hexsha
stringlengths 40
40
| size
int64 6
14.9M
| ext
stringclasses 1
value | lang
stringclasses 1
value | max_stars_repo_path
stringlengths 6
260
| max_stars_repo_name
stringlengths 6
119
| max_stars_repo_head_hexsha
stringlengths 40
41
| max_stars_repo_licenses
list | max_stars_count
int64 1
191k
⌀ | max_stars_repo_stars_event_min_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_stars_repo_stars_event_max_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_issues_repo_path
stringlengths 6
260
| max_issues_repo_name
stringlengths 6
119
| max_issues_repo_head_hexsha
stringlengths 40
41
| max_issues_repo_licenses
list | max_issues_count
int64 1
67k
⌀ | max_issues_repo_issues_event_min_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_issues_repo_issues_event_max_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_forks_repo_path
stringlengths 6
260
| max_forks_repo_name
stringlengths 6
119
| max_forks_repo_head_hexsha
stringlengths 40
41
| max_forks_repo_licenses
list | max_forks_count
int64 1
105k
⌀ | max_forks_repo_forks_event_min_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_forks_repo_forks_event_max_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | avg_line_length
float64 2
1.04M
| max_line_length
int64 2
11.2M
| alphanum_fraction
float64 0
1
| cells
list | cell_types
list | cell_type_groups
list |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
4a3018bf9f835bf9cde5f5d1043aa4ed2ca8cee2
| 31,081 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
models/ML_Pipeline_Preparation.ipynb
|
AntonioBauer/DisasterResponsePipelines
|
561c99e2f938f41ce857aec2e83846b399d2a8e6
|
[
"FTL",
"CNRI-Python",
"RSA-MD"
] | null | null | null |
models/ML_Pipeline_Preparation.ipynb
|
AntonioBauer/DisasterResponsePipelines
|
561c99e2f938f41ce857aec2e83846b399d2a8e6
|
[
"FTL",
"CNRI-Python",
"RSA-MD"
] | null | null | null |
models/ML_Pipeline_Preparation.ipynb
|
AntonioBauer/DisasterResponsePipelines
|
561c99e2f938f41ce857aec2e83846b399d2a8e6
|
[
"FTL",
"CNRI-Python",
"RSA-MD"
] | 1 |
2021-01-23T14:53:52.000Z
|
2021-01-23T14:53:52.000Z
| 39.796415 | 337 | 0.519835 |
[
[
[
"# ML Pipeline Preparation\nFollow the instructions below to help you create your ML pipeline.\n### 1. Import libraries and load data from database.\n- Import Python libraries\n- Load dataset from database with [`read_sql_table`](https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/generated/pandas.read_sql_table.html)\n- Define feature and target variables X and Y",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# import libraries\nimport sys\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nfrom sqlalchemy import create_engine\n\nimport nltk\nnltk.download(['punkt', 'wordnet', 'stopwords'])\nfrom nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize\nfrom nltk.stem import WordNetLemmatizer\nfrom nltk.corpus import stopwords\nfrom nltk.stem.porter import PorterStemmer\nfrom nltk.tokenize import RegexpTokenizer\n\nfrom nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize\nfrom nltk.stem import WordNetLemmatizer\nfrom sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline\nfrom sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nfrom sklearn.multioutput import MultiOutputClassifier\nfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier\nfrom sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV\nfrom sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer, TfidfTransformer\nfrom sklearn.metrics import classification_report\nfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, precision_score, recall_score, f1_score\n\nimport re\nimport pickle",
"[nltk_data] Downloading package punkt to /root/nltk_data...\n[nltk_data] Package punkt is already up-to-date!\n[nltk_data] Downloading package wordnet to /root/nltk_data...\n[nltk_data] Package wordnet is already up-to-date!\n[nltk_data] Downloading package stopwords to /root/nltk_data...\n[nltk_data] Package stopwords is already up-to-date!\n"
],
[
"# load data from database into DataFrame df\nengine = create_engine('sqlite:///DisasterResponse.db')\ndf = pd.read_sql('DisasterData', con=engine)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# split Dataframe df into X and y\nX = df['message']\ny = df.iloc[:, 4:]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 2. Write a tokenization function to process your text data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def tokenize(text):\n\n # tokenize text and instantiate lemmatizer\n tokens = word_tokenize(text)\n lemmatizer = WordNetLemmatizer()\n \n # remove stopwords\n tokens = [token for token in tokens if token not in stopwords.words('english')]\n \n # remove punctuaction\n tokens = [token for token in tokens if token.isalpha()]\n\n # create clean tokens\n clean_tokens = []\n for tok in tokens:\n clean_tok = lemmatizer.lemmatize(tok).lower().strip()\n clean_tokens.append(clean_tok)\n\n return clean_tokens",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 3. Build a machine learning pipeline\nThis machine pipeline should take in the `message` column as input and output classification results on the other 36 categories in the dataset. You may find the [MultiOutputClassifier](http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.multioutput.MultiOutputClassifier.html) helpful for predicting multiple target variables.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# build pipeline for the text transformation and for estimator\npipeline = Pipeline([\n ('vect', CountVectorizer(tokenizer = tokenize)),\n ('tfidf', TfidfTransformer()),\n ('clf', MultiOutputClassifier(RandomForestClassifier()))\n])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 4. Train pipeline\n- Split data into train and test sets\n- Train pipeline",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# split data into training and test data\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%%time\n# train data\npipeline.fit(X_train, y_train)",
"CPU times: user 2min 37s, sys: 7.35 s, total: 2min 45s\nWall time: 2min 45s\n"
],
[
"y_test.columns",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 5. Test your model\nReport the f1 score, precision and recall for each output category of the dataset. You can do this by iterating through the columns and calling sklearn's `classification_report` on each.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# predict responses for basic model\nY_pred = pipeline.predict(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# print classification_report\nprint(classification_report(y_test, Y_pred, target_names = y_test.columns, digits = 2))",
" precision recall f1-score support\n\n related 0.87 0.91 0.89 5105\n request 0.82 0.44 0.57 1140\n offer 0.00 0.00 0.00 33\n aid_related 0.75 0.60 0.66 2739\n medical_help 0.60 0.07 0.12 546\n medical_products 0.88 0.11 0.19 355\n search_and_rescue 0.54 0.04 0.08 173\n security 0.00 0.00 0.00 123\n military 0.69 0.10 0.17 226\n child_alone 0.00 0.00 0.00 0\n water 0.86 0.29 0.43 414\n food 0.80 0.60 0.69 727\n shelter 0.83 0.30 0.44 592\n clothing 0.69 0.12 0.20 95\n money 0.80 0.02 0.05 161\n missing_people 0.50 0.01 0.02 86\n refugees 0.53 0.04 0.07 204\n death 0.78 0.16 0.27 313\n other_aid 0.40 0.05 0.09 858\ninfrastructure_related 0.11 0.00 0.00 445\n transport 0.65 0.06 0.12 313\n buildings 0.74 0.12 0.20 353\n electricity 0.75 0.07 0.12 132\n tools 0.00 0.00 0.00 34\n hospitals 0.00 0.00 0.00 63\n shops 0.00 0.00 0.00 26\n aid_centers 0.00 0.00 0.00 85\n other_infrastructure 0.17 0.00 0.01 307\n weather_related 0.86 0.59 0.70 1864\n floods 0.89 0.36 0.52 547\n storm 0.79 0.41 0.54 641\n fire 0.33 0.01 0.03 71\n earthquake 0.88 0.73 0.79 626\n cold 0.52 0.14 0.22 122\n other_weather 0.41 0.03 0.06 346\n direct_report 0.75 0.32 0.44 1294\n\n avg / total 0.74 0.49 0.54 21159\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"### 6. Improve your model\nUse grid search to find better parameters. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# build pipeline for the text transformation and for estimator\ncv_pipeline = Pipeline([\n ('vect', CountVectorizer(tokenizer=tokenize)),\n ('tfidf', TfidfTransformer()),\n ('clf', MultiOutputClassifier(RandomForestClassifier()))\n])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"MultiOutputClassifier(RandomForestClassifier()).get_params()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# reduced hyperparameter tuning and cross validation due to runtime\nparameters = {\n 'clf__estimator__n_estimators': [4, 6, 9],\n 'clf__estimator__min_samples_split': [2, 3, 5],\n}\n \n\ncv_forest = GridSearchCV(cv_pipeline, param_grid = parameters, cv = 2, verbose = 2, n_jobs = 4)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%%time\n# train improved model\ncv_forest.fit(X_train, y_train)",
"Fitting 2 folds for each of 9 candidates, totalling 18 fits\n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=2, clf__estimator__n_estimators=4 \n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=2, clf__estimator__n_estimators=4 \n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=2, clf__estimator__n_estimators=6 \n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=2, clf__estimator__n_estimators=6 \n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=2, clf__estimator__n_estimators=4, total= 7.8min\n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=2, clf__estimator__n_estimators=9 \n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=2, clf__estimator__n_estimators=4, total= 7.8min\n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=2, clf__estimator__n_estimators=9 \n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=2, clf__estimator__n_estimators=6, total= 8.2min\n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=3, clf__estimator__n_estimators=4 \n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=2, clf__estimator__n_estimators=6, total= 8.2min\n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=3, clf__estimator__n_estimators=4 \n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=3, clf__estimator__n_estimators=4, total= 7.8min\n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=3, clf__estimator__n_estimators=6 \n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=3, clf__estimator__n_estimators=4, total= 7.8min\n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=3, clf__estimator__n_estimators=6 \n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=2, clf__estimator__n_estimators=9, total= 8.8min\n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=3, clf__estimator__n_estimators=9 \n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=2, clf__estimator__n_estimators=9, total= 8.9min\n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=3, clf__estimator__n_estimators=9 \n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=3, clf__estimator__n_estimators=6, total= 8.2min\n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=5, clf__estimator__n_estimators=4 \n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=3, clf__estimator__n_estimators=6, total= 8.2min\n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=5, clf__estimator__n_estimators=4 \n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=3, clf__estimator__n_estimators=9, total= 8.7min\n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=5, clf__estimator__n_estimators=6 \n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=3, clf__estimator__n_estimators=9, total= 8.7min\n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=5, clf__estimator__n_estimators=6 \n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=5, clf__estimator__n_estimators=4, total= 7.8min\n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=5, clf__estimator__n_estimators=9 \n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=5, clf__estimator__n_estimators=4, total= 7.8min\n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=5, clf__estimator__n_estimators=9 \n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=5, clf__estimator__n_estimators=6, total= 8.1min\n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=5, clf__estimator__n_estimators=6, total= 8.1min\n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=5, clf__estimator__n_estimators=9, total= 5.0min\n[CV] clf__estimator__min_samples_split=5, clf__estimator__n_estimators=9, total= 4.9min\n"
],
[
"# display the best performing parameters\ncv_forest.best_params_",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 7. Test your model\nShow the accuracy, precision, and recall of the tuned model. \n\nSince this project focuses on code quality, process, and pipelines, there is no minimum performance metric needed to pass. However, make sure to fine tune your models for accuracy, precision and recall to make your project stand out - especially for your portfolio!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# predict responses for improved model\nY_pred_cv = cv_forest.predict(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# print classification_report\nprint(classification_report(y_test, Y_pred_cv, target_names = y_test.columns, digits = 2))",
" precision recall f1-score support\n\n related 0.87 0.89 0.88 5105\n request 0.79 0.39 0.52 1140\n offer 0.00 0.00 0.00 33\n aid_related 0.74 0.55 0.63 2739\n medical_help 0.60 0.09 0.15 546\n medical_products 0.70 0.08 0.14 355\n search_and_rescue 0.53 0.05 0.09 173\n security 0.00 0.00 0.00 123\n military 0.56 0.09 0.15 226\n child_alone 0.00 0.00 0.00 0\n water 0.81 0.32 0.46 414\n food 0.82 0.43 0.56 727\n shelter 0.79 0.26 0.39 592\n clothing 1.00 0.05 0.10 95\n money 0.78 0.09 0.16 161\n missing_people 0.00 0.00 0.00 86\n refugees 0.53 0.08 0.14 204\n death 0.80 0.15 0.25 313\n other_aid 0.42 0.05 0.09 858\ninfrastructure_related 0.31 0.02 0.03 445\n transport 0.66 0.11 0.18 313\n buildings 0.60 0.09 0.15 353\n electricity 0.67 0.09 0.16 132\n tools 0.00 0.00 0.00 34\n hospitals 0.00 0.00 0.00 63\n shops 0.00 0.00 0.00 26\n aid_centers 0.00 0.00 0.00 85\n other_infrastructure 0.17 0.01 0.01 307\n weather_related 0.82 0.57 0.67 1864\n floods 0.84 0.28 0.42 547\n storm 0.77 0.37 0.50 641\n fire 0.33 0.01 0.03 71\n earthquake 0.87 0.66 0.75 626\n cold 0.68 0.16 0.25 122\n other_weather 0.47 0.05 0.10 346\n direct_report 0.72 0.29 0.41 1294\n\n avg / total 0.73 0.46 0.52 21159\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"### 8. Try improving your model further. Here are a few ideas:\n* try other machine learning algorithms\n* add other features besides the TF-IDF",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"I'm going to use the KNeighborsClassifier like in my previous submission and see how well it performs in this case.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# using KNeighborsClassifier\npipeline_knn = Pipeline([\n ('vect', CountVectorizer(tokenizer = tokenize)),\n ('tfidf', TfidfTransformer()),\n ('clf', MultiOutputClassifier(KNeighborsClassifier()))\n])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# train KNeighborsClassifier model\npipeline_knn.fit(X_train, y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# predict responses for KNeighborsClassifier model\nY_pred_knn = pipeline_knn.predict(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# print classification_report\nprint(classification_report(y_test, Y_pred_knn, target_names = y_test.columns, digits = 2))",
" precision recall f1-score support\n\n related 0.80 0.99 0.88 5105\n request 0.75 0.09 0.16 1140\n offer 0.00 0.00 0.00 33\n aid_related 0.78 0.05 0.09 2739\n medical_help 0.00 0.00 0.00 546\n medical_products 0.50 0.00 0.01 355\n search_and_rescue 0.00 0.00 0.00 173\n security 0.00 0.00 0.00 123\n military 0.00 0.00 0.00 226\n child_alone 0.00 0.00 0.00 0\n water 0.73 0.05 0.09 414\n food 0.75 0.07 0.12 727\n shelter 0.84 0.04 0.07 592\n clothing 0.50 0.02 0.04 95\n money 0.75 0.02 0.04 161\n missing_people 0.00 0.00 0.00 86\n refugees 0.00 0.00 0.00 204\n death 0.78 0.02 0.04 313\n other_aid 0.50 0.01 0.02 858\ninfrastructure_related 0.50 0.00 0.00 445\n transport 0.00 0.00 0.00 313\n buildings 1.00 0.01 0.02 353\n electricity 0.00 0.00 0.00 132\n tools 0.00 0.00 0.00 34\n hospitals 0.00 0.00 0.00 63\n shops 0.00 0.00 0.00 26\n aid_centers 0.00 0.00 0.00 85\n other_infrastructure 0.00 0.00 0.00 307\n weather_related 0.80 0.06 0.11 1864\n floods 0.50 0.00 0.00 547\n storm 0.75 0.01 0.03 641\n fire 0.00 0.00 0.00 71\n earthquake 0.81 0.14 0.24 626\n cold 1.00 0.01 0.02 122\n other_weather 0.75 0.01 0.02 346\n direct_report 0.73 0.06 0.11 1294\n\n avg / total 0.67 0.27 0.27 21159\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"### 9. Export your model as a pickle file",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pickle_out = open('model.pkl','wb')\npickle.dump(cv_forest, pickle_out)\npickle_out.close()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 10. Use this notebook to complete `train.py`\nUse the template file attached in the Resources folder to write a script that runs the steps above to create a database and export a model based on a new dataset specified by the user.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a301978d2b7fcffd2e4a8064a6f891c1c4fdfff
| 316,244 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/graph_generator.ipynb
|
dschaub95/pyconcorde
|
8b4a7af120071e939445050efdf613412475cb26
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/graph_generator.ipynb
|
dschaub95/pyconcorde
|
8b4a7af120071e939445050efdf613412475cb26
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/graph_generator.ipynb
|
dschaub95/pyconcorde
|
8b4a7af120071e939445050efdf613412475cb26
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null | 215.425068 | 101,302 | 0.806169 |
[
[
[
"%load_ext autoreload\n%autoreload 2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from TSP_utils import TSP_solver, TSP_plotter, TSP_generator, TSP_loader\nimport numpy as np\nimport networkx as nx\nimport tqdm\nimport tsplib95\nimport time\nimport sys",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"solver = TSP_solver()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"folder = 'test_sets'\nNUM_NODES = 10\ngenerator = TSP_generator(g_type='tsp_2d', num_min=NUM_NODES, num_max=NUM_NODES)\nnum_graphs = 1000\ngraph_list = generator.gen_graphs(num_graphs=num_graphs)\nsave_path = f'../{folder}/synthetic_n_{NUM_NODES}_{num_graphs}'\ngenerator.save_nx_as_tsp(graph_list, save_path, scale=6, start_index=0)\nsolver.add_lengths_and_sols(data_dir=save_path, scale_factor=10**6, lengths_name='lengths.txt', sols_name='solutions.txt')",
"TSP_Problem_0.tsp\nTSP_Problem_1.tsp\nTSP_Problem_2.tsp\nTSP_Problem_3.tsp\nTSP_Problem_4.tsp\nTSP_Problem_5.tsp\nTSP_Problem_6.tsp\nTSP_Problem_7.tsp\nTSP_Problem_8.tsp\nTSP_Problem_9.tsp\nTSP_Problem_10.tsp\nTSP_Problem_11.tsp\nTSP_Problem_12.tsp\nTSP_Problem_13.tsp\nTSP_Problem_14.tsp\nTSP_Problem_15.tsp\nTSP_Problem_16.tsp\nTSP_Problem_17.tsp\nTSP_Problem_18.tsp\nTSP_Problem_19.tsp\nTSP_Problem_20.tsp\nTSP_Problem_21.tsp\nTSP_Problem_22.tsp\nTSP_Problem_23.tsp\nTSP_Problem_24.tsp\nTSP_Problem_25.tsp\nTSP_Problem_26.tsp\nTSP_Problem_27.tsp\nTSP_Problem_28.tsp\nTSP_Problem_29.tsp\nTSP_Problem_30.tsp\nTSP_Problem_31.tsp\nTSP_Problem_32.tsp\nTSP_Problem_33.tsp\nTSP_Problem_34.tsp\nTSP_Problem_35.tsp\nTSP_Problem_36.tsp\nTSP_Problem_37.tsp\nTSP_Problem_38.tsp\nTSP_Problem_39.tsp\nTSP_Problem_40.tsp\nTSP_Problem_41.tsp\nTSP_Problem_42.tsp\nTSP_Problem_43.tsp\nTSP_Problem_44.tsp\nTSP_Problem_45.tsp\nTSP_Problem_46.tsp\nTSP_Problem_47.tsp\nTSP_Problem_48.tsp\nTSP_Problem_49.tsp\nTSP_Problem_50.tsp\nTSP_Problem_51.tsp\nTSP_Problem_52.tsp\nTSP_Problem_53.tsp\nTSP_Problem_54.tsp\nTSP_Problem_55.tsp\nTSP_Problem_56.tsp\nTSP_Problem_57.tsp\nTSP_Problem_58.tsp\nTSP_Problem_59.tsp\nTSP_Problem_60.tsp\nTSP_Problem_61.tsp\nTSP_Problem_62.tsp\nTSP_Problem_63.tsp\nTSP_Problem_64.tsp\nTSP_Problem_65.tsp\nTSP_Problem_66.tsp\nTSP_Problem_67.tsp\nTSP_Problem_68.tsp\nTSP_Problem_69.tsp\nTSP_Problem_70.tsp\nTSP_Problem_71.tsp\nTSP_Problem_72.tsp\nTSP_Problem_73.tsp\nTSP_Problem_74.tsp\nTSP_Problem_75.tsp\nTSP_Problem_76.tsp\nTSP_Problem_77.tsp\nTSP_Problem_78.tsp\nTSP_Problem_79.tsp\nTSP_Problem_80.tsp\nTSP_Problem_81.tsp\nTSP_Problem_82.tsp\nTSP_Problem_83.tsp\nTSP_Problem_84.tsp\nTSP_Problem_85.tsp\nTSP_Problem_86.tsp\nTSP_Problem_87.tsp\nTSP_Problem_88.tsp\nTSP_Problem_89.tsp\nTSP_Problem_90.tsp\nTSP_Problem_91.tsp\nTSP_Problem_92.tsp\nTSP_Problem_93.tsp\nTSP_Problem_94.tsp\nTSP_Problem_95.tsp\nTSP_Problem_96.tsp\nTSP_Problem_97.tsp\nTSP_Problem_98.tsp\nTSP_Problem_99.tsp\nTSP_Problem_100.tsp\nTSP_Problem_101.tsp\nTSP_Problem_102.tsp\nTSP_Problem_103.tsp\nTSP_Problem_104.tsp\nTSP_Problem_105.tsp\nTSP_Problem_106.tsp\nTSP_Problem_107.tsp\nTSP_Problem_108.tsp\nTSP_Problem_109.tsp\nTSP_Problem_110.tsp\nTSP_Problem_111.tsp\nTSP_Problem_112.tsp\nTSP_Problem_113.tsp\nTSP_Problem_114.tsp\nTSP_Problem_115.tsp\nTSP_Problem_116.tsp\nTSP_Problem_117.tsp\nTSP_Problem_118.tsp\nTSP_Problem_119.tsp\nTSP_Problem_120.tsp\nTSP_Problem_121.tsp\nTSP_Problem_122.tsp\nTSP_Problem_123.tsp\nTSP_Problem_124.tsp\nTSP_Problem_125.tsp\nTSP_Problem_126.tsp\nTSP_Problem_127.tsp\nTSP_Problem_128.tsp\nTSP_Problem_129.tsp\nTSP_Problem_130.tsp\nTSP_Problem_131.tsp\nTSP_Problem_132.tsp\nTSP_Problem_133.tsp\nTSP_Problem_134.tsp\nTSP_Problem_135.tsp\nTSP_Problem_136.tsp\nTSP_Problem_137.tsp\nTSP_Problem_138.tsp\nTSP_Problem_139.tsp\nTSP_Problem_140.tsp\nTSP_Problem_141.tsp\nTSP_Problem_142.tsp\nTSP_Problem_143.tsp\nTSP_Problem_144.tsp\nTSP_Problem_145.tsp\nTSP_Problem_146.tsp\nTSP_Problem_147.tsp\nTSP_Problem_148.tsp\nTSP_Problem_149.tsp\nTSP_Problem_150.tsp\nTSP_Problem_151.tsp\nTSP_Problem_152.tsp\nTSP_Problem_153.tsp\nTSP_Problem_154.tsp\nTSP_Problem_155.tsp\nTSP_Problem_156.tsp\nTSP_Problem_157.tsp\nTSP_Problem_158.tsp\nTSP_Problem_159.tsp\nTSP_Problem_160.tsp\nTSP_Problem_161.tsp\nTSP_Problem_162.tsp\nTSP_Problem_163.tsp\nTSP_Problem_164.tsp\nTSP_Problem_165.tsp\nTSP_Problem_166.tsp\nTSP_Problem_167.tsp\nTSP_Problem_168.tsp\nTSP_Problem_169.tsp\nTSP_Problem_170.tsp\nTSP_Problem_171.tsp\nTSP_Problem_172.tsp\nTSP_Problem_173.tsp\nTSP_Problem_174.tsp\nTSP_Problem_175.tsp\nTSP_Problem_176.tsp\nTSP_Problem_177.tsp\nTSP_Problem_178.tsp\nTSP_Problem_179.tsp\nTSP_Problem_180.tsp\nTSP_Problem_181.tsp\nTSP_Problem_182.tsp\nTSP_Problem_183.tsp\nTSP_Problem_184.tsp\nTSP_Problem_185.tsp\nTSP_Problem_186.tsp\nTSP_Problem_187.tsp\nTSP_Problem_188.tsp\nTSP_Problem_189.tsp\nTSP_Problem_190.tsp\nTSP_Problem_191.tsp\nTSP_Problem_192.tsp\nTSP_Problem_193.tsp\nTSP_Problem_194.tsp\nTSP_Problem_195.tsp\nTSP_Problem_196.tsp\nTSP_Problem_197.tsp\nTSP_Problem_198.tsp\nTSP_Problem_199.tsp\nTSP_Problem_200.tsp\nTSP_Problem_201.tsp\nTSP_Problem_202.tsp\nTSP_Problem_203.tsp\nTSP_Problem_204.tsp\nTSP_Problem_205.tsp\nTSP_Problem_206.tsp\nTSP_Problem_207.tsp\nTSP_Problem_208.tsp\nTSP_Problem_209.tsp\nTSP_Problem_210.tsp\nTSP_Problem_211.tsp\nTSP_Problem_212.tsp\nTSP_Problem_213.tsp\nTSP_Problem_214.tsp\nTSP_Problem_215.tsp\nTSP_Problem_216.tsp\nTSP_Problem_217.tsp\nTSP_Problem_218.tsp\nTSP_Problem_219.tsp\nTSP_Problem_220.tsp\nTSP_Problem_221.tsp\nTSP_Problem_222.tsp\nTSP_Problem_223.tsp\nTSP_Problem_224.tsp\nTSP_Problem_225.tsp\nTSP_Problem_226.tsp\nTSP_Problem_227.tsp\nTSP_Problem_228.tsp\nTSP_Problem_229.tsp\nTSP_Problem_230.tsp\nTSP_Problem_231.tsp\nTSP_Problem_232.tsp\nTSP_Problem_233.tsp\nTSP_Problem_234.tsp\nTSP_Problem_235.tsp\nTSP_Problem_236.tsp\nTSP_Problem_237.tsp\nTSP_Problem_238.tsp\nTSP_Problem_239.tsp\nTSP_Problem_240.tsp\nTSP_Problem_241.tsp\nTSP_Problem_242.tsp\nTSP_Problem_243.tsp\nTSP_Problem_244.tsp\nTSP_Problem_245.tsp\nTSP_Problem_246.tsp\nTSP_Problem_247.tsp\nTSP_Problem_248.tsp\nTSP_Problem_249.tsp\nTSP_Problem_250.tsp\nTSP_Problem_251.tsp\nTSP_Problem_252.tsp\nTSP_Problem_253.tsp\nTSP_Problem_254.tsp\nTSP_Problem_255.tsp\nTSP_Problem_256.tsp\nTSP_Problem_257.tsp\nTSP_Problem_258.tsp\nTSP_Problem_259.tsp\nTSP_Problem_260.tsp\nTSP_Problem_261.tsp\nTSP_Problem_262.tsp\nTSP_Problem_263.tsp\nTSP_Problem_264.tsp\nTSP_Problem_265.tsp\nTSP_Problem_266.tsp\nTSP_Problem_267.tsp\nTSP_Problem_268.tsp\nTSP_Problem_269.tsp\nTSP_Problem_270.tsp\nTSP_Problem_271.tsp\nTSP_Problem_272.tsp\nTSP_Problem_273.tsp\nTSP_Problem_274.tsp\nTSP_Problem_275.tsp\nTSP_Problem_276.tsp\nTSP_Problem_277.tsp\nTSP_Problem_278.tsp\nTSP_Problem_279.tsp\nTSP_Problem_280.tsp\nTSP_Problem_281.tsp\nTSP_Problem_282.tsp\nTSP_Problem_283.tsp\nTSP_Problem_284.tsp\nTSP_Problem_285.tsp\nTSP_Problem_286.tsp\nTSP_Problem_287.tsp\nTSP_Problem_288.tsp\nTSP_Problem_289.tsp\nTSP_Problem_290.tsp\nTSP_Problem_291.tsp\nTSP_Problem_292.tsp\nTSP_Problem_293.tsp\nTSP_Problem_294.tsp\nTSP_Problem_295.tsp\nTSP_Problem_296.tsp\nTSP_Problem_297.tsp\nTSP_Problem_298.tsp\nTSP_Problem_299.tsp\nTSP_Problem_300.tsp\nTSP_Problem_301.tsp\nTSP_Problem_302.tsp\nTSP_Problem_303.tsp\nTSP_Problem_304.tsp\nTSP_Problem_305.tsp\nTSP_Problem_306.tsp\nTSP_Problem_307.tsp\nTSP_Problem_308.tsp\nTSP_Problem_309.tsp\nTSP_Problem_310.tsp\nTSP_Problem_311.tsp\nTSP_Problem_312.tsp\nTSP_Problem_313.tsp\nTSP_Problem_314.tsp\nTSP_Problem_315.tsp\nTSP_Problem_316.tsp\nTSP_Problem_317.tsp\nTSP_Problem_318.tsp\nTSP_Problem_319.tsp\nTSP_Problem_320.tsp\nTSP_Problem_321.tsp\nTSP_Problem_322.tsp\nTSP_Problem_323.tsp\nTSP_Problem_324.tsp\nTSP_Problem_325.tsp\nTSP_Problem_326.tsp\nTSP_Problem_327.tsp\nTSP_Problem_328.tsp\nTSP_Problem_329.tsp\nTSP_Problem_330.tsp\nTSP_Problem_331.tsp\nTSP_Problem_332.tsp\nTSP_Problem_333.tsp\nTSP_Problem_334.tsp\nTSP_Problem_335.tsp\nTSP_Problem_336.tsp\nTSP_Problem_337.tsp\nTSP_Problem_338.tsp\nTSP_Problem_339.tsp\nTSP_Problem_340.tsp\nTSP_Problem_341.tsp\nTSP_Problem_342.tsp\nTSP_Problem_343.tsp\nTSP_Problem_344.tsp\nTSP_Problem_345.tsp\nTSP_Problem_346.tsp\nTSP_Problem_347.tsp\nTSP_Problem_348.tsp\nTSP_Problem_349.tsp\nTSP_Problem_350.tsp\nTSP_Problem_351.tsp\nTSP_Problem_352.tsp\nTSP_Problem_353.tsp\nTSP_Problem_354.tsp\nTSP_Problem_355.tsp\nTSP_Problem_356.tsp\nTSP_Problem_357.tsp\nTSP_Problem_358.tsp\nTSP_Problem_359.tsp\nTSP_Problem_360.tsp\nTSP_Problem_361.tsp\nTSP_Problem_362.tsp\nTSP_Problem_363.tsp\nTSP_Problem_364.tsp\nTSP_Problem_365.tsp\nTSP_Problem_366.tsp\nTSP_Problem_367.tsp\nTSP_Problem_368.tsp\nTSP_Problem_369.tsp\nTSP_Problem_370.tsp\nTSP_Problem_371.tsp\nTSP_Problem_372.tsp\nTSP_Problem_373.tsp\nTSP_Problem_374.tsp\nTSP_Problem_375.tsp\nTSP_Problem_376.tsp\nTSP_Problem_377.tsp\nTSP_Problem_378.tsp\nTSP_Problem_379.tsp\nTSP_Problem_380.tsp\nTSP_Problem_381.tsp\nTSP_Problem_382.tsp\nTSP_Problem_383.tsp\nTSP_Problem_384.tsp\nTSP_Problem_385.tsp\nTSP_Problem_386.tsp\nTSP_Problem_387.tsp\nTSP_Problem_388.tsp\nTSP_Problem_389.tsp\nTSP_Problem_390.tsp\nTSP_Problem_391.tsp\nTSP_Problem_392.tsp\nTSP_Problem_393.tsp\nTSP_Problem_394.tsp\nTSP_Problem_395.tsp\nTSP_Problem_396.tsp\nTSP_Problem_397.tsp\nTSP_Problem_398.tsp\nTSP_Problem_399.tsp\nTSP_Problem_400.tsp\nTSP_Problem_401.tsp\nTSP_Problem_402.tsp\nTSP_Problem_403.tsp\nTSP_Problem_404.tsp\nTSP_Problem_405.tsp\nTSP_Problem_406.tsp\nTSP_Problem_407.tsp\nTSP_Problem_408.tsp\nTSP_Problem_409.tsp\nTSP_Problem_410.tsp\nTSP_Problem_411.tsp\nTSP_Problem_412.tsp\nTSP_Problem_413.tsp\nTSP_Problem_414.tsp\nTSP_Problem_415.tsp\nTSP_Problem_416.tsp\nTSP_Problem_417.tsp\nTSP_Problem_418.tsp\nTSP_Problem_419.tsp\nTSP_Problem_420.tsp\nTSP_Problem_421.tsp\nTSP_Problem_422.tsp\nTSP_Problem_423.tsp\nTSP_Problem_424.tsp\nTSP_Problem_425.tsp\nTSP_Problem_426.tsp\nTSP_Problem_427.tsp\nTSP_Problem_428.tsp\nTSP_Problem_429.tsp\nTSP_Problem_430.tsp\nTSP_Problem_431.tsp\nTSP_Problem_432.tsp\nTSP_Problem_433.tsp\nTSP_Problem_434.tsp\nTSP_Problem_435.tsp\nTSP_Problem_436.tsp\nTSP_Problem_437.tsp\nTSP_Problem_438.tsp\nTSP_Problem_439.tsp\nTSP_Problem_440.tsp\nTSP_Problem_441.tsp\nTSP_Problem_442.tsp\nTSP_Problem_443.tsp\nTSP_Problem_444.tsp\nTSP_Problem_445.tsp\nTSP_Problem_446.tsp\nTSP_Problem_447.tsp\nTSP_Problem_448.tsp\nTSP_Problem_449.tsp\nTSP_Problem_450.tsp\nTSP_Problem_451.tsp\nTSP_Problem_452.tsp\nTSP_Problem_453.tsp\nTSP_Problem_454.tsp\nTSP_Problem_455.tsp\nTSP_Problem_456.tsp\nTSP_Problem_457.tsp\nTSP_Problem_458.tsp\nTSP_Problem_459.tsp\nTSP_Problem_460.tsp\nTSP_Problem_461.tsp\nTSP_Problem_462.tsp\nTSP_Problem_463.tsp\nTSP_Problem_464.tsp\nTSP_Problem_465.tsp\nTSP_Problem_466.tsp\nTSP_Problem_467.tsp\nTSP_Problem_468.tsp\nTSP_Problem_469.tsp\nTSP_Problem_470.tsp\nTSP_Problem_471.tsp\nTSP_Problem_472.tsp\nTSP_Problem_473.tsp\nTSP_Problem_474.tsp\nTSP_Problem_475.tsp\nTSP_Problem_476.tsp\nTSP_Problem_477.tsp\nTSP_Problem_478.tsp\nTSP_Problem_479.tsp\nTSP_Problem_480.tsp\nTSP_Problem_481.tsp\nTSP_Problem_482.tsp\nTSP_Problem_483.tsp\nTSP_Problem_484.tsp\nTSP_Problem_485.tsp\nTSP_Problem_486.tsp\nTSP_Problem_487.tsp\nTSP_Problem_488.tsp\nTSP_Problem_489.tsp\nTSP_Problem_490.tsp\nTSP_Problem_491.tsp\nTSP_Problem_492.tsp\nTSP_Problem_493.tsp\nTSP_Problem_494.tsp\nTSP_Problem_495.tsp\nTSP_Problem_496.tsp\nTSP_Problem_497.tsp\nTSP_Problem_498.tsp\nTSP_Problem_499.tsp\nTSP_Problem_500.tsp\nTSP_Problem_501.tsp\nTSP_Problem_502.tsp\nTSP_Problem_503.tsp\nTSP_Problem_504.tsp\nTSP_Problem_505.tsp\nTSP_Problem_506.tsp\nTSP_Problem_507.tsp\nTSP_Problem_508.tsp\nTSP_Problem_509.tsp\nTSP_Problem_510.tsp\nTSP_Problem_511.tsp\nTSP_Problem_512.tsp\nTSP_Problem_513.tsp\nTSP_Problem_514.tsp\nTSP_Problem_515.tsp\nTSP_Problem_516.tsp\nTSP_Problem_517.tsp\nTSP_Problem_518.tsp\nTSP_Problem_519.tsp\nTSP_Problem_520.tsp\nTSP_Problem_521.tsp\nTSP_Problem_522.tsp\nTSP_Problem_523.tsp\nTSP_Problem_524.tsp\nTSP_Problem_525.tsp\nTSP_Problem_526.tsp\nTSP_Problem_527.tsp\nTSP_Problem_528.tsp\nTSP_Problem_529.tsp\nTSP_Problem_530.tsp\nTSP_Problem_531.tsp\nTSP_Problem_532.tsp\nTSP_Problem_533.tsp\nTSP_Problem_534.tsp\nTSP_Problem_535.tsp\nTSP_Problem_536.tsp\nTSP_Problem_537.tsp\nTSP_Problem_538.tsp\nTSP_Problem_539.tsp\nTSP_Problem_540.tsp\nTSP_Problem_541.tsp\nTSP_Problem_542.tsp\nTSP_Problem_543.tsp\nTSP_Problem_544.tsp\nTSP_Problem_545.tsp\nTSP_Problem_546.tsp\nTSP_Problem_547.tsp\nTSP_Problem_548.tsp\nTSP_Problem_549.tsp\nTSP_Problem_550.tsp\nTSP_Problem_551.tsp\nTSP_Problem_552.tsp\nTSP_Problem_553.tsp\nTSP_Problem_554.tsp\nTSP_Problem_555.tsp\nTSP_Problem_556.tsp\nTSP_Problem_557.tsp\nTSP_Problem_558.tsp\nTSP_Problem_559.tsp\nTSP_Problem_560.tsp\nTSP_Problem_561.tsp\nTSP_Problem_562.tsp\nTSP_Problem_563.tsp\nTSP_Problem_564.tsp\nTSP_Problem_565.tsp\nTSP_Problem_566.tsp\nTSP_Problem_567.tsp\nTSP_Problem_568.tsp\nTSP_Problem_569.tsp\nTSP_Problem_570.tsp\nTSP_Problem_571.tsp\nTSP_Problem_572.tsp\nTSP_Problem_573.tsp\nTSP_Problem_574.tsp\nTSP_Problem_575.tsp\nTSP_Problem_576.tsp\nTSP_Problem_577.tsp\nTSP_Problem_578.tsp\nTSP_Problem_579.tsp\nTSP_Problem_580.tsp\nTSP_Problem_581.tsp\nTSP_Problem_582.tsp\nTSP_Problem_583.tsp\nTSP_Problem_584.tsp\nTSP_Problem_585.tsp\nTSP_Problem_586.tsp\nTSP_Problem_587.tsp\nTSP_Problem_588.tsp\nTSP_Problem_589.tsp\nTSP_Problem_590.tsp\nTSP_Problem_591.tsp\nTSP_Problem_592.tsp\nTSP_Problem_593.tsp\nTSP_Problem_594.tsp\nTSP_Problem_595.tsp\nTSP_Problem_596.tsp\nTSP_Problem_597.tsp\nTSP_Problem_598.tsp\nTSP_Problem_599.tsp\nTSP_Problem_600.tsp\nTSP_Problem_601.tsp\nTSP_Problem_602.tsp\nTSP_Problem_603.tsp\nTSP_Problem_604.tsp\nTSP_Problem_605.tsp\nTSP_Problem_606.tsp\nTSP_Problem_607.tsp\nTSP_Problem_608.tsp\nTSP_Problem_609.tsp\nTSP_Problem_610.tsp\nTSP_Problem_611.tsp\nTSP_Problem_612.tsp\nTSP_Problem_613.tsp\nTSP_Problem_614.tsp\nTSP_Problem_615.tsp\nTSP_Problem_616.tsp\nTSP_Problem_617.tsp\nTSP_Problem_618.tsp\nTSP_Problem_619.tsp\nTSP_Problem_620.tsp\nTSP_Problem_621.tsp\nTSP_Problem_622.tsp\nTSP_Problem_623.tsp\nTSP_Problem_624.tsp\nTSP_Problem_625.tsp\nTSP_Problem_626.tsp\nTSP_Problem_627.tsp\nTSP_Problem_628.tsp\nTSP_Problem_629.tsp\nTSP_Problem_630.tsp\nTSP_Problem_631.tsp\nTSP_Problem_632.tsp\nTSP_Problem_633.tsp\nTSP_Problem_634.tsp\nTSP_Problem_635.tsp\nTSP_Problem_636.tsp\nTSP_Problem_637.tsp\nTSP_Problem_638.tsp\nTSP_Problem_639.tsp\nTSP_Problem_640.tsp\nTSP_Problem_641.tsp\nTSP_Problem_642.tsp\nTSP_Problem_643.tsp\nTSP_Problem_644.tsp\nTSP_Problem_645.tsp\nTSP_Problem_646.tsp\nTSP_Problem_647.tsp\nTSP_Problem_648.tsp\nTSP_Problem_649.tsp\nTSP_Problem_650.tsp\nTSP_Problem_651.tsp\nTSP_Problem_652.tsp\nTSP_Problem_653.tsp\nTSP_Problem_654.tsp\nTSP_Problem_655.tsp\nTSP_Problem_656.tsp\nTSP_Problem_657.tsp\nTSP_Problem_658.tsp\nTSP_Problem_659.tsp\nTSP_Problem_660.tsp\nTSP_Problem_661.tsp\nTSP_Problem_662.tsp\nTSP_Problem_663.tsp\nTSP_Problem_664.tsp\nTSP_Problem_665.tsp\nTSP_Problem_666.tsp\nTSP_Problem_667.tsp\nTSP_Problem_668.tsp\nTSP_Problem_669.tsp\nTSP_Problem_670.tsp\nTSP_Problem_671.tsp\nTSP_Problem_672.tsp\nTSP_Problem_673.tsp\nTSP_Problem_674.tsp\nTSP_Problem_675.tsp\nTSP_Problem_676.tsp\nTSP_Problem_677.tsp\nTSP_Problem_678.tsp\nTSP_Problem_679.tsp\nTSP_Problem_680.tsp\nTSP_Problem_681.tsp\nTSP_Problem_682.tsp\nTSP_Problem_683.tsp\nTSP_Problem_684.tsp\nTSP_Problem_685.tsp\nTSP_Problem_686.tsp\nTSP_Problem_687.tsp\nTSP_Problem_688.tsp\nTSP_Problem_689.tsp\nTSP_Problem_690.tsp\nTSP_Problem_691.tsp\nTSP_Problem_692.tsp\nTSP_Problem_693.tsp\nTSP_Problem_694.tsp\nTSP_Problem_695.tsp\nTSP_Problem_696.tsp\nTSP_Problem_697.tsp\nTSP_Problem_698.tsp\nTSP_Problem_699.tsp\nTSP_Problem_700.tsp\nTSP_Problem_701.tsp\nTSP_Problem_702.tsp\nTSP_Problem_703.tsp\nTSP_Problem_704.tsp\nTSP_Problem_705.tsp\nTSP_Problem_706.tsp\nTSP_Problem_707.tsp\nTSP_Problem_708.tsp\nTSP_Problem_709.tsp\nTSP_Problem_710.tsp\nTSP_Problem_711.tsp\nTSP_Problem_712.tsp\nTSP_Problem_713.tsp\nTSP_Problem_714.tsp\nTSP_Problem_715.tsp\nTSP_Problem_716.tsp\nTSP_Problem_717.tsp\nTSP_Problem_718.tsp\nTSP_Problem_719.tsp\nTSP_Problem_720.tsp\nTSP_Problem_721.tsp\nTSP_Problem_722.tsp\nTSP_Problem_723.tsp\nTSP_Problem_724.tsp\nTSP_Problem_725.tsp\nTSP_Problem_726.tsp\nTSP_Problem_727.tsp\nTSP_Problem_728.tsp\nTSP_Problem_729.tsp\nTSP_Problem_730.tsp\nTSP_Problem_731.tsp\nTSP_Problem_732.tsp\nTSP_Problem_733.tsp\nTSP_Problem_734.tsp\nTSP_Problem_735.tsp\nTSP_Problem_736.tsp\nTSP_Problem_737.tsp\nTSP_Problem_738.tsp\nTSP_Problem_739.tsp\nTSP_Problem_740.tsp\nTSP_Problem_741.tsp\nTSP_Problem_742.tsp\nTSP_Problem_743.tsp\nTSP_Problem_744.tsp\nTSP_Problem_745.tsp\nTSP_Problem_746.tsp\nTSP_Problem_747.tsp\nTSP_Problem_748.tsp\nTSP_Problem_749.tsp\nTSP_Problem_750.tsp\nTSP_Problem_751.tsp\nTSP_Problem_752.tsp\nTSP_Problem_753.tsp\nTSP_Problem_754.tsp\nTSP_Problem_755.tsp\nTSP_Problem_756.tsp\nTSP_Problem_757.tsp\nTSP_Problem_758.tsp\nTSP_Problem_759.tsp\nTSP_Problem_760.tsp\nTSP_Problem_761.tsp\nTSP_Problem_762.tsp\nTSP_Problem_763.tsp\nTSP_Problem_764.tsp\nTSP_Problem_765.tsp\nTSP_Problem_766.tsp\nTSP_Problem_767.tsp\nTSP_Problem_768.tsp\nTSP_Problem_769.tsp\nTSP_Problem_770.tsp\nTSP_Problem_771.tsp\nTSP_Problem_772.tsp\nTSP_Problem_773.tsp\nTSP_Problem_774.tsp\nTSP_Problem_775.tsp\nTSP_Problem_776.tsp\nTSP_Problem_777.tsp\nTSP_Problem_778.tsp\nTSP_Problem_779.tsp\nTSP_Problem_780.tsp\nTSP_Problem_781.tsp\nTSP_Problem_782.tsp\nTSP_Problem_783.tsp\nTSP_Problem_784.tsp\nTSP_Problem_785.tsp\nTSP_Problem_786.tsp\nTSP_Problem_787.tsp\nTSP_Problem_788.tsp\nTSP_Problem_789.tsp\nTSP_Problem_790.tsp\nTSP_Problem_791.tsp\nTSP_Problem_792.tsp\nTSP_Problem_793.tsp\nTSP_Problem_794.tsp\nTSP_Problem_795.tsp\nTSP_Problem_796.tsp\nTSP_Problem_797.tsp\nTSP_Problem_798.tsp\nTSP_Problem_799.tsp\nTSP_Problem_800.tsp\nTSP_Problem_801.tsp\nTSP_Problem_802.tsp\nTSP_Problem_803.tsp\nTSP_Problem_804.tsp\nTSP_Problem_805.tsp\nTSP_Problem_806.tsp\nTSP_Problem_807.tsp\nTSP_Problem_808.tsp\nTSP_Problem_809.tsp\nTSP_Problem_810.tsp\nTSP_Problem_811.tsp\nTSP_Problem_812.tsp\nTSP_Problem_813.tsp\nTSP_Problem_814.tsp\nTSP_Problem_815.tsp\nTSP_Problem_816.tsp\nTSP_Problem_817.tsp\nTSP_Problem_818.tsp\nTSP_Problem_819.tsp\nTSP_Problem_820.tsp\nTSP_Problem_821.tsp\nTSP_Problem_822.tsp\nTSP_Problem_823.tsp\nTSP_Problem_824.tsp\nTSP_Problem_825.tsp\nTSP_Problem_826.tsp\nTSP_Problem_827.tsp\nTSP_Problem_828.tsp\nTSP_Problem_829.tsp\nTSP_Problem_830.tsp\nTSP_Problem_831.tsp\nTSP_Problem_832.tsp\nTSP_Problem_833.tsp\nTSP_Problem_834.tsp\nTSP_Problem_835.tsp\nTSP_Problem_836.tsp\nTSP_Problem_837.tsp\nTSP_Problem_838.tsp\nTSP_Problem_839.tsp\nTSP_Problem_840.tsp\nTSP_Problem_841.tsp\nTSP_Problem_842.tsp\nTSP_Problem_843.tsp\nTSP_Problem_844.tsp\nTSP_Problem_845.tsp\nTSP_Problem_846.tsp\nTSP_Problem_847.tsp\nTSP_Problem_848.tsp\nTSP_Problem_849.tsp\nTSP_Problem_850.tsp\nTSP_Problem_851.tsp\nTSP_Problem_852.tsp\nTSP_Problem_853.tsp\nTSP_Problem_854.tsp\nTSP_Problem_855.tsp\nTSP_Problem_856.tsp\nTSP_Problem_857.tsp\nTSP_Problem_858.tsp\nTSP_Problem_859.tsp\nTSP_Problem_860.tsp\nTSP_Problem_861.tsp\nTSP_Problem_862.tsp\nTSP_Problem_863.tsp\nTSP_Problem_864.tsp\nTSP_Problem_865.tsp\nTSP_Problem_866.tsp\nTSP_Problem_867.tsp\nTSP_Problem_868.tsp\nTSP_Problem_869.tsp\nTSP_Problem_870.tsp\nTSP_Problem_871.tsp\nTSP_Problem_872.tsp\nTSP_Problem_873.tsp\nTSP_Problem_874.tsp\nTSP_Problem_875.tsp\nTSP_Problem_876.tsp\nTSP_Problem_877.tsp\nTSP_Problem_878.tsp\nTSP_Problem_879.tsp\nTSP_Problem_880.tsp\nTSP_Problem_881.tsp\nTSP_Problem_882.tsp\nTSP_Problem_883.tsp\nTSP_Problem_884.tsp\nTSP_Problem_885.tsp\nTSP_Problem_886.tsp\nTSP_Problem_887.tsp\nTSP_Problem_888.tsp\nTSP_Problem_889.tsp\nTSP_Problem_890.tsp\nTSP_Problem_891.tsp\nTSP_Problem_892.tsp\nTSP_Problem_893.tsp\nTSP_Problem_894.tsp\nTSP_Problem_895.tsp\nTSP_Problem_896.tsp\nTSP_Problem_897.tsp\nTSP_Problem_898.tsp\nTSP_Problem_899.tsp\nTSP_Problem_900.tsp\nTSP_Problem_901.tsp\nTSP_Problem_902.tsp\nTSP_Problem_903.tsp\nTSP_Problem_904.tsp\nTSP_Problem_905.tsp\nTSP_Problem_906.tsp\nTSP_Problem_907.tsp\nTSP_Problem_908.tsp\nTSP_Problem_909.tsp\nTSP_Problem_910.tsp\nTSP_Problem_911.tsp\nTSP_Problem_912.tsp\nTSP_Problem_913.tsp\nTSP_Problem_914.tsp\nTSP_Problem_915.tsp\nTSP_Problem_916.tsp\nTSP_Problem_917.tsp\nTSP_Problem_918.tsp\nTSP_Problem_919.tsp\nTSP_Problem_920.tsp\nTSP_Problem_921.tsp\nTSP_Problem_922.tsp\nTSP_Problem_923.tsp\nTSP_Problem_924.tsp\nTSP_Problem_925.tsp\nTSP_Problem_926.tsp\nTSP_Problem_927.tsp\nTSP_Problem_928.tsp\nTSP_Problem_929.tsp\nTSP_Problem_930.tsp\nTSP_Problem_931.tsp\nTSP_Problem_932.tsp\nTSP_Problem_933.tsp\nTSP_Problem_934.tsp\nTSP_Problem_935.tsp\nTSP_Problem_936.tsp\nTSP_Problem_937.tsp\nTSP_Problem_938.tsp\nTSP_Problem_939.tsp\nTSP_Problem_940.tsp\nTSP_Problem_941.tsp\nTSP_Problem_942.tsp\nTSP_Problem_943.tsp\nTSP_Problem_944.tsp\nTSP_Problem_945.tsp\nTSP_Problem_946.tsp\nTSP_Problem_947.tsp\nTSP_Problem_948.tsp\nTSP_Problem_949.tsp\nTSP_Problem_950.tsp\nTSP_Problem_951.tsp\nTSP_Problem_952.tsp\nTSP_Problem_953.tsp\nTSP_Problem_954.tsp\nTSP_Problem_955.tsp\nTSP_Problem_956.tsp\nTSP_Problem_957.tsp\nTSP_Problem_958.tsp\nTSP_Problem_959.tsp\nTSP_Problem_960.tsp\nTSP_Problem_961.tsp\nTSP_Problem_962.tsp\nTSP_Problem_963.tsp\nTSP_Problem_964.tsp\nTSP_Problem_965.tsp\nTSP_Problem_966.tsp\nTSP_Problem_967.tsp\nTSP_Problem_968.tsp\nTSP_Problem_969.tsp\nTSP_Problem_970.tsp\nTSP_Problem_971.tsp\nTSP_Problem_972.tsp\nTSP_Problem_973.tsp\nTSP_Problem_974.tsp\nTSP_Problem_975.tsp\nTSP_Problem_976.tsp\nTSP_Problem_977.tsp\nTSP_Problem_978.tsp\nTSP_Problem_979.tsp\nTSP_Problem_980.tsp\nTSP_Problem_981.tsp\nTSP_Problem_982.tsp\nTSP_Problem_983.tsp\nTSP_Problem_984.tsp\nTSP_Problem_985.tsp\nTSP_Problem_986.tsp\nTSP_Problem_987.tsp\nTSP_Problem_988.tsp\nTSP_Problem_989.tsp\nTSP_Problem_990.tsp\nTSP_Problem_991.tsp\nTSP_Problem_992.tsp\nTSP_Problem_993.tsp\nTSP_Problem_994.tsp\nTSP_Problem_995.tsp\nTSP_Problem_996.tsp\nTSP_Problem_997.tsp\nTSP_Problem_998.tsp\nTSP_Problem_999.tsp\n"
],
[
"NUM_MIN = 20\nNUM_MAX = 20\ngenerator = TSP_generator(g_type='tsp_2d', num_min=NUM_MIN, num_max=NUM_MAX)\nnum_graphs = 50000\ngraph_list = generator.gen_graphs(num_graphs=num_graphs)\nsave_path = f'../training_sets/synthetic_nrange_{NUM_MIN}_{NUM_MAX}_{num_graphs}'\ngenerator.save_nx_as_tsp(graph_list, save_path, scale=6, start_index=0)\nsolver.add_lengths_and_sols(data_dir=save_path, scale_factor=10**6, lengths_name='lengths.txt', sols_name='solutions.txt')",
"TSP_Problem_0.tsp\nTSP_Problem_1.tsp\nTSP_Problem_2.tsp\nTSP_Problem_3.tsp\nTSP_Problem_4.tsp\nTSP_Problem_5.tsp\nTSP_Problem_6.tsp\nTSP_Problem_7.tsp\nTSP_Problem_8.tsp\nTSP_Problem_9.tsp\nTSP_Problem_10.tsp\nTSP_Problem_11.tsp\nTSP_Problem_12.tsp\nTSP_Problem_13.tsp\nTSP_Problem_14.tsp\nTSP_Problem_15.tsp\nTSP_Problem_16.tsp\nTSP_Problem_17.tsp\nTSP_Problem_18.tsp\nTSP_Problem_19.tsp\nTSP_Problem_20.tsp\nTSP_Problem_21.tsp\nTSP_Problem_22.tsp\nTSP_Problem_23.tsp\nTSP_Problem_24.tsp\nTSP_Problem_25.tsp\nTSP_Problem_26.tsp\nTSP_Problem_27.tsp\nTSP_Problem_28.tsp\nTSP_Problem_29.tsp\nTSP_Problem_30.tsp\nTSP_Problem_31.tsp\nTSP_Problem_32.tsp\nTSP_Problem_33.tsp\nTSP_Problem_34.tsp\nTSP_Problem_35.tsp\nTSP_Problem_36.tsp\nTSP_Problem_37.tsp\nTSP_Problem_38.tsp\nTSP_Problem_39.tsp\nTSP_Problem_40.tsp\nTSP_Problem_41.tsp\nTSP_Problem_42.tsp\nTSP_Problem_43.tsp\nTSP_Problem_44.tsp\nTSP_Problem_45.tsp\nTSP_Problem_46.tsp\nTSP_Problem_47.tsp\nTSP_Problem_48.tsp\nTSP_Problem_49.tsp\nTSP_Problem_50.tsp\nTSP_Problem_51.tsp\nTSP_Problem_52.tsp\nTSP_Problem_53.tsp\nTSP_Problem_54.tsp\nTSP_Problem_55.tsp\nTSP_Problem_56.tsp\nTSP_Problem_57.tsp\nTSP_Problem_58.tsp\nTSP_Problem_59.tsp\nTSP_Problem_60.tsp\nTSP_Problem_61.tsp\nTSP_Problem_62.tsp\nTSP_Problem_63.tsp\nTSP_Problem_64.tsp\nTSP_Problem_65.tsp\nTSP_Problem_66.tsp\nTSP_Problem_67.tsp\nTSP_Problem_68.tsp\nTSP_Problem_69.tsp\nTSP_Problem_70.tsp\nTSP_Problem_71.tsp\nTSP_Problem_72.tsp\nTSP_Problem_73.tsp\nTSP_Problem_74.tsp\nTSP_Problem_75.tsp\nTSP_Problem_76.tsp\nTSP_Problem_77.tsp\nTSP_Problem_78.tsp\nTSP_Problem_79.tsp\nTSP_Problem_80.tsp\nTSP_Problem_81.tsp\nTSP_Problem_82.tsp\nTSP_Problem_83.tsp\nTSP_Problem_84.tsp\nTSP_Problem_85.tsp\nTSP_Problem_86.tsp\nTSP_Problem_87.tsp\nTSP_Problem_88.tsp\nTSP_Problem_89.tsp\nTSP_Problem_90.tsp\nTSP_Problem_91.tsp\nTSP_Problem_92.tsp\nTSP_Problem_93.tsp\nTSP_Problem_94.tsp\nTSP_Problem_95.tsp\nTSP_Problem_96.tsp\nTSP_Problem_97.tsp\nTSP_Problem_98.tsp\nTSP_Problem_99.tsp\n"
],
[
"NUM_MIN = 40\nNUM_MAX = 50\ngenerator = TSP_generator(g_type='tsp_2d', num_min=NUM_MIN, num_max=NUM_MAX)\n\nnum_graphs = 100\ngraph_list = generator.gen_graphs(num_graphs=num_graphs)\nsave_path = f'valid_sets/synthetic_nrange_{NUM_MIN}_{NUM_MAX}_{num_graphs}'\ngenerator.save_nx_as_tsp(graph_list, save_path, scale=6, start_index=0)\nsolver.add_lengths_and_sols(data_dir=save_path, scale_factor=10**6, lengths_name='lengths.txt', sols_name='solutions.txt')",
"TSP_Problem_0.tsp\nTSP_Problem_1.tsp\nTSP_Problem_2.tsp\nTSP_Problem_3.tsp\nTSP_Problem_4.tsp\nTSP_Problem_5.tsp\nTSP_Problem_6.tsp\nTSP_Problem_7.tsp\nTSP_Problem_8.tsp\nTSP_Problem_9.tsp\nTSP_Problem_10.tsp\nTSP_Problem_11.tsp\nTSP_Problem_12.tsp\nTSP_Problem_13.tsp\nTSP_Problem_14.tsp\nTSP_Problem_15.tsp\nTSP_Problem_16.tsp\nTSP_Problem_17.tsp\nTSP_Problem_18.tsp\nTSP_Problem_19.tsp\nTSP_Problem_20.tsp\nTSP_Problem_21.tsp\nTSP_Problem_22.tsp\nTSP_Problem_23.tsp\nTSP_Problem_24.tsp\nTSP_Problem_25.tsp\nTSP_Problem_26.tsp\nTSP_Problem_27.tsp\nTSP_Problem_28.tsp\nTSP_Problem_29.tsp\nTSP_Problem_30.tsp\nTSP_Problem_31.tsp\nTSP_Problem_32.tsp\nTSP_Problem_33.tsp\nTSP_Problem_34.tsp\nTSP_Problem_35.tsp\nTSP_Problem_36.tsp\nTSP_Problem_37.tsp\nTSP_Problem_38.tsp\nTSP_Problem_39.tsp\nTSP_Problem_40.tsp\nTSP_Problem_41.tsp\nTSP_Problem_42.tsp\nTSP_Problem_43.tsp\nTSP_Problem_44.tsp\nTSP_Problem_45.tsp\nTSP_Problem_46.tsp\nTSP_Problem_47.tsp\nTSP_Problem_48.tsp\nTSP_Problem_49.tsp\nTSP_Problem_50.tsp\nTSP_Problem_51.tsp\nTSP_Problem_52.tsp\nTSP_Problem_53.tsp\nTSP_Problem_54.tsp\nTSP_Problem_55.tsp\nTSP_Problem_56.tsp\nTSP_Problem_57.tsp\nTSP_Problem_58.tsp\nTSP_Problem_59.tsp\nTSP_Problem_60.tsp\nTSP_Problem_61.tsp\nTSP_Problem_62.tsp\nTSP_Problem_63.tsp\nTSP_Problem_64.tsp\nTSP_Problem_65.tsp\nTSP_Problem_66.tsp\nTSP_Problem_67.tsp\nTSP_Problem_68.tsp\nTSP_Problem_69.tsp\nTSP_Problem_70.tsp\nTSP_Problem_71.tsp\nTSP_Problem_72.tsp\nTSP_Problem_73.tsp\nTSP_Problem_74.tsp\nTSP_Problem_75.tsp\nTSP_Problem_76.tsp\nTSP_Problem_77.tsp\nTSP_Problem_78.tsp\nTSP_Problem_79.tsp\nTSP_Problem_80.tsp\nTSP_Problem_81.tsp\nTSP_Problem_82.tsp\nTSP_Problem_83.tsp\nTSP_Problem_84.tsp\nTSP_Problem_85.tsp\nTSP_Problem_86.tsp\nTSP_Problem_87.tsp\nTSP_Problem_88.tsp\nTSP_Problem_89.tsp\nTSP_Problem_90.tsp\nTSP_Problem_91.tsp\nTSP_Problem_92.tsp\nTSP_Problem_93.tsp\nTSP_Problem_94.tsp\nTSP_Problem_95.tsp\nTSP_Problem_96.tsp\nTSP_Problem_97.tsp\nTSP_Problem_98.tsp\nTSP_Problem_99.tsp\n"
],
[
"plotter.plot_nx_graph(test[0], title='Fittness = {}'.format(np.round(test[1], 3)))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\nplotter = gTSP.TSP_plotter()\nplotter.plot_nx_graph(test[0])\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.arange(10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"generator = gTSP.TSP_generator(g_type='tsp_2d', num_min=15, num_max=20)\nmin = np.inf\nfor g in graph_list:\n tmp = generator.calc_control_parameter(g)\n if tmp < min:\n min = tmp\nprint(min)",
"0.8869272752360513\n"
],
[
"solver = gTSP.TSP_solver()\nsolver.calc_best_tour(graph_list[3])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a302eb7c1f7fa7a54635822e060571644e52e5d
| 340,180 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
07_food_vision_milestone_project_1.ipynb
|
Ankur099IIT/Tensorflow-and-DeepLearning
|
ef684d7613902f8c7185e67629440e6abc264789
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2,375 |
2020-11-24T06:18:23.000Z
|
2022-03-31T13:29:55.000Z
|
07_food_vision_milestone_project_1.ipynb
|
Ankur099IIT/Tensorflow-and-DeepLearning
|
ef684d7613902f8c7185e67629440e6abc264789
|
[
"MIT"
] | 41 |
2021-03-03T08:43:52.000Z
|
2022-03-31T19:49:49.000Z
|
07_food_vision_milestone_project_1.ipynb
|
Ankur099IIT/Tensorflow-and-DeepLearning
|
ef684d7613902f8c7185e67629440e6abc264789
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1,036 |
2021-01-17T05:14:41.000Z
|
2022-03-31T10:10:09.000Z
| 100.141301 | 82,790 | 0.775331 |
[
[
[
"<a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/mrdbourke/tensorflow-deep-learning/blob/main/07_food_vision_milestone_project_1.ipynb\" target=\"_parent\"><img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open In Colab\"/></a>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 07. Milestone Project 1: 🍔👁 Food Vision Big™\n\nIn the previous notebook ([transfer learning part 3: scaling up](https://github.com/mrdbourke/tensorflow-deep-learning/blob/main/06_transfer_learning_in_tensorflow_part_3_scaling_up.ipynb)) we built Food Vision mini: a transfer learning model which beat the original results of the [Food101 paper](https://data.vision.ee.ethz.ch/cvl/datasets_extra/food-101/) with only 10% of the data.\n\nBut you might be wondering, what would happen if we used all the data?\n\nWell, that's what we're going to find out in this notebook!\n\nWe're going to be building Food Vision Big™, using all of the data from the Food101 dataset.\n\nYep. All 75,750 training images and 25,250 testing images.\n\nAnd guess what...\n\nThis time **we've got the goal of beating [DeepFood](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/304163308_DeepFood_Deep_Learning-Based_Food_Image_Recognition_for_Computer-Aided_Dietary_Assessment)**, a 2016 paper which used a Convolutional Neural Network trained for 2-3 days to achieve 77.4% top-1 accuracy.\n\n> 🔑 **Note:** **Top-1 accuracy** means \"accuracy for the top softmax activation value output by the model\" (because softmax ouputs a value for every class, but top-1 means only the highest one is evaluated). **Top-5 accuracy** means \"accuracy for the top 5 softmax activation values output by the model\", in other words, did the true label appear in the top 5 activation values? Top-5 accuracy scores are usually noticeably higher than top-1.\n\n| | 🍔👁 Food Vision Big™ | 🍔👁 Food Vision mini |\n|-----|-----|-----|\n| Dataset source | TensorFlow Datasets | Preprocessed download from Kaggle | \n| Train data | 75,750 images | 7,575 images | \n| Test data | 25,250 images | 25,250 images | \n| Mixed precision | Yes | No |\n| Data loading | Performanant tf.data API | TensorFlow pre-built function | \n| Target results | 77.4% top-1 accuracy (beat [DeepFood paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/1606.05675)) | 50.76% top-1 accuracy (beat [Food101 paper](https://data.vision.ee.ethz.ch/cvl/datasets_extra/food-101/static/bossard_eccv14_food-101.pdf)) | \n\n*Table comparing difference between Food Vision Big (this notebook) versus Food Vision mini (previous notebook).*\n\nAlongside attempting to beat the DeepFood paper, we're going to learn about two methods to significantly improve the speed of our model training:\n1. Prefetching\n2. Mixed precision training\n\nBut more on these later.\n\n## What we're going to cover\n\n* Using TensorFlow Datasets to download and explore data\n* Creating preprocessing function for our data\n* Batching & preparing datasets for modelling (**making our datasets run fast**)\n* Creating modelling callbacks\n* Setting up **mixed precision training**\n* Building a feature extraction model (see [transfer learning part 1: feature extraction](https://github.com/mrdbourke/tensorflow-deep-learning/blob/main/04_transfer_learning_in_tensorflow_part_1_feature_extraction.ipynb))\n* Fine-tuning the feature extraction model (see [transfer learning part 2: fine-tuning](https://github.com/mrdbourke/tensorflow-deep-learning/blob/main/05_transfer_learning_in_tensorflow_part_2_fine_tuning.ipynb))\n* Viewing training results on TensorBoard\n\n## How you should approach this notebook\n\nYou can read through the descriptions and the code (it should all run, except for the cells which error on purpose), but there's a better option.\n\nWrite all of the code yourself.\n\nYes. I'm serious. Create a new notebook, and rewrite each line by yourself. Investigate it, see if you can break it, why does it break?\n\nYou don't have to write the text descriptions but writing the code yourself is a great way to get hands-on experience.\n\nDon't worry if you make mistakes, we all do. The way to get better and make less mistakes is to write more code.\n\n> 📖 **Resource:** See the full set of course materials on GitHub: https://github.com/mrdbourke/tensorflow-deep-learning",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Check GPU\n\nFor this notebook, we're going to be doing something different.\n\nWe're going to be using mixed precision training.\n\nMixed precision training was introduced in [TensorFlow 2.4.0](https://blog.tensorflow.org/2020/12/whats-new-in-tensorflow-24.html) (a very new feature at the time of writing).\n\nWhat does **mixed precision training** do?\n\nMixed precision training uses a combination of single precision (float32) and half-preicison (float16) data types to speed up model training (up 3x on modern GPUs).\n\nWe'll talk about this more later on but in the meantime you can read the [TensorFlow documentation on mixed precision](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/mixed_precision) for more details.\n\nFor now, before we can move forward if we want to use mixed precision training, we need to make sure the GPU powering our Google Colab instance (if you're using Google Colab) is compataible. \n\nFor mixed precision training to work, you need access to a GPU with a compute compability score of 7.0+. \n\nGoogle Colab offers P100, K80 and T4 GPUs, however, **the P100 and K80 aren't compatible with mixed precision training**.\n\nTherefore before we proceed we need to make sure we have **access to a Tesla T4 GPU in our Google Colab instance**.\n\nIf you're not using Google Colab, you can find a list of various [Nvidia GPU compute capabilities on Nvidia's developer website](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-gpus#compute).\n\n> 🔑 **Note:** If you run the cell below and see a P100 or K80, try going to to Runtime -> Factory Reset Runtime (note: this will remove any saved variables and data from your Colab instance) and then retry to get a T4.\n>\n> **You can still run the code *without* a GPU capable of mixed precision** (it'll just be a little slower). ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# If using Google Colab, this should output \"Tesla T4\" otherwise, \n# you won't be able to use mixed precision training\n!nvidia-smi -L",
"GPU 0: NVIDIA TITAN RTX (UUID: GPU-64b1678c-cec3-56bb-af0c-8ae69de44cbd)\r\n"
]
],
[
[
"Since mixed precision training was introduced in TensorFlow 2.4.0, make sure you've got at least TensorFlow 2.4.0+.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Hide warning logs (see: https://stackoverflow.com/a/38645250/7900723)\nimport os\nos.environ[\"TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL\"] = \"3\"\n\n# Check TensorFlow version (should be 2.4.0+)\nimport tensorflow as tf\nprint(tf.__version__)",
"2.6.2\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Get helper functions\n\nWe've created a series of helper functions throughout the previous notebooks in the course. Instead of rewriting them (tedious), we'll import the [`helper_functions.py`](https://github.com/mrdbourke/tensorflow-deep-learning/blob/main/extras/helper_functions.py) file from the GitHub repo.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Get helper functions file\nif not os.path.exists(\"helper_functions.py\"):\n print(\"Downloading helper functions...\")\n !wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mrdbourke/tensorflow-deep-learning/main/extras/helper_functions.py\nelse:\n print(\"Helper functions file already exists, skipping download...\")",
"Helper functions file already exists, skipping download...\n"
],
[
"# Import series of helper functions for the notebook (we've created/used these in previous notebooks)\nfrom helper_functions import create_tensorboard_callback, plot_loss_curves, compare_historys",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Use TensorFlow Datasets to Download Data\n\nIn previous notebooks, we've downloaded our food images (from the [Food101 dataset](https://www.kaggle.com/dansbecker/food-101/home)) from Google Storage.\n\nAnd this is a typical workflow you'd use if you're working on your own datasets.\n\nHowever, there's another way to get datasets ready to use with TensorFlow.\n\nFor many of the most popular datasets in the machine learning world (often referred to and used as benchmarks), you can access them through [TensorFlow Datasets (TFDS)](https://www.tensorflow.org/datasets/overview).\n\nWhat is **TensorFlow Datasets**?\n\nA place for prepared and ready-to-use machine learning datasets.\n\nWhy use TensorFlow Datasets?\n\n* Load data already in Tensors\n* Practice on well established datasets\n* Experiment with differet data loading techniques (like we're going to use in this notebook)\n* Experiment with new TensorFlow features quickly (such as mixed precision training)\n\nWhy *not* use TensorFlow Datasets?\n\n* The datasets are static (they don't change, like your real-world datasets would)\n* Might not be suited for your particular problem (but great for experimenting)\n\nTo begin using TensorFlow Datasets we can import it under the alias `tfds`.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Get TensorFlow Datasets\nimport tensorflow_datasets as tfds",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"To find all of the available datasets in TensorFlow Datasets, you can use the `list_builders()` method.\n\nAfter doing so, we can check to see if the one we're after (`\"food101\"`) is present.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# List available datasets\ndatasets_list = tfds.list_builders() # get all available datasets in TFDS\nprint(\"food101\" in datasets_list) # is the dataset we're after available?",
"True\n"
]
],
[
[
"Beautiful! It looks like the dataset we're after is available (note there are plenty more available but we're on Food101).\n\nTo get access to the Food101 dataset from the TFDS, we can use the [`tfds.load()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/datasets/api_docs/python/tfds/load) method.\n\nIn particular, we'll have to pass it a few parameters to let it know what we're after:\n* `name` (str) : the target dataset (e.g. `\"food101\"`)\n* `split` (list, optional) : what splits of the dataset we're after (e.g. `[\"train\", \"validation\"]`)\n * the `split` parameter is quite tricky. See [the documentation for more](https://github.com/tensorflow/datasets/blob/master/docs/splits.md).\n* `shuffle_files` (bool) : whether or not to shuffle the files on download, defaults to `False` \n* `as_supervised` (bool) : `True` to download data samples in tuple format (`(data, label)`) or `False` for dictionary format \n* `with_info` (bool) : `True` to download dataset metadata (labels, number of samples, etc)\n\n> 🔑 **Note:** Calling the `tfds.load()` method will start to download a target dataset to disk if the `download=True` parameter is set (default). This dataset could be 100GB+, so make sure you have space.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Load in the data (takes about 5-6 minutes in Google Colab)\n(train_data, test_data), ds_info = tfds.load(name=\"food101\", # target dataset to get from TFDS\n split=[\"train\", \"validation\"], # what splits of data should we get? note: not all datasets have train, valid, test\n shuffle_files=True, # shuffle files on download?\n as_supervised=True, # download data in tuple format (sample, label), e.g. (image, label)\n with_info=True) # include dataset metadata? if so, tfds.load() returns tuple (data, ds_info)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Wonderful! After a few minutes of downloading, we've now got access to entire Food101 dataset (in tensor format) ready for modelling.\n\nNow let's get a little information from our dataset, starting with the class names.\n\nGetting class names from a TensorFlow Datasets dataset requires downloading the \"`dataset_info`\" variable (by using the `as_supervised=True` parameter in the `tfds.load()` method, **note:** this will only work for supervised datasets in TFDS).\n\nWe can access the class names of a particular dataset using the `dataset_info.features` attribute and accessing `names` attribute of the the `\"label\"` key.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Features of Food101 TFDS\nds_info.features",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Get class names\nclass_names = ds_info.features[\"label\"].names\nclass_names[:10]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Exploring the Food101 data from TensorFlow Datasets\n\nNow we've downloaded the Food101 dataset from TensorFlow Datasets, how about we do what any good data explorer should?\n\nIn other words, \"visualize, visualize, visualize\". \n\nLet's find out a few details about our dataset:\n* The shape of our input data (image tensors)\n* The datatype of our input data\n* What the labels of our input data look like (e.g. one-hot encoded versus label-encoded)\n* Do the labels match up with the class names?\n\nTo do, let's take one sample off the training data (using the [`.take()` method](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/data/Dataset#take)) and explore it. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Take one sample off the training data\ntrain_one_sample = train_data.take(1) # samples are in format (image_tensor, label)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Because we used the `as_supervised=True` parameter in our `tfds.load()` method above, data samples come in the tuple format structure `(data, label)` or in our case `(image_tensor, label)`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# What does one sample of our training data look like?\ntrain_one_sample",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's loop through our single training sample and get some info from the `image_tensor` and `label`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Output info about our training sample\nfor image, label in train_one_sample:\n print(f\"\"\"\n Image shape: {image.shape}\n Image dtype: {image.dtype}\n Target class from Food101 (tensor form): {label}\n Class name (str form): {class_names[label.numpy()]}\n \"\"\")",
"\n Image shape: (512, 289, 3)\n Image dtype: <dtype: 'uint8'>\n Target class from Food101 (tensor form): 45\n Class name (str form): frozen_yogurt\n \n"
]
],
[
[
"Because we set the `shuffle_files=True` parameter in our `tfds.load()` method above, running the cell above a few times will give a different result each time.\n\nChecking these you might notice some of the images have different shapes, for example `(512, 342, 3)` and `(512, 512, 3)` (height, width, color_channels).\n\nLet's see what one of the image tensors from TFDS's Food101 dataset looks like.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# What does an image tensor from TFDS's Food101 look like?\nimage",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# What are the min and max values?\ntf.reduce_min(image), tf.reduce_max(image)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Alright looks like our image tensors have values of between 0 & 255 (standard red, green, blue colour values) and the values are of data type `unit8`.\n\nWe might have to preprocess these before passing them to a neural network. But we'll handle this later.\n\nIn the meantime, let's see if we can plot an image sample.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Plot an image from TensorFlow Datasets\n\nWe've seen our image tensors in tensor format, now let's really adhere to our motto.\n\n\"Visualize, visualize, visualize!\"\n\nLet's plot one of the image samples using [`matplotlib.pyplot.imshow()`](https://matplotlib.org/stable/api/_as_gen/matplotlib.pyplot.imshow.html) and set the title to target class name.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Plot an image tensor\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nplt.imshow(image)\nplt.title(class_names[label.numpy()]) # add title to image by indexing on class_names list\nplt.axis(False);",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Delicious!\n\nOkay, looks like the Food101 data we've got from TFDS is similar to the datasets we've been using in previous notebooks.\n\nNow let's preprocess it and get it ready for use with a neural network.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Create preprocessing functions for our data\n\nIn previous notebooks, when our images were in folder format we used the method [`tf.keras.preprocessing.image_dataset_from_directory()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/preprocessing/image_dataset_from_directory) to load them in.\n\nDoing this meant our data was loaded into a format ready to be used with our models.\n\nHowever, since we've downloaded the data from TensorFlow Datasets, there are a couple of preprocessing steps we have to take before it's ready to model. \n\nMore specifically, our data is currently:\n\n* In `uint8` data type\n* Comprised of all differnet sized tensors (different sized images)\n* Not scaled (the pixel values are between 0 & 255)\n\nWhereas, models like data to be:\n\n* In `float32` data type\n* Have all of the same size tensors (batches require all tensors have the same shape, e.g. `(224, 224, 3)`)\n* Scaled (values between 0 & 1), also called normalized\n\nTo take care of these, we'll create a `preprocess_img()` function which:\n\n* Resizes an input image tensor to a specified size using [`tf.image.resize()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/image/resize)\n* Converts an input image tensor's current datatype to `tf.float32` using [`tf.cast()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/cast)\n\n> 🔑 **Note:** Pretrained EfficientNetBX models in [`tf.keras.applications.efficientnet`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/applications/efficientnet) (what we're going to be using) have rescaling built-in. But for many other model architectures you'll want to rescale your data (e.g. get its values between 0 & 1). This could be incorporated inside your \"`preprocess_img()`\" function (like the one below) or within your model as a [`tf.keras.layers.experimental.preprocessing.Rescaling`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/layers/experimental/preprocessing/Rescaling) layer.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Make a function for preprocessing images\ndef preprocess_img(image, label, img_shape=224):\n \"\"\"\n Converts image datatype from 'uint8' -> 'float32' and reshapes image to\n [img_shape, img_shape, color_channels]\n \"\"\"\n image = tf.image.resize(image, [img_shape, img_shape]) # reshape to img_shape\n return tf.cast(image, tf.float32), label # return (float32_image, label) tuple",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Our `preprocess_img()` function above takes image and label as input (even though it does nothing to the label) because our dataset is currently in the tuple structure `(image, label)`.\n\nLet's try our function out on a target image.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Preprocess a single sample image and check the outputs\npreprocessed_img = preprocess_img(image, label)[0]\nprint(f\"Image before preprocessing:\\n {image[:2]}...,\\nShape: {image.shape},\\nDatatype: {image.dtype}\\n\")\nprint(f\"Image after preprocessing:\\n {preprocessed_img[:2]}...,\\nShape: {preprocessed_img.shape},\\nDatatype: {preprocessed_img.dtype}\")",
"Image before preprocessing:\n [[[145 151 125]\n [157 163 137]\n [159 165 139]\n ...\n [197 209 199]\n [197 209 199]\n [197 207 198]]\n\n [[146 152 126]\n [156 162 136]\n [158 164 138]\n ...\n [197 209 199]\n [197 209 199]\n [199 209 200]]]...,\nShape: (512, 289, 3),\nDatatype: <dtype: 'uint8'>\n\nImage after preprocessing:\n [[[147.19739 153.19739 127.19739]\n [157.22768 163.22768 137.22768]\n [158.09805 164.09805 138.09805]\n ...\n [197. 209. 197.54907]\n [197. 209. 199. ]\n [198.09914 208.38936 199.24425]]\n\n [[154.69467 160.69467 134.69467]\n [155.87053 161.87053 135.87053]\n [158.39908 164.39908 138.39908]\n ...\n [197. 209. 197.54907]\n [197. 209. 199. ]\n [196.32831 206.61853 195.76364]]]...,\nShape: (224, 224, 3),\nDatatype: <dtype: 'float32'>\n"
]
],
[
[
"Excellent! Looks like our `preprocess_img()` function is working as expected.\n\nThe input image gets converted from `uint8` to `float32` and gets reshaped from its current shape to `(224, 224, 3)`.\n\nHow does it look?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# We can still plot our preprocessed image as long as we \n# divide by 255 (for matplotlib capatibility)\nplt.imshow(preprocessed_img/255.)\nplt.title(class_names[label])\nplt.axis(False);",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"All this food visualization is making me hungry. How about we start preparing to model it?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Batch & prepare datasets\n\nBefore we can model our data, we have to turn it into batches.\n\nWhy?\n\nBecause computing on batches is memory efficient.\n\nWe turn our data from 101,000 image tensors and labels (train and test combined) into batches of 32 image and label pairs, thus enabling it to fit into the memory of our GPU.\n\nTo do this in effective way, we're going to be leveraging a number of methods from the [`tf.data` API](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/data).\n\n> 📖 **Resource:** For loading data in the most performant way possible, see the TensorFlow docuemntation on [Better performance with the tf.data API](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/data_performance).\n\nSpecifically, we're going to be using:\n\n* [`map()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/data/Dataset#map) - maps a predefined function to a target dataset (e.g. `preprocess_img()` to our image tensors)\n* [`shuffle()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/data/Dataset#shuffle) - randomly shuffles the elements of a target dataset up `buffer_size` (ideally, the `buffer_size` is equal to the size of the dataset, however, this may have implications on memory)\n* [`batch()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/data/Dataset#batch) - turns elements of a target dataset into batches (size defined by parameter `batch_size`)\n* [`prefetch()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/data/Dataset#prefetch) - prepares subsequent batches of data whilst other batches of data are being computed on (improves data loading speed but costs memory)\n* Extra: [`cache()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/data/Dataset#cache) - caches (saves them for later) elements in a target dataset, saving loading time (will only work if your dataset is small enough to fit in memory, standard Colab instances only have 12GB of memory) \n\nThings to note:\n- Can't batch tensors of different shapes (e.g. different image sizes, need to reshape images first, hence our `preprocess_img()` function)\n- `shuffle()` keeps a buffer of the number you pass it images shuffled, ideally this number would be all of the samples in your training set, however, if your training set is large, this buffer might not fit in memory (a fairly large number like 1000 or 10000 is usually suffice for shuffling)\n- For methods with the `num_parallel_calls` parameter available (such as `map()`), setting it to`num_parallel_calls=tf.data.AUTOTUNE` will parallelize preprocessing and significantly improve speed\n- Can't use `cache()` unless your dataset can fit in memory\n\nWoah, the above is alot. But once we've coded below, it'll start to make sense.\n\nWe're going to through things in the following order:\n\n```\nOriginal dataset (e.g. train_data) -> map() -> shuffle() -> batch() -> prefetch() -> PrefetchDataset\n```\n\nThis is like saying, \n\n> \"Hey, map this preprocessing function across our training dataset, then shuffle a number of elements before batching them together and make sure you prepare new batches (prefetch) whilst the model is looking through the current batch\".\n\n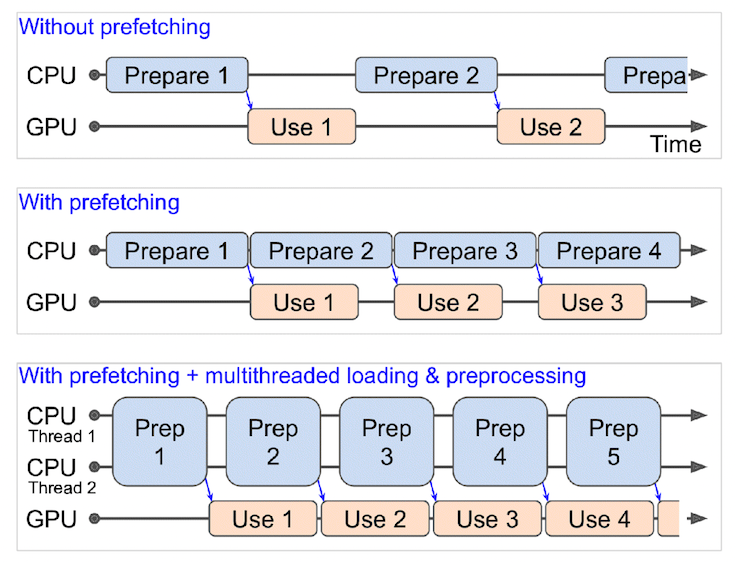\n\n*What happens when you use prefetching (faster) versus what happens when you don't use prefetching (slower). **Source:** Page 422 of [Hands-On Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn, Keras & TensorFlow Book by Aurélien Géron](https://www.oreilly.com/library/view/hands-on-machine-learning/9781492032632/).*\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Map preprocessing function to training data (and paralellize)\ntrain_data = train_data.map(map_func=preprocess_img, num_parallel_calls=tf.data.AUTOTUNE)\n# Shuffle train_data and turn it into batches and prefetch it (load it faster)\ntrain_data = train_data.shuffle(buffer_size=1000).batch(batch_size=32).prefetch(buffer_size=tf.data.AUTOTUNE)\n\n# Map prepreprocessing function to test data\ntest_data = test_data.map(preprocess_img, num_parallel_calls=tf.data.AUTOTUNE)\n# Turn test data into batches (don't need to shuffle)\ntest_data = test_data.batch(32).prefetch(tf.data.AUTOTUNE)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"And now let's check out what our prepared datasets look like.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"train_data, test_data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Excellent! Looks like our data is now in tutples of `(image, label)` with datatypes of `(tf.float32, tf.int64)`, just what our model is after.\n\n> 🔑 **Note:** You can get away without calling the `prefetch()` method on the end of your datasets, however, you'd probably see significantly slower data loading speeds when building a model. So most of your dataset input pipelines should end with a call to [`prefecth()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/data/Dataset#prefetch).\n\nOnward.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Create modelling callbacks\n\nSince we're going to be training on a large amount of data and training could take a long time, it's a good idea to set up some modelling callbacks so we be sure of things like our model's training logs being tracked and our model being checkpointed (saved) after various training milestones.\n\nTo do each of these we'll use the following callbacks:\n* [`tf.keras.callbacks.TensorBoard()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/callbacks/TensorBoard) - allows us to keep track of our model's training history so we can inspect it later (**note:** we've created this callback before have imported it from `helper_functions.py` as `create_tensorboard_callback()`)\n* [`tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/callbacks/ModelCheckpoint) - saves our model's progress at various intervals so we can load it and resuse it later without having to retrain it\n * Checkpointing is also helpful so we can start fine-tuning our model at a particular epoch and revert back to a previous state if fine-tuning offers no benefits",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create TensorBoard callback (already have \"create_tensorboard_callback()\" from a previous notebook)\nfrom helper_functions import create_tensorboard_callback\n\n# Create ModelCheckpoint callback to save model's progress\ncheckpoint_path = \"model_checkpoints/cp.ckpt\" # saving weights requires \".ckpt\" extension\nmodel_checkpoint = tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(checkpoint_path,\n montior=\"val_accuracy\", # save the model weights with best validation accuracy\n save_best_only=True, # only save the best weights\n save_weights_only=True, # only save model weights (not whole model)\n verbose=1) # don't print out whether or not model is being saved ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Setup mixed precision training\n\nWe touched on mixed precision training above.\n\nHowever, we didn't quite explain it.\n\nNormally, tensors in TensorFlow default to the float32 datatype (unless otherwise specified).\n\nIn computer science, float32 is also known as [single-precision floating-point format](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single-precision_floating-point_format). The 32 means it usually occupies 32 bits in computer memory.\n\nYour GPU has a limited memory, therefore it can only handle a number of float32 tensors at the same time.\n\nThis is where mixed precision training comes in.\n\nMixed precision training involves using a mix of float16 and float32 tensors to make better use of your GPU's memory.\n\nCan you guess what float16 means?\n\nWell, if you thought since float32 meant single-precision floating-point, you might've guessed float16 means [half-precision floating-point format](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Half-precision_floating-point_format). And if you did, you're right! And if not, no trouble, now you know.\n\nFor tensors in float16 format, each element occupies 16 bits in computer memory.\n\nSo, where does this leave us?\n\nAs mentioned before, when using mixed precision training, your model will make use of float32 and float16 data types to use less memory where possible and in turn run faster (using less memory per tensor means more tensors can be computed on simultaneously).\n\nAs a result, using mixed precision training can improve your performance on modern GPUs (those with a compute capability score of 7.0+) by up to 3x.\n\nFor a more detailed explanation, I encourage you to read through the [TensorFlow mixed precision guide](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/mixed_precision) (I'd highly recommend at least checking out the summary).\n\n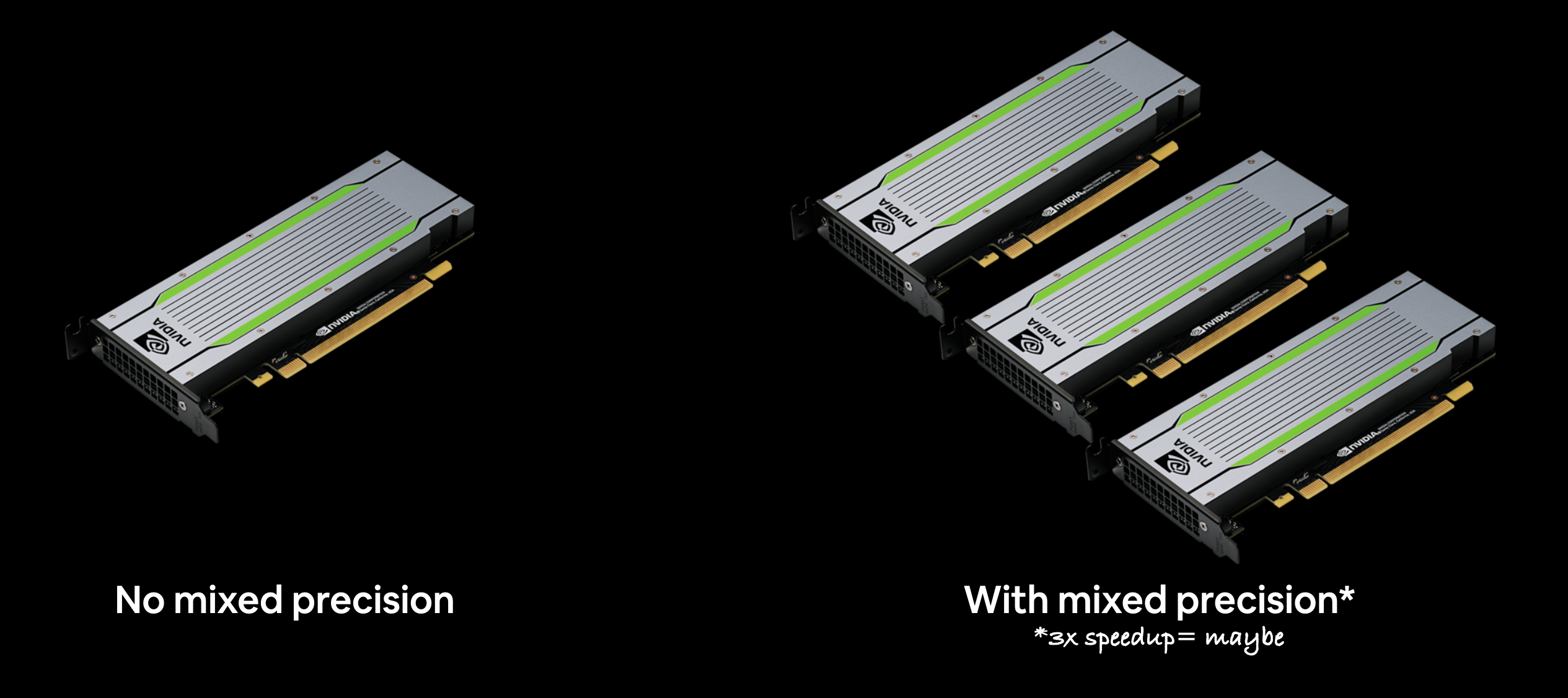\n*Because mixed precision training uses a combination of float32 and float16 data types, you may see up to a 3x speedup on modern GPUs.*\n\n> 🔑 **Note:** If your GPU doesn't have a score of over 7.0+ (e.g. P100 in Colab), mixed precision won't work (see: [\"Supported Hardware\"](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/mixed_precision#supported_hardware) in the mixed precision guide for more).\n\n> 📖 **Resource:** If you'd like to learn more about precision in computer science (the detail to which a numerical quantity is expressed by a computer), see the [Wikipedia page](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Precision_(computer_science)) (and accompanying resources). \n\nOkay, enough talk, let's see how we can turn on mixed precision training in TensorFlow.\n\nThe beautiful thing is, the [`tensorflow.keras.mixed_precision`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/mixed_precision/) API has made it very easy for us to get started.\n\nFirst, we'll import the API and then use the [`set_global_policy()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/mixed_precision/set_global_policy) method to set the *dtype policy* to `\"mixed_float16\"`.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Turn on mixed precision training\nfrom tensorflow.keras import mixed_precision\nmixed_precision.set_global_policy(policy=\"mixed_float16\") # set global policy to mixed precision ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Nice! As long as the GPU you're using has a compute capability of 7.0+ the cell above should run without error.\n\nNow we can check the global dtype policy (the policy which will be used by layers in our model) using the [`mixed_precision.global_policy()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/mixed_precision/global_policy) method.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mixed_precision.global_policy() # should output \"mixed_float16\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Great, since the global dtype policy is now `\"mixed_float16\"` our model will automatically take advantage of float16 variables where possible and in turn speed up training.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Build feature extraction model\n\nCallbacks: ready to roll.\n\nMixed precision: turned on.\n\nLet's build a model.\n\nBecause our dataset is quite large, we're going to move towards fine-tuning an existing pretrained model (EfficienetNetB0).\n\nBut before we get into fine-tuning, let's set up a feature-extraction model.\n\nRecall, the typical order for using transfer learning is:\n\n1. Build a feature extraction model (replace the top few layers of a pretrained model) \n2. Train for a few epochs with lower layers frozen\n3. Fine-tune if necessary with multiple layers unfrozen\n\n\n*Before fine-tuning, it's best practice to train a feature extraction model with custom top layers.*\n\nTo build the feature extraction model (covered in [Transfer Learning in TensorFlow Part 1: Feature extraction](https://github.com/mrdbourke/tensorflow-deep-learning/blob/main/04_transfer_learning_in_tensorflow_part_1_feature_extraction.ipynb)), we'll:\n* Use `EfficientNetB0` from [`tf.keras.applications`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/applications) pre-trained on ImageNet as our base model\n * We'll download this without the top layers using `include_top=False` parameter so we can create our own output layers\n* Freeze the base model layers so we can use the pre-learned patterns the base model has found on ImageNet\n* Put together the input, base model, pooling and output layers in a [Functional model](https://keras.io/guides/functional_api/)\n* Compile the Functional model using the Adam optimizer and [sparse categorical crossentropy](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/losses/SparseCategoricalCrossentropy) as the loss function (since our labels **aren't** one-hot encoded)\n* Fit the model for 3 epochs using the TensorBoard and ModelCheckpoint callbacks\n\n> 🔑 **Note:** Since we're using mixed precision training, our model needs a separate output layer with a hard-coded `dtype=float32`, for example, `layers.Activation(\"softmax\", dtype=tf.float32)`. This ensures the outputs of our model are returned back to the float32 data type which is more numerically stable than the float16 datatype (important for loss calculations). See the [\"Building the model\"](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/mixed_precision#building_the_model) section in the TensorFlow mixed precision guide for more.\n\n\n*Turning mixed precision on in TensorFlow with 3 lines of code.*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from tensorflow.keras import layers\nfrom tensorflow.keras.layers.experimental import preprocessing\n\n# Create base model\ninput_shape = (224, 224, 3)\nbase_model = tf.keras.applications.EfficientNetB0(include_top=False)\nbase_model.trainable = False # freeze base model layers\n\n# Create Functional model \ninputs = layers.Input(shape=input_shape, name=\"input_layer\", dtype=tf.float16)\n# Note: EfficientNetBX models have rescaling built-in but if your model didn't you could have a layer like below\n# x = preprocessing.Rescaling(1./255)(x)\nx = base_model(inputs, training=False) # set base_model to inference mode only\nx = layers.GlobalAveragePooling2D(name=\"pooling_layer\")(x)\nx = layers.Dense(len(class_names))(x) # want one output neuron per class \n# Separate activation of output layer so we can output float32 activations\noutputs = layers.Activation(\"softmax\", dtype=tf.float32, name=\"softmax_float32\")(x) \nmodel = tf.keras.Model(inputs, outputs)\n\n# Compile the model\nmodel.compile(loss=\"sparse_categorical_crossentropy\", # Use sparse_categorical_crossentropy when labels are *not* one-hot\n optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(),\n metrics=[\"accuracy\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Check out our model\nmodel.summary()",
"Model: \"model_1\"\n_________________________________________________________________\nLayer (type) Output Shape Param # \n=================================================================\ninput_layer (InputLayer) [(None, 224, 224, 3)] 0 \n_________________________________________________________________\nefficientnetb0 (Functional) (None, None, None, 1280) 4049571 \n_________________________________________________________________\npooling_layer (GlobalAverage (None, 1280) 0 \n_________________________________________________________________\ndense_1 (Dense) (None, 101) 129381 \n_________________________________________________________________\nsoftmax_float32 (Activation) (None, 101) 0 \n=================================================================\nTotal params: 4,178,952\nTrainable params: 129,381\nNon-trainable params: 4,049,571\n_________________________________________________________________\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Checking layer dtype policies (are we using mixed precision?)\n\nModel ready to go!\n\nBefore we said the mixed precision API will automatically change our layers' dtype policy's to whatever the global dtype policy is (in our case it's `\"mixed_float16\"`).\n\nWe can check this by iterating through our model's layers and printing layer attributes such as `dtype` and `dtype_policy`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Check the dtype_policy attributes of layers in our model\nfor layer in model.layers:\n print(layer.name, layer.trainable, layer.dtype, layer.dtype_policy) # Check the dtype policy of layers",
"input_layer True float16 <Policy \"float16\">\nefficientnetb0 False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\npooling_layer True float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\ndense_1 True float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nsoftmax_float32 True float32 <Policy \"float32\">\n"
]
],
[
[
"Going through the above we see:\n* `layer.name` (str) : a layer's human-readable name, can be defined by the `name` parameter on construction\n* `layer.trainable` (bool) : whether or not a layer is trainable (all of our layers are trainable except the efficientnetb0 layer since we set it's `trainable` attribute to `False`\n* `layer.dtype` : the data type a layer stores its variables in\n* `layer.dtype_policy` : the data type a layer computes in\n\n> 🔑 **Note:** A layer can have a dtype of `float32` and a dtype policy of `\"mixed_float16\"` because it stores its variables (weights & biases) in `float32` (more numerically stable), however it computes in `float16` (faster).\n\nWe can also check the same details for our model's base model.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Check the layers in the base model and see what dtype policy they're using\nfor layer in model.layers[1].layers[:20]: # only check the first 20 layers to save output space\n print(layer.name, layer.trainable, layer.dtype, layer.dtype_policy)",
"input_2 False float32 <Policy \"float32\">\nrescaling_1 False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nnormalization_1 False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nstem_conv_pad False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nstem_conv False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nstem_bn False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nstem_activation False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_dwconv False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_bn False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_activation False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_se_squeeze False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_se_reshape False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_se_reduce False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_se_expand False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_se_excite False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_project_conv False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_project_bn False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock2a_expand_conv False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock2a_expand_bn False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock2a_expand_activation False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\n"
]
],
[
[
"> 🔑 **Note:** The mixed precision API automatically causes layers which can benefit from using the `\"mixed_float16\"` dtype policy to use it. It also prevents layers which shouldn't use it from using it (e.g. the normalization layer at the start of the base model).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Fit the feature extraction model\n\nNow that's one good looking model. Let's fit it to our data shall we?\n\nThree epochs should be enough for our top layers to adjust their weights enough to our food image data.\n\nTo save time per epoch, we'll also only validate on 15% of the test data.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Fit the model with callbacks\nhistory_101_food_classes_feature_extract = model.fit(train_data, \n epochs=3,\n steps_per_epoch=len(train_data),\n validation_data=test_data,\n validation_steps=int(0.15 * len(test_data)),\n callbacks=[create_tensorboard_callback(\"training_logs\", \n \"efficientnetb0_101_classes_all_data_feature_extract\"),\n model_checkpoint])",
"Saving TensorBoard log files to: training_logs/efficientnetb0_101_classes_all_data_feature_extract/20211215-112338\nEpoch 1/3\n2368/2368 [==============================] - 55s 22ms/step - loss: 1.8217 - accuracy: 0.5565 - val_loss: 1.2271 - val_accuracy: 0.6774\n\nEpoch 00001: val_loss improved from inf to 1.22710, saving model to model_checkpoints/cp.ckpt\nEpoch 2/3\n2368/2368 [==============================] - 51s 21ms/step - loss: 1.2942 - accuracy: 0.6655 - val_loss: 1.1317 - val_accuracy: 0.6989\n\nEpoch 00002: val_loss improved from 1.22710 to 1.13174, saving model to model_checkpoints/cp.ckpt\nEpoch 3/3\n2368/2368 [==============================] - 51s 22ms/step - loss: 1.1446 - accuracy: 0.7017 - val_loss: 1.0912 - val_accuracy: 0.7058\n\nEpoch 00003: val_loss improved from 1.13174 to 1.09125, saving model to model_checkpoints/cp.ckpt\n"
]
],
[
[
"Nice, looks like our feature extraction model is performing pretty well. How about we evaluate it on the whole test dataset?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Evaluate model (unsaved version) on whole test dataset\nresults_feature_extract_model = model.evaluate(test_data)\nresults_feature_extract_model",
"790/790 [==============================] - 14s 18ms/step - loss: 1.0924 - accuracy: 0.7053\n"
]
],
[
[
"And since we used the `ModelCheckpoint` callback, we've got a saved version of our model in the `model_checkpoints` directory.\n\nLet's load it in and make sure it performs just as well.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Load and evaluate checkpoint weights\n\nWe can load in and evaluate our model's checkpoints by:\n\n1. Cloning our model using [`tf.keras.models.clone_model()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/models/clone_model) to make a copy of our feature extraction model with reset weights.\n2. Calling the `load_weights()` method on our cloned model passing it the path to where our checkpointed weights are stored.\n3. Calling `evaluate()` on the cloned model with loaded weights.\n\nA reminder, checkpoints are helpful for when you perform an experiment such as fine-tuning your model. In the case you fine-tune your feature extraction model and find it doesn't offer any improvements, you can always revert back to the checkpointed version of your model.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Clone the model we created (this resets all weights)\ncloned_model = tf.keras.models.clone_model(model)\ncloned_model.summary()",
"Model: \"model_1\"\n_________________________________________________________________\nLayer (type) Output Shape Param # \n=================================================================\ninput_layer (InputLayer) [(None, 224, 224, 3)] 0 \n_________________________________________________________________\nefficientnetb0 (Functional) (None, None, None, 1280) 4049571 \n_________________________________________________________________\npooling_layer (GlobalAverage (None, 1280) 0 \n_________________________________________________________________\ndense_1 (Dense) (None, 101) 129381 \n_________________________________________________________________\nsoftmax_float32 (Activation) (None, 101) 0 \n=================================================================\nTotal params: 4,178,952\nTrainable params: 129,381\nNon-trainable params: 4,049,571\n_________________________________________________________________\n"
],
[
"!ls model_checkpoints/",
"checkpoint cp.ckpt.data-00000-of-00001 cp.ckpt.index\r\n"
],
[
"# Where are our checkpoints stored?\ncheckpoint_path",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Load checkpointed weights into cloned_model\ncloned_model.load_weights(checkpoint_path)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Each time you make a change to your model (including loading weights), you have to recompile.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Compile cloned_model (with same parameters as original model)\ncloned_model.compile(loss=\"sparse_categorical_crossentropy\",\n optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(),\n metrics=[\"accuracy\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Evalaute cloned model with loaded weights (should be same score as trained model)\nresults_cloned_model_with_loaded_weights = cloned_model.evaluate(test_data)",
"790/790 [==============================] - 15s 18ms/step - loss: 1.7466 - accuracy: 0.5401\n"
]
],
[
[
"Our cloned model with loaded weight's results should be very close to the feature extraction model's results (if the cell below errors, something went wrong).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Loaded checkpoint weights should return very similar results to checkpoint weights prior to saving\nimport numpy as np\nassert np.isclose(results_feature_extract_model, results_cloned_model_with_loaded_weights).all() # check if all elements in array are close",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Cloning the model preserves `dtype_policy`'s of layers (but doesn't preserve weights) so if we wanted to continue fine-tuning with the cloned model, we could and it would still use the mixed precision dtype policy.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Check the layers in the base model and see what dtype policy they're using\nfor layer in cloned_model.layers[1].layers[:20]: # check only the first 20 layers to save space\n print(layer.name, layer.trainable, layer.dtype, layer.dtype_policy)",
"input_2 True float32 <Policy \"float32\">\nrescaling_1 False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nnormalization_1 False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nstem_conv_pad False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nstem_conv False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nstem_bn False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nstem_activation False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_dwconv False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_bn False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_activation False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_se_squeeze False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_se_reshape False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_se_reduce False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_se_expand False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_se_excite False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_project_conv False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_project_bn False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock2a_expand_conv False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock2a_expand_bn False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock2a_expand_activation False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Save the whole model to file\n\nWe can also save the whole model using the [`save()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/Model#save) method.\n\nSince our model is quite large, you might want to save it to Google Drive (if you're using Google Colab) so you can load it in for use later.\n\n> 🔑 **Note:** Saving to Google Drive requires mounting Google Drive (go to Files -> Mount Drive).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# ## Saving model to Google Drive (optional)\n\n# # Create save path to drive \n# save_dir = \"drive/MyDrive/tensorflow_course/food_vision/07_efficientnetb0_feature_extract_model_mixed_precision/\"\n# # os.makedirs(save_dir) # Make directory if it doesn't exist\n\n# # Save model\n# model.save(save_dir)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can also save it directly to our Google Colab instance.\n\n> 🔑 **Note:** Google Colab storage is ephemeral and your model will delete itself (along with any other saved files) when the Colab session expires.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Save model locally (if you're using Google Colab, your saved model will Colab instance terminates)\nsave_dir = \"07_efficientnetb0_feature_extract_model_mixed_precision\"\nmodel.save(save_dir)",
"INFO:tensorflow:Assets written to: 07_efficientnetb0_feature_extract_model_mixed_precision/assets\n"
]
],
[
[
"And again, we can check whether or not our model saved correctly by loading it in and evaluating it.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Load model previously saved above\nloaded_saved_model = tf.keras.models.load_model(save_dir)",
"WARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block3b_activation_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_143555) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block5a_expand_activation_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_145084) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block5b_expand_activation_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_108907) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block6b_se_reduce_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_109467) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block3b_expand_activation_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_143461) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block7a_activation_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_109925) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block5c_expand_activation_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_109074) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block5a_se_reduce_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_145246) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block3b_se_reduce_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_108162) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block4a_activation_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_143989) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block4c_se_reduce_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_144834) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block5b_activation_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_145543) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block3b_se_reduce_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_143623) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block6c_se_reduce_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_147234) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block5c_activation_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_145955) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block2b_se_reduce_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_107836) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block6b_expand_activation_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_109400) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block6d_se_reduce_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_147646) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block5a_activation_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_108779) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block6d_activation_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_109758) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block2a_expand_activation_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_142275) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block5a_se_reduce_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_108822) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block6a_se_reduce_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_109315) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block1a_activation_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_142004) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block4b_expand_activation_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_144260) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_efficientnetb0_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_136248) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block2b_se_reduce_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_142824) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block6a_expand_activation_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_146273) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block7a_activation_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_147990) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block1a_activation_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_107482) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block2b_activation_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_107793) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block3a_expand_activation_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_143074) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block5c_se_reduce_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_109141) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block5b_se_reduce_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_108974) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block4c_expand_activation_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_108588) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block3a_activation_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_107967) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block5a_activation_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_145178) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block5a_expand_activation_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_108755) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block3a_se_reduce_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_143258) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block5c_se_reduce_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_146023) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\nWARNING:absl:Importing a function (__inference_block5b_activation_layer_call_and_return_conditional_losses_108931) with ops with unsaved custom gradients. Will likely fail if a gradient is requested.\n"
]
],
[
[
"Loading a `SavedModel` also retains all of the underlying layers `dtype_policy` (we want them to be `\"mixed_float16\"`).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Check the layers in the base model and see what dtype policy they're using\nfor layer in loaded_saved_model.layers[1].layers[:20]: # check only the first 20 layers to save output space\n print(layer.name, layer.trainable, layer.dtype, layer.dtype_policy)",
"input_2 True float32 <Policy \"float32\">\nrescaling_1 False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nnormalization_1 False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nstem_conv_pad False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nstem_conv False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nstem_bn False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nstem_activation False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_dwconv False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_bn False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_activation False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_se_squeeze False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_se_reshape False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_se_reduce False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_se_expand False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_se_excite False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_project_conv False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_project_bn False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock2a_expand_conv False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock2a_expand_bn False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock2a_expand_activation False float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\n"
],
[
"# Check loaded model performance (this should be the same as results_feature_extract_model)\nresults_loaded_saved_model = loaded_saved_model.evaluate(test_data)\nresults_loaded_saved_model",
"790/790 [==============================] - 16s 19ms/step - loss: 1.0924 - accuracy: 0.7053\n"
],
[
"# The loaded model's results should equal (or at least be very close) to the model's results prior to saving\n# Note: this will only work if you've instatiated results variables \nimport numpy as np\nassert np.isclose(results_feature_extract_model, results_loaded_saved_model).all()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"That's what we want! Our loaded model performing as it should.\n\n> 🔑 **Note:** We spent a fair bit of time making sure our model saved correctly because training on a lot of data can be time-consuming, so we want to make sure we don't have to continaully train from scratch.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Preparing our model's layers for fine-tuning\n\nOur feature-extraction model is showing some great promise after three epochs. But since we've got so much data, it's probably worthwhile that we see what results we can get with fine-tuning (fine-tuning usually works best when you've got quite a large amount of data).\n\nRemember our goal of beating the [DeepFood paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1606.05675.pdf)?\n\nThey were able to achieve 77.4% top-1 accuracy on Food101 over 2-3 days of training.\n\nDo you think fine-tuning will get us there?\n\nLet's find out.\n\nTo start, let's load in our saved model.\n\n> 🔑 **Note:** It's worth remembering a traditional workflow for fine-tuning is to freeze a pre-trained base model and then train only the output layers for a few iterations so their weights can be updated inline with your custom data (feature extraction). And then unfreeze a number or all of the layers in the base model and continue training until the model stops improving.\n\nLike all good cooking shows, I've saved a model I prepared earlier (the feature extraction model from above) to Google Storage.\n\nWe can download it to make sure we're using the same model going forward.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Download the saved model from Google Storage\n!wget https://storage.googleapis.com/ztm_tf_course/food_vision/07_efficientnetb0_feature_extract_model_mixed_precision.zip ",
"--2021-12-15 11:50:25-- https://storage.googleapis.com/ztm_tf_course/food_vision/07_efficientnetb0_feature_extract_model_mixed_precision.zip\nResolving storage.googleapis.com (storage.googleapis.com)... 142.250.67.16, 142.250.71.80, 172.217.24.48, ...\nConnecting to storage.googleapis.com (storage.googleapis.com)|142.250.67.16|:443... connected.\nHTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK\nLength: 16976857 (16M) [application/zip]\nSaving to: '07_efficientnetb0_feature_extract_model_mixed_precision.zip’\n\n07_efficientnetb0_f 100%[===================>] 16.19M 12.1MB/s in 1.3s \n\n2021-12-15 11:50:27 (12.1 MB/s) - '07_efficientnetb0_feature_extract_model_mixed_precision.zip’ saved [16976857/16976857]\n\n"
],
[
"# Unzip the SavedModel downloaded from Google Stroage\n!mkdir downloaded_gs_model # create new dir to store downloaded feature extraction model\n!unzip 07_efficientnetb0_feature_extract_model_mixed_precision.zip -d downloaded_gs_model",
"mkdir: cannot create directory ‘downloaded_gs_model’: File exists\nArchive: 07_efficientnetb0_feature_extract_model_mixed_precision.zip\n creating: downloaded_gs_model/07_efficientnetb0_feature_extract_model_mixed_precision/\n creating: downloaded_gs_model/07_efficientnetb0_feature_extract_model_mixed_precision/variables/\n inflating: downloaded_gs_model/07_efficientnetb0_feature_extract_model_mixed_precision/variables/variables.data-00000-of-00001 \n inflating: downloaded_gs_model/07_efficientnetb0_feature_extract_model_mixed_precision/variables/variables.index \n inflating: downloaded_gs_model/07_efficientnetb0_feature_extract_model_mixed_precision/saved_model.pb \n creating: downloaded_gs_model/07_efficientnetb0_feature_extract_model_mixed_precision/assets/\n"
],
[
"# Load and evaluate downloaded GS model\ntf.get_logger().setLevel('INFO') # hide warning logs\nloaded_gs_model = tf.keras.models.load_model(\"downloaded_gs_model/07_efficientnetb0_feature_extract_model_mixed_precision\")",
"WARNING:tensorflow:SavedModel saved prior to TF 2.5 detected when loading Keras model. Please ensure that you are saving the model with model.save() or tf.keras.models.save_model(), *NOT* tf.saved_model.save(). To confirm, there should be a file named \"keras_metadata.pb\" in the SavedModel directory.\n"
],
[
"# Get a summary of our downloaded model\nloaded_gs_model.summary()",
"Model: \"model\"\n_________________________________________________________________\nLayer (type) Output Shape Param # \n=================================================================\ninput_layer (InputLayer) [(None, 224, 224, 3)] 0 \n_________________________________________________________________\nefficientnetb0 (Functional) (None, None, None, 1280) 4049571 \n_________________________________________________________________\npooling_layer (GlobalAverage (None, 1280) 0 \n_________________________________________________________________\ndense (Dense) (None, 101) 129381 \n_________________________________________________________________\nsoftmax_float32 (Activation) (None, 101) 0 \n=================================================================\nTotal params: 4,178,952\nTrainable params: 129,381\nNon-trainable params: 4,049,571\n_________________________________________________________________\n"
]
],
[
[
"And now let's make sure our loaded model is performing as expected.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# How does the loaded model perform?\nresults_loaded_gs_model = loaded_gs_model.evaluate(test_data)\nresults_loaded_gs_model",
"790/790 [==============================] - 16s 19ms/step - loss: 1.0881 - accuracy: 0.7065\n"
]
],
[
[
"Great, our loaded model is performing as expected.\n\nWhen we first created our model, we froze all of the layers in the base model by setting `base_model.trainable=False` but since we've loaded in our model from file, let's check whether or not the layers are trainable or not.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Are any of the layers in our model frozen?\nfor layer in loaded_gs_model.layers:\n layer.trainable = True # set all layers to trainable\n print(layer.name, layer.trainable, layer.dtype, layer.dtype_policy) # make sure loaded model is using mixed precision dtype_policy (\"mixed_float16\")",
"input_layer True float32 <Policy \"float32\">\nefficientnetb0 True float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\npooling_layer True float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\ndense True float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nsoftmax_float32 True float32 <Policy \"float32\">\n"
]
],
[
[
"Alright, it seems like each layer in our loaded model is trainable. But what if we got a little deeper and inspected each of the layers in our base model?\n\n> 🤔 **Question:** *Which layer in the loaded model is our base model?*\n\nBefore saving the Functional model to file, we created it with five layers (layers below are 0-indexed):\n0. The input layer\n1. The pre-trained base model layer (`tf.keras.applications.EfficientNetB0`)\n2. The pooling layer\n3. The fully-connected (dense) layer\n4. The output softmax activation (with float32 dtype)\n\nTherefore to inspect our base model layer, we can access the `layers` attribute of the layer at index 1 in our model.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Check the layers in the base model and see what dtype policy they're using\nfor layer in loaded_gs_model.layers[1].layers[:20]:\n print(layer.name, layer.trainable, layer.dtype, layer.dtype_policy)",
"input_1 True float32 <Policy \"float32\">\nrescaling True float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nnormalization True float32 <Policy \"float32\">\nstem_conv_pad True float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nstem_conv True float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nstem_bn True float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nstem_activation True float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_dwconv True float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_bn True float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_activation True float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_se_squeeze True float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_se_reshape True float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_se_reduce True float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_se_expand True float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_se_excite True float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_project_conv True float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock1a_project_bn True float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock2a_expand_conv True float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock2a_expand_bn True float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\nblock2a_expand_activation True float32 <Policy \"mixed_float16\">\n"
]
],
[
[
"Wonderful, it looks like each layer in our base model is trainable (unfrozen) and every layer which should be using the dtype policy `\"mixed_policy16\"` is using it.\n\nSince we've got so much data (750 images x 101 training classes = 75750 training images), let's keep all of our base model's layers unfrozen.\n\n> 🔑 **Note:** If you've got a small amount of data (less than 100 images per class), you may want to only unfreeze and fine-tune a small number of layers in the base model at a time. Otherwise, you risk overfitting.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## A couple more callbacks\n\nWe're about to start fine-tuning a deep learning model with over 200 layers using over 100,000 (75k+ training, 25K+ testing) images, which means our model's training time is probably going to be much longer than before.\n\n> 🤔 **Question:** *How long does training take?*\n\nIt could be a couple of hours or in the case of the [DeepFood paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1606.05675.pdf) (the baseline we're trying to beat), their best performing model took 2-3 days of training time.\n\nYou will really only know how long it'll take once you start training.\n\n> 🤔 **Question:** *When do you stop training?*\n\nIdeally, when your model stops improving. But again, due to the nature of deep learning, it can be hard to know when exactly a model will stop improving.\n\nLuckily, there's a solution: the [`EarlyStopping` callback](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/callbacks/EarlyStopping).\n\nThe `EarlyStopping` callback monitors a specified model performance metric (e.g. `val_loss`) and when it stops improving for a specified number of epochs, automatically stops training. \n\nUsing the `EarlyStopping` callback combined with the `ModelCheckpoint` callback saving the best performing model automatically, we could keep our model training for an unlimited number of epochs until it stops improving.\n\nLet's set both of these up to monitor our model's `val_loss`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Setup EarlyStopping callback to stop training if model's val_loss doesn't improve for 3 epochs\nearly_stopping = tf.keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(monitor=\"val_loss\", # watch the val loss metric\n patience=3) # if val loss decreases for 3 epochs in a row, stop training\n\n# Create ModelCheckpoint callback to save best model during fine-tuning\ncheckpoint_path = \"fine_tune_checkpoints/\"\nmodel_checkpoint = tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(checkpoint_path,\n save_best_only=True,\n monitor=\"val_loss\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Woohoo! Fine-tuning callbacks ready.\n\nIf you're planning on training large models, the `ModelCheckpoint` and `EarlyStopping` are two callbacks you'll want to become very familiar with. \n\nWe're almost ready to start fine-tuning our model but there's one more callback we're going to implement: [`ReduceLROnPlateau`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/callbacks/ReduceLROnPlateau).\n\nRemember how the learning rate is the most important model hyperparameter you can tune? (if not, treat this as a reminder).\n\nWell, the `ReduceLROnPlateau` callback helps to tune the learning rate for you.\n\nLike the `ModelCheckpoint` and `EarlyStopping` callbacks, the `ReduceLROnPlateau` callback montiors a specified metric and when that metric stops improving, it reduces the learning rate by a specified factor (e.g. divides the learning rate by 10).\n\n> 🤔 **Question:** *Why lower the learning rate?*\n\nImagine having a coin at the back of the couch and you're trying to grab with your fingers. \n\nNow think of the learning rate as the size of the movements your hand makes towards the coin. \n\nThe closer you get, the smaller you want your hand movements to be, otherwise the coin will be lost.\n\nOur model's ideal performance is the equivalent of grabbing the coin. So as training goes on and our model gets closer and closer to it's ideal performance (also called **convergence**), we want the amount it learns to be less and less.\n\nTo do this we'll create an instance of the `ReduceLROnPlateau` callback to monitor the validation loss just like the `EarlyStopping` callback. \n\nOnce the validation loss stops improving for two or more epochs, we'll reduce the learning rate by a factor of 5 (e.g. `0.001` to `0.0002`).\n\nAnd to make sure the learning rate doesn't get too low (and potentially result in our model learning nothing), we'll set the minimum learning rate to `1e-7`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Creating learning rate reduction callback\nreduce_lr = tf.keras.callbacks.ReduceLROnPlateau(monitor=\"val_loss\", \n factor=0.2, # multiply the learning rate by 0.2 (reduce by 5x)\n patience=2,\n verbose=1, # print out when learning rate goes down \n min_lr=1e-7)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Learning rate reduction ready to go!\n\nNow before we start training, we've got to recompile our model.\n\nWe'll use sparse categorical crossentropy as the loss and since we're fine-tuning, we'll use a 10x lower learning rate than the Adam optimizers default (`1e-4` instead of `1e-3`). ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Compile the model\nloaded_gs_model.compile(loss=\"sparse_categorical_crossentropy\", # sparse_categorical_crossentropy for labels that are *not* one-hot\n optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(0.0001), # 10x lower learning rate than the default\n metrics=[\"accuracy\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Okay, model compiled.\n\nNow let's fit it on all of the data. \n\nWe'll set it up to run for up to 100 epochs. \n\nSince we're going to be using the `EarlyStopping` callback, it might stop before reaching 100 epochs.\n\n> 🔑 **Note:** Running the cell below will set the model up to fine-tune all of the pre-trained weights in the base model on all of the Food101 data. Doing so with **unoptimized** data pipelines and **without** mixed precision training will take a fairly long time per epoch depending on what type of GPU you're using (about 15-20 minutes on Colab GPUs). But don't worry, **the code we've written above will ensure it runs much faster** (more like 4-5 minutes per epoch).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Start to fine-tune (all layers)\nhistory_101_food_classes_all_data_fine_tune = loaded_gs_model.fit(train_data,\n epochs=100, # fine-tune for a maximum of 100 epochs\n steps_per_epoch=len(train_data),\n validation_data=test_data,\n validation_steps=int(0.15 * len(test_data)), # validation during training on 15% of test data\n callbacks=[create_tensorboard_callback(\"training_logs\", \"efficientb0_101_classes_all_data_fine_tuning\"), # track the model training logs\n model_checkpoint, # save only the best model during training\n early_stopping, # stop model after X epochs of no improvements\n reduce_lr]) # reduce the learning rate after X epochs of no improvements",
"Saving TensorBoard log files to: training_logs/efficientb0_101_classes_all_data_fine_tuning/20211215-115307\nEpoch 1/100\n2368/2368 [==============================] - 141s 57ms/step - loss: 0.9242 - accuracy: 0.7500 - val_loss: 0.8070 - val_accuracy: 0.7725\nINFO:tensorflow:Assets written to: fine_tune_checkpoints/assets\n"
]
],
[
[
"> 🔑 **Note:** If you didn't use mixed precision or use techniques such as [`prefetch()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/data/Dataset#prefetch) in the *Batch & prepare datasets* section, your model fine-tuning probably takes up to 2.5-3x longer per epoch (see the output below for an example).\n\n| | Prefetch and mixed precision | No prefetch and no mixed precision |\n|-----|-----|-----|\n| Time per epoch | ~280-300s | ~1127-1397s |\n\n*Results from fine-tuning Food Vision Big™ on Food101 dataset using an EfficienetNetB0 backbone using a Google Colab Tesla T4 GPU.*\n\n```\nSaving TensorBoard log files to: training_logs/efficientB0_101_classes_all_data_fine_tuning/20200928-013008\nEpoch 1/100\n2368/2368 [==============================] - 1397s 590ms/step - loss: 1.2068 - accuracy: 0.6820 - val_loss: 1.1623 - val_accuracy: 0.6894\nEpoch 2/100\n2368/2368 [==============================] - 1193s 504ms/step - loss: 0.9459 - accuracy: 0.7444 - val_loss: 1.1549 - val_accuracy: 0.6872\nEpoch 3/100\n2368/2368 [==============================] - 1143s 482ms/step - loss: 0.7848 - accuracy: 0.7838 - val_loss: 1.0402 - val_accuracy: 0.7142\nEpoch 4/100\n2368/2368 [==============================] - 1127s 476ms/step - loss: 0.6599 - accuracy: 0.8149 - val_loss: 0.9599 - val_accuracy: 0.7373\n```\n*Example fine-tuning time for non-prefetched data as well as non-mixed precision training (~2.5-3x longer per epoch).*\n\nLet's make sure we save our model before we start evaluating it.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# # Save model to Google Drive (optional)\n# loaded_gs_model.save(\"/content/drive/MyDrive/tensorflow_course/food_vision/07_efficientnetb0_fine_tuned_101_classes_mixed_precision/\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Save model locally (note: if you're using Google Colab and you save your model locally, it will be deleted when your Google Colab session ends)\nloaded_gs_model.save(\"07_efficientnetb0_fine_tuned_101_classes_mixed_precision\")",
"INFO:tensorflow:Assets written to: 07_efficientnetb0_fine_tuned_101_classes_mixed_precision/assets\n"
]
],
[
[
"Looks like our model has gained a few performance points from fine-tuning, let's evaluate on the whole test dataset and see if managed to beat the [DeepFood paper's](https://arxiv.org/abs/1606.05675) result of 77.4% accuracy.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Evaluate mixed precision trained loaded model\nresults_loaded_gs_model_fine_tuned = loaded_gs_model.evaluate(test_data) \nresults_loaded_gs_model_fine_tuned",
"790/790 [==============================] - 15s 19ms/step - loss: 1.0241 - accuracy: 0.7985\n"
]
],
[
[
"Woohoo!!!! It looks like our model beat the results mentioned in the DeepFood paper for Food101 (DeepFood's 77.4% top-1 accuracy versus our ~79% top-1 accuracy).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Download fine-tuned model from Google Storage\n\nAs mentioned before, training models can take a significant amount of time.\n\nAnd again, like any good cooking show, here's something we prepared earlier...\n\nIt's a fine-tuned model exactly like the one we trained above but it's saved to Google Storage so it can be accessed, imported and evaluated.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Download and evaluate fine-tuned model from Google Storage\n!wget https://storage.googleapis.com/ztm_tf_course/food_vision/07_efficientnetb0_fine_tuned_101_classes_mixed_precision.zip",
"--2021-12-15 12:07:25-- https://storage.googleapis.com/ztm_tf_course/food_vision/07_efficientnetb0_fine_tuned_101_classes_mixed_precision.zip\nResolving storage.googleapis.com (storage.googleapis.com)... 142.250.204.16, 172.217.167.80, 142.250.66.240, ...\nConnecting to storage.googleapis.com (storage.googleapis.com)|142.250.204.16|:443... connected.\nHTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK\nLength: 46790356 (45M) [application/zip]\nSaving to: '07_efficientnetb0_fine_tuned_101_classes_mixed_precision.zip’\n\n07_efficientnetb0_f 100%[===================>] 44.62M 13.0MB/s in 3.5s \n\n2021-12-15 12:07:29 (12.7 MB/s) - '07_efficientnetb0_fine_tuned_101_classes_mixed_precision.zip’ saved [46790356/46790356]\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"The downloaded model comes in zip format (`.zip`) so we'll unzip it into the Google Colab instance.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Unzip fine-tuned model\n!mkdir downloaded_fine_tuned_gs_model # create separate directory for fine-tuned model downloaded from Google Storage\n!unzip 07_efficientnetb0_fine_tuned_101_classes_mixed_precision -d downloaded_fine_tuned_gs_model",
"Archive: 07_efficientnetb0_fine_tuned_101_classes_mixed_precision.zip\n creating: downloaded_fine_tuned_gs_model/07_efficientnetb0_fine_tuned_101_classes_mixed_precision/\n creating: downloaded_fine_tuned_gs_model/07_efficientnetb0_fine_tuned_101_classes_mixed_precision/variables/\n inflating: downloaded_fine_tuned_gs_model/07_efficientnetb0_fine_tuned_101_classes_mixed_precision/variables/variables.data-00000-of-00001 \n inflating: downloaded_fine_tuned_gs_model/07_efficientnetb0_fine_tuned_101_classes_mixed_precision/variables/variables.index \n inflating: downloaded_fine_tuned_gs_model/07_efficientnetb0_fine_tuned_101_classes_mixed_precision/saved_model.pb \n creating: downloaded_fine_tuned_gs_model/07_efficientnetb0_fine_tuned_101_classes_mixed_precision/assets/\n"
]
],
[
[
"Now we can load it using the [`tf.keras.models.load_model()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/keras/save_and_load) method and get a summary (it should be the exact same as the model we created above).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Load in fine-tuned model from Google Storage and evaluate\nloaded_fine_tuned_gs_model = tf.keras.models.load_model(\"downloaded_fine_tuned_gs_model/07_efficientnetb0_fine_tuned_101_classes_mixed_precision\")",
"WARNING:tensorflow:SavedModel saved prior to TF 2.5 detected when loading Keras model. Please ensure that you are saving the model with model.save() or tf.keras.models.save_model(), *NOT* tf.saved_model.save(). To confirm, there should be a file named \"keras_metadata.pb\" in the SavedModel directory.\n"
],
[
"# Get a model summary (same model architecture as above)\nloaded_fine_tuned_gs_model.summary()",
"Model: \"model\"\n_________________________________________________________________\nLayer (type) Output Shape Param # \n=================================================================\ninput_layer (InputLayer) [(None, 224, 224, 3)] 0 \n_________________________________________________________________\nefficientnetb0 (Functional) (None, None, None, 1280) 4049571 \n_________________________________________________________________\npooling_layer (GlobalAverage (None, 1280) 0 \n_________________________________________________________________\ndense (Dense) (None, 101) 129381 \n_________________________________________________________________\nsoftmax_float32 (Activation) (None, 101) 0 \n=================================================================\nTotal params: 4,178,952\nTrainable params: 4,136,929\nNon-trainable params: 42,023\n_________________________________________________________________\n"
]
],
[
[
"Finally, we can evaluate our model on the test data (this requires the `test_data` variable to be loaded.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Note: Even if you're loading in the model from Google Storage, you will still need to load the test_data variable for this cell to work\nresults_downloaded_fine_tuned_gs_model = loaded_fine_tuned_gs_model.evaluate(test_data)\nresults_downloaded_fine_tuned_gs_model",
"790/790 [==============================] - 16s 19ms/step - loss: 0.9072 - accuracy: 0.8016\n"
]
],
[
[
"Excellent! Our saved model is performing as expected (better results than the DeepFood paper!).\n\nCongrautlations! You should be excited! You just trained a computer vision model with competitive performance to a research paper and in far less time (our model took ~20 minutes to train versus DeepFood's quoted 2-3 days).\n\nIn other words, you brought Food Vision life!\n\nIf you really wanted to step things up, you could try using the [`EfficientNetB4`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/applications/EfficientNetB4) model (a larger version of `EfficientNetB0`). At at the time of writing, the EfficientNet family has the [state of the art classification results](https://paperswithcode.com/sota/fine-grained-image-classification-on-food-101) on the Food101 dataset.\n\n> 📖 **Resource:** To see which models are currently performing the best on a given dataset or problem type as well as the latest trending machine learning research, be sure to check out [paperswithcode.com](http://paperswithcode.com/) and [sotabench.com](https://sotabench.com/).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## View training results on TensorBoard\n\nSince we tracked our model's fine-tuning training logs using the `TensorBoard` callback, let's upload them and inspect them on TensorBoard.dev.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# !tensorboard dev upload --logdir ./training_logs \\\n# --name \"Fine-tuning EfficientNetB0 on all Food101 Data\" \\\n# --description \"Training results for fine-tuning EfficientNetB0 on Food101 Data with learning rate 0.0001\" \\",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Viewing at our [model's training curves on TensorBoard.dev](https://tensorboard.dev/experiment/2KINdYxgSgW2bUg7dIvevw/), it looks like our fine-tuning model gains boost in performance but starts to overfit as training goes on.\n\nSee the training curves on TensorBoard.dev here: https://tensorboard.dev/experiment/2KINdYxgSgW2bUg7dIvevw/\n\nTo fix this, in future experiments, we might try things like:\n* A different iteration of `EfficientNet` (e.g. `EfficientNetB4` instead of `EfficientNetB0`).\n* Unfreezing less layers of the base model and training them rather than unfreezing the whole base model in one go.\n\nYou can also view and delete past experiments on TensorBoard.dev with the following commands.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# View past TensorBoard experiments\n# !tensorboard dev list",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Delete past TensorBoard experiments\n# !tensorboard dev delete --experiment_id YOUR_EXPERIMENT_ID\n\n# Example\n# !tensorboard dev delete --experiment_id OAE6KXizQZKQxDiqI3cnUQ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Exercises \n\n1. Use the same evaluation techniques on the large-scale Food Vision model as you did in the previous notebook ([Transfer Learning Part 3: Scaling up](https://github.com/mrdbourke/tensorflow-deep-learning/blob/main/06_transfer_learning_in_tensorflow_part_3_scaling_up.ipynb)). More specifically, it would be good to see:\n * A confusion matrix between all of the model's predictions and true labels.\n * A graph showing the f1-scores of each class.\n * A visualization of the model making predictions on various images and comparing the predictions to the ground truth.\n * For example, plot a sample image from the test dataset and have the title of the plot show the prediction, the prediction probability and the ground truth label. \n2. Take 3 of your own photos of food and use the Food Vision model to make predictions on them. How does it go? Share your images/predictions with the other students.\n3. Retrain the model (feature extraction and fine-tuning) we trained in this notebook, except this time use [`EfficientNetB4`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/applications/EfficientNetB4) as the base model instead of `EfficientNetB0`. Do you notice an improvement in performance? Does it take longer to train? Are there any tradeoffs to consider?\n4. Name one important benefit of mixed precision training, how does this benefit take place?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Extra-curriculum\n\n* Read up on learning rate scheduling and the [learning rate scheduler callback](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/callbacks/LearningRateScheduler). What is it? And how might it be helpful to this project?\n* Read up on TensorFlow data loaders ([improving TensorFlow data loading performance](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/data_performance)). Is there anything we've missed? What methods you keep in mind whenever loading data in TensorFlow? Hint: check the summary at the bottom of the page for a gret round up of ideas.\n* Read up on the documentation for [TensorFlow mixed precision training](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/mixed_precision). What are the important things to keep in mind when using mixed precision training?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4a303be7f98326c8c84f797632edd0eac94d82b7
| 4,409 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
src/bayes/proportion/proportion_binomial.ipynb
|
shigeodayo/ex_design_analysis
|
58eda66a2b77d17f8443a286af4a7090111b072c
|
[
"MIT"
] | 10 |
2020-05-24T12:09:54.000Z
|
2021-03-03T10:14:52.000Z
|
src/bayes/proportion/proportion_binomial.ipynb
|
shigeodayo/ex_design_analysis
|
58eda66a2b77d17f8443a286af4a7090111b072c
|
[
"MIT"
] | 6 |
2020-05-24T13:14:09.000Z
|
2022-03-12T00:53:24.000Z
|
src/bayes/proportion/proportion_binomial.ipynb
|
shigeodayo/ex_design_analysis
|
58eda66a2b77d17f8443a286af4a7090111b072c
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2020-05-26T05:42:52.000Z
|
2020-05-26T05:42:52.000Z
| 22.155779 | 142 | 0.528465 |
[
[
[
"# Estimation of population proportion (Binomial distribution)\nAlternative of z-test and chi-square test",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Enable the commands below when running this program on Google Colab.\n# !pip install arviz==0.7\n# !pip install pymc3==3.8\n# !pip install Theano==1.0.4\n\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nfrom scipy import stats\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn as sns\n\nimport pymc3 as pm\n\nimport math\n\nplt.style.use('seaborn-darkgrid')\nnp.set_printoptions(precision=3)\npd.set_option('display.precision', 3)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Q. Is the ratio of Soba lovers higher than that of Udon lovers?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"SOBA_LOVER = 220 # Number of people who love Soba\nUDON_LOVER = 180 # Number of people who love Udon\n\nN = SOBA_LOVER + UDON_LOVER\n\nprint(SOBA_LOVER / N)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Bayesian analysis",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"with pm.Model() as model:\n # Prior distribution\n p = pm.Uniform('p', 0, 1)\n\n # Likelihood\n y_pred = pm.Binomial('y_pred', n=400, p=p, observed=SOBA_LOVER)\n \n # Odds\n odds = pm.Deterministic('odds', p / (1 - p))\n\n trace = pm.sample(21000, chains=5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"chain = trace[1000:]\npm.traceplot(chain)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pm.summary(chain)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('There are {:.3f} times as many Soba lovers than as Udon lovers.'.format(chain['odds'].mean()))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### RQ1: 「蕎麦好き」が「うどん好き」より多いか?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print('Probability of there are more Soba lovers than Udon lovers: {:.3f} %'.format((chain['p'] > 0.5).mean() * 100))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### RQ2: 「蕎麦好き」は「うどん好き」の1.4倍より多くいるか?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print('Probability of there are 1.4 times as many Soba lovers than as Udon lovers: {:.3f} %'.format((chain['odds'] > 1.4).mean() * 100))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('At least {:.3f} times as many (95%).'.format(np.quantile(chain['odds'], 0.05)))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pm.plot_posterior(chain['odds'], credible_interval=0.95, point_estimate='mode')\nplt.xlabel('Odds')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a30500a62ad3df1b7fc10131d3b086102cc9e34
| 3,379 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/load_pdf.ipynb
|
arijitthegame/simpletopics
|
cd8ead00595805e0adc5975d25e102ecd097d691
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/load_pdf.ipynb
|
arijitthegame/simpletopics
|
cd8ead00595805e0adc5975d25e102ecd097d691
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2021-07-01T21:24:25.000Z
|
2021-07-02T19:20:18.000Z
|
notebooks/load_pdf.ipynb
|
arijitthegame/simpletopics
|
cd8ead00595805e0adc5975d25e102ecd097d691
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-05-20T19:41:05.000Z
|
2021-05-20T19:41:05.000Z
| 23.303448 | 88 | 0.498668 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport os\nimport time\nimport glob\n\nfrom sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer\nfrom sklearn.decomposition import TruncatedSVD\nfrom sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# main\ntxtfolder = '/home/ngr/gdrive/simpletopics/data/processed/'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\ndocuments = glob.glob(os.path.join(txtfolder, '*.txt')) \nvectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(input='filename', \n decode_error='ignore',\n stop_words='english', \n use_idf=True, \n smooth_idf=True)\n\nwords = [i for i in vectorizer.get_feature_names() if not i.isnumeric()]\nA = vectorizer.fit_transform(documents)\nA = A[:, [i for i,v in enumerate(vectorizer.get_feature_names()) if v in words]]\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"A",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"[i for i in words if i.startswith('imm')]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a3060191c1bc6b130892d86c5dd82428a78afe0
| 213,738 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
junk/.ipynb_checkpoints/hw7-checkpoint.ipynb
|
Lavendulaa/programming-in-python-for-data-science
|
bc41da8afacf4c180ae0ff9c6dc26a7e6292252f
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2020-06-26T20:15:44.000Z
|
2020-06-26T20:15:44.000Z
|
junk/.ipynb_checkpoints/hw7-checkpoint.ipynb
|
Lavendulaa/programming-in-python-for-data-science
|
bc41da8afacf4c180ae0ff9c6dc26a7e6292252f
|
[
"MIT"
] | 20 |
2020-06-15T23:05:20.000Z
|
2020-09-01T22:07:45.000Z
|
junk/hw7.ipynb
|
UBC-MDS/MCL-programming-in-python
|
22836d9013d3e3d1b1074678ba7dc3ee2e66f398
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2020-06-25T20:53:13.000Z
|
2020-06-25T20:53:13.000Z
| 49.033723 | 36,216 | 0.584351 |
[
[
[
"# CPSC 330 hw7",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### BEGIN SOLUTION\nfrom sklearn.impute import SimpleImputer\nfrom sklearn.compose import ColumnTransformer\nfrom sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler, OrdinalEncoder, OneHotEncoder\n\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import Ridge\nfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV, RandomizedSearchCV\n\nfrom sklearn.metrics import r2_score\n### END SOLUTION",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Instructions\nrubric={points:5}\n\nFollow the [homework submission instructions](https://github.students.cs.ubc.ca/cpsc330-2019w-t2/home/blob/master/docs/homework_instructions.md). ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Exercise 1: time series prediction\n\nIn this exercise we'll be looking at a [dataset of avocado prices](https://www.kaggle.com/neuromusic/avocado-prices). You should start by downloading the dataset. As usual, please do not commit it to your repos.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df = pd.read_csv(\"avocado.csv\", parse_dates=[\"Date\"], index_col=0)\ndf.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df[\"Date\"].min()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df[\"Date\"].max()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"It looks like the data ranges from the start of 2015 to March 2018 (~2 years ago), for a total of 3.25 years or so. Let's split the data so that we have a 6 months of test data.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"split_date = '20170925'\ndf_train = df[df[\"Date\"] <= split_date]\ndf_test = df[df[\"Date\"] > split_date]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"assert len(df_train) + len(df_test) == len(df)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### 1(a)\nrubric={points:3}\n\nIn the Rain is Australia dataset from Lecture 16, we had different measurements for each Location. What about this dataset: for which categorical feature(s), if any, do we have separate measurements? Justify your answer by referencing the dataset.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### BEGIN SOLUTION",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df.sort_values(by=\"Date\").head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"From the above, we definitely see measurements on the same day at different regresion. Let's now group by region.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df.sort_values(by=[\"region\", \"Date\"]).head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"From the above we see that, even in Albany, we have two measurements on the same date. This seems to be due to the type of avocado.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df.sort_values(by=[\"region\", \"type\", \"Date\"]).head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Great, now we have a sequence of dates with a single row per date. So, the answer is that we have a separate timeseries for each combination of `region` and `type`.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### END SOLUTION",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### 1(b)\nrubric={points:3}\n\nIn the Rain in Australia dataset, the measurements were generally equally spaced but with some exceptions. How about with this dataset? Justify your answer by referencing the dataset.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### BEGIN SOLUTION",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"I think it's not unreasonable to do this on `df` rather than `df_train`, but either way is fine. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for name, group in df.groupby(['region', 'type']):\n print(\"%-40s %s\" % (name, group[\"Date\"].sort_values().diff().min()))",
"('Albany', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Albany', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Atlanta', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Atlanta', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('BaltimoreWashington', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('BaltimoreWashington', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Boise', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Boise', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Boston', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Boston', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('BuffaloRochester', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('BuffaloRochester', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('California', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('California', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Charlotte', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Charlotte', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Chicago', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Chicago', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('CincinnatiDayton', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('CincinnatiDayton', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Columbus', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Columbus', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('DallasFtWorth', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('DallasFtWorth', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Denver', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Denver', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Detroit', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Detroit', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('GrandRapids', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('GrandRapids', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('GreatLakes', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('GreatLakes', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('HarrisburgScranton', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('HarrisburgScranton', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('HartfordSpringfield', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('HartfordSpringfield', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Houston', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Houston', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Indianapolis', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Indianapolis', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Jacksonville', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Jacksonville', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('LasVegas', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('LasVegas', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('LosAngeles', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('LosAngeles', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Louisville', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Louisville', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('MiamiFtLauderdale', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('MiamiFtLauderdale', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Midsouth', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Midsouth', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Nashville', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Nashville', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('NewOrleansMobile', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('NewOrleansMobile', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('NewYork', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('NewYork', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Northeast', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Northeast', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('NorthernNewEngland', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('NorthernNewEngland', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Orlando', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Orlando', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Philadelphia', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Philadelphia', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('PhoenixTucson', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('PhoenixTucson', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Pittsburgh', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Pittsburgh', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Plains', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Plains', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Portland', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Portland', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('RaleighGreensboro', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('RaleighGreensboro', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('RichmondNorfolk', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('RichmondNorfolk', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Roanoke', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Roanoke', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Sacramento', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Sacramento', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('SanDiego', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('SanDiego', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('SanFrancisco', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('SanFrancisco', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Seattle', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Seattle', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('SouthCarolina', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('SouthCarolina', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('SouthCentral', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('SouthCentral', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Southeast', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Southeast', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Spokane', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Spokane', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('StLouis', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('StLouis', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Syracuse', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Syracuse', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Tampa', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Tampa', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('TotalUS', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('TotalUS', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('West', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('West', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('WestTexNewMexico', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('WestTexNewMexico', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n"
],
[
"for name, group in df.groupby(['region', 'type']):\n print(\"%-40s %s\" % (name, group[\"Date\"].sort_values().diff().max()))",
"('Albany', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Albany', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Atlanta', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Atlanta', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('BaltimoreWashington', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('BaltimoreWashington', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Boise', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Boise', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Boston', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Boston', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('BuffaloRochester', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('BuffaloRochester', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('California', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('California', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Charlotte', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Charlotte', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Chicago', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Chicago', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('CincinnatiDayton', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('CincinnatiDayton', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Columbus', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Columbus', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('DallasFtWorth', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('DallasFtWorth', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Denver', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Denver', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Detroit', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Detroit', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('GrandRapids', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('GrandRapids', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('GreatLakes', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('GreatLakes', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('HarrisburgScranton', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('HarrisburgScranton', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('HartfordSpringfield', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('HartfordSpringfield', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Houston', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Houston', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Indianapolis', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Indianapolis', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Jacksonville', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Jacksonville', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('LasVegas', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('LasVegas', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('LosAngeles', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('LosAngeles', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Louisville', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Louisville', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('MiamiFtLauderdale', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('MiamiFtLauderdale', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Midsouth', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Midsouth', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Nashville', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Nashville', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('NewOrleansMobile', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('NewOrleansMobile', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('NewYork', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('NewYork', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Northeast', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Northeast', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('NorthernNewEngland', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('NorthernNewEngland', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Orlando', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Orlando', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Philadelphia', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Philadelphia', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('PhoenixTucson', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('PhoenixTucson', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Pittsburgh', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Pittsburgh', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Plains', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Plains', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Portland', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Portland', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('RaleighGreensboro', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('RaleighGreensboro', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('RichmondNorfolk', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('RichmondNorfolk', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Roanoke', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Roanoke', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Sacramento', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Sacramento', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('SanDiego', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('SanDiego', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('SanFrancisco', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('SanFrancisco', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Seattle', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Seattle', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('SouthCarolina', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('SouthCarolina', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('SouthCentral', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('SouthCentral', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Southeast', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Southeast', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Spokane', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Spokane', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('StLouis', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('StLouis', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Syracuse', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Syracuse', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Tampa', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('Tampa', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('TotalUS', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('TotalUS', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('West', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('West', 'organic') 7 days 00:00:00\n('WestTexNewMexico', 'conventional') 7 days 00:00:00\n('WestTexNewMexico', 'organic') 21 days 00:00:00\n"
]
],
[
[
"It looks almost perfect - just organic avocados in WestTexNewMexico seems to be missing a couple measurements.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"name",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"group[\"Date\"].sort_values().diff().value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"So, in one case there's a 2-week jump, and in one cast there's a 3-week jump.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"group[\"Date\"].sort_values().reset_index(drop=True).diff().sort_values()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can see the anomalies occur at index 48 and 127. (Note: I had to `reset_index` because the index was not unique to each row.)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"group[\"Date\"].sort_values().reset_index(drop=True)[45:50]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can spot the first anomaly: a 2-week jump from Nov 29, 2015 to Dec 13, 2015.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"group[\"Date\"].sort_values().reset_index(drop=True)[125:130]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"And we can spot the second anomaly: a 3-week jump from June 11, 2017 to July 2, 2017.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### END SOLUTION",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### 1(c)\nrubric={points:1}\n\nIn the Rain is Australia dataset, each location was a different place in Australia. For this dataset, look at the names of the regions. Do you think the regions are also all distinct, or are there overlapping regions? Justify your answer by referencing the data.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### BEGIN SOLUTION",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df[\"region\"].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"There seems to be a hierarchical structure here: `TotalUS` is split into bigger regions like `West`, `Southeast`, `Northeast`, `Midsouth`; and `California` is split into cities like `Sacramento`, `SanDiego`, `LosAngeles`. It's a bit hard to figure out what's going on.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df.query(\"region == 'TotalUS' and type == 'conventional' and Date == '20150104'\")[\"Total Volume\"].values[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.query(\"region != 'TotalUS' and type == 'conventional' and Date == '20150104'\")[\"Total Volume\"].sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Since the individual regions sum up to more than the total US, it seems that some of the other regions are double-counted, which is consistent with a hierarchical structure. For example, Los Angeles is probalby double counted because it's within `LosAngeles` but also within `California`. What a mess!",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### END SOLUTION",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We will use the entire dataset despite any location-based weirdness uncovered in the previous part.\n\nWe will be trying to forecast the avocado price, which is the `AveragePrice` column. The function below is adapted from Lecture 16, with some improvements.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def create_lag_feature(df, orig_feature, lag, groupby, new_feature_name=None, clip=False):\n \"\"\"\n Creates a new feature that's a lagged version of an existing one.\n \n NOTE: assumes df is already sorted by the time columns and has unique indices.\n \n Parameters\n ----------\n df : pandas.core.frame.DataFrame\n The dataset.\n orig_feature : str\n The column name of the feature we're copying\n lag : int\n The lag; negative lag means values from the past, positive lag means values from the future\n groupby : list\n Column(s) to group by in case df contains multiple time series\n new_feature_name : str\n Override the default name of the newly created column\n clip : bool\n If True, remove rows with a NaN values for the new feature\n \n Returns\n -------\n pandas.core.frame.DataFrame\n A new dataframe with the additional column added.\n \"\"\"\n \n if new_feature_name is None:\n if lag < 0:\n new_feature_name = \"%s_lag%d\" % (orig_feature, -lag)\n else:\n new_feature_name = \"%s_ahead%d\" % (orig_feature, lag)\n \n new_df = df.assign(**{new_feature_name : np.nan})\n for name, group in new_df.groupby(groupby): \n if lag < 0: # take values from the past\n new_df.loc[group.index[-lag:],new_feature_name] = group.iloc[:lag][orig_feature].values\n else: # take values from the future\n new_df.loc[group.index[:-lag], new_feature_name] = group.iloc[lag:][orig_feature].values\n \n if clip:\n new_df = new_df.dropna(subset=[new_feature_name])\n \n return new_df",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We first sort our dataframe properly:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_sort = df.sort_values(by=[\"region\", \"type\", \"Date\"]).reset_index(drop=True)\ndf_sort",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We then call `create_lag_feature`. This creates a new column in the dataset `AveragePriceNextWeek`, which is the following week's `AveragePrice`. We have set `clip=True` which means it will remove rows where the target would be missing.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_hastarget = create_lag_feature(df_sort, \"AveragePrice\", +1, [\"region\", \"type\"], \"AveragePriceNextWeek\", clip=True)\ndf_hastarget",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"I will now split the data:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_train = df_hastarget[df_hastarget[\"Date\"] <= split_date]\ndf_test = df_hastarget[df_hastarget[\"Date\"] > split_date]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### 1(d)\nrubric={points:1}\n\nWhy was it reasonable for me to do this operation _before_ splitting the data, despite the fact that this usually constitutes a violation of the Golden Rule?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### BEGIN SOLUTION\n\nBecause we were only looking at the dates and creating the future feature. The difference is that the very last time point in our training set now contains the average price from the first time point in our test set. This is a realistic scenario if we wre actually using this model to forecast, so it's not a major concern.\n\n### END SOLUTION",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### 1(e)\nrubric={points:1}\n\nNext we will want to build some models to forecast the average avocado price a week in advance. Before we start with any ML, let's try a baseline: just predicting the previous week's `AveragePrice`. What $R^2$ do you get with this approach?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### BEGIN SOLUTION",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"r2_score(df_train[\"AveragePriceNextWeek\"], df_train[\"AveragePrice\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"r2_score(df_test[\"AveragePriceNextWeek\"], df_test[\"AveragePrice\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Interesting that this is a less effective prediction strategy in the later part of the dataset. I guess that means the price was fluctuating more in late 2017 / early 2018?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### END SOLUTION",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### 1(f)\nrubric={points:10}\n\nBuild some models to forecast the average avocado price. Experiment with a few approachs for encoding the date. Justify the decisions you make. Which approach worked best? Report your test score and briefly discuss your results.\n\nBenchmark: you should be able to achieve $R^2$ of at least 0.79 on the test set. I got to 0.80, but not beyond that. Let me know if you do better!\n\nNote: because we only have 2 splits here, we need to be a bit wary of overfitting on the test set. Try not to test on it a ridiculous number of times. If you are interested in some proper ways of dealing with this, see for example sklearn's [TimeSeriesSplit](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.model_selection.TimeSeriesSplit.html), which is like cross-validation for time series data.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### BEGIN SOLUTION",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_train.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"(df_train.loc[:, \"Small Bags\": \"XLarge Bags\"].sum(axis=1) - df_train[\"Total Bags\"]).abs().max()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"It seems that `Total Bags` is (approximately) the sum of the other 3 bag features, so I will drop `Total Bags`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"(df_train.loc[:, \"4046\": \"4770\"].sum(axis=1) - df_train[\"Total Volume\"]).abs().max()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"It seems that `Total Volume` is _not_ the sum of the 3 avocado types, so I will keep all 4 columns.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_train.info()",
