question_slug
stringlengths 3
77
| title
stringlengths 1
183
| slug
stringlengths 12
45
| summary
stringlengths 1
160
⌀ | author
stringlengths 2
30
| certification
stringclasses 2
values | created_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| updated_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| hit_count
int64 0
10.6M
| has_video
bool 2
classes | content
stringlengths 4
576k
| upvotes
int64 0
11.5k
| downvotes
int64 0
358
| tags
stringlengths 2
193
| comments
int64 0
2.56k
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
create-components-with-same-value
|
BFS
|
bfs-by-votrubac-1e9j
|
If we split the tree into i components, the target value of each component is sum / i. \n\nNote that we cannot split into i components if sum % i != 0. \n\nFor
|
votrubac
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-15T18:56:59.375915+00:00
|
2022-10-19T17:24:22.816257+00:00
| 2,118 | false |
If we split the tree into `i` components, the target value of each component is `sum / i`. \n\nNote that we cannot split into `i` components if `sum % i != 0`. \n\nFor each target value, we can unambiguously discover all components starting from leaves. This works because we have a tree, not a graph. \n\nWhen processing from leaves, we track the value of the current component:\n- If the value is greater than the target, we cannot split the tree.\n- If the value is less, we add it to the parent.\n\t- There is no more than one parent as we go from a leaf.\n- If the value is equal, we do not add it to the parent.\n\t- It will start a new component from that parent.\n\nThus, the solution is to try to `sum / n, sum / (n - 1), ..., sum / 2` values, and use BFS to check if we can do the split.\n\n**Complexity Analysis**\n- Time: O(n * N nm), where m is max(nums), and N is a function returning the number of divisors.\n\t- BFS is O(n), and we do it for each divisor of sum. \n\t- The maximum sum is `nm`, and N(nm) is the number of divisors. \n\t- In the average case, the number of divisorts/target values that won\'t be fast-pruned in BFS can be esitmated as `log2 nm`.\n- Memory: O(n)\n\n**C++**\n`cnt[i]` is the number of edges for node `i`. We start from leaves - nodes with one edge.\n\nAs we process a neighboring node, we decrease its number of edges. When that number becomes `1` - this node becomes a \u201Cleaf\u201D and we add it to the BFS queue.\n\nNote that it also prevents a node from being processed twice - since next time `cnt[i]` would become zero.\n```cpp\nbool bfs(int val, vector<vector<int>> &al, vector<int> q, vector<int> n, vector<int> cnt) {\n while(!q.empty()) {\n vector<int> q1;\n for (auto i : q) {\n if (n[i] > val)\n return false;\n for (auto j : al[i]) {\n n[j] += n[i] < val ? n[i] : 0;\n if (--cnt[j] == 1)\n q1.push_back(j);\n }\n }\n swap(q, q1);\n }\n return true;\n}\nint componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n int n = nums.size(), sum = accumulate(begin(nums), end(nums), 0);\n if (sum % n == 0 && all_of(begin(nums), end(nums), [&](int v){ return v == sum / n; }))\n return n - 1;\n vector<vector<int>> al(n);\n for (auto &e : edges) {\n al[e[0]].push_back(e[1]);\n al[e[1]].push_back(e[0]);\n }\n vector<int> q, cnt(n);\n for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {\n cnt[i] = al[i].size();\n if (al[i].size() == 1)\n q.push_back(i);\n }\n for (int i = n - 1; i > 1; --i)\n if (sum % i == 0 && bfs(sum / i, al, q, nums, cnt))\n return i - 1;\n return 0;\n}\n```
| 32 | 1 |
['C']
| 4 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
[Python3] post-order dfs
|
python3-post-order-dfs-by-ye15-kj28
|
Please pull this commit for solutions of biweekly 89. \n\n\nclass Solution:\n def componentValue(self, nums: List[int], edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n
|
ye15
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-15T19:21:29.568560+00:00
|
2022-10-15T19:23:54.295783+00:00
| 803 | false |
Please pull this [commit](https://github.com/gaosanyong/leetcode/commit/b09317beeb5fa2ae0b6d2537172ab52647a75cea) for solutions of biweekly 89. \n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def componentValue(self, nums: List[int], edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n tree = [[] for _ in nums]\n for u, v in edges: \n tree[u].append(v)\n tree[v].append(u)\n \n def fn(u, p):\n """Post-order dfs."""\n ans = nums[u]\n for v in tree[u]: \n if v != p: ans += fn(v, u)\n return 0 if ans == cand else ans\n \n total = sum(nums)\n for cand in range(1, total//2+1): \n if total % cand == 0 and fn(0, -1) == 0: return total//cand-1\n return 0 \n```
| 15 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 3 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Python solution
|
python-solution-by-leetcode_dafu-d6fq
|
Solution: find the total sum of node vals. if our tree can be split, the sum of each subtree must equal one divisor of the total sum. check if we can split the
|
leetcode_dafu
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-15T16:00:46.985338+00:00
|
2022-10-15T16:07:22.491042+00:00
| 910 | false |
Solution: find the total sum of node vals. if our tree can be split, the sum of each subtree must equal one divisor of the total sum. check if we can split the tree for every divisor of the total sum. To save time:\n\n1. skip divisors smaller than the largest node val\n2. check divisors from low to high. We terminate after finding the first divisor that can split the tree, which leads to the max edge removals\n\n\nHow many divisors we may check in the worst case? For a num N, the common approximate upper bound of # of divisors is N^1/3. \nthe exact bounds for the number of divisors of any n-digit number are (http://oeis.org/A066150): 4, 12, 32, 64, 128, 240, 448, 768, 1344\n\n nums = [1,5,5,4,11]\n edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[1,3],[3,4]]\n\n tree=collections.defaultdict(set)\n for i,j in edges:\n tree[i].add(j)\n tree[j].add(i)\n \n def check(cur,prev,target):\n val=nums[cur]\n for kid in tree[cur]-{prev}:\n i=check(kid,cur,target)\n if i==-1: return -1\n val+=i \n return val%target if val<=target else -1\n \n tot=sum(nums)\n for n in range(min(tot//max(nums),len(nums)),0,-1): # for simplicity, i do not use O(n^1/2) approach to find all factors here\n if not tot%n and check(0,-1,tot//n)==0:\n return n-1
| 11 | 0 |
['Python']
| 3 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
C++ || Easy understanding || explained
|
c-easy-understanding-explained-by-user76-k66k
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n //to count\n int countIt(vector<int> arr, int x,int &sum){\n int count=0;\n for(auto &itr:arr){\n
|
user7609a
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-15T19:02:56.801244+00:00
|
2022-10-15T19:02:56.801281+00:00
| 710 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n //to count\n int countIt(vector<int> arr, int x,int &sum){\n int count=0;\n for(auto &itr:arr){\n if(itr==x) count++;\n sum+=itr;\n }\n return count;\n }\n \n\n //dfs traversal\n int dfs(vector<int> &nums, int cur, vector<int> adj[], int prev, int target){\n \n int curSum=nums[cur];\n \n for(auto &itr : adj[cur]){\n if(itr==prev) continue; // avoid going backside in graph else infi loop\n curSum+=dfs(nums,itr,adj,cur,target);\n }\n \n //on returning back in recursion if you get target break \n //it there and start sum from 0 for next\n \n if(curSum==target) return 0;\n else return curSum;\n }\n \n //main() start\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n vector<int> adj[nums.size()];\n \n //make graph\n for(auto &itr:edges){\n adj[itr[0]].push_back(itr[1]);\n adj[itr[1]].push_back(itr[0]);\n }\n \n //if all are of same nums[i] divide each node as individual also get total sum\n int sum=0;\n if(countIt(nums,nums[0],sum)==nums.size()) return nums.size()-1;\n \n //check for what it is dividable\n for(int i=nums.size()-1;i>=2;i--){\n if(sum%i != 0) continue; // not dividable in i parts\n int res=dfs(nums,0,adj,-1, sum/i); //array , start , graph , parent, target\n if(res==0) return i-1; // edges removed = total components divided into -1 \n }\n \n \n return 0;\n }\n};\n```
| 10 | 2 |
['Depth-First Search', 'C']
| 3 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
python 3 || dfs, some explanation || T/S: 53% / 30%
|
python-3-dfs-some-explanation-ts-53-30-b-758z
|
\nclass Solution:\n def componentValue(self, nums: List[int], edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n\n def dfs(a, b): # if this subtre
|
Spaulding_
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-20T17:09:49.788979+00:00
|
2024-06-23T17:16:36.998711+00:00
| 493 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def componentValue(self, nums: List[int], edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n\n def dfs(a, b): # if this subtree has sum value of div, make it zero\n \n tally = nums[a]\n for c in graph[a]: \n if c != b:\n tally += dfs(c, a)\n \n return tally if tally != div else 0\n \n graph = defaultdict(list)\n n, sm, mx, mn = len(nums), sum(nums), max(nums), min(nums)\n\n for a, b in edges: # build the graph\n graph[a].append(b)\n graph[b].append(a)\n \n for div in range(mx, sm//mn): # consider each potential divisor of sm\n if not(sm%div or dfs(0, n-1)): # if divisor and whole tree has sum-value of zero, success\n return sm//div-1 # number of deletions is one less than number of components\n\n return 0 # no successes\n```\n[https://leetcode.com/submissions/detail/826733562/](https://leetcode.com/submissions/detail/826733562/)\n\nI could be wrong, but I think that time complexity is *O*(*N* ^2) and space complexity is *O*(*N*), in which *N* ~ `len(nums)` and *N* ~ `len(nums)`.
| 8 | 0 |
['Python']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Easy Java Solution
|
easy-java-solution-by-sumitk7970-1qah
|
```\nclass Solution {\n int[] nums;\n public int componentValue(int[] nums, int[][] edges) {\n int n = nums.length;\n this.nums = nums;\n
|
Sumitk7970
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-15T19:13:49.290675+00:00
|
2022-10-15T19:13:49.290730+00:00
| 775 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n int[] nums;\n public int componentValue(int[] nums, int[][] edges) {\n int n = nums.length;\n this.nums = nums;\n List<Integer>[] graph = new ArrayList[n];\n for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {\n graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();\n }\n for(int[] e : edges) {\n graph[e[0]].add(e[1]);\n graph[e[1]].add(e[0]);\n }\n \n int sum = 0;\n for(int i : nums) {\n sum += i;\n }\n \n for(int k=n; k>0; k--) {\n if(sum % k != 0) continue;\n int ans = helper(graph, 0, -1, sum / k);\n if(ans == 0) return k-1;\n }\n return 0;\n }\n \n private int helper(List<Integer>[] graph, int i, int prev, int target) {\n if(graph[i].size() == 1 && graph[i].get(0) == prev) {\n if(nums[i] > target) return -1;\n if(nums[i] == target) return 0;\n return nums[i];\n }\n \n int sum = nums[i];\n for(int k : graph[i]) {\n if(k == prev) continue;\n int ans = helper(graph, k, i, target);\n if(ans == -1) return -1;\n sum += ans;\n }\n \n if(sum > target) return -1;\n if(sum == target) return 0;\n return sum;\n }\n}
| 8 | 0 |
['Java']
| 1 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
[Python] Get factors of sum all nodes then check
|
python-get-factors-of-sum-all-nodes-then-x1bo
|
Intuition\n- Sum of each connected component must be values in factors of sum(nums), and at least max(nums).\n- So get factors of sum all nodes then check if we
|
hiepit
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-15T16:12:03.617132+00:00
|
2022-10-15T17:57:22.606152+00:00
| 1,001 | false |
# Intuition\n- Sum of each connected component must be values in factors of `sum(nums)`, and at least `max(nums)`.\n- So get factors of sum all nodes then check if we can split into connected component, where sum of each connected component is equal to factor.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: `O(sqrt(SUM_ALL_NODE) + N*log(SUM_ALL_NODE))`, where `SUM_ALL_NODE <= 10^6` is number of all nodes, `N <= 2*10^4` is number of nodes.\n - `factors` is up to `log(SUM_ALL_NODE)` elements.\n - `dfs()` function cost `O(N)`\n\n- Space complexity: `O(log(SUM_ALL_NODE) + N)`\n\n# Code\n```python\nclass Solution:\n def getFactors(self, x):\n factors = []\n for i in range(1, int(sqrt(x)) + 1):\n if x % i != 0: continue\n factors.append(i)\n if x // i != i: factors.append(x // i)\n return factors\n\n def componentValue(self, nums: List[int], edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n n = len(nums)\n graph = defaultdict(list)\n for a, b in edges:\n graph[a].append(b)\n graph[b].append(a)\n\n self.cntRemainZero = 0\n def dfs(u, p, sumPerComponent): # return remain of the subtree with root `u`\n remain = nums[u]\n for v in graph[u]:\n if v == p: continue\n remain += dfs(v, u, sumPerComponent)\n \n remain %= sumPerComponent\n if remain == 0:\n self.cntRemainZero += 1\n \n return remain\n \n def isGood(sumPerComponent, expectedNumOfComponents):\n self.cntRemainZero = 0\n dfs(0, -1, sumPerComponent)\n return self.cntRemainZero == expectedNumOfComponents\n \n sumAllNodes, maxNum = sum(nums), max(nums)\n for sumPerComponent in sorted(self.getFactors(sumAllNodes)):\n if sumPerComponent < maxNum: continue # at least maxNum\n expectedNumOfComponents = sumAllNodes // sumPerComponent\n if isGood(sumPerComponent, expectedNumOfComponents):\n return expectedNumOfComponents - 1 # Need to cut `numOfComponent - 1` edges to make `numOfComponent` connected component\n \n return 0\n```
| 7 | 3 |
['Python3']
| 3 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
DFS math solution [EXPLAINED]
|
dfs-math-solution-explained-by-r9n-od7o
|
IntuitionSplit the tree into parts where the sum of node values in each part is the same. We do this by exploring all ways to divide the total sum of node value
|
r9n
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-25T00:32:38.761461+00:00
|
2024-12-25T00:32:38.761461+00:00
| 54 | false |
# Intuition
Split the tree into parts where the sum of node values in each part is the same. We do this by exploring all ways to divide the total sum of node values evenly, using the tree structure to check if such a division is possible.
# Approach
Traverse the tree using DFS and calculate subtree sums while checking if they can match a target sum, using an adjacency list for efficient neighbor lookups.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
O(n . divisors of total_sum),since DFS runs O(n) for each divisor of the total sum.
- Space complexity:
O(n), for the adjacency list and recursive call stack.
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def componentValue(self, nums, edges):
from collections import defaultdict
# Create an adjacency list for the tree
graph = defaultdict(list)
for a, b in edges:
graph[a].append(b)
graph[b].append(a)
total_sum = sum(nums)
def is_valid(target):
"""Check if it's possible to partition the tree into components with the target sum."""
visited = [False] * len(nums)
def dfs(node):
visited[node] = True
current_sum = nums[node]
for neighbor in graph[node]:
if not visited[neighbor]:
subtree_sum = dfs(neighbor)
if subtree_sum == -1:
return -1
current_sum += subtree_sum
if current_sum > target:
return -1
return current_sum if current_sum < target else 0
for i in range(len(nums)):
if not visited[i]:
if dfs(i) == -1:
return False
return True
# Find the maximum number of deletable edges
for k in range(total_sum, 0, -1):
if total_sum % k == 0:
target = total_sum // k
if is_valid(target):
return k - 1
return 0
```
| 6 | 0 |
['Array', 'Math', 'Tree', 'Depth-First Search', 'Enumeration', 'Python3']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Explanation of everyone's short code | C++
|
explanation-of-everyones-short-code-c-by-j0a5
|
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n unordered_map> adj;\n vector arr;\n \n int dfs(int src,int parent,int target)\n {\n int sum=arr[src]; //m
|
kunalrautela
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-16T07:38:58.755867+00:00
|
2022-10-16T07:38:58.755896+00:00
| 194 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n unordered_map<int,vector<int>> adj;\n vector<int> arr;\n \n int dfs(int src,int parent,int target)\n {\n int sum=arr[src]; //mai apne subtree ka sum nikal rha hu -> to pehle apni val\n \n for(auto i:adj[src])\n if(i!=parent)\n sum+=dfs(i,src,target); \n \n if(sum==target) //bhai mera subtree pura hai mai ab alag component bngya\n return 0; //thats why mera sb kuch bhuja (as if i dont exist. return 0)\n \n return sum; //agar mai target ke equal nahi to kya pta parent ko help kru \n }\n \n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n \n //Step 1 Make graph\n arr=nums;\n for(auto e:edges)\n {\n adj[e[1]].push_back(e[0]);\n adj[e[0]].push_back(e[1]);\n }\n \n //Step 2 Calculate sum\n int sum=0;\n for(auto i:nums)\n sum+=i;\n \n /* Step 3 -> 18 sum hai agar to kitne possible ways hai bnane ke compo :\n -> 1 compoent bnaega 18 sum ka \n -> 2 compoent bnaega 9 sum ka \n -> 3 compoent bnaega 6 sum ka \n -> 6 compoent bnaega 3 sum ka \n -> 9 compoent bnaega 2 sum ka\n -> 18 component bnaega 1 sum ka */\n \n for(int i=sum;i>=1;i--) \n {\n if(sum%i==0) // i components bn skte kya with every component val = n/i\n {\n//IMPORTANT -> i components bn pa rhe hai to edges i-1 remove hogi (Simple logic -> 2 compoent bnane hote to ek edge remove krte)\n if(dfs(0,-1,sum/i)==0) \n return i-1; \n }\n }\n return 0;\n }\n};
| 6 | 1 |
[]
| 1 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
✅C++|| DFS || Easy Solution
|
c-dfs-easy-solution-by-indresh149-dpf3
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> arr;\n vector<vector<int>> g;\n \n int dfs(int ind,int parent,const int target)\n {\n int val =
|
indresh149
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-16T07:10:12.361878+00:00
|
2022-10-16T07:10:12.361923+00:00
| 941 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> arr;\n vector<vector<int>> g;\n \n int dfs(int ind,int parent,const int target)\n {\n int val = arr[ind];\n \n for(auto it : g[ind]){\n if(it == parent) continue;\n val += dfs(it,ind,target);\n }\n \n if(val == target) return 0;\n return val;\n }\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n g.clear(),arr.clear();\n int n = nums.size();\n g.resize(n),arr.resize(n);\n int sum = 0;\n \n for(auto i: edges){\n g[i[0]].push_back(i[1]);\n g[i[1]].push_back(i[0]);\n }\n \n for(int j=0;j<n;j++){\n sum += nums[j];\n arr[j] = nums[j];\n }\n \n int result = 0;\n for(int parts = 1;parts <= n;parts++){\n if(sum%parts != 0) continue;\n if(dfs(0,-1,sum/parts) !=0) continue;\n \n result = max(result,parts-1);\n }\n return result;\n }\n};\n```\n**Please upvote if it was helpful for you, thank you!**
| 6 | 0 |
['Graph', 'C']
| 1 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Solution based in intuiton (full explained)
|
solution-based-in-intuiton-full-explaine-rog5
|
Intuition\nWe define W as the total weight of the tree and x as the total weight of each component after erase some edges and finally k as the number of compone
|
BetoSCL
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-15T17:10:50.690930+00:00
|
2022-10-15T17:38:04.054870+00:00
| 651 | false |
# Intuition\nWe define **W** as the total weight of the tree and **x** as the total weight of each component after erase some edges and finally **k** as the number of components left\n\nFirst of all we know that if a tree can be divided into many components with the same weight **x** the total weight of the tree must be a multiple of x that is **W = kx** for some **k** then we can iterate over all divisors of the total weight of the tree and try to find if it can be partitioned into k components such that they all have weight = **x**\n\nAnd here\'s the main intuition, if we need to make each component weigh = **x**, we know we\'ll get $$\\frac{W}{x} = k$$ components, so there must be exactly k subtrees with weight equal to a multiple of **x**\n\n# Example \nWe use the same tree of first example \n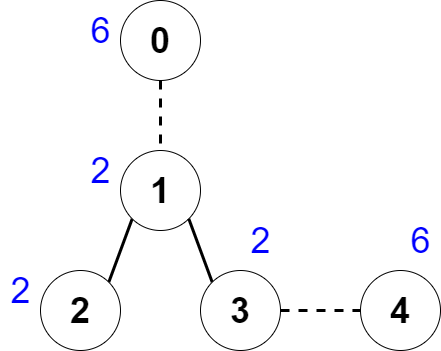\n\nFirst we get the weight of each subtree (the root doesn\'t matter)\n\nFor our example, the weights of each subtree with root 0 from node 0 to n-1 are:\n**[18,12,2,8,6]**\n\nAnd then we try to find the solution for some x. \n\nFor x = 9: (remember that **x** is some divisor of **W**)\nwe find that only one of the subtrees has weight = **kx** but intuition says we need to find exactly $$\\frac{W}{x} = \\frac{18}{9} =2 $$ so this divisor is invalid\n\nFor x = 6:\nIn this case we find that the subtree of nodes **[0, 1, 4]** with weights **[18, 12, 6]** are multiples of **x = 6** and we have exactly 3 which is equal to **$$k = \\frac{W}{x} = \\frac{18}{6} = 3 $$** so we can say that it is a valid division of the tree, that is, there must be some way to delete some edges (exactly k-1) so that each component has weight = **x**\n\n\n# Approach sumary\nIterate over all divisors **x** of **W** and find if there are exactly **$$\\frac{W}{x}$$** subtrees whose weight $$w_{i} \\% x = 0 $$ and if this condition is valid we update the answer with **$$\\max( ans, \\frac{W}{x} -1)$$** (ans at the beginning is 0) \n# Complexity\n$$O(sqrt(W) \\times n)$$ (\\sqrt doesn\'t render)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<bool> vis;\n vector<int> Nums;\n vector<int> graph[20007];\n vector<int> sz;\n void solve(int u){\n sz[u] = Nums[u];\n vis[u] = true;\n for(auto v:graph[u]){\n if(vis[v])continue;\n solve(v);\n sz[u]+=sz[v];\n }\n }\n \n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n int n = nums.size();\n Nums = nums;\n vis.resize(n);\n sz.resize(n);\n // Create the graph with adjacent list\n for(int i = 0;i<edges.size();i++){\n int u = edges[i][0];\n int v = edges[i][1];\n graph[u].push_back(v);\n graph[v].push_back(u);\n }\n int ans = 0;\n \n // Dfs to get the weight of each subtree (well known algorithm)\n // The root does not matter\n solve(0);\n\n // Define W as the total weight of the tree\n int W = accumulate(nums.begin(),nums.end(),0);\n \n for(int x = 1;x*x<=W;x++){\n if(W%x ==0){\n // Check for every divisor\n int cont = 0;\n for(int j = 0;j<n;j++){\n // Count every subtree with weight multiple of x\n if(sz[j]%x ==0){\n cont++;\n }\n }\n int k = W/x;\n // Check the condition that must be exactly W/x components and update the answer\n // To make k components in a tree we need to erase k-1 edges \n if(cont == k )\n ans = max(ans,k-1);\n \n if((W/x)==x)continue;\n\n // The same for the other divisor W/x\n int otherDiv = W/x;\n cont = 0;\n for(int j = 0;j<n;j++){\n if(sz[j]%otherDiv==0){\n cont++;\n }\n }\n k = W/otherDiv;\n if(cont==k)\n ans = max(ans,k-1);\n }\n }\n return ans;\n \n }\n};\n```
| 6 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
[Python3] Math + Topological Sort - Simple Solution
|
python3-math-topological-sort-simple-sol-5bn3
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
dolong2110
|
NORMAL
|
2024-03-13T16:45:33.987085+00:00
|
2024-03-13T16:45:33.987114+00:00
| 110 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def componentValue(self, nums: List[int], edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n n, s = len(nums), sum(nums)\n if n < 2: return 0\n g = [[] for _ in range(n)]\n in_degree = [0 for _ in range(n)]\n for u, v in edges:\n g[u].append(v)\n g[v].append(u)\n in_degree[u] += 1\n in_degree[v] += 1\n \n def is_cuttable(f: int) -> bool:\n d, values = in_degree.copy(), nums.copy()\n dq = collections.deque(u for u in range(n) if d[u] == 1)\n while dq:\n u = dq.popleft()\n d[u] = 0\n if values[u] > f: return False\n elif values[u] == f: values[u] = 0\n for v in g[u]:\n if d[v] == 0: continue\n d[v] -= 1\n values[v] += values[u]\n if d[v] == 1: dq.append(v)\n return True\n\n factor_nums = [i for i in range(1, s + 1) if s % i == 0]\n for f in factor_nums:\n if is_cuttable(f): return s // f - 1\n \n return 0\n```\n\nThis is similar to this [problem](https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-number-of-k-divisible-components/solutions/4870785/python3-cut-leaf-bfs-topological-sort-simple-solution/)
| 3 | 0 |
['Math', 'Topological Sort', 'Python3']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Explained, C++
|
explained-c-by-404akhan-wbbt
|
Each component\'s sum can be only divisor of the total sum. Thus we only need to check those (~100 divisors max of a number).\n\nFor each candidate sum, we will
|
404akhan
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-15T16:12:08.178599+00:00
|
2022-10-15T16:12:08.178650+00:00
| 654 | false |
Each component\'s sum can be only divisor of the total sum. Thus we only need to check those (~100 divisors max of a number).\n\nFor each candidate sum, we will spend linear time to check whether it is possible to divide tree into such components with given sum, using dfs.\n\nRun dfs, and keep track of the subtree visited, when the sum of nodes in the subtree becomes equal to the potential sum, we will update our sum of subnodes to zero, and will count again until we go through entire tree. If at some point the sum is greater than potential sum, that means we cant build such a division into subtrees.\n\nAt the end, we know into how many components we were able to divide. From which we infer number of edges deleted and pick max.\n\nComplexity: n * D(sum of nodes). \nD(s) number of divisors of s.\n\n```\n#include <bits/stdc++.h>\n\nusing namespace std;\n\n#define forn(i, n) for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)\n#define forbn(i, b, n) for(int i = b; i < n; ++i)\n#define sz(v) (int)v.size()\n#define pb push_back\n\ntypedef vector<int> vi;\n\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\tstatic const int N = 20 * 1001;\n\tvi gr[N];\n\tvi gl_nums;\n\t\n \n\tint dfs(int target_sm, int node, int pr = -1) {\n\t\tint loc_sm = gl_nums[node];\n\t\t\n\t\tfor(int to: gr[node]) {\n\t\t\tif(to != pr) {\n\t\t\t\tint rem = dfs(target_sm, to, node);\n\t\t\t\tloc_sm += rem;\n\t\t\t\tif(rem < 0)\n\t\t\t\t\treturn -1;\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t}\n\t\t\n\t\tif(loc_sm == target_sm) {\n\t\t\treturn 0;\n\t\t} \n\t\tif(loc_sm > target_sm) {\n\t\t\treturn -1;\n\t\t}\n\t\treturn loc_sm;\n\t}\n\t\n \n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n \tint total = 0;\n \tfor(int to: nums) {\n \t\tgl_nums.pb(to);\n \t\ttotal += to;\n \t}\n \t\n \tforn(i, sz(edges)) {\n \t\tint a = edges[i][0];\n \t\tint b = edges[i][1];\n \t\t\n \t\tgr[a].pb(b);\n \t\tgr[b].pb(a);\n \t}\n \t\n \tforbn(d, 1, total + 1) {\n \t\tif(total % d == 0) {\n \t\t\tint ans = dfs(d, 0);\n \t\t\tif(ans == 0) {\n \t\t\t\tint k = total / d;\n \t\t\t\treturn k - 1;\n \t\t\t}\n \t\t}\n \t}\n return -1;\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Clear & short Explanation - DFS - O( sqrt(sum) * N ) - comments added
|
clear-short-explanation-dfs-o-sqrtsum-n-8qq9p
|
\n# Approach\nFactorize sum and try all poosible factors..\nfor each factor i the target is sum/i;\n\nnow to check if each factor can be our answer we are runni
|
bhavya_kawatra13
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-07T20:22:23.379858+00:00
|
2023-02-07T20:22:23.379890+00:00
| 309 | false |
\n# Approach\nFactorize sum and try all poosible factors..\nfor each factor i the target is sum/i;\n\nnow to check if each factor can be our answer we are running a dfs, \nin which if any component reaches the sum of exactly targeted value (val is used in code), then we return 0 for that component or we can say we deleted that.. \nat at the end if we are able to delete the root also then we are good and this factor is one of our answer..\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O( sqrt(sum) * N )\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(N)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<vector<int>>g;\n vector<int>A;\n\n // dfs function will check whether split is possible or not\n // if it is possible then it will return 0;\n int dfs(int r,int prnt,int val){\n int c=A[r];\n for(auto i:g[r]){\n if(i!=prnt){\n c+=dfs(i,r,val);\n }\n }\n if(c==val)return 0;\n else return c;\n }\n int componentValue(vector<int>& a, vector<vector<int>>& ed) {\n int s=0;\n A=a;\n for(auto i:a)s+=i;\n\n // factorizing sum\n vector<int>f;\n for(int i=1;i*i<=s;i++){\n if(s%i==0){\n f.push_back(i);\n if(s/i!=i)f.push_back(s/i);\n }\n }\n\n // making tree\n int n=a.size(),ans=1;\n g.assign(n+1,vector<int>());\n for(auto i:ed){\n g[i[0]].push_back(i[1]);\n g[i[1]].push_back(i[0]);\n }\n\n // checking for each factor, can it be our ans?\n for(auto i:f){\n if(i<=n&&!dfs(0,-1,s/i)){\n ans=max(ans,i);\n }\n }\n return ans-1;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Math', 'Tree', 'Depth-First Search', 'Enumeration', 'C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
✅ C++ Simple + Clean | Simple modified DFS | Heavily Commented 100% | Beginner Friendly
|
c-simple-clean-simple-modified-dfs-heavi-250v
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n // dfs traversal of graph\n int dfs(vector<int>&nums, vector<vector<int>>&g, int cur, int parent, int target)\n {\n
