hexsha
stringlengths 40
40
| size
int64 6
14.9M
| ext
stringclasses 1
value | lang
stringclasses 1
value | max_stars_repo_path
stringlengths 6
260
| max_stars_repo_name
stringlengths 6
119
| max_stars_repo_head_hexsha
stringlengths 40
41
| max_stars_repo_licenses
list | max_stars_count
int64 1
191k
⌀ | max_stars_repo_stars_event_min_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_stars_repo_stars_event_max_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_issues_repo_path
stringlengths 6
260
| max_issues_repo_name
stringlengths 6
119
| max_issues_repo_head_hexsha
stringlengths 40
41
| max_issues_repo_licenses
list | max_issues_count
int64 1
67k
⌀ | max_issues_repo_issues_event_min_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_issues_repo_issues_event_max_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_forks_repo_path
stringlengths 6
260
| max_forks_repo_name
stringlengths 6
119
| max_forks_repo_head_hexsha
stringlengths 40
41
| max_forks_repo_licenses
list | max_forks_count
int64 1
105k
⌀ | max_forks_repo_forks_event_min_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_forks_repo_forks_event_max_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | avg_line_length
float64 2
1.04M
| max_line_length
int64 2
11.2M
| alphanum_fraction
float64 0
1
| cells
list | cell_types
list | cell_type_groups
list |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
4a70559d1244ccd6e9080979d79fe5eee92712f2
| 18,342 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
distribute_MICE_results.ipynb
|
d-farnham/EIA_Cleaned_Hourly_Electricity_Demand_Code
|
61608bf7324af5597960aff5efbf1e0fba1a92b2
|
[
"MIT"
] | 5 |
2020-03-25T03:50:15.000Z
|
2021-08-23T05:10:51.000Z
|
distribute_MICE_results.ipynb
|
d-farnham/EIA_Cleaned_Hourly_Electricity_Demand_Code
|
61608bf7324af5597960aff5efbf1e0fba1a92b2
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2020-03-25T17:55:08.000Z
|
2020-04-01T19:46:01.000Z
|
distribute_MICE_results.ipynb
|
d-farnham/EIA_Cleaned_Hourly_Electricity_Demand_Code
|
61608bf7324af5597960aff5efbf1e0fba1a92b2
|
[
"MIT"
] | 8 |
2019-11-14T00:09:32.000Z
|
2021-01-06T21:03:13.000Z
| 39.192308 | 326 | 0.49542 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nfrom datetime import datetime\nimport os",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Define Which Input Files to Use\nThe default settings will use the input files recently produced in Step 1) using the notebook `get_eia_demand_data.ipynb`. For those interested in reproducing the exact results included in the repository, you will need to point to the files containing the original `raw` EIA demand data that we querried on 10 Sept 2019.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"merge_with_step1_files = False # used to run step 2 on the most recent files\nmerge_with_10sept2019_files = True # used to reproduce the documented results\nassert((merge_with_step1_files != merge_with_10sept2019_files) and \n (merge_with_step1_files == True or merge_with_10sept2019_files == True)), \"One of these must be true: 'merge_with_step1_files' and 'merge_with_10sept2019_files'\"\n\nif merge_with_step1_files:\n input_path = './data'\n\nif merge_with_10sept2019_files:\n # input_path is the path to the downloaded data from Zenodo: https://zenodo.org/record/3517197\n input_path = '/BASE/PATH/TO/ZENODO'\n input_path += '/data/release_2019_Oct/original_eia_files'\n assert(os.path.exists(input_path)), f\"You must set the base directory for the Zenodo data {input_path} does not exist\"\n # If you did not run step 1, make the /data directory\n if not os.path.exists('./data'):\n os.mkdir('./data')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Make the output directories",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Make output directories\nout_base = './data/final_results'\nif not os.path.exists(out_base):\n os.mkdir(out_base)\n for subdir in ['balancing_authorities', 'regions', 'interconnects', 'contiguous_US']:\n os.mkdir(f\"{out_base}/{subdir}\")\n print(f\"Final results files will be located here: {out_base}/{subdir}\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Useful functions",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# All 56 balancing authorities that have demand (BA)\ndef return_all_regions():\n return [\n 'AEC', 'AECI', 'CPLE', 'CPLW',\n 'DUK', 'FMPP', 'FPC',\n 'FPL', 'GVL', 'HST', 'ISNE',\n 'JEA', 'LGEE', 'MISO', 'NSB',\n 'NYIS', 'PJM', 'SC',\n 'SCEG', 'SOCO',\n 'SPA', 'SWPP', 'TAL', 'TEC',\n 'TVA', 'ERCO',\n 'AVA', 'AZPS', 'BANC', 'BPAT',\n 'CHPD', 'CISO', 'DOPD',\n 'EPE', 'GCPD', 'IID',\n 'IPCO', 'LDWP', 'NEVP', 'NWMT',\n 'PACE', 'PACW', 'PGE', 'PNM',\n 'PSCO', 'PSEI', 'SCL', 'SRP',\n 'TEPC', 'TIDC', 'TPWR', 'WACM',\n 'WALC', 'WAUW',\n 'OVEC', 'SEC',\n ]\n\n# All 54 \"usable\" balancing authorities (BA) (excludes OVEC and SEC)\n# These 2 have significant\n# enough reporting problems that we do not impute cleaned data for them.\ndef return_usable_BAs():\n return [\n 'AEC', 'AECI', 'CPLE', 'CPLW',\n 'DUK', 'FMPP', 'FPC',\n 'FPL', 'GVL', 'HST', 'ISNE',\n 'JEA', 'LGEE', 'MISO', 'NSB',\n 'NYIS', 'PJM', 'SC',\n 'SCEG', 'SOCO',\n 'SPA', 'SWPP', 'TAL', 'TEC',\n 'TVA', 'ERCO',\n 'AVA', 'AZPS', 'BANC', 'BPAT',\n 'CHPD', 'CISO', 'DOPD',\n 'EPE', 'GCPD', 'IID',\n 'IPCO', 'LDWP', 'NEVP', 'NWMT',\n 'PACE', 'PACW', 'PGE', 'PNM',\n 'PSCO', 'PSEI', 'SCL', 'SRP',\n 'TEPC', 'TIDC', 'TPWR', 'WACM',\n 'WALC', 'WAUW',\n # 'OVEC', 'SEC',\n ]\n\n# mapping of each balancing authority (BA) to its associated\n# U.S. interconnect (IC).\ndef return_ICs_from_BAs():\n return {\n 'EASTERN_IC' : [\n 'AEC', 'AECI', 'CPLE', 'CPLW',\n 'DUK', 'FMPP', 'FPC',\n 'FPL', 'GVL', 'HST', 'ISNE',\n 'JEA', 'LGEE', 'MISO', 'NSB',\n 'NYIS', 'PJM', 'SC',\n 'SCEG', 'SOCO',\n 'SPA', 'SWPP', 'TAL', 'TEC',\n 'TVA',\n 'OVEC', 'SEC',\n ],\n 'TEXAS_IC' : [\n 'ERCO',\n ],\n 'WESTERN_IC' : [\n 'AVA', 'AZPS', 'BANC', 'BPAT',\n 'CHPD', 'CISO', 'DOPD',\n 'EPE', 'GCPD',\n 'IID',\n 'IPCO', 'LDWP', 'NEVP', 'NWMT',\n 'PACE', 'PACW', 'PGE', 'PNM',\n 'PSCO', 'PSEI', 'SCL', 'SRP',\n 'TEPC', 'TIDC', 'TPWR', 'WACM',\n 'WALC', 'WAUW',\n ]\n }\n\n# Defines a mapping between the balancing authorities (BAs)\n# and their locally defined region based on EIA naming.\n# This uses a json file defining the mapping.\ndef return_BAs_per_region_map():\n\n regions = {\n 'CENT' : 'Central',\n 'MIDW' : 'Midwest',\n 'TEN' : 'Tennessee',\n 'SE' : 'Southeast',\n 'FLA' : 'Florida',\n 'CAR' : 'Carolinas',\n 'MIDA' : 'Mid-Atlantic',\n 'NY' : 'New York',\n 'NE' : 'New England',\n 'TEX' : 'Texas',\n 'CAL' : 'California',\n 'NW' : 'Northwest',\n 'SW' : 'Southwest'\n }\n\n rtn_map = {}\n for k, v in regions.items():\n rtn_map[k] = []\n\n # Load EIA's Blancing Authority Acronym table\n # https://www.eia.gov/realtime_grid/\n df = pd.read_csv('data/balancing_authority_acronyms.csv',\n skiprows=1) # skip first row as it is source info\n\n # Loop over all rows and fill map\n for idx in df.index:\n\n # Skip Canada and Mexico\n if df.loc[idx, 'Region'] in ['Canada', 'Mexico']:\n continue\n\n reg_acronym = ''\n # Get region to acronym\n for k, v in regions.items():\n if v == df.loc[idx, 'Region']:\n reg_acronym = k\n break\n assert(reg_acronym != '')\n\n rtn_map[reg_acronym].append(df.loc[idx, 'Code'])\n\n tot = 0\n for k, v in rtn_map.items():\n tot += len(v)\n print(f\"Total US48 BAs mapped {tot}. Recall 11 are generation only.\")\n\n return rtn_map\n\n\n# Assume the MICE results file is a subset of the original hours\ndef trim_rows_to_match_length(mice, df):\n mice_start = mice.loc[0, 'date_time']\n mice_end = mice.loc[len(mice.index)-1, 'date_time']\n to_drop = []\n for idx in df.index:\n if df.loc[idx, 'date_time'] != mice_start:\n to_drop.append(idx)\n else: # stop once equal\n break\n for idx in reversed(df.index):\n if df.loc[idx, 'date_time'] != mice_end:\n to_drop.append(idx)\n else: # stop once equal\n break\n \n df = df.drop(to_drop, axis=0)\n df = df.reset_index()\n assert(len(mice.index) == len(df.index))\n return df\n\n\n# Load balancing authority files already containing the full MICE results.\n# Aggregate associated regions into regional, interconnect, or CONUS files.\n# Treat 'MISSING' and 'EMPTY' values as zeros when aggregating.\ndef merge_BAs(region, bas, out_base, folder):\n \n print(region, bas)\n \n # Remove BAs which are generation only as well as SEC and OVEC.\n # See main README regarding SEC and OVEC.\n usable_BAs = return_usable_BAs()\n good_bas = []\n for ba in bas:\n if ba in usable_BAs:\n good_bas.append(ba)\n \n \n first_ba = good_bas.pop()\n master = pd.read_csv(f'{out_base}/balancing_authorities/{first_ba}.csv', na_values=['MISSING', 'EMPTY'])\n master = master.fillna(0)\n \n master = master.drop(['category', 'forecast demand (MW)'], axis=1)\n \n for ba in good_bas:\n df = pd.read_csv(f'{out_base}/balancing_authorities/{ba}.csv', na_values=['MISSING', 'EMPTY'])\n df = df.fillna(0)\n master['raw demand (MW)'] += df['raw demand (MW)']\n master['cleaned demand (MW)'] += df['cleaned demand (MW)']\n \n master.to_csv(f'{out_base}/{folder}/{region}.csv', index=False)\n \n\n# Do both the distribution of balancing authority level results to new BA files\n# and generate regional, interconnect, and CONUS aggregate files.\ndef distribute_MICE_results(raw_demand_file_loc, screening_file, mice_results_csv, out_base):\n\n # Load screening results\n screening = pd.read_csv(screening_file)\n # Load MICE results\n mice = pd.read_csv(mice_results_csv)\n screening = trim_rows_to_match_length(mice, screening)\n \n # Distribute to single BA results files first\n print(\"Distribute MICE results per-balancing authority:\")\n for ba in return_usable_BAs():\n print(ba)\n df = pd.read_csv(f\"{raw_demand_file_loc}/{ba}.csv\")\n df = trim_rows_to_match_length(mice, df)\n \n df_out = pd.DataFrame({\n 'date_time': df['date_time'],\n 'raw demand (MW)': df['demand (MW)'],\n 'category': screening[f'{ba}_category'],\n 'cleaned demand (MW)': mice[ba],\n 'forecast demand (MW)': df['forecast demand (MW)']\n })\n \n \n df_out.to_csv(f'./{out_base}/balancing_authorities/{ba}.csv', index=False)\n\n # Aggregate balancing authority level results into EIA regions\n print(\"\\nEIA regional aggregation:\")\n for region, bas in return_BAs_per_region_map().items():\n merge_BAs(region, bas, out_base, 'regions')\n \n # Aggregate balancing authority level results into CONUS interconnects\n print(\"\\nCONUS interconnect aggregation:\")\n for region, bas in return_ICs_from_BAs().items():\n merge_BAs(region, bas, out_base, 'interconnects')\n \n # Aggregate balancing authority level results into CONUS total\n print(\"\\nCONUS total aggregation:\")\n merge_BAs('CONUS', return_usable_BAs(), out_base, 'contiguous_US')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Run the distribution and aggregation",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# The output file generated by Step 2 listing the categories for each time step\nscreening_file = './data/csv_MASTER.csv'\n# The output file generated by Step 3 which runs the MICE algo and has the cleaned demand values\nmice_file = 'MICE_output/mean_impute_csv_MASTER.csv'\n\n\ndistribute_MICE_results(input_path, screening_file, mice_file, out_base)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Test distribution and aggregation\nThis cell simply checks that the results all add up.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Compare each value in the vectors\ndef compare(vect1, vect2):\n cnt = 0\n clean = True\n for v1, v2 in zip(vect1, vect2):\n if v1 != v2:\n print(f\"Error at idx {cnt} {v1} != {v2}\")\n clean = False\n cnt += 1\n return clean\n \n\ndef test_aggregation(raw_demand_file_loc, screening_file, mice_results_csv, out_base):\n\n # Load MICE results\n usable_BAs = return_usable_BAs()\n mice = pd.read_csv(mice_results_csv)\n\n # Sum all result BAs\n tot_imp = np.zeros(len(mice.index))\n for col in mice.columns:\n if col not in usable_BAs:\n continue\n tot_imp += mice[col]\n\n # Sum Raw\n tot_raw = np.zeros(len(mice.index))\n for ba in return_usable_BAs():\n df = pd.read_csv(f\"{raw_demand_file_loc}/{ba}.csv\", na_values=['MISSING', 'EMPTY'])\n df = trim_rows_to_match_length(mice, df)\n df = df.fillna(0)\n\n tot_raw += df['demand (MW)']\n \n # Check BA results distribution\n print(\"\\nBA Distribution:\")\n new_tot_raw = np.zeros(len(mice.index))\n new_tot_clean = np.zeros(len(mice.index))\n for ba in return_usable_BAs():\n df = pd.read_csv(f\"{out_base}/balancing_authorities/{ba}.csv\", na_values=['MISSING', 'EMPTY'])\n df = df.fillna(0)\n new_tot_raw += df['raw demand (MW)']\n new_tot_clean += df['cleaned demand (MW)']\n \n assert(compare(tot_raw, new_tot_raw)), \"Error in raw sums.\"\n assert(compare(tot_imp, new_tot_clean)), \"Error in imputed values.\"\n print(\"BA Distribution okay!\")\n \n \n # Check aggregate balancing authority level results into EIA regions\n print(\"\\nEIA regional aggregation:\")\n new_tot_raw = np.zeros(len(mice.index))\n new_tot_clean = np.zeros(len(mice.index))\n for region, bas in return_BAs_per_region_map().items():\n df = pd.read_csv(f\"{out_base}/regions/{region}.csv\")\n new_tot_raw += df['raw demand (MW)']\n new_tot_clean += df['cleaned demand (MW)']\n \n assert(compare(tot_raw, new_tot_raw)), \"Error in raw sums.\"\n assert(compare(tot_imp, new_tot_clean)), \"Error in imputed values.\"\n print(\"Regional sums okay!\")\n \n # Aggregate balancing authority level results into CONUS interconnects\n print(\"\\nCONUS interconnect aggregation:\")\n new_tot_raw = np.zeros(len(mice.index))\n new_tot_clean = np.zeros(len(mice.index))\n for region, bas in return_ICs_from_BAs().items():\n df = pd.read_csv(f\"{out_base}/interconnects/{region}.csv\")\n new_tot_raw += df['raw demand (MW)']\n new_tot_clean += df['cleaned demand (MW)']\n \n assert(compare(tot_raw, new_tot_raw)), \"Error in raw sums.\"\n assert(compare(tot_imp, new_tot_clean)), \"Error in imputed values.\"\n print(\"Interconnect sums okay!\")\n \n \n # Aggregate balancing authority level results into CONUS total\n print(\"\\nCONUS total aggregation:\")\n new_tot_raw = np.zeros(len(mice.index))\n new_tot_clean = np.zeros(len(mice.index))\n df = pd.read_csv(f\"{out_base}/contiguous_US/CONUS.csv\")\n new_tot_raw += df['raw demand (MW)']\n new_tot_clean += df['cleaned demand (MW)']\n \n assert(compare(tot_raw, new_tot_raw)), \"Error in raw sums.\"\n assert(compare(tot_imp, new_tot_clean)), \"Error in imputed values.\"\n print(\"CONUS sums okay!\")\n\n\ntest_aggregation(input_path, screening_file, mice_file, out_base)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a706a2256a6eb82b3671cbbb2ab1ab69d7950b9
| 1,939 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Arquivo aulas/Modulo 2/MOD2-aula2.ipynb
|
Sevi042/CursoPython
|
9bb26d602ef1cc5c3da0edab21bea1563f560aae
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Arquivo aulas/Modulo 2/MOD2-aula2.ipynb
|
Sevi042/CursoPython
|
9bb26d602ef1cc5c3da0edab21bea1563f560aae
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Arquivo aulas/Modulo 2/MOD2-aula2.ipynb
|
Sevi042/CursoPython
|
9bb26d602ef1cc5c3da0edab21bea1563f560aae
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 17.159292 | 65 | 0.46983 |
[
[
[
"# Tipos de variáveis\n\n\nUma variável é um objeto, afinal tudo é objeto no python\n\n int - inteiro\n string - texto\n float - decimal (ponto flutuante)\n bool ou boolean",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"faturamento = 1000\nprint(type(faturamento))",
"<class 'int'>\n"
],
[
"faturamento = 1000.00\nprint(type(faturamento))",
"<class 'float'>\n"
],
[
"faturamento = '1000.00'\nprint(type(faturamento))",
"<class 'str'>\n"
],
[
"ganha_bonus = True\nprint(type(ganha_bonus))",
"<class 'bool'>\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a70732486375c038c7986f75b82f5798e62b02d
| 56,747 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
models/baseline_hierarchical/baseline-rhinolophus.ipynb
|
FrankFundel/BAT
|
70c422d9af093a5c5e4d7486f7a206bc87478a9e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
models/baseline_hierarchical/baseline-rhinolophus.ipynb
|
FrankFundel/BAT
|
70c422d9af093a5c5e4d7486f7a206bc87478a9e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
models/baseline_hierarchical/baseline-rhinolophus.ipynb
|
FrankFundel/BAT
|
70c422d9af093a5c5e4d7486f7a206bc87478a9e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 57.032161 | 18,612 | 0.669551 |
[
[
[
"# Dataset",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import sys\nsys.path.append('../../datasets/')\nfrom prepare_individuals import prepare, germanBats\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport torch\nimport numpy as np\nimport tqdm\nimport pickle\n\nclasses = germanBats",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"patch_len = 44 # 88 bei 44100, 44 bei 22050 = 250ms ~ 25ms\n\nX_train, Y_train, X_test, Y_test, X_val, Y_val = prepare(\"../../datasets/prepared.h5\", classes, patch_len)",
"100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 18/18 [00:15<00:00, 1.19it/s]\n100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 18/18 [00:06<00:00, 2.69it/s]\n100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 18/18 [00:03<00:00, 4.56it/s]\n"
],
[
"with open('../call_nocall.indices', 'rb') as file:\n indices, labels = pickle.load(file)\n \n train_indices = indices[0][:len(X_train)]\n test_indices = indices[1][:len(X_test)]\n val_indices = indices[2][:len(X_val)]\n \n X_train = X_train[train_indices]\n X_test = X_test[test_indices]\n X_val = X_val[val_indices]\n \n Y_train = Y_train[train_indices]\n Y_test = Y_test[test_indices]\n Y_val = Y_val[val_indices]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(\"Total calls:\", len(X_train) + len(X_test) + len(X_val))\nprint(X_train.shape, Y_train.shape)",
"Total calls: 33868\n(19839, 44, 257) (19839,)\n"
],
[
"'''species = [0, 1]\ndef filterSpecies(s, X, Y):\n idx = np.in1d(Y, s)\n return X[idx], Y[idx]\n\nX_train, Y_train = filterSpecies(species, X_train, Y_train)\nX_test, Y_test = filterSpecies(species, X_test, Y_test)\nX_val, Y_val = filterSpecies(species, X_val, Y_val)\n\nclasses = {\n \"Rhinolophus ferrumequinum\": 0,\n \"Rhinolophus hipposideros\": 1,\n}'''\n\nspecies = np.asarray([0, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2])\n\nY_train = species[Y_train]\nY_test = species[Y_test]\nY_val = species[Y_val]\n\nclasses = {\n \"Rhinolophus ferrumequinum\": 0,\n \"Rhinolophus hipposideros\": 1,\n \"Other\": 2,\n}\n\nprint(\"Total calls:\", len(X_train) + len(X_test) + len(X_val))\nprint(X_train.shape, Y_train.shape)",
"Total calls: 33868\n(19839, 44, 257) (19839,)\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import time\nimport datetime\nimport tqdm\nimport torch.nn as nn\nimport torchvision\nfrom torch.cuda.amp import autocast\nfrom torch.utils.data import TensorDataset, DataLoader\nfrom timm.data.mixup import Mixup",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"use_stochdepth = False\nuse_mixedprecision = False\nuse_imbalancedsampler = False\nuse_sampler = True\nuse_cosinescheduler = False\nuse_reduceonplateu = False\nuse_nadam = False\nuse_mixup = False",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mixup_args = {\n 'mixup_alpha': 1.,\n 'cutmix_alpha': 0.,\n 'cutmix_minmax': None,\n 'prob': 1.0,\n 'switch_prob': 0.,\n 'mode': 'batch',\n 'label_smoothing': 0,\n 'num_classes': len(list(classes))}\nmixup_fn = Mixup(**mixup_args)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class Block(nn.Module):\n def __init__(self, num_layers, in_channels, out_channels, identity_downsample=None, stride=1):\n assert num_layers in [18, 34, 50, 101, 152], \"should be a a valid architecture\"\n super(Block, self).__init__()\n self.num_layers = num_layers\n if self.num_layers > 34:\n self.expansion = 4\n else:\n self.expansion = 1\n \n # ResNet50, 101, and 152 include additional layer of 1x1 kernels\n self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)\n self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)\n if self.num_layers > 34:\n self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1)\n else:\n # for ResNet18 and 34, connect input directly to (3x3) kernel (skip first (1x1))\n self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1)\n \n self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)\n self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels * self.expansion, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)\n self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels * self.expansion)\n self.relu = nn.ReLU()\n self.identity_downsample = identity_downsample\n\n def forward(self, x):\n identity = x\n if self.num_layers > 34:\n x = self.conv1(x)\n x = self.bn1(x)\n x = self.relu(x)\n x = self.conv2(x)\n x = self.bn2(x)\n x = self.relu(x)\n x = self.conv3(x)\n x = self.bn3(x)\n\n if self.identity_downsample is not None:\n identity = self.identity_downsample(identity)\n\n x = torchvision.ops.stochastic_depth(input=x, p=0.25, mode='batch', training=self.training) # randomly zero input tensor\n x += identity\n x = self.relu(x)\n return x",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class ResNet(nn.Module):\n def __init__(self, num_layers, block, image_channels, num_classes):\n assert num_layers in [18, 34, 50, 101, 152], f'ResNet{num_layers}: Unknown architecture! Number of layers has ' \\\n f'to be 18, 34, 50, 101, or 152 '\n super(ResNet, self).__init__()\n if num_layers < 50:\n self.expansion = 1\n else:\n self.expansion = 4\n if num_layers == 18:\n layers = [2, 2, 2, 2]\n elif num_layers == 34 or num_layers == 50:\n layers = [3, 4, 6, 3]\n elif num_layers == 101:\n layers = [3, 4, 23, 3]\n else:\n layers = [3, 8, 36, 3]\n self.in_channels = 64\n self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(image_channels, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3)\n self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)\n self.relu = nn.ReLU()\n self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)\n\n # ResNetLayers\n self.layer1 = self.make_layers(num_layers, block, layers[0], intermediate_channels=64, stride=1)\n self.layer2 = self.make_layers(num_layers, block, layers[1], intermediate_channels=128, stride=2)\n self.layer3 = self.make_layers(num_layers, block, layers[2], intermediate_channels=256, stride=2)\n self.layer4 = self.make_layers(num_layers, block, layers[3], intermediate_channels=512, stride=2)\n\n self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))\n self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * self.expansion, num_classes)\n\n def forward(self, x):\n x = self.conv1(x)\n x = self.bn1(x)\n x = self.relu(x)\n x = self.maxpool(x)\n\n x = self.layer1(x)\n x = self.layer2(x)\n x = self.layer3(x)\n x = self.layer4(x)\n\n x = self.avgpool(x)\n x = x.reshape(x.shape[0], -1)\n x = self.fc(x)\n return x\n\n def make_layers(self, num_layers, block, num_residual_blocks, intermediate_channels, stride):\n layers = []\n\n identity_downsample = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(self.in_channels, intermediate_channels*self.expansion, kernel_size=1, stride=stride),\n nn.BatchNorm2d(intermediate_channels*self.expansion))\n layers.append(block(num_layers, self.in_channels, intermediate_channels, identity_downsample, stride))\n self.in_channels = intermediate_channels * self.expansion # 256\n for i in range(num_residual_blocks - 1):\n layers.append(block(num_layers, self.in_channels, intermediate_channels)) # 256 -> 64, 64*4 (256) again\n return nn.Sequential(*layers)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def train_epoch(model, epoch, criterion, optimizer, scheduler, dataloader, device):\n model.train()\n \n running_loss = 0.0\n running_corrects = 0\n \n num_batches = len(dataloader)\n num_samples = len(dataloader.dataset)\n \n for batch, (inputs, labels) in enumerate(tqdm.tqdm(dataloader)):\n # Transfer Data to GPU if available\n inputs, labels = inputs.to(device), labels.to(device)\n if use_mixup:\n inputs, labels = mixup_fn(inputs, labels)\n \n # Clear the gradients\n optimizer.zero_grad()\n \n with autocast(enabled=use_mixedprecision):\n # Forward Pass\n outputs = model(inputs)\n _, predictions = torch.max(outputs, 1)\n\n # Compute Loss\n loss = criterion(outputs, labels)\n \n # Calculate gradients\n loss.backward()\n \n # Update Weights\n optimizer.step()\n \n # Calculate Loss\n running_loss += loss.item() * inputs.size(0)\n if use_mixup:\n running_corrects += (predictions == torch.max(labels, 1)[1]).sum().item()\n else:\n running_corrects += (predictions == labels).sum().item()\n \n # Perform learning rate step\n if use_cosinescheduler:\n scheduler.step(epoch + batch / num_batches)\n \n epoch_loss = running_loss / num_samples\n epoch_acc = running_corrects / num_samples\n \n return epoch_loss, epoch_acc",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def test_epoch(model, epoch, criterion, optimizer, dataloader, device):\n model.eval()\n \n num_batches = len(dataloader)\n num_samples = len(dataloader.dataset)\n \n with torch.no_grad():\n running_loss = 0.0\n running_corrects = 0\n\n for batch, (inputs, labels) in enumerate(tqdm.tqdm(dataloader)):\n # Transfer Data to GPU if available\n inputs, labels = inputs.to(device), labels.to(device)\n if use_mixup:\n labels = torch.nn.functional.one_hot(labels.to(torch.int64), num_classes=len(list(classes))).float()\n\n # Clear the gradients\n optimizer.zero_grad()\n\n # Forward Pass\n outputs = model(inputs)\n _, predictions = torch.max(outputs, 1)\n\n # Compute Loss\n loss = criterion(outputs, labels)\n\n # Update Weights\n # optimizer.step()\n\n # Calculate Loss\n running_loss += loss.item() * inputs.size(0)\n if use_mixup:\n running_corrects += (predictions == torch.max(labels, 1)[1]).sum().item()\n else:\n running_corrects += (predictions == labels).sum().item()\n\n epoch_loss = running_loss / num_samples\n epoch_acc = running_corrects / num_samples\n \n return epoch_loss, epoch_acc",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from torchsampler import ImbalancedDatasetSampler\nfrom torch.utils.data import WeightedRandomSampler\n\nbatch_size = 64\nepochs = 40\nlr = 0.01\nwarmup_epochs = 5\nwd = 0.01\n\n'''# Experiment: wrong sampling\nX = np.concatenate([X_train, X_test, X_val])\nY = np.concatenate([Y_train, Y_test, Y_val])\n\nfull_data = TensorDataset(torch.Tensor(np.expand_dims(X, axis=1)), torch.from_numpy(Y))\ntrain_size = int(0.75 * len(full_data))\ntest_size = len(full_data) - train_size\nval_size = int(0.2 * test_size)\ntest_size -= val_size\n\ntrain_data, test_data, val_data = torch.utils.data.random_split(full_data, [train_size, test_size, val_size],\n generator=torch.Generator().manual_seed(42))'''\n\ntrain_data = TensorDataset(torch.Tensor(np.expand_dims(X_train, axis=1)), torch.from_numpy(Y_train))\ntest_data = TensorDataset(torch.Tensor(np.expand_dims(X_test, axis=1)), torch.from_numpy(Y_test))\nval_data = TensorDataset(torch.Tensor(np.expand_dims(X_val, axis=1)), torch.from_numpy(Y_val))\n\nif use_imbalancedsampler:\n train_loader = DataLoader(train_data, sampler=ImbalancedDatasetSampler(train_data), batch_size=batch_size)\n test_loader = DataLoader(test_data, sampler=ImbalancedDatasetSampler(test_data), batch_size=batch_size)\n val_loader = DataLoader(val_data, sampler=ImbalancedDatasetSampler(val_data), batch_size=batch_size)\nelif use_sampler:\n def getSampler(y):\n _, counts = np.unique(y, return_counts=True)\n weights = [len(y)/c for c in counts]\n samples_weights = [weights[t] for t in y]\n return WeightedRandomSampler(samples_weights, len(y))\n \n train_loader = DataLoader(train_data, sampler=getSampler(Y_train), batch_size=batch_size)\n test_loader = DataLoader(test_data, sampler=getSampler(Y_test), batch_size=batch_size)\n val_loader = DataLoader(val_data, sampler=getSampler(Y_val), batch_size=batch_size)\nelse:\n train_loader = DataLoader(train_data, batch_size=batch_size)\n test_loader = DataLoader(test_data, batch_size=batch_size)\n val_loader = DataLoader(val_data, batch_size=batch_size)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model = ResNet(18, Block, image_channels=1, num_classes=len(list(classes)))\ndevice = torch.device(\"cuda:0\" if torch.cuda.is_available() else \"cpu\")\nif torch.cuda.device_count() > 1:\n print(\"Let's use\", torch.cuda.device_count(), \"GPUs!\")\n model = nn.DataParallel(model, device_ids=[0, 1])\nmodel.to(device)\nprint(device)",
"cuda:0\n"
],
[
"import wandb\n\nwandb.init(project=\"BAT-baseline-hierarchical\", entity=\"frankfundel\")\n\nwandb.config = {\n \"learning_rate\": lr,\n \"epochs\": epochs,\n \"batch_size\": batch_size\n}\n\ncriterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()\nif use_mixup:\n criterion = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()\n\noptimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=lr)\nif use_nadam:\n optimizer = torch.optim.NAdam(model.parameters(), lr=lr, weight_decay=wd)\n\nscheduler = None\nif use_cosinescheduler:\n scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.CosineAnnealingWarmRestarts(optimizer=optimizer, T_0=warmup_epochs, T_mult=1)\nif use_reduceonplateu:\n scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.ReduceLROnPlateau(optimizer)\n\nmin_val_loss = np.inf\n\ntorch.autograd.set_detect_anomaly(True)",
"Failed to detect the name of this notebook, you can set it manually with the WANDB_NOTEBOOK_NAME environment variable to enable code saving.\n\u001b[34m\u001b[1mwandb\u001b[0m: Currently logged in as: \u001b[33mfrankfundel\u001b[0m (use `wandb login --relogin` to force relogin)\n"
],
[
"for epoch in range(epochs):\n end = time.time()\n print(f\"==================== Starting at epoch {epoch} ====================\", flush=True)\n \n train_loss, train_acc = train_epoch(model, epoch, criterion, optimizer, scheduler, train_loader, device)\n print('Training loss: {:.4f} Acc: {:.4f}'.format(train_loss, train_acc), flush=True)\n \n val_loss, val_acc = test_epoch(model, epoch, criterion, optimizer, val_loader, device)\n print('Validation loss: {:.4f} Acc: {:.4f}'.format(val_loss, val_acc), flush=True)\n \n if use_reduceonplateu:\n scheduler.step(val_loss)\n \n wandb.log({\n \"train_loss\": train_loss,\n \"train_acc\": train_acc,\n \"val_loss\": val_loss,\n \"val_acc\": val_acc,\n })\n \n if min_val_loss > val_loss:\n print('val_loss decreased, saving model', flush=True)\n min_val_loss = val_loss\n \n # Saving State Dict\n torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'baseline_rhinolophus.pth')",
"==================== Starting at epoch 0 ====================\n"
],
[
"wandb.finish()",
"\n"
],
[
"model.load_state_dict(torch.load('baseline_rhinolophus.pth'))\ncompiled_model = torch.jit.script(model)\ntorch.jit.save(compiled_model, 'baseline_rhinolophus.pt')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix\nimport seaborn as sn\nimport pandas as pd\n\nY_pred = []\nY_true = []\ncorrects = 0\n\nmodel.eval()\n\n# iterate over test data\nfor inputs, labels in tqdm.tqdm(test_loader):\n output = model(inputs.cuda()) # Feed Network\n\n output = (torch.max(output, 1)[1]).data.cpu().numpy()\n Y_pred.extend(output) # Save Prediction\n\n labels = labels.data.cpu().numpy()\n Y_true.extend(labels) # Save Truth",
"100%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 138/138 [00:10<00:00, 13.66it/s]\n"
],
[
"# Build confusion matrix\ncf_matrix = confusion_matrix(Y_true, Y_pred)\ndf_cm = pd.DataFrame(cf_matrix / np.sum(cf_matrix, axis=-1), index = [i for i in classes],\n columns = [i for i in classes])\nplt.figure(figsize = (12,7))\nsn.heatmap(df_cm, annot=True)\nplt.savefig('baseline_rhinolophus_cf.png')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.metrics import f1_score\ncorrects = np.equal(Y_pred, Y_true).sum()\nprint(\"Test accuracy:\", corrects/len(Y_pred))\nprint(\"F1-score:\", f1_score(Y_true, Y_pred, average=None).mean())",
"Test accuracy: 0.9605799728137744\nF1-score: 0.9606633026340764\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a7074911a9b12f1269d025a3be0a4a466a4e21e
| 84,352 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
files/supernova-plot-update/New Plot.ipynb
|
agude/agude.github.io
|
4d20535b03e7804c6a6c1e48e944a2e6e4d2808e
|
[
"MIT"
] | 9 |
2015-09-25T13:52:23.000Z
|
2021-03-04T17:50:00.000Z
|
files/supernova-plot-update/New Plot.ipynb
|
quynhneo/agude.github.io
|
153de74df0146a1dcfb527f723b0816e5e2ee6a4
|
[
"MIT"
] | 37 |
2018-09-27T02:58:50.000Z
|
2021-12-27T17:43:57.000Z
|
files/supernova-plot-update/New Plot.ipynb
|
quynhneo/agude.github.io
|
153de74df0146a1dcfb527f723b0816e5e2ee6a4
|
[
"MIT"
] | 7 |
2017-08-18T04:55:58.000Z
|
2021-12-02T01:54:19.000Z
| 537.273885 | 80,220 | 0.943238 |
[
[
[
"from numpy import array, log\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn as sns\n\n# Set plotting style\nsns.set_style(\"ticks\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"labels = ['May 17', 'May 20', 'June 02', 'June 06']\nfiles = [\n \"sn2002cx-20020517-fast.flm\",\n \"sn2002cx-20020520-fast.flm\",\n \"sn2002cx-20020602-fast.flm\",\n \"sn2002cx-20020606-fast.flm\",\n]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def normalize_area(wavelengths, fluxes):\n \"\"\"Takes a binned spectrum as two arrays and returns the flux normalized to\n an area of 1000.\n\n Args:\n wavelengths (array): The wavelengths of the center of each bin of the\n spectrum.\n fluxes (array): The flux value for each bin.\n\n Returns:\n array: The flux values normalized to have a total area of 1000.\n\n \"\"\"\n desired_area = 1000\n bin_width = wavelengths[1] - wavelengths[0]\n area = sum(fluxes) * bin_width\n normed_fluxes = (fluxes / area) * desired_area\n\n return normed_fluxes",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Work on spectra\nfig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 6))\n\nfor i, file in enumerate(files):\n offset = (len(files) - i) * 3\n\n # Open data\n with open(file) as f:\n cont = f.read()\n\n cont = cont.splitlines()\n\n # Process data\n wavelengths = []\n fluxes = []\n for line in cont:\n if line.startswith('#'):\n continue\n\n sline = line.split()\n wavelengths.append(float(sline[0]))\n fluxes.append(float(sline[1]))\n\n # Normalize the area of the flux\n fluxes = array(fluxes)\n fluxes = log(normalize_area(wavelengths, fluxes))\n fluxes = fluxes + offset\n\n # Plot\n plot = plt.plot(wavelengths, fluxes, label=labels[i])\n # These numbers below were selected through trial and error\n # to offset the spectra date labels nicely\n text_y = 10.8 - (2.9 * i)\n ax.text(6900, text_y, labels[i], fontsize=20, color=plot[0].get_color())\n\n# Remove y ticks\nplt.yticks([])\n\nsns.despine()\n\nplt.xlabel(r'Wavelength (Å)', fontsize=18)\nplt.ylabel('Normalized Log(Flux) + Offset', fontsize=18)\nplt.title('SN 2002cx Spectra', fontsize=22)\n\nplt.savefig(\"/tmp/SN_2002cx_Spectra_log.svg\", bbox_inches=\"tight\")\n\nplt.show()",
"/home/agude/bin/anaconda/lib/python3.6/site-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:26: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in log\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a707ecc77cd1f02bbc8ed3727759f509cea173d
| 85,155 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
figures/Figure7.ipynb
|
adamamiller/bright_transient_survey
|
88e7b1b09cf2048e892121141581d994709845a0
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-03-11T18:39:51.000Z
|
2021-03-11T18:39:51.000Z
|
figures/Figure7.ipynb
|
steveschulze/bright_transient_survey
|
88e7b1b09cf2048e892121141581d994709845a0
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
figures/Figure7.ipynb
|
steveschulze/bright_transient_survey
|
88e7b1b09cf2048e892121141581d994709845a0
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2020-03-23T21:24:50.000Z
|
2021-03-11T18:39:55.000Z
| 68.951417 | 34,247 | 0.662392 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\n\nfrom scipy.stats import ks_2samp, chi2\nimport scipy\n\nfrom astropy.table import Table\nimport astropy\n\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom matplotlib.ticker import MultipleLocator\nfrom matplotlib.colors import colorConverter\nimport matplotlib",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%matplotlib notebook",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('numpy version: {}'.format(np.__version__))\nprint('pandas version: {}'.format(pd.__version__))\nprint('matplotlib version: {}'.format(matplotlib.__version__))\nprint('scipy version: {}'.format(scipy.__version__))",
"numpy version: 1.15.4\npandas version: 0.23.4\nmatplotlib version: 3.0.1\nscipy version: 1.2.0\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Figure 7\n\nCreate Figure 7 (the host-galaxy offset of ASAS-SN SNe relative to SNe in the ZTF BTS) in [Fremling et al. 2020](https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2019arXiv191012973F/abstract).\n\nData for ASAS-SN are from [Holoien et al. 2019](https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2019MNRAS.484.1899H/abstract).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# BTS data\nbts_df = pd.read_hdf('../data/final_rcf_table.h5')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"z_sn = bts_df.z_sn.values\nz_host = bts_df.z_host.values\n\nnorm_Ia = np.where( ( (bts_df.sn_type == 'Ia-norm') | \n (bts_df.sn_type == 'Ia') | \n (bts_df.sn_type == 'Ia-91bg') | \n (bts_df.sn_type == 'Ia-91T') | \n (bts_df.sn_type == 'Ia-99aa') | \n (bts_df.sn_type == 'ia')\n | (bts_df.sn_type == 'Ia-norm*')\n | (bts_df.sn_type == 'Ia-91T*')\n | (bts_df.sn_type == 'Ia-91T**')\n | (bts_df.sn_type == 'SN Ia')\n )\n )\n\nnorm_cc = np.where( (bts_df.sn_type == 'IIb') | \n (bts_df.sn_type == 'Ib') | \n (bts_df.sn_type == 'IIP') | \n (bts_df.sn_type == 'Ib/c') | \n (bts_df.sn_type == 'Ic-norm') | \n (bts_df.sn_type == 'IIn') | \n (bts_df.sn_type == 'IIL') | \n (bts_df.sn_type == 'Ic-broad') | \n (bts_df.sn_type == 'II') | \n (bts_df.sn_type == 'II-pec') | \n (bts_df.sn_type == 'Ib-pec') | \n (bts_df.sn_type == 'Ic') | \n (bts_df.sn_type == 'Ic-BL') | \n (bts_df.sn_type == 'IIP*') | \n (bts_df.sn_type == 'II*') | \n (bts_df.sn_type == 'Ibn') | \n (bts_df.sn_type == 'II**') | \n (bts_df.sn_type == 'Ib-norm') | \n (bts_df.sn_type == 'IIn*')\n )\n\nhas_host_z = np.where((z_host > 0) & np.isfinite(z_host))\nno_host = np.where((z_host < 0) | np.isnan(z_host))\n\nhas_host_cc = np.intersect1d(has_host_z, norm_cc)\nhas_host_ia = np.intersect1d(has_host_z, norm_Ia)\n\nno_host_cc = np.intersect1d(no_host, norm_cc)\nno_host_ia = np.intersect1d(no_host, norm_Ia)\n\nz_mix = z_sn.copy()\nz_mix[has_host_z] = z_host[has_host_z]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Read in SN data from ASAS-SN",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"n_asas_ia = 0\nn_asas_91T = 0\nn_asas_91bg = 0\nn_asas_ii = 0\nn_asas_ibc = 0\nn_asas_slsn = 0\nasas_offset = np.array([])\n\nfor release in ['1','2','3','4']:\n tab1 = '../data/ASAS_SN/bright_sn_catalog_{}/table1.txt'.format(release)\n tab2 = '../data/ASAS_SN/bright_sn_catalog_{}/table2.txt'.format(release)\n\n asassn_tab1 = Table.read(tab1, format='cds')\n asassn_tab2 = Table.read(tab2, format='cds')\n\n n_asas_ia += len(np.where( (asassn_tab1['Type'] == 'Ia') | \n (asassn_tab1['Type'] == 'Ia-91T') | \n (asassn_tab1['Type'] == 'Ia-91bg') | \n (asassn_tab1['Type'] == 'Ia+CSM') |\n (asassn_tab1['Type'] == 'Ia-pec') |\n (asassn_tab1['Type'] == 'Ia-00cx') |\n (asassn_tab1['Type'] == 'Ia-06bt') |\n (asassn_tab1['Type'] == 'Ia-07if') |\n (asassn_tab1['Type'] == 'Ia-09dc') |\n (asassn_tab1['Type'] == 'Ia-02cx')\n )[0])\n\n n_asas_91T += len(np.where( (asassn_tab1['Type'] == 'Ia-91T') )[0])\n n_asas_91bg += len(np.where( (asassn_tab1['Type'] == 'Ia-91bg') )[0])\n\n \n n_asas_ii += len(np.where( (asassn_tab1['Type'] == 'II') | \n (asassn_tab1['Type'] == 'IIP') | \n (asassn_tab1['Type'] == 'IIb') | \n (asassn_tab1['Type'] == 'II-pec') | \n (asassn_tab1['Type'] == 'IIn') |\n (asassn_tab1['Type'] == 'IIn-pec') |\n (asassn_tab1['Type'] == 'IIn/LBV') |\n (asassn_tab1['Type'] == 'IIn-09ip') \n )[0])\n\n n_asas_ibc += len(np.where( (asassn_tab1['Type'] == 'Ib') | \n (asassn_tab1['Type'] == 'Ib/c') | \n (asassn_tab1['Type'] == 'Ibn') | \n (asassn_tab1['Type'] == 'Ic') |\n (asassn_tab1['Type'] == 'Ic-pec') |\n (asassn_tab1['Type'] == 'Ib/c-BL') |\n (asassn_tab1['Type'] == 'Ic-BL')\n )[0])\n\n n_asas_slsn += len(np.where( (asassn_tab1['Type'] == 'SLSN-II') | \n (asassn_tab1['Type'] == 'SLSN-I')\n )[0])\n \n n_asas_ia += len(np.where( ( (asassn_tab2['Type'] == 'Ia') | \n (asassn_tab2['Type'] == 'Ia-91T') | \n (asassn_tab2['Type'] == 'Ia-91bg') | \n (asassn_tab2['Type'] == 'Ia+CSM') |\n (asassn_tab2['Type'] == 'Ia-pec') |\n (asassn_tab2['Type'] == 'Ia-00cx') |\n (asassn_tab2['Type'] == 'Ia-06bt') |\n (asassn_tab2['Type'] == 'Ia-07if') |\n (asassn_tab2['Type'] == 'Ia-09dc') |\n (asassn_tab2['Type'] == 'Ia-02cx')\n ) & \n (asassn_tab2['Recovered'] == 'Yes')\n )[0])\n\n n_asas_91T += len(np.where( (asassn_tab2['Type'] == 'Ia-91T') & \n (asassn_tab2['Recovered'] == 'Yes')\n )[0])\n n_asas_91bg += len(np.where( (asassn_tab2['Type'] == 'Ia-91bg') & \n (asassn_tab2['Recovered'] == 'Yes')\n )[0])\n\n n_asas_ii += len(np.where( ( (asassn_tab2['Type'] == 'II') | \n (asassn_tab2['Type'] == 'IIP') | \n (asassn_tab2['Type'] == 'IIb') | \n (asassn_tab2['Type'] == 'II-pec') | \n (asassn_tab2['Type'] == 'IIn') |\n (asassn_tab2['Type'] == 'IIn-pec') |\n (asassn_tab2['Type'] == 'IIn/LBV') |\n (asassn_tab2['Type'] == 'IIn-09ip')\n ) & \n (asassn_tab2['Recovered'] == 'Yes')\n )[0])\n\n n_asas_ibc += len(np.where( ( (asassn_tab2['Type'] == 'Ib') | \n (asassn_tab2['Type'] == 'Ib/c') | \n (asassn_tab2['Type'] == 'Ibn') | \n (asassn_tab2['Type'] == 'Ic') |\n (asassn_tab2['Type'] == 'Ic-pec') |\n (asassn_tab2['Type'] == 'Ib/c-BL') |\n (asassn_tab2['Type'] == 'Ic-BL')\n ) &\n (asassn_tab2['Recovered'] == 'Yes')\n )[0])\n\n n_asas_slsn += len(np.where( ( (asassn_tab2['Type'] == 'SLSN-II') | \n (asassn_tab2['Type'] == 'SLSN-I')\n ) & \n (asassn_tab2['Recovered'] == 'Yes')\n )[0])\n\n asas_offset = np.append(asas_offset, np.array(asassn_tab1['Offset'][asassn_tab1['HostName'] != 'None'], dtype=float))\n asas_offset = np.append(asas_offset, \n np.array(asassn_tab2['Offset'][np.where((asassn_tab2['Recovered'] == 'Yes') & \n (asassn_tab2['SNName'] != 'PS16dtm'))], dtype=float))\n \ntot_asas = n_asas_ia + n_asas_ii + n_asas_ibc + n_asas_slsn",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"bts_df.columns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"not_ambiguous = np.where(np.isfinite(bts_df.sep))\n\nbrighter_than_17 = np.where((bts_df.g_max < 17) | (bts_df.r_max < 17))\nbright_bts = np.intersect1d(not_ambiguous, brighter_than_17)\nprint(len(bright_bts))",
"79\n"
],
[
"color_dict = {'blue': '#2C5361',\n 'orange': '#DB6515', \n 'yellow': '#CA974C', \n 'maroon': '#3B2525', \n 'purple': '#A588AC',\n 'beige': '#D2A176'}\n\n\nfig, ax1 = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(6,8/3))\nax1.plot(np.sort(bts_df.sep.iloc[bright_bts]), \n np.arange(len(bts_df.sep.iloc[bright_bts]))/float(len(bts_df.sep.iloc[bright_bts])),\n label = 'ZTF BTS',\n lw=3, color=color_dict['orange'])\n\nax1.plot(np.sort(asas_offset),\n np.arange(len(asas_offset))/float(len(asas_offset)),\n label = 'ASAS-SN', \n lw=2, dashes=[6, 1],\n color=color_dict['blue'])\n \nax1.set_xlabel('SN offset (arcsec)',fontsize=14)\nax1.legend(loc=4, fontsize=13)\nax1.set_xlim(-1, 24)\nax1.set_ylim(0,1)\nax1.xaxis.set_minor_locator(MultipleLocator(1))\nax1.yaxis.set_minor_locator(MultipleLocator(.1))\nax1.set_ylabel('cumulative $f_\\mathrm{SN}$',fontsize=14)\nax1.tick_params(top=True,right=True,labelsize=11,which='both')\n\nfig.subplots_adjust(left=0.105,bottom=0.2,top=0.97,right=0.98, hspace=0.3)\nfig.savefig('ZTF_ASASSN_offset.pdf')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### KS test",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"ks_2samp(bts_df.sep.iloc[bright_bts], asas_offset)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### $\\chi^2$ test",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"logbins = np.logspace(-2,1.57,11)\nztf_cnts, _ = np.histogram(bts_df.sep.iloc[bright_bts], \n range=(0,25), bins=50)\n# bins=logbins)\nasas_cnts, _ = np.histogram(asas_offset, \n range=(0,25), bins=50)\n# bins=logbins)\n\nnot_empty = np.where((ztf_cnts > 0) & (asas_cnts > 0))\n\nk1 = np.sqrt(np.sum(asas_cnts[not_empty])/np.sum(ztf_cnts[not_empty]))\nk2 = np.sqrt(np.sum(ztf_cnts[not_empty])/np.sum(asas_cnts[not_empty]))\n\nchisq_test = np.sum((k1*ztf_cnts[not_empty] - k2*asas_cnts[not_empty])**2 / (ztf_cnts[not_empty] + asas_cnts[not_empty]))\n\ndof = len(not_empty[0])\nchisq = scipy.stats.chi2(dof)\nprint(chisq_test, dof, chisq.sf(chisq_test))",
"37.41029978962741 32 0.23456771688085984\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a708f40bf23a06a4af6f43ff9bf50c199888b88
| 5,684 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
warp.ipynb
|
kbro18/CarND-Advanced-Lane-Lines
|
411b8aedfeb5f5349d1ddbc2adb81251fde62c98
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
warp.ipynb
|
kbro18/CarND-Advanced-Lane-Lines
|
411b8aedfeb5f5349d1ddbc2adb81251fde62c98
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
warp.ipynb
|
kbro18/CarND-Advanced-Lane-Lines
|
411b8aedfeb5f5349d1ddbc2adb81251fde62c98
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 33.046512 | 171 | 0.529381 |
[
[
[
"import cv2\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport matplotlib.image as mpimg\nimport glob\nimport time\nimport os\nfrom utils import calibrate_cam, weighted_img, warp\nprint(\"ready\")",
"ready\n"
],
[
"def warpTest(img, img_name):\n imshape = img.shape\n bot_x = 0.13*imshape[1] # offset from bottom corner\n top_x = 0.04*imshape[1] # offset from centre of image\n top_y = 0.63*imshape[0]\n bot_y = imshape[0] \n vertices = np.array([[(bot_x,bot_y),((imshape[1]/2) - top_x, top_y), ((imshape[1]/2) + top_x, top_y), (imshape[1] - bot_x,bot_y)]], dtype=np.int32)\n \n x = [vertices[0][0][0], vertices[0][1][0], vertices[0][2][0], vertices[0][3][0]]\n y = [vertices[0][0][1], vertices[0][1][1], vertices[0][2][1], vertices[0][3][1]]\n roi_lines = np.copy(img)*0\n for i in range(0, len(x)-1):\n cv2.line(roi_lines,(x[i],y[i]),(x[i+1],y[i+1]),(0,0,255),3)\n roi_img = weighted_img(img, roi_lines, α=0.8, β=1., γ=0.)\n cv2.imwrite(\"./test_images_output/\" + img_name[:-4] +\"/02_\" + img_name[:-4] + \"_roi.jpg\" , cv2.cvtColor(roi_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))\n print(\"x:\\n\", x)\n print(\"________\\ny:\\n\", y)\n src = np.float32([[x[0],y[0]], [x[1],y[1]], [x[2],y[2]], [x[3],y[3]]])\n dst = np.float32([[x[0],y[0]], [x[0],y[1]], [x[3],y[2]], [x[3],y[3]]])\n dst = np.float32([[x[0],y[0]], [x[0],0], [x[3],0], [x[3],y[3]]])\n print(\"________\\nsrc:\\n\", src)\n print(\"________\\ndst:\\n\", dst)\n \n roi_mask = np.zeros_like(img) \n ignore_mask_color = (255,255,255) \n cv2.fillPoly(roi_mask, vertices, ignore_mask_color)\n masked_img = cv2.bitwise_and(img, roi_mask)\n cv2.imwrite(\"./test_images_output/\" + img_name[:-4] +\"/03_\" + img_name[:-4] + \"_masked.jpg\" , cv2.cvtColor(masked_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))\n \n M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(src, dst)\n warped_img = cv2.warpPerspective(img, M, (imshape[1],imshape[0]))\n cv2.imwrite(\"./test_images_output/\" + img_name[:-4] +\"/04_\" + img_name[:-4] + \"_warped.jpg\" , cv2.cvtColor(warped_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))\n return warped_img",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"calibration_imgs = glob.glob(\"camera_cal/calibration*.jpg\")\nret, mtx, dist = calibrate_cam(calibration_imgs)\nprint(ret)",
"0.921982464824774\n"
],
[
"test_imgs = glob.glob(\"test_images/*.jpg\")\nfor img_name in test_imgs:\n if not os.path.exists(\"./test_images_output/\" + img_name[12:-4]):\n os.makedirs(\"./test_images_output/\" + img_name[12:-4])\n print(img_name[12:])\n img = mpimg.imread(img_name)\n cv2.imwrite(\"./test_images_output/\" + img_name[12:-4] +\"/00_\" + img_name[12:-4] + \"_original.jpg\" , cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))\n undistorted_img = cv2.undistort(img, mtx, dist, None, mtx)\n cv2.imwrite(\"./test_images_output/\" + img_name[12:-4] +\"/01_\" + img_name[12:-4] + \"_undistorted.jpg\" , cv2.cvtColor(undistorted_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))\n warped_img = warp(undistorted_img, img_name[12:])\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"test_imgs = glob.glob(\"test_images/*.jpg\")\nfor img_name in test_imgs:\n if not os.path.exists(\"./test_images_output/\" + img_name[12:-4]):\n os.makedirs(\"./test_images_output/\" + img_name[12:-4])\n print(img_name[12:])\n img = mpimg.imread(img_name)\n undistorted_img = cv2.undistort(img, mtx, dist, None, mtx)\n warped_img = warp(undistorted_img, img_name[12:])\n cv2.imwrite(\"./test_images_output/\" + img_name[12:-4] +\"/05_\" + img_name[12:-4] + \"_warpFunction.jpg\" , cv2.cvtColor(warped_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))",
"test6.jpg\ntest5.jpg\ntest4.jpg\ntest1.jpg\ntest3.jpg\ntest2.jpg\nstraight_lines2.jpg\nstraight_lines1.jpg\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a709057e440c5e781d459f4c239979d0ff286c0
| 39,091 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
src/recommenders/featurization.ipynb
|
jdavidagudelo/tensorflow-tutorials
|
fa706b7f5ef7b33dc605c8161617494c3be231db
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
src/recommenders/featurization.ipynb
|
jdavidagudelo/tensorflow-tutorials
|
fa706b7f5ef7b33dc605c8161617494c3be231db
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
src/recommenders/featurization.ipynb
|
jdavidagudelo/tensorflow-tutorials
|
fa706b7f5ef7b33dc605c8161617494c3be231db
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 33.75734 | 521 | 0.611726 |
[
[
[
"##### Copyright 2020 The TensorFlow Authors.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#@title Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the \"License\");\n# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.\n# You may obtain a copy of the License at\n#\n# https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0\n#\n# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software\n# distributed under the License is distributed on an \"AS IS\" BASIS,\n# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.\n# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and\n# limitations under the License.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Using side features: feature preprocessing\n\n<table class=\"tfo-notebook-buttons\" align=\"left\">\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/recommenders/examples/movielens\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/tf_logo_32px.png\" />View on TensorFlow.org</a>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/tensorflow/recommenders/blob/main/docs/examples/featurization.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/colab_logo_32px.png\" />Run in Google Colab</a>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://github.com/tensorflow/recommenders/blob/main/docs/examples/featurization.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/GitHub-Mark-32px.png\" />View source on GitHub</a>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a href=\"https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow_docs/recommenders/docs/examples/featurization.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/download_logo_32px.png\" />Download notebook</a>\n </td>\n</table>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"One of the great advantages of using a deep learning framework to build recommender models is the freedom to build rich, flexible feature representations.\n\nThe first step in doing so is preparing the features, as raw features will usually not be immediately usable in a model.\n\nFor example:\n\n- User and item ids may be strings (titles, usernames) or large, noncontiguous integers (database IDs).\n- Item descriptions could be raw text.\n- Interaction timestamps could be raw Unix timestamps.\n\nThese need to be appropriately transformed in order to be useful in building models:\n\n- User and item ids have to be translated into embedding vectors: high-dimensional numerical representations that are adjusted during training to help the model predict its objective better.\n- Raw text needs to be tokenized (split into smaller parts such as individual words) and translated into embeddings.\n- Numerical features need to be normalized so that their values lie in a small interval around 0.\n\nFortunately, by using TensorFlow we can make such preprocessing part of our model rather than a separate preprocessing step. This is not only convenient, but also ensures that our pre-processing is exactly the same during training and during serving. This makes it safe and easy to deploy models that include even very sophisticated pre-processing.\n\nIn this tutorial, we are going to focus on recommenders and the preprocessing we need to do on the [MovieLens dataset](https://grouplens.org/datasets/movielens/). If you're interested in a larger tutorial without a recommender system focus, have a look at the full [Keras preprocessing guide](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/keras/preprocessing_layers). ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## The MovieLens dataset\n\nLet's first have a look at what features we can use from the MovieLens dataset:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#!pip install -q --upgrade tensorflow-datasets",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import pprint\n\nimport tensorflow_datasets as tfds\n\nratings = tfds.load(\"movielens/100k-ratings\", split=\"train\")\n\nfor x in ratings.take(1).as_numpy_iterator():\n pprint.pprint(x)",
"2021-07-29 14:36:24.534680: W tensorflow/stream_executor/platform/default/dso_loader.cc:64] Could not load dynamic library 'libcudart.so.11.0'; dlerror: libcudart.so.11.0: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory\n2021-07-29 14:36:24.534704: I tensorflow/stream_executor/cuda/cudart_stub.cc:29] Ignore above cudart dlerror if you do not have a GPU set up on your machine.\n"
]
],
[
[
"There are a couple of key features here:\n\n- Movie title is useful as a movie identifier.\n- User id is useful as a user identifier.\n- Timestamps will allow us to model the effect of time.\n\nThe first two are categorical features; timestamps are a continuous feature.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Turning categorical features into embeddings\n\nA [categorical feature](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Categorical_variable) is a feature that does not express a continuous quantity, but rather takes on one of a set of fixed values.\n\nMost deep learning models express these feature by turning them into high-dimensional vectors. During model training, the value of that vector is adjusted to help the model predict its objective better.\n\nFor example, suppose that our goal is to predict which user is going to watch which movie. To do that, we represent each user and each movie by an embedding vector. Initially, these embeddings will take on random values - but during training, we will adjust them so that embeddings of users and the movies they watch end up closer together.\n\nTaking raw categorical features and turning them into embeddings is normally a two-step process:\n\n1. Firstly, we need to translate the raw values into a range of contiguous integers, normally by building a mapping (called a \"vocabulary\") that maps raw values (\"Star Wars\") to integers (say, 15).\n2. Secondly, we need to take these integers and turn them into embeddings.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Defining the vocabulary\n\nThe first step is to define a vocabulary. We can do this easily using Keras preprocessing layers.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport tensorflow as tf\n\nmovie_title_lookup = tf.keras.layers.experimental.preprocessing.StringLookup()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The layer itself does not have a vocabulary yet, but we can build it using our data.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"movie_title_lookup.adapt(ratings.map(lambda x: x[\"movie_title\"]))\n\nprint(f\"Vocabulary: {movie_title_lookup.get_vocabulary()[:3]}\")",
"Vocabulary: ['', '[UNK]', 'Star Wars (1977)']\n"
]
],
[
[
"Once we have this we can use the layer to translate raw tokens to embedding ids:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"movie_title_lookup([\"Star Wars (1977)\", \"One Flew Over the Cuckoo's Nest (1975)\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Note that the layer's vocabulary includes one (or more!) unknown (or \"out of vocabulary\", OOV) tokens. This is really handy: it means that the layer can handle categorical values that are not in the vocabulary. In practical terms, this means that the model can continue to learn about and make recommendations even using features that have not been seen during vocabulary construction.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Using feature hashing\n\nIn fact, the `StringLookup` layer allows us to configure multiple OOV indices. If we do that, any raw value that is not in the vocabulary will be deterministically hashed to one of the OOV indices. The more such indices we have, the less likley it is that two different raw feature values will hash to the same OOV index. Consequently, if we have enough such indices the model should be able to train about as well as a model with an explicit vocabulary without the disdvantage of having to maintain the token list.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We can take this to its logical extreme and rely entirely on feature hashing, with no vocabulary at all. This is implemented in the `tf.keras.layers.experimental.preprocessing.Hashing` layer.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# We set up a large number of bins to reduce the chance of hash collisions.\nnum_hashing_bins = 200_000\n\nmovie_title_hashing = tf.keras.layers.experimental.preprocessing.Hashing(\n num_bins=num_hashing_bins\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can do the lookup as before without the need to build vocabularies:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"movie_title_hashing([\"Star Wars (1977)\", \"One Flew Over the Cuckoo's Nest (1975)\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Defining the embeddings\n\nNow that we have integer ids, we can use the [`Embedding`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/layers/Embedding) layer to turn those into embeddings.\n\nAn embedding layer has two dimensions: the first dimension tells us how many distinct categories we can embed; the second tells us how large the vector representing each of them can be.\n\nWhen creating the embedding layer for movie titles, we are going to set the first value to the size of our title vocabulary (or the number of hashing bins). The second is up to us: the larger it is, the higher the capacity of the model, but the slower it is to fit and serve.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"movie_title_embedding = tf.keras.layers.Embedding(\n # Let's use the explicit vocabulary lookup.\n input_dim=movie_title_lookup.vocab_size(),\n output_dim=32\n)",
"WARNING:tensorflow:vocab_size is deprecated, please use vocabulary_size.\n"
]
],
[
[
"We can put the two together into a single layer which takes raw text in and yields embeddings.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"movie_title_model = tf.keras.Sequential([movie_title_lookup, movie_title_embedding])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Just like that, we can directly get the embeddings for our movie titles:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"movie_title_model([\"Star Wars (1977)\"])",
"WARNING:tensorflow:Layers in a Sequential model should only have a single input tensor, but we receive a <class 'list'> input: ['Star Wars (1977)']\nConsider rewriting this model with the Functional API.\n"
]
],
[
[
"We can do the same with user embeddings:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"user_id_lookup = tf.keras.layers.experimental.preprocessing.StringLookup()\nuser_id_lookup.adapt(ratings.map(lambda x: x[\"user_id\"]))\n\nuser_id_embedding = tf.keras.layers.Embedding(user_id_lookup.vocab_size(), 32)\n\nuser_id_model = tf.keras.Sequential([user_id_lookup, user_id_embedding])",
"WARNING:tensorflow:vocab_size is deprecated, please use vocabulary_size.\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Normalizing continuous features\n\nContinuous features also need normalization. For example, the `timestamp` feature is far too large to be used directly in a deep model:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for x in ratings.take(3).as_numpy_iterator():\n print(f\"Timestamp: {x['timestamp']}.\")",
"Timestamp: 879024327.\nTimestamp: 875654590.\nTimestamp: 882075110.\n"
]
],
[
[
"We need to process it before we can use it. While there are many ways in which we can do this, discretization and standardization are two common ones.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Standardization\n\n[Standardization](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Feature_scaling#Standardization_(Z-score_Normalization)) rescales features to normalize their range by subtracting the feature's mean and dividing by its standard deviation. It is a common preprocessing transformation.\n\nThis can be easily accomplished using the [`tf.keras.layers.experimental.preprocessing.Normalization`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/layers/experimental/preprocessing/Normalization) layer:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"timestamp_normalization = tf.keras.layers.experimental.preprocessing.Normalization()\ntimestamp_normalization.adapt(ratings.map(lambda x: x[\"timestamp\"]).batch(1024))\n\nfor x in ratings.take(3).as_numpy_iterator():\n print(f\"Normalized timestamp: {timestamp_normalization(x['timestamp'])}.\")",
"Normalized timestamp: [[-0.84293723]].\nNormalized timestamp: [[-1.4735204]].\nNormalized timestamp: [[-0.27203268]].\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Discretization\n\nAnother common transformation is to turn a continuous feature into a number of categorical features. This makes good sense if we have reasons to suspect that a feature's effect is non-continuous.\n\nTo do this, we first need to establish the boundaries of the buckets we will use for discretization. The easiest way is to identify the minimum and maximum value of the feature, and divide the resulting interval equally:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"max_timestamp = ratings.map(lambda x: x[\"timestamp\"]).reduce(\n tf.cast(0, tf.int64), tf.maximum).numpy().max()\nmin_timestamp = ratings.map(lambda x: x[\"timestamp\"]).reduce(\n np.int64(1e9), tf.minimum).numpy().min()\n\ntimestamp_buckets = np.linspace(\n min_timestamp, max_timestamp, num=1000)\n\nprint(f\"Buckets: {timestamp_buckets[:3]}\")",
"Buckets: [8.74724710e+08 8.74743291e+08 8.74761871e+08]\n"
]
],
[
[
"Given the bucket boundaries we can transform timestamps into embeddings:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"timestamp_embedding_model = tf.keras.Sequential([\n tf.keras.layers.experimental.preprocessing.Discretization(timestamp_buckets.tolist()),\n tf.keras.layers.Embedding(len(timestamp_buckets) + 1, 32)\n])\n\nfor timestamp in ratings.take(1).map(lambda x: x[\"timestamp\"]).batch(1).as_numpy_iterator():\n print(f\"Timestamp embedding: {timestamp_embedding_model(timestamp)}.\") ",
"Timestamp embedding: [[ 0.04547194 0.04779687 0.00122223 0.00176687 -0.04119935 0.03958721\n -0.0040681 -0.0426871 -0.04356153 0.04099916 0.0092079 0.00338521\n -0.01376065 -0.03042089 0.03177242 0.03973057 0.01073965 0.02446422\n 0.01654053 0.02857013 -0.01100773 0.01856038 0.02352443 0.03842402\n -0.04413103 0.02203031 0.04415288 -0.00496578 -0.024371 0.02586483\n -0.04456453 -0.04328077]].\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Processing text features\n\nWe may also want to add text features to our model. Usually, things like product descriptions are free form text, and we can hope that our model can learn to use the information they contain to make better recommendations, especially in a cold-start or long tail scenario.\n\nWhile the MovieLens dataset does not give us rich textual features, we can still use movie titles. This may help us capture the fact that movies with very similar titles are likely to belong to the same series.\n\nThe first transformation we need to apply to text is tokenization (splitting into constituent words or word-pieces), followed by vocabulary learning, followed by an embedding.\n\nThe Keras [`tf.keras.layers.experimental.preprocessing.TextVectorization`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/layers/experimental/preprocessing/TextVectorization) layer can do the first two steps for us:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"title_text = tf.keras.layers.experimental.preprocessing.TextVectorization()\ntitle_text.adapt(ratings.map(lambda x: x[\"movie_title\"]))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's try it out:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for row in ratings.batch(1).map(lambda x: x[\"movie_title\"]).take(1):\n print(title_text(row))",
"tf.Tensor([[ 32 266 162 2 267 265 53]], shape=(1, 7), dtype=int64)\n"
]
],
[
[
"Each title is translated into a sequence of tokens, one for each piece we've tokenized.\n\nWe can check the learned vocabulary to verify that the layer is using the correct tokenization:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"title_text.get_vocabulary()[40:45]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This looks correct: the layer is tokenizing titles into individual words.\n\nTo finish the processing, we now need to embed the text. Because each title contains multiple words, we will get multiple embeddings for each title. For use in a donwstream model these are usually compressed into a single embedding. Models like RNNs or Transformers are useful here, but averaging all the words' embeddings together is a good starting point.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Putting it all together\n\nWith these components in place, we can build a model that does all the preprocessing together.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### User model\n\nThe full user model may look like the following:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class UserModel(tf.keras.Model):\n \n def __init__(self):\n super().__init__()\n\n self.user_embedding = tf.keras.Sequential([\n user_id_lookup,\n tf.keras.layers.Embedding(user_id_lookup.vocab_size(), 32),\n ])\n self.timestamp_embedding = tf.keras.Sequential([\n tf.keras.layers.experimental.preprocessing.Discretization(timestamp_buckets.tolist()),\n tf.keras.layers.Embedding(len(timestamp_buckets) + 2, 32)\n ])\n self.normalized_timestamp = tf.keras.layers.experimental.preprocessing.Normalization()\n\n def call(self, inputs):\n\n # Take the input dictionary, pass it through each input layer,\n # and concatenate the result.\n return tf.concat([\n self.user_embedding(inputs[\"user_id\"]),\n self.timestamp_embedding(inputs[\"timestamp\"]),\n self.normalized_timestamp(inputs[\"timestamp\"])\n ], axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's try it out:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"user_model = UserModel()\n\nuser_model.normalized_timestamp.adapt(\n ratings.map(lambda x: x[\"timestamp\"]).batch(128))\n\nfor row in ratings.batch(1).take(1):\n print(f\"Computed representations: {user_model(row)[0, :3]}\")",
"WARNING:tensorflow:vocab_size is deprecated, please use vocabulary_size.\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Movie model\nWe can do the same for the movie model:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class MovieModel(tf.keras.Model):\n \n def __init__(self):\n super().__init__()\n\n max_tokens = 10_000\n\n self.title_embedding = tf.keras.Sequential([\n movie_title_lookup,\n tf.keras.layers.Embedding(movie_title_lookup.vocab_size(), 32)\n ])\n self.title_text_embedding = tf.keras.Sequential([\n tf.keras.layers.experimental.preprocessing.TextVectorization(max_tokens=max_tokens),\n tf.keras.layers.Embedding(max_tokens, 32, mask_zero=True),\n # We average the embedding of individual words to get one embedding vector\n # per title.\n tf.keras.layers.GlobalAveragePooling1D(),\n ])\n\n def call(self, inputs):\n return tf.concat([\n self.title_embedding(inputs[\"movie_title\"]),\n self.title_text_embedding(inputs[\"movie_title\"]),\n ], axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's try it out:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"movie_model = MovieModel()\n\nmovie_model.title_text_embedding.layers[0].adapt(\n ratings.map(lambda x: x[\"movie_title\"]))\n\nfor row in ratings.batch(1).take(1):\n print(f\"Computed representations: {movie_model(row)[0, :3]}\")",
"WARNING:tensorflow:vocab_size is deprecated, please use vocabulary_size.\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Next steps\n\nWith the two models above we've taken the first steps to representing rich features in a recommender model: to take this further and explore how these can be used to build an effective deep recomender model, take a look at our Deep Recommenders tutorial.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a70a26666b118c85962e56bf246ce4af49e5912
| 10,868 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
warp-by-vector-eigenmodes.ipynb
|
UttamBasu/ipygany_examples
|
5b619951977a0e89f2c63a172d55a637519231d8
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
warp-by-vector-eigenmodes.ipynb
|
UttamBasu/ipygany_examples
|
5b619951977a0e89f2c63a172d55a637519231d8
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
warp-by-vector-eigenmodes.ipynb
|
UttamBasu/ipygany_examples
|
5b619951977a0e89f2c63a172d55a637519231d8
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 112.041237 | 6,501 | 0.505245 |
[
[
[
"%matplotlib inline\nfrom pyvista import set_plot_theme\nset_plot_theme('document')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Displaying eigenmodes of vibration using `warp_by_vector`\n=========================================================\n\nThis example applies the `warp_by_vector` filter to a cube whose\neigenmodes have been computed using the Ritz method, as outlined in\nVisscher, William M., Albert Migliori, Thomas M. Bell, et Robert A.\nReinert. \\\"On the normal modes of free vibration of inhomogeneous and\nanisotropic elastic objects\\\". The Journal of the Acoustical Society of\nAmerica 90, n.4 (october 1991): 2154-62.\n<https://asa.scitation.org/doi/10.1121/1.401643>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"First, let\\'s solve the eigenvalue problem for a vibrating cube. We use\na crude approximation (by choosing a low max polynomial order) to get a\nfast computation.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nfrom scipy.linalg import eigh\n\nimport pyvista as pv\n\n\ndef analytical_integral_rppd(p, q, r, a, b, c):\n \"\"\"Returns the analytical value of the RPPD integral, i.e. the integral\n of x**p * y**q * z**r for (x, -a, a), (y, -b, b), (z, -c, c).\"\"\"\n if p < 0:\n return 0.\n elif q < 0:\n return 0.\n elif r < 0.:\n return 0.\n else:\n return a ** (p + 1) * b ** (q + 1) * c ** (r + 1) * \\\n ((-1) ** p + 1) * ((-1) ** q + 1) * ((-1) ** r + 1) \\\n / ((p + 1) * (q + 1) * (r + 1))\n\n\ndef make_cijkl_E_nu(E=200, nu=0.3):\n \"\"\"Makes cijkl from E and nu.\n Default values for steel are: E=200 GPa, nu=0.3.\"\"\"\n lambd = E * nu / (1 + nu) / (1 - 2 * nu)\n mu = E / 2 / (1 + nu)\n cij = np.zeros((6, 6))\n cij[(0, 1, 2), (0, 1, 2)] = lambd + 2 * mu\n cij[(0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2), (1, 2, 0, 2, 0, 1)] = lambd\n cij[(3, 4, 5), (3, 4, 5)] = mu\n # check symmetry\n assert np.allclose(cij, cij.T)\n # convert to order 4 tensor\n coord_mapping = {(1, 1): 1,\n (2, 2): 2,\n (3, 3): 3,\n (2, 3): 4,\n (1, 3): 5,\n (1, 2): 6,\n (2, 1): 6,\n (3, 1): 5,\n (3, 2): 4}\n\n cijkl = np.zeros((3, 3, 3, 3))\n for i in range(3):\n for j in range(3):\n for k in range(3):\n for l in range(3):\n u = coord_mapping[(i + 1, j + 1)]\n v = coord_mapping[(k + 1, l + 1)]\n cijkl[i, j, k, l] = cij[u - 1, v - 1]\n return cijkl, cij\n\n\ndef get_first_N_above_thresh(N, freqs, thresh, decimals=3):\n \"\"\"Returns first N unique frequencies with amplitude above threshold based\n on first decimals.\"\"\"\n unique_freqs, unique_indices = np.unique(\n np.round(freqs, decimals=decimals), return_index=True)\n nonzero = unique_freqs > thresh\n unique_freqs, unique_indices = unique_freqs[nonzero], unique_indices[\n nonzero]\n return unique_freqs[:N], unique_indices[:N]\n\n\ndef assemble_mass_and_stiffness(N, F, geom_params, cijkl):\n \"\"\"This routine assembles the mass and stiffness matrix.\n It first builds an index of basis functions as a quadruplet of\n component and polynomial order for (x^p, y^q, z^r) of maximum order N.\n\n This routine only builds the symmetric part of the matrix to speed\n things up.\n \"\"\"\n # building coordinates\n triplets = []\n for p in range(N + 1):\n for q in range(N - p + 1):\n for r in range(N - p - q + 1):\n triplets.append((p, q, r))\n assert len(triplets) == (N + 1) * (N + 2) * (N + 3) // 6\n\n quadruplets = []\n for i in range(3):\n for triplet in triplets:\n quadruplets.append((i, *triplet))\n assert len(quadruplets) == 3 * (N + 1) * (N + 2) * (N + 3) // 6\n\n # assembling the mass and stiffness matrix in a single loop\n R = len(triplets)\n E = np.zeros((3 * R, 3 * R)) # the mass matrix\n G = np.zeros((3 * R, 3 * R)) # the stiffness matrix\n for index1, quad1 in enumerate(quadruplets):\n I, p1, q1, r1 = quad1\n for index2, quad2 in enumerate(quadruplets[index1:]):\n index2 = index2 + index1\n J, p2, q2, r2 = quad2\n G[index1, index2] = cijkl[I, 1 - 1, J, 1 - 1] * p1 * p2 * F(\n p1 + p2 - 2, q1 + q2, r1 + r2, **geom_params) + \\\n cijkl[I, 1 - 1, J, 2 - 1] * p1 * q2 * F(\n p1 + p2 - 1, q1 + q2 - 1, r1 + r2,\n **geom_params) + \\\n cijkl[I, 1 - 1, J, 3 - 1] * p1 * r2 * F(\n p1 + p2 - 1, q1 + q2, r1 + r2 - 1,\n **geom_params) + \\\n cijkl[I, 2 - 1, J, 1 - 1] * q1 * p2 * F(\n p1 + p2 - 1, q1 + q2 - 1, r1 + r2,\n **geom_params) + \\\n cijkl[I, 2 - 1, J, 2 - 1] * q1 * q2 * F(\n p1 + p2, q1 + q2 - 2, r1 + r2, **geom_params) + \\\n cijkl[I, 2 - 1, J, 3 - 1] * q1 * r2 * F(\n p1 + p2, q1 + q2 - 1, r1 + r2 - 1,\n **geom_params) + \\\n cijkl[I, 3 - 1, J, 1 - 1] * r1 * p2 * F(\n p1 + p2 - 1, q1 + q2, r1 + r2 - 1,\n **geom_params) + \\\n cijkl[I, 3 - 1, J, 2 - 1] * r1 * q2 * F(\n p1 + p2, q1 + q2 - 1, r1 + r2 - 1,\n **geom_params) + \\\n cijkl[I, 3 - 1, J, 3 - 1] * r1 * r2 * F(\n p1 + p2, q1 + q2, r1 + r2 - 2, **geom_params)\n G[index2, index1] = G[\n index1, index2] # since stiffness matrix is symmetric\n if I == J:\n E[index1, index2] = F(p1 + p2, q1 + q2, r1 + r2, **geom_params)\n E[index2, index1] = E[\n index1, index2] # since mass matrix is symmetric\n return E, G, quadruplets\n\n\nN = 8 # maximum order of x^p y^q z^r polynomials\nrho = 8.0 # g/cm^3\nl1, l2, l3 = .2, .2, .2 # all in cm\ngeometry_parameters = {'a': l1 / 2., 'b': l2 / 2., 'c': l3 / 2.}\ncijkl, cij = make_cijkl_E_nu(200, 0.3) # Gpa, without unit\nE, G, quadruplets = assemble_mass_and_stiffness(N, analytical_integral_rppd,\n geometry_parameters, cijkl)\n\n# solving the eigenvalue problem using symmetric solver\nw, vr = eigh(a=G, b=E)\nomegas = np.sqrt(np.abs(w) / rho) * 1e5 # convert back to Hz\nfreqs = omegas / (2 * np.pi)\n# expected values from (Bernard 2014, p.14),\n# error depends on polynomial order ``N``\nexpected_freqs_kHz = np.array(\n [704.8, 949., 965.2, 1096.3, 1128.4, 1182.8, 1338.9, 1360.9])\ncomputed_freqs_kHz, mode_indices = get_first_N_above_thresh(8, freqs / 1e3,\n thresh=1,\n decimals=1)\nprint('found the following first unique eigenfrequencies:')\nfor ind, (freq1, freq2) in enumerate(\n zip(computed_freqs_kHz, expected_freqs_kHz)):\n error = np.abs(freq2 - freq1) / freq1 * 100.\n print(\n f\"freq. {ind + 1:1}: {freq1:8.1f} kHz,\" + \\\n f\" expected: {freq2:8.1f} kHz, error: {error:.2f} %\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now, let\\'s display a mode on a mesh of the cube.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create the 3D NumPy array of spatially referenced data\n# (nx by ny by nz)\nnx, ny, nz = 30, 31, 32\n\nx = np.linspace(-l1 / 2., l1 / 2., nx)\ny = np.linspace(-l2 / 2., l2 / 2., ny)\nx, y = np.meshgrid(x, y)\nz = np.zeros_like(x) + l3 / 2.\ngrid = pv.StructuredGrid(x, y, z)\n\nslices = []\nfor zz in np.linspace(-l3 / 2., l3 / 2., nz)[::-1]:\n slice = grid.points.copy()\n slice[:, -1] = zz\n slices.append(slice)\n\nvol = pv.StructuredGrid()\nvol.points = np.vstack(slices)\nvol.dimensions = [*grid.dimensions[0:2], nz]\n\nfor i, mode_index in enumerate(mode_indices):\n eigenvector = vr[:, mode_index]\n displacement_points = np.zeros_like(vol.points)\n for weight, (component, p, q, r) in zip(eigenvector, quadruplets):\n displacement_points[:, component] += weight * vol.points[:, 0] ** p * \\\n vol.points[:, 1] ** q * \\\n vol.points[:, 2] ** r\n if displacement_points.max() > 0.:\n displacement_points /= displacement_points.max()\n vol[f'eigenmode_{i:02}'] = displacement_points\n\nwarpby = 'eigenmode_00'\nwarped = vol.warp_by_vector(warpby, factor=0.04)\nwarped.translate([-1.5 * l1, 0., 0.], inplace=True)\np = pv.Plotter()\np.add_mesh(vol, style='wireframe', scalars=warpby)\np.add_mesh(warped, scalars=warpby)\np.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Finally, let\\'s make a gallery of the first 8 unique eigenmodes.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"p = pv.Plotter(shape=(2, 4))\nfor i in range(2):\n for j in range(4):\n p.subplot(i, j)\n current_index = 4 * i + j\n vector = f\"eigenmode_{current_index:02}\"\n p.add_text(\n f\"mode {current_index},\" + \\\n f\" freq. {computed_freqs_kHz[current_index]:.1f} kHz\",\n font_size=10)\n p.add_mesh(vol.warp_by_vector(vector, factor=0.03), scalars=vector)\np.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a70a82e4efb3f1bae0c1b3ec7c4b12fcab38d4f
| 95,537 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
initial.ipynb
|
skgrunblatt/FoFreeAST
|
de2703f460ce613c0b180eb7caae267735fa44a7
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2018-06-24T03:31:23.000Z
|
2018-06-24T03:31:23.000Z
|
initial.ipynb
|
skgrunblatt/FoFreeAST
|
de2703f460ce613c0b180eb7caae267735fa44a7
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
initial.ipynb
|
skgrunblatt/FoFreeAST
|
de2703f460ce613c0b180eb7caae267735fa44a7
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2018-10-08T17:39:44.000Z
|
2018-10-08T17:39:44.000Z
| 348.675182 | 32,320 | 0.93726 |
[
[
[
"%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\nimport autocorr\n\nfrom scipy.ndimage.filters import gaussian_filter\n\nfrom astropy.stats import LombScargle",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data = np.loadtxt('230763211.dat.ts')\nt = np.array(data[:, 0]*0.0864)\ny = np.array(data[:, 1]*1e3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = 0.01 / (np.max(t) - np.min(t))\nfreq = np.arange(10.0, 0.5 / np.median(np.diff(t)), df)\nlen(freq)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model = LombScargle(t, y)\npower = model.power(freq)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.loglog(freq, power)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def estimate_background(x, y, log_width=0.005):\n count = np.zeros(len(x), dtype=int)\n bkg = np.zeros_like(x)\n x0 = np.log10(x[0])\n while x0 < np.log10(x[-1]):\n m = np.abs(np.log10(x) - x0) < log_width\n bkg[m] += np.median(y[m])\n count[m] += 1\n x0 += 0.5 * log_width\n return bkg / count\n\nbkg = estimate_background(freq, power)\nplt.loglog(freq, power)\nplt.plot(freq, bkg)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.plot(freq, power / bkg)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = freq[1] - freq[0]\nsmoothed_ps = gaussian_filter(power / bkg, 5 / df)\n\n# And the autocorrelation function of a lightly smoothed power spectrum\nacor_func = autocorr.function_1d(gaussian_filter(power / bkg, 0.5 / df))\nlags = df*np.arange(len(acor_func))\nacor_func = acor_func[lags < 30]\nlags = lags[lags < 30]\n\n# Find the peaks\ndef find_peaks(z):\n peak_inds = (z[1:-1] > z[:-2]) * (z[1:-1] > z[2:])\n peak_inds = np.arange(1, len(z)-1)[peak_inds]\n peak_inds = peak_inds[np.argsort(z[peak_inds])][::-1]\n return peak_inds\n\npeak_freqs = freq[find_peaks(smoothed_ps)]\nnu_max = peak_freqs[peak_freqs > 5][0]\n\n# Expected delta_nu: Stello et al (2009)\ndnu_expected = 0.263 * nu_max ** 0.772\npeak_lags = lags[find_peaks(acor_func)]\ndelta_nu = peak_lags[np.argmin(np.abs(peak_lags - dnu_expected))]\nprint(\"nu_max = {0}, delta_nu = {1}\".format(nu_max, delta_nu))",
"nu_max = 105.09194928492161, delta_nu = 9.460775505433745\n"
],
[
"plt.plot(freq,smoothed_ps)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a70ad5ae0e002aadddf5487d8e915dfc024ae69
| 18,162 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
ML algorithms/classification/K-Nearest-neighbors-CustCat.ipynb
|
srishtipoudel/Machine_Learning_Notes
|
a30bc0b0d9617d68b4bac82911f0ea9242410acd
|
[
"MIT"
] | 6 |
2021-05-10T12:06:06.000Z
|
2021-07-19T16:29:30.000Z
|
ML algorithms/classification/K-Nearest-neighbors-CustCat.ipynb
|
srishtipoudel/Machine_Learning_Notes
|
a30bc0b0d9617d68b4bac82911f0ea9242410acd
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
ML algorithms/classification/K-Nearest-neighbors-CustCat.ipynb
|
srishtipoudel/Machine_Learning_Notes
|
a30bc0b0d9617d68b4bac82911f0ea9242410acd
|
[
"MIT"
] | 4 |
2021-05-24T16:11:21.000Z
|
2021-07-17T14:19:52.000Z
| 18,162 | 18,162 | 0.693811 |
[
[
[
"<center>\n <img src=\"https://cf-courses-data.s3.us.cloud-object-storage.appdomain.cloud/IBMDeveloperSkillsNetwork-ML0101EN-SkillsNetwork/labs/Module%203/images/IDSNlogo.png\" width=\"300\" alt=\"cognitiveclass.ai logo\" />\n</center>\n\n# K-Nearest Neighbors\n\nEstimated time needed: **25** minutes\n\n## Objectives\n\nAfter completing this lab you will be able to:\n\n- Use K Nearest neighbors to classify data\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In this Lab you will load a customer dataset, fit the data, and use K-Nearest Neighbors to predict a data point. But what is **K-Nearest Neighbors**?\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**K-Nearest Neighbors** is an algorithm for supervised learning. Where the data is 'trained' with data points corresponding to their classification. Once a point is to be predicted, it takes into account the 'K' nearest points to it to determine it's classification.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Here's an visualization of the K-Nearest Neighbors algorithm.\n\n<img src=\"https://cf-courses-data.s3.us.cloud-object-storage.appdomain.cloud/IBMDeveloperSkillsNetwork-ML0101EN-SkillsNetwork/labs/Module%203/images/KNN_Diagram.png\">\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In this case, we have data points of Class A and B. We want to predict what the star (test data point) is. If we consider a k value of 3 (3 nearest data points) we will obtain a prediction of Class B. Yet if we consider a k value of 6, we will obtain a prediction of Class A.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In this sense, it is important to consider the value of k. But hopefully from this diagram, you should get a sense of what the K-Nearest Neighbors algorithm is. It considers the 'K' Nearest Neighbors (points) when it predicts the classification of the test point.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<h1>Table of contents</h1>\n\n<div class=\"alert alert-block alert-info\" style=\"margin-top: 20px\">\n <ol>\n <li><a href=\"#about_dataset\">About the dataset</a></li>\n <li><a href=\"#visualization_analysis\">Data Visualization and Analysis</a></li>\n <li><a href=\"#classification\">Classification</a></li>\n </ol>\n</div>\n<br>\n<hr>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!pip install scikit-learn==0.23.1",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Lets load required libraries\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nfrom sklearn import preprocessing\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<div id=\"about_dataset\">\n <h2>About the dataset</h2>\n</div>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Imagine a telecommunications provider has segmented its customer base by service usage patterns, categorizing the customers into four groups. If demographic data can be used to predict group membership, the company can customize offers for individual prospective customers. It is a classification problem. That is, given the dataset, with predefined labels, we need to build a model to be used to predict class of a new or unknown case. \n\nThe example focuses on using demographic data, such as region, age, and marital, to predict usage patterns. \n\nThe target field, called **custcat**, has four possible values that correspond to the four customer groups, as follows:\n 1- Basic Service\n 2- E-Service\n 3- Plus Service\n 4- Total Service\n\nOur objective is to build a classifier, to predict the class of unknown cases. We will use a specific type of classification called K nearest neighbour.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Lets download the dataset. To download the data, we will use !wget to download it from IBM Object Storage.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!wget -O teleCust1000t.csv https://cf-courses-data.s3.us.cloud-object-storage.appdomain.cloud/IBMDeveloperSkillsNetwork-ML0101EN-SkillsNetwork/labs/Module%203/data/teleCust1000t.csv",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Did you know?** When it comes to Machine Learning, you will likely be working with large datasets. As a business, where can you host your data? IBM is offering a unique opportunity for businesses, with 10 Tb of IBM Cloud Object Storage: [Sign up now for free](http://cocl.us/ML0101EN-IBM-Offer-CC)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Load Data From CSV File\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df = pd.read_csv('teleCust1000t.csv')\ndf.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<div id=\"visualization_analysis\">\n <h2>Data Visualization and Analysis</h2> \n</div>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Let’s see how many of each class is in our data set\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df['custcat'].value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### 281 Plus Service, 266 Basic-service, 236 Total Service, and 217 E-Service customers\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"You can easily explore your data using visualization techniques:\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df.hist(column='income', bins=50)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Feature set\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Lets define feature sets, X:\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df.columns",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"To use scikit-learn library, we have to convert the Pandas data frame to a Numpy array:\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"X = df[['region', 'tenure','age', 'marital', 'address', 'income', 'ed', 'employ','retire', 'gender', 'reside']] .values #.astype(float)\nX[0:5]\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"What are our labels?\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"y = df['custcat'].values\ny[0:5]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Normalize Data\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Data Standardization give data zero mean and unit variance, it is good practice, especially for algorithms such as KNN which is based on distance of cases:\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"X = preprocessing.StandardScaler().fit(X).transform(X.astype(float))\nX[0:5]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Train Test Split\n\nOut of Sample Accuracy is the percentage of correct predictions that the model makes on data that that the model has NOT been trained on. Doing a train and test on the same dataset will most likely have low out-of-sample accuracy, due to the likelihood of being over-fit.\n\nIt is important that our models have a high, out-of-sample accuracy, because the purpose of any model, of course, is to make correct predictions on unknown data. So how can we improve out-of-sample accuracy? One way is to use an evaluation approach called Train/Test Split.\nTrain/Test Split involves splitting the dataset into training and testing sets respectively, which are mutually exclusive. After which, you train with the training set and test with the testing set. \n\nThis will provide a more accurate evaluation on out-of-sample accuracy because the testing dataset is not part of the dataset that have been used to train the data. It is more realistic for real world problems.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split( X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=4)\nprint ('Train set:', X_train.shape, y_train.shape)\nprint ('Test set:', X_test.shape, y_test.shape)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<div id=\"classification\">\n <h2>Classification</h2>\n</div>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<h3>K nearest neighbor (KNN)</h3>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Import library\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Classifier implementing the k-nearest neighbors vote.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Training\n\nLets start the algorithm with k=4 for now:\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"k = 4\n#Train Model and Predict \nneigh = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors = k).fit(X_train,y_train)\nneigh",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Predicting\n\nwe can use the model to predict the test set:\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"yhat = neigh.predict(X_test)\nyhat[0:5]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Accuracy evaluation\n\nIn multilabel classification, **accuracy classification score** is a function that computes subset accuracy. This function is equal to the jaccard_score function. Essentially, it calculates how closely the actual labels and predicted labels are matched in the test set.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn import metrics\nprint(\"Train set Accuracy: \", metrics.accuracy_score(y_train, neigh.predict(X_train)))\nprint(\"Test set Accuracy: \", metrics.accuracy_score(y_test, yhat))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Practice\n\nCan you build the model again, but this time with k=6?\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# write your code here\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<details><summary>Click here for the solution</summary>\n\n```python\nk = 6\nneigh6 = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors = k).fit(X_train,y_train)\nyhat6 = neigh6.predict(X_test)\nprint(\"Train set Accuracy: \", metrics.accuracy_score(y_train, neigh6.predict(X_train)))\nprint(\"Test set Accuracy: \", metrics.accuracy_score(y_test, yhat6))\n\n```\n\n</details>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### What about other K?\n\nK in KNN, is the number of nearest neighbors to examine. It is supposed to be specified by the User. So, how can we choose right value for K?\nThe general solution is to reserve a part of your data for testing the accuracy of the model. Then chose k =1, use the training part for modeling, and calculate the accuracy of prediction using all samples in your test set. Repeat this process, increasing the k, and see which k is the best for your model.\n\nWe can calculate the accuracy of KNN for different Ks.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Ks = 10\nmean_acc = np.zeros((Ks-1))\nstd_acc = np.zeros((Ks-1))\n\nfor n in range(1,Ks):\n \n #Train Model and Predict \n neigh = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors = n).fit(X_train,y_train)\n yhat=neigh.predict(X_test)\n mean_acc[n-1] = metrics.accuracy_score(y_test, yhat)\n\n \n std_acc[n-1]=np.std(yhat==y_test)/np.sqrt(yhat.shape[0])\n\nmean_acc",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Plot model accuracy for Different number of Neighbors\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plt.plot(range(1,Ks),mean_acc,'g')\nplt.fill_between(range(1,Ks),mean_acc - 1 * std_acc,mean_acc + 1 * std_acc, alpha=0.10)\nplt.fill_between(range(1,Ks),mean_acc - 3 * std_acc,mean_acc + 3 * std_acc, alpha=0.10,color=\"green\")\nplt.legend(('Accuracy ', '+/- 1xstd','+/- 3xstd'))\nplt.ylabel('Accuracy ')\nplt.xlabel('Number of Neighbors (K)')\nplt.tight_layout()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print( \"The best accuracy was with\", mean_acc.max(), \"with k=\", mean_acc.argmax()+1) ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<h2>Want to learn more?</h2>\n\nIBM SPSS Modeler is a comprehensive analytics platform that has many machine learning algorithms. It has been designed to bring predictive intelligence to decisions made by individuals, by groups, by systems – by your enterprise as a whole. A free trial is available through this course, available here: <a href=\"https://www.ibm.com/analytics/spss-statistics-software\">SPSS Modeler</a>\n\nAlso, you can use Watson Studio to run these notebooks faster with bigger datasets. Watson Studio is IBM's leading cloud solution for data scientists, built by data scientists. With Jupyter notebooks, RStudio, Apache Spark and popular libraries pre-packaged in the cloud, Watson Studio enables data scientists to collaborate on their projects without having to install anything. Join the fast-growing community of Watson Studio users today with a free account at <a href=\"https://www.ibm.com/cloud/watson-studio\">Watson Studio</a>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Thank you for completing this lab!\n\n## Author\n\nSaeed Aghabozorgi\n\n### Other Contributors\n\n<a href=\"https://www.linkedin.com/in/joseph-s-50398b136/\" target=\"_blank\">Joseph Santarcangelo</a>\n\n## Change Log\n\n| Date (YYYY-MM-DD) | Version | Changed By | Change Description |\n| ----------------- | ------- | ---------- | ---------------------------------- |\n| 2021-01-21 | 2.4 | Lakshmi | Updated sklearn library |\n| 2020-11-20 | 2.3 | Lakshmi | Removed unused imports |\n| 2020-11-17 | 2.2 | Lakshmi | Changed plot function of KNN |\n| 2020-11-03 | 2.1 | Lakshmi | Changed URL of csv |\n| 2020-08-27 | 2.0 | Lavanya | Moved lab to course repo in GitLab |\n| | | | |\n| | | | |\n\n## <h3 align=\"center\"> © IBM Corporation 2020. All rights reserved. <h3/>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4a70d7d05b019105a5dfbeee7b6eb8ea5c9bdb66
| 1,906 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
GeneticDrawing.ipynb
|
faheywf/genetic-drawing
|
917deae8205d5b3d69a7929262b05e65c1d269b2
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2,091 |
2020-06-05T11:59:47.000Z
|
2022-03-31T23:59:20.000Z
|
GeneticDrawing.ipynb
|
faheywf/genetic-drawing
|
917deae8205d5b3d69a7929262b05e65c1d269b2
|
[
"MIT"
] | 10 |
2020-06-05T14:34:07.000Z
|
2021-12-12T21:36:05.000Z
|
GeneticDrawing.ipynb
|
faheywf/genetic-drawing
|
917deae8205d5b3d69a7929262b05e65c1d269b2
|
[
"MIT"
] | 207 |
2020-06-05T12:04:10.000Z
|
2022-02-19T22:32:49.000Z
| 24.435897 | 94 | 0.559811 |
[
[
[
"import cv2\nimport os\nimport time\nfrom IPython.display import clear_output\nfrom genetic_drawing import *",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#load the example image and set the generator for 100 stages with 20 generations each\ngen = GeneticDrawing('example.jpg', seed=time.time())\nout = gen.generate(100, 20)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#load a custom mask and set a smaller brush size for finer details\ngen.sampling_mask = cv2.cvtColor(cv2.imread(\"mask.jpg\"), cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)\ngen.brushesRange = [[0.05, 0.1], [0.1, 0.2]]\n#keep drawing on top of our previous result\nout = gen.generate(40, 30)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#save all the images from the image buffer\nif not os.path.exists('out'):\n os.mkdir(\"out\")\nfor i in range(len(gen.imgBuffer)):\n cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(\"out\", f\"{i:06d}.png\"), gen.imgBuffer[i])\n#if you want to save only last image, run below\n# cv2.imwrite(\"out/final.png', out)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a70e81e4e89cb9773ffb95d6729c1cc99dd45db
| 4,220 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
example-1-Dataset.ipynb
|
abhimanyu1990/Pytorch-Examples
|
dfae06c9b6bfbf7cce16be0c2106b24786a8152b
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
example-1-Dataset.ipynb
|
abhimanyu1990/Pytorch-Examples
|
dfae06c9b6bfbf7cce16be0c2106b24786a8152b
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
example-1-Dataset.ipynb
|
abhimanyu1990/Pytorch-Examples
|
dfae06c9b6bfbf7cce16be0c2106b24786a8152b
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 22.210526 | 259 | 0.509953 |
[
[
[
"In this example we will understand and create custom pytorch Dataset. Dataset is one of the important tool \nprovided by PyTorch which is quite useful in processing and loading data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from torch.utils.data import Dataset\nimport torch",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\nclass custom_set(Dataset):\n def __init__ (self, length=5, transform=None):\n self.x=3*torch.ones(length,2)\n self.y=torch.ones(length,1)\n self.len = length\n self.transform = transform\n \n def __getitem__ (self, index):\n val = self.x[index],self.y[index]\n if self.transform:\n val = self.transform(val)\n return val\n \n def __len__(self):\n return self.len\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Above we are creating a subclass custom_set of DataSet. Dataset is abstract class from torch.\n\nunderstanding torch.ones(5,2)\n 1. It returns the tensor filled with scalar value 1.\n 2. Here, we are dfining two dimensional tensor of length 5.\n 3. self.x = 3*torch.ones(length,2) \n x value will be represeted as \n self.x = [3,3],[3,3],[3,3],[3,3],[3,3]\n index = 0 , 1 , 2 , 3 , 4",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# creating object of class custom_set\ndataset = custom_set()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Accessing value at index 1\ndataset[1]\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"It calls the function dataset.__getitem__(1). In __getitem__ function we have used transform = None. This means we are not applying any data transformation. Transformation is used for normalization and standardization of data which is not in this scope ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# to find the length of dataset \ndataset.len",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dataset.__getitem__(1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The above code \"dataset.len\" calls the function dataset.__len__(), defined it the class custom_set",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dataset.__len__()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"raw",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"raw"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a70f5f4591c858e9e757718f53677430426dc09
| 53,101 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
misc/kijang-emas-bank-negara.ipynb
|
felix-zg/Stock-Prediction-Models
|
d05751496b6d8920353661d7c682a3e4f27af295
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
misc/kijang-emas-bank-negara.ipynb
|
felix-zg/Stock-Prediction-Models
|
d05751496b6d8920353661d7c682a3e4f27af295
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
misc/kijang-emas-bank-negara.ipynb
|
felix-zg/Stock-Prediction-Models
|
d05751496b6d8920353661d7c682a3e4f27af295
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 40.442498 | 8,459 | 0.65914 |
[
[
[
"# Welcome to Kijang Emas analysis!\n\n\n\nI was found around last week (18th March 2019), our Bank Negara opened public APIs for certain data, it was really cool and I want to help people get around with the data and what actually they can do with the data!\n\nWe are going to cover 2 things here,\n\n1. Data Analytics\n2. Predictive Modelling (Linear regression, ARIMA, LSTM)\n\nHell, I know nothing about Kijang Emas.\n\n**Again, do not use this code to buy something on the real world (if got positive return, please donate some to me)**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import requests",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Data gathering\n\nTo get the data is really simple, use this link to get kijang emas data, https://api.bnm.gov.my/public/kijang-emas/year/{year}/month/{month}\n\nNow, I want to get data from january 2018 - march 2019.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### 2018 data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data_2018 = []\nfor i in range(12):\n data_2018.append(requests.get(\n 'https://api.bnm.gov.my/public/kijang-emas/year/2018/month/%d'%(i + 1),\n headers = {'Accept': 'application/vnd.BNM.API.v1+json'},\n ).json())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### 2019 data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data_2019 = []\nfor i in range(3):\n data_2019.append(requests.get(\n 'https://api.bnm.gov.my/public/kijang-emas/year/2019/month/%d'%(i + 1),\n headers = {'Accept': 'application/vnd.BNM.API.v1+json'},\n ).json())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Take a peak our data ya",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data_2018[0]['data'][:5]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Again, I got zero knowledge on kijang emas and I don't really care about the value, and I don't know what the value represented.\n\nNow I want to parse `effective_date` and `buying` from `one_oz`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"timestamp, selling = [], []\nfor month in data_2018 + data_2019:\n for day in month['data']:\n timestamp.append(day['effective_date'])\n selling.append(day['one_oz']['selling'])\n \nlen(timestamp), len(selling)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Going to import matplotlib and seaborn for visualization, I really seaborn because of the font and colors, thats all, hah!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn as sns\nimport numpy as np\nsns.set()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize = (15, 5))\nplt.plot(selling)\nplt.xticks(np.arange(len(timestamp))[::15], timestamp[::15], rotation = '45')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Perfect!\n\nSo now let's we start our Data analytics.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Distribution study",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plt.figure(figsize = (15, 5))\nsns.distplot(selling)\nplt.show()",
"/Users/felixweizmann/Documents/GitHub/Stock-Prediction-Models/venv/lib/python3.7/site-packages/seaborn/distributions.py:2551: FutureWarning: `distplot` is a deprecated function and will be removed in a future version. Please adapt your code to use either `displot` (a figure-level function with similar flexibility) or `histplot` (an axes-level function for histograms).\n warnings.warn(msg, FutureWarning)\n/Users/felixweizmann/Documents/GitHub/Stock-Prediction-Models/venv/lib/python3.7/site-packages/seaborn/distributions.py:2589: RuntimeWarning: Mean of empty slice.\n line, = ax.plot(a.mean(), 0)\n/Users/felixweizmann/Documents/GitHub/Stock-Prediction-Models/venv/lib/python3.7/site-packages/numpy/core/_methods.py:161: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in double_scalars\n ret = ret.dtype.type(ret / rcount)\n/Users/felixweizmann/Documents/GitHub/Stock-Prediction-Models/venv/lib/python3.7/site-packages/numpy/lib/histograms.py:908: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in true_divide\n return n/db/n.sum(), bin_edges\n"
]
],
[
[
"Look at this, already normal distribution, coincidence? (I really wanted to show off unit scaling skills, too bad :/ )\n\nNow let's change our into Pandas, for lagging analysis.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\ndf = pd.DataFrame({'timestamp':timestamp, 'selling':selling})\ndf.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def df_shift(df, lag = 0, start = 1, skip = 1, rejected_columns = []):\n df = df.copy()\n if not lag:\n return df\n cols = {}\n for i in range(start, lag + 1, skip):\n for x in list(df.columns):\n if x not in rejected_columns:\n if not x in cols:\n cols[x] = ['{}_{}'.format(x, i)]\n else:\n cols[x].append('{}_{}'.format(x, i))\n for k, v in cols.items():\n columns = v\n dfn = pd.DataFrame(data = None, columns = columns, index = df.index)\n i = start - 1\n for c in columns:\n dfn[c] = df[k].shift(periods = i)\n i += skip\n df = pd.concat([df, dfn], axis = 1, join_axes = [df.index])\n return df",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Shifted and moving average are not same.**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_crosscorrelated = df_shift(\n df, lag = 12, start = 4, skip = 2, rejected_columns = ['timestamp']\n)\ndf_crosscorrelated['ma7'] = df_crosscorrelated['selling'].rolling(7).mean()\ndf_crosscorrelated['ma14'] = df_crosscorrelated['selling'].rolling(14).mean()\ndf_crosscorrelated['ma21'] = df_crosscorrelated['selling'].rolling(21).mean()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## why we lagged or shifted to certain units?\n\nVirals took some time, impacts took some time, same goes to price lot / unit.\n\nNow I want to `lag` for until 12 units, `start` at 4 units shifted, `skip` every 2 units.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_crosscorrelated.head(10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize = (20, 4))\nplt.subplot(1, 3, 1)\nplt.scatter(df_crosscorrelated['selling'], df_crosscorrelated['selling_4'])\nmse = (\n (df_crosscorrelated['selling_4'] - df_crosscorrelated['selling']) ** 2\n).mean()\nplt.title('close vs shifted 4, average change: %f'%(mse))\nplt.subplot(1, 3, 2)\nplt.scatter(df_crosscorrelated['selling'], df_crosscorrelated['selling_8'])\nmse = (\n (df_crosscorrelated['selling_8'] - df_crosscorrelated['selling']) ** 2\n).mean()\nplt.title('close vs shifted 8, average change: %f'%(mse))\nplt.subplot(1, 3, 3)\nplt.scatter(df_crosscorrelated['selling'], df_crosscorrelated['selling_12'])\nmse = (\n (df_crosscorrelated['selling_12'] - df_crosscorrelated['selling']) ** 2\n).mean()\nplt.title('close vs shifted 12, average change: %f'%(mse))\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Keep increasing and increasing!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plt.figure(figsize = (10, 5))\nplt.scatter(\n df_crosscorrelated['selling'],\n df_crosscorrelated['selling_4'],\n label = 'close vs shifted 4',\n)\nplt.scatter(\n df_crosscorrelated['selling'],\n df_crosscorrelated['selling_8'],\n label = 'close vs shifted 8',\n)\nplt.scatter(\n df_crosscorrelated['selling'],\n df_crosscorrelated['selling_12'],\n label = 'close vs shifted 12',\n)\nplt.legend()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize = (15, 5))\ndf_crosscorrelated.plot(\n x = 'timestamp', y = ['selling', 'ma7', 'ma14', 'ma21'], ax = ax\n)\nplt.xticks(np.arange(len(timestamp))[::10], timestamp[::10], rotation = '45')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"As you can see, even moving average 7 already not followed sudden trending (blue line), means that, **dilation rate required less than 7 days! so fast!**\n\n#### How about correlation?\n\nWe want to study linear relationship between, how many days required to give impact to future sold units?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"colormap = plt.cm.RdBu\nplt.figure(figsize = (15, 5))\nplt.title('cross correlation', y = 1.05, size = 16)\n\nsns.heatmap(\n df_crosscorrelated.iloc[:, 1:].corr(),\n linewidths = 0.1,\n vmax = 1.0,\n cmap = colormap,\n linecolor = 'white',\n annot = True,\n)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Based on this correlation map, look at selling vs selling_X,\n\n**selling_X from 4 to 12 is getting lower, means that, if today is 50 mean, next 4 days should increased by 0.95 * 50 mean, and continue.**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Outliers\n\nSimple, we can use Z-score to detect outliers, which timestamps gave very uncertain high and low value.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"std_selling = (selling - np.mean(selling)) / np.std(selling)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def detect(signal, treshold = 2.0):\n detected = []\n for i in range(len(signal)):\n if np.abs(signal[i]) > treshold:\n detected.append(i)\n return detected",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Based on z-score table, 2.0 already positioned at 97.772% of the population.\n\nhttps://d2jmvrsizmvf4x.cloudfront.net/6iEAaVSaT3aGP52HMzo3_z-score-02.png",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"outliers = detect(std_selling)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize = (15, 7))\nplt.plot(selling)\nplt.plot(\n np.arange(len(selling)),\n selling,\n 'X',\n label = 'outliers',\n markevery = outliers,\n c = 'r',\n)\nplt.legend()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can see that, **we have positive and negative outliers**. What happened to our local market on that days? So we should study sentiment from local news to do risk analysis.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Give us predictive modelling!\n\nOkay okay.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Predictive modelling\n\nLike I said, I want to compare with 3 models,\n\n1. Linear regression\n2. ARIMA\n3. LSTM Tensorflow (sorry Pytorch, not used to it)\n\nWhich models give the best accuracy and lowest error rate?\n\n**I want to split first timestamp 80% for train, another 20% timestamp for test.**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"train_selling = selling[: int(0.8 * len(selling))]\ntest_selling = selling[int(0.8 * len(selling)) :]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Beware of `:`!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"future_count = len(test_selling)\nfuture_count",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Our model should forecast 61 future days ahead.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Linear regression",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%time\nlinear_regression = LinearRegression().fit(\n np.arange(len(train_selling)).reshape((-1, 1)), train_selling\n)\nlinear_future = linear_regression.predict(\n np.arange(len(train_selling) + future_count).reshape((-1, 1))\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Took me 594 us to train linear regression from sklearn. Very quick!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize = (15, 5))\nax.plot(selling, label = '20% test trend')\nax.plot(train_selling, label = '80% train trend')\nax.plot(linear_future, label = 'forecast linear regression')\nplt.xticks(\n np.arange(len(timestamp))[::10],\n np.arange(len(timestamp))[::10],\n rotation = '45',\n)\nplt.legend()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Oh no, if based on linear relationship, the trend is going down!",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### ARIMA\n\nStands for Auto-regressive Moving Average.\n\n3 important parameters you need to know about ARIMA, ARIMA(p, d, q). You will able to see what is `p`, `d`, `q` from wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Autoregressive_integrated_moving_average.\n\n`p` for the order (number of time lags).\n\n`d` for degree of differencing.\n\n`q` for the order of the moving-average.\n\nOr,\n\n`p` is how long the periods we need to look back.\n\n`d` is the skip value during calculating future differences.\n\n`q` is how many periods for moving average.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import statsmodels.api as sm\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler\nfrom itertools import product\n\nQs = range(0, 2)\nqs = range(0, 2)\nPs = range(0, 2)\nps = range(0, 2)\nD = 1\nparameters = product(ps, qs, Ps, Qs)\nparameters_list = list(parameters)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Problem with ARIMA, you cannot feed a high value, so we need to scale, simplest we can use, minmax scaling.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"minmax = MinMaxScaler().fit(np.array([train_selling]).T)\nminmax_values = minmax.transform(np.array([train_selling]).T)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now using naive meshgrid parameter searching, which pairs of parameters are the best! **Lower is better!**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"best_aic = float('inf')\nfor param in parameters_list:\n try:\n model = sm.tsa.statespace.SARIMAX(\n minmax_values[:, 0],\n order = (param[0], D, param[1]),\n seasonal_order = (param[2], D, param[3], future_count),\n ).fit(disp = -1)\n except Exception as e:\n print(e)\n continue\n aic = model.aic\n print(aic)\n if aic < best_aic and aic:\n best_model = model\n best_aic = aic\n\narima_future = best_model.get_prediction(\n start = 0, end = len(train_selling) + (future_count - 1)\n)\narima_future = minmax.inverse_transform(\n np.expand_dims(arima_future.predicted_mean, axis = 1)\n)[:, 0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize = (15, 5))\nax.plot(selling, label = '20% test trend')\nax.plot(train_selling, label = '80% train trend')\nax.plot(linear_future, label = 'forecast linear regression')\nax.plot(arima_future, label = 'forecast ARIMA')\nplt.xticks(\n np.arange(len(timestamp))[::10],\n np.arange(len(timestamp))[::10],\n rotation = '45',\n)\nplt.legend()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Perfect!\n\nNow we left,\n\n#### RNN + LSTM",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import tensorflow as tf",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class Model:\n def __init__(\n self,\n learning_rate,\n num_layers,\n size,\n size_layer,\n output_size,\n forget_bias = 0.1,\n ):\n def lstm_cell(size_layer):\n return tf.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMCell(size_layer, state_is_tuple = False)\n\n rnn_cells = tf.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell(\n [lstm_cell(size_layer) for _ in range(num_layers)],\n state_is_tuple = False,\n )\n self.X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, (None, None, size))\n self.Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, (None, output_size))\n drop = tf.contrib.rnn.DropoutWrapper(\n rnn_cells, output_keep_prob = forget_bias\n )\n self.hidden_layer = tf.placeholder(\n tf.float32, (None, num_layers * 2 * size_layer)\n )\n self.outputs, self.last_state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(\n drop, self.X, initial_state = self.hidden_layer, dtype = tf.float32\n )\n self.logits = tf.layers.dense(self.outputs[-1], output_size)\n self.cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(self.Y - self.logits))\n self.optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(\n self.cost\n )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Naively defined neural network parameters, no meshgrid here. this parameters came from my dream, believe me :)**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"num_layers = 1\nsize_layer = 128\nepoch = 500\ndropout_rate = 0.6\nskip = 10",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Same goes to LSTM, we need to scale our value becaused LSTM use sigmoid and tanh functions during feed-forward, we don't want any gradient vanishing during backpropagation.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df = pd.DataFrame({'values': train_selling})\nminmax = MinMaxScaler().fit(df)\ndf_log = minmax.transform(df)\ndf_log = pd.DataFrame(df_log)\ndf_log.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tf.reset_default_graph()\nmodelnn = Model(\n learning_rate = 0.001, \n num_layers = num_layers, \n size = df_log.shape[1], \n size_layer = size_layer, \n output_size = df_log.shape[1], \n forget_bias = dropout_rate\n)\nsess = tf.InteractiveSession()\nsess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%%time\n\nfor i in range(epoch):\n init_value = np.zeros((1, num_layers * 2 * size_layer))\n total_loss = 0\n for k in range(0, df_log.shape[0] - 1, skip):\n index = min(k + skip, df_log.shape[0] -1)\n batch_x = np.expand_dims(\n df_log.iloc[k : index, :].values, axis = 0\n )\n batch_y = df_log.iloc[k + 1 : index + 1, :].values\n last_state, _, loss = sess.run(\n [modelnn.last_state, modelnn.optimizer, modelnn.cost],\n feed_dict = {\n modelnn.X: batch_x,\n modelnn.Y: batch_y,\n modelnn.hidden_layer: init_value,\n },\n )\n init_value = last_state\n total_loss += loss\n total_loss /= ((df_log.shape[0] - 1) / skip)\n if (i + 1) % 100 == 0:\n print('epoch:', i + 1, 'avg loss:', total_loss)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = pd.DataFrame({'values': train_selling})\nminmax = MinMaxScaler().fit(df)\ndf_log = minmax.transform(df)\ndf_log = pd.DataFrame(df_log)\nfuture_day = future_count\n\noutput_predict = np.zeros((df_log.shape[0] + future_day, df_log.shape[1]))\noutput_predict[0] = df_log.iloc[0]\nupper_b = (df_log.shape[0] // skip) * skip\ninit_value = np.zeros((1, num_layers * 2 * size_layer))\nfor k in range(0, (df_log.shape[0] // skip) * skip, skip):\n out_logits, last_state = sess.run(\n [modelnn.logits, modelnn.last_state],\n feed_dict = {\n modelnn.X: np.expand_dims(\n df_log.iloc[k : k + skip], axis = 0\n ),\n modelnn.hidden_layer: init_value,\n },\n )\n init_value = last_state\n output_predict[k + 1 : k + skip + 1] = out_logits\n\nif upper_b < df_log.shape[0]:\n out_logits, last_state = sess.run(\n [modelnn.logits, modelnn.last_state],\n feed_dict = {\n modelnn.X: np.expand_dims(df_log.iloc[upper_b:], axis = 0),\n modelnn.hidden_layer: init_value,\n },\n )\n init_value = last_state\n output_predict[upper_b + 1 : df_log.shape[0] + 1] = out_logits\n df_log.loc[df_log.shape[0]] = out_logits[-1]\n future_day = future_day - 1\n \nfor i in range(future_day):\n out_logits, last_state = sess.run(\n [modelnn.logits, modelnn.last_state],\n feed_dict = {\n modelnn.X: np.expand_dims(df_log.iloc[-skip:], axis = 0),\n modelnn.hidden_layer: init_value,\n },\n )\n init_value = last_state\n output_predict[df_log.shape[0]] = out_logits[-1]\n df_log.loc[df_log.shape[0]] = out_logits[-1]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_log = minmax.inverse_transform(output_predict)\nlstm_future = df_log[:,0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize = (15, 5))\nax.plot(selling, label = '20% test trend')\nax.plot(train_selling, label = '80% train trend')\nax.plot(linear_future, label = 'forecast linear regression')\nax.plot(arima_future, label = 'forecast ARIMA')\nax.plot(lstm_future, label='forecast lstm')\nplt.xticks(\n np.arange(len(timestamp))[::10],\n np.arange(len(timestamp))[::10],\n rotation = '45',\n)\nplt.legend()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.metrics import r2_score\nfrom scipy.stats import pearsonr, spearmanr",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Accuracy based on correlation coefficient, **higher is better!**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def calculate_accuracy(real, predict):\n r2 = r2_score(real, predict)\n if r2 < 0:\n r2 = 0\n\n def change_percentage(val): \n # minmax, we know that correlation is between -1 and 1\n if val > 0:\n return val\n else:\n return val + 1\n\n pearson = pearsonr(real, predict)[0]\n spearman = spearmanr(real, predict)[0]\n pearson = change_percentage(pearson)\n spearman = change_percentage(spearman)\n return {\n 'r2': r2 * 100,\n 'pearson': pearson * 100,\n 'spearman': spearman * 100,\n }",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Distance error for mse and rmse, **lower is better!**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def calculate_distance(real, predict):\n mse = ((real - predict) ** 2).mean()\n rmse = np.sqrt(mse)\n return {'mse': mse, 'rmse': rmse}",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Now let's check distance error using Mean Square Error and Root Mean Square Error\n\nValidating based on 80% training timestamps",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"linear_cut = linear_future[: len(train_selling)]\narima_cut = arima_future[: len(train_selling)]\nlstm_cut = lstm_future[: len(train_selling)]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Linear regression",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"calculate_distance(train_selling, linear_cut)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"calculate_accuracy(train_selling, linear_cut)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"ARIMA",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"calculate_distance(train_selling, arima_cut)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"calculate_accuracy(train_selling, arima_cut)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"LSTM",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"calculate_distance(train_selling, lstm_cut)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"calculate_accuracy(train_selling, lstm_cut)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**LSTM learn better during training session!**\n\nHow about another 20%?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"linear_cut = linear_future[len(train_selling) :]\narima_cut = arima_future[len(train_selling) :]\nlstm_cut = lstm_future[len(train_selling) :]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Linear regression",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"calculate_distance(test_selling, linear_cut)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"calculate_accuracy(test_selling, linear_cut)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"ARIMA",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"calculate_distance(test_selling, arima_cut)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"calculate_accuracy(test_selling, arima_cut)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"LSTM",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"calculate_distance(test_selling, lstm_cut)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"calculate_accuracy(test_selling, lstm_cut)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**LSTM is the best model based on testing!**\n\nDeep learning won again!",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"I guess that's all for now, **again, do not use these models to buy any stocks or trends!**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4a710ba98921a01c25a99fef08b6ef8ce4c4c495
| 13,825 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
python/ch13/13.7-statsville-revisited.ipynb
|
krishnonwork/mathematical-methods-in-deep-learning
|
12a7e7a9981f8639b4524b7977bd185f82c04e2d
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2020-03-20T20:46:58.000Z
|
2020-03-20T20:46:58.000Z
|
python/ch13/13.7-statsville-revisited.ipynb
|
sthagen/mathematical-methods-in-deep-learning-ipython
|
12a7e7a9981f8639b4524b7977bd185f82c04e2d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
python/ch13/13.7-statsville-revisited.ipynb
|
sthagen/mathematical-methods-in-deep-learning-ipython
|
12a7e7a9981f8639b4524b7977bd185f82c04e2d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 36.096606 | 478 | 0.571284 |
[
[
[
"import torch\nfrom torch.distributions import Normal\nimport math",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let us revisit the problem of predicting if a resident of Statsville is female based on the height. For this purpose, we have collected a set of height samples from adult female residents in Statsville. Unfortunately, due to unforseen circumstances we have collected a very small sample from the residents. Armed with our knowledge of Bayesian inference, we do not want to let this deter us from trying to build a model.\n\nFrom physical considerations, we can assume that the distribution of heights is Gaussian. Our goal is to estimate the parameters ($\\mu$, $\\sigma$) of this Gaussian.\n\n\nLet us first create the dataset by sampling 5 points from a Gaussian distribution with $\\mu$=152 and $\\sigma$=8. In real life scenarios, we do not know the mean and standard deviation of the true distribution. But for the sake of this example, let's assume that the mean height is 152cm and standard deviation is 8cm.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"torch.random.manual_seed(0)\nnum_samples = 5\ntrue_dist = Normal(152, 8)\nX = true_dist.sample((num_samples, 1))\nprint('Dataset shape: {}'.format(X.shape))",
"Dataset shape: torch.Size([5, 1])\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Maximum Likelihood Estimate\n\nIf we relied on Maximum Likelihood estimation, our approach would be simply to compute the mean and standard deviation of the dataset, and use this normal distribution as our model.\n\n$$\\mu_{MLE} = \\frac{1}{N}\\sum_{i=1}^nx_i$$\n$$\\sigma_{MLE} = \\frac{1}{N}\\sum_{i=1}^n(x_i - \\mu)^2$$\n\nOnce we estimate the parameters, we can find out the probability that a sample lies in the range using the following formula\n$$ p(a < X <= b) = \\int_{a}^b p(X) dX $$\n\nHowever, when the amount of data is low, the MLE estimates are not as reliable. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mle_mu, mle_std = X.mean(), X.std()\nmle_dist = Normal(mle_mu, mle_std)\n\nprint(f\"MLE: mu {mle_mu:0.2f} std {mle_std:0.2f}\")",
"MLE: mu 149.68 std 11.52\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Bayesian Inference\n\nCan we do better than MLE? \n\nOne potential method to do this is to use Bayesian inference with a good prior. How does one go about selecting a good prior? Well, lets say from another survey, we know that the average and the standard deviation of height of adult female residents in Neighborville, the neighboring town. Additionally, we have no reason to believe that the distribution of heights at Statsville is significantly different. So we can use this information to \"initialize\" our prior. \n\nLets say the the mean height of adult female resident in Neighborville is 150 cm with a standard deviation of 9 cm.\n\nWe can use this information as our prior. The prior distribution encodes our beliefs on the parameter values.\n\nGiven that we are dealing with an unknown mean, and unknown variance, we will model the prior as a Normal Gamma distribution. \n\n$$p\\left( \\theta \\middle\\vert X \\right) = p \\left( X \\middle\\vert \\theta \\right) p \\left( \\theta \\right)\\\\\np\\left( \\theta \\middle\\vert X \\right) = Normal-Gamma\\left( \\mu_{n}, \\lambda_{n}, \\alpha_{n}, \\beta_{n} \\right) \\\\\np \\left( X \\middle\\vert \\theta \\right) = \\mathbb{N}\\left( \\mu, \\lambda^{ -\\frac{1}{2} } \\right) \\\\\np \\left( \\theta \\right) = Normal-Gamma\\left( \\mu_{0}, \\lambda_{0}, \\alpha_{0}, \\beta_{0} \\right)$$\n\nWe will choose a prior, $p \\left(\\theta \\right)$, such that \n$$ \\mu_{0} = 150 \\\\\n \\lambda_{0} = 100 \\\\\n \\alpha_{0} = 100.5 \\\\\n \\beta_{0} = 8100 $$\n \n$$p \\left( \\theta \\right) = Normal-Gamma\\left( 150, 100, 100.5 , 8100 \\right)$$\n\n\nWe will compute the posterior, $p\\left( \\theta \\middle\\vert X \\right)$, using Bayesian inference.\n\n$$\\mu_{n} = \\frac{ \\left( n \\bar{x} + \\mu_{0} \\lambda_{0} \\right) }{ n + \\lambda_{0} } \\\\\n\\lambda_{n} = n + \\lambda_{0} \\\\\n\\alpha_{n} = \\frac{n}{2} + \\alpha_{0} \\\\\n\\beta_{n} = \\frac{ ns }{ 2 } + \\beta_{ 0 } + \\frac{ n \\lambda_{0} } { 2 \\left( n + \\lambda_{0} \\right) } \\left( \\bar{x} - \\mu_{0} \\right)^{ 2 }$$\n\n$$p\\left( \\theta \\middle\\vert X \\right) = Normal-Gamma\\left( \\mu_{n}, \\lambda_{n}, \\alpha_{n}, \\beta_{n} \\right)$$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class NormalGamma():\n def __init__(self, mu_, lambda_, alpha_, beta_):\n self.mu_ = mu_\n self.lambda_ = lambda_\n self.alpha_ = alpha_\n self.beta_ = beta_\n \n @property\n def mean(self):\n return self.mu_, self.alpha_/ self.beta_\n\n \n @property\n def mode(self):\n return self.mu_, (self.alpha_-0.5)/ self.beta_",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def inference_unknown_mean_variance(X, prior_dist):\n mu_mle = X.mean()\n sigma_mle = X.std()\n n = X.shape[0]\n # Parameters of the prior\n mu_0 = prior_dist.mu_\n lambda_0 = prior_dist.lambda_\n alpha_0 = prior_dist.alpha_\n beta_0 = prior_dist.beta_\n \n # Parameters of posterior\n mu_n = (n * mu_mle + mu_0 * lambda_0) / (lambda_0 + n) \n lambda_n = n + lambda_0\n alpha_n = n / 2 + alpha_0\n beta_n = (n / 2 * sigma_mle ** 2) + beta_0 + (0.5* n * lambda_0 * (mu_mle - mu_0) **2 /(n + lambda_0)) \n posterior_dist = NormalGamma(mu_n, lambda_n, alpha_n, beta_n)\n \n return posterior_dist",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Let us initialize the prior based on our beliefs\nprior_dist = NormalGamma(150, 100, 10.5, 810)\n\n# We compute the posterior distribution\nposterior_dist = inference_unknown_mean_variance(X, prior_dist)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"How do we use the posterior distribution?\n\nNote that the posterior distribution is a distribution on the parameters $\\mu$ and $\\lambda$. It is important to note that the posterior and prior are distributions in the parameter space. The likelihood is a distribution on the data space.\n\n\nOnce we learn the posterior distribution, one way to use the distribution is to look at the mode of the distribution i.e the parameter values which have the highest probability density. Using these point estimates leads us to Maximum A Posteriori / MAP estimation.\n\nAs usual, we will obtain the maxima of the posterior probability density function $p\\left( \\mu, \\sigma \\middle\\vert X \\right) = Normal-Gamma\\left( \\mu, \\sigma ; \\;\\; \\mu_{n}, \\lambda_{n}, \\alpha_{n}, \\beta_{n} \\right) $.\n\nThis function attains its maxima when\n\n$$\\mu = \\mu_{n} \\\\\n\\lambda = \\frac{ \\alpha_{n} - \\frac{1}{2} } { \\beta_{n} }$$\n\nWe notice that the MAP estimates for $\\mu$ and $\\sigma$ are better than the MLE estimates. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# With the Normal Gamma formulation, the unknown parameters are mu and precision\nmap_mu, map_precision = posterior_dist.mode\n\n# We can compute the standard deviation using precision.\nmap_std = math.sqrt(1 / map_precision)\n\nmap_dist = Normal(map_mu, map_std)\nprint(f\"MAP: mu {map_mu:0.2f} std {map_std:0.2f}\")",
"MAP: mu 149.98 std 9.56\n"
]
],
[
[
"How did we arrive at the values of the parameters for the prior distribution? \n\nLet us consider the case when we have 0 data points. In this case, posterior will become equal to the prior. If we use the mode of this posterior for our MAP estimate, we see that the mu and std parameters are the same as the $\\mu$ and $\\sigma$ of adult female residents in Neighborville.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"prior_mu, prior_precision = prior_dist.mode\nprior_std = math.sqrt(1 / prior_precision)\nprint(f\"Prior: mu {prior_mu:0.2f} std {prior_std:0.2f}\")",
"Prior: mu 150.00 std 9.00\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Inference\n\nLet us say we want to find out the probability that a height between 150 and 155 belongs to an adult female resident. We can now use the the MAP estimates for $\\mu$ and $\\sigma$ to compute this value. \n\nSince our prior was good, we notice that the MAP serves as a better estimator than MLE at low values of n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"a, b = torch.Tensor([150]), torch.Tensor([155])\n\ntrue_prob = true_dist.cdf(b) - true_dist.cdf(a)\nprint(f'True probability: {true_prob}')\n\nmap_prob = map_dist.cdf(b) - map_dist.cdf(a)\nprint(f'MAP probability: {map_prob}')\n\nmle_prob = mle_dist.cdf(b) - mle_dist.cdf(a)\nprint('MLE probability: {}'.format(mle_prob))",
"True probability: tensor([0.2449])\nMAP probability: tensor([0.1995])\nMLE probability: tensor([0.1669])\n"
]
],
[
[
"Let us say we receive more samples, how do we incorporate this information into our model? We can now set the prior to our current posterior and run inference again to obtain the new posterior. This process can be done interatively.\n\n$$ p \\left( \\theta \\right)_{n} = p\\left( \\theta \\middle\\vert X \\right)_{n-1}$$\n$$ p\\left( \\theta \\middle\\vert X \\right)_{n}=inference\\_unknown\\_mean\\_variance(X_{n}, p \\left( \\theta \\right)_{n})$$\n\nWe also notice that as the number of data points increases, the MAP starts to converge towards the true values of $\\mu$ and $\\sigma$ respectively",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"num_batches, batch_size = 20, 10\nfor i in range(num_batches):\n X_i = true_dist.sample((batch_size, 1))\n prior_i = posterior_dist\n posterior_dist = inference_unknown_mean_variance(X_i, prior_i)\n map_mu, map_precision = posterior_dist.mode\n\n # We can compute the standard deviation using precision.\n map_std = math.sqrt(1 / map_precision)\n map_dist = Normal(map_mu, map_std)\n if i % 5 == 0:\n print(f\"MAP at batch {i}: mu {map_mu:0.2f} std {map_std:0.2f}\")\nprint(f\"MAP at batch {i}: mu {map_mu:0.2f} std {map_std:0.2f}\")",
"MAP at batch 0: mu 149.98 std 8.84\nMAP at batch 5: mu 150.65 std 8.98\nMAP at batch 10: mu 150.70 std 8.77\nMAP at batch 15: mu 151.15 std 8.79\nMAP at batch 19: mu 151.04 std 8.70\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a7129e3f7daaea5fef65b44588de191420a5aac
| 79,161 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
01-data-formats/lab.ipynb
|
davidhoksza/bioinformatics-algo-labs
|
96b10b0e38e1dbd1be550d174f7398569a4ae67d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
01-data-formats/lab.ipynb
|
davidhoksza/bioinformatics-algo-labs
|
96b10b0e38e1dbd1be550d174f7398569a4ae67d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
01-data-formats/lab.ipynb
|
davidhoksza/bioinformatics-algo-labs
|
96b10b0e38e1dbd1be550d174f7398569a4ae67d
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-12-06T19:40:47.000Z
|
2021-12-06T19:40:47.000Z
| 96.30292 | 21,703 | 0.732836 |
[
[
[
"# Labs - Biopython and data formats\n\n## Outline\n\n- Managing dependencies in Python with environments\n- Biopython \n - Sequences (parsing, representation, manipulation)\n - Structures (parsing, representation, manipulation)\n\n### 1. Python environments\n\n- handles issues with dependencies versions\n- ensures reproducibility\n- does not clutter users' global site-packages directory\n\n`python3 -m venv venv/ # Creates an environment called venv/`\n`source venv/bin/activate`\n`pip install biopython`\n`pip freeze > requirements.txt`\n`(venv) % deactivate`\n\nOn a different machine, the environment can be replicated by creating a new environment and running\n\n`pip install -r requirements.txt`\n\n### 2. Biopython\n\nBiopython is a library consisting of tools for both sequence and structure bioinformatics. Among other things it enables parsing, handling and storing molecular data present in common formats such as FASTA, PDB or mmCIF.\n\nInstall biopython using `pip install biopython`\n\nFunctionality divided into packages list of which is available in the [docs](https://biopython.org/docs/1.75/api/Bio.html). \n\nMain sequence and structure packages:\n - [Bio.Seq](https://biopython.org/docs/latest/api/Bio.Seq.html)\n - [Bio.Align](https://biopython.org/docs/latest/api/Bio.Align.html) \n - [Bio.SeqIO](https://biopython.org/docs/latest/api/Bio.SeqIO.html)\n - [Bio.PDB](https://biopython.org/docs/latest/api/Bio.PDB.html) \n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
" \n#### Sequences \n \n Loading a sequence from a string: ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from Bio.Seq import Seq\nseq = Seq(\"AGTACACTG\")\nprint(seq)",
"AGTACACTG\n"
]
],
[
[
"This creates a [sequence object](https://biopython.org/docs/latest/api/Bio.Seq.html) with a couple of fancy methods, especially when it comes to nuclotide sequences such as `reverse_complement` or `translate`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(seq.translate())\nprint(seq.reverse_complement().transcribe())\nprint(seq.reverse_complement().transcribe().translate())",
"STL\nCAGUGUACU\nQCT\n"
],
[
"coding_dna = Seq(\"ATGGCCATTGTAATGGGCCGCTGAAAGGGTGCCCGATAG\")\nprint(coding_dna.translate())\nprint(coding_dna.translate(to_stop=True))\nprint(coding_dna.translate(table=2))\nprint(coding_dna.translate(table=2, to_stop=True))",
"MAIVMGR*KGAR*\nMAIVMGR\nMAIVMGRWKGAR*\nMAIVMGRWKGAR\n"
]
],
[
[
"Notice, in the example above we used different genetic tables. Check [NCBI genetic codes](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Utils/wprintgc.cgi) for details.\n\nTo list all the methods, run, e.g., one of the following:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(dir(seq))\nprint(help(seq))",
"['__abstractmethods__', '__add__', '__bytes__', '__class__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__dict__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__imul__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__module__', '__mul__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__radd__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__rmul__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__slots__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', '__weakref__', '_abc_impl', '_data', 'back_transcribe', 'complement', 'complement_rna', 'count', 'count_overlap', 'encode', 'endswith', 'find', 'index', 'join', 'lower', 'lstrip', 'replace', 'reverse_complement', 'reverse_complement_rna', 'rfind', 'rindex', 'rsplit', 'rstrip', 'split', 'startswith', 'strip', 'tomutable', 'transcribe', 'translate', 'ungap', 'upper']\nb'AGTACACTG'\n"
]
],
[
[
"Methods for accessing by position are available as well.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(seq[3])\nprint(seq[3:5])\nprint(seq[::-1])",
"A\nAC\nGTCACATGA\n"
]
],
[
[
"If needed, the Seq object can be converted into a string.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(str(seq))\nprint(str(seq).translate({65: 88}))",
"AGTACACTG\nXGTXCXCTG\n"
]
],
[
[
"To parse sequence from a file, you can use [Bio.SeqIO](https://biopython.org/docs/latest/api/Bio.SeqIO.html). [Here](https://biopython.org/wiki/SeqIO#file-formats) is the list of supported formats. The format name is passed into the `parse` method.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from Bio import SeqIO\n\nsars2_it = SeqIO.parse(\"R1A-B_SARS2.fasta\", \"fasta\")\nfor seq_record in sars2_it: \n print(seq_record.id)\n print(repr(seq_record.seq))\n print(len(seq_record))\nsars2_seq_recs = list(sars2_it)",
"sp|P0DTD1|R1AB_SARS2\nSeq('MESLVPGFNEKTHVQLSLPVLQVRDVLVRGFGDSVEEVLSEARQHLKDGTCGLV...VNN')\n7096\nsp|P0DTC1|R1A_SARS2\nSeq('MESLVPGFNEKTHVQLSLPVLQVRDVLVRGFGDSVEEVLSEARQHLKDGTCGLV...FAV')\n4405\n"
]
],
[
[
"The result is an iterator of [SeqRecord](https://biopython.org/docs/latest/api/Bio.SeqRecord.html)s. Other attributes of `SeqRecord` such as features or annotations are more relevant for other formats, such as genbank. The underlying gene for the two isoforms (R1A_SARS2/P0DTC1 and R1AB_SARS2/P0DTD1) is ORF1ab and the two isoforms are caused by ribosomal slippage during translation (see, e.g., [here](https://www.science.org/doi/full/10.1126/science.abf3546)). Both reading frames R1A_SARS2 and R1AB_SARS2 are polyproteins and are encoded by the same [gene](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/43740578). Let's explore this.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"gb_rec = list(SeqIO.parse(\"NC_045512.gb\", \"genbank\"))[0]\nprint(gb_rec.)",
"NC_045512.2\n"
],
[
"print(gb_rec.annotations)\nprint(gb_rec.features)",
"{'molecule_type': 'ss-RNA', 'topology': 'linear', 'data_file_division': 'VRL', 'date': '18-JUL-2020', 'accessions': ['NC_045512'], 'sequence_version': 2, 'keywords': ['RefSeq'], 'source': 'Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)', 'organism': 'Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2', 'taxonomy': ['Viruses', 'Riboviria', 'Orthornavirae', 'Pisuviricota', 'Pisoniviricetes', 'Nidovirales', 'Cornidovirineae', 'Coronaviridae', 'Orthocoronavirinae', 'Betacoronavirus', 'Sarbecovirus'], 'references': [Reference(title='A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China', ...), Reference(title='Programmed ribosomal frameshifting in decoding the SARS-CoV genome', ...), Reference(title='The structure of a rigorously conserved RNA element within the SARS virus genome', ...), Reference(title=\"A phylogenetically conserved hairpin-type 3' untranslated region pseudoknot functions in coronavirus RNA replication\", ...), Reference(title='Direct Submission', ...), Reference(title='Direct Submission', ...)], 'comment': \"REVIEWED REFSEQ: This record has been curated by NCBI staff. The\\nreference sequence is identical to MN908947.\\nOn Jan 17, 2020 this sequence version replaced NC_045512.1.\\nAnnotation was added using homology to SARSr-CoV NC_004718.3. ###\\nFormerly called 'Wuhan seafood market pneumonia virus.' If you have\\nquestions or suggestions, please email us at [email protected]\\nand include the accession number NC_045512.### Protein structures\\ncan be found at\\nhttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/structure/?term=sars-cov-2.### Find\\nall other Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2\\n(SARS-CoV-2) sequences at\\nhttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/sars-cov-2-seqs/\\nCOMPLETENESS: full length.\", 'structured_comment': OrderedDict([('Assembly-Data', OrderedDict([('Assembly Method', 'Megahit v. V1.1.3'), ('Sequencing Technology', 'Illumina')]))])}\n[SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(0), ExactPosition(29903), strand=1), type='source'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(0), ExactPosition(265), strand=1), type=\"5'UTR\"), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(265), ExactPosition(21555), strand=1), type='gene'), SeqFeature(CompoundLocation([FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(265), ExactPosition(13468), strand=1), FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(13467), ExactPosition(21555), strand=1)], 'join'), type='CDS', location_operator='join'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(265), ExactPosition(805), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(805), ExactPosition(2719), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(2719), ExactPosition(8554), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(8554), ExactPosition(10054), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(10054), ExactPosition(10972), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(10972), ExactPosition(11842), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(11842), ExactPosition(12091), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(12091), ExactPosition(12685), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(12685), ExactPosition(13024), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(13024), ExactPosition(13441), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(CompoundLocation([FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(13441), ExactPosition(13468), strand=1), FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(13467), ExactPosition(16236), strand=1)], 'join'), type='mat_peptide', location_operator='join'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(16236), ExactPosition(18039), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(18039), ExactPosition(19620), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(19620), ExactPosition(20658), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(20658), ExactPosition(21552), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(265), ExactPosition(13483), strand=1), type='CDS'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(265), ExactPosition(805), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(805), ExactPosition(2719), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(2719), ExactPosition(8554), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(8554), ExactPosition(10054), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(10054), ExactPosition(10972), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(10972), ExactPosition(11842), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(11842), ExactPosition(12091), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(12091), ExactPosition(12685), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(12685), ExactPosition(13024), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(13024), ExactPosition(13441), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(13441), ExactPosition(13480), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(13475), ExactPosition(13503), strand=1), type='stem_loop'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(13487), ExactPosition(13542), strand=1), type='stem_loop'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(21562), ExactPosition(25384), strand=1), type='gene'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(21562), ExactPosition(25384), strand=1), type='CDS'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(25392), ExactPosition(26220), strand=1), type='gene'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(25392), ExactPosition(26220), strand=1), type='CDS'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(26244), ExactPosition(26472), strand=1), type='gene'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(26244), ExactPosition(26472), strand=1), type='CDS'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(26522), ExactPosition(27191), strand=1), type='gene'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(26522), ExactPosition(27191), strand=1), type='CDS'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(27201), ExactPosition(27387), strand=1), type='gene'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(27201), ExactPosition(27387), strand=1), type='CDS'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(27393), ExactPosition(27759), strand=1), type='gene'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(27393), ExactPosition(27759), strand=1), type='CDS'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(27755), ExactPosition(27887), strand=1), type='gene'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(27755), ExactPosition(27887), strand=1), type='CDS'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(27893), ExactPosition(28259), strand=1), type='gene'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(27893), ExactPosition(28259), strand=1), type='CDS'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(28273), ExactPosition(29533), strand=1), type='gene'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(28273), ExactPosition(29533), strand=1), type='CDS'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(29557), ExactPosition(29674), strand=1), type='gene'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(29557), ExactPosition(29674), strand=1), type='CDS'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(29608), ExactPosition(29644), strand=1), type='stem_loop'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(29628), ExactPosition(29657), strand=1), type='stem_loop'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(29674), ExactPosition(29903), strand=1), type=\"3'UTR\"), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(29727), ExactPosition(29768), strand=1), type='stem_loop')]\n"
],
[
"gb_rec.features",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's obtain all CDS (coding sequence) features.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(gb_rec.features)\ncds = [seq_feature for seq_feature in gb_rec.features if seq_feature.type == 'CDS']",
"[SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(0), ExactPosition(29903), strand=1), type='source'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(0), ExactPosition(265), strand=1), type=\"5'UTR\"), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(265), ExactPosition(21555), strand=1), type='gene'), SeqFeature(CompoundLocation([FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(265), ExactPosition(13468), strand=1), FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(13467), ExactPosition(21555), strand=1)], 'join'), type='CDS', location_operator='join'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(265), ExactPosition(805), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(805), ExactPosition(2719), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(2719), ExactPosition(8554), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(8554), ExactPosition(10054), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(10054), ExactPosition(10972), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(10972), ExactPosition(11842), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(11842), ExactPosition(12091), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(12091), ExactPosition(12685), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(12685), ExactPosition(13024), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(13024), ExactPosition(13441), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(CompoundLocation([FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(13441), ExactPosition(13468), strand=1), FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(13467), ExactPosition(16236), strand=1)], 'join'), type='mat_peptide', location_operator='join'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(16236), ExactPosition(18039), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(18039), ExactPosition(19620), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(19620), ExactPosition(20658), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(20658), ExactPosition(21552), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(265), ExactPosition(13483), strand=1), type='CDS'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(265), ExactPosition(805), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(805), ExactPosition(2719), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(2719), ExactPosition(8554), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(8554), ExactPosition(10054), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(10054), ExactPosition(10972), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(10972), ExactPosition(11842), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(11842), ExactPosition(12091), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(12091), ExactPosition(12685), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(12685), ExactPosition(13024), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(13024), ExactPosition(13441), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(13441), ExactPosition(13480), strand=1), type='mat_peptide'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(13475), ExactPosition(13503), strand=1), type='stem_loop'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(13487), ExactPosition(13542), strand=1), type='stem_loop'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(21562), ExactPosition(25384), strand=1), type='gene'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(21562), ExactPosition(25384), strand=1), type='CDS'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(25392), ExactPosition(26220), strand=1), type='gene'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(25392), ExactPosition(26220), strand=1), type='CDS'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(26244), ExactPosition(26472), strand=1), type='gene'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(26244), ExactPosition(26472), strand=1), type='CDS'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(26522), ExactPosition(27191), strand=1), type='gene'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(26522), ExactPosition(27191), strand=1), type='CDS'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(27201), ExactPosition(27387), strand=1), type='gene'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(27201), ExactPosition(27387), strand=1), type='CDS'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(27393), ExactPosition(27759), strand=1), type='gene'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(27393), ExactPosition(27759), strand=1), type='CDS'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(27755), ExactPosition(27887), strand=1), type='gene'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(27755), ExactPosition(27887), strand=1), type='CDS'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(27893), ExactPosition(28259), strand=1), type='gene'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(27893), ExactPosition(28259), strand=1), type='CDS'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(28273), ExactPosition(29533), strand=1), type='gene'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(28273), ExactPosition(29533), strand=1), type='CDS'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(29557), ExactPosition(29674), strand=1), type='gene'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(29557), ExactPosition(29674), strand=1), type='CDS'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(29608), ExactPosition(29644), strand=1), type='stem_loop'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(29628), ExactPosition(29657), strand=1), type='stem_loop'), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(29674), ExactPosition(29903), strand=1), type=\"3'UTR\"), SeqFeature(FeatureLocation(ExactPosition(29727), ExactPosition(29768), strand=1), type='stem_loop')]\n"
],
[
"cds[0].extract(gb_rec.seq).translate()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now, let's get the DNA sequence for the the polyprotein 1ab.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"aa_seq = cds[0].extract(gb_rec.seq).translate()\nprint(aa_seq[-10:])\nprint(gb_rec.seq.translate()[-10:])",
"ISSDVLVNN*\nKKKKKKKKKK\n"
]
],
[
[
"To write a sequence into a file, use `SeqIO.write`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"SeqIO.write([gb_rec, SeqIO.SeqRecord(aa_seq, id=\"id\", description=\"aa\")], \"fasta_from_gb.fasta\", \"fasta\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now, carry out the following tasks by yourselfs:\n- Obtain the protein sequnece for polyprotein 1ab and check with UniProt that it matches (just by eyeballing).\n- Obtain the protein sequence for the polyprotien 1a.\n- Obtain protein sequences for all the proteins and list them together with their names\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(cds[1].extract(gb_rec.seq).translate())",
"MESLVPGFNEKTHVQLSLPVLQVRDVLVRGFGDSVEEVLSEARQHLKDGTCGLVEVEKGVLPQLEQPYVFIKRSDARTAPHGHVMVELVAELEGIQYGRSGETLGVLVPHVGEIPVAYRKVLLRKNGNKGAGGHSYGADLKSFDLGDELGTDPYEDFQENWNTKHSSGVTRELMRELNGGAYTRYVDNNFCGPDGYPLECIKDLLARAGKASCTLSEQLDFIDTKRGVYCCREHEHEIAWYTERSEKSYELQTPFEIKLAKKFDTFNGECPNFVFPLNSIIKTIQPRVEKKKLDGFMGRIRSVYPVASPNECNQMCLSTLMKCDHCGETSWQTGDFVKATCEFCGTENLTKEGATTCGYLPQNAVVKIYCPACHNSEVGPEHSLAEYHNESGLKTILRKGGRTIAFGGCVFSYVGCHNKCAYWVPRASANIGCNHTGVVGEGSEGLNDNLLEILQKEKVNINIVGDFKLNEEIAIILASFSASTSAFVETVKGLDYKAFKQIVESCGNFKVTKGKAKKGAWNIGEQKSILSPLYAFASEAARVVRSIFSRTLETAQNSVRVLQKAAITILDGISQYSLRLIDAMMFTSDLATNNLVVMAYITGGVVQLTSQWLTNIFGTVYEKLKPVLDWLEEKFKEGVEFLRDGWEIVKFISTCACEIVGGQIVTCAKEIKESVQTFFKLVNKFLALCADSIIIGGAKLKALNLGETFVTHSKGLYRKCVKSREETGLLMPLKAPKEIIFLEGETLPTEVLTEEVVLKTGDLQPLEQPTSEAVEAPLVGTPVCINGLMLLEIKDTEKYCALAPNMMVTNNTFTLKGGAPTKVTFGDDTVIEVQGYKSVNITFELDERIDKVLNEKCSAYTVELGTEVNEFACVVADAVIKTLQPVSELLTPLGIDLDEWSMATYYLFDESGEFKLASHMYCSFYPPDEDEEEGDCEEEEFEPSTQYEYGTEDDYQGKPLEFGATSAALQPEEEQEEDWLDDDSQQTVGQQDGSEDNQTTTIQTIVEVQPQLEMELTPVVQTIEVNSFSGYLKLTDNVYIKNADIVEEAKKVKPTVVVNAANVYLKHGGGVAGALNKATNNAMQVESDDYIATNGPLKVGGSCVLSGHNLAKHCLHVVGPNVNKGEDIQLLKSAYENFNQHEVLLAPLLSAGIFGADPIHSLRVCVDTVRTNVYLAVFDKNLYDKLVSSFLEMKSEKQVEQKIAEIPKEEVKPFITESKPSVEQRKQDDKKIKACVEEVTTTLEETKFLTENLLLYIDINGNLHPDSATLVSDIDITFLKKDAPYIVGDVVQEGVLTAVVIPTKKAGGTTEMLAKALRKVPTDNYITTYPGQGLNGYTVEEAKTVLKKCKSAFYILPSIISNEKQEILGTVSWNLREMLAHAEETRKLMPVCVETKAIVSTIQRKYKGIKIQEGVVDYGARFYFYTSKTTVASLINTLNDLNETLVTMPLGYVTHGLNLEEAARYMRSLKVPATVSVSSPDAVTAYNGYLTSSSKTPEEHFIETISLAGSYKDWSYSGQSTQLGIEFLKRGDKSVYYTSNPTTFHLDGEVITFDNLKTLLSLREVRTIKVFTTVDNINLHTQVVDMSMTYGQQFGPTYLDGADVTKIKPHNSHEGKTFYVLPNDDTLRVEAFEYYHTTDPSFLGRYMSALNHTKKWKYPQVNGLTSIKWADNNCYLATALLTLQQIELKFNPPALQDAYYRARAGEAANFCALILAYCNKTVGELGDVRETMSYLFQHANLDSCKRVLNVVCKTCGQQQTTLKGVEAVMYMGTLSYEQFKKGVQIPCTCGKQATKYLVQQESPFVMMSAPPAQYELKHGTFTCASEYTGNYQCGHYKHITSKETLYCIDGALLTKSSEYKGPITDVFYKENSYTTTIKPVTYKLDGVVCTEIDPKLDNYYKKDNSYFTEQPIDLVPNQPYPNASFDNFKFVCDNIKFADDLNQLTGYKKPASRELKVTFFPDLNGDVVAIDYKHYTPSFKKGAKLLHKPIVWHVNNATNKATYKPNTWCIRCLWSTKPVETSNSFDVLKSEDAQGMDNLACEDLKPVSEEVVENPTIQKDVLECNVKTTEVVGDIILKPANNSLKITEEVGHTDLMAAYVDNSSLTIKKPNELSRVLGLKTLATHGLAAVNSVPWDTIANYAKPFLNKVVSTTTNIVTRCLNRVCTNYMPYFFTLLLQLCTFTRSTNSRIKASMPTTIAKNTVKSVGKFCLEASFNYLKSPNFSKLINIIIWFLLLSVCLGSLIYSTAALGVLMSNLGMPSYCTGYREGYLNSTNVTIATYCTGSIPCSVCLSGLDSLDTYPSLETIQITISSFKWDLTAFGLVAEWFLAYILFTRFFYVLGLAAIMQLFFSYFAVHFISNSWLMWLIINLVQMAPISAMVRMYIFFASFYYVWKSYVHVVDGCNSSTCMMCYKRNRATRVECTTIVNGVRRSFYVYANGGKGFCKLHNWNCVNCDTFCAGSTFISDEVARDLSLQFKRPINPTDQSSYIVDSVTVKNGSIHLYFDKAGQKTYERHSLSHFVNLDNLRANNTKGSLPINVIVFDGKSKCEESSAKSASVYYSQLMCQPILLLDQALVSDVGDSAEVAVKMFDAYVNTFSSTFNVPMEKLKTLVATAEAELAKNVSLDNVLSTFISAARQGFVDSDVETKDVVECLKLSHQSDIEVTGDSCNNYMLTYNKVENMTPRDLGACIDCSARHINAQVAKSHNIALIWNVKDFMSLSEQLRKQIRSAAKKNNLPFKLTCATTRQVVNVVTTKIALKGGKIVNNWLKQLIKVTLVFLFVAAIFYLITPVHVMSKHTDFSSEIIGYKAIDGGVTRDIASTDTCFANKHADFDTWFSQRGGSYTNDKACPLIAAVITREVGFVVPGLPGTILRTTNGDFLHFLPRVFSAVGNICYTPSKLIEYTDFATSACVLAAECTIFKDASGKPVPYCYDTNVLEGSVAYESLRPDTRYVLMDGSIIQFPNTYLEGSVRVVTTFDSEYCRHGTCERSEAGVCVSTSGRWVLNNDYYRSLPGVFCGVDAVNLLTNMFTPLIQPIGALDISASIVAGGIVAIVVTCLAYYFMRFRRAFGEYSHVVAFNTLLFLMSFTVLCLTPVYSFLPGVYSVIYLYLTFYLTNDVSFLAHIQWMVMFTPLVPFWITIAYIICISTKHFYWFFSNYLKRRVVFNGVSFSTFEEAALCTFLLNKEMYLKLRSDVLLPLTQYNRYLALYNKYKYFSGAMDTTSYREAACCHLAKALNDFSNSGSDVLYQPPQTSITSAVLQSGFRKMAFPSGKVEGCMVQVTCGTTTLNGLWLDDVVYCPRHVICTSEDMLNPNYEDLLIRKSNHNFLVQAGNVQLRVIGHSMQNCVLKLKVDTANPKTPKYKFVRIQPGQTFSVLACYNGSPSGVYQCAMRPNFTIKGSFLNGSCGSVGFNIDYDCVSFCYMHHMELPTGVHAGTDLEGNFYGPFVDRQTAQAAGTDTTITVNVLAWLYAAVINGDRWFLNRFTTTLNDFNLVAMKYNYEPLTQDHVDILGPLSAQTGIAVLDMCASLKELLQNGMNGRTILGSALLEDEFTPFDVVRQCSGVTFQSAVKRTIKGTHHWLLLTILTSLLVLVQSTQWSLFFFLYENAFLPFAMGIIAMSAFAMMFVKHKHAFLCLFLLPSLATVAYFNMVYMPASWVMRIMTWLDMVDTSLSGFKLKDCVMYASAVVLLILMTARTVYDDGARRVWTLMNVLTLVYKVYYGNALDQAISMWALIISVTSNYSGVVTTVMFLARGIVFMCVEYCPIFFITGNTLQCIMLVYCFLGYFCTCYFGLFCLLNRYFRLTLGVYDYLVSTQEFRYMNSQGLLPPKNSIDAFKLNIKLLGVGGKPCIKVATVQSKMSDVKCTSVVLLSVLQQLRVESSSKLWAQCVQLHNDILLAKDTTEAFEKMVSLLSVLLSMQGAVDINKLCEEMLDNRATLQAIASEFSSLPSYAAFATAQEAYEQAVANGDSEVVLKKLKKSLNVAKSEFDRDAAMQRKLEKMADQAMTQMYKQARSEDKRAKVTSAMQTMLFTMLRKLDNDALNNIINNARDGCVPLNIIPLTTAAKLMVVIPDYNTYKNTCDGTTFTYASALWEIQQVVDADSKIVQLSEISMDNSPNLAWPLIVTALRANSAVKLQNNELSPVALRQMSCAAGTTQTACTDDNALAYYNTTKGGRFVLALLSDLQDLKWARFPKSDGTGTIYTELEPPCRFVTDTPKGPKVKYLYFIKGLNNLNRGMVLGSLAATVRLQAGNATEVPANSTVLSFCAFAVDAAKAYKDYLASGGQPITNCVKMLCTHTGTGQAITVTPEANMDQESFGGASCCLYCRCHIDHPNPKGFCDLKGKYVQIPTTCANDPVGFTLKNTVCTVCGMWKGYGCSCDQLREPMLQSADAQSFLNGFAV*\n"
],
[
"#print(cds[1].extract(gb_rec.seq).translate())\n\npeptides = [print(\"{}: {}\".format(ft.qualifiers['protein_id'], ft.extract(gb_rec.seq).translate())) for ft in gb_rec.features if ft.type == 'mat_peptide']\n",
"['YP_009725297.1']: MESLVPGFNEKTHVQLSLPVLQVRDVLVRGFGDSVEEVLSEARQHLKDGTCGLVEVEKGVLPQLEQPYVFIKRSDARTAPHGHVMVELVAELEGIQYGRSGETLGVLVPHVGEIPVAYRKVLLRKNGNKGAGGHSYGADLKSFDLGDELGTDPYEDFQENWNTKHSSGVTRELMRELNGG\n['YP_009725298.1']: AYTRYVDNNFCGPDGYPLECIKDLLARAGKASCTLSEQLDFIDTKRGVYCCREHEHEIAWYTERSEKSYELQTPFEIKLAKKFDTFNGECPNFVFPLNSIIKTIQPRVEKKKLDGFMGRIRSVYPVASPNECNQMCLSTLMKCDHCGETSWQTGDFVKATCEFCGTENLTKEGATTCGYLPQNAVVKIYCPACHNSEVGPEHSLAEYHNESGLKTILRKGGRTIAFGGCVFSYVGCHNKCAYWVPRASANIGCNHTGVVGEGSEGLNDNLLEILQKEKVNINIVGDFKLNEEIAIILASFSASTSAFVETVKGLDYKAFKQIVESCGNFKVTKGKAKKGAWNIGEQKSILSPLYAFASEAARVVRSIFSRTLETAQNSVRVLQKAAITILDGISQYSLRLIDAMMFTSDLATNNLVVMAYITGGVVQLTSQWLTNIFGTVYEKLKPVLDWLEEKFKEGVEFLRDGWEIVKFISTCACEIVGGQIVTCAKEIKESVQTFFKLVNKFLALCADSIIIGGAKLKALNLGETFVTHSKGLYRKCVKSREETGLLMPLKAPKEIIFLEGETLPTEVLTEEVVLKTGDLQPLEQPTSEAVEAPLVGTPVCINGLMLLEIKDTEKYCALAPNMMVTNNTFTLKGG\n['YP_009725299.1']: APTKVTFGDDTVIEVQGYKSVNITFELDERIDKVLNEKCSAYTVELGTEVNEFACVVADAVIKTLQPVSELLTPLGIDLDEWSMATYYLFDESGEFKLASHMYCSFYPPDEDEEEGDCEEEEFEPSTQYEYGTEDDYQGKPLEFGATSAALQPEEEQEEDWLDDDSQQTVGQQDGSEDNQTTTIQTIVEVQPQLEMELTPVVQTIEVNSFSGYLKLTDNVYIKNADIVEEAKKVKPTVVVNAANVYLKHGGGVAGALNKATNNAMQVESDDYIATNGPLKVGGSCVLSGHNLAKHCLHVVGPNVNKGEDIQLLKSAYENFNQHEVLLAPLLSAGIFGADPIHSLRVCVDTVRTNVYLAVFDKNLYDKLVSSFLEMKSEKQVEQKIAEIPKEEVKPFITESKPSVEQRKQDDKKIKACVEEVTTTLEETKFLTENLLLYIDINGNLHPDSATLVSDIDITFLKKDAPYIVGDVVQEGVLTAVVIPTKKAGGTTEMLAKALRKVPTDNYITTYPGQGLNGYTVEEAKTVLKKCKSAFYILPSIISNEKQEILGTVSWNLREMLAHAEETRKLMPVCVETKAIVSTIQRKYKGIKIQEGVVDYGARFYFYTSKTTVASLINTLNDLNETLVTMPLGYVTHGLNLEEAARYMRSLKVPATVSVSSPDAVTAYNGYLTSSSKTPEEHFIETISLAGSYKDWSYSGQSTQLGIEFLKRGDKSVYYTSNPTTFHLDGEVITFDNLKTLLSLREVRTIKVFTTVDNINLHTQVVDMSMTYGQQFGPTYLDGADVTKIKPHNSHEGKTFYVLPNDDTLRVEAFEYYHTTDPSFLGRYMSALNHTKKWKYPQVNGLTSIKWADNNCYLATALLTLQQIELKFNPPALQDAYYRARAGEAANFCALILAYCNKTVGELGDVRETMSYLFQHANLDSCKRVLNVVCKTCGQQQTTLKGVEAVMYMGTLSYEQFKKGVQIPCTCGKQATKYLVQQESPFVMMSAPPAQYELKHGTFTCASEYTGNYQCGHYKHITSKETLYCIDGALLTKSSEYKGPITDVFYKENSYTTTIKPVTYKLDGVVCTEIDPKLDNYYKKDNSYFTEQPIDLVPNQPYPNASFDNFKFVCDNIKFADDLNQLTGYKKPASRELKVTFFPDLNGDVVAIDYKHYTPSFKKGAKLLHKPIVWHVNNATNKATYKPNTWCIRCLWSTKPVETSNSFDVLKSEDAQGMDNLACEDLKPVSEEVVENPTIQKDVLECNVKTTEVVGDIILKPANNSLKITEEVGHTDLMAAYVDNSSLTIKKPNELSRVLGLKTLATHGLAAVNSVPWDTIANYAKPFLNKVVSTTTNIVTRCLNRVCTNYMPYFFTLLLQLCTFTRSTNSRIKASMPTTIAKNTVKSVGKFCLEASFNYLKSPNFSKLINIIIWFLLLSVCLGSLIYSTAALGVLMSNLGMPSYCTGYREGYLNSTNVTIATYCTGSIPCSVCLSGLDSLDTYPSLETIQITISSFKWDLTAFGLVAEWFLAYILFTRFFYVLGLAAIMQLFFSYFAVHFISNSWLMWLIINLVQMAPISAMVRMYIFFASFYYVWKSYVHVVDGCNSSTCMMCYKRNRATRVECTTIVNGVRRSFYVYANGGKGFCKLHNWNCVNCDTFCAGSTFISDEVARDLSLQFKRPINPTDQSSYIVDSVTVKNGSIHLYFDKAGQKTYERHSLSHFVNLDNLRANNTKGSLPINVIVFDGKSKCEESSAKSASVYYSQLMCQPILLLDQALVSDVGDSAEVAVKMFDAYVNTFSSTFNVPMEKLKTLVATAEAELAKNVSLDNVLSTFISAARQGFVDSDVETKDVVECLKLSHQSDIEVTGDSCNNYMLTYNKVENMTPRDLGACIDCSARHINAQVAKSHNIALIWNVKDFMSLSEQLRKQIRSAAKKNNLPFKLTCATTRQVVNVVTTKIALKGG\n['YP_009725300.1']: KIVNNWLKQLIKVTLVFLFVAAIFYLITPVHVMSKHTDFSSEIIGYKAIDGGVTRDIASTDTCFANKHADFDTWFSQRGGSYTNDKACPLIAAVITREVGFVVPGLPGTILRTTNGDFLHFLPRVFSAVGNICYTPSKLIEYTDFATSACVLAAECTIFKDASGKPVPYCYDTNVLEGSVAYESLRPDTRYVLMDGSIIQFPNTYLEGSVRVVTTFDSEYCRHGTCERSEAGVCVSTSGRWVLNNDYYRSLPGVFCGVDAVNLLTNMFTPLIQPIGALDISASIVAGGIVAIVVTCLAYYFMRFRRAFGEYSHVVAFNTLLFLMSFTVLCLTPVYSFLPGVYSVIYLYLTFYLTNDVSFLAHIQWMVMFTPLVPFWITIAYIICISTKHFYWFFSNYLKRRVVFNGVSFSTFEEAALCTFLLNKEMYLKLRSDVLLPLTQYNRYLALYNKYKYFSGAMDTTSYREAACCHLAKALNDFSNSGSDVLYQPPQTSITSAVLQ\n['YP_009725301.1']: SGFRKMAFPSGKVEGCMVQVTCGTTTLNGLWLDDVVYCPRHVICTSEDMLNPNYEDLLIRKSNHNFLVQAGNVQLRVIGHSMQNCVLKLKVDTANPKTPKYKFVRIQPGQTFSVLACYNGSPSGVYQCAMRPNFTIKGSFLNGSCGSVGFNIDYDCVSFCYMHHMELPTGVHAGTDLEGNFYGPFVDRQTAQAAGTDTTITVNVLAWLYAAVINGDRWFLNRFTTTLNDFNLVAMKYNYEPLTQDHVDILGPLSAQTGIAVLDMCASLKELLQNGMNGRTILGSALLEDEFTPFDVVRQCSGVTFQ\n['YP_009725302.1']: SAVKRTIKGTHHWLLLTILTSLLVLVQSTQWSLFFFLYENAFLPFAMGIIAMSAFAMMFVKHKHAFLCLFLLPSLATVAYFNMVYMPASWVMRIMTWLDMVDTSLSGFKLKDCVMYASAVVLLILMTARTVYDDGARRVWTLMNVLTLVYKVYYGNALDQAISMWALIISVTSNYSGVVTTVMFLARGIVFMCVEYCPIFFITGNTLQCIMLVYCFLGYFCTCYFGLFCLLNRYFRLTLGVYDYLVSTQEFRYMNSQGLLPPKNSIDAFKLNIKLLGVGGKPCIKVATVQ\n['YP_009725303.1']: SKMSDVKCTSVVLLSVLQQLRVESSSKLWAQCVQLHNDILLAKDTTEAFEKMVSLLSVLLSMQGAVDINKLCEEMLDNRATLQ\n['YP_009725304.1']: AIASEFSSLPSYAAFATAQEAYEQAVANGDSEVVLKKLKKSLNVAKSEFDRDAAMQRKLEKMADQAMTQMYKQARSEDKRAKVTSAMQTMLFTMLRKLDNDALNNIINNARDGCVPLNIIPLTTAAKLMVVIPDYNTYKNTCDGTTFTYASALWEIQQVVDADSKIVQLSEISMDNSPNLAWPLIVTALRANSAVKLQ\n['YP_009725305.1']: NNELSPVALRQMSCAAGTTQTACTDDNALAYYNTTKGGRFVLALLSDLQDLKWARFPKSDGTGTIYTELEPPCRFVTDTPKGPKVKYLYFIKGLNNLNRGMVLGSLAATVRLQ\n['YP_009725306.1']: AGNATEVPANSTVLSFCAFAVDAAKAYKDYLASGGQPITNCVKMLCTHTGTGQAITVTPEANMDQESFGGASCCLYCRCHIDHPNPKGFCDLKGKYVQIPTTCANDPVGFTLKNTVCTVCGMWKGYGCSCDQLREPMLQ\n['YP_009725307.1']: SADAQSFLNRVCGVSAARLTPCGTGTSTDVVYRAFDIYNDKVAGFAKFLKTNCCRFQEKDEDDNLIDSYFVVKRHTFSNYQHEETIYNLLKDCPAVAKHDFFKFRIDGDMVPHISRQRLTKYTMADLVYALRHFDEGNCDTLKEILVTYNCCDDDYFNKKDWYDFVENPDILRVYANLGERVRQALLKTVQFCDAMRNAGIVGVLTLDNQDLNGNWYDFGDFIQTTPGSGVPVVDSYYSLLMPILTLTRALTAESHVDTDLTKPYIKWDLLKYDFTEERLKLFDRYFKYWDQTYHPNCVNCLDDRCILHCANFNVLFSTVFPPTSFGPLVRKIFVDGVPFVVSTGYHFRELGVVHNQDVNLHSSRLSFKELLVYAADPAMHAASGNLLLDKRTTCFSVAALTNNVAFQTVKPGNFNKDFYDFAVSKGFFKEGSSVELKHFFFAQDGNAAISDYDYYRYNLPTMCDIRQLLFVVEVVDKYFDCYDGGCINANQVIVNNLDKSAGFPFNKWGKARLYYDSMSYEDQDALFAYTKRNVIPTITQMNLKYAISAKNRARTVAGVSICSTMTNRQFHQKLLKSIAATRGATVVIGTSKFYGGWHNMLKTVYSDVENPHLMGWDYPKCDRAMPNMLRIMASLVLARKHTTCCSLSHRFYRLANECAQVLSEMVMCGGSLYVKPGGTSSGDATTAYANSVFNICQAVTANVNALLSTDGNKIADKYVRNLQHRLYECLYRNRDVDTDFVNEFYAYLRKHFSMMILSDDAVVCFNSTYASQGLVASIKNFKSVLYYQNNVFMSEAKCWTETDLTKGPHEFCSQHTMLVKQGDDYVYLPYPDPSRILGAGCFVDDIVKTDGTLMIERFVSLAIDAYPLTKHPNQEYADVFHLYLQYIRKLHDELTGHMLDMYSVMLTNDNTSRYWEPEFYEAMYTPHTVLQ\n['YP_009725308.1']: AVGACVLCNSQTSLRCGACIRRPFLCCKCCYDHVISTSHKLVLSVNPYVCNAPGCDVTDVTQLYLGGMSYYCKSHKPPISFPLCANGQVFGLYKNTCVGSDNVTDFNAIATCDWTNAGDYILANTCTERLKLFAAETLKATEETFKLSYGIATVREVLSDRELHLSWEVGKPRPPLNRNYVFTGYRVTKNSKVQIGEYTFEKGDYGDAVVYRGTTTYKLNVGDYFVLTSHTVMPLSAPTLVPQEHYVRITGLYPTLNISDEFSSNVANYQKVGMQKYSTLQGPPGTGKSHFAIGLALYYPSARIVYTACSHAAVDALCEKALKYLPIDKCSRIIPARARVECFDKFKVNSTLEQYVFCTVNALPETTADIVVFDEISMATNYDLSVVNARLRAKHYVYIGDPAQLPAPRTLLTKGTLEPEYFNSVCRLMKTIGPDMFLGTCRRCPAEIVDTVSALVYDNKLKAHKDKSAQCFKMFYKGVITHDVSSAINRPQIGVVREFLTRNPAWRKAVFISPYNSQNAVASKILGLPTQTVDSSQGSEYDYVIFTQTTETAHSCNVNRFNVAITRAKVGILCIMSDRDLYDKLQFTSLEIPRRNVATLQ\n['YP_009725309.1']: AENVTGLFKDCSKVITGLHPTQAPTHLSVDTKFKTEGLCVDIPGIPKDMTYRRLISMMGFKMNYQVNGYPNMFITREEAIRHVRAWIGFDVEGCHATREAVGTNLPLQLGFSTGVNLVAVPTGYVDTPNNTDFSRVSAKPPPGDQFKHLIPLMYKGLPWNVVRIKIVQMLSDTLKNLSDRVVFVLWAHGFELTSMKYFVKIGPERTCCLCDRRATCFSTASDTYACWHHSIGFDYVYNPFMIDVQQWGFTGNLQSNHDLYCQVHGNAHVASCDAIMTRCLAVHECFVKRVDWTIEYPIIGDELKINAACRKVQHMVVKAALLADKFPVLHDIGNPKAIKCVPQADVEWKFYDAQPCSDKAYKIEELFYSYATHSDKFTDGVCLFWNCNVDRYPANSIVCRFDTRVLSNLNLPGCDGGSLYVNKHAFHTPAFDKSAFVNLKQLPFFYYSDSPCESHGKQVVSDIDYVPLKSATCITRCNLGGAVCRHHANEYRLYLDAYNMMISAGFSLWVYKQFDTYNLWNTFTRLQ\n['YP_009725310.1']: SLENVAFNVVNKGHFDGQQGEVPVSIINNTVYTKVDGVDVELFENKTTLPVNVAFELWAKRNIKPVPEVKILNNLGVDIAANTVIWDYKRDAPAHISTIGVCSMTDIAKKPTETICAPLTVFFDGRVDGQVDLFRNARNGVLITEGSVKGLQPSVGPKQASLNGVTLIGEAVKTQFNYYKKVDGVVQQLPETYFTQSRNLQEFKPRSQMEIDFLELAMDEFIERYKLEGYAFEHIVYGDFSHSQLGGLHLLIGLAKRFKESPFELEDFIPMDSTVKNYFITDAQTGSSKCVCSVIDLLLDDFVEIIKSQDLSVVSKVVKVTIDYTEISFMLWCKDGHVETFYPKLQ\n['YP_009725311.1']: SSQAWQPGVAMPNLYKMQRMLLEKCDLQNYGDSATLPKGIMMNVAKYTQLCQYLNTLTLAVPYNMRVIHFGAGSDKGVAPGTAVLRQWLPTGTLLVDSDLNDFVSDADSTLIGDCATVHTANKWDLIISDMYDPKTKNVTKENDSKEGFFTYICGFIQQKLALGGSVAIKITEHSWNADLYKLMGHFAWWTAFVTNVNASSSEAFLIGCNYLGKPREQIDGYVMHANYIFWRNTNPIQLSSYSLFDMSKFPLKLRGTAVMSLKEGQINDMILSLLSKGRLIIRENNRVVISSDVLVNN\n['YP_009742608.1']: MESLVPGFNEKTHVQLSLPVLQVRDVLVRGFGDSVEEVLSEARQHLKDGTCGLVEVEKGVLPQLEQPYVFIKRSDARTAPHGHVMVELVAELEGIQYGRSGETLGVLVPHVGEIPVAYRKVLLRKNGNKGAGGHSYGADLKSFDLGDELGTDPYEDFQENWNTKHSSGVTRELMRELNGG\n['YP_009742609.1']: AYTRYVDNNFCGPDGYPLECIKDLLARAGKASCTLSEQLDFIDTKRGVYCCREHEHEIAWYTERSEKSYELQTPFEIKLAKKFDTFNGECPNFVFPLNSIIKTIQPRVEKKKLDGFMGRIRSVYPVASPNECNQMCLSTLMKCDHCGETSWQTGDFVKATCEFCGTENLTKEGATTCGYLPQNAVVKIYCPACHNSEVGPEHSLAEYHNESGLKTILRKGGRTIAFGGCVFSYVGCHNKCAYWVPRASANIGCNHTGVVGEGSEGLNDNLLEILQKEKVNINIVGDFKLNEEIAIILASFSASTSAFVETVKGLDYKAFKQIVESCGNFKVTKGKAKKGAWNIGEQKSILSPLYAFASEAARVVRSIFSRTLETAQNSVRVLQKAAITILDGISQYSLRLIDAMMFTSDLATNNLVVMAYITGGVVQLTSQWLTNIFGTVYEKLKPVLDWLEEKFKEGVEFLRDGWEIVKFISTCACEIVGGQIVTCAKEIKESVQTFFKLVNKFLALCADSIIIGGAKLKALNLGETFVTHSKGLYRKCVKSREETGLLMPLKAPKEIIFLEGETLPTEVLTEEVVLKTGDLQPLEQPTSEAVEAPLVGTPVCINGLMLLEIKDTEKYCALAPNMMVTNNTFTLKGG\n['YP_009742610.1']: APTKVTFGDDTVIEVQGYKSVNITFELDERIDKVLNEKCSAYTVELGTEVNEFACVVADAVIKTLQPVSELLTPLGIDLDEWSMATYYLFDESGEFKLASHMYCSFYPPDEDEEEGDCEEEEFEPSTQYEYGTEDDYQGKPLEFGATSAALQPEEEQEEDWLDDDSQQTVGQQDGSEDNQTTTIQTIVEVQPQLEMELTPVVQTIEVNSFSGYLKLTDNVYIKNADIVEEAKKVKPTVVVNAANVYLKHGGGVAGALNKATNNAMQVESDDYIATNGPLKVGGSCVLSGHNLAKHCLHVVGPNVNKGEDIQLLKSAYENFNQHEVLLAPLLSAGIFGADPIHSLRVCVDTVRTNVYLAVFDKNLYDKLVSSFLEMKSEKQVEQKIAEIPKEEVKPFITESKPSVEQRKQDDKKIKACVEEVTTTLEETKFLTENLLLYIDINGNLHPDSATLVSDIDITFLKKDAPYIVGDVVQEGVLTAVVIPTKKAGGTTEMLAKALRKVPTDNYITTYPGQGLNGYTVEEAKTVLKKCKSAFYILPSIISNEKQEILGTVSWNLREMLAHAEETRKLMPVCVETKAIVSTIQRKYKGIKIQEGVVDYGARFYFYTSKTTVASLINTLNDLNETLVTMPLGYVTHGLNLEEAARYMRSLKVPATVSVSSPDAVTAYNGYLTSSSKTPEEHFIETISLAGSYKDWSYSGQSTQLGIEFLKRGDKSVYYTSNPTTFHLDGEVITFDNLKTLLSLREVRTIKVFTTVDNINLHTQVVDMSMTYGQQFGPTYLDGADVTKIKPHNSHEGKTFYVLPNDDTLRVEAFEYYHTTDPSFLGRYMSALNHTKKWKYPQVNGLTSIKWADNNCYLATALLTLQQIELKFNPPALQDAYYRARAGEAANFCALILAYCNKTVGELGDVRETMSYLFQHANLDSCKRVLNVVCKTCGQQQTTLKGVEAVMYMGTLSYEQFKKGVQIPCTCGKQATKYLVQQESPFVMMSAPPAQYELKHGTFTCASEYTGNYQCGHYKHITSKETLYCIDGALLTKSSEYKGPITDVFYKENSYTTTIKPVTYKLDGVVCTEIDPKLDNYYKKDNSYFTEQPIDLVPNQPYPNASFDNFKFVCDNIKFADDLNQLTGYKKPASRELKVTFFPDLNGDVVAIDYKHYTPSFKKGAKLLHKPIVWHVNNATNKATYKPNTWCIRCLWSTKPVETSNSFDVLKSEDAQGMDNLACEDLKPVSEEVVENPTIQKDVLECNVKTTEVVGDIILKPANNSLKITEEVGHTDLMAAYVDNSSLTIKKPNELSRVLGLKTLATHGLAAVNSVPWDTIANYAKPFLNKVVSTTTNIVTRCLNRVCTNYMPYFFTLLLQLCTFTRSTNSRIKASMPTTIAKNTVKSVGKFCLEASFNYLKSPNFSKLINIIIWFLLLSVCLGSLIYSTAALGVLMSNLGMPSYCTGYREGYLNSTNVTIATYCTGSIPCSVCLSGLDSLDTYPSLETIQITISSFKWDLTAFGLVAEWFLAYILFTRFFYVLGLAAIMQLFFSYFAVHFISNSWLMWLIINLVQMAPISAMVRMYIFFASFYYVWKSYVHVVDGCNSSTCMMCYKRNRATRVECTTIVNGVRRSFYVYANGGKGFCKLHNWNCVNCDTFCAGSTFISDEVARDLSLQFKRPINPTDQSSYIVDSVTVKNGSIHLYFDKAGQKTYERHSLSHFVNLDNLRANNTKGSLPINVIVFDGKSKCEESSAKSASVYYSQLMCQPILLLDQALVSDVGDSAEVAVKMFDAYVNTFSSTFNVPMEKLKTLVATAEAELAKNVSLDNVLSTFISAARQGFVDSDVETKDVVECLKLSHQSDIEVTGDSCNNYMLTYNKVENMTPRDLGACIDCSARHINAQVAKSHNIALIWNVKDFMSLSEQLRKQIRSAAKKNNLPFKLTCATTRQVVNVVTTKIALKGG\n['YP_009742611.1']: KIVNNWLKQLIKVTLVFLFVAAIFYLITPVHVMSKHTDFSSEIIGYKAIDGGVTRDIASTDTCFANKHADFDTWFSQRGGSYTNDKACPLIAAVITREVGFVVPGLPGTILRTTNGDFLHFLPRVFSAVGNICYTPSKLIEYTDFATSACVLAAECTIFKDASGKPVPYCYDTNVLEGSVAYESLRPDTRYVLMDGSIIQFPNTYLEGSVRVVTTFDSEYCRHGTCERSEAGVCVSTSGRWVLNNDYYRSLPGVFCGVDAVNLLTNMFTPLIQPIGALDISASIVAGGIVAIVVTCLAYYFMRFRRAFGEYSHVVAFNTLLFLMSFTVLCLTPVYSFLPGVYSVIYLYLTFYLTNDVSFLAHIQWMVMFTPLVPFWITIAYIICISTKHFYWFFSNYLKRRVVFNGVSFSTFEEAALCTFLLNKEMYLKLRSDVLLPLTQYNRYLALYNKYKYFSGAMDTTSYREAACCHLAKALNDFSNSGSDVLYQPPQTSITSAVLQ\n['YP_009742612.1']: SGFRKMAFPSGKVEGCMVQVTCGTTTLNGLWLDDVVYCPRHVICTSEDMLNPNYEDLLIRKSNHNFLVQAGNVQLRVIGHSMQNCVLKLKVDTANPKTPKYKFVRIQPGQTFSVLACYNGSPSGVYQCAMRPNFTIKGSFLNGSCGSVGFNIDYDCVSFCYMHHMELPTGVHAGTDLEGNFYGPFVDRQTAQAAGTDTTITVNVLAWLYAAVINGDRWFLNRFTTTLNDFNLVAMKYNYEPLTQDHVDILGPLSAQTGIAVLDMCASLKELLQNGMNGRTILGSALLEDEFTPFDVVRQCSGVTFQ\n['YP_009742613.1']: SAVKRTIKGTHHWLLLTILTSLLVLVQSTQWSLFFFLYENAFLPFAMGIIAMSAFAMMFVKHKHAFLCLFLLPSLATVAYFNMVYMPASWVMRIMTWLDMVDTSLSGFKLKDCVMYASAVVLLILMTARTVYDDGARRVWTLMNVLTLVYKVYYGNALDQAISMWALIISVTSNYSGVVTTVMFLARGIVFMCVEYCPIFFITGNTLQCIMLVYCFLGYFCTCYFGLFCLLNRYFRLTLGVYDYLVSTQEFRYMNSQGLLPPKNSIDAFKLNIKLLGVGGKPCIKVATVQ\n['YP_009742614.1']: SKMSDVKCTSVVLLSVLQQLRVESSSKLWAQCVQLHNDILLAKDTTEAFEKMVSLLSVLLSMQGAVDINKLCEEMLDNRATLQ\n['YP_009742615.1']: AIASEFSSLPSYAAFATAQEAYEQAVANGDSEVVLKKLKKSLNVAKSEFDRDAAMQRKLEKMADQAMTQMYKQARSEDKRAKVTSAMQTMLFTMLRKLDNDALNNIINNARDGCVPLNIIPLTTAAKLMVVIPDYNTYKNTCDGTTFTYASALWEIQQVVDADSKIVQLSEISMDNSPNLAWPLIVTALRANSAVKLQ\n['YP_009742616.1']: NNELSPVALRQMSCAAGTTQTACTDDNALAYYNTTKGGRFVLALLSDLQDLKWARFPKSDGTGTIYTELEPPCRFVTDTPKGPKVKYLYFIKGLNNLNRGMVLGSLAATVRLQ\n['YP_009742617.1']: AGNATEVPANSTVLSFCAFAVDAAKAYKDYLASGGQPITNCVKMLCTHTGTGQAITVTPEANMDQESFGGASCCLYCRCHIDHPNPKGFCDLKGKYVQIPTTCANDPVGFTLKNTVCTVCGMWKGYGCSCDQLREPMLQ\n['YP_009725312.1']: SADAQSFLNGFAV\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### Structures\nStructure processing is managed by the [Bio.PDB](https://biopython.org/docs/latest/api/Bio.PDB.html) package.\n\nTo read a structure from a PDB file, use the `PDBParser`. We will be using the 3C-like proteinase protein, which is one of the processed proteins present in the ORF1a discussed above. One of it's structures is [7ALH](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbe/entry/pdb/7alh). To see all the proteins, I suggest checking out the PDBe-KB page for [P0DTD1](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbe/pdbe-kb/protein/P0DTD1).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from Bio.PDB.PDBParser import PDBParser\nparser = PDBParser(PERMISSIVE=1)\nstructure = parser.get_structure(\"7alh\", \"7alh.ent\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"As the PDB format is considered deprecated, one should use the mmCIF file instead. This is done the same way as in case of PDB files.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from Bio.PDB.MMCIFParser import MMCIFParser\nparser = MMCIFParser()\nstructure = parser.get_structure(\"7alh\", \"7alh.cif\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"To retrieve the individual CIF dictionary fields, one can use the `MMCIF2Dict` module.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from Bio.PDB.MMCIFParser import MMCIF2Dict\nmmcif_dict = MMCIF2Dict(\"7alh.cif\")\nprint(mmcif_dict[\"_citation.title\"])",
"['Crystal structure of the main protease (3CLpro/Mpro) of SARS-CoV-2 at 1.65A resolution (spacegroup C2).']\n"
]
],
[
[
"The structure record has the structure->model->chain->residue architecture.\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Each of the levels in the hierarchy is represented by a submodule in Bio.PDB, namely [Bio.Structure](https://biopython.org/docs/latest/api/Bio.PDB.Modul.html), [Bio.Module](https://biopython.org/docs/latest/api/Bio.PDB.Module.html),[Bio.Chain](https://biopython.org/docs/latest/api/Bio.PDB.Chain.html),[Bio.Residue](https://biopython.org/docs/latest/api/Bio.PDB.Residue.html) and [Bio.Atom](https://biopython.org/docs/latest/api/Bio.PDB.Atom.html). For details regarding IDs, check the [section on ID](https://biopython.org/docs/1.75/api/Bio.PDB.Entity.html#Bio.PDB.Entity.Entity.get_full_id) of the Entity class which is the superclass of the Module/Chain/Residue/Atom classes.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(structure.get_list())\n\nprint('---------- MODEL INFO ----------')\n\nmodel = structure[0]\nprint(\"Full ID: {}\\nID: {}\".format(model.get_full_id(), model.get_id()))\nprint(model.get_list())\n\nprint('---------- CHAIN INFO ----------')\nchain = model['A']\nprint(\"Full ID: {}\\nID: {}\".format(chain.get_full_id(), chain.get_id()))\nprint(chain.get_list())\n\nprint('---------- RESIDUE INFO ----------')\nres = chain[(' ',1,' ')]\nprint(\"Full ID: {}\\nID: {}\".format(res.get_full_id(), res.get_id()))\nprint(res.get_resname())\nres = chain[1]\nprint(res.get_resname())\n\nprint(res.get_list())\nprint('---------- ATOM INFO ----------')\natom=res['CA']\nprint(\"Full ID: {}\\nID: {}\".format(atom.get_full_id(), atom.get_id()))\nprint(\"{}\\n{}\\n{}\\n{}\".format(atom.get_name(), atom.get_id(), atom.get_coord(), atom.get_fullname()))\nprint(atom.get_vector())\n",