"<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>\nInt64Index: 15441 entries, 0 to 18222\nData columns (total 14 columns):\n # Column Non-Null Count Dtype \n--- ------ -------------- ----- \n 0 Date 15441 non-null datetime64[ns]\n 1 AveragePrice 15441 non-null float64 \n 2 Total Volume 15441 non-null float64 \n 3 4046 15441 non-null float64 \n 4 4225 15441 non-null float64 \n 5 4770 15441 non-null float64 \n 6 Total Bags 15441 non-null float64 \n 7 Small Bags 15441 non-null float64 \n 8 Large Bags 15441 non-null float64 \n 9 XLarge Bags 15441 non-null float64 \n 10 type 15441 non-null object \n 11 year 15441 non-null int64 \n 12 region 15441 non-null object \n 13 AveragePriceNextWeek 15441 non-null float64 \ndtypes: datetime64[ns](1), float64(10), int64(1), object(2)\nmemory usage: 1.8+ MB\n"
]
],
[
[
"It seems there are no null values, so I will not do any imputation.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Will plot a single time series for exploration purposes:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_train.query(\"region == 'TotalUS'\").set_index(\"Date\").groupby(\"type\")[\"AveragePrice\"].plot(legend=True);",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_train.query(\"region == 'TotalUS' and type == 'conventional'\").plot(x=\"Date\", y=\"Total Volume\");",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We see some seasonality in the total volume, but not much in the average price - interesting.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"I will not scale the `AveragePrice` because I am not scaling `AveragePriceNextWeek` either, and it may be helpful to keep them the same. Alternatively, it may have been effective to predict the _change_ in price instead of next's week's price.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"numeric_features = [\"Total Volume\", \"4046\", \"4225\", \"4770\", \"Small Bags\", \"Large Bags\", \"XLarge Bags\", \"year\"]\ncategorical_features = [\"type\", \"region\"]\nkeep_features = [\"AveragePrice\"]\ndrop_features = [\"Date\", \"Total Bags\"] \ntarget_feature = \"AveragePriceNextWeek\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Next, I grab the `preprocess_features` function from Lecture 16, with a minor modification to allow un-transformed features via `keep_features`:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def preprocess_features(df_train, df_test, \n numeric_features, \n categorical_features, \n keep_features, \n drop_features, \n target_feature):\n \n all_features = numeric_features + categorical_features + keep_features + drop_features + [target_feature]\n if set(df_train.columns) != set(all_features):\n print(\"Missing columns\", set(df_train.columns) - set(all_features))\n print(\"Extra columns\", set(all_features) - set(df_train.columns))\n raise Exception(\"Columns do not match\")\n \n # Put the columns in the order we want\n df_train = df_train[all_features]\n df_test = df_test[all_features]\n \n numeric_transformer = Pipeline([\n ('imputer', SimpleImputer(strategy='median')),\n ('scaler', StandardScaler())\n ])\n categorical_transformer = Pipeline([\n ('imputer', SimpleImputer(strategy='most_frequent')),\n ('onehot', OneHotEncoder(sparse=False, drop='first'))\n ])\n preprocessor = ColumnTransformer([\n ('numeric', numeric_transformer, numeric_features),\n ('categorical', categorical_transformer, categorical_features)\n ], remainder='passthrough')\n preprocessor.fit(df_train);\n\n if len(categorical_features) > 0:\n ohe = preprocessor.named_transformers_['categorical'].named_steps['onehot']\n ohe_feature_names = list(ohe.get_feature_names(categorical_features))\n new_columns = numeric_features + ohe_feature_names + keep_features + drop_features + [target_feature]\n else:\n new_columns = all_features\n\n X_train_enc = pd.DataFrame(preprocessor.transform(df_train), index=df_train.index, columns=new_columns)\n X_test_enc = pd.DataFrame(preprocessor.transform(df_test), index=df_test.index, columns=new_columns)\n \n X_train_enc = X_train_enc.drop(columns=drop_features + [target_feature])\n X_test_enc = X_test_enc.drop( columns=drop_features + [target_feature])\n \n y_train = df_train[target_feature]\n y_test = df_test[ target_feature]\n \n return X_train_enc, y_train, X_test_enc, y_test",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_train_enc, y_train, df_test_enc, y_test = preprocess_features(df_train, df_test, \n numeric_features, \n categorical_features, \n keep_features, \n drop_features, \n target_feature)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_train_enc.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lr = Ridge()\nlr.fit(df_train_enc, y_train);",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lr.score(df_train_enc, y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lr.score(df_test_enc, y_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lr_coef = pd.DataFrame(data=np.squeeze(lr.coef_), index=df_train_enc.columns, columns=[\"Coef\"])\nlr_coef.sort_values(by=\"Coef\", ascending=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This is not a very impressive showing. We're doing almost the same as the baseline.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Let's see if encoding the date helps at all. We'll try to OHE the month.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_train_month = df_train.assign(Month=df_train[\"Date\"].apply(lambda x: x.month))\ndf_test_month = df_test.assign( Month=df_test[ \"Date\"].apply(lambda x: x.month))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_train_month_enc, y_train, df_test_month_enc, y_test = preprocess_features(df_train_month, df_test_month, \n numeric_features, \n categorical_features + [\"Month\"], \n keep_features, \n drop_features, \n target_feature)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_train_month_enc.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lr = Ridge()\nlr.fit(df_train_month_enc, y_train);",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lr.score(df_train_month_enc, y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lr.score(df_test_month_enc, y_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"A tiny bit better.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pd.DataFrame(data=np.squeeze(lr.coef_), index=df_train_month_enc.columns, columns=[\"Coef\"]).sort_values(by=\"Coef\", ascending=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's add some lag features. I'm arbitrarily deciding on 4 lags for `AveragePrice` (the most important feature).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def add_lags(df):\n df = create_lag_feature(df, \"AveragePrice\", -1, [\"region\", \"type\"])\n df = create_lag_feature(df, \"AveragePrice\", -2, [\"region\", \"type\"])\n df = create_lag_feature(df, \"AveragePrice\", -3, [\"region\", \"type\"])\n df = create_lag_feature(df, \"AveragePrice\", -4, [\"region\", \"type\"])\n return df\n\ndf_train_month_lag = add_lags(df_train_month)\ndf_test_month_lag = add_lags(df_test_month)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_train_month_lag",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_train_month_lag_enc, y_train, df_test_month_lag_enc, y_test = preprocess_features(df_train_month_lag, df_test_month_lag, \n numeric_features + [\"AveragePrice_lag1\", \"AveragePrice_lag2\", \"AveragePrice_lag3\", \"AveragePrice_lag4\"], \n categorical_features + [\"Month\"], \n keep_features, \n drop_features, \n target_feature)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lr = Ridge()\nlr.fit(df_train_month_lag_enc, y_train);",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lr.score(df_train_month_lag_enc, y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lr.score(df_test_month_lag_enc, y_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This did not seem to help.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pd.DataFrame(data=np.squeeze(lr.coef_), index=df_train_month_lag_enc.columns, columns=[\"Coef\"]).sort_values(by=\"Coef\", ascending=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can also try a random forest:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"rf = RandomForestRegressor() \nrf.fit(df_train_month_lag_enc, y_train);",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"rf.score(df_train_month_lag_enc, y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"rf.score(df_test_month_lag_enc, y_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"For the random forest it may be helpful to model the difference between today and tomorrow. The linear model does not care about this because it just corresponds to changing the coefficient corresponding to `AveragePrice` by 1, but for the random forest it may help:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"rf = RandomForestRegressor() \nrf.fit(df_train_month_lag_enc, y_train - df_train_month_lag_enc[\"AveragePrice\"]);",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"r2_score(y_train, rf.predict(df_train_month_lag_enc) + df_train_month_lag_enc[\"AveragePrice\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"r2_score(y_test, rf.predict(df_test_month_lag_enc) + df_test_month_lag_enc[\"AveragePrice\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This massively overfits when we do this shifting. Let's try a simpler model...",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"rf = RandomForestRegressor(max_depth=8) \nrf.fit(df_train_month_lag_enc, y_train - df_train_month_lag_enc[\"AveragePrice\"]);",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"r2_score(y_train, rf.predict(df_train_month_lag_enc) + df_train_month_lag_enc[\"AveragePrice\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"r2_score(y_test, rf.predict(df_test_month_lag_enc) + df_test_month_lag_enc[\"AveragePrice\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Doesn't realy help.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Also, we can just confirm that this shifting has no effect on the linear model (well, a small effect because it's `Ridge` instead of `LinearRegression`, but small):",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"lr = Ridge() \nlr.fit(df_train_month_lag_enc, y_train - df_train_month_lag_enc[\"AveragePrice\"]);",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"r2_score(y_train, lr.predict(df_train_month_lag_enc) + df_train_month_lag_enc[\"AveragePrice\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"r2_score(y_test, lr.predict(df_test_month_lag_enc) + df_test_month_lag_enc[\"AveragePrice\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Indeed, this is essentially the same score we had before.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Overall, adding the month helped, but adding the lagged price was surprisingly unhelpful. Perhaps lagged version of other features would have been better, or other representations of the time of year, or dealing with the regions and avocado types a bit more carefully. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### END SOLUTION",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### 1(g)\nrubric={points:3}\n\nWe talked a little bit about _seasonality_, which is the idea of a periodic component to the time series. For example, in Lecture 16 we attempted to capture this by encoding the month. Something we didn't discuss is _trends_, which are long-term variations in the quantity of interest. Aside from the effects of climate change, the amount of rain in Australia is likely to vary during the year but less likely to have long-term trends over the years. Avocado prices, on the other hand, could easily exhibit trends: for example avocados may just cost more in 2020 than they did in 2015.\n\nBriefly discuss in ~1 paragraph: to what extent, if any, was your model above able to account for seasonality? What about trends?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### BEGIN SOLUTION\n\nI tried to take seasonality into account by having the month as an OHE variable. As far as trends are concerned, the year is also a numeric variable in the model, so it could learn that the price in 2017 is higher than in 2015, say. However, there are very few years in the training set (2015, 16, 17), so that is not a lot of data to learn from. Perhaps including the number of months since the start of the dataset, or something like that, would enable the model to do a bit better with trends. Nonetheless, extrapolating is very hard so we can't necessarily trust our models' handing of trend. \n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pd.DataFrame(data=np.squeeze(lr.coef_), index=df_train_month_lag_enc.columns, columns=[\"Coef\"]).loc[\"year\"]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"It seems that our linear model learned a small positive trend for the year. It would be cool to use SHAP and see what the random forest is doing.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### END SOLUTION",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Exercise 2: very short answer questions\n\nEach question is worth 2 points.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### 2(a)\nrubric={points:4}\n\nThe following questions pertain to Lecture 16 on time series data:\n\n1. Sometimes a time series has missing time points or, worse, time points that are unequally spaced in general. Give an example of a real world situation where the time series data would have unequally spaced time points.\n2. In class we discussed two approaches to using temporal information: encoding the date as one or more features, and creating lagged versions of features. Which of these (one/other/both/neither) two approaches would struggle with unequally spaced time points? Briefly justify your answer.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### BEGIN SOLUTION\n\n1. Many many examples: credit card transactions, log files, basically any situation where the frequency of the measurements could not be chosen by the person taking the measurements. \n2. Encoding the date as, e.g. OHE month works just fine with unequally spaced points. However, the lag features are more problematic, because the \"previous\" measurement will be a different length of time away in each case. \n\n### END SOLUTION",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### 2(b)\nrubric={points:10}\n\nThe following questions pertain to Lecture 17 on survival analysis. We'll consider the use case of customer churn analysis.\n\n1. What is the problem with simply labeling customers are \"churned\" or \"not churned\" and using standard supervised learning techniques, as we did in hw4?\n2. Consider customer A who just joined last week vs. customer B who has been with the service for a year. Who do you expect will leave the service first: probably customer A, probably customer B, or we don't have enough information to answer? (This is a bit tricky - it's OK if you don't know the answer, but try to argue your case.)\n3. One of the true/false questions from class was: \"If a customer is censored after 5 months with the service, then all customers are censored after 5 months (i.e. no values of `tenure` above 5).\" What is the answer if all customers joined the service at the same time? Briefly explain.\n4. One of the true/false questions from class was: \"If a customer is censored after 5 months with the service, then all customers are censored after 5 months (i.e. no values of `tenure` above 5).\" What is the answer if customers did not necessarily join the service at the same time? Briefly explain.\n5. If a customer's survival function is almost flat during a certain period, how do we interpret that?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### BEGIN SOLUTION\n\n1. The \"not churned\" are censored - we don't know if they will churn shortly or in a long time. These people have the same label and our model will be impacted negatively.\n2. Not enough information - it depends! Imagine a subscription service where you have to pay a starter fee after a month and then pay a huge fee after a year. Well, customer B just paid that huge fee and will probably stay a while, whereas customer A may leave before paying the huge fee, so customer A will probably leave first. But imagine a service where people are more and more likely to leave every day, e.g. a movie service with only 100 movies, so you can run out easily. In that case customer B will probably leave first.\n3. True. If all started at the same time, and a customer is censored after 5 months, that means they all started 5 months ago and are all censored after 5 months.\n4. False. That particular customer started 5 months ago, but you may have another customer who started much longer ago.\n5. The customer is very unlikely to leave during that period.\n\n### END SOLUTION",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### 2(c)\nrubric={points:10}\n\nThe following questions pertain to Lecture 18 on clustering.\n\n1. What's the main difference between unsupervised and supervised learning?\n2. When choosing $k$ in $k$-means, why not just choose the $k$ that leads to the smallest inertia (sum of squared distances within clusters)?\n3. You decide to use clustering for _outlier detection_; that is, to detect instances that are very atypical compared to all the rest. How might you do this with $k$-means?\n4. You decide to use clustering for _outlier detection_; that is, to detect instances that are very atypical compared to all the rest. How might you do this with DBSCAN?\n5. For hierarchical clustering, we briefly discussed a few different methods for merging clusters: single linkage, average linkage, etc. Why do we have this added complication here - can't we just minimize distance like we did with $k$-means? ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### BEGIN SOLUTION\n\n1. Supervised has target values ($y$), unsupervised does not.\n2. Because inertia decreases with $k$, so you'd just choose $k=n$, which is not interesting.\n3. Look for examples that are very far away from their cluster mean.\n4. Look for examples that were not assigned to any cluster.\n5. With $k$-means we had to find the distance between a point and a cluster mean. Here, we need to find the distance between two clusters, and, importantly, we have no cluster means. So it's ambiguous how to definite distance between two clusters.\n\n### END SOLUTION",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4a3075b11daf299b1ca98e2833b7dad5e21eda18
| 25,987 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
jupyter/lasso-structure-learning.ipynb
|
oneoffcoder/lasso-bbn
|
f3e16bb23fe1b76f5a02eeb7b784044501fed922
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
jupyter/lasso-structure-learning.ipynb
|
oneoffcoder/lasso-bbn
|
f3e16bb23fe1b76f5a02eeb7b784044501fed922
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
jupyter/lasso-structure-learning.ipynb
|
oneoffcoder/lasso-bbn
|
f3e16bb23fe1b76f5a02eeb7b784044501fed922
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 60.575758 | 13,328 | 0.721322 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd\n\ndf = pd.read_csv('../data/data-binary.csv')\ndf.dtypes",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression\n\ndef get_model(df, X_cols, y_col, solver='liblinear', penalty='l1', C=0.2):\n X = df[X_cols]\n y = df[y_col]\n \n model = LogisticRegression(penalty=penalty, solver=solver, C=C)\n model.fit(X, y)\n \n return model\n\ndef extract_model_params(y, fields, model):\n child = {'child': y}\n intercepts = {'intercept': model.intercept_[0]}\n coefs = {field: coef for field, coef in zip(fields, model.coef_[0])}\n others = {field: 0.0 for field in fields[len(coefs):]}\n \n p = {**child, **intercepts}\n p = {**p, **coefs}\n p = {**p, **others}\n \n return p\n \nargs = [(list(df.columns[0:index]), y) for index, y in enumerate(df.columns) if index > 0]\nmodels = [(y_col, get_model(df, X_cols, y_col)) for X_cols, y_col in args]\nparam_df = pd.DataFrame([extract_model_params(y, df.columns, model) for y, model in models])\nparam_df",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import networkx as nx\nfrom networkx.algorithms.dag import is_directed_acyclic_graph\nfrom itertools import chain\n\ndef get_structure(param_df, threshold=0.0):\n def get_edges(r, nodes):\n edges = []\n ch = r['child']\n for pa in nodes:\n if pa == ch:\n break\n if abs(r[pa]) > threshold:\n edge = (pa, ch)\n edges.append(edge)\n return edges\n\n nodes = [v for v in param_df.columns if v not in ['child', 'intercept']]\n edges = list(chain(*[get_edges(r, nodes) for _, r in param_df.iterrows()]))\n\n g = nx.DiGraph()\n\n for n in nodes:\n g.add_node(n)\n\n for edge in edges:\n g.add_edge(*edge)\n if not is_directed_acyclic_graph(g):\n g.remove_edge(*edge)\n \n return g\n\ng = get_structure(param_df)\n\nprint(g.nodes())\nprint(g.edges())",
"['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']\n[('a', 'c'), ('a', 'd'), ('b', 'c'), ('b', 'd'), ('b', 'e'), ('d', 'e')]\n"
],
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\nfig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(5, 5))\n\nnx.draw(g, with_labels=True, font_weight='bold', node_color='r', ax=ax)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ddf = df.copy(deep=True)\nfor col in ddf.columns:\n ddf[col] = ddf[col].astype(str)\n \nddf.dtypes",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from itertools import combinations\nimport numpy as np\n\ndef get_parameters(ddf, g):\n def get_filters(ch, parents, domains):\n pas = parents[ch]\n if len(pas) == 0:\n ch_domain = domains[ch]\n return [f'{ch}==\"{v}\"' for v in ch_domain]\n else:\n vals = [[(pa, v) for v in domains[pa]] for pa in pas]\n vals = vals + [[(ch, v) for v in domains[ch]]]\n vals = chain(*vals)\n vals = combinations(vals, len(pas) + 1)\n vals = filter(lambda tups: tups[0][0] != tups[1][0] and tups[0][0] != tups[2][0] and tups[1][0] != tups[2][0], vals)\n vals = map(lambda tups: ' and '.join([f'{t[0]}==\"{t[1]}\"' for t in tups]), vals)\n vals = list(vals)\n return vals\n\n def get_total(filters, n):\n counts = [ddf.query(f).shape[0] for f in filters]\n counts = [counts[i:i + n] for i in range(0, len(counts), n)]\n counts = [list(np.array(arr) / sum(arr)) for arr in counts]\n counts = list(chain(*counts))\n return counts\n\n nodes = list(g.nodes())\n \n domains = {n: sorted(list(ddf[n].unique())) for n in nodes}\n parents = {ch: list(g.predecessors(ch)) for ch in nodes}\n\n return {ch: get_total(get_filters(ch, parents, domains), len(domains[ch])) for ch in nodes}\n\nget_parameters(ddf, g)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a30794f9fa83fda580bc67973d543fdabb5999e
| 170,894 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Python_Stock/Candlestick_Patterns/Candlestick_Hanging_Man.ipynb
|
chunsj/Stock_Analysis_For_Quant
|
5f28ef9537885a695245d26f3010592a29d45a34
|
[
"MIT"
] | 962 |
2019-07-17T09:57:41.000Z
|
2022-03-29T01:55:20.000Z
|
Python_Stock/Candlestick_Patterns/Candlestick_Hanging_Man.ipynb
|
chunsj/Stock_Analysis_For_Quant
|
5f28ef9537885a695245d26f3010592a29d45a34
|
[
"MIT"
] | 5 |
2020-04-29T16:54:30.000Z
|
2022-02-10T02:57:30.000Z
|
Python_Stock/Candlestick_Patterns/Candlestick_Hanging_Man.ipynb
|
chunsj/Stock_Analysis_For_Quant
|
5f28ef9537885a695245d26f3010592a29d45a34
|
[
"MIT"
] | 286 |
2019-08-04T10:37:58.000Z
|
2022-03-28T06:31:56.000Z
| 230.626181 | 58,121 | 0.840345 |
[
[
[
"# Candlestick Hanging Man",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"https://www.investopedia.com/articles/active-trading/040914/understanding-hanging-man-optimistic-candlestick-pattern.asp",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport talib\n\nimport warnings\nwarnings.filterwarnings(\"ignore\")\n\n# yahoo finance is used to fetch data \nimport yfinance as yf\nyf.pdr_override()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# input\nsymbol = 'AMD'\nstart = '2018-01-01'\nend = '2021-10-08'\n\n# Read data \ndf = yf.download(symbol,start,end)\n\n# View Columns\ndf.head()",
"[*********************100%***********************] 1 of 1 completed\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Candlestick with Hanging Man",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from matplotlib import dates as mdates\nimport datetime as dt\n\ndfc = df.copy()\ndfc['VolumePositive'] = dfc['Open'] < dfc['Adj Close']\n#dfc = dfc.dropna()\ndfc = dfc.reset_index()\ndfc['Date'] = pd.to_datetime(dfc['Date'])\ndfc['Date'] = dfc['Date'].apply(mdates.date2num)\ndfc.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from mplfinance.original_flavor import candlestick_ohlc\n\nfig = plt.figure(figsize=(14,10))\nax = plt.subplot(2, 1, 1)\ncandlestick_ohlc(ax,dfc.values, width=0.5, colorup='g', colordown='r', alpha=1.0)\nax.xaxis_date()\nax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(mdates.DateFormatter('%d-%m-%Y'))\nax.grid(True, which='both')\nax.minorticks_on()\naxv = ax.twinx()\ncolors = dfc.VolumePositive.map({True: 'g', False: 'r'})\naxv.bar(dfc.Date, dfc['Volume'], color=colors, alpha=0.4)\naxv.axes.yaxis.set_ticklabels([])\naxv.set_ylim(0, 3*df.Volume.max())\nax.set_title('Stock '+ symbol +' Closing Price')\nax.set_ylabel('Price')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"hanging_man = talib.CDLHANGINGMAN(df['Open'], df['High'], df['Low'], df['Close'])\n\nhanging_man = hanging_man[hanging_man != 0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df['hanging_man'] = talib.CDLHANGINGMAN(df['Open'], df['High'], df['Low'], df['Close'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.loc[df['hanging_man'] !=0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df['Adj Close'].loc[df['hanging_man'] !=0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df['Adj Close'].loc[df['hanging_man'] !=0].index",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"hanging_man",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"hanging_man.index",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig = plt.figure(figsize=(20,16))\nax = plt.subplot(2, 1, 1)\ncandlestick_ohlc(ax,dfc.values, width=0.5, colorup='g', colordown='r', alpha=1.0)\nax.xaxis_date()\nax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(mdates.DateFormatter('%d-%m-%Y'))\nax.grid(True, which='both')\nax.minorticks_on()\naxv = ax.twinx()\nax.plot_date(df['Adj Close'].loc[df['hanging_man'] !=0].index, df['Adj Close'].loc[df['hanging_man'] !=0],\n 'Dc', # marker style 'o', color 'g'\n fillstyle='none', # circle is not filled (with color)\n ms=10.0) \ncolors = dfc.VolumePositive.map({True: 'g', False: 'r'})\naxv.bar(dfc.Date, dfc['Volume'], color=colors, alpha=0.4)\naxv.axes.yaxis.set_ticklabels([])\naxv.set_ylim(0, 3*df.Volume.max())\nax.set_title('Stock '+ symbol +' Closing Price')\nax.set_ylabel('Price')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Plot Certain dates",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df = df['2021-07-01':'2021-08-01']\ndfc = df.copy()\ndfc['VolumePositive'] = dfc['Open'] < dfc['Adj Close']\n#dfc = dfc.dropna()\ndfc = dfc.reset_index()\ndfc['Date'] = pd.to_datetime(dfc['Date'])\ndfc['Date'] = dfc['Date'].apply(mdates.date2num)\ndfc.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig = plt.figure(figsize=(20,16))\nax = plt.subplot(2, 1, 1)\nax.set_facecolor('black')\ncandlestick_ohlc(ax,dfc.values, width=0.5, colorup='tan', colordown='gold', alpha=1.0)\nax.xaxis_date()\nax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(mdates.DateFormatter('%d-%m-%Y'))\n#ax.grid(True, which='both')\n#ax.minorticks_on()\naxv = ax.twinx()\nax.plot_date(df['Adj Close'].loc[df['hanging_man'] !=0].index, df['Adj Close'].loc[df['hanging_man'] !=0],\n 'dr', # marker style 'o', color 'g'\n fillstyle='none', # circle is not filled (with color)\n ms=20.0) \ncolors = dfc.VolumePositive.map({True: 'tan', False: 'gold'})\naxv.bar(dfc.Date, dfc['Volume'], color=colors, alpha=0.4)\naxv.axes.yaxis.set_ticklabels([])\naxv.set_ylim(0, 3*df.Volume.max())\nax.set_title('Stock '+ symbol +' Closing Price')\nax.set_ylabel('Price')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Highlight Candlestick",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from matplotlib.dates import date2num\nfrom datetime import datetime\n\nfig = plt.figure(figsize=(20,16))\nax = plt.subplot(2, 1, 1)\ncandlestick_ohlc(ax,dfc.values, width=0.5, colorup='g', colordown='r', alpha=1.0)\nax.xaxis_date()\nax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(mdates.DateFormatter('%d-%m-%Y'))\n#ax.grid(True, which='both')\n#ax.minorticks_on()\naxv = ax.twinx()\nax.axvspan(date2num(datetime(2021,7,19)), date2num(datetime(2021,7,21)), \n label=\"Hanging Man Bearish\",color=\"red\", alpha=0.3)\nax.legend()\ncolors = dfc.VolumePositive.map({True: 'g', False: 'r'})\naxv.bar(dfc.Date, dfc['Volume'], color=colors, alpha=0.4)\naxv.axes.yaxis.set_ticklabels([])\naxv.set_ylim(0, 3*df.Volume.max())\nax.set_title('Stock '+ symbol +' Closing Price')\nax.set_ylabel('Price')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a307f7ba4525ec65fd4af0902bb1ba333312b2c
| 4,770 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
DSA/graph/findJudge.ipynb
|
lance-lh/Data-Structures-and-Algorithms
|
c432654edaeb752536e826e88bcce3ed2ab000fb
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2019-03-27T13:00:28.000Z
|
2019-03-27T13:00:28.000Z
|
DSA/graph/findJudge.ipynb
|
lance-lh/Data-Structures-and-Algorithms
|
c432654edaeb752536e826e88bcce3ed2ab000fb
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
DSA/graph/findJudge.ipynb
|
lance-lh/Data-Structures-and-Algorithms
|
c432654edaeb752536e826e88bcce3ed2ab000fb
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 37.857143 | 1,657 | 0.512998 |
[
[
[
"In a town, there are N people labelled from 1 to N. There is a rumor that one of these people is secretly the town judge.\n\nIf the town judge exists, then:\n\nThe town judge trusts nobody.\nEverybody (except for the town judge) trusts the town judge.\nThere is exactly one person that satisfies properties 1 and 2.\nYou are given trust, an array of pairs trust[i] = [a, b] representing that the person labelled a trusts the person labelled b.\n\nIf the town judge exists and can be identified, return the label of the town judge. Otherwise, return -1.\n\n \n\nExample 1:\n\n Input: N = 2, trust = [[1,2]]\n Output: 2\nExample 2:\n\n Input: N = 3, trust = [[1,3],[2,3]]\n Output: 3\nExample 3:\n\n Input: N = 3, trust = [[1,3],[2,3],[3,1]]\n Output: -1\nExample 4:\n\n Input: N = 3, trust = [[1,2],[2,3]]\n Output: -1\nExample 5:\n\n Input: N = 4, trust = [[1,3],[1,4],[2,3],[2,4],[4,3]]\n Output: 3\n \n\nNote:\n\n 1 <= N <= 1000\n trust.length <= 10000\n trust[i] are all different\n trust[i][0] != trust[i][1]\n 1 <= trust[i][0], trust[i][1] <= N",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def findJudge(N, trust):\n '''\n :param N: int\n :param trust: List[List[int]]\n :return: int\n '''\n # if judge exists, it has N - 1 votes\n # we consider each person as a vertex and each trust relationship as a directed edge\n\n # note that: N is the num of people\n # N + 1 is the num of sub-list\n a = [0] * (N + 1)\n for i in trust:\n a[i[1]] += 1\n # why ?\n a[i[0]] -= 1\n\n for j in range(1, len(a)):\n if a[j] == N - 1:\n return j\n\n return -1\n\n# test\nN = 4\ntrust = [[1,3],[1,4],[2,3],[2,4],[4,3]]\nprint(findJudge(N, trust))",
"3\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a30998ba9b4f22cef8e5183ffbb36523daba0f5
| 13,831 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
frameworks/tensorflow/get_started_mnist_train.ipynb
|
AmintorDusko/amazon-sagemaker-examples
|
ed0bfa6d0d9291dd0f1562231579d8dd51bf1ed4
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
frameworks/tensorflow/get_started_mnist_train.ipynb
|
AmintorDusko/amazon-sagemaker-examples
|
ed0bfa6d0d9291dd0f1562231579d8dd51bf1ed4
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2022-03-15T20:04:30.000Z
|
2022-03-15T20:04:30.000Z
|
frameworks/tensorflow/get_started_mnist_train.ipynb
|
vivekmadan2/amazon-sagemaker-examples
|
4ccb050067c5305a50db750df3444dbc85600d5f
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2022-03-19T17:04:30.000Z
|
2022-03-19T17:04:30.000Z
| 35.646907 | 557 | 0.614634 |
[
[
[
"# Train an MNIST model with TensorFlow\n\nMNIST is a widely-used dataset for handwritten digit classification. It consists of 70,000 labeled 28x28 pixel grayscale images of hand-written digits. The dataset is split into 60,000 training images and 10,000 test images. There are 10 classes (one for each of the 10 digits). This tutorial will show how to train a TensorFlow V2 model on MNIST model on SageMaker.\n\n## Runtime\n\nThis notebook takes approximately 5 minutes to run.\n\n## Contents\n\n1. [TensorFlow Estimator](#TensorFlow-Estimator)\n1. [Implement the training entry point](#Implement-the-training-entry-point)\n1. [Set hyperparameters](#Set-hyperparameters)\n1. [Set up channels for training and testing data](#Set-up-channels-for-training-and-testing-data)\n1. [Run the training script on SageMaker](#Run-the-training-script-on-SageMaker)\n1. [Inspect and store model data](#Inspect-and-store-model-data)\n1. [Test and debug the entry point before running the training container](#Test-and-debug-the-entry-point-before-running-the-training-container)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import os\nimport json\n\nimport sagemaker\nfrom sagemaker.tensorflow import TensorFlow\nfrom sagemaker import get_execution_role\n\nsess = sagemaker.Session()\n\nrole = get_execution_role()\n\noutput_path = \"s3://\" + sess.default_bucket() + \"/DEMO-tensorflow/mnist\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## TensorFlow Estimator\n\nThe `TensorFlow` class allows you to run your training script on SageMaker\ninfrastracture in a containerized environment. In this notebook, we\nrefer to this container as the \"training container.\" \n\nConfigure it with the following parameters to set up the environment:\n\n- `entry_point`: A user-defined Python file used by the training container as the instructions for training. We will further discuss this file in the next subsection.\n\n- `role`: An IAM role to make AWS service requests\n\n- `instance_type`: The type of SageMaker instance to run your training script. Set it to `local` if you want to run the training job on the SageMaker instance you are using to run this notebook.\n\n- `model_dir`: S3 bucket URI where the checkpoint data and models can be exported to during training (default: None). \nTo disable having model_dir passed to your training script, set `model_dir`=False\n\n- `instance_count`: The number of instances to run your training job on. Multiple instances are needed for distributed training.\n\n- `output_path`: the S3 bucket URI to save training output (model artifacts and output files).\n\n- `framework_version`: The TensorFlow version to use.\n\n- `py_version`: The Python version to use.\n\nFor more information, see the [EstimatorBase API reference](https://sagemaker.readthedocs.io/en/stable/api/training/estimators.html#sagemaker.estimator.EstimatorBase).\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Implement the training entry point\n\nThe entry point for training is a Python script that provides all \nthe code for training a TensorFlow model. It is used by the SageMaker \nTensorFlow Estimator (`TensorFlow` class above) as the entry point for running the training job.\n\nUnder the hood, SageMaker TensorFlow Estimator downloads a docker image\nwith runtime environments \nspecified by the parameters to initiate the\nestimator class and it injects the training script into the \ndocker image as the entry point to run the container.\n\nIn the rest of the notebook, we use *training image* to refer to the \ndocker image specified by the TensorFlow Estimator and *training container*\nto refer to the container that runs the training image. \n\nThis means your training script is very similar to a training script\nyou might run outside Amazon SageMaker, but it can access the useful environment \nvariables provided by the training image. See [the complete list of environment variables](https://github.com/aws/sagemaker-training-toolkit/blob/master/ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLES.md) for a complete \ndescription of all environment variables your training script\ncan access. \n\nIn this example, we use the training script `code/train.py`\nas the entry point for our TensorFlow Estimator. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!pygmentize 'code/train.py'",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Set hyperparameters\n\nIn addition, the TensorFlow estimator allows you to parse command line arguments\nto your training script via `hyperparameters`.\n\n<span style=\"color:red\"> Note: local mode is not supported in SageMaker Studio. </span>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Set local_mode to be True if you want to run the training script on the machine that runs this notebook\n\nlocal_mode = False\n\nif local_mode:\n instance_type = \"local\"\nelse:\n instance_type = \"ml.c4.xlarge\"\n\nest = TensorFlow(\n entry_point=\"train.py\",\n source_dir=\"code\", # directory of your training script\n role=role,\n framework_version=\"2.3.1\",\n model_dir=False, # don't pass --model_dir to your training script\n py_version=\"py37\",\n instance_type=instance_type,\n instance_count=1,\n volume_size=250,\n output_path=output_path,\n hyperparameters={\n \"batch-size\": 512,\n \"epochs\": 1,\n \"learning-rate\": 1e-3,\n \"beta_1\": 0.9,\n \"beta_2\": 0.999,\n },\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The training container runs your training script like:\n\n```\npython train.py --batch-size 32 --epochs 1 --learning-rate 0.001 --beta_1 0.9 --beta_2 0.999\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Set up channels for training and testing data\n\nTell `TensorFlow` estimator where to find the training and \ntesting data. It can be a path to an S3 bucket, or a path\nin your local file system if you use local mode. In this example,\nwe download the MNIST data from a public S3 bucket and upload it \nto your default bucket. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import logging\nimport boto3\nfrom botocore.exceptions import ClientError\n\n# Download training and testing data from a public S3 bucket\n\n\ndef download_from_s3(data_dir=\"./data\", train=True):\n \"\"\"Download MNIST dataset and convert it to numpy array\n\n Args:\n data_dir (str): directory to save the data\n train (bool): download training set\n\n Returns:\n None\n \"\"\"\n\n if not os.path.exists(data_dir):\n os.makedirs(data_dir)\n\n if train:\n images_file = \"train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz\"\n labels_file = \"train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz\"\n else:\n images_file = \"t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz\"\n labels_file = \"t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz\"\n\n # download objects\n s3 = boto3.client(\"s3\")\n bucket = f\"sagemaker-sample-files\"\n for obj in [images_file, labels_file]:\n key = os.path.join(\"datasets/image/MNIST\", obj)\n dest = os.path.join(data_dir, obj)\n if not os.path.exists(dest):\n s3.download_file(bucket, key, dest)\n return\n\n\ndownload_from_s3(\"./data\", True)\ndownload_from_s3(\"./data\", False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Upload to the default bucket\n\nprefix = \"DEMO-mnist\"\nbucket = sess.default_bucket()\nloc = sess.upload_data(path=\"./data\", bucket=bucket, key_prefix=prefix)\n\nchannels = {\"training\": loc, \"testing\": loc}",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The keys of the `channels` dictionary are passed to the training image,\nand it creates the environment variable `SM_CHANNEL_<key name>`. \n\nIn this example, `SM_CHANNEL_TRAINING` and `SM_CHANNEL_TESTING` are created in the training image (see \nhow `code/train.py` accesses these variables). For more information,\nsee: [SM_CHANNEL_{channel_name}](https://github.com/aws/sagemaker-training-toolkit/blob/master/ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLES.md#sm_channel_channel_name).\n\nIf you want, you can create a channel for validation:\n```\nchannels = {\n 'training': train_data_loc,\n 'validation': val_data_loc,\n 'test': test_data_loc\n}\n```\nYou can then access this channel within your training script via\n`SM_CHANNEL_VALIDATION`.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Run the training script on SageMaker\nNow, the training container has everything to run your training\nscript. Start the container by calling the `fit()` method.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"est.fit(inputs=channels)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Inspect and store model data\n\nNow, the training is finished, and the model artifact has been saved in \nthe `output_path`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tf_mnist_model_data = est.model_data\nprint(\"Model artifact saved at:\\n\", tf_mnist_model_data)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We store the variable `tf_mnist_model_data` in the current notebook kernel. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%store tf_mnist_model_data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Test and debug the entry point before running the training container\n\nThe entry point `code/train.py` provided here has been tested and it can be runs in the training container. \nWhen you develop your own training script, it is a good practice to simulate the container environment \nin the local shell and test it before sending it to SageMaker, because debugging in a containerized environment\nis rather cumbersome. The following script shows how you can test your training script:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!pygmentize code/test_train.py",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Conclusion\n\nIn this notebook, we trained a TensorFlow model on the MNIST dataset by fitting a SageMaker estimator. For next steps on how to deploy the trained model and perform inference, see [Deploy a Trained TensorFlow V2 Model](https://sagemaker-examples.readthedocs.io/en/latest/frameworks/tensorflow/get_started_mnist_deploy.html).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a30aa04a5e521b867999fafe2de05892f649c80
| 325,056 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
docs/Tutorial_mass_algorithm.ipynb
|
gmarkall/stumpy
|
b72911468467932f21e5ec601946173e2337076b
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
docs/Tutorial_mass_algorithm.ipynb
|
gmarkall/stumpy
|
b72911468467932f21e5ec601946173e2337076b
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
docs/Tutorial_mass_algorithm.ipynb
|
gmarkall/stumpy
|
b72911468467932f21e5ec601946173e2337076b
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null | 1,062.27451 | 109,764 | 0.957872 |
[
[
[
"# MASS Algorithm Tutorial\n\nThis notebook is a tutorial on how to use STUMPY and the MASS algorithm [1] to compute a **distance profile**, a vector containing all of the distances from a query subsequence to the subsequences of a time series.\n\nIn this tutorial we are going to reproduce one of the use case mentioned in this [presentation](https://www.cs.unm.edu/~mueen/Simple_Case_Studies_Using_MASS.pptx).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Load Libraries and Data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%matplotlib inline\nimport numpy as np\nfrom os import path\nimport pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport urllib.request ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def change_plot_size(width, height, plt):\n fig_size = plt.rcParams[\"figure.figsize\"]\n fig_size[0] = width\n fig_size[1] = height\n plt.rcParams[\"figure.figsize\"] = fig_size\n plt.rcParams['xtick.direction'] = 'out'\n \nchange_plot_size(20, 6, plt)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The use case dataset is the \"Sony AIBO robot dog dataset\" and comes from an accelerometer inside a Sony AIBO robot dog ([dataset source](https://www.cs.ucr.edu/~eamonn/time_series_data_2018/)). The query comes from a period when the dog was walking on carpet, the time series data we will search comes from a time the robot walked on cement (for 5000 data points), then carpet (for 3000 data points), then back onto cement.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#load SampleTarget (time series)\nst_url = 'https://www.cs.unm.edu/~mueen/robot_dog.txt'\nst_txt = urllib.request.urlopen(st_url)\nsample_target = pd.read_csv(st_txt, sep=\"\\s+\", header = None)[0]\n\n#load Pattern (query subsequence)\npattern_url = 'https://www.cs.unm.edu/~mueen/carpet_query.txt'\npattern_txt = urllib.request.urlopen(pattern_url)\npattern = pd.read_csv(pattern_txt, sep=\"\\s+\", header = None)[0]\n\npattern.shape, sample_target.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Plot Data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plt.plot(sample_target)\nplt.title('Robot Dog Accelerometer Sample')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.plot(pattern)\nplt.title('Carpet Walk - Query Subsequence')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Distance Profile",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"What we want to do is to perform a similarity search for our query subsequence (dog walking on the carpet). Thus, we search for a known pattern (the dog walking on the Carpet) in the entire time series and returns the most similar subsequences. To do so in Python, we can simply use the STUMPY function `core.mass`",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from stumpy.core import mass\ndistance_profile = mass(pattern, sample_target)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#find k indexes pointing to k most similar subsequences \nk = 16\nmin_idxs = np.argpartition(distance_profile, k)[:k]\nmin_idxs = min_idxs[np.argsort(distance_profile[min_idxs])]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#quick test\nnp.sort(distance_profile)[:k][0] == distance_profile[min_idxs][0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#plot top k patterns\nm = len(pattern)\nplt.plot(sample_target, alpha=0.5)\nplt.xlim((2000, 10000)) #limit x axis for better visualization\nfor i in range(k):\n plt.plot(\n list(range(min_idxs[i], (min_idxs[i] + m))),\n sample_target[min_idxs[i] : (min_idxs[i] + m)],\n c = np.random.rand(3,),\n linewidth=3.0,\n )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Note that the best matches all occur during the carpet walking period (5000 - 8000 range). The best match is plotted below together with the query subsequence to show their similarity.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#Plot Best Match\nfig, axs = plt.subplots(2)\n\n# pattern\naxs[0].plot(pattern)\n# best match\naxs[1].plot(sample_target[min_idxs[0] : (min_idxs[0] + m)])\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## References\n\n[1] Abdullah Mueen, Yan Zhu, Michael Yeh, Kaveh Kamgar, Krishnamurthy Viswanathan, Chetan Kumar Gupta and Eamonn Keogh (2015), The Fastest Similarity Search Algorithm for Time Series Subsequences under Euclidean Distance, URL: http://www.cs.unm.edu/~mueen/FastestSimilaritySearch.html",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a30adbeafdcf2efac47c46621a6bded9f41ac9a
| 196,607 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
example_analysis.ipynb
|
pgrobecker/cemag
|
3d23841d8f7f4074abf4c59913c0e6077e8af0be
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
example_analysis.ipynb
|
pgrobecker/cemag
|
3d23841d8f7f4074abf4c59913c0e6077e8af0be
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
example_analysis.ipynb
|
pgrobecker/cemag
|
3d23841d8f7f4074abf4c59913c0e6077e8af0be
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 143.090975 | 11,828 | 0.85057 |
[
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom cemag import entropy, prior_params, find_error_probability, std_eff",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Loading expression Data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The included dataset contains log2(TPM) normalized RNA-seq data for various tissues taken from adult zebrafish at different ages. \n\nFor details see [Kijima, Y. et al. Age-associated different transcriptome profiling in zebrafish and rat: insight into diversity of vertebrate aging. bioRxiv 478438 (2018)](https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/478438v1.abstract). The raw data is available here: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/PRJDB7713 ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# load dataset\nexpression_df = pd.read_csv('./data/gene_expression.tab', sep='\\t', index_col=0)\ndata = expression_df.values\nexpression_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# make DataFrame for column attributes\nca = pd.DataFrame([c.split('_') for c in expression_df.columns], \n columns=['tissue', 'age', 'replicate'])\nca.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ca.groupby(['tissue', 'age']).count()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Inferring marker genes",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Marker genes between two groups of samples\n\nHere, we simply want to find marker genes that can differentiate between samples taken from the brain at ages 2 months and 39 months. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# define groups that are compared against each other\ngroups = [['brain', '2mo'], ['brain', '39mo']]\ngroups_idx = [np.flatnonzero((ca.tissue == t)&(ca.age == a)) for t, a in groups]\ngroups_idx",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# relative a priori size of different groups,\n# discounting potential differences in no. of replicates\nnc = [1,1]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# calculate conditional class entropy\n# the parameters k, N determine how accurately the integrals are calculated\n# one can start with smaller values and see how much of a difference it makes\nH_result = entropy(data, groups_idx, ncond=nc, k=6, N=1e2)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# when there are only two classes, we can invert the entropy function\n# H=p*log(p) and infer the probability p of misclassification given gene expression a measurement\n# The function find_error_probability is an analytical solution valid only for small p \np_result = find_error_probability(H_result)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# create sorted list of top marker genes\ndf_result = pd.DataFrame({'H(c|x)':H_result, 'p_e':p_result}, index=expression_df.index)\ndf_result = df_result.sort_values(by='p_e')\ndf_result.head(20)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# check expression of top marker genes in both groups\nfor gene in df_result.index[:10]:\n plot_data = tuple(expression_df.loc[gene][group].values for group in groups_idx)\n plt.figure(figsize=(2,2))\n plt.boxplot(plot_data, labels=['{}_{}'.format(tissue, age) for tissue, age in groups])\n plt.suptitle(gene)\n plt.ylabel('log2(TPM)')\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Marker genes between more than two groups of samples\n\nHere, we simply want to find marker genes that can differentiate between samples taken from the brain at all ages (2 months, 7 months, 16 months, and 39 months). ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# define groups that are compared against each other\ngroups = [['brain', '2mo'], ['brain', '7mo'], ['brain', '16mo'], ['brain', '39mo']]\ngroups_idx = [np.flatnonzero((ca.tissue == t)&(ca.age == a)) for t, a in groups]\ngroups_idx\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# relative a priori size of different groups,\n# discounting potential differences in no. of replicates\nnc = [1,1,1,1]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# calculate conditional class entropy\n# the parameters k, N determine how accurately the integrals are calculated\n# one can start with smaller values and see how much of a difference it makes\nH_result = entropy(data, groups_idx, ncond=nc, k=6, N=1e2)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# create sorted list of top marker genes\ndf_result = pd.DataFrame({'H(c|x)':H_result}, index=expression_df.index)\ndf_result = df_result.sort_values(by='H(c|x)')\ndf_result.head(20)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# For each set of replicates, we want to estimate the effective standard deviation of the measurements\n# For this, we need to estimate the prior distribution of variances first in each set, which have two parameters\n\nparams = [prior_params(data[group]) for group in groups_idx]\nparams",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# For this kind of data, it is more appropriate to plot time courses\n# we can estimate error bars using the std_eff function\n\nplot_color = '#377eb8'\nfor gene in df_result.index[:10]:\n plot_data = tuple(expression_df.loc[gene][group].values for group in groups_idx)\n plt.figure(figsize=(2,2))\n y_mean = np.array([y.mean() for y in plot_data])\n n = len(y_mean)\n x = np.arange(n)\n plt.plot(x, y_mean, color=plot_color)\n for xi, y, (a,b) in zip(x, plot_data, params):\n y_std = std_eff(y, a, b) # estimate effective standard deviation\n plt.errorbar(xi, y=y.mean(), yerr=y_std, color=plot_color)\n plt.plot([xi]*len(y), y, 'x', color=plot_color)\n plt.xticks(ticks=x, labels=['{}_{}'.format(tissue, age) for tissue, age in groups],\n rotation=45)\n plt.suptitle(gene)\n plt.ylabel('log2(TPM)')\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a30b109b0237a899b7eff3a906feae8702c2cbd
| 125,294 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
House Prices- Advanced Regression Techniques/ML/Kaggle kernel.ipynb
|
PadmarajBhat/Kaggle-Dataset-Exploration
|
2bfa56eb582c658eacd82df5660da15dd541bd8a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
House Prices- Advanced Regression Techniques/ML/Kaggle kernel.ipynb
|
PadmarajBhat/Kaggle-Dataset-Exploration
|
2bfa56eb582c658eacd82df5660da15dd541bd8a
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2019-02-03T07:39:58.000Z
|
2019-02-04T16:55:14.000Z
|
House Prices- Advanced Regression Techniques/ML/Kaggle kernel.ipynb
|
PadmarajBhat/Kaggle-Dataset-Exploration
|
2bfa56eb582c658eacd82df5660da15dd541bd8a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 89.687903 | 9,330 | 0.617125 |
[
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom collections import Counter\nimport datetime\n\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom IPython import display\n\nfrom scipy import stats\nimport math\nimport random\n\nfrom sklearn import preprocessing\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import ShuffleSplit, train_test_split, cross_val_score, StratifiedShuffleSplit\nfrom sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_log_error\n\nfrom xgboost import XGBRegressor",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"train_File = '../input/train.csv'\ntest_File = '../input/test.csv'\n#train_File = 'train.csv'\n#test_File = 'test.csv'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dd = display.display",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 1. Gather",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def loadData():\n df_train = pd.read_csv(train_File)\n df_test = pd.read_csv(test_File)\n \n df = pd.concat([df_train, df_test], axis=0,sort=True,ignore_index=True)\n \n return df\n\ndf_before_clean = loadData()\ndd(df_before_clean)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 2. Assess Data : Inspecting Data for Quality and Tidiness Issues\n#### 2.1 Quality Issues : Issues with content - missing, duplicate or incorrect data. a.k.a Dirty data \n* 2.1.a Completeness : *\"Are there any rows, columns or cells missing values?\"*\n * 35 columns have the missing values: \n \n ['Alley', 'BsmtCond', 'BsmtExposure', 'BsmtFinSF1', 'BsmtFinSF2', 'BsmtFinType1', 'BsmtFinType2', 'BsmtFullBath', 'BsmtHalfBath', 'BsmtQual', 'BsmtUnfSF', 'Electrical', 'Exterior1st', 'Exterior2nd', 'Fence', 'FireplaceQu', 'Functional', 'GarageArea', 'GarageCars', 'GarageCond', 'GarageFinish', 'GarageQual', 'GarageType', 'GarageYrBlt', 'KitchenQual', 'LotFrontage', 'MSZoning', 'MasVnrArea', 'MasVnrType', 'MiscFeature', 'PoolQC', 'SalePrice', 'SaleType', 'TotalBsmtSF', 'Utilities']\n###### \n* 2.1.b Validity : *\"Does the data comply to the data schema like duplicate patient id or zip code being < 5 digits or float data type?\"*\n###### \n * Following are Categorical Variables but currently are being considered as integer/float:\n\n * MSSubClass\n * OverallQual\n * OverallCond\n * FireplaceQu\n * MoSold\n###### \n * Following variables are supposed to be Integer type but Box-Cox or Scaling will anyway type cast them to float:\n\n * LotFrontage, LotArea, YearBuilt, YearRemodAdd, MasVnrArea, BsmtFinSF1, BsmtFinSF2, BsmtUnfSF, TotalBsmtSF, 1stFlrSF, 2ndFlrSF, LowQualFinSF, GrLivArea, BsmtFullBath, BsmtHalfBath, FullBath, HalfBath, BedroomAbvGr, KitchenAbvGr, TotRmsAbvGrd, Fireplaces, GarageCars, GarageArea, WoodDeckSF, OpenPorchSF, EnclosedPorch, 3SsnPorch, ScreenPorch, PoolArea, MiscVal, YrSold, SalePrice\n * GarageYrBlt will be NA when garage is not available for the house and hence this variable needs to be dropped as it does not comply to the schema.\n \n###### \n \n* 2.1.c Accuracy : *\"Wrong data that is valid. like hieght = 300 inches; it still complies to the standard i.e. inches but data is in accurate.\"*\n###### \n * MSZoning has 4 missing entries. Also, we do not have data samples to Agricultre (A), Industrial (I), Residential Low Density Park (RP). Therefore, there exist a probability that missing entries will be replaced with wrong data which are valid for the variables.\n###### \n * Similarly, Utilites has 2 missing entries. Also, we do not have data samples for NoSewr ((Electricity, Gas, and Water (Septic Tank)) and ELO (Electricity only)\n###### \n * Exterior1st, has no missing values in training data set. But has no samples for 'Other' and 'PreCast' Material. Testing data has one missing sample for the variable.\n###### \n * Exterior2nd has no missing values in the training data set. But has no samples for \"PreCast\" material. Testing data has one missing sample for the variable.\n###### \n * MasVnrType has 8 missing values in training data set. It has total of 5 valid values.But there are no samples for \"CBlock\" (Cylinder block). One in testing set also has a record with missing value for this variable.\n###### \n * ExterQual has no samples for \"Po\" but fortunately there are no missing values for it in both training or testing data.\n###### \n * BsmtQual has 37 missing entries. It has no samples for \"Po\" ((Poor (<70 inches)). Testing data set has 46 missing entries.\n###### \n * BsmtCond has 37 missing entries. It has no samples for \"Ex\" (Excellent). There are 46 missing entries in the testing dataset.\n###### \n * KitchenQual has no training samples on \"Po\" but testing sample has a missing entry.\n * Functional has no training samples for \"Po\" but testing sample has a missing entry.\n * PoolQC has no samples for \"Typ\" but testing sample has missing values.\n * SaleType has no samples for \"VWD\" but testing sample has a missing value record.\n###### \n###### \n* 2.1.d Consistency : *\"Both valid and accurate but inconsistent. state = california and CA\"*\n###### \n * BsmtExposure has training samples as NA for both No Basement and also for missing values. There are also 2 testing samples with missing values as NA.\n###### \n * BsmtFinType2 has training samples as NA for both No Basement and also for missing values.\n###### \n * TotalBsmtSF has both 0 and NA representing as missing basement.\n###### \n * BsmtExposure has NA for both missing and no basement houses.\n * BsmtFinType2 has NA for both missing and no basement for a house.\n \n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### 2.2 Tidiness Issues: Issues with structure - untidy or messy data\n* 2.2.a Each observation is a row\n * No Issues: Each observation is a unique house (no duplicate records)\n###### \n* 2.2.b Each variable is a column\n * No Issues: There are no colummns with multi data or concatenated data.\n###### \n* 2.2.c Each observational unit is a table\n * No Issues: There are no cross referring keys present in the table. Bsmt* and Garage* variables do form a logical group but there is no unique identities to the group.\n###### ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"##### Hypothesis 1: Bsmt__ variables are NA when TotalBsmtSF is 0\n##### Proof:\n* BsmtFinType1 is NA when TotalBsmtSF is 0\n* BsmtUnfSF is 0 whenever TotalBsmtSF is 0; Even in testing set it is NA only when TotalBsmtSF is NA\n* BsmtFullBath is 0 whenever TotalBsmtSF is 0; Even in testin set it is NA only when TotalBsmtSF is NA or 0.\n* BsmtHalfBath is 0 whenever TotalBsmtSF is 0; Even in testin set it is NA only when TotalBsmtSF is NA or 0.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"##### Key Observations:\n* Dataset has House Prices which were sold in between 2006 - 2010.\n* Surprised to see no bathroom and no bedroom but with kitchen Houses !!! Where do they sleep and shit after the heavy meal ?\n* NA value in GarageType can be easily mis interpreted as missing value. However, it is not true. NA in GarageType clearly indicates no garage because in both train and testing dataset GarageArea = 0 in all those cases. Similarly, GarageYrBlt, GarageFinish, GarageQual, GarageCond are also NA when GarageArea = 0. And GarageCars,GarageArea = 0 ==> GarageArea = 0.\n* How do we verify NA in Fence as missing entry or No Fence ??\n* How do we verify NA in MiscFeatures as None or missing value ?? Note that MiscVal is zero for NA, Othr & Shed.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 2.1.a Completeness : *\"Are there any rows, columns or cells missing values?\"*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def missingValueAssessment(df):\n nan_columns = df.columns[df.isna().any()].tolist()\n print('NaN columns :', nan_columns, \"\\n# :\", len(nan_columns))\n \n print(\"Duplicated rows count: \", df[df.duplicated()].shape)\n df = df.fillna('NA')\n print(\"Duplicated rows count: \", df[df.duplicated()].shape)\n \nmissingValueAssessment(df_before_clean)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 2.2.a Each observation is a row",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def checkHouseIsRepeated(df):\n df_temp = df.groupby(['SalePrice','GrLivArea','YearBuilt','YearRemodAdd']).agg('count').reset_index()[['SalePrice','GrLivArea','YearBuilt','YearRemodAdd','Id']]\n dd(\"Samples with same 'SalePrice','GrLivArea','YearBuilt','YearRemodAdd' : \",df_temp[df_temp.Id > 1])\n \n \ncheckHouseIsRepeated(df_before_clean)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"* As there are no time series data: as in there is no variable indicating the time of the reading carried out, It is safe to assume the reading was done at one shot and there would not be any duplicate entries of a house.\n* With the above assumption, group by 'SalePrice','GrLivArea','YearBuilt','YearRemodAdd' count indicates that there are no duplicate records.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_before_clean.info()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 3.0 Cleaning Data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"##### Let us first do the cleaning activities where we have high confidence of imputing the values as listed in the above Assessment summary.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def convertOrdinalToNumber(df):\n \n #Convert ordinal categorical values to numeric values\n \n \n Ordinal_columns = ['BsmtCond','BsmtQual','ExterCond','ExterQual',\n 'FireplaceQu','GarageCond','GarageQual','HeatingQC',\n 'PoolQC','KitchenQual']\n \n #Thankfully panda converts the missing values to -1 here\n for c in Ordinal_columns:\n \n df[c] = pd.Categorical(df[c], categories=['NA','Po', 'Fa', 'TA', 'Gd', 'Ex'], \n ordered=True).codes\n dd(c, df[c].unique())\n \n \n df['BsmtExposure'] = pd.Categorical(df['BsmtExposure'],\n categories=['NA', 'No', 'Mn', 'Av', 'Gd'],\n ordered=True).codes\n \n df['GarageFinish'] = pd.Categorical(df['GarageFinish'],\n categories=['NA', 'Unf', 'RFn', 'Fin'],\n ordered=True).codes\n \n df['PavedDrive'] = pd.Categorical(df['PavedDrive'],\n categories=['N', 'P', 'Y'],\n ordered=True).codes\n \n df['Utilities'] = pd.Categorical(df['Utilities'],\n categories=['ELO', 'NoSeWa', 'NoSewr', 'AllPub'],\n ordered=True).codes\n \n df['LotShape'] = pd.Categorical(df['LotShape'],\n categories=['Reg', 'IR1', 'IR2', 'IR3'],\n ordered=True).codes\n \n df['LandSlope'] = pd.Categorical(df['LandSlope'],\n categories=['Gtl', 'Mod', 'Sev'],\n ordered=True).codes\n \n df['Functional'] = pd.Categorical(df['Functional'],\n categories=['Sal', 'Sev', 'Maj2', 'Maj1', 'Mod',\n 'Min2', 'Min1', 'Typ'],\n ordered=True).codes\n \n df['BsmtFinType1'] = pd.Categorical(df['BsmtFinType1'],\n categories=['NA', 'Unf', 'LwQ', 'Rec', 'BLQ',\n 'ALQ', 'GLQ'],\n ordered=True).codes\n \n df['BsmtFinType2'] = pd.Categorical(df['BsmtFinType2'],\n categories=['NA', 'Unf', 'LwQ', 'Rec', 'BLQ',\n 'ALQ', 'GLQ'],\n ordered=True).codes\n \n dd('BldgType',df['BldgType'].unique(),df[df['BldgType'].isna()]) #'1Fam', '2fmCon', 'Duplex', 'TwnhsE', 'Twnhs']\n df['BldgType'] = pd.Categorical(df['BldgType'],\n categories=['1Fam', '2fmCon', 'Duplex', 'Twnhs', 'TwnhsE'],\n ordered=True).codes\n dd('BldgType',df['BldgType'].unique())\n \n df['HouseStyle'] = pd.Categorical(df['HouseStyle'],\n categories=['1Story', '1.5Unf', '1.5Fin', '2Story', '2.5Unf', '2.5Fin', 'SFoyer', 'SLvl'],\n ordered=True).codes\n \n df['LandContour'] = pd.Categorical(df['LandContour'],\n categories=['Low', 'Lvl', 'Bnk', 'HLS'],\n ordered=True).codes\n \n df['Electrical'] = pd.Categorical(df['Electrical'],\n categories=['Mix', 'FuseP', 'FuseF', 'FuseA', 'SBrkr'],\n ordered=True).codes\n \n return df",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def cleanStage1(df):\n \n #convert data type\n #we are being little lineant to give float64 for YearBuilt, YrSold but those guys are going to be box-coxed \n #so let them at least enjoy the bigger size for now\n \n #Before changing thier data type, let us first convert them to continuous variable wherever applicable. \n #i.e. YearBuilt, YearRemodAdd, YrSold & MoSold\n \n df['AgeInMonths'] = df.YearBuilt.apply(lambda x: (2019 - x)*12)\n \n df['AgeWhenSold'] = (df.YrSold - df.YearBuilt) * 12 + df.MoSold\n \n df['AgeWhenRemod'] = (df.YearRemodAdd - df.YearBuilt) * 12\n \n df= df.drop(['YearBuilt', 'YrSold', 'MoSold', 'YearRemodAdd'],axis=1)\n \n float64_variables = ['LotFrontage', 'LotArea', 'AgeInMonths', 'AgeWhenRemod', 'MasVnrArea', \\\n 'TotalBsmtSF', '1stFlrSF', '2ndFlrSF', 'LowQualFinSF', 'GrLivArea', 'BsmtFullBath', \\\n 'BsmtHalfBath', 'FullBath', 'HalfBath', 'BedroomAbvGr', 'KitchenAbvGr', 'TotRmsAbvGrd', 'Fireplaces',\\\n 'GarageCars', 'GarageArea', 'WoodDeckSF', 'OpenPorchSF', 'EnclosedPorch', '3SsnPorch', 'ScreenPorch', \\\n 'PoolArea', 'MiscVal', 'AgeWhenSold', 'SalePrice', 'OverallQual', 'OverallCond']\n \n for c in float64_variables:\n df[c] = df[c].astype(np.float64)\n \n '''int_to_categorical_variables = ['MSSubClass',]\n for c in int_to_categorical_variables:\n df[c] = df[c].astype(str)'''\n \n dd(len(df.columns[df.isna().any()].tolist()), df.columns[df.isna().any()].tolist())\n df = convertOrdinalToNumber(df)\n \n dd(\"Number of na columns : \",len([c for c in list(df) if (-1 in df[c].unique()) or (df[df[c].isna()].shape[0] > 0)]))\n dd(\"To be imputed columns : \", [c for c in list(df) if (-1 in df[c].unique()) or (df[df[c].isna()].shape[0] > 0)])\n \n dd(df.KitchenQual.unique())\n dd(df.BsmtCond.unique())\n #return\n \n #As per our data analysis TotalBsmtSF = 0 when TotalBsmtSF is missing.\n df.loc[df.TotalBsmtSF.isna(), 'TotalBsmtSF'] = 0\n\n #BsmtQual\tBsmtCond\tBsmtExposure\tBsmtFinType1\tBsmtFinType2\tBsmtFullBath\tBsmtHalfBath\n #BsmtFinSF1\tBsmtFinSF2\tBsmtUnfSF\n bsmt_cols = [c for c in list(df) if 'Bsmt' in c]\n df.loc[df.TotalBsmtSF == 0, bsmt_cols] = 0\n\n #verify almighty pandas half line solution to assignment\n dd(df[df.TotalBsmtSF== 0][bsmt_cols])\n \n dd(df.GarageType.unique())\n\n #GarageYrBlt\tGarageFinish GarageQual\tGarageCond GarageCars\tGarageArea\n df['GarageType'] = df.GarageType.fillna(\"NA\")\n gar_cols = [c for c in list(df) if ('Garage' in c) and ('GarageType' not in c)]\n df.loc[df.GarageType == \"NA\", gar_cols] = 0\n \n dd(df[df.GarageType== \"NA\"][gar_cols+['GarageType']])\n\n #drop obsolete columns\n df = df.drop(['Id','GarageYrBlt'], axis=1)\n df['SalePrice'] = df.SalePrice.fillna(0)\n \n \n dd(df.KitchenQual.unique())\n dd(df.BsmtCond.unique())\n\n return df\n\ndf_stage_1 = cleanStage1(df_before_clean.copy())\ndf_stage_1.info()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_stage_1[df_stage_1.BsmtCond == -1]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_stage_1[df_stage_1.GarageArea.isna()]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### We had map when TotalBsmtSF =0 , there are couple of entries when it is TotalBsmtSF != 0. We may have to other Bsmt- attributes to impute the values for it but we will do such analysis after the straight forward missing value imputation.\n\n##### Similarly, Garage variables are not completely imputed yet.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"##### We have now 25 columns to look after for the first round of cleaning.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dd(\"Total columns in the input dataset : \",df_stage_1.shape[1])\ndd(\"Number of na columns : \",len([c for c in list(df_stage_1) if (-1 in df_stage_1[c].unique()) or (df_stage_1[df_stage_1[c].isna()].shape[0] > 0)]))\ndd(\"To be imputed columns : \", [c for c in list(df_stage_1) if (-1 in df_stage_1[c].unique()) or (df_stage_1[df_stage_1[c].isna()].shape[0] > 0)])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### Before Imputing let us find if there are further more ordinal variables",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"_= [dd(c,df_stage_1[c].unique()) for c in df_stage_1.select_dtypes(include=np.object) ]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def checkOrdinal(df):\n df['TotalSqFt'] = df['GrLivArea'] + df['TotalBsmtSF']\n dd(df.groupby('BldgType').agg('median').reset_index().sort_values('TotRmsAbvGrd')[['BldgType', 'TotalSqFt','TotRmsAbvGrd','BedroomAbvGr']])\n dd(df.groupby('BldgType').agg('max').reset_index().sort_values('TotRmsAbvGrd')[['BldgType', 'TotalSqFt','TotRmsAbvGrd','BedroomAbvGr']])\n \n \n dd(df.groupby('HouseStyle').agg('median').reset_index().sort_values('TotalSqFt')[['HouseStyle', 'TotalSqFt','TotRmsAbvGrd','BedroomAbvGr']])\n dd(df.groupby('HouseStyle').agg('max').reset_index().sort_values('TotalSqFt')[['HouseStyle', 'TotalSqFt','TotRmsAbvGrd','BedroomAbvGr']])\n \ncheckOrdinal(df_stage_1.copy())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### We know from the domain knowledge \"type of dwelling\" that 1Fam < 2FmCon < Duplx < Twnhs. Now, between the town houses, I am finalizing the sequence through Total sq ft. \n* final ordinal variable : 1Fam < 2FmCon < Duplx < Twnhs < TwnhsE",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"##### Similarly, for HouseStyle we have ,\n* 1Story < 1.5Unf < 1.5Fin < 2Story < 2.5Unf < 2.5Fin < SFoyer < SLvl\n\n##### I had confusion between Unf and Fin but I relied on again sq. ft, rooms and bedrooms. I could not get enough material to defend Sfoyer and SLvl, so again relied on those 3 parameters.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"##### With domain knowledge(common sense) For LandContour,\n* Low < Lvl < Bnk < HLS",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def checkOrdinal1(df):\n dd(df.groupby('MSZoning').agg('sum').reset_index().sort_values('TotRmsAbvGrd')[['MSZoning','TotRmsAbvGrd']])\ncheckOrdinal1(df_stage_1.copy())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### Let us first see all the NaN values",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def plotNAs(df):\n nan_columns = df.columns[df.isna().any()].tolist()\n #nan_columns.remove('SalePrice')\n for c in df.fillna('NotAvailable')[nan_columns]:\n df[[c,'SalePrice']].fillna('NotAvailable').\\\n groupby(by=c).agg('count').\\\n plot.bar(legend=None, title=\"Frequency Plot for \"+c)\n plt.xticks(rotation=45)\n plt.show()\nplotNAs(df_stage_1.copy())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 1. Alley",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def outerLandScape(df_temp):\n df = df_temp.copy()\n print(\"Initial Shape : \", df.shape)\n \n beyond_house = ['Neighborhood','Street', 'PavedDrive', 'Alley']\n df_temp = df.groupby(beyond_house).agg('count').reset_index()[['Neighborhood','Street', 'PavedDrive', 'Alley',\"SalePrice\"]]\n dd()\n \n def getAlley(Street, Neighborhood, PavedDrive):\n try:\n alley = df_temp[\n (df_temp['Street'] == Street ) &\n (df_temp['Neighborhood'] == Neighborhood ) &\n (df_temp['PavedDrive'] == PavedDrive) \n ]['Alley'].tolist()[0]\n except:\n alley = 'NA'\n \n return alley\n \n \n df['Alley'] = df.Alley.fillna(\"NA\")\n df[['Alley','SalePrice']].fillna(0).\\\n groupby(by='Alley').agg('count').\\\n plot.bar(legend=None, title=\"Frequency Plot for \"+'Alley')\n plt.xticks(rotation=45)\n plt.show()\n \n na_alley_count = df[df.Alley == \"NA\"].shape[0]\n gr_alley_count = df[df.Alley == \"Grvl\"].shape[0]\n pa_alley_count = df[df.Alley == \"Pave\"].shape[0]\n \n \n df['Alley'] = df.apply( lambda x: getAlley (x['Street']\n ,x['Neighborhood']\n ,x['PavedDrive']\n ) if x['Alley'] == \"NA\" else x['Alley']\n ,axis=1)\n \n \n df[['Alley','SalePrice']].fillna(0).\\\n groupby(by='Alley').agg('count').\\\n plot.bar(legend=None, title=\"Frequency Plot for \"+'Alley')\n plt.xticks(rotation=45)\n plt.show()\n \n \n print(\"Alley Snapshot Before : NA -\", na_alley_count,\"Grvl - \", gr_alley_count, \"Pave - \", pa_alley_count)\n print(\"Alley Snapshot After : NA -\", df[df.Alley == \"NA\"].shape[0],\n \"Grvl - \", df[df.Alley == \"Grvl\"].shape[0], \"Pave - \", df[df.Alley == \"Pave\"].shape[0]\n )\n \n return df\n\ndf_alley = outerLandScape(df_stage_1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def outerLandScape2():\n df_train = pd.read_csv(train_File)\n df_test = pd.read_csv(test_File)\n \n df = pd.concat([df_train, df_test], axis=0,sort=True,ignore_index=True)\n print(\"Initial Shape : \", df.shape)\n \n '''beyond_house = [ 'MSZoning','Street', 'LotShape', 'LandContour', 'LotConfig', 'LandSlope', 'Neighborhood',\n 'Condition1', 'Condition2', 'BldgType', 'HouseStyle', 'PavedDrive','SaleCondition','Fence', 'Alley']\n df_temp = df[beyond_house].copy()\n for c in beyond_house:\n df_temp = df_temp[df_temp[c].notna()]#.reset_index()\n print(c, df_temp.shape)'''\n #display.display(df_temp)\n \n #beyond_house = ['Neighborhood','Street', 'PavedDrive', 'Alley']\n #df = df.fillna('NNN')\n beyond_house = ['Neighborhood','Street','Alley']\n #beyond_house = ['Street', 'Alley']\n \n #display.display(df.groupby(beyond_house).agg('count').reset_index()[['Neighborhood','Street', 'PavedDrive', 'Alley','Id']])\n display.display(df.groupby(beyond_house).agg('count').reset_index()[['Neighborhood','Street', 'Alley','Id']])\n \n \nouterLandScape2()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### We can have the above table mapping missing Alley variable values. I am here assuming that Street and Alley would intersect. Therefore, there is a pattern with respect to location regarding the type of material used.\n\n* However, the variable itself might not have such significance to target variable and hence can we can drop the imputation to it. The model which uses this variable would give lower significance level during training.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 2. Electrical",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def electricalWrangling(df_temp):\n df = df_temp.copy()\n df1 = df_temp.copy()\n print(\"No of missing entries :\", df[df.Electrical == -1].shape[0])\n df['Electrical'] = df.Electrical.fillna('NA')\n display.display(df[['Neighborhood','Electrical', 'SalePrice']].groupby(['Neighborhood','Electrical']).agg('count'))\n \n #df1['Electrical'] = df1.Electrical.fillna('SBrkr')\n df1.loc[df1['Electrical'] == -1,'Electrical'] = 4\n display.display(df1[['Neighborhood','Electrical', 'SalePrice']].groupby(['Neighborhood','Electrical']).agg('count'))\n \n \n \n return df1\n \ndf_electrical = electricalWrangling(df_stage_1.drop('Alley',axis=1))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### At Timber, most of them have SBrkr as electrical system. So, it is a safe bet to have the missing entry replaced with 'SBrkr'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 3. Exterior1st & Exterior2nd",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def exteriorWrangle(df_temp):\n df = df_temp.copy()\n dd(df.shape)\n dd(df[df.Exterior1st == df.Exterior2nd].shape)\n dd(df[df.Exterior1st.isna()][['Exterior1st','Exterior2nd', 'Neighborhood','ExterQual', 'ExterCond', 'MSSubClass']])\n dd(df[df.Exterior2nd.isna()][['Exterior1st','Exterior2nd', 'Neighborhood','ExterQual', 'ExterCond','MSSubClass']])\n dt = df.\\\n groupby(['Exterior1st','Exterior2nd', 'Neighborhood','ExterQual', 'ExterCond', 'MSSubClass']).\\\n agg('count').reset_index().\\\n sort_values(by=['MSSubClass','SalePrice'],ascending=False)[['Exterior1st','Exterior2nd', 'Neighborhood','ExterQual', 'ExterCond','MSSubClass','SalePrice']]\n #dd(dt)\n dd(dt[(dt.MSSubClass == 30) & (dt.Neighborhood == 'Edwards')].head())\n \n def bestExt1(Neighborhood,ExterQual, ExterCond, MSSubClass):\n return dt[(dt.Neighborhood == Neighborhood)&\n (dt.ExterQual == ExterQual)&\n (dt.ExterCond == ExterCond)&\n (dt.MSSubClass == MSSubClass)]['Exterior1st'].tolist()[0]\n \n def bestExt2(Neighborhood,ExterQual, ExterCond, MSSubClass):\n return dt[(dt.Neighborhood == Neighborhood)&\n (dt.ExterQual == ExterQual)&\n (dt.ExterCond == ExterCond)&\n (dt.MSSubClass == MSSubClass)]['Exterior2nd'].tolist()[0]\n \n df['Exterior1st'] = df.Exterior1st.fillna('NA')\n df['Exterior2nd'] = df.Exterior2nd.fillna('NA')\n \n df['Exterior1st'] = df.apply(lambda x: bestExt1(\n x['Neighborhood'], x['ExterQual'], x['ExterCond'], x['MSSubClass']\n ) if x['Exterior1st'] ==\"NA\" else x['Exterior1st'], axis=1)\n df['Exterior2nd'] = df.apply(lambda x: bestExt2(\n x['Neighborhood'], x['ExterQual'], x['ExterCond'], x['MSSubClass']\n ) if x['Exterior2nd'] ==\"NA\" else x['Exterior2nd'], axis=1)\n \n dd(df[df.index == 2151][['Exterior1st','Exterior2nd', 'Neighborhood','ExterQual', 'ExterCond', 'MSSubClass']])\n return df\n \n\n \ndf_ext = exteriorWrangle(df_electrical)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### it is observed that many of the houses have Exterior1st and Exterior2nd same values per neighborhood. Therefore, we will create a matrix of neighborhood and Exterior1st. We will first populate Exterior1st from neighborhood value and then we will populate Exterior2nd from Exterior1st.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 4. Fence",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def fenceWrangling(df_temp):\n df = df_temp.copy()\n\n print(\"Count of missing Fence : \",df[df.Fence.isna()].shape)\n \n df['Fence'] = df.Fence.fillna('NA')\n \n #dd(df.groupby(['MSSubClass', 'Neighborhood','Fence', ]).agg('count').reset_index()[['MSSubClass', 'Neighborhood','Fence', 'SalePrice']])\n dd(df.groupby(['Neighborhood','Fence', ]).agg('count').reset_index()[['Neighborhood','Fence', 'SalePrice']])\n return df\n \ndf_fence = fenceWrangling(df_ext)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### It is too tedious to decide if missing value indicates \"NA\" - No Fence or the entry was missing. What does actually Fence depend on ?\n* For now i m going to rely on NA for the missing entry. Safest assumption.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"##### It is too risky to map from othe rvariables. Though it seems like it depends on LotArea or LotFrontage. It is not very clear if it depends solely on one of the variable or sort of combination of others. Let us keep it NA for missing values, so that it would mean no fence available.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def plotMinusOnes(df):\n minusOneCols = [c for c in list(df) if -1 in df[c].unique()]\n \n for c in df[minusOneCols]:\n df[[c,'SalePrice']].\\\n groupby(by=c).agg('count').\\\n plot.bar(legend=None, title=\"Frequency Plot for \"+c)\n plt.xticks(rotation=45)\n plt.show()\nplotMinusOnes(df_stage_1.copy())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 5.0 Functional",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def functionalWrangle(df):\n print(\"Unique values in Functional variable Before: \", df.Functional.unique())\n print(\"How many missing entries are there in Functional variable : \",df[df.Functional == -1].shape[0])\n \n co_qu_columns = [c for c in list(df) if (\"Co\" in c) or (\"Qu\" in c)]\n co_qu_columns.append('SalePrice')\n co_qu_columns.append('Functional')\n print(\"Quality and Condition Related columns : \", co_qu_columns)\n \n dd(\"Samples with missing functional feature values : \" , df[df.Functional == -1][co_qu_columns])\n \n dd(\"Let us see the samples which have similar Overall Condition and Quality\")\n dd(df[(df.OverallCond == 5) & (df.OverallQual == 1)][co_qu_columns])\n dd(df[(df.OverallCond == 1) & (df.OverallQual == 4)][co_qu_columns])\n \n df.loc[df.Functional == -1, \"Functional\"] = 7\n \n print(\"Unique values in Functional variable : \", df.Functional.unique())\n \n return df\n \ndf_funct = functionalWrangle(df_fence.copy())\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### the rule itself says, assume typical unless deductions are warranted. However, there is no entry of salvage in our data set. Though it is not mandatory to have all categorical values has to be there in the dataset but it always raises the question why not that variable ? Can *Cond and *Qu variable give us hint of not 'Sal' ?\n\n* I am actually tempted to put 'Sal' but due to lack of samples for Sal, I will be putting it as 'Typ'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 6. LotFrontage",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def LotFrontagecheck(df):\n\n print(\"Number of samples with missing LotFrontage variable values (Before): \", df[df.LotFrontage.isna()].shape[0])\n df_LotFrontage = df[['Neighborhood','LotFrontage']].groupby('Neighborhood').agg(lambda x:x.value_counts().index[0]).reset_index()\n df_dict = dict([tuple(x) for x in df_LotFrontage.values])\n print(\"\\nLotFrontage median valued per Neighborhood \", df_dict)\n \n df['LotFrontage'] =df.LotFrontage.fillna(-1)\n df['LotFrontage'] =df.apply(lambda x: df_dict[x['Neighborhood']] if x['LotFrontage'] == -1 else x['LotFrontage'],axis=1)\n print(\"\\nNumber of samples with missing LotFrontage variable values (After): \", df[df.LotFrontage.isna()].shape[0])\n \n\n return df\n \ndf_lot = LotFrontagecheck(df_funct.copy())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### LotFrontage: taking neighborhood as reference most occuring distance is used for filling missing values. Inspiration: neighboring house have same distance to road /gate.\n\n* Lot area > 10000 & LotFrontage > 200 seems like outliers",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 7. MSZoning",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def msZoningWrangle(df):\n \n zone_related = ['LotShape', 'LandContour', 'Utilities', 'LotConfig', 'LandSlope', 'Neighborhood', 'Condition1',\n 'Condition2', 'BldgType', 'OverallQual', 'OverallCond', 'MSZoning'\n ]\n \n temp = df.groupby(['Neighborhood','MSSubClass','MSZoning']).\\\n agg('count').reset_index().\\\n sort_values(by=['SalePrice'],ascending=False)[['Neighborhood','MSSubClass','MSZoning','SalePrice']]\n dd(temp[(temp.Neighborhood == 'IDOTRR') |(temp.Neighborhood == 'Mitchel')])\n \n def returnmsZone(Neighborhood,MSSubClass):\n return temp[(temp.Neighborhood == Neighborhood) &\n (temp.MSSubClass == MSSubClass)]['MSZoning'].tolist()[0]\n \n dd(df[df.MSZoning.isna()][['Neighborhood','MSSubClass','MSZoning']])\n df['MSZoning'] = df.MSZoning.fillna(\"NA\")\n df['MSZoning'] = df.apply(lambda x: returnmsZone(x['Neighborhood'], x['MSSubClass']) \n if x['MSZoning'] == \"NA\" else x['MSZoning'], axis=1)\n \n dd(df[df.index.isin([1915,2216,2250,2904])][['Neighborhood','MSSubClass','MSZoning']])\n\n return df\n\ndf_ms = msZoningWrangle(df_lot.copy()) ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### MSZoning is general zoning classification. Therefore, it must be specific to an area and hence 'Neighborhood' is the variable to our rescue. MSZoning = RL when neighbor is 'Mitchel' and RM when neighbor is IDOTRR and they are is missing.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 8.0 MasVnrType & MasVnrArea",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def MasVnrTypeCheck(df_temp):\n #df = pd.read_csv('train.csv')\n df=df_temp.copy()\n print(df[df.MasVnrType.isna()].shape, )\n #display.display(df[['Neighborhood','MasVnrType','Id']].groupby(['Neighborhood','MasVnrType']).agg('count').reset_index())\n \n dd(df[['MasVnrType','MasVnrArea']][df.MasVnrType.isna()].head())\n dd(df[['MasVnrType','MasVnrArea']][df.MasVnrArea.isna()].head())\n dd(df[['MasVnrType','MasVnrArea']][df.MasVnrArea == 0].head())\n dd(df[['MasVnrType','MasVnrArea']][df.MasVnrType == 'None'].head())\n \n df['MasVnrType'] = df.MasVnrType.fillna(\"None\")\n df['MasVnrArea'] = df.MasVnrArea.fillna(0)\n\n df['MasVnrArea'] = df['MasVnrArea'].astype(np.float64)\n\n return df\ndf_mas = MasVnrTypeCheck(df_ms)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"* MasVnrArea nan count is equivalent to MasVnrType count.\n* MasVnrArea == 0 is already present \n* whenever MasVnrArea == 0 MasVnrType is also None \n* Therefore, MasVnrArea will be mapped to zero when MasVnrType = None\n\n##### Outlier: area > 1400 is only one sample which has low sale price. Its overall condition and quality is moderate and there are enough sample for those bands.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 9. MiscFeature",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def miscFeatureWrangle(df):\n #df = df_temp.copy()\n df_df = df.fillna('NA').groupby(['MiscFeature','MiscVal']).agg('count').reset_index()[['MiscFeature','MiscVal','SalePrice']]\n \n dd(\"Before :\",df_df[df_df.MiscVal == 0])\n dd(df_df[df_df.MiscFeature == \"NA\"])\n #dd(df_df[df_df.MiscVal == \"NA\"])\n \n df['MiscFeature'] = df.apply(lambda x: \"NA\" if x['MiscVal'] == 0 else x['MiscFeature'],axis=1)\n df['MiscFeature'] = df.apply(lambda x: \"Gar2\" if x['MiscVal'] == 17000.0 else x['MiscFeature'],axis=1)\n \n df_df = df.fillna('NA').groupby(['MiscFeature','MiscVal']).agg('count').reset_index()[['MiscFeature','MiscVal','SalePrice']]\n \n dd(\"After :\",df_df[df_df.MiscVal == 0])\n dd(df_df[df_df.MiscFeature == \"NA\"])\n return df\n \ndf_misc = miscFeatureWrangle(df_mas.copy())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"* When MiscVal == 0 ; MiscFeature is mostly NA (None). Note that it can be Shed or Other too. Will park it for next level fine tuning.\n* High Values are dedicated to 'Gar2'. Therefore, testing set missing value is gar2 for sure.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 10. PoolQC",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def poolWrangling(df):\n\n print(\"Count of Samples which have PoolQC valid values : \", df[df.PoolQC != -1].shape[0] )\n print(\"Count of missing PoolQC : \",df[df.PoolQC == -1].shape[0])\n \n dd(\"Pattern of missing PoolQC vs Overall Cond n Qual\", df[df.PoolQC == -1][['PoolArea', 'PoolQC','OverallCond','OverallQual']].head())\n dd(\"Pattern of PoolQC when PoolArea = 0\",df[df.PoolArea == 0][['PoolArea', 'PoolQC','OverallCond','OverallQual']]['PoolQC'].unique())\n dd(\"Dataset samples with PoolArea missing \",df[df.PoolArea.isna()])\n \n dd(\"PoolQC vs Overall Cond and Qual : \" , df.groupby(['OverallCond','OverallQual','PoolQC']).agg('count').reset_index()[['OverallCond','OverallQual','PoolQC','SalePrice']])\n \n df.loc[(df['PoolArea'] == 0) & (df['PoolQC'] == -1), 'PoolQC'] = 0\n df.loc[(df['PoolArea'] > 0) & (df['PoolQC'] == -1), 'PoolQC'] = 2\n \n dd(df[df.PoolQC == -1][['PoolArea', 'PoolQC','OverallCond','OverallQual']])\n dd(Counter(df.PoolQC))\n \n return df\n \ndf_pool = poolWrangling(df_misc.copy())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### When PoolArea is 0 PoolQC will be NA (no pool). When PoolArea > 0 it appears to be good candidates for \"Fa\".",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* when PoolQC should be \"NA\" when PoolArea = 0 [Thumb rule / Common sense]\n* Missing values have characterstics matching with that of \"Fair\" condition. It may be \"TA\" but we dont have enough evidence or rather no evidence for that.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 11. SaleType",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def saleTypeWrangling(df):\n\n dd(df[df.SaleType.isna()][['MSSubClass', 'MSZoning', 'SaleCondition','SaleType']])\n df1 = df.groupby(['MSSubClass', 'MSZoning', 'SaleCondition','SaleType']).\\\n agg('count').reset_index().sort_values('SalePrice',ascending=False)[['MSSubClass', 'MSZoning', 'SaleCondition','SaleType', 'SalePrice']]\n dd(df1[df1.MSSubClass == 20])\n \n def popSaleType(MSSubClass, MSZoning, SaleCondition):\n return df1[(df1.MSSubClass == MSSubClass) &\n (df1.MSZoning == MSZoning) &\n (df1.SaleCondition == SaleCondition)\n ]['SaleType'].tolist()[0]\n \n df['SaleType'] = df.SaleType.fillna(\"NA\")\n df['SaleType'] = df.apply(lambda x: popSaleType(x['MSSubClass'], x['MSZoning'], x['SaleCondition']) \n if x['SaleType'] == \"NA\" else x['SaleType']\n ,\n axis = 1)\n dd(df[df.index == 2489][['MSSubClass', 'MSZoning', 'SaleCondition','SaleType']])\n \n return df\n \ndf_sale = saleTypeWrangling(df_pool.copy()) ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 12. Utilities",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def utilWrangling(df):\n dd(\"Missing entries for Utilities : \",df[df.Utilities == -1][['Neighborhood','Utilities']])\n \n df1 = df.groupby(['Neighborhood','Utilities']).agg('count').reset_index().\\\n sort_values('SalePrice',ascending=False)[['Neighborhood','Utilities','SalePrice']]\n dd(\"Relation between Neighborhood and Utilities : \",df1)\n \n def returnUtil(Neighborhood):\n return df1[(df1.Neighborhood == Neighborhood)][\"Utilities\"].tolist()[0]\n \n \n df['Utilities'] = df.apply(lambda x: returnUtil(x['Neighborhood']) if x['Utilities'] == -1 else x[\"Utilities\"],axis=1)\n \n dd(\"Post imputation :\", df[df.index.isin([1915,1945])][['Neighborhood','Utilities']])\n return df\n \ndf_util = utilWrangling(df_sale.copy())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 13. KitchenQual",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def kitchenQual(df):\n \n dd(\"Missing samples for KitchenQual\", df[df.KitchenQual == -1][['OverallCond', 'OverallQual', 'KitchenAbvGr', 'KitchenQual']])\n \n df1 = df.groupby(['OverallCond', 'OverallQual', 'KitchenAbvGr', 'KitchenQual']).agg('count').\\\n reset_index().sort_values('SalePrice', ascending= False)[['OverallCond', 'OverallQual', 'KitchenAbvGr', 'KitchenQual']]\n dd(\"Kitchen Table : \", df1)\n def returnkqual(OverallCond, OverallQual, KitchenAbvGr):\n return df1[(df1.OverallCond == OverallCond)&\n (df1.OverallQual == OverallQual) &\n (df1.KitchenAbvGr == KitchenAbvGr)\n ]['KitchenQual'].tolist()[0]\n \n df['KitchenQual'] = df.apply(lambda x: returnkqual(x['OverallCond'], x['OverallQual'],x['KitchenAbvGr'])\n if x['KitchenQual'] == -1 else x['KitchenQual']\n ,axis=1)\n dd(df[df.index == 1555][['OverallCond', 'OverallQual', 'KitchenAbvGr', 'KitchenQual']])\n return df\n\ndf_kitchen = kitchenQual(df_util.copy())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Checkpoint - 1",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plotNAs(df_kitchen.copy())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plotMinusOnes(df_kitchen.copy())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def bsmtInterpolate(df):\n bsmt_column = ['BsmtCond', 'BsmtExposure', 'BsmtFinType1', 'BsmtFinType2', 'BsmtQual']\n print(bsmt_column)\n \n bsmt_column2 = [c for c in list(df) if 'Bsmt' in c]\n \n dd(\"BsmtCond missing entries : \", df[df.BsmtCond == -1][bsmt_column])\n bsmt_index = []\n bsmt_index += list(df[df.BsmtCond == -1].index)\n \n dd(\"BsmtExposure missing entries : \", df[df.BsmtExposure == -1][bsmt_column])\n bsmt_index += list(df[df.BsmtExposure == -1].index)\n \n dd(\"BsmtFinType1 missing entries :\",df[df.BsmtFinType1 == -1][bsmt_column])\n bsmt_index += list(df[df.BsmtFinType1 == -1].index)\n \n dd(\"BsmtFinType2 missing entries :\",df[df.BsmtFinType2 == -1][bsmt_column])\n bsmt_index += list(df[df.BsmtFinType2 == -1].index)\n \n dd(\"BsmtQual missing entries : \", df[df.BsmtQual == -1][bsmt_column])\n bsmt_index += list(df[df.BsmtQual == -1].index)\n \n df1 = df.groupby(bsmt_column).agg('count').reset_index().sort_values('SalePrice', ascending=False)[(bsmt_column + ['SalePrice'])]\n df1 = df1.sort_values('SalePrice',ascending=False)\n #dd(df1)\n \n def getBsmtCond(BsmtExposure, BsmtFinType1, BsmtFinType2, BsmtQual):\n return df1[(df1.BsmtExposure == BsmtExposure)&\n (df1.BsmtFinType1 == BsmtFinType1)&\n (df1.BsmtFinType2 == BsmtFinType2)&\n (df1.BsmtQual == BsmtQual) \n ]['BsmtCond'].tolist()[0]\n \n def getBsmtExposure(BsmtCond, BsmtFinType1, BsmtFinType2, BsmtQual):\n return df1[(df1.BsmtCond == BsmtCond)&\n (df1.BsmtFinType1 == BsmtFinType1)&\n (df1.BsmtFinType2 == BsmtFinType2)&\n (df1.BsmtQual == BsmtQual) \n ]['BsmtExposure'].tolist()[0]\n \n def getBsmtFinType1(BsmtExposure, BsmtCond, BsmtFinType2, BsmtQual):\n return df1[(df1.BsmtExposure == BsmtExposure)&\n (df1.BsmtCond == BsmtCond)&\n (df1.BsmtFinType2 == BsmtFinType2)&\n (df1.BsmtQual == BsmtQual) \n ]['BsmtFinType1'].tolist()[0]\n \n def getBsmtFinType2(BsmtExposure, BsmtFinType1, BsmtCond, BsmtQual):\n return df1[(df1.BsmtExposure == BsmtExposure)&\n (df1.BsmtFinType1 == BsmtFinType1)&\n (df1.BsmtCond == BsmtCond)&\n (df1.BsmtQual == BsmtQual) \n ]['BsmtFinType2'].tolist()[0]\n \n def getBsmtQual(BsmtExposure, BsmtFinType1, BsmtFinType2, BsmtCond):\n return df1[(df1.BsmtExposure == BsmtExposure)&\n (df1.BsmtFinType1 == BsmtFinType1)&\n (df1.BsmtFinType2 == BsmtFinType2)&\n (df1.BsmtCond == BsmtCond) \n ]['BsmtQual'].tolist()[0]\n \n #['BsmtCond', 'BsmtExposure', 'BsmtFinType1', 'BsmtFinType2', 'BsmtQual']\n df['BsmtCond'] = df.apply(lambda x: getBsmtCond(x['BsmtExposure'], x['BsmtFinType1'], x['BsmtFinType2'], x['BsmtQual'])\n if x['BsmtCond'] == -1 else x['BsmtCond']\n , axis = 1)\n \n df['BsmtExposure'] = df.apply(lambda x: getBsmtExposure(x['BsmtCond'], x['BsmtFinType1'], x['BsmtFinType2'], x['BsmtQual'])\n if x['BsmtExposure'] == -1 else x['BsmtExposure']\n , axis = 1)\n \n df['BsmtFinType1'] = df.apply(lambda x: getBsmtFinType1(x['BsmtExposure'], x['BsmtCond'], x['BsmtFinType2'], x['BsmtQual'])\n if x['BsmtFinType1'] == -1 else x['BsmtFinType1']\n , axis = 1)\n\n df['BsmtFinType2'] = df.apply(lambda x: getBsmtFinType2(x['BsmtExposure'], x['BsmtFinType1'], x['BsmtCond'], x['BsmtQual'])\n if x['BsmtFinType2'] == -1 else x['BsmtFinType2']\n , axis = 1)\n \n df['BsmtQual'] = df.apply(lambda x: getBsmtQual(x['BsmtExposure'], x['BsmtFinType1'], x['BsmtFinType2'], x['BsmtCond'])\n if x['BsmtQual'] == -1 else x['BsmtQual']\n , axis = 1)\n \n dd(\"Post imputation :\", df[df.index.isin(bsmt_index)][bsmt_column])\n \n return df\ndf_bsmt_final = bsmtInterpolate(df_kitchen.copy())\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Garage*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def garageWrangling(df):\n garage_columns = [c for c in df.select_dtypes(exclude=np.number) if \"Garage\" in c]\n print(garage_columns)\n garage_col2 = [c for c in list(df) if \"Garage\" in c]\n grp_by = ['GarageType','MiscFeature','OverallQual','OverallCond','GarageFinish','GarageQual','GarageCond',\\\n 'GarageArea','GarageCars']\n \n new_col = list(set(garage_col2 + grp_by + ['MiscFeature']))\n \n miss_index = []\n for c in garage_col2:\n df_temp = df[df[c] == -1][new_col]\n dd(\"Missing Entries for \"+c+ \" : \",df_temp)\n miss_index += list(df_temp.index)\n \n \n df1 = df.groupby(grp_by).agg('count').reset_index().sort_values('SalePrice',ascending=False)[grp_by + ['SalePrice']]\n dd(\"when garage type == Detchd : \", df1[df1.GarageType == 'Detchd'])\n \n def getGarageArea( GarageType, MiscFeature, OverallQual, OverallCond):\n return df1[\n (df1.GarageType == GarageType) &\n (df1.MiscFeature == MiscFeature) &\n (df1.OverallQual == OverallQual) &\n (df1.OverallCond == OverallCond)\n ]['GarageArea'].tolist()[0]\n \n def getGarageCars( GarageType, MiscFeature, OverallQual, OverallCond):\n return df1[\n (df1.GarageType == GarageType) &\n (df1.MiscFeature == MiscFeature) &\n (df1.OverallQual == OverallQual) &\n (df1.OverallCond == OverallCond)\n ]['GarageCars'].tolist()[0]\n \n def getGarageCond(GarageType, MiscFeature, OverallQual, OverallCond):\n return df1[\n (df1.GarageType == GarageType) &\n (df1.MiscFeature == MiscFeature) &\n (df1.OverallQual == OverallQual) &\n (df1.OverallCond == OverallCond)\n ]['GarageCond'].tolist()[0]\n \n def getGarageFinish(GarageType, MiscFeature, OverallQual, OverallCond):\n return df1[\n (df1.GarageType == GarageType) &\n (df1.MiscFeature == MiscFeature) &\n (df1.OverallQual == OverallQual) &\n (df1.OverallCond == OverallCond)\n ]['GarageFinish'].tolist()[0]\n \n def getGarageQual(GarageType, MiscFeature, OverallQual, OverallCond):\n return df1[\n (df1.GarageType == GarageType) &\n (df1.MiscFeature == MiscFeature) &\n (df1.OverallQual == OverallQual) &\n (df1.OverallCond == OverallCond)\n ]['GarageQual'].tolist()[0]\n \n df['GarageArea'] = df['GarageArea'].fillna(\"NA\")\n df['GarageArea'] = df.apply(lambda x: getGarageArea( x['GarageType'], x['MiscFeature'], x['OverallQual'], x['OverallCond'])\n if x['GarageArea'] ==\"NA\" else x['GarageArea']\n ,axis =1)\n \n df['GarageCars'] = df['GarageCars'].fillna(\"NA\")\n df['GarageCars'] = df.apply(lambda x: getGarageCars( x['GarageType'], x['MiscFeature'], x['OverallQual'], x['OverallCond'])\n if x['GarageCars'] ==\"NA\" else x['GarageCars']\n ,axis =1)\n \n df['GarageCond'] = df.apply(lambda x: getGarageCond( x['GarageType'], x['MiscFeature'], x['OverallQual'], x['OverallCond'])\n if x['GarageCond'] == -1 else x['GarageCond']\n ,axis =1)\n \n df['GarageFinish'] = df.apply(lambda x: getGarageFinish( x['GarageType'], x['MiscFeature'], x['OverallQual'], x['OverallCond'])\n if x['GarageFinish'] == -1 else x['GarageFinish']\n ,axis =1)\n \n df['GarageQual'] = df.apply(lambda x: getGarageQual( x['GarageType'], x['MiscFeature'], x['OverallQual'], x['OverallCond'])\n if x['GarageQual'] == -1 else x['GarageQual']\n ,axis =1)\n \n dd(df[df.index.isin(miss_index)][new_col])\n return df\ndf_garage_final = garageWrangling(df_bsmt_final.copy())\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Checkpoint 2",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plotNAs(df_garage_final.copy())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plotMinusOnes(df_garage_final.copy())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"did_we_miss_them = ['MSSubClass', 'OverallQual', 'OverallCond', 'FireplaceQu', ]\nfor c in did_we_miss_them:\n dd(c, df_garage_final[c].unique())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def FireplaceWrangling(df_temp):\n df = pd.read_csv(train_File)\n print(\"Count of missing FireplaceQu : \",df[df.FireplaceQu.isna()].shape[0])\n dd(\"Count of Fireplaces == 0\",df[['Fireplaces', 'FireplaceQu']][df.Fireplaces == 0].shape)\n dd(df[['Fireplaces', 'FireplaceQu']][df.FireplaceQu.isna()].head())\n dd(\"When FireplaceQu == NA, Fireplaces:\", df[['Fireplaces', 'FireplaceQu']][df.FireplaceQu.isna()]['Fireplaces'].unique())\n dd(\"When Fireplaces == 0, FireplaceQu:\",df[['Fireplaces', 'FireplaceQu']][df.Fireplaces == 0]['FireplaceQu'].unique())\n \n #now we have NA as nan in our wrangled dataset; ideally this should not be problem but let us be consistent.\n df = df_temp.copy()\n \n df['FireplaceQu'] = df.apply(lambda x: 0 if x['Fireplaces'] == 0 else x['FireplaceQu'], axis=1 )\n \n dd(\"Post imputing :\",df.FireplaceQu.unique())\n \n return df\n \ndf_fire = FireplaceWrangling(df_garage_final.copy())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### FireplaceQu will be mapped to NA (no fireplace) whenever Fireplaces = 0",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"##### TotalBsmtSF = 0 indicates there is no basement. \n* Therefore, BsmtQual = BsmtCond = BsmtExposure = BsmtFinType1 = BsmtFinType2 = \"NA\"; when TotalBsmtSF = 0 \n\n* Outlier: (df.BsmtFinSF1 > 2000) & (df.SalePrice < 200000) (2 of them) are outlier because it not only brings the co relation down but also there are enough samples for outlier's overall condition and quality samples.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"##### Let us check the datatype if it is corrupted due to our imputate operation",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"post_imputing_cols = list(df_fire.select_dtypes(include=np.object))\ncols_need_change = [c for c in list(df_before_clean.select_dtypes(include=np.number)) if c in post_imputing_cols]\n\n#dd(df_before_clean[df_before_clean.MasVnrArea == 'BrkFace'])\n\n'''for c in post_imputing_cols:\n if c in cols_need_change:\n print(c)\n df_fire[c] = df_fire[c].astype(np.float64)'''\nprint()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"post_imputing_cols = list(df_fire.select_dtypes(include=np.number))\n[c for c in list(df_before_clean.select_dtypes(include=np.number)) if c not in post_imputing_cols]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"post_imputing_cols = list(df_fire.select_dtypes(include=np.object))\n[c for c in list(df_before_clean.select_dtypes(include=np.object)) if c not in post_imputing_cols]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"post_imputing_cols = list(df_fire.select_dtypes(include=np.number))\n\n_= [dd(c,df_fire[c].unique()) for c in list(df_fire.select_dtypes(exclude=np.number))]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(\"Are there any missing entries for numerical variables ?: \", len([dd(df_fire[c].unique() ) for c in post_imputing_cols if -1 in df_fire[c].unique()]) > 0)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Outliers",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(\"Shape of the imputed dataset : \", df_fire.shape)\ndf_out = df_fire[df_fire.SalePrice > 0].copy()\nprint(\"Shape of the Outlier Analysis dataset : \", df_out.shape)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def computeCorrCols(df):\n df_corr = df.corr()\n \n df1 = df_corr.stack().reset_index().rename(columns={'level_0': \"C1\", \"level_1\": \"C2\", 0 : \"Corr_val\"})\n \n df1['Corr_val']= df1['Corr_val'].abs()\n df1 = df1[df1['Corr_val'] < 1].sort_values('Corr_val',ascending=False)\n df1 = df1.drop_duplicates('Corr_val').reset_index(drop=True)\n dd(df1)\n \n return df1\ndf_corr = computeCorrCols(df_out.copy())\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def checkCorr(df_old):\n df = pd.get_dummies(df_old)\n corr_target = []\n df_corr = df.corr()\n for c in list(df_corr):\n corr_target.append((c, np.abs(df_corr.loc[c,'SalePrice'])))\n\n dd(\"Top 15 Numerical Variables with High Corr value for SalePrice :\",\n [x for x in sorted(corr_target,key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True) if '_' not in x[0]][1:15])\n \n dd(\"Top 15 Variables (All Types) with High Corr value for SalePrice :\",\n [x for x in sorted(corr_target,key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)][1:15])\n\ncheckCorr(df_out.copy())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### There may be so many outliers but let us target the ones which are not only numerical but also impact the target variables. Let us target top 5 variables for outlier removal. i.e. OverallQual, GrLivArea, ExterQual, KitchenQual, GarageCars & TotalBsmtSF.\n\n* Note that I am not selecte GarageArea for outlier detection following reasons:\n * it has high co relation with GarageCars\n * GarageCars and GarageArea both gets imputed in our last steps but the error margin is less for GarageCars when compared to GarageArea\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_out.GarageCars.unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def topCorrWithOthers(df):\n top_5_corr = ['OverallQual', 'GrLivArea', 'ExterQual', 'KitchenQual', 'GarageCars', 'TotalBsmtSF']\n print(\"Co relation of the top 5 columns with others : \")\n for c in top_5_corr:\n dd(c, df_corr[(df_corr.C1 == c) | (df_corr.C2 == c)].head())\n \ntopCorrWithOthers(df_fire.copy())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#df_out['SalePrice'] = df_out['SalePrice'] / df_out.GrLivArea",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 1. OverallQual Outlier Check",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def overallQualOutlier(df):\n df.plot.scatter(\"OverallQual\", \"SalePrice\", title=\"Before Removal of Outlier\")\n df_corr = df.corr()\n print(\"Co relation before removing the outlier : \",df_corr.loc['OverallQual','SalePrice']) \n df1 = df[(df.OverallQual != 10) | (df.SalePrice >200000 )]\n df1 = df1[(df1.OverallQual != 4) | (df1.SalePrice <200000 )]\n df1 = df1[(df1.SalePrice >125000 ) | (df1.OverallQual != 7)]\n df1 = df1[(df1.OverallQual != 8) | (df1.SalePrice >125000 )]\n df1 = df1[(df1.OverallQual != 7) | (df1.SalePrice <360000)]\n df1 = df1[(df1.OverallQual != 8) | (df1.SalePrice < 460000)]\n #.plot.scatter(\"OverallQual\", \"SalePrice\", title=\"Zoomed view on a outlier\")\n \n print(\"Outlier Count: \", df.shape[0]-df1.shape[0])\n df1.plot.scatter(\"OverallQual\", \"SalePrice\", title=\"After Removal of Outlier\")\n df_corr = df1.corr()\n print(\"Co relation After removing the outlier : \",df_corr.loc['OverallQual','SalePrice'])\n return df1\ndf_overallqual = overallQualOutlier(df_out.copy())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 2. GrLivArea Outlier Check",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def grLivAreaOutlier(df):\n df.plot.scatter(\"GrLivArea\", \"SalePrice\", title=\"Before Removal of Outlier\")\n df_corr = df.corr()\n print(\"Co relation before removing the outlier : \",df_corr.loc['GrLivArea','SalePrice'])\n df1 = df[(df.GrLivArea < 4000) | (df.SalePrice >250000 )]\n df1 = df1[(df1.GrLivArea > 2000) | (df1.SalePrice < 380000)]\n df1 = df1[(df1.GrLivArea < 3300) | (df1.SalePrice > 220000)]\n print(\"Outlier Count: \", df.shape[0]-df1.shape[0])\n \n #df1[(df1.GrLivArea > 3000)&(df.SalePrice <300000)].plot.scatter(\"GrLivArea\", \"SalePrice\", title=\"Zoomed look on a outlier\")\n \n df1.plot.scatter(\"GrLivArea\", \"SalePrice\", title=\"After Removal of Outlier\")\n \n #dd(corr(df1.GrLivArea, df1.SalePrice))\n \n df_corr = df1.corr()\n print(\"Co relation After removing the outlier : \",df_corr.loc['GrLivArea','SalePrice'])\n \n return df1\ndf_liv = grLivAreaOutlier(df_overallqual.copy())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 3. ExterQual Outlier Check",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def exernalQualOutlier(df):\n df.plot.scatter(\"ExterQual\", \"SalePrice\", title=\"Before Removal of Outlier\")\n df_corr = df.corr()\n print(\"Co relation before removing the outlier : \",df_corr.loc['ExterQual','SalePrice'])\n \n print(df['SalePrice'][df.ExterQual == 4].min(), df['SalePrice'][df.ExterQual == 4].max())\n #df1 = df[(df.SalePrice)]\n df1 = df[(df.ExterQual != 4) | ((df.SalePrice != 52000.0) & ( df.SalePrice != 745000.0))]\n \n print(\"Outlier Count : \", df.shape[0]-df[(df.ExterQual != 4) | ((df.SalePrice != 52000.0) & ( df.SalePrice != 745000.0))].shape[0])\n df_corr = df1.corr()\n print(\"Co relation After removing the outlier : \",df_corr.loc['ExterQual','SalePrice'])\n df1.plot.scatter(\"ExterQual\", \"SalePrice\", title=\"After Removal of Outlier\")\n \n return df1\n\ndf_external_qual = exernalQualOutlier(df_liv.copy())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 4. KitchenQual Outlier Check",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def kitchenQualOutlier(df):\n df.plot.scatter(\"KitchenQual\", \"SalePrice\", title=\"Before Removal of Outlier\")\n df_corr = df.corr()\n print(\"Co relation before removing the outlier : \",df_corr.loc['KitchenQual','SalePrice'])\n print(\"Max values when KitchenQual == 3 :\", df[df.KitchenQual == 3]['SalePrice'].max())\n print(\"Max values when KitchenQual == 4 :\", df[df.KitchenQual == 4]['SalePrice'].max())\n df1 = df[(df.KitchenQual != 3) | ( df.SalePrice != 359100.0) ]\n df1 = df1[ (df1.KitchenQual != 4) | ( df1.SalePrice != 625000.0)]\n print(\"Outlier Count : \", df.shape[0] - df1.shape[0])\n df_corr = df1.corr()\n print(\"Co relation After removing the outlier : \",df_corr.loc['KitchenQual','SalePrice'])\n df1.plot.scatter(\"KitchenQual\", \"SalePrice\", title=\"After Removal of Outlier\")\n return df1\n \ndf_kitchen_qual = kitchenQualOutlier(df_external_qual.copy())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 5. GarageCars Outlier Check",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def garageCarsOutlier(df):\n df.plot.scatter(\"GarageCars\", \"SalePrice\", title=\"Before Removal of Outlier\")\n df_corr = df.corr()\n print(\"Co relation before removing the outlier : \",df_corr.loc['GarageCars','SalePrice'])\n \n df1 = df[(df.GarageCars < 4)]\n \n print(\"Outlier Count : \", df[(df.GarageCars == 4)].shape[0])\n df_corr = df1.corr()\n print(\"Co relation After removing the outlier : \",df_corr.loc['GarageCars','SalePrice'])\n df1.plot.scatter(\"GarageCars\", \"SalePrice\", title=\"After Removal of Outlier\")\n return df1\n \ndf_gar_car = garageCarsOutlier(df_kitchen_qual.copy())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 6. TotalBsmtSF Outlier Check",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def totalBsmtSFOutlier(df):\n df.plot.scatter(\"TotalBsmtSF\", \"SalePrice\", title=\"Before Removal of Outlier\")\n df_corr = df.corr()\n print(\"Co relation before removing the outlier : \",df_corr.loc['TotalBsmtSF','SalePrice'])\n df[df.TotalBsmtSF >3000].plot.scatter(\"TotalBsmtSF\", \"SalePrice\", title=\"Zoomed look on Outlier\")\n df[df.TotalBsmtSF >3100].plot.scatter(\"TotalBsmtSF\", \"SalePrice\", title=\"Further Zoomed look on Outlier\")\n df[(df.TotalBsmtSF >1000) & (df.TotalBsmtSF <1500) & (df.SalePrice <100000)].plot.scatter(\"TotalBsmtSF\", \"SalePrice\", title=\"Further Zoomed look Outlier 2\")\n df[(df.TotalBsmtSF >2000) & (df.TotalBsmtSF <2500) & (df.SalePrice <210000)].plot.scatter(\"TotalBsmtSF\", \"SalePrice\", title=\"Further Zoomed look Outlier 3\")\n \n df1 = df[(df.TotalBsmtSF < 3000) | (df.SalePrice > 300000)]\n df1 = df1[(df1.TotalBsmtSF < 1000) | (df1.TotalBsmtSF > 1500) | (df1.SalePrice > 65000)]\n df1 = df1[(df1.TotalBsmtSF < 2000) | (df1.TotalBsmtSF > 2500) | (df1.SalePrice > 150000)]\n \n print(\"Outlier Count : \", df.shape[0] - df1.shape[0])\n df_corr = df1.corr()\n print(\"Co relation After removing the outlier : \",df_corr.loc['TotalBsmtSF','SalePrice'])\n df1.plot.scatter(\"TotalBsmtSF\", \"SalePrice\", title=\"After Removal of Outlier\")\n \n return df1\n\ndf_tot = totalBsmtSFOutlier(df_gar_car.copy())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"checkCorr(df_tot.copy())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### We have so far identified 31 outliers altogether from 6 variables from our input data set. These outliers have increased the co relation with target variable.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"##### Let us check with XGBoost for the score.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def preProcessData(df, log=False):\n \n print(\"Shape of the data set before pre processing : \", df.shape )\n\n #get dummies\n if log:\n print(\"Categorical columns : \", list(df.select_dtypes(exclude=np.number)))\n df = pd.get_dummies(df, dtype=np.float64)\n \n print(\"\\n\\nShape of the data set after pre processing : \", df.shape )\n \n if log:\n print(\"Columns in the data set are : \",list(df))\n\n return df\n\ndf_prep = preProcessData(df_fire.copy())\ndf_prep.info()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"list(df_prep)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def removeOutlier(df):\n \n print(\"Shape before removing outlier : \", df.shape)\n '''df = df[(df.GrLivArea < 4000) | (df.SalePrice >250000) | (df.SalePrice == 0) ]\n df = df[(df.GarageCars < 4) | (df.SalePrice == 0)]\n df = df[((df.GarageArea < 1200) | (df.SalePrice > 300000)) | (df.SalePrice ==0)]\n df = df[((df.TotalBsmtSF < 3000) | (df.SalePrice > 300000)) | (df.SalePrice ==0)]'''\n df = df[(df.GrLivArea < 3000)| (df.SalePrice ==0)]\n df = df[(df.SalePrice < 200)| (df.SalePrice ==0)]\n print(\"Shape after removing outlier : \", df.shape)\n \n df1 = pd.concat([df_tot,df[df.SalePrice == 0]])\n \n return df1\n\ndf_out_removed = removeOutlier(df_fire.copy())\ndf_out_removed.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from IPython import display\ndef transformTarget(df_temp, revert=False ):\n '''df = df_temp.copy()\n #df['new_variable'] = df.BedroomAbvGr * .1 + df.FullBath *.25 + df.HalfBath * .5 + df.BsmtFullBath *.75 + df.BsmtHalfBath * 1\n #df['new_variable'] = df.BedroomAbvGr * .1 + df.FullBath *.25 + df.HalfBath * .5 + df.BsmtFullBath *.75 + df.BsmtHalfBath * .1\n df['new_variable'] = df.BedroomAbvGr.apply(lambda x: x if x > 0 else 1)\n #print(\"new_variable calculated\")\n #display.display(df[df.new_variable.isna()])\n \n if not revert:\n df['sales_per_new'] = df['SalePrice']/ df.new_variable\n #display.display(df[df.sales_per_new.isna()])\n y = np.array(df['sales_per_new'].apply( lambda x: math.log(x)))\n return y\n \n df['sales_per_new'] = df['SalePrice']* df.new_variable\n #print(\"sales_per_new calculated\")\n #display.display(df[df.sales_per_new.isna()])'''\n #return np.log( df_temp.SalePrice / df_temp.GrLivArea)\n return np.log(df_temp['SalePrice'])\n #return (df_temp['SalePrice'])\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def newBoxCoxTranformation(df_temp,target,testFile=False, log=False):\n df = df_temp.copy()\n #assuming that only numerical features are presented\n if log:\n print(\"Shape of the dataset initial : \", df.shape)\n \n if not testFile:\n df =df[df.SalePrice >0]\n if log:\n print(\"Shape of the dataset before transformation : \", df.shape)\n \n #display.display(df[df['SalePrice'].isna()])\n y = transformTarget(df)\n X= df.drop([target],axis = 1)\n #X=df.drop(target, axis=1)\n x_columns = list(X)\n #print(x_columns)\n #X = preprocessing.RobustScaler().fit_transform(X)\n #X = preprocessing.MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(1, 2)).fit_transform(X)\n #X_testx = preprocessing.MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(1, 2)).fit_transform(X,y)\n #X_testxx = preprocessing.MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(1, 2)).fit_transform(X,df.SalePrice)\n #print(np.unique(X == X_testx))\n #print(np.unique(X == X_testxx))\n #print(np.unique(X_testx == X_testxx))\n '''X = pd.DataFrame(X, columns=x_columns)\n \n for c in list(X):\n if True:\n #if len(X[c].unique()) in [1,2]:\n if log:\n print(\"Skipping Transformation for \", c, \"because unique values are :\",X[c].unique())\n else:\n if log:\n print(\"Boxcoxing : \", c)\n X[c] = stats.boxcox(X[c])[0]'''\n \n #X = preprocessing.MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(1, 2)).fit_transform(X)\n X = preprocessing.StandardScaler().fit_transform(X)\n #X = preprocessing.RobustScaler().fit_transform(X)\n #X = X.values\n if log:\n print(\"Shape of the dataset after transformation : \", X.shape, y.shape)\n return X,y\n else:\n df = df[df.SalePrice == 0.0]\n if log:\n print(\"Shape of the dataset before transformation : \", df.shape)\n X=df.drop(target,axis = 1)\n x_columns = list(X)\n #print(x_columns)\n #X = preprocessing.RobustScaler().fit_transform(X)\n #X = preprocessing.MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(1, 2)).fit_transform(X)\n \n '''X = pd.DataFrame(X, columns=x_columns)\n for c in list(X):\n if True:\n #if len(X[c].unique()) in [1,2]:\n if log:\n print(\"Skipping Transformation for \", c, \"because unique values are :\",X[c].unique())\n else:\n if log:\n print(\"Boxcoxing : \", c)\n X[c] = stats.boxcox(X[c])[0]'''\n \n \n #X = preprocessing.power_transform( X, method='box-cox')\n #X = preprocessing.MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(1, 2)).fit_transform(X)\n X = preprocessing.StandardScaler().fit_transform(X)\n #X = preprocessing.RobustScaler().fit_transform(X)\n #X = X.values\n if log:\n print(\"Shape of the dataset after transformation : \", X.shape)\n return X\n \n#df_fire_b = df_fire.copy()\n#df_fire_b['SalePrice'] = df_fire_b['SalePrice'] / df_fire_b.GrLivArea\ndf_out_removed = removeOutlier(df_fire.copy())\ndf_prep = preProcessData(df_out_removed.copy())\n#df_prep = preProcessData(df_fire.copy())\n#df_prep['SalePrice'] = df_prep['SalePrice'] / df_prep['OverallQual']\ndf_prep['SalePrice'] = df_prep['SalePrice'] / df_prep['GrLivArea']\nX = newBoxCoxTranformation(df_prep.copy(),'SalePrice',True,False) \nX,y = newBoxCoxTranformation(df_prep.copy(),'SalePrice',False,False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X,y, test_size=0.5, random_state=random.randint(1,500))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#reg = XGBRegressor(max_depth=4, n_estimators=200)\n'''reg = XGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.25,\n colsample_bytree=0.5, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=100,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.0, reg_lambda=0.0, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=1) #0.13073788936978095'''\n\n'''reg = XGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.5,\n colsample_bytree=0.75, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=800,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.5, reg_lambda=0.5, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5) #.144'''\n'''reg = XGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.5,\n colsample_bytree=0.75, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=5, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=100,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.35, reg_lambda=0.35, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=1)#0.13515'''\n'''reg = XGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.75,\n colsample_bytree=0.5, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=6, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=100,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.1, reg_lambda=0.6, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=1) #0.13495'''\n'''reg = XGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.25,\n colsample_bytree=0.75, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=5, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=100,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.1, reg_lambda=0.35, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5) #0.13486'''\n'''reg = XGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.75,\n colsample_bytree=0.5, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=300,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.25, reg_lambda=0.25, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5)'''\n'''reg = XGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.25,\n colsample_bytree=0.25, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=600,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.25, reg_lambda=0.25, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5) #0.13....'''\n'''reg = XGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.25,\n colsample_bytree=0.5, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=500,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.25, reg_lambda=0.25, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5) #0.131...'''\n'''reg = XGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.75,\n colsample_bytree=0.25, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=500,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.0, reg_lambda=0.5, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5) #0.126'''\n'''reg = XGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.5,\n colsample_bytree=0.75, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=4, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=300,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.0, reg_lambda=0.5, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5) #0.13...'''\n'''reg=XGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.25,\n colsample_bytree=0.5, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=500,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.25, reg_lambda=0.75, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5) #0.129'''\n'''reg = XGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.25,\n colsample_bytree=0.75, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=500,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.0, reg_lambda=0.5, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5) #0.127'''\n'''reg = XGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.5,\n colsample_bytree=0.5, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.05, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=500,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.5, reg_lambda=0.5, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5)#126xx'''\n'''reg = XGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.25,\n colsample_bytree=0.75, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=500,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.0, reg_lambda=0.5, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5)'''\n'''reg = XGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.75,\n colsample_bytree=0.25, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=600,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.25, reg_lambda=0.5, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5)'''\n\n'''reg = XGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.75,\n colsample_bytree=0.25, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=600,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.25, reg_lambda=0.5, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5) #damn 0.13...'''\n\n'''reg = XGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.5,\n colsample_bytree=0.5, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=500,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.5, reg_lambda=0.5, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5) #0.1622'''\n\n'''reg = XGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.75,\n colsample_bytree=0.25, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=600,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.0, reg_lambda=0.5, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5)'''\n\n'''reg = XGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.5,\n colsample_bytree=0.75, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=400,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.25, reg_lambda=0.5, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5)#0.14'''\n'''reg = XGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.75,\n colsample_bytree=0.25, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=600,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.0, reg_lambda=0.5, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5)'''\nreg = XGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.5,\n colsample_bytree=0.5, gamma=0.05, learning_rate=0.05,\n max_delta_step=0, max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None,\n n_estimators=3000, n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear',\n random_state=0, reg_alpha=0.5, reg_lambda=0.5, scale_pos_weight=1,\n seed=None, silent=True, subsample=0.5)\n\n'''reg=XGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.75,\n colsample_bytree=0.25, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=500,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.0, reg_lambda=0.25, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5)# 0.126'''\nreg.fit(X_train,y_train)\nreg.score(X_test,y_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#np.sqrt(mean_squared_log_error((y_test), (reg.predict(X_test))))\nnp.sqrt(mean_squared_log_error(np.exp(y_test), np.exp(reg.predict(X_test))))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"reg",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def dummyCrossValidation(loop_count):\n for i in range(loop_count):\n X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X,y, test_size=0.5, random_state=random.randint(1,500))\n #reg = XGBRegressor(max_depth=3, n_estimators=100, reg_alpha=.5, reg_lambda=.5)\n reg.fit(X_train,y_train)\n \n print(\"R2 Score: \", reg.score(X_test,y_test))\n #print(\"RMSLE Score : \", np.sqrt(mean_squared_log_error((y_test), (reg.predict(X_test)))))\n print(\"RMSLE Score : \", np.sqrt(mean_squared_log_error(np.exp(y_test), np.exp(reg.predict(X_test)))))\ndummyCrossValidation(10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"reg.fit(X,y)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def checkTheTrainFile(reg,df_prep):\n df_train = pd.read_csv(train_File)\n #df_tra['SalePrice'] = 0.0\n \n #df_train = pd.read_csv(train_File)\n #df_concat = pd.concat([df_train,df_test])\n\n #print(df_test[df_test.TotalBsmtSF.isna()])\n #return\n #df = giveMeWrangledData(df_concat,True)\n \n #print(df.info())\n #df = preProcessData(df)\n #print(df.info())\n #dt = df_prep.copy()\n \n #df_prep = preProcessData(df_fire.copy())\n #dt = dt[dt.SalePrice > 0]\n df_prep1 = df_prep.copy()\n df_prep1 = df_prep1[df_prep1['SalePrice'] > 0]\n df_prep1['New_SalePrice'] = 0.0\n \n df_prep = df_prep[df_prep['SalePrice'] > 0]\n df_prep['SalePrice'] = 0\n \n X = newBoxCoxTranformation(df_prep.copy(),'SalePrice',True)\n #print(np.sqrt(mean_squared_log_error(y, reg.predict(X))))\n \n df_prep1['New_SalePrice'] = list(np.exp(reg.predict(X)))\n #df_prep1['New_SalePrice'] = reg.predict(X)\n df_prep1['New_SalePrice'] = df_prep1['New_SalePrice'] * df_prep1.GrLivArea\n df_prep1['SalePrice'] = df_prep1['SalePrice'] * df_prep1.GrLivArea\n \n #df_prep1['New_SalePrice'] = df_prep1['New_SalePrice'] * df_prep1.OverallQual\n #df_prep1['SalePrice'] = df_prep1['SalePrice'] * df_prep1.OverallQual\n \n df_train_score = df_prep1[df_prep1.SalePrice > 0]\n \n print(np.sqrt(mean_squared_log_error(df_train_score['SalePrice'], df_train_score['New_SalePrice'])))\n \n #return df_test, X, reg.predict(X)\n#df_test, X_dummy, y_dummy= checkTheTestFile(reg)\ncheckTheTrainFile(reg,df_prep.copy())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def checkTheTestFile(reg):\n df_test = pd.read_csv(test_File)\n df_test['SalePrice'] = 0.0\n print(df_test.shape)\n \n #df_train = pd.read_csv(train_File)\n #df_concat = pd.concat([df_train,df_test])\n\n #print(df_test[df_test.TotalBsmtSF.isna()])\n #return\n #df = giveMeWrangledData(df_concat,True)\n \n #print(df.info())\n #df = preProcessData(df)\n #print(df.info())\n X = newBoxCoxTranformation(df_prep.copy(),'SalePrice',True)\n #print(np.sqrt(mean_squared_log_error(y, reg.predict(X))))\n #df_test['SalePrice'] = (reg.predict(X))\n df_test['SalePrice'] = np.exp(reg.predict(X)) \n df_test['SalePrice'] = df_test['SalePrice'] * df_test.GrLivArea\n #df_test['SalePrice'] = df_test['SalePrice'] * df_test.OverallQual\n \n return df_test, X, reg.predict(X)\ndf_test, X_dummy, y_dummy= checkTheTestFile(reg)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_test[['Id','SalePrice']].to_csv('smubmission.csv',index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_test[['Id','SalePrice']]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def forCrossValidationStratifiedShuffleSplit(df):\n sss = StratifiedShuffleSplit(n_splits=10, test_size=.5, random_state=1986)\n #print(\"Number of Splits configured :\", sss.get_n_splits(df, df.BldgType))\n \n for train_index, test_index in sss.split(df, df.BldgType):\n yield train_index, test_index\n \n for train_index, test_index in sss.split(df, df.OverallQual):\n yield train_index, test_index",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_train = pd.read_csv(train_File)\ndef crossValidationScoring(reg,X,y):\n return -np.sqrt(mean_squared_log_error(np.exp(y), \n np.exp(reg.predict(X))\n ))\n #return np.sqrt(mean_squared_log_error(np.exp(y), \n # np.exp(reg.predict(X\n # ))\n # ))\n\n #return np.sqrt(mean_squared_log_error((y), \n # (reg.predict(X))\n # ))\nmean_temp_rmsle = np.mean(cross_val_score(reg,X,y,cv= 5,scoring='neg_mean_squared_log_error'))\nprint(\"RMSE with without target variable transformation : \", np.sqrt(mean_temp_rmsle * -1))\n\nmean_temp_rmsle = np.mean(cross_val_score(reg, X, y,\n cv= 5,\n scoring=crossValidationScoring))\nprint(\"RMSE with post target variable transformation : \", mean_temp_rmsle)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV\ndef gridSearchCVImp():\n start_time =datetime.datetime.now()\n #reg = XGBRegressor(n_jobs =2, reg_alpha=.5, reg_lambda=.5, subsample=.5)\n reg = XGBRegressor(n_jobs =2,subsample=.5, learning_rate=0.05)\n \n parameters = {\n 'max_depth':list(range(3,4)),\n 'colsample_bylevel' : np.arange(0.25, 1.0, 0.25),\n 'n_estimators' : list(range(200,600,100)),\n 'colsample_bytree' : np.arange(0.25, 1.0, 0.25),\n 'reg_alpha': np.arange(0.0, 1.0, 0.25),\n 'reg_lambda': np.arange(0.25, 1.0, 0.25)\n }\n cv= ShuffleSplit(n_splits=5, test_size=.05, random_state=1986)\n reg_grid = GridSearchCV(reg, parameters, \n #cv=forCrossValidationStratifiedShuffleSplit(df_train),\n cv=cv,\n n_jobs = 2,\n #scoring = 'neg_median_absolute_error',\n #scoring = 'neg_mean_absolute_error',\n #scoring = 'neg_mean_squared_log_error',\n scoring = crossValidationScoring,\n verbose=1,\n #error_score ='raise'\n error_score =5\n #pre_dispatch = 2\n )\n reg_grid.fit(X,y)\n \n print(\"Total time for the gridserach\", datetime.datetime.now() - start_time)\n \n return reg_grid\nreg_grid = gridSearchCVImp()\nprint(reg_grid.best_estimator_)\nprint(reg_grid.best_score_)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(np.sqrt(reg_grid.best_score_ * -1))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"This statement is written just to keep the kaggle kernel up during the gridsearch.This again to keep the session live.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Conservative GridSearch : testsize : .5, scoring: r2\n\nTotal time for the gridserach 0:54:19.899125\n\nXGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.25,\n colsample_bytree=0.5, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=500,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.25, reg_lambda=0.25, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5)\n \n0.9153911325136409",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Conservative GridSearch : testsize : .5, scoring: neg_msle\n\nTotal time for the gridserach 0:55:00.412282\n\nXGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.25,\n colsample_bytree=0.5, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=500,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.25, reg_lambda=0.25, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5)\n \n-7.906906622834065e-05",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Conservative GridSearch : testsize : .5, scoring: negative RMSLE\n\nTotal time for the gridserach 0:50:49.492892\n\nXGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.25,\n colsample_bytree=0.5, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=500,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.25, reg_lambda=0.25, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5)\n \n-0.11425853874531103 ==> Kaggle Score gave 0.131.....",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Optimistic GridSearch: testsize: .1 scoring: negative RMSLE\n\nTotal time for the gridserach 1:34:16.138500\n\nXGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.75,\n colsample_bytree=0.25, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=500,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.0, reg_lambda=0.5, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5)\n \n-0.1135887234582907",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Optimistic GridSearch testsize : .1 , scoring: negative RMSLE, target transformation : per OverallQual\n\nTotal time for the gridserach 1:05:27.602182\n\nXGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.5,\n colsample_bytree=0.75, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=4, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=300,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.0, reg_lambda=0.5, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5)\n \n-0.12313052538188561",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Optimistic GridSearch testsize : .1 , scoring: negative RMSLE, target transformation : per GrLivArea\n\nTotal time for the gridserach 0:52:42.390855\n\nXGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.25,\n colsample_bytree=0.5, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=500,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.25, reg_lambda=0.75, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5)\n \n-0.11300130870279539\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Conservative Grid Search, testsize : .5, negative RMSLE, target transformation: per GrLivArea\n\nTotal time for the gridserach 0:30:47.246428\n\nXGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.25,\n colsample_bytree=0.75, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=500,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.0, reg_lambda=0.5, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5)\n \n-0.1140592041230081",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Conservative Grid Search, testsize : .5, negative RMSLE, target transformation: per GrLivArea\nWith all variables to boxcox \n\nTotal time for the gridserach 0:18:57.023773\n\nXGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.25,\n colsample_bytree=0.75, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=500,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.0, reg_lambda=0.5, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5)\n \n-0.11473189632093529",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Conservative Grid Search, testsize : .5, negative RMSLE, target transformation: per GrLivArea\nWith all variables to boxcox \nWith 300 - 900 estimator\n\nTotal time for the gridserach 0:20:53.198464\n\nXGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.25,\n colsample_bytree=0.75, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=500,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.0, reg_lambda=0.5, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5)\n \n-0.11473189632093529",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Conservative Grid Search, testsize : .5, negative RMSLE, target transformation: per GrLivArea\nWith all variables to boxcox and with minmax scaling instead to standard scaling\n\nTotal time for the gridserach 0:12:38.560831\n\nXGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.75,\n colsample_bytree=0.25, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=600,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.25, reg_lambda=0.5, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5)\n \n-0.11470853780134761",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Conservative Grid Search, testsize : .5, negative RMSLE, target transformation: per GrLivArea\nWith all variables to boxcox and with no scaling post box cox\n\nTotal time for the gridserach 0:09:23.388481\n\nXGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.75,\n colsample_bytree=0.25, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=600,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.25, reg_lambda=0.5, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5)\n \n-0.11470853780134761",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Optimistic Grid Search, testsize : .05, negative RMSLE, target transformation: per GrLivArea\nWith all variables to boxcox and with no scaling post box cox\n\nTotal time for the gridserach 0:31:17.912847\n \nXGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.5,\n colsample_bytree=0.5, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=500,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.5, reg_lambda=0.5, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5)\n\n-0.1032861306860222",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Conservative Grid Search, testsize : .5, negative RMSLE, target transformation: per GrLivArea\nWith all variables to boxcox and with no scaling post box cox & 2 more ordinal variables converted to number.\n\nTotal time for the gridserach 0:16:43.250894\n\nXGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.75,\n colsample_bytree=0.25, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=600,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.0, reg_lambda=0.5, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5)\n \n-0.11436784398304499",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Conservative Grid Search, testsize : .5, negative RMSLE, target transformation: per GrLivArea\nWith all variables to boxcox and with no scaling post box cox & 2 more ordinal variables converted to number.\nand robust scaling before boxcox\n\nTotal time for the gridserach 0:12:00.972793\n\nXGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.75,\n colsample_bytree=0.25, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=600,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.0, reg_lambda=0.5, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5)\n \n-0.11436784398304499\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"How robust is robustscaler ?\n\nTotal time for the gridserach 0:12:36.182610\n\nXGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.5,\n colsample_bytree=0.75, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=400,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.25, reg_lambda=0.5, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5)\n \n-0.12788816069618766",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"How much does the standard scaler help post boxcox\n\nTotal time for the gridserach 0:11:45.913461\n\nXGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.75,\n colsample_bytree=0.25, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=600,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.0, reg_lambda=0.5, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5)\n \n-0.11468293397638228",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Robustscaler went transperant with standard scaler post box cox\n\nTotal time for the gridserach 0:11:52.590051\n\nXGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.75,\n colsample_bytree=0.25, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=600,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.0, reg_lambda=0.5, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5)\n \n-0.11468293397638228",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Optimistic grid search for estimator between 500- 800 with standard scaler post boxcox\n\nTotal time for the gridserach 0:20:25.400043\n\nXGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.75,\n colsample_bytree=0.25, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=500,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.0, reg_lambda=0.25, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5)\n \n-0.1028989248977331 #0.12646",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Optimistic grid search for estimator between 200- 600 with standard scaler post boxcox\nTotal time for the gridserach 0:16:03.879108\n\nXGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.75,\n colsample_bytree=0.25, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=500,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.0, reg_lambda=0.25, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5)\n \n-0.1028989248977331",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"1. OverallQual target transformation\n2. GrLivArea target transformation\n3. Less number of outliers removal\n4. Imputing based on high co related variables.\n5. boxcox for the dataset\n6. min max post boxcox\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Next Steps to follow are :\n1. optimistic grid search with standard scaling post box cox - This would be with the anticipation of the best score which we got post first round of ordinal numerical variation. Expectation is that since standard scaling is done optimistic search i.e. testcase = 0.05 will be equivalent to testing with the full training set and the value should be equivalent to kaggle score.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"With no boxcox but standard scaler:\n\nTotal time for the gridserach 0:16:46.997090\n\nXGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.75,\n colsample_bytree=0.25, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=500,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.0, reg_lambda=0.25, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5)\n \n-0.1028989248977331 #kaggle score : 0.12646",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"no box cox but with robust scaler\n\nTotal time for the gridserach 0:16:41.065970\n\nXGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.75,\n colsample_bytree=0.25, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=500,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.0, reg_lambda=0.25, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5)\n \n-0.10308985379081549 # 0.12759",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"no box cox but robust scaler conservative search\n\nTotal time for the gridserach 0:09:37.766766\n\nXGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.25,\n colsample_bytree=0.25, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=500,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.0, reg_lambda=0.25, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5)\n -0.11388498877762311 #0.13298",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"no box cox and min max\n\nTotal time for the gridserach 0:16:47.306173\nXGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.75,\n colsample_bytree=0.25, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0,\n max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=500,\n n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0,\n reg_alpha=0.0, reg_lambda=0.25, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,\n silent=True, subsample=0.5)\n-0.1028989248977331\n\nwith learning rate 0.05\n\nTotal time for the gridserach 0:16:47.242496\n\nXGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=0.25,\n colsample_bytree=0.75, gamma=0, learning_rate=0.05,\n max_delta_step=0, max_depth=3, min_child_weight=1, missing=None,\n n_estimators=500, n_jobs=2, nthread=None, objective='reg:linear',\n random_state=0, reg_alpha=0.0, reg_lambda=0.75, scale_pos_weight=1,\n seed=None, silent=True, subsample=0.5)\n \n-0.10392091407197643",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#1 https://www.kaggle.com/zenstat/simple-linear-regression-example SaleCondition condition mapping to ordinal values as 0/1 after comparing the relation with target variable.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"https://www.kaggle.com/jatinmittal0001/housing-price-prediction - talks about the ensembling the elastic_net and lasso with 30:70 ratio.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Found an interesting kernel on easy implementation of stacking approach: https://www.kaggle.com/aiden98/house-prices-error-0-11433",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Found an interesting article on model selection: http://blog.minitab.com/blog/how-to-choose-the-best-regression-model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4a30b5256cc4c1e824495445bfb0a4c2a8500e6f
| 19,603 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
tema1/spaces.ipynb
|
jmiguelespino/ia-course
|
7a6904385aaad8575baf8e2a41b76f55c690115d
|
[
"MIT"
] | 112 |
2018-11-19T17:23:40.000Z
|
2022-03-29T05:36:14.000Z
|
tema1/spaces.ipynb
|
jmiguelespino/ia-course
|
7a6904385aaad8575baf8e2a41b76f55c690115d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
tema1/spaces.ipynb
|
jmiguelespino/ia-course
|
7a6904385aaad8575baf8e2a41b76f55c690115d
|
[
"MIT"
] | 187 |
2018-11-28T11:38:02.000Z
|
2022-03-16T11:18:39.000Z
| 38.894841 | 1,696 | 0.533082 |
[
[
[
"# Clonamos el repositorio para obtener los dataSet\n\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!git clone https://github.com/joanby/ia-course.git",
"Cloning into 'ia-course'...\nremote: Enumerating objects: 375, done.\u001b[K\nremote: Total 375 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 375\u001b[K\nReceiving objects: 100% (375/375), 32.53 MiB | 17.19 MiB/s, done.\nResolving deltas: 100% (67/67), done.\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Damos acceso a nuestro Drive",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from google.colab import drive\ndrive.mount('/content/drive')",
"Go to this URL in a browser: https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/auth?client_id=947318989803-6bn6qk8qdgf4n4g3pfee6491hc0brc4i.apps.googleusercontent.com&redirect_uri=urn%3aietf%3awg%3aoauth%3a2.0%3aoob&scope=email%20https%3a%2f%2fwww.googleapis.com%2fauth%2fdocs.test%20https%3a%2f%2fwww.googleapis.com%2fauth%2fdrive%20https%3a%2f%2fwww.googleapis.com%2fauth%2fdrive.photos.readonly%20https%3a%2f%2fwww.googleapis.com%2fauth%2fpeopleapi.readonly&response_type=code\n\nEnter your authorization code:\n··········\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Test it",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!ls '/content/drive/My Drive' ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#Google colab tools",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from google.colab import files # Para manejar los archivos y, por ejemplo, exportar a su navegador\nimport glob # Para manejar los archivos y, por ejemplo, exportar a su navegador\nfrom google.colab import drive # Montar tu Google drive",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Instalar dependencias de Renderizado, tarda alrededor de 45 segundos\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!apt-get update > /dev/null 2>&1\n!apt-get install python-opengl -y > /dev/null 2>&1\n!apt install xvfb -y --fix-missing > /dev/null 2>&1\n!apt-get install ffmpeg > /dev/null 2>&1\n!apt-get install x11-utils > /dev/null 2>&1\n!apt-get install pyglet > /dev/null 2>&1\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Instalar OpenAi Gym",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!pip install gym pyvirtualdisplay > /dev/null 2>&1\n!pip install piglet > /dev/null 2>&1\n!pip install 'gym[box2d]' > /dev/null 2>&1\n#por si quieres algun environment en concreto\n#!pip install atari_py > /dev/null 2>&1\n#!pip install gym[atari] > /dev/null 2>&1",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Todos los imports necesarios en google colab y helpers para poder visualizar OpenAi",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import gym\nfrom gym import logger as gymlogger\nfrom gym.wrappers import Monitor\ngymlogger.set_level(40) #error only\nimport numpy as np\nimport random\nimport matplotlib\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n%matplotlib inline\nimport math\nimport glob\nimport io\nimport base64\nfrom IPython.display import HTML\n\nfrom IPython import display as ipythondisplay",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Activamos una vista, seria como crear un plot de una grafica en python",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from pyvirtualdisplay import Display\ndisplay = Display(visible=0, size=(1400, 900)) #Puedes modificar el high and width de la pantalla\ndisplay.start()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Este código crea una pantalla virtual para dibujar imágenes del juego. \n## Si se ejecuta localmente, simplemente ignóralo",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import os\nif type(os.environ.get('DISPLAY')) is not str or \\\n len(os.environ.get('DISPLAY')) == 0:\n !bash ../xvfb start\n %env DISPLAY=:1",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Funciones de utilidad para permitir la grabación de video del ambiente del gimnasio y su visualización\n## Para habilitar la visualizacion por pantalla , tan solo haz \"**environment = wrap_env(environment)**\", por ejemplo: **environment = wrap_env(gym.make(\"MountainCar-v0\"))**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import io\nimport glob\nimport base64\nfrom IPython.display import HTML\nfrom IPython import display as ipythondisplay\n\ndef show_video():\n mp4list = glob.glob('video/*.mp4')\n if len(mp4list) > 0:\n mp4 = mp4list[0]\n video = io.open(mp4, 'r+b').read()\n encoded = base64.b64encode(video)\n\n content = ipythondisplay.display(HTML(data='''\n <video alt=\"test\" autoplay loop controls style=\"height: 400px;\">\n <source src=\"data:video/mp4;base64,{0}\" type=\"video/mp4\" />\n </video>\n '''.format(encoded.decode('ascii'))))\n else: \n print(\"Couldn't find video\")\n\ndef wrap_env(env):\n env = gym.wrappers.Monitor(env, './video', force=True)\n return env",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Nuestro Script",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"environment = wrap_env(gym.make(\"Qbert-v0\"))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from gym.spaces import *\nimport sys",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Box -> R^n (x1,x2,x3,...,xn), xi [low, high]\n#gym.spaces.Box(low = -10, high = 10, shape = (2,)) # (x,y), -10<x,y<10\n\n# Discrete -> Números enteros entre 0 y n-1, {0,1,2,3,...,n-1}\n#gym.spaces.Discrete(5) # {0,1,2,3,4}\n\n#Dict -> Diccionario de espacios más complejos\n#gym.spaces.Dict({\n# \"position\": gym.spaces.Discrete(3), #{0,1,2}\n# \"velocity\": gym.spaces.Discrete(2) #{0,1}\n# })\n\n\n# Multi Binary -> {T,F}^n (x1,x2,x3,...xn), xi {T,F}\n# gym.spaces.MultiBinary(3)# (x,y,z), x,y,z = T|F\n\n# Multi Discreto -> {a,a+1,a+2..., b}^m\n#gym.spaces.MultiDiscrete([-10,10],[0,1])\n\n# Tuple -> Producto de espacios simples\n#gym.spaces.Tuple((gym.spaces.Discrete(3), gym.spaces.Discrete(2)))#{0,1,2}x{0,1}\n\n# prng -> Random Seed\n\n\ndef print_spaces(space):\n print(space)\n if isinstance(space, Box):#Comprueba si el space subministrado es de tipo Box\n print(\"\\n Cota inferior: \", space.low)\n print(\"\\n Cota superior: \", space.high)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# main",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sys.argv=['self.py','CartPole-v0'] #Aqui Cambia el nombre para ver el environment\nif __name__ == \"__main__\":\n environment = gym.make(sys.argv[1]) ## El usuario debe llamar al script con el nombre del entorno como parámetro\n print(\"Espacio de estados:\")\n print_spaces(environment.observation_space)\n print(\"Espacio de acciones: \")\n print_spaces(environment.action_space)\n try:\n print(\"Descripción de las acciones: \", environment.unwrapped.get_action_meanings())\n except AttributeError:\n pass",
"Espacio de estados:\nBox(4,)\n\n Cota inferior: [-4.8000002e+00 -3.4028235e+38 -4.1887903e-01 -3.4028235e+38]\n\n Cota superior: [4.8000002e+00 3.4028235e+38 4.1887903e-01 3.4028235e+38]\nEspacio de acciones: \nDiscrete(2)\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a30c47f79d0e60e6bb1413942d34e235d0b022b
| 245,310 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Py_Finance_01.ipynb
|
revendrat/FinancialMathematics
|
8d95d0425e7c56ffe162bb2ae3051229a6f3a59a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Py_Finance_01.ipynb
|
revendrat/FinancialMathematics
|
8d95d0425e7c56ffe162bb2ae3051229a6f3a59a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Py_Finance_01.ipynb
|
revendrat/FinancialMathematics
|
8d95d0425e7c56ffe162bb2ae3051229a6f3a59a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 51.138211 | 37,593 | 0.448836 |
[
[
[
"<a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/revendrat/FinancialMathematics/blob/main/Py_Finance_01.ipynb\" target=\"_parent\"><img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open In Colab\"/></a>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#install yahoo finance\n%pip install yfinance",
"Collecting yfinance\n Downloading yfinance-0.1.70-py2.py3-none-any.whl (26 kB)\nRequirement already satisfied: numpy>=1.15 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from yfinance) (1.21.5)\nRequirement already satisfied: multitasking>=0.0.7 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from yfinance) (0.0.10)\nRequirement already satisfied: pandas>=0.24.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from yfinance) (1.3.5)\nCollecting lxml>=4.5.1\n Downloading lxml-4.8.0-cp37-cp37m-manylinux_2_17_x86_64.manylinux2014_x86_64.manylinux_2_24_x86_64.whl (6.4 MB)\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 6.4 MB 1.3 MB/s \n\u001b[?25hCollecting requests>=2.26\n Downloading requests-2.27.1-py2.py3-none-any.whl (63 kB)\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 63 kB 1.8 MB/s \n\u001b[?25hRequirement already satisfied: python-dateutil>=2.7.3 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from pandas>=0.24.0->yfinance) (2.8.2)\nRequirement already satisfied: pytz>=2017.3 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from pandas>=0.24.0->yfinance) (2018.9)\nRequirement already satisfied: six>=1.5 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from python-dateutil>=2.7.3->pandas>=0.24.0->yfinance) (1.15.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: idna<4,>=2.5 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from requests>=2.26->yfinance) (2.10)\nRequirement already satisfied: urllib3<1.27,>=1.21.1 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from requests>=2.26->yfinance) (1.24.3)\nRequirement already satisfied: certifi>=2017.4.17 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from requests>=2.26->yfinance) (2021.10.8)\nRequirement already satisfied: charset-normalizer~=2.0.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages (from requests>=2.26->yfinance) (2.0.12)\nInstalling collected packages: requests, lxml, yfinance\n Attempting uninstall: requests\n Found existing installation: requests 2.23.0\n Uninstalling requests-2.23.0:\n Successfully uninstalled requests-2.23.0\n Attempting uninstall: lxml\n Found existing installation: lxml 4.2.6\n Uninstalling lxml-4.2.6:\n Successfully uninstalled lxml-4.2.6\n\u001b[31mERROR: pip's dependency resolver does not currently take into account all the packages that are installed. This behaviour is the source of the following dependency conflicts.\ngoogle-colab 1.0.0 requires requests~=2.23.0, but you have requests 2.27.1 which is incompatible.\ndatascience 0.10.6 requires folium==0.2.1, but you have folium 0.8.3 which is incompatible.\u001b[0m\nSuccessfully installed lxml-4.8.0 requests-2.27.1 yfinance-0.1.70\n"
],
[
"# import packages & modules\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport yfinance as yf\nfrom pylab import mpl, plt",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# suppress scientific notation\npd.options.display.float_format = '{:.5f}'.format",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.style.use('seaborn')\nmpl.rcParams['font.family'] = 'serif'\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Analyse Infosys stock\n#define the ticker symbol\ntickerSymbol = 'INFY.NS'\n\n#get data on this ticker\ntickerData = yf.Ticker(tickerSymbol)\n\n#get the historical prices for this ticker\ninfy = tickerData.history(period='1d', start='2017-1-1', end='2022-4-3')\n\n#see your data\ninfy.info()",
"<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>\nDatetimeIndex: 1298 entries, 2017-01-02 to 2022-04-01\nData columns (total 7 columns):\n # Column Non-Null Count Dtype \n--- ------ -------------- ----- \n 0 Open 1298 non-null float64\n 1 High 1298 non-null float64\n 2 Low 1298 non-null float64\n 3 Close 1298 non-null float64\n 4 Volume 1298 non-null int64 \n 5 Dividends 1298 non-null float64\n 6 Stock Splits 1298 non-null float64\ndtypes: float64(6), int64(1)\nmemory usage: 81.1 KB\n"
],
[
