hexsha
stringlengths 40
40
| size
int64 6
14.9M
| ext
stringclasses 1
value | lang
stringclasses 1
value | max_stars_repo_path
stringlengths 6
260
| max_stars_repo_name
stringlengths 6
119
| max_stars_repo_head_hexsha
stringlengths 40
41
| max_stars_repo_licenses
list | max_stars_count
int64 1
191k
⌀ | max_stars_repo_stars_event_min_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_stars_repo_stars_event_max_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_issues_repo_path
stringlengths 6
260
| max_issues_repo_name
stringlengths 6
119
| max_issues_repo_head_hexsha
stringlengths 40
41
| max_issues_repo_licenses
list | max_issues_count
int64 1
67k
⌀ | max_issues_repo_issues_event_min_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_issues_repo_issues_event_max_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_forks_repo_path
stringlengths 6
260
| max_forks_repo_name
stringlengths 6
119
| max_forks_repo_head_hexsha
stringlengths 40
41
| max_forks_repo_licenses
list | max_forks_count
int64 1
105k
⌀ | max_forks_repo_forks_event_min_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_forks_repo_forks_event_max_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | avg_line_length
float64 2
1.04M
| max_line_length
int64 2
11.2M
| alphanum_fraction
float64 0
1
| cells
list | cell_types
list | cell_type_groups
list |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
4a749b4fe40d648f8e882b7c1d4860dda19cb923
| 508 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/0 Instrucciones.ipynb
|
jestivalv/Maths
|
92221c4a5ec7938f940be5b2be6c06b2270e1212
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/0 Instrucciones.ipynb
|
jestivalv/Maths
|
92221c4a5ec7938f940be5b2be6c06b2270e1212
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/0 Instrucciones.ipynb
|
jestivalv/Maths
|
92221c4a5ec7938f940be5b2be6c06b2270e1212
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 14.514286 | 39 | 0.476378 |
[
[
[
"# Con Esc - 1 ponemos cabecera h1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Con Esc -2 Cabecera h2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Con Esc - 3 Cabecera h3",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4a749f598fac031c3a8a55c6abd8712f2f376aee
| 88,350 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
oldbabylonian/start.ipynb
|
sethbam9/tutorials
|
c259636682304cb516e9048ca8df5a3ab92c62cc
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2019-07-17T18:51:26.000Z
|
2019-07-24T19:45:23.000Z
|
oldbabylonian/start.ipynb
|
sethbam9/tutorials
|
c259636682304cb516e9048ca8df5a3ab92c62cc
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2019-01-16T10:56:50.000Z
|
2020-11-16T16:30:48.000Z
|
oldbabylonian/start.ipynb
|
sethbam9/tutorials
|
c259636682304cb516e9048ca8df5a3ab92c62cc
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2020-12-17T15:41:33.000Z
|
2021-11-03T18:23:07.000Z
| 35.241324 | 13,198 | 0.527187 |
[
[
[
"<img align=\"right\" src=\"images/tf.png\" width=\"128\"/>\n<img align=\"right\" src=\"images/ninologo.png\" width=\"128\"/>\n<img align=\"right\" src=\"images/dans.png\" width=\"128\"/>\n\n# Tutorial\n\nThis notebook gets you started with using\n[Text-Fabric](https://annotation.github.io/text-fabric/) for coding in the Old-Babylonian Letter corpus (cuneiform).\n\nFamiliarity with the underlying\n[data model](https://annotation.github.io/text-fabric/tf/about/datamodel.html)\nis recommended.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Installing Text-Fabric\n\n### Python\n\nYou need to have Python on your system. Most systems have it out of the box,\nbut alas, that is python2 and we need at least python **3.6**.\n\nInstall it from [python.org](https://www.python.org) or from\n[Anaconda](https://www.anaconda.com/download).\n\n### TF itself\n\n```\npip3 install text-fabric\n```\n\n### Jupyter notebook\n\nYou need [Jupyter](http://jupyter.org).\n\nIf it is not already installed:\n\n```\npip3 install jupyter\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Tip\nIf you cloned the repository containing this tutorial,\nfirst copy its parent directory to somewhere outside your clone of the repo,\nbefore computing with this it.\n\nIf you pull changes from the repository later, it will not conflict with\nyour computations.\n\nWhere you put your tutorial directory is up to you.\nIt will work from any directory.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Old Babylonian data\n\nText-Fabric will fetch the data set for you from the newest github release binaries.\n\nThe data will be stored in the `text-fabric-data` in your home directory.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Features\nThe data of the corpus is organized in features.\nThey are *columns* of data.\nThink of the corpus as a gigantic spreadsheet, where row 1 corresponds to the\nfirst sign, row 2 to the second sign, and so on, for all 200,000 signs.\n\nThe information which reading each sign has, constitutes a column in that spreadsheet.\nThe Old Babylonian corpus contains nearly 60 columns, not only for the signs, but also for thousands of other\ntextual objects, such as clusters, lines, columns, faces, documents.\n\nInstead of putting that information in one big table, the data is organized in separate columns.\nWe call those columns **features**.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%load_ext autoreload\n%autoreload 2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import os\nimport collections",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Incantation\n\nThe simplest way to get going is by this *incantation*:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from tf.app import use",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"For the very last version, use `hot`.\n\nFor the latest release, use `latest`.\n\nIf you have cloned the repos (TF app and data), use `clone`.\n\nIf you do not want/need to upgrade, leave out the checkout specifiers.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"A = use(\"oldbabylonian:clone\", checkout=\"clone\", hoist=globals())\n# A = use('oldbabylonian:hot', checkout=\"hot\", hoist=globals())\n# A = use('oldbabylonian:latest', checkout=\"latest\", hoist=globals())\n# A = use('oldbabylonian', hoist=globals())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You can see which features have been loaded, and if you click on a feature name, you find its documentation.\nIf you hover over a name, you see where the feature is located on your system.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## API\n\nThe result of the incantation is that we have a bunch of special variables at our disposal\nthat give us access to the text and data of the corpus.\n\nAt this point it is helpful to throw a quick glance at the text-fabric API documentation\n(see the links under **API Members** above).\n\nThe most essential thing for now is that we can use `F` to access the data in the features\nwe've loaded.\nBut there is more, such as `N`, which helps us to walk over the text, as we see in a minute.\n\nThe **API members** above show you exactly which new names have been inserted in your namespace.\nIf you click on these names, you go to the API documentation for them.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Search\nText-Fabric contains a flexible search engine, that does not only work for the data,\nof this corpus, but also for other corpora and data that you add to corpora.\n\n**Search is the quickest way to come up-to-speed with your data, without too much programming.**\n\nJump to the dedicated [search](search.ipynb) search tutorial first, to whet your appetite.\n\nThe real power of search lies in the fact that it is integrated in a programming environment.\nYou can use programming to:\n\n* compose dynamic queries\n* process query results\n\nTherefore, the rest of this tutorial is still important when you want to tap that power.\nIf you continue here, you learn all the basics of data-navigation with Text-Fabric.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Counting\n\nIn order to get acquainted with the data, we start with the simple task of counting.\n\n## Count all nodes\nWe use the\n[`N.walk()` generator](https://annotation.github.io/text-fabric/tf/core/nodes.html#tf.core.nodes.Nodes.walk)\nto walk through the nodes.\n\nWe compared the TF data to a gigantic spreadsheet, where the rows correspond to the signs.\nIn Text-Fabric, we call the rows `slots`, because they are the textual positions that can be filled with signs.\n\nWe also mentioned that there are also other textual objects.\nThey are the clusters, lines, faces and documents.\nThey also correspond to rows in the big spreadsheet.\n\nIn Text-Fabric we call all these rows *nodes*, and the `N()` generator\ncarries us through those nodes in the textual order.\n\nJust one extra thing: the `info` statements generate timed messages.\nIf you use them instead of `print` you'll get a sense of the amount of time that\nthe various processing steps typically need.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"A.indent(reset=True)\nA.info(\"Counting nodes ...\")\n\ni = 0\nfor n in N.walk():\n i += 1\n\nA.info(\"{} nodes\".format(i))",
" 0.00s Counting nodes ...\n 0.05s 334667 nodes\n"
]
],
[
[
"Here you see it: over 300,000 nodes.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## What are those nodes?\nEvery node has a type, like sign, or line, face.\nBut what exactly are they?\n\nText-Fabric has two special features, `otype` and `oslots`, that must occur in every Text-Fabric data set.\n`otype` tells you for each node its type, and you can ask for the number of `slot`s in the text.\n\nHere we go!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"F.otype.slotType",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"F.otype.maxSlot",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"F.otype.maxNode",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"F.otype.all",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"C.levels.data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This is interesting: above you see all the textual objects, with the average size of their objects,\nthe node where they start, and the node where they end.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Count individual object types\nThis is an intuitive way to count the number of nodes in each type.\nNote in passing, how we use the `indent` in conjunction with `info` to produce neat timed\nand indented progress messages.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"A.indent(reset=True)\nA.info(\"counting objects ...\")\n\nfor otype in F.otype.all:\n i = 0\n\n A.indent(level=1, reset=True)\n\n for n in F.otype.s(otype):\n i += 1\n\n A.info(\"{:>7} {}s\".format(i, otype))\n\nA.indent(level=0)\nA.info(\"Done\")",
" 0.00s counting objects ...\n | 0.00s 1285 documents\n | 0.00s 2834 faces\n | 0.00s 27375 lines\n | 0.01s 76505 words\n | 0.00s 23449 clusters\n | 0.02s 203219 signs\n 0.04s Done\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Viewing textual objects\n\nYou can use the A API (the extra power) to display cuneiform text.\n\nSee the [display](display.ipynb) tutorial.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Feature statistics\n\n`F`\ngives access to all features.\nEvery feature has a method\n`freqList()`\nto generate a frequency list of its values, higher frequencies first.\nHere are the repeats of numerals (the `-1` comes from a `n(rrr)`:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"F.repeat.freqList()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Signs have types and clusters have types. We can count them separately:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"F.type.freqList(\"cluster\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"F.type.freqList(\"sign\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Finally, the flags:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"F.flags.freqList()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Word matters\n\n## Top 20 frequent words\n\nWe represent words by their essential symbols, collected in the feature *sym* (which also exists for signs).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for (w, amount) in F.sym.freqList(\"word\")[0:20]:\n print(f\"{amount:>5} {w}\")",
" 7089 x\n 4071 a-na\n 2517 u3\n 2361 sza\n 1645 um-ma\n 1440 i-na\n 1365 ...\n 1140 qi2-bi2-ma\n 1075 la\n 796 u2-ul\n 776 d⁼utu\n 626 d⁼marduk\n 585 ku3-babbar\n 551 ki-ma\n 540 asz-szum\n 407 hi-a\n 388 lu\n 381 1(disz)\n 363 ki-a-am\n 341 szum-ma\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Word distribution\n\nLet's do a bit more fancy word stuff.\n\n### Hapaxes\n\nA hapax can be found by picking the words with frequency 1\n\nWe print 20 hapaxes.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for w in [w for (w, amount) in F.sym.freqList(\"word\") if amount == 1][0:20]:\n print(f'\"{w}\"')",
"\"...-BU-szu\"\n\"...-BU-um\"\n\"...-DI\"\n\"...-IG-ti-sza\"\n\"...-SZI\"\n\"...-ZU\"\n\"...-a-tim\"\n\"...-ab-ba-lam\"\n\"...-am-ma\"\n\"...-an\"\n\"...-ar\"\n\"...-ar-ra\"\n\"...-ba-lam\"\n\"...-da-an-ni\"\n\"...-d⁼en-lil2\"\n\"...-d⁼la-ga-ma-al\"\n\"...-ha-ar\"\n\"...-hu\"\n\"...-im\"\n\"...-ir\"\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Small occurrence base\n\nThe occurrence base of a word are the documents in which occurs.\n\nWe compute the occurrence base of each word.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"occurrenceBase = collections.defaultdict(set)\n\nfor w in F.otype.s(\"word\"):\n pNum = T.sectionFromNode(w)[0]\n occurrenceBase[F.sym.v(w)].add(pNum)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"An overview of how many words have how big occurrence bases:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"occurrenceSize = collections.Counter()\n\nfor (w, pNums) in occurrenceBase.items():\n occurrenceSize[len(pNums)] += 1\n\noccurrenceSize = sorted(\n occurrenceSize.items(),\n key=lambda x: (-x[1], x[0]),\n)\n\nfor (size, amount) in occurrenceSize[0:10]:\n print(f\"base size {size:>4} : {amount:>5} words\")\nprint(\"...\")\nfor (size, amount) in occurrenceSize[-10:]:\n print(f\"base size {size:>4} : {amount:>5} words\")",
"base size 1 : 11957 words\nbase size 2 : 1817 words\nbase size 3 : 745 words\nbase size 4 : 367 words\nbase size 5 : 229 words\nbase size 6 : 150 words\nbase size 7 : 128 words\nbase size 9 : 75 words\nbase size 8 : 74 words\nbase size 10 : 64 words\n...\nbase size 459 : 1 words\nbase size 624 : 1 words\nbase size 626 : 1 words\nbase size 649 : 1 words\nbase size 736 : 1 words\nbase size 967 : 1 words\nbase size 1031 : 1 words\nbase size 1119 : 1 words\nbase size 1169 : 1 words\nbase size 1255 : 1 words\n"
]
],
[
[
"Let's give the predicate *private* to those words whose occurrence base is a single document.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"privates = {w for (w, base) in occurrenceBase.items() if len(base) == 1}\nlen(privates)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Peculiarity of documents\n\nAs a final exercise with words, lets make a list of all documents, and show their\n\n* total number of words\n* number of private words\n* the percentage of private words: a measure of the peculiarity of the document",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"docList = []\n\nempty = set()\nordinary = set()\n\nfor d in F.otype.s(\"document\"):\n pNum = T.documentName(d)\n words = {F.sym.v(w) for w in L.d(d, otype=\"word\")}\n a = len(words)\n if not a:\n empty.add(pNum)\n continue\n o = len({w for w in words if w in privates})\n if not o:\n ordinary.add(pNum)\n continue\n p = 100 * o / a\n docList.append((pNum, a, o, p))\n\ndocList = sorted(docList, key=lambda e: (-e[3], -e[1], e[0]))\n\nprint(f\"Found {len(empty):>4} empty documents\")\nprint(f\"Found {len(ordinary):>4} ordinary documents (i.e. without private words)\")",
"Found 7 empty documents\nFound 30 ordinary documents (i.e. without private words)\n"
],
[
"print(\n \"{:<20}{:>5}{:>5}{:>5}\\n{}\".format(\n \"document\",\n \"#all\",\n \"#own\",\n \"%own\",\n \"-\" * 35,\n )\n)\n\nfor x in docList[0:20]:\n print(\"{:<20} {:>4} {:>4} {:>4.1f}%\".format(*x))\nprint(\"...\")\nfor x in docList[-20:]:\n print(\"{:<20} {:>4} {:>4} {:>4.1f}%\".format(*x))",
"document #all #own %own\n-----------------------------------\nP292935 20 11 55.0%\nP510702 39 21 53.8%\nP386445 40 20 50.0%\nP510808 28 14 50.0%\nP313381 24 12 50.0%\nP510849 16 8 50.0%\nP510657 4 2 50.0%\nP292931 48 23 47.9%\nP305788 17 8 47.1%\nP313326 45 21 46.7%\nP292992 28 13 46.4%\nP292810 26 12 46.2%\nP305774 13 6 46.2%\nP510641 13 6 46.2%\nP292984 24 11 45.8%\nP481778 24 11 45.8%\nP373043 104 47 45.2%\nP491917 29 13 44.8%\nP355749 226 100 44.2%\nP365938 25 11 44.0%\n...\nP510540 21 1 4.8%\nP372962 22 1 4.5%\nP275094 24 1 4.2%\nP372895 24 1 4.2%\nP385995 24 1 4.2%\nP510732 24 1 4.2%\nP386005 27 1 3.7%\nP510730 27 1 3.7%\nP372914 28 1 3.6%\nP372900 30 1 3.3%\nP372929 30 1 3.3%\nP510528 30 1 3.3%\nP413618 31 1 3.2%\nP510661 64 2 3.1%\nP510535 32 1 3.1%\nP365118 34 1 2.9%\nP510663 34 1 2.9%\nP510817 36 1 2.8%\nP275114 40 1 2.5%\nP372420 61 1 1.6%\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Locality API\nWe travel upwards and downwards, forwards and backwards through the nodes.\nThe Locality-API (`L`) provides functions: `u()` for going up, and `d()` for going down,\n`n()` for going to next nodes and `p()` for going to previous nodes.\n\nThese directions are indirect notions: nodes are just numbers, but by means of the\n`oslots` feature they are linked to slots. One node *contains* an other node, if the one is linked to a set of slots that contains the set of slots that the other is linked to.\nAnd one if next or previous to an other, if its slots follow or precede the slots of the other one.\n\n`L.u(node)` **Up** is going to nodes that embed `node`.\n\n`L.d(node)` **Down** is the opposite direction, to those that are contained in `node`.\n\n`L.n(node)` **Next** are the next *adjacent* nodes, i.e. nodes whose first slot comes immediately after the last slot of `node`.\n\n`L.p(node)` **Previous** are the previous *adjacent* nodes, i.e. nodes whose last slot comes immediately before the first slot of `node`.\n\nAll these functions yield nodes of all possible otypes.\nBy passing an optional parameter, you can restrict the results to nodes of that type.\n\nThe result are ordered according to the order of things in the text.\n\nThe functions return always a tuple, even if there is just one node in the result.\n\n## Going up\nWe go from the first word to the document it contains.\nNote the `[0]` at the end. You expect one document, yet `L` returns a tuple.\nTo get the only element of that tuple, you need to do that `[0]`.\n\nIf you are like me, you keep forgetting it, and that will lead to weird error messages later on.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"firstDoc = L.u(1, otype=\"document\")[0]\nprint(firstDoc)",
"226669\n"
]
],
[
[
"And let's see all the containing objects of sign 3:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"s = 3\nfor otype in F.otype.all:\n if otype == F.otype.slotType:\n continue\n up = L.u(s, otype=otype)\n upNode = \"x\" if len(up) == 0 else up[0]\n print(\"sign {} is contained in {} {}\".format(s, otype, upNode))",
"sign 3 is contained in document 226669\nsign 3 is contained in face 227954\nsign 3 is contained in line 230788\nsign 3 is contained in word 258164\nsign 3 is contained in cluster 203222\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Going next\nLet's go to the next nodes of the first document.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"afterFirstDoc = L.n(firstDoc)\nfor n in afterFirstDoc:\n print(\n \"{:>7}: {:<13} first slot={:<6}, last slot={:<6}\".format(\n n,\n F.otype.v(n),\n E.oslots.s(n)[0],\n E.oslots.s(n)[-1],\n )\n )\nsecondDoc = L.n(firstDoc, otype=\"document\")[0]",
" 348: sign first slot=348 , last slot=348 \n 258314: word first slot=348 , last slot=349 \n 230824: line first slot=348 , last slot=355 \n 227956: face first slot=348 , last slot=482 \n 226670: document first slot=348 , last slot=500 \n"
]
],
[
[
"## Going previous\n\nAnd let's see what is right before the second document.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for n in L.p(secondDoc):\n print(\n \"{:>7}: {:<13} first slot={:<6}, last slot={:<6}\".format(\n n,\n F.otype.v(n),\n E.oslots.s(n)[0],\n E.oslots.s(n)[-1],\n )\n )",
" 226669: document first slot=1 , last slot=347 \n 227955: face first slot=164 , last slot=347 \n 230823: line first slot=330 , last slot=347 \n 203293: cluster first slot=345 , last slot=347 \n 258313: word first slot=347 , last slot=347 \n 347: sign first slot=347 , last slot=347 \n"
]
],
[
[
"## Going down",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We go to the faces of the first document, and just count them.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"faces = L.d(firstDoc, otype=\"face\")\nprint(len(faces))",
"2\n"
]
],
[
[
"## The first line\nWe pick two nodes and explore what is above and below them:\nthe first line and the first word.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for n in [\n F.otype.s(\"word\")[0],\n F.otype.s(\"line\")[0],\n]:\n A.indent(level=0)\n A.info(\"Node {}\".format(n), tm=False)\n A.indent(level=1)\n A.info(\"UP\", tm=False)\n A.indent(level=2)\n A.info(\"\\n\".join([\"{:<15} {}\".format(u, F.otype.v(u)) for u in L.u(n)]), tm=False)\n A.indent(level=1)\n A.info(\"DOWN\", tm=False)\n A.indent(level=2)\n A.info(\"\\n\".join([\"{:<15} {}\".format(u, F.otype.v(u)) for u in L.d(n)]), tm=False)\nA.indent(level=0)\nA.info(\"Done\", tm=False)",
"Node 258163\n | UP\n | | 203220 cluster\n | | 230788 line\n | | 227954 face\n | | 226669 document\n | DOWN\n | | 203220 cluster\n | | 1 sign\n | | 2 sign\nNode 230788\n | UP\n | | 227954 face\n | | 226669 document\n | DOWN\n | | 258163 word\n | | 203220 cluster\n | | 1 sign\n | | 2 sign\n | | 258164 word\n | | 203221 cluster\n | | 203222 cluster\n | | 3 sign\n | | 4 sign\n | | 5 sign\n | | 203223 cluster\n | | 6 sign\n | | 7 sign\nDone\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Text API\n\nSo far, we have mainly seen nodes and their numbers, and the names of node types.\nYou would almost forget that we are dealing with text.\nSo let's try to see some text.\n\nIn the same way as `F` gives access to feature data,\n`T` gives access to the text.\nThat is also feature data, but you can tell Text-Fabric which features are specifically\ncarrying the text, and in return Text-Fabric offers you\na Text API: `T`.\n\n## Formats\nCuneiform text can be represented in a number of ways:\n\n* original ATF, with bracketings and flags\n* essential symbols: readings and graphemes, repeats and fractions (of numerals), no flags, no clusterings\n* unicode symbols\n\nIf you wonder where the information about text formats is stored:\nnot in the program text-fabric, but in the data set.\nIt has a feature `otext`, which specifies the formats and which features\nmust be used to produce them. `otext` is the third special feature in a TF data set,\nnext to `otype` and `oslots`.\nIt is an optional feature.\nIf it is absent, there will be no `T` API.\n\nHere is a list of all available formats in this data set.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sorted(T.formats)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Using the formats\n\nThe ` T.text()` function is central to get text representations of nodes. Its most basic usage is\n\n```python\nT.text(nodes, fmt=fmt)\n```\nwhere `nodes` is a list or iterable of nodes, usually word nodes, and `fmt` is the name of a format.\nIf you leave out `fmt`, the default `text-orig-full` is chosen.\n\nThe result is the text in that format for all nodes specified:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"T.text([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11], fmt=\"text-orig-plain\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"There is also another usage of this function:\n\n```python\nT.text(node, fmt=fmt)\n```\n\nwhere `node` is a single node.\nIn this case, the default format is *ntype*`-orig-full` where *ntype* is the type of `node`.\n\nIf the format is defined in the corpus, it will be used. Otherwise, the word nodes contained in `node` will be looked up\nand represented with the default format `text-orig-full`.\n\nIn this way we can sensibly represent a lot of different nodes, such as documents, faces, lines, clusters, words and signs.\n\nWe compose a set of example nodes and run `T.text` on them:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"exampleNodes = [\n F.otype.s(\"sign\")[0],\n F.otype.s(\"word\")[0],\n F.otype.s(\"cluster\")[0],\n F.otype.s(\"line\")[0],\n F.otype.s(\"face\")[0],\n F.otype.s(\"document\")[0],\n]\nexampleNodes",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for n in exampleNodes:\n print(f\"This is {F.otype.v(n)} {n}:\")\n print(T.text(n))\n print(\"\")",
"This is sign 1:\n[a-\n\nThis is word 258163:\n[a-na] \n\nThis is cluster 203220:\n[a-na] \n\nThis is line 230788:\n[a-na] _{d}suen_-i-[din-nam]\n\nThis is face 227954:\n[a-na] _{d}suen_-i-[din-nam]qi2-bi2-[ma]um-ma _{d}en-lil2_-sza-du-u2-ni-ma_{d}utu_ u3 _{d}[marduk]_ a-na da-ri-a-[tim]li-ba-al-li-t,u2-u2-ka{disz}sze-ep-_{d}suen a2-gal2 [dumu] um-mi-a-mesz_ki-a-am u2-lam-mi-da-an-ni um-[ma] szu-u2-[ma]{disz}sa-am-su-ba-ah-li sza-pi2-ir ma-[tim]2(esze3) _a-sza3_ s,i-[bi]-it {disz}[ku]-un-zu-lum _sza3-gud__a-sza3 a-gar3_ na-ag-[ma-lum] _uru_ x x x{ki}sza _{d}utu_-ha-zi-[ir] isz-tu _mu 7(disz) kam_ id-di-nu-szumu3 i-na _uru_ x-szum{ki} sza-ak-nu id-di-a-am-ma2(esze3) _a-sza3 szuku_ i-li-ib-bu s,i-bi-it _nagar-mesz__a-sza3 a-gar3 uru_ ra-bu-um x [...]x x x x x x [...]$ rest broken\n\nThis is document 226669:\n[a-na] _{d}suen_-i-[din-nam]qi2-bi2-[ma]um-ma _{d}en-lil2_-sza-du-u2-ni-ma_{d}utu_ u3 _{d}[marduk]_ a-na da-ri-a-[tim]li-ba-al-li-t,u2-u2-ka{disz}sze-ep-_{d}suen a2-gal2 [dumu] um-mi-a-mesz_ki-a-am u2-lam-mi-da-an-ni um-[ma] szu-u2-[ma]{disz}sa-am-su-ba-ah-li sza-pi2-ir ma-[tim]2(esze3) _a-sza3_ s,i-[bi]-it {disz}[ku]-un-zu-lum _sza3-gud__a-sza3 a-gar3_ na-ag-[ma-lum] _uru_ x x x{ki}sza _{d}utu_-ha-zi-[ir] isz-tu _mu 7(disz) kam_ id-di-nu-szumu3 i-na _uru_ x-szum{ki} sza-ak-nu id-di-a-am-ma2(esze3) _a-sza3 szuku_ i-li-ib-bu s,i-bi-it _nagar-mesz__a-sza3 a-gar3 uru_ ra-bu-um x [...]x x x x x x [...]$ rest broken$ beginning broken[x x] x x [...][x x] x [...][x x] x s,i-bi-it _gir3-se3#-ga#_[x x] x x x-ir ub-lamin-na-me-er-max _[a-sza3_ s,i]-bi-it ku-un-zu-lum_a-[sza3 a-gar3_ na-ag]-ma-lum _uru gan2_ x x{ki}a-[na] sa-[am-su]-ba-ah-[la] x x li ig bumi-im-ma _a-sza3_ s,i-bi-[it] _nagar-mesz_u2-ul na-di-isz-szuma-na ki-ma i-[na] _dub e2-gal_-limsza _{d}utu_-ha-zi-ir ub-lam in-na-am-ruasz-t,u3-ra-am _dub_ [usz]-ta-bi-la-kuma-wa-tim sza ma-ah-hi-rum u2-lam-ma-du-u2-maasz-szum _e2-gal_-lim la lum-mu-[di ...]_dub_-pi2 u2-sza-ab-ba-x [...]x ti u2-ul a-ga-am-ma-[x ...]u2-ul a-sza-ap-pa-[x ...][at-ta] ki-ma ti-du-u2 wa-ar-ka-az-zu pu-ru-us [x x ...]\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Using the formats\nNow let's use those formats to print out the first line in this corpus.\n\nNote that only the formats starting with `text-` are usable for this.\n\nFor the `layout-` formats, see [display](display.ipynb).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for fmt in sorted(T.formats):\n if fmt.startswith(\"text-\"):\n print(\"{}:\\n\\t{}\".format(fmt, T.text(range(1, 12), fmt=fmt)))",
"text-orig-full:\n\t[a-na] _{d}suen_-i-[din-nam]qi2-bi2-[ma]um-\ntext-orig-plain:\n\ta-na d⁼suen-i-din-namqi2-bi2-maum-\ntext-orig-rich:\n\ta-na d⁼suen-i-din-namqi₂-bi₂-maum-\ntext-orig-unicode:\n\t𒀀𒈾 𒀭𒂗𒍪𒄿𒁷𒉆𒆠𒉈𒈠𒌝\n"
]
],
[
[
"If we do not specify a format, the **default** format is used (`text-orig-full`).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"T.text(range(1, 12))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"firstLine = F.otype.s(\"line\")[0]\nT.text(firstLine)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"T.text(firstLine, fmt=\"text-orig-unicode\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The important things to remember are:\n\n* you can supply a list of slot nodes and get them represented in all formats\n* you can get non-slot nodes `n` in default format by `T.text(n)`\n* you can get non-slot nodes `n` in other formats by `T.text(n, fmt=fmt, descend=True)`",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Whole text in all formats in just 2 seconds\nPart of the pleasure of working with computers is that they can crunch massive amounts of data.\nThe text of the Old Babylonian Letters is a piece of cake.\n\nIt takes just ten seconds to have that cake and eat it.\nIn nearly a dozen formats.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"A.indent(reset=True)\nA.info(\"writing plain text of all letters in all text formats\")\n\ntext = collections.defaultdict(list)\n\nfor ln in F.otype.s(\"line\"):\n for fmt in sorted(T.formats):\n if fmt.startswith(\"text-\"):\n text[fmt].append(T.text(ln, fmt=fmt, descend=True))\n\nA.info(\"done {} formats\".format(len(text)))\n\nfor fmt in sorted(text):\n print(\"{}\\n{}\\n\".format(fmt, \"\\n\".join(text[fmt][0:5])))",
" 0.00s writing plain text of all letters in all text formats\n 1.70s done 4 formats\ntext-orig-full\n[a-na] _{d}suen_-i-[din-nam]\nqi2-bi2-[ma]\num-ma _{d}en-lil2_-sza-du-u2-ni-ma\n_{d}utu_ u3 _{d}[marduk]_ a-na da-ri-a-[tim]\nli-ba-al-li-t,u2-u2-ka\n\ntext-orig-plain\na-na d⁼suen-i-din-nam\nqi2-bi2-ma\num-ma d⁼en-lil2-sza-du-u2-ni-ma\nd⁼utu u3 d⁼marduk a-na da-ri-a-tim\nli-ba-al-li-t,u2-u2-ka\n\ntext-orig-rich\na-na d⁼suen-i-din-nam\nqi₂-bi₂-ma\num-ma d⁼en-lil₂-ša-du-u₂-ni-ma\nd⁼utu u₃ d⁼marduk a-na da-ri-a-tim\nli-ba-al-li-ṭu₂-u₂-ka\n\ntext-orig-unicode\n𒀀𒈾 𒀭𒂗𒍪𒄿𒁷𒉆\n𒆠𒉈𒈠\n𒌝𒈠 𒀭𒂗𒆤𒊭𒁺𒌑𒉌𒈠\n𒀭𒌓 𒅇 𒀭𒀫𒌓 𒀀𒈾 𒁕𒊑𒀀𒁴\n𒇷𒁀𒀠𒇷𒌅𒌑𒅗\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"### The full plain text\nWe write all formats to file, in your `Downloads` folder.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for fmt in T.formats:\n if fmt.startswith(\"text-\"):\n with open(os.path.expanduser(f\"~/Downloads/{fmt}.txt\"), \"w\") as f:\n f.write(\"\\n\".join(text[fmt]))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Sections\n\nA section in the letter corpus is a document, a face or a line.\nKnowledge of sections is not baked into Text-Fabric.\nThe config feature `otext.tf` may specify three section levels, and tell\nwhat the corresponding node types and features are.\n\nFrom that knowledge it can construct mappings from nodes to sections, e.g. from line\nnodes to tuples of the form:\n\n (p-number, face specifier, line number)\n\nYou can get the section of a node as a tuple of relevant document, face, and line nodes.\nOr you can get it as a passage label, a string.\n\nYou can ask for the passage corresponding to the first slot of a node, or the one corresponding to the last slot.\n\nIf you are dealing with document and face nodes, you can ask to fill out the line and face parts as well.\n\nHere are examples of getting the section that corresponds to a node and vice versa.\n\n**NB:** `sectionFromNode` always delivers a verse specification, either from the\nfirst slot belonging to that node, or, if `lastSlot`, from the last slot\nbelonging to that node.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"someNodes = (\n F.otype.s(\"sign\")[100000],\n F.otype.s(\"word\")[10000],\n F.otype.s(\"cluster\")[5000],\n F.otype.s(\"line\")[15000],\n F.otype.s(\"face\")[1000],\n F.otype.s(\"document\")[500],\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for n in someNodes:\n nType = F.otype.v(n)\n d = f\"{n:>7} {nType}\"\n first = A.sectionStrFromNode(n)\n last = A.sectionStrFromNode(n, lastSlot=True, fillup=True)\n tup = (\n T.sectionTuple(n),\n T.sectionTuple(n, lastSlot=True, fillup=True),\n )\n print(f\"{d:<16} - {first:<18} {last:<18} {tup}\")",
" 100001 sign - P313335 obverse:8 P313335 obverse:8 ((227310, 229370, 244327), (227310, 229370, 244327))\n 268163 word - P510665 obverse:9 P510665 obverse:9 ((226821, 228295, 234114), (226821, 228295, 234114))\n 208220 cluster - P510766 obverse:9 P510766 obverse:9 ((226925, 228516, 236231), (226925, 228516, 236231))\n 245788 line - P313410 obverse:12' P313410 obverse:12' ((227376, 229516, 245788), (227376, 229516, 245788))\n 228954 face - P292765 reverse P292765 reverse:12 ((227126, 228954), (227126, 228954, 240157))\n 227169 document - P382526 P382526 left:2 ((227169,), (227169, 229057, 241107))\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Clean caches\n\nText-Fabric pre-computes data for you, so that it can be loaded faster.\nIf the original data is updated, Text-Fabric detects it, and will recompute that data.\n\nBut there are cases, when the algorithms of Text-Fabric have changed, without any changes in the data, that you might\nwant to clear the cache of precomputed results.\n\nThere are two ways to do that:\n\n* Locate the `.tf` directory of your dataset, and remove all `.tfx` files in it.\n This might be a bit awkward to do, because the `.tf` directory is hidden on Unix-like systems.\n* Call `TF.clearCache()`, which does exactly the same.\n\nIt is not handy to execute the following cell all the time, that's why I have commented it out.\nSo if you really want to clear the cache, remove the comment sign below.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# TF.clearCache()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Next steps\n\nBy now you have an impression how to compute around in the corpus.\nWhile this is still the beginning, I hope you already sense the power of unlimited programmatic access\nto all the bits and bytes in the data set.\n\nHere are a few directions for unleashing that power.\n\n* **[display](display.ipynb)** become an expert in creating pretty displays of your text structures\n* **[search](search.ipynb)** turbo charge your hand-coding with search templates\n* **[exportExcel](exportExcel.ipynb)** make tailor-made spreadsheets out of your results\n* **[share](share.ipynb)** draw in other people's data and let them use yours\n* **[similarLines](similarLines.ipynb)** spot the similarities between lines\n\n---\n\nSee the [cookbook](cookbook) for recipes for small, concrete tasks.\n\nCC-BY Dirk Roorda",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a74b587973dc79a0e5e40a132468ab67b0b0574
| 370,979 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
experiments/tl_3v2.wisig+cores/oracle.run1.framed-cores_wisig/trials/1/trial.ipynb
|
stevester94/csc500-notebooks
|
4c1b04c537fe233a75bed82913d9d84985a89177
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
experiments/tl_3v2.wisig+cores/oracle.run1.framed-cores_wisig/trials/1/trial.ipynb
|
stevester94/csc500-notebooks
|
4c1b04c537fe233a75bed82913d9d84985a89177
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
experiments/tl_3v2.wisig+cores/oracle.run1.framed-cores_wisig/trials/1/trial.ipynb
|
stevester94/csc500-notebooks
|
4c1b04c537fe233a75bed82913d9d84985a89177
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 109.239988 | 133,603 | 0.593632 |
[
[
[
"# Transfer Learning Template",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%load_ext autoreload\n%autoreload 2\n%matplotlib inline\n\n \nimport os, json, sys, time, random\nimport numpy as np\nimport torch\nfrom torch.optim import Adam\nfrom easydict import EasyDict\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\nfrom steves_models.steves_ptn import Steves_Prototypical_Network\n\nfrom steves_utils.lazy_iterable_wrapper import Lazy_Iterable_Wrapper\nfrom steves_utils.iterable_aggregator import Iterable_Aggregator\nfrom steves_utils.ptn_train_eval_test_jig import PTN_Train_Eval_Test_Jig\nfrom steves_utils.torch_sequential_builder import build_sequential\nfrom steves_utils.torch_utils import get_dataset_metrics, ptn_confusion_by_domain_over_dataloader\nfrom steves_utils.utils_v2 import (per_domain_accuracy_from_confusion, get_datasets_base_path)\nfrom steves_utils.PTN.utils import independent_accuracy_assesment\n\nfrom torch.utils.data import DataLoader\n\nfrom steves_utils.stratified_dataset.episodic_accessor import Episodic_Accessor_Factory\n\nfrom steves_utils.ptn_do_report import (\n get_loss_curve,\n get_results_table,\n get_parameters_table,\n get_domain_accuracies,\n)\n\nfrom steves_utils.transforms import get_chained_transform",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Allowed Parameters\nThese are allowed parameters, not defaults\nEach of these values need to be present in the injected parameters (the notebook will raise an exception if they are not present)\n\nPapermill uses the cell tag \"parameters\" to inject the real parameters below this cell.\nEnable tags to see what I mean",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"required_parameters = {\n \"experiment_name\",\n \"lr\",\n \"device\",\n \"seed\",\n \"dataset_seed\",\n \"n_shot\",\n \"n_query\",\n \"n_way\",\n \"train_k_factor\",\n \"val_k_factor\",\n \"test_k_factor\",\n \"n_epoch\",\n \"patience\",\n \"criteria_for_best\",\n \"x_net\",\n \"datasets\",\n \"torch_default_dtype\",\n \"NUM_LOGS_PER_EPOCH\",\n \"BEST_MODEL_PATH\",\n \"x_shape\",\n}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from steves_utils.CORES.utils import (\n ALL_NODES,\n ALL_NODES_MINIMUM_1000_EXAMPLES,\n ALL_DAYS\n)\n\nfrom steves_utils.ORACLE.utils_v2 import (\n ALL_DISTANCES_FEET_NARROWED,\n ALL_RUNS,\n ALL_SERIAL_NUMBERS,\n)\n\nstandalone_parameters = {}\nstandalone_parameters[\"experiment_name\"] = \"STANDALONE PTN\"\nstandalone_parameters[\"lr\"] = 0.001\nstandalone_parameters[\"device\"] = \"cuda\"\n\nstandalone_parameters[\"seed\"] = 1337\nstandalone_parameters[\"dataset_seed\"] = 1337\n\nstandalone_parameters[\"n_way\"] = 8\nstandalone_parameters[\"n_shot\"] = 3\nstandalone_parameters[\"n_query\"] = 2\nstandalone_parameters[\"train_k_factor\"] = 1\nstandalone_parameters[\"val_k_factor\"] = 2\nstandalone_parameters[\"test_k_factor\"] = 2\n\n\nstandalone_parameters[\"n_epoch\"] = 50\n\nstandalone_parameters[\"patience\"] = 10\nstandalone_parameters[\"criteria_for_best\"] = \"source_loss\"\n\nstandalone_parameters[\"datasets\"] = [\n {\n \"labels\": ALL_SERIAL_NUMBERS,\n \"domains\": ALL_DISTANCES_FEET_NARROWED,\n \"num_examples_per_domain_per_label\": 100,\n \"pickle_path\": os.path.join(get_datasets_base_path(), \"oracle.Run1_framed_2000Examples_stratified_ds.2022A.pkl\"),\n \"source_or_target_dataset\": \"source\",\n \"x_transforms\": [\"unit_mag\", \"minus_two\"],\n \"episode_transforms\": [],\n \"domain_prefix\": \"ORACLE_\"\n },\n {\n \"labels\": ALL_NODES,\n \"domains\": ALL_DAYS,\n \"num_examples_per_domain_per_label\": 100,\n \"pickle_path\": os.path.join(get_datasets_base_path(), \"cores.stratified_ds.2022A.pkl\"),\n \"source_or_target_dataset\": \"target\",\n \"x_transforms\": [\"unit_power\", \"times_zero\"],\n \"episode_transforms\": [],\n \"domain_prefix\": \"CORES_\"\n } \n]\n\nstandalone_parameters[\"torch_default_dtype\"] = \"torch.float32\" \n\n\n\nstandalone_parameters[\"x_net\"] = [\n {\"class\": \"nnReshape\", \"kargs\": {\"shape\":[-1, 1, 2, 256]}},\n {\"class\": \"Conv2d\", \"kargs\": { \"in_channels\":1, \"out_channels\":256, \"kernel_size\":(1,7), \"bias\":False, \"padding\":(0,3), },},\n {\"class\": \"ReLU\", \"kargs\": {\"inplace\": True}},\n {\"class\": \"BatchNorm2d\", \"kargs\": {\"num_features\":256}},\n\n {\"class\": \"Conv2d\", \"kargs\": { \"in_channels\":256, \"out_channels\":80, \"kernel_size\":(2,7), \"bias\":True, \"padding\":(0,3), },},\n {\"class\": \"ReLU\", \"kargs\": {\"inplace\": True}},\n {\"class\": \"BatchNorm2d\", \"kargs\": {\"num_features\":80}},\n {\"class\": \"Flatten\", \"kargs\": {}},\n\n {\"class\": \"Linear\", \"kargs\": {\"in_features\": 80*256, \"out_features\": 256}}, # 80 units per IQ pair\n {\"class\": \"ReLU\", \"kargs\": {\"inplace\": True}},\n {\"class\": \"BatchNorm1d\", \"kargs\": {\"num_features\":256}},\n\n {\"class\": \"Linear\", \"kargs\": {\"in_features\": 256, \"out_features\": 256}},\n]\n\n# Parameters relevant to results\n# These parameters will basically never need to change\nstandalone_parameters[\"NUM_LOGS_PER_EPOCH\"] = 10\nstandalone_parameters[\"BEST_MODEL_PATH\"] = \"./best_model.pth\"\n\n\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Parameters\nparameters = {\n \"experiment_name\": \"tl_3Av2:oracle.run1.framed -> cores+wisig\",\n \"device\": \"cuda\",\n \"lr\": 0.0001,\n \"x_shape\": [2, 200],\n \"n_shot\": 3,\n \"n_query\": 2,\n \"train_k_factor\": 3,\n \"val_k_factor\": 2,\n \"test_k_factor\": 2,\n \"torch_default_dtype\": \"torch.float32\",\n \"n_epoch\": 50,\n \"patience\": 3,\n \"criteria_for_best\": \"target_accuracy\",\n \"x_net\": [\n {\"class\": \"nnReshape\", \"kargs\": {\"shape\": [-1, 1, 2, 200]}},\n {\n \"class\": \"Conv2d\",\n \"kargs\": {\n \"in_channels\": 1,\n \"out_channels\": 256,\n \"kernel_size\": [1, 7],\n \"bias\": False,\n \"padding\": [0, 3],\n },\n },\n {\"class\": \"ReLU\", \"kargs\": {\"inplace\": True}},\n {\"class\": \"BatchNorm2d\", \"kargs\": {\"num_features\": 256}},\n {\n \"class\": \"Conv2d\",\n \"kargs\": {\n \"in_channels\": 256,\n \"out_channels\": 80,\n \"kernel_size\": [2, 7],\n \"bias\": True,\n \"padding\": [0, 3],\n },\n },\n {\"class\": \"ReLU\", \"kargs\": {\"inplace\": True}},\n {\"class\": \"BatchNorm2d\", \"kargs\": {\"num_features\": 80}},\n {\"class\": \"Flatten\", \"kargs\": {}},\n {\"class\": \"Linear\", \"kargs\": {\"in_features\": 16000, \"out_features\": 256}},\n {\"class\": \"ReLU\", \"kargs\": {\"inplace\": True}},\n {\"class\": \"BatchNorm1d\", \"kargs\": {\"num_features\": 256}},\n {\"class\": \"Linear\", \"kargs\": {\"in_features\": 256, \"out_features\": 256}},\n ],\n \"NUM_LOGS_PER_EPOCH\": 10,\n \"BEST_MODEL_PATH\": \"./best_model.pth\",\n \"n_way\": 16,\n \"datasets\": [\n {\n \"labels\": [\n \"1-10.\",\n \"1-11.\",\n \"1-15.\",\n \"1-16.\",\n \"1-17.\",\n \"1-18.\",\n \"1-19.\",\n \"10-4.\",\n \"10-7.\",\n \"11-1.\",\n \"11-14.\",\n \"11-17.\",\n \"11-20.\",\n \"11-7.\",\n \"13-20.\",\n \"13-8.\",\n \"14-10.\",\n \"14-11.\",\n \"14-14.\",\n \"14-7.\",\n \"15-1.\",\n \"15-20.\",\n \"16-1.\",\n \"16-16.\",\n \"17-10.\",\n \"17-11.\",\n \"17-2.\",\n \"19-1.\",\n \"19-16.\",\n \"19-19.\",\n \"19-20.\",\n \"19-3.\",\n \"2-10.\",\n \"2-11.\",\n \"2-17.\",\n \"2-18.\",\n \"2-20.\",\n \"2-3.\",\n \"2-4.\",\n \"2-5.\",\n \"2-6.\",\n \"2-7.\",\n \"2-8.\",\n \"3-13.\",\n \"3-18.\",\n \"3-3.\",\n \"4-1.\",\n \"4-10.\",\n \"4-11.\",\n \"4-19.\",\n \"5-5.\",\n \"6-15.\",\n \"7-10.\",\n \"7-14.\",\n \"8-18.\",\n \"8-20.\",\n \"8-3.\",\n \"8-8.\",\n ],\n \"domains\": [1, 2, 3, 4, 5],\n \"num_examples_per_domain_per_label\": -1,\n \"pickle_path\": \"/mnt/wd500GB/CSC500/csc500-main/datasets/cores.stratified_ds.2022A.pkl\",\n \"source_or_target_dataset\": \"target\",\n \"x_transforms\": [\"unit_mag\", \"take_200\"],\n \"episode_transforms\": [],\n \"domain_prefix\": \"C_\",\n },\n {\n \"labels\": [\n \"1-10\",\n \"1-12\",\n \"1-14\",\n \"1-16\",\n \"1-18\",\n \"1-19\",\n \"1-8\",\n \"10-11\",\n \"10-17\",\n \"10-4\",\n \"10-7\",\n \"11-1\",\n \"11-10\",\n \"11-19\",\n \"11-20\",\n \"11-4\",\n \"11-7\",\n \"12-19\",\n \"12-20\",\n \"12-7\",\n \"13-14\",\n \"13-18\",\n \"13-19\",\n \"13-20\",\n \"13-3\",\n \"13-7\",\n \"14-10\",\n \"14-11\",\n \"14-12\",\n \"14-13\",\n \"14-14\",\n \"14-19\",\n \"14-20\",\n \"14-7\",\n \"14-8\",\n \"14-9\",\n \"15-1\",\n \"15-19\",\n \"15-6\",\n \"16-1\",\n \"16-16\",\n \"16-19\",\n \"16-20\",\n \"17-10\",\n \"17-11\",\n \"18-1\",\n \"18-10\",\n \"18-11\",\n \"18-12\",\n \"18-13\",\n \"18-14\",\n \"18-15\",\n \"18-16\",\n \"18-17\",\n \"18-19\",\n \"18-2\",\n \"18-20\",\n \"18-4\",\n \"18-5\",\n \"18-7\",\n \"18-8\",\n \"18-9\",\n \"19-1\",\n \"19-10\",\n \"19-11\",\n \"19-12\",\n \"19-13\",\n \"19-14\",\n \"19-15\",\n \"19-19\",\n \"19-2\",\n \"19-20\",\n \"19-3\",\n \"19-4\",\n \"19-6\",\n \"19-7\",\n \"19-8\",\n \"19-9\",\n \"2-1\",\n \"2-13\",\n \"2-15\",\n \"2-3\",\n \"2-4\",\n \"2-5\",\n \"2-6\",\n \"2-7\",\n \"2-8\",\n \"20-1\",\n \"20-12\",\n \"20-14\",\n \"20-15\",\n \"20-16\",\n \"20-18\",\n \"20-19\",\n \"20-20\",\n \"20-3\",\n \"20-4\",\n \"20-5\",\n \"20-7\",\n \"20-8\",\n \"3-1\",\n \"3-13\",\n \"3-18\",\n \"3-2\",\n \"3-8\",\n \"4-1\",\n \"4-10\",\n \"4-11\",\n \"5-1\",\n \"5-5\",\n \"6-1\",\n \"6-15\",\n \"6-6\",\n \"7-10\",\n \"7-11\",\n \"7-12\",\n \"7-13\",\n \"7-14\",\n \"7-7\",\n \"7-8\",\n \"7-9\",\n \"8-1\",\n \"8-13\",\n \"8-14\",\n \"8-18\",\n \"8-20\",\n \"8-3\",\n \"8-8\",\n \"9-1\",\n \"9-7\",\n ],\n \"domains\": [1, 2, 3, 4],\n \"num_examples_per_domain_per_label\": -1,\n \"pickle_path\": \"/mnt/wd500GB/CSC500/csc500-main/datasets/wisig.node3-19.stratified_ds.2022A.pkl\",\n \"source_or_target_dataset\": \"target\",\n \"x_transforms\": [\"unit_mag\", \"take_200\"],\n \"episode_transforms\": [],\n \"domain_prefix\": \"W_\",\n },\n {\n \"labels\": [\n \"3123D52\",\n \"3123D65\",\n \"3123D79\",\n \"3123D80\",\n \"3123D54\",\n \"3123D70\",\n \"3123D7B\",\n \"3123D89\",\n \"3123D58\",\n \"3123D76\",\n \"3123D7D\",\n \"3123EFE\",\n \"3123D64\",\n \"3123D78\",\n \"3123D7E\",\n \"3124E4A\",\n ],\n \"domains\": [32, 38, 8, 44, 14, 50, 20, 26],\n \"num_examples_per_domain_per_label\": 2000,\n \"pickle_path\": \"/mnt/wd500GB/CSC500/csc500-main/datasets/oracle.Run1_framed_2000Examples_stratified_ds.2022A.pkl\",\n \"source_or_target_dataset\": \"source\",\n \"x_transforms\": [\"unit_mag\", \"take_200\", \"resample_20Msps_to_25Msps\"],\n \"episode_transforms\": [],\n \"domain_prefix\": \"O_\",\n },\n ],\n \"seed\": 1337,\n \"dataset_seed\": 1337,\n}\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Set this to True if you want to run this template directly\nSTANDALONE = False\nif STANDALONE:\n print(\"parameters not injected, running with standalone_parameters\")\n parameters = standalone_parameters\n\nif not 'parameters' in locals() and not 'parameters' in globals():\n raise Exception(\"Parameter injection failed\")\n\n#Use an easy dict for all the parameters\np = EasyDict(parameters)\n\nif \"x_shape\" not in p:\n p.x_shape = [2,256] # Default to this if we dont supply x_shape\n\n\nsupplied_keys = set(p.keys())\n\nif supplied_keys != required_parameters:\n print(\"Parameters are incorrect\")\n if len(supplied_keys - required_parameters)>0: print(\"Shouldn't have:\", str(supplied_keys - required_parameters))\n if len(required_parameters - supplied_keys)>0: print(\"Need to have:\", str(required_parameters - supplied_keys))\n raise RuntimeError(\"Parameters are incorrect\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"###################################\n# Set the RNGs and make it all deterministic\n###################################\nnp.random.seed(p.seed)\nrandom.seed(p.seed)\ntorch.manual_seed(p.seed)\n\ntorch.use_deterministic_algorithms(True) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"###########################################\n# The stratified datasets honor this\n###########################################\ntorch.set_default_dtype(eval(p.torch_default_dtype))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"###################################\n# Build the network(s)\n# Note: It's critical to do this AFTER setting the RNG\n###################################\nx_net = build_sequential(p.x_net)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"start_time_secs = time.time()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"p.domains_source = []\np.domains_target = []\n\n\ntrain_original_source = []\nval_original_source = []\ntest_original_source = []\n\ntrain_original_target = []\nval_original_target = []\ntest_original_target = []",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# global_x_transform_func = lambda x: normalize(x.to(torch.get_default_dtype()), \"unit_power\") # unit_power, unit_mag\n# global_x_transform_func = lambda x: normalize(x, \"unit_power\") # unit_power, unit_mag",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def add_dataset(\n labels,\n domains,\n pickle_path,\n x_transforms,\n episode_transforms,\n domain_prefix,\n num_examples_per_domain_per_label,\n source_or_target_dataset:str,\n iterator_seed=p.seed,\n dataset_seed=p.dataset_seed,\n n_shot=p.n_shot,\n n_way=p.n_way,\n n_query=p.n_query,\n train_val_test_k_factors=(p.train_k_factor,p.val_k_factor,p.test_k_factor),\n):\n \n if x_transforms == []: x_transform = None\n else: x_transform = get_chained_transform(x_transforms)\n \n if episode_transforms == []: episode_transform = None\n else: raise Exception(\"episode_transforms not implemented\")\n \n episode_transform = lambda tup, _prefix=domain_prefix: (_prefix + str(tup[0]), tup[1])\n\n\n eaf = Episodic_Accessor_Factory(\n labels=labels,\n domains=domains,\n num_examples_per_domain_per_label=num_examples_per_domain_per_label,\n iterator_seed=iterator_seed,\n dataset_seed=dataset_seed,\n n_shot=n_shot,\n n_way=n_way,\n n_query=n_query,\n train_val_test_k_factors=train_val_test_k_factors,\n pickle_path=pickle_path,\n x_transform_func=x_transform,\n )\n\n train, val, test = eaf.get_train(), eaf.get_val(), eaf.get_test()\n train = Lazy_Iterable_Wrapper(train, episode_transform)\n val = Lazy_Iterable_Wrapper(val, episode_transform)\n test = Lazy_Iterable_Wrapper(test, episode_transform)\n\n if source_or_target_dataset==\"source\":\n train_original_source.append(train)\n val_original_source.append(val)\n test_original_source.append(test)\n\n p.domains_source.extend(\n [domain_prefix + str(u) for u in domains]\n )\n elif source_or_target_dataset==\"target\":\n train_original_target.append(train)\n val_original_target.append(val)\n test_original_target.append(test)\n p.domains_target.extend(\n [domain_prefix + str(u) for u in domains]\n )\n else:\n raise Exception(f\"invalid source_or_target_dataset: {source_or_target_dataset}\")\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for ds in p.datasets:\n add_dataset(**ds)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# from steves_utils.CORES.utils import (\n# ALL_NODES,\n# ALL_NODES_MINIMUM_1000_EXAMPLES,\n# ALL_DAYS\n# )\n\n# add_dataset(\n# labels=ALL_NODES,\n# domains = ALL_DAYS,\n# num_examples_per_domain_per_label=100,\n# pickle_path=os.path.join(get_datasets_base_path(), \"cores.stratified_ds.2022A.pkl\"),\n# source_or_target_dataset=\"target\",\n# x_transform_func=global_x_transform_func,\n# domain_modifier=lambda u: f\"cores_{u}\"\n# )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# from steves_utils.ORACLE.utils_v2 import (\n# ALL_DISTANCES_FEET,\n# ALL_RUNS,\n# ALL_SERIAL_NUMBERS,\n# )\n\n\n# add_dataset(\n# labels=ALL_SERIAL_NUMBERS,\n# domains = list(set(ALL_DISTANCES_FEET) - {2,62}),\n# num_examples_per_domain_per_label=100,\n# pickle_path=os.path.join(get_datasets_base_path(), \"oracle.Run2_framed_2000Examples_stratified_ds.2022A.pkl\"),\n# source_or_target_dataset=\"source\",\n# x_transform_func=global_x_transform_func,\n# domain_modifier=lambda u: f\"oracle1_{u}\"\n# )\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# from steves_utils.ORACLE.utils_v2 import (\n# ALL_DISTANCES_FEET,\n# ALL_RUNS,\n# ALL_SERIAL_NUMBERS,\n# )\n\n\n# add_dataset(\n# labels=ALL_SERIAL_NUMBERS,\n# domains = list(set(ALL_DISTANCES_FEET) - {2,62,56}),\n# num_examples_per_domain_per_label=100,\n# pickle_path=os.path.join(get_datasets_base_path(), \"oracle.Run2_framed_2000Examples_stratified_ds.2022A.pkl\"),\n# source_or_target_dataset=\"source\",\n# x_transform_func=global_x_transform_func,\n# domain_modifier=lambda u: f\"oracle2_{u}\"\n# )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# add_dataset(\n# labels=list(range(19)),\n# domains = [0,1,2],\n# num_examples_per_domain_per_label=100,\n# pickle_path=os.path.join(get_datasets_base_path(), \"metehan.stratified_ds.2022A.pkl\"),\n# source_or_target_dataset=\"target\",\n# x_transform_func=global_x_transform_func,\n# domain_modifier=lambda u: f\"met_{u}\"\n# )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# # from steves_utils.wisig.utils import (\n# # ALL_NODES_MINIMUM_100_EXAMPLES,\n# # ALL_NODES_MINIMUM_500_EXAMPLES,\n# # ALL_NODES_MINIMUM_1000_EXAMPLES,\n# # ALL_DAYS\n# # )\n\n# import steves_utils.wisig.utils as wisig\n\n\n# add_dataset(\n# labels=wisig.ALL_NODES_MINIMUM_100_EXAMPLES,\n# domains = wisig.ALL_DAYS,\n# num_examples_per_domain_per_label=100,\n# pickle_path=os.path.join(get_datasets_base_path(), \"wisig.node3-19.stratified_ds.2022A.pkl\"),\n# source_or_target_dataset=\"target\",\n# x_transform_func=global_x_transform_func,\n# domain_modifier=lambda u: f\"wisig_{u}\"\n# )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"###################################\n# Build the dataset\n###################################\ntrain_original_source = Iterable_Aggregator(train_original_source, p.seed)\nval_original_source = Iterable_Aggregator(val_original_source, p.seed)\ntest_original_source = Iterable_Aggregator(test_original_source, p.seed)\n\n\ntrain_original_target = Iterable_Aggregator(train_original_target, p.seed)\nval_original_target = Iterable_Aggregator(val_original_target, p.seed)\ntest_original_target = Iterable_Aggregator(test_original_target, p.seed)\n\n# For CNN We only use X and Y. And we only train on the source.\n# Properly form the data using a transform lambda and Lazy_Iterable_Wrapper. Finally wrap them in a dataloader\n\ntransform_lambda = lambda ex: ex[1] # Original is (<domain>, <episode>) so we strip down to episode only\n\ntrain_processed_source = Lazy_Iterable_Wrapper(train_original_source, transform_lambda)\nval_processed_source = Lazy_Iterable_Wrapper(val_original_source, transform_lambda)\ntest_processed_source = Lazy_Iterable_Wrapper(test_original_source, transform_lambda)\n\ntrain_processed_target = Lazy_Iterable_Wrapper(train_original_target, transform_lambda)\nval_processed_target = Lazy_Iterable_Wrapper(val_original_target, transform_lambda)\ntest_processed_target = Lazy_Iterable_Wrapper(test_original_target, transform_lambda)\n\ndatasets = EasyDict({\n \"source\": {\n \"original\": {\"train\":train_original_source, \"val\":val_original_source, \"test\":test_original_source},\n \"processed\": {\"train\":train_processed_source, \"val\":val_processed_source, \"test\":test_processed_source}\n },\n \"target\": {\n \"original\": {\"train\":train_original_target, \"val\":val_original_target, \"test\":test_original_target},\n \"processed\": {\"train\":train_processed_target, \"val\":val_processed_target, \"test\":test_processed_target}\n },\n})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from steves_utils.transforms import get_average_magnitude, get_average_power\n\nprint(set([u for u,_ in val_original_source]))\nprint(set([u for u,_ in val_original_target]))\n\ns_x, s_y, q_x, q_y, _ = next(iter(train_processed_source))\nprint(s_x)\n\n# for ds in [\n# train_processed_source,\n# val_processed_source,\n# test_processed_source,\n# train_processed_target,\n# val_processed_target,\n# test_processed_target\n# ]:\n# for s_x, s_y, q_x, q_y, _ in ds:\n# for X in (s_x, q_x):\n# for x in X:\n# assert np.isclose(get_average_magnitude(x.numpy()), 1.0)\n# assert np.isclose(get_average_power(x.numpy()), 1.0)\n ",
"{'O_50', 'O_8', 'O_44', 'O_32', 'O_26', 'O_20', 'O_38', 'O_14'}\n"
],
[
"###################################\n# Build the model\n###################################\n# easfsl only wants a tuple for the shape\nmodel = Steves_Prototypical_Network(x_net, device=p.device, x_shape=tuple(p.x_shape))\noptimizer = Adam(params=model.parameters(), lr=p.lr)",
"(2, 200)\n"
],
[
"###################################\n# train\n###################################\njig = PTN_Train_Eval_Test_Jig(model, p.BEST_MODEL_PATH, p.device)\n\njig.train(\n train_iterable=datasets.source.processed.train,\n source_val_iterable=datasets.source.processed.val,\n target_val_iterable=datasets.target.processed.val,\n num_epochs=p.n_epoch,\n num_logs_per_epoch=p.NUM_LOGS_PER_EPOCH,\n patience=p.patience,\n optimizer=optimizer,\n criteria_for_best=p.criteria_for_best,\n)",
"epoch: 1, [batch: 1 / 6720], examples_per_second: 46.3796, train_label_loss: 2.9812, \n"
],
[
"total_experiment_time_secs = time.time() - start_time_secs",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"###################################\n# Evaluate the model\n###################################\nsource_test_label_accuracy, source_test_label_loss = jig.test(datasets.source.processed.test)\ntarget_test_label_accuracy, target_test_label_loss = jig.test(datasets.target.processed.test)\n\nsource_val_label_accuracy, source_val_label_loss = jig.test(datasets.source.processed.val)\ntarget_val_label_accuracy, target_val_label_loss = jig.test(datasets.target.processed.val)\n\nhistory = jig.get_history()\n\ntotal_epochs_trained = len(history[\"epoch_indices\"])\n\nval_dl = Iterable_Aggregator((datasets.source.original.val,datasets.target.original.val))\n\nconfusion = ptn_confusion_by_domain_over_dataloader(model, p.device, val_dl)\nper_domain_accuracy = per_domain_accuracy_from_confusion(confusion)\n\n# Add a key to per_domain_accuracy for if it was a source domain\nfor domain, accuracy in per_domain_accuracy.items():\n per_domain_accuracy[domain] = {\n \"accuracy\": accuracy,\n \"source?\": domain in p.domains_source\n }\n\n# Do an independent accuracy assesment JUST TO BE SURE!\n# _source_test_label_accuracy = independent_accuracy_assesment(model, datasets.source.processed.test, p.device)\n# _target_test_label_accuracy = independent_accuracy_assesment(model, datasets.target.processed.test, p.device)\n# _source_val_label_accuracy = independent_accuracy_assesment(model, datasets.source.processed.val, p.device)\n# _target_val_label_accuracy = independent_accuracy_assesment(model, datasets.target.processed.val, p.device)\n\n# assert(_source_test_label_accuracy == source_test_label_accuracy)\n# assert(_target_test_label_accuracy == target_test_label_accuracy)\n# assert(_source_val_label_accuracy == source_val_label_accuracy)\n# assert(_target_val_label_accuracy == target_val_label_accuracy)\n\nexperiment = {\n \"experiment_name\": p.experiment_name,\n \"parameters\": dict(p),\n \"results\": {\n \"source_test_label_accuracy\": source_test_label_accuracy,\n \"source_test_label_loss\": source_test_label_loss,\n \"target_test_label_accuracy\": target_test_label_accuracy,\n \"target_test_label_loss\": target_test_label_loss,\n \"source_val_label_accuracy\": source_val_label_accuracy,\n \"source_val_label_loss\": source_val_label_loss,\n \"target_val_label_accuracy\": target_val_label_accuracy,\n \"target_val_label_loss\": target_val_label_loss,\n \"total_epochs_trained\": total_epochs_trained,\n \"total_experiment_time_secs\": total_experiment_time_secs,\n \"confusion\": confusion,\n \"per_domain_accuracy\": per_domain_accuracy,\n },\n \"history\": history,\n \"dataset_metrics\": get_dataset_metrics(datasets, \"ptn\"),\n}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ax = get_loss_curve(experiment)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"get_results_table(experiment)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"get_domain_accuracies(experiment)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(\"Source Test Label Accuracy:\", experiment[\"results\"][\"source_test_label_accuracy\"], \"Target Test Label Accuracy:\", experiment[\"results\"][\"target_test_label_accuracy\"])\nprint(\"Source Val Label Accuracy:\", experiment[\"results\"][\"source_val_label_accuracy\"], \"Target Val Label Accuracy:\", experiment[\"results\"][\"target_val_label_accuracy\"])",
"Source Test Label Accuracy: 0.8865234375 Target Test Label Accuracy: 0.6338877688172043\nSource Val Label Accuracy: 0.8833984375 Target Val Label Accuracy: 0.6387877747252747\n"
],
[
"json.dumps(experiment)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a74bb475fb60a232c495d3de786b65d365be035
| 12,815 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
linear_numpy_short.ipynb
|
kalz2q/myjupyternotebooks
|
daab7169bd6e515c94207371471044bd5992e009
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-09-16T03:45:19.000Z
|
2021-09-16T03:45:19.000Z
|
linear_numpy_short.ipynb
|
kalz2q/myjupyternotebooks
|
daab7169bd6e515c94207371471044bd5992e009
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
linear_numpy_short.ipynb
|
kalz2q/myjupyternotebooks
|
daab7169bd6e515c94207371471044bd5992e009
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 23.131769 | 240 | 0.349824 |
[
[
[
"<a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/kalz2q/mycolabnotebooks/blob/master/linear_numpy_short.ipynb\" target=\"_parent\"><img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open In Colab\"/></a>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# numpy と 線形代数\n\n線形代数を学ぶには numpy と sympy の両方が必要である。 \n\nnumpy でないと機械学習なのど高速な計算ができないし、sympy でないと数式処理ができない。\n\n* 行列計算\n* 行列方程式を解く\n* 逆行列と行列式を計算する\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 行列計算\n\n次の例を考える\n\n$$\nA = \\begin{pmatrix}\n5 & 6 & 2\\\\\n4 & 7 & 19\\\\\n0 & 3 & 12\n\\end{pmatrix}\n$$\n\n$$\nB = \\begin{pmatrix}\n14 & -2 & 12\\\\\n4 & 4 & 5\\\\\n5 & 5 & 1\n\\end{pmatrix}\n$$\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"numpy を使うためには import する必要がある。",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nA = np.matrix([[5, 6, 2],\n [4, 7, 19],\n [0, 3, 12]])\nB = np.matrix([[14, -2, 12],\n [4, 4, 5],\n [5, 5, 1]])\nprint(A)\nprint(B)",
"[[ 5 6 2]\n [ 4 7 19]\n [ 0 3 12]]\n[[14 -2 12]\n [ 4 4 5]\n [ 5 5 1]]\n"
]
],
[
[
"同じことを sympy でやってみると次のようになる。",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 同じことを sympy でやってみると\nfrom sympy import *\nA_sympy = Matrix([[5, 6, 2],\n [4, 7, 19],\n [0, 3, 12]])\nB_sympy = Matrix([[14, -2, 12],\n [4, 4, 5],\n [5, 5, 1]])\ndisplay(A_sympy)\ndisplay(B_sympy)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"次の計算をする\n\n* $5A$\n* $A ^ 3$ \n* $A + B$;\n* $A - B$;\n* $AB$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(A)\nprint(5 * A)\nprint(A**2)\nprint(A**3)\nprint(A+B)\nprint(A-B)\nprint(A*B)\n",
"[[ 5 6 2]\n [ 4 7 19]\n [ 0 3 12]]\n[[25 30 10]\n [20 35 95]\n [ 0 15 60]]\n[[ 49 78 148]\n [ 48 130 369]\n [ 12 57 201]]\n[[ 557 1284 3356]\n [ 760 2305 6994]\n [ 288 1074 3519]]\n[[19 4 14]\n [ 8 11 24]\n [ 5 8 13]]\n[[ -9 8 -10]\n [ 0 3 14]\n [ -5 -2 11]]\n[[104 24 92]\n [179 115 102]\n [ 72 72 27]]\n"
]
],
[
[
"# いまここ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"---\n練習問題 $\\quad$ Compute $A ^ 2 - 2 A + 3$ with:\n\n$$A = \n\\begin{pmatrix}\n1 & -1\\\\\n2 & 1\n\\end{pmatrix}\n$$\n\n---\n\n## Solving Matrix equations\n\nWe can use Numpy to (efficiently) solve large systems of equations of the form:\n\n$$Ax=b$$\n\nLet us illustrate that with:\n\n$$\nA = \\begin{pmatrix}\n5 & 6 & 2\\\\\n4 & 7 & 19\\\\\n0 & 3 & 12\n\\end{pmatrix}\n$$\n\n$$\nb = \\begin{pmatrix}\n-1\\\\\n2\\\\\n1 \n\\end{pmatrix}\n$$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"A = np.matrix([[5, 6, 2],\n [4, 7, 19],\n [0, 3, 12]])\nb = np.matrix([[-1], [2], [1]])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We use the `linalg.solve` command:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x = np.linalg.solve(A, b)\nx",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can verify our result:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"A * x",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"---\n練習問題 $\\quad$ 行列方程式 $Bx=b$ を解く。\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"---\n# 逆行列と行列式を求める\n\n逆行列は次のようにして求められる。",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 逆行列は inv を使って求める\nAinv = np.linalg.inv(A)\nAinv",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"$A^{-1}A=\\mathbb{1}$ となることを確認する。",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"A * Ainv",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"若干見にくいが、[[1,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,1]] であることがわかる。\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"行列式は次のように求める。",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 行列式\nnp.linalg.det(A)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"---\n\n練習問題 $\\quad$ 行列 $B$ の逆行列と行列式を求める。\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4a74c4ca121fabcbcf3a21d53925319accec0e8e
| 42,859 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
data/10-MSE-vs-MAE.ipynb
|
IIMostro/machine-learning
|
8da0975c64985673d4ea64018631563ebfc19612
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
data/10-MSE-vs-MAE.ipynb
|
IIMostro/machine-learning
|
8da0975c64985673d4ea64018631563ebfc19612
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
data/10-MSE-vs-MAE.ipynb
|
IIMostro/machine-learning
|
8da0975c64985673d4ea64018631563ebfc19612
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 115.522911 | 14,132 | 0.838797 |
[
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom sklearn import datasets",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 波士顿房价预测",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"boston = datasets.load_boston()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(boston.DESCR)",
".. _boston_dataset:\n\nBoston house prices dataset\n---------------------------\n\n**Data Set Characteristics:** \n\n :Number of Instances: 506 \n\n :Number of Attributes: 13 numeric/categorical predictive. Median Value (attribute 14) is usually the target.\n\n :Attribute Information (in order):\n - CRIM per capita crime rate by town\n - ZN proportion of residential land zoned for lots over 25,000 sq.ft.\n - INDUS proportion of non-retail business acres per town\n - CHAS Charles River dummy variable (= 1 if tract bounds river; 0 otherwise)\n - NOX nitric oxides concentration (parts per 10 million)\n - RM average number of rooms per dwelling\n - AGE proportion of owner-occupied units built prior to 1940\n - DIS weighted distances to five Boston employment centres\n - RAD index of accessibility to radial highways\n - TAX full-value property-tax rate per $10,000\n - PTRATIO pupil-teacher ratio by town\n - B 1000(Bk - 0.63)^2 where Bk is the proportion of blacks by town\n - LSTAT % lower status of the population\n - MEDV Median value of owner-occupied homes in $1000's\n\n :Missing Attribute Values: None\n\n :Creator: Harrison, D. and Rubinfeld, D.L.\n\nThis is a copy of UCI ML housing dataset.\nhttps://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/housing/\n\n\nThis dataset was taken from the StatLib library which is maintained at Carnegie Mellon University.\n\nThe Boston house-price data of Harrison, D. and Rubinfeld, D.L. 'Hedonic\nprices and the demand for clean air', J. Environ. Economics & Management,\nvol.5, 81-102, 1978. Used in Belsley, Kuh & Welsch, 'Regression diagnostics\n...', Wiley, 1980. N.B. Various transformations are used in the table on\npages 244-261 of the latter.\n\nThe Boston house-price data has been used in many machine learning papers that address regression\nproblems. \n \n.. topic:: References\n\n - Belsley, Kuh & Welsch, 'Regression diagnostics: Identifying Influential Data and Sources of Collinearity', Wiley, 1980. 244-261.\n - Quinlan,R. (1993). Combining Instance-Based and Model-Based Learning. In Proceedings on the Tenth International Conference of Machine Learning, 236-243, University of Massachusetts, Amherst. Morgan Kaufmann.\n\n"
],
[
"boston.feature_names",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x = boston.data[: ,5] #只是用rm 房间数量的特征",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"y = boston.target",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"y.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.scatter(x, y)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x = x[y < 50.0]\ny = y[y < 50.0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.scatter(x, y)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 使用简单的线性回归",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, random_state=666)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x_train.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
" from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"reg = LinearRegression()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"reg.fit(x_train.reshape(1, -1), y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a74c63813da7fe8382845bc2c98cb4605b1b241
| 3,366 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/in-class/Week 2.ipynb
|
thePortus/programming-the-past
|
74581b1ed9a51b8662a2f59b8ef752ad18417901
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2019-11-23T19:32:06.000Z
|
2020-03-06T16:31:01.000Z
|
notebooks/in-class/Week 2.ipynb
|
thePortus/programming-the-past
|
74581b1ed9a51b8662a2f59b8ef752ad18417901
|
[
"MIT"
] | 5 |
2020-03-24T18:00:27.000Z
|
2021-08-23T20:30:52.000Z
|
notebooks/in-class/Week 2.ipynb
|
thePortus/programming-the-past
|
74581b1ed9a51b8662a2f59b8ef752ad18417901
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-03-23T10:27:41.000Z
|
2021-03-23T10:27:41.000Z
| 19.344828 | 81 | 0.481581 |
[
[
[
"# Week 2\n---",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Basic Syntax\n\nThis is where I tell you all hope is not lost if you don't understand this.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# this is a comment, it will be ignored when this runs\nother_answer = \"answer\"\nanswer = \"other_answer\"\nprint(answer)\n",
"other_answer\n"
],
[
"other_answer = \"answer\"\nanswer = \"other_answer\nprint(answer)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Basic Functions",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# printing nothing\nprint()\n\n# multiple arguments\nx = \"Dave\"\ny = \"Thomas\"\nprint(x, y)\n\n# foreign characters work as well\nπ = 3.14159\nprint(π)\n\n# keyword arguments\nprint(\"This is the first group of text\", end=\"\")\nprint(\"This is the second group of text\")\n\n# putting quotes in strings using \" inside of '\nprint('Professor Thomas is really \"awesome\"')\n\n# putting quotes in strings using special backslash escape character\nprint(\"Professor Thomas is really \\\"awesome\\\"\")",
"\nDave Thomas\n3.14159\nThis is the first group of textThis is the second group of text\nProfessor Thomas is really \"awesome\"\nProfessor Thomas is really \"awesome\"\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Conditions",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x = False\ny = False\nz = \"Luck\"\n\nif (x == True and y == True) or z == \"Duck\":\n print('Bingo!')\nelse:\n print('Not bingo!')",
"Not bingo!\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a74f771c68872461aa9f81d2c2f93d467339ae9
| 2,448 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Chapter4_Iterables/Strings/strings2.ipynb
|
kernbeisser/UdemyPythonPro
|
000d5e66031bcc22b2d8f115edfbd5ef0e80d5b9
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Chapter4_Iterables/Strings/strings2.ipynb
|
kernbeisser/UdemyPythonPro
|
000d5e66031bcc22b2d8f115edfbd5ef0e80d5b9
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Chapter4_Iterables/Strings/strings2.ipynb
|
kernbeisser/UdemyPythonPro
|
000d5e66031bcc22b2d8f115edfbd5ef0e80d5b9
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 19.902439 | 80 | 0.51634 |
[
[
[
"# FIRSTNAME LASTNAME\ntext = \"Hello my name is Jan Schaffranek:\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"my_firstname = my_name.split(' ')\n\nprint(my_firstname)",
"['Hello', 'my', '', 'name', 'is', 'Jan', 'Schaffranek:']\n"
],
[
"my_firstname_start_idx = my_name.find('Yan')\nprint(my_firstname_start_idx)\n\nmy_firstname = my_name[my_firstname_start_idx:my_firstname_start_idx+3]\nprint(my_firstname)",
"-1\n\n"
],
[
"my_firstname = 'Peter'\nmy_lastname = 'Peterson'\n\nmy_name = my_firstname + ' ' + my_lastname\nprint(my_name)",
"Peter Peterson\n"
],
[
"friend_names = ['Jan', 'Peter', 'Dennis']\n\noutput_str = ''\nfor name in friend_names:\n output_str += name + ' '\n\nprint(output_str)",
"Jan Peter Dennis \n"
],
[
"output_str2 = ''.join(friend_names)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a74f7dcdcbebeb0ac30c2850d9fde726c0120ea
| 278,684 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
reinforcement_learning/rl_deepracer_robomaker_coach_gazebo/deepracer_rl.ipynb
|
connorgoggins/amazon-sagemaker-examples
|
7117ceb3fbad1376d9af32aac858633c40e63219
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 3 |
2020-09-10T15:02:36.000Z
|
2020-09-13T17:37:23.000Z
|
reinforcement_learning/rl_deepracer_robomaker_coach_gazebo/deepracer_rl.ipynb
|
connorgoggins/amazon-sagemaker-examples
|
7117ceb3fbad1376d9af32aac858633c40e63219
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 4 |
2020-09-26T01:30:01.000Z
|
2022-02-10T02:20:35.000Z
|
reinforcement_learning/rl_deepracer_robomaker_coach_gazebo/deepracer_rl.ipynb
|
connorgoggins/amazon-sagemaker-examples
|
7117ceb3fbad1376d9af32aac858633c40e63219
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2020-09-09T08:35:51.000Z
|
2020-09-09T08:35:51.000Z
| 61.22232 | 948 | 0.646162 |
[
[
[
"# Distributed DeepRacer RL training with SageMaker and RoboMaker\n\n---\n## Introduction\n\n\nIn this notebook, we will train a fully autonomous 1/18th scale race car using reinforcement learning using Amazon SageMaker RL and AWS RoboMaker's 3D driving simulator. [AWS RoboMaker](https://console.aws.amazon.com/robomaker/home#welcome) is a service that makes it easy for developers to develop, test, and deploy robotics applications. \n\nThis notebook provides a jailbreak experience of [AWS DeepRacer](https://console.aws.amazon.com/deepracer/home#welcome), giving us more control over the training/simulation process and RL algorithm tuning.\n\n\n\n\n---\n## How it works? \n\n\n\nThe reinforcement learning agent (i.e. our autonomous car) learns to drive by interacting with its environment, e.g., the track, by taking an action in a given state to maximize the expected reward. The agent learns the optimal plan of actions in training by trial-and-error through repeated episodes. \n \nThe figure above shows an example of distributed RL training across SageMaker and two RoboMaker simulation envrionments that perform the **rollouts** - execute a fixed number of episodes using the current model or policy. The rollouts collect agent experiences (state-transition tuples) and share this data with SageMaker for training. SageMaker updates the model policy which is then used to execute the next sequence of rollouts. This training loop continues until the model converges, i.e. the car learns to drive and stops going off-track. More formally, we can define the problem in terms of the following: \n\n1. **Objective**: Learn to drive autonomously by staying close to the center of the track.\n2. **Environment**: A 3D driving simulator hosted on AWS RoboMaker.\n3. **State**: The driving POV image captured by the car's head camera, as shown in the illustration above.\n4. **Action**: Six discrete steering wheel positions at different angles (configurable)\n5. **Reward**: Positive reward for staying close to the center line; High penalty for going off-track. This is configurable and can be made more complex (for e.g. steering penalty can be added).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Prequisites",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Run these command if you wish to modify the SageMaker and Robomaker code\n<span style=\"color:red\">Note: Make sure you have atleast 25 GB of space when you are planning to modify the Sagemaker and Robomaker code</span>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# #\n# # Run these commands only for the first time\n# #\n# # Clean the build directory if present\n# !python3 sim_app_bundler.py --clean\n\n# # Download Robomaker simApp from the deepracer public s3 bucket\n# simulation_application_bundle_location = \"s3://deepracer-managed-resources-us-east-1/deepracer-simapp.tar.gz\"\n# !aws s3 cp {simulation_application_bundle_location} ./\n\n# # Untar the simapp bundle\n# !python3 sim_app_bundler.py --untar ./deepracer-simapp.tar.gz\n\n# # Now modify the simapp(Robomaker) from build directory and run this command.\n\n# # Most of the simapp files can be found here (Robomaker changes). You can modify them in these locations\n# # bundle/opt/install/sagemaker_rl_agent/lib/python3.5/site-packages/\n# # bundle/opt/install/deepracer_simulation_environment/share/deepracer_simulation_environment/\n# # bundle/opt/install/deepracer_simulation_environment/lib/deepracer_simulation_environment/\n\n# # # Copying the notebook src/markov changes to the simapp (For sagemaker container)\n# !rsync -av ./src/markov/ ./build/simapp/bundle/opt/install/sagemaker_rl_agent/lib/python3.5/site-packages/markov\n\n# print(\"############################################\")\n# print(\"This command execution takes around >2 min...\")\n# !python3 sim_app_bundler.py --tar",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Imports",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"To get started, we'll import the Python libraries we need, set up the environment with a few prerequisites for permissions and configurations.\n\nYou can run this notebook from your local machine or from a SageMaker notebook instance. In both of these scenarios, you can run the following to launch a training job on SageMaker and a simulation job on RoboMaker.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import boto3\nimport sagemaker\nimport sys\nimport os\nimport re\nimport numpy as np\nimport subprocess\nimport yaml\nsys.path.append(\"common\")\nsys.path.append(\"./src\")\nfrom misc import get_execution_role, wait_for_s3_object\nfrom docker_utils import build_and_push_docker_image\nfrom sagemaker.rl import RLEstimator, RLToolkit, RLFramework\nfrom time import gmtime, strftime\nimport time\nfrom IPython.display import Markdown\nfrom markdown_helper import *",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Initializing basic parameters",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Select the instance type\ninstance_type = \"ml.c4.2xlarge\"\n#instance_type = \"ml.p2.xlarge\"\n#instance_type = \"ml.c5.4xlarge\"\n\n# Starting SageMaker session\nsage_session = sagemaker.session.Session()\n\n# Create unique job name.\njob_name_prefix = 'deepracer-notebook'\n\n# Duration of job in seconds (1 hours)\njob_duration_in_seconds = 3600\n\n# AWS Region\naws_region = sage_session.boto_region_name\nif aws_region not in [\"us-west-2\", \"us-east-1\", \"eu-west-1\"]:\n raise Exception(\"This notebook uses RoboMaker which is available only in US East (N. Virginia),\"\n \"US West (Oregon) and EU (Ireland). Please switch to one of these regions.\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Setup S3 bucket\nSet up the linkage and authentication to the S3 bucket that we want to use for checkpoint and metadata.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# S3 bucket\ns3_bucket = sage_session.default_bucket()\n\n# SDK appends the job name and output folder\ns3_output_path = 's3://{}/'.format(s3_bucket)\n\n#Ensure that the S3 prefix contains the keyword 'sagemaker'\ns3_prefix = job_name_prefix + \"-sagemaker-\" + strftime(\"%y%m%d-%H%M%S\", gmtime())\n\n# Get the AWS account id of this account\nsts = boto3.client(\"sts\")\naccount_id = sts.get_caller_identity()['Account']\n\nprint(\"Using s3 bucket {}\".format(s3_bucket))\nprint(\"Model checkpoints and other metadata will be stored at: \\ns3://{}/{}\".format(s3_bucket, s3_prefix))",
"Using s3 bucket sagemaker-us-east-1-376804254363\nModel checkpoints and other metadata will be stored at: \ns3://sagemaker-us-east-1-376804254363/deepracer-notebook-sagemaker-200901-020536\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Create an IAM role\nEither get the execution role when running from a SageMaker notebook `role = sagemaker.get_execution_role()` or, when running from local machine, use utils method `role = get_execution_role('role_name')` to create an execution role.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"try:\n sagemaker_role = sagemaker.get_execution_role()\nexcept:\n sagemaker_role = get_execution_role('sagemaker')\n\nprint(\"Using Sagemaker IAM role arn: \\n{}\".format(sagemaker_role))",
"Using Sagemaker IAM role arn: \narn:aws:iam::376804254363:role/service-role/AmazonSageMaker-ExecutionRole-20200811T143087\n"
]
],
[
[
"> Please note that this notebook cannot be run in `SageMaker local mode` as the simulator is based on AWS RoboMaker service.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Permission setup for invoking AWS RoboMaker from this notebook\nIn order to enable this notebook to be able to execute AWS RoboMaker jobs, we need to add one trust relationship to the default execution role of this notebook.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"display(Markdown(generate_help_for_robomaker_trust_relationship(sagemaker_role)))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Permission setup for Sagemaker to S3 bucket\n\nThe sagemaker writes the Redis IP address, models to the S3 bucket. This requires PutObject permission on the bucket. Make sure the sagemaker role you are using as this permissions.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"display(Markdown(generate_s3_write_permission_for_sagemaker_role(sagemaker_role)))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Permission setup for Sagemaker to create KinesisVideoStreams\n\nThe sagemaker notebook has to create a kinesis video streamer. You can observer the car making epsiodes in the kinesis video streamer.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"display(Markdown(generate_kinesis_create_permission_for_sagemaker_role(sagemaker_role)))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Build and push docker image\n\nThe file ./Dockerfile contains all the packages that are installed into the docker. Instead of using the default sagemaker container. We will be using this docker container.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%time\nfrom copy_to_sagemaker_container import get_sagemaker_docker, copy_to_sagemaker_container, get_custom_image_name\ncpu_or_gpu = 'gpu' if instance_type.startswith('ml.p') else 'cpu'\nrepository_short_name = \"sagemaker-docker-%s\" % cpu_or_gpu\ncustom_image_name = get_custom_image_name(repository_short_name)\ntry:\n print(\"Copying files from your notebook to existing sagemaker container\")\n sagemaker_docker_id = get_sagemaker_docker(repository_short_name)\n copy_to_sagemaker_container(sagemaker_docker_id, repository_short_name)\nexcept Exception as e:\n print(\"Creating sagemaker container\")\n docker_build_args = {\n 'CPU_OR_GPU': cpu_or_gpu, \n 'AWS_REGION': boto3.Session().region_name,\n }\n custom_image_name = build_and_push_docker_image(repository_short_name, build_args=docker_build_args)\n print(\"Using ECR image %s\" % custom_image_name)",