"[<Model id=0>]\n---------- MODEL INFO ----------\nFull ID: ('7alh', 0)\nID: 0\n[<Chain id=A>]\n---------- CHAIN INFO ----------\nFull ID: ('7alh', 0, 'A')\nID: A\n[<Residue SER het= resseq=1 icode= >, <Residue GLY het= resseq=2 icode= >, <Residue PHE het= resseq=3 icode= >, <Residue ARG het= resseq=4 icode= >, <Residue LYS het= resseq=5 icode= >, <Residue MET het= resseq=6 icode= >, <Residue ALA het= resseq=7 icode= >, <Residue PHE het= resseq=8 icode= >, <Residue PRO het= resseq=9 icode= >, <Residue SER het= resseq=10 icode= >, <Residue GLY het= resseq=11 icode= >, <Residue LYS het= resseq=12 icode= >, <Residue VAL het= resseq=13 icode= >, <Residue GLU het= resseq=14 icode= >, <Residue GLY het= resseq=15 icode= >, <Residue CYS het= resseq=16 icode= >, <Residue MET het= resseq=17 icode= >, <Residue VAL het= resseq=18 icode= >, <Residue GLN het= resseq=19 icode= >, <Residue VAL het= resseq=20 icode= >, <Residue THR het= resseq=21 icode= >, <Residue CYS het= resseq=22 icode= >, <Residue GLY het= resseq=23 icode= >, <Residue THR het= resseq=24 icode= >, <Residue THR het= resseq=25 icode= >, <Residue THR het= resseq=26 icode= >, <Residue LEU het= resseq=27 icode= >, <Residue ASN het= resseq=28 icode= >, <Residue GLY het= resseq=29 icode= >, <Residue LEU het= resseq=30 icode= >, <Residue TRP het= resseq=31 icode= >, <Residue LEU het= resseq=32 icode= >, <Residue ASP het= resseq=33 icode= >, <Residue ASP het= resseq=34 icode= >, <Residue VAL het= resseq=35 icode= >, <Residue VAL het= resseq=36 icode= >, <Residue TYR het= resseq=37 icode= >, <Residue CYS het= resseq=38 icode= >, <Residue PRO het= resseq=39 icode= >, <Residue ARG het= resseq=40 icode= >, <Residue HIS het= resseq=41 icode= >, <Residue VAL het= resseq=42 icode= >, <Residue ILE het= resseq=43 icode= >, <Residue CYS het= resseq=44 icode= >, <Residue THR het= resseq=45 icode= >, <Residue SER het= resseq=46 icode= >, <Residue GLU het= resseq=47 icode= >, <Residue ASP het= resseq=48 icode= >, <Residue MET het= resseq=49 icode= >, <Residue LEU het= resseq=50 icode= >, <Residue ASN het= resseq=51 icode= >, <Residue PRO het= resseq=52 icode= >, <Residue ASN het= resseq=53 icode= >, <Residue TYR het= resseq=54 icode= >, <Residue GLU het= resseq=55 icode= >, <Residue ASP het= resseq=56 icode= >, <Residue LEU het= resseq=57 icode= >, <Residue LEU het= resseq=58 icode= >, <Residue ILE het= resseq=59 icode= >, <Residue ARG het= resseq=60 icode= >, <Residue LYS het= resseq=61 icode= >, <Residue SER het= resseq=62 icode= >, <Residue ASN het= resseq=63 icode= >, <Residue HIS het= resseq=64 icode= >, <Residue ASN het= resseq=65 icode= >, <Residue PHE het= resseq=66 icode= >, <Residue LEU het= resseq=67 icode= >, <Residue VAL het= resseq=68 icode= >, <Residue GLN het= resseq=69 icode= >, <Residue ALA het= resseq=70 icode= >, <Residue GLY het= resseq=71 icode= >, <Residue ASN het= resseq=72 icode= >, <Residue VAL het= resseq=73 icode= >, <Residue GLN het= resseq=74 icode= >, <Residue LEU het= resseq=75 icode= >, <Residue ARG het= resseq=76 icode= >, <Residue VAL het= resseq=77 icode= >, <Residue ILE het= resseq=78 icode= >, <Residue GLY het= resseq=79 icode= >, <Residue HIS het= resseq=80 icode= >, <Residue SER het= resseq=81 icode= >, <Residue MET het= resseq=82 icode= >, <Residue GLN het= resseq=83 icode= >, <Residue ASN het= resseq=84 icode= >, <Residue CYS het= resseq=85 icode= >, <Residue VAL het= resseq=86 icode= >, <Residue LEU het= resseq=87 icode= >, <Residue LYS het= resseq=88 icode= >, <Residue LEU het= resseq=89 icode= >, <Residue LYS het= resseq=90 icode= >, <Residue VAL het= resseq=91 icode= >, <Residue ASP het= resseq=92 icode= >, <Residue THR het= resseq=93 icode= >, <Residue ALA het= resseq=94 icode= >, <Residue ASN het= resseq=95 icode= >, <Residue PRO het= resseq=96 icode= >, <Residue LYS het= resseq=97 icode= >, <Residue THR het= resseq=98 icode= >, <Residue PRO het= resseq=99 icode= >, <Residue LYS het= resseq=100 icode= >, <Residue TYR het= resseq=101 icode= >, <Residue LYS het= resseq=102 icode= >, <Residue PHE het= resseq=103 icode= >, <Residue VAL het= resseq=104 icode= >, <Residue ARG het= resseq=105 icode= >, <Residue ILE het= resseq=106 icode= >, <Residue GLN het= resseq=107 icode= >, <Residue PRO het= resseq=108 icode= >, <Residue GLY het= resseq=109 icode= >, <Residue GLN het= resseq=110 icode= >, <Residue THR het= resseq=111 icode= >, <Residue PHE het= resseq=112 icode= >, <Residue SER het= resseq=113 icode= >, <Residue VAL het= resseq=114 icode= >, <Residue LEU het= resseq=115 icode= >, <Residue ALA het= resseq=116 icode= >, <Residue CYS het= resseq=117 icode= >, <Residue TYR het= resseq=118 icode= >, <Residue ASN het= resseq=119 icode= >, <Residue GLY het= resseq=120 icode= >, <Residue SER het= resseq=121 icode= >, <Residue PRO het= resseq=122 icode= >, <Residue SER het= resseq=123 icode= >, <Residue GLY het= resseq=124 icode= >, <Residue VAL het= resseq=125 icode= >, <Residue TYR het= resseq=126 icode= >, <Residue GLN het= resseq=127 icode= >, <Residue CYS het= resseq=128 icode= >, <Residue ALA het= resseq=129 icode= >, <Residue MET het= resseq=130 icode= >, <Residue ARG het= resseq=131 icode= >, <Residue PRO het= resseq=132 icode= >, <Residue ASN het= resseq=133 icode= >, <Residue PHE het= resseq=134 icode= >, <Residue THR het= resseq=135 icode= >, <Residue ILE het= resseq=136 icode= >, <Residue LYS het= resseq=137 icode= >, <Residue GLY het= resseq=138 icode= >, <Residue SER het= resseq=139 icode= >, <Residue PHE het= resseq=140 icode= >, <Residue LEU het= resseq=141 icode= >, <Residue ASN het= resseq=142 icode= >, <Residue GLY het= resseq=143 icode= >, <Residue SER het= resseq=144 icode= >, <Residue CYS het= resseq=145 icode= >, <Residue GLY het= resseq=146 icode= >, <Residue SER het= resseq=147 icode= >, <Residue VAL het= resseq=148 icode= >, <Residue GLY het= resseq=149 icode= >, <Residue PHE het= resseq=150 icode= >, <Residue ASN het= resseq=151 icode= >, <Residue ILE het= resseq=152 icode= >, <Residue ASP het= resseq=153 icode= >, <Residue TYR het= resseq=154 icode= >, <Residue ASP het= resseq=155 icode= >, <Residue CYS het= resseq=156 icode= >, <Residue VAL het= resseq=157 icode= >, <Residue SER het= resseq=158 icode= >, <Residue PHE het= resseq=159 icode= >, <Residue CYS het= resseq=160 icode= >, <Residue TYR het= resseq=161 icode= >, <Residue MET het= resseq=162 icode= >, <Residue HIS het= resseq=163 icode= >, <Residue HIS het= resseq=164 icode= >, <Residue MET het= resseq=165 icode= >, <Residue GLU het= resseq=166 icode= >, <Residue LEU het= resseq=167 icode= >, <Residue PRO het= resseq=168 icode= >, <Residue THR het= resseq=169 icode= >, <Residue GLY het= resseq=170 icode= >, <Residue VAL het= resseq=171 icode= >, <Residue HIS het= resseq=172 icode= >, <Residue ALA het= resseq=173 icode= >, <Residue GLY het= resseq=174 icode= >, <Residue THR het= resseq=175 icode= >, <Residue ASP het= resseq=176 icode= >, <Residue LEU het= resseq=177 icode= >, <Residue GLU het= resseq=178 icode= >, <Residue GLY het= resseq=179 icode= >, <Residue ASN het= resseq=180 icode= >, <Residue PHE het= resseq=181 icode= >, <Residue TYR het= resseq=182 icode= >, <Residue GLY het= resseq=183 icode= >, <Residue PRO het= resseq=184 icode= >, <Residue PHE het= resseq=185 icode= >, <Residue VAL het= resseq=186 icode= >, <Residue ASP het= resseq=187 icode= >, <Residue ARG het= resseq=188 icode= >, <Residue GLN het= resseq=189 icode= >, <Residue THR het= resseq=190 icode= >, <Residue ALA het= resseq=191 icode= >, <Residue GLN het= resseq=192 icode= >, <Residue ALA het= resseq=193 icode= >, <Residue ALA het= resseq=194 icode= >, <Residue GLY het= resseq=195 icode= >, <Residue THR het= resseq=196 icode= >, <Residue ASP het= resseq=197 icode= >, <Residue THR het= resseq=198 icode= >, <Residue THR het= resseq=199 icode= >, <Residue ILE het= resseq=200 icode= >, <Residue THR het= resseq=201 icode= >, <Residue VAL het= resseq=202 icode= >, <Residue ASN het= resseq=203 icode= >, <Residue VAL het= resseq=204 icode= >, <Residue LEU het= resseq=205 icode= >, <Residue ALA het= resseq=206 icode= >, <Residue TRP het= resseq=207 icode= >, <Residue LEU het= resseq=208 icode= >, <Residue TYR het= resseq=209 icode= >, <Residue ALA het= resseq=210 icode= >, <Residue ALA het= resseq=211 icode= >, <Residue VAL het= resseq=212 icode= >, <Residue ILE het= resseq=213 icode= >, <Residue ASN het= resseq=214 icode= >, <Residue GLY het= resseq=215 icode= >, <Residue ASP het= resseq=216 icode= >, <Residue ARG het= resseq=217 icode= >, <Residue TRP het= resseq=218 icode= >, <Residue PHE het= resseq=219 icode= >, <Residue LEU het= resseq=220 icode= >, <Residue ASN het= resseq=221 icode= >, <Residue ARG het= resseq=222 icode= >, <Residue PHE het= resseq=223 icode= >, <Residue THR het= resseq=224 icode= >, <Residue THR het= resseq=225 icode= >, <Residue THR het= resseq=226 icode= >, <Residue LEU het= resseq=227 icode= >, <Residue ASN het= resseq=228 icode= >, <Residue ASP het= resseq=229 icode= >, <Residue PHE het= resseq=230 icode= >, <Residue ASN het= resseq=231 icode= >, <Residue LEU het= resseq=232 icode= >, <Residue VAL het= resseq=233 icode= >, <Residue ALA het= resseq=234 icode= >, <Residue MET het= resseq=235 icode= >, <Residue LYS het= resseq=236 icode= >, <Residue TYR het= resseq=237 icode= >, <Residue ASN het= resseq=238 icode= >, <Residue TYR het= resseq=239 icode= >, <Residue GLU het= resseq=240 icode= >, <Residue PRO het= resseq=241 icode= >, <Residue LEU het= resseq=242 icode= >, <Residue THR het= resseq=243 icode= >, <Residue GLN het= resseq=244 icode= >, <Residue ASP het= resseq=245 icode= >, <Residue HIS het= resseq=246 icode= >, <Residue VAL het= resseq=247 icode= >, <Residue ASP het= resseq=248 icode= >, <Residue ILE het= resseq=249 icode= >, <Residue LEU het= resseq=250 icode= >, <Residue GLY het= resseq=251 icode= >, <Residue PRO het= resseq=252 icode= >, <Residue LEU het= resseq=253 icode= >, <Residue SER het= resseq=254 icode= >, <Residue ALA het= resseq=255 icode= >, <Residue GLN het= resseq=256 icode= >, <Residue THR het= resseq=257 icode= >, <Residue GLY het= resseq=258 icode= >, <Residue ILE het= resseq=259 icode= >, <Residue ALA het= resseq=260 icode= >, <Residue VAL het= resseq=261 icode= >, <Residue LEU het= resseq=262 icode= >, <Residue ASP het= resseq=263 icode= >, <Residue MET het= resseq=264 icode= >, <Residue CYS het= resseq=265 icode= >, <Residue ALA het= resseq=266 icode= >, <Residue SER het= resseq=267 icode= >, <Residue LEU het= resseq=268 icode= >, <Residue LYS het= resseq=269 icode= >, <Residue GLU het= resseq=270 icode= >, <Residue LEU het= resseq=271 icode= >, <Residue LEU het= resseq=272 icode= >, <Residue GLN het= resseq=273 icode= >, <Residue ASN het= resseq=274 icode= >, <Residue GLY het= resseq=275 icode= >, <Residue MET het= resseq=276 icode= >, <Residue ASN het= resseq=277 icode= >, <Residue GLY het= resseq=278 icode= >, <Residue ARG het= resseq=279 icode= >, <Residue THR het= resseq=280 icode= >, <Residue ILE het= resseq=281 icode= >, <Residue LEU het= resseq=282 icode= >, <Residue GLY het= resseq=283 icode= >, <Residue SER het= resseq=284 icode= >, <Residue ALA het= resseq=285 icode= >, <Residue LEU het= resseq=286 icode= >, <Residue LEU het= resseq=287 icode= >, <Residue GLU het= resseq=288 icode= >, <Residue ASP het= resseq=289 icode= >, <Residue GLU het= resseq=290 icode= >, <Residue PHE het= resseq=291 icode= >, <Residue THR het= resseq=292 icode= >, <Residue PRO het= resseq=293 icode= >, <Residue PHE het= resseq=294 icode= >, <Residue ASP het= resseq=295 icode= >, <Residue VAL het= resseq=296 icode= >, <Residue VAL het= resseq=297 icode= >, <Residue ARG het= resseq=298 icode= >, <Residue GLN het= resseq=299 icode= >, <Residue CYS het= resseq=300 icode= >, <Residue SER het= resseq=301 icode= >, <Residue GLY het= resseq=302 icode= >, <Residue VAL het= resseq=303 icode= >, <Residue THR het= resseq=304 icode= >, <Residue PHE het= resseq=305 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=401 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=402 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=403 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=404 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=405 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=406 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=407 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=408 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=409 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=410 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=411 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=412 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=413 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=414 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=415 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=416 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=417 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=418 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=419 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=420 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=421 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=422 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=423 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=424 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=425 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=426 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=427 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=428 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=429 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=430 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=431 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=432 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=433 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=434 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=435 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=436 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=437 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=438 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=439 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=440 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=441 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=442 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=443 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=444 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=445 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=446 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=447 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=448 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=449 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=450 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=451 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=452 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=453 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=454 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=455 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=456 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=457 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=458 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=459 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=460 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=461 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=462 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=463 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=464 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=465 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=466 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=467 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=468 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=469 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=470 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=471 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=472 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=473 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=474 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=475 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=476 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=477 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=478 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=479 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=480 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=481 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=482 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=483 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=484 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=485 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=486 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=487 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=488 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=489 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=490 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=491 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=492 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=493 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=494 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=495 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=496 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=497 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=498 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=499 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=500 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=501 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=502 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=503 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=504 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=505 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=506 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=507 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=508 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=509 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=510 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=511 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=512 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=513 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=514 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=515 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=516 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=517 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=518 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=519 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=520 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=521 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=522 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=523 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=524 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=525 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=526 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=527 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=528 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=529 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=530 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=531 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=532 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=533 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=534 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=535 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=536 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=537 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=538 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=539 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=540 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=541 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=542 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=543 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=544 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=545 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=546 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=547 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=548 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=549 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=550 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=551 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=552 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=553 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=554 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=555 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=556 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=557 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=558 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=559 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=560 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=561 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=562 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=563 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=564 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=565 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=566 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=567 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=568 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=569 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=570 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=571 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=572 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=573 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=574 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=575 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=576 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=577 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=578 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=579 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=580 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=581 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=582 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=583 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=584 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=585 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=586 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=587 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=588 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=589 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=590 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=591 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=592 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=593 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=594 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=595 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=596 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=597 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=598 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=599 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=600 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=601 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=602 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=603 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=604 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=605 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=606 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=607 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=608 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=609 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=610 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=611 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=612 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=613 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=614 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=615 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=616 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=617 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=618 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=619 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=620 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=621 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=622 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=623 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=624 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=625 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=626 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=627 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=628 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=629 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=630 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=631 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=632 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=633 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=634 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=635 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=636 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=637 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=638 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=639 icode= >, <Residue HOH het=W resseq=640 icode= >]\n---------- RESIDUE INFO ----------\nFull ID: ('7alh', 0, 'A', (' ', 1, ' '))\nID: (' ', 1, ' ')\nSER\nSER\n[<Atom N>, <Atom CA>, <Atom C>, <Atom O>, <Atom CB>, <Atom OG>, <Atom H1>, <Atom H2>, <Atom H3>, <Atom HA>, <Atom HB2>, <Atom HB3>, <Atom HG>]\n---------- ATOM INFO ----------\nFull ID: ('7alh', 0, 'A', (' ', 1, ' '), ('CA', ' '))\nID: CA\nCA\nCA\n[ -1.88186 -21.36393 38.35414]\nCA\n<Vector -1.88, -21.36, 38.35>\n"
]
],
[
[
"To download a file from PDB, one can use the PDBList module.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from Bio.PDB.PDBList import PDBList\npdbl = PDBList()\npbl_7lkr=pdbl.retrieve_pdb_file(\"7LKR\", file_format=\"mmCif\", pdir=\".\")",
"Structure exists: '.\\7lkr.cif' \n"
],
[
"from Bio.PDB.MMCIFParser import MMCIFParser\nparser = MMCIFParser()\nstructure = parser.get_structure(\"7lkr\", \"7lkr.cif\")",
"c:\\python39\\lib\\site-packages\\Bio\\PDB\\StructureBuilder.py:89: PDBConstructionWarning: WARNING: Chain A is discontinuous at line 4467.\n warnings.warn(\nc:\\python39\\lib\\site-packages\\Bio\\PDB\\StructureBuilder.py:89: PDBConstructionWarning: WARNING: Chain B is discontinuous at line 4531.\n warnings.warn(\nc:\\python39\\lib\\site-packages\\Bio\\PDB\\StructureBuilder.py:89: PDBConstructionWarning: WARNING: Chain A is discontinuous at line 4608.\n warnings.warn(\nc:\\python39\\lib\\site-packages\\Bio\\PDB\\StructureBuilder.py:89: PDBConstructionWarning: WARNING: Chain B is discontinuous at line 4774.\n warnings.warn(\n"
]
],
[
[
"Tasks:\n- Iterate over all atoms of the structure\n- List all water residues (the first field of the residue id is 'W')\n- How many water molecules is in the recrod?\n- How many heteroatoms are there in the recod (the first field of the residue id is 'H').\n- Find a structure in PDB with at least one ligand (different from water) and write a code which lists all the ligands.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a712ddddb5b93a063d3e338eedd3d27af98dd90
| 29,144 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/benchmark_simple_model.ipynb
|
Maximophone/seldon-core
|
d737332b464fc2c22fd120adcdbe0e9644034ae5
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/benchmark_simple_model.ipynb
|
Maximophone/seldon-core
|
d737332b464fc2c22fd120adcdbe0e9644034ae5
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/benchmark_simple_model.ipynb
|
Maximophone/seldon-core
|
d737332b464fc2c22fd120adcdbe0e9644034ae5
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 34.449173 | 271 | 0.461604 |
[
[
[
"# Throughtput Benchmarking Seldon-Core on GCP Kubernetes\n\nThe notebook will provide a benchmarking of seldon-core for maximum throughput test. We will run a stub model and test using REST and gRPC predictions. This will provide a maximum theoretical throughtput for model deployment in the given infrastructure scenario:\n \n * 1 replica of the model running on n1-standard-16 GCP node\n \nFor a real model the throughput would be less. Future benchmarks will test realistic models scenarios.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Create Cluster",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Create a cluster of 4 nodes of machine type n1-standard-16 \n\n```bash\nPROJECT=seldon-core-benchmarking\nZONE=europe-west1-b\ngcloud beta container --project \"${PROJECT}\" clusters create \"loadtest\" \\\n --zone \"${ZONE}\" \\\n --username \"admin\" \\\n --cluster-version \"1.9.3-gke.0\" \\\n --machine-type \"n1-standard-16\" \\\n --image-type \"COS\" \\\n --disk-size \"100\" \\\n --num-nodes \"4\" \\\n --network \"default\" \\\n --enable-cloud-logging \\\n --enable-cloud-monitoring \\\n --subnetwork \"default\"\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Install helm",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!kubectl -n kube-system create sa tiller\n!kubectl create clusterrolebinding tiller --clusterrole cluster-admin --serviceaccount=kube-system:tiller\n!helm init --service-account tiller",
"serviceaccount \"tiller\" created\nclusterrolebinding \"tiller\" created\n$HELM_HOME has been configured at /home/clive/.helm.\n\nTiller (the Helm server-side component) has been installed into your Kubernetes Cluster.\nHappy Helming!\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Start Seldon-Core CRD",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!helm install ../helm-charts/seldon-core-crd --name seldon-core-crd",
"NAME: seldon-core-crd\nLAST DEPLOYED: Wed Mar 7 15:14:11 2018\nNAMESPACE: default\nSTATUS: DEPLOYED\n\nRESOURCES:\n==> v1beta1/CustomResourceDefinition\nNAME AGE\nseldondeployments.machinelearning.seldon.io 1s\n\n\nNOTES:\nNOTES: TODO\n\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Cordon off loadtest nodes",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!kubectl get nodes",
"NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION\r\ngke-loadtest-default-pool-e2e99314-7zb5 Ready <none> 1m v1.9.3-gke.0\r\ngke-loadtest-default-pool-e2e99314-gbjx Ready <none> 1m v1.9.3-gke.0\r\ngke-loadtest-default-pool-e2e99314-hcvx Ready <none> 1m v1.9.3-gke.0\r\ngke-loadtest-default-pool-e2e99314-tb2p Ready <none> 1m v1.9.3-gke.0\r\n"
]
],
[
[
"We cordon off first 3 nodes so seldon-core and the model will not be deployed on the 1 remaining node.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!kubectl cordon $(kubectl get nodes -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')\n!kubectl cordon $(kubectl get nodes -o jsonpath='{.items[1].metadata.name}')\n!kubectl cordon $(kubectl get nodes -o jsonpath='{.items[2].metadata.name}')",
"node \"gke-loadtest-default-pool-e2e99314-7zb5\" cordoned\nnode \"gke-loadtest-default-pool-e2e99314-gbjx\" cordoned\nnode \"gke-loadtest-default-pool-e2e99314-hcvx\" cordoned\n"
]
],
[
[
"Label the nodes so they can be used by locust.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!kubectl label nodes $(kubectl get nodes -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') role=locust\n!kubectl label nodes $(kubectl get nodes -o jsonpath='{.items[1].metadata.name}') role=locust\n!kubectl label nodes $(kubectl get nodes -o jsonpath='{.items[2].metadata.name}') role=locust",
"node \"gke-loadtest-default-pool-e2e99314-7zb5\" labeled\nnode \"gke-loadtest-default-pool-e2e99314-gbjx\" labeled\nnode \"gke-loadtest-default-pool-e2e99314-hcvx\" labeled\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Start seldon-core",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!helm install ../helm-charts/seldon-core --name seldon-core \\\n --set cluster_manager.rbac=true \\\n --set apife.enabled=true \\\n --set engine.image.tag=0.1.6_SNAPSHOT_loadtest \\\n --set cluster_manager.image.tag=0.1.6_SNAPSHOT_loadtest\n ",
"NAME: seldon-core\nLAST DEPLOYED: Wed Mar 7 15:15:11 2018\nNAMESPACE: default\nSTATUS: DEPLOYED\n\nRESOURCES:\n==> v1beta1/ClusterRoleBinding\nNAME AGE\nseldon 1s\n\n==> v1/Pod(related)\nNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE\nredis-df886d999-rl5l8 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s\n\n==> v1beta1/Deployment\nNAME DESIRED CURRENT UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE\nseldon-apiserver 1 0 0 0 1s\nseldon-cluster-manager 1 0 0 0 1s\nredis 1 1 1 0 1s\n\n==> v1/Service\nNAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE\nseldon-apiserver NodePort 10.3.246.186 <none> 8080:31873/TCP,5000:30398/TCP 1s\nredis ClusterIP 10.3.240.223 <none> 6379/TCP 0s\n\n==> v1/ServiceAccount\nNAME SECRETS AGE\nseldon 1 1s\n\n\nNOTES:\nNOTES: TODO\n\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"Wait for seldon-core to start",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!kubectl get pods -o wide",
"NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE\r\nredis-df886d999-rl5l8 1/1 Running 0 31s 10.0.2.5 gke-loadtest-default-pool-e2e99314-tb2p\r\nseldon-apiserver-64ccd4c5f4-xcclp 1/1 Running 0 31s 10.0.2.7 gke-loadtest-default-pool-e2e99314-tb2p\r\nseldon-cluster-manager-68c8c6b5bf-tbc5b 1/1 Running 0 31s 10.0.2.6 gke-loadtest-default-pool-e2e99314-tb2p\r\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Create Stub Deployment",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!pygmentize resources/loadtest_simple_model.json",
"{\r\n \u001b[34;01m\"apiVersion\"\u001b[39;49;00m: \u001b[33m\"machinelearning.seldon.io/v1alpha1\"\u001b[39;49;00m,\r\n \u001b[34;01m\"kind\"\u001b[39;49;00m: \u001b[33m\"SeldonDeployment\"\u001b[39;49;00m,\r\n \u001b[34;01m\"metadata\"\u001b[39;49;00m: {\r\n \u001b[34;01m\"labels\"\u001b[39;49;00m: {\r\n \u001b[34;01m\"app\"\u001b[39;49;00m: \u001b[33m\"seldon\"\u001b[39;49;00m\r\n },\r\n \u001b[34;01m\"name\"\u001b[39;49;00m: \u001b[33m\"seldon-core-loadtest\"\u001b[39;49;00m\r\n },\r\n \u001b[34;01m\"spec\"\u001b[39;49;00m: {\r\n \u001b[34;01m\"annotations\"\u001b[39;49;00m: {\r\n \u001b[34;01m\"project_name\"\u001b[39;49;00m: \u001b[33m\"loadtest\"\u001b[39;49;00m,\r\n \u001b[34;01m\"deployment_version\"\u001b[39;49;00m: \u001b[33m\"v1\"\u001b[39;49;00m\r\n },\r\n \u001b[34;01m\"name\"\u001b[39;49;00m: \u001b[33m\"loadtest\"\u001b[39;49;00m,\r\n \u001b[34;01m\"oauth_key\"\u001b[39;49;00m: \u001b[33m\"oauth-key\"\u001b[39;49;00m,\r\n \u001b[34;01m\"oauth_secret\"\u001b[39;49;00m: \u001b[33m\"oauth-secret\"\u001b[39;49;00m,\r\n \u001b[34;01m\"predictors\"\u001b[39;49;00m: [\r\n {\r\n \u001b[34;01m\"componentSpec\"\u001b[39;49;00m: {\r\n \u001b[34;01m\"spec\"\u001b[39;49;00m: {\r\n \u001b[34;01m\"containers\"\u001b[39;49;00m: [\r\n ],\r\n \u001b[34;01m\"terminationGracePeriodSeconds\"\u001b[39;49;00m: \u001b[34m20\u001b[39;49;00m\r\n }\r\n },\r\n \u001b[34;01m\"graph\"\u001b[39;49;00m: {\r\n \u001b[34;01m\"children\"\u001b[39;49;00m: [],\r\n \u001b[34;01m\"name\"\u001b[39;49;00m: \u001b[33m\"stub\"\u001b[39;49;00m,\r\n \u001b[34;01m\"endpoint\"\u001b[39;49;00m: {\r\n\t\t\t\u001b[34;01m\"type\"\u001b[39;49;00m : \u001b[33m\"REST\"\u001b[39;49;00m\r\n\t\t },\r\n \u001b[34;01m\"type\"\u001b[39;49;00m: \u001b[33m\"MODEL\"\u001b[39;49;00m,\r\n\t\t \u001b[34;01m\"implementation\"\u001b[39;49;00m: \u001b[33m\"SIMPLE_MODEL\"\u001b[39;49;00m\r\n },\r\n \u001b[34;01m\"name\"\u001b[39;49;00m: \u001b[33m\"loadtest\"\u001b[39;49;00m,\r\n \u001b[34;01m\"replicas\"\u001b[39;49;00m: \u001b[34m1\u001b[39;49;00m,\r\n\t\t\u001b[34;01m\"annotations\"\u001b[39;49;00m: {\r\n\t\t \u001b[34;01m\"predictor_version\"\u001b[39;49;00m : \u001b[33m\"v1\"\u001b[39;49;00m\r\n\t\t}\r\n }\r\n ]\r\n }\r\n}\r\n"
],
[
"!kubectl apply -f resources/loadtest_simple_model.json",
"seldondeployment \"seldon-core-loadtest\" created\r\n"
]
],
[
[
"Wait for deployment to be running.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!kubectl get seldondeployments seldon-core-loadtest -o jsonpath='{.status}'",
"map[predictorStatus:[map[name:loadtest-loadtest replicas:1 replicasAvailable:1]]]"
]
],
[
[
"## Run benchmark",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Uncorden the first 3 nodes so they can be used to schedule locust",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!kubectl uncordon $(kubectl get nodes -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')\n!kubectl uncordon $(kubectl get nodes -o jsonpath='{.items[1].metadata.name}')\n!kubectl uncordon $(kubectl get nodes -o jsonpath='{.items[2].metadata.name}')",
"node \"gke-loadtest-default-pool-e2e99314-7zb5\" uncordoned\nnode \"gke-loadtest-default-pool-e2e99314-gbjx\" uncordoned\nnode \"gke-loadtest-default-pool-e2e99314-hcvx\" uncordoned\n"
]
],
[
[
"## gRPC\nStart locust load test for gRPC",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!helm install ../helm-charts/seldon-core-loadtesting --name loadtest \\\n --set locust.host=loadtest:5001 \\\n --set locust.script=predict_grpc_locust.py \\\n --set oauth.enabled=false \\\n --set oauth.key=oauth-key \\\n --set oauth.secret=oauth-secret \\\n --set locust.hatchRate=1 \\\n --set locust.clients=256 \\\n --set loadtest.sendFeedback=0 \\\n --set locust.minWait=0 \\\n --set locust.maxWait=0 \\\n --set replicaCount=64 ",
"NAME: loadtest\nLAST DEPLOYED: Wed Mar 7 15:17:44 2018\nNAMESPACE: default\nSTATUS: DEPLOYED\n\nRESOURCES:\n==> v1/Service\nNAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE\nlocust-master-1 NodePort 10.3.253.118 <none> 5557:30970/TCP,5558:30185/TCP,8089:30505/TCP 1s\n\n==> v1/Pod(related)\nNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE\nlocust-slave-1-2kc26 0/1 Pending 0 0s\nlocust-slave-1-2ngks 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-4kxg4 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-5h67f 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-62c7w 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-68skx 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-6qnwx 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-9d4vm 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-b9fgb 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-bf7nq 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-bpzrm 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-bqc4g 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-cr2f8 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-f2lnr 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-fxb5j 0/1 Pending 0 0s\nlocust-slave-1-gmmlc 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-hs9q2 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-jl4dz 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-khkc6 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-kwknl 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-l5vjh 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-ls2nv 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-n2xft 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-njvwf 0/1 Pending 0 0s\nlocust-slave-1-q88tf 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-r28vx 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-rldrp 0/1 Pending 0 0s\nlocust-slave-1-sbrz5 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-sj2rg 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-sm9mb 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-stfrc 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-t67gv 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-t8x4t 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-tnhdp 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-vtm4p 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-vx6c5 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-x2mfm 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-zrbx2 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-master-1-n7hrr 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 1s\n\n==> v1/ReplicationController\nNAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE\nlocust-slave-1 64 0 0 1s\nlocust-master-1 1 1 0 1s\n\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"To download stats use \n\n```bash\nif [ \"$#\" -ne 2 ]; then\n echo \"Illegal number of parameters: <experiment> <rest|grpc>\"\nfi\n\nEXPERIMENT=$1\nTYPE=$2\n\nMASTER=`kubectl get pod -l name=locust-master-1 -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}'`\n\nkubectl cp ${MASTER}:stats_distribution.csv ${EXPERIMENT}_${TYPE}_stats_distribution.csv\nkubectl cp ${MASTER}:stats_requests.csv ${EXPERIMENT}_${TYPE}_stats_requests.csv\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"You can get live stats by viewing the logs of the locust master",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!kubectl logs $(kubectl get pod -l name=locust-master-1 -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') --tail=10",
" grpc loadtest:5001 875872 0(0.00%) 1 0 5020 | 1 26458.80\r\n--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\r\n Total 875872 0(0.00%) 26458.80\r\n\r\n Name # reqs # fails Avg Min Max | Median req/s\r\n--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\r\n grpc loadtest:5001 917872 0(0.00%) 1 0 5020 | 1 25319.50\r\n--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\r\n Total 917872 0(0.00%) 25319.50\r\n\r\n"
],
[
"!helm delete loadtest --purge",
"release \"loadtest\" deleted\r\n"
]
],
[
[
"## REST \nRun REST benchmark",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!helm install ../helm-charts/seldon-core-loadtesting --name loadtest \\\n --set locust.host=http://loadtest:8000 \\\n --set oauth.enabled=false \\\n --set oauth.key=oauth-key \\\n --set oauth.secret=oauth-secret \\\n --set locust.hatchRate=1 \\\n --set locust.clients=256 \\\n --set loadtest.sendFeedback=0 \\\n --set locust.minWait=0 \\\n --set locust.maxWait=0 \\\n --set replicaCount=64",
"NAME: loadtest\nLAST DEPLOYED: Wed Mar 7 15:20:13 2018\nNAMESPACE: default\nSTATUS: DEPLOYED\n\nRESOURCES:\n==> v1/ReplicationController\nNAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE\nlocust-slave-1 64 0 0 1s\nlocust-master-1 1 1 0 1s\n\n==> v1/Service\nNAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE\nlocust-master-1 NodePort 10.3.243.232 <none> 5557:31799/TCP,5558:32699/TCP,8089:30737/TCP 1s\n\n==> v1/Pod(related)\nNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE\nlocust-slave-1-29sc7 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-4h2jz 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-545xr 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-55vbz 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-59lff 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-dtcvq 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-dzh8c 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-f4h26 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-hdk4v 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-hnfb7 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-j2w82 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-jtcsp 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-jvzjs 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-kkhpg 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-krhlk 0/1 Pending 0 0s\nlocust-slave-1-kwwx2 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-lq2xn 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-ls2vj 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-m8r6d 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-mrcrb 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-pvdgp 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-pvqxp 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-q77j9 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-r4ss5 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-rm5rn 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-rpgt4 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-rs28s 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-tjhvl 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-vk2lg 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-vsxd7 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-vv8s8 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-vx9bn 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-slave-1-zjlt4 0/1 Pending 0 1s\nlocust-master-1-5jh2d 0/1 Pending 0 1s\n\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"Get stats as per gRPC and/or monitor",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!kubectl logs $(kubectl get pod -l name=locust-master-1 -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') --tail=10",
" POST predictions 250653 0(0.00%) 5 2 5011 | 4 11907.80\r\n--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\r\n Total 250653 0(0.00%) 11907.80\r\n\r\n Name # reqs # fails Avg Min Max | Median req/s\r\n--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\r\n POST predictions 272674 0(0.00%) 5 2 5011 | 4 11785.90\r\n--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\r\n Total 272674 0(0.00%) 11785.90\r\n\r\n"
],
[
"!helm delete loadtest --purge",
"release \"loadtest\" deleted\r\n"
],
[
"!kubectl cordon $(kubectl get nodes -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')\n!kubectl cordon $(kubectl get nodes -o jsonpath='{.items[1].metadata.name}')\n!kubectl cordon $(kubectl get nodes -o jsonpath='{.items[2].metadata.name}')",
"node \"gke-loadtest-default-pool-e2e99314-7zb5\" cordoned\nnode \"gke-loadtest-default-pool-e2e99314-gbjx\" cordoned\nnode \"gke-loadtest-default-pool-e2e99314-hcvx\" cordoned\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Tear Down",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!kubectl delete -f resources/loadtest_simple_model.json",
"seldondeployment \"seldon-core-loadtest\" deleted\r\n"
],
[
"!helm delete seldon-core --purge",
"release \"seldon-core\" deleted\r\n"
],
[
"!helm delete seldon-core-crd --purge",
"release \"seldon-core-crd\" deleted\r\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a7130e0ffb1fded9d2ada5c8b203a21997776ef
| 41,878 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
site/en/guide/distribute_strategy_tf1.ipynb
|
shawnkoon/docs
|
c13cd44cfab572fe5a7111afd60bb0bfd9596039
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 2 |
2021-07-05T19:07:31.000Z
|
2021-11-17T11:09:30.000Z
|
site/en/guide/distribute_strategy_tf1.ipynb
|
shawnkoon/docs
|
c13cd44cfab572fe5a7111afd60bb0bfd9596039
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
site/en/guide/distribute_strategy_tf1.ipynb
|
shawnkoon/docs
|
c13cd44cfab572fe5a7111afd60bb0bfd9596039
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2019-11-10T04:01:29.000Z
|
2019-11-10T04:01:29.000Z
| 46.8434 | 1,144 | 0.623167 |
[
[
[
"##### Copyright 2018 The TensorFlow Authors.\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#@title Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the \"License\");\n# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.\n# You may obtain a copy of the License at\n#\n# https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0\n#\n# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software\n# distributed under the License is distributed on an \"AS IS\" BASIS,\n# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.\n# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and\n# limitations under the License.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Distributed Training in TensorFlow",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<table class=\"tfo-notebook-buttons\" align=\"left\">\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/alpha/guide/distribute_strategy\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/tf_logo_32px.png\" />View on TensorFlow.org</a>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/tensorflow/docs/blob/master/site/en/r2/guide/distribute_strategy.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/colab_logo_32px.png\" />Run in Google Colab</a>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://github.com/tensorflow/docs/blob/master/site/en/r2/guide/distribute_strategy.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/GitHub-Mark-32px.png\" />View source on GitHub</a>\n </td>\n</table>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Overview\n\n`tf.distribute.Strategy` is a TensorFlow API to distribute training\nacross multiple GPUs, multiple machines or TPUs. Using this API, users can distribute their existing models and training code with minimal code changes.\n\n`tf.distribute.Strategy` has been designed with these key goals in mind:\n* Easy to use and support multiple user segments, including researchers, ML engineers, etc.\n* Provide good performance out of the box.\n* Easy switching between strategies.\n\n`tf.distribute.Strategy` can be used with TensorFlow's high level APIs, [tf.keras](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/keras) and [tf.estimator](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/estimators), with just a couple of lines of code change. It also provides an API that can be used to distribute custom training loops (and in general any computation using TensorFlow).\nIn TensorFlow 2.0, users can execute their programs eagerly, or in a graph using [`tf.function`](../tutorials/eager/tf_function.ipynb). `tf.distribute.Strategy` intends to support both these modes of execution. Note that we may talk about training most of the time in this guide, but this API can also be used for distributing evaluation and prediction on different platforms.\n\nAs you will see in a bit, very few changes are needed to use `tf.distribute.Strategy` with your code. This is because we have changed the underlying components of TensorFlow to become strategy-aware. This includes variables, layers, models, optimizers, metrics, summaries, and checkpoints. \n\nIn this guide, we will talk about various types of strategies and how one can use them in a different situations. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import TensorFlow\nfrom __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function\nimport tensorflow as tf #gpu",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Types of strategies\n`tf.distribute.Strategy` intends to cover a number of use cases along different axes. Some of these combinations are currently supported and others will be added in the future. Some of these axes are:\n* Syncronous vs asynchronous training: These are two common ways of distributing training with data parallelism. In sync training, all workers train over different slices of input data in sync, and aggregating gradients at each step. In async training, all workers are independently training over the input data and updating variables asynchronously. Typically sync training is supported via all-reduce and async through parameter server architecture.\n* Hardware platform: Users may want to scale their training onto multiple GPUs on one machine, or multiple machines in a network (with 0 or more GPUs each), or on Cloud TPUs.\n\nIn order to support these use cases, we have 4 strategies available. In the next section we will talk about which of these are supported in which scenarios in TF nightly at this time.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### MirroredStrategy\n`tf.distribute.MirroredStrategy` support synchronous distributed training on multiple GPUs on one machine. It creates one replica per GPU device. Each variable in the model is mirrored across all the replicas. Together, these variables form a single conceptual variable called `MirroredVariable`. These variables are kept in sync with each other by applying identical updates.\n\nEfficient all-reduce algorithms are used to communicate the variable updates across the devices.\nAll-reduce aggregates tensors across all the devices by adding them up, and makes them available on each device.\nIt’s a fused algorithm that is very efficient and can reduce the overhead of synchronization significantly. There are many all-reduce algorithms and implementations available, depending on the type of communication available between devices. By default, it uses NVIDIA NCCL as the all-reduce implementation. The user can also choose between a few other options we provide, or write their own.\n\nHere is the simplest way of creating `MirroredStrategy`:\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mirrored_strategy = tf.distribute.MirroredStrategy()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This will create a `MirroredStrategy` instance which will use all the GPUs that are visible to TensorFlow, and use NCCL as the cross device communication.\n\nIf you wish to use only some of the GPUs on your machine, you can do so like this:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mirrored_strategy = tf.distribute.MirroredStrategy(devices=[\"/gpu:0\", \"/gpu:1\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"If you wish to override the cross device communication, you can do so using the `cross_device_ops` argument by supplying an instance of `tf.distribute.CrossDeviceOps`. Currently we provide `tf.distribute.HierarchicalCopyAllReduce` and `tf.distribute.ReductionToOneDevice` as 2 other options other than `tf.distribute.NcclAllReduce` which is the default.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mirrored_strategy = tf.distribute.MirroredStrategy(\n cross_device_ops=tf.distribute.HierarchicalCopyAllReduce())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### MultiWorkerMirroredStrategy\n\n`tf.distribute.experimental.MultiWorkerMirroredStrategy` is very similar to `MirroredStrategy`. It implements synchronous distributed training across multiple workers, each with potentially multiple GPUs. Similar to `MirroredStrategy`, it creates copies of all variables in the model on each device across all workers. \n\nIt uses [CollectiveOps](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/python/ops/collective_ops.py) as the multi-worker all-reduce communication method used to keep variables in sync. A collective op is a single op in the TensorFlow graph which can automatically choose an all-reduce algorithm in the TensorFlow runtime according to hardware, network topology and tensor sizes. \n\nIt also implements additional performance optimizations. For example, it includes a static optimization that converts multiple all-reductions on small tensors into fewer all-reductions on larger tensors. In addition, we are designing it to have a plugin architecture - so that in the future, users will be able to plugin algorithms that are better tuned for their hardware. Note that collective ops also implement other collective operations such as broadcast and all-gather. \n\nHere is the simplest way of creating `MultiWorkerMirroredStrategy`: ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"multiworker_strategy = tf.distribute.experimental.MultiWorkerMirroredStrategy()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"`MultiWorkerMirroredStrategy` currently allows you to choose between two different implementations of collective ops. `CollectiveCommunication.RING` implements ring-based collectives using gRPC as the communication layer. `CollectiveCommunication.NCCL` uses [Nvidia's NCCL](https://developer.nvidia.com/nccl) to implement collectives. `CollectiveCommunication.AUTO` defers the choice to the runtime. The best choice of collective implementation depends upon the number and kind of GPUs, and the network interconnect in the cluster. You can specify them like so:\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"multiworker_strategy = tf.distribute.experimental.MultiWorkerMirroredStrategy(\n tf.distribute.experimental.CollectiveCommunication.NCCL)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\nOne of the key differences to get multi worker training going, as compared to multi-GPU training, is the multi-worker setup. \"TF_CONFIG\" environment variable is the standard way in TensorFlow to specify the cluster configuration to each worker that is part of the cluster. See section on [\"TF_CONFIG\" below](#TF_CONFIG) for more details on how this can be done. \n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Note: This strategy is [`experimental`](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/version_compat#what_is_not_covered) as we are currently improving it and making it work for more scenarios. As part of this, please expect the APIs to change in the future.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### TPUStrategy\n`tf.distribute.experimental.TPUStrategy` lets users run their TensorFlow training on Tensor Processing Units (TPUs). TPUs are Google's specialized ASICs designed to dramatically accelerate machine learning workloads. They are available on Google Colab, the [TensorFlow Research Cloud](https://www.tensorflow.org/tfrc) and [Google Compute Engine](https://cloud.google.com/tpu).\n\nIn terms of distributed training architecture, TPUStrategy is the same `MirroredStrategy` - it implements synchronous distributed training. TPUs provide their own implementation of efficient all-reduce and other collective operations across multiple TPU cores, which are used in `TPUStrategy`. \n\nHere is how you would instantiate `TPUStrategy`.\nNote: To run this code in Colab, you should select TPU as the Colab runtime. See [Using TPUs]( tpu.ipynb) guide for a runnable version.\n\n```\nresolver = tf.distribute.cluster_resolver.TPUClusterResolver()\ntf.tpu.experimental.initialize_tpu_system(resolver)\ntpu_strategy = tf.distribute.experimental.TPUStrategy(resolver)\n```\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"`TPUClusterResolver` instance helps locate the TPUs. In Colab, you don't need to specify any arguments to it. If you want to use this for Cloud TPUs, you will need to specify the name of your TPU resource in `tpu` argument. We also need to initialize the tpu system explicitly at the start of the program. This is required before TPUs can be used for computation and should ideally be done at the beginning because it also wipes out the TPU memory so all state will be lost. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Note: This strategy is [`experimental`](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/version_compat#what_is_not_covered) as we are currently improving it and making it work for more scenarios. As part of this, please expect the APIs to change in the future.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### ParameterServerStrategy\n`tf.distribute.experimental.ParameterServerStrategy` supports parameter servers training. It can be used either for multi-GPU synchronous local training or asynchronous multi-machine training. When used to train locally on one machine, variables are not mirrored, instead they are placed on the CPU and operations are replicated across all local GPUs. In a multi-machine setting, some machines are designated as workers and some as parameter servers. Each variable of the model is placed on one parameter server. Computation is replicated across all GPUs of the all the workers.\n\nIn terms of code, it looks similar to other strategies:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"ps_strategy = tf.distribute.experimental.ParameterServerStrategy()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"For multi worker training, \"TF_CONFIG\" needs to specify the configuration of parameter servers and workers in your cluster, which you can read more about in [\"TF_CONFIG\" below](#TF_CONFIG) below. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\nSo far we've talked about what are the different stategies available and how you can instantiate them. In the next few sections, we will talk about the different ways in which you can use them to distribute your training. We will show short code snippets in this guide and link off to full tutorials which you can run end to end. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Using `tf.distribute.Strategy` with Keras\nWe've integrated `tf.distribute.Strategy` into `tf.keras` which is TensorFlow's implementation of the\n[Keras API specification](https://keras.io). `tf.keras` is a high-level API to build and train models. By integrating into `tf.keras` backend, we've made it seamless for Keras users to distribute their training written in the Keras training framework. The only things that need to change in a user's program are: (1) Create an instance of the appropriate `tf.distribute.Strategy` and (2) Move the creation and compiling of Keras model inside `strategy.scope`. \n\nHere is a snippet of code to do this for a very simple Keras model with one dense layer:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mirrored_strategy = tf.distribute.MirroredStrategy()\nwith mirrored_strategy.scope():\n model = tf.keras.Sequential([tf.keras.layers.Dense(1, input_shape=(1,))])\n model.compile(loss='mse', optimizer='sgd')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"In this example we used `MirroredStrategy` so we can run this on a machine with multiple GPUs. `strategy.scope()` indicated which parts of the code to run distributed. Creating a model inside this scope allows us to create mirrored variables instead of regular variables. Compiling under the scope allows us to know that the user intends to train this model using this strategy. Once this is setup, you can fit your model like you would normally. `MirroredStrategy` takes care of replicating the model's training on the available GPUs, aggregating gradients etc.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensors(([1.], [1.])).repeat(100).batch(10)\nmodel.fit(dataset, epochs=2)\nmodel.evaluate(dataset)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Here we used a `tf.data.Dataset` to provide the training and eval input. You can also use numpy arrays:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\ninputs, targets = np.ones((100, 1)), np.ones((100, 1))\nmodel.fit(inputs, targets, epochs=2, batch_size=10)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"In both cases (dataset or numpy), each batch of the given input is divided equally among the multiple replicas. For instance, if using `MirroredStrategy` with 2 GPUs, each batch of size 10 will get divided among the 2 GPUs, with each receiving 5 input examples in each step. Each epoch will then train faster as you add more GPUs. Typically, you would want to increase your batch size as you add more accelerators so as to make effective use of the extra computing power. You will also need to re-tune your learning rate, depending on the model. You can use `strategy.num_replicas_in_sync` to get the number of replicas.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Compute global batch size using number of replicas.\nBATCH_SIZE_PER_REPLICA = 5\nglobal_batch_size = (BATCH_SIZE_PER_REPLICA * \n mirrored_strategy.num_replicas_in_sync)\ndataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensors(([1.], [1.])).repeat(100)\ndataset = dataset.batch(global_batch_size)\n\nLEARNING_RATES_BY_BATCH_SIZE = {5: 0.1, 10: 0.15}\nlearning_rate = LEARNING_RATES_BY_BATCH_SIZE[global_batch_size]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### What's supported now?\n\nIn [TF nightly release](https://pypi.org/project/tf-nightly-gpu/), we now support training with Keras using all strategies.\n\nNote: When using `MultiWorkerMirorredStrategy` for multiple workers or `TPUStrategy` with more than one host with Keras, currently the user will have to explicitly shard or shuffle the data for different workers, but we will change this in the future to automatically shard the input data intelligently. \n\n### Examples and Tutorials\n\nHere is a list of tutorials and examples that illustrate the above integration end to end with Keras:\n1. [Tutorial](../tutorials/distribute/keras.ipynb) to train MNIST with `MirroredStrategy`.\n2. Official [ResNet50](https://github.com/tensorflow/models/blob/master/official/resnet/keras/keras_imagenet_main.py) training with ImageNet data using `MirroredStrategy`.\n3. [ResNet50](https://github.com/tensorflow/tpu/blob/master/models/experimental/resnet50_keras/resnet50.py) trained with Imagenet data on Cloud TPus with `TPUStrategy`.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Using `tf.distribute.Strategy` with Estimator\n`tf.estimator` is a distributed training TensorFlow API that originally supported the async parameter server approach. Like with Keras, we've integrated `tf.distribute.Strategy` into `tf.Estimator` so that a user who is using Estimator for their training can easily change their training is distributed with very few changes to your their code. With this, estimator users can now do synchronous distributed training on multiple GPUs and multiple workers, as well as use TPUs. \n\nThe usage of `tf.distribute.Strategy` with Estimator is slightly different than the Keras case. Instead of using `strategy.scope`, now we pass the strategy object into the [`RunConfig`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/estimator/RunConfig) for the Estimator. \n\nHere is a snippet of code that shows this with a premade estimator `LinearRegressor` and `MirroredStrategy`:\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mirrored_strategy = tf.distribute.MirroredStrategy()\nconfig = tf.estimator.RunConfig(\n train_distribute=mirrored_strategy, eval_distribute=mirrored_strategy)\nregressor = tf.estimator.LinearRegressor(\n feature_columns=[tf.feature_column.numeric_column('feats')],\n optimizer='SGD',\n config=config)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We use a premade Estimator here, but the same code works with a custom Estimator as well. `train_evaluate` determines how training will be distributed, and `eval_distribute` determines how evaluation will be distributed. This is another difference from Keras where we use the same strategy for both training and eval. \n\nNow we can train and evaluate this Estimator with an input function:\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def input_fn():\n dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensors(({\"feats\":[1.]}, [1.]))\n return dataset.repeat(1000).batch(10)\nregressor.train(input_fn=input_fn, steps=10)\nregressor.evaluate(input_fn=input_fn, steps=10)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Another difference to highlight here between Estimator and Keras is the input handling. In Keras, we mentioned that each batch of the dataset is split across the multiple replicas. In Estimator, however, the user provides an `input_fn` and have full control over how they want their data to be distributed across workers and devices. We do not do automatic splitting of batch, nor automatically shard the data across different workers. The provided `input_fn` is called once per worker, thus giving one dataset per worker. Then one batch from that dataset is fed to one replica on that worker, thereby consuming N batches for N replicas on 1 worker. In other words, the dataset returned by the `input_fn` should provide batches of size `PER_REPLICA_BATCH_SIZE`. And the global batch size for a step can be obtained as `PER_REPLICA_BATCH_SIZE * strategy.num_replicas_in_sync`. When doing multi worker training, users will also want to either split their data across the workers, or shuffle with a random seed on each. You can see an example of how to do this in the [multi-worker tutorial](../tutorials/distribute/multi_worker.ipynb). ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We showed an example of using `MirroredStrategy` with Estimator. You can also use `TPUStrategy` with Estimator as well, in the exact same way:\n```\nconfig = tf.estimator.RunConfig(\n train_distribute=tpu_strategy, eval_distribute=tpu_strategy)\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"And similarly, you can use multi worker and parameter server strategies as well. The code remains the same, but you need to use `tf.estimator.train_and_evaluate`, and set \"TF_CONFIG\" environment variables for each binary running in your cluster.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### What's supported now?\n\nIn TF nightly release, we support training with Estimator using all strategies. \n\n### Examples and Tutorials\nHere are some examples that show end to end usage of various strategies with Estimator:\n\n1. [End to end example](https://github.com/tensorflow/ecosystem/tree/master/distribution_strategy) for multi worker training in tensorflow/ecosystem using Kuberentes templates. This example starts with a Keras model and converts it to an Estimator using the `tf.keras.estimator.model_to_estimator` API. \n2. Official [ResNet50](https://github.com/tensorflow/models/blob/master/official/resnet/imagenet_main.py) model, which can be trained using either `MirroredStrategy` or `MultiWorkerMirroredStrategy`.\n3. [ResNet50](https://github.com/tensorflow/tpu/blob/master/models/experimental/distribution_strategy/resnet_estimator.py) example with TPUStrategy.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Using `tf.distribute.Strategy` with custom training loops\nAs you've seen, using `tf.distrbute.Strategy` with high level APIs is only a couple lines of code change. With a little more effort, `tf.distrbute.Strategy` can also be used by other users who are not using these frameworks.\n\nTensorFlow is used for a wide variety of use cases and some users (such as researchers) require more flexibility and control over their training loops. This makes it hard for them to use the high level frameworks such as Estimator or Keras. For instance, someone using a GAN may want to take a different number of generator or discriminator steps each round. Similarly, the high level frameworks are not very suitable for Reinforcement Learning training. So these users will usually write their own training loops. \n\nFor these users, we provide a core set of methods through the `tf.distrbute.Strategy` classes. Using these may require minor restructuring of the code initially, but once that is done, the user should be able to switch between GPUs / TPUs / multiple machines by just changing the strategy instance.\n\nHere we will show a brief snippet illustrating this use case for a simple training example using the same Keras model as before. \nNote: These APIs are still experimental and we are improving them to make them more user friendly.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"First, we create the model and optimizer inside the strategy's scope. This ensures that any variables created with the model and optimizer are mirrored variables.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"with mirrored_strategy.scope():\n model = tf.keras.Sequential([tf.keras.layers.Dense(1, input_shape=(1,))])\n optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Next, we create the input dataset and call `make_dataset_iterator` to distribute the dataset based on the strategy. This API is expected to change in the near future.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"with mirrored_strategy.scope():\n dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensors(([1.], [1.])).repeat(1000).batch(\n global_batch_size)\n input_iterator = mirrored_strategy.make_dataset_iterator(dataset)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Then, we define one step of the training. We will use `tf.GradientTape` to compute gradients and optimizer to apply those gradients to update our model's variables. To distribute this training step, we put in in a function `step_fn` and pass it to `strategy.experimental_run` along with the iterator created before:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def train_step():\n def step_fn(inputs):\n features, labels = inputs\n logits = model(features)\n cross_entropy = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(\n logits=logits, labels=labels) \n loss = tf.reduce_sum(cross_entropy) * (1.0 / global_batch_size)\n train_op = optimizer.minimize(loss)\n with tf.control_dependencies([train_op]):\n return tf.identity(loss)\n\n per_replica_losses = mirrored_strategy.experimental_run(\n step_fn, input_iterator)\n mean_loss = mirrored_strategy.reduce(\n tf.distribute.ReduceOp.MEAN, per_replica_losses)\n return mean_loss",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"A few other things to note in the code above: \n1. We used `tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits` to compute the loss. And then we scaled the total loss by the global batch size. This is important because all the replicas are training in sync and number of examples in each step of training is the global batch. If you're using TensorFlow's standard losses from `tf.losses` or `tf.keras.losses`, they are distribution aware and will take care of the scaling by number of replicas whenever a strategy is in scope. \n2. We used the `strategy.reduce` API to aggregate the results returned by `experimental_run`. `experimental_run` returns results from each local replica in the strategy, and there are multiple ways to consume this result. You can `reduce` them to get an aggregated value. You can also do `strategy.unwrap(results)`* to get the list of values contained in the result, one per local replica.\n\n*expected to change\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Finally, once we have defined the training step, we can initialize the iterator and variables and run the training in a loop:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"with mirrored_strategy.scope():\n iterator_init = input_iterator.initialize()\n var_init = tf.global_variables_initializer()\n loss = train_step()\n with tf.Session() as sess:\n sess.run([iterator_init, var_init])\n for _ in range(10):\n print(sess.run(loss))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"In the example above, we used `make_dataset_iterator` to provide input to your training. We also provide two additional APIs: `make_input_fn_iterator` and `make_experimental_numpy_iterator` to support other kinds of inputs. See their documentation in `tf.distribute.Strategy` and how they differ from `make_dataset_iterator`.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"This covers the simplest case of using `tf.distribute.Strategy` API to do distribute custom training loops. We are in the process of improving these APIs. Since this use case requres more work on the part of the user, we will be publishing a separate detailed guide for this use case in the future.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### What's supported now?\nIn TF nightly release, we support training with custom training loops using `MirroredStrategy` and `TPUStrategy` as shown above. Support for other strategies will be coming in soon. `MultiWorkerMirorredStrategy` support will be coming in the future.\n\n### Examples and Tutorials\nHere are some examples for using distribution strategy with custom training loops:\n1. [Example](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/5456cc28f3f8d9c17c645d9a409e495969e584ae/tensorflow/contrib/distribute/python/examples/mnist_tf1_tpu.py) to train MNIST using `TPUStrategy`.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Other topics\nIn this section, we will cover some topics that are relevant to multiple use cases.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a id=\"TF_CONFIG\">\n### Setting up TF\\_CONFIG environment variable\n</a>\nFor multi-worker training, as mentioned before, you need to us set \"TF\\_CONFIG\" environment variable for each\nbinary running in your cluster. The \"TF\\_CONFIG\" environment variable is a JSON string which specifies what\ntasks constitute a cluster, their addresses and each task's role in the cluster. We provide a Kubernetes template in the\n[tensorflow/ecosystem](https://github.com/tensorflow/ecosystem) repo which sets\n\"TF\\_CONFIG\" for your training tasks. \n\nOne example of \"TF\\_CONFIG\" is:\n```\nos.environ[\"TF_CONFIG\"] = json.dumps({\n \"cluster\": {\n \"worker\": [\"host1:port\", \"host2:port\", \"host3:port\"],\n \"ps\": [\"host4:port\", \"host5:port\"]\n },\n \"task\": {\"type\": \"worker\", \"index\": 1}\n})\n```\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"This \"TF\\_CONFIG\" specifies that there are three workers and two ps tasks in the\ncluster along with their hosts and ports. The \"task\" part specifies that the\nrole of the current task in the cluster, worker 1 (the second worker). Valid roles in a cluster is\n\"chief\", \"worker\", \"ps\" and \"evaluator\". There should be no \"ps\" job except when using `tf.distribute.experimental.ParameterServerStrategy`. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## What's next?\n\n`tf.distribute.Strategy` is actively under development. We welcome you to try it out and provide and your feedback via [issues on GitHub](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/issues/new).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4a713627f3e4b335721166edf73af4d9556397af
| 11,805 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
code/Project_3.ipynb
|
dreamofjade/ModSimPy
|
12bc71e5ecd122e96e57f4659d1e79c2c6ec7361
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
code/Project_3.ipynb
|
dreamofjade/ModSimPy
|
12bc71e5ecd122e96e57f4659d1e79c2c6ec7361
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
code/Project_3.ipynb
|
dreamofjade/ModSimPy
|
12bc71e5ecd122e96e57f4659d1e79c2c6ec7361
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 28.107143 | 328 | 0.374756 |
[
[
[
"# Project 3",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Configure Jupyter so figures appear in the notebook\n%matplotlib inline\n\n# Configure Jupyter to display the assigned value after an assignment\n%config InteractiveShell.ast_node_interactivity='last_expr_or_assign'\n\n# import functions from the modsim.py module\nfrom modsim import *\nfrom numpy import *",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"m = UNITS.meter\ns = UNITS.second\nkg = UNITS.kilogram\ndegree = UNITS.degree",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"params = Params(x = 0 * m, \n y = 5000 * m,\n g = 3.7 * m/s**2,\n mass = 900 * kg,\n diameter = 1.5 * m,\n rho = 1.2 * 0.006 * kg/m**3,\n C_d = 0.3,\n angle = 45 * degree,\n velocity = 50 * m / s,\n t_end = 20 * s)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def make_system(params):\n \"\"\"Make a system object.\n \n params: Params object with angle, velocity, x, y,\n diameter, duration, g, mass, rho, and C_d\n \n returns: System object\n \"\"\"\n unpack(params)\n \n # convert angle to degrees\n theta = np.deg2rad(angle)\n \n # compute x and y components of velocity\n vx, vy = pol2cart(theta, velocity)\n \n # make the initial state\n init = State(x=x, y=y, vx=vx, vy=vy)\n \n # compute area from diameter\n area = np.pi * (diameter/2)**2\n \n return System(params, init=init, area=area)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def drag_force(V, system):\n \"\"\"Computes drag force in the opposite direction of `V`.\n \n V: velocity\n system: System object with rho, C_d, area\n \n returns: Vector drag force\n \"\"\"\n unpack(system)\n mag = -rho * V.mag**2 * C_d * area / 2\n direction = V.hat()\n f_drag = mag * direction\n return f_drag",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def slope_func(state, t, system):\n \"\"\"Computes derivatives of the state variables.\n \n state: State (x, y, x velocity, y velocity)\n t: time\n system: System object with g, rho, C_d, area, mass\n \n returns: sequence (vx, vy, ax, ay)\n \"\"\"\n x, y, vx, vy = state\n unpack(system)\n\n V = Vector(vx, vy) \n a_drag = drag_force(V, system) / mass\n a_grav = Vector(0, -g)\n \n a = a_grav + a_drag\n \n return vx, vy, a.x, a.y",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def event_func(state, t, system):\n \"\"\"Stop when the y coordinate is 0.\n \n state: State object\n t: time\n system: System object\n \n returns: y coordinate\n \"\"\"\n x, y, vx, vy = state\n return y",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"make_system(params)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"drag_force(velocity, system)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a713e2f17ef364437d67b5a4bedf9e6575a5989
| 288,122 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/test.show_clusters.ipynb
|
BiCroLab/nucleAI
|
1fa1ea23e5b0f282b51e8a57f428f8e8cfc51589
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-05-25T13:40:56.000Z
|
2021-05-25T13:40:56.000Z
|
notebooks/test.show_clusters.ipynb
|
BiCroLab/nucleAI
|
1fa1ea23e5b0f282b51e8a57f428f8e8cfc51589
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/test.show_clusters.ipynb
|
BiCroLab/nucleAI
|
1fa1ea23e5b0f282b51e8a57f428f8e8cfc51589
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-05-25T13:41:06.000Z
|
2021-05-25T13:41:06.000Z
| 776.609164 | 219,804 | 0.948747 |
[
[
[
"import os\nimport glob\nimport pickle\nimport sys \n\nsys.path.insert(0, '../py')\nfrom graviti import *\n\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\n\nfrom matplotlib import pyplot\n\nimport warnings\nwarnings.filterwarnings('ignore')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = pd.read_pickle('../py/df_clusters.pkl')\ndf.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import seaborn\nseaborn.set(style='white')\n\nfg = seaborn.FacetGrid(data=df[['x_umap','y_umap','UMAP_cluster_ID']], \n hue='UMAP_cluster_ID')\nfg.map(pyplot.scatter, 'x_umap', 'y_umap').add_legend()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\nfg = seaborn.FacetGrid(data=df[['x_umap','y_umap','label']], \n hue='label',size=10)\nfg.map(pyplot.scatter, 'x_umap', 'y_umap',s=5,alpha=0.5).add_legend()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fg = seaborn.FacetGrid(data=df[['x_pca','y_pca','PCA_cluster_ID']], \n hue='PCA_cluster_ID')\nfg.map(pyplot.scatter, 'x_pca', 'y_pca').add_legend()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.to_csv('df_clusters.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Study the statistics of the covd barycenters",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"barycenters = np.load('../py/covd_barycenters.npy')\n\ninfile = open('list_of_cancerID.pkl','rb')\ncancerID = pickle.load(infile)\ninfile.close\nprint(barycenters.shape,len(cancerID))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = pd.DataFrame([[s] for s in barycenters],columns= ['barycenters'])\ndf['cancerID'] = cancerID",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#result = df.groupby(['cancerID'], as_index=False).agg({'barycenters':['mean']})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"groups = df.groupby('cancerID')\ndata = np.zeros((10,36))\nrow = 0\ncancer_list = []\nfor name, group in groups:\n cancer_list.append(name)\n #group.x, group.y, marker='o', linestyle='', ms=3, label=name, alpha=0.75\n data[row,:] = group['barycenters'].mean()\n row += 1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import umap\nreducer = umap.UMAP(n_components=2)\nembedding = reducer.fit_transform(data)\nx = embedding[:,0]\ny = embedding[:,1]\ndf_plot = pd.DataFrame(dict(x=x, y=y, label=cancer_list))\nimport seaborn as sns; sns.set()\nfig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10,10))\nax = sns.scatterplot(x=\"x\", y=\"y\", hue=\"label\",data=df_plot)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pca = PCA(n_components=2)\nembedding = pca.fit_transform(data)\nx = embedding[:,0]\ny = embedding[:,1]\ndf_plot = pd.DataFrame(dict(x=x, y=y, label=cancer_list))\nimport seaborn as sns; sns.set()\nfig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10,10))\nax = sns.scatterplot(x=\"x\", y=\"y\", hue=\"label\",data=df_plot)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a7163eff7ee8caf32f94db8ac91bb046e8b0dc3
| 7,097 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Examples/notebooks/Streamlines.ipynb
|
paulbrodersen/BrainRender
|
772684d5fb52cd827e88357cda995f36c0ad2e60
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Examples/notebooks/Streamlines.ipynb
|
paulbrodersen/BrainRender
|
772684d5fb52cd827e88357cda995f36c0ad2e60
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Examples/notebooks/Streamlines.ipynb
|
paulbrodersen/BrainRender
|
772684d5fb52cd827e88357cda995f36c0ad2e60
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 41.023121 | 618 | 0.653938 |
[
[
[
"# Streamlines tutorial\nIn this tutorial you will learn how to download and render streamline data to display connectivity data. In brief, injections of anterogradely transported viruses are performed in wild type and CRE-driver mouse lines. The viruses express fluorescent proteins so that efferent projections from the injection locations can be traced everywhere in the brain. The images with the fluorescence data are acquired and registered to the Allen Coordinates reference frame. The traces of the streamlines are then extracted using a fast marching algorithm (by [https://neuroinformatics.nl](https://neuroinformatics.nl)).\n\n<img src=\"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/BrancoLab/BrainRender/master/Docs/Media/streamlines2.png\" width=\"600\" height=\"350\">\n\nThe connectivity data are produced as part of the Allen Brain Atlas [Mouse Connectivity project](http://connectivity.brain-map.org).\n\nThe first step towards being able to render streamlines data is to identify the set of experiments you are interested in (i.e. injections in the primary visual cortex of wild type mice]. To do so you can use the experiments explorer at [http://connectivity.brain-map.org].\n\nOnce you have selected the experiments, you can download metadata about them using the 'download data as csv' option at the bottom of the page. This metadata .csv is what we can then use to get a link to the data to download. \n\nFirst we do the usual set up steps to get brainrender up and running\n### Setup\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# We begin by adding the current path to sys.path to make sure that the imports work correctly\nimport sys\nsys.path.append('../')\nimport os\n\n# Set up VTKPLOTTER to work in Jupyter notebooks\nfrom vtkplotter import *\n\n\n# Import variables\nfrom brainrender import * # <- these can be changed to personalize the look of your renders\n\n# Import brainrender classes and useful functions\nfrom brainrender.scene import Scene\nfrom brainrender.Utils.parsers.streamlines import StreamlinesAPI\nfrom brainrender.Utils.data_io import listdir\n\nstreamlines_api = StreamlinesAPI()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Downloading data\nIf you have streamlines data already saved somewhere, you can skip this section.\n\n### Manual download\nTo download streamlines data, you have two options (see the [user guide](Docs/UserGuide.md) for more details. \nIf you head to [http://connectivity.brain-map.org](http://connectivity.brain-map.org) you can download a .csv file with the experiment IDs of interest. Then you can use the following function to download the streamline data: ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# parse .csv file\n# Make sure to put the path to your downloaded file here\nfilepaths, data = streamlines_api.extract_ids_from_csv(\"Examples/example_files/experiments_injections.csv\", \n download=True) ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The `filepaths` variable stores the paths to the .json files that have been saved by the `streamlines_api`, the `data` variable already contains the streamlines data. You can pass either `filepaths` or `data` to `scene.add_streamlines` (see below) to render your streamlines data. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Automatic download\nIf you know that you simply want to download the data to a specific target structure, then you can let brainrender take care of downloading the data for you. This is how:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"filepaths, data = streamlines_api.download_streamlines_for_region(\"CA1\") # <- get the streamlines for CA1",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Once you have downloaded the streamlines data, it's time to render it in your scene. \n\n## Rendering streamlines data\nYou can pass either `data` or `filepaths` to `scene.add_streamlines`, just make sure to use the correct keyword argument (unimaginatively called `data` and `filepath`).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Start by creating a scene\nscene = Scene(jupyter=True)\n\n\n# you can then pass this list of filepaths to add_streamlines.\nscene.add_streamlines(data, color=\"green\")\n\n# alternative you can pass a string with the path to a single file or a list of paths to the .json files that you \n# created in some other way. \n\n# then you can just render your scene\nscene.render()\n\nvp = Plotter(axes=0)\nvp.show(scene.get_actors(), viewup=(10, 0.7, 0))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"add_streamliens takes a few arguments that let you personalize the look of the streamlines:\n* `colorby`: you can pass the acronym to a brain region, then the default color of that region will be used for the streamliens\n* `color`: alternatively you can specify the color of the streamlines directly.\n* `alpha`, `radius`: you can change the transparency and the thickness of the actors used to render the streamlines.\n* `show_injection_site`: if set as True, a sphere will be rendered at the locations that correspond to the injections sytes. \n\n\nDon't forget to check the other examples to lear more about how to use brainrender to make amazing 3D renderings!\nAlso, you can find a list of variables you can play around with in brainrender.variables.py\nPlaying around with these variables will allow you to make the rendering look exactly how you want them to be. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a716a62e5391f1822d0178ae43c9a91f965f7e4
| 92,468 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
fit_a_stright_line.ipynb
|
moshebou/50-ways-to-fit-a-straight-line
|
a5e0b3dc8eec153d6a4dc48170b427771e35e225
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-09-01T06:44:18.000Z
|
2021-09-01T06:44:18.000Z
|
fit_a_stright_line.ipynb
|
moshebou/50-ways-to-fit-a-straight-line
|
a5e0b3dc8eec153d6a4dc48170b427771e35e225
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
fit_a_stright_line.ipynb
|
moshebou/50-ways-to-fit-a-straight-line
|
a5e0b3dc8eec153d6a4dc48170b427771e35e225
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 149.867099 | 22,669 | 0.64817 |
[
[
[
"!pip install plotly -U",
"Requirement already up-to-date: plotly in /usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages (4.14.3)\nRequirement already satisfied, skipping upgrade: six in /usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages (from plotly) (1.15.0)\nRequirement already satisfied, skipping upgrade: retrying>=1.3.3 in /usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages (from plotly) (1.3.3)\n"
],
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom plotly import graph_objs as go\nimport plotly as py\nfrom scipy import optimize\nprint(\"hello\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Generate the data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"m = np.random.rand()\nn = np.random.rand()\nnum_of_points = 100\nx = np.random.random(num_of_points)\ny = x*m + n + 0.15*np.random.random(num_of_points)\nfig = go.Figure(data=[go.Scatter(x=x, y=y, mode='markers', name='all points')],\n layout=go.Layout(\n xaxis=dict(range=[np.min(x), np.max(x)], autorange=False),\n yaxis=dict(range=[np.min(y), np.max(y)], autorange=False)\n )\n )\nfig.show()\nprint(\"m=\" + str(m) + \" n=\" + str(n) )\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# fmin\ndef stright_line_fmin(x,y):\n dist_func = lambda p: (((y-x*p[0]-p[1])**2).mean())\n p_opt = optimize.fmin(dist_func, np.array([0,0]))\n return p_opt",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"stright_line_fmin(x,y)",
"Optimization terminated successfully.\n Current function value: 0.001687\n Iterations: 65\n Function evaluations: 127\n"
],
[
"# PCA\ndef straight_line_pca(x,y):\n \n X = np.append(x-x.mean(),y-y.mean(), axis=1)\n # Data matrix X, assumes 0-centered\n \n n, m = X.shape\n # Compute covariance matrix\n C = np.dot(X.T, X) / (n-1)\n # Eigen decomposition\n eigen_vals, eigen_vecs = np.linalg.eig(C)\n # Project X onto PC space\n X_pca_inv = np.dot(np.array([[1,0],[-1,0]]), np.linalg.inv(eigen_vecs))\n X_pca = np.dot(X, eigen_vecs)\n x_min = (x-x.mean()).min()\n x_max = (x-x.mean()).max()\n fig = go.Figure(data=[\n go.Scatter(x=x.ravel(), y=y.ravel(), mode='markers', name='all points'),\n go.Scatter(x=X_pca_inv[:, 0]+x.mean(), y=X_pca_inv[:,1]+y.mean(), mode='lines', name='pca estimation')])\n fig.show()\n return X_pca_inv[1, 1]/X_pca_inv[1, 0], y.mean() - x.mean()*X_pca_inv[1, 1]/X_pca_inv[1, 0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"c = straight_line_pca(x[:, np.newaxis],y[:, np.newaxis])\nc",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#leaset squares\ndef least_square_fit(x, y):\n # model: y_i = h*x_i\n # cost: (Y-h*X)^T * (Y-h*X)\n # solution: h = (X^t *X)^-1 * X^t * Y\n return np.dot(np.linalg.inv(np.dot(x.transpose(), x)), np.dot(x.transpose() , y))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"least_square_fit(np.append(x[:, np.newaxis], np.ones_like(x[:, np.newaxis]), axis=1), y)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# SVd\ndef svd_fit(x, y):\n # model: y_i = h*x_i\n # minimize: [x_0, 1, -y_0; x1, 1, -y_1; ...]*[h, 1] = Xh = 0\n # do so by: eigenvector coresponds to smallest eigenvalue of X\n X = np.append(x, -y, axis=1)\n u, s, vh = np.linalg.svd(X)\n return vh[-1, :2]/vh[-1,-1]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"m_, n_ = svd_fit(np.append(x[:, np.newaxis], np.ones_like(x[:, np.newaxis]), axis=1), y[:, np.newaxis])\nprint(m_, n_)",
"(0.7445827664252567, 0.6595856086525708)\n"
],
[
"#Ransac\ndef ransac(src_pnts, distance_func, model_func, num_of_points_to_determine_model, \n dist_th, inliers_ratio=0.7, p=0.95):\n \"\"\"Summary or Description of the Function\n\n Parameters:\n src_pnt : data points used by Ransac to find the model\n distance_func : a function pointer to a distance function. \n The distance function takes a model and a point and calculate the cost\n p : success probabilaty\n\n Returns:\n int:Returning value\n\n \"\"\"\n\n min_x = src_pnts[:, 0].min()\n max_x = src_pnts[:, 0].max()\n print(min_x, max_x)\n num_of_points = src_pnts.shape[0]\n num_of_iter = int(np.ceil(np.log(1-p)/np.log(1-inliers_ratio**num_of_points_to_determine_model)))\n proposed_line = []\n max_num_of_inliers = 0\n for i in range(num_of_iter):\n indx = np.random.permutation(num_of_points)[:num_of_points_to_determine_model]\n curr_model = model_func(src_pnts[indx, :])\n x=np.array([min_x, max_x])\n y=curr_model(x)\n print(y)\n d = distance_func(curr_model, src_pnts)\n num_of_inliers = np.sum(d<dist_th)\n proposed_line.append((curr_model, x, y, indx, d, num_of_inliers))\n if num_of_inliers > max_num_of_inliers:\n max_num_of_inliers = num_of_inliers\n best_model = curr_model\n return best_model, proposed_line\n \n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def stright_line_from_two_points(pnts):\n m = (pnts[1, 1]-pnts[0,1])/(pnts[1,0]-pnts[0,0])\n n = (pnts[1,0]*pnts[0,1]-pnts[0,0]*pnts[1,1])/(pnts[1,0]-pnts[0,0])\n mod_func = lambda x : x*m + n\n return mod_func",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"src_pnts = np.array([x, y]).transpose()\ndistance_func = lambda model, pnts : (model(pnts[:, 0]) - pnts[:, 1])**2\nmodel_func = stright_line_from_two_points\nnum_of_points_to_determine_model = 2\ndist_th = 0.2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"best_model, ransac_run = ransac(src_pnts, distance_func, model_func, num_of_points_to_determine_model, dist_th)\nprint(x.min())\nprint(x.max())\nx_ransac = np.array([x.min(), x.max()])\ny_ransac = best_model(x_ransac)\nprint(y_ransac)",
"(0.005363911267647348, 0.939533173015347)\n[0.62125787 1.45704118]\n[0.57324424 1.39458894]\n[-2.81628889 3.38873782]\n[0.54967848 1.60171453]\n[0.57742033 1.72106373]\n0.005363911267647348\n0.939533173015347\n[0.62125787 1.45704118]\n"
],
[
"scatter_xy = go.Scatter(x=x, y=y, mode='markers', name=\"all points\")\nframes=[go.Frame(\n data=[scatter_xy, \n go.Scatter(x=x[item[3]], y=y[item[3]], mode='markers', line=dict(width=2, color=\"red\"), name=\"selected points\"), \n go.Scatter(x=item[1], y=item[2], mode='lines', name='current line')]) for item in ransac_run]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig = go.Figure(\n data=[go.Scatter(x=x, y=y, mode='markers', name='all points'), \n go.Scatter(x=x, y=y, mode='markers', name=\"selected points\"), \n go.Scatter(x=x, y=y, mode='markers', name=\"current line\"),\n go.Scatter(x=x_ransac, y=y_ransac, mode='lines', name=\"best selection\")],\n layout=go.Layout(\n xaxis=dict(range=[np.min(x), np.max(x)], autorange=False),\n yaxis=dict(range=[np.min(y), np.max(y)], autorange=False),\n title=\"Ransac guesses\",\n updatemenus=[dict(\n type=\"buttons\",\n buttons=[dict(label=\"Play\",\n method=\"animate\",\n args=[None])])]\n ),\n frames=frames\n)\n\nfig.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a7176db02372879b6221a570cf0ff2709cbb5b8
| 20,250 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
lazy_widefield_psf.ipynb
|
zacsimile/random
|
cfc1837afe069c3ed856af08a7464634b5198853
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
lazy_widefield_psf.ipynb
|
zacsimile/random
|
cfc1837afe069c3ed856af08a7464634b5198853
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
lazy_widefield_psf.ipynb
|
zacsimile/random
|
cfc1837afe069c3ed856af08a7464634b5198853
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 113.764045 | 14,120 | 0.83042 |
[
[
[
"%pylab inline",
"Populating the interactive namespace from numpy and matplotlib\n"
],
[
"wvl = 488 # wavelength [nm]\nNA = 1.2 # numerical aperture \nn = 1.33 # refractive index of propagating medium\npixel_size = 50 # effective camera pixel size [nm]\nchip_size = 128 # pixels\n\ndef widefield_psf_2d(wvl, NA, n, pixel_size, chip_size, z=0.0):\n \"\"\"\n Construct the electric field for a widefield PSF in 2d.\n \n Parameters\n ----------\n wvl : float\n Wavelength of emitted light in nm.\n NA : float\n Numerical aperture of the optical system\n n : float\n Refractive index surrounding point source\n pixel_size : float\n Effective pixel size of camera chip in nm\n chip_size : int\n How many pixels on the camera chip?\n z : float\n Depth from focus\n \n Returns\n -------\n psf : np.array \n Array of np.complex values describing electric field of the PSF.\n \"\"\"\n # Create frequency space\n # f = np.arange(-chip_size//2,chip_size//2)/(pixel_size*chip_size) # <cycles per chip>*<cycle size [nm^-1]>\n # If f above is used, we need an additional ifftshift\n f = np.fft.fftfreq(chip_size, pixel_size)*wvl/n\n X, Y = np.meshgrid(f,f)\n\n # Create an aperture in frequency space\n # Clip on 1/<spatial resolution of the system> (spatial frequency)\n # Note the \"missing\" factor of 2 since we are thresholding on radius\n # rescale by refractive index\n aperture = (X*X+Y*Y) <= (NA/n)**2\n\n # The pupil can also contain aberrations, but they must\n # be clipped by aperture \n k = 2.0*np.pi/(n*wvl)\n pf = np.exp(1j*k*z*np.sqrt(1-np.minimum(X*X+Y*Y,1)))\n pupil = aperture*pf\n\n # Take the inverse fourier transform of the pupil\n # to get the point spread function\n psf = np.fft.fftshift(np.fft.ifft2(np.fft.ifftshift(pupil)))\n \n return psf\n\ndef amplitude_psf(psf):\n \"\"\" Return the amplitude of a PSF, described by its electric field. \"\"\"\n return np.abs(psf)\n\ndef intensity_psf(psf):\n \"\"\" Return the intensity of a PSF, described by its electric field. \"\"\"\n return np.abs(psf*np.conj(psf))\n\n# psf = widefield_psf_2d(wvl, NA, n, pixel_size, chip_size)\nres_z = 2*wvl/(NA*NA)\npsf_z = np.array([widefield_psf_2d(wvl, NA, n, pixel_size, chip_size,z=i) for i in np.arange(-chip_size//2,chip_size//2)*2*pixel_size])\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, axs = plt.subplots(1,2,figsize=(12,6))\nn_steps=chip_size\noffset = chip_size//2+n_steps//8\nfs = 24\nsl = slice(chip_size//2-n_steps//4,chip_size//2+n_steps//4)\npsf_im = intensity_psf(psf_z[sl,psf_z.shape[1]//2,sl]).T\naxs[0].imshow(psf_im, cmap='gray',vmax=1.5e-3)\naxs[0].annotate(\"\", xy=(20, offset-25), xytext=(10, offset-25),\n arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle=\"->\",color='white',linewidth=2),\n color='white')\naxs[0].annotate(\"\", xy=(10, offset-34.6), xytext=(10, offset-24.6),\n arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle=\"->\",color='white',linewidth=2),\n color='white')\naxs[0].annotate(\"x\", xy=(5, offset-27.5),color=\"white\",fontsize=fs)\naxs[0].annotate(\"z\", xy=(12.5, offset-20),color=\"white\",fontsize=fs)\naxs[0].set_xticks([])\naxs[0].set_yticks([])\n\notf_im = intensity_psf(np.fft.ifftshift(np.fft.fft2(intensity_psf(psf_z[:,psf_z.shape[1]//2,:]))))[sl,sl].T\naxs[1].imshow(otf_im,cmap='gray',vmax=3e-2)\naxs[1].annotate(\"\", xy=(20, offset-25), xytext=(10, offset-25),\n arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle=\"->\",color='white',linewidth=2),\n color='white')\naxs[1].annotate(\"\", xy=(10, offset-34.6), xytext=(10, offset-24.6),\n arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle=\"->\",color='white',linewidth=2),\n color='white')\naxs[1].annotate(\"k$_x$\", xy=(5, offset-27.5),color=\"white\",fontsize=fs)\naxs[1].annotate(\"k$_z$\", xy=(12.5, offset-20),color=\"white\",fontsize=fs)\naxs[1].set_xticks([])\naxs[1].set_yticks([])\nfig.tight_layout()\nplt.savefig('introduction-simple-psf.png', dpi=600)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a7188f825184c277153dc792267994c22ad7da9
| 5,415 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
csg_datafusion_stats_analysis_fmp_dicoms_db_acute.ipynb
|
lrq3000/csg_datafusion
|
075279929a1025fc9333a34ffc33873ea7e8f3df
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
csg_datafusion_stats_analysis_fmp_dicoms_db_acute.ipynb
|
lrq3000/csg_datafusion
|
075279929a1025fc9333a34ffc33873ea7e8f3df
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
csg_datafusion_stats_analysis_fmp_dicoms_db_acute.ipynb
|
lrq3000/csg_datafusion
|
075279929a1025fc9333a34ffc33873ea7e8f3df
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2018-12-10T15:15:51.000Z
|
2020-11-14T04:29:10.000Z
| 29.590164 | 149 | 0.586704 |
[
[
[
"# DB acute analysis\nBy Stephen Karl Larroque @ Coma Science Group, GIGA Research, University of Liege\nCreation date: 2018-05-27\nLicense: MIT\nv1.0.3\n\nDESCRIPTION:\nCalculate whether patients were acute at the time of MRI acquisition (28 days included by default).\nThis expects as input a csv file with both the accident date and dicom date (see other scripts). The result will be saved as a new csv file.\n\nINSTALL NOTE:\nYou need to pip install pandas before launching this script.\nTested on Python 2.7.13\n\nUSAGE:\nInput the csv demographics file that is the output of the notebook stats_analysis_fmp_dicoms_db.ipynb\n\nTODO:\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Forcefully autoreload all python modules\n%load_ext autoreload\n%autoreload 2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# AUX FUNCTIONS\n\nimport os, sys\n\ncur_path = os.path.realpath('.')\nsys.path.append(os.path.join(cur_path, 'csg_fileutil_libs'))\n\nimport re\n\nfrom csg_fileutil_libs.aux_funcs import save_df_as_csv, _tqdm, reorder_cols_df, find_columns_matching, convert_to_datetype\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Nice plots!\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nplt.style.use('ggplot')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# PARAMETERS\n\n# FileMakerPro (FMP) database, cleaned with the provided script\nfmp_agg_csv = r'databases_output\\fmp_db_subjects_aggregated.csv_etiosedatfixed_dicomsdatediag_dicompathsedat.csv'\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Import the csv dbs as dataframes\nimport pandas as pd\nimport ast\n\ncf_agg = pd.read_csv(fmp_agg_csv, sep=';', low_memory=False).dropna(axis=0, how='all') # drop empty lines\ncf_agg.set_index('Name', inplace=True)\ncf_agg",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def df_extract_first_date(x):\n if not pd.isnull(x):\n try:\n x2 = ast.literal_eval(x)\n except SyntaxError as exc:\n x2 = ast.literal_eval(\"['\"+x+\"']\")\n return x2[0].split(':')[0]\n else:\n return x\nfirst_crsr_date = cf_agg['CRSr::Date and subscores'].apply(df_extract_first_date)\ncf_agg['CRSr first date'] = first_crsr_date\ncf_agg",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Convert to datetime the columns we need, to ease date calculations\ncf_agg2 = convert_to_datetype(cf_agg, 'Date of Accident', '%d/%m/%Y', errors='coerce')\ncf_agg2 = convert_to_datetype(cf_agg2, 'CRSr first date', '%d/%m/%Y', errors='coerce')\ncf_agg2 = convert_to_datetype(cf_agg2, 'Dicom Date Sync With CRS-R', '%Y-%m-%d', errors='coerce')\ncf_agg2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Acute from a random CRS-R date\ncf_agg2['Days random CRSr since accident'] = cf_agg2['CRSr first date'] - cf_agg2['Date of Accident']\ncf_agg2['Days random CRSr since accident']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Acute from dicom date\ncf_agg2['Days scan since accident'] = cf_agg2['Dicom Date Sync With CRS-R'] - cf_agg2['Date of Accident']\ncf_agg2.loc[:, ['Name', 'CRSr::Best Computed Outcome', 'CRSr::Best Diagnosis', 'Final diagnosis', 'Days scan since accident']]\ncf_agg2['AcuteDicom'] = (cf_agg2['Days scan since accident'] <= pd.Timedelta('28 days'))\n# Nullify if no dicom date available (then cannot know if acute or not)\ncf_agg2.loc[cf_agg2['Dicom Date Sync With CRS-R'].isnull(), ['Days scan since accident', 'Days random CRSr since accident']] = None\ncf_agg2.loc[cf_agg2['Dicom Date Sync With CRS-R'].isnull() | cf_agg2['Date of Accident'].isnull(), 'AcuteDicom'] = ''\n# Save as csv\nsave_df_as_csv(cf_agg2, fmp_agg_csv+'_acute.csv', fields_order=False, keep_index=False)\ncf_agg2",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a71942afe4aee8bae17d1a12d266fe058141448
| 209,525 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Codes/Data Integration.ipynb
|
cathyxinxyz/Capstone_Project_1
|
b62dd89c1626704e7991cbb1b22fa54b46f6b056
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Codes/Data Integration.ipynb
|
cathyxinxyz/Capstone_Project_1
|
b62dd89c1626704e7991cbb1b22fa54b46f6b056
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Codes/Data Integration.ipynb
|
cathyxinxyz/Capstone_Project_1
|
b62dd89c1626704e7991cbb1b22fa54b46f6b056
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 48.311045 | 6,303 | 0.410099 |
[
[
[
"This is the collection of codes that read food atlas datasets and CDC health indicator datasets from Github repository, integrate datasets and cleaning data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#merge food atlas datasets into one\nimport pandas as pd\n\nOverall_folder='C:/Users/cathy/Capstone_project_1/'\n\ndfs=list()\nurl_folder='https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cathyxinxyz/Capstone_Project_1/master/Datasets/Food_atlas/'\n\nfilenames=['ACCESS','ASSISTANCE','HEALTH','INSECURITY','LOCAL','PRICES_TAXES','RESTAURANTS','SOCIOECONOMIC','STORES']\nfor i,filename in enumerate(filenames):\n filepath=url_folder+filename+\".csv\" \n d=pd.read_csv(filepath,index_col='FIPS',encoding=\"ISO-8859-1\")\n #append datasets to the list and drop the redundent columns:'State' and 'County'\n if i!=0:\n dfs.append(d.drop(['State', 'County'], axis=1))\n else:\n dfs.append(d)\n\n#merge datasets\ndf_merge=pd.concat(dfs, join='outer', axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print (df_merge.head(5))",
" State County LACCESS_POP10 LACCESS_POP15 PCH_LACCESS_POP_10_15 \\\nFIPS \n1001 AL Autauga 18428.439690 17496.693040 -5.056026 \n1003 AL Baldwin 35210.814080 30561.264430 -13.204891 \n1005 AL Barbour 5722.305602 6069.523628 6.067799 \n1007 AL Bibb 1044.867327 969.378841 -7.224696 \n1009 AL Blount 1548.175559 3724.428242 140.568857 \n\n PCT_LACCESS_POP10 PCT_LACCESS_POP15 LACCESS_LOWI10 LACCESS_LOWI15 \\\nFIPS \n1001 33.769657 32.062255 5344.427472 6543.676824 \n1003 19.318473 16.767489 9952.144027 9886.831137 \n1005 20.840972 22.105560 3135.676086 2948.790251 \n1007 4.559753 4.230324 491.449066 596.162829 \n1009 2.700840 6.497380 609.027708 1650.959482 \n\n PCH_LACCESS_LOWI_10_15 ... PCH_SNAPS_12_16 SNAPSPTH12 \\\nFIPS ... \n1001 22.439248 ... 30.957684 0.674004 \n1003 -0.656270 ... 58.313251 0.725055 \n1005 -5.959985 ... 11.961722 1.280590 \n1007 21.307144 ... 29.230770 0.719122 \n1009 171.081177 ... 68.421051 0.657144 \n\n SNAPSPTH16 PCH_SNAPSPTH_12_16 WICS08 WICS12 PCH_WICS_08_12 \\\nFIPS \n1001 0.884221 31.189270 6 5 -16.66667 \n1003 1.050042 44.822353 25 27 8.00000 \n1005 1.502022 17.291382 6 7 16.66667 \n1007 0.927439 28.968229 6 5 -16.66667 \n1009 1.109109 68.777138 10 6 -40.00000 \n\n WICSPTH08 WICSPTH12 PCH_WICSPTH_08_12 \nFIPS \n1001 0.119156 0.090067 -24.412460 \n1003 0.141875 0.141517 -0.252126 \n1005 0.201099 0.257344 27.968330 \n1007 0.277919 0.221268 -20.383970 \n1009 0.173028 0.103760 -40.033200 \n\n[5 rows x 279 columns]\n"
]
],
[
[
"Check columns for missing values",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_merge.describe()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"number_null_values_percol=df_merge.isnull().sum(axis=0)\n#columns with over 100 missing values\ncols_with_over_5_percent_null_values=number_null_values_percol[number_null_values_percol>0.05*df_merge.shape[0]]\nprint (cols_with_over_5_percent_null_values.index)",
"Index(['REDEMP_SNAPS12', 'REDEMP_SNAPS16', 'PCH_REDEMP_SNAPS_12_16',\n 'PCT_FREE_LUNCH14', 'PCT_REDUCED_LUNCH14', 'PC_WIC_REDEMP08',\n 'PC_WIC_REDEMP12', 'PCH_PC_WIC_REDEMP_08_12', 'REDEMP_WICS08',\n 'REDEMP_WICS12', 'PCH_REDEMP_WICS_08_12', 'PCT_HSPA15',\n 'PCT_LOCLSALE07', 'PCT_LOCLSALE12', 'DIRSALES07', 'DIRSALES12',\n 'PCH_DIRSALES_07_12', 'PC_DIRSALES07', 'PC_DIRSALES12',\n 'PCH_PC_DIRSALES_07_12', 'PCH_FMRKT_09_16', 'PCH_FMRKTPTH_09_16',\n 'FMRKT_SNAP16', 'PCT_FMRKT_SNAP16', 'FMRKT_WIC16', 'PCT_FMRKT_WIC16',\n 'FMRKT_WICCASH16', 'PCT_FMRKT_WICCASH16', 'FMRKT_SFMNP16',\n 'PCT_FMRKT_SFMNP16', 'FMRKT_CREDIT16', 'PCT_FMRKT_CREDIT16',\n 'FMRKT_FRVEG16', 'PCT_FMRKT_FRVEG16', 'FMRKT_ANMLPROD16',\n 'PCT_FMRKT_ANMLPROD16', 'FMRKT_BAKED16', 'PCT_FMRKT_BAKED16',\n 'FMRKT_OTHERFOOD16', 'PCT_FMRKT_OTHERFOOD16', 'PCH_VEG_FARMS_07_12',\n 'VEG_ACRES07', 'VEG_ACRES12', 'PCH_VEG_ACRES_07_12', 'VEG_ACRESPTH07',\n 'VEG_ACRESPTH12', 'PCH_VEG_ACRESPTH_07_12', 'PCH_FRESHVEG_FARMS_07_12',\n 'FRESHVEG_ACRES07', 'FRESHVEG_ACRES12', 'PCH_FRESHVEG_ACRES_07_12',\n 'FRESHVEG_ACRESPTH07', 'FRESHVEG_ACRESPTH12',\n 'PCH_FRESHVEG_ACRESPTH_07_12', 'PCH_ORCHARD_FARMS_07_12',\n 'ORCHARD_ACRES07', 'ORCHARD_ACRES12', 'PCH_ORCHARD_ACRES_07_12',\n 'ORCHARD_ACRESPTH07', 'ORCHARD_ACRESPTH12',\n 'PCH_ORCHARD_ACRESPTH_07_12', 'PCH_BERRY_FARMS_07_12', 'BERRY_ACRES07',\n 'BERRY_ACRES12', 'PCH_BERRY_ACRES_07_12', 'BERRY_ACRESPTH07',\n 'BERRY_ACRESPTH12', 'PCH_BERRY_ACRESPTH_07_12', 'PCH_SLHOUSE_07_12',\n 'PCH_GHVEG_FARMS_07_12', 'GHVEG_SQFT07', 'GHVEG_SQFT12',\n 'PCH_GHVEG_SQFT_07_12', 'GHVEG_SQFTPTH07', 'GHVEG_SQFTPTH12',\n 'PCH_GHVEG_SQFTPTH_07_12', 'PCH_CSA_07_12', 'PCH_AGRITRSM_OPS_07_12',\n 'AGRITRSM_RCT07', 'AGRITRSM_RCT12', 'PCH_AGRITRSM_RCT_07_12',\n 'FARM_TO_SCHOOL13', 'PCH_SPECS_09_14', 'PCH_SPECSPTH_09_14'],\n dtype='object')\n"
],
[
"#drop these columns first\ndf_merge=df_merge.drop(list(cols_with_over_5_percent_null_values.index), axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_merge.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#check number of remaining columns\nprint (df_merge.columns)",
"Index(['State', 'County', 'LACCESS_POP10', 'LACCESS_POP15',\n 'PCH_LACCESS_POP_10_15', 'PCT_LACCESS_POP10', 'PCT_LACCESS_POP15',\n 'LACCESS_LOWI10', 'LACCESS_LOWI15', 'PCH_LACCESS_LOWI_10_15',\n ...\n 'PCH_SNAPS_12_16', 'SNAPSPTH12', 'SNAPSPTH16', 'PCH_SNAPSPTH_12_16',\n 'WICS08', 'WICS12', 'PCH_WICS_08_12', 'WICSPTH08', 'WICSPTH12',\n 'PCH_WICSPTH_08_12'],\n dtype='object', length=195)\n"
]
],
[
[
"categorizes columns into three groups: category data ('State' and 'County'), count data, percent data, # per 1000 pop, and percent change\n\ncolumns to keep: category data ('State' and 'County'), percent data, # per 1000 pop, and percent change; remove count data because it is not adjusted by population size\n\nEach column name is highly abstract and unreadable, need to extract info from the variable information provided by Food_atlas",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"url='https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cathyxinxyz/Capstone_Project_1/master/Datasets/Food_atlas/variable_info.csv'\nvar_info_df=pd.read_csv(url,encoding=\"ISO-8859-1\", index_col='Variable Code')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"further filter varaibles based on following principles:\ni. keep variables that are adjusted by population size: '% change', 'Percent', '# per 1,000 pop','Percentage points';\nii. keep variables that are mostly valuable for analysis\niii. keep variables where values are valid: e.g. no negative values for variables with units as 'Percent' or '# per 1,000 pop'.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#units to keep: '% change', 'Percent', '# per 1,000 pop','Percentage points'\n#var_info_df['Units'].isin(['Percent', '# per 1,000 pop','Dollars'])\nvar_info_df_subset=var_info_df[var_info_df['Units'].isin(['Percent', '# per 1,000 pop','Dollars'])]\nvar_subset=list(var_info_df_subset.index)\nvar_subset.extend(['State', 'County'])\n#print (var_subset)\ndf_subset=df_merge.loc[:, var_subset]\n#print (df_merge.shape)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print (df_subset.shape)",
"(3143, 106)\n"
],
[
"#check weather each column has valid values:\n####### columns with units 'Percent' should have values between 0 and 100, any value that fall out of this range should be changed to NaN values\n###### \n######\n######\n\n#Replace invalid values with np.nan\nimport numpy as np\n\nfor c in df_subset.columns: \n if c in var_info_df.index:\n if var_info_df.loc[c]['Units'] =='Percent': \n df_subset[c][(df_subset[c]<0)|(df_subset[c]>100)]=np.nan\n elif var_info_df.loc[c]['Units'] =='# per 1,000 pop':\n df_subset[c][(df_subset[c]<0)|(df_subset[c]>1000)]=np.nan\n elif var_info_df.loc[c]['Units'] =='Dollars':\n df_subset[c][(df_subset[c]<0)]=np.nan ",
"C:\\anaconda\\lib\\site-packages\\ipykernel_launcher.py:13: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#indexing-view-versus-copy\n del sys.path[0]\nC:\\anaconda\\lib\\site-packages\\ipykernel_launcher.py:15: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#indexing-view-versus-copy\n from ipykernel import kernelapp as app\nC:\\anaconda\\lib\\site-packages\\ipykernel_launcher.py:17: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#indexing-view-versus-copy\n"
],
[
"df_subset.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"get the average of variables measured at two time points",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"var_tup_dict={}\nfor c in df_subset.columns: \n if c in var_info_df.index:\n k=(var_info_df.loc[c]['Category Name'],var_info_df.loc[c]['Sub_subcategory Name'],var_info_df.loc[c]['Units'])\n if k not in var_tup_dict.keys():\n var_tup_dict[k]=list()\n var_tup_dict[k].append(c)\nprint (var_tup_dict)",
"{('Access and Proximity to Grocery Store', 'Overall', 'Percent'): ['PCT_LACCESS_POP10', 'PCT_LACCESS_POP15'], ('Access and Proximity to Grocery Store', 'Low income', 'Percent'): ['PCT_LACCESS_LOWI10', 'PCT_LACCESS_LOWI15'], ('Access and Proximity to Grocery Store', 'no car', 'Percent'): ['PCT_LACCESS_HHNV10', 'PCT_LACCESS_HHNV15'], ('Access and Proximity to Grocery Store', 'SNAP', 'Percent'): ['PCT_LACCESS_SNAP15'], ('Access and Proximity to Grocery Store', 'Children', 'Percent'): ['PCT_LACCESS_CHILD10', 'PCT_LACCESS_CHILD15'], ('Access and Proximity to Grocery Store', 'Seniors', 'Percent'): ['PCT_LACCESS_SENIORS10', 'PCT_LACCESS_SENIORS15'], ('Access and Proximity to Grocery Store', 'White', 'Percent'): ['PCT_LACCESS_WHITE15'], ('Access and Proximity to Grocery Store', 'Black', 'Percent'): ['PCT_LACCESS_BLACK15'], ('Access and Proximity to Grocery Store', 'Hispanic ethnicity', 'Percent'): ['PCT_LACCESS_HISP15'], ('Access and Proximity to Grocery Store', 'Asian', 'Percent'): ['PCT_LACCESS_NHASIAN15'], ('Access and Proximity to Grocery Store', 'American Indian or Alaska Native', 'Percent'): ['PCT_LACCESS_NHNA15'], ('Access and Proximity to Grocery Store', 'Hawaiian or Pacific Islander', 'Percent'): ['PCT_LACCESS_NHPI15'], ('Access and Proximity to Grocery Store', 'Multiracial', 'Percent'): ['PCT_LACCESS_MULTIR15'], ('Store Availability', 'Grocery', '# per 1,000 pop'): ['GROCPTH09', 'GROCPTH14'], ('Store Availability', 'Supercenters', '# per 1,000 pop'): ['SUPERCPTH09', 'SUPERCPTH14'], ('Store Availability', 'Convenience', '# per 1,000 pop'): ['CONVSPTH09', 'CONVSPTH14'], ('Store Availability', 'Specialized', '# per 1,000 pop'): ['SPECSPTH09', 'SPECSPTH14'], ('Store Availability', 'SNAP-authorized', '# per 1,000 pop'): ['SNAPSPTH12', 'SNAPSPTH16'], ('Store Availability', 'WIC-authorized', '# per 1,000 pop'): ['WICSPTH08', 'WICSPTH12'], ('Restaurant Availability and Expenditures', 'Fast-food', '# per 1,000 pop'): ['FFRPTH09', 'FFRPTH14'], ('Restaurant Availability and Expenditures', 'Full-service', '# per 1,000 pop'): ['FSRPTH09', 'FSRPTH14'], ('Restaurant Availability and Expenditures', 'fast food', 'Dollars'): ['PC_FFRSALES07', 'PC_FFRSALES12'], ('Restaurant Availability and Expenditures', 'restaurants', 'Dollars'): ['PC_FSRSALES07', 'PC_FSRSALES12'], ('Food Assistance', 'SNAP participants', 'Percent'): ['PCT_SNAP12'], ('Food Assistance', 'SNAP participants ', 'Percent'): ['PCT_SNAP16'], ('Food Assistance', 'SNAP participants/eligible pop', 'Percent'): ['SNAP_PART_RATE08', 'SNAP_PART_RATE13'], ('Food Assistance', 'National School Lunch Program participants ', 'Percent'): ['PCT_NSLP09', 'PCT_NSLP15'], ('Food Assistance', 'Students eligible for free lunch', 'Percent'): ['PCT_FREE_LUNCH09', 'PCT_FREE_LUNCH14'], ('Food Assistance', 'Students eligible for reduced-price lunch', 'Percent'): ['PCT_REDUCED_LUNCH09', 'PCT_REDUCED_LUNCH14'], ('Food Assistance', 'School Breakfast Program participants', 'Percent'): ['PCT_SBP09', 'PCT_SBP15'], ('Food Assistance', 'Summer Food Program participants', 'Percent'): ['PCT_SFSP09', 'PCT_SFSP15'], ('Food Assistance', 'WIC participants', 'Percent'): ['PCT_WIC09', 'PCT_WIC15'], ('Food Assistance', nan, 'Percent'): ['PCT_CACFP09', 'PCT_CACFP15'], ('Food Insecurity', 'Household food insecurity', 'Percent'): ['FOODINSEC_10_12', 'FOODINSEC_13_15'], ('Food Insecurity', 'Household very low food security', 'Percent'): ['VLFOODSEC_10_12', 'VLFOODSEC_13_15'], ('Food Insecurity', 'Household child food insecurity', 'Percent'): ['FOODINSEC_CHILD_01_07', 'FOODINSEC_CHILD_03_11'], ('Food Prices and Taxes', 'Soda/retail stores', 'Percent'): ['SODATAX_STORES14'], ('Food Prices and Taxes', 'Soda/vending', 'Percent'): ['SODATAX_VENDM14'], ('Food Prices and Taxes', 'Chip & pretzel sales tax/ retail stores', 'Percent'): ['CHIPSTAX_STORES14', 'CHIPSTAX_VENDM14'], ('Food Prices and Taxes', 'General food sales tax/ retail stores', 'Percent'): ['FOOD_TAX14'], ('Local Foods', 'Farms', 'Percent'): ['PCT_LOCLFARM07', 'PCT_LOCLFARM12'], ('Local Foods', 'Direct farm sales', 'Percent'): ['PCT_LOCLSALE07', 'PCT_LOCLSALE12'], ('Local Foods', 'Direct farm sales per capita', 'Dollars'): ['PC_DIRSALES07', 'PC_DIRSALES12'], ('Local Foods', 'overall', '# per 1,000 pop'): ['FMRKTPTH09', 'FMRKTPTH16'], ('Local Foods', 'SNAP', 'Percent'): ['PCT_FMRKT_SNAP16'], ('Local Foods', 'WIC', 'Percent'): ['PCT_FMRKT_WIC16'], ('Local Foods', 'WIC Cash', 'Percent'): ['PCT_FMRKT_WICCASH16'], ('Local Foods', 'SFMNP', 'Percent'): ['PCT_FMRKT_SFMNP16'], ('Local Foods', 'credit cards', 'Percent'): ['PCT_FMRKT_CREDIT16'], ('Local Foods', 'fruit & vegetables', 'Percent'): ['PCT_FMRKT_FRVEG16'], ('Local Foods', 'animal products', 'Percent'): ['PCT_FMRKT_ANMLPROD16'], ('Local Foods', 'baked/prepared food', 'Percent'): ['PCT_FMRKT_BAKED16'], ('Local Foods', 'other food', 'Percent'): ['PCT_FMRKT_OTHERFOOD16'], ('Local Foods', 'Agritourism receipts', 'Dollars'): ['AGRITRSM_RCT07', 'AGRITRSM_RCT12'], ('Health and Physical Activity', 'Adult diabetes rate', 'Percent'): ['PCT_DIABETES_ADULTS08', 'PCT_DIABETES_ADULTS13'], ('Health and Physical Activity', 'Adult obesity rate', 'Percent'): ['PCT_OBESE_ADULTS08', 'PCT_OBESE_ADULTS13'], ('Health and Physical Activity', 'High schoolers physically active', 'Percent'): ['PCT_HSPA15'], ('Health and Physical Activity', 'Recreation & fitness facilities', '# per 1,000 pop'): ['RECFACPTH09', 'RECFACPTH14'], ('Socioeconomic Characteristics', 'White', 'Percent'): ['PCT_NHWHITE10'], ('Socioeconomic Characteristics', 'Black', 'Percent'): ['PCT_NHBLACK10'], ('Socioeconomic Characteristics', 'Hispanic', 'Percent'): ['PCT_HISP10'], ('Socioeconomic Characteristics', 'Asian', 'Percent'): ['PCT_NHASIAN10'], ('Socioeconomic Characteristics', 'American Indian or Alaska Native', 'Percent'): ['PCT_NHNA10'], ('Socioeconomic Characteristics', 'Hawaiian or Pacific Islander', 'Percent'): ['PCT_NHPI10'], ('Socioeconomic Characteristics', '>=65', 'Percent'): ['PCT_65OLDER10'], ('Socioeconomic Characteristics', '<18', 'Percent'): ['PCT_18YOUNGER10'], ('Socioeconomic Characteristics', 'Median household income', 'Dollars'): ['MEDHHINC15'], ('Socioeconomic Characteristics', 'Poverty rate', 'Percent'): ['POVRATE15'], ('Socioeconomic Characteristics', 'Child poverty rate', 'Percent'): ['CHILDPOVRATE15']}\n"
],
[
"n=1\nvar_name_cat_subcat=list()\nfor k in var_tup_dict.keys():\n df_subset['var'+str(n)]=(df_subset[var_tup_dict[k][0]]+df_subset[var_tup_dict[k][-1]])/2\n var_name_cat_subcat.append(['var'+str(n), k[0], k[1]])\n df_subset=df_subset.drop(var_tup_dict[k], axis=1)\n n+=1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_subset.columns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_subset.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"further drop variables that have redundent information",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dropped=['var'+str(n) for n in [24,25, 42]]\ndropped.extend(['var'+str(n) for n in range(45,54)])\ndropped.extend(['var'+str(n) for n in [55,56]])\ndf_subset=df_subset.drop(dropped, axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_subset.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_subset=df_subset.drop(['var28','var29','var43','var54','var57'],axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"var_name_info_df=pd.DataFrame(var_name_cat_subcat, columns=['variable','category', 'sub_category'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"var_name_info_df.to_csv('C:/Users/cathy/Capstone_project_1/Datasets/Food_atlas/Var_name_info.csv',index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_subset.to_csv(Overall_folder+'Datasets/food_environment.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Integrate CDC Datasets together",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\ndfs=list()\nsub_folder=Overall_folder+'/Datasets/CDC/'\nfilenames=['Diabetes_prevalence',\n 'Obesity_prevalence',\n 'Physical_inactive_prevalence']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for filename in filenames:\n filepath=sub_folder+filename+\".csv\" \n df=pd.read_csv(filepath,index_col='FIPS')\n \n \n if 'Diabetes' in filename:\n df.columns=df.columns.astype(str)+'_db'\n elif 'Obesity' in filename:\n df.columns=df.columns.astype(str)+'_ob'\n elif 'Physical' in filename:\n df.columns=df.columns.astype(str)+'_phy'\n dfs.append(df)\n#merge datasets\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"CDC_merge=pd.concat(dfs, join='outer', axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"CDC_merge.info()",
"<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>\nInt64Index: 3224 entries, 1001 to 72153\nData columns (total 30 columns):\n2004_db 3224 non-null object\n2005_db 3224 non-null object\n2006_db 3224 non-null object\n2007_db 3224 non-null object\n2008_db 3224 non-null object\n2009_db 3224 non-null object\n2010_db 3224 non-null object\n2011_db 3224 non-null object\n2012_db 3224 non-null object\n2013_db 3224 non-null object\n2004_ob 3224 non-null object\n2005_ob 3224 non-null object\n2006_ob 3224 non-null object\n2007_ob 3224 non-null object\n2008_ob 3224 non-null object\n2009_ob 3224 non-null object\n2010_ob 3224 non-null object\n2011_ob 3146 non-null object\n2012_ob 3146 non-null object\n2013_ob 3146 non-null object\n2004_phy 3224 non-null object\n2005_phy 3224 non-null object\n2006_phy 3224 non-null object\n2007_phy 3224 non-null object\n2008_phy 3224 non-null object\n2009_phy 3224 non-null object\n2010_phy 3224 non-null object\n2011_phy 3224 non-null object\n2012_phy 3146 non-null object\n2013_phy 3146 non-null object\ndtypes: object(30)\nmemory usage: 780.8+ KB\n"
],
[
"#Find out the non numeric entries in CDC_merge\nfor c in CDC_merge.columns:\n num_non_numeric=sum(CDC_merge.applymap(lambda x: isinstance(x, (int, float)))[c])\n if num_non_numeric>0:\n print(c, num_non_numeric, CDC_merge[pd.to_numeric(CDC_merge[c], errors='coerce').isnull()])",
"2011_ob 78 2004_db 2005_db 2006_db 2007_db 2008_db 2009_db 2010_db \\\nFIPS \n2201 5.8 6.1000000000000005 5.9 6.8 7.4 No Data No Data \n2232 5.8 6.1000000000000005 6.6 6.9 5.2 No Data No Data \n2280 5.4 6.2 6.4 7 7 No Data No Data \n72001 11.4 10.9 12.8 12.7 14.3 14.7 15.4 \n72003 12.4 14.9 16.3 15.5 14.7 14.6 16.4 \n72005 12.8 14.6 16.3 14.9 15.4 15 15.9 \n72007 11.1 12.9 14 14.7 14.7 15.1 15 \n72009 13 13.6 13.7 13.2 13.2 12.5 13.9 \n72011 12.1 13.8 15.3 14.9 14.7 14.8 16.9 \n72013 13.8 14.5 14.8 15.3 16.4 17.9 17.2 \n72015 13.6 13.9 13.4 13.8 14.1 14.1 14.2 \n72017 12.7 13.9 13.8 13.5 14.8 16.4 17.4 \n72019 11.9 12.9 12.6 13 13.5 13.8 14.7 \n72021 11.6 11 11.6 11.3 11.8 12.6 13.9 \n72023 11.6 11.4 12.1 12.3 14.1 15.2 15.7 \n72025 11.3 13 13.3 14.1 13.3 13.9 13 \n72027 11.5 11.7 13.2 13.4 13.8 13.6 15.6 \n72029 11.4 12.1 11.7 11.9 12.1 13.1 14.8 \n72031 10.9 12 13 13.7 13.3 14 14.9 \n72033 12.7 12.4 13.1 12.2 13.3 13.5 14.8 \n72035 11 10.8 11.4 11.5 13.3 14.4 15 \n72037 12 12.5 13.9 13.4 12.3 12.5 15.4 \n72039 13.9 14.1 13.9 13.9 15.4 16.1 16.8 \n72041 12 12.1 11.3 10.5 12.4 13.4 13.7 \n72043 11.2 11.4 12.4 12.8 13.3 14.7 14.5 \n72045 12.6 14 13.5 13.4 14 13.9 15.6 \n72047 12.2 13 13.6 12.6 13.4 12.9 15.4 \n72049 10.5 10.6 13 13.6 13 14.7 12.7 \n72051 11.5 12 11.8 13.2 12 12.1 12.9 \n72053 14.7 15.2 15.7 13.6 13.3 14 15.6 \n... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... \n72095 13.6 16.5 15.5 16.5 15.9 16.9 17.6 \n72097 13.2 14.9 16.1 16.8 15.7 16 15.1 \n72099 11.9 12.8 14.2 13.7 13.9 13.8 14.9 \n72101 12.1 13.2 13.3 12.7 13.5 13.6 15.3 \n72103 14 14.4 14.5 13.1 12.9 12.7 15 \n72105 12.6 13.4 13.9 13.7 13.6 12.9 14.7 \n72107 12.9 13.9 14.3 13.8 14.3 14.4 15.4 \n72109 13.9 15.3 15.5 14.6 15.5 16.1 17.8 \n72111 12.8 12.8 12.9 12 14.4 14.5 16.7 \n72113 13.4 13.4 13.8 13 14.3 14.8 15.6 \n72115 13.9 14.4 15.6 16.3 16.9 15.7 17.2 \n72117 12.6 15 17.5 18.6 17.4 17 18.2 \n72119 12.1 12.2 12.7 12.3 12.8 14.1 14.5 \n72121 12.7 13.5 13.8 14.5 14.8 15.2 15 \n72123 12.2 11.7 12.7 12.1 13.6 14.2 16.1 \n72125 13.9 14.6 15.8 16.3 16.2 16.4 17.5 \n72127 11.3 10.8 11.6 11.7 12.8 12.4 12.5 \n72129 10.7 11.9 12.5 12.9 13.3 14.1 15.1 \n72131 13.8 15.6 15.5 16.5 16.2 16.9 17.9 \n72133 11.2 10.3 11.1 11.2 12.1 13.2 12.6 \n72135 9.5 9.2 9.5 9.4 9.7 9.9 11.5 \n72137 11.5 11.5 11.9 11.8 11.1 11.9 12.7 \n72139 8.9 9 10.1 11.5 11.7 12.8 12.2 \n72141 13.5 13.6 14 14.4 15.8 16.6 15.3 \n72143 11.9 12.4 12.7 13.4 13.7 14.2 14.8 \n72145 11.4 12.6 15 15.2 14.5 12.9 14.1 \n72147 11.3 12.2 14 16.4 16.3 17 14.8 \n72149 11 11 12 11.9 12.3 11.9 14 \n72151 13.1 14.6 14.3 14.2 13.7 14.1 15.6 \n72153 13.7 13.7 13.5 13 14 13.4 15.6 \n\n 2011_db 2012_db 2013_db ... 2004_phy 2005_phy 2006_phy 2007_phy \\\nFIPS ... \n2201 No Data No Data No Data ... 22.7 26.8 29 26.8 \n2232 No Data No Data No Data ... 21.4 22.5 23 25.2 \n2280 No Data No Data No Data ... 18.4 18.9 20.2 23.1 \n72001 18.3 20.7 21.8 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72003 16.2 15.3 16.1 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72005 15.2 15.1 16 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72007 15.3 16.2 16.8 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72009 14 14.3 14.9 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72011 17.4 17.1 17.9 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72013 16.1 15.5 16.7 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72015 16.4 18.2 18.9 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72017 16.9 17.7 17.5 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72019 14.4 14.3 14.4 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72021 15.8 15.1 15.2 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72023 16.1 15.9 17.7 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72025 14.2 14 15.3 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72027 15.7 16.4 17.1 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72029 15.3 16.3 15.4 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72031 16 15.8 16.1 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72033 16.5 15.9 15.9 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72035 14.4 13.9 14.3 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72037 18 18 18.5 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72039 16 16.7 17.9 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72041 13.6 12.9 13.6 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72043 16.5 15.9 18 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72045 15.4 15.1 15.5 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72047 15 15.4 16.4 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72049 17.6 20.4 24.3 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72051 15.2 14.7 14.7 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72053 17.4 17.9 19 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... \n72095 17.3 17.5 17.8 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72097 15.7 15.6 16.8 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72099 14.6 15.6 16.9 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72101 15.6 15.7 16.5 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72103 15.8 17.2 17.4 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72105 15.3 15.8 16 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72107 14.8 15.1 16.6 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72109 18.5 19.4 20.1 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72111 16.3 16.6 17.3 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72113 16 15.6 16.3 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72115 15.8 17.1 17.4 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72117 17.3 17.7 17.5 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72119 14.9 15 17.2 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72121 16.9 17.8 18.6 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72123 17.1 18.4 18.6 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72125 17.1 16.8 16.6 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72127 12.9 13.7 13.9 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72129 15 15.1 16.5 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72131 18.7 19.5 19.2 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72133 14.3 13.4 15 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72135 12.9 13.1 13.1 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72137 15 14.6 14.4 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72139 13.4 12.9 13.7 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72141 15.2 15.6 18.1 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72143 15.8 16 16.2 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72145 15.2 16.7 17.7 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72147 18.6 19.2 22.6 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72149 15 15.2 16.1 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72151 15.5 15.4 16.6 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72153 15.5 17.1 17.2 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n\n 2008_phy 2009_phy 2010_phy 2011_phy 2012_phy 2013_phy \nFIPS \n2201 25.3 No Data No Data No Data No Data No Data \n2232 22.1 No Data No Data No Data No Data No Data \n2280 24.6 No Data No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72001 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72003 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72005 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72007 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72009 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72011 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72013 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72015 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72017 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72019 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72021 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72023 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72025 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72027 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72029 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72031 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72033 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72035 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72037 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72039 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72041 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72043 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72045 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72047 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72049 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72051 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72053 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n... ... ... ... ... ... ... \n72095 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72097 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72099 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72101 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72103 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72105 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72107 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72109 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72111 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72113 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72115 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72117 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72119 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72121 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72123 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72125 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72127 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72129 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72131 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72133 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72135 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72137 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72139 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72141 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72143 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72145 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72147 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72149 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72151 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72153 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n\n[81 rows x 30 columns]\n2012_ob 78 2004_db 2005_db 2006_db 2007_db 2008_db 2009_db 2010_db \\\nFIPS \n2201 5.8 6.1000000000000005 5.9 6.8 7.4 No Data No Data \n2232 5.8 6.1000000000000005 6.6 6.9 5.2 No Data No Data \n2280 5.4 6.2 6.4 7 7 No Data No Data \n72001 11.4 10.9 12.8 12.7 14.3 14.7 15.4 \n72003 12.4 14.9 16.3 15.5 14.7 14.6 16.4 \n72005 12.8 14.6 16.3 14.9 15.4 15 15.9 \n72007 11.1 12.9 14 14.7 14.7 15.1 15 \n72009 13 13.6 13.7 13.2 13.2 12.5 13.9 \n72011 12.1 13.8 15.3 14.9 14.7 14.8 16.9 \n72013 13.8 14.5 14.8 15.3 16.4 17.9 17.2 \n72015 13.6 13.9 13.4 13.8 14.1 14.1 14.2 \n72017 12.7 13.9 13.8 13.5 14.8 16.4 17.4 \n72019 11.9 12.9 12.6 13 13.5 13.8 14.7 \n72021 11.6 11 11.6 11.3 11.8 12.6 13.9 \n72023 11.6 11.4 12.1 12.3 14.1 15.2 15.7 \n72025 11.3 13 13.3 14.1 13.3 13.9 13 \n72027 11.5 11.7 13.2 13.4 13.8 13.6 15.6 \n72029 11.4 12.1 11.7 11.9 12.1 13.1 14.8 \n72031 10.9 12 13 13.7 13.3 14 14.9 \n72033 12.7 12.4 13.1 12.2 13.3 13.5 14.8 \n72035 11 10.8 11.4 11.5 13.3 14.4 15 \n72037 12 12.5 13.9 13.4 12.3 12.5 15.4 \n72039 13.9 14.1 13.9 13.9 15.4 16.1 16.8 \n72041 12 12.1 11.3 10.5 12.4 13.4 13.7 \n72043 11.2 11.4 12.4 12.8 13.3 14.7 14.5 \n72045 12.6 14 13.5 13.4 14 13.9 15.6 \n72047 12.2 13 13.6 12.6 13.4 12.9 15.4 \n72049 10.5 10.6 13 13.6 13 14.7 12.7 \n72051 11.5 12 11.8 13.2 12 12.1 12.9 \n72053 14.7 15.2 15.7 13.6 13.3 14 15.6 \n... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... \n72095 13.6 16.5 15.5 16.5 15.9 16.9 17.6 \n72097 13.2 14.9 16.1 16.8 15.7 16 15.1 \n72099 11.9 12.8 14.2 13.7 13.9 13.8 14.9 \n72101 12.1 13.2 13.3 12.7 13.5 13.6 15.3 \n72103 14 14.4 14.5 13.1 12.9 12.7 15 \n72105 12.6 13.4 13.9 13.7 13.6 12.9 14.7 \n72107 12.9 13.9 14.3 13.8 14.3 14.4 15.4 \n72109 13.9 15.3 15.5 14.6 15.5 16.1 17.8 \n72111 12.8 12.8 12.9 12 14.4 14.5 16.7 \n72113 13.4 13.4 13.8 13 14.3 14.8 15.6 \n72115 13.9 14.4 15.6 16.3 16.9 15.7 17.2 \n72117 12.6 15 17.5 18.6 17.4 17 18.2 \n72119 12.1 12.2 12.7 12.3 12.8 14.1 14.5 \n72121 12.7 13.5 13.8 14.5 14.8 15.2 15 \n72123 12.2 11.7 12.7 12.1 13.6 14.2 16.1 \n72125 13.9 14.6 15.8 16.3 16.2 16.4 17.5 \n72127 11.3 10.8 11.6 11.7 12.8 12.4 12.5 \n72129 10.7 11.9 12.5 12.9 13.3 14.1 15.1 \n72131 13.8 15.6 15.5 16.5 16.2 16.9 17.9 \n72133 11.2 10.3 11.1 11.2 12.1 13.2 12.6 \n72135 9.5 9.2 9.5 9.4 9.7 9.9 11.5 \n72137 11.5 11.5 11.9 11.8 11.1 11.9 12.7 \n72139 8.9 9 10.1 11.5 11.7 12.8 12.2 \n72141 13.5 13.6 14 14.4 15.8 16.6 15.3 \n72143 11.9 12.4 12.7 13.4 13.7 14.2 14.8 \n72145 11.4 12.6 15 15.2 14.5 12.9 14.1 \n72147 11.3 12.2 14 16.4 16.3 17 14.8 \n72149 11 11 12 11.9 12.3 11.9 14 \n72151 13.1 14.6 14.3 14.2 13.7 14.1 15.6 \n72153 13.7 13.7 13.5 13 14 13.4 15.6 \n\n 2011_db 2012_db 2013_db ... 2004_phy 2005_phy 2006_phy 2007_phy \\\nFIPS ... \n2201 No Data No Data No Data ... 22.7 26.8 29 26.8 \n2232 No Data No Data No Data ... 21.4 22.5 23 25.2 \n2280 No Data No Data No Data ... 18.4 18.9 20.2 23.1 \n72001 18.3 20.7 21.8 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72003 16.2 15.3 16.1 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72005 15.2 15.1 16 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72007 15.3 16.2 16.8 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72009 14 14.3 14.9 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72011 17.4 17.1 17.9 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72013 16.1 15.5 16.7 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72015 16.4 18.2 18.9 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72017 16.9 17.7 17.5 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72019 14.4 14.3 14.4 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72021 15.8 15.1 15.2 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72023 16.1 15.9 17.7 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72025 14.2 14 15.3 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72027 15.7 16.4 17.1 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72029 15.3 16.3 15.4 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72031 16 15.8 16.1 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72033 16.5 15.9 15.9 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72035 14.4 13.9 14.3 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72037 18 18 18.5 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72039 16 16.7 17.9 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72041 13.6 12.9 13.6 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72043 16.5 15.9 18 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72045 15.4 15.1 15.5 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72047 15 15.4 16.4 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72049 17.6 20.4 24.3 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72051 15.2 14.7 14.7 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72053 17.4 17.9 19 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... \n72095 17.3 17.5 17.8 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72097 15.7 15.6 16.8 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72099 14.6 15.6 16.9 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72101 15.6 15.7 16.5 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72103 15.8 17.2 17.4 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72105 15.3 15.8 16 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72107 14.8 15.1 16.6 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72109 18.5 19.4 20.1 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72111 16.3 16.6 17.3 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72113 16 15.6 16.3 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72115 15.8 17.1 17.4 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72117 17.3 17.7 17.5 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72119 14.9 15 17.2 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72121 16.9 17.8 18.6 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72123 17.1 18.4 18.6 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72125 17.1 16.8 16.6 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72127 12.9 13.7 13.9 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72129 15 15.1 16.5 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72131 18.7 19.5 19.2 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72133 14.3 13.4 15 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72135 12.9 13.1 13.1 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72137 15 14.6 14.4 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72139 13.4 12.9 13.7 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72141 15.2 15.6 18.1 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72143 15.8 16 16.2 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72145 15.2 16.7 17.7 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72147 18.6 19.2 22.6 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72149 15 15.2 16.1 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72151 15.5 15.4 16.6 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72153 15.5 17.1 17.2 ... No Data No Data No Data No Data \n\n 2008_phy 2009_phy 2010_phy 2011_phy 2012_phy 2013_phy \nFIPS \n2201 25.3 No Data No Data No Data No Data No Data \n2232 22.1 No Data No Data No Data No Data No Data \n2280 24.6 No Data No Data No Data No Data No Data \n72001 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72003 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72005 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72007 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72009 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72011 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72013 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72015 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72017 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72019 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72021 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72023 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72025 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72027 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72029 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72031 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72033 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72035 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72037 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72039 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72041 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72043 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72045 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72047 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72049 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72051 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72053 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n... ... ... ... ... ... ... \n72095 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72097 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72099 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72101 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72103 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72105 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72107 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72109 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72111 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72113 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72115 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72117 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72119 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72121 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72123 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72125 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72127 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72129 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72131 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72133 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72135 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72137 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72139 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72141 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72143 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72145 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72147 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72149 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72151 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n72153 No Data No Data No Data No Data NaN NaN \n\n[81 rows x 30 columns]\n"
],
[
"#It turns out that some entries are 'No Data' or NaN, so I replace the 'No Data' with NaN values\nCDC_merge=CDC_merge.replace('No Data', np.nan)\nCDC_merge=CDC_merge.astype(float)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#now check the CDC_merge\nCDC_merge.info()",
"<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>\nInt64Index: 3224 entries, 1001 to 72153\nData columns (total 30 columns):\n2004_db 3219 non-null float64\n2005_db 3219 non-null float64\n2006_db 3219 non-null float64\n2007_db 3219 non-null float64\n2008_db 3219 non-null float64\n2009_db 3221 non-null float64\n2010_db 3221 non-null float64\n2011_db 3221 non-null float64\n2012_db 3221 non-null float64\n2013_db 3220 non-null float64\n2004_ob 3141 non-null float64\n2005_ob 3141 non-null float64\n2006_ob 3141 non-null float64\n2007_ob 3141 non-null float64\n2008_ob 3141 non-null float64\n2009_ob 3143 non-null float64\n2010_ob 3143 non-null float64\n2011_ob 3143 non-null float64\n2012_ob 3143 non-null float64\n2013_ob 3142 non-null float64\n2004_phy 3141 non-null float64\n2005_phy 3141 non-null float64\n2006_phy 3141 non-null float64\n2007_phy 3141 non-null float64\n2008_phy 3141 non-null float64\n2009_phy 3143 non-null float64\n2010_phy 3143 non-null float64\n2011_phy 3143 non-null float64\n2012_phy 3143 non-null float64\n2013_phy 3142 non-null float64\ndtypes: float64(30)\nmemory usage: 780.8 KB\n"
],
[
"#choose the latest prevalence of diabetes, obesity and physical inactivity to merge with df_tp \nCDC_subset=CDC_merge[['2013_db','2013_ob','2011_phy','2012_phy','2013_phy']]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"CDC_subset['prevalence of physical inactivity']=(CDC_subset['2011_phy']+CDC_subset['2012_phy']+CDC_subset['2013_phy'])/3",
"C:\\anaconda\\lib\\site-packages\\ipykernel_launcher.py:1: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#indexing-view-versus-copy\n \"\"\"Entry point for launching an IPython kernel.\n"
],
[
"CDC_subset.head(5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"CDC_subset.rename(columns={'2013_db': 'prevalence of diabetes', '2013_ob': 'prevalence of obesity'}, inplace=True)",
"C:\\anaconda\\lib\\site-packages\\pandas\\core\\frame.py:2746: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#indexing-view-versus-copy\n **kwargs)\n"
],
[
"CDC_subset[['prevalence of diabetes', 'prevalence of obesity', 'prevalence of physical inactivity']].to_csv(Overall_folder+'Datasets/Db_ob_phy.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Integrating geography dataset",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df=pd.read_excel(Overall_folder+'Datasets/geography/ruralurbancodes2013.xls')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.head(5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df=df.set_index('FIPS')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_RUCC_info=pd.DataFrame()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_RUCC_info['RUCC_2013']=df['RUCC_2013'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df[df['RUCC_2013']==1]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df[df['RUCC_2013']==4]['Description'].unique()[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"description_dict={1:df[df['RUCC_2013']==1]['Description'].unique()[0],\n 2:df[df['RUCC_2013']==2]['Description'].unique()[0],\n 3:df[df['RUCC_2013']==3]['Description'].unique()[0],\n 4:df[df['RUCC_2013']==4]['Description'].unique()[0],\n 5:df[df['RUCC_2013']==5]['Description'].unique()[0],\n 6:df[df['RUCC_2013']==6]['Description'].unique()[0],\n 7:df[df['RUCC_2013']==7]['Description'].unique()[0],\n 8:df[df['RUCC_2013']==8]['Description'].unique()[0],\n 9:df[df['RUCC_2013']==9]['Description'].unique()[0]}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"description_dict",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_RUCC_info['RUCC_2013']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_RUCC_info['categories']=df_RUCC_info['RUCC_2013'].map(description_dict)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_RUCC_info",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_RUCC_info.to_csv(Overall_folder+'Datasets/rural_urban_category.csv', index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.to_csv(Overall_folder+'Datasets/rural_urban_codes.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df[['RUCC_2013']].to_csv(Overall_folder+'Datasets/RUCC_codes.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Integrate information of uninsured population from 2011 to 2013",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def Guess_skiprows(filename, firstcol):\n for n in range(100):\n try:\n df=pd.read_csv(filename, skiprows=n)\n if 'year' in df.columns[0]:\n print (n, df.columns)\n skiprows=n\n break \n except:\n next\n return skiprows",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import pandas as pd\n\ndef Extract_number(x):\n import re\n \n if type(x)==str:\n num_string=''.join(re.findall('\\d+', x ))\n if num_string !='':\n return float(num_string)\n else:\n return None\n elif type(x) in [int, float]:\n return x",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def Choose_Subset(df):\n df=df[df['agecat']==0]\n df=df[df['sexcat']==0]\n df=df[df['racecat']==0]\n df=df[df['iprcat']==0]\n return df",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_dicts={}\nyears=[2011, 2012, 2013]\nfor year in years:\n filename='C:/Users/cathy/Capstone_Project_1/Datasets/SAHIE/sahie_{}.csv'.format(year)\n firstcol='year'\n skiprows=Guess_skiprows(filename, firstcol)\n\n df=pd.read_csv(filename, skiprows=skiprows)\n \n df=Choose_Subset(df)\n \n df['FIPS']=df['statefips'].apply((lambda x:('0'+str(x))[-2:]))+df['countyfips'].apply((lambda x:('00'+str(x))[-3:]))\n \n df['FIPS']=df['FIPS'].astype(int)\n df=df.set_index('FIPS')\n \n df['NUI']=df['NUI'].apply(Extract_number)\n \n df_dicts[year]=df[['NUI']]",
"C:\\anaconda\\lib\\site-packages\\IPython\\core\\interactiveshell.py:2802: DtypeWarning: Columns (0,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22) have mixed types. Specify dtype option on import or set low_memory=False.\n if self.run_code(code, result):\nC:\\anaconda\\lib\\site-packages\\IPython\\core\\interactiveshell.py:2802: DtypeWarning: Columns (9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22) have mixed types. Specify dtype option on import or set low_memory=False.\n if self.run_code(code, result):\n"
],
[
"df_dem=pd.read_csv('C:/Users/cathy/Capstone_Project_1/Datasets/Food_atlas/Supplemental_data_county.csv', encoding=\"ISO-8859-1\", index_col='FIPS')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for year in years:\n df_dem['Population Estimate, {}'.format(year)]=df_dem['Population Estimate, {}'.format(year)].apply(lambda x:float(''.join(x.split(','))))\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_combineds=list()\nfor year in years:\n df_combined=pd.concat([df_dicts[year], df_dem['Population Estimate, {}'.format(year)]],axis=1, join='inner')\n df_combined['frac_uninsured_{}'.format(year)]=df_combined['NUI']/df_combined['Population Estimate, {}'.format(year)]\n df_combineds.append(df_combined['frac_uninsured_{}'.format(year)])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_frac_nui=pd.concat(df_combineds, axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_frac_nui",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import numpy as np\n\ndf_frac_nui['frac_uninsured']=(df_frac_nui['frac_uninsured_2011']+df_frac_nui['frac_uninsured_2012']+df_frac_nui['frac_uninsured_2013'])/3",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_frac_nui['frac_uninsured']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_frac_nui[['frac_uninsured']].to_csv('C:/Users/cathy/Capstone_Project_1/Datasets/Uninsured.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Integrate all datasets",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"filenames=['food_environment', 'Db_ob_phy', 'Uninsured', 'RUCC_codes']\nOverall_folder='C:/Users/cathy/Capstone_Project_1/'\ndfs=list()\nfor filename in filenames:\n df=pd.read_csv(Overall_folder+'Datasets/'+filename+'.csv', index_col='FIPS', encoding=\"ISO-8859-1\")\n dfs.append(df)\n \ndf_merge=pd.concat(dfs, axis=1, join='inner')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_merge.info()",
"<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>\nInt64Index: 3141 entries, 1001 to 56045\nData columns (total 57 columns):\nState 3141 non-null object\nCounty 3141 non-null object\nvar1 3094 non-null float64\nvar2 3122 non-null float64\nvar3 3139 non-null float64\nvar4 3122 non-null float64\nvar5 3122 non-null float64\nvar6 3122 non-null float64\nvar7 3122 non-null float64\nvar8 3122 non-null float64\nvar9 3122 non-null float64\nvar10 3122 non-null float64\nvar11 3122 non-null float64\nvar12 3122 non-null float64\nvar13 3122 non-null float64\nvar14 3141 non-null float64\nvar15 3141 non-null float64\nvar16 3141 non-null float64\nvar17 3141 non-null float64\nvar18 3141 non-null float64\nvar19 3141 non-null float64\nvar20 3141 non-null float64\nvar21 3141 non-null float64\nvar22 3141 non-null float64\nvar23 3141 non-null float64\nvar26 3141 non-null float64\nvar27 3141 non-null float64\nvar30 3141 non-null float64\nvar31 3141 non-null float64\nvar32 3141 non-null float64\nvar33 3141 non-null float64\nvar34 3141 non-null float64\nvar35 3141 non-null float64\nvar36 3141 non-null float64\nvar37 3141 non-null float64\nvar38 3141 non-null float64\nvar39 3141 non-null float64\nvar40 3141 non-null float64\nvar41 3074 non-null float64\nvar44 3135 non-null float64\nvar58 3141 non-null float64\nvar59 3141 non-null float64\nvar60 3141 non-null float64\nvar61 3141 non-null float64\nvar62 3141 non-null float64\nvar63 3141 non-null float64\nvar64 3141 non-null float64\nvar65 3141 non-null float64\nvar66 3141 non-null float64\nvar67 3139 non-null float64\nvar68 3139 non-null float64\nvar69 3139 non-null float64\nprevalence of diabetes 3141 non-null float64\nprevalence of obesity 3141 non-null float64\nprevalence of physical inactivity 3141 non-null float64\nfrac_uninsured 3140 non-null float64\nRUCC_2013 3141 non-null int64\ndtypes: float64(54), int64(1), object(2)\nmemory usage: 1.4+ MB\n"
],
[
"df_merge.to_csv(Overall_folder+'Datasets/combined.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"combine state, county, fips code file into one for map",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df=pd.read_csv(Overall_folder+'Datasets/Food_atlas/Supplemental_data_county.csv',encoding=\"ISO-8859-1\", index_col='FIPS')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.info()",
"<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>\nInt64Index: 3142 entries, 1001 to 56045\nData columns (total 9 columns):\nState 3142 non-null object\nCounty 3142 non-null object\n2010 Census Population 3142 non-null object\nPopulation Estimate, 2011 3142 non-null object\nPopulation Estimate, 2012 3142 non-null object\nPopulation Estimate, 2013 3142 non-null object\nPopulation Estimate, 2014 3142 non-null object\nPopulation Estimate, 2015 3142 non-null object\nPopulation Estimate, 2016 3142 non-null object\ndtypes: object(9)\nmemory usage: 245.5+ KB\n"
],
[
"df['State']=df['State'].apply((lambda x:x.lower()))\ndf['County']=df['County'].apply((lambda x:x.lower()))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df['State']=df['State'].apply((lambda x:(\"\").join(x.split(' '))))\ndf['County']=df['County'].apply((lambda x:(\"\").join(x.split(' '))))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df['County']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df[['State', 'County']].to_csv(Overall_folder+'Datasets/state_county_name.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a71a5e753cb7a36d2c1cc2d66721b9c90266f1e
| 4,167 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
ipynb/Germany-Bayern-LK-Augsburg.ipynb
|
RobertRosca/oscovida.github.io
|
d609949076e3f881e38ec674ecbf0887e9a2ec25
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | null | null | null |
ipynb/Germany-Bayern-LK-Augsburg.ipynb
|
RobertRosca/oscovida.github.io
|
d609949076e3f881e38ec674ecbf0887e9a2ec25
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | null | null | null |
ipynb/Germany-Bayern-LK-Augsburg.ipynb
|
RobertRosca/oscovida.github.io
|
d609949076e3f881e38ec674ecbf0887e9a2ec25
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | null | null | null | 29.13986 | 180 | 0.515719 |
[
[
[
"# Germany: LK Augsburg (Bayern)\n\n* Homepage of project: https://oscovida.github.io\n* [Execute this Jupyter Notebook using myBinder](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/oscovida/binder/master?filepath=ipynb/Germany-Bayern-LK-Augsburg.ipynb)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import datetime\nimport time\n\nstart = datetime.datetime.now()\nprint(f\"Notebook executed on: {start.strftime('%d/%m/%Y %H:%M:%S%Z')} {time.tzname[time.daylight]}\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%config InlineBackend.figure_formats = ['svg']\nfrom oscovida import *",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"overview(country=\"Germany\", subregion=\"LK Augsburg\");",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# load the data\ncases, deaths, region_label = germany_get_region(landkreis=\"LK Augsburg\")\n\n# compose into one table\ntable = compose_dataframe_summary(cases, deaths)\n\n# show tables with up to 500 rows\npd.set_option(\"max_rows\", 500)\n\n# display the table\ntable",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Explore the data in your web browser\n\n- If you want to execute this notebook, [click here to use myBinder](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/oscovida/binder/master?filepath=ipynb/Germany-Bayern-LK-Augsburg.ipynb)\n- and wait (~1 to 2 minutes)\n- Then press SHIFT+RETURN to advance code cell to code cell\n- See http://jupyter.org for more details on how to use Jupyter Notebook",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Acknowledgements:\n\n- Johns Hopkins University provides data for countries\n- Robert Koch Institute provides data for within Germany\n- Open source and scientific computing community for the data tools\n- Github for hosting repository and html files\n- Project Jupyter for the Notebook and binder service\n- The H2020 project Photon and Neutron Open Science Cloud ([PaNOSC](https://www.panosc.eu/))\n\n--------------------",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(f\"Download of data from Johns Hopkins university: cases at {fetch_cases_last_execution()} and \"\n f\"deaths at {fetch_deaths_last_execution()}.\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# to force a fresh download of data, run \"clear_cache()\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(f\"Notebook execution took: {datetime.datetime.now()-start}\")\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a71a60caf7d772ac6ced87931a797dfa9d50e49
| 37,641 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
site/en/tutorials/estimators/boosted_trees_model_understanding.ipynb
|
christophmeyer/docs
|
f0b5959f682adce50ace43b190140188134e33d5
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 4 |
2019-08-20T11:59:23.000Z
|
2020-01-12T13:42:50.000Z
|
site/en/tutorials/estimators/boosted_trees_model_understanding.ipynb
|
christophmeyer/docs
|
f0b5959f682adce50ace43b190140188134e33d5
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
site/en/tutorials/estimators/boosted_trees_model_understanding.ipynb
|
christophmeyer/docs
|
f0b5959f682adce50ace43b190140188134e33d5
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2020-11-01T15:12:58.000Z
|
2020-11-01T15:12:58.000Z
| 33.668157 | 532 | 0.514784 |
[
[
[
"##### Copyright 2019 The TensorFlow Authors.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#@title Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the \"License\");\n# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.\n# You may obtain a copy of the License at\n#\n# https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0\n#\n# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software\n# distributed under the License is distributed on an \"AS IS\" BASIS,\n# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.\n# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and\n# limitations under the License.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Gradient Boosted Trees: Model understanding",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<table class=\"tfo-notebook-buttons\" align=\"left\">\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/estimators/boosted_trees_model_understanding\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/tf_logo_32px.png\" />View on TensorFlow.org</a>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/tensorflow/docs/blob/master/site/en/tutorials/estimators/boosted_trees_model_understanding.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/colab_logo_32px.png\" />Run in Google Colab</a>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://github.com/tensorflow/docs/tree/master/site/en/tutorials/estimators/boosted_trees_model_understanding.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/GitHub-Mark-32px.png\" />View source on GitHub</a>\n </td>\n</table>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\nFor an end-to-end walkthrough of training a Gradient Boosting model check out the [boosted trees tutorial](https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/estimators/boosted_trees). In this tutorial you will:\n\n* Learn how to interpret a Boosted Trees model both *locally* and *globally*\n* Gain intution for how a Boosted Trees model fits a dataset\n\n## How to interpret Boosted Trees models both locally and globally\n\nLocal interpretability refers to an understanding of a model’s predictions at the individual example level, while global interpretability refers to an understanding of the model as a whole. Such techniques can help machine learning (ML) practitioners detect bias and bugs during the model development stage\n\nFor local interpretability, you will learn how to create and visualize per-instance contributions. To distinguish this from feature importances, we refer to these values as directional feature contributions (DFCs).\n\nFor global interpretability you will retrieve and visualize gain-based feature importances, [permutation feature importances](https://www.stat.berkeley.edu/~breiman/randomforest2001.pdf) and also show aggregated DFCs.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Load the titanic dataset\nYou will be using the titanic dataset, where the (rather morbid) goal is to predict passenger survival, given characteristics such as gender, age, class, etc.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals\n\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport tensorflow as tf\n\ntf.logging.set_verbosity(tf.logging.ERROR)\ntf.set_random_seed(123)\n\n# Load dataset.\ndftrain = pd.read_csv('https://storage.googleapis.com/tfbt/titanic_train.csv')\ndfeval = pd.read_csv('https://storage.googleapis.com/tfbt/titanic_eval.csv')\ny_train = dftrain.pop('survived')\ny_eval = dfeval.pop('survived')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"For a description of the features, please review the prior tutorial.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Create feature columns, input_fn, and the train the estimator",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Preprocess the data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Create the feature columns, using the original numeric columns as is and one-hot-encoding categorical variables.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"fc = tf.feature_column\nCATEGORICAL_COLUMNS = ['sex', 'n_siblings_spouses', 'parch', 'class', 'deck',\n 'embark_town', 'alone']\nNUMERIC_COLUMNS = ['age', 'fare']\n\ndef one_hot_cat_column(feature_name, vocab):\n return fc.indicator_column(\n fc.categorical_column_with_vocabulary_list(feature_name,\n vocab))\nfeature_columns = []\nfor feature_name in CATEGORICAL_COLUMNS:\n # Need to one-hot encode categorical features.\n vocabulary = dftrain[feature_name].unique()\n feature_columns.append(one_hot_cat_column(feature_name, vocabulary))\n\nfor feature_name in NUMERIC_COLUMNS:\n feature_columns.append(fc.numeric_column(feature_name,\n dtype=tf.float32))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Build the input pipeline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Create the input functions using the `from_tensor_slices` method in the [`tf.data`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/data) API to read in data directly from Pandas.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Use entire batch since this is such a small dataset.\nNUM_EXAMPLES = len(y_train)\n\ndef make_input_fn(X, y, n_epochs=None, shuffle=True):\n y = np.expand_dims(y, axis=1)\n def input_fn():\n dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((X.to_dict(orient='list'), y))\n if shuffle:\n dataset = dataset.shuffle(NUM_EXAMPLES)\n # For training, cycle thru dataset as many times as need (n_epochs=None).\n dataset = (dataset\n .repeat(n_epochs)\n .batch(NUM_EXAMPLES))\n return dataset\n return input_fn\n\n# Training and evaluation input functions.\ntrain_input_fn = make_input_fn(dftrain, y_train)\neval_input_fn = make_input_fn(dfeval, y_eval, shuffle=False, n_epochs=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Train the model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"params = {\n 'n_trees': 50,\n 'max_depth': 3,\n 'n_batches_per_layer': 1,\n # You must enable center_bias = True to get DFCs. This will force the model to\n # make an initial prediction before using any features (e.g. use the mean of\n # the training labels for regression or log odds for classification when\n # using cross entropy loss).\n 'center_bias': True\n}\n\nest = tf.estimator.BoostedTreesClassifier(feature_columns, **params)\nest.train(train_input_fn, max_steps=100)\nresults = est.evaluate(eval_input_fn)\npd.Series(results).to_frame()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"For performance reasons, when your data fits in memory, we recommend use the `boosted_trees_classifier_train_in_memory` function. However if training time is not of a concern or if you have a very large dataset and want to do distributed training, use the `tf.estimator.BoostedTrees` API shown above.\n\n\nWhen using this method, you should not batch your input data, as the method operates on the entire dataset.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"in_memory_params = dict(params)\ndel in_memory_params['n_batches_per_layer']\n# In-memory input_fn does not use batching.\ndef make_inmemory_train_input_fn(X, y):\n y = np.expand_dims(y, axis=1)\n def input_fn():\n return dict(X), y\n return input_fn\ntrain_input_fn = make_inmemory_train_input_fn(dftrain, y_train)\n\n# Train the model.\nest = tf.contrib.estimator.boosted_trees_classifier_train_in_memory(\n train_input_fn,\n feature_columns,\n **in_memory_params)\nprint(est.evaluate(eval_input_fn))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Model interpretation and plotting",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn as sns\nsns_colors = sns.color_palette('colorblind')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Local interpretability\nNext you will output the directional feature contributions (DFCs) to explain individual predictions using the approach outlined in [Palczewska et al](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1312.1121.pdf) and by Saabas in [Interpreting Random Forests](http://blog.datadive.net/interpreting-random-forests/) (this method is also available in scikit-learn for Random Forests in the [`treeinterpreter`](https://github.com/andosa/treeinterpreter) package). The DFCs are generated with:\n\n`pred_dicts = list(est.experimental_predict_with_explanations(pred_input_fn))`\n\n(Note: The method is named experimental as we may modify the API before dropping the experimental prefix.)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pred_dicts = list(est.experimental_predict_with_explanations(eval_input_fn))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create DFC Pandas dataframe.\nlabels = y_eval.values\nprobs = pd.Series([pred['probabilities'][1] for pred in pred_dicts])\ndf_dfc = pd.DataFrame([pred['dfc'] for pred in pred_dicts])\ndf_dfc.describe().T",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"A nice property of DFCs is that the sum of the contributions + the bias is equal to the prediction for a given example.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Sum of DFCs + bias == probabality.\nbias = pred_dicts[0]['bias']\ndfc_prob = df_dfc.sum(axis=1) + bias\nnp.testing.assert_almost_equal(dfc_prob.values,\n probs.values)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Plot DFCs for an individual passenger.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Plot results.\nID = 182\nexample = df_dfc.iloc[ID] # Choose ith example from evaluation set.\nTOP_N = 8 # View top 8 features.\nsorted_ix = example.abs().sort_values()[-TOP_N:].index\nax = example[sorted_ix].plot(kind='barh', color=sns_colors[3])\nax.grid(False, axis='y')\n\nax.set_title('Feature contributions for example {}\\n pred: {:1.2f}; label: {}'.format(ID, probs[ID], labels[ID]))\nax.set_xlabel('Contribution to predicted probability')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The larger magnitude contributions have a larger impact on the model's prediction. Negative contributions indicate the feature value for this given example reduced the model's prediction, while positive values contribute an increase in the prediction.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Improved plotting\nLet's make the plot nice by color coding based on the contributions' directionality and add the feature values on figure.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Boilerplate code for plotting :)\ndef _get_color(value):\n \"\"\"To make positive DFCs plot green, negative DFCs plot red.\"\"\"\n green, red = sns.color_palette()[2:4]\n if value >= 0: return green\n return red\n\ndef _add_feature_values(feature_values, ax):\n \"\"\"Display feature's values on left of plot.\"\"\"\n x_coord = ax.get_xlim()[0]\n OFFSET = 0.15\n for y_coord, (feat_name, feat_val) in enumerate(feature_values.items()):\n t = plt.text(x_coord, y_coord - OFFSET, '{}'.format(feat_val), size=12)\n t.set_bbox(dict(facecolor='white', alpha=0.5))\n from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties\n font = FontProperties()\n font.set_weight('bold')\n t = plt.text(x_coord, y_coord + 1 - OFFSET, 'feature\\nvalue',\n fontproperties=font, size=12)\n\ndef plot_example(example):\n TOP_N = 8 # View top 8 features.\n sorted_ix = example.abs().sort_values()[-TOP_N:].index # Sort by magnitude.\n example = example[sorted_ix]\n colors = example.map(_get_color).tolist()\n ax = example.to_frame().plot(kind='barh',\n color=[colors],\n legend=None,\n alpha=0.75,\n figsize=(10,6))\n ax.grid(False, axis='y')\n ax.set_yticklabels(ax.get_yticklabels(), size=14)\n\n # Add feature values.\n _add_feature_values(dfeval.iloc[ID][sorted_ix], ax)\n return ax",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Plot example.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"example = df_dfc.iloc[ID] # Choose IDth example from evaluation set.\nax = plot_example(example)\nax.set_title('Feature contributions for example {}\\n pred: {:1.2f}; label: {}'.format(ID, probs[ID], labels[ID]))\nax.set_xlabel('Contribution to predicted probability', size=14)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You can also plot the example's DFCs compare with the entire distribution using a voilin plot.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Boilerplate plotting code.\ndef dist_violin_plot(df_dfc, ID):\n # Initialize plot.\n fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(10, 6))\n\n # Create example dataframe.\n TOP_N = 8 # View top 8 features.\n example = df_dfc.iloc[ID]\n ix = example.abs().sort_values()[-TOP_N:].index\n example = example[ix]\n example_df = example.to_frame(name='dfc')\n\n # Add contributions of entire distribution.\n parts=ax.violinplot([df_dfc[w] for w in ix],\n vert=False,\n showextrema=False,\n widths=0.7,\n positions=np.arange(len(ix)))\n face_color = sns_colors[0]\n alpha = 0.15\n for pc in parts['bodies']:\n pc.set_facecolor(face_color)\n pc.set_alpha(alpha)\n\n # Add feature values.\n _add_feature_values(dfeval.iloc[ID][sorted_ix], ax)\n\n # Add local contributions.\n ax.scatter(example,\n np.arange(example.shape[0]),\n color=sns.color_palette()[2],\n s=100,\n marker=\"s\",\n label='contributions for example')\n\n # Legend\n # Proxy plot, to show violinplot dist on legend.\n ax.plot([0,0], [1,1], label='eval set contributions\\ndistributions',\n color=face_color, alpha=alpha, linewidth=10)\n legend = ax.legend(loc='lower right', shadow=True, fontsize='x-large',\n frameon=True)\n legend.get_frame().set_facecolor('white')\n\n # Format plot.\n ax.set_yticks(np.arange(example.shape[0]))\n ax.set_yticklabels(example.index)\n ax.grid(False, axis='y')\n ax.set_xlabel('Contribution to predicted probability', size=14)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Plot this example.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dist_violin_plot(df_dfc, ID)\nplt.title('Feature contributions for example {}\\n pred: {:1.2f}; label: {}'.format(ID, probs[ID], labels[ID]))\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Finally, third-party tools, such as [LIME](https://github.com/marcotcr/lime) and [shap](https://github.com/slundberg/shap), can also help understand individual predictions for a model.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Global feature importances\n\nAdditionally, you might want to understand the model as a whole, rather than studying individual predictions. Below, you will compute and use:\n\n* Gain-based feature importances using `est.experimental_feature_importances`\n* Permutation importances\n* Aggregate DFCs using `est.experimental_predict_with_explanations`\n\nGain-based feature importances measure the loss change when splitting on a particular feature, while permutation feature importances are computed by evaluating model performance on the evaluation set by shuffling each feature one-by-one and attributing the change in model performance to the shuffled feature.\n\nIn general, permutation feature importance are preferred to gain-based feature importance, though both methods can be unreliable in situations where potential predictor variables vary in their scale of measurement or their number of categories and when features are correlated ([source](https://bmcbioinformatics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1471-2105-9-307)). Check out [this article](http://explained.ai/rf-importance/index.html) for an in-depth overview and great discussion on different feature importance types.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Gain-based feature importances",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Gain-based feature importances are built into the TensorFlow Boosted Trees estimators using `est.experimental_feature_importances`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"importances = est.experimental_feature_importances(normalize=True)\ndf_imp = pd.Series(importances)\n\n# Visualize importances.\nN = 8\nax = (df_imp.iloc[0:N][::-1]\n .plot(kind='barh',\n color=sns_colors[0],\n title='Gain feature importances',\n figsize=(10, 6)))\nax.grid(False, axis='y')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Average absolute DFCs\nYou can also average the absolute values of DFCs to understand impact at a global level.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Plot.\ndfc_mean = df_dfc.abs().mean()\nN = 8\nsorted_ix = dfc_mean.abs().sort_values()[-N:].index # Average and sort by absolute.\nax = dfc_mean[sorted_ix].plot(kind='barh',\n color=sns_colors[1],\n title='Mean |directional feature contributions|',\n figsize=(10, 6))\nax.grid(False, axis='y')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You can also see how DFCs vary as a feature value varies.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"FEATURE = 'fare'\nfeature = pd.Series(df_dfc[FEATURE].values, index=dfeval[FEATURE].values).sort_index()\nax = sns.regplot(feature.index.values, feature.values, lowess=True)\nax.set_ylabel('contribution')\nax.set_xlabel(FEATURE)\nax.set_xlim(0, 100)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Permutation feature importance",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def permutation_importances(est, X_eval, y_eval, metric, features):\n \"\"\"Column by column, shuffle values and observe effect on eval set.\n\n source: http://explained.ai/rf-importance/index.html\n A similar approach can be done during training. See \"Drop-column importance\"\n in the above article.\"\"\"\n baseline = metric(est, X_eval, y_eval)\n imp = []\n for col in features:\n save = X_eval[col].copy()\n X_eval[col] = np.random.permutation(X_eval[col])\n m = metric(est, X_eval, y_eval)\n X_eval[col] = save\n imp.append(baseline - m)\n return np.array(imp)\n\ndef accuracy_metric(est, X, y):\n \"\"\"TensorFlow estimator accuracy.\"\"\"\n eval_input_fn = make_input_fn(X,\n y=y,\n shuffle=False,\n n_epochs=1)\n return est.evaluate(input_fn=eval_input_fn)['accuracy']\nfeatures = CATEGORICAL_COLUMNS + NUMERIC_COLUMNS\nimportances = permutation_importances(est, dfeval, y_eval, accuracy_metric,\n features)\ndf_imp = pd.Series(importances, index=features)\n\nsorted_ix = df_imp.abs().sort_values().index\nax = df_imp[sorted_ix][-5:].plot(kind='barh', color=sns_colors[2], figsize=(10, 6))\nax.grid(False, axis='y')\nax.set_title('Permutation feature importance')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Visualizing model fitting",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Lets first simulate/create training data using the following formula:\n\n\n$$z=x* e^{-x^2 - y^2}$$\n\n\nWhere \\\\(z\\\\) is the dependent variable you are trying to predict and \\\\(x\\\\) and \\\\(y\\\\) are the features.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from numpy.random import uniform, seed\nfrom matplotlib.mlab import griddata\n\n# Create fake data\nseed(0)\nnpts = 5000\nx = uniform(-2, 2, npts)\ny = uniform(-2, 2, npts)\nz = x*np.exp(-x**2 - y**2)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Prep data for training.\ndf = pd.DataFrame({'x': x, 'y': y, 'z': z})\n\nxi = np.linspace(-2.0, 2.0, 200),\nyi = np.linspace(-2.1, 2.1, 210),\nxi,yi = np.meshgrid(xi, yi)\n\ndf_predict = pd.DataFrame({\n 'x' : xi.flatten(),\n 'y' : yi.flatten(),\n})\npredict_shape = xi.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def plot_contour(x, y, z, **kwargs):\n # Grid the data.\n plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))\n # Contour the gridded data, plotting dots at the nonuniform data points.\n CS = plt.contour(x, y, z, 15, linewidths=0.5, colors='k')\n CS = plt.contourf(x, y, z, 15,\n vmax=abs(zi).max(), vmin=-abs(zi).max(), cmap='RdBu_r')\n plt.colorbar() # Draw colorbar.\n # Plot data points.\n plt.xlim(-2, 2)\n plt.ylim(-2, 2)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You can visualize the function. Redder colors correspond to larger function values.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"zi = griddata(x, y, z, xi, yi, interp='linear')\nplot_contour(xi, yi, zi)\nplt.scatter(df.x, df.y, marker='.')\nplt.title('Contour on training data')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fc = [tf.feature_column.numeric_column('x'),\n tf.feature_column.numeric_column('y')]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def predict(est):\n \"\"\"Predictions from a given estimator.\"\"\"\n predict_input_fn = lambda: tf.data.Dataset.from_tensors(dict(df_predict))\n preds = np.array([p['predictions'][0] for p in est.predict(predict_input_fn)])\n return preds.reshape(predict_shape)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"First let's try to fit a linear model to the data.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"train_input_fn = make_input_fn(df, df.z)\nest = tf.estimator.LinearRegressor(fc)\nest.train(train_input_fn, max_steps=500);",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plot_contour(xi, yi, predict(est))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"It's not a very good fit. Next let's try to fit a GBDT model to it and try to understand how the model fits the function.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def create_bt_est(n_trees):\n return tf.estimator.BoostedTreesRegressor(fc,\n n_batches_per_layer=1,\n n_trees=n_trees)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"N_TREES = [1,2,3,4,10,20,50,100]\nfor n in N_TREES:\n est = create_bt_est(n)\n est.train(train_input_fn, max_steps=500)\n plot_contour(xi, yi, predict(est))\n plt.text(-1.8, 2.1, '# trees: {}'.format(n), color='w', backgroundcolor='black', size=20)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"As you increase the number of trees, the model's predictions better approximates the underlying function.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Conclusion",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In this tutorial you learned how to interpret Boosted Trees models using directional feature contributions and feature importance techniques. These techniques provide insight into how the features impact a model's predictions. Finally, you also gained intution for how a Boosted Tree model fits a complex function by viewing the decision surface for several models.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4a71ac871b7a5d269fdcb593da8b58432156b436