"# verify the top 5 records\ninfy.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# verify the bottom 5 records\n\ninfy.tail()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#pandas.Dataframe.shift(# lags)\n#Using shift(1), we can get the row just above the present row. Here, # lags is 1.\n#log() is a function given in numpy package in python. It calculates the natural log of the value given inside it.\ninfy['LogReturn'] = np.log(infy['Close']/infy['Close'].shift(1))\n\n#print() function prints the value inside it on the console.\ninfy['LogReturn'].head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"infy['LogReturn'].head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sma_180=180\ninfy['sma_180'] = infy['LogReturn'].rolling(sma_180).sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# plot the sma_180 against time\ninfy['sma_180'].plot(figsize=(10,6))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"infy.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"infy.tail()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"infy.iloc[1]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Verify random values of LogReturn and sma_180\ninfy[['LogReturn', 'sma_180']].iloc[175:185]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Build the strategy \n# Create the 'position' column that has strategy based on sum of last 180 days log returns with following criteria\n# sma_180 >0 is Buy, < 0 is Sell & Na is No Position for trade\ninfy['position'] = np.where(infy['sma_180'].isna(), 'No Position', np.where(infy['sma_180'] > 0, 'Buy', 'Sell'))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# likewise create a column 'position indicator' that stores numeric values of strategy as mentioned below\n# 1 is buy, -1 is sell & 0 is no position indicator\ninfy['position_indicator'] = np.where(infy['sma_180'].isna(), 0, np.where(infy['sma_180'] > 0, 1, -1))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Verify random values of LogReturn, sma_180, position and position_indicator\ninfy[['LogReturn', 'sma_180', 'position', 'position_indicator']].iloc[175:185]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"infy['position'] = np.where(infy['sma_180'] >0, 'Buy', 'Sell')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"infy[['LogReturn', 'sma_180', 'position']].iloc[175:185]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"infy.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"infy.tail()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"infy['position_indicator'] = np.where(infy['sma_180'] >0, 1, -1)\ninfy[['LogReturn', 'sma_180', 'position', 'position_indicator']].iloc[175:185]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# rebalance every month\n# send the data frame and date to rebalance\n# if the position_indicator is negative (sum of 180 days log returns is negative) then change the strategy to sell.\n# Otherwise, remain with past strategy\n# Record the past and current strategy and return details on a rebalanced_strategy dataframeac\ndef rebalance(data, date):\n rebalanced_strategy = pd.DataFrame({'review_date':[], 'previous_position':[], 'rebalanced_position':[]})\n #df = pd.DataFrame(data)\n date = pd.to_datetime(date)\n temp_vals = data.loc[date]\n temp_rebalance = 'Buy'\n if (temp_vals['position_indicator'] < 1):\n temp_rebalance = 'Sell'\n print(\" temp_rebalance \", temp_rebalance)\n temp_df = pd.DataFrame({'review_date':[date], 'previous_position':[temp_vals['position']], 'rebalanced_position':[temp_rebalance]})\n\n rebalanced_strategy = rebalanced_strategy.append(temp_df)\n print(\" rebalanced_strategy \", rebalanced_strategy)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# test the rebalance strategy\nrebalance(infy[['position', 'position_indicator']], '2017-09-27')",
" temp_rebalance Sell\n rebalanced_strategy review_date previous_position rebalanced_position\n0 2017-09-27 Sell Sell\n"
],
[
"rebalance(infy[['position', 'position_indicator']], '2022-03-28')",
" rebalanced_strategy review_date previous_position rebalanced_position\n0 2022-03-28 Buy Buy\n"
],
[
"# Comparing the results with buy & hold strategy of Infosys NSE\n# Multiplies the position_indicator values with previous da log returns of Infosys NSE stock to avoid foresight bias\n# Foresight bias implies that trade is placed given today's data, and returns are made on tomorrow\ninfy['strategy_sma180'] = infy['position_indicator'].shift(1)*infy['LogReturn']\n\n# round the decimal to fourth place and verify the first 5 values\ninfy.round(4).head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\ninfy.round(4).head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Fetch the returns of buy & hold strategy and 180 days sum of log returns strategy\ninfy[['LogReturn', 'strategy_sma180']].sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Use anti-log(e) to get the returns value\nnp.exp(infy[['LogReturn', 'strategy_sma180']].sum())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Optimising the look back period with multiple iterations of past values of log returns\n\n# import product module from itertools\nfrom itertools import product\n# select the random values for finding optimal values\nsma1 = range(20, 61, 4)\nsma2 = range(180, 201, 10)\n# create results data frame\nresults = pd.DataFrame()\n\n# write a for loop for different values of look back periods \nfor SMA1, SMA2 in product(sma1, sma2):\n # create a temporary data frame\n data_opt = pd.DataFrame()\n # Drop all Nan & NaT values\n data_opt.dropna(inplace=True)\n # pass log returns of Infosys NSE to data_opt dataframe\n data_opt['Returns'] = infy['LogReturn'] \n # Create log returns of Infosys NSE to data_opt dataframe\n data_opt['SMA1'] = data_opt['Returns'].rolling(SMA1).sum()\n data_opt['SMA2'] = data_opt['Returns'].rolling(SMA2).sum()\n # Drop all Nan & NaT values\n data_opt.dropna(inplace=True)\n # if sma1 look back period's sum of log returns is greater than sma2 look back period's sum of log returns, then buy, otherwise sell\n data_opt['Position'] = np.where(data_opt['SMA1'] > data_opt['SMA2'], 1, -1)\n # Drop all Nan & NaT values\n data_opt.dropna(inplace=True)\n # calculate the returns of strategy based sma1 greater than sma2 (foresight bias method)\n data_opt['Strategy'] = data_opt['Position'].shift(1) * data_opt['Returns']\n # Drop all Nan & NaT values\n data_opt.dropna(inplace=True)\n\n # calculate the performance of strategy\n perf = np.exp(data_opt[['Returns', 'Strategy']].sum())\n\n # create a dataframe with values of sma1, sma2 (look back periods, returns and strategy values)\n results = results.append(pd.DataFrame(\n {'SMA1': SMA1, 'SMA2': SMA2,\n 'MARKET': perf['Returns'],\n 'STRATEGY': perf['Strategy'],\n 'OUT': perf['Strategy'] - perf['Returns']},\n index=[0]), ignore_index=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Optimising the look back period with multiple iterations of past values of log returns\n\n# import product module from itertools\nfrom itertools import product\n# select the random values for finding optimal values\nsma1 = range(20, 61, 4)\n#sma2 = range(180, 201, 10)\n# create results data frame\nresults = pd.DataFrame()\n\n# write a for loop for different values of look back periods \nfor SMA1, SMA2 in product(sma1, sma2):\n # create a temporary data frame\n data_opt = pd.DataFrame()\n # Drop all Nan & NaT values\n data_opt.dropna(inplace=True)\n # pass log returns of Infosys NSE to data_opt dataframe\n data_opt['Returns'] = infy['LogReturn'] \n # Create log returns of Infosys NSE to data_opt dataframe\n data_opt['SMA1'] = data_opt['Returns'].rolling(SMA1).sum()\n #data_opt['SMA2'] = data_opt['Returns'].rolling(SMA2).sum()\n # Drop all Nan & NaT values\n data_opt.dropna(inplace=True)\n # if sma1 look back period's sum of log returns is greater than 0 then buy, otherwise sell\n data_opt['Position'] = np.where(data_opt['SMA1'] >0, 1, -1)\n # Drop all Nan & NaT values\n data_opt.dropna(inplace=True)\n # calculate the returns of strategy based sma1 greater than sma2 (foresight bias method)\n data_opt['Strategy'] = data_opt['Position'].shift(1) * data_opt['Returns']\n # Drop all Nan & NaT values\n data_opt.dropna(inplace=True)\n\n # calculate the performance of strategy\n perf = np.exp(data_opt[['Returns', 'Strategy']].sum())\n\n # create a dataframe with values of sma1, sma2 (look back periods, returns and strategy values)\n results = results.append(pd.DataFrame(\n {'SMA1': SMA1, \n 'MARKET': perf['Returns'],\n 'STRATEGY': perf['Strategy'],\n 'OUT': perf['Strategy'] - perf['Returns']},\n index=[0]), ignore_index=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"results.info()",
"<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>\nRangeIndex: 33 entries, 0 to 32\nData columns (total 4 columns):\n # Column Non-Null Count Dtype \n--- ------ -------------- ----- \n 0 SMA1 33 non-null int64 \n 1 MARKET 33 non-null float64\n 2 STRATEGY 33 non-null float64\n 3 OUT 33 non-null float64\ndtypes: float64(3), int64(1)\nmemory usage: 1.2 KB\n"
],
[
"results.sort_values('OUT', ascending=False).head(7)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"results.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"results.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"results",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data_opt.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data_opt.tail()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
" data_opt['Position'].shift(1) * data_opt['Returns']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"results.sort_values('OUT', ascending=True).head(7)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a30caddf4f7d91a917526c9c82f4e2b471a2b15
| 71,728 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Chunking.ipynb
|
VaradrajPoojari/NLP_Chunking
|
d1663d8cbdf5b2b551152f5d6f21c4f5b7850456
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Chunking.ipynb
|
VaradrajPoojari/NLP_Chunking
|
d1663d8cbdf5b2b551152f5d6f21c4f5b7850456
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Chunking.ipynb
|
VaradrajPoojari/NLP_Chunking
|
d1663d8cbdf5b2b551152f5d6f21c4f5b7850456
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 26.945154 | 404 | 0.419613 |
[
[
[
"## Objectives",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"- Identify noun phrase chunks using POS tags\n- Extract information from noun phrases in the Penn Treebank",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Dowloading Lexicons",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import nltk\nnltk.download(\"punkt\")\nnltk.download(\"treebank\")\nnltk.download(\"averaged_perceptron_tagger\")\nnltk.download(\"wordnet\")",
"[nltk_data] Downloading package punkt to\n[nltk_data] /Users/varadrajrameshpoojary/nltk_data...\n[nltk_data] Package punkt is already up-to-date!\n[nltk_data] Downloading package treebank to\n[nltk_data] /Users/varadrajrameshpoojary/nltk_data...\n[nltk_data] Package treebank is already up-to-date!\n[nltk_data] Downloading package averaged_perceptron_tagger to\n[nltk_data] /Users/varadrajrameshpoojary/nltk_data...\n[nltk_data] Package averaged_perceptron_tagger is already up-to-\n[nltk_data] date!\n[nltk_data] Downloading package wordnet to\n[nltk_data] /Users/varadrajrameshpoojary/nltk_data...\n[nltk_data] Package wordnet is already up-to-date!\n"
]
],
[
[
"Code to access relevant modules (you can add to this as needed):",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from nltk.corpus import treebank\nfrom nltk import word_tokenize, pos_tag, RegexpParser\nfrom nltk.tree import Tree\nfrom nltk.chunk.util import ChunkScore\nfrom nltk.stem import WordNetLemmatizer ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Simple NP chunking",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We start by building a basic NP chunker. A simple approach to the task of NP chunking is to assume that a sequence of words is an NP if \n\n* it contains only determiners, nouns, pronouns, and adjectives,\n* and it contains at least one noun or pronoun. \n\nThe first letters of relevant POS tags are provided for you in the sets `NP_POS` and `NP_HEAD_POS`. \n\nWe write a function which takes a raw sentence (a string) and \n\n1. tokenizes and POS tags it using NLTK,\n1. finds all contiguous sequences of words that fit the above description, and returns them. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"NP_POS = {\"DT\", \"NN\", \"JJ\", \"PR\"} # these are the first two letters of the POS that you should consider potential parts of NP chunks \nNP_HEAD_POS = {\"NN\", \"PR\"} # each chunk must have at least one of these\n\ndef get_chunks(sentence):\n '''Extracts noun phrases from a sentence corresponding to the part-of-speech tags in optional_POS,\n requiring at least one of the POS tags in required_POS. Returns the chunks as a list of strings'''\n # your code here\n chunks=[]\n list_1=[]\n tags= set()\n tagged_sent = pos_tag(word_tokenize(sentence))\n for word,tag in tagged_sent:\n if tag[:2] in NP_POS:\n list_1.append(word)\n tags.add(tag[:2])\n else:\n if len(tags & NP_HEAD_POS)>0:\n chunks.append(\" \".join(list_1))\n list_1= []\n tags= set()\n if len(tags & NP_HEAD_POS)>0:\n chunks.append(\" \".join(list_1))\n return chunks ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Here are a few examples which show you the input format for `get_chunks` and the intended output format.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"assert(sorted(get_chunks(\"the quick brown fox jumped over the lazy dog\"))) == sorted([\"the quick brown fox\", \"the lazy dog\"])\nassert(get_chunks(\"life is good\")) == [\"life\"]\nassert(get_chunks(\"life is good and chickens are tasty\")) == [\"life\",\"chickens\"]\nprint(\"Success!\")",
"Success!\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Regex chunking",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Created three different NLTK regex noun chunkers using the `RegexpParser` class:\n\n1. `simple_chunk` which exactly duplicates the logic from above.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tagged_sent = pos_tag(word_tokenize(\"I gave John my old Globe and Mail\"))\nsimple_chunk = RegexpParser(\"NP: {(<DT.*|NN.*|JJ.*|PR.*>*)(<NN.*|PR.*>)(<DT.*|NN.*|JJ.*|PR.*>*)}\")\nprint(simple_chunk.parse(tagged_sent))",
"(S\n (NP I/PRP)\n gave/VBD\n (NP John/NNP my/PRP$ old/JJ Globe/NNP)\n and/CC\n (NP Mail/NNP))\n"
]
],
[
[
"\n2. `ordered_chunk` which captures the standard English NP word order, defined by the following properties:\n\n * The syntactic head of an NP is either a personal pronoun, common noun or proper noun. Every NP has to contain at least one of these. Note that there can be more.\n * If the head is a noun, it can be preceded by a determiner (also called an article) as in _the dog_ or a possessive pronoun as in _my dogs_. \n * If the head is a noun, it can be preceded by one or more adjectives as in _beautiful weather_.\n * If a determiner or possessive pronoun occurs, it has to be the first token of the NP. \n * If the syntactic head is a noun, it can be preceded by an adjective as in _the grey dog_ and _grey dogs_.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tagged_sent = pos_tag(word_tokenize(\"I gave John my old Globe and Mail\"))\nordered_chunk = RegexpParser(\"NP: {(<DT.*|PRP\\$>?<JJ.*>*<NN.*>+)|(<PRP>+)}\")\nprint(ordered_chunk.parse(tagged_sent))",
"(S\n (NP I/PRP)\n gave/VBD\n (NP John/NNP)\n (NP my/PRP$ old/JJ Globe/NNP)\n and/CC\n (NP Mail/NNP))\n"
]
],
[
[
"\n3. `conj_chunk` which allows for coordination of two NPs matching `ordered_chunk` using a coordinate conjunction `CC`. Note that often there is only one determiner in a coordinated NP as in \"the Globe and Mail\", however, \"the Globe and the Mail\" is also grammatical. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tagged_sent = pos_tag(word_tokenize(\"I gave John my old Globe and MAIL and mail\"))\nconj_chunk = RegexpParser(\"NP: {((<DT.*|PRP\\$>?<JJ.*>*<NN.*>+)|(<PRP>+))(<CC>((<DT.*|PRP\\$>?<JJ.*>*<NN.*>+)|(<PRP>+)))*}\")\nprint(conj_chunk.parse(tagged_sent))",
"(S\n (NP I/PRP)\n gave/VBD\n (NP John/NNP)\n (NP my/PRP$ old/JJ Globe/NNP and/CC MAIL/NNP and/CC mail/NN))\n"
],
[
"sent = \"I gave John my old Globe and Mail\"\nassert (str(simple_chunk.parse(pos_tag(word_tokenize(sent)))) == str(Tree.fromstring(\"(S (NP I/PRP) gave/VBD (NP John/NNP my/PRP$ old/JJ Globe/NNP) and/CC (NP Mail/NNP))\")))\nassert (str(ordered_chunk.parse(pos_tag(word_tokenize(sent)))) == str(Tree.fromstring(\"(S (NP I/PRP) gave/VBD (NP John/NNP) (NP my/PRP$ old/JJ Globe/NNP) and/CC (NP Mail/NNP))\")))\nassert (str(conj_chunk.parse(pos_tag(word_tokenize(sent)))) == str(Tree.fromstring(\"(S (NP I/PRP) gave/VBD (NP John/NNP) (NP my/PRP$ old/JJ Globe/NNP and/CC Mail/NNP))\")))\nprint(\"Success!\")",
"Success!\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Chunking evaluation and improvement\n\nEvaluation our regular expression chunkers by comparing their output to gold standard chunks extrated from the Penn Treebank.\n\n\nFirst, we will create a new test set for our chunkers by pulling out noun phrases from the Penn Treebank. We start by creating a function `convert_to_chunk` which converts standard syntactic trees into shallow chunk trees, where all phrases except `NP` have been flattened. \n\nYour `convert_to_chunk` function should take a list of syntax trees as input and return a list of chunk trees as output. Here is an example of a syntax tree and the corresponding chunk tree:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def is_wanted_NP(tree):\n '''returns False if the NLTK tree of a NP has either other NPs or traces (\"*\") within it'''\n if tree.label() != \"NP\":\n return False\n \n subtrees = list(tree.subtrees())[1:]\n if any([subtree.label().startswith(\"NP\") for subtree in subtrees]):\n return False\n # your code here\n\n if \"*\" in tree.leaves():\n return False\n return True\n\ndef convert_to_chunk_(tree,chunks):\n '''Recursively finds any shallow NPs in the tree, converting the parse into the NLTK chunk format.\n The list of chunks is returned'''\n # your code here\n\n for inner_tree in tree:\n if is_wanted_NP(inner_tree):\n chunks.append(Tree(inner_tree.label(), inner_tree.pos()))\n elif inner_tree.height()==2:\n chunks.append(inner_tree.pos()[0])\n else:\n chunks = (convert_to_chunk_(inner_tree, chunks))\n return chunks\n\ntree = Tree.fromstring(\"(S (NP (DT the) (NN dog)) (VP (VBD saw) (NP (DT the) (NN cat))))\")\nassert(convert_to_chunk_(tree,[]) == [Tree('NP', [('the', 'DT'), ('dog', 'NN')]), ('saw', 'VBD'), Tree('NP', [('the', 'DT'),('cat','NN')])])\n\ndef convert_to_chunk(tree):\n return Tree(\"S\",convert_to_chunk_(tree,[]))\n\n\ntreebank_test = []\n\nfor parsed_sent in treebank.parsed_sents():\n treebank_test.append(convert_to_chunk(parsed_sent))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now, we evaluate the three regex chunkers from Exercise 2 using the built-in NLTK chunk evaluation system.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(\"simple chunk\")\nprint(simple_chunk.evaluate(treebank_test))\nprint(\"ordered chunk\")\nprint(ordered_chunk.evaluate(treebank_test))\nprint(\"conj chunk\")\nprint(conj_chunk.evaluate(treebank_test))",
"simple chunk\nChunkParse score:\n IOB Accuracy: 75.4%%\n Precision: 50.3%%\n Recall: 65.4%%\n F-Measure: 56.9%%\nordered chunk\nChunkParse score:\n IOB Accuracy: 75.5%%\n Precision: 50.6%%\n Recall: 66.8%%\n F-Measure: 57.6%%\nconj chunk\nChunkParse score:\n IOB Accuracy: 75.3%%\n Precision: 50.8%%\n Recall: 64.4%%\n F-Measure: 56.8%%\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### looking for errors",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dev_set = treebank.tagged_sents()[:50]\ntest_set = treebank.tagged_sents()[50:]\nfor tagged, gold_tree in zip(dev_set,treebank_test):\n sys_tree = ordered_chunk.parse(tagged)\n print(\"SYS:\",sys_tree)\n print(\"GOLD:\",gold_tree)",
"SYS: (S\n (NP Pierre/NNP Vinken/NNP)\n ,/,\n 61/CD\n (NP years/NNS)\n old/JJ\n ,/,\n will/MD\n join/VB\n (NP the/DT board/NN)\n as/IN\n (NP a/DT nonexecutive/JJ director/NN Nov./NNP)\n 29/CD\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n (NP Pierre/NNP Vinken/NNP)\n ,/,\n (NP 61/CD years/NNS)\n old/JJ\n ,/,\n will/MD\n join/VB\n (NP the/DT board/NN)\n as/IN\n (NP a/DT nonexecutive/JJ director/NN)\n Nov./NNP\n 29/CD\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n (NP Mr./NNP Vinken/NNP)\n is/VBZ\n (NP chairman/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP Elsevier/NNP N.V./NNP)\n ,/,\n (NP the/DT Dutch/NNP)\n publishing/VBG\n (NP group/NN)\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n Mr./NNP\n Vinken/NNP\n is/VBZ\n (NP chairman/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP Elsevier/NNP N.V./NNP)\n ,/,\n (NP the/DT Dutch/NNP publishing/VBG group/NN)\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n (NP Rudolph/NNP Agnew/NNP)\n ,/,\n 55/CD\n (NP years/NNS)\n old/JJ\n and/CC\n (NP former/JJ chairman/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP Consolidated/NNP Gold/NNP Fields/NNP PLC/NNP)\n ,/,\n was/VBD\n named/VBN\n *-1/-NONE-\n (NP a/DT nonexecutive/JJ director/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP this/DT British/JJ industrial/JJ conglomerate/NN)\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n (NP Rudolph/NNP Agnew/NNP)\n ,/,\n (NP 55/CD years/NNS)\n old/JJ\n and/CC\n (NP former/JJ chairman/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP Consolidated/NNP Gold/NNP Fields/NNP PLC/NNP)\n ,/,\n was/VBD\n named/VBN\n *-1/-NONE-\n (NP a/DT nonexecutive/JJ director/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP this/DT British/JJ industrial/JJ conglomerate/NN)\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n (NP A/DT form/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP asbestos/NN)\n once/RB\n used/VBN\n */-NONE-\n */-NONE-\n to/TO\n make/VB\n (NP Kent/NNP cigarette/NN filters/NNS)\n has/VBZ\n caused/VBN\n (NP a/DT high/JJ percentage/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP cancer/NN deaths/NNS)\n among/IN\n (NP a/DT group/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP workers/NNS)\n exposed/VBN\n */-NONE-\n to/TO\n (NP it/PRP)\n more/RBR\n than/IN\n 30/CD\n (NP years/NNS)\n ago/IN\n ,/,\n (NP researchers/NNS)\n reported/VBD\n 0/-NONE-\n *T*-1/-NONE-\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n (NP A/DT form/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP asbestos/NN)\n once/RB\n used/VBN\n */-NONE-\n */-NONE-\n to/TO\n make/VB\n (NP Kent/NNP cigarette/NN filters/NNS)\n has/VBZ\n caused/VBN\n (NP a/DT high/JJ percentage/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP cancer/NN deaths/NNS)\n among/IN\n (NP a/DT group/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP workers/NNS)\n exposed/VBN\n */-NONE-\n to/TO\n (NP it/PRP)\n (NP more/RBR than/IN 30/CD years/NNS)\n ago/IN\n ,/,\n researchers/NNS\n reported/VBD\n 0/-NONE-\n *T*-1/-NONE-\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n (NP The/DT asbestos/NN fiber/NN)\n ,/,\n (NP crocidolite/NN)\n ,/,\n is/VBZ\n unusually/RB\n resilient/JJ\n once/IN\n (NP it/PRP)\n enters/VBZ\n (NP the/DT lungs/NNS)\n ,/,\n with/IN\n even/RB\n (NP brief/JJ exposures/NNS)\n to/TO\n (NP it/PRP)\n causing/VBG\n (NP symptoms/NNS)\n that/WDT\n *T*-1/-NONE-\n show/VBP\n up/RP\n (NP decades/NNS)\n later/JJ\n ,/,\n (NP researchers/NNS)\n said/VBD\n 0/-NONE-\n *T*-2/-NONE-\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n (NP The/DT asbestos/NN fiber/NN)\n ,/,\n (NP crocidolite/NN)\n ,/,\n is/VBZ\n unusually/RB\n resilient/JJ\n once/IN\n it/PRP\n enters/VBZ\n (NP the/DT lungs/NNS)\n ,/,\n with/IN\n (NP even/RB brief/JJ exposures/NNS)\n to/TO\n (NP it/PRP)\n causing/VBG\n (NP symptoms/NNS)\n that/WDT\n *T*-1/-NONE-\n show/VBP\n up/RP\n (NP decades/NNS)\n later/JJ\n ,/,\n researchers/NNS\n said/VBD\n 0/-NONE-\n *T*-2/-NONE-\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n (NP Lorillard/NNP Inc./NNP)\n ,/,\n (NP the/DT unit/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP New/JJ York-based/JJ Loews/NNP Corp./NNP)\n that/WDT\n *T*-2/-NONE-\n makes/VBZ\n (NP Kent/NNP cigarettes/NNS)\n ,/,\n stopped/VBD\n using/VBG\n (NP crocidolite/NN)\n in/IN\n (NP its/PRP$ Micronite/NN cigarette/NN filters/NNS)\n in/IN\n 1956/CD\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n (NP Lorillard/NNP Inc./NNP)\n ,/,\n (NP the/DT unit/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP New/JJ York-based/JJ Loews/NNP Corp./NNP)\n that/WDT\n *T*-2/-NONE-\n makes/VBZ\n (NP Kent/NNP cigarettes/NNS)\n ,/,\n stopped/VBD\n using/VBG\n (NP crocidolite/NN)\n in/IN\n (NP its/PRP$ Micronite/NN cigarette/NN filters/NNS)\n in/IN\n (NP 1956/CD)\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n Although/IN\n (NP preliminary/JJ findings/NNS)\n were/VBD\n reported/VBN\n *-2/-NONE-\n more/RBR\n than/IN\n (NP a/DT year/NN)\n ago/IN\n ,/,\n (NP the/DT latest/JJS results/NNS)\n appear/VBP\n in/IN\n (NP today/NN)\n 's/POS\n (NP New/NNP England/NNP Journal/NNP)\n of/IN\n (NP Medicine/NNP)\n ,/,\n (NP a/DT forum/NN)\n likely/JJ\n */-NONE-\n to/TO\n bring/VB\n (NP new/JJ attention/NN)\n to/TO\n (NP the/DT problem/NN)\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n Although/IN\n preliminary/JJ\n findings/NNS\n were/VBD\n reported/VBN\n (NP *-2/-NONE-)\n (NP more/RBR than/IN a/DT year/NN)\n ago/IN\n ,/,\n the/DT\n latest/JJS\n results/NNS\n appear/VBP\n in/IN\n (NP today/NN 's/POS)\n New/NNP\n England/NNP\n Journal/NNP\n of/IN\n (NP Medicine/NNP)\n ,/,\n (NP a/DT forum/NN)\n likely/JJ\n */-NONE-\n to/TO\n bring/VB\n (NP new/JJ attention/NN)\n to/TO\n (NP the/DT problem/NN)\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n (NP A/DT Lorillard/NNP spokewoman/NN)\n said/VBD\n ,/,\n ``/``\n This/DT\n is/VBZ\n (NP an/DT old/JJ story/NN)\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n A/DT\n Lorillard/NNP\n spokewoman/NN\n said/VBD\n ,/,\n ``/``\n This/DT\n is/VBZ\n an/DT\n old/JJ\n story/NN\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n (NP We/PRP)\n 're/VBP\n talking/VBG\n about/IN\n (NP years/NNS)\n ago/IN\n before/IN\n (NP anyone/NN)\n heard/VBD\n of/IN\n (NP asbestos/NN)\n having/VBG\n (NP any/DT questionable/JJ properties/NNS)\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n We/PRP\n 're/VBP\n talking/VBG\n about/IN\n (NP years/NNS)\n ago/IN\n before/IN\n anyone/NN\n heard/VBD\n of/IN\n asbestos/NN\n having/VBG\n (NP any/DT questionable/JJ properties/NNS)\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n There/EX\n is/VBZ\n (NP no/DT asbestos/NN)\n in/IN\n (NP our/PRP$ products/NNS)\n now/RB\n ./.\n ''/'')\nGOLD: (S\n There/EX\n is/VBZ\n no/DT\n asbestos/NN\n in/IN\n (NP our/PRP$ products/NNS)\n now/RB\n ./.\n ''/'')\nSYS: (S\n (NP Neither/DT Lorillard/NNP)\n nor/CC\n (NP the/DT researchers/NNS)\n who/WP\n *T*-3/-NONE-\n studied/VBD\n (NP the/DT workers/NNS)\n were/VBD\n aware/JJ\n of/IN\n (NP any/DT research/NN)\n on/IN\n (NP smokers/NNS)\n of/IN\n (NP the/DT Kent/NNP cigarettes/NNS)\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n Neither/DT\n (NP Lorillard/NNP)\n nor/CC\n (NP the/DT researchers/NNS)\n who/WP\n *T*-3/-NONE-\n studied/VBD\n (NP the/DT workers/NNS)\n were/VBD\n aware/JJ\n of/IN\n (NP any/DT research/NN)\n on/IN\n (NP smokers/NNS)\n of/IN\n (NP the/DT Kent/NNP cigarettes/NNS)\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n ``/``\n (NP We/PRP)\n have/VBP\n (NP no/DT useful/JJ information/NN)\n on/IN\n whether/IN\n (NP users/NNS)\n are/VBP\n at/IN\n (NP risk/NN)\n ,/,\n ''/''\n said/VBD\n *T*-1/-NONE-\n (NP James/NNP A./NNP Talcott/NNP)\n of/IN\n (NP Boston/NNP)\n 's/POS\n (NP Dana-Farber/NNP Cancer/NNP Institute/NNP)\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n ``/``\n We/PRP\n have/VBP\n (NP no/DT useful/JJ information/NN)\n on/IN\n whether/IN\n users/NNS\n are/VBP\n at/IN\n (NP risk/NN)\n ,/,\n ''/''\n said/VBD\n *T*-1/-NONE-\n (NP James/NNP A./NNP Talcott/NNP)\n of/IN\n (NP Boston/NNP 's/POS)\n Dana-Farber/NNP\n Cancer/NNP\n Institute/NNP\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n (NP Dr./NNP Talcott/NNP)\n led/VBD\n (NP a/DT team/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP researchers/NNS)\n from/IN\n (NP the/DT National/NNP Cancer/NNP Institute/NNP)\n and/CC\n (NP the/DT medical/JJ schools/NNS)\n of/IN\n (NP Harvard/NNP University/NNP)\n and/CC\n (NP Boston/NNP University/NNP)\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n Dr./NNP\n Talcott/NNP\n led/VBD\n (NP a/DT team/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP researchers/NNS)\n from/IN\n (NP the/DT National/NNP Cancer/NNP Institute/NNP)\n and/CC\n (NP the/DT medical/JJ schools/NNS)\n of/IN\n (NP Harvard/NNP University/NNP)\n and/CC\n (NP Boston/NNP University/NNP)\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n (NP The/DT Lorillard/NNP spokeswoman/NN)\n said/VBD\n 0/-NONE-\n (NP asbestos/NN)\n was/VBD\n used/VBN\n *-1/-NONE-\n in/IN\n ``/``\n very/RB\n (NP modest/JJ amounts/NNS)\n ''/''\n in/IN\n */-NONE-\n making/VBG\n (NP paper/NN)\n for/IN\n (NP the/DT filters/NNS)\n in/IN\n the/DT\n early/JJ\n 1950s/CD\n and/CC\n replaced/VBN\n *-1/-NONE-\n with/IN\n (NP a/DT different/JJ type/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP filter/NN)\n in/IN\n 1956/CD\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n The/DT\n Lorillard/NNP\n spokeswoman/NN\n said/VBD\n 0/-NONE-\n asbestos/NN\n was/VBD\n used/VBN\n (NP *-1/-NONE-)\n in/IN\n ``/``\n (NP very/RB modest/JJ amounts/NNS)\n ''/''\n in/IN\n */-NONE-\n making/VBG\n (NP paper/NN)\n for/IN\n (NP the/DT filters/NNS)\n in/IN\n (NP the/DT early/JJ 1950s/CD)\n and/CC\n replaced/VBN\n (NP *-1/-NONE-)\n with/IN\n (NP a/DT different/JJ type/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP filter/NN)\n in/IN\n (NP 1956/CD)\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n From/IN\n 1953/CD\n to/TO\n 1955/CD\n ,/,\n 9.8/CD\n billion/CD\n (NP Kent/NNP cigarettes/NNS)\n with/IN\n (NP the/DT filters/NNS)\n were/VBD\n sold/VBN\n *-3/-NONE-\n ,/,\n (NP the/DT company/NN)\n said/VBD\n 0/-NONE-\n *T*-1/-NONE-\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n From/IN\n (NP 1953/CD)\n to/TO\n (NP 1955/CD)\n ,/,\n (NP 9.8/CD billion/CD Kent/NNP cigarettes/NNS)\n with/IN\n (NP the/DT filters/NNS)\n were/VBD\n sold/VBN\n (NP *-3/-NONE-)\n ,/,\n the/DT\n company/NN\n said/VBD\n 0/-NONE-\n *T*-1/-NONE-\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n Among/IN\n 33/CD\n (NP men/NNS)\n who/WP\n *T*-4/-NONE-\n worked/VBD\n closely/RB\n with/IN\n (NP the/DT substance/NN)\n ,/,\n 28/CD\n *ICH*-1/-NONE-\n have/VBP\n died/VBN\n --/:\n more/JJ\n than/IN\n three/CD\n (NP times/NNS)\n the/DT\n expected/VBN\n (NP number/NN)\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n Among/IN\n (NP 33/CD men/NNS)\n who/WP\n *T*-4/-NONE-\n worked/VBD\n closely/RB\n with/IN\n (NP the/DT substance/NN)\n ,/,\n (NP 28/CD)\n (NP *ICH*-1/-NONE-)\n have/VBP\n died/VBN\n --/:\n more/JJ\n than/IN\n three/CD\n times/NNS\n the/DT\n expected/VBN\n number/NN\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n Four/CD\n of/IN\n the/DT\n five/CD\n surviving/VBG\n (NP workers/NNS)\n have/VBP\n (NP asbestos-related/JJ diseases/NNS)\n ,/,\n including/VBG\n three/CD\n with/IN\n recently/RB\n diagnosed/VBN\n (NP cancer/NN)\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n (NP Four/CD)\n of/IN\n (NP the/DT five/CD surviving/VBG workers/NNS)\n have/VBP\n (NP asbestos-related/JJ diseases/NNS)\n ,/,\n including/VBG\n (NP three/CD)\n with/IN\n (NP recently/RB diagnosed/VBN cancer/NN)\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n (NP The/DT total/NN)\n of/IN\n 18/CD\n (NP deaths/NNS)\n from/IN\n (NP malignant/JJ mesothelioma/NN)\n ,/,\n (NP lung/NN cancer/NN)\n and/CC\n (NP asbestosis/NN)\n was/VBD\n far/RB\n higher/JJR\n than/IN\n */-NONE-\n expected/VBN\n *?*/-NONE-\n ,/,\n (NP the/DT researchers/NNS)\n said/VBD\n 0/-NONE-\n *T*-1/-NONE-\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n (NP The/DT total/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP 18/CD deaths/NNS)\n from/IN\n (NP malignant/JJ mesothelioma/NN)\n ,/,\n (NP lung/NN cancer/NN)\n and/CC\n (NP asbestosis/NN)\n was/VBD\n far/RB\n higher/JJR\n than/IN\n */-NONE-\n expected/VBN\n *?*/-NONE-\n ,/,\n the/DT\n researchers/NNS\n said/VBD\n 0/-NONE-\n *T*-1/-NONE-\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n ``/``\n (NP The/DT morbidity/NN rate/NN)\n is/VBZ\n (NP a/DT striking/JJ finding/NN)\n among/IN\n those/DT\n of/IN\n (NP us/PRP)\n who/WP\n *T*-5/-NONE-\n study/VBP\n (NP asbestos-related/JJ diseases/NNS)\n ,/,\n ''/''\n said/VBD\n *T*-1/-NONE-\n (NP Dr./NNP Talcott/NNP)\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n ``/``\n The/DT\n morbidity/NN\n rate/NN\n is/VBZ\n a/DT\n striking/JJ\n finding/NN\n among/IN\n (NP those/DT)\n of/IN\n (NP us/PRP)\n who/WP\n *T*-5/-NONE-\n study/VBP\n (NP asbestos-related/JJ diseases/NNS)\n ,/,\n ''/''\n said/VBD\n *T*-1/-NONE-\n Dr./NNP\n Talcott/NNP\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n (NP The/DT percentage/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP lung/NN cancer/NN deaths/NNS)\n among/IN\n (NP the/DT workers/NNS)\n at/IN\n (NP the/DT West/NNP Groton/NNP)\n ,/,\n (NP Mass./NNP)\n ,/,\n (NP paper/NN factory/NN)\n appears/VBZ\n *-1/-NONE-\n to/TO\n be/VB\n the/DT\n highest/JJS\n for/IN\n (NP any/DT asbestos/NN workers/NNS)\n studied/VBN\n */-NONE-\n in/IN\n Western/JJ\n industrialized/VBN\n (NP countries/NNS)\n ,/,\n (NP he/PRP)\n said/VBD\n 0/-NONE-\n *T*-2/-NONE-\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n (NP The/DT percentage/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP lung/NN cancer/NN deaths/NNS)\n among/IN\n (NP the/DT workers/NNS)\n at/IN\n (NP\n the/DT\n West/NNP\n Groton/NNP\n ,/,\n Mass./NNP\n ,/,\n paper/NN\n factory/NN)\n appears/VBZ\n *-1/-NONE-\n to/TO\n be/VB\n (NP the/DT highest/JJS)\n for/IN\n (NP any/DT asbestos/NN workers/NNS)\n studied/VBN\n */-NONE-\n in/IN\n (NP Western/JJ industrialized/VBN countries/NNS)\n ,/,\n he/PRP\n said/VBD\n 0/-NONE-\n *T*-2/-NONE-\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n (NP The/DT plant/NN)\n ,/,\n which/WDT\n *T*-1/-NONE-\n is/VBZ\n owned/VBN\n *-4/-NONE-\n by/IN\n (NP Hollingsworth/NNP)\n &/CC\n (NP Vose/NNP Co./NNP)\n ,/,\n was/VBD\n under/IN\n (NP contract/NN)\n *ICH*-2/-NONE-\n with/IN\n (NP Lorillard/NN)\n */-NONE-\n to/TO\n make/VB\n (NP the/DT cigarette/NN filters/NNS)\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n (NP The/DT plant/NN)\n ,/,\n which/WDT\n *T*-1/-NONE-\n is/VBZ\n owned/VBN\n (NP *-4/-NONE-)\n by/IN\n Hollingsworth/NNP\n &/CC\n Vose/NNP\n Co./NNP\n ,/,\n was/VBD\n under/IN\n (NP contract/NN *ICH*-2/-NONE-)\n with/IN\n (NP Lorillard/NN)\n */-NONE-\n to/TO\n make/VB\n (NP the/DT cigarette/NN filters/NNS)\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n (NP The/DT finding/NN)\n probably/RB\n will/MD\n support/VB\n those/DT\n who/WP\n *T*-6/-NONE-\n argue/VBP\n that/IN\n (NP the/DT U.S./NNP)\n should/MD\n regulate/VB\n (NP the/DT class/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP asbestos/NN)\n including/VBG\n (NP crocidolite/NN)\n more/RBR\n stringently/RB\n than/IN\n (NP the/DT common/JJ kind/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP asbestos/NN)\n ,/,\n (NP chrysotile/NN)\n ,/,\n found/VBN\n */-NONE-\n in/IN\n (NP most/JJS schools/NNS)\n and/CC\n (NP other/JJ buildings/NNS)\n ,/,\n (NP Dr./NNP Talcott/NNP)\n said/VBD\n 0/-NONE-\n *T*-1/-NONE-\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n The/DT\n finding/NN\n probably/RB\n will/MD\n support/VB\n (NP those/DT)\n who/WP\n *T*-6/-NONE-\n argue/VBP\n that/IN\n the/DT\n U.S./NNP\n should/MD\n regulate/VB\n (NP the/DT class/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP asbestos/NN)\n including/VBG\n (NP crocidolite/NN)\n more/RBR\n stringently/RB\n than/IN\n (NP the/DT common/JJ kind/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP asbestos/NN)\n ,/,\n (NP chrysotile/NN)\n ,/,\n found/VBN\n */-NONE-\n in/IN\n (NP most/JJS schools/NNS)\n and/CC\n (NP other/JJ buildings/NNS)\n ,/,\n Dr./NNP\n Talcott/NNP\n said/VBD\n 0/-NONE-\n *T*-1/-NONE-\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n (NP The/DT U.S./NNP)\n is/VBZ\n one/CD\n of/IN\n the/DT\n few/JJ\n industrialized/VBN\n (NP nations/NNS)\n that/WDT\n *T*-7/-NONE-\n does/VBZ\n n't/RB\n have/VB\n (NP a/DT higher/JJR standard/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP regulation/NN)\n for/IN\n the/DT\n smooth/JJ\n ,/,\n (NP needle-like/JJ fibers/NNS)\n such/JJ\n as/IN\n (NP crocidolite/NN)\n that/WDT\n *T*-1/-NONE-\n are/VBP\n classified/VBN\n *-5/-NONE-\n as/IN\n (NP amphobiles/NNS)\n ,/,\n according/VBG\n to/TO\n (NP Brooke/NNP T./NNP Mossman/NNP)\n ,/,\n (NP a/DT professor/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP pathlogy/NN)\n at/IN\n (NP the/DT University/NNP)\n of/IN\n (NP Vermont/NNP College/NNP)\n of/IN\n (NP Medicine/NNP)\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n The/DT\n U.S./NNP\n is/VBZ\n (NP one/CD)\n of/IN\n (NP the/DT few/JJ industrialized/VBN nations/NNS)\n that/WDT\n *T*-7/-NONE-\n does/VBZ\n n't/RB\n have/VB\n (NP a/DT higher/JJR standard/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP regulation/NN)\n for/IN\n (NP the/DT smooth/JJ ,/, needle-like/JJ fibers/NNS)\n such/JJ\n as/IN\n (NP crocidolite/NN)\n that/WDT\n *T*-1/-NONE-\n are/VBP\n classified/VBN\n (NP *-5/-NONE-)\n as/IN\n (NP amphobiles/NNS)\n ,/,\n according/VBG\n to/TO\n (NP Brooke/NNP T./NNP Mossman/NNP)\n ,/,\n (NP a/DT professor/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP pathlogy/NN)\n at/IN\n the/DT\n University/NNP\n of/IN\n (NP Vermont/NNP)\n College/NNP\n of/IN\n (NP Medicine/NNP)\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n More/RBR\n (NP common/JJ chrysotile/NN fibers/NNS)\n are/VBP\n curly/JJ\n and/CC\n are/VBP\n more/RBR\n easily/RB\n rejected/VBN\n *-1/-NONE-\n by/IN\n (NP the/DT body/NN)\n ,/,\n (NP Dr./NNP Mossman/NNP)\n explained/VBD\n 0/-NONE-\n *T*-2/-NONE-\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n More/RBR\n common/JJ\n chrysotile/NN\n fibers/NNS\n are/VBP\n curly/JJ\n and/CC\n are/VBP\n more/RBR\n easily/RB\n rejected/VBN\n (NP *-1/-NONE-)\n by/IN\n the/DT\n body/NN\n ,/,\n Dr./NNP\n Mossman/NNP\n explained/VBD\n 0/-NONE-\n *T*-2/-NONE-\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n In/IN\n (NP July/NNP)\n ,/,\n (NP the/DT Environmental/NNP Protection/NNP Agency/NNP)\n imposed/VBD\n (NP a/DT gradual/JJ ban/NN)\n on/IN\n virtually/RB\n (NP all/DT uses/NNS)\n of/IN\n (NP asbestos/NN)\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n In/IN\n (NP July/NNP)\n ,/,\n the/DT\n Environmental/NNP\n Protection/NNP\n Agency/NNP\n imposed/VBD\n (NP a/DT gradual/JJ ban/NN)\n on/IN\n (NP virtually/RB all/DT uses/NNS)\n of/IN\n (NP asbestos/NN)\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n By/IN\n 1997/CD\n ,/,\n almost/RB\n all/DT\n remaining/VBG\n (NP uses/NNS)\n of/IN\n (NP cancer-causing/JJ asbestos/NN)\n will/MD\n be/VB\n outlawed/VBN\n *-6/-NONE-\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n By/IN\n (NP 1997/CD)\n ,/,\n (NP almost/RB all/DT remaining/VBG uses/NNS)\n of/IN\n (NP cancer-causing/JJ asbestos/NN)\n will/MD\n be/VB\n outlawed/VBN\n (NP *-6/-NONE-)\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n About/IN\n 160/CD\n (NP workers/NNS)\n at/IN\n (NP a/DT factory/NN)\n that/WDT\n *T*-8/-NONE-\n made/VBD\n (NP paper/NN)\n for/IN\n (NP the/DT Kent/NNP filters/NNS)\n were/VBD\n exposed/VBN\n *-7/-NONE-\n to/TO\n (NP asbestos/NN)\n in/IN\n the/DT\n 1950s/CD\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n (NP About/IN 160/CD workers/NNS)\n at/IN\n (NP a/DT factory/NN)\n that/WDT\n *T*-8/-NONE-\n made/VBD\n (NP paper/NN)\n for/IN\n (NP the/DT Kent/NNP filters/NNS)\n were/VBD\n exposed/VBN\n (NP *-7/-NONE-)\n to/TO\n (NP asbestos/NN)\n in/IN\n (NP the/DT 1950s/CD)\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n (NP Areas/NNS)\n of/IN\n (NP the/DT factory/NN)\n *ICH*-2/-NONE-\n were/VBD\n particularly/RB\n dusty/JJ\n where/WRB\n (NP the/DT crocidolite/NN)\n was/VBD\n used/VBN\n *-8/-NONE-\n *T*-1/-NONE-\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n (NP Areas/NNS)\n of/IN\n (NP the/DT factory/NN)\n *ICH*-2/-NONE-\n were/VBD\n particularly/RB\n dusty/JJ\n where/WRB\n the/DT\n crocidolite/NN\n was/VBD\n used/VBN\n (NP *-8/-NONE-)\n *T*-1/-NONE-\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n (NP Workers/NNS)\n dumped/VBD\n (NP large/JJ burlap/NN sacks/NNS)\n of/IN\n the/DT\n imported/VBN\n (NP material/NN)\n into/IN\n (NP a/DT huge/JJ bin/NN)\n ,/,\n poured/VBD\n in/RP\n (NP cotton/NN)\n and/CC\n (NP acetate/NN fibers/NNS)\n and/CC\n mechanically/RB\n mixed/VBD\n (NP the/DT dry/JJ fibers/NNS)\n in/IN\n (NP a/DT process/NN)\n used/VBN\n */-NONE-\n */-NONE-\n to/TO\n make/VB\n (NP filters/NNS)\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n Workers/NNS\n dumped/VBD\n (NP large/JJ burlap/NN sacks/NNS)\n of/IN\n (NP the/DT imported/VBN material/NN)\n into/IN\n (NP a/DT huge/JJ bin/NN)\n ,/,\n poured/VBD\n in/RP\n (NP cotton/NN and/CC acetate/NN fibers/NNS)\n and/CC\n mechanically/RB\n mixed/VBD\n (NP the/DT dry/JJ fibers/NNS)\n in/IN\n (NP a/DT process/NN)\n used/VBN\n */-NONE-\n */-NONE-\n to/TO\n make/VB\n (NP filters/NNS)\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n (NP Workers/NNS)\n described/VBD\n ``/``\n (NP clouds/NNS)\n of/IN\n (NP blue/JJ dust/NN)\n ''/''\n that/WDT\n *T*-1/-NONE-\n hung/VBD\n over/IN\n (NP parts/NNS)\n of/IN\n (NP the/DT factory/NN)\n ,/,\n even/RB\n though/IN\n (NP exhaust/NN fans/NNS)\n ventilated/VBD\n (NP the/DT area/NN)\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n Workers/NNS\n described/VBD\n ``/``\n (NP clouds/NNS)\n of/IN\n (NP blue/JJ dust/NN)\n ''/''\n that/WDT\n *T*-1/-NONE-\n hung/VBD\n over/IN\n (NP parts/NNS)\n of/IN\n (NP the/DT factory/NN)\n ,/,\n even/RB\n though/IN\n exhaust/NN\n fans/NNS\n ventilated/VBD\n (NP the/DT area/NN)\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n ``/``\n There/EX\n 's/VBZ\n (NP no/DT question/NN)\n that/IN\n some/DT\n of/IN\n (NP those/DT workers/NNS)\n and/CC\n (NP managers/NNS)\n contracted/VBD\n (NP asbestos-related/JJ diseases/NNS)\n ,/,\n ''/''\n said/VBD\n *T*-1/-NONE-\n (NP Darrell/NNP Phillips/NNP)\n ,/,\n (NP vice/NN president/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP human/JJ resources/NNS)\n for/IN\n (NP Hollingsworth/NNP)\n &/CC\n (NP Vose/NNP)\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n ``/``\n There/EX\n 's/VBZ\n (NP no/DT question/NN)\n that/IN\n (NP some/DT)\n of/IN\n (NP those/DT workers/NNS and/CC managers/NNS)\n contracted/VBD\n (NP asbestos-related/JJ diseases/NNS)\n ,/,\n ''/''\n said/VBD\n *T*-1/-NONE-\n (NP Darrell/NNP Phillips/NNP)\n ,/,\n (NP vice/NN president/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP human/JJ resources/NNS)\n for/IN\n (NP Hollingsworth/NNP &/CC Vose/NNP)\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n ``/``\n But/CC\n (NP you/PRP)\n have/VBP\n *-1/-NONE-\n to/TO\n recognize/VB\n that/IN\n (NP these/DT events/NNS)\n took/VBD\n (NP place/NN)\n 35/CD\n (NP years/NNS)\n ago/IN\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n ``/``\n But/CC\n you/PRP\n have/VBP\n *-1/-NONE-\n to/TO\n recognize/VB\n that/IN\n these/DT\n events/NNS\n took/VBD\n (NP place/NN)\n (NP 35/CD years/NNS)\n ago/IN\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n (NP It/PRP)\n has/VBZ\n (NP no/DT bearing/NN)\n on/IN\n (NP our/PRP$ work/NN force/NN today/NN)\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n It/PRP\n has/VBZ\n (NP no/DT bearing/NN)\n on/IN\n (NP our/PRP$ work/NN force/NN)\n today/NN\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n (NP Yields/NNS)\n on/IN\n (NP money-market/JJ mutual/JJ funds/NNS)\n continued/VBD\n *-1/-NONE-\n to/TO\n slide/VB\n ,/,\n amid/IN\n (NP signs/NNS)\n that/IN\n (NP portfolio/NN managers/NNS)\n expect/VBP\n (NP further/JJ declines/NNS)\n in/IN\n (NP interest/NN rates/NNS)\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n (NP Yields/NNS)\n on/IN\n (NP money-market/JJ mutual/JJ funds/NNS)\n continued/VBD\n *-1/-NONE-\n to/TO\n slide/VB\n ,/,\n amid/IN\n signs/NNS\n that/IN\n portfolio/NN\n managers/NNS\n expect/VBP\n (NP further/JJ declines/NNS)\n in/IN\n (NP interest/NN rates/NNS)\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n (NP The/DT average/JJ seven-day/JJ compound/NN yield/NN)\n of/IN\n the/DT\n 400/CD\n (NP taxable/JJ funds/NNS)\n tracked/VBN\n */-NONE-\n by/IN\n (NP IBC/NNP)\n 's/POS\n (NP Money/NNP Fund/NNP Report/NNP)\n eased/VBD\n (NP a/DT fraction/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP a/DT percentage/NN point/NN)\n to/TO\n 8.45/CD\n (NP %/NN)\n from/IN\n 8.47/CD\n (NP %/NN)\n for/IN\n (NP the/DT week/NN)\n ended/VBD\n (NP Tuesday/NNP)\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n (NP The/DT average/JJ seven-day/JJ compound/NN yield/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP the/DT 400/CD taxable/JJ funds/NNS)\n tracked/VBN\n */-NONE-\n by/IN\n (NP IBC/NNP 's/POS)\n Money/NNP\n Fund/NNP\n Report/NNP\n eased/VBD\n (NP a/DT fraction/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP a/DT percentage/NN point/NN)\n to/TO\n (NP 8.45/CD %/NN)\n from/IN\n (NP 8.47/CD %/NN)\n for/IN\n (NP the/DT week/NN)\n ended/VBD\n Tuesday/NNP\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n (NP Compound/NN yields/NNS)\n assume/VBP\n (NP reinvestment/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP dividends/NNS)\n and/CC\n that/IN\n (NP the/DT current/JJ yield/NN)\n continues/VBZ\n for/IN\n (NP a/DT year/NN)\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n Compound/NN\n yields/NNS\n assume/VBP\n (NP reinvestment/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP dividends/NNS)\n and/CC\n that/IN\n the/DT\n current/JJ\n yield/NN\n continues/VBZ\n for/IN\n (NP a/DT year/NN)\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n (NP Average/JJ maturity/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP the/DT funds/NNS)\n '/POS\n (NP investments/NNS)\n lengthened/VBD\n by/IN\n (NP a/DT day/NN)\n to/TO\n 41/CD\n (NP days/NNS)\n ,/,\n the/DT\n longest/JJS\n since/IN\n (NP early/JJ August/NNP)\n ,/,\n according/VBG\n to/TO\n (NP Donoghue/NNP)\n 's/POS\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n (NP Average/JJ maturity/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP the/DT funds/NNS '/POS)\n investments/NNS\n lengthened/VBD\n by/IN\n (NP a/DT day/NN)\n to/TO\n (NP 41/CD days/NNS)\n ,/,\n (NP the/DT longest/JJS)\n since/IN\n (NP early/JJ August/NNP)\n ,/,\n according/VBG\n to/TO\n (NP Donoghue/NNP 's/POS)\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n (NP Longer/JJR maturities/NNS)\n are/VBP\n thought/VBN\n *-1/-NONE-\n to/TO\n indicate/VB\n declining/VBG\n (NP interest/NN rates/NNS)\n because/IN\n (NP they/PRP)\n permit/VBP\n (NP portfolio/NN managers/NNS)\n to/TO\n retain/VB\n relatively/RB\n (NP higher/JJR rates/NNS)\n for/IN\n (NP a/DT longer/JJR period/NN)\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n Longer/JJR\n maturities/NNS\n are/VBP\n thought/VBN\n *-1/-NONE-\n to/TO\n indicate/VB\n (NP declining/VBG interest/NN rates/NNS)\n because/IN\n they/PRP\n permit/VBP\n portfolio/NN\n managers/NNS\n to/TO\n retain/VB\n (NP relatively/RB higher/JJR rates/NNS)\n for/IN\n (NP a/DT longer/JJR period/NN)\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n (NP Shorter/JJR maturities/NNS)\n are/VBP\n considered/VBN\n *-9/-NONE-\n (NP a/DT sign/NN)\n of/IN\n rising/VBG\n (NP rates/NNS)\n because/IN\n (NP portfolio/NN managers/NNS)\n can/MD\n capture/VB\n (NP higher/JJR rates/NNS)\n sooner/RB\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n Shorter/JJR\n maturities/NNS\n are/VBP\n considered/VBN\n *-9/-NONE-\n (NP a/DT sign/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP rising/VBG rates/NNS)\n because/IN\n portfolio/NN\n managers/NNS\n can/MD\n capture/VB\n (NP higher/JJR rates/NNS)\n sooner/RB\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n (NP The/DT average/JJ maturity/NN)\n for/IN\n (NP funds/NNS)\n open/JJ\n only/RB\n to/TO\n (NP institutions/NNS)\n ,/,\n considered/VBN\n by/IN\n some/DT\n */-NONE-\n to/TO\n be/VB\n (NP a/DT stronger/JJR indicator/NN)\n because/IN\n (NP those/DT managers/NNS)\n watch/VBP\n (NP the/DT market/NN)\n closely/RB\n ,/,\n reached/VBD\n (NP a/DT high/JJ point/NN)\n for/IN\n (NP the/DT year/NN)\n --/:\n 33/CD\n (NP days/NNS)\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n (NP The/DT average/JJ maturity/NN)\n for/IN\n (NP funds/NNS)\n open/JJ\n only/RB\n to/TO\n (NP institutions/NNS)\n ,/,\n considered/VBN\n by/IN\n some/DT\n */-NONE-\n to/TO\n be/VB\n a/DT\n stronger/JJR\n indicator/NN\n because/IN\n those/DT\n managers/NNS\n watch/VBP\n (NP the/DT market/NN)\n closely/RB\n ,/,\n reached/VBD\n (NP a/DT high/JJ point/NN)\n for/IN\n (NP the/DT year/NN)\n --/:\n (NP 33/CD days/NNS)\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n Nevertheless/RB\n ,/,\n said/VBD\n *T*-1/-NONE-\n (NP Brenda/NNP Malizia/NNP Negus/NNP)\n ,/,\n (NP editor/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP Money/NNP Fund/NNP Report/NNP)\n ,/,\n (NP yields/NNS)\n ``/``\n may/MD\n blip/VB\n up/RP\n again/RB\n before/IN\n (NP they/PRP)\n blip/VBP\n down/RP\n ''/''\n because/IN\n of/IN\n (NP recent/JJ rises/NNS)\n in/IN\n (NP short-term/JJ interest/NN rates/NNS)\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n Nevertheless/RB\n ,/,\n said/VBD\n *T*-1/-NONE-\n (NP Brenda/NNP Malizia/NNP Negus/NNP)\n ,/,\n (NP editor/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP Money/NNP Fund/NNP Report/NNP)\n ,/,\n yields/NNS\n ``/``\n may/MD\n blip/VB\n up/RP\n again/RB\n before/IN\n they/PRP\n blip/VBP\n down/RP\n ''/''\n because/IN\n of/IN\n (NP recent/JJ rises/NNS)\n in/IN\n (NP short-term/JJ interest/NN rates/NNS)\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n (NP The/DT yield/NN)\n on/IN\n (NP six-month/JJ Treasury/NNP bills/NNS)\n sold/VBN\n */-NONE-\n at/IN\n (NP Monday/NNP)\n 's/POS\n (NP auction/NN)\n ,/,\n for/IN\n (NP example/NN)\n ,/,\n rose/VBD\n to/TO\n 8.04/CD\n (NP %/NN)\n from/IN\n 7.90/CD\n (NP %/NN)\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n (NP The/DT yield/NN)\n on/IN\n (NP six-month/JJ Treasury/NNP bills/NNS)\n sold/VBN\n */-NONE-\n at/IN\n (NP Monday/NNP 's/POS)\n auction/NN\n ,/,\n for/IN\n (NP example/NN)\n ,/,\n rose/VBD\n to/TO\n (NP 8.04/CD %/NN)\n from/IN\n (NP 7.90/CD %/NN)\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n Despite/IN\n (NP recent/JJ declines/NNS)\n in/IN\n (NP yields/NNS)\n ,/,\n (NP investors/NNS)\n continue/VBP\n *-1/-NONE-\n to/TO\n pour/VB\n (NP cash/NN)\n into/IN\n (NP money/NN funds/NNS)\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n Despite/IN\n (NP recent/JJ declines/NNS)\n in/IN\n (NP yields/NNS)\n ,/,\n investors/NNS\n continue/VBP\n *-1/-NONE-\n to/TO\n pour/VB\n (NP cash/NN)\n into/IN\n (NP money/NN funds/NNS)\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n (NP Assets/NNS)\n of/IN\n the/DT\n 400/CD\n (NP taxable/JJ funds/NNS)\n grew/VBD\n by/IN\n $/$\n 1.5/CD\n billion/CD\n *U*/-NONE-\n during/IN\n (NP the/DT latest/JJS week/NN)\n ,/,\n to/TO\n $/$\n 352.7/CD\n billion/CD\n *U*/-NONE-\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n (NP Assets/NNS)\n of/IN\n (NP the/DT 400/CD taxable/JJ funds/NNS)\n grew/VBD\n by/IN\n (NP $/$ 1.5/CD billion/CD *U*/-NONE-)\n during/IN\n (NP the/DT latest/JJS week/NN)\n ,/,\n to/TO\n (NP $/$ 352.7/CD billion/CD *U*/-NONE-)\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n Typically/RB\n ,/,\n (NP money-fund/NN yields/NNS)\n beat/VBP\n (NP comparable/JJ short-term/JJ investments/NNS)\n because/IN\n (NP portfolio/NN managers/NNS)\n can/MD\n vary/VB\n (NP maturities/NNS)\n and/CC\n go/VB\n after/IN\n (NP the/DT highest/JJS rates/NNS)\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n Typically/RB\n ,/,\n money-fund/NN\n yields/NNS\n beat/VBP\n (NP comparable/JJ short-term/JJ investments/NNS)\n because/IN\n portfolio/NN\n managers/NNS\n can/MD\n vary/VB\n (NP maturities/NNS)\n and/CC\n go/VB\n after/IN\n (NP the/DT highest/JJS rates/NNS)\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n (NP The/DT top/JJ money/NN funds/NNS)\n are/VBP\n currently/RB\n yielding/VBG\n well/RB\n over/IN\n 9/CD\n (NP %/NN)\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n The/DT\n top/JJ\n money/NN\n funds/NNS\n are/VBP\n currently/RB\n yielding/VBG\n (NP well/RB over/IN 9/CD %/NN)\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n (NP Dreyfus/NNP World-Wide/NNP Dollar/NNP)\n ,/,\n (NP the/DT top-yielding/JJ fund/NN)\n ,/,\n had/VBD\n (NP a/DT seven-day/JJ compound/NN yield/NN)\n of/IN\n 9.37/CD\n (NP %/NN)\n during/IN\n (NP the/DT latest/JJS week/NN)\n ,/,\n down/RB\n from/IN\n 9.45/CD\n (NP %/NN)\n (NP a/DT week/NN)\n earlier/JJR\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n (NP Dreyfus/NNP World-Wide/NNP Dollar/NNP)\n ,/,\n (NP the/DT top-yielding/JJ fund/NN)\n ,/,\n had/VBD\n (NP a/DT seven-day/JJ compound/NN yield/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP 9.37/CD %/NN)\n during/IN\n (NP the/DT latest/JJS week/NN)\n ,/,\n down/RB\n from/IN\n (NP 9.45/CD %/NN)\n (NP a/DT week/NN)\n earlier/JJR\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n (NP It/PRP)\n invests/VBZ\n heavily/RB\n in/IN\n (NP dollar-denominated/JJ securities/NNS)\n overseas/RB\n and/CC\n is/VBZ\n currently/RB\n waiving/VBG\n (NP management/NN fees/NNS)\n ,/,\n which/WDT\n *T*-9/-NONE-\n boosts/VBZ\n (NP its/PRP$ yield/NN)\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n It/PRP\n invests/VBZ\n heavily/RB\n in/IN\n (NP dollar-denominated/JJ securities/NNS)\n overseas/RB\n and/CC\n is/VBZ\n currently/RB\n waiving/VBG\n (NP management/NN fees/NNS)\n ,/,\n which/WDT\n *T*-9/-NONE-\n boosts/VBZ\n (NP its/PRP$ yield/NN)\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n (NP The/DT average/JJ seven-day/JJ simple/JJ yield/NN)\n of/IN\n the/DT\n 400/CD\n (NP funds/NNS)\n was/VBD\n 8.12/CD\n (NP %/NN)\n ,/,\n down/RB\n from/IN\n 8.14/CD\n (NP %/NN)\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n (NP The/DT average/JJ seven-day/JJ simple/JJ yield/NN)\n of/IN\n (NP the/DT 400/CD funds/NNS)\n was/VBD\n 8.12/CD\n %/NN\n ,/,\n down/RB\n from/IN\n (NP 8.14/CD %/NN)\n ./.)\nSYS: (S\n (NP The/DT 30-day/JJ simple/JJ yield/NN)\n fell/VBD\n to/TO\n an/DT\n average/JJ\n 8.19/CD\n (NP %/NN)\n from/IN\n 8.22/CD\n (NP %/NN)\n ;/:\n (NP the/DT 30-day/JJ compound/NN yield/NN)\n slid/VBD\n to/TO\n an/DT\n average/JJ\n 8.53/CD\n (NP %/NN)\n from/IN\n 8.56/CD\n (NP %/NN)\n ./.)\nGOLD: (S\n The/DT\n 30-day/JJ\n simple/JJ\n yield/NN\n fell/VBD\n to/TO\n (NP an/DT average/JJ 8.19/CD %/NN)\n from/IN\n (NP 8.22/CD %/NN)\n ;/:\n the/DT\n 30-day/JJ\n compound/NN\n yield/NN\n slid/VBD\n to/TO\n (NP an/DT average/JJ 8.53/CD %/NN)\n from/IN\n (NP 8.56/CD %/NN)\n ./.)\n"
]
],
[
[
"The cd or the cardinal number tag can appear before noun and that must be included in our Parser.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from nltk.corpus import brown\n\nchunk = RegexpParser(\"NP: {((<DT|PRP\\$>?<JJ.*>*<CD.*|NN.*>+)|(<PRP>))(<CC>((<DT|PRP\\$>?<JJ.*>*<CD.*|NN.*>+)|(<PRP>)))*}\")\ntest_set = []\n\nfor parsed_sent in treebank.parsed_sents()[50:]:\n test_set.append(convert_to_chunk(parsed_sent))\n\nprint(chunk.evaluate(test_set))",
"ChunkParse score:\n IOB Accuracy: 78.1%%\n Precision: 52.9%%\n Recall: 71.2%%\n F-Measure: 60.7%%\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Identifying predicates and objects\n\nWe now build a function which extracts predicate-object pairs from syntax trees. For example, for the sentence _I bought the toys_ , your function should identify that the predicate of the sentence is _bought_ and its object is _toys_ , the function should then return the pair `(\"buy\", \"toy\")`. \n\n\nFirst, we write a recursive function `get_head` which takes two arguments: `phrase` and `phrase_type` as input. The `phrase` argument is an NLTK tree representing either an NP or a VP, and `phrase_type` is either `\"N\"` or `\"V\"` for NPs and VPs, respectively. The function should return the **lemmatized** syntactic head of `phrase`. For example, given the following NLTK syntax tree as input\n\n```\n(NP \n (DT the) \n (JJ grey) \n (NN dogs) \n)\n```\n\nThe function should return `dog`. \n\nWe assume that the head is either the right-most token with the appropriate POS `V.*` or `N.*`, or the syntactic head of the right-most child phrase having type `NP.*` or `VP.*` depending on `phrase_type`. This means that we may need to call `get_head` recursively. For example, for \n\n```\n(NP \n (DT the) \n (JJ second) \n (NN incentive) \n (NN plan)\n)\n```\n\nshould return `\"plan\"` which is the right-most noun. As another example, consider \n\n```\n(NP \n (DT the) \n (JJ blue) \n (NN bird)\n (CC and)\n (NP \n (DT the)\n (JJ yellow)\n (NN butterfly)\n )\n)\n```\n\nHere we return \"`butterfly`\" which is the head of the right-most child NP.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# lemmatizer.lemmatize(word,pos) returns the lemma for word. \n# pos should be 'n' for nouns and 'v' for verbs.\nlemmatizer = WordNetLemmatizer()\n\nhead_list = []\ndef get_head(phrase, phrase_type):\n '''returns the lemmatized lexical head assuming the provided phrase_type (\"N\",\"V\",etc.)'''\n head = None\n # your code here\n get_head_(phrase, head, phrase_type)\n if len(head_list) == 0:\n return head\n\n return lemmatizer.lemmatize(head_list[-1],phrase_type.lower())\n\ndef get_head_(phrase, head, phrase_type):\n '''returns the lemmatized lexical head assuming the provided phrase_type (\"N\",\"V\",etc.)'''\n if phrase.label()[:1] == phrase_type and phrase.height() == 2:\n head = phrase.pos()[0][0]\n head_list.append(phrase.pos()[0][0])\n elif phrase.label()[:1] == phrase_type and phrase.height() > 2:\n for sub in phrase:\n get_head_(sub, head, phrase_type)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"assert (get_head(Tree.fromstring(\"(NP (DT the) (JJ second) (NN incentive) (NN plan))\"), \"N\") == \"plan\")\nassert (get_head(Tree.fromstring(\"(NP-SUBJ (NP (DT the) (NNS policies)) (PP (IN of) (NP (NN tomorrow))))\"), \"N\") == \"policy\")\nassert (get_head(Tree.fromstring(\"(VP (VBN offered) (NP (NNS advertisers)))\"),\"V\") == \"offer\")\nprint(\"Success!\")",
"Success!\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"raw",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"raw"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a30d229174dec0eea7196d59997b789d0dd9c61
| 164,174 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
SARS-prediction-with-B-cell-data.ipynb
|
amanaation/SARS-prediction-with-B-cell-data
|
cd1c538e780dca121b5efe6fe4bdcb2133b00195
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
SARS-prediction-with-B-cell-data.ipynb
|
amanaation/SARS-prediction-with-B-cell-data
|
cd1c538e780dca121b5efe6fe4bdcb2133b00195
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
SARS-prediction-with-B-cell-data.ipynb
|
amanaation/SARS-prediction-with-B-cell-data
|
cd1c538e780dca121b5efe6fe4bdcb2133b00195
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 108.796554 | 46,740 | 0.760876 |
[
[
[
"# Importing Required Libraries",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn as sns\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nfrom sklearn import metrics\n%matplotlib inline\nsns.set_style(\"darkgrid\")\nsns.set(style=\"ticks\", color_codes=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\ndata = pd.read_csv(\"input_bcell.csv\")\ndata.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**By checking the value we can see that our class is Unbalanced.**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data[\"target\"].value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.describe()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"columns = []\nfor cols in data.columns:\n if type(data[cols][0]) is not str:\n columns.append(cols)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Including features only with integer or float values.**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data = data[columns]\ndata.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Standardising the values\n**Transforming the features to a scaled version.**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler\n\nscaled_data = StandardScaler()\nscaled_data = scaled_data.fit(data)\nscaled_data = scaled_data.transform(data)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"scaled_data.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Check if any of the features have null values.**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sns.heatmap(data.isnull(), cmap=\"viridis\", yticklabels=False, cbar = False, square = False)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Using Logistic Regression",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression\n\nmodel = LogisticRegression()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\nX = data[data.columns[:-1]]\ny = data[data.columns[-1]]\n\nX_train,X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state = 42, test_size = 0.33,shuffle = True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\nmodel.fit(X_train, y_train)\n",
"c:\\users\\amanm\\appdata\\local\\programs\\python\\python37\\lib\\site-packages\\sklearn\\linear_model\\_logistic.py:764: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge (status=1):\nSTOP: TOTAL NO. of ITERATIONS REACHED LIMIT.\n\nIncrease the number of iterations (max_iter) or scale the data as shown in:\n https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/preprocessing.html\nPlease also refer to the documentation for alternative solver options:\n https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/linear_model.html#logistic-regression\n extra_warning_msg=_LOGISTIC_SOLVER_CONVERGENCE_MSG)\n"
],
[
"\npredictions = model.predict(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, confusion_matrix\n\nprint(confusion_matrix(y_test, predictions))\nprint(\"\\n\")\nprint(classification_report(y_test, predictions))\n",
"[[3399 66]\n [1225 58]]\n\n\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.74 0.98 0.84 3465\n 1 0.47 0.05 0.08 1283\n\n accuracy 0.73 4748\n macro avg 0.60 0.51 0.46 4748\nweighted avg 0.66 0.73 0.64 4748\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Principal Component Analysis",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.decomposition import PCA\n\npca = PCA(n_components=2)\n\npca.fit(scaled_data)\n\nx_pca = pca.transform(scaled_data)\nx_pca.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def plot_pca(y_sklearn, y, title, x_label='Principal Component 1', y_label = 'Principal Component 2'):\n with plt.style.context('seaborn-whitegrid'):\n plt.figure(figsize=(9, 4))\n for lab, col in zip((0,1), ('blue', 'red')):\n plt.scatter(y_sklearn[y==lab, 0],\n y_sklearn[y==lab, 1],\n label=lab,\n c=col)\n plt.xlabel(x_label)\n plt.ylabel(y_label)\n plt.legend(loc='lower center')\n plt.tight_layout()\n plt.title(title)\n plt.show()\nplot_pca(x_pca, y,\"Entire Data\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pca.components_",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"new_data = pd.DataFrame(pca.components_, columns = data.columns)\nnew_data.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sns.set_style(\"darkgrid\")\nplt.figure(figsize=(12,6))\nsns.heatmap(new_data,cmap='plasma',)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Using K Nearest Neighbours",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier\nerror_rate = []\n\nfor i in range(1,50):\n\n knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=i)\n knn.fit(X_train,y_train)\n knn_predictions = knn.predict(X_test)\n error_rate.append(np.mean(knn_predictions != y_test))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sns.set_style(\"darkgrid\")\nplt.plot(range(1,50),error_rate,color='blue',linestyle='dashed', marker='o',\n markerfacecolor='red', markersize=5, )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=2)\nknn.fit(X_train,y_train)\nknn_predictions = knn.predict(X_test)\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(confusion_matrix(y_test, knn_predictions))\n\nprint(\"\\n\")\nprint(classification_report(y_test, knn_predictions))\n",
"[[3286 179]\n [ 996 287]]\n\n\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.77 0.95 0.85 3465\n 1 0.62 0.22 0.33 1283\n\n accuracy 0.75 4748\n macro avg 0.69 0.59 0.59 4748\nweighted avg 0.73 0.75 0.71 4748\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"\n# Using Random Forest Classifier",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier\n\nrandom_model = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators = 600)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"random_model.fit(X_train, y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"random_predictions = random_model.predict(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(confusion_matrix(y_test, random_predictions))\n\nprint(\"\\n\")\nprint(classification_report(y_test, random_predictions))\n",
"[[3192 273]\n [ 417 866]]\n\n\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.88 0.92 0.90 3465\n 1 0.76 0.67 0.72 1283\n\n accuracy 0.85 4748\n macro avg 0.82 0.80 0.81 4748\nweighted avg 0.85 0.85 0.85 4748\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Using Support Vector Machine",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.svm import SVC",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"svc_model = SVC(C = 1000 , gamma = 0.001)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"param_grid = {\"C\":[0.1,1,10,100,1000], \"gamma\":[10,1,0.1,0.001,0.0001]}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"grid_search_model = GridSearchCV(SVC(),param_grid,refit=True,verbose=2)\ngrid_search_model.fit(X_train,y_train)",
"Fitting 5 folds for each of 25 candidates, totalling 125 fits\n[CV] C=0.1, gamma=10 .................................................\n"
],
[
"grid_search_model.best_estimator_\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"svc_model.fit(X_train, y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"svc_predictions = svc_model.predict(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Comapring the accuracy of all the above 4 models",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(\"Logistic Regression : \\n\", confusion_matrix(y_test, predictions))\nprint(\"Support Vector Machine : \\n\",confusion_matrix(y_test, svc_predictions))\nprint(\"Random Forest : \\n\",confusion_matrix(y_test, random_predictions))\nprint(\"K Nearest Neigbiour : \\n\",confusion_matrix(y_test, knn_predictions))\nprint(\"\\n\")\nprint(\"Logistic Regression : \\n\", classification_report(y_test, predictions))\nprint(\"Support Vector Machine : \\n\",classification_report(y_test, svc_predictions))\nprint(\"Random Forest : \\n\",classification_report(y_test, random_predictions))\nprint(\"K Nearest Neigbiour : \\n\",classification_report(y_test, knn_predictions))\n\n",
"Logistic Regression : \n [[3399 66]\n [1225 58]]\nSupport Vector Machine : \n [[3228 237]\n [ 862 421]]\nRandom Forest : \n [[3192 273]\n [ 417 866]]\nK Nearest Neigbiour : \n [[3286 179]\n [ 996 287]]\n\n\nLogistic Regression : \n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.74 0.98 0.84 3465\n 1 0.47 0.05 0.08 1283\n\n accuracy 0.73 4748\n macro avg 0.60 0.51 0.46 4748\nweighted avg 0.66 0.73 0.64 4748\n\nSupport Vector Machine : \n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.79 0.93 0.85 3465\n 1 0.64 0.33 0.43 1283\n\n accuracy 0.77 4748\n macro avg 0.71 0.63 0.64 4748\nweighted avg 0.75 0.77 0.74 4748\n\nRandom Forest : \n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.88 0.92 0.90 3465\n 1 0.76 0.67 0.72 1283\n\n accuracy 0.85 4748\n macro avg 0.82 0.80 0.81 4748\nweighted avg 0.85 0.85 0.85 4748\n\nK Nearest Neigbiour : \n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.77 0.95 0.85 3465\n 1 0.62 0.22 0.33 1283\n\n accuracy 0.75 4748\n macro avg 0.69 0.59 0.59 4748\nweighted avg 0.73 0.75 0.71 4748\n\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a30d94b26e21c13f6dffe088aab2ea943a3612d
| 4,075 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
bus/bus.ipynb
|
brisa-araujo/mex-jul-2019-prework
|
3f2939d4f8fca158eec0eca5d6ad23e2f70249da
|
[
"Unlicense"
] | null | null | null |
bus/bus.ipynb
|
brisa-araujo/mex-jul-2019-prework
|
3f2939d4f8fca158eec0eca5d6ad23e2f70249da
|
[
"Unlicense"
] | null | null | null |
bus/bus.ipynb
|
brisa-araujo/mex-jul-2019-prework
|
3f2939d4f8fca158eec0eca5d6ad23e2f70249da
|
[
"Unlicense"
] | null | null | null | 26.986755 | 160 | 0.532025 |
[
[
[
"# Bus\n\nThis bus has a passenger entry and exit control system to monitor the number of occupants it carries and thus detect when there is too high a capacity.\n\nAt each stop the entry and exit of passengers is represented by a tuple consisting of two integer numbers.\n```\nbus_stop = (in, out)\n```\nThe succession of stops is represented by a list of these tuples.\n```\nstops = [(in1, out1), (in2, out2), (in3, out3), (in4, out4)]\n```\n\n## Goals:\n* lists, tuples\n* while/for loops\n* minimum, maximum, length\n* average, standard deviation\n\n## Tasks\n1. Calculate the number of stops.\n2. Assign to a variable a list whose elements are the number of passengers at each stop (in-out),\n3. Find the maximum occupation of the bus.\n4. Calculate the average occupation. And the standard deviation.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# variables\nbus_stop = (\"in\", \"out\")\nstops = [(\"in1\", \"out1\"), (\"in2\", \"out2\"), (\"in3\", \"out3\"), (\"in4\", \"out4\")]\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 1. Calculate the number of stops.\n\nnumber_stops = len(stops)\nprint(\"The bus made\", number_stops, \"stops\")",
"The bus made 4 stops\n"
],
[
"# 2. Assign a variable a list whose elements are the number of passengers in each stop: \n# Each item depends on the previous item in the list + in - out.\n\n''' I understand this exercise is theoric, since we have no data... \nso what I am doing is just setup the function so that any data of the type can apply.\n'''\n\ndef number_per_stop(a):\n number_list = [a[0][0]-a[0][1]]\n previous_number = a[0][0]-a[0][1]\n i = 1\n for i in range(1,len(a)):\n if previous_number + a[i][0] - a[i][1] < 0:\n return \"Impossible values\"\n else:\n number_list.append(previous_number + a[i][0] - a[i][1])\n previous_number += a[i][0] - a[i][1]\n i += 1\n return number_list\n\npassengers_per_stop = number_per_stop(stops)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 3. Find the maximum occupation of the bus.\n\nmax_occupation = max(passengers_per_stop)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 4. Calculate the average occupation. And the standard deviation.\n'''\nSorry for using numpy for std deviation... it is just too much code for 1 simple statistic :P \n'''\n\navg_occupation = sum(passengers_per_stop)/len(passengers_per_stop)\n\nimport numpy\nstd_occupation = numpy.std(passengers_per_stop)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a30e922b6986ac08723c87b8609e97e7dd76fd8
| 2,039 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
astr-119-hw-2.ipynb
|
audreydo/astr-119-hw-2
|
64cfd8964e0c118e1a312d8f5d421cda97b36e3d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
astr-119-hw-2.ipynb
|
audreydo/astr-119-hw-2
|
64cfd8964e0c118e1a312d8f5d421cda97b36e3d
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2018-10-18T00:48:15.000Z
|
2018-10-25T03:41:58.000Z
|
astr-119-hw-2.ipynb
|
audreydo/astr-119-hw-2
|
64cfd8964e0c118e1a312d8f5d421cda97b36e3d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 23.988235 | 110 | 0.518391 |
[
[
[
"# ASTR 119 - Homework #2, Due Oct. 18\n\nAudrey Do",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%matplotlib inline\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x = np.arange(0, 2*np.pi, 2*np.pi/1000) # create an array ranging from 0 to 2pi in 1000 increments\ny1 = 5.5 * np.cos(2*x) + 5.5\ny2 = 0.02 * np.exp(x)\ny3 = 0.25 * (x**2) + 0.1*np.sin(10*x)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,10)) # set figure size to 10 x 10\n\nplt.plot(x,y1,label=r'$y = 5.5 * cos(2x) + 5.5$') # plot y1\nplt.plot(x,y2,label=r'$y = 0.02 * e^x$') # plot y2\nplt.plot(x,y3,label=r'$y = 0.25x^2 + 0.1sin(10x)$') # plot y3\n\nplt.ylim(-1,10) # set y range from -1 to 10\n\nplt.xlabel(\"Time in Astr 119\") # label x axis as \"Time in Astr 119\"\nplt.ylabel(\"Measures of Awesomeness\") # label y axis as \"Measure of Awesomeness\"\nplt.legend(loc=4,framealpha=0.9) # add a legend with a semitransparent frame in bottom right corner\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a30f2fe7fe885528ca410a371f45068a6d30cef
| 361,498 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
2021/2021-03-12 Data Deep Dive Analsis (tests).ipynb
|
kulla/serlo-evaluations
|
3a53c850ad77fcf7fa793e92d52eeacda1a082a9
|
[
"CC0-1.0"
] | null | null | null |
2021/2021-03-12 Data Deep Dive Analsis (tests).ipynb
|
kulla/serlo-evaluations
|
3a53c850ad77fcf7fa793e92d52eeacda1a082a9
|
[
"CC0-1.0"
] | null | null | null |
2021/2021-03-12 Data Deep Dive Analsis (tests).ipynb
|
kulla/serlo-evaluations
|
3a53c850ad77fcf7fa793e92d52eeacda1a082a9
|
[
"CC0-1.0"
] | null | null | null | 245.249661 | 108,488 | 0.885158 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport mysql.connector\n\nfrom IPython.display import display, Markdown\n\ndb = mysql.connector.connect(\n host=\"localhost\",\n user=\"root\",\n password=\"secret\",\n port=\"3306\",\n database=\"serlo\"\n)\n\n\ndef read_event_log():\n df = pd.read_sql(\"\"\"\n select event_log.id, event_log.date, event_log.actor_id,\n user.username, event_log.event_id, event.name\n from event_log\n join event on event.id = event_log.event_id\n join user on user.id = event_log.actor_id\n order by event_log.id\n \"\"\", db)\n df.set_index(\"id\", inplace=True)\n return df\n\nevent_log = read_event_log()\nevent_log.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from IPython.display import display\n\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\ndef becomes_active(x, delta):\n diff = x-x.min()\n if diff[diff < delta].count() > 10:\n return 1\n else:\n return 0\n\nd = event_log.groupby(\"actor_id\").aggregate({\n \"date\": [\"first\", lambda x: becomes_active(x, pd.Timedelta(\"90days\")), lambda x: becomes_active(x, pd.Timedelta(\"3days\"))],\n \"username\": \"first\",\n})\nd.columns = d.columns.to_flat_index()\nd.rename(columns={\n (\"date\", \"first\"): \"date\",\n (\"date\", \"<lambda_0>\"): \"becomes_active_90days\",\n (\"date\", \"<lambda_1>\"): \"becomes_active_2days\"\n}, inplace=True)\nd.sort_values(\"date\", inplace=True)\nd = d[[\"date\", \"becomes_active_90days\", \"becomes_active_2days\"]]\nd.set_index(\"date\", inplace=True)\nd = d.rolling(\"365d\").mean()\ndisplay(d.head())\nd.plot(figsize=(20,8), ylim=(0,0.4))\nplt.show()\nd[\"diff\"] = d[\"becomes_active_90days\"] - d[\"becomes_active_2days\"]\nd[\"diff\"].plot(figsize=(20,8), ylim=(0,0.2))\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from IPython.display import display\n\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\ndef becomes_active(x, delta):\n diff = x-x.min()\n if diff[diff < delta].count() > 10:\n return 1\n else:\n return 0\n\nd = event_log.groupby(\"actor_id\").aggregate({\n \"date\": [\"first\", lambda x: becomes_active(x, pd.Timedelta(\"90days\")), lambda x: becomes_active(x, pd.Timedelta(\"1days\"))],\n \"username\": \"first\",\n})\nd.columns = d.columns.to_flat_index()\nd.rename(columns={\n (\"date\", \"first\"): \"date\",\n (\"date\", \"<lambda_0>\"): \"becomes_active_90days\",\n (\"date\", \"<lambda_1>\"): \"becomes_active_2days\"\n}, inplace=True)\nd.sort_values(\"date\", inplace=True)\nd = d[[\"date\", \"becomes_active_90days\", \"becomes_active_2days\"]]\nd.set_index(\"date\", inplace=True)\nd = d.rolling(\"90d\").sum()\ndisplay(d.head())\nd.plot(figsize=(20,8))\nplt.show()\nd[\"diff\"] = d[\"becomes_active_90days\"] - d[\"becomes_active_2days\"]\nd[\"diff\"].plot(figsize=(20,8))\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.set_option('display.max_rows', None)\ndf = event_log[event_log[\"event_id\"] == 5].groupby(\"actor_id\").aggregate({\n \"username\": \"first\",\n \"event_id\": \"count\"\n})\ndf.rename(columns = { \"event_id\": \"edits\" }, inplace=True)\ndf.sort_values(\"edits\", inplace=True, ascending=False)\ndf = df.head(136)\ndf.to_csv(\"/tmp/most_active_user.csv\")\ndf",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def read_event_log_all():\n df = pd.read_sql(\"\"\"\n select event_log.id, event.name, event_log.actor_id, user.username,\n event_log.date, event_log.event_id, event_parameter_uuid.uuid_id\n from event_log\n join event on event.id = event_log.event_id\n join user on user.id = event_log.actor_id\n join event_parameter on event_parameter.log_id = event_log.id\n join event_parameter_uuid on event_parameter_uuid.event_parameter_id = event_parameter.id\n where event_parameter.name_id != 8\n \"\"\", db)\n df.set_index(\"id\", inplace=True)\n return df\n\nread_event_log_all().to_csv(\"/tmp/event_log.csv\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df2 = event_log[event_log[\"event_id\"] == 5].copy()\ndf2[\"year\"] = df2[\"date\"].map(lambda x: x.year)\ndf2 = df2[df2[\"year\"] <= 2019].groupby(\"actor_id\").aggregate({\n \"username\": \"first\",\n \"event_id\": \"count\"\n })\ndf2.rename(columns = { \"event_id\": \"edits\" }, inplace=True)\ndf2.sort_values(\"edits\", inplace=True, ascending=False)\ndf2 = df2.head(136)\n\ndf2[~df2[\"username\"].isin(df[\"username\"])].to_csv(\"/tmp/2019.csv\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"p = event_log.copy()\np = p[(p[\"username\"] != \"Legacy\") & (p[\"event_id\"] == 5) & (p[\"username\"] == \"kathongi\")].copy()\np.set_index(\"date\", inplace=True)\np = p.resample(\"1d\").aggregate({\"actor_id\": \"count\" })\np.rename(columns={\"actor_id\": \"edits\"}, inplace=True)\nf = p.tail(100)\n#display(f[f[\"edits\"] <10])\nm = int(f.max())\nf.plot.hist(bins=m, figsize=(20,8))\nf.describe()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a30f7f56f6a38e9e3f76f9ae13c7d1357449c16
| 28,225 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
LGBM(41)/LGBM2(41).ipynb
|
sokolovm19/malware_prediction
|
0d9e5f1a59792e434eabfd19138b6a41e42fc116
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
LGBM(41)/LGBM2(41).ipynb
|
sokolovm19/malware_prediction
|
0d9e5f1a59792e434eabfd19138b6a41e42fc116
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
LGBM(41)/LGBM2(41).ipynb
|
sokolovm19/malware_prediction
|
0d9e5f1a59792e434eabfd19138b6a41e42fc116
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 34.088164 | 362 | 0.329212 |
[
[
[
"import os\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport sklearn\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import KFold\nfrom sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\n%matplotlib inline\n\nimport pandas as pd\nfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier, forest\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nfrom sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom IPython.display import display\nimport numpy as np\nimport scipy\nimport re",
"/python3.7/site-packages/sklearn/utils/deprecation.py:144: FutureWarning: The sklearn.ensemble.forest module is deprecated in version 0.22 and will be removed in version 0.24. The corresponding classes / functions should instead be imported from sklearn.ensemble. Anything that cannot be imported from sklearn.ensemble is now part of the private API.\n warnings.warn(message, FutureWarning)\n"
],
[
"train = pd.read_csv('df2.csv')\nprint('Training set loaded')\nprint(train.shape)",
"Training set loaded\n(1427437, 42)\n"
],
[
"train",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df1, drop = train.drop('Unnamed: 0', axis=1), train['Unnamed: 0']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X, Y = df1.drop('HasDetections', axis=1), df1['HasDetections']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_train, X_val, Y_train, Y_val = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.2, random_state=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import lightgbm as lgb",
"/python3.7/site-packages/lightgbm/__init__.py:48: UserWarning: Starting from version 2.2.1, the library file in distribution wheels for macOS is built by the Apple Clang (Xcode_8.3.3) compiler.\nThis means that in case of installing LightGBM from PyPI via the ``pip install lightgbm`` command, you don't need to install the gcc compiler anymore.\nInstead of that, you need to install the OpenMP library, which is required for running LightGBM on the system with the Apple Clang compiler.\nYou can install the OpenMP library by the following command: ``brew install libomp``.\n \"You can install the OpenMP library by the following command: ``brew install libomp``.\", UserWarning)\n"
],
[
"def print_score(m):\n res = [roc_auc_score(m.predict(X_train), Y_train), roc_auc_score(m.predict(X_val), Y_val), \n m.score(X_train, Y_train), m.score(X_val, Y_val)\n ]\n if hasattr(m, 'oob_score_'): res.append(m.oob_score_)\n print(res)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"m = lgb.LGBMClassifier(boosting_type='gbdt', \n num_leaves=250, \n n_estimators=5000, \n learning_rate=0.02,\n min_data_in_leaf=42,\n feature_fraction= 0.8,\n bagging_freq=5,\n bagging_fraction= 0.8,\n bagging_seed=11,\n lambda_l1= 0.15,\n lambda_l2= 0.15,\n max_depth=-1\n )\n%time m.fit(X_train, Y_train)\n\n%time print_score(m)",
"CPU times: user 44min 13s, sys: 10.3 s, total: 44min 23s\nWall time: 5min 42s\n[0.7035875573476128, 0.664266112411531, 0.7035875507575206, 0.6642133441685816]\nCPU times: user 1h 7min 14s, sys: 4.09 s, total: 1h 7min 18s\nWall time: 8min 29s\n"
],
[
"test = pd.read_csv('test41.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"testing, drop = test.drop('Unnamed: 0', axis=1), test['Unnamed: 0']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_test, Y_test = testing.drop('HasDetections', axis=1), testing['HasDetections']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%time Y_predi = m.predict(X_test)",
"CPU times: user 41min 47s, sys: 3.39 s, total: 41min 50s\nWall time: 5min 21s\n"
],
[
"Y_predi = Y_predi.reshape(Y_predi.shape[0], 1)\nprint(Y_predi)",
"[[0]\n [0]\n [0]\n ...\n [0]\n [0]\n [0]]\n"
],
[
"Y_prediction = pd.DataFrame(Y_predi)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Y_prediction",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Y_prediction.to_csv('Prediction2.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a31021ad2e1fc6f2fcadea7dc9bb8995a9a0fab
| 179,777 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Mini_projects/Bayesian_Inference/inferential_statistics_3-Q.ipynb
|
psanghal/Springboard-Data-Science
|
47224935d7de51355acedee822b3d27ba820548c
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2019-08-07T17:12:03.000Z
|
2019-08-07T17:12:03.000Z
|
Mini_projects/Bayesian_Inference/inferential_statistics_3-Q.ipynb
|
psanghal/Springboard-Data-Science
|
47224935d7de51355acedee822b3d27ba820548c
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Mini_projects/Bayesian_Inference/inferential_statistics_3-Q.ipynb
|
psanghal/Springboard-Data-Science
|
47224935d7de51355acedee822b3d27ba820548c
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2019-11-13T16:08:32.000Z
|
2019-11-13T16:08:32.000Z
| 248.654219 | 93,948 | 0.915134 |
[
[
[
"# Inferential Statistics III - Bayesian",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Introduction",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In the last two subunits, you've encountered two schools for performing inference from samples. The Frequentist school calls upon a body of theory established over the past couple of centuries or so. Under certain assumptions and conditions, this allows us to calculate what we would expect to see if an experiment were to be repeated again and again and again. The expected value of the average of a sample is one such statistic we can calculate a result for, even if the originating distribution is far from normal. The bootstrap school, on the other hand, literally does (virtually) run that experiment again and again and again and empirically observes the multitude of outcomes. It then empirically calculates a statistic of interest. While this can be for exactly the same statistics that frequentism calculates (e.g. the mean of a sample) this empirical approach can also perform inference on statistics that do not have well known sampling distributions. Because of the requirement to repeat many, many redraws (with replacement) from the sample, this approach only became feasible with modern computing power.\n\nAnd thus we come to the Bayesian school of inference. Here we frame our probabilities not so much in terms of \"how many times would I expect this event to occur if the experiment were to be rerun many times\" but rather in terms of \"what is my belief in the likelihood of this event occurring?\" In a Bayesian probabilistic programming context, we can build models for systems and then let the data tell us how likely certain values for our model parameters are. This can be a very useful way to incorporate prior knowledge and deal with limited data. It can just be more than a _little_ fiddly to produce a good model!",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Medical charge data set",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"For the final mini-project of the stats unit, you'll once again return tot he medical charge data you've used for the other mini-projects. Previously, we considered whether we believed that the actual average(non-insured) charge had fallen below a certain threshold.\n\nThe hospital is now reviewing its financial resiliency plan, which requires a model for revenue under a range of conditions that include the number of patients treated. Its current model is based on a confidence interval for the mean, and scaling that by different numbers of patients for each scenario. This approach has a number of limitations, most acutely the breakdown of the central limit theorem for low patient volumes; the current model does not do a good job of reflecting the variability in revenue you would see as the number of cases drops. A bootstrap approach would return samples of the same size as the original. Taking subsamples would restrict the sampling to the values already present in the original sample and would not do a good job of representing the actual variability you might see. What is needed is a better model of individual charges.\n\nSo the problem here is that we want to model the distribution of individual charges and _we also really want to be able to capture our uncertainty about that distribution_ so we can better capture the range of values we might see. This naturally leads us to a powerful, probabilistic approach — we'll use the pymc3 library to perform Bayesian inference.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Loading the data and performing an initial view",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport pymc3 as pm",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import pymc3 as pm\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nfrom numpy.random import seed\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom scipy.stats import gamma\n# there has been some incompatibilty between theano and numpy, if you encounter\n# an error with the latest packages from anaconda, then the included\n# package-list-txt should allow you to create a conda environment with compatible\n# packages.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"medical = pd.read_csv('insurance2.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"medical.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"insurance = medical.charges[medical.insuranceclaim == 1]\nno_insurance = medical.charges[medical.insuranceclaim == 0]\nn_ins = len(insurance)\nn_no_ins = len(no_insurance)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"_ = plt.hist(insurance, bins=30, alpha=0.5, label='insurance claim')\n_ = plt.hist(no_insurance, bins=30, alpha=0.5, label='not insurance claim')\n_ = plt.xlabel('Charge amount')\n_ = plt.ylabel('Frequency')\n_ = plt.legend()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We may suspect from the above that there is some sort of exponential-like distribution at play here. The charges that were not insurance claims seem most like this. The insurance claim charges may possibly be multimodal. The gamma distribution may be applicable and we could test this for the distribution of charges that weren't insurance claims first. Developing our new method for the easiest looking case first is a common and sound approach that can demonstrate a minimum viable solution/product and get, or keep, stakeholders on board.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Initial parameter estimation",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"An initial guess for the gamma distribution's $\\alpha$ and $\\beta$ parameters can be made as described [here](https://wiki.analytica.com/index.php?title=Gamma_distribution).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"alpha_est = np.mean(no_insurance)**2 / np.var(no_insurance)\nbeta_est = np.var(no_insurance) / np.mean(no_insurance)\nalpha_est, beta_est",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Initial simulation",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Let's draw the same number of random variates from this distribution and compare to our observed data.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"seed(47)\nno_ins_model_rvs = gamma(alpha_est, scale=beta_est).rvs(n_no_ins)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"_ = plt.hist(no_ins_model_rvs, bins=30, alpha=0.5, label='simulated')\n_ = plt.hist(no_insurance, bins=30, alpha=0.5, label='observed')\n_ = plt.xlabel('Charge amount')\n_ = plt.ylabel('Frequency')\n_ = plt.legend()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Well it doesn't look too bad! We're not a million miles off. But can we do better? We have a plausible form for the distribution of charge amounts and potential values for that distribution's parameters so we can already draw random variates from that distribution to perform simulations. But we don't know if we have a _best_ estimate for the population parameters, and we also only have a single estimate each for $\\alpha$ and $\\beta$; we aren't capturing our uncertainty in their values. Can we take a Bayesian inference approach to estimate the parameters?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Creating a PyMC3 model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# PyMC3 Gamma seems to use rate = 1/beta\nrate_est = 1/beta_est\n# Initial parameter estimates we'll use below\nalpha_est, rate_est",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"__Q:__ You are now going to create your own PyMC3 model!\n1. Use an [exponential](https://docs.pymc.io/api/distributions/continuous.html#pymc3.distributions.continuous.Exponential) prior for alpha. Call this stochastic variable `alpha_`.\n2. Similarly, use an exponential prior for the rate ([$1/\\beta$](https://wiki.analytica.com/index.php?title=Gamma_distribution)) parameter in PyMC3's [Gamma](https://docs.pymc.io/api/distributions/continuous.html#pymc3.distributions.continuous.Gamma). Call this stochastic variable `rate_` (but it will be supplied as `pm.Gamma`'s `beta` parameter). Hint: to set up a prior with an exponential distribution for $x$ where you have an initial estimate for $x$ of $x_0$, use a scale parameter of $1/x_0$.\n5. Create your Gamma distribution with your `alpha_` and `rate_` stochastic variables and the observed data.\n6. Perform 10000 draws.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Hint: you may find it helpful to work backwards. Start with your `pm.Gamma`, and note the required stochastic variables `alpha` and `beta`. Then, before that, you need to create those stochastic variables using `pm.Exponential` and the correct parameters.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"__A:__",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"with pm.Model() as model: \n alpha_ = pm.Exponential('alpha_', 1/alpha_est)\n rate_ = pm.Exponential('rate_', 1/rate_est) #beta = 1/rate\n no_insurance_charge = pm.Gamma('no_insurance_charge', alpha=alpha_, beta=rate_, observed = no_insurance)\n trace = pm.sample(10000)",
"Auto-assigning NUTS sampler...\nInitializing NUTS using jitter+adapt_diag...\nMultiprocess sampling (4 chains in 4 jobs)\nNUTS: [rate_, alpha_]\nSampling 4 chains: 100%|██████████| 42000/42000 [00:11<00:00, 3647.85draws/s]\nThe acceptance probability does not match the target. It is 0.8788903541644567, but should be close to 0.8. Try to increase the number of tuning steps.\nThe number of effective samples is smaller than 25% for some parameters.\n"
],
[
"trace",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"If you get a warning about acceptance probability not matching the target, and that it's around 0.88 when it should be close to 0.8, don't worry. We encourage you to read up on this and see if you can adjust the parameters and/or arguments to pm.sample, but if your model runs without any additional warnings or errors then you should be doing great!",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"__Q:__ Explore your posteriors for $\\alpha$ and $\\beta$ (from the trace).\n* Calculate the 95% credible interval for $\\alpha$ and $\\beta$.\n* Plot your posterior values of $\\alpha$ and $\\beta$ (both line plots and histograms). \n* Mark your CIs on the histograms.\n* Do they look okay? What would bad plots look like?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"__A:__",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#95% Confidence Interval for Alpha: \nalpha_mean = np.mean(trace.alpha_)\nprint(f\"Alpha Mean is {alpha_mean}\")\n\nconfi_alpha_lower, confi_alpha_upper= np.percentile(trace.alpha_, [2.5, 97.5])\nprint(f\"Confidence Intreval for Alpha is {confi_alpha_lower} & {confi_alpha_upper}\")",
"Alpha Mean is 2.2317456331484307\nConfidence Intreval for Alpha is 1.9949991968177083 & 2.4852708733833455\n"
],
[
"#95% Confidence Interval for Beta: \nbeta_mean = 1/np.mean(trace.rate_) #Beta mean = 1/rate mean\nprint(f\"Beta Mean is {beta_mean}\")\n\nconfi_beta_lower, confi_beta_upper = 1/np.percentile(trace.rate_, [2.5, 97.5])\nprint(f\"Confidence Interval for Beta is {confi_beta_lower} and {confi_beta_upper}\")",
"Beta Mean is 3953.0423598833904\nConfidence Interval for Beta is 4484.814533648446 and 3510.172571679417\n"
],
[
"#Histogram and Line plots for Alpha Posterior Values: \n\n_ = plt.hist(trace.alpha_, bins = 30, edgecolor = 'black')\n_ = plt.axvline(alpha_mean, color= 'red')\n_ = plt.axvline(confi_alpha_lower, color = 'gold', linestyle= '-.')\n_ = plt.axvline(confi_alpha_upper, color = 'gold', linestyle= '-.')\n_ = plt.xlabel('Alpha_')\n_ = plt.ylabel('Count')\n_ = plt.title('Alpha Posterior Values')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Histogram and Line Plots for Beta Posterior Values: \n_ = plt.hist(1/trace.rate_, bins = 30, edgecolor = 'black')\n_ = plt.axvline(beta_mean, color= 'red')\n_ = plt.axvline(confi_beta_lower, color = 'gold', linestyle= '-.')\n_ = plt.axvline(confi_beta_upper, color = 'gold', linestyle= '-.')\n_ = plt.xlabel('Beta_')\n_ = plt.ylabel('Count')\n_ = plt.title('Beta Posterior Values')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"__Q:__ Play around with some of the built-in diagnostic plots for your model. We suggest at least checking out the traceplot for alpha and beta. How do they look?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"__A:__",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#TracePlot: \n_ = pm.traceplot(trace)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Traceplots for alpha and beta looks similar",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"__Q:__ Take your best shot at a new simulated sequence of medical charges using scipy.stat's gamma distribution. Don't forget the difference between functions that take $\\beta$ and functions that use $1/\\beta$ for the scale parameter. Simulate a data set the same size as the number of observations in the data and overlay the two histograms (simulated and observed).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"__A:__",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#Using Scipy Stats:\nseed(47)\nbest_shot_simulated = gamma(alpha_mean, scale = beta_mean).rvs(n_no_ins)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Overlay Histogram: \n_ = plt.hist(best_shot_simulated, bins=30, alpha = 0.5, label ='Simulated')\n_ = plt.hist(no_insurance, bins = 30, alpha = 0.5, label = 'Observed')\n_ = plt.legend()\n_ = plt.xlabel('Non Insured Charges')\n_ = plt.ylabel('Count')\n_ = plt.title('Overlay of Simluated and Observed Non Insured Charges')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Similar to initial simulation",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Summary",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In this exercise, we have postulated a distribution to describe the individual charge amounts for non-insured cases. This distribution has two required parameters, which we do not know, but we used PyMC3 to perform Bayesian inference to find our level of \"belief\" in a range of values for them. We then used the average parameter values to create one simulated data set of the same size as the original, but the distribution of our posteriors for these parameters will allow us to perform simulations of any sample size we desire and for a range of scenarios of different $\\alpha$ and $\\beta$. This could be a powerful tool to model different financial conditions for the hospital. \n\nWell done making it through this tricky subject. Starting think Bayesian _and_ starting to get to grips with something like PyMC3 is no easy task. As a data scientist, the most important thing is to be aware that this statistical approach exists, though you may not actually use this approach as much as you use the other approaches you've learned about. Still, we encourage you to think of ways that this approach could apply to the work that you do in this course and throughout your career. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4a310f0b35666f6e91646ce33e2a3a812c6a44d4
| 3,446 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
analytics/.ipynb_checkpoints/Untitled1-checkpoint.ipynb
|
martin-tauber/thresholdMigration
|
c1e9b9b1cd9ed73b6b7e08da8dff176f04c53e28
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
analytics/.ipynb_checkpoints/Untitled1-checkpoint.ipynb
|
martin-tauber/thresholdMigration
|
c1e9b9b1cd9ed73b6b7e08da8dff176f04c53e28
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
analytics/.ipynb_checkpoints/Untitled1-checkpoint.ipynb
|
martin-tauber/thresholdMigration
|
c1e9b9b1cd9ed73b6b7e08da8dff176f04c53e28
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 43.620253 | 1,286 | 0.635229 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\n\nimport sys\nsys.path.append(\"..\")\nfrom lib.thresholds import FileThresholdSet, InstanceThresholdMigrator\nfrom lib.kmrepository import KMRepository\nfrom lib.policy import PolicyFactory\nfrom lib.solution import SolutionPackManager\nfrom lib.ruleset import RuleSetFactory, RulesetMigrator",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"solutionPackManager = SolutionPackManager(path=\"solutions\", repository = kmRepository)\nrulesets = RuleSetFactory(\"/Users/martin/Development/pcm2cma/in/pconfig/activ\")\n\nrulesetMigrator = RulesetMigrator(rulesets, solutionPackManager, kmRepository)\nrulesetConfigurations = rulesetMigrator.migrate()\n\n# Generate Policies\npolicyFactory = PolicyFactory(None, \"*\", \"*\", False, False, 399, 499, \"owner\", \"group\", False, 30, \"/tmp/agentinfo.csv\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a311da3d7740819f0f3afb8ef46dc19591ee7d6
| 89,319 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
climate_final.ipynb
|
AtreidesArcade/SQLAlchemy-Challenge
|
9efe458a4addf13eb65518c6872409ba716976bf
|
[
"ADSL"
] | null | null | null |
climate_final.ipynb
|
AtreidesArcade/SQLAlchemy-Challenge
|
9efe458a4addf13eb65518c6872409ba716976bf
|
[
"ADSL"
] | null | null | null |
climate_final.ipynb
|
AtreidesArcade/SQLAlchemy-Challenge
|
9efe458a4addf13eb65518c6872409ba716976bf
|
[
"ADSL"
] | null | null | null | 115.998701 | 29,822 | 0.863568 |
[
[
[
"%matplotlib inline\nfrom matplotlib import style\nstyle.use('fivethirtyeight')\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport matplotlib.dates as mdates\nfrom flask import Flask, jsonify",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import datetime as dt\nfrom scipy import stats",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Reflect Tables into SQLAlchemy ORM",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Python SQL toolkit and Object Relational Mapper\nimport sqlalchemy\nfrom sqlalchemy.ext.automap import automap_base \nfrom sqlalchemy.orm import Session\nfrom sqlalchemy import create_engine,inspect, func",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# create engine to hawaii.sqlite\nengine = create_engine(\"sqlite:///Resources/hawaii.sqlite\")\ninspector = inspect(engine)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# reflect an existing database into a new model\nBase = automap_base()\n# reflect the tables\nBase.prepare(engine, reflect=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# View all of the classes that automap found\nBase.classes.keys()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Save references to each table\nMeasurement = Base.classes.measurement\nStation = Base.classes.station",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create our session (link) from Python to the DB\nsession = Session(engine)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"inspector.get_table_names()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"columns = inspector.get_columns('measurement')\nfor column in columns:\n primarykeystr = \"\"\n if column['primary_key'] == 1:\n primarykeystr = \"Primary Key\"\n print(column[\"name\"],column[\"type\"],primarykeystr)",
"id INTEGER Primary Key\nstation TEXT \ndate TEXT \nprcp FLOAT \ntobs FLOAT \n"
],
[
"columns = inspector.get_columns('station')\nfor column in columns:\n primarykeystr = \"\"\n if column['primary_key'] == 1:\n primarykeystr = \"Primary Key\"\n print(column[\"name\"], column[\"type\"], primarykeystr)",
"id INTEGER Primary Key\nstation TEXT \nname TEXT \nlatitude FLOAT \nlongitude FLOAT \nelevation FLOAT \n"
]
],
[
[
"# Exploratory Precipitation Analysis",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#Validate records in the column\nsession.query(func.count(Measurement.date)).all()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Find the earliest starting date\n\nearlieststr = session.query(Measurement.date).order_by(Measurement.date).first()\nlateststr = session.query(Measurement.date).order_by(Measurement.date.desc()).first()\nprint(f\"Earliest: {earlieststr[0]} , Latest: {lateststr[0]}\")",
"Earliest: 2010-01-01 , Latest: 2017-08-23\n"
],
[
"#Find the last/ most recent date record in column\n#Find the the last years worth of data\n#Save to dataFrame\n#Sort vales by date\n#Set Index by date\n\nlatestdate = dt.datetime.strptime(lateststr[0], '%Y-%m-%d')\nquerydate = dt.date(latestdate.year -1, latestdate.month, latestdate.day)\nquerydate\n\nsel = [Measurement.date,Measurement.prcp]\nqueryresult = session.query(*sel).filter(Measurement.date >= querydate).all()\n\nprecipitation = pd.DataFrame(queryresult, columns=['Date','Precipitation'])\nprecipitation = precipitation.dropna(how='any') # clean up non value entries\nprecipitation = precipitation.sort_values([\"Date\"], ascending=True)\nprecipitation = precipitation.set_index(\"Date\")\nprecipitation.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Use Pandas Plotting with Matplotlib to plot the data\n\n# Set plot and plot the chart\nxx = precipitation.index.tolist()\nyy = precipitation['Precipitation'].tolist()\n\nplt.figure(figsize=(10,7))\nplt.bar(xx,yy,width = 5 ,color='g', alpha=0.5, align=\"center\",label='Precipitation')\nplt.tick_params(\n axis='x', \n which='both', \n bottom=False, \n top=False, \n labelbottom=False) \nmajor_ticks = np.arange(0,400,80)\nplt.xticks(major_ticks)\n\nplt.title(f\"Precipitation from {querydate} to {lateststr[0]}\")\nplt.xlabel(\"Date\")\nplt.ylabel(\"Precipitation\")\nplt.grid(which='major', axis='both', linestyle='-')\nplt.legend()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Use Pandas to calcualte the summary statistics for the precipitation data\nprecipitation.describe()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Exploratory Station Analysis",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Design a query to calculate the total number stations in the dataset\nsession.query(Station.id).count()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Design a query to find the most active stations (i.e. what stations have the most rows?)\n# List the stations and the counts in descending order.\nsel = [Measurement.station,func.count(Measurement.id)]\nactivestations = session.query(*sel).\\\n group_by(Measurement.station).\\\n order_by(func.count(Measurement.id).desc()).all()\nactivestations",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Using the most active station id from the previous query, calculate the lowest, highest, and average temperature.\nsel = [func.min(Measurement.tobs),func.max(Measurement.tobs),func.avg(Measurement.tobs)]\nmostactivestationdata = session.query(*sel).\\\n group_by(Measurement.station).\\\n order_by(func.count(Measurement.id).desc()).first()\nmostactivestationdata",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Query the last 12 months of temperature observation data for this station and plot the results as a histogram\nqueryresult = session.query(Measurement.tobs).\\\n filter(Measurement.station == activestations[0][0]).\\\n filter(Measurement.date >= querydate).all()\ntemperatures = list(np.ravel(queryresult))\n\nsel = [Station.station,Station.name,Station.latitude,Station.longitude,Station.elevation]\nqueryresult = session.query(*sel).all()\nstations_desc = pd.DataFrame(queryresult, columns=['Station','Name','Latitude','Longitude','Elevation'])\n\nstationname = stations_desc.loc[stations_desc[\"Station\"] == activestations[0][0],\"Name\"].tolist()[0]\n\nplt.hist(temperatures, bins=12,rwidth=1.0,label='tobs')\nplt.grid(axis='both', alpha=0.75)\nplt.ylabel('Frequency')\nplt.title(f\"Temperature from {querydate} to {lateststr[0]} \\nmeasured at {stationname}\")\nplt.legend()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#func to return the minimum, average, and maximum temperatures for that range of dates\ndef calc_temps(start_date, end_date):\n return session.query(func.min(Measurement.tobs), func.avg(Measurement.tobs), func.max(Measurement.tobs)).\\\n filter(Measurement.date >= start_date).filter(Measurement.date <= end_date).all()\n\n\nprint(calc_temps('2012-02-28', '2012-03-05'))",
"[(62.0, 69.57142857142857, 74.0)]\n"
],
[
"# Use your previous function `calc_temps` to calculate the tmin, tavg, and tmax \nstartdate = '2017-01-01'\nenddate = '2017-01-07'\ntempresult = calc_temps(startdate,enddate)[0]\ntempresult",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
" #Plot the results from your previous query as a bar chart. \n# Use \"Trip Avg Temp\" as title\n# Use the average temperature for y axis\n# Use the peak-to-peak (tmax-tmin) value as the y error bar (yerr)\nx_pos = [0]\ny_pos = [tempresult[1]]\nerror = [(tempresult[2] - tempresult[0])]\n\nw = 3\nh = 5\nd = 70\nplt.figure(figsize=(w, h), dpi=d)\nplt.bar(x_pos,y_pos,color='orange', yerr=error)\nplt.xlim(-0.75,0.75)\nplt.title(\"Trip Avg Temp\")\nplt.ylabel(\"Temp (F)\")\nplt.ylim(0, 100)\nplt.tick_params(axis='x',which='both',bottom=False,top=False,labelbottom=False)\nplt.grid(which='major', axis='x', linestyle='')\nplt.grid(which='major', axis='y', linestyle='-')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Close session",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Close Session\nsession.close()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a31338d1a36cedcf7a281c2363c64c98d23cfb2
| 6,512 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
linear_regression.ipynb
|
Abhishekauti21/dsmp-pre-work
|
718b1c4149306c84d22763df9dcc5959015267f8
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2020-03-29T18:42:36.000Z
|
2020-05-17T10:45:08.000Z
|
linear_regression.ipynb
|
Abhishekauti21/dsmp-pre-work
|
718b1c4149306c84d22763df9dcc5959015267f8
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
linear_regression.ipynb
|
Abhishekauti21/dsmp-pre-work
|
718b1c4149306c84d22763df9dcc5959015267f8
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 21.634551 | 244 | 0.409398 |
[
[
[
"<a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/Abhishekauti21/dsmp-pre-work/blob/master/linear_regression.ipynb\" target=\"_parent\"><img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open In Colab\"/></a>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import re",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"str=\"How are you. How is everything\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"matches=re.findall(\"How\",str)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(matches)",
"['How', 'How']\n"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# match object",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"str",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"matches=re.search(\"How\",str)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(type(matches))",
"<class '_sre.SRE_Match'>\n"
],
[
"print(matches)",
"<_sre.SRE_Match object; span=(0, 3), match='How'>\n"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#search()function",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"txt=\"The rain in spain\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x=re.search(\"\\s\",txt)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(\"The first white-space character is located in position:\",x.start())",
"The first white-space character is located in position: 3\n"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a315a7543f0223839e03b29e29587aa7430cf24
| 15,656 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
MNIST_TF_1.ipynb
|
captain-pool/DraiveX-TF_NN_1
|
a034d726f0280bd1b403f90b20a4c298914e37b5
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2018-07-26T08:30:57.000Z
|
2018-07-26T08:30:57.000Z
|
MNIST_TF_1.ipynb
|
DrAiveX/DraiveX-TF_NN_1
|
a034d726f0280bd1b403f90b20a4c298914e37b5
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
MNIST_TF_1.ipynb
|
DrAiveX/DraiveX-TF_NN_1
|
a034d726f0280bd1b403f90b20a4c298914e37b5
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 56.724638 | 199 | 0.706566 |
[
[
[
"import tensorflow as tf\nfrom tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data",
"/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/h5py/__init__.py:16: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility\n from h5py import h5a, h5d, h5ds, h5f, h5fd, h5g, h5r, h5s, h5t, h5p, h5z\n/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/h5py/_hl/group.py:15: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility\n from h5py import h5g, h5i, h5o, h5r, h5t, h5l, h5p\n/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/scipy/sparse/csgraph/__init__.py:148: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility\n from ._shortest_path import shortest_path, floyd_warshall, dijkstra,\\\n/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/scipy/sparse/csgraph/_validation.py:5: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility\n from ._tools import csgraph_to_dense, csgraph_from_dense,\\\n/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/scipy/sparse/csgraph/__init__.py:150: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility\n from ._traversal import breadth_first_order, depth_first_order, \\\n/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/scipy/sparse/csgraph/__init__.py:152: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility\n from ._min_spanning_tree import minimum_spanning_tree\n/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/scipy/ndimage/measurements.py:36: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility\n from . import _ni_label\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/pandas/_libs/__init__.py:4: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility. Expected 96, got 88\n from .tslib import iNaT, NaT, Timestamp, Timedelta, OutOfBoundsDatetime\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/pandas/__init__.py:26: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility. Expected 96, got 88\n from pandas._libs import (hashtable as _hashtable,\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/pandas/core/dtypes/common.py:6: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility. Expected 96, got 88\n from pandas._libs import algos, lib\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/pandas/core/util/hashing.py:7: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility. Expected 96, got 88\n from pandas._libs import hashing, tslib\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/pandas/core/indexes/base.py:7: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility. Expected 96, got 88\n from pandas._libs import (lib, index as libindex, tslib as libts,\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/pandas/tseries/offsets.py:21: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility. Expected 96, got 88\n import pandas._libs.tslibs.offsets as liboffsets\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/pandas/core/ops.py:16: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility. Expected 96, got 88\n from pandas._libs import algos as libalgos, ops as libops\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/pandas/core/indexes/interval.py:32: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility. Expected 96, got 88\n from pandas._libs.interval import (\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/pandas/core/internals.py:14: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility. Expected 96, got 88\n from pandas._libs import internals as libinternals\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/pandas/core/sparse/array.py:33: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility. Expected 96, got 88\n import pandas._libs.sparse as splib\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/pandas/core/window.py:36: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility. Expected 96, got 88\n import pandas._libs.window as _window\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/pandas/core/groupby/groupby.py:68: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility. Expected 96, got 88\n from pandas._libs import (lib, reduction,\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/pandas/core/reshape/reshape.py:30: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility. Expected 96, got 88\n from pandas._libs import algos as _algos, reshape as _reshape\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/pandas/io/parsers.py:45: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility. Expected 96, got 88\n import pandas._libs.parsers as parsers\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/pandas/io/pytables.py:50: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility. Expected 96, got 88\n from pandas._libs import algos, lib, writers as libwriters\n/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/scipy/spatial/__init__.py:90: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility\n from .ckdtree import *\n/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/scipy/spatial/__init__.py:91: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility\n from .qhull import *\n/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/utils/__init__.py:11: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility\n from .murmurhash import murmurhash3_32\n/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/utils/__init__.py:11: RuntimeWarning: numpy.ufunc size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility\n from .murmurhash import murmurhash3_32\n/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/utils/sparsetools/__init__.py:3: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility\n from ._min_spanning_tree import minimum_spanning_tree\n/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/utils/sparsetools/__init__.py:3: RuntimeWarning: numpy.ufunc size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility\n from ._min_spanning_tree import minimum_spanning_tree\n/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/utils/sparsetools/_graph_validation.py:5: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility\n from ._graph_tools import csgraph_to_dense, csgraph_from_dense,\\\n/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/utils/sparsetools/_graph_validation.py:5: RuntimeWarning: numpy.ufunc size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility\n from ._graph_tools import csgraph_to_dense, csgraph_from_dense,\\\n/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/utils/sparsetools/__init__.py:4: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility\n from ._traversal import connected_components\n/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/utils/sparsetools/__init__.py:4: RuntimeWarning: numpy.ufunc size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility\n from ._traversal import connected_components\n/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/data.py:20: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility\n from ..utils.sparsefuncs import inplace_csr_row_normalize_l1\n/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/data.py:20: RuntimeWarning: numpy.ufunc size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility\n from ..utils.sparsefuncs import inplace_csr_row_normalize_l1\n/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/scipy/special/__init__.py:531: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility\n from ._ufuncs import *\n/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/scipy/stats/distributions.py:35: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility\n from . import vonmises_cython\n/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/scipy/stats/stats.py:252: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility\n from ._rank import rankdata, tiecorrect\n/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/scipy/stats/morestats.py:20: DeprecationWarning: Importing from numpy.testing.decorators is deprecated, import from numpy.testing instead.\n from numpy.testing.decorators import setastest\n/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/metrics/cluster/supervised.py:19: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility\n from .expected_mutual_info_fast import expected_mutual_information\n/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/metrics/cluster/supervised.py:19: RuntimeWarning: numpy.ufunc size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility\n from .expected_mutual_info_fast import expected_mutual_information\n/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/utils/extmath.py:14: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility\n from ._logistic_sigmoid import _log_logistic_sigmoid\n/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/utils/extmath.py:14: RuntimeWarning: numpy.ufunc size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility\n from ._logistic_sigmoid import _log_logistic_sigmoid\n/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/metrics/pairwise.py:52: RuntimeWarning: numpy.dtype size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility\n from .pairwise_fast import _chi2_kernel_fast\n/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/metrics/pairwise.py:52: RuntimeWarning: numpy.ufunc size changed, may indicate binary incompatibility\n from .pairwise_fast import _chi2_kernel_fast\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Creating Variable and Placeholders",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"X=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,28*28*1])\nW=tf.Variable(tf.zeros([28*28*1,10]))\nb=tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))\nY=tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(X,W)+b)\nY_=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10])\ninit=tf.initialize_all_variables()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Creating Loss Function",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cross_entropy=-tf.reduce_sum(Y_*tf.log(Y))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"is_correct=tf.equal(tf.argmax(Y,1),tf.argmax(Y_,1))\naccuracy=tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(is_correct,tf.float32))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"optimizer=tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.003)\nm=optimizer.minimize(cross_entropy)\nsess=tf.Session()\nsess.run(init)\nmnist=input_data.read_data_sets(\"MNIST_Data/\",one_hot=True)",
"Successfully downloaded train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz 9912422 bytes.\nExtracting MNIST_Data/train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz\nSuccessfully downloaded train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz 28881 bytes.\nExtracting MNIST_Data/train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz\nSuccessfully downloaded t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz 1648877 bytes.\nExtracting MNIST_Data/t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz\nSuccessfully downloaded t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz 4542 bytes.\nExtracting MNIST_Data/t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz\n"
],
[
"for i in range(1000):\n batch=mnist.train.next_batch(100)\n b={X:batch[0],Y_:batch[1]}\n sess.run(m,feed_dict=b)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"b={X:mnist.test.images,Y_:mnist.test.labels}\nsess.run([accuracy,cross_entropy],feed_dict=b)",
"/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/IPython/core/formatters.py:92: DeprecationWarning: DisplayFormatter._ipython_display_formatter_default is deprecated: use @default decorator instead.\n def _ipython_display_formatter_default(self):\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/IPython/core/formatters.py:98: DeprecationWarning: DisplayFormatter._formatters_default is deprecated: use @default decorator instead.\n def _formatters_default(self):\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/IPython/core/formatters.py:677: DeprecationWarning: PlainTextFormatter._deferred_printers_default is deprecated: use @default decorator instead.\n def _deferred_printers_default(self):\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/IPython/core/formatters.py:669: DeprecationWarning: PlainTextFormatter._singleton_printers_default is deprecated: use @default decorator instead.\n def _singleton_printers_default(self):\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/IPython/core/formatters.py:672: DeprecationWarning: PlainTextFormatter._type_printers_default is deprecated: use @default decorator instead.\n def _type_printers_default(self):\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/IPython/core/formatters.py:669: DeprecationWarning: PlainTextFormatter._singleton_printers_default is deprecated: use @default decorator instead.\n def _singleton_printers_default(self):\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/IPython/core/formatters.py:672: DeprecationWarning: PlainTextFormatter._type_printers_default is deprecated: use @default decorator instead.\n def _type_printers_default(self):\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/IPython/core/formatters.py:677: DeprecationWarning: PlainTextFormatter._deferred_printers_default is deprecated: use @default decorator instead.\n def _deferred_printers_default(self):\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a3165dbdda2596381ad876ef804cee5592892b3
| 2,838 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
basic-statistics/population_sample_sampling_dist.ipynb
|
tejeshreddy/statistics-with-python
|
34ce76779a5228f671ca9e4173424a9373013307
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
basic-statistics/population_sample_sampling_dist.ipynb
|
tejeshreddy/statistics-with-python
|
34ce76779a5228f671ca9e4173424a9373013307
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
basic-statistics/population_sample_sampling_dist.ipynb
|
tejeshreddy/statistics-with-python
|
34ce76779a5228f671ca9e4173424a9373013307
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 39.971831 | 477 | 0.679704 |
[
[
[
"# Population Distribution, Sample Distribution and Sampling Distribution",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Population Distribution:\nThe population is the whole set of values, or individuals, you are interested in. For example, if you want to know the average height of the residents of India, that is your population, ie, the population of India.\n\nPopulation characteristic are mean (μ), Standard deviation (σ) , proportion (P) , median, percentiles etc. The value of a population characteristic is fixed. This characteristics are called population distribution. They are symbolized by Greek characters as they are population parameters.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Sample Distribution:\nThe sample is a subset of the population, and is the set of values you actually use in your estimation. Let’s think 1000 individual you have selected for your study to know about average height of the residents of India. This sample has some quantity computed from values e.g. mean (x ), Standard deviation (s) , sample proportion etc. This is called sample distribution. The mean and standard deviation are symbolized by Roman characters as they are sample statistics. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Sampling Distribution:\nResearchers often use a sample to draw inferences about the population that sample is from. To do that, they make use of a probability distribution that is very important in the world of statistics: the sampling distribution. It is theoretical distribution. The distribution of sample statistics is called sampling distribution.\n\n\n<img src=\"assets/sampling_dist.png\" width=500>\n\nWe have a population of x values whose histogram is the probability distribution of x. Select a sample of size n from this population and calculate a sample statistic e.g. . This procedure can be repeated indefinitely and generates a population of values for the sample statistic and the histogram is the sampling distribution of the sample statistics.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4a3172d5ab274ac5d6bf2456f41f23ce7a222fbe
| 692,123 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
content/en/modules/fmri_parcellation/atlas_parcellations.ipynb
|
lalou97/psy6983_2021
|
5b551c8ce2d89282fdc537b7302e04dee2b3d79b
|
[
"MIT"
] | 9 |
2020-05-09T04:03:30.000Z
|
2021-07-13T11:39:51.000Z
|
content/en/modules/fmri_parcellation/atlas_parcellations.ipynb
|
lalou97/psy6983_2021
|
5b551c8ce2d89282fdc537b7302e04dee2b3d79b
|
[
"MIT"
] | 42 |
2020-02-28T16:17:49.000Z
|
2020-07-05T16:44:32.000Z
|
content/en/modules/fmri_parcellation/atlas_parcellations.ipynb
|
lalou97/psy6983_2021
|
5b551c8ce2d89282fdc537b7302e04dee2b3d79b
|
[
"MIT"
] | 29 |
2020-02-13T19:01:51.000Z
|
2021-11-11T03:07:20.000Z
| 3,174.876147 | 405,041 | 0.909769 |
[
[
[
"from nilearn.plotting import view_img\nfrom nilearn import datasets\nfrom nilearn import plotting ",
"In /home/lussier/.local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/matplotlib/mpl-data/stylelib/_classic_test.mplstyle: \nThe text.latex.preview rcparam was deprecated in Matplotlib 3.3 and will be removed two minor releases later.\nIn /home/lussier/.local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/matplotlib/mpl-data/stylelib/_classic_test.mplstyle: \nThe mathtext.fallback_to_cm rcparam was deprecated in Matplotlib 3.3 and will be removed two minor releases later.\nIn /home/lussier/.local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/matplotlib/mpl-data/stylelib/_classic_test.mplstyle: Support for setting the 'mathtext.fallback_to_cm' rcParam is deprecated since 3.3 and will be removed two minor releases later; use 'mathtext.fallback : 'cm' instead.\nIn /home/lussier/.local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/matplotlib/mpl-data/stylelib/_classic_test.mplstyle: \nThe validate_bool_maybe_none function was deprecated in Matplotlib 3.3 and will be removed two minor releases later.\nIn /home/lussier/.local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/matplotlib/mpl-data/stylelib/_classic_test.mplstyle: \nThe savefig.jpeg_quality rcparam was deprecated in Matplotlib 3.3 and will be removed two minor releases later.\nIn /home/lussier/.local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/matplotlib/mpl-data/stylelib/_classic_test.mplstyle: \nThe keymap.all_axes rcparam was deprecated in Matplotlib 3.3 and will be removed two minor releases later.\nIn /home/lussier/.local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/matplotlib/mpl-data/stylelib/_classic_test.mplstyle: \nThe animation.avconv_path rcparam was deprecated in Matplotlib 3.3 and will be removed two minor releases later.\nIn /home/lussier/.local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/matplotlib/mpl-data/stylelib/_classic_test.mplstyle: \nThe animation.avconv_args rcparam was deprecated in Matplotlib 3.3 and will be removed two minor releases later.\n/home/lussier/.local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/nilearn/datasets/__init__.py:89: FutureWarning: Fetchers from the nilearn.datasets module will be updated in version 0.9 to return python strings instead of bytes and Pandas dataframes instead of Numpy arrays.\n \"Numpy arrays.\", FutureWarning)\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Fetch atlases",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Schaefer atlas",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"atlas = datasets.fetch_atlas_schaefer_2018()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#plot a static map\nplotting.plot_roi(atlas.maps)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#plot an interactive map\nplotting.view_img(atlas.maps)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Fetch and view three atlases of your choice from nilearn.datasets ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"You may select any 3 atlases from nilearn.datasets. Fetch and view the atlases using the above code as an example. Check out the documentation at nilearn.plotting at https://nilearn.github.io/plotting/index.html to try different viewing methods, edit colours, change viewing options etc.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Compare and discuss",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Compare the atlas parcellations and discuss your observations below. What might be some reasons that parcellation could affect your functional connectivity results?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4a31841a23ea9de872886d67ec3d06bad9ae6da3
| 15,126 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
preprocessing.ipynb
|
sizhit2/myprojects
|
35a1796b2ec103739923805c9f4f96dc3ee4fb03
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
preprocessing.ipynb
|
sizhit2/myprojects
|
35a1796b2ec103739923805c9f4f96dc3ee4fb03
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
preprocessing.ipynb
|
sizhit2/myprojects
|
35a1796b2ec103739923805c9f4f96dc3ee4fb03
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 34.692661 | 182 | 0.451673 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nfrom datetime import datetime",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"movie_all = pd.read_csv('data/all_movie.csv')\nmovie_info = pd.read_csv('data/movie_info.tsv',sep = '\\t')\nreview = pd.read_csv('data/reviews.tsv',sep = '\\t',encoding = 'unicode_escape')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"movie_all_cleaned = movie_all.drop(['Cast 4','Cast 3','Cast 5','Cast 6','Director 2','Director 3','Writer 2','Writer 3','Writer 4'],axis = 1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"movie_info_cleaned = movie_info.drop(['currency'],axis = 1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"merged = pd.merge(movie_all_cleaned,movie_info_cleaned,how = 'right',left_on=['Director 1','Writer 1','Runtime'],right_on= ['director','writer','runtime']).drop_duplicates()\nmerged = merged.drop(['Rating','Genre','Release Date','dvd_date','Director 1','Writer 1'],axis = 1)\nmerged = merged.drop_duplicates()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"movie_final = merged.drop(['Studio','Runtime','Description','Year'],axis = 1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"movie_final['runtime'] = movie_final['runtime'].apply(lambda x: x if pd.isna(x) else float(x[:-8]))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def convert_rating(col):\n scores = [1,0.95,0.85, 0.80, 0.75,0.65,0.60,0.55,0.45,0.40,0.35,0.25,0.20,0.15]\n grades = ['A+','A', 'A-', 'B+', 'B', 'B-', 'C+', 'C', 'C-', 'D+', 'D', 'D-','F+','F']\n if(pd.isna(col)):\n return col\n x = col.split('/')\n try:\n num = float(x[0])\n de = float(x[1])\n if(num < de):\n return num/de\n else:\n return 1.0\n except ValueError:\n try:\n i = grades.index(x[0])\n return scores[i]\n except ValueError:\n return 0.0\n except IndexError:\n return np.abs(float(x[0]) / 10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"review_final = review.copy()\nreview_final['rating'] = review['rating'].apply(convert_rating)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"review_final['fresh'] = review['fresh'].apply(lambda x:1 if x =='fresh' else 0)\nmovie_final['theater_date'] = movie_final['theater_date'].apply(lambda x:x if pd.isna(x) else datetime.strptime(x,'%b %d, %Y').strftime('%Y-%m-%d'))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"movie_final = movie_final.replace('', np.nan, regex=True)\nreview_final = review_final.replace('', np.nan, regex=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"review_final.to_csv('cleaned_review.csv',index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"movie_final.to_csv('cleaned_movie.csv',index=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"movie_all.head(5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"search_engine = movie_all[['Description','Title','Cast 1','Director 1','Writer 1','Year','Genre']]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"search_engine.drop_duplicates().to_csv('search.csv',index=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"avg = review_final.groupby(['id']).mean()['fresh']",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a3198978fe515e7fc38780e82b35a9bd2e834a0
| 409,716 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
spacy-2.1/procs-corpus-seq2seq.ipynb
|
samlet/stack
|
47db17fd4fdab264032f224dca31a4bb1d19b754
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 3 |
2020-01-11T13:55:38.000Z
|
2020-08-25T22:34:15.000Z
|
spacy-2.1/procs-corpus-seq2seq.ipynb
|
samlet/stack
|
47db17fd4fdab264032f224dca31a4bb1d19b754
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
spacy-2.1/procs-corpus-seq2seq.ipynb
|
samlet/stack
|
47db17fd4fdab264032f224dca31a4bb1d19b754
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2021-01-01T05:21:44.000Z
|
2021-01-01T05:21:44.000Z
| 104.947746 | 2,362 | 0.613195 |
[
[
[
"from sagas.train.parallel_corpus import ParallelCorpus\npc=ParallelCorpus()\nrs=pc.load_corpus()\npc.samples",
".. bert service port is localhost\n"
],
[
"prefix='/pi/ai/seq2seq/'\npc=ParallelCorpus()\nrs_zh=pc.load_corpus(f\"{prefix}/cmn-eng/cmn.txt\")\npc.samples",
".. bert service port is localhost\n"
],
[
"def samples(count, file):\n pc=ParallelCorpus()\n pc.samples_count=count\n rs_zh=pc.load_corpus(f\"{prefix}{file}\")\n return pc.samples\n\nsamples(5, 'en_Persian/pes-eng/pes.txt')",
".. bert service port is localhost\n"
],
[
"samples(5, 'ara-eng/ara.txt')",
".. bert service port is localhost\n"
],
[
"from sagas.nlu.uni_cli import UniCli\nfrom sagas.nlu.uni_viz import EnhancedViz\nfrom sagas.nlu.corenlp_parser import get_chunks\nfrom sagas.tool.misc import print_stem_chunks\nimport sagas\n\nserial_numbers='❶❷❸❹❺❻❼❽❾❿'\nlocal=False\ndef viz_sample(lang, sents, engine='corenlp'):\n from sagas.nlu.uni_remote import dep_parse\n \n if local:\n uni=UniCli()\n doc=uni.parsers[engine](lang, sents)\n rs = get_chunks(doc)\n else:\n doc= dep_parse(sents, lang, engine)\n rs= get_chunks(doc)\n for serial, r in enumerate(rs):\n df = sagas.to_df(r['domains'], ['rel', 'index', 'text', 'lemma', 'children', 'features'])\n if 'head' in r:\n cla=\"%s(%s)\"%(r['head'], r['head_pos'])\n else:\n cla='_'\n print(serial_numbers[serial], '%s(%s)' % (r['type'], r['lemma']), cla)\n # sagas.print_df(df)\n display(df)\n print_stem_chunks(r)\n\n cv = EnhancedViz(shape='egg', size='8,5', fontsize=20)\n return cv.analyse_doc(doc, None)\n\nsents_p=samples(1, 'ara-eng/ara.txt')[0]\nprint(sents_p)\nsents=sents_p[1]\nviz_sample('ar', sents)",
".. bert service port is localhost\n('Most Americans liked Roosevelt.', 'أحب أكثر الأمريكيين روزفلت.')\n.. request is {'lang': 'ar', 'sents': 'أحب أكثر الأمريكيين روزفلت.', 'engine': 'corenlp'}\nwords count 5\n❶ verb_domains(أَحَب) _\n"
],
[
"sents_p=samples(1, 'jpn-eng-2019/jpn.txt')[0]\nprint(sents_p)\nsents=sents_p[1]\nviz_sample('ja', sents)",
".. bert service port is localhost\n('Even Tom did that.', 'トムでさえそれをした。')\n.. request is {'lang': 'ja', 'sents': 'トムでさえそれをした。', 'engine': 'corenlp'}\nwords count 8\n❶ verb_domains(する) _\n"
],
[
"sents='what time is it ?'\nviz_sample('en', sents)",
".. request is {'lang': 'en', 'sents': 'what time is it ?', 'engine': 'corenlp'}\nwords count 5\n❶ aux_domains(be) it(pron)\n"
],
[
"sents='what time is it ?'\nviz_sample('en', sents, engine='spacy')",
".. request is {'lang': 'en', 'sents': 'what time is it ?', 'engine': 'spacy'}\nwords count 5\n❶ verb_domains(be) _\n"
],
[
"viz_sample('ja', \"今何時ですか?\")",
".. request is {'lang': 'ja', 'sents': '今何時ですか?', 'engine': 'corenlp'}\nwords count 6\n❶ aux_domains(だ) 何(num)\n"
],
[
"viz_sample('zh', '现在是几点?')",
".. request is {'lang': 'zh', 'sents': '现在是几点?', 'engine': 'corenlp'}\nwords count 4\n❶ verb_domains(现) _\n"
],
[
"viz_sample('zh', '现在是几点?', engine='ltp')",
"是 --> 现在|ADV|nt|O\n? --> 是|HED|v|O\n点 --> 几|ATT|m|O\n是 --> 点|VOB|q|O\n是 --> ?|WP|wp|O\nverb_domains(是) _\n"
],
[
"viz_sample('zh', '现在几点?', engine='ltp')",
"点 --> 现在|ATT|nt|O\n点 --> 几|ATT|m|O\n? --> 点|HED|q|O\n点 --> ?|WP|wp|O\nindex: 1\ttext: 现在 \tlemma: 现在\tupos: NOUN\txpos: nt\nindex: 2\ttext: 几 \tlemma: 几\tupos: NUM\txpos: m\nindex: 3\ttext: 点 \tlemma: 点\tupos: X\txpos: q\nindex: 4\ttext: ? \tlemma: ?\tupos: PUNCT\txpos: wp\n现在 -> att, 3, 点\n几 -> att, 3, 点\n点 -> hed, 0, _root_\n? -> wp, 3, 点\n('现在', 3, 'att')\n('几', 3, 'att')\n('点', 0, 'hed')\n('?', 3, 'wp')\n"
],
[
"viz_sample('zh', '现在几点?', engine='corenlp')",
"❶ verb_domains(现) _\n"
],
[
"viz_sample('en', \"How many laptops do you have?\")",
"verb_domains(have) _\n"
],
[
"viz_sample('zh', \"你有几台笔记本电脑?\", 'ltp')",
"有 --> 你|SBV|r|O\n? --> 有|HED|v|O\n台 --> 几|ATT|m|O\n笔记本 --> 台|ATT|q|O\n电脑 --> 笔记本|ATT|n|O\n有 --> 电脑|VOB|n|O\n有 --> ?|WP|wp|O\nverb_domains(有) _\n"
],
[
"viz_sample('ja', \"ラップトップはいくつありますか?\")",
"verb_domains(ある) _\n"
],
[
"en=\"I have to turn off the lights in the room.\"\nzh=\"我必须关掉房间里的灯。\"\nja=\"部屋の明かりを消さなければなりません。\"\nviz_sample('en', en)",
".. request is {'lang': 'en', 'sents': 'I have to turn off the lights in the room.', 'engine': 'corenlp'}\nwords count 11\n❶ verb_domains(have) _\n"
],
[
"viz_sample('zh', zh, 'ltp')",
".. request is {'lang': 'zh', 'sents': '我必须关掉房间里的灯。', 'engine': 'ltp'}\nwords count 8\n❶ verb_domains(关掉) _\n"
],
[
"viz_sample('ja', ja)",
"❶ verb_domains(消す) _\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a319c3ccd3f621d537a53ec8067716f37c0047e
| 41,398 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
WIP/4 - Gated PixelCNN/gated_pixelcnn_receptive_field.ipynb
|
Mind-the-Pineapple/Autoregressive-models
|
34880e294b0999ddae77965f1f1b18528a7c5add
|
[
"MIT"
] | 14 |
2020-03-19T08:31:21.000Z
|
2021-12-01T02:35:54.000Z
|
WIP/4 - Gated PixelCNN/gated_pixelcnn_receptive_field.ipynb
|
Mind-the-Pineapple/Autoregressive-models
|
34880e294b0999ddae77965f1f1b18528a7c5add
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
WIP/4 - Gated PixelCNN/gated_pixelcnn_receptive_field.ipynb
|
Mind-the-Pineapple/Autoregressive-models
|
34880e294b0999ddae77965f1f1b18528a7c5add
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2020-06-24T14:37:30.000Z
|
2020-08-06T14:24:03.000Z
| 87.522199 | 5,132 | 0.799918 |
[
[
[
"# Gated PixelCNN receptive fields\n\nHi everybody!\nIn this notebook, we will analyse the Gated PixelCNN's block receptive field. Diferent of the original PixelCNN, we expect that the blocks of the Gated PixelCNN do not create blind spots that limit the information flow of the previous pixel in order to model the density probability function.\n\nLet's start!",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"First, we define the masked convolutions involved in the Gated PixelCNN as presented in the post.\n\n*Note: Here we are using float64 to get more precise values of the gradients and avoid false values.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import random as rn\n\nimport matplotlib\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom matplotlib.ticker import FixedLocator\nimport numpy as np\nimport tensorflow as tf\nfrom tensorflow import keras\nfrom tensorflow import nn\nfrom tensorflow.keras import initializers\nfrom tensorflow.keras.utils import Progbar\n\ntf.keras.backend.set_floatx('float64')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class MaskedConv2D(keras.layers.Layer):\n \"\"\"Convolutional layers with masks extended to work with Gated PixelCNN.\n\n Convolutional layers with simple implementation of masks type A and B for\n autoregressive models. Extended version to work with the verticala and horizontal\n stacks from the Gated PixelCNN model.\n\n Arguments:\n mask_type: one of `\"V\"`, `\"A\"` or `\"B\".`\n filters: Integer, the dimensionality of the output space (i.e. the number of output\n filters in the convolution).\n kernel_size: An integer or tuple/list of 2 integers, specifying the height and width\n of the 2D convolution window.\n Can be a single integer to specify the same value for all spatial dimensions.\n strides: An integer or tuple/list of 2 integers, specifying the strides of the\n convolution along the height and width.\n Can be a single integer to specify the same value for all spatial dimensions.\n Specifying any stride value != 1 is incompatible with specifying any\n `dilation_rate` value != 1.\n padding: one of `\"valid\"` or `\"same\"` (case-insensitive).\n kernel_initializer: Initializer for the `kernel` weights matrix.\n bias_initializer: Initializer for the bias vector.\n \"\"\"\n\n def __init__(self,\n mask_type,\n filters,\n kernel_size,\n strides=1,\n padding='same',\n kernel_initializer='glorot_uniform',\n bias_initializer='zeros'):\n super(MaskedConv2D, self).__init__()\n\n assert mask_type in {'A', 'B', 'V'}\n self.mask_type = mask_type\n\n self.filters = filters\n\n if isinstance(kernel_size, int):\n kernel_size = (kernel_size, kernel_size)\n self.kernel_size = kernel_size\n\n self.strides = strides\n self.padding = padding.upper()\n self.kernel_initializer = initializers.get(kernel_initializer)\n self.bias_initializer = initializers.get(bias_initializer)\n\n def build(self, input_shape):\n kernel_h, kernel_w = self.kernel_size\n\n self.kernel = self.add_weight('kernel',\n shape=(kernel_h,\n kernel_w,\n int(input_shape[-1]),\n self.filters),\n initializer=self.kernel_initializer,\n trainable=True)\n\n self.bias = self.add_weight('bias',\n shape=(self.filters,),\n initializer=self.bias_initializer,\n trainable=True)\n\n mask = np.ones(self.kernel.shape, dtype=np.float64)\n\n # Get centre of the filter for even or odd dimensions\n if kernel_h % 2 != 0:\n center_h = kernel_h // 2\n else:\n center_h = (kernel_h - 1) // 2\n\n if kernel_w % 2 != 0:\n center_w = kernel_w // 2\n else:\n center_w = (kernel_w - 1) // 2\n\n if self.mask_type == 'V':\n mask[center_h + 1:, :, :, :] = 0.\n else:\n mask[:center_h, :, :] = 0.\n mask[center_h, center_w + (self.mask_type == 'B'):, :, :] = 0.\n mask[center_h + 1:, :, :] = 0.\n\n self.mask = tf.constant(mask, dtype=tf.float64, name='mask')\n\n def call(self, input):\n masked_kernel = tf.math.multiply(self.mask, self.kernel)\n x = nn.conv2d(input,\n masked_kernel,\n strides=[1, self.strides, self.strides, 1],\n padding=self.padding)\n x = nn.bias_add(x, self.bias)\n return x",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Then, we define th eblock implementation.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class GatedBlock(tf.keras.Model):\n \"\"\" Gated block that compose Gated PixelCNN.\"\"\"\n\n def __init__(self, mask_type, filters, kernel_size):\n super(GatedBlock, self).__init__(name='')\n\n self.mask_type = mask_type\n self.vertical_conv = MaskedConv2D(mask_type='V',\n filters=2 * filters,\n kernel_size=kernel_size)\n\n self.horizontal_conv = MaskedConv2D(mask_type=mask_type,\n filters=2 * filters,\n kernel_size=(1, kernel_size))\n\n self.padding = keras.layers.ZeroPadding2D(padding=((1, 0), 0))\n self.cropping = keras.layers.Cropping2D(cropping=((0, 1), 0))\n\n self.v_to_h_conv = keras.layers.Conv2D(filters=2 * filters, kernel_size=1)\n\n self.horizontal_output = keras.layers.Conv2D(filters=filters, kernel_size=1)\n\n def _gate(self, x):\n tanh_preactivation, sigmoid_preactivation = tf.split(x, 2, axis=-1)\n return tf.nn.tanh(tanh_preactivation) * tf.nn.sigmoid(sigmoid_preactivation)\n\n def call(self, input_tensor):\n v = input_tensor[0]\n h = input_tensor[1]\n\n vertical_preactivation = self.vertical_conv(v)\n\n # Shifting vertical stack feature map down before feed into horizontal stack to\n # ensure causality\n v_to_h = self.padding(vertical_preactivation)\n v_to_h = self.cropping(v_to_h)\n v_to_h = self.v_to_h_conv(v_to_h)\n\n horizontal_preactivation = self.horizontal_conv(h)\n\n v_out = self._gate(vertical_preactivation)\n\n horizontal_preactivation = horizontal_preactivation + v_to_h\n h_activated = self._gate(horizontal_preactivation)\n h_activated = self.horizontal_output(h_activated)\n\n if self.mask_type == 'A':\n h_out = h_activated\n elif self.mask_type == 'B':\n h_out = h + h_activated\n\n return v_out, h_out",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"In order to analyse grow the receptive field grows along the layers, we will start analysing 1 block.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"height = 10\nwidth = 10\nn_channel = 1\n\ndata = tf.random.normal((1, height, width, n_channel))\n\ninputs = keras.layers.Input(shape=(height, width, n_channel))\nv, h = GatedBlock(mask_type='A', filters=1, kernel_size=3)([inputs, inputs])\nmodel = tf.keras.Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=h)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def plot_receptive_field(model, data):\n with tf.GradientTape() as tape:\n tape.watch(data)\n prediction = model(data)\n loss = prediction[:,5,5,0]\n\n gradients = tape.gradient(loss, data)\n\n gradients = np.abs(gradients.numpy().squeeze())\n gradients = (gradients > 0).astype('float64')\n gradients[5, 5] = 0.5\n\n fig = plt.figure()\n ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)\n\n plt.xticks(np.arange(0, 10, step=1))\n plt.yticks(np.arange(0, 10, step=1))\n ax.xaxis.set_minor_locator(FixedLocator(np.arange(0.5, 10.5, step=1)))\n ax.yaxis.set_minor_locator(FixedLocator(np.arange(0.5, 10.5, step=1)))\n plt.grid(which=\"minor\")\n plt.imshow(gradients, vmin=0, vmax=1)\n plt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plot_receptive_field(model, data)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Excellent! Like we expected the block considered all the previous blocks in the same row of the analyssed pixel, and the two rows over it.\n\nNote that this receptive field is different from the original PixelCNN. In the original PixelCNN only one row over the analysed pixel influenced in its prediction (when using one masked convolution). In the Gated PixelCNN, the authors used a vertical stack with effective area of 2x3 per vertical convolution. This is not a problem, since the considered pixels still being the ones in past positions. We believe the main coice for this format is to implement an efficient way to apply the masked convolutions without using masking (which we will discuss in future posts).\n\nFor the next step, we wll verify a model with 2, 3, 4, and 5 layers",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"inputs = keras.layers.Input(shape=(height, width, n_channel))\nv, h = GatedBlock(mask_type='A', filters=1, kernel_size=3)([inputs, inputs])\nv, h = GatedBlock(mask_type='B', filters=1, kernel_size=3)([v, h])\nmodel = tf.keras.Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=h)\n\nplot_receptive_field(model, data)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"inputs = keras.layers.Input(shape=(height, width, n_channel))\nv, h = GatedBlock(mask_type='A', filters=1, kernel_size=3)([inputs, inputs])\nv, h = GatedBlock(mask_type='B', filters=1, kernel_size=3)([v, h])\nv, h = GatedBlock(mask_type='B', filters=1, kernel_size=3)([v, h])\nmodel = tf.keras.Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=h)\n\nplot_receptive_field(model, data)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"inputs = keras.layers.Input(shape=(height, width, n_channel))\nv, h = GatedBlock(mask_type='A', filters=1, kernel_size=3)([inputs, inputs])\nv, h = GatedBlock(mask_type='B', filters=1, kernel_size=3)([v, h])\nv, h = GatedBlock(mask_type='B', filters=1, kernel_size=3)([v, h])\nv, h = GatedBlock(mask_type='B', filters=1, kernel_size=3)([v, h])\nmodel = tf.keras.Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=h)\n\nplot_receptive_field(model, data)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"inputs = keras.layers.Input(shape=(height, width, n_channel))\nv, h = GatedBlock(mask_type='A', filters=1, kernel_size=3)([inputs, inputs])\nv, h = GatedBlock(mask_type='B', filters=1, kernel_size=3)([v, h])\nv, h = GatedBlock(mask_type='B', filters=1, kernel_size=3)([v, h])\nv, h = GatedBlock(mask_type='B', filters=1, kernel_size=3)([v, h])\nv, h = GatedBlock(mask_type='B', filters=1, kernel_size=3)([v, h])\nmodel = tf.keras.Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=h)\n\nplot_receptive_field(model, data)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"As you can notice, the Gated PixelCNN does not create blind spots when adding more and more layers.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a31be0e547fe4795836eb43a4eafd35126383ab
| 563,033 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/Orbits3D-Copy1.ipynb
|
benitocm/practical-astronomy
|
4bfea9d5b2bb49997f35e8c7b1ada2708ee6c978
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/Orbits3D-Copy1.ipynb
|
benitocm/practical-astronomy
|
4bfea9d5b2bb49997f35e8c7b1ada2708ee6c978
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/Orbits3D-Copy1.ipynb
|
benitocm/practical-astronomy
|
4bfea9d5b2bb49997f35e8c7b1ada2708ee6c978
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 129.522199 | 127,843 | 0.816656 |
[
[
[
"%matplotlib notebook\nimport sys\nfrom pathlib import Path\n\nSRC_ROOT_DIR_0 = '/g/wsl_projs/practical-astronomy'\nSRC_ROOT_DIR_1 = '/g/wsl_projs/practical-astronomy/myastro/'\nsys.path.insert(0, SRC_ROOT_DIR_0)\nsys.path.insert(1, SRC_ROOT_DIR_1)\n\n%load_ext autoreload\n%autoreload 2",
"\nBad key \"text.kerning_factor\" on line 4 in\n/home/anybody/apps/anaconda3/envs/py37astro/lib/python3.7/site-packages/matplotlib/mpl-data/stylelib/_classic_test_patch.mplstyle.\nYou probably need to get an updated matplotlibrc file from\nhttps://github.com/matplotlib/matplotlib/blob/v3.1.3/matplotlibrc.template\nor from the matplotlib source distribution\n"
],
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D\nfrom matplotlib.colors import cnames\nfrom matplotlib import animation\nfrom myastro.ephem import calc_orbits_data, EphemrisInput\nfrom myastro.data_catalog import DF_BODYS, DF_COMETS, read_body_elms_for, read_comet_elms_for, CometElms, BodyElems\nfrom myastro.data_catalog import APOFIS\nimport seaborn as sns\nfrom toolz import concat, first\nfrom myastro.graphics_util import OrbitsPlot\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"eph = EphemrisInput(from_date=\"1972.02.01.0\",\n to_date = \"1992.05.01.0\",\n step_dd_hh_hhh = \"50 00.0\",\n equinox_name = \"J2000\")\n\n#PLANETS = ['Earth','Mercury','Venus','Mars']\n#PLANETS = ['Jupiter','Saturn','Uranus','Neptune', 'Pluto']\nPLANETS = ['Jupiter']\n#PLANETS = []\n#PLANETS = ['Jupiter','Saturn']\n#MINOR_BODYS = []\n#MINOR_BODYS = ['Ceres','Pallas','Juno','Vesta']\n#MINOR_BODYS = ['Ceres',APOFIS]\n#MINOR_BODYS = ['Ceres']\n#MINOR_BODYS = []\nMINOR_BODYS=[]\n#COMETS = ['1P/Halley','2P/Encke','10P/Tempel 2','C/1995 O1 (Hale-Bopp)']\nCOMETS = ['C/2019 Q4 (Borisov)']\n#COMETS = ['D/1993 F2-A (Shoemaker-Levy 9)']\nCOMETS = ['C/1988 L1 (Shoemaker-Holt-Rodriquez)'] #, 'C/1980 E1 (Bowell)','C/2019 Q4 (Borisov)']\nCOMETS = ['C/1980 E1 (Bowell)','C/2019 Q4 (Borisov)']\n#COMETS = []\n\norbs, dfs, date_refs = calc_orbits_data(eph, PLANETS, MINOR_BODYS, COMETS)",
"Calculating data for Jupiter\nCalculating data for C/1980 E1 (Bowell)\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Other implementation",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dfs.append(calc_eph_minor_body_perturbed(APOFIS,eph))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"CERES = read_body_elms_for(\"Ceres\",DF_BODYS)\ndfs.append(calc_eph_minor_body_perturbed(CERES,eph))\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#HALLEY = read_comet_elms_for(\"1P/Halley\",DF_COMETS)\n#ENCKE = read_comet_elms_for(\"2P/Encke\",DF_COMETS)\nHALLEY = CometElms(name=\"1P/Halley\",\n epoch_mjd=None ,\n q = 0.5870992 ,\n e = 0.9672725 ,\n i_dg = 162.23932 ,\n Node_dg = 58.14397 ,\n w_dg = 111.84658 ,\n tp_str = \"19860209.44\",\n equinox_name = \"B1950\")\n\nENCKE = CometElms(name=\"2P/Encke\",\n epoch_mjd=None ,\n q = 2.2091404*(1-0.8502196) ,\n e = 0.8502196 ,\n i_dg = 11.94524 ,\n Node_dg = 334.75006 ,\n w_dg = 186.23352 ,\n tp_str = \"19901028.54502\",\n equinox_name = \"J2000\") \n\n\ncomets = [HALLEY,ENCKE]\nfor comet in comets:\n dfs.append(calc_eph_comet(comet,eph))\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cols=['h_x','h_y','h_z']\n# A 3d matrix with shape (a,b,c) where a=n_orbits, b=n_t_samples, c=3\nx_t = np.array([df[cols].to_numpy() for df in dfs])\n\nN_trajectories = len(dfs)\n\n# Set up figure & 3D axis for animation\nfig = plt.figure()\nax = fig.add_axes([0, 0, 1, 1], projection='3d')\n#ax.axis('off')\n\n# choose a different color for each trajectory\ncolors = plt.cm.jet(np.linspace(0, 1, N_trajectories))\n\n# set up lines and points\nlines = sum([ax.plot([], [], [], '-', c=c) for c in colors], [])\npts = sum([ax.plot([], [], [], 'o', c=c) for c in colors], [])\n\nLIMITS=(-1.3,1.3)\n\n# prepare the axes limits\n#ax.set_xlim((-30,30 ))\n#ax.set_ylim((-30,30))\n#ax.set_zlim((-30, 30))\nax.set_xlim(LIMITS)\nax.set_ylim(LIMITS)\nax.set_zlim(LIMITS)\nax.set_xlabel(\"X\")\nax.set_ylabel(\"Y\")\nax.set_zlabel(\"Z\")\n\n# set point-of-view: specified by (altitude degrees, azimuth degrees)\nax.view_init(15, 0)\n# SUN\nax.scatter3D(0,0,0, color='yellow', marker='o', lw=8, label='Sun')\n\n# initialization function: plot the background of each frame\ndef init():\n for line, pt in zip(lines, pts):\n line.set_data([], [])\n line.set_3d_properties([])\n\n pt.set_data([], [])\n pt.set_3d_properties([])\n return lines + pts\n\n# animation function. This will be called sequentially with the frame number\ndef animate(i):\n #print (i)\n # we'll step two time-steps per frame. This leads to nice results.\n i = (2 * i) % x_t.shape[1]\n\n for line, pt, xi in zip(lines, pts, x_t):\n x, y, z = xi[:i].T\n #print (x)\n #print (y)\n #print (z)\n line.set_data(x, y)\n line.set_3d_properties(z)\n\n pt.set_data(x[-1:], y[-1:])\n pt.set_3d_properties(z[-1:])\n\n #ax.view_init(30, 0.3 * i)\n fig.canvas.draw()\n return lines + pts\n\n# instantiate the animator.\nanim = animation.FuncAnimation(fig, animate, init_func=init,frames=500, interval=500, blit=True, repeat=False)\n#anim = animation.FuncAnimation(fig, animate, init_func=init, interval=500, blit=True, repeat=False)\n\n# Save as mp4. This requires mplayer or ffmpeg to be installed\n#anim.save('lorentz_attractor.mp4', fps=15, extra_args=['-vcodec', 'libx264'])\n\nplt.show()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"animate(2)",
"[-0.18314445 -0.21738337 -0.25134806 -0.28499862]\n[-0.37991948 -0.39134127 -0.39518683 -0.39197985]\n[0.5200483 0.49103405 0.46048123 0.42848397]\n[1.37965144 1.3754605 1.37068102 1.36531696]\n"
],
[
"#animate (3)\nlen(orbs)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Next Implementation",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"n_trajectories = len(orbs)\n\n# Set up figure & 3D axis for animation\nfig = plt.figure()\nax = fig.add_axes([0, 0, 1, 1], projection='3d')\n#ax.axis('off')\n\n# choose a different color for each trajectory\ncolors = plt.cm.jet(np.linspace(0, 1, n_trajectories))\n\nlines = []\npts = []\nfor i, (name, mtx) in enumerate(orbs.items()):\n lines.append(ax.plot([], [], [], '--', c=colors[i], label=name,lw=.7))\n pts.append(ax.plot([], [], [], 'o', c=colors[i]))\n #ax.plot3D(mtx[:,0],mtx[:,1],mtx[:,2], c=colors[i], lw=.75, label=name)\nlines = list(concat(lines))\npts = list(concat(pts))\n\n#LIMITS=(-1.3,1.3)\nLIMITS=(-30,30)\n# prepare the axes limits\nax.set_xlim(LIMITS)\nax.set_ylim(LIMITS)\nax.set_zlim(LIMITS)\nax.set_xlabel(\"X\")\nax.set_ylabel(\"Y\")\nax.set_zlabel(\"Z\")\n\n# SUN\nax.scatter3D(0,0,0, color='yellow', marker='o', lw=8, label='Sun')\n\n# set the legend, title and animation encoding type\nax.legend(loc='upper right', prop={'size': 9})\n#ax.set_title(\"Tim-Sitze, Orbits of the Inner Planets\")\n#animation.writer = animation.writers['ffmpeg']\n\naxtext = fig.add_axes([0.0,0.95,0.1,0.05])\n# turn the axis labels/spines/ticks off\naxtext.axis(\"off\")\n\ntime = axtext.text(0.5,0.5, date_refs[0], ha=\"left\", va=\"top\")\n\n# initialization function: plot the background of each frame\ndef init():\n for line, pt in zip(lines, pts):\n line.set_data([], [])\n line.set_3d_properties([])\n\n pt.set_data([], [])\n pt.set_3d_properties([])\n return lines + pts\n\ndef animate(i):\n for line, pt, mtx in zip(lines, pts, orbs.values()):\n xs = mtx[0:i,0] \n ys = mtx[0:i,1]\n zs = mtx[0:i,2]\n line.set_data(xs, ys)\n line.set_3d_properties(zs)\n \n x = xs[-1:]\n y = ys[-1:]\n z = zs[-1:] \n pt.set_data(x, y)\n pt.set_3d_properties(z)\n \n time.set_text(date_refs[i])\n\n #ax.view_init(30, 0.3 * i)\n fig.canvas.draw()\n return lines + pts\n \n# instantiate the animator.\nanim = animation.FuncAnimation(fig, animate, init_func=init, frames=len(date_refs), interval=1000, blit=False, repeat=False)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"animate(4)",
"[2.07666195 2.09028128 2.10388254 2.11746558]\n[-6.24950665 -6.24143339 -6.23335255 -6.22526413]\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Current Implementation",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"fig = plt.figure()\nLIMITS=(-7,7)\norbs_plot = OrbitsPlot(orbs, date_refs, fig, LIMITS)\nanim = animation.FuncAnimation(fig, orbs_plot.animate, init_func=orbs_plot.init, frames=len(date_refs), interval=1000, blit=False, repeat=False)\nplt.show()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = DF_COMETS",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.info()",
"<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>\nRangeIndex: 3633 entries, 0 to 3632\nData columns (total 9 columns):\n # Column Non-Null Count Dtype \n--- ------ -------------- ----- \n 0 Name 3633 non-null object \n 1 Epoch 3633 non-null float64\n 2 q 3633 non-null float64\n 3 e 3633 non-null float64\n 4 i 3633 non-null float64\n 5 w 3633 non-null float64\n 6 Node 3633 non-null float64\n 7 Tp 3633 non-null object \n 8 Ref 3633 non-null object \ndtypes: float64(6), object(3)\nmemory usage: 255.6+ KB\n"
],
[