"Copying files from your notebook to existing sagemaker container\ndocker images sagemaker-docker-cpu | sed -n 2,2p\nCreating sagemaker container\nWARNING! Using --password via the CLI is insecure. Use --password-stdin.\nWARNING! Your password will be stored unencrypted in /home/ec2-user/.docker/config.json.\nConfigure a credential helper to remove this warning. See\nhttps://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/login/#credentials-store\n\nLogin Succeeded\nLogged into ECR\nBuilding docker image sagemaker-docker-cpu from Dockerfile\n$ docker build -t sagemaker-docker-cpu -f Dockerfile . --build-arg CPU_OR_GPU=cpu --build-arg AWS_REGION=us-east-1\nSending build context to Docker daemon 22.67MB\nStep 1/22 : ARG CPU_OR_GPU\nStep 2/22 : ARG AWS_REGION\nStep 3/22 : FROM 520713654638.dkr.ecr.$AWS_REGION.amazonaws.com/sagemaker-tensorflow-scriptmode:1.12.0-$CPU_OR_GPU-py3\n1.12.0-cpu-py3: Pulling from sagemaker-tensorflow-scriptmode\n9ff7e2e5f967: Pulling fs layer\n59856638ac9f: Pulling fs layer\n6f317d6d954b: Pulling fs layer\na9dde5e2a643: Pulling fs layer\n601c9b2daa0d: Pulling fs layer\n07845bcc017a: Pulling fs layer\n1e13c73eef50: Pulling fs layer\n98cfce7034cb: Pulling fs layer\n2f9f8435ab01: Pulling fs layer\n8327741031a8: Pulling fs layer\n3a666bbb2fc3: Pulling fs layer\n594cdbd8b013: Pulling fs layer\na4d7a1014fb2: Pulling fs layer\na9dde5e2a643: Waiting\n6d1799916ac0: Pulling fs layer\n54edfc5311fe: Pulling fs layer\n601c9b2daa0d: Waiting\n07845bcc017a: Waiting\n1e13c73eef50: Waiting\n98cfce7034cb: Waiting\n2f9f8435ab01: Waiting\n8327741031a8: Waiting\n3a666bbb2fc3: Waiting\n594cdbd8b013: Waiting\na4d7a1014fb2: Waiting\n6d1799916ac0: Waiting\n54edfc5311fe: Waiting\n59856638ac9f: Verifying Checksum\n59856638ac9f: Download complete\n6f317d6d954b: Verifying Checksum\n6f317d6d954b: Download complete\na9dde5e2a643: Verifying Checksum\na9dde5e2a643: Download complete\n07845bcc017a: Verifying Checksum\n07845bcc017a: Download complete\n1e13c73eef50: Verifying Checksum\n1e13c73eef50: Download complete\n98cfce7034cb: Verifying Checksum\n98cfce7034cb: Download complete\n2f9f8435ab01: Download complete\n9ff7e2e5f967: Verifying Checksum\n8327741031a8: Verifying Checksum\n8327741031a8: Download complete\n594cdbd8b013: Verifying Checksum\n594cdbd8b013: Download complete\n3a666bbb2fc3: Verifying Checksum\n3a666bbb2fc3: Download complete\n6d1799916ac0: Verifying Checksum\n6d1799916ac0: Download complete\n601c9b2daa0d: Verifying Checksum\n601c9b2daa0d: Download complete\na4d7a1014fb2: Verifying Checksum\na4d7a1014fb2: Download complete\n54edfc5311fe: Verifying Checksum\n54edfc5311fe: Download complete\n9ff7e2e5f967: Pull complete\n59856638ac9f: Pull complete\n6f317d6d954b: Pull complete\na9dde5e2a643: Pull complete\n601c9b2daa0d: Pull complete\n07845bcc017a: Pull complete\n1e13c73eef50: Pull complete\n98cfce7034cb: Pull complete\n2f9f8435ab01: Pull complete\n8327741031a8: Pull complete\n3a666bbb2fc3: Pull complete\n594cdbd8b013: Pull complete\na4d7a1014fb2: Pull complete\n6d1799916ac0: Pull complete\n54edfc5311fe: Pull complete\nDigest: sha256:1036b5e92698629ea1dcf1d2adc6c186b404d38ef93e2c31cb4dd47787a3629b\nStatus: Downloaded newer image for 520713654638.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/sagemaker-tensorflow-scriptmode:1.12.0-cpu-py3\n ---> ba542f0b9706\nStep 4/22 : COPY ./src/markov /opt/amazon/markov\n ---> eb7754c07507\nStep 5/22 : RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y --no-install-recommends build-essential jq libav-tools libjpeg-dev libxrender1 python3.6-dev python3-opengl wget xvfb && apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*\n ---> Running in e428cdf97e72\nGet:1 http://ppa.launchpad.net/deadsnakes/ppa/ubuntu xenial InRelease [18.0 kB]\nGet:2 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial-security InRelease [109 kB]\nGet:3 http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial InRelease [247 kB]\nGet:4 http://ppa.launchpad.net/deadsnakes/ppa/ubuntu xenial/main amd64 Packages [37.2 kB]\nGet:5 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial-security/main amd64 Packages [1167 kB]\nGet:6 http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial-updates InRelease [109 kB]\nGet:7 http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial-backports InRelease [107 kB]\nGet:8 http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial/main amd64 Packages [1558 kB]\nGet:9 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial-security/restricted amd64 Packages [12.7 kB]\nGet:10 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial-security/universe amd64 Packages [637 kB]\nGet:11 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial-security/multiverse amd64 Packages [6680 B]\nGet:12 http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial/restricted amd64 Packages [14.1 kB]\nGet:13 http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial/universe amd64 Packages [9827 kB]\nGet:14 http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial/multiverse amd64 Packages [176 kB]\nGet:15 http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial-updates/main amd64 Packages [1531 kB]\nGet:16 http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial-updates/restricted amd64 Packages [13.1 kB]\nGet:17 http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial-updates/universe amd64 Packages [1038 kB]\nGet:18 http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial-updates/multiverse amd64 Packages [19.7 kB]\nGet:19 http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial-backports/main amd64 Packages [7942 B]\nGet:20 http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu xenial-backports/universe amd64 Packages [9084 B]\nFetched 16.6 MB in 2s (6733 kB/s)\nReading package lists...\nReading package lists...\nBuilding dependency tree...\nReading state information...\nbuild-essential is already the newest version (12.1ubuntu2).\nThe following additional packages will be installed:\n ffmpeg fontconfig-config fonts-dejavu-core freeglut3 libasound2\n libasound2-data libass5 libasyncns0 libavc1394-0 libavcodec-ffmpeg56\n libavdevice-ffmpeg56 libavfilter-ffmpeg5 libavformat-ffmpeg56\n libavresample-ffmpeg2 libavutil-ffmpeg54 libbluray1 libbs2b0 libcaca0\n libcdio-cdda1 libcdio-paranoia1 libcdio13 libcrystalhd3 libdc1394-22\n libdrm-amdgpu1 libdrm-common libdrm-intel1 libdrm-nouveau2 libdrm-radeon1\n libdrm2 libelf1 libflac8 libflite1 libfontconfig1 libfontenc1 libfreetype6\n libfribidi0 libgl1-mesa-dri libgl1-mesa-glx libglapi-mesa libglu1-mesa\n libgme0 libgraphite2-3 libgsm1 libharfbuzz0b libice6 libicu55 libiec61883-0\n libjack-jackd2-0 libjpeg-turbo8 libjpeg-turbo8-dev libjpeg8 libjpeg8-dev\n libllvm6.0 libmodplug1 libmp3lame0 libnuma1 libogg0 libonig2 libopenal-data\n libopenal1 libopencv-core2.4v5 libopencv-imgproc2.4v5 libopenjpeg5 libopus0\n liborc-0.4-0 libpciaccess0 libpixman-1-0 libpng12-0 libpostproc-ffmpeg53\n libpulse0 libpython3.6 libpython3.6-dev libpython3.6-minimal\n libpython3.6-stdlib libraw1394-11 libsamplerate0 libschroedinger-1.0-0\n libsdl1.2debian libsensors4 libshine3 libslang2 libsm6 libsnappy1v5\n libsndfile1 libsodium18 libsoxr0 libspeex1 libssh-gcrypt-4\n libswresample-ffmpeg1 libswscale-ffmpeg3 libtbb2 libtheora0 libtwolame0\n libusb-1.0-0 libva1 libvdpau1 libvorbis0a libvorbisenc2 libvpx3 libwavpack1\n libwebp5 libx11-6 libx11-data libx11-xcb1 libx264-148 libx265-79 libxau6\n libxaw7 libxcb-dri2-0 libxcb-dri3-0 libxcb-glx0 libxcb-present0\n libxcb-shape0 libxcb-shm0 libxcb-sync1 libxcb-xfixes0 libxcb1 libxdamage1\n libxdmcp6 libxext6 libxfixes3 libxfont1 libxi6 libxkbfile1 libxml2 libxmu6\n libxmuu1 libxpm4 libxshmfence1 libxt6 libxv1 libxvidcore4 libxxf86vm1\n libzmq5 libzvbi-common libzvbi0 python3.6 python3.6-minimal ucf x11-common\n x11-xkb-utils xauth xkb-data xserver-common\nSuggested packages:\n ffmpeg-doc libasound2-plugins alsa-utils libbluray-bdj firmware-crystalhd\n alsa-base jackd2 libportaudio2 opus-tools pciutils pulseaudio libraw1394-doc\n lm-sensors speex python3-tk python3-numpy libgle3 python3.6-venv\n python3.6-doc binfmt-support\nRecommended packages:\n libaacs0 libtxc-dxtn-s2tc | libtxc-dxtn-s2tc0 | libtxc-dxtn0 va-driver-all\n | va-driver vdpau-driver-all | vdpau-driver xml-core xfonts-base\nThe following NEW packages will be installed:\n ffmpeg fontconfig-config fonts-dejavu-core freeglut3 jq libasound2\n libasound2-data libass5 libasyncns0 libav-tools libavc1394-0\n libavcodec-ffmpeg56 libavdevice-ffmpeg56 libavfilter-ffmpeg5\n libavformat-ffmpeg56 libavresample-ffmpeg2 libavutil-ffmpeg54 libbluray1\n libbs2b0 libcaca0 libcdio-cdda1 libcdio-paranoia1 libcdio13 libcrystalhd3\n libdc1394-22 libdrm-amdgpu1 libdrm-common libdrm-intel1 libdrm-nouveau2\n libdrm-radeon1 libdrm2 libelf1 libflac8 libflite1 libfontconfig1 libfontenc1\n libfreetype6 libfribidi0 libgl1-mesa-dri libgl1-mesa-glx libglapi-mesa\n libglu1-mesa libgme0 libgraphite2-3 libgsm1 libharfbuzz0b libice6 libicu55\n libiec61883-0 libjack-jackd2-0 libjpeg-dev libjpeg-turbo8 libjpeg-turbo8-dev\n libjpeg8 libjpeg8-dev libllvm6.0 libmodplug1 libmp3lame0 libnuma1 libogg0\n libonig2 libopenal-data libopenal1 libopencv-core2.4v5\n libopencv-imgproc2.4v5 libopenjpeg5 libopus0 liborc-0.4-0 libpciaccess0\n libpixman-1-0 libpng12-0 libpostproc-ffmpeg53 libpulse0 libraw1394-11\n libsamplerate0 libschroedinger-1.0-0 libsdl1.2debian libsensors4 libshine3\n libslang2 libsm6 libsnappy1v5 libsndfile1 libsodium18 libsoxr0 libspeex1\n libssh-gcrypt-4 libswresample-ffmpeg1 libswscale-ffmpeg3 libtbb2 libtheora0\n libtwolame0 libusb-1.0-0 libva1 libvdpau1 libvorbis0a libvorbisenc2 libvpx3\n libwavpack1 libwebp5 libx11-6 libx11-data libx11-xcb1 libx264-148 libx265-79\n libxau6 libxaw7 libxcb-dri2-0 libxcb-dri3-0 libxcb-glx0 libxcb-present0\n libxcb-shape0 libxcb-shm0 libxcb-sync1 libxcb-xfixes0 libxcb1 libxdamage1\n libxdmcp6 libxext6 libxfixes3 libxfont1 libxi6 libxkbfile1 libxml2 libxmu6\n libxmuu1 libxpm4 libxrender1 libxshmfence1 libxt6 libxv1 libxvidcore4\n libxxf86vm1 libzmq5 libzvbi-common libzvbi0 python3-opengl ucf wget\n x11-common x11-xkb-utils xauth xkb-data xserver-common xvfb\nThe following packages will be upgraded:\n libpython3.6 libpython3.6-dev libpython3.6-minimal libpython3.6-stdlib\n python3.6 python3.6-dev python3.6-minimal\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Clean the docker images\nRemove this only when you want to completely remove the docker or clean up the space of the sagemaker instance",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# !docker rm -f $(docker ps -a -q);\n# !docker rmi -f $(docker images -q);",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Configure VPC\n\nSince SageMaker and RoboMaker have to communicate with each other over the network, both of these services need to run in VPC mode. This can be done by supplying subnets and security groups to the job launching scripts. \nWe will check if the deepracer-vpc stack is created and use it if present (This is present if the AWS Deepracer console is used atleast once to create a model). Else we will use the default VPC stack.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"ec2 = boto3.client('ec2')\n\n#\n# Check if the user has Deepracer-VPC and use that if its present. This will have all permission.\n# This VPC will be created when you have used the Deepracer console and created one model atleast\n# If this is not present. Use the default VPC connnection\n#\ndeepracer_security_groups = [group[\"GroupId\"] for group in ec2.describe_security_groups()['SecurityGroups']\\\n if group['GroupName'].startswith(\"aws-deepracer-\")]\n\n# deepracer_security_groups = False\nif(deepracer_security_groups):\n print(\"Using the DeepRacer VPC stacks. This will be created if you run one training job from console.\")\n deepracer_vpc = [vpc['VpcId'] for vpc in ec2.describe_vpcs()['Vpcs'] \\\n if \"Tags\" in vpc for val in vpc['Tags'] \\\n if val['Value'] == 'deepracer-vpc'][0]\n deepracer_subnets = [subnet[\"SubnetId\"] for subnet in ec2.describe_subnets()[\"Subnets\"] \\\n if subnet[\"VpcId\"] == deepracer_vpc]\nelse:\n print(\"Using the default VPC stacks\")\n deepracer_vpc = [vpc['VpcId'] for vpc in ec2.describe_vpcs()['Vpcs'] if vpc[\"IsDefault\"] == True][0]\n\n deepracer_security_groups = [group[\"GroupId\"] for group in ec2.describe_security_groups()['SecurityGroups'] \\\n if 'VpcId' in group and group[\"GroupName\"] == \"default\" and group[\"VpcId\"] == deepracer_vpc]\n\n deepracer_subnets = [subnet[\"SubnetId\"] for subnet in ec2.describe_subnets()[\"Subnets\"] \\\n if subnet[\"VpcId\"] == deepracer_vpc and subnet['DefaultForAz']==True]\n\nprint(\"Using VPC:\", deepracer_vpc)\nprint(\"Using security group:\", deepracer_security_groups)\nprint(\"Using subnets:\", deepracer_subnets)",
"Using the default VPC stacks\nUsing VPC: vpc-0b20d076\nUsing security group: ['sg-79304842']\nUsing subnets: ['subnet-944ce8f2', 'subnet-a91f68e4', 'subnet-0dc8233c', 'subnet-9beb4bc4', 'subnet-6ede7c4f', 'subnet-7e24ba70']\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Create Route Table\nA SageMaker job running in VPC mode cannot access S3 resourcs. So, we need to create a VPC S3 endpoint to allow S3 access from SageMaker container. To learn more about the VPC mode, please visit [this link.](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/sagemaker/latest/dg/train-vpc.html)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#TODO: Explain to customer what CREATE_ROUTE_TABLE is doing\nCREATE_ROUTE_TABLE = True\n\ndef create_vpc_endpoint_table():\n print(\"Creating \")\n try:\n route_tables = [route_table[\"RouteTableId\"] for route_table in ec2.describe_route_tables()['RouteTables']\\\n if route_table['VpcId'] == deepracer_vpc]\n except Exception as e:\n if \"UnauthorizedOperation\" in str(e):\n display(Markdown(generate_help_for_s3_endpoint_permissions(sagemaker_role)))\n else:\n display(Markdown(create_s3_endpoint_manually(aws_region, deepracer_vpc)))\n raise e\n\n print(\"Trying to attach S3 endpoints to the following route tables:\", route_tables)\n \n if not route_tables:\n raise Exception((\"No route tables were found. Please follow the VPC S3 endpoint creation \"\n \"guide by clicking the above link.\"))\n try:\n ec2.create_vpc_endpoint(DryRun=False,\n VpcEndpointType=\"Gateway\",\n VpcId=deepracer_vpc,\n ServiceName=\"com.amazonaws.{}.s3\".format(aws_region),\n RouteTableIds=route_tables)\n print(\"S3 endpoint created successfully!\")\n except Exception as e:\n if \"RouteAlreadyExists\" in str(e):\n print(\"S3 endpoint already exists.\")\n elif \"UnauthorizedOperation\" in str(e):\n display(Markdown(generate_help_for_s3_endpoint_permissions(role)))\n raise e\n else:\n display(Markdown(create_s3_endpoint_manually(aws_region, deepracer_vpc)))\n raise e\n\nif CREATE_ROUTE_TABLE:\n create_vpc_endpoint_table()",
"Creating \nTrying to attach S3 endpoints to the following route tables: ['rtb-31b6c94f']\nS3 endpoint already exists.\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Setup the environment\n\nThe environment is defined in a Python file called “deepracer_racetrack_env.py” and the file can be found at `src/markov/environments/`. This file implements the gym interface for our Gazebo based RoboMakersimulator. This is a common environment file used by both SageMaker and RoboMaker. The environment variable - `NODE_TYPE` defines which node the code is running on. So, the expressions that have `rospy` dependencies are executed on RoboMaker only. \n\nWe can experiment with different reward functions by modifying `reward_function` in `src/markov/rewards/`. Action space and steering angles can be changed by modifying `src/markov/actions/`.json file\n\n### Configure the preset for RL algorithm\n\nThe parameters that configure the RL training job are defined in `src/markov/presets/`. Using the preset file, you can define agent parameters to select the specific agent algorithm. We suggest using Clipped PPO for this example. \nYou can edit this file to modify algorithm parameters like learning_rate, neural network structure, batch_size, discount factor etc.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Uncomment the pygmentize code lines to see the code\n\n# Reward function\n#!pygmentize src/markov/rewards/default.py\n\n# Action space\n#!pygmentize src/markov/actions/single_speed_stereo_shallow.json\n\n# Preset File\n#!pygmentize src/markov/presets/default.py\n#!pygmentize src/markov/presets/preset_attention_layer.py",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Copy custom files to S3 bucket so that sagemaker & robomaker can pick it up",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"s3_location = \"s3://%s/%s\" % (s3_bucket, s3_prefix)\nprint(s3_location)\n\n# Clean up the previously uploaded files\n!aws s3 rm --recursive {s3_location}\n\n!aws s3 cp ./src/artifacts/rewards/default.py {s3_location}/customer_reward_function.py\n\n!aws s3 cp ./src/artifacts/actions/default.json {s3_location}/model/model_metadata.json\n\n#!aws s3 cp src/markov/presets/default.py {s3_location}/presets/preset.py\n#!aws s3 cp src/markov/presets/preset_attention_layer.py {s3_location}/presets/preset.py",
"s3://sagemaker-us-east-1-376804254363/deepracer-notebook-sagemaker-200901-020536\nupload: src/artifacts/rewards/default.py to s3://sagemaker-us-east-1-376804254363/deepracer-notebook-sagemaker-200901-020536/customer_reward_function.py\nupload: src/artifacts/actions/default.json to s3://sagemaker-us-east-1-376804254363/deepracer-notebook-sagemaker-200901-020536/model/model_metadata.json\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Train the RL model using the Python SDK Script mode\n\nNext, we define the following algorithm metrics that we want to capture from cloudwatch logs to monitor the training progress. These are algorithm specific parameters and might change for different algorithm. We use [Clipped PPO](https://coach.nervanasys.com/algorithms/policy_optimization/cppo/index.html) for this example.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metric_definitions = [\n # Training> Name=main_level/agent, Worker=0, Episode=19, Total reward=-102.88, Steps=19019, Training iteration=1\n {'Name': 'reward-training',\n 'Regex': '^Training>.*Total reward=(.*?),'},\n \n # Policy training> Surrogate loss=-0.32664725184440613, KL divergence=7.255815035023261e-06, Entropy=2.83156156539917, training epoch=0, learning_rate=0.00025\n {'Name': 'ppo-surrogate-loss',\n 'Regex': '^Policy training>.*Surrogate loss=(.*?),'},\n {'Name': 'ppo-entropy',\n 'Regex': '^Policy training>.*Entropy=(.*?),'},\n \n # Testing> Name=main_level/agent, Worker=0, Episode=19, Total reward=1359.12, Steps=20015, Training iteration=2\n {'Name': 'reward-testing',\n 'Regex': '^Testing>.*Total reward=(.*?),'},\n]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We use the RLEstimator for training RL jobs.\n\n1. Specify the source directory which has the environment file, preset and training code.\n2. Specify the entry point as the training code\n3. Specify the choice of RL toolkit and framework. This automatically resolves to the ECR path for the RL Container.\n4. Define the training parameters such as the instance count, instance type, job name, s3_bucket and s3_prefix for storing model checkpoints and metadata. **Only 1 training instance is supported for now.**\n4. Set the RLCOACH_PRESET as \"deepracer\" for this example.\n5. Define the metrics definitions that you are interested in capturing in your logs. These can also be visualized in CloudWatch and SageMaker Notebooks.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"estimator = RLEstimator(entry_point=\"training_worker.py\",\n source_dir='src',\n image_name=custom_image_name,\n dependencies=[\"common/\"],\n role=sagemaker_role,\n train_instance_type=instance_type,\n train_instance_count=1,\n output_path=s3_output_path,\n base_job_name=job_name_prefix,\n metric_definitions=metric_definitions,\n train_max_run=job_duration_in_seconds,\n hyperparameters={\n \"s3_bucket\": s3_bucket,\n \"s3_prefix\": s3_prefix,\n \"aws_region\": aws_region,\n \"model_metadata_s3_key\": \"%s/model/model_metadata.json\" % s3_prefix,\n \"reward_function_s3_source\": \"%s/customer_reward_function.py\" % s3_prefix,\n \"batch_size\": \"64\",\n \"num_epochs\": \"10\",\n \"stack_size\": \"1\",\n \"lr\": \"0.0003\",\n \"exploration_type\": \"Categorical\",\n \"e_greedy_value\": \"1\",\n \"epsilon_steps\": \"10000\",\n \"beta_entropy\": \"0.01\",\n \"discount_factor\": \"0.999\",\n \"loss_type\": \"Huber\",\n \"num_episodes_between_training\": \"20\",\n \"max_sample_count\": \"0\",\n \"sampling_frequency\": \"1\"\n# ,\"pretrained_s3_bucket\": \"sagemaker-us-east-1-259455987231\"\n# ,\"pretrained_s3_prefix\": \"deepracer-notebook-sagemaker-200729-202318\"\n },\n subnets=deepracer_subnets,\n security_group_ids=deepracer_security_groups,\n )\n\nestimator.fit(wait=False)\njob_name = estimator.latest_training_job.job_name\nprint(\"Training job: %s\" % job_name)",
"Parameter image_name will be renamed to image_uri in SageMaker Python SDK v2.\n"
],
[
"training_job_arn = estimator.latest_training_job.describe()['TrainingJobArn']",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Create the Kinesis video stream",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"kvs_stream_name = \"dr-kvs-{}\".format(job_name)\n\n!aws --region {aws_region} kinesisvideo create-stream --stream-name {kvs_stream_name} --media-type video/h264 --data-retention-in-hours 24\nprint (\"Created kinesis video stream {}\".format(kvs_stream_name))",
"{\n \"StreamARN\": \"arn:aws:kinesisvideo:us-east-1:376804254363:stream/dr-kvs-deepracer-notebook-2020-09-01-02-12-31-568/1598926352908\"\n}\nCreated kinesis video stream dr-kvs-deepracer-notebook-2020-09-01-02-12-31-568\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Start the Robomaker job",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"robomaker = boto3.client(\"robomaker\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Create Simulation Application",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"robomaker_s3_key = 'robomaker/simulation_ws.tar.gz'\nrobomaker_source = {'s3Bucket': s3_bucket,\n 's3Key': robomaker_s3_key,\n 'architecture': \"X86_64\"}\nsimulation_software_suite={'name': 'Gazebo',\n 'version': '7'}\nrobot_software_suite={'name': 'ROS',\n 'version': 'Kinetic'}\nrendering_engine={'name': 'OGRE',\n 'version': '1.x'}",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Download the DeepRacer bundle provided by RoboMaker service and upload it in our S3 bucket to create a RoboMaker Simulation Application",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"if not os.path.exists('./build/output.tar.gz'):\n print(\"Using the latest simapp from public s3 bucket\")\n # Download Robomaker simApp for the deepracer public s3 bucket\n simulation_application_bundle_location = \"s3://deepracer-managed-resources-us-east-1/deepracer-simapp.tar.gz\"\n !aws s3 cp {simulation_application_bundle_location} ./\n\n # Remove if the Robomaker sim-app is present in s3 bucket\n !aws s3 rm s3://{s3_bucket}/{robomaker_s3_key}\n\n # Uploading the Robomaker SimApp to your S3 bucket\n !aws s3 cp ./deepracer-simapp.tar.gz s3://{s3_bucket}/{robomaker_s3_key}\n\n # Cleanup the locally downloaded version of SimApp\n !rm deepracer-simapp.tar.gz\nelse:\n print(\"Using the simapp from build directory\")\n !aws s3 cp ./build/output.tar.gz s3://{s3_bucket}/{robomaker_s3_key}",
"Using the latest simapp from public s3 bucket\ndownload: s3://deepracer-managed-resources-us-east-1/deepracer-simapp.tar.gz to ./deepracer-simapp.tar.gz\ndelete: s3://sagemaker-us-east-1-376804254363/robomaker/simulation_ws.tar.gz\nupload: ./deepracer-simapp.tar.gz to s3://sagemaker-us-east-1-376804254363/robomaker/simulation_ws.tar.gz\n"
],
[
"app_name = \"deepracer-notebook-application\" + strftime(\"%y%m%d-%H%M%S\", gmtime())\n\nprint(app_name)\ntry:\n response = robomaker.create_simulation_application(name=app_name,\n sources=[robomaker_source],\n simulationSoftwareSuite=simulation_software_suite,\n robotSoftwareSuite=robot_software_suite,\n renderingEngine=rendering_engine)\n simulation_app_arn = response[\"arn\"]\n print(\"Created a new simulation app with ARN:\", simulation_app_arn)\nexcept Exception as e:\n if \"AccessDeniedException\" in str(e):\n display(Markdown(generate_help_for_robomaker_all_permissions(role)))\n raise e\n else:\n raise e",
"deepracer-notebook-application200901-021300\nCreated a new simulation app with ARN: arn:aws:robomaker:us-east-1:376804254363:simulation-application/deepracer-notebook-application200901-021300/1598926380260\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Launch the Simulation job on RoboMaker\n\nWe create [AWS RoboMaker](https://console.aws.amazon.com/robomaker/home#welcome) Simulation Jobs that simulates the environment and shares this data with SageMaker for training. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"s3_yaml_name=\"training_params.yaml\"\nworld_name = \"reInvent2019_track\"\n# Change this for multiple rollouts. This will invoke the specified number of robomaker jobs to collect experience\nnum_simulation_workers = 1\n\nwith open(\"./src/artifacts/yaml/training_yaml_template.yaml\", \"r\") as filepointer:\n yaml_config = yaml.load(filepointer)\n\nyaml_config['WORLD_NAME'] = world_name\nyaml_config['SAGEMAKER_SHARED_S3_BUCKET'] = s3_bucket\nyaml_config['SAGEMAKER_SHARED_S3_PREFIX'] = s3_prefix\nyaml_config['TRAINING_JOB_ARN'] = training_job_arn\nyaml_config['METRICS_S3_BUCKET'] = s3_bucket\nyaml_config['METRICS_S3_OBJECT_KEY'] = \"{}/training_metrics.json\".format(s3_prefix)\nyaml_config['SIMTRACE_S3_BUCKET'] = s3_bucket\nyaml_config['SIMTRACE_S3_PREFIX'] = \"{}/iteration-data/training\".format(s3_prefix)\nyaml_config['AWS_REGION'] = aws_region\nyaml_config['ROBOMAKER_SIMULATION_JOB_ACCOUNT_ID'] = account_id\nyaml_config['KINESIS_VIDEO_STREAM_NAME'] = kvs_stream_name\nyaml_config['REWARD_FILE_S3_KEY'] = \"{}/customer_reward_function.py\".format(s3_prefix)\nyaml_config['MODEL_METADATA_FILE_S3_KEY'] = \"{}/model/model_metadata.json\".format(s3_prefix)\nyaml_config['NUM_WORKERS'] = num_simulation_workers\nyaml_config['MP4_S3_BUCKET'] = s3_bucket\nyaml_config['MP4_S3_OBJECT_PREFIX'] = \"{}/iteration-data/training\".format(s3_prefix)\n\n# Race-type supported for training are TIME_TRIAL, OBJECT_AVOIDANCE, HEAD_TO_BOT\n# If you need to modify more attributes look at the template yaml file\nrace_type = \"TIME_TRIAL\"\n\nif race_type == \"OBJECT_AVOIDANCE\":\n yaml_config['NUMBER_OF_OBSTACLES'] = \"6\"\n yaml_config['RACE_TYPE'] = \"OBJECT_AVOIDANCE\"\n\nelif race_type == \"HEAD_TO_BOT\":\n yaml_config['NUMBER_OF_BOT_CARS'] = \"6\"\n yaml_config['RACE_TYPE'] = \"HEAD_TO_BOT\"\n\n# Printing the modified yaml parameter\nfor key, value in yaml_config.items():\n print(\"{}: {}\".format(key.ljust(40, ' '), value))\n\n# Uploading the modified yaml parameter\nwith open(\"./training_params.yaml\", \"w\") as filepointer:\n yaml.dump(yaml_config, filepointer)\n\n!aws s3 cp ./training_params.yaml {s3_location}/training_params.yaml\n!rm training_params.yaml",
"JOB_TYPE : TRAINING\nWORLD_NAME : reInvent2019_track\nSAGEMAKER_SHARED_S3_BUCKET : sagemaker-us-east-1-376804254363\nSAGEMAKER_SHARED_S3_PREFIX : deepracer-notebook-sagemaker-200901-020536\nTRAINING_JOB_ARN : arn:aws:sagemaker:us-east-1:376804254363:training-job/deepracer-notebook-2020-09-01-02-12-31-568\nMETRICS_S3_BUCKET : sagemaker-us-east-1-376804254363\nMETRICS_S3_OBJECT_KEY : deepracer-notebook-sagemaker-200901-020536/training_metrics.json\nSIMTRACE_S3_BUCKET : sagemaker-us-east-1-376804254363\nSIMTRACE_S3_PREFIX : deepracer-notebook-sagemaker-200901-020536/iteration-data/training\nAWS_REGION : us-east-1\nTARGET_REWARD_SCORE : None\nNUMBER_OF_EPISODES : 0\nROBOMAKER_SIMULATION_JOB_ACCOUNT_ID : 376804254363\nCHANGE_START_POSITION : true\nALTERNATE_DRIVING_DIRECTION : false\nREVERSE_DIR : false\nKINESIS_VIDEO_STREAM_NAME : dr-kvs-deepracer-notebook-2020-09-01-02-12-31-568\nREWARD_FILE_S3_KEY : deepracer-notebook-sagemaker-200901-020536/customer_reward_function.py\nMODEL_METADATA_FILE_S3_KEY : deepracer-notebook-sagemaker-200901-020536/model/model_metadata.json\nNUMBER_OF_RESETS : 0\nCAR_COLOR : Blue\nENABLE_DOMAIN_RANDOMIZATION : false\nNUM_WORKERS : 1\nNUMBER_OF_OBSTACLES : 0\nMIN_DISTANCE_BETWEEN_OBSTACLES : 2.0\nRANDOMIZE_OBSTACLE_LOCATIONS : false\nIS_OBSTACLE_BOT_CAR : false\nNUMBER_OF_BOT_CARS : 0\nIS_LANE_CHANGE : false\nLOWER_LANE_CHANGE_TIME : 3.0\nUPPER_LANE_CHANGE_TIME : 5.0\nLANE_CHANGE_DISTANCE : 1.0\nMIN_DISTANCE_BETWEEN_BOT_CARS : 2.0\nRANDOMIZE_BOT_CAR_LOCATIONS : true\nBOT_CAR_SPEED : 0.2\nMP4_S3_BUCKET : sagemaker-us-east-1-376804254363\nMP4_S3_OBJECT_PREFIX : deepracer-notebook-sagemaker-200901-020536/iteration-data/training\nRACE_TYPE : TIME_TRIAL\nVIDEO_JOB_TYPE : RACING\nDISPLAY_NAME : LongLongRacerNameBlaBlaBla\nRACER_NAME : racer-alias\nMODEL_NAME : bla-bla-model-user-created-in-customer\nLEADERBOARD_TYPE : LEAGUE\nLEADERBOARD_NAME : 2020 MARCH QUALIFIER\n"
],
[
"vpcConfig = {\"subnets\": deepracer_subnets,\n \"securityGroups\": deepracer_security_groups,\n \"assignPublicIp\": True}\n\nresponses = []\nfor job_no in range(num_simulation_workers):\n client_request_token = strftime(\"%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S\", gmtime())\n envriron_vars = {\n \"S3_YAML_NAME\": s3_yaml_name,\n \"SAGEMAKER_SHARED_S3_PREFIX\": s3_prefix,\n \"SAGEMAKER_SHARED_S3_BUCKET\": s3_bucket,\n \"WORLD_NAME\": world_name,\n \"KINESIS_VIDEO_STREAM_NAME\": kvs_stream_name,\n \"APP_REGION\": aws_region,\n \"MODEL_METADATA_FILE_S3_KEY\": \"%s/model/model_metadata.json\" % s3_prefix,\n \"ROLLOUT_IDX\": str(job_no)\n }\n\n simulation_application = {\"application\":simulation_app_arn,\n \"launchConfig\": {\"packageName\": \"deepracer_simulation_environment\",\n \"launchFile\": \"distributed_training.launch\",\n \"environmentVariables\": envriron_vars}\n }\n response = robomaker.create_simulation_job(iamRole=sagemaker_role,\n clientRequestToken=client_request_token,\n maxJobDurationInSeconds=job_duration_in_seconds,\n failureBehavior=\"Fail\",\n simulationApplications=[simulation_application],\n vpcConfig=vpcConfig\n )\n responses.append(response)\n time.sleep(5)\n \n\nprint(\"Created the following jobs:\")\njob_arns = [response[\"arn\"] for response in responses]\nfor job_arn in job_arns:\n print(\"Job ARN\", job_arn)",
"Created the following jobs:\nJob ARN arn:aws:robomaker:us-east-1:376804254363:simulation-job/sim-bd6zlxzwr1ff\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Visualizing the simulations in RoboMaker\nYou can visit the RoboMaker console to visualize the simulations or run the following cell to generate the hyperlinks.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"display(Markdown(generate_robomaker_links(job_arns, aws_region)))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Creating temporary folder top plot metrics",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tmp_dir = \"/tmp/{}\".format(job_name)\nos.system(\"mkdir {}\".format(tmp_dir))\nprint(\"Create local folder {}\".format(tmp_dir))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Plot metrics for training job",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%matplotlib inline\nimport pandas as pd\nimport json\n\ntraining_metrics_file = \"training_metrics.json\"\ntraining_metrics_path = \"{}/{}\".format(s3_prefix, training_metrics_file)\nwait_for_s3_object(s3_bucket, training_metrics_path, tmp_dir)\n\njson_file = \"{}/{}\".format(tmp_dir, training_metrics_file)\nwith open(json_file) as fp: \n data = json.load(fp)\n\ndf = pd.DataFrame(data['metrics'])\nx_axis = 'episode'\ny_axis = 'reward_score'\n\nplt = df.plot(x=x_axis,y=y_axis, figsize=(12,5), legend=True, style='b-')\nplt.set_ylabel(y_axis);\nplt.set_xlabel(x_axis);",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Clean up RoboMaker and SageMaker training job\n\nExecute the cells below if you want to kill RoboMaker and SageMaker job.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# # Cancelling robomaker job\n# for job_arn in job_arns:\n# robomaker.cancel_simulation_job(job=job_arn)\n\n# # Stopping sagemaker training job\n# sage_session.sagemaker_client.stop_training_job(TrainingJobName=estimator._current_job_name)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Evaluation (Time trail, Object avoidance, Head to bot)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"s3_yaml_name=\"evaluation_params.yaml\"\nworld_name = \"reInvent2019_track\"\n\nwith open(\"./src/artifacts/yaml/evaluation_yaml_template.yaml\", \"r\") as filepointer:\n yaml_config = yaml.load(filepointer)\n\nyaml_config['WORLD_NAME'] = world_name\nyaml_config['MODEL_S3_BUCKET'] = s3_bucket\nyaml_config['MODEL_S3_PREFIX'] = s3_prefix\nyaml_config['AWS_REGION'] = aws_region\nyaml_config['METRICS_S3_BUCKET'] = s3_bucket\nyaml_config['METRICS_S3_OBJECT_KEY'] = \"{}/evaluation_metrics.json\".format(s3_prefix)\nyaml_config['SIMTRACE_S3_BUCKET'] = s3_bucket\nyaml_config['SIMTRACE_S3_PREFIX'] = \"{}/iteration-data/evaluation\".format(s3_prefix)\nyaml_config['ROBOMAKER_SIMULATION_JOB_ACCOUNT_ID'] = account_id\nyaml_config['NUMBER_OF_TRIALS'] = \"5\"\nyaml_config['MP4_S3_BUCKET'] = s3_bucket\nyaml_config['MP4_S3_OBJECT_PREFIX'] = \"{}/iteration-data/evaluation\".format(s3_prefix)\n\n# Race-type supported for training are TIME_TRIAL, OBJECT_AVOIDANCE, HEAD_TO_BOT\n# If you need to modify more attributes look at the template yaml file\nrace_type = \"TIME_TRIAL\"\n\nif race_type == \"OBJECT_AVOIDANCE\":\n yaml_config['NUMBER_OF_OBSTACLES'] = \"6\"\n yaml_config['RACE_TYPE'] = \"OBJECT_AVOIDANCE\"\n\nelif race_type == \"HEAD_TO_BOT\":\n yaml_config['NUMBER_OF_BOT_CARS'] = \"6\"\n yaml_config['RACE_TYPE'] = \"HEAD_TO_BOT\"\n\n# Printing the modified yaml parameter\nfor key, value in yaml_config.items():\n print(\"{}: {}\".format(key.ljust(40, ' '), value))\n\n# Uploading the modified yaml parameter\nwith open(\"./evaluation_params.yaml\", \"w\") as filepointer:\n yaml.dump(yaml_config, filepointer)\n\n!aws s3 cp ./evaluation_params.yaml {s3_location}/evaluation_params.yaml\n!rm evaluation_params.yaml",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"num_simulation_workers = 1\n\nenvriron_vars = {\n \"S3_YAML_NAME\": s3_yaml_name,\n \"MODEL_S3_PREFIX\": s3_prefix,\n \"MODEL_S3_BUCKET\": s3_bucket,\n \"WORLD_NAME\": world_name,\n \"KINESIS_VIDEO_STREAM_NAME\": kvs_stream_name,\n \"APP_REGION\": aws_region,\n \"MODEL_METADATA_FILE_S3_KEY\": \"%s/model/model_metadata.json\" % s3_prefix\n}\n\nsimulation_application = {\n \"application\":simulation_app_arn,\n \"launchConfig\": {\n \"packageName\": \"deepracer_simulation_environment\",\n \"launchFile\": \"evaluation.launch\",\n \"environmentVariables\": envriron_vars\n }\n}\n \nvpcConfig = {\"subnets\": deepracer_subnets,\n \"securityGroups\": deepracer_security_groups,\n \"assignPublicIp\": True}\n\nresponses = []\nfor job_no in range(num_simulation_workers):\n response = robomaker.create_simulation_job(clientRequestToken=strftime(\"%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S\", gmtime()),\n outputLocation={ \n \"s3Bucket\": s3_bucket,\n \"s3Prefix\": s3_prefix\n },\n maxJobDurationInSeconds=job_duration_in_seconds,\n iamRole=sagemaker_role,\n failureBehavior=\"Fail\",\n simulationApplications=[simulation_application],\n vpcConfig=vpcConfig)\n responses.append(response)\n\nprint(\"Created the following jobs:\")\njob_arns = [response[\"arn\"] for response in responses]\nfor job_arn in job_arns:\n print(\"Job ARN\", job_arn)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Visualizing the simulations in RoboMaker\nYou can visit the RoboMaker console to visualize the simulations or run the following cell to generate the hyperlinks.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"display(Markdown(generate_robomaker_links(job_arns, aws_region)))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Creating temporary folder top plot metrics",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"evaluation_metrics_file = \"evaluation_metrics.json\"\nevaluation_metrics_path = \"{}/{}\".format(s3_prefix, evaluation_metrics_file)\nwait_for_s3_object(s3_bucket, evaluation_metrics_path, tmp_dir)\n\njson_file = \"{}/{}\".format(tmp_dir, evaluation_metrics_file)\nwith open(json_file) as fp: \n data = json.load(fp)\n\ndf = pd.DataFrame(data['metrics'])\n# Converting milliseconds to seconds\ndf['elapsed_time'] = df['elapsed_time_in_milliseconds']/1000\ndf = df[['trial', 'completion_percentage', 'elapsed_time']]\n\ndisplay(df)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Clean Up Simulation Application Resource",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# robomaker.delete_simulation_application(application=simulation_app_arn)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Clean your S3 bucket (Uncomment the awscli commands if you want to do it)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Uncomment if you only want to clean the s3 bucket\n# sagemaker_s3_folder = \"s3://{}/{}\".format(s3_bucket, s3_prefix)\n# !aws s3 rm --recursive {sagemaker_s3_folder}\n\n# robomaker_s3_folder = \"s3://{}/{}\".format(s3_bucket, job_name)\n# !aws s3 rm --recursive {robomaker_s3_folder}\n\n# robomaker_sim_app = \"s3://{}/{}\".format(s3_bucket, 'robomaker')\n# !aws s3 rm --recursive {robomaker_sim_app}\n\n# model_output = \"s3://{}/{}\".format(s3_bucket, s3_bucket)\n# !aws s3 rm --recursive {model_output}",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Head-to-head Evaluation",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# S3 bucket\ns3_bucket_2 = sage_session.default_bucket()\n\n# Ensure that the S3 prefix contains the keyword 'sagemaker'\n# s3_prefix_2 = \"deepracer-notebook-sagemaker-200422-231836\"\ns3_prefix_2 = \"deepracer-notebook-sagemaker-200422-231836\"\nif not s3_prefix_2:\n raise Exception(\"Please provide the second agents s3_prefix and s3_bucket. The prefix would have sagemaker in between\")\n\nprint(\"Using s3 bucket {}\".format(s3_bucket_2))\nprint(\"Model checkpoints and other metadata will be stored at: \\ns3://{}/{}\".format(s3_bucket_2, s3_prefix_2))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s3_yaml_name=\"evaluation_params.yaml\"\nworld_name = \"reInvent2019_track\"\n\nwith open(\"./src/artifacts/yaml/head2head_yaml_template.yaml\", \"r\") as filepointer:\n yaml_config = yaml.load(filepointer)\n\nyaml_config['WORLD_NAME'] = world_name\nyaml_config['MODEL_S3_BUCKET'] = [s3_bucket,\n s3_bucket_2]\nyaml_config['MODEL_S3_PREFIX'] = [s3_prefix,\n s3_prefix_2]\nyaml_config['MODEL_METADATA_FILE_S3_KEY'] =[\"{}/model/model_metadata.json\".format(s3_prefix),\n \"{}/model/model_metadata.json\".format(s3_prefix_2)]\nyaml_config['AWS_REGION'] = aws_region\nyaml_config['METRICS_S3_BUCKET'] = [s3_bucket,\n s3_bucket_2]\nyaml_config['METRICS_S3_OBJECT_KEY'] = [\"{}/evaluation_metrics.json\".format(s3_prefix),\n \"{}/evaluation_metrics.json\".format(s3_prefix_2)]\nyaml_config['SIMTRACE_S3_BUCKET'] = [s3_bucket,\n s3_bucket_2]\nyaml_config['SIMTRACE_S3_PREFIX'] = [\"{}/iteration-data/evaluation\".format(s3_prefix),\n \"{}/iteration-data/evaluation\".format(s3_prefix_2)]\nyaml_config['ROBOMAKER_SIMULATION_JOB_ACCOUNT_ID'] = account_id\nyaml_config['NUMBER_OF_TRIALS'] = \"5\"\nyaml_config['MP4_S3_BUCKET'] = [s3_bucket,\n s3_bucket_2]\nyaml_config['MP4_S3_OBJECT_PREFIX'] = [\"{}/iteration-data/evaluation\".format(s3_prefix),\n \"{}/iteration-data/evaluation\".format(s3_prefix_2)]\n\n# Race-type supported for training are TIME_TRIAL, OBJECT_AVOIDANCE, HEAD_TO_BOT\n# If you need to modify more attributes look at the template yaml file\nrace_type = \"TIME_TRIAL\"\n\nif race_type == \"OBJECT_AVOIDANCE\":\n yaml_config['NUMBER_OF_OBSTACLES'] = \"6\"\n yaml_config['RACE_TYPE'] = \"OBJECT_AVOIDANCE\"\n\nelif race_type == \"HEAD_TO_BOT\":\n yaml_config['NUMBER_OF_BOT_CARS'] = \"6\"\n yaml_config['RACE_TYPE'] = \"HEAD_TO_BOT\"\n\n# Printing the modified yaml parameter\nfor key, value in yaml_config.items():\n print(\"{}: {}\".format(key.ljust(40, ' '), value))\n\n# Uploading the modified yaml parameter\nwith open(\"./evaluation_params.yaml\", \"w\") as filepointer:\n yaml.dump(yaml_config, filepointer)\n\n!aws s3 cp ./evaluation_params.yaml {s3_location}/evaluation_params.yaml\n!rm evaluation_params.yaml",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"num_simulation_workers = 1\n\nenvriron_vars = {\n \"S3_YAML_NAME\": s3_yaml_name,\n \"MODEL_S3_PREFIX\": s3_prefix,\n \"MODEL_S3_BUCKET\": s3_bucket,\n \"WORLD_NAME\": world_name,\n \"KINESIS_VIDEO_STREAM_NAME\": kvs_stream_name,\n \"APP_REGION\": aws_region,\n \"MODEL_METADATA_FILE_S3_KEY\": \"%s/model/model_metadata.json\" % s3_prefix\n}\n\nsimulation_application = {\n \"application\":simulation_app_arn,\n \"launchConfig\": {\n \"packageName\": \"deepracer_simulation_environment\",\n \"launchFile\": \"evaluation.launch\",\n \"environmentVariables\": envriron_vars\n }\n}\n \nvpcConfig = {\"subnets\": deepracer_subnets,\n \"securityGroups\": deepracer_security_groups,\n \"assignPublicIp\": True}\n\nresponses = []\nfor job_no in range(num_simulation_workers):\n response = robomaker.create_simulation_job(clientRequestToken=strftime(\"%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S\", gmtime()),\n outputLocation={ \n \"s3Bucket\": s3_bucket,\n \"s3Prefix\": s3_prefix\n },\n maxJobDurationInSeconds=job_duration_in_seconds,\n iamRole=sagemaker_role,\n failureBehavior=\"Fail\",\n simulationApplications=[simulation_application],\n vpcConfig=vpcConfig)\n responses.append(response)\n\nprint(\"Created the following jobs:\")\njob_arns = [response[\"arn\"] for response in responses]\nfor job_arn in job_arns:\n print(\"Job ARN\", job_arn)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Visualizing the simulations in RoboMaker\nYou can visit the RoboMaker console to visualize the simulations or run the following cell to generate the hyperlinks.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"display(Markdown(generate_robomaker_links(job_arns, aws_region)))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Creating temporary folder top plot metrics",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"evaluation_metrics_file = \"evaluation_metrics.json\"\nevaluation_metrics_path = \"{}/{}\".format(s3_prefix, evaluation_metrics_file)\nwait_for_s3_object(s3_bucket, evaluation_metrics_path, tmp_dir)\n\njson_file = \"{}/{}\".format(tmp_dir, evaluation_metrics_file)\nwith open(json_file) as fp: \n data = json.load(fp)\n\ndf_1 = pd.DataFrame(data['metrics'])\n# Converting milliseconds to seconds\ndf_1['elapsed_time'] = df_1['elapsed_time_in_milliseconds']/1000\ndf_1 = df_1[['trial', 'completion_percentage', 'elapsed_time']]\n\ndisplay(df_1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"evaluation_metrics_file = \"evaluation_metrics.json\"\nevaluation_metrics_path = \"{}/{}\".format(s3_prefix_2, evaluation_metrics_file)\nwait_for_s3_object(s3_bucket_2, evaluation_metrics_path, tmp_dir)\n\njson_file = \"{}/{}\".format(tmp_dir, evaluation_metrics_file)\nwith open(json_file) as fp: \n data = json.load(fp)\n\ndf_2 = pd.DataFrame(data['metrics'])\n# Converting milliseconds to seconds\ndf_2['elapsed_time'] = df_2['elapsed_time_in_milliseconds']/1000\ndf_2 = df_2[['trial', 'completion_percentage', 'elapsed_time']]\n\ndisplay(df_2)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a74fd7a8f92534a7afd9a249bba235405c4c816
| 18,297 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Notebooks/old/nyul_normalization.ipynb
|
McMasterAI/Radiology-and-AI
|
e7b1559a0673021c583c5b8da624438677253027
|
[
"MIT"
] | 6 |
2021-02-21T19:45:11.000Z
|
2022-03-30T05:38:35.000Z
|
Notebooks/old/nyul_normalization.ipynb
|
basharbme/Radiology-and-AI
|
e7b1559a0673021c583c5b8da624438677253027
|
[
"MIT"
] | 60 |
2020-11-13T23:55:10.000Z
|
2021-03-31T21:20:12.000Z
|
Notebooks/old/nyul_normalization.ipynb
|
basharbme/Radiology-and-AI
|
e7b1559a0673021c583c5b8da624438677253027
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2021-02-21T19:45:04.000Z
|
2021-07-14T20:56:35.000Z
| 18,297 | 18,297 | 0.673116 |
[
[
[
"#!pip install pytorch_lightning\r\n#!pip install torchsummaryX\r\n!pip install webdataset\r\n# !pip install datasets\r\n# !pip install wandb\r\n#!pip install -r MedicalZooPytorch/installation/requirements.txt\r\n#!pip install torch==1.7.1+cu101 torchvision==0.8.2+cu101 torchaudio==0.7.2 -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/torch_stable.html\r\n!git clone https://github.com/McMasterAI/Radiology-and-AI.git #--branch augmentation \r\n!git clone https://github.com/jcreinhold/intensity-normalization.git\r\n! python intensity-normalization/setup.py install\r\n!pip install scikit-fuzzy",
"Collecting webdataset\n Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/16/bc/8b98d07eb97a51584ff305b468a13628f3905964d597c62513f6beacb4a4/webdataset-0.1.40-py3-none-any.whl\nCollecting braceexpand\n Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/bc/63/e944b82d7dc4fbba0199af90f6712626224990fbe7fd3fe323d9a984a679/braceexpand-0.1.6-py2.py3-none-any.whl\nRequirement already satisfied: msgpack in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from webdataset) (1.0.2)\nRequirement already satisfied: torch in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from webdataset) (1.7.0+cu101)\nCollecting simplejson\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/73/96/1e6b19045375890068d7342cbe280dd64ae73fd90b9735b5efb8d1e044a1/simplejson-3.17.2-cp36-cp36m-manylinux2010_x86_64.whl (127kB)\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 133kB 14.6MB/s \n\u001b[?25hCollecting objectio\n Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/86/e3/a132a91c4e9fd5e59c947263c7ef4e3415640fa151344f858e2def8c1726/objectio-0.2.29-py3-none-any.whl\nRequirement already satisfied: Pillow in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from webdataset) (7.0.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: numpy in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from webdataset) (1.19.5)\nRequirement already satisfied: pyyaml in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from webdataset) (3.13)\nRequirement already satisfied: future in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from torch->webdataset) (0.16.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: typing-extensions in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from torch->webdataset) (3.7.4.3)\nRequirement already satisfied: dataclasses in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from torch->webdataset) (0.8)\nCollecting typer\n Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/90/34/d138832f6945432c638f32137e6c79a3b682f06a63c488dcfaca6b166c64/typer-0.3.2-py3-none-any.whl\nRequirement already satisfied: click<7.2.0,>=7.1.1 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from typer->objectio->webdataset) (7.1.2)\nInstalling collected packages: braceexpand, simplejson, typer, objectio, webdataset\nSuccessfully installed braceexpand-0.1.6 objectio-0.2.29 simplejson-3.17.2 typer-0.3.2 webdataset-0.1.40\nCloning into 'Radiology-and-AI'...\nremote: Enumerating objects: 152, done.\u001b[K\nremote: Counting objects: 100% (152/152), done.\u001b[K\nremote: Compressing objects: 100% (98/98), done.\u001b[K\nremote: Total 312 (delta 92), reused 98 (delta 44), pack-reused 160\u001b[K\nReceiving objects: 100% (312/312), 25.81 MiB | 23.06 MiB/s, done.\nResolving deltas: 100% (170/170), done.\nCloning into 'intensity-normalization'...\nremote: Enumerating objects: 184, done.\u001b[K\nremote: Counting objects: 100% (184/184), done.\u001b[K\nremote: Compressing objects: 100% (167/167), done.\u001b[K\nremote: Total 1216 (delta 111), reused 85 (delta 12), pack-reused 1032\u001b[K\nReceiving objects: 100% (1216/1216), 1.03 MiB | 3.33 MiB/s, done.\nResolving deltas: 100% (846/846), done.\nTraceback (most recent call last):\n File \"intensity-normalization/setup.py\", line 39, in <module>\n with open('README.md', encoding=\"utf-8\") as f:\nFileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: 'README.md'\nCollecting scikit-fuzzy\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/6c/f0/5eb5dbe0fd8dfe7d4651a8f4e591a196623a22b9e5339101e559695b4f6c/scikit-fuzzy-0.4.2.tar.gz (993kB)\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 1.0MB 7.9MB/s \n\u001b[?25hRequirement already satisfied: numpy>=1.6.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from scikit-fuzzy) (1.19.5)\nRequirement already satisfied: scipy>=0.9.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from scikit-fuzzy) (1.4.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: networkx>=1.9.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from scikit-fuzzy) (2.5)\nRequirement already satisfied: decorator>=4.3.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from networkx>=1.9.0->scikit-fuzzy) (4.4.2)\nBuilding wheels for collected packages: scikit-fuzzy\n Building wheel for scikit-fuzzy (setup.py) ... \u001b[?25l\u001b[?25hdone\n Created wheel for scikit-fuzzy: filename=scikit_fuzzy-0.4.2-cp36-none-any.whl size=894070 sha256=dc48fb5886148b425bce7c036cabbb78c2f23ba5e7a71fb4a0eb36607a18db2b\n Stored in directory: /root/.cache/pip/wheels/b9/4e/77/da79b16f64ef1738d95486e2731eea09d73e90a72465096600\nSuccessfully built scikit-fuzzy\nInstalling collected packages: scikit-fuzzy\nSuccessfully installed scikit-fuzzy-0.4.2\n"
],
[
"from google.colab import drive\r\ndrive.mount('/content/drive', force_remount=True)",
"Mounted at /content/drive\n"
],
[
"cd drive/MyDrive/MacAI",
"/content/drive/MyDrive/MacAI\n"
],
[
"import sys\r\nsys.path.append('./Radiology-and-AI/Radiology_and_AI')\r\nsys.path.append('./intensity-normalization')\r\nimport os\r\nimport torch\r\nimport numpy as np\r\nimport webdataset as wds",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import intensity_normalization",
"/usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/statsmodels/tools/_testing.py:19: FutureWarning: pandas.util.testing is deprecated. Use the functions in the public API at pandas.testing instead.\n import pandas.util.testing as tm\n"
],
[
"from io import BytesIO\r\nfrom nibabel import FileHolder, Nifti1Image\r\nimport torch\r\nimport numpy as np\r\nfrom scipy.interpolate import RegularGridInterpolator\r\nfrom scipy.ndimage.filters import gaussian_filter\r\nfrom time import time",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\r\nimport seaborn as sns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from scipy.interpolate import interp1d",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"train_dataset = wds.Dataset(\"macai_datasets/brats/train/brats_train.tar.gz\")\r\neval_dataset = wds.Dataset(\"macai_datasets/brats/validation/brats_validation.tar.gz\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def np_img_collator(batch):\r\n bytes_data_list = [list(batch[i].items())[1][1] for i in range(5)]\r\n bytes_data_keys = [list(batch[i].items())[0][1].split('_')[-1] for i in range(5)]\r\n bytes_data_dict = dict(zip(bytes_data_keys,bytes_data_list))\r\n\r\n bb = BytesIO(bytes_data_dict['flair'])\r\n fh = FileHolder(fileobj=bb)\r\n f_flair = Nifti1Image.from_file_map({'header': fh, 'image':fh}).get_fdata()\r\n bb = BytesIO(bytes_data_dict['seg'])\r\n fh = FileHolder(fileobj=bb)\r\n f_seg = Nifti1Image.from_file_map({'header': fh, 'image':fh}).get_fdata()\r\n bb = BytesIO(bytes_data_dict['t1'])\r\n fh = FileHolder(fileobj=bb)\r\n f_t1 = Nifti1Image.from_file_map({'header': fh, 'image':fh}).get_fdata()\r\n bb = BytesIO(bytes_data_dict['t1ce'])\r\n fh = FileHolder(fileobj=bb)\r\n f_t1ce=Nifti1Image.from_file_map({'header':fh, 'image':fh}).get_fdata()\r\n bb = BytesIO(bytes_data_dict['t2'])\r\n fh = FileHolder(fileobj=bb)\r\n f_t2 =Nifti1Image.from_file_map({'header':fh, 'image':fh}).get_fdata()\r\n\r\n padding = [(0, 0), (0, 0), (0, 0)]# last (2,3)\r\n f_flair = np.expand_dims(np.pad(f_flair, padding), axis=0)\r\n f_t1 = np.expand_dims(np.pad(f_t1, padding), axis=0)\r\n f_t2 = np.expand_dims(np.pad(f_t2, padding), axis=0)\r\n f_t1ce = np.expand_dims(np.pad(f_t1ce, padding), axis=0)\r\n\r\n f_seg = np.pad(f_seg, padding)\r\n concat = np.concatenate([f_t1, f_t1ce, f_t2, f_flair], axis=0)\r\n f_seg = np.expand_dims(f_seg, axis=0)\r\n\r\n return ([concat, f_seg])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"train_dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=5,collate_fn=np_img_collator)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def nyul_train_dataloader(dataloader, n_imgs = 4, i_min=1, i_max=99, i_s_min=1, i_s_max=100, l_percentile=10, u_percentile=90, step=20):\r\n \"\"\"\r\n determine the standard scale for the set of images\r\n Args:\r\n img_fns (list): set of NifTI MR image paths which are to be normalized\r\n mask_fns (list): set of corresponding masks (if not provided, estimated)\r\n i_min (float): minimum percentile to consider in the images\r\n i_max (float): maximum percentile to consider in the images\r\n i_s_min (float): minimum percentile on the standard scale\r\n i_s_max (float): maximum percentile on the standard scale\r\n l_percentile (int): middle percentile lower bound (e.g., for deciles 10)\r\n u_percentile (int): middle percentile upper bound (e.g., for deciles 90)\r\n step (int): step for middle percentiles (e.g., for deciles 10)\r\n Returns:\r\n standard_scale (np.ndarray): average landmark intensity for images\r\n percs (np.ndarray): array of all percentiles used\r\n \"\"\"\r\n percss = [np.concatenate(([i_min], np.arange(l_percentile, u_percentile+1, step), [i_max])) for _ in range(n_imgs)]\r\n standard_scales = [np.zeros(len(percss[0])) for _ in range(n_imgs)]\r\n\r\n iteration = 1\r\n for all_img, seg_data in dataloader:\r\n print(iteration)\r\n \r\n # print(seg_data.shape)\r\n mask_data = seg_data\r\n mask_data[seg_data ==0] = 1\r\n mask_data = np.squeeze(mask_data, axis=0)\r\n\r\n #mask_data[mask_data==2] = 0 # ignore edema\r\n\r\n for i in range(n_imgs):\r\n img_data = all_img[i]\r\n\r\n masked = img_data[mask_data > 0]\r\n landmarks = intensity_normalization.normalize.nyul.get_landmarks(masked, percss[i])\r\n min_p = np.percentile(masked, i_min)\r\n max_p = np.percentile(masked, i_max)\r\n f = interp1d([min_p, max_p], [i_s_min, i_s_max])\r\n landmarks = np.array(f(landmarks))\r\n \r\n standard_scales[i] += landmarks\r\n iteration += 1\r\n\r\n standard_scales = [scale / iteration for scale in standard_scales]\r\n return standard_scales, percss",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"standard_scales, percss = nyul_train_dataloader(train_dataloader)",
"1\n2\n3\n4\n5\n6\n7\n8\n9\n10\n11\n12\n13\n14\n15\n16\n17\n18\n19\n20\n21\n22\n23\n24\n25\n26\n27\n28\n29\n30\n31\n32\n33\n34\n35\n36\n37\n38\n39\n40\n41\n42\n43\n44\n45\n46\n47\n48\n49\n50\n51\n52\n53\n54\n55\n56\n57\n58\n59\n60\n61\n62\n63\n64\n65\n66\n67\n68\n69\n70\n71\n72\n73\n74\n75\n76\n77\n78\n79\n80\n81\n82\n83\n84\n85\n86\n87\n88\n89\n90\n91\n92\n93\n94\n95\n96\n97\n98\n99\n100\n101\n102\n103\n104\n105\n106\n107\n108\n109\n110\n111\n112\n113\n114\n115\n116\n117\n118\n119\n120\n121\n122\n123\n124\n125\n126\n127\n128\n129\n130\n131\n132\n133\n134\n135\n136\n137\n138\n139\n140\n141\n142\n143\n144\n145\n146\n147\n148\n149\n150\n151\n152\n153\n154\n155\n156\n157\n158\n159\n160\n161\n162\n163\n164\n165\n166\n167\n168\n169\n170\n171\n172\n173\n174\n175\n176\n177\n178\n179\n180\n181\n182\n183\n184\n185\n186\n187\n188\n189\n190\n191\n192\n193\n194\n195\n196\n197\n198\n199\n200\n201\n202\n203\n204\n205\n206\n207\n208\n209\n210\n211\n212\n213\n214\n215\n216\n217\n218\n219\n220\n221\n222\n223\n224\n225\n226\n227\n228\n229\n230\n231\n232\n233\n234\n235\n236\n237\n238\n239\n240\n241\n242\n243\n244\n245\n246\n247\n248\n249\n250\n251\n252\n253\n254\n255\n256\n257\n258\n259\n260\n261\n262\n263\n264\n265\n266\n267\n268\n269\n270\n271\n272\n273\n274\n275\n276\n277\n278\n279\n280\n281\n282\n283\n284\n285\n286\n287\n288\n289\n290\n291\n292\n293\n294\n"
],
[
"def dataloader_hist_norm(img_data, landmark_percs, standard_scale, seg_data):\r\n \"\"\"\r\n do the Nyul and Udupa histogram normalization routine with a given set of learned landmarks\r\n Args:\r\n img (nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image): image on which to find landmarks\r\n landmark_percs (np.ndarray): corresponding landmark points of standard scale\r\n standard_scale (np.ndarray): landmarks on the standard scale\r\n mask (nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image): foreground mask for img\r\n Returns:\r\n normalized (nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image): normalized image\r\n \"\"\"\r\n mask_data = seg_data\r\n mask_data[seg_data ==0] = 1\r\n mask_data = np.squeeze(mask_data, axis=0)\r\n\r\n masked = img_data[mask_data > 0]\r\n landmarks = intensity_normalization.normalize.nyul.get_landmarks(masked, landmark_percs)\r\n f = interp1d(landmarks, standard_scale, fill_value='extrapolate')\r\n normed = f(img_data)\r\n\r\n z = img_data\r\n z[img_data > 0] = normed[img_data > 0]\r\n return z #normed",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for all_img, seg_data in train_dataloader:\r\n for i, this_img in enumerate(all_img):\r\n if i == 0:\r\n transformed_img = dataloader_hist_norm(this_img, percss[i], standard_scales[i], seg_data)\r\n transformed_img = transformed_img[transformed_img>0]\r\n plt.hist(np.ravel(transformed_img), bins=30)\r\n plt.xlim(0, 150)\r\n plt.show()\r\n # plt.hist(np.ravel(this_img))\r\n # plt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a7511dbd4550017050e97bbdb933eeb633a5eaa
| 46,447 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Pt_1/06_01_Objects_in_BeautifulSoup/06_01_end.ipynb
|
vladcuevas/Python-Data-Science-Labs
|
eb7b2fa94402f396ed6fd5d4de62f89f930da458
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Pt_1/06_01_Objects_in_BeautifulSoup/06_01_end.ipynb
|
vladcuevas/Python-Data-Science-Labs
|
eb7b2fa94402f396ed6fd5d4de62f89f930da458
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Pt_1/06_01_Objects_in_BeautifulSoup/06_01_end.ipynb
|
vladcuevas/Python-Data-Science-Labs
|
eb7b2fa94402f396ed6fd5d4de62f89f930da458
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 56.850673 | 750 | 0.667126 |
[
[
[
"# Chapter 6 - Data Sourcing via Web\n## Part 1 - Objects in BeautifulSoup",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import sys\nprint(sys.version)",
"3.7.3 (default, Apr 24 2019, 15:29:51) [MSC v.1915 64 bit (AMD64)]\n"
],
[
"from bs4 import BeautifulSoup",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### BeautifulSoup objects ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"our_html_document = '''\n<html><head><title>IoT Articles</title></head>\n<body>\n<p class='title'><b>2018 Trends: Best New IoT Device Ideas for Data Scientists and Engineers</b></p>\n\n<p class='description'>It’s almost 2018 and IoT is on the cusp of an explosive expansion. In this article, I offer you a listing of new IoT device ideas that you can use...\n<br>\n<br>\nIt’s almost 2018 and IoT is on the cusp of an explosive expansion. In this article, I offer you a listing of new IoT device ideas that you can use to get practice in designing your first IoT applications.\n<h1>Looking Back at My Coolest IoT Find in 2017</h1>\nBefore going into detail about best new IoT device ideas, here’s the backstory. <span style=\"text-decoration: underline;\"><strong><a href=\"http://bit.ly/LPlNDJj\">Last month Ericsson Digital invited me</a></strong></span> to tour the Ericsson Studio in Kista, Sweden. Up until that visit, <a href=\"http://www.data-mania.com/blog/m2m-vs-iot/\">IoT</a> had been largely theoretical to me. Of course, I know the usual mumbo-jumbo about wearables and IoT-connected fitness trackers. That stuff is all well and good, but it’s somewhat old hat – plus I am not sure we are really benefiting so much from those, so I’m not that impressed.\n\nIt wasn’t until I got to the Ericsson Studio that I became extremely impressed by how far IoT has really come. Relying on the promise of the 5g network expansion, IoT-powered smart devices are on the cusp of an explosive growth in adoption. It was Ericsson’s Smart Car that sent me reeling:<a href=\"bit.ly/LPlNDJj\"><img class=\"aligncenter size-full wp-image-3802\" src=\"http://www.data-mania.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/new-IoT-device-ideas.jpg\" alt=\"Get your new iot device ideas here\" width=\"1024\" height=\"683\" /></a>\n\nThis car is connected to Ericsson’s Connected Vehicle Cloud, an IoT platform that manages services for the Smart Cars to which it’s connected. The Volvo pictured above acts as a drop-off location for groceries that have been ordered by its owner.\n\nTo understand how it works, imagine you’re pulling your normal 9-to-5 and you know you need to grab some groceries on your way home. Well, since you’re smart you’ve used Ericsson IoT platform to connect your car to the local grocery delivery service (<a href=\"http://mat.se/\">Mat.se</a>), so all you need to do is open the Mat.se app and make your usual order. Mat.se automatically handles the payment, grocery selection, delivery, and delivery scheduling. Since your car is IoT-enabled, Mat.se issues its trusted delivery agent a 1-time token to use for opening your car in order to place your groceries in your car for you at 4:40 pm (just before you get off from work).\n\nTo watch some of the amazing IoT device demos I witnessed at Ericsson Studio, make sure to go <span style=\"text-decoration: underline;\"><strong><a href=\"http://bit.ly/LPlNDJj\">watch the videos on this page</a></strong></span>.\n<h1>Future Trends for IoT in 2018</h1>\nNew IoT device ideas won’t do you much good unless you at least know the basic technology trends that are set to impact IoT over the next year(s). These include:\n<ol>\n \t<li><strong>Big Data</strong> & Data Engineering: Sensors that are embedded within IoT devices spin off machine-generated data like it’s going out of style. For IoT to function, the platform must be solidly engineered to handle big data. Be assured, that requires some serious data engineering.</li>\n \t<li><strong>Machine Learning</strong> Data Science: While a lot of IoT devices are still operated according to rules-based decision criteria, the age of artificial intelligence is upon us. IoT will increasingly depend on machine learning algorithms to control device operations so that devices are able to autonomously respond to a complex set of overlapping stimuli.</li>\n \t<li><strong>Blockchain</strong>-Enabled Security: Above all else, IoT networks must be secure. Blockchain technology is primed to meet the security demands that come along with building and expanding the IoT.</li>\n</ol>\n<h1>Best New IoT Device Ideas</h1>\nThis listing of new IoT device ideas has been sub-divided according to the main technology upon which the IoT devices are built. Below I’m providing a list of new IoT device ideas, but for detailed instructions on how to build these IoT applications, I recommend the <a href=\"https://click.linksynergy.com/deeplink?id=*JDLXjeE*wk&mid=39197&murl=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.udemy.com%2Ftopic%2Finternet-of-things%2F%3Fsort%3Dhighest-rated\">IoT courses on Udemy</a> (ß Please note: if you purchase a Udemy course through this link, I may receive a small commission), or courses that are available at <a href=\"http://www.skyfilabs.com/iot-online-courses\">SkyFi</a> and <a href=\"https://www.coursera.org/specializations/iot\">Coursera</a>.\n<h2>Raspberry Pi IoT Ideas</h2>\nUsing Raspberry Pi as open-source hardware, you can build IoT applications that offer any one of the following benefits:\n<ol>\n \t<li>Enable built-in sensing to build a weather station that measures ambient temperature and humidity</li>\n \t<li>Build a system that detects discrepancies in electrical readings to identify electricity theft</li>\n \t<li>Use IoT to build a Servo that is controlled by motion detection readings</li>\n \t<li>Build a smart control switch that operates devices based on external stimuli. Use this for home automation.</li>\n \t<li>Build a music playing application that enables music for each room in your house</li>\n \t<li>Implement biometrics on IoT-connected devices</li>\n</ol>\n<h2>Arduino IoT Ideas</h2>\nThere are a number of new IoT device ideas that deploy Arduino as a microcontroller. These include:\n<ol>\n \t<li>Integrate Arduino with Android to build a remote-control RGB LED device.</li>\n \t<li>Connect PIR sensors across the IoT to implement a smart building.</li>\n \t<li>Build a temperature and sunlight sensor system to remotely monitor and control the conditions of your garden.</li>\n \t<li>Deploy Arduino and IoT to automate your neighborhood streetlights.</li>\n \t<li>Build a smart irrigation system based on IoT-connected temperature and moisture sensors built-in to your agricultural plants.</li>\n</ol>\n[caption id=\"attachment_3807\" align=\"aligncenter\" width=\"300\"]<a href=\"bit.ly/LPlNDJj\"><img class=\"wp-image-3807 size-medium\" src=\"http://www.data-mania.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/IMG_3058-300x295.jpg\" alt=\"\" width=\"300\" height=\"295\" /></a> An IoT Chatbot Tree at the Ericsson Studio[/caption]\n<h2>Wireless (GSM) IoT Ideas</h2>\nSeveral new IoT device ideas are developed around the GSM wireless network. Those are:\n<ol>\n \t<li>Monitor soil moisture to automate agricultural irrigation cycles.</li>\n \t<li>Automate and control the conditions of a greenhouse.</li>\n \t<li>Enable bio-metrics to build a smart security system for your home or office building</li>\n \t<li>Build an autonomously operating fitness application that automatically makes recommendations based on motion detection and heart rate sensors that are embedded on wearable fitness trackers.</li>\n \t<li>Build a healthcare monitoring system that tracks, informs, and automatically alerts healthcare providers based on sensor readings that describe a patients vital statistics (like temperature, pulse, blood pressure, etc).</li>\n</ol>\n<h2>IoT Automation Ideas</h2>\nAlmost all new IoT device ideas offer automation benefits, but to outline a few more ideas:\n<ol>\n \t<li>Build an IoT device that automatically locates and reports the closest nearby parking spot.</li>\n \t<li>Build a motion detection system that automatically issues emails or sms messages to alert home owners of a likely home invasion.</li>\n \t<li>Use temperature sensors connected across the IoT to automatically alert you if your home windows or doors have been left open.</li>\n \t<li>Use bio-metric sensors to build a smart system that automate security for your home or office building</li>\n</ol>\nTo learn more about IoT and what’s happening on the leading edge, be sure to pop over to Ericsson’s Studio Tour recap and <span style=\"text-decoration: underline;\"><strong><a href=\"http://bit.ly/LPlNDJj\">watch these videos</a></strong></span>.\n\n<em>(I captured some of this content on behalf of DevMode Strategies during an invite-only tour of the Ericsson Studio in Kista. Rest assure, the text and opinions are my own</em>)\n<p class='description'>...</p>\n'''",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"our_soup_object = BeautifulSoup(our_html_document, 'html.parser')\nprint(our_soup_object)",
"\n<html><head><title>IoT Articles</title></head>\n<body>\n<p class=\"title\"><b>2018 Trends: Best New IoT Device Ideas for Data Scientists and Engineers</b></p>\n<p class=\"description\">It’s almost 2018 and IoT is on the cusp of an explosive expansion. In this article, I offer you a listing of new IoT device ideas that you can use...\n<br/>\n<br/>\nIt’s almost 2018 and IoT is on the cusp of an explosive expansion. In this article, I offer you a listing of new IoT device ideas that you can use to get practice in designing your first IoT applications.\n<h1>Looking Back at My Coolest IoT Find in 2017</h1>\nBefore going into detail about best new IoT device ideas, here’s the backstory. <span style=\"text-decoration: underline;\"><strong><a href=\"http://bit.ly/LPlNDJj\">Last month Ericsson Digital invited me</a></strong></span> to tour the Ericsson Studio in Kista, Sweden. Up until that visit, <a href=\"http://www.data-mania.com/blog/m2m-vs-iot/\">IoT</a> had been largely theoretical to me. Of course, I know the usual mumbo-jumbo about wearables and IoT-connected fitness trackers. That stuff is all well and good, but it’s somewhat old hat – plus I am not sure we are really benefiting so much from those, so I’m not that impressed.\n\nIt wasn’t until I got to the Ericsson Studio that I became extremely impressed by how far IoT has really come. Relying on the promise of the 5g network expansion, IoT-powered smart devices are on the cusp of an explosive growth in adoption. It was Ericsson’s Smart Car that sent me reeling:<a href=\"bit.ly/LPlNDJj\"><img alt=\"Get your new iot device ideas here\" class=\"aligncenter size-full wp-image-3802\" height=\"683\" src=\"http://www.data-mania.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/new-IoT-device-ideas.jpg\" width=\"1024\"/></a>\n\nThis car is connected to Ericsson’s Connected Vehicle Cloud, an IoT platform that manages services for the Smart Cars to which it’s connected. The Volvo pictured above acts as a drop-off location for groceries that have been ordered by its owner.\n\nTo understand how it works, imagine you’re pulling your normal 9-to-5 and you know you need to grab some groceries on your way home. Well, since you’re smart you’ve used Ericsson IoT platform to connect your car to the local grocery delivery service (<a href=\"http://mat.se/\">Mat.se</a>), so all you need to do is open the Mat.se app and make your usual order. Mat.se automatically handles the payment, grocery selection, delivery, and delivery scheduling. Since your car is IoT-enabled, Mat.se issues its trusted delivery agent a 1-time token to use for opening your car in order to place your groceries in your car for you at 4:40 pm (just before you get off from work).\n\nTo watch some of the amazing IoT device demos I witnessed at Ericsson Studio, make sure to go <span style=\"text-decoration: underline;\"><strong><a href=\"http://bit.ly/LPlNDJj\">watch the videos on this page</a></strong></span>.\n<h1>Future Trends for IoT in 2018</h1>\nNew IoT device ideas won’t do you much good unless you at least know the basic technology trends that are set to impact IoT over the next year(s). These include:\n<ol>\n<li><strong>Big Data</strong> & Data Engineering: Sensors that are embedded within IoT devices spin off machine-generated data like it’s going out of style. For IoT to function, the platform must be solidly engineered to handle big data. Be assured, that requires some serious data engineering.</li>\n<li><strong>Machine Learning</strong> Data Science: While a lot of IoT devices are still operated according to rules-based decision criteria, the age of artificial intelligence is upon us. IoT will increasingly depend on machine learning algorithms to control device operations so that devices are able to autonomously respond to a complex set of overlapping stimuli.</li>\n<li><strong>Blockchain</strong>-Enabled Security: Above all else, IoT networks must be secure. Blockchain technology is primed to meet the security demands that come along with building and expanding the IoT.</li>\n</ol>\n<h1>Best New IoT Device Ideas</h1>\nThis listing of new IoT device ideas has been sub-divided according to the main technology upon which the IoT devices are built. Below I’m providing a list of new IoT device ideas, but for detailed instructions on how to build these IoT applications, I recommend the <a href=\"https://click.linksynergy.com/deeplink?id=*JDLXjeE*wk&mid=39197&murl=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.udemy.com%2Ftopic%2Finternet-of-things%2F%3Fsort%3Dhighest-rated\">IoT courses on Udemy</a> (ß Please note: if you purchase a Udemy course through this link, I may receive a small commission), or courses that are available at <a href=\"http://www.skyfilabs.com/iot-online-courses\">SkyFi</a> and <a href=\"https://www.coursera.org/specializations/iot\">Coursera</a>.\n<h2>Raspberry Pi IoT Ideas</h2>\nUsing Raspberry Pi as open-source hardware, you can build IoT applications that offer any one of the following benefits:\n<ol>\n<li>Enable built-in sensing to build a weather station that measures ambient temperature and humidity</li>\n<li>Build a system that detects discrepancies in electrical readings to identify electricity theft</li>\n<li>Use IoT to build a Servo that is controlled by motion detection readings</li>\n<li>Build a smart control switch that operates devices based on external stimuli. Use this for home automation.</li>\n<li>Build a music playing application that enables music for each room in your house</li>\n<li>Implement biometrics on IoT-connected devices</li>\n</ol>\n<h2>Arduino IoT Ideas</h2>\nThere are a number of new IoT device ideas that deploy Arduino as a microcontroller. These include:\n<ol>\n<li>Integrate Arduino with Android to build a remote-control RGB LED device.</li>\n<li>Connect PIR sensors across the IoT to implement a smart building.</li>\n<li>Build a temperature and sunlight sensor system to remotely monitor and control the conditions of your garden.</li>\n<li>Deploy Arduino and IoT to automate your neighborhood streetlights.</li>\n<li>Build a smart irrigation system based on IoT-connected temperature and moisture sensors built-in to your agricultural plants.</li>\n</ol>\n[caption id=\"attachment_3807\" align=\"aligncenter\" width=\"300\"]<a href=\"bit.ly/LPlNDJj\"><img alt=\"\" class=\"wp-image-3807 size-medium\" height=\"295\" src=\"http://www.data-mania.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/IMG_3058-300x295.jpg\" width=\"300\"/></a> An IoT Chatbot Tree at the Ericsson Studio[/caption]\n<h2>Wireless (GSM) IoT Ideas</h2>\nSeveral new IoT device ideas are developed around the GSM wireless network. Those are:\n<ol>\n<li>Monitor soil moisture to automate agricultural irrigation cycles.</li>\n<li>Automate and control the conditions of a greenhouse.</li>\n<li>Enable bio-metrics to build a smart security system for your home or office building</li>\n<li>Build an autonomously operating fitness application that automatically makes recommendations based on motion detection and heart rate sensors that are embedded on wearable fitness trackers.</li>\n<li>Build a healthcare monitoring system that tracks, informs, and automatically alerts healthcare providers based on sensor readings that describe a patients vital statistics (like temperature, pulse, blood pressure, etc).</li>\n</ol>\n<h2>IoT Automation Ideas</h2>\nAlmost all new IoT device ideas offer automation benefits, but to outline a few more ideas:\n<ol>\n<li>Build an IoT device that automatically locates and reports the closest nearby parking spot.</li>\n<li>Build a motion detection system that automatically issues emails or sms messages to alert home owners of a likely home invasion.</li>\n<li>Use temperature sensors connected across the IoT to automatically alert you if your home windows or doors have been left open.</li>\n<li>Use bio-metric sensors to build a smart system that automate security for your home or office building</li>\n</ol>\nTo learn more about IoT and what’s happening on the leading edge, be sure to pop over to Ericsson’s Studio Tour recap and <span style=\"text-decoration: underline;\"><strong><a href=\"http://bit.ly/LPlNDJj\">watch these videos</a></strong></span>.\n\n<em>(I captured some of this content on behalf of DevMode Strategies during an invite-only tour of the Ericsson Studio in Kista. Rest assure, the text and opinions are my own</em>)\n<p class=\"description\">...</p>\n</p></body></html>\n"
],
[
"print(our_soup_object.prettify()[0:300])",
"<html>\n <head>\n <title>\n IoT Articles\n </title>\n </head>\n <body>\n <p class=\"title\">\n <b>\n 2018 Trends: Best New IoT Device Ideas for Data Scientists and Engineers\n </b>\n </p>\n <p class=\"description\">\n It’s almost 2018 and IoT is on the cusp of an explosive expansion. In this article,\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Tag objects",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Tag names",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"soup_object = BeautifulSoup('<h1 attribute_1 = \"Heading Level 1\"\">Future Trends for IoT in 2018</h1>', \"lxml\")\n\ntag = soup_object.h1\ntype(tag)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(tag)",
"<h1 attribute_1=\"Heading Level 1\">Future Trends for IoT in 2018</h1>\n"
],
[
"tag.name",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tag.name = 'heading 1'\ntag",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tag.name",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Tag attributes",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"soup_object = BeautifulSoup('<h1 attribute_1 = \"Heading Level 1\"\">Future Trends for IoT in 2018</h1>', \"lxml\")\ntag = soup_object.h1\ntag",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tag['attribute_1']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tag.attrs",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tag['attribute_2'] = 'Heading Level 1*'\ntag.attrs",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tag",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"del tag['attribute_2']\ntag",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"del tag['attribute_1']\ntag.attrs",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Navigating a parse tree using tags",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# First we will recreate our original parse tree.\nour_html_document = '''\n<html><head><title>IoT Articles</title></head>\n<body>\n<p class='title'><b>2018 Trends: Best New IoT Device Ideas for Data Scientists and Engineers</b></p>\n\n<p class='description'>It’s almost 2018 and IoT is on the cusp of an explosive expansion. In this article, I offer you a listing of new IoT device ideas that you can use...\n<br>\n<br>\nIt’s almost 2018 and IoT is on the cusp of an explosive expansion. In this article, I offer you a listing of new IoT device ideas that you can use to get practice in designing your first IoT applications.\n<h1>Looking Back at My Coolest IoT Find in 2017</h1>\nBefore going into detail about best new IoT device ideas, here’s the backstory. <span style=\"text-decoration: underline;\"><strong><a href=\"http://bit.ly/LPlNDJj\">Last month Ericsson Digital invited me</a></strong></span> to tour the Ericsson Studio in Kista, Sweden. Up until that visit, <a href=\"http://www.data-mania.com/blog/m2m-vs-iot/\">IoT</a> had been largely theoretical to me. Of course, I know the usual mumbo-jumbo about wearables and IoT-connected fitness trackers. That stuff is all well and good, but it’s somewhat old hat – plus I am not sure we are really benefiting so much from those, so I’m not that impressed.\n\nIt wasn’t until I got to the Ericsson Studio that I became extremely impressed by how far IoT has really come. Relying on the promise of the 5g network expansion, IoT-powered smart devices are on the cusp of an explosive growth in adoption. It was Ericsson’s Smart Car that sent me reeling:<a href=\"bit.ly/LPlNDJj\"><img class=\"aligncenter size-full wp-image-3802\" src=\"http://www.data-mania.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/new-IoT-device-ideas.jpg\" alt=\"Get your new iot device ideas here\" width=\"1024\" height=\"683\" /></a>\n\nThis car is connected to Ericsson’s Connected Vehicle Cloud, an IoT platform that manages services for the Smart Cars to which it’s connected. The Volvo pictured above acts as a drop-off location for groceries that have been ordered by its owner.\n\nTo understand how it works, imagine you’re pulling your normal 9-to-5 and you know you need to grab some groceries on your way home. Well, since you’re smart you’ve used Ericsson IoT platform to connect your car to the local grocery delivery service (<a href=\"http://mat.se/\">Mat.se</a>), so all you need to do is open the Mat.se app and make your usual order. Mat.se automatically handles the payment, grocery selection, delivery, and delivery scheduling. Since your car is IoT-enabled, Mat.se issues its trusted delivery agent a 1-time token to use for opening your car in order to place your groceries in your car for you at 4:40 pm (just before you get off from work).\n\nTo watch some of the amazing IoT device demos I witnessed at Ericsson Studio, make sure to go <span style=\"text-decoration: underline;\"><strong><a href=\"http://bit.ly/LPlNDJj\">watch the videos on this page</a></strong></span>.\n<h1>Future Trends for IoT in 2018</h1>\nNew IoT device ideas won’t do you much good unless you at least know the basic technology trends that are set to impact IoT over the next year(s). These include:\n<ol>\n \t<li><strong>Big Data</strong> & Data Engineering: Sensors that are embedded within IoT devices spin off machine-generated data like it’s going out of style. For IoT to function, the platform must be solidly engineered to handle big data. Be assured, that requires some serious data engineering.</li>\n \t<li><strong>Machine Learning</strong> Data Science: While a lot of IoT devices are still operated according to rules-based decision criteria, the age of artificial intelligence is upon us. IoT will increasingly depend on machine learning algorithms to control device operations so that devices are able to autonomously respond to a complex set of overlapping stimuli.</li>\n \t<li><strong>Blockchain</strong>-Enabled Security: Above all else, IoT networks must be secure. Blockchain technology is primed to meet the security demands that come along with building and expanding the IoT.</li>\n</ol>\n<h1>Best New IoT Device Ideas</h1>\nThis listing of new IoT device ideas has been sub-divided according to the main technology upon which the IoT devices are built. Below I’m providing a list of new IoT device ideas, but for detailed instructions on how to build these IoT applications, I recommend the <a href=\"https://click.linksynergy.com/deeplink?id=*JDLXjeE*wk&mid=39197&murl=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.udemy.com%2Ftopic%2Finternet-of-things%2F%3Fsort%3Dhighest-rated\">IoT courses on Udemy</a> (ß Please note: if you purchase a Udemy course through this link, I may receive a small commission), or courses that are available at <a href=\"http://www.skyfilabs.com/iot-online-courses\">SkyFi</a> and <a href=\"https://www.coursera.org/specializations/iot\">Coursera</a>.\n<h2>Raspberry Pi IoT Ideas</h2>\nUsing Raspberry Pi as open-source hardware, you can build IoT applications that offer any one of the following benefits:\n<ol>\n \t<li>Enable built-in sensing to build a weather station that measures ambient temperature and humidity</li>\n \t<li>Build a system that detects discrepancies in electrical readings to identify electricity theft</li>\n \t<li>Use IoT to build a Servo that is controlled by motion detection readings</li>\n \t<li>Build a smart control switch that operates devices based on external stimuli. Use this for home automation.</li>\n \t<li>Build a music playing application that enables music for each room in your house</li>\n \t<li>Implement biometrics on IoT-connected devices</li>\n</ol>\n<h2>Arduino IoT Ideas</h2>\nThere are a number of new IoT device ideas that deploy Arduino as a microcontroller. These include:\n<ol>\n \t<li>Integrate Arduino with Android to build a remote-control RGB LED device.</li>\n \t<li>Connect PIR sensors across the IoT to implement a smart building.</li>\n \t<li>Build a temperature and sunlight sensor system to remotely monitor and control the conditions of your garden.</li>\n \t<li>Deploy Arduino and IoT to automate your neighborhood streetlights.</li>\n \t<li>Build a smart irrigation system based on IoT-connected temperature and moisture sensors built-in to your agricultural plants.</li>\n</ol>\n[caption id=\"attachment_3807\" align=\"aligncenter\" width=\"300\"]<a href=\"bit.ly/LPlNDJj\"><img class=\"wp-image-3807 size-medium\" src=\"http://www.data-mania.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/IMG_3058-300x295.jpg\" alt=\"\" width=\"300\" height=\"295\" /></a> An IoT Chatbot Tree at the Ericsson Studio[/caption]\n<h2>Wireless (GSM) IoT Ideas</h2>\nSeveral new IoT device ideas are developed around the GSM wireless network. Those are:\n<ol>\n \t<li>Monitor soil moisture to automate agricultural irrigation cycles.</li>\n \t<li>Automate and control the conditions of a greenhouse.</li>\n \t<li>Enable bio-metrics to build a smart security system for your home or office building</li>\n \t<li>Build an autonomously operating fitness application that automatically makes recommendations based on motion detection and heart rate sensors that are embedded on wearable fitness trackers.</li>\n \t<li>Build a healthcare monitoring system that tracks, informs, and automatically alerts healthcare providers based on sensor readings that describe a patients vital statistics (like temperature, pulse, blood pressure, etc).</li>\n</ol>\n<h2>IoT Automation Ideas</h2>\nAlmost all new IoT device ideas offer automation benefits, but to outline a few more ideas:\n<ol>\n \t<li>Build an IoT device that automatically locates and reports the closest nearby parking spot.</li>\n \t<li>Build a motion detection system that automatically issues emails or sms messages to alert home owners of a likely home invasion.</li>\n \t<li>Use temperature sensors connected across the IoT to automatically alert you if your home windows or doors have been left open.</li>\n \t<li>Use bio-metric sensors to build a smart system that automate security for your home or office building</li>\n</ol>\nTo learn more about IoT and what’s happening on the leading edge, be sure to pop over to Ericsson’s Studio Tour recap and <span style=\"text-decoration: underline;\"><strong><a href=\"http://bit.ly/LPlNDJj\">watch these videos</a></strong></span>.\n\n<em>(I captured some of this content on behalf of DevMode Strategies during an invite-only tour of the Ericsson Studio in Kista. Rest assure, the text and opinions are my own</em>)\n<p class='description'>...</p>\n'''\nour_soup_object = BeautifulSoup(our_html_document, 'html.parser')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"our_soup_object.head",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"our_soup_object.title",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"our_soup_object.body.b",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"our_soup_object.body",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"our_soup_object.li",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"our_soup_object.a",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a7515d70e613f33a8f4f4a874a29e899b2c4cdf
| 5,538 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
week4/create_labeled_queries.ipynb
|
sumitsidana/search_with_machine_learning_course
|
0d35803e63867bb5a2933514a4b42b437ad3748e
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2022-03-21T20:44:51.000Z
|
2022-03-21T20:44:51.000Z
|
week4/create_labeled_queries.ipynb
|
sumitsidana/search_with_machine_learning_course
|
0d35803e63867bb5a2933514a4b42b437ad3748e
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
week4/create_labeled_queries.ipynb
|
sumitsidana/search_with_machine_learning_course
|
0d35803e63867bb5a2933514a4b42b437ad3748e
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 30.262295 | 136 | 0.564103 |
[
[
[
"import os\nimport argparse\nimport xml.etree.ElementTree as ET\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport csv\n\n# Useful if you want to perform stemming.\nimport nltk\nstemmer = nltk.stem.PorterStemmer()\n\ncategories_file_name = r'/workspace/datasets/product_data/categories/categories_0001_abcat0010000_to_pcmcat99300050000.xml'\n\nqueries_file_name = r'/workspace/datasets/train.csv'\noutput_file_name = r'/workspace/datasets/labeled_query_data.txt'\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Process arguments.')\n# general = parser.add_argument_group(\"general\")\n# general.add_argument(\"--min_queries\", default=1, help=\"The minimum number of queries per category label (default is 1)\")\n# general.add_argument(\"--output\", default=output_file_name, help=\"the file to output to\")\n\n# args = parser.parse_args()\n# output_file_name = args.output\n\n# if args.min_queries:\n# min_queries = int(args.min_queries)\n\n# The root category, named Best Buy with id cat00000, doesn't have a parent.\n\nmin_queries = 10\nroot_category_id = 'cat00000'\n\ntree = ET.parse(categories_file_name)\nroot = tree.getroot()\n\n# Parse the category XML file to map each category id to its parent category id in a dataframe.\ncategories = []\nparents = []\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for child in root:\n id = child.find('id').text\n cat_path = child.find('path')\n cat_path_ids = [cat.find('id').text for cat in cat_path]\n leaf_id = cat_path_ids[-1]\n if leaf_id != root_category_id:\n categories.append(leaf_id)\n parents.append(cat_path_ids[-2])\nparents_df = pd.DataFrame(list(zip(categories, parents)), columns =['category', 'parent'])\n\n# Read the training data into pandas, only keeping queries with non-root categories in our category tree.\ndf = pd.read_csv(queries_file_name)[['category', 'query']]\ndf = df[df['category'].isin(categories)]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"category_value_counts= pd.DataFrame(df['category'].value_counts().reset_index().\\\n rename(columns = {\"index\": \"category\", \"category\": \"category_count\"}))\nfaulty_categories = list(category_value_counts[category_value_counts['category_count'] < min_queries]['category'])\n\nwhile len(faulty_categories) > 0:\n df.loc[df['category'].isin(faulty_categories), 'category'] = df['category'].\\\n map(parents_df.set_index('category')['parent'])\n category_value_counts= pd.DataFrame(df['category'].value_counts().reset_index().\\\n rename(columns = {\"index\": \"category\", \"category\": \"category_count\"}))\n faulty_categories = list(category_value_counts[category_value_counts['category_count'] < min_queries]['category'])\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# find faulty categories\n\ncategory_value_counts= pd.DataFrame(df['category'].value_counts().reset_index().\\\n rename(columns = {\"index\": \"category\", \"category\": \"category_count\"}))\nfaulty_categories = list(category_value_counts[category_value_counts['category_count'] < min_queries]['category'])\ndf.loc[df['category'].isin(faulty_categories), 'category'] = df['category'].map(parents_df.set_index('category')['parent'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"faulty_categories",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.isnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a751885e5f016ea0ed5e325eaa8f25b11258cb7
| 685,076 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Capstone_project_EDA.ipynb
|
vs1991/ga-learner-dsmp-repo
|
6e4488fa5ea3614e0d4d496681db7295f956be56
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Capstone_project_EDA.ipynb
|
vs1991/ga-learner-dsmp-repo
|
6e4488fa5ea3614e0d4d496681db7295f956be56
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Capstone_project_EDA.ipynb
|
vs1991/ga-learner-dsmp-repo
|
6e4488fa5ea3614e0d4d496681db7295f956be56
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 93.948985 | 28,958 | 0.536952 |
[
[
[
"<a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/vs1991/ga-learner-dsmp-repo/blob/master/Capstone_project_EDA.ipynb\" target=\"_parent\"><img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open In Colab\"/></a>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Loading from drive",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from google.colab import drive",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"drive.mount('../Greyatom',force_remount=True)",
"Go to this URL in a browser: https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/auth?client_id=947318989803-6bn6qk8qdgf4n4g3pfee6491hc0brc4i.apps.googleusercontent.com&redirect_uri=urn%3aietf%3awg%3aoauth%3a2.0%3aoob&scope=email%20https%3a%2f%2fwww.googleapis.com%2fauth%2fdocs.test%20https%3a%2f%2fwww.googleapis.com%2fauth%2fdrive%20https%3a%2f%2fwww.googleapis.com%2fauth%2fdrive.photos.readonly%20https%3a%2f%2fwww.googleapis.com%2fauth%2fpeopleapi.readonly&response_type=code\n\nEnter your authorization code:\n··········\nMounted at ../Greyatom\n"