| 10,999 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notes/L-Files.ipynb
|
innamuris/Panoscloned
|
401a4e276692c65ee96c6fb29b8a5a1445445e29
|
[
"CC0-1.0"
] | null | null | null |
notes/L-Files.ipynb
|
innamuris/Panoscloned
|
401a4e276692c65ee96c6fb29b8a5a1445445e29
|
[
"CC0-1.0"
] | null | null | null |
notes/L-Files.ipynb
|
innamuris/Panoscloned
|
401a4e276692c65ee96c6fb29b8a5a1445445e29
|
[
"CC0-1.0"
] | null | null | null | 28.347938 | 641 | 0.556232 |
[
[
[
"Files and Printing\n------------------\n\n** See also Examples 15, 16, and 17 from Learn Python the Hard Way**\n\nYou'll often be reading data from a file, or writing the output of your python scripts back into a file. Python makes this very easy. You need to open a file in the appropriate mode, using the `open` function, then you can read or write to accomplish your task. The `open` function takes two arguments, the name of the file, and the mode. The mode is a single letter string that specifies if you're going to be reading from a file, writing to a file, or appending to the end of an existing file. The function returns a file object that performs the various tasks you'll be performing: `a_file = open(filename, mode)`. The modes are:\n\n+ `'r'`: open a file for reading\n+ `'w'`: open a file for writing. Caution: this will overwrite any previously existing file\n+ `'a'`: append. Write to the end of a file. \n\nWhen reading, you typically want to iterate through the lines in a file using a for loop, as above. Some other common methods for dealing with files are: \n\n+ `file.read()`: read the entire contents of a file into a string\n+ `file.write(some_string)`: writes to the file, note this doesn't automatically include any new lines. Also note that sometimes writes are buffered- python will wait until you have several writes pending, and perform them all at once\n+ `file.flush()`: write out any buffered writes\n+ `file.close()`: close the open file. This will free up some computer resources occupied by keeping a file open.\n\nHere is an example using files:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Writing a file to disk",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create the file temp.txt, and get it ready for writing\nf = open(\"temp.txt\", \"w\")\nf.write(\"This is my first file! The end!\\n\")\nf.write(\"Oh wait, I wanted to say something else.\")\nf.close()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Let's check that we did everything as expected\n!cat temp.txt",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create a file numbers.txt and write the numbers from 0 to 24 there\nf = open(\"numbers.txt\", \"w\")\nfor num in range(25):\n f.write(str(num)+'\\n')\nf.close()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Let's check that we did everything as expected\n!cat numbers.txt",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Reading a file from disk",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# We now open the file for reading\nf = open(\"temp.txt\", \"r\")\n# And we read the full content of the file in memory, as a big string\ncontent = f.read()\nf.close()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"content",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Once we read the file, we have the lines in a big string. Let's process that big string a little bit:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Read the file in the cell above, the content is in f2_content\n\n# Split the content of the file using the newline character \\n\nlines = content.split(\"\\n\")\n\n# Iterate through the line variable (it is a list of strings)\n# and then print the length of each line\nfor line in lines:\n print(line, \" ===> \", len(line))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# We now open the file for reading\nf = open(\"numbers.txt\", \"r\")\n# And we read the full content of the file in memory, as a big string\ncontent = f.read()\nf.close()\ncontent",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Once we read the file, we have the lines in a big string. Let's process that big string a little bit:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"lines = content.split(\"\\n\") # we get back a list of strings\nprint(lines)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# here we convert the strings into integers, using a list comprehension\n# we have the conditional to avoid trying to parse the string '' that \n# is at the end of the list\nnumbers = [int(line) for line in lines if len(line)>0]\nprint(numbers)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Let's clean up\n!rm temp.txt\n!rm numbers.txt",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Exercise 1\n\n* Write a function that reads a file and returns its content as a list of strings (one string per line). Read the file with filename `data/restaurant-names.txt`. If you stored your notebook under `Student_Notebooks` the full filename is `/home/ubuntu/jupyter/NYU_Notes/2-Introduction_to_Python/data/restaurant-names.txt`",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Exercise 2\n\n* Write a function that reads the n-th column of a CSV file and returns its contents. (Reuse the function that you wrote above.) Then reads the file `data/baseball.csv` and return the content of the 5th column (`team`).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Exercise 3 \n\nThe command below will create a file called `phonetest.txt`. Write code that:\n* Reads the file `phonetest.txt`\n* Write a function that takes as input a string, and removes any non-digit characters\n* Print out the \"clean\" string, without any non-digit characters",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%file phonetest.txt\n679-397-5255\n2126660921\n212-998-0902\n888-888-2222\n800-555-1211\n800 555 1212\n800.555.1213\n(800) 555-1214\n1-800-555-1215\n1(800)555-1216\n800-555-1212-1234\n800-555-1212x1234\n800-555-1212 ext. 1234\nwork 1-(800) 555.1212 #1234",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# your code here",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Solution for exercise 4 (with a lot of comments)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# this function takes as input a phone (string variable)\n# and prints only its digits\ndef clean(phone):\n # We initialize the result variable to be empty. \n # We will append to this variable the digit characters \n result = \"\"\n # This is a set of digits (as **strings**) that will\n # allow us to filter the characters\n digits = {\"0\",\"1\",\"2\",\"3\",\"4\",\"5\",\"6\",\"7\",\"8\",\"9\"}\n # We iterate over all the characters in the string \"phone\"\n # which is a parameter of the function clean\n for c in phone:\n # We check if the character c is a digit\n if c in digits:\n # if it is, we append it to the result\n result = result + c\n # once we are done we return a string variable with the result\n return result \n\n# This is an alternative, one-line solution that uses a list \n# comprehension to create the list of acceptable characters, \n# and then uses the join command to concatenate all the \n# characters in the list into a string. Notice that we use \n# the empty string \"\" as the connector\ndef clean_oneline(phone):\n digits = {\"0\",\"1\",\"2\",\"3\",\"4\",\"5\",\"6\",\"7\",\"8\",\"9\"}\n return \"\".join([c for c in phone if c in digits])\n\n# your code here\n# We open the file\nf = open(\"phonetest.txt\", \"r\")\n# We read the content using the f.read() command\ncontent = f.read()\n# Close the file\nf.close()\n# We split the file into lines\nlines = content.split(\"\\n\")\n# We iterate over the lines, and we clean each one of them\nfor line in lines:\n print(line, \"==>\", clean(line))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Let's clean up\n!rm phonetest.txt",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a71b8efa0a8eaa9ccb5286e4b35cc560287236e
| 5,330 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Guides/python/csvToPandas.ipynb
|
rocketproplab/Guides
|
165f0ffc6ed2ea746de08941077e2c2e0c2af554
|
[
"MIT"
] | 9 |
2017-04-11T01:10:37.000Z
|
2020-11-14T23:08:28.000Z
|
Guides/python/csvToPandas.ipynb
|
rocketproplab/Guides
|
165f0ffc6ed2ea746de08941077e2c2e0c2af554
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Guides/python/csvToPandas.ipynb
|
rocketproplab/Guides
|
165f0ffc6ed2ea746de08941077e2c2e0c2af554
|
[
"MIT"
] | 6 |
2017-04-15T22:36:07.000Z
|
2020-11-14T23:08:29.000Z
| 24.227273 | 376 | 0.513133 |
[
[
[
"# Import csv To Pandas\n\nThis file covers the process of importing excel files into a pandas dataframe.\n\nThe function used is [read_csv](http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/generated/pandas.read_csv.html).\n\n### Step 1\nLets start by importing pandas and os. We will be using pandas to create a dataframe from our data, and os to get file paths.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport os",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Step 2\nNow lets create a variable, <code>filePath</code>, that is a string containing the full path to the file we want to import. The code below looks in the current working directory for the file given a file name input by the user. This isn't necessary, and is just included for convienence. Alternatively, user can input a full path into the <code>filePath</code> variable.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cwd = os.getcwd()\nfileName = 'example.csv'\nfilePath = os.path.join(cwd, fileName)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Step 3\nGreat! Now lets read the data into a dataframe called <code>df</code>.\nThis will allow our data to be accessible by the string in the header.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df = pd.read_csv(filePath,header=0)\nprint(df)",
" Time (s) - Dev1/ai0 Amplitude - Dev1/ai0\n0 0.000 -0.5\n1 0.002 -0.5\n2 0.004 -0.5\n3 0.006 -0.5\n4 0.008 -0.5\n"
]
],
[
[
"Our data is now accessible by a key value. The keys are the column headers in the dataframe. In this example case, those are 'Time (s) - Dev1/ai0' and 'Amplitude - Dev1/ai0'. For example, lets access the data in the first column.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df['Time (s) - Dev1/ai0']",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"What would happen if we tried to access the data with an invalid key, say <code>1</code> for example? Lets try it to find out.\n\nNote: I enclose this code in a <code>try: except:</code> statement in order to prevent a huge error from being generated.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"try:\n df[1]\nexcept KeyError:\n print(\"KeyError: 1 - not a valid key\")",
"KeyError: 1 - not a valid key\n"
]
],
[
[
"So lets say you have a large dataframe with unknown columns. There is a simple way to index them without having prior knowledge of what the dataframe columns are. Namely, the <code>columns</code> method in pandas.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cols = df.columns\nfor col in cols:\n print(df[col])",
"0 0.000\n1 0.002\n2 0.004\n3 0.006\n4 0.008\nName: Time (s) - Dev1/ai0, dtype: float64\n0 -0.5\n1 -0.5\n2 -0.5\n3 -0.5\n4 -0.5\nName: Amplitude - Dev1/ai0, dtype: float64\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a71bef265bfda776d789fc5f27cfbda861b884a
| 82,249 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Gardenkiak/.ipynb_checkpoints/Algoritmoen Konplexutasuna eta Notazio Asintotikoa-checkpoint.ipynb
|
mpenagar/Programazioaren-Oinarriak
|
831dd1c1ec6cbd290f958328acc0132185b89e96
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Gardenkiak/.ipynb_checkpoints/Algoritmoen Konplexutasuna eta Notazio Asintotikoa-checkpoint.ipynb
|
mpenagar/Programazioaren-Oinarriak
|
831dd1c1ec6cbd290f958328acc0132185b89e96
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Gardenkiak/.ipynb_checkpoints/Algoritmoen Konplexutasuna eta Notazio Asintotikoa-checkpoint.ipynb
|
mpenagar/Programazioaren-Oinarriak
|
831dd1c1ec6cbd290f958328acc0132185b89e96
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 25.598817 | 2,255 | 0.488869 |
[
[
[
"# Algoritmoen Konplexutasuna eta Notazio Asintotikoa\n\n<img src=\"../img/konplexutasuna.jpg\" alt=\"Konplexutasuna\" style=\"width: 600px;\"/>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Algoritmoen Konplexutasuna eta Notazio Asintotikoa\n\n* Problema bat algoritmo ezberdinekin ebatzi daitezke\n* Zeren araberea aukeratuko dugu?\n * Ulergarritasuna\n * Inplementatzeko erreztasuna\n * Exekutatzeko behar duen denbora\n * **Denbora Konplexutasuna**\n * Exekutatzeko behar duen memoria\n * **Espazio Konplexutasuna**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"→ Gai honetan **Denbora Konplexutasuna** aztertuko dugu.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Denbora Konplexutasunaren azterketa enpirikoa\n\n* Algoritmo ezberdinen exekuzio denborak neurtu\n\n<center><img src=\"../img/cronometro.jpg\" alt=\"Konplexutasuna\" style=\"width: 300px;\"/></center>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Adibide bat: Ordenazio algoritmoa\n\n* Oinarria: Zerrenda bat ordenatua dago, ondoz-ondoko elementu guztiak ordenatuak badaude",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def isOrdered(z):\n return all(z[i]<=z[i+1] for i in range(len(z)-1))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"isOrdered([1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"isOrdered([1,2,3,4,6,5,7,8,9,10])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Algoritmo zoro bat: Suffle-Sort\n\n1. Zerrendako elementuak nahastu.\n1. Zerrenda ordenatua badago, **AMAITU**\n1. Jauzi **1**-era",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from random import shuffle\ndef shuffleSort(z):\n while not isOrdered(z):\n shuffle(z)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Algoritmoa badabil...",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"z = [2,1,4,3,5,7,6]\nshuffleSort(z)\nprint(z)",
"[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Exekuzio denbora neurtzen I - notebook-eko `%timit`\n\n* https://ipython.readthedocs.io/en/stable/interactive/magics.html#magic-timeit\n* `%timit sententzia` → sententzia exekutatzeko behar den denbora neurtu\n* Defektuz, exekuzio asko egingo ditu, denboraren batazbestekoa eta desbiderapena pantailatik idatziz",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print('Neurketa hastera doa')\n%timeit sum(range(100000))\nprint('Amaitu da:')",
"Neurketa hastera doa\n1.92 ms ± 89.2 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100 loops each)\nAmaitu da:\n"
]
],
[
[
"Algoritmo zoroaren exekuzio denboraren neurketa...",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"z = [2,1,4,3,5,7,6]\n%timeit shuffleSort(z)",
"2.65 µs ± 8.09 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100000 loops each)\n"
]
],
[
[
"→ nahiko bizkorra dirudi....",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"→ **bizkorregia**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* `%timit -n int -r int sententzia` → _loops_ eta _runs_ aukeratu",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"z = [2,1,4,3,5,7,6]\n%timeit -n 1 -r 1 shuffleSort(z)",
"23.3 ms ± 0 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 1 run, 1 loop each)\n"
]
],
[
[
"* x µs → x ms ????\n\n* zerbait txarto dabil...",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Eta 2 *run* egiten baditugu?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"z = [2,1,4,3,5,7,6]\n%timeit -n 1 -r 2 shuffleSort(z)",
"The slowest run took 19032.66 times longer than the fastest. This could mean that an intermediate result is being cached.\n31.9 ms ± 31.9 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 2 runs, 1 loop each)\n"
]
],
[
[
"* `%timeit`-aren lehenengo exekuzioak zerrenda ordenatzen du\n* Bigarrenetik aurrera ordenatua dago\n```python\nz = [2,1,4,3,5,7,6]\n%timeit shuffleSort(z)\n```\n* Ez dugu denbora ongi neurtzen `-n 1 -r 1` jartzen ez badugu",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Exekuzio denbora neurtzen II - notebook-eko `%%timit`\n\n* https://ipython.readthedocs.io/en/stable/interactive/magics.html#magic-timeit\n* `%%timit` zeldako lehen agindua → zelda osoa exekutatzeko behar den denbora neurtu",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%timeit -n 2 -r 3\nprint('Neurketa hastera doa')\nsum(range(100000))\nprint('Amaitu da:')",
"Neurketa hastera doa\nAmaitu da:\nNeurketa hastera doa\nAmaitu da:\nNeurketa hastera doa\nAmaitu da:\nNeurketa hastera doa\nAmaitu da:\nNeurketa hastera doa\nAmaitu da:\nNeurketa hastera doa\nAmaitu da:\n2.02 ms ± 40 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 3 runs, 2 loops each)\n"
]
],
[
[
"Orain ez gara arduratu behar _loops_ eta _runs_ aukeratzeaz",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%timeit\nz = [2,1,4,3,5,7,6]\nshuffleSort(z)",
"48.2 ms ± 16.6 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10 loops each)\n"
]
],
[
[
"→ Neurtzen ari garen denboran, zerrendaren sorrera bere barne du",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%timeit\nz = [2,1,4,3,5,7,6]",
"176 ns ± 5.28 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000000 loops each)\n"
]
],
[
[
"→ guztiz arbuiagarria da",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Exekuzio denbora neurtzen III - `timit` modulua\n\n* https://docs.python.org/3.8/library/timeit.html\n* `timeit.timeit(stmt='pass', setup='pass', timer=<default timer>, number=1000000, globals=None)`\n * `stmt` sententziaren `number` exekuzioek behar duten denbora\n* `timeit.repeat(stmt='pass', setup='pass', timer=<default timer>, repeat=5, number=1000000, globals=None)`\n * `stmt` sententziaren `number` exekuzioek behar duten denbora `repeat` aldiz",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import timeit\ntimeit.timeit('sum(range(100000))',number=1000)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"timeit.repeat('sum(range(100000))',number=100, repeat=10)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"→ Saiatu gintezke `%%timit` moduko bat sortzen, edozein lekutan erabiltzeko.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# prints a timing msm such as:\n# 66.2 ns ± 0.104 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000000 loops each)\ndef mytimeit(stmt='pass',loops=100,runs=7,setup='pass',globals=None):\n z = timeit.repeat(stmt=stmt,number=loops,repeat=runs,setup=setup,globals=globals)\n z = [x/loops for x in z]\n mean = sum(z)/runs\n std = (sum((x-mean)**2 for x in z)/(runs-1))**0.5 if runs>1 else 0.0\n if mean >= 1.0 :\n unit = 's'\n elif mean >= 1e-3 :\n unit = 'ms'\n mean *= 1e3\n std *= 1e3\n elif mean >= 1e-6 :\n unit = 'µs'\n mean *= 1e6\n std *= 1e6\n else :\n unit = 'ns'\n mean *= 1e9\n std *= 1e9\n print(f'{mean:.2f} {unit} ± {std:.2f} {unit} per loop (mean ± std. dev. of {runs} runs, {loops} loops each)')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mytimeit('sum(range(100000))')\n%timeit sum(range(100000))",
"1.84 ms ± 0.01 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100 loops each)\n1.85 ms ± 7.95 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)\n"
]
],
[
[
"Lerro anitzetako kodea neurtzeko:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"stmt='''\nb = 0\nfor i in range(100000):\n b += i\n'''\n\nmytimeit(stmt=stmt)",
"8.38 ms ± 0.05 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100 loops each)\n"
]
],
[
[
"Saia gitezke algoritmo zoroa neurtzen...",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"stmt='''\nz = [2,1,4,3,5,7,6]\nshuffleSort(z)\n'''\n\n# Errorea gertatuko da, timit moduluak beste ingurune batetan exekutatzen\n# duelako kodea, eta beraz shuffleSort funtzioa ez dago definitua\n#mytimeit(stmt=stmt)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"* `globals` argumentuari `globals()` builtin funtzioaren emaitza pasa.\n* https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#globals",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%timeit\nz = [2,1,4,3,5,7,6]\nshuffleSort(z)",
"54.8 ms ± 9.13 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10 loops each)\n"
],
[
"stmt='''\nz = [2,1,4,3,5,7,6]\nshuffleSort(z)\n'''\n\nmytimeit(stmt=stmt,loops=20,globals=globals())",
"46.92 ms ± 15.19 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 20 loops each)\n"
]
],
[
[
"Eta zerrenden `sort` funtzioarekin konparatzen badugu?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%timeit\nz = [2,1,4,3,5,7,6]\nz.sort()",
"318 ns ± 2.26 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000000 loops each)\n"
],
[
"stmt='''\nz = [2,1,4,3,5,7,6]\nz.sort()\n'''\n\nmytimeit(stmt=stmt,globals=globals())",
"317.10 ns ± 5.26 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100 loops each)\n"
],
[
"stmt='''\nz = [2,1,4,3,5,7,6]\nz.sort()\n'''\n\nmytimeit(stmt=stmt,number=1000000,repeat=7,globals=globals())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Gure ordenazio algoritmo zoroaren eta python-eko `sort`-aren arteko ezberdintasuna ikaragarri handituko da **zerrendaren tamaina luzatu ahala**...",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for i in range(11):\n print('---',i,'---')\n z = list(range(i))\n shuffle(z)\n mytimeit('shuffleSort(z)',loops=1,runs=1,globals=globals())",
"--- 0 ---\n6.81 µs ± 0.00 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 1 runs, 1 loops each)\n--- 1 ---\n4.10 µs ± 0.00 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 1 runs, 1 loops each)\n--- 2 ---\n14.20 µs ± 0.00 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 1 runs, 1 loops each)\n--- 3 ---\n21.38 µs ± 0.00 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 1 runs, 1 loops each)\n--- 4 ---\n80.44 µs ± 0.00 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 1 runs, 1 loops each)\n--- 5 ---\n965.17 µs ± 0.00 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 1 runs, 1 loops each)\n--- 6 ---\n6.75 ms ± 0.00 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 1 runs, 1 loops each)\n--- 7 ---\n57.08 ms ± 0.00 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 1 runs, 1 loops each)\n--- 8 ---\n335.99 ms ± 0.00 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 1 runs, 1 loops each)\n--- 9 ---\n2.98 s ± 0.00 s per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 1 runs, 1 loops each)\n--- 10 ---\n"
],
[
"for i in range(11):\n print('---',i,'---')\n z = list(range(i))\n shuffle(z)\n mytimeit('z.sort()',loops=1,runs=1,globals=globals())",
"--- 0 ---\n1.64 µs ± 0.00 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 1 runs, 1 loops each)\n--- 1 ---\n951.81 ns ± 0.00 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 1 runs, 1 loops each)\n--- 2 ---\n1.52 µs ± 0.00 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 1 runs, 1 loops each)\n--- 3 ---\n1.15 µs ± 0.00 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 1 runs, 1 loops each)\n--- 4 ---\n1.22 µs ± 0.00 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 1 runs, 1 loops each)\n--- 5 ---\n1.34 µs ± 0.00 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 1 runs, 1 loops each)\n--- 6 ---\n1.47 µs ± 0.00 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 1 runs, 1 loops each)\n--- 7 ---\n1.44 µs ± 0.00 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 1 runs, 1 loops each)\n--- 8 ---\n1.49 µs ± 0.00 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 1 runs, 1 loops each)\n--- 9 ---\n1.47 µs ± 0.00 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 1 runs, 1 loops each)\n--- 10 ---\n1.60 µs ± 0.00 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 1 runs, 1 loops each)\n"
],
[
"def f1(h):\n b = 0\n for k in h:\n b += k*h[k]\n return b\n\ndef f2(h):\n b = 0\n for k,v in h.items():\n b += k*v\n return b\n\ndef f3(h):\n return sum(k*v for k,v in h.items())\n\nh = {i:i for i in range(10000)}\nprint(f1(h),f2(h),f3(h))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%timeit f1(h)\n%timeit f2(h)\n%timeit f3(h)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Denbora Konplexutasunaren azterketa teorikoa\n\n* Algoritmo ezberdinen exekuzio denborak **estimatu**\n\n<center><img src=\"../img/guessing.gif\" alt=\"Konplexutasuna\" style=\"width: 300px;\"/></center>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Adibide bat: $n^2$ kalkulkatzen\n\n* Berreketa eragiketa existituko ez balitz...",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Hiru algoritmo ezberdin aztertuko ditugu:\n\n<center><img src=\"../img/Konplexutasuna-taula-1.png\" alt=\"Konplexutasuna\"/></center>\n\n<!--\n<table>\n<thead><tr><th><center>Biderkadura</center></th><th><center>Batura</center></th><th><center>Inkrementua</center></th></tr></thead>\n<tbody><tr>\n<td><code>result=n*n</code></td>\n<td><code>result = 0\nfor i in range(n):\n result += n</code></td>\n<td><code>result = 0\nfor i in range(n):\n for j in range(n):\n result += 1</code></td>\n</tr></tbody>\n</table>\n-->",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Oraingoz, analisia errazteko:\n\n<center><img src=\"../img/Konplexutasuna-taula-2.png\" alt=\"Konplexutasuna\"/></center>\n\n<!--\n<table>\n<thead><tr><th><center>Biderkadura</center></th><th><center>Batura</center></th><th><center>Inkrementua</center></th></tr></thead>\n<tbody><tr>\n<td><code>result=n*n</code></td>\n<td><code>result = 0\ni = 0\nwhile i < n :\n result += n\n i += 1</code></td>\n<td><code>result = 0\ni = 0\nwhile i < n :\n j = 0\n while j < n :\n result += 1\n j += 1\n i += 1</code></td>\n</tr></tbody>\n</table>\n-->",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* **Biderkaduran** oinarritutako algoritmoa\n\n<center><img src=\"../img/Konplexutasuna-taula-3.png\" alt=\"Konplexutasuna\"/></center>\n\n<!--\n<table>\n<thead><tr><th><center>Kodea</center></th><th><center>Eragiketa kopurua</center></tr></thead>\n<tbody><tr>\n<td><code>result=n*n</code></td>\n<td><code>→ 1 biderkaketa + 1 esleipen</code></td>\n</tr></tbody>\n</table>\n-->",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* **Baturan** oinarritutako algoritmoa\n\n<center><img src=\"../img/Konplexutasuna-taula-4.png\" alt=\"Konplexutasuna\"/></center>\n\n<!--\n<table>\n<thead><tr><th><center>Kodea</center></th><th><center>Eragiketa kopurua</center></tr></thead>\n<tbody><tr>\n<td><code>result = 0\ni = 0\nwhile i < n :\n result += n\n i += 1</code></td>\n<td><code>→ 1 esleipen\n→ 1 esleipen\n→ (n+1) • (1 konparaketa)\n→ n • (1 batura + 1 esleipen)\n→ n • (1 inkrementu)</code></td>\n</tr></tbody>\n</table>\n-->",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* **Inkrementuan** oinarritutako algoritmoa\n\n<center><img src=\"../img/Konplexutasuna-taula-5.png\" alt=\"Konplexutasuna\"/></center>\n\n<!--\n<table>\n<thead><tr><th><center>Kodea</center></th><th><center>Eragiketa kopurua</center></tr></thead>\n<tbody><tr>\n<td><code>result = 0\ni = 0\nwhile i < n :\n j = 0\n while j < n :\n result += 1\n j += 1\n i += 1</code></td>\n<td><code>→ 1 esleipen\n→ 1 esleipen\n→ (n+1) • (1 konparaketa)\n→ n • (1 esleipen)\n→ n • (n+1) • (1 konparaketa)\n→ n • n • (1 inkrementu)\n→ n • n • (1 inkrementu)\n→ n • (1 inkrementu)</code></td>\n</tr></tbody>\n</table>\n-->",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Demagun oinarrizko eragiketa bakoitzak ondoko denborak behar dituela :\n\n| Biderkadura | Batura | Inkrementua | Esleipena | Konparaketa |\n|:--------:|:--------:|:--------:|:---------:|:--------:|\n| 342$\\mu s$ | 31$\\mu s$ | 1$\\mu s$ | 1$\\mu s$ | 1$\\mu s$ |\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Orduan,\n\n| Algoritmoa | Bider. | Batura | Inkr. | Esleip. | Konpa. | Denbora $\\mu s$ |\n| :------------ | :------: | :------: | :------: | :-------: | :------: | :--------------: |\n| Biderkadura | $\\tiny 1$ | | | $\\tiny 1$ | | $\\tiny 343$ |\n| Batura | | $\\tiny n$ | $\\tiny n$ | $\\tiny n+2$ | $\\tiny n+1$ | $\\tiny 34n+3$ |\n| Inkrementua | | | $\\tiny 2n^2+n$ | $\\tiny n+2$ | $\\tiny n^2+2n+1$ | $\\tiny 3n^2+4n+3$ |\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"| Algoritmoa | Bider. | Batura | Inkr. | Esleip. | Konpa. | Denbora $\\mu s$ |\n|:--------------|:--------:|:--------:|:--------:|:---------:|:--------:|----------:|\n| Biderkadura | $\\tiny 1$ | | | $\\tiny 1$ | | $\\tiny 343$ |\n| Batura | | $\\tiny n$ | $\\tiny n$ | $\\tiny n+2$ | $\\tiny n+1$ | $\\tiny 34n+3$ |\n| Inkrementua | | | $\\tiny 2n^2+n$ | $\\tiny n+2$ | $\\tiny n^2+2n+1$ | $\\tiny 3n^2+4n+3$ |\n\n\n<center><img src=\"../img/Berreketa.png\" alt=\"Konplexutasuna\"/></center>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Oinarrizko eragiketen exekuzio denborak edozein direlarik ere:\n\n| Biderkadura | Batura | Inkrementua | Esleipena | Konparaketa |\n|:--------:|:--------:|:--------:|:---------:|:--------:|\n| $c_1$ | $c_2$ | $c_3$ | $c_4$ | $c_5$ |\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"| Algoritmoa | Bider. | Batura | Inkr. | Esleip. | Konpa. |\n|:--------------|:--------:|:--------:|:--------:|:---------:|:--------:|\n| Biderkadura | $\\tiny 1$ | | | $\\tiny 1$ | | \n| Batura | | $\\tiny n$ | $\\tiny n$ | $\\tiny n+2$ | $\\tiny n+1$ |\n| Inkrementua | | | $\\tiny 2n^2+n$ | $\\tiny n+2$ | $\\tiny n^2+2n+1$ |",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Biderkadura: $c_1 + c_2$ \n* Batura: $(c_2 + c_3 + c_4 +c_5) \\cdot n + (2c_4 + c_5)$\n* Inkrementua: $(2c_3+c_5) \\cdot n^2 + (c_3 + c_4 + 2c_5) \\cdot n + (2c_4+c_5)$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Biderkadura: $c_1 + c_2$ \n* Batura: $(c_2 + c_3 + c_4 +c_5) \\cdot n + (2c_4 + c_5)$\n* Inkrementua: $(2c_3+c_5) \\cdot n^2 + (c_3 + c_4 + 2c_5) \\cdot n + (2c_4+c_5)$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Konstante berriak definituz:\n\n* Biderkadura: $k_1$ \n* Batura: $k_2 n + k_3 $\n* Inkrementua: $k_4 n^2 + k_5 n + k_6$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Berdin dio $k_1 \\dots k_6$ konstanteen balioa zein den, n-ren tamaina handitu ahala:\n* Biderkadura algoritmoak $k_1$ koste **konstantea** izango du\n * n handitu arren, denbora ez da aldatuko.\n* Batura algoritmoak $k_2 n + k_3$ koste **lineala** izango du\n * n bikoiztean, denbora ere bikoiztu egingo da.\n* Inkrementu algoritmoak $k_4 n^2 + k_5 n + k_6$ koste **kuadratikoa** izango du\n * n bikoiztu → denbora laukoiztu\n * n x 10 → t x 100\n * n x 100 → t x 10.000\n * n x 1000 → t x 1.000.000\n * ...\n \n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Denbora Konplexutasunaren azterketa teorikoa:\n\n\n<p><center><em>Algoritmo baten exekuzio denborak problemaren tamainarekiko izango duen konportamolde asintotikoa</em></center></p>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Problemaren Tamaina:\n * $n^2$ kalkulatzean, n\n * Zerrenda bat ordenatzerakoan, zerrendaren luzera\n * ...\n* Batzuetan tamaina bat baina gehiago egon daiteke\n * Matrize batetako elementu maximoan, ilara eta zutabe kopurua\n * ...",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Eragiketetatik pausuetara: azterketa teorikoa sinplifikatzen\n\n\n<center><img src=\"../img/Pausuak.png\" alt=\"Konplexutasuna\" style=\"width: 600px;\"/></center>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Aurreko adibideetan, exekuzio denbora oinarrizko eragiketetan neurtu dugu\n * Esleipena, Batura, Konparaketa, Inkrementua...\n* Amaieran, eragiketa ezberdinen denbora koefizienteak konbinatu egin ditugu:\n * $(2c_3+c_5) \\cdot n^2 + (c_3 + c_4 + 2c_5) \\cdot n + (2c_4+c_5)$ → $k_4 n^2 + k_5 n + k_6$\n* Halako konbinaketak haseratik egin ditzakegu, notazioa errazteko:\n * $k$ → pausuak/urratsak",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Pausua/urratsa\n\n* Denbora konstante batetan exekutatuko den eragiketa multzoa\n * batura → pausu 1\n * 2 batura → pausu 1\n * 10.000 batura → pausu 1\n * ...\n * batura + esleipena → pausu 1\n * 2 x (batura + esleipena) → pausu 1\n * 10.000 x (batura + esleipena ) → pausu 1\n * ...",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"→ **Problemaren tamainarekiko menpekotasunik ez duen eragiketa multzoa** ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<center><img src=\"../img/Pausuak2.png\" alt=\"Konplexutasuna\" /></center>\n\n<!--\n<table>\n<thead><tr><th><center>Kodea</center></th><th><center>Pausu kopurua</center></tr></thead>\n<tbody><tr>\n<td><code>result = 0\ni = 0\nwhile i < n :\n j = 0\n while j < n :\n result += 1\n j += 1\n i += 1</code></td>\n<td><code>\n</tr></tbody>\n</table>\n\n-->",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<center><img src=\"../img/Pausuak3.png\" alt=\"Konplexutasuna\" /></center>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"→ **Pausu Kopurua:** $t(n) = n^2+n+1$ ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Algoritmo originaleetara bueltatuz:**\n\n<img src=\"../img/Konplexutasuna-taula-1.png\" alt=\"Konplexutasuna\"/>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* `range(n)` → 1 pausu\n* `for i in range(n)` → n x 1 pausu",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Biderkadura: $t(n) = 1$\n* Batura: $t(n) = n + 1$\n* Inkrementua: $t(n) = n^2+n+1$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Hiru algoritmoen pausu kopuruak:\n\n* Biderkadura: $t(n) = 1$\n* Batura: $t(n) = n+1$\n* Inkrementua: $t(n) = n^2+n+1$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Pausuak **edozein** direlarik ere:\n * $\\exists \\; n_a , \\forall n \\ge n_a$ Batura Inkrementua baina bizkorragoa den.\n * $\\exists \\; n_b , \\forall n \\ge n_b$ Biderkadura Batura baina bizkorragoa den.\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Kasu On, Txar eta Batazbestekoa \n<br/>\n<br/>\n\n<center><img src=\"../img/GoodUglyBad.jpg\" alt=\"GoodUglyBasd\" /></center>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Algoritmo batek emango dituen pausu kopuruak, problemaren tamaina konstante mantenduta ere, ebazten duen **kasu zehatzaren** araberakoa izan daiteke:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* `if` kontrol egitura\n * Aurrez ez dakigu egia izango ote den\n * batzuetan exekutatu, besteetan ez.\n* `while` kontrol egitura\n * Aurrez ez dakigu zenbat aldiz exekutatuko ote den\n * batzuetan askotan exekutatu, besteetan gutxitan",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Adibide bat: zerrenda batetan balio baten agerpen kopurua kalkulatu",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def kontatu(z,x):\n k = 0\n for y in z:\n if x == y :\n k += 1\n return k",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"* Problemaren tamaina: $n = len(z)$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* `x` $\\ne$ `y` → 1 pausu\n* `x` $=$ `y` → 2 pausu → 1 pausu\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* $t(n) = n + 1$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Adibide bat: zerrenda batetan balio baten lehen agerpenaren posizioa, edo `None`",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def topatu(z,x):\n for i in range(len(z)):\n if x == z[i] :\n return i\n return None",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"* Problemaren tamaina: $n = len(z)$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* `x` $\\ne$ `z[i]` → 1 pausu\n* `x` $=$ `z[i]` → 1 pausu eta *AMAITU*",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* $t(n) = ???$\n * Funtzioak jasotzen duen **zerrenda zehatzaren** araberakoa ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### I - Kasu Ona (*El Bueno*)\n\n```python\ndef topatu(z,x):\n for i in range(len(z)):\n if x == z[i] :\n return i\n return None\n```\n\n* Problemaren tamaina **EDOZEIN** delarik ere, izan dezakegun adibiderik bizkorrena.\n * Zerrendaren tamaina 0 dela esateak ez du balio.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Elementua zerrendaren lehenengo posizioan topatzea.\n\n* $t(n) = 1$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### II - Kasu Txarra (*El Malo*)\n\n```python\ndef topatu(z,x):\n for i in range(len(z)):\n if x == z[i] :\n return i\n return None\n```\n\n* Problemaren tamaina **EDOZEIN** delarik ere, izan dezakegun adibiderik motelena.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Elementua zerrendan ez egotea.\n\n* $t(n) = n+1$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### III - Batazbesteko Kasua (*El Feo*)\n\n```python\ndef topatu(z,x):\n for i in range(len(z)):\n if x == z[i] :\n return i\n return None\n```\n\n* Problemaren tamaina **EDOZEIN** delarik ere, *batazbestean* emango dugun pausu kopurua.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Batazbestekoa kalkulatu ahal izateko, posible diren kasuen gaineko probabilitate banaketa bat definitu beharko genuke eta ondoren kasu bakoitzaren pausu kopurua bere probabilitatearekin pixatu eta batu.\n * Edo integratu, kasu espazioa jarraia balitz",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Horrexegatik esleitu diogu *El Feo* pertsonaia...",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### III - Batazbesteko Kasua (*El Feo*) kalkulatzen...\n\n```python\ndef topatu(z,x):\n for i in range(len(z)):\n if x == z[i] :\n return i\n return None\n```\n\n* Demagun $n$ luzerako zerrenda batetan elementu bat edozein posiziotan topatzeko edo zerrendan ez egoteko probabilitatea berdina dela, hau da, $1/(n+1)$.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* $j$ posizioan dagoen elementua → $t_j(n)=j+1$ pausu",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Zerrendan ez dagoen elementua → $t_{None}(n)=n+1$ pausu",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* $j$ posizioan → $prob(j)=1/(n+1) \\;\\; , \\;\\;t_j(n)=j+1$\n* ez badago → $prob(None)=1/(n+1) \\;\\; , \\;\\;t_{None}(n)=n+1$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"$$t(n) = \\sum_{k \\in kasuak}{prob(k) \\cdot t_k(n)} = \\left(\\sum_{j=0}^{j=n-1}{\\frac{1}{n+1} \\cdot (j+1)} \\right) + \\frac{1}{n+1} \\cdot (n+1)$$ ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"$$= \\left(\\frac{1}{n+1} \\sum_{i=1}^{i=n}{i}\\right) + 1 = \\frac{n}{2}+1$$ ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Konplexutasun Polinomiko eta Ez Polinomikoak \n<br/>\n<br/>\n\n\n<center><img src=\"../img/Konplexutasuna-polinomioak.png\" alt=\"Konplexutasun ez polinomikoak\" /></center>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* `for` kontrol egiturek, askotan, pausu kopuru polinomikoak suposatzen dituzte",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* $t(n)=n$ :\n```python\nfor i in range(n):\n pausu 1\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* $t(n)=n^2$ :\n```python\nfor i in range(n):\n for j in range(n):\n pausu 1\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* $t(n)=n^3$ :\n```python\nfor i in range(n):\n for j in range(n):\n for k in range(n):\n pausu 1\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Indizeak erabiltzen dituzten `for` kontrol egitura *garbietan* (`return/break` ez dutenak), pausu kopurua batukarien bidez nahiko erraz adierazi daiteke",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* `for i in range(n)` $\\equiv$ `for i in range(0,n)` → $\\sum_{i=0}^{n-1}$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* `for j in range(i,n)` → $\\sum_{j=i}^{n-1}$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Kontuan izan gainera:\n\n$$\\sum_{i=a}^{b} 1 = \\sum_{i=b}^{a} 1 = \\max{(a,b)}-\\min{(a,b)}+1$$\n$$\\sum_{i=1}^{n} i = \\sum_{i=n}^{1} i = \\frac{n \\cdot (n+1)}{2}$$\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<span style=\"display:block; margin-top:-20px;\">\n \n```python\nfor i in range(n):\n pausu 1\n```\n\n   →   $t(n) = \\sum_{i=0}^{n-1} 1 = n$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<span style=\"display:block; margin-top:-20px;\">\n \n```python\nfor i in range(n):\n for j in range(n):\n pausu 1\n```\n\n   →   $t(n) = \\sum_{i=0}^{n-1} \\left( \\sum_{j=0}^{n-1} 1 \\right) = \\sum_{i=0}^{n-1} n = n^2$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<span style=\"display:block; margin-top:-20px;\">\n \n```python\nfor i in range(n):\n for j in range(n):\n for k in range(n):\n pausu 1\n```\n\n   →   $t(n) = \\sum_{i=0}^{n-1} \\left( \\sum_{j=0}^{n-1} \\left( \\sum_{k=0}^{n-1} 1 \\right) \\right) = \\sum_{i=0}^{n-1} \\left( \\sum_{j=0}^{n-1} n \\right) = \\sum_{i=0}^{n-1} n^2 = n^3$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Adibide bat:** Zerrenda batetan, bi edozein elementuren biderkadura maximoa\n\n```python\ndef kontatu(z):\n m = z[0]*z[1]\n for i in range(n-1):\n for j in range(i+1,n):\n x = z[i]*z[j]\n if x > m :\n m = x\n return m\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"$$t(n) = 1 + \\sum_{i=0}^{n-2} \\left( \\sum_{j=i+1}^{n-1} 1 \\right) = 1 + \\sum_{i=0}^{n-2} (n-1-i)$$\n\n$$ \\overset{k=n-1-i}{=\\mathrel{\\mkern-3mu}=} \\;\\; 1 + \\sum_{k=n-1}^{1} k = 1 + \\frac{(n-1) \\cdot n}{2} = \\frac{n^2}{2} - \\frac{n}{2} + 1$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* `while` kontrol egiturek, askotan, kasu on eta txarrak sortzen dituzte.\n* Pausu kopuruek ez dute zertan polinomikoak izan behar.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Adibide bat:** $[1,n]$ arteko zenbaki arrunt bat asmatzen. Demagun funtzio bat dugula, `galdera(k)` zeinak zenbakia pentsatu duenari galdetzeko balio duen. Funtzioak `0` bueltatuko du asmatu badugu, `1` bilatzen ari garen zenbakia handiagoa bada edo `-1` txikiagoa bada.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Problemaren tamaina: $n$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* `galdera(k)` : 1 pausu",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Ume oso txiki batek, halako zerbait egiten lezake:\n```python\nfrom random import randrange \ndef asmatu(n):\n x = galdera(randrange(1,n+1))\n while x:\n x = galdera(randrange(1,n+1)) \n print('Asmatu dut zure zenbakia!')\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Kasu Ona (auzazki aukeratutako lehenengo zenbakia): $t(n)=1$\n* Kasu Txarra (ez du sekula topatuko?): $t(n)\\overset{?}{=}\\infty$\n* Batazbesteko kasua: $t(n) = \\sum_{k \\in kasuak}{prob(k) \\cdot t_k(n)} = ??$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Estimazio enpirikoa:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from random import random\nn = 17\nth = 1/n\nN = 100000\nb = 0\nfor i in range(N):\n k = 1\n while random()>th :\n k+= 1\n b += k\nprint(b/N)",
"16.97855\n"
]
],
[
[
"* Kasu Ona (auzazki aukeratutako lehenengo zenbakia): $t(n)=1$\n* Kasu Txarra (ez du sekula topatuko?): $t(n)\\overset{?}{=}\\infty$\n* Batazbesteko kasua: $t(n) = \\sum_{k \\in kasuak}{prob(k) \\cdot t_k(n)} \\overset{enp}{=} n$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<center><img src=\"../img/Ugly.jpg\" alt=\"GoodUglyBasd\" /></center>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Umeak hobeto egiten ikas dezake:\n```python\ndef asmatu(n):\n i = 1\n x = galdera(i)\n while x:\n i += 1\n x = galdera(i)\n print('Asmatu dut zure zenbakia!')\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Kasu Ona (lehenengo zenbakia): $t(n)=1$\n* Kasu Txarra (azken zenbakia): $t(n)=n$\n* Batazbesteko kasua: $t(n) = \\sum_{i=1}^{n} (\\frac{1}{n} \\cdot i)= \\frac{n+1}{2}$\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Adin batetik aurrera, honako hau egin beharko genuke:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def asmatu(n):\n i,j = 1,n\n e = (i+j)//2\n x = galdera(e)\n while x :\n if x == 1 :\n i = e+1\n else :\n j = e-1\n e = (i+j)//2\n x = galdera(e)\n print('Asmatu dut zure zenbakia!')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"* Kasu Ona (justu justu erdian!): $t(n)=1$\n* Kasu Txarra (`i==j` egoerara iristean): $t(n) = \\; ???$\n* Batazbesteko kasua: $t(n) = \\; ???$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"→ Bitxia... bizkorragoa dela suposatzen dugu, baina ez gera gai zuzenean bere bizkortasuna adierazteko",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Iterazio bakoitza: 1 pausu → $t(n) = iterazio\\_kopurua$\n* Iterazio bakoitzean, bilaketa tartea erdira (apur bat txikiagoa) doa:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Iterazio bat: $[i,j] \\; \\approx \\frac{1}{2} [1,n]$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* 2 iterazio: $[i,j] \\; \\approx \\frac{1}{4} [1,n]$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* $k$ iterazio: $[i,j] \\; \\approx \\frac{1}{2^k} [1,n]$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* $i = j \\iff 2^k = n $\n* $k=\\log_2 n\\;$ iterazio izango dira",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Kasu Ona (erdian): $t(n)=1$\n* Kasu Txarra (`i==j` egoerara iristean): $t(n) = \\; \\log_2 n$\n* Batazbesteko kasua: $t(n) = \\; \\sum_{k \\in kasuak}{prob(k) \\cdot t_k(n)}$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Batazbestekoa kalkulatzeko, kasu bakoitzaren probabilitatea aukeratu behar dugu.\n* Demagun zenbaki guztiek probabilitate berdina dutela, $prob(k)=\\frac{1}{n}$\n* 1 pausu: 1 kasu (erdian egotea)\n* 2 pausu: 2 kasu (erdi bakoitzetako erdian egotea)\n* 3 pausu: 4 kasu (laurden bakoitzetako erdian egotea)\n* ...\n* $k$ pausu: $2^{k-1}$ kasu\n* ...\n* $k = \\log_2 n$ pausu : $2^{k-1} = \\frac{n}{2}$ kasu.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"$$\\small t(n) = \\; \\sum_{k \\in kasuak}{prob(k) \\cdot t_k(n)} = \\frac{1}{n} \\cdot \\sum_{k \\in kasuak}{t_k(n)} = \\frac{1}{n} \\cdot \\left( \\sum_{k=1}^{\\log_2 n}{ 2^{k-1} \\cdot k } \\right) \\overset{?}{\\approx} \\log_2 n$$\n\n$$ \\frac{1}{2} \\cdot \\log_2 n \\lt t(n) \\lt \\log_2 n \\;\\;\\; \\to \\;\\;\\; t(n) = \\log_2 n$$\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<center><img src=\"../img/Ugly.jpg\" alt=\"GoodUglyBasd\" /></center>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Algoritmo Errekurtsiboak \n<br/>\n<br/>\n\n<center><img src=\"../img/recursion.png\" alt=\"Algoritmo Errekurtsiboak\" /></center>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Algoritmo errekurtsiboen pausu kopurua espresio errekurtsibo bat erabiliz adierazi ahal da.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def faktoriala(n):\n if n < 2 :\n return 1\n else :\n return n * faktoriala(n-1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"$$\nt(n) = \n \\begin{cases}\n 1 & , & n<2\\\\\n 1+t(n-1) & , & n \\ge 2\\\\\n\\end{cases}\n$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Espresio errekurtsiboa garatu dezakegu:\n\n$$ t(n) = 1 + t(n-1) = 2 + t(n-2) = 3 + t(n-3) = \\ldots $$\n\n$$= k + t(n-k)$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Kasu basera iristeko behar den $k$ konstantea lortu behar dugu:\n\n$$ n-k = 1 \\iff k = n-1$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Eta ordezkatu:\n\n$$\\boxed{\\small t(n) = n - 1 + t(1) = n}$$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def hanoi(a,b,n):\n if n == 1 :\n print(a,'-->',b)\n else :\n c = 6-a-b\n hanoi(a,c,n-1)\n print(a,'-->',b)\n hanoi(c,b,n-1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"$$\nt(n) = \n \\begin{cases}\n 1 & , & n=1\\\\\n 1 + 2 \\cdot t(n-1) & , & n > 1\\\\\n\\end{cases}\n$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"$$t(n) = 1 + 2 \\cdot t(n-1) = 3 + 4 \\cdot t(n-2) = 7 + 8 \\cdot t(n-3) = \\ldots $$\n\n$$= (2^k-1) + 2^k \\cdot t(n-k)$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"$$n-k = 1 \\iff k=n-1$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"$$t(n) = 2^{n-1} - 1 + 2^{n-1} \\cdot 1$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"$$\\boxed{t(n) = 2^n - 1}$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"→ Bagenekien 2 eraztun 3 mugimendu zirela, 3 eraztun 7, 4 eraztun 15, 5 eraztun 31...",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def merge_sort(z):\n n = len(z)\n if n == 1 :\n return z\n else :\n a = merge_sort(z[:n//2])\n b = merge_sort(z[n//2:])\n return merge(a,b)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"* `z[:n//2]` → $\\frac{n}{2}$ pausu\n* `z[n//2:]` → $\\frac{n}{2}$ pausu\n* `merge(a,b)` → $len(a)+len(b)=n$ pausu ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"$$\nt(n) = \n \\begin{cases}\n 1 & , & n=1\\\\\n 1 + 2 n + 2 \\cdot t\\left(\\frac{n}{2}\\right) & , & n > 1\\\\\n\\end{cases}\n$$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def merge_sort(z):\n n = len(z)\n if n > 1 :\n a = z[:n//2]\n b = z[n//2:]\n merge_sort(a)\n merge_sort(b)\n z.clear()\n z.extend(merge(a,b))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"$$\\small{ t(n) = 1 + 2 n + 2 \\cdot t\\left(\\frac{n}{2}\\right) = 3 + 4n + 4 \\cdot t\\left(\\frac{n}{4}\\right) = 7 + 6n + 8 \\cdot t\\left(\\frac{n}{8}\\right) = \\ldots }$$\n\n$$\\small{= (2^k-1) + k \\cdot 2n+ 2^k \\cdot t\\left(\\frac{n}{2^k}\\right)}$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"$$\\small \\frac{n}{2^k} = 1 \\iff k=\\log_2 n$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"$$t(n) = (n-1) + (\\log_2 n) \\cdot 2n + n \\cdot 1 $$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"$$\\boxed{t(n) = 2n \\cdot \\log_2 n + 2n -1}$$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def merge_sort(z):\n n = len(z)\n if n > 1 :\n a = z[:n//2]\n b = z[n//2:]\n merge_sort(a)\n merge_sort(b)\n z.clear()\n z.extend(merge(a,b))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def fib(n):\n if n < 2 :\n return n\n else :\n return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"$$\nt(n) = \n \\begin{cases}\n 1 & , & n < 2\\\\\n 1 + t(n-1) + t(n-2) & , & n \\ge 2\\\\\n\\end{cases}\n$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"$$\\small{ t(n) = 1 + t(n-1) + t(n-2) = (1 + 1) + 2 \\cdot t(n-2) + t(n-3)}$$\n\n$$\\small{= (1+1+2) + 3 \\cdot t(n-3) + 2 \\cdot t(n-4) = (1+1+2+3) + 5 \\cdot t(n-4) + 3 \\cdot t(n-5) }$$\n\n$$\\small{= (1+1+2+3+5) + 8 \\cdot t(n-5) + 5 \\cdot t(n-6)}$$\n\n$$\\small{ = \\ldots = \\left(1 + \\sum_{i=1}^{k}{fib(i)}\\right) + fib(k+1) \\cdot t(n-k) + fib(k) \\cdot t(n-(k+1))}$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Errazagoa izango da goi/behe-borneak ezartzea:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"$$\ng(n) = \n \\begin{cases}\n 1 & , & n < 2\\\\\n 1 + 2 \\cdot t(n-2) & , & n \\ge 2\\\\\n\\end{cases}\n$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"$$\nh(n) = \n \\begin{cases}\n 1 & , & n < 2\\\\\n 1 + 2 \\cdot t(n-1) & , & n \\ge 2\\\\\n\\end{cases}\n$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"$$g(h) < t(n) < h(n)$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"$$g(n) = 1 + 2 \\cdot t(n-2) = 3 + 4 \\cdot t(n-4) = \\ldots = (2^k-1) + 2^k \\cdot t(n-2k)$$\n\n$$n-2k = 0 \\iff k=\\frac{n}{2}$$\n\n$$g(n) = (2^{n/2}-1) + 2^{n/2} \\cdot 1 = 2 \\cdot \\left(\\sqrt{2}\\right)^n - 1$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"$$h(n) = t_{hanoi}(n) = 2^n - 1$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"$$\\boxed{ 2 \\cdot \\left(\\sqrt{2}\\right)^n - 1 \\;<\\; t(n) \\;<\\; 2^n - 1}$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Notazio Asintotikoa\n\n* Algoritmo baten suposatzen dituen $t(n)$ pausu kopurua (kasu on eta kasu txarra) modu konpaktu batean adierazteko notazioa\n\n<center><img src=\"../img/konplexutasuna.jpg\" alt=\"Konplexutasuna\" style=\"width: 600px;\"/></center>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* **Goi Limitea** : *Kasu Txarra*\n\n$$\\small{O\\left( f(n) \\right) = \\{ t : \\mathbb{N} \\to \\mathbb{R}^+ \\;\\;:\\;\\; \\exists c \\in \\mathbb{R}^+ \\land \\exists n_0 \\in \\mathbb{N} \\;\\;:\\;\\; \\forall n \\ge n_0 \\;\\; t(n) \\le c \\cdot f(n) \\}}$$\n\n$$t(n)=an+b \\quad \\to \\quad t(n) \\in O(n)$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* **Behe Limitea** : *Kasu Ona*\n\n$$\\small{\\Omega \\left( f(n) \\right) = \\{ t : \\mathbb{N} \\to \\mathbb{R}^+ \\;\\;:\\;\\; \\exists c \\in \\mathbb{R}^+ \\land \\exists n_0 \\in \\mathbb{N} \\;\\;:\\;\\; \\forall n \\ge n_0 \\;\\; t(n) \\ge c \\cdot f(n) \\}}$$\n\n$$t(n)=an+b \\quad \\to \\quad t(n) \\in \\Omega(n)$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* **Magnitude Orden Zehatza** : *Kasu Txarra* $\\equiv$ *Kasu Ona*\n\n$$\\small{\\Theta \\left( f(n) \\right) = \\{ t : \\mathbb{N} \\to \\mathbb{R}^+ \\;:\\; \\exists c,d \\in \\mathbb{R}^+ \\land \\exists n_0 \\in \\mathbb{N} \\;:\\; \\forall n \\ge n_0 \\; c \\cdot f(n) \\ge t(n) \\ge d \\cdot f(n) \\}}$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"→ $f(n)$ funtziorik sinpleenak erabiliko ditugu: $O(1) \\;,\\; O(n) \\;,\\; O(\\log n) \\;,\\; O(n^2) \\ldots$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Adibide batzuk",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* $t(n) = 3n^2 - 4n + 17$ → $\\Theta(n^2)$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* $t_{txarra}(n) = 4n + 2 \\quad t_{ona}(n) = 117 $ → $O(n) \\quad \\Omega(1)$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* $t_{txarra}(n) = n^2 + n + 1 \\quad t_{ona}(n) = n \\cdot \\log_2 n+ 1 $ → $O(n^2) \\quad \\Omega(n \\cdot \\log n)$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Konplexutasun mailak",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"$$\\small{O(1) < O(\\log n) < O(n) < O(n \\cdot \\log n) < O(n^2) < O(n^3) < O(2^n) < O(n!) }$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Python-en berezko funtzio eta datu egituren pausuak",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Built-in funtzioak `n = len(it)`\n\n* `min(it)` , `max(it)` , `sum(it)` , `reversed(it)` : n\n* `all(it)` , `any(it)` : [1,n]\n* `sorted(it)` : n log n\n* `range()` , `zip(it)` , `enumerate(it)`: 1 ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Zerrendak `n = len(z)`\n\n* `list()` , `[]` , `z[i]` , `z[i] = x` , `len(z)` : 1\n* `z.clear()` : 1\n* `z.append(x)` : 1\n* `z.extend(x)` , `list(x)` : len(x)\n* `z.pop(-i)` , `del z[-i]` , `z.insert(-i,x)` : i\n* `z[i:j]` : j-i\n* `z.copy()` , `z.reverse()` : n\n* `z1 == z2` , `z1 != z2` , `z1 < z2` , ... : [1,n]\n* `z.count(x)` : n\n* `z.index(x)` , `x in z` : [1,n]\n* `z.remove(x)` : n\n* `z.sort()` : n log n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Hiztegiak `n = len(h)`\n\n* `dict()` , `{}` , `h[k]` , `h[k] = v` , `len(h)` , `h.get(k)` , `h.setdefault(k)` : 1\n* `del h[k]` , `h.popitem()` , `h.pop(x)` : 1\n* `h.keys()` , `h.values()` , `h.items()` : 1\n* `x in h` : 1\n* `dict.fromkeys(x)` , `h.update(x)` : len(x)\n* `h.copy()` : n\n* `h.clear()` : 1? n?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Multzoak `n = len(s)`\n\n* `set()` , `len(s)` , `s.add(x)` : 1\n* `s.pop()` , `s.remove(x)` : 1\n* `x in s` : 1\n* `s.update(x)` : len(x)\n* `s.copy()` : n\n* `s.clear()` : 1? n?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4a71d247bf1b3340b253ff95b8702e24180267c0
| 46,527 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
.ipynb_checkpoints/model_schema - copia-checkpoint.ipynb
|
Atorossian93/FastCycle-GAN
|
3507b80e8e1e749ddd937ee28f16f021c882e649
|
[
"Unlicense"
] | 1 |
2021-11-11T15:11:38.000Z
|
2021-11-11T15:11:38.000Z
|
.ipynb_checkpoints/model_schema - copia-checkpoint.ipynb
|
atorossian/FastCycle-GAN
|
3507b80e8e1e749ddd937ee28f16f021c882e649
|
[
"Unlicense"
] | null | null | null |
.ipynb_checkpoints/model_schema - copia-checkpoint.ipynb
|
atorossian/FastCycle-GAN
|
3507b80e8e1e749ddd937ee28f16f021c882e649
|
[
"Unlicense"
] | null | null | null | 46.341633 | 1,514 | 0.563393 |
[
[
[
"# Cycle-GAN",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Model Schema Definition",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The purpose of this notebook is to create in a simple format the schema of the solution proposed to colorize pictures with a Cycle-GAN accelerated with FFT convolutions.<p>To create a simple model schema this notebook will present the code for a Cycle-GAN built as a MVP (Minimum Viable Product) that works with the problem proposed.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import re\nimport os \nimport urllib.request\nimport numpy as np\nimport random\nimport pickle\nfrom PIL import Image\nfrom skimage import color\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom glob import glob\nfrom keras.preprocessing import image\nfrom keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator\nfrom keras.models import Model\nfrom keras.layers import Conv2D, MaxPooling2D, Activation, BatchNormalization, UpSampling2D, Dropout, Flatten, Dense, Input, LeakyReLU, Conv2DTranspose,AveragePooling2D, Concatenate\nfrom keras.models import load_model\nfrom keras.optimizers import Adam\nfrom keras.models import Sequential\nfrom tensorflow.compat.v1 import set_random_seed\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport pickle\nimport keras.backend as K\nimport boto3\nimport time\nfrom copy import deepcopy",
"Using TensorFlow backend.\n"
],
[
"%%time\n%matplotlib inline",
"Wall time: 4 ms\n"
],
[
"#import tqdm seperately and use jupyter notebooks %%capture\n%%capture\nfrom tqdm import tqdm_notebook as tqdm",
"UsageError: Line magic function `%%capture` not found.\n"
],
[
"#enter your bucket name and use boto3 to identify your region if you don't know it\nbucket = None\nregion = boto3.Session().region_name",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#add your bucket then creat the containers to download files and send to bucket\n\nrole = get_execution_role()\n\nbucket = None # customize to your bucket\ncontainers = {'us-west-2': '433757028032.dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/image-classification:latest',\n 'us-east-1': '811284229777.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/image-classification:latest',\n 'us-east-2': '825641698319.dkr.ecr.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/image-classification:latest',\n 'eu-west-1': '685385470294.dkr.ecr.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/image-classification:latest'}\ntraining_image = containers[boto3.Session().region_name]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def download(url):\n '''\n Downloads the file of a given url\n '''\n filename = url.split(\"/\")[-1]\n if not os.path.exists(filename):\n urllib.request.urlretrieve(url, filename)\n\n \ndef upload_to_s3(channel, file):\n '''\n Save file in a given folder in the S3 bucket\n '''\n s3 = boto3.resource('s3')\n data = open(file, \"rb\")\n key = channel + '/' + file\n s3.Bucket(bucket).put_object(Key=key, Body=data)\n\n\n# MPII Human Pose\ndownload('https://datasets.d2.mpi-inf.mpg.de/andriluka14cvpr/mpii_human_pose_v1.tar.gz')\nupload_to_s3('people', 'mpii_human_pose_v1.tar.gz')\n\n#untar the file\n!tar xvzf mpii_human_pose_v1.tar.gz\n\n\n#MIT coastal \ndownload('http://cvcl.mit.edu/scenedatabase/coast.zip')\nupload_to_s3('coast', 'coast.zip')\n\n#unzip the file\n!unzip coast.zip -d ./data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def image_read(file, size=(256,256)):\n '''\n This function loads and resizes the image to the passed size.\n Default image size is set to be 256x256\n '''\n image = image.load_img(file, target_size=size)\n image = image.img_to_array(img)\n return image",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def image_convert(file_paths,size=256,channels=3):\n '''\n Redimensions images to Numpy arrays of a certain size and channels. Default values are set to 256x256x3 for coloured\n images.\n Parameters:\n file_paths: a path to the image files\n size: an int or a 2x2 tuple to define the size of an image\n channels: number of channels to define in the numpy array\n '''\n # If size is an int\n if isinstance(size, int):\n # build a zeros matrix of the size of the image\n all_images_to_array = np.zeros((len(file_paths), size, size, channels), dtype='int64')\n for ind, i in enumerate(file_paths):\n # reads image\n img = image_read(i)\n all_images_to_array[ind] = img.astype('int64')\n print('All Images shape: {} size: {:,}'.format(all_images_to_array.shape, all_images_to_array.size))\n else:\n all_images_to_array = np.zeros((len(file_paths), size[0], size[1], channels), dtype='int64')\n for ind, i in enumerate(file_paths):\n img = read_img(i)\n all_images_to_array[ind] = img.astype('int64')\n print('All Images shape: {} size: {:,}'.format(all_images_to_array.shape, all_images_to_array.size))\n return all_images_to_array",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"file_paths = glob(r'./images/*.jpg')\nX_train = image_convert(file_paths)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def rgb_to_lab(img, l=False, ab=False):\n \"\"\"\n Takes in RGB channels in range 0-255 and outputs L or AB channels in range -1 to 1\n \"\"\"\n img = img / 255\n l = color.rgb2lab(img)[:,:,0]\n l = l / 50 - 1\n l = l[...,np.newaxis]\n\n ab = color.rgb2lab(img)[:,:,1:]\n ab = (ab + 128) / 255 * 2 - 1\n if l:\n return l\n else: return ab\n\ndef lab_to_rgb(img):\n \"\"\"\n Takes in LAB channels in range -1 to 1 and out puts RGB chanels in range 0-255\n \"\"\"\n new_img = np.zeros((256,256,3))\n for i in range(len(img)):\n for j in range(len(img[i])):\n pix = img[i,j]\n new_img[i,j] = [(pix[0] + 1) * 50,(pix[1] +1) / 2 * 255 - 128,(pix[2] +1) / 2 * 255 - 128]\n new_img = color.lab2rgb(new_img) * 255\n new_img = new_img.astype('uint8')\n return new_img",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"L = np.array([rgb_to_lab(image,l=True)for image in X_train])\nAB = np.array([rgb_to_lab(image,ab=True)for image in X_train])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"L_AB_channels = (L,AB)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"with open('l_ab_channels.p','wb') as f:\n pickle.dump(L_AB_channels,f)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def resnet_block(x ,num_conv=2, num_filters=512,kernel_size=(3,3),padding='same',strides=2):\n '''\n This function defines a ResNet Block composed of two convolution layers and that returns the sum of the inputs and the\n convolution outputs.\n Parameters\n x: is the tensor which will be used as input to the convolution layer\n num_conv: is the number of convolutions inside the block\n num_filters: is an int that describes the number of output filters in the convolution\n kernel size: is an int or tuple that describes the size of the convolution window\n padding: padding with zeros the image so that the kernel fits the input image or not. Options: 'valid' or 'same'\n strides: is the number of pixels shifts over the input matrix. \n '''\n input=x\n for i in num_conv:\n \n input=Conv2D(num_filters,kernel_size=kernel_size,padding=padding,strides=strides)(input)\n input=InstanceNormalization()(input)\n input=LeakyReLU(0.2)(input)\n\n\n return (input + x)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Generator",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def generator(input,filters=64,num_enc_layers=4,num_resblock=4,name=\"Generator\"):\n ''' \n The generator per se is an autoencoder built by a series of convolution layers that initially extract features of the\n input image.\n '''\n\n # defining input\n input=Input(shape=(256,256,1))\n x=input\n \n '''\n Adding first layer of the encoder model: 64 filters, 5x5 kernel size, 2 so the input size is reduced to half,\n input size is the image size: (256,256,1), number of channels 1 for the luminosity channel.\n We will use InstanceNormalization through the model and Leaky Relu with and alfa of 0.2\n as activation function for the encoder, while relu as activation for the decoder.\n between both of them, in the latent space we insert 4 resnet blocks.\n '''\n \n \n for lay in num_enc_layers:\n x=Conv2D(filters*lay,(5,5),padding='same',strides=2,input_shape=(256,256,1))(x)\n x=InstanceNormalization()(x)\n x=LeakyReLU(0.2)(x)\n \n x=Conv2D(128,(3,3),padding='same',strides=2)(x)\n x=InstanceNormalization()(x)\n x=LeakyReLU(0.2)(x)\n \n x=Conv2D(256,(3,3),padding='same',strides=2)(x)\n x=InstanceNormalization()(x)\n x=LeakyReLU(0.2)(x)\n \n x=Conv2D(512,(3,3),padding='same',strides=2)(x)\n x=InstanceNormalization()(x)\n x=LeakyReLU(0.2)(x)\n \n '''\n----------------------------------LATENT SPACE---------------------------------------------\n '''\n for r in num_resblock:\n x=resnet_block(x) \n '''\n----------------------------------LATENT SPACE---------------------------------------------\n '''\n \n x=Conv2DTranspose(256,(3,3),padding='same',strides=2)(x)\n x=InstanceNormalization()(x)\n x=Activation('relu')(x)\n \n x=Conv2DTranspose(128,(3,3),padding='same',strides=2)(x)\n x=InstanceNormalization()(x)\n x=Activation('relu')(x)\n \n x=Conv2DTranspose(64,(3,3),padding='same',strides=2)(x)\n x=InstanceNormalization()(x)\n x=Activation('relu')(x)\n \n x=Conv2DTranspose(32,(5,5),padding='same',strides=2)(x)\n x=InstanceNormalization()(x)\n x=Activation('relu')(x)\n \n x=Conv2D(2,(3,3),padding='same')(x)\n output=Activation('tanh')(x)\n \n model=Model(input,output,name=name)\n\n return model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Discriminator",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def discriminator(input,name=\"Discriminator\"):\n # importing libraries\n from keras.layers import Conv2D, MaxPooling2D, Activation, BatchNormalization, UpSampling2D, Dropout, Flatten, Dense, Input, LeakyReLU, Conv2DTranspose,AveragePooling2D, Concatenate\n from tensorflow_addons import InstanceNormalization\n \n # defining input\n input=Input(shape=(256,256,2))\n x=input\n \n x=Conv2D(32,(3,3), padding='same',strides=2,input_shape=(256,256,2))(x)\n x=LeakyReLU(0.2)(x)\n x=Dropout(0.25)(x)\n \n x=Conv2D(64,(3,3),padding='same',strides=2)(x)\n x=BatchNormalization()\n x=LeakyReLU(0.2)(x)\n x=Dropout(0.25)(x)\n \n \n x=Conv2D(128,(3,3), padding='same', strides=2)(x)\n x=BatchNormalization()(x)\n x=LeakyReLU(0.2)(x)\n x=Dropout(0.25)(x)\n \n \n x=Conv2D(256,(3,3), padding='same',strides=2)(x)\n x=BatchNormalization()(x)\n x=LeakyReLU(0.2)(x)\n x=Dropout(0.25)(x)\n \n \n x=Flatten()(x)\n x=Dense(1)(x)\n output=Activation('sigmoid')(x)\n \n model=Model(input,output,name=name)\n \n return model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Building GAN Model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Building discriminators\ndiscriminator_A=discriminator(input_a,\"discriminator_A\")\n\ndiscriminator_B=discriminator(input_b,\"discriminator_A\")\n\ndiscriminator_A.trainable = False\n\ndiscriminator_B.trainable = False\n\n# Building generator\ngenerator_B = generator(input_a,\"Generator_A_B\")\ngenerator_A = generator(input_b,\"Generator_B_A\")\n\ndecision_A=discriminator(generator_a,\"Discriminator_A\")\ndecision_B=discriminator(generator_B,\"Discriminator_B\")\n\ncycle_A=generator(generator_b,\"Generator_B_A\")\ncycle_B=generator(generator_A,\"Generator_A_B\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#creates lists to log the losses and accuracy\ngen_losses = []\ndisc_real_losses = []\ndisc_fake_losses=[] \ndisc_acc = []\n\n#train the generator on a full set of 320 and the discriminator on a half set of 160 for each epoch\n#discriminator is given real and fake y's while generator is always given real y's\n\nn = 320\ny_train_fake = np.zeros([160,1])\ny_train_real = np.ones([160,1])\ny_gen = np.ones([n,1])\n\n#Optional label smoothing\n#y_train_real -= .1\n\n\n#Pick batch size and number of epochs, number of epochs depends on the number of photos per epoch set above\nnum_epochs=1500\nbatch_size=32",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#run and train until photos meet expectations (stop & restart model with tweaks if loss goes to 0 in discriminator)\nfor epoch in tqdm(range(1,num_epochs+1)):\n #shuffle L and AB channels then take a subset corresponding to each networks training size\n np.random.shuffle(X_train_L)\n l = X_train_L[:n]\n np.random.shuffle(X_train_AB)\n ab = X_train_AB[:160]\n \n fake_images = generator.predict(l[:160], verbose=1)\n \n #Train on Real AB channels\n d_loss_real = discriminator.fit(x=ab, y= y_train_real,batch_size=32,epochs=1,verbose=1) \n disc_real_losses.append(d_loss_real.history['loss'][-1])\n \n #Train on fake AB channels\n d_loss_fake = discriminator.fit(x=fake_images,y=y_train_fake,batch_size=32,epochs=1,verbose=1)\n disc_fake_losses.append(d_loss_fake.history['loss'][-1])\n \n #append the loss and accuracy and print loss\n disc_acc.append(d_loss_fake.history['acc'][-1])\n \n\n #Train the gan by producing AB channels from L\n g_loss = combined_network.fit(x=l, y=y_gen,batch_size=32,epochs=1,verbose=1)\n #append and print generator loss\n gen_losses.append(g_loss.history['loss'][-1])\n \n #every 50 epochs it prints a generated photo and every 100 it saves the model under that epoch\n if epoch % 50 == 0:\n print('Reached epoch:',epoch)\n pred = generator.predict(X_test_L[2].reshape(1,256,256,1))\n img = lab_to_rgb(np.dstack((X_test_L[2],pred.reshape(256,256,2))))\n plt.imshow(img)\n plt.show()\n if epoch % 100 == 0:\n generator.save('generator_' + str(epoch)+ '_v3.h5')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"img_height = 256\nimg_width = 256\nimg_layer = 3\nimg_size = img_height * img_width\n\nto_train = True\nto_test = False\nto_restore = False\noutput_path = \"./output\"\ncheck_dir = \"./output/checkpoints/\"\n\n\ntemp_check = 0\n\n\n\nmax_epoch = 1\nmax_images = 100\n\nh1_size = 150\nh2_size = 300\nz_size = 100\nbatch_size = 1\npool_size = 50\nsample_size = 10\nsave_training_images = True\nngf = 32\nndf = 64\n\nclass CycleGAN():\n\n def input_setup(self):\n\n ''' \n This function basically setup variables for taking image input.\n filenames_A/filenames_B -> takes the list of all training images\n self.image_A/self.image_B -> Input image with each values ranging from [-1,1]\n '''\n\n filenames_A = tf.train.match_filenames_once(\"./input/horse2zebra/trainA/*.jpg\") \n self.queue_length_A = tf.size(filenames_A)\n filenames_B = tf.train.match_filenames_once(\"./input/horse2zebra/trainB/*.jpg\") \n self.queue_length_B = tf.size(filenames_B)\n \n filename_queue_A = tf.train.string_input_producer(filenames_A)\n filename_queue_B = tf.train.string_input_producer(filenames_B)\n\n image_reader = tf.WholeFileReader()\n _, image_file_A = image_reader.read(filename_queue_A)\n _, image_file_B = image_reader.read(filename_queue_B)\n\n self.image_A = tf.subtract(tf.div(tf.image.resize_images(tf.image.decode_jpeg(image_file_A),[256,256]),127.5),1)\n self.image_B = tf.subtract(tf.div(tf.image.resize_images(tf.image.decode_jpeg(image_file_B),[256,256]),127.5),1)\n\n \n\n def input_read(self, sess):\n\n\n '''\n It reads the input into from the image folder.\n self.fake_images_A/self.fake_images_B -> List of generated images used for calculation of loss function of Discriminator\n self.A_input/self.B_input -> Stores all the training images in python list\n '''\n\n # Loading images into the tensors\n coord = tf.train.Coordinator()\n threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(coord=coord)\n\n num_files_A = sess.run(self.queue_length_A)\n num_files_B = sess.run(self.queue_length_B)\n\n self.fake_images_A = np.zeros((pool_size,1,img_height, img_width, img_layer))\n self.fake_images_B = np.zeros((pool_size,1,img_height, img_width, img_layer))\n\n\n self.A_input = np.zeros((max_images, batch_size, img_height, img_width, img_layer))\n self.B_input = np.zeros((max_images, batch_size, img_height, img_width, img_layer))\n\n for i in range(max_images): \n image_tensor = sess.run(self.image_A)\n if(image_tensor.size() == img_size*batch_size*img_layer):\n self.A_input[i] = image_tensor.reshape((batch_size,img_height, img_width, img_layer))\n\n for i in range(max_images):\n image_tensor = sess.run(self.image_B)\n if(image_tensor.size() == img_size*batch_size*img_layer):\n self.B_input[i] = image_tensor.reshape((batch_size,img_height, img_width, img_layer))\n\n\n coord.request_stop()\n coord.join(threads)\n\n\n\n\n def model_setup(self):\n\n ''' This function sets up the model to train\n self.input_A/self.input_B -> Set of training images.\n self.fake_A/self.fake_B -> Generated images by corresponding generator of input_A and input_B\n self.lr -> Learning rate variable\n self.cyc_A/ self.cyc_B -> Images generated after feeding self.fake_A/self.fake_B to corresponding generator. This is use to calcualte cyclic loss\n '''\n\n self.input_A = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [batch_size, img_width, img_height, img_layer], name=\"input_A\")\n self.input_B = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [batch_size, img_width, img_height, img_layer], name=\"input_B\")\n \n self.fake_pool_A = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, img_width, img_height, img_layer], name=\"fake_pool_A\")\n self.fake_pool_B = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, img_width, img_height, img_layer], name=\"fake_pool_B\")\n\n self.global_step = tf.Variable(0, name=\"global_step\", trainable=False)\n\n self.num_fake_inputs = 0\n\n self.lr = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[], name=\"lr\")\n\n with tf.variable_scope(\"Model\") as scope:\n self.fake_B = build_generator_resnet_9blocks(self.input_A, name=\"g_A\")\n self.fake_A = build_generator_resnet_9blocks(self.input_B, name=\"g_B\")\n self.rec_A = build_gen_discriminator(self.input_A, \"d_A\")\n self.rec_B = build_gen_discriminator(self.input_B, \"d_B\")\n\n scope.reuse_variables()\n\n self.fake_rec_A = build_gen_discriminator(self.fake_A, \"d_A\")\n self.fake_rec_B = build_gen_discriminator(self.fake_B, \"d_B\")\n self.cyc_A = build_generator_resnet_9blocks(self.fake_B, \"g_B\")\n self.cyc_B = build_generator_resnet_9blocks(self.fake_A, \"g_A\")\n\n scope.reuse_variables()\n\n self.fake_pool_rec_A = build_gen_discriminator(self.fake_pool_A, \"d_A\")\n self.fake_pool_rec_B = build_gen_discriminator(self.fake_pool_B, \"d_B\")\n\n def loss_calc(self):\n\n ''' In this function we are defining the variables for loss calcultions and traning model\n d_loss_A/d_loss_B -> loss for discriminator A/B\n g_loss_A/g_loss_B -> loss for generator A/B\n *_trainer -> Variaous trainer for above loss functions\n *_summ -> Summary variables for above loss functions'''\n\n cyc_loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.abs(self.input_A-self.cyc_A)) + tf.reduce_mean(tf.abs(self.input_B-self.cyc_B))\n \n disc_loss_A = tf.reduce_mean(tf.squared_difference(self.fake_rec_A,1))\n disc_loss_B = tf.reduce_mean(tf.squared_difference(self.fake_rec_B,1))\n \n g_loss_A = cyc_loss*10 + disc_loss_B\n g_loss_B = cyc_loss*10 + disc_loss_A\n\n d_loss_A = (tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(self.fake_pool_rec_A)) + tf.reduce_mean(tf.squared_difference(self.rec_A,1)))/2.0\n d_loss_B = (tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(self.fake_pool_rec_B)) + tf.reduce_mean(tf.squared_difference(self.rec_B,1)))/2.0\n\n \n optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(self.lr, beta1=0.5)\n\n self.model_vars = tf.trainable_variables()\n\n d_A_vars = [var for var in self.model_vars if 'd_A' in var.name]\n g_A_vars = [var for var in self.model_vars if 'g_A' in var.name]\n d_B_vars = [var for var in self.model_vars if 'd_B' in var.name]\n g_B_vars = [var for var in self.model_vars if 'g_B' in var.name]\n \n self.d_A_trainer = optimizer.minimize(d_loss_A, var_list=d_A_vars)\n self.d_B_trainer = optimizer.minimize(d_loss_B, var_list=d_B_vars)\n self.g_A_trainer = optimizer.minimize(g_loss_A, var_list=g_A_vars)\n self.g_B_trainer = optimizer.minimize(g_loss_B, var_list=g_B_vars)\n\n for var in self.model_vars: print(var.name)\n\n #Summary variables for tensorboard\n\n self.g_A_loss_summ = tf.summary.scalar(\"g_A_loss\", g_loss_A)\n self.g_B_loss_summ = tf.summary.scalar(\"g_B_loss\", g_loss_B)\n self.d_A_loss_summ = tf.summary.scalar(\"d_A_loss\", d_loss_A)\n self.d_B_loss_summ = tf.summary.scalar(\"d_B_loss\", d_loss_B)\n\n def save_training_images(self, sess, epoch):\n\n if not os.path.exists(\"./output/imgs\"):\n os.makedirs(\"./output/imgs\")\n\n for i in range(0,10):\n fake_A_temp, fake_B_temp, cyc_A_temp, cyc_B_temp = sess.run([self.fake_A, self.fake_B, self.cyc_A, self.cyc_B],feed_dict={self.input_A:self.A_input[i], self.input_B:self.B_input[i]})\n imsave(\"./output/imgs/fakeB_\"+ str(epoch) + \"_\" + str(i)+\".jpg\",((fake_A_temp[0]+1)*127.5).astype(np.uint8))\n imsave(\"./output/imgs/fakeA_\"+ str(epoch) + \"_\" + str(i)+\".jpg\",((fake_B_temp[0]+1)*127.5).astype(np.uint8))\n imsave(\"./output/imgs/cycA_\"+ str(epoch) + \"_\" + str(i)+\".jpg\",((cyc_A_temp[0]+1)*127.5).astype(np.uint8))\n imsave(\"./output/imgs/cycB_\"+ str(epoch) + \"_\" + str(i)+\".jpg\",((cyc_B_temp[0]+1)*127.5).astype(np.uint8))\n imsave(\"./output/imgs/inputA_\"+ str(epoch) + \"_\" + str(i)+\".jpg\",((self.A_input[i][0]+1)*127.5).astype(np.uint8))\n imsave(\"./output/imgs/inputB_\"+ str(epoch) + \"_\" + str(i)+\".jpg\",((self.B_input[i][0]+1)*127.5).astype(np.uint8))\n\n def fake_image_pool(self, num_fakes, fake, fake_pool):\n ''' This function saves the generated image to corresponding pool of images.\n In starting. It keeps on feeling the pool till it is full and then randomly selects an\n already stored image and replace it with new one.'''\n\n if(num_fakes < pool_size):\n fake_pool[num_fakes] = fake\n return fake\n else :\n p = random.random()\n if p > 0.5:\n random_id = random.randint(0,pool_size-1)\n temp = fake_pool[random_id]\n fake_pool[random_id] = fake\n return temp\n else :\n return fake\n\n\n def train(self):\n\n\n ''' Training Function '''\n\n\n # Load Dataset from the dataset folder\n self.input_setup() \n\n #Build the network\n self.model_setup()\n\n #Loss function calculations\n self.loss_calc()\n \n # Initializing the global variables\n init = tf.global_variables_initializer()\n saver = tf.train.Saver() \n\n with tf.Session() as sess:\n sess.run(init)\n\n #Read input to nd array\n self.input_read(sess)\n\n #Restore the model to run the model from last checkpoint\n if to_restore:\n chkpt_fname = tf.train.latest_checkpoint(check_dir)\n saver.restore(sess, chkpt_fname)\n\n writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(\"./output/2\")\n\n if not os.path.exists(check_dir):\n os.makedirs(check_dir)\n\n # Training Loop\n for epoch in range(sess.run(self.global_step),100): \n print (\"In the epoch \", epoch)\n saver.save(sess,os.path.join(check_dir,\"cyclegan\"),global_step=epoch)\n\n # Dealing with the learning rate as per the epoch number\n if(epoch < 100) :\n curr_lr = 0.0002\n else:\n curr_lr = 0.0002 - 0.0002*(epoch-100)/100\n\n if(save_training_images):\n self.save_training_images(sess, epoch)\n\n # sys.exit()\n\n for ptr in range(0,max_images):\n print(\"In the iteration \",ptr)\n print(\"Starting\",time.time()*1000.0)\n\n # Optimizing the G_A network\n\n _, fake_B_temp, summary_str = sess.run([self.g_A_trainer, self.fake_B, self.g_A_loss_summ],feed_dict={self.input_A:self.A_input[ptr], self.input_B:self.B_input[ptr], self.lr:curr_lr})\n \n writer.add_summary(summary_str, epoch*max_images + ptr) \n fake_B_temp1 = self.fake_image_pool(self.num_fake_inputs, fake_B_temp, self.fake_images_B)\n \n # Optimizing the D_B network\n _, summary_str = sess.run([self.d_B_trainer, self.d_B_loss_summ],feed_dict={self.input_A:self.A_input[ptr], self.input_B:self.B_input[ptr], self.lr:curr_lr, self.fake_pool_B:fake_B_temp1})\n writer.add_summary(summary_str, epoch*max_images + ptr)\n \n \n # Optimizing the G_B network\n _, fake_A_temp, summary_str = sess.run([self.g_B_trainer, self.fake_A, self.g_B_loss_summ],feed_dict={self.input_A:self.A_input[ptr], self.input_B:self.B_input[ptr], self.lr:curr_lr})\n\n writer.add_summary(summary_str, epoch*max_images + ptr)\n \n \n fake_A_temp1 = self.fake_image_pool(self.num_fake_inputs, fake_A_temp, self.fake_images_A)\n\n # Optimizing the D_A network\n _, summary_str = sess.run([self.d_A_trainer, self.d_A_loss_summ],feed_dict={self.input_A:self.A_input[ptr], self.input_B:self.B_input[ptr], self.lr:curr_lr, self.fake_pool_A:fake_A_temp1})\n\n writer.add_summary(summary_str, epoch*max_images + ptr)\n \n self.num_fake_inputs+=1\n \n \n\n sess.run(tf.assign(self.global_step, epoch + 1))\n\n writer.add_graph(sess.graph)\n\n def test(self):\n\n\n ''' Testing Function'''\n\n print(\"Testing the results\")\n\n self.input_setup()\n\n self.model_setup()\n saver = tf.train.Saver()\n init = tf.global_variables_initializer()\n\n with tf.Session() as sess:\n\n sess.run(init)\n\n self.input_read(sess)\n\n chkpt_fname = tf.train.latest_checkpoint(check_dir)\n saver.restore(sess, chkpt_fname)\n\n if not os.path.exists(\"./output/imgs/test/\"):\n os.makedirs(\"./output/imgs/test/\") \n\n for i in range(0,100):\n fake_A_temp, fake_B_temp = sess.run([self.fake_A, self.fake_B],feed_dict={self.input_A:self.A_input[i], self.input_B:self.B_input[i]})\n imsave(\"./output/imgs/test/fakeB_\"+str(i)+\".jpg\",((fake_A_temp[0]+1)*127.5).astype(np.uint8))\n imsave(\"./output/imgs/test/fakeA_\"+str(i)+\".jpg\",((fake_B_temp[0]+1)*127.5).astype(np.uint8))\n imsave(\"./output/imgs/test/inputA_\"+str(i)+\".jpg\",((self.A_input[i][0]+1)*127.5).astype(np.uint8))\n imsave(\"./output/imgs/test/inputB_\"+str(i)+\".jpg\",((self.B_input[i][0]+1)*127.5).astype(np.uint8))\n\n\ndef main():\n \n model = CycleGAN()\n if to_train:\n model.train()\n elif to_test:\n model.test()\n\nif __name__ == '__main__':\n\n main()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a71db6d8af952ca7cd9854e640dadbcdba8c4ca
| 6,867 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
portfolio_exercises/PythonPackageTemplate/polynomial_TMC/polynomial_TMC/Poly Notebook.ipynb
|
TomCanty/DSND_Term2
|
1481606c96d063c6851d74edc7d8b85ba57bfca7
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
portfolio_exercises/PythonPackageTemplate/polynomial_TMC/polynomial_TMC/Poly Notebook.ipynb
|
TomCanty/DSND_Term2
|
1481606c96d063c6851d74edc7d8b85ba57bfca7
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
portfolio_exercises/PythonPackageTemplate/polynomial_TMC/polynomial_TMC/Poly Notebook.ipynb
|
TomCanty/DSND_Term2
|
1481606c96d063c6851d74edc7d8b85ba57bfca7
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 21.129231 | 84 | 0.440658 |
[
[
[
"import polynomial",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import numpy as np",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class Polynomial():\n\n def __init__(self, coef=[0]):\n self.coef = np.array(coef)\n self.exp = self._determine_exponents()\n pass\n\n def _determine_exponents(self):\n # Create list of exponents based on size of array\n return np.array(range(len(self.coef)-1,-1,-1))\n\n def result(self,x):\n # calculates y for the polynomail funciton given x\n return np.power(np.array(self.coef)*x,self.exp).sum()\n\n def __repr__(self):\n rep_str = \"Polynomial: \"\n for i in range(len(self.coef)):\n if self.exp[i] > 0:\n rep_str += str(self.coef[i])+'x^'+str(self.exp[i])+ ' + '\n else:\n rep_str += str(self.coef[i])\n return rep_str\n\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class Derivative(Polynomial):\n\n def __init__(self, coef=[0],order=1):\n Polynomial.__init__(self,coef)\n self.dcoef = self.coef\n self.dexp = self._determine_exponents()\n self.order = order\n if order > self.exp[0]:\n print('Warning: Order larger than the polynomial')\n self.derivate(order)\n\n def derivate(self,order):\n for i in range(1,order+1):\n self.dcoef = np.multiply(self.dcoef,self.dexp)[:-1]\n self.dexp = self.dexp[:-1]-1\n \n def __repr__(self):\n rep_str = \"Polynomial: \"\n der_str = \"Order \" + str(self.order) + \" Derivative: \"\n for i in range(len(self.coef)):\n if self.exp[i] > 0:\n rep_str += str(self.coef[i])+'x^'+str(self.exp[i])+ ' + '\n else:\n rep_str += str(self.coef[i])\n for i in range(len(self.dcoef)):\n if self.dexp[i] > 0:\n der_str += str(self.dcoef[i])+'x^'+str(self.dexp[i])+ ' + '\n else:\n der_str += str(self.dcoef[i])\n return rep_str +' \\n' + der_str\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"poly = Polynomial([1,2,3,4,5])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"poly",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"poly.exp",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"poly.coef",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"poly.result(5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"polyD = Derivative([1,2,3,4,5],order=2)\npolyD",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for i in range(1,order+1):\n print(i)",
"1\n"
],
[
"poly.coef",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"poly.exp",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"string = ''\nfor i in range(len(poly.coef)):\n if poly.exp[i] > 0:\n string += str(poly.coef[i])+'x^'+str(poly.exp[i])+ ' + '\n else:\n string += str(poly.coef[i])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"string",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a71e94865b5875eb960c23bd78e3221322ecf31
| 27,069 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
3-qm/ProjectiveMeasurement.ipynb
|
igelover/math-intro-to-qc
|
4ad535402cb6ccd619c4e4fd5c257ae8c6ce76d3
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2022-01-18T00:26:27.000Z
|
2022-01-18T00:26:27.000Z
|
3-qm/ProjectiveMeasurement.ipynb
|
igelover/math-intro-to-qc
|
4ad535402cb6ccd619c4e4fd5c257ae8c6ce76d3
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
3-qm/ProjectiveMeasurement.ipynb
|
igelover/math-intro-to-qc
|
4ad535402cb6ccd619c4e4fd5c257ae8c6ce76d3
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 63.245327 | 854 | 0.592301 |
[
[
[
"<a href=\"https://qworld.net\" target=\"_blank\" align=\"left\"><img src=\"../qworld/images/header.jpg\" align=\"left\"></a>\n$$\n\\newcommand{\\set}[1]{\\left\\{#1\\right\\}}\n\\newcommand{\\abs}[1]{\\left\\lvert#1\\right\\rvert}\n\\newcommand{\\norm}[1]{\\left\\lVert#1\\right\\rVert}\n\\newcommand{\\inner}[2]{\\left\\langle#1,#2\\right\\rangle}\n\\newcommand{\\bra}[1]{\\left\\langle#1\\right|}\n\\newcommand{\\ket}[1]{\\left|#1\\right\\rangle}\n\\newcommand{\\braket}[2]{\\left\\langle#1|#2\\right\\rangle}\n\\newcommand{\\ketbra}[2]{\\left|#1\\right\\rangle\\left\\langle#2\\right|}\n\\newcommand{\\angleset}[1]{\\left\\langle#1\\right\\rangle}\n\\newcommand{\\expected}[1]{\\left\\langle#1\\right\\rangle}\n\\newcommand{\\dv}[2]{\\frac{d#1}{d#2}}\n\\newcommand{\\real}[0]{\\mathfrak{Re}}\n$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Projective Measurement\n\n_prepared by Israel Gelover_",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### <a name=\"definition_3_6\">Definition 3.6</a> Projector\n\nGiven a subset of vectors $\\set{\\ket{f_i}}_{i=1}^n \\subset \\mathcal{H}$, we define the _Projector_ over the subspace $\\mathcal{F}$ generated by them as:\n\n\\begin{equation*}\n \\begin{split}\n \\hat{P}:\\mathcal{H} &\\to \\mathcal{F} \\\\\n \\ket{\\psi} &\\to \\sum_{i=1}^n \\ket{f_i}\\braket{f_i}{\\psi}\n \\end{split}\n\\end{equation*}\n\nIt is clear that what we obtain from this operator is a linear combination of $\\set{\\ket{f_i}}_{i=1}^n$ and therefore, the resulting vector is an element of the subspace generated by these vectors. And it is precisely this definition what we used to calculate the <a href=\"./WorkedExample.ipynb#5\">Wave function collapse</a>.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### <a name=\"definition_3_7\">Definition 3.7</a> Projective Measurement\n\nA _Projective Measurement_ is described with a self-adjoint operator\n\n\\begin{equation*}\n \\hat{M} = \\sum_m m\\hat{P}_m\n\\end{equation*}\n\nWhere $\\hat{P}_m$ is a projector on the subspace corresponding to the eigenvalue $m$ of $\\hat{M}$.\n\nThis is known as the spectral decomposition of the $\\hat{M}$ operator, and any self-adjoint operator can be expressed in terms of its spectral decomposition. We emphasize that this way of decomposing a projective measurement is very useful to us since it involves the eigenvalues and the projectors associated with these eigenvalues.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Example\n\nLet\n\n\\begin{equation}\\label{op_h}\n \\hat{H} = \\ketbra{0} + i\\ketbra{1}{2} - i\\ketbra{2}{1}\n\\end{equation}\n\nLet us recall that in the example of <a href=\"./WorkedExample.ipynb#3\">Time evlution</a> we saw that this is a self-adjoint operator, therefore we can use it as a projective measurement, and the way to do it is by obtaining its spectral decomposition through the eigenvalues and eigenvectors that we already calculated. That is\n\n\\begin{equation*}\n \\begin{split}\n \\varepsilon_1 = 1 \\qquad&\\qquad \\ket{\\varepsilon_1} = \\ket{0} \\\\\n \\varepsilon_2 = 1 \\qquad&\\qquad \\ket{\\varepsilon_2} = \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{2}}(\\ket{1} + i\\ket{2}) \\\\\n \\varepsilon_3 = -1 \\qquad&\\qquad \\ket{\\varepsilon_3} = \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{2}}(\\ket{1} - i\\ket{2})\n \\end{split}\n\\end{equation*}\n\nNote that we only have two different eigenvalues: $1$ and $-1$. The eigenvalue $1$ has multiplicity $2$ and therefore has associated a subspace of dimension $2$, while the eigenvalue $-1$ has multiplicity $1$ and therefore has associated a subspace of dimension $1$.\n\nThus\n\n\\begin{equation*}\n \\hat{H} = 1\\cdot\\hat{P_1} + (-1)\\cdot\\hat{P_{-1}}\n\\end{equation*}\n\nWhere, from <a href=\"#definition_3_6\">Definition 3.6</a>\n\n\\begin{equation*}\n \\begin{split}\n \\hat{P_1} &= \\ketbra{\\varepsilon_1}{\\varepsilon_1} + \\ketbra{\\varepsilon_2}{\\varepsilon_2} \\\\\n \\hat{P_{-1}} &= \\ketbra{\\varepsilon_3}{\\varepsilon_3}\n \\end{split}\n\\end{equation*}\n\nTherefore\n\n\\begin{equation*}\n \\hat{H} = \\ketbra{\\varepsilon_1}{\\varepsilon_1} + \\ketbra{\\varepsilon_2}{\\varepsilon_2} - \\ketbra{\\varepsilon_3}{\\varepsilon_3}\n\\end{equation*}\n\nSomething that may not be so clear from this result is that in $\\hat{H} = \\ketbra{0} + i\\ketbra{1}{2} - i\\ketbra{2}{1}$ we have $\\hat{H}$ expressed in terms of the base $\\set{\\ket{0}, \\ket{1}, \\ket{2}}$ and what the spectral decomposition is doing is diagonalize the operator $\\hat{H}$, since we are expressing it in terms of its eigenvectors and that what turns out to be is a diagonal matrix, in this case\n\n\\begin{equation*}\n \\hat{H} = \\begin{pmatrix}\n 1 & 0 & 0 \\\\\n 0 & 1 & 0 \\\\\n 0 & 0 & -1\n \\end{pmatrix}\n\\end{equation*}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Measurement Related Postulates\n\nThis formalism of projective measurements allows us on the one hand to group the postulates of quantum mechanics related to measurement in a single formalism, but on the other hand, it also allows us to focus on the state that we want to measure and on the state of the system after the measurement. Let us recall that the postulates of quantum mechanics related to measurement focus on the value that we can measure, that is, on the eigenvalue of an observable that is related to a measurable physical quantity. This formalism allows us to focus on the state in which the vector (that we originally had) ends up after measurement, and so to speak, to put aside for a bit what we are measuring.\n\nIn the following proposition we are going to describe the postulates related to the measurement that we already mentioned, but in a more condensed way in two quantities.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### <a name=\"proposition_3_8\">Proposition 3.8</a>\n\nLet $\\hat{M} = \\sum_m m\\hat{P_m}$ be a projective measurement expressed in terms of its spectral decomposition. ($\\hat{M}$ can be an observable)\n\n1. If the system is in the state $\\ket{\\psi}$, the probability of measuring the eigenvalue $m$ is given by\n\n\\begin{equation*}\n P_\\psi(m) = \\bra{\\psi}\\hat{P_m}\\ket{\\psi}\n\\end{equation*}\n\n2. The state of the system immediately after measuring the eigenvalue $m$ is given by\n\n\\begin{equation*}\n \\ket{\\psi} \\to \\frac{\\hat{P_m}\\ket{\\psi}}{\\sqrt{P(m)}}\n\\end{equation*}\n\n**Proof:**\n\n1. Let's verify the first statement by calculating the expected value. Recall that by <a href=\"#definition_3_6\">Definition 3.6</a>, the $m$ projector applied to $\\ket{\\psi}$ is given by\n\n\\begin{equation*}\n \\hat{P_m}\\ket{\\psi} = \\sum_{i=1}^{g_m} \\ket{m_i}\\braket{m_i}{\\psi}\n\\end{equation*}\n\nwhere $g_m$ is the multiplicity of the eigenvalue $m$. Thus\n\n\\begin{equation*}\n \\begin{split}\n \\bra{\\psi}\\hat{P_m}\\ket{\\psi} &= \\bra{\\psi} \\sum_{i=1}^{g_m} \\ket{m_i}\\braket{m_i}{\\psi} = \\sum_{i=1}^{g_m} \\braket{\\psi}{m_i}\\braket{m_i}{\\psi} \\\\\n &= \\sum_{i=1}^{g_m} \\braket{m_i}{\\psi}^*\\braket{m_i}{\\psi} = \\sum_{i=1}^{g_m} \\abs{\\braket{m_i}{\\psi}}^2 \\\\\n &= P_\\psi(m)\n \\end{split}\n\\end{equation*}\n\nThis last equality is given by <a href=\"./Postulates.ipynb#definition_3_1\">Postulate V</a>.\n\n2. Let's remember that projecting the vector can change its norm and therefore we need to renormalize it. Let us then calculate the magnitude of the projection, calculating the internal product of the projection with itself. In the previous section we gave the expression of the $m$ projector applied to $\\ket{\\psi}$, let's see now that\n\n\\begin{equation*}\n \\bra{\\psi}\\hat{P_m}^* = \\sum_{i=1}^{g_m} \\braket{\\psi}{m_i}\\bra{\\psi}\n\\end{equation*}\n\nThus\n\n\\begin{equation*}\n \\begin{split}\n \\abs{\\hat{P_m}\\ket{\\psi}}^2 &= \\bra{\\psi}\\hat{P_m}^* \\hat{P_m}\\ket{\\psi} \\\\\n &= \\sum_{i=1}^{g_m} \\braket{\\psi}{m_i}\\bra{\\psi} \\sum_{i=1}^{g_m} \\ket{m_i}\\braket{m_i}{\\psi} \\\\\n &= \\sum_{i=1}^{g_m} \\braket{\\psi}{m_i} \\braket{m_i} \\braket{m_i}{\\psi} \\\\\n &= \\sum_{i=1}^{g_m} \\braket{\\psi}{m_i}\\braket{m_i}{\\psi} \\\\\n &= \\sum_{i=1}^{g_m} \\braket{m_i}{\\psi}^*\\braket{m_i}{\\psi} \\\\\n &= \\sum_{i=1}^{g_m} \\abs{\\braket{m_i}{\\psi}}^2 \\\\\n &= P_\\psi(m) \\\\\n \\implies \\\\\n \\abs{\\hat{P_m}\\ket{\\psi}} &= \\sqrt{P_\\psi(m)}\n \\end{split}\n\\end{equation*}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### <a name=\"remark\">Remark</a>\n\nIn summary, with this projector formalism, we can express the measurement-related postulates in two simpler expressions:\n\n**1. The probability of measuring an eigenvalue is the expected value of the projector associated with the eigenvalue.** \n**2. The state of the system after measurement is obtained by applying the projector to the state and renormalizing. The normalization constant is precisely the square root of the probability, calculated in the previous section.**\n\nAs we have already mentioned, this formalism is useful when we are not so interested in what we are going to measure, but rather we are interested in the state of the system after measurement. That is, instead of verifying what is the observable, calculate the eigenvalues of the observable, calculate the probability based on the eigenvectors associated with these eigenvalues, etc. All this, that is required by the quantum mechanics postulates related to measurement in order to find a probability, is already implicit in the projector formalism.\n\nOn the other hand, when we talk about measurements in quantum computing, we usually refer to measurements in the computational basis, and the computational basis is the basis of the Pauli operator $\\hat{\\sigma_z}$. So the observable that is almost always used in quantum computing is $\\hat{\\sigma_z}$, that is, when talking about measuring a qubit, we are talking about measuring the observable $\\hat{\\sigma_z}$ and calculating the probability to find the eigenvalue $+1$ or the eigenvalue $-1$ of $\\hat{\\sigma_z}$. The eigenvalue $+1$ is associated with the qubit $\\ket{0}$ and the eigenvalue $-1$ is associated with the qubit $\\ket{1}$.\n\nObservables are very useful when we are interested in measuring magnitudes that have a physical interpretation such as momentum, position or energy, on the other hand, in quantum computing we are interested in knowing if when the measurement is made the system will be in a state $\\ket{0}$ or in a state $\\ket{1}$, beyond the measured eigenvalue or the observable with which you are working. It is for this reason that this formalism of projective measurements is particularly useful in this area.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Let's see how we can apply it in a concrete example.\n\n### <a name=\"example\">Example</a>\n\nLet $\\ket{\\psi}$ be the state\n\n\\begin{equation*}\n \\ket{\\psi} = \\sqrt{\\frac{3}{8}}\\ket{00} + \\frac{1}{2}\\ket{01} + \\frac{1}{2}\\ket{10} + \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{8}}\\ket{11} \\in \\mathbb{B}^{\\otimes2}\n\\end{equation*}\n\nWe note that the state is normalized, that is, it is a valid state in $\\mathbb{B}^{\\otimes2}$ and thus we can answer the following questions.\n\n**1. What is the probability of finding the first qubit in $\\ket{0}$?**\n\nTo emphasize the previous comments, let's start by considering the following projective measurement, which corresponds to the expression in terms of outer products of the Pauli operator $\\hat{\\sigma_x}$\n\n\\begin{equation*}\n \\hat{M} = (1)\\hat{P_0} + (-1)\\hat{P_1} \\enspace \\text{ where } \\enspace \\hat{P_0} = \\ketbra{0}{0}, \\enspace \\hat{P_1} = \\ketbra{1}{1}\n\\end{equation*}\n\nWe know that to answers this question we need to find the probability of measuring the eigenvalue of $\\hat{M}$ associated with the qubit $\\ket{0}$, but note that according to section **1.** of the previous remark, what is relevant to make this calculation is only $\\hat{P_0}$. That is, we are not interested in the eigenvalue that is measured, nor the observable. To accentuate this fact, we could even have considered any other projective measurement such as\n\n\\begin{equation*}\n \\hat{M} = \\alpha\\hat{P_0} + \\beta\\hat{P_1}\n\\end{equation*}\n\nand this would still be a self-adjoint operator and therefore a valid projective measure, for all $\\alpha,\\beta \\in \\mathbb{R}$.\n\nFor all this to agree with the formalism of the postulates of quantum mechanics, we usually take $\\hat{M} = \\hat{\\sigma_z}$ as we did initially, that is, formally from a physical point of view, what we will do is measure the observable $\\hat{\\sigma_z}$. However, from a mathematical point of view we can measure any projective measurement (self-adjoint operator) that distinguishes with a certain eigenvalue the qubit $\\ket{0}$ and with a different eigenvalue the qubit $\\ket{1}$.\n\nIn summary, what is really relevant for this calculation is the projector of the eigenvalue associated with the state we want to measure, in this case what we want to calculate is $\\bra{\\psi}\\hat{P_0}\\ket{\\psi}$, except that we are working on $\\mathbb{B}^{\\otimes2}$, but that detail will be clarified below.\n\nAccording to section **1.** of the previous remark, to calculate this probability, we must calculate the expected value of a projector, but we cannot simply consider $\\hat{P_0}$ because of the fact that we just mentioned, that we are working on $\\mathbb{B}^{\\otimes2}$. Since in this case the state of the second qubit is not relevant, what we need is the following\n\n\\begin{equation*}\n \\begin{split}\n &\\bra{\\psi}\\hat{P_0}\\otimes\\hat{I}\\ket{\\psi} = \\\\\n &= \\bra{\\psi} \\left[\\ketbra{0}\\otimes\\hat{I}\\left(\\sqrt{\\frac{3}{8}}\\ket{00} + \\frac{1}{2}\\ket{01} + \\frac{1}{2}\\ket{10} + \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{8}}\\ket{11} \\right) \\right] \\\\\n &= \\bra{\\psi} \\left[ \\sqrt{\\frac{3}{8}} \\ketbra{0}\\otimes\\hat{I}\\ket{00} + \\frac{1}{2} \\ketbra{0}\\otimes\\hat{I}\\ket{01} + \\frac{1}{2} \\ketbra{0}\\otimes\\hat{I}\\ket{10} + \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{8}} \\ketbra{0}\\otimes\\hat{I}\\ket{11} \\right] \\\\\n \\end{split}\n\\end{equation*}\n\nLet us recall from <a href=\"../2-math/TensorProduct.ipynb#definition_2_11\">Definition 2.11</a>, that $\\hat{A} \\otimes \\hat{B}(\\ket{a} \\otimes \\ket{b}) = (\\hat{A}\\ket{a})\\otimes(\\hat{B}\\ket{b})$. This means that we must apply the projector $\\ketbra{0}{0}$ to the first qubit and the operator $\\hat{I}$ to the second qubit, since its state is not relevant to us. Thus\n\n\\begin{equation*}\n \\begin{split}\n \\bra{\\psi}\\hat{P_0}\\otimes\\hat{I}\\ket{\\psi} &= \\bra{\\psi} \\left( \\sqrt{\\frac{3}{8}} \\ket{00} + \\frac{1}{2} \\ket{01} \\right) \\\\\n &= \\left(\\sqrt{\\frac{3}{8}}\\bra{00} + \\frac{1}{2}\\bra{01} + \\frac{1}{2}\\bra{10} + \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{8}}\\bra{11}\\right) \\left(\\sqrt{\\frac{3}{8}} \\ket{00} + \\frac{1}{2} \\ket{01}\\right) \\\\\n &= \\left(\\sqrt{\\frac{3}{8}}\\right)\\left(\\sqrt{\\frac{3}{8}}\\right)\\braket{00}{00} + \\left(\\frac{1}{2}\\right)\\left(\\frac{1}{2}\\right)\\braket{01}{01} \\\\\n &= \\frac{3}{8} + \\frac{1}{4} = \\frac{5}{8}\n \\end{split}\n\\end{equation*}\n\nThis is congruent with the intuition given by the fact that the amplitudes associated with the states where the first qubit is $\\ket{0}$ are $\\sqrt{\\frac{3}{8}}$ and $\\frac{1}{2}$ and to calculate the probability of measuring these states, we take the modulus squared of the amplitudes, which is known as _Born's Rule_.\n\nIn summary, formally what we did was calculate the probability of measuring the eigenvalue $+1$ of the observable $\\hat{\\sigma_z}\\otimes\\hat{I}$, which is completely congruent with what the postulates tell us. But as we previously highlighted, for practical issues of carrying out this calculation, the only thing that was relevant, was the projector associated with the state we wanted to measure, we do not need to know the observable or the eigenvalue to measure. Which allows us to put aside a bit the formalism that the postulates entail.\n\n**2. What is the status immediately after measurement?**\n\nSection **2.** of the previous remark tells us that\n\n\\begin{equation*}\n \\begin{split}\n \\ket{\\psi} \\longrightarrow \\frac{\\hat{P_0}\\otimes\\hat{I}\\ket{\\psi}}{\\sqrt{P(\\ket{0})}} &= \\frac{\\hat{P_0}\\otimes\\hat{I}\\ket{\\psi}}{\\sqrt{\\frac{5}{8}}} \\\\\n &= \\sqrt{\\frac{8}{5}}\\hat{P_0}\\otimes\\hat{I}\\ket{\\psi} \\\\\n &= \\sqrt{\\frac{8}{5}}\\left(\\sqrt{\\frac{3}{8}}\\ket{00} + \\frac{1}{2}\\ket{01}\\right) \\\\\n &= \\sqrt{\\frac{3}{5}}\\ket{00} + \\sqrt{\\frac{2}{5}}\\ket{01}\n \\end{split}\n\\end{equation*}\n\nWhere $P(\\ket{0})$ is the probability that we just calculated in the first question. Technically it would have to be the probability of measuring the eigenvalue $+1$, but from what we explained previously, we allow ourselves to use this notation.\n\nNote that this new state is the projection of $\\ket{\\psi}$ over the subspace generated by all the states that have the first qubit in $\\ket{0}$, namely $\\set{\\ket{00}, \\ket{01}}$, therefore this condition is also true. On the other hand, we note that the normalization is correct since $\\abs{\\sqrt{\\frac{3}{5}}}^2 + \\abs{\\sqrt{\\frac{2}{5}}}^2 = \\frac{3}{5} + \\frac{2}{5} = 1$.\n\n**3. What is the probability of measuring some qubit in $\\ket{1}$?**\n\nLet us consider the following events\n\n\\begin{equation*}\n \\begin{split}\n A &= \\text{Measure first qubit in} \\ket{1} \\\\\n B &= \\text{Measure second qubit in} \\ket{1}\n \\end{split}\n\\end{equation*}\n\nRecall from probability theory that\n\n\\begin{equation*}\n P(A \\cup B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A \\cap B)\n\\end{equation*}\n\nSo what we are looking for is\n\n\\begin{equation*}\n \\begin{split}\n P(A \\cup B) &= \\bra{\\psi}\\hat{P_1}\\otimes\\hat{I}\\ket{\\psi} + \\bra{\\psi}\\hat{I}\\otimes\\hat{P_1}\\ket{\\psi} - \\bra{\\psi}\\hat{P_1}\\otimes\\hat{P_1}\\ket{\\psi} \\\\\n &= \\bra{\\psi}\\left(\\frac{1}{2}\\ket{10} + \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{8}}\\ket{11}\\right) + \\bra{\\psi}\\left(\\frac{1}{2}\\ket{01} + \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{8}}\\ket{11}\\right) - \\bra{\\psi}\\left(\\frac{1}{\\sqrt{8}}\\ket{11}\\right) \\\\\n &= \\frac{1}{2}\\braket{\\psi}{10} + \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{8}}\\braket{\\psi}{11} + \\frac{1}{2}\\braket{\\psi}{01} + \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{8}}\\braket{\\psi}{11} - \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{8}}\\braket{\\psi}{11} \\\\\n &= \\left(\\frac{1}{2}\\right)\\left(\\frac{1}{2}\\right) + \\left(\\frac{1}{\\sqrt{8}}\\right)\\left(\\frac{1}{\\sqrt{8}}\\right) + \\left(\\frac{1}{2}\\right)\\left(\\frac{1}{2}\\right) \\\\\n &= \\frac{1}{4} + \\frac{1}{8} + \\frac{1}{4} = \\frac{5}{8}\n \\end{split}\n\\end{equation*}\n\nNote that the amplitudes of the terms of $\\ket{\\psi}$ that have some qubit in $\\ket{1}$ are precisely $\\frac{1}{2}$, $\\frac{1}{2}$ and $\\frac{1}{\\sqrt{8}}$, if we calculate the sum of its squared modules we have exactly\n\n\\begin{equation*}\n \\abs{\\frac{1}{2}}^2 + \\abs{\\frac{1}{2}}^2 + \\abs{\\frac{1}{\\sqrt{8}}}^2 = \\frac{1}{4} + \\frac{1}{4} + \\frac{1}{8} = \\frac{5}{8} = P(AUB)\n\\end{equation*}\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The goal of this section on projective measurement is to highlight that in quantum computing, when we talk about measuring, it is much more practical to ask about the state of the system than the value to be measured, which might not be so relevant in this context. For example, if we have a state $\\ket{\\psi}$ of three qubits, it is easier to think of calculating the probability of measuring $\\ket{010}$ than to think of calculating the probability of measuring a certain eigenvalue of $\\hat{\\sigma_z}\\otimes\\hat{\\sigma_z}\\otimes\\hat{\\sigma_z}$, which is actually what we are doing in the background but without the formalism of the postulates of quantum mechanics. We can say that in quantum computing the state of the system (the qubits themselves) is more relevant than the eigenvalues obtained from measuring $\\hat{\\sigma_z}$.\n\nIt is important to note that in quantum computing, measurement can also be part of an algorithm. When this topic is addressed, it will be clear that many times a measurement is made to project to a certain state that is being sought and continue with the algorithm from that new state. Therefore, being able to know the state of a system after a certain measurement turns out to be very relevant.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### <a name=\"remark_3_9\">Remark 3.9</a>\n\n1. Non-orthogonal states cannot be reliably distinguished by a projective measurement.\n\nLet us remember that if we have a certain state $\\ket{\\psi}$, we measure an observable (self-adjoint operator) and obtain an eigenvalue of that measurement, what the postulates of quantum mechanics regarding the measurement tell us, is that this state $\\ket{\\psi}$ will be projected on the subspace associated with the measured eigenvalue. In terms of the previous section, this means applying a projector to the $\\ket{\\psi}$ state.\n\nWhat do we mean by reliably distinguish them? By using a projective measurement we can measure one of them with probability $1$, and measure the other with probability $0$. For example, if we wanted to distinguish if we have the state $\\ket{\\varphi}$ and not state $\\ket{\\psi}$, we would simply want to measure the expected value of the projector $\\hat{P_\\varphi}$ in $\\ket{\\varphi}$ and get $1$ and in turn get $0$ by measuring it in $\\ket{\\psi}$. Let's see why we can't make this reliable distinction with two states that are not orthogonal using an example.\n\nLet us consider the following non-orthogonal states\n\n\\begin{equation*}\n \\ket{\\psi} = \\ket{0} \\enspace \\text{ y } \\enspace \\ket{\\varphi} = \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{2}}(\\ket{0} + \\ket{1})\n\\end{equation*}\n\nAnd the projector\n\n\\begin{equation*}\n \\hat{P_\\psi} = \\ketbra{\\psi}{\\psi}\n\\end{equation*}\n\nThus we have\n\n\\begin{equation*}\n \\begin{split}\n P(\\ket{\\psi}) &= \\bra{\\psi}\\hat{P_\\psi}\\ket{\\psi} = \\braket{\\psi}{\\psi}\\braket{\\psi}{\\psi} = 1 \\\\\n P(\\ket{\\varphi}) &= \\bra{\\varphi}\\hat{P_\\psi}\\ket{\\varphi} = \\braket{\\varphi}{\\psi}\\braket{\\psi}{\\varphi} = \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{2}}\\frac{1}{\\sqrt{2}} = \\frac{1}{2}\n \\end{split}\n\\end{equation*}\n\nIt should be clear from this particular example that we cannot have a projector that allows us to reliably distinguish two non-orthogonal states.\n\n2. Orthogonal states can be reliably distinguished by a projective measurement.\n\nLet's consider the states\n\n\\begin{equation*}\n \\ket{\\psi} = \\ket{0} \\enspace \\text{ and } \\enspace \\ket{\\varphi} = \\ket{1}\n\\end{equation*}\n\n\\begin{equation*}\n \\begin{split}\n \\hat{P_\\psi} &= \\ketbra{\\psi}{\\psi} \\\\\n \\implies \\\\\n P(\\ket{\\psi}) &= \\bra{\\psi}\\hat{P_\\psi}\\ket{\\psi} = \\braket{\\psi}{\\psi}\\braket{\\psi}{\\psi} = 1 \\\\\n P(\\ket{\\varphi}) &= \\bra{\\varphi}\\hat{P_\\psi}\\ket{\\varphi} = \\braket{\\varphi}{\\psi}\\braket{\\psi}{\\varphi} = 0\n \\end{split}\n\\end{equation*}\n\nIt should be clear from this particular example that we can reliably distinguish orthogonal states.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4a71f0a42489ac5137cc7e905155c33f91af5b26
| 4,554 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Static/requests/google translate/test.ipynb
|
ChanderJindal/webscrape
|
72c58407ff6e685c2504c7e2d67b263c94b02837
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Static/requests/google translate/test.ipynb
|
ChanderJindal/webscrape
|
72c58407ff6e685c2504c7e2d67b263c94b02837
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Static/requests/google translate/test.ipynb
|
ChanderJindal/webscrape
|
72c58407ff6e685c2504c7e2d67b263c94b02837
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 20.986175 | 296 | 0.510321 |
[
[
[
"BaseLink = \"https://translate.google.co.in/?sl=auto&tl=en&text=\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import requests as R\nfrom bs4 import BeautifulSoup as BS",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"text = '''\n江戸川コナン (@conan_file)\n『名探偵コナン100PLUS』発売記念緊急アンケート第2弾!\nみんなが二人でおうちデートしたい『コナン』のキャラは? 理由も教えてね!\n\nこのツイートに返信するか、#コナンおうちデート\nをつけてツイートしてね!\n\n結果は、春頃発売の『名探偵コナン100PLUS SDB』にて発表!\n〆きりは3月3日24時!\n'''",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"TranslateLink = R.get(BaseLink+text)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"TranslateLink",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"f = open(file=\"TranslatedText.txt\",mode=\"w\",encoding=\"utf-8\")\nf.write(str(TranslateLink.text))\nf.close()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"soup = BS(TranslateLink.text,features=\"lxml\")\nmain_div = soup.find('div', class_=\"dePhmb\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"main_div",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"SubDiv1 = main_div.find_all('div',class_=\"eyKpYb\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"SubDiv1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"json_data = TranslateLink.json",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"json_data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"json_data.div",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a71f5d1e9a23b9d98cc05321a734c7eb9d47ecb
| 66,064 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Week 3 - Computational graphs/Week 3 - Exercises Solutions.ipynb
|
zhaw-dl/zhaw-dlcourse-autumn2018
|
7ca4e9f62b72be72d51f365464c009dfde33d02e
|
[
"BSD-4-Clause-UC"
] | 5 |
2019-01-17T20:14:22.000Z
|
2019-03-05T12:26:12.000Z
|
Week 3 - Computational graphs/Week 3 - Exercises Solutions.ipynb
|
michelucci/zhaw-dlcourse-autumn2018
|
7ca4e9f62b72be72d51f365464c009dfde33d02e
|
[
"BSD-4-Clause-UC"
] | null | null | null |
Week 3 - Computational graphs/Week 3 - Exercises Solutions.ipynb
|
michelucci/zhaw-dlcourse-autumn2018
|
7ca4e9f62b72be72d51f365464c009dfde33d02e
|
[
"BSD-4-Clause-UC"
] | 2 |
2019-08-17T17:13:08.000Z
|
2019-11-28T09:54:33.000Z
| 43.838089 | 26,284 | 0.681703 |
[
[
[
"# Neural Networks and Deep Learning for Life Sciences and Health Applications - An introductory course about theoretical fundamentals, case studies and implementations in python and tensorflow",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"(C) Umberto Michelucci 2018 - [email protected] \n\ngithub repository: https://github.com/michelucci/dlcourse2018_students\n\nFall Semester 2018",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import tensorflow as tf\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Solutions to exercises",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Exercise 1 (Difficulty: easy)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Draw and develop in tensorflow with ```tf.constant``` the computational graphs for the following operations\n\nA) ```w1*x1+w2*x2+x1*x1```\n\nB) ```A*x1+3+x2/2```\n\nUse as input values ```x1 = 5``` and ```x2 = 6```",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## A)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"There are several ways of solving this exercise. This is one possible",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Building Phase\nx1 = tf.constant(5.)\nx2 = tf.constant(6.)\n\nw1 = 10.\nw2 = 20.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"z1 = tf.multiply(w1, x1)\nz2 = tf.multiply(w2, x2)\nz3 = tf.multiply(x1, x1)\n\nresult = z1 + z2 + z3",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Evaluation Phase\nwith tf.Session() as sess:\n print(result.eval())",
"195.0\n"
]
],
[
[
"A second way of doing that is the following",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Building Phase\nx1 = tf.constant(5.)\nx2 = tf.constant(6.)\n\nw1 = 10.\nw2 = 20.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"z1 = tf.multiply(w1, x1)\nz2 = tf.multiply(w2, x2)\nz3 = tf.multiply(x1, x1)\n\nresult = z1 + z2 + z3",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Evaluation Phase\nsess = tf.Session()\nprint(sess.run(result))\nsess.close()",
"195.0\n"
]
],
[
[
"But you can also define ```w1``` and ```w2``` as constants too",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Building Phase\nx1 = tf.constant(5.)\nx2 = tf.constant(6.)\n\nw1 = tf.constant(10.)\nw2 = tf.constant(20.)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"z1 = tf.multiply(w1, x1)\nz2 = tf.multiply(w2, x2)\nz3 = tf.multiply(x1, x1)\n\nresult = z1 + z2 + z3",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Evaluation Phase\nsess = tf.Session()\nprint(sess.run(result))\nsess.close()",
"195.0\n"
]
],
[
[
"### B)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Building Phase\nx1 = tf.constant(5.)\nx2 = tf.constant(6.)\nA = tf.constant(10.)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"result = tf.multiply(A, x1) + tf.constant(3.) + tf.divide(x2, 2.)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Evaluation Phase\nsess = tf.Session()\nprint(sess.run(result))\nsess.close()",
"56.0\n"
]
],
[
[
"or you can define the ```result``` in multiple steps",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Building Phase\nz1 = tf.multiply(A, x1)\nz2 = tf.add(z1, 3.)\nz3 = tf.add(z2, tf.divide(x2,2.))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Evaluation Phase\nsess = tf.Session()\nprint(sess.run(result))\nsess.close()",
"56.0\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Exercise 2 (Difficulty: medium)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Draw and develop in tensorflow with ```tf.Variable``` the computational graph for the following operation ```A*(w1*x1+w2*x2)```\n\nbuild the computational graph and then evaluate it two times (without re-building it) with the initial values in the same session\n\nA) ```x1 = 3, x2 = 4```\n\nB) ```x1 = 5, x2 = 7```",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Building Phase\nx1 = tf.Variable(3.)\nx2 = tf.Variable(4.)\nw1 = tf.constant(10.)\nw2 = tf.constant(20.)\nA = tf.constant(30.)\ninit = tf.global_variables_initializer()\n\nz1 = tf.multiply(w1,x1)\nz2 = tf.multiply(w2,x2)\nz3 = tf.add(z1, z2)\nresult = tf.multiply(A, z3)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"To run the same graph twice in the same session you can do the following",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sess = tf.Session()\nprint(sess.run(result, feed_dict = {x1: 3, x2: 4}))\nprint(sess.run(result, feed_dict = {x1: 5, x2: 7}))\nsess.close()",
"3300.0\n5700.0\n"
]
],
[
[
"Or you can write a function that creates a session, evaluates a node, and then close it.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def run_evaluation(x1_, x2_):\n sess = tf.Session()\n print(sess.run(result, feed_dict = {x1: x1_, x2: x2_}))\n sess.close()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"And then you can evalute the node with a call to your function.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"run_evaluation(3,4)",
"3300.0\n"
],
[
"run_evaluation(5,7)",
"5700.0\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Exercise 3 (Difficulty: FUN)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Consider two vectors\n\n``` x1 = [1,2,3,4,5], x2 = [6,7,8,9,10]```\n\ndraw and build in tensorflow the computational graph for the dot-product operation between the two vectors. If you don't know what a dot-product is you can check it here (we covered that in our introductory week) [](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dot_product).\n\nBuild it in two different ways:\n\nA) Do it with loops. Build a computational graph that takes as input scalars and in the session/evaluation phase build a loop to go over all the inputs and then sums the results\n\nB) Do it in one shot with tensorflow. Build a computational graph that takes as input vectors and do the entire operation directly in tensorflow. \n\nHint: you can use in tensorflow two methods: ```tf.reduce_sum(tf.multiply(x1, x2))``` or ```tf.matmul(tf.reshape(x1,[1,5]), tf.reshape(x2, [-1, 1]))```. Try to understand why they work checking the official documentation.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## a)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"first = tf.Variable(0.)\nsecond = tf.Variable(0.)\nmult = tf.multiply(first, second)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x1 = [1,2,3,4,5]\nx2 = [6,7,8,9,10]\n\nsess = tf.Session()\ntotal = 0\nfor i in range(0,len(x1)):\n total = total + sess.run(mult, feed_dict = {first: x1[i], second: x2[i]})\n \nprint(total)",
"130.0\n"
]
],
[
[
"Note that you can do that easily in numpy",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.dot(x1, x2)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## b)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Another way, and much more efficient, is the following",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x1 = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, None) # Let's assume we work with integers\nx2 = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, None) # Let's assume we work with integers\nresult = tf.reduce_sum(tf.multiply(x1, x2))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sess = tf.Session()\nprint(sess.run(result, feed_dict = {x1: [1,2,3,4,5], x2:[6,7,8,9,10]}))\nsess.close()",
"130\n"
]
],
[
[
"Or in with matrices",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x1 = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, None) # Let's assume we work with integers\nx2 = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, None) # Let's assume we work with integers\nresult = tf.matmul(tf.reshape(x1,[1,5]), tf.reshape(x2, [-1, 1]))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sess = tf.Session()\nprint(sess.run(result, feed_dict = {x1: [1,2,3,4,5], x2:[6,7,8,9,10]}))\nsess.close()",
"[[130]]\n"
]
],
[
[
"Note that the result is different in the two cases! In the first we get a scalar, in the second a matrix that has dimensions ```1x1```, because the second method is a matrix multiplication function that will return a matrix (or better a tensor).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## c) (even another way) (BONUS Solution)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"There is actually another way. Tensorflow can perform the dot product directly",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x1 = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, None) # Let's assume we work with integers\nx2 = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, None) # Let's assume we work with integers\nresult = tf.tensordot(x1, x2, axes = 1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sess = tf.Session()\nprint(sess.run(result, feed_dict = {x1: [1,2,3,4,5], x2:[6,7,8,9,10]}))\nsess.close()",
"130\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Exercise 4 (Difficulty: medium)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Write a function that build a computational graph for the operation ```x1+x2``` where the input ```x1``` and ```x2``` are input with given dimensions. Your ```x1``` and ```x2``` should be declared as ```tf.placeholder```. \nYour functions should accept as input:\n\n- dimensions of ```x1``` as list, for example ```[3]```\n- dimensions of ```x2``` as list, for example ```[3]```\n\nThe function should return a tensor ```z = x1 + x2```. \nThen open a session and evaluate ```z``` with the following inputs:\n\n- ```x1 = [4,6,7], x2 = [1,2,9]```\n- ```x1 = [1,2,....., 1000], x2 = [10001, 10002, ...., 11000]```\n\nand print the result.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def build_graph(dim1, dim2):\n tf.reset_default_graph()\n x1 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, dim1)\n x2 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, dim2)\n z = tf.add(x1, x2)\n return z, x1, x2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x1list = [4,6,7]\nx2list = [1,2,9]\n\n\n# Building Phase\nz, x1, x2 = build_graph(len(x1list), len(x2list))\n\nsess = tf.Session()\nprint(sess.run(z, feed_dict = {x1: x1list, x2: x2list}))\nsess.close()",
"[ 5. 8. 16.]\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Note that since you refer to the tensors ```x1``` and ```x2``` in the ```feed_dict``` dictionary you need to have the tensors visible, otherwise you will get an error, therefore you need your function to return no only ```z``` but also ```x1``` and ```x2```.**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x1list = np.arange(1, 1001, 1)\nx2list = np.arange(10001, 11001, 1)\n\n# Building Phase\nz, x1, x2 = build_graph(len(x1list), len(x2list))\n\nsess = tf.Session()\nprint(sess.run(z, feed_dict = {x1: x1list, x2: x2list}))\nsess.close()",
"[10002. 10004. 10006. 10008. 10010. 10012. 10014. 10016. 10018. 10020.\n 10022. 10024. 10026. 10028. 10030. 10032. 10034. 10036. 10038. 10040.\n 10042. 10044. 10046. 10048. 10050. 10052. 10054. 10056. 10058. 10060.\n 10062. 10064. 10066. 10068. 10070. 10072. 10074. 10076. 10078. 10080.\n 10082. 10084. 10086. 10088. 10090. 10092. 10094. 10096. 10098. 10100.\n 10102. 10104. 10106. 10108. 10110. 10112. 10114. 10116. 10118. 10120.\n 10122. 10124. 10126. 10128. 10130. 10132. 10134. 10136. 10138. 10140.\n 10142. 10144. 10146. 10148. 10150. 10152. 10154. 10156. 10158. 10160.\n 10162. 10164. 10166. 10168. 10170. 10172. 10174. 10176. 10178. 10180.\n 10182. 10184. 10186. 10188. 10190. 10192. 10194. 10196. 10198. 10200.\n 10202. 10204. 10206. 10208. 10210. 10212. 10214. 10216. 10218. 10220.\n 10222. 10224. 10226. 10228. 10230. 10232. 10234. 10236. 10238. 10240.\n 10242. 10244. 10246. 10248. 10250. 10252. 10254. 10256. 10258. 10260.\n 10262. 10264. 10266. 10268. 10270. 10272. 10274. 10276. 10278. 10280.\n 10282. 10284. 10286. 10288. 10290. 10292. 10294. 10296. 10298. 10300.\n 10302. 10304. 10306. 10308. 10310. 10312. 10314. 10316. 10318. 10320.\n 10322. 10324. 10326. 10328. 10330. 10332. 10334. 10336. 10338. 10340.\n 10342. 10344. 10346. 10348. 10350. 10352. 10354. 10356. 10358. 10360.\n 10362. 10364. 10366. 10368. 10370. 10372. 10374. 10376. 10378. 10380.\n 10382. 10384. 10386. 10388. 10390. 10392. 10394. 10396. 10398. 10400.\n 10402. 10404. 10406. 10408. 10410. 10412. 10414. 10416. 10418. 10420.\n 10422. 10424. 10426. 10428. 10430. 10432. 10434. 10436. 10438. 10440.\n 10442. 10444. 10446. 10448. 10450. 10452. 10454. 10456. 10458. 10460.\n 10462. 10464. 10466. 10468. 10470. 10472. 10474. 10476. 10478. 10480.\n 10482. 10484. 10486. 10488. 10490. 10492. 10494. 10496. 10498. 10500.\n 10502. 10504. 10506. 10508. 10510. 10512. 10514. 10516. 10518. 10520.\n 10522. 10524. 10526. 10528. 10530. 10532. 10534. 10536. 10538. 10540.\n 10542. 10544. 10546. 10548. 10550. 10552. 10554. 10556. 10558. 10560.\n 10562. 10564. 10566. 10568. 10570. 10572. 10574. 10576. 10578. 10580.\n 10582. 10584. 10586. 10588. 10590. 10592. 10594. 10596. 10598. 10600.\n 10602. 10604. 10606. 10608. 10610. 10612. 10614. 10616. 10618. 10620.\n 10622. 10624. 10626. 10628. 10630. 10632. 10634. 10636. 10638. 10640.\n 10642. 10644. 10646. 10648. 10650. 10652. 10654. 10656. 10658. 10660.\n 10662. 10664. 10666. 10668. 10670. 10672. 10674. 10676. 10678. 10680.\n 10682. 10684. 10686. 10688. 10690. 10692. 10694. 10696. 10698. 10700.\n 10702. 10704. 10706. 10708. 10710. 10712. 10714. 10716. 10718. 10720.\n 10722. 10724. 10726. 10728. 10730. 10732. 10734. 10736. 10738. 10740.\n 10742. 10744. 10746. 10748. 10750. 10752. 10754. 10756. 10758. 10760.\n 10762. 10764. 10766. 10768. 10770. 10772. 10774. 10776. 10778. 10780.\n 10782. 10784. 10786. 10788. 10790. 10792. 10794. 10796. 10798. 10800.\n 10802. 10804. 10806. 10808. 10810. 10812. 10814. 10816. 10818. 10820.\n 10822. 10824. 10826. 10828. 10830. 10832. 10834. 10836. 10838. 10840.\n 10842. 10844. 10846. 10848. 10850. 10852. 10854. 10856. 10858. 10860.\n 10862. 10864. 10866. 10868. 10870. 10872. 10874. 10876. 10878. 10880.\n 10882. 10884. 10886. 10888. 10890. 10892. 10894. 10896. 10898. 10900.\n 10902. 10904. 10906. 10908. 10910. 10912. 10914. 10916. 10918. 10920.\n 10922. 10924. 10926. 10928. 10930. 10932. 10934. 10936. 10938. 10940.\n 10942. 10944. 10946. 10948. 10950. 10952. 10954. 10956. 10958. 10960.\n 10962. 10964. 10966. 10968. 10970. 10972. 10974. 10976. 10978. 10980.\n 10982. 10984. 10986. 10988. 10990. 10992. 10994. 10996. 10998. 11000.\n 11002. 11004. 11006. 11008. 11010. 11012. 11014. 11016. 11018. 11020.\n 11022. 11024. 11026. 11028. 11030. 11032. 11034. 11036. 11038. 11040.\n 11042. 11044. 11046. 11048. 11050. 11052. 11054. 11056. 11058. 11060.\n 11062. 11064. 11066. 11068. 11070. 11072. 11074. 11076. 11078. 11080.\n 11082. 11084. 11086. 11088. 11090. 11092. 11094. 11096. 11098. 11100.\n 11102. 11104. 11106. 11108. 11110. 11112. 11114. 11116. 11118. 11120.\n 11122. 11124. 11126. 11128. 11130. 11132. 11134. 11136. 11138. 11140.\n 11142. 11144. 11146. 11148. 11150. 11152. 11154. 11156. 11158. 11160.\n 11162. 11164. 11166. 11168. 11170. 11172. 11174. 11176. 11178. 11180.\n 11182. 11184. 11186. 11188. 11190. 11192. 11194. 11196. 11198. 11200.\n 11202. 11204. 11206. 11208. 11210. 11212. 11214. 11216. 11218. 11220.\n 11222. 11224. 11226. 11228. 11230. 11232. 11234. 11236. 11238. 11240.\n 11242. 11244. 11246. 11248. 11250. 11252. 11254. 11256. 11258. 11260.\n 11262. 11264. 11266. 11268. 11270. 11272. 11274. 11276. 11278. 11280.\n 11282. 11284. 11286. 11288. 11290. 11292. 11294. 11296. 11298. 11300.\n 11302. 11304. 11306. 11308. 11310. 11312. 11314. 11316. 11318. 11320.\n 11322. 11324. 11326. 11328. 11330. 11332. 11334. 11336. 11338. 11340.\n 11342. 11344. 11346. 11348. 11350. 11352. 11354. 11356. 11358. 11360.\n 11362. 11364. 11366. 11368. 11370. 11372. 11374. 11376. 11378. 11380.\n 11382. 11384. 11386. 11388. 11390. 11392. 11394. 11396. 11398. 11400.\n 11402. 11404. 11406. 11408. 11410. 11412. 11414. 11416. 11418. 11420.\n 11422. 11424. 11426. 11428. 11430. 11432. 11434. 11436. 11438. 11440.\n 11442. 11444. 11446. 11448. 11450. 11452. 11454. 11456. 11458. 11460.\n 11462. 11464. 11466. 11468. 11470. 11472. 11474. 11476. 11478. 11480.\n 11482. 11484. 11486. 11488. 11490. 11492. 11494. 11496. 11498. 11500.\n 11502. 11504. 11506. 11508. 11510. 11512. 11514. 11516. 11518. 11520.\n 11522. 11524. 11526. 11528. 11530. 11532. 11534. 11536. 11538. 11540.\n 11542. 11544. 11546. 11548. 11550. 11552. 11554. 11556. 11558. 11560.\n 11562. 11564. 11566. 11568. 11570. 11572. 11574. 11576. 11578. 11580.\n 11582. 11584. 11586. 11588. 11590. 11592. 11594. 11596. 11598. 11600.\n 11602. 11604. 11606. 11608. 11610. 11612. 11614. 11616. 11618. 11620.\n 11622. 11624. 11626. 11628. 11630. 11632. 11634. 11636. 11638. 11640.\n 11642. 11644. 11646. 11648. 11650. 11652. 11654. 11656. 11658. 11660.\n 11662. 11664. 11666. 11668. 11670. 11672. 11674. 11676. 11678. 11680.\n 11682. 11684. 11686. 11688. 11690. 11692. 11694. 11696. 11698. 11700.\n 11702. 11704. 11706. 11708. 11710. 11712. 11714. 11716. 11718. 11720.\n 11722. 11724. 11726. 11728. 11730. 11732. 11734. 11736. 11738. 11740.\n 11742. 11744. 11746. 11748. 11750. 11752. 11754. 11756. 11758. 11760.\n 11762. 11764. 11766. 11768. 11770. 11772. 11774. 11776. 11778. 11780.\n 11782. 11784. 11786. 11788. 11790. 11792. 11794. 11796. 11798. 11800.\n 11802. 11804. 11806. 11808. 11810. 11812. 11814. 11816. 11818. 11820.\n 11822. 11824. 11826. 11828. 11830. 11832. 11834. 11836. 11838. 11840.\n 11842. 11844. 11846. 11848. 11850. 11852. 11854. 11856. 11858. 11860.\n 11862. 11864. 11866. 11868. 11870. 11872. 11874. 11876. 11878. 11880.\n 11882. 11884. 11886. 11888. 11890. 11892. 11894. 11896. 11898. 11900.\n 11902. 11904. 11906. 11908. 11910. 11912. 11914. 11916. 11918. 11920.\n 11922. 11924. 11926. 11928. 11930. 11932. 11934. 11936. 11938. 11940.\n 11942. 11944. 11946. 11948. 11950. 11952. 11954. 11956. 11958. 11960.\n 11962. 11964. 11966. 11968. 11970. 11972. 11974. 11976. 11978. 11980.\n 11982. 11984. 11986. 11988. 11990. 11992. 11994. 11996. 11998. 12000.]\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Exercise 5 (Difficult: FUN)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Linear Regression with tensorflow",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"https://onlinecourses.science.psu.edu/stat501/node/382/",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Consider the following dataset",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x = [4.0, 4.5, 5.0, 5.5, 6.0, 6.5, 7.0]\ny = [33, 42, 45, 51, 53, 61, 62]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We want to find the best parameters $p_0$ and $p_1$ that minimise the MSE (mean squared error) for the data given, in other words we want to do a linear regression on the data $(x,y)$. Given that a matrix solution to find the best parameter is\n\n$$\n{\\bf p} =(X^TX)^{-1} X^T Y\n$$\n\nwhere $X^T$ is the transpose of the matrix $X$. The matrix $X$ is defined as\n\n$$\nX = \n\\begin{bmatrix}\n1 & x_1 \\\\\n... & ... \\\\\n1 & x_n \n\\end{bmatrix}\n$$\n\nThe matrix $Y$ is simply a matrix $n\\times 1$ containing the values $y_i$.\n\ndimensions are:\n\n- $X$ has dimensions $n\\times 2$\n- $Y$ has dimensions $n\\times 1$\n- ${\\bf p}$ has dimensions $2\\times 1$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Build a computational graph that evaluates $\\bf p$ as given above, given the matrices $X$ and $Y$. Note you will have to build the matrices from the data given at the beginning. If you need more information a beatifully long explanation can be found here https://onlinecourses.science.psu.edu/stat501/node/382/",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Let's convert ```y``` to a floating list... **Remeber tensorflow is really strict with datatypes**.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"y = [float(i) for i in y]\ny",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x = pd.DataFrame(x)\ny = pd.DataFrame(y)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x['b'] = 1\nx.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cols = x.columns.tolist()\ncols = cols[-1:] + cols[:-1]\nprint(cols)",
"['b', 0]\n"
],
[
"x = x[cols]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's build the computational graph: \n\n**NOTE: if you use tf.float32 you will get results that are slightly different than numpy. So be aware. To be safe you can use ```float64```.**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Always try to be as specific \nas you can with dimensions\nThe first dimensions is defined as \"None\" so that we use, in necessary, \nwith different number of observations without rebuilding the graph.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tf.reset_default_graph()\nxinput = tf.placeholder(tf.float64, [None,2])\nyinput = tf.placeholder(tf.float64, [None,1]) ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Multiplication between tensors is somewhat complicated, especially when dealing\nwith tensors with more dimensions. So we use the method\n\nhttps://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/einsum\n\ncheck it out to get more information.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tmp = tf.einsum('ij,jk->ik',tf.transpose(xinput) , xinput)\npart1 = tf.linalg.inv(tmp)\npart2 = tf.einsum('ij,jk->ik',tf.transpose(xinput), yinput)\n\n\npout = tf.einsum('ij,jk->ik', part1, part2)\n# Reference: https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/einsum",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sess = tf.Session()\nprint(\"The best parameters p are:\")\nprint(sess.run(pout, feed_dict = {xinput: x, yinput: y}))\nsess.close()",
"The best parameters p are:\n[[-2.67857143]\n [ 9.5 ]]\n"
]
],
[
[
"If you remember the first week (check https://github.com/michelucci/dlcourse2018_students/blob/master/Week%201%20-%20Mathematic%20introduction/Week%201%20-%20Solution%20to%20exercises.ipynb) you can do the same with ```numpy```",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"part1np = np.linalg.inv(np.matmul(x.transpose() , x))\npart2np = np.matmul(x.transpose(), y)\n\npnp = np.matmul(part1np, part2np)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(pnp)",
"[[-2.67857143]\n [ 9.5 ]]\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Computational Graph for predictions",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The same result we got with tensorflow. Now we can build a graph that will use the ```p``` we have found for predictions",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"p = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [2,1])\nxnode = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 2]) # This time let's be specific with dimensions\n\npred = tf.tensordot(xnode, p, axes = 1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sess = tf.Session()\npred_y = sess.run(pred, feed_dict = {p: pnp, xnode: x})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pred_y",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"And those are the **true** values",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"y",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Plot of the results",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plt.rc('font', family='arial')\nplt.rc('xtick', labelsize='x-small')\nplt.rc('ytick', labelsize='x-small')\n \nplt.tight_layout()\n\nfig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 5))\nax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)\nax.scatter(y, pred_y, lw = 0.3, s = 80)\nax.plot([y.min(), y.max()], [y.min(), y.max()], 'k--', lw = 3)\nax.set_xlabel('Measured Target Value', fontsize = 16);\nax.set_ylabel('Predicted Target Value', fontsize = 16);\n\nplt.tick_params(labelsize=16)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a721100b25a5d9eb377d6489026e6ddc6fa3eee
| 27,363 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
ML - Mistakes to avoid in Machine Learning/01_11_Not_Treating_for_Imbalanced_Data.ipynb
|
ptyadana/probability-and-statistics-for-business-and-data-science
|
6c4d09c70e4c8546461eb7ebc401bb95a0827ef2
|
[
"MIT"
] | 10 |
2021-01-14T15:14:03.000Z
|
2022-02-19T14:06:25.000Z
|
ML - Mistakes to avoid in Machine Learning/01_11_Not_Treating_for_Imbalanced_Data.ipynb
|
ptyadana/probability-and-statistics-for-business-and-data-science
|
6c4d09c70e4c8546461eb7ebc401bb95a0827ef2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
ML - Mistakes to avoid in Machine Learning/01_11_Not_Treating_for_Imbalanced_Data.ipynb
|
ptyadana/probability-and-statistics-for-business-and-data-science
|
6c4d09c70e4c8546461eb7ebc401bb95a0827ef2
|
[
"MIT"
] | 8 |
2021-03-24T13:00:02.000Z
|
2022-03-27T16:32:20.000Z
| 60.006579 | 5,680 | 0.787158 |
[
[
[
"# **Imbalanced Data**\nEncountered in a classification problem in which the number of observations per class are disproportionately distributed.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## **How to treat for Imbalanced Data?**<br>\n\nIntroducing the `imbalanced-learn` (imblearn) package.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport seaborn as sns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.datasets import make_classification",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# make dummy data\nX, y = make_classification(n_samples=5000, n_features=2, n_informative=2,\n n_redundant=0, n_repeated=0, n_classes=3,\n n_clusters_per_class=1,\n weights=[0.01, 0.05, 0.94],\n class_sep=0.8, random_state=0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = pd.DataFrame(X)\ndf.columns = ['feature1', 'feature2']\ndf['target'] = y\n\ndf.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# visualize the data\nsns.countplot(data=df, x=df['target']);",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can see that the data are very heavily imbalanced.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"--------",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 1) Over-Sampling Approach\n\n\n## 1.1) naive approach known as Random Over-Sampling\n+ We will upsample our minority classes, that is sample with replacement until the number of observations is uniform across all classes.\n+ As we can imagine this approach should give us a pause depending on the scale of upsampling we'll be doing.\n+ `from imblearn.over_sampling import RandomOverSampler`\n\n## 1.2) another approach is SMOTE (Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique)\n+ in the case, we generate new observations within the existing feature space over our minority classes.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Now, let's apply an over-sampling approach. For this we'll use **a naive approach known as random over-sampling.**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from imblearn.over_sampling import RandomOverSampler",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ros = RandomOverSampler(random_state=0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_resampled, y_resampled = ros.fit_resample(X, y)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Let's visualize again after random over-sampling",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df = pd.DataFrame(y_resampled, columns=['target'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sns.countplot(data=df, x=df['target']);",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We have increased the size of each of our minority classes to be uniform with that of our majority class through random sampling.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 2) Under-Sampling Technique\n\n## 2.1) Naive approach to randomly under-sample our majority class\n+ this time we actually throwing out data in our majority class until the number of observations is uniform.\n+ `from imblearn.under_sampling import RandomUnderSampler`",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Let's now try an under-sampling technique. Again, we'll start with a naive approach to randomly under-sample our majority class.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from imblearn.under_sampling import RandomUnderSampler",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"rus = RandomUnderSampler(random_state=0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_resampled, y_resampled = rus.fit_resample(X, y)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Visualized the resampled data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df = pd.DataFrame(y_resampled, columns=['target'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sns.countplot(data=df, x='target');",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Data get blanced. However note that there are about 60 observations per class.\n\n**Because of the infrequency of our smallest minority class, we threw out a huge percentage**.\n\nSo you might want to consider other methods for this data (like `k-means` and `near-miss`)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a7215cbf38f87d592d515260414d181a53c8036
| 57,560 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
_source/raw/yelp.ipynb
|
sparsh-ai/reco-tutorials
|
7be837ca7105424aaf43148b334dc9d2e0e66368
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 3 |
2021-08-29T13:18:25.000Z
|
2022-03-08T19:48:32.000Z
|
code/yelp.ipynb
|
sparsh-ai/recsys-colab
|
c0aa0dceca5a4d8ecd42b61c4e906035fe1614f3
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
code/yelp.ipynb
|
sparsh-ai/recsys-colab
|
c0aa0dceca5a4d8ecd42b61c4e906035fe1614f3
|
[
"MIT"
] | 4 |
2021-06-16T03:07:10.000Z
|
2022-03-26T04:22:04.000Z
| 54.301887 | 20,836 | 0.685285 |
[
[
[
"# ~145MB\n!wget -x --load-cookies cookies.txt -O business.zip 'https://www.kaggle.com/yelp-dataset/yelp-dataset/download/py6LEr6zxQNWjebkCW8B%2Fversions%2FlVP0fduiJJo8YKt2vKKr%2Ffiles%2Fyelp_academic_dataset_business.json?datasetVersionNumber=2'\n!unzip business.zip\n!wget -x --load-cookies cookies.txt -O review.zip 'https://www.kaggle.com/yelp-dataset/yelp-dataset/download/py6LEr6zxQNWjebkCW8B%2Fversions%2FlVP0fduiJJo8YKt2vKKr%2Ffiles%2Fyelp_academic_dataset_review.json?datasetVersionNumber=2'\n!unzip review.zip",
"--2020-04-14 12:04:52-- https://www.kaggle.com/yelp-dataset/yelp-dataset/download/py6LEr6zxQNWjebkCW8B%2Fversions%2FlVP0fduiJJo8YKt2vKKr%2Ffiles%2Fyelp_academic_dataset_business.json?datasetVersionNumber=2\nResolving www.kaggle.com (www.kaggle.com)... 35.244.233.98\nConnecting to www.kaggle.com (www.kaggle.com)|35.244.233.98|:443... connected.\nHTTP request sent, awaiting response... 302 Found\nLocation: https://storage.googleapis.com/kaggle-data-sets/10100/1035793/compressed/yelp_academic_dataset_business.json.zip?GoogleAccessId=web-data@kaggle-161607.iam.gserviceaccount.com&Expires=1587125092&Signature=UmAY5gLzNMHqLJGVso3wKR3l0qnvTfCt9g6QQ0C0ss2WovMiy%2BopSaDOXOYGGwi1p4Jb9ROlwON2jSXnPIjpR%2BPtRQK0sTODXy%2FUV1FbGxpa%2BwtwehoqHtbmrXzSI1Zo3OmNrW3TBEFmWHyOEp9Mlkk5cMCewlJ0yutdpG5uNR3I%2BS3v2NZNGfx8cfgg7hrQc9%2FQLk67vHNe5BsgwM01ltus3%2B7IjXpvMKgAamBCdaeIbJqCxr5lL57Jtpi1ahpdlx595lRf7k8nEQaXTKP7YPvVGRWelXMo3dpgvjRKxmaL1mKf5n%2Bj672OGsP8Vy33DTbWERbUBNe6SRNxoVxtBg%3D%3D&response-content-disposition=attachment%3B+filename%3Dyelp_academic_dataset_business.json.zip [following]\n--2020-04-14 12:04:52-- https://storage.googleapis.com/kaggle-data-sets/10100/1035793/compressed/yelp_academic_dataset_business.json.zip?GoogleAccessId=web-data@kaggle-161607.iam.gserviceaccount.com&Expires=1587125092&Signature=UmAY5gLzNMHqLJGVso3wKR3l0qnvTfCt9g6QQ0C0ss2WovMiy%2BopSaDOXOYGGwi1p4Jb9ROlwON2jSXnPIjpR%2BPtRQK0sTODXy%2FUV1FbGxpa%2BwtwehoqHtbmrXzSI1Zo3OmNrW3TBEFmWHyOEp9Mlkk5cMCewlJ0yutdpG5uNR3I%2BS3v2NZNGfx8cfgg7hrQc9%2FQLk67vHNe5BsgwM01ltus3%2B7IjXpvMKgAamBCdaeIbJqCxr5lL57Jtpi1ahpdlx595lRf7k8nEQaXTKP7YPvVGRWelXMo3dpgvjRKxmaL1mKf5n%2Bj672OGsP8Vy33DTbWERbUBNe6SRNxoVxtBg%3D%3D&response-content-disposition=attachment%3B+filename%3Dyelp_academic_dataset_business.json.zip\nResolving storage.googleapis.com (storage.googleapis.com)... 172.217.193.128, 2607:f8b0:400c:c08::80\nConnecting to storage.googleapis.com (storage.googleapis.com)|172.217.193.128|:443... connected.\nHTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK\nLength: 28568278 (27M) [application/zip]\nSaving to: ‘business.zip’\n\nbusiness.zip 100%[===================>] 27.24M 60.1MB/s in 0.5s \n\n2020-04-14 12:04:53 (60.1 MB/s) - ‘business.zip’ saved [28568278/28568278]\n\nArchive: business.zip\n inflating: yelp_academic_dataset_business.json \n--2020-04-14 12:04:58-- https://www.kaggle.com/yelp-dataset/yelp-dataset/download/py6LEr6zxQNWjebkCW8B%2Fversions%2FlVP0fduiJJo8YKt2vKKr%2Ffiles%2Fyelp_academic_dataset_review.json?datasetVersionNumber=2\nResolving www.kaggle.com (www.kaggle.com)... 35.244.233.98\nConnecting to www.kaggle.com (www.kaggle.com)|35.244.233.98|:443... connected.\nHTTP request sent, awaiting response... 302 Found\nLocation: https://storage.googleapis.com/kaggle-data-sets/10100/1035793/compressed/yelp_academic_dataset_review.json.zip?GoogleAccessId=web-data@kaggle-161607.iam.gserviceaccount.com&Expires=1587125098&Signature=rdIFQVbMexsSsfNEDkZUbYJI0zlWS%2BKzu6PnXauin%2Fb1kT%2BtW9RnJBQ6biVJBr1T2MZt2XFDRubXPSar4dXswSsl9QFBVw38xBlctLfrWsrf2TTCdGAQp6%2FQY8E%2BjZErfiat%2FZidJddgnYNfC3IqysOtzWxQBnV1DjJ%2FnznF9mLFdcTao9wsUhl42V2yju2nyXcj0OI%2FMGqeiJ4VBu3YyAVnHppehiiBbKJZdO1VtYKgTCXJZsZ0FY401%2BhpvXYGb8y9FUPv8iSBAExWzUtkIlWjzw1gZYl0dBZRj9i0BICL%2B9ElswIJU%2FxVrpsYuIBIWV9CWpB3lT4NaSXl4F8WHQ%3D%3D&response-content-disposition=attachment%3B+filename%3Dyelp_academic_dataset_review.json.zip [following]\n--2020-04-14 12:04:58-- https://storage.googleapis.com/kaggle-data-sets/10100/1035793/compressed/yelp_academic_dataset_review.json.zip?GoogleAccessId=web-data@kaggle-161607.iam.gserviceaccount.com&Expires=1587125098&Signature=rdIFQVbMexsSsfNEDkZUbYJI0zlWS%2BKzu6PnXauin%2Fb1kT%2BtW9RnJBQ6biVJBr1T2MZt2XFDRubXPSar4dXswSsl9QFBVw38xBlctLfrWsrf2TTCdGAQp6%2FQY8E%2BjZErfiat%2FZidJddgnYNfC3IqysOtzWxQBnV1DjJ%2FnznF9mLFdcTao9wsUhl42V2yju2nyXcj0OI%2FMGqeiJ4VBu3YyAVnHppehiiBbKJZdO1VtYKgTCXJZsZ0FY401%2BhpvXYGb8y9FUPv8iSBAExWzUtkIlWjzw1gZYl0dBZRj9i0BICL%2B9ElswIJU%2FxVrpsYuIBIWV9CWpB3lT4NaSXl4F8WHQ%3D%3D&response-content-disposition=attachment%3B+filename%3Dyelp_academic_dataset_review.json.zip\nResolving storage.googleapis.com (storage.googleapis.com)... 172.217.204.128, 2607:f8b0:400c:c13::80\nConnecting to storage.googleapis.com (storage.googleapis.com)|172.217.204.128|:443... connected.\nHTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK\nLength: 2636909381 (2.5G) [application/zip]\nSaving to: ‘review.zip’\n\nreview.zip 100%[===================>] 2.46G 46.4MB/s in 22s \n\n2020-04-14 12:05:21 (114 MB/s) - ‘review.zip’ saved [2636909381/2636909381]\n\nArchive: review.zip\n inflating: yelp_academic_dataset_review.json \n"
],
[
"import pandas as pd\nfrom six.moves import cPickle\nimport numpy as np\nimport json\nfrom scipy.sparse import csr_matrix\nfrom sklearn.decomposition import TruncatedSVD\nfrom scipy.sparse.linalg import svds\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"business = []\nwith open('/content/yelp_academic_dataset_business.json') as fl:\n for line in fl:\n business.append(json.loads(line))\nbusiness = pd.DataFrame(business)\nbusiness.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"review = []\nwith open('/content/yelp_academic_dataset_review.json') as fl:\n for line in fl:\n review.append(json.loads(line))\nreview = pd.DataFrame(review)\nreview.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"bcols = ['business_id', 'city', 'categories']\nucols = ['business_id', 'user_id', 'review_id', 'stars']\ndf = review[ucols].merge(business[bcols], how = 'outer', on= 'business_id')\ndf = df.dropna()\ndf.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#selecting subset: Phoenix city restaurants\ndfx = df[(df.city == 'Phoenix') & (df.categories.str.contains('.Restaurant.', case= False))]\ndfx.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def get_clean_df(df, min_user_review = 30, min_res_review = 0, cols = ['user_id', 'business_id', 'stars']):\n '''Cleans the df and gets rid of the unwanted cols and also allows to filter the user and business based on the min number of reviews received'''\n df_new = df[cols]\n df_new.dropna(axis = 0, how = 'any', inplace = True)\n df_new[cols[1]+'_freq'] = df_new.groupby(cols[1])[cols[1]].transform('count')\n df_clean = df_new[df_new[cols[1]+'_freq']>=min_res_review]\n df_clean[cols[0]+'_freq'] = df_clean.groupby(cols[0])[cols[0]].transform('count')\n df_clean_2 = df_clean[df_clean[cols[0]+'_freq']>=min_user_review]\n return df_clean_2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from pandas.api.types import CategoricalDtype",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def get_sparse_matrix(df):\n '''Converts the df into a sparse ratings matrix'''\n unique_users = list(df['user_id'].unique())\n unique_bus = list(df['business_id'].unique())\n data = df['stars'].tolist()\n row = df['user_id'].astype(CategoricalDtype(categories=unique_users)).cat.codes\n col = df['business_id'].astype(CategoricalDtype(categories=unique_bus)).cat.codes\n sparse_matrix = csr_matrix((data, (row, col)), shape=(len(unique_users), len(unique_bus)))\n return sparse_matrix",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def get_sparsity(sparse_matrix):\n return 1 - sparse_matrix.nnz/(sparse_matrix.shape[0]*sparse_matrix.shape[1])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data = get_sparse_matrix(get_clean_df(dfx, min_user_review=10))\nprint(get_sparsity(data))\nprint(data.shape)",
"/usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:4: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy\n after removing the cwd from sys.path.\n/usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:5: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy\n \"\"\"\n"
],
[
"def train_val_test_split(sparse_matrix, num_review_val = 2, num_review_test = 2):\n '''Split the rating matrix into train ,val, and test marix that are disjoint matrices'''\n nzrows, nzcols = sparse_matrix.nonzero()\n sparse_matrix_test = csr_matrix(sparse_matrix.shape)\n sparse_matrix_val = csr_matrix(sparse_matrix.shape)\n sparse_matrix_train = sparse_matrix.copy()\n n_users = sparse_matrix.shape[0]\n for u in range(n_users):\n idx = nzcols[np.where(nzrows == u)]\n np.random.shuffle(idx)\n test_idx = idx[-num_review_test:]\n val_idx = idx[-(num_review_val+num_review_test):-num_review_test]\n train_idx = idx[:-(num_review_val+num_review_test)]\n sparse_matrix_test[u,test_idx] = sparse_matrix[u,test_idx]\n sparse_matrix_val[u,val_idx] = sparse_matrix[u,val_idx]\n sparse_matrix_train[u,test_idx] = 0\n sparse_matrix_train[u,val_idx] = 0\n data = np.array(sparse_matrix_train[sparse_matrix_train.nonzero()])[0]\n row = sparse_matrix_train.nonzero()[0]\n col = sparse_matrix_train.nonzero()[1]\n size = sparse_matrix_train.shape\n sparse_matrix_train = csr_matrix((data,(row,col)),shape = size)\n mult = sparse_matrix_train.multiply(sparse_matrix_val)\n mmult = mult.multiply(sparse_matrix_test)\n assert(mmult.nnz == 0)\n return sparse_matrix_train, sparse_matrix_val, sparse_matrix_test",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"train, val, test = train_val_test_split(data)",
"/usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/scipy/sparse/_index.py:118: SparseEfficiencyWarning: Changing the sparsity structure of a csr_matrix is expensive. lil_matrix is more efficient.\n self._set_arrayXarray_sparse(i, j, x)\n"
],
[
"print(train.nnz, val.nnz, test.nnz)",
"82735 10141 10146\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Model Building",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def approx_err(k, A, U, S, Vt):\n rec_A = np.dot(U[:, :k], np.dot(S[:k,:k], Vt[:k, :]))\n idx = np.where(A>0);\n diff = A[idx] - rec_A[idx]\n return np.linalg.norm(diff)**2/diff.shape[1]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# # svd\n# U, S, Vt = np.linalg.svd(train.todense())\n# k = np.linspace(2,40,20, dtype = int)\n# errors_svd_val = {}\n# errors_svd_train = {}\n# for i in k:\n# errors_svd_val[i] = approx_err(i, val.todense(), U, S, Vt)\n# errors_svd_train[i] = approx_err(i, train.todense(), U, S, Vt)\n\n# plt.plot(errors_svd_val.keys(),errors_svd_val.values(), label = 'Validation')\n# plt.plot(errors_svd_train.keys(),errors_svd_train.values(), label = 'Train')\n# plt.xlabel('k')\n# plt.ylabel('MSE')\n# plt.legend()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"ALS",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def get_mse(pred, actual):\n # Ignore zero terms.\n pred = pred[actual.nonzero()].flatten()\n actual = actual[actual.nonzero()].flatten()\n return mean_squared_error(pred, actual)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def als(ratings_matrix, k=40, user_reg=0, res_reg=0, iters=10):\n '''Performs ALS for a given ratings_matrix and returns predictions using the latent vector representation User (U x K) and Restaurant (R x K)'''\n ratings_matrix = ratings_matrix.T\n user_vec = np.random.rand(ratings_matrix.shape[1],k).T\n res_vec = np.random.rand(ratings_matrix.shape[0],k).T\n for i in range(iters):\n for u in range(ratings_matrix.shape[1]):\n user_vec[:,u] = np.linalg.solve(np.dot(res_vec,res_vec.T) + user_reg * np.eye(res_vec.shape[0]), np.dot(res_vec,ratings_matrix[:,u]))\n for r in range(ratings_matrix.shape[0]):\n res_vec[:,r] = np.linalg.solve(np.dot(user_vec,user_vec.T) + res_reg * np.eye(user_vec.shape[0]), np.dot(user_vec,ratings_matrix[r,:].T))\n prediction = np.dot(res_vec.T, user_vec)\n# error = np.mean((ratings_matrix - prediction)**2)\n return np.dot(res_vec.T, user_vec).T",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"num_features = np.linspace(1,20,5,dtype=int)\ntest_error_als = []\ntrain_error_als = []\nfor i in num_features:\n preds_als = als(np.array(train.todense()), k=i, iters = 5)\n test_err = get_mse(preds_als, np.array(val.todense()))\n train_err = get_mse(preds_als, np.array(train.todense()))\n test_error_als.append(test_err)\n train_error_als.append(train_err)\n\nfig = plt.figure(figsize=(8,5))\nplt.plot(num_features,test_error_als,'b-',label = 'validation')\nplt.plot(num_features,train_error_als,'r-', label = 'training')\nplt.title('MSE vs num_features (for ALS)')\nplt.xlabel('Number of features in a feature vector')\nplt.ylabel('MSE')\nplt.legend()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Refer to [this](https://colab.research.google.com/github/HegdeChaitra/Yelp-Recommendation-System/blob/master/Yelp_Reco_System.ipynb#scrollTo=kAoMx5IHUpsi) for further info",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a721769e6256da47ed6365e38b2650a789a073a
| 458,917 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
code/Chapter 04 - Effective Information in Real Networks.ipynb
|
ajayjeswani12/NEW
|
44c9fdf03cbb6e37c8a2c43ff8bf3ac2a686ba82
|
[
"MIT"
] | 63 |
2019-07-19T09:30:18.000Z
|
2022-03-27T18:35:51.000Z
|
code/Chapter 04 - Effective Information in Real Networks.ipynb
|
ajayjeswani12/NEW
|
44c9fdf03cbb6e37c8a2c43ff8bf3ac2a686ba82
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2020-05-30T11:19:36.000Z
|
2020-05-30T11:19:36.000Z
|
code/Chapter 04 - Effective Information in Real Networks.ipynb
|
ajayjeswani12/NEW
|
44c9fdf03cbb6e37c8a2c43ff8bf3ac2a686ba82
|
[
"MIT"
] | 17 |
2019-07-22T18:52:03.000Z
|
2021-10-02T08:09:31.000Z
| 1,103.165865 | 326,272 | 0.949993 |
[
[
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport networkx as nx\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nfrom scipy import stats\nimport scipy as sp\nimport datetime as dt\n\nfrom ei_net import * \n\n# import cmocean as cmo\n\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"##########################################\n############ PLOTTING SETUP ##############\nEI_cmap = \"Greys\"\nwhere_to_save_pngs = \"../figs/pngs/\"\nwhere_to_save_pdfs = \"../figs/pdfs/\"\nsave = True\nplt.rc('axes', axisbelow=True)\nplt.rc('axes', linewidth=2)\n##########################################\n##########################################",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# The emergence of informative higher scales in complex networks",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Chapter 04: Effective Information in Real Networks\n\n$EI$ often grows with network size. To compare networks of different sizes, we examine their *effectiveness*, which is the $EI$ normalized by the size of the network to a value between $0.0$ and $1.0$:\n\n$$ \\text{effectiveness} = \\frac{EI}{\\log_2(N)} $$\n\nAs the noise and/or the degeneracy of a network increases toward their upper possible bounds, the effectiveness of that network will trend to $0.0$. Regardless of its size, a network wherein each node has a deterministic output to a unique target has an effectiveness of $1.0$. \n\nHere, we examine the effectiveness of 84 different networks corresponding to data from real systems. These networks were selected primarily from the [Konect Network Database](http://konect.cc/), which was used because its networks are publicly available, range in size from dozens to tens of thousands of nodes, often have a reasonable interpretation as a causal structure, and they are diverse, ranging from social networks, to power networks, to metabolic networks. We defined four categories of interest: biological, social, informational, and technological. We selected our networks by using all the available networks (under 40,000 nodes) in the domains corresponding to each category within the Konect database, and where it was appropriate, the [Network Repository](http://networkrepository.com/) as well. \n\nLower effectiveness values correspond to structures that either have high degeneracy, low determinism, or a combination of both. In the networks we measured, biological networks on average have lower effectiveness values, whereas technological networks on average have the highest effectiveness. This finding aligns intuitively with what we know about the relationship between $EI$ and network structure, and it also supports long-standing hypotheses about the role of redundancy, degeneracy, and noise in biological systems. On the other hand, technological networks such as power grids, autonomous systems, or airline networks are associated with higher effectiveness values on average. One explanation for this difference is that efficiency in human-made technological networks tends to create sparser, non-degenerate networks with higher effectiveness on average.\n\nPerhaps it might be surprising to find that evolved networks have such low effectiveness. But, as we will show, a low effectiveness can actually indicate that there are informative higher-scale (macroscale) dependencies in the system. That is, a low effectiveness can be reflective of the fact that biological systems often contain higher-scale causal structure, which we demonstrate in the following section.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"________________________",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 4.1 Effectiveness of Real World Networks",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import json\njson_data = open('../data/real_network_ei.json',\"r\").read()\nout_dict = json.loads(json_data)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"list1 = out_dict['Eff']\nlist1 = list(enumerate(list1))\nlist2 = sorted(list1, key=lambda x:x[1])\nordering = list(list(zip(*list2))[0])\neff_vals = list(list(zip(*list2))[1])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"newcos = [\"#ed4f44\",\"#fdcb12\",\"#7f61c3\",\"#00c6c5\",\"#333333\"]\ncols = ['#88002c',\"#ba4b57\",\"#cc5134\",\"#daaa32\",\"#b8ab51\",\"#698b4a\",\"#69d07d\",\"#50c9b5\",\n \"#64b6ff\",\"#786bdb\",\"#573689\",\"#b55083\",\"#c65abb\",\"#bfbfbf\",\"#666666\",\"#333333\"]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(13,20))\n\nfor idx,i in enumerate(ordering):\n co = out_dict['color'][i]\n ef = out_dict['Eff'][i]\n plt.hlines(idx,0,ef,color=co,linewidth=4.5)\n \n\nplt.scatter(eff_vals, list(range(len(eff_vals))), \n edgecolors='w',linewidths=1.5,\n marker='o', s=130, alpha=0.98, \n facecolor=np.array(out_dict['color'])[ordering], zorder=20)\nplt.scatter([0]*len(eff_vals), list(range(len(eff_vals))), \n marker='s', s=65, alpha=0.98,\n edgecolors=np.array(out_dict['newco'])[ordering],\n linewidths=3.5, facecolor='w', zorder=20)\n\ndomainz = ['Biological','Information','Social','Technological']\nfor ii, lab in enumerate(domainz):\n plt.scatter([-1], [-1], marker='s', s=125, \n alpha=0.98,edgecolors=newcos[ii], \n linewidths=4.5, facecolor='w', label=lab)\n \nfor ii, lab in enumerate(sorted(np.unique(out_dict['Category']))):\n plt.plot([-10,-9], [-10,-9], marker='',\n alpha=0.98, linewidth=4.0,\n color=cols[ii], label=lab)\n\nplt.legend(loc=4, fontsize=19, framealpha=0.85)\nplt.yticks(list(range(len(eff_vals))), \n np.array(out_dict['Name'])[ordering], \n fontsize=14)\nplt.xticks(np.linspace(0,1,11), \n [\"%.1f\"%i for i in np.linspace(0,1,11)], \n size=18)\nplt.grid(alpha=0.3, color='#999999', \n linestyle='-', linewidth=2.5)\nplt.xlabel('Effectiveness', size=20)\nplt.xlim(-0.01,1.01)\nplt.ylim(-1,len(eff_vals))\n\nif save:\n plt.savefig(where_to_save_pngs+\"Konect_SortedEffectiveness_withLabels.png\", dpi=425, bbox_inches='tight')\n plt.savefig(where_to_save_pdfs+\"Konect_SortedEffectiveness_withLabels.pdf\", bbox_inches='tight')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 4.2 Statistical Comparison of Effectiveness, by Domain",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"rn_bio = np.array([out_dict['Eff'][i] for i in range(len(out_dict['Eff'])) \\\n if out_dict['Category_EI'][i]=='Biological'])\nrn_inf = np.array([out_dict['Eff'][i] for i in range(len(out_dict['Eff'])) \\\n if out_dict['Category_EI'][i]=='Information'])\nrn_soc = np.array([out_dict['Eff'][i] for i in range(len(out_dict['Eff'])) \\\n if out_dict['Category_EI'][i]=='Social'])\nrn_tec = np.array([out_dict['Eff'][i] for i in range(len(out_dict['Eff'])) \\\n if out_dict['Category_EI'][i]=='Technological'])\n\nlabs = {'biological':0,'social':2,\"information\":1,'technological':3}\na = labs['biological']\nb = labs['social']\n\nall_data = [rn_bio,rn_inf,rn_soc,rn_tec]\n\nfor lab1 in labs.keys():\n a = labs[lab1]\n for lab2 in labs.keys():\n b = labs[lab2]\n if a!=b:\n t,p = sp.stats.ttest_ind(all_data[a], all_data[b], equal_var=False)\n print(\"comparing\",lab1,\" \\t\", \n \"to \\t \",lab2,\" \\t t-statistic = %.7f, \\t p < %.8f\"%(t,p))",
"comparing biological \t to \t social \t t-statistic = -1.2023872, \t p < 0.23744675\ncomparing biological \t to \t information \t t-statistic = -1.9001405, \t p < 0.06608408\ncomparing biological \t to \t technological \t t-statistic = -5.2740596, \t p < 0.00001255\ncomparing social \t to \t biological \t t-statistic = 1.2023872, \t p < 0.23744675\ncomparing social \t to \t information \t t-statistic = -0.9547772, \t p < 0.34621068\ncomparing social \t to \t technological \t t-statistic = -5.6426075, \t p < 0.00000121\ncomparing information \t to \t biological \t t-statistic = 1.9001405, \t p < 0.06608408\ncomparing information \t to \t social \t t-statistic = 0.9547772, \t p < 0.34621068\ncomparing information \t to \t technological \t t-statistic = -4.2445263, \t p < 0.00021821\ncomparing technological \t to \t biological \t t-statistic = 5.2740596, \t p < 0.00001255\ncomparing technological \t to \t social \t t-statistic = 5.6426075, \t p < 0.00000121\ncomparing technological \t to \t information \t t-statistic = 4.2445263, \t p < 0.00021821\n"
],
[
"plt.rc('axes', linewidth=1.5)\nmult = 0.8\n\nfig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=1, figsize=(15*mult, 15*mult))\n\nnoise0 = np.random.uniform(-0.035,0.035,len(all_data[0]))\nnoise1 = np.random.uniform(-0.035,0.035,len(all_data[1]))\nnoise2 = np.random.uniform(-0.035,0.035,len(all_data[2]))\nnoise3 = np.random.uniform(-0.035,0.035,len(all_data[3]))\n\nplt.plot([1]*len(all_data[0]) + noise0, all_data[0],\n marker='o',linestyle='', markeredgecolor='k',\n markersize=6, color=newcos[0])\nplt.plot([3]*len(all_data[1]) + noise1, all_data[1],\n marker='o',linestyle='',markeredgecolor='k',\n markersize=6, color=newcos[1])\nplt.plot([2]*len(all_data[2]) + noise2, all_data[2],\n marker='o',linestyle='',markeredgecolor='k',\n markersize=6, color=newcos[2])\nplt.plot([4]*len(all_data[3]) + noise3, all_data[3],\n marker='o',linestyle='',markeredgecolor='k',\n markersize=6, color=newcos[3]) \n \nparts = ax.violinplot(all_data, positions=[1,3,2,4], \n showmeans=False, showmedians=False, \n showextrema=False, widths=0.75)\nfor i in range(len(parts['bodies'])):\n pc = parts['bodies'][i]\n pc.set_edgecolor(newcos[i])\n pc.set_facecolor(newcos[i])\n pc.set_alpha(0.85)\n pc.set_linewidth(4.0)\nparts = ax.violinplot(all_data, positions=[1,3,2,4], \n showmeans=False, showmedians=False, \n showextrema=False, widths=0.55)\nfor i in range(len(parts['bodies'])):\n pc = parts['bodies'][i]\n pc.set_edgecolor(newcos[i])\n pc.set_facecolor('w')\n pc.set_alpha(0.5)\n pc.set_linewidth(0.0)\n\nplt.hlines([np.mean(data) for data in all_data], \n [0.67, 2.6925, 1.695, 3.74], \n [1.33, 3.3075, 2.305, 4.26], \n linestyles='-', colors=newcos, \n zorder=1, linewidth=4.5)\n\nplt.plot(np.linspace(-10,-20,5), np.linspace(-10,-20,5), \n linestyle='-', marker='>', markersize=18, \n markerfacecolor='w', color='#333333', \n linewidth=3.5, markeredgecolor='k', \n markeredgewidth=2.5, label='Mean', alpha=0.98)\n\nplt.scatter([1,3,2,4], \n [np.mean(data) for data in all_data], \n zorder=20, marker='>', s=450, facecolor='w', \n edgecolors=newcos, linewidths=3.5, alpha=0.98)\n\nax.set_ylabel('Effectiveness', fontsize=22)\nax.set_xticks([y+1 for y in range(len(all_data))])\nax.set_xticklabels(['biological', 'social', \n 'information', 'technological'],\n fontsize=19, rotation=353)\nax.set_yticks(np.linspace(0,1,6))\nax.set_yticklabels([\"%.1f\"%i for i in np.linspace(0,1,6)], fontsize=18)\nax.grid(True, linestyle='-', linewidth=3.0, color='#999999', alpha=0.4)\n\nax.text(1.28,0.07,\"n=%i\"%len(all_data[0]), \n fontsize=22, color=newcos[0])\nax.text(3.20,0.33,\"n=%i\"%len(all_data[1]), \n fontsize=22, color='k')\nax.text(3.20,0.33,\"n=%i\"%len(all_data[1]), \n fontsize=22, color=newcos[1],alpha=0.95)\nax.text(2.26,0.25,\"n=%i\"%len(all_data[2]), \n fontsize=22, color=newcos[2])\nax.text(4.21,0.55,\"n=%i\"%len(all_data[3]), \n fontsize=22, color=newcos[3])\n\nax.text(2.35,1.065,\"**\", fontsize=22)\nax.hlines(1.07, labs['biological']+1+0.025, \n labs['technological']+1-0.025, linewidth=2.0)\nax.vlines(labs['biological']+1+0.025, 1.045, 1.07, linewidth=2.0)\nax.vlines(labs['technological']+1-0.025, 1.045, 1.07, linewidth=2.0)\n\nax.text(3.01,1.012,\"***\", fontsize=22)\nax.hlines(1.015, labs['social']+0.025, \n labs['technological']+1-0.025, linewidth=2.0)\nax.vlines(labs['social']+0.025, 0.995, 1.015, linewidth=2.0)\nax.vlines(labs['technological']+1-0.025, 0.995, 1.015, linewidth=2.0)\n\nax.text(3.47,0.962,\"*\", fontsize=22)\nax.hlines(0.965, labs['information']+2+0.025, \n labs['technological']+1-0.025, linewidth=2.0)\nax.vlines(labs['information']+2+0.025, 0.945, 0.965, linewidth=2.0)\nax.vlines(labs['technological']+1-0.025, 0.945, 0.965, linewidth=2.0)\n\nx1 = ax.plot([], [], marker='.', linestyle='', c='w')\nx2 = ax.plot([], [], marker='.', linestyle='', c='w')\nx3 = ax.plot([], [], marker='.', linestyle='', c='w')\n\nlegs=[x1,x2,x3]\nleg1 = ax.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.009,0.22), fontsize=23, \n ncol=1, columnspacing=2, framealpha=0.95)\nax.legend([l[0] for l in legs], \n [\"p < 1e-06 ***\",\"p < 1e-05 **\",\"p < 1e-03 *\"], \n handletextpad=-1.50,\n bbox_to_anchor=(1.0055,0.16), fontsize=18, ncol=1, \n columnspacing=-3.75, framealpha=0.95)\n\nax.add_artist(leg1)\nax.set_ylim(-0.015, 1.1)\nax.set_xlim(0.25, 4.75)\n\nif save:\n plt.savefig(\n where_to_save_pngs+\\\n \"Konect_Effectiveness_Violinplots.png\", \n dpi=425, bbox_inches='tight')\n plt.savefig(\n where_to_save_pdfs+\\\n \"Konect_Effectiveness_Violinplots.pdf\",\n bbox_inches='tight')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## End of Chapter 04. In [Chapter 05](https://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/jkbren/einet/blob/master/code/Chapter%2005%20-%20Causal%20Emergence%20in%20Preferential%20Attachment%20and%20SBMs.ipynb) we'll start to look at *causal emergence* networks.\n_______________",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a721cf8749e8b8c8966f820f22d1af8360f43a1
| 176,776 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
1. Preprocessing/2. Long vectors.ipynb
|
Llannelongue/B4PPI
|
47984eb496ddfff49814a6d784d02ff3c3d0fbff
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | 4 |
2022-02-10T04:24:30.000Z
|
2022-02-27T23:26:05.000Z
|
1. Preprocessing/2. Long vectors.ipynb
|
Llannelongue/B4PPI
|
47984eb496ddfff49814a6d784d02ff3c3d0fbff
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | null | null | null |
1. Preprocessing/2. Long vectors.ipynb
|
Llannelongue/B4PPI
|
47984eb496ddfff49814a6d784d02ff3c3d0fbff
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | null | null | null | 39.680359 | 21,492 | 0.439958 |
[
[
[
"---\n**Export of unprocessed features**\n\n---",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport os\nimport re\nimport matplotlib as mpl\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn as sns\nfrom sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer\nimport random\nimport pickle\nfrom scipy import sparse\nimport math\nimport pprint\n\nimport sklearn as sk \n\nimport torch\n\nfrom IPython.display import display\n\nfrom toolbox import *\n# from myMLtoolbox import *\n\n%matplotlib inline\nsns.set()\nsns.set_context(\"notebook\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sns.set(rc={'figure.figsize':(14,6)})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cfg = load_cfg()\n\nlogVersions = load_LogVersions()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"---\n**For figures**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from figures_toolbox import *",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mpl.rcParams.update(mpl.rcParamsDefault)\n\nsns.set(\n context='paper',\n style='ticks',\n)\n\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mpl.rcParams.update(performancePlot_style)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Get uniprot list of proteins",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"uniprotIDs = pd.read_csv(\n os.path.join(cfg['rawDataUniProt'], \n \"uniprot_allProteins_Human_v{}.pkl\".format(logVersions['UniProt']['rawData'])),\n header=None,\n names=['uniprotID']\n )\nglance(uniprotIDs)",
"DataFrame: 20,386 rows \t 1 columns\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Hubs",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"path0 = os.path.join(\n cfg['outputPreprocessingIntAct'], \n \"listHubs_20p_v{}.pkl\".format(logVersions['IntAct']['preprocessed']['all'])\n)\n\nwith open(path0, 'rb') as f:\n list_hubs20 = pickle.load(f)\n\nglance(list_hubs20)",
"list: len 3240\n['P42858', 'Q9NRI5', 'A8MQ03', 'P05067', 'P62993']\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Load feature datasets",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"featuresDict = {\n 'bioProcessUniprot': {\n 'path': os.path.join(\n cfg['outputPreprocessingUniprot'], \n \"bioProcessUniprot_v{}--{}.pkl\".format(logVersions['UniProt']['rawData'], logVersions['UniProt']['preprocessed'])\n ),\n 'imputeNA': '0', # '0', 'mean', 'none'\n 'normalise':False,\n 'isBinary': True,\n },\n 'cellCompUniprot': {\n 'path': os.path.join(\n cfg['outputPreprocessingUniprot'], \n \"cellCompUniprot_v{}--{}.pkl\".format(logVersions['UniProt']['rawData'], logVersions['UniProt']['preprocessed'])\n ),\n 'imputeNA': '0',\n 'normalise':False,\n 'isBinary': True,\n },\n 'molFuncUniprot': {\n 'path': os.path.join(\n cfg['outputPreprocessingUniprot'], \n \"molFuncUniprot_v{}--{}.pkl\".format(logVersions['UniProt']['rawData'], logVersions['UniProt']['preprocessed'])\n ),\n 'imputeNA': '0',\n 'normalise':False,\n 'isBinary': True,\n },\n 'domainUniprot': {\n 'path': os.path.join(\n cfg['outputPreprocessingUniprot'], \n \"domainFT_v{}--{}.pkl\".format(logVersions['UniProt']['rawData'], logVersions['UniProt']['preprocessed'])\n ),\n 'imputeNA': '0',\n 'normalise':False,\n 'isBinary': True,\n },\n 'motifUniprot': {\n 'path': os.path.join(\n cfg['outputPreprocessingUniprot'], \n \"motif_v{}--{}.pkl\".format(logVersions['UniProt']['rawData'], logVersions['UniProt']['preprocessed'])\n ),\n 'imputeNA': '0',\n 'normalise':False,\n 'isBinary': True,\n },\n 'Bgee': {\n 'path': os.path.join(\n cfg['outputPreprocessingBgee'],\n \"Bgee_processed_v{}.pkl\".format(logVersions['Bgee']['preprocessed'])\n ),\n 'imputeNA': '0',\n 'normalise':True,\n 'isBinary': False,\n },\n 'tissueCellHPA': {\n 'path': os.path.join(\n cfg['outputPreprocessingHPA'], \n \"tissueIHC_tissueCell_v{}.pkl\".format(logVersions['HPA']['preprocessed']['tissueIHC_tissueCell'])\n ),\n 'imputeNA': '0',\n 'normalise':True,\n 'isBinary': False,\n },\n 'tissueHPA': {\n 'path': os.path.join(\n cfg['outputPreprocessingHPA'], \n \"tissueIHC_tissueOnly_v{}.pkl\".format(logVersions['HPA']['preprocessed']['tissueIHC_tissueOnly'])\n ),\n 'imputeNA': '0',\n 'normalise':True,\n 'isBinary': False,\n },\n 'RNAseqHPA': {\n 'path': os.path.join(\n cfg['outputPreprocessingHPA'], \n \"consensusRNAseq_v{}.pkl\".format(logVersions['HPA']['preprocessed']['consensusRNAseq'])\n ),\n 'imputeNA': 'mean',\n 'normalise':True,\n 'isBinary': False,\n },\n 'subcellularLocationHPA': {\n 'path': os.path.join(\n cfg['outputPreprocessingHPA'], \n \"subcellularLocation_v{}.pkl\".format(logVersions['HPA']['preprocessed']['subcellularLocation'])\n ),\n 'imputeNA': '0',\n 'normalise':False,\n 'isBinary': True,\n },\n 'sequence': {\n 'path': os.path.join(\n cfg['outputPreprocessingUniprot'], \n \"sequenceData_v{}--{}.pkl\".format(logVersions['UniProt']['rawData'], logVersions['UniProt']['preprocessed'])\n ),\n 'imputeNA':'none',\n 'normalise':False,\n 'isBinary': False,\n }\n}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def sneakPeak(featuresDict):\n for feature, details in featuresDict.items():\n df = pd.read_pickle(details['path'])\n print('## ',feature)\n glance(df)\n print()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sneakPeak(featuresDict)",