"df.sort_values('e',ascending=False)[:3]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Set up figure & 3D axis for animation\nfig = plt.figure()\nax = fig.add_axes([0, 0, 1, 1], projection='3d')\n#ax.axis('off')\n\n# choose a different color for each trajectory\ncolors = plt.cm.jet(np.linspace(0, 1, N_trajectories))\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"colors",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lines = []\npts = []\nfor i, (name, mtx) in enumerate(orbs.items()):\n lines.append(ax.plot([], [], [], '-', c=colors[i],label=name))\n pts.append(ax.plot([], [], [], 'o', c=colors[i]))\n #ax.plot3D(mtx[:,0],mtx[:,1],mtx[:,2], c=colors[i], lw=.75, label=name)\nlines = list(concat(lines))\npts = list(concat(pts))\n \n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"LIMITS=(-1.3,1.3)\n# prepare the axes limits\nax.set_xlim(LIMITS)\nax.set_ylim(LIMITS)\nax.set_zlim(LIMITS)\nax.set_xlabel(\"X\")\nax.set_ylabel(\"Y\")\nax.set_zlabel(\"Z\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# initialization function: plot the background of each frame\ndef init():\n for line, pt in zip(lines, pts):\n line.set_data([], [])\n line.set_3d_properties([])\n\n pt.set_data([], [])\n pt.set_3d_properties([])\n return lines + pts\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def animate(i):\n for line, pt, mtx in zip(lines, points, orbs.values()):\n xs = mtx[0:i,0]\n ys = mtx[0:i,1]\n zs = mtx[0:i,2]\n line.set_data(xs, ys)\n line.set_3d_properties(zs)\n\n x = xs[-1:]\n y = ys[-1:]\n z = zs[-1:]\n pt.set_data(x, y)\n pt.set_3d_properties(z)\n\n #ax.view_init(30, 0.3 * i)\n fig.canvas.draw()\n return lines + pts\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"anim = animation.FuncAnimation(fig, animate, init_func=init, interval=500, blit=True, repeat=False)\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"i=3\nxyz[0:i,0] # x\nxs = xyz[0:i,0] ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"xs[-1:]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"xs",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# first plot the constants to be used in our plots\n# plot the sun at the origin\nax.scatter3D(0,0,0, color='yellow', marker='o', lw=8, label='Sun')\n\n# plot the orbit of mercury\nax.plot3D(merc_orb[:,0],merc_orb[:,1],merc_orb[:,2], color='gray', lw=.75, label='Mercury')\n\n# plot the prbit of Venus\nax.plot3D(ven_orb[:,0],ven_orb[:,1],ven_orb[:,2], color='orange', lw=.75, label='Venus')\n\n# plot the orbit of the Earth\nax.plot3D(earth_orb[:,0],earth_orb[:,1],earth_orb[:,2], color='blue', lw=.75, label='Earth')\n\n# plot the orbit of Mars\nax.plot3D(mars_orb[:,0],mars_orb[:,1],mars_orb[:,2], color='red', lw=.75, label='Mars')\n\n\n# get the particles 3d plots. Initially empty\nmerc_particle, = plt.plot([],[],[], marker='.', color='gray', lw=2)\nven_particle, = plt.plot([],[],[], marker='.', color='orange', lw=2)\nearth_particle, = plt.plot([],[],[], marker='.', color='blue', lw=2)\nmars_particle, = plt.plot([],[],[], marker='.', color='red', lw=2)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lines",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cols=['h_x','h_y','h_z']\n# A 3d matrix with shape (a,b,c) where a=n_orbits, b=n_t_samples, c=3\nx_t = np.array([df[cols].to_numpy() for df in dfs])\n\nN_trajectories = len(dfs)\n\n# Set up figure & 3D axis for animation\nfig = plt.figure()\nax = fig.add_axes([0, 0, 1, 1], projection='3d')\n#ax.axis('off')\n\n# choose a different color for each trajectory\ncolors = plt.cm.jet(np.linspace(0, 1, N_trajectories))\n\n# set up lines and points\nlines = sum([ax.plot([], [], [], '-', c=c)\n for c in colors], [])\npts = sum([ax.plot([], [], [], 'o', c=c)\n for c in colors], [])\n\nLIMITS=(-1.3,1.3)\n\n# prepare the axes limits\n#ax.set_xlim((-30,30 ))\n#ax.set_ylim((-30,30))\n#ax.set_zlim((-30, 30))\nax.set_xlim(LIMITS)\nax.set_ylim(LIMITS)\nax.set_zlim(LIMITS)\nax.set_xlabel(\"X\")\nax.set_ylabel(\"Y\")\nax.set_zlabel(\"Z\")\n\n# set point-of-view: specified by (altitude degrees, azimuth degrees)\nax.view_init(15, 0)\n# SUN\nax.scatter3D(0,0,0, color='yellow', marker='o', lw=8, label='Sun')\n\n# initialization function: plot the background of each frame\ndef init():\n for line, pt in zip(lines, pts):\n line.set_data([], [])\n line.set_3d_properties([])\n\n pt.set_data([], [])\n pt.set_3d_properties([])\n return lines + pts\n\n# animation function. This will be called sequentially with the frame number\ndef animate(i):\n # we'll step two time-steps per frame. This leads to nice results.\n i = (2 * i) % x_t.shape[1]\n\n for line, pt, xi in zip(lines, pts, x_t):\n x, y, z = xi[:i].T\n line.set_data(x, y)\n line.set_3d_properties(z)\n\n pt.set_data(x[-1:], y[-1:])\n pt.set_3d_properties(z[-1:])\n\n #ax.view_init(30, 0.3 * i)\n fig.canvas.draw()\n return lines + pts\n\n# instantiate the animator.\n#anim = animation.FuncAnimation(fig, animate, init_func=init,frames=500, interval=500, blit=True, repeat=False)\nanim = animation.FuncAnimation(fig, animate, init_func=init, interval=500, blit=True, repeat=False)\n\n# Save as mp4. This requires mplayer or ffmpeg to be installed\n#anim.save('lorentz_attractor.mp4', fps=15, extra_args=['-vcodec', 'libx264'])\n\nplt.show()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"list1=['a','b','c']\nsum(list1,[''])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a31c41d944bade360a511a9742c1952729f3d25
| 18,096 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
05_q_learn_fin_2_keras.ipynb
|
bastulli/rlfinance
|
5cd969aa2a4dde021fb7554a713f5cf2e242b904
|
[
"MIT"
] | 44 |
2022-01-20T15:07:57.000Z
|
2022-03-28T16:37:17.000Z
|
05_q_learn_fin_2_keras.ipynb
|
bastulli/rlfinance
|
5cd969aa2a4dde021fb7554a713f5cf2e242b904
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
05_q_learn_fin_2_keras.ipynb
|
bastulli/rlfinance
|
5cd969aa2a4dde021fb7554a713f5cf2e242b904
|
[
"MIT"
] | 7 |
2022-01-23T19:54:20.000Z
|
2022-03-23T15:37:25.000Z
| 31.416667 | 160 | 0.478835 |
[
[
[
"<img src='https://certificate.tpq.io/quantsdev_banner_color.png' width=\"250px\" align=\"right\">",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Reinforcement Learning",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"© Dr Yves J Hilpisch | The Python Quants GmbH\n\n[quants@dev Discord Server](https://discord.gg/uJPtp9Awaj) | [@quants_dev](https://twitter.com/quants_dev) | <a href=\"mailto:[email protected]\">[email protected]</a>\n\n<img src=\"https://hilpisch.com/aiif_cover_shadow.png\" width=\"300px\" align=\"left\">",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Imports",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import os\nimport math\nimport random\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nfrom pylab import plt, mpl\nplt.style.use('seaborn')\nmpl.rcParams['font.family'] = 'serif'\nnp.set_printoptions(precision=4, suppress=True)\nos.environ['PYTHONHASHSEED'] = '0'\n%config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'svg'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import warnings as w\nw.simplefilter('ignore')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '4'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import tensorflow as tf",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from tensorflow import keras\nfrom keras.layers import Dense, Dropout\nfrom keras.models import Sequential\nfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from tensorflow.python.framework.ops import disable_eager_execution\ndisable_eager_execution()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def set_seeds(seed=100):\n random.seed(seed)\n np.random.seed(seed)\n tf.random.set_seed(seed)\n env.seed(seed)\n env.action_space.seed(100)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Improved Finance Environment",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class observation_space:\n def __init__(self, n):\n self.shape = (n,)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class action_space:\n def __init__(self, n):\n self.n = n\n def seed(self, seed):\n pass\n def sample(self):\n return random.randint(0, self.n - 1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class Finance:\n url = 'http://hilpisch.com/aiif_eikon_eod_data.csv'\n def __init__(self, symbol, features, window, lags,\n leverage=1, min_performance=0.85,\n start=0, end=None, mu=None, std=None):\n self.symbol = symbol\n self.features = features\n self.n_features = len(features)\n self.window = window\n self.lags = lags\n self.leverage = leverage\n self.min_performance = min_performance\n self.start = start\n self.end = end\n self.mu = mu\n self.std = std\n self.observation_space = observation_space(self.lags)\n self.action_space = action_space(2)\n self._get_data()\n self._prepare_data()\n def _get_data(self):\n self.raw = pd.read_csv(self.url, index_col=0,\n parse_dates=True).dropna()\n def _prepare_data(self):\n self.data = pd.DataFrame(self.raw[self.symbol])\n self.data = self.data.iloc[self.start:]\n self.data['r'] = np.log(self.data / self.data.shift(1))\n self.data.dropna(inplace=True)\n self.data['s'] = self.data[self.symbol].rolling(\n self.window).mean() \n self.data['m'] = self.data['r'].rolling(self.window).mean()\n self.data['v'] = self.data['r'].rolling(self.window).std()\n self.data.dropna(inplace=True)\n if self.mu is None:\n self.mu = self.data.mean()\n self.std = self.data.std()\n self.data_ = (self.data - self.mu) / self.std\n self.data_['d'] = np.where(self.data['r'] > 0, 1, 0)\n self.data_['d'] = self.data_['d'].astype(int)\n if self.end is not None:\n self.data = self.data.iloc[:self.end - self.start]\n self.data_ = self.data_.iloc[:self.end - self.start]\n def _get_state(self):\n return self.data_[self.features].iloc[self.bar -\n self.lags:self.bar]\n def seed(self, seed):\n random.seed(seed)\n np.random.seed(seed)\n def reset(self):\n self.treward = 0\n self.accuracy = 0\n self.performance = 1\n self.bar = self.lags\n state = self.data_[self.features].iloc[self.bar-\n self.lags:self.bar]\n return state.values\n def step(self, action):\n correct = action == self.data_['d'].iloc[self.bar]\n ret = self.data['r'].iloc[self.bar] * self.leverage\n reward_1 = 1 if correct else 0\n reward_2 = abs(ret) if correct else -abs(ret)\n self.treward += reward_1\n self.bar += 1\n self.accuracy = self.treward / (self.bar - self.lags)\n self.performance *= math.exp(reward_2)\n if self.bar >= len(self.data):\n done = True\n elif reward_1 == 1:\n done = False\n elif (self.performance < self.min_performance and\n self.bar > self.lags + 15):\n done = True\n else:\n done = False\n state = self._get_state()\n info = {}\n return state.values, reward_1 + reward_2 * 252, done, info",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"env = Finance('EUR=', ['EUR=', 'r', 'v'], window=10, lags=5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a = env.action_space.sample()\na",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"env.reset()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"env.step(a)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Improved Financial QL Agent",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from collections import deque",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class FQLAgent:\n def __init__(self, hidden_units, learning_rate, learn_env, valid_env, dropout=True):\n self.learn_env = learn_env\n self.valid_env = valid_env\n self.dropout = dropout\n self.epsilon = 1.0\n self.epsilon_min = 0.1\n self.epsilon_decay = 0.98\n self.learning_rate = learning_rate\n self.gamma = 0.95\n self.batch_size = 128\n self.max_treward = 0\n self.trewards = list()\n self.averages = list()\n self.performances = list()\n self.aperformances = list()\n self.vperformances = list()\n self.memory = deque(maxlen=2000)\n self.model = self._build_model(hidden_units, learning_rate)\n \n def _build_model(self, hu, lr):\n model = Sequential()\n model.add(Dense(hu, input_shape=(\n self.learn_env.lags, self.learn_env.n_features),\n activation='relu'))\n if self.dropout:\n model.add(Dropout(0.3, seed=100))\n model.add(Dense(hu, activation='relu'))\n if self.dropout:\n model.add(Dropout(0.3, seed=100))\n model.add(Dense(2, activation='linear'))\n model.compile(\n loss='mse',\n optimizer=keras.optimizers.RMSprop(learning_rate=lr)\n )\n return model\n \n def act(self, state):\n if random.random() <= self.epsilon:\n return self.learn_env.action_space.sample()\n action = self.model.predict(state)[0, 0]\n return np.argmax(action)\n \n def replay(self):\n batch = random.sample(self.memory, self.batch_size)\n for state, action, reward, next_state, done in batch:\n if not done:\n reward += self.gamma * np.amax(\n self.model.predict(next_state)[0, 0])\n target = self.model.predict(state)\n target[0, 0, action] = reward\n self.model.fit(state, target, epochs=1,\n verbose=False)\n if self.epsilon > self.epsilon_min:\n self.epsilon *= self.epsilon_decay\n \n def learn(self, episodes):\n for e in range(1, episodes + 1):\n state = self.learn_env.reset()\n state = np.reshape(state, [1, self.learn_env.lags,\n self.learn_env.n_features])\n for _ in range(10000):\n action = self.act(state)\n next_state, reward, done, info = \\\n self.learn_env.step(action)\n next_state = np.reshape(next_state,\n [1, self.learn_env.lags,\n self.learn_env.n_features])\n self.memory.append([state, action, reward,\n next_state, done])\n state = next_state\n if done:\n treward = _ + 1\n self.trewards.append(treward)\n av = sum(self.trewards[-25:]) / 25\n perf = self.learn_env.performance\n self.averages.append(av)\n self.performances.append(perf)\n self.aperformances.append(\n sum(self.performances[-25:]) / 25)\n self.max_treward = max(self.max_treward, treward)\n templ = 'episode: {:2d}/{} | treward: {:4d} | '\n templ += 'perf: {:5.3f} | av: {:5.1f} | max: {:4d}'\n print(templ.format(e, episodes, treward, perf,\n av, self.max_treward), end='\\r')\n break\n self.validate(e, episodes)\n if len(self.memory) > self.batch_size:\n self.replay()\n print()\n def validate(self, e, episodes):\n state = self.valid_env.reset()\n state = np.reshape(state, [1, self.valid_env.lags,\n self.valid_env.n_features])\n for _ in range(10000):\n action = np.argmax(self.model.predict(state)[0, 0])\n next_state, reward, done, info = self.valid_env.step(action)\n state = np.reshape(next_state, [1, self.valid_env.lags,\n self.valid_env.n_features])\n if done:\n treward = _ + 1\n perf = self.valid_env.performance\n self.vperformances.append(perf)\n if e % 20 == 0:\n templ = 71 * '='\n templ += '\\nepisode: {:2d}/{} | VALIDATION | '\n templ += 'treward: {:4d} | perf: {:5.3f} | '\n templ += 'eps: {:.2f}\\n'\n templ += 71 * '='\n print(templ.format(e, episodes, treward,\n perf, self.epsilon))\n break",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"symbol = 'EUR='\nfeatures = ['r', 's', 'm', 'v']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a = 0\nb = 2000\nc = 500",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"learn_env = Finance(symbol, features, window=10, lags=6,\n leverage=1, min_performance=0.85,\n start=a, end=a + b, mu=None, std=None)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"learn_env.data.info()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"valid_env = Finance(symbol, features, window=learn_env.window,\n lags=learn_env.lags, leverage=learn_env.leverage,\n min_performance=learn_env.min_performance,\n start=a + b, end=a + b + c,\n mu=learn_env.mu, std=learn_env.std)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"valid_env.data.info()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"set_seeds(100)\nagent = FQLAgent(48, 0.0001, learn_env, valid_env, True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"episodes = 61",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%time agent.learn(episodes)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"agent.epsilon",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))\nx = range(1, len(agent.averages) + 1)\ny = np.polyval(np.polyfit(x, agent.averages, deg=3), x)\nplt.plot(agent.averages, label='moving average')\nplt.plot(x, y, 'r--', label='regression')\nplt.xlabel('episodes')\nplt.ylabel('total reward')\nplt.legend();",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))\nx = range(1, len(agent.performances) + 1)\ny = np.polyval(np.polyfit(x, agent.performances, deg=3), x)\ny_ = np.polyval(np.polyfit(x, agent.vperformances, deg=3), x)\nplt.plot(agent.performances[:], label='training')\nplt.plot(agent.vperformances[:], label='validation')\nplt.plot(x, y, 'r--', label='regression (train)')\nplt.plot(x, y_, 'r-.', label='regression (valid)')\nplt.xlabel('episodes')\nplt.ylabel('gross performance')\nplt.legend();",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<img src=\"https://certificate.tpq.io/quantsdev_banner_color.png\" alt=\"quants@dev\" width=\"35%\" align=\"right\" border=\"0\"><br>\n\n[quants@dev Discord Server](https://discord.gg/uJPtp9Awaj) | [@quants_dev](https://twitter.com/quants_dev) | <a href=\"mailto:[email protected]\">[email protected]</a>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a31ce17566c73a8bc9dbaaba4de2d816b54c937
| 4,098 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
CSV/pascaltocsv.ipynb
|
jellycat0327/DundasStreet.AI
|
8517f6bc4a5970ab342802ac0d07e4a0cd0a388d
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
CSV/pascaltocsv.ipynb
|
jellycat0327/DundasStreet.AI
|
8517f6bc4a5970ab342802ac0d07e4a0cd0a388d
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
CSV/pascaltocsv.ipynb
|
jellycat0327/DundasStreet.AI
|
8517f6bc4a5970ab342802ac0d07e4a0cd0a388d
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 30.58209 | 136 | 0.418009 |
[
[
[
"# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-\n \nimport csv\nimport os\nimport glob\nimport sys\n \nclass PascalVOC2CSV(object):\n def __init__(self,xml=[], ann_path='./annotations.csv',classes_path='./classes.csv'):\n '''\n :param xml: 所有Pascal VOC的xml文件路径组成的列表\n :param ann_path: ann_path\n :param classes_path: classes_path\n '''\n self.xml = xml\n self.ann_path = ann_path\n self.classes_path=classes_path\n self.label=[]\n self.annotations=[]\n \n self.data_transfer()\n self.write_file()\n \n \n def data_transfer(self):\n for num, xml_file in enumerate(self.xml):\n try:\n # print(xml_file)\n # 进度输出\n sys.stdout.write('\\r>> Converting image %d/%d' % (\n num + 1, len(self.xml)))\n sys.stdout.flush()\n \n with open(xml_file, 'r') as fp:\n for p in fp:\n if '<filename>' in p:\n self.filen_ame = p.split('>')[1].split('<')[0]\n \n if '<object>' in p:\n # 类别\n d = [next(fp).split('>')[1].split('<')[0] for _ in range(9)]\n self.supercategory = d[0]\n if self.supercategory not in self.label:\n self.label.append(self.supercategory)\n \n # 边界框\n x1 = int(d[-4]);\n y1 = int(d[-3]);\n x2 = int(d[-2]);\n y2 = int(d[-1])\n \n self.annotations.append([os.path.join('JPEGImages',self.filen_ame),x1,y1,x2,y2,self.supercategory])\n except:\n continue\n \n sys.stdout.write('\\n')\n sys.stdout.flush()\n \n def write_file(self,):\n with open(self.ann_path, 'w', newline='') as fp:\n csv_writer = csv.writer(fp, dialect='excel')\n csv_writer.writerows(self.annotations)\n \n class_name=sorted(self.label)\n class_=[]\n for num,name in enumerate(class_name):\n class_.append([name,num])\n with open(self.classes_path, 'w', newline='') as fp:\n csv_writer = csv.writer(fp, dialect='excel')\n csv_writer.writerows(class_)\n \n \nxml_file = glob.glob('./Annotations/*.xml')\n \nPascalVOC2CSV(xml_file)",
">> Converting image 13/13\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
]
] |
4a31d05bd2c4dcd0485c577bdcdc289edb9ec0c8
| 59,370 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
clustering_without_preprocessing.ipynb
|
aktivkohle/cluster-sparse-vectors
|
427c090dc5b3d6b933c2fb751c95f02fa2a80ab9
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
clustering_without_preprocessing.ipynb
|
aktivkohle/cluster-sparse-vectors
|
427c090dc5b3d6b933c2fb751c95f02fa2a80ab9
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
clustering_without_preprocessing.ipynb
|
aktivkohle/cluster-sparse-vectors
|
427c090dc5b3d6b933c2fb751c95f02fa2a80ab9
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 48.229082 | 7,978 | 0.517618 |
[
[
[
"## Run a script which pulls about 7364 unique english language captions and their tfidf vectors from the MySQL databank and brings into scope the variables we need, a sparse matrix and also a matching dataframe with the names of the videos.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%time\n%run prepare_variables.py",
"CPU times: user 9.26 s, sys: 384 ms, total: 9.64 s\nWall time: 9.76 s\n"
],
[
"p.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"p",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### That is very sparse - only 0.05% of the matrix has anything in it.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Run KMeans to find ten clusters among the sparse vectors",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%time\nfrom numpy.random import random \nfrom scipy.sparse import * \nfrom sklearn.cluster import KMeans\n\nkmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=10).fit(p) ",
"CPU times: user 4min 52s, sys: 3.16 s, total: 4min 55s\nWall time: 4min 55s\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Try to find an indication of how many clusters there actually should be",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%time\nnclusters_inertias = []\nfor i in range(3,21):\n kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=i).fit(p)\n ni = (i,kmeans.inertia_)\n nclusters_inertias.append(ni)",
"CPU times: user 1h 37min 19s, sys: 54.4 s, total: 1h 38min 14s\nWall time: 1h 38min 11s\n"
],
[
"nclusters_inertias",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # https://stackoverflow.com/questions/18458734/python-plot-list-of-tuples\n%matplotlib inline\nplt.scatter(*zip(*nclusters_inertias))\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### ...oops that approach was an oversimplification : \n\n> increasing k without penalty will always reduce the amount of error in the resulting clustering, to the extreme case of zero error if each data point is considered its own cluster (i.e., when k equals the number of data points, n)\n\nhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Determining_the_number_of_clusters_in_a_data_set\n\n**without penalty** Good to know that I was about to try running it overnight to a cluster of 40 rather than 20 which still would not have found anything. Will have to implement one of the techniques discussed in the article.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### I manually tested 5,7,10 and 20 clusters and looked at the videos in each cluster. 10 seemed to do best to find clusters without impurities but there are other factors, like the starting points for each cluster",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## How many videos has it found in each cluster?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"videos_df['cluster_labels'] = kmeans.labels_\nvideos_df.groupby('cluster_labels').count()[['videoTitle']]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Sample ten videos randomly from each of those groups:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pd.set_option('display.max_rows', 120)\n\n# https://stackoverflow.com/questions/22472213/python-random-selection-per-group\n\nsize = 10 # sample size\nreplace = False # with replacement\nfn = lambda obj: obj.loc[np.random.choice(obj.index, size, replace),:]\nclustered_sample = videos_df.groupby('cluster_labels', as_index=False).apply(fn)\nclustered_sample[['videoTitle','cluster_labels', 'link']]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a31d10806fef2fe95493ecea6b1b54f8254b51d
| 98,853 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
ProbabilisticModel/PM_Vitterbi_Forward_Backward.ipynb
|
camilleAmaury/MachineLearningMaster1DataScience
|
2c7beb8448a18ebbb8eb81ba3296bbc182f2c53c
|
[
"Unlicense"
] | null | null | null |
ProbabilisticModel/PM_Vitterbi_Forward_Backward.ipynb
|
camilleAmaury/MachineLearningMaster1DataScience
|
2c7beb8448a18ebbb8eb81ba3296bbc182f2c53c
|
[
"Unlicense"
] | null | null | null |
ProbabilisticModel/PM_Vitterbi_Forward_Backward.ipynb
|
camilleAmaury/MachineLearningMaster1DataScience
|
2c7beb8448a18ebbb8eb81ba3296bbc182f2c53c
|
[
"Unlicense"
] | null | null | null | 340.872414 | 92,388 | 0.908885 |
[
[
[
"SLIDE 92 du PDF corrigé\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a = {}\na[0]=np.matrix('0.4 0.6')\na['a']=np.matrix('0.3 0.2 ; 0.1 0.1')\na['b']=np.matrix('0.1 0.3 ; 0.1 0.1')\na['$']=np.matrix('0.1 ; 0.6')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print (np.dot(a[0],a['a']))",
"[[0.18 0.14]]\n"
],
[
"r=a[0]\nr=np.dot(r,a['a'])\nr=np.dot(r,a['$'])\nr",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def parser(string, A):\n prob = A[0]\n for char in string:\n prob = np.dot(prob, A[char])\n return np.dot(prob, A['$'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(parser(\"baab\", a))",
"[[0.004396]]\n"
],
[
"def forward(A, n, string, logs):\n # inner function\n def forward_Initialisation(A, M, i, j, char, logs):\n res = 0\n for k in range(0, M.shape[0]):\n res += A[char][k,i] * M[k, j-1]\n return res\n # process\n \n # initialisation \n M = np.zeros((n, len(string)+1))\n M[0,0] = A[0][0, 0]\n M[1,0] = A[0][0, 1]\n # Iteration\n for j in range(1, M.shape[1]):\n for i in range(0, M.shape[0]):\n M[i,j] = forward_Initialisation(a, M, i, j, string[j-1], True)\n print(M)\n # probability\n proba = 0\n j = M.shape[1]-1\n for i in range(0, M.shape[0]):\n proba += M[i,j] * A['$'][i,0]\n return proba",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"prob = forward(a, 2, \"baab\", True)\nprint(\"P('baab') =\",prob)",
"[[0.4 0.1 0.048 0.0182 0.00316]\n [0.6 0.18 0.038 0.0134 0.0068 ]]\nP('baab') = 0.004396000000000001\n"
],
[
"def backward(A, n, string, logs):\n # inner function\n def forward_Initialisation(A, M, i, j, char, logs):\n res = 0\n for k in range(0, M.shape[0]):\n res += A[char][i,k] * M[k, j]\n return res\n # process\n \n # initialisation\n M = np.zeros((n, len(string)+1))\n j_temp = M.shape[1]-1\n M[0,j_temp] = A['$'][0, 0]\n M[1,j_temp] = A['$'][1, 0]\n print(M)\n # Iteration\n for j in range(M.shape[1]-1, 0, -1):\n for i in range(0, M.shape[0]):\n M[i,j-1] = forward_Initialisation(a, M, i, j, string[j-1], True)\n print(M)\n # probability\n proba = 0\n for k in range(0, M.shape[0]):\n proba += M[k,0] * A[0][0,k]\n return proba",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"prob = backward(a, 2, \"baab\", True)\nprint(\"P('baab') =\",prob)",
"[[0. 0. 0. 0. 0.1]\n [0. 0. 0. 0. 0.6]]\n[[0.00556 0.0265 0.071 0.19 0.1 ]\n [0.00362 0.0097 0.026 0.07 0.6 ]]\nP('baab') = 0.004395999999999999\n"
],
[
"M = np.zeros((2, len('baab')+1))\nj_temp = M.shape[1]-1\nM[0,j_temp] = a['$'][0, 0]\nM[1,j_temp] = a['$'][1, 0]\nprint(M)\n# Iteration\nfor j in range(M.shape[1]-1, 0, -1):\n print(j)",
"[[0. 0. 0. 0. 0.1]\n [0. 0. 0. 0. 0.6]]\n4\n3\n2\n1\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a31d8c2318a744084c13ae48b6273656161d4b4
| 6,539 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Notebooks/Towards real-time simulation.ipynb
|
Mahziron12/TEST1
|
dd1a9fa2605540fc7fa6625db886ea780e17bede
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Notebooks/Towards real-time simulation.ipynb
|
Mahziron12/TEST1
|
dd1a9fa2605540fc7fa6625db886ea780e17bede
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Notebooks/Towards real-time simulation.ipynb
|
Mahziron12/TEST1
|
dd1a9fa2605540fc7fa6625db886ea780e17bede
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 30.556075 | 114 | 0.541673 |
[
[
[
"empty"
]
]
] |
[
"empty"
] |
[
[
"empty"
]
] |
4a31db9d27d8ed916f9b948268ae6a2811a3b5af
| 380,320 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
m&v_inverted_visualization_.ipynb
|
SakshiPriya/inverted-visualization
|
2beb4ab39ce6188568f52f4ef14f7a4af3b5c00c
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
m&v_inverted_visualization_.ipynb
|
SakshiPriya/inverted-visualization
|
2beb4ab39ce6188568f52f4ef14f7a4af3b5c00c
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
m&v_inverted_visualization_.ipynb
|
SakshiPriya/inverted-visualization
|
2beb4ab39ce6188568f52f4ef14f7a4af3b5c00c
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 453.842482 | 276,892 | 0.916013 |
[
[
[
"[View in Colaboratory](https://colab.research.google.com/github/SakshiPriya/inverted-visualization/blob/master/m&v_inverted_visualization_.ipynb)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
" !apt-get install -y -qq software-properties-common python-software-properties module-init-tools\n !add-apt-repository -y ppa:alessandro-strada/ppa 2>&1 > /dev/null\n !apt-get update -qq 2>&1 > /dev/null\n !apt-get -y install -qq google-drive-ocamlfuse fuse\n from google.colab import auth\n auth.authenticate_user()\n from oauth2client.client import GoogleCredentials\n creds = GoogleCredentials.get_application_default()\n import getpass\n !google-drive-ocamlfuse -headless -id={creds.client_id} -secret={creds.client_secret} < /dev/null 2>&1 | grep URL\n vcode = getpass.getpass()\n !echo {vcode} | google-drive-ocamlfuse -headless -id={creds.client_id} -secret={creds.client_secret}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!mkdir -p drive\n!google-drive-ocamlfuse drive\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!pip install torch\n!pip install torchvision\n!pip install pillow==4.0.0",
"Collecting torch\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/49/0e/e382bcf1a6ae8225f50b99cc26effa2d4cc6d66975ccf3fa9590efcbedce/torch-0.4.1-cp36-cp36m-manylinux1_x86_64.whl (519.5MB)\n\u001b[K 100% |████████████████████████████████| 519.5MB 30kB/s \ntcmalloc: large alloc 1073750016 bytes == 0x5a3cc000 @ 0x7f4178aea1c4 0x46d6a4 0x5fcbcc 0x4c494d 0x54f3c4 0x553aaf 0x54e4c8 0x54f4f6 0x553aaf 0x54efc1 0x54f24d 0x553aaf 0x54efc1 0x54f24d 0x553aaf 0x54efc1 0x54f24d 0x551ee0 0x54e4c8 0x54f4f6 0x553aaf 0x54efc1 0x54f24d 0x551ee0 0x54efc1 0x54f24d 0x551ee0 0x54e4c8 0x54f4f6 0x553aaf 0x54e4c8\n\u001b[?25hInstalling collected packages: torch\nSuccessfully installed torch-0.4.1\nCollecting torchvision\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/ca/0d/f00b2885711e08bd71242ebe7b96561e6f6d01fdb4b9dcf4d37e2e13c5e1/torchvision-0.2.1-py2.py3-none-any.whl (54kB)\n\u001b[K 100% |████████████████████████████████| 61kB 5.0MB/s \n\u001b[?25hRequirement already satisfied: six in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from torchvision) (1.11.0)\nCollecting pillow>=4.1.1 (from torchvision)\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/d1/24/f53ff6b61b3d728b90934bddb4f03f8ab584a7f49299bf3bde56e2952612/Pillow-5.2.0-cp36-cp36m-manylinux1_x86_64.whl (2.0MB)\n\u001b[K 100% |████████████████████████████████| 2.0MB 13.2MB/s \n\u001b[?25hRequirement already satisfied: torch in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from torchvision) (0.4.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: numpy in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from torchvision) (1.14.5)\nInstalling collected packages: pillow, torchvision\n Found existing installation: Pillow 4.0.0\n Uninstalling Pillow-4.0.0:\n Successfully uninstalled Pillow-4.0.0\nSuccessfully installed pillow-5.2.0 torchvision-0.2.1\nCollecting pillow==4.0.0\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/37/e8/b3fbf87b0188d22246678f8cd61e23e31caa1769ebc06f1664e2e5fe8a17/Pillow-4.0.0-cp36-cp36m-manylinux1_x86_64.whl (5.6MB)\n\u001b[K 100% |████████████████████████████████| 5.6MB 6.6MB/s \n\u001b[?25hRequirement already satisfied: olefile in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from pillow==4.0.0) (0.45.1)\n\u001b[31mtorchvision 0.2.1 has requirement pillow>=4.1.1, but you'll have pillow 4.0.0 which is incompatible.\u001b[0m\nInstalling collected packages: pillow\n Found existing installation: Pillow 5.2.0\n Uninstalling Pillow-5.2.0:\n Successfully uninstalled Pillow-5.2.0\nSuccessfully installed pillow-4.0.0\n"
],
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport torch\nimport torchvision\nfrom torchvision import transforms,models\nfrom PIL import Image\nfrom torch import optim",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n\nmean=torch.Tensor([0.485, 0.456, 0.406])\nstd=torch.Tensor([0.229, 0.224, 0.225])\ndef transformimage(image):\n transform=transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize((224,224)),transforms.ToTensor(),transforms.Normalize(mean,std)])\n transformedimage=transform(image)\n transformedimage=transformedimage.unsqueeze(0)\n return transformedimage\n \nuntransform=transforms.ToPILImage()\ngrayscale=transforms.Grayscale()\ndef showimage(transformedimage,show,gradient):\n untrans_image=transformedimage.squeeze(0)\n if show==True:\n for i in range(untrans_image.shape[0]):\n untrans_image[i]=untrans_image[i]*(std[i].double())+(mean[i].double())\n \n elif gradient==True:\n untrans_image=(untrans_image-untrans_image.min())/untrans_image.max()\n untrans_image=untrans_image.float()\n untrans_image=untransform(untrans_image)\n plt.figure()\n plt.imshow(untrans_image)\n plt.show()\n return untrans_image\n \n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"listofimages=[['drive/app/goldfish.jpg',1],\n ['drive/app/hamster.jpg',333],\n ['drive/app/jellyfish.jpg',107]]\n\n\nindex=0\nlayervisual=9\nimgpath=listofimages[index][0]\nclassid=listofimages[index][1]\nmodel=models.vgg19(pretrained=True)\nimage=Image.open(imgpath)\nimagetensor=transformimage(image)\ninitial_img=torch.tensor(np.random.normal(0,1,imagetensor.size()),requires_grad=True,dtype=torch.float)\nmodel=model.eval().float()\n\nmodel.to('cpu')\n",
"Downloading: \"https://download.pytorch.org/models/vgg19-dcbb9e9d.pth\" to /content/.torch/models/vgg19-dcbb9e9d.pth\n100.0%\n"
],
[
"def outputoflayer(layerno,inputs):\n i=0\n for layer in model.features:\n inputs=layer(inputs)\n if i==layerno:\n break\n i+=1\n return inputs\n \n\n\n\ndef vectorization(image,power):\n return (image.view(-1)**power).sum()\n\ndef lossfunc(output,target,layer):\n result=0\n lambda_alpha=2.16e-8\n #if layer in range(11):\n #lambda_beta=0.05\n #elif layer in range(21):\n #lambda_beta=0.5\n #else:\n lambda_beta=1e-8\n alpha=6\n beta=2\n \n distance=target-output\n euclidean_loss=vectorization(distance,2)/vectorization(output,2) \n regularizer1=lambda_alpha*vectorization(output,alpha) \n \n \n for i in range(output.size()[2]-1):\n for j in range(output.size()[3]-1):\n result+=( ((output[0,:,i,j+1]-output[0,:,i,j])**2 + (output[0,:,i+1,j]-output[0,:,i,j])**2 )**(beta/2)).sum()\n \n regularizer2=lambda_beta*result\n return euclidean_loss+regularizer1+regularizer2\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"epochno=2000\ntargetimage=outputoflayer(layervisual,imagetensor).detach()\noptimizer=optim.SGD([initial_img],lr=0.001,momentum=0.9)\nfor i in range(epochno):\n optimizer.zero_grad()\n input_image=outputoflayer(layervisual,initial_img)\n loss=lossfunc(input_image,targetimage,layervisual)\n print('loss{}:{}'.format(i,loss))\n loss.backward()\n optimizer.step()\n \n \n",
"loss0:202282.90625\nloss1:73904.890625\nloss2:40051.3671875\nloss3:31736.220703125\nloss4:30877.375\nloss5:28472.771484375\nloss6:25556.58203125\nloss7:22777.57421875\nloss8:20210.115234375\nloss9:18133.037109375\nloss10:16118.3310546875\nloss11:14163.32421875\nloss12:12488.71875\nloss13:11160.427734375\nloss14:9979.5771484375\nloss15:8962.8515625\nloss16:8113.58544921875\nloss17:7385.77978515625\nloss18:6729.2900390625\nloss19:6130.443359375\nloss20:5594.47265625\nloss21:5124.74951171875\nloss22:4715.64501953125\nloss23:4361.23583984375\nloss24:4051.7529296875\nloss25:3779.163330078125\nloss26:3537.065185546875\nloss27:3319.7900390625\nloss28:3122.739990234375\nloss29:2942.314208984375\nloss30:2776.9580078125\nloss31:2624.89599609375\nloss32:2485.33642578125\nloss33:2357.833984375\nloss34:2240.880126953125\nloss35:2134.302978515625\nloss36:2036.893798828125\nloss37:1947.897216796875\nloss38:1866.4366455078125\nloss39:1791.5799560546875\nloss40:1722.6351318359375\nloss41:1659.1199951171875\nloss42:1600.414306640625\nloss43:1545.9405517578125\nloss44:1495.3714599609375\nloss45:1448.3353271484375\nloss46:1404.5499267578125\nloss47:1363.6761474609375\nloss48:1325.4249267578125\nloss49:1289.5567626953125\nloss50:1255.8931884765625\nloss51:1224.2540283203125\nloss52:1194.4852294921875\nloss53:1166.4295654296875\nloss54:1139.96337890625\nloss55:1114.9520263671875\nloss56:1091.3206787109375\nloss57:1068.9290771484375\nloss58:1047.6707763671875\nloss59:1027.4527587890625\nloss60:1008.20751953125\nloss61:989.8889770507812\nloss62:972.43408203125\nloss63:955.7909545898438\nloss64:939.9088745117188\nloss65:924.7178955078125\nloss66:910.1715087890625\nloss67:896.238525390625\nloss68:882.8674926757812\nloss69:870.0198364257812\nloss70:857.6771850585938\nloss71:845.7922973632812\nloss72:834.353759765625\nloss73:823.3405151367188\nloss74:812.718994140625\nloss75:802.4672241210938\nloss76:792.5636596679688\nloss77:782.9825439453125\nloss78:773.7086181640625\nloss79:764.7208251953125\nloss80:756.01318359375\nloss81:747.5820922851562\nloss82:739.40185546875\nloss83:731.4605102539062\nloss84:723.7383422851562\nloss85:716.22607421875\nloss86:708.9168701171875\nloss87:701.8048095703125\nloss88:694.8750610351562\nloss89:688.1211547851562\nloss90:681.5391845703125\nloss91:675.1160888671875\nloss92:668.8406372070312\nloss93:662.7134399414062\nloss94:656.72998046875\nloss95:650.8836059570312\nloss96:645.16943359375\nloss97:639.58251953125\nloss98:634.1151733398438\nloss99:628.757568359375\nloss100:623.511474609375\nloss101:618.3792724609375\nloss102:613.3524169921875\nloss103:608.4260864257812\nloss104:603.5935668945312\nloss105:598.8561401367188\nloss106:594.215087890625\nloss107:589.6589965820312\nloss108:585.1896362304688\nloss109:580.8012084960938\nloss110:576.489501953125\nloss111:572.2600708007812\nloss112:568.1052856445312\nloss113:564.0208740234375\nloss114:560.0068359375\nloss115:556.0614624023438\nloss116:552.1822509765625\nloss117:548.3678588867188\nloss118:544.6203002929688\nloss119:540.9303588867188\nloss120:537.2980346679688\nloss121:533.7255249023438\nloss122:530.2085571289062\nloss123:526.74609375\nloss124:523.3369750976562\nloss125:519.9797973632812\nloss126:516.6742553710938\nloss127:513.419677734375\nloss128:510.2109375\nloss129:507.047119140625\nloss130:503.9302673339844\nloss131:500.8587646484375\nloss132:497.8271789550781\nloss133:494.83770751953125\nloss134:491.8876037597656\nloss135:488.97869873046875\nloss136:486.11004638671875\nloss137:483.27838134765625\nloss138:480.4872131347656\nloss139:477.7335205078125\nloss140:475.01513671875\nloss141:472.33160400390625\nloss142:469.6838073730469\nloss143:467.0693359375\nloss144:464.4868469238281\nloss145:461.9367980957031\nloss146:459.42034912109375\nloss147:456.9337158203125\nloss148:454.4779357910156\nloss149:452.0503234863281\nloss150:449.65380859375\nloss151:447.28387451171875\nloss152:444.9424743652344\nloss153:442.62750244140625\nloss154:440.3414001464844\nloss155:438.0830383300781\nloss156:435.8501892089844\nloss157:433.6424865722656\nloss158:431.45977783203125\nloss159:429.30169677734375\nloss160:427.16790771484375\nloss161:425.0594482421875\nloss162:422.9740295410156\nloss163:420.9105224609375\nloss164:418.86968994140625\nloss165:416.8525085449219\nloss166:414.8572998046875\nloss167:412.8825988769531\nloss168:410.9290771484375\nloss169:408.9979248046875\nloss170:407.08514404296875\nloss171:405.1919860839844\nloss172:403.3193664550781\nloss173:401.4659118652344\nloss174:399.628662109375\nloss175:397.8117980957031\nloss176:396.01361083984375\nloss177:394.2328186035156\nloss178:392.4710998535156\nloss179:390.7256774902344\nloss180:388.9976806640625\nloss181:387.285888671875\nloss182:385.5907287597656\nloss183:383.91107177734375\nloss184:382.248046875\nloss185:380.6004638671875\nloss186:378.96905517578125\nloss187:377.3527526855469\nloss188:375.7502136230469\nloss189:374.1639099121094\nloss190:372.59197998046875\nloss191:371.0353088378906\nloss192:369.4926452636719\nloss193:367.9638671875\nloss194:366.4486999511719\nloss195:364.94818115234375\nloss196:363.4605712890625\nloss197:361.9860534667969\nloss198:360.52386474609375\nloss199:359.0757751464844\nloss200:357.64019775390625\nloss201:356.2170715332031\nloss202:354.80609130859375\nloss203:353.40863037109375\nloss204:352.022705078125\nloss205:350.6480712890625\nloss206:349.28607177734375\nloss207:347.9358215332031\nloss208:346.5970153808594\nloss209:345.2685852050781\nloss210:343.95111083984375\nloss211:342.6451110839844\nloss212:341.3505554199219\nloss213:340.0661926269531\nloss214:338.7913818359375\nloss215:337.5272521972656\nloss216:336.2743225097656\nloss217:335.0320129394531\nloss218:333.799072265625\nloss219:332.5767822265625\nloss220:331.3641052246094\nloss221:330.16156005859375\nloss222:328.96966552734375\nloss223:327.78656005859375\nloss224:326.6127014160156\nloss225:325.44818115234375\nloss226:324.2925109863281\nloss227:323.146484375\nloss228:322.00909423828125\nloss229:320.8808288574219\nloss230:319.7610778808594\nloss231:318.6500549316406\nloss232:317.54730224609375\nloss233:316.4526062011719\nloss234:315.366943359375\nloss235:314.2891540527344\nloss236:313.21929931640625\nloss237:312.15765380859375\nloss238:311.1034240722656\nloss239:310.05694580078125\nloss240:309.01812744140625\nloss241:307.9866943359375\nloss242:306.9629211425781\nloss243:305.9468688964844\nloss244:304.9371643066406\nloss245:303.9346923828125\nloss246:302.9403991699219\nloss247:301.95263671875\nloss248:300.9714660644531\nloss249:299.99713134765625\nloss250:299.02960205078125\nloss251:298.0695495605469\nloss252:297.1158447265625\nloss253:296.1683349609375\nloss254:295.22796630859375\nloss255:294.2948303222656\nloss256:293.3674011230469\nloss257:292.4454650878906\nloss258:291.5306091308594\nloss259:290.6217956542969\nloss260:289.7188415527344\nloss261:288.8221130371094\nloss262:287.9313049316406\nloss263:287.04705810546875\nloss264:286.16864013671875\nloss265:285.2957763671875\nloss266:284.4281005859375\nloss267:283.5668640136719\nloss268:282.71063232421875\nloss269:281.8605041503906\nloss270:281.0153503417969\nloss271:280.17608642578125\nloss272:279.3423156738281\nloss273:278.5139465332031\nloss274:277.6908874511719\nloss275:276.8724670410156\nloss276:276.05865478515625\nloss277:275.25091552734375\nloss278:274.4479675292969\nloss279:273.6498718261719\nloss280:272.8564758300781\nloss281:272.0684509277344\nloss282:271.28485107421875\nloss283:270.5062561035156\nloss284:269.73297119140625\nloss285:268.9642639160156\nloss286:268.2005920410156\nloss287:267.4409484863281\nloss288:266.68621826171875\nloss289:265.93634033203125\nloss290:265.1909484863281\nloss291:264.44976806640625\nloss292:263.7132263183594\nloss293:262.9819641113281\nloss294:262.2548522949219\nloss295:261.5319519042969\nloss296:260.8137512207031\nloss297:260.09942626953125\nloss298:259.38916015625\nloss299:258.6836242675781\nloss300:257.9819030761719\nloss301:257.2833557128906\nloss302:256.5892028808594\nloss303:255.89915466308594\nloss304:255.21315002441406\nloss305:254.53160095214844\nloss306:253.85328674316406\nloss307:253.17849731445312\nloss308:252.50840759277344\nloss309:251.8419189453125\nloss310:251.1786651611328\nloss311:250.5194549560547\nloss312:249.86476135253906\nloss313:249.21340942382812\nloss314:248.5654296875\nloss315:247.92137145996094\nloss316:247.28158569335938\nloss317:246.64454650878906\nloss318:246.01112365722656\nloss319:245.381103515625\nloss320:244.7549591064453\nloss321:244.1321563720703\nloss322:243.51246643066406\nloss323:242.89620971679688\nloss324:242.28311157226562\nloss325:241.67361450195312\nloss326:241.0673828125\nloss327:240.46466064453125\nloss328:239.86509704589844\nloss329:239.26864624023438\nloss330:238.67568969726562\nloss331:238.08624267578125\nloss332:237.4991455078125\nloss333:236.91497802734375\nloss334:236.3340301513672\nloss335:235.7563934326172\nloss336:235.18223571777344\nloss337:234.61065673828125\nloss338:234.04165649414062\nloss339:233.47586059570312\nloss340:232.9126739501953\nloss341:232.35218811035156\nloss342:231.7950439453125\nloss343:231.2408447265625\nloss344:230.68914794921875\nloss345:230.1402130126953\nloss346:229.593994140625\nloss347:229.05056762695312\nloss348:228.5101318359375\nloss349:227.97177124023438\nloss350:227.4363555908203\nloss351:226.90362548828125\nloss352:226.3736114501953\nloss353:225.84613037109375\nloss354:225.32151794433594\nloss355:224.79893493652344\nloss356:224.27951049804688\nloss357:223.76303100585938\nloss358:223.24850463867188\nloss359:222.73654174804688\nloss360:222.22703552246094\nloss361:221.72007751464844\nloss362:221.2156219482422\nloss363:220.7134246826172\nloss364:220.21405029296875\nloss365:219.71730041503906\nloss366:219.22244262695312\nloss367:218.7301788330078\nloss368:218.240478515625\nloss369:217.75279235839844\nloss370:217.26756286621094\nloss371:216.78485107421875\nloss372:216.30429077148438\nloss373:215.82594299316406\nloss374:215.3494873046875\nloss375:214.87525939941406\nloss376:214.4033660888672\nloss377:213.93386840820312\nloss378:213.46669006347656\nloss379:213.0015869140625\nloss380:212.53855895996094\nloss381:212.07713317871094\nloss382:211.6184539794922\nloss383:211.16184997558594\nloss384:210.70741271972656\nloss385:210.25448608398438\nloss386:209.8045196533203\nloss387:209.35653686523438\nloss388:208.91026306152344\nloss389:208.466552734375\nloss390:208.02438354492188\nloss391:207.58432006835938\nloss392:207.14662170410156\nloss393:206.71078491210938\nloss394:206.27674865722656\nloss395:205.8448028564453\nloss396:205.4148406982422\nloss397:204.98696899414062\nloss398:204.56076049804688\nloss399:204.13673400878906\nloss400:203.7149658203125\nloss401:203.2947235107422\nloss402:202.87648010253906\nloss403:202.45989990234375\nloss404:202.04534912109375\nloss405:201.6326446533203\nloss406:201.22177124023438\nloss407:200.81256103515625\nloss408:200.4053192138672\nloss409:199.9998321533203\nloss410:199.59571838378906\nloss411:199.1934814453125\nloss412:198.79290771484375\nloss413:198.3939208984375\nloss414:197.99691772460938\nloss415:197.6016082763672\nloss416:197.2079315185547\nloss417:196.81625366210938\nloss418:196.42587280273438\nloss419:196.03704833984375\nloss420:195.65000915527344\nloss421:195.2648162841797\nloss422:194.8808135986328\nloss423:194.49862670898438\n"
],
[
"img=showimage(initial_img,False,True)\ngrayscale(img)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a31e616bab891ff02b62f28e2088ac9db364a28
| 128,735 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
tutorials/W1D1_BasicsAndPytorch/W1D1_Tutorial1.ipynb
|
raghudiddigi/course-content-dl
|
e6690218ea031d3054bfa4b085e8088103b766fa
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0",
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
tutorials/W1D1_BasicsAndPytorch/W1D1_Tutorial1.ipynb
|
raghudiddigi/course-content-dl
|
e6690218ea031d3054bfa4b085e8088103b766fa
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0",
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
tutorials/W1D1_BasicsAndPytorch/W1D1_Tutorial1.ipynb
|
raghudiddigi/course-content-dl
|
e6690218ea031d3054bfa4b085e8088103b766fa
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0",
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null | 32.127527 | 571 | 0.560127 |
[
[
[
"<a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/NeuromatchAcademy/course-content-dl/blob/main/tutorials/W1D1_BasicsAndPytorch/W1D1_Tutorial1.ipynb\" target=\"_parent\"><img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open In Colab\"/></a>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Tutorial 1: PyTorch\n**Week 1, Day 1: Basics and PyTorch**\n\n**By Neuromatch Academy**\n\n\n__Content creators:__ Shubh Pachchigar, Vladimir Haltakov, Matthew Sargent, Konrad Kording\n\n__Content reviewers:__ Deepak Raya, Siwei Bai, Kelson Shilling-Scrivo\n\n__Content editors:__ Anoop Kulkarni, Spiros Chavlis\n\n__Production editors:__ Arush Tagade, Spiros Chavlis",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Our 2021 Sponsors, including Presenting Sponsor Facebook Reality Labs**\n\n<p align='center'><img src='https://github.com/NeuromatchAcademy/widgets/blob/master/sponsors.png?raw=True'/></p>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"---\n# Tutorial Objectives\n\nThen have a few specific objectives for this tutorial:\n* Learn about PyTorch and tensors\n* Tensor Manipulations\n* Data Loading\n* GPUs and Cuda Tensors\n* Train NaiveNet\n* Get to know your pod\n* Start thinking about the course as a whole",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# @title Tutorial slides\n\n# @markdown These are the slides for the videos in this tutorial today\nfrom IPython.display import IFrame\nIFrame(src=f\"https://mfr.ca-1.osf.io/render?url=https://osf.io/wcjrv/?direct%26mode=render%26action=download%26mode=render\", width=854, height=480)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"---\n# Setup",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Throughout your Neuromatch tutorials, most (probably all!) notebooks contain setup cells. These cells will import the required Python packages (e.g., PyTorch, NumPy); set global or environment variables, and load in helper functions for things like plotting. In some tutorials, you will notice that we install some dependencies even if they are preinstalled on google colab or kaggle. This happens because we have added automation to our repository through [GitHub Actions](https://docs.github.com/en/actions/learn-github-actions/introduction-to-github-actions).\n\nBe sure to run all of the cells in the setup section. Feel free to expand them and have a look at what you are loading in, but you should be able to fulfill the learning objectives of every tutorial without having to look at these cells.\n\nIf you start building your own projects built on this code base we highly recommend looking at them in more detail.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# @title Install dependencies\n!pip install pandas --quiet\n!pip install git+https://github.com/NeuromatchAcademy/evaltools --quiet\n\nfrom evaltools.airtable import AirtableForm",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Imports\nimport time\nimport torch\nimport random\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\nfrom torch import nn\nfrom torchvision import datasets\nfrom torchvision.transforms import ToTensor\nfrom torch.utils.data import DataLoader",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# @title Figure Settings\nimport ipywidgets as widgets\n%config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'retina'\nplt.style.use(\"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/NeuromatchAcademy/content-creation/main/nma.mplstyle\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# @title Helper Functions\n\natform = AirtableForm('appn7VdPRseSoMXEG','W1D1_T1','https://portal.neuromatchacademy.org/api/redirect/to/97e94a29-0b3a-4e16-9a8d-f6838a5bd83d')\n\n\ndef checkExercise1(A, B, C, D):\n \"\"\"\n Helper function for checking exercise.\n\n Args:\n A: torch.Tensor\n B: torch.Tensor\n C: torch.Tensor\n D: torch.Tensor\n Returns:\n Nothing.\n \"\"\"\n errors = []\n # TODO better errors and error handling\n if not torch.equal(A.to(int),torch.ones(20, 21).to(int)):\n errors.append(f\"Got: {A} \\n Expected: {torch.ones(20, 21)} (shape: {torch.ones(20, 21).shape})\")\n if not np.array_equal( B.numpy(),np.vander([1, 2, 3], 4)):\n errors.append(\"B is not a tensor containing the elements of Z \")\n if C.shape != (20, 21):\n errors.append(\"C is not the correct shape \")\n if not torch.equal(D, torch.arange(4, 41, step=2)):\n errors.append(\"D does not contain the correct elements\")\n\n if errors == []:\n print(\"All correct!\")\n\n else:\n [print(e) for e in errors]\n\n\ndef timeFun(f, dim, iterations, device='cpu'):\n iterations = iterations\n t_total = 0\n for _ in range(iterations):\n start = time.time()\n f(dim, device)\n end = time.time()\n t_total += end - start\n print(f\"time taken for {iterations} iterations of {f.__name__}({dim}): {t_total:.5f}\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Important note: Google Colab users**\n\n*Scratch Code Cells*\n\nIf you want to quickly try out something or take a look at the data you can use scratch code cells. They allow you to run Python code, but will not mess up the structure of your notebook.\n\nTo open a new scratch cell go to *Insert* → *Scratch code cell*.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Section 1: Welcome to Neuromatch Deep learning course\n\n*Time estimate: ~25mins*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# @title Video 1: Welcome and History\nfrom ipywidgets import widgets\n\nout2 = widgets.Output()\nwith out2:\n from IPython.display import IFrame\n class BiliVideo(IFrame):\n def __init__(self, id, page=1, width=400, height=300, **kwargs):\n self.id=id\n src = \"https://player.bilibili.com/player.html?bvid={0}&page={1}\".format(id, page)\n super(BiliVideo, self).__init__(src, width, height, **kwargs)\n\n video = BiliVideo(id=f\"BV1Av411n7oL\", width=854, height=480, fs=1)\n print(\"Video available at https://www.bilibili.com/video/{0}\".format(video.id))\n display(video)\n\nout1 = widgets.Output()\nwith out1:\n from IPython.display import YouTubeVideo\n video = YouTubeVideo(id=f\"ca21SNqt78I\", width=854, height=480, fs=1, rel=0)\n print(\"Video available at https://youtube.com/watch?v=\" + video.id)\n display(video)\n\nout = widgets.Tab([out1, out2])\nout.set_title(0, 'Youtube')\nout.set_title(1, 'Bilibili')\n\n# add timing\natform.add_event('Video 1: Welcome and History')\n\ndisplay(out)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*This will be an intensive 3 week adventure. We will all learn Deep Learning. In a group. Groups need standards. Read our \n[Code of Conduct](https://docs.google.com/document/d/1eHKIkaNbAlbx_92tLQelXnicKXEcvFzlyzzeWjEtifM/edit?usp=sharing).\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# @title Video 2: Why DL is cool\nfrom ipywidgets import widgets\n\nout2 = widgets.Output()\nwith out2:\n from IPython.display import IFrame\n class BiliVideo(IFrame):\n def __init__(self, id, page=1, width=400, height=300, **kwargs):\n self.id=id\n src = \"https://player.bilibili.com/player.html?bvid={0}&page={1}\".format(id, page)\n super(BiliVideo, self).__init__(src, width, height, **kwargs)\n\n video = BiliVideo(id=f\"BV1gf4y1j7UZ\", width=854, height=480, fs=1)\n print(\"Video available at https://www.bilibili.com/video/{0}\".format(video.id))\n display(video)\n\nout1 = widgets.Output()\nwith out1:\n from IPython.display import YouTubeVideo\n video = YouTubeVideo(id=f\"l-K6495BN-4\", width=854, height=480, fs=1, rel=0)\n print(\"Video available at https://youtube.com/watch?v=\" + video.id)\n display(video)\n\nout = widgets.Tab([out1, out2])\nout.set_title(0, 'Youtube')\nout.set_title(1, 'Bilibili')\n\n# add timing to airtable\natform.add_event('Video 2: Why DL is cool')\n\ndisplay(out)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Describe what you hope to get out of this course in about 100 words.**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"---\n# Section 2: The Basics of PyTorch\n\n*Time estimate: ~2 hours 05 mins*",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"PyTorch is a Python-based scientific computing package targeted at two sets of\naudiences:\n\n- A replacement for NumPy to use the power of GPUs\n- A deep learning platform that provides significant flexibility\n and speed\n\nAt its core, PyTorch provides a few key features:\n\n- A multidimensional [Tensor](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/tensors.html) object, similar to [NumPy Array](https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.ndarray.html) but with GPU acceleration.\n- An optimized **autograd** engine for automatically computing derivatives.\n- A clean, modular API for building and deploying **deep learning models**.\n\nYou can find more information about PyTorch in the appendix.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Section 2.1: Creating Tensors\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# @title Video 3: Making Tensors\nfrom ipywidgets import widgets\n\nout2 = widgets.Output()\nwith out2:\n from IPython.display import IFrame\n class BiliVideo(IFrame):\n def __init__(self, id, page=1, width=400, height=300, **kwargs):\n self.id=id\n src = \"https://player.bilibili.com/player.html?bvid={0}&page={1}\".format(id, page)\n super(BiliVideo, self).__init__(src, width, height, **kwargs)\n\n video = BiliVideo(id=f\"BV1Rw411d7Uy\", width=854, height=480, fs=1)\n print(\"Video available at https://www.bilibili.com/video/{0}\".format(video.id))\n display(video)\n\nout1 = widgets.Output()\nwith out1:\n from IPython.display import YouTubeVideo\n video = YouTubeVideo(id=f\"jGKd_4tPGrw\", width=854, height=480, fs=1, rel=0)\n print(\"Video available at https://youtube.com/watch?v=\" + video.id)\n display(video)\n\nout = widgets.Tab([out1, out2])\nout.set_title(0, 'Youtube')\nout.set_title(1, 'Bilibili')\n\n# add timing to airtable\natform.add_event('Video 3: Making Tensors')\n\ndisplay(out)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"There are various ways of creating tensors, and when doing any real deep learning project we will usually have to do so.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Construct tensors directly:**\n\n---\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# we can construct a tensor directly from some common python iterables,\n# such as list and tuple nested iterables can also be handled as long as the\n# dimensions make sense\n\n# tensor from a list\na = torch.tensor([0, 1, 2])\n\n#tensor from a tuple of tuples\nb = ((1.0, 1.1), (1.2, 1.3))\nb = torch.tensor(b)\n\n# tensor from a numpy array\nc = np.ones([2, 3])\nc = torch.tensor(c)\n\nprint(f\"Tensor a: {a}\")\nprint(f\"Tensor b: {b}\")\nprint(f\"Tensor c: {c}\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Some common tensor constructors:**\n\n---",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# the numerical arguments we pass to these constructors\n# determine the shape of the output tensor\n\nx = torch.ones(5, 3)\ny = torch.zeros(2)\nz = torch.empty(1, 1, 5)\nprint(f\"Tensor x: {x}\")\nprint(f\"Tensor y: {y}\")\nprint(f\"Tensor z: {z}\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Notice that ```.empty()``` does not return zeros, but seemingly random small numbers. Unlike ```.zeros()```, which initialises the elements of the tensor with zeros, ```.empty()``` just allocates the memory. It is hence a bit faster if you are looking to just create a tensor.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Creating random tensors and tensors like other tensors:**\n\n---",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# there are also constructors for random numbers\n\n# uniform distribution\na = torch.rand(1, 3)\n\n# normal distribution\nb = torch.randn(3, 4)\n\n# there are also constructors that allow us to construct\n# a tensor according to the above constructors, but with\n# dimensions equal to another tensor\n\nc = torch.zeros_like(a)\nd = torch.rand_like(c)\n\nprint(f\"Tensor a: {a}\")\nprint(f\"Tensor b: {b}\")\nprint(f\"Tensor c: {c}\")\nprint(f\"Tensor d: {d}\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*Reproducibility*: \n\n- PyTorch random number generator: You can use `torch.manual_seed()` to seed the RNG for all devices (both CPU and CUDA)\n\n```python\nimport torch\ntorch.manual_seed(0)\n```\n- For custom operators, you might need to set python seed as well:\n\n```python\nimport random\nrandom.seed(0)\n```\n\n- Random number generators in other libraries\n\n```python\nimport numpy as np\nnp.random.seed(0)\n```\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Here, we define for you a function called `set_seed` that does the job for you!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def set_seed(seed=None, seed_torch=True):\n \"\"\"\n Function that controls randomness. NumPy and random modules must be imported.\n\n Args:\n seed : Integer\n A non-negative integer that defines the random state. Default is `None`.\n seed_torch : Boolean\n If `True` sets the random seed for pytorch tensors, so pytorch module\n must be imported. Default is `True`.\n\n Returns:\n Nothing.\n \"\"\"\n if seed is None:\n seed = np.random.choice(2 ** 32)\n random.seed(seed)\n np.random.seed(seed)\n if seed_torch:\n torch.manual_seed(seed)\n torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed)\n torch.cuda.manual_seed(seed)\n torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False\n torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True\n\n print(f'Random seed {seed} has been set.')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now, let's use the `set_seed` function in the previous example. Execute the cell multiple times to verify that the numbers printed are always the same.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def simplefun(seed=True, my_seed=None):\n if seed:\n set_seed(seed=my_seed)\n\n # uniform distribution\n a = torch.rand(1, 3)\n # normal distribution\n b = torch.randn(3, 4)\n\n print(\"Tensor a: \", a)\n print(\"Tensor b: \", b)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"simplefun(seed=True, my_seed=0) # Turn `seed` to `False` or change `my_seed`",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Numpy-like number ranges:**\n---\nThe ```.arange()``` and ```.linspace()``` behave how you would expect them to if you are familar with numpy.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"a = torch.arange(0, 10, step=1)\nb = np.arange(0, 10, step=1)\n\nc = torch.linspace(0, 5, steps=11)\nd = np.linspace(0, 5, num=11)\n\nprint(f\"Tensor a: {a}\\n\")\nprint(f\"Numpy array b: {b}\\n\")\nprint(f\"Tensor c: {c}\\n\")\nprint(f\"Numpy array d: {d}\\n\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Coding Exercise 2.1: Creating Tensors\n\nBelow you will find some incomplete code. Fill in the missing code to construct the specified tensors.\n\nWe want the tensors: \n\n$A:$ 20 by 21 tensor consisting of ones\n\n$B:$ a tensor with elements equal to the elements of numpy array $Z$\n\n$C:$ a tensor with the same number of elements as $A$ but with values $\n\\sim U(0,1)$\n\n$D:$ a 1D tensor containing the even numbers between 4 and 40 inclusive.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def tensor_creation(Z):\n \"\"\"A function that creates various tensors.\n\n Args:\n Z (numpy.ndarray): An array of shape\n\n Returns:\n A : 20 by 21 tensor consisting of ones\n B : a tensor with elements equal to the elements of numpy array Z\n C : a tensor with the same number of elements as A but with values ∼U(0,1)\n D : a 1D tensor containing the even numbers between 4 and 40 inclusive.\n \"\"\"\n #################################################\n ## TODO for students: fill in the missing code\n ## from the first expression\n raise NotImplementedError(\"Student exercise: say what they should have done\")\n #################################################\n A = ...\n B = ...\n C = ...\n D = ...\n\n return A, B, C, D\n\n\n# add timing to airtable\natform.add_event('Coding Exercise 2.1: Creating Tensors')\n\n\n\n# numpy array to copy later\nZ = np.vander([1, 2, 3], 4)\n\n# Uncomment below to check your function!\n# A, B, C, D = tensor_creation(Z)\n# checkExercise1(A, B, C, D)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# to_remove solution\ndef tensor_creation(Z):\n \"\"\"A function that creates various tensors.\n\n Args:\n Z (numpy.ndarray): An array of shape\n\n Returns:\n A : 20 by 21 tensor consisting of ones\n B : a tensor with elements equal to the elements of numpy array Z\n C : a tensor with the same number of elements as A but with values ∼U(0,1)\n D : a 1D tensor containing the even numbers between 4 and 40 inclusive.\n \"\"\"\n\n A = torch.ones(20, 21)\n B = torch.tensor(Z)\n C = torch.rand_like(A)\n D = torch.arange(4, 41, step=2)\n\n return A, B, C, D\n\n# add timing to airtable\natform.add_event('Coding Exercise 2.1: Creating Tensors')\n\n# numpy array to copy later\nZ = np.vander([1, 2, 3], 4)\n\n# Uncomment below to check your function!\nA, B, C, D = tensor_creation(Z)\ncheckExercise1(A, B, C, D)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"```\nAll correct!\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Section 2.2: Operations in PyTorch\n\n**Tensor-Tensor operations**\n\nWe can perform operations on tensors using methods under ```torch.``` \n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# @title Video 4: Tensor Operators\nfrom ipywidgets import widgets\n\nout2 = widgets.Output()\nwith out2:\n from IPython.display import IFrame\n class BiliVideo(IFrame):\n def __init__(self, id, page=1, width=400, height=300, **kwargs):\n self.id=id\n src = \"https://player.bilibili.com/player.html?bvid={0}&page={1}\".format(id, page)\n super(BiliVideo, self).__init__(src, width, height, **kwargs)\n\n video = BiliVideo(id=f\"BV1G44y127As\", width=854, height=480, fs=1)\n print(\"Video available at https://www.bilibili.com/video/{0}\".format(video.id))\n display(video)\n\nout1 = widgets.Output()\nwith out1:\n from IPython.display import YouTubeVideo\n video = YouTubeVideo(id=f\"R1R8VoYXBVA\", width=854, height=480, fs=1, rel=0)\n print(\"Video available at https://youtube.com/watch?v=\" + video.id)\n display(video)\n\nout = widgets.Tab([out1, out2])\nout.set_title(0, 'Youtube')\nout.set_title(1, 'Bilibili')\n\n# add timing to airtable\natform.add_event('Video 4: Tensor Operators')\n\ndisplay(out)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Tensor-Tensor operations**\n\nWe can perform operations on tensors using methods under ```torch.``` ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"a = torch.ones(5, 3)\nb = torch.rand(5, 3)\nc = torch.empty(5, 3)\nd = torch.empty(5, 3)\n\n# this only works if c and d already exist\ntorch.add(a, b, out=c)\n#Pointwise Multiplication of a and b\ntorch.multiply(a, b, out=d)\nprint(c)\nprint(d)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"However, in PyTorch most common Python operators are overridden.\nThe common standard arithmetic operators (+, -, *, /, and **) have all been lifted to elementwise operations",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x = torch.tensor([1, 2, 4, 8])\ny = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3, 4])\nx + y, x - y, x * y, x / y, x**y # The ** operator is exponentiation",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Tensor Methods**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Tensors also have a number of common arithmetic operations built in. A full list of **all** methods can be found in the appendix (there are a lot!) \n\nAll of these operations should have similar syntax to their numpy equivalents.(Feel free to skip if you already know this!)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x = torch.rand(3, 3)\nprint(x)\nprint(\"\\n\")\n# sum() - note the axis is the axis you move across when summing\nprint(f\"Sum of every element of x: {x.sum()}\")\nprint(f\"Sum of the columns of x: {x.sum(axis=0)}\")\nprint(f\"Sum of the rows of x: {x.sum(axis=1)}\")\nprint(\"\\n\")\n\nprint(f\"Mean value of all elements of x {x.mean()}\")\nprint(f\"Mean values of the columns of x {x.mean(axis=0)}\")\nprint(f\"Mean values of the rows of x {x.mean(axis=1)}\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Matrix Operations**\n\nThe ```@``` symbol is overridden to represent matrix multiplication. You can also use ```torch.matmul()``` to multiply tensors. For dot multiplication, you can use ```torch.dot()```, or manipulate the axes of your tensors and do matrix multiplication (we will cover that in the next section). \n\nTransposes of 2D tensors are obtained using ```torch.t()``` or ```Tensor.t```. Note the lack of brackets for ```Tensor.t``` - it is an attribute, not a method.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Coding Exercise 2.2 : Simple tensor operations\n\nBelow are two expressions involving operations on matrices. \n\n$$ \\textbf{A} = \n\\begin{bmatrix}2 &4 \\\\5 & 7 \n\\end{bmatrix} \n\\begin{bmatrix} 1 &1 \\\\2 & 3\n\\end{bmatrix} \n + \n\\begin{bmatrix}10 & 10 \\\\ 12 & 1 \n\\end{bmatrix} \n$$\n\n\nand\n\n\n$$ b = \n\\begin{bmatrix} 3 \\\\ 5 \\\\ 7\n\\end{bmatrix} \\cdot \n\\begin{bmatrix} 2 \\\\ 4 \\\\ 8\n\\end{bmatrix}\n$$\n\nThe code block below that computes these expressions using PyTorch is incomplete - fill in the missing lines.\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def simple_operations(a1: torch.Tensor, a2: torch.Tensor, a3: torch.Tensor):\n ################################################\n ## TODO for students: complete the first computation using the argument matricies\n raise NotImplementedError(\"Student exercise: fill in the missing code to complete the operation\")\n ################################################\n # multiplication of tensor a1 with tensor a2 and then add it with tensor a3\n answer = ...\n return answer\n\n# add timing to airtable\natform.add_event('Coding Exercise 2.2 : Simple tensor operations-simple_operations')\n\n# Computing expression 1:\n\n# init our tensors\na1 = torch.tensor([[2, 4], [5, 7]])\na2 = torch.tensor([[1, 1], [2, 3]])\na3 = torch.tensor([[10, 10], [12, 1]])\n## uncomment to test your function\n# A = simple_operations(a1, a2, a3)\n# print(A)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# to_remove solution\ndef simple_operations(a1: torch.Tensor, a2: torch.Tensor, a3: torch.Tensor):\n # multiplication of tensor a1 with tensor a2 and then add it with tensor a3\n answer = a1 @ a2 + a3\n return answer\n\n# add timing to airtable\natform.add_event('Coding Exercise 2.2 : Simple tensor operations-simple_operations')\n\n\n# Computing expression 1:\n\n# init our tensors\na1 = torch.tensor([[2, 4], [5, 7]])\na2 = torch.tensor([[1, 1], [2, 3]])\na3 = torch.tensor([[10, 10], [12, 1]])\n## uncomment to test your function\nA = simple_operations(a1, a2, a3)\nprint(A)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"```\ntensor([[20, 24],\n [31, 27]])\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def dot_product(b1: torch.Tensor, b2: torch.Tensor):\n ###############################################\n ## TODO for students: complete the first computation using the argument matricies\n raise NotImplementedError(\"Student exercise: fill in the missing code to complete the operation\")\n ###############################################\n # Use torch.dot() to compute the dot product of two tensors\n product = ...\n return product\n\n# add timing to airtable\natform.add_event('Coding Exercise 2.2 : Simple tensor operations-dot_product')\n\n\n# Computing expression 2:\nb1 = torch.tensor([3, 5, 7])\nb2 = torch.tensor([2, 4, 8])\n## Uncomment to test your function\n# b = dot_product(b1, b2)\n# print(b)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# to_remove solution\ndef dot_product(b1: torch.Tensor, b2: torch.Tensor):\n # Use torch.dot() to compute the dot product of two tensors\n product = torch.dot(b1, b2)\n return product\n\n# add timing to airtable\natform.add_event('Coding Exercise 2.2 : Simple tensor operations-dot_product')\n\n\n# Computing expression 2:\nb1 = torch.tensor([3, 5, 7])\nb2 = torch.tensor([2, 4, 8])\n## Uncomment to test your function\nb = dot_product(b1, b2)\nprint(b)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"```\ntensor(82)\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Section 2.3 Manipulating Tensors in Pytorch\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# @title Video 5: Tensor Indexing\nfrom ipywidgets import widgets\n\nout2 = widgets.Output()\nwith out2:\n from IPython.display import IFrame\n class BiliVideo(IFrame):\n def __init__(self, id, page=1, width=400, height=300, **kwargs):\n self.id=id\n src = \"https://player.bilibili.com/player.html?bvid={0}&page={1}\".format(id, page)\n super(BiliVideo, self).__init__(src, width, height, **kwargs)\n\n video = BiliVideo(id=f\"BV1BM4y1K7pD\", width=854, height=480, fs=1)\n print(\"Video available at https://www.bilibili.com/video/{0}\".format(video.id))\n display(video)\n\nout1 = widgets.Output()\nwith out1:\n from IPython.display import YouTubeVideo\n video = YouTubeVideo(id=f\"0d0KSJ3lJbg\", width=854, height=480, fs=1, rel=0)\n print(\"Video available at https://youtube.com/watch?v=\" + video.id)\n display(video)\n\nout = widgets.Tab([out1, out2])\nout.set_title(0, 'Youtube')\nout.set_title(1, 'Bilibili')\n\n# add timing to airtable\natform.add_event('Video 5: Tensor Indexing')\n\ndisplay(out)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Indexing**\n\nJust as in numpy, elements in a tensor can be accessed by index. As in any numpy array, the first element has index 0 and ranges are specified to include the first but before the last element. We can access elements according to their relative position to the end of the list by using negative indices. Indexing is also referred to as slicing.\n\nFor example, [-1] selects the last element; [1:3] selects the second and the third elements, and [:-2] will select all elements excluding the last and second-to-last elements.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x = torch.arange(0, 10)\nprint(x)\nprint(x[-1])\nprint(x[1:3])\nprint(x[:-2])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"When we have multidimensional tensors, indexing rules work the same way as numpy.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# make a 5D tensor\nx = torch.rand(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)\n\nprint(f\" shape of x[0]:{x[0].shape}\")\nprint(f\" shape of x[0][0]:{x[0][0].shape}\")\nprint(f\" shape of x[0][0][0]:{x[0][0][0].shape}\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Flatten and reshape**\n\nThere are various methods for reshaping tensors. It is common to have to express 2D data in 1D format. Similarly, it is also common to have to reshape a 1D tensor into a 2D tensor. We can achieve this with the ```.flatten()``` and ```.reshape()``` methods.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"z = torch.arange(12).reshape(6, 2)\nprint(f\"Original z: \\n {z}\")\n\n# 2D -> 1D\nz = z.flatten()\nprint(f\"Flattened z: \\n {z}\")\n\n# and back to 2D\nz = z.reshape(3, 4)\nprint(f\"Reshaped (3x4) z: \\n {z}\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You will also see the ```.view()``` methods used a lot to reshape tensors. There is a subtle difference between ```.view()``` and ```.reshape()```, though for now we will just use ```.reshape()```. The documentation can be found in the appendix.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Squeezing tensors**\n\nWhen processing batches of data, you will quite often be left with singleton dimensions. e.g. [1,10] or [256, 1, 3]. This dimension can quite easily mess up your matrix operations if you don't plan on it being there...\n\nIn order to compress tensors along their singleton dimensions we can use the ```.squeeze()``` method. We can use the ```.unsqueeze()``` method to do the opposite. \n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x = torch.randn(1, 10)\n# printing the zeroth element of the tensor will not give us the first number!\n\nprint(x.shape)\nprint(f\"x[0]: {x[0]}\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
" Because of that pesky singleton dimension, x[0] gave us the first row instead!\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# lets get rid of that singleton dimension and see what happens now\nx = x.squeeze(0)\nprint(x.shape)\nprint(f\"x[0]: {x[0]}\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# adding singleton dimensions works a similar way, and is often used when tensors\n# being added need same number of dimensions\n\ny = torch.randn(5, 5)\nprint(f\"shape of y: {y.shape}\")\n\n# lets insert a singleton dimension\ny = y.unsqueeze(1)\nprint(f\"shape of y: {y.shape}\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Permutation**\nSometimes our dimensions will be in the wrong order! For example, we may be dealing with RGB images with dim [3x48x64], but our pipeline expects the colour dimension to be the last dimension i.e. [48x64x3]. To get around this we can use ```.permute()```\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# `x` has dimensions [color,image_height,image_width]\nx = torch.rand(3, 48, 64)\n\n# we want to permute our tensor to be [ image_height , image_width , color ]\nx = x.permute(1, 2, 0)\n# permute(1,2,0) means:\n# the 0th dim of my new tensor = the 1st dim of my old tensor\n# the 1st dim of my new tensor = the 2nd\n# the 2nd dim of my new tensor = the 0th\nprint(x.shape)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You may also see ```.transpose()``` used. This works in a similar way as permute, but can only swap two dimensions at once.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Concatenation**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In this example, we concatenate two matrices along rows (axis 0, the first element of the shape) vs. columns (axis 1, the second element of the shape). We can see that the first output tensor’s axis-0 length ( 6 ) is the sum of the two input tensors’ axis-0 lengths ( 3+3 ); while the second output tensor’s axis-1 length ( 8 ) is the sum of the two input tensors’ axis-1 lengths ( 4+4 ).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create two tensors of the same shape\nx = torch.arange(12, dtype=torch.float32).reshape((3, 4))\ny = torch.tensor([[2.0, 1, 4, 3], [1, 2, 3, 4], [4, 3, 2, 1]])\n\n\n#concatenate them along rows\ncat_rows = torch.cat((x, y), dim=0)\n\n# concatenate along columns\ncat_cols = torch.cat((x, y), dim=1)\n\n# printing outputs\nprint('Concatenated by rows: shape{} \\n {}'.format(list(cat_rows.shape), cat_rows))\nprint('\\n Concatenated by colums: shape{} \\n {}'.format(list(cat_cols.shape), cat_cols))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Conversion to Other Python Objects**\n\nConverting to a NumPy tensor, or vice versa, is easy. The converted result does not share memory. This minor inconvenience is actually quite important: when you perform operations on the CPU or on GPUs, you do not want to halt computation, waiting to see whether the NumPy package of Python might want to be doing something else with the same chunk of memory.\n\nWhen converting to a numpy array, the information being tracked by the tensor will be lost i.e. the computational graph. This will be covered in detail when you are introduced to autograd tomorrow! ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x = torch.randn(5)\nprint(f\"x: {x} | x type: {x.type()}\")\n\ny = x.numpy()\nprint(f\"y: {y} | y type: {type(y)}\")\n\nz = torch.tensor(y)\nprint(f\"z: {z} | z type: {z.type()}\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"To convert a size-1 tensor to a Python scalar, we can invoke the item function or Python’s built-in functions.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"a = torch.tensor([3.5])\na, a.item(), float(a), int(a)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Coding Exercise 2.3: Manipulating Tensors\nUsing a combination of the methods discussed above, complete the functions below.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Function A** \n\nThis function takes in two 2D tensors $A$ and $B$ and returns the column sum of A multiplied by the sum of all the elmements of $B$ i.e. a scalar, e.g.,:\n\n$ A = \\begin{bmatrix}\n1 & 1 \\\\\n1 & 1 \n\\end{bmatrix} \\,$\nand\n$ B = \\begin{bmatrix}\n1 & 2 & 3\\\\\n1 & 2 & 3 \n\\end{bmatrix} \\,$\nso\n$ \\, Out = \\begin{bmatrix} 2 & 2 \\\\\n\\end{bmatrix} \\cdot 12 = \\begin{bmatrix}\n24 & 24\\\\\n\\end{bmatrix}$\n\n**Function B** \n\nThis function takes in a square matrix $C$ and returns a 2D tensor consisting of a flattened $C$ with the index of each element appended to this tensor in the row dimension, e.g.,:\n\n$ C = \\begin{bmatrix}\n2 & 3 \\\\\n-1 & 10 \n\\end{bmatrix} \\,$\nso\n$ \\, Out = \\begin{bmatrix}\n0 & 2 \\\\\n1 & 3 \\\\\n2 & -1 \\\\\n3 & 10\n\\end{bmatrix}$\n\n**Hint:** pay close attention to singleton dimensions\n\n**Function C**\n\nThis function takes in two 2D tensors $D$ and $E$. If the dimensions allow it, this function returns the elementwise sum of $D$-shaped $E$, and $D$; else this function returns a 1D tensor that is the concatenation of the two tensors, e.g.,:\n\n$ D = \\begin{bmatrix}\n1 & -1 \\\\\n-1 & 3 \n\\end{bmatrix} \\,$\nand \n$ E = \\begin{bmatrix}\n2 & 3 & 0 & 2 \\\\\n\\end{bmatrix} \\, $\nso\n$ \\, Out = \\begin{bmatrix}\n3 & 2 \\\\\n-1 & 5 \n\\end{bmatrix}$\n\n$ D = \\begin{bmatrix}\n1 & -1 \\\\\n-1 & 3 \n\\end{bmatrix}$\nand\n$ \\, E = \\begin{bmatrix}\n2 & 3 & 0 \\\\\n\\end{bmatrix} \\,$\nso\n$ \\, Out = \\begin{bmatrix}\n1 & -1 & -1 & 3 & 2 & 3 & 0 \n\\end{bmatrix}$\n\n**Hint:** `torch.numel()` is an easy way of finding the number of elements in a tensor\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def functionA(my_tensor1, my_tensor2):\n \"\"\"\n This function takes in two 2D tensors `my_tensor1` and `my_tensor2`\n and returns the column sum of\n `my_tensor1` multiplied by the sum of all the elmements of `my_tensor2`,\n i.e., a scalar.\n\n Args:\n my_tensor1: torch.Tensor\n my_tensor2: torch.Tensor\n Retuns:\n output: torch.Tensor\n The multiplication of the column sum of `my_tensor1` by the sum of\n `my_tensor2`.\n \"\"\"\n ################################################\n ## TODO for students: complete functionA\n raise NotImplementedError(\"Student exercise: complete function A\")\n ################################################\n # TODO multiplication the sum of the tensors\n output = ...\n\n return output\n\n\ndef functionB(my_tensor):\n \"\"\"\n This function takes in a square matrix `my_tensor` and returns a 2D tensor\n consisting of a flattened `my_tensor` with the index of each element\n appended to this tensor in the row dimension.\n\n Args:\n my_tensor: torch.Tensor\n Retuns:\n output: torch.Tensor\n Concatenated tensor.\n \"\"\"\n ################################################\n ## TODO for students: complete functionB\n raise NotImplementedError(\"Student exercise: complete function B\")\n ################################################\n # TODO flatten the tensor `my_tensor`\n my_tensor = ...\n # TODO create the idx tensor to be concatenated to `my_tensor`\n idx_tensor = ...\n # TODO concatenate the two tensors\n output = ...\n\n return output\n\n\ndef functionC(my_tensor1, my_tensor2):\n \"\"\"\n This function takes in two 2D tensors `my_tensor1` and `my_tensor2`.\n If the dimensions allow it, it returns the\n elementwise sum of `my_tensor1`-shaped `my_tensor2`, and `my_tensor2`;\n else this function returns a 1D tensor that is the concatenation of the\n two tensors.\n\n Args:\n my_tensor1: torch.Tensor\n my_tensor2: torch.Tensor\n Retuns:\n output: torch.Tensor\n Concatenated tensor.\n \"\"\"\n ################################################\n ## TODO for students: complete functionB\n raise NotImplementedError(\"Student exercise: complete function C\")\n ################################################\n # TODO check we can reshape `my_tensor2` into the shape of `my_tensor1`\n if ...:\n # TODO reshape `my_tensor2` into the shape of `my_tensor1`\n my_tensor2 = ...\n # TODO sum the two tensors\n output = ...\n else:\n # TODO flatten both tensors\n my_tensor1 = ...\n my_tensor2 = ...\n # TODO concatenate the two tensors in the correct dimension\n output = ...\n\n return output\n\n# add timing to airtable\natform.add_event('Coding Exercise 2.3: Manipulating Tensors')\n\n\n\n## Implement the functions above and then uncomment the following lines to test your code\n# print(functionA(torch.tensor([[1, 1], [1, 1]]), torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3]])))\n# print(functionB(torch.tensor([[2, 3], [-1, 10]])))\n# print(functionC(torch.tensor([[1, -1], [-1, 3]]), torch.tensor([[2, 3, 0, 2]])))\n# print(functionC(torch.tensor([[1, -1], [-1, 3]]), torch.tensor([[2, 3, 0]])))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# to_remove solution\ndef functionA(my_tensor1, my_tensor2):\n \"\"\"\n This function takes in two 2D tensors `my_tensor1` and `my_tensor2`\n and returns the column sum of\n `my_tensor1` multiplied by the sum of all the elmements of `my_tensor2`,\n i.e., a scalar.\n\n Args:\n my_tensor1: torch.Tensor\n my_tensor2: torch.Tensor\n Retuns:\n output: torch.Tensor\n The multiplication of the column sum of `my_tensor1` by the sum of\n `my_tensor2`.\n \"\"\"\n # TODO multiplication the sum of the tensors\n output = my_tensor1.sum(axis=0) * my_tensor2.sum()\n\n return output\n\n\ndef functionB(my_tensor):\n \"\"\"\n This function takes in a square matrix `my_tensor` and returns a 2D tensor\n consisting of a flattened `my_tensor` with the index of each element\n appended to this tensor in the row dimension.\n\n Args:\n my_tensor: torch.Tensor\n Retuns:\n output: torch.Tensor\n Concatenated tensor.\n \"\"\"\n # TODO flatten the tensor `my_tensor`\n my_tensor = my_tensor.flatten()\n # TODO create the idx tensor to be concatenated to `my_tensor`\n idx_tensor = torch.arange(0, len(my_tensor))\n # TODO concatenate the two tensors\n output = torch.cat([idx_tensor.unsqueeze(1), my_tensor.unsqueeze(1)], axis=1)\n\n return output\n\n\ndef functionC(my_tensor1, my_tensor2):\n \"\"\"\n This function takes in two 2D tensors `my_tensor1` and `my_tensor2`.\n If the dimensions allow it, it returns the\n elementwise sum of `my_tensor1`-shaped `my_tensor2`, and `my_tensor2`;\n else this function returns a 1D tensor that is the concatenation of the\n two tensors.\n\n Args:\n my_tensor1: torch.Tensor\n my_tensor2: torch.Tensor\n Retuns:\n output: torch.Tensor\n Concatenated tensor.\n \"\"\"\n # TODO check we can reshape `my_tensor2` into the shape of `my_tensor1`\n if torch.numel(my_tensor1) == torch.numel(my_tensor2):\n # TODO reshape `my_tensor2` into the shape of `my_tensor1`\n my_tensor2 = my_tensor2.reshape(my_tensor1.shape)\n # TODO sum the two tensors\n output = my_tensor1 + my_tensor2\n else:\n # TODO flatten both tensors\n my_tensor1 = my_tensor1.reshape(1, -1)\n my_tensor2 = my_tensor2.reshape(1, -1)\n # TODO concatenate the two tensors in the correct dimension\n output = torch.cat([my_tensor1, my_tensor2], axis=1).squeeze()\n\n return output\n\n# add timing to airtable\natform.add_event('Coding Exercise 2.3: Manipulating Tensors')\n\n\n## Implement the functions above and then uncomment the following lines to test your code\nprint(functionA(torch.tensor([[1, 1], [1, 1]]), torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3]])))\nprint(functionB(torch.tensor([[2, 3], [-1, 10]])))\nprint(functionC(torch.tensor([[1, -1], [-1, 3]]), torch.tensor([[2, 3, 0, 2]])))\nprint(functionC(torch.tensor([[1, -1], [-1, 3]]), torch.tensor([[2, 3, 0]])))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"```\ntensor([24, 24])\ntensor([[ 0, 2],\n [ 1, 3],\n [ 2, -1],\n [ 3, 10]])\ntensor([[ 3, 2],\n [-1, 5]])\ntensor([ 1, -1, -1, 3, 2, 3, 0])\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Section 2.4: GPUs \n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# @title Video 6: GPU vs CPU\nfrom ipywidgets import widgets\n\nout2 = widgets.Output()\nwith out2:\n from IPython.display import IFrame\n class BiliVideo(IFrame):\n def __init__(self, id, page=1, width=400, height=300, **kwargs):\n self.id=id\n src = \"https://player.bilibili.com/player.html?bvid={0}&page={1}\".format(id, page)\n super(BiliVideo, self).__init__(src, width, height, **kwargs)\n\n video = BiliVideo(id=f\"BV1nM4y1K7qx\", width=854, height=480, fs=1)\n print(\"Video available at https://www.bilibili.com/video/{0}\".format(video.id))\n display(video)\n\nout1 = widgets.Output()\nwith out1:\n from IPython.display import YouTubeVideo\n video = YouTubeVideo(id=f\"9Mc9GFUtILY\", width=854, height=480, fs=1, rel=0)\n print(\"Video available at https://youtube.com/watch?v=\" + video.id)\n display(video)\n\nout = widgets.Tab([out1, out2])\nout.set_title(0, 'Youtube')\nout.set_title(1, 'Bilibili')\n\n# add timing to airtable\natform.add_event('Video 6: GPU vs CPU')\n\ndisplay(out)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\nBy default, when we create a tensor it will *not* live on the GPU! ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x = torch.randn(10)\nprint(x.device)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"When using Colab notebooks by default will not have access to a GPU. In order to start using GPUs we need to request one. We can do this by going to the runtime tab at the top of the page. \n\nBy following Runtime -> Change runtime type and selecting \"GPU\" from the Hardware Accelerator dropdown list, we can start playing with sending tensors to GPUs.\n\nOnce you have done this your runtime will restart and you will need to rerun the first setup cell to reimport PyTorch. Then proceed to the next cell.\n\n(For more information on the GPU usage policy you can view in the appendix)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Now we have a GPU**\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The cell below should return True.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(torch.cuda.is_available())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"CUDA is an API developed by Nvidia for interfacing with GPUs. PyTorch provides us with a layer of abstraction, and allows us to launch CUDA kernels using pure Python. *NOTE I am assuming that GPU stuff might be covered in more detail on another day but there could be a bit more detail here.*\n\nIn short, we get the power of parallising our tensor computations on GPUs, whilst only writing (relatively) simple Python!\n\nHere, we define the function `set_device`, which returns the device use in the notebook, i.e., `cpu` or `cuda`. Unless otherwise specified, we use this function on top of every tutorial, and we store the device variable such as\n\n```python\nDEVICE = set_device()\n```\n\nLet's define the function using the PyTorch package `torch.cuda`, which is lazily initialized, so we can always import it, and use `is_available()` to determine if our system supports CUDA.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def set_device():\n device = \"cuda\" if torch.cuda.is_available() else \"cpu\"\n if device != \"cuda\":\n print(\"GPU is not enabled in this notebook. \\n\"\n \"If you want to enable it, in the menu under `Runtime` -> \\n\"\n \"`Hardware accelerator.` and select `GPU` from the dropdown menu\")\n else:\n print(\"GPU is enabled in this notebook. \\n\"\n \"If you want to disable it, in the menu under `Runtime` -> \\n\"\n \"`Hardware accelerator.` and select `None` from the dropdown menu\")\n\n return device",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's make some CUDA tensors!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# common device agnostic way of writing code that can run on cpu OR gpu\n# that we provide for you in each of the tutorials\nDEVICE = set_device()\n\n# we can specify a device when we first create our tensor\nx = torch.randn(2, 2, device=DEVICE)\nprint(x.dtype)\nprint(x.device)\n\n# we can also use the .to() method to change the device a tensor lives on\ny = torch.randn(2, 2)\nprint(f\"y before calling to() | device: {y.device} | dtype: {y.type()}\")\n\ny = y.to(DEVICE)\nprint(f\"y after calling to() | device: {y.device} | dtype: {y.type()}\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Operations between cpu tensors and cuda tensors**\n\nNote that the type of the tensor changed after calling ```.to()```. What happens if we try and perform operations on tensors on devices?\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x = torch.tensor([0, 1, 2], device=DEVICE)\ny = torch.tensor([3, 4, 5], device=\"cpu\")\n\n# Uncomment the following line and run this cell\n# z = x + y",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We cannot combine cuda tensors and cpu tensors in this fashion. If we want to compute an operation that combines tensors on different devices, we need to move them first! We can use the `.to()` method as before, or the `.cpu()` and `.cuda()` methods. Note that using the `.cuda()` will throw an error if CUDA is not enabled in your machine.\n\nGenrally in this course all Deep learning is done on the GPU and any computation is done on the CPU, so sometimes we have to pass things back and forth so you'll see us call.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x = torch.tensor([0, 1, 2], device=DEVICE)\ny = torch.tensor([3, 4, 5], device=\"cpu\")\nz = torch.tensor([6, 7, 8], device=DEVICE)\n\n# moving to cpu\nx = x.to(\"cpu\") # alternatively, you can use x = x.cpu()\nprint(x + y)\n\n# moving to gpu\ny = y.to(DEVICE) # alternatively, you can use y = y.cuda()\nprint(y + z)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Coding Exercise 2.4: Just how much faster are GPUs?\n\nBelow is a simple function. Complete the second function, such that it is performs the same operations as the first function, but entirely on the GPU. We will use the helper function `timeFun(f, dim, iterations, device)`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dim = 10000\niterations = 1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def simpleFun(dim, device):\n \"\"\"\n Args:\n dim: integer\n device: \"cpu\" or \"cuda:0\"\n Returns:\n Nothing.\n \"\"\"\n ###############################################\n ## TODO for students: recreate the above function, but\n ## ensure all computation happens on the GPU\n raise NotImplementedError(\"Student exercise: fill in the missing code to create the tensors\")\n ###############################################\n x = ...\n y = ...\n z = ...\n\n x = ...\n y = ...\n\n del x\n del y\n del z\n\n\n## TODO: Implement the function above and uncomment the following lines to test your code\n# timeFun(f=simpleFun, dim=dim, iterations=iterations)\n# timeFun(f=simpleFun, dim=dim, iterations=iterations, device=DEVICE)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# to_remove solution\ndef simpleFun(dim, device):\n \"\"\"\n Args:\n dim: integer\n device: \"cpu\" or \"cuda\"\n Returns:\n Nothing.\n \"\"\"\n x = torch.rand(dim, dim).to(device)\n y = torch.rand_like(x).to(device)\n z = 2*torch.ones(dim, dim).to(device)\n\n x = x * y\n x = x @ z\n\n\n del x\n del y\n del z\n\n\n## TODO: Implement the function above and uncomment the following lines to test your code\ntimeFun(f=simpleFun, dim=dim, iterations=iterations)\ntimeFun(f=simpleFun, dim=dim, iterations=iterations, device=DEVICE)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Sample output (depends on your hardware)\n\n```\ntime taken for 1 iterations of simpleFun(10000): 28.50481\ntime taken for 1 iterations of simpleFunGPU(10000): 0.91102\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Discuss!**\n\nTry and reduce the dimensions of the tensors and increase the iterations. You can get to a point where the cpu only function is faster than the GPU function. Why might this be?\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Section 2.5: Datasets and Dataloaders\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# @title Video 7: Getting Data\nfrom ipywidgets import widgets\n\nout2 = widgets.Output()\nwith out2:\n from IPython.display import IFrame\n class BiliVideo(IFrame):\n def __init__(self, id, page=1, width=400, height=300, **kwargs):\n self.id=id\n src = \"https://player.bilibili.com/player.html?bvid={0}&page={1}\".format(id, page)\n super(BiliVideo, self).__init__(src, width, height, **kwargs)\n\n video = BiliVideo(id=f\"BV1744y127SQ\", width=854, height=480, fs=1)\n print(\"Video available at https://www.bilibili.com/video/{0}\".format(video.id))\n display(video)\n\nout1 = widgets.Output()\nwith out1:\n from IPython.display import YouTubeVideo\n video = YouTubeVideo(id=f\"LSkjPM1gFu0\", width=854, height=480, fs=1, rel=0)\n print(\"Video available at https://youtube.com/watch?v=\" + video.id)\n display(video)\n\nout = widgets.Tab([out1, out2])\nout.set_title(0, 'Youtube')\nout.set_title(1, 'Bilibili')\n\n# add timing to airtable\natform.add_event('Video 7: Getting Data')\n\ndisplay(out)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"When training neural network models you will be working with large amounts of data. Fortunately, PyTorch offers some great tools that help you organize and manipulate your data samples.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import dataset and dataloaders related packages\nfrom torchvision import datasets\nfrom torchvision.transforms import ToTensor\nfrom torch.utils.data import DataLoader\nfrom torchvision.transforms import Compose, Grayscale",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Datasets**\n\nThe `torchvision` package gives you easy access to many of the publicly available datasets. Let's load the [CIFAR10](https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.html) dataset, which contains color images of 10 different classes, like vehicles and animals.\n\nCreating an object of type `datasets.CIFAR10` will automatically download and load all images from the dataset. The resulting data structure can be treated as a list containing data samples and their corresponding labels.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Download and load the images from the CIFAR10 dataset\ncifar10_data = datasets.CIFAR10(\n root=\"data\", # path where the images will be stored\n download=True, # all images should be downloaded\n transform=ToTensor() # transform the images to tensors\n )\n\n# Print the number of samples in the loaded dataset\nprint(f\"Number of samples: {len(cifar10_data)}\")\nprint(f\"Class names: {cifar10_data.classes}\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We have 50000 samples loaded. Now let's take a look at one of them in detail. Each sample consists of an image and its corresponding label.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Choose a random sample\nrandom.seed(2021)\nimage, label = cifar10_data[random.randint(0, len(cifar10_data))]\nprint(f\"Label: {cifar10_data.classes[label]}\")\nprint(f\"Image size: {image.shape}\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Color images are modeled as 3 dimensional tensors. The first dimension corresponds to the channels (C) of the image (in this case we have RGB images). The second dimensions is the height (H) of the image and the third is the width (W). We can denote this image format as C × H × W.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Coding Exercise 2.5: Display an image from the dataset\n\nLet's try to display the image using `matplotlib`. The code below will not work, because `imshow` expects to have the image in a different format - $H \\times W \\times C$.\n\nYou need to reorder the dimensions of the tensor using the `permute` method of the tensor. PyTorch `torch.permute(*dims)` rearranges the original tensor according to the desired ordering and returns a new multidimensional rotated tensor. The size of the returned tensor remains the same as that of the original.\n\n**Code hint:**\n\n```python\n# create a tensor of size 2 x 4\ninput_var = torch.randn(2, 4)\n# print its size and the tensor\nprint(input_var.size())\nprint(input_var)\n\n# dimensions permuted\ninput_var = input_var.permute(1, 0)\n# print its size and the permuted tensor\nprint(input_var.size())\nprint(input_var)\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# TODO: Uncomment the following line to see the error that arises from the current image format\n# plt.imshow(image)\n\n# TODO: Comment the above line and fix this code by reordering the tensor dimensions\n# plt.imshow(image.permute(...))\n# plt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# to_remove solution\n\n# TODO: Uncomment the following line to see the error that arises from the current image format\n# plt.imshow(image)\n\n# TODO: Comment the above line and fix this code by reordering the tensor dimensions\nplt.imshow(image.permute(1, 2, 0))\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#@title Video 8: Train and Test\nfrom ipywidgets import widgets\n\nout2 = widgets.Output()\nwith out2:\n from IPython.display import IFrame\n class BiliVideo(IFrame):\n def __init__(self, id, page=1, width=400, height=300, **kwargs):\n self.id=id\n src = \"https://player.bilibili.com/player.html?bvid={0}&page={1}\".format(id, page)\n super(BiliVideo, self).__init__(src, width, height, **kwargs)\n\n video = BiliVideo(id=f\"BV1rV411H7s5\", width=854, height=480, fs=1)\n print(\"Video available at https://www.bilibili.com/video/{0}\".format(video.id))\n display(video)\n\nout1 = widgets.Output()\nwith out1:\n from IPython.display import YouTubeVideo\n video = YouTubeVideo(id=f\"JokSIuPs-ys\", width=854, height=480, fs=1, rel=0)\n print(\"Video available at https://youtube.com/watch?v=\" + video.id)\n display(video)\n\nout = widgets.Tab([out1, out2])\nout.set_title(0, 'Youtube')\nout.set_title(1, 'Bilibili')\n\n# add timing to airtable\natform.add_event('Video 8: Train and Test')\n\ndisplay(out)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Training and Test Datasets**\n\nWhen loading a dataset, you can specify if you want to load the training or the test samples using the `train` argument. We can load the training and test datasets separately. For simplicity, today we will not use both datasets separately, but this topic will be adressed in the next days.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Load the training samples\ntraining_data = datasets.CIFAR10(\n root=\"data\",\n train=True,\n download=True,\n transform=ToTensor()\n )\n\n# Load the test samples\ntest_data = datasets.CIFAR10(\n root=\"data\",\n train=False,\n download=True,\n transform=ToTensor()\n )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# @title Video 9: Data Augmentation - Transformations\nfrom ipywidgets import widgets\n\nout2 = widgets.Output()\nwith out2:\n from IPython.display import IFrame\n class BiliVideo(IFrame):\n def __init__(self, id, page=1, width=400, height=300, **kwargs):\n self.id=id\n src = \"https://player.bilibili.com/player.html?bvid={0}&page={1}\".format(id, page)\n super(BiliVideo, self).__init__(src, width, height, **kwargs)\n\n video = BiliVideo(id=f\"BV19B4y1N77t\", width=854, height=480, fs=1)\n print(\"Video available at https://www.bilibili.com/video/{0}\".format(video.id))\n display(video)\n\nout1 = widgets.Output()\nwith out1:\n from IPython.display import YouTubeVideo\n video = YouTubeVideo(id=f\"sjegA9OBUPw\", width=854, height=480, fs=1, rel=0)\n print(\"Video available at https://youtube.com/watch?v=\" + video.id)\n display(video)\n\nout = widgets.Tab([out1, out2])\nout.set_title(0, 'Youtube')\nout.set_title(1, 'Bilibili')\n\n# add timing to airtable\natform.add_event('Video 9: Data Augmentation - Transformations')\n\ndisplay(out)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Dataloader**\n\nAnother important concept is the `Dataloader`. It is a wrapper around the `Dataset` that splits it into minibatches (important for training the neural network) and makes the data iterable. The `shuffle` argument is used to shuffle the order of the samples across the minibatches.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create dataloaders with\ntrain_dataloader = DataLoader(training_data, batch_size=64, shuffle=True)\ntest_dataloader = DataLoader(test_data, batch_size=64, shuffle=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*Reproducibility:* DataLoader will reseed workers following Randomness in multi-process data loading algorithm. Use `worker_init_fn()` and a `generator` to preserve reproducibility:\n\n\n```python\ndef seed_worker(worker_id):\n worker_seed = torch.initial_seed() % 2**32\n numpy.random.seed(worker_seed)\n random.seed(worker_seed)\n\n\ng_seed = torch.Generator()\ng_seed.manual_seed(my_seed)\n\nDataLoader(\n train_dataset,\n batch_size=batch_size,\n num_workers=num_workers,\n worker_init_fn=seed_worker,\n generator=g_seed\n )\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Note:** For the `seed_worker` to have an effect, `num_workers` should be 2 or more.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We can now query the next batch from the data loader and inspect it. For this we need to convert the dataloader object to a Python iterator using the function `iter` and then we can query the next batch using the function `next`.\n\nWe can now see that we have a 4D tensor. This is because we have a 64 images in the batch ($B$) and each image has 3 dimensions: channels ($C$), height ($H$) and width ($W$). So, the size of the 4D tensor is $B \\times C \\times H \\times W$.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Load the next batch\nbatch_images, batch_labels = next(iter(train_dataloader))\nprint('Batch size:', batch_images.shape)\n\n# Display the first image from the batch\nplt.imshow(batch_images[0].permute(1, 2, 0))\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Transformations**\n\nAnother useful feature when loading a dataset is applying transformations on the data - color conversions, normalization, cropping, rotation etc. There are many predefined transformations in the `torchvision.transforms` package and you can also combine them using the `Compose` transform. Checkout the [pytorch documentation](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html) for details.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Coding Exercise 2.6: Load the CIFAR10 dataset as grayscale images\n\nThe goal of this excercise is to load the images from the CIFAR10 dataset as grayscale images. Note that we rerun the `set_seed` function to ensure reproducibility.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def my_data_load():\n ###############################################\n ## TODO for students: recreate the above function, but\n ## ensure all computation happens on the GPU\n raise NotImplementedError(\"Student exercise: fill in the missing code to load the data\")\n ###############################################\n ## TODO Load the CIFAR10 data using a transform that converts the images to grayscale tensors\n data = datasets.CIFAR10(...,\n transform=...)\n # Display a random grayscale image\n image, label = data[random.randint(0, len(data))]\n plt.imshow(image.squeeze(), cmap=\"gray\")\n plt.show()\n\n return data\n\n\nset_seed(seed=2021)\n## After implementing the above code, uncomment the following lines to test your code\n# data = my_data_load()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# to_remove solution\ndef my_data_load():\n\n ## TODO Load the CIFAR10 data using a transform that converts the images to grayscale tensors\n data = datasets.CIFAR10(root=\"data\", download=True,\n transform=Compose([ToTensor(), Grayscale()]))\n # Display a random grayscale image\n image, label = data[random.randint(0, len(data))]\n plt.imshow(image.squeeze(), cmap=\"gray\")\n plt.show()\n\n return data\n\n\nset_seed(seed=2021)\n## After implementing the above code, uncomment the following lines to test your code\ndata = my_data_load()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"---\n# Section 3: Neural Networks\n\n*Time estimate: ~1 hour 30 mins (excluding movie)*",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Now it's time for you to create your first neural network using PyTorch. This section will walk you through the process of:\n- Creating a simple neural network model\n- Training the network\n- Visualizing the results of the network\n- Tweeking the network",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# @title Video 10: CSV Files\nfrom ipywidgets import widgets\n\nout2 = widgets.Output()\nwith out2:\n from IPython.display import IFrame\n class BiliVideo(IFrame):\n def __init__(self, id, page=1, width=400, height=300, **kwargs):\n self.id=id\n src = \"https://player.bilibili.com/player.html?bvid={0}&page={1}\".format(id, page)\n super(BiliVideo, self).__init__(src, width, height, **kwargs)\n\n video = BiliVideo(id=f\"BV1xy4y1T7kv\", width=854, height=480, fs=1)\n print(\"Video available at https://www.bilibili.com/video/{0}\".format(video.id))\n display(video)\n\nout1 = widgets.Output()\nwith out1:\n from IPython.display import YouTubeVideo\n video = YouTubeVideo(id=f\"JrC_UAJWYKU\", width=854, height=480, fs=1, rel=0)\n print(\"Video available at https://youtube.com/watch?v=\" + video.id)\n display(video)\n\nout = widgets.Tab([out1, out2])\nout.set_title(0, 'Youtube')\nout.set_title(1, 'Bilibili')\n\n# add timing to airtable\natform.add_event('Video 10: CSV Files')\n\ndisplay(out)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Section 3.1: Data Loading\n\nFirst we need some sample data to train our network on. You can use the function below to generate an example dataset consisting of 2D points along two interleaving half circles. The data will be stored in a file called `sample_data.csv`. You can inspect the file directly in Colab by going to Files on the left side and opening the CSV file.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# @title Generate sample data\n# @markdown we used `scikit-learn` module\nfrom sklearn.datasets import make_moons\n\n# Create a dataset of 256 points with a little noise\nX, y = make_moons(256, noise=0.1)\n\n# Store the data as a Pandas data frame and save it to a CSV file\ndf = pd.DataFrame(dict(x0=X[:,0], x1=X[:,1], y=y))\ndf.to_csv('sample_data.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now we can load the data from the CSV file using the Pandas library. Pandas provides many functions for reading files in various formats. When loading data from a CSV file, we can reference the columns directly by their names.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Load the data from the CSV file in a Pandas DataFrame\ndata = pd.read_csv(\"sample_data.csv\")\n\n# Create a 2D numpy array from the x0 and x1 columns\nX_orig = data[[\"x0\", \"x1\"]].to_numpy()\n\n# Create a 1D numpy array from the y column\ny_orig = data[\"y\"].to_numpy()\n\n# Print the sizes of the generated 2D points X and the corresponding labels Y\nprint(f\"Size X:{X_orig.shape}\")\nprint(f\"Size y:{y_orig.shape}\")\n\n# Visualize the dataset. The color of the points is determined by the labels `y_orig`.\nplt.scatter(X_orig[:, 0], X_orig[:, 1], s=40, c=y_orig)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Prepare Data for PyTorch**\n\nNow let's prepare the data in a format suitable for PyTorch - convert everything into tensors.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Initialize the device variable\nDEVICE = set_device()\n\n# Convert the 2D points to a float32 tensor\nX = torch.tensor(X_orig, dtype=torch.float32)\n\n# Upload the tensor to the device\nX = X.to(DEVICE)\n\nprint(f\"Size X:{X.shape}\")\n\n# Convert the labels to a long interger tensor\ny = torch.from_numpy(y_orig).type(torch.LongTensor)\n# Upload the tensor to the device\ny = y.to(DEVICE)\n\nprint(f\"Size y:{y.shape}\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Section 3.2: Create a Simple Neural Network",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# @title Video 11: Generating the Neural Network\nfrom ipywidgets import widgets\n\nout2 = widgets.Output()\nwith out2:\n from IPython.display import IFrame\n class BiliVideo(IFrame):\n def __init__(self, id, page=1, width=400, height=300, **kwargs):\n self.id=id\n src = \"https://player.bilibili.com/player.html?bvid={0}&page={1}\".format(id, page)\n super(BiliVideo, self).__init__(src, width, height, **kwargs)\n\n video = BiliVideo(id=f\"BV1fK4y1M74a\", width=854, height=480, fs=1)\n print(\"Video available at https://www.bilibili.com/video/{0}\".format(video.id))\n display(video)\n\nout1 = widgets.Output()\nwith out1:\n from IPython.display import YouTubeVideo\n video = YouTubeVideo(id=f\"PwSzRohUvck\", width=854, height=480, fs=1, rel=0)\n print(\"Video available at https://youtube.com/watch?v=\" + video.id)\n display(video)\n\nout = widgets.Tab([out1, out2])\nout.set_title(0, 'Youtube')\nout.set_title(1, 'Bilibili')\n\n# add timing to airtable\natform.add_event('Video 11: Generating the Neural Network')\n\ndisplay(out)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"For this example we want to have a simple neural network consisting of 3 layers:\n- 1 input layer of size 2 (our points have 2 coordinates)\n- 1 hidden layer of size 16 (you can play with different numbers here)\n- 1 output layer of size 2 (we want the have the scores for the two classes)\n\nDuring the course you will deal with differend kinds of neural networks. On Day 2 we will focus on linear networks, but you will work with some more complicated architectures in the next days. The example here is meant to demonstrate the process of creating and training a neural network end-to-end.\n\n**Programing the Network**\n\nPyTorch provides a base class for all neural network modules called [`nn.Module`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.Module.html). You need to inherit from `nn.Module` and implement some important methods:\n\n`__init__`\n\nIn the `__init__` method you need to define the structure of your network. Here you will specify what layers will the network consist of, what activation functions will be used etc.\n\n`forward`\n\nAll neural network modules need to implement the `forward` method. It specifies the computations the network needs to do when data is passed through it.\n\n`predict`\n\nThis is not an obligatory method of a neural network module, but it is a good practice if you want to quickly get the most likely label from the network. It calls the `forward` method and chooses the label with the highest score.\n\n`train`\n\nThis is also not an obligatory method, but it is a good practice to have. The method will be used to train the network parameters and will be implemented later in the notebook.\n\n\n> Note that you can use the `__call__` method of a module directly and it will invoke the `forward` method: `net()` does the same as `net.forward()`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Inherit from nn.Module - the base class for neural network modules provided by Pytorch\nclass NaiveNet(nn.Module):\n\n # Define the structure of your network\n def __init__(self):\n super(NaiveNet, self).__init__()\n\n # The network is defined as a sequence of operations\n self.layers = nn.Sequential(\n nn.Linear(2, 16), # Transformation from the input to the hidden layer\n nn.ReLU(), # Activation function (ReLU) is a non-linearity which is widely used because it reduces computation. The function returns 0 if it receives any\n # negative input, but for any positive value x, it returns that value back.\n nn.Linear(16, 2), # Transformation from the hidden to the output layer\n )\n\n # Specify the computations performed on the data\n def forward(self, x):\n # Pass the data through the layers\n return self.layers(x)\n\n # Choose the most likely label predicted by the network\n def predict(self, x):\n # Pass the data through the networks\n output = self.forward(x)\n\n # Choose the label with the highest score\n return torch.argmax(output, 1)\n\n # Train the neural network (will be implemented later)\n def train(self, X, y):\n pass",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Check that your network works**\n\nCreate an instance of your model and visualize it",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create new NaiveNet and transfer it to the device\nmodel = NaiveNet().to(DEVICE)\n\n# Print the structure of the network\nprint(model)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Coding Exercise 3.2: Classify some samples\n\nNow let's pass some of the points of our dataset through the network and see if it works. You should not expect the network to actually classify the points correctly, because it has not been trained yet. \n\nThe goal here is just to get some experience with the data structures that are passed to the forward and predict methods and their results.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Get the samples\n# X_samples = ...\n# print(\"Sample input:\\n\", X_samples)\n\n## Do a forward pass of the network\n# output = ...\n# print(\"\\nNetwork output:\\n\", output)\n\n## Predict the label of each point\n# y_predicted = ...\n# print(\"\\nPredicted labels:\\n\", y_predicted)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# to_remove solution\n## Get the samples\nX_samples = X[0:5]\nprint(\"Sample input:\\n\", X_samples)\n\n# Do a forward pass of the network\noutput = model.forward(X_samples)\nprint(\"\\nNetwork output:\\n\", output)\n\n# Predict the label of each point\ny_predicted = model.predict(X_samples)\nprint(\"\\nPredicted labels:\\n\", y_predicted)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"```\nSample input:\n tensor([[ 0.9066, 0.5052],\n [-0.2024, 1.1226],\n [ 1.0685, 0.2809],\n [ 0.6720, 0.5097],\n [ 0.8548, 0.5122]], device='cuda:0')\n\nNetwork output:\n tensor([[ 0.1543, -0.8018],\n [ 2.2077, -2.9859],\n [-0.5745, -0.0195],\n [ 0.1924, -0.8367],\n [ 0.1818, -0.8301]], device='cuda:0', grad_fn=<AddmmBackward>)\n\nPredicted labels:\n tensor([0, 0, 1, 0, 0], device='cuda:0')\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Section 3.3: Train Your Neural Network\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# @title Video 12: Train the Network\nfrom ipywidgets import widgets\n\nout2 = widgets.Output()\nwith out2:\n from IPython.display import IFrame\n class BiliVideo(IFrame):\n def __init__(self, id, page=1, width=400, height=300, **kwargs):\n self.id=id\n src = \"https://player.bilibili.com/player.html?bvid={0}&page={1}\".format(id, page)\n super(BiliVideo, self).__init__(src, width, height, **kwargs)\n\n video = BiliVideo(id=f\"BV1v54y1n7CS\", width=854, height=480, fs=1)\n print(\"Video available at https://www.bilibili.com/video/{0}\".format(video.id))\n display(video)\n\nout1 = widgets.Output()\nwith out1:\n from IPython.display import YouTubeVideo\n video = YouTubeVideo(id=f\"4MIqnE4XPaA\", width=854, height=480, fs=1, rel=0)\n print(\"Video available at https://youtube.com/watch?v=\" + video.id)\n display(video)\n\nout = widgets.Tab([out1, out2])\nout.set_title(0, 'Youtube')\nout.set_title(1, 'Bilibili')\n\n# add timing to airtable\natform.add_event('Video 12: Train the Network')\n\ndisplay(out)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now it is time to train your network on your dataset. Don't worry if you don't fully understand everything yet - we wil cover training in much more details in the next days. For now, the goal is just to see your network in action!\n\nYou will usually implement the `train` method directly when implementing your class `NaiveNet`. Here, we will implement it as a function outside of the class in order to have it in a ceparate cell.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# @title Helper function to plot the decision boundary\n\n# Code adapted from this notebook: https://jonchar.net/notebooks/Artificial-Neural-Network-with-Keras/\n\nfrom pathlib import Path\n\ndef plot_decision_boundary(model, X, y, device):\n # Transfer the data to the CPU\n X = X.cpu().numpy()\n y = y.cpu().numpy()\n\n # Check if the frames folder exists and create it if needed\n frames_path = Path(\"frames\")\n if not frames_path.exists():\n frames_path.mkdir()\n\n # Set min and max values and give it some padding\n x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - .5, X[:, 0].max() + .5\n y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - .5, X[:, 1].max() + .5\n h = 0.01\n\n # Generate a grid of points with distance h between them\n xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h), np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))\n\n # Predict the function value for the whole gid\n grid_points = np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]\n grid_points = torch.from_numpy(grid_points).type(torch.FloatTensor)\n Z = model.predict(grid_points.to(device)).cpu().numpy()\n Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)\n\n # Plot the contour and training examples\n plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral)\n plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, cmap=plt.cm.binary)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Implement the train function given a training dataset X and correcsponding labels y\ndef train(model, X, y):\n # The Cross Entropy Loss is suitable for classification problems\n loss_function = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()\n\n # Create an optimizer (Stochastic Gradient Descent) that will be used to train the network\n learning_rate = 1e-2\n optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)\n\n # Number of epochs\n epochs = 15000\n\n # List of losses for visualization\n losses = []\n\n for i in range(epochs):\n # Pass the data through the network and compute the loss\n # We'll use the whole dataset during the training instead of using batches\n # in to order to keep the code simple for now.\n y_logits = model.forward(X)\n loss = loss_function(y_logits, y)\n\n # Clear the previous gradients and compute the new ones\n optimizer.zero_grad()\n loss.backward()\n\n # Adapt the weights of the network\n optimizer.step()\n\n # Store the loss\n losses.append(loss.item())\n\n # Print the results at every 1000th epoch\n if i % 1000 == 0:\n print(f\"Epoch {i} loss is {loss.item()}\")\n\n plot_decision_boundary(model, X, y, DEVICE)\n plt.savefig('frames/{:05d}.png'.format(i))\n\n return losses\n\n\n# Create a new network instance a train it\nmodel = NaiveNet().to(DEVICE)\nlosses = train(model, X, y)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Plot the loss during training**\n\nPlot the loss during the training to see how it reduces and converges.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plt.plot(np.linspace(1, len(losses), len(losses)), losses)\nplt.xlabel(\"Epoch\")\nplt.ylabel(\"Loss\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# @title Visualize the training process\n# @markdown ### Execute this cell!\n!pip install imageio --quiet\n!pip install pathlib --quiet\n\nimport imageio\nfrom IPython.core.interactiveshell import InteractiveShell\nfrom IPython.display import Image, display\nfrom pathlib import Path\n\nInteractiveShell.ast_node_interactivity = \"all\"\n\n# Make a list with all images\nimages = []\nfor i in range(10):\n filename = \"frames/0\"+str(i)+\"000.png\"\n images.append(imageio.imread(filename))\n# Save the gif\nimageio.mimsave('frames/movie.gif', images)\ngifPath = Path(\"frames/movie.gif\")\nwith open(gifPath,'rb') as f:\n display(Image(data=f.read(), format='png'))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# @title Video 13: Play with it\nfrom ipywidgets import widgets\n\nout2 = widgets.Output()\nwith out2:\n from IPython.display import IFrame\n class BiliVideo(IFrame):\n def __init__(self, id, page=1, width=400, height=300, **kwargs):\n self.id=id\n src = \"https://player.bilibili.com/player.html?bvid={0}&page={1}\".format(id, page)\n super(BiliVideo, self).__init__(src, width, height, **kwargs)\n\n video = BiliVideo(id=f\"BV1Cq4y1W7BH\", width=854, height=480, fs=1)\n print(\"Video available at https://www.bilibili.com/video/{0}\".format(video.id))\n display(video)\n\nout1 = widgets.Output()\nwith out1:\n from IPython.display import YouTubeVideo\n video = YouTubeVideo(id=f\"_GGkapdOdSY\", width=854, height=480, fs=1, rel=0)\n print(\"Video available at https://youtube.com/watch?v=\" + video.id)\n display(video)\n\nout = widgets.Tab([out1, out2])\nout.set_title(0, 'Youtube')\nout.set_title(1, 'Bilibili')\n\n# add timing to airtable\natform.add_event('Video 13: Play with it')\n\ndisplay(out)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Exercise 3.3: Tweak your Network\n\nYou can now play around with the network a little bit to get a feeling of what different parameters are doing. Here are some ideas what you could try:\n- Increase or decrease the number of epochs for training\n- Increase or decrease the size of the hidden layer\n- Add one additional hidden layer\n\nCan you get the network to better fit the data?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# @title Video 14: XOR Widget\nfrom ipywidgets import widgets\n\nout2 = widgets.Output()\nwith out2:\n from IPython.display import IFrame\n class BiliVideo(IFrame):\n def __init__(self, id, page=1, width=400, height=300, **kwargs):\n self.id=id\n src = \"https://player.bilibili.com/player.html?bvid={0}&page={1}\".format(id, page)\n super(BiliVideo, self).__init__(src, width, height, **kwargs)\n\n video = BiliVideo(id=f\"BV1mB4y1N7QS\", width=854, height=480, fs=1)\n print(\"Video available at https://www.bilibili.com/video/{0}\".format(video.id))\n display(video)\n\nout1 = widgets.Output()\nwith out1:\n from IPython.display import YouTubeVideo\n video = YouTubeVideo(id=f\"oTr1nE2rCWg\", width=854, height=480, fs=1, rel=0)\n print(\"Video available at https://youtube.com/watch?v=\" + video.id)\n display(video)\n\nout = widgets.Tab([out1, out2])\nout.set_title(0, 'Youtube')\nout.set_title(1, 'Bilibili')\n\n# add timing to airtable\natform.add_event('Video 14: XOR Widget')\n\ndisplay(out)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Exclusive OR (XOR) logical operation gives a true (`1`) output when the number of true inputs is odd. That is, a true output result if one, and only one, of the inputs to the gate is true. If both inputs are false (`0`) or both are true or false output results. Mathematically speaking, XOR represents the inequality function, i.e., the output is true if the inputs are not alike; otherwise, the output is false.\n\nIn case of two inputs ($X$ and $Y$) the following truth table is applied:\n\n\\begin{array}{ccc}\nX & Y & \\text{XOR} \\\\\n\\hline\n0 & 0 & 0 \\\\\n0 & 1 & 1 \\\\\n1 & 0 & 1 \\\\\n1 & 1 & 0 \\\\\n\\end{array}\n\nHere, with `0`, we denote `False`, and with `1` we denote `True` in boolean terms.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Interactive Demo 3.3: Solving XOR\n\nHere we use an open source and famous visualization widget developed by Tensorflow team available [here](https://github.com/tensorflow/playground).\n* Play with the widget and observe that you can not solve the continuous XOR dataset.\n* Now add one hidden layer with three units, play with the widget, and set weights by hand to solve this dataset perfectly.\n\nFor the second part, you should set the weights by clicking on the connections and either type the value or use the up and down keys to change it by one increment. You could also do the same for the biases by clicking on the tiny square to each neuron's bottom left.\nEven though there are infinitely many solutions, a neat solution when $f(x)$ is ReLU is: \n\n\\begin{equation}\n y = f(x_1)+f(x_2)-f(x_1+x_2)\n\\end{equation}\n\nTry to set the weights and biases to implement this function after you played enough :)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# @markdown ###Play with the parameters to solve XOR\nfrom IPython.display import HTML\nHTML('<iframe width=\"1020\" height=\"660\" src=\"https://playground.arashash.com/#activation=relu&batchSize=10&dataset=xor®Dataset=reg-plane&learningRate=0.03®ularizationRate=0&noise=0&networkShape=&seed=0.91390&showTestData=false&discretize=false&percTrainData=90&x=true&y=true&xTimesY=false&xSquared=false&ySquared=false&cosX=false&sinX=false&cosY=false&sinY=false&collectStats=false&problem=classification&initZero=false&hideText=false\" allowfullscreen></iframe>')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# @markdown Do you think we can solve the discrete XOR (only 4 possibilities) with only 2 hidden units?\nw1_min_xor = 'Select' #@param ['Select', 'Yes', 'No']\nif w1_min_xor == 'No':\n print(\"Correct!\")\nelse:\n print(\"How about giving it another try?\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"---\n# Section 4: Ethics And Course Info\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# @title Video 15: Ethics\nfrom ipywidgets import widgets\n\nout2 = widgets.Output()\nwith out2:\n from IPython.display import IFrame\n class BiliVideo(IFrame):\n def __init__(self, id, page=1, width=400, height=300, **kwargs):\n self.id=id\n src = \"https://player.bilibili.com/player.html?bvid={0}&page={1}\".format(id, page)\n super(BiliVideo, self).__init__(src, width, height, **kwargs)\n\n video = BiliVideo(id=f\"BV1Hw41197oB\", width=854, height=480, fs=1)\n print(\"Video available at https://www.bilibili.com/video/{0}\".format(video.id))\n display(video)\n\nout1 = widgets.Output()\nwith out1:\n from IPython.display import YouTubeVideo\n video = YouTubeVideo(id=f\"Kt6JLi3rUFU\", width=854, height=480, fs=1, rel=0)\n print(\"Video available at https://youtube.com/watch?v=\" + video.id)\n display(video)\n\nout = widgets.Tab([out1, out2])\nout.set_title(0, 'Youtube')\nout.set_title(1, 'Bilibili')\n\ndisplay(out)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# @title Video 16: Be a group\nfrom ipywidgets import widgets\n\nout2 = widgets.Output()\nwith out2:\n from IPython.display import IFrame\n class BiliVideo(IFrame):\n def __init__(self, id, page=1, width=400, height=300, **kwargs):\n self.id=id\n src = \"https://player.bilibili.com/player.html?bvid={0}&page={1}\".format(id, page)\n super(BiliVideo, self).__init__(src, width, height, **kwargs)\n\n video = BiliVideo(id=f\"BV1j44y1272h\", width=854, height=480, fs=1)\n print(\"Video available at https://www.bilibili.com/video/{0}\".format(video.id))\n display(video)\n\nout1 = widgets.Output()\nwith out1:\n from IPython.display import YouTubeVideo\n video = YouTubeVideo(id=f\"Sfp6--d_H1A\", width=854, height=480, fs=1, rel=0)\n print(\"Video available at https://youtube.com/watch?v=\" + video.id)\n display(video)\n\nout = widgets.Tab([out1, out2])\nout.set_title(0, 'Youtube')\nout.set_title(1, 'Bilibili')\n\ndisplay(out)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# @title Video 17: Syllabus\nfrom ipywidgets import widgets\n\nout2 = widgets.Output()\nwith out2:\n from IPython.display import IFrame\n class BiliVideo(IFrame):\n def __init__(self, id, page=1, width=400, height=300, **kwargs):\n self.id=id\n src = \"https://player.bilibili.com/player.html?bvid={0}&page={1}\".format(id, page)\n super(BiliVideo, self).__init__(src, width, height, **kwargs)\n\n video = BiliVideo(id=f\"BV1iB4y1N7uQ\", width=854, height=480, fs=1)\n print(\"Video available at https://www.bilibili.com/video/{0}\".format(video.id))\n display(video)\n\nout1 = widgets.Output()\nwith out1:\n from IPython.display import YouTubeVideo\n video = YouTubeVideo(id=f\"cDvAqG_hAvQ\", width=854, height=480, fs=1, rel=0)\n print(\"Video available at https://youtube.com/watch?v=\" + video.id)\n display(video)\n\nout = widgets.Tab([out1, out2])\nout.set_title(0, 'Youtube')\nout.set_title(1, 'Bilibili')\n\ndisplay(out)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Meet our lecturers:\n\nWeek 1: the building blocks\n* [Konrad Kording](https://kordinglab.com)\n* [Andrew Saxe](https://www.saxelab.org/)\n* [Surya Ganguli](https://ganguli-gang.stanford.edu/)\n* [Ioannis Mitliagkas](http://mitliagkas.github.io/)\n* [Lyle Ungar](https://www.cis.upenn.edu/~ungar/)\n\nWeek 2: making things work\n* [Alona Fyshe](https://webdocs.cs.ualberta.ca/~alona/)\n* [Alexander Ecker](https://eckerlab.org/)\n* [James Evans](https://sociology.uchicago.edu/directory/james-evans)\n* [He He](https://hhexiy.github.io/)\n* [Vikash Gilja](https://tnel.ucsd.edu/bio) and [Akash Srivastava](https://akashgit.github.io/)\n\nWeek 3: more magic\n* [Tim Lillicrap](https://contrastiveconvergence.net/~timothylillicrap/index.php) and [Blake Richards](https://www.mcgill.ca/neuro/blake-richards-phd)\n* [Jane Wang](http://www.janexwang.com/) and [Feryal Behbahani](https://feryal.github.io/)\n* [Tim Lillicrap](https://contrastiveconvergence.net/~timothylillicrap/index.php) and [Blake Richards](https://www.mcgill.ca/neuro/blake-richards-phd)\n* [Josh Vogelstein](https://jovo.me/) and [Vincenzo Lamonaco](https://www.vincenzolomonaco.com/)\n\nNow, go to the [visualization of ICLR papers](https://iclr.cc/virtual/2021/paper_vis.html). Read a few abstracts. Look at the various clusters. Where do you see yourself in this map?\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"---\n# Submit to Airtable",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# @title Video 18: Submission info\nfrom ipywidgets import widgets\n\nout2 = widgets.Output()\nwith out2:\n from IPython.display import IFrame\n class BiliVideo(IFrame):\n def __init__(self, id, page=1, width=400, height=300, **kwargs):\n self.id=id\n src = \"https://player.bilibili.com/player.html?bvid={0}&page={1}\".format(id, page)\n super(BiliVideo, self).__init__(src, width, height, **kwargs)\n\n video = BiliVideo(id=f\"BV1e44y127ti\", width=854, height=480, fs=1)\n print(\"Video available at https://www.bilibili.com/video/{0}\".format(video.id))\n display(video)\n\nout1 = widgets.Output()\nwith out1:\n from IPython.display import YouTubeVideo\n video = YouTubeVideo(id=f\"JwTn7ej2dq8\", width=854, height=480, fs=1, rel=0)\n print(\"Video available at https://youtube.com/watch?v=\" + video.id)\n display(video)\n\nout = widgets.Tab([out1, out2])\nout.set_title(0, 'Youtube')\nout.set_title(1, 'Bilibili')\n\ndisplay(out)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This is Darryl, the Deep Learning Dapper Lion, and he's here to teach you about content submission to airtable.\n<br>\n<img src=\"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/NeuromatchAcademy/course-content-dl/main/tutorials/static/DapperLion.png\" alt=\"Darryl\"> \n<br><br>\nAt the end of each tutorial there will be an <b>Airtable Submission</b> Cell. Run the cell to generate the airtable submission button and click on it to submit your information to airtable.\n<br><br>\nif it is the last tutorial of the day your button will look like this and take you to the end of day survey: \n<br>\n<img src=\"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/NeuromatchAcademy/course-content-dl/main/tutorials/static/SurveyButton.png?raw=1\" alt=\"Survey Button\">\n\notherwise it look like this: \n<br>\n\n<img src=\"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/NeuromatchAcademy/course-content-dl/main/tutorials/static/AirtableSubmissionButton.png?raw=1\" alt=\"Submission Button\"> \n<br><br>\n\nIt is critical that you push the submit button for every tutorial you run. <b><u> even if you don't finish the tutorial, still submit!</b></u>\nSubmitting is the only way we can verify that you attempted each tutorial, which is critical for the award of your completion certificate at the end of the course.\n<br><br><br>\n\nFinally, we try to keep the airtable code as hidden as possible, but if you ever see any calls to `atform` such as `atform.add_event()` in the coding exercises, just know that is for saving airtable information only.<b> It will not affect the code that is being run around it in any way</b> , so please do not modify, comment out, or worry about any of those lines of code.\n<br><br><br>\nNow, lets try submitting today's course to Airtable by running the next cell and clicking the button when it appears. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# @title Airtable Submission Link\nfrom IPython import display\ndisplay.HTML(\n f\"\"\"\n <div>\n <a href= \"{atform.url()}\" target=\"_blank\">\n <img src=\"https://github.com/NeuromatchAcademy/course-content-dl/blob/main/tutorials/static/SurveyButton.png?raw=1\"\n alt=\"button link to survey\" style=\"width:410px\"></a>\n </div>\"\"\" )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"---\n# Bonus - 60 years of Machine Learning Research in one Plot\n\nby [Hendrik Strobelt](http://hendrik.strobelt.com) (MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab) with support from Benjamin Hoover.\n\nIn this notebook we visualize a subset* of 3,300 articles retreived from the AllenAI [S2ORC dataset](https://github.com/allenai/s2orc). We represent each paper by a position that is output of a dimensionality reduction method applied to a vector representation of each paper. The vector representation is output of a neural network.\n\n*The selection is very biased on the keywords and methodology we used to filter. Please see the details section to learn about what we did. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# @title Import `altair` and load the data\n!pip install altair vega_datasets --quiet\nimport requests\nimport altair as alt # altair is defining data visualizations\n\n# Source data files\n# Position data file maps ID to x,y positions\n# original link: http://gltr.io/temp/ml_regexv1_cs_ma_citation+_99perc.pos_umap_cosine_100_d0.1.json\nPOS_FILE = 'https://osf.io/qyrfn/download'\n# original link: http://gltr.io/temp/ml_regexv1_cs_ma_citation+_99perc_clean.csv\n# Metadata file maps ID to title, abstract, author,....\nMETA_FILE = 'https://osf.io/vfdu6/download'\n\n# data loading and wrangling\ndef load_data():\n positions = pd.read_json(POS_FILE)\n positions[['x', 'y']] = positions['pos'].to_list()\n meta = pd.read_csv(META_FILE)\n return positions.merge(meta, left_on='id', right_on='paper_id')\n\n# load data\ndata = load_data()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# @title Define Visualization using ALtair\nYEAR_PERIOD = \"quinquennial\" # @param\nselection = alt.selection_multi(fields=[YEAR_PERIOD], bind='legend')\ndata[YEAR_PERIOD] = (data[\"year\"] / 5.0).apply(np.floor) * 5\nchart = alt.Chart(data[[\"x\", \"y\", \"authors\", \"title\", YEAR_PERIOD, \"citation_count\"]], width=800,\n height=800).mark_circle(radius=2, opacity=0.2).encode(\n alt.Color(YEAR_PERIOD+':O',\n scale=alt.Scale(scheme='viridis', reverse=False, clamp=True, domain=list(range(1955,2020,5))),\n # legend=alt.Legend(title='Total Records')\n ),\n alt.Size('citation_count',\n scale=alt.Scale(type=\"pow\", exponent=1, range=[15, 300])\n ),\n alt.X('x:Q',\n scale=alt.Scale(zero=False), axis=alt.Axis(labels=False)\n ),\n alt.Y('y:Q',\n scale=alt.Scale(zero=False), axis=alt.Axis(labels=False)\n ),\n tooltip=['title', 'authors'],\n # size='citation_count',\n # color=\"decade:O\",\n opacity=alt.condition(selection, alt.value(.8), alt.value(0.2)),\n\n).add_selection(\n selection\n).interactive()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Lets look at the Visualization. Each dot represents one paper. Close dots mean that the respective papers are closer related than distant ones. The color indicates the 5-year period of when the paper was published. The dot size indicates the citation count (within S2ORC corpus) as of July 2020. \n\nThe view is **interactive** and allows for three main interactions. Try them and play around.\n1. hover over a dot to see a tooltip (title, author)\n2. select a year in the legend (right) to filter dots\n2. zoom in/out with scroll -- double click resets view ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"chart",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Questions\n\nBy playing around, can you find some answers to the follwing questions?\n\n1. Can you find topical clusters? What cluster might occur because of a filtering error?\n2. Can you see a temporal trend in the data and clusters?\n2. Can you determine when deep learning methods started booming ?\n3. Can you find the key papers that where written before the DL \"winter\" that define milestones for a cluster? (tipp: look for large dots of different color)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Methods\n\nHere is what we did:\n1. Filtering of all papers who fullfilled the criterria:\n - are categorized as `Computer Science` or `Mathematics` \n - one of the following keywords appearing in title or abstract: `\"machine learning|artificial intelligence|neural network|(machine|computer) vision|perceptron|network architecture| RNN | CNN | LSTM | BLEU | MNIST | CIFAR |reinforcement learning|gradient descent| Imagenet \"`\n2. per year, remove all papers that are below the 99 percentile of citation count in that year\n3. embed each paper by using abstract+title in SPECTER model\n4. project based on embedding using UMAP\n5. visualize using Altair",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Find Authors",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# @title Edit the `AUTHOR_FILTER` variable to full text search for authors.\n\nAUTHOR_FILTER = \"Rush \" # @param space at the end means \"word border\"\n\n### Don't ignore case when searching...\nFLAGS = 0\n### uncomment do ignore case\n# FLAGS = re.IGNORECASE\n\n## --- FILTER CODE.. make it your own ---\nimport re\ndata['issel'] = data['authors'].str.contains(AUTHOR_FILTER, na=False, flags=FLAGS, )\nif data['issel'].mean()<0.0000000001:\n print('No match found')\n\n## --- FROM HERE ON VIS CODE ---\nalt.Chart(data[[\"x\", \"y\", \"authors\", \"title\", YEAR_PERIOD, \"citation_count\", \"issel\"]], width=800,\n height=800) \\\n .mark_circle(stroke=\"black\", strokeOpacity=1).encode(\n alt.Color(YEAR_PERIOD+':O',\n scale=alt.Scale(scheme='viridis', reverse=False),\n # legend=alt.Legend(title='Total Records')\n ),\n alt.Size('citation_count',\n scale=alt.Scale(type=\"pow\", exponent=1, range=[15, 300])\n ),\n alt.StrokeWidth('issel:Q', scale=alt.Scale(type=\"linear\", domain=[0,1], range=[0, 2]), legend=None),\n\n alt.Opacity('issel:Q', scale=alt.Scale(type=\"linear\", domain=[0,1], range=[.2, 1]), legend=None),\n alt.X('x:Q',\n scale=alt.Scale(zero=False), axis=alt.Axis(labels=False)\n ),\n alt.Y('y:Q',\n scale=alt.Scale(zero=False), axis=alt.Axis(labels=False)\n ),\n tooltip=['title', 'authors'],\n).interactive()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"---\n# Appendix\n\n## Official PyTorch resources:\n### Tutorials\nhttps://pytorch.org/tutorials/\n\n### Documentation\n\n https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/tensors.html (tensor methods)\n\n https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/tensors.html#torch.Tensor.view (The view method in particular)\n\n https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/datasets.html (pre-loaded image datasets)\n\n ## Google Colab Resources:\n https://research.google.com/colaboratory/faq.html (FAQ including guidance on GPU usage)\n\n ## Books for reference:\n\nhttps://www.deeplearningbook.org/ (Deep Learning by Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio and Aaron Courville)\n\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a320d103fbac6534f7e2363a5c14eb5fa14f44e
| 39,715 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Logistic Regression2.ipynb
|
Davisy/Logistic-Regression
|
b4ff6fe0dcfb96dc5fdf10922d11e11e59ec50b6
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Logistic Regression2.ipynb
|
Davisy/Logistic-Regression
|
b4ff6fe0dcfb96dc5fdf10922d11e11e59ec50b6
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Logistic Regression2.ipynb
|
Davisy/Logistic-Regression
|
b4ff6fe0dcfb96dc5fdf10922d11e11e59ec50b6
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-04-20T00:30:43.000Z
|
2021-04-20T00:30:43.000Z
| 56.979914 | 22,330 | 0.753015 |
[
[
[
"# Logistic Regression",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Resources:\n\n[Logistic Regression Tutorial for Machine Learning](http://machinelearningmastery.com/logistic-regression-tutorial-for-machine-learning/)\n\n[Logistic Regression for Machine Learning](http://machinelearningmastery.com/logistic-regression-for-machine-learning/)\n\n[How To Implement Logistic Regression With Stochastic Gradient Descent From Scratch With Python](http://machinelearningmastery.com/implement-logistic-regression-stochastic-gradient-descent-scratch-python/)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Logistic regression is the go-to linear classification algorithm for two-class problems. It is easy to implement, easy to understand and gets great results on a wide variety of problems, even when the expectations the method has for your data are violated.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Description\n\n#### Logistic Regression\n\nLogistic regression is named for the function used at the core of the method, the [logistic function](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Logistic_function).\n\nThe logistic function, also called the **Sigmoid function** was developed by statisticians to describe properties of population growth in ecology, rising quickly and maxing out at the carrying capacity of the environment. It’s an S-shaped curve that can take any real-valued number and map it into a value between 0 and 1, but never exactly at those limits.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"$$\\frac{1}{1 + e^{-x}}$$\n\n$e$ is the base of the natural logarithms and $x$ is value that you want to transform via the logistic function.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x = np.linspace(-6, 6, num = 1000)\nplt.figure(figsize = (12,8))\nplt.plot(x, 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))); # Sigmoid Function\nplt.title(\"Sigmoid Function\");",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"***",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The logistic regression equation has a very simiar representation like linear regression. The difference is that the output value being modelled is binary in nature.\n\n$$\\hat{y}=\\frac{e^{\\beta_0+\\beta_1x_1}}{1+\\beta_0+\\beta_1x_1}$$\n\nor\n\n$$\\hat{y}=\\frac{1.0}{1.0+e^{-\\beta_0-\\beta_1x_1}}$$\n\n$\\beta_0$ is the intecept term\n\n$\\beta_1$ is the coefficient for $x_1$\n\n$\\hat{y}$ is the predicted output with real value between 0 and 1. To convert this to binary output of 0 or 1, this would either need to be rounded to an integer value or a cutoff point be provided to specify the class segregation point.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tmp = [0, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tmp",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.round(tmp)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.array(tmp) > 0.7",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"***",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Making Predictions with Logistic Regression",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"$$\\hat{y}=\\frac{1.0}{1.0+e^{-\\beta_0-\\beta_1x_i}}$$\n\n$\\beta_0$ is the intecept term\n\n$\\beta_1$ is the coefficient for $x_i$\n\n$\\hat{y}$ is the predicted output with real value between 0 and 1. To convert this to binary output of 0 or 1, this would either need to be rounded to an integer value or a cutoff point be provided to specify the class segregation point.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dataset = [[-2.0011, 0],\n [-1.4654, 0],\n [0.0965, 0],\n [1.3881, 0],\n [3.0641, 0],\n [7.6275, 1],\n [5.3324, 1],\n [6.9225, 1],\n [8.6754, 1],\n [7.6737, 1]]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's say you have been provided with the coefficient",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"coef = [-0.806605464, 0.2573316]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for row in dataset:\n yhat = 1.0 / (1.0 + np.exp(- coef[0] - coef[1] * row[0]))\n print(\"yhat {0:.4f}, yhat {1}\".format(yhat, round(yhat)))",
"yhat 0.2106, yhat 0.0\nyhat 0.2344, yhat 0.0\nyhat 0.3139, yhat 0.0\nyhat 0.3895, yhat 0.0\nyhat 0.4955, yhat 0.0\nyhat 0.7606, yhat 1.0\nyhat 0.6377, yhat 1.0\nyhat 0.7261, yhat 1.0\nyhat 0.8063, yhat 1.0\nyhat 0.7628, yhat 1.0\n"
]
],
[
[
"***",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Learning the Logistic Regression Model\n\nThe coefficients (Beta values b) of the logistic regression algorithm must be estimated from your training data. This is done using [maximum-likelihood estimation](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Maximum_likelihood_estimation).\n\nMaximum-likelihood estimation is a common learning algorithm used by a variety of machine learning algorithms, although it does make assumptions about the distribution of your data (more on this when we talk about preparing your data).\n\nThe best coefficients would result in a model that would predict a value very close to 1 (e.g. male) for the default class and a value very close to 0 (e.g. female) for the other class. The intuition for maximum-likelihood for logistic regression is that a search procedure seeks values for the coefficients (Beta values) that minimize the error in the probabilities predicted by the model to those in the data (e.g. probability of 1 if the data is the primary class).\n\nWe are not going to go into the math of maximum likelihood. It is enough to say that a minimization algorithm is used to optimize the best values for the coefficients for your training data. This is often implemented in practice using efficient numerical optimization algorithm (like the Quasi-newton method).\n\nWhen you are learning logistic, you can implement it yourself from scratch using the much simpler gradient descent algorithm.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Learning with Stochastic Gradient Descent\n\nLogistic Regression uses gradient descent to update the coefficients.\n\nEach gradient descent iteration, the coefficients are updated using the equation:\n\n$$\\beta=\\beta+\\textrm{learning rate}\\times (y-\\hat{y}) \\times \\hat{y} \\times (1-\\hat{y}) \\times x $$\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"***",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Using Scikit Learn to Estimate Coefficients",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dataset",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X = np.array(dataset)[:, 0:1]\ny = np.array(dataset)[:, 1]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"y",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"clf_LR = LogisticRegression(C=1.0, penalty='l2', tol=0.0001)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"clf_LR.fit(X,y)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"clf_LR.predict(X)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"clf_LR.predict_proba(X)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Further Resources\n\n[A comparison of numerical optimizers for logistic regression](https://tminka.github.io/papers/logreg/)\n\n[PDF: A comparison of numerical optimizers for logistic regression](https://tminka.github.io/papers/logreg/minka-logreg.pdf)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"***",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Classification Exercise",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dataset2 = [[ 0.2, 0. ],\n [ 0.2, 0. ],\n [ 0.2, 0. ],\n [ 0.2, 0. ],\n [ 0.2, 0. ],\n [ 0.4, 0. ],\n [ 0.3, 0. ],\n [ 0.2, 0. ],\n [ 0.2, 0. ],\n [ 0.1, 0. ],\n [ 1.4, 1. ],\n [ 1.5, 1. ],\n [ 1.5, 1. ],\n [ 1.3, 1. ],\n [ 1.5, 1. ],\n [ 1.3, 1. ],\n [ 1.6, 1. ],\n [ 1. , 1. ],\n [ 1.3, 1. ],\n [ 1.4, 1. ]]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X = np.array(dataset2)[:, 0:1]\ny = np.array(dataset2)[:, 1]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"clf_LR = LogisticRegression(C=1.0, penalty='l2', tol=0.0001)\n\nclf_LR.fit(X,y)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"y_pred = clf_LR.predict(X)\nclf_LR.predict(X)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.column_stack((y_pred, y))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"***",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a321c0e5a794acc1b57642d79ded43fd3ab75a3
| 434,399 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
desafios_aula02.ipynb
|
justapixel/QuarentenaDados
|
6eb06ea8d02b822c0e98c5b611c67147fec0413f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
desafios_aula02.ipynb
|
justapixel/QuarentenaDados
|
6eb06ea8d02b822c0e98c5b611c67147fec0413f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
desafios_aula02.ipynb
|
justapixel/QuarentenaDados
|
6eb06ea8d02b822c0e98c5b611c67147fec0413f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 774.329768 | 51,363 | 0.721434 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn as sns\n\nmovies = pd.read_csv(\"ml-latest-small/movies.csv\")\nmovies_rating = pd.read_csv(\"ml-latest-small/ratings.csv\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sum_movies_genres = movies[\"genres\"].str.get_dummies('|').sum()\nmovies_by_genre = sum_movies_genres.sort_values(ascending=False)\nmovies_by_genre",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Desafio 1 do [Guilherme Silveira](https://twitter.com/guilhermecaelum)\n## Rotacionar os thicks (os nomes dos generos) do gráfico de barras verdes (o último), de forma a deixar as legendas mais legíveis.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sns.set_style(\"whitegrid\")\n\nmovies_by_genre = sum_movies_genres.sort_values(ascending=False)\nplt.figure(figsize=(16,8))\ngr = sns.barplot(x=movies_by_genre.index,\n y=movies_by_genre.values,\n palette=sns.color_palette(\"BuGn_r\", n_colors=len(movies_by_genre) + 4))\ngr.set_xticklabels(movies_by_genre.index.array, rotation=90, ha='right')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Desafio 2 do [Paulo Silveira](https://twitter.com/paulo_caelum)\n## Encontar vários filmes com médias próximas e distribuições diferentes, use a função **plot_filmes(n)** para plotar.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def plot_movie(id):\n rating_movie = movies_rating.query(f\"movieId=={id}\")['rating']\n rating_movie.plot(kind='hist')\n return rating_movie.describe()\n\nrating = movies_rating.groupby(\"movieId\")['rating'].mean()\n\nmovies_with_mean = movies.join(rating, on=\"movieId\")\n\ncount_votes_by_movieId = movies_rating.groupby('movieId')['rating'].count()\ncount_votes_by_movieId.rename('votes', inplace=True)\n\nmovies_with_rating_and_votes = movies_with_mean.join(count_votes_by_movieId, on=\"movieId\").round({'rating':1})\nmovies_clean = movies_with_rating_and_votes.query(\"votes > 100\").sort_values(by=\"votes\", ascending=False)\nmovies_clean",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"movies_clean.query(\"rating == 3\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plot_movie(344)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plot_movie(586)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plot_movie(185)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plot_movie(434)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Desafio 3 do [Paulo Silveira](https://twitter.com/paulo_caelum)\n\n### Criar o boxplot dos 10 filmes com mais votos (não é com maior média, é com mais votos!). Não apenas plot mas também analise e tente tirar conclusões.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"movies_id = movies_clean.head(10)[\"movieId\"].tolist()\nplt.figure(figsize=(16, 8))\nsns.boxplot(data = movies_rating.query(f\"movieId in {movies_id}\"), x =\"movieId\", y=\"rating\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Dentre os 10, o filme de id 318 possui a melhor distribuição de notas.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Desafio 4 do [Guilherme Silveira](https://twitter.com/guilhermecaelum)\n\n### Configurar a visualização do boxplot gerado pelo seaborn (último boxplot plotado na aula). Configurar o tamanho e colocar o nome dos filmes nos thicks.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))\nboxplot_data = movies_rating.query(\"movieId in [1,2,919,46578]\").merge(movies[[\"movieId\", \"title\"]], on=\"movieId\")\nsns.boxplot(data = boxplot_data, x = \"title\", y=\"rating\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Desafio 5 do [Allan Spadini](https://twitter.com/allanspadini)\n### Calcular moda, média e mediana dos filmes. Explore filmes com notas mais próximas de 0.5, 3 e 5.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def movies_3m(id):\n movie_3m = movies_rating.query(f\"movieId=={id}\")['rating']\n movie_title = movies.query(f\"movieId=={id}\")['title']\n print(movie_title.values[0])\n print(\"Média = \", movie_3m.mean())\n print(\"Mediana = \", movie_3m.median())\n print(\"Moda = \", movie_3m.mode()[0])\n print('\\n')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for n in movies_with_mean.query(\"rating > 0.1 and rating < 1\")[\"movieId\"].head(5):\n movies_3m(n)",
"Amityville Curse, The (1990)\nMédia = 0.75\nMediana = 0.75\nModa = 0.5\n\n\nGypsy (1962)\nMédia = 0.5\nMediana = 0.5\nModa = 0.5\n\n\nHouse Party 2 (1991)\nMédia = 0.75\nMediana = 0.75\nModa = 0.5\n\n\nKiller Shrews, The (1959)\nMédia = 0.5\nMediana = 0.5\nModa = 0.5\n\n\nHorrors of Spider Island (Ein Toter Hing im Netz) (1960)\nMédia = 0.5\nMediana = 0.5\nModa = 0.5\n\n\n"
],
[
"for n in movies_with_mean.query(\"rating > 2.4 and rating < 3.6\")[\"movieId\"].head(5):\n movies_3m(n)",
"Jumanji (1995)\nMédia = 3.4318181818181817\nMediana = 3.5\nModa = 4.0\n\n\nGrumpier Old Men (1995)\nMédia = 3.2596153846153846\nMediana = 3.0\nModa = 3.0\n\n\nFather of the Bride Part II (1995)\nMédia = 3.0714285714285716\nMediana = 3.0\nModa = 3.0\n\n\nSabrina (1995)\nMédia = 3.185185185185185\nMediana = 3.0\nModa = 3.0\n\n\nTom and Huck (1995)\nMédia = 2.875\nMediana = 3.0\nModa = 3.0\n\n\n"
],
[
"for n in movies_with_mean.query(\"rating > 4 and rating <= 5\")[\"movieId\"].head(5):\n movies_3m(n)",
"Persuasion (1995)\nMédia = 4.2272727272727275\nMediana = 4.5\nModa = 4.5\n\n\nCity of Lost Children, The (Cité des enfants perdus, La) (1995)\nMédia = 4.0131578947368425\nMediana = 4.0\nModa = 4.0\n\n\nCry, the Beloved Country (1995)\nMédia = 4.25\nMediana = 4.25\nModa = 3.5\n\n\nUsual Suspects, The (1995)\nMédia = 4.237745098039215\nMediana = 4.5\nModa = 5.0\n\n\nLamerica (1994)\nMédia = 5.0\nMediana = 5.0\nModa = 5.0\n\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Desafio 6 da [Thais André](https://twitter.com/thais_tandre)\n### Plotar o boxplot e o histograma um do lado do outro (na mesma figura ou em figuras distintas, mas um do lado do outro).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def plot_movie_box(id):\n rating_movie = movies_rating.query(f\"movieId=={id}\")['rating']\n fig, (ax, ax2) = plt.subplots(ncols=2, sharey=False, figsize=(16, 8))\n rating_movie.plot(ax = ax, kind='hist')\n rating_movie.plot.box().plot()\n plt.show()\n return rating_movie.describe()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plot_movie_box(919)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Desafio 7 do [Thiago Gonçalves](https://twitter.com/tgcsantos)\n### Criar um gráfico de notas médias por ano (média geral considerando todos os filmes lançados naquele ano).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"movies_with_mean['release_date'] = movies['title'].str.extract('.*\\((.*)\\).*', expand = False)\nmovies_with_mean",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"movies_with_mean.sort_values(by='release_date')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mean_by_date = movies_with_mean.dropna().groupby('release_date').mean().reset_index()[['release_date', 'rating']]\nmean_by_date.sort_values(by=\"release_date\", ascending=False, inplace=True)\nmean_by_date",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(16,8))\ngr = sns.barplot(\n x=mean_by_date['release_date'].head(10),\n y=mean_by_date['rating'].head(10)\n )\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a3225d68c71944230aa55b611b831159d8c2e39
| 9,437 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/users/reuben/hugo-experiments.ipynb
|
OpenSecuritySummit/jp-2020
|
f822a583e531cd3b316c2475066f7613c4f9681c
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/users/reuben/hugo-experiments.ipynb
|
OpenSecuritySummit/jp-2020
|
f822a583e531cd3b316c2475066f7613c4f9681c
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/users/reuben/hugo-experiments.ipynb
|
OpenSecuritySummit/jp-2020
|
f822a583e531cd3b316c2475066f7613c4f9681c
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2020-06-14T16:08:34.000Z
|
2020-06-14T16:08:34.000Z
| 109.732558 | 1,997 | 0.694394 |
[
[
[
"from oss_hugo.API_Hugo_OSS import API_Hugo_OSS\n\nimport pandas as pd\n\n# pd.set_option('display.max_colwidth', -1)\npd.set_option('display.max_rows', 1000)\npd.set_option('display.max_columns', None)\n\nhugo = API_Hugo_OSS()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"hugo.df_sessions() # the .head(20) command will show the top 20 ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a323b93bf62eceaf8fc550c547ba61d7c2b3fb9
| 41,248 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
docs/2notebook/2_Constraints.ipynb
|
Ashiq5/TextAttack
|
257c5440b5a8d00d921b760bc06d5dbd7d28928d
|
[
"MIT"
] | 7 |
2021-10-30T03:44:53.000Z
|
2021-11-24T08:18:38.000Z
|
docs/2notebook/2_Constraints.ipynb
|
Ashiq5/TextAttack
|
257c5440b5a8d00d921b760bc06d5dbd7d28928d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
docs/2notebook/2_Constraints.ipynb
|
Ashiq5/TextAttack
|
257c5440b5a8d00d921b760bc06d5dbd7d28928d
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2021-03-28T09:02:57.000Z
|
2021-12-28T01:17:20.000Z
| 53.568831 | 2,389 | 0.635255 |
[
[
[