],
[
"cd ../Greyatom/'My Drive'/'my first book'/'capstone project'",
"/Greyatom/My Drive/my first book/capstone project\n"
],
[
"ls",
" Cusomer_Cleaned.csv JTD_Cleaned.csv\n Customer_Data.csv JTD.csv\n'customer datas legend .xlsx' 'Mahindra problem description of the data.docx'\n Final_invoice.csv Plant_Cleaned.csv\n Invoice_Cleaned.csv 'Plant Master_real.xlsx - Sheet1.csv'\n Invoice_Data.csv\n"
],
[
"import pandas as pd \nimport numpy as np \nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt \nimport seaborn as sns \nimport plotly\n\n\nimport plotly\nimport plotly.graph_objs as go\nfrom plotly.offline import iplot\nimport plotly.express as px",
"/usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/statsmodels/tools/_testing.py:19: FutureWarning: pandas.util.testing is deprecated. Use the functions in the public API at pandas.testing instead.\n import pandas.util.testing as tm\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Loading Files",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#cleaned invoice data\ninv=pd.read_csv('Invoice_Cleaned.csv')\ninv=inv.drop(columns=['Unnamed: 0'])\ninv['Customer No.'] = inv['Customer No.'].str.lstrip('0')\n\n\ninv.head()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#cleaned customer data\ncustomer=pd.read_csv('Cusomer_Cleaned.csv')\ncustomer=customer.drop(columns=['Unnamed: 0','Business Partner'])\n\ncustomer['Customer No.'] = customer['Customer No.'].astype(str)\ncustomer['Data Origin'].value_counts()\n",
"/usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/IPython/core/interactiveshell.py:2718: DtypeWarning:\n\nColumns (1,2) have mixed types.Specify dtype option on import or set low_memory=False.\n\n"
],
[
"#cleaned jtd data\njtd=pd.read_csv('JTD_Cleaned.csv')\njtd=jtd.drop(columns=['Unnamed: 0'])\n\njtd.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plant=pd.read_csv('Plant_Cleaned.csv')\nplant=plant.drop(columns=['Unnamed: 0'])\n\nplant.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#jtd_grouped=jtd.groupby(['DBM Order','Item Category'],as_index=False).agg({\"Net value\":'sum',\"Order Quantity\":\"sum\"})\n#inv_jtd=pd.merge(inv,jtd_grouped,how=\"left\",left_on='Job Card No',right_on='DBM Order')\n\ninv_cust=pd.merge(inv,customer,on='Customer No.',how='left')\ninv_plant=pd.merge(inv,plant,on='Plant',how='left')\ninv_cust_plant=pd.merge(inv_cust,plant,on='Plant',how='left')\n\n#inv_jtd_customer=pd.merge(inv_jtd,customer,how='left',on='Customer No.')\n#combined_data=pd.merge(inv_jtd_customer,plant,on='Plant',how='left')\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"inv_cust_plant.isnull().sum()/len(inv_cust_plant)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"inv_cust_plant=inv_cust_plant.drop(columns=['Name 1','House number and street','PO Box'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"inv_cust_plant.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# **EDA** ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Revenue Analysis\n\n1. Year Wise revenue Analysis\n2. Order Wise revenue Analysis\n3. Make wise revenue Analysis\n4. State wise revenus Analyise\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"year_income=inv_cust_plant.groupby(['Job Year','Job Month'],as_index=False)['Total Amt Wtd Tax.'].sum()\n\n\nfig = px.line(year_income, x=\"Job Month\", y=\"Total Amt Wtd Tax.\", color='Job Year')\nfig.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"order_income=inv_cust_plant.groupby(['Job Year','Order Type'],as_index=False)['Total Amt Wtd Tax.'].sum()\n\n\nfig = px.line(order_income, x=\"Job Year\", y=\"Total Amt Wtd Tax.\", color='Order Type')\n\nfig.update_layout(title='Year Wise Order Revenue')\n\nfig.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"make_income=inv_cust_plant.groupby(['Job Year','Make'],as_index=False)['Total Amt Wtd Tax.'].sum()\n\n\nfig = px.line(make_income, x=\"Job Year\", y=\"Total Amt Wtd Tax.\", color='Make')\n\nfig.update_layout(title='Year Wise Make/Car Revenue')\n\nfig.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"state_income=inv_cust_plant.groupby(['Job Year','State'],as_index=False)['Total Amt Wtd Tax.'].sum()\n\n\nfig = px.line(state_income, x=\"Job Year\", y=\"Total Amt Wtd Tax.\", color='State')\n\nfig.update_layout(title='State wise Revenue')\n\nfig.show()\n#model_income.sort_values(by='Total Amt Wtd Tax.',ascending=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Source Income ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#source affecting to more income \nsource_income=inv_cust_plant.groupby(['Job Year','Data Origin'],as_index=False)['Total Amt Wtd Tax.'].sum()\n\n\nfig = px.line(source_income, x=\"Job Year\", y=\"Total Amt Wtd Tax.\", color='Data Origin')\n\nfig.update_layout(title='Source wise income ')\n\nfig.show()\n#model_income.sort_values(by='Total Amt Wtd Tax.',ascending=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Labour Revenue Analysis?\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n# Mean labour charges according to each order \nlabour_charge=inv_cust_plant[['Labour Total','Order Type']]\nlab=pd.DataFrame(labour_charge.groupby(['Order Type'])['Labour Total'].mean()).rename(columns={'Labour total':'Mean Labour Cost'}).reset_index()\nlab.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig = px.bar(lab, y='Labour Total', x='Order Type')\nfig.update_layout(template='ggplot2', title=\"Mean Labour charges for various order type\")\n\nfig.show()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"labor_year_income=inv_cust_plant.groupby(['Job Year','Job Month'],as_index=False)['Labour Total'].sum()\n\n\nfig = px.line(labor_year_income, x=\"Job Year\", y=\"Labour Total\", color='Job Month')\nfig.update_layout(template='ggplot2', title=\"labor Charges For various months \")\nfig.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"month_income=inv_cust_plant.groupby(['Job Month'],as_index=False)['Labour Total'].sum()\n\n\nfig = px.line(month_income, x=\"Job Month\", y=\"Labour Total\")\nfig.update_layout(template='ggplot2', title=\"Overall Labor costing during various months \")\nfig.show()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"order_year_income=inv_cust_plant.groupby(['Order Type','Job Year'],as_index=False)['Labour Total'].sum()\n\n\nfig = px.line(order_year_income, x=\"Job Year\", y=\"Labour Total\", color='Order Type')\nfig.update_layout(template='ggplot2', title=\"labor Charges For various order in all years \")\nfig.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Total number of plants in each state",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#total number of plants in each states\nstate=pd.crosstab(columns=plant['State'],index='Plant')\nstate.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"city=pd.crosstab(columns=plant['City'],index='Plant')\ncity.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Number of plants in each city",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#graphical representation of number of plants in each state\nplt.figure(figsize=(15,4))\nplt.xticks(rotation=90)\nsns.set(style='darkgrid')\nax=sns.barplot(plant['State'].value_counts().index,plant['State'].value_counts())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#graphical representation of number of plants in each city\nplt.figure(figsize=(15,4))\nplt.xticks(rotation=90)\nsns.set(style='darkgrid')\nax=sns.barplot(plant['City'].value_counts().head(30).index,plant['City'].value_counts().head(30))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Number of plants according to various zones",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#divide states into zones \nnorthern_zone =['Chandigarh','Delhi','Haryana','Himachal Pradesh','Jammu and Kashmir','Ladakh'\n ,'Punjab','Rajasthan','Uttarakhand','Uttar Pradesh']\n\nnorth_eastern_Zone =[ ]\n\neastern_zone =['Bihar', 'Jharkhand', 'Odisha','West Bengal','Assam', 'Arunachal Pradesh', 'Manipur', 'Meghalaya', 'Mizoram', 'Nagaland']\n\ncentral_western_zone=['Madhya Pradesh', 'Chhattisgarh', 'Goa', 'Gujarat', 'Maharashtra']\n\nsouthern_zone =[ 'Andhra Pradesh', 'Karnataka', 'Kerala', 'Puducherry', 'Tamil Nadu','Telangana']\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"f1=plant['State'].isin(northern_zone)\nf2=plant['State'].isin(eastern_zone)\nf3=plant['State'].isin(central_western_zone)\nf4=plant['State'].isin(southern_zone)\n#filt5=plant['State'].isin(north_eastern_Zone)\n\nn_state =plant.loc[f1]\ne_state =plant.loc[f2]\nc_w_state=plant.loc[f3]\ns_state =plant.loc[f4]\n#north_east_state=plant.loc[filt5]\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"trace1=go.Bar(\n y = n_state['State'].value_counts().values,\n x = n_state['State'].value_counts().index,\n name = \"Northern Zone\",\n marker = dict(color = 'rgba(255, 174, 255, 0.5)',\n line=dict(color='rgb(0,0,0)',width=1.5)))\n\ntrace2 = go.Bar(\n y =s_state['State'].value_counts().values,\n x = s_state['State'].value_counts().index,\n name = \"Southern Zone\",\n marker = dict(color = 'rgba(155, 255, 128, 0.5)',\n line=dict(color='rgb(0,0,0)',width=1.5))) \n\ntrace3 = go.Bar(\n y =e_state['State'].value_counts().values ,\n x = e_state['State'].value_counts().index,\n name = \"Eastern Zone\",\n marker = dict(color = 'rgba(355, 355,1000, 0.5)',\n line=dict(color='rgb(0,0,0)',width=1.5))) \n\n\ntrace4 = go.Bar(\n y =c_w_state['State'].value_counts().values ,\n x = c_w_state['State'].value_counts().index,\n name = \"Central and Western Zone\",\n marker = dict(color = 'rgba(255, 225,1, 0.5)',\n line=dict(color='rgb(0,0,0)',width=1.5)))\n\n\n\n\nfig = go.Figure(data = [trace1,trace2,trace3,trace4])\n\nfig.update_layout(template='ggplot2', title=\"Plant Count in various state\")\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n#fig, axs=plt.subplots(nrows=2,ncols=2,figsize=(16.5,10))\n\n#sns.barplot(north_state['State'].value_counts().values,north_state['State'].value_counts().index,ax=axs[0,0])\n#axs[0,0].set_title('Northern Zone')\n\n#sns.barplot(east_state['State'].value_counts().values,east_state['State'].value_counts().index,ax=axs[0,1])\n#axs[0,1].set_title('Eastern Zone')\n\n#sns.barplot(cent_west_state['State'].value_counts().values,cent_west_state['State'].value_counts().index,ax=axs[1,0])\n#axs[1,0].set_title('Cental & Western Zone')\n\n#sns.barplot(south_state['State'].value_counts().values,south_state['State'].value_counts().index,ax=axs[1,1])\n#axs[1,1].set_title('Southern Zone')\n\n#sns.barplot(north_east_state['State'].value_counts().values,north_east_state['State'].value_counts().index,ax=axs[2,0])\n#axs[2,0].set_title('North Eastern Zone')\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Location Based Analysis",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#k=inv_plant[inv_plant['State']=='Maharashtra']\n\n#for i in ['CITY','City','State','District','Regn No']:\n # print(k[i].value_counts())\n #print('*'*80)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"inv_plant.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n \n#city=[]\n#state=[]\n#car_count=[]\n \n#for i in loc1['City'].unique():\n # city.append(i)\n # car_count.append(len(loc1[loc1['City']==i]['Regn No'].value_counts()))\n #state.append(loc1[loc1['City']==i]['State'].value_counts().index)\n #print('*'*60)\n\n\n#k=loc[loc['State']=='Kerala']\n#len(k[k['City']=='Kottayam']['Regn No'].value_counts())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#plant_most_cars=pd.DataFrame({'City':city,'State':state,'Total Unique Cars':car_count})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#plant_most_cars.sort_values(by=['Total Unique Cars'],inplace=True,ascending=False)\n#plant_most_cars",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#sns.barplot(plant_most_cars['Total Unique Cars'].head(10),plant_most_cars['City'].head(10))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n \nfilt1=inv_plant['State'].isin(northern_zone)\nnorth_state=inv_plant.loc[filt1]\n\n\nfilt2=inv_plant['State'].isin(eastern_zone)\neast_state=inv_plant.loc[filt2]\n\n\nfilt3=inv_plant['State'].isin(central_western_zone)\ncent_west_state=inv_plant.loc[filt3]\n\nfilt4=inv_plant['State'].isin(southern_zone)\nsouth_state=inv_plant.loc[filt4]\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# **Which** **make** **and** **model** **is** **more** popular?\n\n1. Make popular in various zones\n2. Model popular in various zone \n3. Make with most sales\n\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#graphical representation of famous makes among various zones \n\nfrom plotly.subplots import make_subplots\nfig = make_subplots(rows=4, cols=2)\n#for northern zone \nfig.add_trace(go.Bar(\n y = north_state['Make'].value_counts().head(5).values,\n x = north_state['Make'].value_counts().head(5).index,\n marker=dict(color=[1, 2, 3,4,5])),\n 1, 1)\nfig.add_trace(go.Bar(\n y = north_state['Model'].value_counts().head(5).values,\n x = north_state['Model'].value_counts().head(5).index,\n marker=dict(color=[15,8,9,10,11])),\n 1, 2)\nfig.update_xaxes(title_text=\"Make count('northern Zone )\", row=1, col=1)\nfig.update_xaxes(title_text=\"Model count('northern Zone )\", row=1, col=2)\n\n#figure for eastern zone \nfig.add_trace(go.Bar(\n y = east_state['Make'].value_counts().head(5).values,\n x = east_state['Make'].value_counts().head(5).index,\n marker=dict(color=[1, 2, 3,4,5])),\n 2, 1)\nfig.add_trace(go.Bar(\n y = east_state['Model'].value_counts().head(5).values,\n x = east_state['Model'].value_counts().head(5).index,\n marker=dict(color=[15,8,9,10,11])),\n 2, 2)\nfig.update_xaxes(title_text=\"Make count('Eastern Zone )\", row=2, col=1)\nfig.update_xaxes(title_text=\"Model count('Eastern Zone )\", row=2, col=2)\n\n#figure for southern zone \nfig.add_trace(go.Bar(\n y = south_state['Make'].value_counts().head(5).values,\n x = south_state['Make'].value_counts().head(5).index,\n marker=dict(color=[1, 2, 3,4,5])),\n 3, 1)\nfig.add_trace(go.Bar(\n y = south_state['Model'].value_counts().head(5).values,\n x = south_state['Model'].value_counts().head(5).index,\n marker=dict(color=[15,8,9,10,11])),\n 3, 2)\nfig.update_xaxes(title_text=\"Make count('Southern Zone )\", row=3, col=1)\nfig.update_xaxes(title_text=\"Model count('Southern Zone )\", row=3, col=2)\n\n#figure for centeral and western zone \nfig.add_trace(go.Bar(\n y = cent_west_state['Make'].value_counts().head(5).values,\n x = cent_west_state['Make'].value_counts().head(5).index,\n marker=dict(color=[1, 2, 3,4,5])),\n 4, 1)\nfig.add_trace(go.Bar(\n y = cent_west_state['Model'].value_counts().head(5).values,\n x = cent_west_state['Model'].value_counts().head(5).index,\n marker=dict(color=[15,8,9,10,11])),\n 4, 2)\nfig.update_xaxes(title_text=\"Central & Western Zone )\", row=4, col=1)\nfig.update_xaxes(title_text=\"Central & Western Zone )\", row=4, col=2)\n\nfig.update_layout(template='ggplot2', title=\"Zonal Count\",height=1100, width=1100)\n\n\nfig.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#sns.scatterplot(inv_plant[inv_plant[\"Make\"]==\"PORCHE\"][\"Total Amt Wtd Tax.\"],inv_cust_plant['Total Amt Wtd Tax.'])\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# which area has most cars?\n\n\n1. Zone wise \n2. Top 5 States\n\n\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#according to zones\ndata=[['Northern Zone',north_state['Make'].count()],['Eastern Zone',east_state['Make'].count()],\n ['Central & Western Zone',cent_west_state['Make'].count()],['Southern Zone',south_state['Make'].count()]]\noverall=pd.DataFrame(data,columns=['Zones','Count'])\noverall.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import plotly.graph_objects as go\n#graphical representation of most cars in various zones\ncolors = ['gold', 'mediumturquoise', 'darkorange', 'lightgreen']\n\nfig = go.Figure(data=[go.Pie(labels=overall['Zones'],\n values=overall['Count'])])\nfig.update_traces(hoverinfo='label+percent', textinfo='value', textfont_size=20,\n marker=dict(colors=colors, line=dict(color='#000000', width=2)))\nfig.update_layout(template='ygridoff', title=\"Zone Wise Car Count\")\n\nfig.show()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n#overall car count in each state\ncar1=[]\nstate1=[]\nfor i in inv_plant['State'].unique():\n car1.append(inv_plant[inv_plant['State']==i]['Make'].count())\n state1.append(i)\n\ndf1=pd.DataFrame({'States':state1,'car count':car1})\ndf1=df1.sort_values(by='car count',ascending=False)\ndf1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#state wise count\n\ncolors = ['gold', 'mediumturquoise', 'darkorange', 'lightgreen']\n\nfig = go.Figure(data=[go.Pie(labels=df1['States'][0:10],\n values=df1['car count'][0:10])])\nfig.update_traces(hoverinfo='label+percent', textinfo='value', textfont_size=20,\n marker=dict(colors=colors, line=dict(color='#000000', width=2)))\nfig.update_layout(template='ggplot2', title=\" Top 10 State wise count car count\")\nfig.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# which service structure is popular in different zones ?\n\n\n\n1. Northern Zone \n2. Eastern Zone \n3. Central and western Zone\n4. Southern Zone \n\n\n\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## **Northern** Zone",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"one=pd.DataFrame(north_state.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False).loc['Uttar Pradesh'])\n#one=pd.DataFrame(loc1.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False))\none=one.rename(columns={'Order Type':'count'})\none=one.reset_index()\none.head()\n\ntwo=pd.DataFrame(north_state.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False).loc['Haryana'])\n#one=pd.DataFrame(loc1.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False))\ntwo=two.rename(columns={'Order Type':'count'})\ntwo=two.reset_index()\ntwo.head()\n\nthree=pd.DataFrame(north_state.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False).loc['Punjab'])\n#one=pd.DataFrame(loc1.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False))\nthree=three.rename(columns={'Order Type':'count'})\nthree=three.reset_index()\nthree.head()\n\n\nfour=pd.DataFrame(north_state.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False).loc['Uttarakhand'])\n#one=pd.DataFrame(loc1.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False))\nfour=four.rename(columns={'Order Type':'count'})\nfour=four.reset_index()\nfour.head()\n\n\nfive=pd.DataFrame(north_state.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False).loc['Himachal Pradesh'])\n#one=pd.DataFrame(loc1.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False))\nfive=five.rename(columns={'Order Type':'count'})\nfive=five.reset_index()\n\n\n\n\nsix=pd.DataFrame(north_state.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False).loc['Rajasthan'])\n#one=pd.DataFrame(loc1.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False))\nsix=six.rename(columns={'Order Type':'count'})\nsix=six.reset_index()\n\n\nseven=pd.DataFrame(north_state.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False).loc['Chandigarh'])\n#one=pd.DataFrame(loc1.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False))\nseven=seven.rename(columns={'Order Type':'count'})\nseven=seven.reset_index()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"trace1=go.Bar(\n y = one['count'],\n x = one['Order Type'],\n name = \"Uttar Pradesh\",\n marker = dict(color = 'rgba(255, 174, 255, 0.5)',\n line=dict(color='rgb(0,0,0)',width=1.5)))\n\ntrace2 = go.Bar(\n y =two['count'],\n x = two['Order Type'],\n name = \"Haryana\",\n marker = dict(color = 'rgba(155, 255, 128, 0.5)',\n line=dict(color='rgb(0,0,0)',width=1.5))) \n\ntrace3 = go.Bar(\n y =three['count'] ,\n x = three['Order Type'],\n name = \"Punjab\",\n marker = dict(color = 'rgba(355, 355,1000, 0.5)',\n line=dict(color='rgb(0,0,0)',width=1.5))) \n\n\ntrace4 = go.Bar(\n y =four['count'] ,\n x = four['Order Type'],\n name = \"Uttarakhand\",\n marker = dict(color = 'rgba(255, 225,1, 0.5)',\n line=dict(color='rgb(0,0,0)',width=1.5)))\n\ntrace5 = go.Bar(\n y =five['count'] ,\n x = five['Order Type'],\n name = \"Himachal Pradesh\",\n marker = dict(color = 'DarkSlateGrey',\n line=dict(color='rgb(0,0,0)',width=1.5)))\n\ntrace6 = go.Bar(\n y =six['count'] ,\n x = six['Order Type'],\n name = \"Rajasthan\",\n marker = dict(color = 'goldenrod',\n line=dict(color='rgb(0,0,0)',width=1.5)))\n\ntrace7 = go.Bar(\n y =seven['count'] ,\n x = seven['Order Type'],\n name = \"Chandigarh\",\n marker = dict(color = 'darksalmon',\n line=dict(color='rgb(0,0,0)',width=1.5)))\n\n\n\nfig = go.Figure(data = [trace1,trace2,trace3,trace4,trace5,trace6,trace7])\nfig.update_layout(template='plotly_dark', title=\"Famous order typ in Northern Zone\")\n\niplot(fig)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Central and Western Zone ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"one=pd.DataFrame(cent_west_state.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False).loc['Maharashtra'])\n#one=pd.DataFrame(loc1.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False))\none=one.rename(columns={'Order Type':'count'})\none=one.reset_index()\none.head()\n\n\n\ntwo=pd.DataFrame(cent_west_state.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False).loc['Gujarat'])\n#one=pd.DataFrame(loc1.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False))\ntwo=two.rename(columns={'Order Type':'count'})\ntwo=two.reset_index()\ntwo.head()\n\nthree=pd.DataFrame(cent_west_state.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False).loc['Madhya Pradesh'])\n#one=pd.DataFrame(loc1.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False))\nthree=three.rename(columns={'Order Type':'count'})\nthree=three.reset_index()\nthree.head()\n\n\nfour=pd.DataFrame(cent_west_state.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False).loc['Chhattisgarh'])\n#one=pd.DataFrame(loc1.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False))\nfour=four.rename(columns={'Order Type':'count'})\nfour=four.reset_index()\nfour.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"trace1=go.Bar(\n y = one['count'],\n x = one['Order Type'],\n name = \"Maharashtra\",\n marker = dict(color = 'rgba(255, 174, 255, 0.5)',\n line=dict(color='rgb(0,0,0)',width=1.5)))\n\ntrace2 = go.Bar(\n y =two['count'],\n x = two['Order Type'],\n name = \"Gujarat\",\n marker = dict(color = 'rgba(155, 255, 128, 0.5)',\n line=dict(color='rgb(0,0,0)',width=1.5))) \n\ntrace3 = go.Bar(\n y =three['count'] ,\n x = three['Order Type'],\n name = \"Rajasthan\",\n marker = dict(color = 'rgba(355, 355,1000, 0.5)',\n line=dict(color='rgb(0,0,0)',width=1.5))) \n\n\ntrace4 = go.Bar(\n y =four['count'] ,\n x = four['Order Type'],\n name = \"Chhattisgarh\",\n marker = dict(color = 'rgba(255, 225,1, 0.5)',\n line=dict(color='rgb(0,0,0)',width=1.5)))\n\n\nfig = go.Figure(data = [trace1,trace2,trace3,trace4])\nfig.update_layout(template='plotly_dark', title=\"Famous order in Central & Western Zone\")\n\niplot(fig)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## eastern and north eastern zone ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"one=pd.DataFrame(east_state.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False).loc['Bihar'])\n#one=pd.DataFrame(loc1.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False))\none=one.rename(columns={'Order Type':'count'})\none=one.reset_index()\none.head()\n\ntwo=pd.DataFrame(east_state.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False).loc['West Bengal'])\n#one=pd.DataFrame(loc1.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False))\ntwo=two.rename(columns={'Order Type':'count'})\ntwo=two.reset_index()\ntwo.head()\n\nthree=pd.DataFrame(east_state.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False).loc['Odisha'])\n#one=pd.DataFrame(loc1.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False))\nthree=three.rename(columns={'Order Type':'count'})\nthree=three.reset_index()\nthree.head()\n\n\nfour=pd.DataFrame(east_state.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False).loc['Jharkhand'])\n#one=pd.DataFrame(loc1.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False))\nfour=four.rename(columns={'Order Type':'count'})\nfour=four.reset_index()\nfour.head()\n\n\nfive=pd.DataFrame(east_state.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False).loc['Assam'])\n#one=pd.DataFrame(loc1.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False))\nfive=five.rename(columns={'Order Type':'count'})\nfive=five.reset_index()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n\ntrace1=go.Bar(\n y = one['count'],\n x = one['Order Type'],\n name = \"Bihar\",\n marker = dict(color = 'rgba(255, 174, 255, 0.5)',\n line=dict(color='rgb(0,0,0)',width=1.5)))\n\ntrace2 = go.Bar(\n y =two['count'],\n x = two['Order Type'],\n name = \"West Bengal\",\n marker = dict(color = 'rgba(155, 255, 128, 0.5)',\n line=dict(color='rgb(0,0,0)',width=1.5))) \n\ntrace3 = go.Bar(\n y =three['count'] ,\n x = three['Order Type'],\n name = \"Odisha\",\n marker = dict(color = 'rgba(355, 355,1000, 0.5)',\n line=dict(color='rgb(0,0,0)',width=1.5))) \n\n\ntrace4 = go.Bar(\n y =four['count'] ,\n x = four['Order Type'],\n name = \"Jharkhand\",\n marker = dict(color = 'rgba(255, 225,1, 0.5)',\n line=dict(color='rgb(0,0,0)',width=1.5)))\n\ntrace5 = go.Bar(\n y =five['count'] ,\n x = five['Order Type'],\n name = \"Assam\",\n marker = dict(color = 'DarkSlateGrey',\n line=dict(color='rgb(0,0,0)',width=1.5)))\n\n\n\nfig = go.Figure(data = [trace1,trace2,trace3,trace4,trace5])\nfig.update_layout(template='plotly_dark', title=\"Famous order in North Eastern Zone\")\n\niplot(fig)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Southern Zone ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"one=pd.DataFrame(south_state.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False).loc['Telangana'])\n#one=pd.DataFrame(loc1.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False))\none=one.rename(columns={'Order Type':'count'})\none=one.reset_index()\none.head()\n\ntwo=pd.DataFrame(south_state.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False).loc['Tamil Nadu'])\n#one=pd.DataFrame(loc1groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False))\ntwo=two.rename(columns={'Order Type':'count'})\ntwo=two.reset_index()\ntwo.head()\n\nthree=pd.DataFrame(south_state.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False).loc['Karnataka'])\n#one=pd.DataFrame(loc1.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False))\nthree=three.rename(columns={'Order Type':'count'})\nthree=three.reset_index()\nthree.head()\n\n\nfour=pd.DataFrame(south_state.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False).loc['Puducherry'])\n#one=pd.DataFrame(loc1.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False))\nfour=four.rename(columns={'Order Type':'count'})\nfour=four.reset_index()\nfour.head()\n\n\nfive=pd.DataFrame(south_state.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False).loc['Andhra Pradesh'])\n#one=pd.DataFrame(loc1.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False))\nfive=five.rename(columns={'Order Type':'count'})\nfive=five.reset_index()\n\n\nsix=pd.DataFrame(south_state.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False).loc['Kerala'])\n#one=pd.DataFrame(loc1.groupby(['State'])['Order Type'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False))\nsix=six.rename(columns={'Order Type':'count'})\nsix=six.reset_index()\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n\n\ntrace1=go.Bar(\n y = one['count'],\n x = one['Order Type'],\n name = \"Telangana\",\n marker = dict(color = 'rgba(255, 174, 255, 0.5)',\n line=dict(color='rgb(0,0,0)',width=1.5)))\n\ntrace2 = go.Bar(\n y =two['count'],\n x = two['Order Type'],\n name = \"Tamil Nadu\",\n marker = dict(color = 'rgba(155, 255, 128, 0.5)',\n line=dict(color='rgb(0,0,0)',width=1.5))) \n\ntrace3 = go.Bar(\n y =three['count'] ,\n x = three['Order Type'],\n name = \"Karnataka\",\n marker = dict(color = 'rgba(355, 355,1000, 0.5)',\n line=dict(color='rgb(0,0,0)',width=1.5))) \n\n\ntrace4 = go.Bar(\n y =four['count'] ,\n x = four['Order Type'],\n name = \"Puducherry\",\n marker = dict(color = 'rgba(255, 225,1, 0.5)',\n line=dict(color='rgb(0,0,0)',width=1.5)))\n\ntrace5 = go.Bar(\n y =five['count'] ,\n x = five['Order Type'],\n name = \"Andhra Pradesh\",\n marker = dict(color = 'DarkSlateGrey',\n line=dict(color='rgb(0,0,0)',width=1.5)))\n\ntrace6 = go.Bar(\n y =six['count'] ,\n x = six['Order Type'],\n name = \"Kerala\",\n marker = dict(color = 'goldenrod',\n line=dict(color='rgb(0,0,0)',width=1.5)))\n\n#trace7 = go.Bar(\n # y =seven['count'] ,\n # x = seven['Order Type'],\n # name = \"Chandigarh\",\n # marker = dict(color = 'darksalmon',\n # line=dict(color='rgb(0,0,0)',width=1.5)))\n\n\n\nfig = go.Figure(data = [trace1,trace2,trace3,trace4,trace5,trace6])\nfig.update_layout(template='plotly_dark', title=\"Famous order in Southern Zone\")\n\niplot(fig)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Service Structure for particular car ?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"one=pd.DataFrame(inv_plant.groupby(['Order Type'])['Make'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False)).loc['Running Repairs']\none=one.rename(columns={'Make':'count'})\none=one.reset_index()\none\n\ntwo=pd.DataFrame(inv_plant.groupby(['Order Type'])['Make'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False)).loc['Accidental']\ntwo=two.rename(columns={'Make':'count'})\ntwo=two.reset_index()\ntwo\n\nthree=pd.DataFrame(inv_plant.groupby(['Order Type'])['Make'].value_counts().sort_values(ascending=False)).loc['Mechanical']\nthree=three.rename(columns={'Make':'count'})\nthree=three.reset_index()\nthree",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n\n\ntrace1=go.Bar(\n y = one['count'][0:5],\n x = one['Make'][0:5],\n name = \"Running repairs\",\n marker = dict(color = 'rgba(255, 174, 255, 0.5)',\n line=dict(color='rgb(0,0,0)',width=1.5)))\n\ntrace2 = go.Bar(\n y =two['count'][0:5],\n x = two['Make'][0:5],\n name = \"Accidental\",\n marker = dict(color = 'rgba(155, 255, 128, 0.5)',\n line=dict(color='rgb(0,0,0)',width=1.5))) \n\ntrace3 = go.Bar(\n y =three['count'][0:5] ,\n x = three['Make'][0:5],\n name = \"Mechanical\",\n marker = dict(color = 'rgba(355, 355,1000, 0.5)',\n line=dict(color='rgb(0,0,0)',width=1.5))) \n\n\nfig = go.Figure(data = [trace1,trace2,trace3])\nfig.update_layout(template='ggplot2', title=\"Famous order among cars\")\n\niplot(fig)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Seasonal Orders\n\n1. Year Wise Analysis\n2. Overall Ananlysis\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Year Wise",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for_2012=inv_cust_plant[inv_cust_plant['Job Year']==2012]\nfor_2013=inv_cust_plant[inv_cust_plant['Job Year']==2013]\nfor_2014=inv_cust_plant[inv_cust_plant['Job Year']==2014]\nfor_2015=inv_cust_plant[inv_cust_plant['Job Year']==2015]\nfor_2016=inv_cust_plant[inv_cust_plant['Job Year']==2016]\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"inv_cust_plant['Job Year'].value_counts().sort_index().index",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for i in inv_cust_plant['Job Year'].value_counts().sort_index().index:\n year=inv_cust_plant[inv_cust_plant['Job Year']==i]\n rain=[6,7,8,9]\n filt=year['Job Month'].isin(rain)\n rain_data=year.loc[filt]\n###creating dataframes of season wise analysis of order type\n###for rain season:\n rain_df=pd.DataFrame(rain_data['Order Type'].value_counts())\n rain_df=rain_df.rename(columns={'Order Type':'count'})\n rain_df=rain_df.reset_index()\n rain_df=rain_df.rename(columns={'index':'order type'})\n rain_df.head()\n###summer\n summer=[2,3,4,5]\n filt2=year['Job Month'].isin(summer)\n summer_data=year.loc[filt2]\n###winter\n winter=[10,11,12,1]\n filt1=year['Job Month'].isin(winter)\n winter_data=year.loc[filt1]\n winter_data.head()\n###for winter season\n winter_df=pd.DataFrame(winter_data['Order Type'].value_counts())\n winter_df=winter_df.rename(columns={'Order Type':'count'})\n winter_df=winter_df.reset_index()\n winter_df=winter_df.rename(columns={'index':'order type'})\n winter_df.head()\n###for summer season\n summer_df=pd.DataFrame(summer_data['Order Type'].value_counts())\n summer_df=summer_df.rename(columns={'Order Type':'count'})\n summer_df=summer_df.reset_index()\n summer_df=summer_df.rename(columns={'index':'order type'})\n summer_df.head()\n\n colors = ['gold', 'mediumturquoise', 'darkorange', 'lightgreen']\n\n #fig = go.Figure(data=[go.Pie(labels=rain_df['order type'],title='Rainy Season Orders',\n #values=rain_df['count'])])\n #fig.update_traces(hoverinfo='label+percent', textinfo='value', textfont_size=20,\n #marker=dict(colors=colors, line=dict(color='#000000', width=2)))\n #fig.show()\n\n fig = make_subplots(rows=1, cols=3)\n#for northern zone \n\n\n fig = make_subplots(rows=1, cols=3, specs=[[{'type':'domain'}, {'type':'domain'},{'type':'domain'}]],subplot_titles=['WINTER', 'RAIN','SUMMER'])\n fig.add_trace(go.Pie(labels=winter_df['order type'], values=winter_df['count']),\n 1, 1)\n fig.add_trace(go.Pie(labels=rain_df['order type'], values=rain_df['count']),\n 1, 2)\n fig.add_trace(go.Pie(labels=summer_df['order type'], values=summer_df['count']),\n 1, 3)\n print('for the {}'.format(i))\n fig.update_layout(template='ggplot2', title='For the year {}'.format(i))\n fig.show()\n\n",
"for the 2012\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Overall Analysis",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n######Rainy season:\nrain=[6,7,8,9]\nfilt=inv_plant['Job Month'].isin(rain)\nrain_data=inv_plant.loc[filt]\n###creating dataframes of season wise analysis of order type\n###for rain season:\nrain_df=pd.DataFrame(inv_plant['Order Type'].value_counts())\nrain_df=rain_df.rename(columns={'Order Type':'count'})\nrain_df=rain_df.reset_index()\nrain_df=rain_df.rename(columns={'index':'order type'})\nrain_df.head()\n###summer\nsummer=[2,3,4,5]\nfilt2=inv_plant['Job Month'].isin(summer)\nsummer_data=inv_plant.loc[filt2]\n###winter\nwinter=[10,11,12,1]\nfilt1=inv_plant['Job Month'].isin(winter)\nwinter_data=inv_plant.loc[filt1]\nwinter_data.head()\n###for winter season\nwinter_df=pd.DataFrame(winter_data['Order Type'].value_counts())\nwinter_df=winter_df.rename(columns={'Order Type':'count'})\nwinter_df=winter_df.reset_index()\nwinter_df=winter_df.rename(columns={'index':'order type'})\nwinter_df.head()\n###for summer season\nsummer_df=pd.DataFrame(summer_data['Order Type'].value_counts())\nsummer_df=summer_df.rename(columns={'Order Type':'count'})\nsummer_df=summer_df.reset_index()\nsummer_df=summer_df.rename(columns={'index':'order type'})\nsummer_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig = make_subplots(rows=1, cols=3, specs=[[{'type':'domain'}, {'type':'domain'},{'type':'domain'}]],subplot_titles=['WINTER', 'RAIN','SUMMER'])\nfig.add_trace(go.Pie(labels=winter_df['order type'], values=winter_df['count']),\n 1, 1)\nfig.add_trace(go.Pie(labels=rain_df['order type'], values=rain_df['count']),\n 1, 2)\nfig.add_trace(go.Pie(labels=summer_df['order type'], values=summer_df['count']),\n 1, 3)\nprint('for the {}'.format(i))\nfig.update_layout(template='ggplot2', title=\"Overall Orders \")\nfig.show()",
"for the 2016\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Inventory Management",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#combination of customer,invoice,plant and item \ninv_cust_plant_jtd=pd.merge(inv_cust_plant,jtd,left_on='Job Card No',right_on='DBM Order')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"inv_cust_plant",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#inventory management\n#P002 is for parts \n\ninventory=inv_cust_plant_jtd[['Make','Model','Order Type','Item Category','Description','Material','Order Quantity','Net value','Target quantity UoM','Parts Total']]\nz=inventory[inventory['Item Category']=='P002']\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"parts=z.groupby(['Material','Description'],as_index=False)['Net value'].sum().sort_values(by='Net value',ascending=False)#,'Net values':'sum'})\nparts['Net value']=parts['Net value'].apply(lambda x: '{:.2f}'.format(x))\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"trace1 = go.Bar(\n y =parts['Net value'][0:10],\n x = parts['Description'][0:10]\n )\nfig = go.Figure(data = [trace1])\n\nfig.update_layout(template='ggplot2', title=\"Top 10 most sold parts according to revenue\")\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#services code P010\n\nservices=inventory[inventory['Item Category']=='P010']\ns=services.groupby(['Material','Description'],as_index=False)['Net value'].sum().sort_values(by='Net value',ascending=False)#,'Net values':'sum'})\ns['Net value']=s['Net value'].apply(lambda x: '{:.2f}'.format(x))\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"trace1 = go.Bar(\n y =s['Net value'][0:10],\n x =s['Description'][0:10]\n )\nfig = go.Figure(data = [trace1])\n\nfig.update_layout(template='ggplot2', title=\"Top 10 Service provided according to revenue\")\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"make=z.groupby(['Model','Make','Description'],as_index=False)['Net value'].sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ma=[]\ndescription=[]\nfamous_parts=[]\n\nfor i in make['Make'].unique():\n o=make[make['Make']==i].sort_values(by='Net value',ascending=False)\n ma.append(i)\n description.append(o['Description'].iloc[0])\n famous_parts.append(o['Net value'].iloc[0])\n\n\ndf1=pd.DataFrame({'Make':ma,'description':description,'value':famous_parts})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ser=services.groupby(['Model','Make','Description'],as_index=False)['Net value'].sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ma1=[]\ndescription1=[]\nfamous_parts1=[]\n\nfor i in ser['Make'].unique():\n o=ser[ser['Make']==i].sort_values(by='Net value',ascending=False)\n ma1.append(i)\n description1.append(o['Description'].iloc[0])\n famous_parts1.append(o['Net value'].iloc[0])\n\n\ndf2=pd.DataFrame({'Make':ma1,'description':description1,'value':famous_parts1})\ndf2",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Customer Segmentation",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"inv_cust_plant['Invoice_DateTime'] = pd.to_datetime(inv_cust_plant['Invoice_DateTime'])\ninv_cust_plant['Invoice_Date']=inv_cust_plant['Invoice_DateTime'].dt.date\ninv_cust_plant['Invoice_Date'].max()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"clust=inv_cust_plant[['Customer No.','Invoice_Date','Total Amt Wtd Tax.']]\n\n\ntx_user = pd.DataFrame(clust['Customer No.'].unique())\ntx_user.columns = ['CustomerID']\n\n#get the max purchase date for each customer and create a dataframe with it\ntx_max_purchase = clust.groupby('Customer No.').Invoice_Date.max().reset_index()\ntx_max_purchase.columns = ['CustomerID','MaxPurchaseDate']\n\n#we take our observation point as the max invoice date in our dataset\ntx_max_purchase['Recency'] = (tx_max_purchase['MaxPurchaseDate'].max() - tx_max_purchase['MaxPurchaseDate']).dt.days\n\n#merge this dataframe to our new user dataframe\ntx_user = pd.merge(tx_user, tx_max_purchase[['CustomerID','Recency']], on='CustomerID')\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tx_frequency = clust.groupby('Customer No.').Invoice_Date.count().reset_index()\ntx_frequency.columns = ['CustomerID','Frequency']\n\n#add this data to our main dataframe\ntx_user = pd.merge(tx_user, tx_frequency, on='CustomerID')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tx_user.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\ntx_revenue = clust.groupby('Customer No.')['Total Amt Wtd Tax.'].sum().reset_index()\ntx_frequency.columns = ['CustomerID','Revenue']\n#merge it with our main dataframe\ntx_user = pd.merge(tx_user, tx_frequency, on='CustomerID')\ntx_user",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\nsns.distplot(tx_user['Recency'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n\nsns.distplot(np.log(tx_user['Frequency']))\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#tx_user['Revenue']=np.log(tx_user['Revenue'])\n\nsns.distplot(tx_user['Revenue'])\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from scipy import stats\ncustomers_fix = pd.DataFrame()\n#customers_fix[\"Recency\"] = stats.boxcox(tx_user['Recency'])[0]\ncustomers_fix[\"Frequency\"] = stats.boxcox(tx_user['Frequency'])[0]\ncustomers_fix[\"Revenue\"] = pd.Series(np.cbrt(tx_user['Revenue'])).values\ncustomers_fix[\"Recency\"] = pd.Series(np.cbrt(tx_user['Recency'])).values\ncustomers_fix.tail()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Import library\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler\n# Initialize the Object\nscaler = StandardScaler()\n# Fit and Transform The Data\nscaler.fit(customers_fix)\ncustomers_normalized = scaler.transform(customers_fix)\n# Assert that it has mean 0 and variance 1\nprint(customers_normalized.mean(axis = 0).round(2)) # [0. -0. 0.]\nprint(customers_normalized.std(axis = 0).round(2)) # [1. 1. 1.]",
"[-0. -0. 0.]\n[1. 1. 1.]\n"
],
[
"from sklearn.cluster import KMeans\n\n\n\nsse = {}\nfor k in range(1, 11):\n kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=k, random_state=42)\n kmeans.fit(customers_normalized)\n sse[k] = kmeans.inertia_ # SSE to closest cluster centroid\nplt.title('The Elbow Method')\nplt.xlabel('k')\nplt.ylabel('SSE')\nsns.pointplot(x=list(sse.keys()), y=list(sse.values()))\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model = KMeans(n_clusters=3, random_state=42)\nmodel.fit(customers_normalized)\nmodel.labels_.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tx_user[\"Cluster\"] = model.labels_\ntx_user.groupby('Cluster').agg({\n 'Recency':'mean',\n 'Frequency':'mean',\n 'Revenue':['mean', 'count']}).round(2)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a75193f811ccb72cf491d08f391c9f55cd1860d
| 3,724 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
4. Zip Your Project Files and Submit.ipynb
|
carreaza/P3_Implement_SLAM
|
ee6a849c2df6d25df84f131f10e196a83cec29d9
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
4. Zip Your Project Files and Submit.ipynb
|
carreaza/P3_Implement_SLAM
|
ee6a849c2df6d25df84f131f10e196a83cec29d9
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
4. Zip Your Project Files and Submit.ipynb
|
carreaza/P3_Implement_SLAM
|
ee6a849c2df6d25df84f131f10e196a83cec29d9
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 34.165138 | 310 | 0.62782 |
[
[
[
"## Project Submission\n\nWhen you are ready to submit your project, meaning you have checked the [rubric](https://review.udacity.com/#!/rubrics/1428/view) and made sure that you have completed all tasks and answered all questions. Then you are ready to compress your files and submit your solution!\n\nThe following steps assume:\n1. All cells have been *run* in Notebook 3 (and that progress has been saved).\n2. All questions in Notebook 3 have been answered.\n3. Your robot `sense` function in `robot_class.py` is complete.\n\nPlease make sure all your work is saved before moving on. You do not need to change any code in the following cells; this code is to help you submit your project, only.\n\n---\n\nThe first thing we'll do, is convert your notebooks into `.html` files; these files will save the output of each cell and any code/text that you have modified and saved in those notebooks. Note that the second notebook is not included because its completion does not affect whether you pass this project.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!jupyter nbconvert \"1. Robot Moving and Sensing.ipynb\"\n!jupyter nbconvert \"3. Landmark Detection and Tracking.ipynb\"",
"[NbConvertApp] Converting notebook 1. Robot Moving and Sensing.ipynb to html\n[NbConvertApp] Writing 332608 bytes to 1. Robot Moving and Sensing.html\n[NbConvertApp] Converting notebook 3. Landmark Detection and Tracking.ipynb to html\n[NbConvertApp] Writing 419610 bytes to 3. Landmark Detection and Tracking.html\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Zip the project files\n\nNext, we'll zip these notebook files and your `robot_class.py` file into one compressed archive named `project3.zip`.\n\nAfter completing this step you should see this zip file appear in your home directory, where you can download it as seen in the image below, by selecting it from the list and clicking **Download**.\n\n<img src='images/download_ex.png' width=50% height=50%/>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!!apt-get -y update && apt-get install -y zip\n!zip project3.zip -r . [email protected]",
"updating: 3. Landmark Detection and Tracking.html (deflated 79%)\r\nupdating: robot_class.py (deflated 66%)\r\nupdating: 1. Robot Moving and Sensing.html (deflated 81%)\r\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Submit Your Project\n\nAfter creating and downloading your zip file, click on the `Submit` button and follow the instructions for submitting your `project3.zip` file. Congratulations on completing this project and I hope you enjoyed it!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a75238ad7fa9aa209f5743f63f15c0fcb09bc76
| 7,200 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Introduction to Python/Advanced Lists.ipynb
|
Xelepam/Python_Scripts
|
72779c5b1fa4188b7aaf8def39d5d1902002010b
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Introduction to Python/Advanced Lists.ipynb
|
Xelepam/Python_Scripts
|
72779c5b1fa4188b7aaf8def39d5d1902002010b
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Introduction to Python/Advanced Lists.ipynb
|
Xelepam/Python_Scripts
|
72779c5b1fa4188b7aaf8def39d5d1902002010b
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 16.363636 | 313 | 0.430694 |
[
[
[
"l = [1,2,3] ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"l.append(4)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"l",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"l.count(10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"l.count(1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x = [1,2,3]\nx.append([4,5])\nprint(x)",
"[1, 2, 3, [4, 5]]\n"
],
[
"x = [1,2,3]\nx.extend([4,5])\nprint(x)",
"[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]\n"
],
[
"l.index(2)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"l.index(10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"l.insert(2, 'inserted')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"l",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ele = l.pop()\nprint(ele)",
"4\n"
],
[
"l",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"l.pop(0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"l",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"l.remove('inserted')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"l",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"l = [1,2,3,4,3]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"l.remove(3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"l",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"l.reverse()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"l",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"l.sort()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"l",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a753041c9c481621395b95b2ebb338c91c8476f
| 23,902 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
ols_regression.ipynb
|
fieryWalrus1002/potato
|
ecad7ae2fb4d602cd79f402697dc95684cc8ead2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
ols_regression.ipynb
|
fieryWalrus1002/potato
|
ecad7ae2fb4d602cd79f402697dc95684cc8ead2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
ols_regression.ipynb
|
fieryWalrus1002/potato
|
ecad7ae2fb4d602cd79f402697dc95684cc8ead2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 103.471861 | 17,486 | 0.839679 |
[
[
[
"%load_ext blackcellmagic\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom sklearn import linear_model\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nfrom mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D\nfrom pathlib import Path\nfrom sklearn import preprocessing\n\n\n# code from 'aegis4048.github.io', modified for VI and yield\n\n######################################## Data preparation #########################################\n\n# data path\ndf_path = (\n Path.cwd()\n / \"data\"\n / \"processed\"\n / \"Jun22_2020\"\n / \"Jun22_2020_df.csv\"\n)\n\ndf = pd.read_csv(df_path).iloc[:, 2:]\nprint(df.head().iloc[:,0:4])",
"The blackcellmagic extension is already loaded. To reload it, use:\n %reload_ext blackcellmagic\n yield blue-blue-444 blue-green blue-green-531\n0 641.218827 0.013329 -0.419273 -0.445662\n1 697.979880 -0.001042 -0.459447 -0.476955\n2 709.891479 0.008540 -0.433216 -0.455423\n3 674.191672 0.013697 -0.402593 -0.427173\n4 680.430664 0.003195 -0.457388 -0.475037\n"
],
[
"# Train Test Split\ntrain, test = train_test_split(df, test_size=0.2, shuffle=True)\n\nX_train = train.iloc[:, 1:4].values\ny_train = train['yield'].values\n\nX_test = test.iloc[:, 1:4].values\ny_test = test['yield'].values\n\n# scale features\nscaler = preprocessing.StandardScaler()\n\nX_test_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(X_test)\nX_train_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(X_train)",
"824.1496306416666 844.6471607804349\n[ 1.94289029e-16 -9.62193288e-16 -1.07321559e-15] [-2.09976963e-16 3.89302117e-15 -5.23011586e-15]\n"
],
[
"################################################ Train #############################################\n\nols = linear_model.LinearRegression()\nmodel = ols.fit(X_train_scaled, y_train)\nmodel.score(X_train_scaled, y_train)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"############################################## Evaluate ############################################\ny_pred = model.predict(X_test_scaled)\nmodel.score(X_test_scaled, y_test)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"############################################## Plot ################################################\nplt.scatter(y_test, y_pred)\nplt.show()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\nx = X_test_scaled[:,0]\ny = X_test_scaled[:,1]\nz = predicted\n\nplt.style.use('default')\n\nfig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))\n\nax1 = fig.add_subplot(131, projection='3d')\nax2 = fig.add_subplot(132, projection='3d')\nax3 = fig.add_subplot(133, projection='3d')\n\naxes = [ax1, ax2, ax3]\n\nfor ax in axes:\n ax.plot(x, y, z, color='k', zorder=15, linestyle='none', marker='o', alpha=0.5)\n ax.scatter(x, y, predicted, facecolor=(0,0,0,0), s=20, edgecolor='#70b3f0')\n ax.set_xlabel('NDVI', fontsize=12)\n ax.set_ylabel('SAVI', fontsize=12)\n ax.set_zlabel('yield (CWT/A)', fontsize=12)\n ax.locator_params(nbins=4, axis='x')\n ax.locator_params(nbins=5, axis='x')\n\n# ax1.text2D(0.2, 0.32, 'aegis4048.github.io', fontsize=13, ha='center', va='center',\n# transform=ax1.transAxes, color='grey', alpha=0.5)\n# ax2.text2D(0.3, 0.42, 'aegis4048.github.io', fontsize=13, ha='center', va='center',\n# transform=ax2.transAxes, color='grey', alpha=0.5)\n# ax3.text2D(0.85, 0.85, 'aegis4048.github.io', fontsize=13, ha='center', va='center',\n# transform=ax3.transAxes, color='grey', alpha=0.5)\n\nax1.view_init(elev=28, azim=120)\nax2.view_init(elev=4, azim=114)\nax3.view_init(elev=60, azim=165)\n\nfig.suptitle('$R^2 = %.2f$' % r2, fontsize=20)\n\nfig.tight_layout()\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a7538ee998a4e41c8c91cf1209e0c68ce7c7960
| 408,620 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
src/notebooks/1_gensim_lda.ipynb
|
prrao87/topic-modelling
|
b7bceef8711edb097c3afec95c30474ae0789e1f
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2020-11-22T14:55:58.000Z
|
2021-03-13T17:59:26.000Z
|
src/notebooks/1_gensim_lda.ipynb
|
prrao87/topic-modelling
|
b7bceef8711edb097c3afec95c30474ae0789e1f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
src/notebooks/1_gensim_lda.ipynb
|
prrao87/topic-modelling
|
b7bceef8711edb097c3afec95c30474ae0789e1f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 723.221239 | 392,252 | 0.945815 |
[
[
[
"import re\nimport pandas as pd\nimport spacy\nfrom typing import List\nfrom math import sqrt, ceil\n# gensim\nfrom gensim import corpora\nfrom gensim.models.ldamulticore import LdaMulticore\n# plotting\nfrom matplotlib import pyplot as plt\nfrom wordcloud import WordCloud\nimport matplotlib.colors as mcolors\n# progress bars\nfrom tqdm.notebook import tqdm\ntqdm.pandas()",
"unable to import 'smart_open.gcs', disabling that module\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Params",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"params = dict(\n num_topics = 15,\n iterations = 200,\n epochs = 20,\n minDF = 0.02,\n maxDF = 0.8,\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Files\nInput CSV file and stopword files.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"inputfile = \"../../data/nytimes.tsv\"\nstopwordfile = \"../stopwords/custom_stopwords.txt\"\n\ndef get_stopwords():\n # Read in stopwords\n with open(stopwordfile) as f:\n stopwords = []\n for line in f:\n stopwords.append(line.strip(\"\\n\"))\n return stopwords\n\nstopwords = get_stopwords()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Read in New York Times Dataset\nA pre-processed version of the NYT news dataset is read in as a DataFrame.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def read_data(inputfile):\n \"Read in a tab-separated file with date, headline and news content\"\n df = pd.read_csv(inputfile, sep='\\t', header=None,\n names=['date', 'headline', 'content'])\n df['date'] = pd.to_datetime(df['date'], format=\"%Y-%m-%d\")\n return df",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = read_data(inputfile)\ndf.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Clean the input text\nWe clean the text from each article's content to only contain relevant alphanumeric strings (symbols do not add any value to topic modelling).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def clean_data(df):\n \"Extract relevant text from DataFrame using a regex\"\n # Regex pattern for only alphanumeric, hyphenated text with 3 or more chars\n pattern = re.compile(r\"[A-Za-z0-9\\-]{3,50}\")\n df['clean'] = df['content'].str.findall(pattern).str.join(' ')\n return df",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_clean = clean_data(df)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### (Optional) Subset the dataframe for testing\nTest on a subset of the full data for quicker results.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df1 = df_clean.iloc[:2000, :].copy()\n# df1 = df_clean.copy()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Preprocess text for topic modelling",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def lemmatize(text, nlp):\n \"Perform lemmatization and stopword removal in the clean text\"\n doc = nlp(text)\n lemma_list = [str(tok.lemma_).lower() for tok in doc\n if tok.is_alpha and tok.text.lower() not in stopwords]\n return lemma_list\n\ndef preprocess(df):\n \"Preprocess text in each row of the DataFrame\"\n nlp = spacy.load('en_core_web_sm', disable=['parser', 'ner'])\n nlp.add_pipe(nlp.create_pipe('sentencizer'))\n df['lemmas'] = df['clean'].progress_apply(lambda row: lemmatize(row, nlp))\n return df.drop('clean', axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_preproc = preprocess(df1)\ndf_preproc.head(3)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Build LDA Topic Model",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Multicore LDA algorithm",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Choose number of workers for multicore LDA as (num_physical_cores - 1)\ndef run_lda_multicore(text_df, params, workers=7):\n id2word = corpora.Dictionary(text_df['lemmas'])\n # Filter out words that occur in less than 2% documents or more than 50% of the documents.\n id2word.filter_extremes(no_below=params['minDF'], no_above=params['maxDF'])\n corpus = [id2word.doc2bow(text) for text in text_df['lemmas']]\n # LDA Model\n lda_model = LdaMulticore(\n corpus=corpus,\n id2word=id2word,\n workers=workers,\n num_topics=params['num_topics'],\n random_state=1,\n chunksize=2048,\n passes=params['epochs'],\n iterations=params['iterations'],\n )\n return lda_model, corpus",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Wordclouds of most likely words in each topic",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def plot_wordclouds(topics, colormap=\"cividis\"):\n cloud = WordCloud(\n background_color='white',\n width=600,\n height=400,\n colormap=colormap,\n prefer_horizontal=1.0,\n )\n\n num_topics = len(topics)\n fig_width = min(ceil(0.6 * num_topics + 6), 20)\n fig_height = min(ceil(0.65 * num_topics), 20)\n fig = plt.figure(figsize=(fig_width, fig_height))\n\n for idx, word_weights in tqdm(enumerate(topics), total=num_topics):\n ax = fig.add_subplot((num_topics / 5) + 1, 5, idx + 1)\n wordcloud = cloud.generate_from_frequencies(word_weights)\n ax.imshow(wordcloud, interpolation=\"bilinear\")\n ax.set_title('Topic {}'.format(idx + 1))\n ax.set_xticklabels([])\n ax.set_yticklabels([])\n ax.tick_params(length=0)\n\n plt.tick_params(labelsize=14)\n plt.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.1, hspace=0.1)\n plt.margins(x=0.1, y=0.1)\n st = fig.suptitle(\"LDA Topics\", y=0.92)\n fig.savefig(\"pyspark-topics.png\", bbox_extra_artists=[st], bbox_inches='tight')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Run topic model and plot wordclouds",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model, corpus = run_lda_multicore(df_preproc, params)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Convert topic words to a list of dicts",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"topic_list = model.show_topics(formatted=False,\n num_topics=params['num_topics'],\n num_words=15)\ntopics = [dict(item[1]) for item in topic_list]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plot_wordclouds(topics)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a753dabfb883b7f64b7a0ac1deabf8b06ba3b2f
| 14,004 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
how-to-use-azureml/training-with-deep-learning/distributed-cntk-with-custom-docker/distributed-cntk-with-custom-docker.ipynb
|
kenakamu/MachineLearningNotebooks
|
0514eee64b296328d0c98b9a45b74c17b09b7bec
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-01-18T16:19:04.000Z
|
2021-01-18T16:19:04.000Z
|
how-to-use-azureml/training-with-deep-learning/distributed-cntk-with-custom-docker/distributed-cntk-with-custom-docker.ipynb
|
AprilXiaoyanLiu/MachineLearningNotebooks
|
0514eee64b296328d0c98b9a45b74c17b09b7bec
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
how-to-use-azureml/training-with-deep-learning/distributed-cntk-with-custom-docker/distributed-cntk-with-custom-docker.ipynb
|
AprilXiaoyanLiu/MachineLearningNotebooks
|
0514eee64b296328d0c98b9a45b74c17b09b7bec
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2019-08-21T04:24:19.000Z
|
2019-08-21T04:24:19.000Z
| 35.543147 | 542 | 0.563268 |
[
[
[
"Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.\n\nLicensed under the MIT License.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Distributed CNTK using custom docker images\nIn this tutorial, you will train a CNTK model on the [MNIST](http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/) dataset using a custom docker image and distributed training.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Prerequisites\n* Understand the [architecture and terms](https://docs.microsoft.com/azure/machine-learning/service/concept-azure-machine-learning-architecture) introduced by Azure Machine Learning\n* Go through the [configuration notebook](../../../configuration.ipynb) to:\n * install the AML SDK\n * create a workspace and its configuration file (`config.json`)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Check core SDK version number\nimport azureml.core\n\nprint(\"SDK version:\", azureml.core.VERSION)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Diagnostics\nOpt-in diagnostics for better experience, quality, and security of future releases.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from azureml.telemetry import set_diagnostics_collection\n\nset_diagnostics_collection(send_diagnostics=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Initialize workspace\n\nInitialize a [Workspace](https://docs.microsoft.com/azure/machine-learning/service/concept-azure-machine-learning-architecture#workspace) object from the existing workspace you created in the Prerequisites step. `Workspace.from_config()` creates a workspace object from the details stored in `config.json`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from azureml.core.workspace import Workspace\n\nws = Workspace.from_config()\nprint('Workspace name: ' + ws.name,\n 'Azure region: ' + ws.location, \n 'Subscription id: ' + ws.subscription_id, \n 'Resource group: ' + ws.resource_group, sep='\\n')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Create or Attach existing AmlCompute\nYou will need to create a [compute target](https://docs.microsoft.com/azure/machine-learning/service/concept-azure-machine-learning-architecture#compute-target) for training your model. In this tutorial, you create `AmlCompute` as your training compute resource.\n\n**Creation of AmlCompute takes approximately 5 minutes.** If the AmlCompute with that name is already in your workspace this code will skip the creation process.\n\nAs with other Azure services, there are limits on certain resources (e.g. AmlCompute) associated with the Azure Machine Learning service. Please read [this article](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/machine-learning/service/how-to-manage-quotas) on the default limits and how to request more quota.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from azureml.core.compute import ComputeTarget, AmlCompute\nfrom azureml.core.compute_target import ComputeTargetException\n\n# choose a name for your cluster\ncluster_name = \"gpucluster\"\n\ntry:\n compute_target = ComputeTarget(workspace=ws, name=cluster_name)\n print('Found existing compute target.')\nexcept ComputeTargetException:\n print('Creating a new compute target...')\n compute_config = AmlCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size='STANDARD_NC6',\n max_nodes=4)\n\n # create the cluster\n compute_target = ComputeTarget.create(ws, cluster_name, compute_config)\n\n compute_target.wait_for_completion(show_output=True)\n\n# use get_status() to get a detailed status for the current AmlCompute\nprint(compute_target.get_status().serialize())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Upload training data\nFor this tutorial, we will be using the MNIST dataset.\n\nFirst, let's download the dataset. We've included the `install_mnist.py` script to download the data and convert it to a CNTK-supported format. Our data files will get written to a directory named `'mnist'`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import install_mnist\n\ninstall_mnist.main('mnist')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"To make the data accessible for remote training, you will need to upload the data from your local machine to the cloud. AML provides a convenient way to do so via a [Datastore](https://docs.microsoft.com/azure/machine-learning/service/how-to-access-data). The datastore provides a mechanism for you to upload/download data, and interact with it from your remote compute targets. \n\nEach workspace is associated with a default datastore. In this tutorial, we will upload the training data to this default datastore, which we will then mount on the remote compute for training in the next section.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"ds = ws.get_default_datastore()\nprint(ds.datastore_type, ds.account_name, ds.container_name)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The following code will upload the training data to the path `./mnist` on the default datastore.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"ds.upload(src_dir='./mnist', target_path='./mnist')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now let's get a reference to the path on the datastore with the training data. We can do so using the `path` method. In the next section, we can then pass this reference to our training script's `--data_dir` argument. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"path_on_datastore = 'mnist'\nds_data = ds.path(path_on_datastore)\nprint(ds_data)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Train model on the remote compute\nNow that we have the cluster ready to go, let's run our distributed training job.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Create a project directory\nCreate a directory that will contain all the necessary code from your local machine that you will need access to on the remote resource. This includes the training script, and any additional files your training script depends on.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import os\n\nproject_folder = './cntk-distr'\nos.makedirs(project_folder, exist_ok=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Copy the training script `cntk_distr_mnist.py` into this project directory.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import shutil\n\nshutil.copy('cntk_distr_mnist.py', project_folder)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Create an experiment\nCreate an [experiment](https://docs.microsoft.com/azure/machine-learning/service/concept-azure-machine-learning-architecture#experiment) to track all the runs in your workspace for this distributed CNTK tutorial. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from azureml.core import Experiment\n\nexperiment_name = 'cntk-distr'\nexperiment = Experiment(ws, name=experiment_name)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Create an Estimator\nThe AML SDK's base Estimator enables you to easily submit custom scripts for both single-node and distributed runs. You should this generic estimator for training code using frameworks such as sklearn or CNTK that don't have corresponding custom estimators. For more information on using the generic estimator, refer [here](https://docs.microsoft.com/azure/machine-learning/service/how-to-train-ml-models).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from azureml.train.estimator import Estimator\n\nscript_params = {\n '--num_epochs': 20,\n '--data_dir': ds_data.as_mount(),\n '--output_dir': './outputs'\n}\n\nestimator = Estimator(source_directory=project_folder,\n compute_target=compute_target,\n entry_script='cntk_distr_mnist.py',\n script_params=script_params,\n node_count=2,\n process_count_per_node=1,\n distributed_backend='mpi',\n pip_packages=['cntk-gpu==2.6'],\n custom_docker_base_image='microsoft/mmlspark:gpu-0.12',\n use_gpu=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We would like to train our model using a [pre-built Docker container](https://hub.docker.com/r/microsoft/mmlspark/). To do so, specify the name of the docker image to the argument `custom_docker_base_image`. You can only provide images available in public docker repositories such as Docker Hub using this argument. To use an image from a private docker repository, use the constructor's `environment_definition` parameter instead. Finally, we provide the `cntk` package to `pip_packages` to install CNTK 2.6 on our custom image.\n\nThe above code specifies that we will run our training script on `2` nodes, with one worker per node. In order to run distributed CNTK, which uses MPI, you must provide the argument `distributed_backend='mpi'`.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Submit job\nRun your experiment by submitting your estimator object. Note that this call is asynchronous.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"run = experiment.submit(estimator)\nprint(run)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Monitor your run\nYou can monitor the progress of the run with a Jupyter widget. Like the run submission, the widget is asynchronous and provides live updates every 10-15 seconds until the job completes.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from azureml.widgets import RunDetails\n\nRunDetails(run).show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Alternatively, you can block until the script has completed training before running more code.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"run.wait_for_completion(show_output=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a7552d3d470c13b10469b59cda58dcb71ff0902
| 19,084 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
docs/circuits.ipynb
|
JiMu-Bao/Cirq
|
b88069f7b01457e592ad69d6b413642ef11a56b8
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
docs/circuits.ipynb
|
JiMu-Bao/Cirq
|
b88069f7b01457e592ad69d6b413642ef11a56b8
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
docs/circuits.ipynb
|
JiMu-Bao/Cirq
|
b88069f7b01457e592ad69d6b413642ef11a56b8
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 31.285246 | 469 | 0.604119 |
[
[
[
"#@title Copyright 2020 The Cirq Developers\n# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the \"License\");\n# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.\n# You may obtain a copy of the License at\n#\n# https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0\n#\n# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software\n# distributed under the License is distributed on an \"AS IS\" BASIS,\n# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.\n# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and\n# limitations under the License.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Circuits",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<table class=\"tfo-notebook-buttons\" align=\"left\">\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://quantumai.google/cirq/circuits\"><img src=\"https://quantumai.google/site-assets/images/buttons/quantumai_logo_1x.png\" />View on QuantumAI</a>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/quantumlib/Cirq/blob/master/docs/circuits.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://quantumai.google/site-assets/images/buttons/colab_logo_1x.png\" />Run in Google Colab</a>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://github.com/quantumlib/Cirq/blob/master/docs/circuits.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://quantumai.google/site-assets/images/buttons/github_logo_1x.png\" />View source on GitHub</a>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a href=\"https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow_docs/Cirq/docs/circuits.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://quantumai.google/site-assets/images/buttons/download_icon_1x.png\" />Download notebook</a>\n </td>\n</table>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"try:\n import cirq\nexcept ImportError:\n print(\"installing cirq...\")\n !pip install --quiet cirq\n import cirq\n print(\"installed cirq.\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Conceptual overview\n\nThe primary representation of quantum programs in Cirq is the `Circuit` class. A `Circuit` is a collection of `Moments`. A `Moment` is a collection of `Operations` that all act during the same abstract time slice. An `Operation` is a some effect that operates on a specific subset of Qubits, the most common type of `Operation` is a `GateOperation`.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Let's unpack this.\n\nAt the base of this construction is the notion of a qubit. In Cirq, qubits and other quantum objects are identified by instances of subclasses of the `cirq.Qid` base class. Different subclasses of Qid can be used for different purposes. For example, the qubits that Google’s devices use are often arranged on the vertices of a square grid. For this, the class `cirq.GridQubit` subclasses `cirq.Qid`. For example, we can create a 3 by 3 grid of qubits using",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"qubits = [cirq.GridQubit(x, y) for x in range(3) for y in range(3)]\n\nprint(qubits[0])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The next level up is the notion of `cirq.Gate`. A `cirq.Gate` represents a physical process that occurs on a qubit. The important property of a gate is that it can be applied to one or more qubits. This can be done via the `gate.on(*qubits)` method itself or via `gate(*qubits)`, and doing this turns a `cirq.Gate` into a `cirq.Operation`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# This is an Pauli X gate. It is an object instance.\nx_gate = cirq.X\n# Applying it to the qubit at location (0, 0) (defined above)\n# turns it into an operation.\nx_op = x_gate(qubits[0])\n\nprint(x_op)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"A `cirq.Moment` is simply a collection of operations, each of which operates on a different set of qubits, and which conceptually represents these operations as occurring during this abstract time slice. The `Moment` structure itself is not required to be related to the actual scheduling of the operations on a quantum computer, or via a simulator, though it can be. For example, here is a `Moment` in which **Pauli** `X` and a `CZ` gate operate on three qubits:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cz = cirq.CZ(qubits[0], qubits[1])\nx = cirq.X(qubits[2])\nmoment = cirq.Moment(x, cz)\n\nprint(moment)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The above is not the only way one can construct moments, nor even the typical method, but illustrates that a `Moment` is just a collection of operations on disjoint sets of qubits.\n\nFinally, at the top level a `cirq.Circuit` is an ordered series of `cirq.Moment` objects. The first `Moment` in this series contains the first `Operations` that will be applied. Here, for example, is a simple circuit made up of two moments:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cz01 = cirq.CZ(qubits[0], qubits[1])\nx2 = cirq.X(qubits[2])\ncz12 = cirq.CZ(qubits[1], qubits[2])\nmoment0 = cirq.Moment([cz01, x2])\nmoment1 = cirq.Moment([cz12])\ncircuit = cirq.Circuit((moment0, moment1))\n\nprint(circuit)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Note that the above is one of the many ways to construct a `Circuit`, which illustrates the concept that a `Circuit` is an iterable of `Moment` objects.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Constructing circuits\n\nConstructing Circuits as a series of `Moment` objects, with each `Moment` being hand-crafted, is tedious. Instead, we provide a variety of different ways to create a `Circuit`.\n\nOne of the most useful ways to construct a `Circuit` is by appending onto the `Circuit` with the `Circuit.append` method.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from cirq.ops import CZ, H\nq0, q1, q2 = [cirq.GridQubit(i, 0) for i in range(3)]\ncircuit = cirq.Circuit()\ncircuit.append([CZ(q0, q1), H(q2)])\n\nprint(circuit)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This appended a new moment to the qubit, which we can continue to do:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"circuit.append([H(q0), CZ(q1, q2)])\n\nprint(circuit)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"In these two examples, we appended full moments, what happens when we append all of these at once?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"circuit = cirq.Circuit()\ncircuit.append([CZ(q0, q1), H(q2), H(q0), CZ(q1, q2)])\n\nprint(circuit)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We see that here we have again created two `Moment` objects. How did `Circuit` know how to do this? `Circuit`'s `Circuit.append` method (and its cousin, `Circuit.insert`) both take an argument called `strategy` of type `cirq.InsertStrategy`. By default, `InsertStrategy` is `InsertStrategy.NEW_THEN_INLINE`.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### InsertStrategies\n\n`cirq.InsertStrategy` defines how `Operations` are placed in a `Circuit` when requested to be inserted at a given location. Here, a location is identified by the index of the `Moment` (in the `Circuit`) where the insertion is requested to be placed at (in the case of `Circuit.append`, this means inserting at the `Moment`, at an index one greater than the maximum moment index in the `Circuit`). \n\nThere are four such strategies: `InsertStrategy.EARLIEST`, `InsertStrategy.NEW`, `InsertStrategy.INLINE` and `InsertStrategy.NEW_THEN_INLINE`.\n\n`InsertStrategy.EARLIEST`, which is the default, is defined as:\n\n*Scans backward from the insert location until a moment with operations touching qubits affected by the operation to insert is found. The operation is added to the moment just after that location.*\n\nFor example, if we first create an `Operation` in a single moment, and then use `InsertStrategy.EARLIEST`, `Operation` can slide back to this first ` Moment` if there is space:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from cirq.circuits import InsertStrategy\n\ncircuit = cirq.Circuit()\ncircuit.append([CZ(q0, q1)])\ncircuit.append([H(q0), H(q2)], strategy=InsertStrategy.EARLIEST)\n\nprint(circuit)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"After creating the first moment with a `CZ` gate, the second append uses the `InsertStrategy.EARLIEST` strategy. The `H` on `q0` cannot slide back, while the `H` on `q2` can and so ends up in the first `Moment`.\n\nContrast this with `InsertStrategy.NEW` that is defined as:\n\n*Every operation that is inserted is created in a new moment.*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"circuit = cirq.Circuit()\ncircuit.append([H(q0), H(q1), H(q2)], strategy=InsertStrategy.NEW)\n\nprint(circuit)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Here every operator processed by the append ends up in a new moment. `InsertStrategy.NEW` is most useful when you are inserting a single operation and do not want it to interfere with other `Moments`.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Another strategy is `InsertStrategy.INLINE`:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"*Attempts to add the operation to insert into the moment just before the desired insert location. But, if there’s already an existing operation affecting any of the qubits touched by the operation to insert, a new moment is created instead.*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"circuit = cirq.Circuit()\ncircuit.append([CZ(q1, q2)])\ncircuit.append([CZ(q1, q2)])\ncircuit.append([H(q0), H(q1), H(q2)], strategy=InsertStrategy.INLINE)\n\nprint(circuit)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"After two initial `CZ` between the second and third qubit, we try to insert three `H` operations. We see that the `H` on the first qubit is inserted into the previous `Moment`, but the `H` on the second and third qubits cannot be inserted into the previous `Moment`, so a new `Moment` is created.\n\nFinally, we turn to a useful strategy to start a new moment and then start\ninserting from that point, `InsertStrategy.NEW_THEN_INLINE`",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"*Creates a new moment at the desired insert location for the first operation, but then switches to inserting operations according to `InsertStrategy.INLINE`.*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"circuit = cirq.Circuit()\ncircuit.append([H(q0)])\ncircuit.append([CZ(q1,q2), H(q0)], strategy=InsertStrategy.NEW_THEN_INLINE)\n\nprint(circuit)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The first append creates a single moment with an `H` on the first qubit. Then, the append with the `InsertStrategy.NEW_THEN_INLINE` strategy begins by inserting the `CZ` in a new `Moment` (the `InsertStrategy.NEW` in `InsertStrategy.NEW_THEN_INLINE`). Subsequent appending is done `InsertStrategy.INLINE`, so the next `H` on the first qubit is appending in the just created `Moment`.\n\nHere is a picture showing simple examples of appending 1 and then 2 using the different strategies",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Patterns for arguments to append and insert\n\nIn the above examples, we used a series of `Circuit.append `calls with a list of different `Operations` added to the circuit. However, the argument where we have supplied a list can also take more than just list values. For instance:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def my_layer():\n yield CZ(q0, q1)\n yield [H(q) for q in (q0, q1, q2)]\n yield [CZ(q1, q2)]\n yield [H(q0), [CZ(q1, q2)]]\n\ncircuit = cirq.Circuit()\ncircuit.append(my_layer())\n\nfor x in my_layer():\n print(x)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(circuit)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Recall that Python functions with a `yield` are generators. Generators are functions that act as iterators. In the above example, we see that we can iterate `over my_layer()`. In this case, each of the `yield` returns produces what was yielded, and here these are:\n\n* `Operations`, \n* lists of `Operations`,\n* or lists of `Operations` mixed with lists of `Operations`. \n\n\nWhen we pass an iterator to the `append` method, `Circuit` is able to flatten all of these and pass them as one giant list to `Circuit.append` (this also works for `Circuit.insert`).\n\nThe above idea uses the concept of `cirq.OP_TREE`. An `OP_TREE` is not a class, but a *contract*. The basic idea is that, if the input can be iteratively flattened into a list of operations, then the input is an `OP_TREE`.\n\nA very nice pattern emerges from this structure: define generators for sub-circuits, which can vary by size or `Operation` parameters.\n\nAnother useful method to construct a `Circuit` fully formed from an `OP_TREE` is to pass the `OP_TREE` into `Circuit` when initializing it:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"circuit = cirq.Circuit(H(q0), H(q1))\nprint(circuit)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Slicing and iterating over circuits\n\nCircuits can be iterated over and sliced. When they are iterated, each item in the iteration is a moment:\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"circuit = cirq.Circuit(H(q0), CZ(q0, q1))\nfor moment in circuit:\n print(moment)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Slicing a `Circuit`, on the other hand, produces a new `Circuit` with only the moments corresponding to the slice:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"circuit = cirq.Circuit(H(q0), CZ(q0, q1), H(q1), CZ(q0, q1))\nprint(circuit[1:3])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Especially useful is dropping the last moment (which are often just measurements): `circuit[:-1]`, or reversing a circuit: `circuit[::-1]`.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Related\n\n\n- [Transform circuits](transform.ipynb) - features related to circuit optimization and compilation\n- [Import/export circuits](interop.ipynb) - features to serialize/deserialize circuits into/from different formats",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4a755518252c0317d780c63df32ec09efc233b51
| 18,021 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
type_inferencing/example_executions/all4_2x125.ipynb
|
rparundekar/understanding-things-with-semantic-graph-classification
|
63c3f973b18ab33e14129a1f4ea5fcd9ff6dfbac
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
type_inferencing/example_executions/all4_2x125.ipynb
|
rparundekar/understanding-things-with-semantic-graph-classification
|
63c3f973b18ab33e14129a1f4ea5fcd9ff6dfbac
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
type_inferencing/example_executions/all4_2x125.ipynb
|
rparundekar/understanding-things-with-semantic-graph-classification
|
63c3f973b18ab33e14129a1f4ea5fcd9ff6dfbac
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 35.266145 | 203 | 0.549304 |
[
[
[
"from keras.models import Sequential\nfrom keras.layers import Dropout\nfrom keras.layers import Input, Dense, Activation,Dropout\nfrom keras import regularizers\nfrom keras.layers.advanced_activations import LeakyReLU\nfrom keras.layers.normalization import BatchNormalization\n\nimport numpy as np\n# fix random seed for reproducibility\nnp.random.seed(42)\n\nimport pandas as pd",
"Using TensorFlow backend.\n"
],
[
"#Folder for the dataset\ndatasetFolder = '/home/carnd/dbpedia2016/all4_2x125/dataset/'\n\n#Number of files\nnumberOfFiles = 638\n\n#Test split\ntestSplit=0.1\nvalidationSplit=0.2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def load_data(datasetFolder, datasetXFile, datasetYFile, wrap=True, printIt=False):\n #print('Loading X')\n # load file\n with open(datasetFolder + datasetXFile, \"r\") as f:\n head = f.readline()\n cols = head.split(',')\n numberOfCols = len(cols)\n #print(numberOfCols)\n numberOfRows=0\n for line in f:\n numberOfRows+=1\n f.close()\n if(printIt):\n print('Input Features: {} x {}'.format(numberOfRows,numberOfCols))\n if(wrap==True):\n maxY = 8384\n else:\n maxY = numberOfCols-1\n half=(numberOfCols//maxY)*0.5\n dataX = np.zeros([numberOfRows,maxY],np.int8)\n with open(datasetFolder + datasetXFile, \"r\") as f:\n head = f.readline()\n rowCounter=0\n for line in f:\n row=line.split(',')\n for i in range(1, len(row)):\n if(int(row[i])<=0):\n continue;\n val = 1 + ((int(row[i])-1)//maxY);\n if(val>half):\n val = 0 - (val - half)\n dataX[rowCounter][(int(row[i])-1)%maxY]= val\n #if((1 + ((int(row[i])-1)//maxY))>1):\n # print(\"{} data[{}][{}] = {}\".format(int(row[i])-1, rowCounter,(int(row[i])-1)%maxY,1 + ((int(row[i])-1)//maxY)))\n rowCounter+=1\n f.close()\n \n #print('Loading Y')\n # load file\n with open(datasetFolder + datasetYFile, \"r\") as f:\n head = f.readline()\n cols = head.split(',')\n numberOfCols = len(cols)\n #print(numberOfCols)\n numberOfRows=0\n for line in f:\n numberOfRows+=1\n f.close()\n\n if(printIt):\n print('Output Features: {} x {}'.format(numberOfRows,numberOfCols))\n dataY = np.zeros([numberOfRows,(numberOfCols-1)],np.float16)\n with open(datasetFolder + datasetYFile, \"r\") as f:\n head = f.readline()\n rowCounter=0\n for line in f:\n row=line.split(',')\n for i in range(1, len(row)):\n if(int(row[i])<=0):\n continue;\n dataY[rowCounter][(int(row[i])-1)]=1\n rowCounter+=1\n f.close()\n \n\n return dataX, dataY",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dataX, dataY = load_data(datasetFolder,'datasetX_1.csv', 'datasetY_1.csv', printIt=True)",
"Input Features: 4995 x 702242\nOutput Features: 4995 x 526\n"
],
[
"dataX, dataY = load_data(datasetFolder,'datasetX_1.csv', 'datasetY_1.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(dataX.shape)\nprint(dataX[0:5])",
"(4995, 8384)\n[[1 1 1 ..., 0 0 0]\n [0 0 0 ..., 0 0 0]\n [0 0 1 ..., 0 0 0]\n [0 0 1 ..., 0 0 0]\n [1 1 1 ..., 0 0 0]]\n"
],
[
"print(dataY.shape)\nprint(dataY[0:5])",
"(4995, 525)\n[[ 0. 0. 0. ..., 0. 0. 0.]\n [ 0. 1. 1. ..., 0. 0. 0.]\n [ 0. 0. 0. ..., 0. 0. 0.]\n [ 0. 0. 0. ..., 0. 0. 0.]\n [ 0. 0. 0. ..., 0. 0. 0.]]\n"
],
[
"print(\"Input Features for classification: {}\".format(dataX.shape[1]))\nprint(\"Output Classes for classification: {}\".format(dataY.shape[1]))",
"Input Features for classification: 8384\nOutput Classes for classification: 525\n"
],
[