|
HustlerNitin
|
NORMAL
|
2022-11-21T16:08:24.398429+00:00
|
2022-11-21T16:09:58.627084+00:00
| 351 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n // dfs traversal of graph\n int dfs(vector<int>&nums, vector<vector<int>>&g, int cur, int parent, int target)\n {\n int curSum = nums[cur];\n for(auto &nbr : g[cur])\n {\n if(nbr == parent) continue; // avoid going backside in graph else infinite loop\n curSum += dfs(nums, g, nbr, cur,target);\n }\n \n // on returning back in recursion if you get target break \n // it there and start sum from 0 for next\n \n if(curSum == target) \n return 0;\n else \n return curSum;\n }\n \n\t\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) \n {\n int n = nums.size();\n vector<vector<int>>g(n);\n \n // make graph\n for(auto e : edges){\n g[e[0]].push_back(e[1]);\n g[e[1]].push_back(e[0]);\n }\n \n int sum = accumulate(nums.begin(), nums.end(), 0);\n \n // Handle early this Edge case will save time \n // if all values of nums are same divide each node as individual also \n // get total sum, i.e all nodes have same value.\n \n unordered_set<int>st(nums.begin(), nums.end());\n if(st.size() == 1) return n-1;\n \n // start from maximum (i.e n-1) number of components to minimum no. of components that is "2"\n for(int i=n-1;i>=2;i--)\n {\n if(sum%i != 0) continue; // not dividable into "i" components\n \n int ans = dfs(nums, g, 0, -1, sum/i); // value array , graph , start , parent , EachComponentSum\n \n // if ans finally returned to "0" means all components are successfully divided into sum of "sum/i"\n if(ans == 0) return i-1; // edges removed = total components divided into - 1 \n }\n return 0;\n }\n};\n```\n\n----\n***Thanks for Upvoting !***\n\uD83D\uDE42
| 2 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Graph', 'C', 'C++']
| 1 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Simple Logic, DFS+ Factors,C++
|
simple-logic-dfs-factorsc-by-kundanagraw-csjv
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<vector<int>> adj;\n int comp;\n int dfs(vector<int>& nums,int v, int parent,int val) {\n int total = nums[v
|
kundanagrawal001
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-15T18:21:11.867832+00:00
|
2022-10-15T18:21:11.867874+00:00
| 345 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<vector<int>> adj;\n int comp;\n int dfs(vector<int>& nums,int v, int parent,int val) {\n int total = nums[v];\n for(auto x: adj[v]) {\n if(x == parent) continue;\n total += dfs(nums,x, v,val);\n } \n if(total == val) {\n comp--;\n return 0;\n }\n return total;\n }\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n int n = nums.size();\n adj.resize(n);\n for(auto e: edges) {\n adj[e[0]].push_back(e[1]);\n adj[e[1]].push_back(e[0]);\n }\n \n if(count(nums.begin(), nums.end(), nums[0]) == n) return n - 1;\n int sum = accumulate(nums.begin(), nums.end(), 0);\n int res = 0;\n \n for(int i = 2; i * i <= sum; ++i) {\n if(sum % i == 0) {\n comp = i;\n dfs(nums,0, -1,sum / i);\n if(comp == 0) res = max(res, i - 1);\n \n comp = sum / i;\n dfs(nums,0, -1,i);\n if(comp == 0) res = max(res, (sum / i) - 1);\n }\n }\n \n return res;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Python | Factorization + DFS
|
python-factorization-dfs-by-antarestrue-atla
|
Let s = sum(nums). Let t is the sum of a component, which is unknown right now. But, because each component has the same sum, s % t == 0 must hold.\n\nSo firs
|
antarestrue
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-15T16:02:48.293421+00:00
|
2022-10-15T16:25:08.626223+00:00
| 400 | false |
Let `s = sum(nums)`. Let `t` is the sum of a component, which is unknown right now. But, because each component has the same sum, `s % t == 0` must hold.\n\nSo first, we find all the possible `t`s. We can try from `1` to `ceil(sqrt(s))`, and we sort the `t`s from small to large. Remember `t` can be larger than `sqrt(s)`. For `s = i * j`, both `i` and `j` are candidates of `t`.\n\nAnd then, we try using each `t` as the component sum and see if that is feasible. We use a DFS on the tree. For each sub-tree, there are 3 situations:\n1. `sum < t`, then we should not cut off this sub-tree.\n2. `sum == t`, then we should cut off this sub-tree, and `+1` to the cut counter.\n3. `sum > t`, then this `t` is infeasible. Terminate and try next `t`.\n\nIf `t` is feasible, then we can return the cut counter. No need to try the larger `t`s.\n\nThe amount of `t`s is in `O(sqrt(N))`, and DFS costs `O(N)`. Overall is `O(N*sqrt(N))`.\n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def componentValue(self, nums: List[int], edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n n = len(nums)\n if n <= 1: return 0\n s = sum(nums)\n m = max(nums)\n \n f = set()\n for i in range(1, ceil(sqrt(s))):\n if s % i == 0:\n if i >= m:\n f.add(i)\n j = s // i\n if j >= m:\n f.add(j)\n f = sorted(f)\n \n g = [[] for _ in range(n)]\n for a, b in edges:\n g[a].append(b)\n g[b].append(a)\n \n c = 0\n t = 0\n def rec(p, pp):\n nonlocal c\n r = nums[p]\n for q in g[p]:\n if q == pp: continue\n r += rec(q, p)\n if r == t:\n c += 1\n return 0\n elif r > t:\n raise Exception("")\n else:\n return r\n for t in f:\n try:\n c = 0\n rec(0, -1)\n return c-1\n except:\n pass\n```
| 2 | 1 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Recursion', 'Python']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
DFS
|
dfs-by-vats_lc-h1ey
|
Code
|
vats_lc
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T12:57:44.134699+00:00
|
2025-01-12T12:57:44.134699+00:00
| 23 | false |
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
void dfs(int node, int parent, vector<vector<int>>& adj,
vector<int>& values, vector<int>& a, int& comp, int& target) {
values[node] = a[node];
for (auto adjNode : adj[node]) {
if (adjNode == parent)
continue;
dfs(adjNode, node, adj, values, a, comp, target);
values[node] += values[adjNode];
}
if (values[node] == target) {
comp++;
values[node] = 0;
}
}
int componentValue(vector<int>& a, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
int n = a.size();
vector<vector<int>> adj(n);
for (auto i : edges) {
adj[i[0]].push_back(i[1]);
adj[i[1]].push_back(i[0]);
}
int sum = accumulate(a.begin(), a.end(), 0), ans = 0;
if (sum == n)
return n - 1;
for (int i = 2; i * i <= sum; i++) {
if (sum % i)
continue;
int j = sum / i;
vector<int> values(n, 0);
int comp = 0;
dfs(0, -1, adj, values, a, comp, j);
if ((comp * j) == sum)
ans = max(ans, comp - 1);
j = i, comp = 0;
values.resize(n, 0);
dfs(0, -1, adj, values, a, comp, j);
if ((comp * j) == sum)
ans = max(ans, comp - 1);
}
return ans;
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Easiest and Fastest solution (beats 100%)
|
easiest-and-fastest-solution-beats-100-b-g4v4
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Babir
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-23T21:44:24.296471+00:00
|
2024-10-23T21:45:06.841345+00:00
| 68 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n#define ll long long \nint cnt=0;\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n ll dfs(vector<vector<int>> & g, vector<int> & nums, int val, int node, int par){\n ll ans =nums[node];\n for(auto v:g[node]){\n if(v==par) continue;\n ll subt=dfs(g,nums,val,v,node);\n if(subt==val){\n cnt++;\n }\n else{\n ans+=subt;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n int n = nums.size();\n vector<vector<int>> g(n);\n for(auto e:edges){\n g[e[0]].push_back(e[1]);\n g[e[1]].push_back(e[0]);\n }\n vector<int> factors;\n ll sum =0;\n \n \n for(int i =0;i<n;i++){\n sum+=nums[i];\n }\n int i;\n // cout<<sum<<"\\n";\n for(i=1;i*i<=sum;i++){\n if(sum%i==0){\n factors.push_back(i);\n \n }\n \n }\n i--;\n if(i*i==sum){\n i--;\n }\n while(i>=1){\n if(sum%i==0){\n factors.push_back(sum/i);\n\n }\n i--;\n }\n ll ans =0;\n for(int i =0;i<factors.size();i++){\n cnt =0;\n dfs(g,nums,factors[i],0,0);\n // cout<<factors[i]<<" "<<cnt+1<<"\\n";\n if(cnt+1==sum/factors[i]){\n ans=cnt;\n break;\n }\n // cout<<factors[i]<<"\\n";\n }\n return ans;\n\n \n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
C++ || DFS || Math
|
c-dfs-math-by-akash92-8fjm
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nThe goal is to partition the tree into connected components, each having the same sum o
|
akash92
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-25T08:07:25.340973+00:00
|
2024-09-25T08:07:25.341028+00:00
| 93 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThe goal is to partition the tree into connected components, each having the same sum of node values. The total sum of the array should be divisible by the number of components we want to form, which leads us to check the divisors of the sum. For each divisor, we attempt to recursively split the tree.\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1.\tGraph Representation: We represent the tree using an adjacency list based on the edges.\n2.\tDFS Function (f): We perform a depth-first search (DFS) on the tree starting from node 0. As we traverse, we accumulate the node values. If at any point the accumulated value exceeds the target sum for a component, we return an invalid state (a large value).\n\t\u2022\tIf the accumulated value exactly equals the target sum, we reset it to 0 since we successfully formed one component.\n3.\tDivisor Checking: We loop over the possible number of components (starting from n to 2) and check if the total sum can be divided evenly into that many components. For each divisor, we try to partition the tree.\n4.\tReturn Result: The maximum number of components that can be formed is the result.\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n * sqrt(sum(nums)))$$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\n vector<vector<int>> adj;\n vector<int> vis;\n int target;\nprivate:\n int f(int node, vector<int>& nums){\n vis[node] = nums[node];\n for(auto adjNode: adj[node]){\n if(vis[adjNode]) continue;\n vis[node] += f(adjNode, nums);\n if(vis[node] > target) return 1e7;\n }\n if(vis[node] == target) return 0;\n return vis[node];\n }\n\npublic:\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n int n = nums.size();\n int sum = accumulate(nums.begin(), nums.end(), 0);\n adj.resize(n);\n for(auto& it: edges){\n adj[it[0]].push_back(it[1]);\n adj[it[1]].push_back(it[0]);\n }\n\n for (int i=n; i>1; i--) {\n if(sum % i) continue;\n target = sum/i;\n vis = vector<int>(n);\n if(f(0, nums) == 0) return i-1;\n }\n \n return 0;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Math', 'Depth-First Search', 'C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
C++ || BFS with explanation || Beginner Friendly
|
c-bfs-with-explanation-beginner-friendly-m7y1
|
Intuition\nThe problem requires two things to be thought of:\n\nQ1) What could be the sum of each component?\nQ2) How can we check whether the tree could be spl
|
Rock3933
|
NORMAL
|
2023-07-01T19:28:26.231244+00:00
|
2023-07-01T19:28:26.231264+00:00
| 57 | false |
# Intuition\nThe problem requires two things to be thought of:\n\n*Q1) What could be the sum of each component?\nQ2) How can we check whether the tree could be split into components of given sum?*\n\n1) Add the value of all the nodes and try all the possible sums into which this value can be broken down.\n2) Start travelling from the leaf nodes and move towards the root. A leaf node can be considered only if its value equals the sum. If it\'s value is less than the sum then it must give its to its parent. On the other hand if its value is greater than sum we can conclude that the tree cant be broken into clusters of that sum.\n\n*Please upvote if found helpful :)*\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool bfs(int rt, vector<vector<int>> &adj,vector<int>&nums, int sum){\n stack<vector<int>> st;\n vector<int> vis(adj.size());\n queue<int> q;\n q.push(rt);\n vector<int> first={rt};\n st.push(first);\n\n\n while(!q.empty()){\n int siz=q.size();\n vector<int> tem;\n for(int i=0;i<siz;i++){\n int nod=q.front();\n vis[nod]=1;\n q.pop();\n for(auto it:adj[nod]){\n if(!vis[it]){\n q.push(it);\n tem.push_back(it);\n }\n }\n }\n st.push(tem);\n }\n vector<int> pval(adj.size());\n for(int i =0;i<vis.size();i++){\n vis[i]=0;\n }\n while(!st.empty()){\n \n vector<int> tem=st.top();\n for(int i=0;i<tem.size();i++){\n vis[tem[i]]=1;\n if(pval[tem[i]]+nums[tem[i]]>sum){\n return 0;\n }else if(pval[tem[i]]+nums[tem[i]]<sum){\n for(auto it: adj[tem[i]]){\n if(!vis[it]){\n \n pval[it]+=pval[tem[i]]+nums[tem[i]];\n }\n }\n } \n }\n st.pop();\n }\n if(pval[0]+nums[0]!=sum) return 0;\n return 1;\n }\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n int sum=accumulate(nums.begin(),nums.end(),0);\n vector<vector<int>> adj(nums.size());\n for(int i=0;i<edges.size();i++){\n adj[edges[i][0]].push_back(edges[i][1]);\n adj[edges[i][1]].push_back(edges[i][0]);\n }\n int maxi=INT_MIN;\n for(int i=1;i<=sqrt(sum);i++){\n if(sum%i==0){\n if(bfs(0,adj,nums,sum/i)){\n maxi=max(maxi,i-1);\n }\n int quo=sum/i;\n if(bfs(0,adj,nums,sum/quo)){\n maxi=max(maxi,quo-1);\n }\n }\n }\n return maxi;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Breadth-First Search', 'C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Java || 100% faster || Easy Solution || no recursion ||0sec
|
java-100-faster-easy-solution-no-recursi-10da
|
Intuition\n\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Tim
|
sadanandsidhu
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-04T01:05:25.464493+00:00
|
2023-03-04T01:05:25.464532+00:00
| 101 | false |
# Intuition\n\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n int[] nums;\n public int componentValue(int[] nums, int[][] edges) {\n int n = nums.length;\n this.nums = nums;\n List<Integer>[] graph = new ArrayList[n];\n for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {\n graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();\n }\n for(int[] e : edges) {\n graph[e[0]].add(e[1]);\n graph[e[1]].add(e[0]);\n }\n \n int sum = 0;\n for(int i : nums) {\n sum += i;\n }\n \n for(int k=n; k>0; k--) {\n if(sum % k != 0) continue;\n int ans = helper(graph, 0, -1, sum / k);\n if(ans == 0) return k-1;\n }\n return 0;\n }\n \n private int helper(List<Integer>[] graph, int i, int prev, int target) {\n if(graph[i].size() == 1 && graph[i].get(0) == prev) {\n if(nums[i] > target) return -1;\n if(nums[i] == target) return 0;\n return nums[i];\n }\n \n int sum = nums[i];\n for(int k : graph[i]) {\n if(k == prev) continue;\n int ans = helper(graph, k, i, target);\n if(ans == -1) return -1;\n sum += ans;\n }\n \n if(sum > target) return -1;\n if(sum == target) return 0;\n return sum;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
[Python] One Pass DFS to count, optimized with module, O(n) * ((factor of sum(nums)) - max(nums))
|
python-one-pass-dfs-to-count-optimized-w-sn7c
|
First, get all subtree sum dfs start from any node(here is 0).As every compent we get is divisor of sum(nums), we iterate all k in range(max(nums), s). sum(c fo
|
cava
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-26T09:46:59.390922+00:00
|
2022-10-26T09:49:04.586126+00:00
| 56 | false |
First, get all subtree sum dfs start from any node(here is 0).As every compent we get is divisor of sum(nums), we iterate all k in range(max(nums), s). *sum(c for v, c in dt.items() if v % k == 0)* is used to get all subtree sum is k * t(1 <= t <= s // k).\n```\nclass Solution:\n def componentValue(self, nums: List[int], edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n graph = [[] for _ in range(len(nums))]\n for u, v in edges:\n graph[u].append(v)\n graph[v].append(u)\n dt, visited = dict(), set()\n def dfs(v):\n visited.add(v)\n ret = nums[v]\n for u in graph[v]:\n if u not in visited: ret += dfs(u)\n dt[ret] = dt.get(ret, 0) + 1\n return ret\n s = sum(nums)\n dfs(0)\n for k in range(max(nums), s):\n if s % k: continue\n if sum(c for v, c in dt.items() if v % k == 0) == s // k: return s // k - 1\n return 0\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Java | DFS
|
java-dfs-by-conchwu-x1pe
|
\n\t//1.DFS\n //Runtime: 64 ms, faster than 97.17% of Java online submissions for Create Components With Same Value.\n //Memory Usage: 103.1 MB, less than
|
conchwu
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-20T14:27:21.010126+00:00
|
2022-10-20T14:27:21.010165+00:00
| 150 | false |
```\n\t//1.DFS\n //Runtime: 64 ms, faster than 97.17% of Java online submissions for Create Components With Same Value.\n //Memory Usage: 103.1 MB, less than 83.02% of Java online submissions for Create Components With Same Value.\n //Time: O(V + V + E + logV * V); Space: O(V + E + V)\n //Time: O(logV * V); Space: O(V)\n public int componentValue(int[] nums, int[][] edges) {\n if (edges.length == 0) return 0;\n\n //Time: O(V)\n int sum = 0, maxValue = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){\n sum += nums[i];\n maxValue = Math.max(maxValue, nums[i]);\n }\n int maxCount = sum / maxValue;\n if (sum % maxCount == 0 && maxCount == nums.length) return nums.length - 1;\n\n //build graph\n //Time: O(V + E); Space: O(V + E)\n List<Integer>[] graph = new List[nums.length];\n for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();\n for (int[] edge: edges){\n graph[edge[0]].add(edge[1]);\n graph[edge[1]].add(edge[0]);\n }\n\n //Time: O(logV * V); Space:O(V)\n for (int k = maxCount; k > 1; k--)\n if (sum % k == 0 && helper_dfs_sumTarget(nums, graph,0, -1, sum / k) == 0)\n return k - 1;\n return 0;\n }\n\n private int helper_dfs_sumTarget(int[] nums, List<Integer>[] graph,\n int index, int parent, int target) {\n //the sum of value of current subtree\n int sum = nums[index];\n for (int neighbour : graph[index]){\n if (neighbour != parent) {\n sum += helper_dfs_sumTarget(nums, graph, neighbour, index, target);\n if (sum > target) return sum;\n }\n }\n //sum == target means current subtree can be deleted from tree.\n return sum == target ? 0 : sum;\n }\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Java']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
easy short efficient clean code
|
easy-short-efficient-clean-code-by-maver-bqbs
|
\nclass Solution {\ntypedef long long ll;\n#define vi(x) vector<x>\n#define pb push_back\npublic:\n ll n, rem, sum;\n vi(vi(ll))g;\n ll func(const vi(v
|
maverick09
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-17T03:59:51.755538+00:00
|
2022-10-17T04:00:02.420644+00:00
| 379 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\ntypedef long long ll;\n#define vi(x) vector<x>\n#define pb push_back\npublic:\n ll n, rem, sum;\n vi(vi(ll))g;\n ll func(const vi(vi(ll))&g, const vi(int)&val, const ll&nd, const ll&par){\n ll tot=val[nd];\n for(ll child:g[nd]){\n if(child!=par){\n tot+=func(g, val, child, nd);\n }\n }\n if(tot==sum){\n --rem, tot=0;\n }\n return tot;\n }\n int componentValue(vector<int>&v, vector<vector<int>>&e) {\n n=v.size();\n ll tot=accumulate(begin(v), end(v), 0LL), ans=0;\n g.resize(n);\n for(auto edge:e){\n g[edge[0]].pb(edge[1]);\n g[edge[1]].pb(edge[0]);\n }\n for(ll i=1;i<=n;++i){\n if(tot%i){\n continue;\n }\n rem=i, sum=tot/rem;\n func(g, v, 0, -1);\n if(rem==0){\n ans=i;\n }\n }\n return ans-1;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'C']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
✅ [Python] BFS + Topological Sort w/ Explanation | Beats 100%
|
python-bfs-topological-sort-w-explanatio-a3ij
|
Python solution:\n\nclass Solution:\n def componentValue(self, N:List[int], E: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n total_sum, n = sum(nums), len(nums)\n
|
takanuva15
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-16T15:19:43.747477+00:00
|
2022-10-16T15:30:41.735009+00:00
| 175 | false |
Python solution:\n```\nclass Solution:\n def componentValue(self, N:List[int], E: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n total_sum, n = sum(nums), len(nums)\n adj_list, dep_counts = collections.defaultdict(set), [0] * n\n for v1, v2 in edges:\n adj_list[v1].add(v2)\n adj_list[v2].add(v1)\n dep_counts[v1] += 1\n dep_counts[v2] += 1\n\n def can_partition_into_subtrees_with_sum_(target_tree_sum: int) -> bool:\n v_subtree_sums, dep_counts_copy = nums[:], dep_counts[:]\n v_dq = deque([i for i, dep_count in enumerate(dep_counts) if dep_count == 1])\n while v_dq:\n for _ in range(len(v_dq)):\n curr_v = v_dq.pop()\n if v_subtree_sums[curr_v] > target_tree_sum:\n return False\n elif dep_counts_copy[curr_v] == 0: # can\'t come up with a short example to trigger this condition\n continue\n dep_counts_copy[curr_v] = 0\n for next_v in adj_list[curr_v]:\n if v_subtree_sums[curr_v] == target_tree_sum or dep_counts_copy[next_v] > 0:\n dep_counts_copy[next_v] -= 1\n if v_subtree_sums[curr_v] < target_tree_sum:\n v_subtree_sums[next_v] += v_subtree_sums[curr_v]\n if dep_counts_copy[next_v] == 0:\n return v_subtree_sums[next_v] == target_tree_sum\n elif dep_counts_copy[next_v] == 1:\n v_dq.appendleft(next_v)\n return True\n\n for possible_subtree_sum in range(total_sum // n, total_sum):\n if total_sum % possible_subtree_sum == 0 and can_partition_into_subtrees_with_sum_(possible_subtree_sum):\n return total_sum // possible_subtree_sum - 1\n return 0\n```\nI put this together with help from https://leetcode.com/problems/create-components-with-same-value/discuss/2706736/Python-Explanation-with-pictures-BFS and cleaned it up to be easier for me to understand. (Would highly recommend checking out the pictures in the linked post).\n\nHere\'s the explanation I could come up with:\n1. **Only attempt to partition the tree into subtrees with a sum that is a perfect divisor of the total tree sum.**\nThe first thing to realize here (as the problem hint says), is that you can only split the tree into x subtrees if x cleanly divides the sum of nums.\n\t* Ex1: `nums = [1,2,1], sum(nums) = 4`. Here, it\'s obvious that we can\'t split the tree into 3 subtrees (which would be the optimal answer since we would be deleting all edges), because 4/3 is not an integer (ie 4 % 3 != 0)\n\t* Ex2: `nums = [6,8,10], sum(nums) = 24`. Here, it could be possible to split the tree into 3 subtrees with sum 8 since 24 % 3 == 0. In this case, now we need to actually run through the tree and see if we can successfully partition it into 3 subtrees of sum 8 (obviously not possible for the given example).\n\t* This principle provides the setup for the `for`-loop iterating from `[total_sum // n, total_sum)`. The minimum possible valid subtree sum would be `total_sum` split over n subtrees (ie 1-node trees), and the max would be a single tree with all nodes summing to `total_sum` (we don\'t need to manually check the max since it is the default answer if we can\'t do any splits).\n2. **Additional space required for performing the partitioning**\nTo perform the actual partition-checking, we define a function that takes in the required sum that each subtree must have, and attempts to split all the nodes into subtrees with that sum. In order for this function to do its job, it will need:\n\t* An easy way to determine the neighbors of a given node.\n\t\t* We build a standard adjacency list `adj_list` to do this.\n\t* An easy way to track whether a given node has been used up or not.\n\t\t* We build a dependency-count array `dep_counts` (aka the current "degree" of a vertex) to do this.\n\t* An easy way to track the sum of the subtree at the current vertex being considered.\n\t\t* We\'ll use the `nums` array for this.\n\t* Since the partition function could be run multiple times for multiple possible subtree sums, and since we\'ll need to modify the subtree sums and `dep_counts` as we go, we\'ll need to make copies of these arrays each time the function executes. We\'ll use those copies during the function-execution.\n3. **Process the nodes in the tree starting from leaves first**\n\t* \tTo partition the tree into subtrees of sum x, we\'ll start from all the leaf nodes in the tree. The reason we want to start from leaf nodes rather than a middle node is that if a node has multiple neighbors to pick from, we don\'t know ahead-of-time which neighbor should be the correct one to pick such that other nodes in the tree will also be able to correctly form subtrees of sum x.\n\t* \tEx: Given this tree which you want to partition into subtrees of sum 3:\n\t\t```\n 1 2\n \\ /\n 2--1\n / \\\n 3 3\n\t\t```\n\t\tIf you start at the first 2 with 3 neighbors, and you incorrectly pick the "1" to the right to make a subtree of sum 3, then the other nodes will not be able to form subtrees of sum 3. This would require some complex backtracking to undo, so it\'s better to start at the leaf nodes.\n\t* \t(In case you haven\'t already seen it...we\'re going to be running a topological sort lol) We\'ll build a deque of nodes `v_dq`, which will be instantiated with all nodes with `dep_count == 1` (ie leaves).\n4. **Perform the subtree-building in a topological-sort fashion**\nNow we\'ll just do a standard bfs-style iteration of the vertices in the deque which is common to topological sort problems. For all the elements in the deque, we pop off each one and do the following:\n\t* Let `curr_v` be the current vertex we are considering which we just popped off the deque\n\t* If the sum of the subtree at `curr_v` is > than the target sum, we know we\'ve failed the partitioning so we\'ll just return False immediately.\n\t\t* Ex: `nums=[10,2], sum(nums) = 12`, we\'d first try to partition the tree into 2 subtrees of sum 6. We check 10 and its sum is > 6, so we stop immediately.\n\t* Otherwise, if the dep_count of `curr_v` is 0, then we\'ll skip it and move on to the next vertex. I think this case only occurs if we added a vertex to a previous subtree while that vertex was sitting in the deque.\n\t\t* Ex: Unfortunately I can\'t come up with a simple example to demonstrate this. If you have one please let me know. (This condition is necessary to achieve fast runtime)\n\t* Otherwise we\'ll set the dep_count of `curr_v` to 0 to indicate that this node has been used up in a subtree that we\'re building. Now, for each of the neighbors of `curr_v` (denoted `next_v`), we do the following:\n\t\t* if the sum at `curr_v` is already equal to the target sum, then we know this tree is finished. Thus all neighboring nodes should no longer have a dependency on `curr_v` and we\'ll decrement their dep_count by 1. (Note this may cause the `dep_count` of some nodes to fall below 0 - this is not an issue because those nodes would have already been processed in our `v_dq` ahead-of-time due to having a lower dependency-count than us [this is the nature of a topological sort]).\n\t\t\t* if we find after decrementing the neighbor\'s `dep_count` that it\'s `dep_count == 0`, this indicates that we\'ve just processed all nodes in the tree (by the nature of a connected tree where the node with the most edges is processed last). So we\'ll just check whether our `tree_sum == target` and, if so, `return True` (else `return False`).\n\t\t\t* otherwise if the neighbor\'s `dep_count` is now 1, that means it\'s eligible to be processed in the next round of BFS, so we\'ll append it onto `v_dq`.\n\t\t* the only other possibility is that our `tree_sum` is < than the target sum (we already checked the > condition above so we would\'ve returned False by now). For this case, we can only consider neighbors whose `dep_count` is > 0 (otherwise we would end up looking at nodes that were already added to our subtree in the previous iteration).\n\t\t\t* Since we absolutely need another node in our subtree to potentially hit the target, we must add this neighbor into our subtree. (Remember that nodes in `v_dq` have only 1 dependency, which means there\'s only 1 option to pick for increasing our subtree sum.) Thus we will increment the `next_v` tree_sum value by `curr_v` tree_sum value.\n\t\t\t* Afterwards, the same logic as in the previous block applies:\n\t\t\t\t* if the neighbor we just added has `dep_count == 0`, it\'s the last node to be processed in the tree.\n\t\t\t\t* elif the neighbor\'s `dep_count == 1`, it\'s ready to be processed in the next round of BFS.\n\t\t\t\t* otherwise, the neighbor must have other dependencies that should be processed first before deciding if any more nodes should be added to our subtree that the neighbor is now in.\n\t* Note: There is a `return True` condition at the end of the function - this should not execute because our topological sort will handle it in the `if dep_counts_copy[next_v] == 0` condition.\n5. A nice thing to note about the final answer we return: If we are able to successfully partition the given tree into multiple subtrees, then the number of edges that were deleted is going to be exactly the `number of subtrees` - 1.\n\t* Ex: `nums=[8,8,8], sum(nums) = 24`. We can partition into 3 subtrees, which means we\'d remove 2 edges.\n\t\tSince all the nodes are connected in the beginning, to form 2 trees out of 1 tree, you delete one edge. Then to form 3 trees from 2 trees, you delete one more edge. etc.\n\t\t\nSorry if this was a little verbose. Hopefully it\'ll help me understand this if I look at it again a few years from now lol.