"## bioProcessUniprot\nDataFrame: 20,386 rows \t 12,249 columns\n"
]
],
[
[
"# EDA",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Number of GO terms for hubs and lone proteins**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def count_GOterms():\n countGO = uniprotIDs.copy()\n \n for feature, details in featuresDict.items(): \n print(feature)\n if feature != 'sequence':\n df = pd.read_pickle(details['path'])\n\n foo = df.set_index('uniprotID').ne(0).sum(axis=1)\n foo2 = pd.DataFrame(foo)\n foo2.columns = [feature]\n foo2.reset_index()\n \n countGO = countGO.join(foo2, on='uniprotID', how='left')\n \n return countGO\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"countGO = count_GOterms()\nglance(countGO)",
"bioProcessUniprot\ncellCompUniprot\nmolFuncUniprot\ndomainUniprot\nmotifUniprot\nBgee\ntissueCellHPA\ntissueHPA\nRNAseqHPA\nsubcellularLocationHPA\nsequence\nDataFrame: 20,386 rows \t 11 columns\n"
],
[
"countGO.info()",
"<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>\nRangeIndex: 20386 entries, 0 to 20385\nData columns (total 11 columns):\n # Column Non-Null Count Dtype \n--- ------ -------------- ----- \n 0 uniprotID 20386 non-null object \n 1 bioProcessUniprot 20386 non-null int64 \n 2 cellCompUniprot 20386 non-null int64 \n 3 molFuncUniprot 20386 non-null int64 \n 4 domainUniprot 20386 non-null int64 \n 5 motifUniprot 20386 non-null int64 \n 6 Bgee 19090 non-null float64\n 7 tissueCellHPA 10850 non-null float64\n 8 tissueHPA 10850 non-null float64\n 9 RNAseqHPA 18938 non-null float64\n 10 subcellularLocationHPA 12566 non-null float64\ndtypes: float64(5), int64(5), object(1)\nmemory usage: 1.7+ MB\n"
],
[
"countGO['isHub'] = countGO.uniprotID.isin(list_hubs20)\n\nglance(countGO)",
"DataFrame: 20,386 rows \t 12 columns\n"
],
[
"sns.displot(countGO, x=\"bioProcessUniprot\", hue=\"isHub\", kind='kde', common_norm=False);",
"/home/ll582/.conda/envs/PPI-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/matplotlib/cbook/__init__.py:1402: FutureWarning: Support for multi-dimensional indexing (e.g. `obj[:, None]`) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Convert to a numpy array before indexing instead.\n x[:, None]\n/home/ll582/.conda/envs/PPI-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/matplotlib/axes/_base.py:276: FutureWarning: Support for multi-dimensional indexing (e.g. `obj[:, None]`) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Convert to a numpy array before indexing instead.\n x = x[:, np.newaxis]\n/home/ll582/.conda/envs/PPI-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/matplotlib/axes/_base.py:278: FutureWarning: Support for multi-dimensional indexing (e.g. `obj[:, None]`) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Convert to a numpy array before indexing instead.\n y = y[:, np.newaxis]\n"
],
[
"doPlot=False\n\nfor feature in featuresDict.keys():\n if feature != 'sequence':\n foo = countGO.loc[countGO.isHub][feature]\n bar = countGO.loc[~countGO.isHub][feature]\n \n print(f\"{feature}: on average, hubs have {foo.mean():.2f} GO terms, non-hubs have {bar.mean():.2f} (medians {foo.median():.2f} vs {bar.median():.2f})\")\n if doPlot:\n sns.displot(countGO, x=feature, hue=\"isHub\", kind='kde', common_norm=False)\n plt.show();",
"bioProcessUniprot: on average, hubs have 11.54 GO terms, non-hubs have 5.72 (medians 6.00 vs 3.00)\ncellCompUniprot: on average, hubs have 6.11 GO terms, non-hubs have 3.60 (medians 5.00 vs 3.00)\nmolFuncUniprot: on average, hubs have 4.19 GO terms, non-hubs have 2.49 (medians 3.00 vs 2.00)\ndomainUniprot: on average, hubs have 1.09 GO terms, non-hubs have 1.00 (medians 0.00 vs 0.00)\nmotifUniprot: on average, hubs have 0.28 GO terms, non-hubs have 0.16 (medians 0.00 vs 0.00)\nBgee: on average, hubs have 937.01 GO terms, non-hubs have 876.51 (medians 993.00 vs 940.00)\ntissueCellHPA: on average, hubs have 85.08 GO terms, non-hubs have 84.32 (medians 83.00 vs 82.00)\ntissueHPA: on average, hubs have 48.73 GO terms, non-hubs have 48.71 (medians 49.00 vs 49.00)\nRNAseqHPA: on average, hubs have 56.54 GO terms, non-hubs have 52.39 (medians 61.00 vs 60.00)\nsubcellularLocationHPA: on average, hubs have 1.78 GO terms, non-hubs have 1.75 (medians 2.00 vs 2.00)\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Export vectors lengths",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def getVectorsLengths(featuresDict):\n \n vectorsLengths = dict()\n \n for feature, details in featuresDict.items():\n df = pd.read_pickle(details['path'])\n \n assert 'uniprotID' in df.columns\n \n vectorsLengths[feature] = df.shape[1]-1 # -1 to remove uniprotID\n \n return vectorsLengths",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"vectorsLengths = getVectorsLengths(featuresDict)\nprint(vectorsLengths)",
"{'bioProcessUniprot': 12248, 'cellCompUniprot': 1754, 'molFuncUniprot': 4346, 'domainUniprot': 2313, 'motifUniprot': 819, 'Bgee': 1147, 'tissueCellHPA': 189, 'tissueHPA': 62, 'RNAseqHPA': 61, 'subcellularLocationHPA': 33, 'sequence': 1}\n"
],
[
"versionRawImpute_overall = '6-0'\n\nlogVersions['featuresEngineering']['longVectors']['overall'] = versionRawImpute_overall\n\ndump_LogVersions(logVersions)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"with open(os.path.join(\n cfg['outputFeaturesEngineering'],\n \"longVectors_lengths_v{}.pkl\".format(versionRawImpute_overall)\n), 'wb') as f:\n pickle.dump(vectorsLengths, f)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Format long vectors",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def formatRawData(featuresDict, uniprotIDs, vectorsLengths):\n \n out = dict()\n \n out['uniprotID'] = uniprotIDs.uniprotID.to_list()\n \n for feature, details in featuresDict.items():\n print(feature)\n df = pd.read_pickle(details['path'])\n print(' - initial dim:', df.shape)\n \n print(' - merge with reference index list')\n df = uniprotIDs.merge(\n df,\n on = 'uniprotID',\n how='left',\n validate='1:1'\n )\n df.set_index('uniprotID', inplace=True)\n print(' - new dim:', df.shape)\n \n assert details['imputeNA'] in ['0','mean','none']\n if details['imputeNA'] == 'mean':\n print(' - mean imputation')\n meanValues = df.mean(axis = 0, skipna = True)\n meanValues[np.isnan(meanValues)] = 0\n\n df.fillna(meanValues, inplace=True)\n\n # sanity check\n assert df.isna().sum().sum() == 0\n elif details['imputeNA'] == '0':\n print(' - imputate with 0')\n df.fillna(0, inplace=True)\n\n # sanity check\n assert df.isna().sum().sum() == 0\n else:\n print(' - no imputation: {:,} NAs'.format(df.isna().sum().sum()))\n \n if details['normalise']:\n print(' - normalise')\n scal = sk.preprocessing.StandardScaler(copy = False)\n df = scal.fit_transform(df)\n elif feature == 'sequence':\n df = df.sequence.to_list()\n else:\n df = df.values\n \n # compare shape to vectorsLengths\n if feature == 'sequence':\n assert isinstance(df, list)\n else:\n assert df.shape[1] == vectorsLengths[feature]\n \n out[feature] = df.copy()\n \n return out",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def sneakPeak2(featuresDict, n=5):\n for feature, df in featuresDict.items():\n print('## ',feature)\n glance(df, n=n)\n print()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Without normalising binary features",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for feature in featuresDict:\n if featuresDict[feature]['isBinary']:\n featuresDict[feature]['normalise'] = False\n \nfeaturesDict",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"outDict = formatRawData(featuresDict=featuresDict, uniprotIDs=uniprotIDs, vectorsLengths=vectorsLengths)",
"bioProcessUniprot\n - initial dim: (20386, 12249)\n - merge with reference index list\n - new dim: (20386, 12248)\n - imputate with 0\ncellCompUniprot\n - initial dim: (20386, 1755)\n - merge with reference index list\n - new dim: (20386, 1754)\n - imputate with 0\nmolFuncUniprot\n - initial dim: (20386, 4347)\n - merge with reference index list\n - new dim: (20386, 4346)\n - imputate with 0\ndomainUniprot\n - initial dim: (20386, 2314)\n - merge with reference index list\n - new dim: (20386, 2313)\n - imputate with 0\nmotifUniprot\n - initial dim: (20386, 820)\n - merge with reference index list\n - new dim: (20386, 819)\n - imputate with 0\nBgee\n - initial dim: (19090, 1148)\n - merge with reference index list\n - new dim: (20386, 1147)\n - imputate with 0\n - normalise\ntissueCellHPA\n - initial dim: (10850, 190)\n - merge with reference index list\n - new dim: (20386, 189)\n - imputate with 0\n - normalise\ntissueHPA\n - initial dim: (10850, 63)\n - merge with reference index list\n - new dim: (20386, 62)\n - imputate with 0\n - normalise\nRNAseqHPA\n - initial dim: (18938, 62)\n - merge with reference index list\n - new dim: (20386, 61)\n - mean imputation\n - normalise\nsubcellularLocationHPA\n - initial dim: (12566, 34)\n - merge with reference index list\n - new dim: (20386, 33)\n - imputate with 0\nsequence\n - initial dim: (20386, 2)\n - merge with reference index list\n - new dim: (20386, 1)\n - no imputation: 0 NAs\n"
],
[
"sneakPeak2(outDict)",
"## uniprotID\nlist: len 20386\n['A0A024RBG1', 'A0A075B6H7', 'A0A075B6H8', 'A0A075B6H9', 'A0A075B6I0']\n\n## bioProcessUniprot\nnp.array: shape (20386, 12248)\n\n[[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]\n [0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]\n [0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]\n ...\n [0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]\n [0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]\n [0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]]\n\n## cellCompUniprot\nnp.array: shape (20386, 1754)\n\n[[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]\n [0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]\n [0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]\n ...\n [0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]\n [0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]\n [0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]]\n\n## molFuncUniprot\nnp.array: shape (20386, 4346)\n\n[[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]\n [0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]\n [0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]\n ...\n [0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]\n [0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]\n [0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]]\n\n## domainUniprot\nnp.array: shape (20386, 2313)\n\n[[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]\n [0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]\n [0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]\n ...\n [0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]\n [0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]\n [0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]]\n\n## motifUniprot\nnp.array: shape (20386, 819)\n\n[[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]\n [0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]\n [0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]\n ...\n [0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]\n [0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]\n [0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]]\n\n## Bgee\nnp.array: shape (20386, 1147)\n\n[[-0.10658714 0.68210993 0.64575424 ... 0.54472649 0.44463934\n 1.09760362]\n [-0.10658714 -1.49017079 -1.67791238 ... -1.82328592 0.44463934\n -0.57266454]\n [-0.10658714 -1.49017079 -1.67791238 ... -1.82328592 0.44463934\n -0.57266454]\n ...\n [-0.10658714 -0.76607722 -0.90335684 ... -1.82328592 -2.20113346\n -0.57266454]\n [-0.10658714 -0.76607722 -0.90335684 ... -1.82328592 -2.20113346\n -0.57266454]\n [-0.10658714 -1.49017079 -1.67791238 ... -1.82328592 -0.87824706\n -0.57266454]]\n\n## tissueCellHPA\nnp.array: shape (20386, 189)\n\n[[ 2.0749595 -0.01084193 -0.01467305 ... 0.48441489 1.16131334\n 0.62403542]\n [ 0.0226513 -0.01084193 -0.01467305 ... -0.36092683 -0.44069869\n -0.25659493]\n [ 0.0226513 -0.01084193 -0.01467305 ... -0.36092683 -0.44069869\n -0.25659493]\n ...\n [ 0.0226513 -0.01084193 -0.01467305 ... -0.36092683 -0.44069869\n -0.25659493]\n [ 0.0226513 -0.01084193 -0.01467305 ... -0.36092683 -0.44069869\n -0.25659493]\n [ 0.0226513 -0.01084193 -0.01467305 ... -0.36092683 -0.44069869\n -0.25659493]]\n\n## tissueHPA\nnp.array: shape (20386, 62)\n\n[[ 2.0749595 1.12532653 1.08594146 ... 1.07799286 1.16131334\n 0.62403542]\n [ 0.0226513 -0.45370136 -0.49342663 ... -0.49604735 -0.44069869\n -0.25659493]\n [ 0.0226513 -0.45370136 -0.49342663 ... -0.49604735 -0.44069869\n -0.25659493]\n ...\n [ 0.0226513 -0.45370136 -0.49342663 ... -0.49604735 -0.44069869\n -0.25659493]\n [ 0.0226513 -0.45370136 -0.49342663 ... -0.49604735 -0.44069869\n -0.25659493]\n [ 0.0226513 -0.45370136 -0.49342663 ... -0.49604735 -0.44069869\n -0.25659493]]\n\n## RNAseqHPA\nnp.array: shape (20386, 61)\n\n[[-4.02508290e-01 -4.78013516e-01 -4.20137262e-01 ... -2.76648740e-01\n -3.15290044e-01 -6.00891684e-01]\n [ 5.32096259e-15 3.25942180e-15 3.51673001e-15 ... 5.21505197e-15\n 8.51075141e-15 6.15586650e-15]\n [ 5.32096259e-15 3.25942180e-15 3.51673001e-15 ... 5.21505197e-15\n 8.51075141e-15 6.15586650e-15]\n ...\n [-4.02508290e-01 -4.92992221e-01 -3.78700781e-01 ... -2.86889949e-01\n -6.34698518e-01 -5.30499838e-01]\n [ 5.32096259e-15 3.25942180e-15 3.51673001e-15 ... 5.21505197e-15\n 8.51075141e-15 6.15586650e-15]\n [ 5.32096259e-15 3.25942180e-15 3.51673001e-15 ... 5.21505197e-15\n 8.51075141e-15 6.15586650e-15]]\n\n## subcellularLocationHPA\nnp.array: shape (20386, 33)\n\n[[0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.]\n [0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.]\n [0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.]\n ...\n [0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.]\n [0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.]\n [0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.]]\n\n## sequence\nlist: len 20386\n['MMKFKPNQTRTYDREGFKKRAACLCFRSEQEDEVLLVSSSRYPDQWIVPGGGMEPEEEPGGAAVREVYEEAGVKGKLGRLLGIFEQNQDRKHRTYVYVLTVTEILEDWEDSVNIGRKREWFKVEDAIKVLQCHKPVHAEYLEKLKLGCSPANGNSTVPSLPDNNALFVTAAQTSGLPSSVR', 'MEAPAQLLFLLLLWLPDTTREIVMTQSPPTLSLSPGERVTLSCRASQSVSSSYLTWYQQKPGQAPRLLIYGASTRATSIPARFSGSGSGTDFTLTISSLQPEDFAVYYCQQDYNLP', 'MDMRVPAQLLGLLLLWLPGVRFDIQMTQSPSFLSASVGDRVSIICWASEGISSNLAWYLQKPGKSPKLFLYDAKDLHPGVSSRFSGRGSGTDFTLTIISLKPEDFAAYYCKQDFSYP', 'MAWTPLLFLTLLLHCTGSLSQLVLTQSPSASASLGASVKLTCTLSSGHSSYAIAWHQQQPEKGPRYLMKLNSDGSHSKGDGIPDRFSGSSSGAERYLTISSLQSEDEADYYCQTWGTGI', 'MSVPTMAWMMLLLGLLAYGSGVDSQTVVTQEPSFSVSPGGTVTLTCGLSSGSVSTSYYPSWYQQTPGQAPRTLIYSTNTRSSGVPDRFSGSILGNKAALTITGAQADDESDYYCVLYMGSGI']\n\n"
],
[
"sneakPeak2(outDict, n=0)",
"## uniprotID\nlist: len 20386\n\n## bioProcessUniprot\nnp.array: shape (20386, 12248)\n\n\n## cellCompUniprot\nnp.array: shape (20386, 1754)\n\n\n## molFuncUniprot\nnp.array: shape (20386, 4346)\n\n\n## domainUniprot\nnp.array: shape (20386, 2313)\n\n\n## motifUniprot\nnp.array: shape (20386, 819)\n\n\n## Bgee\nnp.array: shape (20386, 1147)\n\n\n## tissueCellHPA\nnp.array: shape (20386, 189)\n\n\n## tissueHPA\nnp.array: shape (20386, 62)\n\n\n## RNAseqHPA\nnp.array: shape (20386, 61)\n\n\n## subcellularLocationHPA\nnp.array: shape (20386, 33)\n\n\n## sequence\nlist: len 20386\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"---\n**Export**\n- v6.1 09/11/2021",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"versionRawLimitedImpute = '6-1'\n\n# logVersions['featuresEngineering'] = dict()\n# logVersions['featuresEngineering']['longVectors']=dict()\nlogVersions['featuresEngineering']['longVectors']['keepBinary'] = versionRawLimitedImpute\n\ndump_LogVersions(logVersions)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"with open(os.path.join(\n cfg['outputFeaturesEngineering'],\n \"longVectors_keepBinary_v{}.pkl\".format(versionRawLimitedImpute)\n), 'wb') as f:\n pickle.dump(outDict, f)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## WITH normalising binary features",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for feature in featuresDict:\n if featuresDict[feature]['isBinary']:\n featuresDict[feature]['normalise'] = True\n \nfeaturesDict",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"outDict2 = formatRawData(featuresDict=featuresDict, uniprotIDs=uniprotIDs, vectorsLengths=vectorsLengths)",
"bioProcessUniprot\n - initial dim: (20386, 12249)\n - merge with reference index list\n - new dim: (20386, 12248)\n - imputate with 0\n - normalise\ncellCompUniprot\n - initial dim: (20386, 1755)\n - merge with reference index list\n - new dim: (20386, 1754)\n - imputate with 0\n - normalise\nmolFuncUniprot\n - initial dim: (20386, 4347)\n - merge with reference index list\n - new dim: (20386, 4346)\n - imputate with 0\n - normalise\ndomainUniprot\n - initial dim: (20386, 2314)\n - merge with reference index list\n - new dim: (20386, 2313)\n - imputate with 0\n - normalise\nmotifUniprot\n - initial dim: (20386, 820)\n - merge with reference index list\n - new dim: (20386, 819)\n - imputate with 0\n - normalise\nBgee\n - initial dim: (19090, 1148)\n - merge with reference index list\n - new dim: (20386, 1147)\n - imputate with 0\n - normalise\ntissueCellHPA\n - initial dim: (10850, 190)\n - merge with reference index list\n - new dim: (20386, 189)\n - imputate with 0\n - normalise\ntissueHPA\n - initial dim: (10850, 63)\n - merge with reference index list\n - new dim: (20386, 62)\n - imputate with 0\n - normalise\nRNAseqHPA\n - initial dim: (18938, 62)\n - merge with reference index list\n - new dim: (20386, 61)\n - mean imputation\n - normalise\nsubcellularLocationHPA\n - initial dim: (12566, 34)\n - merge with reference index list\n - new dim: (20386, 33)\n - imputate with 0\n - normalise\nsequence\n - initial dim: (20386, 2)\n - merge with reference index list\n - new dim: (20386, 1)\n - no imputation: 0 NAs\n"
],
[
"sneakPeak2(outDict2)",
"## uniprotID\nlist: len 20386\n['A0A024RBG1', 'A0A075B6H7', 'A0A075B6H8', 'A0A075B6H9', 'A0A075B6I0']\n\n## bioProcessUniprot\nnp.array: shape (20386, 12248)\n\n[[-0.02323526 -0.01400898 -0.02215341 ... -0.01213184 -0.00700398\n -0.00990536]\n [-0.02323526 -0.01400898 -0.02215341 ... -0.01213184 -0.00700398\n -0.00990536]\n [-0.02323526 -0.01400898 -0.02215341 ... -0.01213184 -0.00700398\n -0.00990536]\n ...\n [-0.02323526 -0.01400898 -0.02215341 ... -0.01213184 -0.00700398\n -0.00990536]\n [-0.02323526 -0.01400898 -0.02215341 ... -0.01213184 -0.00700398\n -0.00990536]\n [-0.02323526 -0.01400898 -0.02215341 ... -0.01213184 -0.00700398\n -0.00990536]]\n\n## cellCompUniprot\nnp.array: shape (20386, 1754)\n\n[[-0.01400898 -0.01715827 -0.01213184 ... -0.00700398 -0.01213184\n -0.00700398]\n [-0.01400898 -0.01715827 -0.01213184 ... -0.00700398 -0.01213184\n -0.00700398]\n [-0.01400898 -0.01715827 -0.01213184 ... -0.00700398 -0.01213184\n -0.00700398]\n ...\n [-0.01400898 -0.01715827 -0.01213184 ... -0.00700398 -0.01213184\n -0.00700398]\n [-0.01400898 -0.01715827 -0.01213184 ... -0.00700398 -0.01213184\n -0.00700398]\n [-0.01400898 -0.01715827 -0.01213184 ... -0.00700398 -0.01213184\n -0.00700398]]\n\n## molFuncUniprot\nnp.array: shape (20386, 4346)\n\n[[-0.00990536 -0.00990536 -0.01853351 ... -0.00990536 -0.02101605\n -0.01213184]\n [-0.00990536 -0.00990536 -0.01853351 ... -0.00990536 -0.02101605\n -0.01213184]\n [-0.00990536 -0.00990536 -0.01853351 ... -0.00990536 -0.02101605\n -0.01213184]\n ...\n [-0.00990536 -0.00990536 -0.01853351 ... -0.00990536 -0.02101605\n -0.01213184]\n [-0.00990536 -0.00990536 -0.01853351 ... -0.00990536 -0.02101605\n -0.01213184]\n [-0.00990536 -0.00990536 -0.01853351 ... -0.00990536 -0.02101605\n -0.01213184]]\n\n## domainUniprot\nnp.array: shape (20386, 2313)\n\n[[-0.00990536 -0.00990536 -0.00990536 ... -0.00990536 -0.02426903\n -0.00990536]\n [-0.00990536 -0.00990536 -0.00990536 ... -0.00990536 -0.02426903\n -0.00990536]\n [-0.00990536 -0.00990536 -0.00990536 ... -0.00990536 -0.02426903\n -0.00990536]\n ...\n [-0.00990536 -0.00990536 -0.00990536 ... -0.00990536 -0.02426903\n -0.00990536]\n [-0.00990536 -0.00990536 -0.00990536 ... -0.00990536 -0.02426903\n -0.00990536]\n [-0.00990536 -0.00990536 -0.00990536 ... -0.00990536 -0.02426903\n -0.00990536]]\n\n## motifUniprot\nnp.array: shape (20386, 819)\n\n[[-0.00700398 -0.00700398 -0.00700398 ... -0.00700398 -0.00990536\n -0.0156629 ]\n [-0.00700398 -0.00700398 -0.00700398 ... -0.00700398 -0.00990536\n -0.0156629 ]\n [-0.00700398 -0.00700398 -0.00700398 ... -0.00700398 -0.00990536\n -0.0156629 ]\n ...\n [-0.00700398 -0.00700398 -0.00700398 ... -0.00700398 -0.00990536\n -0.0156629 ]\n [-0.00700398 -0.00700398 -0.00700398 ... -0.00700398 -0.00990536\n -0.0156629 ]\n [-0.00700398 -0.00700398 -0.00700398 ... -0.00700398 -0.00990536\n -0.0156629 ]]\n\n## Bgee\nnp.array: shape (20386, 1147)\n\n[[-0.10658714 0.68210993 0.64575424 ... 0.54472649 0.44463934\n 1.09760362]\n [-0.10658714 -1.49017079 -1.67791238 ... -1.82328592 0.44463934\n -0.57266454]\n [-0.10658714 -1.49017079 -1.67791238 ... -1.82328592 0.44463934\n -0.57266454]\n ...\n [-0.10658714 -0.76607722 -0.90335684 ... -1.82328592 -2.20113346\n -0.57266454]\n [-0.10658714 -0.76607722 -0.90335684 ... -1.82328592 -2.20113346\n -0.57266454]\n [-0.10658714 -1.49017079 -1.67791238 ... -1.82328592 -0.87824706\n -0.57266454]]\n\n## tissueCellHPA\nnp.array: shape (20386, 189)\n\n[[ 2.0749595 -0.01084193 -0.01467305 ... 0.48441489 1.16131334\n 0.62403542]\n [ 0.0226513 -0.01084193 -0.01467305 ... -0.36092683 -0.44069869\n -0.25659493]\n [ 0.0226513 -0.01084193 -0.01467305 ... -0.36092683 -0.44069869\n -0.25659493]\n ...\n [ 0.0226513 -0.01084193 -0.01467305 ... -0.36092683 -0.44069869\n -0.25659493]\n [ 0.0226513 -0.01084193 -0.01467305 ... -0.36092683 -0.44069869\n -0.25659493]\n [ 0.0226513 -0.01084193 -0.01467305 ... -0.36092683 -0.44069869\n -0.25659493]]\n\n## tissueHPA\nnp.array: shape (20386, 62)\n\n[[ 2.0749595 1.12532653 1.08594146 ... 1.07799286 1.16131334\n 0.62403542]\n [ 0.0226513 -0.45370136 -0.49342663 ... -0.49604735 -0.44069869\n -0.25659493]\n [ 0.0226513 -0.45370136 -0.49342663 ... -0.49604735 -0.44069869\n -0.25659493]\n ...\n [ 0.0226513 -0.45370136 -0.49342663 ... -0.49604735 -0.44069869\n -0.25659493]\n [ 0.0226513 -0.45370136 -0.49342663 ... -0.49604735 -0.44069869\n -0.25659493]\n [ 0.0226513 -0.45370136 -0.49342663 ... -0.49604735 -0.44069869\n -0.25659493]]\n\n## RNAseqHPA\nnp.array: shape (20386, 61)\n\n[[-4.02508290e-01 -4.78013516e-01 -4.20137262e-01 ... -2.76648740e-01\n -3.15290044e-01 -6.00891684e-01]\n [ 5.32096259e-15 3.25942180e-15 3.51673001e-15 ... 5.21505197e-15\n 8.51075141e-15 6.15586650e-15]\n [ 5.32096259e-15 3.25942180e-15 3.51673001e-15 ... 5.21505197e-15\n 8.51075141e-15 6.15586650e-15]\n ...\n [-4.02508290e-01 -4.92992221e-01 -3.78700781e-01 ... -2.86889949e-01\n -6.34698518e-01 -5.30499838e-01]\n [ 5.32096259e-15 3.25942180e-15 3.51673001e-15 ... 5.21505197e-15\n 8.51075141e-15 6.15586650e-15]\n [ 5.32096259e-15 3.25942180e-15 3.51673001e-15 ... 5.21505197e-15\n 8.51075141e-15 6.15586650e-15]]\n\n## subcellularLocationHPA\nnp.array: shape (20386, 33)\n\n[[-0.01400898 -0.12096565 -0.6468028 ... -0.06508804 -0.03641696\n -0.01715827]\n [-0.01400898 -0.12096565 -0.6468028 ... -0.06508804 -0.03641696\n -0.01715827]\n [-0.01400898 -0.12096565 -0.6468028 ... -0.06508804 -0.03641696\n -0.01715827]\n ...\n [-0.01400898 -0.12096565 -0.6468028 ... -0.06508804 -0.03641696\n -0.01715827]\n [-0.01400898 -0.12096565 -0.6468028 ... -0.06508804 -0.03641696\n -0.01715827]\n [-0.01400898 -0.12096565 -0.6468028 ... -0.06508804 -0.03641696\n -0.01715827]]\n\n## sequence\nlist: len 20386\n['MMKFKPNQTRTYDREGFKKRAACLCFRSEQEDEVLLVSSSRYPDQWIVPGGGMEPEEEPGGAAVREVYEEAGVKGKLGRLLGIFEQNQDRKHRTYVYVLTVTEILEDWEDSVNIGRKREWFKVEDAIKVLQCHKPVHAEYLEKLKLGCSPANGNSTVPSLPDNNALFVTAAQTSGLPSSVR', 'MEAPAQLLFLLLLWLPDTTREIVMTQSPPTLSLSPGERVTLSCRASQSVSSSYLTWYQQKPGQAPRLLIYGASTRATSIPARFSGSGSGTDFTLTISSLQPEDFAVYYCQQDYNLP', 'MDMRVPAQLLGLLLLWLPGVRFDIQMTQSPSFLSASVGDRVSIICWASEGISSNLAWYLQKPGKSPKLFLYDAKDLHPGVSSRFSGRGSGTDFTLTIISLKPEDFAAYYCKQDFSYP', 'MAWTPLLFLTLLLHCTGSLSQLVLTQSPSASASLGASVKLTCTLSSGHSSYAIAWHQQQPEKGPRYLMKLNSDGSHSKGDGIPDRFSGSSSGAERYLTISSLQSEDEADYYCQTWGTGI', 'MSVPTMAWMMLLLGLLAYGSGVDSQTVVTQEPSFSVSPGGTVTLTCGLSSGSVSTSYYPSWYQQTPGQAPRTLIYSTNTRSSGVPDRFSGSILGNKAALTITGAQADDESDYYCVLYMGSGI']\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"---\n**Export**\n- v6.1 09/11/2021",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"versionRawImputeAll = '6-1'\n\nlogVersions['featuresEngineering']['longVectors']['imputeAll'] = versionRawImputeAll\n\ndump_LogVersions(logVersions)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"with open(os.path.join(\n cfg['outputFeaturesEngineering'],\n \"longVectors_imputeAll_v{}.pkl\".format(versionRawImputeAll)\n), 'wb') as f:\n pickle.dump(outDict, f)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a721d7b015eeaad217a9a02d3c221012f656db2
| 5,113 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
02_Python_Datatypes_examples/034_capitalize_the_first_character_of_a_string.ipynb
|
peterennis/90_Python_Examples
|
e2a5a4772ab47d8100b6f13713ea3bc9a25a1ee2
|
[
"MIT"
] | 70 |
2021-07-02T07:56:45.000Z
|
2022-03-19T04:13:31.000Z
|
02_Python_Datatypes_examples/034_capitalize_the_first_character_of_a_string.ipynb
|
bbeella/90_Python_Examples
|
fbbb1f484b676648881f4287e8175ce9f6224a5a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
02_Python_Datatypes_examples/034_capitalize_the_first_character_of_a_string.ipynb
|
bbeella/90_Python_Examples
|
fbbb1f484b676648881f4287e8175ce9f6224a5a
|
[
"MIT"
] | 51 |
2021-10-30T10:16:28.000Z
|
2022-03-19T04:11:05.000Z
| 25.187192 | 239 | 0.561314 |
[
[
[
"<small><small><i>\nAll the IPython Notebooks in this **Python Examples** series by Dr. Milaan Parmar are available @ **[GitHub](https://github.com/milaan9/90_Python_Examples)**\n</i></small></small>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Python Program to Capitalize the First Character of a String\n\nIn this example, you will learn to capitalize the first character of a string.\n\nTo understand this example, you should have the knowledge of the following Python programming topics:\n\nTo understand this example, you should have the knowledge of the following **[Python programming](https://github.com/milaan9/01_Python_Introduction/blob/main/000_Intro_to_Python.ipynb)** topics:\n\n* **[Python Strings](https://github.com/milaan9/02_Python_Datatypes/blob/main/002_Python_String.ipynb)**\n* **[Python Strings upper()](https://github.com/milaan9/02_Python_Datatypes/blob/main/002_Python_String_Methods/026_Python_String_upper%28%29.ipynb)**\n* **[Python Strings capitalize()](https://github.com/milaan9/02_Python_Datatypes/blob/main/002_Python_String_Methods/001_Python_String_capitalize%28%29.ipynb)**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Example 1: Using list slicing\n\nmy_string = \"python is Fun\"\n\nprint(my_string[0].upper() + my_string[1:])\n\n'''\n>>Output/Runtime Test Cases:\n \nPython is Fun\n'''",
"Python is Fun\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Explanation:** \n\nIn the above example, **`my_string[0]`** selects the first character and **`upper()`** converts it to uppercase. Likewise, **`my_string[1:]`** selects the remaining characters as they are. Finally they are concatenated using **`+`**.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Example 2: Using inbuilt method capitalize()\n\nmy_string = \"python is Fun\"\ncap_string = my_string.capitalize()\n\nprint(cap_string)\n\n'''\n>>Output/Runtime Test Cases:\n \nPython is fun\n'''",
"Python is fun\n"
]
],
[
[
">**Note:** **`capitalize()`** changes the first character to uppercase; however, changes all other characters to lowercase.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a721f933930cc4a3a89518a03b8b682cc5377e7
| 17,210 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
week1/notebooks/exercises/case_2.2_student/case_2.2_student.ipynb
|
japarra27/ds4a_2019
|
e20a7baecdeaea34711b0cbb569a60357a736b90
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
week1/notebooks/exercises/case_2.2_student/case_2.2_student.ipynb
|
japarra27/ds4a_2019
|
e20a7baecdeaea34711b0cbb569a60357a736b90
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
week1/notebooks/exercises/case_2.2_student/case_2.2_student.ipynb
|
japarra27/ds4a_2019
|
e20a7baecdeaea34711b0cbb569a60357a736b90
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2019-10-24T18:52:38.000Z
|
2019-10-24T18:52:38.000Z
| 43.903061 | 715 | 0.661302 |
[
[
[
"# Case 2.2\n## How do users engage with a mobile app for automobiles?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"_\"It is important to understand what you can do before you learn how to measure how well you seem to have done it.\" – J. Tukey\n\nAs we saw in the previous case, careful data vizualization (DV) can guide or even replace formal statistical analysis and model building. Here, we'll continue with more complex and computationally-intensive visualizations.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Introduction",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Business Context.** A recent trend among car manufacturers is to provide continued support through mobile applications. Features of these apps include services like remote ignition, GPS location, anti-theft mechanisms, maintenance reminders, and promotion pushes. Manufacturers are keen to maximize engagement with their app because they believe this increases relationship depth and brand loyalty with the customer. However, app usage is often limited, with many customers abandoning the app after only a short time period or never even opening it in the first place.\n\nYou are a data scientist for a large luxury automobile company. Your company wants you to uncover behavioral patterns of the users who engage with the app. They believe that if you can find discernible patterns, your company can leverage those insights to give users incentives to use the app more frequently.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Business Problem.** Your employer would like you to answer the following: **\"How do users currently engage with your mobile app and how has that engagement changed over time?\"** ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Analytical Context.** In this case, we will look at data on a subset of 105 customers (out of 1,000 total app users) for the first four weeks after installing the app. This small subset of the data is chosen as a representative sample. Data were collected as part off a beta version of the app.\n\nWe will not just present a catalog of different visualizations but rather, we will look at how domain questions can guide visualizations and how carefully constructed visualizations can generate new questions and insights.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## First look at the data\n\nAs always, let's begin by having a look at the data and computing a few summary statistics. The data set contains \n105 rows and 116 columns. Most of the columns represent app data collected on day $j$ ($1 \\le j \\le 28$):\n\n| Variable name| Description | Values |\n|--------------|--------------|------------|\n| age | Ordinal age, coded: 1 (<= 25), 2 (26-34), 3 (35-50), 4 (50+)| Int: 1-4 | \n| sex | Categorical sex | Char: F, M| \n| device_type | Android or OS X | String: Andr, X|\n| vehicle_class| Luxury or standard vehicle| String: Lx, Std|\n| p_views_j, j=1,...,28| Ordinal page views on day j| Int: 1-5 |\n| major_p_type_j, j=1,...,28| Majority page type| String: Main, Prom, Serv| \n| engagement_time_j, j=1,...,28| Ordinal engagement time per day | Int: 0-5|\n| drive_j, j=1,...,28| Indicator that user drove| Int: 0, 1|",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We see that a lot of the data are **ordinal variables**. An ordinal variable is a categorical variable where the categories are numbers and the relative values of those numbers matter; however, the absolute values of those numbers does not. In other words, for a given ordinal variable $x$, a larger numbered category means \"more of $x$\" than a smaller numbered category; however, the category number does not indicate the actual amount of $x$. For example, here `age` is coded as an ordinal variable; the categorical value of `3` clearly indicates \"more age\" than the categorical value of `1` (35 - 50 years of age vs. under 25 years of age), but the specific category value `3` or `1` is meaningless.\n\nBelow is some more information about some of the other variables:\n\n1. The only allowable mobile platforms are Android (coded `Andr`) or OS X (coded `X`) and this is collected automatically when the app is installed; thus, we expect this variable to have no missing values.\n2. The vehicle identification number was required to sign in and from this `vehicle_class` was automatically populated; thus, we also expect this variable to have no missing values.\n3. The variable `major_p_type_j` is the majority page type for the user on day j. In other words, it's the type of page which is viewed most often. It's coded as a categorical variable taking the values `Main` for maintenance, `Prom` for promotions, and `Serv` for services. Here, services means the app's services (e.g. automatic start, GPS location, etc.), rather than, say, scheduling an appointment to get the car serviced (which would be categorized as maintenance).\n\nFurthermore, a lot of the data here is \"opt-in\" only; that is, it is only recorded if the user was active on the app that day, and missing otherwise. For example, `p_views_j`, `major_p_type_j`, `engagement_time_j`, and `drive_j` are all \"opt-in\" variables.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Exercise 1:\n\nWhat is the significance of the variables mentioned above being opt-in? What insights can we derive from this?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Given this realization about the \"opt-in\" data, it makes sense for us to first understand patterns surrounding what data is missing.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Understanding and visualizing patterns in the missing data\n\nAs you saw in the Python cases, missing data is a staple of almost any dataset we will encounter. This one is no different. This dataset has substantial missing data, with nearly 60% of subjects missing a value for at least one column.\n\nA useful tool to look at the structure of missing data is a **missingness plot**, which is a grid where the rows correspond to individuals and the columns correspond to the variables (so in our case, this will be a 106 x 115 grid). \nThe $(i,j)$-th square of the grid is colored white if variable $j$ was missing for subject $i$. A first pass at a missingness plot gives us:\n\n<img src=\"img/missingnessPlotOne.png\" width=\"1200\">",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Question:\n\nDo you spot any patterns in the missing values here?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Exercise 2:\n\nWhat are some things you can do with the dataset to visualize the missing data better?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In light of this, let's remake the missingness plot with the similar variables grouped together:\n\n<img src=\"img/missingnessPlotTwo.png\" width=\"1200\">",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Exercise 3:\n\nWhat patterns do you notice here? Do these patterns make sense based on your understanding of the problem?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We can make the pattern from Exercise 2 even more apparent by not just grouping the \"opt-in\" data together by type of information conveyed, but by grouping them all together, regardless of type. In this case the missingness plot looks like:\n\n<img src=\"img/missingnessPlotThree.png\" width=\"1200\">",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Exercise 4:\n\nA natural question to ask is 'what percentage of users were still engaged as of a certain day?'. How can we modify the above plot to better visualize this?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<img src=\"img/missingnessPlotFour.png\" width=\"1200\">",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"From this plot it is immediately apparent that some subjects are dropping off and not returning; the data shows a **nearly monotone missingness pattern** which is useful for weighting and multiple imputation schemes (such methods are discussed in future cases on data wrangling). Furthermore, a significant proportion of users were engaged with the app throughout the entire 4-week period.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We now see the power of using contextual knowledge of the problem and dataset itself in the data visualization process. **The preceding four plots all contained the same underlying information, yet the later plots were clearly much easier to draw insights from than the earlier ones.**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Investigating in-app behavior",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Now that we've gleaned basic insights into whether or not users engage with the app at all, it's time to do a more detailed analysis of their behavior within the app. We'll start by looking at page views.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Evaluating patterns in page views\n\nTo stakeholders, page views are a key measure of engagement. Let's identify patterns in the number of page views per day. Recall that page views is an ordinal variable (ordered categorical variable) coded 1-5. Here 1 codes 0-1 actual page views, with 1 indicating that the app was opened and then closed without navigating past the splash page. For each person, we have a sequence of up to 28 observations. Let's first create a parallel coordinates plot with one line per subject:\n\n<img src=\"img/matplotOne.png\" width=\"1200\">\n\nThe preceding plot is extremely difficult to read. But we don't care so much about patterns for any individual user as much as the aggregate set of users. Thus, let's graph a line representing the average page views per person. The following plot shows this in black:\n\n<img src=\"img/matplotTwo.png\" width=\"1200\">\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Exercise 5:\n\nThere seems to be some kind of periodicity in the above smoothed plot. What might explain this pattern?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Clustering by user cohorts\n\nDomain experts who have run qualitative studies of user behavior believe that there are different groups, or **cohorts**, of users, where the users within a single cohort behave similarly. They believe that page view behavior would be more homogeneous within any given cohort. However, these cohorts are not directly observable.\n\nUsing clustering methods (which you will learn about in future cases), we have segregated the users into three groups based on their similarities: \n\n<img src=\"img/matplotG1.png\" width=\"1200\">\n<img src=\"img/matplotG2.png\" width=\"1200\">\n<img src=\"img/matplotG3.png\" width=\"1200\">",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Exercise 6:\n\nDescribe the page view behaviors within each cohort.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Exercise 7:\n\nWhich cohort of users do you think are more likely to look at promotional pages (major page type category `Prom`)?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Analyzing patterns in major page type\n\nLet's have a look at the major page type over time across our three user cohorts:\n\n<img src=\"img/pagetypeG1.png\" width=\"1200\">\n<img src=\"img/pagetypeG2.png\" width=\"1200\">\n<img src=\"img/pagetypeG3.png\" width=\"1200\">",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"From this, we can see that the third group is indeed the most engaged with the promotional pages.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Exercise 8:\n\nWhat are some potential next steps if you wanted to do a deep dive into user page view behavior? What additional data might you want to collect on users?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Predicting dropout from page view behavior\n\nBecause page view behavior is believed to be strongly related to engagement with the app and likelihood of discontinuation, we would like to see if we can predict the point of disengagement by analyzing the page view behavior within each cohort. We start by simply labeling the last observation (i.e. day of usage) for each subject with a large red dot:\n\n<img src=\"img/matplotMissingG1.png\" width=\"1100\">\n<img src=\"img/matplotMissingG2.png\" width=\"1100\">\n<img src=\"img/matplotMissingG3.png\" width=\"1100\">",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Exercise 9:\n\nDo you notice any patterns in page views preceding dropout?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Exercise 10:\n\nWork with a partner. Based on the preceding visualizations, propose an adaptive intervention strategy that monitors a user's page views and then offers them an incentive to continue using the app right when we believe that the incentive would have the most impact. Assume that you can offer at most one such incentive during the first four weeks of app use.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Conclusions\n\nWe explored usage and disengagement patterns among users of a mobile app for a car manufacturer. We saw that most users still remained engaged with the app even after 28 days, and that there were three significantly distinct cohorts of users. We used these patterns to generate ideas for intervention strategies that might be used to increase app usage and reduce disengagement. These visualizations are an excellent starting point for building statistical models or designing experiments to test theories about drivers of disengagement. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Takeaways",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In this case, you looked at more types of plots and how to draw conclusions from them. You also learned how these conclusions can drive further questions and plotting. Some key insights include: \n\n1. Sometimes it is important to reorder the data according to some variable in order to derive insights (as we saw with the missingness plot).\n2. Sometimes additional computation or data manipulation is required in order to tease a meaningful pattern from a data visualization (as we saw with the clustering & averaging for the parallel coordinates plots with the three cohorts).\n3. Domain knoweldge and understanding the context of the problem and data at hand is crucial. Without this, we would never have been able to create the visualizations we did and draw the conclusions we did from the missingness plot and the parallel coordinates plots.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4a722d9f16eecb4311f9472668b0afd1fdd08673
| 16,141 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Analysis/w2vec/w2vec - 500_embedding-v2.ipynb
|
gniehaus/NLP-Earning-Transcripts
|
0001109d388f411bde0fd43a11c65599fd02d5fb
|
[
"AFL-1.1"
] | null | null | null |
Analysis/w2vec/w2vec - 500_embedding-v2.ipynb
|
gniehaus/NLP-Earning-Transcripts
|
0001109d388f411bde0fd43a11c65599fd02d5fb
|
[
"AFL-1.1"
] | null | null | null |
Analysis/w2vec/w2vec - 500_embedding-v2.ipynb
|
gniehaus/NLP-Earning-Transcripts
|
0001109d388f411bde0fd43a11c65599fd02d5fb
|
[
"AFL-1.1"
] | null | null | null | 31.160232 | 264 | 0.517564 |
[
[
[
"import import_ipynb\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom FULL_DATA import final_df\nimport nltk\nnltk.download('punkt')\nfrom nltk.tokenize import sent_tokenize\nfrom nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize\nfrom nltk.probability import FreqDist\nfrom sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer\nfrom sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB\nfrom sklearn import metrics\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression\nfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier\nfrom nltk.corpus import stopwords",
"importing Jupyter notebook from FULL_DATA.ipynb\nimporting Jupyter notebook from Create_Labels.ipynb\n(6383, 4)\n4402\n(4402, 7)\n"
],
[
"#Making Labels\nfinal_df['SENTIMENT'] = [0 if (x > 1 and x<3.4999) else 1 if (x > 3.5 and x<4.49999) else -1 for x in final_df['ratings']]\nprint(final_df['SENTIMENT'].value_counts())\nprint(final_df.shape)\nfinal_df.head()",
" 1 2367\n 0 1144\n-1 866\nName: SENTIMENT, dtype: int64\n(4377, 8)\n"
],
[
"final_df['SENTIMENT'].value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# iterate through each sentence in the file \ndata = [] \nfor i in final_df['TRANSCRIPTS']: \n temp = [] \n # tokenize the sentence into words \n# print(i)\n for j in word_tokenize(i): \n if j in temp:\n pass\n elif j in stopwords.words('english'):\n pass\n else:\n temp.append(j.lower()) \n data.append(temp) \n#data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tf=TfidfVectorizer(lowercase=True,max_df = .9,min_df=.1,ngram_range = (1,1))\ntext_tf= tf.fit_transform(final_df['TRANSCRIPTS'])\ntfidf = dict(zip(tf.get_feature_names(), tf.idf_))\n# tfidf",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Word2Vec\nmax_len = 500\nfrom gensim.models import Word2Vec\nword2vec = Word2Vec(data, min_count=2,size = max_len, window = 5)\nvocabulary = word2vec.wv.vocab",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"avg_list = [] \nimport numpy as np\nfor i in final_df['TRANSCRIPTS']: \n vec = np.zeros(max_len).reshape((1, max_len))\n count = 0\n# print(\"iiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiii\",i)\n for j in word_tokenize(i):\n# print(j)\n try:\n vec += word2vec[j].reshape((1, max_len)) * tfidf[j]\n count += 1.\n except KeyError: \n continue\n if count != 0:\n vec /= count\n avg_list.append(vec[-1])",
"C:\\Users\\Chad\\Anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages\\ipykernel_launcher.py:10: DeprecationWarning: Call to deprecated `__getitem__` (Method will be removed in 4.0.0, use self.wv.__getitem__() instead).\n # Remove the CWD from sys.path while we load stuff.\n"
],
[
"import pandas as pd\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(\n pd.DataFrame(avg_list), final_df['SENTIMENT'], test_size=0.15, random_state=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from keras.utils import to_categorical\nnum_classes = 3\n\ny_train_adjusted = to_categorical(np.array(y_train), num_classes = num_classes)\ny_test_adjusted = to_categorical(np.array(y_test), num_classes = num_classes)",
"Using TensorFlow backend.\n"
],
[
"#Simple Feed-Forward\nimport tensorflow \nfrom tensorflow import keras\nfrom tensorflow.keras import Sequential\nfrom tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense\nfrom tensorflow.keras.layers import LSTM\nfrom tensorflow.keras.layers import Embedding\nfrom tensorflow.keras.layers import Dropout\nfrom tensorflow.keras.layers import Activation\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler\nfrom tensorflow.keras.preprocessing import sequence\nfrom tensorflow.keras.optimizers import SGD\n\nepochs = 1500\n#lr =.1\nnum_classes = 3\nmodel = Sequential()\nmodel.add(Dense(100, activation='sigmoid', input_dim=max_len))\nmodel.add(Dense(100, activation='relu'))\nmodel.add(Dense(num_classes, activation = 'softmax'))\n\n#sgd = SGD(lr=0.05, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True)\nmodel.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer = 'adam', metrics=['acc'])\nmodel.fit(np.array(X_train), y_train_adjusted, epochs=epochs, batch_size=32, verbose=0,validation_data=(np.array(X_test), y_test_adjusted), shuffle=False)",
"WARNING:tensorflow:From C:\\Users\\Chad\\Anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages\\tensorflow\\python\\ops\\resource_variable_ops.py:435: colocate_with (from tensorflow.python.framework.ops) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version.\nInstructions for updating:\nColocations handled automatically by placer.\nWARNING:tensorflow:From C:\\Users\\Chad\\Anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages\\tensorflow\\python\\ops\\math_ops.py:3066: to_int32 (from tensorflow.python.ops.math_ops) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version.\nInstructions for updating:\nUse tf.cast instead.\n"
],
[
"from sklearn import metrics",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"score = model.evaluate(X_test, y_test_adjusted, batch_size=32, verbose=2)\n\ny_prob = model.predict(X_test)\npredicted = np.argmax(y_prob, axis = 1)\n\nsklearn_y_test = np.argmax(y_test_adjusted, axis = 1)\n\nprint(\"Making Sure Accuracy is the same:\",metrics.accuracy_score(sklearn_y_test, predicted))\nprint(\"Feed-Foward Precision:\",metrics.precision_score(sklearn_y_test, predicted, average = 'weighted'))\nprint(\"Feed-Foward Recall:\",metrics.recall_score(sklearn_y_test, predicted, average = 'weighted'))\nprint(\"Feed-Foward F1:\",metrics.f1_score(sklearn_y_test, predicted, average = 'weighted'))",
" - 0s - loss: 3.3570 - acc: 0.6986\nMaking Sure Accuracy is the same: 0.6986301369863014\nFeed-Foward Precision: 0.6933117021780927\nFeed-Foward Recall: 0.6986301369863014\nFeed-Foward F1: 0.695207910276481\n"
],
[
"#For Report - Baseline\n'''\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\n\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(final_df['TRANSCRIPTS'], final_df['SENTIMENT'], test_size=0.15, random_state=1)\n\nprint(y_train)\nprint()\n'''\n \npredicted_baseline = np.full(y_test.size, 1)\n\nprint(\"Baseline Accuracy\",metrics.accuracy_score(y_test, predicted_baseline))\nprint(\"Baseline Precision:\",metrics.precision_score(y_test, predicted_baseline, average = 'weighted'))\nprint(\"Baseline Recall:\",metrics.recall_score(y_test, predicted_baseline, average = 'weighted'))\nprint(\"Baseline F1:\",metrics.f1_score(y_test, predicted_baseline, average = 'weighted'))",
"Baseline Accuracy 0.5601217656012176\nBaseline Precision: 0.31373639230022543\nBaseline Recall: 0.5601217656012176\nBaseline F1: 0.40219475071463046\n"
],
[
"#Printing Confusion Matrix - For Report\nprint(\"Confusion Matrix DL:\")\nprint(metrics.multilabel_confusion_matrix(sklearn_y_test, predicted))",
"Confusion Matrix DL:\n[[[436 59]\n [ 56 106]]\n\n [[199 90]\n [ 75 293]]\n\n [[481 49]\n [ 67 60]]]\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a723b94ed44c29ece472623eab1e98fe0eec903
| 3,209 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
examples/basic_course/06-GeomWF.ipynb
|
fcichos/pyoptools
|
ce0df42d45420f02d351e76d5f11fded4df8969d
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 1 |
2021-05-21T14:11:09.000Z
|
2021-05-21T14:11:09.000Z
|
examples/basic_course/06-GeomWF.ipynb
|
fcichos/pyoptools
|
ce0df42d45420f02d351e76d5f11fded4df8969d
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
examples/basic_course/06-GeomWF.ipynb
|
fcichos/pyoptools
|
ce0df42d45420f02d351e76d5f11fded4df8969d
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 2 |
2015-03-21T23:37:10.000Z
|
2018-10-22T18:03:57.000Z
| 21.393333 | 112 | 0.450296 |
[
[
[
"empty"
]
]
] |
[
"empty"
] |
[
[
"empty"
]
] |
4a724875577f24ac191347f080cc9239fba47091
| 67,014 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
10_Missing_Values/5_Krish_Naik/Missing_Values_titanic_HousePrice.ipynb
|
sureshmecad/Pandas
|
128091e7021158f39eb0ff97e0e63d76e778a52c
|
[
"CNRI-Python"
] | null | null | null |
10_Missing_Values/5_Krish_Naik/Missing_Values_titanic_HousePrice.ipynb
|
sureshmecad/Pandas
|
128091e7021158f39eb0ff97e0e63d76e778a52c
|
[
"CNRI-Python"
] | null | null | null |
10_Missing_Values/5_Krish_Naik/Missing_Values_titanic_HousePrice.ipynb
|
sureshmecad/Pandas
|
128091e7021158f39eb0ff97e0e63d76e778a52c
|
[
"CNRI-Python"
] | null | null | null | 50.462349 | 8,084 | 0.667905 |
[
[
[
"#### Arbitrary Value Imputation\n\nthis technique was derived from kaggle competition\nIt consists of replacing NAN by an arbitrary value",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df=pd.read_csv(\"titanic.csv\", usecols=[\"Age\",\"Fare\",\"Survived\"])\ndf.head()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def impute_nan(df,variable):\n df[variable+'_zero']=df[variable].fillna(0)\n df[variable+'_hundred']=df[variable].fillna(100)\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df['Age'].hist(bins=50)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
" \n### Advantages\n\n- Easy to implement\n- Captures the importance of missingess if there is one\n\n### Disadvantages\n\n- Distorts the original distribution of the variable\n- If missingess is not important, it may mask the predictive power of the original variable by distorting its distribution\n- Hard to decide which value to use",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## How To Handle Categroical Missing Values\n\n##### Frequent Category Imputation",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df.columns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df=pd.read_csv('loan.csv', usecols=['BsmtQual','FireplaceQu','GarageType','SalePrice'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.isnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.isnull().mean().sort_values(ascending=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Compute the frequency with every feature",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df['BsmtQual'].value_counts().plot.bar()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.groupby(['BsmtQual'])['BsmtQual'].count().sort_values(ascending=False).plot.bar()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df['GarageType'].value_counts().plot.bar()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df['FireplaceQu'].value_counts().plot.bar()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df['GarageType'].value_counts().index[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df['GarageType'].mode()[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def impute_nan(df,variable):\n most_frequent_category=df[variable].mode()[0]\n df[variable].fillna(most_frequent_category,inplace=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for feature in ['BsmtQual','FireplaceQu','GarageType']:\n impute_nan(df,feature)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.isnull().mean()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Advantages\n1. Easy To implement\n2. Fater way to implement\n#### Disadvantages\n1. Since we are using the more frequent labels, it may use them in an over respresented way, if there are many nan's\n2. It distorts the relation of the most frequent label",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"##### Adding a variable to capture NAN",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df=pd.read_csv('loan.csv', usecols=['BsmtQual','FireplaceQu','GarageType','SalePrice'])\ndf.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import numpy as np\ndf['BsmtQual_Var']=np.where(df['BsmtQual'].isnull(),1,0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df['BsmtQual'].mode()[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df['BsmtQual'].fillna(frequent,inplace=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df['FireplaceQu_Var']=np.where(df['FireplaceQu'].isnull(),1,0)\nfrequent=df['FireplaceQu'].mode()[0]\ndf['FireplaceQu'].fillna(frequent,inplace=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Suppose if you have more frequent categories, we just replace NAN with a new category",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df=pd.read_csv('loan.csv', usecols=['BsmtQual','FireplaceQu','GarageType','SalePrice'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def impute_nan(df,variable):\n df[variable+\"newvar\"]=np.where(df[variable].isnull(),\"Missing\",df[variable])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for feature in ['BsmtQual','FireplaceQu','GarageType']:\n impute_nan(df,feature)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df=df.drop(['BsmtQual','FireplaceQu','GarageType'],axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a7252206a49d85427a67d80912d09a5bc0d024d
| 743 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
colab/workshop_01.ipynb
|
kecbigmt/rollin-tech
|
c1d408f6195f80df2689b42dd007f7b5a2a6103f
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2018-02-04T11:44:34.000Z
|
2018-04-22T11:35:14.000Z
|
colab/workshop_01.ipynb
|
kecbigmt/rollin-tech
|
c1d408f6195f80df2689b42dd007f7b5a2a6103f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
colab/workshop_01.ipynb
|
kecbigmt/rollin-tech
|
c1d408f6195f80df2689b42dd007f7b5a2a6103f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 20.081081 | 131 | 0.45895 |
[
[
[
"[View in Colaboratory](https://colab.research.google.com/github/kecbigmt/rollin-tech/blob/master/colab/workshop_01.ipynb)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a7262795a0080ae970b4647d0f2b0197d019d90
| 679,595 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/MuscleModeling.ipynb
|
ajapplegate/BMC
|
7f60d36198c07acab805181511f37f31dfe13974
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | 1 |
2019-05-08T20:20:51.000Z
|
2019-05-08T20:20:51.000Z
|
notebooks/MuscleModeling.ipynb
|
ajapplegate/BMC
|
7f60d36198c07acab805181511f37f31dfe13974
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/MuscleModeling.ipynb
|
ajapplegate/BMC
|
7f60d36198c07acab805181511f37f31dfe13974
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | null | null | null | 387.675414 | 319,016 | 0.925688 |
[
[
[
"# Muscle modeling\n\n> Marcos Duarte \n> Laboratory of Biomechanics and Motor Control ([http://demotu.org/](http://demotu.org/)) \n> Federal University of ABC, Brazil",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"There are two major classes of muscle models that have been used in biomechanics and motor control: the Hill-type and Huxley-type models. They differ mainly on how the contractile element is modeled. In Hill-type models, the modeling of the contractile element is phenomenological; arbitrary mathematical functions are used to reproduce experimental observations relating muscle characteristics (such as excitation/activation, muscle length and velocity) with the muscle force. In Huxley-type models, the modeling of the contractile element is mechanistic; the mathematical functions used represent the hypothesized mechanisms for the cross-bridge dynamics (Tsianos and Loeb, 2013). Huxley-type models tend to produce more realistic results than Hill-type models for certain conditions but they have a higher computational demand. For this reason, Hill-type models are more often employed in musculoskeletal modeling and simulation. \n\nHill-type muscle models are presented in several texts (e.g., Erdermir et al. 2007; He et al., 1991; McMahon, 1984; Nigg and Herzog, 2007; Robertson et al., 2013, Thelen, 2003; Tsianos and Loeb, 2013, Winters, 1990; Zajac, 1989; Zatsiorsky and Prilutsky, 2012) and implemented in many software for modeling and simulation of the musculoskeletal dynamics of human movement (e.g., the free and open source software [OpenSim](https://simtk.org/home/opensim)). \n\nNext, let's see a brief overview of a Hill-type muscle model and a basic implementation in Python. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Hill-type muscle model\n\nHill-type models are developed to reproduce the dependence of force with the length and velocity of the muscle-tendon unit and parameters are lumped and made dimensionless in order to represent different muscles with few changes in these parameters. A Hill-type model is complemented with the modeling of the activation dynamics (i.e., the temporal pattern of muscle activation and deactivation as a function of the neural excitation) to produce more realistic results. As a result, the force generated will be a function of three factors: the length and velocity of the muscle-tendon unit and its activation level $a$. \n\nA Hill-type muscle model has three components (see figure below): two for the muscle, an active contractile element (CE) and a passive elastic element (PE) in parallel with the CE, and one component for the tendon, an elastic element (SE) in series with the muscle. In some variations, a damping component is added parallel to the CE as a fourth element. A [pennation angle](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Muscle_architecture) (angle of the pennate fibers with respect to the force-generating axis) is also included in the model. In a simpler approach, the muscle and tendon are assumed massless.\n\n<figure><img src=\"./../images/muscle_hill.png\" width=400 alt=\"Hill-type muscle model.\"/><figcaption><center><i>Figure. A Hill-type muscle model with three components: two for the muscle, an active contractile element, $\\mathsf{CE}$, and a passive elastic element in parallel, $\\mathsf{PE}$, with the $\\mathsf{CE}$, and one component for the tendon, an elastic element in series, $\\mathsf{SE}$, with the muscle. $\\mathsf{L_{MT}}$: muscle–tendon length, $\\mathsf{L_T}$: tendon length, $\\mathsf{L_M}$: muscle fiber length, $\\mathsf{F_T}$: tendon force, $\\mathsf{F_M}$: muscle force, and $α$: pennation angle.</i></center></figcaption>\n\nLet's now revise the models of a Hill-type muscle with three components and activation dynamics by two references: \n 1. [Thelen (2003)](http://simtk-confluence.stanford.edu:8080/display/OpenSim/Thelen+2003+Muscle+Model) with some of the adjustments described in Millard et al. (2013). Hereafter, Thelen2003Muscle or T03.\n 2. [McLean, Su, van den Bogert (2003)](http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14986412). Hereafter, McLean2003Muscle or M03.\n \nFirst, let's import the necessary Python libraries and customize the environment:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nfrom scipy.integrate import ode, odeint\n%matplotlib inline\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt \nimport matplotlib\nmatplotlib.rcParams['lines.linewidth'] = 3\nmatplotlib.rcParams['font.size'] = 13\nmatplotlib.rcParams['lines.markersize'] = 5\nmatplotlib.rc('axes', grid=True, labelsize=14, titlesize=16, ymargin=0.05)\nmatplotlib.rc('legend', numpoints=1, fontsize=11)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Force-length relationship\n\nIn a Hill-type model, the force a muscle can generate depends on its length due to two factors: \n\n1. The active force of the contractile element (CE), which in turn depends on the spatial superposition of the actin and myosin molecules to form cross-bridges at the sarcomere. A maximum number of cross-bridges will be formed at an optimal fiber length, generating a maximum force. When a fiber is too stretched or too shortened, fewer cross-bridges will be formed, decreasing the force generated. \n2. The passive and parallel elastic element (PE), which behaves as a nonlinear spring where no force is generated below a certain length (the slack length) and force increases with the muscle elongation.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Force-length relationship of the contractile element\n\nThelen2003Muscle represented the normalized force-length relationship of the contractile element by a Gaussian function:\n\n\\begin{equation}\n\\bar{f}_{l,CE} = exp\\left[-(\\bar{L}_M-1)^2/\\gamma\\right]\n\\label{}\n\\end{equation}\n\nwhere $\\gamma$ is a shape factor and $\\bar{L}_M$ is the muscle fiber length normalized by the optimal muscle fiber length at which maximal force can be produced, $L_{Mopt}$:\n\n\\begin{equation}\n\\bar{L}_M=\\dfrac{L_M}{L_{Mopt}}\n\\label{}\n\\end{equation}\n\nThelen2003Muscle adopted $\\gamma=0.45$. The actual force produced is obtained multiplying $\\bar{f}_{l,CE}$ by the maximum isometric muscle force, $F_{M0}$. Thelen2003Muscle assumed that the maximum isometric muscle forces for old adults were 30% lower than those used for young adults.\n\nMcLean2003Muscle represented the force-length relationship of the contractile element (not normalized) as a function of muscle length (not normalized) by a quadratic function:\n\n\\begin{equation}\nf_{l,CE} = max \\left\\{ \n \\begin{array}{l l}\n F_{Mmin} \\\\\n F_{M0}\\left[1 - \\left(\\dfrac{L_M-L_{Mopt}}{WL_{Mopt}}\\right)^2\\right]\n\\end{array} \\right.\n\\label{}\n\\end{equation}\n\nwhere $W$ is a dimensionless parameter describing the width of the force-length relationship. A minimum force level $F_{Mmin}$ is employed for numerical stability. \nMcLean2003Muscle adopted $W=1$ and $F_{Mmin}=10 N$. \n\nThe corresponding Python functions are:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def flce_T03(lm=1, gammal=0.45):\n \"\"\"Thelen (2003) force of the contractile element as function of muscle length.\n \n Parameters\n ----------\n lm : float, optional (default=1)\n normalized muscle fiber length\n gammal : float, optional (default=0.45)\n shape factor\n\n Returns\n -------\n fl : float\n normalized force of the muscle contractile element\n \"\"\"\n \n fl = np.exp(-(lm-1)**2/gammal)\n \n return fl",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def flce_M03(lm=1, lmopt=1, fm0=1, fmmin=0.001, wl=1):\n \"\"\"McLean (2003) force of the contractile element as function of muscle length.\n \n Parameters\n ----------\n lm : float, optional (default=1)\n muscle (fiber) length\n lmopt : float, optional (default=1)\n optimal muscle fiber length\n fm0 : float, optional (default=1)\n maximum isometric muscle force\n fmmin : float, optional (default=0.001)\n minimum muscle force\n wl : float, optional (default=1)\n shape factor of the contractile element force-length curve\n\n Returns\n -------\n fl : float\n force of the muscle contractile element\n \"\"\"\n \n fl = np.max([fmmin, fm0*(1 - ((lm - lmopt)/(wl*lmopt))**2)])\n \n return fl",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"And plots of these functions:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"lm = np.arange(0, 2.02, .02)\nfce_T03 = np.zeros(lm.size)\nfce_M03 = np.zeros(lm.size)\nfor i in range(len(lm)):\n fce_T03[i] = flce_T03(lm[i])\n fce_M03[i] = flce_M03(lm[i])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(7, 4))\nplt.plot(lm, fce_T03, 'b', label='T03')\nplt.plot(lm, fce_M03, 'g', label='M03')\nplt.xlabel('Normalized length')\nplt.ylabel('Normalized force')\nplt.legend(loc='best')\nplt.suptitle('Force-length relationship of the contractile element', y=1, fontsize=16)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Similar results when the same parameters are used.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Force-length relationship of the parallel element\n\nThelen2003Muscle represents the normalized force of the parallel (passive) element of the muscle as a function of muscle length (normalized by the optimal muscle fiber length) by an exponential function:\n\n\\begin{equation}\n\\bar{F}_{PE}(\\bar{L}_M) = \\dfrac{exp\\left[k_{PE}(\\bar{L}_M-1)/\\epsilon_{M0}\\right]-1}{exp(k_{PE})-1}\n\\label{}\n\\end{equation}\n\nwhere $k_{PE}$ is an exponential shape factor and $\\epsilon_{M0}$ is the passive muscle strain due to maximum isometric force:\n\n\\begin{equation}\n\\epsilon_{M0}=\\dfrac{L_M(F_{M0})-L_{Mslack}}{L_{Mslack}}\n\\label{}\n\\end{equation}\n\nwhere $L_{Mslack}$ is the muscle slack length. Thelen2003Muscle adopted $L_{Mslack} = L_{Mopt}$. \nThelen2003Muscle adopted $k_{PE}=5$ and $\\epsilon_{M0}=0.6$ for young adults ($\\epsilon_{M0}=0.5$ for old adults). The actual force produced is obtained multiplying $\\bar{F}_{PE}$ by the maximum isometric muscle force, $F_{M0}$.\n\nMcLean2003Muscle represents the force of the parallel (passive) element of the muscle (not normalized) as a function of muscle length (not normalized) by a quadratic function:\n\n\\begin{equation} \nF_{PE}(L_M) = \\left\\{ \n \\begin{array}{l l}\n 0 \\quad & \\text{if} \\quad L_M \\leq L_{Mslack} \\\\\n k_{PE}(L_M - L_{Mslack})^2 \\quad & \\text{if} \\quad L_M > L_{Mslack}\n\\end{array} \\right.\n\\label{}\n\\end{equation}\n\nwhere $k_{PE}$ is a stiffness parameter of the parallel element such that the passive muscle force is equal to the normalized maximum isometric force of the muscle when the CE is stretched to its maximal length for active force production:\n\n\\begin{equation}\nk_{PE} = \\dfrac{F_{M0}}{(WL_{Mopt})^2}\n\\label{}\n\\end{equation}\n\nMcLean2003Muscle adopted $L_{Mslack} = L_{Mopt}$.\n\nThe corresponding Python functions are:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def fpelm_T03(lm=1, kpe=5, epsm0=0.6):\n \"\"\"Thelen (2003) force of the muscle parallel element as function of muscle length.\n \n Parameters\n ----------\n lm : float, optional (default=1)\n normalized muscle fiber length\n kpe : float, optional (default=5)\n exponential shape factor\n epsm0 : float, optional (default=0.6)\n passive muscle strain due to maximum isometric force\n\n Returns\n -------\n fpe : float\n normalized force of the muscle parallel (passive) element\n \"\"\"\n \n if lm < 1:\n fpe = 0\n else:\n fpe = (np.exp(kpe*(lm-1)/epsm0)-1)/(np.exp(kpe)-1)\n \n return fpe",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def fpelm_M03(lm=1, lmopt=1, fm0=1, lmslack=1, wp=1):\n \"\"\"McLean (2003) force of the muscle parallel element as function of muscle length.\n \n Parameters\n ----------\n lm : float, optional (default=1)\n muscle fiber length\n lmopt : float, optional (default=1)\n optimal muscle (fiber) length\n fm0 : float, optional (default=1)\n maximum isometric muscle force\n lmslack : float, optional (default=1)\n muscle slack length\n wp : float, optional (default=1)\n shape factor of the parallel element force-length curve\n\n Returns\n -------\n fpe : float\n force of the muscle parallel (passive) element\n \"\"\"\n \n kpe = fm0/(wp*lmopt)**2\n if lm <= lmslack:\n fpe = 0\n else:\n fpe = kpe*(lm-lmslack)**2\n \n return fpe",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"And plots of these functions:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"lm = np.arange(0, 2.02, .02)\nfpe_T03 = np.zeros(lm.size)\nfpe_M03 = np.zeros(lm.size)\nfor i in range(len(lm)):\n fpe_T03[i] = fpelm_T03(lm[i])\n fpe_M03[i] = fpelm_M03(lm[i])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=2, sharex=True, sharey=True, figsize=(10, 4))\nax1.plot(lm[:86], fce_T03[:86], 'b', label='Active')\nax1.plot(lm[:86], fpe_T03[:86], 'r', label='Passive')\nax1.plot(lm[:86], fce_T03[:86] + fpe_T03[:86], 'g', label='Total')\nax1.text(0.1, 2.6, 'T03')\nax1.set_xlim([0, 1.7])\nax1.set_xlabel('Normalized length')\nax1.set_ylabel('Normalized force')\n#ax1.legend(loc='best')\nax2.plot(lm[:86], fce_M03[:86], 'b', label='Active')\nax2.plot(lm[:86], fpe_M03[:86], 'r', label='Passive')\nax2.plot(lm[:86], fce_M03[:86] + fpe_M03[:86], 'g', label='Total')\nax2.text(0.1, 2.6, 'M03')\nax2.set_xlim([0, 1.7])\nax2.set_xlabel('Normalized length')\nax2.legend(loc='best')\nplt.suptitle('Muscle force-length relationship', y=1, fontsize=16)\nplt.tight_layout()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The results are different at the maximum stretching because Thelen2003Muscle and McLean2003Muscle model differently the passive component. \nThese results were simulated for a maximum muscle activation (an activation level, $a$, of 1, where 0 is no activation). The effect of different activation levels on the total muscle force (but only the active force is affected) is shown in the next figure:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"lm = np.arange(0, 2.02, .02)\nfce_T03_als = np.zeros((lm.size, 5))\nals = [0, 0.25, 0.50, 0.75, 1.0]\nfor j, al in enumerate(als):\n for i in range(len(lm)):\n fce_T03_als[i, j] = flce_T03(lm[i])*al",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=1, sharex=True, sharey=True, figsize=(6, 5))\nfor j, al in enumerate(als):\n ax.plot(lm[:86], fce_T03_als[:86, j] + fpe_T03[:86], label='%.2f'%al)\nax.text(0.1, 2.6, 'T03')\nax.set_xlim([0, 1.7])\nax.set_xlabel('Normalized length')\nax.set_ylabel('Normalized force')\nax.legend(loc='best', title='Activation level')\nax.set_title('Muscle force-length relationship', y=1, fontsize=16)\nplt.tight_layout()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Force-length relationship of the series element (tendon)\n\nThelen2003Muscle represented the tendon force of the series element as a function of the normalized tendon length (in fact, tendon strain) by an exponential function during an initial nonlinear toe region and by a linear function thereafter:\n\n\\begin{equation}\n\\bar{F}_{SE}(\\bar{L}_T) = \\left\\{ \n \\begin{array}{l l}\n \\dfrac{\\bar{F}_{Ttoe}}{exp(k_{Ttoe})-1}\\left[exp(k_{Ttoe}\\epsilon_T/\\epsilon_{Ttoe})-1\\right] \\quad & \\text{if} \\quad \\epsilon_T \\leq \\epsilon_{Ttoe} \\\\\n k_{Tlin}(\\epsilon_T - \\epsilon_{Ttoe}) + \\bar{F}_{Ttoe} \\quad & \\text{if} \\quad \\epsilon_T > \\epsilon_{Ttoe}\n\\end{array} \\right.\n\\label{}\n\\end{equation}\n\nwhere $\\epsilon_{T}$ is the tendon strain:\n\n\\begin{equation}\n\\epsilon_{T} = \\dfrac{L_T-L_{Tslack}}{L_{Tslack}}\n\\label{}\n\\end{equation}\n\n$L_{Tslack}$ is the tendon slack length, $\\epsilon_{Ttoe}$ is the tendon strain above which the tendon exhibits linear behavior, $k_{Ttoe}$ is an exponential shape factor, and $k_{Tlin}$ is a linear scale factor. The parameters are chosen such that the tendon elongation at the normalized maximal isometric force of the muscle is 4% of the tendon length ($\\epsilon_{T0}=0.04$). \nThelen2003Muscle adopted $k_{Ttoe}=3$ and the transition from nonlinear to linear behavior occurs for normalized tendon forces greater than $\\bar{F}_{Ttoe}=0.33$. For continuity of slopes at the transition, $\\epsilon_{Ttoe}=0.609\\epsilon_{T0}$ and $k_{Tlin}=1.712/\\epsilon_{T0}$. The actual force produced is obtained multiplying $\\bar{F}_{SE}$ by the maximum isometric muscle force, $F_{M0}$.\n\nMcLean2003Muscle represented the tendon force (not normalized) of the series element as a function of the tendon length (not normalized) by the same quadratic function used for the force of the muscle passive element:\n\n\\begin{equation}\nF_{SE}(L_T) = \\left\\{ \n \\begin{array}{l l}\n 0 \\quad & \\text{if} \\quad L_T \\leq L_{Tslack} \\\\\n k_T(L_T - L_{Tslack})^2 \\quad & \\text{if} \\quad L_T > L_{Tslack}\n\\end{array} \\right.\n\\label{}\n\\end{equation}\n\nwhere $k_T$ is the tendon stiffness. The stiffness parameter $k_T$ is chosen such that the tendon elongation is 4% at the maximum isometric force, $k_T=(1/\\epsilon_{T0})^2=625$ for $F_{M0}=1$.\n\nThe corresponding Python functions are:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def fselt_T03(lt=1, ltslack=1, epst0=0.04, kttoe=3):\n \"\"\"Thelen (2003) force-length relationship of tendon as function of tendon length.\n \n Parameters\n ----------\n lt : float, optional (default=1)\n normalized tendon length\n ltslack : float, optional (default=1)\n normalized tendon slack length\n epst0 : float, optional (default=0.04)\n tendon strain at the maximal isometric muscle force\n kttoe : float, optional (default=3)\n linear scale factor\n\n Returns\n -------\n fse : float\n normalized force of the tendon series element\n \"\"\"\n\n epst = (lt-ltslack)/ltslack\n fttoe = 0.33\n # values from OpenSim Thelen2003Muscle\n epsttoe = .99*epst0*np.e**3/(1.66*np.e**3 - .67)\n ktlin = .67/(epst0 - epsttoe)\n #\n if epst <= 0:\n fse = 0\n elif epst <= epsttoe:\n fse = fttoe/(np.exp(kttoe)-1)*(np.exp(kttoe*epst/epsttoe)-1)\n else:\n fse = ktlin*(epst-epsttoe) + fttoe\n \n return fse",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def fselt_M03(lt, ltslack=1, fm0=1, epst0=0.04):\n \"\"\"McLean (2003) force-length relationship of tendon as function of tendon length.\n \n Parameters\n ----------\n lt : float, optional (default=1)\n tendon length\n ltslack : float, optional (default=1)\n tendon slack length\n fm0 : float, optional (default=1)\n maximum isometric muscle force\n epst0 : float, optional (default=0.04)\n tendon strain at the maximal isometric muscle force\n\n Returns\n -------\n fse : float\n force of the tendon series element\n \"\"\"\n\n kt = fm0/epst0**2\n if lt <= ltslack:\n fse = 0\n else:\n fse = kt*(lt-ltslack)**2\n \n return fse",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"And plots of these functions:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"lt = np.arange(1, 1.051, .001)\nfse_T03 = np.zeros(lt.size)\nfse_M03 = np.zeros(lt.size)\nfor i in range(len(lt)):\n fse_T03[i] = fselt_T03(lt[i])\n fse_M03[i] = fselt_M03(lt[i])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(7, 4))\nplt.plot(lt-1, fse_T03, 'b', label='T03')\nplt.plot(lt-1, fse_M03, 'g', label='M03')\nplt.plot(0.04, 1, 'ro', markersize=8)\nplt.text(0.04, 0.7, '$\\epsilon_{T0}$', fontsize=22)\nplt.xlabel('Tendon strain')\nplt.ylabel('Normalized force')\nplt.legend(loc='upper left')\nplt.suptitle('Tendon force-length relationship (series element)', y=1, fontsize=16)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Similar results when the same parameters are used.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Force-velocity relationship of the contractile element\n\nThe force-velocity relation of the contractile element for shortening (concentric activation) is based on the well known Hill's equation of a hyperbola describing that the product between force $F$ and velocity $V$ of the contractile element is constant (Winters, 1990; Winters, 1995):\n\n\\begin{equation}\n(F+a')(V+b') = (F_{0}+a')b'\n\\label{}\n\\end{equation}\n\nwhere $a'$, $b'$, and $F_{0}$ are constants. \n\nWe can rewrite the equation above with constants more meaningful to our modeling: \n\n\\begin{equation}\n(F_{M}+A_f F_{Mlen})(V_M+A_f V_{Mmax}) = A_f F_{Mlen}V_{Mmax}(1+A_f)\n\\label{}\n\\end{equation}\n\nwhere $F_{M}$ and $V_M$ are the contractile element force and velocity, respectively, and the three constants are: $V_{Mmax}$, the maximum unloaded velocity (when $F_{M}=0$), $F_{Mlen}$, the maximum isometric force (when $V_M=0$), and $A_f$, a shape factor which specifies the concavity of the hyperbola.\n\nBased on the equation above for the shortening phase and in Winters (1990, 1995) for the lengthening phase, Thelen2003Muscle employed the following force-velocity equation:\n\n\\begin{equation}\nV_M = (0.25+0.75a)\\,V_{Mmax}\\dfrac{\\bar{F}_M-a\\bar{f}_{l,CE}}{b}\n\\label{}\n\\end{equation}\n\nwhere\n\n\\begin{equation}\nb = \\left\\{ \n \\begin{array}{l l l}\n a\\bar{f}_{l,CE} + \\bar{F}_M/A_f \\quad & \\text{if} \\quad \\bar{F}_M \\leq a\\bar{f}_{l,CE} & \\text{(shortening)} \\\\\n \\\\\n \\dfrac{(2+2/A_f)(a\\bar{f}_{l,CE}\\bar{f}_{Mlen} - \\bar{F}_M)}{\\bar{f}_{Mlen}-1} \\quad & \\text{if} \\quad \\bar{F}_M > a\\bar{f}_{l,CE} & \\text{(lengthening)} \n\\end{array} \\right.\n\\label{}\n\\end{equation}\n\nwhere $a$ is the activation level and $\\bar{f}_{Mlen}$ is a constant for the maximum force generated at the lengthening phase (normalized by the maximum isometric force). \nThelen2003Muscle adopted $A_f=0.25$, $V_{Mmax}=10L_{Mopt}/s$, $\\bar{f}_{Mlen}=1.4$ for young adults ($V_{Mmax}=8L_{Mopt}/s$ and $\\bar{f}_{Mlen}=1.8$ for old adults). Note that the dependences of the force with the activation level and with the muscle length are already incorporated in the expression above. \n\nMcLean2013Muscle employed:\n\n\\begin{equation} \n\\bar{f}_{v,CE} = \\left\\{ \n \\begin{array}{l l l}\n \\dfrac{\\lambda(a)V_{Mmax} + V_M}{\\lambda(a)V_{Mmax} - V_M/A_f} \\quad & \\text{if} \\quad V_M \\leq 0 & \\text{(shortening)} \\\\\n \\\\\n \\dfrac{\\bar{f}_{Mlen}V_M + d_1}{V_M + d_1} \\quad & \\text{if} \\quad 0 < V_M \\leq \\gamma d_1 & \\text{(slow lengthening)} \\\\\n \\\\\n d_3 + d_2V_M \\quad & \\text{if} \\quad V_M > \\gamma d_1 & \\text{(fast lengthening)} \n\\end{array} \\right.\n\\label{}\n\\end{equation}\n\nwhere\n\n\\begin{equation}\n\\begin{array}{l l}\n \\lambda(a) = 1-e^{-3.82a} + a\\:e^{-3.82} \\\\\n \\\\\n d_1 = \\dfrac{V_{Mmax}A_f(\\bar{f}_{Mlen}-1)}{S(A_f+1)} \\\\\n \\\\\n d_2 = \\dfrac{S(A_f+1)}{V_{Mmax}A_f(\\gamma+1)^2} \\\\\n \\\\\n d_3 = \\dfrac{(\\bar{f}_{Mlen}-1)\\gamma^2}{(\\gamma+1)^2} + 1\n\\end{array}\n\\label{}\n\\end{equation}\n\nwhere $\\lambda(a)$ is a scaling factor to account for the influence of the activation level $a$ on the force-velocity relationship, $\\bar{f}_{Mlen}$ is the asymptotic (maximum) value of $\\bar{F}_M$, $S$ is a parameter to double the slope of the force-velocity curve at zero velocity, and $\\gamma$ is a dimensionless parameter to ensure the transition between the hyperbolic and linear parts of the lengthening phase. \nMcLean2013Muscle adopted $A_f=0.25$, $V_{Mmax}=10L_{Mopt}/s$, $\\bar{f}_{Mlen}=1.5$, $S=2.0$, and $\\gamma=5.67$.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Let's write these expressions as Python code and visualize them:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def vmfce_T03(fm, flce=1, lmopt=1, a=1, vmmax=1, fmlen=1.4, af=0.25):\n \"\"\"Thelen (2003) velocity of the force-velocity relationship as function of CE force.\n \n Parameters\n ----------\n fm : float\n normalized muscle force\n flce : float, optional (default=1)\n normalized muscle force due to the force-length relationship\n lmopt : float, optional (default=1)\n optimal muscle fiber length\n a : float, optional (default=1)\n muscle activation level\n vmmax : float, optional (default=1)\n maximum muscle velocity for concentric activation\n fmlen : float, optional (default=1.4)\n normalized maximum force generated at the lengthening phase\n af : float, optional (default=0.25)\n shape factor\n\n Returns\n -------\n vm : float\n velocity of the muscle\n \"\"\"\n \n vmmax = vmmax*lmopt\n if fm <= a*flce: # isometric and concentric activation\n b = a*flce + fm/af\n else: # eccentric activation\n b = (2 + 2/af)*(a*flce*fmlen - fm)/(fmlen - 1) \n vm = (0.25 + 0.75*a)*vmmax*(fm - a*flce)/b\n \n return vm",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's find an expression for contractile element force as function of muscle velocity given the equation above, i.e. we want to invert the equation. For that, let's use [Sympy](http://www.sympy.org/):",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def fvce_T03_symb():\n # Thelen (2003) velocity of the force-velocity relationship as function of CE force\n \n from sympy import symbols, solve, collect, Eq\n a, flce, fm, af, fmlen, vmmax = symbols('a, flce, fm, af, fmlen, vmmax', positive=True)\n vm = symbols('vm', real=True)\n \n b = a*flce + fm/af\n vm_eq = Eq(vm - (0.25 + 0.75*a)*vmmax*(fm - a*flce)/b)\n sol = solve(vm_eq, fm)\n print('fm <= a*flce:\\n', collect(sol[0], vmmax),'\\n')\n \n b = (2 + 2/af)*(a*flce*fmlen - fm)/(fmlen - 1)\n vm_eq = Eq(vm - (0.25 + 0.75*a)*vmmax*(fm - a*flce)/b)\n sol = solve(vm_eq, fm)\n print('fm > a*flce:\\n', collect(sol[0], (vmmax*af, fmlen, vm)))\n\nfvce_T03_symb()",
"fm <= a*flce:\n a*af*flce*(4.0*vm + vmmax*(3.0*a + 1))/(-4.0*vm + vmmax*(3.0*a*af + af)) \n\nfm > a*flce:\n a*flce*(af*vmmax*(3.0*a*fmlen - 3.0*a + fmlen - 1) + fmlen*(8.0*af*vm + 8.0*vm))/(af*vmmax*(3.0*a*fmlen - 3.0*a + fmlen - 1) + vm*(8.0*af + 8.0))\n"
]
],
[
[
"And here is the function we need to compute contractile element force as function of muscle velocity:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def fvce_T03(vm=0, flce=1, lmopt=1, a=1, vmmax=1, fmlen=1.4, af=0.25):\n \"\"\"Thelen (2003) force of the contractile element as function of muscle velocity.\n \n Parameters\n ----------\n vm : float, optional (default=0)\n muscle velocity\n flce : float, optional (default=1)\n normalized muscle force due to the force-length relationship\n lmopt : float, optional (default=1)\n optimal muscle fiber length\n a : float, optional (default=1)\n muscle activation level\n vmmax : float, optional (default=1)\n maximum muscle velocity for concentric activation\n fmlen : float, optional (default=1.4)\n normalized maximum force generated at the lengthening phase\n af : float, optional (default=0.25)\n shape factor\n\n Returns\n -------\n fvce : float\n normalized force of the muscle contractile element\n \"\"\"\n\n vmmax = vmmax*lmopt\n if vm <= 0: # isometric and concentric activation\n fvce = af*a*flce*(4*vm + vmmax*(3*a + 1))/(-4*vm + vmmax*af*(3*a + 1))\n else: # eccentric activation\n fvce = a*flce*(af*vmmax*(3*a*fmlen - 3*a + fmlen - 1) + 8*vm*fmlen*(af + 1))/\\\n (af*vmmax*(3*a*fmlen - 3*a + fmlen - 1) + 8*vm*(af + 1))\n \n return fvce",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Here is the Python function for the McLean (2003) model:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def fvce_M03(vm=0, lmopt=1, a=1, vmmax=1, fmlen=1.5, af=0.25, s=2, gammav=5.67):\n \"\"\"McLean (2003) contractile element force as function of muscle velocity.\n \n Parameters\n ----------\n vm : float, optional (default=0)\n muscle velocity\n lmopt : float, optional (default=1)\n optimal muscle fiber length\n a : float, optional (default=1)\n muscle activation level\n vmmax : float, optional (default=1)\n maximum muscle velocity for concentric activation\n fmlen : float, optional (default=1.5)\n normalized maximum force generated at the lengthening phase\n af : float, optional (default=0.25)\n shape factor\n s : float, optional (default=2)\n to double the slope of the force-velocity curve at zero velocity\n gammav : float, optional (default=5.67)\n to ensure the smooth transition of the lengthening phase\n\n Returns\n -------\n fvce : float\n normalized force of the muscle contractile element\n \"\"\"\n\n vmmax = vmmax*lmopt\n d1 = vmmax*af*(fmlen - 1)/(s*(af + 1))\n d2 = s*(af + 1)/(vmmax*af*(gammav + 1)**2)\n d3 = (fmlen - 1)*gammav**2/(gammav + 1)**2 + 1\n lbd = 1 - np.exp(-3.82*a) + a*np.exp(-3.82)\n if vm <= 0: # isometric and concentric activation\n fvce = (lbd*vmmax + vm)/(lbd*vmmax - vm/af)\n elif 0 < vm <= gammav*d1: # slow lengthening\n fvce = (fmlen*vm + d1)/(vm + d1)\n elif vm > gammav*d1: # fast lengthening\n fvce = d3 + d2*vm\n \n return fvce",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can invert this equation to get an expression for muscle velocity as function of the contractile element force:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def vmfce_M03(fvce=1, lmopt=1, a=1, vmmax=1, fmlen=1.5, af=0.25, s=2, gammav=5.67):\n \"\"\"McLean (2003) contractile element velocity as function of CE force.\n \n Parameters\n ----------\n fvce : float, optional (default=1)\n normalized muscle force\n lmopt : float, optional (default=1)\n optimal muscle fiber length\n a : float, optional (default=1)\n muscle activation level\n vmmax : float, optional (default=1)\n maximum muscle velocity for concentric activation\n fmlen : float, optional (default=1.5)\n normalized maximum force generated at the lengthening phase\n af : float, optional (default=0.25)\n shape factor\n s : float, optional (default=2)\n to double the slope of the force-velocity curve at zero velocity\n gammav : float, optional (default=5.67)\n to ensure the smooth transition of the lengthening phase\n\n Returns\n -------\n fvce : float\n muscle velocity\n \"\"\"\n \n vmmax = vmmax*lmopt\n d1 = vmmax*af*(fmlen - 1)/(s*(af + 1))\n d2 = s*(af + 1)/(vmmax*af*(gammav + 1)**2)\n d3 = (fmlen - 1)*gammav**2/(gammav + 1)**2 + 1\n lbd = 1 - np.exp(-3.82*a) + a*np.exp(-3.82)\n if 0 <= fvce <= 1: # isometric and concentric activation\n vm = (lbd*vmmax*(1 - fvce))/(1 + fvce/af)\n elif 1 < fvce <= gammav*d1*d2 + d3: # slow lengthening\n vm = d1*(fvce - 1)/(fmlen - fvce)\n elif fvce > gammav*d1*d2 + d3: # fast lengthening\n vm = (fvce - d3)/d2\n \n return vm",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's use these functions to compute muscle force as a function of the muscle velocity considering two levels of activation:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"vm1_T03 = np.linspace(-1, 1, 201)\nfce1_T03 = np.zeros(vm1_T03.size)\nvm2_T03 = np.linspace(-.63, .63, 201)\nfce2_T03 = np.zeros(vm2_T03.size)\nfor i in range(len(vm1_T03)):\n fce1_T03[i] = fvce_T03(vm=vm1_T03[i])\n fce2_T03[i] = fvce_T03(vm=vm2_T03[i], a=0.5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"vm1_M03 = np.linspace(-1, 1, 201)\nfce1_M03 = np.zeros(vm1_M03.size)\nvm2_M03 = np.linspace(-.63, .63, 201)\nfce2_M03 = np.zeros(vm2_M03.size)\nfor i in range(len(vm1_M03)):\n fce1_M03[i] = fvce_M03(vm=vm1_M03[i])\n fce2_M03[i] = fvce_M03(vm=vm2_M03[i], a=0.5)\nfce2_M03 = fce2_M03*0.5",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=2, sharex=True, sharey=True, figsize=(10, 4))\nax1.plot(vm1_T03, fce1_T03, 'b', label='T03)')\nax1.plot(vm1_M03, fce1_M03, 'g', label='M03)')\nax1.set_ylabel('Normalized force')\nax1.set_xlabel('Normalized velocity')\nax1.text(-.9, 1.5, 'Activation = 1.0')\nax2.plot(vm2_T03, fce2_T03, 'b', label='T03')\nax2.plot(vm2_M03, fce2_M03, 'g', label='M03')\nax2.text(-.9, 1.5, 'Activation = 0.5')\nax2.set_xlabel('Normalized velocity')\nax2.legend(loc='best')\nplt.suptitle('Force-velocity relationship of the contractile element', y=1.05, fontsize=16)\nplt.tight_layout()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Identical results for the shortening phase when $a=1$ and similar results for the lengthening phase when the same parameters are used.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Muscle power\n\nThe muscle power is the product between force and velocity:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"P_T03 = np.abs(fce1_T03*vm1_T03)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's visualize the muscle power only for the concentric phase (muscle shortening):",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(7, 4))\nplt.plot(vm1_T03[:101], fce1_T03[:101], 'b', label='Force')\nplt.xlabel('Normalized velocity')\nplt.ylabel('Normalized force', color='b')\n#plt.legend(loc='upper left')\nplt.gca().invert_xaxis()\nplt.gca().twinx()\nplt.plot(vm1_T03[:101], P_T03[:101], 'g', label='Power')\nplt.ylabel('Normalized power', color='g')\n#plt.legend(loc='upper right')\nplt.suptitle('Muscle power', y=1, fontsize=16)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Force-length-velocity relationship\n\nLet's visualize the effects of the length and velocity on the total (active plus passive) muscle force:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"lms = np.linspace(0, 1.65, 101)\nvms = np.linspace(-1, .76, 101)\nfce_T03 = np.zeros(lms.size)\nfpe_T03 = np.zeros(lms.size)\nfm_T03 = np.zeros((lms.size, vms.size))\nfor i in range(len(lms)):\n fce_T03[i] = flce_T03(lm=lms[i])\n fpe_T03[i] = fpelm_T03(lm=lms[i]) \n for j in range(len(vms)):\n fm_T03[j, i] = fvce_T03(vm=vms[j], flce=fce_T03[i]) + fpe_T03[i]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lms = np.linspace(0, 1.65, 101)\nvms = np.linspace(-1, .76, 101)\nfce_M03 = np.zeros(lms.size)\nfpe_M03 = np.zeros(lms.size)\nfm_M03 = np.zeros((lms.size, vms.size))\nfor i in range(len(lms)):\n fce_M03[i] = flce_M03(lm=lms[i])\n fpe_M03[i] = fpelm_M03(lm=lms[i]) \n for j in range(len(vms)):\n fm_M03[j, i] = fvce_M03(vm=vms[j])*fce_M03[i] + fpe_M03[i]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D\n\ndef flv3dplot(ax, lm, vm, fm, model):\n # 3d plot\n lm2, vm2 = np.meshgrid(lm, vm)\n ax.plot_surface(lm2, vm2, fm, rstride=2, cstride=2, cmap=plt.cm.coolwarm,\n linewidth=.5, antialiased=True)\n ax.plot(np.ones(vms.size), vms, fm[:, np.argmax(lm>=1)], 'w', linewidth=4)\n ax.plot(lm, np.zeros(lm.size), fm[np.argmax(vm>=0),:], 'w', linewidth=4)\n ax.set_xlim3d(lm[0], lm[-1])\n ax.set_ylim3d(vm[0], vm[-1])\n #ax.set_zlim3d(np.min(fm), np.max(fm))\n ax.set_zlim3d(0, 2)\n ax.set_xlabel('Normalized length')\n ax.set_ylabel('Normalized velocity')\n ax.set_zlabel('Normalized force')\n ax.view_init(20, 225)\n ax.locator_params(nbins=6)\n ax.text(-0.4, 0.7, 2.5, model, fontsize=14)\n \nfig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))\nax1 = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 1, projection='3d')\nflv3dplot(ax1, lms, vms, fm_T03, 'T03')\nax2 = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 2, projection='3d')\nflv3dplot(ax2, lms, vms, fm_M03, 'M03')\nplt.suptitle('Force-length-velocity relationship', y=1, fontsize=16)\nplt.tight_layout()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Activation dynamics\n\nActivation dynamics represents the fact that a muscle cannot instantly activate or deactivate because of the electrical and chemical processes involved and it is usually integrated with a Hill-type model. In its simplest form, the activation dynamics is generally represented as a first-order ODE. \n\nThelen2003Muscle employed the following first-order [ordinary differential equation (ODE)](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ordinary_differential_equation):\n\n\\begin{equation}\n\\frac{\\mathrm{d}a}{\\mathrm{d}t} = \\dfrac{u-a}{\\tau(a, u)}\n\\label{}\n\\end{equation}\n\nwith a lower activation bound to both activation and excitation.\n\nwhere $u$ and $a$ are the muscle excitation and activation, respectively (both are function of time), and $\\tau$ is a variable time constant to represent the activation and deactivation times, given by:\n\n\\begin{equation} \n\\tau(a, u) = \\left\\{ \n \\begin{array}{l l}\n t_{act}(0.5+1.5a) \\quad & \\text{if} \\quad u > a\\\\\n \\dfrac{t_{deact}}{(0.5+1.5a)} \\quad & \\text{if} \\quad u \\leq a\n\\end{array} \\right.\n\\label{}\n\\end{equation}\n\nThelen2003Muscle adopted activation, $t_{act}$, and deactivation, $t_{deact}$, time constants for young adults equal to 15 and 50 ms, respectively (for old adults, Thelen2003Muscle adopted 15 and 60 ms, respectively).\n\nMcLean2003Muscle expressed the activation dynamics as the following first-order ODE:\n\n\\begin{equation}\n\\dfrac{\\mathrm{d}a}{\\mathrm{d}t} = (u - a)(c_1u + c_2)\n\\label{}\n\\end{equation}\n\nwith a lower activation bound to both activation and excitation.\n\nwhere $c_1 + c_2$ is the activation rate constant (when $u = 1$), the inverse of $t_{act}$, and $c_2$ is the deactivation rate constant (when $u = 0$), the inverse of $t_{deact}$. \nMcLean2003Muscle adopted $c_1=3.3 s^{-1}$ and $c_2=16.7 s^{-1}$, resulting in time constants of 50 ms and 60 ms for activation and deactivation, respectively.\n\nIn Python, the numeric first-order ODE for the activation dynamics presented in Thelen2003Muscle can be expressed as:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def actdyn_T03(t, a, t_act, t_deact, u_max, u_min, t0=0, t1=1):\n \"\"\"Thelen (2003) activation dynamics, the derivative of `a` at `t`.\n\n Parameters\n ----------\n t : float\n time instant [s]\n a : float (0 <= a <= 1)\n muscle activation\n t_act : float\n activation time constant [s]\n t_deact : float\n deactivation time constant [s]\n u_max : float (0 < u_max <= 1), optional (default=1)\n maximum value for muscle excitation\n u_min : float (0 < u_min < 1), optional (default=0.01)\n minimum value for muscle excitation\n t0 : float [s], optional (default=0)\n initial time instant for muscle excitation equals to u_max\n t1 : float [s], optional (default=1)\n final time instant for muscle excitation equals to u_max\n\n Returns\n -------\n adot : float \n derivative of `a` at `t`\n \"\"\"\n\n u = excitation(t, u_max, u_min)\n if u > a:\n adot = (u - a)/(t_act*(0.5 + 1.5*a))\n else:\n adot = (u - a)/(t_deact/(0.5 + 1.5*a))\n\n return adot",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"In Python, the numeric first-order ODE for the activation dynamics presented in McLean2003Muscle can be expressed as:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def actdyn_M03(t, a, t_act, t_deact, u_max=1, u_min=0.01, t0=0, t1=1):\n \"\"\"McLean (2003) activation dynamics, the derivative of `a` at `t`.\n\n Parameters\n ----------\n t : float\n time instant [s]\n a : float (0 <= a <= 1)\n muscle activation\n t_act : float\n activation time constant [s]\n t_deact : float\n deactivation time constant [s]\n u_max : float (0 < u_max <= 1), optional (default=1)\n maximum value for muscle excitation\n u_min : float (0 < u_min < 1), optional (default=0.01)\n minimum value for muscle excitation\n t0 : float [s], optional (default=0)\n initial time instant for muscle excitation equals to u_max\n t1 : float [s], optional (default=1)\n final time instant for muscle excitation equals to u_max\n\n Returns\n -------\n adot : float \n derivative of `a` at `t`\n \"\"\"\n \n c2 = 1/t_deact\n c1 = 1/t_act - c2\n u = excitation(t, u_max, u_min)\n adot = (u - a)*(c1*u + c2)\n \n return adot",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's simulate the activation signal for a rectangular function as excitation signal:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def excitation(t, u_max=1, u_min=0.01, t0=0.1, t1=0.4):\n \"\"\"Excitation signal, a square wave.\n \n Parameters\n ----------\n t : float\n time instant [s]\n u_max : float (0 < u_max <= 1), optional (default=1)\n maximum value for muscle excitation\n u_min : float (0 < u_min < 1), optional (default=0.01)\n minimum value for muscle excitation\n t0 : float [s], optional (default=0.1)\n initial time instant for muscle excitation equals to u_max\n t1 : float [s], optional (default=0.4)\n final time instant for muscle excitation equals to u_max\n\n Returns\n -------\n u : float (0 < u <= 1)\n excitation signal\n \"\"\"\n \n u = u_min\n if t >= t0 and t <= t1:\n u = u_max\n \n return u",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We will solve the equation for $a$ by numerical integration using the [`scipy.integrate.ode`](http://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy-0.14.0/reference/generated/scipy.integrate.ode.html) class of numeric integrators, particularly the `dopri5`, an explicit runge-kutta method of order (4)5 due to Dormand and Prince (a.k.a. ode45 in Matlab):",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import warnings\ndef actdyn_ode45(fun, t0=0, t1=1, a0=0, t_act=0.015, t_deact=0.050, u_max=1, u_min=0.01):\n # Runge-Kutta (4)5 due to Dormand & Prince with variable stepsize ODE solver\n \n f = ode(fun).set_integrator('dopri5', nsteps=1, max_step=0.01, atol=1e-8) \n f.set_initial_value(a0, t0).set_f_params(t_act, t_deact, u_max, u_min)\n # suppress Fortran warning\n warnings.filterwarnings(\"ignore\", category=UserWarning)\n data = []\n while f.t < t1:\n f.integrate(t1, step=True)\n data.append([f.t, excitation(f.t, u_max, u_min), np.max([f.y, u_min])])\n warnings.resetwarnings()\n data = np.array(data)\n \n return data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Solving the problem for two different maximum excitation levels:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# using the values for t_act and t_deact from Thelen2003Muscle for both models\nact1_T03 = actdyn_ode45(fun=actdyn_T03, u_max=1.0)\nact2_T03 = actdyn_ode45(fun=actdyn_T03, u_max=0.5)\nact1_M03 = actdyn_ode45(fun=actdyn_M03, u_max=1.0)\nact2_M03 = actdyn_ode45(fun=actdyn_M03, u_max=0.5)\n# using the values for t_act and t_deact from McLean2003Muscle\nact3_M03 = actdyn_ode45(fun=actdyn_M03, u_max=1.0, t_act=0.050, t_deact=0.060)\nact4_M03 = actdyn_ode45(fun=actdyn_M03, u_max=0.5, t_act=0.050, t_deact=0.060)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"And the results:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"fig, axs = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2, sharex=True, sharey=True, figsize=(10, 6))\naxs[0, 0].plot(act1_T03[:, 0], act1_T03[:, 1], 'r:', label='Excitation')\naxs[0, 0].plot(act1_T03[:, 0], act1_T03[:, 2], 'b', label='T03 [15, 50] ms')\naxs[0, 0].plot(act1_M03[:, 0], act1_M03[:, 2], 'g', label='M03 [15, 50] ms')\naxs[0, 0].set_ylabel('Level')\naxs[0, 1].plot(act2_T03[:, 0], act2_T03[:, 1], 'r:', label='Excitation')\naxs[0, 1].plot(act2_T03[:, 0], act2_T03[:, 2], 'b', label='T03 [15, 50] ms')\naxs[0, 1].plot(act2_M03[:, 0], act2_M03[:, 2], 'g', label='M03 [15, 50] ms')\naxs[1, 1].set_xlabel('Time (s)')\naxs[0, 1].legend()\naxs[1, 0].plot(act1_T03[:, 0], act1_T03[:, 1], 'r:', label='Excitation')\naxs[1, 0].plot(act1_T03[:, 0], act1_T03[:, 2], 'b', label='T03 [15, 50] ms')\naxs[1, 0].plot(act3_M03[:, 0], act3_M03[:, 2], 'g', label='M03 [50, 60] ms')\naxs[1, 0].set_xlabel('Time (s)')\naxs[1, 0].set_ylabel('Level')\naxs[1, 1].plot(act2_T03[:, 0], act2_T03[:, 1], 'r:', label='Excitation')\naxs[1, 1].plot(act2_T03[:, 0], act2_T03[:, 2], 'b', label='T03 [15, 50] ms')\naxs[1, 1].plot(act4_M03[:, 0], act4_M03[:, 2], 'g', label='M03 [50, 60] ms')\naxs[1, 1].set_xlabel('Time (s)')\naxs[1, 1].legend()\nplt.suptitle('Activation dynamics', y=1, fontsize=16)\nplt.tight_layout()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Similar results when the same parameters are used (first row), but different bahavior when the typical values of each study are compared (second row).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Muscle modeling parameters\n\nWe have seen two types of parameters in the muscle modeling: parameters related to the mathematical functions used to model the muscle and tendon behavior and parameters related to the properties of specific muscles and tendons (e.g., maximum isometric force, optimal fiber length, pennation angle, and tendon slack). In general the first type of parameters are independent of the muscle-tendon unit being modeled (but dependent of the model!) while the second type of parameters is changed for each muscle-tendon unit (for instance, see http://isbweb.org/data/delp/ for some of these parameters).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Limitations of Hill-type muscle models\n\nAs with any modeling, Hill-type muscle models are a simplification of the reality. For instance, a typical Hill-type muscle model (as implemented here) does not capture time-dependent muscle behavior, such as force depression after quick muscle shortening, force enhancement after quick muscle lengthening, viscoelastic properties (creep and relaxation), and muscle fatigue (Zatsiorsky and Prilutsky, 2012). There are enhanced models that capture these properties but it seems their complexity are not worthy for the most common applications of human movement simulation.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Exercises\n\n1. The results presented in this text depend on the parameters used in the model. These parameters may vary because of different properties of the muscle and tendon but also because different mathematical functions may be used. \n a. Change some of the parameters and reproduce the plots shown here and discuss these results (e.g., use the parameters for different muscles from OpenSim or the data from [http://isbweb.org/data/delp/](http://isbweb.org/data/delp/)). \n b. Select another reference (e.g., Anderson, 2007) about muscle modeling that uses different mathematical functions and repeat the previous item.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## References\n\n- Anderson C (2007) [Equations for Modeling the Forces Generated by Muscles and Tendons](https://docs.google.com/viewer?url=https%3A%2F%2Fsimtk.org%2Fdocman%2Fview.php%2F124%2F604%2FMuscleAndTendonForcesClayAnderson20070521.doc) ([PDF](https://drive.google.com/open?id=0BxbW72zV7WmUVUh0MldGOGZ6aHc&authuser=0)). BioE215 Physics-based Simulation of Biological Structures. \n- Erdemir A, McLean S, Herzog W, van den Bogert AJ (2007) [Model-based estimation of muscle forces exerted during movements](http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17070969). Clinical Biomechanics, 22, 131–154. \n- He J, Levine WS, Loeb GE (1991) [Feedback gains for correcting small perturbations to standing posture](https://drive.google.com/open?id=0BxbW72zV7WmUekRXY09GSEhUVlE&authuser=0). IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 36, 322–332. \n- McLean SG, Su A, van den Bogert AJ (2003) [Development and validation of a 3-D model to predict knee joint loading during dynamic movement](http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14986412). Journal of Biomechanical Engineering, 125, 864-74. \n- McMahon TA (1984) [Muscles, Reflexes, and Locomotion](https://archive.org/details/McMahonTAMusclesReflexesAndLocomotionPrincetonUniversityPress1984). Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey. \n- Millard M, Uchida T, Seth A, Delp SL (2013) [Flexing computational muscle: modeling and simulation of musculotendon dynamics](http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23445050). Journal of Biomechanical Engineering, 135, 021005. \n- Nigg BM and Herzog W (2006) [Biomechanics of the Musculo-skeletal System](https://books.google.com.br/books?id=hOIeAQAAIAAJ&dq=editions:ISBN0470017678). 3rd Edition. Wiley. \n- Robertson G, Caldwell G, Hamill J, Kamen G (2013) [Research Methods in Biomechanics](http://books.google.com.br/books?id=gRn8AAAAQBAJ). 2nd Edition. Human Kinetics. \n- Thelen DG (2003) [Adjustment of muscle mechanics model parameters to simulate dynamic contractions in older adults](http://homepages.cae.wisc.edu/~thelen/pubs/jbme03.pdf). Journal of Biomechanical Engineering, 125(1):70–77.\n- Tsianos GA and Loeb GE (2013) [Muscle Physiology and Modeling](http://www.scholarpedia.org/article/Muscle_Physiology_and_Modeling). Scholarpedia, 8(10):12388. \n- Winters JM (1990) [Hill-based muscle models: a systems engineering perspective](http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007%2F978-1-4613-9030-5_5). In [Multiple Muscle Systems: Biomechanics and Movement Organization](http://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-1-4613-9030-5), edited by JM Winters and SL Woo, Springer-Verlag, New York. \n- Winters JM (1995) [An Improved Muscle-Reflex Actuator for Use in Large-Scale Neuromusculoskeletal Models](http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7486344). Annals of Biomedical Engineering, 23, 359–374. \n- Zajac FE (1989) [Muscle and tendon: properties, models, scaling and application to biomechanics and motor control](http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2676342). Critical Reviews in Biomedical Engineering 17:359-411. \n- Zatsiorsky V and Prilutsky B (2012) [Biomechanics of Skeletal Muscles](http://books.google.com.br/books?id=THXfHT8L5MEC). Human Kinetics. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4a7263641ab5bbc40f6fd168409dfcbfbd06ee50
| 39,041 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Resources/Generator/GenerateData.ipynb
|
British2/Supervised_Machine_Learning
|
bda9136f97c1dca5c56c9c019a80304fa00e0d31
|
[
"ADSL"
] | null | null | null |
Resources/Generator/GenerateData.ipynb
|
British2/Supervised_Machine_Learning
|
bda9136f97c1dca5c56c9c019a80304fa00e0d31
|
[
"ADSL"
] | null | null | null |
Resources/Generator/GenerateData.ipynb
|
British2/Supervised_Machine_Learning
|
bda9136f97c1dca5c56c9c019a80304fa00e0d31
|
[
"ADSL"
] | null | null | null | 61.38522 | 2,530 | 0.519659 |
[
[
[
"!wget https://resources.lendingclub.com/LoanStats_2019Q1.csv.zip\n!wget https://resources.lendingclub.com/LoanStats_2019Q2.csv.zip\n!wget https://resources.lendingclub.com/LoanStats_2019Q3.csv.zip\n!wget https://resources.lendingclub.com/LoanStats_2019Q4.csv.zip\n!wget https://resources.lendingclub.com/LoanStats_2020Q1.csv.zip",
"'wget' is not recognized as an internal or external command,\noperable program or batch file.\n'wget' is not recognized as an internal or external command,\noperable program or batch file.\n'wget' is not recognized as an internal or external command,\noperable program or batch file.\n'wget' is not recognized as an internal or external command,\noperable program or batch file.\n'wget' is not recognized as an internal or external command,\noperable program or batch file.\n"
],
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nfrom pathlib import Path\nfrom collections import Counter\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"columns = [\n \"loan_amnt\", \"int_rate\", \"installment\", \"home_ownership\", \"annual_inc\", \n \"verification_status\", \"pymnt_plan\", \"dti\", \"delinq_2yrs\", \n \"inq_last_6mths\", \"open_acc\", \"pub_rec\", \"revol_bal\", \"total_acc\", \n \"initial_list_status\", \"out_prncp\", \"out_prncp_inv\", \"total_pymnt\", \n \"total_pymnt_inv\", \"total_rec_prncp\", \"total_rec_int\", \n \"total_rec_late_fee\", \"recoveries\", \"collection_recovery_fee\", \n \"last_pymnt_amnt\", \"collections_12_mths_ex_med\", \"policy_code\", \n \"application_type\", \"acc_now_delinq\", \"tot_coll_amt\", \"tot_cur_bal\", \n \"open_acc_6m\", \"open_act_il\", \"open_il_12m\", \"open_il_24m\", \n \"mths_since_rcnt_il\", \"total_bal_il\", \"il_util\", \"open_rv_12m\", \n \"open_rv_24m\", \"max_bal_bc\", \"all_util\", \"total_rev_hi_lim\", \"inq_fi\", \n \"total_cu_tl\", \"inq_last_12m\", \"acc_open_past_24mths\", \"avg_cur_bal\", \n \"bc_open_to_buy\", \"bc_util\", \"chargeoff_within_12_mths\", \"delinq_amnt\", \n \"mo_sin_old_il_acct\", \"mo_sin_old_rev_tl_op\", \"mo_sin_rcnt_rev_tl_op\", \n \"mo_sin_rcnt_tl\", \"mort_acc\", \"mths_since_recent_bc\", \n \"mths_since_recent_inq\", \"num_accts_ever_120_pd\", \"num_actv_bc_tl\",\n \"num_actv_rev_tl\", \"num_bc_sats\", \"num_bc_tl\", \"num_il_tl\", \n \"num_op_rev_tl\", \"num_rev_accts\", \"num_rev_tl_bal_gt_0\", \"num_sats\", \n \"num_tl_120dpd_2m\", \"num_tl_30dpd\", \"num_tl_90g_dpd_24m\", \n \"num_tl_op_past_12m\", \"pct_tl_nvr_dlq\", \"percent_bc_gt_75\", \n \"pub_rec_bankruptcies\", \"tax_liens\", \"tot_hi_cred_lim\", \n \"total_bal_ex_mort\", \"total_bc_limit\", \"total_il_high_credit_limit\", \n \"hardship_flag\", \"debt_settlement_flag\",\n \"loan_status\"\n]\n\ntarget = \"loan_status\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Load the data\ndf1 = pd.read_csv(Path('../Resources/LoanStats_2019Q1.csv.zip'), skiprows=1)[:-2]\ndf2 = pd.read_csv(Path('../Resources/LoanStats_2019Q2.csv.zip'), skiprows=1)[:-2]\ndf3 = pd.read_csv(Path('../Resources/LoanStats_2019Q3.csv.zip'), skiprows=1)[:-2]\ndf4 = pd.read_csv(Path('../Resources/LoanStats_2019Q4.csv.zip'), skiprows=1)[:-2]\n\ndf = pd.concat([df1, df2, df3, df4]).loc[:, columns].copy()\n\n# Drop the null columns where all values are null\ndf = df.dropna(axis='columns', how='all')\n\n# Drop the null rows\ndf = df.dropna()\n\n# Remove the `Issued` loan status\nissued_mask = df['loan_status'] != 'Issued'\ndf = df.loc[issued_mask]\n\n# convert interest rate to numerical\ndf['int_rate'] = df['int_rate'].str.replace('%', '')\ndf['int_rate'] = df['int_rate'].astype('float') / 100\n\n\n# Convert the target column values to low_risk and high_risk based on their values\nx = {'Current': 'low_risk'} \ndf = df.replace(x)\n\nx = dict.fromkeys(['Late (31-120 days)', 'Late (16-30 days)', 'Default', 'In Grace Period'], 'high_risk') \ndf = df.replace(x)\n\n\nlow_risk_rows = df[df[target] == 'low_risk']\nhigh_risk_rows = df[df[target] == 'high_risk']\n\n#df = pd.concat([low_risk_rows, high_risk_rows.sample(n=len(low_risk_rows), replace=True)])\ndf = pd.concat([low_risk_rows.sample(n=len(high_risk_rows), random_state=42), high_risk_rows])\ndf = df.reset_index(drop=True)\ndf = df.rename({target:'target'}, axis=\"columns\")\ndf",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.to_csv('2019loans.csv', index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Load the data\nvalidate_df = pd.read_csv(Path('../Resources/LoanStats_2020Q1.csv.zip'), skiprows=1)[:-2]\nvalidate_df = validate_df.loc[:, columns].copy()\n\n# Drop the null columns where all values are null\nvalidate_df = validate_df.dropna(axis='columns', how='all')\n\n# Drop the null rows\nvalidate_df = validate_df.dropna()\n\n# Remove the `Issued` loan status\nissued_mask = validate_df[target] != 'Issued'\nvalidate_df = validate_df.loc[issued_mask]\n\n# convert interest rate to numerical\nvalidate_df['int_rate'] = validate_df['int_rate'].str.replace('%', '')\nvalidate_df['int_rate'] = validate_df['int_rate'].astype('float') / 100\n\n\n# Convert the target column values to low_risk and high_risk based on their values\nx = dict.fromkeys(['Current', 'Fully Paid'], 'low_risk') \nvalidate_df = validate_df.replace(x)\n\nx = dict.fromkeys(['Late (31-120 days)', 'Late (16-30 days)', 'Default', 'In Grace Period', 'Charged Off'], 'high_risk') \nvalidate_df = validate_df.replace(x)\n\nlow_risk_rows = validate_df[validate_df[target] == 'low_risk']\nhigh_risk_rows = validate_df[validate_df[target] == 'high_risk']\n\nvalidate_df = pd.concat([low_risk_rows.sample(n=len(high_risk_rows), random_state=37), high_risk_rows])\nvalidate_df = validate_df.reset_index(drop=True)\nvalidate_df = validate_df.rename({target:'target'}, axis=\"columns\")\nvalidate_df",
"Z:\\Travis\\anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages\\IPython\\core\\interactiveshell.py:3063: DtypeWarning: Columns (0,138,139,140) have mixed types.Specify dtype option on import or set low_memory=False.\n interactivity=interactivity, compiler=compiler, result=result)\n"
],
[
"validate_df.to_csv('2020Q1loans.csv', index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a727133377631d1a6bae2cac075041c47831f4c
| 7,732 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/report_wrangle.ipynb
|
janhenner/TwitterDataWrangling
|
d3e7e17712225816f206d02b6d605a8a1877cb5a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/report_wrangle.ipynb
|
janhenner/TwitterDataWrangling
|
d3e7e17712225816f206d02b6d605a8a1877cb5a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/report_wrangle.ipynb
|
janhenner/TwitterDataWrangling
|
d3e7e17712225816f206d02b6d605a8a1877cb5a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 86.876404 | 2,915 | 0.728919 |
[
[
[
"##### Internal Document\n# DAND Project WeRateDogs: Wrangling report",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"WeRateDogs is a Twitter account that rates people's dogs with a humorous comment about the dog. We wrangle the WeRateDogs Tweets. We provide a cleaned dataset for further analysis.\n\nWe combine three datasets:\n1. WeRateDogs Twitter archive download by WeRateDogs.\n2. Data downloaded using the Twitter API.\n3. Predictions of the pictures' content.\n\nConcerning 1: WeRateDogs downloaded their Twitter archive and sent it to Udacity. The format is CSV. Some enhancement of the data is included. Namely, from the Tweet texts, the dogs' names and dogs stages are extracted. Dogs stages are made up of dog categories from WeRateDogs.\n\nConcerning 2: Using the Twitter API all information from WeRateDogs can be downloaded. The exceptions are the enhancements mentioned under (1) and the predictions of the pictures.\n\nConcerning 3: The images in the WeRateDogs Twitter archive were run through a neural network to classify breeds of dogs. The data is provided as a link to TSV file. \n\nMuch Tweet information can be obtained through both (1) and (2). Because the ETL steps obtaining the data directly from the source are more transparent, we prefer to collect the data from the Twitter API. The API is called Tweepy.\n\nOur approach is to collect all the data which is available via the API. We select the relevant columns later. Thus we can easily expand the analysis to data not considered before.\n\nOur goal is to produce a high-quality dataset. We prefer a complete dataset over collecting as much data as possible. This means we combine the information from all sources and drop observations with missing data. Most notably, the predictions in (3) are only available up to August 2017. WeRateDogs started in November 2015. What we accept are missing dog names and dog stages.\n\nBased on the Tweet IDs in (1) we collect the data from the API. We do not filter the IDs we request over the API based on the date given in (1). Instead, we filter the date directly at the source: for each Tweet ID data is collected using the Twitter API. The data returned is only accepted when the tweet is from before 02.08.2017. Also, retweets are filtered here.\n\nThe Twitter API runs about 30 minutes to check 2,356 IDs in (1). Of those IDs, 2,325 are considered relevant. Additionally to the acceptance criteria mentioned, a small number of Tweets were deleted from Twitter as of 12.05.2019. Unexpectedly, the Twitter output contains a small 2-digit number of duplicates. One instance of the duplicates is dropped. Because of the runtime of data collection using the API, the data is stored on disc.\n\nData completeness and tidiness is reached combining all three datasets, dropping columns which are duplicated or not relevant for the analysis, and melting the dog stages. From this, we end up with 2,065 observations. That is the number of lines in (3) minus Tweets no more available.\n\nAssessing data quality, we decide to correct the data type for the Tweet creation timestamp and improve the rating information. The rating information is wrong e.g. when similar patterns are in the Tweet. An example is \"3 1/2 legged (...) 9/10\", where 9/10 is the rating. Rating denominator is not 10 when multiple dogs on a single picture are rated. Instead of scaling, due to the small number of such pictures those observations are dropped. After this, we are down to 2,045 observations.\n\nThe dogs' names are wrongly extracted in (1) for certain cases. Then wrongly \"a\", \"an\", and \"the\" are given as names. We correct these cases.\n\nThe cleaned dataset is stored in CSV format.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# words:\ntext = \"WeRateDogs is a Twitter account that rates people's dogs with a humorous comment about the dog. We wrangle the WeRateDogs Tweets. We provide a cleaned dataset for further analysis. We combine three datasets: 1. WeRateDogs Twitter archive download by WeRateDogs. 2. Data downloaded using the Twitter API. 3. Predictions of the pictures content. CMuch Tweet information can be obtained through both (1) and (2). Because the ETL steps obtaining the data directly from the source are more transparent, we prefer to collect the data from the Twitter API. The API is called Tweepy. Our approach is to collect all the data which is available via the API. We select the relevant columns later. Thus we can easily expand the analysis to data not considered before. Our goal is to produce a high quality dataset. We prefer a complete dataset over collecting as much data as possible. This means we combine the information from all sources and drop observations with missing data. Most notably, the predictions in (3) are only available up to August 2017. WeRateDogs was started November 2015. What we accept is missing dog names and dog stages.Based on the Tweet IDs in (1) we collect the data from the API. We do not filter the IDs we request over the API based on the date given in (1). Instead, we filter the date directly at the source: for each Tweet ID data is collected using the Twitter API. The data returned is only accepted when the tweet is from before 02.08.2017. Also retweets are filtered here.The Twitter API runs about 30 minutes to check 2,356 IDs in (1). Of those IDs 2,325 are considered relevant. Additionally to the acceptance criteria mentioned, a small amount of Tweets were deleted from Twitter as of 12.05.2019. Unexpectedly, the Twitter output contains a small 2-digit number of duplicates. One instance of the duplicates is dropped. Because of the runtime of data collection using the API, the data is stored on disc.Data completeness and tidiness is reached combining all three datasets, dropping columns which are duplicated or not relevant for the analysis, and melting the dog stages. From this we end up with 2,065 observations. That is the number of lines in (3) minus Tweets no more available. Assessing data quality, we decide to correct the data type for the Tweet creation timestamp and improve the rating information. The rating information is wrong e.g. when similar patterns are in the Tweet. An example is '3 1/2 legged (...) 9/10', where 9/10 is the rating. Ratings denominator is not 10 when multiple dogs on a single picture are rated. Instead of scaling, due to the small amount of such pictures those observations are dropped. After this we are down to 2,045 observations. The dogs names are wrongly extracted in (1) for certain cases. Then wrongly 'a', 'an', and 'the' are given as names. We correct these ceses. The cleaned dataset is stored in csv format.\"\nprint('This report has', len(text.split(' ')), 'words.')",
"This report has 491 words.\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a728439a8b1da6d19df29565b85981c15ea8ee1
| 3,904 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/Ch03_Processing_Wrangling_and_Visualizing_Data/notebook_website_crawler.ipynb
|
guptasanjeev/practical-machine-learning-with-python
|
bc42a88552128bc19c6852e1f4be1d718710a291
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1,989 |
2017-11-29T02:34:45.000Z
|
2022-03-30T18:18:51.000Z
|
notebooks/Ch03_Processing_Wrangling_and_Visualizing_Data/notebook_website_crawler.ipynb
|
guptasanjeev/practical-machine-learning-with-python
|
bc42a88552128bc19c6852e1f4be1d718710a291
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 29 |
2018-01-21T04:17:23.000Z
|
2022-03-17T10:59:50.000Z
|
notebooks/Ch03_Processing_Wrangling_and_Visualizing_Data/notebook_website_crawler.ipynb
|
guptasanjeev/practical-machine-learning-with-python
|
bc42a88552128bc19c6852e1f4be1d718710a291
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1,617 |
2017-12-22T16:13:58.000Z
|
2022-03-31T15:58:08.000Z
| 23.377246 | 513 | 0.548668 |
[
[
[
"# Crawling Web Pages\n\nThis notebook crawls apress.com's blog post to:\n+ extract content related to blog post using regex",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# import required libraries\nimport re\nimport requests",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Utility",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def extract_blog_content(content):\n \"\"\"This function extracts blog post content using regex\n\n Args:\n content (request.content): String content returned from requests.get\n\n Returns:\n str: string content as per regex match\n\n \"\"\"\n content_pattern = re.compile(r'<div class=\"cms-richtext\">(.*?)</div>')\n result = re.findall(content_pattern, content)\n return result[0] if result else \"None\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Crawl the Web",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Set the URL and blog post to be parsed",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"base_url = \"http://www.apress.com/in/blog/all-blog-posts\"\nblog_suffix = \"/wannacry-how-to-prepare/12302194\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Use requests library to make a get request",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"response = requests.get(base_url+blog_suffix)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Identify and Parse blog content using python's regex library (re)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"if response.status_code == 200:\n content = response.text.encode('utf-8', 'ignore').decode('utf-8', 'ignore')\n content = content.replace(\"\\n\", '')\n blog_post_content = extract_blog_content(content)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"View first 500 characters of the blogpost",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"blog_post_content[0:500]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a728b4891774371ca491d9824dfec102048a100
| 12,018 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/bytopic/xarray/01_getting_started_with_xarray.ipynb
|
jukent/ncar-python-tutorial
|
85c899e865c1861777e99764ef697219355e0585
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | 38 |
2019-09-10T05:00:52.000Z
|
2021-12-06T17:39:14.000Z
|
notebooks/bytopic/xarray/01_getting_started_with_xarray.ipynb
|
jukent/ncar-python-tutorial
|
85c899e865c1861777e99764ef697219355e0585
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | 60 |
2019-08-28T22:34:17.000Z
|
2021-01-25T22:53:21.000Z
|
notebooks/bytopic/xarray/01_getting_started_with_xarray.ipynb
|
NCAR/ncar-pangeo-tutorial
|
54d536d40cfaf6f8990c58edb438286c19d32a67
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | 22 |
2019-08-29T18:11:57.000Z
|
2021-01-07T02:23:46.000Z
| 36.978462 | 1,322 | 0.535031 |
[
[
[
"# Getting Started With Xarray",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<h1>Table of Contents<span class=\"tocSkip\"></span></h1>\n<div class=\"toc\"><ul class=\"toc-item\"><li><span><a href=\"#Getting-Started-With-Xarray\" data-toc-modified-id=\"Getting-Started-With-Xarray-1\"><span class=\"toc-item-num\">1 </span>Getting Started With Xarray</a></span><ul class=\"toc-item\"><li><span><a href=\"#Learning-Objectives\" data-toc-modified-id=\"Learning-Objectives-1.1\"><span class=\"toc-item-num\">1.1 </span>Learning Objectives</a></span></li><li><span><a href=\"#What-Is-Xarray?\" data-toc-modified-id=\"What-Is-Xarray?-1.2\"><span class=\"toc-item-num\">1.2 </span>What Is Xarray?</a></span></li><li><span><a href=\"#Core-Data-Structures\" data-toc-modified-id=\"Core-Data-Structures-1.3\"><span class=\"toc-item-num\">1.3 </span>Core Data Structures</a></span><ul class=\"toc-item\"><li><span><a href=\"#DataArray\" data-toc-modified-id=\"DataArray-1.3.1\"><span class=\"toc-item-num\">1.3.1 </span><code>DataArray</code></a></span></li><li><span><a href=\"#Dataset\" data-toc-modified-id=\"Dataset-1.3.2\"><span class=\"toc-item-num\">1.3.2 </span><code>Dataset</code></a></span></li></ul></li><li><span><a href=\"#Going-Further\" data-toc-modified-id=\"Going-Further-1.4\"><span class=\"toc-item-num\">1.4 </span>Going Further</a></span></li></ul></li></ul></div>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Learning Objectives\n\n- Provide an overview of xarray\n- Describe the core xarray data structures, the DataArray and the Dataset, and the components that make them up\n- Create xarray DataArrays/Datasets out of raw numpy arrays\n- Create xarray objects with and without indexes\n- View and set attributes",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## What Is Xarray?\n\n\nUnlabeled, N-dimensional arrays of numbers (e.g., NumPy’s ndarray) are the most widely used data structure in scientific computing. However, they lack a meaningful representation of the metadata associated with their data. Implementing such functionality is left to individual users and domain-specific packages. xarray is a useful tool for parallelizing and working with large datasets in the geosciences. xarry expands on the capabilities of NumPy arrays, providing a lot of streamline data manipulation.\n\nXarray's interface is based largely on the netCDF data model (variables, attributes, and dimensions), but it goes beyond the traditional netCDF interfaces to provide functionality similar to netCDF-java's Common Data Model (CDM).\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n## Core Data Structures\n\n\n- xarray has 2 fundamental data structures:\n - `DataArray`, which holds single multi-dimensional variables and its coordinates\n - `Dataset`, which holds multiple variables that potentially share the same coordinates\n \n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n \n### `DataArray`\n\nThe DataArray is xarray's implementation of a labeled, multi-dimensional array. It has several key properties:\n\n| Attribute \t| Description \t|\n|-----------\t|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\t|\n| `data` \t| `numpy.ndarray` or `dask.array` holding the array's values. \t|\n| `dims` \t| dimension names for each axis. For example:(`x`, `y`, `z`) (`lat`, `lon`, `time`). \t|\n| `coords` \t| a dict-like container of arrays (coordinates) that label each point (e.g., 1-dimensional arrays of numbers, datetime objects or strings) \t|\n| `attrs` \t| an `OrderedDict` to hold arbitrary attributes/metadata (such as units) \t|\n| `name` \t| an arbitrary name of the array \t|",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import packages\nimport numpy as np\nimport xarray as xr",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create some sample data\ndata = 2 + 6 * np.random.exponential(size=(5, 3, 4))\ndata",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"To create a basic `DataArray`, you can pass this numpy array of random data to `xr.DataArray`",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"prec = xr.DataArray(data)\nprec",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<div class=\"alert alert-block alert-warning\">\n \nXarray automatically generates some basic dimension names for us.\n\n</div>\n\nYou can also pass in your own dimension names and coordinate values:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Use pandas to create an array of datetimes\nimport pandas as pd\ntimes = pd.date_range('2019-04-01', periods=5)\ntimes",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Use numpy to create array of longitude and latitude values\nlons = np.linspace(-150, -60, 4)\nlats = np.linspace(10, 80, 3)\nlons, lats",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"coords = {'time': times, 'lat': lats, 'lon': lons}\ndims = ['time', 'lat', 'lon']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Add name, coords, dims to our data\nprec = xr.DataArray(data, dims=dims, coords=coords, name='prec')\nprec",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This is already improved upon from the original numpy array, because we have names for each of the dimensions (or axis in NumPy parlance). \n\nWe can also add attributes to an existing `DataArray`:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"prec.attrs['units'] = 'mm'\nprec.attrs['standard_name'] = 'precipitation'\nprec",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### `Dataset`\n\n- Xarray's `Dataset` is a dict-like container of labeled arrays (`DataArrays`) with aligned dimensions. - It is designed as an in-memory representation of a netCDF dataset. \n- In addition to the dict-like interface of the dataset itself, which can be used to access any `DataArray` in a `Dataset`. Datasets have the following key properties:\n\n\n| Attribute \t| Description \t|\n|-------------\t|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\t|\n| `data_vars` \t| OrderedDict of `DataArray` objects corresponding to data variables. \t|\n| `dims` \t| dictionary mapping from dimension names to the fixed length of each dimension (e.g., {`lat`: 6, `lon`: 6, `time`: 8}). \t|\n| `coords` \t| a dict-like container of arrays (coordinates) that label each point (e.g., 1-dimensional arrays of numbers, datetime objects or strings) \t|\n| `attrs` \t| OrderedDict to hold arbitrary metadata pertaining to the dataset. \t|\n| `name` \t| an arbitrary name of the dataset \t|",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"- DataArray objects inside a Dataset may have any number of dimensions but are presumed to share a common coordinate system. \n- Coordinates can also have any number of dimensions but denote constant/independent quantities, unlike the varying/dependent quantities that belong in data.\n\n\nTo create a `Dataset` from scratch, we need to supply dictionaries for any variables (`data_vars`), coordinates (`coords`) and attributes (`attrs`):",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dset = xr.Dataset({'precipitation' : prec})\ndset",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's add some toy `temperature` data array to this existing dataset:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"temp_data = 283 + 5 * np.random.randn(5, 3, 4)\ntemp = xr.DataArray(data=temp_data, dims=['time', 'lat', 'lon'],\n coords={'time': times, 'lat': lats, 'lon': lons},\n name='temp',\n attrs={'standard_name': 'air_temperature', 'units': 'kelvin'})\ntemp",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Now add this data array to our existing dataset\ndset['temperature'] = temp\ndset.attrs['history'] = 'Created for the xarray tutorial'\ndset.attrs['author'] = 'foo and bar'\ndset",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Going Further\n \nXarray Documentation on Data Structures: http://xarray.pydata.org/en/latest/data-structures.html\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<div class=\"alert alert-block alert-success\">\n <p>Next: <a href=\"02_io.ipynb\">I/O</a></p>\n</div>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4a7297b7f9d1968cfa62a2369b603ed5ecd3d658
| 68,139 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/Reverse-path-tool.ipynb
|
alphagov/govuk-user-journey-analysis-tools
|
3c83478df2f463053ad3f6ced6ab63d90d0a372e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/Reverse-path-tool.ipynb
|
alphagov/govuk-user-journey-analysis-tools
|
3c83478df2f463053ad3f6ced6ab63d90d0a372e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/Reverse-path-tool.ipynb
|
alphagov/govuk-user-journey-analysis-tools
|
3c83478df2f463053ad3f6ced6ab63d90d0a372e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 50.398669 | 555 | 0.585304 |
[
[
[
"# Reporting on user journeys to a GOV.UK page\n\nCalculate the count and proportion of sessions that have the same journey behaviour.\n\nThis script finds sessions that visit a specific page (`DESIRED_PAGE`) in their journey. From the first or last visit to\n`DESIRED_PAGE` in the session, the journey is subsetted to include the last N pages including `DESIRED_PAGE`\n(`NUMBER_OF_STAGES`). \n\nThe count and proportion of sessions visiting distinct, subsetted journeys are compiled together, and returned as a\nsorted list in descending order split by subsetted journeys including the entrance page.\n\n## Arguments\n\n- `START_DATE`: String in YYYYMMDD format defining the start date of your query.\n- `END_DATE`: String in YYYYMMDD format defining the end date of your query.\n- `DESIRED_PAGE`: String of the desired GOV.UK page path of interest.\n- `FIRST_HIT`: Boolean flag indicating that the `FIRST` hit to the `DESIRED_PAGE` in the session is used for the subsetted journey. If this option is selected, `LAST_HIT` cannot be selected. \n- `LAST_HIT`: Boolean flag indicating that the `LAST` hit to the `DESIRED_PAGE` in the session is used for the subsetted journey. If this option is selected, `FIRST_HIT` cannot be selected. \n- `NUMBER_OF_STAGES`: Integer defining how many pages in the past (including `DESIRED_PAGE`) should be considered when subsetting the user journeys. Note that journeys with fewer pages than `NUMBER_OF_STAGES` will always be included.\n- `PAGE_TYPE`: Boolean flag indicating that `PAGE` page paths are required. One of `PAGE_TYPE` or `EVENT_TYPE` must be selected.\n- `EVENT_TYPE`: Boolean flag indicating that `EVENT` page paths are required. One of `PAGE_TYPE` or `EVENT_TYPE` must be selected.\n- `DEVICE_DESKTOP`: Boolean flag indicating that desktop devices should be included in this query. One of `DEVICE_DESKTOP`, `DEVICE_MOBILE`, `DEVICE_TABLET`, or `DEVICE_ALL` must be selected. However, `DEVICE_TABLET` cannot be selected if `DEVICE_ALL` is selected.\n- `DEVICE_MOBILE`: Boolean flag indicating that mobile devices should be included in this query. One of `DEVICE_DESKTOP`, `DEVICE_MOBILE`, `DEVICE_TABLET`, or `DEVICE_ALL` must be selected. However, `DEVICE_MOBILE` cannot be selected if `DEVICE_ALL` is selected.\n- `DEVICE_TABLET`: Boolean flag indicating that tablet devices should be included in this query. One of `DEVICE_DESKTOP`, `DEVICE_MOBILE`, `DEVICE_TABLET`, or `DEVICE_ALL` must be selected. However, `DEVICE_TABLET` cannot be selected if `DEVICE_ALL` is selected.\n- `DEVICE_ALL`: Boolean flag indicating that all devices should be segmented but included in this query. One of `DEVICE_DESKTOP`, `DEVICE_MOBILE`, `DEVICE_TABLET`, or `DEVICE_ALL` must be selected. However, `DEVICE_ALL` cannot be selected if `DEVICE_DESKTOP`, `DEVICE_MOBILE`, or `DEVICE_TABLET` is selected. \n\n### Optional arguments\n\n- `QUERY_STRING`: Boolean flag. If `TRUE`, remove query strings from all page paths. If `FALSE`, keep query strings in all page paths. \n- `FLAG_EVENTS`: Boolean flag. If `TRUE`, all `EVENT` page paths will have a ` [E]` suffix. This is useful if both `PAGE_TYPE` and `EVENT_TYPE` are selected, so you can differentiate between the same page path with different types. If `FALSE`, no suffix is appended to `EVENT` page paths.\n- `EVENT_CATEGORY`: Boolean flag. If `TRUE`, all event categorys will be displayed. \n- `EVENT_ACTION`: Boolean flag. If `TRUE`, all event actions will be displayed. \n- `EVENT_LABEL`: Boolean flag. If `TRUE`, all event labels will be displayed. \n- `ENTRANCE_PAGE`: Boolean flag. If `TRUE`, if the subsetted journey contains the entrance page this is flagged. \n- `EXIT_PAGE`: Boolean flag. If `TRUE`, if the subsetted journey contains the exit page this is flagged. \n- `REMOVE_DESIRED_PAGE_REFRESHES`: Boolean flag. If `TRUE` sequential page paths of the same type are removed when the query calculates the first/last visit to the desired page. In other words, it will only use the first visit in a series of sequential visits to desired page if they have the same type. Other visits to the desired page will remain, as will any other desired page refreshes.\n- `TRUNCATE_SEARCHES`: Boolean flag. If `TRUE`, all GOV.UK search page paths are truncated to `Sitesearch ({TYPE}): {KEYWORDS}`, where `{TYPE}` is the GOV.UK search content type, and `{KEYWORDS}` are the search keywords. If there are no keywords, this is set to `none`. If `FALSE`, GOV.UK search page paths are not truncated.\n\n## Returns\n\nA csv file containing a Google BigQuery result showing the subsetted user journey containing `PAGE_TYPE` and/or `EVENT_TYPE` page paths in order from the first or last visit to `DESIRED_PAGE` with a maximum length `NUMBER_OF_STAGES`. The results are presented in descending order, with the most popular subsetted user journey first.\n\nResults show:\n- `flagEntrance`: Subsetted journeys that incorporate the first page visited during a session are flagged if selected\n- `flagExit`: Subsetted journeys that incorporate the last page visited during a session are flagged if selected\n- `deviceCategories`: The device category/ies of the subsetted journeys\n- `totalSessions`: The total number of sessions\n- `countSessions`: The total number of sessions per subsetted journey\n- `proportionSessions`: The proportion of sessions per subsetted journey\n- `goalPreviousStepX`: The X previous page path following the `DESIRED_PAGE`; X corresponding to `NUMBER_OF_STAGES`\n- `goal`: The `DESIRED_PAGE`\n\nA second csv file showing the count for each previous step page path, regardless of the overall subsetted journey. The results are presented in descending order, with the most popular previous step first. \n\nResults show: \n- `goalPreviousStepX`: The X previous step page path; X corresponding to `NUMBER_OF_STAGES`\n- `countsGoalPreviousStepX`: The number of sessions that visited the page path at step X\n- `goal`: The `DESIRED_PAGE`\n- `countsGoal`: The number of unique subsetted journeys \n\n## Assumptions\n\n- Only exact matches to `DESIRED_PAGE` are currently supported.\n- Other visits to `DESIRED_PAGE` are ignored, only the first or last visit is used.\n- If `REMOVE_DESIRED_PAGE_REFRESHES` is `TRUE`, and there is more than one page type (`PAGE_TYPE` and `EVENT_TYPE` are both selected), only the first visit in page refreshes to the same `DESIRED_PAGE` and page type are used to determine which is the first/last visit.\n- Journeys shorter than the number of desired stages (`NUMBER_OF_STAGES`) are always included.\n- GOV.UK search page paths are assumed to have the format `/search/{TYPE}?keywords={KEYWORDS}{...}`, where `{TYPE}` is the GOV.UK search content type, `{KEYWORDS}` are the search keywords, where each keyword is\n separated by `+`, and `{...}` are any other parts of the search query that are not keyword-related (if they exist).\n- GOV.UK search page titles are assumed to have the format `{KEYWORDS} - {TYPE} - GOV.UK`, where `{TYPE}` is the GOV.UK search content type, and `{KEYWORDS}` are the search keywords.\n- If `ENTRANCE_PAGE` is `FALSE`, each journey (row) contains both instances where the entrance page is included, and the entrance page is not included. Therefore, if there are more page paths than `NUMBER_OF_STAGES`, this will not be flagged. \n- If `EXIT_PAGE` is `FALSE`, each journey (row) contains both instances where the exit page is included, and the exit page is not included. Therefore, if there are more page paths than `NUMBER_OF_STAGES`, this will not be flagged. \n- If `DEVICE_ALL` is selected in combination with either `DEVICE_DESKTOP`, `DEVICE_MOBILE`, and/or `DEVICE_TABLET`, then the analysis will use `DEVICE_ALL` and ignore all other arguments. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from datetime import datetime\n\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport plotly.graph_objects as go\nfrom google.cloud import bigquery\nfrom google.colab import auth, files\nfrom IPython.core.interactiveshell import InteractiveShell\nfrom oauth2client.client import GoogleCredentials\n\n!pip install --upgrade gspread -q\nimport gspread\n\n!pip install gspread_formatting -q\nimport gspread_formatting as gsf\n\n# Allow multiline outputs\nInteractiveShell.ast_node_interactivity = \"all\"\n\n# Authenticate the user - follow the link and the prompts to get an authentication token\nauth.authenticate_user()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# @markdown ## Set query parameters\n# @markdown Define the start and end dates\nSTART_DATE = \"2022-01-04\" # @param {type:\"date\"}\nEND_DATE = \"2022-01-04\" # @param {type:\"date\"}\n\n# @markdown Set the desired page path - must start with '/'\nDESIRED_PAGE = \"/coronavirus\" # @param {type:\"string\"}\n\n# @markdown Set the hit to the desired page in the session; select one option only\nFIRST_HIT = False # @param {type:\"boolean\"}\nLAST_HIT = True # @param {type:\"boolean\"}\n\n# @markdown Set the number of pages, including `DESIRED_PAGE` to include in the subsetted journeys\nNUMBER_OF_STAGES = 4 # @param {type:\"integer\"}\n\n# @markdown Set the page types; at least one must be checked\nPAGE_TYPE = True # @param {type:\"boolean\"}\nEVENT_TYPE = False # @param {type:\"boolean\"}\n\n# @markdown Set the device categories; select one or more devices `[DEVICE_DESKTOP, DEVICE_MOBILE, DEVICE_TABLET]`, OR select all device categories divided up but included in the same analysis `[DEVICE_ALL]`\nDEVICE_DESKTOP = True # @param {type:\"boolean\"}\nDEVICE_MOBILE = True # @param {type:\"boolean\"}\nDEVICE_TABLET = True # @param {type:\"boolean\"}\nDEVICE_ALL = False # @param {type:\"boolean\"}\n\n# @markdown ### Other options\n\n# @markdown Remove query strings from all page paths\nQUERY_STRING = False # @param {type:\"boolean\"}\n\n# @markdown Add a ` [E]` suffix to EVENT page paths - easier to differentiate between PAGE and\n# @markdown EVENT types for the same page path\nFLAG_EVENTS = False # @param {type:\"boolean\"}\n\n# @markdown Add event information suffix to EVENT page paths\nEVENT_CATEGORY = False # @param {type:\"boolean\"}\nEVENT_ACTION = False # @param {type:\"boolean\"}\nEVENT_LABEL = False # @param {type:\"boolean\"}\n\n# @markdown Include entrance page flag\nENTRANCE_PAGE = True # @param {type:\"boolean\"}\n\n# @markdown Include exit page flag\nEXIT_PAGE = True # @param {type:\"boolean\"}\n\n# @markdown Remove page refreshes when determining the last visit to `DESIRED_PAGE`\nREMOVE_DESIRED_PAGE_REFRESHES = True # @param {type:\"boolean\"}\n\n# @markdown Truncate search pages to only show the search content type, and search keywords\nTRUNCATE_SEARCHES = True # @param {type:\"boolean\"}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Convert the inputted start and end date into `YYYYMMDD` formats\nQUERY_START_DATE = datetime.strptime(START_DATE, \"%Y-%m-%d\").strftime(\"%Y%m%d\")\nQUERY_END_DATE = datetime.strptime(END_DATE, \"%Y-%m-%d\").strftime(\"%Y%m%d\")\n\n# Check that `DESIRED_PAGE` starts with '/'\nassert DESIRED_PAGE.startswith(\n \"/\"\n), f\"`DESIRED_PAGE` must start with '/': {DESIRED_PAGE}\"\n\n# Check that only one of `FIRST_HIT` or `LAST_HIT` is selected\nif FIRST_HIT and LAST_HIT:\n raise AssertionError(\"Only one of `FIRST_HIT` or `LAST_HIT` can be checked!\")\n\n# Compile the query page types\nif PAGE_TYPE and EVENT_TYPE:\n QUERY_PAGE_TYPES = [\"PAGE\", \"EVENT\"]\nelif PAGE_TYPE:\n QUERY_PAGE_TYPES = [\"PAGE\"]\nelif EVENT_TYPE:\n QUERY_PAGE_TYPES = [\"EVENT\"]\nelse:\n raise AssertionError(\"At least one of `PAGE_TYPE` or `EVENT_TYPE` must be checked!\")\n\n# Compile the device categories\nQUERY_DEVICE_CATEGORIES = [\n \"desktop\" if DEVICE_DESKTOP else \"\",\n \"mobile\" if DEVICE_MOBILE else \"\",\n \"tablet\" if DEVICE_TABLET else \"\",\n]\nQUERY_DEVICE_CATEGORIES = [d for d in QUERY_DEVICE_CATEGORIES if d]\nassert (bool(QUERY_DEVICE_CATEGORIES)) | (DEVICE_ALL), (\n f\"At least one of `DEVICE_DESKTOP`, `DEVICE_MOBILE`, `DEVICE_TABLET`\"\n + f\" or `DEVICE_ALL` must be checked!\"\n)\n\n# Set the notebook execution date\nNOTEBOOK_EXECUTION_DATE = datetime.now().strftime(\"%Y%m%d\")\n\n# Define the output file names\nOUTPUT_FILE = (\n f\"{NOTEBOOK_EXECUTION_DATE}_user_journeys_{QUERY_START_DATE}_{QUERY_END_DATE}_\"\n + f\"{'_'.join(QUERY_DEVICE_CATEGORIES)}.csv\"\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"query = \"\"\"\nWITH\n get_session_data AS (\n -- Get all the session data between `start_date` and `end_date`, subsetting for specific `page_type`s. As\n -- some pages might be dropped by the subsetting, recalculate `hitNumber` as `journeyNumber` so the values\n -- are sequential.\n SELECT\n CONCAT(fullVisitorId, \"-\", visitId) AS sessionId,\n ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY fullVisitorId, visitId ORDER BY hits.hitNumber) AS journeyNumber,\n ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY fullVisitorId, visitId ORDER BY hits.hitNumber DESC) AS revJourneyNumber,\n hits.type,\n device.deviceCategory,\n hits.page.pagePath,\n CONCAT(\n IF(@queryString, REGEXP_REPLACE(hits.page.pagePath, r'[?#].*', ''), hits.page.pagePath), -- modify this line to `hits.page.pageTitle` if required\n IF(hits.type = \"EVENT\" AND @flagEvents, IF ((@eventCategory OR @eventAction OR @eventLabel), \" [E\", \"[E]\"), \"\"),\n IF(hits.type = \"EVENT\" AND @eventCategory, CONCAT(IF ((@flagEvents), \", \", \" [\"), hits.eventInfo.eventCategory, IF ((@eventAction OR @eventLabel), \"\", \"]\")), \"\"),\n IF(hits.type = \"EVENT\" AND @eventAction, CONCAT(IF ((@flagEvents OR @eventCategory), \", \", \" [\"), hits.eventInfo.eventAction, IF ((@eventLabel), \"\", \"]\")), \"\"),\n IF(hits.type = \"EVENT\" AND @eventLabel, CONCAT(IF ((@flagEvents OR @eventCategory OR @eventAction), \", \", \" [\"), hits.eventInfo.eventLabel, \"]\"), \"\") \n ) AS pageId\n FROM `govuk-bigquery-analytics.87773428.ga_sessions_*`\n CROSS JOIN UNNEST(hits) AS hits\n WHERE _TABLE_SUFFIX BETWEEN @startDate AND @endDate\n AND hits.type IN UNNEST(@pageType)\n AND (CASE WHEN @deviceAll THEN device.deviceCategory in UNNEST([\"mobile\", \"desktop\", \"tablet\"]) END \n OR CASE WHEN @deviceCategories IS NOT NULL THEN device.deviceCategory in UNNEST(@deviceCategories) END )\n ),\n get_search_content_type_and_keywords AS (\n -- Extract the content type and keywords (if any) for GOV.UK search pages.\n SELECT\n *,\n IFNULL(\n REGEXP_EXTRACT(pagePath, r\"^/search/([^ ?#/]+)\"),\n REGEXP_EXTRACT(pagePath, r\"^.+ - ([^-]+) - GOV.UK$\")\n ) AS searchContentType,\n IFNULL(\n REPLACE(REGEXP_EXTRACT(pagePath, r\"^/search/[^ ?#/]+\\?keywords=([^&]+)\"), \"+\", \" \"),\n REGEXP_EXTRACT(pagePath, r\"^(.+)- [^-]+ - GOV.UK$\")\n ) AS searchKeywords\n FROM get_session_data\n ),\n compile_search_entry AS (\n -- Truncate the search page into an entry of the search content type and keywords (if any).\n SELECT\n * EXCEPT (searchContentType, searchKeywords),\n CONCAT(\n \"Sitesearch (\",\n searchContentType,\n \"):\",\n COALESCE(searchKeywords, \"none\")\n ) AS search_entry\n FROM get_search_content_type_and_keywords\n ),\n replace_escape_characters AS ( \n -- Replace \\ with / as otherwise following REGEXP_REPLACE will not execute \n SELECT\n *,\n REGEXP_REPLACE(search_entry, r\"\\\\\\\\\", \"/\") AS searchEntryEscapeRemoved\n FROM compile_search_entry \n ), \n revise_search_pageids AS (\n -- Replace `pageId` for search pages with the compiled entries if selected by the user.\n SELECT\n * REPLACE (\n IFNULL(IF(@truncatedSearches, REGEXP_REPLACE(pageId, r\"^/search/.*\", searchEntryEscapeRemoved), pageId), pageId) AS pageId\n )\n FROM replace_escape_characters\n ),\n identify_page_refreshes AS (\n -- Lag the page `type` and `pageId` columns. This helps identify page refreshes that can be removed in the\n -- next CTE\n SELECT\n *,\n LAG(type) OVER (PARTITION BY sessionId ORDER BY journeyNumber) AS lagType,\n LAG(pageId) OVER (PARTITION BY sessionId ORDER BY journeyNumber) AS lagPageId\n FROM revise_search_pageids\n ),\n identify_hit_to_desired_page AS (\n -- Get the first/last hit to the desired page. Ignores previous visits to the desired page. Page refreshes of the\n -- desired page are also ignored if the correct option is declared.\n SELECT\n sessionId,\n deviceCategory,\n CASE \n WHEN @firstHit THEN MIN(journeyNumber) \n WHEN @lastHit THEN MAX(journeyNumber) \n END AS desiredPageJourneyNumber\n FROM identify_page_refreshes\n WHERE pageId = @desiredPage\n AND IF(\n @desiredPageRemoveRefreshes,\n (\n lagPageId IS NULL\n OR pageId != lagPageId\n OR IF(ARRAY_LENGTH(@pageType) > 1, pageId = lagPageId AND type != lagType, FALSE)\n ),\n TRUE\n )\n GROUP BY sessionId, deviceCategory\n ),\n subset_journey_to_hit_of_desired_page AS (\n -- Subset all user journeys to the first/last hit of the desired page.\n SELECT revise_search_pageids.*\n FROM revise_search_pageids\n INNER JOIN identify_hit_to_desired_page\n ON revise_search_pageids.sessionId = identify_hit_to_desired_page.sessionId\n AND revise_search_pageids.deviceCategory = identify_hit_to_desired_page.deviceCategory\n AND revise_search_pageids.journeyNumber <= identify_hit_to_desired_page.desiredPageJourneyNumber\n ),\n calculate_stages AS (\n -- Calculate the number of stages from the first/last hit to the desired page, where the first/last hit to the desired\n -- page is '1'.\n SELECT\n *,\n ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY sessionId ORDER BY journeyNumber DESC) AS reverseDesiredPageJourneyNumber\n FROM subset_journey_to_hit_of_desired_page\n ),\n subset_journey_to_number_of_stages AS (\n -- Compile the subsetted user journeys together for each session in reverse order (first/last hit to the desired\n -- page first), delimited by \" <<< \".\n SELECT DISTINCT\n sessionId,\n deviceCategory,\n MIN(journeyNumber) OVER (PARTITION BY sessionId) = 1 AS flagEntrance,\n MIN(revJourneyNumber) OVER (PARTITION BY sessionId) = 1 AS flagExit,\n STRING_AGG(pageId, \" <<< \") OVER (\n PARTITION BY sessionId\n ORDER BY reverseDesiredPageJourneyNumber ROWS BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING\n ) AS userJourney\n FROM calculate_stages\n WHERE reverseDesiredPageJourneyNumber <= @numberOfStages\n ),\n count_distinct_journeys AS (\n -- Count the number of sessions for each distinct subsetted user journey, split by whether the sessions\n -- entered on the first page of the subsetted journey or not\n SELECT\n CASE WHEN @entrancePage THEN CAST(flagEntrance AS STRING) ELSE 'no flag' END AS flagEntrance,\n CASE WHEN @exitPage THEN CAST(flagExit AS STRING) ELSE 'no flag' END AS flagExit,\n CASE WHEN @deviceAll THEN CAST(deviceCategory AS STRING) ELSE ARRAY_TO_STRING(@deviceCategories, \", \") END AS deviceCategory,\n userJourney,\n (SELECT COUNT(sessionId) FROM subset_journey_to_number_of_stages) AS totalSessions,\n COUNT(sessionId) AS countSessions\n FROM subset_journey_to_number_of_stages\n GROUP BY\n flagEntrance, flagExit, deviceCategory, userJourney\n )\nSELECT\n *,\n countSessions / totalSessions AS proportionSessions\nFROM count_distinct_journeys\nORDER BY countSessions DESC;\n\"\"\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Initialise a Google BigQuery client, and define a the query parameters\nclient = bigquery.Client(project=\"govuk-bigquery-analytics\", location=\"EU\")\nquery_parameters = [\n bigquery.ScalarQueryParameter(\"startDate\", \"STRING\", QUERY_START_DATE),\n bigquery.ScalarQueryParameter(\"endDate\", \"STRING\", QUERY_END_DATE),\n bigquery.ArrayQueryParameter(\"pageType\", \"STRING\", QUERY_PAGE_TYPES),\n bigquery.ScalarQueryParameter(\"firstHit\", \"BOOL\", FIRST_HIT),\n bigquery.ScalarQueryParameter(\"lastHit\", \"BOOL\", LAST_HIT),\n bigquery.ArrayQueryParameter(\"deviceCategories\", \"STRING\", QUERY_DEVICE_CATEGORIES),\n bigquery.ScalarQueryParameter(\"deviceAll\", \"BOOL\", DEVICE_ALL),\n bigquery.ScalarQueryParameter(\"flagEvents\", \"BOOL\", FLAG_EVENTS),\n bigquery.ScalarQueryParameter(\"eventCategory\", \"BOOL\", EVENT_CATEGORY),\n bigquery.ScalarQueryParameter(\"eventAction\", \"BOOL\", EVENT_ACTION),\n bigquery.ScalarQueryParameter(\"eventLabel\", \"BOOL\", EVENT_LABEL),\n bigquery.ScalarQueryParameter(\"truncatedSearches\", \"BOOL\", TRUNCATE_SEARCHES),\n bigquery.ScalarQueryParameter(\"desiredPage\", \"STRING\", DESIRED_PAGE),\n bigquery.ScalarQueryParameter(\"queryString\", \"BOOL\", QUERY_STRING),\n bigquery.ScalarQueryParameter(\"entrancePage\", \"BOOL\", ENTRANCE_PAGE),\n bigquery.ScalarQueryParameter(\"exitPage\", \"BOOL\", EXIT_PAGE),\n bigquery.ScalarQueryParameter(\n \"desiredPageRemoveRefreshes\", \"BOOL\", REMOVE_DESIRED_PAGE_REFRESHES\n ),\n bigquery.ScalarQueryParameter(\"numberOfStages\", \"INT64\", NUMBER_OF_STAGES),\n]\n\n# Dry run the query, asking for user input to confirm the query execution size is okay\nbytes_processed = client.query(\n query,\n job_config=bigquery.QueryJobConfig(query_parameters=query_parameters, dry_run=True),\n).total_bytes_processed\n\n# Compile a message, and flag to the user for a response; if not \"yes\", terminate execution\nuser_message = (\n f\"This query will process {bytes_processed / (1024 ** 3):.1f} GB when run, \"\n + f\"which is approximately ${bytes_processed / (1024 ** 4)*5:.3f}. Continue ([yes])? \"\n)\nif input(user_message).lower() != \"yes\":\n raise RuntimeError(\"Stopped execution!\")\n\n# Execute the query, and return as a pandas DataFrame\ndf_raw = client.query(\n query, job_config=bigquery.QueryJobConfig(query_parameters=query_parameters)\n).to_dataframe()\ndf_raw.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_stages = (\n df_raw.set_index(\n [\"flagEntrance\", \"flagExit\", \"deviceCategory\", \"userJourney\"], drop=False\n )[\"userJourney\"]\n .str.split(\" <<< \", expand=True)\n .iloc[:, ::-1]\n)\ndf_stages.columns = [\n *[f\"goalPreviousStep{c+1}\" for c in df_stages.columns[1:]],\n \"goalCompletionLocation\",\n]\n\ndf = df_raw.merge(\n df_stages,\n how=\"left\",\n left_on=[\"flagEntrance\", \"flagExit\", \"deviceCategory\", \"userJourney\"],\n right_index=True,\n validate=\"1:1\",\n)\ndf.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Outputs",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Output the results to a CSV file, and download it\ndf.to_csv(OUTPUT_FILE)\nfiles.download(OUTPUT_FILE)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Amalgamate the previous steps to provide a summary of the most popular pages (regardless of order of steps)\nall_data = []\nfor c in df.columns[6:]:\n df_amal = (\n df.groupby([c])\n .size()\n .reset_index(name=f\"counts{c}\")\n .sort_values([f\"counts{c}\"], ascending=False)\n )\n all_data.append(df_amal)\n\ndf2 = pd.concat(all_data, axis=0, ignore_index=True)\ndf2 = df2.apply(lambda x: pd.Series(x.dropna().values))\ndf2.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Save amalgamation of previous steps to file\nfilename = \"previous_steps_amalgamated.csv\"\noutput = df2.to_csv(filename, index=False)\nfiles.download(filename)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Presenting results as a Sankey diagram\n\nRun this code to create a pseduo Sankey diagram to summarise the top 10 and remainder journeys. \n\nNotes:\n* If you want to view `EVENT` hit information, consider using the google sheets template instead. The Sankey diagram can only present a limited number of characters, and therefore it is likely that `EVENT` hit information will be lost\n* The plot is best when `NUMBER_OF_STAGES` <= 4. More characters are truncated the greater the number of stages, which will impact the coherence and quality of the diagram \n* Because of the above, the Sankey plot cannot be created when `NUMBER_OF_STAGES` is equal to or greater than 8\n* If, for example, `NUMBER_OF_STAGES` = 5, but the max journey length is 4, then re-do the analysis with `NUMBER_OF_STAGES` = 4. Less characters will be truncated\n* When the plot is created, it is possible to drag the nodes to a different position. This is particularly useful when you have wide nodes, such as nodes with a proportion greater than 70%, as sometimes these nodes will overlap\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Raise an error if `NUMBER_OF_STAGES` >= 8\nassert NUMBER_OF_STAGES < 8, f\"`NUMBER_OF_STAGES` must be equal to or less than 7\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Filter the data to show the top 10 journeys only and order columns\ndf_top = df.iloc[:, np.r_[5, 4, 6 : len(df.columns)]].iloc[:, ::-1].head(10)\n\n# Transpose df, and replace the first instance of nan value for each journey with '[Entrance]'\nfor column in df_top.transpose():\n df_top.loc[column] = df_top.loc[column].fillna(\"Entrance\", limit=1)\n\n# Sum count and proportion for top 10 journeys\ntop_10_count = df_top[\"countSessions\"].sum()\ntop_10_count = f\"{top_10_count:,}\"\ntop_10_prop = df_top[\"proportionSessions\"].sum() * 100\ntop_10_prop = top_10_prop.round(decimals=1)\n\n# Create 11th journey `Other journeys` which amalgamates the remainding journeys\njourney_remainder = [\n [df[10:][\"countSessions\"].sum(axis=0)],\n [df[10:][\"proportionSessions\"].sum(axis=0)],\n [DESIRED_PAGE],\n [\"Other journeys\"],\n]\njourney_remainder = pd.DataFrame(data=journey_remainder).transpose()\njourney_remainder.columns = [\n \"countSessions\",\n \"proportionSessions\",\n \"goalCompletionLocation\",\n \"goalPreviousStep1\",\n]\ndf_top = df_top.append(journey_remainder, ignore_index=True)\ndf_top[\"proportionSessions\"] = df_top[\"proportionSessions\"].astype(\"float\")\ndf_prop = df_top[\"proportionSessions\"] * 100\ndf_prop = df_prop.round(decimals=1)\n\n# Amalgamate countSessions and proportionSessions\ndf_top[\"proportionSessions\"] = df_top[\"proportionSessions\"] * 100\ndf_top[\"proportionSessions\"] = df_top[\"proportionSessions\"].round(decimals=1)\ndf_top[\"countSessions\"] = [f\"{val:,}\" for val in df_top[\"countSessions\"]]\ndf_top[\"sessions\"] = (\n \" [\"\n + df_top[\"countSessions\"].astype(str)\n + \": \"\n + df_top[\"proportionSessions\"].astype(str)\n + \"%]\"\n)\n\n# Get total number of sessions\ntotal_sessions = df_raw[\"totalSessions\"][0]\ntotal_sessions = f\"{total_sessions:,}\"\n\n# Drop redundant columns\ndf_top = df_top.drop(\n [\"countSessions\", \"totalSessions\", \"proportionSessions\"], axis=1\n).dropna(axis=1, how=\"all\")\n\n# Create a title for the figure\nfigure_title = (\n f\"<b>Reverse Path Tool: `{DESIRED_PAGE}`</b><br>[{START_DATE} to {END_DATE}]\"\n)\n\n# Define node colours\ndesired_page_node_colour = [\"rgb(136,34,85)\"]\nnode_colour = [\n \"rgb(222,29,29)\",\n \"rgb(82,188,163)\",\n \"rgb(153,201,69)\",\n \"rgb(204,97,196)\",\n \"rgb(36,121,108)\",\n \"rgb(218,165,27)\",\n \"rgb(47,138,196)\",\n \"rgb(118,78,115)\",\n \"rgb(237,100,90)\",\n \"rgb(229,134,6)\",\n \"rgb(136,34,85)\",\n]\nwhite_colour = [\"rgb(255,255,255)\"]\ngrey_colour = [\"rgb(192,192,192)\"]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create `x_coord` parameter, and truncate page path characters depending on `NUMBER_OF_STAGES`\ndf_top = df_top.astype(str)\n\nif NUMBER_OF_STAGES <= 2:\n # create `x_coord`\n x_coord = list(np.linspace(1.05, 0.01, 2))\n\n for column in df_top:\n # truncate characters and add '...' where string lengths are more than 92\n df_top[column] = df_top[column].where(\n df_top[column].str.len() < 92, df_top[column].str[:92] + \"...\"\n )\n # for the last `goal`, truncate characters and add '...' where string lengths are more than 55\n df_top.iloc[:, 0] = df_top.iloc[:, 0].where(\n df_top.iloc[:, 0].str.len() < 55, df_top.iloc[:, 0].str[:55] + \"...\"\n )\n\nelif NUMBER_OF_STAGES == 3:\n x_coord = [1.05, 0.40, 0.01]\n\n for column in df_top:\n df_top[column] = df_top[column].where(\n df_top[column].str.len() < 55, df_top[column].str[:55] + \"...\"\n )\n df_top.iloc[:, 0] = df_top.iloc[:, 0].where(\n df_top.iloc[:, 0].str.len() < 35, df_top.iloc[:, 0].str[:35] + \"...\"\n )\nelif NUMBER_OF_STAGES == 4:\n x_coord = [1.05, 0.54, 0.29, 0.01]\n\n for column in df_top:\n df_top[column] = df_top[column].where(\n df_top[column].str.len() < 36, df_top[column].str[:36] + \"...\"\n )\n df_top.iloc[:, 0] = df_top.iloc[:, 0].where(\n df_top.iloc[:, 0].str.len() < 30, df_top.iloc[:, 0].str[:30] + \"...\"\n )\nelif NUMBER_OF_STAGES == 5:\n x_coord = [1.05, 0.63, 0.45, 0.25, 0.001]\n\n for column in df_top.iloc[:, 1:]:\n df_top[column] = df_top[column].where(\n df_top[column].str.len() < 27, df_top[column].str[:27] + \"...\"\n )\n df_top.iloc[:, 0] = df_top.iloc[:, 0].where(\n df_top.iloc[:, 0].str.len() < 22, df_top.iloc[:, 0].str[:22] + \"...\"\n )\n\nelif NUMBER_OF_STAGES == 6:\n x_coord = [1.05, 0.68, 0.55, 0.40, 0.25, 0.01]\n\n for column in df_top:\n df_top[column] = df_top[column].where(\n df_top[column].str.len() < 22, df_top[column].str[:22] + \"...\"\n )\n\nelse:\n x_coord = [1.05, 0.75, 0.6, 0.45, 0.30, 0.15, 0.01]\n\n for column in df_top:\n df_top[column] = df_top[column].where(\n df_top[column].str.len() < 15, df_top[column].str[:15] + \"...\"\n )\n\n# Remove `None` or 'nan' values\nlabel_list = [\n [x for x in y if str(x) != \"None\" and str(x) != \"nan\"]\n for y in df_top.values.tolist()\n]\n\n# Concatanate count and proportion in the last `goalPreviousStep` field\nlabel_list_concatanated = []\n\nfor lists in label_list:\n temp = []\n temp = lists[:-2] + [(\" \".join(lists[-2:]))]\n label_list_concatanated.append(temp)\n\n# Get length for each journey\njourney_lengths = [len(n) for n in label_list_concatanated]\n\n# Create `x_coord` paramater\nx_coord_list = [x_coord[1 : journey_lengths[x]] for x in range(11)]\nx_coord_unnested = [item for sublist in x_coord_list for item in sublist]\nx_coord_unnested.insert(0, 0.97)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create `y_coord` parameter\ny_coord = [0.1]\n\nfor index in range(0, 10):\n\n if index == 0 and df_prop[index] <= 30:\n prev_elem = y_coord[0]\n y_coord.append(prev_elem + 0.1)\n\n elif index == 0 and df_prop[index] >= 30 and df_prop[index] <= 50:\n prev_elem = y_coord[0]\n y_coord.append(prev_elem + 0.2)\n\n elif index == 0 and df_prop[index] >= 50 and df_prop[index] <= 70:\n prev_elem = y_coord[0]\n y_coord.append(prev_elem + 0.25)\n\n elif index == 0 and df_prop[index] >= 70 and df_prop[index] <= 90:\n prev_elem = y_coord[0]\n y_coord.append(prev_elem + 0.3)\n\n elif index == 0 and df_prop[index] >= 90 and df_prop[index] <= 100:\n prev_elem = y_coord[0]\n y_coord.append(prev_elem + 0.4)\n\n elif index >= 1 and index <= 8 and df_prop[index] <= 10:\n prev_elem = y_coord[index]\n y_coord.append(prev_elem + 0.05)\n\n elif index >= 1 and index <= 8 and df_prop[index] >= 10 and df_prop[index] <= 30:\n prev_elem = y_coord[index]\n y_coord.append(prev_elem + 0.1)\n\n elif index >= 1 and index <= 8 and df_prop[index] >= 30 and df_prop[index] <= 50:\n prev_elem = y_coord[index]\n y_coord.append(prev_elem + 0.2)\n\n elif index >= 1 and index <= 8 and df_prop[index] >= 50 and df_prop[index] <= 70:\n prev_elem = y_coord[index]\n y_coord.append(prev_elem + 0.3)\n\n elif index >= 1 and index <= 8 and df_prop[index] >= 70 and df_prop[index] <= 100:\n prev_elem = y_coord[index]\n y_coord.append(prev_elem + 0.5)\n\n elif index == 9:\n y_coord.append(0.9)\n\ny_coord_list = [[y_coord[y]] * (journey_lengths[y] - 1) for y in range(0, 11)]\ny_coord_unnested = [item for sublist in y_coord_list for item in sublist]\ny_coord_unnested.insert(0, 0.5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Get previous item function\nfrom itertools import chain, islice, tee\n\n\ndef previous(some_iterable):\n prevs, items = tee(some_iterable, 2)\n prevs = chain([None], prevs)\n return zip(prevs, items)\n\n\n# Create new list of lists with node number\nnode_no_list = []\n\nfor prevlength, length in previous(journey_lengths):\n if prevlength is None:\n temp1 = list(range(0, length))\n node_no_list.append(temp1)\n\n elif temp1 != [] and len(node_no_list) == 1:\n temp2 = list(range(temp1[-1] + 1, temp1[-1] + length + 1))\n node_no_list.append(temp2)\n\n else:\n node_no_list.append(\n list(range(node_no_list[-1][-1] + 1, node_no_list[-1][-1] + length + 1))\n )\n\n# Replace every first value with '0'\nfor journey in node_no_list:\n journey[0] = 0",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Within `node_no_list`, combine the source and target values\nsource_target_list = []\n\nfor journey in node_no_list:\n number_of_pairs = len(journey) - 1\n\n for prev_elem, elem in previous(journey):\n if prev_elem is None:\n continue\n\n elif prev_elem is not None:\n temp = []\n temp.append(prev_elem)\n temp.append(elem)\n\n source_target_list.append(temp)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create `source` and `target` parameter\nsource = [item[0] for item in source_target_list]\ntarget = [item[1] for item in source_target_list]\n\n# Unnest `label_list_concatanated` to create `label` parameter\nlabel_list_unnested = [item for sublist in label_list_concatanated for item in sublist]\n\n# Create `color` paramater\ncolours = [\n desired_page_node_colour + [node_colour[colour]] * (journey_lengths[colour] - 1)\n for colour in range(11)\n]\ncolours_unnested = [item for sublist in colours for item in sublist]\n\n# Create `link_color` parameter\nlink_colour = [\n grey_colour * (journey_lengths[colour] - 1) + white_colour for colour in range(11)\n]\nlink_colour_unnested = [item for sublist in link_colour for item in sublist]\n\n# Create `value` parameter based on proportion\namin, amax = min(df_prop), max(df_prop)\nval = [((val - amin) / (amax - amin)) for i, val in enumerate(df_prop)]\nval_list = [[val[y]] * (journey_lengths[y] - 1) for y in range(0, 11)]\nval_list_unnested = [item for sublist in val_list for item in sublist]\n\n# Replace `0.0` with the second lowest number, as otherwise journeys with value `0.0` will not display\nval_list_unnested = [\n sorted(set(val_list_unnested))[1] if item == 0.0 else item\n for item in val_list_unnested\n]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create figure\nfig = go.Figure(\n data=[\n go.Sankey(\n node=dict(\n x=x_coord_unnested,\n y=y_coord_unnested,\n pad=35,\n thickness=35,\n line=dict(color=\"white\", width=0.5),\n label=label_list_unnested,\n color=colours_unnested,\n ),\n arrangement=\"freeform\", # 'fixed' 'snap' 'freeform' 'perpendicular'\n link=dict(source=source, target=target, value=val_list_unnested),\n )\n ]\n)\n\n# Add annotations\nfig = fig.add_annotation(\n x=1.05,\n y=1.1,\n text=f\"<br>Total visits and proportion for the top 10 journeys: {top_10_count} [{top_10_prop}%]\",\n showarrow=False,\n font=dict(family=\"Arial\", size=22),\n align=\"right\",\n)\n\nfig = fig.add_annotation(\n x=1.05,\n y=0.485,\n text=f\"<br>Total visits:<br>{total_sessions}\",\n showarrow=False,\n font=dict(family=\"Arial\", size=19),\n align=\"center\",\n)\n\n# Update layout\nfig.update_layout(\n title_text=figure_title,\n font=dict(family=\"Arial\", size=19, color=\"black\"),\n title_font_size=30,\n width=1700,\n height=900,\n hovermode=False,\n xaxis={\n \"showgrid\": False,\n \"zeroline\": False,\n \"visible\": False,\n },\n yaxis={\n \"showgrid\": False,\n \"zeroline\": False,\n \"visible\": False,\n },\n plot_bgcolor=\"rgba(0,0,0,0)\",\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Presenting results in Google sheets\nHere's an [example of how you could present the results](https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1vSFXnPE8XozpRhI1G3x4tl5oro3pUIgZnoFmJ_AjPbY/edit#gid=1115034830) to facilitate sharing with colleagues. To do this, run the code below.\n\nThis code uses a [template google sheet](https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1E54VgFepSCxNfNKNtxp8eQXme7wGOAEauTqgzEuz3iM/edit?usp=drive_web&ouid=114104082491527752510) to create a new google sheet in `GOV.UK teams/2021-2022/Data labs/Requests/User journey tools/Path tools: google sheets result tables`, with the title: `{START_DATE} to {END_DATE} - Reverse path tool - {DESIRED_PAGE}`. This template can present up to 6 `NUMBER_OF_STAGES`. Copy or delete the formatting on the newly created google sheet if more or less stages are required. \n\nIt is advisable to present the results like this when the page paths are long, and if you want to visualise `EVENT` hits, as well as `PAGE` hits.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Authentication\ngc = gspread.authorize(GoogleCredentials.get_application_default())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Set up data\ndf_top = (\n df.iloc[:, np.r_[6 : len(df.columns), 4, 5]].iloc[:, ::-1].head(10)\n) # Filter the data to show the top 10 journeys only and order columns\ndf_top[\"proportionSessions\"] = (\n df_top[\"proportionSessions\"] * 100\n) # Convert proportion to %\ndf_top[\"proportionSessions\"] = df_top[\"proportionSessions\"].round(\n decimals=2\n) # Round % 2 decimal places\n\n# Tranpose df, reverse order df, and replace the first instance of na value for each journey with `[Entrance]`\nfor column in df_top.transpose():\n df_top.loc[column] = df_top.loc[column].fillna(\"Entrance\", limit=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create google sheet in `GOV.UK teams/2021-2022/Data labs/Requests/Path tools`\ngc.copy(\n \"1E54VgFepSCxNfNKNtxp8eQXme7wGOAEauTqgzEuz3iM\", # pragma: allowlist secret\n title=f\"{START_DATE} to {END_DATE} - Reverse path tool - {DESIRED_PAGE}\",\n copy_permissions=True,\n)\nsheet = gc.open(f\"{START_DATE} to {END_DATE} - Reverse path tool - {DESIRED_PAGE}\")\nworksheet = sheet.worksheet(\"reverse_path_tool\")\nprint(\"\\n\", sheet.url)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Fill spreadsheet\n\n# Replace df nan values with ''\ndf_top = df_top.fillna(\"\")\n\n# Update title header cells\ntitle = f\"Reverse path tool: `{DESIRED_PAGE}`\"\nworksheet.update(\"B1\", f\"{title}\")\nworksheet.update(\"B2\", f\"{START_DATE} to {END_DATE}\")\n\n# Update `% of sessions` cells\ncell_range = list(map(\"C{}\".format, range(4, 14)))\nsessions = list(map(\"{}%\".format, list(df_top[\"proportionSessions\"])))\n[worksheet.update(cell, sessionProp) for cell, sessionProp in zip(cell_range, sessions)]\n\n# Update `No of. sessions` cells\ncell_range = list(map(\"D{}\".format, range(4, 14)))\nsessions = list(df_top[\"countSessions\"])\n[\n worksheet.update(cell, sessionCount)\n for cell, sessionCount in zip(cell_range, sessions)\n]\n\n# Update `Goal page` cells\ncell_range = list(map(\"F{}\".format, range(4, 14)))\ngoal = list(df_top[\"goalCompletionLocation\"])\n[worksheet.update(cell, goalPage) for cell, goalPage in zip(cell_range, goal)]\n\n## Update `Previous step N` cells\n\n# Get cell ID letter for all `Previous step N` cells (start from cell `H`, skip 1, until cell `Z`)\ncell_letters = [chr(c) for c in range(ord(\"h\"), ord(\"z\") + 1, 2)]\ncell_letters = cell_letters[\n :NUMBER_OF_STAGES\n] # only keep the numer of elements that match NUMBER_OF_STAGES\n\n# Get cell ID number for all `Previous step N` cells\ncell_numbers = list(range(4, 14))\ncell_numbers = [str(x) for x in cell_numbers]\n\n# Combine cell ID letter and number to create a list of cell IDs for `Previous step N` cells\ngoal_previous_step_cells = []\nfor letter in cell_letters:\n for number in cell_numbers:\n goal_previous_step_cells.append(letter + number)\n\n\n# Create a list of the `Previous step N` paths\ngoal_previous_step = []\nfor step in range(1, NUMBER_OF_STAGES):\n goal_previous_step.extend(df_top[f\"goalPreviousStep{step}\"])\n\n# Update `Previous step N` cells\n[\n worksheet.update(cell, goalPage)\n for cell, goalPage in zip(goal_previous_step_cells, goal_previous_step)\n]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Original SQL query",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"```sql\n/*\nCalculate the count and proportion of sessions that have the same journey behaviour.\n\nThis script finds sessions that visit a specific page (`desiredPage`) in their journey. From the first/last visit to\n`desiredPage` in the session, the journey is subsetted to include the last N pages including `desiredPage`\n(`numberofStages`). \n\nThe count and proportion of sessions visiting distinct, subsetted journeys are compiled together, and returned as a\nsorted list in descending order split by subsetted journeys including the entrance page.\n\nArguments:\n\n startDate: String in YYYYMMDD format defining the start date of your query.\n endDate: String in YYYYMMDD format defining the end date of your query.\n pageType: String array containing comma-separated strings of page types. Must contain one or more of \"PAGE\" and\n \"EVENT\".\n firstHit: Boolean flag. If TRUE the first hit to the desired page is used for the subsetted journey. If set to TRUE, \n `lastHit` must be set to FALSE.\n lastHit: Boolean flag. If TRUE the last hit to the desired page is used for the subsetted journey. If set to TRUE, \n `firstHit` must be set to FALSE.\n deviceCategories: String array containing comma-separated strings of device categories. Can contain one or more\n of \"mobile\", \"desktop\", and \"tablet\".\n deviceAll: Boolean flag. If TRUE all device categories are included in the query but divided into their respective \n categories. This must to set to TRUE if deviceCategories is left blank. If deviceCategories is not left blank, \n this must be set to FALSE. \n flagEvents: Boolean flag. If TRUE, all \"EVENT\" page paths will have a \" [E]\" suffix. This is useful if `pageType`\n contains both \"PAGE\" and \"EVENT\" so you can differentiate between the same page path with different types. If\n FALSE, no suffix is appended to \"EVENT\" page paths.\n eventCategory: Boolean flag. If TRUE, all \"EVENT\" page paths will be followed by the \" [eventCategory]\". If FALSE, \n no \" [eventCategory]\" suffix is appended to \"EVENT\" page paths. \n eventAction: Boolean flag. If TRUE, all \"EVENT\" page paths will be followed by the \" [eventAction]\". If FALSE, no \n \" [eventAction]\" suffix is appended to \"EVENT\" page paths. \n eventLabel: Boolean flag. If TRUE, all \"EVENT\" page paths will be followed by the \" [eventLabel]\". If FALSE, no \n \" [eventLabel]\" suffix is appended to \"EVENT\" page paths. \n truncatedSearches: Boolean flag. If TRUE, all GOV.UK search page paths are truncated to\n \"Sitesearch ({TYPE}): {KEYWORDS}\", where `{TYPE}` is the GOV.UK search content type, and `{KEYWORDS}` are the\n search keywords. If there are no keywords, this is set to `none`. If FALSE, GOV.UK search page paths are\n not truncated.\n desiredPage: String of the desired GOV.UK page path of interest.\n queryString: If TRUE, remove query string from all page paths. If FALSE, keep query strings for all page paths. \n desiredPageRemoveRefreshes: Boolean flag. If TRUE sequential page paths of the same type are removed when the query\n calculates the first/last visit to the desired page. In other words, it will only use the first visit in a series\n of sequential visits to desired page if they have the same type. Other earlier visits to the desired page will\n remain, as will any earlier desired page refreshes.\n numberOfStages: Integer defining how many pages in the past (including `desiredPage`) should be considered when\n subsetting the user journeys. Note that journeys with fewer pages than `numberOfStages` will always be\n included.\n entrancePage: Boolean flag. If TRUE, if the subsetted journey contains the entrance page this is flagged. If FALSE \n no flag is used (e.g. the journey contains both instances where the entrance page is included, and the\n entrance page is not included).\n exitPage: Boolean flag. If TRUE, if the subsetted journey contains the exit page this is flagged. If FALSE \n no flag is used (e.g. the journey contains both instances where the exit page is included, and the\n exit page is not included).\n\nReturns:\n\n A Google BigQuery result containing the subsetted user journey containing `pageType` page paths in reverse from\n the first/last visit to `desiredPage` with a maximum length `numberOfStages`. Counts and the proportion of sessions\n that have this subsetted journey are also shown. Subsetted journeys that incorporate the first page or last page visited by a \n session are flagged if selected. The device category/ies of the subsetted journeys are also included. The results \n are presented in descending order, with the most popular subsetted user journey first.\n\nAssumptions:\n\n - Only exact matches to `desiredPage` are currently supported.\n - Previous visits to `desiredPage` are ignored, only the last visit is used.\n - If `desiredPageRemoveRefreshes` is TRUE, and there is more than one page type (`pageType`), only the first visit\n in page refreshes to the same `desiredPage` and page type are used to determine which is the first/last visit.\n - Journeys shorter than the number of desired stages (`numberOfStages`) are always included.\n - GOV.UK search page paths are assumed to have the format `/search/{TYPE}?keywords={KEYWORDS}{...}`, where\n `{TYPE}` is the GOV.UK search content type, `{KEYWORDS}` are the search keywords, where each keyword is\n separated by `+`, and `{...}` are any other parts of the search query that are not keyword-related (if they\n exist).\n - GOV.UK search page titles are assumed to have the format `{KEYWORDS} - {TYPE} - GOV.UK`, where `{TYPE}` is the\n GOV.UK search content type, and `{KEYWORDS}` are the search keywords.\n - If `entrancePage` is FALSE, each journey (row) contains both instances where the entrance page is included, \n and the entrance page is not included. Therefore, if there are more page paths than `numberOfStages`, this \n will not be flagged. \n - If `deviceAll` is set to TRUE, and `deviceCategories` set to 'desktop', 'mobile', and/or 'tablet', the \n query will use `deviceAll` and ignore all other arguments. \n*/\n\n-- Declare query variables\nDECLARE startDate DEFAULT \"20210628\";\nDECLARE endDate DEFAULT \"20210628\";\nDECLARE pageType DEFAULT [\"PAGE\", \"EVENT\"];\nDECLARE firstHit DEFAULT TRUE;\nDECLARE lastHit DEFAULT FALSE; \nDECLARE deviceCategories DEFAULT [\"desktop\", \"mobile\", \"tablet\"];\nDECLARE deviceAll DEFAULT FALSE;\nDECLARE flagEvents DEFAULT TRUE;\nDECLARE eventCategory DEFAULT TRUE;\nDECLARE eventAction DEFAULT TRUE;\nDECLARE eventLabel DEFAULT TRUE;\nDECLARE truncatedSearches DEFAULT TRUE;\nDECLARE desiredPage DEFAULT \"/trade-tariff\";\nDECLARE queryString DEFAULT TRUE; \nDECLARE desiredPageRemoveRefreshes DEFAULT TRUE;\nDECLARE numberOfStages DEFAULT 3;\nDECLARE entrancePage DEFAULT TRUE; \nDECLARE exitPage DEFAULT TRUE; \n\nWITH\n get_session_data AS (\n -- Get all the session data between `start_date` and `end_date`, subsetting for specific `page_type`s. As\n -- some pages might be dropped by the subsetting, recalculate `hitNumber` as `journeyNumber` so the values\n -- are sequential.\n SELECT\n CONCAT(fullVisitorId, \"-\", visitId) AS sessionId,\n ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY fullVisitorId, visitId ORDER BY hits.hitNumber) AS journeyNumber,\n ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY fullVisitorId, visitId ORDER BY hits.hitNumber DESC) AS revJourneyNumber,\n hits.type,\n device.deviceCategory,\n hits.page.pagePath,\n CONCAT(\n IF(queryString, REGEXP_REPLACE(hits.page.pagePath, r'[?#].*', ''), hits.page.pagePath), -- modify this line to `hits.page.pageTitle` if required\n IF(hits.type = \"EVENT\" AND flagEvents, IF ((eventCategory OR eventAction OR eventLabel), \" [E\", \"[E]\"), \"\"),\n IF(hits.type = \"EVENT\" AND eventCategory, CONCAT(IF ((flagEvents), \", \", \" [\"), hits.eventInfo.eventCategory, IF ((eventAction OR eventLabel), \"\", \"]\")), \"\"),\n IF(hits.type = \"EVENT\" AND eventAction, CONCAT(IF ((flagEvents OR eventCategory), \", \", \" [\"), hits.eventInfo.eventAction, IF ((eventLabel), \"\", \"]\")), \"\"),\n IF(hits.type = \"EVENT\" AND eventLabel, CONCAT(IF ((flagEvents OR eventCategory OR eventAction), \", \", \" [\"), hits.eventInfo.eventLabel, \"]\"), \"\") \n ) AS pageId\n FROM `govuk-bigquery-analytics.87773428.ga_sessions_*`\n CROSS JOIN UNNEST(hits) AS hits\n WHERE _TABLE_SUFFIX BETWEEN startDate AND endDate\n AND hits.type IN UNNEST(pageType)\n AND (CASE WHEN deviceAll THEN device.deviceCategory in UNNEST([\"mobile\", \"desktop\", \"tablet\"]) END \n OR CASE WHEN deviceCategories IS NOT NULL THEN device.deviceCategory in UNNEST(deviceCategories) END )\n ),\n get_search_content_type_and_keywords AS (\n -- Extract the content type and keywords (if any) for GOV.UK search pages.\n SELECT\n *,\n IFNULL(\n REGEXP_EXTRACT(pagePath, r\"^/search/([^ ?#/]+)\"),\n REGEXP_EXTRACT(pagePath, r\"^.+ - ([^-]+) - GOV.UK$\")\n ) AS searchContentType,\n IFNULL(\n REPLACE(REGEXP_EXTRACT(pagePath, r\"^/search/[^ ?#/]+\\?keywords=([^&]+)\"), \"+\", \" \"),\n REGEXP_EXTRACT(pagePath, r\"^(.+)- [^-]+ - GOV.UK$\")\n ) AS searchKeywords\n FROM get_session_data\n ),\n compile_search_entry AS (\n -- Truncate the search page into an entry of the search content type and keywords (if any).\n SELECT\n * EXCEPT (searchContentType, searchKeywords),\n CONCAT(\n \"Sitesearch (\",\n searchContentType,\n \"):\",\n COALESCE(searchKeywords, \"none\")\n ) AS search_entry\n FROM get_search_content_type_and_keywords\n ),\n replace_escape_characters AS (\n -- Replace \\ with / as otherwise following REGEXP_REPLACE will not execute \n SELECT\n *,\n REGEXP_REPLACE(search_entry, r\"\\\\\", \"/\") AS searchEntryEscapeRemoved\n FROM compile_search_entry \n ), \n revise_search_pageids AS (\n -- Replace `pageId` for search pages with the compiled entries if selected by the user.\n SELECT\n * REPLACE (\n IFNULL(IF(truncatedSearches, (REGEXP_REPLACE(pageId, r\"^/search/.*\", searchEntryEscapeRemoved)), pageId), pageId) AS pageId\n )\n FROM replace_escape_characters\n ),\n identify_page_refreshes AS (\n -- Lag the page `type` and `pageId` columns. This helps identify page refreshes that can be removed in the\n -- next CTE\n SELECT\n *,\n LAG(type) OVER (PARTITION BY sessionId ORDER BY journeyNumber) AS lagType,\n LAG(pageId) OVER (PARTITION BY sessionId ORDER BY journeyNumber) AS lagPageId\n FROM revise_search_pageids\n ),\n identify_hit_to_desired_page AS (\n -- Get the first/last hit to the desired page. Ignores previous visits to the desirted page. Page refreshes of the\n -- desired page are also ignored if the correct option is declared.\n SELECT\n sessionId,\n deviceCategory,\n CASE \n WHEN firstHit THEN MIN(journeyNumber) \n WHEN lastHit THEN MAX(journeyNumber) \n END AS desiredPageJourneyNumber\n FROM identify_page_refreshes\n WHERE pageId = desiredPage\n AND IF(\n desiredPageRemoveRefreshes,\n (\n lagPageId IS NULL\n OR pageId != lagPageId\n OR IF(ARRAY_LENGTH(pageType) > 1, pageId = lagPageId AND type != lagType, FALSE)\n ),\n TRUE\n )\n GROUP BY sessionId, deviceCategory \n ),\n subset_journey_to_hit_of_desired_page AS (\n -- Subset all user journeys to the first/last hit of the desired page.\n SELECT revise_search_pageids.*\n FROM revise_search_pageids\n INNER JOIN identify_hit_to_desired_page\n ON revise_search_pageids.sessionId = identify_hit_to_desired_page.sessionId\n AND revise_search_pageids.deviceCategory = identify_hit_to_desired_page.deviceCategory\n AND revise_search_pageids.journeyNumber <= identify_hit_to_desired_page.desiredPageJourneyNumber\n ),\n calculate_stages AS (\n -- Calculate the number of stages from the first/last hit to the desired page, where the first/last hit to the desired\n -- page is '1'.\n SELECT\n *,\n ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY sessionId ORDER BY journeyNumber DESC) AS reverseDesiredPageJourneyNumber\n FROM subset_journey_to_hit_of_desired_page\n ),\n subset_journey_to_number_of_stages AS (\n -- Compile the subsetted user journeys together for each session in reverse order (first/last hit to the desired\n -- page first), delimited by \" <<< \".\n SELECT DISTINCT\n sessionId,\n deviceCategory,\n MIN(journeyNumber) OVER (PARTITION BY sessionId) = 1 AS flagEntrance,\n MIN(revJourneyNumber) OVER (PARTITION BY sessionId) = 1 AS flagExit,\n STRING_AGG(pageId, \" <<< \") OVER (\n PARTITION BY sessionId\n ORDER BY reverseDesiredPageJourneyNumber ROWS BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING\n ) AS userJourney\n FROM calculate_stages\n WHERE reverseDesiredPageJourneyNumber <= numberOfStages\n ),\n count_distinct_journeys AS (\n -- Count the number of sessions for each distinct subsetted user journey, split by whether the sessions\n -- entered on the first page of the subsetted journey or not\n SELECT\n CASE WHEN entrancePage \n THEN CAST(flagEntrance AS STRING) \n ELSE 'no flag' \n END AS flagEntrance,\n CASE WHEN exitPage \n THEN CAST(flagExit AS STRING) \n ELSE 'no flag' \n END AS flagExit,\n CASE WHEN deviceAll\n THEN CAST(deviceCategory AS STRING) \n ELSE ARRAY_TO_STRING(deviceCategories, \", \") \n END AS deviceCategory,\n userJourney,\n (SELECT COUNT(sessionId) FROM subset_journey_to_number_of_stages) AS totalSessions,\n COUNT(sessionId) AS countSessions\n FROM subset_journey_to_number_of_stages\n GROUP BY\n flagEntrance, flagExit, deviceCategory, userJourney\n )\nSELECT\n *,\n countSessions / totalSessions AS proportionSessions\nFROM count_distinct_journeys\nORDER BY countSessions DESC;\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4a72a839790813d6487bc6cf19e6c8d252a88b02