"deepModel = Sequential(name='Deep Model (5 Dense Layers)')\ndeepModel.add(Dense(2048, input_dim=dataX.shape[1], init='glorot_normal'))\ndeepModel.add(BatchNormalization())\ndeepModel.add(Activation('relu'))\ndeepModel.add(Dropout(0.2))\ndeepModel.add(Dense(1024, init='glorot_normal'))\ndeepModel.add(BatchNormalization())\ndeepModel.add(Activation('relu'))\ndeepModel.add(Dropout(0.2))\ndeepModel.add(Dense(768, init='glorot_normal'))\ndeepModel.add(BatchNormalization())\ndeepModel.add(Activation('relu'))\ndeepModel.add(Dropout(0.2))\ndeepModel.add(Dense(512, init='glorot_normal'))\ndeepModel.add(BatchNormalization())\ndeepModel.add(Activation('relu'))\ndeepModel.add(Dropout(0.2))\ndeepModel.add(Dense(256, init='glorot_normal'))\ndeepModel.add(BatchNormalization())\ndeepModel.add(Activation('relu'))\ndeepModel.add(Dropout(0.2))\ndeepModel.add(Dense(dataY.shape[1], activation='sigmoid', init='glorot_normal'))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Compile model\nimport keras.backend as K\n\ndef count_predictions(y_true, y_pred):\n true_positives = K.sum(K.round(K.clip(y_true * y_pred, 0, 1)))\n predicted_positives = K.sum(K.round(K.clip(y_pred, 0, 1)))\n possible_positives = K.sum(K.round(K.clip(y_true, 0, 1)))\n return true_positives, predicted_positives, possible_positives\n\ndef f1score(y_true, y_pred):\n true_positives, predicted_positives, possible_positives = count_predictions(y_true, y_pred)\n precision = true_positives / (predicted_positives + K.epsilon())\n recall = true_positives / (possible_positives + K.epsilon())\n f1score = 2.0 * precision * recall / (precision+recall+ K.epsilon())\n return f1score\n\ndef fBetaScore(y_true, y_pred, beta):\n true_positives, predicted_positives, possible_positives = count_predictions(y_true, y_pred)\n precision = true_positives / (predicted_positives + K.epsilon())\n recall = true_positives / (possible_positives + K.epsilon())\n f1score = (1+(beta*beta)) * precision * recall / ((beta*beta*precision)+recall+ K.epsilon())\n return f1score\n\n\ndeepModel.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='nadam', metrics=[f1score])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def fit_data(model, dataX, dataY):\n # Fit the model\n #model.fit(dataX, dataY, nb_epoch=5, verbose=2, batch_size=256)\n return model.train_on_batch(dataX, dataY)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def countPredictions(y_true, y_pred):\n true_positives = np.sum(np.round(y_pred*y_true))\n predicted_positives = np.sum(np.round(y_pred))\n possible_positives = np.sum(y_true)\n return true_positives, predicted_positives, possible_positives",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Randomize the list of numbers so we can split train and test dataset\nlistOfFiles=list(range(1,numberOfFiles+1))\nimport random\nrandom.shuffle(listOfFiles)\nsplitIndex=int((1-(testSplit+validationSplit))*numberOfFiles)\ntestSplitIndex=int((1-(testSplit))*numberOfFiles)\n\n\nnumberOfEons = 8\n \nfor eon in range(0, numberOfEons):\n print('{}. Eon {}/{}'.format(eon+1,eon+1, numberOfEons))\n for trainIndex in range(0,splitIndex):\n dataX, dataY = load_data(datasetFolder,'datasetX_{}.csv'.format(listOfFiles[trainIndex]), 'datasetY_{}.csv'.format(listOfFiles[trainIndex]))\n #print('Model = {}'.format(model.name))\n deepModel.fit(dataX, dataY, nb_epoch=1, verbose=0, batch_size=256)\n print('Learning deep model for file {} / {} : datasetX/Y_{}'.format(trainIndex+1, splitIndex, listOfFiles[trainIndex]), end='\\r')\n #sc=deepModel.test_on_batch(dataX,dataY)\n #loss = sc[0]\n #f1score = sc[1]\n #loss, f1score=fit_data(deepModel,dataX, dataY)\n #print('Learning deep model for file {} / {} : datasetX/Y_{} loss={:.4f} f1score={:.4f}'.format(trainIndex+1, splitIndex, listOfFiles[trainIndex], loss, f1score), end='\\r')\n\n counts = {} \n counts[deepModel.name] = {'true_positives':0, 'predicted_positives':0, 'possible_positives':0}\n for testIndex in range(splitIndex, testSplitIndex):\n dataX, dataY = load_data(datasetFolder,'datasetX_{}.csv'.format(listOfFiles[testIndex]), 'datasetY_{}.csv'.format(listOfFiles[testIndex]))\n predY=deepModel.predict_on_batch(dataX)\n true_positives, predicted_positives, possible_positives = countPredictions(dataY, predY)\n counts[deepModel.name]['true_positives'] += true_positives\n counts[deepModel.name]['predicted_positives'] += predicted_positives\n counts[deepModel.name]['possible_positives'] += possible_positives\n print ('Validating deep model {} / {} : - true +ve:{} pred +ve:{} possible +ve:{}'.format(testIndex+1, testSplitIndex, true_positives,predicted_positives,possible_positives), end='\\r')\n\n count = counts[deepModel.name]\n precision = (count['true_positives'])/(count['predicted_positives']+0.0001)\n recall = (count['true_positives'])/(count['possible_positives']+0.0001)\n f1score = 2.0 * precision * recall / (precision+recall+0.0001)\n print(' - Model = {} \\t f1-score = {:.4f}\\t precision = {:.4f} \\t recall = {:.4f}'.format(deepModel.name, f1score, precision, recall))\n\ncounts = {} \ncounts[deepModel.name] = {'true_positives':0, 'predicted_positives':0, 'possible_positives':0}\nfor testIndex in range(testSplitIndex, numberOfFiles):\n dataX, dataY = load_data(datasetFolder,'datasetX_{}.csv'.format(listOfFiles[testIndex]), 'datasetY_{}.csv'.format(listOfFiles[testIndex]))\n predY=deepModel.predict_on_batch(dataX)\n true_positives, predicted_positives, possible_positives = countPredictions(dataY, predY)\n counts[deepModel.name]['true_positives'] += true_positives\n counts[deepModel.name]['predicted_positives'] += predicted_positives\n counts[deepModel.name]['possible_positives'] += possible_positives\n print ('Testing deep model {} / {} : - true +ve:{} pred +ve:{} possible +ve:{}'.format(testIndex+1, numberOfFiles, true_positives,predicted_positives,possible_positives), end='\\r')\n\ncount = counts[deepModel.name]\nprecision = (count['true_positives'])/(count['predicted_positives']+0.0001)\nrecall = (count['true_positives'])/(count['possible_positives']+0.0001)\nf1score = 2.0 * precision * recall / (precision+recall+0.0001)\nprint(' - Final Test Score for {} \\t f1-score = {:.4f}\\t precision = {:.4f} \\t recall = {:.4f}'.format(deepModel.name, f1score, precision, recall))\n\ndeepModel.save('deepModelDBpediaOntologyTypes.h5')",
"1. Eon 1/8\n - Model = Deep Model (5 Dense Layers) \t f1-score = 0.9112\t precision = 0.9350 \t recall = 0.8886\n2. Eon 2/8\n - Model = Deep Model (5 Dense Layers) \t f1-score = 0.9174\t precision = 0.9359 \t recall = 0.8997\n3. Eon 3/8\n - Model = Deep Model (5 Dense Layers) \t f1-score = 0.9195\t precision = 0.9365 \t recall = 0.9032\n4. Eon 4/8\n - Model = Deep Model (5 Dense Layers) \t f1-score = 0.9194\t precision = 0.9340 \t recall = 0.9054\n5. Eon 5/8\n - Model = Deep Model (5 Dense Layers) \t f1-score = 0.9205\t precision = 0.9368 \t recall = 0.9048\n6. Eon 6/8\n - Model = Deep Model (5 Dense Layers) \t f1-score = 0.9202\t precision = 0.9359 \t recall = 0.9051\n7. Eon 7/8\n - Model = Deep Model (5 Dense Layers) \t f1-score = 0.9203\t precision = 0.9351 \t recall = 0.9061\n8. Eon 8/8\n - Model = Deep Model (5 Dense Layers) \t f1-score = 0.9199\t precision = 0.9350 \t recall = 0.9053\n - Final Test Score for Deep Model (5 Dense Layers) \t f1-score = 0.9200\t precision = 0.9352 \t recall = 0.9054\n"
]
],
[
[
"1. Eon 1/8\n - Model = Deep Model (5 Dense Layers) \t f1-score = 0.9112\t precision = 0.9350 \t recall = 0.8886\n2. Eon 2/8\n - Model = Deep Model (5 Dense Layers) \t f1-score = 0.9174\t precision = 0.9359 \t recall = 0.8997\n3. Eon 3/8\n - Model = Deep Model (5 Dense Layers) \t f1-score = 0.9195\t precision = 0.9365 \t recall = 0.9032\n4. Eon 4/8\n - Model = Deep Model (5 Dense Layers) \t f1-score = 0.9194\t precision = 0.9340 \t recall = 0.9054\n5. Eon 5/8\n - Model = Deep Model (5 Dense Layers) \t f1-score = 0.9205\t precision = 0.9368 \t recall = 0.9048\n6. Eon 6/8\n - Model = Deep Model (5 Dense Layers) \t f1-score = 0.9202\t precision = 0.9359 \t recall = 0.9051\n7. Eon 7/8\n - Model = Deep Model (5 Dense Layers) \t f1-score = 0.9203\t precision = 0.9351 \t recall = 0.9061\n8. Eon 8/8\n - Model = Deep Model (5 Dense Layers) \t f1-score = 0.9199\t precision = 0.9350 \t recall = 0.9053\n - Final Test Score for Deep Model (5 Dense Layers) \t f1-score = 0.9200\t precision = 0.9352 \t recall = 0.9054",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a756cabc4635aaaa8f882be745c43c45191d3d5
| 130,176 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
docs/using/interaction/init_trad_bug.ipynb
|
karban8/tardis
|
f1ab565ba76a106719ce01088135465cbfdf3191
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 176 |
2015-02-26T07:26:59.000Z
|
2022-03-16T18:26:22.000Z
|
docs/using/interaction/init_trad_bug.ipynb
|
karban8/tardis
|
f1ab565ba76a106719ce01088135465cbfdf3191
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 1,474 |
2015-02-12T13:02:16.000Z
|
2022-03-31T09:05:54.000Z
|
docs/using/interaction/init_trad_bug.ipynb
|
karban8/tardis
|
f1ab565ba76a106719ce01088135465cbfdf3191
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 434 |
2015-02-07T17:15:41.000Z
|
2022-03-23T04:49:38.000Z
| 76.081823 | 561 | 0.630792 |
[
[
[
"# Initial_t_rad Bug\n\nThe purpose of this notebook is to demonstrate the bug associated with setting the initial_t_rad tardis.plasma property.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pwd",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import tardis\nimport numpy as np",
"/anaconda2/envs/tardis/lib/python3.6/site-packages/tqdm/autonotebook/__init__.py:14: TqdmExperimentalWarning: Using `tqdm.autonotebook.tqdm` in notebook mode. Use `tqdm.tqdm` instead to force console mode (e.g. in jupyter console)\n \" (e.g. in jupyter console)\", TqdmExperimentalWarning)\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Density and Abundance test files\n\nBelow are the density and abundance data from the test files used for demonstrating this bug.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"density_dat = np.loadtxt('data/density.txt',skiprows=1)\nabund_dat = np.loadtxt('data/abund.dat', skiprows=1)\n\nprint(density_dat)\nprint(abund_dat)",
"[[0.00000000e+00 2.90000000e+03 4.28253781e-16]\n [1.00000000e+00 3.00000000e+03 4.12668886e-16]\n [2.00000000e+00 3.10000000e+03 3.94940562e-16]\n [3.00000000e+00 3.20000000e+03 3.80047743e-16]\n [4.00000000e+00 3.30000000e+03 3.63720829e-16]\n [5.00000000e+00 3.40000000e+03 3.53372945e-16]\n [6.00000000e+00 3.50000000e+03 3.46148955e-16]\n [7.00000000e+00 3.60000000e+03 3.37683976e-16]\n [8.00000000e+00 3.70000000e+03 3.30780715e-16]\n [9.00000000e+00 3.80000000e+03 3.26689004e-16]\n [1.00000000e+01 3.90000000e+03 3.23089580e-16]]\n[[0. 1. ]\n [0.1 0.9]\n [0.2 0.8]\n [0.3 0.7]\n [0.4 0.6]\n [0.5 0.5]\n [0.6 0.4]\n [0.7 0.3]\n [0.8 0.2]\n [0.9 0.1]]\n"
]
],
[
[
"## No initial_t_rad\n\nBelow we run a simple tardis simulation where `initial_t_rad` is not set. The simulation has v_inner_boundary = 3350 km/s and v_outer_boundary = 3750 km/s, both within the velocity range in the density file. The simulation runs fine.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"no_init_trad = tardis.run_tardis('data/config_no_init_trad.yml')",
"[\u001b[1mpy.warnings \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] /anaconda2/envs/tardis/lib/python3.6/importlib/_bootstrap.py:219: QAWarning: pyne.data is not yet QA compliant.\n return f(*args, **kwds)\n (\u001b[1mwarnings.py\u001b[0m:99)\n[\u001b[1mpy.warnings \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] /anaconda2/envs/tardis/lib/python3.6/importlib/_bootstrap.py:219: QAWarning: pyne.material is not yet QA compliant.\n return f(*args, **kwds)\n (\u001b[1mwarnings.py\u001b[0m:99)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.model.base \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] Abundances have not been normalized to 1. - normalizing (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:394)\n[\u001b[1mpy.warnings \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] /anaconda2/envs/tardis/lib/python3.6/site-packages/astropy/units/quantity.py:1067: AstropyDeprecationWarning: The truth value of a Quantity is ambiguous. In the future this will raise a ValueError.\n AstropyDeprecationWarning)\n (\u001b[1mwarnings.py\u001b[0m:99)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.plasma.standard_plasmas\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Reading Atomic Data from /Users/marcwilliamson/Research/TARDIS/tardis-refdata/atom_data/kurucz_cd23_chianti_H_He.h5 (\u001b[1mstandard_plasmas.py\u001b[0m:74)\n[\u001b[1mpy.warnings \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] /anaconda2/envs/tardis/lib/python3.6/site-packages/IPython/core/interactiveshell.py:3296: PerformanceWarning: indexing past lexsort depth may impact performance.\n exec(code_obj, self.user_global_ns, self.user_ns)\n (\u001b[1mwarnings.py\u001b[0m:99)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.io.atom_data.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Read Atom Data with UUID=6f7b09e887a311e7a06b246e96350010 and MD5=864f1753714343c41f99cb065710cace. (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:184)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.io.atom_data.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Non provided atomic data: synpp_refs, photoionization_data (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:187)\n[\u001b[1mpy.warnings \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] /anaconda2/envs/tardis/lib/python3.6/site-packages/astropy/units/quantity.py:1067: AstropyDeprecationWarning: The truth value of a Quantity is ambiguous. In the future this will raise a ValueError.\n AstropyDeprecationWarning)\n (\u001b[1mwarnings.py\u001b[0m:99)\n[\u001b[1mpy.warnings \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] /Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/plasma/properties/ion_population.py:63: FutureWarning: \nPassing list-likes to .loc or [] with any missing label will raise\nKeyError in the future, you can use .reindex() as an alternative.\n\nSee the documentation here:\nhttps://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#deprecate-loc-reindex-listlike\n partition_function.index].dropna())\n (\u001b[1mwarnings.py\u001b[0m:99)\n[\u001b[1mpy.warnings \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] /anaconda2/envs/tardis/lib/python3.6/site-packages/astropy/units/quantity.py:1067: AstropyDeprecationWarning: The truth value of a Quantity is ambiguous. In the future this will raise a ValueError.\n AstropyDeprecationWarning)\n (\u001b[1mwarnings.py\u001b[0m:99)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Starting iteration 1/20 (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:266)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Luminosity emitted = 7.60257e+41 erg / s Luminosity absorbed = 2.81189e+40 erg / s Luminosity requested = 1.22640e+42 erg / s (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:357)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Plasma stratification:\n\t t_rad next_t_rad w next_w\n\tShell \n\t0 9464.058312 9484.781155 0.439255 0.464482\n\n (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:348)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] t_inner 9464.848 K -- next t_inner 12021.255 K (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:350)\n[\u001b[1mpy.warnings \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] /Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/plasma/properties/ion_population.py:63: FutureWarning: \nPassing list-likes to .loc or [] with any missing label will raise\nKeyError in the future, you can use .reindex() as an alternative.\n\nSee the documentation here:\nhttps://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#deprecate-loc-reindex-listlike\n partition_function.index].dropna())\n (\u001b[1mwarnings.py\u001b[0m:99)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Starting iteration 2/20 (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:266)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Luminosity emitted = 1.60837e+42 erg / s Luminosity absorbed = 5.98006e+40 erg / s Luminosity requested = 1.22640e+42 erg / s (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:357)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Plasma stratification:\n\t t_rad next_t_rad w next_w\n\tShell \n\t0 9484.781155 12054.327238 0.464482 0.464327\n\n (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:348)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] t_inner 12021.255 K -- next t_inner 10497.194 K (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:350)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Starting iteration 3/20 (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:266)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Luminosity emitted = 9.75339e+41 erg / s Luminosity absorbed = 1.31663e+41 erg / s Luminosity requested = 1.22640e+42 erg / s (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:357)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Plasma stratification:\n\t t_rad next_t_rad w next_w\n\tShell \n\t0 12054.327238 10542.291939 0.464327 0.509656\n\n (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:348)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] t_inner 10497.194 K -- next t_inner 11770.965 K (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:350)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Starting iteration 4/20 (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:266)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Luminosity emitted = 1.41912e+42 erg / s Luminosity absorbed = 1.52432e+41 erg / s Luminosity requested = 1.22640e+42 erg / s (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:357)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Plasma stratification:\n\t t_rad next_t_rad w next_w\n\tShell \n\t0 10542.291939 11750.092484 0.509656 0.512801\n\n (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:348)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] t_inner 11770.965 K -- next t_inner 10942.574 K (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:350)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Starting iteration 5/20 (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:266)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Luminosity emitted = 1.11236e+42 erg / s Luminosity absorbed = 1.52914e+41 erg / s Luminosity requested = 1.22640e+42 erg / s (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:357)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Plasma stratification:\n\t t_rad next_t_rad w next_w\n\tShell \n\t0 11750.092484 10938.987367 0.512801 0.525724\n\n (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:348)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] t_inner 10942.574 K -- next t_inner 11489.809 K (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:350)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Starting iteration 6/20 (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:266)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Luminosity emitted = 1.29924e+42 erg / s Luminosity absorbed = 1.66012e+41 erg / s Luminosity requested = 1.22640e+42 erg / s (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:357)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Iteration converged 1/4 consecutive times. (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:194)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Plasma stratification:\n\t t_rad next_t_rad w next_w\n\tShell \n\t0 10938.987367 11456.397166 0.525724 0.521184\n\n (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:348)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] t_inner 11489.809 K -- next t_inner 11163.104 K (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:350)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Starting iteration 7/20 (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:266)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Luminosity emitted = 1.16874e+42 erg / s Luminosity absorbed = 1.57467e+41 erg / s Luminosity requested = 1.22640e+42 erg / s (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:357)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Iteration converged 2/4 consecutive times. (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:194)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Plasma stratification:\n\t t_rad next_t_rad w next_w\n\tShell \n\t0 11456.397166 11225.829447 0.521184 0.516013\n\n (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:348)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] t_inner 11163.104 K -- next t_inner 11435.147 K (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:350)\n"
],
[
"no_init_trad.model.velocity",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"no_init_trad.model.no_of_shells, no_init_trad.model.no_of_raw_shells",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('raw velocity: \\n',no_init_trad.model.raw_velocity)\nprint('raw velocity shape: ',no_init_trad.model.raw_velocity.shape)\nprint('(v_boundary_inner, v_boundary_outer) = (%i, %i)'%\n (no_init_trad.model.v_boundary_inner.to('km/s').value, no_init_trad.model.v_boundary_outer.to('km/s').value))\nprint('v_boundary_inner_index: ', no_init_trad.model.v_boundary_inner_index)\nprint('v_boundary_outer_index: ', no_init_trad.model.v_boundary_outer_index)\nprint('t_rad', no_init_trad.model.t_rad)",
"raw velocity: \n [2.9e+08 3.0e+08 3.1e+08 3.2e+08 3.3e+08 3.4e+08 3.5e+08 3.6e+08 3.7e+08\n 3.8e+08 3.9e+08] cm / s\nraw velocity shape: (11,)\n(v_boundary_inner, v_boundary_outer) = (3350, 3750)\nv_boundary_inner_index: 4\nv_boundary_outer_index: 10\nt_rad [11372.82371614 11426.15383155 11420.35713928 11382.47864204\n 11375.63115928] K\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Debugging",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%debug\ninit_trad = tardis.run_tardis('data/config_init_trad.yml')",
"NOTE: Enter 'c' at the ipdb> prompt to continue execution.\n> \u001b[0;32m<string>\u001b[0m(2)\u001b[0;36m<module>\u001b[0;34m()\u001b[0m\n\nipdb> b tardis/plasma/properties/j_blues:34\nBreakpoint 1 at /Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/plasma/properties/j_blues.py:34\nipdb> c\n[\u001b[1mtardis.model.base \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] Abundances have not been normalized to 1. - normalizing (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:368)\n[\u001b[1mpy.warnings \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] /anaconda2/envs/tardis/lib/python3.6/site-packages/astropy/units/quantity.py:1067: AstropyDeprecationWarning: The truth value of a Quantity is ambiguous. In the future this will raise a ValueError.\n AstropyDeprecationWarning)\n (\u001b[1mwarnings.py\u001b[0m:99)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.plasma.standard_plasmas\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Reading Atomic Data from /Users/marcwilliamson/Research/TARDIS/tardis-refdata/atom_data/kurucz_cd23_chianti_H_He.h5 (\u001b[1mstandard_plasmas.py\u001b[0m:74)\n[\u001b[1mpy.warnings \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] /anaconda2/envs/tardis/lib/python3.6/bdb.py:434: PerformanceWarning: indexing past lexsort depth may impact performance.\n exec(cmd, globals, locals)\n (\u001b[1mwarnings.py\u001b[0m:99)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.io.atom_data.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Read Atom Data with UUID=6f7b09e887a311e7a06b246e96350010 and MD5=864f1753714343c41f99cb065710cace. (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:184)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.io.atom_data.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Non provided atomic data: synpp_refs, photoionization_data (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:187)\n[\u001b[1mpy.warnings \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] /anaconda2/envs/tardis/lib/python3.6/site-packages/astropy/units/quantity.py:1067: AstropyDeprecationWarning: The truth value of a Quantity is ambiguous. In the future this will raise a ValueError.\n AstropyDeprecationWarning)\n (\u001b[1mwarnings.py\u001b[0m:99)\n> \u001b[0;32m/Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/plasma/properties/j_blues.py\u001b[0m(34)\u001b[0;36mcalculate\u001b[0;34m()\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 32 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0;34m@\u001b[0m\u001b[0mstaticmethod\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 33 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0;32mdef\u001b[0m \u001b[0mcalculate\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m(\u001b[0m\u001b[0mlines\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mnu\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mt_rad\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mw\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m)\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m:\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[1;31m1\u001b[0;32m--> 34 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0mj_blues\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mw\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m*\u001b[0m \u001b[0mintensity_black_body\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m(\u001b[0m\u001b[0mnu\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mvalues\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m[\u001b[0m\u001b[0mnp\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mnewaxis\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m]\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mT\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mt_rad\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m)\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 35 \u001b[0;31m j_blues = pd.DataFrame(j_blues, index=lines.index,\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 36 \u001b[0;31m columns=np.arange(len(t_rad)))\n\u001b[0m\nipdb> n\nValueError: operands could not be broadcast together with shapes (5,) (247,6)\n> \u001b[0;32m/Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/plasma/properties/j_blues.py\u001b[0m(34)\u001b[0;36mcalculate\u001b[0;34m()\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 32 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0;34m@\u001b[0m\u001b[0mstaticmethod\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 33 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0;32mdef\u001b[0m \u001b[0mcalculate\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m(\u001b[0m\u001b[0mlines\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mnu\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mt_rad\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mw\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m)\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m:\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[1;31m1\u001b[0;32m--> 34 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0mj_blues\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mw\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m*\u001b[0m \u001b[0mintensity_black_body\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m(\u001b[0m\u001b[0mnu\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mvalues\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m[\u001b[0m\u001b[0mnp\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mnewaxis\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m]\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mT\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mt_rad\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m)\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 35 \u001b[0;31m j_blues = pd.DataFrame(j_blues, index=lines.index,\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 36 \u001b[0;31m columns=np.arange(len(t_rad)))\n\u001b[0m\nipdb> restart\nRestarting\n> \u001b[0;32m<string>\u001b[0m(2)\u001b[0;36m<module>\u001b[0;34m()\u001b[0m\n\nipdb> c\n[\u001b[1mtardis.model.base \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] Abundances have not been normalized to 1. - normalizing (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:368)\n[\u001b[1mpy.warnings \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] /anaconda2/envs/tardis/lib/python3.6/site-packages/astropy/units/quantity.py:1067: AstropyDeprecationWarning: The truth value of a Quantity is ambiguous. In the future this will raise a ValueError.\n AstropyDeprecationWarning)\n (\u001b[1mwarnings.py\u001b[0m:99)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.plasma.standard_plasmas\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Reading Atomic Data from /Users/marcwilliamson/Research/TARDIS/tardis-refdata/atom_data/kurucz_cd23_chianti_H_He.h5 (\u001b[1mstandard_plasmas.py\u001b[0m:74)\n[\u001b[1mpy.warnings \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] /anaconda2/envs/tardis/lib/python3.6/bdb.py:434: PerformanceWarning: indexing past lexsort depth may impact performance.\n exec(cmd, globals, locals)\n (\u001b[1mwarnings.py\u001b[0m:99)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.io.atom_data.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Read Atom Data with UUID=6f7b09e887a311e7a06b246e96350010 and MD5=864f1753714343c41f99cb065710cace. (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:184)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.io.atom_data.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Non provided atomic data: synpp_refs, photoionization_data (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:187)\n[\u001b[1mpy.warnings \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] /anaconda2/envs/tardis/lib/python3.6/site-packages/astropy/units/quantity.py:1067: AstropyDeprecationWarning: The truth value of a Quantity is ambiguous. In the future this will raise a ValueError.\n AstropyDeprecationWarning)\n (\u001b[1mwarnings.py\u001b[0m:99)\n> \u001b[0;32m/Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/plasma/properties/j_blues.py\u001b[0m(34)\u001b[0;36mcalculate\u001b[0;34m()\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 32 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0;34m@\u001b[0m\u001b[0mstaticmethod\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 33 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0;32mdef\u001b[0m \u001b[0mcalculate\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m(\u001b[0m\u001b[0mlines\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mnu\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mt_rad\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mw\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m)\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m:\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[1;31m1\u001b[0;32m--> 34 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0mj_blues\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mw\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m*\u001b[0m \u001b[0mintensity_black_body\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m(\u001b[0m\u001b[0mnu\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mvalues\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m[\u001b[0m\u001b[0mnp\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mnewaxis\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m]\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mT\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mt_rad\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m)\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 35 \u001b[0;31m j_blues = pd.DataFrame(j_blues, index=lines.index,\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 36 \u001b[0;31m columns=np.arange(len(t_rad)))\n\u001b[0m\nipdb> t_rad\narray([11000., 11000., 11000., 11000., 11000., 11000.])\nipdb> lines.shape\n(247, 9)\nipdb> intensity_black_body(nu.values[np.newaxis].T, t_rad)\narray([[3.45300820e-23, 3.45300820e-23, 3.45300820e-23, 3.45300820e-23,\n 3.45300820e-23, 3.45300820e-23],\n [3.45300820e-23, 3.45300820e-23, 3.45300820e-23, 3.45300820e-23,\n 3.45300820e-23, 3.45300820e-23],\n [1.17024224e-22, 1.17024224e-22, 1.17024224e-22, 1.17024224e-22,\n 1.17024224e-22, 1.17024224e-22],\n ...,\n [1.65889253e-10, 1.65889253e-10, 1.65889253e-10, 1.65889253e-10,\n 1.65889253e-10, 1.65889253e-10],\n [1.65754663e-10, 1.65754663e-10, 1.65754663e-10, 1.65754663e-10,\n 1.65754663e-10, 1.65754663e-10],\n [8.99221749e-11, 8.99221749e-11, 8.99221749e-11, 8.99221749e-11,\n 8.99221749e-11, 8.99221749e-11]])\nipdb> intensity_black_body(nu.values[np.newaxis].T, t_rad).shape\n(247, 6)\nipdb> lines.shape\n(247, 9)\nipdb> nu.shape\n(247,)\nipdb> restart\nRestarting\n> \u001b[0;32m<string>\u001b[0m(2)\u001b[0;36m<module>\u001b[0;34m()\u001b[0m\n\nipdb> b tardis/simulation/base:436\nBreakpoint 2 at /Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/simulation/base.py:436\nipdb> c\n[\u001b[1mtardis.model.base \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] Abundances have not been normalized to 1. - normalizing (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:368)\n[\u001b[1mpy.warnings \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] /anaconda2/envs/tardis/lib/python3.6/site-packages/astropy/units/quantity.py:1067: AstropyDeprecationWarning: The truth value of a Quantity is ambiguous. In the future this will raise a ValueError.\n AstropyDeprecationWarning)\n (\u001b[1mwarnings.py\u001b[0m:99)\n> \u001b[0;32m/Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/simulation/base.py\u001b[0m(436)\u001b[0;36mfrom_config\u001b[0;34m()\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 434 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0mplasma\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mkwargs\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m[\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m'plasma'\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m]\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 435 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0;32melse\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m:\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[1;31m2\u001b[0;32m-> 436 \u001b[0;31m plasma = assemble_plasma(config, model,\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 437 \u001b[0;31m atom_data=kwargs.get('atom_data', None))\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 438 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0;32mif\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m'runner'\u001b[0m \u001b[0;32min\u001b[0m \u001b[0mkwargs\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m:\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\n"
],
[
"init_trad = tardis.run_tardis('data/config_init_trad.yml')",
"[\u001b[1mtardis.model.base \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] Abundances have not been normalized to 1. - normalizing (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:394)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.plasma.standard_plasmas\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Reading Atomic Data from /Users/marcwilliamson/Research/TARDIS/tardis-refdata/atom_data/kurucz_cd23_chianti_H_He.h5 (\u001b[1mstandard_plasmas.py\u001b[0m:74)\n[\u001b[1mpy.warnings \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] /anaconda2/envs/tardis/lib/python3.6/site-packages/IPython/core/interactiveshell.py:3296: PerformanceWarning: indexing past lexsort depth may impact performance.\n exec(code_obj, self.user_global_ns, self.user_ns)\n (\u001b[1mwarnings.py\u001b[0m:99)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.io.atom_data.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Read Atom Data with UUID=6f7b09e887a311e7a06b246e96350010 and MD5=864f1753714343c41f99cb065710cace. (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:184)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.io.atom_data.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Non provided atomic data: synpp_refs, photoionization_data (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:187)\n[\u001b[1mpy.warnings \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] /anaconda2/envs/tardis/lib/python3.6/site-packages/astropy/units/quantity.py:1067: AstropyDeprecationWarning: The truth value of a Quantity is ambiguous. In the future this will raise a ValueError.\n AstropyDeprecationWarning)\n (\u001b[1mwarnings.py\u001b[0m:99)\n[\u001b[1mpy.warnings \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] /Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/plasma/properties/ion_population.py:63: FutureWarning: \nPassing list-likes to .loc or [] with any missing label will raise\nKeyError in the future, you can use .reindex() as an alternative.\n\nSee the documentation here:\nhttps://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#deprecate-loc-reindex-listlike\n partition_function.index].dropna())\n (\u001b[1mwarnings.py\u001b[0m:99)\n[\u001b[1mpy.warnings \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] /anaconda2/envs/tardis/lib/python3.6/site-packages/astropy/units/quantity.py:1067: AstropyDeprecationWarning: The truth value of a Quantity is ambiguous. In the future this will raise a ValueError.\n AstropyDeprecationWarning)\n (\u001b[1mwarnings.py\u001b[0m:99)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Starting iteration 1/20 (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:266)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Luminosity emitted = 5.98252e+41 erg / s Luminosity absorbed = 1.50141e+41 erg / s Luminosity requested = 1.22640e+42 erg / s (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:357)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Plasma stratification:\n\t t_rad next_t_rad w next_w\n\tShell \n\t0 11000.0 10177.195287 0.408333 0.538077\n\t5 11000.0 10160.603522 0.229156 0.282716\n\n (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:348)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] t_inner 10172.718 K -- next t_inner 14565.035 K (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:350)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Starting iteration 2/20 (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:266)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Luminosity emitted = 1.82691e+42 erg / s Luminosity absorbed = 2.82152e+41 erg / s Luminosity requested = 1.22640e+42 erg / s (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:357)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Plasma stratification:\n\t t_rad next_t_rad w next_w\n\tShell \n\t0 10177.195287 14593.630626 0.538077 0.496563\n\t5 10160.603522 14511.556871 0.282716 0.275395\n\n (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:348)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] t_inner 14565.035 K -- next t_inner 11933.532 K (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:350)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Starting iteration 3/20 (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:266)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Luminosity emitted = 9.71423e+41 erg / s Luminosity absorbed = 2.55207e+41 erg / s Luminosity requested = 1.22640e+42 erg / s (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:357)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Plasma stratification:\n\t t_rad next_t_rad w next_w\n\tShell \n\t0 14593.630626 11959.523175 0.496563 0.536576\n\t5 14511.556871 11863.444513 0.275395 0.288444\n\n (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:348)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] t_inner 11933.532 K -- next t_inner 13408.534 K (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:350)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Starting iteration 4/20 (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:266)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Luminosity emitted = 1.34841e+42 erg / s Luminosity absorbed = 3.56350e+41 erg / s Luminosity requested = 1.22640e+42 erg / s (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:357)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Plasma stratification:\n\t t_rad next_t_rad w next_w\n\tShell \n\t0 11959.523175 13397.442807 0.536576 0.545853\n\t5 11863.444513 13434.561796 0.288444 0.279834\n\n (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:348)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] t_inner 13408.534 K -- next t_inner 12787.534 K (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:350)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Starting iteration 5/20 (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:266)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Luminosity emitted = 1.18228e+42 erg / s Luminosity absorbed = 3.17468e+41 erg / s Luminosity requested = 1.22640e+42 erg / s (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:357)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Plasma stratification:\n\t t_rad next_t_rad w next_w\n\tShell \n\t0 13397.442807 12761.259654 0.545853 0.549926\n\t5 13434.561796 12694.451547 0.279834 0.291458\n\n (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:348)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] t_inner 12787.534 K -- next t_inner 13023.975 K (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:350)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Starting iteration 6/20 (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:266)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Luminosity emitted = 1.24451e+42 erg / s Luminosity absorbed = 3.27235e+41 erg / s Luminosity requested = 1.22640e+42 erg / s (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:357)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Iteration converged 1/4 consecutive times. (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:194)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Plasma stratification:\n\t t_rad next_t_rad w next_w\n\tShell \n\t0 12761.259654 12957.006442 0.549926 0.556939\n\t5 12694.451547 12962.669431 0.291458 0.289348\n\n (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:348)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] t_inner 13023.975 K -- next t_inner 12928.870 K (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:350)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Starting iteration 7/20 (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:266)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Luminosity emitted = 1.20889e+42 erg / s Luminosity absorbed = 3.17537e+41 erg / s Luminosity requested = 1.22640e+42 erg / s (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:357)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Iteration converged 2/4 consecutive times. (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:194)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Plasma stratification:\n\t t_rad next_t_rad w next_w\n\tShell \n\t0 12957.006442 13011.562529 0.556939 0.528909\n\t5 12962.669431 12911.385086 0.289348 0.287062\n\n (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:348)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] t_inner 12928.870 K -- next t_inner 13022.158 K (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:350)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Starting iteration 8/20 (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:266)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Luminosity emitted = 1.23931e+42 erg / s Luminosity absorbed = 3.40055e+41 erg / s Luminosity requested = 1.22640e+42 erg / s (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:357)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Iteration converged 3/4 consecutive times. (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:194)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Plasma stratification:\n\t t_rad next_t_rad w next_w\n\tShell \n\t0 13011.562529 12935.144806 0.528909 0.559823\n\t5 12911.385086 12870.837942 0.287062 0.295395\n\n (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:348)\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Debugging",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Debugging No initial_t_radiative run to compare with Yes initial_t_radiative run\n\n\nWe place two breakpoints:\n\nbreak 1. tardis/base:37 --> Stops in the run_tardis() function when the simulation is initialized.\n\nbreak 2. tardis/simulation/base:436 --> Stops after the Radial1DModel has been built from the config file, but before the plasma has been initialized.\n\n## IMPORTANT:\n\nWe check the model.t_radiative property INSIDE the assemble_plasma function. Notice that it has len(model.t_radiative) = model.no_of_shells = 5",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%debug\nno_init_trad = tardis.run_tardis('config_no_init_trad.yml')",
"NOTE: Enter 'c' at the ipdb> prompt to continue execution.\nNone\n> \u001b[0;32m<string>\u001b[0m(2)\u001b[0;36m<module>\u001b[0;34m()\u001b[0m\n\nipdb> b tardis/base:37\nBreakpoint 1 at /Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/base.py:37\nipdb> b tardis/simulation/base:436\nBreakpoint 2 at /Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/simulation/base.py:436\nipdb> c\n> \u001b[0;32m/Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/base.py\u001b[0m(37)\u001b[0;36mrun_tardis\u001b[0;34m()\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 35 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0mtardis_config\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mConfiguration\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mfrom_config_dict\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m(\u001b[0m\u001b[0mconfig\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m)\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 36 \u001b[0;31m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[1;31m1\u001b[0;32m--> 37 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0msimulation\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mSimulation\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mfrom_config\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m(\u001b[0m\u001b[0mtardis_config\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0matom_data\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m=\u001b[0m\u001b[0matom_data\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m)\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 38 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0;32mfor\u001b[0m \u001b[0mcb\u001b[0m \u001b[0;32min\u001b[0m \u001b[0msimulation_callbacks\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m:\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 39 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0msimulation\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0madd_callback\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m(\u001b[0m\u001b[0mcb\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m)\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\nipdb> c\n[\u001b[1mtardis.model.base \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] Abundances have not been normalized to 1. - normalizing (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:367)\n> \u001b[0;32m/Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/simulation/base.py\u001b[0m(436)\u001b[0;36mfrom_config\u001b[0;34m()\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 434 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0mplasma\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mkwargs\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m[\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m'plasma'\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m]\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 435 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0;32melse\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m:\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[1;31m2\u001b[0;32m-> 436 \u001b[0;31m plasma = assemble_plasma(config, model,\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 437 \u001b[0;31m atom_data=kwargs.get('atom_data', None))\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 438 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0;32mif\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m'runner'\u001b[0m \u001b[0;32min\u001b[0m \u001b[0mkwargs\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m:\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\nipdb> s\n> \u001b[0;32m/Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/simulation/base.py\u001b[0m(437)\u001b[0;36mfrom_config\u001b[0;34m()\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 435 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0;32melse\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m:\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[1;31m2\u001b[0;32m 436 \u001b[0;31m plasma = assemble_plasma(config, model,\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m--> 437 \u001b[0;31m atom_data=kwargs.get('atom_data', None))\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 438 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0;32mif\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m'runner'\u001b[0m \u001b[0;32min\u001b[0m \u001b[0mkwargs\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m:\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 439 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0mrunner\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mkwargs\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m[\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m'runner'\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m]\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\nipdb> s\n--Call--\n> \u001b[0;32m/Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/plasma/standard_plasmas.py\u001b[0m(33)\u001b[0;36massemble_plasma\u001b[0;34m()\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 31 \u001b[0;31m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 32 \u001b[0;31m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m---> 33 \u001b[0;31m\u001b[0;32mdef\u001b[0m \u001b[0massemble_plasma\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m(\u001b[0m\u001b[0mconfig\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mmodel\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0matom_data\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m=\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32mNone\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m)\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m:\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 34 \u001b[0;31m \"\"\"\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 35 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0mCreate\u001b[0m \u001b[0ma\u001b[0m \u001b[0mBasePlasma\u001b[0m \u001b[0minstance\u001b[0m \u001b[0;32mfrom\u001b[0m \u001b[0ma\u001b[0m \u001b[0mConfiguration\u001b[0m \u001b[0mobject\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\nipdb> n\n> \u001b[0;32m/Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/plasma/standard_plasmas.py\u001b[0m(52)\u001b[0;36massemble_plasma\u001b[0;34m()\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 50 \u001b[0;31m \"\"\"\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 51 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0;31m# Convert the nlte species list to a proper format.\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m---> 52 \u001b[0;31m nlte_species = [species_string_to_tuple(s) for s in\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 53 \u001b[0;31m config.plasma.nlte.species]\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 54 \u001b[0;31m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\nipdb> model.t_radiative\n<Quantity [9464.0583115 , 9461.69144847, 9458.53747203, 9455.38559759,\n 9453.02306994] K>\nipdb> model.no_of_shells\n5\nipdb> len(model.t_radiative)==model.no_of_shells\nTrue\nipdb> exit\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Debugging Yes initial_t_radiative run\n\n\n\nWe place the same two breakpoints as above:\n\nbreak 1. tardis/base:37 --> Stops in the run_tardis() function when the simulation is initialized.\n\nbreak 2. tardis/simulation/base:436 --> Stops after the Radial1DModel has been built from the config file, but before the plasma has been initialized.\n\n## IMPORTANT:\n\nWe check the model.t_radiative property INSIDE the assemble_plasma function. Notice that it has len(model.t_radiative) = 6 which is NOT EQUAL to model.no_of_shells = 5",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%debug\ninit_trad = tardis.run_tardis('config_init_trad.yml')",
"NOTE: Enter 'c' at the ipdb> prompt to continue execution.\nNone\n> \u001b[0;32m<string>\u001b[0m(2)\u001b[0;36m<module>\u001b[0;34m()\u001b[0m\n\nipdb> b tardis/base:37\nBreakpoint 1 at /Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/base.py:37\nipdb> b tardis/simulation/base:436\nBreakpoint 2 at /Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/simulation/base.py:436\nipdb> c\n> \u001b[0;32m/Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/base.py\u001b[0m(37)\u001b[0;36mrun_tardis\u001b[0;34m()\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 35 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0mtardis_config\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mConfiguration\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mfrom_config_dict\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m(\u001b[0m\u001b[0mconfig\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m)\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 36 \u001b[0;31m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[1;31m1\u001b[0;32m--> 37 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0msimulation\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mSimulation\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mfrom_config\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m(\u001b[0m\u001b[0mtardis_config\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0matom_data\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m=\u001b[0m\u001b[0matom_data\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m)\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 38 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0;32mfor\u001b[0m \u001b[0mcb\u001b[0m \u001b[0;32min\u001b[0m \u001b[0msimulation_callbacks\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m:\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 39 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0msimulation\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0madd_callback\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m(\u001b[0m\u001b[0mcb\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m)\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\nipdb> c\n[\u001b[1mtardis.model.base \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] Abundances have not been normalized to 1. - normalizing (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:367)\n> \u001b[0;32m/Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/simulation/base.py\u001b[0m(436)\u001b[0;36mfrom_config\u001b[0;34m()\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 434 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0mplasma\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mkwargs\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m[\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m'plasma'\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m]\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 435 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0;32melse\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m:\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[1;31m2\u001b[0;32m-> 436 \u001b[0;31m plasma = assemble_plasma(config, model,\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 437 \u001b[0;31m atom_data=kwargs.get('atom_data', None))\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 438 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0;32mif\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m'runner'\u001b[0m \u001b[0;32min\u001b[0m \u001b[0mkwargs\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m:\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\nipdb> s\n> \u001b[0;32m/Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/simulation/base.py\u001b[0m(437)\u001b[0;36mfrom_config\u001b[0;34m()\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 435 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0;32melse\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m:\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[1;31m2\u001b[0;32m 436 \u001b[0;31m plasma = assemble_plasma(config, model,\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m--> 437 \u001b[0;31m atom_data=kwargs.get('atom_data', None))\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 438 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0;32mif\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m'runner'\u001b[0m \u001b[0;32min\u001b[0m \u001b[0mkwargs\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m:\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 439 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0mrunner\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mkwargs\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m[\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m'runner'\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m]\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\nipdb> s\n--Call--\n> \u001b[0;32m/Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/plasma/standard_plasmas.py\u001b[0m(33)\u001b[0;36massemble_plasma\u001b[0;34m()\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 31 \u001b[0;31m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 32 \u001b[0;31m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m---> 33 \u001b[0;31m\u001b[0;32mdef\u001b[0m \u001b[0massemble_plasma\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m(\u001b[0m\u001b[0mconfig\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mmodel\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0matom_data\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m=\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32mNone\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m)\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m:\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 34 \u001b[0;31m \"\"\"\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 35 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0mCreate\u001b[0m \u001b[0ma\u001b[0m \u001b[0mBasePlasma\u001b[0m \u001b[0minstance\u001b[0m \u001b[0;32mfrom\u001b[0m \u001b[0ma\u001b[0m \u001b[0mConfiguration\u001b[0m \u001b[0mobject\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\nipdb> n\n> \u001b[0;32m/Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/plasma/standard_plasmas.py\u001b[0m(52)\u001b[0;36massemble_plasma\u001b[0;34m()\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 50 \u001b[0;31m \"\"\"\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 51 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0;31m# Convert the nlte species list to a proper format.\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m---> 52 \u001b[0;31m nlte_species = [species_string_to_tuple(s) for s in\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 53 \u001b[0;31m config.plasma.nlte.species]\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 54 \u001b[0;31m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\nipdb> model.t_radiative\n<Quantity [11000., 11000., 11000., 11000., 11000., 11000.] K>\nipdb> len(model.t_radiative) == model.no_of_shells\nFalse\nipdb> exit\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Checking model.t_radiative initialization when YES initial_t_rad\n\nIn the above debugging blocks, we have identified the following discrepancy INSIDE assemble_plasma(): \n\n### len(model.t_radiative) = 6 when YES initial_t_rad\n### len(model.t_radiative) = 5 when NO initial_t_rad\n\nTherefore, we investigate in the following debugging block how model.t_radiative is initialized. We place a breakpoint at tardis/simulation/base:432 and step INSIDE the Radial1DModel initialization.\n\nBreakpoints:\n\nbreak 1. tardis/simulation/base:432 --> Stops so that we can step INSIDE Radial1DModel initialization from_config().\n\nbreak 2. tardis/model/base:330 --> Where temperature is handled INSIDE Radial1DModel initialization from_config().\n\nbreak 3. tardis/model/base:337 --> `t_radiative` is initialized. It has the same length as `velocity` which is the raw velocities from the density file.\n\nbreak 4. tardis/model/base:374 --> init() for Radial1DModel is called. We check values of relevant variables.\n\nbreak 5. tardis/model/base:76 --> Stops at first line of Radial1DModel init() function.\n\nbreak 6. tardis/model/base:101 --> self.\\_t\\_radiative is set.\n\nbreak 7. tardis/model/base:140 --> Stops at first line of self.t_radiative setter.\n\nbreak 8. tardis/model/base:132 --> Stops at first line of self.t_radiative getter.\n\nbreak 9. tardis/model/base:108 --> Stop right after self.\\_t\\_radiative is set. NOTICE that neither the setter nor the getter was called. __IMPORTANT:__ at line 108, we have len(self.\\_t\\_radiative) = 10. __TO DO:__ Check len(self.\\_t\\_radiative) at line 108 in the NO initial\\_t\\_rad case.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%debug\ninit_trad = tardis.run_tardis('config_init_trad.yml')",
"NOTE: Enter 'c' at the ipdb> prompt to continue execution.\nNone\n> \u001b[0;32m<string>\u001b[0m(2)\u001b[0;36m<module>\u001b[0;34m()\u001b[0m\n\nipdb> b tardis/model/base:101\nBreakpoint 1 at /Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/model/base.py:101\nipdb> c\n[\u001b[1mtardis.model.base \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] Abundances have not been normalized to 1. - normalizing (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:367)\n> \u001b[0;32m/Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/model/base.py\u001b[0m(101)\u001b[0;36m__init__\u001b[0;34m()\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 99 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0mself\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mt_inner\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mt_inner\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 100 \u001b[0;31m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[1;31m1\u001b[0;32m-> 101 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0;32mif\u001b[0m \u001b[0mt_radiative\u001b[0m \u001b[0;32mis\u001b[0m \u001b[0;32mNone\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m:\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 102 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0mlambda_wien_inner\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mconstants\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mb_wien\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m/\u001b[0m \u001b[0mself\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mt_inner\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 103 \u001b[0;31m self._t_radiative = constants.b_wien / (lambda_wien_inner * (\n\u001b[0m\nipdb> n\n> \u001b[0;32m/Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/model/base.py\u001b[0m(106)\u001b[0;36m__init__\u001b[0;34m()\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 104 \u001b[0;31m 1 + (self.v_middle - self.v_boundary_inner) / constants.c))\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 105 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0;32melse\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m:\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m--> 106 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0mself\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0m_t_radiative\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mt_radiative\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 107 \u001b[0;31m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 108 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0;32mif\u001b[0m \u001b[0mdilution_factor\u001b[0m \u001b[0;32mis\u001b[0m \u001b[0;32mNone\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m:\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\nipdb> b tardis/model/base:108\nBreakpoint 2 at /Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/model/base.py:108\nipdb> b tardis/model/base:140\nBreakpoint 3 at /Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/model/base.py:140\nipdb> b tardis/model/base:132\nBreakpoint 4 at /Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/model/base.py:132\nipdb> c\n> \u001b[0;32m/Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/model/base.py\u001b[0m(108)\u001b[0;36m__init__\u001b[0;34m()\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 106 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0mself\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0m_t_radiative\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mt_radiative\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 107 \u001b[0;31m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[1;31m2\u001b[0;32m-> 108 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0;32mif\u001b[0m \u001b[0mdilution_factor\u001b[0m \u001b[0;32mis\u001b[0m \u001b[0;32mNone\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m:\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 109 \u001b[0;31m self.dilution_factor = 0.5 * (1 - np.sqrt(\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 110 \u001b[0;31m 1 - (self.r_inner[0] ** 2 / self.r_middle ** 2).to(1).value))\n\u001b[0m\nipdb> self._t_radiative\n<Quantity [11000., 11000., 11000., 11000., 11000., 11000., 11000., 11000.,\n 11000., 11000.] K>\nipdb> exit\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Checking self.\\_t\\_radiative initialization when NO initial_t_rad at line 108\n\n__IMPORTANT:__ We find that len(self.\\_t\\_radiative) = 5. This is a DISCREPANCY with the YES initial_t_rad case.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%debug\nno_init_trad = tardis.run_tardis('config_no_init_trad.yml')",
"NOTE: Enter 'c' at the ipdb> prompt to continue execution.\nNone\n> \u001b[0;32m<string>\u001b[0m(2)\u001b[0;36m<module>\u001b[0;34m()\u001b[0m\n\nipdb> b tardis/model/base:101\nBreakpoint 1 at /Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/model/base.py:101\nipdb> c\n[\u001b[1mtardis.model.base \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] Abundances have not been normalized to 1. - normalizing (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:367)\n> \u001b[0;32m/Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/model/base.py\u001b[0m(101)\u001b[0;36m__init__\u001b[0;34m()\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 99 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0mself\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mt_inner\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mt_inner\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 100 \u001b[0;31m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[1;31m1\u001b[0;32m-> 101 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0;32mif\u001b[0m \u001b[0mt_radiative\u001b[0m \u001b[0;32mis\u001b[0m \u001b[0;32mNone\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m:\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 102 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0mlambda_wien_inner\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mconstants\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mb_wien\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m/\u001b[0m \u001b[0mself\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mt_inner\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 103 \u001b[0;31m self._t_radiative = constants.b_wien / (lambda_wien_inner * (\n\u001b[0m\nipdb> n\n> \u001b[0;32m/Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/model/base.py\u001b[0m(102)\u001b[0;36m__init__\u001b[0;34m()\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 100 \u001b[0;31m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[1;31m1\u001b[0;32m 101 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0;32mif\u001b[0m \u001b[0mt_radiative\u001b[0m \u001b[0;32mis\u001b[0m \u001b[0;32mNone\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m:\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m--> 102 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0mlambda_wien_inner\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mconstants\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mb_wien\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m/\u001b[0m \u001b[0mself\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mt_inner\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 103 \u001b[0;31m self._t_radiative = constants.b_wien / (lambda_wien_inner * (\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 104 \u001b[0;31m 1 + (self.v_middle - self.v_boundary_inner) / constants.c))\n\u001b[0m\nipdb> n\n> \u001b[0;32m/Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/model/base.py\u001b[0m(103)\u001b[0;36m__init__\u001b[0;34m()\u001b[0m\n\u001b[1;31m1\u001b[0;32m 101 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0;32mif\u001b[0m \u001b[0mt_radiative\u001b[0m \u001b[0;32mis\u001b[0m \u001b[0;32mNone\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m:\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 102 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0mlambda_wien_inner\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mconstants\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mb_wien\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m/\u001b[0m \u001b[0mself\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mt_inner\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m--> 103 \u001b[0;31m self._t_radiative = constants.b_wien / (lambda_wien_inner * (\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 104 \u001b[0;31m 1 + (self.v_middle - self.v_boundary_inner) / constants.c))\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 105 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0;32melse\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m:\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\nipdb> l\n\u001b[1;32m 98 \u001b[0m \u001b[0;32melse\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m:\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[1;32m 99 \u001b[0m \u001b[0mself\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mt_inner\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mt_inner\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[1;32m 100 \u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[1;31m1\u001b[1;32m 101 \u001b[0m \u001b[0;32mif\u001b[0m \u001b[0mt_radiative\u001b[0m \u001b[0;32mis\u001b[0m \u001b[0;32mNone\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m:\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[1;32m 102 \u001b[0m \u001b[0mlambda_wien_inner\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mconstants\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mb_wien\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m/\u001b[0m \u001b[0mself\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mt_inner\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m--> 103 \u001b[0;31m self._t_radiative = constants.b_wien / (lambda_wien_inner * (\n\u001b[0m\u001b[1;32m 104 \u001b[0m 1 + (self.v_middle - self.v_boundary_inner) / constants.c))\n\u001b[1;32m 105 \u001b[0m \u001b[0;32melse\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m:\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[1;32m 106 \u001b[0m \u001b[0mself\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0m_t_radiative\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mt_radiative\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[1;32m 107 \u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[1;32m 108 \u001b[0m \u001b[0;32mif\u001b[0m \u001b[0mdilution_factor\u001b[0m \u001b[0;32mis\u001b[0m \u001b[0;32mNone\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m:\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\nipdb> b tardis/model/base:108\nBreakpoint 2 at /Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/model/base.py:108\nipdb> b tardis/model/base:140\nBreakpoint 3 at /Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/model/base.py:140\nipdb> b tardis/model/base:132\nBreakpoint 4 at /Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/model/base.py:132\nipdb> c\n[\u001b[1mpy.warnings \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] /anaconda2/envs/tardis/lib/python3.6/site-packages/astropy/units/quantity.py:1067: AstropyDeprecationWarning: The truth value of a Quantity is ambiguous. In the future this will raise a ValueError.\n AstropyDeprecationWarning)\n (\u001b[1mwarnings.py\u001b[0m:99)\n> \u001b[0;32m/Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/model/base.py\u001b[0m(108)\u001b[0;36m__init__\u001b[0;34m()\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 106 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0mself\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0m_t_radiative\u001b[0m \u001b[0;34m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mt_radiative\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 107 \u001b[0;31m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[1;31m2\u001b[0;32m-> 108 \u001b[0;31m \u001b[0;32mif\u001b[0m \u001b[0mdilution_factor\u001b[0m \u001b[0;32mis\u001b[0m \u001b[0;32mNone\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m:\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 109 \u001b[0;31m self.dilution_factor = 0.5 * (1 - np.sqrt(\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 110 \u001b[0;31m 1 - (self.r_inner[0] ** 2 / self.r_middle ** 2).to(1).value))\n\u001b[0m\nipdb> self._t_radiative\n<Quantity [9464.0583115 , 9461.69144847, 9458.53747203, 9455.38559759,\n 9453.02306994] K>\nipdb> exit\n"
]
],
[
[
"## CODE CHANGE:\n\nWe propose the following change to tardis/model/base:106\n\n__Line 106 Before Change:__ `self._t_radiative = t_radiative`\n\n__Line 106 After Change:__ `self._t_radiative = t_radiative[1:1 + self.no_of_shells]`\n\nt_radiative\\[0\\] corresponds to the temperature within the inner boundary, and so should be ignored. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"init_trad = tardis.run_tardis('config_init_trad.yml')",
"[\u001b[1mpy.warnings \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] /anaconda2/envs/tardis/lib/python3.6/importlib/_bootstrap.py:219: QAWarning: pyne.data is not yet QA compliant.\n return f(*args, **kwds)\n (\u001b[1mwarnings.py\u001b[0m:99)\n[\u001b[1mpy.warnings \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] /anaconda2/envs/tardis/lib/python3.6/importlib/_bootstrap.py:219: QAWarning: pyne.material is not yet QA compliant.\n return f(*args, **kwds)\n (\u001b[1mwarnings.py\u001b[0m:99)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.model.base \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] Abundances have not been normalized to 1. - normalizing (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:367)\n[\u001b[1mpy.warnings \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] /anaconda2/envs/tardis/lib/python3.6/site-packages/astropy/units/quantity.py:1067: AstropyDeprecationWarning: The truth value of a Quantity is ambiguous. In the future this will raise a ValueError.\n AstropyDeprecationWarning)\n (\u001b[1mwarnings.py\u001b[0m:99)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.plasma.standard_plasmas\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Reading Atomic Data from /Users/marcwilliamson/Research/TARDIS/tardis-refdata/atom_data/kurucz_cd23_chianti_H_He.h5 (\u001b[1mstandard_plasmas.py\u001b[0m:74)\n[\u001b[1mpy.warnings \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] /anaconda2/envs/tardis/lib/python3.6/site-packages/IPython/core/interactiveshell.py:3296: PerformanceWarning: indexing past lexsort depth may impact performance.\n exec(code_obj, self.user_global_ns, self.user_ns)\n (\u001b[1mwarnings.py\u001b[0m:99)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.io.atom_data.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Read Atom Data with UUID=6f7b09e887a311e7a06b246e96350010 and MD5=864f1753714343c41f99cb065710cace. (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:184)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.io.atom_data.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Non provided atomic data: synpp_refs, photoionization_data (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:187)\n[\u001b[1mpy.warnings \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] /anaconda2/envs/tardis/lib/python3.6/site-packages/astropy/units/quantity.py:1067: AstropyDeprecationWarning: The truth value of a Quantity is ambiguous. In the future this will raise a ValueError.\n AstropyDeprecationWarning)\n (\u001b[1mwarnings.py\u001b[0m:99)\n[\u001b[1mpy.warnings \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] /Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/plasma/properties/ion_population.py:63: FutureWarning: \nPassing list-likes to .loc or [] with any missing label will raise\nKeyError in the future, you can use .reindex() as an alternative.\n\nSee the documentation here:\nhttps://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#deprecate-loc-reindex-listlike\n partition_function.index].dropna())\n (\u001b[1mwarnings.py\u001b[0m:99)\n[\u001b[1mpy.warnings \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] /anaconda2/envs/tardis/lib/python3.6/site-packages/astropy/units/quantity.py:1067: AstropyDeprecationWarning: The truth value of a Quantity is ambiguous. In the future this will raise a ValueError.\n AstropyDeprecationWarning)\n (\u001b[1mwarnings.py\u001b[0m:99)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Starting iteration 1/20 (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:266)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Luminosity emitted = 6.99873e+41 erg / s Luminosity absorbed = 8.78774e+40 erg / s Luminosity requested = 1.22640e+42 erg / s (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:357)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Plasma stratification:\n\t t_rad next_t_rad w next_w\n\tShell \n\t0 11000.0 9480.001506 0.439255 0.516372\n\n (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:348)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] t_inner 9464.848 K -- next t_inner 12529.122 K (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:350)\n[\u001b[1mpy.warnings \u001b[0m][\u001b[1;33mWARNING\u001b[0m] /Users/marcwilliamson/src/dev/tardis/tardis/plasma/properties/ion_population.py:63: FutureWarning: \nPassing list-likes to .loc or [] with any missing label will raise\nKeyError in the future, you can use .reindex() as an alternative.\n\nSee the documentation here:\nhttps://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#deprecate-loc-reindex-listlike\n partition_function.index].dropna())\n (\u001b[1mwarnings.py\u001b[0m:99)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Starting iteration 2/20 (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:266)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Luminosity emitted = 1.81607e+42 erg / s Luminosity absorbed = 6.48628e+40 erg / s Luminosity requested = 1.22640e+42 erg / s (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:357)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Plasma stratification:\n\t t_rad next_t_rad w next_w\n\tShell \n\t0 9480.001506 12575.745392 0.516372 0.460796\n\n (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:348)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] t_inner 12529.122 K -- next t_inner 10296.058 K (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:350)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Starting iteration 3/20 (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:266)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Luminosity emitted = 9.13387e+41 erg / s Luminosity absorbed = 1.26685e+41 erg / s Luminosity requested = 1.22640e+42 erg / s (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:357)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Plasma stratification:\n\t t_rad next_t_rad w next_w\n\tShell \n\t0 12575.745392 10311.711267 0.460796 0.518384\n\n (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:348)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] t_inner 10296.058 K -- next t_inner 11930.539 K (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:350)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Starting iteration 4/20 (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:266)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Luminosity emitted = 1.49508e+42 erg / s Luminosity absorbed = 1.38767e+41 erg / s Luminosity requested = 1.22640e+42 erg / s (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:357)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Plasma stratification:\n\t t_rad next_t_rad w next_w\n\tShell \n\t0 10311.711267 11931.816104 0.518384 0.501568\n\n (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:348)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] t_inner 11930.539 K -- next t_inner 10805.487 K (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:350)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Starting iteration 5/20 (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:266)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Luminosity emitted = 1.06943e+42 erg / s Luminosity absorbed = 1.45352e+41 erg / s Luminosity requested = 1.22640e+42 erg / s (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:357)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Plasma stratification:\n\t t_rad next_t_rad w next_w\n\tShell \n\t0 11931.816104 10806.647371 0.501568 0.521923\n\n (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:348)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] t_inner 10805.487 K -- next t_inner 11571.347 K (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:350)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Starting iteration 6/20 (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:266)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Luminosity emitted = 1.33219e+42 erg / s Luminosity absorbed = 1.63948e+41 erg / s Luminosity requested = 1.22640e+42 erg / s (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:357)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Plasma stratification:\n\t t_rad next_t_rad w next_w\n\tShell \n\t0 10806.647371 11489.044309 0.521923 0.530125\n\n (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:348)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] t_inner 11571.347 K -- next t_inner 11102.402 K (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:350)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Starting iteration 7/20 (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:266)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Luminosity emitted = 1.14086e+42 erg / s Luminosity absorbed = 1.63206e+41 erg / s Luminosity requested = 1.22640e+42 erg / s (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:357)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Iteration converged 1/4 consecutive times. (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:194)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Plasma stratification:\n\t t_rad next_t_rad w next_w\n\tShell \n\t0 11489.044309 11163.609414 0.530125 0.515142\n\n (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:348)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] t_inner 11102.402 K -- next t_inner 11511.109 K (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:350)\n[\u001b[1mtardis.simulation.base\u001b[0m][\u001b[1;37mINFO\u001b[0m ] Starting iteration 8/20 (\u001b[1mbase.py\u001b[0m:266)\n"
],
[
"import numpy as np\na = np.array([1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a[3:8]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"2 in a",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.argwhere(a==6)[0][0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.searchsorted(a, 6.5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"if (2 in a) and (3.5 in a):\n print('hi')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"assert 1==1.2, \"test\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a[3:6]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a756eca8f604268860c55d9a7b120e9c175c0bd
| 4,236 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Crypto/Strategy Backtesting/Backtesting Pipeline.ipynb
|
darkeclipz/jupyter-notebooks
|
5de784244ad9db12cfacbbec3053b11f10456d7e
|
[
"Unlicense"
] | 1 |
2018-08-28T12:16:12.000Z
|
2018-08-28T12:16:12.000Z
|
Crypto/Strategy Backtesting/Backtesting Pipeline.ipynb
|
darkeclipz/jupyter-notebooks
|
5de784244ad9db12cfacbbec3053b11f10456d7e
|
[
"Unlicense"
] | null | null | null |
Crypto/Strategy Backtesting/Backtesting Pipeline.ipynb
|
darkeclipz/jupyter-notebooks
|
5de784244ad9db12cfacbbec3053b11f10456d7e
|
[
"Unlicense"
] | null | null | null | 24.485549 | 91 | 0.429887 |
[
[
[
"# Imports",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%pylab inline\nfrom datetime import datetime, timedelta\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nfrom matplotlib import gridspec\nimport poloniex as plnx\nimport ta_lib as ta",
"Populating the interactive namespace from numpy and matplotlib\n"
],
[
"pair = 'USDT_BTC'\ntimeframe = 15 * 60\nend = datetime.utcnow()\nstart = end - timedelta(days=31)\nchart = plnx.get_chart(pair, timeframe, start, end)\nta.ema(chart, 8)\nta.ema(chart, 21)\nta.ema(chart, 55)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"chart[53:55]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for i in range(55, len(chart.index)):\n break",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a758eb3073c010b77b04fa2a7c45fc74854efda
| 134,042 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
D3/.ipynb_checkpoints/train-checkpoint.ipynb
|
LichUnHappy/Real-time-Anomaly-Detection
|
5ca88c6dc950bffee30454fea548c7ed7a5a50ce
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
D3/.ipynb_checkpoints/train-checkpoint.ipynb
|
LichUnHappy/Real-time-Anomaly-Detection
|
5ca88c6dc950bffee30454fea548c7ed7a5a50ce
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
D3/.ipynb_checkpoints/train-checkpoint.ipynb
|
LichUnHappy/Real-time-Anomaly-Detection
|
5ca88c6dc950bffee30454fea548c7ed7a5a50ce