| 1 | 0 |
['Breadth-First Search', 'Topological Sort', 'Python']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
C++ || Easy To Understand || 100% Fast Solution
|
c-easy-to-understand-100-fast-solution-b-vkre
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nDiving the total sum into equal parts and then simply DFS call\n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Sankalp_Sharma_29
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-16T10:58:05.756683+00:00
|
2022-10-16T10:58:05.756718+00:00
| 70 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nDiving the total sum into equal parts and then simply DFS call\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(N*root(N))\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:O(N)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n int n=nums.size();\n vector<vector<int>> adj(n);\n int sum=0;\n for (int i=0; i<n; ++i)\n sum+=nums[i];\n for(auto &x:edges)\n {\n adj[x[0]].push_back(x[1]);\n \n adj[x[1]].push_back(x[0]);\n }\n \n for(int i=n;i>1;i--)\n {\n if(sum%i) continue;\n \n if(dfs(nums,adj,0,-1,sum/i)==0)\n return i-1;\n }\n return 0;\n }\n private:\n int dfs(vector<int> &nums,vector<vector<int>> &adj,int node,int par,int target)\n {\n int s=nums[node];\n for(auto &it:adj[node])\n {\n if(it==par) continue;\n s+=dfs(nums,adj,it,node,target);\n }\n if(s==target)\n return 0;\n else\n return s;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 1 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Faster solution O(MloglogM) where M is the sum of nodes
|
faster-solution-omloglogm-where-m-is-the-4b8b
|
Prerequisite\nChoose an arbitrary root to make the tree rooted. 0 is the root thereafter.\nThe sum of nodes in the subtree (subtree-sum thereafter) rooted at ea
|
cai_lw
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-15T17:42:43.784269+00:00
|
2022-10-15T17:42:43.784311+00:00
| 258 | false |
## Prerequisite\nChoose an arbitrary root to make the tree rooted. 0 is the root thereafter.\nThe sum of nodes in the subtree (subtree-sum thereafter) rooted at each node can be found by a simple DFS in O(N).\nLet M be the sum of all nodes, or in other words, the subtree-sum of the root.\n\n## Lemma\nThis solution is based on the following not so intuitive lemma:\n> For any divisor D of M, the tree can be divided into connected components (CCs) with the same sum D, if and only if D divides exactly M/D nodes\' subtree-sum.\n## Proof\n### "=>" direction\nFor any CC, consider its unique node closest to the root. The subtree rooted at this node is disconnected from the rest of the tree, so this subtree must consist of one or more CCs in their entirety. Therefore this node\'s subtree-sum is the sum of one more CCs and is divisible by D.\nConversely, if a node is not a CC\'s closest node to the root, let sub-CC be the intersection of this CC and the subtree rooted at this node. Note that sub-CC is a proper subset of CC, since this node\'s parent must also belong to this CC. Also, since nodes are all positive, sub-CC\'s sum is positive and strictly smaller than that of CC. The subtree-sum of this node is the sum of sub-CC and zero or more other CCs in their entirety, so if the subtree-sum divisible by D, the sub-CC\'s sum must be at least D, and the CC\'s sum is strictly larger than D, a contradiction.\nWe have shown that a node\'s subtree-sum is divisible by D if and only if it\'s a CC\'s unique closest node to the root. Since there are exactly M/D CCs, there are exactly M/D nodes whose subtree-sum is divisible by D.\n### "<=" direction:\nRemove all edges between non-root nodes whose subtree-sum is divisible by D and their parents. This splits the tree into M/D CCs. Each CC\'s sum must be positive and divisible by D, and thus at least D. Also, none of the CC\'s sum could larger than D since otherwise their sum will be larger than M, a contradition. Therefore all CC\'s sums are exactly D, and we found a valid solution.\n## Algorithm\nUse an array or a hashmap to count the number of subtree-sums equal to x for every integer x from 1 to M (inclusive). Let\'s call it `count`.\nEnumerate all divisors of D of M, starting from the smallest. The number of subtree-sums divisible by D is given by `count[D]+count[D*2]+...+count[M]`. If it is exactly M/D, return M/D-1.\nFor each D, it takes M/D steps to compute the summation. Therefore the complexity is the sum of M/D over all D\'s, which is the same as the sum of all D\'s. This is at most O(MloglogM). See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Divisor_function#Growth_rate\n## Code\n### C++\n```\nclass Solution {\n void dfs(int u,vector<int> &subsum,const vector<vector<int>> &adj,vector<bool> &vis){\n vis[u]=true;\n for(int v:adj[u])\n if(!vis[v]){\n dfs(v,subsum,adj,vis);\n subsum[u]+=subsum[v];\n }\n }\npublic:\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n int n=nums.size();\n vector<vector<int>> adj(n);\n for(auto &e:edges){\n adj[e[0]].push_back(e[1]);\n adj[e[1]].push_back(e[0]);\n }\n vector<bool> vis(n);\n dfs(0,nums,adj,vis);\n int tot=nums[0];\n vector<int> cnt(tot+1);\n for(int x:nums)\n cnt[x]++;\n for(int d=1;d<tot;d++)\n if(tot%d==0){\n int c=0;\n for(int i=d;i<tot;i+=d)\n c+=cnt[i];\n if((c+1)*d==tot)\n return c;\n }\n return 0;\n }\n};\n```\n### Python\n```\nclass Solution:\n def dfs(self, u):\n self.vis[u]=True\n for v in self.adj[u]:\n if not self.vis[v]:\n self.dfs(v)\n self.subsum[u]+=self.subsum[v]\n def componentValue(self, nums: List[int], edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n n=len(nums)\n self.adj=[list() for _ in range(n)]\n for u,v in edges:\n self.adj[u].append(v)\n self.adj[v].append(u)\n self.vis=[False]*n\n self.subsum=nums\n self.dfs(0)\n cnt=[0]*(max(self.subsum)+1)\n for s in self.subsum:\n cnt[s]+=1\n tot=self.subsum[0]\n for d in range(1,tot):\n if tot%d==0:\n c=0\n for i in range(d,tot,d):\n c+=cnt[i]\n if (c+1)*d==tot:\n return c\n return 0\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'C', 'Python']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
C++| DSU + Factorization | O(N*root(sum))
|
c-dsu-factorization-onrootsum-by-kumarab-792q
|
Hint: sum of all node values = (no. of component) * (value of component)\nThe problem is divided into two steps:\n1. find the value of component (say target). w
|
kumarabhi98
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-15T16:30:47.694763+00:00
|
2022-10-15T16:33:31.581807+00:00
| 626 | false |
`Hint: sum of all node values = (no. of component) * (value of component)`\nThe problem is divided into two steps:\n1. find the value of component (say **target**). we will check for possible values.\n1. check if there are possible partitions with the target value, if yes find no. of Max component. Max edges removed = (max no. of component -1)\n\n* To find the value of component, we will use the Factorization method and check for all of those values.\n* To check the no. of max partition, I have used DSU. Now a question arrises, what is the criteria for the union of nodes and check the **Value of a component**? To do this, first find all node with degree 1 and push into the queue. Now union all these node with its direct parent. But before this, first check that if the value of component is equal to the **target** value. if it is, then insert its parent to a *set* ( which will mark this compenent as lock ). Also, avoid the union operation with any of the nodes whose component is locked.\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int n;\n int find(vector<int>& nums,int i){\n if(nums[i]==-1) return i;\n else return nums[i] = find(nums,nums[i]);\n }\n void union_(vector<int>& nums,vector<int>& sum,int x,int y){\n int i = find(nums,x), j = find(nums,y);\n if(i==j) return;\n if(i<j) {nums[j] = i; sum[i]+=sum[j];}\n else {nums[i] = j; sum[j]+=sum[i];}\n }\n int dfs(vector<int>& val,vector<int> deg,vector<vector<int>>& nums,int target){\n queue<int> q;\n vector<int> dp(n+1,-1), sum(n+1,-1);\n for(int i = 0; i<n;++i) {\n sum[i] = val[i];\n if(deg[i]==1){\n q.push(i); deg[i] = 0;\n }\n }\n unordered_set<int> st;\n while(!q.empty()){\n int s = q.size();\n while(s--){\n int in = q.front(); q.pop();\n int pt = find(dp,in); bool is = 1;\n if(sum[pt]==target){ \n st.insert(find(dp,in)); is = 0;\n }\n if(sum[pt]>target) return 1;\n for(int i = 0; i<nums[in].size();++i){\n int j = nums[in][i];\n int p = find(dp,j);\n if(deg[j] && st.find(p)==st.end()){\n deg[j]--;\n if(is) union_(dp,sum,in,j);\n if(deg[j]==1) q.push(j);\n }\n }\n }\n }\n int re = 0;\n for(int i = 0; i<n;++i){\n if(dp[i]==-1){\n if(sum[i]==target) re++;\n else return 1;\n }\n }\n return re;\n }\n int componentValue(vector<int>& val, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n n = val.size();\n vector<int> deg(n+1,0);\n vector<vector<int>> nums(n+1);\n for(int i = 0; i<edges.size();++i){\n deg[edges[i][0]]++; deg[edges[i][1]]++;\n nums[edges[i][0]].push_back(edges[i][1]);\n nums[edges[i][1]].push_back(edges[i][0]);\n }\n int sum = 0,re = 0;\n for(int i = 0; i<n;++i) sum+=val[i];\n for(int i = 1;i*i<=sum;++i){\n if(sum%i==0){\n re = max(re,dfs(val,deg,nums,i)-1);\n re = max(re,dfs(val,deg,nums,sum/i)-1);\n }\n }\n return re;\n }\n};\n```\n***Comment for any queries. Upvote if it helps***
| 1 | 0 |
['C']
| 1 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
c++||DFS
|
cdfs-by-praveenkumarnew2019-oml0
|
int ans=0;\n int dfs(vector adj[],int sv,int p,vector& nums,int sum,int & f){\n int s=0;\n for(auto c:adj[sv]){\n if(c!=p){\n
|
praveenkumarnew2019
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-15T16:01:24.518030+00:00
|
2022-10-15T16:01:24.518085+00:00
| 242 | false |
int ans=0;\n int dfs(vector<int> adj[],int sv,int p,vector<int>& nums,int sum,int & f){\n int s=0;\n for(auto c:adj[sv]){\n if(c!=p){\n s+=dfs(adj,c,sv,nums,sum,f);\n \n }\n }\n if(s+nums[sv]==sum)return 0;\n else if(s+nums[sv]>sum){\n f=1;\n return 0;\n }\n return s+nums[sv];\n \n \n }\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n int n=nums.size();\n vector<int> adj[n];\n for(auto e:edges){\n adj[e[0]].push_back(e[1]);\n adj[e[1]].push_back(e[0]);\n }\n \n int sum=0;\n for(auto k:nums)sum+=k;\n for(int i=1;i<=sum;i++){\n if(sum%i==0)\n {\n int f=0;\n dfs(adj,0,0,nums,i,f);\n if(f==0) {\n return sum/i-1;\n }\n }\n \n }\n int f=0;\n dfs(adj,0,0,nums,6,f);\n if(f==0) {\n cout<<f<<" ";\n }\n return -1;\n \n }
| 1 | 1 |
['Depth-First Search']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Test2
|
test2-by-strotest-hbqo
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
StroTest
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-27T15:01:54.073069+00:00
|
2025-01-27T15:01:54.073069+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <numeric>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
int n = nums.size();
int total_sum = accumulate(nums.begin(), nums.end(), 0);
vector<int> divisors = getDivisors(total_sum);
vector<vector<int>> adj(n);
for (auto& e : edges) {
adj[e[0]].push_back(e[1]);
adj[e[1]].push_back(e[0]);
}
for (int k : divisors) {
int d = total_sum / k;
if (d == 0) continue;
if (isPossible(d, adj, nums, total_sum)) {
return k - 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
private:
vector<int> getDivisors(int S) {
vector<int> divisors;
for (int i = 1; i * i <= S; ++i) {
if (S % i == 0) {
divisors.push_back(i);
if (i != S / i) {
divisors.push_back(S / i);
}
}
}
sort(divisors.rbegin(), divisors.rend());
return divisors;
}
bool isPossible(int d, vector<vector<int>>& adj, vector<int>& nums, int total_sum) {
int count = 0;
int sum = dfs(0, -1, d, count, adj, nums);
return (sum == 0 && count == (total_sum / d));
}
int dfs(int node, int parent, int d, int& count, vector<vector<int>>& adj, vector<int>& nums) {
int sum = nums[node];
for (int child : adj[node]) {
if (child == parent) continue;
int child_sum = dfs(child, node, d, count, adj, nums);
if (child_sum == -1) {
return -1;
}
sum += child_sum;
if (sum > d) {
return -1;
}
}
if (sum == d) {
++count;
return 0;
}
return sum;
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Java Solution
|
java-solution-by-nishaanth2696-flxl
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
nishaanth2696
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-25T18:05:11.400737+00:00
|
2025-01-25T18:05:11.400737+00:00
| 5 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
// n = 5
// nums = [6,2,2,2,6]
// graph = [[1], [0,2,3], [1], [1,4], [3]]
// sum = 18
// k = 5 -> 4 -> 3
// 18%5 != 0 -> continue
// 18%4 != 0 -> continue
// 18%3 == 0 -> ans = helper(graph, 0, -1, 6, nums)
// helperSum = 6
public int componentValue(int[] nums, int[][] edges) {
int n = nums.length;
List<Integer>[] adjList = new ArrayList[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
adjList[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for (int[] edge: edges) {
adjList[edge[0]].add(edge[1]);
adjList[edge[1]].add(edge[0]);
}
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
sum = sum + nums[i];
}
for (int k = n; k > 0; k--) {
if (sum % k != 0) {
continue;
}
int ans = helper(adjList, 0, -1, sum / k, nums);
if (ans == 0) {
return k - 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
public int helper(List<Integer>[] adjList, int index, int prev, int target, int[] nums) {
if (adjList[index].size() == 1 && adjList[index].get(0) == prev) {
if(nums[index] > target) {
return -1;
}
if (nums[index] == target) {
return 0;
}
return nums[index];
}
int helperSum = nums[index];
for (int k: adjList[index]) {
if (k == prev) {
continue;
}
int ans = helper(adjList, k, index, target, nums);
if (ans == -1) {
return -1;
}
helperSum = helperSum + ans;
}
if (helperSum > target) {
return -1;
}
if (helperSum == target) {
return 0;
}
return helperSum;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
c++ solution
|
c-solution-by-dilipsuthar60-it6m
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<vector<int>>dp;\n int find(int node,vector<int>&nums,int &count,int req,int p=-1){\n int sum=nums[node];\n
|
dilipsuthar17
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-24T16:25:21.763985+00:00
|
2024-12-24T16:25:21.764015+00:00
| 2 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<vector<int>>dp;\n int find(int node,vector<int>&nums,int &count,int req,int p=-1){\n int sum=nums[node];\n for(auto &it:dp[node]){\n if(it!=p){\n sum+=find(it,nums,count,req,node);\n }\n }\n if(sum==req){\n count++;\n return 0;\n }\n return sum;\n }\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n int n=edges.size();\n dp=vector<vector<int>>(n+1);\n for(auto &it:edges){\n dp[it[0]].push_back(it[1]);\n dp[it[1]].push_back(it[0]);\n }\n int sum=accumulate(nums.begin(),nums.end(),0);\n int ans=0;\n for(int i=1;i*i<=sum;i++){\n if(sum%i==0){\n int count=0;\n find(0,nums,count,sum/i);\n if(count==i){\n ans=max(ans,i-1);\n }\n count=0;\n find(0,nums,count,i);\n if(count==sum/i){\n ans=max(ans,sum/i-1);\n }\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C', 'C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
C++ 23 solution
|
c-23-solution-by-cookie55-vluv
|
IntuitionFocus on the subtree, how can we determine valid subtrees?
Comparing the subtree sum to a specific valid value was paramount. It was trivial to see tha
|
COOKIE55
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-26T05:48:25.007616+00:00
|
2024-12-26T05:48:25.007616+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
Focus on the subtree, how can we determine valid subtrees?
Comparing the subtree sum to a specific valid value was paramount. It was trivial to see that (number of splits + 1) * component_value = total sum of all the nodes. Using that logic, we have to determine a valid componentValue. So we check that each subtree equals componentValue
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
Explained above
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
$$O(ND)$$, D for divisors, n for number of elements in tree.
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(D + )
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
// Function to find all divisors of a number in ascending order
vector<long long> findDivisors(long long n) {
vector<long long> divisors;
for(long long i = 1; i < sqrt(n); ++i){
if(n % i == 0){
divisors.push_back(i);
if(n / i != i){
divisors.push_back(n / i);
}
}
}
sort(divisors.begin(), divisors.end());
return divisors;
}
// Recursive DFS to calculate subtree sums and count valid splits
long long dfs(int node, int parent, int divisor, const vector<vector<int>> &adj_list, const vector<int> &nums, int &count) {
long long current_sum = nums[node];
for(auto &neighbor : adj_list[node]){
if(neighbor != parent){
current_sum += dfs(neighbor, node, divisor, adj_list, nums, count);
}
}
if(current_sum == divisor){
count++;
return 0; // Reset sum after a valid split
}
return current_sum;
}
int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
int n = nums.size();
// Step 1: Build the adjacency list
vector<vector<int>> adj_list(n, vector<int>());
for(auto &edge : edges){
int a = edge[0];
int b = edge[1];
adj_list[a].push_back(b);
adj_list[b].push_back(a);
}
// Step 2: Calculate the total sum
long long total_sum = 0;
for(auto &num : nums){
total_sum += num;
}
// Step 3: Find all divisors of the total sum
vector<long long> divisors = findDivisors(total_sum);
// Remove the total_sum itself as we cannot split the entire tree
divisors.pop_back();
// Step 4: Iterate over divisors in ascending order to maximize splits
// Alternatively, sort in descending order to find the first valid k quickly
sort(divisors.begin(), divisors.end(), [&](const long long &a, const long long &b) -> bool {
return a < b; // Ascending order for maximizing splits
});
int max_splits = 0;
for(auto it = divisors.begin(); it != divisors.end(); ++it){
long long d = *it;
// The number of components we need
int k = total_sum / d;
int count = 0;
// Perform DFS to check if we can split the tree into k components with sum d
dfs(0, -1, d, adj_list, nums, count);
if(count == k){
max_splits = max(max_splits, count - 1);
}
}
return max_splits;
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
DFS Solution
|
dfs-solution-by-emin-35-5q7w
|
IntuitionThe problem requires dividing the tree into components of equal value by removing edges. Initially, the solution can be thought of as exploring potenti
|
Emin-35
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-21T18:42:17.513225+00:00
|
2024-12-21T18:42:17.513225+00:00
| 8 | false |
# Intuition
The problem requires dividing the tree into components of equal value by removing edges. Initially, the solution can be thought of as exploring potential "component values" (sum of values in each component) and checking if the tree can be split accordingly. This approach stems from the observation that the total sum of all node values must be divisible by the desired component value.
# Approach
1. **Graph Representation**: Represent the tree as an adjacency list for easy traversal.
2. **Sum and Divisors**: Calculate the total sum of node values. Iterate through all possible divisors of this total sum as potential "component values."
3. **DFS Validation**: Use Depth-First Search (DFS) to determine if the tree can be split into components where the sum of each component equals the target value.
- If a subtree forms a valid component, return `0` for that branch, indicating that the component is complete.
- If a subtree's sum exceeds the target, the current configuration is invalid.
4. **Result Calculation**: For each valid "component value," calculate the number of edges removed (`total_sum // target - 1`), which represents the maximum number of components.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
- Constructing the adjacency list takes $$O(n)$$.
- Testing all divisors of `total_sum` involves a loop over potential divisors (approximately $$O(\sqrt {{total\_sum}})$$) with a DFS call for each divisor. Each DFS traversal is $$O(n)$$.
- Overall complexity: $$O(n \times \sqrt {\text{total\_sum}})$$.
- Space complexity:
- The adjacency list uses $$O(n)$$ space.
- The recursion stack for DFS can go up to $$O(n)$$.
- Overall complexity: $$O(n)$$.
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def componentValue(self, nums: List[int], edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:
if len(nums) == 1:
return 0
adj_list = defaultdict(list)
for i, j in edges:
adj_list[i].append(j)
adj_list[j].append(i)
total_sum = sum(nums)
# Helper function to perform DFS and check if the tree can be split with `target` as the component value
def dfs(curr, parent, target):
total = nums[curr]
for child in adj_list[curr]:
if child != parent:
subtree_sum = dfs(child, curr, target)
# If the subtree can't form a valid component, return a large number to indicate failure
if subtree_sum == -1:
return -1
total += subtree_sum
# If this subtree forms a valid component, "cut" it and return 0
if total == target:
return 0
# Otherwise, return the current total for further propagation
return total if total < target else -1
# Try all possible component values (divisors of total_sum)
for target in range(1, total_sum + 1):
if total_sum % target == 0:
# Try to partition the tree with this target value
if dfs(0, -1, target) == 0:
# If successful, calculate the number of edges removed
return total_sum // target - 1
return 0
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
EASY JAVA DFS Solution
|
easy-java-dfs-solution-by-debrup7703-4guo
|
Code
|
Debrup7703
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-21T10:22:45.093594+00:00
|
2024-12-21T10:22:45.093594+00:00
| 9 | false |
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
int res=0;
public int dfs(List<List<Integer>> adj,int node,int vis[],int k,int[] nums,int s){
vis[node]=1;
int sum=nums[node];
for(int j:adj.get(node)){
if(vis[j]==1) continue;
sum+=dfs(adj,j,vis,k,nums,s);
}
if(sum==k && (s-sum)%k==0){
res++;
return 0;
}
return sum;
}
public int componentValue(int[] nums, int[][] edges) {
List<List<Integer>> adj=new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
int n=nums.length;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) adj.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
for(int[] i:edges){
adj.get(i[0]).add(i[1]);
adj.get(i[1]).add(i[0]);
}
int sum=0;
int min=Integer.MAX_VALUE,max=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for(int i:nums) {
max=Math.max(max,i);
min=Math.min(i,min);
sum+=i;
}
int ans=-1;
for(int i=max;i<=sum;i++){
if(sum%i!=0) continue;
res=0;
int vis[]=new int[n];
int x=dfs(adj,0,vis,i,nums,sum);
if(x!=0) continue;
ans=Math.max(ans,res);
}
return ans-1;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Tree', 'Java']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Intuitive understandable code || java
|
intuitive-understandable-code-java-by-el-uqrv
|
IntuitionIn this problem, we want to split a tree into multiple connected components such that each component has the same sum of node values. To do this, we fi
|
ElhombreShivamIsHere
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-21T09:59:20.455199+00:00
|
2024-12-21T09:59:20.455199+00:00
| 7 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
In this problem, we want to split a tree into multiple connected components such that each component has the same sum of node values. To do this, we first calculate the total sum of all the node values. We then check all possible ways to divide this sum by trying different divisors, which represent the target sum for each component. For each divisor, we use Depth-First Search (DFS) to explore if it's possible to split the tree into parts where each part's sum matches the target value. If we find a valid way to split, we count how many edges we can remove to create these components. The goal is to maximize the number of edges we can remove while still forming components with equal sums.