| 14,484 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
5_Input_and_Output_Solutions.ipynb
|
MinKyungNet/numpy_exercises
|
f0999827c02404f02604afd69da9a39c8b52e0f9
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
5_Input_and_Output_Solutions.ipynb
|
MinKyungNet/numpy_exercises
|
f0999827c02404f02604afd69da9a39c8b52e0f9
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
5_Input_and_Output_Solutions.ipynb
|
MinKyungNet/numpy_exercises
|
f0999827c02404f02604afd69da9a39c8b52e0f9
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 28.91018 | 128 | 0.411212 |
[
[
[
"# Input and Output",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from __future__ import print_function\nimport numpy as np",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"author = \"kyubyong. https://github.com/Kyubyong/numpy_exercises\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.__version__",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from datetime import date\nprint(date.today())",
"2017-04-01\n"
]
],
[
[
"## NumPy binary files (NPY, NPZ)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Q1. Save x into `temp.npy` and load it.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x = np.arange(10)\nnp.save('temp.npy', x) # Actually you can omit the extension. If so, it will be added automatically.\n\n# Check if there exists the 'temp.npy' file.\nimport os\nif os.path.exists('temp.npy'):\n x2 = np.load('temp.npy')\n print(np.array_equal(x, x2))\n",
"True\n"
]
],
[
[
"Q2. Save x and y into a single file 'temp.npz' and load it.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x = np.arange(10)\ny = np.arange(11, 20)\nnp.savez('temp.npz', x=x, y=y)\n# np.savez_compressed('temp.npz', x=x, y=y) # If you want to save x and y into a single file in compressed .npz format.\nwith np.load('temp.npz') as data:\n x2 = data['x']\n y2 = data['y']\n print(np.array_equal(x, x2))\n print(np.array_equal(y, y2))\n",
"True\nTrue\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Text files",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Q3. Save x to 'temp.txt' in string format and load it.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x = np.arange(10).reshape(2, 5)\nheader = 'num1 num2 num3 num4 num5'\nnp.savetxt('temp.txt', x, fmt=\"%d\", header=header) \nnp.loadtxt('temp.txt')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Q4. Save `x`, `y`, and `z` to 'temp.txt' in string format line by line, then load it.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x = np.arange(10)\ny = np.arange(11, 21)\nz = np.arange(22, 32)\nnp.savetxt('temp.txt', (x, y, z), fmt='%d')\nnp.loadtxt('temp.txt')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Q5. Convert `x` into bytes, and load it as array.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4])\nx_bytes = x.tostring() # Don't be misled by the function name. What it really does is it returns bytes.\nx2 = np.fromstring(x_bytes, dtype=x.dtype) # returns a 1-D array even if x is not.\nprint(np.array_equal(x, x2))\n",
"True\n"
]
],
[
[
"Q6. Convert `a` into an ndarray and then convert it into a list again.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"a = [[1, 2], [3, 4]]\nx = np.array(a)\na2 = x.tolist()\nprint(a == a2)",
"True\n"
]
],
[
[
"## String formatting¶",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Q7. Convert `x` to a string, and revert it.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x = np.arange(10).reshape(2,5)\nx_str = np.array_str(x)\nprint(x_str, \"\\n\", type(x_str))\nx_str = x_str.replace(\"[\", \"\") # [] must be stripped\nx_str = x_str.replace(\"]\", \"\")\nx2 = np.fromstring(x_str, dtype=x.dtype, sep=\" \").reshape(x.shape)\nassert np.array_equal(x, x2)\n\n",
"[[0 1 2 3 4]\n [5 6 7 8 9]] \n <class 'str'>\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Text formatting options",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Q8. Print `x` such that all elements are displayed with precision=1, no suppress.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x = np.random.uniform(size=[10,100])\nnp.set_printoptions(precision=1, threshold=np.nan, suppress=True)\nprint(x)",
"[[ 0.5 0. 0.8 0.2 0.3 0.2 0.2 1. 0.4 0.8 0.6 0.2 0.5 0.1\n 0.4 0.1 0.9 0.6 0.1 0.5 0.8 0.8 0.8 0. 0.6 0.8 0.4 0.3\n 0.8 0.2 0.7 0.7 0.2 1. 0.8 0.1 0.2 0.1 0.3 0.1 0.5 0.9\n 0.6 0.9 0.6 0.5 0.8 0.3 0.3 0.5 0.1 0.6 0.1 0.3 0.6 0.2\n 0.4 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.6 0. 0.3 0.8 0.5 0.7 0.9 0.8 0.6\n 0.9 0.8 0.4 0.4 0.7 0.8 0. 0.1 0.5 0.4 0.7 1. 0.1 0.2\n 0.6 0.3 0.9 0.1 0.6 0.4 0.3 0.8 0.3 0.6 0.6 0.3 1. 0.2\n 0.9 0.2]\n [ 0.9 0.2 0.4 0.9 0.5 0.6 0.1 0.7 0. 0. 0.1 0.8 0.8 1. 0.2\n 0.8 0.3 0.2 1. 0.6 1. 0.3 0.4 0.4 0.7 0.5 0.4 0.8 0.5\n 0.9 0.3 0.5 0.7 0.4 0.2 0.3 0.9 0. 0.6 0.8 0.3 0.5 0.2\n 0.3 0. 0.6 0.5 0.2 0.5 0.8 0.2 0.8 0. 0.9 0. 0.7 0.1\n 0.4 0.2 0.5 0.6 0.2 0.6 0.1 0.1 0. 0.5 0.9 0.4 0.5 0.8\n 0.5 0.1 0.7 0. 1. 0.5 0.4 0.2 0. 1. 0.4 0.1 0.7 0.7\n 0.4 0.8 0.4 0.6 0.6 0.5 0.8 0.8 0.2 0.2 0.3 0.2 0.5 0.9\n 0.5]\n [ 0.3 0.6 0.4 0.5 0.5 0. 0.7 0.1 0. 0.9 0.5 0.7 0.6 0.3\n 0.9 0.5 0.1 0.4 0.1 0.9 0.8 0.6 0.8 0.8 0.1 0.4 0.9 0.1 1.\n 0.7 0.4 0.3 0.8 0.3 0.8 0.8 0.2 0.7 0.2 0.8 0.3 0.9 0.1\n 0.9 0.2 0.8 0.9 0.6 0.1 0.3 0.4 1. 0.1 0.7 0.3 0.9 0.3\n 0.5 0.9 0. 0.6 0. 0.8 0.1 0.9 0. 0.8 0.6 0.5 0.5 0.2 1.\n 0.4 0. 0.2 0. 0.9 0.9 0.8 0.2 0.7 0.3 0.2 0.1 1. 0.4\n 0.5 0.4 0.8 0.8 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.4 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.8 0.7 0.6]\n [ 0.2 0.6 0.9 0.7 0.1 0.1 1. 0.5 0.8 0.3 1. 0.4 0.1 0.5\n 0.6 0.8 0.8 0.8 0.1 1. 0.8 0. 0.7 0.6 0.8 0.2 0.5 0.9\n 0.4 0.8 0.7 0.2 0.8 0.6 0.9 0.6 0.9 0.8 0.9 1. 0.6 0.6\n 0.7 0.1 0.5 0.3 0. 0.8 0. 0.5 0.8 0.3 0.8 0.7 0.1 0.5\n 0.2 0.1 0.7 0. 0. 0.6 0. 0.8 0.7 0.1 0.4 0.1 0.2 0.1\n 0.9 0.6 0.9 0.3 0.4 0.9 0.2 0.6 0.8 0.9 0.6 0.8 0.5 0.1\n 0.6 1. 0. 0.7 0.7 0.4 0.1 0.9 0.4 0.1 0.7 0.6 0.3 0.9\n 0.3 0.5]\n [ 0.9 0.3 0.1 0.1 0.2 0.4 0.3 0.5 0.2 0. 0.5 0.4 0.5 0.3\n 0.6 1. 0.1 0.7 0.6 0.2 0.3 0.3 0.1 0.5 0.6 0. 0.6 0.7\n 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.6 0.1 0.9 0.9 0.1 0.9 0.1 0.6 0.6 0. 0.1\n 0.6 0.4 0.3 0.1 0.9 0.8 0.1 0.2 0.8 0.4 0.7 0.8 0.6 0.4\n 0.9 0.3 0.6 0.7 0.4 0.8 0.3 0. 0. 0.9 0.3 0.3 0.8 0.5\n 0.8 1. 0.2 0.6 0.6 0.2 0.2 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.6 0.4 0.4 0.8\n 0.2 0.5 0.7 0.7 0.1 0.9 0.5 0.6 0.3 0.3 0.6 0.8 0.6 0.8\n 0.4 0.3]\n [ 0.3 1. 0.6 0.9 0.6 1. 0.7 0.9 0.4 0.3 0.9 0.9 0.3 0.8\n 0.3 0.6 0.7 0.3 0.1 0.1 0.4 0.3 0.6 0.5 0.1 0.6 0.1 0.5\n 0.9 0.5 0.5 0.6 0.4 0.4 0.3 1. 0.6 0.6 0.3 0.1 0.4 0.7\n 0.7 0.1 0.5 0.1 0.3 0.1 0.6 0.7 0. 0.1 0.2 0.4 0.1 0.4\n 0.7 0.3 0.2 0.9 0.5 0. 0.4 0.9 1. 0.4 0. 0.2 0.3 0.9\n 0.3 0. 0.8 0.9 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.5 0. 0.9 0.6 0.6 0.1 0.6\n 0.9 0.1 0.8 0.6 0.6 0.5 0.7 1. 0.5 0.3 0.3 0.4 0.6 0.6 1.\n 0.2]\n [ 0.7 0.7 0.9 0.2 0.6 0.3 0.9 0.2 0.9 0.8 0.5 0.3 0.9 0.5 1.\n 0.6 0.9 0.5 0.5 0.1 0.8 0.3 0.9 0.5 0.7 1. 0.6 0.7 0.1\n 0.7 0.9 0.4 0.8 0.9 0.4 1. 0.1 1. 0.5 0.1 0.4 0.7 1. 0.4\n 0.3 0.2 0.2 0.6 0.6 0.3 0.7 0.5 0.7 0.1 0.3 0.5 1. 0.8\n 0.4 0.8 0.8 0.7 0.1 0.2 0.4 0.3 0.4 0.3 0.5 0.4 0.6 0.3\n 0.1 0.7 0.8 0.6 0.6 0.2 0.7 0.9 0.9 0.7 0.3 0.9 0.4 0.6 0.\n 0.4 0.4 0.2 0.8 0.3 0.1 0.2 0.6 0.5 0.9 0.8 0.9 0.7]\n [ 0.8 0.7 0.7 0.6 0.9 0.1 0.4 0.9 1. 0.3 0. 0.2 0.1 0.5\n 0.8 0.1 0.7 0.7 0.6 1. 0.7 1. 0.4 0.6 0.2 0.4 0.4 0.6 0.\n 0.1 1. 0.5 0.1 0.2 0.8 0.2 0.1 0.4 0.7 0.5 0.4 1. 0.5\n 0.5 0.4 0.8 0.2 0.1 0.7 0.2 0.1 0.4 0.3 0.6 0.9 0.9 0.9\n 0.9 0.1 0.1 0. 1. 0. 0.1 0.4 0.6 1. 0.4 0.9 0.3 0.2\n 0.7 0. 0.3 0.2 0.7 0.4 0.3 0.9 0.3 0. 0.5 0.2 0.3 0.1\n 0.2 0. 0.1 0.6 0.9 0.2 0.5 0.8 0.7 0. 0.4 0.8 0.8 0.5\n 0.2]\n [ 0.2 0.3 0. 0.1 0.8 0.4 0.1 0.2 0. 0.7 0. 1. 0.6 0.7\n 0.3 0.3 0.7 0.9 0.3 0.7 0.1 0.1 0.5 0.6 0.3 0.8 0.7 0.1\n 0.6 0.6 0.3 0.2 0.3 0.3 1. 0.1 0.1 0.2 0.4 0.4 0.6 0.5\n 0.7 0.7 0.2 0. 0.8 0.3 0.9 0.1 0.1 0.4 0.4 0.5 0.3 0.9\n 0.6 0.9 0.3 0.5 0. 0.4 0.8 1. 0.3 0.5 0.7 0.5 0.8 0.7\n 0.6 0.3 0.1 0.2 0.5 1. 0.9 0.5 0.6 0.6 0.2 0.8 0.6 0. 0.5\n 0.6 0.8 0.5 0.8 0.8 0.9 0.7 0.9 0.5 0.2 1. 1. 0.1 0.3\n 0.3]\n [ 0. 0.3 0.4 0.7 0.2 0.9 0.2 0.3 0.6 0.8 0.4 0.7 0.3 0.5\n 0.6 0.3 0.7 0. 0.1 0.1 0.9 0. 0.7 0.7 0.1 0.6 0.6 0. 0.3\n 0.5 0.9 0.3 0.1 0.3 0.1 0.9 0.6 0.3 0.3 0.4 0.4 0.2 0.3\n 0.1 0.5 0.3 0.8 0. 0.8 0.6 0.2 0.7 0.4 0.8 0.2 0.9 1. 1.\n 0.7 0.9 0.1 0.2 0. 0.5 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.7 0.7 0.5 0.9 0.2\n 0.2 0.1 0.2 0.1 0.7 1. 0.6 0.3 0.9 1. 0.3 0.3 0.7 0.9\n 0.5 0.8 0.9 0.7 0.2 0.7 0.3 0.1 0.9 0.2 0.5 0.6 0.3 0.4]]\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Base-n representations",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Q9. Convert 12 into a binary number in string format.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"out1 = np.binary_repr(12)\nout2 = np.base_repr(12, base=2)\nassert out1 == out2 # But out1 is better because it's much faster.\nprint(out1)",
"1100\n"
]
],
[
[
"Q10. Convert 12 into a hexadecimal number in string format.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.base_repr(1100, base=16)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a72b7fa82fb68ff6c347549ce7f613f6f311154
| 243,866 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
climate_starter.ipynb
|
ybefidi/SQLAlchemy-Homework
|
5a0188c8c473f6d971780a64fe2c8ca6ba42cf9e
|
[
"ADSL"
] | null | null | null |
climate_starter.ipynb
|
ybefidi/SQLAlchemy-Homework
|
5a0188c8c473f6d971780a64fe2c8ca6ba42cf9e
|
[
"ADSL"
] | null | null | null |
climate_starter.ipynb
|
ybefidi/SQLAlchemy-Homework
|
5a0188c8c473f6d971780a64fe2c8ca6ba42cf9e
|
[
"ADSL"
] | null | null | null | 129.923282 | 64,539 | 0.745364 |
[
[
[
"%matplotlib inline\nfrom matplotlib import style\nstyle.use('fivethirtyeight')\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import datetime as dt",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Reflect Tables into SQLAlchemy ORM",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Python SQL toolkit and Object Relational Mapper\nimport sqlalchemy\nfrom sqlalchemy.ext.automap import automap_base\nfrom sqlalchemy.orm import Session\nfrom sqlalchemy import create_engine, func",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"engine = create_engine(\"sqlite:///Resources/hawaii.sqlite\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# reflect an existing database into a new model\nBase = automap_base()\n# reflect the tables\nBase.prepare(engine, reflect=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# We can view all of the classes that automap found\nBase.classes.keys()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Save references to each table\nMeasurement = Base.classes.measurement\nStation = Base.classes.station",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create our session (link) from Python to the DB\nsession = Session(engine)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Exploratory Climate Analysis",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Design a query to retrieve the last 12 months of precipitation data and plot the results\n\n# Calculate the date 1 year ago from the last data point in the database\n\n# Perform a query to retrieve the data and precipitation scores\n\n# Save the query results as a Pandas DataFrame and set the index to the date column\n\n# Sort the dataframe by date\n\n# Use Pandas Plotting with Matplotlib to plot the data\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"last_date = session.query(func.max(Measurement.date)).first()\nprint(last_date)",
"('2017-08-23',)\n"
],
[
"last_date2=str(last_date)\nyear = int(last_date2[2]+ last_date2[3]+ last_date2[4]+ last_date2[5])\nprint(year)\nmonth = int(last_date2[7]+ last_date2[8])\nprint(month)\nday = int(last_date2[10]+ last_date2[11])\nprint(day)",
"2017\n8\n23\n"
],
[
"query_date = dt.date(year, month, day) - dt.timedelta(days=365)\nprint(\"Query Date: \", query_date)",
"Query Date: 2016-08-23\n"
],
[
"maxdate = dt.date(year, month, day)\nprcp_list = [] \nprcp_list = session.query(Measurement.date, Measurement.prcp).\\\n filter(Measurement.date > query_date).filter(Measurement.date <= maxdate).\\\n all()\n\nprint(prcp_list)",
"[('2016-08-24', 0.08), ('2016-08-25', 0.08), ('2016-08-26', 0.0), ('2016-08-27', 0.0), ('2016-08-28', 0.01), ('2016-08-29', 0.0), ('2016-08-30', 0.0), ('2016-08-31', 0.13), ('2016-09-01', 0.0), ('2016-09-02', 0.0), ('2016-09-03', 0.0), ('2016-09-04', 0.03), ('2016-09-05', None), ('2016-09-06', None), ('2016-09-07', 0.05), ('2016-09-08', 0.0), ('2016-09-09', 0.03), ('2016-09-10', 0.0), ('2016-09-11', 0.05), ('2016-09-12', 0.0), ('2016-09-13', 0.02), ('2016-09-14', 1.32), ('2016-09-15', 0.42), ('2016-09-16', 0.06), ('2016-09-17', 0.05), ('2016-09-18', 0.0), ('2016-09-19', 0.0), ('2016-09-20', 0.0), ('2016-09-21', 0.0), ('2016-09-22', 0.02), ('2016-09-23', 0.0), ('2016-09-24', 0.0), ('2016-09-25', 0.0), ('2016-09-26', 0.06), ('2016-09-27', 0.02), ('2016-09-28', 0.0), ('2016-09-29', 0.0), ('2016-09-30', 0.0), ('2016-10-01', 0.0), ('2016-10-02', 0.0), ('2016-10-03', 0.0), ('2016-10-04', 0.0), ('2016-10-05', 0.0), ('2016-10-06', 0.0), ('2016-10-07', 0.0), ('2016-10-08', 0.0), ('2016-10-09', 0.0), ('2016-10-10', 0.0), ('2016-10-11', 0.0), ('2016-10-12', 0.0), ('2016-10-13', 0.0), ('2016-10-14', 0.0), ('2016-10-15', 0.0), ('2016-10-16', 0.0), ('2016-10-17', 0.01), ('2016-10-18', 0.0), ('2016-10-19', 0.0), ('2016-10-20', 0.0), ('2016-10-21', 0.05), ('2016-10-22', 0.15), ('2016-10-23', 0.01), ('2016-10-24', 0.0), ('2016-10-25', 0.03), ('2016-10-26', 0.0), ('2016-10-27', 0.0), ('2016-10-28', 0.0), ('2016-10-29', 0.0), ('2016-10-30', 0.24), ('2016-10-31', 0.03), ('2016-11-01', 0.0), ('2016-11-02', 0.0), ('2016-11-03', 0.0), ('2016-11-04', 0.0), ('2016-11-05', 0.0), ('2016-11-06', 0.0), ('2016-11-07', 0.0), ('2016-11-08', 0.07), ('2016-11-09', 0.0), ('2016-11-10', 0.0), ('2016-11-11', 0.0), ('2016-11-12', 0.0), ('2016-11-13', 0.0), ('2016-11-14', 0.0), ('2016-11-15', 0.0), ('2016-11-16', 0.0), ('2016-11-17', 0.0), ('2016-11-18', 0.0), ('2016-11-19', 0.03), ('2016-11-20', 0.05), ('2016-11-21', 0.01), ('2016-11-22', 0.13), ('2016-11-23', 0.14), ('2016-11-24', 0.05), ('2016-11-25', 0.05), ('2016-11-26', 0.05), ('2016-11-27', 0.0), ('2016-11-28', 0.01), ('2016-11-29', 0.0), ('2016-11-30', 0.14), ('2016-12-01', 0.12), ('2016-12-02', 0.03), ('2016-12-03', 0.0), ('2016-12-04', 0.03), ('2016-12-05', 0.43), ('2016-12-06', 0.02), ('2016-12-07', 0.0), ('2016-12-08', 0.03), ('2016-12-09', 0.52), ('2016-12-10', 0.05), ('2016-12-11', 0.04), ('2016-12-12', 0.01), ('2016-12-13', 0.05), ('2016-12-14', 0.03), ('2016-12-15', 0.0), ('2016-12-16', 0.0), ('2016-12-17', 0.01), ('2016-12-18', 0.13), ('2016-12-19', 0.01), ('2016-12-20', 0.0), ('2016-12-21', 0.0), ('2016-12-22', 0.01), ('2016-12-23', 0.01), ('2016-12-24', 0.01), ('2016-12-25', 0.0), ('2016-12-26', 0.02), ('2016-12-27', 0.0), ('2016-12-28', 0.02), ('2016-12-29', 0.04), ('2016-12-30', 0.12), ('2016-12-31', 0.01), ('2017-01-01', 0.0), ('2017-01-02', 0.0), ('2017-01-03', 0.0), ('2017-01-04', 0.0), ('2017-01-05', 0.0), ('2017-01-06', 0.0), ('2017-01-07', 0.0), ('2017-01-08', 0.0), ('2017-01-09', 0.0), ('2017-01-10', 0.0), ('2017-01-11', 0.0), ('2017-01-12', 0.0), ('2017-01-13', 0.0), ('2017-01-14', 0.0), ('2017-01-15', 0.0), ('2017-01-16', 0.0), ('2017-01-17', 0.0), ('2017-01-18', 0.0), ('2017-01-19', 0.0), ('2017-01-20', 0.0), ('2017-01-21', 0.0), ('2017-01-22', 0.16), ('2017-01-23', 0.0), ('2017-01-24', 0.04), ('2017-01-25', 0.03), ('2017-01-26', 0.0), ('2017-01-27', 0.0), ('2017-01-28', 0.0), ('2017-01-29', 0.18), ('2017-01-30', 0.0), ('2017-01-31', 0.0), ('2017-02-01', 0.0), ('2017-02-02', 0.0), ('2017-02-03', 0.0), ('2017-02-04', 0.0), ('2017-02-05', 0.0), ('2017-02-06', 0.0), ('2017-02-07', 0.51), ('2017-02-08', 0.0), ('2017-02-09', 0.0), ('2017-02-10', 0.0), ('2017-02-11', 0.31), ('2017-02-12', 2.62), ('2017-02-13', 0.01), ('2017-02-14', 0.0), ('2017-02-15', 0.0), ('2017-02-16', 0.07), ('2017-02-17', 0.0), ('2017-02-18', 0.0), ('2017-02-19', 0.0), ('2017-02-20', 0.0), ('2017-02-21', 0.06), ('2017-02-22', 0.06), ('2017-02-23', 0.01), ('2017-02-24', 0.0), ('2017-02-25', 0.03), ('2017-02-26', 0.0), ('2017-02-27', 0.0), ('2017-02-28', 0.0), ('2017-03-01', 1.19), ('2017-03-02', 0.73), ('2017-03-03', 0.47), ('2017-03-04', 0.0), ('2017-03-05', 0.35), ('2017-03-06', 0.0), ('2017-03-07', 0.0), ('2017-03-08', 0.0), ('2017-03-09', 0.0), ('2017-03-10', 0.0), ('2017-03-11', 0.0), ('2017-03-12', 0.0), ('2017-03-13', 0.0), ('2017-03-14', 0.0), ('2017-03-15', 0.0), ('2017-03-16', 0.0), ('2017-03-17', 0.0), ('2017-03-18', 0.0), ('2017-03-19', 0.0), ('2017-03-20', 0.0), ('2017-03-21', 0.0), ('2017-03-22', 0.0), ('2017-03-23', 0.0), ('2017-03-24', 0.02), ('2017-03-25', 0.0), ('2017-03-26', 0.0), ('2017-03-27', 0.0), ('2017-03-28', 0.0), ('2017-03-29', 0.0), ('2017-03-30', 0.0), ('2017-03-31', 0.0), ('2017-04-01', 0.0), ('2017-04-02', 0.0), ('2017-04-03', 0.0), ('2017-04-04', 0.0), ('2017-04-05', 0.0), ('2017-04-06', 0.0), ('2017-04-07', 0.0), ('2017-04-08', 0.0), ('2017-04-09', 0.0), ('2017-04-10', 0.0), ('2017-04-11', 0.0), ('2017-04-12', 0.0), ('2017-04-13', 0.0), ('2017-04-14', 0.26), ('2017-04-15', 0.01), ('2017-04-16', 0.0), ('2017-04-17', 0.02), ('2017-04-18', 0.0), ('2017-04-19', 0.02), ('2017-04-20', 0.05), ('2017-04-21', 0.23), ('2017-04-22', 0.32), ('2017-04-23', 0.03), ('2017-04-24', 0.0), ('2017-04-25', 0.0), ('2017-04-26', 0.0), ('2017-04-27', 0.0), ('2017-04-28', 0.0), ('2017-04-29', 0.12), ('2017-04-30', 0.89), ('2017-05-01', 0.26), ('2017-05-02', 0.0), ('2017-05-03', 0.0), ('2017-05-04', 0.0), ('2017-05-05', 0.0), ('2017-05-06', 0.0), ('2017-05-07', 0.0), ('2017-05-08', 0.0), ('2017-05-10', 0.0), ('2017-05-11', 0.01), ('2017-05-12', 0.0), ('2017-05-13', 0.0), ('2017-05-14', 0.0), ('2017-05-15', 0.05), ('2017-05-16', 0.01), ('2017-05-17', 0.0), ('2017-05-18', 0.01), ('2017-05-19', 0.0), ('2017-05-20', 0.0), ('2017-05-21', 0.0), ('2017-05-22', 0.0), ('2017-05-23', 0.08), ('2017-05-24', 0.13), ('2017-05-25', 0.15), ('2017-05-27', 0.01), ('2017-05-28', 0.02), ('2017-05-29', 0.0), ('2017-05-30', 0.26), ('2017-05-31', 0.02), ('2017-06-01', 0.0), ('2017-06-02', 0.0), ('2017-06-03', 0.02), ('2017-06-04', 0.0), ('2017-06-05', 0.0), ('2017-06-06', 0.0), ('2017-06-07', 0.0), ('2017-06-08', 0.0), ('2017-06-09', 0.0), ('2017-06-10', 0.04), ('2017-06-11', 0.08), ('2017-06-12', 0.02), ('2017-06-13', 0.0), ('2017-06-14', 0.0), ('2017-06-15', 0.0), ('2017-06-16', 0.0), ('2017-06-17', 0.0), ('2017-06-18', 0.05), ('2017-06-19', 0.0), ('2017-06-20', 0.02), ('2017-06-21', 0.0), ('2017-06-22', 0.0), ('2017-06-23', 0.0), ('2017-06-24', 0.06), ('2017-06-25', 0.0), ('2017-06-26', 0.0), ('2017-06-27', 0.0), ('2017-06-28', 0.0), ('2017-06-29', 0.0), ('2017-06-30', 0.08), ('2017-07-01', 0.02), ('2017-07-02', 0.02), ('2017-07-03', 0.04), ('2017-07-04', 0.04), ('2017-07-05', 0.0), ('2017-07-06', 0.0), ('2017-07-07', 0.0), ('2017-07-08', 0.0), ('2017-07-09', 0.0), ('2017-07-10', 0.0), ('2017-07-11', 0.0), ('2017-07-12', 0.0), ('2017-07-13', 0.07), ('2017-07-14', 0.02), ('2017-07-15', 0.0), ('2017-07-16', 0.02), ('2017-07-17', 0.03), ('2017-07-18', 0.05), ('2017-07-20', 0.03), ('2017-07-21', 0.0), ('2017-07-22', 0.03), ('2017-07-23', 0.0), ('2017-07-24', 0.05), ('2017-07-25', 0.0), ('2017-07-26', 0.0), ('2017-07-27', 0.0), ('2017-07-28', 0.0), ('2017-07-29', 0.0), ('2017-07-30', 0.0), ('2017-07-31', 0.0), ('2017-08-01', 0.02), ('2017-08-02', 0.0), ('2017-08-03', 0.0), ('2017-08-04', 0.02), ('2017-08-05', 0.0), ('2017-08-06', 0.0), ('2017-08-07', 0.0), ('2017-08-08', 0.0), ('2017-08-09', 0.0), ('2017-08-10', 0.0), ('2017-08-11', 0.0), ('2017-08-12', 0.0), ('2017-08-13', 0.0), ('2017-08-14', 0.0), ('2017-08-15', 0.02), ('2017-08-18', 0.0), ('2017-08-19', 0.0), ('2017-08-20', 0.0), ('2017-08-21', 0.0), ('2017-08-22', 0.0), ('2017-08-23', 0.0), ('2016-08-24', 2.15), ('2016-08-25', 0.08), ('2016-08-26', 0.03), ('2016-08-27', 0.18), ('2016-08-28', 0.14), ('2016-08-29', 0.17), ('2016-08-30', 0.0), ('2016-08-31', 0.1), ('2016-09-01', 0.0), ('2016-09-02', 0.02), ('2016-09-03', 0.07), ('2016-09-04', 0.03), ('2016-09-05', 0.11), ('2016-09-06', 0.05), ('2016-09-07', 0.1), ('2016-09-08', 0.22), ('2016-09-09', 0.01), ('2016-09-10', 0.01), ('2016-09-11', 0.18), ('2016-09-12', 0.04), ('2016-09-13', 0.37), ('2016-09-14', 0.9), ('2016-09-15', 0.12), ('2016-09-16', 0.01), ('2016-09-17', 0.04), ('2016-09-18', 0.0), ('2016-09-19', 0.01), ('2016-09-20', 0.09), ('2016-09-21', 0.06), ('2016-09-22', 0.09), ('2016-09-23', 0.15), ('2016-09-24', 0.0), ('2016-09-25', 0.02), ('2016-09-26', 0.06), ('2016-09-27', 0.12), ('2016-09-28', 0.08), ('2016-09-29', 0.49), ('2016-09-30', 0.31), ('2016-10-01', 0.14), ('2016-10-02', 0.02), ('2016-10-03', 0.04), ('2016-10-04', 0.0), ('2016-10-05', 0.0), ('2016-10-06', 0.05), ('2016-10-07', 0.0), ('2016-10-08', 0.0), ('2016-10-09', 0.0), ('2016-10-10', 0.0), ('2016-10-11', 0.02), ('2016-10-12', 0.03), ('2016-10-13', 0.0), ('2016-10-14', 0.0), ('2016-10-15', 0.0), ('2016-10-16', 0.0), ('2016-10-17', 0.03), ('2016-10-18', 0.05), ('2016-10-19', 0.06), ('2016-10-20', 0.0), ('2016-10-21', 0.15), ('2016-10-22', 0.1), ('2016-10-23', 0.01), ('2016-10-24', 0.0), ('2016-10-25', 0.04), ('2016-10-26', 0.06), ('2016-10-27', 0.11), ('2016-10-28', 0.02), ('2016-10-29', 0.02), ('2016-10-30', 0.1), ('2016-10-31', 0.03), ('2016-11-01', 0.01), ('2016-11-02', 0.0), ('2016-11-03', 0.0), ('2016-11-04', 0.0), ('2016-11-05', 0.02), ('2016-11-06', 0.02), ('2016-11-07', 0.0), ('2016-11-08', 0.14), ('2016-11-09', 0.08), ('2016-11-10', 0.0), ('2016-11-11', 0.0), ('2016-11-12', 0.0), ('2016-11-13', 0.0), ('2016-11-14', 0.06), ('2016-11-15', 0.0), ('2016-11-16', 0.14), ('2016-11-17', 0.03), ('2016-11-18', 0.01), ('2016-11-19', 0.11), ('2016-11-20', 0.11), ('2016-11-21', 0.02), ('2016-11-22', 0.41), ('2016-11-23', 0.03), ('2016-11-24', 0.2), ('2016-11-25', 0.05), ('2016-11-26', 0.05), ('2016-11-27', 0.06), ('2016-11-28', 0.02), ('2016-11-29', 0.04), ('2016-11-30', 0.05), ('2016-12-01', 0.33), ('2016-12-02', 0.3), ('2016-12-03', 0.04), ('2016-12-04', 0.1), ('2016-12-05', 0.34), ('2016-12-06', 0.02), ('2016-12-07', 0.17), ('2016-12-08', 0.03), ('2016-12-09', 0.34), ('2016-12-10', 0.02), ('2016-12-11', 0.02), ('2016-12-12', 0.01), ('2016-12-13', 0.1), ('2016-12-14', 0.05), ('2016-12-15', 0.02), ('2016-12-16', 0.01), ('2016-12-17', 0.11), ('2016-12-18', 0.29), ('2016-12-19', 0.21), ('2016-12-20', 0.02), ('2016-12-21', 0.03), ('2016-12-22', 0.17), ('2016-12-23', 0.1), ('2016-12-24', 0.14), ('2016-12-25', 0.03), ('2016-12-26', 0.26), ('2016-12-27', 0.03), ('2016-12-28', 0.09), ('2016-12-29', 0.18), ('2016-12-30', 0.21), ('2016-12-31', 0.62), ('2017-01-01', 0.29), ('2017-01-02', 0.0), ('2017-01-03', 0.0), ('2017-01-04', 0.0), ('2017-01-05', 0.0), ('2017-01-06', 0.0), ('2017-01-07', 0.06), ('2017-01-08', 0.0), ('2017-01-09', 0.0), ('2017-01-10', 0.0), ('2017-01-11', 0.0), ('2017-01-12', 0.0), ('2017-01-13', 0.0), ('2017-01-14', 0.0), ('2017-01-15', 0.0), ('2017-01-16', 0.0), ('2017-01-17', 0.0), ('2017-01-18', 0.0), ('2017-01-19', 0.0), ('2017-01-20', 0.0), ('2017-01-21', 0.04), ('2017-01-22', 0.01), ('2017-01-23', 0.08), ('2017-01-24', 0.15), ('2017-01-25', 0.12), ('2017-01-26', 0.0), ('2017-01-27', 0.0), ('2017-01-28', 0.14), ('2017-01-29', 0.0), ('2017-01-30', 0.0), ('2017-01-31', 0.0), ('2017-02-01', 0.0), ('2017-02-02', 0.0), ('2017-02-03', 0.0), ('2017-02-04', 0.0), ('2017-02-05', 0.0), ('2017-02-06', 0.16), ('2017-02-07', 1.08), ('2017-02-08', 1.08), ('2017-02-09', 0.02), ('2017-02-10', 0.0), ('2017-02-11', 1.0), ('2017-02-12', 1.07), ('2017-02-13', 2.9), ('2017-02-14', 0.0), ('2017-02-15', 0.0), ('2017-02-16', 0.0), ('2017-02-17', 0.8), ('2017-02-18', 0.0), ('2017-02-19', 0.0), ('2017-02-20', 0.0), ('2017-02-21', 0.0), ('2017-02-22', 0.06), ('2017-02-23', 0.0), ('2017-02-24', 0.0), ('2017-02-25', 0.0), ('2017-02-26', 0.0), ('2017-02-27', 0.0), ('2017-02-28', 0.16), ('2017-03-01', 2.2), ('2017-03-02', 1.45), ('2017-03-03', 0.54), ('2017-03-04', 0.0), ('2017-03-05', 0.1), ('2017-03-06', 0.51), ('2017-03-07', 0.0), ('2017-03-08', 0.0), ('2017-03-09', 0.8), ('2017-03-10', 0.13), ('2017-03-11', 0.03), ('2017-03-12', 0.0), ('2017-03-13', 0.0), ('2017-03-14', 0.0), ('2017-03-15', 0.0), ('2017-03-16', 0.0), ('2017-03-17', 0.19), ('2017-03-18', 0.0), ('2017-03-19', 0.0), ('2017-03-20', 0.0), ('2017-03-21', 0.0), ('2017-03-22', 0.0), ('2017-03-23', 0.0), ('2017-03-24', 0.6), ('2017-03-25', 0.13), ('2017-03-26', 0.0), ('2017-03-27', 0.0), ('2017-03-28', 0.03), ('2017-03-29', 0.0), ('2017-03-30', 0.08), ('2017-03-31', 0.0), ('2017-04-01', 0.0), ('2017-04-02', 0.0), ('2017-04-03', 0.08), ('2017-04-04', 0.04), ('2017-04-05', 0.04), ('2017-04-06', 0.0), ('2017-04-07', 0.0), ('2017-04-08', 0.0), ('2017-04-09', 0.0), ('2017-04-10', 0.01), ('2017-04-11', 0.03), ('2017-04-12', 0.03), ('2017-04-13', 0.27), ('2017-04-14', 0.69), ('2017-04-15', 0.45), ('2017-04-16', 0.49), ('2017-04-17', 0.41), ('2017-04-18', 0.08), ('2017-04-19', 0.02), ('2017-04-20', 0.33), ('2017-04-21', 1.16), ('2017-04-22', 1.01), ('2017-04-23', 0.02), ('2017-04-24', 0.0), ('2017-04-25', 0.0), ('2017-04-26', 0.0), ('2017-04-27', 0.1), ('2017-04-28', 2.6), ('2017-04-29', 0.35), ('2017-04-30', 1.21), ('2017-05-01', 0.07), ('2017-05-02', 0.03), ('2017-05-03', 0.01), ('2017-05-04', 0.0), ('2017-05-05', 0.0), ('2017-05-06', 0.0), ('2017-05-07', 0.07), ('2017-05-08', 0.22), ('2017-05-09', 1.62), ('2017-05-10', 0.05), ('2017-05-11', 0.03), ('2017-05-12', 0.04), ('2017-05-13', 0.02), ('2017-05-14', 0.05), ('2017-05-15', 0.08), ('2017-05-16', 0.03), ('2017-05-17', 0.02), ('2017-05-18', 0.09), ('2017-05-19', 0.02), ('2017-05-20', 0.0), ('2017-05-21', 0.0), ('2017-05-22', 0.0), ('2017-05-23', 0.02), ('2017-05-24', 0.58), ('2017-05-25', 0.37), ('2017-05-26', 0.02), ('2017-05-27', 0.0), ('2017-05-28', 0.29), ('2017-05-29', 0.02), ('2017-05-30', 0.2), ('2017-05-31', 0.1), ('2017-06-01', 0.03), ('2017-06-02', 0.1), ('2017-06-03', 0.2), ('2017-06-04', 0.15), ('2017-06-05', 0.0), ('2017-06-06', 0.0), ('2017-06-07', 0.0), ('2017-06-08', 0.02), ('2017-06-09', 0.02), ('2017-06-10', 0.21), ('2017-06-11', 0.24), ('2017-06-12', 0.19), ('2017-06-13', 0.36), ('2017-06-14', 0.27), ('2017-06-15', 0.17), ('2017-06-16', 0.02), ('2017-06-17', 0.35), ('2017-06-18', 0.25), ('2017-06-19', 0.05), ('2017-06-20', 0.05), ('2017-06-21', 0.02), ('2017-06-22', 0.1), ('2017-06-23', 0.0), ('2017-06-24', 0.0), ('2017-06-25', 0.08), ('2017-06-26', 0.02), ('2017-06-27', 0.0), ('2017-06-28', 0.01), ('2017-06-29', 0.03), ('2017-06-30', 0.04), ('2017-07-01', 0.06), ('2017-07-02', 0.05), ('2017-07-03', 0.13), ('2017-07-04', 0.03), ('2017-07-05', 0.0), ('2017-07-06', 0.0), ('2017-07-07', 0.02), ('2017-07-08', 0.02), ('2017-07-09', 0.09), ('2017-07-10', 0.0), ('2017-07-11', 0.01), ('2017-07-12', 0.01), ('2017-07-13', 0.33), ('2017-07-14', 0.05), ('2017-07-15', 0.03), ('2017-07-16', 0.07), ('2017-07-17', 0.12), ('2017-07-18', 0.03), ('2017-07-19', 0.0), ('2017-07-20', 0.12), ('2017-07-21', 0.0), ('2017-07-22', 0.07), ('2017-07-23', 0.06), ('2017-07-24', 0.58), ('2017-07-25', 0.03), ('2017-07-26', 0.06), ('2017-07-27', 0.0), ('2017-07-28', 0.13), ('2017-07-29', 0.06), ('2017-07-30', 0.0), ('2017-07-31', 0.0), ('2016-08-24', 2.28), ('2016-08-25', 0.0), ('2016-08-26', 0.02), ('2016-08-27', 0.02), ('2016-08-28', 0.14), ('2016-08-29', 0.04), ('2016-08-31', None), ('2016-09-01', 0.0), ('2016-09-02', 0.19), ('2016-09-05', None), ('2016-09-06', 0.04), ('2016-09-07', 0.23), ('2016-09-08', 0.01), ('2016-09-09', 0.29), ('2016-09-12', None), ('2016-09-13', 0.32), ('2016-09-14', 1.84), ('2016-09-15', 0.07), ('2016-09-16', 0.07), ('2016-09-19', None), ('2016-09-20', 0.25), ('2016-09-21', 0.02), ('2016-09-22', 0.17), ('2016-09-23', 0.15), ('2016-09-24', 0.0), ('2016-09-25', 0.0), ('2016-09-26', 0.02), ('2016-09-27', 0.0), ('2016-09-28', 0.0), ('2016-09-29', 0.2), ('2016-09-30', 0.06), ('2016-10-01', 0.08), ('2016-10-02', 0.03), ('2016-10-03', 0.03), ('2016-10-04', 0.0), ('2016-10-05', 0.0), ('2016-10-06', 0.0), ('2016-10-07', 0.0), ('2016-10-10', None), ('2016-10-11', 0.04), ('2016-10-12', 0.0), ('2016-10-13', 0.02), ('2016-10-14', 0.0), ('2016-10-15', 0.02), ('2016-10-17', None), ('2016-10-18', 0.03), ('2016-10-19', 0.0), ('2016-10-20', 0.01), ('2016-10-21', 0.03), ('2016-10-23', None), ('2016-10-24', 0.01), ('2016-10-25', 0.0), ('2016-10-27', 0.2), ('2016-10-28', 0.07), ('2016-10-29', 0.26), ('2016-10-30', 0.14), ('2016-10-31', 0.0), ('2016-11-01', 0.0), ('2016-11-02', 0.0), ('2016-11-03', 0.0), ('2016-11-04', 0.0), ('2016-11-05', 0.0), ('2016-11-06', 0.0), ('2016-11-07', 0.13), ('2016-11-08', 0.02), ('2016-11-09', 0.17), ('2016-11-10', 0.0), ('2016-11-11', 0.0), ('2016-11-12', 0.0), ('2016-11-13', 0.0), ('2016-11-14', 0.05), ('2016-11-15', 0.0), ('2016-11-16', 0.18), ('2016-11-17', 0.0), ('2016-11-22', None), ('2016-11-25', None), ('2016-11-26', 0.02), ('2016-11-27', 0.03), ('2016-11-28', 0.0), ('2016-11-29', 0.04), ('2016-11-30', 0.03), ('2016-12-01', 0.07), ('2016-12-02', 0.4), ('2016-12-03', 0.26), ('2016-12-04', 0.0), ('2016-12-05', 0.2), ('2016-12-07', None), ('2016-12-08', 0.02), ('2016-12-09', 0.26), ('2016-12-10', 0.0), ('2016-12-12', None), ('2016-12-13', 0.34), ('2016-12-14', 0.12), ('2016-12-15', 0.07), ('2016-12-16', 0.0), ('2016-12-17', 0.0), ('2016-12-18', 0.04), ('2016-12-19', 0.0), ('2016-12-20', 0.0), ('2016-12-21', 0.09), ('2016-12-22', 0.05), ('2016-12-23', 0.03), ('2016-12-24', 0.13), ('2016-12-26', None), ('2016-12-27', 0.02), ('2016-12-28', 0.01), ('2016-12-29', 0.56), ('2016-12-30', 0.29), ('2016-12-31', 0.36), ('2017-01-01', 0.0), ('2017-01-02', 0.01), ('2017-01-03', 0.0), ('2017-01-04', 0.0), ('2017-01-05', 0.0), ('2017-01-06', 0.59), ('2017-01-07', 0.0), ('2017-01-08', 0.03), ('2017-01-09', 0.0), ('2017-01-10', 0.0), ('2017-01-11', 0.0), ('2017-01-13', None), ('2017-01-14', 0.0), ('2017-01-16', None), ('2017-01-17', 0.0), ('2017-01-18', 0.0), ('2017-01-19', 0.0), ('2017-01-20', 0.0), ('2017-01-21', 0.02), ('2017-01-23', None), ('2017-01-25', None), ('2017-01-26', 0.01), ('2017-01-27', 0.0), ('2017-01-28', 0.0), ('2017-01-30', None), ('2017-01-31', 0.0), ('2017-02-01', 0.0), ('2017-02-02', 0.0), ('2017-02-03', 0.0), ('2017-02-05', None), ('2017-02-06', 0.04), ('2017-02-07', 0.9), ('2017-02-08', 0.0), ('2017-02-09', 0.0), ('2017-02-10', 0.0), ('2017-02-11', 2.39), ('2017-02-12', 1.91), ('2017-02-13', 0.0), ('2017-02-14', 0.0), ('2017-02-15', 0.0), ('2017-02-16', 0.62), ('2017-02-17', 0.06), ('2017-02-20', None), ('2017-02-21', 0.0), ('2017-02-22', 0.11), ('2017-02-23', 0.0), ('2017-02-24', 0.0), ('2017-02-26', None), ('2017-02-27', 0.0), ('2017-02-28', 0.04), ('2017-03-01', 1.12), ('2017-03-03', None), ('2017-03-06', None), ('2017-03-07', 0.0), ('2017-03-08', 0.0), ('2017-03-09', 0.5), ('2017-03-10', 0.13), ('2017-03-12', None), ('2017-03-13', 0.0), ('2017-03-14', 0.0), ('2017-03-16', None), ('2017-03-17', 0.06), ('2017-03-18', 0.0), ('2017-03-20', None), ('2017-03-21', 0.0), ('2017-03-22', 0.0), ('2017-03-23', 0.0), ('2017-03-24', 0.15), ('2017-03-27', None), ('2017-03-28', 0.0), ('2017-03-29', 0.03), ('2017-03-30', 0.03), ('2017-03-31', 0.0), ('2017-04-01', 0.0), ('2017-04-02', 0.0), ('2017-04-03', 0.09), ('2017-04-04', 0.0), ('2017-04-05', 0.07), ('2017-04-06', 0.0), ('2017-04-07', 0.0), ('2017-04-09', None), ('2017-04-10', 0.0), ('2017-04-11', 0.16), ('2017-04-12', 0.29), ('2017-04-13', 0.0), ('2017-04-14', 0.29), ('2017-04-17', None), ('2017-04-18', 0.12), ('2017-04-19', 0.0), ('2017-04-20', 0.0), ('2017-04-21', 1.05), ('2017-04-22', 0.7), ('2017-04-24', None), ('2017-04-25', 0.0), ('2017-04-26', 0.14), ('2017-04-27', 0.02), ('2017-04-28', 0.09), ('2017-04-29', 0.95), ('2017-04-30', 1.17), ('2017-05-01', 0.03), ('2017-05-02', 0.01), ('2017-05-03', 0.01), ('2017-05-04', 0.08), ('2017-05-05', 0.28), ('2017-05-06', 0.06), ('2017-05-08', 0.95), ('2017-05-09', 0.52), ('2017-05-10', 0.0), ('2017-05-12', None), ('2017-05-15', None), ('2017-05-16', 0.05), ('2017-05-17', 0.0), ('2017-05-18', 0.16), ('2017-05-19', 0.01), ('2017-05-20', 0.01), ('2017-05-22', None), ('2017-05-23', 0.11), ('2017-05-24', 0.1), ('2017-05-25', 0.07), ('2017-05-26', 0.0), ('2017-05-27', 0.0), ('2017-05-28', 0.02), ('2017-05-29', 0.0), ('2017-05-30', 0.04), ('2017-05-31', 0.0), ('2017-06-01', 0.0), ('2017-06-02', 0.15), ('2017-06-03', 0.16), ('2017-06-04', 0.05), ('2017-06-05', 0.02), ('2017-06-06', 0.0), ('2017-06-07', 0.0), ('2017-06-08', 0.01), ('2017-06-09', 0.0), ('2017-06-10', 0.53), ('2017-06-11', 0.14), ('2017-06-12', 0.35), ('2017-06-13', 0.1), ('2017-06-14', 0.21), ('2017-06-15', 0.3), ('2017-06-16', 0.02), ('2017-06-17', 0.02), ('2017-06-18', 0.18), ('2017-06-19', 0.19), ('2017-06-20', 0.17), ('2017-06-23', None), ('2017-06-26', None), ('2017-06-29', None), ('2017-06-30', 0.0), ('2017-07-03', None), ('2017-07-05', None), ('2017-07-07', None), ('2017-07-08', 0.06), ('2017-07-09', 0.0), ('2017-07-10', 0.0), ('2017-07-11', 0.0), ('2017-07-12', 0.02), ('2017-07-13', 0.3), ('2017-07-14', 0.0), ('2017-07-15', 0.01), ('2017-07-16', 0.12), ('2017-07-17', 0.16), ('2017-07-18', 0.0), ('2017-07-19', 0.09), ('2017-07-20', 0.0), ('2017-07-21', 0.0), ('2017-07-22', 0.12), ('2017-07-23', 0.07), ('2017-07-24', 1.19), ('2017-07-25', 0.12), ('2017-07-26', 0.02), ('2017-07-27', 0.0), ('2017-07-28', 0.14), ('2017-07-29', 0.02), ('2017-07-31', None), ('2017-08-01', 0.12), ('2017-08-02', 0.05), ('2017-08-03', 0.01), ('2017-08-04', 0.04), ('2017-08-06', 0.0), ('2017-08-07', 0.0), ('2017-08-08', 0.1), ('2017-08-09', 0.0), ('2017-08-10', 0.0), ('2017-08-11', 0.0), ('2017-08-13', None), ('2017-08-14', 0.01), ('2017-08-15', 0.0), ('2017-08-16', 0.0), ('2017-08-17', 0.0), ('2017-08-18', 0.0), ('2017-08-19', 0.0), ('2017-08-20', 0.01), ('2017-08-21', 0.02), ('2017-08-23', 0.0), ('2016-08-24', None), ('2016-08-25', 0.0), ('2016-08-26', 0.04), ('2016-08-29', None), ('2016-08-30', 0.02), ('2016-08-31', None), ('2016-09-01', None), ('2016-09-02', None), ('2016-09-08', None), ('2016-09-09', None), ('2016-09-12', None), ('2016-09-13', None), ('2016-09-14', None), ('2016-09-15', None), ('2016-09-16', 0.0), ('2016-09-19', None), ('2016-09-20', 0.0), ('2016-09-22', 0.06), ('2016-09-23', 0.0), ('2016-09-26', None), ('2016-09-28', 0.0), ('2016-09-29', 0.04), ('2016-09-30', None), ('2016-10-03', None), ('2016-10-04', None), ('2016-10-05', None), ('2016-10-06', 0.07), ('2016-10-07', None), ('2016-10-11', None), ('2016-10-13', None), ('2016-10-17', None), ('2016-10-18', None), ('2016-10-19', None), ('2016-10-20', None), ('2016-10-21', None), ('2016-10-24', None), ('2016-10-25', 0.4), ('2016-10-26', 0.2), ('2016-10-27', None), ('2016-10-28', None), ('2016-10-31', None), ('2016-11-04', None), ('2016-11-07', None), ('2016-11-09', 0.0), ('2016-11-14', 0.02), ('2016-11-15', None), ('2016-11-16', None), ('2016-11-17', None), ('2016-11-18', None), ('2016-11-21', None), ('2016-11-22', None), ('2016-11-23', None), ('2016-11-28', None), ('2016-11-29', None), ('2016-11-30', None), ('2016-12-01', None), ('2016-12-02', None), ('2016-12-05', None), ('2016-12-06', None), ('2016-12-07', None), ('2016-12-08', 0.27), ('2016-12-09', None), ('2016-12-12', 0.02), ('2016-12-13', None), ('2016-12-14', None), ('2016-12-15', None), ('2016-12-16', None), ('2016-12-19', None), ('2016-12-20', None), ('2016-12-21', 0.06), ('2016-12-22', None), ('2016-12-23', None), ('2016-12-28', None), ('2016-12-29', None), ('2016-12-30', None), ('2017-01-09', None), ('2017-01-10', None), ('2017-01-11', None), ('2017-01-12', None), ('2017-01-13', None), ('2017-01-17', 0.0), ('2017-01-18', 0.0), ('2017-01-19', None), ('2017-01-20', None), ('2017-01-23', None), ('2017-01-24', None), ('2017-01-25', None), ('2017-01-26', 0.0), ('2017-01-27', 0.0), ('2017-01-30', 0.05), ('2017-01-31', 0.0), ('2017-02-01', 0.0), ('2017-02-02', 0.0), ('2017-02-03', 0.0), ('2017-02-06', None), ('2017-02-07', 0.0), ('2017-02-08', 0.0), ('2017-02-09', 0.0), ('2017-02-10', 0.0), ('2017-02-13', None), ('2017-02-14', 0.0), ('2017-02-15', None), ('2017-02-16', None), ('2017-02-17', 0.0), ('2017-02-21', None), ('2017-02-22', 0.17), ('2017-02-23', 0.0), ('2017-02-24', 0.0), ('2017-02-27', None), ('2017-02-28', None), ('2017-03-01', 2.4), ('2017-03-02', 0.44), ('2017-03-03', 0.14), ('2017-03-06', None), ('2017-03-07', None), ('2017-03-08', None), ('2017-03-09', 0.0), ('2017-03-10', 0.0), ('2017-03-13', None), ('2017-03-14', 0.06), ('2017-03-15', 0.0), ('2017-03-16', None), ('2017-03-17', None), ('2017-03-28', None), ('2017-03-29', None), ('2017-03-30', None), ('2017-03-31', 0.0), ('2017-04-03', None), ('2017-04-04', 0.0), ('2017-04-05', 0.0), ('2017-04-06', 0.0), ('2017-04-07', 0.0), ('2017-04-10', None), ('2017-04-11', None), ('2017-04-12', None), ('2017-04-13', None), ('2017-04-17', None), ('2017-04-18', 0.0), ('2017-04-19', None), ('2017-04-20', None), ('2017-04-21', None), ('2017-04-24', None), ('2017-04-25', None), ('2017-04-27', None), ('2017-04-28', None), ('2017-06-02', None), ('2017-06-05', None), ('2017-06-06', None), ('2017-06-07', None), ('2017-06-08', None), ('2017-06-09', None), ('2017-06-13', None), ('2017-06-14', None), ('2017-06-15', None), ('2017-06-16', None), ('2017-06-19', None), ('2017-06-20', None), ('2017-06-21', None), ('2017-06-22', 0.0), ('2017-06-23', 0.0), ('2017-06-26', None), ('2017-06-27', 0.0), ('2017-06-28', 0.0), ('2017-06-29', 0.0), ('2017-06-30', 0.12), ('2017-07-03', None), ('2017-07-05', None), ('2017-07-06', None), ('2017-07-07', None), ('2017-07-10', None), ('2017-07-11', None), ('2017-07-12', None), ('2017-07-13', None), ('2017-07-18', 0.0), ('2017-07-19', 0.0), ('2017-07-20', 0.0), ('2017-07-21', 0.0), ('2017-07-25', 0.0), ('2017-07-26', None), ('2017-07-27', None), ('2017-07-28', 0.01), ('2017-07-31', None), ('2016-08-24', 1.22), ('2016-08-25', 0.21), ('2016-08-26', 0.0), ('2016-08-27', 0.0), ('2016-08-28', 0.14), ('2016-08-29', 0.0), ('2016-08-30', 0.0), ('2016-08-31', 0.25), ('2016-09-02', None), ('2016-09-03', 0.08), ('2016-09-04', 0.74), ('2016-09-05', 0.02), ('2016-09-06', 0.03), ('2016-09-07', 0.11), ('2016-09-08', 0.01), ('2016-09-09', 0.23), ('2016-09-10', 0.14), ('2016-09-11', 0.12), ('2016-09-12', 0.15), ('2016-09-13', 0.46), ('2016-09-14', 1.19), ('2016-09-15', 0.17), ('2016-09-16', 0.01), ('2016-09-17', 0.0), ('2016-09-18', 0.04), ('2016-09-19', 0.05), ('2016-09-20', 0.04), ('2016-09-21', 0.0), ('2016-09-22', 0.01), ('2016-09-23', 0.0), ('2016-09-24', 0.0), ('2016-09-25', 0.0), ('2016-09-26', 0.34), ('2016-09-27', 0.05), ('2016-09-28', 0.0), ('2016-09-29', 0.18), ('2016-09-30', 0.15), ('2016-10-01', 0.07), ('2016-10-02', 0.0), ('2016-10-03', 0.0), ('2016-10-04', 0.0), ('2016-10-05', 0.0), ('2016-10-06', 0.0), ('2016-10-07', 0.0), ('2016-10-08', 0.0), ('2016-10-09', 0.0), ('2016-10-10', 0.0), ('2016-10-11', 0.0), ('2016-10-12', 0.0), ('2016-10-13', 0.0), ('2016-10-14', 0.0), ('2016-10-15', 0.0), ('2016-10-16', 0.0), ('2016-10-17', 0.12), ('2016-10-18', 0.02), ('2016-10-19', 0.0), ('2016-10-21', None), ('2016-10-22', 0.0), ('2016-10-23', 0.0), ('2016-10-24', 0.0), ('2016-10-25', 0.12), ('2016-10-26', 0.02), ('2016-10-27', 0.08), ('2016-10-28', 0.06), ('2016-10-29', 0.01), ('2016-10-30', 0.0), ('2016-10-31', 0.13), ('2016-11-01', 0.01), ('2016-11-02', 0.0), ('2016-11-03', 0.0), ('2016-11-04', 0.0), ('2016-11-05', 0.02), ('2016-11-06', 0.0), ('2016-11-07', 0.0), ('2016-11-08', 0.15), ('2016-11-09', 0.0), ('2016-11-10', 0.0), ('2016-11-11', 0.0), ('2016-11-12', 0.0), ('2016-11-13', 0.0), ('2016-11-14', 0.0), ('2016-11-15', 0.0), ('2016-11-16', 0.07), ('2016-11-17', 0.0), ('2016-11-18', 0.02), ('2016-11-19', 0.13), ('2016-11-20', 0.4), ('2016-11-21', 0.07), ('2016-11-22', 0.31), ('2016-11-23', 0.03), ('2016-11-24', 0.21), ('2016-11-25', 0.11), ('2016-11-26', 0.03), ('2016-11-27', 0.0), ('2016-11-28', 0.0), ('2016-11-29', 0.06), ('2016-11-30', 0.0), ('2016-12-01', 0.16), ('2016-12-02', 0.01), ('2016-12-03', 0.02), ('2016-12-04', 0.32), ('2016-12-05', 0.45), ('2016-12-06', 0.0), ('2016-12-07', 0.07), ('2016-12-08', 0.01), ('2016-12-10', None), ('2016-12-11', 0.06), ('2016-12-12', 0.0), ('2016-12-13', 0.15), ('2016-12-14', 0.05), ('2016-12-15', 0.0), ('2016-12-16', 0.0), ('2016-12-17', 0.16), ('2016-12-18', 0.27), ('2016-12-19', 0.02), ('2016-12-20', 0.01), ('2016-12-21', 0.06), ('2016-12-22', 0.14), ('2016-12-23', 0.02), ('2016-12-24', 0.06), ('2016-12-25', 0.0), ('2016-12-26', 0.06), ('2016-12-27', 0.0), ('2016-12-28', 0.06), ('2016-12-29', 0.05), ('2016-12-30', 0.07), ('2017-01-01', None), ('2017-01-03', None), ('2017-01-04', 0.18), ('2017-01-05', 0.42), ('2017-01-06', 0.01), ('2017-01-07', 0.0), ('2017-01-08', 0.0), ('2017-01-09', 0.0), ('2017-01-10', 0.0), ('2017-01-12', None), ('2017-01-15', None), ('2017-01-16', 0.0), ('2017-01-18', None), ('2017-01-19', 0.0), ('2017-01-20', 0.0), ('2017-01-21', 0.11), ('2017-01-22', 0.04), ('2017-01-23', 0.0), ('2017-01-24', 0.08), ('2017-01-25', 0.0), ('2017-01-26', 0.0), ('2017-01-27', 0.0), ('2017-01-29', None), ('2017-01-30', 0.0), ('2017-01-31', 0.0), ('2017-02-01', 0.0), ('2017-02-02', 0.0), ('2017-02-03', 0.0), ('2017-02-04', 0.0), ('2017-02-05', 0.0), ('2017-02-06', 0.0), ('2017-02-07', 1.8), ('2017-02-08', 0.0), ('2017-02-09', 0.0), ('2017-02-10', 0.0), ('2017-02-11', 5.04), ('2017-02-12', 0.07), ('2017-02-13', 0.0), ('2017-02-15', None), ('2017-02-16', 0.67), ('2017-02-17', 0.06), ('2017-02-18', 0.01), ('2017-02-20', None), ('2017-02-22', 0.13), ('2017-02-23', 0.0), ('2017-02-24', 0.0), ('2017-02-26', None), ('2017-02-27', 0.0), ('2017-02-28', 0.0), ('2017-03-01', 0.59), ('2017-03-02', 1.48), ('2017-03-03', 0.25), ('2017-03-04', 0.0), ('2017-03-06', None), ('2017-03-09', None), ('2017-03-10', 0.0), ('2017-03-11', 0.0), ('2017-03-12', 0.0), ('2017-03-13', 0.0), ('2017-03-14', 0.0), ('2017-03-15', 0.0), ('2017-03-16', 0.0), ('2017-03-17', 0.35), ('2017-03-18', 0.0), ('2017-03-19', 0.0), ('2017-03-20', 0.0), ('2017-03-21', 0.0), ('2017-03-22', 0.0), ('2017-03-23', 0.02), ('2017-03-24', 0.07), ('2017-03-25', 0.43), ('2017-03-26', 0.0), ('2017-03-27', 0.0), ('2017-03-28', 0.0), ('2017-03-29', 0.08), ('2017-03-30', 0.0), ('2017-03-31', 0.0), ('2017-04-01', 0.0), ('2017-04-02', 0.0), ('2017-04-03', 0.0), ('2017-04-04', 0.0), ('2017-04-05', 0.0), ('2017-04-06', 0.0), ('2017-04-07', 0.0), ('2017-04-09', None), ('2017-04-10', 0.0), ('2017-04-11', 0.0), ('2017-04-12', 0.0), ('2017-04-13', 0.0), ('2017-04-14', 0.36), ('2017-04-15', 0.0), ('2017-04-16', 0.0), ('2017-04-17', 0.3), ('2017-04-18', 0.15), ('2017-04-19', 0.0), ('2017-04-20', 0.35), ('2017-04-21', 2.36), ('2017-04-24', None), ('2017-04-25', 0.0), ('2017-04-26', 0.01), ('2017-04-27', 0.0), ('2017-04-28', 0.0), ('2017-04-29', 6.25), ('2017-04-30', 1.31), ('2017-05-01', 0.07), ('2017-05-02', 0.0), ('2017-05-03', 0.0), ('2017-05-04', 0.0), ('2017-05-05', 0.0), ('2017-05-06', 0.0), ('2017-05-07', 0.0), ('2017-05-08', 0.0), ('2017-05-09', 0.68), ('2017-05-10', 0.06), ('2017-05-11', 0.0), ('2017-05-12', 0.0), ('2017-05-13', 0.0), ('2017-05-14', 0.0), ('2017-05-15', 0.06), ('2017-05-16', 0.0), ('2017-05-17', 0.0), ('2017-05-18', 0.46), ('2017-05-20', None), ('2017-05-21', 0.0), ('2017-05-22', 0.0), ('2017-05-23', 0.0), ('2017-05-24', 0.61), ('2017-05-25', 0.55), ('2017-05-26', 0.0), ('2017-05-27', 0.0), ('2017-05-28', 0.0), ('2017-05-29', 0.0), ('2017-05-30', 0.11), ('2017-05-31', 0.0), ('2017-06-01', 0.0), ('2017-06-02', 0.0), ('2017-06-03', 0.15), ('2017-06-04', 0.0), ('2017-06-05', 0.0), ('2017-06-06', 0.0), ('2017-06-07', 0.0), ('2017-06-08', 0.0), ('2017-06-09', 0.0), ('2017-06-10', 0.13), ('2017-06-11', 0.25), ('2017-06-12', 0.14), ('2017-06-13', 0.03), ('2017-06-14', 0.06), ('2017-06-15', 0.0), ('2017-06-16', 0.0), ('2017-06-17', 0.0), ('2017-06-18', 0.0), ('2017-06-19', 0.01), ('2017-06-21', None), ('2017-06-22', 0.0), ('2017-06-23', 0.05), ('2017-06-24', 0.0), ('2017-06-25', 0.0), ('2017-06-26', 0.0), ('2017-06-27', 0.0), ('2017-06-28', 0.0), ('2017-06-29', 0.0), ('2017-06-30', 0.07), ('2017-07-02', None), ('2017-07-03', 0.02), ('2017-07-05', None), ('2017-07-06', 0.0), ('2017-07-07', 0.0), ('2017-07-08', 0.0), ('2017-07-09', 0.0), ('2017-07-10', 0.0), ('2017-07-11', 0.0), ('2017-07-12', 0.0), ('2017-07-13', 0.11), ('2017-07-14', 0.0), ('2017-07-15', 0.0), ('2017-07-16', 0.0), ('2017-07-17', 0.0), ('2017-07-18', 0.0), ('2017-07-19', 0.0), ('2017-07-20', 0.33), ('2017-07-21', 0.0), ('2017-07-22', 0.0), ('2017-07-24', None), ('2017-07-25', 0.05), ('2017-07-26', 0.0), ('2017-07-27', 0.0), ('2017-07-28', 0.0), ('2017-07-29', 0.0), ('2017-07-30', 0.0), ('2017-07-31', 0.0), ('2017-08-01', 0.0), ('2017-08-02', 0.0), ('2017-08-03', 0.0), ('2017-08-04', 0.0), ('2017-08-06', 0.0), ('2017-08-07', 0.0), ('2017-08-08', 0.0), ('2017-08-10', 0.0), ('2017-08-11', 0.0), ('2017-08-12', 0.0), ('2017-08-13', 0.0), ('2017-08-14', 0.08), ('2017-08-15', 0.06), ('2017-08-16', 0.07), ('2017-08-17', 0.05), ('2017-08-19', None), ('2017-08-21', None), ('2017-08-22', 0.0), ('2017-08-23', 0.08), ('2016-08-24', 2.15), ('2016-08-25', 0.06), ('2016-08-26', 0.01), ('2016-08-27', 0.12), ('2016-08-28', 0.6), ('2016-08-29', 0.35), ('2016-08-30', 0.0), ('2016-08-31', 0.24), ('2016-09-01', 0.02), ('2016-09-02', 0.01), ('2016-09-03', 0.12), ('2016-09-04', 0.14), ('2016-09-05', 0.03), ('2016-09-06', 0.11), ('2016-09-07', 0.16), ('2016-09-08', 0.07), ('2016-09-09', 0.16), ('2016-09-10', 0.09), ('2016-09-11', 0.3), ('2016-09-12', 0.31), ('2016-09-13', 0.34), ('2016-09-14', 2.33), ('2016-09-15', 0.83), ('2016-09-16', 0.06), ('2016-09-17', 0.36), ('2016-09-18', 0.07), ('2016-09-19', 0.01), ('2016-09-20', 0.22), ('2016-09-21', 0.07), ('2016-09-22', 0.34), ('2016-09-23', 0.94), ('2016-09-24', 0.01), ('2016-09-25', 0.03), ('2016-09-26', 0.17), ('2016-09-27', 0.17), ('2016-09-28', 0.0), ('2016-09-29', 0.59), ('2016-09-30', 0.25), ('2016-10-01', 0.14), ('2016-10-02', 0.06), ('2016-10-03', 0.16), ('2016-10-04', 0.03), ('2016-10-05', 0.01), ('2016-10-06', 0.0), ('2016-10-07', 0.0), ('2016-10-08', 0.0), ('2016-10-09', 0.0), ('2016-10-10', 0.0), ('2016-10-11', 0.28), ('2016-10-12', 0.03), ('2016-10-13', 0.0), ('2016-10-14', 0.0), ('2016-10-15', 0.04), ('2016-10-16', 0.0), ('2016-10-17', 0.01), ('2016-10-18', 0.02), ('2016-10-19', 0.11), ('2016-10-20', 0.0), ('2016-10-21', 0.0), ('2016-10-22', 0.15), ('2016-10-23', 0.02), ('2016-10-24', 0.08), ('2016-10-25', 0.11), ('2016-10-26', 0.01), ('2016-10-27', 0.22), ('2016-10-28', 0.05), ('2016-10-29', 0.1), ('2016-10-30', 0.16), ('2016-10-31', 0.07), ('2016-11-01', 0.1), ('2016-11-02', 0.0), ('2016-11-03', 0.0), ('2016-11-04', 0.0), ('2016-11-05', 0.03), ('2016-11-06', 0.01), ('2016-11-07', 0.0), ('2016-11-08', 0.21), ('2016-11-09', 0.11), ('2016-11-10', 0.0), ('2016-11-11', 0.0), ('2016-11-12', 0.0), ('2016-11-13', 0.0), ('2016-11-14', 0.0), ('2016-11-15', 0.0), ('2016-11-16', 0.24), ('2016-11-17', 0.01), ('2016-11-18', 0.0), ('2016-11-19', 0.11), ('2016-11-20', 0.39), ('2016-11-21', 0.11), ('2016-11-22', 2.05), ('2016-11-23', 0.25), ('2016-11-24', 0.3), ('2016-11-25', 0.08), ('2016-11-26', 0.06), ('2016-11-27', 0.17), ('2016-11-28', 0.0), ('2016-11-29', 0.09), ('2016-11-30', 0.05), ('2016-12-01', 0.37), ('2016-12-02', 0.35), ('2016-12-03', 0.77), ('2016-12-04', 0.04), ('2016-12-05', 0.22), ('2016-12-06', 0.0), ('2016-12-07', 0.12), ('2016-12-08', 0.07), ('2016-12-09', 0.31), ('2016-12-10', 0.02), ('2016-12-11', 0.0), ('2016-12-12', 0.0), ('2016-12-13', 0.04), ('2016-12-14', 0.92), ('2016-12-15', 0.14), ('2016-12-16', 0.03), ('2016-12-17', 0.07), ('2016-12-18', 0.16), ('2016-12-19', 0.03), ('2016-12-20', 0.0), ('2016-12-21', 0.11), ('2016-12-22', 0.86), ('2016-12-23', 0.24), ('2016-12-24', 0.2), ('2016-12-25', 0.02), ('2016-12-26', 0.22), ('2016-12-27', 0.05), ('2016-12-28', 0.09), ('2016-12-29', 0.52), ('2016-12-30', 0.29), ('2016-12-31', 0.25), ('2017-01-01', 0.03), ('2017-01-02', 0.01), ('2017-01-03', 0.0), ('2017-01-04', 0.0), ('2017-01-05', 0.06), ('2017-01-06', 0.1), ('2017-01-07', 0.0), ('2017-01-08', 0.0), ('2017-01-09', 0.0), ('2017-01-10', 0.0), ('2017-01-11', 0.0), ('2017-01-12', 0.0), ('2017-01-13', 0.0), ('2017-01-14', 0.01), ('2017-01-15', 0.0), ('2017-01-16', 0.0), ('2017-01-17', 0.0), ('2017-01-18', 0.0), ('2017-01-19', 0.02), ('2017-01-20', 0.0), ('2017-01-21', 0.03), ('2017-01-22', 0.09), ('2017-01-23', 0.01), ('2017-01-24', 0.13), ('2017-01-25', 0.79), ('2017-01-26', 0.0), ('2017-01-27', 0.03), ('2017-01-28', 0.0), ('2017-01-29', 0.26), ('2017-01-30', 0.0), ('2017-01-31', 0.0), ('2017-02-01', 0.0), ('2017-02-02', 0.0), ('2017-02-03', 0.0), ('2017-02-04', 0.0), ('2017-02-05', 0.0), ('2017-02-06', 0.18), ('2017-02-07', 1.32), ('2017-02-08', 0.0), ('2017-02-09', 0.0), ('2017-02-10', 0.0), ('2017-02-11', 1.73), ('2017-02-12', 2.98), ('2017-02-13', 0.01), ('2017-02-14', 0.0), ('2017-02-15', 0.01), ('2017-02-16', 0.73), ('2017-02-17', 0.13), ('2017-02-18', 0.0), ('2017-02-19', 0.09), ('2017-02-20', 0.0), ('2017-02-21', 0.0), ('2017-02-22', 0.06), ('2017-02-23', 0.0), ('2017-02-24', 0.0), ('2017-02-25', 0.0), ('2017-02-26', 0.0), ('2017-02-27', 0.0), ('2017-02-28', 0.04), ('2017-03-01', 2.12), ('2017-03-02', 1.88), ('2017-03-03', 0.27), ('2017-03-04', 0.0), ('2017-03-05', 0.41), ('2017-03-06', 0.03), ('2017-03-07', 0.0), ('2017-03-08', 0.0), ('2017-03-09', 0.65), ('2017-03-10', 0.03), ('2017-03-11', 0.01), ('2017-03-12', 0.0), ('2017-03-13', 0.0), ('2017-03-14', 0.0), ('2017-03-15', 0.06), ('2017-03-16', 0.0), ('2017-03-17', 0.12), ('2017-03-18', 0.0), ('2017-03-19', 0.0), ('2017-03-20', 0.02), ('2017-03-21', 0.09), ('2017-03-22', 0.0), ('2017-03-23', 0.0), ('2017-03-24', 0.12), ('2017-03-25', 0.93), ('2017-03-26', 0.0), ('2017-03-27', 0.01), ('2017-03-28', 0.0), ('2017-03-29', 0.01), ('2017-03-30', 0.04), ('2017-03-31', 0.01), ('2017-04-01', 0.21), ('2017-04-02', 0.0), ('2017-04-03', 0.26), ('2017-04-04', 0.09), ('2017-04-05', 0.1), ('2017-04-06', 0.06), ('2017-04-07', 0.0), ('2017-04-08', 0.0), ('2017-04-09', 0.0), ('2017-04-10', 0.01), ('2017-04-11', 0.03), ('2017-04-12', 0.11), ('2017-04-13', 0.59), ('2017-04-14', 2.3), ('2017-04-15', 0.38), ('2017-04-16', 0.47), ('2017-04-17', 1.04), ('2017-04-18', 2.03), ('2017-04-19', 0.02), ('2017-04-20', 0.05), ('2017-04-21', 1.74), ('2017-04-22', 1.58), ('2017-04-23', 0.06), ('2017-04-24', 0.01), ('2017-04-25', 0.0), ('2017-04-26', 0.02), ('2017-04-27', 0.19), ('2017-04-28', 0.76), ('2017-04-29', 0.37), ('2017-04-30', 1.04), ('2017-05-01', 0.13), ('2017-05-02', 0.01), ('2017-05-03', 0.01), ('2017-05-04', 0.0), ('2017-05-05', 0.0), ('2017-05-06', 0.0), ('2017-05-07', 0.02), ('2017-05-08', 0.73), ('2017-05-09', 1.58), ('2017-05-10', 0.2), ('2017-05-11', 0.12), ('2017-05-12', 0.02), ('2017-05-13', 0.12), ('2017-05-14', 0.17), ('2017-05-15', 0.09), ('2017-05-16', 0.03), ('2017-05-17', 0.07), ('2017-05-18', 0.13), ('2017-05-19', 0.01), ('2017-05-20', 0.02), ('2017-05-21', 0.01), ('2017-05-22', 0.06), ('2017-05-23', 0.06), ('2017-05-24', 0.3), ('2017-05-25', 0.2), ('2017-05-26', 0.0), ('2017-05-27', 0.0), ('2017-05-28', 0.08), ('2017-05-29', 0.4), ('2017-05-30', 1.12), ('2017-05-31', 0.25), ('2017-06-01', 0.0), ('2017-06-02', 0.09), ('2017-06-03', 0.08), ('2017-06-04', 0.13), ('2017-06-05', 0.05), ('2017-06-06', 0.0), ('2017-06-07', 0.0), ('2017-06-08', 0.0), ('2017-06-09', 0.02), ('2017-06-10', 0.62), ('2017-06-11', 0.74), ('2017-06-12', 0.24), ('2017-06-13', 0.24), ('2017-06-14', 0.22), ('2017-06-15', 0.55), ('2017-06-16', 0.06), ('2017-06-17', 0.07), ('2017-06-18', 0.24), ('2017-06-19', 0.08), ('2017-06-20', 0.0), ('2017-06-21', 0.19), ('2017-06-22', 0.06), ('2017-06-23', 0.12), ('2017-06-24', 0.36), ('2017-06-25', 0.02), ('2017-06-26', 0.06), ('2017-06-27', 0.01), ('2017-06-28', 0.0), ('2017-06-29', 0.0), ('2017-06-30', 0.01), ('2017-07-01', 0.08), ('2017-07-02', 0.15), ('2017-07-03', 0.15), ('2017-07-04', 0.08), ('2017-07-05', 0.0), ('2017-07-06', 0.0), ('2017-07-07', 0.18), ('2017-07-08', 0.0), ('2017-07-09', 0.11), ('2017-07-10', 0.02), ('2017-07-11', 0.02), ('2017-07-12', 0.28), ('2017-07-13', 0.32), ('2017-07-14', 0.2), ('2017-07-15', 0.05), ('2017-07-16', 0.1), ('2017-07-17', 0.21), ('2017-07-18', 0.05), ('2017-07-19', 0.05), ('2017-07-20', 0.06), ('2017-07-21', 0.03), ('2017-07-22', 0.2), ('2017-07-23', 0.2), ('2017-07-24', 0.61), ('2017-07-25', 0.11), ('2017-07-26', 0.12), ('2017-07-27', 0.01), ('2017-07-28', 0.09), ('2017-07-29', 0.23), ('2017-07-30', 0.0), ('2017-07-31', 0.0), ('2017-08-04', 0.0), ('2017-08-05', 0.06), ('2017-08-06', 0.0), ('2017-08-13', 0.0), ('2017-08-14', 0.0), ('2017-08-15', 0.32), ('2017-08-16', 0.12), ('2017-08-17', 0.01), ('2017-08-18', 0.06), ('2016-08-24', 1.45), ('2016-08-25', 0.11), ('2016-08-27', None), ('2016-08-28', 2.07), ('2016-08-29', 0.9), ('2016-08-30', 0.05), ('2016-08-31', 2.46), ('2016-09-01', 0.01), ('2016-09-02', 0.03), ('2016-09-03', 1.0), ('2016-09-04', 0.44), ('2016-09-05', 0.18), ('2016-09-06', 1.0), ('2016-09-07', 1.35), ('2016-09-08', 0.15), ('2016-09-09', 0.35), ('2016-09-10', 1.16), ('2016-09-11', 0.6), ('2016-09-12', 1.04), ('2016-09-13', 1.2), ('2016-09-14', 6.7), ('2016-09-15', 3.35), ('2016-09-16', 0.61), ('2016-09-17', 0.23), ('2016-09-18', 0.42), ('2016-09-19', 0.25), ('2016-09-20', 0.43), ('2016-09-21', 1.02), ('2016-09-22', 0.75), ('2016-09-23', 0.33), ('2016-09-24', 0.27), ('2016-09-25', 0.04), ('2016-09-26', 1.02), ('2016-09-27', 1.0), ('2016-09-28', 0.05), ('2016-09-29', 1.49), ('2016-09-30', 0.38), ('2016-10-01', 1.02), ('2016-10-02', 0.61), ('2016-10-03', 0.46), ('2016-10-04', 3.46), ('2016-10-05', 0.81), ('2016-10-06', 0.04), ('2016-10-07', 0.01), ('2016-10-08', 0.04), ('2016-10-09', 0.0), ('2016-10-10', 0.0), ('2016-10-11', 0.35), ('2016-10-12', 0.02), ('2016-10-13', 0.06), ('2016-10-14', 0.0), ('2016-10-15', 0.33), ('2016-10-16', 0.0), ('2016-10-17', 0.38), ('2016-10-18', 0.48), ('2016-10-19', 0.0), ('2016-10-20', 1.0), ('2016-10-21', 0.09), ('2016-10-22', 1.37), ('2016-10-23', 0.24), ('2016-10-24', 0.7), ('2016-10-25', 0.4), ('2016-10-26', 0.0), ('2016-10-27', 1.25), ('2016-10-28', 0.37), ('2016-10-29', 0.25), ('2016-10-30', 0.95), ('2016-10-31', 1.35), ('2016-11-01', 0.09), ('2016-11-02', 0.04), ('2016-11-03', 0.02), ('2016-11-04', 0.06), ('2016-11-05', 0.38), ('2016-11-06', 0.05), ('2016-11-07', 0.05), ('2016-11-08', 0.53), ('2016-11-09', 0.04), ('2016-11-10', 0.01), ('2016-11-11', 0.0), ('2016-11-12', 0.0), ('2016-11-13', 0.0), ('2016-11-14', 0.02), ('2016-11-15', 0.05), ('2016-11-16', 0.91), ('2016-11-17', 0.02), ('2016-11-20', None), ('2016-11-21', 2.87), ('2016-11-22', 2.11), ('2016-11-23', 0.22), ('2016-11-24', 0.72), ('2016-11-25', 1.03), ('2016-11-26', 0.3), ('2016-11-27', 0.29), ('2016-11-28', 0.69), ('2016-11-29', 0.2), ('2016-11-30', 0.79), ('2016-12-01', 0.72), ('2016-12-02', 1.27), ('2016-12-03', 1.62), ('2016-12-04', 0.31), ('2016-12-05', 1.6), ('2016-12-06', 0.0), ('2016-12-07', 0.02), ('2016-12-08', 0.03), ('2016-12-09', 0.42), ('2016-12-10', 0.04), ('2016-12-11', 0.13), ('2016-12-12', 0.01), ('2016-12-13', 0.09), ('2016-12-14', 0.33), ('2016-12-15', 0.03), ('2016-12-16', 0.0), ('2016-12-18', None), ('2016-12-19', 0.15), ('2016-12-20', 0.0), ('2016-12-21', 0.55), ('2016-12-22', 1.24), ('2016-12-23', 0.83), ('2016-12-24', 1.08), ('2016-12-25', 0.38), ('2016-12-26', 1.48), ('2016-12-27', 0.14), ('2016-12-28', 0.14), ('2016-12-29', 1.03), ('2016-12-30', 2.37), ('2016-12-31', 0.9), ('2017-01-01', 0.03), ('2017-01-02', 0.0), ('2017-01-03', 0.0), ('2017-01-04', 0.0), ('2017-01-05', 0.47), ('2017-01-06', 0.1), ('2017-01-07', 0.0), ('2017-01-08', 0.03), ('2017-01-09', 0.0), ('2017-01-10', 0.0), ('2017-01-11', 0.0), ('2017-01-12', 0.0), ('2017-01-13', 0.0), ('2017-01-14', 0.0), ('2017-01-15', 0.01), ('2017-01-16', 0.0), ('2017-01-17', 0.0), ('2017-01-18', 0.07), ('2017-01-19', 0.0), ('2017-01-20', 0.0), ('2017-01-21', 0.08), ('2017-01-22', 0.72), ('2017-01-23', 0.85), ('2017-01-24', 1.85), ('2017-01-25', 2.64), ('2017-01-26', 0.1), ('2017-01-27', 0.03), ('2017-01-28', 0.0), ('2017-01-29', 0.55), ('2017-01-30', 0.0), ('2017-01-31', 0.0), ('2017-02-01', 0.0), ('2017-02-02', 0.0), ('2017-02-04', None), ('2017-02-05', 0.0), ('2017-02-06', 0.0), ('2017-02-07', 1.79), ('2017-02-08', 0.0), ('2017-02-09', 0.0), ('2017-02-10', 0.0), ('2017-02-11', 0.73), ('2017-02-12', 1.83), ('2017-02-13', 0.0), ('2017-02-14', 0.01), ('2017-02-15', 0.07), ('2017-02-16', 0.13), ('2017-02-18', None), ('2017-02-19', 0.1), ('2017-02-20', 0.0), ('2017-02-21', 0.07), ('2017-02-22', 0.32), ('2017-02-23', 0.0), ('2017-02-24', 0.0), ('2017-02-25', 0.12), ('2017-02-26', 0.0), ('2017-02-27', 0.0), ('2017-02-28', 0.58), ('2017-03-01', 2.0), ('2017-03-02', 0.58), ('2017-03-03', 0.56), ('2017-03-04', 0.0), ('2017-03-05', 0.35), ('2017-03-06', 0.0), ('2017-03-07', 0.0), ('2017-03-08', 0.0), ('2017-03-09', 0.01), ('2017-03-10', 0.0), ('2017-03-11', 0.0), ('2017-03-13', None), ('2017-03-14', 0.0), ('2017-03-15', 0.0), ('2017-03-16', 0.0), ('2017-03-18', None), ('2017-03-19', 0.0), ('2017-03-20', 0.0), ('2017-03-21', 0.0), ('2017-03-22', 0.0), ('2017-03-23', 0.03), ('2017-03-24', 0.17), ('2017-03-25', 0.48), ('2017-03-26', 0.0), ('2017-03-27', 0.0), ('2017-03-28', 0.68), ('2017-03-29', 0.07), ('2017-03-31', None), ('2017-04-01', 0.2), ('2017-04-02', 0.0), ('2017-04-03', 0.23), ('2017-04-04', 0.02), ('2017-04-05', 0.45), ('2017-04-06', 0.0), ('2017-04-08', None), ('2017-04-09', 0.0), ('2017-04-10', 0.0), ('2017-04-11', 0.25), ('2017-04-12', 0.65), ('2017-04-13', 0.23), ('2017-04-14', 2.82), ('2017-04-15', 0.9), ('2017-04-16', 0.11), ('2017-04-17', 1.3), ('2017-04-18', 0.98), ('2017-04-19', 0.14), ('2017-04-20', 0.0), ('2017-04-21', 1.84), ('2017-04-22', 1.35), ('2017-04-23', 0.35), ('2017-04-24', 0.05), ('2017-04-25', 0.0), ('2017-04-26', 0.22), ('2017-04-27', 0.11), ('2017-04-28', 0.79), ('2017-04-29', 0.0), ('2017-04-30', 0.8), ('2017-05-01', 0.25), ('2017-05-02', 0.0), ('2017-05-04', None), ('2017-05-05', 0.1), ('2017-05-06', 0.0), ('2017-05-07', 0.03), ('2017-05-08', 1.11), ('2017-05-09', 0.23), ('2017-05-10', 0.55), ('2017-05-11', 0.44), ('2017-05-12', 0.1), ('2017-05-13', 0.1), ('2017-05-14', 1.0), ('2017-05-15', 0.6), ('2017-05-16', 0.3), ('2017-05-17', 0.06), ('2017-05-18', 0.0), ('2017-05-20', None), ('2017-05-21', 0.0), ('2017-05-22', 0.3), ('2017-05-23', 0.44), ('2017-05-24', 2.17), ('2017-05-25', 0.88), ('2017-05-26', 0.0), ('2017-05-27', 0.5), ('2017-05-28', 0.0), ('2017-05-30', None), ('2017-06-01', 0.01), ('2017-06-03', None), ('2017-06-04', 0.82), ('2017-06-05', 0.01), ('2017-06-06', 0.0), ('2017-06-07', 0.01), ('2017-06-08', 0.0), ('2017-06-10', None), ('2017-06-11', 0.7), ('2017-06-12', 0.81), ('2017-06-13', 0.65), ('2017-06-14', 0.81), ('2017-06-15', 1.69), ('2017-06-16', 0.1), ('2017-06-17', 0.1), ('2017-06-18', 0.7), ('2017-06-19', 0.4), ('2017-06-20', 0.31), ('2017-06-21', 0.3), ('2017-06-22', 0.28), ('2017-06-23', 0.5), ('2017-06-24', 0.22), ('2017-06-25', 0.5), ('2017-06-26', 0.02), ('2017-06-27', 0.1), ('2017-06-28', 0.02), ('2017-06-29', 0.04), ('2017-06-30', 0.2), ('2017-07-01', 0.1), ('2017-07-02', 0.5), ('2017-07-03', 0.4), ('2017-07-04', 0.0), ('2017-07-05', 0.0), ('2017-07-06', 0.02), ('2017-07-07', 0.3), ('2017-07-08', 0.02), ('2017-07-09', 0.0), ('2017-07-10', 0.02), ('2017-07-11', 0.0), ('2017-07-12', 0.05), ('2017-07-13', 0.68), ('2017-07-14', 0.68), ('2017-07-15', 0.1), ('2017-07-16', 0.5), ('2017-07-17', 0.39), ('2017-07-18', 2.4), ('2017-07-19', 0.27), ('2017-07-20', 0.7), ('2017-07-21', 0.1), ('2017-07-22', 4.0), ('2017-07-23', 0.8), ('2017-07-24', 0.84), ('2017-07-25', 0.3), ('2017-07-26', 0.3), ('2017-07-27', 0.0), ('2017-07-28', 0.4), ('2017-07-29', 0.3), ('2017-07-30', 0.3), ('2017-07-31', 0.0), ('2017-08-01', None), ('2017-08-02', 0.25), ('2017-08-03', 0.06), ('2017-08-05', None), ('2017-08-06', None), ('2017-08-07', 0.05), ('2017-08-08', 0.34), ('2017-08-09', 0.15), ('2017-08-10', 0.07), ('2017-08-11', None), ('2017-08-12', 0.14), ('2017-08-13', None), ('2017-08-14', 0.22), ('2017-08-15', 0.42), ('2017-08-16', 0.42), ('2017-08-17', 0.13), ('2017-08-18', None), ('2017-08-19', 0.09), ('2017-08-20', None), ('2017-08-21', 0.56), ('2017-08-22', 0.5), ('2017-08-23', 0.45)]\n"
],
[
"prcpdf = pd.DataFrame(prcp_list)\nprcpdf['date'] = pd.to_datetime(prcpdf['date'])\nprcpdf.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"prcpdf2 = prcpdf.set_index('date')\nprcpdf2.rename(columns = {'prcp': 'Precipitaion'}, inplace=True)\nprcpdf2.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"prcpdf2.plot(figsize=(15, 8),sort_columns=True,rot=50,use_index=True,legend=True)\nplt.xlabel('Date')\nplt.ylabel(\"Precipitation\")\nplt.title(\"Precipitation \", fontsize=20)\nplt.savefig('barplot1')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Use Pandas to calcualte the summary statistics for the precipitation data\nprcpdf2.describe()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Design a query to show how many stations are available in this dataset?\nstationcount = []\nstationcount = session.query(Station.station).count()\nprint(stationcount)",
"9\n"
],
[
"# What are the most active stations? (i.e. what stations have the most rows)?\n# List the stations and the counts in descending order.\ns_results = session.query(Measurement.station, func.count(Measurement.station)).\\\n group_by(Measurement.station).\\\n order_by(func.count(Measurement.station).desc()).all()\ns_results",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Using the station id from the previous query, calculate the lowest temperature recorded, \n# highest temperature recorded, and average temperature of the most active station?\n\nbest_station = s_results[0][0]\nsession.query(func.min(Measurement.tobs), func.avg(Measurement.tobs), func.max(Measurement.tobs)).\\\n filter(Measurement.station == best_station).all()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Choose the station with the highest number of temperature observations.\n# Query the last 12 months of temperature observation data for this station and plot the results as a histogram\n\nstationhits[0][0]\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"hist_list = [] \nhist_list = session.query(Measurement.station, Measurement.date, Measurement.tobs).\\\n filter(Measurement.station == stationhits[0][0]).filter(Measurement.date > query_date).\\\n filter(Measurement.date <= maxdate).\\\n all()\n\nhist_df = pd.DataFrame(hist_list)\nhist_df.head()\n\nhist_df['date'] = pd.to_datetime(hist_df['date'])\nhist_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"hist_temps=hist_df['tobs']\nplt.hist(hist_temps, bins=12)\nplt.title(\"Temperature Observations \", fontsize=20)\nplt.ylabel('Frequency', fontsize=16)\nlabels = ['tobs']\nplt.legend(labels)\nplt.savefig('histogram1')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# This function called `calc_temps` will accept start date and end date in the format '%Y-%m-%d' \n# and return the minimum, average, and maximum temperatures for that range of dates\ndef calc_temps(start_date, end_date):\n \"\"\"TMIN, TAVG, and TMAX for a list of dates.\n \n Args:\n start_date (string): A date string in the format %Y-%m-%d\n end_date (string): A date string in the format %Y-%m-%d\n \n Returns:\n TMIN, TAVE, and TMAX\n \"\"\"\n \n return session.query(func.min(Measurement.tobs), func.avg(Measurement.tobs), func.max(Measurement.tobs)).\\\n filter(Measurement.date >= start_date).filter(Measurement.date <= end_date).all()\n\n# function usage example\nprint(calc_temps('2012-02-28', '2012-03-05'))",
"[(62.0, 69.57142857142857, 74.0)]\n"
],
[
"# Use your previous function `calc_temps` to calculate the tmin, tavg, and tmax \n# for your trip using the previous year's data for those same dates.\ndef calc_temps(start_date, end_date):\n c_results = session.query(func.min(Measurement.tobs), func.avg(Measurement.tobs), func.max(Measurement.tobs)).\\\n filter(Measurement.date >= start_date).\\\n filter(Measurement.date <= end_date).all()\n return c_results\ncalc_temps('2017-01-01', '2017-12-31')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"results = calc_temps('2017-07-02', '2017-07-08')\nresults",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Plot the results from your previous query as a bar chart. \n# Use \"Trip Avg Temp\" as your Title\n# Use the average temperature for the y value\n# Use the peak-to-peak (tmax-tmin) value as the y error bar (yerr)\nfig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=plt.figaspect(2.))\npeak = results[0][2] - results[0][0]\nbar = ax.bar(1, results[0][1], yerr = peak, color = \"coral\")\nplt.title(\"Trip Avg Temp\")\nplt.ylabel(\"Temperature (F)\")\nfig.show()",
"C:\\Users\\user\\Anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages\\ipykernel_launcher.py:10: UserWarning: Matplotlib is currently using module://ipykernel.pylab.backend_inline, which is a non-GUI backend, so cannot show the figure.\n # Remove the CWD from sys.path while we load stuff.\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Optional Challenge Assignment",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create a query that will calculate the daily normals \n# (i.e. the averages for tmin, tmax, and tavg for all historic data matching a specific month and day)\n\ndef daily_normals(date):\n \"\"\"Daily Normals.\n \n Args:\n date (str): A date string in the format '%m-%d'\n \n Returns:\n A list of tuples containing the daily normals, tmin, tavg, and tmax\n \n \"\"\"\n \n sel = [func.min(Measurement.tobs), func.avg(Measurement.tobs), func.max(Measurement.tobs)]\n return session.query(*sel).filter(func.strftime(\"%m-%d\", Measurement.date) == date).all()\n \ndaily_normals(\"01-01\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# calculate the daily normals for your trip\n# push each tuple of calculations into a list called `normals`\n\n# Set the start and end date of the trip\n\n# Use the start and end date to create a range of dates\n\n# Stip off the year and save a list of %m-%d strings\n\n# Loop through the list of %m-%d strings and calculate the normals for each date\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Load the previous query results into a Pandas DataFrame and add the `trip_dates` range as the `date` index\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Plot the daily normals as an area plot with `stacked=False`\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a72c4cbd7af1ec6136f07c57b59a66971de6a5b
| 284,733 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
colab_notebooks/Notebook10_AHyperparameterSearch.ipynb
|
ai2es/WAF_ML_Tutorial_Part1
|
034aa52303172161aa6435238ffe1b5d84e969b6
|
[
"CC0-1.0"
] | null | null | null |
colab_notebooks/Notebook10_AHyperparameterSearch.ipynb
|
ai2es/WAF_ML_Tutorial_Part1
|
034aa52303172161aa6435238ffe1b5d84e969b6
|
[
"CC0-1.0"
] | 1 |
2022-03-29T14:34:27.000Z
|
2022-03-29T14:34:27.000Z
|
colab_notebooks/Notebook10_AHyperparameterSearch.ipynb
|
ai2es/WAF_ML_Tutorial_Part1
|
034aa52303172161aa6435238ffe1b5d84e969b6
|
[
"CC0-1.0"
] | 1 |
2022-03-28T21:40:09.000Z
|
2022-03-28T21:40:09.000Z
| 284,733 | 284,733 | 0.943393 |
[
[
[
"[](http://colab.research.google.com/github/ai2es/WAF_ML_Tutorial_Part1/blob/main/colab_notebooks/Notebook10_AHyperparameterSearch.ipynb)\n\n# Notebook 10: A hyperparameter search\n\n### Goal: Show an example of hyperparameter tuning \n\n#### Background\n\nIf you look at any of the ML method documentation, you will find there are alot of switches and nobs you can play with. See this page on ```RandomForestRegressor``` [click](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.ensemble.RandomForestRegressor.html). Most of these switches and nobs are considered *hyperparameters*. In otherwords, these are parameters you can change that may or may not influence the machine learning model performance. Since every machine learning task is different, you often can *tune* your choice of these hyperparameters to get a better performing model. This notebook sets out to show you one way to do a hyperparameter search with random forest. \n\n#### Step 0: Get the github repo (we need some of the functions there)\n\nThe first step with all of these Google Colab notebooks will be to grab the github repo and cd into the notebooks directory. \n\nTo run things from the command line, put a ```!``` before your code\n\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#get the github repo \n!git clone https://github.com/ai2es/WAF_ML_Tutorial_Part1.git \n\n#cd into the repo so the paths work \nimport os \nos.chdir('/content/WAF_ML_Tutorial_Part1/jupyter_notebooks/')",
"Cloning into 'WAF_ML_Tutorial_Part1'...\nremote: Enumerating objects: 301, done.\u001b[K\nremote: Counting objects: 100% (301/301), done.\u001b[K\nremote: Compressing objects: 100% (197/197), done.\u001b[K\nremote: Total 301 (delta 139), reused 236 (delta 96), pack-reused 0\u001b[K\nReceiving objects: 100% (301/301), 195.77 MiB | 14.92 MiB/s, done.\nResolving deltas: 100% (139/139), done.\nChecking out files: 100% (100/100), done.\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Import packages and load data for Regression\nIn the paper we do this hyperparameter tuning with the random forest regression example. So let's load in the regression dataset.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"###################################### Load training data ######################################\n#import some helper functions for our other directory.\nimport sys\nsys.path.insert(1, '../scripts/')\nfrom aux_functions import load_n_combine_df\nimport numpy as np\n(X_train,y_train),(X_validate,y_validate),_ = load_n_combine_df(path_to_data='../datasets/sevir/',features_to_keep=np.arange(0,36,1),class_labels=False,dropzeros=True)\n\n#remember since we have all 36 predictors we need to scale the inputs \nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler\n#create scaling object \nscaler = StandardScaler()\n#fit scaler to training data\nscaler.fit(X_train)\n#transform feature data into scaled space \nX_train = scaler.transform(X_train)\nX_validate = scaler.transform(X_validate)\n################################################################################################\n\n#import other packages we will need \nimport pandas as pd \nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\nimport matplotlib.patheffects as path_effects\npe1 = [path_effects.withStroke(linewidth=2,\n foreground=\"k\")]\npe2 = [path_effects.withStroke(linewidth=2,\n foreground=\"w\")]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Determine what parameter 'sweeps' you wish to do \n\nRight now I would like you to go check out the random forest document page: [here](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.ensemble.RandomForestRegressor.html). \n\nWe will go ahead and systematically vary some of these hyperparameters. More specifically, we will play with\n\n1. Tree depth (i.e., number of branches).\n2. Number of Trees \n\nWhile one could always do more hyperparameter tests, for now this will get you started on generally how to do it. Let's vary the depth of trees from 1 to 10, and we will incrementally increase it. Then for the number of trees lets do 1, 5, 10, 25, 50, 100. Note we did 1000 in the paper, but something you will notice is that the deeper the tree and the more numerous trees it takes longer to train your models. So for it not to take forever in this tutorial, we will cut it to 100. \n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#vary depth of trees from 1 to 10. \ndepth = np.arange(1,11,1)\n#vary the number of trees in the forest from 1 to 100 \nn_tree = [1,5,10,25,50,100]\n\n#build out the parameter sets we will test. \nsets = []\n#for each number of trees, set their depth\nfor n in n_tree:\n for d in depth:\n sets.append([n,d])\n \nprint(sets,len(sets))",
"[[1, 1], [1, 2], [1, 3], [1, 4], [1, 5], [1, 6], [1, 7], [1, 8], [1, 9], [1, 10], [5, 1], [5, 2], [5, 3], [5, 4], [5, 5], [5, 6], [5, 7], [5, 8], [5, 9], [5, 10], [10, 1], [10, 2], [10, 3], [10, 4], [10, 5], [10, 6], [10, 7], [10, 8], [10, 9], [10, 10], [25, 1], [25, 2], [25, 3], [25, 4], [25, 5], [25, 6], [25, 7], [25, 8], [25, 9], [25, 10], [50, 1], [50, 2], [50, 3], [50, 4], [50, 5], [50, 6], [50, 7], [50, 8], [50, 9], [50, 10], [100, 1], [100, 2], [100, 3], [100, 4], [100, 5], [100, 6], [100, 7], [100, 8], [100, 9], [100, 10]] 60\n"
]
],
[
[
"As you can see, we have built out 60 different parameters to try out! \n\nTo make the code a bit more concise, let's define a functiont that will calculate all our metrics for us. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from gewitter_functions import get_bias,get_mae,get_rmse,get_r2\n#define a function to calcualte all the metrics, and return a vector with all 4. \ndef get_metrics(model,X,y):\n yhat = model.predict(X)\n mae = get_mae(y,yhat)\n rmse = get_rmse(y,yhat)\n bias = get_bias(y,yhat)\n r2 = get_r2(y,yhat)\n return np.array([bias,mae,rmse,r2])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Okay, now we are ready to do the hyperparameter sweep. \n\nWARNING, this took 60 mins on google colab with n_jobs set to 4. So if you dont have that kind of time, go ahead and jump past this cell, and just load the pre-computed metrics I have. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# import the progress bar so we can see how long this will take\nimport tqdm \n\n#import RandomForest \nfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor\n\n#do our hyperparameter search!\n# for each set of parameters,train a new model and evaluate it \nfor i,s in enumerate(tqdm.tqdm(sets)):\n #initialize the model \n reg = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=s[0],max_depth=s[1],n_jobs=4)\n #train the model\n reg.fit(X_train,y_train)\n #get the metrics on both the training dataset and the validation dataset. \n met_train = get_metrics(reg,X_train,y_train)\n met_val = get_metrics(reg,X_validate,y_validate)\n \n #this if statement lets us stack the observations up. \n if i ==0:\n #if the first loop, rename things\n all_scores_val = met_val \n all_scores_train = met_train\n else:\n #otherwise, stack it on \n all_scores_val = np.vstack([all_scores_val,met_val])\n all_scores_train = np.vstack([all_scores_train,met_train])\n \n del reg \n\n#import pandas for easy writing and reading functions \nimport pandas as pd\n\n#this takes a hot min to run, so lets save them when we are done. \ndf_val = pd.DataFrame(all_scores_val,columns=['Bias','MeanAbsoluteError','RootMeanSquaredError','Rsquared'])\ndf_val.to_csv('../datasets/hyperparametersearch/validation_metrics.csv',index=False)\ndf_train = pd.DataFrame(all_scores_train,columns=['Bias','MeanAbsoluteError','RootMeanSquaredError','Rsquared'])\ndf_train.to_csv('../datasets/hyperparametersearch/train_metrics.csv',index=False)",
"100%|██████████| 60/60 [55:56<00:00, 55.95s/it] \n"
]
],
[
[
"Since that took about 30 mins, we dont want to do that EVERY time we load this notebook, so lets save the results out to a file (i.e., a comma separated values file format) to allow for quick and easy reading later on. (this dataset is already made for you in the ```datasets``` folder in the repo.). ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_val = pd.read_csv('../datasets/hyperparametersearch/validation_metrics.csv').to_numpy()\ndf_train = pd.read_csv('../datasets/hyperparametersearch/train_metrics.csv').to_numpy()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"And there we go, we have successfully trained 60 models with various different configurations to see if any one particular configuration does better than another. So, how do we check which one is doing best? Well we can look at the validation dataset results, here I named it ```all_scores_val```. This will show us the general performance on the validation data. So lets take a look at that now. In the next cell is some code to plot up that matrix we saved out in the last cell. \n\nThe figure I want to make has a metric on each panel. The x-axis will be the tree depth, then each color will be the number of trees. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#matplotlib things\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt \nimport matplotlib\nfrom matplotlib.ticker import (MultipleLocator, FormatStrFormatter,\n AutoMinorLocator)\n\n#make default resolution of figures much higher (i.e., High definition)\n%config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'retina'\n\n#plot parameters that I personally like, feel free to make these your own.\nmatplotlib.rcParams['axes.facecolor'] = [0.9,0.9,0.9] #makes a grey background to the axis face\nmatplotlib.rcParams['axes.labelsize'] = 14 #fontsize in pts\nmatplotlib.rcParams['axes.titlesize'] = 14 \nmatplotlib.rcParams['xtick.labelsize'] = 12 \nmatplotlib.rcParams['ytick.labelsize'] = 12 \nmatplotlib.rcParams['legend.fontsize'] = 12 \nmatplotlib.rcParams['legend.facecolor'] = 'w' \nmatplotlib.rcParams['savefig.transparent'] = False\n\n#make a 2 row, 2 column plot (4 total subplots)\nfig,axes = plt.subplots(2,2,figsize=(5,5))\n#set background color to white, otherwise its transparent when you copy paste it out of this notebook. \nfig.set_facecolor('w')\n\n#lets ravel the 2x2 axes matrix to a 4x1 shape. This makes looping easier (in my opinion). \naxes = axes.ravel()\n\n########### colormap stuff ###########\n# I want to color each line by the number of trees. So this bit of code does that for us.\n#get func to plot it\nfrom aux_functions import make_colorbar\n#grab colormap\ncmap = matplotlib.cm.cividis\n#set up the boundaries to each color \nnorm = matplotlib.colors.BoundaryNorm(n_tree, cmap.N)\n#make a mappable so we can get the color based on the number of trees. \nscalarMap = matplotlib.cm.ScalarMappable(norm=norm, cmap=cmap)\n######################################\n\ntitles = ['Bias','MAE','RMSE','$R^{2}$']\nfor j,ax in enumerate(axes):\n for i,ii in enumerate(n_tree):\n color_choice =scalarMap.to_rgba(ii)\n ax.plot(np.arange(1,11,1),df_val[(i*10):(i+1)*10,j],'o-',color=color_choice,ms=3)\n # ax.plot(np.arange(1,11,1),df_train[(i*10):(i+1)*10,j],'o--',color=color_choice,ms=3)\n ax.set_title(titles[j])\n ax.set_xlim([0,12])\n ax.grid('on')\n # ax.xaxis.grid(True, which='minor')\n # For the minor ticks, use no labels; default NullFormatter.\n ax.xaxis.set_minor_locator(MultipleLocator(1))\n ax.yaxis.set_minor_locator(MultipleLocator(2.5))\n \naxes[2].set_xlabel('Tree Depth')\naxes[3].set_xlabel('Tree Depth')\n\n########### draw and fill the colorbar ###########\nax_cbar = fig.add_axes([1.025, 0.4, 0.015,0.33])\ncbar = make_colorbar(ax_cbar,1,100,cmap)\ncbar.set_label('# of trees')\n##################################################\n\nplt.tight_layout()",
"/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:63: UserWarning: This figure includes Axes that are not compatible with tight_layout, so results might be incorrect.\n"
]
],
[
[
"A reminder that each x-axis as the tree depth (i.e., number of decisions; branches) and the y-axis is the metric that is indicated in the title. The color corresponds to the number of trees used in the random forest, with 1 being the darkest color and 100 being the lightest. \n\nAs we can see, and noted in the paper, basically beyond using just 1 tree, which means its a decision tree, the number of trees doesnt have a large effect on the overall performance, while the number of trees seems to have a more appreciable effect. While this is helpful to find generally which models are performing better than others, there is a group of models that all seem to have similar performance with a tree depth greater than 5. \n\nIn order to truly assess which one is best to use, we need to include the training data metrics. This is where we will diagnose when a model becomes *overfit*. Overfitting is when the training data performance is really good, but the validation performance is not good. To diagnose this, you compare on the plot when the training data continues to improve its performance while the validation performance starts to degrade or worsen. So lets add the training curves to the same plot as above.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#make a 2 row, 2 column plot (4 total subplots)\nfig,axes = plt.subplots(2,2,figsize=(5,5))\n#set background color to white, otherwise its transparent when you copy paste it out of this notebook. \nfig.set_facecolor('w')\n\n#lets ravel the 2x2 axes matrix to a 4x1 shape. This makes looping easier (in my opinion). \naxes = axes.ravel()\n\n########### colormap stuff ###########\n# I want to color each line by the number of trees. So this bit of code does that for us.\n#get func to plot it\nfrom aux_functions import make_colorbar\n#grab colormap\ncmap = matplotlib.cm.cividis\n#set up the boundaries to each color \nnorm = matplotlib.colors.BoundaryNorm(n_tree, cmap.N)\n#make a mappable so we can get the color based on the number of trees. \nscalarMap = matplotlib.cm.ScalarMappable(norm=norm, cmap=cmap)\n######################################\n\ntitles = ['Bias','MAE','RMSE','$R^{2}$']\nfor j,ax in enumerate(axes):\n for i,ii in enumerate(n_tree):\n color_choice =scalarMap.to_rgba(ii)\n ax.plot(np.arange(1,11,1),df_val[(i*10):(i+1)*10,j],'o-',color=color_choice,ms=3)\n ax.plot(np.arange(1,11,1),df_train[(i*10):(i+1)*10,j],'^--',color=color_choice,ms=3)\n ax.axvline(8,ls='--',color='k')\n ax.set_title(titles[j])\n ax.set_xlim([0,12])\n ax.grid('on')\n # ax.xaxis.grid(True, which='minor')\n # For the minor ticks, use no labels; default NullFormatter.\n ax.xaxis.set_minor_locator(MultipleLocator(1))\n ax.yaxis.set_minor_locator(MultipleLocator(2.5))\n \naxes[2].set_xlabel('Tree Depth')\naxes[3].set_xlabel('Tree Depth')\n\n########### draw and fill the colorbar ###########\nax_cbar = fig.add_axes([1.025, 0.4, 0.015,0.33])\ncbar = make_colorbar(ax_cbar,1,100,cmap)\ncbar.set_label('# of trees')\n##################################################\n\nplt.tight_layout()",
"/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:45: UserWarning: This figure includes Axes that are not compatible with tight_layout, so results might be incorrect.\n"
]
],
[
[
"Okay, now we have the training curves in the dashed lines and triangle markers. I have also drawn a vertical dashed black line on the tree depth that seems to maximize performance before overfitting. We can see at a tree depth of 8, the $R^{2}$ value for the training data now out performs the validation data, while the other metrics are effectively the same as 5,6, and 7. Thats why we suggest random forest of > 1 tree and depth of 8 is likely a good model to continue on and use. \n\nI hope this was enough to give you an example of how to do hyperparameter tuning. I encourage you to go ahead and try it with the other models!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a72c7768adfea4bc10d19893ba2ddedb90092ac
| 50,613 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
main/nbs/poc/gpt-2-Copy1.ipynb
|
jason424217/Artificial-Code-Gen
|
a6e2c097c5ffe8cb0929e6703035b526f477e514
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
main/nbs/poc/gpt-2-Copy1.ipynb
|
jason424217/Artificial-Code-Gen
|
a6e2c097c5ffe8cb0929e6703035b526f477e514
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
main/nbs/poc/gpt-2-Copy1.ipynb
|
jason424217/Artificial-Code-Gen
|
a6e2c097c5ffe8cb0929e6703035b526f477e514
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 39.915615 | 269 | 0.50487 |
[
[
[
"# Load the tensorboard notebook extension\n%load_ext tensorboard",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cd /tf/src/data/gpt-2/",
"/tf/src/data/gpt-2\n"
],
[
"! pip3 install -r requirements.txt",
"Collecting fire>=0.1.3 (from -r requirements.txt (line 1))\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/d9/69/faeaae8687f4de0f5973694d02e9d6c3eb827636a009157352d98de1129e/fire-0.2.1.tar.gz (76kB)\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 81kB 3.6MB/s eta 0:00:011\n\u001b[?25hCollecting regex==2017.4.5 (from -r requirements.txt (line 2))\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/36/62/c0c0d762ffd4ffaf39f372eb8561b8d491a11ace5a7884610424a8b40f95/regex-2017.04.05.tar.gz (601kB)\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 604kB 11.2MB/s eta 0:00:01\n\u001b[?25hCollecting requests==2.21.0 (from -r requirements.txt (line 3))\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/7d/e3/20f3d364d6c8e5d2353c72a67778eb189176f08e873c9900e10c0287b84b/requests-2.21.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl (57kB)\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 61kB 15.3MB/s eta 0:00:01\n\u001b[?25hCollecting tqdm==4.31.1 (from -r requirements.txt (line 4))\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/6c/4b/c38b5144cf167c4f52288517436ccafefe9dc01b8d1c190e18a6b154cd4a/tqdm-4.31.1-py2.py3-none-any.whl (48kB)\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 51kB 15.0MB/s eta 0:00:01\n\u001b[?25hCollecting toposort==1.5 (from -r requirements.txt (line 5))\n Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/e9/8a/321cd8ea5f4a22a06e3ba30ef31ec33bea11a3443eeb1d89807640ee6ed4/toposort-1.5-py2.py3-none-any.whl\nRequirement already satisfied: six in /usr/lib/python3/dist-packages (from fire>=0.1.3->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (1.11.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: termcolor in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from fire>=0.1.3->-r requirements.txt (line 1)) (1.1.0)\nCollecting urllib3<1.25,>=1.21.1 (from requests==2.21.0->-r requirements.txt (line 3))\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/01/11/525b02e4acc0c747de8b6ccdab376331597c569c42ea66ab0a1dbd36eca2/urllib3-1.24.3-py2.py3-none-any.whl (118kB)\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 122kB 13.0MB/s eta 0:00:01\n\u001b[?25hCollecting certifi>=2017.4.17 (from requests==2.21.0->-r requirements.txt (line 3))\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/69/1b/b853c7a9d4f6a6d00749e94eb6f3a041e342a885b87340b79c1ef73e3a78/certifi-2019.6.16-py2.py3-none-any.whl (157kB)\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 163kB 13.2MB/s eta 0:00:01\n\u001b[?25hCollecting chardet<3.1.0,>=3.0.2 (from requests==2.21.0->-r requirements.txt (line 3))\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/bc/a9/01ffebfb562e4274b6487b4bb1ddec7ca55ec7510b22e4c51f14098443b8/chardet-3.0.4-py2.py3-none-any.whl (133kB)\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 143kB 14.6MB/s eta 0:00:01\n\u001b[?25hRequirement already satisfied: idna<2.9,>=2.5 in /usr/lib/python3/dist-packages (from requests==2.21.0->-r requirements.txt (line 3)) (2.6)\nBuilding wheels for collected packages: fire, regex\n Building wheel for fire (setup.py) ... \u001b[?25ldone\n\u001b[?25h Stored in directory: /root/.cache/pip/wheels/31/9c/c0/07b6dc7faf1844bb4688f46b569efe6cafaa2179c95db821da\n Building wheel for regex (setup.py) ... \u001b[?25ldone\n\u001b[?25h Stored in directory: /root/.cache/pip/wheels/75/07/38/3c16b529d50cb4e0cd3dbc7b75cece8a09c132692c74450b01\nSuccessfully built fire regex\nInstalling collected packages: fire, regex, urllib3, certifi, chardet, requests, tqdm, toposort\nSuccessfully installed certifi-2019.6.16 chardet-3.0.4 fire-0.2.1 regex-2017.4.5 requests-2.21.0 toposort-1.5 tqdm-4.31.1 urllib3-1.24.3\n\u001b[33mWARNING: You are using pip version 19.1.1, however version 19.2.1 is available.\nYou should consider upgrading via the 'pip install --upgrade pip' command.\u001b[0m\n"
],
[
"! python3 download_model.py 117M",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import fire\nimport json\nimport os\nimport numpy as np\nimport tensorflow as tf\nimport regex as re\nfrom functools import lru_cache\nfrom statistics import median\nimport argparse\nimport time\nimport tqdm\nfrom tensorflow.core.protobuf import rewriter_config_pb2\nimport glob\nimport pickle\n\ntf.__version__",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Encoding",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\"\"\"Byte pair encoding utilities\"\"\"\n\n\n@lru_cache()\ndef bytes_to_unicode():\n \"\"\"\n Returns list of utf-8 byte and a corresponding list of unicode strings.\n The reversible bpe codes work on unicode strings.\n This means you need a large # of unicode characters in your vocab if you want to avoid UNKs.\n When you're at something like a 10B token dataset you end up needing around 5K for decent coverage.\n This is a signficant percentage of your normal, say, 32K bpe vocab.\n To avoid that, we want lookup tables between utf-8 bytes and unicode strings.\n And avoids mapping to whitespace/control characters the bpe code barfs on.\n \"\"\"\n bs = list(range(ord(\"!\"), ord(\"~\")+1))+list(range(ord(\"¡\"), ord(\"¬\")+1))+list(range(ord(\"®\"), ord(\"ÿ\")+1))\n cs = bs[:]\n n = 0\n for b in range(2**8):\n if b not in bs:\n bs.append(b)\n cs.append(2**8+n)\n n += 1\n cs = [chr(n) for n in cs]\n return dict(zip(bs, cs))\n\ndef get_pairs(word):\n \"\"\"Return set of symbol pairs in a word.\n\n Word is represented as tuple of symbols (symbols being variable-length strings).\n \"\"\"\n pairs = set()\n prev_char = word[0]\n for char in word[1:]:\n pairs.add((prev_char, char))\n prev_char = char\n return pairs\n\nclass Encoder:\n def __init__(self, encoder, bpe_merges, errors='replace'):\n self.encoder = encoder\n self.decoder = {v:k for k,v in self.encoder.items()}\n self.errors = errors # how to handle errors in decoding\n self.byte_encoder = bytes_to_unicode()\n self.byte_decoder = {v:k for k, v in self.byte_encoder.items()}\n self.bpe_ranks = dict(zip(bpe_merges, range(len(bpe_merges))))\n self.cache = {}\n\n # Should haved added re.IGNORECASE so BPE merges can happen for capitalized versions of contractions\n self.pat = re.compile(r\"\"\"'s|'t|'re|'ve|'m|'ll|'d| ?\\p{L}+| ?\\p{N}+| ?[^\\s\\p{L}\\p{N}]+|\\s+(?!\\S)|\\s+\"\"\")\n\n def bpe(self, token):\n if token in self.cache:\n return self.cache[token]\n word = tuple(token)\n pairs = get_pairs(word)\n\n if not pairs:\n return token\n\n while True:\n bigram = min(pairs, key = lambda pair: self.bpe_ranks.get(pair, float('inf')))\n if bigram not in self.bpe_ranks:\n break\n first, second = bigram\n new_word = []\n i = 0\n while i < len(word):\n try:\n j = word.index(first, i)\n new_word.extend(word[i:j])\n i = j\n except:\n new_word.extend(word[i:])\n break\n\n if word[i] == first and i < len(word)-1 and word[i+1] == second:\n new_word.append(first+second)\n i += 2\n else:\n new_word.append(word[i])\n i += 1\n new_word = tuple(new_word)\n word = new_word\n if len(word) == 1:\n break\n else:\n pairs = get_pairs(word)\n word = ' '.join(word)\n self.cache[token] = word\n return word\n\n def encode(self, text):\n bpe_tokens = []\n for token in re.findall(self.pat, text):\n token = ''.join(self.byte_encoder[b] for b in token.encode('utf-8'))\n bpe_tokens.extend(self.encoder[bpe_token] for bpe_token in self.bpe(token).split(' '))\n return bpe_tokens\n\n def decode(self, tokens):\n text = ''.join([self.decoder[token] for token in tokens])\n text = bytearray([self.byte_decoder[c] for c in text]).decode('utf-8', errors=self.errors)\n return text\n\ndef get_encoder(model_name, models_dir):\n with open(os.path.join(models_dir, model_name, 'encoder.json'), 'r') as f:\n encoder = json.load(f)\n with open(os.path.join(models_dir, model_name, 'vocab.bpe'), 'r', encoding=\"utf-8\") as f:\n bpe_data = f.read()\n bpe_merges = [tuple(merge_str.split()) for merge_str in bpe_data.split('\\n')[1:-1]]\n return Encoder(\n encoder=encoder,\n bpe_merges=bpe_merges,\n )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class HParams():\n n_vocab=50257\n n_ctx=1024\n n_embd=768\n n_head=12\n n_layer=12\n \n def __init__(self, n_vocab, n_ctx, n_embd, n_head, n_layer):\n self.n_vocab = n_vocab\n self.n_ctx = n_ctx\n self.n_embd = n_embd\n self.n_head = n_head\n self.n_layer = n_layer",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def default_hparams():\n return HParams(\n n_vocab=50257,\n n_ctx=1024,\n n_embd=768,\n n_head=12,\n n_layer=12,\n )\n\ndef shape_list(x):\n \"\"\"Deal with dynamic shape in tensorflow cleanly.\"\"\"\n static = x.shape.as_list()\n dynamic = tf.shape(input=x)\n return [dynamic[i] if s is None else s for i, s in enumerate(static)]\n\ndef gelu(x):\n return 0.5 * x * (1 + tf.tanh(np.sqrt(2 / np.pi) * (x + 0.044715 * tf.pow(x, 3))))\n\ndef norm(x, scope, *, axis=-1, epsilon=1e-5):\n \"\"\"Normalize to mean = 0, std = 1, then do a diagonal affine transform.\"\"\"\n with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope(scope):\n n_state = x.shape[-1]\n g = tf.compat.v1.get_variable('g', [n_state], initializer=tf.compat.v1.constant_initializer(1), use_resource=False)\n b = tf.compat.v1.get_variable('b', [n_state], initializer=tf.compat.v1.constant_initializer(0), use_resource=False)\n u = tf.reduce_mean(input_tensor=x, axis=axis, keepdims=True)\n s = tf.reduce_mean(input_tensor=tf.square(x-u), axis=axis, keepdims=True)\n x = (x - u) * tf.math.rsqrt(s + epsilon)\n x = x*g + b\n return x\n\ndef split_states(x, n):\n \"\"\"Reshape the last dimension of x into [n, x.shape[-1]/n].\"\"\"\n *start, m = shape_list(x)\n return tf.reshape(x, start + [n, m//n])\n\ndef merge_states(x):\n \"\"\"Smash the last two dimensions of x into a single dimension.\"\"\"\n *start, a, b = shape_list(x)\n return tf.reshape(x, start + [a*b])\n\ndef conv1d(x, scope, nf, *, w_init_stdev=0.02):\n with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope(scope):\n *start, nx = shape_list(x)\n w = tf.compat.v1.get_variable('w', [1, nx, nf], initializer=tf.compat.v1.random_normal_initializer(stddev=w_init_stdev), use_resource=False)\n b = tf.compat.v1.get_variable('b', [nf], initializer=tf.compat.v1.constant_initializer(0), use_resource=False)\n c = tf.reshape(tf.matmul(tf.reshape(x, [-1, nx]), tf.reshape(w, [-1, nf]))+b, start+[nf])\n return c\n\ndef attention_mask(nd, ns, *, dtype):\n \"\"\"1's in the lower triangle, counting from the lower right corner.\n\n Same as tf.matrix_band_part(tf.ones([nd, ns]), -1, ns-nd), but doesn't produce garbage on TPUs.\n \"\"\"\n i = tf.range(nd)[:,None]\n j = tf.range(ns)\n m = i >= j - ns + nd\n return tf.cast(m, dtype)\n\n\ndef attn(x, scope, n_state, *, past, hparams):\n assert x.shape.ndims == 3 # Should be [batch, sequence, features]\n assert n_state % hparams.n_head == 0\n if past is not None:\n assert past.shape.ndims == 5 # Should be [batch, 2, heads, sequence, features], where 2 is [k, v]\n\n def split_heads(x):\n # From [batch, sequence, features] to [batch, heads, sequence, features]\n return tf.transpose(a=split_states(x, hparams.n_head), perm=[0, 2, 1, 3])\n\n def merge_heads(x):\n # Reverse of split_heads\n return merge_states(tf.transpose(a=x, perm=[0, 2, 1, 3]))\n\n def mask_attn_weights(w):\n # w has shape [batch, heads, dst_sequence, src_sequence], where information flows from src to dst.\n _, _, nd, ns = shape_list(w)\n b = attention_mask(nd, ns, dtype=w.dtype)\n b = tf.reshape(b, [1, 1, nd, ns])\n w = w*b - tf.cast(1e10, w.dtype)*(1-b)\n return w\n\n def multihead_attn(q, k, v):\n # q, k, v have shape [batch, heads, sequence, features]\n w = tf.matmul(q, k, transpose_b=True)\n w = w * tf.math.rsqrt(tf.cast(v.shape[-1], w.dtype))\n\n w = mask_attn_weights(w)\n w = tf.nn.softmax(w, axis=-1)\n a = tf.matmul(w, v)\n return a\n\n with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope(scope):\n c = conv1d(x, 'c_attn', n_state*3)\n q, k, v = map(split_heads, tf.split(c, 3, axis=2))\n present = tf.stack([k, v], axis=1)\n if past is not None:\n pk, pv = tf.unstack(past, axis=1)\n k = tf.concat([pk, k], axis=-2)\n v = tf.concat([pv, v], axis=-2)\n a = multihead_attn(q, k, v)\n a = merge_heads(a)\n a = conv1d(a, 'c_proj', n_state)\n return a, present\n\n\ndef mlp(x, scope, n_state, *, hparams):\n with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope(scope):\n nx = x.shape[-1]\n h = gelu(conv1d(x, 'c_fc', n_state))\n h2 = conv1d(h, 'c_proj', nx)\n return h2\n\ndef block(x, scope, *, past, hparams):\n with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope(scope):\n nx = x.shape[-1]\n a, present = attn(norm(x, 'ln_1'), 'attn', nx, past=past, hparams=hparams)\n x = x + a\n m = mlp(norm(x, 'ln_2'), 'mlp', nx*4, hparams=hparams)\n x = x + m\n return x, present\n\ndef past_shape(*, hparams, batch_size=None, sequence=None):\n return [batch_size, hparams.n_layer, 2, hparams.n_head, sequence, hparams.n_embd // hparams.n_head]\n\ndef expand_tile(value, size):\n \"\"\"Add a new axis of given size.\"\"\"\n value = tf.convert_to_tensor(value=value, name='value')\n ndims = value.shape.ndims\n return tf.tile(tf.expand_dims(value, axis=0), [size] + [1]*ndims)\n\ndef positions_for(tokens, past_length):\n batch_size = tf.shape(input=tokens)[0]\n nsteps = tf.shape(input=tokens)[1]\n return expand_tile(past_length + tf.range(nsteps), batch_size)\n\ndef clf(x, ny, w_init=tf.compat.v1.random_normal_initializer(stddev=0.02), b_init=tf.compat.v1.constant_initializer(0), train=False):\n with tf.variable_scope('clf'):\n nx = shape_list(x)[-1]\n w = tf.compat.v1.get_variable(\"w\", [nx, ny], initializer=w_init)\n b = tf.compat.v1.get_variable(\"b\", [ny], initializer=b_init)\n return tf.matmul(x, w)+b\n\ndef model(hparams, X, past=None, scope='model', reuse=tf.compat.v1.AUTO_REUSE):\n with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope(scope, reuse=reuse):\n results = {}\n batch, sequence = shape_list(X)\n\n wpe = tf.compat.v1.get_variable('wpe', [hparams.n_ctx, hparams.n_embd],\n initializer=tf.compat.v1.random_normal_initializer(stddev=0.01), use_resource=False)\n wte = tf.compat.v1.get_variable('wte', [hparams.n_vocab, hparams.n_embd],\n initializer=tf.compat.v1.random_normal_initializer(stddev=0.02), use_resource=False)\n past_length = 0 if past is None else tf.shape(input=past)[-2]\n h = tf.gather(wte, X) + tf.gather(wpe, positions_for(X, past_length))\n\n # Transformer\n presents = []\n pasts = tf.unstack(past, axis=1) if past is not None else [None] * hparams.n_layer\n assert len(pasts) == hparams.n_layer\n for layer, past in enumerate(pasts):\n h, present = block(h, 'h%d' % layer, past=past, hparams=hparams)\n presents.append(present)\n results['present'] = tf.stack(presents, axis=1)\n h = norm(h, 'ln_f')\n \n # Classification on h vector (from paper https://openai.com/blog/language-unsupervised/)\n clf_h = tf.reshape(h, [-1, hparams.n_embd])\n pool_idx = tf.cast(tf.argmax(tf.cast(tf.equal(X[:, :, 0], hparams.n_vocab), tf.float32), 1), tf.int32)\n clf_h = tf.gather(clf_h, tf.range(shape_list(X)[0], dtype=tf.int32)*n_ctx+pool_idx)\n\n clf_h = tf.reshape(clf_h, [-1, 2, hparams.n_embd])\n if train and clf_pdrop > 0:\n shape = shape_list(clf_h)\n shape[1] = 1\n clf_h = tf.nn.dropout(clf_h, 1-clf_pdrop, shape)\n clf_h = tf.reshape(clf_h, [-1, n_embd])\n clf_logits = clf(clf_h, 1, train=train)\n clf_logits = tf.reshape(clf_logits, [-1, 2])\n results['clf_logits'] = clf_logits\n\n # Language model loss. Do tokens <n predict token n?\n h_flat = tf.reshape(h, [batch*sequence, hparams.n_embd])\n logits = tf.matmul(h_flat, wte, transpose_b=True)\n logits = tf.reshape(logits, [batch, sequence, hparams.n_vocab])\n results['logits'] = logits\n return results",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def model(X, M, Y, train=False, reuse=False):\n with tf.variable_scope('model', reuse=reuse):\n we = tf.get_variable(\"we\", [n_vocab+n_special+n_ctx, n_embd], initializer=tf.random_normal_initializer(stddev=0.02))\n we = dropout(we, embd_pdrop, train)\n\n X = tf.reshape(X, [-1, n_ctx, 2])\n M = tf.reshape(M, [-1, n_ctx])\n\n h = embed(X, we)\n for layer in range(n_layer):\n h = block(h, 'h%d'%layer, train=train, scale=True)\n\n lm_h = tf.reshape(h[:, :-1], [-1, n_embd])\n lm_logits = tf.matmul(lm_h, we, transpose_b=True)\n lm_losses = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=lm_logits, labels=tf.reshape(X[:, 1:, 0], [-1]))\n lm_losses = tf.reshape(lm_losses, [shape_list(X)[0], shape_list(X)[1]-1])\n lm_losses = tf.reduce_sum(lm_losses*M[:, 1:], 1)/tf.reduce_sum(M[:, 1:], 1)\n\n clf_h = tf.reshape(h, [-1, n_embd])\n pool_idx = tf.cast(tf.argmax(tf.cast(tf.equal(X[:, :, 0], clf_token), tf.float32), 1), tf.int32)\n clf_h = tf.gather(clf_h, tf.range(shape_list(X)[0], dtype=tf.int32)*n_ctx+pool_idx)\n\n clf_h = tf.reshape(clf_h, [-1, 2, n_embd])\n if train and clf_pdrop > 0:\n shape = shape_list(clf_h)\n shape[1] = 1\n clf_h = tf.nn.dropout(clf_h, 1-clf_pdrop, shape)\n clf_h = tf.reshape(clf_h, [-1, n_embd])\n clf_logits = clf(clf_h, 1, train=train)\n clf_logits = tf.reshape(clf_logits, [-1, 2])\n\n clf_losses = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=clf_logits, labels=Y)\n return clf_logits, clf_losses, lm_losses",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Sample from Model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def top_k_logits(logits, k):\n if k == 0:\n # no truncation\n return logits\n\n def _top_k():\n values, _ = tf.nn.top_k(logits, k=k)\n min_values = values[:, -1, tf.newaxis]\n return tf.compat.v1.where(\n logits < min_values,\n tf.ones_like(logits, dtype=logits.dtype) * -1e10,\n logits,\n )\n return tf.cond(\n pred=tf.equal(k, 0),\n true_fn=lambda: logits,\n false_fn=lambda: _top_k(),\n )\n\n\ndef sample_sequence(*, hparams, length, start_token=None, batch_size=None, context=None, temperature=1, top_k=0):\n if start_token is None:\n assert context is not None, 'Specify exactly one of start_token and context!'\n else:\n assert context is None, 'Specify exactly one of start_token and context!'\n context = tf.fill([batch_size, 1], start_token)\n\n def step(hparams, tokens, past=None):\n lm_output = model(hparams=hparams, X=tokens, past=past, reuse=tf.compat.v1.AUTO_REUSE)\n\n logits = lm_output['logits'][:, :, :hparams.n_vocab]\n presents = lm_output['present']\n presents.set_shape(past_shape(hparams=hparams, batch_size=batch_size))\n return {\n 'logits': logits,\n 'presents': presents,\n }\n\n def body(past, prev, output):\n next_outputs = step(hparams, prev, past=past)\n logits = next_outputs['logits'][:, -1, :] / tf.cast(temperature, dtype=tf.float32)\n logits = top_k_logits(logits, k=top_k)\n samples = tf.random.categorical(logits=logits, num_samples=1, dtype=tf.int32)\n return [\n next_outputs['presents'] if past is None else tf.concat([past, next_outputs['presents']], axis=-2),\n samples,\n tf.concat([output, samples], axis=1)\n ]\n\n past, prev, output = body(None, context, context)\n\n def cond(*args):\n return True\n\n _, _, tokens = tf.while_loop(\n cond=cond, body=body,\n maximum_iterations=length - 1,\n loop_vars=[\n past,\n prev,\n output\n ],\n shape_invariants=[\n tf.TensorShape(past_shape(hparams=hparams, batch_size=batch_size)),\n tf.TensorShape([batch_size, None]),\n tf.TensorShape([batch_size, None]),\n ],\n back_prop=False,\n )\n\n return tokens",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from pathlib import Path\ndef load_dataset(enc, path):\n paths = []\n if os.path.isfile(path):\n # Simple file\n paths.append(path)\n elif os.path.isdir(path):\n # Directory\n for i, (dirpath, _, fnames) in enumerate(os.walk(path)):\n for fname in fnames:\n paths.append(os.path.join(dirpath, fname))\n else:\n # Assume glob\n paths = glob.glob(path)\n\n \n token_chunks = []\n raw_text = ''\n for i, path in enumerate(tqdm.tqdm(paths)):\n# if i >= 10000: break\n try:\n with open(path, 'r') as fp:\n raw_text += fp.read()\n raw_text += '<|endoftext|>'\n tokens = np.stack(enc.encode(raw_text))\n token_chunks.append(tokens)\n raw_text = ''\n except Exception as e:\n print(e)\n return token_chunks\n\ndef binary_search(f, lo, hi):\n if f(lo) or not f(hi):\n return None\n while hi > lo + 1:\n mid = (lo + hi) // 2\n if f(mid):\n hi = mid\n else:\n lo = mid\n return hi\n\n\nclass Sampler(object):\n \"\"\"Fairly samples a slice from a set of variable sized chunks.\n\n 'Fairly' means that the distribution is the same as sampling from one concatenated chunk,\n but without crossing chunk boundaries.\"\"\"\n\n def __init__(self, chunks, seed=None):\n self.chunks = chunks\n self.total_size = sum(chunk.shape[0] for chunk in chunks)\n self.boundaries = [0]\n for i in range(len(chunks)):\n self.boundaries.append(self.boundaries[-1] + chunks[i].shape[0])\n self.rs = np.random.RandomState(seed=seed)\n\n def sample(self, length):\n assert length < self.total_size // len(\n self.chunks\n ), \"Dataset files are too small to sample {} tokens at a time\".format(\n length)\n while True:\n index = self.rs.randint(0, self.total_size - length - 1)\n i = binary_search(lambda j: self.boundaries[j] > index, 0,\n len(self.boundaries) - 1) - 1\n if self.boundaries[i + 1] > index + length:\n within_chunk = index - self.boundaries[i]\n return self.chunks[i][within_chunk:within_chunk + length]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class Args():\n def __init__(self, trn_dataset, model_name, combine, batch_size, learning_rate, optimizer, noise, top_k, top_p, run_name, sample_every, sample_length, sample_num, save_every, val_dataset, val_batch_size, val_batch_count, val_every, pretrained, iterations):\n self.trn_dataset = trn_dataset\n self.model_name = model_name\n self.combine = combine\n self.batch_size = batch_size\n self.learning_rate = learning_rate\n self.optimizer = optimizer\n self.noise = noise\n self.top_k = top_k\n self.top_p = top_p\n self.run_name = run_name\n self.sample_every = sample_every\n self.sample_length = sample_length\n self.sample_num = sample_num\n self.save_every = save_every\n self.val_dataset = val_dataset\n self.val_batch_size = val_batch_size\n self.val_batch_count = val_batch_count\n self.val_every = val_every\n self.pretrained = pretrained\n self.iterations = iterations",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"args = Args(\n trn_dataset=\"/tf/src/data/methods/DATA00M_[god-r]/train\",\n model_name=\"117M\",\n combine=50000,\n batch_size=1, # DO NOT TOUCH. INCREASING THIS WILL RAIN DOWN HELL FIRE ONTO YOUR COMPUTER.\n learning_rate=0.00002,\n optimizer=\"sgd\",\n noise=0.0,\n top_k=40,\n top_p=0.0,\n run_name=\"m4\",\n sample_every=100,\n sample_length=1023,\n sample_num=1,\n save_every=1000,\n val_dataset=\"/tf/src/data/methods/DATA00M_[god-r]/valid\",\n val_batch_size=1,\n val_batch_count=40,\n val_every=100,\n pretrained=True,\n iterations=493000\n )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"enc = get_encoder(args.model_name, \"models\")\ntrn_set = load_dataset(enc, args.trn_dataset)\nval_set = load_dataset(enc, args.val_dataset)\nlen(trn_set), len(val_set)",
" 0%| | 729/972771 [00:13<6:50:51, 39.43it/s]"
],
[
"# DATASET_SIZE = len(dataset)\n# TRN_SET_SIZE = int(DATASET_SIZE * 0.8)\n# VAL_SET_SIZE = int(DATASET_SIZE * 0.1)\n# TST_SET_SIZE = int(DATASET_SIZE * 0.1)\n\n# trn_set = dataset[:TRN_SET_SIZE]\n# val_set = dataset[TRN_SET_SIZE:TRN_SET_SIZE + VAL_SET_SIZE]\n# tst_set = dataset[-TST_SET_SIZE:]\n# DATASET_SIZE, len(trn_set), len(val_set), len(tst_set)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"CHECKPOINT_DIR = 'checkpoint'\nSAMPLE_DIR = 'samples'\n\ntrn_losses = []\ntrn_avgs = []\nval_losses = []",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Restore previous metrics \nwith open(os.path.join(CHECKPOINT_DIR, args.run_name, 'metrics.pickle'), 'rb') as f:\n loss_dict = pickle.load(f)\n \ntrn_losses = loss_dict[\"trn_losses\"]\ntrn_avgs = loss_dict[\"avg_trn_losses\"]\nval_losses = loss_dict[\"val_losses\"]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(trn_losses), len(trn_avgs), len(val_losses)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def maketree(path):\n try:\n os.makedirs(path)\n except:\n pass\n\n\ndef randomize(context, hparams, p):\n if p > 0:\n mask = tf.random.uniform(shape=tf.shape(input=context)) < p\n noise = tf.random.uniform(shape=tf.shape(input=context), minval=0, maxval=hparams.n_vocab, dtype=tf.int32)\n return tf.compat.v1.where(mask, noise, context)\n else:\n return context\n\n\ndef main():\n enc = get_encoder(args.model_name, \"models\")\n hparams = default_hparams()\n\n if args.sample_length > hparams.n_ctx:\n raise ValueError(\n \"Can't get samples longer than window size: %s\" % hparams.n_ctx)\n\n config = tf.compat.v1.ConfigProto()\n config.gpu_options.allow_growth = True\n config.graph_options.rewrite_options.layout_optimizer = rewriter_config_pb2.RewriterConfig.OFF\n with tf.compat.v1.Session(config=config) as sess:\n context = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.int32, [args.batch_size, None])\n context_in = randomize(context, hparams, args.noise)\n output = model(hparams=hparams, X=context_in)\n \n val_context = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.int32, [args.val_batch_size, None])\n val_output = model(hparams=hparams, X=val_context)\n \n\n tf_sample = sample_sequence(\n hparams=hparams,\n length=args.sample_length,\n context=context,\n batch_size=args.batch_size,\n temperature=1.0,\n top_k=args.top_k)\n\n all_vars = [v for v in tf.compat.v1.trainable_variables() if 'model' in v.name]\n train_vars = all_vars\n\n if args.optimizer == 'adam':\n opt = tf.compat.v1.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=args.learning_rate)\n elif args.optimizer == 'sgd':\n opt = tf.compat.v1.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=args.learning_rate)\n else:\n exit('Bad optimizer:', args.optimizer)\n\n \n \n ## Collect Metrics for Tensorboard\n with tf.compat.v1.name_scope('metrics'):\n with tf.compat.v1.name_scope('train'):\n trn_loss = tf.reduce_mean(\n input_tensor=tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(\n labels=context[:, 1:], logits=output['logits'][:, :-1]))\n trn_loss_summ = tf.compat.v1.summary.scalar('loss', trn_loss)\n \n trn_med_ph = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=None,name='median')\n trn_med_summ = tf.compat.v1.summary.scalar('median', trn_med_ph)\n \n trn_mean_ph = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=None,name='mean')\n trn_mean_summ = tf.compat.v1.summary.scalar('mean', trn_mean_ph)\n \n with tf.compat.v1.name_scope('valid'):\n val_loss = tf.reduce_mean(\n input_tensor=tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(\n labels=val_context[:, 1:], logits=val_output['logits'][:, :-1]))\n val_loss_summ = tf.compat.v1.summary.scalar('loss', val_loss)\n\n\n\n val_med_ph = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=None,name='median')\n val_med_summ = tf.compat.v1.summary.scalar('median', val_med_ph)\n \n \n \n trn_summaries = tf.compat.v1.summary.merge([trn_loss_summ, trn_med_summ, trn_mean_summ])\n val_summaries = tf.compat.v1.summary.merge([val_loss_summ, val_med_summ])\n\n opt_grads = tf.gradients(ys=trn_loss, xs=train_vars)\n opt_grads = list(zip(opt_grads, train_vars))\n opt_apply = opt.apply_gradients(opt_grads)\n\n trn_summ_log = tf.compat.v1.summary.FileWriter(os.path.join(CHECKPOINT_DIR, args.run_name, 'train'))\n val_summ_log = tf.compat.v1.summary.FileWriter(os.path.join(CHECKPOINT_DIR, args.run_name, 'valid'))\n \n saver = tf.compat.v1.train.Saver(\n var_list=all_vars,\n max_to_keep=5,\n keep_checkpoint_every_n_hours=2)\n sess.run(tf.compat.v1.global_variables_initializer())\n\n ckpt = tf.train.latest_checkpoint(\n os.path.join(CHECKPOINT_DIR, args.run_name))\n if ckpt is None:\n # Get fresh GPT weights if new run.\n ckpt = tf.train.latest_checkpoint(\n os.path.join('models', args.model_name))\n\n if args.pretrained == True:\n print('Loading checkpoint', ckpt)\n saver.restore(sess, ckpt)\n\n print('Loading dataset...')\n data_sampler = Sampler(trn_set)\n if args.val_every > 0:\n val_chunks = val_set\n print('dataset has', data_sampler.total_size, 'tokens')\n print('Training...')\n\n if args.val_every > 0:\n # Sample from validation set once with fixed seed to make\n # it deterministic during training as well as across runs.\n val_data_sampler = Sampler(val_chunks, seed=1)\n val_batches = [[val_data_sampler.sample(512) for _ in range(args.val_batch_size)]\n for _ in range(args.val_batch_count)]\n\n counter = 1\n counter_path = os.path.join(CHECKPOINT_DIR, args.run_name, 'counter')\n if os.path.exists(counter_path):\n # Load the step number if we're resuming a run\n # Add 1 so we don't immediately try to save again\n with open(counter_path, 'r') as fp:\n counter = int(fp.read()) + 1\n\n def save():\n maketree(os.path.join(CHECKPOINT_DIR, args.run_name))\n print(\n 'Saving',\n os.path.join(CHECKPOINT_DIR, args.run_name,\n 'model-{}').format(counter))\n saver.save(\n sess,\n os.path.join(CHECKPOINT_DIR, args.run_name, 'model'),\n global_step=counter)\n with open(counter_path, 'w') as fp:\n fp.write(str(counter) + '\\n')\n \n # Save metrics such as losses\n metrics = {\n \"trn_losses\": trn_losses,\n \"avg_trn_losses\": trn_avgs,\n \"val_losses\": val_losses\n }\n\n with open(os.path.join(CHECKPOINT_DIR, args.run_name, 'metrics.pickle'), 'wb') as f:\n pickle.dump(metrics, f, protocol=pickle.HIGHEST_PROTOCOL)\n\n def generate_samples():\n print('Generating samples...')\n context_tokens = data_sampler.sample(1)\n all_text = []\n index = 0\n while index < args.sample_num:\n out = sess.run(\n tf_sample,\n feed_dict={context: args.batch_size * [context_tokens]})\n for i in range(min(args.sample_num - index, args.batch_size)):\n text = enc.decode(out[i])\n text = '======== SAMPLE {} ========\\n{}\\n'.format(\n index + 1, text)\n all_text.append(text)\n index += 1\n print(text)\n maketree(os.path.join(SAMPLE_DIR, args.run_name))\n with open(\n os.path.join(SAMPLE_DIR, args.run_name,\n 'samples-{}').format(counter), 'w') as fp:\n fp.write('\\n'.join(all_text))\n \n def validation():\n print('Calculating validation loss...')\n losses = []\n for batch in tqdm.tqdm(val_batches):\n losses.append(sess.run(val_loss, feed_dict={val_context: batch}))\n v_val_loss = np.mean(losses)\n val_losses.append(v_val_loss)\n v_summary = sess.run(val_summaries, feed_dict={val_loss: v_val_loss, val_med_ph: median(losses)})\n val_summ_log.add_summary(v_summary, counter)\n val_summ_log.flush()\n print(\n '[{counter} | {time:2.2f}] validation loss = {loss:2.2f}'\n .format(\n counter=counter,\n time=time.time() - start_time,\n loss=v_val_loss))\n\n def sample_batch():\n return [data_sampler.sample(256) for _ in range(args.batch_size)]\n\n\n avg_trn_loss = (0.0, 0.1)\n# trn_losses = [0.0]\n# val_losses = []\n start_time = time.time()\n# trn_avgs = []\n\n try:\n for _ in range(args.iterations):\n if counter % args.save_every == 0:\n save()\n if counter % args.sample_every == 0:\n generate_samples()\n if args.val_every > 0 and (counter % args.val_every == 0 or counter == 1):\n validation()\n \n if _ == 0:\n avg = 0\n else: avg = avg_trn_loss[0] / avg_trn_loss[1]\n\n (_, v_loss, v_summary) = sess.run(\n (opt_apply, trn_loss, trn_summaries),\n feed_dict={context: sample_batch(), trn_med_ph: median(trn_losses), trn_mean_ph: avg})\n trn_losses.append(v_loss)\n \n trn_summ_log.add_summary(v_summary, counter)\n\n avg_trn_loss = (avg_trn_loss[0] * 0.99 + v_loss,\n avg_trn_loss[1] * 0.99 + 1.0)\n\n trn_avgs.append(avg)\n print(\n '[{counter} | {time:2.2f}] loss={loss:2.2f} avg={avg:2.2f}'\n .format(\n counter=counter,\n time=time.time() - start_time,\n loss=v_loss,\n avg=avg_trn_loss[0] / avg_trn_loss[1]))\n\n counter += 1\n except KeyboardInterrupt:\n print('interrupted')\n save()\n \n save()\nif __name__ == '__main__':\n main()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%tensorboard --logdir ./checkpoint/unconditional_experiment/",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"! curl -X POST -H 'Content-type: application/json' --data '{\"text\":\"from: semeru tower 1\\nstatus: model 4 finished training\"}' https://hooks.slack.com/services/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",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Reading in the data\nwith open(os.path.join(CHECKPOINT_DIR, args.run_name, 'metrics.pickle'), 'rb') as f:\n loss_dict = pickle.load(f)\n \nloss_dict",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a72e30f52945b7c573f12c5b1c7445ae02f5e86
| 2,655 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Flowers.ipynb
|
patriciamedyna/bear_voila
|
22f55012101a11f909263493e82123ff680d3465
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Flowers.ipynb
|
patriciamedyna/bear_voila
|
22f55012101a11f909263493e82123ff680d3465
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Flowers.ipynb
|
patriciamedyna/bear_voila
|
22f55012101a11f909263493e82123ff680d3465
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 21.585366 | 120 | 0.527307 |
[
[
[
"#hide\nfrom utils import *\nfrom fastai2.vision.all import *\nfrom fastai2.vision.widgets import *",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# The Amazing Flowers Classifier!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"path = Path()\nlearn_inf = load_learner(path/'export.pkl',cpu=True)\nbtn_upload = widgets.FileUpload()\nout_pl = widgets.Output()\nlbl_pred = widgets.Label()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def on_click(change):\n img = PILImage.create(btn_upload.data[-1])\n out_pl.clear_output()\n with out_pl: display(img.to_thumb(128,128))\n pred,pred_idx,probs = learn_inf.predict(img)\n lbl_pred.value = f'Prediction: {pred}; Probability: {probs[pred_idx]:.04f}'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"btn_upload.observe(on_click, names=['data'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"display(VBox([widgets.Label('Select your flower!'), \n btn_upload, out_pl, lbl_pred]))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a72eef2945169c525dbea1350d4edb6ec4dc766
| 41,283 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/Collaborative_Filtering_Model_Process.ipynb
|
Lambda-School-Labs/betterreads-ds
|
7817f97922a9b6dab36f11345c1a94b8527c56e2
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2020-04-15T19:55:35.000Z
|
2020-09-10T16:23:36.000Z
|
notebooks/Collaborative_Filtering_Model_Process.ipynb
|
Lambda-School-Labs/betterreads-ds
|
7817f97922a9b6dab36f11345c1a94b8527c56e2
|
[
"MIT"
] | 26 |
2020-03-11T16:40:26.000Z
|
2020-05-29T17:47:05.000Z
|
notebooks/Collaborative_Filtering_Model_Process.ipynb
|
Lambda-School-Labs/betterreads-ds
|
7817f97922a9b6dab36f11345c1a94b8527c56e2
|
[
"MIT"
] | 7 |
2020-02-18T16:41:32.000Z
|
2020-07-31T22:02:33.000Z
| 30.58 | 126 | 0.366979 |
[
[
[
"**KNN model of 10k dataset**\n\n\n_using data found on kaggle from Goodreads_\n\n\n_books.csv contains information for 10,000 books, such as ISBN, authors, title, year_\n\n\n_ratings.csv is a collection of user ratings on these books, from 1 to 5 stars_",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# imports\n\n\nimport numpy as pd\nimport pandas as pd\nimport pickle\n\n\nfrom sklearn.neighbors import NearestNeighbors\nfrom scipy.sparse import csr_matrix\n\nimport re",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Books dataset**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"books = pd.read_csv('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/zygmuntz/goodbooks-10k/master/books.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(books.shape)\nbooks.head()",
"(10000, 23)\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Ratings dataset**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"ratings = pd.read_csv('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/zygmuntz/goodbooks-10k/master/ratings.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(ratings.shape)\nratings.head()",
"(5976479, 3)\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Trim down the data**\n\n_In order to make a user rating matrix we will only need bood_id and title._\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cols = ['book_id', 'title']\n\nbooks = books[cols]\nbooks.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Clean up book titles**\n\n_Book titles are messy, special characters, empty spaces, brackets clutter up the titles_",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def clean_book_titles(title):\n title = re.sub(r'\\([^)]*\\)', '', title) # handles brackets\n title = re.sub(' + ', ' ', title) #compresses multi spaces into a single space\n title = title.strip() # handles special characters\n return title",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"books['title'] = books['title'].apply(clean_book_titles)\n\nbooks.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**neat-o**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Create feature matrix**\n\n_Combine datasets to get a new dataset of user ratings for each book_",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"books_ratings = pd.merge(ratings, books, on='book_id')\n\nprint(books_ratings.shape)\n\nbooks_ratings.head()\n",
"(5976479, 4)\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Remove rows with same user_id and book title**\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"user_ratings = books_ratings.drop_duplicates(['user_id', 'title'])\n\nprint(user_ratings.shape)\nuser_ratings.head()",
"(5972713, 4)\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Pivot table to create user_ratings matrix**\n\n_Each column is a user and each row is a book. The entries in the martix are the user's rating for that book._",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"user_matrix = user_ratings.pivot(index='title', columns='user_id', values='rating').fillna(0)\n\nuser_matrix.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"user_matrix.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Compress the matrix since it is extremely sparse**\n\n_Whole lotta zeros_\n\n_",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"compressed = csr_matrix(user_matrix.values)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# build and train knn\n\n# unsupervised learning\n# using cosine to measure space/distance\n\nknn = NearestNeighbors(algorithm='brute', metric='cosine')\n\nknn.fit(compressed)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def get_recommendations(book_title, matrix=user_matrix, model=knn, topn=2):\n book_index = list(matrix.index).index(book_title)\n distances, indices = model.kneighbors(matrix.iloc[book_index,:].values.reshape(1,-1), n_neighbors=topn+1)\n print('Recommendations for {}:'.format(matrix.index[book_index]))\n for i in range(1, len(distances.flatten())):\n print('{}. {}, distance = {}'.format(i, matrix.index[indices.flatten()[i]], \"%.3f\"%distances.flatten()[i]))\n print()\n \nget_recommendations(\"Harry Potter and the Sorcerer's Stone\")\nget_recommendations(\"Pride and Prejudice\")\nget_recommendations(\"Matilda\")",
"Recommendations for Harry Potter and the Sorcerer's Stone:\n1. Harry Potter and the Prisoner of Azkaban, distance = 0.320\n2. Harry Potter and the Chamber of Secrets, distance = 0.327\n\nRecommendations for Pride and Prejudice:\n1. Jane Eyre, distance = 0.421\n2. Sense and Sensibility, distance = 0.434\n\nRecommendations for Matilda:\n1. The Witches, distance = 0.501\n2. The BFG, distance = 0.525\n\n"
],
[
"pickle.dump(knn, open('knn_model.pkl','wb'))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a730558d195620b5d39dddc57bb8d48c7b594e5
| 224,925 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
classes/Aula_5_NLTK_Python_para_PLN.ipynb
|
jonatas-88/course_usp_icmc_nlp
|
6fb45e5ac3ae8637a586b10b4c668bda7014128e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
classes/Aula_5_NLTK_Python_para_PLN.ipynb
|
jonatas-88/course_usp_icmc_nlp
|
6fb45e5ac3ae8637a586b10b4c668bda7014128e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
classes/Aula_5_NLTK_Python_para_PLN.ipynb
|
jonatas-88/course_usp_icmc_nlp
|
6fb45e5ac3ae8637a586b10b4c668bda7014128e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 42.326872 | 14,430 | 0.323912 |
[
[
[
"# Importando o NLTK\n\nImportar um módulo ou biblioteca significa informar para o programa que você está criando/executando que precisa daquela biblioteca específica.\n\nÉ possível fazer uma analogia, imagine que você precisa estudar para as provas de Matemática e Português. Você pega seus livros para estudar. Nessa analogia os livros são as \"bibliotecas externas\" nas quais você quer estudar o assunto.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import nltk",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Fazendo o download dos dados complementares do NLTK\n\nOs desenvolvedores do NLTK decidiram manter o arquivo de instalação (pip install nltk) com o mínimo de arquivos possível para facilitar o download e instalação. Portanto, eles permitem fazer o download dos arquivos complementares de acordo com a demanda dos desenvolvedores. \n\nPara fazer isso, basta executar o código abaixo e seguir as instruções apresentadas.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"nltk.download()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# O que encontramos no NLTK?\n\nAs células abaixo apresentam o exemplo de um dos córpus em Português que podemos acessar com o NLTK. \n\nMACMORPHO - http://nilc.icmc.usp.br/macmorpho/",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Mostrar as palavras existentes no MACMorpho\n# Observe que elas estão dispostas em uma estrutura de Lista\n# Observe também a estrutura para acessar o córpus e seus tokens, imagine \n# que está acessando uma estrutura de árvore, com uma raiz e vários ramos filhos.\n\nnltk.corpus.mac_morpho.words()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"nltk.corpus.mac_morpho.sents()[1]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"nltk.corpus.mac_morpho.tagged_words()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"nltk.corpus.mac_morpho.tagged_sents()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Primeira tarefa com o NLTK - a Tokenização\n\nObserve que essa é a forma mais simples de tokenizar um texto usando o NLTK.\n\nA função (trecho de código pré-desenvolvido que executa uma ação) *word_tokenize()* recebe um texto e retorna uma lista de tokens.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"nltk.word_tokenize(\"Com um passe de Eli Manning para Plaxico Burress a 39 segundos do fim, o New York Giants anotou o touchdown decisivo e derrubou o favorito New England Patriots por 17 a 14 neste domingo, em Glendale, no Super Bowl XLII.\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Formas adicionais avançadas para tokenização de um texto\n\nO conceito utilizado nas células seguintes é o de Expressões Regulares. \n\nExpressões regulares (chamadas REs, ou regexes ou padrões regex) são essencialmente uma mini linguagem de programação altamente especializada incluída dentro do Python. \n\nUsando esta pequena linguagem, você especifica as regras para o conjunto de strings possíveis que você quer combinar; esse conjunto pode conter sentenças em inglês, endereços de e-mail, ou comandos TeX ou qualquer coisa que você queira. Você poderá então perguntar coisas como “Essa string se enquadra dentro do padrão?” ou “Existe alguma parte da string que se enquadra nesse padrão?”. Você também pode usar as REs para modificar uma string ou dividi-la de diversas formas.\n\nhttps://docs.python.org/pt-br/3.8/howto/regex.html\n\nhttps://www.w3schools.com/python/python_regex.asp\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Informando ao programa que vamos utilizar a classe RegexpTokenizer\n# observe que é outra forma de fazer a 'importação' de um módulo\nfrom nltk.tokenize import RegexpTokenizer\n\n# Nosso texto\ntexto = \"Com um passe de Eli Manning para Plaxico Burress a 39 segundos do fim, o New York Giants anotou o touchdown decisivo e derrubou o favorito New England Patriots por 17 a 14 neste domingo, em Glendale, no Super Bowl XLII.\"\n\n# Criando o \"objeto\" que vai tokenizar nosso texto.\n# Nesse caso usamos uma expressão regular que vai retornar todos os tokens\n# textuais (letras do alfabeto, números e underscore). \n# Não queremos os símbolos.\ntokenizer = RegexpTokenizer(r'\\w+')\n\n# Executando o método do objeto tokenizador\ntokens = tokenizer.tokenize(texto)\n\n# Nossos tokens :)\ntokens",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Informando ao programa que vamos utilizar a classe RegexpTokenizer\n# observe que é outra forma de fazer a 'importação' de um módulo\nfrom nltk.tokenize import RegexpTokenizer\n\n# Nosso texto\ntexto = \"Com um passe de Eli Manning para Plaxico Burress a 39 segundos do fim, o New York Giants anotou o touchdown decisivo e derrubou o favorito New England Patriots por 17 a 14 neste domingo, em Glendale, no Super Bowl XLII.\"\n\n# Criando o \"objeto\" que vai tokenizar nosso texto.\n# Nesse caso usamos uma expressão regular que vai retornar somente os tokens\n# com letras maiúsculas e minúsculas. Não queremos os símbolos e números.\ntokenizer = RegexpTokenizer(r'[a-zA-Z]\\w+')\n\ntokens = tokenizer.tokenize(texto)\ntokens",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Frequência de tokens\n\nMuitas vezes é interessante saber a frequencia em que os tokens aparecem em um texto. Com a classe *FreqDist* podemos calcular facilmente.\n\n**Nesse primeiro exemplo, como será a frequencia usando todos os tokens?**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Nosso texto\ntexto = \"Com um passe de Eli Manning para Plaxico Burress a 39 segundos do fim, o New York Giants anotou o touchdown decisivo e derrubou o favorito New England Patriots por 17 a 14 neste domingo, em Glendale, no Super Bowl XLII.\"\n\n# Tokenizamos nosso texto usando a word_tokenize\ntokens = nltk.word_tokenize(texto)\n\n# Calculando nossa frequencia de palavras\nfrequencia = nltk.FreqDist(tokens)\n\n# Recuperamos a lista de frequencia usando a função most_common()\nfrequencia.most_common()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**E se excluírmos as pontuações?**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from nltk.tokenize import RegexpTokenizer\ntexto = \"Com um passe de Eli Manning para Plaxico Burress a 39 segundos do fim, o New York Giants anotou o touchdown decisivo e derrubou o favorito New England Patriots por 17 a 14 neste domingo, em Glendale, no Super Bowl XLII.\"\n\ntokenizer = RegexpTokenizer(r'\\w+')\ntokens = tokenizer.tokenize(texto)\n\nfrequencia = nltk.FreqDist(tokens)\nfrequencia.most_common()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Acessando córpus externos\n\nComo já foi apresentado, podemos acessar nossos arquivos que estão no Google Drive apenas \"montando\" nosso drive no ícone na barra à esquerda. \n\nPara acessar o conteúdo do arquivo, devemos usar a função *open()* que está embutida no python. Essa função retorna o arquivo no formato que o python entende. Para lermos o seu conteúdo devemos usar a função *read()*.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Abrindo nosso córpus\n# Nesse código concatenamos a função open com a função read\n# Sem concatenar teríamos a seguinte construção\n# infile = open('/content/drive/MyDrive/recursos/corpus_teste.txt')\n# corpus = infile.read()\n\ncorpus = open('/content/drive/MyDrive/recursos/corpus_teste.txt').read()\nprint(corpus)",
"Giants batem os Patriots no Super Bowl XLII\nAzarões acabam com a invencibilidade de New England e ficam com o título da temporada\n04/02/2008 - 01h07m - Atualizado em 04/02/2008 - 09h49m\n\nCom um passe de Eli Manning para Plaxico Burress a 39 segundos do fim, o New York Giants anotou o touchdown decisivo e derrubou o favorito New England Patriots por 17 a 14 neste domingo, em Glendale, no Super Bowl XLII. O resultado, uma das maiores zebras da história do Super Bowl, acabou com a temporada perfeita de Tom Brady e companhia, que esperavam fazer história ao levantar o troféu da NFL sem sofrer uma derrota no ano. \n\nA vitória dos Giants, porém, também ficará para a história. Pela primeira vez, irmãos quarterbacks triunfam no Super Bowl em temporadas consecutivas. No ano passado, Peyton Manning, irmão de Eli, chegou ao título máximo da NFL pelo Indianapolis Colts.\n\nA partida\n\nOs Giants começaram com a posse de bola, e mostraram logo que iriam alongar ao máximo suas posses de bola. Misturando corridas com Brandon Jacobs e passes curtos, o time de Nova York chegou à red zone logo na primeira campanha. O avanço, no entanto, parou na linha de 17 jardas e Lawrence Tynes converteu o field goal de 32 jardas para abrir o placar.\n\nEli Manning e companhia ficaram 9m54s com a bola, mas o ataque dos Patriots não entrou em campo frio. Logo no retorno do kickoff, o running back Laurence Maroney avançou 43 jardas, deixando Tom Brady em boa posição. Com passes curtos, os Patriots chegaram à linha de 17 jardas e, graças a uma penalidade (interferência de passe) do linebacker Antonio Pierce, alcançaram a linha de uma jarda. Maroney avançou pelo chão e anotou o primeiro touchdown do jogo.\n\nOs Giants pareciam rumo à virada na campanha seguinte. Manning achou Amani Toomer para um avanço de 38 jardas, e o time de Nova York entrou novamente na red zone. Com a bola na linha de 14 jardas dos Patriots, os Giants sofreram um revés. Manning passou para Steve Smith, que soltou a bola. Ellis Hobbs aproveitou, tomou a posse para os Patriots, e avançou 23 jardas. \n\nA defesa de Nova York manteve o jogo equilibrado. Com dois sacks seguidos, os Giants forçaram o punt e recuperaram a bola. Mas a campanha seguinte provou ser outra decepção para Nova York. O time chegou à linha de 25 jardas, mas Manning sofreu um sack e cometeu um fumble, e o ataque voltou para a linha de 39 jardas, não conseguindo pontuar mais uma vez.\n\nOs Patriots tiveram uma última chance de marcar antes do intervalo, mas, a 22 segundos do fim do segundo período, Brady foi novamente sacado. Desta vez, ele cometeu o fumble e os Giants tomaram a posse de bola. Manning tentou um passe longo, de 50 jardas, nos últimos segundos, mas não teve sucesso. \n\nO jogo continuou amarrado no terceiro quarto, com as defesas levando a melhor sobre os ataques. A única chance de pontuar do período foi dos Patriots, que chegaram à linha de 31 jardas dos Giants. O técnico Bill Bellichick, porém, optou por uma quarta descida em vez de um field goal. Brady tentou um passe para Jabar Gaffney, mas não conseguiu completar.\n\nO último período começou arrasador para os Giants. na primeira jogada, Manning achou o tight end Kevin Boss, para um incrível avanço de 45 jardas, que deixou o time na linha de 35 dos Patriots. Outro lançamento, desta vez para Steve Smith, marcou o avanço até a linha de 12 jardas. Duas jogadas depois, David Tyree pegou um passe de cinco jardas na end zone para anotar o touchdown e virar o jogo.\n\nNa hora da decisão, o ataque dos Patriots voltou a funcionar. Com uma série de passes curtos e variados, Brady achou Wes Welker, Randy Moss e Kevin Faulk seguidas vezes até chegar à red zone. A 2m45s do fim, o quarterback conectou mais uma vez com Moss, que se desmarcou e ficou livre na lateral direita da end zone.\n\nQuando os fãs de New England já comemoravam a vitória, o inesperado aconteceu. Em uma jogada incrível, Eli Manning se soltou de dois marcadores que o seguravam pela camisa e, na corrida, lançou para Amani Toomer. O wide receiver, bem marcado, saltou e conseguiu a fazer recepção para um avanço de 32 jardas, deixando os Giants na linha de 24 de New England.\n\nQuatro jogadas depois, a 39 segundos do fim, Manning achou Plaxico Burress na end zone para conseguir o touchdown do título.\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Agora vamos tokenizar e calcular a frequência do nosso corpus inteiro :)**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from nltk.tokenize import RegexpTokenizer\n\n# Não quero símbolos\ntokenizer = RegexpTokenizer(r'\\w+')\ntokens = tokenizer.tokenize(corpus)\n\nfrequencia = nltk.FreqDist(tokens)\nfrequencia.most_common()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Agrupando minúsculas e maiúsculas\n\nNas células anteriores percebemos que alguns tokens estão com o texto em maiúsculas e outros em minúsculas. O python considera que são tokens diferentes apenas por conter letras com \"caixa\" diferente. Portanto, precisamos agrupar todas as palavras que sabemos que são a mesma coisa. O modo mais simples é converter todas para minúsculas ou maiúsculas.\n\nVimos que podemos modificar uma string para minúsculas ou maiúsculas apenas usando as funções *.lower()* ou *.upper()*, respectivamente.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Vamos usar o tokenizador do tipo Regex\nfrom nltk.tokenize import RegexpTokenizer\n\n# Vamos considerar apenas as letras\ntokenizer = RegexpTokenizer(r'[a-zA-Z]\\w*')\n\n# Tokenizamos o corpus\ntokens = tokenizer.tokenize(corpus)\n\n# Nesse trecho queremos criar uma nova lista com todos os tokens convertidos em\n# minúsculas. Para fazer isso \"caminhamos\" na nossa lista de tokens e executamos\n# em cada um a função .lower() e adicionamos esse token convertido na nova lista.\nnova_lista = []\n\nfor token in tokens:\n nova_lista.append(token.lower())\n\n# Com todos os tokens convertidos para minúsculas, calcularemos as suas frequencias :)\nfrequencia = nltk.FreqDist(nova_lista)\nfrequencia.most_common()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Tokens que não nos interessam\n\nAlguns tokens que são muito frequentes não ajudam na análise de um texto.\nVeja como exemplo a lista de tokens anterior, no topo da lista estão artigos, preposições e etc. No nosso caso não são interessantes. \n\nO NLTK possui uma lista de tokens considerados desinteressantes e que podem ser removidos de uma lista de tokens sem problemas. Em PLN os chamamos de *stopwords*.\n\nPara removê-los da nossa lista de tokens, precisamos comparar um a um com a lista de *stopwords*. Caso um token seja uma *stopword* o removeremos da lista de tokens.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Acessamos a lista de stopwords do NLTK, para a língua portuguesa\nstopwords = nltk.corpus.stopwords.words('portuguese')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Mais uma vez usarmos o tokenizador de Regex\nfrom nltk.tokenize import RegexpTokenizer\n\n# Somente as palavras\ntokenizer = RegexpTokenizer(r'[a-zA-Z]\\w*')\ntokens = tokenizer.tokenize(corpus)\n\n# agora além de convertermos a lista de tokens em minúsculas, vamos comparar\n# cada token com a lista de stopwords. Somente vamos adicionar à nova lista \n# os tokens que não forem stopwords\nnova_lista = []\n\nfor token in tokens:\n if token.lower() not in stopwords:\n nova_lista.append(token.lower())\n\n# E agora calculamos a frequencia novamente\nfrequencia = nltk.FreqDist(nova_lista)\nfrequencia.most_common()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# List Comprehension\n\nA técnica de *list comprehension* é uma forma diferente e avançada de criar uma lista. Não é obrigatório saber usá-la, mas é muito interessante conhecer sua construção.\n\nO python entende que é uma *list comprehension* quando criamos um laço de repetição entre colchetes: [i for i in range(10)]. Essa construção criará a seguinte lista: [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]. Veja que é possível fazer isso sem essa construção.\n\nUma forma genérica de imaginar uma *list comprehension* é montar a seguinte estrutura: \n\n<*lista_final* = **[** *elemento_da_lista* **for** *elemento_da_lista* **in** *lista_de_elementos* **]**>\n\nLembrando que você poderá acrescentar alguma condição para o elemento ser acrescentado na lista:\n\n<*lista_final* = **[** *elemento_da_lista* **for** *elemento_da_lista* **in** *lista_de_elementos* **if** *condição* **]**>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from nltk.tokenize import RegexpTokenizer\n\ntokenizer = RegexpTokenizer(r'[a-zA-Z]\\w*')\ntokens = tokenizer.tokenize(corpus)\n\nnova_lista = []\n\n#for token in tokens:\n# if token.lower() not in stopwords:\n# nova_lista.append(token.lower())\n\nnova_lista = [token.lower() for token in tokens if token.lower() not in stopwords]\n\nfrequencia = nltk.FreqDist(nova_lista)\nfrequencia.most_common()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Utilizando ngrams",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Abrindo nosso córpus\n# Nesse código concatenamos a função open com a função read\n# Sem concatenar teríamos a seguinte construção\n# infile = open('/content/drive/MyDrive/recursos/corpus_teste.txt')\n# corpus = infile.read()\n\ncorpus = open('/content/drive/MyDrive/recursos/corpus_teste.txt').read()\nprint(corpus)",
"Giants batem os Patriots no Super Bowl XLII\nAzarões acabam com a invencibilidade de New England e ficam com o título da temporada\n04/02/2008 - 01h07m - Atualizado em 04/02/2008 - 09h49m\n\nCom um passe de Eli Manning para Plaxico Burress a 39 segundos do fim, o New York Giants anotou o touchdown decisivo e derrubou o favorito New England Patriots por 17 a 14 neste domingo, em Glendale, no Super Bowl XLII. O resultado, uma das maiores zebras da história do Super Bowl, acabou com a temporada perfeita de Tom Brady e companhia, que esperavam fazer história ao levantar o troféu da NFL sem sofrer uma derrota no ano. \n\nA vitória dos Giants, porém, também ficará para a história. Pela primeira vez, irmãos quarterbacks triunfam no Super Bowl em temporadas consecutivas. No ano passado, Peyton Manning, irmão de Eli, chegou ao título máximo da NFL pelo Indianapolis Colts.\n\nA partida\n\nOs Giants começaram com a posse de bola, e mostraram logo que iriam alongar ao máximo suas posses de bola. Misturando corridas com Brandon Jacobs e passes curtos, o time de Nova York chegou à red zone logo na primeira campanha. O avanço, no entanto, parou na linha de 17 jardas e Lawrence Tynes converteu o field goal de 32 jardas para abrir o placar.\n\nEli Manning e companhia ficaram 9m54s com a bola, mas o ataque dos Patriots não entrou em campo frio. Logo no retorno do kickoff, o running back Laurence Maroney avançou 43 jardas, deixando Tom Brady em boa posição. Com passes curtos, os Patriots chegaram à linha de 17 jardas e, graças a uma penalidade (interferência de passe) do linebacker Antonio Pierce, alcançaram a linha de uma jarda. Maroney avançou pelo chão e anotou o primeiro touchdown do jogo.\n\nOs Giants pareciam rumo à virada na campanha seguinte. Manning achou Amani Toomer para um avanço de 38 jardas, e o time de Nova York entrou novamente na red zone. Com a bola na linha de 14 jardas dos Patriots, os Giants sofreram um revés. Manning passou para Steve Smith, que soltou a bola. Ellis Hobbs aproveitou, tomou a posse para os Patriots, e avançou 23 jardas. \n\nA defesa de Nova York manteve o jogo equilibrado. Com dois sacks seguidos, os Giants forçaram o punt e recuperaram a bola. Mas a campanha seguinte provou ser outra decepção para Nova York. O time chegou à linha de 25 jardas, mas Manning sofreu um sack e cometeu um fumble, e o ataque voltou para a linha de 39 jardas, não conseguindo pontuar mais uma vez.\n\nOs Patriots tiveram uma última chance de marcar antes do intervalo, mas, a 22 segundos do fim do segundo período, Brady foi novamente sacado. Desta vez, ele cometeu o fumble e os Giants tomaram a posse de bola. Manning tentou um passe longo, de 50 jardas, nos últimos segundos, mas não teve sucesso. \n\nO jogo continuou amarrado no terceiro quarto, com as defesas levando a melhor sobre os ataques. A única chance de pontuar do período foi dos Patriots, que chegaram à linha de 31 jardas dos Giants. O técnico Bill Bellichick, porém, optou por uma quarta descida em vez de um field goal. Brady tentou um passe para Jabar Gaffney, mas não conseguiu completar.\n\nO último período começou arrasador para os Giants. na primeira jogada, Manning achou o tight end Kevin Boss, para um incrível avanço de 45 jardas, que deixou o time na linha de 35 dos Patriots. Outro lançamento, desta vez para Steve Smith, marcou o avanço até a linha de 12 jardas. Duas jogadas depois, David Tyree pegou um passe de cinco jardas na end zone para anotar o touchdown e virar o jogo.\n\nNa hora da decisão, o ataque dos Patriots voltou a funcionar. Com uma série de passes curtos e variados, Brady achou Wes Welker, Randy Moss e Kevin Faulk seguidas vezes até chegar à red zone. A 2m45s do fim, o quarterback conectou mais uma vez com Moss, que se desmarcou e ficou livre na lateral direita da end zone.\n\nQuando os fãs de New England já comemoravam a vitória, o inesperado aconteceu. Em uma jogada incrível, Eli Manning se soltou de dois marcadores que o seguravam pela camisa e, na corrida, lançou para Amani Toomer. O wide receiver, bem marcado, saltou e conseguiu a fazer recepção para um avanço de 32 jardas, deixando os Giants na linha de 24 de New England.\n\nQuatro jogadas depois, a 39 segundos do fim, Manning achou Plaxico Burress na end zone para conseguir o touchdown do título.\n"
],
[
"from nltk import bigrams\nfrom nltk import trigrams\nfrom nltk import ngrams",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tokens = nltk.word_tokenize(corpus)\n\ntokens_bigrams = list(bigrams(tokens))\n\ntokens_bigrams",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tokens_trigrams = list(trigrams(tokens))\n\ntokens_trigrams",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tokens_ngrams = list(ngrams(tokens, 4))\n\ntokens_ngrams",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Reconhecer entidades nomeadas",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from nltk import bigrams\nfrom nltk import trigrams\n\nbigramas = list(bigrams(tokens))\ntrigramas = list(trigrams(tokens))\n\nfor bigrama in bigramas:\n if bigrama[0][0].isupper() and bigrama[1][0].isupper():\n print(bigrama)",
"('Super', 'Bowl')\n('Bowl', 'XLII')\n('XLII', 'Azarões')\n('New', 'England')\n('Eli', 'Manning')\n('Plaxico', 'Burress')\n('New', 'York')\n('York', 'Giants')\n('New', 'England')\n('England', 'Patriots')\n('Super', 'Bowl')\n('Bowl', 'XLII')\n('Super', 'Bowl')\n('Tom', 'Brady')\n('Super', 'Bowl')\n('Peyton', 'Manning')\n('Indianapolis', 'Colts')\n('Os', 'Giants')\n('Brandon', 'Jacobs')\n('Nova', 'York')\n('Lawrence', 'Tynes')\n('Eli', 'Manning')\n('Laurence', 'Maroney')\n('Tom', 'Brady')\n('Antonio', 'Pierce')\n('Os', 'Giants')\n('Amani', 'Toomer')\n('Nova', 'York')\n('Steve', 'Smith')\n('Ellis', 'Hobbs')\n('Nova', 'York')\n('Nova', 'York')\n('Os', 'Patriots')\n('Bill', 'Bellichick')\n('Jabar', 'Gaffney')\n('Kevin', 'Boss')\n('Steve', 'Smith')\n('David', 'Tyree')\n('Wes', 'Welker')\n('Randy', 'Moss')\n('Kevin', 'Faulk')\n('New', 'England')\n('Eli', 'Manning')\n('Amani', 'Toomer')\n('New', 'England')\n('Plaxico', 'Burress')\n"
],
[
"for trigrama in trigramas:\n if trigrama[0][0].isupper() and trigrama[1][0].isupper() and trigrama[2][0].isupper():\n print(trigrama)",
"('Super', 'Bowl', 'XLII')\n('Bowl', 'XLII', 'Azarões')\n('New', 'York', 'Giants')\n('New', 'England', 'Patriots')\n('Super', 'Bowl', 'XLII')\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Stemming e Lematização",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import nltk\n\nstemmer = nltk.RSLPStemmer()\n\nprint(stemmer.stem(\"Amigão\"))\nprint(stemmer.stem(\"amigo\"))\nprint(stemmer.stem(\"amigos\"))\nprint(stemmer.stem(\"propuseram\"))\nprint(stemmer.stem(\"propõem\"))\nprint(stemmer.stem(\"propondo\"))",
"amig\namig\namig\npropus\npropõ\nprop\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Etiquetador",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from nltk.corpus import mac_morpho\nfrom nltk.tag import UnigramTagger\n\ntokens = nltk.word_tokenize(corpus)\n\nsentencas_treino = mac_morpho.tagged_sents()\netiquetador = UnigramTagger(sentencas_treino)\n\netiquetado = etiquetador.tag(tokens)\n\nprint(etiquetado)",
"[('Giants', 'NPROP'), ('batem', 'V'), ('os', 'ART'), ('Patriots', None), ('no', 'KC'), ('Super', 'NPROP'), ('Bowl', 'NPROP'), ('XLII', None), ('Azarões', None), ('acabam', 'VAUX'), ('com', 'PREP'), ('a', 'ART'), ('invencibilidade', 'N'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('New', 'NPROP'), ('England', 'NPROP'), ('e', 'KC'), ('ficam', 'V'), ('com', 'PREP'), ('o', 'ART'), ('título', 'N'), ('da', 'NPROP'), ('temporada', 'N'), ('04/02/2008', None), ('-', '-'), ('01h07m', None), ('-', '-'), ('Atualizado', None), ('em', 'PREP|+'), ('04/02/2008', None), ('-', '-'), ('09h49m', None), ('Com', 'PREP'), ('um', 'ART'), ('passe', 'N'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('Eli', 'NPROP'), ('Manning', 'NPROP'), ('para', 'PREP'), ('Plaxico', None), ('Burress', None), ('a', 'ART'), ('39', 'NUM'), ('segundos', 'N'), ('do', 'NPROP'), ('fim', 'N'), (',', ','), ('o', 'ART'), ('New', 'NPROP'), ('York', 'NPROP'), ('Giants', 'NPROP'), ('anotou', 'V'), ('o', 'ART'), ('touchdown', 'N|EST'), ('decisivo', 'ADJ'), ('e', 'KC'), ('derrubou', 'V'), ('o', 'ART'), ('favorito', 'N'), ('New', 'NPROP'), ('England', 'NPROP'), ('Patriots', None), ('por', 'PREP|+'), ('17', 'NUM'), ('a', 'ART'), ('14', 'NUM'), ('neste', None), ('domingo', 'N'), (',', ','), ('em', 'PREP|+'), ('Glendale', None), (',', ','), ('no', 'KC'), ('Super', 'NPROP'), ('Bowl', 'NPROP'), ('XLII', None), ('.', '.'), ('O', 'ART'), ('resultado', 'N'), (',', ','), ('uma', 'ART'), ('das', 'NPROP'), ('maiores', 'ADJ'), ('zebras', None), ('da', 'NPROP'), ('história', 'N'), ('do', 'NPROP'), ('Super', 'NPROP'), ('Bowl', 'NPROP'), (',', ','), ('acabou', 'VAUX'), ('com', 'PREP'), ('a', 'ART'), ('temporada', 'N'), ('perfeita', 'ADJ'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('Tom', 'NPROP'), ('Brady', 'NPROP'), ('e', 'KC'), ('companhia', 'N'), (',', ','), ('que', 'PRO-KS-REL'), ('esperavam', 'V'), ('fazer', 'V'), ('história', 'N'), ('ao', 'PREP'), ('levantar', 'V'), ('o', 'ART'), ('troféu', 'N'), ('da', 'NPROP'), ('NFL', None), ('sem', 'PREP'), ('sofrer', 'V'), ('uma', 'ART'), ('derrota', 'N'), ('no', 'KC'), ('ano', 'N'), ('.', '.'), ('A', 'ART'), ('vitória', 'N'), ('dos', 'NPROP'), ('Giants', 'NPROP'), (',', ','), ('porém', 'KC'), (',', ','), ('também', 'PDEN'), ('ficará', 'V'), ('para', 'PREP'), ('a', 'ART'), ('história', 'N'), ('.', '.'), ('Pela', 'NPROP'), ('primeira', 'ADJ'), ('vez', 'N'), (',', ','), ('irmãos', 'N'), ('quarterbacks', None), ('triunfam', None), ('no', 'KC'), ('Super', 'NPROP'), ('Bowl', 'NPROP'), ('em', 'PREP|+'), ('temporadas', 'N'), ('consecutivas', 'ADJ'), ('.', '.'), ('No', 'KC'), ('ano', 'N'), ('passado', 'PCP'), (',', ','), ('Peyton', None), ('Manning', 'NPROP'), (',', ','), ('irmão', 'N'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('Eli', 'NPROP'), (',', ','), ('chegou', 'V'), ('ao', 'PREP'), ('título', 'N'), ('máximo', 'N'), ('da', 'NPROP'), ('NFL', None), ('pelo', 'PDEN'), ('Indianapolis', None), ('Colts', None), ('.', '.'), ('A', 'ART'), ('partida', 'N'), ('Os', 'ART'), ('Giants', 'NPROP'), ('começaram', 'VAUX'), ('com', 'PREP'), ('a', 'ART'), ('posse', 'N'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('bola', 'N'), (',', ','), ('e', 'KC'), ('mostraram', 'V'), ('logo', 'ADV'), ('que', 'PRO-KS-REL'), ('iriam', 'VAUX'), ('alongar', 'V'), ('ao', 'PREP'), ('máximo', 'N'), ('suas', 'PROADJ'), ('posses', 'N'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('bola', 'N'), ('.', '.'), ('Misturando', None), ('corridas', 'N'), ('com', 'PREP'), ('Brandon', None), ('Jacobs', 'NPROP'), ('e', 'KC'), ('passes', 'N'), ('curtos', 'ADJ'), (',', ','), ('o', 'ART'), ('time', 'N'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('Nova', 'NPROP'), ('York', 'NPROP'), ('chegou', 'V'), ('à', 'NPROP'), ('red', 'N|EST'), ('zone', None), ('logo', 'ADV'), ('na', 'NPROP'), ('primeira', 'ADJ'), ('campanha', 'N'), ('.', '.'), ('O', 'ART'), ('avanço', 'N'), (',', ','), ('no', 'KC'), ('entanto', 'KC'), (',', ','), ('parou', 'V'), ('na', 'NPROP'), ('linha', 'N'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('17', 'NUM'), ('jardas', 'N'), ('e', 'KC'), ('Lawrence', 'NPROP'), ('Tynes', None), ('converteu', 'V'), ('o', 'ART'), ('field', 'N|EST'), ('goal', 'N|EST'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('32', 'NUM'), ('jardas', 'N'), ('para', 'PREP'), ('abrir', 'V'), ('o', 'ART'), ('placar', 'N'), ('.', '.'), ('Eli', 'NPROP'), ('Manning', 'NPROP'), ('e', 'KC'), ('companhia', 'N'), ('ficaram', 'V'), ('9m54s', None), ('com', 'PREP'), ('a', 'ART'), ('bola', 'N'), (',', ','), ('mas', 'KC'), ('o', 'ART'), ('ataque', 'N'), ('dos', 'NPROP'), ('Patriots', None), ('não', 'ADV'), ('entrou', 'V'), ('em', 'PREP|+'), ('campo', 'N'), ('frio', 'N'), ('.', '.'), ('Logo', 'ADV'), ('no', 'KC'), ('retorno', 'N'), ('do', 'NPROP'), ('kickoff', None), (',', ','), ('o', 'ART'), ('running', 'N|EST'), ('back', 'N|EST'), ('Laurence', 'NPROP'), ('Maroney', None), ('avançou', 'V'), ('43', 'NUM'), ('jardas', 'N'), (',', ','), ('deixando', 'V'), ('Tom', 'NPROP'), ('Brady', 'NPROP'), ('em', 'PREP|+'), ('boa', 'ADJ'), ('posição', 'N'), ('.', '.'), ('Com', 'PREP'), ('passes', 'N'), ('curtos', 'ADJ'), (',', ','), ('os', 'ART'), ('Patriots', None), ('chegaram', 'V'), ('à', 'NPROP'), ('linha', 'N'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('17', 'NUM'), ('jardas', 'N'), ('e', 'KC'), (',', ','), ('graças', 'PREP|+'), ('a', 'ART'), ('uma', 'ART'), ('penalidade', None), ('(', '('), ('interferência', 'N'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('passe', 'N'), (')', ')'), ('do', 'NPROP'), ('linebacker', None), ('Antonio', 'NPROP'), ('Pierce', 'NPROP'), (',', ','), ('alcançaram', 'V'), ('a', 'ART'), ('linha', 'N'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('uma', 'ART'), ('jarda', None), ('.', '.'), ('Maroney', None), ('avançou', 'V'), ('pelo', 'PDEN'), ('chão', 'N'), ('e', 'KC'), ('anotou', 'V'), ('o', 'ART'), ('primeiro', 'ADJ'), ('touchdown', 'N|EST'), ('do', 'NPROP'), ('jogo', 'N'), ('.', '.'), ('Os', 'ART'), ('Giants', 'NPROP'), ('pareciam', 'V'), ('rumo', 'PREP|+'), ('à', 'NPROP'), ('virada', 'N'), ('na', 'NPROP'), ('campanha', 'N'), ('seguinte', 'ADJ'), ('.', '.'), ('Manning', 'NPROP'), ('achou', 'V'), ('Amani', None), ('Toomer', None), ('para', 'PREP'), ('um', 'ART'), ('avanço', 'N'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('38', 'NUM'), ('jardas', 'N'), (',', ','), ('e', 'KC'), ('o', 'ART'), ('time', 'N'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('Nova', 'NPROP'), ('York', 'NPROP'), ('entrou', 'V'), ('novamente', 'ADV'), ('na', 'NPROP'), ('red', 'N|EST'), ('zone', None), ('.', '.'), ('Com', 'PREP'), ('a', 'ART'), ('bola', 'N'), ('na', 'NPROP'), ('linha', 'N'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('14', 'NUM'), ('jardas', 'N'), ('dos', 'NPROP'), ('Patriots', None), (',', ','), ('os', 'ART'), ('Giants', 'NPROP'), ('sofreram', 'V'), ('um', 'ART'), ('revés', None), ('.', '.'), ('Manning', 'NPROP'), ('passou', 'V'), ('para', 'PREP'), ('Steve', 'NPROP'), ('Smith', 'NPROP'), (',', ','), ('que', 'PRO-KS-REL'), ('soltou', 'V'), ('a', 'ART'), ('bola', 'N'), ('.', '.'), ('Ellis', 'NPROP'), ('Hobbs', None), ('aproveitou', 'V'), (',', ','), ('tomou', 'V'), ('a', 'ART'), ('posse', 'N'), ('para', 'PREP'), ('os', 'ART'), ('Patriots', None), (',', ','), ('e', 'KC'), ('avançou', 'V'), ('23', 'NUM'), ('jardas', 'N'), ('.', '.'), ('A', 'ART'), ('defesa', 'N'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('Nova', 'NPROP'), ('York', 'NPROP'), ('manteve', 'V'), ('o', 'ART'), ('jogo', 'N'), ('equilibrado', 'PCP'), ('.', '.'), ('Com', 'PREP'), ('dois', 'NUM'), ('sacks', None), ('seguidos', 'PCP'), (',', ','), ('os', 'ART'), ('Giants', 'NPROP'), ('forçaram', 'V'), ('o', 'ART'), ('punt', None), ('e', 'KC'), ('recuperaram', None), ('a', 'ART'), ('bola', 'N'), ('.', '.'), ('Mas', 'KC'), ('a', 'ART'), ('campanha', 'N'), ('seguinte', 'ADJ'), ('provou', 'V'), ('ser', 'VAUX'), ('outra', 'PROADJ'), ('decepção', 'N'), ('para', 'PREP'), ('Nova', 'NPROP'), ('York', 'NPROP'), ('.', '.'), ('O', 'ART'), ('time', 'N'), ('chegou', 'V'), ('à', 'NPROP'), ('linha', 'N'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('25', 'NUM'), ('jardas', 'N'), (',', ','), ('mas', 'KC'), ('Manning', 'NPROP'), ('sofreu', 'V'), ('um', 'ART'), ('sack', None), ('e', 'KC'), ('cometeu', 'V'), ('um', 'ART'), ('fumble', 'N|EST'), (',', ','), ('e', 'KC'), ('o', 'ART'), ('ataque', 'N'), ('voltou', 'V'), ('para', 'PREP'), ('a', 'ART'), ('linha', 'N'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('39', 'NUM'), ('jardas', 'N'), (',', ','), ('não', 'ADV'), ('conseguindo', 'V'), ('pontuar', None), ('mais', 'ADV'), ('uma', 'ART'), ('vez', 'N'), ('.', '.'), ('Os', 'ART'), ('Patriots', None), ('tiveram', 'V'), ('uma', 'ART'), ('última', 'ADJ'), ('chance', 'N'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('marcar', 'V'), ('antes', 'ADV'), ('do', 'NPROP'), ('intervalo', 'N'), (',', ','), ('mas', 'KC'), (',', ','), ('a', 'ART'), ('22', 'NUM'), ('segundos', 'N'), ('do', 'NPROP'), ('fim', 'N'), ('do', 'NPROP'), ('segundo', 'PREP'), ('período', 'N'), (',', ','), ('Brady', 'NPROP'), ('foi', 'VAUX'), ('novamente', 'ADV'), ('sacado', 'PCP'), ('.', '.'), ('Desta', 'ADV'), ('vez', 'N'), (',', ','), ('ele', 'PROPESS'), ('cometeu', 'V'), ('o', 'ART'), ('fumble', 'N|EST'), ('e', 'KC'), ('os', 'ART'), ('Giants', 'NPROP'), ('tomaram', 'V'), ('a', 'ART'), ('posse', 'N'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('bola', 'N'), ('.', '.'), ('Manning', 'NPROP'), ('tentou', 'V'), ('um', 'ART'), ('passe', 'N'), ('longo', 'ADJ'), (',', ','), ('de', 'PREP'), ('50', 'NUM'), ('jardas', 'N'), (',', ','), ('nos', 'PROPESS'), ('últimos', 'ADJ'), ('segundos', 'N'), (',', ','), ('mas', 'KC'), ('não', 'ADV'), ('teve', 'V'), ('sucesso', 'N'), ('.', '.'), ('O', 'ART'), ('jogo', 'N'), ('continuou', 'V'), ('amarrado', 'PCP'), ('no', 'KC'), ('terceiro', 'ADJ'), ('quarto', 'N'), (',', ','), ('com', 'PREP'), ('as', 'ART'), ('defesas', 'N'), ('levando', 'V'), ('a', 'ART'), ('melhor', 'ADJ'), ('sobre', 'PREP'), ('os', 'ART'), ('ataques', 'N'), ('.', '.'), ('A', 'ART'), ('única', 'ADJ'), ('chance', 'N'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('pontuar', None), ('do', 'NPROP'), ('período', 'N'), ('foi', 'VAUX'), ('dos', 'NPROP'), ('Patriots', None), (',', ','), ('que', 'PRO-KS-REL'), ('chegaram', 'V'), ('à', 'NPROP'), ('linha', 'N'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('31', 'NUM'), ('jardas', 'N'), ('dos', 'NPROP'), ('Giants', 'NPROP'), ('.', '.'), ('O', 'ART'), ('técnico', 'N'), ('Bill', 'NPROP'), ('Bellichick', None), (',', ','), ('porém', 'KC'), (',', ','), ('optou', 'V'), ('por', 'PREP|+'), ('uma', 'ART'), ('quarta', 'N'), ('descida', 'N'), ('em', 'PREP|+'), ('vez', 'N'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('um', 'ART'), ('field', 'N|EST'), ('goal', 'N|EST'), ('.', '.'), ('Brady', 'NPROP'), ('tentou', 'V'), ('um', 'ART'), ('passe', 'N'), ('para', 'PREP'), ('Jabar', None), ('Gaffney', None), (',', ','), ('mas', 'KC'), ('não', 'ADV'), ('conseguiu', 'V'), ('completar', 'V'), ('.', '.'), ('O', 'ART'), ('último', 'ADJ'), ('período', 'N'), ('começou', 'VAUX'), ('arrasador', None), ('para', 'PREP'), ('os', 'ART'), ('Giants', 'NPROP'), ('.', '.'), ('na', 'NPROP'), ('primeira', 'ADJ'), ('jogada', 'N'), (',', ','), ('Manning', 'NPROP'), ('achou', 'V'), ('o', 'ART'), ('tight', None), ('end', None), ('Kevin', 'NPROP'), ('Boss', None), (',', ','), ('para', 'PREP'), ('um', 'ART'), ('incrível', 'ADJ'), ('avanço', 'N'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('45', 'NUM'), ('jardas', 'N'), (',', ','), ('que', 'PRO-KS-REL'), ('deixou', 'V'), ('o', 'ART'), ('time', 'N'), ('na', 'NPROP'), ('linha', 'N'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('35', 'NUM'), ('dos', 'NPROP'), ('Patriots', None), ('.', '.'), ('Outro', 'PROADJ'), ('lançamento', 'N'), (',', ','), ('desta', 'PROADJ'), ('vez', 'N'), ('para', 'PREP'), ('Steve', 'NPROP'), ('Smith', 'NPROP'), (',', ','), ('marcou', 'V'), ('o', 'ART'), ('avanço', 'N'), ('até', 'PREP'), ('a', 'ART'), ('linha', 'N'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('12', 'NUM'), ('jardas', 'N'), ('.', '.'), ('Duas', 'NUM'), ('jogadas', 'N'), ('depois', 'ADV'), (',', ','), ('David', 'NPROP'), ('Tyree', None), ('pegou', 'V'), ('um', 'ART'), ('passe', 'N'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('cinco', 'NUM'), ('jardas', 'N'), ('na', 'NPROP'), ('end', None), ('zone', None), ('para', 'PREP'), ('anotar', 'V'), ('o', 'ART'), ('touchdown', 'N|EST'), ('e', 'KC'), ('virar', 'V'), ('o', 'ART'), ('jogo', 'N'), ('.', '.'), ('Na', 'NPROP'), ('hora', 'N'), ('da', 'NPROP'), ('decisão', 'N'), (',', ','), ('o', 'ART'), ('ataque', 'N'), ('dos', 'NPROP'), ('Patriots', None), ('voltou', 'V'), ('a', 'ART'), ('funcionar', 'V'), ('.', '.'), ('Com', 'PREP'), ('uma', 'ART'), ('série', 'N'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('passes', 'N'), ('curtos', 'ADJ'), ('e', 'KC'), ('variados', 'PCP'), (',', ','), ('Brady', 'NPROP'), ('achou', 'V'), ('Wes', None), ('Welker', None), (',', ','), ('Randy', 'NPROP'), ('Moss', 'NPROP'), ('e', 'KC'), ('Kevin', 'NPROP'), ('Faulk', None), ('seguidas', 'PCP'), ('vezes', 'N'), ('até', 'PREP'), ('chegar', 'V'), ('à', 'NPROP'), ('red', 'N|EST'), ('zone', None), ('.', '.'), ('A', 'ART'), ('2m45s', None), ('do', 'NPROP'), ('fim', 'N'), (',', ','), ('o', 'ART'), ('quarterback', 'N|EST'), ('conectou', None), ('mais', 'ADV'), ('uma', 'ART'), ('vez', 'N'), ('com', 'PREP'), ('Moss', 'NPROP'), (',', ','), ('que', 'PRO-KS-REL'), ('se', 'PROPESS'), ('desmarcou', None), ('e', 'KC'), ('ficou', 'V'), ('livre', 'ADJ'), ('na', 'NPROP'), ('lateral', 'N'), ('direita', 'N'), ('da', 'NPROP'), ('end', None), ('zone', None), ('.', '.'), ('Quando', 'KS'), ('os', 'ART'), ('fãs', 'N'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('New', 'NPROP'), ('England', 'NPROP'), ('já', 'ADV'), ('comemoravam', 'V'), ('a', 'ART'), ('vitória', 'N'), (',', ','), ('o', 'ART'), ('inesperado', 'ADJ'), ('aconteceu', 'V'), ('.', '.'), ('Em', 'PREP|+'), ('uma', 'ART'), ('jogada', 'N'), ('incrível', 'ADJ'), (',', ','), ('Eli', 'NPROP'), ('Manning', 'NPROP'), ('se', 'PROPESS'), ('soltou', 'V'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('dois', 'NUM'), ('marcadores', 'N'), ('que', 'PRO-KS-REL'), ('o', 'ART'), ('seguravam', None), ('pela', 'NPROP'), ('camisa', 'N'), ('e', 'KC'), (',', ','), ('na', 'NPROP'), ('corrida', 'N'), (',', ','), ('lançou', 'V'), ('para', 'PREP'), ('Amani', None), ('Toomer', None), ('.', '.'), ('O', 'ART'), ('wide', 'N|EST'), ('receiver', None), (',', ','), ('bem', 'ADV'), ('marcado', 'PCP'), (',', ','), ('saltou', 'V'), ('e', 'KC'), ('conseguiu', 'V'), ('a', 'ART'), ('fazer', 'V'), ('recepção', 'N'), ('para', 'PREP'), ('um', 'ART'), ('avanço', 'N'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('32', 'NUM'), ('jardas', 'N'), (',', ','), ('deixando', 'V'), ('os', 'ART'), ('Giants', 'NPROP'), ('na', 'NPROP'), ('linha', 'N'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('24', 'NUM'), ('de', 'PREP'), ('New', 'NPROP'), ('England', 'NPROP'), ('.', '.'), ('Quatro', 'NUM'), ('jogadas', 'N'), ('depois', 'ADV'), (',', ','), ('a', 'ART'), ('39', 'NUM'), ('segundos', 'N'), ('do', 'NPROP'), ('fim', 'N'), (',', ','), ('Manning', 'NPROP'), ('achou', 'V'), ('Plaxico', None), ('Burress', None), ('na', 'NPROP'), ('end', None), ('zone', None), ('para', 'PREP'), ('conseguir', 'V'), ('o', 'ART'), ('touchdown', 'N|EST'), ('do', 'NPROP'), ('título', 'N'), ('.', '.')]\n"
],
[
"from nltk.corpus import mac_morpho\nfrom nltk.tag import UnigramTagger\nfrom nltk.tag import DefaultTagger\n\ntokens = nltk.word_tokenize(corpus)\n\n# Dessa vez utilizaremos o DefaultTagger para definir uma etiqueta padrão\netiq_padrao = DefaultTagger('N')\nsentencas_treino = mac_morpho.tagged_sents()\netiquetador = UnigramTagger(sentencas_treino, backoff=etiq_padrao)\n\netiquetado = etiquetador.tag(tokens)\n\netiquetado",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from nltk.chunk import RegexpParser\n\npattern = 'NP: {<NPROP><NPROP> | <N><N>}'\nanalise_gramatical = RegexpParser(pattern)\n\narvore = analise_gramatical.parse(etiquetado)\nprint(arvore)",
"(S\n Giants/NPROP\n batem/V\n os/ART\n Patriots/N\n no/KC\n (NP Super/NPROP Bowl/NPROP)\n (NP XLII/N Azarões/N)\n acabam/VAUX\n com/PREP\n a/ART\n invencibilidade/N\n de/PREP\n (NP New/NPROP England/NPROP)\n e/KC\n ficam/V\n com/PREP\n o/ART\n título/N\n da/NPROP\n (NP temporada/N 04/02/2008/N)\n -/-\n 01h07m/N\n -/-\n Atualizado/N\n em/PREP|+\n 04/02/2008/N\n -/-\n 09h49m/N\n Com/PREP\n um/ART\n passe/N\n de/PREP\n (NP Eli/NPROP Manning/NPROP)\n para/PREP\n (NP Plaxico/N Burress/N)\n a/ART\n 39/NUM\n segundos/N\n do/NPROP\n fim/N\n ,/,\n o/ART\n (NP New/NPROP York/NPROP)\n Giants/NPROP\n anotou/V\n o/ART\n touchdown/N|EST\n decisivo/ADJ\n e/KC\n derrubou/V\n o/ART\n favorito/N\n (NP New/NPROP England/NPROP)\n Patriots/N\n por/PREP|+\n 17/NUM\n a/ART\n 14/NUM\n (NP neste/N domingo/N)\n ,/,\n em/PREP|+\n Glendale/N\n ,/,\n no/KC\n (NP Super/NPROP Bowl/NPROP)\n XLII/N\n ./.\n O/ART\n resultado/N\n ,/,\n uma/ART\n das/NPROP\n maiores/ADJ\n zebras/N\n da/NPROP\n história/N\n (NP do/NPROP Super/NPROP)\n Bowl/NPROP\n ,/,\n acabou/VAUX\n com/PREP\n a/ART\n temporada/N\n perfeita/ADJ\n de/PREP\n (NP Tom/NPROP Brady/NPROP)\n e/KC\n companhia/N\n ,/,\n que/PRO-KS-REL\n esperavam/V\n fazer/V\n história/N\n ao/PREP\n levantar/V\n o/ART\n troféu/N\n da/NPROP\n NFL/N\n sem/PREP\n sofrer/V\n uma/ART\n derrota/N\n no/KC\n ano/N\n ./.\n A/ART\n vitória/N\n (NP dos/NPROP Giants/NPROP)\n ,/,\n porém/KC\n ,/,\n também/PDEN\n ficará/V\n para/PREP\n a/ART\n história/N\n ./.\n Pela/NPROP\n primeira/ADJ\n vez/N\n ,/,\n (NP irmãos/N quarterbacks/N)\n triunfam/N\n no/KC\n (NP Super/NPROP Bowl/NPROP)\n em/PREP|+\n temporadas/N\n consecutivas/ADJ\n ./.\n No/KC\n ano/N\n passado/PCP\n ,/,\n Peyton/N\n Manning/NPROP\n ,/,\n irmão/N\n de/PREP\n Eli/NPROP\n ,/,\n chegou/V\n ao/PREP\n (NP título/N máximo/N)\n da/NPROP\n NFL/N\n pelo/PDEN\n (NP Indianapolis/N Colts/N)\n ./.\n A/ART\n partida/N\n Os/ART\n Giants/NPROP\n começaram/VAUX\n com/PREP\n a/ART\n posse/N\n de/PREP\n bola/N\n ,/,\n e/KC\n mostraram/V\n logo/ADV\n que/PRO-KS-REL\n iriam/VAUX\n alongar/V\n ao/PREP\n máximo/N\n suas/PROADJ\n posses/N\n de/PREP\n bola/N\n ./.\n (NP Misturando/N corridas/N)\n com/PREP\n Brandon/N\n Jacobs/NPROP\n e/KC\n passes/N\n curtos/ADJ\n ,/,\n o/ART\n time/N\n de/PREP\n (NP Nova/NPROP York/NPROP)\n chegou/V\n à/NPROP\n red/N|EST\n zone/N\n logo/ADV\n na/NPROP\n primeira/ADJ\n campanha/N\n ./.\n O/ART\n avanço/N\n ,/,\n no/KC\n entanto/KC\n ,/,\n parou/V\n na/NPROP\n linha/N\n de/PREP\n 17/NUM\n jardas/N\n e/KC\n Lawrence/NPROP\n Tynes/N\n converteu/V\n o/ART\n field/N|EST\n goal/N|EST\n de/PREP\n 32/NUM\n jardas/N\n para/PREP\n abrir/V\n o/ART\n placar/N\n ./.\n (NP Eli/NPROP Manning/NPROP)\n e/KC\n companhia/N\n ficaram/V\n 9m54s/N\n com/PREP\n a/ART\n bola/N\n ,/,\n mas/KC\n o/ART\n ataque/N\n dos/NPROP\n Patriots/N\n não/ADV\n entrou/V\n em/PREP|+\n (NP campo/N frio/N)\n ./.\n Logo/ADV\n no/KC\n retorno/N\n do/NPROP\n kickoff/N\n ,/,\n o/ART\n running/N|EST\n back/N|EST\n Laurence/NPROP\n Maroney/N\n avançou/V\n 43/NUM\n jardas/N\n ,/,\n deixando/V\n (NP Tom/NPROP Brady/NPROP)\n em/PREP|+\n boa/ADJ\n posição/N\n ./.\n Com/PREP\n passes/N\n curtos/ADJ\n ,/,\n os/ART\n Patriots/N\n chegaram/V\n à/NPROP\n linha/N\n de/PREP\n 17/NUM\n jardas/N\n e/KC\n ,/,\n graças/PREP|+\n a/ART\n uma/ART\n penalidade/N\n (/(\n interferência/N\n de/PREP\n passe/N\n )/)\n do/NPROP\n linebacker/N\n (NP Antonio/NPROP Pierce/NPROP)\n ,/,\n alcançaram/V\n a/ART\n linha/N\n de/PREP\n uma/ART\n jarda/N\n ./.\n Maroney/N\n avançou/V\n pelo/PDEN\n chão/N\n e/KC\n anotou/V\n o/ART\n primeiro/ADJ\n touchdown/N|EST\n do/NPROP\n jogo/N\n ./.\n Os/ART\n Giants/NPROP\n pareciam/V\n rumo/PREP|+\n à/NPROP\n virada/N\n na/NPROP\n campanha/N\n seguinte/ADJ\n ./.\n Manning/NPROP\n achou/V\n (NP Amani/N Toomer/N)\n para/PREP\n um/ART\n avanço/N\n de/PREP\n 38/NUM\n jardas/N\n ,/,\n e/KC\n o/ART\n time/N\n de/PREP\n (NP Nova/NPROP York/NPROP)\n entrou/V\n novamente/ADV\n na/NPROP\n red/N|EST\n zone/N\n ./.\n Com/PREP\n a/ART\n bola/N\n na/NPROP\n linha/N\n de/PREP\n 14/NUM\n jardas/N\n dos/NPROP\n Patriots/N\n ,/,\n os/ART\n Giants/NPROP\n sofreram/V\n um/ART\n revés/N\n ./.\n Manning/NPROP\n passou/V\n para/PREP\n (NP Steve/NPROP Smith/NPROP)\n ,/,\n que/PRO-KS-REL\n soltou/V\n a/ART\n bola/N\n ./.\n Ellis/NPROP\n Hobbs/N\n aproveitou/V\n ,/,\n tomou/V\n a/ART\n posse/N\n para/PREP\n os/ART\n Patriots/N\n ,/,\n e/KC\n avançou/V\n 23/NUM\n jardas/N\n ./.\n A/ART\n defesa/N\n de/PREP\n (NP Nova/NPROP York/NPROP)\n manteve/V\n o/ART\n jogo/N\n equilibrado/PCP\n ./.\n Com/PREP\n dois/NUM\n sacks/N\n seguidos/PCP\n ,/,\n os/ART\n Giants/NPROP\n forçaram/V\n o/ART\n punt/N\n e/KC\n recuperaram/N\n a/ART\n bola/N\n ./.\n Mas/KC\n a/ART\n campanha/N\n seguinte/ADJ\n provou/V\n ser/VAUX\n outra/PROADJ\n decepção/N\n para/PREP\n (NP Nova/NPROP York/NPROP)\n ./.\n O/ART\n time/N\n chegou/V\n à/NPROP\n linha/N\n de/PREP\n 25/NUM\n jardas/N\n ,/,\n mas/KC\n Manning/NPROP\n sofreu/V\n um/ART\n sack/N\n e/KC\n cometeu/V\n um/ART\n fumble/N|EST\n ,/,\n e/KC\n o/ART\n ataque/N\n voltou/V\n para/PREP\n a/ART\n linha/N\n de/PREP\n 39/NUM\n jardas/N\n ,/,\n não/ADV\n conseguindo/V\n pontuar/N\n mais/ADV\n uma/ART\n vez/N\n ./.\n Os/ART\n Patriots/N\n tiveram/V\n uma/ART\n última/ADJ\n chance/N\n de/PREP\n marcar/V\n antes/ADV\n do/NPROP\n intervalo/N\n ,/,\n mas/KC\n ,/,\n a/ART\n 22/NUM\n segundos/N\n do/NPROP\n fim/N\n do/NPROP\n segundo/PREP\n período/N\n ,/,\n Brady/NPROP\n foi/VAUX\n novamente/ADV\n sacado/PCP\n ./.\n Desta/ADV\n vez/N\n ,/,\n ele/PROPESS\n cometeu/V\n o/ART\n fumble/N|EST\n e/KC\n os/ART\n Giants/NPROP\n tomaram/V\n a/ART\n posse/N\n de/PREP\n bola/N\n ./.\n Manning/NPROP\n tentou/V\n um/ART\n passe/N\n longo/ADJ\n ,/,\n de/PREP\n 50/NUM\n jardas/N\n ,/,\n nos/PROPESS\n últimos/ADJ\n segundos/N\n ,/,\n mas/KC\n não/ADV\n teve/V\n sucesso/N\n ./.\n O/ART\n jogo/N\n continuou/V\n amarrado/PCP\n no/KC\n terceiro/ADJ\n quarto/N\n ,/,\n com/PREP\n as/ART\n defesas/N\n levando/V\n a/ART\n melhor/ADJ\n sobre/PREP\n os/ART\n ataques/N\n ./.\n A/ART\n única/ADJ\n chance/N\n de/PREP\n pontuar/N\n do/NPROP\n período/N\n foi/VAUX\n dos/NPROP\n Patriots/N\n ,/,\n que/PRO-KS-REL\n chegaram/V\n à/NPROP\n linha/N\n de/PREP\n 31/NUM\n jardas/N\n (NP dos/NPROP Giants/NPROP)\n ./.\n O/ART\n técnico/N\n Bill/NPROP\n Bellichick/N\n ,/,\n porém/KC\n ,/,\n optou/V\n por/PREP|+\n uma/ART\n (NP quarta/N descida/N)\n em/PREP|+\n vez/N\n de/PREP\n um/ART\n field/N|EST\n goal/N|EST\n ./.\n Brady/NPROP\n tentou/V\n um/ART\n passe/N\n para/PREP\n (NP Jabar/N Gaffney/N)\n ,/,\n mas/KC\n não/ADV\n conseguiu/V\n completar/V\n ./.\n O/ART\n último/ADJ\n período/N\n começou/VAUX\n arrasador/N\n para/PREP\n os/ART\n Giants/NPROP\n ./.\n na/NPROP\n primeira/ADJ\n jogada/N\n ,/,\n Manning/NPROP\n achou/V\n o/ART\n (NP tight/N end/N)\n Kevin/NPROP\n Boss/N\n ,/,\n para/PREP\n um/ART\n incrível/ADJ\n avanço/N\n de/PREP\n 45/NUM\n jardas/N\n ,/,\n que/PRO-KS-REL\n deixou/V\n o/ART\n time/N\n na/NPROP\n linha/N\n de/PREP\n 35/NUM\n dos/NPROP\n Patriots/N\n ./.\n Outro/PROADJ\n lançamento/N\n ,/,\n desta/PROADJ\n vez/N\n para/PREP\n (NP Steve/NPROP Smith/NPROP)\n ,/,\n marcou/V\n o/ART\n avanço/N\n até/PREP\n a/ART\n linha/N\n de/PREP\n 12/NUM\n jardas/N\n ./.\n Duas/NUM\n jogadas/N\n depois/ADV\n ,/,\n David/NPROP\n Tyree/N\n pegou/V\n um/ART\n passe/N\n de/PREP\n cinco/NUM\n jardas/N\n na/NPROP\n (NP end/N zone/N)\n para/PREP\n anotar/V\n o/ART\n touchdown/N|EST\n e/KC\n virar/V\n o/ART\n jogo/N\n ./.\n Na/NPROP\n hora/N\n da/NPROP\n decisão/N\n ,/,\n o/ART\n ataque/N\n dos/NPROP\n Patriots/N\n voltou/V\n a/ART\n funcionar/V\n ./.\n Com/PREP\n uma/ART\n série/N\n de/PREP\n passes/N\n curtos/ADJ\n e/KC\n variados/PCP\n ,/,\n Brady/NPROP\n achou/V\n (NP Wes/N Welker/N)\n ,/,\n (NP Randy/NPROP Moss/NPROP)\n e/KC\n Kevin/NPROP\n Faulk/N\n seguidas/PCP\n vezes/N\n até/PREP\n chegar/V\n à/NPROP\n red/N|EST\n zone/N\n ./.\n A/ART\n 2m45s/N\n do/NPROP\n fim/N\n ,/,\n o/ART\n quarterback/N|EST\n conectou/N\n mais/ADV\n uma/ART\n vez/N\n com/PREP\n Moss/NPROP\n ,/,\n que/PRO-KS-REL\n se/PROPESS\n desmarcou/N\n e/KC\n ficou/V\n livre/ADJ\n na/NPROP\n (NP lateral/N direita/N)\n da/NPROP\n (NP end/N zone/N)\n ./.\n Quando/KS\n os/ART\n fãs/N\n de/PREP\n (NP New/NPROP England/NPROP)\n já/ADV\n comemoravam/V\n a/ART\n vitória/N\n ,/,\n o/ART\n inesperado/ADJ\n aconteceu/V\n ./.\n Em/PREP|+\n uma/ART\n jogada/N\n incrível/ADJ\n ,/,\n (NP Eli/NPROP Manning/NPROP)\n se/PROPESS\n soltou/V\n de/PREP\n dois/NUM\n marcadores/N\n que/PRO-KS-REL\n o/ART\n seguravam/N\n pela/NPROP\n camisa/N\n e/KC\n ,/,\n na/NPROP\n corrida/N\n ,/,\n lançou/V\n para/PREP\n (NP Amani/N Toomer/N)\n ./.\n O/ART\n wide/N|EST\n receiver/N\n ,/,\n bem/ADV\n marcado/PCP\n ,/,\n saltou/V\n e/KC\n conseguiu/V\n a/ART\n fazer/V\n recepção/N\n para/PREP\n um/ART\n avanço/N\n de/PREP\n 32/NUM\n jardas/N\n ,/,\n deixando/V\n os/ART\n (NP Giants/NPROP na/NPROP)\n linha/N\n de/PREP\n 24/NUM\n de/PREP\n (NP New/NPROP England/NPROP)\n ./.\n Quatro/NUM\n jogadas/N\n depois/ADV\n ,/,\n a/ART\n 39/NUM\n segundos/N\n do/NPROP\n fim/N\n ,/,\n Manning/NPROP\n achou/V\n (NP Plaxico/N Burress/N)\n na/NPROP\n (NP end/N zone/N)\n para/PREP\n conseguir/V\n o/ART\n touchdown/N|EST\n do/NPROP\n título/N\n ./.)\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a730597dcf7584c7ac1640e6443b8a9cd0230b6