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 270.245968 | 43,556 | 0.914855 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport sklearn\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport matplotlib\nfrom joblib import dump\nfrom sklearn.ensemble import IsolationForest",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Load the data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"X_train = pd.read_csv('./Datasets/train.csv')\nX_test = pd.read_csv('./Datasets/test.csv')\nX_train.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Train the basic classifier",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Base model; without contamination.\nclf = IsolationForest(n_estimators = 100, random_state=16).fit(X_train)\nclf",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"predictions = clf.predict(X_train)\npredictions",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a = np.linspace(-2, 70, 100)\na.ravel()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Visualization",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Plot of the base model's decision frontier.\n\nplt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [15, 15]\n\nxx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-2, 70, 100), np.linspace(-2, 70, 100))\nprint(xx.ravel())\nZ = clf.decision_function(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])\nprint(Z.shape)\nprint(Z.min())\nZ = Z.reshape(xx.shape)\nplt.title(\"Decision Boundary (base model)\")\n\n# This draws the \"soft\" or secondary boundaries.\nplt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, levels=np.linspace(Z.min(), 0, 8), cmap=plt.cm.PuBu, alpha=0.5)\n# This draws the line that separates the hard from the soft boundaries.\nplt.contour(xx, yy, Z, levels=[0], linewidths=2, colors='g')\n# This draws the hard boundary\nplt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, levels=[0, Z.max()], colors='palevioletred')\nplt.scatter(X_train.iloc[:, 0],\n X_train.iloc[:, 1],\n edgecolors='k')\nplt.xlabel('Mean')\nplt.ylabel('SD')\nplt.grid(True)\nplt.show()",
"[-2. -1.27272727 -0.54545455 ... 68.54545455 69.27272727\n 70. ]\n(10000,)\n-0.371078126851377\n"
],
[
"# With contamination.\nclf = IsolationForest(n_estimators = 100, random_state=16, contamination=0.001).fit(X_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Plot of the contamination model's decision frontier.\nplt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [15, 15]\n\nxx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-2, 70, 100), np.linspace(-2, 70, 100))\nZ = clf.decision_function(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])\nZ = Z.reshape(xx.shape)\nplt.title(\"Decision Boundary (with contamination)\")\nplt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, levels=np.linspace(\n Z.min(), 0, 8), cmap=plt.cm.PuBu, alpha=0.5)\nplt.contour(xx, yy, Z, levels=[0], linewidths=2, colors='g')\nplt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, levels=[0, Z.max()], colors='palevioletred')\nplt.scatter(X_test.iloc[:, 0],\n X_test.iloc[:, 1],\n cmap = matplotlib.colors.ListedColormap(['blue', 'red']), edgecolors='k')\nplt.xlabel('Mean')\nplt.ylabel('SD')\nplt.grid(True)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"predictions = clf.predict(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_predictions = pd.concat([X_test, pd.Series(predictions)], axis=1)\ndf_predictions.columns = ['mean', 'sd', 'output']\ndf_predictions",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Plot of the test dataset and the contamination model's decision frontier.\nplt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [15, 15]\n\nxx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-2, 70, 100), np.linspace(-2, 70, 100))\nZ = clf.decision_function(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])\nZ = Z.reshape(xx.shape)\nplt.title(\"Decision Boundary (with contamination)\")\nplt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, levels=np.linspace(\n Z.min(), 0, 8), cmap=plt.cm.PuBu, alpha=0.5)\nplt.contour(xx, yy, Z, levels=[0], linewidths=2, colors='darkred')\nplt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, levels=[0, Z.max()], colors='palevioletred')\n\n# output 1 means normal\nplt.scatter(df_predictions[df_predictions['output'] == 1 ].iloc[:, 0],\n df_predictions[df_predictions['output'] == 1 ].iloc[:, 1],\n c='blue', edgecolors='k')\n\n# output -1 means abnormal\nplt.scatter(df_predictions[df_predictions['output'] == -1 ].iloc[:, 0],\n df_predictions[df_predictions['output'] == -1 ].iloc[:, 1],\n c='red', edgecolors='k')\nplt.xlabel('Mean')\nplt.ylabel('SD')\nplt.grid(True)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Export the model.\ndump(clf, 'model.joblib') ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a7598e9309e3115d98a9ef946a48b37ef66230c
| 1,163 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
examples/kaggle_submit/predict.ipynb
|
lightforever/kaggler
|
c78fdb77ec9c4ec8ff11beea50b90cab20903ad9
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 166 |
2019-08-21T20:00:04.000Z
|
2020-05-14T16:13:57.000Z
|
examples/kaggle_submit/predict.ipynb
|
lightforever/kaggler
|
c78fdb77ec9c4ec8ff11beea50b90cab20903ad9
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 14 |
2019-08-22T07:58:39.000Z
|
2020-04-13T13:59:07.000Z
|
examples/kaggle_submit/predict.ipynb
|
lightforever/kaggler
|
c78fdb77ec9c4ec8ff11beea50b90cab20903ad9
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 22 |
2019-08-23T12:37:20.000Z
|
2020-04-20T10:06:29.000Z
| 18.460317 | 90 | 0.514187 |
[
[
[
"max_count = 25",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import pandas as pd\ndf = pd.read_csv(\"../input/deepfake-detection-challenge/sample_submission.csv\")\nif max_count is not None:\n df = df[:max_count]\ndf.to_csv('submission.csv', index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a759abcf6b29dc9ce9de62aa4371d5f64f1637a
| 17,933 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
_20201015_coco_labeledbbox_final.ipynb
|
mccallion/rory
|
164f7dedf30f6c91cb4a3f7bafc4e62b971bb1be
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
_20201015_coco_labeledbbox_final.ipynb
|
mccallion/rory
|
164f7dedf30f6c91cb4a3f7bafc4e62b971bb1be
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 2 |
2021-05-20T21:10:18.000Z
|
2021-09-28T05:33:24.000Z
|
_20201015_coco_labeledbbox_final.ipynb
|
mccallion/rory
|
164f7dedf30f6c91cb4a3f7bafc4e62b971bb1be
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 30.241147 | 914 | 0.447666 |
[
[
[
"<h1>Table of Contents<span class=\"tocSkip\"></span></h1>\n<div class=\"toc\"><ul class=\"toc-item\"><li><span><a href=\"#In-This-Notebook\" data-toc-modified-id=\"In-This-Notebook-1\"><span class=\"toc-item-num\">1 </span>In This Notebook</a></span></li><li><span><a href=\"#Final-Result\" data-toc-modified-id=\"Final-Result-2\"><span class=\"toc-item-num\">2 </span>Final Result</a></span></li><li><span><a href=\"#Loss-Function-Notes-&-Scratch\" data-toc-modified-id=\"Loss-Function-Notes-&-Scratch-3\"><span class=\"toc-item-num\">3 </span>Loss Function Notes & Scratch</a></span><ul class=\"toc-item\"><li><span><a href=\"#Notes\" data-toc-modified-id=\"Notes-3.1\"><span class=\"toc-item-num\">3.1 </span>Notes</a></span></li><li><span><a href=\"#Scratch-Work\" data-toc-modified-id=\"Scratch-Work-3.2\"><span class=\"toc-item-num\">3.2 </span>Scratch Work</a></span></li></ul></li></ul></div>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# In This Notebook",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Context**\n\nI worked on this notebook after getting back from my PNW van trip with Rose, Tim, and Eva. I started on a Thursday and ended on a Monday.\n\nThe notes on loss function in section 3 was critically important to coming up with the final solution. While working on this notebook, I dug into the depths of the Learner class and studied callbacks.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Breakthroughs in this notebook:**\n- **Massively improved results.** Achieved by changing the weights of CEL and MSE in the loss function. Before, I was weighting CEL by 10; now I'm weighting MSE by 5.\n- **Added metrics.** MSE, CEL, and ACC were all added.\n- **`view_results` working.**\n- **`show_batch` working.**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Final Result",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from fastai.vision.all import *\n\n\n### Params ###\nim_size = 224\nbatch_size = 64\npath = Path('/home/rory/data/coco2017')\nvalid_split = .15\n\n\n### Load data (singles) ###\n# Grab cols\ndef grab_cols(df, cols):\n \"\"\"Expects: DataFrame df; str or list of strs cols. Returns: L or an LoL.\"\"\"\n def _grab_col(df, col):\n return L((ColReader(col)(df)).to_list())\n \n if isinstance(cols, str): return _grab_col(df, cols)\n if len(cols)==1: return _grab_col(df, cols)\n if len(cols)>=2:\n r=L()\n for c in cols:\n r.append(_grab_col(df,c))\n return r\ndf = pd.read_pickle(path/'singles.pkl')\nimp, lbl, bbox = grab_cols(df, ['im','lbl','bbox'])\nbbox = bbox.map(lambda x:list(x)) # fixed pickle bug; lists incorrectly unpickled as tups\n# Create getters for pipeline\nimp2lbl = {p:l for p,l in zip(imp,lbl)}\nimp2bbox = {p:b for p,b in zip(imp,bbox)}\ndef get_lbl(p): return imp2lbl[p]\ndef get_bbox(p): return imp2bbox[p]\n\n\n### Datasets ###\ndss_tfms = [[PILImage.create],\n [get_bbox, TensorBBox.create],\n [get_lbl, Categorize()]]\nsplits = RandomSplitter(valid_split)(imp)\ndss = Datasets(imp, tfms=dss_tfms, splits=splits)\n\n\n### DataLoaders ###\ncpu_tfms = [BBoxLabeler(), PointScaler(), Resize(im_size, method='squish'), ToTensor()]\ngpu_tfms = [IntToFloatTensor(), Normalize.from_stats(*imagenet_stats)]\ndls = dss.dataloaders(bs=batch_size,after_item=cpu_tfms,after_batch=gpu_tfms,drop_last=True)\ndls.n_inp = 1\n\n\n### Model ###\nclass custom_module(Module):\n \n def __init__(self, body, head):\n self.body, self.head = body, head\n\n def forward(self, x):\n return self.head(self.body(x))\nbody = create_body(resnet34, pretrained=True)\nhead = create_head(1024, 4+dss.c, ps=0.5)\nmod = custom_module(body, head)\n\n\n### Loss ###\ndef mse(f, bb, lbl): return MSELossFlat()(f[:,:4], torch.squeeze(bb))\ndef cel(f, bb, lbl): return CrossEntropyLossFlat()(f[:,4:], lbl)\ndef lbb_loss(f, bb, lbl): return 5*mse(f,bb,lbl) + cel(f,bb,lbl)\ndef acc(f, bb, lbl): return accuracy(f[:,4:], lbl)\n\n\n### Training ###\nlearner = Learner(dls, mod, loss_func=lbb_loss, metrics=[mse, cel, acc])\nlr_min, _ = learner.lr_find(); print(\"lr_min:\", lr_min)\nlearner.fit_one_cycle(10, lr=lr_min)\n\n\n### Results ###\ndef view_results(learner, n=16, nrows=4, ncols=4, offset=0):\n # get batch of ims & targs, get preds\n ims, targ_bbs, targ_lbls = learner.dls.one_batch()\n preds = learner.model(ims)\n pred_bbs, pred_lbls = preds[:,:4], preds[:,4:].argmax(dim=-1)\n decoded_ims = Pipeline(gpu_tfms).decode(ims)\n \n # show grid results\n for i,ctx in enumerate(get_grid(n, nrows, ncols)):\n idx = i+offset*n\n # title\n pred_cls = dls.vocab[pred_lbls[idx].item()]\n targ_cls = dls.vocab[targ_lbls[idx].item()]\n icon = '✔️' if pred_cls==targ_cls else '✖️'\n title = f\"{icon} P {pred_cls} : A {targ_cls}\"\n # im\n show_image(decoded_ims[idx], ctx=ctx, title=title)\n # bbs\n pred_bb = TensorBBox(pred_bbs[idx])\n targ_bb = TensorBBox(targ_bbs[idx])\n ((pred_bb+1)*224//2).show(ctx=ctx, color='magenta')\n ((targ_bb+1)*224//2).show(ctx=ctx);\nview_results(learner)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Loss Function Notes & Scratch",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Notes",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"My notes from my journal\n1. `xb,yb = b`\n2. `p = mod(xb)`\n3. `alpha = cel(mb) / rmse(mb); beta = 1`\n4. `if epoch <= 3: gamma=10; else: gamma=1` (do later)\n5. `loss(p, yb): rmse(p[0:4],yb[0])*alpha*gamma + cel(p[4:],yb[1])*beta`",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Method chain for learning (from https://github.com/fastai/fastai/blob/master/fastai/learner.py#L163)\n1. `learner.fit_one_cycle()`\n2. → `.fit()`\n3. → `._do_fit()`\n4. → `._do_epoch()`\n5. → `._do_epoch_train(); ._do_epoch_validate()` (rest of chain follows `_do_epoch_train`)\n6. → `.dl = .dls.train; .all_batches()`\n7. → `.n_iter = len(.dl); for o in enum(.dl): .one_batch(*o)` o=(i,b)\n8. → `.iter = i; ._split(b); ._do_one_batch()` (item 9 has `_split`, item 10 has `_do_one_batch`)\n9. → `._split(b)`: `i = dls.n_inp; .xb, .yb = b[:i], b[i:]`\n10. → `._do_one_batch()`:\n - `.pred = .model(*xb)`\n - `.loss = .loss_func(.pred, *.yb)`\n - `._backward()` → `.loss.backward()`\n - `._step()` → `.opt.step()`\n - `.opt.zero_grad()`",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Scratch Work",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"learner = Learner(dls, mod, loss_func=lbb_loss)\nlearner.dl = learner.dls.train\nlearner.b = learner.dl.one_batch()\nlearner._split(learner.b)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"learner.pred = learner.model(learner.xb[0])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"learner.pred.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"learner.pred[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"learner.yb[0].shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"[learner.yb[0].shape[0], learner.yb[0].shape[-1]]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"learner.yb",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"learner.pred[:,4:].shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"(learner.pred[:,4:]).argmax(dim=-1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"torch.squeeze(learner.yb[0]).shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"learner.metrics",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def cel_loss(pred, targ_bb, targ_lbl):\n# mse = MSELossFlat()(pred[:,:4], torch.squeeze(targ_bb))\n cel = CrossEntropyLossFlat()(pred[:,4:], targ_lbl)\n return cel",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lbb_loss(learner.pred, learner.yb[0], learner.yb[1])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a75b19ae12e99f4c9060d889c6918ab1a99d627
| 749,456 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
choronic kidney.ipynb
|
ankitkumar0/chornic-kidney
|
4518d0ccf261d4ce1c3f796ea8ee44eeb4633b96
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
choronic kidney.ipynb
|
ankitkumar0/chornic-kidney
|
4518d0ccf261d4ce1c3f796ea8ee44eeb4633b96
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
choronic kidney.ipynb
|
ankitkumar0/chornic-kidney
|
4518d0ccf261d4ce1c3f796ea8ee44eeb4633b96
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 52.946379 | 126,904 | 0.628244 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport os",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import numpy as np",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import plotly.express as px\nimport seaborn as sns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"os.chdir(\"E:\\\\PYTHON NOTES\\\\projects\\\\100 data science projeect\\\\choronic kidney\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data=pd.read_csv(\"kidney_disease.csv\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.describe()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"columns=pd.read_csv(\"data_description.txt\",sep=\"-\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"columns=columns.reset_index()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"columns.columns=[\"cols\",\"abb_col_names\"]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"columns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.columns=columns[\"abb_col_names\"].values",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.info()",
"<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>\nRangeIndex: 400 entries, 0 to 399\nData columns (total 26 columns):\n # Column Non-Null Count Dtype \n--- ------ -------------- ----- \n 0 id 400 non-null int64 \n 1 age 391 non-null float64\n 2 blood pressure 388 non-null float64\n 3 specific gravity 353 non-null float64\n 4 albumin 354 non-null float64\n 5 sugar 351 non-null float64\n 6 red blood cells 248 non-null object \n 7 pus cell 335 non-null object \n 8 pus cell clumps 396 non-null object \n 9 bacteria 396 non-null object \n 10 blood glucose random 356 non-null float64\n 11 blood urea 381 non-null float64\n 12 serum creatinine 383 non-null float64\n 13 sodium 313 non-null float64\n 14 potassium 312 non-null float64\n 15 haemoglobin 348 non-null float64\n 16 packed cell volume 330 non-null object \n 17 white blood cell count 295 non-null object \n 18 red blood cell count 270 non-null object \n 19 ypertension 398 non-null object \n 20 diabetes mellitus 398 non-null object \n 21 coronary artery disease 398 non-null object \n 22 appetite 399 non-null object \n 23 pedal edema 399 non-null object \n 24 anemia 399 non-null object \n 25 class 400 non-null object \ndtypes: float64(11), int64(1), object(14)\nmemory usage: 81.4+ KB\n"
],
[
"def convert_dtype(data,col):\n data[col]=pd.to_numeric(data[col],errors=\"coerce\")\n \n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"features=[\"packed cell volume\",\"white blood cell count\",\"red blood cell count\"]\nfor feature in features:\n convert_dtype(data,feature)\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.drop(\"id\",axis=1,inplace=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.info()",
"<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>\nRangeIndex: 400 entries, 0 to 399\nData columns (total 25 columns):\n # Column Non-Null Count Dtype \n--- ------ -------------- ----- \n 0 age 391 non-null float64\n 1 blood pressure 388 non-null float64\n 2 specific gravity 353 non-null float64\n 3 albumin 354 non-null float64\n 4 sugar 351 non-null float64\n 5 red blood cells 248 non-null object \n 6 pus cell 335 non-null object \n 7 pus cell clumps 396 non-null object \n 8 bacteria 396 non-null object \n 9 blood glucose random 356 non-null float64\n 10 blood urea 381 non-null float64\n 11 serum creatinine 383 non-null float64\n 12 sodium 313 non-null float64\n 13 potassium 312 non-null float64\n 14 haemoglobin 348 non-null float64\n 15 packed cell volume 329 non-null float64\n 16 white blood cell count 294 non-null float64\n 17 red blood cell count 269 non-null float64\n 18 ypertension 398 non-null object \n 19 diabetes mellitus 398 non-null object \n 20 coronary artery disease 398 non-null object \n 21 appetite 399 non-null object \n 22 pedal edema 399 non-null object \n 23 anemia 399 non-null object \n 24 class 400 non-null object \ndtypes: float64(14), object(11)\nmemory usage: 78.2+ KB\n"
],
[
"def extract_cat_num(data):\n cat_col=[col for col in data.columns if data[col].dtype==\"O\"]\n num_col=[col for col in data.columns if data[col].dtype!=\"O\"]\n return cat_col,num_col\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cat_col,num_col=extract_cat_num(data)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"num_col",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for col in cat_col:\n print(\"{} has {} values\".format(col,data[col].unique()))\n print(\"\\n\")",
"red blood cells has [nan 'normal' 'abnormal'] values\n\n\npus cell has ['normal' 'abnormal' nan] values\n\n\npus cell clumps has ['notpresent' 'present' nan] values\n\n\nbacteria has ['notpresent' 'present' nan] values\n\n\nypertension has ['yes' 'no' nan] values\n\n\ndiabetes mellitus has ['yes' 'no' ' yes' '\\tno' '\\tyes' nan] values\n\n\ncoronary artery disease has ['no' 'yes' '\\tno' nan] values\n\n\nappetite has ['good' 'poor' nan] values\n\n\npedal edema has ['no' 'yes' nan] values\n\n\nanemia has ['no' 'yes' nan] values\n\n\nclass has ['ckd' 'ckd\\t' 'notckd'] values\n\n\n"
],
[
"data[\"diabetes mellitus\"].replace(to_replace={\"\\tno\":\"no\",\"\\tyes\":\"yes\"},inplace=True)\ndata[\"coronary artery disease\"]=data[\"coronary artery disease\"].replace(to_replace=\"\\tno\",value=\"no\")\ndata[\"class\"]=data[\"class\"].replace(to_replace=\"ckd\\t\",value=\"ckd\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for col in cat_col:\n print(\"{} has {} values\".format(col,data[col].unique()))\n print(\"\\n\")",
"red blood cells has [nan 'normal' 'abnormal'] values\n\n\npus cell has ['normal' 'abnormal' nan] values\n\n\npus cell clumps has ['notpresent' 'present' nan] values\n\n\nbacteria has ['notpresent' 'present' nan] values\n\n\nypertension has ['yes' 'no' nan] values\n\n\ndiabetes mellitus has ['yes' 'no' ' yes' nan] values\n\n\ncoronary artery disease has ['no' 'yes' nan] values\n\n\nappetite has ['good' 'poor' nan] values\n\n\npedal edema has ['no' 'yes' nan] values\n\n\nanemia has ['no' 'yes' nan] values\n\n\nclass has ['ckd' 'notckd'] values\n\n\n"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(30,20))\n \nfor i ,feature in enumerate (num_col):\n plt.subplot(5,3,i+1)\n data[feature].hist() \n plt.title(feature) \n \n \n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(30,20))\nfor i, feature in enumerate(cat_col):\n plt.subplot(4,3,i+1)\n sns.countplot(data[feature])\n plt.title(feature)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sns.countplot(data[\"class\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(10,8))\ndata.corr()\nsns.heatmap(data.corr(),annot=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.groupby([\"red blood cells\",\"class\"])[\"red blood cell count\"].agg([\"count\",\"mean\",\"median\",\"max\",\"min\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"px.violin(data,x=\"class\",y=\"red blood cell count\",color=\"class\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"px.scatter(data,x=\"haemoglobin\",y=\"packed cell volume\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import warnings\nfrom warnings import filterwarnings\nfilterwarnings(\"ignore\")\n\ngrid=sns.FacetGrid(data,hue='class',aspect=2)\ngrid.map(sns.kdeplot,'red blood cell count')\ngrid.add_legend()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def violin(col):\n fig=px.violin(data,x=\"class\",y=col,color=\"class\",box=True)\n return fig.show()\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def scatter(col1,col2):\n fig=px.scatter(data,x=col1,y=col2,color=\"class\")\n return fig.show()\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def kdeplot(feature):\n grid=sns.FacetGrid(data,hue=\"class\",aspect=2)\n grid.map(sns.kdeplot,feature)\n grid.add_legend()\n \n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.columns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"kdeplot(\"haemoglobin\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"kdeplot(\"packed cell volume\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"scatter(\"packed cell volume\",\"red blood cell count\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"scatter(\"haemoglobin\",\"red blood cell count\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.columns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"violin(\"red blood cell count\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"scatter(\"red blood cell count\",\"albumin\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.isnull().sum().sort_values(ascending=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## missing value filed with random sample\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df=data.copy()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df[\"red blood cells\"].isnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"random_sample=df[\"red blood cells\"].dropna().sample(df[\"red blood cells\"].isnull().sum())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df[df[\"red blood cells\"].isnull()].index",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"random_sample.index",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"random_sample.index=df[df[\"red blood cells\"].isnull()].index",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"random_sample.index",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"random_sample",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.loc[df[\"red blood cells\"].isnull(),\"red blood cells\"]=random_sample",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df[\"red blood cells\"].isnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## missing impuation funtiom",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def Random_value_impuation(feature):\n random_sample=df[feature].dropna().sample(df[feature].isnull().sum())\n random_sample.index=df[df[feature].isnull()].index\n df.loc[df[feature].isnull(),feature]=random_sample",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for col in num_col:\n Random_value_impuation(col)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df[num_col].isnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df[cat_col].isnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Random_value_impuation(\"pus cell\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df[\"pus cell clumps\"].mode()[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def impute_mode(feature):\n mode=df[feature].mode()[0]\n df[feature]=df[feature].fillna(mode)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for col in cat_col:\n impute_mode(col)\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df[cat_col].isnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## lable encoding",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for col in cat_col:\n print(\"{} has {} categories\".format(col,df[col].nunique()))",
"red blood cells has 2 categories\npus cell has 2 categories\npus cell clumps has 2 categories\nbacteria has 2 categories\nypertension has 2 categories\ndiabetes mellitus has 3 categories\ncoronary artery disease has 2 categories\nappetite has 2 categories\npedal edema has 2 categories\nanemia has 2 categories\nclass has 2 categories\n"
],
[
"from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"le=LabelEncoder()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for col in cat_col:\n df[col]=le.fit_transform(df[col])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.feature_selection import SelectKBest",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.feature_selection import chi2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ind_col=[col for col in df.columns if col!=\"class\"]\ndep_col=\"class\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x=df[ind_col]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"y=df[dep_col]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"order_rank_feature=SelectKBest(score_func=chi2,k=20)\norder_feature=order_rank_feature.fit(x,y)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"order_feature.scores_",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"datascore=pd.DataFrame(order_feature.scores_,columns=[\"score\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"datascore",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dfcols=pd.DataFrame(x.columns)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dfcols",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"feature_rank=pd.concat([dfcols,datascore],axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"feature_rank.columns=[\"features\",\"score\"]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"feature_rank",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"feature_rank.nlargest(10,\"score\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"selected_columns=feature_rank.nlargest(10,\"score\")['features'].values",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x_new=df[selected_columns]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x_new.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(x_new,y,random_state=0,test_size=0.25)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from xgboost import XGBClassifier",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"xgb=XGBClassifier()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"params={\"learning_rate\":[0.05,0.20,0.25],\n \"max_depth\":[5,8,10],\n \"min_child_weight\":[1,3,5,7],\n \"gamma\":[0.0,0.1,0.2,0.4],\n \"colsample_bytree\":[0.3,0.4,0.7]\n }",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.model_selection import RandomizedSearchCV",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"random_serach=RandomizedSearchCV(xgb,param_distributions=params,n_iter=5,scoring=\"roc_auc\",n_jobs=-1,cv=5,verbose=3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"random_serach.fit(x_train,y_train)",
"Fitting 5 folds for each of 5 candidates, totalling 25 fits\n"
],
[
"random_serach.best_estimator_",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"random_serach.best_params_",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"classifier=XGBClassifier(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=1,\n colsample_bynode=1, colsample_bytree=0.4, gamma=0.1, gpu_id=-1,\n importance_type='gain', interaction_constraints='',\n learning_rate=0.2, max_delta_step=0, max_depth=5,\n min_child_weight=1,monotone_constraints='()',\n n_estimators=100, n_jobs=0, num_parallel_tree=1,\n objective='binary:logistic', random_state=0, reg_alpha=0,\n reg_lambda=1, scale_pos_weight=1, subsample=1, tree_method='exact',\n validate_parameters=1, verbosity=None)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"classifier.fit(x_train,y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"y_pred=classifier.predict(x_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix,accuracy_score",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"confusion_matrix(y_pred,y_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"accuracy_score(y_pred,y_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a75b9be4c0ecd9baeb1d0306ae37fa6c3cfbbd5
| 21,934 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/baseline.ipynb
|
subhadarship/GermEval2021
|
c131b88a90bbb236afb57cff6302f7a2afd99346
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/baseline.ipynb
|
subhadarship/GermEval2021
|
c131b88a90bbb236afb57cff6302f7a2afd99346
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/baseline.ipynb
|
subhadarship/GermEval2021
|
c131b88a90bbb236afb57cff6302f7a2afd99346
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 42.923679 | 1,092 | 0.589313 |
[
[
[
"# Baseline",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import os\nfrom typing import Any, Dict\n\nimport numpy as np\nimport nltk\nimport pandas as pd\nfrom sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression\nfrom sklearn.metrics import f1_score",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Utilities",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def train_validate_test_logistic_regression_model(train_dict: Dict[str, Any],\n dev_dict: Dict[str, Any],\n C: float, random_seed: int) -> Dict[str, float]:\n \"\"\"Train and validate logistic regression model with tfidf word features\"\"\"\n\n # define tfidf vectorizer\n vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(\n max_features=None,\n encoding='utf-8',\n tokenizer=nltk.word_tokenize,\n ngram_range=(1, 1),\n )\n\n # fit vectorizer\n vectorizer.fit(train_dict['text'])\n\n train_X = vectorizer.transform(train_dict['text'])\n dev_X = vectorizer.transform(dev_dict['text'])\n\n # Define Logistic Regression model\n model = LogisticRegression(\n solver='liblinear',\n random_state=random_seed,\n verbose=False,\n C=C,\n )\n # Fit the model to training data\n model.fit(\n train_X,\n train_dict['labels']\n )\n\n # make prediction using the trained model\n train_pred = model.predict(train_X)\n dev_pred = model.predict(dev_X)\n\n # compute F1 scores\n train_f1 = f1_score(y_pred=train_pred, y_true=train_dict['labels'], average='macro', labels=['0', '1'])\n dev_f1 = f1_score(y_pred=dev_pred, y_true=dev_dict['labels'], average='macro', labels=['0', '1'])\n\n return {\n 'train_f1': train_f1,\n 'dev_f1': dev_f1,\n }\n\n\ndef pick_best_dev_score(scores_dict: Dict[float, Dict[str, float]]) -> Dict[str, float]:\n best_val = {'dev_f1': -1}\n for k, val in scores_dict.items():\n if val['dev_f1'] > best_val['dev_f1']:\n best_val = val\n return best_val",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Load data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"DATA_DIR = os.path.join('../data/GermEval21_Toxic_Train')\nassert os.path.isdir(DATA_DIR)\ntrain_df = pd.read_csv(os.path.join(DATA_DIR, 'train.csv'), encoding='utf-8', sep=',')\ndev_df = pd.read_csv(os.path.join(DATA_DIR, 'dev.csv'), encoding='utf-8', sep=',')\n\ntrain_di = {\n 'text': train_df['comment_text'],\n 'labels': train_df['Sub3_FactClaiming'].astype(str),\n}\ndev_di = {\n 'text': dev_df['comment_text'],\n 'labels': dev_df['Sub3_FactClaiming'].astype(str),\n}",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Train and evaluate",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"scores_dict = {}\nfor c in [1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0]:\n scores_dict[c] = train_validate_test_logistic_regression_model(\n train_dict=train_di,\n dev_dict=dev_di,\n C=c,\n random_seed=123,\n )",
"C:\\Users\\subhadarshi\\AppData\\Local\\Continuum\\anaconda2\\envs\\multiindic\\lib\\site-packages\\sklearn\\feature_extraction\\text.py:489: UserWarning: The parameter 'token_pattern' will not be used since 'tokenizer' is not None'\n warnings.warn(\"The parameter 'token_pattern' will not be used\"\nC:\\Users\\subhadarshi\\AppData\\Local\\Continuum\\anaconda2\\envs\\multiindic\\lib\\site-packages\\sklearn\\feature_extraction\\text.py:489: UserWarning: The parameter 'token_pattern' will not be used since 'tokenizer' is not None'\n warnings.warn(\"The parameter 'token_pattern' will not be used\"\nC:\\Users\\subhadarshi\\AppData\\Local\\Continuum\\anaconda2\\envs\\multiindic\\lib\\site-packages\\sklearn\\feature_extraction\\text.py:489: UserWarning: The parameter 'token_pattern' will not be used since 'tokenizer' is not None'\n warnings.warn(\"The parameter 'token_pattern' will not be used\"\nC:\\Users\\subhadarshi\\AppData\\Local\\Continuum\\anaconda2\\envs\\multiindic\\lib\\site-packages\\sklearn\\feature_extraction\\text.py:489: UserWarning: The parameter 'token_pattern' will not be used since 'tokenizer' is not None'\n warnings.warn(\"The parameter 'token_pattern' will not be used\"\nC:\\Users\\subhadarshi\\AppData\\Local\\Continuum\\anaconda2\\envs\\multiindic\\lib\\site-packages\\sklearn\\feature_extraction\\text.py:489: UserWarning: The parameter 'token_pattern' will not be used since 'tokenizer' is not None'\n warnings.warn(\"The parameter 'token_pattern' will not be used\"\n"
],
[
"scores_dict",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pick_best_dev_score(scores_dict)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Train using 5-fold cross-validation data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"CROSS_VALIDATION_DATA_DIR = os.path.join('../data/cross_validation')\nresults_dict = {}\nfor fold_name in ['fold_A', 'fold_B', 'fold_C', 'fold_D', 'fold_E']:\n print(f'*** {fold_name} ***')\n data_dir = os.path.join(CROSS_VALIDATION_DATA_DIR, fold_name)\n assert os.path.isdir(data_dir)\n train_df = pd.read_csv(os.path.join(data_dir, 'train.csv'), encoding='utf-8', sep=',')\n dev_df = pd.read_csv(os.path.join(data_dir, 'dev.csv'), encoding='utf-8', sep=',')\n\n train_di = {\n 'text': train_df['comment_text'],\n 'labels': train_df['Sub3_FactClaiming'].astype(str),\n }\n dev_di = {\n 'text': dev_df['comment_text'],\n 'labels': dev_df['Sub3_FactClaiming'].astype(str),\n }\n\n scores_dict = {}\n for c in [1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0]:\n scores_dict[c] = train_validate_test_logistic_regression_model(\n train_dict=train_di,\n dev_dict=dev_di,\n C=c,\n random_seed=123,\n )\n\n results_dict[fold_name] = scores_dict",
"*** fold_A ***\n"
],
[
"fold_names = ['fold_A', 'fold_B', 'fold_C', 'fold_D', 'fold_E']\ntrain_f1_means = []\ntrain_f1_stds = []\ndev_f1_means = []\ndev_f1_stds = []\nCs = []\nfor c in [1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0]:\n Cs.append(c)\n train_f1_means.append(\n np.mean([results_dict[fold_name][c]['train_f1'] for fold_name in fold_names])\n )\n train_f1_stds.append(\n np.std([results_dict[fold_name][c]['train_f1'] for fold_name in fold_names])\n )\n dev_f1_means.append(\n np.mean([results_dict[fold_name][c]['dev_f1'] for fold_name in fold_names])\n )\n dev_f1_stds.append(\n np.std([results_dict[fold_name][c]['dev_f1'] for fold_name in fold_names])\n )\ntable_dict = {\n 'C': Cs,\n 'train_f1': [f'{train_f1_mean:0.3f} ± {train_f1_std:0.2f}' for train_f1_mean, train_f1_std in\n zip(train_f1_means, train_f1_stds)],\n 'dev_f1': [f'{dev_f1_mean:0.3f} ± {dev_f1_std:0.2f}' for dev_f1_mean, dev_f1_std in zip(dev_f1_means, dev_f1_stds)],\n}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.DataFrame(table_dict)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a75bc7134bab6e544482110bde327132ffa4f83
| 447,939 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Udemy/StockPrediction/google_colab/1-2_sp500_monthly.ipynb
|
Aquaware/StudyOfML
|
b2fb134dbe7c9b6991aa56d0c869d6856fc782e0
|
[
"Unlicense"
] | null | null | null |
Udemy/StockPrediction/google_colab/1-2_sp500_monthly.ipynb
|
Aquaware/StudyOfML
|
b2fb134dbe7c9b6991aa56d0c869d6856fc782e0
|
[
"Unlicense"
] | null | null | null |
Udemy/StockPrediction/google_colab/1-2_sp500_monthly.ipynb
|
Aquaware/StudyOfML
|
b2fb134dbe7c9b6991aa56d0c869d6856fc782e0
|
[
"Unlicense"
] | null | null | null | 447,939 | 447,939 | 0.892468 |
[
[
[
"\n\n```\nimport torch\nimport torch.nn as nn\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import torch\nimport torch.nn as nn\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\n# Start: 1970-10-01\n# End: 2020-09-31\n\nstock_data = pd.read_csv(\n \"/content/drive/My Drive/data/stock_data/^GSCP.csv\",\n index_col=0,\n parse_dates=True\n)\n\nstock_data\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"stock_data = pd.read_csv(\n \"/content/drive/My Drive/data/stock_data/^GSPC.csv\",\n index_col = 0,\n parse_dates=True\n)\n\nstock_data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\nstock_data.drop(\n [\"Open\", \"High\", \"Low\", \"Close\", \"Volume\"],\n axis=\"columns\",\n inplace=True\n)\n\nstock_data\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"stock_data.drop(\n [\"Open\", \"High\", \"Low\", \"Close\", \"Volume\"],\n axis=\"columns\",\n inplace=True\n)\n\nstock_data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\nstock_data.plot(figsize=(12, 4))\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"stock_data.plot(figsize=(12, 4))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\n# Convert a feature into a one-dimensional Numpy Array\ny = stock_data[\"Adj Close\"].values\ny\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"y = stock_data[\"Adj Close\"].values\ny",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\n# Normalization: \nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\n# Converts a one-dimensional Numpy Array to a two-dimensional Numpy Array\nscaler = MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(-1, 1))\nscaler.fit(y.reshape(-1, 1))\ny = scaler.transform(y.reshape(-1, 1))\ny\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"scaler = MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(-1, 1))\nscaler.fit(y.reshape(-1, 1))\ny = scaler.transform(y.reshape(-1, 1))\ny",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\n# Convert a two-dimensional Numpy Array to a one-dimensional Pytorch Tensor\ny = torch.FloatTensor(y).view(-1)\ny\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"y = torch.FloatTensor(y).view(-1)\ny",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\n# Separate normalized data for training and testing\ntest_size = 24\n\ntrain_seq = y[:-test_size]\ntest_seq = y[-test_size:]\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"test_size = 24\n\n# train_seq = y[:-test_size]\n# test_seq = y[-test_size:]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\n# Plot y, train_seq and test_seq\nplt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))\nplt.xlim(-20, len(y)+20)\nplt.grid(True)\nplt.plot(y)\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))\nplt.xlim(-20, len(y)+20)\nplt.grid(True)\nplt.plot(y)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\ntrain_window_size = 12\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"train_window_size = 12",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\ndef input_data(seq, ws):\n out = []\n L = len(seq)\n \n for i in range(L-ws):\n window = seq[i:i+ws]\n label = seq[i+ws:i+ws+1]\n out.append((window, label))\n \n return out\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def input_data(seq, ws):\n out = []\n L = len(seq)\n\n for i in range(L-ws):\n window = seq[i:i+ws]\n label = seq[i+ws:i+ws+1]\n out.append((window, label))\n \n return out",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\ntrain_data = input_data(train_seq, train_window_size)\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# train_data = input_data(train_seq, train_window_size)\ntrain_data = input_data(y, train_window_size)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\nprint(\"The Number of Training Data: \", len(train_data))\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 600-24-12=564\nprint(\"The Nunber of Training Data: \", len(train_data))",
"The Nunber of Training Data: 588\n"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\nclass Model(nn.Module):\n\n \n def __init__(self, input=1, h=50, output=1):\n \n super().__init__()\n self.hidden_size = h\n \n self.lstm = nn.LSTM(input, h)\n self.fc = nn.Linear(h, output)\n\n self.hidden = (\n torch.zeros(1, 1, h),\n torch.zeros(1, 1, h)\n )\n \n \n def forward(self, seq):\n \n out, _ = self.lstm(\n seq.view(len(seq), 1, -1),\n self.hidden\n )\n\n out = self.fc(\n out.view(len(seq), -1)\n )\n \n return out[-1]\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class Model(nn.Module):\n\n\n def __init__(self, input=1, h=50, output=1):\n super().__init__()\n self.hidden_size = h\n\n self.lstm = nn.LSTM(input, h)\n self.fc = nn.Linear(h, output)\n\n self.hidden = (\n torch.zeros(1, 1, h),\n torch.zeros(1, 1, h)\n )\n \n\n def forward(self, seq):\n\n out, _ = self.lstm(\n seq.view(len(seq), 1, -1),\n self.hidden\n )\n\n out = self.fc(\n out.view(len(seq), -1)\n )\n\n return out[-1]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\ntorch.manual_seed(123)\nmodel = Model()\n# mean squared error loss 平均二乗誤差損失\ncriterion = nn.MSELoss()\n# stochastic gradient descent 確率的勾配降下\noptimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"torch.manual_seed(123)\nmodel = Model()\ncriterion = nn.MSELoss()\noptimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\nepochs = 10\ntrain_losses = []\ntest_losses = []\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"epochs = 10\ntrain_losses = []\ntest_losses = []",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\ndef run_train():\n model.train()\n \n for train_window, correct_label in train_data:\n\n optimizer.zero_grad()\n \n model.hidden = (\n torch.zeros(1, 1, model.hidden_size),\n torch.zeros(1, 1, model.hidden_size) \n )\n \n train_predicted_label = model.forward(train_window)\n train_loss = criterion(train_predicted_label, correct_label)\n \n train_loss.backward()\n optimizer.step()\n \n train_losses.append(train_loss)\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def run_train():\n model.train()\n\n for train_window, correct_label in train_data:\n\n optimizer.zero_grad()\n\n model.hidden = (\n torch.zeros(1, 1, model.hidden_size),\n torch.zeros(1, 1, model.hidden_size)\n )\n\n train_predicted_label = model.forward(train_window)\n train_loss = criterion(train_predicted_label, correct_label)\n\n train_loss.backward()\n optimizer.step()\n\n train_losses.append(train_loss)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\n# Extract the value of an element from a one-dimensional Tensor with a single element\na = torch.tensor([3])\na\n# a.item()\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"a = torch.tensor([3])\na.item()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\ndef run_test():\n model.eval()\n \n for i in range(test_size):\n \n test_window = torch.FloatTensor(extending_seq[-test_size:])\n \n \n # print()\n # print(\"The Length of Extending Sequence: \", len(extending_seq))\n # print(\"The Length of window\", len(test_window))\n # print()\n \n\n # Stop storing parameters by not computing the slope, so as not to consume memory\n with torch.no_grad():\n \n model.hidden = (\n torch.zeros(1, 1, model.hidden_size),\n torch.zeros(1, 1, model.hidden_size) \n )\n \n test_predicted_label = model.forward(test_window)\n extending_seq.append(test_predicted_label.item())\n \n test_loss = criterion(\n torch.FloatTensor(extending_seq[-test_size:]),\n y[len(y)-test_size:]\n )\n \n test_losses.append(test_loss)\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def run_test():\n model.eval()\n\n for i in range(test_size):\n\n test_window = torch.FloatTensor(extending_seq[-test_size:])\n\n with torch.no_grad():\n\n model.hidden = (\n torch.zeros(1, 1, model.hidden_size),\n torch.zeros(1, 1, model.hidden_size)\n ) \n \n test_predicted_label = model.forward(test_window)\n extending_seq.append(test_predicted_label.item())\n \n test_loss = criterion(\n torch.FloatTensor(extending_seq[-test_size:]),\n y[len(y)-test_size:]\n )\n\n test_losses.append(test_loss)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\ntrain_seq[-test_size:]\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# train_seq[-test_size:]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\ntrain_seq[-test_size:].tolist()\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# train_seq[-test_size:].tolist()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\nfor epoch in range(epochs):\n\n print()\n print(f'Epoch: {epoch+1}')\n\n run_train()\n\n extending_seq = train_seq[-test_size:].tolist()\n \n run_test()\n\n plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))\n plt.xlim(-20, len(y)+20)\n plt.grid(True)\n\n plt.plot(y.numpy())\n \n plt.plot(\n range(len(y)-test_size, len(y)),\n extending_seq[-test_size:]\n )\n \n plt.show()\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for epoch in range(epochs):\n\n print()\n print(f'Epoch: {epoch+1}')\n\n run_train()\n\n # extending_seq = train_seq[-test_size:].tolist()\n extending_seq = y[-test_size:].tolist()\n\n run_test()\n\n plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))\n # plt.xlim(-20, len(y)+20)\n plt.xlim(-20, len(y)+50)\n plt.grid(True)\n\n plt.plot(y.numpy())\n\n plt.plot(\n # range(len(y)-test_size, len(y)),\n range(len(y), len(y)+test_size),\n extending_seq[-test_size:]\n )\n\n plt.show()",
"\nEpoch: 1\n"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\nplt.plot(train_losses)\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plt.plot(train_losses)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\nplt.plot(test_losses)\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plt.plot(test_losses)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\n# List\npredicted_normalized_labels_list = extending_seq[-test_size:]\npredicted_normalized_labels_list\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"predicted_normalized_labels_list = extending_seq[-test_size:]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\n# Convert a list to a one-dimensional Numpy Array\npredicted_normalized_labels_array_1d = np.array(predicted_normalized_labels_list)\npredicted_normalized_labels_array_1d\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"predicted_normalized_labels_array_1d = np.array(predicted_normalized_labels_list)\npredicted_normalized_labels_array_1d",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\n# Converts a one-dimensional Numpy Array to a two-dimensional Numpy Array\npredicted_normalized_labels_array_2d = predicted_normalized_labels_array_1d.reshape(-1, 1)\npredicted_normalized_labels_array_2d\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"predicted_normalized_labels_array_2d = predicted_normalized_labels_array_1d.reshape(-1, 1)\npredicted_normalized_labels_array_2d",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\n# From a normalized number to a true number.\npredicted_labels_array_2d = scaler.inverse_transform(predicted_normalized_labels_array_2d)\npredicted_labels_array_2d\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"predicted_labels_array_2d = scaler.inverse_transform(predicted_normalized_labels_array_2d)\npredicted_labels_array_2d",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\nlen(predicted_labels_array_2d)\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"len(predicted_labels_array_2d)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\nstock_data[\"Adj Close\"][-test_size:]\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"stock_data[\"Adj Close\"][-test_size:]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\nlen(stock_data[\"Adj Close\"][-test_size:])\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"len(stock_data[\"Adj Close\"][-test_size:])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\nstock_data.index\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"stock_data.index",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\n# Either way of writing works.\nx_2018_10_to_2020_09 = np.arange('2018-10', '2020-10', dtype='datetime64[M]')\n# x_2018_10_to_2020_09 = np.arange('2018-10-01', '2020-10-31', dtype='datetime64[M]')\n\nx_2018_10_to_2020_09\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# x_2018_10_to_2020_09 = np.arange('2018-10', '2020-10', dtype='datetime64[M]')\n# x_2018_10_to_2020_09\n\nx_2020_10_to_2022_09 = np.arange('2020-10', '2022-10', dtype='datetime64[M]')\nx_2020_10_to_2022_09",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\nlen(x_2018_10_to_2020_09)\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# len(x_2018_10_to_2020_09)\nlen(x_2020_10_to_2022_09)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n```\nfig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))\nplt.title('Stock Price Prediction')\nplt.ylabel('Price')\nplt.grid(True)\nplt.autoscale(axis='x', tight=True)\nfig.autofmt_xdate()\n\nplt.plot(stock_data[\"Adj Close\"]['2016-01':])\nplt.plot(x_2018_10_to_2020_09, predicted_labels_array_2d)\nplt.show()\n```\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))\nplt.title('Stock Price Prediction')\nplt.ylabel('Price')\nplt.grid(True)\nplt.autoscale(axis='x', tight=True)\nfig.autofmt_xdate()\n\nplt.plot(stock_data[\"Adj Close\"]['2016-01':])\n# plt.plot(x_2018_10_to_2020_09, predicted_labels_array_2d)\nplt.plot(x_2020_10_to_2022_09, predicted_labels_array_2d)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a75c9f5c41702c1d5481d58ad6ed4b8324f33da
| 10,251 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Untitled.ipynb
|
BartvLaatum/lsde_stylegan
|
508ba77ee38e02e47f801519dd7cdf75c1378432
|
[
"BSD-Source-Code"
] | null | null | null |
Untitled.ipynb
|
BartvLaatum/lsde_stylegan
|
508ba77ee38e02e47f801519dd7cdf75c1378432
|
[
"BSD-Source-Code"
] | null | null | null |
Untitled.ipynb
|
BartvLaatum/lsde_stylegan
|
508ba77ee38e02e47f801519dd7cdf75c1378432
|
[
"BSD-Source-Code"
] | null | null | null | 42.359504 | 274 | 0.57848 |
[
[
[
"import projector\nimport numpy as np\nimport dnnlib\nfrom dnnlib import tflib\nimport pickle\nimport tensorflow as tf\nimport PIL\nimport os\nimport tqdm",
"C:\\Users\\hbpva\\Anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages\\tensorflow\\python\\framework\\dtypes.py:516: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or '1type' as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / '(1,)type'.\n _np_qint8 = np.dtype([(\"qint8\", np.int8, 1)])\nC:\\Users\\hbpva\\Anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages\\tensorflow\\python\\framework\\dtypes.py:517: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or '1type' as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / '(1,)type'.\n _np_quint8 = np.dtype([(\"quint8\", np.uint8, 1)])\nC:\\Users\\hbpva\\Anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages\\tensorflow\\python\\framework\\dtypes.py:518: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or '1type' as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / '(1,)type'.\n _np_qint16 = np.dtype([(\"qint16\", np.int16, 1)])\nC:\\Users\\hbpva\\Anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages\\tensorflow\\python\\framework\\dtypes.py:519: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or '1type' as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / '(1,)type'.\n _np_quint16 = np.dtype([(\"quint16\", np.uint16, 1)])\nC:\\Users\\hbpva\\Anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages\\tensorflow\\python\\framework\\dtypes.py:520: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or '1type' as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / '(1,)type'.\n _np_qint32 = np.dtype([(\"qint32\", np.int32, 1)])\nC:\\Users\\hbpva\\Anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages\\tensorflow\\python\\framework\\dtypes.py:525: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or '1type' as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / '(1,)type'.\n np_resource = np.dtype([(\"resource\", np.ubyte, 1)])\nC:\\Users\\hbpva\\Anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages\\tensorboard\\compat\\tensorflow_stub\\dtypes.py:541: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or '1type' as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / '(1,)type'.\n _np_qint8 = np.dtype([(\"qint8\", np.int8, 1)])\nC:\\Users\\hbpva\\Anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages\\tensorboard\\compat\\tensorflow_stub\\dtypes.py:542: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or '1type' as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / '(1,)type'.\n _np_quint8 = np.dtype([(\"quint8\", np.uint8, 1)])\nC:\\Users\\hbpva\\Anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages\\tensorboard\\compat\\tensorflow_stub\\dtypes.py:543: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or '1type' as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / '(1,)type'.\n _np_qint16 = np.dtype([(\"qint16\", np.int16, 1)])\nC:\\Users\\hbpva\\Anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages\\tensorboard\\compat\\tensorflow_stub\\dtypes.py:544: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or '1type' as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / '(1,)type'.\n _np_quint16 = np.dtype([(\"quint16\", np.uint16, 1)])\nC:\\Users\\hbpva\\Anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages\\tensorboard\\compat\\tensorflow_stub\\dtypes.py:545: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or '1type' as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / '(1,)type'.\n _np_qint32 = np.dtype([(\"qint32\", np.int32, 1)])\nC:\\Users\\hbpva\\Anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages\\tensorboard\\compat\\tensorflow_stub\\dtypes.py:550: FutureWarning: Passing (type, 1) or '1type' as a synonym of type is deprecated; in a future version of numpy, it will be understood as (type, (1,)) / '(1,)type'.\n np_resource = np.dtype([(\"resource\", np.ubyte, 1)])\n"
],
[
"network_pkl = \"https://nvlabs-fi-cdn.nvidia.com/stylegan2-ada/pretrained/ffhq.pkl\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def project(network_pkl: str, target_fname: str, outdir: str, save_video: bool, seed: int):\n # Load networks.\n tflib.init_tf({'rnd.np_random_seed': seed})\n print('Loading networks from \"%s\"...' % network_pkl)\n with dnnlib.util.open_url(network_pkl) as fp:\n _G, _D, Gs = pickle.load(fp)\n\n # Load target image.\n # files = [f for f in listdir(target_fname) if isfile(join(target_fname, f))]\n # for i in range(len(files)):\n # path = target_fname + files[i]\n target_pil = PIL.Image.open(target_fname)\n w, h = target_pil.size\n s = min(w, h)\n target_pil = target_pil.crop(((w - s) // 2, (h - s) // 2, (w + s) // 2, (h + s) // 2))\n target_pil= target_pil.convert('RGB')\n target_pil = target_pil.resize((Gs.output_shape[3], Gs.output_shape[2]), PIL.Image.ANTIALIAS)\n target_uint8 = np.array(target_pil, dtype=np.uint8)\n target_float = target_uint8.astype(np.float32).transpose([2, 0, 1]) * (2 / 255) - 1\n\n # Initialize projector.\n proj = projector.Projector()\n proj.set_network(Gs)\n proj.start([target_float])\n\n # Setup output directory.\n# os.makedirs(outdir, exist_ok=True)\n # target_pil.save(f'{outdir}/target.png')\n# writer = None\n# if save_video:\n# writer = imageio.get_writer(f'{outdir}/proj.mp4', mode='I', fps=60, codec='libx264', bitrate='16M')\n\n# # Run projector.\n with tqdm.trange(proj.num_steps) as t:\n for step in t:\n assert step == proj.cur_step\n# if writer is not None:\n# writer.append_data(np.concatenate([target_uint8, proj.images_uint8[0]], axis=1))\n dist, loss = proj.step()\n t.set_postfix(dist=f'{dist[0]:.4f}', loss=f'{loss:.2f}')\n\n # Save results.\n # PIL.Image.fromarray(proj.images_uint8[0], 'RGB').save(f'{outdir}/proj.png')\n# np.savez('out/dlatents.npz', dlatents=proj.dlatents)\n return proj.dlatents\n# if writer is not None:\n# writer.close()\n \n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dlatent = project(network_pkl, \"images/002_02.png\", \"out/\", False, 303)",
"Loading networks from \"https://nvlabs-fi-cdn.nvidia.com/stylegan2-ada/pretrained/ffhq.pkl\"...\nSetting up TensorFlow plugin \"fused_bias_act.cu\": Loading... Done.\nSetting up TensorFlow plugin \"upfirdn_2d.cu\": Loading... Done.\nProjector: Computing W midpoint and stddev using 10000 samples...\nProjector: std = 10.0058\nProjector: Setting up noise inputs...\nProjector: Building image output graph...\nProjector: Building loss graph...\nProjector: Building noise regularization graph...\nProjector: Setting up optimizer...\nProjector: Preparing target images...\nProjector: Initializing optimization state...\n"
],
[
"dlatent.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tflib.init_tf({'rnd.np_random_seed': 303})\nwith dnnlib.util.open_url(network_pkl) as fp:\n _G, _D, Gs = pickle.load(fp)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data = np.load('out/dlatents.npz')\ndlat = data[data.files[0]]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"image_float_expr = tf.cast(Gs.components.synthesis.get_output_for(dlat), tf.float32)\nimages_uint8_expr = tflib.convert_images_to_uint8(image_float_expr, nchw_to_nhwc=True)[0]\nimg = PIL.Image.fromarray(tflib.run(images_uint8_expr), 'RGB')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"img.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a75cbb22718dbc66e10359d45e2cb995a1efcdc
| 51,211 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
HMM Tagger.ipynb
|
vijender412/HMM-Tagger
|
8e5c6e191058b645f42ac0408311c49eb2e076c9
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
HMM Tagger.ipynb
|
vijender412/HMM-Tagger
|
8e5c6e191058b645f42ac0408311c49eb2e076c9
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
HMM Tagger.ipynb
|
vijender412/HMM-Tagger
|
8e5c6e191058b645f42ac0408311c49eb2e076c9
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 42.6403 | 660 | 0.592548 |
[
[
[
"# Project: Part of Speech Tagging with Hidden Markov Models \n---\n### Introduction\n\nPart of speech tagging is the process of determining the syntactic category of a word from the words in its surrounding context. It is often used to help disambiguate natural language phrases because it can be done quickly with high accuracy. Tagging can be used for many NLP tasks like determining correct pronunciation during speech synthesis (for example, _dis_-count as a noun vs dis-_count_ as a verb), for information retrieval, and for word sense disambiguation.\n\nIn this notebook, you'll use the [Pomegranate](http://pomegranate.readthedocs.io/) library to build a hidden Markov model for part of speech tagging using a \"universal\" tagset. Hidden Markov models have been able to achieve [>96% tag accuracy with larger tagsets on realistic text corpora](http://www.coli.uni-saarland.de/~thorsten/publications/Brants-ANLP00.pdf). Hidden Markov models have also been used for speech recognition and speech generation, machine translation, gene recognition for bioinformatics, and human gesture recognition for computer vision, and more. \n\n\n\nThe notebook already contains some code to get you started. You only need to add some new functionality in the areas indicated to complete the project; you will not need to modify the included code beyond what is requested. Sections that begin with **'IMPLEMENTATION'** in the header indicate that you must provide code in the block that follows. Instructions will be provided for each section, and the specifics of the implementation are marked in the code block with a 'TODO' statement. Please be sure to read the instructions carefully!",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<div class=\"alert alert-block alert-info\">\n**Note:** Once you have completed all of the code implementations, you need to finalize your work by exporting the iPython Notebook as an HTML document. Before exporting the notebook to html, all of the code cells need to have been run so that reviewers can see the final implementation and output. You must then **export the notebook** by running the last cell in the notebook, or by using the menu above and navigating to **File -> Download as -> HTML (.html)** Your submissions should include both the `html` and `ipynb` files.\n</div>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<div class=\"alert alert-block alert-info\">\n**Note:** Code and Markdown cells can be executed using the `Shift + Enter` keyboard shortcut. Markdown cells can be edited by double-clicking the cell to enter edit mode.\n</div>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### The Road Ahead\nYou must complete Steps 1-3 below to pass the project. The section on Step 4 includes references & resources you can use to further explore HMM taggers.\n\n- [Step 1](#Step-1:-Read-and-preprocess-the-dataset): Review the provided interface to load and access the text corpus\n- [Step 2](#Step-2:-Build-a-Most-Frequent-Class-tagger): Build a Most Frequent Class tagger to use as a baseline\n- [Step 3](#Step-3:-Build-an-HMM-tagger): Build an HMM Part of Speech tagger and compare to the MFC baseline\n- [Step 4](#Step-4:-[Optional]-Improving-model-performance): (Optional) Improve the HMM tagger",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<div class=\"alert alert-block alert-warning\">\n**Note:** Make sure you have selected a **Python 3** kernel in Workspaces or the hmm-tagger conda environment if you are running the Jupyter server on your own machine.\n</div>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Jupyter \"magic methods\" -- only need to be run once per kernel restart\n%load_ext autoreload\n%aimport helpers, tests\n%autoreload 1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# import python modules -- this cell needs to be run again if you make changes to any of the files\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\n\nfrom IPython.core.display import HTML\nfrom itertools import chain\nfrom collections import Counter, defaultdict\nfrom helpers import show_model, Dataset\nfrom pomegranate import State, HiddenMarkovModel, DiscreteDistribution",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Step 1: Read and preprocess the dataset\n---\nWe'll start by reading in a text corpus and splitting it into a training and testing dataset. The data set is a copy of the [Brown corpus](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brown_Corpus) (originally from the [NLTK](https://www.nltk.org/) library) that has already been pre-processed to only include the [universal tagset](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1104.2086.pdf). You should expect to get slightly higher accuracy using this simplified tagset than the same model would achieve on a larger tagset like the full [Penn treebank tagset](https://www.ling.upenn.edu/courses/Fall_2003/ling001/penn_treebank_pos.html), but the process you'll follow would be the same.\n\nThe `Dataset` class provided in helpers.py will read and parse the corpus. You can generate your own datasets compatible with the reader by writing them to the following format. The dataset is stored in plaintext as a collection of words and corresponding tags. Each sentence starts with a unique identifier on the first line, followed by one tab-separated word/tag pair on each following line. Sentences are separated by a single blank line.\n\nExample from the Brown corpus. \n```\nb100-38532\nPerhaps\tADV\nit\tPRON\nwas\tVERB\nright\tADJ\n;\t.\n;\t.\n\nb100-35577\n...\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data = Dataset(\"tags-universal.txt\", \"brown-universal.txt\", train_test_split=0.8)\n\nprint(\"There are {} sentences in the corpus.\".format(len(data)))\nprint(\"There are {} sentences in the training set.\".format(len(data.training_set)))\nprint(\"There are {} sentences in the testing set.\".format(len(data.testing_set)))\n\nassert len(data) == len(data.training_set) + len(data.testing_set), \\\n \"The number of sentences in the training set + testing set should sum to the number of sentences in the corpus\"",
"There are 57340 sentences in the corpus.\nThere are 45872 sentences in the training set.\nThere are 11468 sentences in the testing set.\n"
]
],
[
[
"### The Dataset Interface\n\nYou can access (mostly) immutable references to the dataset through a simple interface provided through the `Dataset` class, which represents an iterable collection of sentences along with easy access to partitions of the data for training & testing. Review the reference below, then run and review the next few cells to make sure you understand the interface before moving on to the next step.\n\n```\nDataset-only Attributes:\n training_set - reference to a Subset object containing the samples for training\n testing_set - reference to a Subset object containing the samples for testing\n\nDataset & Subset Attributes:\n sentences - a dictionary with an entry {sentence_key: Sentence()} for each sentence in the corpus\n keys - an immutable ordered (not sorted) collection of the sentence_keys for the corpus\n vocab - an immutable collection of the unique words in the corpus\n tagset - an immutable collection of the unique tags in the corpus\n X - returns an array of words grouped by sentences ((w11, w12, w13, ...), (w21, w22, w23, ...), ...)\n Y - returns an array of tags grouped by sentences ((t11, t12, t13, ...), (t21, t22, t23, ...), ...)\n N - returns the number of distinct samples (individual words or tags) in the dataset\n\nMethods:\n stream() - returns an flat iterable over all (word, tag) pairs across all sentences in the corpus\n __iter__() - returns an iterable over the data as (sentence_key, Sentence()) pairs\n __len__() - returns the nubmer of sentences in the dataset\n```\n\nFor example, consider a Subset, `subset`, of the sentences `{\"s0\": Sentence((\"See\", \"Spot\", \"run\"), (\"VERB\", \"NOUN\", \"VERB\")), \"s1\": Sentence((\"Spot\", \"ran\"), (\"NOUN\", \"VERB\"))}`. The subset will have these attributes:\n\n```\nsubset.keys == {\"s1\", \"s0\"} # unordered\nsubset.vocab == {\"See\", \"run\", \"ran\", \"Spot\"} # unordered\nsubset.tagset == {\"VERB\", \"NOUN\"} # unordered\nsubset.X == ((\"Spot\", \"ran\"), (\"See\", \"Spot\", \"run\")) # order matches .keys\nsubset.Y == ((\"NOUN\", \"VERB\"), (\"VERB\", \"NOUN\", \"VERB\")) # order matches .keys\nsubset.N == 7 # there are a total of seven observations over all sentences\nlen(subset) == 2 # because there are two sentences\n```\n\n<div class=\"alert alert-block alert-info\">\n**Note:** The `Dataset` class is _convenient_, but it is **not** efficient. It is not suitable for huge datasets because it stores multiple redundant copies of the same data.\n</div>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Sentences\n\n`Dataset.sentences` is a dictionary of all sentences in the training corpus, each keyed to a unique sentence identifier. Each `Sentence` is itself an object with two attributes: a tuple of the words in the sentence named `words` and a tuple of the tag corresponding to each word named `tags`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"key = 'b100-38532'\nprint(\"Sentence: {}\".format(key))\nprint(\"words:\\n\\t{!s}\".format(data.sentences[key].words))\nprint(\"tags:\\n\\t{!s}\".format(data.sentences[key].tags))",
"Sentence: b100-38532\nwords:\n\t('Perhaps', 'it', 'was', 'right', ';', ';')\ntags:\n\t('ADV', 'PRON', 'VERB', 'ADJ', '.', '.')\n"
]
],
[
[
"<div class=\"alert alert-block alert-info\">\n**Note:** The underlying iterable sequence is **unordered** over the sentences in the corpus; it is not guaranteed to return the sentences in a consistent order between calls. Use `Dataset.stream()`, `Dataset.keys`, `Dataset.X`, or `Dataset.Y` attributes if you need ordered access to the data.\n</div>\n\n#### Counting Unique Elements\n\nYou can access the list of unique words (the dataset vocabulary) via `Dataset.vocab` and the unique list of tags via `Dataset.tagset`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(\"There are a total of {} samples of {} unique words in the corpus.\"\n .format(data.N, len(data.vocab)))\nprint(\"There are {} samples of {} unique words in the training set.\"\n .format(data.training_set.N, len(data.training_set.vocab)))\nprint(\"There are {} samples of {} unique words in the testing set.\"\n .format(data.testing_set.N, len(data.testing_set.vocab)))\nprint(\"There are {} words in the test set that are missing in the training set.\"\n .format(len(data.testing_set.vocab - data.training_set.vocab)))\n\nassert data.N == data.training_set.N + data.testing_set.N, \\\n \"The number of training + test samples should sum to the total number of samples\"",
"There are a total of 1161192 samples of 56057 unique words in the corpus.\nThere are 928458 samples of 50536 unique words in the training set.\nThere are 232734 samples of 25112 unique words in the testing set.\nThere are 5521 words in the test set that are missing in the training set.\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### Accessing word and tag Sequences\nThe `Dataset.X` and `Dataset.Y` attributes provide access to ordered collections of matching word and tag sequences for each sentence in the dataset.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# accessing words with Dataset.X and tags with Dataset.Y \nfor i in range(2): \n print(\"Sentence {}:\".format(i + 1), data.X[i])\n print()\n print(\"Labels {}:\".format(i + 1), data.Y[i])\n print()",
"Sentence 1: ('Mr.', 'Podger', 'had', 'thanked', 'him', 'gravely', ',', 'and', 'now', 'he', 'made', 'use', 'of', 'the', 'advice', '.')\n\nLabels 1: ('NOUN', 'NOUN', 'VERB', 'VERB', 'PRON', 'ADV', '.', 'CONJ', 'ADV', 'PRON', 'VERB', 'NOUN', 'ADP', 'DET', 'NOUN', '.')\n\nSentence 2: ('But', 'there', 'seemed', 'to', 'be', 'some', 'difference', 'of', 'opinion', 'as', 'to', 'how', 'far', 'the', 'board', 'should', 'go', ',', 'and', 'whose', 'advice', 'it', 'should', 'follow', '.')\n\nLabels 2: ('CONJ', 'PRT', 'VERB', 'PRT', 'VERB', 'DET', 'NOUN', 'ADP', 'NOUN', 'ADP', 'ADP', 'ADV', 'ADV', 'DET', 'NOUN', 'VERB', 'VERB', '.', 'CONJ', 'DET', 'NOUN', 'PRON', 'VERB', 'VERB', '.')\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### Accessing (word, tag) Samples\nThe `Dataset.stream()` method returns an iterator that chains together every pair of (word, tag) entries across all sentences in the entire corpus.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# use Dataset.stream() (word, tag) samples for the entire corpus\nprint(\"\\nStream (word, tag) pairs:\\n\")\nfor i, pair in enumerate(data.stream()):\n print(\"\\t\", pair)\n if i > 5: break",
"\nStream (word, tag) pairs:\n\n\t ('Mr.', 'NOUN')\n\t ('Podger', 'NOUN')\n\t ('had', 'VERB')\n\t ('thanked', 'VERB')\n\t ('him', 'PRON')\n\t ('gravely', 'ADV')\n\t (',', '.')\n"
]
],
[
[
"\nFor both our baseline tagger and the HMM model we'll build, we need to estimate the frequency of tags & words from the frequency counts of observations in the training corpus. In the next several cells you will complete functions to compute the counts of several sets of counts. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Step 2: Build a Most Frequent Class tagger\n---\n\nPerhaps the simplest tagger (and a good baseline for tagger performance) is to simply choose the tag most frequently assigned to each word. This \"most frequent class\" tagger inspects each observed word in the sequence and assigns it the label that was most often assigned to that word in the corpus.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### IMPLEMENTATION: Pair Counts\n\nComplete the function below that computes the joint frequency counts for two input sequences.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from collections import Counter, defaultdict\ndef pair_counts(sequences_A, sequences_B):\n \"\"\"Return a dictionary keyed to each unique value in the first sequence list\n that counts the number of occurrences of the corresponding value from the\n second sequences list.\n \n For example, if sequences_A is tags and sequences_B is the corresponding\n words, then if 1244 sequences contain the word \"time\" tagged as a NOUN, then\n you should return a dictionary such that pair_counts[NOUN][time] == 1244\n \"\"\"\n # TODO: Finish this function!\n result = defaultdict(lambda: defaultdict(int))\n\n for tag,word in zip(sequences_A,sequences_B):\n result[tag][word]+=1\n\n return result\n raise NotImplementedError\n\n\n# Calculate C(t_i, w_i)\ntags = [tag for i, (word, tag) in enumerate(data.training_set.stream())]\nwords = [word for i, (word, tag) in enumerate(data.training_set.stream())]\nemission_counts = pair_counts(tags,words)\n\nassert len(emission_counts) == 12,\"Uh oh. There should be 12 tags in your dictionary.\"\nassert max(emission_counts[\"NOUN\"], key=emission_counts[\"NOUN\"].get) == 'time', \\\n \"Hmmm...'time' is expected to be the most common NOUN.\"\nHTML('<div class=\"alert alert-block alert-success\">Your emission counts look good!</div>')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### IMPLEMENTATION: Most Frequent Class Tagger\n\nUse the `pair_counts()` function and the training dataset to find the most frequent class label for each word in the training data, and populate the `mfc_table` below. The table keys should be words, and the values should be the appropriate tag string.\n\nThe `MFCTagger` class is provided to mock the interface of Pomegranite HMM models so that they can be used interchangeably.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create a lookup table mfc_table where mfc_table[word] contains the tag label most frequently assigned to that word\nfrom collections import namedtuple\n\nFakeState = namedtuple(\"FakeState\", \"name\")\n\nclass MFCTagger:\n # NOTE: You should not need to modify this class or any of its methods\n missing = FakeState(name=\"<MISSING>\")\n \n def __init__(self, table):\n self.table = defaultdict(lambda: MFCTagger.missing)\n self.table.update({word: FakeState(name=tag) for word, tag in table.items()})\n \n def viterbi(self, seq):\n \"\"\"This method simplifies predictions by matching the Pomegranate viterbi() interface\"\"\"\n return 0., list(enumerate([\"<start>\"] + [self.table[w] for w in seq] + [\"<end>\"]))\n\n\n# TODO: calculate the frequency of each tag being assigned to each word (hint: similar, but not\n# the same as the emission probabilities) and use it to fill the mfc_table\n\nword_counts = pair_counts(words,tags)\n\nmfc_table = dict((word, max(tags.keys(), key=lambda key: tags[key])) for word, tags in word_counts.items())\n\n# DO NOT MODIFY BELOW THIS LINE\nmfc_model = MFCTagger(mfc_table) # Create a Most Frequent Class tagger instance\n\nassert len(mfc_table) == len(data.training_set.vocab), \"\"\nassert all(k in data.training_set.vocab for k in mfc_table.keys()), \"\"\nassert sum(int(k not in mfc_table) for k in data.testing_set.vocab) == 5521, \"\"\nHTML('<div class=\"alert alert-block alert-success\">Your MFC tagger has all the correct words!</div>')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Making Predictions with a Model\nThe helper functions provided below interface with Pomegranate network models & the mocked MFCTagger to take advantage of the [missing value](http://pomegranate.readthedocs.io/en/latest/nan.html) functionality in Pomegranate through a simple sequence decoding function. Run these functions, then run the next cell to see some of the predictions made by the MFC tagger.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def replace_unknown(sequence):\n \"\"\"Return a copy of the input sequence where each unknown word is replaced\n by the literal string value 'nan'. Pomegranate will ignore these values\n during computation.\n \"\"\"\n return [w if w in data.training_set.vocab else 'nan' for w in sequence]\n\ndef simplify_decoding(X, model):\n \"\"\"X should be a 1-D sequence of observations for the model to predict\"\"\"\n _, state_path = model.viterbi(replace_unknown(X))\n return [state[1].name for state in state_path[1:-1]] # do not show the start/end state predictions",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Example Decoding Sequences with MFC Tagger",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for key in data.testing_set.keys[:3]:\n print(\"Sentence Key: {}\\n\".format(key))\n print(\"Predicted labels:\\n-----------------\")\n print(simplify_decoding(data.sentences[key].words, mfc_model))\n print()\n print(\"Actual labels:\\n--------------\")\n print(data.sentences[key].tags)\n print(\"\\n\")",
"Sentence Key: b100-28144\n\nPredicted labels:\n-----------------\n['CONJ', 'NOUN', 'NUM', '.', 'NOUN', 'NUM', '.', 'NOUN', 'NUM', '.', 'CONJ', 'NOUN', 'NUM', '.', '.', 'NOUN', '.', '.']\n\nActual labels:\n--------------\n('CONJ', 'NOUN', 'NUM', '.', 'NOUN', 'NUM', '.', 'NOUN', 'NUM', '.', 'CONJ', 'NOUN', 'NUM', '.', '.', 'NOUN', '.', '.')\n\n\nSentence Key: b100-23146\n\nPredicted labels:\n-----------------\n['PRON', 'VERB', 'DET', 'NOUN', 'ADP', 'ADJ', 'ADJ', 'NOUN', 'VERB', 'VERB', '.', 'ADP', 'VERB', 'DET', 'NOUN', 'ADP', 'NOUN', 'ADP', 'DET', 'NOUN', '.']\n\nActual labels:\n--------------\n('PRON', 'VERB', 'DET', 'NOUN', 'ADP', 'ADJ', 'ADJ', 'NOUN', 'VERB', 'VERB', '.', 'ADP', 'VERB', 'DET', 'NOUN', 'ADP', 'NOUN', 'ADP', 'DET', 'NOUN', '.')\n\n\nSentence Key: b100-35462\n\nPredicted labels:\n-----------------\n['DET', 'ADJ', 'NOUN', 'VERB', 'VERB', 'VERB', 'ADP', 'DET', 'ADJ', 'ADJ', 'NOUN', 'ADP', 'DET', 'ADJ', 'NOUN', '.', 'ADP', 'ADJ', 'NOUN', '.', 'CONJ', 'ADP', 'DET', '<MISSING>', 'ADP', 'ADJ', 'ADJ', '.', 'ADJ', '.', 'CONJ', 'ADJ', 'NOUN', 'ADP', 'ADV', 'NOUN', '.']\n\nActual labels:\n--------------\n('DET', 'ADJ', 'NOUN', 'VERB', 'VERB', 'VERB', 'ADP', 'DET', 'ADJ', 'ADJ', 'NOUN', 'ADP', 'DET', 'ADJ', 'NOUN', '.', 'ADP', 'ADJ', 'NOUN', '.', 'CONJ', 'ADP', 'DET', 'NOUN', 'ADP', 'ADJ', 'ADJ', '.', 'ADJ', '.', 'CONJ', 'ADJ', 'NOUN', 'ADP', 'ADJ', 'NOUN', '.')\n\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Evaluating Model Accuracy\n\nThe function below will evaluate the accuracy of the MFC tagger on the collection of all sentences from a text corpus. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def accuracy(X, Y, model):\n \"\"\"Calculate the prediction accuracy by using the model to decode each sequence\n in the input X and comparing the prediction with the true labels in Y.\n \n The X should be an array whose first dimension is the number of sentences to test,\n and each element of the array should be an iterable of the words in the sequence.\n The arrays X and Y should have the exact same shape.\n \n X = [(\"See\", \"Spot\", \"run\"), (\"Run\", \"Spot\", \"run\", \"fast\"), ...]\n Y = [(), (), ...]\n \"\"\"\n correct = total_predictions = 0\n for observations, actual_tags in zip(X, Y):\n \n # The model.viterbi call in simplify_decoding will return None if the HMM\n # raises an error (for example, if a test sentence contains a word that\n # is out of vocabulary for the training set). Any exception counts the\n # full sentence as an error (which makes this a conservative estimate).\n try:\n most_likely_tags = simplify_decoding(observations, model)\n correct += sum(p == t for p, t in zip(most_likely_tags, actual_tags))\n except:\n pass\n total_predictions += len(observations)\n return correct / total_predictions",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Evaluate the accuracy of the MFC tagger\nRun the next cell to evaluate the accuracy of the tagger on the training and test corpus.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mfc_training_acc = accuracy(data.training_set.X, data.training_set.Y, mfc_model)\nprint(\"training accuracy mfc_model: {:.2f}%\".format(100 * mfc_training_acc))\n\nmfc_testing_acc = accuracy(data.testing_set.X, data.testing_set.Y, mfc_model)\nprint(\"testing accuracy mfc_model: {:.2f}%\".format(100 * mfc_testing_acc))\n\nassert mfc_training_acc >= 0.955, \"Uh oh. Your MFC accuracy on the training set doesn't look right.\"\nassert mfc_testing_acc >= 0.925, \"Uh oh. Your MFC accuracy on the testing set doesn't look right.\"\nHTML('<div class=\"alert alert-block alert-success\">Your MFC tagger accuracy looks correct!</div>')",
"training accuracy mfc_model: 95.72%\ntesting accuracy mfc_model: 93.01%\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Step 3: Build an HMM tagger\n---\nThe HMM tagger has one hidden state for each possible tag, and parameterized by two distributions: the emission probabilties giving the conditional probability of observing a given **word** from each hidden state, and the transition probabilities giving the conditional probability of moving between **tags** during the sequence.\n\nWe will also estimate the starting probability distribution (the probability of each **tag** being the first tag in a sequence), and the terminal probability distribution (the probability of each **tag** being the last tag in a sequence).\n\nThe maximum likelihood estimate of these distributions can be calculated from the frequency counts as described in the following sections where you'll implement functions to count the frequencies, and finally build the model. The HMM model will make predictions according to the formula:\n\n$$t_i^n = \\underset{t_i^n}{\\mathrm{argmax}} \\prod_{i=1}^n P(w_i|t_i) P(t_i|t_{i-1})$$\n\nRefer to Speech & Language Processing [Chapter 10](https://web.stanford.edu/~jurafsky/slp3/10.pdf) for more information.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### IMPLEMENTATION: Unigram Counts\n\nComplete the function below to estimate the co-occurrence frequency of each symbol over all of the input sequences. The unigram probabilities in our HMM model are estimated from the formula below, where N is the total number of samples in the input. (You only need to compute the counts for now.)\n\n$$P(tag_1) = \\frac{C(tag_1)}{N}$$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def unigram_counts(sequences):\n \"\"\"Return a dictionary keyed to each unique value in the input sequence list that\n counts the number of occurrences of the value in the sequences list. The sequences\n collection should be a 2-dimensional array.\n \n For example, if the tag NOUN appears 275558 times over all the input sequences,\n then you should return a dictionary such that your_unigram_counts[NOUN] == 275558.\n \"\"\"\n # TODO: Finish this function!\n return Counter(sequences)\n raise NotImplementedError\n\n# TODO: call unigram_counts with a list of tag sequences from the training set\ntag_unigrams = unigram_counts(tags)\n\nassert set(tag_unigrams.keys()) == data.training_set.tagset, \\\n \"Uh oh. It looks like your tag counts doesn't include all the tags!\"\nassert min(tag_unigrams, key=tag_unigrams.get) == 'X', \\\n \"Hmmm...'X' is expected to be the least common class\"\nassert max(tag_unigrams, key=tag_unigrams.get) == 'NOUN', \\\n \"Hmmm...'NOUN' is expected to be the most common class\"\nHTML('<div class=\"alert alert-block alert-success\">Your tag unigrams look good!</div>')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### IMPLEMENTATION: Bigram Counts\n\nComplete the function below to estimate the co-occurrence frequency of each pair of symbols in each of the input sequences. These counts are used in the HMM model to estimate the bigram probability of two tags from the frequency counts according to the formula: $$P(tag_2|tag_1) = \\frac{C(tag_2|tag_1)}{C(tag_2)}$$\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def bigram_counts(sequences):\n \"\"\"Return a dictionary keyed to each unique PAIR of values in the input sequences\n list that counts the number of occurrences of pair in the sequences list. The input\n should be a 2-dimensional array.\n \n For example, if the pair of tags (NOUN, VERB) appear 61582 times, then you should\n return a dictionary such that your_bigram_counts[(NOUN, VERB)] == 61582\n \"\"\"\n\n # TODO: Finish this function!\n d = Counter(sequences)\n return d\n raise NotImplementedError\n\n# TODO: call bigram_counts with a list of tag sequences from the training set\ntags = [tag for i, (word, tag) in enumerate(data.stream())]\nnew_d = [(tags[i],tags[i+1]) for i in range(0,len(tags)-2,2)]\ntag_bigrams = bigram_counts(new_d)\n\nassert len(tag_bigrams) == 144, \\\n \"Uh oh. There should be 144 pairs of bigrams (12 tags x 12 tags)\"\nassert min(tag_bigrams, key=tag_bigrams.get) in [('X', 'NUM'), ('PRON', 'X')], \\\n \"Hmmm...The least common bigram should be one of ('X', 'NUM') or ('PRON', 'X').\"\nassert max(tag_bigrams, key=tag_bigrams.get) in [('DET', 'NOUN')], \\\n \"Hmmm...('DET', 'NOUN') is expected to be the most common bigram.\"\nHTML('<div class=\"alert alert-block alert-success\">Your tag bigrams look good!</div>')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### IMPLEMENTATION: Sequence Starting Counts\nComplete the code below to estimate the bigram probabilities of a sequence starting with each tag.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def starting_counts(sequences):\n \"\"\"Return a dictionary keyed to each unique value in the input sequences list\n that counts the number of occurrences where that value is at the beginning of\n a sequence.\n \n For example, if 8093 sequences start with NOUN, then you should return a\n dictionary such that your_starting_counts[NOUN] == 8093\n \"\"\"\n # TODO: Finish this function!\n d = Counter(sequences)\n return d\n raise NotImplementedError\n\n# TODO: Calculate the count of each tag starting a sequence\nstarting_tag = [i[0] for i in data.Y]\ntag_starts = starting_counts(starting_tag)\n\nassert len(tag_starts) == 12, \"Uh oh. There should be 12 tags in your dictionary.\"\nassert min(tag_starts, key=tag_starts.get) == 'X', \"Hmmm...'X' is expected to be the least common starting bigram.\"\nassert max(tag_starts, key=tag_starts.get) == 'DET', \"Hmmm...'DET' is expected to be the most common starting bigram.\"\nHTML('<div class=\"alert alert-block alert-success\">Your starting tag counts look good!</div>')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### IMPLEMENTATION: Sequence Ending Counts\nComplete the function below to estimate the bigram probabilities of a sequence ending with each tag.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def ending_counts(sequences):\n \"\"\"Return a dictionary keyed to each unique value in the input sequences list\n that counts the number of occurrences where that value is at the end of\n a sequence.\n \n For example, if 18 sequences end with DET, then you should return a\n dictionary such that your_starting_counts[DET] == 18\n \"\"\"\n # TODO: Finish this function!\n d = Counter(sequences)\n return d\n raise NotImplementedError\n\n# TODO: Calculate the count of each tag ending a sequence\nending_tag = [i[len(i)-1] for i in data.Y]\ntag_ends = ending_counts(ending_tag)\n\nassert len(tag_ends) == 12, \"Uh oh. There should be 12 tags in your dictionary.\"\nassert min(tag_ends, key=tag_ends.get) in ['X', 'CONJ'], \"Hmmm...'X' or 'CONJ' should be the least common ending bigram.\"\nassert max(tag_ends, key=tag_ends.get) == '.', \"Hmmm...'.' is expected to be the most common ending bigram.\"\nHTML('<div class=\"alert alert-block alert-success\">Your ending tag counts look good!</div>')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### IMPLEMENTATION: Basic HMM Tagger\nUse the tag unigrams and bigrams calculated above to construct a hidden Markov tagger.\n\n- Add one state per tag\n - The emission distribution at each state should be estimated with the formula: $P(w|t) = \\frac{C(t, w)}{C(t)}$\n- Add an edge from the starting state `basic_model.start` to each tag\n - The transition probability should be estimated with the formula: $P(t|start) = \\frac{C(start, t)}{C(start)}$\n- Add an edge from each tag to the end state `basic_model.end`\n - The transition probability should be estimated with the formula: $P(end|t) = \\frac{C(t, end)}{C(t)}$\n- Add an edge between _every_ pair of tags\n - The transition probability should be estimated with the formula: $P(t_2|t_1) = \\frac{C(t_1, t_2)}{C(t_1)}$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"basic_model = HiddenMarkovModel(name=\"base-hmm-tagger\")\n\n# TODO: create states with emission probability distributions P(word | tag) and add to the model\ntags = [tag for i, (word, tag) in enumerate(data.stream())]\nwords = [word for i, (word, tag) in enumerate(data.stream())]\n\n#Calling functions\ntags_count=unigram_counts(tags)\ntag_words_count=pair_counts(tags,words)\n\nstarting_tag = [i[0] for i in data.Y]\nending_tag = [i[-1] for i in data.Y]\n\nstarting_tag_counts = starting_counts(starting_tag)\nending_tag_counts = ending_counts(ending_tag) \n\nstates = []\nfor tag, words_dict in tag_words_count.items():\n total = float(sum(words_dict.values()))\n distribution = {word: count/total for word, count in words_dict.items()}\n tag_emissions = DiscreteDistribution(distribution)\n tag_state = State(tag_emissions, name=tag)\n states.append(tag_state)\n\n# (Hint: you may need to loop & create/add new states)\nbasic_model.add_states()\n\nstart_prob={} #a dict to store \n\nfor tag in tags:\n start_prob[tag]=starting_tag_counts[tag]/tags_count[tag]\n\nfor tag_state in states :\n basic_model.add_transition(basic_model.start,tag_state,start_prob[tag_state.name]) \n\nend_prob={}\n\nfor tag in tags:\n end_prob[tag]=ending_tag_counts[tag]/tags_count[tag]\nfor tag_state in states :\n basic_model.add_transition(tag_state,basic_model.end,end_prob[tag_state.name])\n \n\n# TODO: add edges between states for the observed transition frequencies P(tag_i | tag_i-1)\n# (Hint: you may need to loop & add transitions\n# basic_model.add_transition()\n\ntransition_prob_pair={}\n\nfor key in tag_bigrams.keys():\n transition_prob_pair[key]=tag_bigrams.get(key)/tags_count[key[0]]\nfor tag_state in states :\n for next_tag_state in states :\n basic_model.add_transition(tag_state,next_tag_state,transition_prob_pair[(tag_state.name,next_tag_state.name)])\n\n\n# NOTE: YOU SHOULD NOT NEED TO MODIFY ANYTHING BELOW THIS LINE\n# finalize the model\nbasic_model.bake()\n\nassert all(tag in set(s.name for s in basic_model.states) for tag in data.training_set.tagset), \\\n \"Every state in your network should use the name of the associated tag, which must be one of the training set tags.\"\nassert basic_model.edge_count() == 168, \\\n (\"Your network should have an edge from the start node to each state, one edge between every \" +\n \"pair of tags (states), and an edge from each state to the end node.\")\nHTML('<div class=\"alert alert-block alert-success\">Your HMM network topology looks good!</div>')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"hmm_training_acc = accuracy(data.training_set.X, data.training_set.Y, basic_model)\nprint(\"training accuracy basic hmm model: {:.2f}%\".format(100 * hmm_training_acc))\n\nhmm_testing_acc = accuracy(data.testing_set.X, data.testing_set.Y, basic_model)\nprint(\"testing accuracy basic hmm model: {:.2f}%\".format(100 * hmm_testing_acc))\n\nassert hmm_training_acc > 0.97, \"Uh oh. Your HMM accuracy on the training set doesn't look right.\"\nassert hmm_testing_acc > 0.955, \"Uh oh. Your HMM accuracy on the testing set doesn't look right.\"\nHTML('<div class=\"alert alert-block alert-success\">Your HMM tagger accuracy looks correct! Congratulations, you\\'ve finished the project.</div>')",