"# The importance of constraints\n\nConstraints determine which potential adversarial examples are valid inputs to the model. When determining the efficacy of an attack, constraints are everything. After all, an attack that looks very powerful may just be generating nonsense. Or, perhaps more nefariously, an attack may generate a real-looking example that changes the original label of the input. That's why you should always clearly define the *constraints* your adversarial examples must meet. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/QData/TextAttack/blob/master/docs/2notebook/2_Constraints.ipynb)\n\n[](https://github.com/QData/TextAttack/blob/master/docs/2notebook/2_Constraints.ipynb)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Classes of constraints\n\nTextAttack evaluates constraints using methods from three groups:\n\n- **Overlap constraints** determine if a perturbation is valid based on character-level analysis. For example, some attacks are constrained by edit distance: a perturbation is only valid if it perturbs some small number of characters (or fewer).\n\n- **Grammaticality constraints** filter inputs based on syntactical information. For example, an attack may require that adversarial perturbations do not introduce grammatical errors.\n\n- **Semantic constraints** try to ensure that the perturbation is semantically similar to the original input. For example, we may design a constraint that uses a sentence encoder to encode the original and perturbed inputs, and enforce that the sentence encodings be within some fixed distance of one another. (This is what happens in subclasses of `textattack.constraints.semantics.sentence_encoders`.)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### A new constraint\n\nTo add our own constraint, we need to create a subclass of `textattack.constraints.Constraint`. We can implement one of two functions, either `_check_constraint` or `_check_constraint_many`:\n\n- `_check_constraint` determines whether candidate `TokenizedText` `transformed_text`, transformed from `current_text`, fulfills a desired constraint. It returns either `True` or `False`.\n- `_check_constraint_many` determines whether each of a list of candidates `transformed_texts` fulfill the constraint relative to `current_text`. This is here in case your constraint can be vectorized. If not, just implement `_check_constraint`, and `_check_constraint` will be executed for each `(transformed_text, current_text)` pair.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### A custom constraint\n\n\nFor fun, we're going to see what happens when we constrain an attack to only allow perturbations that substitute out a named entity for another. In linguistics, a **named entity** is a proper noun, the name of a person, organization, location, product, etc. Named Entity Recognition is a popular NLP task (and one that state-of-the-art models can perform quite well). \n\n\n### NLTK and Named Entity Recognition\n\n**NLTK**, the Natural Language Toolkit, is a Python package that helps developers write programs that process natural language. NLTK comes with predefined algorithms for lots of linguistic tasks– including Named Entity Recognition.\n\nFirst, we're going to write a constraint class. In the `_check_constraints` method, we're going to use NLTK to find the named entities in both `current_text` and `transformed_text`. We will only return `True` (that is, our constraint is met) if `transformed_text` has substituted one named entity in `current_text` for another.\n\nLet's import NLTK and download the required modules:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import nltk\nnltk.download('punkt') # The NLTK tokenizer\nnltk.download('maxent_ne_chunker') # NLTK named-entity chunker\nnltk.download('words') # NLTK list of words",
"[nltk_data] Downloading package punkt to /u/edl9cy/nltk_data...\n[nltk_data] Package punkt is already up-to-date!\n[nltk_data] Downloading package maxent_ne_chunker to\n[nltk_data] /u/edl9cy/nltk_data...\n[nltk_data] Package maxent_ne_chunker is already up-to-date!\n[nltk_data] Downloading package words to /u/edl9cy/nltk_data...\n[nltk_data] Package words is already up-to-date!\n"
]
],
[
[
"### NLTK NER Example\n\nHere's an example of using NLTK to find the named entities in a sentence:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sentence = ('In 2017, star quarterback Tom Brady led the Patriots to the Super Bowl, '\n 'but lost to the Philadelphia Eagles.')\n\n# 1. Tokenize using the NLTK tokenizer.\ntokens = nltk.word_tokenize(sentence)\n\n# 2. Tag parts of speech using the NLTK part-of-speech tagger.\ntagged = nltk.pos_tag(tokens)\n\n# 3. Extract entities from tagged sentence.\nentities = nltk.chunk.ne_chunk(tagged)\nprint(entities)",
"(S\n In/IN\n 2017/CD\n ,/,\n star/NN\n quarterback/NN\n (PERSON Tom/NNP Brady/NNP)\n led/VBD\n the/DT\n (ORGANIZATION Patriots/NNP)\n to/TO\n the/DT\n (ORGANIZATION Super/NNP Bowl/NNP)\n ,/,\n but/CC\n lost/VBD\n to/TO\n the/DT\n (ORGANIZATION Philadelphia/NNP Eagles/NNP)\n ./.)\n"
]
],
[
[
"It looks like `nltk.chunk.ne_chunk` gives us an `nltk.tree.Tree` object where named entities are also `nltk.tree.Tree` objects within that tree. We can take this a step further and grab the named entities from the tree of entities:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 4. Filter entities to just named entities.\nnamed_entities = [entity for entity in entities if isinstance(entity, nltk.tree.Tree)]\nprint(named_entities)",
"[Tree('PERSON', [('Tom', 'NNP'), ('Brady', 'NNP')]), Tree('ORGANIZATION', [('Patriots', 'NNP')]), Tree('ORGANIZATION', [('Super', 'NNP'), ('Bowl', 'NNP')]), Tree('ORGANIZATION', [('Philadelphia', 'NNP'), ('Eagles', 'NNP')])]\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Caching with `@functools.lru_cache`\n\nA little-known feature of Python 3 is `functools.lru_cache`, a decorator that allows users to easily cache the results of a function in an LRU cache. We're going to be using the NLTK library quite a bit to tokenize, parse, and detect named entities in sentences. These sentences might repeat themselves. As such, we'll use this decorator to cache named entities so that we don't have to perform this expensive computation multiple times.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Putting it all together: getting a list of Named Entity Labels from a sentence\n\nNow that we know how to tokenize, parse, and detect named entities using NLTK, let's put it all together into a single helper function. Later, when we implement our constraint, we can query this function to easily get the entity labels from a sentence. We can even use `@functools.lru_cache` to try and speed this process up.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import functools\n\[email protected]_cache(maxsize=2**14)\ndef get_entities(sentence):\n tokens = nltk.word_tokenize(sentence)\n tagged = nltk.pos_tag(tokens)\n # Setting `binary=True` makes NLTK return all of the named\n # entities tagged as NNP instead of detailed tags like\n #'Organization', 'Geo-Political Entity', etc.\n entities = nltk.chunk.ne_chunk(tagged, binary=True)\n return entities.leaves()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"And let's test our function to make sure it works:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sentence = 'Jack Black starred in the 2003 film classic \"School of Rock\".'\nget_entities(sentence)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We flattened the tree of entities, so the return format is a list of `(word, entity type)` tuples. For non-entities, the `entity_type` is just the part of speech of the word. `'NNP'` is the indicator of a named entity (a proper noun, according to NLTK). Looks like we identified three named entities here: 'Jack' and 'Black', 'School', and 'Rock'. as a 'GPE'. (Seems that the labeler thinks Rock is the name of a place, a city or something.) Whatever technique NLTK uses for named entity recognition may be a bit rough, but it did a pretty decent job here!",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Creating our NamedEntityConstraint\n\nNow that we know how to detect named entities using NLTK, let's create our custom constraint.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from textattack.constraints import Constraint\n\nclass NamedEntityConstraint(Constraint):\n \"\"\" A constraint that ensures `transformed_text` only substitutes named entities from `current_text` with other named entities.\n \"\"\"\n def _check_constraint(self, transformed_text, current_text):\n transformed_entities = get_entities(transformed_text.text)\n current_entities = get_entities(current_text.text)\n # If there aren't named entities, let's return False (the attack\n # will eventually fail).\n if len(current_entities) == 0:\n return False\n if len(current_entities) != len(transformed_entities):\n # If the two sentences have a different number of entities, then \n # they definitely don't have the same labels. In this case, the \n # constraint is violated, and we return False.\n return False\n else:\n # Here we compare all of the words, in order, to make sure that they match.\n # If we find two words that don't match, this means a word was swapped \n # between `current_text` and `transformed_text`. That word must be a named entity to fulfill our\n # constraint.\n current_word_label = None\n transformed_word_label = None\n for (word_1, label_1), (word_2, label_2) in zip(current_entities, transformed_entities):\n if word_1 != word_2:\n # Finally, make sure that words swapped between `x` and `x_adv` are named entities. If \n # they're not, then we also return False.\n if (label_1 not in ['NNP', 'NE']) or (label_2 not in ['NNP', 'NE']):\n return False \n # If we get here, all of the labels match up. Return True!\n return True\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Testing our constraint\n\nWe need to create an attack and a dataset to test our constraint on. We went over all of this in the transformations tutorial, so let's gloss over this part for now.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import the model\nimport transformers\nfrom textattack.models.tokenizers import AutoTokenizer\nfrom textattack.models.wrappers import HuggingFaceModelWrapper\n\nmodel = transformers.AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(\"textattack/albert-base-v2-yelp-polarity\")\ntokenizer = AutoTokenizer(\"textattack/albert-base-v2-yelp-polarity\")\n\nmodel_wrapper = HuggingFaceModelWrapper(model, tokenizer)\n\n# Create the goal function using the model\nfrom textattack.goal_functions import UntargetedClassification\ngoal_function = UntargetedClassification(model_wrapper)\n\n# Import the dataset\nfrom textattack.datasets import HuggingFaceDataset\ndataset = HuggingFaceDataset(\"yelp_polarity\", None, \"test\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from textattack.transformations import WordSwapEmbedding\nfrom textattack.search_methods import GreedySearch\nfrom textattack.shared import Attack\nfrom textattack.constraints.pre_transformation import RepeatModification, StopwordModification\n\n# We're going to the `WordSwapEmbedding` transformation. Using the default settings, this\n# will try substituting words with their neighbors in the counter-fitted embedding space. \ntransformation = WordSwapEmbedding(max_candidates=15) \n\n# We'll use the greedy search method again\nsearch_method = GreedySearch()\n\n# Our constraints will be the same as Tutorial 1, plus the named entity constraint\nconstraints = [RepeatModification(),\n StopwordModification(),\n NamedEntityConstraint(False)]\n\n# Now, let's make the attack using these parameters. \nattack = Attack(goal_function, constraints, transformation, search_method)\n\nprint(attack)",
"Attack(\n (search_method): GreedySearch\n (goal_function): UntargetedClassification\n (transformation): WordSwapEmbedding(\n (max_candidates): 15\n (embedding_type): paragramcf\n )\n (constraints): \n (0): NamedEntityConstraint(\n (compare_against_original): False\n )\n (1): RepeatModification\n (2): StopwordModification\n (is_black_box): True\n)\n"
]
],
[
[
"Now, let's use our attack. We're going to attack samples until we achieve 5 successes. (There's a lot to check here, and since we're using a greedy search over all potential word swap positions, each sample will take a few minutes. This will take a few hours to run on a single core.)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from textattack.loggers import CSVLogger # tracks a dataframe for us.\nfrom textattack.attack_results import SuccessfulAttackResult\n\nresults_iterable = attack.attack_dataset(dataset)\nlogger = CSVLogger(color_method='html')\n\nnum_successes = 0\nwhile num_successes < 5:\n result = next(results_iterable)\n if isinstance(result, SuccessfulAttackResult):\n logger.log_attack_result(result)\n num_successes += 1\n print(f'{num_successes} of 5 successes complete.')",
"1 of 5 successes complete.\n2 of 5 successes complete.\n3 of 5 successes complete.\n4 of 5 successes complete.\n5 of 5 successes complete.\n"
]
],
[
[
"Now let's visualize our 5 successes in color:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\npd.options.display.max_colwidth = 480 # increase column width so we can actually read the examples\n\nfrom IPython.core.display import display, HTML\ndisplay(HTML(logger.df[['original_text', 'perturbed_text']].to_html(escape=False)))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Conclusion\n\nOur constraint seems to have done its job: it filtered out attacks that did not swap out a named entity for another, according to the NLTK named entity detector. However, we can see some problems inherent in the detector: it often thinks the first word of a given sentence is a named entity, probably due to capitalization. \n\nWe did manage to produce some nice adversarial examples! \"Sigh\" beacame \"Inahles\" and the prediction shifted from negative to positive.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a32553dc2821eb703cd91054c2022ff2a272d53
| 1,094 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
content/assignments/mid_proj-placeholder.ipynb
|
irr223/ledatascifi-2022
|
76c137167df1e3e3c343ef016a592cdb8908b1bf
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
content/assignments/mid_proj-placeholder.ipynb
|
irr223/ledatascifi-2022
|
76c137167df1e3e3c343ef016a592cdb8908b1bf
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2022-01-30T18:34:22.000Z
|
2022-02-10T15:48:48.000Z
|
content/assignments/mid_proj-placeholder.ipynb
|
irr223/ledatascifi-2022
|
76c137167df1e3e3c343ef016a592cdb8908b1bf
|
[
"MIT"
] | 14 |
2022-01-26T10:45:19.000Z
|
2022-03-28T15:59:56.000Z
| 26.047619 | 267 | 0.601463 |
[
[
[
"# Midterm aka Assignment 5 - Our first real data science project\n\nIn this project, you will have to get (scrape) data, clean it yourself, and parse the data to construct measures to use in exploratory analysis. This project will show you that production-level analysis at a huge scale is within reach for everyone in class. \n\nMore details will be posted soon, but you can ask me in person for an update anytime!\n\n\n\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a325ac3328e1837cc312baa4119f4c8584233bb
| 3,010 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Chapter6_ObjectOriented/inheritance.ipynb
|
tomex74/UdemyPythonPro
|
b4b83483fa2d3337a2860d53ff38e68eb38b3ac4
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Chapter6_ObjectOriented/inheritance.ipynb
|
tomex74/UdemyPythonPro
|
b4b83483fa2d3337a2860d53ff38e68eb38b3ac4
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Chapter6_ObjectOriented/inheritance.ipynb
|
tomex74/UdemyPythonPro
|
b4b83483fa2d3337a2860d53ff38e68eb38b3ac4
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 19.050633 | 79 | 0.451163 |
[
[
[
"class A:\n def __init__(self):\n print(\"Init A called!\")\n self.a = 1\n\nclass B(A):\n def __init__(self):\n super().__init__()\n print(\"Init B called!\")\n self.b = self.a * 2\n\nclass C(A):\n def __init__(self):\n super().__init__()\n print(\"Init C called!\")\n self.c = self.a / 2\n\nclass D(B, C):\n def __init__(self):\n super().__init__()\n print(\"Init D called!\")\n self.d = self.b + self.c\n print(self.d)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a = A()",
"Init A called!\n"
],
[
"b = B()\n",
"Init A called!\nInit B called!\n"
],
[
"c = C()",
"Init A called!\nInit C called!\n"
],
[
"d = D()",
"Init A called!\nInit C called!\nInit B called!\nInit D called!\n2.5\n"
],
[
"D.mro()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a326a48e5061129cac45f537ade422ff8405958
| 6,626 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Modulo2/.ipynb_checkpoints/5. SELENIUM-checkpoint.ipynb
|
gdelgador/Curso-WebScraping
|
7ca6c810ba26aaa1f71f177144e1cbcfc7f114ee
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2021-09-14T04:38:02.000Z
|
2021-09-14T04:38:02.000Z
|
Modulo2/.ipynb_checkpoints/5. SELENIUM-checkpoint.ipynb
|
gdelgador/Curso-WebScraping
|
7ca6c810ba26aaa1f71f177144e1cbcfc7f114ee
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Modulo2/.ipynb_checkpoints/5. SELENIUM-checkpoint.ipynb
|
gdelgador/Curso-WebScraping
|
7ca6c810ba26aaa1f71f177144e1cbcfc7f114ee
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 28.683983 | 1,033 | 0.58527 |
[
[
[
"# INICIANDO CON [SELENIUM](https://selenium-python.readthedocs.io/getting-started.html)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Selenium es una <b>herramientas de testeo para el desarrollo de páginas web</b>. La cual es muy útil para estos fines ya que permite:\n- Automatización web.\n- Selección de campos mediante nombres ID, XPATH, etc.\n- Entre otros",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Selenium trabaja con diversos navegadores, tambien conocidos como navegadores sin cabecera como <a href=\"https://chromedriver.chromium.org/\">google chrome</a> y <a href=\"https://github.com/mozilla/geckodriver\">firefox.</a>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"El uso de selenium es muy simple y puede servir como un buen punto de partida para el desarrollo de extractores web.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Ejemplo Extración con selenium",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from selenium import webdriver",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# inicializando webdriver y página web\ndriver = webdriver.Chrome(\"./drivers/chromedriver.exe\")\nurl=\"https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anexo:Pa%C3%ADses\"\ndriver.get(url)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Selenium posee un conjunto de elemtos para la realización de extracción de la data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sel_table = driver.find_element_by_xpath('//table')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tr = sel_table.find_element_by_css_selector('thead > tr')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for row in driver.find_elements_by_css_selector(\"tr\"):\n cell = row.find_elements_by_tag_name(\"td\")[1]\n print(cell.text)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Al finalizar cerramos el navegador\ndriver.quit()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# <a href=https://github.com/tryolabs/requestium >REQUESTIUM</a> : Requests + Selenium + lxml",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Requestium es una <b>librería de Python que combina el poder de Requests, Selenium y Parsel</b> en una única herramienta integrada para automatizar acciones web.\nLa librería fue creada para escribir scripts de automatización web que se escriben utilizando principalmente Solicitudes, pero que pueden cambiar sin problemas a Selenium para las partes pesadas de JavaScript del sitio web, mientras se mantiene la sesión.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### USO DE REQUESTIUM",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#importando la librería\nfrom requestium import Session, Keys",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# iniciando \ns = Session(webdriver_path='./drivers/chromedriver.exe',\n browser='chrome',#navegador\n default_timeout=15 # tiempo de espera\n #webdriver_options={'arguments': ['headless']} #-> sirve para manejar el navegador en modo silencioso\n )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#página a navegar\nurl='https://github.com/tryolabs/requestium'\ns.driver.get(url)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#cerrar el navegador\ns.driver.quit()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a326c22d622a7abe1149a9e822434d1b48d867a
| 9,836 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
02_Compile_Exploited_CVEs.ipynb
|
NadimKawwa/CybersecurityThreatIdentification
|
e088dbb861342676337b4c9d385e6abfb6463291
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2021-01-15T10:28:54.000Z
|
2021-11-09T17:55:45.000Z
|
02_Compile_Exploited_CVEs.ipynb
|
NadimKawwa/CybersecurityThreatIdentification
|
e088dbb861342676337b4c9d385e6abfb6463291
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
02_Compile_Exploited_CVEs.ipynb
|
NadimKawwa/CybersecurityThreatIdentification
|
e088dbb861342676337b4c9d385e6abfb6463291
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2021-02-05T17:35:48.000Z
|
2021-04-23T18:56:21.000Z
| 24.226601 | 101 | 0.468381 |
[
[
[
"import os\nimport glob\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nfrom tqdm import tqdm\nimport pickle\nfrom copy import copy",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sources_with_data_text = os.path.join('data', 'sources_with_data.txt')\nwith open (sources_with_data_text, mode='r') as f:\n lines = f.readlines()\n \n#check we closed the file\nassert f.closed\n\n\n#strip the spaces at the end\nlines = [l.strip() for l in lines]\n#keep only CVEs and drop the rest\nlines = [l for l in lines if 'CVE' in l]\n\nunique_cve = (set(lines))\n\nprint(\"Found {} unique CVEs in {}\".format(len(unique_cve), sources_with_data_text))",
"Found 152 unique CVEs in data/sources_with_data.txt\n"
],
[
"def load_obj(path ):\n with open(path, 'rb') as f:\n return pickle.load(f)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#create list of dicts\nbroadcom_arr=[]\nfor file in tqdm(glob.glob('broadcom_dicts/*.pkl')):\n obj = load_obj(file)\n #if array is not empty\n if obj['CVE']:\n broadcom_arr.extend(obj['CVE'])\n \n\nbroadcom_cve = (set(broadcom_arr))\n\nprint(\"Found {} unique CVEs in {}\".format(len(broadcom_cve), 'broadcom dicts'))",
"100%|██████████| 6609/6609 [00:00<00:00, 13552.40it/s]"
],
[
"cve_in_wild = copy(broadcom_cve)\ncve_in_wild.update(unique_cve)\n#cve_in_wild = list(cve_in_wild)\nprint(\"Found {} unique CVEs overll\".format(len(cve_in_wild)))",
"Found 1479 unique CVEs overll\n"
],
[
"#fix some inconsistencies in data collection\n#manual fixes\ncve_in_wild = [cve.replace('1)', '') for cve in cve_in_wild]\ncve_in_wild = [cve.replace('service', '') for cve in cve_in_wild]\ncve_in_wild = [cve.replace('3)', '') for cve in cve_in_wild]\ncve_in_wild = [cve.replace('_3', '') for cve in cve_in_wild]\ncve_in_wild = [cve for cve in cve_in_wild if len(cve)>=11]\ncve_in_wild = [cve.replace('(', '') for cve in cve_in_wild]\ncve_in_wild = [cve.replace(')', '') for cve in cve_in_wild]\n\n\n## more manual fixes to corrupted data\ncve_in_wild = [cve.replace('CVE2019-7278', 'CVE-2019-7278') for cve in cve_in_wild]\ncve_in_wild = [cve.replace('2CVE-2006-3643', 'CVE-2006-3643') for cve in cve_in_wild]\ncve_in_wild = [cve.replace('CVE2019-7279', 'CVE-2019-7279') for cve in cve_in_wild]\ncve_in_wild = [cve.replace('CVE-2018_16858', 'CVE-2018-16858') for cve in cve_in_wild]\ncve_in_wild = [cve.replace('CVE 2014-6278', 'CVE-2014-6278') for cve in cve_in_wild]\ncve_in_wild = [cve.replace('CVE-209-18935', 'CVE-2019-18935') for cve in cve_in_wild]\ncve_in_wild = [cve.replace('CVE_2009-3729', 'CVE-2009-3729') for cve in cve_in_wild]\ncve_in_wild = [cve.replace('CVE-20190-11539', 'CVE-2019-11539') for cve in cve_in_wild]\ncve_in_wild = [cve.replace('CVE-2190-11539', 'CVE-2019-11539') for cve in cve_in_wild]\n\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dates = set([x.split('-')[1] for x in cve_in_wild])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for x in cve_in_wild:\n if '2190' in x:\n print(x)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dates",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(\"First exploit was recorded in {}\".format(min(dates)))",
"First exploit was recorded in 1999\n"
],
[
"print(\"Last exploit was recorded in {}\".format(max(dates)))",
"Last exploit was recorded in 2020\n"
],
[
"target_cve_dict = {}\ndf_nvd = pd.read_csv(os.path.join('data', 'nvdcve_combined.csv'))\nfor cve in df_nvd['ID']:\n if cve in cve_in_wild:\n target_cve_dict[cve] = 1\n else:\n target_cve_dict[cve] = 0\n \ndf_target = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(target_cve_dict, orient='index', columns=['in_the_wild'])\ndf_target['ID'] = df_target.index\ndf_target = df_target.reset_index(drop=True)\n\n#rearrange\ndf_target = df_target[['ID', 'in_the_wild']]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_target.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_target['in_the_wild'].mean()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dates = []",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a327e614e5dd79239816a4c53706d8bda36e383
| 20,176 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Cap04/.ipynb_checkpoints/03_PCA-checkpoint.ipynb
|
arianerfrancisco/Python-Ciencia-de-Dados
|
4083eebb5e1e610c04025564af4114154f865cdd
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2022-03-25T00:18:40.000Z
|
2022-03-25T00:18:40.000Z
|
LinkedIn/Cap04/03_PCA.ipynb
|
ThiagoKS-7/Python_para_Data_Science
|
9b6bb8ce3ce089cf17896726099974081a7efade
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
LinkedIn/Cap04/03_PCA.ipynb
|
ThiagoKS-7/Python_para_Data_Science
|
9b6bb8ce3ce089cf17896726099974081a7efade
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 72.837545 | 13,750 | 0.787173 |
[
[
[
"___\n# Capítulo 4 - Redução de Dimensionalidade\n\n## Seção 3 - Análise de componentes principais (PCA)\n___",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport seaborn as sns \n\nfrom matplotlib import rcParams\n\nfrom sklearn import datasets\nfrom sklearn.decomposition import PCA\n\n\n%matplotlib inline\nrcParams['figure.figsize'] = 5, 4\nsns.set_style('whitegrid')\n\niris = datasets.load_iris()\nX = iris.data\nnomes_das_variaveis = iris.feature_names\nX[0:5,]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### PCA no conjunto de dados iris\n#### Razão da Variância\n\nPara investigar quantos % dos nossos dados originais estão compactados em cada componente",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pca = PCA()\niris_pca = pca.fit_transform(X)\n\npca.explained_variance_ratio_",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Variância Cumulativa",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pca.explained_variance_ratio_.sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Componentes Principais",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"os dois primeiros componentes tem > 97.7% dos dados ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"comps = pd.DataFrame(pca.components_, columns=nomes_das_variaveis)\ncomps",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Heatmap",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sns.heatmap(comps)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a328da0499fc535a4ecc7941f2e17d91faace02
| 54,313 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
in_progress/Tutorial-GiRaFFE_NRPy_Main_Driver.ipynb
|
goncalo-andrade/nrpytutorial
|
4fbcb51c936864b442daefd176bd6a5277c00116
|
[
"BSD-2-Clause"
] | 1 |
2020-06-09T16:16:21.000Z
|
2020-06-09T16:16:21.000Z
|
in_progress/Tutorial-GiRaFFE_NRPy_Main_Driver.ipynb
|
goncalo-andrade/nrpytutorial
|
4fbcb51c936864b442daefd176bd6a5277c00116
|
[
"BSD-2-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
in_progress/Tutorial-GiRaFFE_NRPy_Main_Driver.ipynb
|
goncalo-andrade/nrpytutorial
|
4fbcb51c936864b442daefd176bd6a5277c00116
|
[
"BSD-2-Clause"
] | null | null | null | 54.751008 | 696 | 0.6288 |
[
[
[
"<script async src=\"https://www.googletagmanager.com/gtag/js?id=UA-59152712-8\"></script>\n<script>\n window.dataLayer = window.dataLayer || [];\n function gtag(){dataLayer.push(arguments);}\n gtag('js', new Date());\n\n gtag('config', 'UA-59152712-8');\n</script>\n\n# `GiRaFFE_NRPy`: Main Driver\n\n## Author: Patrick Nelson\n\n<a id='intro'></a>\n\n**Notebook Status:** <font color=Red><b> Validation in progress </b></font>\n\n**Validation Notes:** This code assembles the various parts needed for GRFFE evolution in order.\n\n### NRPy+ Source Code for this module:\n* [GiRaFFE_NRPy/GiRaFFE_NRPy_Main_Driver.py](../../edit/in_progress/GiRaFFE_NRPy/GiRaFFE_NRPy_Main_Driver.py)\n\n### Other critical files (in alphabetical order): \n* [GiRaFFE_NRPy/Afield_flux.py](../../edit/in_progress/GiRaFFE_NRPy/Afield_flux.py) [\\[**tutorial**\\]](Tutorial-GiRaFFE_NRPy-Afield_flux.ipynb) Generates the expressions to find the flux term of the induction equation.\n* [GiRaFFE_NRPy/GiRaFFE_NRPy_A2B.py](../../edit/in_progress/GiRaFFE_NRPy/GiRaFFE_NRPy_A2B.py) [\\[**tutorial**\\]](Tutorial-GiRaFFE_NRPy-A2B.ipynb) Generates the driver to compute the magnetic field from the vector potential/\n* [GiRaFFE_NRPy/GiRaFFE_NRPy_BCs.py](../../edit/in_progress/GiRaFFE_NRPy/GiRaFFE_NRPy_BCs.py) [\\[**tutorial**\\]](Tutorial-GiRaFFE_NRPy-BCs.ipynb) Generates the code to apply boundary conditions to the vector potential, scalar potential, and three-velocity.\n* [GiRaFFE_NRPy/GiRaFFE_NRPy_C2P_P2C.py](../../edit/in_progress/GiRaFFE_NRPy/GiRaFFE_NRPy_C2P_P2C.py) [\\[**tutorial**\\]](Tutorial-GiRaFFE_NRPy-C2P_P2C.ipynb) Generates the conservative-to-primitive and primitive-to-conservative solvers.\n* [GiRaFFE_NRPy/GiRaFFE_NRPy_Metric_Face_Values.py](../../edit/in_progress/GiRaFFE_NRPy/GiRaFFE_NRPy_Metric_Face_Values.py) [\\[**tutorial**\\]](Tutorial-GiRaFFE_NRPy-Metric_Face_Values.ipynb) Generates code to interpolate metric gridfunctions to cell faces.\n* [GiRaFFE_NRPy/GiRaFFE_NRPy_PPM.py](../../edit/in_progress/GiRaFFE_NRPy/GiRaFFE_NRPy_PPM.py) [\\[**tutorial**\\]](Tutorial-GiRaFFE_NRPy-PPM.ipynb) Genearates code to reconstruct primitive variables on cell faces.\n* [GiRaFFE_NRPy/GiRaFFE_NRPy_Source_Terms.py](../../edit/in_progress/GiRaFFE_NRPy/GiRaFFE_NRPy_Source_Terms.py) [\\[**tutorial**\\]](Tutorial-GiRaFFE_NRPy-Source_Terms.ipynb) Genearates code to compute the $\\tilde{S}_i$ source term.\n* [GiRaFFE_NRPy/Stilde_flux.py](../../edit/in_progress/GiRaFFE_NRPy/Stilde_flux.py) [\\[**tutorial**\\]](Tutorial-GiRaFFE_NRPy-Stilde_flux.ipynb) Generates the expressions to find the flux term of the Poynting flux evolution equation.\n* [../GRFFE/equations.py](../../edit/GRFFE/equations.py) [\\[**tutorial**\\]](../Tutorial-GRFFE_Equations-Cartesian.ipynb) Generates code necessary to compute the source terms.\n* [../GRHD/equations.py](../../edit/GRHD/equations.py) [\\[**tutorial**\\]](../Tutorial-GRHD_Equations-Cartesian.ipynb) Generates code necessary to compute the source terms.\n\n## Introduction: \nHaving written all the various algorithms that will go into evolving the GRFFE equations forward through time, we are ready to write a start-to-finish module to do so. However, to help keep things more organized, we will first create a dedicated module to assemble the various functions we need to run, in order, to perform the evolution. This will reduce the length of the standalone C code, improving that notebook's readability.\n\n<a id='prelim'></a>\n# Table of Contents\n$$\\label{prelim}$$\n\nDuring a given RK substep, we will perform the following steps in this order, based on the order used in the original `GiRaFFE`:\n0. [Step 0](#prelim): Preliminaries\n1. [Step 1](#rhs): Calculate the right-hand sides\n 1. [Step 1.a](#parenthetical): Calculate the portion of the gauge terms for $A_k$, $(\\alpha \\Phi - \\beta^j A_j)$ and $\\Phi$, $(\\alpha\\sqrt{\\gamma}A^j - \\beta^j [\\sqrt{\\gamma} \\Phi])$ *inside* the parentheses to be finite-differenced.\n * **GRFFE/equations.py**, **GRHD/equations.py**\n 1. [Step 1.b](#source): Calculate the source terms of $\\partial_t A_i$, $\\partial_t \\tilde{S}_i$, and $\\partial_t [\\sqrt{\\gamma} \\Phi]$ right-hand sides\n * **GRFFE/equations.py**, **GRHD/equations.py**, **GiRaFFE_NRPy/GiRaFFE_NRPy_Source_Terms**\n 1. [Step 1.c](#flux): Calculate the Flux terms\n * In each direction: \n * Interpolate the metric gridfunctions to cell faces\n * **GiRaFFE_NRPy/GiRaFFE_NRPy_Metric_Face_Values.py**\n * Reconstruct primitives $\\bar{v}^i$ and $B^i$ on cell faces with the piecewise-parabolic method\n * **GiRaFFE_NRPy/GiRaFFE_NRPy_PPM.py**\n * Compute the fluxes of $\\tilde{S}_i$ and $A_i$ and add the appropriate combinations to the evolution equation right-hand sides\n * **GiRaFFE_NRPy/Stilde_flux.py**, **GiRaFFE_NRPy/Afield_flux.py**\n1. [Step 2](#poststep): Recover the primitive variables and apply boundary conditions (post-step)\n 1. [Step 2.a](#potential_bc): Apply boundary conditions to $A_i$ and $\\sqrt{\\gamma} \\Phi$\n * **GiRaFFE_NRPy/GiRaFFE_NRPy_BCs.py**\n 1. [Step 2.b](#a2b): Compute $B^i$ from $A_i$\n * **GiRaFFE_NRPy/GiRaFFE_NRPy_A2B.py**\n 1. [Step 2.c](#c2p): Run the Conservative-to-Primitive solver\n * This applies fixes to $\\tilde{S}_i$, then computes $\\bar{v}^i$. A current sheet prescription is then applied to $\\bar{v}^i$, and $\\tilde{S}_i$ is recomputed to be consistent.\n * **GiRaFFE_NRPy/GiRaFFE_NRPy_C2P_P2C.py**\n 1. [Step 2.d](#velocity_bc): Apply outflow boundary conditions to $\\bar{v}^i$\n * **GiRaFFE_NRPy/GiRaFFE_NRPy_BCs.py**\n1. [Step 3](#write_out): Write out the C code function\n1. [Step 3](#code_validation): Self-Validation against `GiRaFFE_NRPy_Main_Drive.py`\n1. [Step 5](#latex_pdf_output): Output this notebook to $\\LaTeX$-formatted PDF file\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a id='prelim'></a>\n\n# Step 0: Preliminaries \\[Back to [top](#toc)\\]\n$$\\label{prelim}$$\n\nWe begin by importing the NRPy+ core functionality. We also import the Levi-Civita symbol, the GRHD module, and the GRFFE module.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Step 0: Add NRPy's directory to the path\n# https://stackoverflow.com/questions/16780014/import-file-from-parent-directory\nimport os,sys\nnrpy_dir_path = os.path.join(\"..\")\nif nrpy_dir_path not in sys.path:\n sys.path.append(nrpy_dir_path)\n\nfrom outputC import * # NRPy+: Core C code output module\nimport finite_difference as fin # NRPy+: Finite difference C code generation module\nimport NRPy_param_funcs as par # NRPy+: Parameter interface\nimport grid as gri # NRPy+: Functions having to do with numerical grids\nimport loop as lp # NRPy+: Generate C code loops\nimport indexedexp as ixp # NRPy+: Symbolic indexed expression (e.g., tensors, vectors, etc.) support\nimport reference_metric as rfm # NRPy+: Reference metric support\nimport cmdline_helper as cmd # NRPy+: Multi-platform Python command-line interface\n\nthismodule = \"GiRaFFE_NRPy_Main_Driver\"\n\npar.set_parval_from_str(\"grid::GridFuncMemAccess\",\"ETK\")\npar.set_parval_from_str(\"finite_difference::FD_CENTDERIVS_ORDER\",2)\n\nout_dir = os.path.join(\"GiRaFFE_standalone_Ccodes\")\ncmd.mkdir(out_dir)\n\nCoordSystem = \"Cartesian\"\n\npar.set_parval_from_str(\"reference_metric::CoordSystem\",CoordSystem)\nrfm.reference_metric() # Create ReU, ReDD needed for rescaling B-L initial data, generating BSSN RHSs, etc.\n\n# Default Kreiss-Oliger dissipation strength\ndefault_KO_strength = 0.1\ndiss_strength = par.Cparameters(\"REAL\", thismodule, \"diss_strength\", default_KO_strength)\n\noutCparams = \"outCverbose=False,CSE_sorting=none\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id='rhs'></a>\n\n# Step 1: Calculate the right-hand sides \\[Back to [top](#toc)\\]\n$$\\label{rhs}$$\n\n<a id='parenthetical'></a>\n\nIn the method of lines using Runge-Kutta methods, each timestep involves several \"RK substeps\" during which we will run the same set of function calls. These can be divided into two groups: one in which the RHSs themselves are calculated, and a second in which boundary conditions are applied and auxiliary variables updated (the post-step). Here, we focus on that first group.\n\n## Step 1.a: Calculate the portion of the gauge terms for $A_k$, $(\\alpha \\Phi - \\beta^j A_j)$ and $\\Phi$, $(\\alpha\\sqrt{\\gamma}A^j - \\beta^j [\\sqrt{\\gamma} \\Phi])$ *inside* the parentheses to be finite-differenced. \\[Back to [top](#toc)\\]\n$$\\label{parenthetical}$$\n\nThe source terms of our evolution equations consist of two terms that are derivatives of some parenthetical quantity. We can save some effort and execution time (at the cost of memory needed) by computing these parentheticals, storing them, and then finite-differencing that stored variable. For more information, see the notebook for the [implementation](Tutorial-GiRaFFE_NRPy-Source_Terms.ipynb) and the [validation](Tutorial-Start_to_Finish_UnitTest-GiRaFFE_NRPy-Source_Terms.ipynb), as well as [Tutorial-GRFFE_Equations-Cartesian](../Tutorial-GRFFE_Equations-Cartesian.ipynb) and [Tutorial-GRHD_Equations-Cartesian](../Tutorial-GRHD_Equations-Cartesian.ipynb) for the terms themselves. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import GRHD.equations as GRHD # NRPy+: Generate general relativistic hydrodynamics equations\nimport GRFFE.equations as GRFFE # NRPy+: Generate general relativisitic force-free electrodynamics equations\n\ngammaDD = ixp.register_gridfunctions_for_single_rank2(\"AUXEVOL\",\"gammaDD\",\"sym01\",DIM=3)\nbetaU = ixp.register_gridfunctions_for_single_rank1(\"AUXEVOL\",\"betaU\",DIM=3)\nalpha = gri.register_gridfunctions(\"AUXEVOL\",\"alpha\")\nAD = ixp.register_gridfunctions_for_single_rank1(\"EVOL\",\"AD\")\nBU = ixp.register_gridfunctions_for_single_rank1(\"AUXEVOL\",\"BU\")\nValenciavU = ixp.register_gridfunctions_for_single_rank1(\"AUXEVOL\",\"ValenciavU\")\npsi6Phi = gri.register_gridfunctions(\"EVOL\",\"psi6Phi\")\nStildeD = ixp.register_gridfunctions_for_single_rank1(\"EVOL\",\"StildeD\")\n\nPhievolParenU = ixp.register_gridfunctions_for_single_rank1(\"AUXEVOL\",\"PhievolParenU\",DIM=3)\nAevolParen = gri.register_gridfunctions(\"AUXEVOL\",\"AevolParen\")\n\nGRHD.compute_sqrtgammaDET(gammaDD)\nGRFFE.compute_AD_source_term_parenthetical_for_FD(GRHD.sqrtgammaDET,betaU,alpha,psi6Phi,AD)\nGRFFE.compute_psi6Phi_rhs_parenthetical(gammaDD,GRHD.sqrtgammaDET,betaU,alpha,AD,psi6Phi)\n\nparens_to_print = [\\\n lhrh(lhs=gri.gfaccess(\"auxevol_gfs\",\"AevolParen\"),rhs=GRFFE.AevolParen),\\\n lhrh(lhs=gri.gfaccess(\"auxevol_gfs\",\"PhievolParenU0\"),rhs=GRFFE.PhievolParenU[0]),\\\n lhrh(lhs=gri.gfaccess(\"auxevol_gfs\",\"PhievolParenU1\"),rhs=GRFFE.PhievolParenU[1]),\\\n lhrh(lhs=gri.gfaccess(\"auxevol_gfs\",\"PhievolParenU2\"),rhs=GRFFE.PhievolParenU[2]),\\\n ]\n\nsubdir = \"RHSs\"\ncmd.mkdir(os.path.join(out_dir, subdir))\ndesc = \"Calculate quantities to be finite-differenced for the GRFFE RHSs\"\nname = \"calculate_parentheticals_for_RHSs\"\noutCfunction(\n outfile = os.path.join(out_dir,subdir,name+\".h\"), desc=desc, name=name,\n params =\"const paramstruct *restrict params,const REAL *restrict in_gfs,REAL *restrict auxevol_gfs\",\n body = fin.FD_outputC(\"returnstring\",parens_to_print,params=outCparams).replace(\"IDX4\",\"IDX4S\"),\n loopopts =\"AllPoints\",\n rel_path_for_Cparams=os.path.join(\"../\"))",
"Output C function calculate_parentheticals_for_RHSs() to file GiRaFFE_standalone_Ccodes\\RHSs\\calculate_parentheticals_for_RHSs.h\n"
]
],
[
[
"<a id='source'></a>\n\n## Step 1.b: Calculate the source terms of $\\partial_t A_i$, $\\partial_t \\tilde{S}_i$, and $\\partial_t [\\sqrt{\\gamma} \\Phi]$ right-hand sides \\[Back to [top](#toc)\\]\n$$\\label{source}$$\n\nWith the parentheticals stored in memory from the previous step, we can now now calculate the terms on the RHS of $A_i$ and $[\\sqrt{\\gamma} \\Phi]$ that involve the derivatives of those terms. We also compute the other term in the RHS of $[\\sqrt{\\gamma} \\Phi]$, which is a straightforward damping term. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"xi_damping = par.Cparameters(\"REAL\",thismodule,\"xi_damping\",0.1)\nGRFFE.compute_psi6Phi_rhs_damping_term(alpha,psi6Phi,xi_damping)\n\nAevolParen_dD = ixp.declarerank1(\"AevolParen_dD\",DIM=3)\nPhievolParenU_dD = ixp.declarerank2(\"PhievolParenU_dD\",\"nosym\",DIM=3)\n\nA_rhsD = ixp.zerorank1()\npsi6Phi_rhs = GRFFE.psi6Phi_damping\n\nfor i in range(3):\n A_rhsD[i] += -AevolParen_dD[i]\n psi6Phi_rhs += -PhievolParenU_dD[i][i]\n\n# Add Kreiss-Oliger dissipation to the GRFFE RHSs:\n# psi6Phi_dKOD = ixp.declarerank1(\"psi6Phi_dKOD\")\n# AD_dKOD = ixp.declarerank2(\"AD_dKOD\",\"nosym\")\n# for i in range(3):\n# psi6Phi_rhs += diss_strength*psi6Phi_dKOD[i]*rfm.ReU[i] # ReU[i] = 1/scalefactor_orthog_funcform[i]\n# for j in range(3):\n# A_rhsD[j] += diss_strength*AD_dKOD[j][i]*rfm.ReU[i] # ReU[i] = 1/scalefactor_orthog_funcform[i]\n\nRHSs_to_print = [\\\n lhrh(lhs=gri.gfaccess(\"rhs_gfs\",\"AD0\"),rhs=A_rhsD[0]),\\\n lhrh(lhs=gri.gfaccess(\"rhs_gfs\",\"AD1\"),rhs=A_rhsD[1]),\\\n lhrh(lhs=gri.gfaccess(\"rhs_gfs\",\"AD2\"),rhs=A_rhsD[2]),\\\n lhrh(lhs=gri.gfaccess(\"rhs_gfs\",\"psi6Phi\"),rhs=psi6Phi_rhs),\\\n ]\n\ndesc = \"Calculate AD gauge term and psi6Phi RHSs\"\nname = \"calculate_AD_gauge_psi6Phi_RHSs\"\nsource_Ccode = outCfunction(\n outfile = \"returnstring\", desc=desc, name=name,\n params =\"const paramstruct *params,const REAL *in_gfs,const REAL *auxevol_gfs,REAL *rhs_gfs\",\n body = fin.FD_outputC(\"returnstring\",RHSs_to_print,params=outCparams).replace(\"IDX4\",\"IDX4S\"),\n loopopts =\"InteriorPoints\",\n rel_path_for_Cparams=os.path.join(\"../\")).replace(\"= NGHOSTS\",\"= NGHOSTS_A2B\").replace(\"NGHOSTS+Nxx0\",\"Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS0-NGHOSTS_A2B\").replace(\"NGHOSTS+Nxx1\",\"Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS1-NGHOSTS_A2B\").replace(\"NGHOSTS+Nxx2\",\"Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS2-NGHOSTS_A2B\")\n# Note the above .replace() functions. These serve to expand the loop range into the ghostzones, since\n# the second-order FD needs fewer than some other algorithms we use do.\nwith open(os.path.join(out_dir,subdir,name+\".h\"),\"w\") as file:\n file.write(source_Ccode)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We also need to compute the source term of the $\\tilde{S}_i$ evolution equation. This term involves derivatives of the four metric, so we can save some effort here by taking advantage of the interpolations done of the metric gridfunctions to the cell faces, which will allow us to take a finite-difference derivative with the accuracy of a higher order and the computational cost of a lower order. However, it will require some more complicated coding, detailed in [Tutorial-GiRaFFE_NRPy-Source_Terms](Tutorial-GiRaFFE_NRPy-Source_Terms.ipynb) ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import GiRaFFE_NRPy.GiRaFFE_NRPy_Source_Terms as source\n# Declare this symbol:\nsqrt4pi = par.Cparameters(\"REAL\",thismodule,\"sqrt4pi\",\"sqrt(4.0*M_PI)\")\n\nsource.write_out_functions_for_StildeD_source_term(os.path.join(out_dir,subdir),outCparams,gammaDD,betaU,alpha,\n ValenciavU,BU,sqrt4pi)",
"Output C function calculate_StildeD0_source_term() to file GiRaFFE_standalone_Ccodes\\RHSs\\calculate_StildeD0_source_term.h\nOutput C function calculate_StildeD1_source_term() to file GiRaFFE_standalone_Ccodes\\RHSs\\calculate_StildeD1_source_term.h\nOutput C function calculate_StildeD2_source_term() to file GiRaFFE_standalone_Ccodes\\RHSs\\calculate_StildeD2_source_term.h\n"
]
],
[
[
"<a id='flux'></a>\n\n## Step 1.c: Calculate the Flux terms \\[Back to [top](#toc)\\]\n$$\\label{flux}$$\n\nNow, we will compute the flux terms of $\\partial_t A_i$ and $\\partial_t \\tilde{S}_i$. To do so, we will first need to interpolate the metric gridfunctions to cell faces and to reconstruct the primitives on the cell faces using the code detailed in [Tutorial-GiRaFFE_NRPy-Metric_Face_Values](Tutorial-GiRaFFE_NRPy-Metric_Face_Values.ipynb) and in [Tutorial-GiRaFFE_NRPy-PPM](Tutorial-GiRaFFE_NRPy-PPM.ipynb).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"subdir = \"FCVAL\"\ncmd.mkdir(os.path.join(out_dir, subdir))\nimport GiRaFFE_NRPy.GiRaFFE_NRPy_Metric_Face_Values as FCVAL\nFCVAL.GiRaFFE_NRPy_FCVAL(os.path.join(out_dir,subdir))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"subdir = \"PPM\"\ncmd.mkdir(os.path.join(out_dir, subdir))\nimport GiRaFFE_NRPy.GiRaFFE_NRPy_PPM as PPM\nPPM.GiRaFFE_NRPy_PPM(os.path.join(out_dir,subdir))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Here, we will write the function to compute the electric field contribution to the induction equation RHS. This is coded with documentation in [Tutorial-GiRaFFE_NRPy-Afield_flux](Tutorial-GiRaFFE_NRPy-Afield_flux.ipynb). The electric field in the $i^{\\rm th}$ direction, it will contribute to the $j^{\\rm th}$ and $k^{\\rm th}$ component of the electric field. That is, in Cartesian coordinates, the component $x$ of the electric field will be the average of the values computed on the cell faces in the $\\pm y$- and $\\pm z$-directions, and so forth for the other components. This ultimately results in the six functions we create below.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import GiRaFFE_NRPy.Afield_flux as Af\n\n# We will pass values of the gridfunction on the cell faces into the function. This requires us\n# to declare them as C parameters in NRPy+. We will denote this with the _face infix/suffix.\nalpha_face = gri.register_gridfunctions(\"AUXEVOL\",\"alpha_face\")\ngamma_faceDD = ixp.register_gridfunctions_for_single_rank2(\"AUXEVOL\",\"gamma_faceDD\",\"sym01\")\nbeta_faceU = ixp.register_gridfunctions_for_single_rank1(\"AUXEVOL\",\"beta_faceU\")\n\n# We'll need some more gridfunctions, now, to represent the reconstructions of BU and ValenciavU\n# on the right and left faces\nValenciav_rU = ixp.register_gridfunctions_for_single_rank1(\"AUXEVOL\",\"Valenciav_rU\",DIM=3)\nB_rU = ixp.register_gridfunctions_for_single_rank1(\"AUXEVOL\",\"B_rU\",DIM=3)\nValenciav_lU = ixp.register_gridfunctions_for_single_rank1(\"AUXEVOL\",\"Valenciav_lU\",DIM=3)\nB_lU = ixp.register_gridfunctions_for_single_rank1(\"AUXEVOL\",\"B_lU\",DIM=3)\n\nsubdir = \"RHSs\"\nAf.generate_Afield_flux_function_files(out_dir,subdir,alpha_face,gamma_faceDD,beta_faceU,\\\n Valenciav_rU,B_rU,Valenciav_lU,B_lU,True)",
"Output C function calculate_E_field_D0_right() to file GiRaFFE_standalone_Ccodes\\RHSs\\calculate_E_field_D0_right.h\nOutput C function calculate_E_field_D0_left() to file GiRaFFE_standalone_Ccodes\\RHSs\\calculate_E_field_D0_left.h\nOutput C function calculate_E_field_D1_right() to file GiRaFFE_standalone_Ccodes\\RHSs\\calculate_E_field_D1_right.h\nOutput C function calculate_E_field_D1_left() to file GiRaFFE_standalone_Ccodes\\RHSs\\calculate_E_field_D1_left.h\nOutput C function calculate_E_field_D2_right() to file GiRaFFE_standalone_Ccodes\\RHSs\\calculate_E_field_D2_right.h\nOutput C function calculate_E_field_D2_left() to file GiRaFFE_standalone_Ccodes\\RHSs\\calculate_E_field_D2_left.h\n"
]
],
[
[
"We must do something similar here, albeit a bit simpler. For instance, the $x$ component of $\\partial_t \\tilde{S}_i$ will be a finite difference of the flux throught the faces in the $\\pm x$ direction; for further detail, see [Tutorial-GiRaFFE_NRPy-Stilde_flux](Tutorial-GiRaFFE_NRPy-Stilde_flux.ipynb).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import GiRaFFE_NRPy.Stilde_flux as Sf\nsubdir = \"RHSs\"\nSf.generate_C_code_for_Stilde_flux(os.path.join(out_dir,subdir), True, alpha_face,gamma_faceDD,beta_faceU,\n Valenciav_rU,B_rU,Valenciav_lU,B_lU,sqrt4pi)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id='poststep'></a>\n\n# Step 2: Recover the primitive variables and apply boundary conditions \\[Back to [top](#toc)\\]\n$$\\label{poststep}$$\n\nWith the RHSs computed, we can now recover the primitive variables, which are the Valencia three-velocity $\\bar{v}^i$ and the magnetic field $B^i$. We can also apply boundary conditions to the vector potential and velocity. By doing this at each RK substep, we can help ensure the accuracy of the following substeps. \n\n<a id='potential_bc'></a>\n\n## Step 2.a: Apply boundary conditions to $A_i$ and $\\sqrt{\\gamma} \\Phi$ \\[Back to [top](#toc)\\]\n$$\\label{potential_bc}$$\n\nFirst, we will apply boundary conditions to the vector potential, $A_i$, and the scalar potential $\\sqrt{\\gamma} \\Phi$. The file we generate here contains both functions we need for BCs, as documented in [Tutorial-GiRaFFE_NRPy-BCs](Tutorial-GiRaFFE_NRPy-BCs.ipynb).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"subdir = \"boundary_conditions\"\ncmd.mkdir(os.path.join(out_dir,subdir))\nimport GiRaFFE_NRPy.GiRaFFE_NRPy_BCs as BC\nBC.GiRaFFE_NRPy_BCs(os.path.join(out_dir,subdir))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id='a2b'></a>\n\n## Step 2.b: Compute $B^i$ from $A_i$ \\[Back to [top](#toc)\\]\n$$\\label{a2b}$$\n\nNow, we will calculate the magnetic field as the curl of the vector potential at all points in our domain; this requires care to be taken in the ghost zones, which is detailed in [Tutorial-GiRaFFE_NRPy-A2B](Tutorial-GiRaFFE_NRPy-A2B.ipynb).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"subdir = \"A2B\"\ncmd.mkdir(os.path.join(out_dir,subdir))\nimport GiRaFFE_NRPy.GiRaFFE_NRPy_A2B as A2B\nA2B.GiRaFFE_NRPy_A2B(os.path.join(out_dir,subdir),gammaDD,AD,BU)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id='c2p'></a>\n\n## Step 2.c: Run the Conservative-to-Primitive solver \\[Back to [top](#toc)\\]\n$$\\label{c2p}$$\n\nWith these functions, we apply fixes to the Poynting flux, and use that to update the three-velocity. Then, we apply our current sheet prescription to the velocity, and recompute the Poynting flux to agree with the now-fixed velocity. More detail can be found in [Tutorial-GiRaFFE_NRPy-C2P_P2C](Tutorial-GiRaFFE_NRPy-C2P_P2C.ipynb).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import GiRaFFE_NRPy.GiRaFFE_NRPy_C2P_P2C as C2P_P2C\nC2P_P2C.GiRaFFE_NRPy_C2P(StildeD,BU,gammaDD,betaU,alpha)\n\nvalues_to_print = [\\\n lhrh(lhs=gri.gfaccess(\"in_gfs\",\"StildeD0\"),rhs=C2P_P2C.outStildeD[0]),\\\n lhrh(lhs=gri.gfaccess(\"in_gfs\",\"StildeD1\"),rhs=C2P_P2C.outStildeD[1]),\\\n lhrh(lhs=gri.gfaccess(\"in_gfs\",\"StildeD2\"),rhs=C2P_P2C.outStildeD[2]),\\\n lhrh(lhs=gri.gfaccess(\"auxevol_gfs\",\"ValenciavU0\"),rhs=C2P_P2C.ValenciavU[0]),\\\n lhrh(lhs=gri.gfaccess(\"auxevol_gfs\",\"ValenciavU1\"),rhs=C2P_P2C.ValenciavU[1]),\\\n lhrh(lhs=gri.gfaccess(\"auxevol_gfs\",\"ValenciavU2\"),rhs=C2P_P2C.ValenciavU[2])\\\n ]\n\nsubdir = \"C2P\"\ncmd.mkdir(os.path.join(out_dir,subdir))\ndesc = \"Apply fixes to \\tilde{S}_i and recompute the velocity to match with current sheet prescription.\"\nname = \"GiRaFFE_NRPy_cons_to_prims\"\noutCfunction(\n outfile = os.path.join(out_dir,subdir,name+\".h\"), desc=desc, name=name,\n params =\"const paramstruct *params,REAL *xx[3],REAL *auxevol_gfs,REAL *in_gfs\",\n body = fin.FD_outputC(\"returnstring\",values_to_print,params=outCparams).replace(\"IDX4\",\"IDX4S\"),\n loopopts =\"AllPoints,Read_xxs\",\n rel_path_for_Cparams=os.path.join(\"../\"))",
"Output C function GiRaFFE_NRPy_cons_to_prims() to file GiRaFFE_standalone_Ccodes\\C2P\\GiRaFFE_NRPy_cons_to_prims.h\n"
],
[
"# TINYDOUBLE = par.Cparameters(\"REAL\",thismodule,\"TINYDOUBLE\",1e-100)\n\nC2P_P2C.GiRaFFE_NRPy_P2C(gammaDD,betaU,alpha, ValenciavU,BU, sqrt4pi)\n\nvalues_to_print = [\\\n lhrh(lhs=gri.gfaccess(\"in_gfs\",\"StildeD0\"),rhs=C2P_P2C.StildeD[0]),\\\n lhrh(lhs=gri.gfaccess(\"in_gfs\",\"StildeD1\"),rhs=C2P_P2C.StildeD[1]),\\\n lhrh(lhs=gri.gfaccess(\"in_gfs\",\"StildeD2\"),rhs=C2P_P2C.StildeD[2]),\\\n ]\n\ndesc = \"Recompute StildeD after current sheet fix to Valencia 3-velocity to ensure consistency between conservative & primitive variables.\"\nname = \"GiRaFFE_NRPy_prims_to_cons\"\noutCfunction(\n outfile = os.path.join(out_dir,subdir,name+\".h\"), desc=desc, name=name,\n params =\"const paramstruct *params,REAL *auxevol_gfs,REAL *in_gfs\",\n body = fin.FD_outputC(\"returnstring\",values_to_print,params=outCparams).replace(\"IDX4\",\"IDX4S\"),\n loopopts =\"AllPoints\",\n rel_path_for_Cparams=os.path.join(\"../\"))",
"Output C function GiRaFFE_NRPy_prims_to_cons() to file GiRaFFE_standalone_Ccodes\\C2P\\GiRaFFE_NRPy_prims_to_cons.h\n"
]
],
[
[
"<a id='velocity_bc'></a>\n\n## Step 2.d: Apply outflow boundary conditions to $\\bar{v}^i$ \\[Back to [top](#toc)\\]\n$$\\label{velocity_bc}$$\n\nNow, we can apply outflow boundary conditions to the Valencia three-velocity. This specific type of boundary condition helps avoid numerical error \"flowing\" into our grid. \n\nThis function has already been generated [above](#potential_bc).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a id='write_out'></a>\n\n# Step 3: Write out the C code function \\[Back to [top](#toc)\\]\n$$\\label{write_out}$$\n\nNow, we have generated all the functions we will need for the `GiRaFFE` evolution. So, we will now assemble our evolution driver. This file will first `#include` all of the files we just generated for easy access. Then, we will write a function that calls these functions in the correct order, iterating over the flux directions as necessary. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%writefile $out_dir/GiRaFFE_NRPy_Main_Driver.h\n// Structure to track ghostzones for PPM:\ntypedef struct __gf_and_gz_struct__ {\n REAL *gf;\n int gz_lo[4],gz_hi[4];\n} gf_and_gz_struct;\n// Some additional constants needed for PPM:\nconst int VX=0,VY=1,VZ=2,BX=3,BY=4,BZ=5;\nconst int NUM_RECONSTRUCT_GFS = 6;\n\n// Include ALL functions needed for evolution\n#include \"RHSs/calculate_parentheticals_for_RHSs.h\"\n#include \"RHSs/calculate_AD_gauge_psi6Phi_RHSs.h\"\n#include \"PPM/reconstruct_set_of_prims_PPM_GRFFE_NRPy.c\"\n#include \"FCVAL/interpolate_metric_gfs_to_cell_faces.h\"\n#include \"RHSs/calculate_StildeD0_source_term.h\"\n#include \"RHSs/calculate_StildeD1_source_term.h\"\n#include \"RHSs/calculate_StildeD2_source_term.h\"\n#include \"../calculate_E_field_flat_all_in_one.h\"\n#include \"RHSs/calculate_Stilde_flux_D0.h\"\n#include \"RHSs/calculate_Stilde_flux_D1.h\"\n#include \"RHSs/calculate_Stilde_flux_D2.h\"\n#include \"boundary_conditions/GiRaFFE_boundary_conditions.h\"\n#include \"A2B/driver_AtoB.h\"\n#include \"C2P/GiRaFFE_NRPy_cons_to_prims.h\"\n#include \"C2P/GiRaFFE_NRPy_prims_to_cons.h\"\n\nvoid override_BU_with_old_GiRaFFE(const paramstruct *restrict params,REAL *restrict auxevol_gfs,const int n) {\n#include \"set_Cparameters.h\"\n char filename[100];\n sprintf(filename,\"BU0_override-%08d.bin\",n);\n FILE *out2D = fopen(filename, \"rb\");\n fread(auxevol_gfs+BU0GF*Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS0*Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS1*Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS2,\n sizeof(double),Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS0*Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS1*Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS2,out2D);\n fclose(out2D);\n sprintf(filename,\"BU1_override-%08d.bin\",n);\n out2D = fopen(filename, \"rb\");\n fread(auxevol_gfs+BU1GF*Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS0*Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS1*Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS2,\n sizeof(double),Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS0*Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS1*Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS2,out2D);\n fclose(out2D);\n sprintf(filename,\"BU2_override-%08d.bin\",n);\n out2D = fopen(filename, \"rb\");\n fread(auxevol_gfs+BU2GF*Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS0*Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS1*Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS2,\n sizeof(double),Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS0*Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS1*Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS2,out2D);\n fclose(out2D);\n}\n\nvoid GiRaFFE_NRPy_RHSs(const paramstruct *restrict params,REAL *restrict auxevol_gfs,const REAL *restrict in_gfs,REAL *restrict rhs_gfs) {\n#include \"set_Cparameters.h\"\n // First thing's first: initialize the RHSs to zero!\n#pragma omp parallel for\n for(int ii=0;ii<Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS0*Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS1*Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS2*NUM_EVOL_GFS;ii++) {\n rhs_gfs[ii] = 0.0;\n }\n // Next calculate the easier source terms that don't require flux directions\n // This will also reset the RHSs for each gf at each new timestep.\n calculate_parentheticals_for_RHSs(params,in_gfs,auxevol_gfs);\n calculate_AD_gauge_psi6Phi_RHSs(params,in_gfs,auxevol_gfs,rhs_gfs);\n\n // Now, we set up a bunch of structs of pointers to properly guide the PPM algorithm.\n // They also count the number of ghostzones available.\n gf_and_gz_struct in_prims[NUM_RECONSTRUCT_GFS], out_prims_r[NUM_RECONSTRUCT_GFS], out_prims_l[NUM_RECONSTRUCT_GFS];\n int which_prims_to_reconstruct[NUM_RECONSTRUCT_GFS],num_prims_to_reconstruct;\n const int Nxxp2NG012 = Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS0*Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS1*Nxx_plus_2NGHOSTS2;\n\n REAL *temporary = auxevol_gfs + Nxxp2NG012*AEVOLPARENGF; //We're not using this anymore\n // This sets pointers to the portion of auxevol_gfs containing the relevant gridfunction.\n int ww=0;\n in_prims[ww].gf = auxevol_gfs + Nxxp2NG012*VALENCIAVU0GF;\n out_prims_r[ww].gf = auxevol_gfs + Nxxp2NG012*VALENCIAV_RU0GF;\n out_prims_l[ww].gf = auxevol_gfs + Nxxp2NG012*VALENCIAV_LU0GF;\n ww++;\n in_prims[ww].gf = auxevol_gfs + Nxxp2NG012*VALENCIAVU1GF;\n out_prims_r[ww].gf = auxevol_gfs + Nxxp2NG012*VALENCIAV_RU1GF;\n out_prims_l[ww].gf = auxevol_gfs + Nxxp2NG012*VALENCIAV_LU1GF;\n ww++;\n in_prims[ww].gf = auxevol_gfs + Nxxp2NG012*VALENCIAVU2GF;\n out_prims_r[ww].gf = auxevol_gfs + Nxxp2NG012*VALENCIAV_RU2GF;\n out_prims_l[ww].gf = auxevol_gfs + Nxxp2NG012*VALENCIAV_LU2GF;\n ww++;\n in_prims[ww].gf = auxevol_gfs + Nxxp2NG012*BU0GF;\n out_prims_r[ww].gf = auxevol_gfs + Nxxp2NG012*B_RU0GF;\n out_prims_l[ww].gf = auxevol_gfs + Nxxp2NG012*B_LU0GF;\n ww++;\n in_prims[ww].gf = auxevol_gfs + Nxxp2NG012*BU1GF;\n out_prims_r[ww].gf = auxevol_gfs + Nxxp2NG012*B_RU1GF;\n out_prims_l[ww].gf = auxevol_gfs + Nxxp2NG012*B_LU1GF;\n ww++;\n in_prims[ww].gf = auxevol_gfs + Nxxp2NG012*BU2GF;\n out_prims_r[ww].gf = auxevol_gfs + Nxxp2NG012*B_RU2GF;\n out_prims_l[ww].gf = auxevol_gfs + Nxxp2NG012*B_LU2GF;\n ww++;\n\n // Prims are defined AT ALL GRIDPOINTS, so we set the # of ghostzones to zero:\n for(int i=0;i<NUM_RECONSTRUCT_GFS;i++) for(int j=1;j<=3;j++) { in_prims[i].gz_lo[j]=0; in_prims[i].gz_hi[j]=0; }\n // Left/right variables are not yet defined, yet we set the # of gz's to zero by default:\n for(int i=0;i<NUM_RECONSTRUCT_GFS;i++) for(int j=1;j<=3;j++) { out_prims_r[i].gz_lo[j]=0; out_prims_r[i].gz_hi[j]=0; }\n for(int i=0;i<NUM_RECONSTRUCT_GFS;i++) for(int j=1;j<=3;j++) { out_prims_l[i].gz_lo[j]=0; out_prims_l[i].gz_hi[j]=0; }\n\n ww=0;\n which_prims_to_reconstruct[ww]=VX; ww++;\n which_prims_to_reconstruct[ww]=VY; ww++;\n which_prims_to_reconstruct[ww]=VZ; ww++;\n which_prims_to_reconstruct[ww]=BX; ww++;\n which_prims_to_reconstruct[ww]=BY; ww++;\n which_prims_to_reconstruct[ww]=BZ; ww++;\n num_prims_to_reconstruct=ww;\n\n // In each direction, perform the PPM reconstruction procedure.\n // Then, add the fluxes to the RHS as appropriate.\n for(int flux_dirn=0;flux_dirn<3;flux_dirn++) {\n // In each direction, interpolate the metric gfs (gamma,beta,alpha) to cell faces.\n interpolate_metric_gfs_to_cell_faces(params,auxevol_gfs,flux_dirn+1);\n // Then, reconstruct the primitive variables on the cell faces.\n // This function is housed in the file: \"reconstruct_set_of_prims_PPM_GRFFE_NRPy.c\"\n reconstruct_set_of_prims_PPM_GRFFE_NRPy(params, auxevol_gfs, flux_dirn+1, num_prims_to_reconstruct,\n which_prims_to_reconstruct, in_prims, out_prims_r, out_prims_l, temporary);\n // For example, if flux_dirn==0, then at gamma_faceDD00(i,j,k) represents gamma_{xx}\n // at (i-1/2,j,k), Valenciav_lU0(i,j,k) is the x-component of the velocity at (i-1/2-epsilon,j,k),\n // and Valenciav_rU0(i,j,k) is the x-component of the velocity at (i-1/2+epsilon,j,k).\n\n if(flux_dirn==0) {\n // Next, we calculate the source term for StildeD. Again, this also resets the rhs_gfs array at\n // each new timestep.\n calculate_StildeD0_source_term(params,auxevol_gfs,rhs_gfs);\n // Now, compute the electric field on each face of a cell and add it to the RHSs as appropriate\n //calculate_E_field_D0_right(params,auxevol_gfs,rhs_gfs);\n //calculate_E_field_D0_left(params,auxevol_gfs,rhs_gfs);\n // Finally, we calculate the flux of StildeD and add the appropriate finite-differences\n // to the RHSs.\n calculate_Stilde_flux_D0(params,auxevol_gfs,rhs_gfs);\n }\n else if(flux_dirn==1) {\n calculate_StildeD1_source_term(params,auxevol_gfs,rhs_gfs);\n //calculate_E_field_D1_right(params,auxevol_gfs,rhs_gfs);\n //calculate_E_field_D1_left(params,auxevol_gfs,rhs_gfs);\n calculate_Stilde_flux_D1(params,auxevol_gfs,rhs_gfs);\n }\n else {\n calculate_StildeD2_source_term(params,auxevol_gfs,rhs_gfs);\n //calculate_E_field_D2_right(params,auxevol_gfs,rhs_gfs);\n //calculate_E_field_D2_left(params,auxevol_gfs,rhs_gfs);\n calculate_Stilde_flux_D2(params,auxevol_gfs,rhs_gfs);\n }\n for(int count=0;count<=1;count++) {\n // This function is written to be general, using notation that matches the forward permutation added to AD2,\n // i.e., [F_HLL^x(B^y)]_z corresponding to flux_dirn=0, count=1.\n // The SIGN parameter is necessary because\n // -E_z(x_i,y_j,z_k) = 0.25 ( [F_HLL^x(B^y)]_z(i+1/2,j,k)+[F_HLL^x(B^y)]_z(i-1/2,j,k)\n // -[F_HLL^y(B^x)]_z(i,j+1/2,k)-[F_HLL^y(B^x)]_z(i,j-1/2,k) )\n // Note the negative signs on the reversed permutation terms!\n\n // By cyclically permuting with flux_dirn, we\n // get contributions to the other components, and by incrementing count, we get the backward permutations:\n // Let's suppose flux_dirn = 0. Then we will need to update Ay (count=0) and Az (count=1):\n // flux_dirn=count=0 -> AD0GF+(flux_dirn+1+count)%3 = AD0GF + (0+1+0)%3=AD1GF <- Updating Ay!\n // (flux_dirn)%3 = (0)%3 = 0 Vx\n // (flux_dirn-count+2)%3 = (0-0+2)%3 = 2 Vz . Inputs Vx, Vz -> SIGN = -1 ; 2.0*((REAL)count)-1.0=-1 check!\n // flux_dirn=0,count=1 -> AD0GF+(flux_dirn+1+count)%3 = AD0GF + (0+1+1)%3=AD2GF <- Updating Az!\n // (flux_dirn)%3 = (0)%3 = 0 Vx\n // (flux_dirn-count+2)%3 = (0-1+2)%3 = 1 Vy . Inputs Vx, Vy -> SIGN = +1 ; 2.0*((REAL)count)-1.0=2-1=+1 check!\n // Let's suppose flux_dirn = 1. Then we will need to update Az (count=0) and Ax (count=1):\n // flux_dirn=1,count=0 -> AD0GF+(flux_dirn+1+count)%3 = AD0GF + (1+1+0)%3=AD2GF <- Updating Az!\n // (flux_dirn)%3 = (1)%3 = 1 Vy\n // (flux_dirn-count+2)%3 = (1-0+2)%3 = 0 Vx . Inputs Vy, Vx -> SIGN = -1 ; 2.0*((REAL)count)-1.0=-1 check!\n // flux_dirn=count=1 -> AD0GF+(flux_dirn+1+count)%3 = AD0GF + (1+1+1)%3=AD0GF <- Updating Ax!\n // (flux_dirn)%3 = (1)%3 = 1 Vy\n // (flux_dirn-count+2)%3 = (1-1+2)%3 = 2 Vz . Inputs Vy, Vz -> SIGN = +1 ; 2.0*((REAL)count)-1.0=2-1=+1 check!\n // Let's suppose flux_dirn = 2. Then we will need to update Ax (count=0) and Ay (count=1):\n // flux_dirn=2,count=0 -> AD0GF+(flux_dirn+1+count)%3 = AD0GF + (2+1+0)%3=AD0GF <- Updating Ax!\n // (flux_dirn)%3 = (2)%3 = 2 Vz\n // (flux_dirn-count+2)%3 = (2-0+2)%3 = 1 Vy . Inputs Vz, Vy -> SIGN = -1 ; 2.0*((REAL)count)-1.0=-1 check!\n // flux_dirn=2,count=1 -> AD0GF+(flux_dirn+1+count)%3 = AD0GF + (2+1+1)%3=AD1GF <- Updating Ay!\n // (flux_dirn)%3 = (2)%3 = 2 Vz\n // (flux_dirn-count+2)%3 = (2-1+2)%3 = 0 Vx . Inputs Vz, Vx -> SIGN = +1 ; 2.0*((REAL)count)-1.0=2-1=+1 check!\n calculate_E_field_flat_all_in_one(params,\n &auxevol_gfs[IDX4ptS(VALENCIAV_RU0GF+(flux_dirn)%3, 0)],&auxevol_gfs[IDX4ptS(VALENCIAV_RU0GF+(flux_dirn-count+2)%3, 0)],\n &auxevol_gfs[IDX4ptS(VALENCIAV_LU0GF+(flux_dirn)%3, 0)],&auxevol_gfs[IDX4ptS(VALENCIAV_LU0GF+(flux_dirn-count+2)%3, 0)],\n &auxevol_gfs[IDX4ptS(B_RU0GF +(flux_dirn)%3, 0)],&auxevol_gfs[IDX4ptS(B_RU0GF +(flux_dirn-count+2)%3, 0)],\n &auxevol_gfs[IDX4ptS(B_LU0GF +(flux_dirn)%3, 0)],&auxevol_gfs[IDX4ptS(B_LU0GF +(flux_dirn-count+2)%3, 0)],\n &auxevol_gfs[IDX4ptS(B_RU0GF +(flux_dirn-count+2)%3, 0)],\n &auxevol_gfs[IDX4ptS(B_LU0GF +(flux_dirn-count+2)%3, 0)],\n &rhs_gfs[IDX4ptS(AD0GF+(flux_dirn+1+count)%3,0)], 2.0*((REAL)count)-1.0, flux_dirn);\n }\n }\n}\n\nvoid GiRaFFE_NRPy_post_step(const paramstruct *restrict params,REAL *xx[3],REAL *restrict auxevol_gfs,REAL *restrict evol_gfs,const int n) {\n // First, apply BCs to AD and psi6Phi. Then calculate BU from AD\n apply_bcs_potential(params,evol_gfs);\n driver_A_to_B(params,evol_gfs,auxevol_gfs);\n //override_BU_with_old_GiRaFFE(params,auxevol_gfs,n);\n // Apply fixes to StildeD, then recompute the velocity at the new timestep.\n // Apply the current sheet prescription to the velocities\n GiRaFFE_NRPy_cons_to_prims(params,xx,auxevol_gfs,evol_gfs);\n // Then, recompute StildeD to be consistent with the new velocities\n //GiRaFFE_NRPy_prims_to_cons(params,auxevol_gfs,evol_gfs);\n // Finally, apply outflow boundary conditions to the velocities.\n apply_bcs_velocity(params,auxevol_gfs);\n}",
"Overwriting GiRaFFE_standalone_Ccodes/GiRaFFE_NRPy_Main_Driver.h\n"
]
],
[
[
"<a id='code_validation'></a>\n\n# Step 4: Self-Validation against `GiRaFFE_NRPy_Main_Drive.py` \\[Back to [top](#toc)\\]\n$$\\label{code_validation}$$\n\nTo validate the code in this tutorial we check for agreement between the files\n\n1. that were generated in this tutorial and\n1. those that are generated in the module `GiRaFFE_NRPy_Main_Driver.py`\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"gri.glb_gridfcs_list = []\n# Define the directory that we wish to validate against:\nvaldir = os.path.join(\"GiRaFFE_validation_Ccodes\")\ncmd.mkdir(valdir)\n\nimport GiRaFFE_NRPy.GiRaFFE_NRPy_Main_Driver as md\nmd.GiRaFFE_NRPy_Main_Driver_generate_all(valdir)\n\n",
"Output C function calculate_parentheticals_for_RHSs() to file GiRaFFE_validation_Ccodes\\RHSs\\calculate_parentheticals_for_RHSs.h\nOutput C function calculate_StildeD0_source_term() to file GiRaFFE_validation_Ccodes\\RHSs\\calculate_StildeD0_source_term.h\nOutput C function calculate_StildeD1_source_term() to file GiRaFFE_validation_Ccodes\\RHSs\\calculate_StildeD1_source_term.h\nOutput C function calculate_StildeD2_source_term() to file GiRaFFE_validation_Ccodes\\RHSs\\calculate_StildeD2_source_term.h\nOutput C function calculate_E_field_D0_right() to file GiRaFFE_validation_Ccodes\\RHSs\\calculate_E_field_D0_right.h\nOutput C function calculate_E_field_D0_left() to file GiRaFFE_validation_Ccodes\\RHSs\\calculate_E_field_D0_left.h\nOutput C function calculate_E_field_D1_right() to file GiRaFFE_validation_Ccodes\\RHSs\\calculate_E_field_D1_right.h\nOutput C function calculate_E_field_D1_left() to file GiRaFFE_validation_Ccodes\\RHSs\\calculate_E_field_D1_left.h\nOutput C function calculate_E_field_D2_right() to file GiRaFFE_validation_Ccodes\\RHSs\\calculate_E_field_D2_right.h\nOutput C function calculate_E_field_D2_left() to file GiRaFFE_validation_Ccodes\\RHSs\\calculate_E_field_D2_left.h\nOutput C function GiRaFFE_NRPy_cons_to_prims() to file GiRaFFE_validation_Ccodes\\C2P\\GiRaFFE_NRPy_cons_to_prims.h\nOutput C function GiRaFFE_NRPy_prims_to_cons() to file GiRaFFE_validation_Ccodes\\C2P\\GiRaFFE_NRPy_prims_to_cons.h\n"
]
],
[
[
"With both sets of codes generated, we can now compare them against each other.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import difflib\nimport sys\n\nprint(\"Printing difference between original C code and this code...\")\n# Open the files to compare\nfiles = [\"GiRaFFE_NRPy_Main_Driver.h\",\n \"RHSs/calculate_parentheticals_for_RHSs.h\",\n \"RHSs/calculate_AD_gauge_psi6Phi_RHSs.h\",\n \"PPM/reconstruct_set_of_prims_PPM_GRFFE_NRPy.c\",\n \"PPM/loop_defines_reconstruction_NRPy.h\",\n \"FCVAL/interpolate_metric_gfs_to_cell_faces.h\",\n \"RHSs/calculate_StildeD0_source_term.h\",\n \"RHSs/calculate_StildeD1_source_term.h\",\n \"RHSs/calculate_StildeD2_source_term.h\",\n \"RHSs/calculate_E_field_D0_right.h\",\n \"RHSs/calculate_E_field_D0_left.h\",\n \"RHSs/calculate_E_field_D1_right.h\",\n \"RHSs/calculate_E_field_D1_left.h\",\n \"RHSs/calculate_E_field_D2_right.h\",\n \"RHSs/calculate_E_field_D2_left.h\",\n \"RHSs/calculate_Stilde_flux_D0.h\",\n \"RHSs/calculate_Stilde_flux_D1.h\",\n \"RHSs/calculate_Stilde_flux_D2.h\",\n \"boundary_conditions/GiRaFFE_boundary_conditions.h\",\n \"A2B/driver_AtoB.h\",\n \"C2P/GiRaFFE_NRPy_cons_to_prims.h\",\n \"C2P/GiRaFFE_NRPy_prims_to_cons.h\"]\n\nfor file in files:\n print(\"Checking file \" + file)\n with open(os.path.join(valdir,file)) as file1, open(os.path.join(out_dir,file)) as file2:\n # Read the lines of each file\n file1_lines = file1.readlines()\n file2_lines = file2.readlines()\n num_diffs = 0\n for line in difflib.unified_diff(file1_lines, file2_lines, fromfile=os.path.join(valdir,file), tofile=os.path.join(out_dir,file)):\n sys.stdout.writelines(line)\n num_diffs = num_diffs + 1\n if num_diffs == 0:\n print(\"No difference. TEST PASSED!\")\n else:\n print(\"ERROR: Disagreement found with .py file. See differences above.\")\n sys.exit(1)",
"Printing difference between original C code and this code...\nChecking file GiRaFFE_NRPy_Main_Driver.h\nNo difference. TEST PASSED!\nChecking file RHSs/calculate_parentheticals_for_RHSs.h\nNo difference. TEST PASSED!\nChecking file RHSs/calculate_AD_gauge_psi6Phi_RHSs.h\nNo difference. TEST PASSED!\nChecking file PPM/reconstruct_set_of_prims_PPM_GRFFE_NRPy.c\nNo difference. TEST PASSED!\nChecking file PPM/loop_defines_reconstruction_NRPy.h\nNo difference. TEST PASSED!\nChecking file FCVAL/interpolate_metric_gfs_to_cell_faces.h\nNo difference. TEST PASSED!\nChecking file RHSs/calculate_StildeD0_source_term.h\nNo difference. TEST PASSED!\nChecking file RHSs/calculate_StildeD1_source_term.h\nNo difference. TEST PASSED!\nChecking file RHSs/calculate_StildeD2_source_term.h\nNo difference. TEST PASSED!\nChecking file RHSs/calculate_E_field_D0_right.h\nNo difference. TEST PASSED!\nChecking file RHSs/calculate_E_field_D0_left.h\nNo difference. TEST PASSED!\nChecking file RHSs/calculate_E_field_D1_right.h\nNo difference. TEST PASSED!\nChecking file RHSs/calculate_E_field_D1_left.h\nNo difference. TEST PASSED!\nChecking file RHSs/calculate_E_field_D2_right.h\nNo difference. TEST PASSED!\nChecking file RHSs/calculate_E_field_D2_left.h\nNo difference. TEST PASSED!\nChecking file RHSs/calculate_Stilde_flux_D0.h\nNo difference. TEST PASSED!\nChecking file RHSs/calculate_Stilde_flux_D1.h\nNo difference. TEST PASSED!\nChecking file RHSs/calculate_Stilde_flux_D2.h\nNo difference. TEST PASSED!\nChecking file boundary_conditions/GiRaFFE_boundary_conditions.h\nNo difference. TEST PASSED!\nChecking file A2B/driver_AtoB.h\nNo difference. TEST PASSED!\nChecking file C2P/GiRaFFE_NRPy_cons_to_prims.h\nNo difference. TEST PASSED!\nChecking file C2P/GiRaFFE_NRPy_prims_to_cons.h\nNo difference. TEST PASSED!\n"
]
],
[
[
"<a id='latex_pdf_output'></a>\n\n# Step 4: Output this notebook to $\\LaTeX$-formatted PDF file \\[Back to [top](#toc)\\]\n$$\\label{latex_pdf_output}$$\n\nThe following code cell converts this Jupyter notebook into a proper, clickable $\\LaTeX$-formatted PDF file. After the cell is successfully run, the generated PDF may be found in the root NRPy+ tutorial directory, with filename\n[Tutorial-GiRaFFE_NRPy_Main_Driver](TTutorial-GiRaFFE_NRPy_Main_Driver.pdf) (Note that clicking on this link may not work; you may need to open the PDF file through another means.)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import cmdline_helper as cmd # NRPy+: Multi-platform Python command-line interface\ncmd.output_Jupyter_notebook_to_LaTeXed_PDF(\"Tutorial-GiRaFFE_NRPy_Main_Driver\")",
"Notebook output to PDF is only supported on Linux systems, with pdflatex installed.\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a329739d88349b05812acea10d66c3addfe5965
| 315,851 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
lyrics-generation-with-lstm.ipynb
|
abhinav-neil/lyrics-generator-lstm
|
00a80e835520650acce40537b23583148f823782
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
lyrics-generation-with-lstm.ipynb
|
abhinav-neil/lyrics-generator-lstm
|
00a80e835520650acce40537b23583148f823782
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
lyrics-generation-with-lstm.ipynb
|
abhinav-neil/lyrics-generator-lstm
|
00a80e835520650acce40537b23583148f823782
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 315,851 | 315,851 | 0.935441 |
[
[
[
"## 1. Introduction\n\nNotebook for generating lyrics using LSTM network. The dataset contains all the songs recorded by Bob Dylan. Stages:\n1. EDA\n - Summary statistics on dataset: distribution of no. of characters, words, sentences in collection\n - Histograms & wordclouds\n2. Preprocessing\n - Create corpus of all words from lyrics\n - Cleaning: remove special characters, convert to lowercase\n - Create mapping of unique chars to indices\n - Create features and targets (categorical)\n3. Model\n - Train LSTM model, one character at a time\n - Visualize learning and loss\n4. Generation\n - Generate lyrics from seed phrase, one character at a time, using model predictions",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Imports\n# Core\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport seaborn as sns\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport string, os, sys, warnings, random, io\nwarnings.filterwarnings(\"ignore\")\n\n# NLP\nimport tensorflow as tf\nfrom tensorflow import keras\nfrom tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical\nfrom tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential, load_model\nfrom tensorflow.keras.layers import LSTM, Dense, Dropout\nimport nltk\nimport re\nfrom wordcloud import WordCloud, STOPWORDS, ImageColorGenerator\nfrom PIL import Image",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# TPU config (for LSTM)\ntpu = tf.distribute.cluster_resolver.TPUClusterResolver.connect()\ntpu_strategy = tf.distribute.experimental.TPUStrategy(tpu)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id=\"2\"></a>\n## 2. EDA",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Load song lyrics dataset\ndf_songs = pd.read_csv(\"../input/bob-dylan-songs/clear.csv\")\ndf_songs.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_songs.info()",
"<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>\nRangeIndex: 345 entries, 0 to 344\nData columns (total 4 columns):\n # Column Non-Null Count Dtype \n--- ------ -------------- ----- \n 0 release_year 345 non-null int64 \n 1 album 345 non-null object\n 2 title 345 non-null object\n 3 lyrics 345 non-null object\ndtypes: int64(1), object(3)\nmemory usage: 10.9+ KB\n"
]
],
[
[
"### 2.1 Summary stats",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Get numbers of characters,words and sentences in each song\ndf_songs[\"n_chars\"] = df_songs[\"lyrics\"].apply(len)\ndf_songs[\"n_words\"]=df_songs.apply(lambda row: nltk.word_tokenize(row[\"lyrics\"]), axis=1).apply(len)\ndf_songs[\"n_lines\"] = df_songs[\"lyrics\"].str.split('\\n').apply(len)\ndf_songs.describe()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Plot distribution of chars, words, sentences in lyrics\nfig, axs = plt.subplots(3, 1, figsize=(15, 10))\nfig.suptitle('Distribution of characters, words and lines')\nsns.histplot(data=df_songs, x='n_chars', ax=axs[0])\nsns.histplot(data=df_songs, x='n_words', ax=axs[1])\nsns.histplot(data=df_songs, x='n_lines', ax=axs[2])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 2.2 Wordcloud",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Generate a wordcloud\nstopwords = set(STOPWORDS)\nwc = WordCloud(stopwords=stopwords, background_color=\"#007399\",colormap=\"cividis\", max_words=100)\nwc.generate(\" \".join(df_songs.lyrics))\nplt.figure(figsize=(12,12))\nplt.imshow(wc, interpolation=\"bilinear\")\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Sample lyrics\nsong_idx = 100\nprint(df_songs.loc[song_idx, :])\ndf_songs.loc[song_idx, 'lyrics'].split('\\n')[:30]",
"release_year 1967\nalbum John Wesley Harding\ntitle The Ballad of Frankie Lee and Judas Priest\nlyrics Well, Frankie Lee and Judas Priest\\n \\n They w...\nn_chars 3160\nn_words 682\nn_lines 195\nName: 100, dtype: object\n"
]
],
[
[
"## 3. Preprocessing",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_songs.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 3.1 Create corpus",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create corpus from lyrics\ncorpus = ''\nfor text in df_songs.lyrics:\n corpus += text\n \ncorpus = corpus.lower()\nprint(\"Number of unique characters:\", len(set(corpus)))",
"Number of unique characters: 65\n"
]
],
[
[
"### 3.2 Cleaning",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(sorted(set(corpus)))",
"['\\n', '\\x0b', ' ', '!', '\"', \"'\", '(', ')', ',', '-', '.', '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', ':', ';', '?', '`', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j', 'k', 'l', 'm', 'n', 'o', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u', 'v', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z', '¥', '©', 'é', 'ñ', 'ó', 'ü', '–', '—', '‘', '’', '“', '”', '…', '\\u2028']\n"
],
[
"special_chars = ['\\x0b', '\"', '(', ')', '`', '¥', '©', 'é', 'ñ', 'ó', 'ü', '—', '“', '”', '…', '\\u2028']\nfor symbol in special_chars:\n corpus = corpus.replace(symbol,\"\")\n# corpus = re.sub(\"[^A-Za-z0-9'.,?!\\n\\w]\",\"\",corpus)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(sorted(set(corpus)))",
"['\\n', ' ', '!', \"'\", ',', '-', '.', '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', ':', ';', '?', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j', 'k', 'l', 'm', 'n', 'o', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u', 'v', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z', '–', '‘', '’']\n"
],
[
"# Sample section\ncorpus[:1000]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id=\"3.3\"></a>\n### 3.3 Create inputs from mapping",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Map characters in corpus to indices\nsymb = sorted(list(set(corpus)))\n\nlen_corpus = len(corpus) \nlen_symb = len(symb)\n\nmapping = dict((c, i) for i, c in enumerate(symb))\nreverse_mapping = dict((i, c) for i, c in enumerate(symb))\n\nprint(\"Total number of characters:\", len_corpus)\nprint(\"Number of unique characters:\", len_symb)",
"Total number of characters: 548593\nNumber of unique characters: 49\n"
],
[
"#Splitting the corpus in equal length of strings and output target\nlength = 50\nfeatures = []\ntargets = []\nfor i in range(0, len_corpus - length, 1):\n feature = corpus[i:i + length]\n target = corpus[i + length]\n features.append([mapping[j] for j in feature])\n targets.append(mapping[target])\n \n# len_datapoints = len(targets)\n# print(\"Total number of sequences in the Corpus:\", len_datapoints)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# reshape X and normalize\nX = (np.reshape(features, (len(targets), length, 1)))/ float(len_symb)\n\n# one hot encode the output variable\ny = to_categorical(targets)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 4. Model",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 4.1 Training",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#Initialising the Model\nwith tpu_strategy.scope():\n model = Sequential()\n model.add(LSTM(256, input_shape=(X.shape[1], X.shape[2])))\n model.add(Dense(y.shape[1], activation='softmax'))\n model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam')\nmodel.summary()",
"Model: \"sequential_1\"\n_________________________________________________________________\nLayer (type) Output Shape Param # \n=================================================================\nlstm_1 (LSTM) (None, 256) 264192 \n_________________________________________________________________\ndense_1 (Dense) (None, 49) 12593 \n=================================================================\nTotal params: 276,785\nTrainable params: 276,785\nNon-trainable params: 0\n_________________________________________________________________\n"
],
[
"%%time\n#Training the Model\nhistory = model.fit(X, y, batch_size=256*tpu_strategy.num_replicas_in_sync, epochs=50)",
"Epoch 1/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 9s 17ms/step - loss: 3.0756\nEpoch 2/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.8562\nEpoch 3/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.7715\nEpoch 4/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.7011\nEpoch 5/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.6631\nEpoch 6/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.6197\nEpoch 7/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.5924\nEpoch 8/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.5620\nEpoch 9/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 15ms/step - loss: 2.5384\nEpoch 10/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.5131\nEpoch 11/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.4917\nEpoch 12/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.4776\nEpoch 13/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.4531\nEpoch 14/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.4365\nEpoch 15/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.4230\nEpoch 16/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.4080\nEpoch 17/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.3956\nEpoch 18/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.3771\nEpoch 19/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.3650\nEpoch 20/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.3521\nEpoch 21/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.3401\nEpoch 22/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.3273\nEpoch 23/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.3163\nEpoch 24/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.3031\nEpoch 25/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.2936\nEpoch 26/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.2769\nEpoch 27/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.2668\nEpoch 28/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.2554\nEpoch 29/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.2430\nEpoch 30/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.2358\nEpoch 31/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.2212\nEpoch 32/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.2130\nEpoch 33/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.2000\nEpoch 34/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.1906\nEpoch 35/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.1847\nEpoch 36/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.1698\nEpoch 37/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.1566\nEpoch 38/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.1508\nEpoch 39/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.1393\nEpoch 40/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.1305\nEpoch 41/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.1199\nEpoch 42/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.1059\nEpoch 43/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.1020\nEpoch 44/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.0921\nEpoch 45/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.0868\nEpoch 46/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 2.0705\nEpoch 47/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 15ms/step - loss: 2.0658\nEpoch 48/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 15ms/step - loss: 2.0601\nEpoch 49/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 15ms/step - loss: 2.0467\nEpoch 50/50\n268/268 [==============================] - 4s 15ms/step - loss: 2.0418\nCPU times: user 1min 10s, sys: 13.3 s, total: 1min 24s\nWall time: 3min 17s\n"
]
],
[
[
"model.save(\"generator_v2.h5\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 4.2 Evaluation",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Evaluation\nhistory_df = pd.DataFrame(history.history)\n#Plotting the learning curve\n\nfig = plt.figure(figsize=(12,6))\nfig.suptitle(\"Learning plot for model Loss\")\npl = sns.lineplot(data=history_df[\"loss\"])\npl.set(ylabel =\"Training Loss\")\npl.set(xlabel =\"Epochs\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 5. Generation",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# The function to generate text from model\ndef generate(seed,char_count, temperature=1.0):\n generated= \"\"\n seed = seed \n seed_idx=[mapping[char] for char in seed]\n generated += seed \n # Generating new text of given length\n for i in range(char_count):\n seed_idx=[mapping[char] for char in seed]\n x_pred = np.reshape(seed_idx, (1, len(seed_idx), 1))/len_symb\n prediction = model.predict(x_pred, verbose=0)[0] \n # Getting the index of the next most probable index\n prediction = np.asarray(prediction).astype('float64')\n prediction = np.log(prediction) / temperature\n# exp_preds = np.exp(prediction)\n# prediction = exp_preds / np.sum(exp_preds)\n# probas = np.random.multinomial(1, prediction, 1)\n index = np.argmax(prediction)\n next_char = reverse_mapping[index] \n # Generating new text\n generated += next_char\n seed = seed[1:] + next_char\n \n return generated",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"song = generate(\"the answer my friend, is blowi\", 50, 2.0)\nsong.split('\\n')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"song = generate(\"the times they ar\", 200)\nsong.split('\\n')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a32a1b6947245cf8d89f041999cc4c55f7684cd
| 29,925 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
User Independence Analysis/ipynb/.ipynb_checkpoints/Pre-Processing -checkpoint.ipynb
|
ramanathanmurugappan/User-Independent-Human-Stress-Detection
|
56d8fc52ecc3e8751ef07304eb349f88ab5d08df
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
User Independence Analysis/ipynb/.ipynb_checkpoints/Pre-Processing -checkpoint.ipynb
|
ramanathanmurugappan/User-Independent-Human-Stress-Detection
|
56d8fc52ecc3e8751ef07304eb349f88ab5d08df
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
User Independence Analysis/ipynb/.ipynb_checkpoints/Pre-Processing -checkpoint.ipynb
|
ramanathanmurugappan/User-Independent-Human-Stress-Detection
|
56d8fc52ecc3e8751ef07304eb349f88ab5d08df
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2020-09-29T17:48:39.000Z
|
2021-05-06T17:55:53.000Z
| 42.628205 | 2,553 | 0.544829 |
[
[
[
"import os\nimport pickle\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom scipy import stats \nimport scipy.signal as scisig\nimport scipy.stats\nimport cvxEDA",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# dir(cvxEDA)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fs_dict = {'ACC': 32, 'BVP': 64, 'EDA': 4, 'TEMP': 4, 'label': 700, 'Resp': 700, 'ECG':700}\nWINDOW_IN_SECONDS = 1\nlabel_dict = {'baseline': 0, 'stress': 1, 'amusement': 2, 'meditation':3}\nint_to_label = {0: 'baseline', 1: 'stress', 2: 'amusement', 3:'meditation'}\nfeat_names = None\nsavePath = 'fresh_start'\nsubject_feature_path = '/subject_feats'\n\nif not os.path.exists(savePath):\n os.makedirs(savePath)\nif not os.path.exists(savePath + subject_feature_path):\n os.makedirs(savePath + subject_feature_path)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# cvxEDA\ndef eda_stats(y):\n Fs = fs_dict['EDA']\n yn = (y - y.mean()) / y.std()\n [r, p, t, l, d, e, obj] = cvxEDA.cvxEDA(yn, 1. / Fs)\n return [r, p, t, l, d, e, obj]\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class SubjectData:\n\n def __init__(self, main_path, subject_number):\n self.name = f'S{subject_number}'\n self.subject_keys = ['signal', 'label', 'subject']\n self.signal_keys = ['chest', 'wrist']\n self.chest_keys = ['ACC', 'ECG', 'EMG', 'EDA', 'Temp', 'Resp']\n self.wrist_keys = ['ACC', 'BVP', 'EDA', 'TEMP']\n with open(os.path.join(main_path, self.name) + '/' + self.name + '.pkl', 'rb') as file:\n self.data = pickle.load(file, encoding='latin1')\n self.labels = self.data['label']\n\n def get_wrist_data(self):\n data = self.data['signal']['wrist']\n data.update({'Resp': self.data['signal']['chest']['Resp']})\n data.update({'ECG': self.data['signal']['chest']['ECG']})\n data.update({'EMG': self.data['signal']['chest']['EMG']})\n data.update({'c_EDA': self.data['signal']['chest']['EDA']})\n data.update({'c_Temp': self.data['signal']['chest']['Temp']})\n data.update({'c_ACC': self.data['signal']['chest']['ACC']})\n return data\n\n def get_chest_data(self):\n return self.data['signal']['chest']\n\n def extract_features(self): # only wrist\n results = \\\n {\n key: get_statistics(self.get_wrist_data()[key].flatten(), self.labels, key)\n for key in self.wrist_keys\n }\n return results",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def butter_lowpass(cutoff, fs, order=5):\n # Filtering Helper functions\n nyq = 0.5 * fs\n normal_cutoff = cutoff / nyq\n b, a = scisig.butter(order, normal_cutoff, btype='low', analog=False)\n return b, a\n\n\ndef butter_lowpass_filter(data, cutoff, fs, order=5):\n # Filtering Helper functions\n b, a = butter_lowpass(cutoff, fs, order=order)\n y = scisig.lfilter(b, a, data)\n return y\n\ndef get_slope(series):\n linreg = scipy.stats.linregress(np.arange(len(series)), series )\n slope = linreg[0]\n return slope\n\ndef get_window_stats(data, label=-1):\n mean_features = np.mean(data)\n std_features = np.std(data)\n min_features = np.amin(data)\n max_features = np.amax(data)\n\n features = {'mean': mean_features, 'std': std_features, 'min': min_features, 'max': max_features,\n 'label': label}\n return features\n\n\ndef get_net_accel(data):\n return (data['ACC_x'] ** 2 + data['ACC_y'] ** 2 + data['ACC_z'] ** 2).apply(lambda x: np.sqrt(x))\n\n\ndef get_peak_freq(x):\n f, Pxx = scisig.periodogram(x, fs=8)\n psd_dict = {amp: freq for amp, freq in zip(Pxx, f)}\n peak_freq = psd_dict[max(psd_dict.keys())]\n return peak_freq",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# https://github.com/MITMediaLabAffectiveComputing/eda-explorer/blob/master/AccelerometerFeatureExtractionScript.py\ndef filterSignalFIR(eda, cutoff=0.4, numtaps=64):\n f = cutoff / (fs_dict['ACC'] / 2.0)\n FIR_coeff = scisig.firwin(numtaps, f)\n\n return scisig.lfilter(FIR_coeff, 1, eda)\n\n\ndef compute_features(e4_data_dict, labels, norm_type=None):\n # Dataframes for each sensor type\n eda_df = pd.DataFrame(e4_data_dict['EDA'], columns=['EDA'])\n bvp_df = pd.DataFrame(e4_data_dict['BVP'], columns=['BVP'])\n acc_df = pd.DataFrame(e4_data_dict['ACC'], columns=['ACC_x', 'ACC_y', 'ACC_z'])\n temp_df = pd.DataFrame(e4_data_dict['TEMP'], columns=['TEMP'])\n label_df = pd.DataFrame(labels, columns=['label'])\n resp_df = pd.DataFrame(e4_data_dict['Resp'], columns=['Resp'])\n \n ecg_df = pd.DataFrame(e4_data_dict['ECG'], columns=['ECG'])\n emg_df = pd.DataFrame(e4_data_dict['EMG'], columns=['EMG'])\n c_temp_df = pd.DataFrame(e4_data_dict['c_Temp'], columns=['c_Temp'])\n c_acc_df = pd.DataFrame(e4_data_dict['c_ACC'], columns=['c_ACC_x', 'c_ACC_y', 'c_ACC_z'])\n \n # Filter EDA\n eda_df['EDA'] = butter_lowpass_filter(eda_df['EDA'], 1.0, fs_dict['EDA'], 6)\n \n # Filter ACM\n for _ in acc_df.columns:\n acc_df[_] = filterSignalFIR(acc_df.values)\n\n # Adding indices for combination due to differing sampling frequencies\n eda_df.index = [(1 / fs_dict['EDA']) * i for i in range(len(eda_df))]\n bvp_df.index = [(1 / fs_dict['BVP']) * i for i in range(len(bvp_df))]\n acc_df.index = [(1 / fs_dict['ACC']) * i for i in range(len(acc_df))]\n temp_df.index = [(1 / fs_dict['TEMP']) * i for i in range(len(temp_df))]\n label_df.index = [(1 / fs_dict['label']) * i for i in range(len(label_df))]\n resp_df.index = [(1 / fs_dict['Resp']) * i for i in range(len(resp_df))]\n \n ecg_df.index = [(1 / fs_dict['ECG']) * i for i in range(len(ecg_df))]\n emg_df.index = [(1 / fs_dict['ECG']) * i for i in range(len(emg_df))] #ECG fz = EMG fz\n c_temp_df.index = [(1 / fs_dict['ECG']) * i for i in range(len(c_temp_df))]\n c_acc_df.index = [(1 / fs_dict['ECG']) * i for i in range(len(c_acc_df))]\n \n # Change indices to datetime\n eda_df.index = pd.to_datetime(eda_df.index, unit='s')\n bvp_df.index = pd.to_datetime(bvp_df.index, unit='s')\n temp_df.index = pd.to_datetime(temp_df.index, unit='s')\n acc_df.index = pd.to_datetime(acc_df.index, unit='s')\n label_df.index = pd.to_datetime(label_df.index, unit='s')\n resp_df.index = pd.to_datetime(resp_df.index, unit='s')\n \n ecg_df.index = pd.to_datetime(ecg_df.index , unit='s')\n emg_df.index = pd.to_datetime(emg_df.index , unit='s')\n c_temp_df.index = pd.to_datetime(c_temp_df.index , unit='s')\n c_acc_df.index = pd.to_datetime(c_acc_df.index, unit='s')\n \n # New EDA features\n r, p, t, l, d, e, obj = eda_stats(eda_df['EDA'])\n eda_df['EDA_phasic'] = r\n eda_df['EDA_smna'] = p\n eda_df['EDA_tonic'] = t\n \n \n \n # Combined dataframe - not used yet\n df = eda_df.join(bvp_df, how='outer')\n df = df.join(temp_df, how='outer')\n df = df.join(acc_df, how='outer')\n df = df.join(resp_df, how='outer')\n df = df.join(label_df, how='outer')\n df = df.join(ecg_df, how='outer')\n df = df.join(emg_df, how='outer')\n df = df.join(c_temp_df, how='outer')\n df = df.join(c_acc_df, how='outer')\n df['label'] = df['label'].fillna(method='bfill')\n df.reset_index(drop=True, inplace=True)\n\n if norm_type is 'std':\n # std norm\n df = (df - df.mean()) / df.std()\n elif norm_type is 'minmax':\n # minmax norm\n df = (df - df.min()) / (df.max() - df.min())\n\n # Groupby\n grouped = df.groupby('label')\n baseline = grouped.get_group(1)\n stress = grouped.get_group(2)\n amusement = grouped.get_group(3)\n meditation = grouped.get_group(4)\n \n# print (\"$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$\")\n# print (df)\n# print (grouped.groups.keys())\n# print (\"$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$\")\n \n return grouped, baseline, stress, amusement, meditation\n\n\ndef get_samples(data, n_windows, label):\n global feat_names\n global WINDOW_IN_SECONDS\n\n samples = []\n # Using label freq (700 Hz) as our reference frequency due to it being the largest\n # and thus encompassing the lesser ones in its resolution.\n window_len = fs_dict['label'] * WINDOW_IN_SECONDS\n\n for i in range(n_windows):\n # Get window of data\n w = data[window_len * i: window_len * (i + 1)]\n\n # Add/Calc rms acc\n # w['net_acc'] = get_net_accel(w)\n w = pd.concat([w, get_net_accel(w)])\n #w.columns = ['net_acc', 'ACC_x', 'ACC_y', 'ACC_z', 'BVP',\n # 'EDA', 'EDA_phasic', 'EDA_smna', 'EDA_tonic', 'TEMP',\n # 'label']\n cols = list(w.columns)\n cols[0] = 'net_acc'\n w.columns = cols\n \n # Calculate stats for window\n wstats = get_window_stats(data=w, label=label)\n\n # Seperating sample and label\n x = pd.DataFrame(wstats).drop('label', axis=0)\n y = x['label'][0]\n x.drop('label', axis=1, inplace=True)\n\n if feat_names is None:\n feat_names = []\n for row in x.index:\n for col in x.columns:\n feat_names.append('_'.join([row, col]))\n\n # sample df\n wdf = pd.DataFrame(x.values.flatten()).T\n wdf.columns = feat_names\n wdf = pd.concat([wdf, pd.DataFrame({'label': y}, index=[0])], axis=1)\n \n # More feats\n wdf['BVP_peak_freq'] = get_peak_freq(w['BVP'].dropna())\n wdf['TEMP_slope'] = get_slope(w['TEMP'].dropna())\n samples.append(wdf)\n\n return pd.concat(samples)\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def make_patient_data(subject_id):\n global savePath\n global WINDOW_IN_SECONDS\n\n # Make subject data object for Sx\n subject = SubjectData(main_path='WESAD', subject_number=subject_id)\n\n # Empatica E4 data - now with resp\n e4_data_dict = subject.get_wrist_data()\n# e4_data_dict = subject.get_chest_data()\n\n # norm type\n norm_type = None\n\n # The 3 classes we are classifying\n grouped, baseline, stress, amusement, meditation = compute_features(e4_data_dict, subject.labels, norm_type)\n\n # print(f'Available windows for {subject.name}:')\n n_baseline_wdws = int(len(baseline) / (fs_dict['label'] * WINDOW_IN_SECONDS))\n n_stress_wdws = int(len(stress) / (fs_dict['label'] * WINDOW_IN_SECONDS))\n n_amusement_wdws = int(len(amusement) / (fs_dict['label'] * WINDOW_IN_SECONDS))\n n_meditation_wdws = int(len(meditation) / (fs_dict['label'] * WINDOW_IN_SECONDS))\n # print(f'Baseline: {n_baseline_wdws}\\nStress: {n_stress_wdws}\\nAmusement: {n_amusement_wdws}\\n')\n\n #\n baseline_samples = get_samples(baseline, n_baseline_wdws, 0)\n # Downsampling\n # baseline_samples = baseline_samples[::2]\n stress_samples = get_samples(stress, n_stress_wdws, 1)\n amusement_samples = get_samples(amusement, n_amusement_wdws, 2)\n meditation_samples = get_samples(meditation, n_meditation_wdws, 3)\n\n all_samples = pd.concat([baseline_samples, stress_samples, amusement_samples,meditation_samples])\n all_samples = pd.concat([all_samples.drop('label', axis=1), pd.get_dummies(all_samples['label'])], axis=1)\n \n # Selected Features\n # all_samples = all_samples[['EDA_mean', 'EDA_std', 'EDA_min', 'EDA_max',\n # 'BVP_mean', 'BVP_std', 'BVP_min', 'BVP_max',\n # 'TEMP_mean', 'TEMP_std', 'TEMP_min', 'TEMP_max',\n # 'net_acc_mean', 'net_acc_std', 'net_acc_min', 'net_acc_max',\n # 0, 1, 2]]\n # Save file as csv (for now)\n all_samples.to_csv(f'{savePath}{subject_feature_path}/S{subject_id}_feats_4.csv')\n\n # Does this save any space?\n subject = None\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def combine_files(subjects):\n df_list = []\n for s in subjects:\n df = pd.read_csv(f'{savePath}{subject_feature_path}/S{s}_feats_4.csv', index_col=0)\n df['subject'] = s\n df_list.append(df)\n\n df = pd.concat(df_list)\n \n# df.info()\n \n df['label'] = (df['0'].astype(str) + df['1'].astype(str) + df['2'].astype(str)+ df['3'].astype(str)).apply(lambda x: x.index('1'))\n \n# print (df)\n \n# print (\"***************************8\")\n# df['label']\n# print (\"***************************8\")\n\n df.drop(['0', '1', '2','3'], axis=1, inplace=True)\n\n df.reset_index(drop=True, inplace=True)\n\n df.to_csv(f'{savePath}/may14_feats4_chest.csv')\n\n counts = df['label'].value_counts()\n print('Number of samples per class:')\n print (counts)\n for label, number in zip(counts.index, counts.values):\n print(f'{int_to_label[label]}: {number}')\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"if __name__ == '__main__':\n\n subject_ids = [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17]\n# subject_ids = [2]\n for patient in subject_ids:\n print(f'Processing data for S{patient}...')\n make_patient_data(patient)\n\n combine_files(subject_ids)\n print('Processing complete.')",
"Processing data for S2...\n"
],
[
"pre = pd.read_csv(\"fresh_start/may14_feats4_chest.csv\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pre['subject'].value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pre['label'].value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pre.info()",
"<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>\nRangeIndex: 785 entries, 0 to 784\nData columns (total 73 columns):\nUnnamed: 0 785 non-null int64\nnet_acc_mean 785 non-null float64\nnet_acc_std 785 non-null float64\nnet_acc_min 785 non-null float64\nnet_acc_max 785 non-null float64\nACC_x_mean 785 non-null float64\nACC_x_std 785 non-null float64\nACC_x_min 785 non-null float64\nACC_x_max 785 non-null float64\nACC_y_mean 785 non-null float64\nACC_y_std 785 non-null float64\nACC_y_min 785 non-null float64\nACC_y_max 785 non-null float64\nACC_z_mean 785 non-null float64\nACC_z_std 785 non-null float64\nACC_z_min 785 non-null float64\nACC_z_max 785 non-null float64\nBVP_mean 785 non-null float64\nBVP_std 785 non-null float64\nBVP_min 785 non-null float64\nBVP_max 785 non-null float64\nECG_mean 785 non-null float64\nECG_std 785 non-null float64\nECG_min 785 non-null float64\nECG_max 785 non-null float64\nEDA_mean 785 non-null float64\nEDA_std 785 non-null float64\nEDA_min 785 non-null float64\nEDA_max 785 non-null float64\nEDA_phasic_mean 785 non-null float64\nEDA_phasic_std 785 non-null float64\nEDA_phasic_min 785 non-null float64\nEDA_phasic_max 785 non-null float64\nEDA_smna_mean 785 non-null float64\nEDA_smna_std 785 non-null float64\nEDA_smna_min 785 non-null float64\nEDA_smna_max 785 non-null float64\nEDA_tonic_mean 785 non-null float64\nEDA_tonic_std 785 non-null float64\nEDA_tonic_min 785 non-null float64\nEDA_tonic_max 785 non-null float64\nEMG_mean 785 non-null float64\nEMG_std 785 non-null float64\nEMG_min 785 non-null float64\nEMG_max 785 non-null float64\nResp_mean 785 non-null float64\nResp_std 785 non-null float64\nResp_min 785 non-null float64\nResp_max 785 non-null float64\nTEMP_mean 785 non-null float64\nTEMP_std 785 non-null float64\nTEMP_min 785 non-null float64\nTEMP_max 785 non-null float64\nc_ACC_x_mean 785 non-null float64\nc_ACC_x_std 785 non-null float64\nc_ACC_x_min 785 non-null float64\nc_ACC_x_max 785 non-null float64\nc_ACC_y_mean 785 non-null float64\nc_ACC_y_std 785 non-null float64\nc_ACC_y_min 785 non-null float64\nc_ACC_y_max 785 non-null float64\nc_ACC_z_mean 785 non-null float64\nc_ACC_z_std 785 non-null float64\nc_ACC_z_min 785 non-null float64\nc_ACC_z_max 785 non-null float64\nc_Temp_mean 785 non-null float64\nc_Temp_std 785 non-null float64\nc_Temp_min 785 non-null float64\nc_Temp_max 785 non-null float64\nBVP_peak_freq 785 non-null float64\nTEMP_slope 785 non-null float64\nsubject 785 non-null int64\nlabel 785 non-null int64\ndtypes: float64(70), int64(3)\nmemory usage: 447.8 KB\n"
],
[
"pre.to_csv('fresh_start/60s_window_wrist_chest.csv',index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a32a4f6e71f7b56d9767b681986f3f595e08873
| 4,792 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Data_Analysis/sql_operations.ipynb
|
sharif-42/All_About_DS
|
c8fa254bb27943ff23f15c9f4175f51a596f30d0
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Data_Analysis/sql_operations.ipynb
|
sharif-42/All_About_DS
|
c8fa254bb27943ff23f15c9f4175f51a596f30d0
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2020-05-22T09:46:32.000Z
|
2021-08-23T20:44:49.000Z
|
Data_Analysis/sql_operations.ipynb
|
sharif-42/All_About_DS
|
c8fa254bb27943ff23f15c9f4175f51a596f30d0
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 23.605911 | 58 | 0.370618 |
[
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Load Data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"t1 = pd.read_csv('dataset/table1.csv')\nt2 = pd.read_csv('dataset/table2.csv')\nt1.head()\nt2.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Join to table",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"t3 = pd.merge(t1,t2,on='user_id')\nt3",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a32a71ce3e2e1e696326cb44ae6f1f9700cb467
| 927,104 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/2019.01.14 Error Compound.ipynb
|
gnestor/jupyterlab-omnisci
|
34690c9c52a7cf34030e05d71c7536bef53a6c5c
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/2019.01.14 Error Compound.ipynb
|
gnestor/jupyterlab-omnisci
|
34690c9c52a7cf34030e05d71c7536bef53a6c5c
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/2019.01.14 Error Compound.ipynb
|
gnestor/jupyterlab-omnisci
|
34690c9c52a7cf34030e05d71c7536bef53a6c5c
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 2,695.069767 | 696,738 | 0.968705 |
[
[
[
"import altair as alt\nimport ibis\nimport jupyterlab_omnisci",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"alt.data_transformers.enable('ibis')\nalt.renderers.enable(\"ibis\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"omnisci_cli = ibis.mapd.connect(\n host='metis.mapd.com', user='mapd', password='HyperInteractive',\n port=443, database='mapd', protocol= 'https'\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"t = omnisci_cli.table('flights_donotmodify')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Let's try and find the city pairs which had the worst average arrival and departure delays\naad = t.arrdelay.mean().name('aad')\nadd = t.depdelay.mean().name('add')\nct = t.count().name('ct')\n\nfilters = [t.dest_city.notnull(), \n t.origin_city.notnull(),\n t.arrdelay > 0,\n t.depdelay > 0,\n t.carrier_name.notnull(),\n t.flight_year == 2008]\n\nexpr = t.filter(filters)\\\n.group_by([t.dest_city, t.origin_city, t.carrier_name])\\\n.having([ct > 1000, aad > 30, add > 30])\\\n.aggregate([aad,add, ct])\\\n.sort_by([('aad', False),('add', False)])\n\nprint(expr.compile())",
"SELECT *\nFROM (\n SELECT \"dest_city\", \"origin_city\", \"carrier_name\", avg(\"arrdelay\") AS aad,\n avg(\"depdelay\") AS add, count(*) AS ct\n FROM flights_donotmodify\n WHERE (\"dest_city\" IS NOT NULL) AND\n (\"origin_city\" IS NOT NULL) AND\n (\"arrdelay\" > 0) AND\n (\"depdelay\" > 0) AND\n (\"carrier_name\" IS NOT NULL) AND\n (\"flight_year\" = 2008)\n GROUP BY dest_city, origin_city, carrier_name\n HAVING count(*) > 1000 AND avg(\"arrdelay\") > 30 AND avg(\"depdelay\") > 30\n) t0\nORDER BY \"aad\" DESC, \"add\" DESC\n"
],
[
"\nad = t.arrdelay.mean().name('ad')\ndd = t.depdelay.mean().name('dd')\nflt_bet = t.count().name('fbp')\norigin = t.origin_city.name('origin')\ndest = t.dest_city.name('dest')\n\nfbp_expr = t.group_by([origin, dest]).aggregate(flt_bet)\n#print(fbp_expr.compile())\n\nexpr = t\\\n.group_by(['origin_city','dest_city'])\\\n.having([ad.notnull(), dd.notnull(), ad > 10, dd > 10])\\\n.aggregate([ad,dd])\n\n#print(expr.compile())\n\nfc = fbp_expr.view()\n\n#Create a join expr - for all pairs of cities with at least 5000 flights between the pair, \n#find where there were at least an average delay of 10 mins for both arrival and departure\njoin_expr = fc[(fc.fbp > 5000) ]\\\n.inner_join(expr,[(fc.origin == expr.origin_city),(fc.dest == expr.dest_city)])[expr, fc.fbp]\\\n.sort_by([('ad',False),('dd',False)]).limit(100)\n\n#print(join_expr.compile())\n\nchart = alt.Chart(join_expr).mark_circle().encode(\n alt.X(alt.repeat(\"column\"), type='quantitative'),\n alt.Y(alt.repeat(\"row\"), type='quantitative'),\n color='fbp:N'\n).properties(\n width=150,\n height=150\n).repeat(\n row=['dd', 'ad', 'fbp'],\n column=['dd', 'ad', 'fbp']\n).interactive()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"chart",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"hc = alt.Chart(expr).mark_rect().encode(\nx = 'dest_city:N',\ny = 'origin_city:N',\ncolor = \"aad:Q\"\n).facet(\ncolumn=\"carrier_name:N\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"hc",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a32b8cc0d5604179a24e6e0cf987a42e70ee1a8
| 1,663 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
pset_challenging_ext/exercises/solutions/nb/p19.ipynb
|
mottaquikarim/pydev-psets
|
9749e0d216ee0a5c586d0d3013ef481cc21dee27
|
[
"MIT"
] | 5 |
2019-04-08T20:05:37.000Z
|
2019-12-04T20:48:45.000Z
|
pset_challenging_ext/exercises/solutions/nb/p19.ipynb
|
mottaquikarim/pydev-psets
|
9749e0d216ee0a5c586d0d3013ef481cc21dee27
|
[
"MIT"
] | 8 |
2019-04-15T15:16:05.000Z
|
2022-02-12T10:33:32.000Z
|
pset_challenging_ext/exercises/solutions/nb/p19.ipynb
|
mottaquikarim/pydev-psets
|
9749e0d216ee0a5c586d0d3013ef481cc21dee27
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2019-04-10T00:14:42.000Z
|
2020-02-26T20:35:21.000Z
| 33.938776 | 207 | 0.559832 |
[
[
[
"empty"
]
]
] |
[
"empty"
] |
[
[
"empty"
]
] |
4a32b991ba9ea0a80a8636a698738d738caf879a
| 74,765 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
examples/.ipynb_checkpoints/scikit-allel-example-checkpoint.ipynb
|
malariagen/datalab
|
f0f35b92337672d1ab173641671a23880c394e74
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
examples/.ipynb_checkpoints/scikit-allel-example-checkpoint.ipynb
|
malariagen/datalab
|
f0f35b92337672d1ab173641671a23880c394e74
|
[
"MIT"
] | 62 |
2018-10-11T12:01:20.000Z
|
2020-10-20T16:39:24.000Z
|
examples/scikit-allel-example.ipynb
|
malariagen/datalab
|
f0f35b92337672d1ab173641671a23880c394e74
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2018-07-09T11:29:43.000Z
|
2018-07-09T11:29:43.000Z
| 101.859673 | 23,276 | 0.79346 |
[
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport zarr\nimport pandas as pd\nimport dask.array as da\nimport allel\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Cluster setup",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from dask_kubernetes import KubeCluster\n#cluster = KubeCluster(n_workers=30)\n#cluster\n\ncluster= KubeCluster()\ncluster.scale_up(6)\ncluster.adapt(minimum=0, maximum=6)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from dask.distributed import Client\nclient = Client(cluster)\nclient",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# client.get_versions(check=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Data setup",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"storage_path = 'ag1000g-release/phase2.AR1/variation/main/zarr/all/ag1000g.phase2.ar1'\n\n# GCS configuration\nimport gcsfs\ngcs_bucket_fs = gcsfs.GCSFileSystem(project='malariagen-jupyterhub', token='anon', access='read_only')\n#store = gcsfs.mapping.GCSMap(storage_path, gcs=gcs_bucket_fs, check=False, create=False)\nstore = gcs_bucket_fs.get_mapper(storage_path)\n# S3 or compatible object storage configuration\n#import s3fs\n#s3 = s3fs.S3FileSystem(anon=True, client_kwargs=dict(region_name='eu-west-2'))\n#store = s3.get_mapper(root=storage_path)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"callset = zarr.open_consolidated(store)\ncallset",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"chrom = '3R'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"gtz = callset[chrom]['calldata/GT']\ngtz",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# gtz.info",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"gt = allel.GenotypeDaskArray(gtz)\ngt",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_samples = pd.read_csv('ftp://ngs.sanger.ac.uk/production/ag1000g/phase2/AR1/samples/samples.meta.txt', \n sep='\\t')\ndf_samples.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Subset data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pop = 'GHcol'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"loc_pass_variants = callset[chrom]['variants/FILTER_PASS'][:]\nloc_pass_variants",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(loc_pass_variants), np.count_nonzero(loc_pass_variants)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"loc_pop_samples = df_samples[df_samples.population == pop].index.values\nloc_pop_samples",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(loc_pop_samples)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"gt_pass_pop = gt.subset(loc_pass_variants, loc_pop_samples)\ngt_pass_pop",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Allele count computation",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# watch the dask dashboard while this is computing\nac_pass_pop = gt_pass_pop.count_alleles(max_allele=3).compute()\nac_pass_pop",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ac_pass_pop.count_segregating()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Multi-population test for selection",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def population_allele_counts(chrom, pop):\n gtz = callset[chrom]['calldata/GT']\n gt = allel.GenotypeDaskArray(gtz)\n loc_pass_variants = callset[chrom]['variants/FILTER_PASS'][:]\n loc_pop_samples = df_samples[df_samples.population == pop].index.values\n gt_pass_pop = gt.subset(loc_pass_variants, loc_pop_samples)\n ac_pass_pop = gt_pass_pop.count_alleles(max_allele=3)\n return ac_pass_pop\n\n\ndef pbs(chrom, pop1, pop2, pop3, window_size=100, min_maf=0.02, normed=True):\n \n # load variant positions\n loc_pass_variants = callset[chrom]['variants/FILTER_PASS'][:]\n pos = callset[chrom]['variants/POS'][:][loc_pass_variants]\n \n # load allele counts\n ac1 = population_allele_counts(chrom, pop1)\n ac2 = population_allele_counts(chrom, pop2)\n ac3 = population_allele_counts(chrom, pop3)\n ac1, ac2, ac3 = da.compute(ac1, ac2, ac3)\n ac1 = allel.AlleleCountsArray(ac1)\n ac2 = allel.AlleleCountsArray(ac2)\n ac3 = allel.AlleleCountsArray(ac3)\n\n # locate segregating variants at sufficient frequency\n ac = ac1 + ac2 + ac3\n loc_seg = ac.is_biallelic_01() & (ac.to_frequencies()[:, :2].min(axis=1) > min_maf)\n pos = pos[loc_seg]\n ac1 = ac1[loc_seg]\n ac2 = ac2[loc_seg]\n ac3 = ac3[loc_seg]\n \n # setup windows\n starts = allel.moving_statistic(pos, statistic=lambda v: v[0], size=window_size)\n starts[0] = 1 # fix to start of sequence\n ends = np.append(starts[1:] - 1, [np.max(pos)])\n\n # compute pbs\n res = allel.pbs(ac1, ac2, ac3, window_size=window_size, normed=normed)\n\n return starts, ends, res\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# watch the dask dashboard\nstarts, ends, y = pbs('3R', 'BFgam', 'UGgam', 'GW')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(14, 3))\nx = (starts + ends) / 2\nax.plot(x, y, marker='o', linestyle=' ', mfc='none', mec='k', markersize=2)\nax.set_xlabel('Genome position (bp)')\nax.set_ylabel('PBS');",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# watch the dask dashboard\nstarts, ends, y = pbs('3R', 'BFcol', 'UGgam', 'GW')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(14, 3))\nx = (starts + ends) / 2\nax.plot(x, y, marker='o', linestyle=' ', mfc='none', mec='k', markersize=2)\nax.set_xlabel('Genome position (bp)')\nax.set_ylabel('PBS');",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a32bad2005937ed4de710c793d560ce20314620
| 15,177 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
More Python Data Tools - Microsoft/08.Testing a model.ipynb
|
ptyadana/probability-and-statistics-for-business-and-data-science
|
6c4d09c70e4c8546461eb7ebc401bb95a0827ef2
|
[
"MIT"
] | 10 |
2021-01-14T15:14:03.000Z
|
2022-02-19T14:06:25.000Z
|
More Python Data Tools - Microsoft/08.Testing a model.ipynb
|
ptyadana/probability-and-statistics-for-business-and-data-science
|
6c4d09c70e4c8546461eb7ebc401bb95a0827ef2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
More Python Data Tools - Microsoft/08.Testing a model.ipynb
|
ptyadana/probability-and-statistics-for-business-and-data-science
|
6c4d09c70e4c8546461eb7ebc401bb95a0827ef2
|
[
"MIT"
] | 8 |
2021-03-24T13:00:02.000Z
|
2022-03-27T16:32:20.000Z
| 29.469903 | 141 | 0.389998 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 1) Load Data and Explore Data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"delays_df = pd.read_csv(\"Data/Lots_of_flight_data.csv\")\ndelays_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"delays_df.info()",
"<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>\nRangeIndex: 300000 entries, 0 to 299999\nData columns (total 16 columns):\n # Column Non-Null Count Dtype \n--- ------ -------------- ----- \n 0 FL_DATE 300000 non-null object \n 1 OP_UNIQUE_CARRIER 300000 non-null object \n 2 TAIL_NUM 299660 non-null object \n 3 OP_CARRIER_FL_NUM 300000 non-null int64 \n 4 ORIGIN 300000 non-null object \n 5 DEST 300000 non-null object \n 6 CRS_DEP_TIME 300000 non-null int64 \n 7 DEP_TIME 296825 non-null float64\n 8 DEP_DELAY 296825 non-null float64\n 9 CRS_ARR_TIME 300000 non-null int64 \n 10 ARR_TIME 296574 non-null float64\n 11 ARR_DELAY 295832 non-null float64\n 12 CRS_ELAPSED_TIME 300000 non-null int64 \n 13 ACTUAL_ELAPSED_TIME 295832 non-null float64\n 14 AIR_TIME 295832 non-null float64\n 15 DISTANCE 300000 non-null int64 \ndtypes: float64(6), int64(5), object(5)\nmemory usage: 36.6+ MB\n"
]
],
[
[
"## 2) Cleaning up data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"delays_df.dropna(inplace=True)\ndelays_df.info()",
"<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>\nInt64Index: 295832 entries, 0 to 299999\nData columns (total 16 columns):\n # Column Non-Null Count Dtype \n--- ------ -------------- ----- \n 0 FL_DATE 295832 non-null object \n 1 OP_UNIQUE_CARRIER 295832 non-null object \n 2 TAIL_NUM 295832 non-null object \n 3 OP_CARRIER_FL_NUM 295832 non-null int64 \n 4 ORIGIN 295832 non-null object \n 5 DEST 295832 non-null object \n 6 CRS_DEP_TIME 295832 non-null int64 \n 7 DEP_TIME 295832 non-null float64\n 8 DEP_DELAY 295832 non-null float64\n 9 CRS_ARR_TIME 295832 non-null int64 \n 10 ARR_TIME 295832 non-null float64\n 11 ARR_DELAY 295832 non-null float64\n 12 CRS_ELAPSED_TIME 295832 non-null int64 \n 13 ACTUAL_ELAPSED_TIME 295832 non-null float64\n 14 AIR_TIME 295832 non-null float64\n 15 DISTANCE 295832 non-null int64 \ndtypes: float64(6), int64(5), object(5)\nmemory usage: 38.4+ MB\n"
]
],
[
[
"## 3) Setting up Features and Labels data sets",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#features\nX = delays_df.loc[:, [\"DISTANCE\", \"CRS_ELAPSED_TIME\"]]\n\n#labels\ny = delays_df.loc[:, [\"ARR_DELAY\"]]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 4) Splitting into Training and Testing sets",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(\n X,\n y,\n test_size = 0.3,\n random_state = 42\n )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 5) Set up & Train Model : this case Linear Regression\n\nUse Scikitlearn LinearRegression fit method to train a linear regression model based on the training data stored in X_train and y_train",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression\n\nregressor = LinearRegression() # Create a scikit learn LinearRegression object\nregressor.fit(X_train, y_train) # Use the fit method to train the model using your training data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### The regressor object now contains your trained Linear Regression model",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 6) Test the Model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"y_predict = regressor.predict(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"y_predict",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### manually compare with actual results",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"y_test.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a32cd8cfc632551055e81a23b84b28312bf01ee
| 91,303 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
analysis/regression.ipynb
|
vsumanbabu/ai-trading-breeakout-strategy
|
f841f1f499cdceb7298cf0b2c44148e3dfdceff3
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
analysis/regression.ipynb
|
vsumanbabu/ai-trading-breeakout-strategy
|
f841f1f499cdceb7298cf0b2c44148e3dfdceff3
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
analysis/regression.ipynb
|
vsumanbabu/ai-trading-breeakout-strategy
|
f841f1f499cdceb7298cf0b2c44148e3dfdceff3
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 375.73251 | 82,548 | 0.932248 |
[
[
[
"\n# Regression",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Install packages",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import sys\n!{sys.executable} -m pip install -r requirements.txt",
"Requirement already satisfied: statsmodels==0.9.0 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from -r requirements.txt (line 1)) (0.9.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: colour==0.1.5 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from -r requirements.txt (line 2)) (0.1.5)\nRequirement already satisfied: numpy==1.14.5 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from -r requirements.txt (line 3)) (1.14.5)\nRequirement already satisfied: pandas==0.21.1 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from -r requirements.txt (line 4)) (0.21.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: plotly==2.2.3 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from -r requirements.txt (line 5)) (2.2.3)\nRequirement already satisfied: scikit-learn==0.19.1 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from -r requirements.txt (line 6)) (0.19.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: six==1.11.0 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from -r requirements.txt (line 7)) (1.11.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: patsy in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from statsmodels==0.9.0->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (0.4.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: pytz>=2011k in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from pandas==0.21.1->-r requirements.txt (line 4)) (2017.3)\nRequirement already satisfied: python-dateutil>=2 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from pandas==0.21.1->-r requirements.txt (line 4)) (2.6.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: requests in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from plotly==2.2.3->-r requirements.txt (line 5)) (2.18.4)\nRequirement already satisfied: decorator>=4.0.6 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from plotly==2.2.3->-r requirements.txt (line 5)) (4.0.11)\nRequirement already satisfied: nbformat>=4.2 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from plotly==2.2.3->-r requirements.txt (line 5)) (4.4.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: chardet<3.1.0,>=3.0.2 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from requests->plotly==2.2.3->-r requirements.txt (line 5)) (3.0.4)\nRequirement already satisfied: idna<2.7,>=2.5 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from requests->plotly==2.2.3->-r requirements.txt (line 5)) (2.6)\nRequirement already satisfied: urllib3<1.23,>=1.21.1 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from requests->plotly==2.2.3->-r requirements.txt (line 5)) (1.22)\nRequirement already satisfied: certifi>=2017.4.17 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from requests->plotly==2.2.3->-r requirements.txt (line 5)) (2019.11.28)\nRequirement already satisfied: jsonschema!=2.5.0,>=2.4 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from nbformat>=4.2->plotly==2.2.3->-r requirements.txt (line 5)) (2.6.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: traitlets>=4.1 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from nbformat>=4.2->plotly==2.2.3->-r requirements.txt (line 5)) (4.3.2)\nRequirement already satisfied: ipython-genutils in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from nbformat>=4.2->plotly==2.2.3->-r requirements.txt (line 5)) (0.2.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: jupyter-core in /opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from nbformat>=4.2->plotly==2.2.3->-r requirements.txt (line 5)) (4.4.0)\n"
],
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport os\nimport helper\nimport quiz_tests\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.style.use('ggplot')\nplt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (14, 8)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Simulate two stock prices\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# just set the seed for the random number generator\nnp.random.seed(100)\n# use returns to create a price series\ndrift = 100\nr0 = pd.Series(np.random.normal(0, 1, 1000))\ns0 = pd.Series(np.cumsum(r0), name='s0') + drift\n\nnoise1 = np.random.normal(0, 0.4, 1000)\ndrift1 = 50\nr1 = r0 + noise1\ns1 = pd.Series(np.cumsum(r1), name='s1') + drift1\n\nnoise2 = np.random.normal(0, 0.4, 1000)\ndrift2 = 60\nr2 = r0 + noise2\ns2 = pd.Series(np.cumsum(r2), name='s2') + drift2\n\npd.concat([s1, s2], axis=1).plot(figsize=(15,6))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Solution: Linear Regression\n\nNote that the LinearRegression().fit() expects 2D numpy arrays. Since s1 and s2 are pandas series, we can use Series.values to get the values as a numpy array. Since these are 1D arrays, we can use numpy.reshape(-1,1) to make these 1000 row by 1 column 2 dimensional arrays. \n\nThe coefficients of the linear regression, $\\beta$ and $intercept$ for the regression line: \n$y = \\beta \\times x + intercept$ \nCan be obtained after fitting to the data. Use `LinearRegression.coef_` for the slope (beta coefficients) and `LinearRegression.intercept_` for the intercept. You may want to practice accessing these outside of the function definition, to see if you'll need additional brackets `[]` to access the values.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def regression_slope_and_intercept(xSeries, ySeries):\n \"\"\"\n xSeries: pandas series, x variable\n ySeries: pandas series, y variable\n \"\"\"\n lr = LinearRegression()\n #TODO: get the values from each series, reshape to be 2 dimensional\n #set s1 to the x variable, s2 to the y variable\n xVar = xSeries.values.reshape(-1,1)\n yVar = ySeries.values.reshape(-1,1)\n \n #TODO: call LinearRegression.fit(). Pass in the x variable then y variable\n lr.fit(xVar,yVar);\n \n #TODO: obtain the slope and intercept\n slope = lr.coef_[0][0]\n intercept = lr.intercept_[0]\n \n return (slope, intercept)\n\nquiz_tests.test_regression_slope_and_intercept(regression_slope_and_intercept);",
"Tests Passed\n"
],
[
"slope, intercept = regression_slope_and_intercept(s1,s2);\nprint(f\"slope {slope:.2f} and intercept {intercept:.2f}\")",
"slope 0.74 and intercept 30.62\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a32dca4232480cd6579ee5129172dbaf3b7d2ca
| 29,747 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
TRN_Notebooks/KO_GoldStandard.ipynb
|
simonsfoundation/Th17_TRN_Networks
|
5b2c9427e1651b42ac913ab45dff5318bd33480b
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2019-03-06T19:37:57.000Z
|
2019-03-06T19:37:57.000Z
|
TRN_Notebooks/KO_GoldStandard.ipynb
|
simonsfoundation/Th17_TRN_Networks
|
5b2c9427e1651b42ac913ab45dff5318bd33480b
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
TRN_Notebooks/KO_GoldStandard.ipynb
|
simonsfoundation/Th17_TRN_Networks
|
5b2c9427e1651b42ac913ab45dff5318bd33480b
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2022-02-24T22:53:03.000Z
|
2022-02-24T22:53:03.000Z
| 41.779494 | 139 | 0.412176 |
[
[
[
"# Visualization of the KO Gold Standard from:\n# Miraldi et al. (2018) \"Leveraging chromatin accessibility data for transcriptional regulatory network inference in Th17 Cells\"\n\n# TO START: In the menu above, choose \"Cell\" --> \"Run All\", and network + heatmap will load\n# NOTE: Default limits networks to TF-TF edges in top 1 TF / gene model (.93 quantile), to see the full \n# network hit \"restore\" (in the drop-down menu in cell below) and set threshold to 0 and hit \"threshold\"\n# You can search for gene names in the search box below the network (hit \"Match\"), and find regulators (\"targeted by\")\n# Change \"canvas\" to \"SVG\" (drop-down menu in cell below) to enable drag interactions with nodes & labels\n# Change \"SVG\" to \"canvas\" to speed up layout operations\n# More info about jp_gene_viz and user interface instructions are available on Github: \n# https://github.com/simonsfoundation/jp_gene_viz/blob/master/doc/dNetwork%20widget%20overview.ipynb\n\n# directory containing gene expression data and network folder\ndirectory = \".\"\n# folder containing networks\nnetPath = 'Networks'\n# network file name\nnetworkFile = 'KO75_KOrk_1norm_sp.tsv'\n# title for network figure\nnetTitle = 'KO Gold Standard'\n# name of gene expression file\nexpressionFile = 'Th0_Th17_48hTh.txt'\n# column of gene expression file to color network nodes\nrnaSampleOfInt = 'Th17(48h)'\n# edge cutoff, TF KO edges from Yosef et al. (2013) Nature. and Ciofani et al. (2012) Cell. are not on comparable scales\nedgeCutoff = 0",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import sys\nif \"..\" not in sys.path:\n sys.path.append(\"..\")\nfrom jp_gene_viz import dNetwork\ndNetwork.load_javascript_support()\n# from jp_gene_viz import multiple_network\nfrom jp_gene_viz import LExpression\nLExpression.load_javascript_support()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Load network linked to gene expression data\nL = LExpression.LinkedExpressionNetwork()\nL.show() ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Load Network and Heatmap\nL.load_network(directory + '/' + netPath + '/' + networkFile)\nL.load_heatmap(directory + '/' + expressionFile)\nN = L.network\nN.set_title(netTitle)\nN.threshhold_slider.value = edgeCutoff\nN.apply_click(None)\nN.draw()\n# Add labels to nodes\nN.labels_button.value=True\nN.restore_click()\n# Limit to TFs only, remove unconnected TFs, choose and set network layout\nN.tf_only_click()\nN.connected_only_click()\nN.layout_dropdown.value = 'fruchterman_reingold'\nN.layout_click()\n\n# Interact with Heatmap\n# Limit genes in heatmap to network genes\nL.gene_click(None) \n# Z-score heatmap values\nL.expression.transform_dropdown.value = 'Z score' \nL.expression.apply_transform() \n# Choose a column in the heatmap (e.g., 48h Th17) to color nodes\nL.expression.col = rnaSampleOfInt\nL.condition_click(None)\n\n# Switch SVG layout to get line colors, then switch back to faster canvas mode\nN.force_svg(None)",
"('Reading network', './Networks/KO75_KOrk_1norm_sp.tsv')\n('Loading saved layout', './Networks/KO75_KOrk_1norm_sp.tsv.layout.json')\nOmitting edges, using canvas, and fast layout default because the network is large\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a32dfcebe6dbc8c54b76041bb8a598c49949610
| 4,538 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
4-assets/BOOKS/Jupyter-Notebooks/Overflow/09-Guessing_Game_Challenge.ipynb
|
impastasyndrome/Lambda-Resource-Static-Assets
|
7070672038620d29844991250f2476d0f1a60b0a
|
[
"MIT"
] | 8 |
2020-09-02T03:59:02.000Z
|
2022-01-08T23:36:19.000Z
|
4-assets/BOOKS/Jupyter-Notebooks/Overflow/09-Guessing_Game_Challenge.ipynb
|
impastasyndrome/Lambda-Resource-Static-Assets
|
7070672038620d29844991250f2476d0f1a60b0a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
4-assets/BOOKS/Jupyter-Notebooks/Overflow/09-Guessing_Game_Challenge.ipynb
|
impastasyndrome/Lambda-Resource-Static-Assets
|
7070672038620d29844991250f2476d0f1a60b0a
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2020-11-18T12:13:05.000Z
|
2021-02-24T19:31:50.000Z
| 25.784091 | 225 | 0.568312 |
[
[
[
"___\n\n<a href='https://www.udemy.com/user/joseportilla/'><img src='../Pierian_Data_Logo.png'/></a>\n___\n<center><em>Content Copyright by Pierian Data</em></center>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Guessing Game Challenge\n\nLet's use `while` loops to create a guessing game.\n\nThe Challenge:\n\nWrite a program that picks a random integer from 1 to 100, and has players guess the number. The rules are:\n\n1. If a player's guess is less than 1 or greater than 100, say \"OUT OF BOUNDS\"\n2. On a player's first turn, if their guess is\n * within 10 of the number, return \"WARM!\"\n * further than 10 away from the number, return \"COLD!\"\n3. On all subsequent turns, if a guess is \n * closer to the number than the previous guess return \"WARMER!\"\n * farther from the number than the previous guess, return \"COLDER!\"\n4. When the player's guess equals the number, tell them they've guessed correctly *and* how many guesses it took!\n\nYou can try this from scratch, or follow the steps outlined below. A separate Solution notebook has been provided. Good luck!\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### First, pick a random integer from 1 to 100 using the random module and assign it to a variable\n\nNote: `random.randint(a,b)` returns a random integer in range `[a, b]`, including both end points.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Next, print an introduction to the game and explain the rules",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Create a list to store guesses\n\nHint: zero is a good placeholder value. It's useful because it evaluates to \"False\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Write a `while` loop that asks for a valid guess. Test it a few times to make sure it works.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"while True:\n \n pass",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Write a `while` loop that compares the player's guess to our number. If the player guesses correctly, break from the loop. Otherwise, tell the player if they're warmer or colder, and continue asking for guesses.\n\nSome hints:\n* it may help to sketch out all possible combinations on paper first!\n* you can use the `abs()` function to find the positive difference between two numbers\n* if you append all new guesses to the list, then the previous guess is given as `guesses[-2]`",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"while True:\n\n # we can copy the code from above to take an input\n\n pass",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"That's it! You've just programmed your first game!\n\nIn the next section we'll learn how to turn some of these repetitive actions into *functions* that can be called whenever we need them.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Good Job!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4a32f2018e40bcd0f0d581305dfbcedf419002cb
| 110,527 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
code/emr-binary-classification.ipynb
|
vlada-rozova/ventilation-duration
|
d7a28334c3528f017a58c565b89a3561d83c1c9e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
code/emr-binary-classification.ipynb
|
vlada-rozova/ventilation-duration
|
d7a28334c3528f017a58c565b89a3561d83c1c9e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
code/emr-binary-classification.ipynb
|
vlada-rozova/ventilation-duration
|
d7a28334c3528f017a58c565b89a3561d83c1c9e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 38.45755 | 125 | 0.391189 |
[
[
[
"# Model development using MIMIC-IV EMR data only (Strategies 0-3)\n\n1. Summary statistics\n2. Feature selection (to add)\n3. Model development\n4. Hyperparameter tuning (to add)\n5. Evaluation of the final model and error analysis (to add)\n\n<img src=\"../results/class distribution.jpeg\" alt=\"Groups\" style=\"width: 400px;\"/>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport utils\nfrom time import time\n\nimport copy, math, os, pickle, time \nimport scipy.stats as ss\n\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV, RandomizedSearchCV\n\nfrom sklearn.svm import SVC\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression\nfrom sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB, ComplementNB\nfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier, GradientBoostingClassifier\nfrom sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier\nfrom sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier\n\nfrom sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline\n\nfrom sklearn.calibration import CalibratedClassifierCV, calibration_curve\n\nfrom sklearn.metrics import average_precision_score, roc_auc_score, accuracy_score, f1_score, precision_recall_curve\n\n# To show all columns in a dataframe\npd.options.display.max_info_columns=250\npd.options.display.max_columns=500\n\n# To make pretty plots\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn as sns\n\nplt.style.use('seaborn-ticks')\nsns.set_style('ticks')\nplt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (6, 4)\nplt.rcParams['axes.titlesize'] = 22\nplt.rcParams['axes.labelsize'] = 20\nplt.rcParams['xtick.labelsize'] = 16\nplt.rcParams['ytick.labelsize'] = 16\n\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Load and prepare the data\n* For a simple model predicting PMV add \"S0\" to filename and set label to \"over72h\"\n* For strategy S1 add \"S1\" to filename and set label to \"over72h\"\n* For strategy S2 add \"S2\" to filename and set label to \"over72h\"\n* For strategy S3 add \"S3\" to filename and set label to \"good_outcome\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_train = pd.read_csv(\"../data/mimic-emr-ft98-train-S0.csv\")\ndf_train.drop(columns=[\"starttime\", \"endtime\"], inplace=True)\n\nlabel = \"over72h\"\n\nprint(df_train.shape)\ndf_train.head()",
"(10121, 103)\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Summary statistics**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_train.describe()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Drop constant variables**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_train = df_train.loc[:, df_train.apply(pd.Series.nunique) != 1]\ndf_train.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Assign cluster numbers based on severity scores",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_train = utils.cluster_by_severity(df_train)",
"Using 24 severity scores...\n0 3614\n1 3266\n3 1678\n2 1563\nName: cluster, dtype: int64\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Feature selection",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"features=None\n# features = df_train.select_dtypes(np.number).columns[1:-2].tolist()\n# features = [\"apsiii\",\n# \"peep_min\",\n# \"resp_rate_min\",\n# \"paraplegia\",\n# \"neuroblocker\",\n# \"vasopressin\",\n# \"chronic_pulmonary_disease\",\n# \"cerebrovascular_disease\",\n# \"congestive_heart_failure\",\n# \"diabetes_with_cc\",\n# \"ph_max\"]\n# features = [\"apsiii\",\n# \"peep_min\",\n# \"resp_rate_min\",\n# \"paraplegia\",\n# \"neuroblocker\",\n# \"vasopressin\",\n# \"height\",\n# \"chronic_pulmonary_disease\",\n# \"cerebrovascular_disease\",\n# \"congestive_heart_failure\",\n# \"diabetes_with_cc\"]\n# features = [\"heart_rate_max\", \"heart_rate_min\", \n# \"peep_max\", \"ph_max\", \n# \"resp_rate_max\", \"resp_rate_min\", \n# \"spo2_min\", \"temp_max\", \"temp_min\"]\n# features = [\"resp_rate_max\",\n# \"resp_rate_min\",\n# \"temp_max\",\n# \"temp_min\",\n# \"spo2_min\",\n# \"glucose_max\",\n# \"mbp_arterial_max\",\n# \"apsiii\",\n# \"glucose_min\",\n# \"heart_rate_min\",\n# \"heart_rate_max\",\n# \"ph_max\",\n# \"co2_total_min\",\n# \"co2_total_max\",\n# \"mbp_ni_min\",\n# \"peep_min\"]\n# features = ['ph_max', 'spo2_min',\n# 'heart_rate_min', 'heart_rate_max', \n# 'resp_rate_min', 'resp_rate_max',\n# 'temp_min', 'temp_max', \n# 'glucose_max', 'glucose_min', \n# 'co2_total_max', 'co2_total_min', \n# 'mbp_max', 'mbp_ni_min', \n# 'apsiii', \n# 'peep_max', 'peep_min']\n\nX_train, y_train = utils.get_X_and_y(df_train, features=features, label=label)\nprint(X_train.shape, y_train.shape)\n\npreprocessor = utils.define_preprocessor(X_train.columns)",
"(10121, 98) (10121,)\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Model development",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# class_names = (\"MV <= 72 hours\", \"MV > 72 hours\")\n# class_names = (\"Bad outcome\", \"Good outcome\")\n\nclfs = (\n LogisticRegression(max_iter=1000),\n# KNeighborsClassifier(),\n# SVC(),\n# DecisionTreeClassifier(),\n# RandomForestClassifier(),\n GradientBoostingClassifier(),\n# CalibratedClassifierCV(GradientBoostingClassifier(), method='isotonic', cv=3)\n)\n\nfor clf in clfs:\n pipe = Pipeline(steps=[('preprocessor', preprocessor),\n ('classifier', clf)])\n scores = utils.benchmark_cv_score(pipe, X_train, y_train)",
"________________________________________________________________________________\n\nModel training: \nLogisticRegression(max_iter=1000)\ntrain time: 3.389s\n\nAverage test_Precision: 0.676 (+/- 0.02)\nAverage test_Recall: 0.676 (+/- 0.02)\nAverage test_F1: 0.676 (+/- 0.02)\nAverage test_ROC AUC: 0.740 (+/- 0.03)\nAverage test_PR AUC: 0.748 (+/- 0.04)\n________________________________________________________________________________\n\nModel training: \nGradientBoostingClassifier()\ntrain time: 20.169s\n\nAverage test_Precision: 0.692 (+/- 0.02)\nAverage test_Recall: 0.691 (+/- 0.02)\nAverage test_F1: 0.691 (+/- 0.02)\nAverage test_ROC AUC: 0.763 (+/- 0.02)\nAverage test_PR AUC: 0.772 (+/- 0.02)\n"
],
[
"from scipy.stats import mannwhitneyu, ttest_ind\nprint(mannwhitneyu(scores_S0['test_roc'], scores_S2['test_roc'], alternative=\"two-sided\"))\nprint(ttest_ind(scores_S0['test_roc'], scores_S2['test_roc']))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Compare full and reduced models",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"X_train, y_train = utils.get_X_and_y(df_train, features=None, label=label)\nprint(X_train.shape, y_train.shape)\n\npreprocessor = utils.define_preprocessor(X_train.columns)\nclf = GradientBoostingClassifier()\n\npipe = Pipeline(steps=[('preprocessor', preprocessor),\n ('classifier', clf)])\n\ny_proba_full = utils.benchmark_cv(pipe, X_train, y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_train, y_train = utils.get_X_and_y(df_train, features=features, label=label)\nprint(X_train.shape, y_train.shape)\n\npreprocessor = utils.define_preprocessor(X_train.columns)\nclf = GradientBoostingClassifier()\n\npipe = Pipeline(steps=[('preprocessor', preprocessor),\n ('classifier', clf)])\n\ny_proba_small = utils.benchmark_cv(pipe, X_train, y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score, roc_curve\n\nplt.figure();\nsns.lineplot(x=[0, 1], y=[0, 1], color=sns.color_palette()[0], lw=2, linestyle='--', label=\"Chance\")\n\nfpr, tpr, _ = roc_curve(y_train, y_proba_full[:,-1])\nroc_auc = roc_auc_score(y_train, y_proba_full[:,-1])\nsns.lineplot(x=fpr, y=tpr, lw=3, color=sns.color_palette()[1], \n label=\"All features: AUC = %0.2f\" % roc_auc)\n\nfpr, tpr, _ = roc_curve(y_train, y_proba_small[:,-1])\nroc_auc = roc_auc_score(y_train, y_proba_small[:,-1])\nsns.lineplot(x=fpr, y=tpr, lw=3, color=sns.color_palette()[2], \n label=\"15 features: AUC = %0.2f\" % roc_auc)\n\nplt.xlim([0.0, 1.0])\nplt.ylim([0.0, 1.05])\nplt.xlabel(\"False Positive Rate\")\nplt.ylabel(\"True Positive Rate\")\nplt.title(\"ROC curve\")\nplt.legend(loc=\"lower right\", fontsize=14);\n\nplt.savefig(\"../results/Feature selection ROC CV\", bbox_inches='tight', dpi=300, transparent=False, pad_inches=0);",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Model calibration",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"preprocessor = utils.define_preprocessor(X_train.columns)\nclf = GradientBoostingClassifier()\ncalibrated_clf = CalibratedClassifierCV(clf, method='isotonic', cv=3)\n\npipe = Pipeline(steps=[('preprocessor', preprocessor),\n ('classifier', clf)])\ncalibrated_pipe = Pipeline(steps=[('preprocessor', preprocessor),\n ('classifier', calibrated_clf)])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Run cross validation to calibrate the model**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"y_proba = utils.benchmark_cv(pipe, X_train, y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"y_proba_c = utils.benchmark_cv(calibrated_pipe, X_train, y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Diagnostic plots**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sns.lineplot(x=[0, 1], y=[0, 1], \n color=sns.color_palette()[0], \n lw=2, linestyle='--', \n label=\"Perfectly calibrated\")\n\nfop, mpv = calibration_curve(y_train, y_proba[:,1], n_bins=30, normalize=False)\nsns.lineplot(x=mpv, y=fop, \n lw=3, marker='.', markersize=15, \n color=sns.color_palette()[1],\n label=\"Uncalibrated\");\n\nfop, mpv = calibration_curve(y_train, y_proba_c[:,1], n_bins=30, normalize=False)\nsns.lineplot(x=mpv, y=fop, \n lw=3, marker='.', markersize=15, \n color=sns.color_palette()[2],\n label=\"Calibrated\");\n\nplt.legend(fontsize=16, loc=\"upper left\");\nplt.xlabel(\"Mean predicted value\");\nplt.ylabel(\"Fraction of positives\");\n\nplt.savefig(\"../results/15ft_calibration.png\", bbox_inches='tight', dpi=300, pad_inches=0);",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sns.histplot(y_proba[:,1], bins=10, stat=\"count\", \n color=sns.color_palette()[1], lw=3, fill=False, \n label=\"Uncalibrated\");\nsns.histplot(y_proba_c[:,1], bins=10, stat=\"count\", \n color=sns.color_palette()[2], lw=3, fill=False, \n label=\"Calibrated\");\nplt.ylim([0, 3800]);\nplt.legend(fontsize=16, loc=\"upper right\");\nplt.xlabel(\"Mean predicted value\");\n\nplt.savefig(\"../results/15ft_probabilities.png\", bbox_inches='tight', dpi=300, pad_inches=0);",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Threshold selection",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def select_threshold(y_train, y_proba):\n precision, recall, thresholds = precision_recall_curve(y_train, y_proba)\n fscore = (2 * precision * recall) / (precision + recall)\n idx = np.argmax(fscore)\n thresh = thresholds[idx]\n print('Best threshold is %.3f, F1 score=%.3f' % (thresh, fscore[idx]))\n return thresh",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"preprocessor = utils.define_preprocessor(X_train.columns)\nclf = GradientBoostingClassifier()\n\npipe = Pipeline(steps=[('preprocessor', preprocessor),\n ('classifier', clf)])\ny_proba = utils.benchmark_cv(pipe, X_train, y_train)",
"________________________________________________________________________________\n\nModel training: \ntrain time: 68.685s\n"
],
[
"thresh = select_threshold(y_train, y_proba)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_train[\"y_proba\"] = y_proba[:,1]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"select_threshold(df_train[df_train.cluster==3].over72h, df_train[df_train.cluster==3].y_proba)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Evaluation using CV",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_train[\"y_pred\"] = utils.evaluate_model(y_train, y_proba, (\"MV < 72h\", \"MV >= 72h\"), \n \"CV, cluster 3\", thresh=thresh, digits=3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_train[\"outcome\"] = 0\ndf_train.loc[(df_train.over72h == 0) & (df_train.y_pred == 0), \"outcome\"] = \"TN\"\ndf_train.loc[(df_train.over72h == 1) & (df_train.y_pred == 0), \"outcome\"] = \"FN\"\ndf_train.loc[(df_train.over72h == 0) & (df_train.y_pred == 1), \"outcome\"] = \"FP\"\ndf_train.loc[(df_train.over72h == 1) & (df_train.y_pred == 1), \"outcome\"] = \"TP\"\ndf_train.outcome.value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tmp = pd.DataFrame((df_train.groupby(\"cluster\").outcome.value_counts() / \n df_train.groupby('cluster').size() * 100).unstack())\ntmp",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"color = sns.color_palette(\"Set1\")\n\ntmp.plot(kind=\"bar\", stacked=True, color=color, alpha=0.8);\nplt.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1, 0.5), fontsize=16);",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.metrics import classification_report\n# Cluster 1\nprint(classification_report(df_train[df_train.cluster==0].over72h, df_train[df_train.cluster==0].y_pred, digits=3))\nprint(classification_report(df_train[df_train.cluster==1].over72h, df_train[df_train.cluster==1].y_pred, digits=3))\nprint(classification_report(df_train[df_train.cluster==2].over72h, df_train[df_train.cluster==2].y_pred, digits=3))\nprint(classification_report(df_train[df_train.cluster==3].over72h, df_train[df_train.cluster==3].y_pred, digits=3))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Model evaluation on MIMIC data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"preprocessor = utils.define_preprocessor(X_train.columns)\nclf = GradientBoostingClassifier()\n\npipe = Pipeline(steps=[('preprocessor', preprocessor),\n ('classifier', clf)])\npipe.fit(X_train, y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Feature importance**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"feature_weights = pd.DataFrame(zip(X_train.columns, pipe['classifier'].feature_importances_), \n columns=[\"feature\", \"weight\"]).sort_values(by=\"weight\", ascending=False)\n\nplt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (4, 6)\n\nax = sns.barplot(y=\"feature\", x=\"weight\", data=feature_weights, orient=\"h\");\n\nplt.ylabel(\"Feature\");\nplt.xlabel(\"Relative importance\");\nplt.xlim([0, 0.35]);\n\nutils.show_values_on_bars(ax, orient=\"h\", space=0.01)\n\nplt.savefig(\"../results/Feature importance\", bbox_inches='tight', dpi=300, transparent=False, pad_inches=0);",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"feature_weights.feature.tolist()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Test set**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_test = pd.read_csv(\"../data/mimic-emr-test-S0.csv\")\ndf_test.drop(columns=[\"starttime\", \"endtime\"], inplace=True)\n\nprint(df_test.shape)\ndf_test.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_test = df_test.loc[:, df_test.apply(pd.Series.nunique) != 1]\ndf_test.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_test, y_test = utils.get_X_and_y(df_test, features=features, label=label)\nprint(X_test.shape, y_test.shape)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"y_proba_test = pipe.predict_proba(X_test)\nutils.evaluate_model(y_test, y_proba_test, (\"MV < 72h\", \"MV >= 72h\"), \"test\", digits=3, \n save_figures=False, filename=\"../results/mimic-test\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### External validation on eICU data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_eicu = pd.read_csv(\"../data/eicu-ft17.csv\")\nprint(df_eicu.shape)\ndf_eicu.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_eicu.over72h.value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_eicu.rename({\"mbp_arterial_max\": \"mbp_max\"}, axis=1, inplace=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_eicu, y_eicu = utils.get_X_and_y(df_eicu, features=features, label=label)\nprint(X_eicu.shape, y_eicu.shape)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"y_proba_eicu = pipe.predict_proba(X_eicu)\nutils.evaluate_model(y_eicu, y_proba_eicu, (\"MV < 72h\", \"MV >= 72h\"), \"eICU\", digits=3, \n save_figures=False, filename=\"../results/eicu\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.metrics import f1_score, auc, roc_auc_score\nroc_auc = roc_auc_score(y_eicu, y_proba_eicu[:,-1])\nroc_auc",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score, roc_curve\n\nplt.figure();\nsns.lineplot(x=[0, 1], y=[0, 1], color=sns.color_palette()[0], lw=2, linestyle='--', label=\"Chance\")\n\n# fpr, tpr, _ = roc_curve(y_test, y_proba_test[:,-1])\n# roc_auc = roc_auc_score(y_test, y_proba_test[:,-1])\n# sns.lineplot(x=fpr, y=tpr, lw=3, color=sns.color_palette()[1], \n# label=\"MIMIC-IV: AUC = %0.2f\" % roc_auc)\n\nfpr, tpr, _ = roc_curve(y_eicu, y_proba_eicu[:,-1])\nroc_auc = roc_auc_score(y_eicu, y_proba_eicu[:,-1])\nsns.lineplot(x=fpr, y=tpr, lw=3, color=sns.color_palette()[2], \n label=\"eICU: AUC = %0.2f\" % roc_auc)\n\nplt.xlim([0.0, 1.0])\nplt.ylim([0.0, 1.05])\nplt.xlabel(\"False Positive Rate\")\nplt.ylabel(\"True Positive Rate\")\nplt.title(\"ROC curve\")\nplt.legend(loc=\"lower right\", fontsize=14);\n\n# plt.savefig(\"../results/ROC mimic vs eicu\", bbox_inches='tight', dpi=300, pad_inches=0);",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a33037e7b3661966400f94e502c33c016796f23
| 220,769 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
climate_analysis.ipynb
|
retroxsky06/surfs_up
|
c90af2c3dda140eeb19f9bd550c26f078639c725
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
climate_analysis.ipynb
|
retroxsky06/surfs_up
|
c90af2c3dda140eeb19f9bd550c26f078639c725
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
climate_analysis.ipynb
|
retroxsky06/surfs_up
|
c90af2c3dda140eeb19f9bd550c26f078639c725
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 43.034893 | 23,512 | 0.443341 |
[
[
[
"# import dependencies\n%matplotlib inline\nfrom matplotlib import style\nstyle.use('fivethirtyeight')\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import datetime as dt",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Reflect Tables into SQLAlchemy ORM",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Python SQL toolkit and Object Relational Mapper\nimport sqlalchemy\nfrom sqlalchemy.ext.automap import automap_base\nfrom sqlalchemy.orm import Session\nfrom sqlalchemy import create_engine, func",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#SETUP SQLALCHEMY ENVIRONMENT\n#create engine function prepaers the db to be connected later\n\nengine = create_engine(\"sqlite:///hawaii.sqlite\")\n\n#add automap base: helps your code to function properly\nBase = automap_base()\n\n# reflect the schema from the tables to our code:\nBase.prepare(engine, reflect=True)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"engine = create_engine(\"sqlite:///hawaii.sqlite\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# reflect an existing database into a new model\nBase = automap_base()\n\n# reflect the tables\nBase.prepare(engine, reflect=True)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# We can view all of the classes that automap found\nBase.classes.keys()\n\n#This code references the classes that were mapped in each table.\n#Base.classes: gives accesses to all classes\n#keys(): references all the names of the classes",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Save references to each table\n# syntax: Base.classes.<class name>\n# assign variables \n\nMeasurement = Base.classes.measurement\nStation = Base.classes.station",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create our session (link) from Python to the DB\nsession = Session(engine)\n\n# session essentially allows us to query for data.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Exploratory Climate Analysis",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Design a query to retrieve the last 12 months of precipitation data and plot the results. \n#Starting from the last data point in the database. \n# prev_year = dt.date(2017, 8, 23)\n\n# Calculate the date one year from the last date in data set.\nprev_year = dt.date(2017, 8, 23) - dt.timedelta(days=365)\n\n# Perform a query to retrieve the data and precipitation scores\nresults = []\nresults = session.query(Measurement.date, Measurement.prcp).filter(Measurement.date >= prev_year).all()\n\n# print(results)\n\n# Save the query results as a Pandas DataFrame and set the index to the date column\n# this saves our query results in two columns, date and precipitation. \ndf = pd.DataFrame(results, columns=['date','precipitation'])\n\n\ndf.set_index(df['date'], inplace=True)\n\n# Use Pandas Plotting with Matplotlib to plot the data\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(df)",
" date precipitation\ndate \n2016-08-23 2016-08-23 0.00\n2016-08-24 2016-08-24 0.08\n2016-08-25 2016-08-25 0.08\n2016-08-26 2016-08-26 0.00\n2016-08-27 2016-08-27 0.00\n... ... ...\n2017-08-19 2017-08-19 0.09\n2017-08-20 2017-08-20 NaN\n2017-08-21 2017-08-21 0.56\n2017-08-22 2017-08-22 0.50\n2017-08-23 2017-08-23 0.45\n\n[2230 rows x 2 columns]\n"
],
[
"\n# print the DataFrame without the index so we can see just the date and precipitation.\n# onvert the DataFrame to strings, and then we'll set our index to \"False.\" \n# This will allow us to print the DataFrame without the index\n\nprint(df.to_string(index=False))",