You can check for reference the question [https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-number-of-k-divisible-components/description/?envType=daily-question&envId=2024-12-21](2872). Its very similar to this question.
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
int[] nums;
public int componentValue(int[] nums, int[][] edges) {
int n = nums.length;
this.nums = nums;
List<Integer>[] graph = new ArrayList[n];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for(int[] e : edges) {
graph[e[0]].add(e[1]);
graph[e[1]].add(e[0]);
}
int sum = 0;
for(int i : nums) {
sum += i;
}
for(int k=n; k>0; k--) {
if(sum % k != 0) continue;
int ans = helper(graph, 0, -1, sum / k);
if(ans == 0) return k-1;
}
return 0;
}
private int helper(List<Integer>[] graph, int i, int prev, int target) {
if(graph[i].size() == 1 && graph[i].get(0) == prev) {
if(nums[i] > target) return -1;
if(nums[i] == target) return 0;
return nums[i];
}
int sum = nums[i];
for(int k : graph[i]) {
if(k == prev) continue;
int ans = helper(graph, k, i, target);
if(ans == -1) return -1;
sum += ans;
}
if(sum > target) return -1;
if(sum == target) return 0;
return sum;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Simple DFS
|
simple-dfs-by-mbhagyesh07-hx41
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
mbhagyesh07
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-21T05:46:18.583337+00:00
|
2024-12-21T05:46:18.583337+00:00
| 15 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
DFS
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int ans=0;
int dfs(int i,vector<int>adj[],vector<int>&v,vector<int>&nums,int k)
{
v[i]=1;
int s=nums[i];
for(auto it:adj[i])
{
if(!v[it])
{
s+=dfs(it,adj,v,nums,k);
}
}
if(s==k)
{
ans++;
return 0;
}
return s;
}
int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& e) {
if(e.size()==0) return 0;
const int n=nums.size();
vector<int>adj[n];
for(int i=0;i<e.size();i++)
{
adj[e[i][0]].push_back(e[i][1]);
adj[e[i][1]].push_back(e[i][0]);
}
int k=-1e9;
int s=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
s+=nums[i];
k=max(k,nums[i]);
}
vector<int>fac;
for(int i=1;i*i<=s;i++)
{
if(s%i==0)
{
fac.push_back(i);
if(s/i!=i) fac.push_back(s/i);
}
}
sort(fac.begin(),fac.end());
for(int i=0;i<fac.size();i++)
{
if(fac[i]>=k)
{
ans=0;
vector<int>v(n,0);
dfs(0,adj,v,nums,fac[i]);
if(ans>0 && ans*fac[i]==s)
{
return ans-1;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
python3 DFS
|
python3-dfs-by-maxorgus-dhee
| null |
MaxOrgus
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-11T03:12:59.467792+00:00
|
2024-12-11T03:12:59.467792+00:00
| 12 | false |
possible component sums should be a factor of the total sum and larger than the biggest element in M, as well as a possible subtree sum.\n\ntry every component sum satisfying these conditions.\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def componentValue(self, nums: List[int], edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n N = len(nums)\n m = min(nums)\n M = max(nums)\n graph = {i:set([]) for i in range(N)}\n for u,v in edges:\n graph[u].add(v)\n graph[v].add(u)\n S = sum(nums)\n factors = set([])\n for i in range(1,int(sqrt(S))+2):\n if S % i == 0:\n if i>=M:factors.add(i)\n if S // i >= M: factors.add(S//i)\n self.subtreesum = [0]*N\n @cache\n def dfs(node,parent):\n res = nums[node]\n for child in graph[node]:\n if child == parent:\n continue\n res += dfs(child,node)\n self.subtreesum[node] = res\n return res\n dfs(0,-1)\n Sums = set(self.subtreesum)\n factors = factors&Sums\n self.reses = {f:0 for f in factors}\n @cache\n def dfs2(node,parent,f):\n currs = nums[node]\n for child in graph[node]:\n if child == parent:continue\n currs += dfs2(child,node,f)\n if currs == f:\n currs = 0\n self.reses[f]+=1\n if node == 0 and currs!=0: self.reses[f] = 0\n return currs\n for f in factors:\n dfs2(0,-1,f)\n return max(self.reses[a] for a in self.reses)-1\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n \n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Python3']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Implementation
|
implementation-by-nanoray22-dev-6ejq
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nThe problem requires splitting a tree into connected components such that each componen
|
Nanoray22-dev
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-28T16:29:20.007338+00:00
|
2024-11-28T16:29:20.007368+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThe problem requires splitting a tree into connected components such that each component has the same sum of node values. Since the structure is a tree, we know there are \uD835\uDC5B \u2212 1 edges, and removing edges creates separate components.\n\nThe key insight is that the target sum for each component must be a divisor of the total sum of node values (\uD835\uDC46). By iterating over the divisors of \uD835\uDC46\n\nS, we can test if it\'s possible to divide the tree into components with the target sum.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nCalculate the Total Sum:\n\nCompute \uD835\uDC46 the total sum of all node values.\nDetermine all divisors of \uD835\uDC46, as only these divisors can be possible values for the target sum of each component.\n\n- Check for Valid Divisors:\n\nFor each divisor k, calculate targetSum = \uD835\uDC46/\uD835\uDC58\n\nVerify if it\'s feasible to split the tree into \uD835\uDC58 components with a sum of targetSum.\n\n- DFS for Validation:\n\nPerform a depth-first search (DFS) to calculate the sum of nodes in each subtree.\n\nIf a subtree\'s sum equals targetSum, it is considered a valid component, and the DFS continues for the rest of the tree.\n\nIf a subtree\u2019s sum exceeds targetSum, the divisor \uD835\uDC58 is invalid, and we try the next divisor.\n\n- Result:\n\nThe maximum \uD835\uDC58\u22121 for which the tree can be divided is the maximum number of edges that can be removed.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```csharp []\npublic class Solution \n{\n private int[] nums;\n\n public int ComponentValue(int[] nums, int[][] edges) \n {\n int n = nums.Length;\n this.nums = nums;\n\n var graph = new List<int>[n];\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n graph[i] = new List<int>();\n }\n foreach (var edge in edges) {\n graph[edge[0]].Add(edge[1]);\n graph[edge[1]].Add(edge[0]);\n }\n\n int sum = nums.Sum();\n\n for (int k = n; k > 0; k--) {\n if (sum % k != 0) continue;\n int target = sum / k;\n\n if (Helper(graph, 0, -1, target) == 0) {\n return k - 1; \n }\n }\n\n return 0;\n }\n\n private int Helper(List<int>[] graph, int node, int parent, int target) {\n // Caso base: nodo hoja\n if (graph[node].Count == 1 && graph[node][0] == parent) {\n if (nums[node] > target) return -1;\n return nums[node] == target ? 0 : nums[node];\n }\n\n int sum = nums[node];\n foreach (int neighbor in graph[node]) {\n if (neighbor == parent) continue;\n int result = Helper(graph, neighbor, node, target);\n if (result == -1) return -1;\n sum += result;\n }\n\n // Validar la suma obtenida\n if (sum > target) return -1;\n return sum == target ? 0 : sum;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C#']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Python (Simple DFS)
|
python-simple-dfs-by-rnotappl-33ep
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
rnotappl
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-28T09:06:27.453892+00:00
|
2024-10-28T09:28:19.968942+00:00
| 6 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def componentValue(self, nums, edges):\n n, total, max_val, min_val, graph = len(nums), sum(nums), max(nums), min(nums), defaultdict(list)\n\n for i,j in edges:\n graph[i].append(j)\n graph[j].append(i)\n\n dict1 = defaultdict(int)\n\n def function(node,parent):\n result = nums[node]\n\n for neighbor in graph[node]:\n if neighbor != parent:\n result += function(neighbor,node)\n\n dict1[result] += 1 \n\n return result\n\n function(0,-1)\n\n for target in range(max_val,total):\n count = 0\n if total%target == 0:\n for key,val in dict1.items():\n if key%target == 0:\n count += val \n if count == total//target:\n return total//target - 1 \n\n return 0\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
dfs + factorization
|
dfs-factorization-by-amit_shinde-p16q
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
amit_shinde
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-16T20:14:35.196422+00:00
|
2024-10-16T20:14:35.196446+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int comp ;\n map<int ,vector<int>>mp ;\n int dfs(int node, int tar, int par, vector<int>& nums) {\n // cout<<node<<endl;\n int sum = nums[node];\n for (auto it : mp[node]) {\n if (it != par) {\n sum += dfs(it, tar, node, nums);\n }\n }\n if (sum == tar) {\n comp--; \n return 0; \n }\n return sum;\n }\n\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n int sum = 0 ;\n for(int i : nums) sum += i ;\n int t = sqrt(sum) ;\n int op = 0 ;\n \n for (auto& it : edges) {\n \n mp[it[0]].push_back(it[1]);\n mp[it[1]].push_back(it[0]);\n }\n\n for (int i = 1 ; i <= t ; i++){\n if(sum%i == 0){\n int a = sum/i ;\n int b = i ;\n comp = sum/a ;\n // cout<<a<<endl;\n \n int ans = dfs(0 , a , -1 , nums ) ;\n // cout<<comp<<endl;\n if(comp == 0){\n op = max(op , (sum/a) - 1 ) ;\n }\n comp = sum/b ;\n ans = dfs(0 , b , - 1 , nums) ;\n if(comp == 0 ){\n op = max(op , (sum/b) - 1) ;\n }\n // cout<<a<<" "<<b<<endl;\n }\n }\n return op ;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Easy Dfs Solution
|
easy-dfs-solution-by-kvivekcodes-z3ie
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
kvivekcodes
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-15T06:48:20.070336+00:00
|
2024-10-15T06:48:20.070376+00:00
| 9 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int cnt_ans;\n int dfs(int ver, int par, int cnt, vector<vector<int>>& g, vector<int>& nums){\n\n int sum = nums[ver];\n for(auto child: g[ver]){\n if(child == par) continue;\n int child_sum = dfs(child, ver, cnt, g, nums);\n if(child_sum > cnt) return 1e6;\n if(child_sum == cnt){\n cnt_ans++;\n }\n else sum += child_sum;\n }\n if(sum > cnt) return 1e6;\n return sum;\n }\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n int n = nums.size();\n vector<vector<int> > g(n);\n for(auto it: edges){\n g[it[0]].push_back(it[1]);\n g[it[1]].push_back(it[0]);\n }\n\n int sum = 0;\n for(auto it: nums) sum += it;\n\n vector<int> facs;\n for(int i = 1; i <= sum; i++){\n if(sum % i == 0) facs.push_back(i);\n }\n\n\n int ans = 0;\n for(auto it: facs){\n cnt_ans = 0;\n if(dfs(0, -1, it, g, nums) != it) continue;\n ans = max(ans, cnt_ans);\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Tree', 'Depth-First Search', 'C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
DFS | Partition by factors
|
dfs-partition-by-factors-by-wayne02-spsy
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Wayne02
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-15T23:46:59.622904+00:00
|
2024-09-15T23:46:59.622921+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(Nlog(N))\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:O(N*N)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int n ; \n vector <vector <int>> g ; \n int cnt = 0 ;\n\n int dfs(int node , int par , int tar , vector <int> &arr){\n int sum = arr[node] ; \n for(int i = 0; i < (int)g[node].size() ; i++){\n if(par == g[node][i]) continue ; \n sum += dfs(g[node][i] , node , tar , arr) ; \n }\n if(sum == tar){\n cnt ++ ; \n return 0 ; \n }\n return sum ; \n }\n\n\n\n\n int componentValue(vector<int>& arr, vector<vector<int>>& e) {\n n = (int)arr.size() ; \n int sum = 0 ; \n g.resize(n) ; \n for(int i =0 ; i < n ; i++){\n sum += arr[i] ; \n } \n vector <int> fac ; \n for(int i =1 ;i*i <= sum ; i++){\n if(sum%i == 0){\n fac.push_back(i) ; \n if(i*i != sum){\n fac.push_back(sum/i) ; \n }\n }\n }\n sort(fac.begin() , fac.end()) ;\n\n for(int i =0 ; i < (int)e.size() ; i++){\n int u = e[i][0] ; \n int v = e[i][1] ; \n g[u].push_back(v) ; \n g[v].push_back(u) ; \n } \n\n int ans = 0 ; \n for(int i =0 ;i < (int)fac.size() ; i++){\n cnt = 0 ; \n int x = dfs(0 , -1 , fac[i] , arr) ;\n if(x == 0){\n ans = max(ans , cnt ) ; \n } \n }\n return ans-1 ; \n\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Normal DFS approach, but with prime factorization to minimize search space, Clean code
|
normal-dfs-approach-but-with-prime-facto-5haa
|
Intuition\nThe main two insights here is that you need to root the tree at a given node, and that whatever sum each group of nodes have, it needs to be able to
|
teodor_spaeren
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-31T11:59:19.983823+00:00
|
2024-07-31T11:59:19.983854+00:00
| 10 | false |
# Intuition\nThe main two insights here is that you need to root the tree at a given node, and that whatever sum each group of nodes have, it needs to be able to divide the sum of all nodes.\n\n# Approach\n\nMy approach is fairly standard, the only difference is that I figure out the prime factors of the sum, and using them, I only search for valid divisors of the given number. In practice this is not much faster, but it does cut down the search space by a lot.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: I don\'t know\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: I don\'t know\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\ninline const auto optimize = []() {\n std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);\n std::cin.tie(nullptr);\n std::cout.tie(nullptr);\n return 0;\n}();\n\nclass Solution {\n\n using GRAPH = std::vector<std::vector<int>>;\n\n static constexpr int dfs(const GRAPH& G, const std::vector<int>& nums,\n const int target, const int parent,\n const int cur) {\n std::int64_t sum = nums[cur];\n\n for (const auto next : G[cur]) {\n if (next == parent)\n continue;\n\n sum += dfs(G, nums, target, cur, next);\n if (target < sum)\n return std::numeric_limits<int>::max();\n }\n\n return (sum == target) ? 0 : sum;\n }\n\n static constexpr int tryAllPrimes(const int numSum, const GRAPH& G,\n const std::vector<int>& nums,\n const std::vector<std::pair<int, int>>& primes,\n const int soFar, const int curIdx) {\n if (curIdx == -1) {\n const int target = numSum / soFar;\n if (dfs(G, nums, target, -1, 0) == 0)\n return soFar - 1;\n else\n return 0;\n }\n\n const auto [prime, cnt] = primes[curIdx];\n int cur = soFar;\n for (int i = 0; i <= cnt; i++) {\n const int res =\n tryAllPrimes(numSum, G, nums, primes, cur, curIdx - 1);\n if (0 < res) {\n return res;\n }\n\n cur /= prime;\n }\n\n return 0;\n }\n\npublic:\n static constexpr int\n componentValue(const std::vector<int>& nums,\n const std::vector<std::vector<int>>& edges) {\n const int N = nums.size();\n const int numSum = std::reduce(nums.begin(), nums.end(), 0);\n\n GRAPH G(N);\n for (const auto& edge : edges) {\n const auto a = edge[0];\n const auto b = edge[1];\n G[a].push_back(b);\n G[b].push_back(a);\n }\n\n auto primes = primeFactor(N, numSum);\n\n return tryAllPrimes(numSum, G, nums, primes, numSum, primes.size()-1);\n }\n\nprivate:\n static constexpr std::vector<std::pair<int, int>>\n primeFactor(const int N, const int target) {\n // Let\'s get all the primes up to N, which is the maximum number of\n // parts we can split it into\n const int maxPrime = static_cast<int>(std::sqrt(N)) + 1;\n\n // The max prime we want to test is N\n // because primes above that, is not interesting to us.\n\n std::vector<unsigned char> isComp(maxPrime + 1);\n std::vector<std::pair<int, int>> primes;\n\n int curTarget = target;\n for (int i = 2; i <= maxPrime; i++) {\n if (isComp[i])\n continue;\n\n if (curTarget < i) {\n break;\n }\n\n int times = 0;\n while (i <= curTarget && (curTarget % i == 0)) {\n times++;\n curTarget /= i;\n }\n if (0 < times) {\n primes.emplace_back(i, times);\n }\n\n for (int j = i + i; j <= maxPrime; j += i) {\n isComp[j] = true;\n }\n }\n\n if (1 < curTarget) {\n primes.emplace_back(curTarget, 1);\n }\n\n return primes;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Math', 'Tree', 'Depth-First Search', 'Graph', 'Number Theory', 'C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Python (Simple DFS)
|
python-simple-dfs-by-rnotappl-pjl7
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
rnotappl
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-15T12:16:13.418244+00:00
|
2024-07-15T12:16:13.418268+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def componentValue(self, nums, edges):\n if not edges:\n return 0\n\n n, dict1, result = len(nums), defaultdict(list), sum(nums)\n\n for i,j in edges:\n dict1[i].append(j)\n dict1[j].append(i)\n\n def function(node,parent,i):\n total = nums[node]\n\n for neighbor in dict1[node]:\n if neighbor != parent:\n total += function(neighbor,node,i)\n\n return total if total != i else 0\n\n for i in range(max(nums),result//min(nums)):\n if result%i == 0 and function(0,-1,i) == 0:\n return result//i - 1\n\n return 0\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
JAVA SOLUTION
|
java-solution-by-danish_jamil-mt1s
|
Intuition\n\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Tim
|
Danish_Jamil
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-10T06:27:42.708282+00:00
|
2024-07-10T06:27:42.708316+00:00
| 8 | false |
# Intuition\n\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n int[] nums;\n public int componentValue(int[] nums, int[][] edges) {\n int n = nums.length;\n this.nums = nums;\n List<Integer>[] graph = new ArrayList[n];\n for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {\n graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();\n }\n for(int[] e : edges) {\n graph[e[0]].add(e[1]);\n graph[e[1]].add(e[0]);\n }\n \n int sum = 0;\n for(int i : nums) {\n sum += i;\n }\n \n for(int k=n; k>0; k--) {\n if(sum % k != 0) continue;\n int ans = helper(graph, 0, -1, sum / k);\n if(ans == 0) return k-1;\n }\n return 0;\n }\n \n private int helper(List<Integer>[] graph, int i, int prev, int target) {\n if(graph[i].size() == 1 && graph[i].get(0) == prev) {\n if(nums[i] > target) return -1;\n if(nums[i] == target) return 0;\n return nums[i];\n }\n \n int sum = nums[i];\n for(int k : graph[i]) {\n if(k == prev) continue;\n int ans = helper(graph, k, i, target);\n if(ans == -1) return -1;\n sum += ans;\n }\n \n if(sum > target) return -1;\n if(sum == target) return 0;\n return sum;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Easy DFS + Math || C++
|
easy-dfs-math-c-by-atma-627j
|
Intuition\nLet\'s say each component has value x. It may be possible to make such component only when sum of all nodes is divisible by x. Given the constraints,
|
Atma_
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-04T05:48:30.369434+00:00
|
2024-07-04T05:48:30.369469+00:00
| 8 | false |
# Intuition\nLet\'s say each component has value x. It may be possible to make such component only when sum of all nodes is divisible by x. Given the constraints, total sum of all nodes <= 1e6. Number of divisors of a number n are approximately \u221Bn, which means n\u221B1e6 should pass here. So just iterate over all divisors and try to divide tree into components with value equal to that divisor.\n\n# Approach\nWe will iterate over all divisors of total sum of all nodes (sum), and then do dfs to try dividing tree into components with value equal to that divisor. Whenever we get value of a subtree equal to divisor, we disconnect it with it\'s parent (remove one edge).\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n\u221B(sum))\n\n- Space complexity: O(n)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n int dfs(int node, int parent, vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& graph, int& remedges, int i){\n int cur=0;\n for(auto& g:graph[node]){\n if(g==parent) continue;\n cur+=dfs(g,node,nums,graph,remedges,i);\n }\n cur+=nums[node];\n if(cur==i){\n cur=0;\n remedges++;\n }\n return cur;\n }\n \n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n int n=nums.size();\n vector<vector<int>> graph(n);\n for(auto& e:edges){\n graph[e[0]].push_back(e[1]);\n graph[e[1]].push_back(e[0]);\n }\n int ans=0,total=accumulate(nums.begin(),nums.end(),0),\n mini=*min_element(nums.begin(),nums.end());\n for(int i=mini;i<=total/2;++i){\n if(total%i==0){\n int remedges=0;\n if(dfs(0,-1,nums,graph,remedges,i)==0){\n ans=max(ans,remedges-1);\n }\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Array', 'Math', 'Tree', 'Depth-First Search', 'Enumeration', 'C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Easy java DFS
|
easy-java-dfs-by-gadepalli_keerthana-8j94
|
\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\n public int componentValue(int[] nums, int[][] edges) {\n Map<Integer, Set<Integer>> graph = new HashMap();\n int
|
gadepalli_keerthana
|
NORMAL
|
2024-06-22T09:23:12.264783+00:00
|
2024-06-22T09:23:12.264811+00:00
| 5 | false |
\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int componentValue(int[] nums, int[][] edges) {\n Map<Integer, Set<Integer>> graph = new HashMap();\n int sum = 0;\n int maxValue = 0;\n for(int index = 0; index < nums.length; index += 1) {\n sum += nums[index];\n maxValue = Math.max(maxValue, nums[index]);\n }\n for(int index = 0; index < edges.length; index += 1) {\n int u = edges[index][0];\n int v = edges[index][1];\n Set<Integer> children1 = graph.getOrDefault(u, new HashSet());\n children1.add(v);\n graph.put(u, children1);\n\n Set<Integer> children2 = graph.getOrDefault(v, new HashSet());\n children2.add(u);\n graph.put(v, children2);\n }\n int ans = 0;\n int n = nums.length;\n int maxCount = sum / maxValue;\n for(int index = maxCount; index > 1 ; index -= 1) {\n if(sum % index == 0) {\n boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];\n int ans2 = isPossible(graph, sum/index, 0, nums, visited);\n if(ans2 == 0) {\n return (index - 1);\n }\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n private int isPossible(Map<Integer, Set<Integer>> graph, int targetSum, int start, int[] nums, boolean[] visited) {\n \n if(nums[start] > targetSum) return nums[start];\n visited[start] = true;\n Set<Integer> children = graph.getOrDefault(start, new HashSet());\n int childSum = nums[start];\n for(Integer child: children) {\n if(!visited[child]) {\n int tempAns = isPossible(graph, targetSum, child, nums, visited);\n childSum += tempAns;\n }\n } \n if(childSum == targetSum) {\n return 0;\n }\n return childSum;\n }\n\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Py/Rust DFS and try all divisors with detailed explanation
|
pyrust-dfs-and-try-all-divisors-with-det-6dhh
|
Intuition\n\nFirst you can find the sum of all values in the tree and lets assume it is s, then potentially you can try to split a tree into every divisor of s.
|
salvadordali
|
NORMAL
|
2024-06-21T20:50:29.392269+00:00
|
2024-06-21T20:50:29.392293+00:00
| 0 | false |
# Intuition\n\nFirst you can find the sum of all values in the tree and lets assume it is `s`, then potentially you can try to split a tree into every divisor of `s`. If this divisor is `d` and you can divide into them, then the number of cuts will be `s / d - 1`. So you try from the smallest divisor to the latest one and if you can divide, return that number of cuts.\n\nNow the question is narrowed down to: You have a tree and whether it is possible to cut it into chunks where each of them has sum of nodes equal to `d`. There are might be multiple approaches to do it, but an easy approach is to use DFS.\n\nIn dfs you need to keep track your current node, your previous node (to not run dfs on nodes you already ran) and sum you need to achieve. And inside of it you maintain your own sum. If the sum becomes equal to divisor, we can make a cut and the sum becomes zero. \n\nIn the end if the sum is not equal to 0, it means you can\'t divide them into chunks. One improvement you can do is do short-cirquit if sum becomes > divisor (I do not do it, but this can trim fast).\n\n# Complexity\n\nLet $k$ be the number of divisors of the sum. Based on my understanding [from this page](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Divisor_function) on average it grows roughly logarithmic. As the sum is bounded by 50 * n, the complexity will not be high.\n\n- Time complexity: $O(n \\cdot k)$\n- Space complexity: $O(n)$\n\n# Code\n```Python []\nclass Solution:\n\n def componentValue(self, nums: List[int], edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n def dfs(node_curr, node_prev, num):\n res = nums[node_curr]\n\n for node_next in tree[node_curr]:\n if node_prev == node_next:\n continue\n\n res += dfs(node_next, node_curr, num)\n\n return res if res != num else 0\n\n tree, s = [[] for _ in range(len(edges) + 1)], sum(nums)\n for v1, v2 in edges:\n tree[v1].append(v2)\n tree[v2].append(v1)\n\n for i in range(1, s + 1):\n if s % i == 0 and dfs(0, -1, i) == 0:\n return s // i - 1\n\n return 0\n```\n```Rust []\nimpl Solution {\n\n fn dfs(tree: &Vec<Vec<usize>>, nums: &Vec<i32>, node_curr: usize, node_prev: usize, s: i32) -> i32 {\n let mut res = nums[node_curr];\n for i in 0 .. tree[node_curr].len() {\n let node_next = tree[node_curr][i];\n if node_next == node_prev {\n continue;\n }\n\n res += Self::dfs(tree, nums, node_next, node_curr, s);\n }\n\n if res == s {\n return 0;\n }\n return res;\n }\n\n pub fn component_value(nums: Vec<i32>, edges: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {\n let s = nums.iter().sum::<i32>();\n let mut tree = vec![Vec::new(); nums.len() + 1];\n for e in edges {\n tree[e[0] as usize].push(e[1] as usize);\n tree[e[1] as usize].push(e[0] as usize);\n }\n\n for i in 1 ..= s {\n if s % i == 0 && Self::dfs(&tree, &nums, 0, usize::MAX, i) == 0 {\n return s / i - 1;\n }\n }\n\n return 0;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python', 'Rust']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
C++ code using DFS
|
c-code-using-dfs-by-sting285-u9bm
|
Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n pair<int, int>solve(vector<int>adj[], int par, int node, vector<int>&nums, int value){\n pair<int, int>res;\n\n
|
Sting285
|
NORMAL
|
2024-06-17T09:57:25.864557+00:00
|
2024-06-17T09:57:25.864586+00:00
| 6 | false |
# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n pair<int, int>solve(vector<int>adj[], int par, int node, vector<int>&nums, int value){\n pair<int, int>res;\n\n int val1 = nums[node], val2 = 0;\n\n for(auto it: adj[node]){\n if(it == par)\n continue;\n auto temp = solve(adj, node, it, nums, value);\n\n if(temp.first == -1){\n return {-1, -1};\n }\n\n val1+=temp.first;\n val2+=temp.second;\n }\n\n if(val1 > value){\n return {-1, -1};\n }\n\n if(val1 == value){\n return {0, val2+1};\n }\n\n return {val1, val2};\n }\n\n bool isPossible(vector<int>adj[], int root, vector<int>&nums, int countComp, int value){\n auto temp = solve(adj, -1, 0, nums, value);\n if(temp.second == countComp && temp.first == 0)\n return true;\n \n return false;\n }\n\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n int sum = 0, maxi = 0;\n for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){\n maxi = max(maxi, nums[i]);\n sum+=nums[i];\n }\n\n vector<int>values;\n for(int i=sum/maxi;i>=1;i--){\n if(sum%i == 0)\n values.push_back(i);\n }\n\n int n = nums.size();\n vector<int>adj[n];\n\n for(auto it: edges){\n adj[it[0]].push_back(it[1]);\n adj[it[1]].push_back(it[0]);\n }\n\n for(int i=0;i<values.size();i++){\n if(isPossible(adj, 0, nums, values[i], sum/values[i]))\n return values[i] - 1;\n }\n\n return 0;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Graph', 'C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
C++ Simple DP Solution
|
c-simple-dp-solution-by-rj_9999-kv5b
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
rj_9999
|
NORMAL
|
2024-05-25T02:14:36.666551+00:00
|
2024-05-25T02:14:36.666578+00:00
| 5 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\nvoid dfs(int curr_node,vector<int>edg[],int par,vector<int>&sub_sum,vector<int>&nums){\n sub_sum[curr_node]=nums[curr_node];\n for(int i=0;i<edg[curr_node].size();i++){\n if(edg[curr_node][i]!=par){\n dfs(edg[curr_node][i],edg,curr_node,sub_sum,nums);\n sub_sum[curr_node]=sub_sum[curr_node]+sub_sum[edg[curr_node][i]];\n }\n }\n}\nint dfs2(int curr_node,vector<int>edg[],int par,vector<int>&sub_sum,int &s){\n int curr=sub_sum[curr_node];\n int cmp=0;\n if(curr==s){\n return 1;\n }\n for(int i=0;i<edg[curr_node].size();i++){\n if(edg[curr_node][i]!=par){\n cmp=cmp+dfs2(edg[curr_node][i],edg,curr_node,sub_sum,s);\n }\n }\n curr=sub_sum[curr_node]-cmp*s;\n if(curr==s){\n cmp=cmp+1;\n return cmp;\n }\n return cmp;\n}\n\n\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n if(edges.size()==0)return 0;\n vector<int>sub_sum(nums.size(),0);\n int root=0;\n vector<int>edg[nums.size()];\n for(int i=0;i<edges.size();i++){\n int nd1=edges[i][0];\n int nd2=edges[i][1];\n edg[nd1].push_back(nd2);\n edg[nd2].push_back(nd1);\n }\n dfs(0,edg,-1,sub_sum,nums);\n int s=0;\n for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++)s=s+nums[i];\n int ans=0;\n for(int i=1;i<=nums.size();i++){\n if(s%i==0){\n int curr=s/i;\n int hp2=dfs2(0,edg,-1,sub_sum,curr);\n if(hp2==i)ans=max(ans,hp2);\n }\n }\n ans=ans-1;\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Tree', 'C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Javascript - Topological Sort + BFS
|
javascript-topological-sort-bfs-by-faust-e9qq
|
Code\n\n/**\n * @param {number[]} nums\n * @param {number[][]} edges\n * @return {number}\n */\nvar componentValue = function (nums, edges) {\n const n = nums.