"training accuracy basic hmm model: 97.49%\ntesting accuracy basic hmm model: 96.09%\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Example Decoding Sequences with the HMM Tagger",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for key in data.testing_set.keys[:3]:\n print(\"Sentence Key: {}\\n\".format(key))\n print(\"Predicted labels:\\n-----------------\")\n print(simplify_decoding(data.sentences[key].words, basic_model))\n print()\n print(\"Actual labels:\\n--------------\")\n print(data.sentences[key].tags)\n print(\"\\n\")",
"Sentence Key: b100-28144\n\nPredicted labels:\n-----------------\n['CONJ', 'NOUN', 'NUM', '.', 'NOUN', 'NUM', '.', 'NOUN', 'NUM', '.', 'CONJ', 'NOUN', 'NUM', '.', '.', 'NOUN', '.', '.']\n\nActual labels:\n--------------\n('CONJ', 'NOUN', 'NUM', '.', 'NOUN', 'NUM', '.', 'NOUN', 'NUM', '.', 'CONJ', 'NOUN', 'NUM', '.', '.', 'NOUN', '.', '.')\n\n\nSentence Key: b100-23146\n\nPredicted labels:\n-----------------\n['PRON', 'VERB', 'DET', 'NOUN', 'ADP', 'ADJ', 'ADJ', 'NOUN', 'VERB', 'VERB', '.', 'ADP', 'VERB', 'DET', 'NOUN', 'ADP', 'NOUN', 'ADP', 'DET', 'NOUN', '.']\n\nActual labels:\n--------------\n('PRON', 'VERB', 'DET', 'NOUN', 'ADP', 'ADJ', 'ADJ', 'NOUN', 'VERB', 'VERB', '.', 'ADP', 'VERB', 'DET', 'NOUN', 'ADP', 'NOUN', 'ADP', 'DET', 'NOUN', '.')\n\n\nSentence Key: b100-35462\n\nPredicted labels:\n-----------------\n['DET', 'ADJ', 'NOUN', 'VERB', 'VERB', 'VERB', 'ADP', 'DET', 'ADJ', 'ADJ', 'NOUN', 'ADP', 'DET', 'ADJ', 'NOUN', '.', 'ADP', 'ADJ', 'NOUN', '.', 'CONJ', 'ADP', 'DET', 'NOUN', 'ADP', 'ADJ', 'ADJ', '.', 'ADJ', '.', 'CONJ', 'ADJ', 'NOUN', 'ADP', 'ADJ', 'NOUN', '.']\n\nActual labels:\n--------------\n('DET', 'ADJ', 'NOUN', 'VERB', 'VERB', 'VERB', 'ADP', 'DET', 'ADJ', 'ADJ', 'NOUN', 'ADP', 'DET', 'ADJ', 'NOUN', '.', 'ADP', 'ADJ', 'NOUN', '.', 'CONJ', 'ADP', 'DET', 'NOUN', 'ADP', 'ADJ', 'ADJ', '.', 'ADJ', '.', 'CONJ', 'ADJ', 'NOUN', 'ADP', 'ADJ', 'NOUN', '.')\n\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"\n## Finishing the project\n---\n\n<div class=\"alert alert-block alert-info\">\n**Note:** **SAVE YOUR NOTEBOOK**, then run the next cell to generate an HTML copy. You will zip & submit both this file and the HTML copy for review.\n</div>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!!jupyter nbconvert *.ipynb",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Step 4: [Optional] Improving model performance\n---\nThere are additional enhancements that can be incorporated into your tagger that improve performance on larger tagsets where the data sparsity problem is more significant. The data sparsity problem arises because the same amount of data split over more tags means there will be fewer samples in each tag, and there will be more missing data tags that have zero occurrences in the data. The techniques in this section are optional.\n\n- [Laplace Smoothing](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Additive_smoothing) (pseudocounts)\n Laplace smoothing is a technique where you add a small, non-zero value to all observed counts to offset for unobserved values.\n\n- Backoff Smoothing\n Another smoothing technique is to interpolate between n-grams for missing data. This method is more effective than Laplace smoothing at combatting the data sparsity problem. Refer to chapters 4, 9, and 10 of the [Speech & Language Processing](https://web.stanford.edu/~jurafsky/slp3/) book for more information.\n\n- Extending to Trigrams\n HMM taggers have achieved better than 96% accuracy on this dataset with the full Penn treebank tagset using an architecture described in [this](http://www.coli.uni-saarland.de/~thorsten/publications/Brants-ANLP00.pdf) paper. Altering your HMM to achieve the same performance would require implementing deleted interpolation (described in the paper), incorporating trigram probabilities in your frequency tables, and re-implementing the Viterbi algorithm to consider three consecutive states instead of two.\n\n### Obtain the Brown Corpus with a Larger Tagset\nRun the code below to download a copy of the brown corpus with the full NLTK tagset. You will need to research the available tagset information in the NLTK docs and determine the best way to extract the subset of NLTK tags you want to explore. If you write the following the format specified in Step 1, then you can reload the data using all of the code above for comparison.\n\nRefer to [Chapter 5](http://www.nltk.org/book/ch05.html) of the NLTK book for more information on the available tagsets.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import nltk\nfrom nltk import pos_tag, word_tokenize\nfrom nltk.corpus import brown\n\nnltk.download('brown')\ntraining_corpus = nltk.corpus.brown\ntraining_corpus.tagged_sents()[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a75d3d93b831c34b4d7f96f48bd9326e741049f
| 4,451 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
test/cpp/Updateleafflag.ipynb
|
Crop2ML-Catalog/SQ_Wheat_Phenology
|
8e9ec229e5f0754d0f4b9d79ac96a084d75dde67
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2018-12-06T07:54:25.000Z
|
2022-02-03T16:31:33.000Z
|
test/cpp/Updateleafflag.ipynb
|
Crop2ML-Catalog/SQ_Wheat_Phenology
|
8e9ec229e5f0754d0f4b9d79ac96a084d75dde67
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2018-12-06T07:51:42.000Z
|
2020-11-14T18:03:12.000Z
|
test/cpp/Updateleafflag.ipynb
|
Crop2ML-Catalog/SQ_Wheat_Phenology
|
8e9ec229e5f0754d0f4b9d79ac96a084d75dde67
|
[
"MIT"
] | 5 |
2018-12-10T12:11:46.000Z
|
2022-03-04T10:52:03.000Z
| 45.418367 | 338 | 0.536059 |
[
[
[
"empty"
]
]
] |
[
"empty"
] |
[
[
"empty"
]
] |
4a75e34843ae7e85805e7015a6f6a9056e27e2ae
| 94,945 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/dnn5.ipynb
|
maxrousseau/dl-anesthesia
|
e5de2ecfc9d9e954f3ee36eedb13332589dfc27e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/dnn5.ipynb
|
maxrousseau/dl-anesthesia
|
e5de2ecfc9d9e954f3ee36eedb13332589dfc27e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/dnn5.ipynb
|
maxrousseau/dl-anesthesia
|
e5de2ecfc9d9e954f3ee36eedb13332589dfc27e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 166.570175 | 34,488 | 0.836263 |
[
[
[
"# Deep Neural Network with 5 Input Features\n\nIn this notebook we will train a deep neural network using 5 input feature to perform binary classification of our dataset.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Setup\n\nWe first need to import the libraries and frameworks to help us create and train our model. \n\n- Numpy will allow us to manipulate our input data\n- Matplotlib gives us easy graphs to visualize performance\n- Sklearn helps us with data normalization and shuffling\n- Keras is our deep learning frameworks which makes it easy to create and train our model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#!bin/env/python3\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import Normalizer\nfrom sklearn.utils import shuffle\n\nfrom tensorflow.keras import models\nfrom tensorflow.keras import layers",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Load Data\n\nHere we load the numpy array that we create previously. Let's check the dimension to make sure they are correctly formatted.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"X = np.load(\"../db/x3.npy\")\nY = np.load(\"../db/y3.npy\")\n\nprint(\"X: \" + str(X.shape))\nprint(\"Y: \" + str(Y.shape))",
"X: (3559, 30)\nY: (3559,)\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Data Preparation\n\nThe neural network will perform better during training if data is normalized. We also want to shuffle the inputs to avoid training out model on a skewed dataset.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"transformer = Normalizer().fit(X)\nX = transformer.transform(X) # normalizes data according to columns\nX, Y = shuffle(X, Y, random_state=0) # shuffle the samples",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Training - Test Split\n\nIdeally we would split our dataset into a training, validation and test set. For this example we will only use a training and validation set. The training set will have 3000 samples and the validation set will contain the remaining samples.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"X_train = X[:3000]\nY_train = Y[:3000]\n\n\nX_test = X[3000:]\nY_test = Y[3000:]\n\n# 3000 training samples\nprint(\"Input training tensor: \" + str(X_train.shape))\nprint(\"Label training tensor: \" + str(Y_train.shape) + \"\\n\")\n\n# 559 test/validation samples\nprint(\"Input validation tensor: \" + str(X_test.shape))\nprint(\"Label validation tensor: \" + str(Y_test.shape))",
"Input training tensor: (3000, 30)\nLabel training tensor: (3000,)\n\nInput validation tensor: (559, 30)\nLabel validation tensor: (559,)\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Defining our model\n\nHere we finally create our model which in this case will be fully connected deep neural network with three hidden layer and a dropout layer. \n\nWe also choose an optimizer (RMSprop), a loss function (binary crossentropy) and our metric for evaluation (accuracy).\n\nWe can also take a look at the size of our model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"nn = models.Sequential()\nnn.add(layers.Dense(200, activation='relu', input_shape=(30,)))\nnn.add(layers.Dense(100, activation='relu'))\nnn.add(layers.Dropout(0.5))\nnn.add(layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))\n\nnn.compile(\n optimizer='rmsprop',\n loss='binary_crossentropy',\n metrics=['accuracy']\n )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Training\n\nHere we actually train the model we defined above. We can specify the batch size (30) and the number of epochs. We also specify the validation set to evaluate how our model performs on data it has never seen after each epochs. This is important so that we can identify when the model begin to overfit to the training data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"history = nn.fit(\n X_train,\n Y_train,\n epochs=100,\n batch_size=30,\n validation_data=(X_test,Y_test)\n )\n\nhistory_dict = history.history\nnn.summary()\n\nprint(\"Training accuracy: \" + str(history_dict['accuracy'][-1]))\nprint(\"Training loss: \" + str(history_dict['loss'][-1]) + \"\\n\")\n\nprint(\"Validation accuracy: \" + str(history_dict['val_accuracy'][-1]))\nprint(\"Validation loss: \" + str(history_dict['val_loss'][-1]))",
"Epoch 1/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.5304 - accuracy: 0.7343 - val_loss: 0.5210 - val_accuracy: 0.7388\nEpoch 2/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5268 - accuracy: 0.7317 - val_loss: 0.5168 - val_accuracy: 0.7335\nEpoch 3/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5301 - accuracy: 0.7383 - val_loss: 0.5056 - val_accuracy: 0.7388\nEpoch 4/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5255 - accuracy: 0.7370 - val_loss: 0.5317 - val_accuracy: 0.7209\nEpoch 5/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5307 - accuracy: 0.7373 - val_loss: 0.5211 - val_accuracy: 0.7388\nEpoch 6/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5253 - accuracy: 0.7393 - val_loss: 0.5217 - val_accuracy: 0.7191\nEpoch 7/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5268 - accuracy: 0.7387 - val_loss: 0.5022 - val_accuracy: 0.7370\nEpoch 8/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5271 - accuracy: 0.7447 - val_loss: 0.4996 - val_accuracy: 0.7442\nEpoch 9/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5288 - accuracy: 0.7443 - val_loss: 0.5300 - val_accuracy: 0.7299\nEpoch 10/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5227 - accuracy: 0.7433 - val_loss: 0.5167 - val_accuracy: 0.7191\nEpoch 11/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5298 - accuracy: 0.7400 - val_loss: 0.5050 - val_accuracy: 0.7317\nEpoch 12/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5220 - accuracy: 0.7483 - val_loss: 0.5179 - val_accuracy: 0.7263\nEpoch 13/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5224 - accuracy: 0.7410 - val_loss: 0.5118 - val_accuracy: 0.7299\nEpoch 14/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5234 - accuracy: 0.7380 - val_loss: 0.5196 - val_accuracy: 0.7156\nEpoch 15/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5190 - accuracy: 0.7493 - val_loss: 0.5134 - val_accuracy: 0.7388\nEpoch 16/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5202 - accuracy: 0.7407 - val_loss: 0.5172 - val_accuracy: 0.7245\nEpoch 17/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5209 - accuracy: 0.7387 - val_loss: 0.4957 - val_accuracy: 0.7406\nEpoch 18/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5172 - accuracy: 0.7477 - val_loss: 0.4999 - val_accuracy: 0.7496\nEpoch 19/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5164 - accuracy: 0.7443 - val_loss: 0.5037 - val_accuracy: 0.7406\nEpoch 20/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5157 - accuracy: 0.7487 - val_loss: 0.4983 - val_accuracy: 0.7352\nEpoch 21/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5071 - accuracy: 0.7427 - val_loss: 0.5077 - val_accuracy: 0.7370\nEpoch 22/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5158 - accuracy: 0.7483 - val_loss: 0.5099 - val_accuracy: 0.7156\nEpoch 23/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5159 - accuracy: 0.7470 - val_loss: 0.5112 - val_accuracy: 0.7209\nEpoch 24/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5101 - accuracy: 0.7477 - val_loss: 0.5046 - val_accuracy: 0.7352\nEpoch 25/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5086 - accuracy: 0.7530 - val_loss: 0.4935 - val_accuracy: 0.7513\nEpoch 26/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.5188 - accuracy: 0.7423 - val_loss: 0.5010 - val_accuracy: 0.7406\nEpoch 27/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5079 - accuracy: 0.7497 - val_loss: 0.4980 - val_accuracy: 0.7424\nEpoch 28/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.5142 - accuracy: 0.7470 - val_loss: 0.4926 - val_accuracy: 0.7496\nEpoch 29/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.5061 - accuracy: 0.7523 - val_loss: 0.5129 - val_accuracy: 0.7478\nEpoch 30/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5115 - accuracy: 0.7480 - val_loss: 0.4986 - val_accuracy: 0.7299\nEpoch 31/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5102 - accuracy: 0.7457 - val_loss: 0.5051 - val_accuracy: 0.7549\nEpoch 32/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.5165 - accuracy: 0.7480 - val_loss: 0.5007 - val_accuracy: 0.7442\nEpoch 33/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5087 - accuracy: 0.7463 - val_loss: 0.4918 - val_accuracy: 0.7549\nEpoch 34/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5075 - accuracy: 0.7433 - val_loss: 0.5016 - val_accuracy: 0.7496\nEpoch 35/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.5015 - accuracy: 0.7473 - val_loss: 0.4887 - val_accuracy: 0.7567\nEpoch 36/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5009 - accuracy: 0.7490 - val_loss: 0.4910 - val_accuracy: 0.7603\nEpoch 37/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5038 - accuracy: 0.7500 - val_loss: 0.5166 - val_accuracy: 0.7317\nEpoch 38/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5075 - accuracy: 0.7577 - val_loss: 0.4901 - val_accuracy: 0.7531\nEpoch 39/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5089 - accuracy: 0.7567 - val_loss: 0.4959 - val_accuracy: 0.7513\nEpoch 40/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.4986 - accuracy: 0.7540 - val_loss: 0.4934 - val_accuracy: 0.7460\nEpoch 41/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5095 - accuracy: 0.7467 - val_loss: 0.5211 - val_accuracy: 0.7335\nEpoch 42/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5042 - accuracy: 0.7557 - val_loss: 0.4946 - val_accuracy: 0.7424\nEpoch 43/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4989 - accuracy: 0.7590 - val_loss: 0.4920 - val_accuracy: 0.7531\nEpoch 44/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4997 - accuracy: 0.7550 - val_loss: 0.5020 - val_accuracy: 0.7352\nEpoch 45/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4981 - accuracy: 0.7520 - val_loss: 0.4858 - val_accuracy: 0.7728\nEpoch 46/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5041 - accuracy: 0.7527 - val_loss: 0.4948 - val_accuracy: 0.7531\nEpoch 47/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.5029 - accuracy: 0.7550 - val_loss: 0.5062 - val_accuracy: 0.7406\nEpoch 48/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4976 - accuracy: 0.7507 - val_loss: 0.4908 - val_accuracy: 0.7567\nEpoch 49/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5018 - accuracy: 0.7517 - val_loss: 0.4996 - val_accuracy: 0.7299\nEpoch 50/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4990 - accuracy: 0.7613 - val_loss: 0.4836 - val_accuracy: 0.7460\nEpoch 51/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4965 - accuracy: 0.7557 - val_loss: 0.4892 - val_accuracy: 0.7478\nEpoch 52/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.5051 - accuracy: 0.7503 - val_loss: 0.5013 - val_accuracy: 0.7478\nEpoch 53/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4952 - accuracy: 0.7483 - val_loss: 0.5063 - val_accuracy: 0.7406\nEpoch 54/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4978 - accuracy: 0.7620 - val_loss: 0.4944 - val_accuracy: 0.7442\nEpoch 55/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.4915 - accuracy: 0.7543 - val_loss: 0.5020 - val_accuracy: 0.7496\nEpoch 56/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4981 - accuracy: 0.7600 - val_loss: 0.4911 - val_accuracy: 0.7513\nEpoch 57/100\n100/100 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4988 - accuracy: 0.7530 - val_loss: 0.4887 - val_accuracy: 0.7496\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Evaluating the Model\n\nAfter our training we get ~75% accuracy on our validation data. When looking at our loss, we can see that our model is indeed learning and it does not seem to be overfitting too much as the training and validation accuracies remain fairly consistent troughout training.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"loss_values = history_dict['loss']\nval_loss_values = history_dict['val_loss']\nepochs = range(1, len(loss_values) + 1)\n\nplt.plot(epochs, loss_values, 'bo', label='Training loss')\nplt.plot(epochs, val_loss_values, 'b', label='Validation loss')\nplt.title('Losses')\nplt.xlabel('Epoch')\nplt.ylabel('Loss Evaluation')\nplt.legend()\nplt.show()\n\nplt.clf()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"loss_values = history_dict['accuracy']\nval_loss_values = history_dict['val_accuracy']\nepochs = range(1, len(loss_values) + 1)\n\nplt.plot(epochs, loss_values, 'bo', label='Training accuracy')\nplt.plot(epochs, val_loss_values, 'b', label='Validation accuracy')\nplt.title('Accuracy Evaluation')\nplt.xlabel('Epoch')\nplt.ylabel('Accuracy')\nplt.legend()\nplt.show()\n\nplt.clf()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## The last step\n\nIf we were happy with our model tuning the last step would be to save our model and evaluate on the test set.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a75ea44a0c94c485ea7615c7435c0baa5bd3722
| 38,433 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
code/.ipynb_checkpoints/nominee_count_degree_analysis-checkpoint.ipynb
|
DS4A-84/DS4A_Group84_Project
|
6f9244689156b818e4081727fef574caa038c419
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
code/.ipynb_checkpoints/nominee_count_degree_analysis-checkpoint.ipynb
|
DS4A-84/DS4A_Group84_Project
|
6f9244689156b818e4081727fef574caa038c419
|
[
"MIT"
] | 14 |
2021-06-21T02:50:35.000Z
|
2021-08-05T01:59:27.000Z
|
code/nominee_count_degree_analysis.ipynb
|
DS4A-84/DS4A_Group84_Project
|
6f9244689156b818e4081727fef574caa038c419
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-06-26T21:59:51.000Z
|
2021-06-26T21:59:51.000Z
| 91.07346 | 23,876 | 0.764785 |
[
[
[
"#!/usr/bin/python\n\n# DS4A Project\n# Group 84\n# using node/edge info to create network graph\n# and do social network analysis\n\nfrom os import path\nimport pandas as pd\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression\n\n\nnominee_count_degree_data_path = '../data/nominee_degree_counts_data.csv'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def load_dataset(filepath):\n df = pd.read_csv(filepath)\n return df\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = load_dataset(nominee_count_degree_data_path)\nprint(df.head(2))",
" name winner gender birthYear year_film \\\n0 Abigail Breslin False F 1996 2006 \n1 Adam Driver False M 1983 2018 \n\n category ceremonyAge num_times_nominated degree \\\n0 ACTRESS IN A SUPPORTING ROLE 10 1 17 \n1 ACTOR IN A SUPPORTING ROLE 35 2 34 \n\n year \n0 2006 \n1 2018 \n"
],
[
"df.loc[(df.winner == False),'winner']=0\ndf.loc[(df.winner == True),'winner']=1\ndf.loc[(df.gender == 'F'),'gender']=0\ndf.loc[(df.gender == 'M'),'gender']=1\ndf.winner = df.winner.astype('int64', copy=False)\ndf.gender = df.gender.astype('int64', copy=False)\nprint(df.info())\nprint(df.head(2))",
"<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>\nRangeIndex: 1696 entries, 0 to 1695\nData columns (total 10 columns):\n # Column Non-Null Count Dtype \n--- ------ -------------- ----- \n 0 name 1696 non-null object\n 1 winner 1696 non-null int64 \n 2 gender 1696 non-null int64 \n 3 birthYear 1696 non-null int64 \n 4 year_film 1696 non-null int64 \n 5 category 1696 non-null object\n 6 ceremonyAge 1696 non-null int64 \n 7 num_times_nominated 1696 non-null int64 \n 8 degree 1696 non-null int64 \n 9 year 1696 non-null int64 \ndtypes: int64(8), object(2)\nmemory usage: 132.6+ KB\nNone\n name winner gender birthYear year_film \\\n0 Abigail Breslin 0 0 1996 2006 \n1 Adam Driver 0 1 1983 2018 \n\n category ceremonyAge num_times_nominated degree \\\n0 ACTRESS IN A SUPPORTING ROLE 10 1 17 \n1 ACTOR IN A SUPPORTING ROLE 35 2 34 \n\n year \n0 2006 \n1 2018 \n"
],
[
"X = df[['gender','ceremonyAge','num_times_nominated','degree']]\ny = df['winner']\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.feature_selection import RFE\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nfrom sklearn import metrics\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=0)\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"clf = LogisticRegression(random_state=0).fit(X_train, y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"clf.predict(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('Accuracy of logistic regression classifier on test set: {:.2f}'.format(clf.score(X_test, y_test)))",
"Accuracy of logistic regression classifier on test set: 0.80\n"
],
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nfrom sklearn import preprocessing\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt \nfrom sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score\nfrom sklearn.metrics import roc_curve\nlogit_roc_auc = roc_auc_score(y_test, clf.predict(X_test))\nfpr, tpr, thresholds = roc_curve(y_test, clf.predict_proba(X_test)[:,1])\nplt.figure()\nplt.plot(fpr, tpr, label='Logistic Regression (area = %0.2f)' % logit_roc_auc)\nplt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1],'r--')\nplt.xlim([0.0, 1.0])\nplt.ylim([0.0, 1.05])\nplt.xlabel('False Positive Rate')\nplt.ylabel('True Positive Rate')\nplt.title('Receiver operating characteristic')\nplt.legend(loc=\"lower right\")\nplt.savefig('Log_ROC')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"y_pred = clf.predict(X_test)\nprint('Accuracy of logistic regression classifier on test set: {:.2f}'.format(clf.score(X_test, y_test)))",
"Accuracy of logistic regression classifier on test set: 0.80\n"
],
[
"from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix\nconfusion_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)\nprint(confusion_matrix)",
"[[407 0]\n [102 0]]\n"
],
[
"from sklearn.metrics import classification_report\nprint(classification_report(y_test, y_pred))",
" precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.80 1.00 0.89 407\n 1 0.00 0.00 0.00 102\n\n accuracy 0.80 509\n macro avg 0.40 0.50 0.44 509\nweighted avg 0.64 0.80 0.71 509\n\n"
],
[
"import statsmodels.api as sm\nlogit_model=sm.Logit(y_train,X_train)\nresult=logit_model.fit()\nprint(result.summary2())\n\n\nlogit_model=sm.Logit(y,X)\nresult=logit_model.fit()\nprint(result.summary2())",
"Optimization terminated successfully.\n Current function value: 0.525785\n Iterations 6\n Results: Logit\n===================================================================\nModel: Logit Pseudo R-squared: -0.028 \nDependent Variable: winner AIC: 1256.2145\nDate: 2021-07-28 01:21 BIC: 1276.5313\nNo. Observations: 1187 Log-Likelihood: -624.11 \nDf Model: 3 LL-Null: -607.05 \nDf Residuals: 1183 LLR p-value: 1.0000 \nConverged: 1.0000 Scale: 1.0000 \nNo. Iterations: 6.0000 \n-------------------------------------------------------------------\n Coef. Std.Err. z P>|z| [0.025 0.975]\n-------------------------------------------------------------------\ngender -0.1661 0.1467 -1.1321 0.2576 -0.4536 0.1214\nceremonyAge -0.0263 0.0038 -6.9115 0.0000 -0.0337 -0.0188\nnum_times_nominated -0.0943 0.0277 -3.4094 0.0007 -0.1485 -0.0401\ndegree 0.0064 0.0029 2.1864 0.0288 0.0007 0.0122\n===================================================================\n\nOptimization terminated successfully.\n Current function value: 0.522136\n Iterations 5\n Results: Logit\n===================================================================\nModel: Logit Pseudo R-squared: -0.027 \nDependent Variable: winner AIC: 1779.0868\nDate: 2021-07-28 01:21 BIC: 1800.8309\nNo. Observations: 1696 Log-Likelihood: -885.54 \nDf Model: 3 LL-Null: -862.09 \nDf Residuals: 1692 LLR p-value: 1.0000 \nConverged: 1.0000 Scale: 1.0000 \nNo. Iterations: 5.0000 \n-------------------------------------------------------------------\n Coef. Std.Err. z P>|z| [0.025 0.975]\n-------------------------------------------------------------------\ngender -0.1408 0.1226 -1.1489 0.2506 -0.3811 0.0994\nceremonyAge -0.0305 0.0032 -9.4408 0.0000 -0.0368 -0.0241\nnum_times_nominated -0.0586 0.0216 -2.7137 0.0067 -0.1010 -0.0163\ndegree 0.0071 0.0025 2.8608 0.0042 0.0022 0.0120\n===================================================================\n\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a75f1a466892548cd4a316aa7399afc45b84066
| 320,060 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
04_timeseries.ipynb
|
Keikokunitoki/sccm-datathon
|
28a19b3e2e398ed7e231e89fcfb8e06daa9a1818
|
[
"MIT"
] | 11 |
2020-02-07T23:14:51.000Z
|
2021-05-18T08:39:08.000Z
|
04_timeseries.ipynb
|
Keikokunitoki/sccm-datathon
|
28a19b3e2e398ed7e231e89fcfb8e06daa9a1818
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
04_timeseries.ipynb
|
Keikokunitoki/sccm-datathon
|
28a19b3e2e398ed7e231e89fcfb8e06daa9a1818
|
[
"MIT"
] | 8 |
2020-02-14T13:35:36.000Z
|
2021-11-03T18:55:16.000Z
| 123.958172 | 129,512 | 0.797747 |
[
[
[
"<a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/MIT-LCP/sccm-datathon/blob/master/04_timeseries.ipynb\" target=\"_parent\"><img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open In Colab\"/></a>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# eICU Collaborative Research Database\n\n# Notebook 4: Timeseries for a single patient\n\nThis notebook explores timeseries data for a single patient.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Load libraries and connect to the database",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import libraries\nimport numpy as np\nimport os\nimport pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\n# Make pandas dataframes prettier\nfrom IPython.display import display, HTML\n\n# Access data using Google BigQuery.\nfrom google.colab import auth\nfrom google.cloud import bigquery",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# authenticate\nauth.authenticate_user()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Set up environment variables\nproject_id='sccm-datathon'\nos.environ[\"GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT\"]=project_id",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Selecting a single patient stay\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### The patient table\n\nThe patient table includes general information about the patient admissions (for example, demographics, admission and discharge details). See: http://eicu-crd.mit.edu/eicutables/patient/",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Display the patient table\n%%bigquery\n\nSELECT *\nFROM `physionet-data.eicu_crd_demo.patient`",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"patient.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### The `vitalperiodic` table\n\nThe `vitalperiodic` table comprises data that is consistently interfaced from bedside vital signs monitors into eCareManager. Data are generally interfaced as 1 minute averages, and archived into the `vitalperiodic` table as 5 minute median values. For more detail, see: http://eicu-crd.mit.edu/eicutables/vitalPeriodic/",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Get periodic vital signs for a single patient stay\n%%bigquery vitalperiodic\n\nSELECT *\nFROM `physionet-data.eicu_crd_demo.vitalperiodic`\nWHERE patientunitstayid = 210014",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"vitalperiodic.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# sort the values by the observationoffset (time in minutes from ICU admission)\nvitalperiodic = vitalperiodic.sort_values(by='observationoffset')\nvitalperiodic.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# subselect the variable columns\ncolumns = ['observationoffset','temperature','sao2','heartrate','respiration',\n 'cvp','etco2','systemicsystolic','systemicdiastolic','systemicmean',\n 'pasystolic','padiastolic','pamean','icp']\n\nvitalperiodic = vitalperiodic[columns].set_index('observationoffset')\nvitalperiodic.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# plot the data\nplt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [12,8]\n\ntitle = 'Vital signs (periodic) for patientunitstayid = {} \\n'.format(patientunitstayid)\nax = vitalperiodic.plot(title=title, marker='o')\n\nax.legend(loc='center left', bbox_to_anchor=(1.0, 0.5))\nax.set_xlabel(\"Minutes after admission to the ICU\")\nax.set_ylabel(\"Absolute value\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Questions\n\n- Which variables are available for this patient?\n- What is the peak heart rate during the period?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### The vitalaperiodic table\n\nThe vitalAperiodic table provides invasive vital sign data that is recorded at irregular intervals. See: http://eicu-crd.mit.edu/eicutables/vitalAperiodic/\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Get aperiodic vital signs\n%%bigquery vitalaperiodic\n\nSELECT *\nFROM `physionet-data.eicu_crd_demo.vitalaperiodic`\nWHERE patientunitstayid = 210014",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# display the first few rows of the dataframe\nvitalaperiodic.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# sort the values by the observationoffset (time in minutes from ICU admission)\nvitalaperiodic = vitalaperiodic.sort_values(by='observationoffset')\nvitalaperiodic.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# subselect the variable columns\ncolumns = ['observationoffset','noninvasivesystolic','noninvasivediastolic',\n 'noninvasivemean','paop','cardiacoutput','cardiacinput','svr',\n 'svri','pvr','pvri']\n\nvitalaperiodic = vitalaperiodic[columns].set_index('observationoffset')\nvitalaperiodic.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# plot the data\nplt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [12,8]\ntitle = 'Vital signs (aperiodic) for patientunitstayid = {} \\n'.format(patientunitstayid)\nax = vitalaperiodic.plot(title=title, marker='o')\n\nax.legend(loc='center left', bbox_to_anchor=(1.0, 0.5))\nax.set_xlabel(\"Minutes after admission to the ICU\")\nax.set_ylabel(\"Absolute value\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Questions\n\n- What do the non-invasive variables measure?\n- How do you think the mean is calculated?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 3.4. The lab table",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Get labs\n%%bigquery lab\n\nSELECT *\nFROM `physionet-data.eicu_crd_demo.lab`\nWHERE patientunitstayid = 210014",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lab.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# sort the values by the offset time (time in minutes from ICU admission)\nlab = lab.sort_values(by='labresultoffset')\nlab.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lab = lab.set_index('labresultoffset')\ncolumns = ['labname','labresult','labmeasurenamesystem']\nlab = lab[columns]\nlab.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# list the distinct labnames\nlab['labname'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# pivot the lab table to put variables into columns\nlab = lab.pivot(columns='labname', values='labresult')\nlab.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# plot laboratory tests of interest\nlabs_to_plot = ['creatinine','pH','BUN', 'glucose', 'potassium']\nlab[labs_to_plot].head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# plot the data\nplt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [12,8]\ntitle = 'Laboratory test results for patientunitstayid = {} \\n'.format(patientunitstayid)\nax = lab[labs_to_plot].plot(title=title, marker='o',ms=10, lw=0)\nax.legend(loc='center left', bbox_to_anchor=(1.0, 0.5))\nax.set_xlabel(\"Minutes after admission to the ICU\")\nax.set_ylabel(\"Absolute value\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a76098e785649197acc7bf9c791c28fec6b6af8
| 12,349 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Documents/wikipedia_companies.ipynb
|
carlosdenner/business_atlas
|
8f95bbd07384baa6c5e51776690103e418b3875e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Documents/wikipedia_companies.ipynb
|
carlosdenner/business_atlas
|
8f95bbd07384baa6c5e51776690103e418b3875e
|
[
"MIT"
] | 4 |
2021-04-14T19:18:46.000Z
|
2021-11-02T16:11:36.000Z
|
Documents/wikipedia_companies.ipynb
|
carlosdenner/business_atlas
|
8f95bbd07384baa6c5e51776690103e418b3875e
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2021-09-01T03:05:21.000Z
|
2021-11-01T16:54:26.000Z
| 35.485632 | 215 | 0.538829 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd\n\nfrom IPython.core.display import display, HTML\ndisplay(HTML(\"<style>.container {width:90% !important;}</style>\"))\n# Don't wrap repr(DataFrame) across additional lines\npd.set_option(\"display.expand_frame_repr\", True)\n\n# Set max rows displayed in output to 25\npd.set_option(\"display.max_rows\", 25)\n%matplotlib inline\n%matplotlib widget",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# ASK WIKIPEDIA FOR LIST OF COMPANIES\n# pip install sparqlwrapper\n# https://rdflib.github.io/sparqlwrapper/\n\nimport sys\nfrom SPARQLWrapper import SPARQLWrapper, JSON\n\nendpoint_url = \"https://query.wikidata.org/sparql\"\n\nquery = \"\"\"#List of `instances of` \"business enterprise\"\nSELECT ?com ?comLabel ?inception ?industry ?industryLabel ?coordinate ?country ?countryLabel WHERE {\n ?com (wdt:P31/(wdt:P279*)) wd:Q4830453;\n wdt:P625 ?coordinate.\n SERVICE wikibase:label { bd:serviceParam wikibase:language \"en\". }\n OPTIONAL { ?com wdt:P571 ?inception. }\n OPTIONAL { ?com wdt:P452 ?industry. }\n OPTIONAL { ?com wdt:P17 ?country. }\n}\"\"\"\n\ndef get_results(endpoint_url, query):\n user_agent = \"WDQS-example Python/%s.%s\" % (sys.version_info[0], sys.version_info[1])\n # TODO adjust user agent; see https://w.wiki/CX6\n sparql = SPARQLWrapper(endpoint_url, agent=user_agent)\n sparql.setQuery(query)\n sparql.setReturnFormat(JSON)\n return sparql.query().convert()\n\nresults = get_results(endpoint_url, query)\n\nfor result in results[\"results\"][\"bindings\"]:\n print(result)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#PUT THE DATA ON THE RIGHT FORMAT into pandas\nimport os\nimport json\nimport pandas as pd\nfrom pandas.io.json import json_normalize\n\n# Get the dataset, and transform string into floats for plotting\ndataFrame = pd.json_normalize(results[\"results\"][\"bindings\"]) #in a serialized json-based format\ndf = pd.DataFrame(dataFrame) # into pandas\np = r'(?P<latitude>-?\\d+\\.\\d+).*?(?P<longitude>-?\\d+\\.\\d+)' #get lat/lon from string coordinates\ndf[['longitude', 'latitude']] = df['coordinate.value'].str.extract(p, expand=True)\ndf['latitude'] = pd.to_numeric(df['latitude'], downcast='float')\ndf['longitude'] = pd.to_numeric(df['longitude'], downcast='float')\ndata = pd.DataFrame(df, columns = ['latitude','longitude','comLabel.value','coordinate.value', 'inception.value', 'industryLabel.value', 'com.value', 'industry.value', 'country.value','countryLabel.value'])\ndata=data.dropna(subset=['latitude', 'longitude'])\ndata.rename(columns={'comLabel.value':'company'}, inplace=True)\ndata.rename(columns={'coordinate.value':'coordinate'}, inplace=True)\ndata.rename(columns={'inception.value':'inception'}, inplace=True)\ndata.rename(columns={'industryLabel.value':'industry'}, inplace=True)\ndata.rename(columns={'com.value':'id'}, inplace=True)\ndata.rename(columns={'industry.value':'id_industry'}, inplace=True)\ndata.rename(columns={'country.value':'id_country'}, inplace=True)\ndata.rename(columns={'countryLabel.value':'country'}, inplace=True)\ndata = pd.DataFrame (data) #cluster maps works ONLY with dataframe\nprint(data.shape)\nprint(data.sample(5))\nprint(data.info())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#DATA index cleaning\nfrom sqlalchemy import create_engine\nfrom pandas.io import sql\nimport re\n\nIDs=[]\nfor name in data['id']:\n ID_n = name.rsplit('/', 1)[1]\n ID = re.findall('\\d+', ID_n)\n #print(ID[0], ID_n)\n IDs.append(ID[0])\ndata ['ID'] = IDs\nprint (data['ID'].describe())\ndata['ID']= data['ID'].astype(int)\n#print (data['ID'].describe())\ndata.rename(columns={'id':'URL'}, inplace=True)\ndata['company_foundation'] = data['inception'].str.extract(r'(\\d{4})')\npd.to_numeric(data['company_foundation'])\ndata = data.set_index(['ID'])\nprint(data.columns)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#GET company-industry relationship data\nindustries = data.dropna(subset=['id_industry'])\n#print(industries)\n\nindustries.groupby('id_industry')[['company', 'country']].apply(lambda x: x.values.tolist())\nprint(industries.info())\n\nindustries = pd.DataFrame (industries)\nprint(industries.sample(3))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"IDs=[]\nfor name in industries['id_industry']:\n ID_n = name.rsplit('/', 1)[1]\n ID = re.findall('\\d+', ID_n)\n# print(ID, ID_n)\n IDs.append(ID[0])\n \nindustries ['ID_industry'] = IDs\nindustries['ID_industry']= industries['ID_industry'].astype(int)\nindustries.set_index([industries.index, 'ID_industry'], inplace=True)\nindustries['id_wikipedia']=industries['id_industry']\nindustries.drop('id_industry', axis=1, inplace=True) \n\nindustries = pd.DataFrame(industries)\nprint(industries.info())\nprint(industries.sample(3))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import plotly.express as px\nimport plotly.io as pio\n\npx.defaults.template = \"ggplot2\"\npx.defaults.color_continuous_scale = px.colors.sequential.Blackbody\n#px.defaults.width = 600\n#px.defaults.height = 400\n\n#data = data.dropna(subset=['country'])\n\nfig = px.scatter(data.dropna(subset=['country']), x=\"latitude\", y=\"longitude\", color=\"country\")# width=400)\nfig.show()\n#break born into quarters and use it for the x axis; y has number of companies;\n\n#fig = px.density_heatmap(countries_industries, x=\"country\", y=\"companies\", template=\"seaborn\")\nfig = px.density_heatmap(data, x=\"latitude\", y=\"longitude\")#, template=\"seaborn\")\nfig.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#COMPANIES IN COUNTRIES\nfig = px.histogram(data.dropna(subset=['country', 'industry']), x=\"country\",\n title='COMPANIES IN COUNTRIES',\n # labels={'industry':'industries'}, # can specify one label per df column\n opacity=0.8,\n log_y=False, # represent bars with log scale\n # color_discrete_sequence=['indianred'], # color of histogram bars\n color='industry',\n # marginal=\"rug\", # can be `box`, `violin`\n # hover_data=\"companies\"\n barmode='overlay'\n )\nfig.show()\n\n#INDUSTRIES IN COUNTRIES\nfig = px.histogram(data.dropna(subset=['industry', 'country']), x=\"industry\",\n title='INDUSTRIES IN COUNTRIES',\n # labels={'industry':'industries'}, # can specify one label per df column\n opacity=0.8,\n log_y=False, # represent bars with log scale\n # color_discrete_sequence=['indianred'], # color of histogram bars\n color='country',\n # marginal=\"rug\", # can be `box`, `violin`\n # hover_data=\"companies\"\n barmode='overlay'\n )\nfig.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#THIS IS THE 2D MAP I COULD FIND, :)\nimport plotly.graph_objects as go\ndata['text'] = 'COMPANY: '+ data['company'] + '<br>COUNTRY: ' + data['country'] + '<br>FOUNDATION: ' + data['company_foundation'].astype(str)\n\nfig = go.Figure(data=go.Scattergeo(\n locationmode = 'ISO-3',\n lon = data['longitude'],\n lat = data['latitude'],\n text = data['text'],\n mode = 'markers',\n marker = dict(\n size = 3,\n opacity = 0.8,\n reversescale = True,\n autocolorscale = False,\n symbol = 'square',\n line = dict(width=1, color='rgba(102, 102, 102)'),\n # colorgroup='country'\n # colorscale = 'Blues',\n # cmin = 0,\n # color = df['cnt'],\n # cmax = df['cnt'].max(),\n # colorbar_title=\"Incoming flights<br>February 2011\"\n )))\n\nfig.update_layout(\n title = 'Companies of the World<br>',\n geo = dict(\n scope='world',\n # projection_type='albers usa',\n showland = True,\n landcolor = \"rgb(250, 250, 250)\",\n subunitcolor = \"rgb(217, 217, 217)\",\n countrycolor = \"rgb(217, 217, 217)\",\n countrywidth = 0.5,\n subunitwidth = 0.5\n ),\n )\nfig.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(data.info())\nimport tkinter as tk\nfrom tkinter import filedialog\nfrom pandas import DataFrame\n\nroot= tk.Tk()\ncanvas1 = tk.Canvas(root, width = 300, height = 300, bg = 'lightsteelblue2', relief = 'raised')\ncanvas1.pack()\n\ndef exportCSV ():\n global df\n \n export_file_path = filedialog.asksaveasfilename(defaultextension='.csv')\n data.to_csv (export_file_path, index = True, header=True)\n\nsaveAsButton_CSV = tk.Button(text='Export CSV', command=exportCSV, bg='green', fg='white', font=('helvetica', 12, 'bold'))\ncanvas1.create_window(150, 150, window=saveAsButton_CSV)\n\nroot.mainloop()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a7615abec49ebed6f3267455d7da3a2d45a4eec
| 181,093 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
examples/notebooks/cache_dataset_speed.ipynb
|
xidchen/MONAI
|
4eae383f1abbbb62a69e054c016a3b4e53af3ea7
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
examples/notebooks/cache_dataset_speed.ipynb
|
xidchen/MONAI
|
4eae383f1abbbb62a69e054c016a3b4e53af3ea7
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
examples/notebooks/cache_dataset_speed.ipynb
|
xidchen/MONAI
|
4eae383f1abbbb62a69e054c016a3b4e53af3ea7
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 416.305747 | 111,160 | 0.932018 |
[
[
[
"# Cache Dataset Tutorial and Speed Test",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"This tutorial shows how to accelerate PyTorch medical DL program based on MONAI CacheDataset. \nIt's modified from the Spleen 3D segmentation tutorial notebook.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Copyright 2020 MONAI Consortium\n# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the \"License\");\n# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.\n# You may obtain a copy of the License at\n# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0\n# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software\n# distributed under the License is distributed on an \"AS IS\" BASIS,\n# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.\n# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and\n# limitations under the License.\n\nimport os\nimport glob\nimport time\nimport numpy as np\nimport torch\nfrom torch.utils.data import DataLoader\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom monai.data import Dataset, CacheDataset\nfrom monai.transforms import \\\n Compose, LoadNiftid, AddChanneld, ScaleIntensityRanged, CropForegroundd, \\\n RandCropByPosNegLabeld, RandAffined, Spacingd, Orientationd, ToTensord\nfrom monai.data import list_data_collate\nfrom monai.inferers import sliding_window_inference\nfrom monai.networks.layers import Norm\nfrom monai.networks.nets import UNet\nfrom monai.losses import DiceLoss\nfrom monai.metrics import compute_meandice\nfrom monai.utils import set_determinism",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Set MSD Spleen dataset path",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data_root = '/workspace/data/medical/Task09_Spleen'\ntrain_images = sorted(glob.glob(os.path.join(data_root, 'imagesTr', '*.nii.gz')))\ntrain_labels = sorted(glob.glob(os.path.join(data_root, 'labelsTr', '*.nii.gz')))\ndata_dicts = [{'image': image_name, 'label': label_name}\n for image_name, label_name in zip(train_images, train_labels)]\ntrain_files, val_files = data_dicts[:-9], data_dicts[-9:]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Setup transforms for training and validation\n \nDeterministic transforms during training: \n- LoadNiftid \n- AddChanneld \n- Spacingd \n- Orientationd \n- ScaleIntensityRanged \n \nNon-deterministic transforms: \n- RandCropByPosNegLabeld \n- ToTensord\n\nAll the validation transforms are deterministic. \nThe results of all the deterministic transforms will be cached to accelerate training.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def transformations():\n train_transforms = Compose([\n LoadNiftid(keys=['image', 'label']),\n AddChanneld(keys=['image', 'label']),\n Spacingd(keys=['image', 'label'], pixdim=(1.5, 1.5, 2.), interp_order=('bilinear', 'nearest')),\n Orientationd(keys=['image', 'label'], axcodes='RAS'),\n ScaleIntensityRanged(keys=['image'], a_min=-57, a_max=164, b_min=0.0, b_max=1.0, clip=True),\n CropForegroundd(keys=['image', 'label'], source_key='image'),\n # randomly crop out patch samples from big image based on pos / neg ratio\n # the image centers of negative samples must be in valid image area\n RandCropByPosNegLabeld(keys=['image', 'label'], label_key='label', size=(96, 96, 96), pos=1,\n neg=1, num_samples=4, image_key='image', image_threshold=0),\n ToTensord(keys=['image', 'label'])\n ])\n val_transforms = Compose([\n LoadNiftid(keys=['image', 'label']),\n AddChanneld(keys=['image', 'label']),\n Spacingd(keys=['image', 'label'], pixdim=(1.5, 1.5, 2.), interp_order=('bilinear', 'nearest')),\n Orientationd(keys=['image', 'label'], axcodes='RAS'),\n ScaleIntensityRanged(keys=['image'], a_min=-57, a_max=164, b_min=0.0, b_max=1.0, clip=True),\n CropForegroundd(keys=['image', 'label'], source_key='image'),\n ToTensord(keys=['image', 'label'])\n ])\n return train_transforms, val_transforms",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Define a typical PyTorch training process",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def train_process(train_ds, val_ds):\n \n # use batch_size=2 to load images and use RandCropByPosNegLabeld\n # to generate 2 x 4 images for network training\n train_loader = DataLoader(train_ds, batch_size=2, shuffle=True, num_workers=4, collate_fn=list_data_collate)\n val_loader = DataLoader(val_ds, batch_size=1, num_workers=4)\n device = torch.device('cuda:0')\n model = UNet(dimensions=3, in_channels=1, out_channels=2, channels=(16, 32, 64, 128, 256),\n strides=(2, 2, 2, 2), num_res_units=2, norm=Norm.BATCH).to(device)\n loss_function = DiceLoss(to_onehot_y=True, softmax=True)\n optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), 1e-4)\n\n epoch_num = 2\n val_interval = 1 # do validation for every epoch\n best_metric = -1\n best_metric_epoch = -1\n epoch_loss_values = list()\n metric_values = list()\n epoch_times = list()\n total_start = time.time()\n for epoch in range(epoch_num):\n epoch_start = time.time()\n print('-' * 10)\n print('epoch {}/{}'.format(epoch + 1, epoch_num))\n model.train()\n epoch_loss = 0\n step = 0\n for batch_data in train_loader:\n step_start = time.time()\n step += 1\n inputs, labels = batch_data['image'].to(device), batch_data['label'].to(device)\n optimizer.zero_grad()\n outputs = model(inputs)\n loss = loss_function(outputs, labels)\n loss.backward()\n optimizer.step()\n epoch_loss += loss.item()\n print('{}/{}, train_loss: {:.4f}, step time: {:.4f}'.format(\n step, len(train_ds) // train_loader.batch_size, loss.item(), time.time() - step_start))\n epoch_loss /= step\n epoch_loss_values.append(epoch_loss)\n print('epoch {} average loss: {:.4f}'.format(epoch + 1, epoch_loss))\n\n if (epoch + 1) % val_interval == 0:\n model.eval()\n with torch.no_grad():\n metric_sum = 0.\n metric_count = 0\n for val_data in val_loader:\n val_inputs, val_labels = val_data['image'].to(device), val_data['label'].to(device)\n roi_size = (160, 160, 160)\n sw_batch_size = 4\n val_outputs = sliding_window_inference(val_inputs, roi_size, sw_batch_size, model)\n value = compute_meandice(y_pred=val_outputs, y=val_labels, include_background=False,\n to_onehot_y=True, mutually_exclusive=True)\n metric_count += len(value)\n metric_sum += value.sum().item()\n metric = metric_sum / metric_count\n metric_values.append(metric)\n if metric > best_metric:\n best_metric = metric\n best_metric_epoch = epoch + 1\n torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'best_metric_model.pth')\n print('saved new best metric model')\n print('current epoch: {} current mean dice: {:.4f} best mean dice: {:.4f} at epoch {}'.format(\n epoch + 1, metric, best_metric, best_metric_epoch))\n print('time consuming of epoch {} is: {:.4f}'.format(epoch + 1, time.time() - epoch_start))\n epoch_times.append(time.time() - epoch_start)\n print('train completed, best_metric: {:.4f} at epoch: {}, total time: {:.4f}'.format(\n best_metric, best_metric_epoch, time.time() - total_start))\n return epoch_num, time.time() - total_start, epoch_loss_values, metric_values, epoch_times",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Enable deterministic training and define regular Datasets",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"set_determinism(seed=0)\ntrain_trans, val_trans = transformations()\ntrain_ds = Dataset(data=train_files, transform=train_trans)\nval_ds = Dataset(data=val_files, transform=val_trans)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Train with regular Dataset",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"epoch_num, total_time, epoch_loss_values, metric_values, epoch_times = train_process(train_ds, val_ds)\nprint('Total training time of {} epochs with regular Dataset: {:.4f}'.format(epoch_num, total_time))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Enable deterministic training and define Cache Datasets",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"set_determinism(seed=0)\ntrain_trans, val_trans = transformations()\ncache_init_start = time.time()\ncache_train_ds = CacheDataset(data=train_files, transform=train_trans, cache_rate=1.0, num_workers=4)\ncache_val_ds = CacheDataset(data=val_files, transform=val_trans, cache_rate=1.0, num_workers=4)\ncache_init_time = time.time() - cache_init_start",
"Load and cache transformed data...\n32/32 [==============================] \nLoad and cache transformed data...\n9/9 [==============================] \n"
]
],
[
[
"## Train with Cache Dataset",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"epoch_num, cache_total_time, cache_epoch_loss_values, cache_metric_values, cache_epoch_times = \\\n train_process(cache_train_ds, cache_val_ds)\nprint('Total training time of {} epochs with CacheDataset: {:.4f}'.format(epoch_num, cache_total_time))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Plot training loss and validation metrics",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plt.figure('train', (12, 12))\nplt.subplot(2, 2, 1)\nplt.title('Regular Epoch Average Loss')\nx = [i + 1 for i in range(len(epoch_loss_values))]\ny = epoch_loss_values\nplt.xlabel('epoch')\nplt.grid(alpha=0.4, linestyle=':')\nplt.plot(x, y, color='red')\n\nplt.subplot(2, 2, 2)\nplt.title('Regular Val Mean Dice')\nx = [i + 1 for i in range(len(metric_values))]\ny = metric_values\nplt.xlabel('epoch')\nplt.grid(alpha=0.4, linestyle=':')\nplt.plot(x, y, color='red')\n\nplt.subplot(2, 2, 3)\nplt.title('Cache Epoch Average Loss')\nx = [i + 1 for i in range(len(epoch_loss_values))]\ny = epoch_loss_values\nplt.xlabel('epoch')\nplt.grid(alpha=0.4, linestyle=':')\nplt.plot(x, y, color='green')\n\nplt.subplot(2, 2, 4)\nplt.title('Cache Val Mean Dice')\nx = [i + 1 for i in range(len(metric_values))]\ny = metric_values\nplt.xlabel('epoch')\nplt.grid(alpha=0.4, linestyle=':')\nplt.plot(x, y, color='green')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Plot total time and every epoch time",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plt.figure('train', (12, 6))\nplt.subplot(1, 2, 1)\nplt.title('Total Train Time(600 epochs)')\nplt.bar('regular', total_time, 1, label='Regular Dataset', color='red')\nplt.bar('cache', cache_init_time + cache_total_time, 1, label='Cache Dataset', color='green')\nplt.bar('cache', cache_init_time, 1, label='Cache Init', color='orange')\nplt.ylabel('secs')\nplt.grid(alpha=0.4, linestyle=':')\nplt.legend(loc='best')\n\nplt.subplot(1, 2, 2)\nplt.title('Epoch Time')\nx = [i + 1 for i in range(len(epoch_times))]\nplt.xlabel('epoch')\nplt.ylabel('secs')\nplt.plot(x, epoch_times, label='Regular Dataset', color='red')\nplt.plot(x, cache_epoch_times, label='Cache Dataset', color='green')\nplt.grid(alpha=0.4, linestyle=':')\nplt.legend(loc='best')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a7617aac65532fe951549e847a4f237a32c4732
| 411,454 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
random_signals/power_spectral_densities.ipynb
|
Fun-pee/signal-processing
|
205d5e55e3168a1ec9da76b569af92c0056619aa
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2020-09-21T10:15:40.000Z
|
2020-09-21T13:36:40.000Z
|
random_signals/power_spectral_densities.ipynb
|
thegodparticle/digital-signal-processing-lecture
|
205d5e55e3168a1ec9da76b569af92c0056619aa
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
random_signals/power_spectral_densities.ipynb
|
thegodparticle/digital-signal-processing-lecture
|
205d5e55e3168a1ec9da76b569af92c0056619aa
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 67.551141 | 38,018 | 0.615571 |
[
[
[
"# Random Signals\n\n*This jupyter notebook is part of a [collection of notebooks](../index.ipynb) on various topics of Digital Signal Processing. Please direct questions and suggestions to [[email protected]](mailto:[email protected]).*",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Auto Power Spectral Density\n\nThe (auto-) [power spectral density](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spectral_density#Power_spectral_density) (PSD) is defined as the Fourier transformation of the [auto-correlation function](correlation_functions.ipynb) (ACF).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Definition\n\nFor a continuous-amplitude, real-valued, wide-sense stationary (WSS) random signal $x[k]$ the PSD is given as\n\n\\begin{equation}\n\\Phi_{xx}(\\mathrm{e}^{\\,\\mathrm{j}\\,\\Omega}) = \\mathcal{F}_* \\{ \\varphi_{xx}[\\kappa] \\},\n\\end{equation}\n\nwhere $\\mathcal{F}_* \\{ \\cdot \\}$ denotes the [discrete-time Fourier transformation](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Discrete-time_Fourier_transform) (DTFT) and $\\varphi_{xx}[\\kappa]$ the ACF of $x[k]$. Note that the DTFT is performed with respect to $\\kappa$. The ACF of a random signal of finite length $N$ can be expressed by way of a linear convolution\n\n\\begin{equation}\n\\varphi_{xx}[\\kappa] = \\frac{1}{N} \\cdot x_N[k] * x_N[-k].\n\\end{equation}\n\nTaking the DTFT of the left- and right-hand side results in\n\n\\begin{equation}\n\\Phi_{xx}(\\mathrm{e}^{\\,\\mathrm{j}\\,\\Omega}) = \\frac{1}{N} \\, X_N(\\mathrm{e}^{\\,\\mathrm{j}\\,\\Omega})\\, X_N(\\mathrm{e}^{-\\,\\mathrm{j}\\,\\Omega}) = \n\\frac{1}{N} \\, | X_N(\\mathrm{e}^{\\,\\mathrm{j}\\,\\Omega}) |^2.\n\\end{equation}\n\nThe last equality results from the definition of the magnitude and the symmetry of the DTFT for real-valued signals. The spectrum $X_N(\\mathrm{e}^{\\,\\mathrm{j}\\,\\Omega})$ quantifies the amplitude density of the signal $x_N[k]$. It can be concluded from above result that the PSD quantifies the squared amplitude or power density of a random signal. This explains the term power spectral density.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Properties\n\nThe properties of the PSD can be deduced from the properties of the ACF and the DTFT as:\n\n1. From the link between the PSD $\\Phi_{xx}(\\mathrm{e}^{\\,\\mathrm{j}\\,\\Omega})$ and the spectrum $X_N(\\mathrm{e}^{\\,\\mathrm{j}\\,\\Omega})$ derived above it can be concluded that the PSD is real valued\n\n $$\\Phi_{xx}(\\mathrm{e}^{\\,\\mathrm{j}\\,\\Omega}) \\in \\mathbb{R}$$\n\n2. From the even symmetry $\\varphi_{xx}[\\kappa] = \\varphi_{xx}[-\\kappa]$ of the ACF it follows that\n\n $$ \\Phi_{xx}(\\mathrm{e}^{\\,\\mathrm{j} \\, \\Omega}) = \\Phi_{xx}(\\mathrm{e}^{\\,-\\mathrm{j}\\, \\Omega}) $$\n\n3. The PSD of an uncorrelated random signal is given as\n\n $$ \\Phi_{xx}(\\mathrm{e}^{\\,\\mathrm{j} \\, \\Omega}) = (\\sigma_x^2 + \\mu_x^2) \\cdot {\\bot \\!\\! \\bot \\!\\! \\bot}\\left( \\frac{\\Omega}{2 \\pi} \\right) ,$$\n \n which can be deduced from the [ACF of an uncorrelated signal](correlation_functions.ipynb#Properties).\n\n4. The quadratic mean of a random signal is given as\n\n $$ E\\{ x[k]^2 \\} = \\varphi_{xx}[\\kappa=0] = \\frac{1}{2\\pi} \\int\\limits_{-\\pi}^{\\pi} \\Phi_{xx}(\\mathrm{e}^{\\,\\mathrm{j}\\, \\Omega}) \\,\\mathrm{d} \\Omega $$\n\n The last relation can be found by expressing the ACF via the inverse DTFT of $\\Phi_{xx}$ and considering that $\\mathrm{e}^{\\mathrm{j} \\Omega \\kappa} = 1$ when evaluating the integral for $\\kappa=0$.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Example - Power Spectral Density of a Speech Signal\n\nIn this example the PSD $\\Phi_{xx}(\\mathrm{e}^{\\,\\mathrm{j} \\,\\Omega})$ of a speech signal of length $N$ is estimated by applying a discrete Fourier transformation (DFT) to its ACF. For a better interpretation of the PSD, the frequency axis $f = \\frac{\\Omega}{2 \\pi} \\cdot f_s$ has been chosen for illustration, where $f_s$ denotes the sampling frequency of the signal. The speech signal constitutes a recording of the vowel 'o' spoken from a German male, loaded into variable `x`.\n\nIn Python the ACF is stored in a vector with indices $0, 1, \\dots, 2N - 2$ corresponding to the lags $\\kappa = (0, 1, \\dots, 2N - 2)^\\mathrm{T} - (N-1)$. When computing the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) of the ACF numerically by the fast Fourier transform (FFT) one has to take this shift into account. For instance, by multiplying the DFT $\\Phi_{xx}[\\mu]$ by $\\mathrm{e}^{\\mathrm{j} \\mu \\frac{2 \\pi}{2N - 1} (N-1)}$.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom scipy.io import wavfile\n%matplotlib inline\n\n# read audio file\nfs, x = wavfile.read('../data/vocal_o_8k.wav')\nx = np.asarray(x, dtype=float)\nN = len(x)\n\n# compute ACF\nacf = 1/N * np.correlate(x, x, mode='full')\n# compute PSD\npsd = np.fft.fft(acf)\npsd = psd * np.exp(1j*np.arange(2*N-1)*2*np.pi*(N-1)/(2*N-1))\nf = np.fft.fftfreq(2*N-1, d=1/fs)\n\n# plot PSD\nplt.figure(figsize = (10, 4))\nplt.plot(f, np.real(psd))\nplt.title('Estimated power spectral density')\nplt.ylabel(r'$\\hat{\\Phi}_{xx}(e^{j \\Omega})$')\nplt.xlabel(r'$f / Hz$')\nplt.axis([0, 500, 0, 1.1*max(np.abs(psd))])\nplt.grid()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Exercise**\n\n* What does the PSD tell you about the average spectral contents of a speech signal?\n\nSolution: The speech signal exhibits a harmonic structure with the dominant fundamental frequency $f_0 \\approx 100$ Hz and a number of harmonics $f_n \\approx n \\cdot f_0$ for $n > 0$. This due to the fact that vowels generate random signals which are in good approximation periodic. To generate vowels, the sound produced by the periodically vibrating vowel folds is filtered by the resonance volumes and articulators above the voice box. The spectrum of periodic signals is a line spectrum.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Cross-Power Spectral Density\n\nThe cross-power spectral density is defined as the Fourier transformation of the [cross-correlation function](correlation_functions.ipynb#Cross-Correlation-Function) (CCF).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Definition\n\nFor two continuous-amplitude, real-valued, wide-sense stationary (WSS) random signals $x[k]$ and $y[k]$, the cross-power spectral density is given as\n\n\\begin{equation}\n\\Phi_{xy}(\\mathrm{e}^{\\,\\mathrm{j} \\, \\Omega}) = \\mathcal{F}_* \\{ \\varphi_{xy}[\\kappa] \\},\n\\end{equation}\n\nwhere $\\varphi_{xy}[\\kappa]$ denotes the CCF of $x[k]$ and $y[k]$. Note again, that the DTFT is performed with respect to $\\kappa$. The CCF of two random signals of finite length $N$ and $M$ can be expressed by way of a linear convolution\n\n\\begin{equation}\n\\varphi_{xy}[\\kappa] = \\frac{1}{N} \\cdot x_N[k] * y_M[-k].\n\\end{equation}\n\nNote the chosen $\\frac{1}{N}$-averaging convention corresponds to the length of signal $x$. If $N \\neq M$, care should be taken on the interpretation of this normalization. In case of $N=M$ the $\\frac{1}{N}$-averaging yields a [biased estimator](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bias_of_an_estimator) of the CCF, which consistently should be denoted with $\\hat{\\varphi}_{xy,\\mathrm{biased}}[\\kappa]$.\n\n\nTaking the DTFT of the left- and right-hand side from above cross-correlation results in\n\n\\begin{equation}\n\\Phi_{xy}(\\mathrm{e}^{\\,\\mathrm{j}\\,\\Omega}) = \\frac{1}{N} \\, X_N(\\mathrm{e}^{\\,\\mathrm{j}\\,\\Omega})\\, Y_M(\\mathrm{e}^{-\\,\\mathrm{j}\\,\\Omega}).\n\\end{equation}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Properties\n\n1. The symmetries of $\\Phi_{xy}(\\mathrm{e}^{\\,\\mathrm{j}\\, \\Omega})$ can be derived from the symmetries of the CCF and the DTFT as\n\n $$ \\underbrace {\\Phi_{xy}(\\mathrm{e}^{\\,\\mathrm{j}\\, \\Omega}) = \\Phi_{xy}^*(\\mathrm{e}^{-\\,\\mathrm{j}\\, \\Omega})}_{\\varphi_{xy}[\\kappa] \\in \\mathbb{R}} = \n\\underbrace {\\Phi_{yx}(\\mathrm{e}^{\\,- \\mathrm{j}\\, \\Omega}) = \\Phi_{yx}^*(\\mathrm{e}^{\\,\\mathrm{j}\\, \\Omega})}_{\\varphi_{yx}[-\\kappa] \\in \\mathbb{R}},$$\n\n from which $|\\Phi_{xy}(\\mathrm{e}^{\\,\\mathrm{j}\\, \\Omega})| = |\\Phi_{yx}(\\mathrm{e}^{\\,\\mathrm{j}\\, \\Omega})|$ can be concluded.\n\n2. The cross PSD of two uncorrelated random signals is given as\n\n $$ \\Phi_{xy}(\\mathrm{e}^{\\,\\mathrm{j} \\, \\Omega}) = \\mu_x^2 \\mu_y^2 \\cdot {\\bot \\!\\! \\bot \\!\\! \\bot}\\left( \\frac{\\Omega}{2 \\pi} \\right) $$\n \n which can be deduced from the CCF of an uncorrelated signal.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Example - Cross-Power Spectral Density\n\nThe following example estimates and plots the cross PSD $\\Phi_{xy}(\\mathrm{e}^{\\,\\mathrm{j}\\, \\Omega})$ of two random signals $x_N[k]$ and $y_M[k]$ of finite lengths $N = 64$ and $M = 512$.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"N = 64 # length of x\nM = 512 # length of y\n\n# generate two uncorrelated random signals\nnp.random.seed(1)\nx = 2 + np.random.normal(size=N)\ny = 3 + np.random.normal(size=M)\nN = len(x)\nM = len(y)\n\n# compute cross PSD via CCF\nacf = 1/N * np.correlate(x, y, mode='full')\npsd = np.fft.fft(acf)\npsd = psd * np.exp(1j*np.arange(N+M-1)*2*np.pi*(M-1)/(2*M-1))\npsd = np.fft.fftshift(psd)\nOm = 2*np.pi * np.arange(0, N+M-1) / (N+M-1)\nOm = Om - np.pi\n\n# plot results\nplt.figure(figsize=(10, 4))\nplt.stem(Om, np.abs(psd), basefmt='C0:', use_line_collection=True)\nplt.title('Biased estimator of cross power spectral density')\nplt.ylabel(r'$|\\hat{\\Phi}_{xy}(e^{j \\Omega})|$')\nplt.xlabel(r'$\\Omega$')\nplt.grid()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Exercise**\n\n* What does the cross PSD $\\Phi_{xy}(\\mathrm{e}^{\\,\\mathrm{j} \\, \\Omega})$ tell you about the statistical properties of the two random signals?\n\nSolution: The cross PSD $\\Phi_{xy}(\\mathrm{e}^{\\,\\mathrm{j} \\, \\Omega})$ is essential only non-zero for $\\Omega=0$. It hence can be concluded that the two random signals are not mean-free and uncorrelated to each other.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Copyright**\n\nThis notebook is provided as [Open Educational Resource](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Open_educational_resources). Feel free to use the notebook for your own purposes. The text is licensed under [Creative Commons Attribution 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), the code of the IPython examples under the [MIT license](https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT). Please attribute the work as follows: *Sascha Spors, Digital Signal Processing - Lecture notes featuring computational examples*.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4a7627bbdfce5e6c56851c73fad3308f41c63d6a
| 1,436 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Untitled.ipynb
|
calebsanfo/IncubatorImaging
|
720a11353b0fa9928792d7ed91fe1f02000dca9a
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2019-12-02T15:48:16.000Z
|
2019-12-02T15:48:16.000Z
|
Untitled.ipynb
|
calebsanfo/IncubatorImaging
|
720a11353b0fa9928792d7ed91fe1f02000dca9a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Untitled.ipynb
|
calebsanfo/IncubatorImaging
|
720a11353b0fa9928792d7ed91fe1f02000dca9a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 17.728395 | 53 | 0.473538 |
[
[
[
"import serial\nimport time\n\nard = serial.Serial('COM1', 9600, timeout=5)\n\ndef goto(x, y):\n message = str(x)+','+str(y)\n message = message.encode()\n ard.write(message)\n print(ard.readline())\n time.sleep(.5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"goto(1,1)",
"b''\n"
],
[
"import cv2\n\ncv2.namedWindow(\"preview\")\nvc = cv2.VideoCapture(0)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a7636fa6e9e9ef21f2cc880c08331c8784fd2ea
| 29,660 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Accuracy Test.ipynb
|
adammuhammadd/Mobile_Phones_Prices_Clustering
|
d64c8fb2b240e7a8a0ebeffd76825dcd3be9bf5f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Accuracy Test.ipynb
|
adammuhammadd/Mobile_Phones_Prices_Clustering
|
d64c8fb2b240e7a8a0ebeffd76825dcd3be9bf5f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Accuracy Test.ipynb
|
adammuhammadd/Mobile_Phones_Prices_Clustering
|
d64c8fb2b240e7a8a0ebeffd76825dcd3be9bf5f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 34.812207 | 99 | 0.331457 |
[
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport pandas as pd",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = pd.read_csv('phones_data_after_preprocessing.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df1= df.drop(['Unnamed: 0'], axis=1)\ndf1.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X=df1.iloc[:, [4, 9]].values\nY=df1.iloc[:, [0,1,2,3,5,6,7,8,10,11,12]].values",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Y",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nX_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size = 0.2, random_state = 0) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_train",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Y_train",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_test",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Y_test",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.cluster import KMeans",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Menjalankan K-Means Clustering ke dalam dataset\nkmeans = KMeans(n_clusters = 3, init = 'k-means++', random_state = 42)\ny_true=kmeans.fit_predict(X_train, Y_train)\ny_true",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters = 3, init = 'k-means++', random_state = 42)\ny_pred=kmeans.fit_predict(X_test)\ny_pred",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.sum(y_true)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.sum(y_pred)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score\nprint('Accuracy score: ', accuracy_score(y_pred, y_test))",
"Accuracy score: 1.0\n"
],
[
"from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix\nconfusion_matrix(y_pred, y_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.metrics import classification_report\nprint(classification_report(y_pred, y_test))",
" precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 1.00 1.00 1.00 42\n 1 1.00 1.00 1.00 188\n 2 1.00 1.00 1.00 15\n\n accuracy 1.00 245\n macro avg 1.00 1.00 1.00 245\nweighted avg 1.00 1.00 1.00 245\n\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a7639eb5a687a98634b036964939c3aa4847360
| 248,036 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
examples/politeness-strategies/Politeness_Strategies_in_MT-mediated_Communication.ipynb
|
CornellNLP/Cornell-Conversational-Analysis-Toolkit
|
0bc4d1a4baf25eec0861440dc3166c60d4cbe339
|
[
"MIT"
] | 371 |
2016-07-19T22:10:13.000Z
|
2022-03-28T08:04:32.000Z
|
examples/politeness-strategies/Politeness_Strategies_in_MT-mediated_Communication.ipynb
|
CornellNLP/Cornell-Conversational-Analysis-Toolkit
|
0bc4d1a4baf25eec0861440dc3166c60d4cbe339
|
[
"MIT"
] | 92 |
2017-07-25T22:04:11.000Z
|
2022-03-29T13:46:07.000Z
|
examples/politeness-strategies/Politeness_Strategies_in_MT-mediated_Communication.ipynb
|
CornellNLP/Cornell-Conversational-Analysis-Toolkit
|
0bc4d1a4baf25eec0861440dc3166c60d4cbe339
|
[
"MIT"
] | 105 |
2016-07-04T15:04:53.000Z
|
2022-03-30T01:36:38.000Z
| 260.542017 | 135,364 | 0.914408 |
[
[
[
"# Politeness strategies in MT-mediated communication\n\nIn this notebook, we demo how to extract politeness strategies using ConvoKit's `PolitenessStrategies` module both in English and in Chinese. We will make use of this functionality to assess the degree to which politeness strategies are preserved in machine-translated texts.\n\nThe politeness strategies considered are adapted from operationalizations in the following papers:\n\n- English: [A computational approach to politeness with application to social factors](https://www.cs.cornell.edu/~cristian/Politeness.html), [The politeness Package: Detecting Politeness in Natural Language](https://journal.r-project.org/archive/2018/RJ-2018-079/RJ-2018-079.pdf)\n\n- Chinese: [Studying Politeness across Cultures using English Twitter and Mandarin Weibo](https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/3415190)\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import os\nfrom collections import defaultdict, Counter\nfrom tqdm import tqdm\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nfrom scipy.stats import pearsonr\nimport spacy\n\nfrom convokit import Corpus, Speaker, Utterance, download\nfrom convokit import TextParser, PolitenessStrategies\n\nimport seaborn as sns\nfrom matplotlib import pyplot as plt\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 1. Preparing diagnostic test sets \n\nWe sample utterances from Wikipedia Talkpages discussions in both English and Chinese. In particular, we use the medium-sized `wiki-corpus` shipped by ConvoKit as the source for sampling English utterances (as shown below), and we sampled a subset of utterances from [WikiConv](https://www.cs.cornell.edu/~cristian/index_files/wikiconv-conversation-corpus.pdf) (Chinese) as shared in [figshare](https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/WikiConv_-_Chinese/7376012). \n\nFor those who would like to skip the preparatory steps and go straight to our analysis exploring how to assess the permeability of politeness signals in machine-translated communication ([Part 2 of this notebook](#2.-Computing-permeability-for-politeness-strategies)), we have made the sampled corpora directly downloadable via ConvoKit as `wiki-sampled-en-corpus` and `wiki-sampled-zh-corpus`.\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 1.1. English data: `wiki-corpus`\n\nThe medium-sized Wikipedia dataset is provided by ConvoKit as `wiki-corpus` ([documentation](https://convokit.cornell.edu/documentation/wiki.html)). Note that ConvoKit also offers a more complete collection of Wikipedia Talkpage discussions: [the Cornell Wikiconv Dataset](https://convokit.cornell.edu/documentation/wikiconv.html). We choose to use `wiki-corpus` as it is already sufficiently large for our purpose. \n\nTo load the corpus, see options in the cell below. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# OPTION 1: DOWNLOAD CORPUS \n# UNCOMMENT THESE LINES TO DOWNLOAD CORPUS\n# DATA_DIR = '<YOUR DIRECTORY>'\n# WIKI_ROOT_DIR = download('wiki-corpus', data_dir=DATA_DIR)\n\n# OPTION 2: READ PREVIOUSLY-DOWNLOADED CORPUS FROM DISK\n# UNCOMMENT THIS LINE AND REPLACE WITH THE DIRECTORY WHERE THE WIKI-CORPUS IS LOCATED\n# WIKI_ROOT_DIR = '<YOUR DIRECTORY>'\n\ncorpus = Corpus(filename=WIKI_ROOT_DIR)\n\n# load parses\ncorpus.load_info('utterance',['parsed'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Overall stats of the dataset \ncorpus.print_summary_stats()",
"Number of Speakers: 38462\nNumber of Utterances: 391294\nNumber of Conversations: 125292\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### Extracting strategies for sampling\n\nIn the case when the corpus is not dependency parsed, it will need to go through an additional step of parsing, which can be achieved via `TextParser`. See [this demo](https://github.com/CornellNLP/Cornell-Conversational-Analysis-Toolkit/blob/master/examples/politeness-strategies/politeness_demo.ipynb) for an example. As the `wiki-corpus` ships with pre-computed dependency parses (which we already loaded as you may notice), we can go straight to politeness strategy extraction. \n\nHere, we will focus on a set of local strategies, and hence specify that we will want to extract with strategy collection _politeness_local_. For other available options, refer to the [documentation](https://convokit.cornell.edu/documentation/politenessStrategies.html) for details.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"ps_local = PolitenessStrategies(strategy_collection=\"politeness_local\", verbose=10000)\n\n# By default, strategy extraction results are saved under \"politeness_strategies\". \ncorpus = ps_local.transform(corpus, markers=True)",
"10000/391294 utterances processed\n20000/391294 utterances processed\n30000/391294 utterances processed\n40000/391294 utterances processed\n50000/391294 utterances processed\n60000/391294 utterances processed\n70000/391294 utterances processed\n80000/391294 utterances processed\n90000/391294 utterances processed\n100000/391294 utterances processed\n110000/391294 utterances processed\n120000/391294 utterances processed\n130000/391294 utterances processed\n140000/391294 utterances processed\n150000/391294 utterances processed\n160000/391294 utterances processed\n170000/391294 utterances processed\n180000/391294 utterances processed\n190000/391294 utterances processed\n200000/391294 utterances processed\n210000/391294 utterances processed\n220000/391294 utterances processed\n230000/391294 utterances processed\n240000/391294 utterances processed\n250000/391294 utterances processed\n260000/391294 utterances processed\n270000/391294 utterances processed\n280000/391294 utterances processed\n290000/391294 utterances processed\n300000/391294 utterances processed\n310000/391294 utterances processed\n320000/391294 utterances processed\n330000/391294 utterances processed\n340000/391294 utterances processed\n350000/391294 utterances processed\n360000/391294 utterances processed\n370000/391294 utterances processed\n380000/391294 utterances processed\n390000/391294 utterances processed\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### Computing strategy prevalance \n\nWe can first take a glimpse over utterance-level strategy prevalence, i.e., proportion of utterances in the dataset that use the politeness strategy. This can be easily done using `summarize()`. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_prevalence = ps_local.summarize(corpus)\ndf_prevalence",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Sampling \n\nTo assess permeability of these strategies, we sample 1000 instances for each strategy. The results will be saved to a smaller `wiki-sampled-en` corpus, which may be directly downloaded via ConvoKit if one wants to skip the intermediate steps (which will take a while to run) see [Part 2 of this notebook](#2.-Computing-permeability-for-politeness-strategies). ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# utterance-level strategy uses\ndf_feat = pd.DataFrame.from_dict({utt.id: utt.meta['politeness_strategies'] \\\n for utt in corpus.iter_utterances()}, orient='index')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# sampling from least common to most\nsorted_strategies = df_prevalence.sort_values().index\nsampled_ids, samples = set(), []\n\nfor k in sorted_strategies:\n df_sample = df_feat[(~df_feat.index.isin(sampled_ids)) & (df_feat[k]==1)].sample(1000, random_state=42)\n df_sample['strategy'] = k\n samples.append(df_sample[['strategy']])\n sampled_ids.update(df_sample.index)\n \ndf_en_sample = pd.concat(samples)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# saving as a convokit corpus\nfor i, info in df_en_sample.itertuples():\n utt = corpus.get_utterance(i)\n utt.add_meta('selected', True)\n utt.add_meta('strategy', info)\n\n# filter only selected utterances \n# (not that this does not maintain conversation structure)\nwiki_sampled_en = corpus.filter_utterances_by(lambda utt:'selected' in utt.meta and utt.meta['selected'])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Translating \n\nTo determine the degree to which politeness markers are perserved in translation, we will make comparisons between original and translated texts. To set it up, we two rounds of translations, forming a English -> Chinese -> English loop, i.e., we first translate the English texts into Chinese, and then translate the Chinese translations back into English. \n\nWe use [EasyNMT](https://github.com/UKPLab/EasyNMT) to perform translations between English and Chinese, using models from [Opus-MT](https://github.com/Helsinki-NLP/Opus-MT) from [Helsinki-NLP](https://blogs.helsinki.fi/language-technology/). ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from easynmt import EasyNMT",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# texts to be translated\ndf_utts = wiki_sampled_en.get_utterances_dataframe(exclude_meta=True)\n\n# translation model\nmodel = EasyNMT('opus-mt', cache_folder=\"/belafonte_sauna/liye_translations/easynmt/\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_utts['en-zh'] = model.translate(list(df_utts['text']), \\\n target_lang='zh', \\\n source_lang='en', \\\n show_progress_bar=True,\n batch_size=8, \\\n perform_sentence_splitting=False)",
"100%|██████████| 18000/18000.0 [2:28:46<00:00, 2.02it/s]\n"
],
[
"df_utts['en-back'] = model.translate(list(df_utts['en-zh']), \\\n target_lang='en', \\\n source_lang='zh', \\\n show_progress_bar=True,\n batch_size=8, \\\n perform_sentence_splitting=False)",
"100%|██████████| 18000/18000.0 [1:09:48<00:00, 4.30it/s]\n"
]
],
[
[
"We add these translated texts as meta data to our sampled corpus, and parse them to prepare for later strategy extraction.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from convokit.text_processing.textParser import TextParser",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for row in df_utts[['text', 'en-zh', 'en-back']].itertuples():\n idx, trans, backtrans = row[0], row[2], row[3]\n utt = wiki_sampled_en.get_utterance(idx)\n utt.add_meta('en-zh', trans)\n utt.add_meta('en-back', backtrans)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# parser to parse back-translated English texts \nen_parser = TextParser(output_field='en_parsed', input_field='en-back', \\\n verbosity=5000)\n\n# parer to parse translated texts in Chinese\nspacy_zh = spacy.load('zh_core_web_sm', disable=['ner'])\nzh_parser = TextParser(output_field='zh_parsed', input_field='en-zh', \\\n spacy_nlp=spacy_zh, verbosity=5000)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"wiki_sampled_en = en_parser.transform(wiki_sampled_en)\nwiki_sampled_en = zh_parser.transform(wiki_sampled_en)",
"5000/18000 utterances processed\n10000/18000 utterances processed\n15000/18000 utterances processed\n18000/18000 utterances processed\n5000/18000 utterances processed\n10000/18000 utterances processed\n15000/18000 utterances processed\n18000/18000 utterances processed\n"
],
[
"# We can then save the corpus using wiki_sampled_en.dump(YOUR_OUT_DIR)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 1.2 Chinese data: [WikiConv](https://www.cs.cornell.edu/~cristian/index_files/wikiconv-conversation-corpus.pdf)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"For the Chinese data, we start utterances from [WikiConv](https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/WikiConv_-_Chinese/7376012) and similarly sampled 1000 instances for a subset of strategies from the collection \"_politeness-cscw-zh_\". The corpus is saved as `wiki-sampled-zh-corpus`, with all textual data (i.e., both the original utterance texts and the the corresponding translations) tokenized and parsed. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"wiki_sampled_zh = Corpus(download('wiki-sampled-zh-corpus'))",
"Dataset already exists at /belafonte_sauna/liye_translations/convokit_mt/test/wiki-sampled-en-corpus\n"
],
[
"# Inspect the meta data avaible, should have the following:\n# 'parsed' contains the dependency parses for the utterance text \n# 'zh-en' and 'zh-back' contains the translations and back translations for utterance texts respectively \n# 'en_parsed' and 'zh_parsed' contain the respective parses, which we will use for strategy extractions\nwiki_sampled_zh.meta_index",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 2. Computing permeability for politeness strategies ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"With the two sampled datasets tokenized and parsed, we are now ready to the degree to which strategies are perserved vs. lost in different translation directions. \n\nWe make two types of comparisons:\n\n* First, we consider a direct comparison between the original vs. translated texts. In particular, we check strategies used in utterances in English texts and Chinese texts with respective politeness strategy operationalizations to make comparisons. \n\n* Second, we consider comparing the original vs. the backtranslated texts using the same strategy operationalization and compare strategies detected. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Download the data if Part 1 of the notebook is skipped \n\n# replace with where you'd like the corpora to be saved \nDATA_DIR = '/belafonte_sauna/liye_translations/convokit_mt/test/'\n\nwiki_sampled_en = Corpus(download('wiki-sampled-en-corpus', data_dir=DATA_DIR))\nwiki_sampled_zh = Corpus(download('wiki-sampled-zh-corpus', data_dir=DATA_DIR))",