| 86,293 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
inauguralproject/inauguralproject.ipynb
|
AskerNC/projects-2021-m-m
|
9c2a38f2082faaddca034d615cdd5ec94c2c0a1a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
inauguralproject/inauguralproject.ipynb
|
AskerNC/projects-2021-m-m
|
9c2a38f2082faaddca034d615cdd5ec94c2c0a1a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
inauguralproject/inauguralproject.ipynb
|
AskerNC/projects-2021-m-m
|
9c2a38f2082faaddca034d615cdd5ec94c2c0a1a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 217.911616 | 25,632 | 0.914199 |
[
[
[
"# Inaugural Project\n\n**Team:** M&M\n\n**Members:** Markus Gorgone Larsen (hbk716) & Matias Bjørn Frydensberg Hall (pkt593)\n\n**Imports and set magics:**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport copy\nfrom types import SimpleNamespace\nfrom scipy import optimize\n%matplotlib inline\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nplt.style.use('seaborn-whitegrid')\n\n# Autoreload modules when code is run\n%load_ext autoreload\n%autoreload 2\n\n# local modules\nimport inauguralproject",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Question 1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"'We consider a household solving the following maximisation problem when looking to buy a home:\n\n\n$$\n\\begin{aligned}\nc^*, h^* & = \\text{arg}\\max_{c,h}c^{1-\\phi}h^\\phi\\\\\n& \\text{s.t.}\\\\\n\\tilde{p}_h & = p_h\\epsilon\\\\\nm & = \\tau(p_h, \\tilde{p}_h) + c\\\\\n\\tau(p_h, \\tilde{p}_h) & = rp_h +\\tau^g\\tilde{p}_h + \\tau^p max\\{\\tilde{p}_h - \\bar{p}, 0\\}\n\\end{aligned}\n$$\n\nWhere $c$ is consumption, $h$ is housing quality, $p_h$ is the price of housing, $\\epsilon$ is the public housing assement factor, $\\phi$ is the Cobb-Douglas weights, $m$ is cash-on-hand, $r$ is the mortgage interest rate, $\\tau^g$ is the base housing tax, $\\tau^p$ is the progressive housing tax and $\\bar{p}$ is the cutoff price for the progressive tax.\n\nAs utility is monotonically increasing in consumption and housing quality, and $\\tau$ is a function of h, we can define consumption as:\n$$\nc = m - \\tau(p_h, \\tilde{p}_h)\n$$\n\nPlugging c into the utility function we get the following:\n$$\nh^* = \\text{arg}\\max_{h}(m - rh +\\tau^gh\\epsilon + \\tau^p max\\{h\\epsilon - \\bar{p}, 0\\})^{1-\\phi}h^\\phi\n$$\n\nThe utility function and optimisation function is defined in the module and used to solve the households problem",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# a. Create simplenamespace and set parameter values\npar = SimpleNamespace()\n\npar.phi = 0.3\npar.epsilon = 0.5\npar.r = 0.03\npar.tau_g = 0.012\npar.tau_p = 0.004\npar.p_bar = 3\npar.m = 0.5\npar.seed = 1\n\n# b. Compute optimal housing quality, consumption and utility\nh_star, c_star, u_star = inauguralproject.u_optimize(par)\n\n# c. Print solution\nprint(f'The household will choose optimal housing = {h_star:.2f}, which implies optimal consumption = {c_star:.2f} and utility = {u_star:.2f}')",
"The household will choose optimal housing = 4.17, which implies optimal consumption = 0.35 and utility = 0.74\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Question 2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"First we create an array of equally spaced values of m using linespace for values between 0.4 and 1.5. We also create arrays as contains for h, c and u values. We then find the optimal values by looping over the values of m. Finally we plot the two graphs. We observe that when m is in the range of 0.72 to about 0.75 optimal housing is unchanged at 6, while consumption increase more rapidly in this range. This is due to the cutoff price. In this range it is more benificial for the household to spend little more than 70% on consumption due to the fact that higher housing quality would increase taxes which in the interval offsets the higher utility from higher housing quality.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# a. Create array of m's and container for h*, c* and u*\nN = 1000\nm_vec = np.linspace(0.4, 1.5, N)\nh_vec = np.zeros(N)\nc_vec = np.zeros(N)\nu_vec = np.zeros(N)\n\n# b. Loop the optimise function over the m_vec array\nfor i in range(N):\n par.m = m_vec[i]\n h_vec[i], c_vec[i], u_vec[i] = inauguralproject.u_optimize(par)\n\n# c. Create graph and plot\ninauguralproject.two_figures(m_vec, c_vec, \"Consumption\", \"$m$\", \"$c$\", m_vec, h_vec, \"House Quality\", \"$m$\", \"$h$\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Question 3",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In the module we define a function to calculate the total tax burden given the utility function.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# a. Adding population size, mean and standard deviation to namespace of parameters\npar.pop = 10000\npar.mu = -0.4\npar.sigma = 0.35\n\n# b. Compute the total tax burden\nT = inauguralproject.tax_total(par)\n\n# c. Print the answer\nprint(f'The average tax burden pr. household is {T/par.pop:.3f}')",
"The average tax burden pr. household is 0.036\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Bonus",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Using the parameters an array of lognormal distributed m's is created. We also create containers for the h, c and u values. We then find the optimal values by looping over the values of m. Finally we plot the findings as histograms. <br>\nBoth the distribution of m and h resembel right skewed normal distrubutions, not suprising given m's log-normal distribution. There is nothing odd about m's distrubution, but the distrubution of h is odd since it has a large concentration around a value of 6. This is due to the effect of the progressive tax as described in question 2.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# a. Resetting seed and create array of m's and container for h*, c* and u* in our population\nnp.random.seed(par.seed)\n\nm_pop = np.random.lognormal(par.mu, par.sigma, par.pop)\nh_pop = np.zeros(par.pop)\nc_pop = np.zeros(par.pop)\nu_pop = np.zeros(par.pop)\n\n# b. Compute optimal housing quality, consumption and utility for whole population\nfor i in range(par.pop):\n par.m = m_pop[i]\n h_pop[i], c_pop[i], u_pop[i] = inauguralproject.u_optimize(par)\n \n# c. Create histograms to plot distributions\nbonus1 = plt.figure(dpi=100)\nax_left = bonus1.add_subplot(1,1,1)\nax_left.hist(m_pop,bins=100,density=True,alpha=0.5,label='cash-on-hand')\nax_left.set_xbound(0, 2.5)\nax_left.set_xlabel('Cash-on-hand')\nax_left.set_ylabel('Probability density')\nax_left.set_title('Distribution of cash-on-hand')\n\nbonus2 = plt.figure(dpi=100)\nax_right = bonus2.add_subplot(1,1,1)\nax_right.hist(h_pop,bins=100,density=True,alpha=0.5,label='housing')\nax_right.set_xbound(1,20)\nax_right.set_xlabel('$h^*$')\nax_right.set_ylabel('Probability density')\nax_right.set_title('Distribution of housing quality');",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Question 4",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We create a new namespace and change parametervalues. Then we use our tax function to find the total tax burden. We find that the average tax burden increases after the reform.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# a. Create a new namespace of parameters by copy and change parameter values\npar2 = copy.copy(par)\n\npar2.epsilon = 0.8\npar2.tau_g = 0.01\npar2.tau_p = 0.009\npar2.p_bar = 8\n\n# b. Compute the total tax after the reform\nT_reform = inauguralproject.tax_total(par2)\n\n# c. Print the answer\nprint(f'The average tax burden pr. household after the reform is {T_reform/par.pop:.3f}')",
"The average tax burden pr. household after the reform is 0.045\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Question 5",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We add the tax burden found in Q3 as the policy maker's tax burden goal. We then compute the new $\\tau_g$ using the root optimising function as defined in the module. Lastly we check that the tax burden is indeed the same as before the reform.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# a. Add the tax burden goal as a parameter\npar2.T_goal = T\n\n# b. Calculate the new tau_g and tax burden hereof and add to parameters\ntau_g = inauguralproject.base_tax_pct(par2)\npar2.tau_g = tau_g\nT_reform2 = inauguralproject.tax_total(par2)\n\n\n# c. Print solution\nprint(f'The base tax level that leaves the average tax burden unchanged at {T_reform2/par2.pop:.3f} is tau_g = {tau_g:.4f}')",
"The base tax level that leaves the average tax burden unchanged at 0.036 is tau_g = 0.0077\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Conclusion",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In this assignment we have solved a households utility maximisation problem with respect to housing quality and other consumption. When plotting the optimal housing quality and other consumption for cash-on-hand in the range 0.4 to 1.5, we observe a flat housing quality curve at a value of 6 in the interval of 0.72 to about 0.75, while consumption increase at a higher rate in that interval. As described earlier in the assignment this is a consequence of the progressive housing tax where the extra cost of housing offsets the utility gain from better housing quality, so just increasing consumption gives the household the highest utility.\n\nIn Q3 we calculate the average tax burden pr. household in a population with lognormally distributed cash-on-hand. We also plot the distributions of cash-on-hand and housing quality, and notice that the cash-on-hand look as expected, but there is a cluster of households who choose a housing quality of 6. This is of course due to the progressive housing tax as described above. In Q4 we find that the average tax burden pr. household increase after the tax reform.\n\nAt last in Q5 we find that in order to keep the tax burden pr. household the same as before the reform the policy maker should set the base housing tax to 0.77%. This change in the reform would redistribute wealth from households with more cash-on-hand to households with less, as households paying the progressive tax, whould finance the decrease in the base housing tax.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4a730ed2dac1bd147ab4e8279015bffd688ae9b8
| 124,310 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
ML-101 Modules/Module 03/Lesson 02/Practice 2/Winequality - Practice.ipynb
|
MaksymDz/data-science
|
dd8c1fc3f60439eb4286ecad37034a7c13a48da6
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-02-03T20:15:08.000Z
|
2021-02-03T20:15:08.000Z
|
ML-101 Modules/Module 03/Lesson 02/Practice 2/Winequality - Practice.ipynb
|
MaksymDz/data-science
|
dd8c1fc3f60439eb4286ecad37034a7c13a48da6
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
ML-101 Modules/Module 03/Lesson 02/Practice 2/Winequality - Practice.ipynb
|
MaksymDz/data-science
|
dd8c1fc3f60439eb4286ecad37034a7c13a48da6
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 65.807305 | 13,052 | 0.709484 |
[
[
[
"# \"Wine Quality.\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### _\"Quality ratings of Portuguese white wines\" (Classification task)._",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Table of Contents\n\n\n## Part 0: Introduction\n\n### Overview\nThe dataset that's we see here contains 12 columns and 4898 entries of data about Portuguese white wines.\n \n**Метаданные:**\n \n* **fixed acidity** \n\n* **volatile acidity**\n\n* **citric acid** \n\n* **residual sugar** \n\n* **chlorides** \n\n* **free sulfur dioxide** \n\n* **total sulfur dioxide**\n\n* **density** \n\n* **pH** \n\n* **sulphates** \n\n* **alcohol** \n\n* **quality** - score between 3 and 9\n\n\n### Questions:\n \nPredict which wines are 'Good/1' and 'Not Good/0' (use binary classification; check balance of classes; calculate perdictions; choose the best model)\n\n\n## [Part 1: Import, Load Data](#Part-1:-Import,-Load-Data.)\n* ### Import libraries, Read data from ‘.csv’ file\n\n## [Part 2: Exploratory Data Analysis](#Part-2:-Exploratory-Data-Analysis.)\n* ### Info, Head, Describe\n* ### Encoding 'quality' attribute\n* ### 'quality' attribute value counts and visualisation\n* ### Resampling of an imbalanced dataset\n* ### Random under-sampling of an imbalanced dataset\n* ### Random over-sampling of an imbalanced dataset\n\n## [Part 3: Data Wrangling and Transformation](#Part-3:-Data-Wrangling-and-Transformation.)\n* ### Creating datasets for ML part\n* ### StandardScaler\n* ### 'Train\\Test' splitting method\n\n## [Part 4: Machine Learning](#Part-4:-Machine-Learning.)\n* ### Build, train and evaluate models without hyperparameters\n * #### Logistic Regression, K-Nearest Neighbors, Decision Trees \n * #### Classification report\n * #### Confusion Matrix\n * #### ROC-AUC score\n* ### Build, train and evaluate models with hyperparameters\n * #### Logistic Regression, K-Nearest Neighbors, Decision Trees \n * #### Classification report\n * #### Confusion Matrix\n * #### ROC-AUC score\n\n## [Conclusion](#Conclusion.)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Part 1: Import, Load Data.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* ### Import libraries",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# import standard libraries\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n%matplotlib inline\nimport seaborn as sns\nsns.set()\n\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, GridSearchCV\nfrom sklearn.metrics import classification_report, confusion_matrix, roc_auc_score\n\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression\nfrom sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier\nfrom sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier\n\nimport warnings\nwarnings.filterwarnings('ignore')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"* ### Read data from ‘.csv’ file",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# read data from '.csv' file\ndata = pd.read_csv(\"winequality.csv\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Part 2: Exploratory Data Analysis.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* ### Info",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# print the full summary of the dataset \ndata.info()",
"<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>\nRangeIndex: 4898 entries, 0 to 4897\nData columns (total 12 columns):\n # Column Non-Null Count Dtype \n--- ------ -------------- ----- \n 0 fixed acidity 4898 non-null float64\n 1 volatile acidity 4898 non-null float64\n 2 citric acid 4898 non-null float64\n 3 residual sugar 4898 non-null float64\n 4 chlorides 4898 non-null float64\n 5 free sulfur dioxide 4898 non-null float64\n 6 total sulfur dioxide 4898 non-null float64\n 7 density 4898 non-null float64\n 8 pH 4898 non-null float64\n 9 sulphates 4898 non-null float64\n 10 alcohol 4898 non-null float64\n 11 quality 4898 non-null int64 \ndtypes: float64(11), int64(1)\nmemory usage: 459.3 KB\n"
]
],
[
[
"* ### Head",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# preview of the first 5 lines of the loaded data \ndata.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"* ### Describe",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data.describe()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"* ### Encoding 'quality' attribute",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# lambda function; wine quality from 3-6 == 0, from 7-9 == 1.\ndata[\"quality\"] = data[\"quality\"].apply(lambda x: 0 if x < 7 else 1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# preview of the first 5 lines of the loaded data \ndata.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"* ### 'quality' attribute value counts and visualisation",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data[\"quality\"].value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# visualisation plot\nsns.countplot(x=\"quality\", data=data);",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"* ### Resampling of an imbalanced dataset",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# class count\ncount_class_0, count_class_1 = data['quality'].value_counts()\n\n# divide by class\nclass_0 = data[data[\"quality\"] == 0]\nclass_1 = data[data[\"quality\"] == 1]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"* ### Random under-sampling of an imbalanced dataset",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#class_0_under = class_0.sample(count_class_1)\n#data_under = pd.concat([class_0_under, class_1], axis=0)\n#sns.countplot(x=\"quality\", data=data_under);",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"* ### Random over-sampling of an imbalanced dataset",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class_1_over = class_1.sample(count_class_0, replace=True)\ndata_over = pd.concat([class_0, class_1_over], axis=0)\nsns.countplot(x=\"quality\", data=data_over);",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Part 3: Data Wrangling and Transformation.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* ### Creating datasets for ML part",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# set 'X' for features' and y' for the target ('quality').\n#X = data.drop('quality', axis=1)\n#y = data['quality']\n\n# for under-sampling dataset \n#X = data_under.drop('quality', axis=1)\n#y = data_under['quality']\n\n# for over-sampling dataset \nX = data_over.drop('quality', axis=1)\ny = data_over['quality']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# preview of the first 5 lines of the loaded data \nX.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"* ### 'Train\\Test' split",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# apply 'Train\\Test' splitting method\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# print shape of X_train and y_train\nX_train.shape, y_train.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# print shape of X_test and y_test\nX_test.shape, y_test.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"* ### StandardScaler",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# StandardScaler \nsc = StandardScaler()\ndata_sc_train = pd.DataFrame(sc.fit_transform(X_train), columns=X.columns)\ndata_sc_test = pd.DataFrame(sc.transform(X_test), columns=X.columns)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data_sc_train.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data_sc_test.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Part 4: Machine Learning.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* ### Build, train and evaluate models without hyperparameters",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Logistic Regression\n* K-Nearest Neighbors\n* Decision Trees\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Logistic Regression\nLR = LogisticRegression()\nLR.fit(data_sc_train, y_train)\nLR_pred = LR.predict(data_sc_test)\n\n# K-Nearest Neighbors\nKNN = KNeighborsClassifier()\nKNN.fit(data_sc_train, y_train)\nKNN_pred = KNN.predict(data_sc_test)\n\n# Decision Tree\nDT = DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=0)\nDT.fit(data_sc_train, y_train)\nDT_pred = DT.predict(data_sc_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"* ### Classification report",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(f\"LogisticRegression: \\n {classification_report(y_test, LR_pred, digits=6)} \")",
"LogisticRegression: \n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.732240 0.699739 0.715621 766\n 1 0.713930 0.745455 0.729352 770\n\n accuracy 0.722656 1536\n macro avg 0.723085 0.722597 0.722486 1536\nweighted avg 0.723062 0.722656 0.722504 1536\n \n"
],
[
"print(f\"KNeighborsClassifier: \\n {classification_report(y_test, KNN_pred, digits=6)} \")",
"KNeighborsClassifier: \n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.922705 0.748042 0.826244 766\n 1 0.789071 0.937662 0.856973 770\n\n accuracy 0.843099 1536\n macro avg 0.855888 0.842852 0.841608 1536\nweighted avg 0.855714 0.843099 0.841649 1536\n \n"
],
[
"print(f\"DecisionTreeClassifier: \\n {classification_report(y_test, DT_pred, digits=6)} \")",
"DecisionTreeClassifier: \n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.958092 0.865535 0.909465 766\n 1 0.877962 0.962338 0.918216 770\n\n accuracy 0.914062 1536\n macro avg 0.918027 0.913936 0.913840 1536\nweighted avg 0.917923 0.914062 0.913852 1536\n \n"
]
],
[
[
"* ### Confusion matrix",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sns.heatmap(confusion_matrix(y_test, LR_pred), annot=True);",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sns.heatmap(confusion_matrix(y_test, KNN_pred), annot=True);",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sns.heatmap(confusion_matrix(y_test, DT_pred), annot=True);",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"* ### ROC-AUC score",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"roc_auc_score(y_test, DT_pred)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"* ### Build, train and evaluate models with hyperparameters",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Logistic Regression\nLR = LogisticRegression()\nLR_params = {'C':[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10], 'penalty':['l1', 'l2', 'elasticnet', 'none'], 'solver':['lbfgs', 'newton-cg', 'liblinear', 'sag', 'saga'], 'random_state':[0]}\nLR1 = GridSearchCV(LR, param_grid = LR_params)\nLR1.fit(X_train, y_train)\nLR1_pred = LR1.predict(X_test)\n\n# K-Nearest Neighbors\nKNN = KNeighborsClassifier()\nKNN_params = {'n_neighbors':[5,7,9,11]}\nKNN1 = GridSearchCV(KNN, param_grid = KNN_params) \nKNN1.fit(X_train, y_train)\nKNN1_pred = KNN1.predict(X_test)\n\n# Decision Tree\nDT = DecisionTreeClassifier()\nDT_params = {'max_depth':[2,10,15,20], 'criterion':['gini', 'entropy'], 'random_state':[0]}\nDT1 = GridSearchCV(DT, param_grid = DT_params)\nDT1.fit(X_train, y_train)\nDT1_pred = DT1.predict(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# print the best hyper parameters set\nprint(f\"LogisticRegression: {LR1.best_params_}\")\nprint(f\"KNeighborsClassifier: {KNN1.best_params_}\")\nprint(f\"DecisionTreeClassifier: {DT1.best_params_}\")",
"LogisticRegression: {'C': 1, 'penalty': 'none', 'random_state': 0, 'solver': 'newton-cg'}\nKNeighborsClassifier: {'n_neighbors': 5}\nDecisionTreeClassifier: {'criterion': 'entropy', 'max_depth': 20, 'random_state': 0}\n"
]
],
[
[
"* ### Classification report",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(f\"LogisticRegression: \\n {classification_report(y_test, LR1_pred, digits=6)} \")\nprint(f\"KNeighborsClassifier: \\n {classification_report(y_test, KNN1_pred, digits=6)} \")\nprint(f\"DecisionTreeClassifier: \\n {classification_report(y_test, DT1_pred, digits=6)} \")",
"LogisticRegression: \n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.732606 0.701044 0.716478 766\n 1 0.714819 0.745455 0.729816 770\n\n accuracy 0.723307 1536\n macro avg 0.723713 0.723249 0.723147 1536\nweighted avg 0.723689 0.723307 0.723164 1536\n \nKNeighborsClassifier: \n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.858506 0.704961 0.774194 766\n 1 0.750827 0.884416 0.812165 770\n\n accuracy 0.794922 1536\n macro avg 0.804666 0.794688 0.793179 1536\nweighted avg 0.804526 0.794922 0.793229 1536\n \nDecisionTreeClassifier: \n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.957507 0.882507 0.918478 766\n 1 0.891566 0.961039 0.925000 770\n\n accuracy 0.921875 1536\n macro avg 0.924537 0.921773 0.921739 1536\nweighted avg 0.924451 0.921875 0.921748 1536\n \n"
]
],
[
[
"* ### Confusion matrix",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# confusion matrix of DT model\nconf_mat_DT1 = confusion_matrix(y_test, DT1_pred)\n\n# visualisation\nsns.heatmap(conf_mat_DT1, annot=True);",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"* ### ROC-AUC score",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"roc_auc_score(y_test, DT1_pred)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Conclusion.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# submission of .csv file with predictions\nsub = pd.DataFrame()\nsub['ID'] = X_test.index\nsub['quality'] = DT1_pred\nsub.to_csv('WinePredictionsTest.csv', index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Question**: Predict which wines are 'Good/1' and 'Not Good/0' (use binary classification; check balance of classes; calculate perdictions; choose the best model).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Answers**:\n\n1. Binary classification was applied.\n\n2. Classes were highly imbalanced. \n\n3. Three options were applied in order to calculate the best predictions:\n * Calculate predictions with imbalanced dataset\n * Calculate predictions with random under-sampling technique of an imbalanced dataset\n * Calculate predictions with random over-sampling technique of an imbalanced dataset (the best solution)\n \n4. Three ML models were used: Logistic Regression, KNN, Decision Tree (without and with hyper parameters).\n\n5. The best result was choosen: \n * Random over-sampling dataset with 3838 enteties in class '0' and 3838 enteties in class '1', 7676 enteties in total.\n * Train/Test split: test_size=0.2, random_state=0\n * Decision Tree model with hyper parameters tuning, with an accuracy score equal 0.921875 and ROC-AUC score equal 0.921773.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4a7320740f0eab10ee4dac7394cd6df95b996962
| 78,718 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
NeuronalNetworkPureNumpy_binaryClassification.ipynb
|
RihaChri/PureNumpyBinaryClassification
|
ffbbf2954bc9d788fd1d64359d31b3c2029889a6
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
NeuronalNetworkPureNumpy_binaryClassification.ipynb
|
RihaChri/PureNumpyBinaryClassification
|
ffbbf2954bc9d788fd1d64359d31b3c2029889a6
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
NeuronalNetworkPureNumpy_binaryClassification.ipynb
|
RihaChri/PureNumpyBinaryClassification
|
ffbbf2954bc9d788fd1d64359d31b3c2029889a6
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 308.698039 | 53,886 | 0.884474 |
[
[
[
"<a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/RihaChri/PureNumpyBinaryClassification/blob/main/NeuronalNetworkPureNumpy_binaryClassification.ipynb\" target=\"_parent\"><img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open In Colab\"/></a>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import scipy.io\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n#------------Activations-------------------------------------------------------\ndef sigmoid_kroko(Z):\n A = 1/(1+np.exp(-Z))\n cache = Z\n #np.exp statt math.exp da dies auch mit Vektoren geht\n #+Numbers between 0 and 1\n #-Prone to zero gradients\n #eher geeignet für letzten Layer\n return A, cache\ndef relu_kroko(Z):\n A = np.maximum(0,Z)\n cache = Z \n return A, cache\ndef relu_backward_kroko(dA, cache):\n Z = cache\n dZ = np.array(dA, copy=True) # just converting dz to a correct object.\n dZ[Z <= 0] = 0\n return dZ\ndef sigmoid_backward_kroko(dA, cache):\n Z = cache\n s = 1/(1+np.exp(-Z))\n dZ = dA * s * (1-s)\n return dZ\n#------------------------------------------------------------------------------\ndef initialize_parameters(layer_dims):#initialisierung a la He--> teilungsfaktor macht geringes W und damit größeren Gradienten\n np.random.seed(3)\n parameters = {}\n L = len(layer_dims) # number of layers in the network\n for l in range(1, L):\n parameters['W' + str(l)] = np.random.randn(layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l-1]) / np.sqrt(layer_dims[l-1])\n parameters['b' + str(l)] = np.zeros((layer_dims[l], 1))\n assert(parameters['W' + str(l)].shape == (layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l-1]))\n assert(parameters['b' + str(l)].shape == (layer_dims[l], 1))\n return parameters\n#------------------------------------------------------------------------------\ndef model(X, Y, layers_dims, learning_rate = 0.3, num_iterations = 30000, print_cost = True, lambd = 0, keep_prob = 1): \n grads = {}\n costs = [] # to keep track of the cost\n parameters = initialize_parameters(layers_dims)\n for i in range(0, num_iterations):\n AL, caches, Dropouts = forward_propagation(X, parameters, keep_prob)\n cost = compute_cost(AL, Y, caches, lambd)\n gradients = backward_propagation(AL, X, Y, caches, keep_prob, Dropouts, lambd)\n parameters = update_parameters(parameters, gradients, learning_rate)\n if print_cost and i % 10000 == 0: print(\"Cost after iteration {}: {}\".format(i, cost))\n if print_cost and i % 1000 == 0: costs.append(cost)\n plt.figure(\"\"\"first figure\"\"\")\n plt.plot(costs); plt.ylabel('cost');plt.xlabel('iterations (x1,000)');plt.title(\"Learning rate =\" + str(learning_rate));plt.show()\n return parameters \n#------------------------------------------------------------------------------\ndef linear_forward(A, W, b):#A.shape=(n_l-1,m), d.h. X.shape=(n_1,m), W.shape=(n_l,n_l-1),b.shape=(n_l,1)\n Z = np.dot(W,A)+b#(n_l,n_l-1) * A.shape=(n_l-1,m) = (n_l,m)\n cache = (A, W, b)\n return Z, cache\ndef linear_activation_forward(A_prev, W, b, activation): #A.shape=(n_l,m), W.shape=(n_l,n_l-1),b.shape=(n_l,1)\n if activation == \"sigmoid\":\n Z, linear_cache = linear_forward(A_prev, W, b)\n A, activation_cache = sigmoid_kroko(Z)\n elif activation == \"relu\":\n Z, linear_cache = linear_forward(A_prev, W, b)\n A, activation_cache = relu_kroko(Z)\n cache = (linear_cache, activation_cache)\n return A, cache\ndef forward_propagation(X, parameters, keep_prob):\n caches = []\n Dropouts= []\n A = X\n L = len(parameters) // 2\n np.random.seed(1)\n for l in range(1, L):#1 bis L-1\n A_prev = A \n A, cache = linear_activation_forward(A_prev, parameters['W' + str(l)], parameters['b' + str(l)], activation = \"relu\")\n D = np.random.rand(A.shape[0], A.shape[1]) #Dropout \n D = D < keep_prob #Dropout \n A = A * D #Dropout \n A = A / keep_prob #Dropout\n Dropouts.append(D)\n caches.append(cache) #linear_cache, activation_cache = cache\n AL, cache = linear_activation_forward(A, parameters['W' + str(L)], parameters['b' + str(L)], activation = \"sigmoid\")\n caches.append(cache)\n return AL, caches, Dropouts\ndef linear_backward(dZ, cache, lambd):#dZ=(n_l,m)\n A_prev, W, b = cache #A_prev.shape=(n_l-1,m), W.shape=(n_l,n_l-1) b.shape=(n_l,1)\n m = A_prev.shape[1]\n dW = np.dot(dZ,A_prev.T)/m + lambd/m * W #dZ=(n_l,m) * (m*n_l-1) = (n_l,n_l-1) + (n_l,n_l-1)\n db = np.sum(dZ, axis=1,keepdims=True)/m #b.shape=(n_l,1)\n #keepdims=true sonst wird aus Spaltenvektor in Zeilenvektor, bzw die eine dimension fällt sonst raus\n dA_prev = np.dot(W.T,dZ)#(n_l-1,n_l) * (n_l,m) = (n_l-1 , m)\n return dA_prev, dW, db\ndef linear_activation_backward(dA, cache, activation, lambd):\n linear_cache, activation_cache = cache\n if activation == \"relu\":\n dZ = relu_backward_kroko(dA, activation_cache)\n dA_prev, dW, db = linear_backward(dZ, linear_cache, lambd)\n elif activation == \"sigmoid\":\n dZ = sigmoid_backward_kroko(dA, activation_cache)\n dA_prev, dW, db = linear_backward(dZ, linear_cache, lambd)\n return dA_prev, dW, db\n#------------------------------------------------------------------------------\ndef backward_propagation(AL, X, Y, caches, keep_prob, Dropouts, lambd):\n L = len(caches)\n gradients = {}\n gradients[\"dZ\" + str(L)] = AL - Y #Die alternative dAL = - (np.divide(Y, AL) - np.divide(1 - Y, 1 - AL)) würde dich evtl durch null teilen lassen\n linear_cache, activation = caches[L-1]\n gradients[\"dA\" + str(L-1)], gradients[\"dW\" + str(L)], gradients[\"db\" + str(L)]=linear_backward(gradients[\"dZ\" + str(L)], linear_cache, lambd)\n gradients[\"dA\" + str(L-1)] = gradients[\"dA\" + str(L-1)] * Dropouts[L-2]/keep_prob\n for l in reversed(range(L-1)):\n current_cache = caches[l]\n gradients[\"dA\" + str(l)], gradients[\"dW\" + str(l+1)], gradients[\"db\" + str(l+1)] = linear_activation_backward(gradients[\"dA\" + str(l+1)], current_cache, \"relu\", lambd)\n if l>0: gradients[\"dA\" + str(l)]= gradients[\"dA\" + str(l)] * Dropouts[l-1]/ keep_prob #dA0 bekommt kein Dropout \n return gradients\n#------------------------------------------------------------------------------\ndef compute_cost(AL, Y, caches, lambd):#A.shape=(n_L,m), Y.shape=(n_L,m)\n m = Y.shape[1]\n L=len(caches)\n cross_entropy = np.nansum(-(Y*np.log(AL)+(1-Y)*np.log(1-AL)),axis=1)/m#Kostenfuntion für Klassifizierung zw. 0 und 1\n L2_regularization=0\n for l in range(0,L):\n (linear_cache, activation_cache)=caches[l]\n A,W,b = linear_cache\n L2_regularization += np.nansum(np.square(W)) * 1/m * lambd/2\n cost = cross_entropy+L2_regularization\n cost = np.squeeze(cost)#Dimensionen mit nur einem Eintrag werden gelöscht, i.e. aus [[17]] wird 17\n return cost\ndef update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate):\n n = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural networks\n for k in range(n):\n parameters[\"W\" + str(k+1)] = parameters[\"W\" + str(k+1)] - learning_rate * grads[\"dW\" + str(k+1)]\n parameters[\"b\" + str(k+1)] = parameters[\"b\" + str(k+1)] - learning_rate * grads[\"db\" + str(k+1)]\n return parameters\ndef predict(X, y, parameters):\n m = X.shape[1]\n p = np.zeros((1,m), dtype = np.int)\n AL, caches, _ = forward_propagation(X, parameters, keep_prob=1.0)\n for i in range(0, AL.shape[1]):\n if AL[0,i] > 0.5: p[0,i] = 1\n else: p[0,i] = 0\n print(\"Accuracy: \" + str(np.mean((p[0,:] == y[0,:]))))\n return p\n#------------------------------------------------------------------------------\ndata = scipy.io.loadmat('/content/drive/MyDrive/Colab Notebooks/PureNumpy/NeuronalNetwork-binaryClassification/data.mat')\ntrain_X = data['X'].T\ntrain_Y = data['y'].T\ntest_X = data['Xval'].T\ntest_Y = data['yval'].T\n\nplt.figure(\"\"\"second figure\"\"\")\nplt.scatter(train_X[0, :], train_X[1, :], c=train_Y[0,:], s=40, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral);\n\nlayers_dims = [train_X.shape[0], 40, 5, 3, 1]\nprint(\"train_X.shape: \"+str(train_X.shape))\nprint(\"train_Y.shape: \"+str(train_Y.shape))\nparameters = model(train_X, train_Y, layers_dims, keep_prob = 1, learning_rate = 0.09, lambd=0.7)\nprint (\"On the train set:\")\npredictions_train = predict(train_X, train_Y, parameters)\nprint (\"On the test set:\")\npredictions_test = predict(test_X, test_Y, parameters)\n\n",
"train_X.shape: (2, 211)\ntrain_Y.shape: (1, 211)\nCost after iteration 0: 0.7760264977289945\nCost after iteration 10000: 0.24669274317839368\nCost after iteration 20000: 0.24372267094983083\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a73217574de36bc995d64e1be6abf094d4bc568
| 281,355 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
analysis/perturb_k562/cell_cycle.ipynb
|
yelabucsf/scrna-parameter-estimation
|
218ef38b87f8d777d5abcb04913212cbcb21ecb1
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2021-03-17T20:31:54.000Z
|
2022-03-17T19:24:37.000Z
|
analysis/perturb_k562/cell_cycle.ipynb
|
yelabucsf/scrna-parameter-estimation
|
218ef38b87f8d777d5abcb04913212cbcb21ecb1
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-08-23T20:55:07.000Z
|
2021-08-23T20:55:07.000Z
|
analysis/perturb_k562/cell_cycle.ipynb
|
yelabucsf/scrna-parameter-estimation
|
218ef38b87f8d777d5abcb04913212cbcb21ecb1
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2020-04-06T05:43:31.000Z
|
2020-04-06T05:43:31.000Z
| 133.660333 | 43,604 | 0.873828 |
[
[
[
"# Perturb-seq K562 co-expression",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import scanpy as sc\nimport seaborn as sns\nimport pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport scipy.stats as stats\nimport itertools\nfrom pybedtools import BedTool\nimport pickle as pkl\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.set_option('max_columns', None)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import sys\nsys.path.append('/home/ssm-user/Github/scrna-parameter-estimation/dist/memento-0.0.6-py3.8.egg')\nsys.path.append('/home/ssm-user/Github/misc-seq/miscseq/')\nimport encode\nimport memento",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data_path = '/data_volume/memento/k562/'",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Read the guide labled K562 data\n\nFrom perturbseq paper",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"adata = sc.read(data_path + 'h5ad/filtered-cellcycle.h5ad')",
"Variable names are not unique. To make them unique, call `.var_names_make_unique`.\n"
],
[
"guides = adata.obs.guides.drop_duplicates().tolist()\nguides = [g for g in guides if ('INTER' not in g and 'nan' not in g)]\nko_genes = adata.obs.query('KO == 1')['KO_GENE'].drop_duplicates().tolist()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"adata.X = adata.X.tocsr()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Setup memento",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"adata.obs['q'] = 0.07",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"memento.setup_memento(adata, q_column='q', filter_mean_thresh=0.07)",
"/home/ssm-user/Github/scrna-parameter-estimation/dist/memento-0.0.6-py3.8.egg/memento/main.py:68: RankWarning: Polyfit may be poorly conditioned\n all_res_var = estimator._residual_variance(all_m, all_v, estimator._fit_mv_regressor(all_m, all_v))\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Get moments from all groups",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"adata_moments = adata.copy().copy()",
"Variable names are not unique. To make them unique, call `.var_names_make_unique`.\nVariable names are not unique. To make them unique, call `.var_names_make_unique`.\n"
],
[
"memento.create_groups(adata_moments, label_columns=['phase'])\nmemento.compute_1d_moments(adata_moments, min_perc_group=.9)",
"/home/ssm-user/anaconda3/envs/single_cell/lib/python3.8/site-packages/pandas/core/arrays/categorical.py:2487: FutureWarning: The `inplace` parameter in pandas.Categorical.remove_unused_categories is deprecated and will be removed in a future version.\n res = method(*args, **kwargs)\n"
],
[
"moment_df = memento.get_1d_moments(adata_moments)\nmoment_df = moment_df[0].merge(moment_df[1], on='gene', suffixes=('_m', '_v'))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"moment_df = moment_df[['gene','sg^G1_m', 'sg^S_m', 'sg^G2M_m', 'sg^G1_v', 'sg^S_v', 'sg^G2M_v']]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Cell cycle 1D moments",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"adata.obs['s_phase'] = (adata.obs.phase == 'S').astype(int)\nadata.obs['g1_phase'] = (adata.obs.phase == 'G1').astype(int)\nadata.obs['g2m_phase'] = (adata.obs.phase == 'G2M').astype(int)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"g1_s = adata[adata.obs.phase.isin(['S', 'G1'])].copy().copy()\ns_g2 = adata[adata.obs.phase.isin(['S', 'G2M'])].copy().copy()\ng2_g1 = adata[adata.obs.phase.isin(['G1', 'G2M'])].copy().copy()",
"/home/ssm-user/anaconda3/envs/single_cell/lib/python3.8/site-packages/pandas/core/arrays/categorical.py:2487: FutureWarning: The `inplace` parameter in pandas.Categorical.remove_unused_categories is deprecated and will be removed in a future version.\n res = method(*args, **kwargs)\nVariable names are not unique. To make them unique, call `.var_names_make_unique`.\nVariable names are not unique. To make them unique, call `.var_names_make_unique`.\nVariable names are not unique. To make them unique, call `.var_names_make_unique`.\nVariable names are not unique. To make them unique, call `.var_names_make_unique`.\nVariable names are not unique. To make them unique, call `.var_names_make_unique`.\nVariable names are not unique. To make them unique, call `.var_names_make_unique`.\n"
],
[
"memento.create_groups(g1_s, label_columns=['s_phase', 'leiden'])\nmemento.compute_1d_moments(g1_s, min_perc_group=.9)\n\nmemento.create_groups(s_g2, label_columns=['g2m_phase', 'leiden'])\nmemento.compute_1d_moments(s_g2, min_perc_group=.9)\n\nmemento.create_groups(g2_g1, label_columns=['g1_phase', 'leiden'])\nmemento.compute_1d_moments(g2_g1, min_perc_group=.9)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"memento.ht_1d_moments(\n g1_s, \n formula_like='1 + s_phase',\n cov_column='s_phase', \n num_boot=20000, \n verbose=1,\n num_cpus=70)\n\nmemento.ht_1d_moments(\n s_g2, \n formula_like='1 + g2m_phase',\n cov_column='g2m_phase', \n num_boot=20000, \n verbose=1,\n num_cpus=70)\n\nmemento.ht_1d_moments(\n g2_g1, \n formula_like='1 + g1_phase',\n cov_column='g1_phase', \n num_boot=20000, \n verbose=1,\n num_cpus=70)\n\ng1_s.write(data_path + 'cell_cycle/g1_s.h5ad')\ns_g2.write(data_path + 'cell_cycle/s_g2.h5ad')\ng2_g1.write(data_path + 'cell_cycle/g2_g1.h5ad')",
"[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Using backend LokyBackend with 70 concurrent workers.\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 60 tasks | elapsed: 6.1s\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 310 tasks | elapsed: 12.0s\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 660 tasks | elapsed: 19.4s\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 1110 tasks | elapsed: 28.3s\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 1660 tasks | elapsed: 39.3s\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 2310 tasks | elapsed: 51.7s\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 3060 tasks | elapsed: 1.1min\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 3910 tasks | elapsed: 1.4min\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 4860 tasks | elapsed: 1.8min\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 5910 tasks | elapsed: 2.1min\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 7060 tasks | elapsed: 2.5min\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 8310 tasks | elapsed: 3.0min\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 8481 out of 8481 | elapsed: 3.2min finished\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Using backend LokyBackend with 70 concurrent workers.\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 60 tasks | elapsed: 1.9s\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 310 tasks | elapsed: 8.2s\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 660 tasks | elapsed: 15.6s\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 1110 tasks | elapsed: 25.2s\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 1660 tasks | elapsed: 36.5s\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 2310 tasks | elapsed: 49.9s\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 3060 tasks | elapsed: 1.1min\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 3910 tasks | elapsed: 1.4min\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 4860 tasks | elapsed: 1.8min\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 5910 tasks | elapsed: 2.2min\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 7060 tasks | elapsed: 2.6min\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 8434 out of 8434 | elapsed: 3.3min finished\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Using backend LokyBackend with 70 concurrent workers.\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 60 tasks | elapsed: 2.0s\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 310 tasks | elapsed: 8.7s\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 660 tasks | elapsed: 17.2s\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 1110 tasks | elapsed: 27.4s\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 1660 tasks | elapsed: 40.3s\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 2310 tasks | elapsed: 54.6s\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 3060 tasks | elapsed: 1.2min\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 3910 tasks | elapsed: 1.6min\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 4860 tasks | elapsed: 1.9min\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 5910 tasks | elapsed: 2.4min\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 7060 tasks | elapsed: 2.8min\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 8310 tasks | elapsed: 3.3min\n[Parallel(n_jobs=70)]: Done 8691 out of 8691 | elapsed: 3.7min finished\n... storing 'memento_group' as categorical\n... storing 'memento_group' as categorical\n... storing 'memento_group' as categorical\n"
],
[
"def get_1d_dfs(subset):\n\n df = memento.get_1d_ht_result(subset)\n df['dv_fdr'] = memento.util._fdrcorrect(df['dv_pval'])\n df['de_fdr'] = memento.util._fdrcorrect(df['de_pval'])\n \n return df",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"g1_s_1d = get_1d_dfs(g1_s)\ns_g2_1d = get_1d_dfs(s_g2)\ng2_g1_1d = get_1d_dfs(g2_g1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(10,3))\nplt.subplot(1,3,1)\nplt.scatter(g1_s_1d['de_coef'], g1_s_1d['dv_coef'], s=1)\nplt.subplot(1,3,2)\nplt.scatter(s_g2_1d['de_coef'], s_g2_1d['dv_coef'], s=1)\nplt.subplot(1,3,3)\nplt.scatter(g2_g1_1d['de_coef'], g2_g1_1d['dv_coef'], s=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sig_genes = set(\n g1_s_1d.query('dv_fdr < 0.01 & (dv_coef < -1 | dv_coef > 1)').gene.tolist() +\\\n s_g2_1d.query('dv_fdr < 0.01 & (dv_coef < -1 | dv_coef > 1)').gene.tolist() + \\\n g2_g1_1d.query('dv_fdr < 0.01 & (dv_coef < -1 | dv_coef > 1)').gene.tolist())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### GSEA + scatterplots",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def plot_scatters(gene_set, name, c='k'):\n plt.figure(figsize=(10,3))\n plt.subplot(1,3,1)\n plt.scatter(g1_s_1d['de_coef'], g1_s_1d['dv_coef'], s=1, color='gray')\n plt.scatter(g1_s_1d.query('gene in @gene_set')['de_coef'], g1_s_1d.query('gene in @gene_set')['dv_coef'], s=15, color=c)\n plt.xlabel('G1->S')\n# plt.xlim(-1.2,1.2); plt.ylim(-1.2,1.2);\n\n plt.subplot(1,3,2)\n plt.scatter(s_g2_1d['de_coef'], s_g2_1d['dv_coef'], s=1, color='gray')\n plt.scatter(s_g2_1d.query('gene in @gene_set')['de_coef'], s_g2_1d.query('gene in @gene_set')['dv_coef'], s=15, color=c)\n plt.title(name)\n plt.xlabel('S->G2M')\n# plt.xlim(-1.2,1.2); plt.ylim(-1.2,1.2);\n\n plt.subplot(1,3,3)\n plt.scatter(g2_g1_1d['de_coef'], g2_g1_1d['dv_coef'], s=1, color='gray')\n plt.scatter(g2_g1_1d.query('gene in @gene_set')['de_coef'], g2_g1_1d.query('gene in @gene_set')['dv_coef'], s=15, color=c)\n plt.xlabel('G2M->G1')\n# plt.xlim(-1.2,1.2); plt.ylim(-1.2,1.2);\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import gseapy as gp\nfrom gseapy.plot import gseaplot\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pre_res = gp.prerank(\n rnk=s_g2_1d.query('de_coef > 0 & de_fdr < 0.01')[['gene','dv_coef']].sort_values('dv_coef'), \n gene_sets='GO_Biological_Process_2018',\n processes=4,\n permutation_num=100, # reduce number to speed up testing\n outdir=None, seed=6)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"terms = pre_res.res2d.index\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"gsea_table = pre_res.res2d.sort_index().sort_values('fdr')\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"gsea_table.head(5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"terms = gsea_table.index\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"idx=0\ngseaplot(rank_metric=pre_res.ranking, term=terms[idx], **pre_res.results[terms[idx]])\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"gsea_table = pre_res.res2d.sort_index().sort_values('fdr')\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"stress_genes",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"stress_genes = gsea_table['ledge_genes'].iloc[0].split(';')\nplot_scatters(stress_genes, 'chaperones')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cell_cycle_genes = [x.strip() for x in open('./regev_lab_cell_cycle_genes.txt')]\nplot_scatters(cell_cycle_genes, 'cell cycle')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"manual_gene_set = g1_s_1d.query('dv_coef < -1 & de_coef < -0.5').gene.tolist()\nplot_scatters(manual_gene_set, 'G1 genes')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"manual_gene_set",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Get any hits for KOs",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"guides = adata.obs.guides.drop_duplicates().tolist()\nguides = [g for g in guides if ('INTER' not in g and 'nan' not in g)]\nko_genes = adata.obs.query('KO == 1')['KO_GENE'].drop_duplicates().tolist()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Get moments for the gene classes",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for g in ko_genes:\n \n print(g)\n \n subset = adata[adata.obs.WT | (adata.obs.KO_GENE == g)].copy().copy()\n \n memento.create_groups(subset, label_columns=['KO', 'leiden'])\n memento.compute_1d_moments(subset, min_perc_group=.9)\n \n target_genes = list(set(subset.var.index)-set(ko_genes))\n# memento.compute_2d_moments(subset, gene_pairs=list(itertools.product([g], target_genes)))\n \n memento.ht_1d_moments(\n subset, \n formula_like='1 + KO',\n cov_column='KO', \n num_boot=10000, \n verbose=1,\n num_cpus=70)\n \n# subset.write(data_path + '2d_self_h5ad/{}.h5ad'.format(g))\n \n break",
"/home/ssm-user/anaconda3/envs/single_cell/lib/python3.8/site-packages/pandas/core/arrays/categorical.py:2487: FutureWarning: The `inplace` parameter in pandas.Categorical.remove_unused_categories is deprecated and will be removed in a future version.\n res = method(*args, **kwargs)\nVariable names are not unique. To make them unique, call `.var_names_make_unique`.\nVariable names are not unique. To make them unique, call `.var_names_make_unique`.\n"
],
[
"df = memento.get_1d_ht_result(subset)\ndf['de_fdr'] = memento.util._fdrcorrect(df['de_pval'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.query('de_fdr < 0.1')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.hist(df['dv_pval'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(10, 3))\nplt.subplot(1, 2, 1)\nplt.plot(moment_df.query('gene in @stress_genes').iloc[:, 1:4].values.T)\nplt.xticks([0,1,2],['G1', 'S', 'G2M'])\nplt.title('Mean')\n\nplt.subplot(1, 2, 2)\nplt.plot(moment_df.query('gene in @stress_genes').iloc[:, 4:].values.T)\nplt.xticks([0,1,2],['G1', 'S', 'G2M'])\nplt.title('Variability')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.plot(moment_df.query('gene in @stress_genes').iloc[:, 4:].values.T)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df['dv_pval'].hist(bins=50)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Find self-DC genes",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for g in ko_genes:\n \n subset = adata[adata.obs.WT | (adata.obs.KO_GENE == g)].copy().copy()\n \n memento.create_groups(subset, label_columns=['KO'])\n memento.compute_1d_moments(subset, min_perc_group=.9)\n \n if g not in subset.var.index:\n continue\n \n target_genes = list(set(subset.var.index)-set(ko_genes))\n# memento.compute_2d_moments(subset, gene_pairs=list(itertools.product([g], target_genes)))\n \n memento.ht_1d_moments(\n subset, \n formula_like='1 + KO',\n cov_column='KO', \n num_boot=10000, \n verbose=1,\n num_cpus=70)\n \n# subset.write(data_path + '2d_self_h5ad/{}.h5ad'.format(g))\n \n break",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = memento.get_1d_ht_result(subset)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = memento.get_1d_ht_result(subset)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df['de_pval'].hist(bins=50)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for g, result in result_1d_dict.items():\n \n result.to_csv(data_path + '/result_1d/{}.csv'.format(g), index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Get 1D results",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"result_1d_dict = {g:pd.read_csv(data_path + '/result_1d/{}.csv'.format(g)) for g in guides if ('INTER' not in g and 'nan' not in g)}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"g = 'p_sgGABPA_9'\ndf = result_1d_dict[g]\ndf.query('de_fdr < 0.1 | dv_fdr < 0.1')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for g in guides:\n \n df = result_1d_dict[g]\n df['de_fdr'] = memento.util._fdrcorrect(df['de_pval'])\n df['dv_fdr'] = memento.util._fdrcorrect(df['dv_pval'])\n \n print(g, df.query('de_fdr < 0.15').shape[0], df.query('dv_fdr < 0.15').shape[0])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### DV shift plots",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for g in guides:\n df = result_1d_dict[g]\n plt.figure()\n sns.kdeplot(df['dv_coef']);\n plt.plot([0, 0], [0, 2])\n plt.title(g)\n plt.xlim(-2, 2)\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### within WT",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"adata[adata.obs.WT].obs.guides.value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"subset = adata[(adata.obs.guides=='p_INTERGENIC393453') | (adata.obs.guides=='p_INTERGENIC216151') ].copy().copy()\n\nmemento.create_groups(subset, label_columns=['guides'])\nmemento.compute_1d_moments(subset, min_perc_group=.9)\n\nmemento.ht_1d_moments(\n subset, \n formula_like='1 + guides',\n cov_column='guides', \n num_boot=10000, \n verbose=1,\n num_cpus=14)\n\nwt_result = memento.get_1d_ht_result(subset)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sns.kdeplot(wt_result.dv_coef)\nplt.title('WT')\nplt.plot([0, 0], [0, 2])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Get the change in magnitude for each guide",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"coef_mag = []\nfor g, df in result_1d_dict.items():\n coef_mag.append((g, df['de_coef'].abs().median()))\ncoef_mag = pd.DataFrame(coef_mag, columns=['guide', 'de_mag'])\ncoef_mag['gene'] = coef_mag['guide'].str.split('_').str[1].str[2:]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Get WT variability of each TF",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"wt_adata = adata[adata.obs['WT']].copy().copy()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tfs = adata.obs.query('KO==1').KO_GENE.drop_duplicates().tolist()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"memento.create_groups(wt_adata, label_columns=['KO'])\nmemento.compute_1d_moments(wt_adata, min_perc_group=.9,)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tf_moments = memento.get_1d_moments(wt_adata, groupby='KO')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Compare WT variability to De mag",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"merged = coef_mag.merge(tf_moments[1], on='gene')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"stats.spearmanr(merged['de_mag'], merged['KO_0'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.scatter(merged['de_mag'], merged['KO_0'])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Number of TF binding sites within 5k(?) KB\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"enc = encode.Encode('/home/ssm-user/Github/misc-seq/miscseq/GRCh38Genes.bed')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"encode_links = {\n 'ELK1':'https://www.encodeproject.org/files/ENCFF119SCQ/@@download/ENCFF119SCQ.bed.gz',\n 'ELF1':'https://www.encodeproject.org/files/ENCFF133TSU/@@download/ENCFF133TSU.bed.gz',\n 'IRF1':'https://www.encodeproject.org/files/ENCFF203LRV/@@download/ENCFF203LRV.bed.gz',\n 'ETS1':'https://www.encodeproject.org/files/ENCFF461PRP/@@download/ENCFF461PRP.bed.gz',\n 'EGR1':'https://www.encodeproject.org/files/ENCFF375RDB/@@download/ENCFF375RDB.bed.gz',\n 'YY1':'https://www.encodeproject.org/files/ENCFF635XCI/@@download/ENCFF635XCI.bed.gz',\n 'GABPA':'https://www.encodeproject.org/files/ENCFF173GUD/@@download/ENCFF173GUD.bed.gz',\n 'E2F4':'https://www.encodeproject.org/files/ENCFF225TLP/@@download/ENCFF225TLP.bed.gz',\n 'NR2C2':'https://www.encodeproject.org/files/ENCFF263VIC/@@download/ENCFF263VIC.bed.gz',\n 'CREB1':'https://www.encodeproject.org/files/ENCFF193LLN/@@download/ENCFF193LLN.bed.gz'\n}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"bed_objs = {tf:enc.get_encode_peaks(link) for tf,link in encode_links.items()}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"target_genes = {tf:enc.get_peak_genes_bed(bed_obj, 0).query('distance==0').gene.tolist() for tf, bed_obj in bed_objs.items()}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x = wt_adata[:, 'EGR1'].X.todense().A1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.bincount(x.astype(int))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x.mean()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.hist(x, bins=20)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"target_numbers = []\nfor tf in encode_links.keys():\n target_numbers.append((tf, len(target_genes[tf])))\ntarget_numbers = pd.DataFrame(target_numbers, columns=['gene', 'num_targets'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"merged = target_numbers.merge(tf_moments[1], on='gene')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"stats.pearsonr(merged.query('gene != \"EGR1\"')['num_targets'], merged.query('gene != \"EGR1\"')['KO_0'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.scatter(merged['num_targets'], merged['KO_0'])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Try with all ENCODE",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"merged",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"all_encode = pd.read_csv('gene_attribute_matrix.txt', sep='\\t', index_col=0, low_memory=False).iloc[2:, 2:].astype(float)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"target_counts = pd.DataFrame(all_encode.sum(axis=0), columns=['num_targets']).reset_index().rename(columns={'index':'gene'})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x = target_counts.query('gene in @tfs').sort_values('gene')['num_targets']\ny = merged.sort_values('gene')['num_targets']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"merged2 = target_counts.merge(tf_moments[1], on='gene')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.scatter(merged2['num_targets'], merged2['KO_0'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"merged2",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Get gene list",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"wt_adata = adata[adata.obs['WT']].copy().copy()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"memento.create_groups(wt_adata, label_columns=['KO'])\nmemento.compute_1d_moments(wt_adata, min_perc_group=.9)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.hist(np.log(wt_adata.uns['memento']['1d_moments']['sg^0'][0]))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"wt_high_genes = wt_adata.var.index[np.log(wt_adata.uns['memento']['1d_moments']['sg^0'][0]) > -1].tolist()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Create labels for X genes",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"chr_locations = pd.read_csv('chr_locations.bed', sep='\\t').rename(columns={'#chrom':'chr'}).drop_duplicates('geneName')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"chr_locations.index=chr_locations.geneName",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"adata.var = adata.var.join(chr_locations, how='left')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Filter X-chromosomal genes",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"adata_X = adata[:, (adata.var.chr=='chrX') | adata.var.chr.isin(['chr1', 'chr2', 'chr3'])].copy()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"adata_X",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Escape genes",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"par_genes = \"\"\"PLCXD1 GTPBP6 PPP2R3B SHOX CRLF2 CSF2RA IL3RA SLC25A6 ASMTL P2RY8 ASMT DHRSXY ZBED1 CD99 XG IL9R SPRY3 VAMP7\"\"\".split()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"escape_genes = \"\"\"EIF1AX\nUSP9X\nEIF2S3\nCTPS2\nTRAPPC2\nHDHD1\nZFX\nDDX3X\nRAB9A\nAP1S2\nGEMIN8\nRPS4X\nSMC1A\nZRSR2\nSTS\nFUNDC1\nPNPLA4\nUBA1\nARSD\nNLGN4X\nGPM6B\nMED14\nCD99\nRBBP7\nSYAP1\nPRKX\nOFD1\nCXorf38\nTXLNG\nKDM5C\nGYG2\nTBL1X\nCA5B\nXIST\nRENBP\nHCFC1\nUSP11\nPLCXD1\nSLC25A6\nASMTL\nDHRSX\nXG\nTMEM27\nARHGAP4\nGAB3\nPIR\nTMEM187\nDOCK11\nEFHC2\nRIBC1\nNAP1L3\nCA5BP1\nMXRA5\nKAL1\nPCDH11X\nKDM6A\nPLS3\nCITED1\nL1CAM\nALG13\nBCOR\"\"\".split()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Run 1d memento",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"adata_X.obs['is_female'] = (adata_X.obs['Sex'] == 'Female').astype(int)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"adata_X.obs.is_female.value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"memento.create_groups(adata_X, label_columns=['is_female', 'ind_cov'])\nmemento.compute_1d_moments(adata_X, min_perc_group=.9)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"memento.ht_1d_moments(\n adata_X, \n formula_like='1 + is_female',\n cov_column='is_female', \n num_boot=20000, \n verbose=1,\n num_cpus=13)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"result_1d = memento.get_1d_ht_result(adata_X)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"result_1d['dv_fdr'] = memento.util._fdrcorrect(result_1d['dv_pval'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sns.distplot(result_1d.dv_coef)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x_chr_genes = adata.var.index[adata.var.chr=='chrX'].tolist()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"result_1d['escape'] = result_1d['gene'].isin(escape_genes)\nresult_1d['par'] = result_1d['gene'].isin(par_genes)\nresult_1d['x_chr'] = result_1d['gene'].isin(x_chr_genes)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sns.distplot(result_1d.query('~x_chr').dv_coef)\nsns.distplot(result_1d.query('x_chr').dv_coef)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sns.boxplot(x='x_chr', y='dv_coef', data=result_1d)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dv_genes = result_1d.query('dv_fdr < 0.1').gene.tolist()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"result_1d['dv'] = result_1d.gene.isin(dv_genes)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"result_1d.query('~dv & ~x_chr & dv_coef > 0').shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a = [[193, 14],\n [23,5]]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"stats.chi2_contingency(a)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"result_1d.query('dv_fdr < 0.1').x_chr.mean()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"result_1d.x_chr.mean()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Run memento for each subset, comparing to control",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cts = [['ciliated'], ['bc','basal']]\n# tps = ['3', '6', '9', '24', '48']\ntps = ['3', '6', '9', '24', '48']\n\nstims = ['alpha', 'beta', 'gamma', 'lambda']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import os\ndone_files = os.listdir('/data_volume/ifn_hbec/binary_test_deep/')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for ct in cts:\n for tp in tps:\n for stim in stims:\n \n fname = '{}_{}_{}_20200320.h5ad'.format('-'.join(ct), stim, tp)\n \n if fname in done_files:\n print('Skipping', fname)\n continue\n\n print('starting', ct, tp, stim)\n\n adata_stim = adata.copy()[\n adata.obs.cell_type.isin(ct) & \\\n adata.obs.stim.isin(['control', stim]) & \\\n adata.obs.time.isin(['0',tp]), :].copy()\n time_converter={0:0, int(tp):1}\n adata_stim.obs['time_step'] = adata_stim.obs['time'].astype(int).apply(lambda x: time_converter[x])\n\n memento.create_groups(adata_stim, label_columns=['time_step', 'donor'])\n memento.compute_1d_moments(adata_stim, min_perc_group=.9)\n\n memento.ht_1d_moments(\n adata_stim, \n formula_like='1 + time_step',\n cov_column='time_step', \n num_boot=10000, \n verbose=1,\n num_cpus=13)\n\n del adata_stim.uns['memento']['mv_regressor']\n\n adata_stim.write('/data_volume/ifn_hbec/binary_test_deep/{}_{}_{}_20200320.h5ad'.format(\n '-'.join(ct), stim, tp))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a7321d071c701504783eb0a19c63d915825c459
| 44,064 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Ejemplos Qiskit/Qiskit example.ipynb
|
javpelle/TFGInformatica
|
fabdf42d4c266fc5f88f66d2eb59e9f0b144a2cb
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Ejemplos Qiskit/Qiskit example.ipynb
|
javpelle/TFGInformatica
|
fabdf42d4c266fc5f88f66d2eb59e9f0b144a2cb
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Ejemplos Qiskit/Qiskit example.ipynb
|
javpelle/TFGInformatica
|
fabdf42d4c266fc5f88f66d2eb59e9f0b144a2cb
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 161.406593 | 19,212 | 0.899669 |
[
[
[
"#initialization\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n%matplotlib inline\nimport numpy as np\n\n# importing Qiskit\nfrom qiskit import IBMQ, BasicAer\nfrom qiskit.providers.ibmq import least_busy\nfrom qiskit import QuantumCircuit, ClassicalRegister, QuantumRegister, execute\n\n# import basic plot tools\nfrom qiskit.tools.visualization import plot_histogram",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def phase_oracle(circuit, register):\n circuit.cz(qr[2],qr[0])\n circuit.cz(qr[2],qr[1])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def n_controlled_Z(circuit, controls, target):\n \"\"\"Implement a Z gate with multiple controls\"\"\"\n if (len(controls) > 2):\n raise ValueError('The controlled Z with more than 2 controls is not implemented')\n elif (len(controls) == 1):\n circuit.h(target)\n circuit.cx(controls[0], target)\n circuit.h(target)\n elif (len(controls) == 2):\n circuit.h(target)\n circuit.ccx(controls[0], controls[1], target)\n circuit.h(target)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def inversion_about_average(circuit, register, n, barriers):\n \"\"\"Apply inversion about the average step of Grover's algorithm.\"\"\"\n circuit.h(register)\n circuit.x(register)\n \n if barriers:\n circuit.barrier()\n \n n_controlled_Z(circuit, [register[j] for j in range(n-1)], register[n-1])\n \n if barriers:\n circuit.barrier()\n \n circuit.x(register)\n circuit.h(register)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"barriers = True\n\nqr = QuantumRegister(3)\ncr = ClassicalRegister(3)\n\ngroverCircuit = QuantumCircuit(qr,cr)\ngroverCircuit.h(qr)\n\nif barriers:\n groverCircuit.barrier()\n\nphase_oracle(groverCircuit, qr)\n\nif barriers:\n groverCircuit.barrier()\n\ninversion_about_average(groverCircuit, qr, 3, barriers)\n\nif barriers:\n groverCircuit.barrier()\n\ngroverCircuit.measure(qr,cr)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"groverCircuit.draw(output=\"mpl\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"backend = BasicAer.get_backend('qasm_simulator')\nshots = 1024\nresults = execute(groverCircuit, backend=backend, shots=shots).result()\nanswer = results.get_counts()\nanswer",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#from qiskit import IBMQ\n#IBMQ.save_account('8fb564aa5ec8cc13346cc6ffb53d99e10f8298a762bf5b3495245b6ea683d76b40f9e9495fe6cfe9c68ef2c559c15a03347f29073f37a2f1defc77df583ee270')\n\n\nIBMQ.load_account()\nprovider = IBMQ.get_provider(hub='ibm-q')\nbackend = least_busy(provider.backends(filters=lambda x: x.configuration().n_qubits <= 5 and \n not x.configuration().simulator and x.status().operational==True))\nprint(\"least busy backend: \", backend)",
"C:\\ProgramData\\Anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages\\qiskit\\providers\\ibmq\\ibmqfactory.py:181: UserWarning: Credentials are already in use. The existing account in the session will be replaced.\n warnings.warn('Credentials are already in use. The existing '\n"
],
[
"# Run our circuit on the least busy backend. Monitor the execution of the job in the queue\nfrom qiskit.tools.monitor import job_monitor\n\nshots = 1024\njob = execute(groverCircuit, backend=backend, shots=shots)\n\njob_monitor(job, interval = 2)",
"Job Status: job has successfully run\n"
],
[
"# Get the results from the computation\nresults = job.result()\nanswer = results.get_counts(groverCircuit)\nplot_histogram(answer)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a732a2b51f8a2945b763d8c6bad7a5a8743a98f
| 8,189 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Python Fundamentals/Module_5_Required_FINAL_Project_Python_Fundamentals.ipynb
|
sdavi187/pythonteachingcode
|
98cdf3fddaf152854d91187408c7d32a6d36db0e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Python Fundamentals/Module_5_Required_FINAL_Project_Python_Fundamentals.ipynb
|
sdavi187/pythonteachingcode
|
98cdf3fddaf152854d91187408c7d32a6d36db0e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Python Fundamentals/Module_5_Required_FINAL_Project_Python_Fundamentals.ipynb
|
sdavi187/pythonteachingcode
|
98cdf3fddaf152854d91187408c7d32a6d36db0e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 38.088372 | 415 | 0.545732 |
[
[
[
"# Final Project Required Coding Activity \nIntroduction to Python (Unit 2) Fundamentals \n \nAll course .ipynb Jupyter Notebooks are available from the project files download topic in Module 1, Section 1. \n\nThis activity is based on modules 1 - 4 and is similar to exercises in the Jupyter Notebooks **`Practice_MOD03_IntroPy.ipynb`** and **`Practice_MOD04_IntroPy.ipynb`** which you may have completed as practice.\n\n| **Assignment Requirements** |\n|:-------------------------------|\n|This program requires the use of **`print`** output and use of **`input`**, **`for`**/**`in`** loop, **`if`**, file **`open`**, **`.readline`**, **`.append`**, **`.strip`**, **`len`**. and function **`def`** and **`return`**. The code should also consider using most of the following (`.upper()` or `.lower()`, `.title()`, `print(\"hello\",end=\"\")` `else`, `elif`, `range()`, `while`, `.close()`) |\n\n\n## Program: Element_Quiz \nIn this program the user enters the name of any 5 of the first 20 Atomic Elements and is given a grade and test report for items correct and incorrect. \n\n\n### Sample input and output: \n```\nlist any 5 of the first 20 elements in the Period table\nEnter the name of an element: argon\nEnter the name of an element: chlorine\nEnter the name of an element: sodium\nEnter the name of an element: argon\nargon was already entered <--no duplicates allowed\nEnter the name of an element: helium\nEnter the name of an element: gold\n\n80 % correct\nFound: Argon Chlorine Sodium Helium \nNot Found: Gold \n``` \n\n\n### Create get_names() Function to collect input of 5 unique element names \n\n- The function accepts no arguments and returns a list of 5 input strings (element names) \n- define a list to hold the input\n- collect input of a element name \n- if input it is **not** already in the list add the input to the list \n- don't allow empty strings as input \n- once 5 unique inputs **return** the list \n\n\n### Create the Program flow \n\n#### import the file into the Jupyter Notebook environment \n\n- use `!curl` to download https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MicrosoftLearning/intropython/master/elements1_20.txt\" as `elements1_20.txt` \n- open the file with the first 20 elements \n- read one line at a time to get element names, remove any whitespace (spaces, newlines) and save each element name, as lowercase, into a list \n\n\n#### Call the get_names() function \n\n- the return value will be the quiz responses list \n\n#### check if responses are in the list of elements \nIterate through 5 responses \n- compare each response to the list of 20 elements\n - any response that is in the list of 20 elements is correct and should be added to a list of correct responses \n - if not in the list of 20 elements then add to a list of incorrect responses \n\n#### calculate the % correct \n \n - find the the number of items in the correct responses and divide by 5, this will result in answers like 1.0, .8, .6,... \n - to get the % multiple the calculated answer above by 100, this will result in answers like 100, 80, 60... \n - *hint: instead of dividing by 5 and then multiplying by 100, the number of correct responses can be multiplied by 20* \n\n#### Print output \n\n- print the Score % right \n- print each of the correct responses \n- print each of the incorrect responses \n\n\n### create Element_Quiz\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# [] create Element_Quiz\n# [] copy and paste in edX assignment page\n!curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MicrosoftLearning/intropython/master/elements1_20.txt -o elements.txt\nguesses = []\ncorrect = []\nincorrect = []\nelements = []\nelements_file = open(\"elements.txt\",\"r\")\n\n \ndef get_names():\n guesses = []\n i = 0\n \n while i < 5:\n temp_guess = input(\"Name one of the first 20 elements of the Periodic Table of Elements: \").lower()\n \n if temp_guess in guesses:\n print (\"You have already guessed that element.\")\n elif temp_guess == \"\":\n print (\"Emtpy answers are not allowed\")\n else:\n guesses.append(temp_guess)\n i += 1\n \n return guesses\n\nindex = 0\n\nwhile True:\n \n temp = elements_file.readline().strip(\"\\n \").lower()\n if temp == \"\":\n break\n else:\n elements.append(temp)\n \nguess = get_names()\n\nindex = 0\n\nfor index in guess:\n if index in elements:\n correct.append(index)\n else:\n incorrect.append(index)\n \nprint (\"Found: \", end=\"\")\nfor x in correct: \n print (x, end=\" \")\nprint (\"\")\n \nprint (\"Not Found: \", end=\"\")\nfor x in incorrect:\n print (x, end=\" \")\nprint (\"\")\n\nprint (\"Score: \" + str((len(correct)/5)*100) + \"%\")\n\n \nelements_file.close()\n \n\n\n",
" % Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current\n Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed\n\n 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 0\n100 161 100 161 0 0 1102 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 1110\n"
]
],
[
[
"Submit this by creating a python file (.py) and submitting it in D2L. Be sure to test that it works. Know that For this to work correctly in Python rather than Jupyter, you would need to switch to using import os rather than !curl. To convert !curl to run in the normal python interpreter try a method such as importing the os library and calling os.system(cmd) with your shell command in the cmd variable. \n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a7347024a3983331bf1d09f85ebc7daba48ff10
| 2,556 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Supervised Learning/Perceptron/NOT_Perceptron.ipynb
|
nilaychauhan/machine_learning
|
1154a0e72d4c7848876b8321661210490baf9b95
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Supervised Learning/Perceptron/NOT_Perceptron.ipynb
|
nilaychauhan/machine_learning
|
1154a0e72d4c7848876b8321661210490baf9b95
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Supervised Learning/Perceptron/NOT_Perceptron.ipynb
|
nilaychauhan/machine_learning
|
1154a0e72d4c7848876b8321661210490baf9b95
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 30.428571 | 142 | 0.48748 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd\n\n# TODO: Set weight1, weight2, and bias\nweight1 = -1.0\nweight2 = -2.0\nbias = 1.0\n\n\n# DON'T CHANGE ANYTHING BELOW\n# Inputs and outputs\ntest_inputs = [(0, 0), (0, 1), (1, 0), (1, 1)]\ncorrect_outputs = [True, False, True, False]\noutputs = []\n\n# Generate and check output\nfor test_input, correct_output in zip(test_inputs, correct_outputs):\n linear_combination = weight1 * test_input[0] + weight2 * test_input[1] + bias\n output = int(linear_combination >= 0)\n is_correct_string = 'Yes' if output == correct_output else 'No'\n outputs.append([test_input[0], test_input[1], linear_combination, output, is_correct_string])\n\n# Print output\nnum_wrong = len([output[4] for output in outputs if output[4] == 'No'])\noutput_frame = pd.DataFrame(outputs, columns=['Input 1', ' Input 2', ' Linear Combination', ' Activation Output', ' Is Correct'])\nif not num_wrong:\n print('Nice! You got it all correct.\\n')\nelse:\n print('You got {} wrong. Keep trying!\\n'.format(num_wrong))\nprint(output_frame.to_string(index=False))",
"Nice! You got it all correct.\n\n Input 1 Input 2 Linear Combination Activation Output Is Correct\n 0 0 1.0 1 Yes\n 0 1 -1.0 0 Yes\n 1 0 0.0 1 Yes\n 1 1 -2.0 0 Yes\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
]
] |
4a73510b8c43dfb321d1730a0d4886ea6c4d3744
| 16,009 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Day74_Gradient Descent_Math.ipynb
|
hengbinxu/ML100-Days
|
ed0eb6e32882239599df57486af3dc398f160d4c
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2019-01-02T01:18:27.000Z
|
2019-01-02T01:18:27.000Z
|
Day74_Gradient Descent_Math.ipynb
|
hengbinxu/ML100-Days
|
ed0eb6e32882239599df57486af3dc398f160d4c
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Day74_Gradient Descent_Math.ipynb
|
hengbinxu/ML100-Days
|
ed0eb6e32882239599df57486af3dc398f160d4c
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 63.527778 | 10,360 | 0.793491 |
[
[
[
"matplotlib: 載入繪圖的工具包\nrandom, numpy: 載入數學運算的工具包",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import matplotlib\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n%matplotlib inline \n#適用於 Jupyter Notebook, 宣告直接在cell 內印出執行結果\nimport random as random\nimport numpy as np\nimport csv",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# ydata = b + w * xdata \n給定曲線的曲線範圍",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 給定初始的data\nx_data = [ 338., 333., 328., 207., 226., 25., 179., 60., 208., 606.]\ny_data = [ 640., 633., 619., 393., 428., 27., 193., 66., 226., 1591.]\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#給定神經網路參數:bias 跟weight\nx = np.arange(-200,-100,1) #給定bias\ny = np.arange(-5,5,0.1) #給定weight",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Z = np.zeros((len(x), len(y)))\n#meshgrid返回的兩個矩陣X、Y必定是行數、列數相等的,且X、Y的行數都等\n#meshgrid函數用兩個坐標軸上的點在平面上畫格。\nX, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)\nfor i in range(len(x)):\n for j in range(len(y)):\n b = x[i]\n w = y[j]\n Z[j][i] = 0 \n for n in range(len(x_data)):\n Z[j][i] = Z[j][i] + (y_data[n] - b - w*x_data[n])**2\n Z[j][i] = Z[j][i]/len(x_data)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# ydata = b + w * xdata \nb = -120 # initial b\nw = -4 # initial w\nlr = 0.000001 # learning rate\niteration = 100000\n\n# Store initial values for plotting.\nb_history = [b]\nw_history = [w]\n\n#給定初始值\nlr_b = 0.0\nlr_w = 0.0",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"在微積分裡面,對多元函數的參數求∂偏導數,把求得的各個參數的偏導數以向量的形式寫出來,就是梯度。\n比如函數f(x), 對x求偏導數,求得的梯度向量就是(∂f/∂x),簡稱grad f(x)或者▽f (x)。\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"'''\nLoss = (實際ydata – 預測ydata)\nGradient = -2*input * Loss \n調整後的權重 = 原權重 – Learning * Gradient\n'''\n# Iterations\nfor i in range(iteration):\n \n b_grad = 0.0\n w_grad = 0.0\n for n in range(len(x_data)): \n b_grad = b_grad - 2.0*(y_data[n] - b - w*x_data[n])*1.0\n w_grad = w_grad - 2.0*(y_data[n] - b - w*x_data[n])*x_data[n]\n \n lr_b = lr_b + b_grad ** 2\n lr_w = lr_w + w_grad ** 2\n \n # Update parameters.\n b = b - lr * b_grad \n w = w - lr * w_grad\n \n # Store parameters for plotting\n b_history.append(b)\n w_history.append(w)\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# plot the figure\nplt.contourf(x,y,Z, 50, alpha=0.5, cmap=plt.get_cmap('jet'))\nplt.plot([-188.4], [2.67], 'x', ms=12, markeredgewidth=3, color='orange')\nplt.plot(b_history, w_history, 'o-', ms=3, lw=1.5, color='black')\nplt.xlim(-200,-100)\nplt.ylim(-5,5)\nplt.xlabel(r'$b$', fontsize=16)\nplt.ylabel(r'$w$', fontsize=16)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a735927bf020f3f9304ab86b2951e4961180cb2
| 351,566 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
introductory-tutorials/intro-to-julia/08. Plotting.ipynb
|
ljbelenky/JuliaTutorials
|
de4a74717e2debebfbddd815848da5292c1755e5
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
introductory-tutorials/intro-to-julia/08. Plotting.ipynb
|
ljbelenky/JuliaTutorials
|
de4a74717e2debebfbddd815848da5292c1755e5
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
introductory-tutorials/intro-to-julia/08. Plotting.ipynb
|
ljbelenky/JuliaTutorials
|
de4a74717e2debebfbddd815848da5292c1755e5
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 256.430343 | 50,838 | 0.684275 |
[
[
[
"empty"
]
]
] |
[
"empty"
] |
[
[
"empty"
]
] |
4a73630658b21f1d62d473df01da2fde3ac52e77
| 155,722 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
06_Stats/Wind_Stats/Exercises_with_solutions.ipynb
|
henrylam07/pandas_exercises
|
75f3b7343d131d4ee67bf23932e4c1ed42ad0704
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 2 |
2020-02-25T13:00:50.000Z
|
2020-02-25T13:00:53.000Z
|
06_Stats/Wind_Stats/Exercises_with_solutions.ipynb
|
saltaro/pandas_exercises
|
59a33f0ee30a8886fb90d2db70d821950282a1d4
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
06_Stats/Wind_Stats/Exercises_with_solutions.ipynb
|
saltaro/pandas_exercises
|
59a33f0ee30a8886fb90d2db70d821950282a1d4
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 11 |
2020-10-30T00:41:11.000Z
|
2022-01-15T02:56:23.000Z
| 37.478219 | 346 | 0.382297 |
[
[
[
"# Wind Statistics",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Introduction:\n\nThe data have been modified to contain some missing values, identified by NaN. \nUsing pandas should make this exercise\neasier, in particular for the bonus question.\n\nYou should be able to perform all of these operations without using\na for loop or other looping construct.\n\n\n1. The data in 'wind.data' has the following format:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\"\"\"\nYr Mo Dy RPT VAL ROS KIL SHA BIR DUB CLA MUL CLO BEL MAL\n61 1 1 15.04 14.96 13.17 9.29 NaN 9.87 13.67 10.25 10.83 12.58 18.50 15.04\n61 1 2 14.71 NaN 10.83 6.50 12.62 7.67 11.50 10.04 9.79 9.67 17.54 13.83\n61 1 3 18.50 16.88 12.33 10.13 11.17 6.17 11.25 NaN 8.50 7.67 12.75 12.71\n\"\"\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
" The first three columns are year, month and day. The\n remaining 12 columns are average windspeeds in knots at 12\n locations in Ireland on that day. \n\n More information about the dataset go [here](wind.desc).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Step 1. Import the necessary libraries",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport datetime",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Step 2. Import the dataset from this [address](https://github.com/guipsamora/pandas_exercises/blob/master/06_Stats/Wind_Stats/wind.data)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Step 3. Assign it to a variable called data and replace the first 3 columns by a proper datetime index.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# parse_dates gets 0, 1, 2 columns and parses them as the index\ndata_url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/guipsamora/pandas_exercises/master/06_Stats/Wind_Stats/wind.data'\ndata = pd.read_csv(data_url, sep = \"\\s+\", parse_dates = [[0,1,2]]) \ndata.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Step 4. Year 2061? Do we really have data from this year? Create a function to fix it and apply it.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# The problem is that the dates are 2061 and so on...\n\n# function that uses datetime\ndef fix_century(x):\n year = x.year - 100 if x.year > 1989 else x.year\n return datetime.date(year, x.month, x.day)\n\n# apply the function fix_century on the column and replace the values to the right ones\ndata['Yr_Mo_Dy'] = data['Yr_Mo_Dy'].apply(fix_century)\n\n# data.info()\ndata.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Step 5. Set the right dates as the index. Pay attention at the data type, it should be datetime64[ns].",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# transform Yr_Mo_Dy it to date type datetime64\ndata[\"Yr_Mo_Dy\"] = pd.to_datetime(data[\"Yr_Mo_Dy\"])\n\n# set 'Yr_Mo_Dy' as the index\ndata = data.set_index('Yr_Mo_Dy')\n\ndata.head()\n# data.info()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Step 6. Compute how many values are missing for each location over the entire record. \n#### They should be ignored in all calculations below. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# \"Number of non-missing values for each location: \"\ndata.isnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Step 7. Compute how many non-missing values there are in total.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#number of columns minus the number of missing values for each location\ndata.shape[0] - data.isnull().sum()\n\n#or\n\ndata.notnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Step 8. Calculate the mean windspeeds of the windspeeds over all the locations and all the times.\n#### A single number for the entire dataset.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data.sum().sum() / data.notna().sum().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Step 9. Create a DataFrame called loc_stats and calculate the min, max and mean windspeeds and standard deviations of the windspeeds at each location over all the days \n\n#### A different set of numbers for each location.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data.describe(percentiles=[])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Step 10. Create a DataFrame called day_stats and calculate the min, max and mean windspeed and standard deviations of the windspeeds across all the locations at each day.\n\n#### A different set of numbers for each day.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# create the dataframe\nday_stats = pd.DataFrame()\n\n# this time we determine axis equals to one so it gets each row.\nday_stats['min'] = data.min(axis = 1) # min\nday_stats['max'] = data.max(axis = 1) # max \nday_stats['mean'] = data.mean(axis = 1) # mean\nday_stats['std'] = data.std(axis = 1) # standard deviations\n\nday_stats.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Step 11. Find the average windspeed in January for each location. \n#### Treat January 1961 and January 1962 both as January.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data.loc[data.index.month == 1].mean()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Step 12. Downsample the record to a yearly frequency for each location.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data.groupby(data.index.to_period('A')).mean()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Step 13. Downsample the record to a monthly frequency for each location.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data.groupby(data.index.to_period('M')).mean()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Step 14. Downsample the record to a weekly frequency for each location.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data.groupby(data.index.to_period('W')).mean()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Step 15. Calculate the min, max and mean windspeeds and standard deviations of the windspeeds across all locations for each week (assume that the first week starts on January 2 1961) for the first 52 weeks.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# resample data to 'W' week and use the functions\nweekly = data.resample('W').agg(['min','max','mean','std'])\n\n# slice it for the first 52 weeks and locations\nweekly.loc[weekly.index[1:53], \"RPT\":\"MAL\"] .head(10)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a7368253dd2a54c8298edfbd0bbc680ec76e4f9
| 4,092 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
chapter1/homework/201611680829.ipynb
|
hpishacker/python_tutorial
|
9005f0db9dae10bdc1d1c3e9e5cf2268036cd5bd
|
[
"MIT"
] | 76 |
2017-09-26T01:07:26.000Z
|
2021-02-23T03:06:25.000Z
|
chapter1/homework/201611680829.ipynb
|
hpishacker/python_tutorial
|
9005f0db9dae10bdc1d1c3e9e5cf2268036cd5bd
|
[
"MIT"
] | 5 |
2017-12-10T08:40:11.000Z
|
2020-01-10T03:39:21.000Z
|
chapter1/homework/201611680829.ipynb
|
hacker-14/python_tutorial
|
4a110b12aaab1313ded253f5207ff263d85e1b56
|
[
"MIT"
] | 112 |
2017-09-26T01:07:30.000Z
|
2021-11-25T19:46:51.000Z
| 19.578947 | 47 | 0.415934 |
[
[
[
"a=str(input('请输入你的名字'))\nx=float(input('请输入你的生日(如:1.1)'))\n\nif 3.21<=x<=4.19:\n print(a,'你是白羊座')\nelif 4.20<=x<=5.20:\n print(a,'你是金牛座')\nelif 5.21<=x<=6.21:\n print(a,'你是双子座')\nelif 6.22<=x<=7.22:\n print(a,'你是巨蟹座')\nelif 7.23<=x<=8.22:\n print(a,'你是狮子座')\nelif 8.23<=x<=9.22:\n print(a,'你是处女座')\nelif 9.23<=x<=10.23:\n print(a,'你是天秤座')\nelif 10.24<=x<=11.22:\n print(a,'你是天蝎座')\nelif 11.23<=x<=12.21:\n print(a,'你是射手座')\nelse:\n 12.22<=x<=12.31 or 1.1<=x<=1.19\n print(a,'你是摩羯座')",
"请输入你的名字Andrew\n请输入你的生日(如:1.1)1.5\nAndrew 你是摩羯座\n"
],
[
"n=int(input('请输入整数n'))\nm=int(input('请输入整数m'))\nx=input('您需要的计算是:请输入‘+’,‘*’,‘%’,‘//’')\n \nif x=='+':\n print(m+n)\nelif x=='*':\n print(m*n)\nelif x=='%':\n print(m%n)\nelif x=='//':\n print(m//n)",
"请输入整数n2\n请输入整数m3\n您需要的计算是:请输入‘+’,‘*’,‘%’,‘//’*\n6\n"
],
[
"n=float(input('请输入北京PM2.5指数'))\nif 0<=n<=50:\n print('参加户外活动吸收新鲜空气')\nelif 50<n<=100:\n print('可正常进行室外活动')\nelif 100<n<=150:\n print('敏感人群减少户外活动')\nelif 150<n<=200:\n print('对敏感人群影响较大')\nelif 200<n<=300:\n print('所有人群减少户外活动')\nelif 300<n<=500:\n print('不要在室外逗留')\nelse:\n n>500\n print('打开空气净化器,戴防雾霾口罩')",
"请输入北京PM2.5指数176\n对敏感人群影响较大\n"
],
[
"print('hello')\nprint('\\n')\nprint('123')",
"hello\n\n\n123\n"
],
[
"n=int(input('请输入想输入的整数个数'))\nmid=0\na=int(input('请输入一个整数'))\nb=int(input('请输入一个整数'))\nif a>=b:\n max=a\n min=b\nelse:\n max=b\n min=a\ni=2\nwhile i<n:\n x=int(input('请输入一个整数'))\n if x>min and x<max:\n mid=x\n elif x>=max:\n mid=max\n max=x\n else:\n mid=min\n min=x\n i=i+1\nprint(mid)",
"请输入想输入的整数个数5\n请输入一个整数1\n请输入一个整数3\n请输入一个整数5\n请输入一个整数7\n请输入一个整数9\n7\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a736e49915d7566f2ac7332cc9ba4c6be7eafd7
| 49,887 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/chap15.ipynb
|
yuanquan010/ThinkBayes2
|
7ce1546cfbb7d733ceb5d42ce821dd7c5ac2d23d
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-04-14T01:29:57.000Z
|
2021-04-14T01:29:57.000Z
|
notebooks/chap15.ipynb
|
yuanquan010/ThinkBayes2
|
7ce1546cfbb7d733ceb5d42ce821dd7c5ac2d23d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/chap15.ipynb
|
yuanquan010/ThinkBayes2
|
7ce1546cfbb7d733ceb5d42ce821dd7c5ac2d23d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 25.996352 | 375 | 0.565979 |
[
[
[
"# Mark and Recapture",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Think Bayes, Second Edition\n\nCopyright 2020 Allen B. Downey\n\nLicense: [Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0)](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# If we're running on Colab, install empiricaldist\n# https://pypi.org/project/empiricaldist/\n\nimport sys\nIN_COLAB = 'google.colab' in sys.modules\n\nif IN_COLAB:\n !pip install empiricaldist",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Get utils.py\n\nimport os\n\nif not os.path.exists('utils.py'):\n !wget https://github.com/AllenDowney/ThinkBayes2/raw/master/soln/utils.py",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from utils import set_pyplot_params\nset_pyplot_params()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This chapter introduces \"mark and recapture\" experiments, in which we sample individuals from a population, mark them somehow, and then take a second sample from the same population. Seeing how many individuals in the second sample are marked, we can estimate the size of the population.\n\nExperiments like this were originally used in ecology, but turn out to be useful in many other fields. Examples in this chapter include software engineering and epidemiology.\n\nAlso, in this chapter we'll work with models that have three parameters, so we'll extend the joint distributions we've been using to three dimensions.\n\nBut first, grizzly bears.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## The Grizzly Bear Problem\n\nIn 1996 and 1997 researchers deployed bear traps in locations in British Columbia and Alberta, Canada, in an effort to estimate the population of grizzly bears. They describe the experiment in [this article](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/229195465_Estimating_Population_Size_of_Grizzly_Bears_Using_Hair_Capture_DNA_Profiling_and_Mark-Recapture_Analysis).\n\nThe \"trap\" consists of a lure and several strands of barbed wire intended to capture samples of hair from bears that visit the lure. Using the hair samples, the researchers use DNA analysis to identify individual bears.\n\nDuring the first session, the researchers deployed traps at 76 sites. Returning 10 days later, they obtained 1043 hair samples and identified 23 different bears. During a second 10-day session they obtained 1191 samples from 19 different bears, where 4 of the 19 were from bears they had identified in the first batch.\n\nTo estimate the population of bears from this data, we need a model for the probability that each bear will be observed during each session. As a starting place, we'll make the simplest assumption, that every bear in the population has the same (unknown) probability of being sampled during each session.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"With these assumptions we can compute the probability of the data for a range of possible populations.\n\nAs an example, let's suppose that the actual population of bears is 100.\n\nAfter the first session, 23 of the 100 bears have been identified.\nDuring the second session, if we choose 19 bears at random, what is the probability that 4 of them were previously identified?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"I'll define\n\n* $N$: actual population size, 100.\n\n* $K$: number of bears identified in the first session, 23.\n\n* $n$: number of bears observed in the second session, 19 in the example.\n\n* $k$: number of bears in the second session that were previously identified, 4.\n\nFor given values of $N$, $K$, and $n$, the probability of finding $k$ previously-identified bears is given by the [hypergeometric distribution](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypergeometric_distribution):\n\n$$\\binom{K}{k} \\binom{N-K}{n-k}/ \\binom{N}{n}$$\n\nwhere the [binomial coefficient](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Binomial_coefficient), $\\binom{K}{k}$, is the number of subsets of size $k$ we can choose from a population of size $K$.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"To understand why, consider: \n\n* The denominator, $\\binom{N}{n}$, is the number of subsets of $n$ we could choose from a population of $N$ bears.\n\n* The numerator is the number of subsets that contain $k$ bears from the previously identified $K$ and $n-k$ from the previously unseen $N-K$.\n\nSciPy provides `hypergeom`, which we can use to compute this probability for a range of values of $k$.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nfrom scipy.stats import hypergeom\n\nN = 100\nK = 23\nn = 19\n\nks = np.arange(12)\nps = hypergeom(N, K, n).pmf(ks)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The result is the distribution of $k$ with given parameters $N$, $K$, and $n$.\nHere's what it looks like.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom utils import decorate\n\nplt.bar(ks, ps)\n\ndecorate(xlabel='Number of bears observed twice',\n ylabel='PMF',\n title='Hypergeometric distribution of k (known population 100)')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The most likely value of $k$ is 4, which is the value actually observed in the experiment. \nThat suggests that $N=100$ is a reasonable estimate of the population, given this data.\n\nWe've computed the distribution of $k$ given $N$, $K$, and $n$.\nNow let's go the other way: given $K$, $n$, and $k$, how can we estimate the total population, $N$?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## The Update\n\nAs a starting place, let's suppose that, prior to this study, an expert estimates that the local bear population is between 50 and 500, and equally likely to be any value in that range.\n\nI'll use `make_uniform` to make a uniform distribution of integers in this range.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nfrom utils import make_uniform\n\nqs = np.arange(50, 501)\nprior_N = make_uniform(qs, name='N')\nprior_N.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"So that's our prior.\n\nTo compute the likelihood of the data, we can use `hypergeom` with constants `K` and `n`, and a range of values of `N`. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Ns = prior_N.qs\nK = 23\nn = 19\nk = 4\n\nlikelihood = hypergeom(Ns, K, n).pmf(k)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can compute the posterior in the usual way.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"posterior_N = prior_N * likelihood\nposterior_N.normalize()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"And here's what it looks like.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"posterior_N.plot(color='C4')\n\ndecorate(xlabel='Population of bears (N)',\n ylabel='PDF',\n title='Posterior distribution of N')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The most likely value is 109.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"posterior_N.max_prob()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"But the distribution is skewed to the right, so the posterior mean is substantially higher.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"posterior_N.mean()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"And the credible interval is quite wide.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"posterior_N.credible_interval(0.9)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This solution is relatively simple, but it turns out we can do a little better if we model the unknown probability of observing a bear explicitly.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Two Parameter Model\n\nNext we'll try a model with two parameters: the number of bears, `N`, and the probability of observing a bear, `p`.\n\nWe'll assume that the probability is the same in both rounds, which is probably reasonable in this case because it is the same kind of trap in the same place.\n\nWe'll also assume that the probabilities are independent; that is, the probability a bear is observed in the second round does not depend on whether it was observed in the first round. This assumption might be less reasonable, but for now it is a necessary simplification.\n\nHere are the counts again:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"K = 23\nn = 19\nk = 4",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"For this model, I'll express the data in a notation that will make it easier to generalize to more than two rounds: \n\n* `k10` is the number of bears observed in the first round but not the second,\n\n* `k01` is the number of bears observed in the second round but not the first, and\n\n* `k11` is the number of bears observed in both rounds.\n\nHere are their values.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"k10 = 23 - 4\nk01 = 19 - 4\nk11 = 4",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Suppose we know the actual values of `N` and `p`. We can use them to compute the likelihood of this data.\n\nFor example, suppose we know that `N=100` and `p=0.2`.\nWe can use `N` to compute `k00`, which is the number of unobserved bears.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"N = 100\n\nobserved = k01 + k10 + k11\nk00 = N - observed\nk00",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"For the update, it will be convenient to store the data as a list that represents the number of bears in each category.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x = [k00, k01, k10, k11]\nx",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now, if we know `p=0.2`, we can compute the probability a bear falls in each category. For example, the probability of being observed in both rounds is `p*p`, and the probability of being unobserved in both rounds is `q*q` (where `q=1-p`).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"p = 0.2\nq = 1-p\ny = [q*q, q*p, p*q, p*p]\ny",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now the probability of the data is given by the [multinomial distribution](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multinomial_distribution):\n\n$$\\frac{N!}{\\prod x_i!} \\prod y_i^{x_i}$$\n\nwhere $N$ is actual population, $x$ is a sequence with the counts in each category, and $y$ is a sequence of probabilities for each category.\n\nSciPy provides `multinomial`, which provides `pmf`, which computes this probability.\nHere is the probability of the data for these values of `N` and `p`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from scipy.stats import multinomial\n\nlikelihood = multinomial.pmf(x, N, y)\nlikelihood",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"That's the likelihood if we know `N` and `p`, but of course we don't. So we'll choose prior distributions for `N` and `p`, and use the likelihoods to update it. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## The Prior\n\nWe'll use `prior_N` again for the prior distribution of `N`, and a uniform prior for the probability of observing a bear, `p`:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"qs = np.linspace(0, 0.99, num=100)\nprior_p = make_uniform(qs, name='p')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can make a joint distribution in the usual way.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from utils import make_joint\n\njoint_prior = make_joint(prior_p, prior_N)\njoint_prior.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The result is a Pandas `DataFrame` with values of `N` down the rows and values of `p` across the columns.\nHowever, for this problem it will be convenient to represent the prior distribution as a 1-D `Series` rather than a 2-D `DataFrame`.\nWe can convert from one format to the other using `stack`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from empiricaldist import Pmf\n\njoint_pmf = Pmf(joint_prior.stack())\njoint_pmf.head(3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"type(joint_pmf)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"type(joint_pmf.index)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"joint_pmf.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The result is a `Pmf` whose index is a `MultiIndex`.\nA `MultiIndex` can have more than one column; in this example, the first column contains values of `N` and the second column contains values of `p`.\n\nThe `Pmf` has one row (and one prior probability) for each possible pair of parameters `N` and `p`.\nSo the total number of rows is the product of the lengths of `prior_N` and `prior_p`.\n\nNow we have to compute the likelihood of the data for each pair of parameters.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## The Update\n\nTo allocate space for the likelihoods, it is convenient to make a copy of `joint_pmf`:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"likelihood = joint_pmf.copy()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"As we loop through the pairs of parameters, we compute the likelihood of the data as in the previous section, and then store the result as an element of `likelihood`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"observed = k01 + k10 + k11\n\nfor N, p in joint_pmf.index:\n k00 = N - observed\n x = [k00, k01, k10, k11]\n q = 1-p\n y = [q*q, q*p, p*q, p*p]\n likelihood[N, p] = multinomial.pmf(x, N, y)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now we can compute the posterior in the usual way.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"posterior_pmf = joint_pmf * likelihood\nposterior_pmf.normalize()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We'll use `plot_contour` again to visualize the joint posterior distribution.\nBut remember that the posterior distribution we just computed is represented as a `Pmf`, which is a `Series`, and `plot_contour` expects a `DataFrame`.\n\nSince we used `stack` to convert from a `DataFrame` to a `Series`, we can use `unstack` to go the other way.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"joint_posterior = posterior_pmf.unstack()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"And here's what the result looks like.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from utils import plot_contour\n\nplot_contour(joint_posterior)\n\ndecorate(title='Joint posterior distribution of N and p')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The most likely values of `N` are near 100, as in the previous model. The most likely values of `p` are near 0.2.\n\nThe shape of this contour indicates that these parameters are correlated. If `p` is near the low end of the range, the most likely values of `N` are higher; if `p` is near the high end of the range, `N` is lower. \n\nNow that we have a posterior `DataFrame`, we can extract the marginal distributions in the usual way.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from utils import marginal\n\nposterior2_p = marginal(joint_posterior, 0)\nposterior2_N = marginal(joint_posterior, 1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Here's the posterior distribution for `p`:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"posterior2_p.plot(color='C1')\n\ndecorate(xlabel='Probability of observing a bear',\n ylabel='PDF',\n title='Posterior marginal distribution of p')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The most likely values are near 0.2.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Here's the posterior distribution for `N` based on the two-parameter model, along with the posterior we got using the one-parameter (hypergeometric) model.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"posterior_N.plot(label='one-parameter model', color='C4')\nposterior2_N.plot(label='two-parameter model', color='C1')\n\ndecorate(xlabel='Population of bears (N)',\n ylabel='PDF',\n title='Posterior marginal distribution of N')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"With the two-parameter model, the mean is a little lower and the 90% credible interval is a little narrower.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(posterior_N.mean(), \n posterior_N.credible_interval(0.9))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(posterior2_N.mean(), \n posterior2_N.credible_interval(0.9))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The two-parameter model yields a narrower posterior distribution for `N`, compared to the one-parameter model, because it takes advantage of an additional source of information: the consistency of the two observations.\n\nTo see how this helps, consider a scenario where `N` is relatively low, like 138 (the posterior mean of the two-parameter model).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"N1 = 138",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Given that we saw 23 bears during the first trial and 19 during the second, we can estimate the corresponding value of `p`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mean = (23 + 19) / 2\np = mean/N1\np",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"With these parameters, how much variability do you expect in the number of bears from one trial to the next? We can quantify that by computing the standard deviation of the binomial distribution with these parameters.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from scipy.stats import binom\n\nbinom(N1, p).std()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now let's consider a second scenario where `N` is 173, the posterior mean of the one-parameter model. The corresponding value of `p` is lower.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"N2 = 173\np = mean/N2\np",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"In this scenario, the variation we expect to see from one trial to the next is higher.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"binom(N2, p).std()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"So if the number of bears we observe is the same in both trials, that would be evidence for lower values of `N`, where we expect more consistency.\nIf the number of bears is substantially different between the two trials, that would be evidence for higher values of `N`.\n\nIn the actual data, the difference between the two trials is low, which is why the posterior mean of the two-parameter model is lower.\nThe two-parameter model takes advantage of additional information, which is why the credible interval is narrower.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Joint and Marginal Distributions\n\nMarginal distributions are called \"marginal\" because in a common visualization they appear in the margins of the plot.\n\nSeaborn provides a class called `JointGrid` that creates this visualization.\nThe following function uses it to show the joint and marginal distributions in a single plot.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nfrom seaborn import JointGrid\n\ndef joint_plot(joint, **options):\n \"\"\"Show joint and marginal distributions.\n \n joint: DataFrame that represents a joint distribution\n options: passed to JointGrid\n \"\"\"\n # get the names of the parameters\n x = joint.columns.name\n x = 'x' if x is None else x\n\n y = joint.index.name\n y = 'y' if y is None else y\n\n # make a JointGrid with minimal data\n data = pd.DataFrame({x:[0], y:[0]})\n g = JointGrid(x=x, y=y, data=data, **options)\n\n # replace the contour plot\n g.ax_joint.contour(joint.columns, \n joint.index, \n joint, \n cmap='viridis')\n \n # replace the marginals\n marginal_x = marginal(joint, 0)\n g.ax_marg_x.plot(marginal_x.qs, marginal_x.ps)\n \n marginal_y = marginal(joint, 1)\n g.ax_marg_y.plot(marginal_y.ps, marginal_y.qs)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"joint_plot(joint_posterior)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"A `JointGrid` is a concise way to represent the joint and marginal distributions visually.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## The Lincoln Index Problem\n\nIn [an excellent blog post](http://www.johndcook.com/blog/2010/07/13/lincoln-index/), John D. Cook wrote about the Lincoln index, which is a way to estimate the\nnumber of errors in a document (or program) by comparing results from\ntwo independent testers.\nHere's his presentation of the problem:\n\n> \"Suppose you have a tester who finds 20 bugs in your program. You\nwant to estimate how many bugs are really in the program. You know\nthere are at least 20 bugs, and if you have supreme confidence in your\ntester, you may suppose there are around 20 bugs. But maybe your\ntester isn't very good. Maybe there are hundreds of bugs. How can you\nhave any idea how many bugs there are? There's no way to know with one\ntester. But if you have two testers, you can get a good idea, even if\nyou don't know how skilled the testers are.\"\n\nSuppose the first tester finds 20 bugs, the second finds 15, and they\nfind 3 in common; how can we estimate the number of bugs?\n\nThis problem is similar to the Grizzly Bear problem, so I'll represent the data in the same way.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"k10 = 20 - 3\nk01 = 15 - 3\nk11 = 3",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"But in this case it is probably not reasonable to assume that the testers have the same probability of finding a bug.\nSo I'll define two parameters, `p0` for the probability that the first tester finds a bug, and `p1` for the probability that the second tester finds a bug.\n\nI will continue to assume that the probabilities are independent, which is like assuming that all bugs are equally easy to find. That might not be a good assumption, but let's stick with it for now.\n\nAs an example, suppose we know that the probabilities are 0.2 and 0.15.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"p0, p1 = 0.2, 0.15",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can compute the array of probabilities, `y`, like this:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def compute_probs(p0, p1):\n \"\"\"Computes the probability for each of 4 categories.\"\"\"\n q0 = 1-p0\n q1 = 1-p1\n return [q0*q1, q0*p1, p0*q1, p0*p1]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"y = compute_probs(p0, p1)\ny",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"With these probabilities, there is a \n68% chance that neither tester finds the bug and a\n3% chance that both do. \n\nPretending that these probabilities are known, we can compute the posterior distribution for `N`.\nHere's a prior distribution that's uniform from 32 to 350 bugs.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"qs = np.arange(32, 350, step=5) \nprior_N = make_uniform(qs, name='N')\nprior_N.head(3)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"I'll put the data in an array, with 0 as a place-keeper for the unknown value `k00`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data = np.array([0, k01, k10, k11])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"And here are the likelihoods for each value of `N`, with `ps` as a constant.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"likelihood = prior_N.copy()\nobserved = data.sum()\nx = data.copy()\n\nfor N in prior_N.qs:\n x[0] = N - observed\n likelihood[N] = multinomial.pmf(x, N, y)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can compute the posterior in the usual way.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"posterior_N = prior_N * likelihood\nposterior_N.normalize()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"And here's what it looks like.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"posterior_N.plot(color='C4')\n\ndecorate(xlabel='Number of bugs (N)',\n ylabel='PMF',\n title='Posterior marginal distribution of n with known p1, p2')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(posterior_N.mean(), \n posterior_N.credible_interval(0.9))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"With the assumption that `p0` and `p1` are known to be `0.2` and `0.15`, the posterior mean is 102 with 90% credible interval (77, 127).\nBut this result is based on the assumption that we know the probabilities, and we don't.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Three-parameter Model\n\nWhat we need is a model with three parameters: `N`, `p0`, and `p1`.\nWe'll use `prior_N` again for the prior distribution of `N`, and here are the priors for `p0` and `p1`:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"qs = np.linspace(0, 1, num=51)\nprior_p0 = make_uniform(qs, name='p0')\nprior_p1 = make_uniform(qs, name='p1')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now we have to assemble them into a joint prior with three dimensions.\nI'll start by putting the first two into a `DataFrame`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"joint2 = make_joint(prior_p0, prior_N)\njoint2.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now I'll stack them, as in the previous example, and put the result in a `Pmf`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"joint2_pmf = Pmf(joint2.stack())\njoint2_pmf.head(3)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can use `make_joint` again to add in the third parameter.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"joint3 = make_joint(prior_p1, joint2_pmf)\njoint3.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The result is a `DataFrame` with values of `N` and `p0` in a `MultiIndex` that goes down the rows and values of `p1` in an index that goes across the columns.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"joint3.head(3)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now I'll apply `stack` again:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"joint3_pmf = Pmf(joint3.stack())\njoint3_pmf.head(3)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The result is a `Pmf` with a three-column `MultiIndex` containing all possible triplets of parameters.\n\nThe number of rows is the product of the number of values in all three priors, which is almost 170,000.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"joint3_pmf.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"That's still small enough to be practical, but it will take longer to compute the likelihoods than in the previous examples.\n\nHere's the loop that computes the likelihoods; it's similar to the one in the previous section:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"likelihood = joint3_pmf.copy()\nobserved = data.sum()\nx = data.copy()\n\nfor N, p0, p1 in joint3_pmf.index:\n x[0] = N - observed\n y = compute_probs(p0, p1)\n likelihood[N, p0, p1] = multinomial.pmf(x, N, y)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can compute the posterior in the usual way.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"posterior_pmf = joint3_pmf * likelihood\nposterior_pmf.normalize()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now, to extract the marginal distributions, we could unstack the joint posterior as we did in the previous section.\nBut `Pmf` provides a version of `marginal` that works with a `Pmf` rather than a `DataFrame`.\nHere's how we use it to get the posterior distribution for `N`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"posterior_N = posterior_pmf.marginal(0)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"And here's what it looks look.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"posterior_N.plot(color='C4')\n\ndecorate(xlabel='Number of bugs (N)',\n ylabel='PDF',\n title='Posterior marginal distributions of N')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"posterior_N.mean()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The posterior mean is 105 bugs, which suggests that there are still many bugs the testers have not found.\n\nHere are the posteriors for `p0` and `p1`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"posterior_p1 = posterior_pmf.marginal(1)\nposterior_p2 = posterior_pmf.marginal(2)\n\nposterior_p1.plot(label='p1')\nposterior_p2.plot(label='p2')\n\ndecorate(xlabel='Probability of finding a bug',\n ylabel='PDF',\n title='Posterior marginal distributions of p1 and p2')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"posterior_p1.mean(), posterior_p1.credible_interval(0.9)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"posterior_p2.mean(), posterior_p2.credible_interval(0.9)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Comparing the posterior distributions, the tester who found more bugs probably has a higher probability of finding bugs. The posterior means are about 23% and 18%. But the distributions overlap, so we should not be too sure.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"This is the first example we've seen with three parameters.\nAs the number of parameters increases, the number of combinations increases quickly.\nThe method we've been using so far, enumerating all possible combinations, becomes impractical if the number of parameters is more than 3 or 4.\n\nHowever there are other methods that can handle models with many more parameters, as we'll see in <<_MCMC>>.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Summary\n\nThe problems in this chapter are examples of [mark and recapture](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mark_and_recapture) experiments, which are used in ecology to estimate animal populations. They also have applications in engineering, as in the Lincoln index problem. And in the exercises you'll see that they are used in epidemiology, too.\n\nThis chapter introduces two new probability distributions:\n\n* The hypergeometric distribution is a variation of the binomial distribution in which samples are drawn from the population without replacement. \n\n* The multinomial distribution is a generalization of the binomial distribution where there are more than two possible outcomes.\n\nAlso in this chapter, we saw the first example of a model with three parameters. We'll see more in subsequent chapters.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Exercises",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Exercise:** [In an excellent paper](http://chao.stat.nthu.edu.tw/wordpress/paper/110.pdf), Anne Chao explains how mark and recapture experiments are used in epidemiology to estimate the prevalence of a disease in a human population based on multiple incomplete lists of cases.\n\nOne of the examples in that paper is a study \"to estimate the number of people who were infected by hepatitis in an outbreak that occurred in and around a college in northern Taiwan from April to July 1995.\"\n\nThree lists of cases were available:\n\n1. 135 cases identified using a serum test. \n\n2. 122 cases reported by local hospitals. \n\n3. 126 cases reported on questionnaires collected by epidemiologists.\n\nIn this exercise, we'll use only the first two lists; in the next exercise we'll bring in the third list.\n\nMake a joint prior and update it using this data, then compute the posterior mean of `N` and a 90% credible interval.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The following array contains 0 as a place-holder for the unknown value of `k00`, followed by known values of `k01`, `k10`, and `k11`. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data2 = np.array([0, 73, 86, 49])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"These data indicate that there are 73 cases on the second list that are not on the first, 86 cases on the first list that are not on the second, and 49 cases on both lists.\n\nTo keep things simple, we'll assume that each case has the same probability of appearing on each list. So we'll use a two-parameter model where `N` is the total number of cases and `p` is the probability that any case appears on any list.\n\nHere are priors you can start with (but feel free to modify them).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"qs = np.arange(200, 500, step=5)\nprior_N = make_uniform(qs, name='N')\nprior_N.head(3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"qs = np.linspace(0, 0.98, num=50)\nprior_p = make_uniform(qs, name='p')\nprior_p.head(3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Solution goes here",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Solution goes here",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Solution goes here",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Solution goes here",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Solution goes here",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Solution goes here",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Solution goes here",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Solution goes here",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Exercise:** Now let's do the version of the problem with all three lists. Here's the data from Chou's paper:\n\n```\nHepatitis A virus list\nP Q E Data\n1 1 1 k111 =28\n1 1 0 k110 =21\n1 0 1 k101 =17\n1 0 0 k100 =69\n0 1 1 k011 =18\n0 1 0 k010 =55\n0 0 1 k001 =63\n0 0 0 k000 =??\n```\n\nWrite a loop that computes the likelihood of the data for each pair of parameters, then update the prior and compute the posterior mean of `N`. How does it compare to the results using only the first two lists?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Here's the data in a NumPy array (in reverse order).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data3 = np.array([0, 63, 55, 18, 69, 17, 21, 28])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Again, the first value is a place-keeper for the unknown `k000`. The second value is `k001`, which means there are 63 cases that appear on the third list but not the first two. And the last value is `k111`, which means there are 28 cases that appear on all three lists.\n\nIn the two-list version of the problem we computed `ps` by enumerating the combinations of `p` and `q`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"q = 1-p\nps = [q*q, q*p, p*q, p*p]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We could do the same thing for the three-list version, computing the probability for each of the eight categories. But we can generalize it by recognizing that we are computing the cartesian product of `p` and `q`, repeated once for each list.\n\nAnd we can use the following function (based on [this StackOverflow answer](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/58242078/cartesian-product-of-arbitrary-lists-in-pandas/58242079#58242079)) to compute Cartesian products:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def cartesian_product(*args, **options):\n \"\"\"Cartesian product of sequences.\n \n args: any number of sequences\n options: passes to `MultiIndex.from_product`\n \n returns: DataFrame with one column per sequence\n \"\"\"\n index = pd.MultiIndex.from_product(args, **options)\n return pd.DataFrame(index=index).reset_index()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Here's an example with `p=0.2`:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"p = 0.2\nt = (1-p, p)\ndf = cartesian_product(t, t, t)\ndf",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"To compute the probability for each category, we take the product across the columns:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"y = df.prod(axis=1)\ny",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now you finish it off from there.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Solution goes here",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Solution goes here",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Solution goes here",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Solution goes here",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Solution goes here",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Solution goes here",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Solution goes here",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Solution goes here",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a737503936b6fc13acc763d2821e41ed85bc9b7
| 24,197 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
README.ipynb
|
c-feldmann/UniProtAPI
|
817aefd040ab5436243cfc21cbfebdddcd3aea4d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
README.ipynb
|
c-feldmann/UniProtAPI
|
817aefd040ab5436243cfc21cbfebdddcd3aea4d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
README.ipynb
|
c-feldmann/UniProtAPI
|
817aefd040ab5436243cfc21cbfebdddcd3aea4d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 32.479195 | 257 | 0.438691 |
[
[
[
"# UniProtClient\nPython classes in this package allow convenient access to [UniProt](https://www.uniprot.org/) for protein ID mapping and information retrieval.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Installation in Conda\nIf not already installed, install **pip** and **git**: \n```\nconda install git\nconda install pip\n```\nThen install via pip:\n```\npip install git+git://github.com/c-feldmann/UniProtClient\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Usage\n### Mapping\nProtein IDs differ from database to database. The class *UniProtMapper* can be utilized for mapping of protein IDs from one database to corresponding IDs of another database, specified by [letter codes](https://www.uniprot.org/help/api_idmapping). ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from UniProtClient import UniProtMapper\norigin_database = 'P_GI' # PubChem Gene ID\ntarget_database = 'ACC' # UniProt Accession\ngi_2_acc_mappig = UniProtMapper(origin_database, target_database)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The obtained object has a function called `map_protein_ids`, which takes a list of strings with protein IDs as input, returning a pandas DataFrame. The DataFrame has two columns: \"From\" and \"To\" referring to the origin and target ID, respectively.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"gi_numbers = ['224586929', '224586929', '4758208'] # IDs should be represented as a list of strings\n# a pandas DataFrame is returned containing the columns \"From\" and \"To\"\nmapping_df = gi_2_acc_mappig.map_protein_ids(gi_numbers)\nuniprot_accessions = mapping_df['To'].tolist()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mapping_df",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Protein information\nUniProt provides a varity of protein specific information, such as protein family, organism, function, EC-number, and many more.\nThe class *UniProtProteinInfo* is initialized with [column identifier](https://www.uniprot.org/help/uniprotkb%5Fcolumn%5Fnames) specifing the requested information. Spaces in column names should be substituted by underscores. \nIf no columns are specified the default is used:\n\n| Column-ID |\n|:------:|\n| id |\n| entry_name |\n| protein_names |\n| families |\n| organism |\n| ec |\n| genes(PREFERRED) |\n| go(molecular_function) |\n\nThe column \"protein_names\" contains all protein names, where secondary names are given in brackets or parenthesis. If this column is requested, the primary name is extracted and added as a new column, called \"primary_name\".",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from UniProtClient import UniProtProteinInfo\ninfo = UniProtProteinInfo()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"info.load_protein_info([\"B4DZW8\", \"Q9Y2R2\", \"P51452\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Protein Families\nIf downloaded, the string 'protein_families' is parsed automatically. It is split into the categories subfamily, family\nand superfamily.\nSome proteins belong to multiple families. The default behaviour is to extract the individual categories and merge them\ninto a `; ` seperated string.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Extending column with. Not important for extraction.\nimport pandas as pd\npd.set_option('max_colwidth', 400)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"info = UniProtProteinInfo(merge_multi_fam_associations=\"string\") # Default behaviour\ninfo.load_protein_info([\"Q923J1\"])[[\"organism\", \"subfamily\", \"family\", \"superfamily\"]]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Setting `merge_multi_fam_associations` to `'list'` will arrange each family association in a list. To keep types consitent this applies to protiens with only one family as well.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"info = UniProtProteinInfo(merge_multi_fam_associations=\"list\") # Default behaviour\ninfo.load_protein_info([\"Q923J1\", \"Q9Y2R2\"])[[\"organism\", \"subfamily\", \"family\", \"superfamily\"]]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
" Setting `merge_multi_fam_associations` to `None` will create for each family association an\nindividual row where remaining protein information are identical.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"info = UniProtProteinInfo(merge_multi_fam_associations=None)\ninfo.load_protein_info([\"Q923J1\"])[[\"organism\", \"subfamily\", \"family\", \"superfamily\"]]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a73837750d114135784a6cfced4e0f45cf568e2
| 72,147 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
courses/machine_learning/deepdive2/introduction_to_tensorflow/labs/write_low_level_code.ipynb
|
KayvanShah1/training-data-analyst
|
3f778a57b8e6d2446af40ca6063b2fd9c1b4bc88
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 6,140 |
2016-05-23T16:09:35.000Z
|
2022-03-30T19:00:46.000Z
|
courses/machine_learning/deepdive2/introduction_to_tensorflow/labs/write_low_level_code.ipynb
|
KayvanShah1/training-data-analyst
|
3f778a57b8e6d2446af40ca6063b2fd9c1b4bc88
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1,384 |
2016-07-08T22:26:41.000Z
|
2022-03-24T16:39:43.000Z
|
courses/machine_learning/deepdive2/introduction_to_tensorflow/labs/write_low_level_code.ipynb
|
KayvanShah1/training-data-analyst
|
3f778a57b8e6d2446af40ca6063b2fd9c1b4bc88
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 5,110 |
2016-05-27T13:45:18.000Z
|
2022-03-31T18:40:42.000Z
| 75.388715 | 21,393 | 0.820478 |
[
[
[
"# Writing Low-Level TensorFlow Code\n\n\n**Learning Objectives**\n\n 1. Practice defining and performing basic operations on constant Tensors\n 2. Use Tensorflow's automatic differentiation capability\n 3. Learn how to train a linear regression from scratch with TensorFLow\n\n\n## Introduction \n\nIn this notebook, we will start by reviewing the main operations on Tensors in TensorFlow and understand how to manipulate TensorFlow Variables. We explain how these are compatible with python built-in list and numpy arrays. \n\nThen we will jump to the problem of training a linear regression from scratch with gradient descent. The first order of business will be to understand how to compute the gradients of a function (the loss here) with respect to some of its arguments (the model weights here). The TensorFlow construct allowing us to do that is `tf.GradientTape`, which we will describe. \n\nAt last we will create a simple training loop to learn the weights of a 1-dim linear regression using synthetic data generated from a linear model. \n\nAs a bonus exercise, we will do the same for data generated from a non linear model, forcing us to manual engineer non-linear features to improve our linear model performance.\n\nEach learning objective will correspond to a __#TODO__ in this student lab notebook -- try to complete this notebook first and then review the [solution notebook](https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/training-data-analyst/blob/master/courses/machine_learning/deepdive2/introduction_to_tensorflow/solutions/write_low_level_code.ipynb)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nfrom matplotlib import pyplot as plt\nimport tensorflow as tf",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(tf.__version__)",
"2.5.0\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Operations on Tensors",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Variables and Constants",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Tensors in TensorFlow are either contant (`tf.constant`) or variables (`tf.Variable`).\nConstant values can not be changed, while variables values can be.\n\nThe main difference is that instances of `tf.Variable` have methods allowing us to change \ntheir values while tensors constructed with `tf.constant` don't have these methods, and\ntherefore their values can not be changed. When you want to change the value of a `tf.Variable`\n`x` use one of the following method: \n\n* `x.assign(new_value)`\n* `x.assign_add(value_to_be_added)`\n* `x.assign_sub(value_to_be_subtracted`\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x = tf.constant([2, 3, 4])\nx",
"<tf.Tensor: shape=(3,), dtype=int32, numpy=array([2, 3, 4], dtype=int32)>\n"
],
[
"x = tf.Variable(2.0, dtype=tf.float32, name='my_variable')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x.assign(45.8)\nx",
"<tf.Variable 'my_variable:0' shape=() dtype=float32, numpy=45.8>\n"
],
[
"x.assign_add(4) \nx",
"<tf.Variable 'my_variable:0' shape=() dtype=float32, numpy=49.8>\n"
],
[
"x.assign_sub(3)\nx",
"<tf.Variable 'my_variable:0' shape=() dtype=float32, numpy=46.8>\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Point-wise operations",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Tensorflow offers similar point-wise tensor operations as numpy does:\n \n* `tf.add` allows to add the components of a tensor \n* `tf.multiply` allows us to multiply the components of a tensor\n* `tf.subtract` allow us to substract the components of a tensor\n* `tf.math.*` contains the usual math operations to be applied on the components of a tensor\n* and many more...\n\nMost of the standard arithmetic operations (`tf.add`, `tf.substrac`, etc.) are overloaded by the usual corresponding arithmetic symbols (`+`, `-`, etc.)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Lab Task #1:** Performing basic operations on Tensors \n1. In the first cell, define two constants `a` and `b` and compute their sum in c and d respectively, below using `tf.add` and `+` and verify both operations produce the same values.\n2. In the second cell, compute the product of the constants `a` and `b` below using `tf.multiply` and `*` and verify both operations produce the same values.\n3. In the third cell, compute the exponential of the constant `a` using `tf.math.exp`. Note, you'll need to specify the type for this operation.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# TODO 1a\na = # TODO -- Your code here.\nb = # TODO -- Your code here.\nc = # TODO -- Your code here.\nd = # TODO -- Your code here.\n\nprint(\"c:\", c)\nprint(\"d:\", d)",
"c: tf.Tensor([ 8 2 10], shape=(3,), dtype=int32)\nd: tf.Tensor([ 8 2 10], shape=(3,), dtype=int32)\n"
],
[
"# TODO 1b\na = # TODO -- Your code here.\nb = # TODO -- Your code here.\nc = # TODO -- Your code here.\nd = # TODO -- Your code here.\n\nprint(\"c:\", c)\nprint(\"d:\", d)",
"c: tf.Tensor([15 -3 16], shape=(3,), dtype=int32)\nd: tf.Tensor([15 -3 16], shape=(3,), dtype=int32)\n"
],
[
"# TODO 1c\n# tf.math.exp expects floats so we need to explicitly give the type\na = # TODO -- Your code here.\nb = # TODO -- Your code here.\n\nprint(\"b:\", b)",
"b: tf.Tensor([ 148.41316 20.085537 2980.958 ], shape=(3,), dtype=float32)\n"
]
],
[
[
"### NumPy Interoperability\n\nIn addition to native TF tensors, tensorflow operations can take native python types and NumPy arrays as operands. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# native python list\na_py = [1, 2] \nb_py = [3, 4] ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tf.add(a_py, b_py)",
"<tf.Tensor: shape=(2,), dtype=int32, numpy=array([4, 6], dtype=int32)>\n"
],
[
"# numpy arrays\na_np = np.array([1, 2])\nb_np = np.array([3, 4])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tf.add(a_np, b_np) ",
"<tf.Tensor: shape=(2,), dtype=int64, numpy=array([4, 6])>\n"
],
[
"# native TF tensor\na_tf = tf.constant([1, 2])\nb_tf = tf.constant([3, 4])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tf.add(a_tf, b_tf)",
"<tf.Tensor: shape=(2,), dtype=int32, numpy=array([4, 6], dtype=int32)>\n"
]
],
[
[
"You can convert a native TF tensor to a NumPy array using .numpy()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"a_tf.numpy()",
"array([1, 2], dtype=int32)\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Linear Regression\n\nNow let's use low level tensorflow operations to implement linear regression.\n\nLater in the course you'll see abstracted ways to do this using high level TensorFlow.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Toy Dataset\n\nWe'll model the following function:\n\n\\begin{equation}\ny= 2x + 10\n\\end{equation}",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"X = tf.constant(range(10), dtype=tf.float32)\nY = 2 * X + 10\n\nprint(\"X:{}\".format(X))\nprint(\"Y:{}\".format(Y))",
"X:[0. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9.]\nY:[10. 12. 14. 16. 18. 20. 22. 24. 26. 28.]\n"
]
],
[
[
"Let's also create a test dataset to evaluate our models:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"X_test = tf.constant(range(10, 20), dtype=tf.float32)\nY_test = 2 * X_test + 10\n\nprint(\"X_test:{}\".format(X_test))\nprint(\"Y_test:{}\".format(Y_test))",
"X_test:[10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19.]\nY_test:[30. 32. 34. 36. 38. 40. 42. 44. 46. 48.]\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### Loss Function",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The simplest model we can build is a model that for each value of x returns the sample mean of the training set:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"y_mean = Y.numpy().mean()\n\n\ndef predict_mean(X):\n y_hat = [y_mean] * len(X)\n return y_hat\n\nY_hat = predict_mean(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Using mean squared error, our loss is:\n\\begin{equation}\nMSE = \\frac{1}{m}\\sum_{i=1}^{m}(\\hat{Y}_i-Y_i)^2\n\\end{equation}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"For this simple model the loss is then:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"errors = (Y_hat - Y)**2\nloss = tf.reduce_mean(errors)\nloss.numpy()",
"33.0\n"
]
],
[
[
"This values for the MSE loss above will give us a baseline to compare how a more complex model is doing.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Now, if $\\hat{Y}$ represents the vector containing our model's predictions when we use a linear regression model\n\\begin{equation}\n\\hat{Y} = w_0X + w_1\n\\end{equation}\n\nwe can write a loss function taking as arguments the coefficients of the model:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def loss_mse(X, Y, w0, w1):\n Y_hat = w0 * X + w1\n errors = (Y_hat - Y)**2\n return tf.reduce_mean(errors)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Gradient Function\n\nTo use gradient descent we need to take the partial derivatives of the loss function with respect to each of the weights. We could manually compute the derivatives, but with Tensorflow's automatic differentiation capabilities we don't have to!\n\nDuring gradient descent we think of the loss as a function of the parameters $w_0$ and $w_1$. Thus, we want to compute the partial derivative with respect to these variables. \n\nFor that we need to wrap our loss computation within the context of `tf.GradientTape` instance which will record gradient information:\n\n```python\nwith tf.GradientTape() as tape:\n loss = # computation \n```\n\nThis will allow us to later compute the gradients of any tensor computed within the `tf.GradientTape` context with respect to instances of `tf.Variable`:\n\n```python\ngradients = tape.gradient(loss, [w0, w1])\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We illustrate this procedure by computing the loss gradients with respect to the model weights:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Lab Task #2:** Complete the function below to compute the loss gradients with respect to the model weights `w0` and `w1`. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# TODO 2\ndef compute_gradients(X, Y, w0, w1):\n # TODO -- Your code here.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"w0 = tf.Variable(0.0)\nw1 = tf.Variable(0.0)\n\ndw0, dw1 = compute_gradients(X, Y, w0, w1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(\"dw0:\", dw0.numpy())",
"dw0: -204.0\n"
],
[
"print(\"dw1\", dw1.numpy())",
"dw1 -38.0\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Training Loop\n\nHere we have a very simple training loop that converges. Note we are ignoring best practices like batching, creating a separate test set, and random weight initialization for the sake of simplicity.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Lab Task #3:** Complete the `for` loop below to train a linear regression. \n1. Use `compute_gradients` to compute `dw0` and `dw1`.\n2. Then, re-assign the value of `w0` and `w1` using the `.assign_sub(...)` method with the computed gradient values and the `LEARNING_RATE`.\n3. Finally, for every 100th step , we'll compute and print the `loss`. Use the `loss_mse` function we created above to compute the `loss`. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# TODO 3\nSTEPS = 1000\nLEARNING_RATE = .02\nMSG = \"STEP {step} - loss: {loss}, w0: {w0}, w1: {w1}\\n\"\n\n\nw0 = tf.Variable(0.0)\nw1 = tf.Variable(0.0)\n\n\nfor step in range(0, STEPS + 1):\n\n dw0, dw1 = # TODO -- Your code here.\n\n if step % 100 == 0:\n loss = # TODO -- Your code here.\n print(MSG.format(step=step, loss=loss, w0=w0.numpy(), w1=w1.numpy()))\n",
"STEP 0 - loss: 35.70719528198242, w0: 4.079999923706055, w1: 0.7599999904632568\nSTEP 100 - loss: 2.6017532348632812, w0: 2.4780430793762207, w1: 7.002389907836914\nSTEP 200 - loss: 0.26831889152526855, w0: 2.153517961502075, w1: 9.037351608276367\nSTEP 300 - loss: 0.027671903371810913, w0: 2.0493006706237793, w1: 9.690855979919434\nSTEP 400 - loss: 0.0028539239428937435, w0: 2.0158326625823975, w1: 9.90071964263916\nSTEP 500 - loss: 0.0002943490108009428, w0: 2.005084753036499, w1: 9.96811580657959\nSTEP 600 - loss: 3.0356444767676294e-05, w0: 2.0016329288482666, w1: 9.989760398864746\nSTEP 700 - loss: 3.1322738323069643e-06, w0: 2.0005245208740234, w1: 9.996710777282715\nSTEP 800 - loss: 3.2238213520940917e-07, w0: 2.0001683235168457, w1: 9.998944282531738\nSTEP 900 - loss: 3.369950718479231e-08, w0: 2.000054359436035, w1: 9.999658584594727\nSTEP 1000 - loss: 3.6101481803996194e-09, w0: 2.0000178813934326, w1: 9.99988842010498\n"
]
],
[
[
"Now let's compare the test loss for this linear regression to the test loss from the baseline model that outputs always the mean of the training set:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"loss = loss_mse(X_test, Y_test, w0, w1)\nloss.numpy()",
"2.4563633e-08\n"
]
],
[
[
"This is indeed much better!",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Bonus",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Try modeling a non-linear function such as: $y=xe^{-x^2}$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"X = tf.constant(np.linspace(0, 2, 1000), dtype=tf.float32)\nY = X * tf.exp(-X**2)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%matplotlib inline\n\nplt.plot(X, Y)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def make_features(X):\n f1 = tf.ones_like(X) # Bias.\n f2 = X\n f3 = tf.square(X)\n f4 = tf.sqrt(X)\n f5 = tf.exp(X)\n return tf.stack([f1, f2, f3, f4, f5], axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def predict(X, W):\n return tf.squeeze(X @ W, -1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def loss_mse(X, Y, W):\n Y_hat = predict(X, W)\n errors = (Y_hat - Y)**2\n return tf.reduce_mean(errors)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def compute_gradients(X, Y, W):\n with tf.GradientTape() as tape:\n loss = loss_mse(Xf, Y, W)\n return tape.gradient(loss, W)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"STEPS = 2000\nLEARNING_RATE = .02\n\n\nXf = make_features(X)\nn_weights = Xf.shape[1]\n\nW = tf.Variable(np.zeros((n_weights, 1)), dtype=tf.float32)\n\n# For plotting\nsteps, losses = [], []\nplt.figure()\n\n\nfor step in range(1, STEPS + 1):\n\n dW = compute_gradients(X, Y, W)\n W.assign_sub(dW * LEARNING_RATE)\n\n if step % 100 == 0:\n loss = loss_mse(Xf, Y, W)\n steps.append(step)\n losses.append(loss)\n plt.clf()\n plt.plot(steps, losses)\n\n\nprint(\"STEP: {} MSE: {}\".format(STEPS, loss_mse(Xf, Y, W)))\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# The .figure() method will create a new figure, or activate an existing figure.\nplt.figure()\n# The .plot() is a versatile function, and will take an arbitrary number of arguments. For example, to plot x versus y.\nplt.plot(X, Y, label='actual')\nplt.plot(X, predict(Xf, W), label='predicted')\n# The .legend() method will place a legend on the axes.\nplt.legend()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Copyright 2021 Google Inc. Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the \"License\"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an \"AS IS\" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a7383ad95ca37180a6509926a54033f606a6431
| 689,965 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
state_of_the_union_analysis-p2.ipynb
|
omidzargham/state-of-the-union-analysis
|
fd258f1e92fcc915a9480247c70873a2035f4ee5
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
state_of_the_union_analysis-p2.ipynb
|
omidzargham/state-of-the-union-analysis
|
fd258f1e92fcc915a9480247c70873a2035f4ee5
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
state_of_the_union_analysis-p2.ipynb
|
omidzargham/state-of-the-union-analysis
|
fd258f1e92fcc915a9480247c70873a2035f4ee5
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 876.702668 | 360,002 | 0.937821 |
[
[
[
"# An analysis of the State of the Union speeches - Part 2",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%matplotlib inline\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport seaborn as sns\nfrom string import punctuation\nfrom nltk import punkt, word_tokenize, sent_tokenize\nfrom nltk.corpus import stopwords\nfrom nltk.stem import SnowballStemmer\nfrom collections import Counter\nimport shelve\n\nplt.style.use('seaborn-dark')\nplt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (10, 6)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's start by loading some of the data created in the previous part, so we can continue where we left off:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"addresses = pd.read_hdf('results/df1.h5', 'addresses')\nwith shelve.open('results/vars1') as db:\n speeches = db['speeches']",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's double-check that we're getting the full set of speeches:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(addresses.shape)\nprint(len(speeches))",
"(227, 3)\n227\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Basic text analysis\n\nLet's ask a few basic questions about this text, by populating our `addresses` dataframe with some extra information. As a reminder, so far we have:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"addresses.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now, let's add the following information to this DF:\n\n* `n_words`: number of words in the speech\n* `n_uwords`: number of *unique* words in the speech\n* `n_swords`: number of *unique, stemmed* words in the speech\n* `n_chars`: number of letters in the speech\n* `n_sent`: number of sentences in the speech\n\nFor this level of complexity, it's probably best if we go with NLTK. Remember, that `speeches` is our list with all the speeches, indexed in the same way as the `addresses` dataframe:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def tokenize_word(doc):\n \"\"\"word tokenizer\n \n Parameters\n ----------\n doc : string\n A document to be tokenized\n \n Returns\n -------\n tokens\n \"\"\"\n tokens = [token.lower() for token in word_tokenize(doc)]\n return tokens",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def clean_word_tokenize(doc):\n \"\"\"custom word toenizer which removes stop words and punctuation\n \n Parameters\n ----------\n doc : string\n A document to be tokenized\n \n Returns\n -------\n tokens\n \"\"\"\n stop = stopwords.words(\"english\") + list(punctuation)\n tokens = [token.lower() for token in word_tokenize(doc)\n if token not in stop]\n return tokens",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now we compute these quantities for each speech, as well as saving the set of unique, stemmed words for each speech, which we'll need later to construct the complete term-document matrix across all speeches.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"n_sent = []\nn_words_all=[]\nn_uwords=[]\nn_chars = []\nn_words=[]\nn_swords=[]\nstemmer = SnowballStemmer('english')\nspeeches_cleaned = []\nspeech_words = []\n# go through our list of speeches and compute these metrics for each speech\nfor speech in speeches:\n stemmed = []\n #all characters in speech\n n_chars.append(len(speech))\n #unique words before removing stop words and punctuation\n tokens_all = tokenize_word(speech)\n tokens_all_counter = Counter(tokens_all)\n #number of sentences\n sent_tokens = sent_tokenize(speech)\n n_sent.append(len(sent_tokens))\n #add all words before removing stop words and punctuation\n n_words_all.append(len(tokens_all))\n \n #words with stop words and punctuation removed\n tokens = clean_word_tokenize(speech)\n tokens_counter = Counter(tokens)\n n_words.append(len(tokens))\n #unique words with stop words and punctuation removed\n n_uwords.append(len(tokens_counter.values()))\n \n #stemmed words\n for token in tokens:\n s = stemmer.stem(token.lower())\n stemmed.append(s)\n #unique, stemmed words\n stemmed_counter = Counter(stemmed)\n #save our unique stemmed words into speech_words for later use\n speech_words.append(list(stemmed_counter.keys()))\n #save our stemmed (non-unique) words into speeches_cleaned for later use\n speeches_cleaned.append(stemmed)\n #number of unique stemmed words\n n_swords.append(len(stemmed_counter))\n\n#save these values into our addresses dataframe\naddresses['n_sent'] = pd.Series(n_sent)\naddresses['n_words_all'] = pd.Series(n_words_all) \naddresses['n_words'] = pd.Series(n_words)\naddresses['n_uwords'] = pd.Series(n_uwords)\naddresses['n_swords'] = pd.Series(n_swords)\naddresses['n_chars'] = pd.Series(n_chars)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#a look at our updated dataframe\npd.options.display.precision = 0\naddresses.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's look at a summary of these ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pd.options.display.precision = 2\naddresses.describe()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Visualizing characteristics of the speeches\n\nNow we explore some of the relationships between the speeches, their authors, and time.\n\nHow properties of the speeches change over time.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# plot of how changes speech over time\nchangeintime=pd.DataFrame(addresses['date'])\nchangeintime['n_sent']=np.log(addresses.n_sent)\nchangeintime['n_words']=np.log(addresses.n_words)\nchangeintime['n_words_pervocb']= (addresses.n_uwords) / (addresses.n_words)\nchangeintime['avgsent_length']= (addresses.n_words) / (addresses.n_sent)\nchangeintime['avgword_length']= (addresses.n_chars) / (addresses.n_words)\nchangeintime['fra_stopword']= (addresses.n_words_all - addresses.n_words) / addresses.n_words\n\nchangeintime.index= changeintime.date\nchangeintime = changeintime.drop('date',axis=1)\n\nfig,axes= plt.subplots(3,2,figsize=(25,20), sharex= True)\nfig.suptitle('Change in speech characteristics over time')\n\naxes[0,0].plot_date(x=changeintime.index, y= changeintime.n_sent, linestyle='solid', marker='None')\naxes[0,0].set_title('Log number of sentences')\naxes[0,0].set_ylabel(\"Log number of sentences\")\naxes[0,0].set_xlabel(\"Date\")\naxes[0,1].plot_date(x=changeintime.index, y= changeintime.n_words, linestyle='solid', marker='None')\naxes[0,1].set_title('Log number of words')\naxes[0,1].set_ylabel(\"Log number of words\")\naxes[0,1].set_xlabel(\"Date\")\naxes[1,0].plot_date(x=changeintime.index, y= changeintime.n_words_pervocb, linestyle='solid', marker='None')\naxes[1,0].set_title('Vocabulary size per word')\naxes[1,0].set_ylabel(\"Vocabulary size per word\")\naxes[1,0].set_xlabel(\"Date\")\naxes[1,1].plot_date(x=changeintime.index, y= changeintime.avgsent_length, linestyle='solid', marker='None')\naxes[1,1].set_title('Average sentence length')\naxes[1,1].set_ylabel(\"Average sentence length\")\naxes[1,1].set_xlabel(\"Date\")\naxes[2,0].plot_date(x=changeintime.index, y= changeintime.avgword_length, linestyle='solid', marker='None')\naxes[2,0].set_title('Average word length')\naxes[2,0].set_ylabel(\"Average word length\")\naxes[2,0].set_xlabel(\"Date\")\naxes[2,1].plot_date(x=changeintime.index, y= changeintime.fra_stopword, linestyle='solid', marker='None')\naxes[2,1].set_title('Fraction of stop words')\naxes[2,1].set_ylabel(\"Fraction of stop words\")\naxes[2,1].set_xlabel(\"Date\")\n\nplt.savefig(\"fig/speech_changes.png\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"These charts clearly suggest that the average word and average sentence lengths for the State of the Union speeches have decreased over time, as evidenced by the steady drop in their respective values on their plots. This drop is consistent with what we can expect based on historical trends of the English language. Interestingly, the fraction of stop words has decreased on average as well. Taking the log of the number of words and sentences in each speech, we can see a substantial increase for roughly the first 30 years, while the vocabulary size of each word experienced the opposite. After this period, there is a great deal of variation so we are unable to discern a clear pattern in that data.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Now for the distributions by president",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# violin plots by president instead of over time\npresidentdis= pd.DataFrame(addresses.president)\npresidentdis['n_sent']=np.log(addresses.n_sent)\npresidentdis['n_words']=np.log(addresses.n_words)\npresidentdis['n_words_pervocb']= (addresses.n_uwords) / (addresses.n_words)\npresidentdis['avgsent_length']= (addresses.n_words) / (addresses.n_sent)\npresidentdis['avgword_length']= (addresses.n_chars) / (addresses.n_words)\npresidentdis['fra_stopword']= (addresses.n_words_all - addresses.n_words) / addresses.n_words\n\nfig,axes= plt.subplots(3,2,figsize=(25,20), sharex= True)\nfig.suptitle('Speech characteristics by President')\n\nsns.violinplot(x='president', y='n_sent', data= presidentdis , ax=axes[0,0])\naxes[0,0].set_title('Log number of sentences')\naxes[0,0].set_ylabel(\"Log number of sentences\")\naxes[0,0].set_xlabel(\"president\")\nplt.setp( axes[0,0].xaxis.get_majorticklabels(), rotation=90)\n\nsns.violinplot(x='president', y='n_words', data= presidentdis , ax=axes[0,1])\naxes[0,1].set_title('Log number of words')\naxes[0,1].set_ylabel(\"Log number of words\")\naxes[0,1].set_xlabel(\"president\")\nplt.setp( axes[0,1].xaxis.get_majorticklabels(), rotation=90)\n\nsns.violinplot(x='president', y='n_words_pervocb', data= presidentdis , ax=axes[1,0])\naxes[1,0].set_title('Vocabulary size per word')\naxes[1,0].set_ylabel(\"Vocabulary size per word\")\naxes[1,0].set_xlabel(\"president\")\nplt.setp( axes[1,0].xaxis.get_majorticklabels(), rotation=90)\n\nsns.violinplot(x='president', y='avgsent_length', data= presidentdis , ax=axes[1,1])\naxes[1,1].set_title('Average sentence length')\naxes[1,1].set_ylabel(\"Average sentence length\")\naxes[1,1].set_xlabel(\"president\")\nplt.setp( axes[1,1].xaxis.get_majorticklabels(), rotation=90)\n\nsns.violinplot(x='president', y='avgword_length', data= presidentdis , ax=axes[2,0])\naxes[2,0].set_title('Average word length')\naxes[2,0].set_ylabel(\"Average word length\")\naxes[2,0].set_xlabel(\"president\")\nplt.setp( axes[2,0].xaxis.get_majorticklabels(), rotation=90)\n\nsns.violinplot(x='president', y='fra_stopword', data= presidentdis , ax=axes[2,1])\naxes[2,1].set_title('Fraction of stop words')\naxes[2,1].set_ylabel(\"Fraction of stop words\")\naxes[2,1].set_xlabel(\"president\")\nplt.setp( axes[2,1].xaxis.get_majorticklabels(), rotation=90)\n\nplt.savefig(\"fig/speech_characteristics.png\");",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"By changing the x axis from time to presidents, we are able to see the data more discretely in that it is easier to see the data as partitions based on each president's induvidual speeches frozen in time. Displaying the previous plots as violin plot also revealed one particular president's speeches as an outlier - Herbert Hoover. Digging into the text of his speeches, we noticed that he tended to reference numbers and figures in his speeches far more often than other presidents, which led to the glaring distinction in the data for the average length and number of characters in each word. The violin plots also reveal flat lines for Zachary Taylor and Donald Trump due to the dataset only containing 1 speech for each of them, whereas the other presidents had multiple speeches. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Intermediate results storage\n\nSince this may have taken a while, we now serialize the results we have for further use. Note that we don't overwrite our original dataframe file, so we can load both (even though in this notebook we reused the name `addresses`):",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"addresses.to_hdf('results/df2.h5', 'addresses')\nwith shelve.open('results/vars2') as db:\n db['speech_words'] = speech_words # will contain the set of unique, stemmed words for each speech\n db['speeches_cleaned'] = speeches_cleaned # stemmed/cleaned versions of each speech, without collapsing into unique word sets",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a73879dbdd3b0e9feba79fafd8ce2c68671a3b2
| 13,011 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Assets/Tools/musical_difficulty_modeling.ipynb
|
elkwolf/ear-training
|
1d210dd4723e2edd50969fb693f0110b81e849ec
|
[
"MIT"
] | 6 |
2020-06-01T18:39:26.000Z
|
2020-10-15T12:54:08.000Z
|
Assets/Tools/musical_difficulty_modeling.ipynb
|
elkwolf/ear-training
|
1d210dd4723e2edd50969fb693f0110b81e849ec
|
[
"MIT"
] | 11 |
2020-06-03T01:35:47.000Z
|
2021-04-06T18:58:00.000Z
|
Assets/Tools/musical_difficulty_modeling.ipynb
|
elkwolf/ear-training
|
1d210dd4723e2edd50969fb693f0110b81e849ec
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2021-03-30T17:28:11.000Z
|
2021-03-30T17:37:04.000Z
| 35.452316 | 142 | 0.560987 |
[
[
[
"## Modeling the musical difficulty",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import ipywidgets as widgets\nfrom IPython.display import Audio, display, clear_output\nfrom ipywidgets import interactive\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn as sns\nimport numpy as np",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"distributions = {\n \"krumhansl_kessler\": [\n 0.15195022732711172, 0.0533620483369227, 0.08327351040918879,\n 0.05575496530270399, 0.10480976310122037, 0.09787030390045463,\n 0.06030150753768843, 0.1241923905240488, 0.05719071548217276,\n 0.08758076094759511, 0.05479779851639147, 0.06891600861450106,\n\n 0.14221523253201526, 0.06021118849696697, 0.07908335205571781,\n 0.12087171422152324, 0.05841383958660975, 0.07930802066951245,\n 0.05706582790384183, 0.1067175915524601, 0.08941810829027184,\n 0.06043585711076162, 0.07503931700741405, 0.07121995057290496\n ],\n \"sapp\": [\n 0.2222222222222222, 0.0, 0.1111111111111111, 0.0,\n 0.1111111111111111, 0.1111111111111111, 0.0, 0.2222222222222222,\n 0.0, 0.1111111111111111, 0.0, 0.1111111111111111,\n\n 0.2222222222222222, 0.0, 0.1111111111111111, 0.1111111111111111,\n 0.0, 0.1111111111111111, 0.0, 0.2222222222222222,\n 0.1111111111111111, 0.0, 0.05555555555555555, 0.05555555555555555\n ],\n \"aarden_essen\": [\n 0.17766092893562843, 0.001456239417504233, 0.1492649402940239,\n 0.0016018593592562562, 0.19804892078043168, 0.11358695456521818,\n 0.002912478835008466, 0.2206199117520353, 0.001456239417504233,\n 0.08154936738025305, 0.002329979068008373, 0.049512180195127924,\n\n 0.18264800547944018, 0.007376190221285707, 0.14049900421497014,\n 0.16859900505797015, 0.0070249402107482066, 0.14436200433086013,\n 0.0070249402107482066, 0.18616100558483017, 0.04566210136986304,\n 0.019318600579558018, 0.07376190221285707, 0.017562300526869017\n ],\n \"bellman_budge\": [\n 0.168, 0.0086, 0.1295, 0.0141, 0.1349, 0.1193,\n 0.0125, 0.2028, 0.018000000000000002, 0.0804, 0.0062, 0.1057,\n\n 0.1816, 0.0069, 0.12990000000000002,\n 0.1334, 0.010700000000000001, 0.1115,\n 0.0138, 0.2107, 0.07490000000000001,\n 0.015300000000000001, 0.0092, 0.10210000000000001\n ],\n \"temperley\": [\n 0.17616580310880825, 0.014130946773433817, 0.11493170042392838,\n 0.019312293923692884, 0.15779557230334432, 0.10833725859632594,\n 0.02260951483749411, 0.16839378238341965, 0.02449364107395195,\n 0.08619877531794629, 0.013424399434762127, 0.09420631182289213,\n\n 0.1702127659574468, 0.020081281377002155, 0.1133158020559407,\n 0.14774085584508725, 0.011714080803251255, 0.10996892182644036,\n 0.02510160172125269, 0.1785799665311977, 0.09658140090843893,\n 0.016017212526894576, 0.03179536218025341, 0.07889074826679417\n ],\n 'albrecht_shanahan1': [\n 0.238, 0.006, 0.111, 0.006, 0.137, 0.094,\n 0.016, 0.214, 0.009, 0.080, 0.008, 0.081,\n\n 0.220, 0.006, 0.104, 0.123, 0.019, 0.103,\n 0.012, 0.214, 0.062, 0.022, 0.061, 0.052\n ],\n 'albrecht_shanahan2': [\n 0.21169, 0.00892766, 0.120448, 0.0100265, 0.131444, 0.0911768, 0.0215947, 0.204703, 0.012894, 0.0900445, 0.012617, 0.0844338,\n\n 0.201933, 0.009335, 0.107284, 0.124169, 0.0199224, 0.108324,\n 0.014314, 0.202699, 0.0653907, 0.0252515, 0.071959, 0.049419\n ] \n}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def compute_threshold(dist_max, dist_min, d, cutoff): \n if d < cutoff: \n thresh = dist_max - d * ((dist_max - dist_min) / cutoff)\n else:\n thresh = 0.0\n return thresh\n\ndef clipped_distribution(orig_dist, d, cutoff):\n # make a copy of the original distribution\n copy = np.array(orig_dist)\n # compute the threshold to get rid of difficult notes at initial difficulties\n threshold = compute_threshold(max(copy), min(copy), d, cutoff)\n # remove the most difficult notes for low difficulties\n copy[copy < threshold] = 0.0\n # norm-1 of the distribution\n copy = copy / sum(copy)\n return copy, threshold",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def scaled_distribution(clipped_dist, h, d):\n # make a copy of the original distribution\n copy = np.array(clipped_dist) \n # compute the scaling factor based on handicap parameter and difficulty (user input)\n scaling = h - (h * d)\n # scale the distribution\n copy = copy ** scaling\n # norm-1 of the distribution\n copy = copy / sum(copy)\n return copy",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def f(dist_name, clipping, handicap, difficulty):\n # create the figures\n f, (axmaj, axmin) = plt.subplots(2, 3, sharex=True, sharey=True)\n \n # get the original distributions for major and minor keys\n dist = np.array(distributions[dist_name])\n major = dist[:12]\n minor = dist[12:]\n \n # clip the distributions for lower difficulties\n clipped_major, major_threshold = clipped_distribution(major, difficulty, clipping)\n clipped_minor, minor_threshold = clipped_distribution(minor, difficulty, clipping)\n \n # get the scaled distribution according to difficulty, handicap, and initial clipping \n scaled_major = scaled_distribution(clipped_major, handicap, difficulty)\n scaled_minor = scaled_distribution(clipped_minor, handicap, difficulty)\n \n ylim_major = max(max(np.amax(major), np.amax(clipped_major)), np.amax(scaled_major))\n ylim_minor = max(max(np.amax(minor), np.amax(clipped_minor)), np.amax(scaled_minor))\n \n # prepare to plot\n x = np.array(['C', 'C#', 'D', 'Eb', 'E', 'F',\n 'F#', 'G', 'Ab', 'A', 'Bb', 'B']) \n \n sns.barplot(x=x, y=major, ax=axmaj[0]) \n axmaj[0].set_title(\"Original Major\")\n axmaj[0].axhline(major_threshold, color=\"k\", clip_on=True)\n axmaj[0].set_ylim(0, ylim_major)\n \n sns.barplot(x=x, y=clipped_major, ax=axmaj[1])\n axmaj[1].set_title(\"Clipped Major\")\n axmaj[1].set_ylim(0, ylim_major)\n \n sns.barplot(x=x, y=scaled_major, ax=axmaj[2])\n axmaj[2].set_title(\"Scaled Major\")\n axmaj[2].set_ylim(0, ylim_major)\n \n sns.barplot(x=x, y=minor, ax=axmin[0])\n axmin[0].set_title(\"Original Minor\")\n axmin[0].axhline(minor_threshold, color=\"k\", clip_on=True)\n axmin[0].set_ylim(0, ylim_minor)\n \n sns.barplot(x=x, y=clipped_minor, ax=axmin[1])\n axmin[1].set_title(\"Clipped Minor\")\n axmin[1].set_ylim(0, ylim_minor)\n \n sns.barplot(x=x, y=scaled_minor, ax=axmin[2])\n axmin[2].set_title(\"Scaled Minor\")\n axmin[2].set_ylim(0, ylim_minor)\n \n plt.tight_layout(h_pad=2) \n return scaled_major, scaled_minor",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"distribution_name = list(distributions.keys())\nhandicap = widgets.IntSlider(min=1, max=10, value=2, continuous_update=False)\ndifficulty = widgets.FloatSlider(min=0.0, max=1.0, value=0.5, step=0.01, continuous_update=False)\nclipping = widgets.FloatSlider(min=0.2, max=0.8, step=0.1, value=0.2, continuous_update=False)\nw = interactive(f, dist_name=distribution_name, handicap=handicap, difficulty=difficulty, clipping=clipping)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"rate = 16000.\nduration = .1\nt = np.linspace(0., duration, int(rate * duration))\n\nnotes = range(12)\nfreqs = 220. * 2**(np.arange(3, 3 + len(notes)) / 12.)\n\ndef synth(f):\n x = np.sin(f * 2. * np.pi * t) * np.sin(t * np.pi / duration)\n display(Audio(x, rate=rate, autoplay=True)) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def sample_major_distribution(b):\n with output_major:\n major = w.result[0]\n note = np.random.choice(np.arange(12), p=major)\n synth(freqs[note])\n clear_output(wait=duration)\n\ndef sample_minor_distribution(b):\n with output_minor:\n minor = w.result[1]\n note = np.random.choice(np.arange(12), p=minor)\n synth(freqs[note])\n clear_output(wait=duration)\n\ndisplay(w)\n \nsample_major = widgets.Button(description=\"C Major\")\noutput_major = widgets.Output()\ndisplay(sample_major, output_major) \n \nsample_minor = widgets.Button(description=\"C Minor\")\noutput_minor = widgets.Output()\ndisplay(sample_minor, output_minor)\n\nsample_major.on_click(sample_major_distribution)\nsample_minor.on_click(sample_minor_distribution)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a738a6d0e10603759c7a0790a90884349544e97
| 150,179 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
110project2.ipynb
|
yihd/110project2
|
75e282c31388577cca365462ef9d196497219b47
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
110project2.ipynb
|
yihd/110project2
|
75e282c31388577cca365462ef9d196497219b47
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
110project2.ipynb
|
yihd/110project2
|
75e282c31388577cca365462ef9d196497219b47
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 254.540678 | 37,356 | 0.917638 |
[
[
[
"Implementation Task1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We implement the 1D example of least square problem for the IGD",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# generate a vector of random numbers which obeys the given distribution.\n#\n# n: length of the vector\n# mu: mean value\n# sigma: standard deviation.\n# dist: choices for the distribution, you need to implement at least normal \n# distribution and uniform distribution.\n#\n# For normal distribution, you can use ``numpy.random.normal`` to generate.\n# For uniform distribution, the interval to sample will be [mu - sigma/sqrt(3), mu + sigma/sqrt(3)].\n\ndef generate_random_numbers(n, mu, sigma, dist=\"normal\"):\n # write your code here.\n if dist == \"normal\":\n return np.random.normal(mu, sigma, n)\n elif dist == \"uniform\":\n return np.random.uniform(mu - sigma/np.sqrt(3),mu + sigma/np.sqrt(3),n)\n else:\n raise Exception(\"The distribution {unknown_dist} is not implemented\".format(unknown_dist=dist))\n \n \n# test your code:\ny_test = generate_random_numbers(5, 0, 0.1, \"normal\")\ny_test",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"y1 = generate_random_numbers(105, 0.5, 1.0, \"normal\")\ny2 = generate_random_numbers(105, 0.5, 1.0, \"uniform\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# IGD, the ordering is permitted to have replacement. \n#\n#\ndef IGD_wr_task1(y): # repeat\n x = 0\n n = len(y)\n ordering = np.random.choice(n, n, replace=True)\n # implement the algorithm's iteration of IGD. Your result should return the the final xk\n # at the last iteration and also the history of objective function at each xk.\n f = np.empty(n) # empty array for histories \n X = np.empty(n) # empty array for xk\n for k in range(n):\n gamma = 1/(k+1)\n x = x - gamma*(x - y[ordering[k]])\n f[k] = 0.5*np.sum((x - y)**2)\n X[k] = x\n return x, f, X\n \n# IGD, the ordering is not permitted to have replacement.\n#\n#\ndef IGD_wo_task1(y): # no repeat\n x = 0\n n = len(y)\n ordering = np.random.choice(n, n, replace=False)\n # implement the algorithm's iteration of IGD. Your result should return the the final xk\n # at the last iteration and also the history of objective function at each xk.\n f = np.empty(n)\n X = np.empty(n)\n for k in range(n):\n gamma = 1/(k+1)\n x = x - gamma*(x - y[ordering[k]])\n f[k] = 0.5*np.sum((x - y)**2)\n X[k] = x\n return x, f, X",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Using y1\nx_wr, wr_solu, X1 = IGD_wr_task1(y1)\nprint(\"Final x using placement:\", x_wr)\nx_wo, wo_solu, X2 = IGD_wo_task1(y1)\nprint(\"Final x without using placement:\", x_wo)\n\nX = np.linspace(0,105,105)\nplt.plot(X,wr_solu)\nplt.plot(X,wo_solu)\nplt.legend([\"With Placement\",\"Without Placement\"])\nplt.xlabel(\"# of iterations\")\nplt.ylabel(\"Histories\")\nplt.show()",
"Final x using placement: 0.2663730095558731\nFinal x without using placement: 0.28426350883742385\n"
],
[
"# Average of x with placement\nprint(np.sum(X1[:5])/5) # first 5\nprint(np.sum(X1[5:10])/5) # next 5\nprint(np.sum(X1[10:15])/5) # next 5\nprint()\n# Average of x without placement\nprint(np.sum(X2[:5])/5)\nprint(np.sum(X2[5:10])/5)\nprint(np.sum(X2[10:15])/5)",
"0.13137918660272563\n0.26167266891993646\n0.17112348060655022\n\n0.7410972866071879\n0.8046691880007153\n0.7799250842602097\n"
],
[
"# Using y2\nx_wr, wr_solu, X1 = IGD_wr_task1(y2)\nprint(\"Final x using placement:\", x_wr)\nx_wo, wo_solu, X2 = IGD_wo_task1(y2)\nprint(\"Final x without using placement:\", x_wo)\n\nX = np.linspace(0,105,105)\nplt.plot(X,wr_solu)\nplt.plot(X,wo_solu)\nplt.legend([\"With Placement\",\"Without Placement\"])\nplt.xlabel(\"# of iterations\")\nplt.ylabel(\"Histories\")\nplt.show()",
"Final x using placement: 0.5463006350584854\nFinal x without using placement: 0.504752965604123\n"
]
],
[
[
"We calculate average of x with replacement and x without replacement to see more clear",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Average of x with placement\nprint(np.sum(X1[:5])/5) # first 5\nprint(np.sum(X1[5:10])/5) # next 5\nprint(np.sum(X1[10:15])/5) # next 5\nprint()\n# Average of x without placement\nprint(np.sum(X2[:5])/5)\nprint(np.sum(X2[5:10])/5)\nprint(np.sum(X2[10:15])/5)\nprint(np.sum(X2[70:75])/5) #average of x70 to x75",
"0.4922610558902911\n0.6927994277891283\n0.6444977495143807\n\n0.5538058747181607\n0.5010424728146283\n0.5053951601723541\n0.4986285911006706\n"
]
],
[
[
"Ordering without replacement is better because it is more steady, and we can conclude that xk will converge to 0.5 and the xk+1 will converge to 0.5 as well",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Implementation task2",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# IGD, the ordering is permitted to have replacement. \n#\n#\ndef IGD_wr_task2(y, beta):\n x = 0\n n = len(beta)\n ordering = np.random.choice(n, n, replace=True)\n f = np.empty(n)\n gamma = 0.05*np.amin(1/beta)\n for k in range(n):\n x = x - gamma*beta[ordering[k]]*(x - y)\n f[k] = 0.5*np.sum(beta*(x - y)**2)\n return x, f\n\n# IGD, the ordering is not permitted to have replacement.\n#\n#\ndef IGD_wo_task2(y, beta):\n x = 0\n n = len(beta)\n ordering = np.random.choice(n, n, replace=False)\n f = np.empty(n)\n gamma = 0.05*np.amin(1/beta)\n for k in range(n):\n x = x - gamma*beta[ordering[k]]*(x - y)\n f[k] = 0.5*np.sum(beta*(x - y)**2)\n return x, f",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"N = 30\nbeta = np.random.uniform(1,2,N)\ny = 2\nx_wr, wr_solu = IGD_wr_task2(y, beta)\nprint(\"Final x using placement:\", x_wr)\nx_wo, wo_solu = IGD_wr_task2(y, beta)\nprint(\"Final x without using placement:\", x_wo)\n\nX = np.linspace(0,N,N)\nplt.plot(X,wr_solu)\nplt.plot(X,wo_solu)\nplt.legend([\"With Placement\",\"Without Placement\"])\nplt.xlabel(\"# of iterations\")\nplt.ylabel(\"Histories\")\nplt.show()",