|
faustaleonardo
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-12T00:18:47.180399+00:00
|
2024-04-12T00:18:47.180422+00:00
| 7 | false |
# Code\n```\n/**\n * @param {number[]} nums\n * @param {number[][]} edges\n * @return {number}\n */\nvar componentValue = function (nums, edges) {\n const n = nums.length;\n const degrees = new Array(n).fill(0);\n const graph = new Array(n).fill().map((_) => []);\n\n for (const [v1, v2] of edges) {\n graph[v1].push(v2);\n graph[v2].push(v1);\n degrees[v1]++;\n degrees[v2]++;\n }\n\n let sum = 0;\n const queue = [];\n for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n if (degrees[i] === 1) queue.push(i);\n sum += nums[i];\n }\n\n for (let i = n; i >= 1; i--) {\n if (sum % i !== 0) continue;\n const result = bfs(\n sum / i,\n degrees.slice(),\n queue.slice(),\n nums.slice(),\n graph\n );\n if (result) return i - 1;\n }\n\n return 0;\n};\n\nfunction bfs(target, degrees, queue, nums, graph) {\n while (queue.length) {\n const curr = queue.shift();\n degrees[curr] = 0;\n for (const next of graph[curr]) {\n if (nums[curr] !== target) nums[next] += nums[curr];\n degrees[next]--;\n if (degrees[next] === 0) return nums[next] === target;\n if (degrees[next] === 1) queue.push(next);\n }\n }\n\n return false; // unreachable\n}\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Breadth-First Search', 'Topological Sort', 'JavaScript']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Java Solution Topological Sort
|
java-solution-topological-sort-by-ndsjqw-w9h9
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
ndsjqwbbb
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-09T06:05:46.356776+00:00
|
2024-04-09T06:05:46.356821+00:00
| 6 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int componentValue(int[] nums, int[][] edges) {\n int n = nums.length;\n if(n == 1){\n return 0;\n }\n Map<Integer, List<Integer>> map = new HashMap<>();\n int[] indegree = new int[n];\n for(int[] edge : edges){\n int current = edge[0];\n int next = edge[1];\n map.putIfAbsent(current, new ArrayList<>());\n map.get(current).add(next);\n indegree[current]++;\n map.putIfAbsent(next, new ArrayList<>());\n map.get(next).add(current);\n indegree[next]++;\n }\n int total = 0;\n for(int num : nums){\n total += num;\n }\n List<Integer> factors = new ArrayList<>();\n for(int i = 1; i * i <= total; i++){\n if(total % i != 0){\n continue;\n }\n factors.add(i);\n factors.add(total / i);\n }\n Collections.sort(factors);\n for(int factor : factors){\n Set<Integer> visited = new HashSet<>();\n Queue<Integer> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();\n int[] indegreenew = new int[n];\n int[] sum = new int[n];\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){\n indegreenew[i] = indegree[i];\n sum[i] = nums[i];\n }\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){\n if(indegreenew[i] == 1){\n queue.offer(i);\n visited.add(i);\n }\n }\n boolean flag = false;\n while(!queue.isEmpty()){\n int current = queue.poll();\n if(sum[current] > factor){\n flag = true;\n break;\n }\n else if(sum[current] == factor){\n sum[current] = 0;\n }\n List<Integer> neighbors = map.get(current);\n for(int nei : neighbors){\n if(visited.contains(nei)){\n continue;\n }\n indegreenew[nei]--;\n sum[nei] += sum[current];\n if(indegreenew[nei] == 1){\n queue.offer(nei);\n visited.add(nei);\n }\n }\n }\n if(!flag){\n return total/factor - 1;\n }\n }\n return 0;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Find all divisors
|
find-all-divisors-by-priyanshukumarsingh-jxpg
|
Intuition\nBasic intution behind the solution is that maximum sum that can be formed would be 5021e5 sou there would be less number of divisors for this.\n\n# A
|
priyanshukumarsingh98266
|
NORMAL
|
2024-03-04T14:06:07.536789+00:00
|
2024-03-04T14:06:07.536817+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition\nBasic intution behind the solution is that maximum sum that can be formed would be $$50*2*1e5$$ sou there would be less number of divisors for this.\n\n# Approach\nFind if we can create subtrees with a particular sum.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n void findfactors(vector<int>&factors, int sum)\n {\n for(int i=1; i<=sqrt(sum); i++)\n {\n if(sum%i==0)\n {\n factors.push_back(i);\n if(i!=sum/i) factors.push_back(sum/i);\n }\n }\n }\n\n int dfs(int node, int par, vector<int>v[], int divs, vector<int>&nums)\n {\n int sum=nums[node];\n bool flag = true;\n for(int i=0; i<v[node].size(); i++)\n {\n int child=v[node][i];\n if(child!=par)\n {\n int z1=dfs(child,node,v,divs,nums);\n sum+=z1;\n if(z1==-1) flag=false;\n }\n }\n if(flag==false || sum>divs) return -1;\n if(sum==divs) sum=0;\n return sum; \n }\n\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n int sum=0,n=edges.size();\n for(int i=0; i<nums.size(); i++) sum+=nums[i];\n vector<int>v[n+1];\n for(int i=0; i<n; i++)\n {\n v[edges[i][0]].push_back(edges[i][1]);\n v[edges[i][1]].push_back(edges[i][0]);\n }\n vector<int>factors;\n findfactors(factors,sum);\n int ans=0;\n for(int i=0; i<factors.size(); i++)\n {\n if(dfs(0,-1,v,factors[i],nums)==0) ans=max(ans,sum/factors[i]-1);\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Short DFS in Python3, Faster Than 77%
|
short-dfs-in-python3-faster-than-77-by-m-nslj
|
Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \nMerging the solutions from bottom to up with DFS. The only cut is that the size of candidate compone
|
metaphysicalist
|
NORMAL
|
2024-01-13T17:14:13.448888+00:00
|
2024-01-13T17:14:13.448916+00:00
| 12 | false |
# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nMerging the solutions from bottom to up with DFS. The only cut is that the size of candidate components should divide the sum of all nodes. The cut is very important for the time complexity. \n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def componentValue(self, nums: List[int], edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n overall_total = sum(nums)\n graph = defaultdict(set)\n for a, b in edges:\n graph[a].add(b)\n graph[b].add(a)\n\n def dfs(v=0, parent=-1):\n nonlocal overall_total\n res = {}\n total = nums[v]\n for u in graph[v]:\n if u != parent:\n r = dfs(u, v)\n k = next(iter(r.keys()))\n total += r[k][0] * k + r[k][1]\n for k in r:\n if overall_total % k != 0:\n continue\n if k not in res:\n res[k] = [r[k][0], r[k][1], 1]\n else:\n res[k][0] += r[k][0]\n res[k][1] += r[k][1]\n res[k][2] += 1\n \n solutions = {total: (1, 0)}\n for k in res:\n if overall_total % k != 0:\n continue\n remains = total - (k * res[k][0])\n if remains == k:\n solutions[k] = (res[k][0] + 1, 0)\n elif remains < k:\n solutions[k] = (res[k][0], remains)\n return solutions\n\n ans = dfs()\n k = min(k for k, v in ans.items() if v[1] == 0)\n return ans[k][0] - 1\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Math', 'Depth-First Search', 'Python3']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Check all factors greedily
|
check-all-factors-greedily-by-theabbie-zag8
|
\nfrom collections import *\n\nclass Solution:\n def maxsplits(self, graph, i, prev, k, values):\n res = 0\n curr = values[i]\n res = 0\
|
theabbie
|
NORMAL
|
2024-01-02T05:31:00.528268+00:00
|
2024-01-02T05:31:00.528322+00:00
| 2 | false |
```\nfrom collections import *\n\nclass Solution:\n def maxsplits(self, graph, i, prev, k, values):\n res = 0\n curr = values[i]\n res = 0\n for j in graph[i]:\n if j != prev:\n ncurr, nres = self.maxsplits(graph, j, i, k, values)\n curr += ncurr\n res += nres\n if curr == k:\n res += 1\n curr = 0\n return curr, res\n \n def componentValue(self, nums: List[int], edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n graph = defaultdict(set)\n for a, b in edges:\n graph[a].add(b)\n graph[b].add(a)\n res = 0\n total = sum(nums)\n s = 1\n while s * s <= total:\n if total % s == 0:\n x = self.maxsplits(graph, 0, -1, s, nums)\n if x[0] == 0:\n res = max(res, x[1] - 1)\n if s * s < total:\n x = self.maxsplits(graph, 0, -1, total // s, nums)\n if x[0] == 0:\n res = max(res, x[1] - 1)\n s += 1\n \xA0 \xA0 \xA0 \xA0return res \n```
| 0 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Short DFS Code C++
|
short-dfs-code-c-by-tejasdesh18-qutb
|
Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n int dfs( int node, int parent, vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& adj, int &components, int sum ){\n int va
|
tejasdesh18
|
NORMAL
|
2023-12-27T19:58:02.083190+00:00
|
2023-12-27T19:58:20.384177+00:00
| 7 | false |
# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n int dfs( int node, int parent, vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& adj, int &components, int sum ){\n int val = nums[node];\n for( int nextNode: adj[node] ){\n if( nextNode==parent ) continue;\n val += dfs( nextNode, node, nums, adj, components, sum );\n }\n\n if( val == sum ){ \n components--;\n return 0;\n }\n return val;\n }\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n \n int n = nums.size(), sum = accumulate(nums.begin(),nums.end(),0), ans = 0, maxi = *max_element(nums.begin(), nums.end());;\n\n vector<vector<int>> adj(n);\n \n for( auto v: edges ){\n adj[v[0]].push_back(v[1]);\n adj[v[1]].push_back(v[0]);\n }\n\n \n for( int i=sum; i>=maxi; i-- )\n if( sum%i==0 ){\n int components = sum/i;\n dfs( 0, -1, nums, adj, components, i );\n if(components==0) ans = max(ans, (sum/i) - 1);\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Java
|
java-by-gadmo-lkbm
|
for each possible sum (that can be devided between nodes to fit total)Start from the leaves and bfs, at any time add to the Queue just nodes that have up to 1 u
|
gadmo
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-23T12:15:41.497250+00:00
|
2023-10-23T12:20:20.758698+00:00
| 2 | false |
for each possible sum (that can be devided between nodes to fit total)Start from the leaves and bfs, at any time add to the Queue just nodes that have up to 1 unseen neighbor, code explains the details.\n\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int componentValue(int[] nums, int[][] edges) {\n int n = nums.length, total = 0, root = -1; \n for (int num : nums) total += num;\n List [] egdesFrom = new List[n];\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) egdesFrom[i] = new ArrayList();\n for (int [] e : edges) {\n egdesFrom[e[0]].add(e[1]);\n egdesFrom[e[1]].add(e[0]);\n }\n List<Integer> leaves = new ArrayList();\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) if (egdesFrom[i].size() == 1) leaves.add(i); // nodes with one edge in the graph -> only one diraction to go to add to sum\n\n for (int ans = n - 1; ans > 0; ans--){ // try to delete ans edges\n if (total % (ans + 1) != 0) continue; // leads to ans + 1 components\n int sum = total / (ans + 1); // sum of each component\n if (leavesUpSum(sum, egdesFrom, Arrays.copyOf(nums, n), leaves)) return ans;\n }\n return 0;\n }\n\n private boolean leavesUpSum(int sum, List [] graph, int[] nums, List<Integer> leaves){\n boolean seen[] = new boolean[nums.length];\n Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList();\n for (int leaf : leaves) q.add(leaf);\n while(!q.isEmpty()){ // bfs\n int size = q.size();\n for (int j = 0; j < size; j++){\n int cur = q.poll(), i = 0, neighbor = -1;\n if (seen[cur]) continue;\n if (nums[cur] > sum) return false;\n // find the unseen neighbor if exist (can\'t have two unseen neighbors - otherwise not in Q yet)\n while (i < graph[cur].size() && seen[(int)graph[cur].get(i)]) i++; \n if (i < graph[cur].size()) neighbor = (int)graph[cur].get(i);\n\n seen[cur] = true;\n if (nums[cur] < sum) {\n if (neighbor == -1) return false;\n nums[neighbor] += nums[cur];\n }\n if (neighbor != -1) q.offer(neighbor);\n }\n }\n return true;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Java🔥Easy to Understand
|
javaeasy-to-understand-by-sanchit_jain-ncnr
|
\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\n int components=0;\n public int getans(ArrayList<Integer>[] graph,int src,int par,int[]nums,int k){\n int sum =0;\n
|
Sanchit_Jain
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-03T16:42:41.049299+00:00
|
2023-10-03T16:42:41.049337+00:00
| 5 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n int components=0;\n public int getans(ArrayList<Integer>[] graph,int src,int par,int[]nums,int k){\n int sum =0;\n for(int nbr : graph[src]){\n if(nbr!=par){\n sum+=getans(graph,nbr,src,nums,k);\n }\n }\n sum+=nums[src];\n if(sum==k) components++;\n return sum==k?0:sum;\n }\n public int componentValue(int[] nums, int[][] edges) {\n ArrayList<Integer>[] graph = new ArrayList[nums.length];\n for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++) graph[i]=new ArrayList<>();\n for(int [] e : edges){\n int u = e[0];\n int v = e[1];\n graph[u].add(v);\n graph[v].add(u);\n }\n int sum=0;\n int maxm=0;\n for(int ele:nums){\n sum+=ele;\n maxm=Math.max(maxm,ele);\n }\n int maxComponents = 0;\n for(int i=maxm;i<=sum;i++){\n components=0;\n if(sum%i==0){\n int x = getans(graph,0,-1,nums,i);\n if(x==0){\n // System.out.println(i + " " + components);\n maxComponents=Math.max(maxComponents,components);\n }\n }\n }\n return maxComponents-1;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Easy C++ Solution
|
easy-c-solution-by-clary_shadowhunters-53zj
|
\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool check(vector<int>&nums,vector<vector<int>>&adj,int target)\n {\n int n=nums.size();\n vector<int>te
|
Clary_ShadowHunters
|
NORMAL
|
2023-09-07T16:59:36.593098+00:00
|
2023-09-07T16:59:36.593120+00:00
| 15 | false |
\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool check(vector<int>&nums,vector<vector<int>>&adj,int target)\n {\n int n=nums.size();\n vector<int>temp(n,0);\n if (traverse(0,nums,adj,target,temp)==0) return true;\n return false;\n }\n \n int traverse(int node,vector<int>&nums,vector<vector<int>>&adj,int target,vector<int>&temp)\n {\n temp[node]=nums[node];\n for (auto it:adj[node])\n {\n if (temp[it]) continue;\n temp[node]+=traverse(it,nums,adj,target,temp);\n if (temp[node]>target) return 1e5;\n }\n if (temp[node]==target) return 0;\n return temp[node];\n }\n\n\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) \n {\n int n=nums.size();\n vector<vector<int>>adj(n);\n for (auto it:edges)\n {\n adj[it[0]].push_back(it[1]);\n adj[it[1]].push_back(it[0]);\n }\n int sum=0;\n for (auto it:nums) sum+=it;\n for (int i=n;i>1;i--)\n {\n if (sum%i) continue;\n if (check(nums,adj,sum/i)) return i-1;\n }\n return 0;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
🎯 Detailed Easy 2 DFS solution. Complete Explanation.
|
detailed-easy-2-dfs-solution-complete-ex-3aky
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nSuppose we are able to divide the tree into k components each having value x then, kx =
|
neembu_mirch
|
NORMAL
|
2023-07-31T07:50:53.862998+00:00
|
2023-07-31T07:50:53.863015+00:00
| 16 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nSuppose we are able to divide the tree into $$k$$ components each having value $$x$$ then, $$k*x = total\\; sum\\; of\\; value\\; of\\; each\\; node$$. Since $$k$$ is an integer, $$x$$ must be a factor of $$total\\; sum$$. We calculate the $$total\\; sum$$ and try to find if each of it\'s factor can be the value of each component. If the value of each component is $$x$$ then number of components is $$ k = (total\\; sum)/ x$$. To form $$k$$ components we need to remove $$k-1$$ edges.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n`subtree[x] stores the sum of the tree rooted at x. sub() function calculates subtree[] array first`.\nIn the `dfs()` function :\n- *adj* is the adjacency list.\n- *req* is required value of each component.\n- *k* is number of components to be formed.\n- *par* is parent node to avoid infinite recursion.\n- *nums* is the value array.\n\nIf I am at an edge `x -- y` and `subtree[y]% req == 0 and subtree[y]/req == k-1` then I can remove this edge `(k-1 is remaining number of components)`. It means after removing the edge `x -- y` , we can still form `k-1` components with the tree rooted at `y`.If only 1 component is remaining we return true. We do this over all factors of `total sum` and take the max.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;O(n * sqrt(sum) )$$\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;O(n)$$\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> adj[20005];\n int subtree[20005];\n int sub(int x, int par, vector<int> &nums){\n int sum = nums[x];\n for(auto y: adj[x]){\n if(y!=par){\n sum+=sub(y,x,nums);\n }\n }\n return subtree[x] = sum;\n }\n bool dfs(int x , int par , int &k, int req, vector<int> & nums){\n \n if(k==1){\n return true;\n }\n for(auto y: adj[x]){\n if(y==par) continue;\n if(subtree[y]%req==0&&subtree[y]/req==k-1){\n k--;\n }\n if(dfs(y,x,k,req,nums)) {\n return true;\n }\n }\n \n return false;\n }\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n for(auto v:edges){\n adj[v[0]].push_back(v[1]);\n adj[v[1]].push_back(v[0]);\n }\n cout<<nums.size()<<endl;\n sub(0,-1,nums);\n int tot = 0;\n unordered_set<int> s;\n for(auto x:nums){\n tot+=x;\n s.insert(x);\n }\n/* if each node has the same value we can delete all n-1 edges dfs*/\n if(s.size()==1) return nums.size()-1;\n\n int ans=1;\n for(int i =1 ;i*i<=tot;i++){\n if(tot%i==0){\n int k= tot/i;\n if(dfs(0,-1,k,i,nums)){\n ans = max(ans,tot/i);\n }\n k = i;\n if(dfs(0,-1,k,tot/i,nums)){\n ans = max(ans,i);\n }\n }\n }\n return ans-1;\n \n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Math', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Depth-First Search', 'C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Very simple and straightforward dfs solution
|
very-simple-and-straightforward-dfs-solu-3x40
|
Intuition\nFirst think if the nums is not there then how you approach\n\n# Approach\nstep1 -> Find the all the divisors of sum(nums[i])\nstep -> check for each
|
51_KING
|
NORMAL
|
2023-07-21T05:47:18.998781+00:00
|
2023-07-21T05:47:18.998800+00:00
| 14 | false |
# Intuition\nFirst think if the nums is not there then how you approach\n\n# Approach\nstep1 -> Find the all the divisors of sum(nums[i])\nstep -> check for each divisor wheather can we split into sum/divisor or not If yes the update ans as max(ans,divisor-1);\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(Number of node*no of divisor of sum(nums[i])+ sum(nums[i]))\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(1)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\nbool flag; // yes can split\nint dfs(int curr,vector <vector<int>> &adj,int par,int k,vector <int> &cost)\n{\n int ans = cost[curr];\n for(auto &x:adj[curr])\n {\n if(par!=x)\n ans+=dfs(x,adj,curr,k,cost);\n }\n if(ans>k)\n {\n flag = false;\n return 0;\n }\n else if(ans==k)\n ans=0;\n return ans;\n}\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n int n = nums.size();\n vector <vector<int>> adj(n);\n for(auto &x:edges)\n {\n adj[x[0]].push_back(x[1]);\n adj[x[1]].push_back(x[0]);\n }\n int sum = 0;\n int maxEdgeCanRemove = 0;\n for(auto &x:nums) sum+=x;\n for(int i=1;i<=sum;i++)\n {\n if(sum%i==0)\n {\n flag = true;\n dfs(0,adj,-1,sum/i,nums);\n if(flag)\n maxEdgeCanRemove = max(maxEdgeCanRemove,i-1);\n }\n }\n return maxEdgeCanRemove;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Number Theory', 'C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
✅C++|| DFS || Easiest and Simplest Solution
|
c-dfs-easiest-and-simplest-solution-by-m-aug7
|
\n# Approach\nIdea is to keep the sum of subtree of each node, and store them in an array, say s. Now for all the factors fac of A (A is the sum of values of al
|
MrGamer2801
|
NORMAL
|
2023-06-19T14:11:47.406408+00:00
|
2023-06-19T14:11:47.406425+00:00
| 26 | false |
\n# Approach\nIdea is to keep the sum of subtree of each node, and store them in an array, say `s`. Now for all the factors `fac` of `A` (`A` is the sum of values of all the nodes.), check if there are exactly ` A / fac ` elemens in s that are divisible by `fac`.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n log(A))\nA is the sum of values of all the nodes.\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n int dfs(int node, vector<int> &s, vector<int> &nums, vector<vector<int>> &mp, vector<int> &vis)\n {\n vis[node] = 1;\n for(auto x: mp[node])\n if(vis[x]==0)\n s[node]+=dfs(x, s, nums, mp, vis);\n s[node]+=nums[node];\n return s[node];\n }\n\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n vector<vector<int>> mp(nums.size());\n for(auto x: edges){\n mp[x[0]].push_back(x[1]);\n mp[x[1]].push_back(x[0]);\n }\n int sum = 0;\n vector<int> s(nums.size(), 0), vis(nums.size(), 0);\n sum = dfs(0, s, nums, mp, vis);\n for(int i=1; i<sum; i++)\n {\n if(sum%i!=0)\n {\n int div=0;\n for(auto x: s)\n if(x%i==0)\n x++;\n if(x==sum/i)\n return sum/i-1;\n }\n }\n return 0;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Python || Factorization || DFS
|
python-factorization-dfs-by-in_sidious-1o3j
|
Time Complexity - O(sqrt(sum)*n)\n\nclass Solution:\n def componentValue(self, nums: List[int], edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n ssum=sum(nums)\n
|
iN_siDious
|
NORMAL
|
2023-04-21T18:02:11.095068+00:00
|
2023-04-21T18:02:11.095095+00:00
| 11 | false |
Time Complexity - O(sqrt(sum)*n)\n```\nclass Solution:\n def componentValue(self, nums: List[int], edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n ssum=sum(nums)\n n=len(nums)\n facs=set()\n for i in range(1,int(sqrt(ssum))+1):\n if ssum%i==0: \n facs.add(ssum//i)\n facs.add(i)\n graph=defaultdict(list)\n for u,v in edges:\n graph[u].append(v)\n graph[v].append(u)\n def dfs(node,par,gg):\n nonlocal cnt\n val=nums[node]\n for nei in graph[node]:\n if nei==par: continue\n val+=dfs(nei,node,gg)\n if val==gg:\n cnt+=1\n val=0\n return val\n for f in sorted(list(facs),reverse=True):\n cnt=0\n dfs(0,-1,ssum//f)\n if cnt==f:\n return f-1\n return 0\n \n \n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Python']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
JavaScript || Beats 100%
|
javascript-beats-100-by-zanooybg23-7w3l
|
Code\n\nvar componentValue = function(nums, edges) {\n var dfs = function(nums, g, cur, parent, target) {\n var curSum = nums[cur];\n for (var
|
zanooybg23
|
NORMAL
|
2023-04-05T20:10:33.824426+00:00
|
2023-04-05T20:10:33.824456+00:00
| 29 | false |
# Code\n```\nvar componentValue = function(nums, edges) {\n var dfs = function(nums, g, cur, parent, target) {\n var curSum = nums[cur];\n for (var i = 0; i < g[cur].length; i++) {\n var nbr = g[cur][i];\n if (nbr === parent) continue;\n curSum += dfs(nums, g, nbr, cur, target);\n }\n \n if (curSum === target) {\n return 0;\n } else {\n return curSum;\n }\n };\n \n var n = nums.length;\n var g = new Array(n);\n for (var i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n g[i] = [];\n }\n \n for (var i = 0; i < edges.length; i++) {\n var e = edges[i];\n g[e[0]].push(e[1]);\n g[e[1]].push(e[0]);\n }\n \n var sum = 0;\n for (var i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {\n sum += nums[i];\n }\n \n var st = {};\n for (var i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {\n st[nums[i]] = true;\n }\n var numDistinctValues = Object.keys(st).length;\n \n if (numDistinctValues === 1) {\n return n - 1;\n }\n \n for (var i = n - 1; i >= 2; i--) {\n if (sum % i !== 0) continue;\n \n var ans = dfs(nums, g, 0, -1, sum / i);\n \n if (ans === 0) return i - 1;\n }\n \n return 0;\n};\n\n\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
C++ dfs faster than 70%
|
c-dfs-faster-than-70-by-idvjojo123-69cb
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int b,sum;\n vector<int> F;\n void dfs(int x,int limit,vector<int>& nums,vector<vector<int>>& A,vector<int>& kt,vector<in
|
idvjojo123
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-26T08:12:06.108392+00:00
|
2023-03-26T08:12:06.108426+00:00
| 22 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int b,sum;\n vector<int> F;\n void dfs(int x,int limit,vector<int>& nums,vector<vector<int>>& A,vector<int>& kt,vector<int>& value)\n {\n kt[x]=1;\n value[x]=nums[x];\n for(int i=0;i<=A[x].size()-1;i++)\n {\n if(kt[A[x][i]]==0)\n {\n dfs(A[x][i],limit,nums,A,kt,value);\n if(b==1) return;\n value[x]=value[x]+value[A[x][i]];\n }\n }\n if(value[x]>limit) b=1;\n else if(value[x]==limit) value[x]=0;\n }\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n if(edges.empty()!=0) return 0;\n vector<int> kt,temp(nums.size(),0),value;\n vector<vector<int>> A(nums.size());\n for(int i=0;i<=edges.size()-1;i++)\n {\n A[edges[i][0]].push_back(edges[i][1]);\n A[edges[i][1]].push_back(edges[i][0]);\n }\n for(int i=0;i<=nums.size()-1;i++)\n sum=sum+nums[i];\n for(int i=1;i<=sum;i++)\n if(sum%i==0) F.push_back(i);\n for(int i=0;i<=F.size()-1;i++)\n {\n b=0;\n kt=temp;\n value=temp;\n dfs(0,F[i],nums,A,kt,value);\n if(b==0) return sum/F[i]-1;\n }\n return 0;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'C']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