"Dataset already exists at /belafonte_sauna/liye_translations/convokit_mt/test/wiki-sampled-en-corpus\nDataset already exists at /belafonte_sauna/liye_translations/convokit_mt/test/wiki-sampled-zh-corpus\n"
],
[
"wiki_sampled_en.print_summary_stats()",
"Number of Speakers: 7290\nNumber of Utterances: 18000\nNumber of Conversations: 16583\n"
],
[
"wiki_sampled_zh.print_summary_stats()",
"Number of Speakers: 2933\nNumber of Utterances: 12000\nNumber of Conversations: 1\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Extracting strategies \n\nAs a first step, we extract strategies for all translations and back-translations. We will need two politeness strategy transformers: \n\n* for texts in English, we will again use the strategy collection _politeness_local_ \n* for texts in Chinese, we will be using the strategy collection _politeness-cscw-zh_.\n\nMore details of different politeness strategy collections can be found at the [documentation page]( https://convokit.cornell.edu/documentation/politenessStrategies.html).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"ps_zh = PolitenessStrategies(parse_attribute_name='zh_parsed', \\\n strategy_attribute_name=\"zh_strategies\", \\\n strategy_collection=\"politeness_cscw_zh\", \n verbose=5000)\n\nps_en = PolitenessStrategies(parse_attribute_name='en_parsed', \\\n strategy_attribute_name=\"en_strategies\", \\\n strategy_collection=\"politeness_local\",\n verbose=5000)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# extracting for English samples\nwiki_sampled_en = ps_zh.transform(wiki_sampled_en)\nwiki_sampled_en = ps_en.transform(wiki_sampled_en)",
"5000/18000 utterances processed\n10000/18000 utterances processed\n15000/18000 utterances processed\n5000/18000 utterances processed\n10000/18000 utterances processed\n15000/18000 utterances processed\n"
],
[
"# extracting for Chinese samples\nwiki_sampled_zh = ps_zh.transform(wiki_sampled_zh)\nwiki_sampled_zh = ps_en.transform(wiki_sampled_zh)",
"5000/12000 utterances processed\n10000/12000 utterances processed\n5000/12000 utterances processed\n10000/12000 utterances processed\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Making comparisons",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We consider permeability of a politeness strategy _s_ as the percentage utterances in a given collection containing such markers for which the translated version also contains (potentially different) markers from the same set.\n \nAs mentioned earlier, we estimate permeability both with translations and backtranslations. Note that each approach has its own limitations, and thus both of them are at best _proxies_ for strategy permeability and should be not read as the groundtruth values.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Mapping between strategy names in different collections \n# Note that the collections are not exactly equivalent, \n# i.e., there are strategies we can't find a close match between the two collections\n\nen2zh = {'Actually': 'factuality',\n 'Adverb.Just': None,\n 'Affirmation': 'praise',\n 'Apology': 'apologetic',\n 'By.The.Way': 'indirect_btw',\n 'Conj.Start': 'start_so',\n 'Filler': None,\n 'For.Me': None,\n 'For.You': None,\n 'Gratitude': 'gratitude',\n 'Greeting':'greeting',\n 'Hedges':'hedge',\n 'Indicative':'can_you',\n 'Please': 'please',\n 'Please.Start': 'start_please',\n 'Reassurance': None,\n 'Subjunctive': 'could_you',\n 'Swearing': 'taboo'\n }\n\nzh2en = {v:k for k,v in en2zh.items() if v}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# add utterance-level assessing result to utterance metadata for the English corpus\nfor utt in wiki_sampled_en.iter_utterances():\n \n # strategy names in English and Chinese \n en_name = utt.retrieve_meta('strategy')\n zh_name = en2zh[en_name]\n \n # translations\n if zh_name:\n trans_status = utt.retrieve_meta('zh_strategies')[zh_name]\n utt.add_meta('translation_result', trans_status)\n else:\n # when a comparison isn't applicable, we use the value -1 \n utt.add_meta('translation_result', -1)\n \n # back translations \n backtrans_status = utt.retrieve_meta('en_strategies')[en_name]\n utt.add_meta('backtranslation_result', backtrans_status)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# add utterance-level assessing result to utterance metadata for the Chinese corpus\nfor utt in wiki_sampled_zh.iter_utterances():\n \n # strategy names in English and Chinese \n zh_name = utt.retrieve_meta('strategy')\n en_name = zh2en[zh_name]\n \n # translations\n if en_name:\n trans_status = utt.retrieve_meta('en_strategies')[en_name]\n utt.add_meta('translation_result', trans_status)\n \n # back translations \n backtrans_status = utt.retrieve_meta('zh_strategies')[zh_name]\n utt.add_meta('backtranslation_result', backtrans_status)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can then export these utterance-level assessing results to pandas DataFrames (via `get_attribute_table`) for easy aggregation and plotting. The utterance metadata we need are:\n\n * strategy: the strategy to be checked for the utterance \n * translation_result: whether the checked strategy remains in the translated text\n * backtranslation_result: whether the checked strategy remains in the back-translated text",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### A. English -> Chinese",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# results for the English corpus \nres_df_en = wiki_sampled_en.get_attribute_table(obj_type='utterance', \\\n attrs=['strategy', \\\n 'translation_result', \\\n 'backtranslation_result'])\n\nres_df_en.columns = ['strategy', 'en->zh', 'en->zh->en']\n\n# strategy-level permeability, -1 means the strategy is not applicable \npermeability_df_en = res_df_en.groupby('strategy').sum() / 1000",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# As a reference, we include permeability computed through an informal small-scale human annotations \n# (50 instances, one annotator)\nreference = {'Actually': 0.7, 'Adverb.Just': 0.62, 'Affirmation': 0.8, 'Apology': 0.94, 'By.The.Way': 0.42,\n 'Conj.Start': 0.66, 'Filler': 0.58, 'For.Me': 0.62, 'For.You': 0.52, 'Gratitude': 0.86,\n 'Greeting': 0.52, 'Hedges': 0.68, 'Indicative': 0.64, 'Please': 0.72, 'Please.Start': 0.82,\n 'Reassurance': 0.88, 'Subjunctive': 0.0, 'Swearing': 0.3}\n\npermeability_df_en['reference'] = [reference[name] for name in permeability_df_en.index]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# As further context, we can inlcude information about strategy prevalence on our plot\nprevalence_en = dict(df_prevalence*100)\npermeability_df_en.index = [f\"{name} ({prevalence_en[name]:.1f}%)\" for name in permeability_df_en.index]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(9, 12))\nsns.set(font_scale=1.2)\n\n# cells that are not applicable are masked in white\nwith sns.axes_style(\"white\"):\n sns.heatmap(permeability_df_en, annot=True, cmap=\"Greens\", fmt=\".1%\", mask=permeability_df_en==-1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### B. Chinese -> English",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# results for the English corpus \nres_df_zh = wiki_sampled_zh.get_attribute_table(obj_type='utterance', \\\n attrs=['strategy', \\\n 'translation_result', \\\n 'backtranslation_result'])\n\n# convert names to make it easier to compare between directions \nres_df_zh['strategy'] = res_df_zh['strategy'].apply(lambda name:zh2en[name])\n\nres_df_zh.columns = ['strategy', 'zh->en', 'zh->en->zh'] \npermeability_df_zh = res_df_zh.groupby('strategy').sum() / 1000",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# as the original dataset for the Chinese corpus is quite large\n# we present strategy prevalence results directly\n\nprevalence_zh = {'apologetic': 0.6, 'can_you': 0.3, 'could_you': 0.0, \n 'factuality': 0.4,'gratitude': 3.1, 'greeting': 0.0, \n 'hedge': 42.8, 'indirect_btw': 0.1,\n 'praise': 0.4, 'please': 25.4, \n 'start_please': 17.7, 'start_so': 0.7, 'taboo': 0.4}\n\npermeability_df_zh.index = [f\"{name} ({prevalence_zh[en2zh[name]]:.1f}%)\" for name in permeability_df_zh.index]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(6, 9))\nsns.set(font_scale=1.2)\nwith sns.axes_style(\"white\"):\n sns.heatmap(permeability_df_zh, annot=True, cmap=\"Blues\", fmt=\".1%\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a7645173e3bbf4ec2f2d138c3ad091e1bd0fe08
| 13,835 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Python_IBM/PY0101EN-4-2-WriteFile.ipynb
|
ClaudiaCCordeiro/Curso_IBM
|
2123ebf48e0657f61998f38fe803203be51877ff
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Python_IBM/PY0101EN-4-2-WriteFile.ipynb
|
ClaudiaCCordeiro/Curso_IBM
|
2123ebf48e0657f61998f38fe803203be51877ff
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Python_IBM/PY0101EN-4-2-WriteFile.ipynb
|
ClaudiaCCordeiro/Curso_IBM
|
2123ebf48e0657f61998f38fe803203be51877ff
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 24.530142 | 716 | 0.539574 |
[
[
[
"<div class=\"alert alert-block alert-info\" style=\"margin-top: 20px\">\n <a href=\"https://cocl.us/topNotebooksPython101Coursera\">\n <img src=\"https://s3-api.us-geo.objectstorage.softlayer.net/cf-courses-data/CognitiveClass/PY0101EN/Ad/TopAd.png\" width=\"750\" align=\"center\">\n </a>\n</div>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a href=\"https://cognitiveclass.ai/\">\n <img src=\"https://s3-api.us-geo.objectstorage.softlayer.net/cf-courses-data/CognitiveClass/PY0101EN/Ad/CCLog.png\" width=\"200\" align=\"center\">\n</a>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<h1>Write and Save Files in Python</h1>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<p><strong>Welcome!</strong> This notebook will teach you about write the text to file in the Python Programming Language. By the end of this lab, you'll know how to write to file and copy the file.</p>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<h2>Table of Contents</h2>\n<div class=\"alert alert-block alert-info\" style=\"margin-top: 20px\">\n <ul>\n <li><a href=\"write\">Writing Files</a></li>\n <li><a href=\"copy\">Copy a File</a></li>\n </ul>\n <p>\n Estimated time needed: <strong>15 min</strong>\n </p>\n</div>\n\n<hr>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<h2 id=\"write\">Writing Files</h2>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
" We can open a file object using the method <code>write()</code> to save the text file to a list. To write the mode, argument must be set to write <b>w</b>. Let’s write a file <b>Example2.txt</b> with the line: <b>“This is line A”</b>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Write line to file\n\nwith open('/resources/data/Example2.txt', 'w') as writefile:\n writefile.write(\"This is line A\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
" We can read the file to see if it worked:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Read file\n\nwith open('/resources/data/Example2.txt', 'r') as testwritefile:\n print(testwritefile.read())",
"This is line A\n"
]
],
[
[
"We can write multiple lines:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Write lines to file\n\nwith open('/resources/data/Example2.txt', 'w') as writefile:\n writefile.write(\"This is line A\\n\")\n writefile.write(\"This is line B\\n\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The method <code>.write()</code> works similar to the method <code>.readline()</code>, except instead of reading a new line it writes a new line. The process is illustrated in the figure , the different colour coding of the grid represents a new line added to the file after each method call.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<img src=\"https://s3-api.us-geo.objectstorage.softlayer.net/cf-courses-data/CognitiveClass/PY0101EN/Chapter%204/Images/WriteLine.png\" width=\"500\" />",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"You can check the file to see if your results are correct ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Check whether write to file\n\nwith open('/resources/data/Example2.txt', 'r') as testwritefile:\n print(testwritefile.read())",
"This is line A\nThis is line B\n\n"
]
],
[
[
" By setting the mode argument to append **a** you can append a new line as follows:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Write a new line to text file\n\nwith open('/resources/data/Example2.txt', 'a') as testwritefile:\n testwritefile.write(\"This is line C\\n\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
" You can verify the file has changed by running the following cell:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Verify if the new line is in the text file\n\nwith open('/resources/data/Example2.txt', 'r') as testwritefile:\n print(testwritefile.read())",
"This is line A\nThis is line B\nThis is line C\n\n"
]
],
[
[
" We write a list to a <b>.txt</b> file as follows:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Sample list of text\n\nLines = [\"This is line A\\n\", \"This is line B\\n\", \"This is line C\\n\"]\nLines",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Write the strings in the list to text file\n\nwith open('Example2.txt', 'w') as writefile:\n for line in Lines:\n print(line)\n writefile.write(line)",
"This is line A\n\nThis is line B\n\nThis is line C\n\n"
]
],
[
[
" We can verify the file is written by reading it and printing out the values: ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Verify if writing to file is successfully executed\n\nwith open('Example2.txt', 'r') as testwritefile:\n print(testwritefile.read())",
"This is line A\nThis is line B\nThis is line C\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"We can again append to the file by changing the second parameter to <b>a</b>. This adds the code:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Append the line to the file\n\nwith open('Example2.txt', 'a') as testwritefile:\n testwritefile.write(\"This is line D\\n\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can see the results of appending the file: ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Verify if the appending is successfully executed\n\nwith open('Example2.txt', 'r') as testwritefile:\n print(testwritefile.read())",
"This is line A\nThis is line B\nThis is line C\nThis is line D\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"<hr>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<h2 id=\"copy\">Copy a File</h2> ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Let's copy the file <b>Example2.txt</b> to the file <b>Example3.txt</b>:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Copy file to another\n\nwith open('Example2.txt','r') as readfile:\n with open('Example3.txt','w') as writefile:\n for line in readfile:\n writefile.write(line)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can read the file to see if everything works:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Verify if the copy is successfully executed\n\nwith open('Example3.txt','r') as testwritefile:\n print(testwritefile.read())",
"This is line A\nThis is line B\nThis is line C\nThis is line D\n\n"
]
],
[
[
" After reading files, we can also write data into files and save them in different file formats like **.txt, .csv, .xls (for excel files) etc**. Let's take a look at some examples.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Now go to the directory to ensure the <b>.txt</b> file exists and contains the summary data that we wrote.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<hr>\n<h2>The last exercise!</h2>\n<p>Congratulations, you have completed your first lesson and hands-on lab in Python. However, there is one more thing you need to do. The Data Science community encourages sharing work. The best way to share and showcase your work is to share it on GitHub. By sharing your notebook on GitHub you are not only building your reputation with fellow data scientists, but you can also show it off when applying for a job. Even though this was your first piece of work, it is never too early to start building good habits. So, please read and follow <a href=\"https://cognitiveclass.ai/blog/data-scientists-stand-out-by-sharing-your-notebooks/\" target=\"_blank\">this article</a> to learn how to share your work.\n<hr>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<div class=\"alert alert-block alert-info\" style=\"margin-top: 20px\">\n<h2>Get IBM Watson Studio free of charge!</h2>\n <p><a href=\"https://cocl.us/bottemNotebooksPython101Coursera\"><img src=\"https://s3-api.us-geo.objectstorage.softlayer.net/cf-courses-data/CognitiveClass/PY0101EN/Ad/BottomAd.png\" width=\"750\" align=\"center\"></a></p>\n</div>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<h3>About the Authors:</h3> \n<p><a href=\"https://www.linkedin.com/in/joseph-s-50398b136/\" target=\"_blank\">Joseph Santarcangelo</a> is a Data Scientist at IBM, and holds a PhD in Electrical Engineering. His research focused on using Machine Learning, Signal Processing, and Computer Vision to determine how videos impact human cognition. Joseph has been working for IBM since he completed his PhD.</p>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Other contributors: <a href=\"www.linkedin.com/in/jiahui-mavis-zhou-a4537814a\">Mavis Zhou</a>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<hr>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<p>Copyright © 2018 IBM Developer Skills Network. This notebook and its source code are released under the terms of the <a href=\"https://cognitiveclass.ai/mit-license/\">MIT License</a>.</p>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4a7648b13663926a1e1d5fd90a2c63755b5e5d88
| 40,235 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
site/en/tutorials/text/text_generation.ipynb
|
martinkosela/docs
|
b3c129474f252497e2ba768539872c1e5ee0343a
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
site/en/tutorials/text/text_generation.ipynb
|
martinkosela/docs
|
b3c129474f252497e2ba768539872c1e5ee0343a
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
site/en/tutorials/text/text_generation.ipynb
|
martinkosela/docs
|
b3c129474f252497e2ba768539872c1e5ee0343a
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 32.188 | 493 | 0.526258 |
[
[
[
"##### Copyright 2019 The TensorFlow Authors.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#@title Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the \"License\");\n# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.\n# You may obtain a copy of the License at\n#\n# https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0\n#\n# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software\n# distributed under the License is distributed on an \"AS IS\" BASIS,\n# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.\n# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and\n# limitations under the License.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Text generation with an RNN",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<table class=\"tfo-notebook-buttons\" align=\"left\">\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/text/text_generation\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/tf_logo_32px.png\" />View on TensorFlow.org</a>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/tensorflow/docs/blob/master/site/en/tutorials/text/text_generation.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/colab_logo_32px.png\" />Run in Google Colab</a>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://github.com/tensorflow/docs/blob/master/site/en/tutorials/text/text_generation.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/GitHub-Mark-32px.png\" />View source on GitHub</a>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a href=\"https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow_docs/docs/site/en/tutorials/text/text_generation.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/download_logo_32px.png\" />Download notebook</a>\n </td>\n</table>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"This tutorial demonstrates how to generate text using a character-based RNN. We will work with a dataset of Shakespeare's writing from Andrej Karpathy's [The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Recurrent Neural Networks](http://karpathy.github.io/2015/05/21/rnn-effectiveness/). Given a sequence of characters from this data (\"Shakespear\"), train a model to predict the next character in the sequence (\"e\"). Longer sequences of text can be generated by calling the model repeatedly.\n\nNote: Enable GPU acceleration to execute this notebook faster. In Colab: *Runtime > Change runtime type > Hardware acclerator > GPU*. If running locally make sure TensorFlow version >= 1.11.\n\nThis tutorial includes runnable code implemented using [tf.keras](https://www.tensorflow.org/programmers_guide/keras) and [eager execution](https://www.tensorflow.org/programmers_guide/eager). The following is sample output when the model in this tutorial trained for 30 epochs, and started with the string \"Q\":\n\n<pre>\nQUEENE:\nI had thought thou hadst a Roman; for the oracle,\nThus by All bids the man against the word,\nWhich are so weak of care, by old care done;\nYour children were in your holy love,\nAnd the precipitation through the bleeding throne.\n\nBISHOP OF ELY:\nMarry, and will, my lord, to weep in such a one were prettiest;\nYet now I was adopted heir\nOf the world's lamentable day,\nTo watch the next way with his father with his face?\n\nESCALUS:\nThe cause why then we are all resolved more sons.\n\nVOLUMNIA:\nO, no, no, no, no, no, no, no, no, no, no, no, no, no, no, no, no, no, no, no, no, it is no sin it should be dead,\nAnd love and pale as any will to that word.\n\nQUEEN ELIZABETH:\nBut how long have I heard the soul for this world,\nAnd show his hands of life be proved to stand.\n\nPETRUCHIO:\nI say he look'd on, if I must be content\nTo stay him from the fatal of our country's bliss.\nHis lordship pluck'd from this sentence then for prey,\nAnd then let us twain, being the moon,\nwere she such a case as fills m\n</pre>\n\nWhile some of the sentences are grammatical, most do not make sense. The model has not learned the meaning of words, but consider:\n\n* The model is character-based. When training started, the model did not know how to spell an English word, or that words were even a unit of text.\n\n* The structure of the output resembles a play—blocks of text generally begin with a speaker name, in all capital letters similar to the dataset.\n\n* As demonstrated below, the model is trained on small batches of text (100 characters each), and is still able to generate a longer sequence of text with coherent structure.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Setup",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Import TensorFlow and other libraries",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals\n\ntry:\n # %tensorflow_version only exists in Colab.\n %tensorflow_version 2.x\nexcept Exception:\n pass\nimport tensorflow as tf\n\nimport numpy as np\nimport os\nimport time",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Download the Shakespeare dataset\n\nChange the following line to run this code on your own data.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"path_to_file = tf.keras.utils.get_file('shakespeare.txt', 'https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/shakespeare.txt')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Read the data\n\nFirst, look in the text:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Read, then decode for py2 compat.\ntext = open(path_to_file, 'rb').read().decode(encoding='utf-8')\n# length of text is the number of characters in it\nprint ('Length of text: {} characters'.format(len(text)))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Take a look at the first 250 characters in text\nprint(text[:250])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# The unique characters in the file\nvocab = sorted(set(text))\nprint ('{} unique characters'.format(len(vocab)))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Process the text",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Vectorize the text\n\nBefore training, we need to map strings to a numerical representation. Create two lookup tables: one mapping characters to numbers, and another for numbers to characters.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Creating a mapping from unique characters to indices\nchar2idx = {u:i for i, u in enumerate(vocab)}\nidx2char = np.array(vocab)\n\ntext_as_int = np.array([char2idx[c] for c in text])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now we have an integer representation for each character. Notice that we mapped the character as indexes from 0 to `len(unique)`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print('{')\nfor char,_ in zip(char2idx, range(20)):\n print(' {:4s}: {:3d},'.format(repr(char), char2idx[char]))\nprint(' ...\\n}')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Show how the first 13 characters from the text are mapped to integers\nprint ('{} ---- characters mapped to int ---- > {}'.format(repr(text[:13]), text_as_int[:13]))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### The prediction task",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Given a character, or a sequence of characters, what is the most probable next character? This is the task we're training the model to perform. The input to the model will be a sequence of characters, and we train the model to predict the output—the following character at each time step.\n\nSince RNNs maintain an internal state that depends on the previously seen elements, given all the characters computed until this moment, what is the next character?\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Create training examples and targets\n\nNext divide the text into example sequences. Each input sequence will contain `seq_length` characters from the text.\n\nFor each input sequence, the corresponding targets contain the same length of text, except shifted one character to the right.\n\nSo break the text into chunks of `seq_length+1`. For example, say `seq_length` is 4 and our text is \"Hello\". The input sequence would be \"Hell\", and the target sequence \"ello\".\n\nTo do this first use the `tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices` function to convert the text vector into a stream of character indices.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# The maximum length sentence we want for a single input in characters\nseq_length = 100\nexamples_per_epoch = len(text)//(seq_length+1)\n\n# Create training examples / targets\nchar_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(text_as_int)\n\nfor i in char_dataset.take(5):\n print(idx2char[i.numpy()])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The `batch` method lets us easily convert these individual characters to sequences of the desired size.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sequences = char_dataset.batch(seq_length+1, drop_remainder=True)\n\nfor item in sequences.take(5):\n print(repr(''.join(idx2char[item.numpy()])))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"For each sequence, duplicate and shift it to form the input and target text by using the `map` method to apply a simple function to each batch:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def split_input_target(chunk):\n input_text = chunk[:-1]\n target_text = chunk[1:]\n return input_text, target_text\n\ndataset = sequences.map(split_input_target)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Print the first examples input and target values:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for input_example, target_example in dataset.take(1):\n print ('Input data: ', repr(''.join(idx2char[input_example.numpy()])))\n print ('Target data:', repr(''.join(idx2char[target_example.numpy()])))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Each index of these vectors are processed as one time step. For the input at time step 0, the model receives the index for \"F\" and trys to predict the index for \"i\" as the next character. At the next timestep, it does the same thing but the `RNN` considers the previous step context in addition to the current input character.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for i, (input_idx, target_idx) in enumerate(zip(input_example[:5], target_example[:5])):\n print(\"Step {:4d}\".format(i))\n print(\" input: {} ({:s})\".format(input_idx, repr(idx2char[input_idx])))\n print(\" expected output: {} ({:s})\".format(target_idx, repr(idx2char[target_idx])))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Create training batches\n\nWe used `tf.data` to split the text into manageable sequences. But before feeding this data into the model, we need to shuffle the data and pack it into batches.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Batch size\nBATCH_SIZE = 64\n\n# Buffer size to shuffle the dataset\n# (TF data is designed to work with possibly infinite sequences,\n# so it doesn't attempt to shuffle the entire sequence in memory. Instead,\n# it maintains a buffer in which it shuffles elements).\nBUFFER_SIZE = 10000\n\ndataset = dataset.shuffle(BUFFER_SIZE).batch(BATCH_SIZE, drop_remainder=True)\n\ndataset",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Build The Model",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Use `tf.keras.Sequential` to define the model. For this simple example three layers are used to define our model:\n\n* `tf.keras.layers.Embedding`: The input layer. A trainable lookup table that will map the numbers of each character to a vector with `embedding_dim` dimensions;\n* `tf.keras.layers.GRU`: A type of RNN with size `units=rnn_units` (You can also use a LSTM layer here.)\n* `tf.keras.layers.Dense`: The output layer, with `vocab_size` outputs.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Length of the vocabulary in chars\nvocab_size = len(vocab)\n\n# The embedding dimension\nembedding_dim = 256\n\n# Number of RNN units\nrnn_units = 1024",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def build_model(vocab_size, embedding_dim, rnn_units, batch_size):\n model = tf.keras.Sequential([\n tf.keras.layers.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim,\n batch_input_shape=[batch_size, None]),\n tf.keras.layers.GRU(rnn_units,\n return_sequences=True,\n stateful=True,\n recurrent_initializer='glorot_uniform'),\n tf.keras.layers.Dense(vocab_size)\n ])\n return model",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model = build_model(\n vocab_size = len(vocab),\n embedding_dim=embedding_dim,\n rnn_units=rnn_units,\n batch_size=BATCH_SIZE)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"For each character the model looks up the embedding, runs the GRU one timestep with the embedding as input, and applies the dense layer to generate logits predicting the log-likelihood of the next character:\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Try the model\n\nNow run the model to see that it behaves as expected.\n\nFirst check the shape of the output:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for input_example_batch, target_example_batch in dataset.take(1):\n example_batch_predictions = model(input_example_batch)\n print(example_batch_predictions.shape, \"# (batch_size, sequence_length, vocab_size)\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"In the above example the sequence length of the input is `100` but the model can be run on inputs of any length:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model.summary()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"To get actual predictions from the model we need to sample from the output distribution, to get actual character indices. This distribution is defined by the logits over the character vocabulary.\n\nNote: It is important to _sample_ from this distribution as taking the _argmax_ of the distribution can easily get the model stuck in a loop.\n\nTry it for the first example in the batch:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sampled_indices = tf.random.categorical(example_batch_predictions[0], num_samples=1)\nsampled_indices = tf.squeeze(sampled_indices,axis=-1).numpy()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This gives us, at each timestep, a prediction of the next character index:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sampled_indices",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Decode these to see the text predicted by this untrained model:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(\"Input: \\n\", repr(\"\".join(idx2char[input_example_batch[0]])))\nprint()\nprint(\"Next Char Predictions: \\n\", repr(\"\".join(idx2char[sampled_indices ])))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Train the model",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"At this point the problem can be treated as a standard classification problem. Given the previous RNN state, and the input this time step, predict the class of the next character.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Attach an optimizer, and a loss function",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The standard `tf.keras.losses.sparse_categorical_crossentropy` loss function works in this case because it is applied across the last dimension of the predictions.\n\nBecause our model returns logits, we need to set the `from_logits` flag.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def loss(labels, logits):\n return tf.keras.losses.sparse_categorical_crossentropy(labels, logits, from_logits=True)\n\nexample_batch_loss = loss(target_example_batch, example_batch_predictions)\nprint(\"Prediction shape: \", example_batch_predictions.shape, \" # (batch_size, sequence_length, vocab_size)\")\nprint(\"scalar_loss: \", example_batch_loss.numpy().mean())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Configure the training procedure using the `tf.keras.Model.compile` method. We'll use `tf.keras.optimizers.Adam` with default arguments and the loss function.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss=loss)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Configure checkpoints",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Use a `tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint` to ensure that checkpoints are saved during training:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Directory where the checkpoints will be saved\ncheckpoint_dir = './training_checkpoints'\n# Name of the checkpoint files\ncheckpoint_prefix = os.path.join(checkpoint_dir, \"ckpt_{epoch}\")\n\ncheckpoint_callback=tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(\n filepath=checkpoint_prefix,\n save_weights_only=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Execute the training",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"To keep training time reasonable, use 10 epochs to train the model. In Colab, set the runtime to GPU for faster training.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"EPOCHS=10",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"history = model.fit(dataset, epochs=EPOCHS, callbacks=[checkpoint_callback])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Generate text",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Restore the latest checkpoint",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"To keep this prediction step simple, use a batch size of 1.\n\nBecause of the way the RNN state is passed from timestep to timestep, the model only accepts a fixed batch size once built.\n\nTo run the model with a different `batch_size`, we need to rebuild the model and restore the weights from the checkpoint.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tf.train.latest_checkpoint(checkpoint_dir)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model = build_model(vocab_size, embedding_dim, rnn_units, batch_size=1)\n\nmodel.load_weights(tf.train.latest_checkpoint(checkpoint_dir))\n\nmodel.build(tf.TensorShape([1, None]))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model.summary()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### The prediction loop\n\nThe following code block generates the text:\n\n* It Starts by choosing a start string, initializing the RNN state and setting the number of characters to generate.\n\n* Get the prediction distribution of the next character using the start string and the RNN state.\n\n* Then, use a categorical distribution to calculate the index of the predicted character. Use this predicted character as our next input to the model.\n\n* The RNN state returned by the model is fed back into the model so that it now has more context, instead than only one character. After predicting the next character, the modified RNN states are again fed back into the model, which is how it learns as it gets more context from the previously predicted characters.\n\n\n\n\nLooking at the generated text, you'll see the model knows when to capitalize, make paragraphs and imitates a Shakespeare-like writing vocabulary. With the small number of training epochs, it has not yet learned to form coherent sentences.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def generate_text(model, start_string):\n # Evaluation step (generating text using the learned model)\n\n # Number of characters to generate\n num_generate = 1000\n\n # Converting our start string to numbers (vectorizing)\n input_eval = [char2idx[s] for s in start_string]\n input_eval = tf.expand_dims(input_eval, 0)\n\n # Empty string to store our results\n text_generated = []\n\n # Low temperatures results in more predictable text.\n # Higher temperatures results in more surprising text.\n # Experiment to find the best setting.\n temperature = 1.0\n\n # Here batch size == 1\n model.reset_states()\n for i in range(num_generate):\n predictions = model(input_eval)\n # remove the batch dimension\n predictions = tf.squeeze(predictions, 0)\n\n # using a categorical distribution to predict the character returned by the model\n predictions = predictions / temperature\n predicted_id = tf.random.categorical(predictions, num_samples=1)[-1,0].numpy()\n\n # We pass the predicted character as the next input to the model\n # along with the previous hidden state\n input_eval = tf.expand_dims([predicted_id], 0)\n\n text_generated.append(idx2char[predicted_id])\n\n return (start_string + ''.join(text_generated))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(generate_text(model, start_string=u\"ROMEO: \"))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The easiest thing you can do to improve the results it to train it for longer (try `EPOCHS=30`).\n\nYou can also experiment with a different start string, or try adding another RNN layer to improve the model's accuracy, or adjusting the temperature parameter to generate more or less random predictions.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Advanced: Customized Training\n\nThe above training procedure is simple, but does not give you much control.\n\nSo now that you've seen how to run the model manually let's unpack the training loop, and implement it ourselves. This gives a starting point if, for example, to implement _curriculum learning_ to help stabilize the model's open-loop output.\n\nWe will use `tf.GradientTape` to track the gradients. You can learn more about this approach by reading the [eager execution guide](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/eager).\n\nThe procedure works as follows:\n\n* First, initialize the RNN state. We do this by calling the `tf.keras.Model.reset_states` method.\n\n* Next, iterate over the dataset (batch by batch) and calculate the *predictions* associated with each.\n\n* Open a `tf.GradientTape`, and calculate the predictions and loss in that context.\n\n* Calculate the gradients of the loss with respect to the model variables using the `tf.GradientTape.grads` method.\n\n* Finally, take a step downwards by using the optimizer's `tf.train.Optimizer.apply_gradients` method.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model = build_model(\n vocab_size = len(vocab),\n embedding_dim=embedding_dim,\n rnn_units=rnn_units,\n batch_size=BATCH_SIZE)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"@tf.function\ndef train_step(inp, target):\n with tf.GradientTape() as tape:\n predictions = model(inp)\n loss = tf.reduce_mean(\n tf.keras.losses.sparse_categorical_crossentropy(\n target, predictions, from_logits=True))\n grads = tape.gradient(loss, model.trainable_variables)\n optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, model.trainable_variables))\n\n return loss",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Training step\nEPOCHS = 10\n\nfor epoch in range(EPOCHS):\n start = time.time()\n\n # initializing the hidden state at the start of every epoch\n # initally hidden is None\n hidden = model.reset_states()\n\n for (batch_n, (inp, target)) in enumerate(dataset):\n loss = train_step(inp, target)\n\n if batch_n % 100 == 0:\n template = 'Epoch {} Batch {} Loss {}'\n print(template.format(epoch+1, batch_n, loss))\n\n # saving (checkpoint) the model every 5 epochs\n if (epoch + 1) % 5 == 0:\n model.save_weights(checkpoint_prefix.format(epoch=epoch))\n\n print ('Epoch {} Loss {:.4f}'.format(epoch+1, loss))\n print ('Time taken for 1 epoch {} sec\\n'.format(time.time() - start))\n\nmodel.save_weights(checkpoint_prefix.format(epoch=epoch))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a76540d83704c4ee555dd77a6e50ff1df13a170
| 14,989 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
SRC/Data_Extraction/DataManage.ipynb
|
Joearrowsmith/Algo-Trading-System-ManAHL18-PofC
|
23c08bd17483b9a5cd58ce9961f7f4db9da3fa09
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
SRC/Data_Extraction/DataManage.ipynb
|
Joearrowsmith/Algo-Trading-System-ManAHL18-PofC
|
23c08bd17483b9a5cd58ce9961f7f4db9da3fa09
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
SRC/Data_Extraction/DataManage.ipynb
|
Joearrowsmith/Algo-Trading-System-ManAHL18-PofC
|
23c08bd17483b9a5cd58ce9961f7f4db9da3fa09
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2018-04-21T18:08:33.000Z
|
2018-04-21T21:38:06.000Z
| 47.13522 | 177 | 0.428381 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport os\nimport datetime as dt\nfrom alpha_vantage.timeseries import TimeSeries",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def getStoredData(srtdt, enddt, ticker):\n #currently assumes that csv data is organised in format: Date,Open,High,Low,Close,Adj Close,Volume\n #also assumes that the name of the csv is the same as that as the ticker\n path = r'C:\\Users\\Edward Stables\\Documents\\Programming\\Jupyter\\Man AHL\\Data\\Initial Datasets'\n beginning_of_time='2000-01-01'#sets the earliest date required to be stored\n os.chdir(path) #sets the directory for the files\n \n try:\n #attempt to load the csv file from the path directory\n frame = pd.read_csv(ticker+'.csv')\n #set 'date' as index\n frame = frame.set_index(['date'])\n \n if dt.datetime.strptime(frame.index[-1], '%Y-%m-%d').date() < dt.datetime.today().date(): \n #if the data is not up-to-date:\n updateData = getData(dt.datetime.strptime(frame.index[-1], '%Y-%m-%d').date().strftime('%Y-%m-%d'), dt.datetime.today().date().strftime('%Y-%m-%d'), ticker)\n #appends the new data to the imported data\n frame = frame.append(updateData[1:])\n frame = partition(frame)\n #saves the data back to storage\n frame.to_csv(ticker+'.csv')\n \n except FileNotFoundError:\n #if the file doesn't exist then send a request to get the data for the ticker's dates#\n with open(ticker+'.csv', \"w\"):\n pass\n #gets the new data, from 1/1/2000 to the current day\n frame = getData(beginning_of_time, dt.datetime.today().date().strftime('%Y-%m-%d'), ticker)\n frame = partition(frame)\n #saves it to disk\n frame.to_csv(ticker+'.csv')\n #reads the requested value from disk\n frame = pd.read_csv(ticker+'.csv')\n #sets date as index\n frame = frame.set_index(['date'])\n \n #returns the selected values\n return frame[(frame.index >= srtdt) & (frame.index <= enddt)]\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def getData(strdt, enddt, tic):\n API_KEY = '4U0DSJC208E4D8R7'\n #makes api call\n ts = TimeSeries(key=API_KEY, output_format='pandas')\n data, meta_data = ts.get_daily(symbol=tic, outputsize='full')\n #selects required data from full datarange returned\n dataRange = data.loc[strdt: enddt]\n return dataRange",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(getStoredData('2000-01','2018-04-20', 'MSFT'))",
" 1. open 2. high 3. low 4. close 5. volume flaggaussian \\\ndate \n2000-01-03 117.370 118.620 112.000 116.56 26614200.0 0 \n2000-01-04 113.560 117.120 112.250 112.62 27059500.0 0 \n2000-01-05 111.120 116.370 109.370 113.81 32029800.0 0 \n2000-01-06 112.190 113.870 108.370 110.00 27488300.0 0 \n2000-01-07 108.620 112.250 107.310 111.44 31006800.0 0 \n2000-01-10 113.440 113.690 111.370 112.25 22481800.0 0 \n2000-01-11 111.500 114.250 108.690 109.37 23371800.0 0 \n2000-01-12 108.500 108.870 104.440 105.81 33266200.0 0 \n2000-01-13 104.370 108.620 101.500 107.81 41572000.0 0 \n2000-01-14 107.190 113.940 105.750 112.25 36708200.0 0 \n2000-01-18 111.810 116.500 111.750 115.31 40741800.0 0 \n2000-01-19 110.500 111.500 106.000 107.00 48784100.0 0 \n2000-01-20 107.060 109.690 105.870 106.00 28174900.0 0 \n2000-01-21 107.000 107.250 103.250 103.75 34208100.0 0 \n2000-01-24 103.800 105.690 100.810 101.25 31798800.0 0 \n2000-01-25 101.000 103.870 99.560 102.81 29911600.0 0 \n2000-01-26 102.440 103.500 99.120 99.37 24682500.0 0 \n2000-01-27 99.890 101.190 97.250 98.75 31827400.0 0 \n2000-01-28 98.120 100.250 97.250 98.25 29112700.0 0 \n2000-01-31 97.620 98.190 94.870 97.87 36597100.0 0 \n2000-02-01 98.500 103.250 97.690 102.94 35098300.0 0 \n2000-02-02 102.440 103.940 100.500 100.81 24957800.0 0 \n2000-02-03 102.060 104.190 100.120 103.62 24593000.0 0 \n2000-02-04 104.370 108.000 104.140 106.56 27682700.0 0 \n2000-02-07 106.810 106.870 104.250 106.62 20002900.0 0 \n2000-02-08 106.440 110.000 106.440 109.94 28114500.0 0 \n2000-02-09 109.440 109.440 103.870 104.00 27545000.0 0 \n2000-02-10 103.890 106.560 102.500 106.00 27263900.0 0 \n2000-02-11 104.870 104.870 99.120 99.94 57779500.0 0 \n2000-02-14 101.230 101.750 99.060 99.62 40514300.0 0 \n... ... ... ... ... ... ... \n2018-03-09 95.290 96.540 95.000 96.54 36145524.0 0 \n2018-03-12 96.500 97.210 96.040 96.77 25333720.0 0 \n2018-03-13 97.000 97.240 93.970 94.41 34445391.0 0 \n2018-03-14 95.120 95.410 93.500 93.85 31576898.0 0 \n2018-03-15 93.530 94.580 92.830 94.18 26279014.0 0 \n2018-03-16 94.680 95.380 93.920 94.60 47329521.0 0 \n2018-03-19 93.740 93.900 92.110 92.89 31752589.0 0 \n2018-03-20 93.050 93.770 93.000 93.13 21787780.0 0 \n2018-03-21 92.930 94.050 92.210 92.48 23753263.0 0 \n2018-03-22 91.265 91.750 89.660 89.79 37578166.0 0 \n2018-03-23 89.500 90.460 87.080 87.18 42159397.0 0 \n2018-03-26 90.610 94.000 90.400 93.78 55031149.0 0 \n2018-03-27 94.940 95.139 88.510 89.47 53704562.0 0 \n2018-03-28 89.820 91.230 88.873 89.39 52501146.0 0 \n2018-03-29 90.180 92.290 88.400 91.27 45867548.0 0 \n2018-04-02 90.470 90.880 87.510 88.52 48515417.0 0 \n2018-04-03 89.575 90.050 87.890 89.71 37213837.0 0 \n2018-04-04 87.850 92.760 87.730 92.33 35559956.0 0 \n2018-04-05 92.435 93.065 91.400 92.38 29771881.0 0 \n2018-04-06 91.490 92.460 89.480 90.23 38026000.0 0 \n2018-04-09 91.040 93.170 90.620 90.77 31533943.0 0 \n2018-04-10 92.390 93.280 91.640 92.88 26939883.0 0 \n2018-04-11 92.010 93.290 91.480 91.86 24872110.0 0 \n2018-04-12 92.430 94.160 92.430 93.58 26758879.0 0 \n2018-04-13 94.050 94.180 92.440 93.08 23346063.0 0 \n2018-04-16 94.070 94.660 93.420 94.17 20288083.0 0 \n2018-04-17 95.000 96.540 94.880 96.07 26771000.0 0 \n2018-04-18 96.220 96.720 95.520 96.44 21043287.0 0 \n2018-04-19 96.440 97.070 95.340 96.11 23552541.0 0 \n2018-04-20 95.910 96.110 94.050 95.00 31133384.0 0 \n\n flagsimple flagyearly \ndate \n2000-01-03 0 0 \n2000-01-04 0 0 \n2000-01-05 0 0 \n2000-01-06 0 0 \n2000-01-07 0 0 \n2000-01-10 0 0 \n2000-01-11 0 0 \n2000-01-12 0 0 \n2000-01-13 0 0 \n2000-01-14 0 0 \n2000-01-18 0 0 \n2000-01-19 0 0 \n2000-01-20 0 0 \n2000-01-21 0 0 \n2000-01-24 0 0 \n2000-01-25 0 0 \n2000-01-26 0 0 \n2000-01-27 0 0 \n2000-01-28 0 0 \n2000-01-31 0 0 \n2000-02-01 0 0 \n2000-02-02 0 0 \n2000-02-03 0 0 \n2000-02-04 0 0 \n2000-02-07 0 0 \n2000-02-08 0 0 \n2000-02-09 0 0 \n2000-02-10 0 0 \n2000-02-11 0 0 \n2000-02-14 0 0 \n... ... ... \n2018-03-09 1 0 \n2018-03-12 1 0 \n2018-03-13 1 0 \n2018-03-14 1 0 \n2018-03-15 1 0 \n2018-03-16 1 0 \n2018-03-19 1 0 \n2018-03-20 1 0 \n2018-03-21 1 0 \n2018-03-22 1 0 \n2018-03-23 1 0 \n2018-03-26 1 0 \n2018-03-27 1 0 \n2018-03-28 1 0 \n2018-03-29 1 0 \n2018-04-02 1 0 \n2018-04-03 1 0 \n2018-04-04 1 0 \n2018-04-05 1 0 \n2018-04-06 1 0 \n2018-04-09 1 0 \n2018-04-10 1 0 \n2018-04-11 1 0 \n2018-04-12 1 0 \n2018-04-13 1 0 \n2018-04-16 1 0 \n2018-04-17 1 0 \n2018-04-18 1 0 \n2018-04-19 1 0 \n2018-04-20 1 0 \n\n[4604 rows x 8 columns]\n"
],
[
"#adds the flag values for whether data should be used for training or testing\ndef partition(table):\n rowcount = len(table.index) #number of rows in the dataset\n flags = [0]*rowcount \n\n #flagsimple gives a train/test split of 70/30 from the start of the dataset to the end\n #this division is not recommended, use for validation purposes\n divide = round(rowcount*0.7)\n index = 0\n while index < rowcount:\n if index >= divide :\n flags[index] = 1\n index += 1\n table = table.assign(flagsimple=flags)\n \n #yearly 70:30 split, gives the same split as above, but performs it over a yearly interval \n #252 business days in a year, therfore a split of 176:76\n flags = [0]*rowcount\n index = 0\n for i in range(rowcount): \n if index < 177:\n flags[i] = 0\n index += 1\n elif index < 253:\n flags [i] = 1\n index += 1\n else:\n index = 0\n table = table.assign(flagyearly=flags)\n \n #gaussian based distribution of values\n #currently giving a zero output, someone needs to check the code (I'm too tired right now)\n #should form a skewed gaussian distibution limited to between 5 and 150, with mean 30 and standard deviation 10\n #the train and test times are currently set as the same distribution.\n index = 0\n flags = [0]*rowcount \n\n while index < rowcount:\n rand = 0 \n while rand < 5 | rand > 150:\n rand = round(rn.gauss(30, 10))\n \n for i in range(rand):\n flags[i] = 0\n index += 1\n for i in range(rand):\n flags[i] = 1\n index += 1\n index += 1\n table=table.assign(flaggaussian=flags)\n \n return table",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a765419b5f457cef97b58e050d9d346769a6328
| 202,183 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
.ipynb_checkpoints/Consistency-checkpoint.ipynb
|
IntelligentQuadruped/Vision_Analysis
|
95b8a23abd9773e2e62f0849e9ddd81465851ff3
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
.ipynb_checkpoints/Consistency-checkpoint.ipynb
|
IntelligentQuadruped/Vision_Analysis
|
95b8a23abd9773e2e62f0849e9ddd81465851ff3
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
.ipynb_checkpoints/Consistency-checkpoint.ipynb
|
IntelligentQuadruped/Vision_Analysis
|
95b8a23abd9773e2e62f0849e9ddd81465851ff3
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 1,347.886667 | 73,548 | 0.947533 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport os\nimport seaborn",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data_dir1 = \"./test/vor\"\ndata_dir2 = \"./test/rbf\"\ndata_dir3 = \"./test/ags\"\ntrials1 = ['log_vor.txt','log_vor2.txt','log_vor3.txt','log_vor4.txt']\ntrials2 = ['log_rbf.txt','log_rbf2.txt','log_rbf3.txt','log_rbf4.txt']\ntrials3 = ['log_ags.txt','log_ags2.txt','log_ags3.txt','log_ags4.txt']\nfor i,f1,f2,f3 in enumerate(zip(trials1,trials2,trials3)):\n vor = pd.read_table(os.path.join(data_dir1,f1),header=None,names=[\"Voronoi + AGS\"])[:70]\n rbf = pd.read_table(os.path.join(data_dir2,f2),header=None,names=[\"RBF + AGS\"])[:70]\n ags = pd.read_table(os.path.join(data_dir3,f3),header=None,names=[\"AGS Only\"])[:70]\n df = pd.concat([vor, rbf, ags], axis=1, )\n plt.figure()\n df.plot()\n plt.xlabel(\"Time Steps\")\n plt.ylabel(\"Turning Command\")\n plt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a7658fae8d53f4572bdbcf10d2d239131531a63
| 50,740 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
course1/Assignment 3.ipynb
|
dileep-kishore/datascience
|
9780605409f2234a862512236446024ba4db7d9e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
course1/Assignment 3.ipynb
|
dileep-kishore/datascience
|
9780605409f2234a862512236446024ba4db7d9e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
course1/Assignment 3.ipynb
|
dileep-kishore/datascience
|
9780605409f2234a862512236446024ba4db7d9e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 36.346705 | 449 | 0.363067 |
[
[
[
"---\n\n_You are currently looking at **version 1.5** of this notebook. To download notebooks and datafiles, as well as get help on Jupyter notebooks in the Coursera platform, visit the [Jupyter Notebook FAQ](https://www.coursera.org/learn/python-data-analysis/resources/0dhYG) course resource._\n\n---",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Assignment 3 - More Pandas\nThis assignment requires more individual learning then the last one did - you are encouraged to check out the [pandas documentation](http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/) to find functions or methods you might not have used yet, or ask questions on [Stack Overflow](http://stackoverflow.com/) and tag them as pandas and python related. And of course, the discussion forums are open for interaction with your peers and the course staff.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Question 1 (20%)\nLoad the energy data from the file `Energy Indicators.xls`, which is a list of indicators of [energy supply and renewable electricity production](Energy%20Indicators.xls) from the [United Nations](http://unstats.un.org/unsd/environment/excel_file_tables/2013/Energy%20Indicators.xls) for the year 2013, and should be put into a DataFrame with the variable name of **energy**.\n\nKeep in mind that this is an Excel file, and not a comma separated values file. Also, make sure to exclude the footer and header information from the datafile. The first two columns are unneccessary, so you should get rid of them, and you should change the column labels so that the columns are:\n\n`['Country', 'Energy Supply', 'Energy Supply per Capita', '% Renewable']`\n\nConvert `Energy Supply` to gigajoules (there are 1,000,000 gigajoules in a petajoule). For all countries which have missing data (e.g. data with \"...\") make sure this is reflected as `np.NaN` values.\n\nRename the following list of countries (for use in later questions):\n\n```\"Republic of Korea\": \"South Korea\",\n\"United States of America\": \"United States\",\n\"United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland\": \"United Kingdom\",\n\"China, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region\": \"Hong Kong\"```\n\nThere are also several countries with numbers and/or parenthesis in their name. Be sure to remove these, \n\ne.g. \n\n`'Bolivia (Plurinational State of)'` should be `'Bolivia'`, \n\n`'Switzerland17'` should be `'Switzerland'`.\n\n<br>\n\nNext, load the GDP data from the file `world_bank.csv`, which is a csv containing countries' GDP from 1960 to 2015 from [World Bank](http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.MKTP.CD). Call this DataFrame **GDP**. \n\nMake sure to skip the header, and rename the following list of countries:\n\n```\"Korea, Rep.\": \"South Korea\", \n\"Iran, Islamic Rep.\": \"Iran\",\n\"Hong Kong SAR, China\": \"Hong Kong\"```\n\n<br>\n\nFinally, load the [Sciamgo Journal and Country Rank data for Energy Engineering and Power Technology](http://www.scimagojr.com/countryrank.php?category=2102) from the file `scimagojr-3.xlsx`, which ranks countries based on their journal contributions in the aforementioned area. Call this DataFrame **ScimEn**.\n\nJoin the three datasets: GDP, Energy, and ScimEn into a new dataset (using the intersection of country names). Use only the last 10 years (2006-2015) of GDP data and only the top 15 countries by Scimagojr 'Rank' (Rank 1 through 15). \n\nThe index of this DataFrame should be the name of the country, and the columns should be ['Rank', 'Documents', 'Citable documents', 'Citations', 'Self-citations',\n 'Citations per document', 'H index', 'Energy Supply',\n 'Energy Supply per Capita', '% Renewable', '2006', '2007', '2008',\n '2009', '2010', '2011', '2012', '2013', '2014', '2015'].\n\n*This function should return a DataFrame with 20 columns and 15 entries.*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def load_energy():\n skiprows = list(range(16)) + [17]\n df1 = pd.read_excel('../data/course1_downloads/Energy Indicators.xls', skiprows=skiprows, header=0, skip_footer=38,\n usecols=[2,3,4,5])\n df1.replace(to_replace=r'\\([^)]*\\)', value='', inplace=True, regex=True)\n df1.replace(to_replace=r'\\d+$', value='', inplace=True, regex=True)\n df1.replace(to_replace='...', value=np.nan, inplace=True)\n df1.columns = ['Country', 'Energy Supply', 'Energy Supply per Capita', '% Renewable'] \n to_replace = [\"Republic of Korea\", \"United States of America\", \"United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland\", \"China, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region\"]\n value = [\"South Korea\", \"United States\", \"United Kingdom\", \"Hong Kong\"]\n energy = df1.replace(to_replace=to_replace, value=value)\n return energy\n\ndef load_gdp():\n df = pd.read_csv('../data/course1_downloads/world_bank.csv', skiprows=4)\n to_replace = [\"Korea, Rep.\", \"Iran, Islamic Rep.\", \"Hong Kong SAR, China\"]\n value = [\"South Korea\", \"Hong Kong\", \"Iran\"]\n gdp = df.replace(to_replace=to_replace, value=value)\n return gdp\n\ndef load_scimen():\n df = pd.read_excel('../data/course1_downloads/scimagojr-3.xlsx')\n return df\n\ndef answer_one():\n energy = load_energy()\n GDP = load_gdp()\n ScimEn = load_scimen()\n # Join these three now\n return ScimEn\n\nanswer_one()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Question 2 (6.6%)\nThe previous question joined three datasets then reduced this to just the top 15 entries. When you joined the datasets, but before you reduced this to the top 15 items, how many entries did you lose?\n\n*This function should return a single number.*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%HTML\n<svg width=\"800\" height=\"300\">\n <circle cx=\"150\" cy=\"180\" r=\"80\" fill-opacity=\"0.2\" stroke=\"black\" stroke-width=\"2\" fill=\"blue\" />\n <circle cx=\"200\" cy=\"100\" r=\"80\" fill-opacity=\"0.2\" stroke=\"black\" stroke-width=\"2\" fill=\"red\" />\n <circle cx=\"100\" cy=\"100\" r=\"80\" fill-opacity=\"0.2\" stroke=\"black\" stroke-width=\"2\" fill=\"green\" />\n <line x1=\"150\" y1=\"125\" x2=\"300\" y2=\"150\" stroke=\"black\" stroke-width=\"2\" fill=\"black\" stroke-dasharray=\"5,3\"/>\n <text x=\"300\" y=\"165\" font-family=\"Verdana\" font-size=\"35\">Everything but this!</text>\n</svg>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def answer_two():\n return \"ANSWER\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<br>\n\nAnswer the following questions in the context of only the top 15 countries by Scimagojr Rank (aka the DataFrame returned by `answer_one()`)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Question 3 (6.6%)\nWhat is the average GDP over the last 10 years for each country? (exclude missing values from this calculation.)\n\n*This function should return a Series named `avgGDP` with 15 countries and their average GDP sorted in descending order.*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def answer_three():\n Top15 = answer_one()\n return \"ANSWER\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Question 4 (6.6%)\nBy how much had the GDP changed over the 10 year span for the country with the 6th largest average GDP?\n\n*This function should return a single number.*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def answer_four():\n Top15 = answer_one()\n return \"ANSWER\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Question 5 (6.6%)\nWhat is the mean `Energy Supply per Capita`?\n\n*This function should return a single number.*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def answer_five():\n Top15 = answer_one()\n return \"ANSWER\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Question 6 (6.6%)\nWhat country has the maximum % Renewable and what is the percentage?\n\n*This function should return a tuple with the name of the country and the percentage.*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def answer_six():\n Top15 = answer_one()\n return \"ANSWER\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Question 7 (6.6%)\nCreate a new column that is the ratio of Self-Citations to Total Citations. \nWhat is the maximum value for this new column, and what country has the highest ratio?\n\n*This function should return a tuple with the name of the country and the ratio.*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def answer_seven():\n Top15 = answer_one()\n return \"ANSWER\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Question 8 (6.6%)\n\nCreate a column that estimates the population using Energy Supply and Energy Supply per capita. \nWhat is the third most populous country according to this estimate?\n\n*This function should return a single string value.*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def answer_eight():\n Top15 = answer_one()\n return \"ANSWER\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Question 9 (6.6%)\nCreate a column that estimates the number of citable documents per person. \nWhat is the correlation between the number of citable documents per capita and the energy supply per capita? Use the `.corr()` method, (Pearson's correlation).\n\n*This function should return a single number.*\n\n*(Optional: Use the built-in function `plot9()` to visualize the relationship between Energy Supply per Capita vs. Citable docs per Capita)*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def answer_nine():\n Top15 = answer_one()\n return \"ANSWER\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def plot9():\n import matplotlib as plt\n %matplotlib inline\n \n Top15 = answer_one()\n Top15['PopEst'] = Top15['Energy Supply'] / Top15['Energy Supply per Capita']\n Top15['Citable docs per Capita'] = Top15['Citable documents'] / Top15['PopEst']\n Top15.plot(x='Citable docs per Capita', y='Energy Supply per Capita', kind='scatter', xlim=[0, 0.0006])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#plot9() # Be sure to comment out plot9() before submitting the assignment!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Question 10 (6.6%)\nCreate a new column with a 1 if the country's % Renewable value is at or above the median for all countries in the top 15, and a 0 if the country's % Renewable value is below the median.\n\n*This function should return a series named `HighRenew` whose index is the country name sorted in ascending order of rank.*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def answer_ten():\n Top15 = answer_one()\n return \"ANSWER\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Question 11 (6.6%)\nUse the following dictionary to group the Countries by Continent, then create a dateframe that displays the sample size (the number of countries in each continent bin), and the sum, mean, and std deviation for the estimated population of each country.\n\n```python\nContinentDict = {'China':'Asia', \n 'United States':'North America', \n 'Japan':'Asia', \n 'United Kingdom':'Europe', \n 'Russian Federation':'Europe', \n 'Canada':'North America', \n 'Germany':'Europe', \n 'India':'Asia',\n 'France':'Europe', \n 'South Korea':'Asia', \n 'Italy':'Europe', \n 'Spain':'Europe', \n 'Iran':'Asia',\n 'Australia':'Australia', \n 'Brazil':'South America'}\n```\n\n*This function should return a DataFrame with index named Continent `['Asia', 'Australia', 'Europe', 'North America', 'South America']` and columns `['size', 'sum', 'mean', 'std']`*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def answer_eleven():\n Top15 = answer_one()\n return \"ANSWER\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Question 12 (6.6%)\nCut % Renewable into 5 bins. Group Top15 by the Continent, as well as these new % Renewable bins. How many countries are in each of these groups?\n\n*This function should return a __Series__ with a MultiIndex of `Continent`, then the bins for `% Renewable`. Do not include groups with no countries.*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def answer_twelve():\n Top15 = answer_one()\n return \"ANSWER\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Question 13 (6.6%)\nConvert the Population Estimate series to a string with thousands separator (using commas). Do not round the results.\n\ne.g. 317615384.61538464 -> 317,615,384.61538464\n\n*This function should return a Series `PopEst` whose index is the country name and whose values are the population estimate string.*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def answer_thirteen():\n Top15 = answer_one()\n return \"ANSWER\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Optional\n\nUse the built in function `plot_optional()` to see an example visualization.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def plot_optional():\n import matplotlib as plt\n %matplotlib inline\n Top15 = answer_one()\n ax = Top15.plot(x='Rank', y='% Renewable', kind='scatter', \n c=['#e41a1c','#377eb8','#e41a1c','#4daf4a','#4daf4a','#377eb8','#4daf4a','#e41a1c',\n '#4daf4a','#e41a1c','#4daf4a','#4daf4a','#e41a1c','#dede00','#ff7f00'], \n xticks=range(1,16), s=6*Top15['2014']/10**10, alpha=.75, figsize=[16,6]);\n\n for i, txt in enumerate(Top15.index):\n ax.annotate(txt, [Top15['Rank'][i], Top15['% Renewable'][i]], ha='center')\n\n print(\"This is an example of a visualization that can be created to help understand the data. \\\nThis is a bubble chart showing % Renewable vs. Rank. The size of the bubble corresponds to the countries' \\\n2014 GDP, and the color corresponds to the continent.\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#plot_optional() # Be sure to comment out plot_optional() before submitting the assignment!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a7659aa22e3f52f74e7adfff9dfc5a755f2fa51
| 49,340 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
09_Time_Series/Apple_Stock/Solutions.ipynb
|
fareed37/Pandas_excercises
|
04e3406805a62d1a39498fb235d05bb72b9ec97b
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 1 |
2020-12-31T18:03:34.000Z
|
2020-12-31T18:03:34.000Z
|
pandas/09_Time_Series/Apple_Stock/Solutions.ipynb
|
cntfk2017/Udemy_Python_Hand_On
|
52f2a5585bfdea95d893f961c8c21844072e93c7
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
pandas/09_Time_Series/Apple_Stock/Solutions.ipynb
|
cntfk2017/Udemy_Python_Hand_On
|
52f2a5585bfdea95d893f961c8c21844072e93c7
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 2 |
2019-09-23T14:26:48.000Z
|
2020-05-25T07:09:26.000Z
| 72.346041 | 31,323 | 0.734921 |
[
[
[
"# Apple Stock",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Introduction:\n\nWe are going to use Apple's stock price.\n\n\n### Step 1. Import the necessary libraries",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\n\n# visualization\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Step 2. Import the dataset from this [address](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/guipsamora/pandas_exercises/master/09_Time_Series/Apple_Stock/appl_1980_2014.csv)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Step 3. Assign it to a variable apple",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Step 4. Check out the type of the columns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Step 5. Transform the Date column as a datetime type",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Step 6. Set the date as the index",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Step 7. Is there any duplicate dates?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# NO! All are unique",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Step 8. Ops...it seems the index is from the most recent date. Make the first entry the oldest date.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Step 9. Get the last business day of each month",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Step 10. What is the difference in days between the first day and the oldest",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Step 11. How many months in the data we have?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Step 12. Plot the 'Adj Close' value. Set the size of the figure to 13.5 x 9 inches",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### BONUS: Create your own question and answer it.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4a7662a86f84938f8c5d14186fb5aa79ead0bcfd
| 140,457 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Type babelfy.ipynb
|
supervitis/CSVAnalyzer
|
c8a97875741eef60d4fda4e2381599884535cdfd
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Type babelfy.ipynb
|
supervitis/CSVAnalyzer
|
c8a97875741eef60d4fda4e2381599884535cdfd
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Type babelfy.ipynb
|
supervitis/CSVAnalyzer
|
c8a97875741eef60d4fda4e2381599884535cdfd
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 95.160569 | 40,652 | 0.751411 |
[
[
[
"import sys\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nfrom bs4 import BeautifulSoup\nimport urllib\nfrom threading import Thread\nfrom queue import Queue\nimport math\nimport requests\nimport time \nfrom datetime import timedelta\nimport pickle\nfrom datetime import datetime\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = pd.read_csv('output2.csv', encoding=\"utf-8\", delimiter=\",\")\ndf.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"del df['22']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df2 = df.copy()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df2.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dfNew = pd.DataFrame(columns=('singleJaccard', 'Jaccard', 'type'))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for column in df2:\n dfNew.loc[column] = df2[column].mean(),df2[column].mean(),df2[column].mean()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = pd.read_csv('output3.csv', encoding=\"utf-8\", delimiter=\",\")\ndf.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"del df['22']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.describe()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for column in df2:\n dfNew.loc[column] = df[column].mean(),df2[column].mean(),df2[column].mean()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dfNew['type'] = \"string\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dfNew",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df['type'] = ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import pylab\npylab.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.Tags.plot.hist()\npylab.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"string, string, string, string, string, string, string, string, string, string, string, string, date, date, date, date, string, string, string, string, string,penis",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a766bcb27dca04f377655d770fc6b8616452ab7
| 22,807 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
ipynb/cifar10_hist.ipynb
|
wittawatj/kernel-mod
|
147a05888855a15d72b28a734752a91d93018604
|
[
"MIT"
] | 20 |
2018-10-26T16:18:56.000Z
|
2020-11-10T01:08:56.000Z
|
ipynb/cifar10_hist.ipynb
|
wittawatj/kernel-mod
|
147a05888855a15d72b28a734752a91d93018604
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
ipynb/cifar10_hist.ipynb
|
wittawatj/kernel-mod
|
147a05888855a15d72b28a734752a91d93018604
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2019-12-08T21:08:53.000Z
|
2020-11-10T01:08:57.000Z
| 33.294891 | 129 | 0.54663 |
[
[
[
"Notebook to plot the histogram of the power criterion values of Rel-UME test.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%matplotlib inline\n%load_ext autoreload\n%autoreload 2\n\n#%config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'svg'\n#%config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'pdf'\n\nimport freqopttest.tst as tst\nimport kmod\nimport kgof\nimport kgof.goftest as gof\n# submodules\nfrom kmod import data, density, kernel, util, plot, glo, log\nfrom kmod.ex import cifar10 as cf10\nimport kmod.ex.exutil as exu\n\nfrom kmod import mctest as mct\nimport matplotlib\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport pickle\nimport os\nimport autograd.numpy as np\nimport scipy.stats as stats\nimport numpy.testing as testing",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# plot.set_default_matplotlib_options()\n# font options\nfont = {\n #'family' : 'normal',\n #'weight' : 'bold',\n 'size' : 20,\n}\n\nplt.rc('font', **font)\nplt.rc('lines', linewidth=2)\nmatplotlib.rcParams['pdf.fonttype'] = 42\nmatplotlib.rcParams['ps.fonttype'] = 42",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# def store_path(fname):\n# \"\"\"\n# Construct a full path for saving/loading files.\n# \"\"\"\n# return os.path.join('cifar10', fname)\ndisplay(list(zip(range(10), cf10.cifar10_classes)))\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Histogram of power criterion values\n\nFirst construct four samples: $X \\sim P, Y \\sim Q, Z \\sim R$, and a pool W to be used as test location candidates.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# class_spec = [\n# # (class, #points for p, #points for q, #points for r, #points for the pool)\n# ('airplane', 2000, 0, 0, 1500),\n# ('cat', 0, 2000, 2000, 1500),\n# ('truck', 1500, 1500, 1500, 1500),\n \n# ]\n\n# class_spec = [\n# # (class, #points for p, #points for q, #points for r, #points for the pool)\n# ('airplane', 1000, 0, 0, 300),\n# ('cat', 0, 1000, 1000, 300),\n# ('truck', 1500, 1500, 1500, 300),\n \n# ]\nclass_spec = [\n # (class, #points for p, #points for q, #points for r, #points for the pool)\n ('ship', 2000, 0, 0, 1000),\n ('airplane', 0, 2000, 1500, 1000),\n ('dog', 1500, 1500, 1500, 1000), \n ('bird', 0, 0, 500, 1000),\n]\n# class_spec = [\n# # (class, #points for p, #points for q, #points for r, #points for the pool)\n# ('horse', 2000, 0, 0, 1000),\n# ('deer', 0, 2000, 1500, 1000),\n# ('dog', 1500, 1500, 1500, 1000), \n# ('automobile', 0, 0, 500, 1000),\n# ]\n# class_spec = [\n# # (class, #points for p, #points for q, #points for r, #points for the pool)\n# ('airplane', 2000, 0, 0, 1000),\n# ('automobile', 0, 2000, 1500, 1000),\n# ('cat', 1500, 1500, 1500, 1000), \n# ('frog', 0, 0, 500, 1000),\n# ]\n#class_spec = [\n # (class, #points for p, #points for q, #points for r, #points for the pool)\n# ('airplane', 2000, 0, 0, 1000),\n# ('automobile', 0, 2000, 2000, 1000),\n# ('cat', 1500, 1500, 1500, 1000), \n#]\n\n# class_spec = [\n# # (class, #points for p, #points for q, #points for r, #points for the pool)\n# ('airplane', 200, 0, 0, 150),\n# ('cat', 0, 200, 200, 150),\n# ('truck', 150, 150, 150, 150),\n \n# ]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# check sizes\nhist_classes = [z[0] for z in class_spec]\np_sizes = [z[1] for z in class_spec]\nq_sizes = [z[2] for z in class_spec]\nr_sizes = [z[3] for z in class_spec]\npool_sizes = [z[4] for z in class_spec]\n\n# make sure p,q,r have the same sample size\nassert sum(p_sizes) == sum(q_sizes)\nassert sum(q_sizes) == sum(r_sizes)\n\n# cannot use more than 6000 from each class\nfor i, cs in enumerate(class_spec):\n class_used = sum(cs[1:])\n if class_used > 6000:\n raise ValueError('class \"{}\" requires more than 6000 points. Was {}.'.format(cs[0], class_used))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# images as numpy arrays\nlist_Ximgs = []\nlist_Yimgs = []\nlist_Zimgs = []\nlist_poolimgs = []\n\n# features\nlist_X = []\nlist_Y = []\nlist_Z = []\nlist_pool = []\n# class labels\nlist_Xlabels = []\nlist_Ylabels = []\nlist_Zlabels = []\nlist_poollabels = []",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# seed used for subsampling\nseed = 368\nwith util.NumpySeedContext(seed=seed):\n for i, cs in enumerate(class_spec):\n # load class data\n class_i = cs[0]\n imgs_i = cf10.load_data_array(class_i)\n feas_i = cf10.load_feature_array(class_i)\n\n # split each class according to the spec\n class_sizes_i = cs[1:]\n # imgs_i, feas_i may contain more than what we need in total for a class. Subsample\n sub_ind = util.subsample_ind(imgs_i.shape[0], sum(class_sizes_i), seed=seed+1)\n sub_ind = list(sub_ind)\n assert len(sub_ind) == sum(class_sizes_i)\n \n xyzp_imgs_i = util.multi_way_split(imgs_i[sub_ind,:], class_sizes_i)\n xyzp_feas_i = util.multi_way_split(feas_i[sub_ind,:], class_sizes_i)\n \n # assignment\n list_Ximgs.append(xyzp_imgs_i[0])\n list_Yimgs.append(xyzp_imgs_i[1])\n list_Zimgs.append(xyzp_imgs_i[2])\n list_poolimgs.append(xyzp_imgs_i[3])\n \n list_X.append(xyzp_feas_i[0])\n list_Y.append(xyzp_feas_i[1])\n list_Z.append(xyzp_feas_i[2])\n list_pool.append(xyzp_feas_i[3])\n \n # class labels\n class_ind_i = cf10.cifar10_class_ind_dict[class_i]\n list_Xlabels.append(np.ones(class_sizes_i[0])*class_ind_i)\n list_Ylabels.append(np.ones(class_sizes_i[1])*class_ind_i)\n list_Zlabels.append(np.ones(class_sizes_i[2])*class_ind_i)\n list_poollabels.append(np.ones(class_sizes_i[3])*class_ind_i)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Finally we have the samples (features and images)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# stack the lists. For the \"histogram\" purpose, we don't actually need\n# images for X, Y, Z. Only images for the pool.\nXimgs = np.vstack(list_Ximgs)\nYimgs = np.vstack(list_Yimgs)\nZimgs = np.vstack(list_Zimgs)\npoolimgs = np.vstack(list_poolimgs)\n\n# features\nX = np.vstack(list_X)\nY = np.vstack(list_Y)\nZ = np.vstack(list_Z)\npool = np.vstack(list_pool)\n\n# labels\nXlabels = np.hstack(list_Xlabels)\nYlabels = np.hstack(list_Ylabels)\nZlabels = np.hstack(list_Zlabels)\npoollabels = np.hstack(list_poollabels)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# sanity check\nXYZP = [(X, Ximgs, Xlabels), (Y, Yimgs, Ylabels), (Z, Zimgs, Zlabels), (pool, poolimgs, poollabels)]\nfor f, fimgs, flabels in XYZP:\n assert f.shape[0] == fimgs.shape[0]\n assert fimgs.shape[0] == flabels.shape[0]\nassert X.shape[0] == sum(p_sizes)\nassert Y.shape[0] == sum(q_sizes)\nassert Z.shape[0] == sum(r_sizes)\nassert pool.shape[0] == sum(pool_sizes)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## The actual histogram",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def eval_test_locations(X, Y, Z, loc_pool, k, func_inds, reg=1e-6):\n \"\"\"\n Use X, Y, Z to estimate the Rel-UME power criterion function and evaluate\n the function at each point (individually) in loc_pool (2d numpy array).\n \n * k: a kernel\n * func_inds: list of indices of the functions to evaluate. See below.\n * reg: regularization parameter in the power criterion\n \n Return an m x (up to) 5 numpy array where m = number of candidates in the\n pool. The columns can be (as specified in func_inds): \n 0. power criterion\n 1. evaluation of the relative witness (or the test statistic of UME_SC)\n 2. evaluation of MMD witness(p, r) (not squared)\n 3. evaluation of witness(q, r)\n 4. evaluate of witness(p, q)\n \n \"\"\"\n datap = data.Data(X)\n dataq = data.Data(Y)\n datar = data.Data(Z)\n\n powcri_func = mct.SC_UME.get_power_criterion_func(datap, dataq, datar, k, k, reg=1e-7)\n relwit_func = mct.SC_UME.get_relative_sqwitness(datap, dataq, datar, k, k)\n witpr = tst.MMDWitness(k, X, Z)\n witqr = tst.MMDWitness(k, Y, Z)\n witpq = tst.MMDWitness(k, X, Y)\n \n funcs = [powcri_func, relwit_func, witpr, witqr, witpq]\n # select the functions according to func_inds\n list_evals = [funcs[i](loc_pool) for i in func_inds]\n stack_evals = np.vstack(list_evals)\n return stack_evals.T\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Gaussian kernel with median heuristic\nmedxz = util.meddistance(np.vstack((X, Z)), subsample=1000)\nmedyz = util.meddistance(np.vstack((Y, Z)), subsample=1000)\nk = kernel.KGauss(np.mean([medxz, medyz])**2)\nprint('Gaussian width: {}'.format(k.sigma2**0.5))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# histogram. This will take some time.\nfunc_inds = np.array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4])\npool_evals = eval_test_locations(X, Y, Z, loc_pool=pool, k=k, func_inds=func_inds, reg=1e-6)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pow_cri_values = pool_evals[:, func_inds==0].reshape(-1)\ntest_stat_values = pool_evals[:, func_inds==1].reshape(-1)\nwitpr_values = pool_evals[:, func_inds==2]\nwitqr_values = pool_evals[:, func_inds==3]\nwitpq_values = pool_evals[:, func_inds==4].reshape(-1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4))\na = 0.6\nplt.figure(figsize=(4,4))\nplt.hist(pow_cri_values, bins=15, label='Power Criterion', alpha=a);\nplt.hist(witpr_values, bins=15, label='Power Criterion', alpha=a);\nplt.hist(witqr_values, bins=15, label='Power Criterion', alpha=a);\nplt.hist(witpq_values, bins=15, label='Power Criterion', alpha=a);",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Save the results\n# package things to save\ndatapack = {\n 'class_spec': class_spec,\n 'seed': seed,\n 'poolimgs': poolimgs,\n 'X': X,\n 'Y': Y,\n 'Z': Z,\n 'pool': pool,\n 'medxz': medxz,\n 'medyz': medyz,\n 'func_inds': func_inds,\n 'pool_evals': pool_evals,\n}\n\n\nlines = [ '_'.join(str(x) for x in cs) for cs in class_spec]\nfname = '-'.join(lines) + '-seed{}.pkl'.format(seed)\nwith open(fname, 'wb') as f:\n # expect result to be a dictionary\n pickle.dump(datapack, f)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Code for running the experiment ends here. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Plot the results \n\nThis section can be run by loading the previously saved results.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# load the results\n# fname = 'airplane_2000_0_0_1000-automobile_0_2000_1500_1000-cat_1500_1500_1500_1000-frog_0_0_500_1000-seed368.pkl'\n# fname = 'ship_2000_0_0_1000-airplane_0_2000_1500_1000-automobile_1500_1500_1500_1000-bird_0_0_500_1000-seed368.pkl'\n# fname = 'ship_2000_0_0_1000-dog_0_2000_1500_1000-automobile_1500_1500_1500_1000-bird_0_0_500_1000-seed368.pkl'\nfname = 'ship_2000_0_0_1000-airplane_0_2000_1500_1000-dog_1500_1500_1500_1000-bird_0_0_500_1000-seed368.pkl'\n# fname = 'horse_2000_0_0_1000-deer_0_2000_1500_1000-dog_1500_1500_1500_1000-airplane_0_0_500_1000-seed368.pkl'\n# fname = 'horse_2000_0_0_1000-deer_0_2000_1500_1000-dog_1500_1500_1500_1000-automobile_0_0_500_1000-seed368.pkl'\n# fname = 'horse_2000_0_0_1000-deer_0_2000_2000_1000-dog_1500_1500_1500_1000-seed368.pkl'\n#fname = 'airplane_2000_0_0_1000-automobile_0_2000_2000_1000-cat_1500_1500_1500_1000-seed368.pkl'\nwith open(fname, 'rb') as f:\n # expect a dictionary\n L = pickle.load(f)\n\n# load the variables\nclass_spec = L['class_spec']\nseed = L['seed']\npoolimgs = L['poolimgs']\nX = L['X']\nY = L['Y']\nZ = L['Z']\npool = L['pool']\nmedxz = L['medxz']\nmedyz = L['medyz']\nfunc_inds = L['func_inds']\npool_evals = L['pool_evals']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pow_cri_values = pool_evals[:, func_inds==0].reshape(-1)\ntest_stat_values = pool_evals[:, func_inds==1].reshape(-1)\nwitpq_values = pool_evals[:, func_inds==4].reshape(-1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# plot the histogram\nplt.figure(figsize=(6, 4))\na = 0.6\nplt.figure(figsize=(4,4))\nplt.hist(pow_cri_values, bins=15, label='Power Criterion', alpha=a);\n# plt.hist(test_stat_values, label='Stat.', alpha=a);\n# plt.legend()\nplt.savefig('powcri_hist_locs_pool.pdf', bbox_inches='tight')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))\nplt.hist(test_stat_values, label='Stat.', alpha=a);\nplt.legend()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def reshape_3c_rescale(img_in_stack):\n img = img_in_stack.reshape([3, 32, 32])\n # h x w x c\n img = img.transpose([1, 2, 0])/255.0\n return img\n\ndef plot_lowzerohigh(images, values, text_in_title='', grid_rows=2,\n grid_cols=10, figsize=(13, 3)):\n \"\"\"\n Sort the values in three different ways (ascending, descending, absolute ascending).\n Plot the images corresponding to the top-k sorted values. k is determined\n by the grid size.\n \"\"\"\n low_inds, zeros_inds, high_inds = util.top_lowzerohigh(values)\n \n plt.figure(figsize=figsize)\n exu.plot_images_grid(images[low_inds], reshape_3c_rescale, grid_rows, grid_cols)\n# plt.suptitle('{} Low'.format(text_in_title))\n plt.savefig('powcri_low_region.pdf', bbox_inches='tight')\n \n plt.figure(figsize=figsize)\n exu.plot_images_grid(images[zeros_inds], reshape_3c_rescale, grid_rows, grid_cols)\n# plt.suptitle('{} Near Zero'.format(text_in_title))\n plt.savefig('powcri_zero_region.pdf', bbox_inches='tight')\n \n plt.figure(figsize=figsize)\n exu.plot_images_grid(images[high_inds], reshape_3c_rescale, grid_rows, grid_cols)\n# plt.suptitle('{} High'.format(text_in_title))\n plt.savefig('powcri_high_region.pdf', bbox_inches='tight')\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"grid_rows = 2\ngrid_cols = 5\nfigsize = (5, 3)\nplot_lowzerohigh(poolimgs, pow_cri_values, 'Power Criterion.', grid_rows, grid_cols, figsize)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# plot_lowzerohigh(poolimgs, rel_wit_values, 'Test statistic.', grid_rows, grid_cols, figsize)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import matplotlib.gridspec as gridspec\n\ndef plot_images_grid_witness(images, func_img=None, grid_rows=4, grid_cols=4, witness_pq=None, scale=100.):\n \"\"\"\n Plot images in a grid, starting from index 0 to the maximum size of the\n grid. \n\n images: stack of images images[i] is one image\n func_img: function to run on each image before plotting\n \"\"\"\n gs1 = gridspec.GridSpec(grid_rows, grid_cols)\n gs1.update(wspace=0.2, hspace=0.8) # set the spacing between axes. \n wit_sign = np.sign(witness_pq)\n\n for i in range(grid_rows*grid_cols):\n if func_img is not None:\n img = func_img(images[i])\n else:\n img = images[i]\n if witness_pq is not None:\n sign = wit_sign[i]\n if sign > 0:\n color = 'red'\n else:\n color = 'blue'\n \n# plt.subplot(grid_rows, grid_cols, i+1)\n ax = plt.subplot(gs1[i])\n if witness_pq is not None:\n ax.text(0.5, -0.6, \"{:1.2f}\".format(scale*witness_pq[i]), ha=\"center\",\n color=color, transform=ax.transAxes)\n plt.imshow(img)\n plt.axis('off')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def plot_lowzerohigh(images, values, text_in_title='', grid_rows=2,\n grid_cols=10, figsize=(13, 3), wit_pq=None, skip_length=1):\n \"\"\"\n Sort the values in three different ways (ascending, descending, absolute ascending).\n Plot the images corresponding to the top-k sorted values. k is determined\n by the grid size.\n \"\"\"\n low_inds, zeros_inds, high_inds = util.top_lowzerohigh(values)\n \n low_inds = low_inds[::skip_length]\n zeros_inds = zeros_inds[::skip_length]\n high_inds = high_inds[::skip_length]\n\n plt.figure(figsize=figsize)\n plot_images_grid_witness(images[low_inds], reshape_3c_rescale, grid_rows, grid_cols, wit_pq[low_inds])\n # plt.suptitle('{} Low'.format(text_in_title))\n # plt.savefig('powcri_low_region.pdf', bbox_inches='tight')\n \n plt.figure(figsize=figsize)\n plot_images_grid_witness(images[zeros_inds], reshape_3c_rescale, grid_rows, grid_cols, wit_pq[zeros_inds])\n # plt.suptitle('{} Near Zero'.format(text_in_title))\n # plt.savefig('powcri_zero_region.pdf', bbox_inches='tight')\n \n plt.figure(figsize=figsize)\n plot_images_grid_witness(images[high_inds[:]], reshape_3c_rescale, grid_rows, grid_cols, wit_pq[high_inds])\n # plt.suptitle('{} High'.format(text_in_title))\n # plt.savefig('powcri_high_region.pdf', bbox_inches='tight')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"grid_rows = 3\ngrid_cols = 5\nfigsize = (8, 3)\nplot_lowzerohigh(poolimgs, pow_cri_values, 'Power Criterion.', grid_rows, grid_cols, figsize, witpq_values, skip_length=40)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a766e5c5dc4257eca9ba326b1d3ba8243dd3a60