"Final x using placement: 1.342759236314443\nFinal x without using placement: 1.330831634316972\n"
],
[
"N = 80\nbeta = np.random.uniform(1,2,N)\ny = 2\nx_wr, wr_solu = IGD_wr_task2(y, beta)\nprint(\"Final x using placement:\", x_wr)\nx_wo, wo_solu = IGD_wr_task2(y, beta)\nprint(\"Final x without using placement:\", x_wo)\n\nX = np.linspace(0,N,N)\nplt.plot(X,wr_solu)\nplt.plot(X,wo_solu)\nplt.legend([\"With Placement\",\"Without Placement\"])\nplt.xlabel(\"# of iterations\")\nplt.ylabel(\"Histories\")\nplt.show()",
"Final x using placement: 1.8986687835469165\nFinal x without using placement: 1.905963291134642\n"
]
],
[
[
"After big iterations, both of the methods can approach to the final results. However, without replacement works better since it approaches faster to the result.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Implementation task3",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# generation of exact solution and data y and matrix A.\n\ndef generate_problem_task3(m, n, rho):\n A = np.random.normal(0., 1.0, (m, n))\n x = np.random.random(n) # uniform in (0,1)\n w = np.random.normal(0., rho, m)\n y = A@x + w\n return A, x, y",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"A, xstar, y = generate_problem_task3(200, 100, 0.01)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# In these two functions, we could only focus on the first n steps and try to make comparisons on these data only.\n# In practice, it requires more iterations to converge, due to the matrix might not be easy to deal with.\n# You can put the ordering loop into a naive loop: namely, we simply perform the IGD code several rounds.\n#\n#\n#\n# IGD, the ordering is permitted to have replacement. \n#\n#\ndef IGD_wr_task3(y, A, xstar):\n n = A.shape[1]\n m = A.shape[0]\n x = np.zeros(n)\n f = np.empty(n)\n conv = np.empty(n)\n gamma = 1e-3\n for i in range(3): # performing IGD for three rounds\n ordering = np.random.choice(n, n, replace=True)\n for k in range(n):\n x = x - gamma*A[ordering[k]]*(A[ordering[k]]@x - y[ordering[k]])\n f[k] = np.sum((A[k]@x - y[k])**2)\n conv[k] = LA.norm(x - xstar)\n return x, f, conv \n\n# IGD, the ordering is not permitted to have replacement.\n#\n#\ndef IGD_wo_task3(y, A, xstar):\n n = A.shape[1]\n x = np.zeros(n)\n f = np.empty(n)\n conv = np.empty(n)\n gamma = 1e-3\n for i in range(3): # performing IGD for three rounds\n ordering = np.random.choice(n, n, replace=False)\n for k in range(n):\n x = x - gamma*A[ordering[k]]*(A[ordering[k]]@x - y[ordering[k]])\n f[k] = np.sum((A[k]@x - y[k])**2)\n conv[k] = LA.norm(x - xstar)\n return x, f, conv",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"N = A.shape[1]\nx_wr, wr_solu, wr_conv = IGD_wr_task3(y, A, xstar)\nx_wo, wo_solu, wo_conv = IGD_wo_task3(y, A, xstar)\n\nX = np.linspace(0,N,N)\nplt.plot(X,wr_solu)\nplt.plot(X,wo_solu)\nplt.legend([\"With Placement\",\"Without Placement\"])\nplt.xlabel(\"# of iterations\")\nplt.ylabel(\"Histories\")\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Histories of norm(xk - xstar) \nX = np.linspace(0,N,N)\nplt.plot(X,wr_conv)\nplt.plot(X,wo_conv)\nplt.legend([\"With Placement\",\"Without Placement\"])\nplt.xlabel(\"# of iterations\")\nplt.ylabel(\"norm\")\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Ordering without placement is still better because it beneaths the plot of with placement, which means the second method converges faster to the true solution than the first one.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a739d43c4cc39af6e0cc6f8f08cd43464c8ed14
| 40,903 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/generate_sample_db_2.ipynb
|
ednad/ooi-ui-services
|
a45e4386a692887057449c1dd3c62a87f57d6582
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/generate_sample_db_2.ipynb
|
ednad/ooi-ui-services
|
a45e4386a692887057449c1dd3c62a87f57d6582
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/generate_sample_db_2.ipynb
|
ednad/ooi-ui-services
|
a45e4386a692887057449c1dd3c62a87f57d6582
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 37.491292 | 308 | 0.575117 |
[
[
[
"empty"
]
]
] |
[
"empty"
] |
[
[
"empty"
]
] |
4a73a42b0cc323244d2860675bcd2bde7f11c25f
| 224,174 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
01_LaLiga_stats.ipynb
|
enliktjioe/nn2020-football
|
c5717b8248f1290a1c876c09c5848d281d5ea93b
|
[
"MIT"
] | 4 |
2020-06-15T06:05:30.000Z
|
2022-01-27T15:55:59.000Z
|
01_LaLiga_stats.ipynb
|
enliktjioe/nn2020-football
|
c5717b8248f1290a1c876c09c5848d281d5ea93b
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
01_LaLiga_stats.ipynb
|
enliktjioe/nn2020-football
|
c5717b8248f1290a1c876c09c5848d281d5ea93b
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 23.950214 | 110 | 0.345995 |
[
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nfrom datetime import datetime as dt\nimport itertools",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"season_1=pd.read_csv(\"2015-16.csv\")[['Date','HomeTeam','AwayTeam','FTHG','FTAG','FTR']]\nseason_2=pd.read_csv(\"2014-15.csv\")[['Date','HomeTeam','AwayTeam','FTHG','FTAG','FTR']]\nseason_3=pd.read_csv(\"2013-14.csv\")[['Date','HomeTeam','AwayTeam','FTHG','FTAG','FTR']]\nseason_4=pd.read_csv(\"2012-13.csv\")[['Date','HomeTeam','AwayTeam','FTHG','FTAG','FTR']]\nseason_5=pd.read_csv(\"2011-12.csv\")[['Date','HomeTeam','AwayTeam','FTHG','FTAG','FTR']]\nseason_6=pd.read_csv(\"2010-11.csv\")[['Date','HomeTeam','AwayTeam','FTHG','FTAG','FTR']]\nseason_7=pd.read_csv(\"2009-10.csv\")[['Date','HomeTeam','AwayTeam','FTHG','FTAG','FTR']]\nseason_8=pd.read_csv(\"2008-09.csv\")[['Date','HomeTeam','AwayTeam','FTHG','FTAG','FTR']]\nseason_9=pd.read_csv(\"2007-08.csv\")[['Date','HomeTeam','AwayTeam','FTHG','FTAG','FTR']]\n\nseason_1.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def parse_date(date):\n# print(type(date))\n data=str(date)\n print(type(date))\n print(date)\n if date==\"\":\n return None\n else:\n return dt.strptime(date,\"%d/%m/%y\").date()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"seasons=[season_1,season_2,season_3,season_4,season_5,season_6,season_7,season_8,season_9]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#apply the above functions\n\nfor season in seasons:\n season.Date=season.Date.apply(parse_date)",
"<class 'str'>\n21/08/15\n<class 'str'>\n22/08/15\n<class 'str'>\n22/08/15\n<class 'str'>\n22/08/15\n<class 'str'>\n22/08/15\n<class 'str'>\n23/08/15\n<class 'str'>\n23/08/15\n<class 'str'>\n23/08/15\n<class 'str'>\n23/08/15\n<class 'str'>\n24/08/15\n<class 'str'>\n28/08/15\n<class 'str'>\n29/08/15\n<class 'str'>\n29/08/15\n<class 'str'>\n29/08/15\n<class 'str'>\n29/08/15\n<class 'str'>\n30/08/15\n<class 'str'>\n30/08/15\n<class 'str'>\n30/08/15\n<class 'str'>\n30/08/15\n<class 'str'>\n30/08/15\n<class 'str'>\n11/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n12/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n12/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n12/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n12/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n13/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n13/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n13/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n13/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n14/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n18/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n19/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n19/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n19/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n19/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n20/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n20/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n20/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n20/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n20/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n22/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n22/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n22/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n23/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n23/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n23/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n23/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n23/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n23/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n24/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n25/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n26/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n26/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n26/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n26/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n26/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n27/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n27/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n27/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n27/09/15\n<class 'str'>\n02/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n03/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n03/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n03/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n03/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n03/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n04/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n04/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n04/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n04/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n17/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n17/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n17/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n17/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n17/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n18/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n18/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n18/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n18/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n19/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n23/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n24/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n24/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n24/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n24/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n25/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n25/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n25/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n25/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n26/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n30/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n31/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n31/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n31/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n31/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n31/10/15\n<class 'str'>\n01/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n01/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n01/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n01/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n06/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n07/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n07/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n07/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n07/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n07/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n08/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n08/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n08/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n08/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n21/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n21/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n21/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n21/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n21/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n22/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n22/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n22/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n22/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n23/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n27/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n28/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n28/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n28/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n28/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n28/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n29/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n29/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n29/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n29/11/15\n<class 'str'>\n05/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n05/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n05/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n05/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n05/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n06/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n06/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n06/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n06/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n07/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n11/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n12/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n12/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n12/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n12/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n12/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n13/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n13/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n13/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n13/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n19/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n19/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n19/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n19/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n20/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n20/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n20/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n20/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n20/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n30/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n30/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n30/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n30/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n30/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n30/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n30/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n30/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n30/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n31/12/15\n<class 'str'>\n02/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n02/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n02/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n03/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n03/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n03/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n03/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n03/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n03/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n04/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n09/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n09/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n09/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n09/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n09/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n10/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n10/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n10/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n10/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n10/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n16/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n16/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n16/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n16/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n17/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n17/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n17/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n17/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n17/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n18/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n22/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n23/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n23/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n23/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n23/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n24/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n24/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n24/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n24/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n25/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n30/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n30/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n30/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n30/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n30/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n31/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n31/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n31/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n31/01/16\n<class 'str'>\n01/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n05/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n06/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n06/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n06/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n06/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n07/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n07/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n07/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n07/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n08/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n12/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n13/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n13/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n13/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n13/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n14/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n14/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n14/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n14/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n14/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n17/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n19/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n20/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n20/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n20/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n20/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n21/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n21/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n21/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n21/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n21/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n26/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n27/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n27/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n27/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n27/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n27/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n28/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n28/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n28/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n28/02/16\n<class 'str'>\n01/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n01/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n02/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n02/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n02/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n02/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n02/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n03/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n03/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n03/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n05/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n05/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n05/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n05/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n06/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n06/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n06/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n06/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n06/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n07/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n11/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n12/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n12/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n12/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n12/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n13/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n13/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n13/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n13/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n14/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n18/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n19/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n19/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n19/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n19/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n19/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n20/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n20/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n20/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n20/03/16\n<class 'str'>\n01/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n02/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n02/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n02/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n02/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n03/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n03/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n03/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n03/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n04/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n08/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n09/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n09/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n09/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n09/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n10/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n10/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n10/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n10/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n11/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n15/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n16/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n16/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n16/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n16/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n17/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n17/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n17/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n17/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n17/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n19/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n19/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n20/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n20/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n20/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n20/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n20/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n20/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n21/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n21/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n22/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n23/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n23/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n23/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n23/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n24/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n24/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n24/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n24/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n25/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n29/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n30/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n30/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n30/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n30/04/16\n<class 'str'>\n01/05/16\n<class 'str'>\n01/05/16\n<class 'str'>\n01/05/16\n<class 'str'>\n01/05/16\n<class 'str'>\n02/05/16\n<class 'str'>\n08/05/16\n<class 'str'>\n08/05/16\n<class 'str'>\n08/05/16\n<class 'str'>\n08/05/16\n<class 'str'>\n08/05/16\n<class 'str'>\n08/05/16\n<class 'str'>\n08/05/16\n<class 'str'>\n08/05/16\n<class 'str'>\n08/05/16\n<class 'str'>\n08/05/16\n<class 'str'>\n13/05/16\n<class 'str'>\n14/05/16\n<class 'str'>\n14/05/16\n<class 'str'>\n14/05/16\n<class 'str'>\n14/05/16\n<class 'str'>\n15/05/16\n<class 'str'>\n15/05/16\n<class 'str'>\n15/05/16\n<class 'str'>\n15/05/16\n<class 'str'>\n15/05/16\n<class 'str'>\n23/08/14\n<class 'str'>\n23/08/14\n<class 'str'>\n23/08/14\n<class 'str'>\n23/08/14\n<class 'str'>\n24/08/14\n<class 'str'>\n24/08/14\n<class 'str'>\n24/08/14\n<class 'str'>\n24/08/14\n<class 'str'>\n25/08/14\n<class 'str'>\n25/08/14\n<class 'str'>\n29/08/14\n<class 'str'>\n29/08/14\n<class 'str'>\n30/08/14\n<class 'str'>\n30/08/14\n<class 'str'>\n30/08/14\n<class 'str'>\n30/08/14\n<class 'str'>\n31/08/14\n<class 'str'>\n31/08/14\n<class 'str'>\n31/08/14\n<class 'str'>\n31/08/14\n<class 'str'>\n12/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n13/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n13/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n13/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n13/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n14/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n14/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n14/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n14/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n15/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n19/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n20/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n20/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n20/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n20/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n21/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n21/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n21/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n21/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n22/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n23/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n23/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n24/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n24/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n24/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n24/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n24/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n24/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n25/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n25/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n26/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n27/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n27/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n27/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n27/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n27/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n28/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n28/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n28/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n28/09/14\n<class 'str'>\n03/10/14\n<class 'str'>\n04/10/14\n<class 'str'>\n04/10/14\n<class 'str'>\n04/10/14\n<class 'str'>\n04/10/14\n<class 'str'>\n04/10/14\n<class 'str'>\n05/10/14\n<class 'str'>\n05/10/14\n<class 'str'>\n05/10/14\n<class 'str'>\n05/10/14\n<class 'str'>\n17/10/14\n<class 'str'>\n18/10/14\n<class 'str'>\n18/10/14\n<class 'str'>\n18/10/14\n<class 'str'>\n18/10/14\n<class 'str'>\n19/10/14\n<class 'str'>\n19/10/14\n<class 'str'>\n19/10/14\n<class 'str'>\n19/10/14\n<class 'str'>\n20/10/14\n<class 'str'>\n24/10/14\n<class 'str'>\n25/10/14\n<class 'str'>\n25/10/14\n<class 'str'>\n25/10/14\n<class 'str'>\n25/10/14\n<class 'str'>\n25/10/14\n<class 'str'>\n26/10/14\n<class 'str'>\n26/10/14\n<class 'str'>\n26/10/14\n<class 'str'>\n26/10/14\n<class 'str'>\n31/10/14\n<class 'str'>\n01/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n01/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n01/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n01/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n02/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n02/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n02/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n02/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n03/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n07/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n08/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n08/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n08/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n08/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n08/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n09/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n09/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n09/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n09/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n21/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n22/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n22/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n22/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n22/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n23/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n23/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n23/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n23/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n24/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n28/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n29/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n29/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n29/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n29/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n30/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n30/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n30/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n30/11/14\n<class 'str'>\n01/12/14\n<class 'str'>\n06/12/14\n<class 'str'>\n06/12/14\n<class 'str'>\n06/12/14\n<class 'str'>\n06/12/14\n<class 'str'>\n07/12/14\n<class 'str'>\n07/12/14\n<class 'str'>\n07/12/14\n<class 'str'>\n07/12/14\n<class 'str'>\n08/12/14\n<class 'str'>\n08/12/14\n<class 'str'>\n12/12/14\n<class 'str'>\n13/12/14\n<class 'str'>\n13/12/14\n<class 'str'>\n13/12/14\n<class 'str'>\n13/12/14\n<class 'str'>\n14/12/14\n<class 'str'>\n14/12/14\n<class 'str'>\n14/12/14\n<class 'str'>\n14/12/14\n<class 'str'>\n15/12/14\n<class 'str'>\n19/12/14\n<class 'str'>\n20/12/14\n<class 'str'>\n20/12/14\n<class 'str'>\n20/12/14\n<class 'str'>\n20/12/14\n<class 'str'>\n21/12/14\n<class 'str'>\n21/12/14\n<class 'str'>\n21/12/14\n<class 'str'>\n21/12/14\n<class 'str'>\n03/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n03/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n03/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n03/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n03/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n04/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n04/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n04/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n04/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n05/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n09/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n10/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n10/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n10/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n10/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n11/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n11/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n11/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n11/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n12/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n16/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n17/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n17/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n17/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n17/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n18/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n18/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n18/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n18/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n18/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n24/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n24/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n24/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n24/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n24/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n25/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n25/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n25/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n25/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n26/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n30/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n31/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n31/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n31/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n31/01/15\n<class 'str'>\n01/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n01/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n01/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n01/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n02/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n04/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n06/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n07/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n07/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n07/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n07/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n08/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n08/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n08/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n08/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n09/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n13/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n14/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n14/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n14/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n14/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n15/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n15/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n15/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n15/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n16/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n20/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n21/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n21/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n21/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n21/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n22/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n22/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n22/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n22/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n23/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n27/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n28/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n28/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n28/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n28/02/15\n<class 'str'>\n01/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n01/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n01/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n01/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n02/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n06/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n07/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n07/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n07/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n07/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n08/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n08/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n08/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n08/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n09/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n13/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n14/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n14/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n14/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n14/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n15/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n15/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n15/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n15/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n16/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n20/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n21/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n21/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n21/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n21/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n21/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n22/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n22/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n22/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n22/03/15\n<class 'str'>\n03/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n04/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n04/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n04/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n04/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n05/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n05/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n05/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n05/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n06/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n07/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n07/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n07/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n08/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n08/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n08/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n08/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n09/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n09/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n09/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n11/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n11/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n11/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n11/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n11/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n12/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n12/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n12/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n12/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n13/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n17/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n18/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n18/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n18/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n18/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n19/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n19/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n19/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n19/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n20/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n24/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n25/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n25/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n25/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n25/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n26/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n26/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n26/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n26/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n27/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n28/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n28/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n28/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n29/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n29/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n29/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n29/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n29/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n30/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n30/04/15\n<class 'str'>\n01/05/15\n<class 'str'>\n02/05/15\n<class 'str'>\n02/05/15\n<class 'str'>\n02/05/15\n<class 'str'>\n02/05/15\n<class 'str'>\n03/05/15\n<class 'str'>\n03/05/15\n<class 'str'>\n03/05/15\n<class 'str'>\n03/05/15\n<class 'str'>\n04/05/15\n<class 'str'>\n"
],
[
"season_1.head(5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#functions adopted from Tewari and Krishna https://github.com/krishnakartik1/LSTM-footballMatchWinner\n\ndef get_goals_scored(season):\n print(\"get_goals_scored\")\n # Create a dictionary with team names as keys\n teams = {}\n for i in season.groupby('HomeTeam').mean().T.columns:\n print(\"check {} \\n\".format(i))\n teams[i] = []\n #print (len(teams[\"Augsburg\"]))\n # the value corresponding to keys is a list containing the match location.\n for i in range(len(season)):\n HTGS = season.iloc[i]['FTHG']\n ATGS = season.iloc[i]['FTAG']\n teams[season.iloc[i].HomeTeam].append(HTGS)\n teams[season.iloc[i].AwayTeam].append(ATGS)\n \n # Create a dataframe for goals scored where rows are teams and cols are matchweek.\n GoalsScored = pd.DataFrame(data=teams, index = [i for i in range(1,39)]).T\n GoalsScored[0] = 0\n # Aggregate to get uptil that point\n for i in range(2,39):\n GoalsScored[i] = GoalsScored[i] + GoalsScored[i-1]\n return GoalsScored\n\n\n\n# Gets the goals conceded agg arranged by teams and matchweek\ndef get_goals_conceded(season):\n # Create a dictionary with team names as keys\n teams = {}\n for i in season.groupby('HomeTeam').mean().T.columns:\n print(\"check {} \\n\".format(i))\n teams[i] = []\n \n # the value corresponding to keys is a list containing the match location.\n for i in range(len(season)):\n ATGC = season.iloc[i]['FTHG']\n HTGC = season.iloc[i]['FTAG']\n teams[season.iloc[i].HomeTeam].append(HTGC)\n teams[season.iloc[i].AwayTeam].append(ATGC)\n \n \n # Create a dataframe for goals scored where rows are teams and cols are matchweek.\n GoalsConceded = pd.DataFrame(data=teams, index = [i for i in range(1,39)]).T\n GoalsConceded[0] = 0\n \n # Aggregate to get uptil that point\n for i in range(2,39):\n GoalsConceded[i] = GoalsConceded[i] + GoalsConceded[i-1]\n return GoalsConceded\n\ndef get_gss(season):\n GC = get_goals_conceded(season)\n GS = get_goals_scored(season)\n \n j = 0\n HTGS = []\n ATGS = []\n HTGC = []\n ATGC = []\n\n for i in range(season.shape[0]):\n ht = season.iloc[i].HomeTeam\n at = season.iloc[i].AwayTeam\n HTGS.append(GS.loc[ht][j])\n ATGS.append(GS.loc[at][j])\n HTGC.append(GC.loc[ht][j])\n ATGC.append(GC.loc[at][j])\n \n if ((i + 1)% 10) == 0:\n j = j + 1\n \n# print(\"check line 87\")\n# print(season.shape,len(HTGS))\n \n season['HTGS'] = HTGS\n season['ATGS'] = ATGS\n season['HTGC'] = HTGC\n season['ATGC'] = ATGC\n \n return season",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#apply the above functions\n\nfor season in seasons:\n season.head()\n season = get_gss(season)\n \nseason_1.head(5)",
"check Ath Bilbao \n\ncheck Ath Madrid \n\ncheck Barcelona \n\ncheck Betis \n\ncheck Celta \n\ncheck Eibar \n\ncheck Espanol \n\ncheck Getafe \n\ncheck Granada \n\ncheck La Coruna \n\ncheck Las Palmas \n\ncheck Levante \n\ncheck Malaga \n\ncheck Real Madrid \n\ncheck Sevilla \n\ncheck Sociedad \n\ncheck Sp Gijon \n\ncheck Valencia \n\ncheck Vallecano \n\ncheck Villarreal \n\nget_goals_scored\ncheck Ath Bilbao \n\ncheck Ath Madrid \n\ncheck Barcelona \n\ncheck Betis \n\ncheck Celta \n\ncheck Eibar \n\ncheck Espanol \n\ncheck Getafe \n\ncheck Granada \n\ncheck La Coruna \n\ncheck Las Palmas \n\ncheck Levante \n\ncheck Malaga \n\ncheck Real Madrid \n\ncheck Sevilla \n\ncheck Sociedad \n\ncheck Sp Gijon \n\ncheck Valencia \n\ncheck Vallecano \n\ncheck Villarreal \n\ncheck Almeria \n\ncheck Ath Bilbao \n\ncheck Ath Madrid \n\ncheck Barcelona \n\ncheck Celta \n\ncheck Cordoba \n\ncheck Eibar \n\ncheck Elche \n\ncheck Espanol \n\ncheck Getafe \n\ncheck Granada \n\ncheck La Coruna \n\ncheck Levante \n\ncheck Malaga \n\ncheck Real Madrid \n\ncheck Sevilla \n\ncheck Sociedad \n\ncheck Valencia \n\ncheck Vallecano \n\ncheck Villarreal \n\nget_goals_scored\ncheck Almeria \n\ncheck Ath Bilbao \n\ncheck Ath Madrid \n\ncheck Barcelona \n\ncheck Celta \n\ncheck Cordoba \n\ncheck Eibar \n\ncheck Elche \n\ncheck Espanol \n\ncheck Getafe \n\ncheck Granada \n\ncheck La Coruna \n\ncheck Levante \n\ncheck Malaga \n\ncheck Real Madrid \n\ncheck Sevilla \n\ncheck Sociedad \n\ncheck Valencia \n\ncheck Vallecano \n\ncheck Villarreal \n\ncheck Almeria \n\ncheck Ath Bilbao \n\ncheck Ath Madrid \n\ncheck Barcelona \n\ncheck Betis \n\ncheck Celta \n\ncheck Elche \n\ncheck Espanol \n\ncheck Getafe \n\ncheck Granada \n\ncheck Levante \n\ncheck Malaga \n\ncheck Osasuna \n\ncheck Real Madrid \n\ncheck Sevilla \n\ncheck Sociedad \n\ncheck Valencia \n\ncheck Valladolid \n\ncheck Vallecano \n\ncheck Villarreal \n\nget_goals_scored\ncheck Almeria \n\ncheck Ath Bilbao \n\ncheck Ath Madrid \n\ncheck Barcelona \n\ncheck Betis \n\ncheck Celta \n\ncheck Elche \n\ncheck Espanol \n\ncheck Getafe \n\ncheck Granada \n\ncheck Levante \n\ncheck Malaga \n\ncheck Osasuna \n\ncheck Real Madrid \n\ncheck Sevilla \n\ncheck Sociedad \n\ncheck Valencia \n\ncheck Valladolid \n\ncheck Vallecano \n\ncheck Villarreal \n\ncheck Ath Bilbao \n\ncheck Ath Madrid \n\ncheck Barcelona \n\ncheck Betis \n\ncheck Celta \n\ncheck Espanol \n\ncheck Getafe \n\ncheck Granada \n\ncheck La Coruna \n\ncheck Levante \n\ncheck Malaga \n\ncheck Mallorca \n\ncheck Osasuna \n\ncheck Real Madrid \n\ncheck Sevilla \n\ncheck Sociedad \n\ncheck Valencia \n\ncheck Valladolid \n\ncheck Vallecano \n\ncheck Zaragoza \n\nget_goals_scored\ncheck Ath Bilbao \n\ncheck Ath Madrid \n\ncheck Barcelona \n\ncheck Betis \n\ncheck Celta \n\ncheck Espanol \n\ncheck Getafe \n\ncheck Granada \n\ncheck La Coruna \n\ncheck Levante \n\ncheck Malaga \n\ncheck Mallorca \n\ncheck Osasuna \n\ncheck Real Madrid \n\ncheck Sevilla \n\ncheck Sociedad \n\ncheck Valencia \n\ncheck Valladolid \n\ncheck Vallecano \n\ncheck Zaragoza \n\ncheck Ath Bilbao \n\ncheck Ath Madrid \n\ncheck Barcelona \n\ncheck Betis \n\ncheck Espanol \n\ncheck Getafe \n\ncheck Granada \n\ncheck Levante \n\ncheck Malaga \n\ncheck Mallorca \n\ncheck Osasuna \n\ncheck Real Madrid \n\ncheck Santander \n\ncheck Sevilla \n\ncheck Sociedad \n\ncheck Sp Gijon \n\ncheck Valencia \n\ncheck Vallecano \n\ncheck Villarreal \n\ncheck Zaragoza \n\nget_goals_scored\ncheck Ath Bilbao \n\ncheck Ath Madrid \n\ncheck Barcelona \n\ncheck Betis \n\ncheck Espanol \n\ncheck Getafe \n\ncheck Granada \n\ncheck Levante \n\ncheck Malaga \n\ncheck Mallorca \n\ncheck Osasuna \n\ncheck Real Madrid \n\ncheck Santander \n\ncheck Sevilla \n\ncheck Sociedad \n\ncheck Sp Gijon \n\ncheck Valencia \n\ncheck Vallecano \n\ncheck Villarreal \n\ncheck Zaragoza \n\ncheck Almeria \n\ncheck Ath Bilbao \n\ncheck Ath Madrid \n\ncheck Barcelona \n\ncheck Espanol \n\ncheck Getafe \n\ncheck Hercules \n\ncheck La Coruna \n\ncheck Levante \n\ncheck Malaga \n\ncheck Mallorca \n\ncheck Osasuna \n\ncheck Real Madrid \n\ncheck Santander \n\ncheck Sevilla \n\ncheck Sociedad \n\ncheck Sp Gijon \n\ncheck Valencia \n\ncheck Villarreal \n\ncheck Zaragoza \n\nget_goals_scored\ncheck Almeria \n\ncheck Ath Bilbao \n\ncheck Ath Madrid \n\ncheck Barcelona \n\ncheck Espanol \n\ncheck Getafe \n\ncheck Hercules \n\ncheck La Coruna \n\ncheck Levante \n\ncheck Malaga \n\ncheck Mallorca \n\ncheck Osasuna \n\ncheck Real Madrid \n\ncheck Santander \n\ncheck Sevilla \n\ncheck Sociedad \n\ncheck Sp Gijon \n\ncheck Valencia \n\ncheck Villarreal \n\ncheck Zaragoza \n\ncheck Almeria \n\ncheck Ath Bilbao \n\ncheck Ath Madrid \n\ncheck Barcelona \n\ncheck Espanol \n\ncheck Getafe \n\ncheck La Coruna \n\ncheck Malaga \n\ncheck Mallorca \n\ncheck Osasuna \n\ncheck Real Madrid \n\ncheck Santander \n\ncheck Sevilla \n\ncheck Sp Gijon \n\ncheck Tenerife \n\ncheck Valencia \n\ncheck Valladolid \n\ncheck Villarreal \n\ncheck Xerez \n\ncheck Zaragoza \n\nget_goals_scored\ncheck Almeria \n\ncheck Ath Bilbao \n\ncheck Ath Madrid \n\ncheck Barcelona \n\ncheck Espanol \n\ncheck Getafe \n\ncheck La Coruna \n\ncheck Malaga \n\ncheck Mallorca \n\ncheck Osasuna \n\ncheck Real Madrid \n\ncheck Santander \n\ncheck Sevilla \n\ncheck Sp Gijon \n\ncheck Tenerife \n\ncheck Valencia \n\ncheck Valladolid \n\ncheck Villarreal \n\ncheck Xerez \n\ncheck Zaragoza \n\ncheck Almeria \n\ncheck Ath Bilbao \n\ncheck Ath Madrid \n\ncheck Barcelona \n\ncheck Betis \n\ncheck Espanol \n\ncheck Getafe \n\ncheck La Coruna \n\ncheck Malaga \n\ncheck Mallorca \n\ncheck Numancia \n\ncheck Osasuna \n\ncheck Real Madrid \n\ncheck Recreativo \n\ncheck Santander \n\ncheck Sevilla \n\ncheck Sp Gijon \n\ncheck Valencia \n\ncheck Valladolid \n\ncheck Villarreal \n\nget_goals_scored\ncheck Almeria \n\ncheck Ath Bilbao \n\ncheck Ath Madrid \n\ncheck Barcelona \n\ncheck Betis \n\ncheck Espanol \n\ncheck Getafe \n\ncheck La Coruna \n\ncheck Malaga \n\ncheck Mallorca \n\ncheck Numancia \n\ncheck Osasuna \n\ncheck Real Madrid \n\ncheck Recreativo \n\ncheck Santander \n\ncheck Sevilla \n\ncheck Sp Gijon \n\ncheck Valencia \n\ncheck Valladolid \n\ncheck Villarreal \n\ncheck Almeria \n\ncheck Ath Bilbao \n\ncheck Ath Madrid \n\ncheck Barcelona \n\ncheck Betis \n\ncheck Espanol \n\ncheck Getafe \n\ncheck La Coruna \n\ncheck Levante \n\ncheck Mallorca \n\ncheck Murcia \n\ncheck Osasuna \n\ncheck Real Madrid \n\ncheck Recreativo \n\ncheck Santander \n\ncheck Sevilla \n\ncheck Valencia \n\ncheck Valladolid \n\ncheck Villarreal \n\ncheck Zaragoza \n\nget_goals_scored\ncheck Almeria \n\ncheck Ath Bilbao \n\ncheck Ath Madrid \n\ncheck Barcelona \n\ncheck Betis \n\ncheck Espanol \n\ncheck Getafe \n\ncheck La Coruna \n\ncheck Levante \n\ncheck Mallorca \n\ncheck Murcia \n\ncheck Osasuna \n\ncheck Real Madrid \n\ncheck Recreativo \n\ncheck Santander \n\ncheck Sevilla \n\ncheck Valencia \n\ncheck Valladolid \n\ncheck Villarreal \n\ncheck Zaragoza \n\n"
],
[
"season_1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#functions adopted from Tewari and Krishna https://github.com/krishnakartik1/LSTM-footballMatchWinner\n\ndef get_points(result):\n if result == 'W':\n return 3\n elif result == 'D':\n return 1\n else:\n return 0\n \n\ndef get_cuml_points(matchres):\n matchres_points = matchres.applymap(get_points)\n for i in range(2,38):\n matchres_points[i] = matchres_points[i] + matchres_points[i-1]\n \n matchres_points.insert(column =0, loc = 0, value = [0*i for i in range(20)])\n return matchres_points\n\n\ndef get_matchres(season):\n print(\"here\")\n # Create a dictionary with team names as keys\n teams = {}\n for i in season.groupby('HomeTeam').mean().T.columns:\n teams[i] = []\n\n # the value corresponding to keys is a list containing the match result\n for i in range(len(season)):\n if season.iloc[i].FTR == 'H':\n teams[season.iloc[i].HomeTeam].append('W')\n teams[season.iloc[i].AwayTeam].append('L')\n elif season.iloc[i].FTR == 'A':\n teams[season.iloc[i].AwayTeam].append('W')\n teams[season.iloc[i].HomeTeam].append('L')\n else:\n teams[season.iloc[i].AwayTeam].append('D')\n teams[season.iloc[i].HomeTeam].append('D')\n\n \n return pd.DataFrame(data=teams, index = [i for i in range(1,39)]).T\n\ndef get_agg_points(season):\n matchres = get_matchres(season)\n cum_pts = get_cuml_points(matchres)\n HTP = []\n ATP = []\n j = 0\n for i in range(season.shape[0]):\n ht = season.iloc[i].HomeTeam\n at = season.iloc[i].AwayTeam\n HTP.append(cum_pts.loc[ht][j])\n ATP.append(cum_pts.loc[at][j])\n\n if ((i + 1)% 10) == 0:\n j = j + 1\n \n season['HTP'] = HTP\n season['ATP'] = ATP\n return season",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#apply the above functions\n\nfor season in seasons:\n season.head()\n season = get_agg_points(season)\n \nseason_1.head(40)",
"here\nhere\nhere\nhere\nhere\nhere\nhere\nhere\nhere\n"
],
[
"la_liga = pd.concat(seasons)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"la_liga",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"la_liga.to_csv('la_liga_stats.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a73a6ab2c1dcf0d6cda567a9dbf2034d696ed35
| 2,298 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
ideas/idea_plywood_notebook.ipynb
|
kolibril13/plywood
|
fd0fa258a52016dbb97d4887039c16449dc3bf00
|
[
"MIT"
] | 4 |
2022-01-30T07:09:44.000Z
|
2022-02-20T19:22:03.000Z
|
ideas/idea_plywood_notebook.ipynb
|
kolibril13/plywood-gallery
|
6a33e688165374cb01548e6f62e60944e6f46e9b
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
ideas/idea_plywood_notebook.ipynb
|
kolibril13/plywood-gallery
|
6a33e688165374cb01548e6f62e60944e6f46e9b
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 15.32 | 77 | 0.436466 |
[
[
[
"import numpy as np\na = 10\nb = 0",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a = a + 20\nprint(a)",
"30\n"
],
[
"a = a + 2\nprint(a)",
"12\n"
],
[
"b = np.pi\nprint(b)",
"3.141592653589793\n"
],
[
"b",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a = a * 4\nprint(a)",
"40\n"
],
[
"a = a + 2\nprint(a)",
"42\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a73b6430e76274f5f0a4e52b31a7809dc2c2fca
| 568,660 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
starter_code/WeatherPy.ipynb
|
ptlhrs7/python-api-challenge
|
097210738af303198154beccfbfa8370d7b1725b
|
[
"ADSL"
] | null | null | null |
starter_code/WeatherPy.ipynb
|
ptlhrs7/python-api-challenge
|
097210738af303198154beccfbfa8370d7b1725b
|
[
"ADSL"
] | null | null | null |
starter_code/WeatherPy.ipynb
|
ptlhrs7/python-api-challenge
|
097210738af303198154beccfbfa8370d7b1725b
|
[
"ADSL"
] | null | null | null | 321.095426 | 53,716 | 0.918767 |
[
[
[
"# WeatherPy\n----\n\n#### Note\n* Instructions have been included for each segment. You do not have to follow them exactly, but they are included to help you think through the steps.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Dependencies and Setup\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport requests\nimport time\nfrom datetime import datetime\nfrom scipy.stats import linregress\n\n# Import API key\nfrom api_keys import weather_api_key\n\n# Incorporated citipy to determine city based on latitude and longitude\nfrom citipy import citipy\n\n# Output File (CSV)\noutput_data_file = \"output_data/cities.csv\"\n\n# Range of latitudes and longitudes\nlat_range = (-90, 90)\nlng_range = (-180, 180)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Generate Cities List",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# List for holding lat_lngs and cities\nlat_lngs = []\ncities = []\n\n# Create a set of random lat and lng combinations\nlats = np.random.uniform(lat_range[0], lat_range[1], size=1500)\nlngs = np.random.uniform(lng_range[0], lng_range[1], size=1500)\nlat_lngs = zip(lats, lngs)\n\n# Identify nearest city for each lat, lng combination\nfor lat_lng in lat_lngs:\n city = citipy.nearest_city(lat_lng[0], lat_lng[1]).city_name\n \n # If the city is unique, then add it to a our cities list\n if city not in cities:\n cities.append(city)\n\n# Print the city count to confirm sufficient count\nlen(cities)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Perform API Calls\n* Perform a weather check on each city using a series of successive API calls.\n* Include a print log of each city as it'sbeing processed (with the city number and city name).\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#Lists and counters\ncity_list = []\ncloud_list = []\ncountry_list = []\ndate_list = []\nhumidity_list = []\nlats_list = []\nlngs_list = []\ntemp_max_list = []\nwind_speed_list = []\nindex_counter = 0\nset_counter = 1\n\nprint(\"Beginning Data Retrieval \")\nprint(\"-------------------------------\")\n\nbase_url = \"http://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather?\"\nunits = \"imperial\"\nquery_url = f\"{base_url}appid={weather_api_key}&units={units}&q=\"\n\n#For loop matching city names with city_list\nfor index, city in enumerate(cities, start = 1):\n try:\n response = requests.get(query_url + city).json()\n city_list.append(response[\"name\"])\n cloud_list.append(response[\"clouds\"][\"all\"])\n country_list.append(response[\"sys\"][\"country\"])\n date_list.append(response[\"dt\"])\n humidity_list.append(response[\"main\"][\"humidity\"])\n lats_list.append(response[\"coord\"][\"lat\"])\n lngs_list.append(response[\"coord\"][\"lon\"])\n temp_max_list.append(response['main']['temp_max'])\n wind_speed_list.append(response[\"wind\"][\"speed\"])\n if index_counter > 49:\n index_counter = 0\n set_counter = set_counter + 1\n \n else:\n index_counter = index_counter + 1\n \n print(f\"Processing Record {index_counter} of Set {set_counter} | {city}\")\n \n except(KeyError, IndexError):\n print(\"City not found. Skipping...\")\n \nprint(\"-------------------------------\")\nprint(\"Data Retrieval Complete\")\nprint(\"-------------------------------\")\n ",
"Beginning Data Retrieval \n-------------------------------\nCity not found. Skipping...\nProcessing Record 1 of Set 1 | georgetown\nProcessing Record 2 of Set 1 | port alfred\nProcessing Record 3 of Set 1 | vermilion\nProcessing Record 4 of Set 1 | provideniya\nProcessing Record 5 of Set 1 | tiksi\nProcessing Record 6 of Set 1 | valparaiso\nProcessing Record 7 of Set 1 | krasnoselkup\nProcessing Record 8 of Set 1 | watsa\nProcessing Record 9 of Set 1 | upernavik\nProcessing Record 10 of Set 1 | port elizabeth\nProcessing Record 11 of Set 1 | rikitea\nProcessing Record 12 of Set 1 | chuy\nProcessing Record 13 of Set 1 | cape town\nProcessing Record 14 of Set 1 | jamestown\nProcessing Record 15 of Set 1 | busselton\nProcessing Record 16 of Set 1 | firovo\nProcessing Record 17 of Set 1 | talnakh\nProcessing Record 18 of Set 1 | alofi\nProcessing Record 19 of Set 1 | albany\nProcessing Record 20 of Set 1 | todos santos\nProcessing Record 21 of Set 1 | johvi\nProcessing Record 22 of Set 1 | vanimo\nProcessing Record 23 of Set 1 | cidreira\nProcessing Record 24 of Set 1 | lompoc\nProcessing Record 25 of Set 1 | petropavlovsk-kamchatskiy\nProcessing Record 26 of Set 1 | torbay\nProcessing Record 27 of Set 1 | portachuelo\nCity not found. Skipping...\nProcessing Record 28 of Set 1 | hermanus\nProcessing Record 29 of Set 1 | castro\nProcessing Record 30 of Set 1 | fukue\nProcessing Record 31 of Set 1 | ushuaia\nProcessing Record 32 of Set 1 | bredasdorp\nProcessing Record 33 of Set 1 | vaini\nProcessing Record 34 of Set 1 | pimenta bueno\nProcessing Record 35 of Set 1 | saint-philippe\nProcessing Record 36 of Set 1 | marystown\nProcessing Record 37 of Set 1 | chara\nProcessing Record 38 of Set 1 | monroe\nProcessing Record 39 of Set 1 | shubarshi\nProcessing Record 40 of Set 1 | lebu\nProcessing Record 41 of Set 1 | saskylakh\nProcessing Record 42 of Set 1 | segovia\nProcessing Record 43 of Set 1 | ibra\nProcessing Record 44 of Set 1 | poum\nProcessing Record 45 of Set 1 | ancud\nProcessing Record 46 of Set 1 | ferrol\nCity not found. Skipping...\nProcessing Record 47 of Set 1 | hasaki\nProcessing Record 48 of Set 1 | faanui\nProcessing Record 49 of Set 1 | kavieng\nProcessing Record 50 of Set 1 | tasiilaq\nProcessing Record 0 of Set 2 | cao bang\nProcessing Record 1 of Set 2 | punta arenas\nProcessing Record 2 of Set 2 | oksfjord\nProcessing Record 3 of Set 2 | tam ky\nProcessing Record 4 of Set 2 | port-gentil\nProcessing Record 5 of Set 2 | hobart\nProcessing Record 6 of Set 2 | khatanga\nProcessing Record 7 of Set 2 | aksu\nProcessing Record 8 of Set 2 | qaanaaq\nProcessing Record 9 of Set 2 | mataura\nProcessing Record 10 of Set 2 | jiuquan\nProcessing Record 11 of Set 2 | longyearbyen\nProcessing Record 12 of Set 2 | naberera\nProcessing Record 13 of Set 2 | venado tuerto\nProcessing Record 14 of Set 2 | bambous virieux\nProcessing Record 15 of Set 2 | east london\nProcessing Record 16 of Set 2 | hithadhoo\nProcessing Record 17 of Set 2 | gat\nProcessing Record 18 of Set 2 | arman\nCity not found. Skipping...\nProcessing Record 19 of Set 2 | luderitz\nProcessing Record 20 of Set 2 | marawi\nProcessing Record 21 of Set 2 | santa josefa\nProcessing Record 22 of Set 2 | butaritari\nProcessing Record 23 of Set 2 | barrow\nProcessing Record 24 of Set 2 | puerto ayora\nProcessing Record 25 of Set 2 | ilulissat\nProcessing Record 26 of Set 2 | salinopolis\nProcessing Record 27 of Set 2 | atuona\nProcessing Record 28 of Set 2 | katsuura\nProcessing Record 29 of Set 2 | guapi\nProcessing Record 30 of Set 2 | baculin\nCity not found. Skipping...\nProcessing Record 31 of Set 2 | sisimiut\nCity not found. Skipping...\nProcessing Record 32 of Set 2 | kununurra\nProcessing Record 33 of Set 2 | toora-khem\nProcessing Record 34 of Set 2 | khash\nProcessing Record 35 of Set 2 | pangnirtung\nProcessing Record 36 of Set 2 | sarahan\nProcessing Record 37 of Set 2 | bathsheba\nProcessing Record 38 of Set 2 | forestville\nProcessing Record 39 of Set 2 | kruisfontein\nProcessing Record 40 of Set 2 | banda aceh\nProcessing Record 41 of Set 2 | saint-augustin\nProcessing Record 42 of Set 2 | bemidji\nProcessing Record 43 of Set 2 | manubul\nProcessing Record 44 of Set 2 | hovd\nProcessing Record 45 of Set 2 | kalispell\nProcessing Record 46 of Set 2 | fort nelson\nProcessing Record 47 of Set 2 | berlevag\nProcessing Record 48 of Set 2 | hassleholm\nProcessing Record 49 of Set 2 | ponta delgada\nProcessing Record 50 of Set 2 | richards bay\nProcessing Record 0 of Set 3 | llallagua\nProcessing Record 1 of Set 3 | tuktoyaktuk\nProcessing Record 2 of Set 3 | yazman\nProcessing Record 3 of Set 3 | atambua\nProcessing Record 4 of Set 3 | esperance\nProcessing Record 5 of Set 3 | arvika\nProcessing Record 6 of Set 3 | avarua\nProcessing Record 7 of Set 3 | mount pleasant\nProcessing Record 8 of Set 3 | quesnel\nProcessing Record 9 of Set 3 | dikson\nProcessing Record 10 of Set 3 | port lincoln\nProcessing Record 11 of Set 3 | sao filipe\nProcessing Record 12 of Set 3 | bluff\nProcessing Record 13 of Set 3 | saint-francois\nProcessing Record 14 of Set 3 | victoria\nProcessing Record 15 of Set 3 | san michele al tagliamento\nProcessing Record 16 of Set 3 | canakkale\nProcessing Record 17 of Set 3 | afrikanda\nProcessing Record 18 of Set 3 | rognan\nProcessing Record 19 of Set 3 | mar del plata\nProcessing Record 20 of Set 3 | praia da vitoria\nProcessing Record 21 of Set 3 | necochea\nCity not found. Skipping...\nProcessing Record 22 of Set 3 | tomatlan\nProcessing Record 23 of Set 3 | moerai\nProcessing Record 24 of Set 3 | bontang\nCity not found. Skipping...\nProcessing Record 25 of Set 3 | norman wells\nProcessing Record 26 of Set 3 | kodiak\nProcessing Record 27 of Set 3 | novaya igirma\nProcessing Record 28 of Set 3 | ambon\nProcessing Record 29 of Set 3 | nanortalik\nProcessing Record 30 of Set 3 | aitape\nProcessing Record 31 of Set 3 | garowe\nProcessing Record 32 of Set 3 | aswan\nProcessing Record 33 of Set 3 | casper\nProcessing Record 34 of Set 3 | bolivar\nProcessing Record 35 of Set 3 | las vegas\nProcessing Record 36 of Set 3 | souillac\nProcessing Record 37 of Set 3 | aklavik\nProcessing Record 38 of Set 3 | camopi\nProcessing Record 39 of Set 3 | san rafael\nProcessing Record 40 of Set 3 | gusau\nProcessing Record 41 of Set 3 | kaitangata\nProcessing Record 42 of Set 3 | constitucion\nProcessing Record 43 of Set 3 | lagoa\nProcessing Record 44 of Set 3 | yellowknife\nProcessing Record 45 of Set 3 | kahului\nProcessing Record 46 of Set 3 | mount gambier\nProcessing Record 47 of Set 3 | homer\nProcessing Record 48 of Set 3 | krikellos\nProcessing Record 49 of Set 3 | puerto baquerizo moreno\nProcessing Record 50 of Set 3 | shankargarh\nProcessing Record 0 of Set 4 | kapaa\nProcessing Record 1 of Set 4 | amga\nProcessing Record 2 of Set 4 | kyrylivka\nProcessing Record 3 of Set 4 | lavrentiya\nProcessing Record 4 of Set 4 | severo-kurilsk\nProcessing Record 5 of Set 4 | dunedin\nProcessing Record 6 of Set 4 | ayorou\nProcessing Record 7 of Set 4 | tubmanburg\nCity not found. Skipping...\nProcessing Record 8 of Set 4 | tilichiki\nProcessing Record 9 of Set 4 | tanabe\nProcessing Record 10 of Set 4 | tazmalt\nProcessing Record 11 of Set 4 | humaita\nProcessing Record 12 of Set 4 | nabire\nProcessing Record 13 of Set 4 | san patricio\nCity not found. Skipping...\nProcessing Record 14 of Set 4 | qitaihe\nCity not found. Skipping...\nProcessing Record 15 of Set 4 | batagay-alyta\nProcessing Record 16 of Set 4 | riyadh\nProcessing Record 17 of Set 4 | kavaratti\nProcessing Record 18 of Set 4 | okhotsk\nProcessing Record 19 of Set 4 | touros\nProcessing Record 20 of Set 4 | taseyevo\nCity not found. Skipping...\nProcessing Record 21 of Set 4 | laguna\nProcessing Record 22 of Set 4 | ponta do sol\nCity not found. Skipping...\nProcessing Record 23 of Set 4 | new norfolk\nProcessing Record 24 of Set 4 | saldanha\nProcessing Record 25 of Set 4 | wajima\nProcessing Record 26 of Set 4 | bangui\nProcessing Record 27 of Set 4 | airai\nProcessing Record 28 of Set 4 | bud\nProcessing Record 29 of Set 4 | chapais\nCity not found. Skipping...\nProcessing Record 30 of Set 4 | saint-pierre\nProcessing Record 31 of Set 4 | hamilton\nProcessing Record 32 of Set 4 | mayahi\nProcessing Record 33 of Set 4 | zarinsk\nProcessing Record 34 of Set 4 | ambilobe\nProcessing Record 35 of Set 4 | launceston\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Convert Raw Data to DataFrame\n* Export the city data into a .csv.\n* Display the DataFrame",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#Create a dataframe using information from data retrieval\nweather_data = pd.DataFrame({\n \"City\" : city_list,\n \"Lat\" : lats_list,\n \"Lng\" : lngs_list,\n \"Max Temp\" : temp_max_list,\n \"Humidity\" : humidity_list,\n \"Clouds\" : cloud_list,\n \"Wind Speed\" : wind_speed_list,\n \"Country\" : country_list,\n \"Date\" : date_list \n})\n\n#Save weather data to a cities csv file\nweather_data.to_csv(\"../output_data/cities.csv\", index=False)\n\n#Display dataframe\nweather_data.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Inspect the data and remove the cities where the humidity > 100%.\n----\nSkip this step if there are no cities that have humidity > 100%. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#check if there are any cities with Humidity >100% \nweather_data[\"Humidity\"].describe()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Get the indices of cities that have humidity over 100%.\nhumidity_101 = weather_data[(weather_data[\"Humidity\"] > 100)].index\nhumidity_101",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Make a new DataFrame equal to the city data to drop all humidity outliers by index.\n# Passing \"inplace=False\" will make a copy of the city_data DataFrame, which we call \"clean_city_data\".\n\nclean_city_data = weather_data.drop(humidity_101, inplace=False)\nclean_city_data.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Export the filtered city data into a csv\nclean_city_data.to_csv(\"../output_data/clean_city_data.csv\", index_label=\"City_ID\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Plotting the Data\n* Use proper labeling of the plots using plot titles (including date of analysis) and axes labels.\n* Save the plotted figures as .pngs.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Latitude vs. Temperature Plot",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"date_now = datetime.date(datetime.now())\n\n# Create a scatter plot for latitude vs max temperature.\nx_values = clean_city_data[\"Lat\"]\ny_values = clean_city_data[\"Max Temp\"]\n\nfig1, ax1 = plt.subplots(figsize=(7,4))\nplt.scatter(x_values, y_values, edgecolor=\"black\", linewidth=1, marker=\"o\", alpha=0.8)\nplt.title(f\"City Latitude vs Max Temperature {date_now}\")\nplt.xlabel(\"Latitude\")\nplt.ylabel(\"Max Temperature (F)\")\nplt.grid()\n\n# Save the figure\nplt.savefig(\"../output_data/latitude_vs_max_temp.png\", bbox_inches=\"tight\")\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Latitude vs. Humidity Plot",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x_values = clean_city_data[\"Lat\"]\ny_values = clean_city_data[\"Humidity\"]\n\nfig1, ax1 = plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 4))\nplt.scatter(x_values, y_values, edgecolor=\"black\", linewidth=1, marker=\"o\", alpha=0.8)\nplt.xlabel(\"Latitude\")\nplt.ylabel(\"Humidity (%)\")\nplt.title(f\"City Latitude vs Humidity {date_now}\")\nplt.grid()\n\n# Save the figure\nplt.savefig(\"../output_data/latitude_vs_humidity.png\", bbox_inches=\"tight\")\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Latitude vs. Cloudiness Plot",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create a scatter plot for latitude vs cloudiness.\nx_values = clean_city_data[\"Lat\"]\ny_values = clean_city_data[\"Clouds\"]\n\nfig1, ax1 = plt.subplots(figsize=(7,4))\nmarkersize=12\nplt.scatter(x_values, y_values, edgecolor=\"black\", linewidth=1, marker=\"o\", alpha=0.8)\nplt.xlabel(\"Latitude\")\nplt.ylabel(\"Cloudiness (%)\")\nplt.title(f\"City Latitude vs Cloudiness {date_now}\")\nplt.grid()\n\n# Save the figure\nplt.savefig(\"../output_data/latitude_vs_cloudiness.png\", bbox_inches=\"tight\")\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Latitude vs. Wind Speed Plot",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create a scatter plot for latitude vs wind speed.\nx_values = clean_city_data[\"Lat\"]\ny_values = clean_city_data[\"Wind Speed\"]\n\nfig1, ax1 = plt.subplots(figsize=(7,4))\nmarkersize=12\nplt.scatter(x_values, y_values, edgecolor=\"black\", linewidth=1, marker=\"o\", alpha=0.8)\n\nplt.xlabel(\"Latitude\")\nplt.ylabel(\"Wind Speed (mph)\")\nplt.title(f\"City Latitude vs Wind Speed {date_now}\")\nplt.grid()\n\n# Save the figure\nplt.savefig(\"../output_data/latitude_vs_wind_speed.png\", bbox_inches=\"tight\")\nplt.show()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Linear Regression",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create a function to create Linear Regression plots for remaining activities\ndef plot_linear_regression(x_values, y_values, x_label, y_label, hemisphere, text_coordinates, ylim=None):\n (slope, intercept, rvalue, pvalue, stderr) = linregress(x_values, y_values)\n\n # Get regression values\n regress_values = x_values * slope + intercept\n \n # Create line equation string\n line_eq = \"y = \" + str(round(slope,2)) + \"x +\" + str(round(intercept,2))\n \n # Generate plots \n fig1, ax1 = plt.subplots(figsize=(7,4))\n plt.scatter(x_values, y_values, edgecolor=\"black\", linewidth=1, marker=\"o\", alpha=0.8)\n plt.plot(x_values,regress_values,\"r-\")\n date_now = datetime.date(datetime.now())\n plt.title(f\"{hemisphere} Hemisphere - {x_label} vs {y_label} {date_now}\",fontsize = 15)\n plt.xlabel(x_label,fontsize=14)\n plt.ylabel(y_label,fontsize=14)\n if ylim is not None:\n plt.ylim(0, ylim)\n plt.annotate(line_eq, text_coordinates, fontsize=20, color=\"red\")\n \n # Print r square value\n print(f\"The r-squared is: {rvalue**2}\")\n # correlation = linregress.pearsonr(x_values, y_values)\n # print(f\"The correlation between both factors is {round(correlation[0],2)}\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create Northern and Southern Hemisphere DataFrames\nnorthern_hemi_weather_df = clean_city_data.loc[clean_city_data[\"Lat\"] >= 0]\nsouthern_hemi_weather_df = clean_city_data.loc[clean_city_data[\"Lat\"] < 0]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Northern Hemisphere - Max Temp vs. Latitude Linear Regression",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create a scatter plot for latitude vs max temp (northern hemisphere)\nx_values = northern_hemi_weather_df[\"Lat\"]\ny_values = northern_hemi_weather_df[\"Max Temp\"]\nplot_linear_regression(x_values, y_values, \"Latitude\", \"Max Temp (F)\", \"Northern\", (10, 10))\n\n# Save the figure\nplt.savefig(\"../output_data/northern_hem_linear_lat_vs_max_temp.png\", bbox_inches=\"tight\")\nplt.show()",
"The r-squared is: 0.7535071398282818\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### Southern Hemisphere - Max Temp vs. Latitude Linear Regression",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create a scatter plot for latitude vs cloudiness (southern hemisphere)\nx_values = southern_hemi_weather_df[\"Lat\"]\ny_values = southern_hemi_weather_df[\"Max Temp\"]\nplot_linear_regression(x_values, y_values, \"Latitude\", \"Max Temp (F)\", \"Southern\", (-52, 75))\n\n# Save the figure\nplt.savefig(\"../output_data/southern_hem_linear_lat_vs_max_temp.png\", bbox_inches=\"tight\")\nplt.show()",
"The r-squared is: 0.5504700389097332\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### Northern Hemisphere - Humidity (%) vs. Latitude Linear Regression",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create a scatter plot for latitude vs humditiy (northern hemisphere)\nx_values = northern_hemi_weather_df['Lat']\ny_values = northern_hemi_weather_df['Humidity']\nplot_linear_regression(x_values, y_values, \"Latitude\", \"Humidity (%)\", \"Northern\",(50,50))\nplt.savefig(\"../output_data/northern_hem_linear_lat_vs_humidity.png\", bbox_inches=\"tight\")\nplt.show()",
"The r-squared is: 0.005332445379105486\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### Southern Hemisphere - Humidity (%) vs. Latitude Linear Regression",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create a scatter plot for latitude vs humditiy (southern hemisphere)\nx_values = southern_hemi_weather_df['Lat']\ny_values = southern_hemi_weather_df['Humidity']\nplot_linear_regression(x_values, y_values, \"Latitude\", \"Humidity (%)\", \"Southern\",(50, 50), 100)\nplt.savefig(\"../output_data/southern_hem_linear_lat_vs_humudity.png\", bbox_inches=\"tight\")\nplt.show()",
"The r-squared is: 0.007100946871600586\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### Northern Hemisphere - Cloudiness (%) vs. Latitude Linear Regression",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create a scatter plot for latitude vs cloudiness (northern hemisphere)\nx_values = northern_hemi_weather_df['Lat']\ny_values = northern_hemi_weather_df['Clouds']\nplot_linear_regression(x_values, y_values, \"Latitude\", \"Cloudiness (%)\", \"Northern\", (20, 60))\n\nplt.savefig(\"../output_data/northern_hem_linear_lat_vs_cloudiness.png\", bbox_inches=\"tight\")\nplt.show()",
"The r-squared is: 0.02538408983570023\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### Southern Hemisphere - Cloudiness (%) vs. Latitude Linear Regression",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create a scatter plot for latitude vs cloudiness (southern hemisphere)\nx_values = southern_hemi_weather_df['Lat']\ny_values = southern_hemi_weather_df['Clouds']\nplot_linear_regression(x_values, y_values, \"Latitude\", \"Cloudiness(%)\", \"Southern\",(-45, 60))\nplt.savefig(\"../output_data/southern_hem_linear_lat_vs_cloudiness.png\", bbox_inches=\"tight\")\nplt.show()",
"The r-squared is: 0.007620333886184847\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### Northern Hemisphere - Wind Speed (mph) vs. Latitude Linear Regression",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create a scatter plot for latitude vs wind speed(northern hemisphere)\nx_values = northern_hemi_weather_df['Lat']\ny_values = northern_hemi_weather_df['Wind Speed']\nplot_linear_regression(x_values, y_values, \"Latitude\", \"Wind Speed (mph)\", \"Northern\",(20, 25))\nplt.savefig(\"../output_data/northern_hem_linear_lat_vs_wind_speed.png\", bbox_inches=\"tight\")\nplt.show()",
"The r-squared is: 0.02123365311318519\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### Southern Hemisphere - Wind Speed (mph) vs. Latitude Linear Regression",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create a scatter plot for latitude vs wind speed (southern hemisphere)\nx_values = southern_hemi_weather_df['Lat']\ny_values = southern_hemi_weather_df['Wind Speed']\nplot_linear_regression(x_values, y_values, \"Latitude\", \"Wind Speed (mph)\", \"Southern\",(-40, 25), ylim=40)\nplt.savefig(\"../output_data/southern_hem_linear_lat_vs_wind_speed.png\", bbox_inches=\"tight\")\nplt.show()",
"The r-squared is: 0.04097966629956104\n"
],
[
"#Reference: https://github.com/poonam-ux/Python_API_WeatherPy_VacationPy ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a73bc831f757a21d067b5cf184100b2a4974f69
| 66,070 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/ONS Boundaries.ipynb
|
isleofdata/geodata
|
bfb8e723f0a0861ee9df48e4fbac8ec2ecdfcbb6
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/ONS Boundaries.ipynb
|
isleofdata/geodata
|
bfb8e723f0a0861ee9df48e4fbac8ec2ecdfcbb6
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 2 |
2019-02-28T21:16:28.000Z
|
2019-02-28T22:46:26.000Z
|
notebooks/ONS Boundaries.ipynb
|
isleofdata/geodata
|
bfb8e723f0a0861ee9df48e4fbac8ec2ecdfcbb6
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 94.116809 | 31,972 | 0.795989 |
[
[
[
"# ONS Boundaries\n\nFragments associated with grabbing boundaries data.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Wards (December 2018) Full Extent Boundaries GB\nhttp://geoportal.statistics.gov.uk/datasets/wards-december-2018-full-extent-boundaries-gb",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!wget https://opendata.arcgis.com/datasets/52182cdda64d4b15984f6446ca7ee7fd_1.zip?outSR=%7B%22wkid%22%3A27700%2C%22latestWkid%22%3A27700%7D -O wards_fullextent.zip",
"--2019-03-06 14:06:04-- https://opendata.arcgis.com/datasets/52182cdda64d4b15984f6446ca7ee7fd_1.zip?outSR=%7B%22wkid%22%3A27700%2C%22latestWkid%22%3A27700%7D\nResolving opendata.arcgis.com (opendata.arcgis.com)... 34.197.13.10, 52.7.213.26\nConnecting to opendata.arcgis.com (opendata.arcgis.com)|34.197.13.10|:443... connected.\nHTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK\nLength: unspecified [application/octet-stream]\nSaving to: ‘wards_fullextent.zip’\n\nwards_fullextent.zi [ <=> ] 88.51M 39.0MB/s in 2.3s \n\n2019-03-06 14:06:07 (39.0 MB/s) - ‘wards_fullextent.zip’ saved [92814270]\n\n"
],
[
"!unzip wards_fullextent.zip",
"Archive: wards_fullextent.zip\n inflating: Wards_December_2018_Full_Extent_Boundaries_GB.shp \n inflating: Wards_December_2018_Full_Extent_Boundaries_GB.shx \n extracting: Wards_December_2018_Full_Extent_Boundaries_GB.cpg \n inflating: Wards_December_2018_Full_Extent_Boundaries_GB.prj \n inflating: Wards_December_2018_Full_Extent_Boundaries_GB.xml \n inflating: Wards_December_2018_Full_Extent_Boundaries_GB.dbf \n"
],
[
"! spatialite adminboundaries.db \".loadshp ./Wards_December_2018_Full_Extent_Boundaries_GB wardboundaries UTF-8 27700\"",
"SpatiaLite version ..: 4.3.0a\tSupported Extensions:\n\t- 'VirtualShape'\t[direct Shapefile access]\n\t- 'VirtualDbf'\t\t[direct DBF access]\n\t- 'VirtualXL'\t\t[direct XLS access]\n\t- 'VirtualText'\t\t[direct CSV/TXT access]\n\t- 'VirtualNetwork'\t[Dijkstra shortest path]\n\t- 'RTree'\t\t[Spatial Index - R*Tree]\n\t- 'MbrCache'\t\t[Spatial Index - MBR cache]\n\t- 'VirtualSpatialIndex'\t[R*Tree metahandler]\n\t- 'VirtualElementary'\t[ElemGeoms metahandler]\n\t- 'VirtualXPath'\t[XML Path Language - XPath]\n\t- 'VirtualFDO'\t\t[FDO-OGR interoperability]\n\t- 'VirtualGPKG'\t[OGC GeoPackage interoperability]\n\t- 'VirtualBBox'\t\t[BoundingBox tables]\n\t- 'SpatiaLite'\t\t[Spatial SQL - OGC]\nPROJ.4 version ......: Rel. 4.9.3, 15 August 2016\nGEOS version ........: 3.6.2-CAPI-1.10.2 4d2925d6\nTARGET CPU ..........: x86_64-linux-gnu\nthe SPATIAL_REF_SYS table already contains some row(s)\n========\nLoading shapefile at './Wards_December_2018_Full_Extent_Boundaries_GB' into SQLite table 'wardboundaries'\n\nBEGIN;\nCREATE TABLE \"wardboundaries\" (\n\"PK_UID\" INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,\n\"objectid\" INTEGER,\n\"wd18cd\" TEXT,\n\"wd18nm\" TEXT,\n\"wd18nmw\" TEXT,\n\"bng_e\" INTEGER,\n\"bng_n\" INTEGER,\n\"long\" DOUBLE,\n\"lat\" DOUBLE,\n\"st_areasha\" DOUBLE,\n\"st_lengths\" DOUBLE);\nSELECT AddGeometryColumn('wardboundaries', 'Geometry', 27700, 'MULTIPOLYGON', 'XY');\nCOMMIT;\n\nInserted 8652 rows into 'wardboundaries' from SHAPEFILE\n========\n"
],
[
"! spatialite adminboundaries.db \"SELECT CreateSpatialIndex('wardboundaries', 'Geometry');\"",
"SpatiaLite version ..: 4.3.0a\tSupported Extensions:\n\t- 'VirtualShape'\t[direct Shapefile access]\n\t- 'VirtualDbf'\t\t[direct DBF access]\n\t- 'VirtualXL'\t\t[direct XLS access]\n\t- 'VirtualText'\t\t[direct CSV/TXT access]\n\t- 'VirtualNetwork'\t[Dijkstra shortest path]\n\t- 'RTree'\t\t[Spatial Index - R*Tree]\n\t- 'MbrCache'\t\t[Spatial Index - MBR cache]\n\t- 'VirtualSpatialIndex'\t[R*Tree metahandler]\n\t- 'VirtualElementary'\t[ElemGeoms metahandler]\n\t- 'VirtualXPath'\t[XML Path Language - XPath]\n\t- 'VirtualFDO'\t\t[FDO-OGR interoperability]\n\t- 'VirtualGPKG'\t[OGC GeoPackage interoperability]\n\t- 'VirtualBBox'\t\t[BoundingBox tables]\n\t- 'SpatiaLite'\t\t[Spatial SQL - OGC]\nPROJ.4 version ......: Rel. 4.9.3, 15 August 2016\nGEOS version ........: 3.6.2-CAPI-1.10.2 4d2925d6\nTARGET CPU ..........: x86_64-linux-gnu\n1\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Spatialite Read Demo\n\nExample of how to read data from Spatialite database.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#Set up the db connection and load in the spatialite extension\nimport sqlite3\n\n#!whereis mod_spatialite.so\nshared_lib = '/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/mod_spatialite.so'\ndbpath = 'adminboundaries.db' \n\n# Create connection and load spatialite extension\nconn = sqlite3.connect(dbpath)\n\n# Enable SpatialLite extension\nconn.enable_load_extension(True)\nconn.load_extension(shared_lib)\n\n# Initialise spatial table support\nconn.execute('SELECT InitSpatialMetadata(1)')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#We can make a simple pandas query\npd.read_sql('SELECT * FROM wardboundaries LIMIT 3', conn)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"More usefully, we can read queries into a geopandas dataframe if we make sure we return a specified geometry column:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import geopandas as gpd\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# SQL must wrap the geometry in hex(st_asbinary(...))\nsql = \"SELECT wd18nm, Hex(ST_AsBinary(Geometry)) AS Geometry FROM wardboundaries LIMIT 2;\"\ngpd.GeoDataFrame.from_postgis(sql, conn, geom_col='Geometry').head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"gpd.GeoDataFrame.from_postgis(sql, conn, geom_col='Geometry').plot();",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Select ward by name - we need to make sure we return a geometry column from the geopandas dataframe\nsql = \"SELECT wd18nm, Hex(ST_AsBinary(Geometry)) AS Geometry FROM wardboundaries WHERE wd18nm='Arreton and Newchurch';\"\ngpd.GeoDataFrame.from_postgis(sql, conn, geom_col='Geometry')\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can select neighbouring wards too:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"q='''\nSELECT w1.wd18nm AS \"Ward\",\n w2.wd18nm AS \"Neighbour\", Hex(ST_AsBinary(w2.Geometry)) AS Geometry \nFROM wardboundaries AS w1,\n wardboundaries AS w2\nWHERE (Touches(w1.Geometry, w2.Geometry) OR w1.wd18nm=w2.wd18nm)\nAND w1.wd18nm='Arreton and Newchurch';\n'''\n\ngpd.GeoDataFrame.from_postgis(q, conn, geom_col='Geometry')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"gpd.GeoDataFrame.from_postgis(q, conn, geom_col='Geometry').plot(facecolor=\"none\", edgecolor='black',);",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a73c1115d10172870575f6495de51e69f7cd745
| 19,594 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
nbs/01a_losses.ipynb
|
MrRobot2211/fastai
|
f75cd0e811125c01a687d1e3a44ecdd7d0233e15
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 2 |
2021-04-12T14:24:54.000Z
|
2021-11-10T12:29:13.000Z
|
nbs/01a_losses.ipynb
|
MrRobot2211/fastai
|
f75cd0e811125c01a687d1e3a44ecdd7d0233e15
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
nbs/01a_losses.ipynb
|
MrRobot2211/fastai
|
f75cd0e811125c01a687d1e3a44ecdd7d0233e15
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2021-04-08T07:06:33.000Z
|
2021-04-08T07:06:33.000Z
| 36.830827 | 557 | 0.602889 |
[
[
[
"#hide\n#skip\n! [ -e /content ] && pip install -Uqq fastai # upgrade fastai on colab",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# default_exp losses\n# default_cls_lvl 3",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#export\nfrom fastai.imports import *\nfrom fastai.torch_imports import *\nfrom fastai.torch_core import *\nfrom fastai.layers import *",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#hide\nfrom nbdev.showdoc import *",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Loss Functions\n> Custom fastai loss functions",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# export\nclass BaseLoss():\n \"Same as `loss_cls`, but flattens input and target.\"\n activation=decodes=noops\n def __init__(self, loss_cls, *args, axis=-1, flatten=True, floatify=False, is_2d=True, **kwargs):\n store_attr(\"axis,flatten,floatify,is_2d\")\n self.func = loss_cls(*args,**kwargs)\n functools.update_wrapper(self, self.func)\n\n def __repr__(self): return f\"FlattenedLoss of {self.func}\"\n @property\n def reduction(self): return self.func.reduction\n @reduction.setter\n def reduction(self, v): self.func.reduction = v\n\n def _contiguous(self,x):\n return TensorBase(x.transpose(self.axis,-1).contiguous()) if isinstance(x,torch.Tensor) else x\n\n def __call__(self, inp, targ, **kwargs):\n inp,targ = map(self._contiguous, (inp,targ))\n if self.floatify and targ.dtype!=torch.float16: targ = targ.float()\n if targ.dtype in [torch.int8, torch.int16, torch.int32]: targ = targ.long()\n if self.flatten: inp = inp.view(-1,inp.shape[-1]) if self.is_2d else inp.view(-1)\n return self.func.__call__(inp, targ.view(-1) if self.flatten else targ, **kwargs)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Wrapping a general loss function inside of `BaseLoss` provides extra functionalities to your loss functions:\n- flattens the tensors before trying to take the losses since it's more convenient (with a potential tranpose to put `axis` at the end)\n- a potential `activation` method that tells the library if there is an activation fused in the loss (useful for inference and methods such as `Learner.get_preds` or `Learner.predict`)\n- a potential <code>decodes</code> method that is used on predictions in inference (for instance, an argmax in classification)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The `args` and `kwargs` will be passed to `loss_cls` during the initialization to instantiate a loss function. `axis` is put at the end for losses like softmax that are often performed on the last axis. If `floatify=True`, the `targs` will be converted to floats (useful for losses that only accept float targets like `BCEWithLogitsLoss`), and `is_2d` determines if we flatten while keeping the first dimension (batch size) or completely flatten the input. We want the first for losses like Cross Entropy, and the second for pretty much anything else.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# export\n@delegates()\nclass CrossEntropyLossFlat(BaseLoss):\n \"Same as `nn.CrossEntropyLoss`, but flattens input and target.\"\n y_int = True\n @use_kwargs_dict(keep=True, weight=None, ignore_index=-100, reduction='mean')\n def __init__(self, *args, axis=-1, **kwargs): super().__init__(nn.CrossEntropyLoss, *args, axis=axis, **kwargs)\n def decodes(self, x): return x.argmax(dim=self.axis)\n def activation(self, x): return F.softmax(x, dim=self.axis)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tst = CrossEntropyLossFlat()\noutput = torch.randn(32, 5, 10)\ntarget = torch.randint(0, 10, (32,5))\n#nn.CrossEntropy would fail with those two tensors, but not our flattened version.\n_ = tst(output, target)\ntest_fail(lambda x: nn.CrossEntropyLoss()(output,target))\n\n#Associated activation is softmax\ntest_eq(tst.activation(output), F.softmax(output, dim=-1))\n#This loss function has a decodes which is argmax\ntest_eq(tst.decodes(output), output.argmax(dim=-1))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#In a segmentation task, we want to take the softmax over the channel dimension\ntst = CrossEntropyLossFlat(axis=1)\noutput = torch.randn(32, 5, 128, 128)\ntarget = torch.randint(0, 5, (32, 128, 128))\n_ = tst(output, target)\n\ntest_eq(tst.activation(output), F.softmax(output, dim=1))\ntest_eq(tst.decodes(output), output.argmax(dim=1))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"[Focal Loss](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1708.02002.pdf) is the same as cross entropy except easy-to-classify observations are down-weighted in the loss calculation. The strength of down-weighting is proportional to the size of the `gamma` parameter. Put another way, the larger `gamma` the less the easy-to-classify observations contribute to the loss.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# export\nclass FocalLossFlat(CrossEntropyLossFlat):\n \"\"\"\n Same as CrossEntropyLossFlat but with focal paramter, `gamma`. Focal loss is introduced by Lin et al. \n https://arxiv.org/pdf/1708.02002.pdf. Note the class weighting factor in the paper, alpha, can be \n implemented through pytorch `weight` argument in nn.CrossEntropyLoss.\n \"\"\"\n y_int = True\n @use_kwargs_dict(keep=True, weight=None, ignore_index=-100, reduction='mean')\n def __init__(self, *args, gamma=2, axis=-1, **kwargs):\n self.gamma = gamma\n self.reduce = kwargs.pop('reduction') if 'reduction' in kwargs else 'mean'\n super().__init__(*args, reduction='none', axis=axis, **kwargs)\n def __call__(self, inp, targ, **kwargs):\n ce_loss = super().__call__(inp, targ, **kwargs)\n pt = torch.exp(-ce_loss)\n fl_loss = (1-pt)**self.gamma * ce_loss\n return fl_loss.mean() if self.reduce == 'mean' else fl_loss.sum() if self.reduce == 'sum' else fl_loss",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Compare focal loss with gamma = 0 to cross entropy\nfl = FocalLossFlat(gamma=0)\nce = CrossEntropyLossFlat()\noutput = torch.randn(32, 5, 10)\ntarget = torch.randint(0, 10, (32,5))\ntest_close(fl(output, target), ce(output, target))\n#Test focal loss with gamma > 0 is different than cross entropy\nfl = FocalLossFlat(gamma=2)\ntest_ne(fl(output, target), ce(output, target))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#In a segmentation task, we want to take the softmax over the channel dimension\nfl = FocalLossFlat(gamma=0, axis=1)\nce = CrossEntropyLossFlat(axis=1)\noutput = torch.randn(32, 5, 128, 128)\ntarget = torch.randint(0, 5, (32, 128, 128))\ntest_close(fl(output, target), ce(output, target), eps=1e-4)\ntest_eq(fl.activation(output), F.softmax(output, dim=1))\ntest_eq(fl.decodes(output), output.argmax(dim=1))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# export\n@delegates()\nclass BCEWithLogitsLossFlat(BaseLoss):\n \"Same as `nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss`, but flattens input and target.\"\n @use_kwargs_dict(keep=True, weight=None, reduction='mean', pos_weight=None)\n def __init__(self, *args, axis=-1, floatify=True, thresh=0.5, **kwargs):\n if kwargs.get('pos_weight', None) is not None and kwargs.get('flatten', None) is True:\n raise ValueError(\"`flatten` must be False when using `pos_weight` to avoid a RuntimeError due to shape mismatch\")\n if kwargs.get('pos_weight', None) is not None: kwargs['flatten'] = False\n super().__init__(nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss, *args, axis=axis, floatify=floatify, is_2d=False, **kwargs)\n self.thresh = thresh\n\n def decodes(self, x): return x>self.thresh\n def activation(self, x): return torch.sigmoid(x)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tst = BCEWithLogitsLossFlat()\noutput = torch.randn(32, 5, 10)\ntarget = torch.randn(32, 5, 10)\n#nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss would fail with those two tensors, but not our flattened version.\n_ = tst(output, target)\ntest_fail(lambda x: nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()(output,target))\noutput = torch.randn(32, 5)\ntarget = torch.randint(0,2,(32, 5))\n#nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss would fail with int targets but not our flattened version.\n_ = tst(output, target)\ntest_fail(lambda x: nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()(output,target))\n\ntst = BCEWithLogitsLossFlat(pos_weight=torch.ones(10))\noutput = torch.randn(32, 5, 10)\ntarget = torch.randn(32, 5, 10)\n_ = tst(output, target)\ntest_fail(lambda x: nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()(output,target))\n\n#Associated activation is sigmoid\ntest_eq(tst.activation(output), torch.sigmoid(output))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# export\n@use_kwargs_dict(weight=None, reduction='mean')\ndef BCELossFlat(*args, axis=-1, floatify=True, **kwargs):\n \"Same as `nn.BCELoss`, but flattens input and target.\"\n return BaseLoss(nn.BCELoss, *args, axis=axis, floatify=floatify, is_2d=False, **kwargs)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tst = BCELossFlat()\noutput = torch.sigmoid(torch.randn(32, 5, 10))\ntarget = torch.randint(0,2,(32, 5, 10))\n_ = tst(output, target)\ntest_fail(lambda x: nn.BCELoss()(output,target))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# export\n@use_kwargs_dict(reduction='mean')\ndef MSELossFlat(*args, axis=-1, floatify=True, **kwargs):\n \"Same as `nn.MSELoss`, but flattens input and target.\"\n return BaseLoss(nn.MSELoss, *args, axis=axis, floatify=floatify, is_2d=False, **kwargs)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tst = MSELossFlat()\noutput = torch.sigmoid(torch.randn(32, 5, 10))\ntarget = torch.randint(0,2,(32, 5, 10))\n_ = tst(output, target)\ntest_fail(lambda x: nn.MSELoss()(output,target))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#hide\n#cuda\n#Test losses work in half precision\nif torch.cuda.is_available():\n output = torch.sigmoid(torch.randn(32, 5, 10)).half().cuda()\n target = torch.randint(0,2,(32, 5, 10)).half().cuda()\n for tst in [BCELossFlat(), MSELossFlat()]: _ = tst(output, target)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# export\n@use_kwargs_dict(reduction='mean')\ndef L1LossFlat(*args, axis=-1, floatify=True, **kwargs):\n \"Same as `nn.L1Loss`, but flattens input and target.\"\n return BaseLoss(nn.L1Loss, *args, axis=axis, floatify=floatify, is_2d=False, **kwargs)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#export\nclass LabelSmoothingCrossEntropy(Module):\n y_int = True\n def __init__(self, eps:float=0.1, weight=None, reduction='mean'): \n store_attr()\n\n def forward(self, output, target):\n c = output.size()[1]\n log_preds = F.log_softmax(output, dim=1)\n if self.reduction=='sum': loss = -log_preds.sum()\n else:\n loss = -log_preds.sum(dim=1) #We divide by that size at the return line so sum and not mean\n if self.reduction=='mean': loss = loss.mean()\n return loss*self.eps/c + (1-self.eps) * F.nll_loss(log_preds, target.long(), weight=self.weight, reduction=self.reduction)\n\n def activation(self, out): return F.softmax(out, dim=-1)\n def decodes(self, out): return out.argmax(dim=-1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lmce = LabelSmoothingCrossEntropy()\noutput = torch.randn(32, 5, 10)\ntarget = torch.randint(0, 10, (32,5))\ntest_eq(lmce(output.flatten(0,1), target.flatten()), lmce(output.transpose(-1,-2), target))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"On top of the formula we define:\n- a `reduction` attribute, that will be used when we call `Learner.get_preds`\n- `weight` attribute to pass to BCE.\n- an `activation` function that represents the activation fused in the loss (since we use cross entropy behind the scenes). It will be applied to the output of the model when calling `Learner.get_preds` or `Learner.predict`\n- a <code>decodes</code> function that converts the output of the model to a format similar to the target (here indices). This is used in `Learner.predict` and `Learner.show_results` to decode the predictions ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#export\n@delegates()\nclass LabelSmoothingCrossEntropyFlat(BaseLoss):\n \"Same as `LabelSmoothingCrossEntropy`, but flattens input and target.\"\n y_int = True\n @use_kwargs_dict(keep=True, eps=0.1, reduction='mean')\n def __init__(self, *args, axis=-1, **kwargs): super().__init__(LabelSmoothingCrossEntropy, *args, axis=axis, **kwargs)\n def activation(self, out): return F.softmax(out, dim=-1)\n def decodes(self, out): return out.argmax(dim=-1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Export -",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#hide\nfrom nbdev.export import *\nnotebook2script()",
"Converted 00_torch_core.ipynb.\nConverted 01_layers.ipynb.\nConverted 01a_losses.ipynb.\nConverted 02_data.load.ipynb.\nConverted 03_data.core.ipynb.\nConverted 04_data.external.ipynb.\nConverted 05_data.transforms.ipynb.\nConverted 06_data.block.ipynb.\nConverted 07_vision.core.ipynb.\nConverted 08_vision.data.ipynb.\nConverted 09_vision.augment.ipynb.\nConverted 09b_vision.utils.ipynb.\nConverted 09c_vision.widgets.ipynb.\nConverted 10_tutorial.pets.ipynb.\nConverted 10b_tutorial.albumentations.ipynb.\nConverted 11_vision.models.xresnet.ipynb.\nConverted 12_optimizer.ipynb.\nConverted 13_callback.core.ipynb.\nConverted 13a_learner.ipynb.\nConverted 13b_metrics.ipynb.\nConverted 14_callback.schedule.ipynb.\nConverted 14a_callback.data.ipynb.\nConverted 15_callback.hook.ipynb.\nConverted 15a_vision.models.unet.ipynb.\nConverted 16_callback.progress.ipynb.\nConverted 17_callback.tracker.ipynb.\nConverted 18_callback.fp16.ipynb.\nConverted 18a_callback.training.ipynb.\nConverted 18b_callback.preds.ipynb.\nConverted 19_callback.mixup.ipynb.\nConverted 20_interpret.ipynb.\nConverted 20a_distributed.ipynb.\nConverted 21_vision.learner.ipynb.\nConverted 22_tutorial.imagenette.ipynb.\nConverted 23_tutorial.vision.ipynb.\nConverted 24_tutorial.siamese.ipynb.\nConverted 24_vision.gan.ipynb.\nConverted 30_text.core.ipynb.\nConverted 31_text.data.ipynb.\nConverted 32_text.models.awdlstm.ipynb.\nConverted 33_text.models.core.ipynb.\nConverted 34_callback.rnn.ipynb.\nConverted 35_tutorial.wikitext.ipynb.\nConverted 36_text.models.qrnn.ipynb.\nConverted 37_text.learner.ipynb.\nConverted 38_tutorial.text.ipynb.\nConverted 39_tutorial.transformers.ipynb.\nConverted 40_tabular.core.ipynb.\nConverted 41_tabular.data.ipynb.\nConverted 42_tabular.model.ipynb.\nConverted 43_tabular.learner.ipynb.\nConverted 44_tutorial.tabular.ipynb.\nConverted 45_collab.ipynb.\nConverted 46_tutorial.collab.ipynb.\nConverted 50_tutorial.datablock.ipynb.\nConverted 60_medical.imaging.ipynb.\nConverted 61_tutorial.medical_imaging.ipynb.\nConverted 65_medical.text.ipynb.\nConverted 70_callback.wandb.ipynb.\nConverted 71_callback.tensorboard.ipynb.\nConverted 72_callback.neptune.ipynb.\nConverted 73_callback.captum.ipynb.\nConverted 74_callback.azureml.ipynb.\nConverted 97_test_utils.ipynb.\nConverted 99_pytorch_doc.ipynb.\nConverted dev-setup.ipynb.\nConverted index.ipynb.\nConverted quick_start.ipynb.\nConverted tutorial.ipynb.\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a73d04231282adfde37397e6f50b05269cc1145
| 2,153 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
_build/jupyter_execute/content/research_interests.ipynb
|
sayanadhikari/homesa
|
e0b982d3b46fa94ebccb71a26fa2371f73128478
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
_build/jupyter_execute/content/research_interests.ipynb
|
sayanadhikari/homesa
|
e0b982d3b46fa94ebccb71a26fa2371f73128478
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
_build/jupyter_execute/content/research_interests.ipynb
|
sayanadhikari/homesa
|
e0b982d3b46fa94ebccb71a26fa2371f73128478
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 34.174603 | 173 | 0.629819 |
[
[
[
"(research_interests)=\n\n# Research Interests\n\n## Primary Research\n* Plasma interaction with spacecraft bodies and Langmuir probes in the polar ionosphere.\n* Ion dynamics and sheath structure in Inertial Electrostatic Confinement Fusion machines.\n* Magnetized Plasma Sheaths. \n* Dust charging in laboratory and astrophysical plasmas.\n## Numerical Tools/Codes\n- Kinetic\n - [XOOPIC (X11-based Object Oriented Particle in Cell code), Michigan State University, USA](https://ptsg.egr.msu.edu/).\n - [PINC (Particle-In-Cell code)](https://github.com/pincproject/PINC), University of Oslo, Norway.\n - [PICSP (Particle-in-Cell Simulation of Plasma)](https://github.com/sayanadhikari/picsp), Centre of Plasma Physics, Institute for Plasma Research, India.\n - [Gkeyll Vlasov-Maxwell code](https://gkeyll.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html), Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL), USA.\n- Fluid\n - [IDFM - (Ion Dynamics using Fluid Modeling)](https://github.com/sayanadhikari/ion-dynamics-mag), Centre of Plasma Physics, Institute for Plasma Research, India.\n\nApart from above, I am also a Python enthusiast and I try to use this language to develop visualization toolkits and basic machine learning models.\n\n<!-- ```{figure} /_static/lecture_specific/about_py/python_vs_matlab.png\n:scale: 72%\n``` -->",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a73d186e9e03447f011e1aacc548826582f7923
| 205,910 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
models/dataset/dataset_generator_json.ipynb
|
ussaema/Box_Office_Sales_Estimation
|
ea5de0b3a39eeb83993c0ea8b27f2dcae99f65dd
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
models/dataset/dataset_generator_json.ipynb
|
ussaema/Box_Office_Sales_Estimation
|
ea5de0b3a39eeb83993c0ea8b27f2dcae99f65dd
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
models/dataset/dataset_generator_json.ipynb
|
ussaema/Box_Office_Sales_Estimation
|
ea5de0b3a39eeb83993c0ea8b27f2dcae99f65dd
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 205,910 | 205,910 | 0.931538 |
[
[
[
"# Module 1: Dataset",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Import",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# not all libraries are used\n!pip install imdbpy\nfrom bs4 import BeautifulSoup\nimport urllib.request\nimport urllib.parse\nimport re\nimport csv\nimport time\nimport datetime\nimport imdb\nimport ast\nfrom tqdm import tnrange, tqdm_notebook\nimport sys\nfrom urllib.request import HTTPError\nimport warnings\nimport html\nimport json\nimport os\nimport math\nimport inspect",
"Collecting imdbpy\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/95/23/60a7244a2d3473c80f71ae8dad832047058dc346525b3a6eacad78bc8d62/IMDbPY-6.7-py3-none-any.whl (285kB)\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 286kB 5.2MB/s \n\u001b[?25hRequirement already satisfied: lxml in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from imdbpy) (4.2.6)\nRequirement already satisfied: SQLAlchemy in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from imdbpy) (1.3.5)\nInstalling collected packages: imdbpy\nSuccessfully installed imdbpy-6.7\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Setup google drive",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"root_dir = '/root/aml/'\ndrive_dir = root_dir + 'My Drive/AML/'\ngit_rep = 'Git'\ngit_dir = drive_dir + git_rep+'/'\ndataset_dir = git_dir + 'datasets'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Run this cell to mount your Google Drive.\nfrom google.colab import drive\ndrive.mount(root_dir, force_remount=True) # run this line every time you have changed something in you drive\nos.chdir(drive_dir)",
"Go to this URL in a browser: https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/auth?client_id=947318989803-6bn6qk8qdgf4n4g3pfee6491hc0brc4i.apps.googleusercontent.com&redirect_uri=urn%3Aietf%3Awg%3Aoauth%3A2.0%3Aoob&scope=email%20https%3A%2F%2Fwww.googleapis.com%2Fauth%2Fdocs.test%20https%3A%2F%2Fwww.googleapis.com%2Fauth%2Fdrive%20https%3A%2F%2Fwww.googleapis.com%2Fauth%2Fdrive.photos.readonly%20https%3A%2F%2Fwww.googleapis.com%2Fauth%2Fpeopleapi.readonly&response_type=code\n\nEnter your authorization code:\n··········\nMounted at /root/aml/\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Utility functions",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"_WARNINGS = False\n\ndef urlopen(url, mobile = False):\n try:\n if mobile:\n urlheader = {'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (iPhone; CPU iPhone OS 5_0 like Mac OS X) AppleWebKit/534.46' ,\n 'Accept': 'text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8',\n 'Accept-Charset': 'ISO-8859-1,utf-8;q=0.7,*;q=0.3',\n 'Accept-Encoding': 'none',\n 'Accept-Language': 'en-US,en;q=0.8',\n 'Connection': 'keep-alive'}\n else:\n urlheader = {'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) ' \n 'AppleWebKit/537.11 (KHTML, like Gecko) '\n 'Chrome/23.0.1271.64 Safari/537.11',\n 'Accept': 'text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8',\n 'Accept-Charset': 'ISO-8859-1,utf-8;q=0.7,*;q=0.3',\n 'Accept-Encoding': 'none',\n 'Accept-Language': 'en-US,en;q=0.8',\n 'Connection': 'keep-alive'\n }\n #header2 = 'Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux i686) AppleWebKit/537.17 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/24.0.1312.27 Safari/537.17'\n return urllib.request.urlopen(urllib.request.Request(url=url, data=None, headers=urlheader)).read().decode('utf-8')\n except HTTPError as e:\n if (_WARNINGS):\n time.sleep(5);\n warnings.warn(str(e))\n return urlopen(url)\n else:\n raise e\n\ndef wrap_error(func):\n def func_wrapper(*args, **kwargs):\n if (_WARNINGS):\n try:\n return func(*args, **kwargs)\n except Exception as e:\n warnings.warn(datetime.datetime.now().strftime(\"%d-%m-%Y %H:%M\")+\" - \"+\"Function \"+ func.__name__ + \" \"+str(e))\n else:\n return func(*args, **kwargs)\n return func_wrapper",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## MoviesDataset class",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Definition of the class",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class MoviesDataset:\n def __init__(self):\n self.Youtube_urlroot = \"https://www.youtube.com\"\n self.Imdb_urlroot = \"https://www.imdb.com\"\n self.TheNumbers_urlroot = \"https://www.the-numbers.com\"\n self.max_number_movies = 16439\n self.number_movies_per_page = 100\n \n self.IMDb = imdb.IMDb()\n self.data = {}\n self.filename = \"MoviesDataset\"\n \n def NewJSON(self):\n with open(self.filename+'.json', 'w') as jsonFile:\n load = {}\n json.dump(load, jsonFile)\n jsonFile.close()\n self.estimatedSize = 0\n \n # append to the created json file\n @wrap_error\n def AppendJSON(self, movie):\n with open(self.filename+'.json', \"r+\") as jsonFile:\n load = json.load(jsonFile)\n load[movie['boxOffice']['id']-1] = movie\n jsonFile.seek(0) # rewind\n json.dump(load, jsonFile)\n jsonFile.truncate()\n return os.path.getsize(self.filename+'.json')/1000000, len(load)\n #jsonFile.close()\n \n # load dataset\n def Load(self, filename = None):\n if not filename:\n filename = self.filename\n else:\n self.filename = filename\n with open(filename+'.json', \"r+\") as jsonFile:\n self.data = json.load(jsonFile)\n jsonFile.seek(0) # rewind\n json.dump(self.data, jsonFile)\n jsonFile.truncate()\n \n #retrieve data from TheNumbers\n @wrap_error\n def BoxOfficeRetrieve(self, item):\n data = {}\n data['id']=int(item[0].text.replace(',',''))\n data['name']=item[2].text\n data['year']=int(item[1].text)\n data['url']=item[2].find_all('a')[0]['href']\n data['revenue_total']= int(item[3].text.replace(',','').replace('$',''))\n # retrieve first week revenue\n url = urllib.parse.urljoin(\"http://www.the-numbers.com\", data['url'])\n html = urlopen(url, False)\n soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')\n div = soup.findAll(attrs={'id':'box_office_chart'})\n if len(div) >0:\n div = div[0]\n tables = div.findAll(\"table\")\n data['revenue_week1']= int(div.findAll(\"td\")[2].text.replace(',','').replace('$',''))\n else:\n return None, data['name']\n # retrieve country\n url = url[:url.index('#')]+'#tab=summary'\n html = urlopen(url, False)\n soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')\n table = soup.findAll(\"table\")[3]\n data['country'] = [i.text for i in table.findAll(\"tr\")[-1].findAll(\"td\")[1].findAll(\"a\")]\n return data, data['name']\n \n \n #search imdb id\n @wrap_error\n def IMDbSearch(self, movie_name, movie_year):\n try:\n result = self.IMDb.search_movie(movie_name)\n #print(result)\n score = 0\n for item in result:\n try:\n if (item['kind'] == 'movie' and item['year'] == movie_year):\n if (len(set(list(str(item).lower().split(\" \"))).intersection(list(movie_name.lower().split(\" \"))))>score):\n return item.movieID\n except KeyError:\n if (item['kind'] == 'movie'):\n if (len(set(list(str(item).lower().split(\" \"))).intersection(list(movie_name.lower().split(\" \"))))>score):\n return item.movieID\n for item in result:\n try:\n if (item['kind'] == 'episode' and item['year'] == movie_year):\n if (len(set(list(str(item).lower().split(\" \"))).intersection(list(movie_name.lower().split(\" \"))))>score):\n return item.movieID\n except KeyError:\n if (item['kind'] == 'episode'):\n if (len(set(list(str(item).lower().split(\" \"))).intersection(list(movie_name.lower().split(\" \"))))>score):\n return item.movieID\n return None\n except:\n print('Movie:' + movie_name + ' - year:' + str(movie_year) + ' could not be found in IMDb')\n return None\n \n @wrap_error\n def IMDbRetrieve(self, movie_name, movie_year):\n id = self.IMDbSearch(movie_name, movie_year)\n data = {}\n if id:\n url = 'https://www.imdb.com/title/tt'+str(id)\n html = urlopen(url)\n soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')\n load = json.loads(soup.find('script', type='application/ld+json').text)\n data.update(load)\n if 'embedUrl' in urlopen(urllib.parse.urljoin(self.Imdb_urlroot, data['url'])):\n url = urllib.parse.urljoin(self.Imdb_urlroot, data['trailer']['embedUrl'])\n html = urlopen(url)\n script = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser').find_all('script')[-3].text\n load = json.loads(script[script.index('push(')+len('push('):script.index(');')])\n data['video'] = load\n return data\n \n \n #retrieve data from Youtube (also for Mobile device, defined by the url header information)\n @wrap_error\n def YoutubeRetrieve(self, movie_name, movie_year):\n data = {}\n query = urllib.parse.quote(movie_name+' '+str(movie_year)+' official trailer')\n url = 'https://www.google.com/search?biw=1620&bih=889&tbs=srcf%3AH4sIAAAAAAAAANOuzC8tKU1K1UvOz1UrSM0vyIEwSzJSy4sSC8DsssSizNSSSoiSnMTK5NS8kqLEHL2UVLX0zPREEA0AcHJbJEcAAAA&tbm=vid&q='+query\n #print(url)\n html = urlopen(url, mobile=True)\n soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')\n div = soup.findAll(attrs={'class':'mnr-c Tyz4ad'})\n if len(div):\n try:\n pos = 0\n while not('watch?v=' in str(div[pos])):\n pos += 1\n div = div[pos]\n\n href = div.find_all('a')[0]['href']\n #print(href)\n data['name'] = soup.findAll(attrs={'class':'lCT7Rc Rqb6rf'})[0].text\n data['url'] = '/watch?v='+str(href[href.index('watch?v=')+len('watch?v='):])\n return data\n except IndexError:\n return None\n else:\n return None\n \n #retrieve is based on the list of TheNumbers\n def Generate(self, movies_id, filename = None, save = True, new = True):\n def getMoviesIDList(movies_id):\n if isinstance(movies_id, list):\n if len(movies_id) >= 2:\n if isinstance(movies_id[0], str) or isinstance(movies_id[-1], str):\n if (movies_id[0] is 'start'):\n start_id = 1\n movies_id = list(range(start_id, movies_id[-1]+1))\n if (movies_id[-1] is 'end'):\n end_id = self.max_number_movies\n movies_id = list(range(movies_id[0], end_id+1))\n else:\n movies_id = list(set(movies_id) & set(list(range(1,self.max_number_movies+1))))\n movies_id.sort()\n else:\n raise Exception(\"movies_id arg must be a list of the at least 2 ids\")\n return list(movies_id)\n def id2page(id):\n return math.floor((id-1)/self.number_movies_per_page)*100+1\n def getMoviesList(page, ids):\n url = urllib.parse.urljoin(self.TheNumbers_urlroot, \"/box-office-records/domestic/all-movies/cumulative/all-time/\") + str(page)\n html = urlopen(url)\n soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')\n tables = soup.findAll(\"table\")\n if tables:\n first_table = tables[0]\n first_table = first_table.find_all('tr')[1:]\n return [i for i in first_table if int(i.find_all('td')[0].text.replace(',', '')) in ids]\n else:\n return None\n def getOneMovie (page_movies, id):\n for movie in page_movies:\n if int(movie.find_all('td')[0].text.replace(',', '')) == id:\n return movie.find_all('td')\n raise\n return None\n \n \n if filename:\n self.filename = filename\n if save:\n if new:\n self.NewJSON()\n else:\n self.data = []\n \n #regroup\n movies_id = getMoviesIDList(movies_id)\n \n pbar_pages = tqdm_notebook(list(set([id2page(id) for id in movies_id])), file=sys.stdout, ncols = 800)\n pbar_movies = tqdm_notebook(movies_id, file=sys.stdout, ncols = 800)\n current_page = id2page(movies_id[0])\n page_movies = getMoviesList(current_page, list(set(movies_id) & set(range(current_page, current_page+100))))\n one_movie = getOneMovie(page_movies, movies_id[0])\n pbar_pages.set_description(('Page %d: ') % (current_page))\n for id in pbar_movies:\n if id2page(id) != current_page:\n current_page = id2page(id)\n page_movies = getMoviesList(current_page, list(set(movies_id) & set(range(current_page, current_page+100))))\n pbar_pages.update()\n \n boxoffice_data, imdb_data, youtube_data = None, None, None\n #get the movie line\n one_movie = getOneMovie(page_movies, id)\n if (one_movie):\n #retrieve box office\n boxoffice_data, movie_name = self.BoxOfficeRetrieve(item = one_movie)\n if boxoffice_data:\n #retrieve IMDb\n imdb_data = self.IMDbRetrieve(movie_name = boxoffice_data['name'], movie_year = boxoffice_data['year'])\n if imdb_data:\n #retrieve youtube\n #print(boxoffice_data['name'])\n youtube_data = self.YoutubeRetrieve(movie_name = imdb_data['name'], movie_year = boxoffice_data['year'])\n if youtube_data:\n #all data retrieved and ready to be stored\n movie = {'boxOffice' : boxoffice_data}\n movie.update(imdb_data)\n if not 'video' in movie: #trailer in imdb was not found\n movie['video'] = {'videos': {'videoMetadata':{}}}\n movie['video']['videos']['videoMetadata'].update({'youtube': youtube_data})\n print(str(id)+': ', movie['name'], ' stored')\n #save in json file and update bar\n if save:\n current_size, json_length = self.AppendJSON(movie)\n self.estimatedSize = current_size + current_size/json_length*(len(movies_id))\n pbar_pages.set_description(('Page %d estimated total size %d.3MB: ') % (current_page, self.estimatedSize))\n else:\n self.data.append(movie)\n pbar_movies.set_description(str(id)+': '+movie_name)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### creation of movies object",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"movies = MoviesDataset()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### dataset generation",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**movies.Generate**:\n\n* **interval** : list(range(#id_start, #id_end+1)), [4, 32, 501], [#id_start, 'end'], ['start', #id_end]\n* **filename**: \"MoviesDataset\" (the name of the generated json file)\n* **save**: True, False (if True, save the retrieved movies in the json file, if False, the data will be stored in the variable movies.data)\n* **new**: True, False (create a new json file, be careful, this will overwrite the existing json file named $filename)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"os.chdir(dataset_dir)\nmovies.Generate(movies_id = [16364, 'end'], filename='Dataset', save = True, new = False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### load dataset",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**movies.Load**:\n\n* **filename**: \"MoviesDataset\" (the name of the json file to be loaded, the result will be stored in the instance movies.data), no value means the file movies.filename will be used, which is \"MoviesDataset\" per default",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"movies.Load(filename = 'Dataset')\nprint(len(movies.data))",
"9178\n"
]
],
[
[
"### filter",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Download the software HugeDataViewer and open your dataset to see how the dataset is structured.\n\nThere are the most important instructions of using dict in Python for our project: (for more, see python wiki)\n\n* Get the movie of id=#id\n```\nmovies.data[str(#id)]\n```\n* Get list of movies given a condition\n```\n[item for id, item in movies.data.items() if item['boxOffice']['country'][0] == 'United States']\n```\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"movies.data.get(str(4)).get('actor')[0].get('name')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"[item for id, item in movies.data.items() if item.get('boxOffice').get('name') == 'Minions']",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The returned data is stored in movies.data as a dict and has the following structure:\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a73e72b4eb96fddebf944e212117116fbb6d31d
| 1,329 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Stack/1223/1410. HTML Entity Parser.ipynb
|
YuHe0108/Leetcode
|
90d904dde125dd35ee256a7f383961786f1ada5d
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2020-08-05T11:47:47.000Z
|
2020-08-05T11:47:47.000Z
|
Stack/1223/1410. HTML Entity Parser.ipynb
|
YuHe0108/LeetCode
|
b9e5de69b4e4d794aff89497624f558343e362ad
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Stack/1223/1410. HTML Entity Parser.ipynb
|
YuHe0108/LeetCode
|
b9e5de69b4e4d794aff89497624f558343e362ad
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 18.985714 | 88 | 0.506396 |
[
[
[
"import html\nclass Solution:\n def entityParser(self, text: str) -> str:\n text = text.replace('⁄','/')\n return html.unescape(text)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"solution = Solution()\nsolution.entityParser(text = \"& is an HTML entity but &ambassador; is not.\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a73ee6e915de5355901f177ea96c5033bd72ee1
| 5,601 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
jupyter/load_mxnet_model.ipynb
|
andreabrduque/djl
|
06997ce4320d656cd133a509c36f6d1a5ade4d07
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
jupyter/load_mxnet_model.ipynb
|
andreabrduque/djl
|
06997ce4320d656cd133a509c36f6d1a5ade4d07
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
jupyter/load_mxnet_model.ipynb
|
andreabrduque/djl
|
06997ce4320d656cd133a509c36f6d1a5ade4d07
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 29.324607 | 215 | 0.596322 |
[
[
[
"# Load MXNet model\n\nIn this tutorial, you learn how to load an existing MXNet model and use it to run a prediction task.\n\n\n## Preparation\n\nThis tutorial requires the installation of Java Kernel. For more information on installing the Java Kernel, see the [README](https://github.com/deepjavalibrary/djl/blob/master/jupyter/README.md).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"// %mavenRepo snapshots https://oss.sonatype.org/content/repositories/snapshots/\n\n%maven ai.djl:api:0.16.0\n%maven ai.djl:model-zoo:0.16.0\n%maven ai.djl.mxnet:mxnet-engine:0.16.0\n%maven ai.djl.mxnet:mxnet-model-zoo:0.16.0\n%maven org.slf4j:slf4j-simple:1.7.32",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import java.awt.image.*;\nimport java.nio.file.*;\nimport ai.djl.*;\nimport ai.djl.inference.*;\nimport ai.djl.ndarray.*;\nimport ai.djl.modality.*;\nimport ai.djl.modality.cv.*;\nimport ai.djl.modality.cv.util.*;\nimport ai.djl.modality.cv.transform.*;\nimport ai.djl.modality.cv.translator.*;\nimport ai.djl.translate.*;\nimport ai.djl.training.util.*;\nimport ai.djl.util.*;",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Step 1: Prepare your MXNet model\n\nThis tutorial assumes that you have a MXNet model trained using Python. A MXNet symbolic model usually contains the following files:\n* Symbol file: {MODEL_NAME}-symbol.json - a json file that contains network information about the model\n* Parameters file: {MODEL_NAME}-{EPOCH}.params - a binary file that stores the parameter weight and bias\n* Synset file: synset.txt - an optional text file that stores classification classes labels\n\nThis tutorial uses a pre-trained MXNet `resnet18_v1` model.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We use `DownloadUtils` for downloading files from internet.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"DownloadUtils.download(\"https://mlrepo.djl.ai/model/cv/image_classification/ai/djl/mxnet/resnet/0.0.1/resnet18_v1-symbol.json\", \"build/resnet/resnet18_v1-symbol.json\", new ProgressBar());\nDownloadUtils.download(\"https://mlrepo.djl.ai/model/cv/image_classification/ai/djl/mxnet/resnet/0.0.1/resnet18_v1-0000.params.gz\", \"build/resnet/resnet18_v1-0000.params\", new ProgressBar());\nDownloadUtils.download(\"https://mlrepo.djl.ai/model/cv/image_classification/ai/djl/mxnet/synset.txt\", \"build/resnet/synset.txt\", new ProgressBar());\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Step 2: Load your model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Path modelDir = Paths.get(\"build/resnet\");\nModel model = Model.newInstance(\"resnet\");\nmodel.load(modelDir, \"resnet18_v1\");",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Step 3: Create a `Translator`",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Pipeline pipeline = new Pipeline();\npipeline.add(new CenterCrop()).add(new Resize(224, 224)).add(new ToTensor());\nTranslator<Image, Classifications> translator = ImageClassificationTranslator.builder()\n .setPipeline(pipeline)\n .optSynsetArtifactName(\"synset.txt\")\n .optApplySoftmax(true)\n .build();",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Step 4: Load image for classification",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"var img = ImageFactory.getInstance().fromUrl(\"https://resources.djl.ai/images/kitten.jpg\");\nimg.getWrappedImage()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Step 5: Run inference",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Predictor<Image, Classifications> predictor = model.newPredictor(translator);\nClassifications classifications = predictor.predict(img);\n\nclassifications",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Summary\n\nNow, you can load any MXNet symbolic model and run inference.\n\nYou might also want to check out [load_pytorch_model.ipynb](https://github.com/deepjavalibrary/djl/blob/master/jupyter/load_pytorch_model.ipynb) which demonstrates loading a local model using the ModelZoo API.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a73efc804046dcd587b8b69be3c4e6f68ff3624
| 904,159 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/2017-09-09(tau_p effects).ipynb
|
h-mayorquin/attractor_sequences
|
885271f30d73a58a7aad83b55949e4e32ba0b45a
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2016-08-19T18:58:51.000Z
|
2016-08-19T18:58:51.000Z
|
notebooks/2017-09-09(tau_p effects).ipynb
|
h-mayorquin/attractor_sequences
|
885271f30d73a58a7aad83b55949e4e32ba0b45a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/2017-09-09(tau_p effects).ipynb
|
h-mayorquin/attractor_sequences
|
885271f30d73a58a7aad83b55949e4e32ba0b45a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 858.650522 | 194,736 | 0.940195 |
[
[
[
"# Tau_p effects",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pprint\nimport subprocess\nimport sys \nsys.path.append('../')\n\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport matplotlib\nimport matplotlib.gridspec as gridspec\nfrom mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1 import make_axes_locatable\nimport seaborn as sns\n\n%matplotlib inline\n\nnp.set_printoptions(suppress=True, precision=2)\n\nsns.set(font_scale=2.0)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Git machinery",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"run_old_version = False\nif run_old_version:\n hash_when_file_was_written = 'beb606918461c91b007f25a007b71466d94cf516'\n hash_at_the_moment = subprocess.check_output([\"git\", 'rev-parse', 'HEAD']).strip()\n print('Actual hash', hash_at_the_moment)\n \n print('Hash of the commit used to run the simulation', hash_when_file_was_written)\n subprocess.call(['git', 'checkout', hash_when_file_was_written])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from network import Protocol, BCPNNFast, NetworkManager\nfrom analysis_functions import calculate_recall_success_sequences, calculate_recall_success\nfrom analysis_functions import calculate_recall_time_quantities, calculate_excitation_inhibition_ratio\nfrom analysis_functions import calculate_total_connections\nfrom plotting_functions import plot_weight_matrix, plot_winning_pattern",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## How do the probabilities evolve in time depending on tau_p",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### An example",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Patterns parameters\nhypercolumns = 4\nminicolumns = 20\nn_patterns = 10\n\n# Manager properties\ndt = 0.001\nT_recalling = 5.0\nvalues_to_save = ['o', 'p_pre', 'p_post', 'p_co', 'w']\n\n# Protocol\ntraining_time = 0.1\ninter_sequence_interval = 1.0\ninter_pulse_interval = 0.0\nepochs = 3\n\n# Network parameters\ntau_z_pre = 0.150\ntau_p = 500.0\n\n# Build the network\nnn = BCPNNFast(hypercolumns, minicolumns, tau_p=tau_p, tau_z_pre=tau_z_pre)\n\n# Build the manager\nmanager = NetworkManager(nn=nn, dt=dt, values_to_save=values_to_save)\n\n# Build protocol\n\nprotocol = Protocol()\nsequences = [[i for i in range(n_patterns)]]\n\nprotocol.cross_protocol(sequences, training_time=training_time,\n inter_sequence_interval=inter_sequence_interval, epochs=epochs)\n\nmanager.run_network_protocol(protocol=protocol, verbose=True)",
"('epochs', 0)\n('epochs', 1)\n('epochs', 2)\n"
],
[
"manager\nplot_weight_matrix(manager.nn)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig = plt.figure(figsize=(16, 12))\nax1 = fig.add_subplot(221)\nax2 = fig.add_subplot(222)\nax3 = fig.add_subplot(223)\nax4 = fig.add_subplot(224)\n\no = manager.history['o']\np_pre = manager.history['p_pre']\np_co = manager.history['p_co']\nw = manager.history['w']\n\npattern_1 = 3\npattern_2 = 4\n\ntime = np.arange(0, manager.T_total, dt)\n\nax1.plot(time, o[:, pattern_1])\nax1.plot(time, o[:, pattern_2])\nax1.set_ylabel('activity')\nax1.set_xlabel('Time')\n\nax2.plot(time, p_pre[:, pattern_1])\nax2.plot(time, p_pre[:, pattern_2])\nax2.set_ylabel('p')\nax2.set_xlabel('Time')\n\nax3.plot(time, p_co[:, pattern_2, pattern_1])\nax3.set_ylabel('p_co')\nax3.set_xlabel('Time')\n\nax4.plot(time, w[:, pattern_2, pattern_1])\nax4.set_ylabel('w')\nax4.set_xlabel('Time');\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"nn.g_w = 15.0\nnn.g_w_ampa = 15.0",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"total, mean, std, success = calculate_recall_time_quantities(manager, T_recall, T_cue, n, sequences)\nprint('success', success)",
"('success', 100.0)\n"
],
[
"plot_winning_pattern(manager)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig = plt.figure(figsize=(16, 12))\nax1 = fig.add_subplot(221)\nax2 = fig.add_subplot(222)\nax3 = fig.add_subplot(223)\nax4 = fig.add_subplot(224)\n\no = manager.history['o']\np_pre = manager.history['p_pre']\np_co = manager.history['p_co']\nw = manager.history['w']\n\npattern_1 = 3\npattern_2 = 4\n\ntime = np.arange(0, manager.T_total, dt)\n\nax1.plot(time, o[:, pattern_1])\nax1.plot(time, o[:, pattern_2])\nax1.set_ylabel('activity')\nax1.set_xlabel('Time')\n\nax2.plot(time, p_pre[:, pattern_1])\nax2.plot(time, p_pre[:, pattern_2])\nax2.set_ylabel('p')\nax2.set_xlabel('Time')\n\nax3.plot(time, p_co[:, pattern_2, pattern_1])\nax3.set_ylabel('p_co')\nax3.set_xlabel('Time')\n\nax4.plot(time, w[:, pattern_2, pattern_1])\nax4.set_ylabel('w')\nax4.set_xlabel('Time');",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Multiple values of tau_p",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tau_p_list = [5.0, 20.0, 100.0, 1000.0]\ntau_p_list = [10.0, 20.0, 30.0, 40.0]\ntau_p_list = [1, 10, 100, 1000]\n\nfig = plt.figure(figsize=(16, 12))\nax1 = fig.add_subplot(221)\nax2 = fig.add_subplot(222)\nax3 = fig.add_subplot(223)\nax4 = fig.add_subplot(224)\n\npattern_1 = 3\npattern_2 = 4\n\n# Patterns parameters\nhypercolumns = 4\nminicolumns = 20\nn_patterns = 10\n\n# Manager properties\ndt = 0.001\nT_recalling = 5.0\nvalues_to_save = ['o', 'p_pre', 'p_post', 'p_co', 'w']\n\n# Protocol\ntraining_time = 0.1\ninter_sequence_interval = 1.0\ninter_pulse_interval = 0.0\nepochs = 3\n\n# Network parameters\ntau_z_pre = 0.150\ntau_p = 10.0\n\nfor tau_p in tau_p_list:\n # Build the network\n nn = BCPNNFast(hypercolumns, minicolumns, tau_p=tau_p, tau_z_pre=tau_z_pre)\n\n # Build the manager\n manager = NetworkManager(nn=nn, dt=dt, values_to_save=values_to_save)\n\n # Build protocol\n\n protocol = Protocol()\n sequences = [[i for i in range(n_patterns)]]\n\n protocol.cross_protocol(sequences, training_time=training_time,\n inter_sequence_interval=inter_sequence_interval, epochs=epochs)\n\n manager.run_network_protocol(protocol=protocol, verbose=False)\n \n # Plotting\n o = manager.history['o']\n p_pre = manager.history['p_pre']\n p_post = manager.history['p_post']\n p_co = manager.history['p_co']\n w = manager.history['w']\n\n pattern_1 = 3\n pattern_2 = 4\n\n time = np.arange(0, manager.T_total, dt)\n \n if False:\n ax1.plot(time, o[:, pattern_1])\n ax1.plot(time, o[:, pattern_2])\n ax1.set_ylabel('activity')\n ax1.set_xlabel('Time')\n \n ax1.plot(time, p_post[:, pattern_1], label=str(tau_p))\n ax1.plot(time, p_post[:, pattern_2], label=str(tau_p))\n ax1.set_ylabel('p')\n ax1.set_xlabel('Time')\n\n ax2.plot(time, p_pre[:, pattern_1], label=str(tau_p))\n ax2.plot(time, p_pre[:, pattern_2], label=str(tau_p))\n ax2.set_ylabel('p')\n ax2.set_xlabel('Time')\n\n ax3.plot(time, p_co[:, pattern_2, pattern_1])\n ax3.set_ylabel('p_co')\n ax3.set_xlabel('Time')\n\n ax4.plot(time, w[:, pattern_2, pattern_1])\n ax4.set_ylabel('w')\n ax4.set_xlabel('Time')\n \nax1.legend()\nax2.legend();",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Convergence and final weights based on tau_p",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tau_p_vector = np.logspace(1.0, 2.0, num=15)\nweights = []\nweights_inhibition = []\nweights_ampa = []\nweights_free_attactor = []\nexc_inh_ratio = []\nexc_inh_ratio_ampa = []\nmean_recall_time = []\nrecall_successes = []\n\nfrom_pattern_inh = 0\n\nfrom_pattern = 3\nto_pattern = 4\n\nT_recall = 5.0\nT_cue = 0.100\nI_cue = 0\nn = 1\n\nfor tau_p in tau_p_vector:\n print('tau_p', tau_p)\n # Patterns parameters\n hypercolumns = 4\n minicolumns = 20\n n_patterns = 10\n\n # Manager properties\n dt = 0.001\n T_recalling = 5.0\n values_to_save = ['o']\n\n # Protocol\n training_time = 0.1\n inter_sequence_interval = 1.0\n inter_pulse_interval = 0.0\n epochs = 3\n\n # Build the network\n nn = BCPNNFast(hypercolumns, minicolumns, tau_p=tau_p, tau_z_pre=tau_z_pre)\n\n # Build the manager\n manager = NetworkManager(nn=nn, dt=dt, values_to_save=values_to_save)\n\n # Build protocol\n\n protocol = Protocol()\n sequences = [[i for i in range(n_patterns)]]\n\n protocol.cross_protocol(sequences, training_time=training_time,\n inter_sequence_interval=inter_sequence_interval, epochs=epochs)\n\n manager.run_network_protocol(protocol=protocol, verbose=False)\n \n total, mean, std, success = calculate_recall_time_quantities(manager, T_recall, T_cue, n, sequences)\n mean_ratio, std_ratio, aux = calculate_excitation_inhibition_ratio(nn, sequences, ampa=False)\n mean_ratio_ampa, std_ratio, aux = calculate_excitation_inhibition_ratio(nn, sequences, ampa=True)\n \n # Store\n weights.append(nn.w[to_pattern, from_pattern])\n weights_inhibition.append(nn.w[to_pattern, from_pattern_inh])\n weights_ampa.append(nn.w_ampa[0, minicolumns])\n weights_free_attactor.append(nn.w[to_pattern, n_patterns + 2])\n exc_inh_ratio.append(mean_ratio)\n exc_inh_ratio_ampa.append(mean_ratio_ampa)\n mean_recall_time.append(mean)\n recall_successes.append(success)",
"('tau_p', 10.0)\n('tau_p', 11.787686347935873)\n('tau_p', 13.894954943731374)\n('tau_p', 16.378937069540637)\n('tau_p', 19.306977288832496)\n('tau_p', 22.758459260747887)\n('tau_p', 26.826957952797258)\n('tau_p', 31.622776601683793)\n('tau_p', 37.275937203149397)\n('tau_p', 43.939705607607905)\n('tau_p', 51.794746792312097)\n('tau_p', 61.054022965853264)\n('tau_p', 71.968567300115211)\n('tau_p', 84.834289824407165)\n('tau_p', 100.0)\n"
],
[
"fig = plt.figure(figsize=(16, 12))\nax1 = fig.add_subplot(211)\nax2 = fig.add_subplot(212)\n\nax1.plot(tau_p_vector, weights, '*-', markersize=15, label='weights')\nax1.plot(tau_p_vector, weights_inhibition, '*-', markersize=15, label='weights inh')\nax1.plot(tau_p_vector, weights_free_attactor, '*-', markersize=15, label='free_attractor')\nax1.plot(tau_p_vector, weights_ampa, '*-', markersize=15, label='weights ampa')\n\nax2.plot(tau_p_vector, recall_successes, '*-', markersize=15, label='recall')\n\nax1.set_xscale('log')\nax1.set_xlabel('tau_p')\nax1.legend()\n\nax2.set_xscale('log')\nax2.set_xlabel('tau_p')\nax2.legend();",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig = plt.figure(figsize=(16, 12))\nax1 = fig.add_subplot(211)\nax2 = fig.add_subplot(212)\n\nax1.plot(tau_p_vector, exc_inh_ratio, '*-', markersize=15, label='exc inh ratio')\nax1.plot(tau_p_vector, exc_inh_ratio_ampa, '*-', markersize=15, label='exc inh ratio ampa')\nax2.plot(tau_p_vector, recall_successes, '*-', markersize=15, label='recall')\n\nax1.set_xscale('log')\nax1.set_xlabel('tau_p')\nax1.legend()\n\nax2.set_xscale('log')\nax2.set_xlabel('tau_p')\nax2.legend();",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Two sequences assymetry in values",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tau_p_vector = np.logspace(1.0, 4.0, num=20)\nconnectivities_1_list = []\nconnectivities_2_list = []\nconnectivities_3_list = []\nconnectivities_4_list = []\nconnectivities_5_list = []\nconnectivities_6_list = []\n\n# Patterns parameters\nhypercolumns = 4\nminicolumns = 35\n\n# Manager properties\ndt = 0.001\nT_recalling = 5.0\nvalues_to_save = ['o']\n\n# Protocol\ntraining_time = 0.1\ninter_sequence_interval = 2.0\ninter_pulse_interval = 0.0\nepochs = 3\n\ntau_z_pre = 0.150\nsigma = 0\ntau_p = 1000.0\n\nfor tau_p in tau_p_vector:\n print('tau p', tau_p)\n\n # Build the network\n nn = BCPNNFast(hypercolumns, minicolumns, tau_z_pre=tau_z_pre, sigma=sigma, tau_p=tau_p)\n\n # Build the manager\n manager = NetworkManager(nn=nn, dt=dt, values_to_save=values_to_save)\n\n # Build a protocol\n protocol = Protocol()\n sequences = [[0, 1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12, 13, 14], [15, 16, 17, 18, 19], \n [20, 21, 22, 23 ,24], [25, 26, 27, 28, 29]]\n protocol.cross_protocol(sequences, training_time=training_time,\n inter_sequence_interval=inter_sequence_interval, epochs=epochs)\n\n # Train\n manager.run_network_protocol(protocol=protocol, verbose=False)\n\n\n from_pattern = 3\n to_pattern = 4\n connectivity_seq_1 = calculate_total_connections(manager, from_pattern, to_pattern, ampa=False, normalize=True)\n\n from_pattern = 8\n to_pattern = 9\n connectivity_seq_2 = calculate_total_connections(manager, from_pattern, to_pattern, ampa=False, normalize=True)\n\n from_pattern = 13\n to_pattern = 14\n connectivity_seq_3 = calculate_total_connections(manager, from_pattern, to_pattern, ampa=False, normalize=True)\n\n from_pattern = 13\n to_pattern = 14\n connectivity_seq_3 = calculate_total_connections(manager, from_pattern, to_pattern, ampa=False, normalize=True)\n\n from_pattern = 18\n to_pattern = 19\n connectivity_seq_4 = calculate_total_connections(manager, from_pattern, to_pattern, ampa=False, normalize=True)\n \n from_pattern = 23\n to_pattern = 24\n connectivity_seq_5 = calculate_total_connections(manager, from_pattern, to_pattern, ampa=False, normalize=True)\n \n from_pattern = 28\n to_pattern = 29\n connectivity_seq_6 = calculate_total_connections(manager, from_pattern, to_pattern, ampa=False, normalize=True)\n\n connectivities_1_list.append(connectivity_seq_1)\n connectivities_2_list.append(connectivity_seq_2)\n connectivities_3_list.append(connectivity_seq_3)\n connectivities_4_list.append(connectivity_seq_4)\n connectivities_5_list.append(connectivity_seq_5)\n connectivities_6_list.append(connectivity_seq_6)",
"('tau p', 10.0)\n('tau p', 14.384498882876629)\n('tau p', 20.691380811147901)\n('tau p', 29.763514416313178)\n('tau p', 42.813323987193932)\n('tau p', 61.584821106602639)\n('tau p', 88.586679041008225)\n('tau p', 127.42749857031335)\n('tau p', 183.29807108324357)\n('tau p', 263.66508987303581)\n('tau p', 379.26901907322497)\n('tau p', 545.55947811685144)\n('tau p', 784.75997035146065)\n('tau p', 1128.8378916846884)\n('tau p', 1623.776739188721)\n('tau p', 2335.7214690901214)\n('tau p', 3359.8182862837812)\n('tau p', 4832.9302385717519)\n('tau p', 6951.9279617756056)\n('tau p', 10000.0)\n"
],
[
"fig = plt.figure(figsize=(16, 12))\nax = fig.add_subplot(111)\nax.plot(tau_p_vector, connectivities_1_list, '*-', markersize=15, label='1')\nax.plot(tau_p_vector, connectivities_2_list, '*-', markersize=15, label='2')\nax.plot(tau_p_vector, connectivities_3_list, '*-', markersize=15, label='3')\nax.plot(tau_p_vector, connectivities_4_list, '*-', markersize=15, label='4')\nax.plot(tau_p_vector, connectivities_5_list, '*-', markersize=15, label='5')\nax.plot(tau_p_vector, connectivities_6_list, '*-', markersize=15, label='6')\n\nax.set_xscale('log')\nax.set_xlabel('tau_p')\nax.set_ylabel('Connectivities')\n\nax.legend();",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Do previous sequences stick?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Patterns parameters\nhypercolumns = 4\nminicolumns = 40\nn_patterns = 10\n\n# Manager properties\ndt = 0.001\nT_recall = 5.0\nT_cue = 0.100\nn = 1\nvalues_to_save = ['o']\n\n# Protocol\ntraining_time = 0.1\ninter_sequence_interval = 1.0\ninter_pulse_interval = 0.0\nepochs = 3\n\nsigma = 0\ntau_z_pre = 0.200\ntau_p = 100.0\n\n# Sequence structure\noverlap = 2\nnumber_of_sequences = 5\nhalf_width = 2\n\n# Build the network\nnn = BCPNNFast(hypercolumns, minicolumns, tau_z_pre=tau_z_pre, sigma=sigma, tau_p=tau_p)\n# Buidl the manager\nmanager = NetworkManager(nn=nn, dt=dt, values_to_save=values_to_save)\n\n# Build chain protocol\nchain_protocol = Protocol()\nunits_to_overload = [i for i in range(overlap)]\nsequences = chain_protocol.create_overload_chain(number_of_sequences, half_width, units_to_overload)\nchain_protocol.cross_protocol(sequences, training_time=training_time,\n inter_sequence_interval=inter_sequence_interval, epochs=epochs)\n\n# Run the manager\nmanager.run_network_protocol(protocol=chain_protocol, verbose=True)\n\nprint(sequences)\n\nnn.g_w = 15.0\nnn.g_w_ampa = 1.0\nnn.tau_z_pre = 0.050\nnn.tau_a = 2.7\nsuccesses = calculate_recall_success_sequences(manager, T_recall=T_recall, T_cue=T_cue, n=n,\n sequences=sequences)",
"('epochs', 0)\n('epochs', 1)\n('epochs', 2)\n[[2, 3, 0, 1, 4, 5], [6, 7, 0, 1, 8, 9], [10, 11, 0, 1, 12, 13], [14, 15, 0, 1, 16, 17], [18, 19, 0, 1, 20, 21]]\n"
],
[
"successes",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plot_weight_matrix(manager.nn)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ampa = False\n\nfrom_pattern = 1\nto_pattern = 4\nconnectivity_seq_1 = calculate_total_connections(manager, from_pattern, to_pattern, ampa=ampa, normalize=True)\n\nfrom_pattern = 1\nto_pattern = 8\nconnectivity_seq_2 = calculate_total_connections(manager, from_pattern, to_pattern, ampa=ampa, normalize=True)\n\nfrom_pattern = 1\nto_pattern = 12\nconnectivity_seq_3 = calculate_total_connections(manager, from_pattern, to_pattern, ampa=ampa, normalize=True)\n\nfrom_pattern = 1\nto_pattern = 16\nconnectivity_seq_4 = calculate_total_connections(manager, from_pattern, to_pattern, ampa=ampa, normalize=True)\n\nfrom_pattern = 1\nto_pattern = 20\nconnectivity_seq_5 = calculate_total_connections(manager, from_pattern, to_pattern, ampa=ampa, normalize=True)\n\nprint('connectivit 1', connectivity_seq_1)\nprint('connectivit 2', connectivity_seq_2)\nprint('connectivit 3', connectivity_seq_3)\nprint('connectivit 4', connectivity_seq_4)\nprint('connectivit 5', connectivity_seq_5)",
"('connectivit 1', 0.4893826834917856)\n('connectivit 2', 0.49538605154872928)\n('connectivit 3', 0.50087836784628958)\n('connectivit 4', 0.50347189368509138)\n('connectivit 5', 0.50413806217879065)\n"
],
[
"from analysis_functions import calculate_timings\nnn.g_w = 15.0\nnn.g_w_ampa = 1.0\nnn.tau_a = 2.7 \nnn.tau_z_pre = 0.500\n\nprint(nn.get_parameters())\nT_recall = 5.0\nT_cue = 0.100\nn = 1\nsequence = 0\npatterns_indexes = sequences[sequence]\nsuccess_1 = calculate_recall_success(manager, T_recall=T_recall, I_cue=patterns_indexes[0],\n T_cue=T_cue, n=n, patterns_indexes=patterns_indexes)\ntimings = calculate_timings(manager, remove=0.010)\nprint('succes', success_1)\n\nplot_winning_pattern(manager)\nprint(patterns_indexes)\nprint(timings)",
"{'tau_z_post': 0.005, 'tau_m': 0.05, 'G': 1.0, 'tau_z_pre': 0.5, 'sigma': 0, 'g_w': 15.0, 'tau_z_post_ampa': 0.005, 'epsilon': 1e-20, 'tau_a': 2.7, 'g_beta': 1, 'g_w_ampa': 1.0, 'g_I': 10.0, 'tau_z_pre_ampa': 0.005, 'g_a': 97.0, 'k': 0, 'tau_p': 100.0}\n('succes', 100.0)\n[2, 3, 0, 1, 4, 5]\n[(2, 0.26600000000000001, 0.0, 0.26500000000000001), (3, 0.441, 0.26500000000000001, 0.70499999999999996), (0, 0.23900000000000002, 0.70499999999999996, 0.94300000000000006), (1, 1.056, 0.94300000000000006, 1.998), (4, 0.13100000000000001, 1.998, 2.1280000000000001), (5, 2.9710000000000001, 2.1280000000000001, 5.0979999999999999)]\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### Git machinery",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"if run_old_version:\n subprocess.call(['git', 'checkout', 'master'])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a73f3e62236d75150e47ddad2f7ef04b9a9d30c
| 8,895 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
test/Navigation.ipynb
|
jensakut/Reinforced_Bananas_DQN
|
3f6a02c97e15b28b193e70c50ec910adcf7e6817
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
test/Navigation.ipynb
|
jensakut/Reinforced_Bananas_DQN
|
3f6a02c97e15b28b193e70c50ec910adcf7e6817
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
test/Navigation.ipynb
|
jensakut/Reinforced_Bananas_DQN
|
3f6a02c97e15b28b193e70c50ec910adcf7e6817
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 34.746094 | 310 | 0.561889 |
[
[
[
"# Navigation\n\n---\n\nIn this notebook, you will learn how to use the Unity ML-Agents environment for the first project of the [Deep Reinforcement Learning Nanodegree](https://www.udacity.com/course/deep-reinforcement-learning-nanodegree--nd893).\n\n### 1. Start the Environment\n\nWe begin by importing some necessary packages. If the code cell below returns an error, please revisit the project instructions to double-check that you have installed [Unity ML-Agents](https://github.com/Unity-Technologies/ml-agents/blob/master/docs/Installation.md) and [NumPy](http://www.numpy.org/).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from unityagents import UnityEnvironment\nimport numpy as np",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Next, we will start the environment! **_Before running the code cell below_**, change the `file_name` parameter to match the location of the Unity environment that you downloaded.\n\n- **Mac**: `\"path/to/Banana.app\"`\n- **Windows** (x86): `\"path/to/Banana_Windows_x86/Banana.exe\"`\n- **Windows** (x86_64): `\"path/to/Banana_Windows_x86_64/Banana.exe\"`\n- **Linux** (x86): `\"path/to/Banana_Linux/Banana.x86\"`\n- **Linux** (x86_64): `\"path/to/Banana_Linux/Banana.x86_64\"`\n- **Linux** (x86, headless): `\"path/to/Banana_Linux_NoVis/Banana.x86\"`\n- **Linux** (x86_64, headless): `\"path/to/Banana_Linux_NoVis/Banana.x86_64\"`\n\nFor instance, if you are using a Mac, then you downloaded `Banana.app`. If this file is in the same folder as the notebook, then the line below should appear as follows:\n```\nenv = UnityEnvironment(file_name=\"Banana.app\")\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"env = UnityEnvironment(file_name=\"../banana_env/Banana.x86_64\")",
"INFO:unityagents:\n'Academy' started successfully!\nUnity Academy name: Academy\n Number of Brains: 1\n Number of External Brains : 1\n Lesson number : 0\n Reset Parameters :\n\t\t\nUnity brain name: BananaBrain\n Number of Visual Observations (per agent): 0\n Vector Observation space type: continuous\n Vector Observation space size (per agent): 37\n Number of stacked Vector Observation: 1\n Vector Action space type: discrete\n Vector Action space size (per agent): 4\n Vector Action descriptions: , , , \n"
]
],
[
[
"Environments contain **_brains_** which are responsible for deciding the actions of their associated agents. Here we check for the first brain available, and set it as the default brain we will be controlling from Python.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# get the default brain\nbrain_name = env.brain_names[0]\nbrain = env.brains[brain_name]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 2. Examine the State and Action Spaces\n\nThe simulation contains a single agent that navigates a large environment. At each time step, it has four actions at its disposal:\n- `0` - walk forward \n- `1` - walk backward\n- `2` - turn left\n- `3` - turn right\n\nThe state space has `37` dimensions and contains the agent's velocity, along with ray-based perception of objects around agent's forward direction. A reward of `+1` is provided for collecting a yellow banana, and a reward of `-1` is provided for collecting a blue banana. \n\nRun the code cell below to print some information about the environment.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# reset the environment\nenv_info = env.reset(train_mode=True)[brain_name]\n\n# number of agents in the environment\nprint('Number of agents:', len(env_info.agents))\n\n# number of actions\naction_size = brain.vector_action_space_size\nprint('Number of actions:', action_size)\n\n# examine the state space \nstate = env_info.vector_observations[0]\nprint('States look like:', state)\nstate_size = len(state)\nprint('States have length:', state_size)",
"Number of agents: 1\nNumber of actions: 4\nStates look like: [1. 0. 0. 0. 0.84408134 0.\n 0. 1. 0. 0.0748472 0. 1.\n 0. 0. 0.25755 1. 0. 0.\n 0. 0.74177343 0. 1. 0. 0.\n 0.25854847 0. 0. 1. 0. 0.09355672\n 0. 1. 0. 0. 0.31969345 0.\n 0. ]\nStates have length: 37\n"
]
],
[
[
"### 3. Take Random Actions in the Environment\n\nIn the next code cell, you will learn how to use the Python API to control the agent and receive feedback from the environment.\n\nOnce this cell is executed, you will watch the agent's performance, if it selects an action (uniformly) at random with each time step. A window should pop up that allows you to observe the agent, as it moves through the environment. \n\nOf course, as part of the project, you'll have to change the code so that the agent is able to use its experience to gradually choose better actions when interacting with the environment!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"env_info = env.reset(train_mode=False)[brain_name] # reset the environment\nstate = env_info.vector_observations[0] # get the current state\nscore = 0 # initialize the score\nwhile True:\n action = np.random.randint(action_size) # select an action\n env_info = env.step(action)[brain_name] # send the action to the environment\n next_state = env_info.vector_observations[0] # get the next state\n reward = env_info.rewards[0] # get the reward\n done = env_info.local_done[0] # see if episode has finished\n score += reward # update the score\n state = next_state # roll over the state to next time step\n if done: # exit loop if episode finished\n break\n \nprint(\"Score: {}\".format(score))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"When finished, you can close the environment.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"env.close()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 4. It's Your Turn!\n\nNow it's your turn to train your own agent to solve the environment! When training the environment, set `train_mode=True`, so that the line for resetting the environment looks like the following:\n```python\nenv_info = env.reset(train_mode=True)[brain_name]\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a73f711a1cd9fea0be60eef01ea8e8f63ed2b47
| 213,590 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
home_credit_risk_feature_analysis_week4.ipynb
|
Katayounb/week4-assignment
|
912817996bd9cb07b5025b4c46fecdf12f90ec18
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
home_credit_risk_feature_analysis_week4.ipynb
|
Katayounb/week4-assignment
|
912817996bd9cb07b5025b4c46fecdf12f90ec18
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
home_credit_risk_feature_analysis_week4.ipynb
|
Katayounb/week4-assignment
|
912817996bd9cb07b5025b4c46fecdf12f90ec18
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 32.669012 | 284 | 0.336678 |
[
[
[
"## Session 4 : Feature engineering - Home Credit Risk\n\n##### Student: Katayoun B.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n%matplotlib inline \nimport seaborn as sns\nimport glob",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Understanding the tables and loading all",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def load_data(path):\n data_path = path \n df_files = glob.glob(data_path+\"*.csv\")\n df_files = sorted(df_files, key=str.lower)\n return df_files",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_files = load_data('/Users/katy/desktop/ml/homework3/home_credit_risk/')\ndf_files",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"csvs = len(df_files)\ncsvs",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# creating datafram for each csv\nfor x in range(csvs):\n if x == 0:\n print(df_files[0])\n main_df = pd.read_csv(df_files[0])\n #print(train_df)\n if x == 1:\n print(df_files[1])\n bureau_df = pd.read_csv(df_files[1])\n if x == 2:\n print(df_files[2])\n bureau_balance_df = pd.read_csv(df_files[2])\n if x == 3:\n print(df_files[3])\n credit_balance_df = pd.read_csv(df_files[3])\n if x == 4:\n print(df_files[4])\n installments_df = pd.read_csv(df_files[4])\n if x == 5:\n print(df_files[5])\n pos_cash_df = pd.read_csv(df_files[5])\n if x == 6:\n print(df_files[6])\n prev_df = pd.read_csv(df_files[6])",
"/Users/katy/desktop/ml/homework3/home_credit_risk/application_train.csv\n/Users/katy/desktop/ml/homework3/home_credit_risk/bureau.csv\n/Users/katy/desktop/ml/homework3/home_credit_risk/bureau_balance.csv\n/Users/katy/desktop/ml/homework3/home_credit_risk/credit_card_balance.csv\n/Users/katy/desktop/ml/homework3/home_credit_risk/installments_payments.csv\n/Users/katy/desktop/ml/homework3/home_credit_risk/POS_CASH_balance.csv\n/Users/katy/desktop/ml/homework3/home_credit_risk/previous_application.csv\n"
],
[
"print(main_df.shape)\nmain_df.head()",
"(307511, 122)\n"
],
[
"#print(main_df.columns.values)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Assignment 1: complete feature analysis for main table\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"1. To create a new feature between 'AMT_CREDIT', 'AMT_INCOME_TOTAL'\n2. I want to call this new feature 'HIGH_INCOME', One(1) for 'HIGH_INCOME' and Zero(0) for less than mean value wich is 3.9",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"main_df[['AMT_CREDIT','AMT_INCOME_TOTAL']]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"main_df['HIGH_INCOME'] = main_df['AMT_CREDIT'] / main_df['AMT_INCOME_TOTAL']\nmain_df['HIGH_INCOME'].mean()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"main_df['HIGH_INCOME'] = main_df['HIGH_INCOME'].apply(lambda x : 0 if x < 3 else 1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"main_df[['SK_ID_CURR', 'AMT_CREDIT', 'AMT_INCOME_TOTAL', 'HIGH_INCOME']]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"1. I create a new feature called 'RISKY_NEW_JOB_FLAG', I assume if they switched the phone number recently that means they changed the job recently.\n2. if this number is bigger 180 days ( 6 months - max number of months to pass probation ), ignore this otherwise flag as a risky with new job 'RISKY_NEW_JOB_FLAG'.\n3. one(1) for risky, Zero(0) for not-risky.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"main_df['DAYS_LAST_PHONE_CHANGE']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"main_df['RISKY_NEW_JOB_FLAG'] = main_df['DAYS_LAST_PHONE_CHANGE'].abs()\nmain_df['RISKY_NEW_JOB_FLAG'] = main_df['RISKY_NEW_JOB_FLAG'].apply(lambda x : 0 if x < 180 else 1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"main_df[['SK_ID_CURR', 'RISKY_NEW_JOB_FLAG']]\n# Then we might drop that col, just an idea",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Create a new feature called 'IF_EMPLOYED', zero (0) is not-employed any more, one (1) for employed. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"main_df['IF_EMPLOYED'] = main_df['DAYS_EMPLOYED'].apply(lambda x : 0 if x > 0 else 1)\nmain_df[['SK_ID_CURR', 'IF_EMPLOYED']]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# check if flaged them correctly\nmain_df.loc[main_df.IF_EMPLOYED == 0]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"1. Create a new feature called 'DAYS_EMPLOYED_PCT' to show the number of work experience (senior or junior). \n2. calculating the percentage of 'DAYS_EMPLOYED' and 'DAYS_BIRTH', \n3. if this nubmer is bigger than > 0.2 I assume that persion is a senior or at least has enough work experience. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"main_df['DAYS_EMPLOYED_PCT'] = main_df['DAYS_EMPLOYED'] / main_df['DAYS_BIRTH']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"main_df['DAYS_EMPLOYED_PCT'] = main_df['DAYS_EMPLOYED_PCT'].abs()\nmain_df['DAYS_EMPLOYED_PCT'] = round(main_df['DAYS_EMPLOYED_PCT'])\nmain_df[['SK_ID_CURR', 'DAYS_EMPLOYED_PCT']]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"main_df['DAYS_EMPLOYED_PCT'] = main_df['DAYS_EMPLOYED_PCT'].apply(lambda x : 0 if x < 0.2 else 1)\nmain_df[['SK_ID_CURR', 'DAYS_EMPLOYED_PCT']]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Assignment 2: team up to expand more features with crazy brain storming",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# bureau_df",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(bureau_df.shape)\nbureau_df.head()",
"(1716428, 17)\n"
],
[
"bureau_df.loc[bureau_df.CREDIT_ACTIVE=='Closed']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"bureau_df.groupby('SK_ID_CURR')['SK_ID_BUREAU'].size()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(bureau_df.columns.values)",
"['SK_ID_CURR' 'SK_ID_BUREAU' 'CREDIT_ACTIVE' 'CREDIT_CURRENCY'\n 'DAYS_CREDIT' 'CREDIT_DAY_OVERDUE' 'DAYS_CREDIT_ENDDATE'\n 'DAYS_ENDDATE_FACT' 'AMT_CREDIT_MAX_OVERDUE' 'CNT_CREDIT_PROLONG'\n 'AMT_CREDIT_SUM' 'AMT_CREDIT_SUM_DEBT' 'AMT_CREDIT_SUM_LIMIT'\n 'AMT_CREDIT_SUM_OVERDUE' 'CREDIT_TYPE' 'DAYS_CREDIT_UPDATE' 'AMT_ANNUITY']\n"
]
],
[
[
"One client open different credit card reporting to credit bureau",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"agg_df = pd.DataFrame(bureau_df.groupby('SK_ID_CURR')['SK_ID_BUREAU'].size()).reset_index()\nagg_df.columns = ['SK_ID_CURR','BU_count']\nagg_df.sort_values('BU_count',inplace=True,ascending=False)\nagg_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"bureau_df.loc[bureau_df.SK_ID_CURR==120860]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"1. lets look at CREDIT_DAY_OVERDUE and AMT_CREDIT_MAX_OVERDUE",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"bureau_df['CREDIT_DAY_OVERDUE']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"bureau_temp_df = bureau_df.loc[bureau_df.CREDIT_DAY_OVERDUE > 40]\nbureau_temp_df.sort_values('AMT_CREDIT_MAX_OVERDUE',inplace=True,ascending=False)\nbureau_temp_df[['SK_ID_CURR','SK_ID_BUREAU','CREDIT_DAY_OVERDUE','AMT_CREDIT_MAX_OVERDUE']]",
"/Users/katy/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:2: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy\n \n"
]
],
[
[
"supposed credit duration:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# supposed credit duration:\nbureau_df['SUPPOSED_DURATION_CREDIT'] = bureau_df['DAYS_CREDIT_ENDDATE'] - bureau_df['DAYS_CREDIT']\nbureau_df['SUPPOSED_DURATION_CREDIT']",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"actual credit duration:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"bureau_df['ACTUAL_DURATION_CREDIT'] = bureau_df['DAYS_ENDDATE_FACT'] - bureau_df['DAYS_CREDIT']\nbureau_df['ACTUAL_DURATION_CREDIT']",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"diff between credit duration and actuall duration:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"bureau_df['DIFF_DURATION_CREDIT'] = bureau_df['ACTUAL_DURATION_CREDIT'] - bureau_df['SUPPOSED_DURATION_CREDIT']\nbureau_df['DIFF_DURATION_CREDIT'] ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Assignment 3: team up and create features for credit_balance",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# bureau_balance",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Status of Credit Bureau loan during the month\nC means closed, \nX means status unknown, \n0 means no DPD, \n1 means maximal did during month between 1-30, \n2 means DPD 31-60,… 5 means DPD 120+ or sold or written off ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"bureau_balance_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"lets create a new feature called BB_NO_DPD, if 'STATUS' == 0 ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"bureau_balance_df['BB_NO_DPD'] = bureau_balance_df['STATUS'].apply(lambda x: True if x==0 else False)\nbureau_balance_df[['SK_ID_BUREAU', 'BB_NO_DPD']]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# credit_balance",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"credit_balance_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"credit_balance_df.columns",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Note: please pay more attention to col: \"MONTHS_BALANCE\" per user, because it indicates the date of the credit and balance away from current application. I suggest that focus on one user and apply your idea to all users after. This is time series data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# let us take ID 378907 as example\ntemp_df = credit_balance_df.loc[credit_balance_df.SK_ID_CURR==378907]\ntemp_df.sort_values('MONTHS_BALANCE',inplace=True,ascending=False)",
"/Users/katy/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:3: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy\n This is separate from the ipykernel package so we can avoid doing imports until\n"
],
[
"temp_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Assignment 4: team up and create features for installment history",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# installment.csv",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"installments_df.loc[installments_df.AMT_INSTALMENT!=installments_df.AMT_PAYMENT]\ninstallments_df[['SK_ID_PREV', 'AMT_PAYMENT']]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"installments_df[['SK_ID_PREV', 'AMT_INSTALMENT']]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"lets see if the difference between AMT_INSTALMENT and AMT_PAYMENT, give us anything intresting ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"installments_df['AMT_INSTALMENT_DIFF'] = installments_df[ 'AMT_INSTALMENT'] - installments_df[ 'AMT_PAYMENT']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"installments_df[['SK_ID_PREV', 'AMT_INSTALMENT_DIFF']]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Lets see the difference between: \n1. DAYS_ENTRY_PAYMENT - When was the installments of previous credit paid actually (relative to application date of current loan)\n2. DAYS_INSTALMENT- When the installment of previous credit was supposed to be paid (relative to application date of current loan)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"installments_df[ 'DAYS_INSTALMENT']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"installments_df['DAYS_INSTALMENT_DIFF'] = (installments_df[ 'DAYS_ENTRY_PAYMENT'] - installments_df[ 'DAYS_INSTALMENT']).clip(lower=0)\ninstallments_df['DAYS_INSTALMENT_DIFF']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"installments_df[['SK_ID_CURR', 'SK_ID_PREV', 'DAYS_INSTALMENT_DIFF']]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"DAYS_INSTALMENT, which indidates the days of paying installent, you need to sort them by each client",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"temp_installments_df = installments_df.loc[installments_df.SK_ID_CURR==378907]\ntemp_installments_df.sort_values('DAYS_INSTALMENT',inplace=True,ascending=False)",
"/Users/katy/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:2: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy\n \n"
]
],
[
[
"let see it for SK_ID_CURR==378907",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"temp_installments_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Assignment 5: complete feature engineering by sorting by \"MONTHS_BALANCE\"\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# pos_cash.csv",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pos_cash_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"1. SK_DPD refers to the dpd (days past due) for any amounts(even if it is small); \n2. SK_DPD_DEF refers to the dpd (days past due) for those relatively \"significant\" amounts. Which saying, we should take SK_DPD_DEF as the ideal column for evaluating the customer's dpd behaviors.\n3. SK_DPD is often bigger than SK_DPD_DEF\n******\n4. New Feature: Created a new feature called \"SK_DPD_DEF_risk\" has values 0,1, One(1) for high risk, Zero(0) for low risk applicant. (High Risk - applicants with more than 30 days -ast due. ) ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pos_cash_df['SK_DPD_DEF_risk'] = (pos_cash_df['SK_DPD_DEF'] > 30).astype(int)\npos_cash_df[['SK_ID_PREV','SK_DPD_DEF_risk']]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"1. We know that SK_DPD is often bigger than SK_DPD_DEF, lets create New Freature call \"SK_DPD_diff\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pos_cash_df['SK_DPD_diff'] = pos_cash_df['SK_DPD'] - pos_cash_df['SK_DPD_DEF']\npos_cash_df[['SK_ID_PREV','SK_DPD_diff']]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a = sorted(pos_cash_df['MONTHS_BALANCE'])\nprint(a)\n#pos_cash_df[['SK_ID_PREV','MONTHS_BALANCE']]",
"IOPub data rate exceeded.\nThe notebook server will temporarily stop sending output\nto the client in order to avoid crashing it.\nTo change this limit, set the config variable\n`--NotebookApp.iopub_data_rate_limit`.\n\nCurrent values:\nNotebookApp.iopub_data_rate_limit=1000000.0 (bytes/sec)\nNotebookApp.rate_limit_window=3.0 (secs)\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Assignment 6: complete feature engineering for this table\n#### prev_df.csv\nThis file shows the previous activity for clients in the bank(not in other banks), you can independently process it and merge into the main table as new features",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"prev_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"here are some features I made to help you\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"1. AMT_CREDIT - Final credit amount on the previous application. This differs from AMT_APPLICATION in a way that the AMT_APPLICATION is the amount for which the client initially applied for, but during our approval process he could have received different amount - AMT_CREDIT\n\n2. AMT_APPLICATION\tFor how much credit did client ask on the previous application\n3. Creating new feature called: 'RATE_AMT_CREDIT' = how much client asked / final amount recieved, if the number bigger than 1, meaning he is a preferable client. \n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"prev_df['RATE_AMT_CREDIT'] = prev_df['AMT_APPLICATION']/prev_df['AMT_CREDIT']\nprev_df[['SK_ID_PREV', 'RATE_AMT_CREDIT']]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"1. AMT_CREDIT - Final credit amount on the previous application. This differs from AMT_APPLICATION in a way that the AMT_APPLICATION is the amount for which the client initially applied for, but during our approval process he could have received different amount - AMT_CREDIT\n2. AMT_ANNUITY- Annuity (a fixed sum of money paid to someone each year) of previous application\n3. Creating new feature called: 'RATE_ANN_CREDIT' = Annuity of previous application / final amount recieved",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"prev_df['RATE_ANN_CREDIT'] = prev_df['AMT_ANNUITY']/prev_df['AMT_CREDIT']\nprev_df[['SK_ID_PREV', 'RATE_ANN_CREDIT']]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"1. 'AMT_DOWN_PAYMENT' - Down payment on the previous application\n2. AMT_CREDIT - Final credit amount on the previous application. This differs from AMT_APPLICATION in a way that the AMT_APPLICATION is the amount for which the client initially applied for, but during our approval process he could have received different amount - AMT_CREDIT\n3. Creating new feature called: 'RATE_DOWNPAY_CREDIT' = Down payment on the previous application / Final credit amount on the previous application, 'RATE_DOWNPAY_CREDIT' would be one (1) if it's less or equal to 0, otherwise will be one (0)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"prev_df['RATE_DOWNPAY_CREDIT'] = prev_df['AMT_DOWN_PAYMENT']/prev_df['AMT_CREDIT']\nprev_df[['SK_ID_PREV', 'RATE_DOWNPAY_CREDIT']]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"prev_df['RATE_DOWNPAY_CREDIT'] = prev_df['RATE_DOWNPAY_CREDIT'].apply(lambda x: 1 if x < 0 or x ==0 else 0)\nprev_df[['SK_ID_PREV', 'RATE_DOWNPAY_CREDIT']]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"1. AMT_ANNUITY - Annuity (a fixed sum of money paid to someone each year) of previous application\n2. AMT_APPLICATION - is the amount for which the client initially applied for, but during our approval process he could have received different amount - AMT_CREDIT\n3. Creating new feature called: 'RATE_ANN_APPT' = Annuity of previous application / amount client initially applied for",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"prev_df['RATE_ANN_APP'] = prev_df['AMT_ANNUITY']/prev_df['AMT_APPLICATION']\nprev_df[['SK_ID_PREV', 'RATE_ANN_APP']]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# In real scenario it would be useful to encode 'CODE_REJECT_REASON', but I have no way of encoding and understanding XAP or HC \nprev_df[['SK_ID_PREV', 'CODE_REJECT_REASON']]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Was the previous application for CASH, POS, CAR, …\nThis might help to find out which have own a car",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"prev_df[['SK_ID_PREV', 'NAME_PORTFOLIO']]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Through which channel we acquired the client on the previous application\nThis might be helpful for marketing",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"prev_df[['SK_ID_PREV', 'CHANNEL_TYPE']]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"NAME_TYPE_SUITE - Who accompanied client when applying for the previous application, we can create a new feature to find who needed a co-signer, We assume that those with accompany needed a Co-Signer. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"prev_df[['SK_ID_PREV', 'NAME_TYPE_SUITE']]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Create Co_SIGNER flag - True for having co-signer and false for not having\nNote: this an assumption, in real case we do more investigation ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"prev_df['CO_SIGNER'] = prev_df['NAME_TYPE_SUITE'].apply(lambda x: False if x is np.nan else True)\nprev_df[['SK_ID_PREV', 'CO_SIGNER']]\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a73fdcd025a63f6a8126cfcf3f60b15e8be3faf
| 6,211 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Introduction to TensorFlow for Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning/Exercise2-Question.ipynb
|
yupyub/Coursera_TF
|
94ff2f7ce9f5d20138df1ceb7d11d26da758b20c
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Introduction to TensorFlow for Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning/Exercise2-Question.ipynb
|
yupyub/Coursera_TF
|
94ff2f7ce9f5d20138df1ceb7d11d26da758b20c
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Introduction to TensorFlow for Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning/Exercise2-Question.ipynb
|
yupyub/Coursera_TF
|
94ff2f7ce9f5d20138df1ceb7d11d26da758b20c
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 31.688776 | 225 | 0.535502 |
[
[
[
"## Exercise 2\nIn the course you learned how to do classificaiton using Fashion MNIST, a data set containing items of clothing. There's another, similar dataset called MNIST which has items of handwriting -- the digits 0 through 9.\n\nWrite an MNIST classifier that trains to 99% accuracy or above, and does it without a fixed number of epochs -- i.e. you should stop training once you reach that level of accuracy.\n\nSome notes:\n1. It should succeed in less than 10 epochs, so it is okay to change epochs= to 10, but nothing larger\n2. When it reaches 99% or greater it should print out the string \"Reached 99% accuracy so cancelling training!\"\n3. If you add any additional variables, make sure you use the same names as the ones used in the class\n\nI've started the code for you below -- how would you finish it? ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import tensorflow as tf\nfrom os import path, getcwd, chdir\n\n# DO NOT CHANGE THE LINE BELOW. If you are developing in a local\n# environment, then grab mnist.npz from the Coursera Jupyter Notebook\n# and place it inside a local folder and edit the path to that location\npath = f\"{getcwd()}/../tmp2/mnist.npz\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# GRADED FUNCTION: train_mnist\ndef train_mnist():\n # Please write your code only where you are indicated.\n # please do not remove # model fitting inline comments.\n\n # YOUR CODE SHOULD START HERE\n class myCallBack(tf.keras.callbacks.Callback):\n def on_epoch_end(self, epoch, logs={}):\n if(logs.get('acc')>0.99):\n print(\"\\nReached 99% accuracy so cancelling training!\")\n self.model.stop_training = True\n # YOUR CODE SHOULD END HERE\n\n mnist = tf.keras.datasets.mnist\n \n (x_train, y_train),(x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data(path=path)\n # YOUR CODE SHOULD START HERE\n x_train = x_train / 255.0\n x_test = x_test / 255.0\n #x_train = t_train/255.0\n #x_test = x_test/255.0\n # YOUR CODE SHOULD END HERE\n callbacks = myCallBack()\n model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([\n # YOUR CODE SHOULD START HERE\n tf.keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28,28)),\n tf.keras.layers.Dense(512, activation=tf.nn.relu),\n tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation=tf.nn.softmax)\n # YOUR CODE SHOULD END HERE\n ])\n\n model.compile(optimizer='adam',\n loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',\n metrics=['accuracy'])\n \n # model fitting\n history = model.fit(\n # YOUR CODE SHOULD START HERE\n x_train, y_train, epochs=10, callbacks=[callbacks]\n # YOUR CODE SHOULD END HERE\n )\n # model fitting\n return history.epoch, history.history['acc'][-1]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"train_mnist()",
"Epoch 1/10\n60000/60000 [==============================] - 9s 155us/sample - loss: 0.2025 - acc: 0.9401\nEpoch 2/10\n60000/60000 [==============================] - 9s 153us/sample - loss: 0.0813 - acc: 0.9755\nEpoch 3/10\n60000/60000 [==============================] - 9s 152us/sample - loss: 0.0530 - acc: 0.9839\nEpoch 4/10\n60000/60000 [==============================] - 9s 155us/sample - loss: 0.0381 - acc: 0.9881\nEpoch 5/10\n59744/60000 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.0277 - acc: 0.9909\nReached 99% accuracy so cancelling training!\n60000/60000 [==============================] - 9s 151us/sample - loss: 0.0276 - acc: 0.9910\n"
],
[
"# Now click the 'Submit Assignment' button above.\n# Once that is complete, please run the following two cells to save your work and close the notebook",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%%javascript\n<!-- Save the notebook -->\nIPython.notebook.save_checkpoint();",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%%javascript\nIPython.notebook.session.delete();\nwindow.onbeforeunload = null\nsetTimeout(function() { window.close(); }, 1000);",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a7412b295849e469af6ad9e27fc02b67963418b
| 28,034 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
sagemaker_processing/fairness_and_explainability/fairness_and_explainability_jsonlines_format.ipynb
|
qidewenwhen/amazon-sagemaker-examples
|
77f7ad7970381a3c9ab74fc8604ab8903ec55c9b
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
sagemaker_processing/fairness_and_explainability/fairness_and_explainability_jsonlines_format.ipynb
|
qidewenwhen/amazon-sagemaker-examples
|
77f7ad7970381a3c9ab74fc8604ab8903ec55c9b
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2022-03-15T20:04:30.000Z
|
2022-03-15T20:04:30.000Z
|
sagemaker_processing/fairness_and_explainability/fairness_and_explainability_jsonlines_format.ipynb
|
vivekmadan2/amazon-sagemaker-examples
|
4ccb050067c5305a50db750df3444dbc85600d5f
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2022-03-19T17:04:30.000Z
|
2022-03-19T17:04:30.000Z
| 39.652051 | 629 | 0.633053 |
[
[
[