c++ | easy | fast
|
c-easy-fast-by-venomhighs7-7qe7
|
\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> arr;\n vector<vector<int>> g;\n \n int dfs(int ind,int parent,const int target)\n {\n
|
venomhighs7
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-11T05:40:31.832251+00:00
|
2023-03-11T05:40:31.832286+00:00
| 35 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> arr;\n vector<vector<int>> g;\n \n int dfs(int ind,int parent,const int target)\n {\n int val = arr[ind];\n \n for(auto it : g[ind]){\n if(it == parent) continue;\n val += dfs(it,ind,target);\n }\n \n if(val == target) return 0;\n return val;\n }\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n g.clear(),arr.clear();\n int n = nums.size();\n g.resize(n),arr.resize(n);\n int sum = 0;\n \n for(auto i: edges){\n g[i[0]].push_back(i[1]);\n g[i[1]].push_back(i[0]);\n }\n \n for(int j=0;j<n;j++){\n sum += nums[j];\n arr[j] = nums[j];\n }\n \n int result = 0;\n for(int parts = 1;parts <= n;parts++){\n if(sum%parts != 0) continue;\n if(dfs(0,-1,sum/parts) !=0) continue;\n \n result = max(result,parts-1);\n }\n return result;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
C++ || SOLUTION || DFS
|
c-solution-dfs-by-_himanshu_12-v4v4
|
Optimized Approach\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n int sum=0;\n // sum of
|
_himanshu_12
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-08T09:53:25.552739+00:00
|
2023-02-08T09:53:25.552784+00:00
| 35 | false |
# Optimized Approach\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n int sum=0;\n // sum of all values which are associated with every node\n for(auto num: nums) // TC: O(n)\n sum+=num;\n \n int n=nums.size(); // TC: O(n)\n vector<int>inEdge(n,0); // SC, TC: O(n)\n vector<vector<int>>adjList(n,vector<int>()); // TC,SC: O(n)\n for(auto it: edges)\n {\n adjList[it[0]].push_back(it[1]);\n adjList[it[1]].push_back(it[0]);\n inEdge[it[0]]++;\n inEdge[it[1]]++;\n }\n \n // deciding the root of tree\n int root=0;\n // TC: O(n)\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n if(inEdge[i]==1)\n {root=i;\n break;}\n \n\n // making list of divisor of sum, so that we can find out that in what numbers of component can we divide the whole tree\n vector<int>divisor; // SC: O(sum)\n int i=1;\n while(i<=sum) // TC: O(sum)\n {\n if(sum%i==0)\n divisor.push_back(i);\n i++;\n }\n\n \n // use dfs \n // TC: O(sum*(V+E))\n // SC: O(sum(V+E+n))\n for(auto it=divisor.rbegin();it!=divisor.rend();it++)\n { int cnt=0;\n vector<int>visited(n,0);\n dfs(adjList,nums,root,sum/(*it),cnt,visited);\n // if number of component is equal to divisor\n if(cnt==*it)\n return *it-1; // no. of component = no. of deleted edge+1\n \n }\n \n return 0;\n \n }\n int dfs(vector<vector<int>>&adjList,vector<int>&nums,int node,int target,int &cnt,vector<int>&visited)\n {\n // mark as visited\n visited[node]=1;\n \n int load=0;\n // traverse over neighbors\n for(auto adjNode: adjList[node])\n {\n if(!visited[adjNode])\n load+=dfs(adjList,nums,adjNode,target,cnt,visited); \n }\n load+=nums[node];\n if(load==target)\n {cnt++;\n load=0;}\n return load;\n }\n};\n```\n\n# Brute Force Approach\n```\nclass Solution {\n private:\n int ans=0;\npublic:\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n vector<int>consider(edges.size(),1);\n fun(nums,edges,0,consider);\n return ans;\n }\n void fun(vector<int>&nums, vector<vector<int>>&edges,int index,vector<int>&consider)\n {\n // cout<<"index:"<<index<<" ans:"<<ans<<endl;\n ans=max(makeComp(nums,edges,consider),ans);\n // cout<<endl;\n if(index==edges.size())\n return;\n\n // let delete this\n // pre-calculation\n consider[index]=0;\n fun(nums,edges,index+1,consider);\n // post-calculation\n consider[index]=1;\n \n // not delete this\n fun(nums,edges,index+1,consider);\n \n }\n int find(vector<int>&dsuf,int v)\n {\n if(dsuf[v]<0)\n return v;\n return dsuf[v]=find(dsuf,dsuf[v]);\n }\n void Union(vector<int>&dsuf,int from ,int to)\n {\n from=find(dsuf,from);\n to=find(dsuf,to);\n if(from!=to)\n {\n if(dsuf[from]<dsuf[to])\n {\n dsuf[from]+=dsuf[to];\n dsuf[to]=from;\n }\n else\n {\n dsuf[to]+=dsuf[from];\n dsuf[from]=to;\n }\n }\n }\n int makeComp(vector<int>&nums, vector<vector<int>>&edges,vector<int>&consider)\n { vector<int>dsuf(nums.size(),-1);\n int cnt=0;\n for(int i=0;i<consider.size();i++)\n {\n if(consider[i])\n {\n Union(dsuf,edges[i][0],edges[i][1]);\n }\n else\n cnt++;\n }\n // for(int i=0;i<dsuf.size();i++)\n // cout<<"node:"<<i<<" parent:"<<dsuf[i]<<endl;\n\n unordered_map<int,int>mp;\n for(int i=0;i<dsuf.size();i++)\n {\n if(dsuf[i]<0)\n {\n mp[i]+=nums[i];\n }\n else\n mp[dsuf[i]]+=nums[i];\n }\n unordered_set<int>st;\n for(auto p:mp)\n \n st.insert(p.second);\n \n if(st.size()==1)\n return cnt;\n return 0 ;\n }\n};\n\n\n\nclass Solution {\n private:\n int ans=0;\npublic:\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n vector<int>consider(edges.size(),1);\n fun(nums,edges,0,consider);\n return ans;\n }\n void fun(vector<int>&nums, vector<vector<int>>&edges,int index,vector<int>&consider)\n {\n // cout<<"index:"<<index<<" ans:"<<ans<<endl;\n ans=max(makeComp(nums,edges,consider),ans);\n // cout<<endl;\n if(index==edges.size())\n return;\n\n // let delete this\n // pre-calculation\n consider[index]=0;\n fun(nums,edges,index+1,consider);\n // post-calculation\n consider[index]=1;\n \n // not delete this\n fun(nums,edges,index+1,consider);\n \n }\n int find(vector<int>&dsuf,int v)\n {\n if(dsuf[v]<0)\n return v;\n return dsuf[v]=find(dsuf,dsuf[v]);\n }\n void Union(vector<int>&dsuf,int from ,int to)\n {\n from=find(dsuf,from);\n to=find(dsuf,to);\n if(from!=to)\n {\n if(dsuf[from]<dsuf[to])\n {\n dsuf[from]+=dsuf[to];\n dsuf[to]=from;\n }\n else\n {\n dsuf[to]+=dsuf[from];\n dsuf[from]=to;\n }\n }\n }\n int makeComp(vector<int>&nums, vector<vector<int>>&edges,vector<int>&consider)\n { vector<int>dsuf(nums.size(),-1);\n int cnt=0;\n for(int i=0;i<consider.size();i++)\n {\n if(consider[i])\n {\n Union(dsuf,edges[i][0],edges[i][1]);\n }\n else\n cnt++;\n }\n // for(int i=0;i<dsuf.size();i++)\n // cout<<"node:"<<i<<" parent:"<<dsuf[i]<<endl;\n\n unordered_map<int,int>mp;\n for(int i=0;i<dsuf.size();i++)\n {\n if(dsuf[i]<0)\n {\n mp[i]+=nums[i];\n }\n else\n mp[dsuf[i]]+=nums[i];\n }\n unordered_set<int>st;\n for(auto p:mp)\n \n st.insert(p.second);\n \n if(st.size()==1)\n return cnt;\n return 0 ;\n }\n};\n```\n\n
| 0 | 0 |
['Tree', 'Depth-First Search', 'Graph', 'C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
C++ || SOLUTION || DFS
|
c-solution-dfs-by-_himanshu_12-n4mw
|
Optimized Approach\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n int sum=0;\n // sum of
|
_himanshu_12
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-08T09:53:17.672776+00:00
|
2023-02-08T09:53:17.672816+00:00
| 35 | false |
# Optimized Approach\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n int sum=0;\n // sum of all values which are associated with every node\n for(auto num: nums) // TC: O(n)\n sum+=num;\n \n int n=nums.size(); // TC: O(n)\n vector<int>inEdge(n,0); // SC, TC: O(n)\n vector<vector<int>>adjList(n,vector<int>()); // TC,SC: O(n)\n for(auto it: edges)\n {\n adjList[it[0]].push_back(it[1]);\n adjList[it[1]].push_back(it[0]);\n inEdge[it[0]]++;\n inEdge[it[1]]++;\n }\n \n // deciding the root of tree\n int root=0;\n // TC: O(n)\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n if(inEdge[i]==1)\n {root=i;\n break;}\n \n\n // making list of divisor of sum, so that we can find out that in what numbers of component can we divide the whole tree\n vector<int>divisor; // SC: O(sum)\n int i=1;\n while(i<=sum) // TC: O(sum)\n {\n if(sum%i==0)\n divisor.push_back(i);\n i++;\n }\n\n \n // use dfs \n // TC: O(sum*(V+E))\n // SC: O(sum(V+E+n))\n for(auto it=divisor.rbegin();it!=divisor.rend();it++)\n { int cnt=0;\n vector<int>visited(n,0);\n dfs(adjList,nums,root,sum/(*it),cnt,visited);\n // if number of component is equal to divisor\n if(cnt==*it)\n return *it-1; // no. of component = no. of deleted edge+1\n \n }\n \n return 0;\n \n }\n int dfs(vector<vector<int>>&adjList,vector<int>&nums,int node,int target,int &cnt,vector<int>&visited)\n {\n // mark as visited\n visited[node]=1;\n \n int load=0;\n // traverse over neighbors\n for(auto adjNode: adjList[node])\n {\n if(!visited[adjNode])\n load+=dfs(adjList,nums,adjNode,target,cnt,visited); \n }\n load+=nums[node];\n if(load==target)\n {cnt++;\n load=0;}\n return load;\n }\n};\n```\n\n# Brute Force Approach\n```\nclass Solution {\n private:\n int ans=0;\npublic:\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n vector<int>consider(edges.size(),1);\n fun(nums,edges,0,consider);\n return ans;\n }\n void fun(vector<int>&nums, vector<vector<int>>&edges,int index,vector<int>&consider)\n {\n // cout<<"index:"<<index<<" ans:"<<ans<<endl;\n ans=max(makeComp(nums,edges,consider),ans);\n // cout<<endl;\n if(index==edges.size())\n return;\n\n // let delete this\n // pre-calculation\n consider[index]=0;\n fun(nums,edges,index+1,consider);\n // post-calculation\n consider[index]=1;\n \n // not delete this\n fun(nums,edges,index+1,consider);\n \n }\n int find(vector<int>&dsuf,int v)\n {\n if(dsuf[v]<0)\n return v;\n return dsuf[v]=find(dsuf,dsuf[v]);\n }\n void Union(vector<int>&dsuf,int from ,int to)\n {\n from=find(dsuf,from);\n to=find(dsuf,to);\n if(from!=to)\n {\n if(dsuf[from]<dsuf[to])\n {\n dsuf[from]+=dsuf[to];\n dsuf[to]=from;\n }\n else\n {\n dsuf[to]+=dsuf[from];\n dsuf[from]=to;\n }\n }\n }\n int makeComp(vector<int>&nums, vector<vector<int>>&edges,vector<int>&consider)\n { vector<int>dsuf(nums.size(),-1);\n int cnt=0;\n for(int i=0;i<consider.size();i++)\n {\n if(consider[i])\n {\n Union(dsuf,edges[i][0],edges[i][1]);\n }\n else\n cnt++;\n }\n // for(int i=0;i<dsuf.size();i++)\n // cout<<"node:"<<i<<" parent:"<<dsuf[i]<<endl;\n\n unordered_map<int,int>mp;\n for(int i=0;i<dsuf.size();i++)\n {\n if(dsuf[i]<0)\n {\n mp[i]+=nums[i];\n }\n else\n mp[dsuf[i]]+=nums[i];\n }\n unordered_set<int>st;\n for(auto p:mp)\n \n st.insert(p.second);\n \n if(st.size()==1)\n return cnt;\n return 0 ;\n }\n};\n\n\n\nclass Solution {\n private:\n int ans=0;\npublic:\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n vector<int>consider(edges.size(),1);\n fun(nums,edges,0,consider);\n return ans;\n }\n void fun(vector<int>&nums, vector<vector<int>>&edges,int index,vector<int>&consider)\n {\n // cout<<"index:"<<index<<" ans:"<<ans<<endl;\n ans=max(makeComp(nums,edges,consider),ans);\n // cout<<endl;\n if(index==edges.size())\n return;\n\n // let delete this\n // pre-calculation\n consider[index]=0;\n fun(nums,edges,index+1,consider);\n // post-calculation\n consider[index]=1;\n \n // not delete this\n fun(nums,edges,index+1,consider);\n \n }\n int find(vector<int>&dsuf,int v)\n {\n if(dsuf[v]<0)\n return v;\n return dsuf[v]=find(dsuf,dsuf[v]);\n }\n void Union(vector<int>&dsuf,int from ,int to)\n {\n from=find(dsuf,from);\n to=find(dsuf,to);\n if(from!=to)\n {\n if(dsuf[from]<dsuf[to])\n {\n dsuf[from]+=dsuf[to];\n dsuf[to]=from;\n }\n else\n {\n dsuf[to]+=dsuf[from];\n dsuf[from]=to;\n }\n }\n }\n int makeComp(vector<int>&nums, vector<vector<int>>&edges,vector<int>&consider)\n { vector<int>dsuf(nums.size(),-1);\n int cnt=0;\n for(int i=0;i<consider.size();i++)\n {\n if(consider[i])\n {\n Union(dsuf,edges[i][0],edges[i][1]);\n }\n else\n cnt++;\n }\n // for(int i=0;i<dsuf.size();i++)\n // cout<<"node:"<<i<<" parent:"<<dsuf[i]<<endl;\n\n unordered_map<int,int>mp;\n for(int i=0;i<dsuf.size();i++)\n {\n if(dsuf[i]<0)\n {\n mp[i]+=nums[i];\n }\n else\n mp[dsuf[i]]+=nums[i];\n }\n unordered_set<int>st;\n for(auto p:mp)\n \n st.insert(p.second);\n \n if(st.size()==1)\n return cnt;\n return 0 ;\n }\n};\n```\n\n
| 0 | 0 |
['Tree', 'Depth-First Search', 'Graph', 'C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Java: Optimal solution
|
java-optimal-solution-by-multi-thread-tp5m
|
Code\n\nclass Solution {\n public int dfs(int src,ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> al,int[] nums,int sum,boolean[] vis){\n vis[src]=true;\n int cu
|
Multi-Thread
|
NORMAL
|
2022-12-22T04:05:38.548173+00:00
|
2022-12-22T04:05:38.548219+00:00
| 95 | false |
# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int dfs(int src,ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> al,int[] nums,int sum,boolean[] vis){\n vis[src]=true;\n int curr = nums[src];\n for(Integer z : al.get(src)){\n if(!vis[z]){\n int s = dfs(z,al,nums,sum,vis);\n // if sum is not possible in some subtree\n // it\'s a fail case we return from here\n if(s==-1)\n return s;\n curr+=s;\n }\n }\n // if curr value is greater than sum\n // then we cannot create sum anymore, so return -1\n if(curr>sum)\n return -1;\n // is possible, we will do a split of component and\n // return 0 as sum of the subtree\n if(curr==sum)\n return 0;\n return curr;\n }\n \n public int componentValue(int[] nums, int[][] edges) {\n int sum=0;\n ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> al=new ArrayList<>();\n for(int x : nums){\n sum+=x;\n al.add(new ArrayList<>());\n }\n for(int[] x : edges){\n al.get(x[0]).add(x[1]);\n al.get(x[1]).add(x[0]);\n }\n int ans=0;\n int sq=(int)Math.sqrt(sum);\n // Iterating over each divisor of the total sum\n // as we want a equal split of sum among all components\n for(int i=1;i<=sq;i++){\n if(sum%i==0){\n int z=sum/i;\n boolean vis[]=new boolean[nums.length];\n // Try to make sum as z, if possible\n // then we need to remove i-1 edges only\n // E.g : i=3, sum=18 : then you need sum as 18/3=6\n // for 3 components and 3 components could be made\n // by removing 2(i-1) edges.\n int op=dfs(0,al,nums,z,vis);\n if(op==0){\n // Taking max of all the edge values\n ans=Integer.max(ans,i-1);\n }\n if(sum%z==0){\n Arrays.fill(vis,false);\n // Similarly trying for other values\n op=dfs(0,al,nums,i,vis);\n if(op==0){\n // Taking max of all the edge values\n ans=Integer.max(ans,z-1);\n }\n }\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Tree', 'Java']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
C++ || 91.96% Faster || 90.17% Less Space || Simple
|
c-9196-faster-9017-less-space-simple-by-67jx2
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
recker2903
|
NORMAL
|
2022-12-10T15:11:24.686197+00:00
|
2022-12-10T15:11:24.686241+00:00
| 82 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n #define ll long long\n\n ll dfs(ll curr,ll par,ll target,vector<int>&nums,vector<ll>adj[],ll &count){\n ll sum=nums[curr];\n for(auto &x:adj[curr]){\n if(x!=par){\n sum+=dfs(x,curr,target,nums,adj,count);\n }\n }\n if(sum==target){\n count--;\n return 0;\n }\n return sum;\n }\n \n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n ll n=nums.size(),total=0;\n for(auto &x:nums){\n total+=x;\n }\n vector<ll>adj[n];\n for(auto &x:edges){\n adj[x[0]].push_back(x[1]);\n adj[x[1]].push_back(x[0]);\n }\n set<ll>ss;\n for(ll i=1;i*i<=total;i++){\n if(total%i==0){\n ss.insert(i);ss.insert(total/i);\n }\n }\n for(auto &x:ss){\n if(x==total){\n continue;\n }\n ll count=total/x;\n if(dfs(0,-1,x,nums,adj,count)==0 && count==0){\n return (total/x)-1;\n }\n }\n return 0;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
[Python] DFS+Factors Easy
|
python-dfsfactors-easy-by-matcha_coder-sngo
|
Reply if you need any more clarification\n\nclass Solution:\n def componentValue(self, nums: List[int], edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n # Get All Fa
|
Matcha_coder
|
NORMAL
|
2022-11-24T23:13:23.260373+00:00
|
2022-11-24T23:13:23.260403+00:00
| 60 | false |
Reply if you need any more clarification\n```\nclass Solution:\n def componentValue(self, nums: List[int], edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n # Get All Factors\n factors = set()\n totalTreeSum = sum(nums)\n for factor in range(1,ceil(sqrt(totalTreeSum))):\n if totalTreeSum%factor == 0:\n factors.add(factor)\n factors.add(totalTreeSum//factor)\n maxNum = max(nums)\n \n graph = defaultdict(list)\n \n for u, v in edges:\n graph[u].append(v)\n graph[v].append(u)\n \n def dfs(u,Sum, vis):\n vis.add(u)\n NowSum = nums[u]\n for v in graph[u]:\n if v not in vis:\n NowSum += dfs(v, Sum, vis)\n if NowSum == Sum:\n self.components-=1\n return 0\n elif NowSum < Sum:\n return NowSum\n return 0\n \n \n def isPossible(targetSum, components):\n self.components = components\n dfs(0,targetSum,set())\n return self.components == 0\n \n for factor in sorted(list(factors)):\n # Each component should be atleast maxNum to be made\n if factor < maxNum: continue\n numberOfComponentsPossible = totalTreeSum//factor\n if isPossible(factor,numberOfComponentsPossible):\n return numberOfComponentsPossible-1\n return 0\n \n \n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Math', 'Depth-First Search', 'Graph', 'Python']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Golang | BFS
|
golang-bfs-by-yfw13-ixjg
|
Golang implementation of https://leetcode.com/problems/create-components-with-same-value/discuss/2706736/Python-Explanation-with-pictures-BFS\n\nfunc componentV
|
tw13
|
NORMAL
|
2022-11-19T09:10:32.914985+00:00
|
2022-11-19T09:10:32.915023+00:00
| 39 | false |
- Golang implementation of https://leetcode.com/problems/create-components-with-same-value/discuss/2706736/Python-Explanation-with-pictures-BFS\n```\nfunc componentValue(nums []int, edges [][]int) int {\n maxNum, minNum, sumNums, n := 0, math.MaxInt32, 0, len(nums)\n for _, num := range nums {\n maxNum = max(maxNum, num)\n minNum = min(minNum, num)\n sumNums += num\n }\n G := make(map[int]map[int]struct{})\n degree := make([]int, n)\n for _, edge := range edges {\n a, b := edge[0], edge[1]\n degree[a]++\n degree[b]++\n if _, ok := G[a]; !ok {\n G[a] = make(map[int]struct{})\n }\n G[a][b] = struct{}{}\n if _, ok := G[b]; !ok {\n G[b] = make(map[int]struct{})\n }\n G[b][a] = struct{}{}\n }\n \n for i := minNum; i < sumNums; i++ {\n if sumNums % i == 0 && bfs(i, nums, degree, G) {\n return (sumNums / i) - 1\n }\n }\n return 0\n}\n\nfunc bfs(target int, nums []int, degree []int, G map[int]map[int]struct{}) bool {\n V := make([]int, len(nums))\n copy(V, nums)\n deg := make([]int, len(degree))\n copy(deg, degree)\n \n q := make([]int, 0)\n for i, d := range degree {\n if d == 1 {\n q = append(q, i)\n }\n }\n \n for len(q) > 0 {\n i := q[0]\n q = q[1:]\n deg[i] = 0\n \n for nxt, _ := range G[i] {\n if V[i] != target {\n V[nxt] += V[i]\n }\n deg[nxt]--\n if deg[nxt] == 0 {\n return V[nxt] == target\n } else if deg[nxt] == 1 {\n q = append(q, nxt)\n }\n }\n }\n return false\n}\n\nfunc max(x, y int) int {\n if x > y {\n return x\n }\n return y\n}\n\nfunc min(x, y int) int {\n if x < y {\n return x\n }\n return y\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Go']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
C++ solution, faster than 40% submissions
|
c-solution-faster-than-40-submissions-by-gutp
|
Question : Find the max number of edges that you can delete, such that all sub-components have the same sum.\n\nIdea : \nFirst, calculate the sum of all nodes a
|
slothalan
|
NORMAL
|
2022-11-11T07:03:12.150891+00:00
|
2022-11-11T07:03:12.150945+00:00
| 32 | false |
Question : Find the max number of edges that you can delete, such that all sub-components have the same sum.\n\nIdea : \nFirst, calculate the sum of all nodes as S. To split them into n components, S % n must be 0 (primary school maths).\n\nThen, you can inspect the tree. Each node must belongs to any sub-component.\n\nThe value of all sub-component is (S / n).\n\nSo, if the current node\'s value is already (S / n), it is a sub-component itself. So, remove all the edges between this and the child / children, and if any child\'s sum != (S / n), it is invalid. Why? Because the current node can\'t take in more values.\n\nIf the current node\'s value is < (S / n), then check the children. For all the children with sub-sum < (S / n), group them together. Since it is a tree, those children can only connect to this parent node.\n\nRecall that all nodes must belongs to any sub-component. Therefore, those children with sub-sum < (S / n) can only be grouped with the current parent.\n\n*Imagine that if you left out any child (-_-) with sub-sum < S / n, that child cannot be connected to any other nodes (T_T) (poor child). Since that child cannot be a sub-component, it is invalid.*\n\nSo, that\'s the entire idea (-_-;)\n\n```cpp\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxn;\n int sumn;\n int pat_val, pat_size;\n const static int MAX = 20010;\n bool mk[MAX];\n int edges_del;\n int max_edges_del;\n bool flag;\n std::map<int, vector<int>> T;\n void T_init_insert(int a, int b) {\n if (T.find(a) == T.end()) {\n T[a] = { b };\n }\n else {\n T[a].push_back(b);\n }\n }\n int T_ck(vector<int>& nums, int cur_n) {\n if (!flag)\n return -1;\n if (nums[cur_n] > pat_val) {\n flag = false;\n return -1;\n }\n mk[cur_n] = true;\n int cvaltmp, rescval;\n if (nums[cur_n] == pat_val) {\n for (int des : T[cur_n]) {\n if (!mk[des]) {\n edges_del++;\n int cval = T_ck(nums, des);\n if (!flag)\n return -1;\n if (cval != pat_val) {\n flag = false;\n return -1;\n }\n }\n }\n return pat_val;\n }\n else {\n cvaltmp = 0;\n for (int des : T[cur_n]) {\n if (!mk[des]) {\n int cval = T_ck(nums, des);\n if (cval > pat_val) {\n flag = false;\n return -1;\n }\n else if (cval == pat_val) {\n edges_del++;\n }\n else {\n cvaltmp += cval;\n }\n }\n }\n rescval = nums[cur_n] + cvaltmp;\n if (rescval > pat_val) {\n flag = false;\n return -1;\n }\n return rescval;\n }\n return -1;\n }\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n max_edges_del = 0;\n maxn = -1;\n sumn = 0;\n for (int v : nums) {\n sumn += v;\n maxn = std::max(maxn, v);\n }\n for (vector<int> e : edges) {\n T_init_insert(e[0], e[1]);\n T_init_insert(e[1], e[0]);\n }\n int bound = (int)std::ceil(std::sqrt((sumn * 1.0)));\n for (int d = 1; d < bound; d++) {\n if ((sumn % d) == 0) {\n flag = true;\n edges_del = 0;\n memset(mk, false, sizeof(mk));\n pat_val = d;\n pat_size = sumn / d;\n T_ck(nums, 0);\n \n if (flag) {\n max_edges_del = std::max(max_edges_del, edges_del);\n }\n flag = true;\n edges_del = 0;\n memset(mk, false, sizeof(mk));\n pat_val = sumn / d;\n pat_size = d; \n T_ck(nums, 0);\n if (flag) {\n max_edges_del = std::max(max_edges_del, edges_del);\n }\n }\n }\n return max_edges_del;\n }\n};\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Simple CPP Solution | DFS Only
|
simple-cpp-solution-dfs-only-by-ankit_73-6obc
|
Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<vector<int>>g;\n vector<int>arr;\n \n int dfs(int ind,int par,int target){\n int val=arr[ind];\n
|
Ankit_73
|
NORMAL
|
2022-11-08T18:33:40.160452+00:00
|
2022-11-08T18:33:40.160495+00:00
| 64 | false |
# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<vector<int>>g;\n vector<int>arr;\n \n int dfs(int ind,int par,int target){\n int val=arr[ind];\n \n for(auto it:g[ind]){\n if(it == par) continue;\n \n val += dfs(it,ind,target);\n }\n if( val == target) return 0;\n return val;\n \n }\n \n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& ed) {\n int n=nums.size();\n if(n == 1) return 0;\n \n g.resize(n);\n arr.resize(n);\n \n for(auto i:ed){\n g[i[0]].push_back(i[1]);\n g[i[1]].push_back(i[0]);\n \n }\n \n \n int sum=0;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n sum += nums[i];\n arr[i]= nums[i];\n }\n \n \n int res=0;\n for(int part=1;part<=n;part++){\n if(sum%part !=0 ) continue;\n if(dfs(0,-1,sum/part) == 0){\n res=max(res,part-1);\n }\n }\n \n return res;\n \n \n \n \n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
[C++] || Code for beginners || Easy understanding DFS
|
c-code-for-beginners-easy-understanding-haawx
|
\nclass Solution {\nprivate:\n list<int>* adj;\npublic:\n vector<int> Divisors(int n){\n vector<int> G,L;\n for(int i=1;i<=sqrt(n);i++){\n
|
Decode_Apocalypse
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-31T07:31:08.480170+00:00
|
2022-10-31T07:31:08.480213+00:00
| 27 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\nprivate:\n list<int>* adj;\npublic:\n vector<int> Divisors(int n){\n vector<int> G,L;\n for(int i=1;i<=sqrt(n);i++){\n if(n%i==0){\n if(n/i==i){\n L.push_back(i);\n }\n else{\n G.push_back(n/i);\n L.push_back(i);\n }\n }\n }\n vector<int> res=L;\n for(int i=G.size()-1;i>=0;i--){\n res.push_back(G[i]);\n }\n return res; // returns sorted output\n } \n \n int validate(int node, int sum, vector<int>& nums, int par){\n int currsum=nums[node];\n for(auto nei: adj[node]){\n if(par==nei){\n continue;\n }\n currsum+=validate(nei,sum,nums,node);\n if(currsum>sum){\n return INT_MAX/2;\n }\n }\n if(currsum==sum){ // erasing edge and hence return 0\n return 0;\n }\n return currsum;\n }\n \n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n int sum=accumulate(nums.begin(),nums.end(),0);\n vector<int> div=Divisors(sum);\n int n=nums.size();\n adj=new list<int>[n];\n for(auto edge: edges){\n adj[edge[0]].push_back(edge[1]);\n adj[edge[1]].push_back(edge[0]);\n }\n for(auto d: div){\n if(validate(0,d,nums,-1)==0){\n return sum/d-1;\n }\n }\n return 0;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'C']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