" date precipitation\n2016-08-23 0.00\n2016-08-24 0.08\n2016-08-25 0.08\n2016-08-26 0.00\n2016-08-27 0.00\n2016-08-28 0.01\n2016-08-29 0.00\n2016-08-30 0.00\n2016-08-31 0.13\n2016-09-01 0.00\n2016-09-02 0.00\n2016-09-03 0.00\n2016-09-04 0.03\n2016-09-05 NaN\n2016-09-06 NaN\n2016-09-07 0.05\n2016-09-08 0.00\n2016-09-09 0.03\n2016-09-10 0.00\n2016-09-11 0.05\n2016-09-12 0.00\n2016-09-13 0.02\n2016-09-14 1.32\n2016-09-15 0.42\n2016-09-16 0.06\n2016-09-17 0.05\n2016-09-18 0.00\n2016-09-19 0.00\n2016-09-20 0.00\n2016-09-21 0.00\n2016-09-22 0.02\n2016-09-23 0.00\n2016-09-24 0.00\n2016-09-25 0.00\n2016-09-26 0.06\n2016-09-27 0.02\n2016-09-28 0.00\n2016-09-29 0.00\n2016-09-30 0.00\n2016-10-01 0.00\n2016-10-02 0.00\n2016-10-03 0.00\n2016-10-04 0.00\n2016-10-05 0.00\n2016-10-06 0.00\n2016-10-07 0.00\n2016-10-08 0.00\n2016-10-09 0.00\n2016-10-10 0.00\n2016-10-11 0.00\n2016-10-12 0.00\n2016-10-13 0.00\n2016-10-14 0.00\n2016-10-15 0.00\n2016-10-16 0.00\n2016-10-17 0.01\n2016-10-18 0.00\n2016-10-19 0.00\n2016-10-20 0.00\n2016-10-21 0.05\n2016-10-22 0.15\n2016-10-23 0.01\n2016-10-24 0.00\n2016-10-25 0.03\n2016-10-26 0.00\n2016-10-27 0.00\n2016-10-28 0.00\n2016-10-29 0.00\n2016-10-30 0.24\n2016-10-31 0.03\n2016-11-01 0.00\n2016-11-02 0.00\n2016-11-03 0.00\n2016-11-04 0.00\n2016-11-05 0.00\n2016-11-06 0.00\n2016-11-07 0.00\n2016-11-08 0.07\n2016-11-09 0.00\n2016-11-10 0.00\n2016-11-11 0.00\n2016-11-12 0.00\n2016-11-13 0.00\n2016-11-14 0.00\n2016-11-15 0.00\n2016-11-16 0.00\n2016-11-17 0.00\n2016-11-18 0.00\n2016-11-19 0.03\n2016-11-20 0.05\n2016-11-21 0.01\n2016-11-22 0.13\n2016-11-23 0.14\n2016-11-24 0.05\n2016-11-25 0.05\n2016-11-26 0.05\n2016-11-27 0.00\n2016-11-28 0.01\n2016-11-29 0.00\n2016-11-30 0.14\n2016-12-01 0.12\n2016-12-02 0.03\n2016-12-03 0.00\n2016-12-04 0.03\n2016-12-05 0.43\n2016-12-06 0.02\n2016-12-07 0.00\n2016-12-08 0.03\n2016-12-09 0.52\n2016-12-10 0.05\n2016-12-11 0.04\n2016-12-12 0.01\n2016-12-13 0.05\n2016-12-14 0.03\n2016-12-15 0.00\n2016-12-16 0.00\n2016-12-17 0.01\n2016-12-18 0.13\n2016-12-19 0.01\n2016-12-20 0.00\n2016-12-21 0.00\n2016-12-22 0.01\n2016-12-23 0.01\n2016-12-24 0.01\n2016-12-25 0.00\n2016-12-26 0.02\n2016-12-27 0.00\n2016-12-28 0.02\n2016-12-29 0.04\n2016-12-30 0.12\n2016-12-31 0.01\n2017-01-01 0.00\n2017-01-02 0.00\n2017-01-03 0.00\n2017-01-04 0.00\n2017-01-05 0.00\n2017-01-06 0.00\n2017-01-07 0.00\n2017-01-08 0.00\n2017-01-09 0.00\n2017-01-10 0.00\n2017-01-11 0.00\n2017-01-12 0.00\n2017-01-13 0.00\n2017-01-14 0.00\n2017-01-15 0.00\n2017-01-16 0.00\n2017-01-17 0.00\n2017-01-18 0.00\n2017-01-19 0.00\n2017-01-20 0.00\n2017-01-21 0.00\n2017-01-22 0.16\n2017-01-23 0.00\n2017-01-24 0.04\n2017-01-25 0.03\n2017-01-26 0.00\n2017-01-27 0.00\n2017-01-28 0.00\n2017-01-29 0.18\n2017-01-30 0.00\n2017-01-31 0.00\n2017-02-01 0.00\n2017-02-02 0.00\n2017-02-03 0.00\n2017-02-04 0.00\n2017-02-05 0.00\n2017-02-06 0.00\n2017-02-07 0.51\n2017-02-08 0.00\n2017-02-09 0.00\n2017-02-10 0.00\n2017-02-11 0.31\n2017-02-12 2.62\n2017-02-13 0.01\n2017-02-14 0.00\n2017-02-15 0.00\n2017-02-16 0.07\n2017-02-17 0.00\n2017-02-18 0.00\n2017-02-19 0.00\n2017-02-20 0.00\n2017-02-21 0.06\n2017-02-22 0.06\n2017-02-23 0.01\n2017-02-24 0.00\n2017-02-25 0.03\n2017-02-26 0.00\n2017-02-27 0.00\n2017-02-28 0.00\n2017-03-01 1.19\n2017-03-02 0.73\n2017-03-03 0.47\n2017-03-04 0.00\n2017-03-05 0.35\n2017-03-06 0.00\n2017-03-07 0.00\n2017-03-08 0.00\n2017-03-09 0.00\n2017-03-10 0.00\n2017-03-11 0.00\n2017-03-12 0.00\n2017-03-13 0.00\n2017-03-14 0.00\n2017-03-15 0.00\n2017-03-16 0.00\n2017-03-17 0.00\n2017-03-18 0.00\n2017-03-19 0.00\n2017-03-20 0.00\n2017-03-21 0.00\n2017-03-22 0.00\n2017-03-23 0.00\n2017-03-24 0.02\n2017-03-25 0.00\n2017-03-26 0.00\n2017-03-27 0.00\n2017-03-28 0.00\n2017-03-29 0.00\n2017-03-30 0.00\n2017-03-31 0.00\n2017-04-01 0.00\n2017-04-02 0.00\n2017-04-03 0.00\n2017-04-04 0.00\n2017-04-05 0.00\n2017-04-06 0.00\n2017-04-07 0.00\n2017-04-08 0.00\n2017-04-09 0.00\n2017-04-10 0.00\n2017-04-11 0.00\n2017-04-12 0.00\n2017-04-13 0.00\n2017-04-14 0.26\n2017-04-15 0.01\n2017-04-16 0.00\n2017-04-17 0.02\n2017-04-18 0.00\n2017-04-19 0.02\n2017-04-20 0.05\n2017-04-21 0.23\n2017-04-22 0.32\n2017-04-23 0.03\n2017-04-24 0.00\n2017-04-25 0.00\n2017-04-26 0.00\n2017-04-27 0.00\n2017-04-28 0.00\n2017-04-29 0.12\n2017-04-30 0.89\n2017-05-01 0.26\n2017-05-02 0.00\n2017-05-03 0.00\n2017-05-04 0.00\n2017-05-05 0.00\n2017-05-06 0.00\n2017-05-07 0.00\n2017-05-08 0.00\n2017-05-10 0.00\n2017-05-11 0.01\n2017-05-12 0.00\n2017-05-13 0.00\n2017-05-14 0.00\n2017-05-15 0.05\n2017-05-16 0.01\n2017-05-17 0.00\n2017-05-18 0.01\n2017-05-19 0.00\n2017-05-20 0.00\n2017-05-21 0.00\n2017-05-22 0.00\n2017-05-23 0.08\n2017-05-24 0.13\n2017-05-25 0.15\n2017-05-27 0.01\n2017-05-28 0.02\n2017-05-29 0.00\n2017-05-30 0.26\n2017-05-31 0.02\n2017-06-01 0.00\n2017-06-02 0.00\n2017-06-03 0.02\n2017-06-04 0.00\n2017-06-05 0.00\n2017-06-06 0.00\n2017-06-07 0.00\n2017-06-08 0.00\n2017-06-09 0.00\n2017-06-10 0.04\n2017-06-11 0.08\n2017-06-12 0.02\n2017-06-13 0.00\n2017-06-14 0.00\n2017-06-15 0.00\n2017-06-16 0.00\n2017-06-17 0.00\n2017-06-18 0.05\n2017-06-19 0.00\n2017-06-20 0.02\n2017-06-21 0.00\n2017-06-22 0.00\n2017-06-23 0.00\n2017-06-24 0.06\n2017-06-25 0.00\n2017-06-26 0.00\n2017-06-27 0.00\n2017-06-28 0.00\n2017-06-29 0.00\n2017-06-30 0.08\n2017-07-01 0.02\n2017-07-02 0.02\n2017-07-03 0.04\n2017-07-04 0.04\n2017-07-05 0.00\n2017-07-06 0.00\n2017-07-07 0.00\n2017-07-08 0.00\n2017-07-09 0.00\n2017-07-10 0.00\n2017-07-11 0.00\n2017-07-12 0.00\n2017-07-13 0.07\n2017-07-14 0.02\n2017-07-15 0.00\n2017-07-16 0.02\n2017-07-17 0.03\n2017-07-18 0.05\n2017-07-20 0.03\n2017-07-21 0.00\n2017-07-22 0.03\n2017-07-23 0.00\n2017-07-24 0.05\n2017-07-25 0.00\n2017-07-26 0.00\n2017-07-27 0.00\n2017-07-28 0.00\n2017-07-29 0.00\n2017-07-30 0.00\n2017-07-31 0.00\n2017-08-01 0.02\n2017-08-02 0.00\n2017-08-03 0.00\n2017-08-04 0.02\n2017-08-05 0.00\n2017-08-06 0.00\n2017-08-07 0.00\n2017-08-08 0.00\n2017-08-09 0.00\n2017-08-10 0.00\n2017-08-11 0.00\n2017-08-12 0.00\n2017-08-13 0.00\n2017-08-14 0.00\n2017-08-15 0.02\n2017-08-18 0.00\n2017-08-19 0.00\n2017-08-20 0.00\n2017-08-21 0.00\n2017-08-22 0.00\n2017-08-23 0.00\n2016-08-23 0.15\n2016-08-24 2.15\n2016-08-25 0.08\n2016-08-26 0.03\n2016-08-27 0.18\n2016-08-28 0.14\n2016-08-29 0.17\n2016-08-30 0.00\n2016-08-31 0.10\n2016-09-01 0.00\n2016-09-02 0.02\n2016-09-03 0.07\n2016-09-04 0.03\n2016-09-05 0.11\n2016-09-06 0.05\n2016-09-07 0.10\n2016-09-08 0.22\n2016-09-09 0.01\n2016-09-10 0.01\n2016-09-11 0.18\n2016-09-12 0.04\n2016-09-13 0.37\n2016-09-14 0.90\n2016-09-15 0.12\n2016-09-16 0.01\n2016-09-17 0.04\n2016-09-18 0.00\n2016-09-19 0.01\n2016-09-20 0.09\n2016-09-21 0.06\n2016-09-22 0.09\n2016-09-23 0.15\n2016-09-24 0.00\n2016-09-25 0.02\n2016-09-26 0.06\n2016-09-27 0.12\n2016-09-28 0.08\n2016-09-29 0.49\n2016-09-30 0.31\n2016-10-01 0.14\n2016-10-02 0.02\n2016-10-03 0.04\n2016-10-04 0.00\n2016-10-05 0.00\n2016-10-06 0.05\n2016-10-07 0.00\n2016-10-08 0.00\n2016-10-09 0.00\n2016-10-10 0.00\n2016-10-11 0.02\n2016-10-12 0.03\n2016-10-13 0.00\n2016-10-14 0.00\n2016-10-15 0.00\n2016-10-16 0.00\n2016-10-17 0.03\n2016-10-18 0.05\n2016-10-19 0.06\n2016-10-20 0.00\n2016-10-21 0.15\n2016-10-22 0.10\n2016-10-23 0.01\n2016-10-24 0.00\n2016-10-25 0.04\n2016-10-26 0.06\n2016-10-27 0.11\n2016-10-28 0.02\n2016-10-29 0.02\n2016-10-30 0.10\n2016-10-31 0.03\n2016-11-01 0.01\n2016-11-02 0.00\n2016-11-03 0.00\n2016-11-04 0.00\n2016-11-05 0.02\n2016-11-06 0.02\n2016-11-07 0.00\n2016-11-08 0.14\n2016-11-09 0.08\n2016-11-10 0.00\n2016-11-11 0.00\n2016-11-12 0.00\n2016-11-13 0.00\n2016-11-14 0.06\n2016-11-15 0.00\n2016-11-16 0.14\n2016-11-17 0.03\n2016-11-18 0.01\n2016-11-19 0.11\n2016-11-20 0.11\n2016-11-21 0.02\n2016-11-22 0.41\n2016-11-23 0.03\n2016-11-24 0.20\n2016-11-25 0.05\n2016-11-26 0.05\n2016-11-27 0.06\n2016-11-28 0.02\n2016-11-29 0.04\n2016-11-30 0.05\n2016-12-01 0.33\n2016-12-02 0.30\n2016-12-03 0.04\n2016-12-04 0.10\n2016-12-05 0.34\n2016-12-06 0.02\n2016-12-07 0.17\n2016-12-08 0.03\n2016-12-09 0.34\n2016-12-10 0.02\n2016-12-11 0.02\n2016-12-12 0.01\n2016-12-13 0.10\n2016-12-14 0.05\n2016-12-15 0.02\n2016-12-16 0.01\n2016-12-17 0.11\n2016-12-18 0.29\n2016-12-19 0.21\n2016-12-20 0.02\n2016-12-21 0.03\n2016-12-22 0.17\n2016-12-23 0.10\n2016-12-24 0.14\n2016-12-25 0.03\n2016-12-26 0.26\n2016-12-27 0.03\n2016-12-28 0.09\n2016-12-29 0.18\n2016-12-30 0.21\n2016-12-31 0.62\n2017-01-01 0.29\n2017-01-02 0.00\n2017-01-03 0.00\n2017-01-04 0.00\n2017-01-05 0.00\n2017-01-06 0.00\n2017-01-07 0.06\n2017-01-08 0.00\n2017-01-09 0.00\n2017-01-10 0.00\n2017-01-11 0.00\n2017-01-12 0.00\n2017-01-13 0.00\n2017-01-14 0.00\n2017-01-15 0.00\n2017-01-16 0.00\n2017-01-17 0.00\n2017-01-18 0.00\n2017-01-19 0.00\n2017-01-20 0.00\n2017-01-21 0.04\n2017-01-22 0.01\n2017-01-23 0.08\n2017-01-24 0.15\n2017-01-25 0.12\n2017-01-26 0.00\n2017-01-27 0.00\n2017-01-28 0.14\n2017-01-29 0.00\n2017-01-30 0.00\n2017-01-31 0.00\n2017-02-01 0.00\n2017-02-02 0.00\n2017-02-03 0.00\n2017-02-04 0.00\n2017-02-05 0.00\n2017-02-06 0.16\n2017-02-07 1.08\n2017-02-08 1.08\n2017-02-09 0.02\n2017-02-10 0.00\n2017-02-11 1.00\n2017-02-12 1.07\n2017-02-13 2.90\n2017-02-14 0.00\n2017-02-15 0.00\n2017-02-16 0.00\n2017-02-17 0.80\n2017-02-18 0.00\n2017-02-19 0.00\n2017-02-20 0.00\n2017-02-21 0.00\n2017-02-22 0.06\n2017-02-23 0.00\n2017-02-24 0.00\n2017-02-25 0.00\n2017-02-26 0.00\n2017-02-27 0.00\n2017-02-28 0.16\n2017-03-01 2.20\n2017-03-02 1.45\n2017-03-03 0.54\n2017-03-04 0.00\n2017-03-05 0.10\n2017-03-06 0.51\n2017-03-07 0.00\n2017-03-08 0.00\n2017-03-09 0.80\n2017-03-10 0.13\n2017-03-11 0.03\n2017-03-12 0.00\n2017-03-13 0.00\n2017-03-14 0.00\n2017-03-15 0.00\n2017-03-16 0.00\n2017-03-17 0.19\n2017-03-18 0.00\n2017-03-19 0.00\n2017-03-20 0.00\n2017-03-21 0.00\n2017-03-22 0.00\n2017-03-23 0.00\n2017-03-24 0.60\n2017-03-25 0.13\n2017-03-26 0.00\n2017-03-27 0.00\n2017-03-28 0.03\n2017-03-29 0.00\n2017-03-30 0.08\n2017-03-31 0.00\n2017-04-01 0.00\n2017-04-02 0.00\n2017-04-03 0.08\n2017-04-04 0.04\n2017-04-05 0.04\n2017-04-06 0.00\n2017-04-07 0.00\n2017-04-08 0.00\n2017-04-09 0.00\n2017-04-10 0.01\n2017-04-11 0.03\n2017-04-12 0.03\n2017-04-13 0.27\n2017-04-14 0.69\n2017-04-15 0.45\n2017-04-16 0.49\n2017-04-17 0.41\n2017-04-18 0.08\n2017-04-19 0.02\n2017-04-20 0.33\n2017-04-21 1.16\n2017-04-22 1.01\n2017-04-23 0.02\n2017-04-24 0.00\n2017-04-25 0.00\n2017-04-26 0.00\n2017-04-27 0.10\n2017-04-28 2.60\n2017-04-29 0.35\n2017-04-30 1.21\n2017-05-01 0.07\n2017-05-02 0.03\n2017-05-03 0.01\n2017-05-04 0.00\n2017-05-05 0.00\n2017-05-06 0.00\n2017-05-07 0.07\n2017-05-08 0.22\n2017-05-09 1.62\n2017-05-10 0.05\n2017-05-11 0.03\n2017-05-12 0.04\n2017-05-13 0.02\n2017-05-14 0.05\n2017-05-15 0.08\n2017-05-16 0.03\n2017-05-17 0.02\n2017-05-18 0.09\n2017-05-19 0.02\n2017-05-20 0.00\n2017-05-21 0.00\n2017-05-22 0.00\n2017-05-23 0.02\n2017-05-24 0.58\n2017-05-25 0.37\n2017-05-26 0.02\n2017-05-27 0.00\n2017-05-28 0.29\n2017-05-29 0.02\n2017-05-30 0.20\n2017-05-31 0.10\n2017-06-01 0.03\n2017-06-02 0.10\n2017-06-03 0.20\n2017-06-04 0.15\n2017-06-05 0.00\n2017-06-06 0.00\n2017-06-07 0.00\n2017-06-08 0.02\n2017-06-09 0.02\n2017-06-10 0.21\n2017-06-11 0.24\n2017-06-12 0.19\n2017-06-13 0.36\n2017-06-14 0.27\n2017-06-15 0.17\n2017-06-16 0.02\n2017-06-17 0.35\n2017-06-18 0.25\n2017-06-19 0.05\n2017-06-20 0.05\n2017-06-21 0.02\n2017-06-22 0.10\n2017-06-23 0.00\n2017-06-24 0.00\n2017-06-25 0.08\n2017-06-26 0.02\n2017-06-27 0.00\n2017-06-28 0.01\n2017-06-29 0.03\n2017-06-30 0.04\n2017-07-01 0.06\n2017-07-02 0.05\n2017-07-03 0.13\n2017-07-04 0.03\n2017-07-05 0.00\n2017-07-06 0.00\n2017-07-07 0.02\n2017-07-08 0.02\n2017-07-09 0.09\n2017-07-10 0.00\n2017-07-11 0.01\n2017-07-12 0.01\n2017-07-13 0.33\n2017-07-14 0.05\n2017-07-15 0.03\n2017-07-16 0.07\n2017-07-17 0.12\n2017-07-18 0.03\n2017-07-19 0.00\n2017-07-20 0.12\n2017-07-21 0.00\n2017-07-22 0.07\n2017-07-23 0.06\n2017-07-24 0.58\n2017-07-25 0.03\n2017-07-26 0.06\n2017-07-27 0.00\n2017-07-28 0.13\n2017-07-29 0.06\n2017-07-30 0.00\n2017-07-31 0.00\n2016-08-23 0.05\n2016-08-24 2.28\n2016-08-25 0.00\n2016-08-26 0.02\n2016-08-27 0.02\n2016-08-28 0.14\n2016-08-29 0.04\n2016-08-31 NaN\n2016-09-01 0.00\n2016-09-02 0.19\n2016-09-05 NaN\n2016-09-06 0.04\n2016-09-07 0.23\n2016-09-08 0.01\n2016-09-09 0.29\n2016-09-12 NaN\n2016-09-13 0.32\n2016-09-14 1.84\n2016-09-15 0.07\n2016-09-16 0.07\n2016-09-19 NaN\n2016-09-20 0.25\n2016-09-21 0.02\n2016-09-22 0.17\n2016-09-23 0.15\n2016-09-24 0.00\n2016-09-25 0.00\n2016-09-26 0.02\n2016-09-27 0.00\n2016-09-28 0.00\n2016-09-29 0.20\n2016-09-30 0.06\n2016-10-01 0.08\n2016-10-02 0.03\n2016-10-03 0.03\n2016-10-04 0.00\n2016-10-05 0.00\n2016-10-06 0.00\n2016-10-07 0.00\n2016-10-10 NaN\n2016-10-11 0.04\n2016-10-12 0.00\n2016-10-13 0.02\n2016-10-14 0.00\n2016-10-15 0.02\n2016-10-17 NaN\n2016-10-18 0.03\n2016-10-19 0.00\n2016-10-20 0.01\n2016-10-21 0.03\n2016-10-23 NaN\n2016-10-24 0.01\n2016-10-25 0.00\n2016-10-27 0.20\n2016-10-28 0.07\n2016-10-29 0.26\n2016-10-30 0.14\n2016-10-31 0.00\n2016-11-01 0.00\n2016-11-02 0.00\n2016-11-03 0.00\n2016-11-04 0.00\n2016-11-05 0.00\n2016-11-06 0.00\n2016-11-07 0.13\n2016-11-08 0.02\n2016-11-09 0.17\n2016-11-10 0.00\n2016-11-11 0.00\n2016-11-12 0.00\n2016-11-13 0.00\n2016-11-14 0.05\n2016-11-15 0.00\n2016-11-16 0.18\n2016-11-17 0.00\n2016-11-22 NaN\n2016-11-25 NaN\n2016-11-26 0.02\n2016-11-27 0.03\n2016-11-28 0.00\n2016-11-29 0.04\n2016-11-30 0.03\n2016-12-01 0.07\n2016-12-02 0.40\n2016-12-03 0.26\n2016-12-04 0.00\n2016-12-05 0.20\n2016-12-07 NaN\n2016-12-08 0.02\n2016-12-09 0.26\n2016-12-10 0.00\n2016-12-12 NaN\n2016-12-13 0.34\n2016-12-14 0.12\n2016-12-15 0.07\n2016-12-16 0.00\n2016-12-17 0.00\n2016-12-18 0.04\n2016-12-19 0.00\n2016-12-20 0.00\n2016-12-21 0.09\n2016-12-22 0.05\n2016-12-23 0.03\n2016-12-24 0.13\n2016-12-26 NaN\n2016-12-27 0.02\n2016-12-28 0.01\n2016-12-29 0.56\n2016-12-30 0.29\n2016-12-31 0.36\n2017-01-01 0.00\n2017-01-02 0.01\n2017-01-03 0.00\n2017-01-04 0.00\n2017-01-05 0.00\n2017-01-06 0.59\n2017-01-07 0.00\n2017-01-08 0.03\n2017-01-09 0.00\n2017-01-10 0.00\n2017-01-11 0.00\n2017-01-13 NaN\n2017-01-14 0.00\n2017-01-16 NaN\n2017-01-17 0.00\n2017-01-18 0.00\n2017-01-19 0.00\n2017-01-20 0.00\n2017-01-21 0.02\n2017-01-23 NaN\n2017-01-25 NaN\n2017-01-26 0.01\n2017-01-27 0.00\n2017-01-28 0.00\n2017-01-30 NaN\n2017-01-31 0.00\n2017-02-01 0.00\n2017-02-02 0.00\n2017-02-03 0.00\n2017-02-05 NaN\n2017-02-06 0.04\n2017-02-07 0.90\n2017-02-08 0.00\n2017-02-09 0.00\n2017-02-10 0.00\n2017-02-11 2.39\n2017-02-12 1.91\n2017-02-13 0.00\n2017-02-14 0.00\n2017-02-15 0.00\n2017-02-16 0.62\n2017-02-17 0.06\n2017-02-20 NaN\n2017-02-21 0.00\n2017-02-22 0.11\n2017-02-23 0.00\n2017-02-24 0.00\n2017-02-26 NaN\n2017-02-27 0.00\n2017-02-28 0.04\n2017-03-01 1.12\n2017-03-03 NaN\n2017-03-06 NaN\n2017-03-07 0.00\n2017-03-08 0.00\n2017-03-09 0.50\n2017-03-10 0.13\n2017-03-12 NaN\n2017-03-13 0.00\n2017-03-14 0.00\n2017-03-16 NaN\n2017-03-17 0.06\n2017-03-18 0.00\n2017-03-20 NaN\n2017-03-21 0.00\n2017-03-22 0.00\n2017-03-23 0.00\n2017-03-24 0.15\n2017-03-27 NaN\n2017-03-28 0.00\n2017-03-29 0.03\n2017-03-30 0.03\n2017-03-31 0.00\n2017-04-01 0.00\n2017-04-02 0.00\n2017-04-03 0.09\n2017-04-04 0.00\n2017-04-05 0.07\n2017-04-06 0.00\n2017-04-07 0.00\n2017-04-09 NaN\n2017-04-10 0.00\n2017-04-11 0.16\n2017-04-12 0.29\n2017-04-13 0.00\n2017-04-14 0.29\n2017-04-17 NaN\n2017-04-18 0.12\n2017-04-19 0.00\n2017-04-20 0.00\n2017-04-21 1.05\n2017-04-22 0.70\n2017-04-24 NaN\n2017-04-25 0.00\n2017-04-26 0.14\n2017-04-27 0.02\n2017-04-28 0.09\n2017-04-29 0.95\n2017-04-30 1.17\n2017-05-01 0.03\n2017-05-02 0.01\n2017-05-03 0.01\n2017-05-04 0.08\n2017-05-05 0.28\n2017-05-06 0.06\n2017-05-08 0.95\n2017-05-09 0.52\n2017-05-10 0.00\n2017-05-12 NaN\n2017-05-15 NaN\n2017-05-16 0.05\n2017-05-17 0.00\n2017-05-18 0.16\n2017-05-19 0.01\n2017-05-20 0.01\n2017-05-22 NaN\n2017-05-23 0.11\n2017-05-24 0.10\n2017-05-25 0.07\n2017-05-26 0.00\n2017-05-27 0.00\n2017-05-28 0.02\n2017-05-29 0.00\n2017-05-30 0.04\n2017-05-31 0.00\n2017-06-01 0.00\n2017-06-02 0.15\n2017-06-03 0.16\n2017-06-04 0.05\n2017-06-05 0.02\n2017-06-06 0.00\n2017-06-07 0.00\n2017-06-08 0.01\n2017-06-09 0.00\n2017-06-10 0.53\n2017-06-11 0.14\n2017-06-12 0.35\n2017-06-13 0.10\n2017-06-14 0.21\n2017-06-15 0.30\n2017-06-16 0.02\n2017-06-17 0.02\n2017-06-18 0.18\n2017-06-19 0.19\n2017-06-20 0.17\n2017-06-23 NaN\n2017-06-26 NaN\n2017-06-29 NaN\n2017-06-30 0.00\n2017-07-03 NaN\n2017-07-05 NaN\n2017-07-07 NaN\n2017-07-08 0.06\n2017-07-09 0.00\n2017-07-10 0.00\n2017-07-11 0.00\n2017-07-12 0.02\n2017-07-13 0.30\n2017-07-14 0.00\n2017-07-15 0.01\n2017-07-16 0.12\n2017-07-17 0.16\n2017-07-18 0.00\n2017-07-19 0.09\n2017-07-20 0.00\n2017-07-21 0.00\n2017-07-22 0.12\n2017-07-23 0.07\n2017-07-24 1.19\n2017-07-25 0.12\n2017-07-26 0.02\n2017-07-27 0.00\n2017-07-28 0.14\n2017-07-29 0.02\n2017-07-31 NaN\n2017-08-01 0.12\n2017-08-02 0.05\n2017-08-03 0.01\n2017-08-04 0.04\n2017-08-06 0.00\n2017-08-07 0.00\n2017-08-08 0.10\n2017-08-09 0.00\n2017-08-10 0.00\n2017-08-11 0.00\n2017-08-13 NaN\n2017-08-14 0.01\n2017-08-15 0.00\n2017-08-16 0.00\n2017-08-17 0.00\n2017-08-18 0.00\n2017-08-19 0.00\n2017-08-20 0.01\n2017-08-21 0.02\n2017-08-23 0.00\n2016-08-23 NaN\n2016-08-24 NaN\n2016-08-25 0.00\n2016-08-26 0.04\n2016-08-29 NaN\n2016-08-30 0.02\n2016-08-31 NaN\n2016-09-01 NaN\n2016-09-02 NaN\n2016-09-08 NaN\n2016-09-09 NaN\n2016-09-12 NaN\n2016-09-13 NaN\n2016-09-14 NaN\n2016-09-15 NaN\n2016-09-16 0.00\n2016-09-19 NaN\n2016-09-20 0.00\n2016-09-22 0.06\n2016-09-23 0.00\n2016-09-26 NaN\n2016-09-28 0.00\n2016-09-29 0.04\n2016-09-30 NaN\n2016-10-03 NaN\n2016-10-04 NaN\n2016-10-05 NaN\n2016-10-06 0.07\n2016-10-07 NaN\n2016-10-11 NaN\n2016-10-13 NaN\n2016-10-17 NaN\n2016-10-18 NaN\n2016-10-19 NaN\n2016-10-20 NaN\n2016-10-21 NaN\n2016-10-24 NaN\n2016-10-25 0.40\n2016-10-26 0.20\n2016-10-27 NaN\n2016-10-28 NaN\n2016-10-31 NaN\n2016-11-04 NaN\n2016-11-07 NaN\n2016-11-09 0.00\n2016-11-14 0.02\n2016-11-15 NaN\n2016-11-16 NaN\n2016-11-17 NaN\n2016-11-18 NaN\n2016-11-21 NaN\n2016-11-22 NaN\n2016-11-23 NaN\n2016-11-28 NaN\n2016-11-29 NaN\n2016-11-30 NaN\n2016-12-01 NaN\n2016-12-02 NaN\n2016-12-05 NaN\n2016-12-06 NaN\n2016-12-07 NaN\n2016-12-08 0.27\n2016-12-09 NaN\n2016-12-12 0.02\n2016-12-13 NaN\n2016-12-14 NaN\n2016-12-15 NaN\n2016-12-16 NaN\n2016-12-19 NaN\n2016-12-20 NaN\n2016-12-21 0.06\n2016-12-22 NaN\n2016-12-23 NaN\n2016-12-28 NaN\n2016-12-29 NaN\n2016-12-30 NaN\n2017-01-09 NaN\n2017-01-10 NaN\n2017-01-11 NaN\n2017-01-12 NaN\n2017-01-13 NaN\n2017-01-17 0.00\n2017-01-18 0.00\n2017-01-19 NaN\n2017-01-20 NaN\n2017-01-23 NaN\n2017-01-24 NaN\n2017-01-25 NaN\n2017-01-26 0.00\n2017-01-27 0.00\n2017-01-30 0.05\n2017-01-31 0.00\n2017-02-01 0.00\n2017-02-02 0.00\n2017-02-03 0.00\n2017-02-06 NaN\n2017-02-07 0.00\n2017-02-08 0.00\n2017-02-09 0.00\n2017-02-10 0.00\n2017-02-13 NaN\n2017-02-14 0.00\n2017-02-15 NaN\n2017-02-16 NaN\n2017-02-17 0.00\n2017-02-21 NaN\n2017-02-22 0.17\n2017-02-23 0.00\n2017-02-24 0.00\n2017-02-27 NaN\n2017-02-28 NaN\n2017-03-01 2.40\n2017-03-02 0.44\n2017-03-03 0.14\n2017-03-06 NaN\n2017-03-07 NaN\n2017-03-08 NaN\n2017-03-09 0.00\n2017-03-10 0.00\n2017-03-13 NaN\n2017-03-14 0.06\n2017-03-15 0.00\n2017-03-16 NaN\n2017-03-17 NaN\n2017-03-28 NaN\n2017-03-29 NaN\n2017-03-30 NaN\n2017-03-31 0.00\n2017-04-03 NaN\n2017-04-04 0.00\n2017-04-05 0.00\n2017-04-06 0.00\n2017-04-07 0.00\n2017-04-10 NaN\n2017-04-11 NaN\n2017-04-12 NaN\n2017-04-13 NaN\n2017-04-17 NaN\n2017-04-18 0.00\n2017-04-19 NaN\n2017-04-20 NaN\n2017-04-21 NaN\n2017-04-24 NaN\n2017-04-25 NaN\n2017-04-27 NaN\n2017-04-28 NaN\n2017-06-02 NaN\n2017-06-05 NaN\n2017-06-06 NaN\n2017-06-07 NaN\n2017-06-08 NaN\n2017-06-09 NaN\n2017-06-13 NaN\n2017-06-14 NaN\n2017-06-15 NaN\n2017-06-16 NaN\n2017-06-19 NaN\n2017-06-20 NaN\n2017-06-21 NaN\n2017-06-22 0.00\n2017-06-23 0.00\n2017-06-26 NaN\n2017-06-27 0.00\n2017-06-28 0.00\n2017-06-29 0.00\n2017-06-30 0.12\n2017-07-03 NaN\n2017-07-05 NaN\n2017-07-06 NaN\n2017-07-07 NaN\n2017-07-10 NaN\n2017-07-11 NaN\n2017-07-12 NaN\n2017-07-13 NaN\n2017-07-18 0.00\n2017-07-19 0.00\n2017-07-20 0.00\n2017-07-21 0.00\n2017-07-25 0.00\n2017-07-26 NaN\n2017-07-27 NaN\n2017-07-28 0.01\n2017-07-31 NaN\n2016-08-23 0.02\n2016-08-24 1.22\n2016-08-25 0.21\n2016-08-26 0.00\n2016-08-27 0.00\n2016-08-28 0.14\n2016-08-29 0.00\n2016-08-30 0.00\n2016-08-31 0.25\n2016-09-02 NaN\n2016-09-03 0.08\n2016-09-04 0.74\n2016-09-05 0.02\n2016-09-06 0.03\n2016-09-07 0.11\n2016-09-08 0.01\n2016-09-09 0.23\n2016-09-10 0.14\n2016-09-11 0.12\n2016-09-12 0.15\n2016-09-13 0.46\n2016-09-14 1.19\n2016-09-15 0.17\n2016-09-16 0.01\n2016-09-17 0.00\n2016-09-18 0.04\n2016-09-19 0.05\n2016-09-20 0.04\n2016-09-21 0.00\n2016-09-22 0.01\n2016-09-23 0.00\n2016-09-24 0.00\n2016-09-25 0.00\n2016-09-26 0.34\n2016-09-27 0.05\n2016-09-28 0.00\n2016-09-29 0.18\n2016-09-30 0.15\n2016-10-01 0.07\n2016-10-02 0.00\n2016-10-03 0.00\n2016-10-04 0.00\n2016-10-05 0.00\n2016-10-06 0.00\n2016-10-07 0.00\n2016-10-08 0.00\n2016-10-09 0.00\n2016-10-10 0.00\n2016-10-11 0.00\n2016-10-12 0.00\n2016-10-13 0.00\n2016-10-14 0.00\n2016-10-15 0.00\n2016-10-16 0.00\n2016-10-17 0.12\n2016-10-18 0.02\n2016-10-19 0.00\n2016-10-21 NaN\n2016-10-22 0.00\n2016-10-23 0.00\n2016-10-24 0.00\n2016-10-25 0.12\n2016-10-26 0.02\n2016-10-27 0.08\n2016-10-28 0.06\n2016-10-29 0.01\n2016-10-30 0.00\n2016-10-31 0.13\n2016-11-01 0.01\n2016-11-02 0.00\n2016-11-03 0.00\n2016-11-04 0.00\n2016-11-05 0.02\n2016-11-06 0.00\n2016-11-07 0.00\n2016-11-08 0.15\n2016-11-09 0.00\n2016-11-10 0.00\n2016-11-11 0.00\n2016-11-12 0.00\n2016-11-13 0.00\n2016-11-14 0.00\n2016-11-15 0.00\n2016-11-16 0.07\n2016-11-17 0.00\n2016-11-18 0.02\n2016-11-19 0.13\n2016-11-20 0.40\n2016-11-21 0.07\n2016-11-22 0.31\n2016-11-23 0.03\n2016-11-24 0.21\n2016-11-25 0.11\n2016-11-26 0.03\n2016-11-27 0.00\n2016-11-28 0.00\n2016-11-29 0.06\n2016-11-30 0.00\n2016-12-01 0.16\n2016-12-02 0.01\n2016-12-03 0.02\n2016-12-04 0.32\n2016-12-05 0.45\n2016-12-06 0.00\n2016-12-07 0.07\n2016-12-08 0.01\n2016-12-10 NaN\n2016-12-11 0.06\n2016-12-12 0.00\n2016-12-13 0.15\n2016-12-14 0.05\n2016-12-15 0.00\n2016-12-16 0.00\n2016-12-17 0.16\n2016-12-18 0.27\n2016-12-19 0.02\n2016-12-20 0.01\n2016-12-21 0.06\n2016-12-22 0.14\n2016-12-23 0.02\n2016-12-24 0.06\n2016-12-25 0.00\n2016-12-26 0.06\n2016-12-27 0.00\n2016-12-28 0.06\n2016-12-29 0.05\n2016-12-30 0.07\n2017-01-01 NaN\n2017-01-03 NaN\n2017-01-04 0.18\n2017-01-05 0.42\n2017-01-06 0.01\n2017-01-07 0.00\n2017-01-08 0.00\n2017-01-09 0.00\n2017-01-10 0.00\n2017-01-12 NaN\n2017-01-15 NaN\n2017-01-16 0.00\n2017-01-18 NaN\n2017-01-19 0.00\n2017-01-20 0.00\n2017-01-21 0.11\n2017-01-22 0.04\n2017-01-23 0.00\n2017-01-24 0.08\n2017-01-25 0.00\n2017-01-26 0.00\n2017-01-27 0.00\n2017-01-29 NaN\n2017-01-30 0.00\n2017-01-31 0.00\n2017-02-01 0.00\n2017-02-02 0.00\n2017-02-03 0.00\n2017-02-04 0.00\n2017-02-05 0.00\n2017-02-06 0.00\n2017-02-07 1.80\n2017-02-08 0.00\n2017-02-09 0.00\n2017-02-10 0.00\n2017-02-11 5.04\n2017-02-12 0.07\n2017-02-13 0.00\n2017-02-15 NaN\n2017-02-16 0.67\n2017-02-17 0.06\n2017-02-18 0.01\n2017-02-20 NaN\n2017-02-22 0.13\n2017-02-23 0.00\n2017-02-24 0.00\n2017-02-26 NaN\n2017-02-27 0.00\n2017-02-28 0.00\n2017-03-01 0.59\n2017-03-02 1.48\n2017-03-03 0.25\n2017-03-04 0.00\n2017-03-06 NaN\n2017-03-09 NaN\n2017-03-10 0.00\n2017-03-11 0.00\n2017-03-12 0.00\n2017-03-13 0.00\n2017-03-14 0.00\n2017-03-15 0.00\n2017-03-16 0.00\n2017-03-17 0.35\n2017-03-18 0.00\n2017-03-19 0.00\n2017-03-20 0.00\n2017-03-21 0.00\n2017-03-22 0.00\n2017-03-23 0.02\n2017-03-24 0.07\n2017-03-25 0.43\n2017-03-26 0.00\n2017-03-27 0.00\n2017-03-28 0.00\n2017-03-29 0.08\n2017-03-30 0.00\n2017-03-31 0.00\n2017-04-01 0.00\n2017-04-02 0.00\n2017-04-03 0.00\n2017-04-04 0.00\n2017-04-05 0.00\n2017-04-06 0.00\n2017-04-07 0.00\n2017-04-09 NaN\n2017-04-10 0.00\n2017-04-11 0.00\n2017-04-12 0.00\n2017-04-13 0.00\n2017-04-14 0.36\n2017-04-15 0.00\n2017-04-16 0.00\n2017-04-17 0.30\n2017-04-18 0.15\n2017-04-19 0.00\n2017-04-20 0.35\n2017-04-21 2.36\n2017-04-24 NaN\n2017-04-25 0.00\n2017-04-26 0.01\n2017-04-27 0.00\n2017-04-28 0.00\n2017-04-29 6.25\n2017-04-30 1.31\n2017-05-01 0.07\n2017-05-02 0.00\n2017-05-03 0.00\n2017-05-04 0.00\n2017-05-05 0.00\n2017-05-06 0.00\n2017-05-07 0.00\n2017-05-08 0.00\n2017-05-09 0.68\n2017-05-10 0.06\n2017-05-11 0.00\n2017-05-12 0.00\n2017-05-13 0.00\n2017-05-14 0.00\n2017-05-15 0.06\n2017-05-16 0.00\n2017-05-17 0.00\n2017-05-18 0.46\n2017-05-20 NaN\n2017-05-21 0.00\n2017-05-22 0.00\n2017-05-23 0.00\n2017-05-24 0.61\n2017-05-25 0.55\n2017-05-26 0.00\n2017-05-27 0.00\n2017-05-28 0.00\n2017-05-29 0.00\n2017-05-30 0.11\n2017-05-31 0.00\n2017-06-01 0.00\n2017-06-02 0.00\n2017-06-03 0.15\n2017-06-04 0.00\n2017-06-05 0.00\n2017-06-06 0.00\n2017-06-07 0.00\n2017-06-08 0.00\n2017-06-09 0.00\n2017-06-10 0.13\n2017-06-11 0.25\n2017-06-12 0.14\n2017-06-13 0.03\n2017-06-14 0.06\n2017-06-15 0.00\n2017-06-16 0.00\n2017-06-17 0.00\n2017-06-18 0.00\n2017-06-19 0.01\n2017-06-21 NaN\n2017-06-22 0.00\n2017-06-23 0.05\n2017-06-24 0.00\n2017-06-25 0.00\n2017-06-26 0.00\n2017-06-27 0.00\n2017-06-28 0.00\n2017-06-29 0.00\n2017-06-30 0.07\n2017-07-02 NaN\n2017-07-03 0.02\n2017-07-05 NaN\n2017-07-06 0.00\n2017-07-07 0.00\n2017-07-08 0.00\n2017-07-09 0.00\n2017-07-10 0.00\n2017-07-11 0.00\n2017-07-12 0.00\n2017-07-13 0.11\n2017-07-14 0.00\n2017-07-15 0.00\n2017-07-16 0.00\n2017-07-17 0.00\n2017-07-18 0.00\n2017-07-19 0.00\n2017-07-20 0.33\n2017-07-21 0.00\n2017-07-22 0.00\n2017-07-24 NaN\n2017-07-25 0.05\n2017-07-26 0.00\n2017-07-27 0.00\n2017-07-28 0.00\n2017-07-29 0.00\n2017-07-30 0.00\n2017-07-31 0.00\n2017-08-01 0.00\n2017-08-02 0.00\n2017-08-03 0.00\n2017-08-04 0.00\n2017-08-06 0.00\n2017-08-07 0.00\n2017-08-08 0.00\n2017-08-10 0.00\n2017-08-11 0.00\n2017-08-12 0.00\n2017-08-13 0.00\n2017-08-14 0.08\n2017-08-15 0.06\n2017-08-16 0.07\n2017-08-17 0.05\n2017-08-19 NaN\n2017-08-21 NaN\n2017-08-22 0.00\n2017-08-23 0.08\n2016-08-23 1.79\n2016-08-24 2.15\n2016-08-25 0.06\n2016-08-26 0.01\n2016-08-27 0.12\n2016-08-28 0.60\n2016-08-29 0.35\n2016-08-30 0.00\n2016-08-31 0.24\n2016-09-01 0.02\n2016-09-02 0.01\n2016-09-03 0.12\n2016-09-04 0.14\n2016-09-05 0.03\n2016-09-06 0.11\n2016-09-07 0.16\n2016-09-08 0.07\n2016-09-09 0.16\n2016-09-10 0.09\n2016-09-11 0.30\n2016-09-12 0.31\n2016-09-13 0.34\n2016-09-14 2.33\n2016-09-15 0.83\n2016-09-16 0.06\n2016-09-17 0.36\n2016-09-18 0.07\n2016-09-19 0.01\n2016-09-20 0.22\n2016-09-21 0.07\n2016-09-22 0.34\n2016-09-23 0.94\n2016-09-24 0.01\n2016-09-25 0.03\n2016-09-26 0.17\n2016-09-27 0.17\n2016-09-28 0.00\n2016-09-29 0.59\n2016-09-30 0.25\n2016-10-01 0.14\n2016-10-02 0.06\n2016-10-03 0.16\n2016-10-04 0.03\n2016-10-05 0.01\n2016-10-06 0.00\n2016-10-07 0.00\n2016-10-08 0.00\n2016-10-09 0.00\n2016-10-10 0.00\n2016-10-11 0.28\n2016-10-12 0.03\n2016-10-13 0.00\n2016-10-14 0.00\n2016-10-15 0.04\n2016-10-16 0.00\n2016-10-17 0.01\n2016-10-18 0.02\n2016-10-19 0.11\n2016-10-20 0.00\n2016-10-21 0.00\n2016-10-22 0.15\n2016-10-23 0.02\n2016-10-24 0.08\n2016-10-25 0.11\n2016-10-26 0.01\n2016-10-27 0.22\n2016-10-28 0.05\n2016-10-29 0.10\n2016-10-30 0.16\n2016-10-31 0.07\n2016-11-01 0.10\n2016-11-02 0.00\n2016-11-03 0.00\n2016-11-04 0.00\n2016-11-05 0.03\n2016-11-06 0.01\n2016-11-07 0.00\n2016-11-08 0.21\n2016-11-09 0.11\n2016-11-10 0.00\n2016-11-11 0.00\n2016-11-12 0.00\n2016-11-13 0.00\n2016-11-14 0.00\n2016-11-15 0.00\n2016-11-16 0.24\n2016-11-17 0.01\n2016-11-18 0.00\n2016-11-19 0.11\n2016-11-20 0.39\n2016-11-21 0.11\n2016-11-22 2.05\n2016-11-23 0.25\n2016-11-24 0.30\n2016-11-25 0.08\n2016-11-26 0.06\n2016-11-27 0.17\n2016-11-28 0.00\n2016-11-29 0.09\n2016-11-30 0.05\n2016-12-01 0.37\n2016-12-02 0.35\n2016-12-03 0.77\n2016-12-04 0.04\n2016-12-05 0.22\n2016-12-06 0.00\n2016-12-07 0.12\n2016-12-08 0.07\n2016-12-09 0.31\n2016-12-10 0.02\n2016-12-11 0.00\n2016-12-12 0.00\n2016-12-13 0.04\n2016-12-14 0.92\n2016-12-15 0.14\n2016-12-16 0.03\n2016-12-17 0.07\n2016-12-18 0.16\n2016-12-19 0.03\n2016-12-20 0.00\n2016-12-21 0.11\n2016-12-22 0.86\n2016-12-23 0.24\n2016-12-24 0.20\n2016-12-25 0.02\n2016-12-26 0.22\n2016-12-27 0.05\n2016-12-28 0.09\n2016-12-29 0.52\n2016-12-30 0.29\n2016-12-31 0.25\n2017-01-01 0.03\n2017-01-02 0.01\n2017-01-03 0.00\n2017-01-04 0.00\n2017-01-05 0.06\n2017-01-06 0.10\n2017-01-07 0.00\n2017-01-08 0.00\n2017-01-09 0.00\n2017-01-10 0.00\n2017-01-11 0.00\n2017-01-12 0.00\n2017-01-13 0.00\n2017-01-14 0.01\n2017-01-15 0.00\n2017-01-16 0.00\n2017-01-17 0.00\n2017-01-18 0.00\n2017-01-19 0.02\n2017-01-20 0.00\n2017-01-21 0.03\n2017-01-22 0.09\n2017-01-23 0.01\n2017-01-24 0.13\n2017-01-25 0.79\n2017-01-26 0.00\n2017-01-27 0.03\n2017-01-28 0.00\n2017-01-29 0.26\n2017-01-30 0.00\n2017-01-31 0.00\n2017-02-01 0.00\n2017-02-02 0.00\n2017-02-03 0.00\n2017-02-04 0.00\n2017-02-05 0.00\n2017-02-06 0.18\n2017-02-07 1.32\n2017-02-08 0.00\n2017-02-09 0.00\n2017-02-10 0.00\n2017-02-11 1.73\n2017-02-12 2.98\n2017-02-13 0.01\n2017-02-14 0.00\n2017-02-15 0.01\n2017-02-16 0.73\n2017-02-17 0.13\n2017-02-18 0.00\n2017-02-19 0.09\n2017-02-20 0.00\n2017-02-21 0.00\n2017-02-22 0.06\n2017-02-23 0.00\n2017-02-24 0.00\n2017-02-25 0.00\n2017-02-26 0.00\n2017-02-27 0.00\n2017-02-28 0.04\n2017-03-01 2.12\n2017-03-02 1.88\n2017-03-03 0.27\n2017-03-04 0.00\n2017-03-05 0.41\n2017-03-06 0.03\n2017-03-07 0.00\n2017-03-08 0.00\n2017-03-09 0.65\n2017-03-10 0.03\n2017-03-11 0.01\n2017-03-12 0.00\n2017-03-13 0.00\n2017-03-14 0.00\n2017-03-15 0.06\n2017-03-16 0.00\n2017-03-17 0.12\n2017-03-18 0.00\n2017-03-19 0.00\n2017-03-20 0.02\n2017-03-21 0.09\n2017-03-22 0.00\n2017-03-23 0.00\n2017-03-24 0.12\n2017-03-25 0.93\n2017-03-26 0.00\n2017-03-27 0.01\n2017-03-28 0.00\n2017-03-29 0.01\n2017-03-30 0.04\n2017-03-31 0.01\n2017-04-01 0.21\n2017-04-02 0.00\n2017-04-03 0.26\n2017-04-04 0.09\n2017-04-05 0.10\n2017-04-06 0.06\n2017-04-07 0.00\n2017-04-08 0.00\n2017-04-09 0.00\n2017-04-10 0.01\n2017-04-11 0.03\n2017-04-12 0.11\n2017-04-13 0.59\n2017-04-14 2.30\n2017-04-15 0.38\n2017-04-16 0.47\n2017-04-17 1.04\n2017-04-18 2.03\n2017-04-19 0.02\n2017-04-20 0.05\n2017-04-21 1.74\n2017-04-22 1.58\n2017-04-23 0.06\n2017-04-24 0.01\n2017-04-25 0.00\n2017-04-26 0.02\n2017-04-27 0.19\n2017-04-28 0.76\n2017-04-29 0.37\n2017-04-30 1.04\n2017-05-01 0.13\n2017-05-02 0.01\n2017-05-03 0.01\n2017-05-04 0.00\n2017-05-05 0.00\n2017-05-06 0.00\n2017-05-07 0.02\n2017-05-08 0.73\n2017-05-09 1.58\n2017-05-10 0.20\n2017-05-11 0.12\n2017-05-12 0.02\n2017-05-13 0.12\n2017-05-14 0.17\n2017-05-15 0.09\n2017-05-16 0.03\n2017-05-17 0.07\n2017-05-18 0.13\n2017-05-19 0.01\n2017-05-20 0.02\n2017-05-21 0.01\n2017-05-22 0.06\n2017-05-23 0.06\n2017-05-24 0.30\n2017-05-25 0.20\n2017-05-26 0.00\n2017-05-27 0.00\n2017-05-28 0.08\n2017-05-29 0.40\n2017-05-30 1.12\n2017-05-31 0.25\n2017-06-01 0.00\n2017-06-02 0.09\n2017-06-03 0.08\n2017-06-04 0.13\n2017-06-05 0.05\n2017-06-06 0.00\n2017-06-07 0.00\n2017-06-08 0.00\n2017-06-09 0.02\n2017-06-10 0.62\n2017-06-11 0.74\n2017-06-12 0.24\n2017-06-13 0.24\n2017-06-14 0.22\n2017-06-15 0.55\n2017-06-16 0.06\n2017-06-17 0.07\n2017-06-18 0.24\n2017-06-19 0.08\n2017-06-20 0.00\n2017-06-21 0.19\n2017-06-22 0.06\n2017-06-23 0.12\n2017-06-24 0.36\n2017-06-25 0.02\n2017-06-26 0.06\n2017-06-27 0.01\n2017-06-28 0.00\n2017-06-29 0.00\n2017-06-30 0.01\n2017-07-01 0.08\n2017-07-02 0.15\n2017-07-03 0.15\n2017-07-04 0.08\n2017-07-05 0.00\n2017-07-06 0.00\n2017-07-07 0.18\n2017-07-08 0.00\n2017-07-09 0.11\n2017-07-10 0.02\n2017-07-11 0.02\n2017-07-12 0.28\n2017-07-13 0.32\n2017-07-14 0.20\n2017-07-15 0.05\n2017-07-16 0.10\n2017-07-17 0.21\n2017-07-18 0.05\n2017-07-19 0.05\n2017-07-20 0.06\n2017-07-21 0.03\n2017-07-22 0.20\n2017-07-23 0.20\n2017-07-24 0.61\n2017-07-25 0.11\n2017-07-26 0.12\n2017-07-27 0.01\n2017-07-28 0.09\n2017-07-29 0.23\n2017-07-30 0.00\n2017-07-31 0.00\n2017-08-04 0.00\n2017-08-05 0.06\n2017-08-06 0.00\n2017-08-13 0.00\n2017-08-14 0.00\n2017-08-15 0.32\n2017-08-16 0.12\n2017-08-17 0.01\n2017-08-18 0.06\n2016-08-23 0.70\n2016-08-24 1.45\n2016-08-25 0.11\n2016-08-27 NaN\n2016-08-28 2.07\n2016-08-29 0.90\n2016-08-30 0.05\n2016-08-31 2.46\n2016-09-01 0.01\n2016-09-02 0.03\n2016-09-03 1.00\n2016-09-04 0.44\n2016-09-05 0.18\n2016-09-06 1.00\n2016-09-07 1.35\n2016-09-08 0.15\n2016-09-09 0.35\n2016-09-10 1.16\n2016-09-11 0.60\n2016-09-12 1.04\n2016-09-13 1.20\n2016-09-14 6.70\n2016-09-15 3.35\n2016-09-16 0.61\n2016-09-17 0.23\n2016-09-18 0.42\n2016-09-19 0.25\n2016-09-20 0.43\n2016-09-21 1.02\n2016-09-22 0.75\n2016-09-23 0.33\n2016-09-24 0.27\n2016-09-25 0.04\n2016-09-26 1.02\n2016-09-27 1.00\n2016-09-28 0.05\n2016-09-29 1.49\n2016-09-30 0.38\n2016-10-01 1.02\n2016-10-02 0.61\n2016-10-03 0.46\n2016-10-04 3.46\n2016-10-05 0.81\n2016-10-06 0.04\n2016-10-07 0.01\n2016-10-08 0.04\n2016-10-09 0.00\n2016-10-10 0.00\n2016-10-11 0.35\n2016-10-12 0.02\n2016-10-13 0.06\n2016-10-14 0.00\n2016-10-15 0.33\n2016-10-16 0.00\n2016-10-17 0.38\n2016-10-18 0.48\n2016-10-19 0.00\n2016-10-20 1.00\n2016-10-21 0.09\n2016-10-22 1.37\n2016-10-23 0.24\n2016-10-24 0.70\n2016-10-25 0.40\n2016-10-26 0.00\n2016-10-27 1.25\n2016-10-28 0.37\n2016-10-29 0.25\n2016-10-30 0.95\n2016-10-31 1.35\n2016-11-01 0.09\n2016-11-02 0.04\n2016-11-03 0.02\n2016-11-04 0.06\n2016-11-05 0.38\n2016-11-06 0.05\n2016-11-07 0.05\n2016-11-08 0.53\n2016-11-09 0.04\n2016-11-10 0.01\n2016-11-11 0.00\n2016-11-12 0.00\n2016-11-13 0.00\n2016-11-14 0.02\n2016-11-15 0.05\n2016-11-16 0.91\n2016-11-17 0.02\n2016-11-20 NaN\n2016-11-21 2.87\n2016-11-22 2.11\n2016-11-23 0.22\n2016-11-24 0.72\n2016-11-25 1.03\n2016-11-26 0.30\n2016-11-27 0.29\n2016-11-28 0.69\n2016-11-29 0.20\n2016-11-30 0.79\n2016-12-01 0.72\n2016-12-02 1.27\n2016-12-03 1.62\n2016-12-04 0.31\n2016-12-05 1.60\n2016-12-06 0.00\n2016-12-07 0.02\n2016-12-08 0.03\n2016-12-09 0.42\n2016-12-10 0.04\n2016-12-11 0.13\n2016-12-12 0.01\n2016-12-13 0.09\n2016-12-14 0.33\n2016-12-15 0.03\n2016-12-16 0.00\n2016-12-18 NaN\n2016-12-19 0.15\n2016-12-20 0.00\n2016-12-21 0.55\n2016-12-22 1.24\n2016-12-23 0.83\n2016-12-24 1.08\n2016-12-25 0.38\n2016-12-26 1.48\n2016-12-27 0.14\n2016-12-28 0.14\n2016-12-29 1.03\n2016-12-30 2.37\n2016-12-31 0.90\n2017-01-01 0.03\n2017-01-02 0.00\n2017-01-03 0.00\n2017-01-04 0.00\n2017-01-05 0.47\n2017-01-06 0.10\n2017-01-07 0.00\n2017-01-08 0.03\n2017-01-09 0.00\n2017-01-10 0.00\n2017-01-11 0.00\n2017-01-12 0.00\n2017-01-13 0.00\n2017-01-14 0.00\n2017-01-15 0.01\n2017-01-16 0.00\n2017-01-17 0.00\n2017-01-18 0.07\n2017-01-19 0.00\n2017-01-20 0.00\n2017-01-21 0.08\n2017-01-22 0.72\n2017-01-23 0.85\n2017-01-24 1.85\n2017-01-25 2.64\n2017-01-26 0.10\n2017-01-27 0.03\n2017-01-28 0.00\n2017-01-29 0.55\n2017-01-30 0.00\n2017-01-31 0.00\n2017-02-01 0.00\n2017-02-02 0.00\n2017-02-04 NaN\n2017-02-05 0.00\n2017-02-06 0.00\n2017-02-07 1.79\n2017-02-08 0.00\n2017-02-09 0.00\n2017-02-10 0.00\n2017-02-11 0.73\n2017-02-12 1.83\n2017-02-13 0.00\n2017-02-14 0.01\n2017-02-15 0.07\n2017-02-16 0.13\n2017-02-18 NaN\n2017-02-19 0.10\n2017-02-20 0.00\n2017-02-21 0.07\n2017-02-22 0.32\n2017-02-23 0.00\n2017-02-24 0.00\n2017-02-25 0.12\n2017-02-26 0.00\n2017-02-27 0.00\n2017-02-28 0.58\n2017-03-01 2.00\n2017-03-02 0.58\n2017-03-03 0.56\n2017-03-04 0.00\n2017-03-05 0.35\n2017-03-06 0.00\n2017-03-07 0.00\n2017-03-08 0.00\n2017-03-09 0.01\n2017-03-10 0.00\n2017-03-11 0.00\n2017-03-13 NaN\n2017-03-14 0.00\n2017-03-15 0.00\n2017-03-16 0.00\n2017-03-18 NaN\n2017-03-19 0.00\n2017-03-20 0.00\n2017-03-21 0.00\n2017-03-22 0.00\n2017-03-23 0.03\n2017-03-24 0.17\n2017-03-25 0.48\n2017-03-26 0.00\n2017-03-27 0.00\n2017-03-28 0.68\n2017-03-29 0.07\n2017-03-31 NaN\n2017-04-01 0.20\n2017-04-02 0.00\n2017-04-03 0.23\n2017-04-04 0.02\n2017-04-05 0.45\n2017-04-06 0.00\n2017-04-08 NaN\n2017-04-09 0.00\n2017-04-10 0.00\n2017-04-11 0.25\n2017-04-12 0.65\n2017-04-13 0.23\n2017-04-14 2.82\n2017-04-15 0.90\n2017-04-16 0.11\n2017-04-17 1.30\n2017-04-18 0.98\n2017-04-19 0.14\n2017-04-20 0.00\n2017-04-21 1.84\n2017-04-22 1.35\n2017-04-23 0.35\n2017-04-24 0.05\n2017-04-25 0.00\n2017-04-26 0.22\n2017-04-27 0.11\n2017-04-28 0.79\n2017-04-29 0.00\n2017-04-30 0.80\n2017-05-01 0.25\n2017-05-02 0.00\n2017-05-04 NaN\n2017-05-05 0.10\n2017-05-06 0.00\n2017-05-07 0.03\n2017-05-08 1.11\n2017-05-09 0.23\n2017-05-10 0.55\n2017-05-11 0.44\n2017-05-12 0.10\n2017-05-13 0.10\n2017-05-14 1.00\n2017-05-15 0.60\n2017-05-16 0.30\n2017-05-17 0.06\n2017-05-18 0.00\n2017-05-20 NaN\n2017-05-21 0.00\n2017-05-22 0.30\n2017-05-23 0.44\n2017-05-24 2.17\n2017-05-25 0.88\n2017-05-26 0.00\n2017-05-27 0.50\n2017-05-28 0.00\n2017-05-30 NaN\n2017-06-01 0.01\n2017-06-03 NaN\n2017-06-04 0.82\n2017-06-05 0.01\n2017-06-06 0.00\n2017-06-07 0.01\n2017-06-08 0.00\n2017-06-10 NaN\n2017-06-11 0.70\n2017-06-12 0.81\n2017-06-13 0.65\n2017-06-14 0.81\n2017-06-15 1.69\n2017-06-16 0.10\n2017-06-17 0.10\n2017-06-18 0.70\n2017-06-19 0.40\n2017-06-20 0.31\n2017-06-21 0.30\n2017-06-22 0.28\n2017-06-23 0.50\n2017-06-24 0.22\n2017-06-25 0.50\n2017-06-26 0.02\n2017-06-27 0.10\n2017-06-28 0.02\n2017-06-29 0.04\n2017-06-30 0.20\n2017-07-01 0.10\n2017-07-02 0.50\n2017-07-03 0.40\n2017-07-04 0.00\n2017-07-05 0.00\n2017-07-06 0.02\n2017-07-07 0.30\n2017-07-08 0.02\n2017-07-09 0.00\n2017-07-10 0.02\n2017-07-11 0.00\n2017-07-12 0.05\n2017-07-13 0.68\n2017-07-14 0.68\n2017-07-15 0.10\n2017-07-16 0.50\n2017-07-17 0.39\n2017-07-18 2.40\n2017-07-19 0.27\n2017-07-20 0.70\n2017-07-21 0.10\n2017-07-22 4.00\n2017-07-23 0.80\n2017-07-24 0.84\n2017-07-25 0.30\n2017-07-26 0.30\n2017-07-27 0.00\n2017-07-28 0.40\n2017-07-29 0.30\n2017-07-30 0.30\n2017-07-31 0.00\n2017-08-01 NaN\n2017-08-02 0.25\n2017-08-03 0.06\n2017-08-05 NaN\n2017-08-06 NaN\n2017-08-07 0.05\n2017-08-08 0.34\n2017-08-09 0.15\n2017-08-10 0.07\n2017-08-11 NaN\n2017-08-12 0.14\n2017-08-13 NaN\n2017-08-14 0.22\n2017-08-15 0.42\n2017-08-16 0.42\n2017-08-17 0.13\n2017-08-18 NaN\n2017-08-19 0.09\n2017-08-20 NaN\n2017-08-21 0.56\n2017-08-22 0.50\n2017-08-23 0.45\n"
]
],
[
[
"### 9.2.3 Sort the DataFrame",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n# Sort the dataframe by date\ndf = df.sort_index()\n# code to print the sorted list without the index\nprint(df.to_string(index=False))",
" date precipitation\n2016-08-23 0.00\n2016-08-23 NaN\n2016-08-23 1.79\n2016-08-23 0.05\n2016-08-23 0.15\n2016-08-23 0.70\n2016-08-23 0.02\n2016-08-24 0.08\n2016-08-24 2.15\n2016-08-24 2.28\n2016-08-24 NaN\n2016-08-24 1.45\n2016-08-24 1.22\n2016-08-24 2.15\n2016-08-25 0.08\n2016-08-25 0.00\n2016-08-25 0.21\n2016-08-25 0.06\n2016-08-25 0.00\n2016-08-25 0.11\n2016-08-25 0.08\n2016-08-26 0.03\n2016-08-26 0.01\n2016-08-26 0.00\n2016-08-26 0.04\n2016-08-26 0.02\n2016-08-26 0.00\n2016-08-27 0.18\n2016-08-27 0.12\n2016-08-27 0.00\n2016-08-27 0.00\n2016-08-27 0.02\n2016-08-27 NaN\n2016-08-28 0.60\n2016-08-28 0.14\n2016-08-28 0.01\n2016-08-28 0.14\n2016-08-28 0.14\n2016-08-28 2.07\n2016-08-29 0.00\n2016-08-29 NaN\n2016-08-29 0.04\n2016-08-29 0.00\n2016-08-29 0.17\n2016-08-29 0.90\n2016-08-29 0.35\n2016-08-30 0.00\n2016-08-30 0.02\n2016-08-30 0.00\n2016-08-30 0.05\n2016-08-30 0.00\n2016-08-30 0.00\n2016-08-31 0.10\n2016-08-31 NaN\n2016-08-31 0.24\n2016-08-31 0.13\n2016-08-31 NaN\n2016-08-31 2.46\n2016-08-31 0.25\n2016-09-01 0.00\n2016-09-01 0.02\n2016-09-01 0.00\n2016-09-01 NaN\n2016-09-01 0.01\n2016-09-01 0.00\n2016-09-02 0.00\n2016-09-02 0.03\n2016-09-02 0.02\n2016-09-02 NaN\n2016-09-02 NaN\n2016-09-02 0.01\n2016-09-02 0.19\n2016-09-03 1.00\n2016-09-03 0.08\n2016-09-03 0.12\n2016-09-03 0.00\n2016-09-03 0.07\n2016-09-04 0.03\n2016-09-04 0.14\n2016-09-04 0.74\n2016-09-04 0.03\n2016-09-04 0.44\n2016-09-05 0.02\n2016-09-05 0.03\n2016-09-05 0.11\n2016-09-05 NaN\n2016-09-05 NaN\n2016-09-05 0.18\n2016-09-06 NaN\n2016-09-06 0.05\n2016-09-06 0.03\n2016-09-06 1.00\n2016-09-06 0.11\n2016-09-06 0.04\n2016-09-07 0.16\n2016-09-07 0.05\n2016-09-07 0.11\n2016-09-07 0.10\n2016-09-07 1.35\n2016-09-07 0.23\n2016-09-08 0.07\n2016-09-08 0.01\n2016-09-08 0.15\n2016-09-08 0.22\n2016-09-08 0.01\n2016-09-08 NaN\n2016-09-08 0.00\n2016-09-09 0.23\n2016-09-09 0.35\n2016-09-09 0.29\n2016-09-09 NaN\n2016-09-09 0.01\n2016-09-09 0.03\n2016-09-09 0.16\n2016-09-10 0.00\n2016-09-10 0.14\n2016-09-10 1.16\n2016-09-10 0.01\n2016-09-10 0.09\n2016-09-11 0.30\n2016-09-11 0.12\n2016-09-11 0.18\n2016-09-11 0.05\n2016-09-11 0.60\n2016-09-12 1.04\n2016-09-12 NaN\n2016-09-12 0.04\n2016-09-12 NaN\n2016-09-12 0.31\n2016-09-12 0.00\n2016-09-12 0.15\n2016-09-13 NaN\n2016-09-13 0.02\n2016-09-13 1.20\n2016-09-13 0.32\n2016-09-13 0.46\n2016-09-13 0.34\n2016-09-13 0.37\n2016-09-14 1.32\n2016-09-14 0.90\n2016-09-14 1.19\n2016-09-14 1.84\n2016-09-14 6.70\n2016-09-14 2.33\n2016-09-14 NaN\n2016-09-15 0.42\n2016-09-15 NaN\n2016-09-15 0.17\n2016-09-15 0.12\n2016-09-15 0.07\n2016-09-15 3.35\n2016-09-15 0.83\n2016-09-16 0.61\n2016-09-16 0.00\n2016-09-16 0.06\n2016-09-16 0.07\n2016-09-16 0.06\n2016-09-16 0.01\n2016-09-16 0.01\n2016-09-17 0.00\n2016-09-17 0.23\n2016-09-17 0.04\n2016-09-17 0.36\n2016-09-17 0.05\n2016-09-18 0.00\n2016-09-18 0.07\n2016-09-18 0.04\n2016-09-18 0.42\n2016-09-18 0.00\n2016-09-19 0.25\n2016-09-19 0.01\n2016-09-19 0.05\n2016-09-19 0.00\n2016-09-19 0.01\n2016-09-19 NaN\n2016-09-19 NaN\n2016-09-20 0.00\n2016-09-20 0.09\n2016-09-20 0.22\n2016-09-20 0.00\n2016-09-20 0.04\n2016-09-20 0.25\n2016-09-20 0.43\n2016-09-21 0.06\n2016-09-21 0.00\n2016-09-21 0.07\n2016-09-21 0.02\n2016-09-21 1.02\n2016-09-21 0.00\n2016-09-22 0.75\n2016-09-22 0.09\n2016-09-22 0.06\n2016-09-22 0.01\n2016-09-22 0.17\n2016-09-22 0.34\n2016-09-22 0.02\n2016-09-23 0.33\n2016-09-23 0.00\n2016-09-23 0.94\n2016-09-23 0.15\n2016-09-23 0.00\n2016-09-23 0.15\n2016-09-23 0.00\n2016-09-24 0.00\n2016-09-24 0.27\n2016-09-24 0.00\n2016-09-24 0.00\n2016-09-24 0.00\n2016-09-24 0.01\n2016-09-25 0.00\n2016-09-25 0.02\n2016-09-25 0.03\n2016-09-25 0.00\n2016-09-25 0.00\n2016-09-25 0.04\n2016-09-26 0.02\n2016-09-26 0.17\n2016-09-26 1.02\n2016-09-26 0.06\n2016-09-26 0.34\n2016-09-26 0.06\n2016-09-26 NaN\n2016-09-27 0.12\n2016-09-27 0.05\n2016-09-27 0.00\n2016-09-27 1.00\n2016-09-27 0.17\n2016-09-27 0.02\n2016-09-28 0.00\n2016-09-28 0.00\n2016-09-28 0.00\n2016-09-28 0.05\n2016-09-28 0.08\n2016-09-28 0.00\n2016-09-28 0.00\n2016-09-29 0.20\n2016-09-29 0.00\n2016-09-29 0.04\n2016-09-29 0.59\n2016-09-29 0.49\n2016-09-29 1.49\n2016-09-29 0.18\n2016-09-30 0.25\n2016-09-30 0.31\n2016-09-30 NaN\n2016-09-30 0.38\n2016-09-30 0.00\n2016-09-30 0.06\n2016-09-30 0.15\n2016-10-01 0.00\n2016-10-01 0.14\n2016-10-01 0.08\n2016-10-01 0.14\n2016-10-01 0.07\n2016-10-01 1.02\n2016-10-02 0.61\n2016-10-02 0.00\n2016-10-02 0.02\n2016-10-02 0.03\n2016-10-02 0.06\n2016-10-02 0.00\n2016-10-03 0.03\n2016-10-03 0.46\n2016-10-03 0.00\n2016-10-03 NaN\n2016-10-03 0.04\n2016-10-03 0.16\n2016-10-03 0.00\n2016-10-04 3.46\n2016-10-04 0.00\n2016-10-04 NaN\n2016-10-04 0.03\n2016-10-04 0.00\n2016-10-04 0.00\n2016-10-04 0.00\n2016-10-05 0.81\n2016-10-05 0.00\n2016-10-05 0.01\n2016-10-05 0.00\n2016-10-05 0.00\n2016-10-05 NaN\n2016-10-05 0.00\n2016-10-06 0.00\n2016-10-06 0.00\n2016-10-06 0.04\n2016-10-06 0.07\n2016-10-06 0.00\n2016-10-06 0.05\n2016-10-06 0.00\n2016-10-07 0.00\n2016-10-07 NaN\n2016-10-07 0.00\n2016-10-07 0.00\n2016-10-07 0.01\n2016-10-07 0.00\n2016-10-07 0.00\n2016-10-08 0.04\n2016-10-08 0.00\n2016-10-08 0.00\n2016-10-08 0.00\n2016-10-08 0.00\n2016-10-09 0.00\n2016-10-09 0.00\n2016-10-09 0.00\n2016-10-09 0.00\n2016-10-09 0.00\n2016-10-10 0.00\n2016-10-10 0.00\n2016-10-10 0.00\n2016-10-10 0.00\n2016-10-10 0.00\n2016-10-10 NaN\n2016-10-11 0.00\n2016-10-11 0.04\n2016-10-11 0.28\n2016-10-11 0.02\n2016-10-11 0.00\n2016-10-11 0.35\n2016-10-11 NaN\n2016-10-12 0.03\n2016-10-12 0.00\n2016-10-12 0.02\n2016-10-12 0.00\n2016-10-12 0.03\n2016-10-12 0.00\n2016-10-13 0.00\n2016-10-13 0.06\n2016-10-13 0.00\n2016-10-13 NaN\n2016-10-13 0.02\n2016-10-13 0.00\n2016-10-13 0.00\n2016-10-14 0.00\n2016-10-14 0.00\n2016-10-14 0.00\n2016-10-14 0.00\n2016-10-14 0.00\n2016-10-14 0.00\n2016-10-15 0.00\n2016-10-15 0.02\n2016-10-15 0.00\n2016-10-15 0.33\n2016-10-15 0.04\n2016-10-15 0.00\n2016-10-16 0.00\n2016-10-16 0.00\n2016-10-16 0.00\n2016-10-16 0.00\n2016-10-16 0.00\n2016-10-17 NaN\n2016-10-17 0.01\n2016-10-17 0.01\n2016-10-17 NaN\n2016-10-17 0.12\n2016-10-17 0.03\n2016-10-17 0.38\n2016-10-18 0.02\n2016-10-18 0.00\n2016-10-18 0.05\n2016-10-18 0.02\n2016-10-18 NaN\n2016-10-18 0.03\n2016-10-18 0.48\n2016-10-19 NaN\n2016-10-19 0.00\n2016-10-19 0.11\n2016-10-19 0.00\n2016-10-19 0.00\n2016-10-19 0.00\n2016-10-19 0.06\n2016-10-20 0.00\n2016-10-20 0.01\n2016-10-20 0.00\n2016-10-20 NaN\n2016-10-20 1.00\n2016-10-20 0.00\n2016-10-21 NaN\n2016-10-21 0.15\n2016-10-21 0.09\n2016-10-21 NaN\n2016-10-21 0.03\n2016-10-21 0.05\n2016-10-21 0.00\n2016-10-22 1.37\n2016-10-22 0.15\n2016-10-22 0.15\n2016-10-22 0.10\n2016-10-22 0.00\n2016-10-23 0.02\n2016-10-23 0.00\n2016-10-23 0.01\n2016-10-23 0.01\n2016-10-23 NaN\n2016-10-23 0.24\n2016-10-24 0.01\n2016-10-24 0.00\n2016-10-24 0.08\n2016-10-24 0.70\n2016-10-24 0.00\n2016-10-24 0.00\n2016-10-24 NaN\n2016-10-25 0.40\n2016-10-25 0.04\n2016-10-25 0.00\n2016-10-25 0.11\n2016-10-25 0.03\n2016-10-25 0.40\n2016-10-25 0.12\n2016-10-26 0.00\n2016-10-26 0.06\n2016-10-26 0.01\n2016-10-26 0.00\n2016-10-26 0.20\n2016-10-26 0.02\n2016-10-27 NaN\n2016-10-27 0.00\n2016-10-27 0.11\n2016-10-27 0.08\n2016-10-27 1.25\n2016-10-27 0.22\n2016-10-27 0.20\n2016-10-28 0.05\n2016-10-28 0.07\n2016-10-28 0.06\n2016-10-28 NaN\n2016-10-28 0.00\n2016-10-28 0.02\n2016-10-28 0.37\n2016-10-29 0.02\n2016-10-29 0.26\n2016-10-29 0.25\n2016-10-29 0.00\n2016-10-29 0.01\n2016-10-29 0.10\n2016-10-30 0.10\n2016-10-30 0.14\n2016-10-30 0.24\n2016-10-30 0.95\n2016-10-30 0.16\n2016-10-30 0.00\n2016-10-31 0.00\n2016-10-31 0.13\n2016-10-31 1.35\n2016-10-31 NaN\n2016-10-31 0.07\n2016-10-31 0.03\n2016-10-31 0.03\n2016-11-01 0.01\n2016-11-01 0.10\n2016-11-01 0.00\n2016-11-01 0.01\n2016-11-01 0.00\n2016-11-01 0.09\n2016-11-02 0.04\n2016-11-02 0.00\n2016-11-02 0.00\n2016-11-02 0.00\n2016-11-02 0.00\n2016-11-02 0.00\n2016-11-03 0.00\n2016-11-03 0.00\n2016-11-03 0.00\n2016-11-03 0.00\n2016-11-03 0.00\n2016-11-03 0.02\n2016-11-04 0.00\n2016-11-04 0.00\n2016-11-04 0.00\n2016-11-04 0.00\n2016-11-04 0.06\n2016-11-04 NaN\n2016-11-04 0.00\n2016-11-05 0.00\n2016-11-05 0.02\n2016-11-05 0.03\n2016-11-05 0.38\n2016-11-05 0.02\n2016-11-05 0.00\n2016-11-06 0.00\n2016-11-06 0.00\n2016-11-06 0.05\n2016-11-06 0.02\n2016-11-06 0.01\n2016-11-06 0.00\n2016-11-07 0.13\n2016-11-07 0.00\n2016-11-07 NaN\n2016-11-07 0.05\n2016-11-07 0.00\n2016-11-07 0.00\n2016-11-07 0.00\n2016-11-08 0.21\n2016-11-08 0.53\n2016-11-08 0.15\n2016-11-08 0.07\n2016-11-08 0.02\n2016-11-08 0.14\n2016-11-09 0.11\n2016-11-09 0.17\n2016-11-09 0.00\n2016-11-09 0.00\n2016-11-09 0.08\n2016-11-09 0.04\n2016-11-09 0.00\n2016-11-10 0.00\n2016-11-10 0.00\n2016-11-10 0.00\n2016-11-10 0.00\n2016-11-10 0.00\n2016-11-10 0.01\n2016-11-11 0.00\n2016-11-11 0.00\n2016-11-11 0.00\n2016-11-11 0.00\n2016-11-11 0.00\n2016-11-11 0.00\n2016-11-12 0.00\n2016-11-12 0.00\n2016-11-12 0.00\n2016-11-12 0.00\n2016-11-12 0.00\n2016-11-12 0.00\n2016-11-13 0.00\n2016-11-13 0.00\n2016-11-13 0.00\n2016-11-13 0.00\n2016-11-13 0.00\n2016-11-13 0.00\n2016-11-14 0.00\n2016-11-14 0.00\n2016-11-14 0.02\n2016-11-14 0.00\n2016-11-14 0.02\n2016-11-14 0.06\n2016-11-14 0.05\n2016-11-15 0.00\n2016-11-15 0.00\n2016-11-15 0.05\n2016-11-15 NaN\n2016-11-15 0.00\n2016-11-15 0.00\n2016-11-15 0.00\n2016-11-16 0.14\n2016-11-16 0.18\n2016-11-16 0.24\n2016-11-16 NaN\n2016-11-16 0.91\n2016-11-16 0.00\n2016-11-16 0.07\n2016-11-17 0.00\n2016-11-17 0.00\n2016-11-17 NaN\n2016-11-17 0.02\n2016-11-17 0.03\n2016-11-17 0.00\n2016-11-17 0.01\n2016-11-18 NaN\n2016-11-18 0.01\n2016-11-18 0.00\n2016-11-18 0.02\n2016-11-18 0.00\n2016-11-19 0.13\n2016-11-19 0.03\n2016-11-19 0.11\n2016-11-19 0.11\n2016-11-20 0.05\n2016-11-20 NaN\n2016-11-20 0.11\n2016-11-20 0.40\n2016-11-20 0.39\n2016-11-21 0.07\n2016-11-21 NaN\n2016-11-21 0.11\n2016-11-21 0.01\n2016-11-21 0.02\n2016-11-21 2.87\n2016-11-22 NaN\n2016-11-22 0.41\n2016-11-22 2.11\n2016-11-22 2.05\n2016-11-22 0.31\n2016-11-22 NaN\n2016-11-22 0.13\n2016-11-23 0.14\n2016-11-23 0.25\n2016-11-23 0.03\n2016-11-23 NaN\n2016-11-23 0.03\n2016-11-23 0.22\n2016-11-24 0.20\n2016-11-24 0.72\n2016-11-24 0.30\n2016-11-24 0.05\n2016-11-24 0.21\n2016-11-25 1.03\n2016-11-25 0.11\n2016-11-25 NaN\n2016-11-25 0.05\n2016-11-25 0.08\n2016-11-25 0.05\n2016-11-26 0.06\n2016-11-26 0.30\n2016-11-26 0.05\n2016-11-26 0.03\n2016-11-26 0.02\n2016-11-26 0.05\n2016-11-27 0.17\n2016-11-27 0.06\n2016-11-27 0.00\n2016-11-27 0.03\n2016-11-27 0.29\n2016-11-27 0.00\n2016-11-28 0.01\n2016-11-28 0.00\n2016-11-28 0.02\n2016-11-28 0.00\n2016-11-28 NaN\n2016-11-28 0.69\n2016-11-28 0.00\n2016-11-29 0.06\n2016-11-29 0.04\n2016-11-29 0.09\n2016-11-29 0.04\n2016-11-29 0.20\n2016-11-29 0.00\n2016-11-29 NaN\n2016-11-30 0.14\n2016-11-30 0.05\n2016-11-30 0.00\n2016-11-30 0.03\n2016-11-30 0.05\n2016-11-30 0.79\n2016-11-30 NaN\n2016-12-01 0.16\n2016-12-01 0.07\n2016-12-01 NaN\n2016-12-01 0.12\n2016-12-01 0.37\n2016-12-01 0.72\n2016-12-01 0.33\n2016-12-02 NaN\n2016-12-02 0.01\n2016-12-02 1.27\n2016-12-02 0.03\n2016-12-02 0.40\n2016-12-02 0.30\n2016-12-02 0.35\n2016-12-03 0.02\n2016-12-03 0.26\n2016-12-03 0.04\n2016-12-03 0.77\n2016-12-03 0.00\n2016-12-03 1.62\n2016-12-04 0.04\n2016-12-04 0.10\n2016-12-04 0.03\n2016-12-04 0.32\n2016-12-04 0.00\n2016-12-04 0.31\n2016-12-05 1.60\n2016-12-05 NaN\n2016-12-05 0.20\n2016-12-05 0.34\n2016-12-05 0.45\n2016-12-05 0.22\n2016-12-05 0.43\n2016-12-06 0.02\n2016-12-06 0.00\n2016-12-06 0.00\n2016-12-06 0.02\n2016-12-06 NaN\n2016-12-06 0.00\n2016-12-07 NaN\n2016-12-07 0.00\n2016-12-07 0.07\n2016-12-07 0.02\n2016-12-07 0.12\n2016-12-07 0.17\n2016-12-07 NaN\n2016-12-08 0.01\n2016-12-08 0.07\n2016-12-08 0.03\n2016-12-08 0.03\n2016-12-08 0.02\n2016-12-08 0.27\n2016-12-08 0.03\n2016-12-09 0.26\n2016-12-09 0.34\n2016-12-09 0.52\n2016-12-09 0.31\n2016-12-09 0.42\n2016-12-09 NaN\n2016-12-10 0.00\n2016-12-10 0.02\n2016-12-10 0.05\n2016-12-10 NaN\n2016-12-10 0.02\n2016-12-10 0.04\n2016-12-11 0.00\n2016-12-11 0.02\n2016-12-11 0.13\n2016-12-11 0.06\n2016-12-11 0.04\n2016-12-12 0.01\n2016-12-12 0.01\n2016-12-12 0.00\n2016-12-12 NaN\n2016-12-12 0.02\n2016-12-12 0.00\n2016-12-12 0.01\n2016-12-13 0.10\n2016-12-13 0.15\n2016-12-13 0.04\n2016-12-13 0.09\n2016-12-13 0.05\n2016-12-13 0.34\n2016-12-13 NaN\n2016-12-14 0.33\n2016-12-14 0.05\n2016-12-14 0.05\n2016-12-14 0.92\n2016-12-14 NaN\n2016-12-14 0.03\n2016-12-14 0.12\n2016-12-15 0.00\n2016-12-15 0.02\n2016-12-15 0.14\n2016-12-15 0.03\n2016-12-15 0.07\n2016-12-15 NaN\n2016-12-15 0.00\n2016-12-16 0.00\n2016-12-16 0.00\n2016-12-16 0.03\n2016-12-16 0.00\n2016-12-16 0.01\n2016-12-16 NaN\n2016-12-16 0.00\n2016-12-17 0.01\n2016-12-17 0.00\n2016-12-17 0.16\n2016-12-17 0.07\n2016-12-17 0.11\n2016-12-18 0.27\n2016-12-18 0.04\n2016-12-18 0.29\n2016-12-18 0.16\n2016-12-18 0.13\n2016-12-18 NaN\n2016-12-19 NaN\n2016-12-19 0.02\n2016-12-19 0.21\n2016-12-19 0.03\n2016-12-19 0.01\n2016-12-19 0.15\n2016-12-19 0.00\n2016-12-20 0.00\n2016-12-20 0.02\n2016-12-20 NaN\n2016-12-20 0.01\n2016-12-20 0.00\n2016-12-20 0.00\n2016-12-20 0.00\n2016-12-21 0.09\n2016-12-21 0.03\n2016-12-21 0.00\n2016-12-21 0.11\n2016-12-21 0.06\n2016-12-21 0.06\n2016-12-21 0.55\n2016-12-22 0.86\n2016-12-22 0.14\n2016-12-22 0.01\n2016-12-22 1.24\n2016-12-22 NaN\n2016-12-22 0.05\n2016-12-22 0.17\n2016-12-23 0.03\n2016-12-23 0.10\n2016-12-23 0.24\n2016-12-23 NaN\n2016-12-23 0.02\n2016-12-23 0.83\n2016-12-23 0.01\n2016-12-24 0.13\n2016-12-24 1.08\n2016-12-24 0.20\n2016-12-24 0.01\n2016-12-24 0.14\n2016-12-24 0.06\n2016-12-25 0.02\n2016-12-25 0.00\n2016-12-25 0.38\n2016-12-25 0.03\n2016-12-25 0.00\n2016-12-26 0.02\n2016-12-26 0.06\n2016-12-26 NaN\n2016-12-26 0.22\n2016-12-26 1.48\n2016-12-26 0.26\n2016-12-27 0.00\n2016-12-27 0.05\n2016-12-27 0.00\n2016-12-27 0.02\n2016-12-27 0.03\n2016-12-27 0.14\n2016-12-28 0.09\n2016-12-28 0.09\n2016-12-28 NaN\n2016-12-28 0.01\n2016-12-28 0.06\n2016-12-28 0.14\n2016-12-28 0.02\n2016-12-29 1.03\n2016-12-29 0.18\n2016-12-29 0.04\n2016-12-29 0.05\n2016-12-29 NaN\n2016-12-29 0.56\n2016-12-29 0.52\n2016-12-30 0.21\n2016-12-30 0.29\n2016-12-30 2.37\n2016-12-30 NaN\n2016-12-30 0.12\n2016-12-30 0.29\n2016-12-30 0.07\n2016-12-31 0.62\n2016-12-31 0.25\n2016-12-31 0.90\n2016-12-31 0.36\n2016-12-31 0.01\n2017-01-01 0.03\n2017-01-01 0.03\n2017-01-01 0.00\n2017-01-01 0.29\n2017-01-01 0.00\n2017-01-01 NaN\n2017-01-02 0.00\n2017-01-02 0.01\n2017-01-02 0.00\n2017-01-02 0.00\n2017-01-02 0.01\n2017-01-03 0.00\n2017-01-03 0.00\n2017-01-03 0.00\n2017-01-03 NaN\n2017-01-03 0.00\n2017-01-03 0.00\n2017-01-04 0.00\n2017-01-04 0.18\n2017-01-04 0.00\n2017-01-04 0.00\n2017-01-04 0.00\n2017-01-04 0.00\n2017-01-05 0.47\n2017-01-05 0.00\n2017-01-05 0.00\n2017-01-05 0.42\n2017-01-05 0.00\n2017-01-05 0.06\n2017-01-06 0.10\n2017-01-06 0.00\n2017-01-06 0.01\n2017-01-06 0.00\n2017-01-06 0.59\n2017-01-06 0.10\n2017-01-07 0.00\n2017-01-07 0.06\n2017-01-07 0.00\n2017-01-07 0.00\n2017-01-07 0.00\n2017-01-07 0.00\n2017-01-08 0.00\n2017-01-08 0.03\n2017-01-08 0.00\n2017-01-08 0.00\n2017-01-08 0.03\n2017-01-08 0.00\n2017-01-09 0.00\n2017-01-09 0.00\n2017-01-09 0.00\n2017-01-09 0.00\n2017-01-09 0.00\n2017-01-09 NaN\n2017-01-09 0.00\n2017-01-10 0.00\n2017-01-10 0.00\n2017-01-10 0.00\n2017-01-10 0.00\n2017-01-10 0.00\n2017-01-10 0.00\n2017-01-10 NaN\n2017-01-11 0.00\n2017-01-11 0.00\n2017-01-11 0.00\n2017-01-11 0.00\n2017-01-11 0.00\n2017-01-11 NaN\n2017-01-12 0.00\n2017-01-12 NaN\n2017-01-12 0.00\n2017-01-12 0.00\n2017-01-12 NaN\n2017-01-12 0.00\n2017-01-13 NaN\n2017-01-13 0.00\n2017-01-13 0.00\n2017-01-13 0.00\n2017-01-13 NaN\n2017-01-13 0.00\n2017-01-14 0.01\n2017-01-14 0.00\n2017-01-14 0.00\n2017-01-14 0.00\n2017-01-14 0.00\n2017-01-15 0.00\n2017-01-15 0.00\n2017-01-15 NaN\n2017-01-15 0.00\n2017-01-15 0.01\n2017-01-16 NaN\n2017-01-16 0.00\n2017-01-16 0.00\n2017-01-16 0.00\n2017-01-16 0.00\n2017-01-16 0.00\n2017-01-17 0.00\n2017-01-17 0.00\n2017-01-17 0.00\n2017-01-17 0.00\n2017-01-17 0.00\n2017-01-17 0.00\n2017-01-18 0.07\n2017-01-18 0.00\n2017-01-18 0.00\n2017-01-18 0.00\n2017-01-18 0.00\n2017-01-18 0.00\n2017-01-18 NaN\n2017-01-19 0.00\n2017-01-19 NaN\n2017-01-19 0.00\n2017-01-19 0.02\n2017-01-19 0.00\n2017-01-19 0.00\n2017-01-19 0.00\n2017-01-20 NaN\n2017-01-20 0.00\n2017-01-20 0.00\n2017-01-20 0.00\n2017-01-20 0.00\n2017-01-20 0.00\n2017-01-20 0.00\n2017-01-21 0.03\n2017-01-21 0.08\n2017-01-21 0.04\n2017-01-21 0.02\n2017-01-21 0.11\n2017-01-21 0.00\n2017-01-22 0.01\n2017-01-22 0.72\n2017-01-22 0.04\n2017-01-22 0.09\n2017-01-22 0.16\n2017-01-23 0.00\n2017-01-23 0.85\n2017-01-23 0.01\n2017-01-23 0.08\n2017-01-23 0.00\n2017-01-23 NaN\n2017-01-23 NaN\n2017-01-24 0.13\n2017-01-24 NaN\n2017-01-24 1.85\n2017-01-24 0.08\n2017-01-24 0.15\n2017-01-24 0.04\n2017-01-25 NaN\n2017-01-25 0.12\n2017-01-25 0.79\n2017-01-25 2.64\n2017-01-25 NaN\n2017-01-25 0.03\n2017-01-25 0.00\n2017-01-26 0.00\n2017-01-26 0.00\n2017-01-26 0.00\n2017-01-26 0.01\n2017-01-26 0.10\n2017-01-26 0.00\n2017-01-26 0.00\n2017-01-27 0.03\n2017-01-27 0.00\n2017-01-27 0.03\n2017-01-27 0.00\n2017-01-27 0.00\n2017-01-27 0.00\n2017-01-27 0.00\n2017-01-28 0.00\n2017-01-28 0.00\n2017-01-28 0.14\n2017-01-28 0.00\n2017-01-28 0.00\n2017-01-29 0.00\n2017-01-29 NaN\n2017-01-29 0.26\n2017-01-29 0.18\n2017-01-29 0.55\n2017-01-30 0.00\n2017-01-30 0.00\n2017-01-30 NaN\n2017-01-30 0.00\n2017-01-30 0.05\n2017-01-30 0.00\n2017-01-30 0.00\n2017-01-31 0.00\n2017-01-31 0.00\n2017-01-31 0.00\n2017-01-31 0.00\n2017-01-31 0.00\n2017-01-31 0.00\n2017-01-31 0.00\n2017-02-01 0.00\n2017-02-01 0.00\n2017-02-01 0.00\n2017-02-01 0.00\n2017-02-01 0.00\n2017-02-01 0.00\n2017-02-01 0.00\n2017-02-02 0.00\n2017-02-02 0.00\n2017-02-02 0.00\n2017-02-02 0.00\n2017-02-02 0.00\n2017-02-02 0.00\n2017-02-02 0.00\n2017-02-03 0.00\n2017-02-03 0.00\n2017-02-03 0.00\n2017-02-03 0.00\n2017-02-03 0.00\n2017-02-03 0.00\n2017-02-04 0.00\n2017-02-04 0.00\n2017-02-04 0.00\n2017-02-04 0.00\n2017-02-04 NaN\n2017-02-05 NaN\n2017-02-05 0.00\n2017-02-05 0.00\n2017-02-05 0.00\n2017-02-05 0.00\n2017-02-05 0.00\n2017-02-06 0.00\n2017-02-06 0.00\n2017-02-06 0.00\n2017-02-06 0.04\n2017-02-06 0.16\n2017-02-06 0.18\n2017-02-06 NaN\n2017-02-07 0.90\n2017-02-07 0.00\n2017-02-07 1.32\n2017-02-07 1.08\n2017-02-07 1.80\n2017-02-07 0.51\n2017-02-07 1.79\n2017-02-08 0.00\n2017-02-08 0.00\n2017-02-08 1.08\n2017-02-08 0.00\n2017-02-08 0.00\n2017-02-08 0.00\n2017-02-08 0.00\n2017-02-09 0.00\n2017-02-09 0.00\n2017-02-09 0.00\n2017-02-09 0.00\n2017-02-09 0.00\n2017-02-09 0.02\n2017-02-09 0.00\n2017-02-10 0.00\n2017-02-10 0.00\n2017-02-10 0.00\n2017-02-10 0.00\n2017-02-10 0.00\n2017-02-10 0.00\n2017-02-10 0.00\n2017-02-11 0.73\n2017-02-11 5.04\n2017-02-11 1.73\n2017-02-11 0.31\n2017-02-11 2.39\n2017-02-11 1.00\n2017-02-12 0.07\n2017-02-12 2.62\n2017-02-12 1.91\n2017-02-12 1.07\n2017-02-12 1.83\n2017-02-12 2.98\n2017-02-13 0.00\n2017-02-13 0.00\n2017-02-13 2.90\n2017-02-13 0.00\n2017-02-13 0.01\n2017-02-13 NaN\n2017-02-13 0.01\n2017-02-14 0.00\n2017-02-14 0.01\n2017-02-14 0.00\n2017-02-14 0.00\n2017-02-14 0.00\n2017-02-14 0.00\n2017-02-15 0.00\n2017-02-15 0.00\n2017-02-15 0.01\n2017-02-15 NaN\n2017-02-15 NaN\n2017-02-15 0.07\n2017-02-15 0.00\n2017-02-16 0.07\n2017-02-16 0.67\n2017-02-16 NaN\n2017-02-16 0.62\n2017-02-16 0.73\n2017-02-16 0.00\n2017-02-16 0.13\n2017-02-17 0.06\n2017-02-17 0.06\n2017-02-17 0.80\n2017-02-17 0.13\n2017-02-17 0.00\n2017-02-17 0.00\n2017-02-18 0.00\n2017-02-18 0.00\n2017-02-18 NaN\n2017-02-18 0.00\n2017-02-18 0.01\n2017-02-19 0.00\n2017-02-19 0.10\n2017-02-19 0.09\n2017-02-19 0.00\n2017-02-20 0.00\n2017-02-20 NaN\n2017-02-20 0.00\n2017-02-20 0.00\n2017-02-20 0.00\n2017-02-20 NaN\n2017-02-21 0.07\n2017-02-21 0.00\n2017-02-21 NaN\n2017-02-21 0.00\n2017-02-21 0.00\n2017-02-21 0.06\n2017-02-22 0.06\n2017-02-22 0.06\n2017-02-22 0.17\n2017-02-22 0.13\n2017-02-22 0.32\n2017-02-22 0.11\n2017-02-22 0.06\n2017-02-23 0.00\n2017-02-23 0.00\n2017-02-23 0.01\n2017-02-23 0.00\n2017-02-23 0.00\n2017-02-23 0.00\n2017-02-23 0.00\n2017-02-24 0.00\n2017-02-24 0.00\n2017-02-24 0.00\n2017-02-24 0.00\n2017-02-24 0.00\n2017-02-24 0.00\n2017-02-24 0.00\n2017-02-25 0.00\n2017-02-25 0.00\n2017-02-25 0.12\n2017-02-25 0.03\n2017-02-26 0.00\n2017-02-26 NaN\n2017-02-26 0.00\n2017-02-26 0.00\n2017-02-26 NaN\n2017-02-26 0.00\n2017-02-27 0.00\n2017-02-27 0.00\n2017-02-27 0.00\n2017-02-27 0.00\n2017-02-27 0.00\n2017-02-27 0.00\n2017-02-27 NaN\n2017-02-28 NaN\n2017-02-28 0.04\n2017-02-28 0.00\n2017-02-28 0.58\n2017-02-28 0.16\n2017-02-28 0.00\n2017-02-28 0.04\n2017-03-01 2.12\n2017-03-01 2.40\n2017-03-01 0.59\n2017-03-01 1.19\n2017-03-01 2.20\n2017-03-01 1.12\n2017-03-01 2.00\n2017-03-02 1.45\n2017-03-02 0.58\n2017-03-02 1.48\n2017-03-02 0.73\n2017-03-02 1.88\n2017-03-02 0.44\n2017-03-03 0.54\n2017-03-03 0.56\n2017-03-03 0.14\n2017-03-03 NaN\n2017-03-03 0.47\n2017-03-03 0.25\n2017-03-03 0.27\n2017-03-04 0.00\n2017-03-04 0.00\n2017-03-04 0.00\n2017-03-04 0.00\n2017-03-04 0.00\n2017-03-05 0.41\n2017-03-05 0.35\n2017-03-05 0.10\n2017-03-05 0.35\n2017-03-06 0.00\n2017-03-06 NaN\n2017-03-06 NaN\n2017-03-06 0.03\n2017-03-06 0.51\n2017-03-06 0.00\n2017-03-06 NaN\n2017-03-07 0.00\n2017-03-07 NaN\n2017-03-07 0.00\n2017-03-07 0.00\n2017-03-07 0.00\n2017-03-07 0.00\n2017-03-08 0.00\n2017-03-08 0.00\n2017-03-08 0.00\n2017-03-08 0.00\n2017-03-08 NaN\n2017-03-08 0.00\n2017-03-09 0.50\n2017-03-09 0.00\n2017-03-09 0.65\n2017-03-09 NaN\n2017-03-09 0.00\n2017-03-09 0.80\n2017-03-09 0.01\n2017-03-10 0.00\n2017-03-10 0.03\n2017-03-10 0.13\n2017-03-10 0.00\n2017-03-10 0.00\n2017-03-10 0.00\n2017-03-10 0.13\n2017-03-11 0.00\n2017-03-11 0.01\n2017-03-11 0.00\n2017-03-11 0.03\n2017-03-11 0.00\n2017-03-12 NaN\n2017-03-12 0.00\n2017-03-12 0.00\n2017-03-12 0.00\n2017-03-12 0.00\n2017-03-13 0.00\n2017-03-13 NaN\n2017-03-13 0.00\n2017-03-13 NaN\n2017-03-13 0.00\n2017-03-13 0.00\n2017-03-13 0.00\n2017-03-14 0.00\n2017-03-14 0.00\n2017-03-14 0.00\n2017-03-14 0.00\n2017-03-14 0.00\n2017-03-14 0.00\n2017-03-14 0.06\n2017-03-15 0.00\n2017-03-15 0.00\n2017-03-15 0.00\n2017-03-15 0.00\n2017-03-15 0.00\n2017-03-15 0.06\n2017-03-16 0.00\n2017-03-16 0.00\n2017-03-16 0.00\n2017-03-16 0.00\n2017-03-16 NaN\n2017-03-16 0.00\n2017-03-16 NaN\n2017-03-17 0.06\n2017-03-17 0.35\n2017-03-17 0.00\n2017-03-17 0.12\n2017-03-17 NaN\n2017-03-17 0.19\n2017-03-18 0.00\n2017-03-18 0.00\n2017-03-18 NaN\n2017-03-18 0.00\n2017-03-18 0.00\n2017-03-18 0.00\n2017-03-19 0.00\n2017-03-19 0.00\n2017-03-19 0.00\n2017-03-19 0.00\n2017-03-19 0.00\n2017-03-20 0.00\n2017-03-20 0.00\n2017-03-20 0.02\n2017-03-20 0.00\n2017-03-20 0.00\n2017-03-20 NaN\n2017-03-21 0.00\n2017-03-21 0.09\n2017-03-21 0.00\n2017-03-21 0.00\n2017-03-21 0.00\n2017-03-21 0.00\n2017-03-22 0.00\n2017-03-22 0.00\n2017-03-22 0.00\n2017-03-22 0.00\n2017-03-22 0.00\n2017-03-22 0.00\n2017-03-23 0.00\n2017-03-23 0.00\n2017-03-23 0.00\n2017-03-23 0.02\n2017-03-23 0.03\n2017-03-23 0.00\n2017-03-24 0.02\n2017-03-24 0.15\n2017-03-24 0.17\n2017-03-24 0.60\n2017-03-24 0.12\n2017-03-24 0.07\n2017-03-25 0.48\n2017-03-25 0.43\n2017-03-25 0.00\n2017-03-25 0.13\n2017-03-25 0.93\n2017-03-26 0.00\n2017-03-26 0.00\n2017-03-26 0.00\n2017-03-26 0.00\n2017-03-26 0.00\n2017-03-27 0.00\n2017-03-27 0.00\n2017-03-27 0.00\n2017-03-27 0.01\n2017-03-27 0.00\n2017-03-27 NaN\n2017-03-28 0.03\n2017-03-28 0.00\n2017-03-28 0.00\n2017-03-28 0.00\n2017-03-28 NaN\n2017-03-28 0.00\n2017-03-28 0.68\n2017-03-29 0.03\n2017-03-29 0.00\n2017-03-29 0.00\n2017-03-29 0.01\n2017-03-29 0.07\n2017-03-29 NaN\n2017-03-29 0.08\n2017-03-30 0.00\n2017-03-30 0.00\n2017-03-30 0.04\n2017-03-30 0.08\n2017-03-30 0.03\n2017-03-30 NaN\n2017-03-31 0.01\n2017-03-31 0.00\n2017-03-31 0.00\n2017-03-31 NaN\n2017-03-31 0.00\n2017-03-31 0.00\n2017-03-31 0.00\n2017-04-01 0.21\n2017-04-01 0.00\n2017-04-01 0.00\n2017-04-01 0.20\n2017-04-01 0.00\n2017-04-01 0.00\n2017-04-02 0.00\n2017-04-02 0.00\n2017-04-02 0.00\n2017-04-02 0.00\n2017-04-02 0.00\n2017-04-02 0.00\n2017-04-03 0.26\n2017-04-03 0.08\n2017-04-03 NaN\n2017-04-03 0.00\n2017-04-03 0.23\n2017-04-03 0.09\n2017-04-03 0.00\n2017-04-04 0.04\n2017-04-04 0.00\n2017-04-04 0.09\n2017-04-04 0.00\n2017-04-04 0.00\n2017-04-04 0.00\n2017-04-04 0.02\n2017-04-05 0.00\n2017-04-05 0.00\n2017-04-05 0.10\n2017-04-05 0.45\n2017-04-05 0.04\n2017-04-05 0.07\n2017-04-05 0.00\n2017-04-06 0.00\n2017-04-06 0.00\n2017-04-06 0.00\n2017-04-06 0.00\n2017-04-06 0.00\n2017-04-06 0.00\n2017-04-06 0.06\n2017-04-07 0.00\n2017-04-07 0.00\n2017-04-07 0.00\n2017-04-07 0.00\n2017-04-07 0.00\n2017-04-07 0.00\n2017-04-08 0.00\n2017-04-08 NaN\n2017-04-08 0.00\n2017-04-08 0.00\n2017-04-09 0.00\n2017-04-09 0.00\n2017-04-09 0.00\n2017-04-09 NaN\n2017-04-09 0.00\n2017-04-09 NaN\n2017-04-10 0.00\n2017-04-10 0.00\n2017-04-10 0.00\n2017-04-10 NaN\n2017-04-10 0.01\n2017-04-10 0.01\n2017-04-10 0.00\n2017-04-11 0.03\n2017-04-11 0.00\n2017-04-11 0.03\n2017-04-11 0.16\n2017-04-11 0.00\n2017-04-11 0.25\n2017-04-11 NaN\n2017-04-12 0.00\n2017-04-12 0.03\n2017-04-12 0.65\n2017-04-12 0.11\n2017-04-12 0.00\n2017-04-12 0.29\n2017-04-12 NaN\n2017-04-13 NaN\n2017-04-13 0.23\n2017-04-13 0.27\n2017-04-13 0.00\n2017-04-13 0.59\n2017-04-13 0.00\n2017-04-13 0.00\n2017-04-14 0.36\n2017-04-14 0.69\n2017-04-14 2.30\n2017-04-14 0.26\n2017-04-14 2.82\n2017-04-14 0.29\n2017-04-15 0.90\n2017-04-15 0.01\n2017-04-15 0.00\n2017-04-15 0.38\n2017-04-15 0.45\n2017-04-16 0.49\n2017-04-16 0.47\n2017-04-16 0.11\n2017-04-16 0.00\n2017-04-16 0.00\n2017-04-17 0.30\n2017-04-17 1.30\n2017-04-17 0.41\n2017-04-17 NaN\n2017-04-17 0.02\n2017-04-17 NaN\n2017-04-17 1.04\n2017-04-18 0.98\n2017-04-18 0.15\n2017-04-18 0.12\n2017-04-18 0.00\n2017-04-18 0.08\n2017-04-18 0.00\n2017-04-18 2.03\n2017-04-19 0.02\n2017-04-19 0.02\n2017-04-19 NaN\n2017-04-19 0.02\n2017-04-19 0.14\n2017-04-19 0.00\n2017-04-19 0.00\n2017-04-20 0.05\n2017-04-20 0.00\n2017-04-20 0.00\n2017-04-20 0.35\n2017-04-20 0.33\n2017-04-20 NaN\n2017-04-20 0.05\n2017-04-21 1.84\n2017-04-21 1.74\n2017-04-21 0.23\n2017-04-21 2.36\n2017-04-21 NaN\n2017-04-21 1.16\n2017-04-21 1.05\n2017-04-22 1.01\n2017-04-22 0.32\n2017-04-22 1.35\n2017-04-22 1.58\n2017-04-22 0.70\n2017-04-23 0.35\n2017-04-23 0.02\n2017-04-23 0.06\n2017-04-23 0.03\n2017-04-24 0.01\n2017-04-24 0.00\n2017-04-24 NaN\n2017-04-24 NaN\n2017-04-24 0.05\n2017-04-24 0.00\n2017-04-24 NaN\n2017-04-25 0.00\n2017-04-25 0.00\n2017-04-25 0.00\n2017-04-25 0.00\n2017-04-25 0.00\n2017-04-25 0.00\n2017-04-25 NaN\n2017-04-26 0.00\n2017-04-26 0.00\n2017-04-26 0.01\n2017-04-26 0.14\n2017-04-26 0.22\n2017-04-26 0.02\n2017-04-27 0.11\n2017-04-27 0.00\n2017-04-27 0.19\n2017-04-27 0.10\n2017-04-27 NaN\n2017-04-27 0.00\n2017-04-27 0.02\n2017-04-28 2.60\n2017-04-28 0.00\n2017-04-28 NaN\n2017-04-28 0.76\n2017-04-28 0.09\n2017-04-28 0.79\n2017-04-28 0.00\n2017-04-29 0.95\n2017-04-29 0.00\n2017-04-29 6.25\n2017-04-29 0.37\n2017-04-29 0.35\n2017-04-29 0.12\n2017-04-30 0.89\n2017-04-30 1.21\n2017-04-30 0.80\n2017-04-30 1.31\n2017-04-30 1.17\n2017-04-30 1.04\n2017-05-01 0.03\n2017-05-01 0.07\n2017-05-01 0.26\n2017-05-01 0.13\n2017-05-01 0.25\n2017-05-01 0.07\n2017-05-02 0.00\n2017-05-02 0.01\n2017-05-02 0.01\n2017-05-02 0.00\n2017-05-02 0.03\n2017-05-02 0.00\n2017-05-03 0.00\n2017-05-03 0.01\n2017-05-03 0.01\n2017-05-03 0.01\n2017-05-03 0.00\n2017-05-04 0.00\n2017-05-04 0.00\n2017-05-04 0.08\n2017-05-04 0.00\n2017-05-04 0.00\n2017-05-04 NaN\n2017-05-05 0.00\n2017-05-05 0.10\n2017-05-05 0.28\n2017-05-05 0.00\n2017-05-05 0.00\n2017-05-05 0.00\n2017-05-06 0.00\n2017-05-06 0.00\n2017-05-06 0.00\n2017-05-06 0.00\n2017-05-06 0.00\n2017-05-06 0.06\n2017-05-07 0.00\n2017-05-07 0.02\n2017-05-07 0.07\n2017-05-07 0.00\n2017-05-07 0.03\n2017-05-08 0.73\n2017-05-08 0.22\n2017-05-08 0.00\n2017-05-08 0.95\n2017-05-08 1.11\n2017-05-08 0.00\n2017-05-09 0.68\n2017-05-09 0.52\n2017-05-09 1.58\n2017-05-09 1.62\n2017-05-09 0.23\n2017-05-10 0.05\n2017-05-10 0.55\n2017-05-10 0.06\n2017-05-10 0.00\n2017-05-10 0.00\n2017-05-10 0.20\n2017-05-11 0.44\n2017-05-11 0.00\n2017-05-11 0.12\n2017-05-11 0.01\n2017-05-11 0.03\n2017-05-12 0.00\n2017-05-12 0.10\n2017-05-12 0.00\n2017-05-12 0.04\n2017-05-12 0.02\n2017-05-12 NaN\n2017-05-13 0.00\n2017-05-13 0.00\n2017-05-13 0.10\n2017-05-13 0.12\n2017-05-13 0.02\n2017-05-14 0.17\n2017-05-14 0.05\n2017-05-14 0.00\n2017-05-14 0.00\n2017-05-14 1.00\n2017-05-15 0.08\n2017-05-15 0.06\n2017-05-15 NaN\n2017-05-15 0.60\n2017-05-15 0.05\n2017-05-15 0.09\n2017-05-16 0.03\n2017-05-16 0.05\n2017-05-16 0.03\n2017-05-16 0.01\n2017-05-16 0.30\n2017-05-16 0.00\n2017-05-17 0.02\n2017-05-17 0.06\n2017-05-17 0.00\n2017-05-17 0.00\n2017-05-17 0.07\n2017-05-17 0.00\n2017-05-18 0.01\n2017-05-18 0.16\n2017-05-18 0.00\n2017-05-18 0.13\n2017-05-18 0.46\n2017-05-18 0.09\n2017-05-19 0.00\n2017-05-19 0.01\n2017-05-19 0.02\n2017-05-19 0.01\n2017-05-20 0.00\n2017-05-20 NaN\n2017-05-20 NaN\n2017-05-20 0.01\n2017-05-20 0.00\n2017-05-20 0.02\n2017-05-21 0.01\n2017-05-21 0.00\n2017-05-21 0.00\n2017-05-21 0.00\n2017-05-21 0.00\n2017-05-22 NaN\n2017-05-22 0.06\n2017-05-22 0.00\n2017-05-22 0.30\n2017-05-22 0.00\n2017-05-22 0.00\n2017-05-23 0.11\n2017-05-23 0.00\n2017-05-23 0.06\n2017-05-23 0.44\n2017-05-23 0.08\n2017-05-23 0.02\n2017-05-24 0.10\n2017-05-24 0.13\n2017-05-24 0.61\n2017-05-24 0.58\n2017-05-24 0.30\n2017-05-24 2.17\n2017-05-25 0.55\n2017-05-25 0.20\n2017-05-25 0.15\n2017-05-25 0.07\n2017-05-25 0.37\n2017-05-25 0.88\n2017-05-26 0.00\n2017-05-26 0.00\n2017-05-26 0.02\n2017-05-26 0.00\n2017-05-26 0.00\n2017-05-27 0.50\n2017-05-27 0.00\n2017-05-27 0.00\n2017-05-27 0.01\n2017-05-27 0.00\n2017-05-27 0.00\n2017-05-28 0.00\n2017-05-28 0.02\n2017-05-28 0.29\n2017-05-28 0.02\n2017-05-28 0.00\n2017-05-28 0.08\n2017-05-29 0.00\n2017-05-29 0.00\n2017-05-29 0.02\n2017-05-29 0.00\n2017-05-29 0.40\n2017-05-30 1.12\n2017-05-30 0.04\n2017-05-30 0.11\n2017-05-30 0.20\n2017-05-30 0.26\n2017-05-30 NaN\n2017-05-31 0.02\n2017-05-31 0.25\n2017-05-31 0.00\n2017-05-31 0.00\n2017-05-31 0.10\n2017-06-01 0.01\n2017-06-01 0.00\n2017-06-01 0.03\n2017-06-01 0.00\n2017-06-01 0.00\n2017-06-01 0.00\n2017-06-02 0.00\n2017-06-02 0.09\n2017-06-02 0.10\n2017-06-02 NaN\n2017-06-02 0.00\n2017-06-02 0.15\n2017-06-03 0.16\n2017-06-03 0.20\n2017-06-03 0.08\n2017-06-03 0.15\n2017-06-03 0.02\n2017-06-03 NaN\n2017-06-04 0.00\n2017-06-04 0.13\n2017-06-04 0.15\n2017-06-04 0.82\n2017-06-04 0.05\n2017-06-04 0.00\n2017-06-05 0.05\n2017-06-05 NaN\n2017-06-05 0.00\n2017-06-05 0.00\n2017-06-05 0.02\n2017-06-05 0.01\n2017-06-05 0.00\n2017-06-06 0.00\n2017-06-06 0.00\n2017-06-06 0.00\n2017-06-06 0.00\n2017-06-06 0.00\n2017-06-06 NaN\n2017-06-06 0.00\n2017-06-07 0.00\n2017-06-07 0.00\n2017-06-07 0.00\n2017-06-07 0.00\n2017-06-07 0.00\n2017-06-07 NaN\n2017-06-07 0.01\n2017-06-08 NaN\n2017-06-08 0.00\n2017-06-08 0.00\n2017-06-08 0.00\n2017-06-08 0.01\n2017-06-08 0.02\n2017-06-08 0.00\n2017-06-09 0.00\n2017-06-09 0.00\n2017-06-09 0.00\n2017-06-09 NaN\n2017-06-09 0.02\n2017-06-09 0.02\n2017-06-10 0.62\n2017-06-10 0.04\n2017-06-10 0.21\n2017-06-10 0.13\n2017-06-10 NaN\n2017-06-10 0.53\n2017-06-11 0.24\n2017-06-11 0.14\n2017-06-11 0.74\n2017-06-11 0.08\n2017-06-11 0.25\n2017-06-11 0.70\n2017-06-12 0.02\n2017-06-12 0.35\n2017-06-12 0.81\n2017-06-12 0.24\n2017-06-12 0.14\n2017-06-12 0.19\n2017-06-13 0.65\n2017-06-13 0.00\n2017-06-13 0.24\n2017-06-13 0.03\n2017-06-13 NaN\n2017-06-13 0.10\n2017-06-13 0.36\n2017-06-14 0.00\n2017-06-14 0.22\n2017-06-14 0.06\n2017-06-14 0.81\n2017-06-14 0.27\n2017-06-14 NaN\n2017-06-14 0.21\n2017-06-15 1.69\n2017-06-15 0.00\n2017-06-15 0.17\n2017-06-15 0.30\n2017-06-15 0.00\n2017-06-15 NaN\n2017-06-15 0.55\n2017-06-16 0.02\n2017-06-16 0.10\n2017-06-16 0.00\n2017-06-16 NaN\n2017-06-16 0.06\n2017-06-16 0.02\n2017-06-16 0.00\n2017-06-17 0.07\n2017-06-17 0.02\n2017-06-17 0.00\n2017-06-17 0.10\n2017-06-17 0.35\n2017-06-17 0.00\n2017-06-18 0.70\n2017-06-18 0.24\n2017-06-18 0.05\n2017-06-18 0.18\n2017-06-18 0.25\n2017-06-18 0.00\n2017-06-19 0.19\n2017-06-19 0.40\n2017-06-19 0.00\n2017-06-19 0.01\n2017-06-19 NaN\n2017-06-19 0.05\n2017-06-19 0.08\n2017-06-20 0.00\n2017-06-20 0.05\n2017-06-20 0.31\n2017-06-20 0.17\n2017-06-20 NaN\n2017-06-20 0.02\n2017-06-21 NaN\n2017-06-21 0.00\n2017-06-21 NaN\n2017-06-21 0.30\n2017-06-21 0.19\n2017-06-21 0.02\n2017-06-22 0.28\n2017-06-22 0.00\n2017-06-22 0.10\n2017-06-22 0.00\n2017-06-22 0.00\n2017-06-22 0.06\n2017-06-23 0.50\n2017-06-23 0.05\n2017-06-23 0.00\n2017-06-23 NaN\n2017-06-23 0.12\n2017-06-23 0.00\n2017-06-23 0.00\n2017-06-24 0.22\n2017-06-24 0.00\n2017-06-24 0.06\n2017-06-24 0.00\n2017-06-24 0.36\n2017-06-25 0.08\n2017-06-25 0.00\n2017-06-25 0.00\n2017-06-25 0.50\n2017-06-25 0.02\n2017-06-26 NaN\n2017-06-26 0.02\n2017-06-26 NaN\n2017-06-26 0.02\n2017-06-26 0.00\n2017-06-26 0.06\n2017-06-26 0.00\n2017-06-27 0.10\n2017-06-27 0.00\n2017-06-27 0.00\n2017-06-27 0.00\n2017-06-27 0.01\n2017-06-27 0.00\n2017-06-28 0.00\n2017-06-28 0.02\n2017-06-28 0.00\n2017-06-28 0.01\n2017-06-28 0.00\n2017-06-28 0.00\n2017-06-29 0.04\n2017-06-29 0.00\n2017-06-29 0.00\n2017-06-29 0.03\n2017-06-29 0.00\n2017-06-29 NaN\n2017-06-29 0.00\n2017-06-30 0.07\n2017-06-30 0.01\n2017-06-30 0.04\n2017-06-30 0.00\n2017-06-30 0.12\n2017-06-30 0.20\n2017-06-30 0.08\n2017-07-01 0.06\n2017-07-01 0.10\n2017-07-01 0.08\n2017-07-01 0.02\n2017-07-02 NaN\n2017-07-02 0.05\n2017-07-02 0.02\n2017-07-02 0.15\n2017-07-02 0.50\n2017-07-03 0.40\n2017-07-03 NaN\n2017-07-03 0.13\n2017-07-03 0.15\n2017-07-03 0.02\n2017-07-03 NaN\n2017-07-03 0.04\n2017-07-04 0.00\n2017-07-04 0.08\n2017-07-04 0.04\n2017-07-04 0.03\n2017-07-05 NaN\n2017-07-05 0.00\n2017-07-05 0.00\n2017-07-05 0.00\n2017-07-05 0.00\n2017-07-05 NaN\n2017-07-05 NaN\n2017-07-06 0.00\n2017-07-06 0.00\n2017-07-06 0.02\n2017-07-06 0.00\n2017-07-06 NaN\n2017-07-06 0.00\n2017-07-07 0.02\n2017-07-07 0.30\n2017-07-07 NaN\n2017-07-07 0.18\n2017-07-07 NaN\n2017-07-07 0.00\n2017-07-07 0.00\n2017-07-08 0.00\n2017-07-08 0.02\n2017-07-08 0.00\n2017-07-08 0.00\n2017-07-08 0.02\n2017-07-08 0.06\n2017-07-09 0.00\n2017-07-09 0.00\n2017-07-09 0.00\n2017-07-09 0.09\n2017-07-09 0.00\n2017-07-09 0.11\n2017-07-10 0.00\n2017-07-10 0.00\n2017-07-10 0.02\n2017-07-10 0.00\n2017-07-10 NaN\n2017-07-10 0.02\n2017-07-10 0.00\n2017-07-11 0.02\n2017-07-11 0.01\n2017-07-11 0.00\n2017-07-11 0.00\n2017-07-11 0.00\n2017-07-11 0.00\n2017-07-11 NaN\n2017-07-12 0.05\n2017-07-12 NaN\n2017-07-12 0.02\n2017-07-12 0.01\n2017-07-12 0.28\n2017-07-12 0.00\n2017-07-12 0.00\n2017-07-13 0.33\n2017-07-13 0.30\n2017-07-13 0.11\n2017-07-13 0.07\n2017-07-13 0.32\n2017-07-13 NaN\n2017-07-13 0.68\n2017-07-14 0.00\n2017-07-14 0.68\n2017-07-14 0.02\n2017-07-14 0.00\n2017-07-14 0.05\n2017-07-14 0.20\n2017-07-15 0.00\n2017-07-15 0.01\n2017-07-15 0.03\n2017-07-15 0.10\n2017-07-15 0.00\n2017-07-15 0.05\n2017-07-16 0.50\n2017-07-16 0.07\n2017-07-16 0.02\n2017-07-16 0.10\n2017-07-16 0.12\n2017-07-16 0.00\n2017-07-17 0.12\n2017-07-17 0.21\n2017-07-17 0.00\n2017-07-17 0.16\n2017-07-17 0.03\n2017-07-17 0.39\n2017-07-18 0.00\n2017-07-18 0.05\n2017-07-18 0.00\n2017-07-18 0.05\n2017-07-18 0.00\n2017-07-18 0.03\n2017-07-18 2.40\n2017-07-19 0.05\n2017-07-19 0.00\n2017-07-19 0.09\n2017-07-19 0.27\n2017-07-19 0.00\n2017-07-19 0.00\n2017-07-20 0.70\n2017-07-20 0.00\n2017-07-20 0.00\n2017-07-20 0.12\n2017-07-20 0.03\n2017-07-20 0.33\n2017-07-20 0.06\n2017-07-21 0.03\n2017-07-21 0.00\n2017-07-21 0.00\n2017-07-21 0.10\n2017-07-21 0.00\n2017-07-21 0.00\n2017-07-21 0.00\n2017-07-22 0.20\n2017-07-22 0.00\n2017-07-22 0.07\n2017-07-22 4.00\n2017-07-22 0.12\n2017-07-22 0.03\n2017-07-23 0.07\n2017-07-23 0.20\n2017-07-23 0.06\n2017-07-23 0.00\n2017-07-23 0.80\n2017-07-24 0.84\n2017-07-24 1.19\n2017-07-24 0.58\n2017-07-24 0.05\n2017-07-24 0.61\n2017-07-24 NaN\n2017-07-25 0.05\n2017-07-25 0.03\n2017-07-25 0.12\n2017-07-25 0.30\n2017-07-25 0.00\n2017-07-25 0.11\n2017-07-25 0.00\n2017-07-26 0.30\n2017-07-26 0.06\n2017-07-26 0.00\n2017-07-26 0.12\n2017-07-26 0.02\n2017-07-26 0.00\n2017-07-26 NaN\n2017-07-27 0.00\n2017-07-27 0.00\n2017-07-27 0.00\n2017-07-27 NaN\n2017-07-27 0.01\n2017-07-27 0.00\n2017-07-27 0.00\n2017-07-28 0.13\n2017-07-28 0.40\n2017-07-28 0.00\n2017-07-28 0.14\n2017-07-28 0.09\n2017-07-28 0.00\n2017-07-28 0.01\n2017-07-29 0.02\n2017-07-29 0.06\n2017-07-29 0.23\n2017-07-29 0.00\n2017-07-29 0.30\n2017-07-29 0.00\n2017-07-30 0.30\n2017-07-30 0.00\n2017-07-30 0.00\n2017-07-30 0.00\n2017-07-30 0.00\n2017-07-31 0.00\n2017-07-31 0.00\n2017-07-31 0.00\n2017-07-31 NaN\n2017-07-31 0.00\n2017-07-31 NaN\n2017-07-31 0.00\n2017-08-01 0.02\n2017-08-01 NaN\n2017-08-01 0.12\n2017-08-01 0.00\n2017-08-02 0.00\n2017-08-02 0.25\n2017-08-02 0.05\n2017-08-02 0.00\n2017-08-03 0.01\n2017-08-03 0.00\n2017-08-03 0.06\n2017-08-03 0.00\n2017-08-04 0.00\n2017-08-04 0.04\n2017-08-04 0.00\n2017-08-04 0.02\n2017-08-05 NaN\n2017-08-05 0.00\n2017-08-05 0.06\n2017-08-06 NaN\n2017-08-06 0.00\n2017-08-06 0.00\n2017-08-06 0.00\n2017-08-06 0.00\n2017-08-07 0.00\n2017-08-07 0.05\n2017-08-07 0.00\n2017-08-07 0.00\n2017-08-08 0.00\n2017-08-08 0.34\n2017-08-08 0.00\n2017-08-08 0.10\n2017-08-09 0.00\n2017-08-09 0.00\n2017-08-09 0.15\n2017-08-10 0.00\n2017-08-10 0.07\n2017-08-10 0.00\n2017-08-10 0.00\n2017-08-11 0.00\n2017-08-11 0.00\n2017-08-11 NaN\n2017-08-11 0.00\n2017-08-12 0.00\n2017-08-12 0.14\n2017-08-12 0.00\n2017-08-13 0.00\n2017-08-13 NaN\n2017-08-13 0.00\n2017-08-13 NaN\n2017-08-13 0.00\n2017-08-14 0.08\n2017-08-14 0.01\n2017-08-14 0.22\n2017-08-14 0.00\n2017-08-14 0.00\n2017-08-15 0.06\n2017-08-15 0.42\n2017-08-15 0.32\n2017-08-15 0.00\n2017-08-15 0.02\n2017-08-16 0.42\n2017-08-16 0.12\n2017-08-16 0.07\n2017-08-16 0.00\n2017-08-17 0.13\n2017-08-17 0.01\n2017-08-17 0.00\n2017-08-17 0.05\n2017-08-18 NaN\n2017-08-18 0.06\n2017-08-18 0.00\n2017-08-18 0.00\n2017-08-19 0.00\n2017-08-19 0.09\n2017-08-19 NaN\n2017-08-19 0.00\n2017-08-20 0.00\n2017-08-20 0.01\n2017-08-20 NaN\n2017-08-21 0.56\n2017-08-21 0.02\n2017-08-21 0.00\n2017-08-21 NaN\n2017-08-22 0.00\n2017-08-22 0.50\n2017-08-22 0.00\n2017-08-23 0.00\n2017-08-23 0.00\n2017-08-23 0.08\n2017-08-23 0.45\n"
]
],
[
[
"### 9.2.4 Plot the Data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Use Pandas Plotting with Matplotlib to plot the data\ndf.plot()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Use Pandas to calcualte the summary statistics for the precipitation data\ndf.describe()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### This data gives us a summary of different statistics for the amount of precipitation in a year. The count is the number of times precipitation was observed. The other statistics are the precipitation amounts for each station for each day",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 9.3.1 Find the Number of Stations",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# How many stations are available in this dataset?\nsession.query(func.count(Station.station)).all()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 9.3.2 Determine the Most Active Stations",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# What are the most active stations? (will need to add parameters to the query)\nsession.query(Measurement.station, func.count(Measurement.station)).\\\ngroup_by(Measurement.station).order_by(func.count(Measurement.station).desc()).all()\n# List the stations and the counts in descending order.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### In the left column is the station ID, and on the right are the counts for each station. The counts indicate which stations are most active. We can also see which stations are the least active.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 9.3.3 Find Low, High, and Average Temperatures",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Using the station id from the previous query, calculate the lowest temperature recorded, \n# highest temperature recorded, and average temperature most active station?\nsession.query(func.min(Measurement.tobs), func.max(Measurement.tobs), func.avg(Measurement.tobs)).\\\nfilter(Measurement.station == 'USC00519281').all()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Choose the station with the highest number of temperature observations.\n# Query the last 12 months of temperature observation data for this station and plot the results as a histogram\nresults = session.query(Measurement.tobs).\\\nfilter(Measurement.station == 'USC00519281').\\\nfilter(Measurement.date >= prev_year).all()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(results)",
"[(77.0,), (77.0,), (80.0,), (80.0,), (75.0,), (73.0,), (78.0,), (77.0,), (78.0,), (80.0,), (80.0,), (78.0,), (78.0,), (78.0,), (73.0,), (74.0,), (80.0,), (79.0,), (77.0,), (80.0,), (76.0,), (79.0,), (75.0,), (79.0,), (78.0,), (79.0,), (78.0,), (78.0,), (76.0,), (74.0,), (77.0,), (78.0,), (79.0,), (79.0,), (77.0,), (80.0,), (78.0,), (78.0,), (78.0,), (77.0,), (79.0,), (79.0,), (79.0,), (79.0,), (75.0,), (76.0,), (73.0,), (72.0,), (71.0,), (77.0,), (79.0,), (78.0,), (79.0,), (77.0,), (79.0,), (77.0,), (78.0,), (78.0,), (78.0,), (78.0,), (77.0,), (74.0,), (75.0,), (76.0,), (73.0,), (76.0,), (74.0,), (77.0,), (76.0,), (76.0,), (74.0,), (75.0,), (75.0,), (75.0,), (75.0,), (71.0,), (63.0,), (70.0,), (68.0,), (67.0,), (77.0,), (74.0,), (77.0,), (76.0,), (76.0,), (75.0,), (76.0,), (75.0,), (73.0,), (75.0,), (73.0,), (75.0,), (74.0,), (75.0,), (74.0,), (75.0,), (73.0,), (75.0,), (73.0,), (73.0,), (74.0,), (70.0,), (72.0,), (70.0,), (67.0,), (67.0,), (69.0,), (70.0,), (68.0,), (69.0,), (69.0,), (66.0,), (65.0,), (68.0,), (62.0,), (75.0,), (70.0,), (69.0,), (76.0,), (76.0,), (74.0,), (73.0,), (71.0,), (74.0,), (74.0,), (72.0,), (71.0,), (72.0,), (74.0,), (69.0,), (67.0,), (72.0,), (70.0,), (64.0,), (63.0,), (63.0,), (62.0,), (70.0,), (70.0,), (62.0,), (62.0,), (63.0,), (65.0,), (69.0,), (77.0,), (70.0,), (74.0,), (69.0,), (72.0,), (71.0,), (69.0,), (71.0,), (71.0,), (72.0,), (72.0,), (69.0,), (70.0,), (66.0,), (65.0,), (69.0,), (68.0,), (68.0,), (68.0,), (59.0,), (60.0,), (70.0,), (73.0,), (75.0,), (64.0,), (59.0,), (59.0,), (62.0,), (68.0,), (70.0,), (73.0,), (79.0,), (75.0,), (65.0,), (70.0,), (74.0,), (70.0,), (70.0,), (71.0,), (71.0,), (71.0,), (69.0,), (61.0,), (67.0,), (65.0,), (72.0,), (71.0,), (73.0,), (72.0,), (77.0,), (73.0,), (67.0,), (62.0,), (64.0,), (67.0,), (66.0,), (81.0,), (69.0,), (66.0,), (67.0,), (69.0,), (66.0,), (68.0,), (65.0,), (74.0,), (69.0,), (72.0,), (73.0,), (72.0,), (71.0,), (76.0,), (77.0,), (76.0,), (74.0,), (68.0,), (73.0,), (71.0,), (74.0,), (75.0,), (70.0,), (67.0,), (71.0,), (67.0,), (74.0,), (77.0,), (78.0,), (67.0,), (70.0,), (69.0,), (69.0,), (74.0,), (78.0,), (71.0,), (67.0,), (68.0,), (67.0,), (76.0,), (69.0,), (72.0,), (76.0,), (68.0,), (72.0,), (74.0,), (70.0,), (67.0,), (72.0,), (60.0,), (65.0,), (75.0,), (70.0,), (75.0,), (70.0,), (79.0,), (75.0,), (70.0,), (67.0,), (74.0,), (70.0,), (75.0,), (76.0,), (77.0,), (74.0,), (74.0,), (74.0,), (69.0,), (68.0,), (76.0,), (74.0,), (71.0,), (71.0,), (74.0,), (74.0,), (74.0,), (74.0,), (80.0,), (74.0,), (72.0,), (75.0,), (80.0,), (76.0,), (76.0,), (77.0,), (75.0,), (75.0,), (75.0,), (75.0,), (72.0,), (74.0,), (74.0,), (74.0,), (76.0,), (74.0,), (75.0,), (73.0,), (79.0,), (75.0,), (72.0,), (72.0,), (74.0,), (72.0,), (72.0,), (77.0,), (71.0,), (73.0,), (76.0,), (77.0,), (76.0,), (76.0,), (79.0,), (81.0,), (76.0,), (78.0,), (77.0,), (74.0,), (75.0,), (78.0,), (78.0,), (69.0,), (72.0,), (74.0,), (74.0,), (76.0,), (80.0,), (80.0,), (76.0,), (76.0,), (76.0,), (77.0,), (77.0,), (77.0,), (82.0,), (75.0,), (77.0,), (75.0,), (76.0,), (81.0,), (82.0,), (81.0,), (76.0,), (77.0,), (82.0,), (83.0,), (77.0,), (77.0,), (77.0,), (76.0,), (76.0,), (79.0,)]\n"
],
[
"# insert into a DataFrame\ndf = pd.DataFrame(results, columns=['tobs'])\nprint(df)",
" tobs\n0 77.0\n1 77.0\n2 80.0\n3 80.0\n4 75.0\n.. ...\n347 77.0\n348 77.0\n349 76.0\n350 76.0\n351 79.0\n\n[352 rows x 1 columns]\n"
],
[
"# Create histogram\n# We'll be creating a histogram from the temperature observations. \n# This will allow us to quickly count how many temperature observations we have.\n\ndf.plot.hist(bins=12)\nplt.tight_layout()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Looking at this plot, we can infer that a vast majority of the observations were over 67 degrees. If you count up the bins to the right of 67 degrees, you will get about 325 days where it was over 67 degrees when the temperature was observed.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Write a function called `calc_temps` that will accept start date and end date in the format '%Y-%m-%d' \n# and return the minimum, average, and maximum temperatures for that range of dates\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 9.4.3 Set Up Flask and Create a Route",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pip install flask",
"Requirement already satisfied: flask in /Users/vanessamarie/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.8/site-packages (1.1.2)\nRequirement already satisfied: click>=5.1 in /Users/vanessamarie/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.8/site-packages (from flask) (7.1.2)\nRequirement already satisfied: Jinja2>=2.10.1 in /Users/vanessamarie/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.8/site-packages (from flask) (2.11.3)\nRequirement already satisfied: Werkzeug>=0.15 in /Users/vanessamarie/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.8/site-packages (from flask) (1.0.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: itsdangerous>=0.24 in /Users/vanessamarie/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.8/site-packages (from flask) (1.1.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: MarkupSafe>=0.23 in /Users/vanessamarie/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.8/site-packages (from Jinja2>=2.10.1->flask) (1.1.1)\nNote: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Challenge",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a3315cd9533afbe49a5b5f7a19d0a2ac2240af0
| 15,147 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
advent_of_code_2019/day 08 space image/solution.ipynb
|
jvanelteren/advent_of_code
|
3c547645250adb2d95ebac43d5d2111cdf9b09e9
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-12-23T11:24:11.000Z
|
2021-12-23T11:24:11.000Z
|
advent_of_code_2019/day 08 space image/solution.ipynb
|
jvanelteren/advent_of_code
|
3c547645250adb2d95ebac43d5d2111cdf9b09e9
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
advent_of_code_2019/day 08 space image/solution.ipynb
|
jvanelteren/advent_of_code
|
3c547645250adb2d95ebac43d5d2111cdf9b09e9
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 122.153226 | 9,985 | 0.654321 |
[
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom collections import Counter\np=[int(x) for x in open('input.txt').read()]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"l = [p[i:i+25*6] for i in range(0,len(p),25*6)]\nres = {}\nfor i,x in enumerate(l):\n c = Counter(x)\n res[c[0]] = i\ntarget_layer = res[min(res.keys())]\nCounter(l[target_layer])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"129*15",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pic = []\ndef get_color(i):\n for layer in l:\n res = layer[i]\n if res < 2: return res\n return 2\nfor i in range(25*6):\n pic.append(get_color(i))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pic = np.array(pic).reshape(6,25)\nfrom matplotlib import pyplot as plt\nplt.imshow(pic, interpolation='nearest')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a331f88962af5c6372ba3e1a7558772217804cb
| 24,737 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
homework/hw0/hw0.ipynb
|
Anusha1426/mcis6273_f21_datamining
|
6155f2c6ae1ee1cea416b4c47c3dbb268908b7ce
|
[
"CC0-1.0"
] | null | null | null |
homework/hw0/hw0.ipynb
|
Anusha1426/mcis6273_f21_datamining
|
6155f2c6ae1ee1cea416b4c47c3dbb268908b7ce
|
[
"CC0-1.0"
] | null | null | null |
homework/hw0/hw0.ipynb
|
Anusha1426/mcis6273_f21_datamining
|
6155f2c6ae1ee1cea416b4c47c3dbb268908b7ce
|
[
"CC0-1.0"
] | null | null | null | 48.887352 | 400 | 0.646885 |
[
[
[
"# MCIS6273 Data Mining (Prof. Maull) / Fall 2021 / HW0\n\n**This assignment is worth up to 20 POINTS to your grade total if you complete it on time.**\n\n| Points <br/>Possible | Due Date | Time Commitment <br/>(estimated) |\n|:---------------:|:--------:|:---------------:|\n| 20 | Wednesday, Sep 1 @ Midnight | _up to_ 20 hours |\n\n\n* **GRADING:** Grading will be aligned with the completeness of the objectives.\n\n* **INDEPENDENT WORK:** Copying, cheating, plagiarism and academic dishonesty _are not tolerated_ by University or course policy. Please see the syllabus for the full departmental and University statement on the academic code of honor.\n\n## OBJECTIVES\n* Familiarize yourself with the JupyterLab environment, Markdown and Python\n\n* Familiarize yourself with Github and basic git\n\n* Explore JupyterHub Linux console integrating what you learned in the prior parts of this homework\n\n* Listen to the Talk Python['Podcast'] from June 25, 2021: A Path to Data Science Interview with Sanyam Bhutani\n\n* Explore Python for data munging and analysis, with an introduction to CSV and Pandas\n\n## WHAT TO TURN IN\nYou are being encouraged to turn the assignment in using the provided\nJupyter Notebook. To do so, make a directory in your Lab environment called\n`homework/hw0`. Put all of your files in that directory. Then zip that directory,\nrename it with your name as the first part of the filename (e.g. `maull_hw0_files.zip`), then\ndownload it to your local machine, then upload the `.zip` to Blackboard.\n\nIf you do not know how to do this, please ask, or visit one of the many tutorials out there\non the basics of using zip in Linux.\n\nIf you choose not to use the provided notebook, you will still need to turn in a\n`.ipynb` Jupyter Notebook and corresponding files according to the instructions in\nthis homework.\n\n\n## ASSIGNMENT TASKS\n### (0%) Familiarize yourself with the JupyterLab environment, Markdown and Python \n\nAs stated in the course announcement [Jupyter (https://jupyter.org)](https://jupyter.org) is the\ncore platform we will be using in this course and\nis a popular platform for data scientists around the world. We have a JupyterLab\nsetup for this course so that we can operate in a cloud-hosted environment, free from\nsome of the resource constraints of running Jupyter on your local machine (though you are free to set\nit up on your own and seek my advice if you desire).\n\nYou have been given the information about the Jupyter environment we have setup for our course, and\nthe underlying Python environment will be using is the [Anaconda (https://anaconda.com)](https://anaconda.com)\ndistribution. It is not necessary for this assignment, but you are free to look at the multitude\nof packages installed with Anaconda, though we will not use the majority of them explicitly.\n\nAs you will soon find out, Notebooks are an incredibly effective way to mix code with narrative\nand you can create cells that are entirely code or entirely Markdown. Markdown (MD or `md`) is\na highly readable text format that allows for easy documentation of text files, while allowing\nfor HTML-based rendering of the text in a way that is style-independent.\n\nWe will be using Markdown frequently in this course, and you will learn that there are many different\n\"flavors\" or Markdown. We will only be using the basic flavor, but you will benefit from exploring\nthe \"Github flavored\" Markdown, though you will not be responsible for using it in this course -- only the\n\"basic\" flavor. Please refer to the original course announcement about Markdown.\n\n§ **THERE IS NOTHING TO TURN IN FOR THIS PART.** Play with and become familiar with the basic functions of\nthe Lab environment given to you online in the course Blackboard.\n\n\n§ **PLEASE _CREATE A MARKDOWN DOCUMENT_ CALLED `semester_goals.md` WITH 3 SENTENCES/FRAGMENTS THAT\nANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTION:**\n\n* **What do you wish to accomplish this semester in Data Mining?**\n\nRead the documentation for basic Markdown [here](https://www.markdownguide.org/basic-syntax). \nTurn in the text `.md` file *not* the processed `.html`. In whatever you turn in, \nyou must show the use of *ALL* the following:\n\n* headings (one level is fine),\n* bullets,\n* bold and italics\n\nAgain, the content of your document needs to address the question above and it should live\nin the top level directory of your assignment submission. This part will be graded but no\npoints are awarded for your answer.\n\n\n\n### (0%) Familiarize yourself with Github and basic git \n\n[Github (https://github.com)](https://github.com) is the _de facto_ platform for open source software in the world based\non the very popular [git (https://git-scm.org)](https://git-scm.org) version control system. Git has a sophisticated set\nof tools for version control based on the concept of local repositories for fast commits and remote\nrepositories only when collaboration and remote synchronization is necessary. Github enhances git by providing\ntools and online hosting of public and private repositories to encourage and promote sharing and collaboration.\nGithub hosts some of the world's most widely used open source software.\n\n**If you are already familiar with git and Github, then this part will be very easy!**\n\n§ **CREATE A PUBLIC GITHUB REPO NAMED `\"mcis6273-F21-datamining\"` AND PLACE A README.MD FILE IN IT.**\nCreate your first file called\n`README.md` at the top level of the repository. You can put whatever text you like in the file \n(If you like, use something like [lorem ipsum](https://lipsum.com/)\nto generate random sentences to place in the file.).\nPlease include the link to **your** Github repository that now includes the minimal `README.md`. \nYou don't have to have anything elaborate in that file or the repo. \n\n\n\n### (0%) Explore JupyterHub Linux console integrating what you learned in the prior parts of this homework \n\nThe Linux console in JupyterLab is a great way to perform command-line tasks and is an essential tool\nfor basic scripting that is part of a data scientist's toolkit. Open a console in the lab environment\nand familiarize yourself with your files and basic commands using git as indicated below.\n\n1. In a new JupyterLab command line console, run the `git clone` command to clone the new\n repository you created in the prior part.\n You will want to read the documentation on this \n command (try here [https://www.git-scm.com/docs/git-clone](https://www.git-scm.com/docs/git-clone) to get a good\n start).\n2. Within the same console, modify your `README.md` file, check it in and push it back to your repository, using\n `git push`. Read the [documentation about `git push`](https://git-scm.com/docs/git-push).\n3. The commands `wget` and `curl` are useful for grabbing data and files from remote resources off the web.\n Read the documentation on each of these commands by typing `man wget` or `man curl` in the terminal.\n Make sure you pipe the output to a file or use the proper flags to do so.\n\n§ **THERE IS NOTHING TO TURN IN FOR THIS PART.**\n\n\n\n### (30%) Listen to the Talk Python['Podcast'] from June 25, 2021: A Path to Data Science Interview with Sanyam Bhutani \n\nData science is one of the most important and \"hot\" disciplines today\nand there is a lot going on from data engineering to modeling and\nanalysis.\n\nBhutani is one of the top [Kaggle]() leaders and in this interview\nshares his experience from computer science to data science, \ndocumenting some of the lessons he learned along the way.\n\nPlease listen to this one hour podcast and answer some of the questions below.\nYou can listen to it from one of the two links below:\n\n* [Talk Python['Podcast'] landing page](https://talkpython.fm/episodes/transcript/322/a-path-into-data-science)\n* [direct link to mp3 file](https://downloads.talkpython.fm/podcasts/talkpython/322-starting-in-data-sci.mp3)\n\n§ **PLEASE ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS AFTER LISTENING TO THE PODCAST:**\n\n1. List 3 things that you learned from this podcast?\n**ANSWER**\n(a).Computer science has became more practical these days\n(b).In order to gain knowledge on programming we need more practice in the coding techniques and try to solve concrete problems\n(c).Data science has became first koggle competition and tend to set goals every year\n\n2. What is your reaction to the podcast? Pick at least one point Sanyam brought up in the interview that you agree with and list your reason why.\n**ANSWER**\nThe one thing I agree with Sanyam brought up in this interview is you gain lot of knowledge by learning from lot of forums and discussion board\nand when it comes to the practical knowledge lot of members have the problems in coding techniques and solving the issues.\n3. After listening to the podcast, do you think you are more interested or less interested in a career in Data Science?\n**ANSWER**\nYes I got more interest in Data Science field to develope my career \n\n\n### (70%) Explore Python for data munging and analysis, with an introduction to CSV and Pandas \n\n\nPython's strengths shine when tasked with data munging and analysis. As we will learn throughout\nthe course, there are a number of excellent data sources for open data of all kinds now\navailable for the public. These open data sources are heralding the new era of transparency\nfrom all levels from small municipal data to big government data, from transportation, to science,\nto education.\n\nTo warm up to such datasets, we will be working with an interesting\ndataset from the US Fish and Wildlife Service (FWS). This is a \nwater quality data set taken from a managed national refuge in\nVirginia called Back Bay National Wildlife Refuge, which was \nestablished in 1938. As a function of being managed by the FWS, \nwater quality samples are taken regularly from the marshes within \nthe refuge.\n\nYou can (and should) learn a little more about Back Bay from\nthis link, since it has an interesting history, features and wildlife.\n\n* [https://www.fws.gov/refuge/Back_Bay/about.html](https://www.fws.gov/refuge/Back_Bay/about.html)\n\n\nThe data we will be looking at can be found as a direct download \nfrom data.gov, the US data repository where many datasets from\na variety of sources can be found -- mostly related to the \nmultitude of US government agencies.\n\nThe dataset is a small water quality dataset with several decades\nof water quality data from Back Bay. We will be warming up\nto this dataset with a basic investigation into the shape, content\nand context of the data contained therein.\n\n\nIn this part of the assignment, we will make use of Python libraries to pull the data from the\nendpoint and use [Pandas](https://pandas.pydata.org) to plot the data. The raw CSV data is\nreadily imported into Pandas from the following URL:\n\n* [FWS Water Quality Data 12/20/2020](https://catalog.data.gov/dataset/water-quality-data/resource/f4d736fd-ade9-4e3f-b8e0-ae7fd98b2f87)\n\nPlease take a look at the page, on it you will notice a link \nto the raw CSV file:\n\n* [https://ecos.fws.gov/ServCat/DownloadFile/173741?Reference=117348](https://ecos.fws.gov/ServCat/DownloadFile/173741?Reference=117348)\n\nWe are going to explore this dataset to learn a bit more about the \nwater quality characteristics of Bay Bay over the past couple decades\nor so.\n\n§ **WRITE THE CODE IN YOUR NOTEBOOK TO LOAD AND RESHAPE THE COMPLETE CSV WATER QUALITY DATASET**:\n\nYou will need to perform the following steps:\n\n1. **use [`pandas.read_csv()`](https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/generated/pandas.read_csv.html) method to load the dataset** into a Pandas DataFrame;\n**ANSWER:**\nimport pandas as pd\ndf=pd.read_csv('https://ecos.fws.gov/ServCat/DownloadFile/173741?Reference=117348')\n\n\n2. **clean the data so that the range of years is restricted to the 20 year period from 1999 to 2018**\n**ANSWER:**\n#filter_range=pd.DataFrame({'Year': range(1999, 2018)})\ndf = df[(df['Year'] >= 1999) & (df['Year'] <= 2018)]\n\n3. **store the entire dataset back into a new CSV** file called `back_bay_1998-2018_clean.csv`.\n**ANSWER:**\ndf.to_csv('back_bay_1998-2018_clean.csv')\n\n\n**HINTS:** _Here are some a code hints you might like to study and use to craft a solution:_\n\n* study [`pandas.DataFrame.query()]`](https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/reference/api/pandas.DataFrame.query.html?highlight=query#pandas.DataFrame.query) to learn how to filter and query year ranges\n* study [`pandas.DataFrame.groupby()`](https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/reference/api/pandas.DataFrame.groupby.html?highlight=groupby#pandas.DataFrame.groupby) to understand how to group data\n\n\n§ **USE PANDAS TO LOAD THE CSV DATA TO A DATAFRAME AND ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS:**\n\n1. How many and what are the names of the columns in this dataset?\n**ANSWER:**\nThere are 17 columns in the dataset and below are the column names in dataset.\n\nSite_Id\nUnit_Id\nRead_Date\nSalinity (ppt)\nDissolved Oxygen (mg/L)\npH (standard units)\nSecchi Depth (m)\nWater Depth (m)\nWater Temp (?C)\nAir Temp-Celsius\nAir Temp (?F)\nTime (24:00)\nField_Tech\nDateVerified\nWhoVerified\nAirTemp (C)\nYear\n\n\n2. What is the mean `Dissolved Oxygen (mg/L)` over the entire dataset?\n\n>This is to load the data from csv file into data frame for performing the required operations\n\ndataframe=pd.read_csv('back_bay_1998-2018_clean.csv')\n**ANSWER:**\nmean_dissolved_oxygen = dataframe['Dissolved Oxygen (mg/L)'].mean()\nprint(mean_dissolved_oxygen)\n\n**Result**\n5.8677\n\n>This value is the result obtained from filtered dataset\n\nIn order to find the mean value for the entire dataset\n\nimport pandas as pd\ndf=pd.read_csv('https://ecos.fws.gov/ServCat/DownloadFile/173741?Reference=117348')\n\nmean_dissolved_oxygen = df['Dissolved Oxygen (mg/L)'].mean()\nprint(mean_dissolved_oxygen)\n\n**Result**\n6.646263157894744\n\n3. Which year were the highest number of `AirTemp (C)` data points collected?\n**ANSWER:**\nhighest_data_points = dataframe.groupby('Year').size()\nprint(highest_data_points)\n\n**Result**\nYear\n1999 45\n2000 109\n2001 115\n2002 108\n2003 98\n2004 119\n2005 107\n2006 118\n2007 114\n2008 117\n2009 120\n2010 109\n2011 97\n2012 88\n2013 91\n2014 87\n2015 88\n2016 59\n2017 85\n2018 82\ndtype: int64\n> From the above result 2009 has the highest data points(120)\n\n4. Which year were the least number of `AirTemp (C)` data points collected?\n**ANSWER:**\nlowest_data_points = dataframe.groupby('Year').size()\nprint(lowest_data_points)\n\n**Result**\nYear\n1999 45\n2000 109\n2001 115\n2002 108\n2003 98\n2004 119\n2005 107\n2006 118\n2007 114\n2008 117\n2009 120\n2010 109\n2011 97\n2012 88\n2013 91\n2014 87\n2015 88\n2016 59\n2017 85\n2018 82\ndtype: int64\n\n>From the above result 1999 has the lowest data points i.e (45)\n\n\n\nTo answer these questions, you'll need to dive further into Pandas, which is\nthe standard tool in the Python data science stack for loading, manipulating,\ntransforming, analyzing and preparing data as input to other tools such as\n[Numpy (http://www.numpy.org/)](http://www.numpy.org/), \n[SciKitLearn (http://scikit-learn.org/stable/index.html)](http://scikit-learn.org/stable/index.html), \n[NLTK (http://www.nltk.org/)](http://www.nltk.org/) and others.\n\nFor this assignment, you will only need to learn how to load and select data using Pandas.\n\n* **LOADING DATA**\nThe core data structure in Pandas is the `DataFrame`. You will need to visit\nthe Pandas documentation [(https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/reference/)](https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/reference/)\nto learn more about the library, but to help you along with a hint, read the\ndocumentation on the [`pandas.read_csv()`](https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/generated/pandas.read_csv.html) method.\n\n* **SELECTING DATA**\nThe [tutorial here on indexing and selecting](http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html)\nshould be of great use in understanding how to index and select subsets of\nthe data to answer the questions.\n\n* **GROUPING DATA** You may use [`DataFrame.value_counts()`](https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/reference/api/pandas.DataFrame.value_counts.html?highlight=value_counts#pandas.DataFrame.value_counts) or [`DataFrame.groupby()`](https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/reference/groupby.html) to group\nthe data you need for these questons. You will also find [`DataFrame.groupby()](https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/reference/api/pandas.DataFrame.groupby.html?highlight=groupby#pandas.DataFrame.groupby) and [`DataFrame.describe()`](https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/reference/api/pandas.DataFrame.describe.html?highlight=describe#pandas.DataFrame.describe) very useful.\n\n**CODE HINTS**\n\nHere is example code that should give you clues about the structure\nof your code for this part.\n\n```python\n import pandas as pd\n\n df = pd.read_csv('your_json_file.csv')\n\n # code for question 1 ... and so on\n```\n\n\n§ **EXPLORING WATER SALINITY IN THE DATA**\n\nThe Back ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Bay refuge is on the eastern coast of Virginia and to\nthe east is the Atlantic Ocean. Salinity is a measure of\nthe salt concentration of water, and you can learn a little more\nabout salinity in water [here](https://www.usgs.gov/special-topic/water-science-school/science/saline-water-and-salinity?qt-science_center_objects=0#qt-science_center_objects).\n\nYou will notice that there is a `Site_Id` variable in the data, which \nwe will find refers to the five sampling locations (see the [documentation here](https://ecos.fws.gov/ServCat/Reference/Profile/117348))\nof (1) the Bay, (2) D-Pool (fishing pond), (3) C-Pool, (4) B-Pool and (5) A-Pool.\n\nThe ppt in Salinity is the percent salinity, and so 1 ppt is equivalent to 10000 ppm salinity. Use this information to answer \nthe following questions.\n\n1. Which sampling location has the highest mean ppt? What is the equivalent ppm?\n**Answer**\nimport pandas as pd \ndf=pd.read_csv('https://ecos.fws.gov/ServCat/DownloadFile/173741')\nmean_salinity = df.groupby('Site_Id')['Salinity (ppt)'].mean()\nprint(mean_salinity)\n\n**Result**\nSite_Id\nA 0.329517\nB 0.433765\nBay 1.483154\nC 0.596397\nD 0.099619\n\n>Looking at the result, the Bay has the highest mean ppt of 1.483154. It's equivalent ppm is 14831.54\n\n2. When looking at the mean ppt, which location would you infer is furthest from the influence of ocean water inflows? \n (Assume that higher salinity correlates to closer proximity to the ocean.)\n**Answer**'\nLooking at the mean ppt values of all sampling locations, I would infer D-pool (fishing pond) is furthest from the influence of ocean water. \n\n3. Dig a little deeper into #2, and write why there may be some uncertainty in your answer? (hint: certainty is improved by consistency in data)\n**Answer**\nThere might some uncertainity in the answer that was provided because we can notice some inconsistencies in the data provided. For example there are values for Site_Id which are not mentioned like 'd' and also some blanks. We have to sanitize the data before performing any analysis/operations.\n\n4. Use the data to determine the correlation between `Salinity (ppt)` and `pH (standard units)`. Use the [DataFrame.corr()](https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/reference/api/pandas.core.groupby.DataFrameGroupBy.corr.html?highlight=correlate). You just need to report the correlation value.\n\n**Answer**\ncorrelation_value = df['Salinity (ppt)'].corr(df['pH (standard units)'])\nprint(correlation_value)\n\n**Result**\n0.29607528012371914",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a3321bfbba7b3186739455a660f50054bde2a91
| 21,443 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
examples/grids/smib_milano_ex8p1/smib_milano_ex8p1_4ord_avr/smib_milano_ex8p1_4ord_avr.ipynb
|
pydae/pydae
|
8076bcfeb2cdc865a5fc58561ff8d246d0ed7d9d
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2020-12-20T03:45:26.000Z
|
2020-12-20T03:45:26.000Z
|
examples/grids/smib_milano_ex8p1/smib_milano_ex8p1_4ord_avr/smib_milano_ex8p1_4ord_avr.ipynb
|
pydae/pydae
|
8076bcfeb2cdc865a5fc58561ff8d246d0ed7d9d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
examples/grids/smib_milano_ex8p1/smib_milano_ex8p1_4ord_avr/smib_milano_ex8p1_4ord_avr.ipynb
|
pydae/pydae
|
8076bcfeb2cdc865a5fc58561ff8d246d0ed7d9d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 32.293675 | 2,388 | 0.530476 |
[
[
[
"# SMIB system as in Milano's book example 8.1",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%matplotlib widget",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport scipy.optimize as sopt\nimport ipywidgets\nfrom pydae import ssa\nimport json",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Import system module",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from smib_milano_ex8p1_4ord_avr import smib_milano_ex8p1_4ord_avr_class",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Instantiate system",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"syst = smib_milano_ex8p1_4ord_avr_class()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Initialize the system (backward and foreward)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"events=[{'p_t':0.8, 'v_t':1.1, 'K_a':500, 'T_e':0.1}]\nsyst.initialize(events,xy0=1)\n\nsyst.save_0()\nsyst.report_u()\nsyst.report_x()\nsyst.report_y()",
"p_m = 0.80\nv_ref = 1.11\ndelta = 0.49\nomega = 1.00\ne1q = 1.38\ne1d = 0.28\nv_c = 1.10\nv_d = 0.44\nv_q = 1.01\ni_d = 1.23\ni_q = 0.25\np_e = 0.80\np_t = 0.80\nq_t = 1.13\nv_t = 1.10\ntheta_t = 0.07\nv_f = 3.24\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Simulation",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"syst = smib_milano_ex8p1_4ord_avr_class()\n\n\nevents=[{'p_t':0.8, 'v_t':1.0, 'K_a':400, 'T_e':0.5, 'H':6}]\nsyst.initialize(events,xy0=1)\n\nevents=[{'t_end':1.0},\n {'t_end':15.0, 'p_m':0.8, 'v_ref':1.05}\n ]\n\nsyst.simulate(events,xy0='prev');",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.close('all')\nfig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2,ncols=2, figsize=(10, 5), frameon=False, dpi=50)\n\naxes[0,0].plot(syst.T, syst.get_values('omega'), label=f'$\\omega$')\naxes[0,1].plot(syst.T, syst.get_values('v_t'), label=f'$v_t$')\naxes[1,0].plot(syst.T, syst.get_values('p_t'), label=f'$p_t$')\naxes[1,1].plot(syst.T, syst.get_values('q_t'), label=f'$q_t$')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Run in two time intervals",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"events=[{'t_end':1.0}]\nsyst.run(events)\nevents=[{'t_end':2.0}]\nsyst.run(events)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"syst.get_value('omega')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"events=[{'p_t':0.8, 'v_t':1.0, 'K_a':400, 'T_e':0.5}]\nsyst.initialize(events,xy0=1)\nssa.eval_A(syst)\nssa.damp_report(syst)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"syst.get_value('p_m')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Ts_control = 0.010\ntimes = np.arange(0.0,10,Ts_control)\n\n# Calculate second references\nevents=[{'P_t':0.9, 'Q_t':0.0}]\nsyst.initialize(events,xy0=1.0)\nx_ref = np.copy(syst.struct[0].x)\nv_f_ref = syst.struct[0]['v_f']\np_m_ref = syst.struct[0]['p_m']\n\n# Calculate initial references\nevents=[{'P_t':0.0, 'Q_t':0.0}]\nsyst.initialize(events,xy0=1.0)\nx_0 = np.copy(syst.struct[0].x)\nv_f_0 = syst.get_value('v_f')\np_m_0 = syst.get_value('p_m')\n\n# Control design\nssa.eval_ss(syst)\nQ = np.eye(syst.N_x)*100\nR = np.eye(syst.N_u)\n\nK = ctrl.place(syst.A,syst.B,[-2.0+1j*6,-2.0-1j*6,-100,-101])\nK,S,E = ctrl.lqr(syst.A,syst.B,Q,R)\nAd,Bd = ssa.discretise_time(syst.A,syst.B,Ts_control)\nKd,S,E = ssa.dlqr(Ad,Bd,Q,R)\n\nfor t in times:\n \n x = np.copy(syst.struct[0].x)\n v_f = v_f_0 \n p_m = p_m_0 \n\n if t>1.0: \n u_ctrl = K*(x_ref - x)\n p_m = p_m_ref + u_ctrl[0]\n v_f = v_f_ref + u_ctrl[1]\n \n \n events=[{'t_end':t,'v_f':v_f,'p_m':p_m}]\n syst.run(events)\n\nsyst.post();\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.close('all')\nfig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2,ncols=2, figsize=(10, 5), frameon=False, dpi=50)\n\naxes[0,0].plot(syst.T, syst.get_values('omega'), label=f'$\\omega$')\naxes[0,1].plot(syst.T, syst.get_values('v_1'), label=f'$v_1$')\naxes[1,0].plot(syst.T, syst.get_values('P_t'), label=f'$P_t$')\naxes[1,1].plot(syst.T, syst.get_values('Q_t'), label=f'$Q_t$')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ssa.eval_ss(syst)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from scipy.signal import ss2tf,lti,bode",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"num,den =ss2tf(syst.A,syst.B,syst.C,syst.D,input=0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"G = lti(num[1],den)",
"C:\\programdata\\anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages\\scipy\\signal\\filter_design.py:1622: BadCoefficients: Badly conditioned filter coefficients (numerator): the results may be meaningless\n \"results may be meaningless\", BadCoefficients)\n"
],
[
"w, mag, phase = G.bode()\nplt.figure()\nplt.semilogx(w, mag) # Bode magnitude plot\nplt.figure()\nplt.semilogx(w, phase) # Bode phase plot\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"events=[{'t_end':1.0,'P_t':0.8, 'Q_t':0.5},\n {'t_end':10.0, 'p_m':0.9}\n ]\n\nsyst.simulate(events,xy0=1.0);",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"syst.inputs_run_list\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"0.01/6",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"syst.B",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"syst.struct[0]['Fu']",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a332a51ccbdf3d6892bc7eb9dcc1603a7549d03
| 20,702 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/peller/train_chargenet.ipynb
|
JanWeldert/freeDOM
|
242fc7e76943bb47f2d7cca3f56f77606f260e40
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/peller/train_chargenet.ipynb
|
JanWeldert/freeDOM
|
242fc7e76943bb47f2d7cca3f56f77606f260e40
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 16 |
2020-05-21T02:02:25.000Z
|
2022-03-07T10:41:55.000Z
|
notebooks/peller/train_chargenet.ipynb
|
JanWeldert/freeDOM
|
242fc7e76943bb47f2d7cca3f56f77606f260e40
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 5 |
2020-05-06T09:49:39.000Z
|
2021-05-12T15:58:14.000Z
| 87.350211 | 1,498 | 0.650565 |
[
[
[
"import os\nos.environ[\"CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES\"]=\"0\"\n#os.environ[\"CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES\"]=\"\"\nos.environ[\"HDF5_USE_FILE_LOCKING\"] = \"FALSE\"\n\nimport datetime\n\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport tensorflow as tf\n\n%load_ext autoreload\n%autoreload 2\n\nfrom freedom.utils.dataset import Data\nfrom freedom.utils.callback import Save\n\nfrom freedom.neural_nets.chargenet import get_chargenet",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data = Data(dirs=['/home/iwsatlas1/peller/work/oscNext/level3_v01.03/140000_i3cols','/home/iwsatlas1/peller/work/oscNext/level3_v01.03/120000_i3cols'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"chargenet = get_chargenet(data.labels)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"chargenet.summary()",
"Model: \"model\"\n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nLayer (type) Output Shape Param # Connected to \n==================================================================================================\ninput_1 (InputLayer) [(None, 1)] 0 \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ninput_2 (InputLayer) [(None, 8)] 0 \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nchargenet_trafo (chargenet_traf (None, 9) 0 input_1[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndense (Dense) (None, 32) 320 chargenet_trafo[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndropout (Dropout) (None, 32) 0 dense[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndense_1 (Dense) (None, 64) 2112 dropout[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndropout_1 (Dropout) (None, 64) 0 dense_1[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndense_2 (Dense) (None, 128) 8320 dropout_1[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndropout_2 (Dropout) (None, 128) 0 dense_2[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndense_3 (Dense) (None, 256) 33024 dropout_2[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndropout_3 (Dropout) (None, 256) 0 dense_3[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndense_4 (Dense) (None, 512) 131584 dropout_3[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndropout_4 (Dropout) (None, 512) 0 dense_4[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndense_5 (Dense) (None, 256) 131328 dropout_4[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndropout_5 (Dropout) (None, 256) 0 dense_5[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndense_6 (Dense) (None, 128) 32896 dropout_5[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndropout_6 (Dropout) (None, 128) 0 dense_6[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndense_7 (Dense) (None, 64) 8256 dropout_6[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndropout_7 (Dropout) (None, 64) 0 dense_7[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndense_8 (Dense) (None, 32) 2080 dropout_7[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndropout_8 (Dropout) (None, 32) 0 dense_8[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndense_9 (Dense) (None, 1) 33 dropout_8[0][0] \n==================================================================================================\nTotal params: 349,953\nTrainable params: 349,953\nNon-trainable params: 0\n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\n"
],
[
"optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(0.0001)\nchargenet.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer=optimizer)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"train_id = 'ChargeNet_logE_' + datetime.datetime.now().strftime(\"%d_%b_%Y-%Hh%M\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"callbacks = []\ncallbacks.append(Save(save_every=20, path_template='../../freedom/resources/models/'+train_id+'/epoch_%i', ))\ncallbacks.append(tf.keras.callbacks.TensorBoard(log_dir='../../freedom/resources/logs/'+train_id, histogram_freq=1))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"train_data, test_data = data.get_chargenet_data(train_batch_size=4096,\n test_batch_size=4096,\n )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"hist = chargenet.fit(train_data, epochs=1000, verbose=2, callbacks=callbacks, validation_data=test_data,\n initial_epoch=len(callbacks[0].hist['train_losses']))",
"Epoch 1/1000\n"
],
[
"# best valid loss L7 0.53....52\n# L3: 0.48 ish\n# L3 bigger net: 0.48...0.47 with 12+14,\n# after epoch 400 reduced lr to 0.00001\n# 0.45 with 256 and 12+14, batch size 4096",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a333745dad6dc277374e5e5ca2f9a8586419f66
| 207,814 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/analysis1.ipynb
|
data301-2021-winter1/project-group34-project
|
a989dee5b8c154b274cf8123b93d00e3c80ff2fc
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/analysis1.ipynb
|
data301-2021-winter1/project-group34-project
|
a989dee5b8c154b274cf8123b93d00e3c80ff2fc
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/analysis1.ipynb
|
data301-2021-winter1/project-group34-project
|
a989dee5b8c154b274cf8123b93d00e3c80ff2fc
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 229.882743 | 53,316 | 0.872848 |
[
[
[
"# Simrandeep Brar",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Research question/interests\nMy research question is to determine what show type (movie/tv show & pg/pg-13/mature) are the most popular. I'm researching this question because I wanna see what kind of content people seem to enjoy the most on Netflix. I'll be using multiple supplemental graphs to support my question. The graphs will be 1: Tv shows vs movies released during a time period. 2: The ratings of tv shows during that time. 3: The rating of movies during that time. 4: Comparing the ratings of the most popular tv shows vs the most popular ratings of movies. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#Importing libraries \nimport pandas as pd\nimport seaborn as sns\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pylab as plt\n\nnetflixds = pd.read_csv(\"../data/raw/netflix_titles.csv\")\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Data Analysis Pipeline \n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"##### The data analysis pipeline is used to clean up the dataset by removing all null values and also removing the Description column of the dataset as it wasn't needed for my research question.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"netflix_updated = (netflixds.dropna()\n .reset_index(drop=True)\n .rename(columns={\"listed_in\": \"Genre\", \"release_year\": \"Release Year\", \"type\": \"Type\"})\n .rename(columns={\"title\": \"Title\", \"director\": \"Director\", \"cast\": \"Cast\"})\n .rename(columns={\"show_id\": \"Show ID\", \"country\": \"Country\", \"date_added\": \"Date Added\"})\n .rename(columns={\"rating\": \"Rating\", \"duration\": \"Duration\", \"description\": \"Description\"})\n .drop([\"Description\"], axis = 1)\n .sort_values(by = \"Release Year\", ascending = True)\n \n)\n\nnetflix_updated",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Method Chaining",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"##### I'm using method chaining to help streamline the process and make it universal to most databases. Doing so is much for efficient and easier to read compared to creating a new method each time for each new database.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from methods import project_functions\ndf = project_functions.load_and_process(\"../data/raw/netflix_titles.csv\")\ndf",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Exploratory Data Analysis",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"##### This EDA is to help me get a better understanding on my data set by getting some information and creating some graphs to visualize the data.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Plot 1: The Quantity of Movies vs TV Shows on Netflix",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(16,10))\ngraph1 = sns.countplot(x='Type',data=netflix_updated)\nsns.set(font_scale = 2)\ngraph1.set(title = 'The Quantity of Movies vs TV Shows on Netflix')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Comments",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"##### After viewing the plot above, it's quite obvious that there's a much larger volume of movies available for consumers on Netflix compared TV shows. This isn't really indicitive of too much at the moment as the lower number of tv shows available can be slightly misleading. Although there may be only a few tv shows availble on Netflix, that doesn't account for the all the seasons those shows maybe have. If each season were to be counted as it's own tv show, of course the number of tv shows would go up drastically.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Plot 2: Overall Movie Ratings on Netflix",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"test = netflix_updated.loc[(netflix_updated['Type'] == 'Movie')]\nplt.figure(figsize=(25,10))\nplt.ylim(0, 1800)\ngraph3=sns.countplot(x='Rating', data=test)\nsns.set(font_scale = 2)\ngraph3.set(title = 'Overall Movie Ratings on Netflix')\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Plot 3: Overall TV Show Ratings on Netflix",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"test2 = netflix_updated.loc[(netflix_updated['Type'] == 'TV Show')]\nplt.figure(figsize=(25,10))\nplt.ylim(0, 1800)\ngraph4 = sns.countplot(x='Rating', data=test2)\nsns.set(font_scale = 2)\ngraph4.set(title = 'Overall TV Show Ratings on Netflix')\n\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Comments",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"##### After examining both plots above, we can determine that there's a much larger volume of TV-MA rated content available on Netflix in terms of both films and TV shows. Although this data doesn't conclusively prove that TV-MA content is the most popular on Netflix, it could be inferred that this content is more widely available due to its popularity. As I had also stated above earlier, it's also possible that the amount of tv show content available to watch is close to the movie content availble but just isn't show in the data as additional seasons aren't accounted for.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Plot 4: TV-MA TV Show Quantities vs TV-MA Movie Quantities on Netflix",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"filter1 = netflix_updated.loc[(netflix_updated['Rating'] == 'TV-MA')] \ngraph2=filter1.groupby(['Type','Rating']).size() \ngraph2=graph2.unstack() \ngraph2.plot(figsize=(25,10), kind='bar', title = 'TV-MA Movie Quantities on Netflix vs TV-MA TV Show Quantities ')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Comments",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"##### As can be seen from the prior plots, as well as the graph above, TV-MA rated movies are significantly more common on Netflix compared to TV-MA rated TV shows. I do belive this to be a bit more telling as to what the most popular content on Netflix is although I can't say for certain without knowing how much tv show content is truly available.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Conclusion",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"After taking a look at all of our data and the supplemental graphs I believe I've come to a conclusion regarding my research question. The question was to determine what kind of content was the most popular on Netflix and I believe that is TV-MA rated movies. I believe this to be true because as we can see in the first graph, movies significantly outnumber the available tv shows on the platform. However, this obviously isn't a great indicator as tv shows may have multiple seasons and those seasons don't get counted as a new addition on Netflix.\n\nTaking a look at the next 2 graphs, we can see that the most common type of content on Netflix is TV-MA rated for both movies and tv shows. Taking this into consideration and the sheer difference in available content between the two content types, I believe that TV-MA rated movies are the most popular content on Netflix. \n\nMy reasoning for this is simple. Movie producers are interested in making the most profit possible, it only makes sense for them to create content that helps them achieve this goal. In Netflix's case, they want to add content to the site that helps them bring in new customers and help retain existing customers. So taking this into consideration, the fact that the most commonly available content on Netflix is TV-MA rated movies, I believe it's fair to say that is because it is the most popular and enjoyed content on the platform.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4a333ffa0a3271458cc01c079caed41799e324ae
| 26,354 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/week2_lecture.ipynb
|
ozieblo-repository/202101-data-science-python
|
6ddb86d70f46cc29e4cc63dd57d9be6331f3f60a
|
[
"MIT"
] | 4 |
2020-11-17T13:11:32.000Z
|
2022-03-06T13:08:20.000Z
|
notebooks/week2_lecture.ipynb
|
ozieblo-repository/202101-data-science-python
|
6ddb86d70f46cc29e4cc63dd57d9be6331f3f60a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/week2_lecture.ipynb
|
ozieblo-repository/202101-data-science-python
|
6ddb86d70f46cc29e4cc63dd57d9be6331f3f60a
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2021-02-15T15:28:06.000Z
|
2021-11-15T15:59:26.000Z
| 26.041502 | 346 | 0.57885 |
[
[
[
"# Week 2 - Data handling\n\nThe Python modules `pandas` and `numpy` are useful libraries to handle datasets and apply basic operations on them. \n\nSome of the things we learnt in week 1 using native Python (e.g. accessing, working with and writing data files, and performing operations on them) can be easily achieved using `pandas` instead. `pandas` offers data structures and operations for manipulating different types of datasets - see [documentation](https://pandas.pydata.org/).\n\nWe will only cover `pandas` today, however feel free to explore `numpy` in parallel at your own pace e.g. following [this tutorial](https://numpy.org/devdocs/user/quickstart.html) and combining it with continuing to learn `pandas`.\n\n\n### Aims\n\n- Gain familiarity using `pandas` to handle datasets\n - Create, read and write data\n - Select a subset of variables (columns)\n - Filter rows based on their values\n - Sort datasets\n - Create new columns or modify existing ones\n - Summarise and collapse values in one or more columns to a single summary value\n - Handle missing data\n - Merge datasets\n\n\n### Installing pandas\n\nThe module `pandas` does not come by default as part of the default Anaconda installation. In order to install it in your system, launch the \"Anaconda Prompt (Anaconda3)\" program and run the following command: `conda install pandas`. Once the command finishes execution, `pandas` will be installed in your system\n\n<img src=\"../img/az_conda_prompt.png\" width=\"400\">\n\n**Note:** if you have any issues installing `pandas`, please get in touch with one of the trainers after the lecture\n\n\n### Loading pandas\n\nOnce installed, you can import it e.g. using the alias `pd` as follows:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Reading datasets with `pandas`\n\nWe are going to use the METABRIC dataset `metabric_clinical_and_expression_data.csv` containing information about breast cancer patients as we did in week 1.\n\nPandas allows importing data from various file formats such as csv, xls, json, sql ... \n\nTo read a csv file, use the method `.read_csv()`:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metabric = pd.read_csv(\"../data/metabric_clinical_and_expression_data.csv\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"metabric",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(metabric)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"If you forget to include `../data/` above, or if you include it but your copy of the file is saved somewhere else, you will get an error that ends with a line like this: `FileNotFoundError: File b'metabric_clinical_and_expression_data.csv' does not exist`\n\nGenerally, rows in a `DataFrame` are the **observations** (patients in the case of METABRIC) whereas columns are known as the observed **variables** (Cohort, Age_at_diagnosis ...). \n\nLooking at the column on the far left, you can see the row names of the DataFrame `metabric` assigned using the known 0-based indexing used in Python.\n\nNote that the `.read_csv()` method is not limited to reading csv files. For example, you can also read Tab Separated Value (TSV) files by adding the argument `sep='\\t'`.\n\n\n### Exploring data\n\nThe pandas DataFrame object borrows features from the well-known R's `data.frame` or SQL's `table`. They are 2-dimensional tables whose columns can contain different data types (e.g. boolean, integer, float, categorical/factor). Both the rows and columns are indexed, and can be referred to by number or name.\n\nAn index in a DataFrame refers to the position of an element in the data structure. Using the `.info()` method, we can view basic information about our DataFrame object:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metabric.info()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"As expected, our object is a `DataFrame` (or, to use the full name that Python uses to refer to it internally, a `pandas.core.frame.DataFrame`).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"type(metabric)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"It has 1904 rows (the patients) and 32 columns. The columns consist of integer, floats and strings (object). It uses almost 500 KB of memory.\n\nAs mentioned, a DataFrame is a Python object or data structure, which means it can have **Attributes** and **Methods**.\n\n**Attributes** contain information about the object. You can access them to learn more about the contents of your DataFrame. To do this, use the object variable name `metabric` followed by the attribute name, separated by a `.`. Do not use any () to access attributes.\n\nFor example, the types of data contained in the columns are stored in the `.dtypes` attribute:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metabric.dtypes",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You can access the dimensions of your DataFrame using the `.shape` attribute. The first value is the number of rows, and the second the number of columns:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metabric.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The row and column names can be accessed using the attributes `.index` and `.columns` respectively:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metabric.index",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"metabric.columns",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"If you'd like to transpose `metabric` use the attribute `T`:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metabric.T",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Methods** are functions that are associated with a DataFrame. Because they are functions, you do use () to call them, and can have arguments added inside the parentheses to control their behaviour. For example, the `.info()` command we executed previously was a method.\n\nThe `.head()` method prints the first few rows of the table, while the `.tail()` method prints the last few rows:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metabric.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"metabric.head(3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"metabric.tail()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The `.describe()` method computes summary statistics for the columns (including the count, mean, median, and std):",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metabric.describe()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"In general you can find which **Attributes** and **Methods** are available for your DataFrame using the function `dir()`:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dir(metabric)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We often want to calculate summary statistics grouped by subsets or attributes within fields of our data. For example, we might want to calculate the average survival time for patients with an advanced tumour stage.\n\nThere are two ways to access columns in a DataFrame. The first is using the name of the DataFrame `metabric` followed by a `.` and then followed by the name of the column. The second is using square brackets:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metabric.Survival_time",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"metabric['Survival_time']",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can also compute metrics on specific columns or on the entire DataFrame:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metabric['Survival_time'].mean()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"metabric['Survival_time'].std()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"metabric.mean()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Selecting columns and rows\n\nThe [pandas cheat sheet](https://pandas.pydata.org/Pandas_Cheat_Sheet.pdf) can be very helpful for recalling basic pandas operations.\n\nTo select rows and columns in a DataFrame, we use square brackets `[ ]`. There are two ways to do this: with **positional** indexing, which uses index numbers, and **label-based** indexing which uses column or row names.\n\nTo select the first three rows using their numeric index:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metabric[:3]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The colon `:` defines a range as we saw with slicing lists in week 1.\n\nTo select one column using its name:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metabric['Mutation_count']",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"And we can combine the two like this:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metabric[:3]['Mutation_count']",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"However the following does not work:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metabric[:3,'Mutation_count']",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"To do **positional** indexing for both rows and columns, use `.iloc[]`. The first argument is the numeric index of the rows, and the second the numeric index of the columns:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metabric.iloc[:3,2]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"For **label-based** indexing, use `.loc[]` with the column and row names:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metabric.loc[:3,\"Age_at_diagnosis\"]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Note**: because the rows have numeric indices in this DataFrame, we may think that selecting rows with `.iloc[]` and `.loc[]` is same. As observed above, this is not the case.\n\nIf you'd like to select more than one row:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metabric.loc[:3, ['Cohort', 'Chemotherapy']]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"metabric.loc[:3, 'Cohort':'Chemotherapy']",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Filtering rows\n\nYou can choose rows from a DataFrame that match some specified criteria. The criteria are based on values of variables and can make use of comparison operators such as `==`, `>`, `<` and `!=`.\n\nFor example, to filter `metabric` so that it only contains observations for those patients who died of breast cancer:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metabric[metabric.Vital_status==\"Died of Disease\"]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"To filter based on more than one condition, you can use the operators `&` (and), `|` (or). ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metabric[(metabric.Vital_status==\"Died of Disease\") & (metabric.Age_at_diagnosis>70)]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"For categorical variables e.g. `Vital_status` or `Cohort`, it may be useful to count how many occurrences there is for each category:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metabric['Vital_status'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"metabric['Vital_status'].value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"To filter by more than one category, use the `.isin()` method.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metabric[metabric.Vital_status.isin(['Died of Disease', 'Died of Other Causes'])]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"metabric['Cohort'].value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"To tabulate two categorical variables just like `table` in R, use the function `.crosstab()`:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pd.crosstab(metabric['Vital_status'], metabric['Cohort'])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Define new columns\n\nTo obtain the age of the patient today `Age_today` (new column) based on the `Age_at_diagnosis` (years) and the `Survival_time` (days), you can do the following:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metabric['Age_today'] = metabric['Age_at_diagnosis'] + metabric['Survival_time']/365\nmetabric",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Sort data\n\nTo sort the entire DataFrame according to one of the columns, we can use the `.sort_values()` method. We can store the sorted DataFrame using a new variable name such as `metabric_sorted`:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metabric_sorted = metabric.sort_values('Tumour_size')\nmetabric_sorted",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"metabric_sorted.iloc[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"metabric_sorted.loc[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can also sort the DataFrame in descending order:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metabric_sorted = metabric.sort_values('Tumour_size', ascending=False)\nmetabric_sorted",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Missing data\n\nPandas primarily uses `NaN` to represent missing data, which are by default not included in computations.\n\nThe `.info()` method shown above already gave us a way to find columns containing missing data:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metabric.info()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"To get the locations where values are missing:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pd.isna(metabric)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"metabric.isnull()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"To drop any rows containing at least one column with missing data:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metabric.dropna()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"However, from the other way around, to rather remove columns with at least one row with missing data, you need to use the 'axis' argument:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metabric.dropna(axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Define in which columns to look for missing values before dropping the row:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metabric.dropna(subset = [\"Tumour_size\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"metabric.dropna(subset = [\"Tumour_size\", \"Tumour_stage\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Filling missing data:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metabric.fillna(value=0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"metabric.fillna(value={'Tumour_size':0, 'Tumour_stage':5})",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Grouping\n\nGrouping patients by Cohort and then applying the `.mean()` function to the resulting groups:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metabric.groupby('Cohort')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"metabric.groupby('Cohort').mean()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Grouping by multiple columns forms a hierarchical index, and again we can apply the `.mean()` function:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metabric.groupby(['Cohort', 'Vital_status']).mean()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Pivoting\n\nIn some cases, you may want to re-structure your existing DataFrame. The function `.pivot_table()` is useful for this:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\ndf = pd.DataFrame({'A': ['one', 'one', 'two', 'three'] * 3, 'B': ['A', 'B', 'C'] * 4, 'C': ['foo', 'foo', 'foo', 'bar', 'bar', 'bar'] * 2, 'D': np.random.randn(12), 'E': np.random.randn(12)})\ndf",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.pivot_table(df, values='D', index=['A', 'B'], columns=['C'])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Merge datasets\n\nYou can concatenate DataFrames using the function `concat()`:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metabric_cohort1 = metabric[metabric[\"Cohort\"]==1]\nmetabric_cohort1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"metabric_cohort2 = metabric[metabric[\"Cohort\"]==2]\nmetabric_cohort2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.concat([metabric_cohort1,metabric_cohort2])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Or join datasets using the function `.merge()`:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"left = pd.DataFrame({'key': ['foo', 'foo'], 'lval': [1, 2]})\nleft",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"right = pd.DataFrame({'key': ['foo', 'foo'], 'rval': [4, 5]})\nright",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.merge(left, right, on='key')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"A final example:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"left = pd.DataFrame({'key': ['foo', 'bar'], 'lval': [1, 2]})\nleft",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"right = pd.DataFrame({'key': ['foo', 'bar'], 'rval': [4, 5]})\nright",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.merge(left, right, on='key')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Assignment\n\n1. Write python commands using pandas to learn how to output tables as follows:\n\n - Read the dataset `metabric_clinical_and_expression_data.csv` and store its summary statistics into a new variable called `metabric_summary`.\n - Just like the `.read_csv()` method allows reading data from a file, `pandas` provides a `.to_csv()` method to write `DataFrames` to files. Write your summary statistics object into a file called `metabric_summary.csv`. You can use `help(metabric.to_csv)` to get information on how to use this function.\n - Use the help information to modify the previous step so that you can generate a Tab Separated Value (TSV) file instead \n - Similarly, explore the method `to_excel()` to output an excel spreadsheet containing summary statistics\n\n\n2. Write python commands to perform basic statistics in the metabric dataset and answer the following questions:\n\n - Read the dataset `metabric_clinical_and_expression_data.csv` into a variable e.g. `metabric`.\n - Calculate mean tumour size of patients grouped by vital status and tumour stage\n - Find the cohort of patients and tumour stage where the average expression of genes TP53 and FOXA1 is the highest\n - Do patients with greater tumour size live longer? How about patients with greater tumour stage? How about greater Nottingham_prognostic_index?\n\n\n3. Review the section on missing data presented in the lecture. Consulting the [user's guide section dedicated to missing data](https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/missing_data.html) and any other materials as necessary use the functionality provided by pandas to answer the following questions:\n\n - Which variables (columns) of the metabric dataset have missing data?\n - Find the patients ids who have missing tumour size and/or missing mutation count data. Which cohorts do they belong to?\n - For the patients identified to have missing tumour size data for each cohort, calculate the average tumour size of the patients with tumour size data available within the same cohort to fill in the missing data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a334e79c4fa6b0a24a7db22b6645b01b47b5562
| 998,719 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
MRNet_custom_itemlist_ns.ipynb
|
nswitanek/mrnet-fastai
|
dfc7cbeb74ada91641b46cdbf38e2c85955402eb
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 16 |
2019-04-17T20:46:58.000Z
|
2021-01-09T02:43:50.000Z
|
MRNet_custom_itemlist_ns.ipynb
|
nswitanek/mrnet-fastai
|
dfc7cbeb74ada91641b46cdbf38e2c85955402eb
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 10 |
2019-04-18T04:43:28.000Z
|
2019-05-17T15:47:43.000Z
|
MRNet_custom_itemlist_ns.ipynb
|
nswitanek/mrnet-fastai
|
dfc7cbeb74ada91641b46cdbf38e2c85955402eb
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 7 |
2019-04-18T00:00:22.000Z
|
2021-08-22T17:31:17.000Z
| 410.320049 | 789,652 | 0.905951 |
[
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport os\n\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom fastai.vision import *\nimport torch\n\n#from mrnet_orig import *\nfrom mrnet_itemlist import *\n\n#from ipywidgets import interact, Dropdown, IntSlider\n\n%matplotlib notebook\nplt.style.use('grayscale')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# run tree on my data to see its data structure\n! tree -d ..",
"\u001b[01;34m..\u001b[00m\n├── \u001b[01;34mdata\u001b[00m\n│ ├── \u001b[01;34mtrain\u001b[00m\n│ │ ├── \u001b[01;34maxial\u001b[00m\n│ │ ├── \u001b[01;34mcoronal\u001b[00m\n│ │ └── \u001b[01;34msagittal\u001b[00m\n│ └── \u001b[01;34mvalid\u001b[00m\n│ ├── \u001b[01;34maxial\u001b[00m\n│ ├── \u001b[01;34mcoronal\u001b[00m\n│ └── \u001b[01;34msagittal\u001b[00m\n├── \u001b[01;34mdata24\u001b[00m\n│ ├── \u001b[01;34mtrain\u001b[00m\n│ │ ├── \u001b[01;34maxial\u001b[00m\n│ │ ├── \u001b[01;34mcoronal\u001b[00m\n│ │ └── \u001b[01;34msagittal\u001b[00m\n│ └── \u001b[01;34mvalid\u001b[00m\n│ ├── \u001b[01;34maxial\u001b[00m\n│ ├── \u001b[01;34mcoronal\u001b[00m\n│ └── \u001b[01;34msagittal\u001b[00m\n└── \u001b[01;34mmrnet-fastai\u001b[00m\n ├── \u001b[01;34m__pycache__\u001b[00m\n ├── \u001b[01;34mexp\u001b[00m\n ├── \u001b[01;34mmodels\u001b[00m\n └── \u001b[01;34mpaper-code\u001b[00m\n └── \u001b[01;34mMRNet-master\u001b[00m\n\n24 directories\n"
],
[
"data_path = Path('../data24') # /data24 contains interpolated data where each case-plane has 24 slices",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"caselist = MRNetCaseList.from_folder(path=data_path)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"type(caselist)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"caselist.items[:5] # items are Case numbers as 4-character strings",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"caselist.inner_df # at this point, inner_df is an empty attribute, returning None, since caselist was ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Construct a DataFrame with labels linked to cases. First, do just the \"Abnormal\" label.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"train_abnl = pd.read_csv(data_path/'train-abnormal.csv', header=None,\n names=['Case', 'Abnormal'], \n dtype={'Case': str, 'Abnormal': np.int64})\nvalid_abnl = pd.read_csv(data_path/'valid-abnormal.csv', header=None,\n names=['Case', 'Abnormal'], \n dtype={'Case': str, 'Abnormal': np.int64})\nabnl = train_abnl.append(valid_abnl, ignore_index=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"caselist.link_label_df(df=abnl)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"caselist.inner_df",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now can label from inner_df associated to CaseList.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"casesplit = caselist.split_by_folder()\nll = casesplit.label_from_df()\nlen(ll.train), len(ll.valid)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"casesplit.valid",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"case = casesplit.train.get(0)\ncase.data.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"At this point we have a correctly labeled dataset. It would be possible to do various types of transformations and augmentation on the data, or could convert into a data bunch. Will implement custom transformations/augmentations later.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Can just call `.databunch()` on the labeled list to create a `DataBunch`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data = ll.databunch(bs=8)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.show_batch(4)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x,y = data.one_batch(DatasetType.Train, True, True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x.shape, y.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"smpl = grab_idx(x, 2)\nsmpl.shape, type(smpl)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Calling `.reconstruct` on the PyTorch Tensor returns the same kind of thing as the `.get` method, which in this context is an `MRNetCase`, which we can then display. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tst = data.train_ds.x.reconstruct(smpl)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"type(tst)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tst",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tst.data.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(10,10))\nax.imshow(tst.data[2, 11, :, :])\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Minimal training example\n- [x] import necessary libraries (fastai, mrnet_itemlist)\n- [x] https://docs.fast.ai/data_block.html\n- [x] 1 provide inputs\n- [x] 2 split data into training and validation sets\n- [x] 3 label the inputs\n- [ ] 4 what transforms to apply (none for now)\n- [ ] 5 how to add test set (none for now)\n- [x] 6 how to wrap in dataloaders and create the databunch",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a3364bda18e0a0a1ad2e78d8b313c8aa990af66
| 221,404 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
.ipynb_checkpoints/climate_starter-checkpoint.ipynb
|
markfindley/sqlalchemy-challenge
|
5d443fa9ed5d4537eeee77e8867f90009aafad66
|
[
"ADSL"
] | null | null | null |
.ipynb_checkpoints/climate_starter-checkpoint.ipynb
|
markfindley/sqlalchemy-challenge
|
5d443fa9ed5d4537eeee77e8867f90009aafad66
|
[
"ADSL"
] | null | null | null |
.ipynb_checkpoints/climate_starter-checkpoint.ipynb
|
markfindley/sqlalchemy-challenge
|
5d443fa9ed5d4537eeee77e8867f90009aafad66
|
[
"ADSL"
] | null | null | null | 100.821494 | 64,539 | 0.748442 |
[
[
[
"%matplotlib inline\nfrom matplotlib import style\nstyle.use('fivethirtyeight')\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import datetime as dt",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Reflect Tables into SQLAlchemy ORM",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Python SQL toolkit and Object Relational Mapper\nimport sqlalchemy\nfrom sqlalchemy.ext.automap import automap_base\nfrom sqlalchemy.orm import Session\nfrom sqlalchemy import create_engine, func",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"engine = create_engine(\"sqlite:///Resources/hawaii.sqlite\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# reflect an existing database into a new model\nBase = automap_base()\n# reflect the tables\nBase.prepare(engine, reflect=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# We can view all of the classes that automap found\nBase.classes.keys()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Save references to each table\nMeasurement = Base.classes.measurement\nStation = Base.classes.station",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create our session (link) from Python to the DB\nsession = Session(engine)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Exploratory Climate Analysis",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Design a query to retrieve the last 12 months of precipitation data and plot the results\n\n# Calculate the date 1 year ago from the last data point in the database\n\n# Perform a query to retrieve the data and precipitation scores\n\n# Save the query results as a Pandas DataFrame and set the index to the date column\n\n# Sort the dataframe by date\n\n# Use Pandas Plotting with Matplotlib to plot the data\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Use Pandas to calcualte the summary statistics for the precipitation data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Design a query to show how many stations are available in this dataset?\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# What are the most active stations? (i.e. what stations have the most rows)?\n# List the stations and the counts in descending order.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Using the station id from the previous query, calculate the lowest temperature recorded, \n# highest temperature recorded, and average temperature most active station?\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Choose the station with the highest number of temperature observations.\n# Query the last 12 months of temperature observation data for this station and plot the results as a histogram\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# This function called `calc_temps` will accept start date and end date in the format '%Y-%m-%d' \n# and return the minimum, average, and maximum temperatures for that range of dates\ndef calc_temps(start_date, end_date):\n \"\"\"TMIN, TAVG, and TMAX for a list of dates.\n \n Args:\n start_date (string): A date string in the format %Y-%m-%d\n end_date (string): A date string in the format %Y-%m-%d\n \n Returns:\n TMIN, TAVE, and TMAX\n \"\"\"\n \n return session.query(func.min(Measurement.tobs), func.avg(Measurement.tobs), func.max(Measurement.tobs)).\\\n filter(Measurement.date >= start_date).filter(Measurement.date <= end_date).all()\n\n# function usage example\nprint(calc_temps('2012-02-28', '2012-03-05'))",
"[(62.0, 69.57142857142857, 74.0)]\n"
],
[
"# Use your previous function `calc_temps` to calculate the tmin, tavg, and tmax \n# for your trip using the previous year's data for those same dates.\n",
"62.0 68.36585365853658 74.0\n"
],
[
"# Plot the results from your previous query as a bar chart. \n# Use \"Trip Avg Temp\" as your Title\n# Use the average temperature for the y value\n# Use the peak-to-peak (tmax-tmin) value as the y error bar (yerr)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Calculate the total amount of rainfall per weather station for your trip dates using the previous year's matching dates.\n# Sort this in descending order by precipitation amount and list the station, name, latitude, longitude, and elevation\n\n",
"[('USC00516128', 'MANOA LYON ARBO 785.2, HI US', 21.3331, -157.8025, 152.4, 0.31), ('USC00519281', 'WAIHEE 837.5, HI US', 21.45167, -157.84888999999998, 32.9, 0.25), ('USC00518838', 'UPPER WAHIAWA 874.3, HI US', 21.4992, -158.0111, 306.6, 0.1), ('USC00513117', 'KANEOHE 838.1, HI US', 21.4234, -157.8015, 14.6, 0.060000000000000005), ('USC00511918', 'HONOLULU OBSERVATORY 702.2, HI US', 21.3152, -157.9992, 0.9, 0.0), ('USC00514830', 'KUALOA RANCH HEADQUARTERS 886.9, HI US', 21.5213, -157.8374, 7.0, 0.0), ('USC00517948', 'PEARL CITY, HI US', 21.3934, -157.9751, 11.9, 0.0), ('USC00519397', 'WAIKIKI 717.2, HI US', 21.2716, -157.8168, 3.0, 0.0), ('USC00519523', 'WAIMANALO EXPERIMENTAL FARM, HI US', 21.33556, -157.71139, 19.5, 0.0)]\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Optional Challenge Assignment",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create a query that will calculate the daily normals \n# (i.e. the averages for tmin, tmax, and tavg for all historic data matching a specific month and day)\n\ndef daily_normals(date):\n \"\"\"Daily Normals.\n \n Args:\n date (str): A date string in the format '%m-%d'\n \n Returns:\n A list of tuples containing the daily normals, tmin, tavg, and tmax\n \n \"\"\"\n \n sel = [func.min(Measurement.tobs), func.avg(Measurement.tobs), func.max(Measurement.tobs)]\n return session.query(*sel).filter(func.strftime(\"%m-%d\", Measurement.date) == date).all()\n \ndaily_normals(\"01-01\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# calculate the daily normals for your trip\n# push each tuple of calculations into a list called `normals`\n\n# Set the start and end date of the trip\n\n# Use the start and end date to create a range of dates\n\n# Stip off the year and save a list of %m-%d strings\n\n# Loop through the list of %m-%d strings and calculate the normals for each date\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Load the previous query results into a Pandas DataFrame and add the `trip_dates` range as the `date` index\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Plot the daily normals as an area plot with `stacked=False`\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a336ef97332aafbef5fa9a58e1d2b5adecd54ef
| 6,276 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
random_signals/correlation.ipynb
|
spatialaudio/digital-signal-processing-exercises
|
0e16bc05cb8ed3dee0537371dbb5826db21c86b3
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | 13 |
2019-10-24T14:27:43.000Z
|
2022-02-22T02:14:43.000Z
|
random_signals/correlation.ipynb
|
spatialaudio/digital-signal-processing-exercises
|
0e16bc05cb8ed3dee0537371dbb5826db21c86b3
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | 2 |
2019-11-05T12:51:46.000Z
|
2021-12-17T19:46:19.000Z
|
random_signals/correlation.ipynb
|
spatialaudio/digital-signal-processing-exercises
|
0e16bc05cb8ed3dee0537371dbb5826db21c86b3
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | 6 |
2019-10-24T14:27:51.000Z
|
2021-08-06T17:33:24.000Z
| 33.924324 | 589 | 0.55529 |
[
[
[
"Sascha Spors,\nProfessorship Signal Theory and Digital Signal Processing,\nInstitute of Communications Engineering (INT),\nFaculty of Computer Science and Electrical Engineering (IEF),\nUniversity of Rostock, Germany\n\n# Tutorial Digital Signal Processing\n\n**Correlation**,\nWinter Semester 2021/22 (Course #24505)\n\n- lecture: https://github.com/spatialaudio/digital-signal-processing-lecture\n- tutorial: https://github.com/spatialaudio/digital-signal-processing-exercises\n\nFeel free to contact lecturer [email protected]\n\nWIP...",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# most common used packages for DSP, have a look into other scipy submodules\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib as mpl\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom scipy import signal\n\n\ndef my_xcorr2(x, y, scaleopt='none'):\n N = len(x)\n M = len(y)\n kappa = np.arange(0, N+M-1) - (M-1)\n ccf = signal.correlate(x, y, mode='full', method='auto')\n if N == M:\n if scaleopt == 'none' or scaleopt == 'raw':\n ccf /= 1\n elif scaleopt == 'biased' or scaleopt == 'bias':\n ccf /= N\n elif scaleopt == 'unbiased' or scaleopt == 'unbias':\n ccf /= (N - np.abs(kappa))\n elif scaleopt == 'coeff' or scaleopt == 'normalized':\n ccf /= np.sqrt(np.sum(x**2) * np.sum(y**2))\n else:\n print('scaleopt unknown: we leave output unnormalized')\n return kappa, ccf",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"if True: # test my_xcorr with simple example\n x = np.array([0, 1, 0, 0, 0])\n y = np.array([1, 0, 0])\n # plot my_xcorr2(x, y) vs. my_xcorr2(y, x)\n plt.figure(figsize=(9, 2))\n plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)\n kappa_xy, ccf_xy = my_xcorr2(x, y) \n plt.stem(kappa_xy, ccf_xy, basefmt='C0:', use_line_collection=True)\n plt.xlabel(r'$\\kappa$')\n plt.ylabel(r'$\\varphi_{xy}[\\kappa]$')\n plt.title('cross correlation between x and y')\n plt.grid(True)\n plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)\n kappa_yx, ccf_yx = my_xcorr2(y, x)\n plt.stem(kappa_yx, ccf_yx, basefmt='C0:', use_line_collection=True)\n plt.xlabel(r'$\\kappa$')\n plt.ylabel(r'$\\varphi_{yx}[\\kappa]$')\n plt.title('cross correlation between y and x')\n plt.grid(True)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Normalization schemes for cross correlation of finite length signals\n\ncheck cross correlation\n- of a cosine and a sine signal\n- of a normal pdf process that exhibits some repetition",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"case_str = 'cos_sin'\ncase_str = 'normal_pdf'\n\nif case_str == 'cos_sin':\n Nt = 200 # number of samples for a full period \n x = np.cos(2*np.pi/Nt * 1 * np.arange(0, Nt)) * 2\n y = np.sin(2*np.pi/Nt * 1 * np.arange(0, Nt)) * 2\nelif case_str == 'normal_pdf':\n Nt = 20000\n loc, scale = 2, np.sqrt(2) # mu, sigma\n x = scale * np.random.randn(Nt) + loc\n y = np.roll(x,-7500) # process similarity for offset of 7500 samples\n\nplt.figure(figsize=(8,6))\nplt.subplot(2,2,1)\nkappa, ccf = my_xcorr2(x, y, scaleopt='none')\nplt.plot(kappa, ccf)\nplt.ylabel(r'$\\varphi_{xy}[\\kappa]$')\nplt.title('raw CCF(x,y)')\nplt.grid(True)\n\nplt.subplot(2,2,2)\nkappa, ccf = my_xcorr2(x, y, scaleopt='biased')\nplt.plot(kappa, ccf)\nplt.title('biased CCF(x,y)')\nplt.grid(True)\n\nplt.subplot(2,2,3)\nkappa, ccf = my_xcorr2(x, y, scaleopt='unbiased')\nplt.plot(kappa, ccf)\nplt.xlabel(r'$\\kappa$')\nplt.ylabel(r'$\\varphi_{xy}[\\kappa]$')\nplt.title('unbiased CCF(x,y)')\nplt.grid(True)\n\nplt.subplot(2,2,4)\nkappa, ccf = my_xcorr2(x, y, scaleopt='coeff')\nplt.plot(kappa, ccf)\nplt.xlabel(r'$\\kappa$')\nplt.title('normalized CCF(x,y)')\nplt.grid(True)\n\n# check that the unbiased estimate of the CCF represents the theoretical\n# result best in comparison to the other normalization schemes, at least\n# for the chosen examples",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# **Copyright**\n\nThe notebooks are provided as [Open Educational Resources](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Open_educational_resources). Feel free to use the notebooks for your own purposes. The text is licensed under [Creative Commons Attribution 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), the code of the IPython examples under the [MIT license](https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT). Please attribute the work as follows: *Frank Schultz, Digital Signal Processing - A Tutorial Featuring Computational Examples* with the URL https://github.com/spatialaudio/digital-signal-processing-exercises",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a3379970c12f1cdac6c9ebb00308deb1a0a631c
| 5,954 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Python Basic Assignment -2.ipynb
|
MuhammedAbin/iNeuron-Assignment
|
3bf3eed637d2ccc9cbf61a07efc11a1f0bc5a953
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Python Basic Assignment -2.ipynb
|
MuhammedAbin/iNeuron-Assignment
|
3bf3eed637d2ccc9cbf61a07efc11a1f0bc5a953
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Python Basic Assignment -2.ipynb
|
MuhammedAbin/iNeuron-Assignment
|
3bf3eed637d2ccc9cbf61a07efc11a1f0bc5a953
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 26.941176 | 92 | 0.429123 |
[
[
[
"# 1. Write a Python program to convert kilometers to miles?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 1km = 0.621371 miles\n\nkm=int(input())\nmiles=0.621371*km\nprint(\"{} kilometer in miles is {}\".format(km,miles))",
"2\n2 kilometer in miles is 1.242742\n"
]
],
[
[
"# 2. Write a Python program to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 1 celsius = 32 Fahrenheit\n\ncel=int(input())\nfar=32*cel\nprint(\"{} in Celsius is {} in Fahrenheit\".format(cel,far))",
"2\n2 in Celsius is 64 in Fahrenheit\n"
]
],
[
[
"# 3. Write a Python program to display calendar?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import calendar\nprint(calendar.calendar(2021))",
" 2021\n\n January February March\nMo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su\n 1 2 3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 2 3 4 5 6 7\n 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 8 9 10 11 12 13 14\n11 12 13 14 15 16 17 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 15 16 17 18 19 20 21\n18 19 20 21 22 23 24 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 22 23 24 25 26 27 28\n25 26 27 28 29 30 31 29 30 31\n\n April May June\nMo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su\n 1 2 3 4 1 2 1 2 3 4 5 6\n 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 7 8 9 10 11 12 13\n12 13 14 15 16 17 18 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 14 15 16 17 18 19 20\n19 20 21 22 23 24 25 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 21 22 23 24 25 26 27\n26 27 28 29 30 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 28 29 30\n 31\n\n July August September\nMo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su\n 1 2 3 4 1 1 2 3 4 5\n 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 6 7 8 9 10 11 12\n12 13 14 15 16 17 18 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 13 14 15 16 17 18 19\n19 20 21 22 23 24 25 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 20 21 22 23 24 25 26\n26 27 28 29 30 31 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 27 28 29 30\n 30 31\n\n October November December\nMo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su\n 1 2 3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 2 3 4 5\n 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 6 7 8 9 10 11 12\n11 12 13 14 15 16 17 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 13 14 15 16 17 18 19\n18 19 20 21 22 23 24 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 20 21 22 23 24 25 26\n25 26 27 28 29 30 31 29 30 27 28 29 30 31\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"# 4. Write a Python program to swap two variables without temp variable?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"a=50\nb=10\na=a+b\nb=a-b\na=a-b\nprint(\"After Swapping values are a:{},b:{}\".format(a,b))",
"After Swapping values are a:10,b:50\n"
]
],
[
[
"# 5. Write a Python program to solve quadratic equation?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"a=int(input())\nb=int(input())\nc=int(input())\nd1=(-b + (b ** 2 - 4 * a * c) ** 0.5) / 2 * a\nd2=(-b - (b ** 2 - 4 * a * c) ** 0.5) / 2 * a\nprint(\"solutions are ({},{})\".format(d1,d2))",
"1\n2\n3\nsolutions are ((-0.9999999999999999+1.4142135623730951j),(-1-1.4142135623730951j))\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a33a887f950dc41c6e4fe31d2f813cc6eb13676
| 12,099 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
path_of_ML/Pandas/Melt.ipynb
|
Alferdize/Machine-Learning-in-Python
|
c1e19bd0968dd08217bf1aa2c516a1058a3da521
|
[
"BSD-4-Clause-UC"
] | null | null | null |
path_of_ML/Pandas/Melt.ipynb
|
Alferdize/Machine-Learning-in-Python
|
c1e19bd0968dd08217bf1aa2c516a1058a3da521
|
[
"BSD-4-Clause-UC"
] | null | null | null |
path_of_ML/Pandas/Melt.ipynb
|
Alferdize/Machine-Learning-in-Python
|
c1e19bd0968dd08217bf1aa2c516a1058a3da521
|
[
"BSD-4-Clause-UC"
] | null | null | null | 26.767699 | 53 | 0.318291 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = pd.read_csv(\"weather4.csv\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df1 = pd.melt(df, id_vars=[\"day\"])\ndf1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df1[df1[\"variable\"]==\"chicago\"]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a33aa0f5c1bc167eba78ccfb6194beff0951f64