"# Fairness and Explainability with SageMaker Clarify - JSONLines Format",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"1. [Overview](#Overview)\n1. [Prerequisites and Data](#Prerequisites-and-Data)\n 1. [Initialize SageMaker](#Initialize-SageMaker)\n 1. [Download data](#Download-data)\n 1. [Loading the data: Adult Dataset](#Loading-the-data:-Adult-Dataset) \n 1. [Data inspection](#Data-inspection) \n 1. [Data encoding and upload to S3](#Encode-and-Upload-the-Data) \n1. [Train and Deploy Linear Learner Model](#Train-Linear-Learner-Model)\n 1. [Train Model](#Train-Model)\n 1. [Deploy Model to Endpoint](#Deploy-Model)\n1. [Amazon SageMaker Clarify](#Amazon-SageMaker-Clarify)\n 1. [Detecting Bias](#Detecting-Bias)\n 1. [Writing BiasConfig](#Writing-BiasConfig)\n 1. [Pre-training Bias](#Pre-training-Bias)\n 1. [Post-training Bias](#Post-training-Bias)\n 1. [Viewing the Bias Report](#Viewing-the-Bias-Report)\n 1. [Explaining Predictions](#Explaining-Predictions)\n 1. [Viewing the Explainability Report](#Viewing-the-Explainability-Report)\n1. [Clean Up](#Clean-Up)\n\n## Overview\nAmazon SageMaker Clarify helps improve your machine learning models by detecting potential bias and helping explain how these models make predictions. The fairness and explainability functionality provided by SageMaker Clarify takes a step towards enabling AWS customers to build trustworthy and understandable machine learning models. The product comes with the tools to help you with the following tasks.\n\n* Measure biases that can occur during each stage of the ML lifecycle (data collection, model training and tuning, and monitoring of ML models deployed for inference).\n* Generate model governance reports targeting risk and compliance teams and external regulators.\n* Provide explanations of the data, models, and monitoring used to assess predictions.\n\nThis sample notebook walks you through: \n1. Key terms and concepts needed to understand SageMaker Clarify\n1. Measuring the pre-training bias of a dataset and post-training bias of a model\n1. Explaining the importance of the various input features on the model's decision\n1. Accessing the reports through SageMaker Studio if you have an instance set up.\n\nIn doing so, the notebook will first train a [SageMaker Linear Learner](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/sagemaker/latest/dg/linear-learner.html) model using training dataset, then use SageMaker Clarify to analyze a testing dataset in [SageMaker JSONLines dense format](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/sagemaker/latest/dg/cdf-inference.html#common-in-formats). SageMaker Clarify also supports analyzing CSV dataset, which is illustrated in [another notebook](https://github.com/aws/amazon-sagemaker-examples/blob/master/sagemaker_processing/fairness_and_explainability/fairness_and_explainability.ipynb).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Prerequisites and Data\n### Initialize SageMaker",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sagemaker import Session\n\nsession = Session()\nbucket = session.default_bucket()\nprefix = \"sagemaker/DEMO-sagemaker-clarify-jsonlines\"\nregion = session.boto_region_name\n# Define IAM role\nfrom sagemaker import get_execution_role\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport os\nimport boto3\nfrom datetime import datetime\n\nrole = get_execution_role()\ns3_client = boto3.client(\"s3\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Download data\nData Source: [https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/adult/](https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/adult/)\n\nLet's __download__ the data and save it in the local folder with the name adult.data and adult.test from UCI repository$^{[2]}$.\n\n$^{[2]}$Dua Dheeru, and Efi Karra Taniskidou. \"[UCI Machine Learning Repository](http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml)\". Irvine, CA: University of California, School of Information and Computer Science (2017).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"adult_columns = [\n \"Age\",\n \"Workclass\",\n \"fnlwgt\",\n \"Education\",\n \"Education-Num\",\n \"Marital Status\",\n \"Occupation\",\n \"Relationship\",\n \"Ethnic group\",\n \"Sex\",\n \"Capital Gain\",\n \"Capital Loss\",\n \"Hours per week\",\n \"Country\",\n \"Target\",\n]\nif not os.path.isfile(\"adult.data\"):\n s3_client.download_file(\n \"sagemaker-sample-files\", \"datasets/tabular/uci_adult/adult.data\", \"adult.data\"\n )\n print(\"adult.data saved!\")\nelse:\n print(\"adult.data already on disk.\")\n\nif not os.path.isfile(\"adult.test\"):\n s3_client.download_file(\n \"sagemaker-sample-files\", \"datasets/tabular/uci_adult/adult.test\", \"adult.test\"\n )\n print(\"adult.test saved!\")\nelse:\n print(\"adult.test already on disk.\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Loading the data: Adult Dataset\nFrom the UCI repository of machine learning datasets, this database contains 14 features concerning demographic characteristics of 45,222 rows (32,561 for training and 12,661 for testing). The task is to predict whether a person has a yearly income that is more or less than $50,000.\n\nHere are the features and their possible values:\n1. **Age**: continuous.\n1. **Workclass**: Private, Self-emp-not-inc, Self-emp-inc, Federal-gov, Local-gov, State-gov, Without-pay, Never-worked.\n1. **Fnlwgt**: continuous (the number of people the census takers believe that observation represents).\n1. **Education**: Bachelors, Some-college, 11th, HS-grad, Prof-school, Assoc-acdm, Assoc-voc, 9th, 7th-8th, 12th, Masters, 1st-4th, 10th, Doctorate, 5th-6th, Preschool.\n1. **Education-num**: continuous.\n1. **Marital-status**: Married-civ-spouse, Divorced, Never-married, Separated, Widowed, Married-spouse-absent, Married-AF-spouse.\n1. **Occupation**: Tech-support, Craft-repair, Other-service, Sales, Exec-managerial, Prof-specialty, Handlers-cleaners, Machine-op-inspct, Adm-clerical, Farming-fishing, Transport-moving, Priv-house-serv, Protective-serv, Armed-Forces.\n1. **Relationship**: Wife, Own-child, Husband, Not-in-family, Other-relative, Unmarried.\n1. **Ethnic group**: White, Asian-Pac-Islander, Amer-Indian-Eskimo, Other, Black.\n1. **Sex**: Female, Male.\n * **Note**: this data is extracted from the 1994 Census and enforces a binary option on Sex\n1. **Capital-gain**: continuous.\n1. **Capital-loss**: continuous.\n1. **Hours-per-week**: continuous.\n1. **Native-country**: United-States, Cambodia, England, Puerto-Rico, Canada, Germany, Outlying-US(Guam-USVI-etc), India, Japan, Greece, South, China, Cuba, Iran, Honduras, Philippines, Italy, Poland, Jamaica, Vietnam, Mexico, Portugal, Ireland, France, Dominican-Republic, Laos, Ecuador, Taiwan, Haiti, Columbia, Hungary, Guatemala, Nicaragua, Scotland, Thailand, Yugoslavia, El-Salvador, Trinadad&Tobago, Peru, Hong, Holand-Netherlands.\n\nNext, we specify our binary prediction task: \n15. **Target**: <=50,000, >$50,000.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"training_data = pd.read_csv(\n \"adult.data\", names=adult_columns, sep=r\"\\s*,\\s*\", engine=\"python\", na_values=\"?\"\n).dropna()\n\ntesting_data = pd.read_csv(\n \"adult.test\", names=adult_columns, sep=r\"\\s*,\\s*\", engine=\"python\", na_values=\"?\", skiprows=1\n).dropna()\n\ntraining_data.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Data inspection\nPlotting histograms for the distribution of the different features is a good way to visualize the data. Let's plot a few of the features that can be considered _sensitive_. \nLet's take a look specifically at the Sex feature of a census respondent. In the first plot we see that there are fewer Female respondents as a whole but especially in the positive outcomes, where they form ~$\\frac{1}{7}$th of respondents.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"training_data[\"Sex\"].value_counts().sort_values().plot(kind=\"bar\", title=\"Counts of Sex\", rot=0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"training_data[\"Sex\"].where(training_data[\"Target\"] == \">50K\").value_counts().sort_values().plot(\n kind=\"bar\", title=\"Counts of Sex earning >$50K\", rot=0\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Encode and Upload the Dataset\nHere we encode the training and test data. Encoding input data is not necessary for SageMaker Clarify, but is necessary for the model.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn import preprocessing\n\n\ndef number_encode_features(df):\n result = df.copy()\n encoders = {}\n for column in result.columns:\n if result.dtypes[column] == np.object:\n encoders[column] = preprocessing.LabelEncoder()\n # print('Column:', column, result[column])\n result[column] = encoders[column].fit_transform(result[column].fillna(\"None\"))\n return result, encoders\n\n\ntraining_data, _ = number_encode_features(training_data)\ntesting_data, _ = number_encode_features(testing_data)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Then save the testing dataset to a JSONLines file. The file conforms to [SageMaker JSONLines dense format](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/sagemaker/latest/dg/cdf-inference.html#common-in-formats), with an additional field to hold the ground truth label.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import json\n\n\ndef dump_to_jsonlines_file(df, filename):\n with open(filename, \"w\") as f:\n for _, row in df.iterrows():\n sample = {\"features\": row[0:-1].tolist(), \"label\": int(row[-1])}\n print(json.dumps(sample), file=f)\n\n\ndump_to_jsonlines_file(testing_data, \"test_data.jsonl\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"A quick note about our encoding: the \"Female\" Sex value has been encoded as 0 and \"Male\" as 1.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!head -n 5 test_data.jsonl",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"testing_data.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Lastly, let's upload the data to S3",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sagemaker.s3 import S3Uploader\n\ntest_data_uri = S3Uploader.upload(\"test_data.jsonl\", \"s3://{}/{}\".format(bucket, prefix))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Train Linear Learner Model\n#### Train Model\nSince our focus is on understanding how to use SageMaker Clarify, we keep it simple by using a standard Linear Learner model.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sagemaker.image_uris import retrieve\nfrom sagemaker.amazon.linear_learner import LinearLearner\n\nll = LinearLearner(\n role,\n instance_count=1,\n instance_type=\"ml.m5.xlarge\",\n predictor_type=\"binary_classifier\",\n sagemaker_session=session,\n)\ntraining_target = training_data[\"Target\"].to_numpy().astype(np.float32)\ntraining_features = training_data.drop([\"Target\"], axis=1).to_numpy().astype(np.float32)\nll.fit(ll.record_set(training_features, training_target), logs=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Deploy Model\nHere we create the SageMaker model.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model_name = \"DEMO-clarify-ll-model-{}\".format(datetime.now().strftime(\"%d-%m-%Y-%H-%M-%S\"))\nmodel = ll.create_model(name=model_name)\ncontainer_def = model.prepare_container_def()\nsession.create_model(model_name, role, container_def)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Amazon SageMaker Clarify\nNow that you have your model set up. Let's say hello to SageMaker Clarify!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sagemaker import clarify\n\nclarify_processor = clarify.SageMakerClarifyProcessor(\n role=role, instance_count=1, instance_type=\"ml.m5.xlarge\", sagemaker_session=session\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Detecting Bias\nSageMaker Clarify helps you detect possible pre- and post-training biases using a variety of metrics.\n#### Writing DataConfig and ModelConfig\nA `DataConfig` object communicates some basic information about data I/O to SageMaker Clarify. We specify where to find the input dataset, where to store the output, the target column (`label`), the header names, and the dataset type.\n\nSome special things to note about this configuration for the JSONLines dataset,\n* Argument `features` or `label` is **NOT** header string. Instead, it is a [JSONPath string](https://jmespath.org/specification.html) to locate the features list or label in the dataset. For example, for a sample like below, `features` should be 'data.features.values', and `label` should be 'data.label'. \n\n```\n{\"data\": {\"features\": {\"values\": [25, 2, 226802, 1, 7, 4, 6, 3, 2, 1, 0, 0, 40, 37]}, \"label\": 0}}\n```\n\n* SageMaker Clarify will load the JSONLines dataset into tabular representation for further analysis, and argument `headers` is the list of column names. The label header shall be the last one in the headers list, and the order of feature headers shall be the same as the order of features in a sample.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"bias_report_output_path = \"s3://{}/{}/clarify-bias\".format(bucket, prefix)\nbias_data_config = clarify.DataConfig(\n s3_data_input_path=test_data_uri,\n s3_output_path=bias_report_output_path,\n features=\"features\",\n label=\"label\",\n headers=testing_data.columns.to_list(),\n dataset_type=\"application/jsonlines\",\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"A `ModelConfig` object communicates information about your trained model. To avoid additional traffic to your production models, SageMaker Clarify sets up and tears down a dedicated endpoint when processing.\n* `instance_type` and `instance_count` specify your preferred instance type and instance count used to run your model on during SageMaker Clarify's processing. The testing dataset is small so a single standard instance is good enough to run this example. If your have a large complex dataset, you may want to use a better instance type to speed up, or add more instances to enable Spark parallelization.\n* `accept_type` denotes the endpoint response payload format, and `content_type` denotes the payload format of request to the endpoint.\n* `content_template` is used by SageMaker Clarify to compose the request payload if the content type is JSONLines. To be more specific, the placeholder `$features` will be replaced by the features list from samples. The request payload of a sample from the testing dataset happens to be similar to the sample itself, like `'{\"features\": [25, 2, 226802, 1, 7, 4, 6, 3, 2, 1, 0, 0, 40, 37]}'`, because both the dataset and the model input conform to [SageMaker JSONLines dense format](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/sagemaker/latest/dg/cdf-inference.html#common-in-formats).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model_config = clarify.ModelConfig(\n model_name=model_name,\n instance_type=\"ml.m5.xlarge\",\n instance_count=1,\n accept_type=\"application/jsonlines\",\n content_type=\"application/jsonlines\",\n content_template='{\"features\":$features}',\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"A `ModelPredictedLabelConfig` provides information on the format of your predictions. The argument `label` is a JSONPath string to locate the predicted label in endpoint response. In this case, the response payload for a single sample request looks like `'{\"predicted_label\": 0, \"score\": 0.013525663875043}'`, so SageMaker Clarify can find predicted label `0` by JSONPath `'predicted_label'`. There is also probability score in the response, so it is possible to use another combination of arguments to decide the predicted label by a custom threshold, for example `probability='score'` and `probability_threshold=0.8`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"predictions_config = clarify.ModelPredictedLabelConfig(label=\"predicted_label\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"If you are building your own model, then you may choose a different JSONLines format, as long as it has the key elements like label and features list, and request payload built using `content_template` is supported by the model (you can customize the template but the placeholder of features list must be `$features`). Also, `dataset_type`, `accept_type` and `content_type` don't have to be the same, for example, a use case may use CSV dataset and content type, but JSONLines accept type.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Writing BiasConfig\nSageMaker Clarify also needs information on what the sensitive columns (`facets`) are, what the sensitive features (`facet_values_or_threshold`) may be, and what the desirable outcomes are (`label_values_or_threshold`).\nSageMaker Clarify can handle both categorical and continuous data for `facet_values_or_threshold` and for `label_values_or_threshold`. In this case we are using categorical data.\n\nWe specify this information in the `BiasConfig` API. Here that the positive outcome is earning >$50,000, Sex is a sensitive category, and Female respondents are the sensitive group. `group_name` is used to form subgroups for the measurement of Conditional Demographic Disparity in Labels (CDDL) and Conditional Demographic Disparity in Predicted Labels (CDDPL) with regards to Simpson’s paradox.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"bias_config = clarify.BiasConfig(\n label_values_or_threshold=[1], facet_name=\"Sex\", facet_values_or_threshold=[0], group_name=\"Age\"\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Pre-training Bias\nBias can be present in your data before any model training occurs. Inspecting your data for bias before training begins can help detect any data collection gaps, inform your feature engineering, and hep you understand what societal biases the data may reflect.\n\nComputing pre-training bias metrics does not require a trained model.\n\n#### Post-training Bias\nComputing post-training bias metrics does require a trained model.\n\nUnbiased training data (as determined by concepts of fairness measured by bias metric) may still result in biased model predictions after training. Whether this occurs depends on several factors including hyperparameter choices.\n\n\nYou can run these options separately with `run_pre_training_bias()` and `run_post_training_bias()` or at the same time with `run_bias()` as shown below.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"clarify_processor.run_bias(\n data_config=bias_data_config,\n bias_config=bias_config,\n model_config=model_config,\n model_predicted_label_config=predictions_config,\n pre_training_methods=\"all\",\n post_training_methods=\"all\",\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Viewing the Bias Report\nIn Studio, you can view the results under the experiments tab.\n\n<img src=\"./recordings/bias_report.gif\">\n\nEach bias metric has detailed explanations with examples that you can explore.\n\n<img src=\"./recordings/bias_detail.gif\">\n\nYou could also summarize the results in a handy table!\n\n<img src=\"./recordings/bias_report_chart.gif\">\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"If you're not a Studio user yet, you can access the bias report in pdf, html and ipynb formats in the following S3 bucket:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"bias_report_output_path",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Explaining Predictions\nThere are expanding business needs and legislative regulations that require explanations of _why_ a model made the decision it did. SageMaker Clarify uses SHAP to explain the contribution that each input feature makes to the final decision.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Kernel SHAP algorithm requires a baseline (also known as background dataset). Baseline dataset type shall be the same as `dataset_type` of `DataConfig`, and baseline samples shall only include features. By definition, `baseline` should either be a S3 URI to the baseline dataset file, or an in-place list of samples. In this case we chose the latter, and put the first sample of the test dataset to the list.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# pick up the first line, load as JSON, then exclude the label (i.e., only keep the features)\nwith open(\"test_data.jsonl\") as f:\n baseline_sample = json.loads(f.readline())\ndel baseline_sample[\"label\"]\nbaseline_sample",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Similarly, excluding label header from headers list\nheaders = testing_data.columns.to_list()\nheaders.remove(\"Target\")\nprint(headers)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"shap_config = clarify.SHAPConfig(\n baseline=[baseline_sample], num_samples=15, agg_method=\"mean_abs\", save_local_shap_values=False\n)\n\nexplainability_output_path = \"s3://{}/{}/clarify-explainability\".format(bucket, prefix)\nexplainability_data_config = clarify.DataConfig(\n s3_data_input_path=test_data_uri,\n s3_output_path=explainability_output_path,\n features=\"features\",\n headers=headers,\n dataset_type=\"application/jsonlines\",\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Run the explainability job, note that Kernel SHAP algorithm requires probability prediction, so JSONPath `\"score\"` is used to extract the probability.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"clarify_processor.run_explainability(\n data_config=explainability_data_config,\n model_config=model_config,\n explainability_config=shap_config,\n model_scores=\"score\",\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Viewing the Explainability Report\nAs with the bias report, you can view the explainability report in Studio under the experiments tab\n\n\n<img src=\"./recordings/explainability_detail.gif\">\n\nThe Model Insights tab contains direct links to the report and model insights.\n\nIf you're not a Studio user yet, as with the Bias Report, you can access this report at the following S3 bucket.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"explainability_output_path",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Clean Up\nFinally, don't forget to clean up the resources we set up and used for this demo!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"session.delete_model(model_name)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a7439c9eaee553018c5a4c7c20ca07808b2825a
| 46,251 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
matrix_day3/DW_matrix_day3.ipynb
|
SpaceIntelligenceLab/dw_matrix_day1
|
1cf82a56a09a4d88eb377463e4835dd595d47dd6
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
matrix_day3/DW_matrix_day3.ipynb
|
SpaceIntelligenceLab/dw_matrix_day1
|
1cf82a56a09a4d88eb377463e4835dd595d47dd6
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
matrix_day3/DW_matrix_day3.ipynb
|
SpaceIntelligenceLab/dw_matrix_day1
|
1cf82a56a09a4d88eb377463e4835dd595d47dd6
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 46,251 | 46,251 | 0.735984 |
[
[
[
"#!pip install datadotworld\n#!pip install datadotworld[pandas]\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#!dw configure",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from google.colab import drive\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport datadotworld as dw\n#!pip install imgaug\n#from imgaug import augmenters as iaa\n#from imgaug import parameters as iap\n#import random\n#from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ROOT='/content/drive'\n#drive.mount(ROOT)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ls\n",
"\u001b[0m\u001b[01;34mdata\u001b[0m/ DW_matrix_day3.ipynb\n"
],
[
"cd \"drive/My Drive/Colab Notebooks/dw_matrix_day1\"",
"/content/drive/My Drive/Colab Notebooks/dw_matrix_day1\n"
],
[
"cd matrix_day3/",
"/content/drive/My Drive/Colab Notebooks/dw_matrix_day1/matrix_day3\n"
],
[
"ls",
"\u001b[0m\u001b[01;34mdata\u001b[0m/ DW_matrix_day3.ipynb\n"
],
[
"!echo 'data' > .gitignore",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!git add .gitignore",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data = dw.load_dataset('datafiniti/mens-shoe-prices')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = data.dataframes['7004_1']\ndf.shape",
"/usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/datadotworld/models/dataset.py:209: UserWarning: Unable to set data frame dtypes automatically using 7004_1 schema. Data types may need to be adjusted manually. Error: Integer column has NA values in column 10\n 'Error: {}'.format(resource_name, e))\n/usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/datadotworld/util.py:121: DtypeWarning: Columns (39,45) have mixed types. Specify dtype option on import or set low_memory=False.\n return self._loader_func()\n"
],
[
"df.sample(5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.columns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.prices_currency.unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.prices_currency.value_counts(normalize=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_usd = df[ df.prices_currency == 'USD'].copy()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_usd.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_usd['prices_amountmin'] = df_usd.prices_amountmin.astype(np.float)\ndf_usd['prices_amountmin'].hist()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"filter_max = np.percentile( df_usd['prices_amountmin'],99)\nfilter_max",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_usd_filter = df_usd[ df_usd['prices_amountmin'] < filter_max]\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_usd_filter.prices_amountmin.hist(bins=100)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ls",
"\u001b[0m\u001b[01;34mdata\u001b[0m/ DW_matrix_day3.ipynb\n"
],
[
"cd data/\nls",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cd ..",
"/content/drive/My Drive/Colab Notebooks/dw_matrix_day1/matrix_day3\n"
],
[
"ls",
"\u001b[0m\u001b[01;34mdata\u001b[0m/ DW_matrix_day3.ipynb\n"
],
[
"!git add DW_matrix_day3.ipynb",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!git config --global user.email \"[email protected]\"\n!git config --global user.name \"Space Intelligence Lab\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!git commit -m \"Read Men's Shoes Prices dataset from data.world\"",
"[master 849a921] Read Men's Shoes Prices dataset from data.world\n 2 files changed, 2 insertions(+)\n create mode 100644 matrix_day3/.gitignore\n create mode 100644 matrix_day3/DW_matrix_day3.ipynb\n"
],
[
"!git push -u origin master",
"Branch 'master' set up to track remote branch 'master' from 'origin'.\nEverything up-to-date\n"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a74411b9afc79bf0725740a1d65a50a701e4500
| 43,272 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Projeto_Python_Oficina_Mecanica_V3.ipynb
|
tycianojr/projetopython
|
2137ba387ad182e54e4af5a83b7dd6537386dfe4
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-12-17T16:12:13.000Z
|
2021-12-17T16:12:13.000Z
|
notebook/Projeto_Python_Oficina_Mecanica_V3.ipynb
|
victorog17/Soulcode_Projeto_Python
|
5f1d81139b4d6fe0c20ca4d83d51f0cbf5cd0a53
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebook/Projeto_Python_Oficina_Mecanica_V3.ipynb
|
victorog17/Soulcode_Projeto_Python
|
5f1d81139b4d6fe0c20ca4d83d51f0cbf5cd0a53
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 41.84913 | 427 | 0.463256 |
[
[
[
"<a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/victorog17/Soulcode_Projeto_Python/blob/main/Projeto_Python_Oficina_Mecanica_V2.ipynb\" target=\"_parent\"><img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open In Colab\"/></a>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print('Hello World')",
"Hello World\n"
],
[
"print('Essa Fera Bicho')",
"Essa Fera Bicho\n"
]
],
[
[
"1) Ao executar o algoritmo, deverá aparecer duas opções: \nA - Para acessar o programa ou \n\nF* - Para finalizar o programa (CORRIGIR) \n\nOK",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"2) Caso o usuário digite A, deverá ser direcionado para outra parte do programa que tenha no mínimo 4 funcionalidades que podem ser:\n\nAdicionar produto , adicionar serviço , finalizar a compra , etc.\n\nOK",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"3) A cada produto ou serviço selecionado, deverá aumentar o valor a ser pago na conta , igualmente num caixa de supermercado convencional . considerando que o cliente pode levar mais de uma quantidade do mesmo produto/serviço (ex : 2 caixas de leite , 2 trocas de pneus ) .\n\nOK",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"4) Ao fechar/concluir o processo de seleção de produtos/serviços deve exibir ao cliente o total de valor a ser pago e pedir para que o cliente selecione a forma de pagamento , obrigatoriamente deve existir a forma de pagamento em dinheiro que gere troco , caso o troco seja gerado deve-se informar o valor do troco e quantas cedulas vão ser dadas para o cliente, sempre considere a menor quantidade de cédulas possíveis .",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"5) As cédulas disponíveis são : 50 , 20 , 10 , 5 ,2 e 1 real . Pode descartar valores de centavos\n\nOK",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"6) No processo de finalização da compra deve existir uma opção para o cliente desistir da compra , em caso positivo deve ser perguntado a confirmação da desistência (informando os produtos/serviços que o cliente está desistindo)\n\nOK",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n7) Ao finalizar a compra deve-se voltar a tela inicial Acessar programa / finalizar programa . Quando finalizar deve-se exibir uma mensagem agradecendo a visita, informando o que foi comprado e o valor gasto no estabelecimento\n\nOK",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Lista de Produtos\nlista_prod = [['Pneu(s)', 'Calota(s)', 'Palheta(s)', 'Protetor(es) de Volante', 'Cheirinho(s) de Carro', 'Óleo de Motor', 'Bateria(s)'],[339.00, 15.00, 55.00, 30.00, 15.00, 27.00, 270.00]]\n\n# Lista de Serviços\nlista_serv = [['Troca de Óleo', 'Alinhamento', 'Revisão Geral', 'Troca de Lampada', 'Troca de Correia', 'Troca de Pastilha de Freio'],[200.00, 60.00, 300.00, 40.00, 220.00, 150.00]]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#FUNCIONALIDADES\n\nimport time\n\ndef limparcar(): #FUNÇÃO LIMPEZA DO CARRINHO\n somaFatura = 0\n for y in range(len(carrinho[0])): #AMOSTRA DO CARRINHO\n print(f'[{y+1}] - {carrinho[0][y]} --> R${carrinho[1][y]} Quantidade: {carrinho[2][y]}')\n somaFatura += ((carrinho[1][y])*(carrinho[2][y])) \n print(f\"\\nValor total R${somaFatura:.2f}\") #VALOR TOTAL\n print(\"[S] para sim\\n[N] para não\\n\") #CONFIRMAÇÃO DA AÇÃO\n certeza = input(f'Tem certeza que deseja remover TUDO de seu carrinho? ').upper()[0] \n print('='*50)\n while (certeza != 'S') and (certeza != 'N'):\n certeza = input(\"Opção inválida! Digite [S] para sim [N] para não:\\n\").upper()[0] \n print('='*50)\n if certeza == 'S': #CONFIRMAÇÃO = SIM - LIMPEZA DO CARRINHO\n carrinho[0].clear()\n carrinho[1].clear()\n carrinho[2].clear()\n print(\"Limpando seu carrinho ...\")\n print('='*50)\n time.sleep(3)\n else: #CONFIRMAÇÃO = NÃO\n print(\"Seus produtos foram mantidos no carrinho!\")\n print('='*50)\n time.sleep(3)\n\ndef adcProduto(): #FUNÇÃO ADICIONAR PRODUTO\n while True:\n print(\"Opções de produto:\\n\")\n for i in range(len(lista_prod[0])): #LISTA DE PRODUTOS DISPONÍVEIS\n print(f'[{i+1}] - {lista_prod[0][i]} --> R${lista_prod[1][i]}')\n print(\"\\nPara voltar ao menu principal basta digitar [99] \")\n print('='*50)\n #CARRINHO \n digite = int(input('Adicione um produto ao seu carrinho: '))\n print('='*50)\n if digite >= 1 and digite <= (len(lista_prod[0])): #ESCOLHA DE PRODUTO\n carrinho[0].append(lista_prod[0][digite-1])\n carrinho[1].append(lista_prod[1][digite-1])\n quant = int(input(f'Qual seria a quantidade de \"{lista_prod[0][digite-1]}\" (MÁX. 10): ')) #QUANTIDADE DE PRODUTO\n print('='*50)\n while quant <= 0 or quant > 10:\n quant = int(input('Valor inválido! Digite novamente a quantidade: '))\n print('='*50)\n print(f'Adicionando \"{lista_prod[0][digite-1]}\" ao seu carrinho ...')\n print('='*50)\n time.sleep(3)\n carrinho[2].append(quant)\n elif digite == 99: #SAÍDA DA FUNÇÃO\n print('Saindo ...')\n print('='*50)\n time.sleep(3)\n break\n else: #OPÇÃO INVÁLIDA\n print('Este número não está entre as opções!!')\n print('='*50)\n time.sleep(3)\n \ndef adcServico(): #FUNÇÃO ADICIONAR SERVIÇO\n while True:\n print(\"Opções de serviços:\\n\")\n for x in range(len(lista_serv[0])): #LISTA DE SERVIÇOS DISPONÍVEIS\n print(f'[{x+1}] - {lista_serv[0][x]} --> R${lista_serv[1][x]}')\n print(\"\\nPara voltar ao menu principal basta digitar [99] \")\n print('='*50)\n #CARRINHO \n digite = int(input('Adicione um serviço ao seu carrinho: '))\n print('='*50)\n if digite >= 1 and digite <= (len(lista_serv[0])): #ESCOLHA DE SERVIÇO\n carrinho[0].append(lista_serv[0][digite-1])\n carrinho[1].append(lista_serv[1][digite-1])\n print(f'Adicionando \"{lista_serv[0][digite-1]}\" ao seu carrinho ...')\n print('='*50)\n time.sleep(3)\n carrinho[2].append(1)\n elif digite == 99: #SAÍDA DA FUNÇÃO\n print('Saindo ...')\n print('='*50)\n time.sleep(3)\n break\n else: #OPÇÃO INVÁLIDA\n print('Este número não está entre as opções!!')\n print('='*50)\n time.sleep(3)\n\ndef rmvProduto(): #FUNÇÃO REMOVER PRODUTO/SERVIÇO\n while True:\n print(\"Dentro do carrinho:\\n\")\n for y in range(len(carrinho[0])): #AMOSTRA DO CARRINHO\n print(f'[{y+1}] - {carrinho[0][y]} --> R${carrinho[1][y]} Quantidade: {carrinho[2][y]}')\n print('='*50)\n #ESCOLHA DE OPÇÕES DE REMOÇÃO - PRODUTO OU QUANTIDADE\n print(\"Digite [P] para remover um produto/serviço\\nDigite [Q] para diminuir a quantidade de seu produto\\nDigite [M] para voltar ao MENU PRINCIPAL\")\n produto_ou_quantidade = input(\"\\nEscolha uma das opções acima: \").upper()[0]\n print('='*50)\n while (produto_ou_quantidade != 'P') and (produto_ou_quantidade != 'Q') and ((produto_ou_quantidade != 'M')):\n produto_ou_quantidade = input(\"As únicas opções válidas são [P], [Q] ou [M]: \").upper()[0]\n print('='*50)\n if produto_ou_quantidade == 'M': #SAÍDA DA FUNÇÃO\n print('Saindo ...')\n print('='*50)\n time.sleep(3)\n break\n elif produto_ou_quantidade == 'P': #REMOÇÃO DE PRODUTO\n remove = int(input(\"Informe qual produto irá remover: \"))\n print('='*50)\n while remove < 1 or remove > len(carrinho[0]):\n remove = int(input(\"Este produto não está na lista! Informe novamente qual produto irá remover: \"))\n print('='*50) \n elif produto_ou_quantidade == 'Q': #REMOÇÃO POR QUANTIDADE\n escolheProdRem = int(input(\"Informe de qual item irá reduzir a quantidade: \")) #APONTAR PRODUTO\n print('='*50)\n while escolheProdRem < 1 or escolheProdRem > len(carrinho[2]):\n escolheProdRem = int(input(\"Este produto não está na lista! Informe novamente qual produto irá reduzir a quantidade: \"))\n print('='*50)\n removeQuantidade = int(input(f'Gostaria de remover quantos de \"{carrinho[0][escolheProdRem-1]}\": ')) #REMOÇÃO DA QUANTIDADE DESSE PRODUTO\n print('='*50)\n while removeQuantidade <= 0 or removeQuantidade > carrinho[2][escolheProdRem-1]:\n removeQuantidade = int(input(f'Tirar este valor é impossível! Gostaria de remover quantos de \"{carrinho[0][escolheProdRem-1]}\": '))\n print('='*50)\n print(\"[S] para sim\\n[N] para não\\n\")\n certeza = input(f'Confirme a sua ação: ').upper()[0] #CONFIRMAÇÃO DA AÇÃO\n print('='*50)\n while (certeza != 'S') and (certeza != 'N'):\n certeza = input(\"Opção inválida! Digite [S] para sim [N] para não: \").upper()[0] \n print('='*50)\n if certeza == 'S': #CONFIRMAÇÃO = SIM\n if produto_ou_quantidade == 'P': #REMOÇÃO DO PRODUTO\n del carrinho[0][remove-1]\n del carrinho[1][remove-1]\n del carrinho[2][remove-1]\n elif produto_ou_quantidade == 'Q':\n if removeQuantidade == carrinho[2][escolheProdRem-1]: #SE REMOÇÃO DA QUANTIDADE FOR IGUAL A QUANTIDADE DO CARRINHO\n del carrinho[0][escolheProdRem-1]\n del carrinho[1][escolheProdRem-1]\n del carrinho[2][escolheProdRem-1]\n else:\n carrinho[2][escolheProdRem-1] -= removeQuantidade #REMOVE QUANTIDADE PEDIDA QUANDO MENOR QUE A QUANTIDADE DO PRODUTO\n else: #CONFIRMAÇÃO = NÃO - MANTÉM PRODUTO OU MESMA QUANTIDADE NO CARRINHO\n print(\"O produto não foi removido de seu carrinho!\")\n print('='*50)\n time.sleep(3)\n \ndef extrato(): #FUNÇÃO EXTRATO CARRINHO\n while True:\n somaFatura = 0\n for y in range(len(carrinho[0])): #AMOSTRA DO CARRINHO\n print(f'[{y+1}] - {carrinho[0][y]} --> R${carrinho[1][y]} Quantidade: {carrinho[2][y]}')\n somaFatura += ((carrinho[1][y])*(carrinho[2][y])) \n print(f\"\\nValor total R${somaFatura:.2f}\") #VALOR TOTAL\n sair_extrato = int(input(\"\\nDigite [99] para sair: \"))\n print('='*50)\n while sair_extrato != 99:\n sair_extrato = int(input(\"Dado inválido! Digite 99 para sair: \"))\n print('='*50)\n if sair_extrato == 99: #OPÇÃO DE SAÍDA DA FUNÇÃO\n print(\"Saindo ...\")\n print('='*50)\n time.sleep(3)\n break\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#PROGRAMA\nimport time\n\ncarrinho = [[],[],[]]\nhistorico = [[],[],[]]\n\n#ACESSAR/FINALIZAR\nwhile True:\n print(\"> Para acessar o programa basta digitar [A]\\n> Caso queira finalizar o programa, digite [F]\\n\")\n acessar = str(input(\"Escolha uma opção: \")).upper()[0]\n print('='*50)\n while acessar != 'A' and acessar != 'F': #VALIDAÇÃO ACESSAR/FINALIZAR\n acessar = input(\"Valor inválido! Digite A para acessar o programa ou F para finalizar o programa:\\n\").upper()[0]\n print('='*50)\n if acessar == 'A':\n print('Bem vindo a Oficina Borracha Forte!') #ACESSAR - BOAS VINDAS\n print('='*50)\n time.sleep(3)\n else:\n print('Iremos finalizar o programa ...') #FINALIZAR\n print('='*50)\n time.sleep(3)\n print(f\"Muito obrigado pela visita!\") #AGRADECIMENTO + HISTÓRICO DE COMPRAS\n print('='*50)\n print('NOTA FISCAL\\n')\n somaFatura = 0\n for y in range(len(historico[0])): #AMOSTRA DO HISTÓRICO FINAL DA COMPRA\n print(f'[{y+1}] - {historico[0][y]} --> R${historico[1][y]:.2f} Quantidade: {historico[2][y]}')\n somaFatura += ((historico[1][y])*(historico[2][y])) \n print(f\"\\nValor total R${somaFatura:.2f}\")\n break\n while True:\n print(f\"MENU PRINCIPAL\\n\") #MENU PRINCIPAL \n #OPÇÕES PARA DAR PROCEDIMENTO\n print(\"Escolha a opção que deseja:\\n\\n[1] - Adicionar Produto\\n[2] - Adicionar Serviço\\n[3] - Remover Produto ou Serviço\\n[4] - Limpar carrinho\\n[5] - Extrato\\n[6] - Finalizar Compra\\n[7] - Sair\")\n opcao = int(input(\"\\n\"))\n print('='*50)\n if opcao == 1: #ADICIONAR PRODUTOS AO SEU CARRINHO\n print(\"Carregando ...\")\n print('='*50)\n time.sleep(3)\n while True:\n adcProduto() #FUNÇÃO ADICIONAR PRODUTO\n break \n elif opcao == 2: #ADICIONAR SERVIÇOS AO SEU CARRINHO\n print(\"Carregando ...\")\n print('='*50)\n time.sleep(3)\n while True:\n adcServico() #FUNÇÃO ADICIONAR SERVIÇO\n break\n elif opcao == 3: #REMOVER PRODUTOS/SERVIÇOS DE SEU CARRINHO\n print(\"Carregando ...\")\n print('='*50)\n time.sleep(3)\n while True:\n rmvProduto() #FUNÇÃO REMOVER PRODUTO\n break\n elif opcao == 4: #LIMPAR SEU CARRINHO\n print(\"Carregando ...\")\n print('='*50)\n time.sleep(3)\n while True:\n limparcar() #FUNÇÃO LIMPAR CARRINHO\n break \n elif opcao == 5: #EXTRATO DE SEU CARRINHO\n print(\"Carregando ...\")\n print('='*50)\n time.sleep(3)\n while True:\n extrato() #FUNÇÃO EXTRATO CARRINHO\n break\n elif opcao == 6: #FINALIZAR/DESISTIR DA COMPRA\n print(\"Carregando ...\")\n print('='*50)\n time.sleep(3)\n print(\"Gostaria de dar procedimento a finalização da compra ou gostaria de desistir?\\n\") #CHANCE DE DESISTÊNCIA DA COMPRA\n print(\"[P] para prosseguir\\n[D] para desistir\\n\")\n certeza = input(f'Confirme a sua ação: ').upper()[0] \n print('='*50)\n while (certeza != 'P') and (certeza != 'D'):\n certeza = input(\"Opção inválida! Digite [P] para prosseguir [D] para desistir: \").upper()[0] \n print('='*50)\n if certeza == 'D': #DESISTÊNCIA (1ªCONFIRMAÇÃO) - MOSTRA OS PRODUTOS QUE ESTÁ DESISTINDO\n print(\"Você tem certeza? Essa é o seu carrinho:\\n\")\n for y in range(len(carrinho[0])):\n print(f'[{y+1}] - {carrinho[0][y]} --> R${carrinho[1][y]} Quantidade: {carrinho[2][y]}')\n print('='*50)\n print(\"[S] para sim\\n[N] para não\\n\") #DESISTÊNCIA (2ªCONFIRMAÇÃO) - LIMPEZA DO CARRINHO E SAÍDA DIRETA DO PROGRAMA\n certeza = input(\"Confirme sua ação: \").upper()[0]\n print('='*50)\n while (certeza != 'S') and (certeza != 'N'):\n certeza = input(\"Opção inválida! Confirme sua ação: \").upper()[0]\n print('='*50)\n if certeza == 'S':\n carrinho[0].clear()\n carrinho[1].clear()\n carrinho[2].clear()\n print('VOLTE SEMPRE!')\n print('='*50)\n time.sleep(3)\n break\n else:\n print(\"Voltando ...\")\n print('='*50)\n time.sleep(3)\n\n else: #FINALIZAR COMPRA - FORMA DE PAGAMENTO\n print(\"Qual será a forma de pagamento?\\n\")\n print(\"[C] - Cartão\\n[D] - Dinheiro\\n[P] - PIX\")\n FormaPagamento = str(input(\"\\nEscolha a forma de pagamento: \")).upper()[0]\n print('='*50)\n while (FormaPagamento != 'D') and (FormaPagamento != 'C') and (FormaPagamento != 'P'):\n FormaPagamento = str(input(\"Esta opcção não é válida! Escolha a forma de pagamento: \")).upper()[0]\n print('='*50)\n \n if FormaPagamento == 'D': #FORMA DE PAGAMENTO - DINHEIRO\n somaFatura = 0\n for y in range(len(carrinho[0])): #AMOSTRA DO CARRINHO\n print(f'[{y+1}] - {carrinho[0][y]} --> R${carrinho[1][y]} Quantidade: {carrinho[2][y]}')\n somaFatura += ((carrinho[1][y])*(carrinho[2][y])) \n print(f\"\\nValor total R${somaFatura:.2f}\")\n dinheiro = int(input(\"\\nDigite o valor do pagamento: \"))\n print('='*50)\n while dinheiro < somaFatura:\n dinheiro = int(input(\"Inválido! Digite o valor: \"))\n print('='*50)\n\n troco = dinheiro - somaFatura\n print(f\"Troco do cliente: R${troco}\")\n cont50n = 0\n cont20n = 0\n cont10n = 0\n cont5n = 0\n cont2n = 0\n cont1n = 0\n\n while troco > 0:\n if troco >= 50:\n troco -= 50\n cont50n +=1\n elif troco >= 20:\n troco -= 20\n cont20n += 1\n elif troco >= 10:\n troco -= 10\n cont10n += 1\n elif troco >= 5:\n troco -= 5\n cont5n += 1\n elif troco >= 2:\n troco -= 2\n cont2n += 1\n elif troco >= 1:\n troco -= 1\n cont1n += 1\n\n lista_cont = [cont50n, cont20n, cont10n, cont5n, cont2n, cont1n]\n lista_cedulas = [50, 20, 10, 5, 2, 1]\n\n for i, v in zip(lista_cont, lista_cedulas):\n if i > 0:\n print(f'{i} cédula(s) de {v} reais')\n print('='*50)\n somaFatura = 0\n for i in range(len(carrinho[0])):\n historico[0].append(carrinho[0][i])\n historico[1].append(carrinho[1][i])\n historico[2].append(carrinho[2][i])\n carrinho[0].clear()\n carrinho[1].clear()\n carrinho[2].clear()\n\n elif FormaPagamento == 'C': #FORMA DE PAGAMENTO - CARTÃO\n somaFatura = 0\n for y in range(len(carrinho[0])):\n print(f'[{y+1}] - {carrinho[0][y]} --> R${carrinho[1][y]} Quantidade: {carrinho[2][y]}')\n somaFatura += ((carrinho[1][y])*(carrinho[2][y])) \n print(f\"\\nValor total R${somaFatura:.2f}\")\n print(\"\\n[C] - Crédito\\n[D] - Débito\") #CRÉDITO OU DÉBITO\n credito_debito = str(input(\"\\nEscolha entre Crédito ou Débito: \")).upper()[0]\n print('='*50)\n while (FormaPagamento != 'D') and (FormaPagamento != 'C'):\n credito_debito = str(input(\"Dado inválido! Escolha entre Crédito ou Débito: \")).upper()[0]\n print('='*50)\n if credito_debito == 'C': #CRÉDITO\n print('Obs: Parcelas acima de 3x acarretará juros de 3%. Máximo de parcelas: 10') #\n parcelas = int(input('\\nDeseja parcelar em quantas vezes: '))\n print('='*50)\n while parcelas <= 0 or parcelas > 10:\n parcelas = int(input('Inválido! Deseja parcelar em quantas vezes: '))\n print('='*50)\n if parcelas >= 1 and parcelas <= 3:\n somaFatura /= parcelas\n print(f\"O valor parcelado em {parcelas}x fica: R${somaFatura:.2f}\") #\n print('='*50)\n print(\"Pago com sucesso!\")\n print('='*50)\n somaFatura = 0\n for i in range(len(carrinho[0])):\n historico[0].append(carrinho[0][i])\n historico[1].append(carrinho[1][i])\n historico[2].append(carrinho[2][i])\n carrinho[0].clear()\n carrinho[1].clear()\n carrinho[2].clear()\n time.sleep(3)\n elif parcelas == 0:\n print(f\"O valor parcelado em {parcelas}x fica: R${somaFatura:.2f}\")\n print('='*50)\n print(\"Pago com sucesso!\")\n print('='*50)\n somaFatura = 0\n for i in range(len(carrinho[0])):\n historico[0].append(carrinho[0][i])\n historico[1].append(carrinho[1][i])\n historico[2].append(carrinho[2][i])\n carrinho[0].clear()\n carrinho[1].clear()\n carrinho[2].clear()\n else:\n somaFatura /= parcelas\n somaFatura * 1.03\n print(f\"O valor parcelado em {parcelas}x fica: R${somaFatura:.2f}\")\n print('='*50)\n print(\"Pago com sucesso!\")\n print('='*50)\n somaFatura = 0\n for i in range(len(carrinho[0])):\n historico[0].append(carrinho[0][i])\n historico[1].append(carrinho[1][i])\n historico[2].append(carrinho[2][i])\n carrinho[0].clear()\n carrinho[1].clear()\n carrinho[2].clear()\n time.sleep(3)\n elif credito_debito == 'D': #DÉBITO\n print('Pagamento realizado com sucesso!')\n print('='*50)\n somaFatura = 0\n for i in range(len(carrinho[0])):\n historico[0].append(carrinho[0][i])\n historico[1].append(carrinho[1][i])\n historico[2].append(carrinho[2][i])\n carrinho[0].clear()\n carrinho[1].clear()\n carrinho[2].clear()\n time.sleep(3) \n else: #FORMA DE PAGAMENTO - PIX\n print('='*50)\n print('Pagamento com PIX realizado com sucesso!')\n print('='*50)\n somaFatura = 0\n for i in range(len(carrinho[0])):\n historico[0].append(carrinho[0][i])\n historico[1].append(carrinho[1][i])\n historico[2].append(carrinho[2][i])\n carrinho[0].clear()\n carrinho[1].clear()\n carrinho[2].clear()\n time.sleep(3)\n elif opcao == 7: #SAIR DO PROGRAMA\n print(\"Carregando ...\")\n print('='*50)\n time.sleep(3)\n if len(carrinho[0]) == 0: #CARRINHO SEM ITEM - SAÍDA DIRETA\n print(\"VOLTE SEMPRE!\")\n print('='*50)\n time.sleep(3)\n break\n else:\n print(\"Tem certeza que deseja sair? Todo o conteúdo do seu carrinho será removido.\\n\\n[S] para sim\\n[N] para não\") #CONFIRMAÇÃO DA AÇÃO\n certeza = input(\"\\nConfirme sua ação: \").upper()[0]\n print('='*50)\n while (certeza != 'S') and (certeza != 'N'):\n certeza = input(\"Dado inválido! Digite [S] para sim [N] para não:\\n\").upper()[0]\n print('='*50)\n if certeza == 'S': #LIMPEZA DO CARRINHO\n carrinho[0].clear()\n carrinho[1].clear()\n carrinho[2].clear()\n print(\"Limpando seu carrinho ...\")\n print('='*50)\n print(\"VOLTE SEMPRE!\")\n print('='*50)\n time.sleep(3)\n break\n else: #CASO DESISTA DA AÇÃO - CARRINHO MANTIDO\n print(\"Seus produtos foram mantidos no carrinho!\")\n print('='*50)\n time.sleep(3)\n else: #AVISO DE ALTERNATIVA INVÁLIDA\n print('Insira uma opção valida!')\n print('='*50)\n time.sleep(3)",
"> Para acessar o programa basta digitar [A]\n> Caso queira finalizar o programa, digite [F]\n\nEscolha uma opção: a\n==================================================\nBem vindo a Oficina Borracha Forte!\n==================================================\nMENU PRINCIPAL\n\nEscolha a opção que deseja:\n\n[1] - Adicionar Produto\n[2] - Adicionar Serviço\n[3] - Remover Produto ou Serviço\n[4] - Limpar carrinho\n[5] - Extrato\n[6] - Finalizar Compra\n[7] - Sair\n\n1\n==================================================\nCarregando ...\n==================================================\nOpções de produto:\n\n[1] - Pneu(s) --> R$339.0\n[2] - Calota(s) --> R$15.0\n[3] - Palheta(s) --> R$55.0\n[4] - Protetor(es) de Volante --> R$30.0\n[5] - Cheirinho(s) de Carro --> R$15.0\n[6] - Óleo de Motor --> R$27.0\n[7] - Bateria(s) --> R$270.0\n\nPara voltar ao menu principal basta digitar [99] \n==================================================\nAdicione um produto ao seu carrinho: 4\n==================================================\nQual seria a quantidade de \"Protetor(es) de Volante\" (MÁX. 10): 1\n==================================================\nAdicionando \"Protetor(es) de Volante\" ao seu carrinho ...\n==================================================\nOpções de produto:\n\n[1] - Pneu(s) --> R$339.0\n[2] - Calota(s) --> R$15.0\n[3] - Palheta(s) --> R$55.0\n[4] - Protetor(es) de Volante --> R$30.0\n[5] - Cheirinho(s) de Carro --> R$15.0\n[6] - Óleo de Motor --> R$27.0\n[7] - Bateria(s) --> R$270.0\n\nPara voltar ao menu principal basta digitar [99] \n==================================================\nAdicione um produto ao seu carrinho: 1\n==================================================\nQual seria a quantidade de \"Pneu(s)\" (MÁX. 10): 4\n==================================================\nAdicionando \"Pneu(s)\" ao seu carrinho ...\n==================================================\nOpções de produto:\n\n[1] - Pneu(s) --> R$339.0\n[2] - Calota(s) --> R$15.0\n[3] - Palheta(s) --> R$55.0\n[4] - Protetor(es) de Volante --> R$30.0\n[5] - Cheirinho(s) de Carro --> R$15.0\n[6] - Óleo de Motor --> R$27.0\n[7] - Bateria(s) --> R$270.0\n\nPara voltar ao menu principal basta digitar [99] \n==================================================\nAdicione um produto ao seu carrinho: 99\n==================================================\nSaindo ...\n==================================================\nMENU PRINCIPAL\n\nEscolha a opção que deseja:\n\n[1] - Adicionar Produto\n[2] - Adicionar Serviço\n[3] - Remover Produto ou Serviço\n[4] - Limpar carrinho\n[5] - Extrato\n[6] - Finalizar Compra\n[7] - Sair\n\n2\n==================================================\nCarregando ...\n==================================================\nOpções de serviços:\n\n[1] - Troca de Óleo --> R$200.0\n[2] - Alinhamento --> R$60.0\n[3] - Revisão Geral --> R$300.0\n[4] - Troca de Lampada --> R$40.0\n[5] - Troca de Correia --> R$220.0\n[6] - Troca de Pastilha de Freio --> R$150.0\n\nPara voltar ao menu principal basta digitar [99] \n==================================================\nAdicione um serviço ao seu carrinho: 1\n==================================================\nAdicionando \"Troca de Óleo\" ao seu carrinho ...\n==================================================\nOpções de serviços:\n\n[1] - Troca de Óleo --> R$200.0\n[2] - Alinhamento --> R$60.0\n[3] - Revisão Geral --> R$300.0\n[4] - Troca de Lampada --> R$40.0\n[5] - Troca de Correia --> R$220.0\n[6] - Troca de Pastilha de Freio --> R$150.0\n\nPara voltar ao menu principal basta digitar [99] \n==================================================\nAdicione um serviço ao seu carrinho: 99\n==================================================\nSaindo ...\n==================================================\nMENU PRINCIPAL\n\nEscolha a opção que deseja:\n\n[1] - Adicionar Produto\n[2] - Adicionar Serviço\n[3] - Remover Produto ou Serviço\n[4] - Limpar carrinho\n[5] - Extrato\n[6] - Finalizar Compra\n[7] - Sair\n\n6\n==================================================\nCarregando ...\n==================================================\nGostaria de dar procedimento a finalização da compra ou gostaria de desistir?\n\n[P] para prosseguir\n[D] para desistir\n\nConfirme a sua ação: p\n==================================================\nQual será a forma de pagamento?\n\n[C] - Cartão\n[D] - Dinheiro\n[P] - PIX\n\nEscolha a forma de pagamento: d\n==================================================\n[1] - Protetor(es) de Volante --> R$30.0 Quantidade: 1\n[2] - Pneu(s) --> R$339.0 Quantidade: 4\n[3] - Troca de Óleo --> R$200.0 Quantidade: 1\n\nValor total R$1586.00\n\nDigite o valor do pagamento: 1750\n==================================================\nTroco do cliente: R$164.0\n3 cédula(s) de 50 reais\n1 cédula(s) de 10 reais\n2 cédula(s) de 2 reais\n==================================================\nMENU PRINCIPAL\n\nEscolha a opção que deseja:\n\n[1] - Adicionar Produto\n[2] - Adicionar Serviço\n[3] - Remover Produto ou Serviço\n[4] - Limpar carrinho\n[5] - Extrato\n[6] - Finalizar Compra\n[7] - Sair\n\n7\n==================================================\nCarregando ...\n==================================================\nVOLTE SEMPRE!\n==================================================\n> Para acessar o programa basta digitar [A]\n> Caso queira finalizar o programa, digite [F]\n\nEscolha uma opção: f\n==================================================\nIremos finalizar o programa ...\n==================================================\nMuito obrigado pela visita!\n==================================================\nNOTA FISCAL\n\n[1] - Protetor(es) de Volante --> R$30.00 Quantidade: 1\n[2] - Pneu(s) --> R$339.00 Quantidade: 4\n[3] - Troca de Óleo --> R$200.00 Quantidade: 1\n\nValor total R$1586.00\n"
],
[
"#LEGADO PARA CONSULTA\n#def finalizarCompra():\n# print(\"Gostaria de dar procedimento a finalização da compra ou gostaria de desistir?\\n\")\n# print(\"[S] para sim\\n[N] para não\\n\")\n# certeza = input(f'Confirme a sua ação: ').upper()[0] #MOSTRAR O NOME DO PRODUTO QUE SERÁ APAGADO\n# print('='*50)\n# while (certeza != 'S') and (certeza != 'N'):\n# certeza = input(\"Opção inválida! Digite [S] para sim [N] para não: \").upper()[0] #MOSTRAR O NOME DO PRODUTO QUE SERÁ APAGADO\n# print('='*50)\n# print(\"Qual será a forma de pagamento?\\n\")\n# print(\"[C] - Cartão\\n[D] - Dinheiro\\n[P] - PIX\")\n# FormaPagamento = str(input(\"\\nEscolha a forma de pagamento: \")).upper()[0]\n# print('='*50)\n# while (FormaPagamento != 'D') and (FormaPagamento != 'C') and (FormaPagamento != 'P'):\n# FormaPagamento = str(input(\"Esta opcção não é válida! Escolha a forma de pagamento: \")).upper()[0]\n# print('='*50)\n# \n# if FormaPagamento == 'D':\n# somaFatura = 0\n# for y in range(len(carrinho[0])):\n# print(f'[{y+1}] - {carrinho[0][y]} --> R${carrinho[1][y]} Quantidade ; {carrinho[2][y]}')\n# somaFatura += ((carrinho[1][y])*(carrinho[2][y])) \n# print(f\"\\nValor total R${somaFatura:.2f}\")\n# dinheiro = int(input(\"\\nDigite o valor do pagamento: \"))\n# print('='*50)\n# while dinheiro < somaFatura:\n# dinheiro = int(input(\"Inválido! Digite o valor: \"))\n# print('='*50)\n\n# troco = dinheiro - somaFatura\n# print(f\"Troco do cliente: R${troco}\")\n# cont50n = 0\n# cont20n = 0\n# cont10n = 0\n# cont5n = 0\n# cont2n = 0\n# cont1n = 0\n\n# while troco > 0:\n# if troco >= 50:\n# troco -= 50\n# cont50n +=1\n# elif troco >= 20:\n# troco -= 20\n# cont20n += 1\n# elif troco >= 10:\n# troco -= 10\n# cont10n += 1\n# elif troco >= 5:\n# troco -= 5\n# cont5n += 1\n# elif troco >= 2:\n# troco -= 2\n# cont2n += 1\n# elif troco >= 1:\n# troco -= 1\n# cont1n += 1\n#\n# lista_cont = [cont50n, cont20n, cont10n, cont5n, cont2n, cont1n]\n# lista_cedulas = [50, 20, 10, 5, 2, 1]\n#\n# for i, v in zip(lista_cont, lista_cedulas):\n# if i > 0:\n# print(f'{i} cédula(s) de {v} reais')\n# print('='*50)\n# somaFatura = 0\n# historico = [[],[],[]]\n# for i in range(len(carrinho[0])):\n# historico[0].append(carrinho[0][i])\n# historico[1].append(carrinho[1][i])\n# historico[2].append(carrinho[2][i])\n# print(f\"antes Lista histórico: {historico}\")\n# print(f\"antesLista carrinho: {carrinho}\")\n# carrinho[0].clear()\n# carrinho[1].clear()\n# carrinho[2].clear()\n# print(f\"depois Lista histórico: {historico}\")\n# print(f\"depois Lista carrinho: {carrinho}\")\n#\n# elif FormaPagamento == 'C':\n# somaFatura = 0\n# for y in range(len(carrinho[0])):\n# print(f'[{y+1}] - {carrinho[0][y]} --> R${carrinho[1][y]} Quantidade ; {carrinho[2][y]}')\n# somaFatura += ((carrinho[1][y])*(carrinho[2][y])) \n# print(f\"\\nValor total R${somaFatura:.2f}\")\n# print(\"\\n[C] - Crédito\\n[D] - Débito\")\n# credito_debito = str(input(\"\\nEscolha entre Crédito ou Débito: \")).upper()[0]\n# print('='*50)\n# while (FormaPagamento != 'D') and (FormaPagamento != 'C'):\n# credito_debito = str(input(\"Dado inválido! Escolha entre Crédito ou Débito: \")).upper()[0]\n# print('='*50)\n# if credito_debito == 'C':\n# print('Obs: Parcelas acima de 3x acarretará juros de 3%. Máximo de parcelas: 10')\n# parcelas = int(input('\\nDeseja parcelar em quantas vezes: '))\n# print('='*50)\n# while parcelas <= 0 or parcelas > 10:\n# parcelas = int(input('Inválido! Deseja parcelar em quantas vezes: '))\n# print('='*50)\n# if parcelas >= 1 and parcelas <= 3:\n# somaFatura /= parcelas\n# print(f\"O valor parcelado em {parcelas}x fica: R${somaFatura:.2f}\")\n# print('='*50)\n# print(\"Pago com sucesso!\")\n# print('='*50)\n# somaFatura = 0\n# historico = carrinho.copy()\n# carrinho[0].clear()\n# carrinho[1].clear()\n# carrinho[2].clear()\n# time.sleep(3)\n# elif parcelas == 0:\n# print(f\"O valor parcelado em {parcelas}x fica: R${somaFatura:.2f}\")\n# print('='*50)\n# print(\"Pago com sucesso!\")\n# print('='*50)\n# somaFatura = 0\n# historico = carrinho.copy()\n# carrinho[0].clear()\n# carrinho[1].clear()\n# carrinho[2].clear()\n# time.sleep(3)\n# else:\n# somaFatura /= parcelas\n# somaFatura * 1.03\n# print(f\"O valor parcelado em {parcelas}x fica: R${somaFatura:.2f}\")\n# print('='*50)\n# print(\"Pago com sucesso!\")\n# print('='*50)\n# somaFatura = 0\n# historico = carrinho.copy()\n# carrinho[0].clear()\n# carrinho[1].clear()\n# carrinho[2].clear()\n# time.sleep(3)\n# elif credito_debito == 'D':\n# print('Pagamento realizado com sucesso!')\n# print('='*50)\n# somaFatura = 0\n# historico = carrinho\n# carrinho[0].clear()\n# carrinho[1].clear()\n# carrinho[2].clear()\n# time.sleep(3) \n# else:\n# print('='*50)\n# print('Pagamento com PIX realizado com sucesso!')\n# print('='*50)\n# somaFatura = 0\n# historico = carrinho\n# carrinho[0].clear()\n# carrinho[1].clear()\n# carrinho[2].clear()\n# time.sleep(3)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a74419cfb3eb5e06207807918a15173d6789f59
| 85,631 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
qiskit/advanced/aqua/finance/simulation/fixed_income_pricing.ipynb
|
gvvynplaine/qiskit-iqx-tutorials
|
40af3da7aa86ce190d04f147daf46fbc893a1966
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 13 |
2020-05-19T06:29:20.000Z
|
2021-12-22T16:40:17.000Z
|
qiskit/advanced/aqua/finance/simulation/fixed_income_pricing.ipynb
|
gvvynplaine/qiskit-iqx-tutorials
|
40af3da7aa86ce190d04f147daf46fbc893a1966
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
qiskit/advanced/aqua/finance/simulation/fixed_income_pricing.ipynb
|
gvvynplaine/qiskit-iqx-tutorials
|
40af3da7aa86ce190d04f147daf46fbc893a1966
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 9 |
2020-05-19T08:30:56.000Z
|
2021-09-01T11:30:25.000Z
| 200.07243 | 21,748 | 0.907487 |
[
[
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# _*Qiskit Finance: Pricing Fixed-Income Assets*_ \n\nThe latest version of this notebook is available on https://github.com/Qiskit/qiskit-iqx-tutorials.\n\n***\n### Contributors\nStefan Woerner<sup>[1]</sup>, Daniel Egger<sup>[1]</sup>, Shaohan Hu<sup>[1]</sup>, Stephen Wood<sup>[1]</sup>, Marco Pistoia<sup>[1]</sup>\n### Affiliation\n- <sup>[1]</sup>IBMQ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Introduction\n\nWe seek to price a fixed-income asset knowing the distributions describing the relevant interest rates. The cash flows $c_t$ of the asset and the dates at which they occur are known. The total value $V$ of the asset is thus the expectation value of:\n\n$$V = \\sum_{t=1}^T \\frac{c_t}{(1+r_t)^t}$$\n\nEach cash flow is treated as a zero coupon bond with a corresponding interest rate $r_t$ that depends on its maturity. The user must specify the distribution modeling the uncertainty in each $r_t$ (possibly correlated) as well as the number of qubits he wishes to use to sample each distribution. In this example we expand the value of the asset to first order in the interest rates $r_t$. This corresponds to studying the asset in terms of its duration.\n<br>\n<br>\nThe approximation of the objective function follows the following paper:<br>\n<a href=\"https://arxiv.org/abs/1806.06893\">Quantum Risk Analysis. Woerner, Egger. 2018.</a>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n%matplotlib inline\nimport numpy as np\nfrom qiskit import BasicAer\nfrom qiskit.aqua.algorithms.single_sample.amplitude_estimation.ae import AmplitudeEstimation\nfrom qiskit.aqua.components.uncertainty_models import MultivariateNormalDistribution\nfrom qiskit.finance.components.uncertainty_problems import FixedIncomeExpectedValue",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"backend = BasicAer.get_backend('statevector_simulator')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Uncertainty Model\n\nWe construct a circuit factory to load a multivariate normal random distribution in $d$ dimensions into a quantum state.\nThe distribution is truncated to a given box $\\otimes_{i=1}^d [low_i, high_i]$ and discretized using $2^{n_i}$ grid points, where $n_i$ denotes the number of qubits used for dimension $i = 1,\\ldots, d$.\nThe unitary operator corresponding to the circuit factory implements the following: \n$$\\big|0\\rangle_{n_1}\\ldots\\big|0\\rangle_{n_d} \\mapsto \\big|\\psi\\rangle = \\sum_{i_1=0}^{2^n_-1}\\ldots\\sum_{i_d=0}^{2^n_-1} \\sqrt{p_{i_1,...,i_d}}\\big|i_1\\rangle_{n_1}\\ldots\\big|i_d\\rangle_{n_d},$$\nwhere $p_{i_1, ..., i_d}$ denote the probabilities corresponding to the truncated and discretized distribution and where $i_j$ is mapped to the right interval $[low_j, high_j]$ using the affine map:\n$$ \\{0, \\ldots, 2^{n_{j}}-1\\} \\ni i_j \\mapsto \\frac{high_j - low_j}{2^{n_j} - 1} * i_j + low_j \\in [low_j, high_j].$$\n\nIn addition to the uncertainty model, we can also apply an affine map, e.g. resulting from a principal component analysis. The interest rates used are then given by:\n$$ \\vec{r} = A * \\vec{x} + b,$$\nwhere $\\vec{x} \\in \\otimes_{i=1}^d [low_i, high_i]$ follows the given random distribution.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# can be used in case a principal component analysis has been done to derive the uncertainty model, ignored in this example.\nA = np.eye(2)\nb = np.zeros(2) \n\n# specify the number of qubits that are used to represent the different dimenions of the uncertainty model\nnum_qubits = [2, 2]\n\n# specify the lower and upper bounds for the different dimension\nlow = [0, 0]\nhigh = [0.12, 0.24]\nmu = [0.12, 0.24]\nsigma = 0.01*np.eye(2)\n\n# construct corresponding distribution\nu = MultivariateNormalDistribution(num_qubits, low, high, mu, sigma)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# plot contour of probability density function\nx = np.linspace(low[0], high[0], 2**num_qubits[0])\ny = np.linspace(low[1], high[1], 2**num_qubits[1])\nz = u.probabilities.reshape(2**num_qubits[0], 2**num_qubits[1])\nplt.contourf(x, y, z)\nplt.xticks(x, size=15)\nplt.yticks(y, size=15)\nplt.grid()\nplt.xlabel('$r_1$ (%)', size=15)\nplt.ylabel('$r_2$ (%)', size=15)\nplt.colorbar()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Cash flow, payoff function, and exact expected value\n\nIn the following we define the cash flow per period, the resulting payoff function and evaluate the exact expected value.\n\nFor the payoff function we first use a first order approximation and then apply the same approximation technique as for the linear part of the payoff function of the [European Call Option](european_call_option_pricing.ipynb).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# specify cash flow\ncf = [1.0, 2.0]\nperiods = range(1, len(cf)+1)\n\n# plot cash flow\nplt.bar(periods, cf)\nplt.xticks(periods, size=15)\nplt.yticks(size=15)\nplt.grid()\nplt.xlabel('periods', size=15)\nplt.ylabel('cashflow ($)', size=15)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# estimate real value\ncnt = 0\nexact_value = 0.0\nfor x1 in np.linspace(low[0], high[0], pow(2, num_qubits[0])):\n for x2 in np.linspace(low[1], high[1], pow(2, num_qubits[1])):\n prob = u.probabilities[cnt]\n for t in range(len(cf)):\n # evaluate linear approximation of real value w.r.t. interest rates\n exact_value += prob * (cf[t]/pow(1 + b[t], t+1) - (t+1)*cf[t]*np.dot(A[:, t], np.asarray([x1, x2]))/pow(1 + b[t], t+2))\n cnt += 1\nprint('Exact value: \\t%.4f' % exact_value)",
"Exact value: \t2.1942\n"
],
[
"# specify approximation factor\nc_approx = 0.125\n\n# get fixed income circuit appfactory\nfixed_income = FixedIncomeExpectedValue(u, A, b, cf, c_approx)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# set number of evaluation qubits (samples)\nm = 5\n\n# construct amplitude estimation \nae = AmplitudeEstimation(m, fixed_income)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# result = ae.run(quantum_instance=LegacySimulators.get_backend('qasm_simulator'), shots=100)\nresult = ae.run(quantum_instance=backend)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('Exact value: \\t%.4f' % exact_value)\nprint('Estimated value:\\t%.4f' % result['estimation'])\nprint('Probability: \\t%.4f' % result['max_probability'])",
"Exact value: \t2.1942\nEstimated value:\t2.4600\nProbability: \t0.8487\n"
],
[
"# plot estimated values for \"a\" (direct result of amplitude estimation, not rescaled yet)\nplt.bar(result['values'], result['probabilities'], width=0.5/len(result['probabilities']))\nplt.xticks([0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1], size=15)\nplt.yticks([0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1], size=15)\nplt.title('\"a\" Value', size=15)\nplt.ylabel('Probability', size=15)\nplt.xlim((0,1))\nplt.ylim((0,1))\nplt.grid()\nplt.show()\n\n# plot estimated values for fixed-income asset (after re-scaling and reversing the c_approx-transformation)\nplt.bar(result['mapped_values'], result['probabilities'], width=3/len(result['probabilities']))\nplt.plot([exact_value, exact_value], [0,1], 'r--', linewidth=2)\nplt.xticks(size=15)\nplt.yticks([0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1], size=15)\nplt.title('Estimated Option Price', size=15)\nplt.ylabel('Probability', size=15)\nplt.ylim((0,1))\nplt.grid()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import qiskit.tools.jupyter\n%qiskit_version_table\n%qiskit_copyright",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a7442692b5910a9c0e3e4f983a34e79c877d24c
| 76,886 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Mini-Projects/IMDB Sentiment Analysis - XGBoost (Batch Transform).ipynb
|
bopamo/sagemaker-deployment
|
8a6dff27188a708a80ebd401771ef28398882896
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2019-08-29T21:56:16.000Z
|
2019-08-29T21:56:16.000Z
|
Mini-Projects/IMDB Sentiment Analysis - XGBoost (Batch Transform).ipynb
|
bopamo/sagemaker-deployment
|
8a6dff27188a708a80ebd401771ef28398882896
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Mini-Projects/IMDB Sentiment Analysis - XGBoost (Batch Transform).ipynb
|
bopamo/sagemaker-deployment
|
8a6dff27188a708a80ebd401771ef28398882896
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 63.176664 | 1,306 | 0.661083 |
[
[
[
"# Sentiment Analysis\n\n## Using XGBoost in SageMaker\n\n_Deep Learning Nanodegree Program | Deployment_\n\n---\n\nAs our first example of using Amazon's SageMaker service we will construct a random tree model to predict the sentiment of a movie review. You may have seen a version of this example in a pervious lesson although it would have been done using the sklearn package. Instead, we will be using the XGBoost package as it is provided to us by Amazon.\n\n## Instructions\n\nSome template code has already been provided for you, and you will need to implement additional functionality to successfully complete this notebook. You will not need to modify the included code beyond what is requested. Sections that begin with '**TODO**' in the header indicate that you need to complete or implement some portion within them. Instructions will be provided for each section and the specifics of the implementation are marked in the code block with a `# TODO: ...` comment. Please be sure to read the instructions carefully!\n\nIn addition to implementing code, there may be questions for you to answer which relate to the task and your implementation. Each section where you will answer a question is preceded by a '**Question:**' header. Carefully read each question and provide your answer below the '**Answer:**' header by editing the Markdown cell.\n\n> **Note**: Code and Markdown cells can be executed using the **Shift+Enter** keyboard shortcut. In addition, a cell can be edited by typically clicking it (double-click for Markdown cells) or by pressing **Enter** while it is highlighted.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Step 1: Downloading the data\n\nThe dataset we are going to use is very popular among researchers in Natural Language Processing, usually referred to as the [IMDb dataset](http://ai.stanford.edu/~amaas/data/sentiment/). It consists of movie reviews from the website [imdb.com](http://www.imdb.com/), each labeled as either '**pos**itive', if the reviewer enjoyed the film, or '**neg**ative' otherwise.\n\n> Maas, Andrew L., et al. [Learning Word Vectors for Sentiment Analysis](http://ai.stanford.edu/~amaas/data/sentiment/). In _Proceedings of the 49th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies_. Association for Computational Linguistics, 2011.\n\nWe begin by using some Jupyter Notebook magic to download and extract the dataset.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%mkdir ../data\n!wget -O ../data/aclImdb_v1.tar.gz http://ai.stanford.edu/~amaas/data/sentiment/aclImdb_v1.tar.gz\n!tar -zxf ../data/aclImdb_v1.tar.gz -C ../data",
"mkdir: cannot create directory ‘../data’: File exists\n--2019-08-27 20:38:58-- http://ai.stanford.edu/~amaas/data/sentiment/aclImdb_v1.tar.gz\nResolving ai.stanford.edu (ai.stanford.edu)... 171.64.68.10\nConnecting to ai.stanford.edu (ai.stanford.edu)|171.64.68.10|:80... connected.\nHTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK\nLength: 84125825 (80M) [application/x-gzip]\nSaving to: ‘../data/aclImdb_v1.tar.gz’\n\n../data/aclImdb_v1. 100%[===================>] 80.23M 23.7MB/s in 4.4s \n\n2019-08-27 20:39:02 (18.4 MB/s) - ‘../data/aclImdb_v1.tar.gz’ saved [84125825/84125825]\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Step 2: Preparing the data\n\nThe data we have downloaded is split into various files, each of which contains a single review. It will be much easier going forward if we combine these individual files into two large files, one for training and one for testing.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import os\nimport glob\n\ndef read_imdb_data(data_dir='../data/aclImdb'):\n data = {}\n labels = {}\n \n for data_type in ['train', 'test']:\n data[data_type] = {}\n labels[data_type] = {}\n \n for sentiment in ['pos', 'neg']:\n data[data_type][sentiment] = []\n labels[data_type][sentiment] = []\n \n path = os.path.join(data_dir, data_type, sentiment, '*.txt')\n files = glob.glob(path)\n \n for f in files:\n with open(f) as review:\n data[data_type][sentiment].append(review.read())\n # Here we represent a positive review by '1' and a negative review by '0'\n labels[data_type][sentiment].append(1 if sentiment == 'pos' else 0)\n \n assert len(data[data_type][sentiment]) == len(labels[data_type][sentiment]), \\\n \"{}/{} data size does not match labels size\".format(data_type, sentiment)\n \n return data, labels",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data, labels = read_imdb_data()\nprint(\"IMDB reviews: train = {} pos / {} neg, test = {} pos / {} neg\".format(\n len(data['train']['pos']), len(data['train']['neg']),\n len(data['test']['pos']), len(data['test']['neg'])))",
"IMDB reviews: train = 12500 pos / 12500 neg, test = 12500 pos / 12500 neg\n"
],
[
"from sklearn.utils import shuffle\n\ndef prepare_imdb_data(data, labels):\n \"\"\"Prepare training and test sets from IMDb movie reviews.\"\"\"\n \n #Combine positive and negative reviews and labels\n data_train = data['train']['pos'] + data['train']['neg']\n data_test = data['test']['pos'] + data['test']['neg']\n labels_train = labels['train']['pos'] + labels['train']['neg']\n labels_test = labels['test']['pos'] + labels['test']['neg']\n \n #Shuffle reviews and corresponding labels within training and test sets\n data_train, labels_train = shuffle(data_train, labels_train)\n data_test, labels_test = shuffle(data_test, labels_test)\n \n # Return a unified training data, test data, training labels, test labets\n return data_train, data_test, labels_train, labels_test",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"train_X, test_X, train_y, test_y = prepare_imdb_data(data, labels)\nprint(\"IMDb reviews (combined): train = {}, test = {}\".format(len(train_X), len(test_X)))",
"IMDb reviews (combined): train = 25000, test = 25000\n"
],
[
"train_X[100]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Step 3: Processing the data\n\nNow that we have our training and testing datasets merged and ready to use, we need to start processing the raw data into something that will be useable by our machine learning algorithm. To begin with, we remove any html formatting that may appear in the reviews and perform some standard natural language processing in order to homogenize the data.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import nltk\nnltk.download(\"stopwords\")\nfrom nltk.corpus import stopwords\nfrom nltk.stem.porter import *\nstemmer = PorterStemmer()",
"[nltk_data] Downloading package stopwords to\n[nltk_data] /home/ec2-user/nltk_data...\n[nltk_data] Unzipping corpora/stopwords.zip.\n"
],
[
"import re\nfrom bs4 import BeautifulSoup\n\ndef review_to_words(review):\n text = BeautifulSoup(review, \"html.parser\").get_text() # Remove HTML tags\n text = re.sub(r\"[^a-zA-Z0-9]\", \" \", text.lower()) # Convert to lower case\n words = text.split() # Split string into words\n words = [w for w in words if w not in stopwords.words(\"english\")] # Remove stopwords\n words = [PorterStemmer().stem(w) for w in words] # stem\n \n return words",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import pickle\n\ncache_dir = os.path.join(\"../cache\", \"sentiment_analysis\") # where to store cache files\nos.makedirs(cache_dir, exist_ok=True) # ensure cache directory exists\n\ndef preprocess_data(data_train, data_test, labels_train, labels_test,\n cache_dir=cache_dir, cache_file=\"preprocessed_data.pkl\"):\n \"\"\"Convert each review to words; read from cache if available.\"\"\"\n\n # If cache_file is not None, try to read from it first\n cache_data = None\n if cache_file is not None:\n try:\n with open(os.path.join(cache_dir, cache_file), \"rb\") as f:\n cache_data = pickle.load(f)\n print(\"Read preprocessed data from cache file:\", cache_file)\n except:\n pass # unable to read from cache, but that's okay\n \n # If cache is missing, then do the heavy lifting\n if cache_data is None:\n # Preprocess training and test data to obtain words for each review\n #words_train = list(map(review_to_words, data_train))\n #words_test = list(map(review_to_words, data_test))\n words_train = [review_to_words(review) for review in data_train]\n words_test = [review_to_words(review) for review in data_test]\n \n # Write to cache file for future runs\n if cache_file is not None:\n cache_data = dict(words_train=words_train, words_test=words_test,\n labels_train=labels_train, labels_test=labels_test)\n with open(os.path.join(cache_dir, cache_file), \"wb\") as f:\n pickle.dump(cache_data, f)\n print(\"Wrote preprocessed data to cache file:\", cache_file)\n else:\n # Unpack data loaded from cache file\n words_train, words_test, labels_train, labels_test = (cache_data['words_train'],\n cache_data['words_test'], cache_data['labels_train'], cache_data['labels_test'])\n \n return words_train, words_test, labels_train, labels_test",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Preprocess data\ntrain_X, test_X, train_y, test_y = preprocess_data(train_X, test_X, train_y, test_y)",
"Wrote preprocessed data to cache file: preprocessed_data.pkl\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Extract Bag-of-Words features\n\nFor the model we will be implementing, rather than using the reviews directly, we are going to transform each review into a Bag-of-Words feature representation. Keep in mind that 'in the wild' we will only have access to the training set so our transformer can only use the training set to construct a representation.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nfrom sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer\nfrom sklearn.externals import joblib\n# joblib is an enhanced version of pickle that is more efficient for storing NumPy arrays\n\ndef extract_BoW_features(words_train, words_test, vocabulary_size=5000,\n cache_dir=cache_dir, cache_file=\"bow_features.pkl\"):\n \"\"\"Extract Bag-of-Words for a given set of documents, already preprocessed into words.\"\"\"\n \n # If cache_file is not None, try to read from it first\n cache_data = None\n if cache_file is not None:\n try:\n with open(os.path.join(cache_dir, cache_file), \"rb\") as f:\n cache_data = joblib.load(f)\n print(\"Read features from cache file:\", cache_file)\n except:\n pass # unable to read from cache, but that's okay\n \n # If cache is missing, then do the heavy lifting\n if cache_data is None:\n # Fit a vectorizer to training documents and use it to transform them\n # NOTE: Training documents have already been preprocessed and tokenized into words;\n # pass in dummy functions to skip those steps, e.g. preprocessor=lambda x: x\n vectorizer = CountVectorizer(max_features=vocabulary_size,\n preprocessor=lambda x: x, tokenizer=lambda x: x) # already preprocessed\n features_train = vectorizer.fit_transform(words_train).toarray()\n\n # Apply the same vectorizer to transform the test documents (ignore unknown words)\n features_test = vectorizer.transform(words_test).toarray()\n \n # NOTE: Remember to convert the features using .toarray() for a compact representation\n \n # Write to cache file for future runs (store vocabulary as well)\n if cache_file is not None:\n vocabulary = vectorizer.vocabulary_\n cache_data = dict(features_train=features_train, features_test=features_test,\n vocabulary=vocabulary)\n with open(os.path.join(cache_dir, cache_file), \"wb\") as f:\n joblib.dump(cache_data, f)\n print(\"Wrote features to cache file:\", cache_file)\n else:\n # Unpack data loaded from cache file\n features_train, features_test, vocabulary = (cache_data['features_train'],\n cache_data['features_test'], cache_data['vocabulary'])\n \n # Return both the extracted features as well as the vocabulary\n return features_train, features_test, vocabulary",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Extract Bag of Words features for both training and test datasets\ntrain_X, test_X, vocabulary = extract_BoW_features(train_X, test_X)",
"Wrote features to cache file: bow_features.pkl\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Step 4: Classification using XGBoost\n\nNow that we have created the feature representation of our training (and testing) data, it is time to start setting up and using the XGBoost classifier provided by SageMaker.\n\n### (TODO) Writing the dataset\n\nThe XGBoost classifier that we will be using requires the dataset to be written to a file and stored using Amazon S3. To do this, we will start by splitting the training dataset into two parts, the data we will train the model with and a validation set. Then, we will write those datasets to a file and upload the files to S3. In addition, we will write the test set input to a file and upload the file to S3. This is so that we can use SageMakers Batch Transform functionality to test our model once we've fit it.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\n\n# TODO: Split the train_X and train_y arrays into the DataFrames val_X, train_X and val_y, train_y. Make sure that\n# val_X and val_y contain 10 000 entires while train_X and train_y contain the remaining 15 000 entries.\n\nval_X = pd.DataFrame(train_X[:10000])\ntrain_X = pd.DataFrame(train_X[10000:])\n\nval_y = pd.DataFrame(train_y[:10000])\ntrain_y = pd.DataFrame(train_y[10000:])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The documentation for the XGBoost algorithm in SageMaker requires that the saved datasets should contain no headers or index and that for the training and validation data, the label should occur first for each sample.\n\nFor more information about this and other algorithms, the SageMaker developer documentation can be found on __[Amazon's website.](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/sagemaker/latest/dg/)__",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# First we make sure that the local directory in which we'd like to store the training and validation csv files exists.\ndata_dir = '../data/xgboost'\nif not os.path.exists(data_dir):\n os.makedirs(data_dir)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# First, save the test data to test.csv in the data_dir directory. Note that we do not save the associated ground truth\n# labels, instead we will use them later to compare with our model output.\n\npd.DataFrame(test_X).to_csv(os.path.join(data_dir, 'test.csv'), header=False, index=False)\n\n# TODO: Save the training and validation data to train.csv and validation.csv in the data_dir directory.\n# Make sure that the files you create are in the correct format.\n\n\n# Solution:\npd.concat([val_y, val_X], axis=1).to_csv(os.path.join(data_dir, 'validation.csv'), header=False, index=False)\npd.concat([train_y, train_X], axis=1).to_csv(os.path.join(data_dir, 'train.csv'), header=False, index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# To save a bit of memory we can set text_X, train_X, val_X, train_y and val_y to None.\n\ntest_X = train_X = val_X = train_y = val_y = None",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### (TODO) Uploading Training / Validation files to S3\n\nAmazon's S3 service allows us to store files that can be access by both the built-in training models such as the XGBoost model we will be using as well as custom models such as the one we will see a little later.\n\nFor this, and most other tasks we will be doing using SageMaker, there are two methods we could use. The first is to use the low level functionality of SageMaker which requires knowing each of the objects involved in the SageMaker environment. The second is to use the high level functionality in which certain choices have been made on the user's behalf. The low level approach benefits from allowing the user a great deal of flexibility while the high level approach makes development much quicker. For our purposes we will opt to use the high level approach although using the low-level approach is certainly an option.\n\nRecall the method `upload_data()` which is a member of object representing our current SageMaker session. What this method does is upload the data to the default bucket (which is created if it does not exist) into the path described by the key_prefix variable. To see this for yourself, once you have uploaded the data files, go to the S3 console and look to see where the files have been uploaded.\n\nFor additional resources, see the __[SageMaker API documentation](http://sagemaker.readthedocs.io/en/latest/)__ and in addition the __[SageMaker Developer Guide.](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/sagemaker/latest/dg/)__",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import sagemaker\n\nsession = sagemaker.Session() # Store the current SageMaker session\n\n# S3 prefix (which folder will we use)\nprefix = 'sentiment-xgboost'\n\n# TODO: Upload the test.csv, train.csv and validation.csv files which are contained in data_dir to S3 using sess.upload_data().\ntest_location = session.upload_data(os.path.join(data_dir, 'test.csv'), key_prefix=prefix)\nval_location = session.upload_data(os.path.join(data_dir, 'validation.csv'), key_prefix=prefix)\ntrain_location = session.upload_data(os.path.join(data_dir, 'train.csv'), key_prefix=prefix)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### (TODO) Creating the XGBoost model\n\nNow that the data has been uploaded it is time to create the XGBoost model. To begin with, we need to do some setup. At this point it is worth discussing what a model is in SageMaker. It is easiest to think of a model of comprising three different objects in the SageMaker ecosystem, which interact with one another.\n\n- Model Artifacts\n- Training Code (Container)\n- Inference Code (Container)\n\nThe Model Artifacts are what you might think of as the actual model itself. For example, if you were building a neural network, the model artifacts would be the weights of the various layers. In our case, for an XGBoost model, the artifacts are the actual trees that are created during training.\n\nThe other two objects, the training code and the inference code are then used the manipulate the training artifacts. More precisely, the training code uses the training data that is provided and creates the model artifacts, while the inference code uses the model artifacts to make predictions on new data.\n\nThe way that SageMaker runs the training and inference code is by making use of Docker containers. For now, think of a container as being a way of packaging code up so that dependencies aren't an issue.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sagemaker import get_execution_role\n\n# Our current execution role is require when creating the model as the training\n# and inference code will need to access the model artifacts.\nrole = get_execution_role()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# We need to retrieve the location of the container which is provided by Amazon for using XGBoost.\n# As a matter of convenience, the training and inference code both use the same container.\nfrom sagemaker.amazon.amazon_estimator import get_image_uri\n\ncontainer = get_image_uri(session.boto_region_name, 'xgboost')",
"WARNING:root:There is a more up to date SageMaker XGBoost image.To use the newer image, please set 'repo_version'='0.90-1. For example:\n\tget_image_uri(region, 'xgboost', 0.90-1).\n"
],
[
"# TODO: Create a SageMaker estimator using the container location determined in the previous cell.\n# It is recommended that you use a single training instance of type ml.m4.xlarge. It is also\n# recommended that you use 's3://{}/{}/output'.format(session.default_bucket(), prefix) as the\n# output path.\n\nxgb = None\n\n# Solution:\nxgb = sagemaker.estimator.Estimator(container, # The location of the container we wish to use\n role, # What is our current IAM Role\n train_instance_count=1, # How many compute instances\n train_instance_type='ml.m4.xlarge', # What kind of compute instances\n output_path='s3://{}/{}/output'.format(session.default_bucket(), prefix),\n sagemaker_session=session)\n\n\n# TODO: Set the XGBoost hyperparameters in the xgb object. Don't forget that in this case we have a binary\n# label so we should be using the 'binary:logistic' objective.\n\n\n# Solution:\nxgb.set_hyperparameters(max_depth=5,\n eta=0.2,\n gamma=4,\n min_child_weight=6,\n subsample=0.8,\n silent=0,\n objective='binary:logistic',\n early_stopping_rounds=10,\n num_round=500)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Fit the XGBoost model\n\nNow that our model has been set up we simply need to attach the training and validation datasets and then ask SageMaker to set up the computation.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"s3_input_train = sagemaker.s3_input(s3_data=train_location, content_type='csv')\ns3_input_validation = sagemaker.s3_input(s3_data=val_location, content_type='csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"xgb.fit({'train': s3_input_train, 'validation': s3_input_validation})",
"2019-08-27 21:12:18 Starting - Starting the training job...\n2019-08-27 21:12:21 Starting - Launching requested ML instances...\n2019-08-27 21:13:16 Starting - Preparing the instances for training......\n2019-08-27 21:14:10 Downloading - Downloading input data...\n2019-08-27 21:14:43 Training - Training image download completed. Training in progress..\n\u001b[31mArguments: train\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[2019-08-27:21:14:44:INFO] Running standalone xgboost training.\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[2019-08-27:21:14:44:INFO] File size need to be processed in the node: 238.47mb. Available memory size in the node: 8589.17mb\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[2019-08-27:21:14:44:INFO] Determined delimiter of CSV input is ','\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:14:44] S3DistributionType set as FullyReplicated\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:14:46] 15000x5000 matrix with 75000000 entries loaded from /opt/ml/input/data/train?format=csv&label_column=0&delimiter=,\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[2019-08-27:21:14:46:INFO] Determined delimiter of CSV input is ','\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:14:46] S3DistributionType set as FullyReplicated\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:14:47] 10000x5000 matrix with 50000000 entries loaded from /opt/ml/input/data/validation?format=csv&label_column=0&delimiter=,\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:14:50] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 46 extra nodes, 2 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[0]#011train-error:0.2966#011validation-error:0.2994\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31mMultiple eval metrics have been passed: 'validation-error' will be used for early stopping.\n\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31mWill train until validation-error hasn't improved in 10 rounds.\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:14:52] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 38 extra nodes, 8 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[1]#011train-error:0.2856#011validation-error:0.2858\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:14:53] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 38 extra nodes, 4 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[2]#011train-error:0.271133#011validation-error:0.275\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:14:54] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 42 extra nodes, 4 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[3]#011train-error:0.2648#011validation-error:0.2692\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:14:56] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 32 extra nodes, 4 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[4]#011train-error:0.2622#011validation-error:0.267\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:14:57] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 30 extra nodes, 6 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[5]#011train-error:0.2498#011validation-error:0.2579\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:14:58] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 28 extra nodes, 6 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[6]#011train-error:0.243#011validation-error:0.2535\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:00] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 30 extra nodes, 0 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[7]#011train-error:0.2384#011validation-error:0.2488\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:01] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 40 extra nodes, 2 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[8]#011train-error:0.232#011validation-error:0.2427\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:02] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 24 extra nodes, 6 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[9]#011train-error:0.226933#011validation-error:0.239\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:04] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 42 extra nodes, 2 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[10]#011train-error:0.223#011validation-error:0.2344\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:05] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 28 extra nodes, 10 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[11]#011train-error:0.217667#011validation-error:0.2294\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:06] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 28 extra nodes, 4 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[12]#011train-error:0.215133#011validation-error:0.2254\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:07] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 34 extra nodes, 6 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[13]#011train-error:0.210067#011validation-error:0.2189\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:09] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 30 extra nodes, 2 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[14]#011train-error:0.206867#011validation-error:0.2171\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:10] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 20 extra nodes, 10 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[15]#011train-error:0.205867#011validation-error:0.2139\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:11] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 34 extra nodes, 2 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[16]#011train-error:0.2#011validation-error:0.2109\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:12] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 28 extra nodes, 4 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[17]#011train-error:0.195933#011validation-error:0.2086\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:14] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 30 extra nodes, 10 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[18]#011train-error:0.192333#011validation-error:0.2061\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:15] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 36 extra nodes, 10 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[19]#011train-error:0.189667#011validation-error:0.2036\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:16] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 36 extra nodes, 4 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[20]#011train-error:0.186533#011validation-error:0.2014\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:17] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 24 extra nodes, 10 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21]#011train-error:0.185133#011validation-error:0.2002\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:19] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 26 extra nodes, 6 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[22]#011train-error:0.182333#011validation-error:0.1974\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:20] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 26 extra nodes, 12 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[23]#011train-error:0.179933#011validation-error:0.1941\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:21] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 28 extra nodes, 6 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[24]#011train-error:0.179933#011validation-error:0.1918\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:23] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 32 extra nodes, 8 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[25]#011train-error:0.1772#011validation-error:0.191\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:24] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 26 extra nodes, 10 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[26]#011train-error:0.1744#011validation-error:0.1897\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:25] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 26 extra nodes, 6 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[27]#011train-error:0.172467#011validation-error:0.1874\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:26] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 26 extra nodes, 12 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[28]#011train-error:0.170933#011validation-error:0.1868\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:28] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 22 extra nodes, 12 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[29]#011train-error:0.170867#011validation-error:0.1838\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:29] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 24 extra nodes, 8 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[30]#011train-error:0.169933#011validation-error:0.1839\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:30] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 20 extra nodes, 8 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[31]#011train-error:0.168467#011validation-error:0.1827\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:31] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 28 extra nodes, 10 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[32]#011train-error:0.166267#011validation-error:0.1796\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:33] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 22 extra nodes, 6 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[33]#011train-error:0.164733#011validation-error:0.1815\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:34] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 22 extra nodes, 8 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[34]#011train-error:0.162933#011validation-error:0.1806\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:35] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 26 extra nodes, 8 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[35]#011train-error:0.162267#011validation-error:0.1777\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:36] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 18 extra nodes, 14 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[36]#011train-error:0.1612#011validation-error:0.1769\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:38] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 26 extra nodes, 12 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[37]#011train-error:0.1582#011validation-error:0.1741\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:39] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 30 extra nodes, 14 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[38]#011train-error:0.156333#011validation-error:0.1752\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:40] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 22 extra nodes, 8 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[39]#011train-error:0.153933#011validation-error:0.1748\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:41] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 18 extra nodes, 20 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[40]#011train-error:0.154733#011validation-error:0.1719\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:43] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 22 extra nodes, 10 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[41]#011train-error:0.152267#011validation-error:0.1712\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:44] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 20 extra nodes, 6 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[42]#011train-error:0.151333#011validation-error:0.1703\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:45] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 20 extra nodes, 4 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[43]#011train-error:0.1496#011validation-error:0.1695\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[21:15:47] src/tree/updater_prune.cc:74: tree pruning end, 1 roots, 18 extra nodes, 14 pruned nodes, max_depth=5\u001b[0m\n\u001b[31m[44]#011train-error:0.148733#011validation-error:0.1687\u001b[0m\n"
]
],
[
[
"### (TODO) Testing the model\n\nNow that we've fit our XGBoost model, it's time to see how well it performs. To do this we will use SageMakers Batch Transform functionality. Batch Transform is a convenient way to perform inference on a large dataset in a way that is not realtime. That is, we don't necessarily need to use our model's results immediately and instead we can peform inference on a large number of samples. An example of this in industry might be peforming an end of month report. This method of inference can also be useful to us as it means to can perform inference on our entire test set. \n\nTo perform a Batch Transformation we need to first create a transformer objects from our trained estimator object.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# TODO: Create a transformer object from the trained model. Using an instance count of 1 and an instance type of ml.m4.xlarge\n# should be more than enough.\nxgb_transformer = None\n\n\n# Solution:\nxgb_transformer = xgb.transformer(instance_count = 1, instance_type = 'ml.m4.xlarge')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Next we actually perform the transform job. When doing so we need to make sure to specify the type of data we are sending so that it is serialized correctly in the background. In our case we are providing our model with csv data so we specify `text/csv`. Also, if the test data that we have provided is too large to process all at once then we need to specify how the data file should be split up. Since each line is a single entry in our data set we tell SageMaker that it can split the input on each line.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# TODO: Start the transform job. Make sure to specify the content type and the split type of the test data.\n\n# Solution:\nxgb_transformer.transform(test_location, content_type='text/csv', split_type='Line')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Currently the transform job is running but it is doing so in the background. Since we wish to wait until the transform job is done and we would like a bit of feedback we can run the `wait()` method.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"xgb_transformer.wait()",
"..............................................!\n"
]
],
[
[
"Now the transform job has executed and the result, the estimated sentiment of each review, has been saved on S3. Since we would rather work on this file locally we can perform a bit of notebook magic to copy the file to the `data_dir`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!aws s3 cp --recursive $xgb_transformer.output_path $data_dir",
"Completed 256.0 KiB/369.9 KiB (3.5 MiB/s) with 1 file(s) remaining\rCompleted 369.9 KiB/369.9 KiB (4.9 MiB/s) with 1 file(s) remaining\rdownload: s3://sagemaker-us-east-2-080917825853/xgboost-2019-08-27-21-19-02-911/test.csv.out to ../data/xgboost/test.csv.out\r\n"
]
],
[
[
"The last step is now to read in the output from our model, convert the output to something a little more usable, in this case we want the sentiment to be either `1` (positive) or `0` (negative), and then compare to the ground truth labels.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"predictions = pd.read_csv(os.path.join(data_dir, 'test.csv.out'), header=None)\npredictions = [round(num) for num in predictions.squeeze().values]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score\naccuracy_score(test_y, predictions)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Optional: Clean up\n\nThe default notebook instance on SageMaker doesn't have a lot of excess disk space available. As you continue to complete and execute notebooks you will eventually fill up this disk space, leading to errors which can be difficult to diagnose. Once you are completely finished using a notebook it is a good idea to remove the files that you created along the way. Of course, you can do this from the terminal or from the notebook hub if you would like. The cell below contains some commands to clean up the created files from within the notebook.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# First we will remove all of the files contained in the data_dir directory\n!rm $data_dir/*\n\n# And then we delete the directory itself\n!rmdir $data_dir\n\n# Similarly we will remove the files in the cache_dir directory and the directory itself\n!rm $cache_dir/*\n!rmdir $cache_dir",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a7443a04cc3a0701bc7b7cad61c2ce1f07d02bc
| 22,411 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
index.ipynb
|
guyemerson/intro
|
bba50f6a6e498769d20ad8d4b3a2ed992c26ea9d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
index.ipynb
|
guyemerson/intro
|
bba50f6a6e498769d20ad8d4b3a2ed992c26ea9d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
index.ipynb
|
guyemerson/intro
|
bba50f6a6e498769d20ad8d4b3a2ed992c26ea9d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 34.745736 | 539 | 0.585918 |
[
[
[
"# Introduction to Programming in Python\n\nIn this short introduction, I'll introduce you to the basics of programming, using the Python programming language. By the end of it, you should hopefully be able to write your own HMM POS-tagger.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### First Steps\n\nYou can think of a program as a series of instructions for the computer, which it will follow one after the other. When the computer runs the program, it will create objects and manipulate them, according to our instructions. For example, we could tell it to create some objects representing numbers, add them together, then show us (`print`) the result. If you click on the block of code below to select it, then click on the \"run\" button in the toolbar above (or press ctrl+enter), you should see the output appear underneath.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"kim = 4\njamie = 3\nchris = kim + jamie\nprint(chris)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now try editing the above code to do a different calculation, and then run it again. As well as adding (`+`), we can also subtract (`-`), multiply (`*`), and divide (`/`). Note that `kim`, `jamie`, and `chris` are just names we've assigned to the objects, and you can change the names to whatever you want.\n\nThese named objects are called **variables**. We can also calculate things without explicitly naming the objects, as shown below.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(3 + 4)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"As you work through this notebook, I would encourage you to play with the examples until you feel comfortable with what the code is doing.\n\nIf a line of code can't be interpreted, Python will throw an error. Run the following code, which has a mistake - it will tell you which line caused the error, and give you an error message.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"hamster = 2 = 3\nprint(hamster)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now edit the above code so that it does not throw an error, then run it again.\n\nDon't be worried if you introduce errors as you play with the code in this notebook - finding errors and fixing them is called **debugging**, and is an important part of programming.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Finally, if we write a hash symbol, Python will ignore everything after it in that line. This is called a **comment**, and is useful to document what the code is doing.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"kim = 4 # Define a variable\njamie = 3 # Define another variable\nchris = kim + jamie # Add these objects together, and save the result as a new variable\nprint(chris) # Print the new variable\n\nchris = 10 # If we re-define a variable, it replaces the old value\nprint(chris)\nchris = chris + 1 # We can also assign a new value to a variable based on its current value\nprint(chris)\nchris += 1 # This is shorthand for the line 'chris = chris + 1'\nprint(chris)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Types of Object\n\nThere are many types of object in Python, apart from numbers. Another type is a **string**, to represent text. A string must start and finish with quotes (either single or double quotes, as long as the same kind is used).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"text = \"hello\"\nmore_text = ' world!'\ncombined = text + more_text # '+' will concatenate strings\nprint(combined)\n\nrepeated = text * 5 # '*' will repeat strings\nprint(repeated)\n\nstring_23 = '23' # This is a string\ninteger_23 = 23 # This is an integer\n\n# What do you think will be printed if you uncomment the lines below?\n#print(string_23 * 3)\n#print(integer_23 * 3)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can refer to specific characters in a string, and refer to substrings, using square brackets:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"long_string = \"they fish in rivers in December\"\nletter = long_string[0] # We start counting from zero. This does: letter = \"t\"\nprint(letter)\nanother_letter = long_string[15]\nprint(another_letter)\n\nend = long_string[-1] # If you give a negative number, it counts backwards from the end\nprint(end)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"long_string = \"they fish in rivers in December\"\nsubstring = long_string[0:3] # We can get a substring by specifying start and end points, separated by a colon\nprint(substring) # This prints the first three characters\n\nlong_substring = long_string[5:] # If you don't specify a number, it uses the very start or very end\nprint(long_substring) # This prints everything except the first five characters",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Other important types of object are **lists**, **tuples**, and **dictionaries**. Lists and tuples are made up of several objects in a particular order. Dictionaries map from one set of objects (the **keys**) to another (the **values**), and have no inherent order. Lists are written with square brackets `[]`, tuples with round brackets `()`, and dictionaries with curly brackets `{}`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"my_list = [1, 5, 12, 'dog']\nmy_tuple = ('cat', 17, 18)\nmy_dict = {'banana': 'yellow', 'apple': 'green', 'orange': 'orange'}\n\nprint(my_tuple[0]) # You can refer to elements of a tuple or list, in the same way as for a string\nprint(my_dict['apple']) # You can also look something up in a dictionary in this way\n\n# Lists and dictionaries can also be changed:\nmy_list[1] = 100\nmy_dict['apple'] = 'red'\nprint(my_list)\nprint(my_dict)\n\n# Note you can't change strings or tuples like this (what happens if you try?)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# This dict maps from bigrams (tuples of strings) to integers\ntuple_dict = {('the', 'fish'): 351, ('dog', 'barked'): 233, ('cat', 'barked'): 1}\n\n# If a key is a tuple, the round brackets of the tuple are optional:\nprint(tuple_dict[('the', 'fish')])\nprint(tuple_dict['the', 'fish'])\n\n# Note that you can't use lists and dicts as keys of a dict (because lists and dicts can be changed)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Functions and Methods\n\nSo far, we've written programs where each line is executed exactly once. However, it is often useful to run the same code in different places, and we can do that using a **function**. We've seen one function so far, namely the `print` function. We can also define our own, using the keyword `def`. The function will take some number of arguments (possibly zero), run some code, and `return` a result. The code inside the function is indented (here, indented with 4 spaces).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def add_one(x): # This defines a function 'add_one' which takes one argument 'x'\n y = x + 1 # We create a new object which is one larger\n return y # We return the result\n\nnew_value = add_one(10) # We're calling the add_one function, with x=10\nprint(new_value) # We're calling the print function\nprint(add_one(add_one(0))) # We can also pass the result of one function as the input to another function\n\ndef repeat_substring(string, number): # This function takes two arguments\n substring = string[0:3] # We take the first three letters in the string\n return substring * number # We return this substring, repeated some number of times\n\nprint(repeat_substring('cathode', 3))\n\n# If the print function is given multiple arguments, it prints them all, separated by a space\nprint('and finally,', repeat_substring('doggerel', add_one(1)))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Try writing your own function for \"Pig Latin\" - it should take a string, remove the first letter, put the first letter on the end, then add \"ay\". For example,\n\n\"pig\" -> \"igpay\" (\"ig\" + \"p\" + \"ay\")\n\n\"latin\" -> \"atinlay\" (\"atin\" + \"l\" + \"ay\")\n\n\"eat\" -> \"ateay\" (\"at\" + \"e\" + \"ay\")\n\n(This is a slight simplification of the children's game.)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Some types of object have built-in functions, called **methods**. We can call a method by writing `.` after an object's name, followed by the name of the method. Different types of object have different methods available. Here is one method of strings, called `split`, which splits it up into a list of smaller strings:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tagged_string = \"they_PNP\"\ntoken_tag = tagged_string.split('_') # split whenever we see '_'\nprint(token_tag)\ntoken, tag = tagged_string.split('_') # we can also assign each element to a separate variable\nprint(token, tag)\n\nlong_string = \"they fish in rivers in December\"\ntokens = long_string.split() # if we don't specify what to split on, the function splits on whitespace\nprint(tokens)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Loops\n\nAnother way that we can execute lines multiple times is with a **loop**. If we have an object that has multiple elements (like a list, tuple, or dict), then we can loop through them, and execute some code for each element. We write a loop using the keywords `for` and `in`, and define a new variable that stands for the current element. As with a function, the code inside the loop is indented.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for x in [1, 2, 3, 'pineapple']:\n print(x, 5*x)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"my_dict = {'banana': 'yellow', 'apple': 'green', 'orange': 'orange'}\n\nfor x in my_dict: # This iterates through the keys of the dict\n print('this', x, 'is', my_dict[x])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tuple_dict = {('the', 'fish'): 351, ('dog', 'barked'): 233, ('cat', 'barked'): 1}\n\nfor thing in tuple_dict: # Each x is a tuple\n print(thing[0])\n\nfor p, q in tuple_dict: # We can break the tuple into two parts\n print(p, q, tuple_dict[p,q])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Variables defined inside a loop will be available in the next iteration. For example, let's iterate through a list of tokens and print both the current token and the previous token:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tokens = \"they fish in rivers in December\".split()\n\nprevious = \"nothing yet...\"\nfor current in tokens:\n print('processing new token!')\n print('current token is', current)\n print('previous token was', previous)\n previous = current # Assign a new value to 'previous', in preparation for the next iteration",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"What happens if we get rid of the line `previous = \"nothing yet...\"`?\n\nTry writing a function that will take a list of numbers as input, and return the product of all the numbers.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Logic\n\nSometimes we may want to do different things depending on the value of an object. For example, suppose we have a list of strings, and want to print everything that starts with the letter 'h'. To do this, we write `if`, followed by a condition that can be `True` or `False`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"my_list = 'the hungry hamster has a question to ask'.split()\n\nfor w in my_list:\n if w[0] == 'h': # A *double* equals sign checks for equality\n print(w) # As with loops and function, we indent the code",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Optionally, we can say what to do if the condition is not true, using the keyword `else`:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for w in 'the hungry hamster has a question to ask'.split():\n if w[0] == 'h':\n print(w, 'begins with h')\n else:\n print(w, 'does not begin with h')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Here are a few examples of conditions that we can use:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print('1 == 1', 1 == 1) # Equality\nprint('1 > 2', 1 > 2) # More than\nprint('1 < 2', 1 < 2) # Less than\nprint('1 in [1, 2, 3]', 1 in [1, 2, 3]) # Being in a list\nprint('5 in [1, 2, 3]', 5 in [1, 2, 3])\nprint('\"h\" in \"hamster\"', \"h\" in \"hamster\") # Being in a string\nprint('\"cat\" in {\"cat\": 5, \"the\" : 8}', \"cat\" in {\"cat\": 5, \"the\" : 8}) # Being a key in a dictionary\nprint('\"dog\" in {\"cat\": 5, \"the\" : 8}', \"dog\" in {\"cat\": 5, \"the\" : 8})",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Putting it all together\n\nFor example, let's go through a toy corpus and count how many times each token appears.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"corpus = 'Once upon a time there was a dragon . The dragon liked to fly . The end .'\ntokens = corpus.split()\nfrequency = {} # An empty dictionary, which will map from words to their counts\n\nfor w in tokens:\n if w in frequency: # If we've seen the word before\n frequency[w] += 1 # Add 1 to the count\n else:\n frequency[w] = 1 # Start the count from 1\n\n# Let's print all the words that appear more than once\n\nfor w in frequency:\n if frequency[w] > 1:\n print(w)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"In the above code, we are effectively saying that when a word is not in the `frequency` dictionary, the default value is 0. Because this is a common thing to do, there is a special type of dict called a `defaultdict`, which can be given a default value. The code below effectively does the same thing as the code above.\n\nBecause a `defaultdict` is not a core part of Python, we have to **import** it to make it available. There are many packages which extend Python in various ways, including a number of packages specifically for Natural Language Processing.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from collections import defaultdict # Make defaultdict available\n\ncorpus = 'Once upon a time there was a dragon . The dragon liked to fly . The end .'\ntokens = corpus.split()\nfrequency = defaultdict(int) # The default value will be an int (integer), which defaults to 0\n\nfor w in tokens:\n frequency[w] += 1 # Add 1 to the count\n\n# Let's print all the words that appear more than once\n\nfor w in frequency:\n if frequency[w] > 1:\n print(w)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Writing an HMM POS-tagger\n\nYou should now know enough programming to write your own HMM part-of-speech tagger! Use everything we've covered above to split up the corpus into the bits you need, count the frequencies of the things you need, calculate the relevant probabilities, and finally write a function that will take a tagged string as input, and return the probability of that sequence in the model.\n\nThe comments below should guide you through writing a tagger. You can uncomment lines and complete them, as you need to - lines with '...' are incomplete! If you're halfway through writing the tagger and you're not sure if you're not sure if you've done something right, you can `print` things to check that they're what you expect.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"corpus = \"They_PNP used_VVD to_TO0 can_VVI fish_NN2 in_PRP those_DT0 towns_NN2 ._PUN These_DT0 days_NN2 now_AV0 in_PRP these_DT0 areas_NN2 few_DT0 people_NN2 can_VM0 fish_VVB ._PUN\"\n\n### We need to find the frequency of each tag, each tag-tag bigram, and each tag-token combination\n### First, we need to define the right type of object that will record these frequencies\n### If you want to use a type that hasn't been imported, make sure to import it first\n\n#tag_count = ...\n#tag_tag_count = ...\n#tag_token_count = ...\n\n### Next, we need to calculate these counts by looping over the corpus\n\n#token_tag_list = corpus...\n#previous_tag = ...\n#for token_tag in token_tag_list:\n# token, tag = ...\n# tag_count[...] ...\n# tag_tag_count[...] ...\n# tag_token_count[...] ...\n# previous_tag ...\n\n### Finally, we need to use these counts to calculate the probabilities\n### First define the right type of object\n\n#tag_tag_prob = ...\n#tag_token_prob = ...\n\n### And then do the calculation\n\n#for ... in ...:\n# tag_tag_prob[...] = ...\n\n#for ... in ...:\n# tag_token_prob[...] = ...\n\n### We have now calculated all the probabilities we need for a Hidden Markov Model!\n### Let's define a function that will take a tagged sequence, and calculate the probability of generating it\n### The 'text' variable will be something like \"They_PNP fished_VVD\"\n\n#def prob(text):\n# token_tag_list = ...\n# result = ...\n# previous_tag = ...\n# for token_tag in token_tag_list:\n# token, tag = ...\n# result *= ...\n# result *= ...\n# previous_tag = ...\n# return result\n\n### Now, for the last step! Here are the two sequences we wanted to compare:\n\n#option1 = 'These_DT0 areas_NN2 can_VM0 fish_VVB'\n#option2 = 'These_DT0 areas_NN2 can_VVB fish_NN2'\n\n#prob1 = prob(option1)\n#prob2 = prob(option2)\n\n#print(prob1)\n#print(prob2)\n#print(prob2 > prob1)\n\n### If you change the corpus at the beginning, see how the results change",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a7446d009668d898d57463f6528135bf8cd665c
| 17,178 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
nbs/01a_losses.ipynb
|
hanshin-back/fastai
|
eb98c4a490c319f8136be92cfc1628b5de3f33e2
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2020-11-28T20:01:39.000Z
|
2020-11-28T20:01:39.000Z
|
nbs/01a_losses.ipynb
|
hanshin-back/fastai
|
eb98c4a490c319f8136be92cfc1628b5de3f33e2
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
nbs/01a_losses.ipynb
|
hanshin-back/fastai
|
eb98c4a490c319f8136be92cfc1628b5de3f33e2
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 34.914634 | 557 | 0.59745 |
[
[
[
"#hide\n#skip\n! [ -e /content ] && pip install -Uqq fastai # upgrade fastai on colab",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# default_exp losses\n# default_cls_lvl 3",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#export\nfrom fastai.imports import *\nfrom fastai.torch_imports import *\nfrom fastai.torch_core import *\nfrom fastai.layers import *",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#hide\nfrom nbdev.showdoc import *",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Loss Functions\n> Custom fastai loss functions",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(torch.randn(4,5), torch.randint(0, 2, (4,5)).float(), reduction='none')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"funcs_kwargs",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# export\nclass BaseLoss():\n \"Same as `loss_cls`, but flattens input and target.\"\n activation=decodes=noops\n def __init__(self, loss_cls, *args, axis=-1, flatten=True, floatify=False, is_2d=True, **kwargs):\n store_attr(\"axis,flatten,floatify,is_2d\")\n self.func = loss_cls(*args,**kwargs)\n functools.update_wrapper(self, self.func)\n\n def __repr__(self): return f\"FlattenedLoss of {self.func}\"\n @property\n def reduction(self): return self.func.reduction\n @reduction.setter\n def reduction(self, v): self.func.reduction = v\n\n def __call__(self, inp, targ, **kwargs):\n inp = inp .transpose(self.axis,-1).contiguous()\n targ = targ.transpose(self.axis,-1).contiguous()\n if self.floatify and targ.dtype!=torch.float16: targ = targ.float()\n if targ.dtype in [torch.int8, torch.int16, torch.int32]: targ = targ.long()\n if self.flatten: inp = inp.view(-1,inp.shape[-1]) if self.is_2d else inp.view(-1)\n return self.func.__call__(inp, targ.view(-1) if self.flatten else targ, **kwargs)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Wrapping a general loss function inside of `BaseLoss` provides extra functionalities to your loss functions:\n- flattens the tensors before trying to take the losses since it's more convenient (with a potential tranpose to put `axis` at the end)\n- a potential `activation` method that tells the library if there is an activation fused in the loss (useful for inference and methods such as `Learner.get_preds` or `Learner.predict`)\n- a potential <code>decodes</code> method that is used on predictions in inference (for instance, an argmax in classification)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The `args` and `kwargs` will be passed to `loss_cls` during the initialization to instantiate a loss function. `axis` is put at the end for losses like softmax that are often performed on the last axis. If `floatify=True`, the `targs` will be converted to floats (useful for losses that only accept float targets like `BCEWithLogitsLoss`), and `is_2d` determines if we flatten while keeping the first dimension (batch size) or completely flatten the input. We want the first for losses like Cross Entropy, and the second for pretty much anything else.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# export\n@delegates()\nclass CrossEntropyLossFlat(BaseLoss):\n \"Same as `nn.CrossEntropyLoss`, but flattens input and target.\"\n y_int = True\n @use_kwargs_dict(keep=True, weight=None, ignore_index=-100, reduction='mean')\n def __init__(self, *args, axis=-1, **kwargs): super().__init__(nn.CrossEntropyLoss, *args, axis=axis, **kwargs)\n def decodes(self, x): return x.argmax(dim=self.axis)\n def activation(self, x): return F.softmax(x, dim=self.axis)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tst = CrossEntropyLossFlat()\noutput = torch.randn(32, 5, 10)\ntarget = torch.randint(0, 10, (32,5))\n#nn.CrossEntropy would fail with those two tensors, but not our flattened version.\n_ = tst(output, target)\ntest_fail(lambda x: nn.CrossEntropyLoss()(output,target))\n\n#Associated activation is softmax\ntest_eq(tst.activation(output), F.softmax(output, dim=-1))\n#This loss function has a decodes which is argmax\ntest_eq(tst.decodes(output), output.argmax(dim=-1))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#In a segmentation task, we want to take the softmax over the channel dimension\ntst = CrossEntropyLossFlat(axis=1)\noutput = torch.randn(32, 5, 128, 128)\ntarget = torch.randint(0, 5, (32, 128, 128))\n_ = tst(output, target)\n\ntest_eq(tst.activation(output), F.softmax(output, dim=1))\ntest_eq(tst.decodes(output), output.argmax(dim=1))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# export\n@delegates()\nclass BCEWithLogitsLossFlat(BaseLoss):\n \"Same as `nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss`, but flattens input and target.\"\n @use_kwargs_dict(keep=True, weight=None, reduction='mean', pos_weight=None)\n def __init__(self, *args, axis=-1, floatify=True, thresh=0.5, **kwargs):\n if kwargs.get('pos_weight', None) is not None and kwargs.get('flatten', None) is True:\n raise ValueError(\"`flatten` must be False when using `pos_weight` to avoid a RuntimeError due to shape mismatch\")\n if kwargs.get('pos_weight', None) is not None: kwargs['flatten'] = False\n super().__init__(nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss, *args, axis=axis, floatify=floatify, is_2d=False, **kwargs)\n self.thresh = thresh\n\n def decodes(self, x): return x>self.thresh\n def activation(self, x): return torch.sigmoid(x)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tst = BCEWithLogitsLossFlat()\noutput = torch.randn(32, 5, 10)\ntarget = torch.randn(32, 5, 10)\n#nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss would fail with those two tensors, but not our flattened version.\n_ = tst(output, target)\ntest_fail(lambda x: nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()(output,target))\noutput = torch.randn(32, 5)\ntarget = torch.randint(0,2,(32, 5))\n#nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss would fail with int targets but not our flattened version.\n_ = tst(output, target)\ntest_fail(lambda x: nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()(output,target))\n\ntst = BCEWithLogitsLossFlat(pos_weight=torch.ones(10))\noutput = torch.randn(32, 5, 10)\ntarget = torch.randn(32, 5, 10)\n_ = tst(output, target)\ntest_fail(lambda x: nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()(output,target))\n\n#Associated activation is sigmoid\ntest_eq(tst.activation(output), torch.sigmoid(output))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# export\n@use_kwargs_dict(weight=None, reduction='mean')\ndef BCELossFlat(*args, axis=-1, floatify=True, **kwargs):\n \"Same as `nn.BCELoss`, but flattens input and target.\"\n return BaseLoss(nn.BCELoss, *args, axis=axis, floatify=floatify, is_2d=False, **kwargs)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tst = BCELossFlat()\noutput = torch.sigmoid(torch.randn(32, 5, 10))\ntarget = torch.randint(0,2,(32, 5, 10))\n_ = tst(output, target)\ntest_fail(lambda x: nn.BCELoss()(output,target))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# export\n@use_kwargs_dict(reduction='mean')\ndef MSELossFlat(*args, axis=-1, floatify=True, **kwargs):\n \"Same as `nn.MSELoss`, but flattens input and target.\"\n return BaseLoss(nn.MSELoss, *args, axis=axis, floatify=floatify, is_2d=False, **kwargs)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tst = MSELossFlat()\noutput = torch.sigmoid(torch.randn(32, 5, 10))\ntarget = torch.randint(0,2,(32, 5, 10))\n_ = tst(output, target)\ntest_fail(lambda x: nn.MSELoss()(output,target))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#hide\n#cuda\n#Test losses work in half precision\noutput = torch.sigmoid(torch.randn(32, 5, 10)).half().cuda()\ntarget = torch.randint(0,2,(32, 5, 10)).half().cuda()\nfor tst in [BCELossFlat(), MSELossFlat()]: _ = tst(output, target)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# export\n@use_kwargs_dict(reduction='mean')\ndef L1LossFlat(*args, axis=-1, floatify=True, **kwargs):\n \"Same as `nn.L1Loss`, but flattens input and target.\"\n return BaseLoss(nn.L1Loss, *args, axis=axis, floatify=floatify, is_2d=False, **kwargs)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#export\nclass LabelSmoothingCrossEntropy(Module):\n y_int = True\n def __init__(self, eps:float=0.1, reduction='mean'): self.eps,self.reduction = eps,reduction\n\n def forward(self, output, target):\n c = output.size()[-1]\n log_preds = F.log_softmax(output, dim=-1)\n if self.reduction=='sum': loss = -log_preds.sum()\n else:\n loss = -log_preds.sum(dim=-1) #We divide by that size at the return line so sum and not mean\n if self.reduction=='mean': loss = loss.mean()\n return loss*self.eps/c + (1-self.eps) * F.nll_loss(log_preds, target.long(), reduction=self.reduction)\n\n def activation(self, out): return F.softmax(out, dim=-1)\n def decodes(self, out): return out.argmax(dim=-1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"On top of the formula we define:\n- a `reduction` attribute, that will be used when we call `Learner.get_preds`\n- an `activation` function that represents the activation fused in the loss (since we use cross entropy behind the scenes). It will be applied to the output of the model when calling `Learner.get_preds` or `Learner.predict`\n- a <code>decodes</code> function that converts the output of the model to a format similar to the target (here indices). This is used in `Learner.predict` and `Learner.show_results` to decode the predictions ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#export\n@delegates()\nclass LabelSmoothingCrossEntropyFlat(BaseLoss):\n \"Same as `LabelSmoothingCrossEntropy`, but flattens input and target.\"\n y_int = True\n @use_kwargs_dict(keep=True, eps=0.1, reduction='mean')\n def __init__(self, *args, axis=-1, **kwargs): super().__init__(LabelSmoothingCrossEntropy, *args, axis=axis, **kwargs)\n def activation(self, out): return F.softmax(out, dim=-1)\n def decodes(self, out): return out.argmax(dim=-1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Export -",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#hide\nfrom nbdev.export import *\nnotebook2script()",
"Converted 00_torch_core.ipynb.\nConverted 01_layers.ipynb.\nConverted 01a_losses.ipynb.\nConverted 02_data.load.ipynb.\nConverted 03_data.core.ipynb.\nConverted 04_data.external.ipynb.\nConverted 05_data.transforms.ipynb.\nConverted 06_data.block.ipynb.\nConverted 07_vision.core.ipynb.\nConverted 08_vision.data.ipynb.\nConverted 09_vision.augment.ipynb.\nConverted 09b_vision.utils.ipynb.\nConverted 09c_vision.widgets.ipynb.\nConverted 10_tutorial.pets.ipynb.\nConverted 10b_tutorial.albumentations.ipynb.\nConverted 11_vision.models.xresnet.ipynb.\nConverted 12_optimizer.ipynb.\nConverted 13_callback.core.ipynb.\nConverted 13a_learner.ipynb.\nConverted 13b_metrics.ipynb.\nConverted 14_callback.schedule.ipynb.\nConverted 14a_callback.data.ipynb.\nConverted 15_callback.hook.ipynb.\nConverted 15a_vision.models.unet.ipynb.\nConverted 16_callback.progress.ipynb.\nConverted 17_callback.tracker.ipynb.\nConverted 18_callback.fp16.ipynb.\nConverted 18a_callback.training.ipynb.\nConverted 18b_callback.preds.ipynb.\nConverted 19_callback.mixup.ipynb.\nConverted 20_interpret.ipynb.\nConverted 20a_distributed.ipynb.\nConverted 21_vision.learner.ipynb.\nConverted 22_tutorial.imagenette.ipynb.\nConverted 23_tutorial.vision.ipynb.\nConverted 24_tutorial.siamese.ipynb.\nConverted 24_vision.gan.ipynb.\nConverted 30_text.core.ipynb.\nConverted 31_text.data.ipynb.\nConverted 32_text.models.awdlstm.ipynb.\nConverted 33_text.models.core.ipynb.\nConverted 34_callback.rnn.ipynb.\nConverted 35_tutorial.wikitext.ipynb.\nConverted 36_text.models.qrnn.ipynb.\nConverted 37_text.learner.ipynb.\nConverted 38_tutorial.text.ipynb.\nConverted 39_tutorial.transformers.ipynb.\nConverted 40_tabular.core.ipynb.\nConverted 41_tabular.data.ipynb.\nConverted 42_tabular.model.ipynb.\nConverted 43_tabular.learner.ipynb.\nConverted 44_tutorial.tabular.ipynb.\nConverted 45_collab.ipynb.\nConverted 46_tutorial.collab.ipynb.\nConverted 50_tutorial.datablock.ipynb.\nConverted 60_medical.imaging.ipynb.\nConverted 61_tutorial.medical_imaging.ipynb.\nConverted 65_medical.text.ipynb.\nConverted 70_callback.wandb.ipynb.\nConverted 71_callback.tensorboard.ipynb.\nConverted 72_callback.neptune.ipynb.\nConverted 73_callback.captum.ipynb.\nConverted 74_callback.cutmix.ipynb.\nConverted 97_test_utils.ipynb.\nConverted 99_pytorch_doc.ipynb.\nConverted dev-setup.ipynb.\nConverted index.ipynb.\nConverted quick_start.ipynb.\nConverted tutorial.ipynb.\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a7473a7560751299e622d7f55bc73f9cc5cad45
| 59,156 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
DigitReconnizer.ipynb
|
enikolaev/DigitRecognizer
|
4600eca0836d1dcc2f3911c17633152043681d5d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
DigitReconnizer.ipynb
|
enikolaev/DigitRecognizer
|
4600eca0836d1dcc2f3911c17633152043681d5d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
DigitReconnizer.ipynb
|
enikolaev/DigitRecognizer
|
4600eca0836d1dcc2f3911c17633152043681d5d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 72.942047 | 18,492 | 0.749645 |
[
[
[
"# Getting dataset information ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nfrom matplotlib import pyplot as plt",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x_train = pd.read_csv(\"data/train.csv\")\nx_test = pd.read_csv(\"data/test.csv\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x_test.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"y_train = x_train[\"label\"].values\ny_train.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"y_train[:10]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x_train = x_train.drop(\"label\", axis=1).values\nx_train.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x_test = x_test.values\nx_test.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x_test = x_test.reshape(x_test.shape[0], 28,28)\nx_train = x_train.reshape(x_train.shape[0], 28,28)\nprint(x_train.shape, x_test.shape)",
"(42000, 28, 28) (28000, 28, 28)\n"
],
[
"def draw_mnist(data, nrow = 3, ncol = 3, title=None):\n f, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=nrow, ncols=ncol, sharex=True, sharey=True)\n for i in range(nrow):\n for j in range(ncol):\n ax[i, j].imshow(data[i * ncol + j], cmap=plt.cm.binary)\n if title is None:\n ax[i, j].set_title(i * ncol + j)\n else:\n ax[i, j].set_title(title[i * ncol + j])\n plt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"draw_mnist(x_train, 3, 5, y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"draw_mnist(x_test, 3, 5)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Build model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import tensorflow as tf",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def conv_layer(input, w, b, s = [1,1,1,1], p = 'SAME'):\n conv = tf.nn.conv2d(input, w, s, p)\n conv = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, b)\n return tf.nn.relu(conv)\n\ndef pool_layer(input, size=2, s=[1, 1, 1, 1], p='SAME', ptype='max'):\n pool = tf.nn.max_pool(input, ksize=[1, size, size, 1], strides=s, padding=p)\n return pool\n\ndef fc_layer(input, w, b, relu=False, drop=False, drop_prob=0.5):\n fc = tf.add(tf.matmul(input, w), b)\n if relu:\n fc = tf.nn.relu(fc)\n if drop:\n fc = tf.nn.dropout(fc, drop_prob)\n return fc\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def build_model_short(input):\n \n # conv - relu - pool 1\n w_conv11 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([5, 5, 1, 32]))\n b_conv11 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([32]))\n conv1 = conv_layer(input, w_conv11, b_conv11)\n pool1 = pool_layer(conv1)\n \n # conv - relu - pool 2\n w_conv12 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 32, 64], stddev=0.1))\n b_conv12 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([64])) \n conv2 = conv_layer(pool1, w_conv12, b_conv12)\n pool2 = pool_layer(conv2)\n \n # flat\n conv_size = pool2.get_shape().as_list()\n flat_shape = conv_size[1] * conv_size[2] * conv_size[3]\n flat = tf.reshape(pool2, [conv_size[0], flat_shape])\n \n # fc1 size 100\n fc1_size = 100\n w_fc1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([flat_shape, fc1_size], stddev=0.1))\n b_fc1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([fc1_size], stddev=0.1))\n fc1 = fc_layer(flat, w_fc1, b_fc1, relu=True, drop_prob=0.4)\n\n # fc2 size 10\n fc2_size = 10\n w_fc2 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([fc1_size, fc2_size], stddev=0.1))\n b_fc2 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([fc2_size], stddev=0.1))\n fc2 = fc_layer(fc1, w_fc2, b_fc2)\n \n return fc2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lr = 0.0001\ntrain_batch_size, eval_batch_size = 1000, 1000\nnum_classes = 10\ninput_w, input_h, channels = 28, 28, 1\n\ntrain_input_shape = (train_batch_size, input_w, input_h, channels) \ntrain_input = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=train_input_shape, name='train_input')\ntrain_target = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=(train_batch_size, num_classes), name='train_target')\n\n# eval_input_shape = (eval_batch_size, input_w, input_h, channels) \n# eval_input = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=eval_input_shape)\n# eval_target = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=(eval_batch_size, num_classes))\n\n# gpu0\nmodel_output = build_model_short(train_input)\n# gpu1\n# eval_model_output = build_model_short(eval_input)\n\ncross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=model_output, labels=train_target))\n# eval_cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=eval_model_output, labels=eval_target))\n\noptimazer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=lr).minimize(cross_entropy)\n\ninit = tf.global_variables_initializer()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# data preparation\nEVAL_SIZE = 1000\none_short_labels = np.array([np.array([int(i==number) for i in range(10)]) for number in y_train])\n\neval_data = np.expand_dims(x_train[-EVAL_SIZE:], -1)/255.0\neval_labels = one_short_labels[-EVAL_SIZE:]\n\ninput_data = np.expand_dims(x_train[:-EVAL_SIZE], -1)/255.0\ninput_labels = one_short_labels[:-EVAL_SIZE]\n\nprint('train: ', input_data.shape, input_labels.shape)\nprint('eval: ', eval_data.shape, eval_labels.shape)",
"train: (41000, 28, 28, 1) (41000, 10)\neval: (1000, 28, 28, 1) (1000, 10)\n"
],
[
"epochs = 30\nsess = tf.Session()\nsess.run(init) \n\nfor epoch in range(epochs): \n start_batch = 0\n end_batch = train_batch_size\n while end_batch <= input_data.shape[0]:\n _, cost_train = sess.run([optimazer, cross_entropy], \n feed_dict={train_input: input_data[start_batch:end_batch], \n train_target: input_labels[start_batch:end_batch]}) \n start_batch += train_batch_size\n end_batch += train_batch_size\n\n cost_eval = sess.run(cross_entropy, \n feed_dict={train_input: eval_data, \n train_target: eval_labels}) \n print('epoch: %d, train loss: %f, val loss: %f' % (epoch, cost_train, cost_eval))\n \n ",
"epoch: 0, train loss: 1.851333, val loss: 1.622980\nepoch: 1, train loss: 0.980596, val loss: 0.855028\nepoch: 2, train loss: 0.703367, val loss: 0.627890\nepoch: 3, train loss: 0.527450, val loss: 0.507280\nepoch: 4, train loss: 0.414127, val loss: 0.433220\nepoch: 5, train loss: 0.338037, val loss: 0.375473\nepoch: 6, train loss: 0.285796, val loss: 0.329611\nepoch: 7, train loss: 0.245309, val loss: 0.298355\nepoch: 8, train loss: 0.214143, val loss: 0.275874\nepoch: 9, train loss: 0.188360, val loss: 0.258837\nepoch: 10, train loss: 0.168794, val loss: 0.246166\nepoch: 11, train loss: 0.152037, val loss: 0.232236\nepoch: 12, train loss: 0.136645, val loss: 0.220010\nepoch: 13, train loss: 0.121327, val loss: 0.209671\nepoch: 14, train loss: 0.107960, val loss: 0.200995\nepoch: 15, train loss: 0.094913, val loss: 0.194396\nepoch: 16, train loss: 0.084134, val loss: 0.186222\nepoch: 17, train loss: 0.074216, val loss: 0.178082\nepoch: 18, train loss: 0.065529, val loss: 0.172727\nepoch: 19, train loss: 0.058474, val loss: 0.168404\nepoch: 20, train loss: 0.051800, val loss: 0.164689\nepoch: 21, train loss: 0.045693, val loss: 0.161450\nepoch: 22, train loss: 0.040044, val loss: 0.159257\nepoch: 23, train loss: 0.035245, val loss: 0.156069\nepoch: 24, train loss: 0.031066, val loss: 0.153680\nepoch: 25, train loss: 0.027614, val loss: 0.152965\nepoch: 26, train loss: 0.024542, val loss: 0.150880\nepoch: 27, train loss: 0.022058, val loss: 0.148718\nepoch: 28, train loss: 0.020137, val loss: 0.145793\nepoch: 29, train loss: 0.019001, val loss: 0.143379\n"
],
[
"test_data = np.expand_dims(x_test, -1)\nprint(test_data.shape)\nanswer = np.array([], dtype=np.int32)\nstart_batch = 0\nend_batch = eval_batch_size\n\nwhile end_batch <= test_data.shape[0]:\n pred = sess.run(tf.nn.softmax(model_output), feed_dict={train_input: test_data[start_batch:end_batch]}) \n answer = np.hstack((answer, np.argmax(pred, axis=1, )))\n start_batch += train_batch_size\n end_batch += train_batch_size\n\n\n",
"(28000, 28, 28, 1)\n"
],
[
"sess.close()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"answer.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"answer",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sub_sample = pd.read_csv('data/sample_submission.csv')\nsub_sample.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"submission = pd.DataFrame({'ImageId': range(1, answer.shape[0]+1), 'Label': answer })\n# submission['Label'] = answer\nsubmission.to_csv(\"sub_18_09_18_1.csv\", index=False, encoding='utf-8')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a7475eef0495c315fb071c47c3aa407071d6f1b
| 10,935 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
solutions/ch_11/exercise_2.ipynb
|
rvmuthukumar/Hands-On-Data-Analysis-with-Pandas
|
bda6407ee05c3917817596f5d79013627d5bcc38
|
[
"MIT"
] | 260 |
2019-01-21T01:38:39.000Z
|
2022-03-26T18:49:21.000Z
|
solutions/ch_11/exercise_2.ipynb
|
rvmuthukumar/Hands-On-Data-Analysis-with-Pandas
|
bda6407ee05c3917817596f5d79013627d5bcc38
|
[
"MIT"
] | 8 |
2020-03-13T15:48:56.000Z
|
2021-08-23T21:43:44.000Z
|
solutions/ch_11/exercise_2.ipynb
|
rvmuthukumar/Hands-On-Data-Analysis-with-Pandas
|
bda6407ee05c3917817596f5d79013627d5bcc38
|
[
"MIT"
] | 665 |
2019-07-27T18:28:20.000Z
|
2022-03-23T08:20:35.000Z
| 29.714674 | 230 | 0.478647 |
[
[
[
"# Finding Outliers with k-Means\n\n## Setup",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\n\nimport sqlite3\n\nwith sqlite3.connect('../../ch_11/logs/logs.db') as conn:\n logs_2018 = pd.read_sql(\n \"\"\"\n SELECT * \n FROM logs \n WHERE datetime BETWEEN \"2018-01-01\" AND \"2019-01-01\";\n \"\"\", \n conn, parse_dates=['datetime'], index_col='datetime'\n )\nlogs_2018.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def get_X(log, day):\n \"\"\"\n Get data we can use for the X\n \n Parameters:\n - log: The logs dataframe\n - day: A day or single value we can use as a datetime index slice\n \n Returns: \n A pandas DataFrame\n \"\"\"\n return pd.get_dummies(log[day].assign(\n failures=lambda x: 1 - x.success\n ).query('failures > 0').resample('1min').agg(\n {'username':'nunique', 'failures': 'sum'}\n ).dropna().rename(\n columns={'username':'usernames_with_failures'}\n ).assign(\n day_of_week=lambda x: x.index.dayofweek, \n hour=lambda x: x.index.hour\n ).drop(columns=['failures']), columns=['day_of_week', 'hour'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X = get_X(logs_2018, '2018')\nX.columns",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## k-Means\nSince we want a \"normal\" activity cluster and an \"anomaly\" cluster, we need to make 2 clusters.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.cluster import KMeans\nfrom sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler\n\nkmeans_pipeline = Pipeline([\n ('scale', StandardScaler()),\n ('kmeans', KMeans(random_state=0, n_clusters=2))\n]).fit(X)",
"c:\\users\\molinstefanie\\packt\\venv\\lib\\site-packages\\sklearn\\preprocessing\\data.py:645: DataConversionWarning: Data with input dtype uint8, int64 were all converted to float64 by StandardScaler.\n return self.partial_fit(X, y)\nc:\\users\\molinstefanie\\packt\\venv\\lib\\site-packages\\sklearn\\base.py:464: DataConversionWarning: Data with input dtype uint8, int64 were all converted to float64 by StandardScaler.\n return self.fit(X, **fit_params).transform(X)\n"
]
],
[
[
"The cluster label doesn't mean anything to us, but we can examine the size of each cluster. We don't expect the clusters to be of equal size because anomalous activity doesn't happen as often as normal activity (we presume).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"preds = kmeans_pipeline.predict(X)\npd.Series(preds).value_counts()",
"c:\\users\\molinstefanie\\packt\\venv\\lib\\site-packages\\sklearn\\pipeline.py:331: DataConversionWarning: Data with input dtype uint8, int64 were all converted to float64 by StandardScaler.\n Xt = transform.transform(Xt)\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Evaluating the clustering\n#### Step 1: Get the true labels",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"with sqlite3.connect('../../ch_11/logs/logs.db') as conn:\n hackers_2018 = pd.read_sql(\n 'SELECT * FROM attacks WHERE start BETWEEN \"2018-01-01\" AND \"2019-01-01\";', \n conn, parse_dates=['start', 'end']\n ).assign(\n duration=lambda x: x.end - x.start, \n start_floor=lambda x: x.start.dt.floor('min'),\n end_ceil=lambda x: x.end.dt.ceil('min')\n )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def get_y(datetimes, hackers, resolution='1min'):\n \"\"\"\n Get data we can use for the y (whether or not a hacker attempted a log in during that time).\n \n Parameters:\n - datetimes: The datetimes to check for hackers\n - hackers: The dataframe indicating when the attacks started and stopped\n - resolution: The granularity of the datetime. Default is 1 minute.\n \n Returns:\n A pandas Series of booleans.\n \"\"\"\n date_ranges = hackers.apply(\n lambda x: pd.date_range(x.start_floor, x.end_ceil, freq=resolution), \n axis=1\n )\n dates = pd.Series()\n for date_range in date_ranges:\n dates = pd.concat([dates, date_range.to_series()])\n return datetimes.isin(dates)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"is_hacker = get_y(X.reset_index().datetime, hackers_2018)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Step 2: Calculate Fowlkes Mallows Score\nThis indicates percentage of the observations belong to the same cluster in the true labels and in the predicted labels.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.metrics import fowlkes_mallows_score\n\nfowlkes_mallows_score(is_hacker, preds)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a74821656e9da2e5ec93d0c8c971e0d9440a9f5
| 2,583 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
2017/Day 16.ipynb
|
AwesomeGitHubRepos/adventofcode
|
84ba7963a5d7905973f14bb1c2e3a59165f8b398
|
[
"MIT"
] | 96 |
2018-04-21T07:53:34.000Z
|
2022-03-15T11:00:02.000Z
|
2017/Day 16.ipynb
|
AwesomeGitHubRepos/adventofcode
|
84ba7963a5d7905973f14bb1c2e3a59165f8b398
|
[
"MIT"
] | 17 |
2019-02-07T05:14:47.000Z
|
2021-12-27T12:11:04.000Z
|
2017/Day 16.ipynb
|
AwesomeGitHubRepos/adventofcode
|
84ba7963a5d7905973f14bb1c2e3a59165f8b398
|
[
"MIT"
] | 14 |
2019-02-05T06:34:15.000Z
|
2022-01-24T17:35:00.000Z
| 20.830645 | 65 | 0.441734 |
[
[
[
"def spin(line, x):\n line[:] = line[-x:] + line[:-x]\n\n\ndef exchange(line, a, b):\n line[a], line[b] = line[b], line[a]\n\n\ndef partner(line, a, b):\n exchange(line, line.index(a), line.index(b))\n\n\ndancemoves = {\n 's': spin,\n 'x': exchange,\n 'p': partner,\n}\n\n\ndef dance(moves, dancers='abcdefghijklmnop', repeats=1):\n line = list(dancers)\n \n seen = []\n for i in range(repeats):\n for move in moves:\n move, instr = move[0], move[1:].split('/')\n if move != 'p':\n instr = map(int, instr)\n dancemoves[move](line, *instr)\n key = ''.join(line)\n if key in seen:\n return seen[(repeats - 1) % len(seen)]\n seen.append(key)\n\n return key",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"assert dance(['s1', 'x3/4', 'pe/b'], 'abcde') == 'baedc'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import aocd\n\ndata = aocd.get_data(day=16, year=2017)\nmoves = data.split(',')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('Part 1:', dance(moves))",
"Part 1: ceijbfoamgkdnlph\n"
],
[
"print('Part 2:', dance(moves, repeats=10 ** 9))",
"Part 2: pnhajoekigcbflmd\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a7487732b3cbb554d1f58d3bbbbc9646d23ef06
| 176,829 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
malaria-detection/notebooks/malaria-detection-mwe.ipynb
|
sohilsshah91/hacknights
|
8f474311799d3466f15fe3564431029ed98ed2e6
|
[
"MIT"
] | 9 |
2019-06-20T20:22:50.000Z
|
2022-01-18T11:45:09.000Z
|
malaria-detection/notebooks/malaria-detection-mwe.ipynb
|
sohilsshah91/hacknights
|
8f474311799d3466f15fe3564431029ed98ed2e6
|
[
"MIT"
] | 6 |
2019-07-07T23:25:14.000Z
|
2021-08-23T20:34:56.000Z
|
malaria-detection/notebooks/malaria-detection-mwe.ipynb
|
sohilsshah91/hacknights
|
8f474311799d3466f15fe3564431029ed98ed2e6
|
[
"MIT"
] | 5 |
2019-10-15T23:05:11.000Z
|
2021-09-30T14:24:06.000Z
| 257.018895 | 148,612 | 0.901046 |
[
[
[
"# Detecting malaria in blood smear images\n\n### The Problem\nMalaria is a mosquito-borne disease caused by the parasite _Plasmodium_. There are an estimated 219 million cases of malaria annually, with 435,000 deaths, many of whom are children. Malaria is prevalent in sub-tropical regions of Africa.\n\nMicroscopy is the most common and reliable method for diagnosing malaria and computing parasitic load. \n\nWith this technique, malaria parasites are identified by examining a drop of the patient’s blood, spread out as a “blood smear” on a slide. Prior to examination, the specimen is stained (most often with the Giemsa stain) to give the parasites a distinctive appearance. This technique remains the gold standard for laboratory confirmation of malaria.\n\n\n\nBlood smear from a patient with malaria; microscopic examination shows _Plasmodium falciparum_ parasites (arrows) infecting some of the patient’s red blood cells. (CDC photo)\n\nHowever, the diagnostic accuracy of this technique is dependent on human expertise and can be affectived by and observer's variability.\n\n### Deep learning as a diagnostic aid\nRecent advances in computing and deep learning techniques have led to the applications of large-scale medical image analysis. Here, we aim to use a convolutional neural network (CNN) in order to quickly and accurately classify parasitized from healthy cells from blood smears.\n\nThis notebook is based on the work presented by [Dipanjan Sarkar](https://towardsdatascience.com/detecting-malaria-with-deep-learning-9e45c1e34b60)\n\n\n### About the dataset\nA [dataset](https://ceb.nlm.nih.gov/repositories/malaria-datasets/) of parasitized and unparasitized cells from blood smear slides was collected and annotated by [Rajaraman et al](https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.4568). The dataset contains a total of 27,558 cell images with equal instances of parasitized and uninfected cells from Giemsa-stained thin blood smear slides from 150 P. falciparum-infected and 50 healthy patients collected and photographed at Chittagong Medical College Hospital, Bangladesh. There are also CSV files containing the Patient-ID to cell mappings for the parasitized and uninfected classes. The CSV file for the parasitized class contains 151 patient-ID entries. The slide images for the parasitized patient-ID “C47P8thinOriginal” are read from two different microscope models (Olympus and Motif). The CSV file for the uninfected class contains 201 entries since the normal cells from the infected patients’ slides also make it to the normal cell category (151+50 = 201).\n\nThe data appears along with the publication:\nRajaraman S, Antani SK, Poostchi M, Silamut K, Hossain MA, Maude, RJ, Jaeger S, Thoma GR. (2018) Pre-trained convolutional neural networks as feature extractors toward improved Malaria parasite detection in thin blood smear images. PeerJ6:e4568 https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.4568",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Malaria Dataset\nMedium post:\nhttps://towardsdatascience.com/detecting-malaria-using-deep-learning-fd4fdcee1f5a\n\nData:\nhttps://ceb.nlm.nih.gov/repositories/malaria-datasets/",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Data preprocessing\n\nThe [cell images](https://ceb.nlm.nih.gov/proj/malaria/cell_images.zip) dataset can be downloaded from the [NIH repository](https://ceb.nlm.nih.gov/repositories/malaria-datasets/).\n\nParasitized and healthy cells are sorted into their own folders.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# mkdir ../data/\n# wget https://ceb.nlm.nih.gov/proj/malaria/cell_images.zip\n# unzip cell_images.zip\n\nimport os\n\nos.listdir('../data/cell_images/')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import random\nimport glob\n\n# Get file paths for files\nbase_dir = os.path.join('../data/cell_images')\ninfected_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, 'Parasitized')\nhealthy_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, 'Uninfected')\n\n# Glob is used to identify filepath patterns\ninfected_files = glob.glob(infected_dir+'/*.png')\nhealthy_files = glob.glob(healthy_dir+'/*.png')\n\n# View size of dataset\nlen(infected_files), len(healthy_files)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Our data is evenly split between parasitized and healthy cells/images so we won't need to further balance our data.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Split data into train, test, split sets\n\nWe can aggregate all of our images by adding the filepaths and labels into a single dataframe. \n\nWe'll then shuffle and split the data into a 60/30/10 train/test/validation set.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\n\nnp.random.seed(1)\n\n# Build a dataframe of filenames with labels\nfiles = pd.DataFrame(data={'filename': infected_files, 'label': ['malaria' for i in range(len(infected_files))]})\nfiles = pd.concat([files, pd.DataFrame(data={'filename': healthy_files, 'label': ['healthy' for i in range(len(healthy_files))]})])\nfiles = files.sample(frac=1).reset_index(drop=True) # Shuffle rows\nfiles.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\n\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(files.filename.values, files.label.values, test_size=0.3, random_state=42)\nX_train, X_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(X_train, y_train, test_size=0.1, random_state=42)\n\nX_train.shape, X_val.shape, y_test.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"As the dimensions of each image will vary, we will resize the images to be 125 x 125 pixels. The cv2 module can be used to load and resize images.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import cv2\n\n# Read and resize images \nnrows = 125\nncols = 125\nchannels = 3\n\ncv2.imread(X_train[0], cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)\ncv2.resize(cv2.imread(X_train[0], cv2.IMREAD_COLOR), (nrows, ncols), interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC).shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import threading\nfrom concurrent import futures\n\n# Resize images\nIMG_DIMS = (125, 125)\n\ndef get_img_data_parallel(idx, img, total_imgs):\n if idx % 5000 == 0 or idx == (total_imgs - 1):\n print('{}: working on img num: {}'.format(threading.current_thread().name,\n idx))\n img = cv2.imread(img)\n img = cv2.resize(img, dsize=IMG_DIMS, \n interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)\n img = np.array(img, dtype=np.float32)\n return img\n\nex = futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=None)\nX_train_inp = [(idx, img, len(X_train)) for idx, img in enumerate(X_train)]\nX_val_inp = [(idx, img, len(X_val)) for idx, img in enumerate(X_val)]\nX_test_inp = [(idx, img, len(X_test)) for idx, img in enumerate(X_test)]\n\nprint('Loading Train Images:')\nX_train_map = ex.map(get_img_data_parallel, \n [record[0] for record in X_train_inp],\n [record[1] for record in X_train_inp],\n [record[2] for record in X_train_inp])\nX_train = np.array(list(X_train_map))\n\nprint('\\nLoading Validation Images:')\nX_val_map = ex.map(get_img_data_parallel, \n [record[0] for record in X_val_inp],\n [record[1] for record in X_val_inp],\n [record[2] for record in X_val_inp])\nX_val = np.array(list(X_val_map))\n\nprint('\\nLoading Test Images:')\nX_test_map = ex.map(get_img_data_parallel, \n [record[0] for record in X_test_inp],\n [record[1] for record in X_test_inp],\n [record[2] for record in X_test_inp])\nX_test = np.array(list(X_test_map))\n\nX_train.shape, X_val.shape, X_test.shape",
"Loading Train Images:\nThreadPoolExecutor-0_0: working on img num: 0\nThreadPoolExecutor-0_9: working on img num: 5000\nThreadPoolExecutor-0_15: working on img num: 10000\nThreadPoolExecutor-0_6: working on img num: 15000\nThreadPoolExecutor-0_2: working on img num: 17360\n\nLoading Validation Images:\nThreadPoolExecutor-0_3: working on img num: 0\nThreadPoolExecutor-0_12: working on img num: 1928\n\nLoading Test Images:\nThreadPoolExecutor-0_10: working on img num: 0\nThreadPoolExecutor-0_2: working on img num: 5000\nThreadPoolExecutor-0_11: working on img num: 8267\n"
]
],
[
[
"Using the matplotlib module, we can view a sample of the resized cell images. A brief inspection shows the presence of purple-stained parasites only in malaria-labeled samples.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n%matplotlib inline\n\nplt.figure(1 , figsize = (8 , 8))\nn = 0 \nfor i in range(16):\n n += 1 \n r = np.random.randint(0 , X_train.shape[0] , 1)\n plt.subplot(4 , 4 , n)\n plt.subplots_adjust(hspace = 0.5 , wspace = 0.5)\n plt.imshow(X_train[r[0]]/255.)\n plt.title('{}'.format(y_train[r[0]]))\n plt.xticks([]) , plt.yticks([])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Model training\nWe can set some initial parameters for our model, including batch size, the number of classes, number of epochs, and image dimensions.\n\nWe'll encode the text category labels as 0 or 1.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder\n\nBATCH_SIZE = 64\nNUM_CLASSES = 2\nEPOCHS = 25\nINPUT_SHAPE = (125, 125, 3)\n\nX_train_imgs_scaled = X_train / 255.\nX_val_imgs_scaled = X_val / 255.\n\nle = LabelEncoder()\nle.fit(y_train)\ny_train_enc = le.transform(y_train)\ny_val_enc = le.transform(y_val)\n\nprint(y_train[:6], y_train_enc[:6])",
"['malaria' 'healthy' 'malaria' 'healthy' 'healthy' 'healthy'] [1 0 1 0 0 0]\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Simple CNN model\n\nTo start with, we'll build a simple CNN model with 2 convolution and pooling layers and a dense dropout layer for regularization.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from keras.models import Sequential\nfrom keras.utils import to_categorical\nfrom keras.layers import Conv2D, Dense, MaxPooling2D, Flatten\n\n# Build a simple CNN\nmodel = Sequential()\nmodel.add(Conv2D(32, kernel_size=(5,5), strides=(1,1), activation='relu', input_shape=INPUT_SHAPE))\nmodel.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides=(2,2)))\nmodel.add(Conv2D(64, (5, 5), activation='relu'))\nmodel.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))\nmodel.add(Flatten())\nmodel.add(Dense(1000, activation='relu'))\nmodel.add(Dense(1, activation='softmax'))\n\n# out = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')(drop2)\n\n# model = tf.keras.Model(inputs=inp, outputs=out)\n\nmodel.compile(optimizer='adam',\n loss='binary_crossentropy',\n metrics=['accuracy'])\nmodel.summary()",
"Using TensorFlow backend.\nWARNING: Logging before flag parsing goes to stderr.\nW0721 19:44:35.868954 4626703808 deprecation_wrapper.py:119] From /Users/npg2108/GitHub/hacknights/hacknights/lib/python3.6/site-packages/keras/backend/tensorflow_backend.py:74: The name tf.get_default_graph is deprecated. Please use tf.compat.v1.get_default_graph instead.\n\nW0721 19:44:35.908560 4626703808 deprecation_wrapper.py:119] From /Users/npg2108/GitHub/hacknights/hacknights/lib/python3.6/site-packages/keras/backend/tensorflow_backend.py:517: The name tf.placeholder is deprecated. Please use tf.compat.v1.placeholder instead.\n\nW0721 19:44:35.916497 4626703808 deprecation_wrapper.py:119] From /Users/npg2108/GitHub/hacknights/hacknights/lib/python3.6/site-packages/keras/backend/tensorflow_backend.py:4138: The name tf.random_uniform is deprecated. Please use tf.random.uniform instead.\n\nW0721 19:44:35.937509 4626703808 deprecation_wrapper.py:119] From /Users/npg2108/GitHub/hacknights/hacknights/lib/python3.6/site-packages/keras/backend/tensorflow_backend.py:3976: The name tf.nn.max_pool is deprecated. Please use tf.nn.max_pool2d instead.\n\nW0721 19:44:35.998247 4626703808 deprecation_wrapper.py:119] From /Users/npg2108/GitHub/hacknights/hacknights/lib/python3.6/site-packages/keras/optimizers.py:790: The name tf.train.Optimizer is deprecated. Please use tf.compat.v1.train.Optimizer instead.\n\nW0721 19:44:36.025438 4626703808 deprecation_wrapper.py:119] From /Users/npg2108/GitHub/hacknights/hacknights/lib/python3.6/site-packages/keras/backend/tensorflow_backend.py:3376: The name tf.log is deprecated. Please use tf.math.log instead.\n\nW0721 19:44:36.030886 4626703808 deprecation.py:323] From /Users/npg2108/GitHub/hacknights/hacknights/lib/python3.6/site-packages/tensorflow/python/ops/nn_impl.py:180: add_dispatch_support.<locals>.wrapper (from tensorflow.python.ops.array_ops) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version.\nInstructions for updating:\nUse tf.where in 2.0, which has the same broadcast rule as np.where\n"
]
],
[
[
"We can evaluate the accuracy of model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import datetime\nfrom keras import callbacks\n\n# View accuracy\nlogdir = os.path.join('../tensorboard_logs', \n datetime.datetime.now().strftime(\"%Y%m%d-%H%M%S\"))\ntensorboard_callback = callbacks.TensorBoard(logdir, histogram_freq=1)\nreduce_lr = callbacks.ReduceLROnPlateau(monitor='val_loss', factor=0.5,\n patience=2, min_lr=0.000001)\ncallbacks = [reduce_lr, tensorboard_callback]\n\nhistory = model.fit(x=X_train_imgs_scaled, y=y_train_enc, \n batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,\n epochs=EPOCHS, \n validation_data=(X_val_imgs_scaled, y_val_enc), \n callbacks=callbacks,\n verbose=1)",
"W0721 19:44:43.684452 4626703808 deprecation_wrapper.py:119] From /Users/npg2108/GitHub/hacknights/hacknights/lib/python3.6/site-packages/keras/backend/tensorflow_backend.py:986: The name tf.assign_add is deprecated. Please use tf.compat.v1.assign_add instead.\n\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a748f6ffe0891a2306713a5422e940eaed7fc87
| 18,703 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
donkey_car.ipynb
|
wywincl/donkeycar
|
4ea50985d753a21072f28f0af70cb2206787610d
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
donkey_car.ipynb
|
wywincl/donkeycar
|
4ea50985d753a21072f28f0af70cb2206787610d
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
donkey_car.ipynb
|
wywincl/donkeycar
|
4ea50985d753a21072f28f0af70cb2206787610d
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 52.684507 | 291 | 0.566807 |
[
[
[
"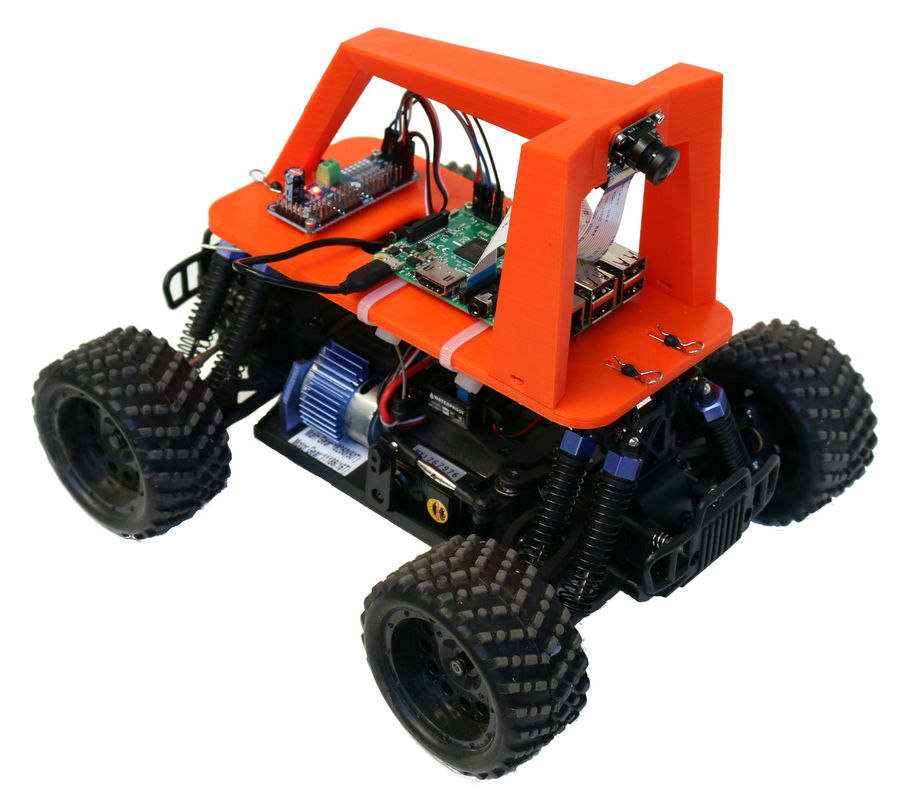\n# Donkey Car指南\n\n|作者 | 修改日期 |\n|-----|------|\n| 汪阳 | 2018/10/30 | \n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 1. 克隆donkeycar代码",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!rm -rf donkey && git clone -b master https://github.com/wroscoe/donkey.git donkey",
"Cloning into 'donkey'...\nremote: Enumerating objects: 1, done.\u001b[K\nremote: Counting objects: 100% (1/1), done.\u001b[K\nremote: Total 6205 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 6204\u001b[K\nReceiving objects: 100% (6205/6205), 30.79 MiB | 8.99 MiB/s, done.\nResolving deltas: 100% (3579/3579), done.\n"
]
],
[
[
"## 2. 安装donkeycar到本地",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!pip3 install -e donkey",
"Obtaining file:///content/donkey\nRequirement already satisfied: numpy in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from donkeycar==2.5.1) (1.14.6)\nRequirement already satisfied: pillow in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from donkeycar==2.5.1) (4.0.0)\nCollecting docopt (from donkeycar==2.5.1)\n Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/a2/55/8f8cab2afd404cf578136ef2cc5dfb50baa1761b68c9da1fb1e4eed343c9/docopt-0.6.2.tar.gz\nRequirement already satisfied: tornado==4.5.3 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from donkeycar==2.5.1) (4.5.3)\nRequirement already satisfied: requests in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from donkeycar==2.5.1) (2.18.4)\nRequirement already satisfied: h5py in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from donkeycar==2.5.1) (2.8.0)\nCollecting python-socketio (from donkeycar==2.5.1)\n Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/45/c5/29e84a694fadea5864ef9530fe815512764497205b4880be32efefbb607f/python_socketio-2.0.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl\nCollecting flask (from donkeycar==2.5.1)\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/7f/e7/08578774ed4536d3242b14dacb4696386634607af824ea997202cd0edb4b/Flask-1.0.2-py2.py3-none-any.whl (91kB)\n\u001b[K 100% |████████████████████████████████| 92kB 4.5MB/s \n\u001b[?25hCollecting eventlet (from donkeycar==2.5.1)\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/86/7e/96e1412f96eeb2f2eca9342dcc4d5bc9305880a448b603b0a8e54439b71c/eventlet-0.24.1-py2.py3-none-any.whl (219kB)\n\u001b[K 100% |████████████████████████████████| 225kB 26.6MB/s \n\u001b[?25hCollecting moviepy (from donkeycar==2.5.1)\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/1f/af/98b68b047c47d9430cb4c9ac899cf9d969de3936f888072991ea74da93a8/moviepy-0.2.3.5.tar.gz (372kB)\n\u001b[K 100% |████████████████████████████████| 378kB 28.0MB/s \n\u001b[?25hRequirement already satisfied: pandas in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from donkeycar==2.5.1) (0.22.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: olefile in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from pillow->donkeycar==2.5.1) (0.46)\nRequirement already satisfied: chardet<3.1.0,>=3.0.2 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from requests->donkeycar==2.5.1) (3.0.4)\nRequirement already satisfied: urllib3<1.23,>=1.21.1 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from requests->donkeycar==2.5.1) (1.22)\nRequirement already satisfied: certifi>=2017.4.17 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from requests->donkeycar==2.5.1) (2018.10.15)\nRequirement already satisfied: idna<2.7,>=2.5 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from requests->donkeycar==2.5.1) (2.6)\nRequirement already satisfied: six in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from h5py->donkeycar==2.5.1) (1.11.0)\nCollecting python-engineio>=2.2.0 (from python-socketio->donkeycar==2.5.1)\n Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/03/6e/44dea849953c21004e288f64d784822c18df25aa043855d87cc1f63c4b41/python_engineio-2.3.2-py2.py3-none-any.whl\nRequirement already satisfied: Werkzeug>=0.14 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from flask->donkeycar==2.5.1) (0.14.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: Jinja2>=2.10 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from flask->donkeycar==2.5.1) (2.10)\nCollecting click>=5.1 (from flask->donkeycar==2.5.1)\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/fa/37/45185cb5abbc30d7257104c434fe0b07e5a195a6847506c074527aa599ec/Click-7.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl (81kB)\n\u001b[K 100% |████████████████████████████████| 81kB 23.3MB/s \n\u001b[?25hCollecting itsdangerous>=0.24 (from flask->donkeycar==2.5.1)\n Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/76/ae/44b03b253d6fade317f32c24d100b3b35c2239807046a4c953c7b89fa49e/itsdangerous-1.1.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl\nCollecting dnspython>=1.15.0 (from eventlet->donkeycar==2.5.1)\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/a6/72/209e18bdfedfd78c6994e9ec96981624a5ad7738524dd474237268422cb8/dnspython-1.15.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl (177kB)\n\u001b[K 100% |████████████████████████████████| 184kB 23.8MB/s \n\u001b[?25hCollecting greenlet>=0.3 (from eventlet->donkeycar==2.5.1)\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/bf/45/142141aa47e01a5779f0fa5a53b81f8379ce8f2b1cd13df7d2f1d751ae42/greenlet-0.4.15-cp36-cp36m-manylinux1_x86_64.whl (41kB)\n\u001b[K 100% |████████████████████████████████| 51kB 20.2MB/s \n\u001b[?25hCollecting monotonic>=1.4 (from eventlet->donkeycar==2.5.1)\n Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/ac/aa/063eca6a416f397bd99552c534c6d11d57f58f2e94c14780f3bbf818c4cf/monotonic-1.5-py2.py3-none-any.whl\nRequirement already satisfied: decorator<5.0,>=4.0.2 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from moviepy->donkeycar==2.5.1) (4.3.0)\nCollecting imageio<3.0,>=2.1.2 (from moviepy->donkeycar==2.5.1)\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/28/b4/cbb592964dfd71a9de6a5b08f882fd334fb99ae09ddc82081dbb2f718c81/imageio-2.4.1.tar.gz (3.3MB)\n\u001b[K 100% |████████████████████████████████| 3.3MB 10.6MB/s \n\u001b[?25hRequirement already satisfied: tqdm<5.0,>=4.11.2 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from moviepy->donkeycar==2.5.1) (4.28.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: python-dateutil>=2 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from pandas->donkeycar==2.5.1) (2.5.3)\nRequirement already satisfied: pytz>=2011k in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from pandas->donkeycar==2.5.1) (2018.6)\nRequirement already satisfied: MarkupSafe>=0.23 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from Jinja2>=2.10->flask->donkeycar==2.5.1) (1.0)\nBuilding wheels for collected packages: docopt, moviepy, imageio\n Running setup.py bdist_wheel for docopt ... \u001b[?25l-\b \bdone\n\u001b[?25h Stored in directory: /root/.cache/pip/wheels/9b/04/dd/7daf4150b6d9b12949298737de9431a324d4b797ffd63f526e\n Running setup.py bdist_wheel for moviepy ... \u001b[?25l-\b \b\\\b \bdone\n\u001b[?25h Stored in directory: /root/.cache/pip/wheels/ad/92/4d/a6c6307d4c2219d002646bd4a5987e31fd5697f6ea7778b2c0\n Running setup.py bdist_wheel for imageio ... \u001b[?25l-\b \b\\\b \b|\b \b/\b \bdone\n\u001b[?25h Stored in directory: /root/.cache/pip/wheels/e0/43/31/605de9372ceaf657f152d3d5e82f42cf265d81db8bbe63cde1\nSuccessfully built docopt moviepy imageio\nInstalling collected packages: docopt, python-engineio, python-socketio, click, itsdangerous, flask, dnspython, greenlet, monotonic, eventlet, imageio, moviepy, donkeycar\n Running setup.py develop for donkeycar\nSuccessfully installed click-7.0 dnspython-1.15.0 docopt-0.6.2 donkeycar eventlet-0.24.1 flask-1.0.2 greenlet-0.4.15 imageio-2.4.1 itsdangerous-1.1.0 monotonic-1.5 moviepy-0.2.3.5 python-engineio-2.3.2 python-socketio-2.0.0\n"
]
],
[
[
"## 3. 创建donkey2自动驾驶小车工程",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!donkey createcar --template donkey2 d2",
"using donkey v2.5.1 ...\nCreating car folder: d2\nmaking dir d2\nCreating data & model folders.\nmaking dir d2/models\nmaking dir d2/data\nmaking dir d2/logs\nCopying car application template: donkey2\nCopying car config defaults. Adjust these before starting your car.\nDonkey setup complete.\n"
]
],
[
[
"## 4. 运行manage.py命令,查看帮助信息",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!cd d2 && python3 manage.py ",
"using donkey v2.5.1 ...\nUsage:\n manage.py (drive) [--model=<model>] [--js] [--chaos]\n manage.py (train) [--tub=<tub1,tub2,..tubn>] (--model=<model>) [--base_model=<base_model>] [--no_cache]\n"
]
],
[
[
"## 5. 上传训练数据并解压缩到指定目录",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!unzip -oq log.zip -d d2/data/",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 6. 训练模型 ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!cd d2 && python3 manage.py train --tub=\"data/log/\" --model=models/mypilot.h5",
"using donkey v2.5.1 ...\nloading config file: /content/d2/config.py\nconfig loaded\ntub_names data/log/\ntrain: 4455, validation: 1114\nsteps_per_epoch 34\nEpoch 1/100\n2018-10-30 02:32:34.060391: I tensorflow/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_gpu_executor.cc:964] successful NUMA node read from SysFS had negative value (-1), but there must be at least one NUMA node, so returning NUMA node zero\n2018-10-30 02:32:34.061007: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:1432] Found device 0 with properties: \nname: Tesla K80 major: 3 minor: 7 memoryClockRate(GHz): 0.8235\npciBusID: 0000:00:04.0\ntotalMemory: 11.17GiB freeMemory: 11.10GiB\n2018-10-30 02:32:34.061060: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:1511] Adding visible gpu devices: 0\n2018-10-30 02:32:35.139713: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:982] Device interconnect StreamExecutor with strength 1 edge matrix:\n2018-10-30 02:32:35.139778: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:988] 0 \n2018-10-30 02:32:35.139824: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:1001] 0: N \n2018-10-30 02:32:35.140176: W tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_bfc_allocator.cc:42] Overriding allow_growth setting because the TF_FORCE_GPU_ALLOW_GROWTH environment variable is set. Original config value was 0.\n2018-10-30 02:32:35.140321: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:1115] Created TensorFlow device (/job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:0 with 10758 MB memory) -> physical GPU (device: 0, name: Tesla K80, pci bus id: 0000:00:04.0, compute capability: 3.7)\n33/34 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 3.8142 - angle_out_loss: 4.2308 - throttle_out_loss: 0.6467\nEpoch 00001: val_loss improved from inf to 2.07851, saving model to models/mypilot.h5\n34/34 [==============================] - 14s 419ms/step - loss: 3.7650 - angle_out_loss: 4.1763 - throttle_out_loss: 0.6351 - val_loss: 2.0785 - val_angle_out_loss: 2.3075 - val_throttle_out_loss: 0.1744\nEpoch 2/100\n33/34 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 1.9221 - angle_out_loss: 2.1329 - throttle_out_loss: 0.2504\nEpoch 00002: val_loss improved from 2.07851 to 1.73459, saving model to models/mypilot.h5\n34/34 [==============================] - 9s 267ms/step - loss: 1.9169 - angle_out_loss: 2.1271 - throttle_out_loss: 0.2508 - val_loss: 1.7346 - val_angle_out_loss: 1.9254 - val_throttle_out_loss: 0.1687\nEpoch 3/100\n33/34 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 1.6160 - angle_out_loss: 1.7933 - throttle_out_loss: 0.2013\nEpoch 00003: val_loss improved from 1.73459 to 1.40012, saving model to models/mypilot.h5\n34/34 [==============================] - 9s 268ms/step - loss: 1.6099 - angle_out_loss: 1.7866 - throttle_out_loss: 0.1998 - val_loss: 1.4001 - val_angle_out_loss: 1.5544 - val_throttle_out_loss: 0.1196\nEpoch 4/100\n33/34 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 1.2878 - angle_out_loss: 1.4288 - throttle_out_loss: 0.1869\nEpoch 00004: val_loss improved from 1.40012 to 1.00291, saving model to models/mypilot.h5\n34/34 [==============================] - 9s 269ms/step - loss: 1.2848 - angle_out_loss: 1.4255 - throttle_out_loss: 0.1855 - val_loss: 1.0029 - val_angle_out_loss: 1.1130 - val_throttle_out_loss: 0.1173\nEpoch 5/100\n33/34 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 1.2149 - angle_out_loss: 1.3481 - throttle_out_loss: 0.1591\nEpoch 00005: val_loss did not improve from 1.00291\n34/34 [==============================] - 9s 268ms/step - loss: 1.2133 - angle_out_loss: 1.3464 - throttle_out_loss: 0.1618 - val_loss: 1.0306 - val_angle_out_loss: 1.1429 - val_throttle_out_loss: 0.1949\nEpoch 6/100\n33/34 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 1.0596 - angle_out_loss: 1.1755 - throttle_out_loss: 0.1595\nEpoch 00006: val_loss improved from 1.00291 to 0.87488, saving model to models/mypilot.h5\n34/34 [==============================] - 9s 268ms/step - loss: 1.0576 - angle_out_loss: 1.1734 - throttle_out_loss: 0.1590 - val_loss: 0.8749 - val_angle_out_loss: 0.9709 - val_throttle_out_loss: 0.1081\nEpoch 7/100\n26/34 [=====================>........] - ETA: 1s - loss: 0.9248 - angle_out_loss: 1.0261 - throttle_out_loss: 0.1324"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.