c++||simple||queue||bfs
|
csimplequeuebfs-by-ankur_singh93806-vg9d
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n bool solve_bfs(int sum,vector<int>nums,vector<vector<int>>&adj,vector<int>cnt,queue<int>q)\n {\n while(!q.empty
|
ankur_singh93806
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-26T10:03:12.862163+00:00
|
2022-10-26T10:03:12.862187+00:00
| 25 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n bool solve_bfs(int sum,vector<int>nums,vector<vector<int>>&adj,vector<int>cnt,queue<int>q)\n {\n while(!q.empty())\n {\n queue<int>q1;\n while(!q.empty())\n {\n int per=q.front();\n q.pop();\n if(nums[per]>sum)\n return 0;\n \n for(auto it:adj[per])\n {\n if(nums[per]!=sum) //if sum is not equal to nums[per]\n nums[it]+=nums[per]; \n \n cnt[it]--;\n if(cnt[it]==1)\n {\n q1.push(it);\n }\n }\n \n }\n q=q1;\n }\n return 1;\n }\n \n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n int sum=0;\n int n=nums.size();\n for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++)\n {\n sum+=nums[i];\n }\n \n vector<vector<int>>adj(n);\n for(int i=0;i<edges.size();i++)\n {\n adj[edges[i][0]].push_back(edges[i][1]);\n adj[edges[i][1]].push_back(edges[i][0]);\n }\n \n vector<int>cnt(n,0);\n queue<int>q;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n cnt[i]=adj[i].size();\n if(cnt[i]==1) //leaf node or root node\n {\n q.push(i);\n }\n }\n \n \n for(int i=n;i>=2;i--)\n {\n if(sum%i==0)\n { \n if(solve_bfs(sum/i,nums,adj,cnt,q))\n return i-1;\n }\n }\n \n return 0;\n \n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Simple Java Solution
|
simple-java-solution-by-piyushkumar2000-gt6c
|
\nclass Solution {\n class Pair{\n int node;\n int val;\n Pair(int node,int val){\n this.node=node;\n this.val=val
|
piyushkumar2000
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-26T06:52:21.279849+00:00
|
2022-10-26T06:52:21.279891+00:00
| 103 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n class Pair{\n int node;\n int val;\n Pair(int node,int val){\n this.node=node;\n this.val=val;\n }\n }\n public int componentValue(int[] nums, int[][] edges) {\n int n=nums.length;\n int sum=0;\n List<List<Integer>> adjList=new ArrayList<>();\n int[] degree=new int[n];\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n sum=sum+nums[i];\n adjList.add(new ArrayList<>());\n }\n for(int[] edge:edges){\n adjList.get(edge[0]).add(edge[1]);\n adjList.get(edge[1]).add(edge[0]);\n degree[edge[0]]++;\n degree[edge[1]]++;\n }\n List<Integer> factors=new ArrayList<>();\n for(int i=1;i<=(int)Math.sqrt(sum);i++){\n if(sum%i==0){\n factors.add(i);\n factors.add(sum/i);\n }\n }\n Collections.sort(factors);\n for(int factor:factors){\n if(sum%factor!=0) continue;\n Queue<Pair> q=new LinkedList<>();\n int[] visited=new int[n];\n int[] numsCopy=new int[n];\n int[] degreeCopy=new int[n];\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++){\n numsCopy[j]=nums[j];\n degreeCopy[j]=degree[j];\n if(degreeCopy[j]==1){\n q.add(new Pair(j,numsCopy[j]));\n visited[j]=1;\n \n } \n }\n int component=0;\n int count=0;\n while(!q.isEmpty()){\n Pair pair=q.remove();\n count++;\n if(numsCopy[pair.node]==factor){\n component++;\n }\n if(numsCopy[pair.node]>factor) break;\n for(int parent:adjList.get(pair.node)){\n if(numsCopy[pair.node]<factor){\n numsCopy[parent]=numsCopy[parent]+numsCopy[pair.node];\n } \n if(visited[parent]==0){\n degreeCopy[parent]--;\n if(degreeCopy[parent]==1){\n q.add(new Pair(parent,numsCopy[parent]));\n visited[parent]=1;\n }\n }\n }\n if(count==n) return component-1;\n }\n }\n return 0;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Graph', 'Java']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Java clear code || faster than 90%
|
java-clear-code-faster-than-90-by-codera-wvdn
|
class Solution {\n int[] nums;\n public int componentValue(int[] nums, int[][] edges) {\n int n = nums.length;\n this.nums = nums;\n
|
coderaman_0502
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-25T19:01:54.797671+00:00
|
2022-10-25T19:01:54.797711+00:00
| 24 | false |
class Solution {\n int[] nums;\n public int componentValue(int[] nums, int[][] edges) {\n int n = nums.length;\n this.nums = nums;\n List<Integer>[] graph = new ArrayList[n];\n for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {\n graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();\n }\n for(int[] e : edges) {\n graph[e[0]].add(e[1]);\n graph[e[1]].add(e[0]);\n }\n \n int sum = 0;\n for(int i : nums) {\n sum += i;\n }\n \n for(int k=n; k>0; k--) {\n if(sum % k != 0) continue;\n int ans = helper(graph, 0, -1, sum / k);\n if(ans == 0) return k-1;\n }\n return 0;\n }\n \n private int helper(List<Integer>[] graph, int i, int prev, int target) {\n if(graph[i].size() == 1 && graph[i].get(0) == prev) {\n if(nums[i] > target) return -1;\n if(nums[i] == target) return 0;\n return nums[i];\n }\n \n int sum = nums[i];\n for(int k : graph[i]) {\n if(k == prev) continue;\n int ans = helper(graph, k, i, target);\n if(ans == -1) return -1;\n sum += ans;\n }\n \n if(sum > target) return -1;\n if(sum == target) return 0;\n return sum;\n }\n}
| 0 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
C++ DFS concise
|
c-dfs-concise-by-sanzenin_aria-3w11
|
```\n int componentValue(vector& nums, vector>& edges) {\n const auto sum = accumulate(nums.begin(), nums.end(), 0); \n vector> g(nums.size());
|
sanzenin_aria
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-24T08:49:30.900960+00:00
|
2022-10-24T08:49:30.901000+00:00
| 29 | false |
```\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n const auto sum = accumulate(nums.begin(), nums.end(), 0); \n vector<vector<int>> g(nums.size());\n for (auto& e:edges) g[e[0]].push_back(e[1]), g[e[1]].push_back(e[0]); \n for (int d=1;d<= sum/2; d++)\n if (sum % d == 0 && dfs(g, nums, 0, -1, d) == 0) return sum/d - 1;\n return 0;\n }\n \n int dfs(const vector<vector<int>>& g, const vector<int>& nums, int i, int par, int d){\n int sum = nums[i];\n for (auto j : g[i]) {\n if (j == par) continue;\n if (int x = dfs(g, nums, j, i, d); x==-1) return -1; //impossible\n else sum += x;\n }\n if (sum > d) return -1;\n return sum == d ? 0 : sum;\n }
| 0 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
[C++] DFS for each divisor of the sum of all nodes in the tree
|
c-dfs-for-each-divisor-of-the-sum-of-all-6a4v
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nThis problem requires the following observations to be solved:\n\n1.) Suppose we are lo
|
aaditya1096
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-23T10:24:23.422200+00:00
|
2022-10-23T10:26:35.792062+00:00
| 78 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThis problem requires the following observations to be solved:\n\n1.) Suppose we are looking to divide the tree into components of sum s, then if a subtree has a sum of s, then it needs to be included in the final answer.\n2.) Following point 1, if there is a tree of sum m*s rooted at some node i and if we have found (m-1) components of sum s in all the subtrees of node i, then it is possible to divide the tree at node i into into m components of sum s.\n3.) We need to consider all the sums that are divisors of the total sum of the tree and choose the lowest sum for which the overall tree can be divided into equal sum components.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nTo check whether the given tree can be divided into equal components of sum "s", we need to check whether the number of components of sum s found in the tree is equal to "totalSum/s", where totalSum is the sum of all the nodes in the overall tree.\n\nThe 2nd observation points to a recursive approach, so we are going to use DFS to count the number of components for each divisor of totalSum.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(N*k) where k is the number of factors of totalSum\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(N) - for storing the tree\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n struct CompositeSum {\n int componentsFound;\n int sum;\n };\n\n CompositeSum dfs(int s, int parent, int targetSum, vector<vector<int>>& tree, \n vector<int>& nums) {\n int currSum = nums[s], currComponents = 0;\n for (int nbr: tree[s]) {\n if (nbr == parent) {\n continue;\n }\n CompositeSum subResult = dfs(nbr, s, targetSum, tree, nums);\n currSum += subResult.sum;\n currComponents += subResult.componentsFound;\n }\n\n if (currSum % targetSum == 0 && (currComponents == currSum/targetSum-1)) {\n currComponents++;\n }\n\n CompositeSum fin = {currComponents, currSum};\n return fin;\n }\n\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n //create the tree\n int N = nums.size();\n vector<vector<int>> tree(N);\n for (vector<int>& edge: edges) {\n tree[edge[0]].push_back(edge[1]);\n tree[edge[1]].push_back(edge[0]);\n }\n\n //calculate the sum and its factors;\n int sum = 0;\n for (int num: nums) {\n sum += num;\n }\n vector<int> factors;\n for (int i = 1; i*i <= sum; i++) {\n if (sum%i == 0) {\n factors.push_back(i);\n factors.push_back(sum/i);\n }\n }\n sort(factors.begin(), factors.end(), greater<int>());\n\n int ans = 0;\n for (int factor: factors) {\n CompositeSum curr = dfs(0, -1, factor, tree, nums);\n if (curr.componentsFound == sum/factor) {\n ans = sum/factor-1;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
C++ || DFS Commented code
|
c-dfs-commented-code-by-sachin-vinod-i0xk
|
C++ code\n\n int isPossible(int target, int src, vector<int> adj[], int par, vector<int> &nums){\n int currSum=nums[src];\n \n for(auto &x:
|
Sachin-Vinod
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-22T13:45:40.201141+00:00
|
2022-10-22T13:45:40.201166+00:00
| 59 | false |
**C++ code**\n```\n int isPossible(int target, int src, vector<int> adj[], int par, vector<int> &nums){\n int currSum=nums[src];\n \n for(auto &x:adj[src]){\n if(x!=par){\n currSum+=isPossible(target,x,adj,src,nums);\n }\n }\n \n //if current node create pair with its child and found target so it will not going to give its value to its parent\n if(currSum==target){\n return 0;\n }\n return currSum;\n }\n \n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n vector<int> adj[nums.size()];\n \n //create graph\n for(auto &x:edges){\n adj[x[0]].push_back(x[1]);\n adj[x[1]].push_back(x[0]);\n }\n \n int sum=0;\n for(auto &x:nums){\n sum+=x;\n }\n // check for each possiblity\n for(int i=nums.size()-1;i>=1;i--){\n if(sum%(i+1)==0){\n if(isPossible(sum/(i+1),0,adj,-1,nums)==0){\n return i;\n }\n }\n }\n return 0;\n }\n\t//code by sachin\n```\n**Upvote if solution was helpful**
| 0 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'C', 'C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Golang
|
golang-by-dynasty919-h8ax
|
\nfunc componentValue(nums []int, edges [][]int) int {\n sum := 0\n for _, v := range nums {\n sum += v\n }\n \n g := make([][]int, len(nu
|
dynasty919
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-22T13:42:48.025406+00:00
|
2022-10-22T13:42:48.025469+00:00
| 23 | false |
```\nfunc componentValue(nums []int, edges [][]int) int {\n sum := 0\n for _, v := range nums {\n sum += v\n }\n \n g := make([][]int, len(nums))\n for _, e := range edges {\n g[e[0]] = append(g[e[0]], e[1])\n g[e[1]] = append(g[e[1]], e[0])\n }\n \n res := 0\n for i := 1; i < sum; i++ {\n if sum % i == 0 {\n res = max(res, search(g, nums, i))\n }\n }\n return res\n}\n\nfunc max(a int,b int) int {\n if a > b {\n return a\n }\n return b\n}\n\nfunc search(g [][]int, nums []int, tar int) int {\n fmt.Println(tar)\n nums2 := make([]int, len(nums))\n copy(nums2, nums)\n \n degree := make([]int, len(nums))\n for i := 0; i < len(nums); i++ {\n degree[i] = len(g[i])\n }\n \n var queue []int\n for i, d := range degree {\n if d == 1 {\n queue = append(queue, i)\n }\n }\n \n res := 0\n for len(queue) > 0 {\n l := len(queue)\n for i := 0; i < l; i++ {\n a := queue[i]\n if nums2[a] > tar {\n return 0\n }\n if degree[a] != 1 {\n continue\n }\n for _, v := range g[a] {\n if degree[v] != 0 {\n degree[v]--\n degree[a]--\n \n if nums2[a] < tar {\n nums2[v] += nums2[a]\n } else {\n res++\n }\n if degree[v] == 1 {\n queue = append(queue, v)\n }\n }\n }\n \n }\n queue = queue[l:]\n }\n return res\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Python | DFS | Easy to Understand
|
python-dfs-easy-to-understand-by-hemantd-chxb
|
\nclass Solution:\n def getFactors(self, num: int) -> List[int]:\n factors = []\n for possibleFactor in range(1, int(sqrt(num)) + 1):\n
|
hemantdhamija
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-22T06:44:07.481320+00:00
|
2022-10-22T06:44:07.481375+00:00
| 61 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def getFactors(self, num: int) -> List[int]:\n factors = []\n for possibleFactor in range(1, int(sqrt(num)) + 1):\n if num % possibleFactor != 0: \n continue\n factors.append(possibleFactor)\n if num // possibleFactor != possibleFactor: \n factors.append(num // possibleFactor)\n return factors\n \n def componentValue(self, nums: List[int], edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n numNodes, self.cntRemainderZero, graph = len(nums), 0, defaultdict(list)\n for node1, node2 in edges:\n graph[node1].append(node2)\n graph[node2].append(node1)\n \n def dfs(node: int, prevNode: int, sumPerComponent: int) -> int:\n remainder = nums[node]\n for neighbor in graph[node]:\n if neighbor == prevNode:\n continue\n remainder += dfs(neighbor, node, sumPerComponent)\n remainder %= sumPerComponent\n if remainder == 0:\n self.cntRemainderZero += 1\n return remainder\n \n def isGood(sumPerComponent: int, expectedNumOfComponents: int) -> bool:\n self.cntRemainderZero = 0\n dfs(0, -1, sumPerComponent)\n return self.cntRemainderZero == expectedNumOfComponents\n \n sumOfAllNodes, maxNode = sum(nums), max(nums)\n for sumPerComponent in sorted(self.getFactors(sumOfAllNodes)):\n if sumPerComponent < maxNode: \n continue\n expectedNumOfComponents = sumOfAllNodes // sumPerComponent\n if isGood(sumPerComponent, expectedNumOfComponents):\n return expectedNumOfComponents - 1\n return 0\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Recursion', 'Python']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
java - complex BFS solution - (commented)
|
java-complex-bfs-solution-commented-by-z-nwjn
|
Runtime: 105 ms, faster than 80.75% of Java online submissions for Create Components With Same Value.\nMemory Usage: 59 MB, less than 88.22% of Java online subm
|
ZX007java
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-21T13:59:57.471843+00:00
|
2022-10-23T13:57:09.295173+00:00
| 131 | false |
Runtime: 105 ms, faster than 80.75% of Java online submissions for Create Components With Same Value.\nMemory Usage: 59 MB, less than 88.22% of Java online submissions for Create Components With Same Value.\n\n\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int componentValue(int[] nums, int[][] edges) {\n if(edges.length == 0) return 0;\n \n fillDivisors(nums);\n constructGraph(edges, nums.length);\n collectAllLeavesAndBFSFromLeaves(nums);\n \n return decoupleGraph(edges.length);\n }\n \n \n//for divisors\n LinkedList<Integer> divisors;\n int sum;\n \n private void fillDivisors(int[] nums) {\n divisors = new LinkedList<>();\n sum = 0;\n for(int x : nums) sum += x;\n \n int n = sum;\n int div = (int)Math.sqrt(n);\n if(n == div * div) divisors.add(div);\n else div++;\n \n while(--div != 0)\n if(n % div == 0){\n divisors.addFirst(div);\n divisors.addLast(n/div);\n }\n \n divisors.pollLast(); \n }\n \n//for graph\n HashSet<Integer>[] graph;\n \n private void constructGraph(int[][] edges, int size){\n graph = new HashSet[size];\n \n for(int[] e: edges){\n if(graph[e[0]] == null) graph[e[0]] = new HashSet<>();\n if(graph[e[1]] == null) graph[e[1]] = new HashSet<>();\n \n graph[e[0]].add(e[1]);\n graph[e[1]].add(e[0]);\n }\n }\n \n//for path from all leaves \n LinkedList<Integer> nodes;\n HashMap<Integer, Integer> table = new HashMap<>();\n \n private void collectAllLeavesAndBFSFromLeaves(int[] nums){\n nodes = new LinkedList<>();\n for(int i = 0; i != graph.length; i++) \n if(graph[i].size() == 1) nodes.add(i);\n \n while(!nodes.isEmpty()){\n int n = nodes.pollLast();\n if(graph[n].size() != 1) continue;\n \n Integer value = table.get(nums[n]);\n value = value == null ? 1 : value + 1;\n table.put(nums[n], value);\n \n for(int next: graph[n]){\n nums[next] += nums[n];\n graph[next].remove(n);\n if(graph[next].size() == 1) nodes.addFirst(next);\n }\n }\n }\n \n//for searching answer\n private int decoupleGraph(int countOfEdges){\n int ans;\n \n for(int d : divisors)\n if( (ans = sum/d - 1) <= countOfEdges){\n int k = 0;\n for(Map.Entry<Integer,Integer> it: table.entrySet())\n if(it.getKey() % d == 0) k += it.getValue();\n \n if(ans <= k) return ans;\n } \n \n return 0;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Factorization || Recursive || C++
|
factorization-recursive-c-by-focus_2000-6qi2
|
class Solution {\nprivate:\n vector a[20000+5];\n pair dfs(int curr,int par,int k,vector &nums)\n {\n bool ans=true;\n int sum=nums[curr]
|
Focus_2000
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-21T12:31:54.406028+00:00
|
2022-10-21T12:32:54.748212+00:00
| 26 | false |
class Solution {\nprivate:\n vector<int> a[20000+5];\n pair<int,bool> dfs(int curr,int par,int k,vector<int> &nums)\n {\n bool ans=true;\n int sum=nums[curr];\n for(auto &it:a[curr])\n {\n if(it!=par)\n {\n pair<int,bool> pp=dfs(it,curr,k,nums);\n ans=ans && pp.second;\n sum+=pp.first;\n }\n }\n \n if(sum==k) \n {\n sum=0;\n ans=ans and true;\n }\n else\n {\n if(sum>k) ans=false;\n }\n \n return {sum,ans};\n }\npublic:\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n \n for(auto &it:edges)\n {\n int x=it[0];\n int y=it[1];\n a[x].push_back(y);\n a[y].push_back(x);\n }\n \n int sum=0;\n for(auto &it:nums) sum+=it;\n \n \n for(int x=1;x<=sum;x++)\n {\n if(sum%x==0 and dfs(0,-1,x,nums).second==true)\n {\n int cc=sum/x;\n return (sum/x)-1;\n }\n }\n return 0;\n }\n};
| 0 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'C']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
C++ || DFS EXPLAINED | stepwise commented
|
c-dfs-explained-stepwise-commented-by-18-k4kq
|
Explanation of DFS: \nImagine standing at the root and going down to child nodes (traversing subtrees)\n1. Assign the current nodes the value of nums[current i
|
18je0001
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-21T08:29:00.872859+00:00
|
2022-10-21T08:29:41.058106+00:00
| 58 | false |
**Explanation of DFS:** \nImagine standing at the root and going down to child nodes (traversing subtrees)\n1. Assign the current nodes the value of nums[current index] to temp[current index] (current index = node 0, 1, 2, 3... here)\n2. Traverse the adjacent nodes of current node. If the child node is not visited call the recursive DFS traversal for these nodes and add the values that they return to the current node value.\nIt means we are at root and we are traversing the children of tree (subtree) and add the values that they return while backtraversing to the root.\n\n3. If after adding DFS traversal values of any child we have `sum at root > target` (target = value of one component),\n we return 1e6 as it is the max sum of whole tree we can have (constraints : max node val = 50, max no. of nodes = 1e4)\n4. If after traversing all the child nodes we see that `sum at current root = target` \nwe can clip off this subtree as one component and return 0 to be added back to root of current root.\n5. Else if `sum at current root < target` \nwe return the value of current root to be added to sum of its root (current root contributing in making a component with its own root)\n\n**If it helps, please UPVOTE : )**\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int dfs(int v, int target, vector<int> &temp, vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& adj)\n {\n temp[v] = nums[v]; //step 1\n \n for(auto u: adj[v]) //step 2\n {\n if(temp[u]) //already visited \n continue;\n \n temp[v] += dfs(u, target, temp, nums, adj);\n \n if(temp[v] > target) //step 3\n return 1e6; \n }\n if(temp[v] == target) //step 4\n return 0;\n return temp[v]; //step 5\n }\n \n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) \n {\n int n = nums.size();\n vector<vector<int>> adj(n); //adjacency list, making graph\n for(auto e: edges)\n {\n adj[e[0]].push_back(e[1]);\n adj[e[1]].push_back(e[0]);\n }\n \n int sum = 0; //sum of all nodes\n for(auto i: nums)\n sum += i;\n \n for(int i=n; i>1; i--) //components = i, edges to be removed = i-1, we see if we can divide the graph into more than 1 component\n {\n if(sum % i != 0) //not possible to divide graph into equal components\n continue;\n \n vector<int> temp(n, 0);\n if(dfs(0, sum/i, temp, nums, adj) == 0) //0 = curr node, sum/i = target sum for each component\n return i-1;\n }\n return 0;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Graph', 'C', 'C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
JAVA | Proper commented code greedy+dfs solution
|
java-proper-commented-code-greedydfs-sol-wz5d
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int componentValue(int[] nums, int[][] edges) {\n int totalSum = 0;\n\n Map<Integer, List<Integer>> graph = new Ha
|
tiwarianand940
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-21T07:51:34.114317+00:00
|
2022-10-21T07:53:57.984518+00:00
| 30 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int componentValue(int[] nums, int[][] edges) {\n int totalSum = 0;\n\n Map<Integer, List<Integer>> graph = new HashMap<>();\n int[] indegree = new int[nums.length];\n\n for (int num : nums) totalSum += num;\n\n for (int[] edge : edges) {\n if (!graph.containsKey(edge[0])) graph.put(edge[0], new ArrayList<>());\n if (!graph.containsKey(edge[1])) graph.put(edge[1], new ArrayList<>());\n\n graph.get(edge[0]).add(edge[1]);\n graph.get(edge[1]).add(edge[0]);\n indegree[edge[0]]++;\n indegree[edge[1]]++;\n }\n\n\n // We will greadily start with max number of components ie, traverse from right to left\n // and check if such configuration is achievable\n for (int i = nums.length; i > 1; i--) {\n\n // If we split the tree into i components, the target value of each component is sum / i.\n // Note that we cannot split into i components if sum % i != 0.\n if (totalSum % i == 0) {\n\n if (bfs(nums.clone(), totalSum / i, graph, indegree.clone())) {\n // return i-1 as edges to be deleted == number of partition - 1\n return i - 1;\n }\n }\n }\n\n return 0;\n }\n\n private boolean bfs(int[] nums, int target, Map<Integer, List<Integer>> graph, int[] indegree) {\n\n Deque<Integer> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();\n for (int i = 0; i < indegree.length; i++) {\n // start from leaves\n if (indegree[i] == 1) queue.addLast(i);\n }\n\n while (!queue.isEmpty()) {\n // leaf nodes\n int curr = queue.removeFirst();\n\n for (int adj : graph.get(curr)) {\n\n // if curr node itself exceeds target then this configuration is indeed impossible to obtain\n if (nums[curr] > target) return false;\n\n // nums[curr] < target is true it means adj can be taken in same component else make a cut\n nums[adj] += nums[curr] < target ? nums[curr] : 0;\n\n // In either cases indegree will be reduced by 1\n indegree[adj]--;\n\n // Repeat the same process\n if (indegree[adj] == 1) {\n queue.addLast(adj);\n }\n\n }\n }\n\n\n return true;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Greedy', 'Depth-First Search', 'Graph']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
DFS | O(N * no.of factors(sum of vals) ) | C++
|
dfs-on-noof-factorssum-of-vals-c-by-aman-ndjv
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n int cnt;\n bool flag;\n \n vector<int> Cal(int num){\n int sq = sqrt(num)+1;\n vector<int> fact;\n
|
Aman9798
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-20T22:22:04.856032+00:00
|
2022-10-20T22:22:04.856071+00:00