| 154,276 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Dominant Color Extraction.ipynb
|
amitguptapc/Image_Segmentation
|
33fd0fce6e87323a2eeb6ba47ae11638b892df54
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Dominant Color Extraction.ipynb
|
amitguptapc/Image_Segmentation
|
33fd0fce6e87323a2eeb6ba47ae11638b892df54
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Dominant Color Extraction.ipynb
|
amitguptapc/Image_Segmentation
|
33fd0fce6e87323a2eeb6ba47ae11638b892df54
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 521.202703 | 86,284 | 0.947024 |
[
[
[
"# Image Segmentation\n\n\n- Segmentation partitions an image into regions having similar visual appearance corresponding to parts of objects\n- We will try to extract the most dominant 'K' Colors using K-Means\n- We can apply K-Means with each pixel will reassigned to the closest of the K Colors, leading to segmentation\n\n<img src=\"img/example.png\" alt=\"Pizza-1\" style=\"width: 800px;\"/>\n\n\n\nFig : Image Segmentation with multiple values of K",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 1. Preprocessing The Image",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from matplotlib import pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport cv2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"im = cv2.imread('img/elephant.jpg')\nim = cv2.cvtColor(im,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)\nprint(im.shape)\n\nplt.axis('off')\nplt.imshow(im)\nplt.show()",
"(330, 500, 3)\n"
],
[
"# Flatten all the 3 Image channels\nall_pixels = im.reshape((-1,3))\nprint(all_pixels.shape)",
"(165000, 3)\n"
]
],
[
[
"### 2. Dominant Color Extraction",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.cluster import KMeans",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dominant_colors = 4\nkm = KMeans(n_clusters=dominant_colors)\nkm.fit(all_pixels)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"centers = km.cluster_centers_\ncenters = np.array(centers,dtype='uint8')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(centers)",
"[[ 1 0 1]\n [174 145 128]\n [ 38 35 64]\n [ 99 95 118]]\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### Plotting the dominant colors",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"i = 1\nprint(\"4 Most Dominant Colors in Image are : \")\nplt.figure(0,figsize=(10,4))\ncolors = []\nfor col in centers:\n plt.subplot(1,4,i);\n plt.axis('off')\n i += 1\n colors.append(col)\n a = np.zeros((100,100,3),dtype='uint8')\n a[:,:,:] = col\n plt.imshow(a)\nplt.show()",
"4 Most Dominant Colors in Image are : \n"
]
],
[
[
"### 3. Segmenting The Image",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"new_img = np.zeros((330*500,3),dtype='uint8')\nprint(new_img.shape)",
"(165000, 3)\n"
],
[
"for ix in range(new_img.shape[0]):\n new_img[ix] = colors[km.labels_[ix]]\nnew_img = new_img.reshape((330,500,3))\n\nplt.figure(1,figsize=(15,15))\nplt.subplot(1,2,1)\nplt.title(\"Original Image\")\nplt.axis('off')\nplt.imshow(im)\nplt.subplot(1,2,2)\n\nplt.title(\"Segmented Image\")\nplt.axis('off')\nplt.imshow(new_img)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a33b792a89a9bfbaeadfd120c3ca17c13d49658
| 181,004 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Latihan/Sinkronisasi Data Sarana/sinkronisasi data kai.ipynb
|
cktheone/DQLab
|
b1eb7e4a1515dfdbe1320c3de206373575a21319
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Latihan/Sinkronisasi Data Sarana/sinkronisasi data kai.ipynb
|
cktheone/DQLab
|
b1eb7e4a1515dfdbe1320c3de206373575a21319
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Latihan/Sinkronisasi Data Sarana/sinkronisasi data kai.ipynb
|
cktheone/DQLab
|
b1eb7e4a1515dfdbe1320c3de206373575a21319
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 33.946737 | 284 | 0.330766 |
[
[
[
"Template untuk mengupdate database bangwas di sinkronkan dengan data aset milik pt kai\n\n- load data yang akan di sinkronkan di line 1 (dataset dr bangwas.web.id belum ada perubahan, jenis dan pemilik masih berupa kode)\n- load data yg jd bencmarking yg sudah diolah dari data aset milik pt kai (relate to data_aset_kai.ipynb, jika ada perubahan - jalankan kembali aplikasinya dan ekpor ulang data outputnya)\n- pastikan format nomor identitas sudah sama(tanpa spasi dan no urut dimulai dr dua digit 01 bukan 1 atau 001)\n- program bisa digunakan untuk mengupdate status, daop, depo dan jenis sarana jika ada perubahan",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\ncolnames=['id', 'kode_sarana', 'kode_sarana_lama', 'id_kartu', 'id_jenis', 'id_sub_jenis', 'seri', 'tahun_dinas', 'id_daops', 'id_depo', 'status', 'negara_asal', 'tgl_uji_pertama', 'tgl_masa_uji', 'tgl_masa_perawatan', 'pabrikan', 'id_pemilik', 'created_at', 'last_update' ] \ndf_sarana = pd.read_csv('../data_source/datsar/tblsarana_nov.csv', sep=\";\", names=colnames)\ndf_sarana.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#slice data yg hanya kepemilikan PT KAI\n#id_pemilik = 2 (untuk KAI)\ndf_kai = df_sarana.loc[(df_sarana['id_pemilik'] == 2)]\ndf_kai",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#import data yang dijadikan rujukan atau bencmarking hasil dari aplikasi data_aset_kai.ipynb\n#pastikan data rujukan sudah sesuai\n\ndf_kai_baru = pd.read_csv('../data_source/datsar/data_kai_after(nov).csv', index_col=0)\ndf_kai_baru",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#hapus kolom yang tidak diinginkan\n#df_kai_baru.drop(columns='Unnamed: 0', inplace=True)\n#df_kai_baru",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#hapus spasi pada nomor_identitas\ndf_kai['kode_sarana'] = df_kai['kode_sarana'].str.strip()\ndf_kai_baru['NOMOR_IDENTITAS'] = df_kai_baru['NOMOR_IDENTITAS'].str.strip()",
"<ipython-input-5-a2d7aef70d7c>:2: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy\n df_kai['kode_sarana'] = df_kai['kode_sarana'].str.strip()\n"
],
[
"#fungsi digunakan untuk mengubah jenis sarana ke kode_sarana sesuai database (sesuaikan apabila ada perubahan)\ndef kode_sarana(jenis_sarana):\n if jenis_sarana == 'LOKOMOTIF' :\n jenis_sarana = 1\n elif jenis_sarana == 'KRL' :\n jenis_sarana = 2\n elif jenis_sarana == 'LRT' :\n jenis_sarana = 2\n elif jenis_sarana == 'KRD' :\n jenis_sarana = 3\n elif jenis_sarana == 'GERBONG' :\n jenis_sarana = 4 \n elif jenis_sarana == 'PERALATAN KHUSUS' :\n jenis_sarana = 9 \n elif jenis_sarana == 'KERETA' :\n jenis_sarana = 11\n elif jenis_sarana == 'RAILBUS' :\n jenis_sarana = 19\n else :\n jenis_sarana = 'undefined'\n \n return jenis_sarana ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_kai_baru['JENIS'] = df_kai_baru['JENIS'].apply(lambda x: kode_sarana(x))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_kai_baru['JENIS'].value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# fungsi untuk ubah nama daop pada kolom DAOP menjadi kode daop(sesuaikan dengan database) \ndef kode_daop(daop):\n if daop == 'DAOP 1' or daop == 'DAOP 1 JAKARTA' :\n daop = 7\n elif daop == 'DAOP 2' or daop == 'DAOP 2 BANDUNG' :\n daop = 8\n elif daop == 'DAOP 3' or daop == 'DAOP 3 CIREBON':\n daop = 9\n elif daop == 'DAOP 4' or daop == 'DAOP 4 SEMARANG' :\n daop = 10\n elif daop == 'DAOP 5' or daop == 'DAOP 5 PURWOKERTO' :\n daop = 11 \n elif daop == 'DAOP 6' or daop == 'DAOP 6 YOGYAKARTA':\n daop = 12 \n elif daop == 'DAOP 7' or daop == 'DAOP 7 MADIUN' :\n daop = 13\n elif daop == 'DAOP 8' or daop == 'DAOP 8 SURABAYA' :\n daop = 14\n elif daop == 'DAOP 9' or daop == 'DAOP 9 JEMBER':\n daop = 15 \n elif daop == 'DIVRE 1' or daop == 'DIVRE I SUMATERA UTARA' or daop == 'DIVRE I' :\n daop = 16 \n elif daop == 'DIVRE 2' or daop == 'DIVRE II SUMATERA BARAT' or daop == 'DIVRE II' :\n daop = 17\n elif daop == 'DIVRE 3' or daop == 'DIVRE III SUMATERA SELATAN' or daop == 'DIVRE III':\n daop = 18\n elif daop == 'DIVRE 4' or daop == 'DIVRE IV LAMPUNG' or daop == 'DIVRE IV' :\n daop = 26\n elif daop == 'BY LT' :\n daop = 18\n elif daop == 'BY MRI' :\n daop = 26\n elif daop == 'PT KAI COMMUTER JABOTABEK' :\n daop = 24\n else :\n daop = 'undefined'\n \n return daop ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_kai_baru['NAMA_DAOP2'] = df_kai_baru['NAMA_DAOP2'].apply(lambda x: kode_daop(x))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_kai_baru['NAMA_DAOP2'].value_counts(dropna=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_kai_baru[df_kai_baru.NAMA_DAOP2 == \"undefined\"]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_kai_baru",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# join/merge data awal dengan data yg dijadikan rujukan dengan tetap mempertahankan data awal, dan menghapus data yg tidak terdapat di data awal \n#(digunakan bila tidak ada pengadaan sarana baru dan perubahan nomor identitas)\nmerge_df = pd.merge(left=df_kai, right=df_kai_baru, how='left', left_on='kode_sarana', right_on='NOMOR_IDENTITAS')\nmerge_df.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# join/merge data awal dengan data yg dijadikan rujukan dengan menambahkan data baru jika terdaapt data baru di rujukan\n# (digunakan bila terdapat penambahan nomor sarana baru karena pengadaan maupun perubahan\n# perhatikan jumlah baris nya kl lebih banyak berarti ada penambahan baru\nmerge_df2 = pd.merge(left=df_kai, right=df_kai_baru, how='outer', left_on='kode_sarana', right_on='NOMOR_IDENTITAS')\nmerge_df2.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#slicing data dari nomor baru tersebut untuk di verifikasi lebih lanjut\ndata_baru = merge_df2.loc[(merge_df2['kode_sarana'].isna()) & (merge_df2['NOMOR_IDENTITAS'].notna())]\ndata_baru.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#mengetahui jumlah nomor baru berdasarkan jenis nya\ndata_baru['JENIS'].value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data_baru",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data_baru.to_csv('../data_source/datsar/kroscek_data.csv', sep=',')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# replace missing value(null value) menjadi string \"NA\" untuk pendefinisian nilai\nmerge_df['NOMOR_IDENTITAS'] = merge_df['NOMOR_IDENTITAS'].fillna(\"NA\")\nmerge_df['NAMA_DAOP2'].fillna(\"NA\", inplace=True)\nmerge_df['JENIS'].fillna(\"NA\", inplace=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#fungsi untuk mengupdate kolom status berdasrkan data rujukan\n# AWAS, jika ada nomor yang mengalami perubahan dan belum terupdate maka status akan otomatis berubah ke Tidak Aktiv\ndef ubah_status(x):\n if x == \"NA\":\n return \"Tidak Aktiv\"\n else:\n return \"Aktiv\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#cek nilai kolom status\nmerge_df['status'].value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# mengupdate status sesuai dg data rujukan\nmerge_df['status']= merge_df['NOMOR_IDENTITAS'].apply(lambda x : ubah_status(x))\nmerge_df['status'].value_counts()\n# bandingkan nilai kolom status dengan sebelum \n# (jika berubah berarti ada perubahan kondisi dari SG ke Konservasi atau sebaliknya)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#fungsi untuk merubah jenis sarana bila ada perubahan/modifikasi ex: bagasi ke SN \n#dg catatan masih menggunakan no lama belum ada penetapanya tp secara fungsi sudah diganti\ndef ubah_jenis(x,y):\n jenis_sarana = \"\"\n if x == y :\n jenis_sarana = x\n elif y == 'NA' :\n jenis_sarana = x\n \n else :\n jenis_sarana = y\n \n return jenis_sarana ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"merge_df['id_jenis'].value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# mengupdate perubahan jenis sarana (bilamana diperlukan)\nmerge_df['id_jenis']= list(map(lambda x, y : ubah_jenis(x,y), merge_df['id_jenis'], merge_df['JENIS']))\nmerge_df['id_jenis'].value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"jumlah_before = df_kai.groupby(['id_jenis','status'])['kode_sarana'].count().reset_index()\n#rekap nilai sebelum dilakukan sinkronisasi\njumlah_before = jumlah_before.pivot_table(index=['id_jenis'], columns='status')\njumlah_before",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"jumlah_after = merge_df.groupby(['id_jenis','status'])['kode_sarana'].count().reset_index()\n#rekap nilai setelah dilakukan sinkronisasi\njumlah_after = jumlah_after.pivot_table(index=['id_jenis'], columns='status')\njumlah_after",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#fungsi untuk merubah nilai pada kolom DAOP yg NA diganti dengan isi dari kolom nama_daop\ndef ubah_daop(x,y):\n daop = \"\"\n if x == 'NA' :\n daop = y \n else :\n daop = x\n \n return daop ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"merge_df['NAMA_DAOP2'].value_counts(dropna=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# ubah na pada kolom daop dengan memanggil fungsi yang telah dibuat cek hasilnya\n# kolom ini yang nantinya digunakan untuk update perubahan lokasi daop\nmerge_df['NAMA_DAOP2']= list(map(lambda x, y : ubah_daop(x,y), merge_df['NAMA_DAOP2'], merge_df['id_daops']))\nmerge_df['NAMA_DAOP2'].value_counts(dropna=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"UPDATE KODE DEPO",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"merge_df['KODE_DEPO'].fillna(0, inplace=True)\nmerge_df['KODE_DEPO'] = merge_df['KODE_DEPO'].astype('int64')\nmerge_df",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#fungsi untuk merubah nilai pada kolom KODE DEPO yg 0 diganti dengan isi dari kolom id_depo(data awal)\ndef ubah_depo(x,y):\n depo = \"\"\n if x == 0 :\n depo = y \n else :\n depo = x\n \n return depo",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"merge_df['KODE_DEPO'].value_counts(dropna=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"merge_df['KODE_DEPO']= list(map(lambda x, y : ubah_depo(x,y), merge_df['KODE_DEPO'], merge_df['id_depo']))\nmerge_df['KODE_DEPO'].value_counts(dropna=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"merge_df['id_depo'].value_counts(dropna=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"merge_df[merge_df.KODE_DEPO == 0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# buat rekap untuk mengetahui jumlah sarana per jenis dan per daop, cocokkan nilainya dengan data armada milik PT KAI\ndata_aktiv2 = merge_df.loc[(merge_df['status'] == \"Aktiv\")]\nrekap = data_aktiv2.groupby(['id_jenis', 'NAMA_DAOP2'])['kode_sarana'].count().reset_index()\nrekap = rekap.pivot_table(index=['id_jenis'], columns='NAMA_DAOP2')\nrekap.fillna(0, inplace=True)\nrekap.columns = rekap.columns.droplevel(0)\nrekap = rekap.astype('int64')\nrekap",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"merge_df['id_jenis'].astype('int64')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"merge_df['id_jenis'] = merge_df['id_jenis'].astype('int64')\nmerge_df['NAMA_DAOP2'] = merge_df['NAMA_DAOP2'].astype('int64')\nmerge_df.dtypes",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#hapus kolom yang tidak diinginkan\nmerge_df.drop(columns=['id_daops','id_depo','NOMOR_IDENTITAS', 'DAOP','DEPO', 'JENIS', 'TAHUN','NAMA_DEPO' ], inplace=True)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"merge_df.columns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# rename kolom DAOP menjadi id_daops\nmerge_df.rename(columns={'NAMA_DAOP2' : 'id_daops', 'KODE_DEPO' : 'id_depo'}, inplace=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"merge_df.columns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# atur urutan kolom seperti dataset semula\nfinal_df = merge_df[['id', 'kode_sarana', 'kode_sarana_lama', 'id_kartu', 'id_jenis', 'id_sub_jenis', 'seri', 'tahun_dinas', 'id_daops', 'id_depo', 'status',\n 'negara_asal', 'tgl_uji_pertama', 'tgl_masa_uji', 'tgl_masa_perawatan',\n 'pabrikan', 'id_pemilik', 'created_at', 'last_update']]\n\nfinal_df\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_sarana.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"final_df.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_nonkai = df_sarana.loc[(df_sarana['id_pemilik'] != 2)]\ndf_nonkai.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x = 14038 - 12269\nprint(x)",
"1769\n"
],
[
"df_sarana2 = final_df.append(df_nonkai, ignore_index=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_sarana2.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_sarana2.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#df_sarana2 = df_sarana2[['id', 'kode_sarana', 'kode_sarana_lama', 'id_kartu', 'id_jenis', 'id_sub_jenis', 'seri', 'tahun_dinas', 'id_daops', 'id_depo', 'status',\n 'negara_asal', 'tgl_uji_pertama', 'tgl_masa_uji', 'tgl_masa_perawatan',\n 'pabrikan', 'id_pemilik', 'created_at', 'last_update']]\n\n#df_sarana2",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# buat rekap untuk mengetahui jumlah sarana per jenis dan kepemilikan, cocokkan nilainya\ndata_aktiv2 = df_sarana2.loc[(df_sarana2['status'] == \"Aktiv\")]\nrekap = data_aktiv2.groupby(['id_jenis', 'id_pemilik'])['kode_sarana'].count().reset_index()\nrekap = rekap.pivot_table(index=['id_jenis'], columns='id_pemilik')\nrekap.fillna(0, inplace=True)\nrekap.columns = rekap.columns.droplevel(0)\nrekap = rekap.astype('int64')\nrekap",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_sarana2.to_csv('../data_source/datsar/tblsarana_update_nov.csv', sep=',')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#merge_df.to_csv('data_source/datsar/kai(update_depo).csv', sep=',')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a33c3bc744eb1fa6942aac956114b34bbdd9a99
| 81,160 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Lab 02b.ipynb
|
shipstone98/AdvCompLabs
|
1bbe0997076b61618117ec430cf0bde8ab228d35
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Lab 02b.ipynb
|
shipstone98/AdvCompLabs
|
1bbe0997076b61618117ec430cf0bde8ab228d35
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Lab 02b.ipynb
|
shipstone98/AdvCompLabs
|
1bbe0997076b61618117ec430cf0bde8ab228d35
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 559.724138 | 43,018 | 0.78567 |
[
[
[
"# Lab 02b - System Dynamics\n## Exercise 03\n#### Constants",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"PRED_POP = 15\nPREY_POP = 110\n\nPRED_BIRTHS = 0.02\nPREY_BIRTHS = 2.2\n\nPRED_DEATHS = 1.08\nPREY_DEATHS = 0.04",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Module Imports",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from matplotlib import pyplot",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Parts A and B",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def model_pred_prey(time_step, sim_len):\n pred_pop = PRED_POP\n prey_pop = PREY_POP\n t = 0\n\n t_list = [ t ]\n pred_list = [ pred_pop ]\n prey_list = [ prey_pop ]\n\n while t <= sim_len:\n t += time_step\n pred_births = pred_pop * PRED_BIRTHS * prey_pop\n prey_births = prey_pop * PREY_BIRTHS\n pred_deaths = pred_pop * PRED_DEATHS\n prey_deaths = prey_pop * PREY_DEATHS * pred_pop\n pred_pop += time_step * (pred_births - pred_deaths)\n prey_pop += time_step * (prey_births - prey_deaths)\n t_list.append(t)\n pred_list.append(pred_pop)\n prey_list.append(prey_pop)\n\n return t_list, pred_list, prey_list",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Part C",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"t_list, pred_list, prey_list = model_pred_prey(0.001, 15)\npyplot.title(\"Predator/prey simulation\")\npyplot.ylabel(\"Population\")\npyplot.xlabel(\"Time (hrs)\")\npyplot.plot(t_list, pred_list, label=\"Predators\")\npyplot.plot(t_list, prey_list, label=\"Prey\")\npyplot.legend()\npyplot.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a33d1c2c3d695b6bf6aeaa53ce101673229a342
| 195,981 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
module2-sampling-confidence-intervals-and-hypothesis-testing/LS_DS_132_Sampling_Confidence_Intervals_and_Hypothesis_Testing_Assignment.ipynb
|
Pdugovich/DS-Unit-1-Sprint-3-Statistical-Tests-and-Experiments
|
cf5abf181992dfe2f39c954ef91ededcd484cb1c
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
module2-sampling-confidence-intervals-and-hypothesis-testing/LS_DS_132_Sampling_Confidence_Intervals_and_Hypothesis_Testing_Assignment.ipynb
|
Pdugovich/DS-Unit-1-Sprint-3-Statistical-Tests-and-Experiments
|
cf5abf181992dfe2f39c954ef91ededcd484cb1c
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
module2-sampling-confidence-intervals-and-hypothesis-testing/LS_DS_132_Sampling_Confidence_Intervals_and_Hypothesis_Testing_Assignment.ipynb
|
Pdugovich/DS-Unit-1-Sprint-3-Statistical-Tests-and-Experiments
|
cf5abf181992dfe2f39c954ef91ededcd484cb1c
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 194.232904 | 111,996 | 0.851878 |
[
[
[
"<a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/Pdugovich/DS-Unit-1-Sprint-3-Statistical-Tests-and-Experiments/blob/master/module2-sampling-confidence-intervals-and-hypothesis-testing/LS_DS_132_Sampling_Confidence_Intervals_and_Hypothesis_Testing_Assignment.ipynb\" target=\"_parent\"><img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open In Colab\"/></a>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Assignment - Build a confidence interval\n\nA confidence interval refers to a neighborhood around some point estimate, the size of which is determined by the desired p-value. For instance, we might say that 52% of Americans prefer tacos to burritos, with a 95% confidence interval of +/- 5%.\n\n52% (0.52) is the point estimate, and +/- 5% (the interval $[0.47, 0.57]$) is the confidence interval. \"95% confidence\" means a p-value $\\leq 1 - 0.95 = 0.05$.\n\nIn this case, the confidence interval includes $0.5$ - which is the natural null hypothesis (that half of Americans prefer tacos and half burritos, thus there is no clear favorite). So in this case, we could use the confidence interval to report that we've failed to reject the null hypothesis.\n\nBut providing the full analysis with a confidence interval, including a graphical representation of it, can be a helpful and powerful way to tell your story. Done well, it is also more intuitive to a layperson than simply saying \"fail to reject the null hypothesis\" - it shows that in fact the data does *not* give a single clear result (the point estimate) but a whole range of possibilities.\n\nHow is a confidence interval built, and how should it be interpreted? It does *not* mean that 95% of the data lies in that interval - instead, the frequentist interpretation is \"if we were to repeat this experiment 100 times, we would expect the average result to lie in this interval ~95 times.\"\n\nFor a 95% confidence interval and a normal(-ish) distribution, you can simply remember that +/-2 standard deviations contains 95% of the probability mass, and so the 95% confidence interval based on a given sample is centered at the mean (point estimate) and has a range of +/- 2 (or technically 1.96) standard deviations.\n\nDifferent distributions/assumptions (90% confidence, 99% confidence) will require different math, but the overall process and interpretation (with a frequentist approach) will be the same.\n\nYour assignment - using the data from the prior module ([congressional voting records](https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Congressional+Voting+Records)):\n\n\n### Confidence Intervals:\n1. Generate and numerically represent a confidence interval\n2. Graphically (with a plot) represent the confidence interval\n3. Interpret the confidence interval - what does it tell you about the data and its distribution?\n\n### Chi-squared tests:\n4. Take a dataset that we have used in the past in class that has **categorical** variables. Pick two of those categorical variables and run a chi-squared tests on that data\n - By hand using Numpy\n - In a single line using Scipy\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Confidence Intervals",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 1) Generate and numerically represent a confidence interval",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!wget https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/voting-records/house-votes-84.data",
"--2019-09-17 23:58:29-- https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/voting-records/house-votes-84.data\nResolving archive.ics.uci.edu (archive.ics.uci.edu)... 128.195.10.252\nConnecting to archive.ics.uci.edu (archive.ics.uci.edu)|128.195.10.252|:443... connected.\nHTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK\nLength: 18171 (18K) [application/x-httpd-php]\nSaving to: ‘house-votes-84.data.2’\n\n\rhouse-votes-84.data 0%[ ] 0 --.-KB/s \rhouse-votes-84.data 100%[===================>] 17.75K --.-KB/s in 0.03s \n\n2019-09-17 23:58:30 (629 KB/s) - ‘house-votes-84.data.2’ saved [18171/18171]\n\n"
],
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport scipy.stats as stats\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport seaborn as sns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"names=['party','handicapped-infants','water-project',\n 'budget','physician-fee-freeze', 'el-salvador-aid',\n 'religious-groups','anti-satellite-ban',\n 'aid-to-contras','mx-missile','immigration',\n 'synfuels', 'education', 'right-to-sue','crime','duty-free',\n 'south-africa']\ndf = pd.read_csv('house-votes-84.data', \n header=None,\n names=names)\nprint(df.shape)\ndf.head()",
"(435, 17)\n"
],
[
"df = df.replace({'?': np.NaN, 'y':1, 'n': 0})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dem = df[df['party'] == 'democrat']\nrep = df[df['party'] == 'republican']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dem['aid-to-contras'].mean()\n\n#Dropping nas to use with function\ndem_contras = dem['aid-to-contras'].dropna()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def sample_confidence_interval(data, confidence_level=0.95):\n data = np.array(data)\n mean = sum(data) / len(data)\n std_error = np.std(data, ddof=1) / (len(data))**(1/2)\n t_value = stats.t.ppf((1 + confidence_level) / 2.0, len(data) - 1)\n margin = t_value * std_error\n return (mean, mean - margin, mean + margin)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Checking to make sure the code works\nsample_confidence_interval(dem_contras)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# I tried a few different styles, but I liked Ryan's graphical\n#representation best\ndem_contras.plot(kind='density', figsize=(10,8))\n#zooming in to get a better view, the margin of error is pretty small\nplt.xlim(left = -0.1, right=1.1)\nplt.grid()\nCI = sample_confidence_interval(dem_contras)\nplt.axvline(x=CI[1], color='red', lw=1)\nplt.axvline(x=CI[2], color='red', lw=1)\nplt.axvline(x=CI[0], color='black', lw=3);",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dem['south-africa'].dropna().plot(kind='density', figsize=(10,8))\nCI = sample_confidence_interval(dem['south-africa'].dropna())\nplt.xlim(left=-.2, right=1.2)\nplt.grid()\nplt.axvline(x=CI[1], color='red')\nplt.axvline(x=CI[2], color='red')\nplt.axvline(x=CI[0], color='black');",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#This graph serves no purpose, and should be ignored. But it looks cool.\nfor issue in df.columns[range(1,17)]:\n dem[issue].dropna().plot(kind='density', figsize=(10,8))\n CI = sample_confidence_interval(dem[issue].dropna())\n plt.axvline(x=CI[1], color='red')\n plt.axvline(x=CI[2], color='red')\n plt.axvline(x=CI[0], color='black');",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##Chi-squared Test",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Loading in a dataset from a previous lecture\n\ndataset_url = 'https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/adult/adult.data'\n\ncolumn_headers = ['age', 'workclass', 'fnlwgt', 'education', 'education-num', \n 'marital-status', 'occupation', 'relationship', 'race', 'sex', \n 'capital-gain', 'capital-loss', 'hours-per-week', \n 'native-country', 'income']\n#Note that having the incorrect number of column headers makes the far left the \"index\", \n\ndf_chi = pd.read_csv(dataset_url, names=column_headers)\nprint(df.shape)\ndf_chi.head(5)\n",
"(435, 17)\n"
],
[
"df_chi['race'].value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_chi['marital-status'].value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Putting the two categorical variables into a crosstab\ncrosstab_table = pd.crosstab(df_chi['sex'], df_chi['race'], margins=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"crosstab_table",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"row_sums = crosstab_table.iloc[0:2, 5].values\ncol_sums = crosstab_table.iloc[2, 0:5].values\ntotal = crosstab_table.loc['All','All']\nprint(row_sums)\nprint(col_sums)\nprint(total)",
"[10771 21790]\n[ 311 1039 3124 271 27816]\n32561\n"
],
[
"#Creating an empty list to fill with expected values\nexpected = []\nfor num in range(len(row_sums)):\n expected_row = []\n for col in col_sums:\n expected_val = col*row_sums[num]/total\n expected_row.append(expected_val)\n expected.append(expected_row)\n \n\nexpected = np.array(expected)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Stretch goals:\n\n1. Write a summary of your findings, mixing prose and math/code/results. *Note* - yes, this is by definition a political topic. It is challenging but important to keep your writing voice *neutral* and stick to the facts of the data. Data science often involves considering controversial issues, so it's important to be sensitive about them (especially if you want to publish).\n2. Apply the techniques you learned today to your project data or other data of your choice, and write/discuss your findings here.\n3. Refactor your code so it is elegant, readable, and can be easily run for all issues.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Resources\n\n- [Interactive visualize the Chi-Squared test](https://homepage.divms.uiowa.edu/~mbognar/applets/chisq.html)\n- [Calculation of Chi-Squared test statistic](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pearson%27s_chi-squared_test)\n- [Visualization of a confidence interval generated by R code](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Confidence-interval.svg)\n- [Expected value of a squared standard normal](https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/264061/expected-value-calculation-for-squared-normal-distribution) (it's 1 - which is why the expected value of a Chi-Squared with $n$ degrees of freedom is $n$, as it's the sum of $n$ squared standard normals)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4a33fd910ae4180252afac1607e56d923de1d3da
| 54,728 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/histogram_khb_kstack_bigtraj.ipynb
|
yizaochen/enmspring
|
84c9aabeb7f87eda43967d86c763b7d600986215
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/histogram_khb_kstack_bigtraj.ipynb
|
yizaochen/enmspring
|
84c9aabeb7f87eda43967d86c763b7d600986215
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/histogram_khb_kstack_bigtraj.ipynb
|
yizaochen/enmspring
|
84c9aabeb7f87eda43967d86c763b7d600986215
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 121.348115 | 18,280 | 0.865663 |
[
[
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom enmspring.spring import BigTrajAgent\ninteractions = ['other', 'backbone', 'stack', 'sugar', 'HB']\nbigtraj_folder = '/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch'",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Part 0: Initialize",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"host = 'a_tract_21mer'\ntype_na = 'bdna+bdna'\nonly_central = True\nb_agent = BigTrajAgent(host, type_na, bigtraj_folder, only_central)",
"/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/0_1000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/500_1500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/1000_2000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/1500_2500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/2000_3000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/2500_3500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/3000_4000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/3500_4500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/4000_5000/pd_dfs exists\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Part 1: Read all DataFrame",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"b_agent.read_all_k_b0_pairtype_df()",
"Read /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/0_1000/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/500_1500/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/1000_2000/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/1500_2500/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/2000_3000/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/2500_3500/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/3000_4000/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/3500_4500/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/4000_5000/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Part 2: Process k-stack and k-HB",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"b_agent.put_all_df_st_into_dict()\nb_agent.put_all_df_hb_into_dict()",
"Read Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Part 3: Histogram",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"k_st_list = b_agent.get_k_st_list()\nk_hb_list = b_agent.get_k_hb_list()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8,4))\n\nax.hist(k_st_list, 50, density=True, facecolor='g', label='stack', alpha=0.75)\nax.hist(k_hb_list, 50, density=True, facecolor='red', label='HB', alpha=0.75)\n\nax.legend()\nplt.tight_layout()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8,4))\n\nax.hist(k_st_list, 50, density=True, facecolor='g', label='stack', alpha=0.75)\nax.hist(k_hb_list, 50, density=True, facecolor='red', label='HB', alpha=0.75)\n\nax.legend()\nplt.tight_layout()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"type_na = 'bdna+bdna'\nonly_central = True\nhosts = ['a_tract_21mer', 'g_tract_21mer', 'atat_21mer', 'gcgc_21mer']\nd_results = dict()\nfor host in hosts:\n b_agent = BigTrajAgent(host, type_na, bigtraj_folder, only_central)\n b_agent.read_all_k_b0_pairtype_df()\n b_agent.put_all_df_st_into_dict()\n b_agent.put_all_df_hb_into_dict()\n \n d_results[host] = dict()\n d_results[host]['st'] = b_agent.get_k_st_list()\n d_results[host]['hb'] = b_agent.get_k_hb_list()",
"/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/0_1000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/500_1500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/1000_2000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/1500_2500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/2000_3000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/2500_3500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/3000_4000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/3500_4500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/4000_5000/pd_dfs exists\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/0_1000/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/500_1500/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/1000_2000/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/1500_2500/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/2000_3000/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/2500_3500/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/3000_4000/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/3500_4500/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/a_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/4000_5000/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/g_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/0_1000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/g_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/500_1500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/g_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/1000_2000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/g_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/1500_2500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/g_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/2000_3000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/g_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/2500_3500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/g_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/3000_4000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/g_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/3500_4500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/g_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/4000_5000/pd_dfs exists\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/g_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/0_1000/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/g_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/500_1500/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/g_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/1000_2000/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/g_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/1500_2500/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/g_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/2000_3000/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/g_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/2500_3500/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/g_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/3000_4000/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/g_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/3500_4500/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/g_tract_21mer/bdna+bdna/4000_5000/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/atat_21mer/bdna+bdna/0_1000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/atat_21mer/bdna+bdna/500_1500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/atat_21mer/bdna+bdna/1000_2000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/atat_21mer/bdna+bdna/1500_2500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/atat_21mer/bdna+bdna/2000_3000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/atat_21mer/bdna+bdna/2500_3500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/atat_21mer/bdna+bdna/3000_4000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/atat_21mer/bdna+bdna/3500_4500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/atat_21mer/bdna+bdna/4000_5000/pd_dfs exists\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/atat_21mer/bdna+bdna/0_1000/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/atat_21mer/bdna+bdna/500_1500/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/atat_21mer/bdna+bdna/1000_2000/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/atat_21mer/bdna+bdna/1500_2500/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/atat_21mer/bdna+bdna/2000_3000/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/atat_21mer/bdna+bdna/2500_3500/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/atat_21mer/bdna+bdna/3000_4000/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/atat_21mer/bdna+bdna/3500_4500/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/atat_21mer/bdna+bdna/4000_5000/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/gcgc_21mer/bdna+bdna/0_1000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/gcgc_21mer/bdna+bdna/500_1500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/gcgc_21mer/bdna+bdna/1000_2000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/gcgc_21mer/bdna+bdna/1500_2500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/gcgc_21mer/bdna+bdna/2000_3000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/gcgc_21mer/bdna+bdna/2500_3500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/gcgc_21mer/bdna+bdna/3000_4000/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/gcgc_21mer/bdna+bdna/3500_4500/pd_dfs exists\n/home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/gcgc_21mer/bdna+bdna/4000_5000/pd_dfs exists\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/gcgc_21mer/bdna+bdna/0_1000/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/gcgc_21mer/bdna+bdna/500_1500/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/gcgc_21mer/bdna+bdna/1000_2000/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/gcgc_21mer/bdna+bdna/1500_2500/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/gcgc_21mer/bdna+bdna/2000_3000/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/gcgc_21mer/bdna+bdna/2500_3500/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/gcgc_21mer/bdna+bdna/3000_4000/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/gcgc_21mer/bdna+bdna/3500_4500/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead /home/ytcdata/bigtraj_fluctmatch/gcgc_21mer/bdna+bdna/4000_5000/pd_dfs/pairtypes_k_b0_cutoff_4.70.csv into df_all_k\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of stacking: df_st\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\nRead Dataframe of HB: df_hb\n"
],
[
"d_rowcols = {'a_tract_21mer':(0,0), 'g_tract_21mer':(0,1), 'atat_21mer':(1,0), 'gcgc_21mer':(1,1)}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2, figsize=(8, 4), sharey=True, sharex=True)\n\nfor host in hosts:\n row_id, col_id = d_rowcols[host]\n ax = axes[row_id, col_id]\n ax.hist(d_results[host]['st'], 50, density=True, facecolor='g', label='stack', alpha=0.75)\n ax.hist(d_results[host]['hb'], 200, density=True, facecolor='red', label='HB', alpha=0.75)\n ax.set_title(host)\n ax.set_xlabel('k (kcal/mol/Å$^2$)')\n ax.set_ylabel('Probability')\n ax.legend(frameon=False)\n \nplt.tight_layout()\nplt.savefig('histogram_kst_khb.pdf')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a3407147b01923ccfe8078873b3fd9d9152f412
| 60,989 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
nbs/dl2/09b_learner-Copy1.ipynb
|
huanzheng/fastai
|
82d25cbb9b950a8f1b94460706f7bceb29300254
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
nbs/dl2/09b_learner-Copy1.ipynb
|
huanzheng/fastai
|
82d25cbb9b950a8f1b94460706f7bceb29300254
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 2 |
2021-09-27T22:53:36.000Z
|
2022-02-26T05:34:00.000Z
|
nbs/dl2/09b_learner-Copy1.ipynb
|
huanzheng/fastai
|
82d25cbb9b950a8f1b94460706f7bceb29300254
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 136.440716 | 31,928 | 0.877699 |
[
[
[
"# Let's kill off `Runner`",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%load_ext autoreload\n%autoreload 2\n\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#export\nfrom exp.nb_09 import *",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"AvgStats",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Imagenette data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"[Jump_to lesson 11 video](https://course.fast.ai/videos/?lesson=11&t=6571)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"path = datasets.untar_data(datasets.URLs.IMAGENETTE_160)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tfms = [make_rgb, ResizeFixed(128), to_byte_tensor, to_float_tensor]\nbs=64\n\nil = ImageList.from_files(path, tfms=tfms)\nsd = SplitData.split_by_func(il, partial(grandparent_splitter, valid_name='val'))\nll = label_by_func(sd, parent_labeler, proc_y=CategoryProcessor())\ndata = ll.to_databunch(bs, c_in=3, c_out=10, num_workers=4)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cbfs = [partial(AvgStatsCallback,accuracy),\n CudaCallback,\n partial(BatchTransformXCallback, norm_imagenette)]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"nfs = [32]*4",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Having a Runner is great but not essential when the `Learner` already has everything needed in its state. We implement everything inside it directly instead of building a second object.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"##### In Lesson 12 Jeremy Howard revisited material in the cell below [Jump_to lesson 12 video](https://course.fast.ai/videos/?lesson=12&t=65)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#export\ndef param_getter(m): return m.parameters()\n\nclass Learner():\n def __init__(self, model, data, loss_func, opt_func=sgd_opt, lr=1e-2, splitter=param_getter,\n cbs=None, cb_funcs=None):\n self.model,self.data,self.loss_func,self.opt_func,self.lr,self.splitter = model,data,loss_func,opt_func,lr,splitter\n self.in_train,self.logger,self.opt = False,print,None\n \n # NB: Things marked \"NEW\" are covered in lesson 12\n # NEW: avoid need for set_runner\n self.cbs = []\n self.add_cb(TrainEvalCallback())\n self.add_cbs(cbs)\n self.add_cbs(cbf() for cbf in listify(cb_funcs))\n\n def add_cbs(self, cbs):\n for cb in listify(cbs): self.add_cb(cb)\n \n def add_cb(self, cb):\n cb.set_runner(self)\n setattr(self, cb.name, cb)\n self.cbs.append(cb)\n\n def remove_cbs(self, cbs):\n for cb in listify(cbs): self.cbs.remove(cb)\n \n def one_batch(self, i, xb, yb):\n try:\n self.iter = i\n self.xb,self.yb = xb,yb; self('begin_batch')\n self.pred = self.model(self.xb); self('after_pred')\n self.loss = self.loss_func(self.pred, self.yb); self('after_loss')\n if not self.in_train: return\n self.loss.backward(); self('after_backward')\n self.opt.step(); self('after_step')\n self.opt.zero_grad()\n except CancelBatchException: self('after_cancel_batch')\n finally: self('after_batch')\n\n def all_batches(self):\n self.iters = len(self.dl)\n try:\n for i,(xb,yb) in enumerate(self.dl): self.one_batch(i, xb, yb)\n except CancelEpochException: self('after_cancel_epoch')\n\n def do_begin_fit(self, epochs):\n self.epochs,self.loss = epochs,tensor(0.)\n self('begin_fit')\n\n def do_begin_epoch(self, epoch):\n self.epoch,self.dl = epoch,self.data.train_dl\n return self('begin_epoch')\n\n def fit(self, epochs, cbs=None, reset_opt=False):\n # NEW: pass callbacks to fit() and have them removed when done\n self.add_cbs(cbs)\n # NEW: create optimizer on fit(), optionally replacing existing\n if reset_opt or not self.opt: self.opt = self.opt_func(self.splitter(self.model), lr=self.lr)\n \n try:\n self.do_begin_fit(epochs)\n for epoch in range(epochs):\n self.do_begin_epoch(epoch)\n if not self('begin_epoch'): self.all_batches()\n\n with torch.no_grad(): \n self.dl = self.data.valid_dl\n if not self('begin_validate'): self.all_batches()\n self('after_epoch')\n \n except CancelTrainException: self('after_cancel_train')\n finally:\n self('after_fit')\n self.remove_cbs(cbs)\n\n ALL_CBS = {'begin_batch', 'after_pred', 'after_loss', 'after_backward', 'after_step',\n 'after_cancel_batch', 'after_batch', 'after_cancel_epoch', 'begin_fit',\n 'begin_epoch', 'begin_validate', 'after_epoch',\n 'after_cancel_train', 'after_fit'}\n \n def __call__(self, cb_name):\n res = False\n assert cb_name in self.ALL_CBS\n for cb in sorted(self.cbs, key=lambda x: x._order): res = cb(cb_name) and res\n return res",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#export\nclass AvgStatsCallback(Callback):\n def __init__(self, metrics):\n self.train_stats,self.valid_stats = AvgStats(metrics,True),AvgStats(metrics,False)\n \n def begin_epoch(self):\n self.train_stats.reset()\n self.valid_stats.reset()\n \n def after_loss(self):\n stats = self.train_stats if self.in_train else self.valid_stats\n with torch.no_grad(): stats.accumulate(self.run)\n \n def after_epoch(self):\n #We use the logger function of the `Learner` here, it can be customized to write in a file or in a progress bar\n self.logger(self.train_stats)\n self.logger(self.valid_stats) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cbfs = [partial(AvgStatsCallback,accuracy),\n CudaCallback,\n partial(BatchTransformXCallback, norm_imagenette)]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#export\ndef get_learner(nfs, data, lr, layer, loss_func=F.cross_entropy,\n cb_funcs=None, opt_func=sgd_opt, **kwargs):\n model = get_cnn_model(data, nfs, layer, **kwargs)\n init_cnn(model)\n return Learner(model, data, loss_func, lr=lr, cb_funcs=cb_funcs, opt_func=opt_func)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"learn = get_learner(nfs, data, 0.4, conv_layer, cb_funcs=cbfs)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%time learn.fit(1)",
"train: [1.8311652646095082, tensor(0.3570, device='cuda:0')]\nvalid: [1.5547332763671875, tensor(0.4880, device='cuda:0')]\nCPU times: user 4.05 s, sys: 1.93 s, total: 5.98 s\nWall time: 18 s\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Check everything works",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Let's check our previous callbacks still work.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cbfs += [Recorder]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"learn = get_learner(nfs, data, 0.4, conv_layer, cb_funcs=cbfs)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"phases = combine_scheds([0.3, 0.7], cos_1cycle_anneal(0.2, 0.6, 0.2))\nsched = ParamScheduler('lr', phases)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"learn.fit(1, sched)",
"train: [1.8860618007891268, tensor(0.3378, device='cuda:0')]\nvalid: [1.775871337890625, tensor(0.3620, device='cuda:0')]\n"
],
[
"learn.recorder.plot_lr()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"learn.recorder.plot_loss()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Export",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!./notebook2script.py 09b_learner.ipynb",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a3413d55deaa2f7142d75b3c9a5acfae48d576b
| 38,545 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
sports/sports-SABTC.ipynb
|
ganymede-io/presentations
|
0f60b1451d9b3d61ecfa124a5d826d38d159a1f0
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | 4 |
2018-03-21T13:30:26.000Z
|
2020-12-16T10:53:04.000Z
|
sports/sports-SABTC.ipynb
|
ganymede-io/presentations
|
0f60b1451d9b3d61ecfa124a5d826d38d159a1f0
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | 3 |
2021-02-05T19:03:02.000Z
|
2022-03-10T20:08:38.000Z
|
sports/sports-SABTC.ipynb
|
ganymede-io/presentations
|
0f60b1451d9b3d61ecfa124a5d826d38d159a1f0
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | 1 |
2021-03-16T04:48:42.000Z
|
2021-03-16T04:48:42.000Z
| 28.135036 | 506 | 0.579712 |
[
[
[
"\n\n\n<h2 align='center'>Data Literacy through Sports Analytics</h2>\n<h3 align='center'>Southern Alberta Teachers' Convention 2021</h3>\n\n<h3 align='center'>Tina Leard (Cybera)<br>\nMichael Lamoureux (University of Calgary)</h3><br>\n\n<h4 align='center'> Slides at: https://tinyurl.com/callysto-data </h4>\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<center><img src='./images/ccby.png' alt=\"CC BY logo\" width='300' /></center>\n\n<p><center><a href='https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/' target='_blank'>CC BY</a>:<br>\nThis license allows reusers to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon the material in any medium or format,<br>\nso long as attribution is given to the creator. \n</center></p>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nfrom pandas import read_csv\nimport plotly.graph_objects as go\nimport plotly.express as px\nfrom plotly import subplots\nfrom plotly.offline import download_plotlyjs, plot,iplot\nimport cufflinks as cf\ncf.go_offline()\n\nfrom IPython.display import YouTubeVideo\n\nfrom ipysheet import sheet, cell, cell_range\n\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Overview\n\n- Data literacy via sports\n- The learning progression\n- Examples of learning and data analysis\n - Professional soccer\n - Ice hockey\n - Field hockey\n- Python, Jupyter, and Callysto",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<center><img src='./images/data_literacy.png' alt='data literacy' width='85%' /></center>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Content and context\n\n(Alberta Education, 2000, 2007, updated 2016, 2017)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Example: professional soccer event data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_soccer = pd.read_csv(\"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/metrica-sports/sample-data/master/data/Sample_Game_1/Sample_Game_1_RawEventsData.csv\"); df_soccer",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Home team passes, second half**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_soccer.loc[lambda df: (df['Team'] == 'Home') & (df['Period'] == 2) & (df['Type'] == 'PASS'), :] \\\n .iplot(kind=\"scatter\",x = \"Start X\", y = \"Start Y\", mode = \"markers\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Bridging expert to novice",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Data visualization learning progression\n<img src='./images/creating_scaffolding.png' alt='scaffolding' width='95%' />",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Data visualization learning progression\n<img src='./images/creating_adapting.png' alt='adapting' width='95%' />",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Communicating mathemtical reasoning (Alberta Education, 2007, updated 2016)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Data gathering learning progression\n<br>\n<center><img src='./images/data_gathering.png' alt='data gathering' width='85%' /></center>\n<br><br><br>Source: <a href='http://oceansofdata.org/sites/oceansofdata.org/files/pervasive-and-persistent-understandings-01-14.pdf' target='_blank'>Pervasive and Persistent Understandings about Data</a>, Kastens (2014)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Authentic learning approach\n\n- Learning design based on interdisciplinary<br>\nconnections and real-world examples\n- Industry-aligned data science analysis process\n- Python, an all-purpose programming language\n- Jupyter notebook, a free industry-standard tool for data scientists\n- CallystoHub, free cloud computing",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Athlete development\n\n### U15 training to train\n- Promotes tactical strategies for in-game decision making, reading the situation and inferring \n- Focuses on the team and the process\n- Situates personal goals within a team approach\n\n### U18 training to compete\n- Emphasizes individual technical and position-specific training",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Youth sports analytics\n\nOnline communication,<br>\nsometimes through shared video analysis spaces\n\nVideo replay during games and training\n\nPost–game video analysis, limitted statistics",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Learning design and flexibility\n<br>\n<img src='./images/flexibility.png' alt='adapting' width='90%' />",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Two data examples\n\n1. Import a csv file and use a Python spreadsheet<br>to create shot maps (ice hockey)\n2. Gather data from video to analyze and make decisions (field hockey)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Data example 1:\n## Using IIHF World Junior Championship data to create graphs and a shot map",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Defining ice hockey net zones:<br> What factors can lead to scoring?\n<!--USA Hockey Goaltender Basics https://www.usahockeygoaltending.com/page/show/890039-stance-->\n||\n|-|-|\n|<img src='./images/hockey_net_zones.png' width='100%'/>|<img src='https://cdn.hockeycanada.ca/hockey-canada/Team-Canada/Men/Under-18/2014-15/2014-15_goalie_camp.jpg?q=60' />|\n||<a href='https://www.hockeycanada.ca/en-ca/news/34-goaltenders-invited-to-2014-poe-camp' target='_blank'>Image source: Hockey Canada</a>|",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%html \n<h2>Data source IIHF: Shot charts</h2><br>\n<iframe width=\"1200\" height=\"600\" src=\"https://www.iihf.com/pdf/503/ihm503a13_77a_3_0\" frameborder=\"0\" ></iframe>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Tally chart\n<img src='./images/hockey_tally.png' alt='tally chart' width='85%' />",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Generating a csv file\n\nZone,Austria,Canada,Czech_Republic,Finland,Germany,Russia,Switzerland,Slovakia,Sweden,USA,Total<br>\none,0,7,0,3,2,0,0,0,3,3,18<br>\ntwo,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,3<br>\nthree,0,5,0,2,2,4,1,0,3,6,23<br>\nfour,0,4,3,2,1,1,0,1,0,3,15<br>\nfive,0,1,0,2,1,0,0,0,0,0,4<br>\nsix,1,1,2,4,0,2,0,1,0,2,13<br>\nseven,0,6,0,1,3,3,1,1,0,9,24<br>\neight,0,5,1,2,2,3,1,2,3,2,21<br>\nnine,0,3,3,0,2,3,2,0,5,0,18<br>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Exploring scoring on net zones ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"hockey_goals_df = pd.read_csv('./data/hockey_goals.csv')\nhockey_goals_df.head(9)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### What do measures of central tendency<br>tell us about the total goals per net zone?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"hockey_goals_df['Total'].sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"hockey_goals_df['Total'].min()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"hockey_goals_df['Total'].max()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"scatter_hockey_goals_df = px.scatter(hockey_goals_df,x=\"Zone\",y=\"Total\",title=\"Total goals per net zone\")\nscatter_hockey_goals_df.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"hockey_goals_df['Total'].mean()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"hockey_goals_df['Total'].median()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"hockey_goals_df['Total'].mode()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Which net zones score above the median? ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"hockey_goals_df = hockey_goals_df.sort_values('Total', ascending=False)\nhockey_goals_df",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"bar_hockey_goals_df = px.bar(hockey_goals_df,\n x=\"Zone\", y=\"Total\")\nbar_hockey_goals_df.update_layout(title_text='Total goals by net zone')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### What connections exist between<br>goalie position and scoring?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"hockey_goals_df = pd.read_csv('./data/hockey_goals.csv') \nhockey_goals_df.Total",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"spread_sheet_hockey_net = sheet(rows=3, columns=3)\n\nmy_cells_net = cell_range([[18,3,23],[15,4,13],[24,21,18]],row_start=0,col_start=0,numeric_format=\"int\")\n\nfigure_hockey_net = go.Figure(data=go.Heatmap(\n z =list(reversed(my_cells_net.value)),\n type = 'heatmap',\n colorscale = 'greys',opacity = 1.0))\n\naxis_template = dict(range = [0,5], autorange = True,\n showgrid = False, zeroline = False,\n showticklabels = False,\n ticks = '' )\n\nfigure_hockey_net.update_layout(margin = dict(t=50,r=200,b=200,l=200),\n xaxis = axis_template,\n yaxis = axis_template,\n showlegend = False,\n width = 800, height = 500, title=\"Ice hockey net zones\",\n autosize = True )\n\n# Add image in the background\nnLanes = 3\nnZones = 3\n\nfigure_hockey_net.add_layout_image(\n dict(\n source=\"images/hockey_net.png\",\n xref=\"x\",\n yref=\"y\",\n x=-0.5,\n y=-.5 + nLanes, #this adjusts the placement of the image\n sizex=nZones,\n sizey=nLanes,\n sizing=\"fill\",\n opacity=1.0,\n layer=\"above\")\n)\n\n# changes in my_cells should trigger this function\ndef calculate(change):\n figure_hockey_net.update_traces(z=list(reversed(my_cells_net.value)))\n \nmy_cells_net.observe(calculate, 'value')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"spread_sheet_hockey_net",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"139",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"figure_hockey_net.update() # Click the keys \"Shift-return\" to update the figure",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Data example 2:\n\n## Analyzing youth field hockey data to make decisions",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<center><img src='./images/learning_cycle1.png' alt=\"Learning design and context\" width='90%' /></center>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Learning design and context notes\n\nThe context is physical education, and the content is statistics. Within physical education, in-game skills, fair play, teamwork, and goal setting are integrated. Those outcomes can be applied to in-game decision making. The goal setting can also be part of the communication resulting from the data analysis. When considering in-game decision making, we can define an action as the result of a decision. Decision making is part of a learning cycle that incorporates a technological feedback loop.\n\n(Field Hokcey Alberta, 2020; Field Hockey Canada, 2020; Alberta Education, 2000)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<center><img src='./images/learning_cycle5.png' alt=\"Learning cycle\" width='90%' /></center>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Learning cycle notes\nThe real situation occurs on the field where a decision is made and an action is executed. Then, the athlete forms a mental representation, processing occurs, and a real model is formed. The real model is integrated into the computational model, which results in a technological feedback, then a connection is made back into game play.\n\n(Butler & Winne, 1995; Cleary & Zimmerman, 2001; Hadwin et al., 2017; Leard & Hadwin, 2001)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<center><img src='./images/computational_thinking.png' alt=\"Computationl thinking\" width='90%' /></center>\n<a href=\"https://app.lucidchart.com/documents/view/8e3186f7-bdfe-46af-9c7f-9c426b80d083\">Connecting data literacy and sports</a>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Computational modelling and data literacy notes\n\nThe definition of computational thinking can vary.\n\nComputational thinking is math reasoning combined with critical thinking plus the power of computers. We can use computers to do work more efficiently for us, like compute thousands of lines of data.\n\nUnder that definition of computational thinking, we can apply computational thinking strategies. The foundational process is decomposing to look for patterns. We can use computer programming to design algorithms to look for patterns. With these algorithms, we can infer through abstractions.\n\nThe abstractions can be in the form of computational models: data visualizations (including graphs from the curriculum), data analyses, and simulations of probability models. The data visualizations can extend beyond the curriculum to support math reasoning.\n\n(Berikan & Özdemir, 2019; Gadanidis, 2020; Guadalupe & Gómez-Blancarte, 2019; Leard & Hadwin, 2001)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<center><img src='./images/analysis_process.png' alt=\"Data science analysis process\" width='90%' /></center>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Data science analysis process notes\n\nThis data science analysis process was modified from how expert data scientists analyze data and aligned to several provincial curricula.\n\nThere are six steps:\n\n1. Understand the problem. What questions are we trying to answer?\n2. Gather the data. Find the data sources, with the extension of big data sets.\n3. Organize the data so we can explore it, usually in the form of a table.\n4. Explore the data to create computational models. Usually, there is more than one model. Look for evidence to answer our questions.\n5. Interpret the data through inferences. Explain how the evidence answers our questions.\n6. Communicate the results. In the context of sports analytics, the communication might be within a team to decide tactical strategies for game play.\n\n(Alberta Education, 2007, updated 2016; Ferri, 2006; Leard & Hadwin, 2001; Manitoba Education and Training, 2020; Ontario Ministry of Education, 2020)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<center><img src='./images/collective.png' alt=\"Collective decision making\" width='90%' /></center>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Learning cycle notes\n\nHow the individual makes decisions within the collective responsibilities and actions of the team can be considered. In-game decision making involves in-game communication with team members, with each athlete referring to their own real model.\n\nWhile in-game decision making will always produce a real model, athletes also need to decide when it is appropriate to connect the real model to the computational model and integrate that connection back into game play.\n\n(BC Ministry of Education, 2020; Hadwin et al., 2017; Leard & Hadwin, 2001)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<center><img src='./images/models.png' alt=\"Models\" width='90%' /></center>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Real model and computational model notes\n\nHow the individual makes decisions within the collective responsibilities and actions of the team can be considered. In-game decision making involves in-game communication with team members, with each athlete referring to their own real model.\n\nWhile in-game decision making will always produce a real model, athletes also need to decide when it is appropriate to connect the real model to the computational model and integrate that connection back into game play.\n\n(Field Hockey Canada, 2020)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<center><img src='./images/data_literacy_sports.png' alt=\"Connecting data literacy and sports\" width='90%' /></center>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<center><img src='./images/field_hockey_game.png' alt=\"Field hockey\" width='90%' /></center>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<center><img src='./images/understand1.png' alt=\"Understand actions\" width='90%' /></center>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"(Field Hockey Alberta, 2020; Field Hockey Canada, 2020)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<center><img src='./images/actions.png' alt=\"Understand viewpoints\" width='90%' /></center>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print ('Passes received')\nYouTubeVideo('mIwiiJO7Rk4?start=2893&end=2915', width='600', height='355')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<center><img src='./images/gather4.png' alt=\"Gather\" width='90%' /></center>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<center><img src='./images/collection_passing.png' alt=\"Passing\" width='90%' /></center>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 3. Organize",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"possession_time_df = read_csv('data/field_hockey_possession_time.csv')\npossession_time_df.head(8)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 4. Explore\nHow does ball possession affect outcomes?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"bar_possession_time_df = px.bar(possession_time_df,x=\"Possession Time (seconds)\",y=\"Quarter\",title=\"Possession per quarter<br>Home 2 shots on net (Q3); Away 1 shot on net (Q1)\",color=\"Team\")\nbar_possession_time_df.update_layout(autosize=False, width=600, height=400)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lanes_home_passes_df = read_csv('data/field_hockey_lanes_home_passes.csv')\nlanes_home_passes_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"circle_lanes_home_passes_df = px.pie(lanes_home_passes_df,values=\"Count\",names=\"Action\",title=\"Passes received, intercepted, and missed for Home team\")\ncircle_lanes_home_passes_df.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"bar_lanes_home_passes_df = px.bar(lanes_home_passes_df,\n x=\"Quarter\", y=\"Count\", color=\"Action\", title=\"Passes per quarter for Home team\")\nbar_lanes_home_passes_df.update_layout(barmode='stack', xaxis={'categoryorder':'array', 'categoryarray':['first','second','third','fourth']})",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 4. Explore passes received\nWhat stays the same and what changes?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"lanes_home_passes_received_df = lanes_home_passes_df[lanes_home_passes_df['Action']=='pass received']\nlanes_home_passes_received_df.head() ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"bar_lanes_home_passes_received_df = px.bar(lanes_home_passes_received_df,\n x=\"Quarter\", y=\"Count\", color=\"Lane\", text=\"Lane\", title=\"Passes received in lanes per quarter for Home team\")\nbar_lanes_home_passes_received_df.update_layout(barmode='stack', xaxis={'categoryorder':'array', 'categoryarray':['first','second','third','fourth']})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_passes_home = pd.read_csv('data/field_hockey_home_passes.csv'); df_passes_home",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_temp_1 = df_passes_home.loc[lambda df: (df['Phase of Play'] == 'attack') &(df['Quarter'] == 'first') ];\ndf_temp_2 = df_passes_home.loc[lambda df: (df['Phase of Play'] == 'attack') &(df['Quarter'] == 'second') ]; \ndf_temp_3 = df_passes_home.loc[lambda df: (df['Phase of Play'] == 'attack') &(df['Quarter'] == 'third') ]; \ndf_temp_4 = df_passes_home.loc[lambda df: (df['Phase of Play'] == 'attack') &(df['Quarter'] == 'fourth') ]; ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#import plotly.tools as tls\nfig_all = subplots.make_subplots(rows=1, cols=4)\nfig_1 = df_temp_1.iplot(kind='heatmap', colorscale='blues', x='Lane', y='Zone', z='Count' , asFigure=True) \nfig_2 = df_temp_2.iplot(kind='heatmap', colorscale='blues', x='Lane', y='Zone', z='Count' , asFigure=True)\nfig_3 = df_temp_3.iplot(kind='heatmap', colorscale='blues', x='Lane', y='Zone', z='Count' , asFigure=True)\nfig_4 = df_temp_4.iplot(kind='heatmap', colorscale='blues', x='Lane', y='Zone', z='Count' , asFigure=True)\nfig_all.append_trace(fig_1['data'][0], 1, 1)\nfig_all.append_trace(fig_2['data'][0], 1, 2)\nfig_all.append_trace(fig_3['data'][0], 1, 3)\nfig_all.append_trace(fig_4['data'][0], 1, 4)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig_all.update_xaxes(showticklabels = False, linecolor='black')\nfig_all.update_yaxes(showticklabels = False, linecolor='black')\niplot(fig_all)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Passes in left outside lane of the opponent's net\n|||||\n|---|---|---|---|\n|**Q1: 29%** (14/49)|**Q2: 41%** (13/32)|**Q3: 38%** (16/42)|**Q4: 28%** (8/29)|",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_passes_home.loc[lambda df: (df['Lane'] == 1) &(df['Phase of Play'] == 'attack') &(df['Quarter']== 'first') ].sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"14/49",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 5. Interpret<br> How can the data exploration inform decision making?\n\n> - Considering the role of passing versus carrying the ball\n> - Keeping the ball out of the zone near the net\n> - Attacking on the outer lanes, especially toward the left side of the opponent's net",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# The technology in this talk\n\n- **Jupyter** notebooks, **Python** programming, **Pandas** for data\n- Free to teachers and students\n- **Callysto.ca** project (CanCode, Cybera, PIMS)\n- This slideshow **IS** a Jupyter notebook! (take a tour)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Callysto resources\n\n- <a href=\"https://www.callysto.ca/starter-kit/\">Callysto starter kit</a> Getting started\n- <a href=\"https://courses.callysto.ca\">courses.callysto.ca</a> Online courses\n- <a href=\"https://www.callysto.ca/weekly-data-visualization/\">Weekly data visualizations</a> Quick activities",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<center><a href='https://www.callysto.ca/learning-modules/'><img src='./images/learning_modules.png' target='_blank' alt=\"Callysto learning modules\" width='90%' /></a></center>\n<center>All free, all open source, aimed at teachers and students</center>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n<p><center>Contact us at <a href=\"mailto:[email protected]\">[email protected]</a><br>\nfor in-class workshops, virtual hackathons...<br>\n <a href=\"https://twitter.com/callysto_canada\">@callysto_canada</a><br>\n <a href=\"https://callysto.ca\">callysto.ca</a><br>\n <a href=\"https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCPdq1SYKA42EZBvUlNQUAng\">YouTube</a>\n</center></p>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Thank you for your attention!\n<center><img src='./images/callysto_logo.png' alt=\"Callysto logo\" width='80%' /></center>\n<center><img src='./images/callysto_partners2.png' alt='Callysto partners' width='80%' /></center>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### References\n\nAlberta Education. (2000). *Physical education* [Program of Studies]. https://education.alberta.ca/media/160191/phys2000.pdf\n\nAlberta Education. (2007, updated 2016). *Mathematics kindergarten to grade 9* [Program of Studies]. https://education.alberta.ca/media/3115252/2016_k_to_9_math_pos.pdf\n\nAlberta Education. (2017). *Career and Ttechnology foundations* [Program of Studies]. https://education.alberta.ca/media/3795641/ctf-program-of-studies-jan-4-2019.pdf\n\nBC Ministry of Education. (2020). *BC's digital literacy framework*. https://www2.gov.bc.ca/assets/gov/education/kindergarten-to-grade-12/teach/teaching-tools/digital-literacy-framework.pdf\n\nBerikan, B., & Özdemir, S. (2019). Investigating “problem-solving with datasets” as an implementation of computational thinking: A literature review. *Journal of Educational Computing Research, 58*(2), 502–534. https://doi.org/10.1177/0735633119845694 \n\nButler, D. L., & Winne, P. H. (1995). Feedback and self-regulated learning: A theoretical synthesis. *Review of Educational Research, 65*(3), 245–281. https://doi.org/10.3102/00346543065003245 \n\nCleary, T. J., & Zimmerman, B. J. (2001). Self-regulation differences during athletic practice by experts, non-experts, and novices. *I Journal of Applied Sport Psychology, 13*(2), 185–206. https://doi.org/10.1080/104132001753149883 \n\nFerri, R. B. (2006). Theoretical and empirical differentiations of phases in the modelling process. *ZDM, 38*(2), 86–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02655883 \n\nField Hockey Alberta (2020). *Tactical Seminars*. http://www.fieldhockey.ab.ca/content/tactical-seminars\n\nField Hockey Canada (2020). *Ahead of the Game*. http://www.fieldhockey.ca/ahead-of-the-game-field-hockey-canada-webinar-series/\n\nGadanidis, G. (2020, September 2). *Shifting from computational thinking to computational modelling in math education* [Online plenary talk]. Changing the Culture 2020, Pacific Institute for the Mathematical Sciences.\n\nGuadalupe, T. & Gómez-Blancarte, A. (2019). Assessment of informal and formal inferential reasoning: A critical research review. *Statistics Education Research Journal, 18*, 8-25. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/335057564_ASSESSMENT_OF_INFORMAL_AND_FORMAL_INFERENTIAL_REASONING_A_CRITICAL_RESEARCH_REVIEW\n\nHadwin, A., Järvelä, S., & Miller, M. (2017). Self-Regulation, Co-Regulation, and Shared Regulation in Collaborative Learning Environments. *Handbook of Self-Regulation of Learning and Performance*, 83–106. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315697048-6 \n\nKastens, K. (2014). *Pervasive and Persistent Understandings about Data*. Oceans of Data Institute. http://oceansofdata.org/sites/oceansofdata.org/files/pervasive-and-persistent-understandings-01-14.pdf\n\nLeard, T., & Hadwin, A. F. (2001, May). *Analyzing logfile data to produce navigation profiles of studying as self-regulated learning* [Paper presentaion]. Canadian Society for the Study of Education, Quebec City, Quebec, Canada.\n\nManitoba Education and Training (2020). *Literacy with ICT across the curriculum: A model for 21st century learning from K-12*. https://www.edu.gov.mb.ca/k12/tech/lict/index.html\n\nOntario Ministry of Education. (2020). *The Ontario curriculum grades 1‐8: Mathematics* [Program of Studies]. https://www.dcp.edu.gov.on.ca/en/curriculum/elementary-mathematics",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4a3420cda91286645d4cd5664f777ca8cc682ae7
| 13,455 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
sst_science/great_lakes_mur_buoy.ipynb
|
sevfour/cloud_science
|
7965c09bfb3ffbb986af24070e745fee9e319542
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
sst_science/great_lakes_mur_buoy.ipynb
|
sevfour/cloud_science
|
7965c09bfb3ffbb986af24070e745fee9e319542
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
sst_science/great_lakes_mur_buoy.ipynb
|
sevfour/cloud_science
|
7965c09bfb3ffbb986af24070e745fee9e319542
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 44.700997 | 129 | 0.591825 |
[
[
[
"#import libraries\nimport numpy.ma as MA\nimport datetime as dt\nfrom datetime import datetime, timedelta\nimport xarray as xr\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport os\nfrom netCDF4 import Dataset # http://code.google.com/p/netcdf4-python/\n\n#subroutine to check for bad values\ndef checkValue(value):\n # Check if value should be a float\n # or flagged as missing\n if value == \"999.0\" or value == \"99.0\":\n value = MA.masked\n else:\n value = float(value)\n return value\n\n#subroutine to read .txt buoy data files\ndef readData(fname):\n f = open(fname)\n # Ignore header\n for i in range(0):\n f.readline() \n col_names = f.readline().split()\n print(col_names)\n col_units = f.readline().split()\n data_block = f.readlines()\n f.close()\n data={}\n for col_name in col_names:\n data[col_name] = MA.zeros(len(data_block), 'f', fill_value = 999.999)\n # Loop through each value: append to each column\n for (line_count, line) in enumerate(data_block):\n items = line.split()\n for (col_count, col_name) in enumerate(col_names):\n value = items[col_count]\n data[col_name][line_count] = checkValue(value)\n ilen=len(data[\"#YY\"])\n data['dtime'] = MA.zeros(len(data_block), 'datetime64[s]')\n for i in range(0,ilen):\n data[\"dtime\"][i]=dt.datetime(data[\"#YY\"][i],data[\"MM\"][i],data[\"DD\"][i],data[\"hh\"][i],data[\"mm\"][i])\n\n return data\n\n#subroutine to read the high resolution CMAN data files\ndef readData_highres(fname):\n print('reading:',fname)\n ds_buoy=Dataset(fname)\n #hourly data\n buoy_time=ds_buoy.variables['time'][:]\n time_index=np.array(buoy_time).astype('datetime64[s]')\n\n #payload 1\n tempgrp = ds_buoy.groups['payload_1']\n\n tempgrp2 = tempgrp.groups['ocean_temperature_sensor_1']\n data=tempgrp2.variables['sea_surface_temperature'][:]\n df_buoy = pd.DataFrame({'sst1' : data,'time' : time_index}).set_index(['time'])\n df_buoy['sst1qc']=tempgrp2.variables['sea_surface_temperature_qc'][:]\n gattrs={}\n gattrs['install_date'] = tempgrp2.install_date\n gattrs['height_of_instrument'] = tempgrp2.height_of_instrument\n df_buoy['sst1'].attrs=gattrs\n\n tempgrp2 = tempgrp.groups['anemometer_1']\n df_buoy['wnd1']=tempgrp2.variables['wind_speed'][:]\n df_buoy['wnd1qc']=tempgrp2.variables['wind_speed_qc'][:]\n df_buoy['wdir1']=tempgrp2.variables['wind_direction'][:]\n df_buoy['wdir1qc']=tempgrp2.variables['wind_direction_qc'][:]\n# data=tempgrp2.variables['continuous_wind_speed'][:]\n gattrs['install_date'] = tempgrp2.install_date\n gattrs['height_of_instrument'] = tempgrp2.height_of_instrument\n df_buoy['wnd1'].attrs=gattrs\n\n tempgrp2 = tempgrp.groups['anemometer_2']\n df_buoy['wnd2']=tempgrp2.variables['wind_speed'][:]\n df_buoy['wnd2qc']=tempgrp2.variables['wind_speed_qc'][:]\n df_buoy['wdir2']=tempgrp2.variables['wind_direction'][:]\n df_buoy['wdir2qc']=tempgrp2.variables['wind_direction_qc'][:]\n gattrs['install_date'] = tempgrp2.install_date\n gattrs['height_of_instrument'] = tempgrp2.height_of_instrument\n df_buoy['wnd2'].attrs=gattrs\n\n tempgrp2 = tempgrp.groups['air_temperature_sensor_1']\n df_buoy['air1']=tempgrp2.variables['air_temperature'][:]\n df_buoy['air1qc']=tempgrp2.variables['air_temperature_qc'][:]\n gattrs['install_date'] = tempgrp2.install_date\n gattrs['height_of_instrument'] = tempgrp2.height_of_instrument\n df_buoy['air1'].attrs=gattrs\n\n tempgrp2 = tempgrp.groups['barometer_1']\n df_buoy['air_pres1']=tempgrp2.variables['air_pressure'][:]\n df_buoy['air_pres1qc']=tempgrp2.variables['air_pressure_qc'][:]\n df_buoy['air_pres_sea_level1']=tempgrp2.variables['air_pressure_at_sea_level'][:]\n df_buoy['air_pres_sea_level1qc']=tempgrp2.variables['air_pressure_at_sea_level_qc'][:]\n gattrs['install_date'] = tempgrp2.install_date\n gattrs['height_of_instrument'] = tempgrp2.height_of_instrument\n df_buoy['air_pres1'].attrs=gattrs\n\n tempgrp2 = tempgrp.groups['barometer_2'] \n df_buoy['air_pres2']=tempgrp2.variables['air_pressure'][:]\n df_buoy['air_pres2qc']=tempgrp2.variables['air_pressure_qc'][:]\n df_buoy['air_pres_sea_level2']=tempgrp2.variables['air_pressure_at_sea_level'][:]\n df_buoy['air_pres_sea_level2qc']=tempgrp2.variables['air_pressure_at_sea_level_qc'][:]\n gattrs['install_date'] = tempgrp2.install_date\n gattrs['height_of_instrument'] = tempgrp2.height_of_instrument\n df_buoy['air_pres2'].attrs=gattrs\n\n \n tempgrp2 = tempgrp.groups['gps_1']\n df_buoy['lat']=tempgrp2.variables['latitude'][:]\n df_buoy['latqc']=tempgrp2.variables['latitude_qc'][:]\n df_buoy['lon']=tempgrp2.variables['longitude'][:]\n df_buoy['lonqc']=tempgrp2.variables['longitude_qc'][:]\n\n #payload 2\n tempgrp = ds_buoy.groups['payload_2']\n\n tempgrp2 = tempgrp.groups['ocean_temperature_sensor_1']\n test=tempgrp2.variables['sea_surface_temperature'][:]\n df_buoy['sst2']=tempgrp2.variables['sea_surface_temperature'][:]\n df_buoy['sst2qc']=tempgrp2.variables['sea_surface_temperature_qc'][:]\n# gattrs['install_date'] = tempgrp2.install_date\n# gattrs['height_of_instrument'] = tempgrp2.height_of_instrument\n# df_buoy['sst2'].attrs=gattrs\n\n tempgrp2 = tempgrp.groups['anemometer_1']\n df_buoy['wnd3']=tempgrp2.variables['wind_speed'][:]\n df_buoy['wnd3qc']=tempgrp2.variables['wind_speed_qc'][:]\n df_buoy['wdir3']=tempgrp2.variables['wind_direction'][:]\n df_buoy['wdir3qc']=tempgrp2.variables['wind_direction_qc'][:]\n# gattrs['install_date'] = tempgrp2.install_date\n# gattrs['height_of_instrument'] = tempgrp2.height_of_instrument\n# df_buoy['wnd3'].attrs=gattrs\n\n tempgrp2 = tempgrp.groups['anemometer_2']\n df_buoy['wnd4']=tempgrp2.variables['wind_speed'][:]\n df_buoy['wnd4qc']=tempgrp2.variables['wind_speed_qc'][:]\n df_buoy['wdir4']=tempgrp2.variables['wind_direction'][:]\n df_buoy['wdir4qc']=tempgrp2.variables['wind_direction_qc'][:]\n# gattrs['install_date'] = tempgrp2.install_date\n# gattrs['height_of_instrument'] = tempgrp2.height_of_instrument\n# df_buoy['wnd4'].attrs=gattrs\n\n tempgrp2 = tempgrp.groups['air_temperature_sensor_1']\n df_buoy['air2']=tempgrp2.variables['air_temperature'][:]\n df_buoy['air2qc']=tempgrp2.variables['air_temperature_qc'][:] \n # gattrs['install_date'] = tempgrp2.install_date\n # gattrs['height_of_instrument'] = tempgrp2.height_of_instrument\n # df_buoy['air2'].attrs=gattrs\n ds_buoy.close() # close the new file\n xr_buoy=xr.Dataset(df_buoy) \n return xr_buoy\n\n#subroutine to read the 10 min CMAN data\ndef readData_highres10(fname):\n ds_buoy=Dataset(fname)\n\n #hourly data\n buoy_time=ds_buoy.variables['time'][:]\n time_index=np.array(buoy_time).astype('datetime64[s]')\n\n #10min data\n buoy_time10=ds_buoy.variables['time10'][:]\n tem=np.array(buoy_time10).astype('datetime64[s]')\n time10_index=tem\n\n #payload 1\n tempgrp = ds_buoy.groups['payload_1']\n \n tempgrp2 = tempgrp.groups['anemometer_1']\n data=tempgrp2.variables['continuous_wind_speed'][:]\n df_buoy10 = pd.DataFrame({'wnd1' : data,'time' : time10_index}).set_index(['time'])\n df_buoy10['wnd1qc']=tempgrp2.variables['continuous_wind_speed_qc'][:]\n df_buoy10['wdir1']=tempgrp2.variables['continuous_wind_direction'][:]\n df_buoy10['wdir1qc']=tempgrp2.variables['continuous_wind_direction_qc'][:]\n\n tempgrp2 = tempgrp.groups['anemometer_2']\n df_buoy10['wnd2']=tempgrp2.variables['continuous_wind_speed'][:]\n df_buoy10['wnd2qc']=tempgrp2.variables['continuous_wind_speed_qc'][:]\n df_buoy10['wdir2']=tempgrp2.variables['continuous_wind_direction'][:]\n df_buoy10['wdir2qc']=tempgrp2.variables['continuous_wind_direction_qc'][:]\n\n #get gps data at lower resolution and map onto highresolution data\n tempgrp2 = tempgrp.groups['gps_1']\n# df_buoy['lat']=tempgrp2.variables['latitude'][:]\n data=tempgrp2.variables['latitude'][:]\n df_buoy = pd.DataFrame({'lat' : data,'time' : time_index}).set_index(['time'])\n df_buoy['latqc']=tempgrp2.variables['latitude_qc'][:]\n df_buoy['lon']=tempgrp2.variables['longitude'][:]\n df_buoy['lonqc']=tempgrp2.variables['longitude_qc'][:]\n\n #payload 2\n tempgrp = ds_buoy.groups['payload_2']\n\n tempgrp2 = tempgrp.groups['anemometer_1']\n df_buoy10['wnd3']=tempgrp2.variables['continuous_wind_speed'][:]\n df_buoy10['wnd3qc']=tempgrp2.variables['continuous_wind_speed_qc'][:]\n df_buoy10['wdir3']=tempgrp2.variables['continuous_wind_direction'][:]\n df_buoy10['wdir3qc']=tempgrp2.variables['continuous_wind_direction_qc'][:]\n\n tempgrp2 = tempgrp.groups['anemometer_2']\n df_buoy10['wnd4']=tempgrp2.variables['continuous_wind_speed'][:]\n df_buoy10['wnd4qc']=tempgrp2.variables['continuous_wind_speed_qc'][:]\n df_buoy10['wdir4']=tempgrp2.variables['continuous_wind_direction'][:]\n df_buoy10['wdir4qc']=tempgrp2.variables['continuous_wind_direction_qc'][:]\n \n ds_buoy.close() # close the new file\n xr_buoy=xr.Dataset(df_buoy)\n xr_buoy10=xr.Dataset(df_buoy10)\n\n time10=xr_buoy10.time\n xr_buoy10['lat']=xr_buoy.lat.interp(time=time10)\n xr_buoy10['latqc']=xr_buoy.latqc.interp(time=time10)\n xr_buoy10['lon']=xr_buoy.lon.interp(time=time10)\n xr_buoy10['lonqc']=xr_buoy.lonqc.interp(time=time10)\n \n return xr_buoy10",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dir_in = 'https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/thredds-ocean/catalog/ndbc/cmanwx/'\nfiles = []\nfor root, dirs, files in os.walk(dir_in, topdown=False):\n for name in files:\n if name.startswith(\"NDBC_45005\") and name.endswith(\"v00.nc\"):\n #continue\n fname_in=os.path.join(root, name)\n #print(fname)\n #fname='F:/data/cruise_data/saildrone/baja-2018/buoy_data/NDBC_46011_201804_D5_v00.nc'\n #in this data time = hourly time10 = 10 min data\n files.append(fname_in)\nprint(files)",
"[]\n"
],
[
" xr_buoy=readData_highres(fname_in)\n #print(xr_buoy)\n fname_out=fname_in[:-3]+'hrly_xrformat.nc'\n xr_buoy.to_netcdf(fname_out)\n xr_buoy10=readData_highres10(fname_in)\n fname_out=fname_in[:-3]+'10min_xrformat.nc'\n xr_buoy10.to_netcdf(fname_out)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a34230c5b3326732b8c1cafc07ad3229c2d2985
| 12,084 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
downloaded_kernels/loan_data/kernel_15.ipynb
|
josepablocam/common-code-extraction
|
a6978fae73eee8ece6f1db09f2f38cf92f03b3ad
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
downloaded_kernels/loan_data/kernel_15.ipynb
|
josepablocam/common-code-extraction
|
a6978fae73eee8ece6f1db09f2f38cf92f03b3ad
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
downloaded_kernels/loan_data/kernel_15.ipynb
|
josepablocam/common-code-extraction
|
a6978fae73eee8ece6f1db09f2f38cf92f03b3ad
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2021-07-12T00:48:08.000Z
|
2021-08-11T12:53:05.000Z
| 12,084 | 12,084 | 0.715078 |
[
[
[
"**Introduction**\nIn this post, you will discover the Keras Python library that provides a clean and convenient way to create a range of deep learning models on top of Theano or TensorFlow.\n\nAll creidts to -- \"http://machinelearningmastery.com/tutorial-first-neural-network-python-keras/\"\n\nLet’s get started.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Dependencies**\n\nAll important libraries and data set are imported below\n\n**Python**\n\nPlease run this script in Python 2 ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import os, sys, re\nimport cPickle as pickle\nfrom keras.models import Sequential\nfrom keras.layers import Dense\nimport time\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\n\nprint (time.time())\ndataset = pd.read_csv(\"loan.csv\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Replace all the missing entries with zeros",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dataset = dataset.fillna(0) ## filling missing values with zeros",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Data Modification**\n\nConvert all kind of categorical data into integral values accordingly and 'Date Column' into real values'",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dataset['application_type'] = dataset['application_type'].astype('category').cat.codes\ndataset['addr_state'] = dataset['addr_state'].astype('category').cat.codes\ndataset['earliest_cr_line'] = pd.to_datetime(dataset['earliest_cr_line'])\ndataset['earliest_cr_line'] = (dataset['earliest_cr_line']-dataset['earliest_cr_line'].min())/np.timedelta64(1,'D')\ndataset['emp_length'] = dataset['emp_length'].astype('category').cat.codes\ndataset['grade'] = dataset['grade'].astype('category').cat.codes\ndataset['home_ownership'] = dataset['home_ownership'].astype('category').cat.codes\ndataset['initial_list_status'] = dataset['initial_list_status'].astype('category').cat.codes\ndataset['issue_d'] = pd.to_datetime(dataset['issue_d'])\ndataset['issue_d'] = (dataset['issue_d']-dataset['issue_d'].min())/np.timedelta64(1,'D')\ndataset['last_credit_pull_d'] = pd.to_datetime(dataset['last_credit_pull_d'])\ndataset['last_credit_pull_d'] = (dataset['last_credit_pull_d']-dataset['last_credit_pull_d'].min())/np.timedelta64(1,'D')\ndataset['last_pymnt_d'] = pd.to_datetime(dataset['last_pymnt_d'])\ndataset['last_pymnt_d'] = (dataset['last_pymnt_d']-dataset['last_pymnt_d'].min())/np.timedelta64(1,'D')\ndataset['loan_status'] = dataset['loan_status'].astype('category').cat.codes\ndataset['next_pymnt_d'] = pd.to_datetime(dataset['next_pymnt_d'])\ndataset['next_pymnt_d'] = (dataset['next_pymnt_d']-dataset['next_pymnt_d'].min())/np.timedelta64(1,'D')\ndataset['purpose'] = dataset['purpose'].astype('category').cat.codes\ndataset['pymnt_plan'] = dataset['pymnt_plan'].astype('category').cat.codes\ndataset['sub_grade'] = dataset['sub_grade'].astype('category').cat.codes\ndataset['term'] = dataset['term'].astype('category').cat.codes\ndataset['verification_status'] = dataset['verification_status'].astype('category').cat.codes\ndataset['verification_status_joint'] = dataset['verification_status_joint'].astype('category').cat.codes\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Storing non numeric or non real columns name in non_numerics array",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"non_numerics = [x for x in dataset.columns\\\nif not (dataset[x].dtype == np.float64 or dataset[x].dtype == np.int8 or dataset[x].dtype == np.int64)]\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Droping non_numerics column for easy modeling",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df = dataset\ndf = df.drop(non_numerics,1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Converting 'loan result status' into two categories 0 and 1. 0 means loan failed or that type of person should not be given loan in future and 1 means loan passed i.e. they are good for extending the loan.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def LoanResult(status):\n if (status == 5) or (status == 1) or (status == 7):\n return 1\n else:\n return 0\n\ndf['loan_status'] = df['loan_status'].apply(LoanResult)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Splitting data into train data and test data with the help of scikit library in the ratio of 3:1",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"train, test = train_test_split(df, test_size = 0.25)\n\n##running complete data set will take a lot of time, hence reduced the data set\nX_train = train.drop('loan_status',1).values[0:50000, :]\nY_train = train['loan_status'].values[0:50000]\n\nX_test = test.drop('loan_status',1).values[0:1000, :]\nY_test = test['loan_status'].values[0:1000]\n\nX_pred = test.drop('loan_status',1).values[1001:2000, :]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Setting the seed for pseudo random numbers generation",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"seed = 8 \nnp.random.seed(seed)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now we will define a three layered neural network model. We create a Sequential model and add layers one at a time until we are happy with our network topology. After that we will set activation function and number of nets in each layer. These are done by heuristics and training the model several times.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create the model \nmodel = Sequential()\n\n# Define the three layered model\nmodel.add(Dense(110, input_dim = 68, kernel_initializer = \"uniform\", activation = \"relu\"))\nmodel.add(Dense(110, kernel_initializer = \"uniform\", activation = \"relu\"))\nmodel.add(Dense(1, kernel_initializer = \"uniform\", activation = \"sigmoid\"))\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now we will compile the model. In this we have to input three parameters viz. loss function, optimizer function and an evaluation metrics. These choices are again by heuristics. Here we are using \"binary_crossentropy\" as loss func, \"adam\" as optimizer func and \"accuracy\" as evaluation metrics.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#\n# Compile the model\nmodel.compile(loss=\"binary_crossentropy\", optimizer= \"adam\", metrics=['accuracy'])\n#\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now we have to fit the data into our model. \nWe can train or fit our model on our loaded data by calling the fit() function on the model.\n\nThe training process will run for a fixed number of iterations through the dataset called epochs, that we must specify using the **epochs** argument. We can also set the number of instances that are evaluated before a weight update in the network is performed, called the batch size and set using the **batch_size** argument.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Fit the model\nmodel.fit(X_train, Y_train, epochs= 22000, batch_size=200)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Evaluate Model**\n\nWe have trained our neural network on the entire dataset and we can evaluate the performance of the network on the test dataset.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"performance = model.evaluate(X_test, Y_test)\nprint(\"%s: %.2f%%\" % (model.metrics_names[1], performance[1]*100))\n#",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Final Prediction**\n\nPredicting using the trained model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Predict using the trained model\nprediction = model.predict(X_pred)\nrounded_predictions = [round(x) for x in prediction]\nprint(rounded_predictions)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a342731254d2bb95e8d439f1a8f0a6c3710c651
| 6,684 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
examples/super-resolution-fastai/DataPrep.ipynb
|
bsircelj/eo-learn
|
e860f46e6e9fb20eecc8a2e0bcb2b6d616d9738d
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2020-08-30T12:40:50.000Z
|
2020-08-30T12:40:50.000Z
|
examples/super-resolution-fastai/DataPrep.ipynb
|
bsircelj/eo-learn
|
e860f46e6e9fb20eecc8a2e0bcb2b6d616d9738d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
examples/super-resolution-fastai/DataPrep.ipynb
|
bsircelj/eo-learn
|
e860f46e6e9fb20eecc8a2e0bcb2b6d616d9738d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 29.444934 | 196 | 0.582136 |
[
[
[
"# Prepare Superresolution Training Data with eo-learn\n\nThere are many examples and resources for training superresolution networks on (satellite) imagery:\n- [MDL4EO](https://mdl4eo.irstea.fr/2019/03/29/enhancement-of-sentinel-2-images-at-1-5m/)\n- [ElementAI HighRes-Net](https://github.com/ElementAI/HighRes-net)\n- [Fast.ai superresolution](https://github.com/fastai/course-v3/blob/master/nbs/dl1/lesson7-superres.ipynb)\n\nWe'll show you how to use `eo-learn` to prepare data for these tasks (and an example of training the network with `fastai`)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"First you'll need to download the [Spacenet Challenge: Paris Data](https://spacenetchallenge.github.io/AOI_Lists/AOI_3_Paris.html). We're using this to get high resolution image chips.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from os import path as op\nfrom glob import glob\nimport datetime\n\nfrom eolearn.io import ImportFromTiff, SentinelHubInputTask\nfrom eolearn.core import FeatureType, LinearWorkflow, EOTask\nfrom sentinelhub import BBox, CRS, DataSource\n\nfrom PIL import Image\nimport numpy as np\nfrom tqdm import tqdm",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"spacenet_images = glob('AOI_3_Paris_Train/RGB-PanSharpen/*.tif')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Import the Spacenet chips into EOPatches, as a feature called \"spacenet\"\ninput_task = ImportFromTiff((FeatureType.DATA_TIMELESS, 'spacenet'))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Add Sentinel 2 L2A to our EOPatches covering the same area\ntime_interval = ('2017-02-28', '2017-04-01') # roughly matching the spacenet dates\n\nadd_l2a = SentinelHubInputTask(\n data_source=DataSource.SENTINEL2_L2A,\n bands=['B04','B03','B02'],\n bands_feature=(FeatureType.DATA, 'TRUE-COLOR-S2-L2A'),\n additional_data=[(FeatureType.MASK, 'dataMask', 'IS_VALID'), (FeatureType.DATA, 'SCL')],\n maxcc=.1,\n time_difference=datetime.timedelta(hours=2),\n max_threads=3,\n resolution=(10,10)\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Save the Spacenet and Sentinel images in separate folders. Resize our images when saving \n\nBIG_SIZE = (256, 256)\nSMALL_SIZE = (64, 64)\nINPUT_FOLDER = 'input'\nTARGET_FOLDER = 'target'\n\nclass CustomSave(EOTask):\n def execute(self, eopatch, image_name=None):\n # if we don't have enough data, don't save\n spacenet_array = eopatch.data_timeless['spacenet']\n data_pct = (np.count_nonzero(spacenet_array) / spacenet_array.size)\n if data_pct < 0.9:\n return eopatch\n \n # resize images, rescale to 8bit\n sentinel_array = eopatch.data[layer][0]\n sentinel_array_8bit = (sentinel_array * 255.).astype(np.uint8)\n sentinel_img = Image.fromarray(sentinel_array_8bit).resize(SMALL_SIZE, resample=Image.BILINEAR)\n sentinel_img.save(op.join(INPUT_FOLDER, f'{image_name}.png'))\n \n spacenet_array_8bit = ((spacenet_array - np.min(spacenet_array, axis=(0, 1))) / (np.max(spacenet_array, axis=(0, 1)) - np.min(spacenet_array, axis=(0, 1))) * 255).astype(np.uint8)\n spacenet_image = Image.fromarray(spacenet_array_8bit).resize(BIG_SIZE, resample=Image.BILINEAR)\n spacenet_image.save(op.join(TARGET_FOLDER, f'{image_name}.png'))\n \n return eopatch\n \ncustom_save = CustomSave()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create this as a EOWorkflow to run over all the images\nprepare_data = LinearWorkflow(\n input_task,\n add_l2a,\n custom_save\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Execute the workflow\npbar = tqdm(total=len(spacenet_images))\nfor image in spacenet_images:\n image_name = op.splitext(op.basename(image))[0].replace('RGB-PanSharpen_AOI_3_Paris_', '')\n workflow_input = {\n input_task: dict(filename=image),\n add_l1c: dict(time_interval=time_interval),\n custom_save: dict(image_name=image_name)\n }\n prepare_data.execute(workflow_input)\n pbar.update(1)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a34273dd8f60690f03df288b701cca7642231b2
| 231,598 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
SSD512_debug.ipynb
|
sloppyjuicy/ssd_detectors
|
acf93082ec7cff616805a97100166fdb264841be
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
SSD512_debug.ipynb
|
sloppyjuicy/ssd_detectors
|
acf93082ec7cff616805a97100166fdb264841be
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
SSD512_debug.ipynb
|
sloppyjuicy/ssd_detectors
|
acf93082ec7cff616805a97100166fdb264841be
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 224.852427 | 191,972 | 0.871903 |
[
[
[
"import cv2\nimport keras\nfrom keras import backend as K\nfrom tensorflow.python.keras.applications import imagenet_utils\nfrom keras.models import Model\nfrom keras.preprocessing import image\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\n#from scipy.misc import imread\nfrom imageio import imread\nimport tensorflow as tf\nimport os\n\nfrom ssd_model import SSD512\nfrom ssd_utils import PriorUtil",
"Using TensorFlow backend.\n"
],
[
"input_shape = (512, 512, 3)\nbatch_size = 32\n\nimage_size = input_shape[:2]\nfrom data_voc import GTUtility\ngt_util = GTUtility('data/VOC2007/')\ngt_util_train, gt_util_val = gt_util.split(0.8)\nnum_classes = gt_util.num_classes\n\nmodel = SSD512(input_shape, num_classes=num_classes)\nprior_util = PriorUtil(model)\n\nmodel.load_weights('./models/ssd512_voc_weights_fixed.hdf5', by_name=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from utils.caffe2keras import compare_output_shape\ncompare_output_shape(model, './models/ssd512_voc_shape.pkl')",
"conv1_1 [64, 512, 512] [512, 512, 64] \nconv1_2 [64, 512, 512] [512, 512, 64] \npool1 [64, 256, 256] [256, 256, 64] \nconv2_1 [128, 256, 256] [256, 256, 128] \nconv2_2 [128, 256, 256] [256, 256, 128] \npool2 [128, 128, 128] [128, 128, 128] \nconv3_1 [256, 128, 128] [128, 128, 256] \nconv3_2 [256, 128, 128] [128, 128, 256] \nconv3_3 [256, 128, 128] [128, 128, 256] \npool3 [256, 64, 64] [64, 64, 256] \nconv4_1 [512, 64, 64] [64, 64, 512] \nconv4_2 [512, 64, 64] [64, 64, 512] \nconv4_3 [512, 64, 64] [64, 64, 512] \npool4 [512, 32, 32] [32, 32, 512] \nconv5_1 [512, 32, 32] [32, 32, 512] \nconv5_2 [512, 32, 32] [32, 32, 512] \nconv5_3 [512, 32, 32] [32, 32, 512] \npool5 [512, 32, 32] [32, 32, 512] \nfc6 [1024, 32, 32] [32, 32, 1024] \nfc7 [1024, 32, 32] [32, 32, 1024] \nconv6_1 [256, 32, 32] [32, 32, 256] \nconv6_2 [512, 16, 16] [16, 16, 512] \nconv7_1 [128, 16, 16] [16, 16, 128] \nconv7_2 [256, 8, 8] [8, 8, 256] \nconv8_1 [128, 8, 8] [8, 8, 128] \nconv8_2 [256, 4, 4] [4, 4, 256] \nconv9_1 [128, 4, 4] [4, 4, 128] \nconv9_2 [256, 2, 2] [2, 2, 256] \nconv10_1 [128, 2, 2] [2, 2, 128] \nconv4_3_norm [512, 64, 64] [64, 64, 512] \nconv10_2 [256, 1, 1] [1, 1, 256] \nconv4_3_norm_mbox_conf [84, 64, 64] [64, 64, 84] \nfc7_mbox_conf [126, 32, 32] [32, 32, 126] \nconv6_2_mbox_conf [126, 16, 16] [16, 16, 126] \nconv7_2_mbox_conf [126, 8, 8] [8, 8, 126] \nconv8_2_mbox_conf [126, 4, 4] [4, 4, 126] \nconv9_2_mbox_conf [84, 2, 2] [2, 2, 84] \nconv10_2_mbox_conf [84, 1, 1] [1, 1, 84] \nconv4_3_norm_mbox_loc [16, 64, 64] [64, 64, 16] \nfc7_mbox_loc [24, 32, 32] [32, 32, 24] \nconv6_2_mbox_loc [24, 16, 16] [16, 16, 24] \nconv7_2_mbox_loc [24, 8, 8] [8, 8, 24] \nconv8_2_mbox_loc [24, 4, 4] [4, 4, 24] \nconv9_2_mbox_loc [16, 2, 2] [2, 2, 16] \nconv10_2_mbox_loc [16, 1, 1] [1, 1, 16] \nconv4_3_norm_mbox_conf_flat [344064] [344064] \nfc7_mbox_conf_flat [129024] [129024] \nconv6_2_mbox_conf_flat [32256] [32256] \nconv7_2_mbox_conf_flat [8064] [8064] \nconv8_2_mbox_conf_flat [2016] [2016] \nconv9_2_mbox_conf_flat [336] [336] \nconv10_2_mbox_conf_flat [84] [84] \nconv4_3_norm_mbox_loc_flat [65536] [65536] \nfc7_mbox_loc_flat [24576] [24576] \nconv6_2_mbox_loc_flat [6144] [6144] \nconv7_2_mbox_loc_flat [1536] [1536] \nconv8_2_mbox_loc_flat [384] [384] \nconv9_2_mbox_loc_flat [64] [64] \nconv10_2_mbox_loc_flat [16] [16] \nmbox_conf [515844] [515844] \nmbox_loc [98256] [98256] \n"
],
[
"from ssd_data import preprocess_image\npo = np.get_printoptions()\nnp.set_printoptions(formatter={'all': '{:+.6e}'.format})\n\nfor layer in model.layers:\n layer_name = layer.name\n \n n = 12; p = 5\n\n file_name = os.path.join('ssd512_voc_activations_fish-bike', layer_name+'.npy')\n try:\n caffe_output = np.load(file_name)\n except FileNotFoundError:\n print(layer_name)\n continue\n \n if len(caffe_output.shape) == 4:\n caffe_output = caffe_output.transpose(0,2,3,1)\n\n input_image = np.round(preprocess_image('pics/fish-bike.jpg', (512,512)), 4)\n f = K.function(model.inputs, [model.get_layer(layer_name).output])\n keras_output = f([[input_image]])[0]\n \n try:\n diff = np.round(caffe_output[0]-keras_output[0], 9)\n except ValueError:\n print(\" %s %s\" % (caffe_output.shape, keras_output.shape))\n print(layer_name)\n continue\n \n min_diff = np.min(diff)\n max_diff = np.max(diff)\n mean_diff = np.mean(diff)\n max_abs_diff = np.max(np.abs(diff))\n diff_ratio = np.nonzero(np.round(diff,4))[0].shape[0] / np.prod(diff.shape)\n \n print('%-28s %10.6f %10.6f %3i%%' % (layer_name, mean_diff, max_abs_diff, diff_ratio*100))\n\nnp.set_printoptions(**po)\nimg_path = './data/images/fish-bike.jpg'\n\nimg = preprocess_image(img_path, size=image_size, lib='skimage')\n\nprint(img.transpose((2, 0, 1))[:,:5,:5])",
"input_1\nconv1_1\nconv1_2\npool1\nconv2_1\nconv2_2\npool2\nconv3_1\nconv3_2\nconv3_3\npool3\nconv4_1\nconv4_2\nconv4_3\npool4\nconv5_1\nconv5_2\nconv5_3\npool5\nfc6\nfc7\nconv6_1\nconv6_2\nconv7_1\nconv7_2\nconv8_1\nconv8_2\nconv9_1\nconv9_2\nconv10_1\nconv4_3_norm\nconv10_2\nconv4_3_norm_mbox_conf\nfc7_mbox_conf\nconv6_2_mbox_conf\nconv7_2_mbox_conf\nconv8_2_mbox_conf\nconv9_2_mbox_conf\nconv10_2_mbox_conf\nconv4_3_norm_mbox_loc\nfc7_mbox_loc\nconv6_2_mbox_loc\nconv7_2_mbox_loc\nconv8_2_mbox_loc\nconv9_2_mbox_loc\nconv10_2_mbox_loc\nconv4_3_norm_mbox_conf_flat\nfc7_mbox_conf_flat\nconv6_2_mbox_conf_flat\nconv7_2_mbox_conf_flat\nconv8_2_mbox_conf_flat\nconv9_2_mbox_conf_flat\nconv10_2_mbox_conf_flat\nconv4_3_norm_mbox_loc_flat\nfc7_mbox_loc_flat\nconv6_2_mbox_loc_flat\nconv7_2_mbox_loc_flat\nconv8_2_mbox_loc_flat\nconv9_2_mbox_loc_flat\nconv10_2_mbox_loc_flat\nmbox_conf\nmbox_loc\nmbox_conf_logits\nmbox_loc_final\nmbox_conf_final\npredictions\n[[[-40.740494 -37.282875 -34.36676 -26.80413 -30.24263 ]\n [-17.333527 -16.461388 -14.007469 -2.7578735 -5.108452 ]\n [ -6.2072372 -9.237984 -7.886551 5.981949 6.4846497 ]\n [ -7.4307632 -8.205444 -4.4833603 10.761452 15.6623 ]\n [ 1.2039642 4.5335693 8.479591 19.349243 24.746628 ]]\n\n [[-49.786774 -46.205734 -43.28962 -35.726982 -39.16549 ]\n [-25.484894 -24.461388 -22.00747 -10.406166 -12.662163 ]\n [-14.50824 -17.322136 -15.963699 -1.3679123 -0.6135254 ]\n [-16.955284 -16.977753 -13.191368 2.283554 7.7613907 ]\n [ -8.886848 -4.557251 -0.52040863 10.616287 16.81305 ]]\n\n [[-57.368256 -53.836594 -50.92047 -43.35784 -46.79634 ]\n [-32.126015 -31.122513 -28.668602 -17.77073 -20.215874 ]\n [-19.014816 -21.99253 -20.655106 -7.513893 -7.262886 ]\n [-17.179535 -18.95282 -15.359337 -0.344635 3.9792328 ]\n [ -5.157387 -3.2515945 0.51278687 11.115387 15.713425 ]]]\n"
]
],
[
[
"caffe preprocessing\n(3, 512, 512)\n[[[-40.7405 -37.2829 -34.3668 -26.8041 -30.2426]\n [-17.3335 -16.4614 -14.0075 -2.7579 -5.1085]\n [ -6.2072 -9.238 -7.8866 5.9819 6.4846]\n [ -7.4308 -8.2054 -4.4834 10.7615 15.6623]\n [ 1.204 4.5336 8.4796 19.3492 24.7466]]\n\n [[-49.7868 -46.2057 -43.2896 -35.727 -39.1655]\n [-25.4849 -24.4614 -22.0075 -10.4062 -12.6622]\n [-14.5082 -17.3221 -15.9637 -1.3679 -0.6135]\n [-16.9553 -16.9778 -13.1914 2.2836 7.7614]\n [ -8.8868 -4.5573 -0.5204 10.6163 16.813 ]]\n\n [[-57.3683 -53.8366 -50.9205 -43.3578 -46.7963]\n [-32.126 -31.1225 -28.6686 -17.7707 -20.2159]\n [-19.0148 -21.9925 -20.6551 -7.5139 -7.2629]\n [-17.1795 -18.9528 -15.3593 -0.3446 3.9792]\n [ -5.1574 -3.2516 0.5128 11.1154 15.7134]]]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"inputs = []\nimages = []\nfor img_path in ['./data/images/fish-bike.jpg',\n './data/images/cat.jpg',\n './data/images/boys.jpg',\n './data/images/car_cat.jpg',\n './data/images/car_cat2.jpg',\n ]:\n images.append(imread(img_path))\n inputs.append(preprocess_image(img_path, image_size))\n\ninputs = np.array(inputs)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"preds = model.predict(inputs, batch_size=1, verbose=1)\n\nresults = [prior_util.decode(p) for p in preds]",
"5/5 [==============================] - 0s 27ms/step\n"
],
[
"plt.figure()\nplt.imshow(images[0])\nres = prior_util.decode(preds[0])\nprior_util.plot_results(classes=gt_util.classes, confidence_threshold=0.5) # 0.1 !!!\nplt.show()\nprint(res)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"caffe model\narray([[ 2. , 0.63118, 0.05004, 0.2005 , 0.94945, 0.98229],\n [ 7. , 0.10457, 0.45818, 0.07994, 0.49172, 0.11543],\n [ 14. , 0.2004 , 0.10655, 0.21848, 0.96107, 0.97251],\n [ 15. , 0.99836, 0.41809, 0.02837, 0.69007, 0.61929]])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# layer activation\npo = np.get_printoptions()\n#np.set_printoptions(formatter={'all': '{:+.6e}'.format})\nnp.set_printoptions(formatter={'all': '{:+.8f}'.format})\n\nprint('%-28s %14s %10s %10s %4s' % ('', 'max activation', 'mean diff', 'max diff', 'ratio'))\n\nfor layer in model.layers:\n layer_name = layer.name\n \n file_name = os.path.join('./caffe_activation_dumps/ssd512_voc_activations_fish-bike', layer_name+'.npy')\n try:\n caffe_output = np.load(file_name)\n except FileNotFoundError:\n print(layer_name)\n continue\n \n if len(caffe_output.shape) == 4:\n caffe_output = caffe_output.transpose(0,2,3,1)\n\n input_image = preprocess_image('./data/images/fish-bike.jpg', input_shape[:2])\n f = K.function(model.inputs, [model.get_layer(layer_name).output])\n keras_output = f([[input_image]])[0]\n\n try:\n diff = np.round(caffe_output[0]-keras_output[0], 9)\n except ValueError:\n print(layer_name)\n continue\n \n max_value = np.max(keras_output)\n min_diff = np.abs(np.min(diff))\n max_diff = np.abs(np.max(diff))\n mean_diff = np.abs(np.mean(diff))\n \n diff_ratio = np.nonzero(np.round(diff,5))[0].shape[0] / np.prod(diff.shape)\n \n print('%-28s %14.6f %10.6f %10.6f %3i%%' % (layer_name, max_value, mean_diff, max_diff, diff_ratio*100))\n \n n = 12; p = 5\n #print(np.round( diff[:n,:n,p], 8))\n\nnp.set_printoptions(po)",
" max activation mean diff max diff ratio\ninput_1\nconv1_1 518.164124 0.000000 0.000031 0%\nconv1_2 1872.668335 0.000000 0.001343 35%\npool1 1872.668335 0.000000 0.001343 43%\nconv2_1 2972.968994 0.000000 0.002686 54%\nconv2_2 4747.130371 0.000000 0.004883 33%\npool2 4747.130371 0.000000 0.004883 52%\nconv3_1 3989.785156 0.000000 0.003662 37%\nconv3_2 3428.608643 0.000001 0.003174 36%\nconv3_3 3365.445068 0.000000 0.003418 14%\npool3 3365.445068 0.000000 0.003418 24%\nconv4_1 2772.205322 0.000000 0.001953 21%\nconv4_2 787.670471 0.000000 0.000854 16%\nconv4_3 559.113831 0.000000 0.000549 9%\npool4 559.113831 0.000000 0.000488 16%\nconv5_1 312.488678 0.000000 0.000168 12%\nconv5_2 162.484543 0.000000 0.000084 9%\nconv5_3 62.775734 0.000000 0.000042 1%\npool5 62.775734 0.000000 0.000042 5%\nfc6 17.861597 0.000000 0.000226 4%\nfc7 4.549523 0.000000 0.000049 0%\nconv6_1 4.778156 0.000000 0.000039 0%\nconv6_2 5.578863 0.019012 2.956600 54%\nconv7_1 5.894940 0.037630 3.489933 72%\nconv7_2 7.663419 0.068775 6.755099 61%\nconv8_1 9.691634 0.100497 5.262675 75%\nconv8_2 11.592814 0.116731 7.740747 68%\nconv9_1 18.754728 0.249361 14.748998 83%\nconv9_2 12.894996 0.516999 12.219683 88%\nconv10_1 15.583832 0.674318 15.024913 88%\nconv4_3_norm 6.635412 0.000000 0.000008 0%\nconv10_2 5.923618 1.021213 6.105431 73%\nconv4_3_norm_mbox_conf 11.731320 0.000000 0.000012 0%\nfc7_mbox_conf 14.705492 0.000000 0.000030 3%\nconv6_2_mbox_conf 15.509990 0.001996 4.523293 100%\nconv7_2_mbox_conf 18.028910 0.002813 9.100971 100%\nconv8_2_mbox_conf 16.830084 0.001444 10.163891 100%\nconv9_2_mbox_conf 16.109234 0.039001 11.190186 100%\nconv10_2_mbox_conf 6.172953 0.067181 4.013759 100%\nconv4_3_norm_mbox_loc 4.038123 0.000000 0.000007 0%\nfc7_mbox_loc 2.898187 0.000000 0.000017 1%\nconv6_2_mbox_loc 3.427546 0.060287 2.158798 100%\nconv7_2_mbox_loc 2.633209 0.084234 2.493238 100%\nconv8_2_mbox_loc 3.269521 0.021421 2.798764 100%\nconv9_2_mbox_loc 0.857027 0.079836 2.533371 100%\nconv10_2_mbox_loc 1.195606 0.017838 1.386647 100%\nconv4_3_norm_mbox_conf_flat 11.731320 0.000000 0.000012 0%\nfc7_mbox_conf_flat 14.705492 0.000000 0.000030 3%\nconv6_2_mbox_conf_flat 15.509990 0.001996 4.523293 100%\nconv7_2_mbox_conf_flat 18.028910 0.002813 9.100971 100%\nconv8_2_mbox_conf_flat 16.830084 0.001444 10.163891 100%\nconv9_2_mbox_conf_flat 16.109234 0.039001 11.190186 100%\nconv10_2_mbox_conf_flat 6.172953 0.067181 4.013759 100%\nconv4_3_norm_mbox_loc_flat 4.038123 0.000000 0.000007 0%\nfc7_mbox_loc_flat 2.898187 0.000000 0.000017 1%\nconv6_2_mbox_loc_flat 3.427546 0.060287 2.158798 100%\nconv7_2_mbox_loc_flat 2.633209 0.084234 2.493238 100%\nconv8_2_mbox_loc_flat 3.269521 0.021421 2.798764 100%\nconv9_2_mbox_loc_flat 0.857027 0.079836 2.533371 100%\nconv10_2_mbox_loc_flat 1.195606 0.017838 1.386647 100%\nmbox_conf 18.028910 0.000160 11.190186 9%\nmbox_loc 4.038123 0.005219 2.798764 8%\nmbox_conf_logits\nmbox_loc_final\nmbox_conf_final\npredictions\n"
],
[
"fstr = '%-28s %-20s %-20s %-12s %-9s %-9s %-28s %-22s %-8s %-8s %-8s'\nprint(fstr % ('', 'input_shape', 'output_shape', 'img_size', 'min_size', 'max_size', 'aspect_ratios', 'variances', 'clip', 'flip', 'step'))\nfor l in model.layers:\n if l.__class__.__name__ == 'PriorBox':\n aspect_ratios = [ round(e, 2) for e in l.aspect_ratios ]\n print(fstr % (l.name, l.input_shape, l.output_shape, l.img_size, l.min_size, l.max_size, aspect_ratios, l.variances, l.clip, l.flip, l.step))",
" input_shape output_shape img_size min_size max_size aspect_ratios variances clip flip step \n"
],
[
"from utils.vis import plot_priorboxes\nfrom ssd_utils import calc_priorboxes\n \nimg_path = 'pics/fish-bike.jpg'\nimage = imread(img_path)\ninput_image = preprocess_image(img_path)\n\nfor layer in model.layers:\n if layer.__class__.__name__ == 'PriorBox':\n prior_boxes = calc_priorboxes(model, layer.name)\n nratios = len(layer.aspect_ratios)\n nlocs = len(prior_boxes)/nratios\n print('%-28s locations: %-6i aspect_ratios: %s' % (layer.name, nlocs, layer.aspect_ratios))\n plot_priorboxes(prior_boxes, image, nratios)\n\n#np.save('ssd512_prior_boxes.npy', calc_priorboxes(model))\n#pb = np.load('ssd512_prior_boxes.npy')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# compare the prior boxes\n\nmbox_priorbox = model.get_layer('mbox_priorbox')\nf = K.function(model.inputs, [mbox_priorbox.output])\npb_keras = f([[input_image]])[0][0][:,:4]\n\npb_caffe = np.load('ssd512_prior_boxes_caffe.npy')\n\nprint(pb_keras[:10])\nprint(np.array([np.min(pb_keras, 0), np.max(pb_keras, 0), np.mean(pb_keras, 0)]))\nprint()\nprint(pb_caffe[:10])\nprint(np.array([np.min(pb_caffe, 0), np.max(pb_caffe, 0), np.mean(pb_caffe, 0)]))\nprint()\npb_diff = pb_keras - pb_caffe\nprint(pb_diff[:10])\nprint(np.mean(pb_diff, 0))\nprint(np.nonzero(np.round(pb_diff, 6))[0])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# compare the positions\n\npos_keras = np.array([pb_keras[:,0]+pb_keras[:,2], pb_keras[:,1]+pb_keras[:,3]]).T/2\npos_caffe = np.array([pb_caffe[:,0]+pb_caffe[:,2], pb_caffe[:,1]+pb_caffe[:,3]]).T/2\npos_diff = pos_keras - pos_caffe\n\nprint(np.array([np.min(pos_keras, 0), np.max(pos_keras, 0), np.mean(pos_keras, 0)]))\nprint()\nprint(np.array([np.min(pos_caffe, 0), np.max(pos_caffe, 0), np.mean(pos_caffe, 0)]))\nprint()\nprint(pos_diff[:20])\nprint(np.nonzero(np.round(pos_diff, 6))[0])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# compute positions\n\nsteps = [8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512]\nimg_width, img_height = 512, 512\nlayer_sizes = (64, 32, 16, 8, 4, 2, 1)\naspect_ratios = ([1.0, 1.0, 2, 0.5], [1.0, 1.0, 2, 0.5, 3, 0.3333333333333333], [1.0, 1.0, 2, 0.5, 3, 0.3333333333333333], [1.0, 1.0, 2, 0.5, 3, 0.3333333333333333], [1.0, 1.0, 2, 0.5, 3, 0.3333333333333333], [1.0, 1.0, 2, 0.5], [1.0, 1.0, 2, 0.5])\n\nidx = 0\nfor i in range(len(layer_sizes)):\n nboxes = len(aspect_ratios[i]) * layer_sizes[i]**2\n print(\"%i %s %i\" % (layer_sizes[i], aspect_ratios[i], nboxes))\n print(np.max(pos_keras[idx:idx+nboxes,0]))\n print(np.max(pos_caffe[idx:idx+nboxes,0]))\n #print(np.min(pos_keras[idx:idx+nboxes,0]))\n #print(np.min(pos_caffe[idx:idx+nboxes,0]))\n \n layer_width = layer_sizes[i]\n \n # keras way\n step_x = img_width / layer_width\n centers_x = np.linspace(step_x / 2., img_width - step_x / 2., layer_width) / img_width\n #centers_x = np.array([(0.5 + i) for i in range(layer_width)]) * step_x / img_width\n print('%-20s %-20s' % (np.max(centers_x), step_x))\n \n # caffe way\n step_x = steps[i]\n centers_x = np.array([(0.5 + i) for i in range(layer_width)]) * step_x / img_width\n print('%-20s %-20s' % (np.max(centers_x), step_x))\n \n print()\n idx += nboxes",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#calucalation of min and max_size\n\nmin_dim = 512\n# conv4_3 ==> 64 x 64\n# fc7 ==> 32 x 32\n# conv6_2 ==> 16 x 16\n# conv7_2 ==> 8 x 8\n# conv8_2 ==> 4 x 4\n# conv9_2 ==> 2 x 2\n# conv10_2 ==> 1 x 1\nmbox_source_layers = ['conv4_3', 'fc7', 'conv6_2', 'conv7_2', 'conv8_2', 'conv9_2', 'conv10_2']\n# in percent %\nmin_ratio = 15\nmax_ratio = 90\nstep = int(np.floor((max_ratio - min_ratio) / (len(mbox_source_layers) - 2)))\nmin_sizes = []\nmax_sizes = []\nfor ratio in range(min_ratio, max_ratio + 1, step):\n min_sizes.append(min_dim * ratio / 100.)\n max_sizes.append(min_dim * (ratio + step) / 100.)\nmin_sizes = [min_dim * 7 / 100.] + min_sizes\nmax_sizes = [min_dim * 15 / 100.] + max_sizes\n\nprint(min_sizes)\nprint(max_sizes)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.set_printoptions(precision=4)\nimport math\n\n# calculation of min_sizes / max_sizes values\n# and why float in prototext and cat to int in PriorBox layer, confusing",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"min_dim = 512\nmbox_source_layers = ['conv4_3', 'fc7', 'conv6_2', 'conv7_2', 'conv8_2', 'conv9_2', 'conv10_2']\nmin_ratio = 15\nmax_ratio = 90\nn = len(mbox_source_layers)\n\nstep = int(math.floor((max_ratio - min_ratio) / (len(mbox_source_layers) - 2)))\nmin_sizes = []\nmax_sizes = []\nfor ratio in range(min_ratio, max_ratio + 1, step):\n min_sizes.append(min_dim * ratio / 100.)\n max_sizes.append(min_dim * (ratio + step) / 100.)\nmin_sizes = [min_dim * 7 / 100.] + min_sizes\nmax_sizes = [min_dim * 15 / 100.] + max_sizes\nprint(min_sizes)\nprint(max_sizes)",
"[35.84, 76.8, 153.6, 230.4, 307.2, 384.0, 460.8]\n[76.8, 153.6, 230.4, 307.2, 384.0, 460.8, 537.6]\n"
],
[
"# naiv approach according to the paper\nnp.linspace(min_ratio, max_ratio, n+1) * min_dim / 100.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# why is it done in the following way?\na = np.linspace(min_ratio, max_ratio, n-1)\na = np.concatenate((np.array([7]), a ,np.array([a[-1]+min_ratio])))\na * min_dim / 100.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# as in pytb\nimport numpy as np\nnp.set_printoptions(precision=1)\n\ns_min = 0.15\ns_max = 0.90\nm = 8\ns = []\nfor k in range(1,m+1):\n s_k = s_min + (s_max - s_min) * (k - 1.0) / (m - 1.0) # equation 2\n s.append(s_k)\nnp.array(s) * 512",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# compute prior box sizes\n\nsteps = [8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512]\nimg_width, img_height = 512, 512\nlayer_sizes = (64, 32, 16, 8, 4, 2, 1)\naspect_ratios = ([1.0, 1.0, 2, 0.5], [1.0, 1.0, 2, 0.5, 3, 0.3333333333333333], [1.0, 1.0, 2, 0.5, 3, 0.3333333333333333], [1.0, 1.0, 2, 0.5, 3, 0.3333333333333333], [1.0, 1.0, 2, 0.5, 3, 0.3333333333333333], [1.0, 1.0, 2, 0.5], [1.0, 1.0, 2, 0.5])\n\nnboxes = []\nunique_size_values_keras = []\nfor i in range(len(layer_sizes)):\n layer_width = layer_height = layer_sizes[i]\n nboxes.append( layer_width * layer_height * len(aspect_ratios[i]) )\n min_size = int(min_sizes[i])\n max_size = int(max_sizes[i])\n box_widths = []\n box_heights = []\n for ar in aspect_ratios[i]:\n if ar == 1 and len(box_widths) > 0:\n box_widths.append(np.sqrt(min_size * max_size))\n box_heights.append(np.sqrt(min_size * max_size))\n else:\n box_widths.append(min_size * np.sqrt(ar))\n box_heights.append(min_size / np.sqrt(ar))\n #print(aspect_ratios[i])\n #print(np.array(box_widths)/img_width)\n #print(np.array(box_heights)/img_height)\n values = np.unique(np.round(np.array(box_widths)/img_width, 4))\n print(values)\n unique_size_values_keras.append(values)\n #print()\nunique_size_values_keras = np.array(unique_size_values_keras)\nprint()\n\n# caffe prior box sizes\nsize_caffe = np.array([pb_caffe[:,2]-pb_caffe[:,0], pb_caffe[:,3]-pb_caffe[:,1]]).T\noffset = 0\nunique_size_values_caffe = []\nfor n in nboxes:\n values = np.unique(np.round(size_caffe[offset:offset+n],4))\n print(values)\n unique_size_values_caffe.append(values)\n offset += n\nunique_size_values_caffe = np.array(unique_size_values_caffe)\nprint()\n\nfor i in range(len(nboxes)):\n try:\n print(unique_size_values_caffe[i] - unique_size_values_keras[i])\n except:\n pass",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"kaffe int min_size, max_size\n[ 0. 0. -0. -0.]\n[-0. -0. -0. 0. 0. -0.]\n[-0. 0. -0. 0. 0. -0.]\n[ 0. 0. 0. -0. -0. 0.]\n[-0. -0. 0. -0. -0. -0.]\n[ 0. 0. 0. 0.]\n[-0. 0. 0. -0.]\nkeras int box_widths, box_heights\n[-0.0005 0. -0.001 -0.0009]\n[ 0.0006 0.0004 -0. -0.0008 -0.0012 -0.0019]\n[-0.0004 0.0012 0. -0.0005 0.0005 -0.0012]\n[ 0.0005 0.0002 0. 0.0007 0.0003 -0.0005]\n[ 0.001 0. 0.0006 0.0002]\n[ 0.0005 0. 0. -0.0009]\nkeras float box_widths, box_heights\n[-0.0012 -0.0016 -0.0023 -0.0018]\n[-0.0007 -0.0008 -0.0012 -0.001 -0.0017 -0.002 ]\n[-0.0004 -0.0006 -0.0008 -0.0006 -0.0011 -0.0013]\n[-0.0002 -0.0003 -0.0004 -0.0002 -0.0005 -0.0006]\n[ 0. 0. -0.0007 0. ]\n[-0.0011 -0.0016 -0.0014 -0.0022]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"fstr = '%-28s %-20s %-20s %-12s %-9s %-9s %-28s %-22s %-8s %-8s %-8s'\nprint(fstr % ('', 'input_shape', 'output_shape', 'img_size', 'min_size', 'max_size', 'aspect_ratios', 'variances', 'clip', 'flip', 'step'))\nfor l in model.layers:\n if l.__class__.__name__ == 'PriorBox':\n aspect_ratios = [ round(r, 2) for r in l.aspect_ratios ]\n print(fstr % (l.name, l.input_shape, l.output_shape, l.img_size, l.min_size, l.max_size, aspect_ratios, l.variances, l.clip, l.flip, l.step))",
" input_shape output_shape img_size min_size max_size aspect_ratios variances clip flip step \nconv4_3_norm_mbox_priorbox (None, 64, 64, 512) (None, 16384, 8) (512, 512) 35 76 [1.0, 1.0, 2, 0.5] [ 0.1 0.1 0.2 0.2] False True None \nfc7_mbox_priorbox (None, 32, 32, 1024) (None, 6144, 8) (512, 512) 76 153 [1.0, 1.0, 2, 0.5, 3, 0.33] [ 0.1 0.1 0.2 0.2] False True None \nconv6_2_mbox_priorbox (None, 16, 16, 512) (None, 1536, 8) (512, 512) 153 230 [1.0, 1.0, 2, 0.5, 3, 0.33] [ 0.1 0.1 0.2 0.2] False True None \nconv7_2_mbox_priorbox (None, 8, 8, 256) (None, 384, 8) (512, 512) 230 307 [1.0, 1.0, 2, 0.5, 3, 0.33] [ 0.1 0.1 0.2 0.2] False True None \nconv8_2_mbox_priorbox (None, 4, 4, 256) (None, 96, 8) (512, 512) 307 384 [1.0, 1.0, 2, 0.5, 3, 0.33] [ 0.1 0.1 0.2 0.2] False True None \nconv9_2_mbox_priorbox (None, 2, 2, 256) (None, 16, 8) (512, 512) 384 460 [1.0, 1.0, 2, 0.5] [ 0.1 0.1 0.2 0.2] False True None \nconv10_2_mbox_priorbox (None, 1, 1, 256) (None, 4, 8) (512, 512) 460 537 [1.0, 1.0, 2, 0.5] [ 0.1 0.1 0.2 0.2] False True None \n"
],
[
"\nlayer_widths = [64, 32, 16, 8, 4, 2, 1]\n\nlayer_widths = []\nfor l in model.layers:\n if l.__class__.__name__ == 'PriorBox':\n layer_widths.append(l.input_shape[1])\n\ngamma = 1.5\nimage_width = image_size[0]\na = image_width / np.array(layer_widths) * gamma\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"raw",
"code",
"raw",
"code",
"raw",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"raw"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"raw"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"raw"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a342772b3541ad9bf64b9782047e3a314a8d7d8
| 205,855 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
06_decision_trees.ipynb
|
eliotest98/handson-ml
|
7a70554ea75b758c35d8568d02e33bffe8176356
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 26,246 |
2016-08-23T01:40:25.000Z
|
2022-03-31T23:48:18.000Z
|
06_decision_trees.ipynb
|
eliotest98/handson-ml
|
7a70554ea75b758c35d8568d02e33bffe8176356
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 616 |
2016-11-01T13:26:38.000Z
|
2022-03-30T12:05:40.000Z
|
06_decision_trees.ipynb
|
eliotest98/handson-ml
|
7a70554ea75b758c35d8568d02e33bffe8176356
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 14,159 |
2016-07-16T23:28:52.000Z
|
2022-03-31T18:40:56.000Z
| 196.614136 | 46,960 | 0.906026 |
[
[
[
"**Chapter 6 – Decision Trees**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"_This notebook contains all the sample code and solutions to the exercises in chapter 6._\n\n<table align=\"left\">\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/ageron/handson-ml/blob/master/06_decision_trees.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/colab_logo_32px.png\" />Run in Google Colab</a>\n </td>\n</table>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Warning**: this is the code for the 1st edition of the book. Please visit https://github.com/ageron/handson-ml2 for the 2nd edition code, with up-to-date notebooks using the latest library versions.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Setup",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"First, let's make sure this notebook works well in both python 2 and 3, import a few common modules, ensure MatplotLib plots figures inline and prepare a function to save the figures:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# To support both python 2 and python 3\nfrom __future__ import division, print_function, unicode_literals\n\n# Common imports\nimport numpy as np\nimport os\n\n# to make this notebook's output stable across runs\nnp.random.seed(42)\n\n# To plot pretty figures\n%matplotlib inline\nimport matplotlib as mpl\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nmpl.rc('axes', labelsize=14)\nmpl.rc('xtick', labelsize=12)\nmpl.rc('ytick', labelsize=12)\n\n# Where to save the figures\nPROJECT_ROOT_DIR = \".\"\nCHAPTER_ID = \"decision_trees\"\nIMAGES_PATH = os.path.join(PROJECT_ROOT_DIR, \"images\", CHAPTER_ID)\nos.makedirs(IMAGES_PATH, exist_ok=True)\n\ndef save_fig(fig_id, tight_layout=True, fig_extension=\"png\", resolution=300):\n path = os.path.join(IMAGES_PATH, fig_id + \".\" + fig_extension)\n print(\"Saving figure\", fig_id)\n if tight_layout:\n plt.tight_layout()\n plt.savefig(path, format=fig_extension, dpi=resolution)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Training and visualizing",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.datasets import load_iris\nfrom sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier\n\niris = load_iris()\nX = iris.data[:, 2:] # petal length and width\ny = iris.target\n\ntree_clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=2, random_state=42)\ntree_clf.fit(X, y)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.tree import export_graphviz\n\ndef image_path(fig_id):\n return os.path.join(IMAGES_PATH, fig_id)\n\nexport_graphviz(\n tree_clf,\n out_file=image_path(\"iris_tree.dot\"),\n feature_names=iris.feature_names[2:],\n class_names=iris.target_names,\n rounded=True,\n filled=True\n )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap\n\ndef plot_decision_boundary(clf, X, y, axes=[0, 7.5, 0, 3], iris=True, legend=False, plot_training=True):\n x1s = np.linspace(axes[0], axes[1], 100)\n x2s = np.linspace(axes[2], axes[3], 100)\n x1, x2 = np.meshgrid(x1s, x2s)\n X_new = np.c_[x1.ravel(), x2.ravel()]\n y_pred = clf.predict(X_new).reshape(x1.shape)\n custom_cmap = ListedColormap(['#fafab0','#9898ff','#a0faa0'])\n plt.contourf(x1, x2, y_pred, alpha=0.3, cmap=custom_cmap)\n if not iris:\n custom_cmap2 = ListedColormap(['#7d7d58','#4c4c7f','#507d50'])\n plt.contour(x1, x2, y_pred, cmap=custom_cmap2, alpha=0.8)\n if plot_training:\n plt.plot(X[:, 0][y==0], X[:, 1][y==0], \"yo\", label=\"Iris-Setosa\")\n plt.plot(X[:, 0][y==1], X[:, 1][y==1], \"bs\", label=\"Iris-Versicolor\")\n plt.plot(X[:, 0][y==2], X[:, 1][y==2], \"g^\", label=\"Iris-Virginica\")\n plt.axis(axes)\n if iris:\n plt.xlabel(\"Petal length\", fontsize=14)\n plt.ylabel(\"Petal width\", fontsize=14)\n else:\n plt.xlabel(r\"$x_1$\", fontsize=18)\n plt.ylabel(r\"$x_2$\", fontsize=18, rotation=0)\n if legend:\n plt.legend(loc=\"lower right\", fontsize=14)\n\nplt.figure(figsize=(8, 4))\nplot_decision_boundary(tree_clf, X, y)\nplt.plot([2.45, 2.45], [0, 3], \"k-\", linewidth=2)\nplt.plot([2.45, 7.5], [1.75, 1.75], \"k--\", linewidth=2)\nplt.plot([4.95, 4.95], [0, 1.75], \"k:\", linewidth=2)\nplt.plot([4.85, 4.85], [1.75, 3], \"k:\", linewidth=2)\nplt.text(1.40, 1.0, \"Depth=0\", fontsize=15)\nplt.text(3.2, 1.80, \"Depth=1\", fontsize=13)\nplt.text(4.05, 0.5, \"(Depth=2)\", fontsize=11)\n\nsave_fig(\"decision_tree_decision_boundaries_plot\")\nplt.show()",
"Saving figure decision_tree_decision_boundaries_plot\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Predicting classes and class probabilities",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tree_clf.predict_proba([[5, 1.5]])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tree_clf.predict([[5, 1.5]])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Sensitivity to training set details",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"X[(X[:, 1]==X[:, 1][y==1].max()) & (y==1)] # widest Iris-Versicolor flower",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"not_widest_versicolor = (X[:, 1]!=1.8) | (y==2)\nX_tweaked = X[not_widest_versicolor]\ny_tweaked = y[not_widest_versicolor]\n\ntree_clf_tweaked = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=2, random_state=40)\ntree_clf_tweaked.fit(X_tweaked, y_tweaked)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(8, 4))\nplot_decision_boundary(tree_clf_tweaked, X_tweaked, y_tweaked, legend=False)\nplt.plot([0, 7.5], [0.8, 0.8], \"k-\", linewidth=2)\nplt.plot([0, 7.5], [1.75, 1.75], \"k--\", linewidth=2)\nplt.text(1.0, 0.9, \"Depth=0\", fontsize=15)\nplt.text(1.0, 1.80, \"Depth=1\", fontsize=13)\n\nsave_fig(\"decision_tree_instability_plot\")\nplt.show()",
"Saving figure decision_tree_instability_plot\n"
],
[
"from sklearn.datasets import make_moons\nXm, ym = make_moons(n_samples=100, noise=0.25, random_state=53)\n\ndeep_tree_clf1 = DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=42)\ndeep_tree_clf2 = DecisionTreeClassifier(min_samples_leaf=4, random_state=42)\ndeep_tree_clf1.fit(Xm, ym)\ndeep_tree_clf2.fit(Xm, ym)\n\nplt.figure(figsize=(11, 4))\nplt.subplot(121)\nplot_decision_boundary(deep_tree_clf1, Xm, ym, axes=[-1.5, 2.5, -1, 1.5], iris=False)\nplt.title(\"No restrictions\", fontsize=16)\nplt.subplot(122)\nplot_decision_boundary(deep_tree_clf2, Xm, ym, axes=[-1.5, 2.5, -1, 1.5], iris=False)\nplt.title(\"min_samples_leaf = {}\".format(deep_tree_clf2.min_samples_leaf), fontsize=14)\n\nsave_fig(\"min_samples_leaf_plot\")\nplt.show()",
"Saving figure min_samples_leaf_plot\n"
],
[
"angle = np.pi / 180 * 20\nrotation_matrix = np.array([[np.cos(angle), -np.sin(angle)], [np.sin(angle), np.cos(angle)]])\nXr = X.dot(rotation_matrix)\n\ntree_clf_r = DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=42)\ntree_clf_r.fit(Xr, y)\n\nplt.figure(figsize=(8, 3))\nplot_decision_boundary(tree_clf_r, Xr, y, axes=[0.5, 7.5, -1.0, 1], iris=False)\n\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.random.seed(6)\nXs = np.random.rand(100, 2) - 0.5\nys = (Xs[:, 0] > 0).astype(np.float32) * 2\n\nangle = np.pi / 4\nrotation_matrix = np.array([[np.cos(angle), -np.sin(angle)], [np.sin(angle), np.cos(angle)]])\nXsr = Xs.dot(rotation_matrix)\n\ntree_clf_s = DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=42)\ntree_clf_s.fit(Xs, ys)\ntree_clf_sr = DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=42)\ntree_clf_sr.fit(Xsr, ys)\n\nplt.figure(figsize=(11, 4))\nplt.subplot(121)\nplot_decision_boundary(tree_clf_s, Xs, ys, axes=[-0.7, 0.7, -0.7, 0.7], iris=False)\nplt.subplot(122)\nplot_decision_boundary(tree_clf_sr, Xsr, ys, axes=[-0.7, 0.7, -0.7, 0.7], iris=False)\n\nsave_fig(\"sensitivity_to_rotation_plot\")\nplt.show()",
"Saving figure sensitivity_to_rotation_plot\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Regression trees",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Quadratic training set + noise\nnp.random.seed(42)\nm = 200\nX = np.random.rand(m, 1)\ny = 4 * (X - 0.5) ** 2\ny = y + np.random.randn(m, 1) / 10",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor\n\ntree_reg = DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=2, random_state=42)\ntree_reg.fit(X, y)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor\n\ntree_reg1 = DecisionTreeRegressor(random_state=42, max_depth=2)\ntree_reg2 = DecisionTreeRegressor(random_state=42, max_depth=3)\ntree_reg1.fit(X, y)\ntree_reg2.fit(X, y)\n\ndef plot_regression_predictions(tree_reg, X, y, axes=[0, 1, -0.2, 1], ylabel=\"$y$\"):\n x1 = np.linspace(axes[0], axes[1], 500).reshape(-1, 1)\n y_pred = tree_reg.predict(x1)\n plt.axis(axes)\n plt.xlabel(\"$x_1$\", fontsize=18)\n if ylabel:\n plt.ylabel(ylabel, fontsize=18, rotation=0)\n plt.plot(X, y, \"b.\")\n plt.plot(x1, y_pred, \"r.-\", linewidth=2, label=r\"$\\hat{y}$\")\n\nplt.figure(figsize=(11, 4))\nplt.subplot(121)\nplot_regression_predictions(tree_reg1, X, y)\nfor split, style in ((0.1973, \"k-\"), (0.0917, \"k--\"), (0.7718, \"k--\")):\n plt.plot([split, split], [-0.2, 1], style, linewidth=2)\nplt.text(0.21, 0.65, \"Depth=0\", fontsize=15)\nplt.text(0.01, 0.2, \"Depth=1\", fontsize=13)\nplt.text(0.65, 0.8, \"Depth=1\", fontsize=13)\nplt.legend(loc=\"upper center\", fontsize=18)\nplt.title(\"max_depth=2\", fontsize=14)\n\nplt.subplot(122)\nplot_regression_predictions(tree_reg2, X, y, ylabel=None)\nfor split, style in ((0.1973, \"k-\"), (0.0917, \"k--\"), (0.7718, \"k--\")):\n plt.plot([split, split], [-0.2, 1], style, linewidth=2)\nfor split in (0.0458, 0.1298, 0.2873, 0.9040):\n plt.plot([split, split], [-0.2, 1], \"k:\", linewidth=1)\nplt.text(0.3, 0.5, \"Depth=2\", fontsize=13)\nplt.title(\"max_depth=3\", fontsize=14)\n\nsave_fig(\"tree_regression_plot\")\nplt.show()",
"Saving figure tree_regression_plot\n"
],
[
"export_graphviz(\n tree_reg1,\n out_file=image_path(\"regression_tree.dot\"),\n feature_names=[\"x1\"],\n rounded=True,\n filled=True\n )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tree_reg1 = DecisionTreeRegressor(random_state=42)\ntree_reg2 = DecisionTreeRegressor(random_state=42, min_samples_leaf=10)\ntree_reg1.fit(X, y)\ntree_reg2.fit(X, y)\n\nx1 = np.linspace(0, 1, 500).reshape(-1, 1)\ny_pred1 = tree_reg1.predict(x1)\ny_pred2 = tree_reg2.predict(x1)\n\nplt.figure(figsize=(11, 4))\n\nplt.subplot(121)\nplt.plot(X, y, \"b.\")\nplt.plot(x1, y_pred1, \"r.-\", linewidth=2, label=r\"$\\hat{y}$\")\nplt.axis([0, 1, -0.2, 1.1])\nplt.xlabel(\"$x_1$\", fontsize=18)\nplt.ylabel(\"$y$\", fontsize=18, rotation=0)\nplt.legend(loc=\"upper center\", fontsize=18)\nplt.title(\"No restrictions\", fontsize=14)\n\nplt.subplot(122)\nplt.plot(X, y, \"b.\")\nplt.plot(x1, y_pred2, \"r.-\", linewidth=2, label=r\"$\\hat{y}$\")\nplt.axis([0, 1, -0.2, 1.1])\nplt.xlabel(\"$x_1$\", fontsize=18)\nplt.title(\"min_samples_leaf={}\".format(tree_reg2.min_samples_leaf), fontsize=14)\n\nsave_fig(\"tree_regression_regularization_plot\")\nplt.show()",
"Saving figure tree_regression_regularization_plot\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Exercise solutions",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 1. to 6.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"See appendix A.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 7.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"_Exercise: train and fine-tune a Decision Tree for the moons dataset._",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a. Generate a moons dataset using `make_moons(n_samples=10000, noise=0.4)`.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Adding `random_state=42` to make this notebook's output constant:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.datasets import make_moons\n\nX, y = make_moons(n_samples=10000, noise=0.4, random_state=42)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"b. Split it into a training set and a test set using `train_test_split()`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\n\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"c. Use grid search with cross-validation (with the help of the `GridSearchCV` class) to find good hyperparameter values for a `DecisionTreeClassifier`. Hint: try various values for `max_leaf_nodes`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV\n\nparams = {'max_leaf_nodes': list(range(2, 100)), 'min_samples_split': [2, 3, 4]}\ngrid_search_cv = GridSearchCV(DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=42), params, n_jobs=-1, verbose=1, cv=3)\n\ngrid_search_cv.fit(X_train, y_train)",
"Fitting 3 folds for each of 294 candidates, totalling 882 fits\n"
],
[
"grid_search_cv.best_estimator_",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"d. Train it on the full training set using these hyperparameters, and measure your model's performance on the test set. You should get roughly 85% to 87% accuracy.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"By default, `GridSearchCV` trains the best model found on the whole training set (you can change this by setting `refit=False`), so we don't need to do it again. We can simply evaluate the model's accuracy:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score\n\ny_pred = grid_search_cv.predict(X_test)\naccuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 8.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"_Exercise: Grow a forest._",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a. Continuing the previous exercise, generate 1,000 subsets of the training set, each containing 100 instances selected randomly. Hint: you can use Scikit-Learn's `ShuffleSplit` class for this.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.model_selection import ShuffleSplit\n\nn_trees = 1000\nn_instances = 100\n\nmini_sets = []\n\nrs = ShuffleSplit(n_splits=n_trees, test_size=len(X_train) - n_instances, random_state=42)\nfor mini_train_index, mini_test_index in rs.split(X_train):\n X_mini_train = X_train[mini_train_index]\n y_mini_train = y_train[mini_train_index]\n mini_sets.append((X_mini_train, y_mini_train))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"b. Train one Decision Tree on each subset, using the best hyperparameter values found above. Evaluate these 1,000 Decision Trees on the test set. Since they were trained on smaller sets, these Decision Trees will likely perform worse than the first Decision Tree, achieving only about 80% accuracy.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.base import clone\n\nforest = [clone(grid_search_cv.best_estimator_) for _ in range(n_trees)]\n\naccuracy_scores = []\n\nfor tree, (X_mini_train, y_mini_train) in zip(forest, mini_sets):\n tree.fit(X_mini_train, y_mini_train)\n \n y_pred = tree.predict(X_test)\n accuracy_scores.append(accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred))\n\nnp.mean(accuracy_scores)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"c. Now comes the magic. For each test set instance, generate the predictions of the 1,000 Decision Trees, and keep only the most frequent prediction (you can use SciPy's `mode()` function for this). This gives you _majority-vote predictions_ over the test set.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Y_pred = np.empty([n_trees, len(X_test)], dtype=np.uint8)\n\nfor tree_index, tree in enumerate(forest):\n Y_pred[tree_index] = tree.predict(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from scipy.stats import mode\n\ny_pred_majority_votes, n_votes = mode(Y_pred, axis=0)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"d. Evaluate these predictions on the test set: you should obtain a slightly higher accuracy than your first model (about 0.5 to 1.5% higher). Congratulations, you have trained a Random Forest classifier!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred_majority_votes.reshape([-1]))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a342c7d0ea543d3f35608f54e3c082d633a8a77
| 51,112 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
modules/dynunet_tutorial.ipynb
|
ronakkaoshik42/tutorials
|
1e5955be4b474d83160e589efc76ef94bb8d6fe4
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2018-06-18T12:09:33.000Z
|
2018-06-18T12:09:33.000Z
|
modules/dynunet_tutorial.ipynb
|
ronakkaoshik42/tutorials
|
1e5955be4b474d83160e589efc76ef94bb8d6fe4
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
modules/dynunet_tutorial.ipynb
|
ronakkaoshik42/tutorials
|
1e5955be4b474d83160e589efc76ef94bb8d6fe4
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2018-06-18T12:13:21.000Z
|
2018-06-18T12:13:21.000Z
| 77.442424 | 15,696 | 0.781539 |
[
[
[
"# Train DynUNet on Decathlon datasets\nThis tutorial shows how to train 3D segmentation tasks on all the 10 decathlon datasets with `DynUNet`.\n\nRefer to papers:\n\n`Automated Design of Deep Learning Methods for Biomedical Image Segmentation <https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.08128>`\n\n`nnU-Net: Self-adapting Framework for U-Net-Based Medical Image Segmentation <https://arxiv.org/abs/1809.10486>`\n\n[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/Project-MONAI/tutorials/blob/master/modules/dynunet_tutorial.ipynb)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Setup environment",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%pip install -q \"monai[itk, ignite, tqdm]\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%pip install -q matplotlib\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Setup imports",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Copyright 2020 MONAI Consortium\n# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the \"License\");\n# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.\n# You may obtain a copy of the License at\n# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0\n# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software\n# distributed under the License is distributed on an \"AS IS\" BASIS,\n# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.\n# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and\n# limitations under the License.\n\nimport os\nimport logging\nimport ignite\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport torch\nimport torch.nn as nn\nimport numpy as np\nfrom monai.apps import DecathlonDataset\nfrom monai.config import print_config\nfrom monai.data import DataLoader\nfrom monai.engines import SupervisedTrainer\nfrom monai.handlers import MeanDice, StatsHandler\nfrom monai.inferers import SimpleInferer\nfrom monai.losses import DiceLoss\nfrom monai.networks.nets import DynUNet\nfrom monai.transforms import (\n AsDiscreted,\n Compose,\n LoadNiftid,\n AddChanneld,\n CropForegroundd,\n Spacingd,\n Orientationd,\n SpatialPadd,\n NormalizeIntensityd,\n RandCropByPosNegLabeld,\n RandZoomd,\n CastToTyped,\n RandGaussianNoised,\n RandGaussianSmoothd,\n RandScaleIntensityd,\n RandFlipd,\n ToTensord,\n)\n\nprint_config()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Select Decathlon task\nThe Decathlon dataset contains 10 tasks, this dynUNet tutorial can support all of them.\n\nJust need to select task ID and other parameters will be automatically selected.\n\n(Tested task 04 locally, epoch time is 8 secs on V100 GPU and best metrics is 0.8828 at epoch: 70)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"task_id = \"04\"\n\ntask_name = {\n \"01\": \"Task01_BrainTumour\",\n \"02\": \"Task02_Heart\",\n \"03\": \"Task03_Liver\",\n \"04\": \"Task04_Hippocampus\",\n \"05\": \"Task05_Prostate\",\n \"06\": \"Task06_Lung\",\n \"07\": \"Task07_Pancreas\",\n \"08\": \"Task08_HepaticVessel\",\n \"09\": \"Task09_Spleen\",\n \"10\": \"Task10_Colon\",\n}\n\npatch_size = {\n \"01\": [128, 128, 128],\n \"02\": [160, 192, 80],\n \"03\": [128, 128, 128],\n \"04\": [40, 56, 40],\n \"05\": [320, 256, 20],\n \"06\": [192, 160, 80],\n \"07\": [224, 224, 40],\n \"08\": [192, 192, 64],\n \"09\": [192, 160, 64],\n \"10\": [192, 160, 56],\n}\n\nspacing = {\n \"01\": [1.0, 1.0, 1.0],\n \"02\": [1.25, 1.25, 1.37],\n \"03\": [0.77, 0.77, 1],\n \"04\": [1.0, 1.0, 1.0],\n \"05\": [0.62, 0.62, 3.6],\n \"06\": [0.79, 0.79, 1.24],\n \"07\": [0.8, 0.8, 2.5],\n \"08\": [0.8, 0.8, 1.5],\n \"09\": [0.79, 0.79, 1.6],\n \"10\": [0.78, 0.78, 3],\n}",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Setup data directory\n\nYou can specify a directory with the `MONAI_DATA_DIRECTORY` environment variable. \nThis allows you to save results and reuse downloads. \nIf not specified a temporary directory will be used.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"directory = os.environ.get(\"MONAI_DATA_DIRECTORY\")\nroot_dir = tempfile.mkdtemp() if directory is None else directory\nprint(root_dir)",
"/workspace/data/medical\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Define train and validation transforms",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"train_transform = Compose(\n [\n LoadNiftid(keys=[\"image\", \"label\"]),\n AddChanneld(keys=[\"image\", \"label\"]),\n CropForegroundd(keys=[\"image\", \"label\"], source_key=\"image\"),\n Spacingd(\n keys=[\"image\", \"label\"],\n pixdim=spacing[task_id],\n mode=(\"bilinear\", \"nearest\"),\n ),\n Orientationd(keys=[\"image\", \"label\"], axcodes=\"RAS\"),\n SpatialPadd(keys=[\"image\", \"label\"], spatial_size=patch_size[task_id]),\n NormalizeIntensityd(keys=[\"image\"], nonzero=False, channel_wise=True),\n RandCropByPosNegLabeld(\n keys=[\"image\", \"label\"],\n label_key=\"label\",\n spatial_size=patch_size[task_id],\n pos=1,\n neg=1,\n num_samples=1,\n image_key=\"image\",\n image_threshold=0,\n ),\n RandZoomd(\n keys=[\"image\", \"label\"],\n min_zoom=0.9,\n max_zoom=1.2,\n mode=(\"trilinear\", \"nearest\"),\n align_corners=(True, None),\n prob=0.16,\n ),\n CastToTyped(keys=[\"image\", \"label\"], dtype=(np.float32, np.uint8)),\n RandGaussianNoised(keys=[\"image\"], std=0.01, prob=0.15),\n RandGaussianSmoothd(\n keys=[\"image\"],\n sigma_x=(0.5, 1.15),\n sigma_y=(0.5, 1.15),\n sigma_z=(0.5, 1.15),\n prob=0.15,\n ),\n RandScaleIntensityd(keys=[\"image\"], factors=0.3, prob=0.15),\n RandFlipd([\"image\", \"label\"], spatial_axis=[0, 1, 2], prob=0.5),\n ToTensord(keys=[\"image\", \"label\"]),\n ]\n)\n\nval_transform = Compose(\n [\n LoadNiftid(keys=[\"image\", \"label\"]),\n AddChanneld(keys=[\"image\", \"label\"]),\n CropForegroundd(keys=[\"image\", \"label\"], source_key=\"image\"),\n Spacingd(\n keys=[\"image\", \"label\"],\n pixdim=spacing[task_id],\n mode=(\"bilinear\", \"nearest\"),\n ),\n Orientationd(keys=[\"image\", \"label\"], axcodes=\"RAS\"),\n SpatialPadd(keys=[\"image\", \"label\"], spatial_size=patch_size[task_id]),\n NormalizeIntensityd(keys=[\"image\"], nonzero=False, channel_wise=True),\n CastToTyped(keys=[\"image\", \"label\"], dtype=(np.float32, np.uint8)),\n ToTensord(keys=[\"image\", \"label\"]),\n ]\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Load data by MONAI DecathlonDataset",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"train_ds = DecathlonDataset(\n root_dir=root_dir,\n task=task_name[task_id],\n transform=train_transform,\n section=\"training\",\n download=False,\n num_workers=4,\n)\ntrain_loader = DataLoader(train_ds, batch_size=2, shuffle=True, num_workers=1)\n\nval_ds = DecathlonDataset(\n root_dir=root_dir,\n task=task_name[task_id],\n transform=val_transform,\n section=\"validation\",\n download=False,\n num_workers=4,\n)\nval_loader = DataLoader(val_ds, batch_size=1, shuffle=False, num_workers=1)",
"208/208 Load and cache transformed data: [==============================]\n52/52 Load and cache transformed data: [==============================]\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Visualize batch of data to check images and labels",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for i in range(2):\n image, label = val_ds[i][\"image\"], val_ds[i][\"label\"]\n plt.figure(\"check\", (12, 8))\n plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)\n plt.title(\"image\")\n plt.imshow(image[0, :, :, 10].detach().cpu(), cmap=\"gray\")\n plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)\n plt.title(\"label\")\n plt.imshow(label[0, :, :, 10].detach().cpu())\n plt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Customize loss function\nHere we combine Dice loss and Cross Entropy loss.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class CrossEntropyLoss(nn.Module):\n def __init__(self):\n super().__init__()\n self.loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()\n\n def forward(self, y_pred, y_true):\n # CrossEntropyLoss target needs to have shape (B, D, H, W)\n # Target from pipeline has shape (B, 1, D, H, W)\n y_true = torch.squeeze(y_true, dim=1).long()\n return self.loss(y_pred, y_true)\n\n\nclass DiceCELoss(nn.Module):\n def __init__(self):\n super().__init__()\n self.dice = DiceLoss(to_onehot_y=True, softmax=True)\n self.cross_entropy = CrossEntropyLoss()\n\n def forward(self, y_pred, y_true):\n dice = self.dice(y_pred, y_true)\n cross_entropy = self.cross_entropy(y_pred, y_true)\n return dice + cross_entropy",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Initialize training components",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"device = torch.device(\"cuda:0\")\nloss = DiceCELoss()\nlearning_rate = 0.01\nmax_epochs = 200\n\nsizes, spacings = patch_size[task_id], spacing[task_id]\nproperties = val_ds.get_properties(keys=[\"labels\", \"modality\"])\nn_class, in_channels = len(properties[\"labels\"]), len(properties[\"modality\"])\nbest_dice, best_epoch = (n_class - 1) * [0], (n_class - 1) * [0]\nstrides, kernels = [], []\n\nwhile True:\n spacing_ratio = [sp / min(spacings) for sp in spacings]\n stride = [2 if ratio <= 2 and size >= 8 else 1 for (ratio, size) in zip(spacing_ratio, sizes)]\n kernel = [3 if ratio <= 2 else 1 for ratio in spacing_ratio]\n if all(s == 1 for s in stride):\n break\n sizes = [i / j for i, j in zip(sizes, stride)]\n spacings = [i * j for i, j in zip(spacings, stride)]\n kernels.append(kernel)\n strides.append(stride)\nstrides.insert(0, len(spacings) * [1])\nkernels.append(len(spacings) * [3])\nnet = DynUNet(\n spatial_dims=3,\n in_channels=in_channels,\n out_channels=n_class,\n kernel_size=kernels,\n strides=strides,\n upsample_kernel_size=strides[1:],\n norm_name=\"instance\",\n deep_supervision=True,\n deep_supr_num=2,\n res_block=False,\n).to(device)\n\noptimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=learning_rate, momentum=0.95)\nscheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.LambdaLR(\n optimizer, lr_lambda=lambda epoch: (1 - epoch / max_epochs) ** 0.9\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## MONAI evaluator\nHere we customized the forward computation, so need to define `_iteration` function.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from monai.engines import SupervisedEvaluator\nfrom monai.handlers import StatsHandler, CheckpointSaver, MeanDice\nfrom monai.inferers import SlidingWindowInferer\n\n\nval_handlers = [\n StatsHandler(output_transform=lambda x: None),\n CheckpointSaver(save_dir=\"./runs/\", save_dict={\"net\": net}, save_key_metric=True),\n]\n\nval_post_transform = Compose(\n [AsDiscreted(keys=(\"pred\", \"label\"), argmax=(True, False), to_onehot=True, n_classes=n_class)]\n)\n\n# Define customized evaluator\nclass DynUNetEvaluator(SupervisedEvaluator):\n def _iteration(self, engine, batchdata):\n inputs, targets = self.prepare_batch(batchdata)\n inputs, targets = inputs.to(engine.state.device), targets.to(engine.state.device)\n flip_inputs = torch.flip(inputs, dims=(2, 3, 4))\n\n def _compute_pred():\n pred = self.inferer(inputs, self.network)\n flip_pred = torch.flip(self.inferer(flip_inputs, self.network), dims=(2, 3, 4))\n return (pred + flip_pred) / 2\n\n # execute forward computation\n self.network.eval()\n with torch.no_grad():\n if self.amp:\n with torch.cuda.amp.autocast():\n predictions = _compute_pred()\n else:\n predictions = _compute_pred()\n return {\"image\": inputs, \"label\": targets, \"pred\": predictions}\n\n\nevaluator = DynUNetEvaluator(\n device=device,\n val_data_loader=val_loader,\n network=net,\n inferer=SlidingWindowInferer(roi_size=patch_size[task_id], sw_batch_size=4, overlap=0.5),\n post_transform=val_post_transform,\n key_val_metric={\n \"val_mean_dice\": MeanDice(\n include_background=False,\n output_transform=lambda x: (x[\"pred\"], x[\"label\"]),\n )\n },\n val_handlers=val_handlers,\n amp=True,\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## MONAI trainer\nHere we customized loss computation progress, so need to define `_iteration` function.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from torch.nn.functional import interpolate\nfrom monai.engines import SupervisedTrainer\nfrom monai.inferers import SimpleInferer\nfrom monai.handlers import LrScheduleHandler, ValidationHandler, StatsHandler\n\n\ntrain_handlers = [\n LrScheduleHandler(lr_scheduler=scheduler, print_lr=True),\n ValidationHandler(validator=evaluator, interval=2, epoch_level=True),\n StatsHandler(tag_name=\"train_loss\", output_transform=lambda x: x[\"loss\"]),\n]\n\n# define customized trainer\nclass DynUNetTrainer(SupervisedTrainer):\n def _iteration(self, engine, batchdata):\n inputs, targets = self.prepare_batch(batchdata)\n inputs, targets = inputs.to(engine.state.device), targets.to(engine.state.device)\n\n def _compute_loss(preds, label):\n labels = [label] + [interpolate(label, pred.shape[2:]) for pred in preds[1:]]\n return sum([0.5 ** i * self.loss_function(p, l) for i, (p, l) in enumerate(zip(preds, labels))])\n\n self.network.train()\n self.optimizer.zero_grad()\n if self.amp and self.scaler is not None:\n with torch.cuda.amp.autocast():\n predictions = self.inferer(inputs, self.network)\n loss = _compute_loss(predictions, targets)\n self.scaler.scale(loss).backward()\n self.scaler.step(self.optimizer)\n self.scaler.update()\n else:\n predictions = self.inferer(inputs, self.network)\n loss = _compute_loss(predictions, targets).mean()\n loss.backward()\n self.optimizer.step()\n return {\"image\": inputs, \"label\": targets, \"pred\": predictions, \"loss\": loss.item()}\n\n\ntrainer = DynUNetTrainer(\n device=device,\n max_epochs=max_epochs,\n train_data_loader=train_loader,\n network=net,\n optimizer=optimizer,\n loss_function=loss,\n inferer=SimpleInferer(),\n post_transform=None,\n key_train_metric=None,\n train_handlers=train_handlers,\n amp=True,\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Execute training with workflows",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import logging\nimport sys\nlogging.basicConfig(stream=sys.stdout, level=logging.INFO)\n\n\ntrainer.run()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Cleanup data directory\n\nRemove directory if a temporary was used.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"if directory is None:\n shutil.rmtree(root_dir)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a34351f4495f765c262c2748720bc3a57946a76
| 29,979 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
lessons/Recommendations/1_Intro_to_Recommendations/4_Collaborative Filtering.ipynb
|
dhamo1/DSND_Term2
|
a5a7083a1025935ca399165d07cf168d6c6078f0
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
lessons/Recommendations/1_Intro_to_Recommendations/4_Collaborative Filtering.ipynb
|
dhamo1/DSND_Term2
|
a5a7083a1025935ca399165d07cf168d6c6078f0
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
lessons/Recommendations/1_Intro_to_Recommendations/4_Collaborative Filtering.ipynb
|
dhamo1/DSND_Term2
|
a5a7083a1025935ca399165d07cf168d6c6078f0
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 41.293388 | 634 | 0.624204 |
[
[
[