| 38 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n int cnt;\n bool flag;\n \n vector<int> Cal(int num){\n int sq = sqrt(num)+1;\n vector<int> fact;\n for(int i=2;i<=sq;i++){\n if(num%i==0){\n int j = num/i;\n fact.push_back(i);\n if(i!=j) fact.push_back(j);\n }\n }\n fact.push_back(1);\n sort(fact.begin(),fact.end());\n return fact;\n }\n \n int Check(vector<vector<int>>& Graph, int node, int f, int par, vector<int>& val){\n if(flag) return -1;\n int sum = val[node];\n for(int next : Graph[node]){\n if(next == par) continue;\n int x = Check(Graph, next, f, node, val);\n if(x==-1) return -1;\n sum += x;\n }\n \n if(sum==f){\n cnt++;\n return 0;\n }else if(sum < f){\n return sum;\n }\n flag = true;\n return -1;\n \n }\n \n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n int N = nums.size();\n if(N==1) return 0;\n int sum = 0;\n for(int i=0;i<N;i++) sum += nums[i];\n \n vector<vector<int>> Graph(N);\n for(auto edge : edges){\n int u = edge[0];\n int v = edge[1];\n Graph[u].push_back(v);\n Graph[v].push_back(u);\n }\n \n vector<int> fact = Cal(sum);\n int Ans = 0;\n for(int f : fact){\n cnt = 0;\n flag = false;\n Check(Graph, 0, f, -1, nums);\n if(!flag){\n Ans = max(Ans,cnt-1);\n } \n }\n return Ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Tree', 'Depth-First Search', 'Recursion']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
C++ | DFS
|
c-dfs-by-chintan26-1hvi
|
Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n int sum = accumulate(nums.begin(),nums.e
|
chintan26
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-20T13:39:29.627986+00:00
|
2022-10-20T13:39:29.628026+00:00
| 67 | false |
# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n int sum = accumulate(nums.begin(),nums.end(),0);\n int n = nums.size();\n vector<int> div;\n vector<vector<int>> adj(n);\n for(auto v:edges)\n {\n adj[v[0]].push_back(v[1]);\n adj[v[1]].push_back(v[0]);\n }\n\n for(int i=1;i*i <= sum;i++)\n {\n if(i*i == sum)\n {\n div.push_back(i);\n }\n else if(sum%i == 0)\n {\n div.push_back(i);\n div.push_back(sum/i);\n }\n }\n\n int ans = 0;\n for(int i:div)\n {\n pair<int,int> temp = divide(adj,0,-1,i,nums);\n\n if(temp.first == 0)\n {\n ans = max(ans,temp.second - 1);\n \n }\n }\n\n return ans;\n\n }\n\n pair<int,int> divide(vector<vector<int>>& adj,int src,int parent,int val,vector<int>& nums)\n {\n \n int sum = nums[src];\n int breaks = 0;\n for(int i:adj[src])\n {\n if(i != parent)\n {\n pair<int,int> temp = divide(adj,i,src,val,nums);\n sum += temp.first;\n breaks += temp.second;\n }\n }\n\n if(sum == val)\n {\n return {0,breaks + 1};\n }\n else\n {\n return {sum,breaks};\n }\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
[C++] DFS
|
c-dfs-by-jonybounce-k6fo
|
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int componentValue(vector& nums, vector>& edges) {\n int size = nums.size();\n int sum = 0;\n for(int n
|
jonybounce
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-19T20:05:51.243034+00:00
|
2022-10-19T20:08:47.859895+00:00
| 28 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n int size = nums.size();\n int sum = 0;\n for(int num: nums) sum += num;\n \n vector<vector<int>> e(size);\n for(vector<int>& edge: edges) {\n e[edge[0]].push_back(edge[1]);\n e[edge[1]].push_back(edge[0]);\n }\n \n vector<int> visited(size, 0);\n bool res;\n int target;\n function<int(int)> dfs = [&](int startNode) {\n if(!res) return 0;\n \n visited[startNode] = target;\n int sum = 0;\n for(int nextNode: e[startNode]) {\n if(visited[nextNode] != target) sum += dfs(nextNode);\n }\n \n sum += nums[startNode];\n if(sum > target) res = false;\n return sum >= target ? 0 : sum;\n };\n \n for(int div = size; div >= 2; div--) {\n if(sum % div) continue;\n \n res = true;\n target = sum / div;\n dfs(0);\n if(res) return div - 1;\n }\n \n return 0;\n }\n};
| 0 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
C++ || BFS || 95% FASTER || Commented Code with explanation
|
c-bfs-95-faster-commented-code-with-expl-numj
|
\nclass Solution {\nprivate:\n bool can_divide_evenly(int comp_val, queue<int> leaf_q, vector<int> cnt_nghbr, vector<int> nums, vector<vector<int>> &G) {\n
|
linear_coder
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-19T06:02:04.518805+00:00
|
2022-10-19T06:02:04.518905+00:00
| 36 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\nprivate:\n bool can_divide_evenly(int comp_val, queue<int> leaf_q, vector<int> cnt_nghbr, vector<int> nums, vector<vector<int>> &G) {\n // we will apply topological sort in some form,\n // roughly similar to BFS, by taking leaf nodes\n // and merging them to their parents.\n while(!leaf_q.empty()) {\n // only leaf nodes, i.e nodes with cnt_nghbr == 1\n // or degree == 1 will enter the queue\n int idx = leaf_q.front();\n leaf_q.pop();\n \n // since we are processing the leaf node, by merging\n // it into its nghbr decrease its cnt_nghbr to 0\n cnt_nghbr[idx]--;\n \n // 3 CASES\n \n // CASE 1: if value at idx is greater than the allowed\n // comp_val because of some reason, we can\'t divide\n // evenly into components\n if(nums[idx] > comp_val)\n return false;\n \n for(int &nghbr: G[idx]) {\n \n // optimisation: if we\'ve already processed a leaf node\n // i.e. if a node\'s degree is zero we will not update its \n // value, becuase it doesn\'t make sense as it will never\n // enter the queue again\n if(cnt_nghbr[nghbr] == 0)\n continue;\n \n // CASE 2: if value at idx is equal to comp_val\n // just decrease the neighbout count, becuase\n // we just completed a component with desired value\n // and can act like we remove that edge\n else if(nums[idx] == comp_val)\n cnt_nghbr[nghbr]--;\n \n // CASE 3: if value is less than the comp_val\n // we add the value to the parent/nghbr node\n // and decrease its neighbour\'s degree by 1\n else {\n nums[nghbr] += nums[idx];\n cnt_nghbr[nghbr]--;\n }\n \n // if nghbr under consideration becomes leaf node\n // push it to the leaf queue\n if(cnt_nghbr[nghbr] == 1)\n leaf_q.push(nghbr);\n }\n }\n return true;\n }\n \npublic:\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n int n = nums.size();\n \n // checking if graph contains all the same value\n int sum = accumulate(nums.begin(), nums.end(), 0);\n int max_ele = *max_element(nums.begin(), nums.end());\n if(sum % n == 0 && count(nums.begin(), nums.end(), sum/n) == n)\n return n-1;\n \n // make adjacency list for the tree(graph)\n vector<vector<int>> G(n);\n for(vector<int> &e: edges) {\n G[e[0]].push_back(e[1]);\n G[e[1]].push_back(e[0]);\n }\n \n // will store the indices of leaf nodes\n queue<int> leaf_q;\n // will sotre the count of neighbors of each node\n vector<int> cnt_nghbr(n, 0);\n for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {\n if(G[i].size() == 1) leaf_q.push(i);\n cnt_nghbr[i] += G[i].size();\n }\n \n // optimisations: \n // 1: start with minimum comp_val possible so that we \n // can get the maximum possible number of components\n // and hence can early stop our solution.\n // 2: comp_val can\'t be less than the max element\n // 3: comp_val cna\'t be more than sum\n // i.e. only one component, no edges removed\n for(int comp_val = max_ele; comp_val <= sum; ++comp_val) {\n // if sum cannot be divided evenly into num_comp\n // with comp_val calues, then continue\n if(sum % comp_val) continue;\n int num_comp = sum / comp_val;\n // because to make "num_comp" componenets\n // we need to remove "num_comp-1" edges \n if(can_divide_evenly(comp_val, leaf_q, cnt_nghbr, nums, G)) return num_comp - 1;\n }\n \n // will never be called b/c in loop condition \n // is comp_val == sum, so it will return 0 anyways\n // there itself if needed\n return 0;\n }\n};```
| 0 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
[CPP-Time-100%] Concise Solution with Topological Sort and Bottom-Up Traversal
|
cpp-time-100-concise-solution-with-topol-weps
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nWe already have many posts using DFS or BFS. Here is an approach using toplogical sort.
|
mkyang
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-18T10:44:26.727943+00:00
|
2022-10-18T10:44:26.727978+00:00
| 49 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nWe already have many posts using DFS or BFS. Here is an approach using toplogical sort. According to the result, this approach beats 99.9+% w.r.t. time and 95+% w.r.t. space. As a result, we decide to share this post.\n\nGiven a target sum, we need to check whether it is possible to partition the tree so that each connected component meets such target. Our idea is quite simple: we always choose the node with least options (i.e. leaf). Either keep going or give up.\n\n1. If the value of current node "*Less Than*" the target, donate its value to its parent, remove the node from tree.\n2. If the value of current node "*Equals*" the target, remove the subtree of current node, add 1 to the counter.\n3. If the value of current node "*Greater Than*" the target, FAIL.\n4. Repeat Step 1~3 on next leaf.\n\nAs you all known, topological sort can give us such an order and meanwhile we can determine the parent of each node (except for the root) accordingly.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(N^2)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nThis is the worst case estimation. The first N is calculated based on the possible numbers of components (we have at most n components). The second N is the number of nodes. Generally, the real performance is much better than this estimation.\n\n- Space complexity: O(N)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n\n# Code\n```\nint n;\nint top [20000];\nint cnt [20000];\nint par [20000];\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n ios::sync_with_stdio(false);\n cin.tie(nullptr);\n n=nums.size();\n if(n==1)\n return 0;\n int m=0, ans=0, tar=0, sum=0;\n vector<vector<int>> edge (n); \n for(int i=0; i<n; ++i) {\n cnt[i]=0;\n par[i]=-1;\n sum+=nums[i];\n tar=max(tar, nums[i]);\n }\n //topo sort + parent of tree\n for(int i=0; i<n-1; ++i) {\n ++cnt[edges[i][0]];\n ++cnt[edges[i][1]];\n edge[edges[i][0]].push_back(edges[i][1]);\n edge[edges[i][1]].push_back(edges[i][0]);\n }\n for(int i=0; i<n; ++i) {\n if(cnt[i]==1) {\n top[m++]=i;\n }\n }\n for(int i=0; i<n; ++i) {\n for(int p : edge[top[i]]) {\n if(par[p]<0) {\n par[top[i]]=p;\n }\n if(--cnt[p]==1) {\n top[m++]=p;\n }\n }\n }\n //check\n for(int i, j, k, m=sum/tar; m && !ans; --m) {\n if(sum%m==0) {\n tar=sum/m;\n for(i=0; i<n; ++i) {\n cnt[i]=nums[i];\n }\n for(i=0, k=-1; i<n; ++i) {\n j=top[i];\n if(cnt[j]>tar) {\n // cout<<j<<":FAIL";\n k=-1;\n break;\n } else if(cnt[j]==tar) {\n // cout<<j<<":REM |";\n ++k;\n } else {\n cnt[par[j]]+=cnt[j];\n // cout<<j<<",";\n }\n }\n // cout<<"~"<<k<<"\\n";\n ans=max(ans, k);\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Greedy', 'Topological Sort']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
Only Do N Times DFS | [CPP] | Explanation
|
only-do-n-times-dfs-cpp-explanation-by-d-i1yx
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> arr;\n vector<vector<int>> g;\n \n int dfs(int idx, int parent, const int target){\n int val = arr[
|
deleted_user
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-18T04:40:37.924129+00:00
|
2022-10-18T04:40:37.924179+00:00
| 52 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> arr;\n vector<vector<int>> g;\n \n int dfs(int idx, int parent, const int target){\n int val = arr[idx];\n for(auto nbr : g[idx]){\n if(nbr == parent) continue;\n val += dfs(nbr,idx,target);\n }\n \n if(val == target) return 0; // we find any one componets give me target value then return 0 bcz we consider that one components\n return val;\n }\n \n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n int n = nums.size(), ttl_sum = 0, res = 0;\n arr.resize(n); g.resize(n);\n \n // Create graph using given edges\n for(auto i : edges){\n g[i[0]].push_back(i[1]);\n g[i[1]].push_back(i[0]);\n }\n \n // Finding total sum of all nodes value \n for(int i = 0; i<n; i++){\n ttl_sum += nums[i];\n arr[i] = nums[i];\n }\n // We find one by one components with target sum % p ---> 1 <= p <= no of nodes\n // bcz we find min one components and max no of nodes components of same value\n // that\'s why we do n time dfs to find we get sum % p vlaue components or not\n for(int p = 1; p <= n; p++){\n if(ttl_sum % p != 0) continue;\n // we get return 0 then we said we create p components of same values and deleted p-1 edges in a tree or graph\n if(dfs(0,-1,ttl_sum/p) != 0) continue;\n res = max(res,p-1);\n }\n \n return res;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Graph', 'C', 'C++']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
C++ || dfs with explanation and comments
|
c-dfs-with-explanation-and-comments-by-u-a6ec
|
\nclass Solution {\n /*\n First, for a number n, the number of divisors of n is O(n^(1/3)). For this problem, the maximum sum of the values in the\n tr
|
user0224B
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-17T19:37:58.656330+00:00
|
2022-10-17T19:40:58.426658+00:00
| 29 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n /*\n First, for a number n, the number of divisors of n is O(n^(1/3)). For this problem, the maximum sum of the values in the\n tree is 2*10^4 * 50 = 10^6, and the maximum number of divisors here is O(100), with this number, we could consider \n iterating through all the divisors of the sum to find the result.\n \n Then we come to the main part of this problem, how to check if the tree can be divided into components of same value, where the\n number fo the components equal to a specific divisor?\n \n With tree problem, it is intuitive to use bfs/dfs here. I am using dfs here, since it is easier to work with recursion. The dfs algorithm\n is shown below, notice that this is a similar dfs algorithm for calculating the size of a tree, we just change size to value here.\n \n The time complexity is O(n logmn), where n is the number of nodes and m is the maximum value in nums.\n O(n) is the time complexity for one dfs traversal and O(logmn) is the maximum number of divisors.\n \n The auxiliary space complexity is O(n) with:\n dfs recursion activation record: O(n)\n neighbors lists: O(n)\n */\n \n int dfs(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& neighbors, int i, int parent, int target) {\n // if the subtree with root i can be divided into components with same value target, then we return 0\n int value = nums[i];\n for (int neighbor : neighbors[i]) {\n if (neighbor != parent) {\n int temp = dfs(nums, neighbors, neighbor, i, target);\n if (temp == -1) return temp; // if the subtree is invalid, then the whole tree must be also invalid\n value += temp;\n }\n }\n if (value > target) return -1; // invalid subtree\n if (value == target) return 0; // find a matched component, cut off the subtree\n return value;\n }\npublic:\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {\n // step 1: find the total sum of the tree\n int sumVal = accumulate(nums.begin(), nums.end(), 0);\n \n // step 2: construct the neighbors lists for each of the node in the tree\n int n = nums.size();\n vector<vector<int>> neighbors(n);\n for (vector<int>& edge : edges) {\n neighbors[edge[0]].push_back(edge[1]);\n neighbors[edge[1]].push_back(edge[0]);\n }\n \n // step 3: traverse all the divisors and perform a dfs to check if we can\n // devide the tree into i components, where i is the divisor\n for (int i = n; i > 1; i--) {\n if (sumVal % i == 0) {\n if (dfs(nums, neighbors, 0, -1, sumVal / i) == 0) return i - 1;\n }\n }\n return 0;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'C']
| 0 |
create-components-with-same-value
|
C++
|
c-by-rony_the_loser-ngk0
|
(```) class Solution {\npublic:\n \n vector> graph;\n \n int dfs(int src, int parent, int target, vector& nums)\n {\n int sum = nums[src]
|
Algo_wizard2020
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-17T07:40:11.256274+00:00
|
2022-10-17T07:40:11.256306+00:00
| 27 | false |
(```) class Solution {\npublic:\n \n vector<vector<int>> graph;\n \n int dfs(int src, int parent, int target, vector<int>& nums)\n {\n int sum = nums[src];\n \n for(auto &x: graph[src])\n {\n if(x != parent)\n {\n sum += dfs(x,src,target, nums);\n }\n }\n \n if(sum == target)\n {\n return 0;\n }\n \n return sum;\n }\n int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) \n {\n \n int n = nums.size();\n \n graph.resize(n);\n \n for(auto &x: edges)\n {\n graph[x[0]].push_back(x[1]);\n graph[x[1]].push_back(x[0]);\n }\n \n int sum = accumulate(nums.begin(),nums.end(), 0);\n \n for(int i=sum; i>=1; i--)\n {\n if(sum % i == 0)\n {\n if(dfs(0,-1, sum/ i, nums) == 0)\n {\n return i-1;\n }\n }\n }\n \n return 0;\n }\n};
| 0 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
find-the-lexicographically-smallest-valid-sequence
|
[Java/C++/Python] Find Smallest Skip Index
|
javacpython-find-smallest-skip-index-by-h2zdi
|
Explanation\nFind the last chance of word1[i] to match word2[j].\nIf we miss word1[i], where i = last[j],\nwe can\'t find almost eqaul string.\n\nItearate each
|
lee215
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-28T18:37:48.593519+00:00
|
2024-09-29T01:38:01.062798+00:00
| 2,134 | false |
# **Explanation**\nFind the `last` chance of `word1[i]` to match `word2[j]`.\nIf we miss `word1[i]`, where `i = last[j]`,\nwe can\'t find almost eqaul string.\n\nItearate each character in `word1`,\nIf it equals to `word2[j]`, we greedliy take it.\nIf it doesn\'t, we try to skip `word2[j]` by checking `i < last[j + 1]`.\n\nThese two cases will make the `res` as smallest as possible.\n\nFinally return the `res` if we found the almoast eqaul string.\n\n<br>\n\n# **Complexity**\nTime `O(n + m)`\nSpace `O(m)`\n<br>\n\n**Java**\n```java\n public int[] validSequence(String word1, String word2) {\n int n = word1.length(), m = word2.length();\n int[] last = new int[m];\n Arrays.fill(last, -1);\n for (int i = n - 1, j = m - 1; i >= 0; --i)\n if (j >= 0 && word1.charAt(i) == word2.charAt(j))\n last[j--] = i;\n int j = 0, res[] = new int[m], skip = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < n && j < m; ++i) {\n if (word1.charAt(i) == word2.charAt(j) || (skip == 0 && (j == m - 1 || i < last[j + 1]))) {\n res[j] = i;\n skip += (word1.charAt(i) != word2.charAt(j)) ? 1 : 0;\n j++;\n }\n }\n return j == m ? res : new int[0];\n }\n```\n\n**C++**\n```cpp\n vector<int> validSequence(string word1, string word2) {\n int n = word1.size(), m = word2.size(), skip = 0;\n vector<int> last(m, -1);\n for (int i = n - 1, j = m - 1; i >= 0; --i)\n if (j >= 0 && word1[i] == word2[j])\n last[j--] = i;\n vector<int> res;\n for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < n && j < m; ++i) {\n if (word1[i] == word2[j] || (skip == 0 && (j == m - 1 || i < last[j + 1]))) {\n res.push_back(i);\n skip += (word1[i] != word2[j++]);\n }\n }\n return res.size() == m ? res : vector<int>();\n }\n```\n\n**Python**\n```py\n def validSequence(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> List[int]:\n n, m = len(word1), len(word2)\n last = [-1] * m\n j = m - 1\n for i in range(n - 1, -1, -1):\n if j >= 0 and word1[i] == word2[j]:\n last[j] = i\n j -= 1\n res = []\n skip = j = 0\n for i, c in enumerate(word1):\n if j == m: break\n if word1[i] == word2[j] or skip == 0 and (j == m - 1 or i < last[j + 1]):\n skip += word1[i] != word2[j]\n res.append(i)\n j += 1\n return res if j == m else []\n```\n
| 37 | 0 |
['C', 'Python', 'Java']
| 9 |
find-the-lexicographically-smallest-valid-sequence
|
Recursion with Greedy
|
recursion-with-greedy-by-thecodeventurer-8lp0
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nThe problem is about finding whether word2 can be matched as a subsequence of word1 wit
|
paardarshee
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-28T16:01:54.702795+00:00
|
2024-10-01T13:43:43.077200+00:00
| 4,240 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThe problem is about finding whether `word2` can be matched as a subsequence of `word1` with at most one mismatch. The idea is to traverse both strings simultaneously, trying to match characters. If a character mismatch occurs, we have one chance to ignore this mismatch (using a flag). Memoization helps to avoid redundant computations by storing previously visited states.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1. Use a recursive function with memoization (via a set) to avoid reprocessing the same state.\n2. The recursive function `start()` takes three parameters: current indices `i` (for `word1`) and `j` (for `word2`), and a `flag` that indicates whether a mismatch is still allowed.\n3. If characters at `i` and `j` match, move both indices forward. If they don\'t match, either skip a character in `word1` (if the flag allows) or continue searching for the next match.\n4. If the entire `word2` is matched, return true and store the indices in the solution vector. Reverse the vector at the end to get the correct order of indices.\n5. If no valid subsequence is found, return an empty vector.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nThe time complexity is approximately $$O(nmlogm)$$, where `m` is the length of `word1` and `n` is the length of `word2`. Each combination of `i` and `j` can be visited once with a possible flag state, making the maximum number of recursive calls.\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nThe space complexity is $$O(n*m)$$ due to the memoization set `s1` storing visited states. \n\n# Code\n```cpp\nclass Solution {\n set<pair<int, pair<int, int>>> s1;\npublic:\n bool start(int i, int j, int flag, string &word1, string &word2, vector<int> &sol) {\n if (j >= word2.size()) return true;\n if (i >= word1.size()) return false;\n if (s1.count({i, {j, flag}})) return false;\n\n bool f1 = false;\n\n if (word1[i] == word2[j]) {\n f1 = start(i + 1, j + 1, flag, word1, word2, sol);\n if (f1) sol.push_back(i);\n return f1;\n } else {\n if (flag > 0) {\n f1 = start(i + 1, j + 1, 0, word1, word2, sol);\n if (f1) {\n sol.push_back(i);\n return true;\n }\n }\n\n while (i < word1.size() && word1[i] != word2[j]) i++;\n if (i < word1.size()) {\n f1 = start(i + 1, j + 1, flag, word1, word2, sol);\n if (f1) {\n sol.push_back(i);\n return true;\n }\n }\n }\n\n s1.insert({i, {j, flag}});\n return f1;\n }\n\n vector<int> validSequence(string word1, string word2) {\n vector<int> sol;\n if (start(0, 0, 1, word1, word2, sol)) {\n reverse(sol.begin(), sol.end());\n if (sol.size() == word2.size()) return sol;\n }\n return {};\n }\n};\n```\n\n# Note :- `This Solution is not working now`\n
| 31 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'C++']
| 15 |
find-the-lexicographically-smallest-valid-sequence
|
C++ Solution
|
c-solution-by-divyaaaaansh-gk9z
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nBasic idea was to check for the smallest index on which, after performing the operation
|
Divyaaaaansh
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-28T16:48:39.544236+00:00
|
2024-09-28T16:48:39.544259+00:00
| 1,616 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nBasic idea was to check for the smallest index on which, after performing the operation, remaining string will contain the pattern\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n- Firstly, iterate from the rear end of `string1` and keep checking at every index, upto which index of `string2`, from the back, you can find a matching subsequence. Store this in an array, say `v`.\n\n- for example lets say my strings are :\n```cpp\nstring1 = "aaabbccdd"\nstring2 = "cbd"\n```\n- for these strings, my array `v` would be :\n```cpp\nv = [ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2 ]\n```\n- In the above example, for index `i=5`, my `v[5]==2`, this means when my pointer on `string1` is currently at 5th index, i can find the pattern `string2[2:]` in `string1`, i.e., `"d"`.\n- similarly for `i=0`, my `v[0]==1`, which implies I can generate the subsequence `string2[1:]`, i.e., `"bd"`\n\n- Once you\'ve precomputed this, start iterating from the start of the `string1` and assume you have to find **completely identical sequence**. (simple two pointer approach using variables `i` for `string1` and `j` for `string2`).\n- At each index, where `string1[i] != string2[j]` , check if by replacing the current index `i` in `string1` with the character at `string2[j]`, I can complete the remaining part of `string2`, i.e., check if `v[i + 1] <= j + 1`. \n- If the condition satisfies, swapping at that particular index would return the lexographically smallest sequence of indices. (refer code below).\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(N)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(N)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> validSequence(string s1, string s2) {\n int n = s1.size(), m = s2.size();\n int j = m - 1;\n vector<int> v(n, 0);\n v.push_back(m);\n \n for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {\n v[i] = v[i + 1];\n if (j >= 0 and s1[i] == s2[j]) {\n v[i] = j;\n j--;\n }\n }\n \n j = 0; \n int swapind = -1;\n \n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n if (s1[i] == s2[j]) {\n j++;\n } else if (v[i + 1] <= j + 1) {\n swapind = j;\n break;\n }\n }\n \n j = 0;\n vector<int> ans;\n \n for (int i = 0; i < n and j < m; i++) {\n if (j == swapind) {\n ans.push_back(i);\n j++;\n } else if (s1[i] == s2[j]) {\n ans.push_back(i);\n j++;\n }\n }\n \n return (ans.size() < m ? vector<int>(0) : ans);\n }\n};\n```
| 23 | 0 |
['C++']
| 4 |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.