"## Recommendations with MovieTweetings: Collaborative Filtering\n\nOne of the most popular methods for making recommendations is **collaborative filtering**. In collaborative filtering, you are using the collaboration of user-item recommendations to assist in making new recommendations. \n\nThere are two main methods of performing collaborative filtering:\n\n1. **Neighborhood-Based Collaborative Filtering**, which is based on the idea that we can either correlate items that are similar to provide recommendations or we can correlate users to one another to provide recommendations.\n\n2. **Model Based Collaborative Filtering**, which is based on the idea that we can use machine learning and other mathematical models to understand the relationships that exist amongst items and users to predict ratings and provide ratings.\n\n\nIn this notebook, you will be working on performing **neighborhood-based collaborative filtering**. There are two main methods for performing collaborative filtering:\n\n1. **User-based collaborative filtering:** In this type of recommendation, users related to the user you would like to make recommendations for are used to create a recommendation.\n\n2. **Item-based collaborative filtering:** In this type of recommendation, first you need to find the items that are most related to each other item (based on similar ratings). Then you can use the ratings of an individual on those similar items to understand if a user will like the new item.\n\nIn this notebook you will be implementing **user-based collaborative filtering**. However, it is easy to extend this approach to make recommendations using **item-based collaborative filtering**. First, let's read in our data and necessary libraries.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport tests as t\nimport progressbar\nfrom scipy.sparse import csr_matrix\nfrom IPython.display import HTML\n\n\n%matplotlib inline\n\n# Read in the datasets\nmovies = pd.read_csv('movies_clean.csv')\nreviews = pd.read_csv('reviews_clean.csv')\n\ndel movies['Unnamed: 0']\ndel reviews['Unnamed: 0']\n\nprint(reviews.head())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Measures of Similarity\n\nWhen using **neighborhood** based collaborative filtering, it is important to understand how to measure the similarity of users or items to one another. \n\nThere are a number of ways in which we might measure the similarity between two vectors (which might be two users or two items). In this notebook, we will look specifically at two measures used to compare vectors:\n\n* **Pearson's correlation coefficient**\n\nPearson's correlation coefficient is a measure of the strength and direction of a linear relationship. The value for this coefficient is a value between -1 and 1 where -1 indicates a strong, negative linear relationship and 1 indicates a strong, positive linear relationship. \n\nIf we have two vectors **x** and **y**, we can define the correlation between the vectors as:\n\n\n$$CORR(x, y) = \\frac{\\text{COV}(x, y)}{\\text{STDEV}(x)\\text{ }\\text{STDEV}(y)}$$\n\nwhere \n\n$$\\text{STDEV}(x) = \\sqrt{\\frac{1}{n-1}\\sum_{i=1}^{n}(x_i - \\bar{x})^2}$$\n\nand \n\n$$\\text{COV}(x, y) = \\frac{1}{n-1}\\sum_{i=1}^{n}(x_i - \\bar{x})(y_i - \\bar{y})$$\n\nwhere n is the length of the vector, which must be the same for both x and y and $\\bar{x}$ is the mean of the observations in the vector. \n\nWe can use the correlation coefficient to indicate how alike two vectors are to one another, where the closer to 1 the coefficient, the more alike the vectors are to one another. There are some potential downsides to using this metric as a measure of similarity. You will see some of these throughout this workbook.\n\n\n* **Euclidean distance**\n\nEuclidean distance is a measure of the straightline distance from one vector to another. Because this is a measure of distance, larger values are an indication that two vectors are different from one another (which is different than Pearson's correlation coefficient).\n\nSpecifically, the euclidean distance between two vectors **x** and **y** is measured as:\n\n$$ \\text{EUCL}(x, y) = \\sqrt{\\sum_{i=1}^{n}(x_i - y_i)^2}$$\n\nDifferent from the correlation coefficient, no scaling is performed in the denominator. Therefore, you need to make sure all of your data are on the same scale when using this metric.\n\n**Note:** Because measuring similarity is often based on looking at the distance between vectors, it is important in these cases to scale your data or to have all data be in the same scale. If some measures are on a 5 point scale, while others are on a 100 point scale, you are likely to have non-optimal results due to the difference in variability of your features. Measures like Pearson and Spearman's correlation coefficients are unit agnostic, which means it is not necessary to scale for these measures. However, many measures used to measure similarity (like euclidean or manhatten distances) are not unit agnostic.\n\nIn this case, we will not need to scale data because they are all on a 10 point scale, but it is always something to keep in mind!\n\n------------\n\n### User-Item Matrix\n\nIn order to calculate the similarities, it is common to put values in a matrix. In this matrix, users are identified by each row, and items are represented by columns. \n\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In the above matrix, you can see that **User 1** and **User 2** both used **Item 1**, and **User 2**, **User 3**, and **User 4** all used **Item 2**. However, there are also a large number of missing values in the matrix for users who haven't used a particular item. A matrix with many missing values (like the one above) is considered **sparse**.\n\nOur first goal for this notebook is to create the above matrix with the **reviews** dataset. However, instead of 1 values in each cell, you should have the actual rating. \n\nThe users will indicate the rows, and the movies will exist across the columns. To create the user-item matrix, we only need the first three columns of the **reviews** dataframe, which you can see by running the cell below.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"user_items = reviews[['user_id', 'movie_id', 'rating']]\nuser_items.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Ceating the User-Item Matrix\n\nIn order to create the user-items matrix (like the one above), I personally started by using a [pivot table](https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/generated/pandas.pivot_table.html). \n\nHowever, I quickly ran into a memory error (a common theme throughout this notebook). I will help you navigate around many of the errors I had, and acheive useful collaborative filtering results! \n\n_____\n\n`1.` Create a matrix where the users are the rows, the movies are the columns, and the ratings exist in each cell, or a NaN exists in cells where a user hasn't rated a particular movie. If you get a memory error (like I did), [this link here](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/39648991/pandas-dataframe-pivot-memory-error) might help you!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create user-by-item matrix\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Check your results below to make sure your matrix is ready for the upcoming sections.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"assert movies.shape[0] == user_by_movie.shape[1], \"Oh no! Your matrix should have {} columns, and yours has {}!\".format(movies.shape[0], user_by_movie.shape[1])\nassert reviews.user_id.nunique() == user_by_movie.shape[0], \"Oh no! Your matrix should have {} rows, and yours has {}!\".format(reviews.user_id.nunique(), user_by_movie.shape[0])\nprint(\"Looks like you are all set! Proceed!\")\nHTML('<img src=\"images/greatjob.webp\">')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"`2.` Now that you have a matrix of users by movies, use this matrix to create a dictionary where the key is each user and the value is an array of the movies each user has rated.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create a dictionary with users and corresponding movies seen\n\ndef movies_watched(user_id):\n '''\n INPUT:\n user_id - the user_id of an individual as int\n OUTPUT:\n movies - an array of movies the user has watched\n '''\n\n return movies\n\n\ndef create_user_movie_dict():\n '''\n INPUT: None\n OUTPUT: movies_seen - a dictionary where each key is a user_id and the value is an array of movie_ids\n \n Creates the movies_seen dictionary\n '''\n \n # Do things - hint this may take some time, so you might want to set up a progress bar to watch things progress\n \n return movies_seen\n\n\n# Use your function to return dictionary\nmovies_seen = create_user_movie_dict()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"`3.` If a user hasn't rated more than 2 movies, we consider these users \"too new\". Create a new dictionary that only contains users who have rated more than 2 movies. This dictionary will be used for all the final steps of this workbook.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Remove individuals who have watched 2 or fewer movies - don't have enough data to make recs\n\ndef create_movies_to_analyze(movies_seen, lower_bound=2):\n '''\n INPUT: \n movies_seen - a dictionary where each key is a user_id and the value is an array of movie_ids\n lower_bound - (an int) a user must have more movies seen than the lower bound to be added to the movies_to_analyze dictionary\n\n OUTPUT: \n movies_to_analyze - a dictionary where each key is a user_id and the value is an array of movie_ids\n \n The movies_seen and movies_to_analyze dictionaries should be the same except that the output dictionary has removed \n \n '''\n \n # Do things to create updated dictionary\n \n return movies_to_analyze\n\n\n# Use your function to return your updated dictionary\nmovies_to_analyze = create_movies_to_analyze(movies_seen)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Run the tests below to check that your movies_to_analyze matches the solution\nassert len(movies_to_analyze) == 23512, \"Oops! It doesn't look like your dictionary has the right number of individuals.\"\nassert len(movies_to_analyze[2]) == 23, \"Oops! User 2 didn't match the number of movies we thought they would have.\"\nassert len(movies_to_analyze[7]) == 3, \"Oops! User 7 didn't match the number of movies we thought they would have.\"\nprint(\"If this is all you see, you are good to go!\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Calculating User Similarities\n\nNow that you have set up the **movies_to_analyze** dictionary, it is time to take a closer look at the similarities between users. Below the sudo code for how I thought about determining the similarity between users:\n\n```\nfor user1 in movies_to_analyze\n for user2 in movies_to_analyze\n see how many movies match between the two users\n if more than two movies in common\n pull the overlapping movies\n compute the distance/similarity metric between ratings on the same movies for the two users\n store the users and the distance metric\n```\n\nHowever, this took a very long time to run, and other methods of performing these operations did not fit on the workspace memory!\n\nTherefore, your task for this question is to look at a few specific examples of the correlation between ratings given by two users. For this question consider you want to compute the [correlation](https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/generated/pandas.DataFrame.corr.html) between users.\n\n`4.` Using the **movies_to_analyze** dictionary and **user_by_movie** dataframe, create a function that computes the correlation between the ratings of similar movies for two users. Then use your function to compare your results to ours using the tests below. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def compute_correlation(user1, user2):\n '''\n INPUT\n user1 - int user_id\n user2 - int user_id\n OUTPUT\n the correlation between the matching ratings between the two users\n '''\n \n return corr #return the correlation",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Read in solution correlations - this will take some time to read in\nimport pickle\ncorrs_import = pickle.load(open(\"corrs.p\", \"rb\"))\ndf_corrs = pd.DataFrame(corrs_import)\ndf_corrs.columns = ['user1', 'user2', 'movie_corr']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Test your function against the solution\nassert compute_correlation(2,2) == df_corrs.query(\"user1 == 2 and user2 == 2\")['movie_corr'][0], \"Oops! The correlation between a user and itself should be 1.0.\"\nassert round(compute_correlation(2,66), 2) == round(df_corrs.query(\"user1 == 2 and user2 == 66\")['movie_corr'][1], 2), \"Oops! The correlation between user 2 and 66 should be about 0.76.\"\nassert np.isnan(compute_correlation(2,104)) == np.isnan(df_corrs.query(\"user1 == 2 and user2 == 104\")['movie_corr'][4]), \"Oops! The correlation between user 2 and 104 should be a NaN.\"\n\nprint(\"If this is all you see, then it looks like your function passed all of our tests!\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Why the NaN's?\n\nIf the function you wrote passed all of the tests, then you have correctly set up your function to calculate the correlation between any two users. The **df_corrs** dataframe created in the cell leading up to the tests holds combinations of users along with their corresponding correlation. \n\n`5.` But one question is why are we still obtaining **NaN** values. Look at the header below for users 2 and 104, they have a correlation of **NaN**, why?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_corrs.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Leave your thoughts here about why the NaN exists, and use the cells below to validate your thoughts. These Nan's ultimately make the correlation coefficient a less than optimal measure of similarity between two users.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Which movies did both user 2 and user 4 see?\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# What were the ratings for each user on those movies?\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"`6.` Because the correlation coefficient proved to be less than optimal for relating user ratings to one another, we could instead calculate the euclidean distance between the ratings. I found [this post](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/1401712/how-can-the-euclidean-distance-be-calculated-with-numpy) particularly helpful when I was setting up my function. This function should be very similar to your previous function. When you feel confident with your function, test it against our results.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def compute_euclidean_dist(user1, user2):\n '''\n INPUT\n user1 - int user_id\n user2 - int user_id\n OUTPUT\n the euclidean distance between user1 and user2\n '''\n \n return dist #return the euclidean distance",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Read in solution euclidean distances - this will take some time to read in\ndf_dists = pickle.load(open(\"dists.p\", \"rb\"))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Test your function against the solution\nassert compute_euclidean_dist(2,2) == df_dists.query(\"user1 == 2 and user2 == 2\")['eucl_dist'][0], \"Oops! The distance between a user and itself should be 0.0.\"\nassert round(compute_euclidean_dist(2,66), 2) == round(df_dists.query(\"user1 == 2 and user2 == 66\")['eucl_dist'][1], 2), \"Oops! The distance between user 2 and 66 should be about 2.24.\"\nassert np.isnan(compute_euclidean_dist(2,104)) == np.isnan(df_dists.query(\"user1 == 2 and user2 == 104\")['eucl_dist'][4]), \"Oops! The distance between user 2 and 104 should be 2.\"\n\nprint(\"If this is all you see, then it looks like your function passed all of our tests!\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Using the Nearest Neighbors to Make Recommendations\n\nIn the previous questions, you read in **df_corrs** and **df_dists**. Therefore, you have a measure of distance and similarity for each user to every other user. These dataframes hold every possible combination of users, as well as the corresponding correlation or euclidean distance, respectively.\n\nBecause of the **NaN** values that exist within **df_corrs**, we will proceed using **df_dists**. You will want to find the users are 'nearest' each user. Then you will want to find the movies the closest neighbors have liked to recommend to each user.\n\nI made use of the following objects:\n\n* df_dists (to obtain the neighbors)\n* user_items (to obtain the movies the neighbors and users have rated)\n* movies (to obtain the names of the movies)\n\n`7.` Complete the functions below, which allow you to find the recommendations for any user. There are three functions which you will need:\n\n* **find_closest_neighbors** - this returns a list of user_ids from closest neighbor to farthest neighbor using euclidean distance\n\n\n* **movies_liked** - returns an array of movie_ids\n\n\n* **movie_names** - takes the output of movies_liked and returns a list of movie names associated with the movie_ids\n\n\n* **make_recommendations** - takes a user id and goes through closest neighbors to return a list of movie names as recommendations\n\n\n* **all_recommendations** = loops through every user and returns a dictionary of with the key as a user_id and the value as a list of movie recommendations",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def find_closest_neighbors(user):\n '''\n INPUT:\n user - (int) the user_id of the individual you want to find the closest users\n OUTPUT:\n closest_neighbors - an array of the id's of the users sorted from closest to farthest away\n '''\n # I treated ties as arbitrary and just kept whichever was easiest to keep using the head method\n # You might choose to do something less hand wavy - order the neighbors\n \n \n \n return closest_neighbors\n \n \n \ndef movies_liked(user_id, min_rating=7):\n '''\n INPUT:\n user_id - the user_id of an individual as int\n min_rating - the minimum rating considered while still a movie is still a \"like\" and not a \"dislike\"\n OUTPUT:\n movies_liked - an array of movies the user has watched and liked\n '''\n \n return movies_liked\n\n\ndef movie_names(movie_ids):\n '''\n INPUT\n movie_ids - a list of movie_ids\n OUTPUT\n movies - a list of movie names associated with the movie_ids\n \n '''\n\n return movie_lst\n \n \ndef make_recommendations(user, num_recs=10):\n '''\n INPUT:\n user - (int) a user_id of the individual you want to make recommendations for\n num_recs - (int) number of movies to return\n OUTPUT:\n recommendations - a list of movies - if there are \"num_recs\" recommendations return this many\n otherwise return the total number of recommendations available for the \"user\"\n which may just be an empty list\n '''\n\n \n return recommendations\n\ndef all_recommendations(num_recs=10):\n '''\n INPUT \n num_recs (int) the (max) number of recommendations for each user\n OUTPUT\n all_recs - a dictionary where each key is a user_id and the value is an array of recommended movie titles\n '''\n \n\n # Apply make recs for each user - \n # hint this may take some time, so you might want to set up a progress bar to watch things progress\n \n \n return all_recs\n\nall_recs = all_recommendations(10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# This make some time - it loads our solution dictionary so you can compare results\nall_recs_sol = pickle.load(open(\"all_recs.p\", \"rb\"))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"assert all_recs[2] == make_recommendations(2), \"Oops! Your recommendations for user 2 didn't match ours.\"\nassert all_recs[26] == make_recommendations(26), \"Oops! It actually wasn't possible to make any recommendations for user 26.\"\nassert all_recs[1503] == make_recommendations(1503), \"Oops! Looks like your solution for user 1503 didn't match ours.\"\nprint(\"If you made it here, you now have recommendations for many users using collaborative filtering!\")\nHTML('<img src=\"images/greatjob.webp\">')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Now What?\n\nIf you made it this far, you have successfully implemented a solution to making recommendations using collaborative filtering. \n\n`8.` Let's do a quick recap of the steps taken to obtain recommendations using collaborative filtering. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Check your understanding of the results by correctly filling in the dictionary below\na = \"pearson's correlation and spearman's correlation\"\nb = 'item based collaborative filtering'\nc = \"there were too many ratings to get a stable metric\"\nd = 'user based collaborative filtering'\ne = \"euclidean distance and pearson's correlation coefficient\"\nf = \"manhatten distance and euclidean distance\"\ng = \"spearman's correlation and euclidean distance\"\nh = \"the spread in some ratings was zero\"\ni = 'content based recommendation'\n\nsol_dict = {\n 'The type of recommendation system implemented here was a ...': # letter here,\n 'The two methods used to estimate user similarity were: ': # letter here,\n 'There was an issue with using the correlation coefficient. What was it?': # letter here\n}\n\nt.test_recs(sol_dict)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Additionally, let's take a closer look at some of the results. There are three objects that you read in to check your results against the solution:\n\n* **df_corrs** - a dataframe of user1, user2, pearson correlation between the two users\n* **df_dists** - a dataframe of user1, user2, euclidean distance between the two users\n* **all_recs_sol** - a dictionary of all recommendations (key = user, value = list of recommendations)\n\nLooping your results from the correlation and euclidean distance functions through every pair of users could have been used to create the first two objects (I don't recommend doing this given how long it will take). \n\n`9.`Use these three objects along with the cells below to correctly fill in the dictionary below and complete this notebook!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"a = 567\nb = 1503\nc = 1319\nd = 1325\ne = 2526710\nf = 0\ng = 'Use another method to make recommendations - content based, knowledge based, or model based collaborative filtering'\n\nsol_dict2 = {\n 'For how many pairs of users were we not able to obtain a measure of similarity using correlation?': # letter here,\n 'For how many pairs of users were we not able to obtain a measure of similarity using euclidean distance?': # letter here,\n 'For how many users were we unable to make any recommendations for using collaborative filtering?': # letter here,\n 'For how many users were we unable to make 10 recommendations for using collaborative filtering?': # letter here,\n 'What might be a way for us to get 10 recommendations for every user?': # letter here \n}\n\nt.test_recs2(sol_dict2)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Use the below cells for any work you need to do!",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Users without recs\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# NaN correlation values\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# NaN euclidean distance values\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Users with less than 10 recs\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a3442a36e91f949504c6886e345e919ee3e6228
| 12,890 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
examples/RL/notebooks/gym_environment.ipynb
|
cdicle-motional/l5kit
|
4dc4ee5391479bb71f0b373f39c316f9eef5a961
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
examples/RL/notebooks/gym_environment.ipynb
|
cdicle-motional/l5kit
|
4dc4ee5391479bb71f0b373f39c316f9eef5a961
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
examples/RL/notebooks/gym_environment.ipynb
|
cdicle-motional/l5kit
|
4dc4ee5391479bb71f0b373f39c316f9eef5a961
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2021-11-19T08:13:46.000Z
|
2021-11-19T08:13:46.000Z
| 35.218579 | 373 | 0.611947 |
[
[
[
"# L5 Closed-loop Gym-compatible Environment\n\nThis notebook demonstrates some of the aspects of our gym-compatible closed-loop environment.\n\nYou will understand the inner workings of our L5Kit environment and an RL policy can be used to rollout the environment. \n\nNote: The training of different RL policies in our environment will be shown in a separate notebook.\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#@title Download L5 Sample Dataset and install L5Kit\nimport os\nRunningInCOLAB = 'google.colab' in str(get_ipython())\nif RunningInCOLAB:\n !wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lyft/l5kit/master/examples/setup_notebook_colab.sh -q\n !sh ./setup_notebook_colab.sh\n os.environ[\"L5KIT_DATA_FOLDER\"] = open(\"./dataset_dir.txt\", \"r\").read().strip()\nelse:\n os.environ[\"L5KIT_DATA_FOLDER\"] = \"/tmp/level5_data\"\n print(\"Not running in Google Colab.\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import gym\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport torch\nimport numpy as np\n\nimport l5kit.environment\nfrom l5kit.configs import load_config_data\nfrom l5kit.environment.envs.l5_env import EpisodeOutputGym, SimulationConfigGym\nfrom l5kit.environment.gym_metric_set import L2DisplacementYawMetricSet\nfrom l5kit.visualization.visualizer.zarr_utils import episode_out_to_visualizer_scene_gym_cle\nfrom l5kit.visualization.visualizer.visualizer import visualize\n\nfrom bokeh.io import output_notebook, show\nfrom prettytable import PrettyTable\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### First, let's configure where our data lives!\nThe data is expected to live in a folder that can be configured using the `L5KIT_DATA_FOLDER` env variable. Your data folder is expected to contain subfolders for the aerial and semantic maps as well as the scenes (`.zarr` files). \nIn this example, the env variable is set to the local data folder. You should make sure the path points to the correct location for you.\n\nWe built our code to work with a human-readable `yaml` config. This config file holds much useful information, however, we will only focus on a few functionalities concerning the creation of our gym environment here",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Dataset is assumed to be on the folder specified\n# in the L5KIT_DATA_FOLDER environment variable\n\n# get environment config\nenv_config_path = '../gym_config.yaml'\ncfg = load_config_data(env_config_path)\nprint(cfg)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### We can look into our current configuration for interesting fields\n\n\\- when loaded in python, the `yaml`file is converted into a python `dict`. \n\n`raster_params` contains all the information related to the transformation of the 3D world onto an image plane:\n - `raster_size`: the image plane size\n - `pixel_size`: how many meters correspond to a pixel\n - `ego_center`: our raster is centered around an agent, we can move the agent in the image plane with this param\n - `map_type`: the rasterizer to be employed. We currently support a satellite-based and a semantic-based one. We will look at the differences further down in this script\n \nThe `raster_params` are used to determine the observation provided by our gym environment to the RL policy.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(f'current raster_param:\\n')\nfor k,v in cfg[\"raster_params\"].items():\n print(f\"{k}:{v}\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Create L5 Closed-loop Environment\n\nWe will now create an instance of the L5Kit gym-compatible environment. As you can see, we need to provide the path to the configuration file of the environment. \n\n1. The `rescale_action` flag rescales the policy action based on dataset statistics. This argument helps for faster convergence during policy training. \n2. The `return_info` flag informs the environment to return the episode output everytime an episode is rolled out. \n\nNote: The environment has already been registered with gym during initialization of L5Kit.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"env = gym.make(\"L5-CLE-v0\", env_config_path=env_config_path, rescale_action=False, return_info=True)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Visualize an observation from the environment\n\nLet us visualize the observation from the environment. We will reset the environment and visualize an observation which is provided by the environment.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"obs = env.reset()\nim = obs[\"image\"].transpose(1, 2, 0)\nim = env.dataset.rasterizer.to_rgb(im)\n\nplt.imshow(im)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Rollout an episode from the environment\n\n### The rollout of an episode in our environment takes place in three steps:\n\n### Gym Environment Update:\n1. Reward Calculation (CLE): Given an action from the policy, the environment will calculate the reward received as a consequence of the action.\n2. Internal State Update: Since we are rolling out the environment in closed-loop, the internal state of the ego is updated based on the action.\n3. Raster rendering: A new raster image is rendered based on the predicted ego position and returned as the observation of next time-step.\n\n### Policy Forward Pass\nThe policy takes as input the observation provided by the environment and outputs the action via a forward pass.\n\n### Inter-process communication\nUsually, we deploy different subprocesses to rollout parallel environments to speed up rollout time during training. Each subprocess rolls out one environemnt. In such scenarios, there is an additional component called inter-process communication: The subprocess outputs (observations) are aggregated and passed to the main process and vice versa (for the actions)\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Dummy Policy\n\nFor this notebook, we will not train the policy but use a dummy policy. Our dummy policy that will move the ego by 10 m/s along the direction of orientation.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class DummyPolicy(torch.nn.Module):\n \"\"\"A policy that advances the ego by constant speed along x-direction.\n\n :param advance_x: the distance to advance per time-step\n \"\"\"\n def __init__(self, advance_x: float = 0.0):\n super(DummyPolicy, self).__init__()\n self.advance_x = advance_x\n\n def forward(self, x):\n positions_and_yaws = torch.zeros(3,)\n positions_and_yaws[..., 0] = self.advance_x\n\n return positions_and_yaws.cpu().numpy()\n\n# We multiple the desired speed by the step-time (inverse of frequency) of data collection\ndesired_speed = 10.0\ndummy_policy = DummyPolicy(cfg[\"model_params\"][\"step_time\"] * desired_speed)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let us now rollout the environment using the dummy policy. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def rollout_episode(env, idx = 0):\n \"\"\"Rollout a particular scene index and return the simulation output.\n\n :param env: the gym environment\n :param idx: the scene index to be rolled out\n :return: the episode output of the rolled out scene\n \"\"\"\n\n # Set the reset_scene_id to 'idx'\n env.reset_scene_id = idx\n \n # Rollout step-by-step\n obs = env.reset()\n while True:\n action = dummy_policy(obs)\n obs, _, done, info = env.step(action)\n if done:\n break\n \n # The episode outputs are present in the key \"sim_outs\"\n sim_out = info[\"sim_outs\"][0]\n return sim_out\n\n# Rollout one episode\nsim_out = rollout_episode(env)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Visualize the episode from the environment\n\nWe can easily visualize the outputs obtained by rolling out episodes in the L5Kit using the Bokeh visualizer.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# might change with different rasterizer\nmap_API = env.dataset.rasterizer.sem_rast.mapAPI\n\ndef visualize_outputs(sim_outs, map_API):\n for sim_out in sim_outs: # for each scene\n vis_in = episode_out_to_visualizer_scene_gym_cle(sim_out, map_API)\n show(visualize(sim_out.scene_id, vis_in))\n\noutput_notebook()\nvisualize_outputs([sim_out], map_API)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Calculate the performance metrics from the episode outputs\n\nWe can also calculate the various quantitative metrics on the rolled out episode output. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def quantify_outputs(sim_outs, metric_set=None):\n metric_set = metric_set if metric_set is not None else L2DisplacementYawMetricSet()\n\n metric_set.evaluate(sim_outs)\n scene_results = metric_set.evaluator.scene_metric_results\n fields = [\"scene_id\", \"FDE\", \"ADE\"]\n table = PrettyTable(field_names=fields)\n tot_fde = 0.0\n tot_ade = 0.0\n for scene_id in scene_results:\n scene_metrics = scene_results[scene_id]\n ade_error = scene_metrics[\"displacement_error_l2\"][1:].mean()\n fde_error = scene_metrics['displacement_error_l2'][-1]\n table.add_row([scene_id, round(fde_error.item(), 4), round(ade_error.item(), 4)])\n tot_fde += fde_error.item()\n tot_ade += ade_error.item()\n\n ave_fde = tot_fde / len(scene_results)\n ave_ade = tot_ade / len(scene_results)\n table.add_row([\"Overall\", round(ave_fde, 4), round(ave_ade, 4)])\n print(table)\n\n\nquantify_outputs([sim_out])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a34453e45e56a2f23a3466d7e1d2e1a29884eb1
| 80,749 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Learning/R_Fundamental.ipynb
|
Maulanaaz/R
|
17425cda964e39bc087faebaf71c7de9b0bb66bb
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2020-10-01T15:52:58.000Z
|
2020-10-01T15:54:30.000Z
|
Learning/R_Fundamental.ipynb
|
Maulanaaz/R
|
17425cda964e39bc087faebaf71c7de9b0bb66bb
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Learning/R_Fundamental.ipynb
|
Maulanaaz/R
|
17425cda964e39bc087faebaf71c7de9b0bb66bb
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 77.419942 | 14,352 | 0.627909 |
[
[
[
"##### Function \"print\" for prints the specified message to the screen, or other standard output device",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(5+5)\nprint(\"Hello World\")\nprint(TRUE)",
"[1] 10\n[1] \"Hello World\"\n[1] TRUE\n"
],
[
"----------------------",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### R is case sensitive",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(\"Me\")\n#Not same with\nprint(\"ME\")\n\nprint(\"01\")\n#Not same with\nprint(\"1\")",
"[1] \"Me\"\n[1] \"ME\"\n[1] \"01\"\n[1] \"1\"\n"
],
[
"----------------------",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"###### \"c\" Function for makes continues number",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"c(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10)\n#Same with\nc(1:10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"----------------------",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### Variable in R",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"a <- \"Hello World\"\nb <- 57\nprint(a)\nprint(b)",
"[1] \"Hello World\"\n[1] 57\n"
],
[
"----------------------",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### Making Vector in R",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Vector <- c(51,45,67)\nprint(Vector)",
"[1] 51 45 67\n"
],
[
"----------------------",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### Continues Vector and Manual Vector",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"manual <- c(10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20)\n#Same with\nvector <- c(10:20)\n\nprint(manual)\nprint(vector)",
" [1] 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20\n [1] 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20\n"
],
[
"----------------------",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### Vector can contains text",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"vector <- c(\"I\",\"Love\",\"You\")\nprint(vector)",
"[1] \"I\" \"Love\" \"You\" \n"
],
[
"----------------------",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### Vector Indexing",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"vector <- c(80,85,87,83,82,98,93,100)\nprint(vector[[2]]) #Print index number 2 from left\nprint(vector[6]) #Print index number 6 from left\nprint(vector[5:8]) #Print index number 5 to 8 from left",
"[1] 85\n[1] 98\n[1] 82 98 93 100\n"
],
[
"----------------------",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### Named Vector",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"named <- c(language=\"R\",machine_learning=\"Yes\",data_mining=\"Yes\")\nprint(named)\nprint(named[\"machine_learning\"]) #Print object named \"machine_learning\"",
" language machine_learning data_mining \n \"R\" \"Yes\" \"Yes\" \nmachine_learning \n \"Yes\" \n"
],
[
"----------------------",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### List",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"alist <- list(\"I\",\"am\",100,\"%\",\"Human\")\nprint(alist)",
"[[1]]\n[1] \"I\"\n\n[[2]]\n[1] \"am\"\n\n[[3]]\n[1] 100\n\n[[4]]\n[1] \"%\"\n\n[[5]]\n[1] \"Human\"\n\n"
],
[
"----------------------",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### List Indexing",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"alist <- list(\"I\",\"am\",100,\"%\",\"Human\")\nprint(alist[3]) #Print index number 3\nprint(alist[1:4]) #Print index number 1 to 4",
"[[1]]\n[1] 100\n\n[[1]]\n[1] \"I\"\n\n[[2]]\n[1] \"am\"\n\n[[3]]\n[1] 100\n\n[[4]]\n[1] \"%\"\n\n"
],
[
"----------------------",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### Data Frame in R",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"jumlah_mahasiswa <- c(450,670,490,421,577)\nfakultas <- c(\"Teknik Pertanian\",\"Sistem Informasi\",\"Statistika\",\"Matematika\",\"Ilmu Komputer\")\ndataframe <- data.frame(fakultas,jumlah_mahasiswa)\nprint(dataframe)",
" fakultas jumlah_mahasiswa\n1 Teknik Pertanian 450\n2 Sistem Informasi 670\n3 Statistika 490\n4 Matematika 421\n5 Ilmu Komputer 577\n"
],
[
"----------------------",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### Taking column from data frame",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"jumlah_mahasiswa <- c(450,670,490,421,577)\nfakultas <- c(\"Teknik Pertanian\",\"Sistem Informasi\",\"Statistika\",\"Matematika\",\"Ilmu Komputer\")\ndataframe <- data.frame(fakultas,jumlah_mahasiswa)\ndataframe$fakultas\ndataframe$jumlah_mahasiswa",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"----------------------",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### Making chart with ggplot2",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"library(ggplot2) #Importing ggplot2 library\njumlah_mahasiswa <- c(450,670,490,421,577)\nfakultas <- c(\"Teknik Pertanian\",\"Sistem Informasi\",\"Statistika\",\"Matematika\",\"Ilmu Komputer\")\ndataframe <- data.frame(prodi,jumlah_mahasiswa)\nplot <- ggplot(dataframe,aes(x=fakultas,y=jumlah_mahasiswa,fill=fakultas))\nplot <- plot + geom_bar(width=0.9,stat=\"identity\")\nplot",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"----------------------",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### Adding title and other informations",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"library(ggplot2) #Importing ggplot2 library\njumlah_mahasiswa <- c(450,670,490,421,577)\nfakultas <- c(\"Teknik Pertanian\",\"Sistem Informasi\",\"Statistika\",\"Matematika\",\"Ilmu Komputer\")\ndataframe <- data.frame(prodi,jumlah_mahasiswa)\nplot <- ggplot(dataframe,aes(x=fakultas,y=jumlah_mahasiswa,fill=fakultas))\nplot <- plot + geom_bar(width=0.9,stat=\"identity\")\nplot <- plot + ggtitle(\"Grafik Jumlah Mahasiswa Terhadap Fakultas\") #Adding title\nplot <- plot + xlab(\"Fakultas\") #Adding bottom information\nplot <- plot + ylab(\"Jumlah Mahasiswa\") # Adding side information\nplot",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"----------------------",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### Reading .xlsx file in R",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"library(openxlsx) #Importing library for reading .xlsx file\nread <- read.xlsx(\"https://academy.dqlab.id/dataset/mahasiswa.xlsx\",sheet = \"Sheet 1\")\nread",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"----------------------",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### Making graph from .xlsx file",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"library(openxlsx) #Importing library for reading .xlsx file\nread <- read.xlsx(\"https://academy.dqlab.id/dataset/mahasiswa.xlsx\",sheet = \"Sheet 1\")\nplot <- ggplot(read,aes(x=Fakultas,y=JUMLAH,fill=Fakultas))\nplot <- plot + geom_bar(width=0.9,stat=\"identity\")\nplot",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Learning Source : www.dqlab.id",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a345709904e007cd7c94ae8f0602636f9fbda68
| 8,727 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
2_ServeToModels/00_Reproduce_WaMDaM_WEAP_paper_Directions_and_Use_Cases.ipynb
|
WamdamProject/JupyteNotebooks
|
d2c256c025268f746698e94ae7333deb7969817d
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
2_ServeToModels/00_Reproduce_WaMDaM_WEAP_paper_Directions_and_Use_Cases.ipynb
|
WamdamProject/JupyteNotebooks
|
d2c256c025268f746698e94ae7333deb7969817d
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
2_ServeToModels/00_Reproduce_WaMDaM_WEAP_paper_Directions_and_Use_Cases.ipynb
|
WamdamProject/JupyteNotebooks
|
d2c256c025268f746698e94ae7333deb7969817d
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null | 44.075758 | 711 | 0.650624 |
[
[
[
"## Instructions to reproduce the WaMDaM / WEAP paper use case results\n\n\n### Open Source Python Software To Manage, Populate, Compare, And Analyze Weap Models And Scenarios \n\n\n#### By Adel M. Abdallah, Feb 2022\n\n### Abstract\nThe Water Evaluation and Planning system (WEAP) is a proprietary systems simulation software that is used globally for water management modeling studies. WEAP has a simple and powerful Application Programming Interface (API), however most WEAP modelers manually populate data into their WEAP area (model), which is error-prone and time-consuming. Remaining modelers use the WEAP API and data and scenarios. \n\nWe contribute open-source Python software that automates and generalizes the processes for WEAP modelers to prepare and load data and run sensitivity analysis for multiple WEAP areas and their scenarios without writing code. The software also allows others to export and store model data and run independent analyses. We demonstrate the software with existing WEAP areas for the 1) Bear River Basin in Idaho and Utah and 2) Weber River Basin in Utah. Results for changes in reservoir capacity, demand, evaporation, and river headflows show estimated demand reliability across all simulation years and scenarios. Demand sites reliability in both the Bear and Weber Rivers models varied from 50% to 100%.\n\nWaMDaM software developments continues at the WaMDaM project on GitHub at https://github.com/WamdamProject",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### The instructions here will help you to reproduce: \n\n* Use Case 1: Estimate and compare how regulated two river basins are based on two existing WEAP models \n \n\n* Use case 2: estimate sensitivity of different water systems’ reliability to meet demand \n\n\n### Required Software \n* Windows 7 or 10 64-bit operating systems, both up to date. \n* Internet connection and Google Chrome v. 69 or FireFox Quantum v. 62.0 browsers \n* Microsoft Excel (versions after 2007) \n* Python 3.7. \n\n* Water Evaluation and Planning System (WEAP) (WEAP requires a license to run the model: Version 2019.2 or newer If you don’t have access to a WEAP license, you will still be able to replicate all the results of the first use. \n\n### Required online accounts (if you don't have them)\n* Free: create a user account at https://openagua.org. After you create the account, email Adel Abdalla @ [email protected] to let him know your username (email) to share a project with you as part of replicating the use case. \n* Free: create a user account at https://www.hydroshare.org/\n\n\n### Difficulty level\nVery little coding or database experience are needed to reproduce the work but some knowledge of coding like in Python and awareness of Structure Query Language (SQL) are a plus. \n\n**Options and required time** \nPlease expect to spend a couple of of hours to complete these directions. This work is 6 years in the making so spending a a couple of hours to learn and reproduce the results is quite amazing! \n\n\n### How to use the Notebook \n\nExecute the Notebook cells that contain Python code by pressing `Shift-Enter`, or by pressing the play button <img style='display:inline;padding-bottom:15px' src='play-button.png'> on the toolbar above. \n\n**Note:** Any changes you make to the live Notebooks are temporary and will be lost once you close it. You always can start a new live Notebook that has the original content. \n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Preperations (step 1-2)\n-----------------------------------------------------------\n\n### Step 1: Setup_local_Jupyter\n\n[01_Step 1_Setup_local_Jupyter](01_Step1_Setup_local_Jupyter.ipynb) \n<br>\n\n### Step 2: Install_WaMDaM_Wizard_Connect to SQLite\n\n \n[02_Step 2_Step2_Install_WaMDaM_Wizard_Connect](02_Step2_Install_WaMDaM_Wizard_Connect.ipynb) \n<br>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n# Use Case 1: Estimate and compare how regulated two river basins are based on two existing WEAP models\n-----------------------------------------------------------\n\n### Step 3: Use WaMDaM Wizard to Extract WEAP models into WaMDaM\n \n[03_Step 3_Step3_Visualize_OpenAgua](03_Step3_Visualize_OpenAgua.ipynb) \n<br>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Use Case 2\n--------------------------------------------------------------\n### Step 4: Create_New_Scenarios_Edit_OpenAgua\n \n[Step4_Create_New_Scenarios_Edit_OpenAgua](https://github.com/WamdamProject/WaMDaM_JupyterNotebooks/blob/master/2_VisualizePublish/04_Step4_Create_New_Scenarios_Edit_OpenAgua.ipynb) \n<br>\n\n\n### Step 5: Download_to_WaMDaM\n \n[Step5_EditOpenAgua_download_to_WaMDaM](https://github.com/WamdamProject/WaMDaM_JupyterNotebooks/blob/master/2_VisualizePublish/05_Step5_download_to_WaMDaM.ipynb) \n<br>\n\n\n\n### Step 6: Serve_NewScenarios_WASH\n \n[Step6_Serve_NewScenarios_WASH](https://github.com/WamdamProject/WaMDaM_JupyterNotebooks/blob/master/2_VisualizePublish/06_Step6_Serve_NewScenarios_WASH.ipynb) \n<br>\n\n\n\n### Step 7: Serve_NewScenarios_WEAP\n \n[Step7_Serve_NewScenarios_WEAP](https://github.com/WamdamProject/WaMDaM_JupyterNotebooks/blob/master/2_VisualizePublish/07_Step7_Serve_NewScenarios_WEAP.ipynb) \n<br>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n# Use Case 3\n\n\n### Step 8: Publish the Bear River and Monterrey models into HydroShare \n[Step8_Publish_HydroShare](https://github.com/WamdamProject/WaMDaM_JupyterNotebooks/blob/master/2_VisualizePublish/08_Step8_Publish_HydroShare.ipynb) \n<br>\n\n### Step 9: Query_Analyze_HydroShare_Monterrey_Mexico\n \n[Step9_Query_Analyze_HydroShare_Monterrey_Mexico](https://github.com/WamdamProject/WaMDaM_JupyterNotebooks/blob/master/2_VisualizePublish/09_Step9_Query_Analyze_HydroShare_Monterrey_Mexico.ipynb) \n<br>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Info\n\n### Sponsors and Credit\nThis material is based upon work [supported](http://docs.wamdam.org/SponsorsCredit/) by the National Science Foundation (NSF) under Grants 1135482 (CI-Water) and 1208732 (iUtah). Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the NSF.\n\n### License\nWaMDaM and its products are disturbed under a BSD 3-Clause [license](http://docs.wamdam.org/License/)\n\n### Authors\n[Adel M. Abdallah](http://adelmabdallah.com/) has been the lead in WaMDaM development as part of his PhD dissertation at Utah State University under the advising of Dr. David Rosenberg. \n\nIf you have questions, feel free to email me at: [[email protected]](mailto:[email protected]) \n\n### Citation\nAdel M. Abdallah, David Rheinheimer, David E. Rosenberg, Steve Knox, Julien J Harou, in review. A Software Ecosystem to Store, Visualize, and Publish Modelling Data for Water Resources Systems. Journal of Hydroinformatics.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# The End :) Congratulations!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4a345a3f9a1a7c3b6e2adda34e112ad3e949a42b
| 42,978 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
site/en-snapshot/tutorials/generative/pix2pix.ipynb
|
justaverygoodboy/docs-l10n
|
8d4857750f2b5e8e6889acbb4b1e2f98ad7ce34e
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2020-09-02T07:40:29.000Z
|
2020-09-02T07:40:29.000Z
|
site/en-snapshot/tutorials/generative/pix2pix.ipynb
|
justaverygoodboy/docs-l10n
|
8d4857750f2b5e8e6889acbb4b1e2f98ad7ce34e
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
site/en-snapshot/tutorials/generative/pix2pix.ipynb
|
justaverygoodboy/docs-l10n
|
8d4857750f2b5e8e6889acbb4b1e2f98ad7ce34e
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 33.136469 | 486 | 0.506492 |
[
[
[
"##### Copyright 2019 The TensorFlow Authors.\n\nLicensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the \"License\");",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#@title Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the \"License\");\n# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.\n# You may obtain a copy of the License at\n#\n# https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0\n#\n# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software\n# distributed under the License is distributed on an \"AS IS\" BASIS,\n# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.\n# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and\n# limitations under the License.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Pix2Pix",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<table class=\"tfo-notebook-buttons\" align=\"left\">\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/generative/pix2pix\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/tf_logo_32px.png\" />View on TensorFlow.org</a>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/tensorflow/docs/blob/master/site/en/tutorials/generative/pix2pix.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/colab_logo_32px.png\" />Run in Google Colab</a>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://github.com/tensorflow/docs/blob/master/site/en/tutorials/generative/pix2pix.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/GitHub-Mark-32px.png\" />View source on GitHub</a>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a href=\"https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow_docs/docs/site/en/tutorials/generative/pix2pix.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/download_logo_32px.png\" />Download notebook</a>\n </td>\n</table>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"This notebook demonstrates image to image translation using conditional GAN's, as described in [Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.07004). Using this technique we can colorize black and white photos, convert google maps to google earth, etc. Here, we convert building facades to real buildings.\n\nIn example, we will use the [CMP Facade Database](http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz/~tylecr1/facade/), helpfully provided by the [Center for Machine Perception](http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz/) at the [Czech Technical University in Prague](https://www.cvut.cz/). To keep our example short, we will use a preprocessed [copy](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~tinghuiz/projects/pix2pix/datasets/) of this dataset, created by the authors of the [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.07004) above.\n\nEach epoch takes around 15 seconds on a single V100 GPU.\n\nBelow is the output generated after training the model for 200 epochs.\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Import TensorFlow and other libraries",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import tensorflow as tf\n\nimport os\nimport time\n\nfrom matplotlib import pyplot as plt\nfrom IPython import display",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!pip install -U tensorboard",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Load the dataset\n\nYou can download this dataset and similar datasets from [here](https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~tinghuiz/projects/pix2pix/datasets). As mentioned in the [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.07004) we apply random jittering and mirroring to the training dataset.\n\n* In random jittering, the image is resized to `286 x 286` and then randomly cropped to `256 x 256`\n* In random mirroring, the image is randomly flipped horizontally i.e left to right.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"_URL = 'https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~tinghuiz/projects/pix2pix/datasets/facades.tar.gz'\n\npath_to_zip = tf.keras.utils.get_file('facades.tar.gz',\n origin=_URL,\n extract=True)\n\nPATH = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(path_to_zip), 'facades/')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"BUFFER_SIZE = 400\nBATCH_SIZE = 1\nIMG_WIDTH = 256\nIMG_HEIGHT = 256",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def load(image_file):\n image = tf.io.read_file(image_file)\n image = tf.image.decode_jpeg(image)\n\n w = tf.shape(image)[1]\n\n w = w // 2\n real_image = image[:, :w, :]\n input_image = image[:, w:, :]\n\n input_image = tf.cast(input_image, tf.float32)\n real_image = tf.cast(real_image, tf.float32)\n\n return input_image, real_image",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"inp, re = load(PATH+'train/100.jpg')\n# casting to int for matplotlib to show the image\nplt.figure()\nplt.imshow(inp/255.0)\nplt.figure()\nplt.imshow(re/255.0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def resize(input_image, real_image, height, width):\n input_image = tf.image.resize(input_image, [height, width],\n method=tf.image.ResizeMethod.NEAREST_NEIGHBOR)\n real_image = tf.image.resize(real_image, [height, width],\n method=tf.image.ResizeMethod.NEAREST_NEIGHBOR)\n\n return input_image, real_image",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def random_crop(input_image, real_image):\n stacked_image = tf.stack([input_image, real_image], axis=0)\n cropped_image = tf.image.random_crop(\n stacked_image, size=[2, IMG_HEIGHT, IMG_WIDTH, 3])\n\n return cropped_image[0], cropped_image[1]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# normalizing the images to [-1, 1]\n\ndef normalize(input_image, real_image):\n input_image = (input_image / 127.5) - 1\n real_image = (real_image / 127.5) - 1\n\n return input_image, real_image",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"@tf.function()\ndef random_jitter(input_image, real_image):\n # resizing to 286 x 286 x 3\n input_image, real_image = resize(input_image, real_image, 286, 286)\n\n # randomly cropping to 256 x 256 x 3\n input_image, real_image = random_crop(input_image, real_image)\n\n if tf.random.uniform(()) > 0.5:\n # random mirroring\n input_image = tf.image.flip_left_right(input_image)\n real_image = tf.image.flip_left_right(real_image)\n\n return input_image, real_image",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"As you can see in the images below\nthat they are going through random jittering\nRandom jittering as described in the paper is to\n\n1. Resize an image to bigger height and width\n2. Randomly crop to the target size\n3. Randomly flip the image horizontally",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(6, 6))\nfor i in range(4):\n rj_inp, rj_re = random_jitter(inp, re)\n plt.subplot(2, 2, i+1)\n plt.imshow(rj_inp/255.0)\n plt.axis('off')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def load_image_train(image_file):\n input_image, real_image = load(image_file)\n input_image, real_image = random_jitter(input_image, real_image)\n input_image, real_image = normalize(input_image, real_image)\n\n return input_image, real_image",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def load_image_test(image_file):\n input_image, real_image = load(image_file)\n input_image, real_image = resize(input_image, real_image,\n IMG_HEIGHT, IMG_WIDTH)\n input_image, real_image = normalize(input_image, real_image)\n\n return input_image, real_image",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Input Pipeline",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"train_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.list_files(PATH+'train/*.jpg')\ntrain_dataset = train_dataset.map(load_image_train,\n num_parallel_calls=tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE)\ntrain_dataset = train_dataset.shuffle(BUFFER_SIZE)\ntrain_dataset = train_dataset.batch(BATCH_SIZE)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"test_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.list_files(PATH+'test/*.jpg')\ntest_dataset = test_dataset.map(load_image_test)\ntest_dataset = test_dataset.batch(BATCH_SIZE)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Build the Generator\n * The architecture of generator is a modified U-Net.\n * Each block in the encoder is (Conv -> Batchnorm -> Leaky ReLU)\n * Each block in the decoder is (Transposed Conv -> Batchnorm -> Dropout(applied to the first 3 blocks) -> ReLU)\n * There are skip connections between the encoder and decoder (as in U-Net).\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"OUTPUT_CHANNELS = 3",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def downsample(filters, size, apply_batchnorm=True):\n initializer = tf.random_normal_initializer(0., 0.02)\n\n result = tf.keras.Sequential()\n result.add(\n tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters, size, strides=2, padding='same',\n kernel_initializer=initializer, use_bias=False))\n\n if apply_batchnorm:\n result.add(tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization())\n\n result.add(tf.keras.layers.LeakyReLU())\n\n return result",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"down_model = downsample(3, 4)\ndown_result = down_model(tf.expand_dims(inp, 0))\nprint (down_result.shape)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def upsample(filters, size, apply_dropout=False):\n initializer = tf.random_normal_initializer(0., 0.02)\n\n result = tf.keras.Sequential()\n result.add(\n tf.keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose(filters, size, strides=2,\n padding='same',\n kernel_initializer=initializer,\n use_bias=False))\n\n result.add(tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization())\n\n if apply_dropout:\n result.add(tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.5))\n\n result.add(tf.keras.layers.ReLU())\n\n return result",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"up_model = upsample(3, 4)\nup_result = up_model(down_result)\nprint (up_result.shape)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def Generator():\n inputs = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=[256,256,3])\n\n down_stack = [\n downsample(64, 4, apply_batchnorm=False), # (bs, 128, 128, 64)\n downsample(128, 4), # (bs, 64, 64, 128)\n downsample(256, 4), # (bs, 32, 32, 256)\n downsample(512, 4), # (bs, 16, 16, 512)\n downsample(512, 4), # (bs, 8, 8, 512)\n downsample(512, 4), # (bs, 4, 4, 512)\n downsample(512, 4), # (bs, 2, 2, 512)\n downsample(512, 4), # (bs, 1, 1, 512)\n ]\n\n up_stack = [\n upsample(512, 4, apply_dropout=True), # (bs, 2, 2, 1024)\n upsample(512, 4, apply_dropout=True), # (bs, 4, 4, 1024)\n upsample(512, 4, apply_dropout=True), # (bs, 8, 8, 1024)\n upsample(512, 4), # (bs, 16, 16, 1024)\n upsample(256, 4), # (bs, 32, 32, 512)\n upsample(128, 4), # (bs, 64, 64, 256)\n upsample(64, 4), # (bs, 128, 128, 128)\n ]\n\n initializer = tf.random_normal_initializer(0., 0.02)\n last = tf.keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose(OUTPUT_CHANNELS, 4,\n strides=2,\n padding='same',\n kernel_initializer=initializer,\n activation='tanh') # (bs, 256, 256, 3)\n\n x = inputs\n\n # Downsampling through the model\n skips = []\n for down in down_stack:\n x = down(x)\n skips.append(x)\n\n skips = reversed(skips[:-1])\n\n # Upsampling and establishing the skip connections\n for up, skip in zip(up_stack, skips):\n x = up(x)\n x = tf.keras.layers.Concatenate()([x, skip])\n\n x = last(x)\n\n return tf.keras.Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=x)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"generator = Generator()\ntf.keras.utils.plot_model(generator, show_shapes=True, dpi=64)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"gen_output = generator(inp[tf.newaxis,...], training=False)\nplt.imshow(gen_output[0,...])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"* **Generator loss**\n * It is a sigmoid cross entropy loss of the generated images and an **array of ones**.\n * The [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.07004) also includes L1 loss which is MAE (mean absolute error) between the generated image and the target image.\n * This allows the generated image to become structurally similar to the target image.\n * The formula to calculate the total generator loss = gan_loss + LAMBDA * l1_loss, where LAMBDA = 100. This value was decided by the authors of the [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.07004).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The training procedure for the generator is shown below:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"LAMBDA = 100",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def generator_loss(disc_generated_output, gen_output, target):\n gan_loss = loss_object(tf.ones_like(disc_generated_output), disc_generated_output)\n\n # mean absolute error\n l1_loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.abs(target - gen_output))\n\n total_gen_loss = gan_loss + (LAMBDA * l1_loss)\n\n return total_gen_loss, gan_loss, l1_loss",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Build the Discriminator\n * The Discriminator is a PatchGAN.\n * Each block in the discriminator is (Conv -> BatchNorm -> Leaky ReLU)\n * The shape of the output after the last layer is (batch_size, 30, 30, 1)\n * Each 30x30 patch of the output classifies a 70x70 portion of the input image (such an architecture is called a PatchGAN).\n * Discriminator receives 2 inputs.\n * Input image and the target image, which it should classify as real.\n * Input image and the generated image (output of generator), which it should classify as fake.\n * We concatenate these 2 inputs together in the code (`tf.concat([inp, tar], axis=-1)`)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def Discriminator():\n initializer = tf.random_normal_initializer(0., 0.02)\n\n inp = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=[256, 256, 3], name='input_image')\n tar = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=[256, 256, 3], name='target_image')\n\n x = tf.keras.layers.concatenate([inp, tar]) # (bs, 256, 256, channels*2)\n\n down1 = downsample(64, 4, False)(x) # (bs, 128, 128, 64)\n down2 = downsample(128, 4)(down1) # (bs, 64, 64, 128)\n down3 = downsample(256, 4)(down2) # (bs, 32, 32, 256)\n\n zero_pad1 = tf.keras.layers.ZeroPadding2D()(down3) # (bs, 34, 34, 256)\n conv = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(512, 4, strides=1,\n kernel_initializer=initializer,\n use_bias=False)(zero_pad1) # (bs, 31, 31, 512)\n\n batchnorm1 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(conv)\n\n leaky_relu = tf.keras.layers.LeakyReLU()(batchnorm1)\n\n zero_pad2 = tf.keras.layers.ZeroPadding2D()(leaky_relu) # (bs, 33, 33, 512)\n\n last = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(1, 4, strides=1,\n kernel_initializer=initializer)(zero_pad2) # (bs, 30, 30, 1)\n\n return tf.keras.Model(inputs=[inp, tar], outputs=last)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"discriminator = Discriminator()\ntf.keras.utils.plot_model(discriminator, show_shapes=True, dpi=64)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"disc_out = discriminator([inp[tf.newaxis,...], gen_output], training=False)\nplt.imshow(disc_out[0,...,-1], vmin=-20, vmax=20, cmap='RdBu_r')\nplt.colorbar()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Discriminator loss**\n * The discriminator loss function takes 2 inputs; **real images, generated images**\n * real_loss is a sigmoid cross entropy loss of the **real images** and an **array of ones(since these are the real images)**\n * generated_loss is a sigmoid cross entropy loss of the **generated images** and an **array of zeros(since these are the fake images)**\n * Then the total_loss is the sum of real_loss and the generated_loss\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"loss_object = tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(from_logits=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def discriminator_loss(disc_real_output, disc_generated_output):\n real_loss = loss_object(tf.ones_like(disc_real_output), disc_real_output)\n\n generated_loss = loss_object(tf.zeros_like(disc_generated_output), disc_generated_output)\n\n total_disc_loss = real_loss + generated_loss\n\n return total_disc_loss",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The training procedure for the discriminator is shown below.\n\nTo learn more about the architecture and the hyperparameters you can refer the [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.07004).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Define the Optimizers and Checkpoint-saver\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"generator_optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(2e-4, beta_1=0.5)\ndiscriminator_optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(2e-4, beta_1=0.5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"checkpoint_dir = './training_checkpoints'\ncheckpoint_prefix = os.path.join(checkpoint_dir, \"ckpt\")\ncheckpoint = tf.train.Checkpoint(generator_optimizer=generator_optimizer,\n discriminator_optimizer=discriminator_optimizer,\n generator=generator,\n discriminator=discriminator)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Generate Images\n\nWrite a function to plot some images during training.\n\n* We pass images from the test dataset to the generator.\n* The generator will then translate the input image into the output.\n* Last step is to plot the predictions and **voila!**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Note: The `training=True` is intentional here since\nwe want the batch statistics while running the model\non the test dataset. If we use training=False, we will get\nthe accumulated statistics learned from the training dataset\n(which we don't want)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def generate_images(model, test_input, tar):\n prediction = model(test_input, training=True)\n plt.figure(figsize=(15,15))\n\n display_list = [test_input[0], tar[0], prediction[0]]\n title = ['Input Image', 'Ground Truth', 'Predicted Image']\n\n for i in range(3):\n plt.subplot(1, 3, i+1)\n plt.title(title[i])\n # getting the pixel values between [0, 1] to plot it.\n plt.imshow(display_list[i] * 0.5 + 0.5)\n plt.axis('off')\n plt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for example_input, example_target in test_dataset.take(1):\n generate_images(generator, example_input, example_target)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Training\n\n* For each example input generate an output.\n* The discriminator receives the input_image and the generated image as the first input. The second input is the input_image and the target_image.\n* Next, we calculate the generator and the discriminator loss.\n* Then, we calculate the gradients of loss with respect to both the generator and the discriminator variables(inputs) and apply those to the optimizer.\n* Then log the losses to TensorBoard.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"EPOCHS = 150",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import datetime\nlog_dir=\"logs/\"\n\nsummary_writer = tf.summary.create_file_writer(\n log_dir + \"fit/\" + datetime.datetime.now().strftime(\"%Y%m%d-%H%M%S\"))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"@tf.function\ndef train_step(input_image, target, epoch):\n with tf.GradientTape() as gen_tape, tf.GradientTape() as disc_tape:\n gen_output = generator(input_image, training=True)\n\n disc_real_output = discriminator([input_image, target], training=True)\n disc_generated_output = discriminator([input_image, gen_output], training=True)\n\n gen_total_loss, gen_gan_loss, gen_l1_loss = generator_loss(disc_generated_output, gen_output, target)\n disc_loss = discriminator_loss(disc_real_output, disc_generated_output)\n\n generator_gradients = gen_tape.gradient(gen_total_loss,\n generator.trainable_variables)\n discriminator_gradients = disc_tape.gradient(disc_loss,\n discriminator.trainable_variables)\n\n generator_optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(generator_gradients,\n generator.trainable_variables))\n discriminator_optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(discriminator_gradients,\n discriminator.trainable_variables))\n\n with summary_writer.as_default():\n tf.summary.scalar('gen_total_loss', gen_total_loss, step=epoch)\n tf.summary.scalar('gen_gan_loss', gen_gan_loss, step=epoch)\n tf.summary.scalar('gen_l1_loss', gen_l1_loss, step=epoch)\n tf.summary.scalar('disc_loss', disc_loss, step=epoch)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The actual training loop:\n\n* Iterates over the number of epochs.\n* On each epoch it clears the display, and runs `generate_images` to show it's progress.\n* On each epoch it iterates over the training dataset, printing a '.' for each example.\n* It saves a checkpoint every 20 epochs.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def fit(train_ds, epochs, test_ds):\n for epoch in range(epochs):\n start = time.time()\n\n display.clear_output(wait=True)\n\n for example_input, example_target in test_ds.take(1):\n generate_images(generator, example_input, example_target)\n print(\"Epoch: \", epoch)\n\n # Train\n for n, (input_image, target) in train_ds.enumerate():\n print('.', end='')\n if (n+1) % 100 == 0:\n print()\n train_step(input_image, target, epoch)\n print()\n\n # saving (checkpoint) the model every 20 epochs\n if (epoch + 1) % 20 == 0:\n checkpoint.save(file_prefix = checkpoint_prefix)\n\n print ('Time taken for epoch {} is {} sec\\n'.format(epoch + 1,\n time.time()-start))\n checkpoint.save(file_prefix = checkpoint_prefix)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This training loop saves logs you can easily view in TensorBoard to monitor the training progress. Working locally you would launch a separate tensorboard process. In a notebook, if you want to monitor with TensorBoard it's easiest to launch the viewer before starting the training.\n\nTo launch the viewer paste the following into a code-cell:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#docs_infra: no_execute\n%load_ext tensorboard\n%tensorboard --logdir {log_dir}",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now run the training loop:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"fit(train_dataset, EPOCHS, test_dataset)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"If you want to share the TensorBoard results _publicly_ you can upload the logs to [TensorBoard.dev](https://tensorboard.dev/) by copying the following into a code-cell.\n\nNote: This requires a Google account.\n\n```\n!tensorboard dev upload --logdir {log_dir}\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Caution: This command does not terminate. It's designed to continuously upload the results of long-running experiments. Once your data is uploaded you need to stop it using the \"interrupt execution\" option in your notebook tool.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"You can view the [results of a previous run](https://tensorboard.dev/experiment/lZ0C6FONROaUMfjYkVyJqw) of this notebook on [TensorBoard.dev](https://tensorboard.dev/).\n\nTensorBoard.dev is a managed experience for hosting, tracking, and sharing ML experiments with everyone.\n\nIt can also included inline using an `<iframe>`:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"display.IFrame(\n src=\"https://tensorboard.dev/experiment/lZ0C6FONROaUMfjYkVyJqw\",\n width=\"100%\",\n height=\"1000px\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Interpreting the logs from a GAN is more subtle than a simple classification or regression model. Things to look for::\n\n* Check that neither model has \"won\". If either the `gen_gan_loss` or the `disc_loss` gets very low it's an indicator that this model is dominating the other, and you are not successfully training the combined model.\n* The value `log(2) = 0.69` is a good reference point for these losses, as it indicates a perplexity of 2: That the discriminator is on average equally uncertain about the two options.\n* For the `disc_loss` a value below `0.69` means the discriminator is doing better than random, on the combined set of real+generated images.\n* For the `gen_gan_loss` a value below `0.69` means the generator i doing better than random at foolding the descriminator.\n* As training progresses the `gen_l1_loss` should go down.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Restore the latest checkpoint and test",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!ls {checkpoint_dir}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# restoring the latest checkpoint in checkpoint_dir\ncheckpoint.restore(tf.train.latest_checkpoint(checkpoint_dir))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Generate using test dataset",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Run the trained model on a few examples from the test dataset\nfor inp, tar in test_dataset.take(5):\n generate_images(generator, inp, tar)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a347ec335bd20195b45ce76db04e6ba26df356f
| 6,902 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
exceptions/Lab/ManagingThrowingAndCatchingExceptions.ipynb
|
csharpfritz/csharp-workshop
|
7d731a5b72635b60e0553a5f3e8f9be1a3755193
|
[
"MIT"
] | 6 |
2021-06-11T18:48:44.000Z
|
2022-01-30T11:52:42.000Z
|
exceptions/Lab/ManagingThrowingAndCatchingExceptions.ipynb
|
csharpfritz/csharp-workshop
|
7d731a5b72635b60e0553a5f3e8f9be1a3755193
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
exceptions/Lab/ManagingThrowingAndCatchingExceptions.ipynb
|
csharpfritz/csharp-workshop
|
7d731a5b72635b60e0553a5f3e8f9be1a3755193
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2021-06-11T18:48:54.000Z
|
2021-12-18T17:26:23.000Z
| 32.556604 | 224 | 0.511736 |
[
[
[
"# Managing Throwing and Catching and Exceptions\n\nIn this workbook, we're going to work with a sample that describes a cashier's till at a store. We'll look at what happens when the cashier makes change for orders, the exceptions thrown and the danger they create.\n\nFirst, let's describe the `Till` class",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"public class Till\n{\n private int OneDollarBills;\n private int FiveDollarBills;\n private int TenDollarBills;\n private int TwentyDollarBills;\n\n public Till(int ones, int fives, int tens = 0, int twenties = 0) =>\n (OneDollarBills, FiveDollarBills, TenDollarBills, TwentyDollarBills) =\n (ones, fives, tens, twenties);\n\n public void MakeChange(int cost, int twenties, int tens = 0, int fives = 0, int ones = 0)\n {\n TwentyDollarBills += twenties;\n TenDollarBills += tens;\n FiveDollarBills += fives;\n OneDollarBills += ones;\n\n int amountPaid = twenties * 20 + tens * 10 + fives * 5 + ones;\n int changeNeeded = amountPaid - cost;\n\n if (changeNeeded < 0)\n throw new InvalidOperationException(\"Not enough money provided\");\n\n Console.WriteLine(\"Cashier Returns:\");\n\n while ((changeNeeded > 19) && (TwentyDollarBills > 0))\n {\n TwentyDollarBills--;\n changeNeeded -= 20;\n Console.WriteLine(\"\\t A twenty\");\n }\n\n while ((changeNeeded > 9) && (TenDollarBills > 0))\n {\n TenDollarBills--;\n changeNeeded -= 10;\n Console.WriteLine(\"\\t A tenner\");\n }\n\n while ((changeNeeded > 4) && (FiveDollarBills > 0))\n {\n FiveDollarBills--;\n changeNeeded -= 5;\n Console.WriteLine(\"\\t A fiver\");\n }\n\n while ((changeNeeded > 0) && (OneDollarBills > 0))\n {\n OneDollarBills--;\n changeNeeded--;\n Console.WriteLine(\"\\t A one\");\n }\n\n if (changeNeeded > 0)\n throw new InvalidOperationException(\"Can't make change. Do you have anything smaller?\");\n }\n\n public void LogTillStatus()\n {\n Console.WriteLine(\"The till currently has:\");\n Console.WriteLine($\"{TwentyDollarBills * 20} in twenties\");\n Console.WriteLine($\"{TenDollarBills * 10} in tens\");\n Console.WriteLine($\"{FiveDollarBills * 5} in fives\");\n Console.WriteLine($\"{OneDollarBills} in ones\");\n Console.WriteLine();\n }\n\n public override string ToString() =>\n $\"The till has {TwentyDollarBills * 20 + TenDollarBills * 10 + FiveDollarBills * 5 + OneDollarBills} dollars\";\n}\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now that we have our `Till`, let's set up our scenario to experiment with.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"// TheBank is our cashier's till we are working with and we'll give it some cash to start with\nvar theBank = new Till(ones: 50, fives: 20, tens: 10, twenties: 5);\n\nvar expectedTotal = 50 * 1 + 20 * 5 + 10 * 10 + 5 * 20;\n\ntheBank.LogTillStatus();\nConsole.WriteLine(theBank);\nConsole.WriteLine($\"Expected till value: {expectedTotal}\");",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now that we have set an initial value for the contents of `TheBank`, let's start working with customers and making change.\n\nWe'll define a number of transactions to run through `TheBank` and also setup a random number generator to give us the feeling of random items being purchased and we'll make change for those customers",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"int transactions = 2;\nvar valueGenerator = new Random((int)DateTime.Now.Ticks);\n\nwhile (transactions-- > 0)\n{\n int itemCost = valueGenerator.Next(2, 50);\n\n int numOnes = itemCost % 2;\n int numFives = (itemCost % 10 > 7) ? 1 : 0;\n int numTens = (itemCost % 20 > 13) ? 1 : 0;\n int numTwenties = (itemCost < 20) ? 1 : 2;\n\n try\n {\n Console.WriteLine($\"Customer making a ${itemCost} purchase\");\n Console.WriteLine($\"\\t Using {numTwenties} twenties\");\n Console.WriteLine($\"\\t Using {numTens} tenners\");\n Console.WriteLine($\"\\t Using {numFives} fivers\");\n Console.WriteLine($\"\\t Using {numOnes} silver dollar coins\");\n\n theBank.MakeChange(itemCost, numTwenties, numTens, numFives, numOnes);\n\n expectedTotal += itemCost;\n }\n catch (InvalidOperationException e)\n {\n Console.WriteLine($\"Could not make transaction: {e.Message}\");\n }\n\n Console.WriteLine(theBank);\n Console.WriteLine($\"Expected till value: {expectedTotal}\");\n Console.WriteLine(\" ------------------------------------------\");\n}",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a348190fd3ff01812979ac7bf6d87e1bbd304d1
| 15,576 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
mnist_fashion/04_consumption/consume-webservice.ipynb
|
timoklimmer/aml-template
|
905882e6ee2ae4046bb819067279deccc5bd36b2
|
[
"MIT"
] | 5 |
2020-07-27T15:24:24.000Z
|
2021-01-22T11:55:58.000Z
|
mnist_fashion/04_consumption/consume-webservice.ipynb
|
timoklimmer/aml-template
|
905882e6ee2ae4046bb819067279deccc5bd36b2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
mnist_fashion/04_consumption/consume-webservice.ipynb
|
timoklimmer/aml-template
|
905882e6ee2ae4046bb819067279deccc5bd36b2
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2020-07-27T15:24:38.000Z
|
2021-07-11T22:14:19.000Z
| 80.28866 | 9,069 | 0.800719 |
[
[
[
"# Consume deployed webservice via REST\nDemonstrates the usage of a deployed model via plain REST.\n\nREST is language-agnostic, so you should be able to query from any REST-capable programming language.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Configuration",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from environs import Env\r\nenv = Env(expand_vars=True)\r\nenv.read_env(\"foundation.env\")\r\nenv.read_env(\"service-principals.env\")\r\n\r\n# image to test\r\nIMAGE_TO_TEST = \"mnist_fashion/04_consumption/random_test_images/random-test-image-9629.png\"\r\n\r\n# endpoint of the scoring webservice\r\nSCORING_URI = \"<add your own scoring REST endpoint here>\"\r\n\r\n# auth method, either \"Token\", \"Keys\" or \"None\".\r\n# also specify additional values depending on auth method\r\nAUTH_METHOD = \"Keys\"\r\nif AUTH_METHOD == \"Keys\":\r\n AUTH_KEY = \"<add your own key here>\"\r\nelif AUTH_METHOD == \"Token\":\r\n REGION = \"eastus\"\r\n SUBSCRIPTION_ID = env(\"SUBSCRIPTION_ID\")\r\n RESOURCE_GROUP = env(\"RESOURCE_GROUP\")\r\n WORKSPACE_NAME = env(\"WORKSPACE_NAME\")\r\n SERVICE_NAME = \"mnist-fashion-service\"\r\n CONSUME_MODEL_SP_TENANT_ID = env(\"CONSUME_MODEL_SP_TENANT_ID\")\r\n CONSUME_MODEL_SP_CLIENT_ID = env(\"CONSUME_MODEL_SP_CLIENT_ID\")\r\n CONSUME_MODEL_SP_CLIENT_SECRET = env(\"CONSUME_MODEL_SP_CLIENT_SECRET\")\r\nelif AUTH_METHOD == \"None\":\r\n pass",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Load a random image and plot it",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\r\nfrom PIL import Image\r\n\r\nimage = Image.open(IMAGE_TO_TEST)\r\nplt.figure()\r\nplt.imshow(image)\r\nplt.colorbar()\r\nplt.grid(False)\r\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Invoke the webservice and show result",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import requests\r\nimport json\r\n\r\n# --- get input data\r\ninput_data = open(IMAGE_TO_TEST, \"rb\").read()\r\n# alternatively for JSON input\r\n#input_data = json.dumps({\"x\": 4711})\r\n\r\n# --- get headers\r\n# Content-Type\r\n# for binary data\r\nheaders = {\"Content-Type\": \"application/octet-stream\"}\r\n# alternatively for JSON data\r\n#headers = {\"Content-Type\": \"application/json\"}\r\n\r\n# Authorization\r\nif AUTH_METHOD == \"Token\":\r\n # get an access token for the service principal to access Azure\r\n azure_access_token = requests.post(\r\n f\"https://login.microsoftonline.com/{CONSUME_MODEL_SP_TENANT_ID}/oauth2/token\",\r\n headers={\"Content-Type\": \"application/x-www-form-urlencoded\"},\r\n data=\"grant_type=client_credentials\"\r\n + \"&resource=https%3A%2F%2Fmanagement.azure.com%2F\"\r\n + f\"&client_id={CONSUME_MODEL_SP_CLIENT_ID}\"\r\n + f\"&client_secret={CONSUME_MODEL_SP_CLIENT_SECRET}\",\r\n ).json()[\"access_token\"]\r\n\r\n # use that token to get another token for accessing the webservice\r\n # note: the token is only valid for a certain period of time.\r\n # after that time, a new token has to be used. the logic\r\n # to do this, is not implemented here yet. you can check\r\n # the current time against the refresh after time to know\r\n # if a new token is required. refreshAfter and expiryOn\r\n # are UNIX timestamps. use time.time() to get the current\r\n # timestamp.\r\n token_response = requests.post(\r\n f\"https://{REGION}.modelmanagement.azureml.net/modelmanagement/v1.0/subscriptions/{SUBSCRIPTION_ID}/resourceGroups/{RESOURCE_GROUP}/providers/Microsoft.MachineLearningServices/workspaces/{WORKSPACE_NAME}/services/{SERVICE_NAME}/token\",\r\n headers={\"Authorization\": f\"Bearer {azure_access_token}\"}\r\n ).json()\r\n access_token = token_response[\"accessToken\"]\r\n access_token_refresh_after = int(token_response[\"refreshAfter\"])\r\n access_token_expiry_on = int(token_response[\"expiryOn\"])\r\n\r\n # finally, use that token to access the webservice\r\n headers[\"Authorization\"] = f\"Bearer {access_token}\"\r\nif AUTH_METHOD == \"Keys\":\r\n headers[\"Authorization\"] = f\"Bearer {AUTH_KEY}\"\r\nif AUTH_METHOD == \"None\":\r\n # do nothing\r\n pass\r\n\r\n# --- make request and display response\r\nresponse = requests.post(SCORING_URI, input_data, headers=headers, verify=True)\r\nprint(response.json())",
"{'predicted_label': 'Sandal', 'confidence': '1.0'}\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a34887ef52d392c7ff8bd7ca15dd0ce11e077b0
| 17,951 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
DecisionTree/04_DT_Iris_data.ipynb
|
Sanjaykkukreja/AIML
|
3d17ecbf5d59db47fece39f9180916ea4d44aa65
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
DecisionTree/04_DT_Iris_data.ipynb
|
Sanjaykkukreja/AIML
|
3d17ecbf5d59db47fece39f9180916ea4d44aa65
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
DecisionTree/04_DT_Iris_data.ipynb
|
Sanjaykkukreja/AIML
|
3d17ecbf5d59db47fece39f9180916ea4d44aa65
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 23.998663 | 280 | 0.535179 |
[
[
[
"# Advanced Certification in AIML\n## A Program by IIIT-H and TalentSprint\n## Not for grades",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Learning Objective",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The objective of this experiment is to understand Decision Tree classifier.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Dataset",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### History\n\nThis is a multivariate dataset introduced by R.A.Fisher (Father of Modern Statistics) for showcasing linear discriminant analysis. This is arguably the best known dataset in Feature Selection literature.\n\n\nThe data set contains 3 classes of 50 instances each, where each class refers to a type of iris plant. One class is linearly separable from the other 2; the latter are NOT linearly separable from each other. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Description\nThe Iris dataset consists of 150 data instances. There are 3 classes (Iris Versicolor, Iris Setosa and Iris Virginica) each have 50 instances. \n\n\nFor each flower we have the below data attributes \n\n- sepal length in cm\n- sepal width in cm\n- petal length in cm\n- petal width in cm\n\nTo make our experiment easy we rename the classes with numbers : \n\n \"0\": setosa\n \"1\": versicolor\n \"2\": virginica",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Challenges\n\nWhen we use the data with large number of features or dimensionality, models usually choke because\n\n 1. Training time increases exponentially with number of features.\n 2. Models have increasing risk of overfitting with increasing number of features.\n \nTo avoid the above mentioned problems while learning about data analysis, we use simple, well behaved, data that reduces the cognitive load, and makes it easier to debug as we are able to better comprehend the data we are working with. \n\nHence, this is a good dataset to work on.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Domain Information",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n\nIris Plants are flowering plants with showy flowers. They are very popular among movie directors as it gives excellent background. \n\nThey are predominantly found in dry, semi-desert, or colder rocky mountainous areas in Europe and Asia. They have long, erect flowering stems and can produce white, yellow, orange, pink, purple, lavender, blue or brown colored flowers. There are 260 to 300 types of iris.\n\n\n\nAs you could see, flowers have 3 sepals and 3 petals. The sepals are usually spreading or drop downwards and the petals stand upright, partly behind the sepal bases. However, the length and width of the sepals and petals vary for each type.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Setup Steps",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Importing Required Packages",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom sklearn.datasets import load_iris\nfrom sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Loading the data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Load data\niris = load_iris()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Checking for the type of iris\nprint(type(iris))",
"<class 'sklearn.utils.Bunch'>\n"
],
[
"# Checking the keys\nprint(iris.keys())",
"dict_keys(['data', 'target', 'target_names', 'DESCR', 'feature_names', 'filename'])\n"
],
[
"# Checking for the type of data\nprint(type(iris.data))",
"<class 'numpy.ndarray'>\n"
],
[
"# Checking for unique target or class values\nprint(set(iris.target))",
"{0, 1, 2}\n"
],
[
"# Let us see how the iris data looks\nprint(iris.data[::15])",
"[[5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2]\n [5.7 4.4 1.5 0.4]\n [4.8 3.1 1.6 0.2]\n [4.8 3. 1.4 0.3]\n [5. 2. 3.5 1. ]\n [6.6 3. 4.4 1.4]\n [5.5 2.6 4.4 1.2]\n [7.6 3. 6.6 2.1]\n [6.9 3.2 5.7 2.3]\n [7.7 3. 6.1 2.3]]\n"
],
[
"# Let us see how the labels \nprint(iris.target[::15])",
"[0 0 0 0 1 1 1 2 2 2]\n"
],
[
"# Storing the data and labels into \"X\" and \"y\" varaibles\nX = iris.data\ny = iris.target",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Splitting the data into train and test sets ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
" # Training and testing set ratio is 70 : 30\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.33, random_state=42)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Let us see the size of train and test sets\nX_train.shape, X_test.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Let us see first five rows of the training data\nX_train[:5]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Training a Decision Tree Classifier ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"decision_tree = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=2)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Training or fitting the model with the train data\ndecision_tree.fit(X_train,y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Testing the trained model\ndecision_tree.predict(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Calculating the score\ndecision_tree.score(X_test,y_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a34a116219585771e95cc93f42fda2f783760ad
| 2,206 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/R/solutions/E.4.4.ipynb
|
rses-dl-course-durham/rses-dl-course-durham.github.io
|
eaa674e612bf7e4ec21ee2038ba86fe2060d67ac
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | 2 |
2021-02-11T08:36:48.000Z
|
2021-02-11T10:16:30.000Z
|
notebooks/R/solutions/E.4.4.ipynb
|
rses-dl-course-durham/rses-dl-course-durham.github.io
|
eaa674e612bf7e4ec21ee2038ba86fe2060d67ac
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | 8 |
2021-04-15T12:20:13.000Z
|
2021-04-23T10:55:25.000Z
|
notebooks/R/solutions/E.4.4.ipynb
|
rses-dl-course/rses-dl-course.github.io
|
bd2880d2db833df5049440af1e554441f75c50e7
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | null | null | null | 33.938462 | 102 | 0.415684 |
[
[
[
"# Create model\nmodel <- keras_model_sequential() %>%\n layer_conv_2d(filters = 32, kernel_size = c(3,3), activation = \"relu\",\n input_shape = c(img_shape, img_shape, 3)) %>%\n layer_max_pooling_2d(c(2,2)) %>%\n\n layer_conv_2d(filters = 64, kernel_size = c(3,3), activation = \"relu\") %>%\n layer_max_pooling_2d(c(2,2)) %>%\n\n layer_conv_2d(filters = 128, kernel_size = c(3,3), activation = \"relu\") %>%\n layer_max_pooling_2d(c(2,2)) %>%\n\n layer_conv_2d(filters = 128, kernel_size = c(3,3), activation = \"relu\") %>%\n layer_max_pooling_2d(c(2,2)) %>% \n layer_dropout(0.5) %>% \n\n layer_flatten() %>%\n layer_dense(512, activation = \"relu\") %>%\n layer_dense(2, activation = \"softmax\")\n\n# Compile the model\nmodel %>% compile(optimizer=\"adam\",\n loss = 'sparse_categorical_crossentropy',\n metrics = \"accuracy\")\n\n# Print summary\nmodel\n\n# Fit model\nepochs <- 40\nhistory <- model %>%\n fit(x = train_data_gen,\n epochs = epochs,\n validation_data = val_data_gen)\n# Print history\nhistory\n\n# Plot history\noptions(repr.plot.width = 12, repr.plot.height = 6)\nplot(history)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
]
] |
4a34a7fecabbe21cee472239bf0efd48355f01ae
| 226,656 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
ex5-Calculate China-Z Index (CZI) with Python.ipynb
|
royalosyin/Calculate-Precipitation-based-Agricultural-Drought-Indices-with-Python
|
a74d79ff6d2b38390801c946cbc882e0664518b7
|
[
"MIT"
] | 14 |
2019-02-20T19:42:33.000Z
|
2021-09-01T08:31:13.000Z
|
ex5-Calculate China-Z Index (CZI) with Python.ipynb
|
kurkutesa/Calculate-Precipitation-based-Agricultural-Drought-Indices-with-Python
|
a74d79ff6d2b38390801c946cbc882e0664518b7
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
ex5-Calculate China-Z Index (CZI) with Python.ipynb
|
kurkutesa/Calculate-Precipitation-based-Agricultural-Drought-Indices-with-Python
|
a74d79ff6d2b38390801c946cbc882e0664518b7
|
[
"MIT"
] | 14 |
2019-05-01T03:22:34.000Z
|
2021-11-08T17:28:58.000Z
| 490.597403 | 122,344 | 0.936009 |
[
[
[
"# Calculate China-Z Index (CZI) with Python\n\nChina Z-Index (CZI) is extensively used by National Climate Centre (NCC) of China to monitor drought conditions throughout\nthe country (Wu et al., 2001; Dogan et al., 2012). CZI assumes that precipitation data follow the Pearson Type III distribution and is related to Wilson–Hilferty cube-root transformation (Wilson and Hilferty, 1931) from chi-square variable to the Z-scale (Kendall and Stuart, 1977). ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Prepare data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data = pd.read_csv('data/prcphq.046037.month.txt', sep=r\"\\s+\", \n skiprows=1, usecols=[1, 2], \n parse_dates=True,\n index_col = 0,\n names=['Date', 'Rain'])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Calculate six-monthly CZI\n\nHere we use all years as a reference period to calculate monthly long-term normals. ZSI = (p-pm)/s",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data['Rain_6'] = data['Rain'].rolling(6).sum()\ndf_6mon = data[['Rain_6']].dropna()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_6mon['CZI'] = np.nan\n\nfor imon in np.arange(1, 13):\n sinds = df_6mon.index.month==imon \n x = df_6mon[sinds] \n zsi = (x -x.mean())/x.std() \n cs = np.power(zsi, 3)/len(x)\n czi = 6.0/cs*np.power((cs/2.0*zsi + 1.0), 1.0/3.0)-6.0/cs + cs/6.0\n df_6mon.loc[sinds, 'CZI'] = czi.values[:,0] ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data['CZI'] = df_6mon['CZI']\ndel df_6mon\ndata.head(7)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Visualize",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"ax = data['CZI'].plot(figsize=(15, 7), )\nax.axhline(1, linestyle='--', color='g')\nax.axhline(-1, linestyle='--', color='r')\nax.set_title('Six-Monthly China-Z Index', fontsize=16)\nax.set_xlim(data.index.min(), data.index.max())\nax.set_ylim(-3, 3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.head(12)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.Rain_6.plot(figsize=(15, 7),)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Summary and discussion\n\nNCC computes CZI only for 1-month time step. However, CZI could be computed for five time steps i.e. 1-, 3-, 6-, 9- and 12-month time step.\n\nMany studies comparing the CZI with that of SPI and Z-score reported similar results (Wu et al., 2001; Morid et al., 2006).\nFurther, Wu et al. (2001) suggested that because of simplicity in calculating drought severity at monthly time step using CZI, it can be preferred over SPI, where rainfall data are often incomplete.\n\n## References\n\nDogan, S., Berktay, A., Singh, V.P., 2012. Comparison of multi-monthly rainfall-based drought severity indices, with application to semi-arid Konya closed basin, Turkey. J. Hydrol. 470–471, 255–268.\n\nKendall, M.G.; Stuart, A. The Advanced Theory of Statistics; Charles Griffin & Company-High Wycombe: London, UK, 1997; pp. 400–401.\n\nMorid, S., Smakhtin, V., Moghaddasi, M., 2006. Comparison of seven meteorological indices for drought monitoring in Iran. Int. J. Climatol. 26, 971–985.\n\nWilson, E.B., Hilferty, M.M., 1931. The Distribution of Chi-Square. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 17, 684–688.\n\nWu, H., Hayes, M.J., Weiss, A., Hu, Q.I., 2001. An evaluation of the standardized precipitation index, the china-Zindex and the statistical Z-Score. Int. J. Climatol.21, 745–758. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/joc.658.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a34ba59411833c867d8f48a4ffefd8c2f3ed2c3
| 4,939 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
07. Link Imaging.ipynb
|
boada/swiftXRT
|
37ae1a17b125678c8ecb1a508b85a35308a175d4
|
[
"MIT"
] | 7 |
2019-02-21T01:31:12.000Z
|
2020-12-01T06:30:25.000Z
|
07. Link Imaging.ipynb
|
boada/swiftXRT
|
37ae1a17b125678c8ecb1a508b85a35308a175d4
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
07. Link Imaging.ipynb
|
boada/swiftXRT
|
37ae1a17b125678c8ecb1a508b85a35308a175d4
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 30.86875 | 95 | 0.495444 |
[
[
[
"import os\nimport sys\nsys.path.append(f'{os.environ[\"HOME\"]}/Projects/planckClusters/catalogs')\nfrom load_catalogs import load_PSZcatalog\nfrom tqdm import tqdm_notebook",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data = load_PSZcatalog()\n\nPS1_dir = f'{os.environ[\"HOME\"]}/Projects/planckClusters/data/extern/PS1'\nSDSS_dir = f'{os.environ[\"HOME\"]}/Projects/planckClusters/data/extern/SDSS'\nDECaLS_dir = f'{os.environ[\"HOME\"]}/Projects/planckClusters/data/extern/DECaLS'\nDES_dir = f'{os.environ[\"HOME\"]}/Projects/planckClusters/data/extern/DES'\noutpath = './data_full_new'\n\nfor name in tqdm_notebook(data['NAME'], total=len(data['NAME'])):\n name = name.replace(' ', '_')\n\n if not os.path.exists(f'{outpath}/{name}'):\n continue\n \n if os.path.isdir(f'{PS1_dir}/{name}'):\n relpath = os.path.relpath(f'{PS1_dir}/{name}', f'{outpath}/{name}')\n\n target_files = ['_PS1stack_g.fits', '_PS1stack_r.fits', '_PS1stack_i.fits',\n '_PS1stack_z.fits', '_PS1stack_y.fits', '_PS1stack_irg.tiff']\n\n for file in target_files:\n try:\n os.symlink(f'{PS1_dir}/{name}/{name}{file}',\n f'{outpath}/{name}/{name}{file}')\n except FileExistsError:\n pass\n\n if os.path.isdir(f'{SDSS_dir}/{name}'):\n relpath = os.path.relpath(f'{SDSS_dir}/{name}', f'{outpath}/{name}')\n\n target_files = ['_SDSSstack_g.fits', '_SDSSstack_r.fits', '_SDSSstack_i.fits',\n '_SDSSstack_z.fits', '_SDSSstack_irg.tiff']\n\n for file in target_files:\n try:\n os.symlink(f'{SDSS_dir}/{name}/{name}{file}',\n f'{outpath}/{name}/{name}{file}')\n except FileExistsError:\n pass\n \n \n if os.path.isdir(f'{DECaLS_dir}/{name}'):\n relpath = os.path.relpath(f'{DECaLS_dir}/{name}', f'{outpath}/{name}')\n\n target_files = ['_DECaLSstack_r.fits', '_DECaLSstack.jpg']\n\n for file in target_files:\n try:\n os.symlink(f'{DECaLS_dir}/{name}/{name}{file}',\n f'{outpath}/{name}/{name}{file}')\n except FileExistsError:\n pass\n \n if os.path.isdir(f'{DES_dir}/{name}'):\n relpath = os.path.relpath(f'{DES_dir}/{name}', f'{outpath}/{name}')\n\n target_files = ['_DESstack_r.fits', '_DESstack.jpg']\n\n for file in target_files:\n try:\n os.symlink(f'{DES_dir}/{name}/{name}{file}',\n f'{outpath}/{name}/{name}{file}')\n except FileExistsError:\n pass",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a34db32bb1d4502954ba4d03b2277503aa27590
| 70,848 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Keras_mnist_LeNet-5_v2.9929.ipynb
|
acphart/Deep_in_mnist
|
56f49b9a00927be0a9fafdf4dc05c8fc4d738e0d
|
[
"MIT"
] | 13 |
2019-01-11T06:18:51.000Z
|
2021-06-05T08:30:41.000Z
|
Keras_mnist_LeNet-5_v2.9929.ipynb
|
acphart/Deep_in_mnist
|
56f49b9a00927be0a9fafdf4dc05c8fc4d738e0d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Keras_mnist_LeNet-5_v2.9929.ipynb
|
acphart/Deep_in_mnist
|
56f49b9a00927be0a9fafdf4dc05c8fc4d738e0d
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2019-05-25T15:19:41.000Z
|
2020-05-27T07:13:19.000Z
| 144.883436 | 53,180 | 0.852233 |
[
[
[
"# Keras mnist LeNet-5 v2\n**此项目为测试修改版的LeNet-5**\n- 目前达到$0.9929$的准确率",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%matplotlib inline\nimport os\nimport PIL\nimport pickle\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport tensorflow as tf\nimport keras\n\nfrom IPython import display\nfrom functools import partial\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import normalize\n\nfrom keras import backend\nfrom keras.utils import np_utils, plot_model\nfrom keras.callbacks import TensorBoard, ModelCheckpoint\nfrom keras.callbacks import LearningRateScheduler, ReduceLROnPlateau\nfrom keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator\n\nfrom keras.models import load_model\nfrom keras.models import Sequential, Model\nfrom keras.layers import Dense, Conv2D, MaxPool2D, Input, AveragePooling2D\nfrom keras.layers import Activation, Dropout, Flatten, BatchNormalization\n\nimport warnings \nwarnings.filterwarnings('ignore')\nnp.random.seed(42)",
"Using TensorFlow backend.\n"
]
],
[
[
"## 准备数据",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"file_path = r\"I:\\Dataset\\mnist\\all_mnist_data.csv\"\nmnist_data = pd.read_csv(file_path)\n\nidx = np.random.permutation(len(mnist_data))\ntrain_data = mnist_data.iloc[idx[: 60000]]\ntest_data = mnist_data.iloc[idx[60000: ]]\n\nX_train = np.array(train_data.drop('0', axis=1)).reshape(-1, 28, 28, 1).astype(\"float32\")\nX_test = np.array(test_data.drop('0', axis=1)).reshape(-1, 28, 28, 1).astype(\"float32\")\n\ny_train = np.array(train_data['0'])\ny_test = np.array(test_data['0'])\ny_train = np_utils.to_categorical(y_train)\ny_test = np_utils.to_categorical(y_test)\n\nx_train = X_train[10000:]\nt_train = y_train[10000:]\nx_val = X_train[:10000]\nt_val = y_train[:10000]\n\nprint(\"\\nimgs of trainset : \", x_train.shape)\nprint(\"labels of trainset : \", t_train.shape)\nprint(\"imgs of valset : \", x_val.shape)\nprint(\"labels of valset : \", t_val.shape)\nprint(\"imgs of testset : \", X_test.shape)\nprint(\"labels of testset : \", y_test.shape)",
"\nimgs of trainset : (50000, 28, 28, 1)\nlabels of trainset : (50000, 10)\nimgs of valset : (10000, 28, 28, 1)\nlabels of valset : (10000, 10)\nimgs of testset : (10000, 28, 28, 1)\nlabels of testset : (10000, 10)\n"
]
],
[
[
"## 搭建模型",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def myCNN():\n model = Sequential()\n\n model.add(Conv2D(filters=16,\n kernel_size=(5, 5),\n padding='same',\n input_shape=(28, 28, 1),\n activation='relu',\n name='conv2d_1'))\n\n model.add(MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2, 2), name='max_pool2d_1'))\n\n model.add(Conv2D(filters=36,\n kernel_size=(5, 5),\n padding='same',\n input_shape=(14, 14, 1),\n activation='relu',\n name='conv2d_2'))\n\n model.add(MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2, 2), name='max_pool2d_2'))\n\n model.add(Dropout(0.25, name='dropout_1'))\n\n model.add(Flatten(name='flatten_1'))\n\n model.add(Dense(128, activation='relu', name='dense_1'))\n model.add(Dropout(0.5, name='dropout_2'))\n\n model.add(Dense(10, activation='softmax', name='dense_2'))\n return model\nmodel = myCNN()\nmodel.summary()",
"_________________________________________________________________\nLayer (type) Output Shape Param # \n=================================================================\nconv2d_1 (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 16) 416 \n_________________________________________________________________\nmax_pool2d_1 (MaxPooling2D) (None, 14, 14, 16) 0 \n_________________________________________________________________\nconv2d_2 (Conv2D) (None, 14, 14, 36) 14436 \n_________________________________________________________________\nmax_pool2d_2 (MaxPooling2D) (None, 7, 7, 36) 0 \n_________________________________________________________________\ndropout_1 (Dropout) (None, 7, 7, 36) 0 \n_________________________________________________________________\nflatten_1 (Flatten) (None, 1764) 0 \n_________________________________________________________________\ndense_1 (Dense) (None, 128) 225920 \n_________________________________________________________________\ndropout_2 (Dropout) (None, 128) 0 \n_________________________________________________________________\ndense_2 (Dense) (None, 10) 1290 \n=================================================================\nTotal params: 242,062\nTrainable params: 242,062\nNon-trainable params: 0\n_________________________________________________________________\n"
]
],
[
[
"### 计算资源的分配",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"config = tf.ConfigProto()\nconfig.gpu_options.per_process_gpu_memory_fraction = 0.2\nsess = tf.Session(config=config)\nbackend.set_session(sess)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 训练",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\"\"\"训练模型并保存模型及训练历史\n保存模型单独创建一个子文件夹modeldir, 保存训练历史则为单个文件hisfile\"\"\"\n\nmodels_name = \"Keras_mnist_LeNet-5_v2\" # 模型名称的公共前缀\nfactor_list = [\"\"] # 此次调参的变量列表\n\nmodel_list = [] # 模型名称列表\nfor i in range(len(factor_list)):\n modelname = models_name + factor_list[i] + \".h5\"\n model_list.append(modelname)\n\n# 创建模型保存子目录modeldir\nif not os.path.isdir(\"saved_models\"): \n os.mkdir(\"saved_models\")\nmodeldir = r\"saved_models\"\n\n# 创建训练历史保存目录\nif not os.path.isdir(\"train_history\"): \n os.mkdir(\"train_history\")\n# 设置训练历史文件路径\nhisfile = r\"train_history\\Keras_mnist_LeNet-5_v2.train_history\" \n# 每个模型及其对应的训练历史作为键值对{modelname: train_history}\n# train_history为字典,含四个key,代表train和val的loss和acc\nmodel_train_history = dict() \n\n\n# 开始训练\nepochs=100\nbatch_size = 32\nsteps_per_epoch=1250\nfor i in range(len(model_list)):\n model = myCNN()\n modelname = model_list[i]\n modelpath = os.path.join(modeldir, modelname) \n \n train_his = np.array([]).reshape(-1, 2)\n val_his = np.array([]).reshape(-1, 2)\n datagen = ImageDataGenerator()\n datagen.fit(x_train)\n model.compile(loss=\"categorical_crossentropy\", \n optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adam(),\n metrics=[\"accuracy\"])\n print(\"\\ntraining model : \", modelname)\n \n ck_epoch, max_val_acc = 0, 0.0\n for epoch in range(epochs+1):\n i = 0\n tr_his = []\n for X, y in datagen.flow(x_train, t_train, batch_size=batch_size):\n his = model.train_on_batch(X, y)\n tr_his.append(his)\n i += 1\n if i >= steps_per_epoch: break\n tr = np.mean(tr_his, axis=0)\n val = model.evaluate(x_val, t_val, verbose=0)\n train_his = np.vstack((train_his, tr))\n val_his = np.vstack((val_his, val))\n if epoch<10 or epoch%5==0:\n print(\"%4d epoch: train acc: %8f loss: %8f val acc: %8f loss: %8f\"%(epoch, tr[1], tr[0], val[1], val[0]))\n # 设置保存模型\n if val[1] > max_val_acc: \n model.save(modelpath)\n print(\"val acc improved from %6f to %6f\"%(max_val_acc, val[1]))\n max_val_acc = val[1]\n ck_epoch = epoch\n model_train_history[modelname] = {\"acc\": train_his[:, 1], \"val_acc\": val_his[:, 1],\n \"loss\": train_his[:, 0], \"val_loss\": val_his[:, 0]}\n\n\"\"\"保存训练历史\"\"\"\nfo = open(hisfile, 'wb')\npickle.dump(model_train_history, fo)\nfo.close() ",
"\ntraining model : Keras_mnist_LeNet-5_v2.h5\n 0 epoch: train acc: 0.922725 loss: 0.248553 val acc: 0.975500 loss: 0.073290\nval acc improved from 0.000000 to 0.975500\n 1 epoch: train acc: 0.974250 loss: 0.088033 val acc: 0.983300 loss: 0.052124\nval acc improved from 0.975500 to 0.983300\n 2 epoch: train acc: 0.979775 loss: 0.069411 val acc: 0.985500 loss: 0.043014\nval acc improved from 0.983300 to 0.985500\n 3 epoch: train acc: 0.982225 loss: 0.060878 val acc: 0.985500 loss: 0.043764\n 4 epoch: train acc: 0.985125 loss: 0.050331 val acc: 0.989400 loss: 0.031212\nval acc improved from 0.985500 to 0.989400\n 5 epoch: train acc: 0.986175 loss: 0.044666 val acc: 0.989900 loss: 0.030585\nval acc improved from 0.989400 to 0.989900\n 6 epoch: train acc: 0.987800 loss: 0.039384 val acc: 0.988800 loss: 0.038796\n 7 epoch: train acc: 0.988525 loss: 0.038216 val acc: 0.988300 loss: 0.037254\n 8 epoch: train acc: 0.990000 loss: 0.033546 val acc: 0.990100 loss: 0.035915\nval acc improved from 0.989900 to 0.990100\n 9 epoch: train acc: 0.990550 loss: 0.031504 val acc: 0.990200 loss: 0.029900\nval acc improved from 0.990100 to 0.990200\n 10 epoch: train acc: 0.991025 loss: 0.028952 val acc: 0.990900 loss: 0.029454\nval acc improved from 0.990200 to 0.990900\nval acc improved from 0.990900 to 0.991300\nval acc improved from 0.991300 to 0.991400\n 15 epoch: train acc: 0.993075 loss: 0.022697 val acc: 0.990300 loss: 0.034392\nval acc improved from 0.991400 to 0.991800\nval acc improved from 0.991800 to 0.992100\nval acc improved from 0.992100 to 0.992700\n 20 epoch: train acc: 0.994150 loss: 0.019887 val acc: 0.991200 loss: 0.033841\nval acc improved from 0.992700 to 0.993100\n 25 epoch: train acc: 0.994925 loss: 0.017861 val acc: 0.992200 loss: 0.032848\n 30 epoch: train acc: 0.995175 loss: 0.016053 val acc: 0.992200 loss: 0.031137\n 35 epoch: train acc: 0.995600 loss: 0.015707 val acc: 0.991600 loss: 0.035695\n 40 epoch: train acc: 0.995325 loss: 0.014632 val acc: 0.992700 loss: 0.037180\n 45 epoch: train acc: 0.996025 loss: 0.012520 val acc: 0.991400 loss: 0.039746\n 50 epoch: train acc: 0.995825 loss: 0.013654 val acc: 0.992700 loss: 0.040660\n 55 epoch: train acc: 0.995600 loss: 0.015995 val acc: 0.992100 loss: 0.048665\nval acc improved from 0.993100 to 0.993200\n 60 epoch: train acc: 0.996750 loss: 0.011147 val acc: 0.992800 loss: 0.045231\n 65 epoch: train acc: 0.996675 loss: 0.011433 val acc: 0.991400 loss: 0.045374\n 70 epoch: train acc: 0.996525 loss: 0.012970 val acc: 0.992100 loss: 0.048299\n 75 epoch: train acc: 0.996950 loss: 0.011898 val acc: 0.991600 loss: 0.059145\n 80 epoch: train acc: 0.997325 loss: 0.010608 val acc: 0.990800 loss: 0.062602\n 85 epoch: train acc: 0.995875 loss: 0.016077 val acc: 0.992400 loss: 0.042106\n 90 epoch: train acc: 0.996725 loss: 0.012706 val acc: 0.992200 loss: 0.052151\n 95 epoch: train acc: 0.997225 loss: 0.011246 val acc: 0.992900 loss: 0.037233\n 100 epoch: train acc: 0.997200 loss: 0.011304 val acc: 0.992200 loss: 0.051990\n"
]
],
[
[
"### 可视化训练过程",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def show_train_history(saved_history, his_img_file): \n modelnames = sorted(list(saved_history.keys()))\n train = [\"acc\", \"loss\"]\n val = [\"val_acc\", \"val_loss\"]\n \n \"\"\"作loss和acc两个图\"\"\"\n fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(16, 5))\n ax = ax.flatten()\n color_add = 0.9/len(saved_history)\n for i in range(2):\n c = 0.05\n for j in range(len(saved_history)):\n modelname = modelnames[j]\n train_history = saved_history[modelname]\n ax[i].plot(train_history[train[i]], \n color=(0, 1-c, 0),\n linestyle=\"-\",\n label=\"train_\"+modelname[21:-3])\n ax[i].plot(train_history[val[i]], \n color=(c, 0, 1-c),\n linestyle=\"-\",\n label=\"val_\"+modelname[21:-3])\n c += color_add\n ax[i].set_title('Train History')\n ax[i].set_ylabel(train[i]) \n ax[i].set_xlabel('Epoch') \n ax[0].legend(loc=\"lower right\")\n ax[1].legend(loc=\"upper right\") \n ax[0].set_ylim(0.9, 1.0)\n ax[1].set_ylim(0, 0.2)\n plt.suptitle(\"LeNet-5_v2\")\n \n print(\"saved img: \", his_img_file)\n plt.savefig(his_img_file)\n plt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\"\"\"载入训练历史并可视化, 并且保存图片\"\"\"\nif not os.path.isdir(\"his_img\"):\n os.mkdir(\"his_img\")\nhis_img_file = r\"his_img\\LeNet-5_v2.png\"\n\nfo2 = open(hisfile, \"rb\")\nsaved_history1 = pickle.load(fo2)\n\nshow_train_history(saved_history1, his_img_file)",
"saved img: his_img\\LeNet-5_v2.png\n"
]
],
[
[
"## 在测试集上测试",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"smodel = load_model(modelpath)\nprint(\"test model: \", os.path.basename(modelpath))\nloss, acc = smodel.evaluate(X_test, y_test)\n\nprint(\"test :acc: %.4f\"%(acc))",
"test model: Keras_mnist_LeNet-5_v2.h5\n10000/10000 [==============================] - 3s 322us/step\ntest :acc: 0.9929\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a34ded035dc7bf32a038e6eebc3c8bdc0249b51
| 24,675 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
bin/temp.ipynb
|
donnaw47/Develop-MCCE
|
15cf6b7dbd8e18f58a6daeb03719e0456f32e938
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
bin/temp.ipynb
|
donnaw47/Develop-MCCE
|
15cf6b7dbd8e18f58a6daeb03719e0456f32e938
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
bin/temp.ipynb
|
donnaw47/Develop-MCCE
|
15cf6b7dbd8e18f58a6daeb03719e0456f32e938
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 89.727273 | 8,836 | 0.793556 |
[
[
[
"class Chain:\n def __init__(self, cid):\n self.cid = cid\n self.res = []\n return\n \n def addres(self, res):\n self.res.append(res)\n return\n \n def printchain(self):\n print(\"chain: %s\" % str(self.cid))\n# for res in self.res:\n# res.printme()\n\nclass Residue:\n def __init__(self, resid):\n self.resid = resid\n self.cid = list(self.resid)[2]\n self.atoms = []\n return\n\n def addatom(self, atom):\n self.atoms.append(atom)\n return\n\n def printme(self):\n print(\"residue: %s\" % str(self.resid))\n# for atom in self.atoms:\n# atom.printline()\n# return\n\nclass Atom:\n def __init__(self, line):\n self.resName = \"\"\n self.xyz = (0, 0, 0)\n self.name = \"\"\n self.cid = \"\"\n self.seq = 0\n self.serial = 0\n self.loadline(line)\n self.resid = (self.resName, self.seq, self.cid)\n return\n\n def loadline(self, line):\n self.serial = int(line[6:11])\n self.name = line[12:16]\n self.resName = line[17:20]\n self.cid = line[21]\n self.seq = int(line[22:26])\n self.xyz = (float(line[30:38]), float(line[38:46]), float(line[46:54]))\n return\n\n def printline(self):\n print(\"ATOM %5d %4s %3s %1s%4d %8.3f%8.3f%8.3f\" % (self.serial, self.name, self.resName, self.cid,\n self.seq, self.xyz[0], self.xyz[1], self.xyz[2]))\n return\n\nfname = '1fn3.pdb'\natomlines = [line for line in open(fname).readlines() if line[:6] == \"ATOM \" or line[:6] == \"HETATM\"]\n\natoms = []\nfor x in atomlines:\n atoms.append(Atom(x))\n\nresidues = []\nfor atom in atoms:\n # is this atom belong to an existing residue,\n in_exisiting_residue = False\n existing_res = None\n for res in residues:\n if atom.resid == res.resid:\n existing_res = res\n in_exisiting_residue = True\n break\n if in_exisiting_residue:\n #if yes, add atom to that residue\n existing_res.addatom(atom)\n else:\n # if not, create a new Residue object and add this atom to the new residue\n new_res = Residue(atom.resid)\n new_res.addatom(atom)\n residues.append(new_res)\n\nchains = []\nfor res in residues:\n in_existing_chain = False\n existing_chain = None\n for chain in chains:\n if res.cid == chain.cid:\n existing_chain = chain\n in_existing_chain = True\n break\n if in_existing_chain:\n existing_chain.addres(res)\n else:\n new_chain = Chain(res.cid)\n new_chain.addres(res)\n chains.append(new_chain)\n \n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"distances = []\nfor chain in chains:\n for res in chain.res:\n seq_skipped = False\n current_seq = res.resid[1]\n if current_seq != len(chain.res):\n next_res = chain.res[current_seq]\n if next_res.resid[1] != current_seq + 1:\n seq_skipped = True\n print('sequence skipped after', res.resid)\n for atom1 in res.atoms: \n if 'C ' in atom1.name:\n C_coord = atom1.xyz\n for atom2 in next_res.atoms:\n if 'N ' in atom2.name:\n N_coord = atom2.xyz\n distance = ((C_coord[0] - N_coord[0])**2 + (C_coord[1] - N_coord[1])**2 + (C_coord[2] - N_coord[2])**2)**.5\n distances.append(distance)\nif seq_skipped == False:\n print('no sequence skipped')\n \n\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\n\nplt.hist(distances)\nplt.title(\"Histogram\")\nplt.xlabel(\"distances\")\nplt.ylabel(\"frequency\")\n\nplt.show()",
"no sequence skipped\n"
],
[
"distances = []\n\nfor res in chains[0].res:\n current_seq = res.resid[1]\n if current_seq != len(chains[0].res):\n next_res = chains[0].res[current_seq]\n for atom1 in res.atoms:\n \n if 'C ' in atom1.name:\n cx = float(atom1.xyz[0])\n cy = float(atom1.xyz[1])\n cz = float(atom1.xyz[2])\n for atom2 in next_res.atoms:\n\n if 'N ' in atom2.name:\n \n nx = float(atom2.xyz[0])\n ny = float(atom2.xyz[1])\n nz = float(atom2.xyz[2])\n distance = ((cx - nx)**2 + (cy - ny)**2 + (cz - nz)**2)**.5\n \n\n distances.append(distance)\n\nprint(len(chains[0].res))\nprint(len(distances))\n\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\n\nplt.hist(distances)\nplt.title(\"Histogram\")\nplt.xlabel(\"distances\")\nplt.ylabel(\"frequency\")\n\nplt.show()",
"159\n140\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a34e38f4f967d43a429873bcaba3976bfa6a4ac
| 112,236 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
machine_learning/lesson 3 - Neural Networks/intro-to-neural-networks.ipynb
|
BreakoutMentors/Data-Science-and-Machine-Learning
|
26bbe39c3e94dc200e8837e2fcba9bdd38222e36
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2020-06-04T15:11:33.000Z
|
2021-09-14T02:12:22.000Z
|
machine_learning/lesson 3 - Neural Networks/intro-to-neural-networks.ipynb
|
BreakoutMentors/Data-Science-and-Machine-Learning
|
26bbe39c3e94dc200e8837e2fcba9bdd38222e36
|
[
"MIT"
] | 19 |
2021-05-27T16:42:42.000Z
|
2022-03-22T23:37:03.000Z
|
machine_learning/lesson 3 - Neural Networks/intro-to-neural-networks.ipynb
|
BreakoutMentors/Data-Science-and-Machine-Learning
|
26bbe39c3e94dc200e8837e2fcba9bdd38222e36
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2020-07-08T21:35:07.000Z
|
2020-07-08T21:35:07.000Z
| 86.735703 | 15,042 | 0.705888 |
[
[
[
"<a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/krmiddlebrook/intro_to_deep_learning/blob/master/machine_learning/lesson%203%20-%20Neural%20Networks/intro-to-neural-networks.ipynb\" target=\"_parent\"><img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open In Colab\"/></a>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Intro to Neural Networks\n<figure><img src='https://mk0analyticsindf35n9.kinstacdn.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/nural-network-banner.gif' width='70%'></img><figcaption>A Feed Forward Neural Network</figcaption>\n</figure>\n\n\n\nIn the previous lesson, we introduced the softmax regression method to solve multi-class classification tasks, implementing a classifer to recognize 10 handwritten digits from the MNIST digits dataset. \n\nWe've come a long way and covered many concepts throughout this series, with each lesson building on the previous material. We've learned how to clean data, create linear models (via linear regression), coerce model outputs into a valid probability distribution (via logistic and softmax regression), train models using Sklearn and Tensorflow, apply the appropriate loss function, and to minimize it with respect to our model's parameters (via optimization algorithms). Now that we have a healthy understanding of these concepts in the context of simple linear models, we are ready to explore neural networks--one of the most exciting and successful methods in modern machine learning! \n\nIn this lesson, we describe deep linear neural networks at a high level, focusing on their structure, and demonstrate how to build one using Tensorflow. \n\nTo make this lesson more approachable, we don't cover every detail about neural networks here, but we aim to provide enough information for you to create your own neural networks and to inspire you to explore deep learning in more detail. \n \nLesson roadmap: \n- High level introduction to *neural networks*.\n- Building neural networks in Python - recreating the feed forward neural network model in 3Blue1Brown's excellent video [But what is a Neural Network? | Deep learning, chapter 1](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aircAruvnKk&t=436s) and training it to classify handwritten digits. As you will see, this simple feed forward neural network achieves impressive results. \n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Neural Networks\nAlthough neural networks only recently became popular, they've been around for quite some time. In fact, they first appeared in machine learning research way back in the late 1950s! But they didn't become popular until after 2012, when researchers built a neural network to classify different kinds of labeled images, achieving groundbreaking results (see [ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional\nNeural Networks](http://papers.nips.cc/paper/4824-imagenet-classification-with-deep-convolutional-neural-networks.pdf)). Since then, neural networks have become widely used in machine learning. Neural networks are successful, in part, because they can effectively learn representations of complex data (e.g., images, text, sound, tabular, etc.), especially given enough data and computing power. \n\nAt a high level, there are three fundemental types of neural networks: 1) encoders, 2) decoders, or 3) a combination of both. We will focus on *encoders*. \n\nEncoder networks take in some input data (i.e., images, texts, sounds, etc.) and output *predictions*, just like the linear models we've been working with. The simplest type of neural networks are called feed forward neural networks (FFNNs), and they consist of many *layers* of *neurons* each *fully-connected* to those in the layer below (from which they receive input) and those above (which they, in turn, influence). \n\nFFNNs may sound complex right now, but hang in there. In many ways FFNNs are the superpowered version of the linear models we already know about. Like the linear models we've discussed (linear/logistic/softmax regression), neural networks can be configured to solve different kinds of tasks: either *regression* or *classification*. \n\n\nHere are some quick facts about neural networks:\n- They are effective models for learning to represent complex data (like images, text, sound, tabular, etc.).\n- Encoder-based networks, which take input data and output predictions, are probably the most common neural networks - they are useful for classification and regression tasks\n- Feed forward neural networks (FFNNs) are the simplest type of neural network. They consist of many *layers* of *neurons* each *fully-connected* to those in the layer below (from which they receive input) and those above (which they, in turn, influence). \n- FFNNs are like linear models on steriods. They have many more parameters than simple linear models, which enables them to learn more complex relationships from the input data. \n- Even though FFNNs are the simplest kind of neural network, they can be very effective. \n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Challenge:** What are two tasks that you think encoder networks might be at good at solving?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Feed Forward Neural Networks\n<figure><img src='https://thumbs.gfycat.com/WeepyConcreteGemsbok-size_restricted.gif' width='100%'></img><figcaption>A Feed Forward Neural Network | <em>Source: <a href='https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aircAruvnKk&t=436s'>3Blue1Brown - But what is a Neural Network? Deep Learning Part 1</a></em></figcaption>\n</figure>\n\nDid you watch the [3Blue1Brown video on neural networks](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aircAruvnKk&t=436s)? If you haven't yet, I highly recommend checking it out (feel free to rewatch it too, it's a great overview of neural networks). I'll frequently be referencing important concepts that the video talks about. \n\nIn the following sections, we will summarize the key concepts behind neural networks. First, we describe the motivation and inspiration behind neural networks. Then, we dive into the structure of neural networks, outlining a few critical pieces that make them work. \n\n*Note, we describe these concepts from the perspective of a feed forward neural network. That said, the fundemental ideas discussed generalize to almost every type of neural network.*",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Neural Networks: Neural Network $=$ Brain?\n<figure><img src='https://github.com/BreakoutMentors/Data-Science-and-Machine-Learning/blob/master/images/neural-network-brain-pizza-yoda-analogy.png?raw=true' width='75%'></img><figcaption>\"Pizza, I like\" - Yoda</figcaption>\n</figure>\n\n\nNo, neural networks $\\neq$ brains.\nWhile neural networks don't actually operate like brains, they were inspired by them. \n\nLet's consider an extremely oversimplified version of the brain. The brain is an organ that uses neurons to process information and make decisions. The neurons are what the brain uses to process data (i.e., information about the world). When some piece of data is sent to a neuron it activates (or dpesn't). The magnitude/strength (i.e., positive or negative) of the activation triggers other groups of neurons to activate (or not). Eventually, this process outputs a decision--based on a combination of the prior triggers and activations--as a response to the input data. As an example, let's say there is a pizza in the kitchen and my nose picks up the scent. The smell of freshly baked dough and melted cheese activates my \"I'm hungry neurons\". Eventually, I can't ignore these neurons any longer, so I run to the kitchen and eat some pizza.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Neural Networks: Neurons\n<figure><img src='https://github.com/BreakoutMentors/Data-Science-and-Machine-Learning/blob/master/images/neuron-3blue1brown.png?raw=true' width='75%'></img><figcaption>Neural Networks: Neuron | <em>Source: <a href='https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aircAruvnKk&t=436s'>3Blue1Brown - But what is a Neural Network? Deep Learning Part 1</a></em></figcaption>\n</figure>\n\n**Neurons** are at the core of neural networks (after all, they are practically in the name). At a high level, a neuron holds a corresponding value (i.e., number) called an **activation**. The activation can be represented by a tiny value, a large value, or a value somewhere in between. A neuron is \"lit up\" (i.e., activated) when its corresponding activation is large, and it is \"dim\" (i.e., not very activated) when its activation is small. Connecting this to the pizza example, my \"I'm hungry neurons\" lit up after I smelled the pizza in the kitchen. \n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Neural Networks: Layers\n<figure><img src='https://miro.medium.com/max/1280/1*_nTmA2RowzQBCqI9BVtmEQ.gif' width='75%'></img><figcaption>The Neural Network's Secret Sauce: Stacking Layers | <em>Source: <a href='https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aircAruvnKk&t=436s'>3Blue1Brown - But what is a Neural Network? Deep Learning Part 1</a></em></figcaption>\n</figure>\n\nThe secret sauce driving neural networks is the technique of *stacking layers*. At a high level, this method enables the neural network to learn an effective representation of the data. The layers that are in between the input layer and the output layer are called *hidden layers*.\n\nA **layer** is composed of a set of **neurons**. We can manually configure the number of neurons we want to have in each layer, except for in the first and last ones. When we add more neurons and layers to the model, we add more parameters (weights and biases) to it. As a result, larger models (models with many parameters) can be computationally expensive, but very effective. This creates a trade-off between computation effeciency and model representation ability (making smaller models as effective as bigger ones is an active area of research). \n\nFor classification tasks, the number of neurons in the last layer is determined by the number of categories/classes in the dataset. While in regression tasks, there is generally only one neurons in the final layer, since we are predicting a continuous value (e.g., the happiness score for a particular country). ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Challenge:** In the above figure (from previous cell), how many layers are in the neural network? How many are hidden layers? How many neurons are in the first layer? How many are in the last layer? ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Neural Networks: Weights & Activation Functions \n<figure><img src='https://thumbs.gfycat.com/BabyishGeneralFruitfly-size_restricted.gif' width='65%'></img><figcaption>Calculating a Neuron's Activation: Connections and Weights (1) | <em>Source: <a href='https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aircAruvnKk&t=436s'>3Blue1Brown - But what is a Neural Network? Deep Learning Part 1</a></em></figcaption>\n</figure>\n\n<figure><img src='https://thumbs.gfycat.com/GlitteringCavernousGoosefish-small.gif' width='65%'></img><figcaption>Calculating a Neuron's Activation: Connections and Weights (2)| <em>Source: <a href='https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aircAruvnKk&t=436s'>3Blue1Brown - But what is a Neural Network? Deep Learning Part 1</a></em></figcaption>\n</figure>\n\nNeural networks pass information through the network using connections between pairs of neurons in adjacent layers. Each connection has a corresponding **weight** parameter that is learned during the model training phase. As shown in the figure above, the activation of a neuron in a subsequent layer is determined by the *weighted sum* of the weights and activations of the neurons in the previous layer (i.e., connections). A **bias** term is added at the end of the weighted sum to control how large/small a neuron's weighted sum must be to activate. Before the neuron receives a final activation value, the weighted sum is *squeezed* by an **activation function**. \n\nActivation functions and parameters (weights and biases)may sound intimidating. Fortunately, you already know a lot about these concepts: 1) the *sigmoid* and *softmax* logit functions are examples of activation functions, 2) linear models (linear/logistic/softmax) use the same *weighted sum* method to activate neurons in subsequent layers, the difference is these networks only have one layer after the input. \n\nAs you may remember from the logistic and softmax lessons, these logit functions convert the inputs to a valid probability space. An activation function, more generally, can be defined as any function that transforms the neuron output. It is common to choose an activation function that normalizes the input between 0 and 1 or -1 and 1. \n\n\nActivation functions play a critical role in building effective deep neural networks. They can help the network converge quickly (find the right parameters) and improve the model's overall performance. \n\nIn the diagrams above, the second layer has one neuron. This neuron is connected to every other neuron in the previous layer. Consequently, it has 784 connections plus one bias term. That's a lot of number crunching! For this reason, we generally select activation functions that can be computed effeciently (quickly). \n\n<figure><img src='https://github.com/BreakoutMentors/Data-Science-and-Machine-Learning/blob/master/images/sigmoid-activation-3Blue1Brown.png?raw=true' width='65%'></img><figcaption>Calculating a Neuron's Activation: Sigmoid Activation Function (2)| <em>Source: <a href='https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aircAruvnKk&t=436s'>3Blue1Brown - But what is a Neural Network? Deep Learning Part 1</a></em></figcaption>\n</figure>\n\nSo far we've only discussed connections and activations in the context of one neuron in a subsequent layer. But, most layers have many neurons. The good news is, we calculate neuron activations in the same way as before. The bad news is, we have to repeat the calculation process many times over. For example, in the diagrams below we see that all 16 neurons in the 2nd layer are connected to every other neuron in the 1st layer (i.e., 784 neurons). Thus, we need to perform $784\\times16$ weights $ + 16$ biases calculations to get the activations for the 16 neurons in the 2nd layer. Doing this by hand would be way too difficult, but luckily, we can make computers do most of the heavy lifting. \n\n<figure><img src='https://github.com/BreakoutMentors/Data-Science-and-Machine-Learning/blob/master/images/2-layer-weights-biases-connections-3Blue1Brown.png?raw=true' width='65%'></img><figcaption>Calculating a Neuron's Activation: Sigmoid Activation Function (2) | <em>Source: <a href='https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aircAruvnKk&t=436s'>3Blue1Brown - But what is a Neural Network? Deep Learning Part 1</a></em></figcaption>\n</figure>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Challenge:** In the below neural network diagram, how many weights and biases are there between the 2nd layer and the 3rd layer? How many total weights and biases are there in the entire network? Hint: all neurons are connected to every other neuron in the previous layer. \n\n<figure><img src='https://thumbs.gfycat.com/DeadlyDeafeningAtlanticblackgoby-poster.jpg' width='65%'></img><figcaption>A Neural Network: Total Weights & Biases | <em>Source: <a href='https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aircAruvnKk&t=436s'>3Blue1Brown - But what is a Neural Network? Deep Learning Part 1</a></em></figcaption>\n</figure>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Building a Neural Network: Summary\nNow that we know a little about neural networks, it's time to make our own! In this section, we demonstrate how to build a neural network in Python using Tensorflow. Specifically, we implement the neural network from 3Blue1Brown's video [But what is a Neural Network? Deep Learning Part 1](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aircAruvnKk&t=436s) to classify 10 types of handwritten digits from the MNIST dataset. Before we start, let's summarize what we know so far about neural networks:\n- *Stacking layers* is their secret sauce - enabling the model to learn an effective representations of the data (most of the time).\n- Layers are comprised of *neurons*. We configure the number of neurons in *hidden layers*. \n- Neurons hold a corresponding *activation* - large activations \"light up\" neurons. \n- The activations of neurons are determined by the weighted sum of their *connections* with the previous layer's neurons - quantified by *weights* and a *bias* term. The resulting output is then squeezed by an *activation function* such as the *sigmoid* function.\n- For classification tasks, the number of neurons in the last layer corresponds to the number of classes/categories in the dataset. \n\nNow, it's time to make our first neural network!",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Classification of Handwritten Digits with a Feed Forward Neural Network\n<figure><img src='https://thumbs.gfycat.com/ViciousUnnaturalAmethystsunbird-max-1mb.gif' width='75%'></img><figcaption>A Neural Network: Total Weights & Biases | <em>Source: <a href='https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aircAruvnKk&t=436s'>3Blue1Brown - But what is a Neural Network? Deep Learning Part 1</a></em></figcaption>\n</figure>\n\nIn this section, we will recreate the feed forward neural network (FFNN) from 3Blue1Brown's video [But what is a Neural Network? Deep Learning Part 1](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aircAruvnKk&t=436s) and use it to classify handwritten digits from the MNIST dataset. This process involves several steps: 1) [loading the dataset](#-Step-1:-Loading-the-Dataset), 2) [building the model](#-Step-2:-Building-the-Model), 3) [training the model](#-Step-3:-Training-the-Model), 4) [testing the model](#-Step-4:-Testing-the-Model).\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Prerequisites: Google Colab + building neural networks in python \nWe recommend that you run this this notebook in the cloud on Google Colab, if you're not already doing so. It's the simplest way to get started. Google Colab gives you free access to specialized compute resources called [GPUs](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Graphics_processing_unit) and [TPUs](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tensor_processing_unit). In modern machine learning these resources are frequently used because they significantly speed up model training compared to using [CPUs](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Central_processing_unit) (your computer is probably using CPUs). At a high level, GPUs and TPUs are special types of computer chips that excel at performing computations on large matrices. They perform mathematical matrix operations like multiplication, addition, subtraction, etc. at a much higher rate (i.e., speed) than CPUs. \n\nNative Python code won't run on GPUs and TPUs because they use specialized operating system *kernels*. We could convert our code to a language that these kernals can understand, but that would be a very tedious and frustrating process. Fortunately, there are several open-source Python libraries exist that do the heavy lifting for us. In particular, the two most popular open-source libraries are [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) and [Tensorflow](https://www.tensorflow.org/). These libraries enable us to build custom neural networks in Python that can run on GPUs and TPUs! \n\nIn this lesson we will use Tensorflow because it is a bit easier to use (while you are learning about neural networks) and it comes preinstalled in Google Colab. It is also possible to [install TensorFlow locally](https://www.tensorflow.org/install/). But, the simple solution is normally best (i.e., use Google Colab).\n \n[tf.keras](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/keras) is the simplest way to build and train neural network models in TensorFlow, so we will use it throughout this lessons.\n\nNote that there's [tf.keras](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/keras) (comes with TensorFlow) and there's [Keras](https://keras.io/) (standalone). You should be using [tf.keras](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/keras) because 1) it comes with TensorFlow so you don't need to install anything extra and 2) it comes with powerful TensorFlow-specific features.\n\nLastly, to accelerate model training time, you may want to run this notebook on a GPU in Google Colab. To do this, click on the \"Runtime\" tab in the top left corner of the notebook, click \"Change runtime type\", and select the \"GPU\" option under \"Hardware accelerator\". ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# TensorFlow and tf.keras\nimport tensorflow as tf\nfrom tensorflow import keras\nfrom tensorflow.keras.layers import Input, Flatten, Dense\n\n# Commonly used modules\nimport numpy as np\nimport os\nimport sys\n\n# Images, plots, display, and visualization\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport pandas as pd\nimport seaborn as sns\nimport cv2\nimport IPython\nfrom six.moves import urllib\n\nprint('Tensorflow version:', tf.__version__)",
"/usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/statsmodels/tools/_testing.py:19: FutureWarning: pandas.util.testing is deprecated. Use the functions in the public API at pandas.testing instead.\n import pandas.util.testing as tm\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Step 1: Loading the Dataset\nThe MNIST dataset contains 70k grayscale images of handwritten digits at a resolution of $28 \\times 28$ pixels. Our goal is to build a classification model to take one of these images as input and predict the most likely digit contained in the image (along with a relative confidence about the prediction):\n\n<figure><img src=\"https://i.imgur.com/ITrm9x4.png\" width=\"65%\"><figcaption><em>Source: <a href=\"https://deeplearning.mit.edu/\">MIT Deep Learning</a></em></figcaption></figure>\n\nLoading the dataset will return four NumPy arrays:\n* The `train_images` and `train_labels` arrays are the *training set*—the data the model uses to learn.\n* The `test_images` and `test_labels` arrays are the *test set*--the data the model is tested on.\n\nThe images are $28\\times28$ NumPy arrays (i.e., the x variables), with pixel values ranging between 0 and 255. The *labels* (i.e., y variable) are an array of integers, ranging from 0 to 9. We will use *one-hot encoding* (the technique we learned about in the logistic regression lesson) to convert these labels to vectors (i.e., arrays with mostly 0s and a 1 at the index that corresponds to the data sample's digit category). We also need to *normalize* the input images by subtracting the mean and standard deviation of the pixels. Normalizing the data encourages our model to learn more generalizable features and helps it perform better on outside data. The final data processing step is \"flattening\" the $28\\times28$ image pixel matrices into $784 \\times 1$ arrays. We reshape the image matrices into arrays because our model expects the input to be a tensor with $784$ features. \n\nNow, let's load the data!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Model / data parameters\nnum_classes = 10\ninput_shape = (-1, 28*28) # this will be used to reshape the 28x28 image pixel matrices into 784 pixel vectors \n\n# the data, split between train and test sets\n(train_images, train_labels), (test_images, test_labels) = keras.datasets.mnist.load_data()\n\n# Normalize train/test images \ntrain_images = train_images.astype(\"float32\")\ntest_images = test_images.astype(\"float32\")\n\nmean = train_images.mean()\nstd = train_images.std()\n\ntrain_images -= mean\ntrain_images /= std\n\ntest_images -= mean\ntest_images /= std\n\nprint(f'normalized images mean and std pixel values: {round(train_images.mean(), 4)}, {round(train_images.std(), 4)}')\n\n\n# Flatten the images.\ntrain_images = train_images.reshape(input_shape)\ntest_images = test_images.reshape(input_shape)\n\nprint(\"train_images shape:\", train_images.shape)\nprint(train_images.shape[0], \"train samples\")\nprint(test_images.shape[0], \"test samples\")\n\n\n# convert class vectors to binary class matrices (i.e., \"one-hot encode\" the y labels)\ntrain_labels = keras.utils.to_categorical(train_labels, num_classes)\ntest_labels = keras.utils.to_categorical(test_labels, num_classes)",
"normalized images mean and std pixel values: -0.0, 1.0\ntrain_images shape: (60000, 784)\n60000 train samples\n10000 test samples\n"
]
],
[
[
"Let's display the first 5 images from the *training set* and display the class name below each image.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(10,2))\nfor i in range(5):\n plt.subplot(1,5,i+1)\n plt.xticks([])\n plt.yticks([])\n plt.grid(False)\n plt.imshow(train_images[i].reshape(28, 28), cmap=plt.cm.binary)\n plt.xlabel(np.argmax(train_labels[i]))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Step 2: Building the Model\nRemember that the secret sauce of neural networks is *stacking layers*? In code, we take advantage of this secret sauce by constructing several layers and combining them to create a neural network model. Building the model is a two step process that involves 1) stacking layers together using `keras.Sequential`, 2) configuring the loss function, optimizer, and metrics to monitor the model using the keras `compile` method. Loss functions, optimizers, and metrics aren't formally discussed in this lesson. Don't worry too much about them for now. They will be described in detail in a future lesson. The goal of this lesson is to introduce the underlying structure of neural networks, and demonstrate how to build/train/test one in Python. Nonetheless, a quick summary about loss functions, optimizers, and metrics can't hurt:\n\n* **Loss function** - measures how accurate the model is during training, we want to minimize the value this function returns using an optimization method.\n* **Optimizer** - defines the optimization method to use to update the model's weights based on the data it sees and its loss function.\n* **Metrics** - monitors the model using a set of user-defined metrics; metrics are calculated at the end of every train and test cycle.\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Building the Model - Step 1: Stacking Layers with `keras.Sequential`**\n\nThe [3Blue1Brown video](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aircAruvnKk&t=436s) used a feed forward neural network with 2 hidden layers to classify handwritten digits. To recreate this neural network, first we need to build a model that 1) takes 784 image pixel feature vectors as input, 2) has 2 hidden layers with 16 neurons and the sigmoid activation function, and 3) includes a final layer with 10 neurons (i.e., there are 10 digit classes so we need 10 neurons) and the *softmax* activation function. The softmax activation function normalizes the activations for the output neurons such that:\n- every activation is between 0 and 1\n- the sum of all activations is 1\n\nNotice that the softmax activation is similar to the sigmoid activation--neuron activations are squeezed between 0 and 1. Softmax differs from sigmoid by constraining the sum of all activations to 1. For multi-class classification problems, where multiple categories/classes are present in the y variable, it is common to use the softmax activation (or a varient) in the final layer. This is because the softmax activation enables us to treat the final neuron activations as confidence values (i.e., probabilities). The neuron with the largest activation is selected as the category/class prediction. \n\nLet's see what this looks like in Python code.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# step 1: stack model layers using keras.Sequential\nmodel = keras.Sequential([\n Input(shape=input_shape[1]), # each input is a 784 feature pixel vector\n Dense(16, activation=\"relu\"), # hidden layer 1\n Dense(16, activation='relu'), # hidden layer 2\n Dense(num_classes, activation=\"softmax\"), # final output layer \n])\n \n# print the model summary to see its structure and the number of parameters (i.e., weights and biases)\nprint(model.summary())",
"Model: \"sequential_2\"\n_________________________________________________________________\nLayer (type) Output Shape Param # \n=================================================================\ndense_6 (Dense) (None, 16) 12560 \n_________________________________________________________________\ndense_7 (Dense) (None, 16) 272 \n_________________________________________________________________\ndense_8 (Dense) (None, 10) 170 \n=================================================================\nTotal params: 13,002\nTrainable params: 13,002\nNon-trainable params: 0\n_________________________________________________________________\nNone\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Building the Model - Step 2: Configuring the Loss Function, Optimizer, & Metrics with the Keras `compile` Method**\n\nThe model structure is defined in step 1, so most of the building process is finished. But, we still need to configure the model's loss function, optimizer, and metrics using the keras `compile` method. We will use binary cross entropy (BCE) for the loss function, the Adam optimization method, and monitor accuracy, precision, and recall of the model.\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# step 2: configure the loss function, optimizer, and model metrics \nmodel.compile(loss=\"categorical_crossentropy\", # BCE loss \n optimizer=\"adam\", # Adam optimization\n metrics=[\"accuracy\", keras.metrics.Precision(), keras.metrics.Recall()] # monitor metrics\n )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now, we can train the model! ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Step 3: Training the Model \n\nTraining the neural network model requires the following steps:\n\n1. Feed the training data to the model—in this example, the `train_images` and `train_labels` arrays.\n2. The model learns to associate images and labels.\n3. We ask the model to make predictions on a test set—in this example, the `test_images` array. We verify that the predictions match the labels from the `test_labels` array. \n\nWe call the `model.fit` method to train the model—the model is \"fit\" to the training data:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# fit the model to the data; train for 20 epochs, use batch size 128, and 10% of the training data \n# for validation to model performance during training, and configure the early stopping callback\nbatch_size = 128\nepochs = 20\n\nhistory = model.fit(train_images, \n train_labels, \n batch_size=batch_size, \n epochs=epochs, \n validation_split=0.1)",
"Epoch 1/20\n422/422 [==============================] - 3s 6ms/step - loss: 0.6800 - accuracy: 0.7844 - precision_2: 0.9133 - recall_2: 0.7094 - val_loss: 0.2499 - val_accuracy: 0.9312 - val_precision_2: 0.9477 - val_recall_2: 0.9182\nEpoch 2/20\n422/422 [==============================] - 2s 5ms/step - loss: 0.2614 - accuracy: 0.9234 - precision_2: 0.9395 - recall_2: 0.9092 - val_loss: 0.1937 - val_accuracy: 0.9468 - val_precision_2: 0.9584 - val_recall_2: 0.9358\nEpoch 3/20\n422/422 [==============================] - 2s 5ms/step - loss: 0.2171 - accuracy: 0.9365 - precision_2: 0.9489 - recall_2: 0.9259 - val_loss: 0.1697 - val_accuracy: 0.9523 - val_precision_2: 0.9613 - val_recall_2: 0.9447\nEpoch 4/20\n422/422 [==============================] - 2s 5ms/step - loss: 0.1930 - accuracy: 0.9426 - precision_2: 0.9530 - recall_2: 0.9341 - val_loss: 0.1611 - val_accuracy: 0.9567 - val_precision_2: 0.9632 - val_recall_2: 0.9517\nEpoch 5/20\n422/422 [==============================] - 2s 5ms/step - loss: 0.1755 - accuracy: 0.9479 - precision_2: 0.9567 - recall_2: 0.9397 - val_loss: 0.1571 - val_accuracy: 0.9557 - val_precision_2: 0.9640 - val_recall_2: 0.9495\nEpoch 6/20\n422/422 [==============================] - 2s 5ms/step - loss: 0.1649 - accuracy: 0.9501 - precision_2: 0.9588 - recall_2: 0.9430 - val_loss: 0.1504 - val_accuracy: 0.9593 - val_precision_2: 0.9659 - val_recall_2: 0.9538\nEpoch 7/20\n422/422 [==============================] - 2s 5ms/step - loss: 0.1558 - accuracy: 0.9527 - precision_2: 0.9602 - recall_2: 0.9466 - val_loss: 0.1511 - val_accuracy: 0.9585 - val_precision_2: 0.9638 - val_recall_2: 0.9542\nEpoch 8/20\n422/422 [==============================] - 2s 5ms/step - loss: 0.1504 - accuracy: 0.9545 - precision_2: 0.9618 - recall_2: 0.9488 - val_loss: 0.1532 - val_accuracy: 0.9610 - val_precision_2: 0.9652 - val_recall_2: 0.9568\nEpoch 9/20\n422/422 [==============================] - 2s 5ms/step - loss: 0.1448 - accuracy: 0.9561 - precision_2: 0.9628 - recall_2: 0.9501 - val_loss: 0.1482 - val_accuracy: 0.9608 - val_precision_2: 0.9655 - val_recall_2: 0.9567\nEpoch 10/20\n422/422 [==============================] - 2s 6ms/step - loss: 0.1378 - accuracy: 0.9589 - precision_2: 0.9653 - recall_2: 0.9533 - val_loss: 0.1446 - val_accuracy: 0.9610 - val_precision_2: 0.9662 - val_recall_2: 0.9570\nEpoch 11/20\n422/422 [==============================] - 2s 5ms/step - loss: 0.1353 - accuracy: 0.9594 - precision_2: 0.9654 - recall_2: 0.9546 - val_loss: 0.1577 - val_accuracy: 0.9575 - val_precision_2: 0.9628 - val_recall_2: 0.9528\nEpoch 12/20\n422/422 [==============================] - 2s 5ms/step - loss: 0.1315 - accuracy: 0.9604 - precision_2: 0.9657 - recall_2: 0.9553 - val_loss: 0.1512 - val_accuracy: 0.9595 - val_precision_2: 0.9659 - val_recall_2: 0.9548\nEpoch 13/20\n422/422 [==============================] - 2s 5ms/step - loss: 0.1278 - accuracy: 0.9611 - precision_2: 0.9669 - recall_2: 0.9567 - val_loss: 0.1616 - val_accuracy: 0.9588 - val_precision_2: 0.9633 - val_recall_2: 0.9533\nEpoch 14/20\n422/422 [==============================] - 2s 5ms/step - loss: 0.1241 - accuracy: 0.9620 - precision_2: 0.9672 - recall_2: 0.9580 - val_loss: 0.1578 - val_accuracy: 0.9562 - val_precision_2: 0.9600 - val_recall_2: 0.9518\nEpoch 15/20\n422/422 [==============================] - 2s 5ms/step - loss: 0.1208 - accuracy: 0.9631 - precision_2: 0.9684 - recall_2: 0.9584 - val_loss: 0.1538 - val_accuracy: 0.9598 - val_precision_2: 0.9634 - val_recall_2: 0.9560\nEpoch 16/20\n422/422 [==============================] - 2s 5ms/step - loss: 0.1196 - accuracy: 0.9638 - precision_2: 0.9694 - recall_2: 0.9596 - val_loss: 0.1488 - val_accuracy: 0.9590 - val_precision_2: 0.9640 - val_recall_2: 0.9547\nEpoch 17/20\n422/422 [==============================] - 2s 5ms/step - loss: 0.1176 - accuracy: 0.9644 - precision_2: 0.9695 - recall_2: 0.9601 - val_loss: 0.1631 - val_accuracy: 0.9560 - val_precision_2: 0.9608 - val_recall_2: 0.9530\nEpoch 18/20\n422/422 [==============================] - 2s 5ms/step - loss: 0.1149 - accuracy: 0.9641 - precision_2: 0.9689 - recall_2: 0.9601 - val_loss: 0.1526 - val_accuracy: 0.9582 - val_precision_2: 0.9634 - val_recall_2: 0.9552\nEpoch 19/20\n422/422 [==============================] - 2s 5ms/step - loss: 0.1113 - accuracy: 0.9661 - precision_2: 0.9713 - recall_2: 0.9621 - val_loss: 0.1538 - val_accuracy: 0.9600 - val_precision_2: 0.9655 - val_recall_2: 0.9560\nEpoch 20/20\n422/422 [==============================] - 2s 5ms/step - loss: 0.1102 - accuracy: 0.9673 - precision_2: 0.9719 - recall_2: 0.9629 - val_loss: 0.1508 - val_accuracy: 0.9587 - val_precision_2: 0.9640 - val_recall_2: 0.9563\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Challenge:** As the model is trained, the loss and metrics are displayed. What is the final precision score on the training data?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Now that we finished training, let's view the results. We'll use the Pandas library to store the training history in a dataframe. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# store the training history in a dataframe\nhist = pd.DataFrame(history.history)\nhist['epoch'] = history.epoch\n\n# see what the hist dataframe looks like\nhist",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now, let's plot the loss function measure on the training and validation sets. The validation set is used to prevent overfitting ([learn more about it here](https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/keras/overfit_and_underfit)). However, because our network is small, the training converges (i.e., reaches an optimal loss value) without noticeably overfitting the data as the plot shows.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def plot_loss():\n plt.figure()\n plt.xlabel('Epoch')\n plt.ylabel('Loss')\n plt.plot(hist['epoch'], hist['loss'], label='Train Error')\n plt.plot(hist['epoch'], hist['val_loss'], label = 'Val Error')\n plt.legend()\n plt.ylim([0,max(hist['loss'].max()+0.2, hist['val_loss'].max()+0.2)])\n\nplot_loss()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now, let's plot accuracy metric on the training and validation set. Similar to the loss metric, we expect the validation accuracy to be a bit lower than the training accuracy. If the validation accuracy is noticeably different than the training one, we might want to do some more analysis. When the validation accuracy is much lower than the training accuracy, the model could be overfitting. When the it is much higher than the training accuracy, the model could be underfitting (this happens less often). However, the plot suggests the model is not overfitting/underfitting the data. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def plot_accuracy():\n plt.figure()\n plt.xlabel('Epoch')\n plt.ylabel('Accuracy')\n plt.plot(hist['epoch'], hist['accuracy'], label='Train Accuracy')\n plt.plot(hist['epoch'], hist['val_accuracy'], label = 'Val Accuracy')\n plt.legend()\n plt.ylim([0,1])\n\nplot_accuracy()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Step 4: Testing the Model\nOur results on the training and validation data look promising, but we want to know whether our model performs well on unknown data. For this, we compare how the model performs on the test dataset:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(test_images.shape)\ntest_loss, test_acc, test_prec, test_rec = model.evaluate(test_images, test_labels)\n\nprint('Test accuracy:', test_acc)",
"(10000, 784)\n313/313 [==============================] - 1s 4ms/step - loss: 0.1632 - accuracy: 0.9549 - precision_2: 0.9594 - recall_2: 0.9521\nTest accuracy: 0.9549000263214111\n"
]
],
[
[
"Let's take a look at a few sample that the network classified incorrectly.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"predictions = np.argmax(model.predict(test_images, batch_size=32), axis=-1)\nis_correct = predictions == np.argmax(test_labels, axis=-1)\n\nmisclassified_indices = np.argwhere(is_correct == False)\n\ndef plot_misclassified(imgs, labels, preds, misclassified_indices, n=5):\n plt.figure(figsize=(10,3))\n for i, idx in enumerate(misclassified_indices[:n]):\n plt.subplot(1, n, i+1)\n plt.xticks([])\n plt.yticks([])\n plt.imshow(imgs[idx].reshape(28, 28), cmap=plt.cm.binary)\n plt.xlabel(f'True: {np.argmax(labels[idx])}, Pred: {preds[idx][0]}')\n\nplot_misclassified(test_images, test_labels, predictions, misclassified_indices)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can see that some of these digits are hard to recognize, even for a human!",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Often times, the accuracy on the test dataset is a little less than the accuracy on the training dataset. Small differences are ok, but we don't want the test results to differ significantly from the training results--this suggests the model is overfitting/underfitting. \n\n**Challenge:** Do you think the difference between the training accuracy and the testing accuracy is significant? Is the model overfitting? Is it underfitting? Are the misclassify images justifiably misclassified (i.e., does it make sense that the model misclassified them)?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Recap\nYou made it! We covered a lot of material in this lesson. Don't worry if it doesn't all make sense yet. The concepts will become more intuitive as you practice building, training, and testing your own neural network models. \n\nLet's summarize what we learned about neural networks:\n- Neural Networks are popular and successful machine learning models that can learn effective representations from data (i.e., images, text, sound). They can and *classification* tasks (see [Part 2](#-Part-2:-Classification-of-MNIST-Digits-with-Convolutional-Neural-Networks)), and also to generate images, text, videos, and sound. \n- Special libraries like Tensorflow and Pytorch enable us to build neural networks in Python and train them on accelerated hardware like GPUs and TPUs. \n- Several steps are involved in making an effective neural network: \n 1. Loading the dataset\n 2. Building the model--stacking several layers and configuring the loss function, optimizer, and metrics.\n 3. Training the model--fitting the model on the training data.\n 4. Evaluating/Testing the model--evaluating the model on the testing data. \n- Once a model is trained, it can be used to make predictions on outside data (see [Part 2, Step 5](#-Step-5:-Make-predictions-on-outside-data)). ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Acknowlegements\n- [MIT Deep Learning Basics](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=O5xeyoRL95U&list=PLrAXtmErZgOeiKm4sgNOknGvNjby9efdf)\n- [Dive into Deep Learning](https://d2l.ai/index.html)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a34e3f48bb5414f3caf56a854cdf2ad2aabd1e1
| 22,601 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
training/trainer.ipynb
|
Verena96/intelligent-systems-project
|
3feb7af9c17cbd99e958027ac45b14cfa769e1ad
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
training/trainer.ipynb
|
Verena96/intelligent-systems-project
|
3feb7af9c17cbd99e958027ac45b14cfa769e1ad
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
training/trainer.ipynb
|
Verena96/intelligent-systems-project
|
3feb7af9c17cbd99e958027ac45b14cfa769e1ad
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 34.505344 | 124 | 0.42799 |
[
[
[
"#Packages\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport os\nimport pickle\nimport random\nfrom sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer, TfidfVectorizer\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression\nfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier\nfrom sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, StratifiedKFold, GridSearchCV,RandomizedSearchCV\nfrom sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler\nfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, f1_score, roc_auc_score, precision_score, recall_score\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score\nfrom sklearn.compose import ColumnTransformer\nimport warnings\nwarnings.filterwarnings(\"ignore\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Environment variables\nDATASET_PATH=os.getenv('DATASET_PATH')\nMODEL_PATH=os.getenv('MODEL_PATH')\nMETRICS_PATH=os.getenv('METRICS_PATH')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Import data\ndf = pd.read_csv(DATASET_PATH)\nprint(df.shape)\ndf.head()",
"(38000, 15)\n"
],
[
"#Check NaN values\ndf.isnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Treating the data and dropping irrelevant columns\ndf=df.drop(['product_id','seller_id','creation_date','order_counts'],axis=1)\ndf=df.dropna()\ndf.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Split data for training and test\nX = df.drop(['category'],axis=1)\ny = df['category']\n\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=42, test_size=0.33)\ncv = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=5)\n\nprint(X_train.shape)\nprint(y_train.shape)",
"(25419, 10)\n(25419,)\n"
],
[
"#Select best parameters for each model tested\ndef choose_model(pip,params,cv,X,y,seed):\n \n CV = RandomizedSearchCV(estimator=pip, \n param_distributions=params,\n cv=cv, \n n_jobs= -1,\n scoring='roc_auc',\n random_state=seed) \n CV.fit(X_train, y_train) \n best_choice = CV.best_estimator_\n\n print('Best choice:','\\n',best_choice)\n\n return best_choice\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Treat text data separately\npreprocess = ColumnTransformer(\n [('query_countvec', CountVectorizer(), 'query'),\n ('title_countvec', CountVectorizer(), 'title'),\n ('concatenated_tags_tfidf', TfidfVectorizer(ngram_range=(1,3)), 'concatenated_tags')],\n remainder='passthrough')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Logistic regression model\npipeline = Pipeline([\n\n ('union',preprocess),\n \n ('scaler', StandardScaler(with_mean=False)),\n \n\n ('clf',LogisticRegression(random_state=42))\n \n ])\n\nparams = [\n {\n \"clf__penalty\": ['l2', 'l1'],\n \"clf__C\": np.logspace(0, 2, 10),\n \"clf__solver\":['newton-cg','saga', 'liblinear']\n }\n] \n\nlogreg_result = choose_model(pip=pipeline,params=params,cv=cv,X=X_train,y=y_train,seed=42)\nacc = cross_val_score(logreg_result, X_train, y_train, cv=cv,scoring='accuracy')\nf1 = cross_val_score(logreg_result, X_train, y_train, cv=cv,scoring='f1_weighted')\nprint(\"%f accuracy with std of %f, and f1-score of %f with std of %f.\" % (acc.mean(), acc.std(),f1.mean(),f1.std()))",
"Best choice: \n Pipeline(steps=[('union',\n ColumnTransformer(remainder='passthrough',\n transformers=[('query_countvec',\n CountVectorizer(), 'query'),\n ('title_countvec',\n CountVectorizer(), 'title'),\n ('concatenated_tags_tfidf',\n TfidfVectorizer(ngram_range=(1,\n 3)),\n 'concatenated_tags')])),\n ('scaler', StandardScaler(with_mean=False)),\n ('clf',\n LogisticRegression(random_state=42, solver='newton-cg'))])\n0.886227 accuracy with std of 0.003398, and f1-score of 0.884573 with std of 0.003645.\n"
],
[
"#Random forest model\npipeline = Pipeline([\n\n ('union',preprocess),\n \n ('scaler', StandardScaler(with_mean=False)),\n\n ('clf',RandomForestClassifier(random_state=42))])\n\nparams = [\n {\n \"clf__n_estimators\": [10, 50, 100, 1000],\n \"clf__max_depth\":[5, 10, 15, 25, 50, None],\n \"clf__min_samples_leaf\":[1, 2, 5, 10, 15, 100],\n \"clf__max_leaf_nodes\": [2, 3,5, 15,20]\n }\n] \n\nrf_result = choose_model(pip=pipeline,params=params,cv=cv,X=X_train,y=y_train,seed=42)\nacc = cross_val_score(rf_result, X_train, y_train, cv=cv,scoring='accuracy')\nf1 = cross_val_score(rf_result, X_train, y_train, cv=cv,scoring='f1_weighted')\nprint(\"%f accuracy with std of %f, and f1-score of %f with std of %f.\" % (acc.mean(), acc.std(),f1.mean(),f1.std()))",
"Best choice: \n Pipeline(steps=[('union',\n ColumnTransformer(remainder='passthrough',\n transformers=[('query_countvec',\n CountVectorizer(), 'query'),\n ('title_countvec',\n CountVectorizer(), 'title'),\n ('concatenated_tags_tfidf',\n TfidfVectorizer(ngram_range=(1,\n 3)),\n 'concatenated_tags')])),\n ('scaler', StandardScaler(with_mean=False)),\n ('clf',\n RandomForestClassifier(max_depth=15, max_leaf_nodes=20,\n min_samples_leaf=2, n_estimators=10,\n random_state=42))])\n0.556552 accuracy with std of 0.013768, and f1-score of 0.466705 with std of 0.020209.\n"
],
[
"#Check metrics and choose final model\npipelines = [logreg_result,rf_result]\n\nresult = pd.DataFrame(columns=['Model','train_acc','test_acc','train_prec','test_prec',\n 'train_rec','test_rec','train_f1','test_f1','train_auc','test_auc'])\n\nfor p in pipelines:\n \n model = p['clf'].__class__.__name__\n tracc = accuracy_score(y_train, p.predict(X_train))\n teacc = accuracy_score(y_test, p.predict(X_test))\n trprec = precision_score(y_train, p.predict(X_train),average='weighted')\n teprec = precision_score(y_test, p.predict(X_test), average='weighted')\n trrec = recall_score(y_train, p.predict(X_train), average='weighted')\n terec = recall_score(y_test, p.predict(X_test), average='weighted')\n trf1 = f1_score(y_train, p.predict(X_train), average='weighted')\n tef1 = f1_score(y_test, p.predict(X_test), average='weighted')\n trauc = roc_auc_score(y_train, p.predict_proba(X_train), multi_class=\"ovo\")\n teauc = roc_auc_score(y_test, p.predict_proba(X_test), multi_class=\"ovo\")\n \n result = result.append({'Model':model,\n 'train_acc':tracc,\n 'test_acc':teacc,\n 'train_prec':trprec,\n 'test_prec':teprec,\n 'train_rec':trrec,\n 'test_rec':terec,\n 'train_f1':trf1,\n 'test_f1':tef1,\n 'train_auc':trauc,\n 'test_auc':teauc},ignore_index=True)\n\nresult ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Save best model\nmodel=logreg_result\nfilepath=MODEL_PATH\npickle.dump(model,open(filepath,'wb'))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Save metrics\npd.DataFrame(result.loc[0]).to_csv(METRICS_PATH)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.