| 20,669 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
examples/integrated_gradients_imdb.ipynb
|
janthiemen/alibi
|
b310d34b1b5f6c4f691678f824c2d2e16f4c0723
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2021-03-14T09:48:09.000Z
|
2021-03-14T09:48:09.000Z
|
examples/integrated_gradients_imdb.ipynb
|
StatMixedML/alibi
|
190d7960630221813f704817ee48cc5af46a9e07
|
[
"ECL-2.0",
"Apache-2.0",
"CC0-1.0"
] | null | null | null |
examples/integrated_gradients_imdb.ipynb
|
StatMixedML/alibi
|
190d7960630221813f704817ee48cc5af46a9e07
|
[
"ECL-2.0",
"Apache-2.0",
"CC0-1.0"
] | 1 |
2021-07-21T15:28:51.000Z
|
2021-07-21T15:28:51.000Z
| 40.687008 | 4,965 | 0.628429 |
[
[
[
"# Integrated gradients for text classification on the IMDB dataset",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In this example, we apply the integrated gradients method to a sentiment analysis model trained on the IMDB dataset. In text classification models, integrated gradients define an attribution value for each word in the input sentence. The attributions are calculated considering the integral of the model gradients with respect to the word embedding layer along a straight path from a baseline instance $x^\\prime$ to the input instance $x.$ A description of the method can be found [here](https://docs.seldon.io/projects/alibi/en/latest/methods/IntegratedGradients.html). Integrated gradients was originally proposed in Sundararajan et al., [\"Axiomatic Attribution for Deep Networks\"](https://arxiv.org/abs/1703.01365)\n\nThe IMDB data set contains 50K movie reviews labelled as positive or negative. \nWe train a convolutional neural network classifier with a single 1-d convolutional layer followed by a fully connected layer. The reviews in the dataset are truncated at 100 words and each word is represented by 50-dimesional word embedding vector. We calculate attributions for the elements of the embedding layer.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import tensorflow as tf\nimport numpy as np\nimport os\nimport pandas as pd\nfrom tensorflow.keras.datasets import imdb\nfrom tensorflow.keras.preprocessing import sequence\nfrom tensorflow.keras.models import Model\nfrom tensorflow.keras.layers import Input, Dense, Embedding, Conv1D, GlobalMaxPooling1D, Dropout \nfrom tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical\nfrom alibi.explainers import IntegratedGradients\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nprint('TF version: ', tf.__version__)\nprint('Eager execution enabled: ', tf.executing_eagerly()) # True",
"TF version: 2.3.1\nEager execution enabled: True\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Load data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Loading the imdb dataset. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"max_features = 10000\nmaxlen = 100",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('Loading data...')\n(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = imdb.load_data(num_words=max_features)\ntest_labels = y_test.copy()\ntrain_labels = y_train.copy()\nprint(len(x_train), 'train sequences')\nprint(len(x_test), 'test sequences')\ny_train, y_test = to_categorical(y_train), to_categorical(y_test)\n\nprint('Pad sequences (samples x time)')\nx_train = sequence.pad_sequences(x_train, maxlen=maxlen)\nx_test = sequence.pad_sequences(x_test, maxlen=maxlen)\nprint('x_train shape:', x_train.shape)\nprint('x_test shape:', x_test.shape)\n\nindex = imdb.get_word_index()\nreverse_index = {value: key for (key, value) in index.items()} ",
"Loading data...\n25000 train sequences\n25000 test sequences\nPad sequences (samples x time)\nx_train shape: (25000, 100)\nx_test shape: (25000, 100)\n"
]
],
[
[
"A sample review from the test set. Note that unknown words are replaced with 'UNK'",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def decode_sentence(x, reverse_index):\n # the `-3` offset is due to the special tokens used by keras\n # see https://stackoverflow.com/questions/42821330/restore-original-text-from-keras-s-imdb-dataset\n return \" \".join([reverse_index.get(i - 3, 'UNK') for i in x])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(decode_sentence(x_test[1], reverse_index)) ",
"a powerful study of loneliness sexual UNK and desperation be patient UNK up the atmosphere and pay attention to the wonderfully written script br br i praise robert altman this is one of his many films that deals with unconventional fascinating subject matter this film is disturbing but it's sincere and it's sure to UNK a strong emotional response from the viewer if you want to see an unusual film some might even say bizarre this is worth the time br br unfortunately it's very difficult to find in video stores you may have to buy it off the internet\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Train Model",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The model includes one convolutional layer and reaches a test accuracy of 0.85. If `save_model = True`, a local folder `../model_imdb` will be created and the trained model will be saved in that folder. If the model was previously saved, it can be loaded by setting `load_model = True`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"batch_size = 32\nembedding_dims = 50\nfilters = 250\nkernel_size = 3\nhidden_dims = 250",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"load_model = False\nsave_model = True",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"filepath = './model_imdb/' # change to directory where model is downloaded\nif load_model:\n model = tf.keras.models.load_model(os.path.join(filepath, 'model.h5'))\nelse:\n print('Build model...')\n \n inputs = Input(shape=(maxlen,), dtype='int32')\n embedded_sequences = Embedding(max_features,\n embedding_dims)(inputs)\n out = Conv1D(filters, \n kernel_size, \n padding='valid', \n activation='relu', \n strides=1)(embedded_sequences)\n out = Dropout(0.4)(out)\n out = GlobalMaxPooling1D()(out)\n out = Dense(hidden_dims, \n activation='relu')(out)\n out = Dropout(0.4)(out)\n outputs = Dense(2, activation='softmax')(out)\n \n model = Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs)\n model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy',\n optimizer='adam',\n metrics=['accuracy'])\n\n print('Train...')\n model.fit(x_train, y_train,\n batch_size=256,\n epochs=3,\n validation_data=(x_test, y_test))\n if save_model: \n if not os.path.exists(filepath):\n os.makedirs(filepath)\n model.save(os.path.join(filepath, 'model.h5')) ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Calculate integrated gradients",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The integrated gradients attributions are calculated with respect to the embedding layer for 10 samples from the test set. Since the model uses a word to vector embedding with vector dimensionality of 50 and sequence length of 100 words, the dimensionality of the attributions is (10, 100, 50). In order to obtain a single attribution value for each word, we sum all the attribution values for the 50 elements of each word's vector representation.\n \nThe default baseline is used in this example which is internally defined as a sequence of zeros. In this case, this corresponds to a sequence of padding characters (**NB:** in general the numerical value corresponding to a \"non-informative\" baseline such as the PAD token will depend on the tokenizer used, make sure that the numerical value of the baseline used corresponds to your desired token value to avoid surprises). The path integral is defined as a straight line from the baseline to the input image. The path is approximated by choosing 50 discrete steps according to the Gauss-Legendre method.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"n_steps = 50\nmethod = \"gausslegendre\"\ninternal_batch_size = 100\nnb_samples = 10\nig = IntegratedGradients(model,\n layer=model.layers[1],\n n_steps=n_steps, \n method=method,\n internal_batch_size=internal_batch_size)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x_test_sample = x_test[:nb_samples]\npredictions = model(x_test_sample).numpy().argmax(axis=1)\nexplanation = ig.explain(x_test_sample, \n baselines=None, \n target=predictions)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Metadata from the explanation object\nexplanation.meta",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Data fields from the explanation object\nexplanation.data.keys()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Get attributions values from the explanation object\nattrs = explanation.attributions[0]\nprint('Attributions shape:', attrs.shape)",
"Attributions shape: (10, 100, 50)\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Sum attributions",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"attrs = attrs.sum(axis=2)\nprint('Attributions shape:', attrs.shape)",
"Attributions shape: (10, 100)\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Visualize attributions",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"i = 1\nx_i = x_test_sample[i]\nattrs_i = attrs[i]\npred = predictions[i]\npred_dict = {1: 'Positive review', 0: 'Negative review'}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('Predicted label = {}: {}'.format(pred, pred_dict[pred]))",
"Predicted label = 1: Positive review\n"
]
],
[
[
"We can visualize the attributions for the text instance by mapping the values of the attributions onto a matplotlib colormap. Below we define some utility functions for doing this.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from IPython.display import HTML\ndef hlstr(string, color='white'):\n \"\"\"\n Return HTML markup highlighting text with the desired color.\n \"\"\"\n return f\"<mark style=background-color:{color}>{string} </mark>\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def colorize(attrs, cmap='PiYG'):\n \"\"\"\n Compute hex colors based on the attributions for a single instance.\n Uses a diverging colorscale by default and normalizes and scales\n the colormap so that colors are consistent with the attributions.\n \"\"\"\n import matplotlib as mpl\n cmap_bound = np.abs(attrs).max()\n norm = mpl.colors.Normalize(vmin=-cmap_bound, vmax=cmap_bound)\n cmap = mpl.cm.get_cmap(cmap)\n \n # now compute hex values of colors\n colors = list(map(lambda x: mpl.colors.rgb2hex(cmap(norm(x))), attrs))\n return colors",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Below we visualize the attribution values (highlighted in the text) having the highest positive attributions. Words with high positive attribution are highlighted in shades of green and words with negative attribution in shades of pink. Stronger shading corresponds to higher attribution values. Positive attributions can be interpreted as increase in probability of the predicted class (\"Positive sentiment\") while negative attributions correspond to decrease in probability of the predicted class.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"words = decode_sentence(x_i, reverse_index).split()\ncolors = colorize(attrs_i)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"HTML(\"\".join(list(map(hlstr, words, colors))))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a767da783fb4107ddcb3cecf9b364c0a83de1e9
| 527,905 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
SourceCodes/P2_evaluation/stacked_LSTM/stackedLLSTM_HP.ipynb
|
AlirezaGhanbarzadehUM/Research_Project_WQD7002
|
3d55e2b93ede1895f33030aaab2e8de93d8bd56c
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
SourceCodes/P2_evaluation/stacked_LSTM/stackedLLSTM_HP.ipynb
|
AlirezaGhanbarzadehUM/Research_Project_WQD7002
|
3d55e2b93ede1895f33030aaab2e8de93d8bd56c
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
SourceCodes/P2_evaluation/stacked_LSTM/stackedLLSTM_HP.ipynb
|
AlirezaGhanbarzadehUM/Research_Project_WQD7002
|
3d55e2b93ede1895f33030aaab2e8de93d8bd56c
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2020-06-20T13:44:38.000Z
|
2020-06-20T13:44:38.000Z
| 527,905 | 527,905 | 0.904428 |
[
[
[
"#@title Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the \"License\");\n# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.\n# You may obtain a copy of the License at\n#\n# https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0\n#\n# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software\n# distributed under the License is distributed on an \"AS IS\" BASIS,\n# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.\n# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and\n# limitations under the License.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import tensorflow as tf\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nprint(tf.__version__)\nfrom google.colab import files\nimport io\nimport pandas as pd\nimport math \n",
"2.2.0-rc4\n"
],
[
"uploaded = files.upload()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"hp = pd.read_csv(io.BytesIO(uploaded['hpq.us.txt']))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"hp['Close'].isnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"hp",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#walmart['ret'] = walmart.close.pct_change(1).mul(100)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"series = hp['Close']\nprint(series)\ntype(series)\ntime = np.arange(0,1259,1)\nprint(\"time_shape :\", time.shape)\nprint(\"series_shape :\", series.shape)",
"0 0.30627\n1 0.31385\n2 0.30996\n3 0.31385\n4 0.31385\n ... \n12070 21.44000\n12071 21.38000\n12072 21.42000\n12073 21.34000\n12074 21.23000\nName: Close, Length: 12075, dtype: float64\ntime_shape : (1259,)\nseries_shape : (12075,)\n"
],
[
"'''usinng returns instead of close price\nseries = walmart['ret']\nprint(series)\ntype(series)\ntime = np.arange(0,1259,1)\nprint(time)\n'''",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"'''\n##adjusting series for using return\nseries = series[1:]\n##slicing time for uisng wih returns\ntime = np.arange(0,1258,1)\n'''",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"series = pd.Series.to_numpy(series)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"##plot the price\ndf = hp.copy()\nplt.figure(figsize = (22,12))\nplt.plot(hp.index, hp['Close'])\nplt.title('Walmart Stock Price')\nplt.xticks(range(0,hp.shape[0],180),hp['Date'].loc[::180],rotation=40)\nplt.ylabel('Price ($)');\nplt.show()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"time = np.arange(0,12075,1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"split_time = 9000\ntime_train = time[:split_time]\nx_train = series[:split_time]\ntime_valid = time[split_time:]\nx_valid = series[split_time:]\n\nwindow_size = 64\nbatch_size = 128\nshuffle_buffer_size = 1000",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"time.shape()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"type(x_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def windowed_dataset(series, window_size, batch_size, shuffle_buffer):\n dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(series)\n dataset = dataset.window(window_size + 1, shift=1, drop_remainder=True)\n dataset = dataset.flat_map(lambda window: window.batch(window_size + 1))\n dataset = dataset.shuffle(shuffle_buffer).map(lambda window: (window[:-1], window[-1]))\n dataset = dataset.batch(batch_size).prefetch(1)\n return dataset",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tf.keras.backend.clear_session()\ntf.random.set_seed(51)\nnp.random.seed(51)\n\ntf.keras.backend.clear_session()\ndataset = windowed_dataset(x_train, window_size, batch_size, shuffle_buffer_size)\n\nmodel = tf.keras.models.Sequential([\n tf.keras.layers.Lambda(lambda x: tf.expand_dims(x, axis=-1),\n input_shape=[None]),\n tf.keras.layers.Bidirectional(tf.keras.layers.LSTM(64, return_sequences=True)),\n tf.keras.layers.Bidirectional(tf.keras.layers.LSTM(32)),\n tf.keras.layers.Dense(1),\n tf.keras.layers.Lambda(lambda x: x * 400.0)\n])\n\nlr_schedule = tf.keras.callbacks.LearningRateScheduler(\n lambda epoch: 1e-8 * 10**(epoch / 20))\noptimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(lr=1e-8, momentum=0.9)\nmodel.compile(loss=tf.keras.losses.Huber(),\n optimizer=optimizer,\n metrics=[\"mse\"])\nhistory = model.fit(dataset, epochs=100, callbacks=[lr_schedule])",
"Epoch 1/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 50.7935 - mse: 4358.9390 - lr: 1.0000e-08\nEpoch 2/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 35.2112 - mse: 2462.2988 - lr: 1.1220e-08\nEpoch 3/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 19.5152 - mse: 1111.5059 - lr: 1.2589e-08\nEpoch 4/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 14.0776 - mse: 649.8337 - lr: 1.4125e-08\nEpoch 5/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 10.5310 - mse: 383.0984 - lr: 1.5849e-08\nEpoch 6/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 7.3477 - mse: 197.6960 - lr: 1.7783e-08\nEpoch 7/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 5.7011 - mse: 109.6505 - lr: 1.9953e-08\nEpoch 8/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 4.9935 - mse: 79.0415 - lr: 2.2387e-08\nEpoch 9/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 4.6201 - mse: 66.6920 - lr: 2.5119e-08\nEpoch 10/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 4.3472 - mse: 59.1012 - lr: 2.8184e-08\nEpoch 11/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 4.1927 - mse: 55.0810 - lr: 3.1623e-08\nEpoch 12/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 4.1057 - mse: 52.0460 - lr: 3.5481e-08\nEpoch 13/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 4.0672 - mse: 50.0676 - lr: 3.9811e-08\nEpoch 14/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 3.9624 - mse: 47.6014 - lr: 4.4668e-08\nEpoch 15/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 3.8544 - mse: 45.4305 - lr: 5.0119e-08\nEpoch 16/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 21ms/step - loss: 3.7903 - mse: 44.0951 - lr: 5.6234e-08\nEpoch 17/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 3.6983 - mse: 43.0176 - lr: 6.3096e-08\nEpoch 18/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 3.5762 - mse: 41.2850 - lr: 7.0795e-08\nEpoch 19/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 3.4260 - mse: 39.2006 - lr: 7.9433e-08\nEpoch 20/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 3.3373 - mse: 36.9527 - lr: 8.9125e-08\nEpoch 21/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 21ms/step - loss: 3.0857 - mse: 33.0809 - lr: 1.0000e-07\nEpoch 22/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 2.8205 - mse: 29.9905 - lr: 1.1220e-07\nEpoch 23/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 2.6292 - mse: 27.7110 - lr: 1.2589e-07\nEpoch 24/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 2.4167 - mse: 24.8748 - lr: 1.4125e-07\nEpoch 25/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 2.2040 - mse: 21.6024 - lr: 1.5849e-07\nEpoch 26/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 2.0313 - mse: 18.8215 - lr: 1.7783e-07\nEpoch 27/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 1.8541 - mse: 15.6415 - lr: 1.9953e-07\nEpoch 28/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 1.6649 - mse: 13.2625 - lr: 2.2387e-07\nEpoch 29/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 1.4490 - mse: 10.4935 - lr: 2.5119e-07\nEpoch 30/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 1.1744 - mse: 7.7337 - lr: 2.8184e-07\nEpoch 31/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.9785 - mse: 5.4936 - lr: 3.1623e-07\nEpoch 32/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.7531 - mse: 3.7172 - lr: 3.5481e-07\nEpoch 33/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.6248 - mse: 2.8412 - lr: 3.9811e-07\nEpoch 34/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.5292 - mse: 2.3022 - lr: 4.4668e-07\nEpoch 35/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.5411 - mse: 2.1705 - lr: 5.0119e-07\nEpoch 36/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.4862 - mse: 1.9705 - lr: 5.6234e-07\nEpoch 37/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.4578 - mse: 1.7390 - lr: 6.3096e-07\nEpoch 38/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.4434 - mse: 1.6958 - lr: 7.0795e-07\nEpoch 39/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.3814 - mse: 1.5448 - lr: 7.9433e-07\nEpoch 40/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.4472 - mse: 1.7744 - lr: 8.9125e-07\nEpoch 41/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.3791 - mse: 1.4559 - lr: 1.0000e-06\nEpoch 42/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.5186 - mse: 1.8882 - lr: 1.1220e-06\nEpoch 43/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.5425 - mse: 2.1501 - lr: 1.2589e-06\nEpoch 44/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.8005 - mse: 3.9007 - lr: 1.4125e-06\nEpoch 45/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 1.3723 - mse: 8.2196 - lr: 1.5849e-06\nEpoch 46/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 3.0746 - mse: 33.9128 - lr: 1.7783e-06\nEpoch 47/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 4.7628 - mse: 41.3601 - lr: 1.9953e-06\nEpoch 48/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 5.0968 - mse: 66.6229 - lr: 2.2387e-06\nEpoch 49/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 5.3534 - mse: 53.3396 - lr: 2.5119e-06\nEpoch 50/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 3.2368 - mse: 21.3087 - lr: 2.8184e-06\nEpoch 51/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 21ms/step - loss: 1.5705 - mse: 8.8408 - lr: 3.1623e-06\nEpoch 52/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 2.5392 - mse: 23.5250 - lr: 3.5481e-06\nEpoch 53/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 2.6155 - mse: 19.5486 - lr: 3.9811e-06\nEpoch 54/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 5.3173 - mse: 91.8807 - lr: 4.4668e-06\nEpoch 55/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 8.6692 - mse: 201.2211 - lr: 5.0119e-06\nEpoch 56/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 10.4280 - mse: 226.2576 - lr: 5.6234e-06\nEpoch 57/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 4.3318 - mse: 38.7385 - lr: 6.3096e-06\nEpoch 58/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 4.3768 - mse: 37.1914 - lr: 7.0795e-06\nEpoch 59/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 4.3416 - mse: 38.7378 - lr: 7.9433e-06\nEpoch 60/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 6.0024 - mse: 63.5052 - lr: 8.9125e-06\nEpoch 61/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 5.6150 - mse: 70.7767 - lr: 1.0000e-05\nEpoch 62/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 7.1291 - mse: 80.5526 - lr: 1.1220e-05\nEpoch 63/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 4.1400 - mse: 36.4216 - lr: 1.2589e-05\nEpoch 64/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 4.5656 - mse: 44.3364 - lr: 1.4125e-05\nEpoch 65/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 4.4740 - mse: 34.9844 - lr: 1.5849e-05\nEpoch 66/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 8.8039 - mse: 189.6736 - lr: 1.7783e-05\nEpoch 67/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 3.9918 - mse: 38.2705 - lr: 1.9953e-05\nEpoch 68/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 5.7576 - mse: 58.4184 - lr: 2.2387e-05\nEpoch 69/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 6.5871 - mse: 80.8445 - lr: 2.5119e-05\nEpoch 70/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 10.6362 - mse: 226.3446 - lr: 2.8184e-05\nEpoch 71/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 8.2095 - mse: 111.3916 - lr: 3.1623e-05\nEpoch 72/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 5.2458 - mse: 38.9821 - lr: 3.5481e-05\nEpoch 73/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 4.2415 - mse: 32.8430 - lr: 3.9811e-05\nEpoch 74/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 5.5912 - mse: 64.0143 - lr: 4.4668e-05\nEpoch 75/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 4.6087 - mse: 37.3286 - lr: 5.0119e-05\nEpoch 76/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 4.4646 - mse: 41.0294 - lr: 5.6234e-05\nEpoch 77/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 8.5108 - mse: 101.1771 - lr: 6.3096e-05\nEpoch 78/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 5.4909 - mse: 53.7439 - lr: 7.0795e-05\nEpoch 79/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 22.3092 - mse: 683.9940 - lr: 7.9433e-05\nEpoch 80/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 12.4800 - mse: 197.9606 - lr: 8.9125e-05\nEpoch 81/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 16.1158 - mse: 427.1535 - lr: 1.0000e-04\nEpoch 82/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 6.2669 - mse: 86.1225 - lr: 1.1220e-04\nEpoch 83/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 16.1074 - mse: 437.4000 - lr: 1.2589e-04\nEpoch 84/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 14.5047 - mse: 313.7844 - lr: 1.4125e-04\nEpoch 85/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 45.5121 - mse: 3370.4336 - lr: 1.5849e-04\nEpoch 86/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 24.4947 - mse: 870.0779 - lr: 1.7783e-04\nEpoch 87/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 31.9242 - mse: 1704.2837 - lr: 1.9953e-04\nEpoch 88/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 33.2835 - mse: 1434.7766 - lr: 2.2387e-04\nEpoch 89/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 42.3057 - mse: 2915.5652 - lr: 2.5119e-04\nEpoch 90/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 103.8296 - mse: 14674.8828 - lr: 2.8184e-04\nEpoch 91/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 47.4886 - mse: 4038.9570 - lr: 3.1623e-04\nEpoch 92/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 54.8404 - mse: 5080.4248 - lr: 3.5481e-04\nEpoch 93/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 84.2343 - mse: 11808.2900 - lr: 3.9811e-04\nEpoch 94/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 37.1050 - mse: 1719.3005 - lr: 4.4668e-04\nEpoch 95/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 41.7691 - mse: 2188.2937 - lr: 5.0119e-04\nEpoch 96/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 46.8449 - mse: 2717.6519 - lr: 5.6234e-04\nEpoch 97/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 52.5965 - mse: 3220.3591 - lr: 6.3096e-04\nEpoch 98/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 58.9789 - mse: 4030.5471 - lr: 7.0795e-04\nEpoch 99/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 66.2660 - mse: 4859.2515 - lr: 7.9433e-04\nEpoch 100/100\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 74.3761 - mse: 6122.0156 - lr: 8.9125e-04\n"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(15,10))\nplt.semilogx(history.history[\"lr\"], history.history[\"loss\"])\nplt.title(\"HP learning rate plot\")\nplt.axis([1e-8, 1e-4, 0, 30])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tf.keras.backend.clear_session()\ntf.random.set_seed(51)\nnp.random.seed(51)\n\ntf.keras.backend.clear_session()\ndataset = windowed_dataset(x_train, window_size, batch_size, shuffle_buffer_size)\n\nmodel = tf.keras.models.Sequential([\n tf.keras.layers.Lambda(lambda x: tf.expand_dims(x, axis=-1),\n input_shape=[None]),\n tf.keras.layers.Bidirectional(tf.keras.layers.LSTM(64, return_sequences=True)),\n tf.keras.layers.Bidirectional(tf.keras.layers.LSTM(32)),\n tf.keras.layers.Dense(1),\n tf.keras.layers.Lambda(lambda x: x * 400.0)\n])\n\n\nmodel.compile(loss=tf.keras.losses.Huber(), optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(lr=1e-6, momentum=0.9),metrics=[\"mse\"])\nhistory = model.fit(dataset,epochs=300,verbose=1)",
"Epoch 1/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 10.4981 - mse: 308.9192\nEpoch 2/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 6.3667 - mse: 79.0194\nEpoch 3/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 2.8412 - mse: 20.4291\nEpoch 4/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 2.1346 - mse: 12.5188\nEpoch 5/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.8821 - mse: 3.2049\nEpoch 6/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.5635 - mse: 1.9792\nEpoch 7/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.7329 - mse: 2.5727\nEpoch 8/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.8364 - mse: 3.0859\nEpoch 9/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.3622 - mse: 1.1315\nEpoch 10/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.5206 - mse: 1.7388\nEpoch 11/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.6112 - mse: 2.3100\nEpoch 12/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.4417 - mse: 1.2424\nEpoch 13/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.5814 - mse: 1.8924\nEpoch 14/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.7964 - mse: 2.6306\nEpoch 15/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 23ms/step - loss: 1.6808 - mse: 10.7386\nEpoch 16/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 1.9771 - mse: 9.7194\nEpoch 17/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 1.8175 - mse: 9.2343\nEpoch 18/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 1.1571 - mse: 4.0809\nEpoch 19/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.8520 - mse: 2.7849\nEpoch 20/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 1.0920 - mse: 5.2015\nEpoch 21/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 1.1812 - mse: 4.8343\nEpoch 22/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.4657 - mse: 1.2762\nEpoch 23/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.3941 - mse: 1.1379\nEpoch 24/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.6638 - mse: 2.6427\nEpoch 25/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 1.2258 - mse: 4.7730\nEpoch 26/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.9531 - mse: 3.4126\nEpoch 27/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 1.0135 - mse: 4.5358\nEpoch 28/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 1.3716 - mse: 7.0219\nEpoch 29/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 1.9582 - mse: 9.2942\nEpoch 30/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 2.2419 - mse: 12.6063\nEpoch 31/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 1.4740 - mse: 6.4649\nEpoch 32/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.3431 - mse: 0.9951\nEpoch 33/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.2092 - mse: 0.5671\nEpoch 34/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.2284 - mse: 0.6106\nEpoch 35/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.2420 - mse: 0.6617\nEpoch 36/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.2840 - mse: 0.7621\nEpoch 37/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.2088 - mse: 0.5504\nEpoch 38/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.2795 - mse: 0.7656\nEpoch 39/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1848 - mse: 0.4827\nEpoch 40/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1997 - mse: 0.5129\nEpoch 41/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 23ms/step - loss: 0.1675 - mse: 0.4340\nEpoch 42/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 23ms/step - loss: 0.3480 - mse: 0.9621\nEpoch 43/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.2627 - mse: 0.6504\nEpoch 44/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.3895 - mse: 1.1767\nEpoch 45/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1764 - mse: 0.4564\nEpoch 46/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1519 - mse: 0.3871\nEpoch 47/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 23ms/step - loss: 0.1474 - mse: 0.3837\nEpoch 48/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1253 - mse: 0.3288\nEpoch 49/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1736 - mse: 0.4506\nEpoch 50/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1948 - mse: 0.5065\nEpoch 51/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.2667 - mse: 0.6921\nEpoch 52/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.3939 - mse: 1.2034\nEpoch 53/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1408 - mse: 0.3687\nEpoch 54/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.3437 - mse: 0.9644\nEpoch 55/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.3845 - mse: 1.0346\nEpoch 56/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.4381 - mse: 1.3551\nEpoch 57/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.2597 - mse: 0.6177\nEpoch 58/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1455 - mse: 0.3774\nEpoch 59/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1509 - mse: 0.3875\nEpoch 60/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1645 - mse: 0.4169\nEpoch 61/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.3550 - mse: 1.0557\nEpoch 62/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.2467 - mse: 0.6735\nEpoch 63/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1992 - mse: 0.5213\nEpoch 64/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1430 - mse: 0.3714\nEpoch 65/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.2057 - mse: 0.5359\nEpoch 66/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.2944 - mse: 0.7771\nEpoch 67/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.2873 - mse: 0.6656\nEpoch 68/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1327 - mse: 0.3217\nEpoch 69/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.2138 - mse: 0.5618\nEpoch 70/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1989 - mse: 0.4622\nEpoch 71/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.3104 - mse: 0.7765\nEpoch 72/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1261 - mse: 0.3159\nEpoch 73/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1509 - mse: 0.3671\nEpoch 74/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1068 - mse: 0.2618\nEpoch 75/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0972 - mse: 0.2399\nEpoch 76/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 23ms/step - loss: 0.0856 - mse: 0.2084\nEpoch 77/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1203 - mse: 0.2948\nEpoch 78/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0854 - mse: 0.2089\nEpoch 79/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1086 - mse: 0.2623\nEpoch 80/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.2085 - mse: 0.5048\nEpoch 81/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1345 - mse: 0.3159\nEpoch 82/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1001 - mse: 0.2397\nEpoch 83/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0903 - mse: 0.2129\nEpoch 84/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.2569 - mse: 0.6644\nEpoch 85/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.6224 - mse: 2.3314\nEpoch 86/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.9347 - mse: 3.8007\nEpoch 87/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.8377 - mse: 3.0322\nEpoch 88/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0908 - mse: 0.2114\nEpoch 89/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1325 - mse: 0.3161\nEpoch 90/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1117 - mse: 0.2627\nEpoch 91/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1233 - mse: 0.2855\nEpoch 92/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0958 - mse: 0.2241\nEpoch 93/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1277 - mse: 0.3023\nEpoch 94/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1372 - mse: 0.3251\nEpoch 95/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1047 - mse: 0.2451\nEpoch 96/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.2268 - mse: 0.6088\nEpoch 97/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.2871 - mse: 0.8621\nEpoch 98/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.2481 - mse: 0.5945\nEpoch 99/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.4448 - mse: 1.7452\nEpoch 100/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.3900 - mse: 1.0138\nEpoch 101/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.2894 - mse: 0.7698\nEpoch 102/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0935 - mse: 0.2141\nEpoch 103/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.2111 - mse: 0.5348\nEpoch 104/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1127 - mse: 0.2505\nEpoch 105/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0827 - mse: 0.1897\nEpoch 106/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0667 - mse: 0.1582\nEpoch 107/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0939 - mse: 0.2126\nEpoch 108/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1611 - mse: 0.3809\nEpoch 109/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1776 - mse: 0.4167\nEpoch 110/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0799 - mse: 0.1807\nEpoch 111/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0980 - mse: 0.2272\nEpoch 112/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0893 - mse: 0.2048\nEpoch 113/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 23ms/step - loss: 0.0599 - mse: 0.1364\nEpoch 114/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0907 - mse: 0.2053\nEpoch 115/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1986 - mse: 0.4959\nEpoch 116/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1183 - mse: 0.2629\nEpoch 117/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1816 - mse: 0.4226\nEpoch 118/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1017 - mse: 0.2246\nEpoch 119/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1665 - mse: 0.3903\nEpoch 120/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.2189 - mse: 0.5479\nEpoch 121/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1699 - mse: 0.3643\nEpoch 122/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1406 - mse: 0.3319\nEpoch 123/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1068 - mse: 0.2399\nEpoch 124/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1022 - mse: 0.2358\nEpoch 125/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1353 - mse: 0.3267\nEpoch 126/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.1326 - mse: 0.3176\nEpoch 127/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0831 - mse: 0.1878\nEpoch 128/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0764 - mse: 0.1737\nEpoch 129/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1626 - mse: 0.3816\nEpoch 130/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0814 - mse: 0.1822\nEpoch 131/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1071 - mse: 0.2441\nEpoch 132/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1033 - mse: 0.2302\nEpoch 133/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0606 - mse: 0.1364\nEpoch 134/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1543 - mse: 0.3556\nEpoch 135/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0963 - mse: 0.2132\nEpoch 136/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1689 - mse: 0.3963\nEpoch 137/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1379 - mse: 0.3270\nEpoch 138/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1775 - mse: 0.4333\nEpoch 139/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0729 - mse: 0.1647\nEpoch 140/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0622 - mse: 0.1371\nEpoch 141/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0666 - mse: 0.1508\nEpoch 142/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0571 - mse: 0.1268\nEpoch 143/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0959 - mse: 0.2116\nEpoch 144/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1238 - mse: 0.2722\nEpoch 145/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0643 - mse: 0.1401\nEpoch 146/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1463 - mse: 0.3437\nEpoch 147/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1092 - mse: 0.2360\nEpoch 148/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 23ms/step - loss: 0.1295 - mse: 0.2983\nEpoch 149/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1523 - mse: 0.3534\nEpoch 150/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0731 - mse: 0.1608\nEpoch 151/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1077 - mse: 0.2396\nEpoch 152/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0837 - mse: 0.1825\nEpoch 153/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.2038 - mse: 0.5275\nEpoch 154/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0956 - mse: 0.2044\nEpoch 155/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0717 - mse: 0.1567\nEpoch 156/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0709 - mse: 0.1556\nEpoch 157/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1384 - mse: 0.3150\nEpoch 158/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.2099 - mse: 0.5207\nEpoch 159/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1069 - mse: 0.2374\nEpoch 160/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1227 - mse: 0.2759\nEpoch 161/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0864 - mse: 0.1883\nEpoch 162/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0507 - mse: 0.1116\nEpoch 163/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0948 - mse: 0.2085\nEpoch 164/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1795 - mse: 0.4250\nEpoch 165/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1226 - mse: 0.2675\nEpoch 166/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0683 - mse: 0.1470\nEpoch 167/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0593 - mse: 0.1318\nEpoch 168/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0748 - mse: 0.1616\nEpoch 169/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1180 - mse: 0.2606\nEpoch 170/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.2122 - mse: 0.5371\nEpoch 171/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.1203 - mse: 0.2666\nEpoch 172/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0625 - mse: 0.1372\nEpoch 173/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0840 - mse: 0.1875\nEpoch 174/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0696 - mse: 0.1533\nEpoch 175/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1432 - mse: 0.3194\nEpoch 176/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1035 - mse: 0.2302\nEpoch 177/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 24ms/step - loss: 0.1529 - mse: 0.3533\nEpoch 178/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 23ms/step - loss: 0.1552 - mse: 0.3541\nEpoch 179/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 26ms/step - loss: 0.2152 - mse: 0.5991\nEpoch 180/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 26ms/step - loss: 0.0727 - mse: 0.1609\nEpoch 181/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 25ms/step - loss: 0.1314 - mse: 0.3057\nEpoch 182/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 25ms/step - loss: 0.0580 - mse: 0.1264\nEpoch 183/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 25ms/step - loss: 0.1461 - mse: 0.3328\nEpoch 184/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 23ms/step - loss: 0.0619 - mse: 0.1345\nEpoch 185/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0608 - mse: 0.1336\nEpoch 186/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1041 - mse: 0.2332\nEpoch 187/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0875 - mse: 0.1949\nEpoch 188/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0886 - mse: 0.1954\nEpoch 189/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.2316 - mse: 0.6031\nEpoch 190/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1698 - mse: 0.3617\nEpoch 191/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1572 - mse: 0.3676\nEpoch 192/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0565 - mse: 0.1240\nEpoch 193/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0475 - mse: 0.1047\nEpoch 194/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0478 - mse: 0.1045\nEpoch 195/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0738 - mse: 0.1608\nEpoch 196/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0771 - mse: 0.1703\nEpoch 197/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1011 - mse: 0.2247\nEpoch 198/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0883 - mse: 0.1895\nEpoch 199/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.2174 - mse: 0.5151\nEpoch 200/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.3678 - mse: 1.1119\nEpoch 201/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 21ms/step - loss: 0.4219 - mse: 1.1836\nEpoch 202/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.3120 - mse: 0.6977\nEpoch 203/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.1271 - mse: 0.2704\nEpoch 204/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.1902 - mse: 0.4834\nEpoch 205/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1171 - mse: 0.2679\nEpoch 206/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0940 - mse: 0.2044\nEpoch 207/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1164 - mse: 0.2531\nEpoch 208/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0812 - mse: 0.1814\nEpoch 209/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0566 - mse: 0.1224\nEpoch 210/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0759 - mse: 0.1669\nEpoch 211/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1213 - mse: 0.2773\nEpoch 212/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0538 - mse: 0.1183\nEpoch 213/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1031 - mse: 0.2258\nEpoch 214/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.2367 - mse: 0.6607\nEpoch 215/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.1705 - mse: 0.4159\nEpoch 216/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.1215 - mse: 0.2812\nEpoch 217/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 21ms/step - loss: 0.1322 - mse: 0.3044\nEpoch 218/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0645 - mse: 0.1427\nEpoch 219/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1180 - mse: 0.2704\nEpoch 220/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0956 - mse: 0.2089\nEpoch 221/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.1125 - mse: 0.2560\nEpoch 222/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0693 - mse: 0.1505\nEpoch 223/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0424 - mse: 0.0922\nEpoch 224/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0870 - mse: 0.1879\nEpoch 225/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0441 - mse: 0.0965\nEpoch 226/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0435 - mse: 0.0955\nEpoch 227/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0703 - mse: 0.1526\nEpoch 228/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1027 - mse: 0.2339\nEpoch 229/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1132 - mse: 0.2537\nEpoch 230/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0618 - mse: 0.1331\nEpoch 231/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0694 - mse: 0.1473\nEpoch 232/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0960 - mse: 0.2156\nEpoch 233/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0912 - mse: 0.2007\nEpoch 234/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0475 - mse: 0.1034\nEpoch 235/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0988 - mse: 0.2125\nEpoch 236/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1107 - mse: 0.2495\nEpoch 237/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1088 - mse: 0.2406\nEpoch 238/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0740 - mse: 0.1610\nEpoch 239/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0669 - mse: 0.1442\nEpoch 240/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0773 - mse: 0.1676\nEpoch 241/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0551 - mse: 0.1209\nEpoch 242/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0370 - mse: 0.0807\nEpoch 243/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0390 - mse: 0.0849\nEpoch 244/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0373 - mse: 0.0809\nEpoch 245/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0605 - mse: 0.1316\nEpoch 246/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0892 - mse: 0.1970\nEpoch 247/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1138 - mse: 0.2526\nEpoch 248/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.1336 - mse: 0.3145\nEpoch 249/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1016 - mse: 0.2181\nEpoch 250/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0841 - mse: 0.1791\nEpoch 251/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0409 - mse: 0.0879\nEpoch 252/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0683 - mse: 0.1481\nEpoch 253/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0659 - mse: 0.1417\nEpoch 254/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0546 - mse: 0.1194\nEpoch 255/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0575 - mse: 0.1229\nEpoch 256/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0540 - mse: 0.1175\nEpoch 257/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0618 - mse: 0.1338\nEpoch 258/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0884 - mse: 0.1931\nEpoch 259/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1067 - mse: 0.2319\nEpoch 260/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1692 - mse: 0.4130\nEpoch 261/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.2116 - mse: 0.5653\nEpoch 262/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.1590 - mse: 0.3850\nEpoch 263/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1319 - mse: 0.2881\nEpoch 264/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.1068 - mse: 0.2213\nEpoch 265/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0538 - mse: 0.1159\nEpoch 266/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0987 - mse: 0.2128\nEpoch 267/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0434 - mse: 0.0938\nEpoch 268/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1178 - mse: 0.2687\nEpoch 269/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0452 - mse: 0.0979\nEpoch 270/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0640 - mse: 0.1385\nEpoch 271/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0832 - mse: 0.1802\nEpoch 272/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0477 - mse: 0.1046\nEpoch 273/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0549 - mse: 0.1188\nEpoch 274/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0394 - mse: 0.0860\nEpoch 275/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0656 - mse: 0.1409\nEpoch 276/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0710 - mse: 0.1518\nEpoch 277/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0445 - mse: 0.0961\nEpoch 278/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.1413 - mse: 0.3212\nEpoch 279/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.2003 - mse: 0.5137\nEpoch 280/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.2258 - mse: 0.5566\nEpoch 281/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.2883 - mse: 0.7161\nEpoch 282/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.1141 - mse: 0.2465\nEpoch 283/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0504 - mse: 0.1075\nEpoch 284/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0591 - mse: 0.1255\nEpoch 285/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0373 - mse: 0.0805\nEpoch 286/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0867 - mse: 0.1850\nEpoch 287/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.1374 - mse: 0.3190\nEpoch 288/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0528 - mse: 0.1141\nEpoch 289/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0951 - mse: 0.2132\nEpoch 290/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0463 - mse: 0.1014\nEpoch 291/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0423 - mse: 0.0914\nEpoch 292/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0602 - mse: 0.1288\nEpoch 293/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0573 - mse: 0.1222\nEpoch 294/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 21ms/step - loss: 0.1278 - mse: 0.2881\nEpoch 295/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0563 - mse: 0.1208\nEpoch 296/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0804 - mse: 0.1734\nEpoch 297/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0737 - mse: 0.1560\nEpoch 298/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 2s 22ms/step - loss: 0.0853 - mse: 0.1854\nEpoch 299/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0512 - mse: 0.1107\nEpoch 300/300\n70/70 [==============================] - 1s 21ms/step - loss: 0.0775 - mse: 0.1662\n"
],
[
"def plot_series(time, series, format=\"-\", start=0, end=None):\n plt.plot(time[start:end], series[start:end], format)\n plt.xlabel(\"Time\")\n plt.ylabel(\"Value\")\n plt.grid(True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"forecast = []\nresults = []\nfor time in range(len(series) - window_size):\n forecast.append(model.predict(series[time:time + window_size][np.newaxis]))\n\nforecast = forecast[split_time-window_size:]\nresults = np.array(forecast)[:, 0, 0]\n\n\nplt.figure(figsize=(17,11))\nplt.title(\"walmart close price prediction\")\nplot_series(time_valid[11000:], x_valid[11000:])\nplot_series(time_valid[11000:], results[11000:])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"time_valid.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(17,11))\nplt.title(\"HP close price prediction\")\nplot_series(time_valid[2400:3075], x_valid[2400:3075])\nplot_series(time_valid[2400:3075], results[2400:3075])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tf.keras.metrics.mean_squared_error(x_valid, results).numpy()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(\"RMSE= \" , math.sqrt(tf.keras.metrics.mean_squared_error(x_valid, results).numpy()))",
"RMSE= 0.6331124948620398\n"
],
[
"import matplotlib.image as mpimg\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\n#-----------------------------------------------------------\n# Retrieve a list of list results on training and test data\n# sets for each training epoch\n#-----------------------------------------------------------\nmse=history.history['mse']\nloss=history.history['loss']\n\nepochs=range(len(loss)) # Get number of epochs\n\n#------------------------------------------------\n# Plot MAE and Loss\n#------------------------------------------------\nplt.figure(figsize=(15,10))\nplt.plot(epochs, mse, 'r')\nplt.plot(epochs, loss, 'b')\nplt.title('MSE and Loss')\nplt.xlabel(\"Epochs\")\nplt.ylabel(\"Accuracy\")\nplt.legend([\"MSE\", \"Loss\"])\n\nplt.figure()\n\nepochs_zoom = epochs[80:]\nmse_zoom = mse[80:]\nloss_zoom = loss[80:300]\n\n\n\n#------------------------------------------------\n# Plot Zoomed MAE and Loss\n#------------------------------------------------\nplt.figure(figsize=(15,10))\nplt.plot(epochs_zoom, mse_zoom, 'r')\nplt.plot(epochs_zoom, loss_zoom, 'b')\nplt.title('MSE and Loss')\nplt.xlabel(\"Epochs\")\nplt.ylabel(\"Accuracy\")\nplt.legend([\"MSE\", \"Loss\"])\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a76818537729d912ecb2e183c6e95dfbcf9d5e0
| 90,002 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
analysis_draft2017b/analysis_cdo_nco_draft2017b.ipynb
|
grandey/p17c-marc-comparison
|
12aebefb3c3ce4d1ced6aad6727c0f25a9b880cd
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
analysis_draft2017b/analysis_cdo_nco_draft2017b.ipynb
|
grandey/p17c-marc-comparison
|
12aebefb3c3ce4d1ced6aad6727c0f25a9b880cd
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2017-07-17T09:15:54.000Z
|
2017-10-31T09:34:44.000Z
|
analysis_draft2017b/analysis_cdo_nco_draft2017b.ipynb
|
grandey/p17c-marc-comparison
|
12aebefb3c3ce4d1ced6aad6727c0f25a9b880cd
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-05-08T09:21:29.000Z
|
2021-05-08T09:21:29.000Z
| 45.709497 | 310 | 0.576732 |
[
[
[
"# analysis_cdo_nco_draft2017b.ipynb\n\n## Purpose\nUse CDO and NCO to analyse CESM simulation output from project [p17c-marc-comparison](https://github.com/grandey/p17c-marc-comparison).\n\n## Requirements\n- Climate Data Operators (CDO)\n- NetCDF Operators (NCO)\n- CESM output data, post-processed to time-series format, as described in [data_management.org](https://github.com/grandey/p17c-marc-comparison/blob/master/manage_data/data_management.org#syncing-to-local-machine-for-analysis). These data are available via https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.5687812.\n\n## Author\nBenjamin S. Grandey, 2017-2018",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"! date",
"Fri Aug 17 15:13:33 +08 2018\r\n"
],
[
"from glob import glob\nimport os\nimport re\nimport shutil",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## CDO and NCO version information\nUseful to record for reproducibility",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"! cdo --version\n! ncks --version",
"Climate Data Operators version 1.9.1 (http://mpimet.mpg.de/cdo)\nCompiled: by root on squall2.local (x86_64-apple-darwin17.2.0) Nov 2 2017 18:28:19\nCXX Compiler: /usr/bin/clang++ -std=gnu++11 -pipe -Os -stdlib=libc++ -arch x86_64 -D_THREAD_SAFE -pthread\nCXX version : unknown\nC Compiler: /usr/bin/clang -pipe -Os -arch x86_64 -D_THREAD_SAFE -pthread\nC version : unknown\nFeatures: DATA PTHREADS HDF5 NC4/HDF5 OPeNDAP SZ UDUNITS2 PROJ.4 CURL FFTW3 SSE4_1\nLibraries: HDF5/1.10.1 proj/4.93 curl/7.56.1\nFiletypes: srv ext ieg grb1 nc1 nc2 nc4 nc4c nc5 \n CDI library version : 1.9.1 of Nov 2 2017 18:27:49\n CGRIBEX library version : 1.9.0 of Sep 29 2017 10:16:02\n NetCDF library version : 4.4.1.1 of Oct 6 2017 14:14:42 $\n HDF5 library version : 1.10.1\n SERVICE library version : 1.4.0 of Nov 2 2017 18:27:47\n EXTRA library version : 1.4.0 of Nov 2 2017 18:27:46\n IEG library version : 1.4.0 of Nov 2 2017 18:27:46\n FILE library version : 1.8.3 of Nov 2 2017 18:27:46\n\nNCO netCDF Operators version 4.6.6 built by root on squall2.local at Nov 3 2017 12:13:40\nncks version 4.6.6\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Directory locations for input and output NetCDF files\nThe data in the input directory (*in_dir*) are available via Figshare: https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.5687812.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Input data directory\nin_dir = os.path.expandvars('$HOME/data/figshare/figshare5687812/')\n#in_dir = os.path.expandvars('$HOME/data/projects/p17c_marc_comparison/output_timeseries/')\n\n# Output data directory\nout_dir = os.path.expandvars('$HOME/data/projects/p17c_marc_comparison/analysis_cdo_nco_draft2017b/')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Clean output data directory",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for filename in glob('{}/*.nc'.format(out_dir)):\n print('Deleting {}'.format(filename.split('/')[-1]))\n os.remove(filename)\nfor filename in glob('{}/*.nco'.format(out_dir)):\n print('Deleting {}'.format(filename.split('/')[-1]))\n os.remove(filename)\nfor filename in glob('{}/*.tmp'.format(out_dir)):\n print('Deleting {}'.format(filename.split('/')[-1]))\n os.remove(filename)\n! date",
"Fri Aug 17 15:13:34 +08 2018\r\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Calculate annual means of standard 2D atmosphere variables",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"variable_list = ['OC_LDG', # MARC pure OC burden, for checking burdens derived using mass-mixing ratios\n 'BURDENSO4', 'BURDENPOM', 'BURDENSOA', 'BURDENBC', # MAM burdens\n 'BURDENSEASALT', 'BURDENDUST', # MAM burdens cont.\n 'TAU_tot', 'AEROD_v', # AOD in MARC, MAM\n 'CDNUMC', # vertically-integrated CDNC\n 'CLDTOT', 'CLDLOW', 'CLDMED', 'CLDHGH', # cloud fraction\n 'TGCLDLWP', 'TGCLDIWP', 'TGCLDCWP', # grid-box average water path\n 'PRECC', 'PRECL', # convective and large-scale precipitation rate (in m/s)\n 'PRECSC', 'PRECSL', # convective and large-scale snow rate (in m/s)\n 'U10', # 10m wind speed\n 'FSNTOA', 'FSNTOANOA', 'FSNTOA_d1', # SW flux at TOA, including clean-sky for MARC, MAM\n 'FSNS', 'FSNSNOA', 'FSNS_d1', # SW flux at surface, including clean-sky for MAM, MAM\n 'CRF', 'SWCF_d1', # SW cloud radiative effect in MARC, MAM\n 'LWCF', # LW cloud radiative effect \n 'FSNTOACNOA', 'FSNTOAC_d1', # SW clear-sky clean-sky flux at TOA in MARC, MAM\n ]\nfor variable in variable_list:\n for model in ['marc_s2', 'mam3', 'mam7']:\n for year in ['1850', '2000']:\n # Check if input file exists\n in_filename = '{}/p17c_{}_{}.cam.h0.{}.nc'.format(in_dir, model, year, variable)\n if os.path.isfile(in_filename):\n print('{}, {}, {}'.format(variable, model, year))\n # Calculate annual means using NCO (with years starting in January)\n annual_filename = '{}/{}_{}_{}_ANN.nc'.format(out_dir, model, year, variable)\n ! ncra -O --mro -d time,,,12,12 {in_filename} {annual_filename}\n print(' Written {}'.format(annual_filename.split('/')[-1]))\n! date ",
"OC_LDG, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_OC_LDG_ANN.nc\nOC_LDG, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_OC_LDG_ANN.nc\nBURDENSO4, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_BURDENSO4_ANN.nc\nBURDENSO4, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_BURDENSO4_ANN.nc\nBURDENSO4, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_BURDENSO4_ANN.nc\nBURDENSO4, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_BURDENSO4_ANN.nc\nBURDENPOM, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_BURDENPOM_ANN.nc\nBURDENPOM, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_BURDENPOM_ANN.nc\nBURDENPOM, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_BURDENPOM_ANN.nc\nBURDENPOM, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_BURDENPOM_ANN.nc\nBURDENSOA, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_BURDENSOA_ANN.nc\nBURDENSOA, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_BURDENSOA_ANN.nc\nBURDENSOA, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_BURDENSOA_ANN.nc\nBURDENSOA, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_BURDENSOA_ANN.nc\nBURDENBC, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_BURDENBC_ANN.nc\nBURDENBC, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_BURDENBC_ANN.nc\nBURDENBC, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_BURDENBC_ANN.nc\nBURDENBC, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_BURDENBC_ANN.nc\nBURDENSEASALT, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_BURDENSEASALT_ANN.nc\nBURDENSEASALT, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_BURDENSEASALT_ANN.nc\nBURDENSEASALT, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_BURDENSEASALT_ANN.nc\nBURDENSEASALT, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_BURDENSEASALT_ANN.nc\nBURDENDUST, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_BURDENDUST_ANN.nc\nBURDENDUST, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_BURDENDUST_ANN.nc\nBURDENDUST, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_BURDENDUST_ANN.nc\nBURDENDUST, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_BURDENDUST_ANN.nc\nTAU_tot, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_TAU_tot_ANN.nc\nTAU_tot, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_TAU_tot_ANN.nc\nAEROD_v, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_AEROD_v_ANN.nc\nAEROD_v, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_AEROD_v_ANN.nc\nAEROD_v, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_AEROD_v_ANN.nc\nAEROD_v, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_AEROD_v_ANN.nc\nCDNUMC, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_CDNUMC_ANN.nc\nCDNUMC, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_CDNUMC_ANN.nc\nCDNUMC, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_CDNUMC_ANN.nc\nCDNUMC, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_CDNUMC_ANN.nc\nCDNUMC, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_CDNUMC_ANN.nc\nCDNUMC, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_CDNUMC_ANN.nc\nCLDTOT, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_CLDTOT_ANN.nc\nCLDTOT, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_CLDTOT_ANN.nc\nCLDTOT, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_CLDTOT_ANN.nc\nCLDTOT, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_CLDTOT_ANN.nc\nCLDTOT, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_CLDTOT_ANN.nc\nCLDTOT, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_CLDTOT_ANN.nc\nCLDLOW, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_CLDLOW_ANN.nc\nCLDLOW, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_CLDLOW_ANN.nc\nCLDLOW, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_CLDLOW_ANN.nc\nCLDLOW, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_CLDLOW_ANN.nc\nCLDLOW, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_CLDLOW_ANN.nc\nCLDLOW, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_CLDLOW_ANN.nc\nCLDMED, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_CLDMED_ANN.nc\nCLDMED, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_CLDMED_ANN.nc\nCLDMED, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_CLDMED_ANN.nc\nCLDMED, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_CLDMED_ANN.nc\nCLDMED, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_CLDMED_ANN.nc\nCLDMED, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_CLDMED_ANN.nc\nCLDHGH, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_CLDHGH_ANN.nc\nCLDHGH, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_CLDHGH_ANN.nc\nCLDHGH, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_CLDHGH_ANN.nc\nCLDHGH, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_CLDHGH_ANN.nc\nCLDHGH, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_CLDHGH_ANN.nc\nCLDHGH, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_CLDHGH_ANN.nc\nTGCLDLWP, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_TGCLDLWP_ANN.nc\nTGCLDLWP, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_TGCLDLWP_ANN.nc\nTGCLDLWP, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_TGCLDLWP_ANN.nc\nTGCLDLWP, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_TGCLDLWP_ANN.nc\nTGCLDLWP, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_TGCLDLWP_ANN.nc\nTGCLDLWP, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_TGCLDLWP_ANN.nc\nTGCLDIWP, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_TGCLDIWP_ANN.nc\nTGCLDIWP, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_TGCLDIWP_ANN.nc\nTGCLDIWP, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_TGCLDIWP_ANN.nc\nTGCLDIWP, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_TGCLDIWP_ANN.nc\nTGCLDIWP, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_TGCLDIWP_ANN.nc\nTGCLDIWP, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_TGCLDIWP_ANN.nc\nTGCLDCWP, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_TGCLDCWP_ANN.nc\nTGCLDCWP, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_TGCLDCWP_ANN.nc\nTGCLDCWP, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_TGCLDCWP_ANN.nc\nTGCLDCWP, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_TGCLDCWP_ANN.nc\nTGCLDCWP, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_TGCLDCWP_ANN.nc\nTGCLDCWP, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_TGCLDCWP_ANN.nc\nPRECC, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_PRECC_ANN.nc\nPRECC, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_PRECC_ANN.nc\nPRECC, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_PRECC_ANN.nc\nPRECC, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_PRECC_ANN.nc\nPRECC, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_PRECC_ANN.nc\nPRECC, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_PRECC_ANN.nc\nPRECL, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_PRECL_ANN.nc\nPRECL, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_PRECL_ANN.nc\nPRECL, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_PRECL_ANN.nc\nPRECL, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_PRECL_ANN.nc\nPRECL, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_PRECL_ANN.nc\nPRECL, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_PRECL_ANN.nc\nPRECSC, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_PRECSC_ANN.nc\nPRECSC, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_PRECSC_ANN.nc\nPRECSC, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_PRECSC_ANN.nc\nPRECSC, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_PRECSC_ANN.nc\nPRECSC, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_PRECSC_ANN.nc\nPRECSC, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_PRECSC_ANN.nc\nPRECSL, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_PRECSL_ANN.nc\nPRECSL, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_PRECSL_ANN.nc\nPRECSL, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_PRECSL_ANN.nc\nPRECSL, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_PRECSL_ANN.nc\nPRECSL, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_PRECSL_ANN.nc\nPRECSL, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_PRECSL_ANN.nc\nU10, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_U10_ANN.nc\nU10, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_U10_ANN.nc\nU10, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_U10_ANN.nc\nU10, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_U10_ANN.nc\nU10, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_U10_ANN.nc\nU10, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_U10_ANN.nc\nFSNTOA, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_FSNTOA_ANN.nc\nFSNTOA, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_FSNTOA_ANN.nc\nFSNTOA, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_FSNTOA_ANN.nc\nFSNTOA, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_FSNTOA_ANN.nc\nFSNTOA, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_FSNTOA_ANN.nc\nFSNTOA, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_FSNTOA_ANN.nc\nFSNTOANOA, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_FSNTOANOA_ANN.nc\nFSNTOANOA, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_FSNTOANOA_ANN.nc\nFSNTOA_d1, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_FSNTOA_d1_ANN.nc\nFSNTOA_d1, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_FSNTOA_d1_ANN.nc\nFSNTOA_d1, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_FSNTOA_d1_ANN.nc\nFSNTOA_d1, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_FSNTOA_d1_ANN.nc\nFSNS, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_FSNS_ANN.nc\nFSNS, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_FSNS_ANN.nc\nFSNS, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_FSNS_ANN.nc\nFSNS, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_FSNS_ANN.nc\nFSNS, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_FSNS_ANN.nc\nFSNS, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_FSNS_ANN.nc\nFSNSNOA, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_FSNSNOA_ANN.nc\nFSNSNOA, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_FSNSNOA_ANN.nc\nFSNS_d1, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_FSNS_d1_ANN.nc\nFSNS_d1, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_FSNS_d1_ANN.nc\nFSNS_d1, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_FSNS_d1_ANN.nc\nFSNS_d1, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_FSNS_d1_ANN.nc\nCRF, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_CRF_ANN.nc\nCRF, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_CRF_ANN.nc\nSWCF_d1, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_SWCF_d1_ANN.nc\nSWCF_d1, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_SWCF_d1_ANN.nc\nSWCF_d1, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_SWCF_d1_ANN.nc\nSWCF_d1, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_SWCF_d1_ANN.nc\nLWCF, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_LWCF_ANN.nc\nLWCF, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_LWCF_ANN.nc\nLWCF, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_LWCF_ANN.nc\nLWCF, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_LWCF_ANN.nc\nLWCF, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_LWCF_ANN.nc\nLWCF, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_LWCF_ANN.nc\nFSNTOACNOA, marc_s2, 1850\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Extract data on specific atmosphere model levels",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"variable_list = ['CCN3', ]\nfor variable in variable_list:\n for model in ['marc_s2', 'mam3', 'mam7']:\n for year in ['1850', '2000']:\n # Check if input file exists\n in_filename = '{}/p17c_{}_{}.cam.h0.{}.nc'.format(in_dir, model, year, variable)\n if os.path.isfile(in_filename): # there is no mam7_1850 simulation\n # Loop over model levels of interest\n for level in [30, 24, 19]: # 30 is bottom level; 24 is ~860hpa; 19 is ~525hPa\n print('{}, {}, {}, ml{}'.format(variable, model, year, level))\n # Select data for model level using CDO\n print(' Selecting data for model level {}'.format(level))\n level_filename = '{}/temp_{}_{}_{}_ml{}.nc'.format(out_dir, model, year, variable, level)\n ! cdo -s sellevidx,{level} {in_filename} {level_filename}\n # Rename variable using NCO\n print(' Renaming variable to {}_ml{}'.format(variable, level))\n ! ncrename -v {variable},{variable}_ml{level} {level_filename} >/dev/null 2>/dev/null\n # Calculate annual means using NCO (with years starting in January)\n print(' Calculating annual means')\n annual_filename = '{}/{}_{}_{}_ml{}_ANN.nc'.format(out_dir, model, year, variable, level)\n ! ncra -O --mro -d time,,,12,12 {level_filename} {annual_filename}\n print(' Written {}'.format(annual_filename.split('/')[-1]))\n # Remove temporary file\n for filename in [level_filename, ]:\n print(' Removing {}'.format(filename.split('/')[-1]))\n os.remove(filename)\n! date",
"CCN3, marc_s2, 1850, ml30\n Selecting data for model level 30\n Renaming variable to CCN3_ml30\n Calculating annual means\n Written marc_s2_1850_CCN3_ml30_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_CCN3_ml30.nc\nCCN3, marc_s2, 1850, ml24\n Selecting data for model level 24\n Renaming variable to CCN3_ml24\n Calculating annual means\n Written marc_s2_1850_CCN3_ml24_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_CCN3_ml24.nc\nCCN3, marc_s2, 1850, ml19\n Selecting data for model level 19\n Renaming variable to CCN3_ml19\n Calculating annual means\n Written marc_s2_1850_CCN3_ml19_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_CCN3_ml19.nc\nCCN3, marc_s2, 2000, ml30\n Selecting data for model level 30\n Renaming variable to CCN3_ml30\n Calculating annual means\n Written marc_s2_2000_CCN3_ml30_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_2000_CCN3_ml30.nc\nCCN3, marc_s2, 2000, ml24\n Selecting data for model level 24\n Renaming variable to CCN3_ml24\n Calculating annual means\n Written marc_s2_2000_CCN3_ml24_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_2000_CCN3_ml24.nc\nCCN3, marc_s2, 2000, ml19\n Selecting data for model level 19\n Renaming variable to CCN3_ml19\n Calculating annual means\n Written marc_s2_2000_CCN3_ml19_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_2000_CCN3_ml19.nc\nCCN3, mam3, 1850, ml30\n Selecting data for model level 30\n Renaming variable to CCN3_ml30\n Calculating annual means\n Written mam3_1850_CCN3_ml30_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_1850_CCN3_ml30.nc\nCCN3, mam3, 1850, ml24\n Selecting data for model level 24\n Renaming variable to CCN3_ml24\n Calculating annual means\n Written mam3_1850_CCN3_ml24_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_1850_CCN3_ml24.nc\nCCN3, mam3, 1850, ml19\n Selecting data for model level 19\n Renaming variable to CCN3_ml19\n Calculating annual means\n Written mam3_1850_CCN3_ml19_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_1850_CCN3_ml19.nc\nCCN3, mam3, 2000, ml30\n Selecting data for model level 30\n Renaming variable to CCN3_ml30\n Calculating annual means\n Written mam3_2000_CCN3_ml30_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_2000_CCN3_ml30.nc\nCCN3, mam3, 2000, ml24\n Selecting data for model level 24\n Renaming variable to CCN3_ml24\n Calculating annual means\n Written mam3_2000_CCN3_ml24_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_2000_CCN3_ml24.nc\nCCN3, mam3, 2000, ml19\n Selecting data for model level 19\n Renaming variable to CCN3_ml19\n Calculating annual means\n Written mam3_2000_CCN3_ml19_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_2000_CCN3_ml19.nc\nCCN3, mam7, 1850, ml30\n Selecting data for model level 30\n Renaming variable to CCN3_ml30\n Calculating annual means\n Written mam7_1850_CCN3_ml30_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_1850_CCN3_ml30.nc\nCCN3, mam7, 1850, ml24\n Selecting data for model level 24\n Renaming variable to CCN3_ml24\n Calculating annual means\n Written mam7_1850_CCN3_ml24_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_1850_CCN3_ml24.nc\nCCN3, mam7, 1850, ml19\n Selecting data for model level 19\n Renaming variable to CCN3_ml19\n Calculating annual means\n Written mam7_1850_CCN3_ml19_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_1850_CCN3_ml19.nc\nCCN3, mam7, 2000, ml30\n Selecting data for model level 30\n Renaming variable to CCN3_ml30\n Calculating annual means\n Written mam7_2000_CCN3_ml30_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_2000_CCN3_ml30.nc\nCCN3, mam7, 2000, ml24\n Selecting data for model level 24\n Renaming variable to CCN3_ml24\n Calculating annual means\n Written mam7_2000_CCN3_ml24_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_2000_CCN3_ml24.nc\nCCN3, mam7, 2000, ml19\n Selecting data for model level 19\n Renaming variable to CCN3_ml19\n Calculating annual means\n Written mam7_2000_CCN3_ml19_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_2000_CCN3_ml19.nc\nFri Aug 17 15:16:38 +08 2018\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Calculate column loadings from MARC mass mixing ratios\n- This is to facilitate comparison with MAM. Although MARC diagnoses some column loadings, the column loading are not available for every aerosol component.\n- Regarding the calculation of the mass in each level, the following reference is helpful: http://nco.sourceforge.net/nco.html#Left-hand-casting. A description of the hybrid vertical coordinate system can be found here: http://www.cesm.ucar.edu/models/atm-cam/docs/usersguide/node25.html.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Calculate column loadings from mass mixing ratios\nfor year in ['1850', '2000']: # loop over emission years\n ! date\n print('year = {}'.format(year))\n # Copy the surface pressure file - necessary for decoding of the hybrid coordinates\n print(' Copying surface pressure file')\n in_filename = '{}/p17c_marc_s2_{}.cam.h0.PS.nc'.format(in_dir, year)\n ps_filename = '{}/temp_marc_s2_{}_PS.nc'.format(out_dir, year)\n shutil.copy2(in_filename, ps_filename)\n # Create file containing NCO commands for calculation of air mass in each model level\n nco_filename = '{}/temp_marc_s2_{}.nco'.format(out_dir, year)\n nco_file = open(nco_filename, 'w')\n nco_file.writelines(['*P_bnds[time,ilev,lat,lon]=hyai*P0+hybi*PS;\\n', # pressures at bounds\n '*P_delta[time,lev,lat,lon]=P_bnds(:,1:30,:,:)-P_bnds(:,0:29,:,:);\\n', # deltas\n 'mass_air=P_delta/9.807;']) # mass of air\n nco_file.close()\n # Calculate mass of air in each model level\n print(' Calculating mass of air in each model level')\n mass_air_filename = '{}/temp_marc_s2_{}_mass_air.nc'.format(out_dir, year)\n ! ncap2 -O -v -S {nco_filename} {ps_filename} {mass_air_filename}\n # Loop over mass mixing ratios for different aerosol components\n for aerosol in ['OC', 'MOS', 'OIM', 'BC', 'MBS', 'BIM',\n 'NUC', 'AIT', 'ACC',\n 'SSLT01', 'SSLT02', 'SSLT03', 'SSLT04', # sea-salt\n 'DST01', 'DST02', 'DST03', 'DST04']: # dust\n ! date\n print(' aerosol = {}'.format(aerosol))\n # Name of corresponding mass mixing ratio variable\n if aerosol[0:3] in ['SSL', 'DST']:\n mmr_aerosol = aerosol\n else:\n mmr_aerosol = 'm{}'.format(aerosol)\n # Copy the mass mixing ratio file\n print(' Copying the file for {}'.format(mmr_aerosol))\n in_filename = '{}/p17c_marc_s2_{}.cam.h0.{}.nc'.format(in_dir, year, mmr_aerosol)\n mmr_filename = '{}/temp_marc_s2_{}_{}.nc'.format(out_dir, year, mmr_aerosol)\n shutil.copy2(in_filename, mmr_filename)\n # Append the mass of air in each model level\n print(' Appending mass_air')\n ! ncks -A {mass_air_filename} {mmr_filename}\n # Calculate the mass of the aerosol\n print(' Calculating the mass of {} in each model level'.format(aerosol))\n mass_aerosol_filename = '{}/temp_marc_s2_{}_mass_{}.nc'.format(out_dir, year, aerosol)\n ! ncap2 -O -s 'mass_{aerosol}=mass_air*{mmr_aerosol}' {mmr_filename} {mass_aerosol_filename}\n # Sum over levels to calculate column loading (and exclude unwanted variables)\n print(' Summing over levels')\n column_filename = '{}/temp_marc_s2_{}_column_{}.nc'.format(out_dir, year, aerosol)\n ! ncwa -O -x -v mass_air,{mmr_aerosol} -a lev -y sum {mass_aerosol_filename} {column_filename}\n # Rename variable\n print(' Renaming variable to c{}_LDG'.format(aerosol))\n ! ncrename -v mass_{aerosol},c{aerosol}_LDG {column_filename} >/dev/null 2>/dev/null\n # Set units and long_name\n print(' Setting units and long_name')\n ! ncatted -a 'units',c{aerosol}_LDG,o,c,'kg/m2' {column_filename}\n ! ncatted -a 'long_name',c{aerosol}_LDG,o,c,'{aerosol} column loading' {column_filename}\n # Calculate annual means (with years starting in January)\n print(' Calculating annual means')\n annual_filename = '{}/marc_s2_{}_c{}_LDG_ANN.nc'.format(out_dir, year, aerosol)\n ! ncra -O --mro -d time,,,12,12 {column_filename} {annual_filename}\n print(' Written {}'.format(annual_filename.split('/')[-1]))\n # Remove three temporary files\n for filename in [mmr_filename, mass_aerosol_filename, column_filename]:\n print(' Removing {}'.format(filename.split('/')[-1]))\n os.remove(filename)\n # Remove another two temporary files\n for filename in [ps_filename, mass_air_filename, nco_filename]:\n print(' Removing {}'.format(filename.split('/')[-1]))\n os.remove(filename)\n! date",
"Fri Aug 17 15:16:38 +08 2018\nyear = 1850\n Copying surface pressure file\n Calculating mass of air in each model level\nFri Aug 17 15:17:26 +08 2018\n aerosol = OC\n Copying the file for mOC\n Appending mass_air\n Calculating the mass of OC in each model level\n Summing over levels\n Renaming variable to cOC_LDG\n Setting units and long_name\n Calculating annual means\n Written marc_s2_1850_cOC_LDG_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_mOC.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_mass_OC.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_column_OC.nc\nFri Aug 17 15:18:23 +08 2018\n aerosol = MOS\n Copying the file for mMOS\n Appending mass_air\n Calculating the mass of MOS in each model level\n Summing over levels\n Renaming variable to cMOS_LDG\n Setting units and long_name\n Calculating annual means\n Written marc_s2_1850_cMOS_LDG_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_mMOS.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_mass_MOS.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_column_MOS.nc\nFri Aug 17 15:19:24 +08 2018\n aerosol = OIM\n Copying the file for mOIM\n Appending mass_air\n Calculating the mass of OIM in each model level\n Summing over levels\n Renaming variable to cOIM_LDG\n Setting units and long_name\n Calculating annual means\n Written marc_s2_1850_cOIM_LDG_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_mOIM.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_mass_OIM.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_column_OIM.nc\nFri Aug 17 15:20:46 +08 2018\n aerosol = BC\n Copying the file for mBC\n Appending mass_air\n Calculating the mass of BC in each model level\n Summing over levels\n Renaming variable to cBC_LDG\n Setting units and long_name\n Calculating annual means\n Written marc_s2_1850_cBC_LDG_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_mBC.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_mass_BC.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_column_BC.nc\nFri Aug 17 15:21:57 +08 2018\n aerosol = MBS\n Copying the file for mMBS\n Appending mass_air\n Calculating the mass of MBS in each model level\n Summing over levels\n Renaming variable to cMBS_LDG\n Setting units and long_name\n Calculating annual means\n Written marc_s2_1850_cMBS_LDG_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_mMBS.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_mass_MBS.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_column_MBS.nc\nFri Aug 17 15:23:11 +08 2018\n aerosol = BIM\n Copying the file for mBIM\n Appending mass_air\n Calculating the mass of BIM in each model level\n Summing over levels\n Renaming variable to cBIM_LDG\n Setting units and long_name\n Calculating annual means\n Written marc_s2_1850_cBIM_LDG_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_mBIM.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_mass_BIM.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_column_BIM.nc\nFri Aug 17 15:24:23 +08 2018\n aerosol = NUC\n Copying the file for mNUC\n Appending mass_air\n Calculating the mass of NUC in each model level\n Summing over levels\n Renaming variable to cNUC_LDG\n Setting units and long_name\n Calculating annual means\n Written marc_s2_1850_cNUC_LDG_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_mNUC.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_mass_NUC.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_column_NUC.nc\nFri Aug 17 15:25:31 +08 2018\n aerosol = AIT\n Copying the file for mAIT\n Appending mass_air\n Calculating the mass of AIT in each model level\n Summing over levels\n Renaming variable to cAIT_LDG\n Setting units and long_name\n Calculating annual means\n Written marc_s2_1850_cAIT_LDG_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_mAIT.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_mass_AIT.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_column_AIT.nc\nFri Aug 17 15:26:37 +08 2018\n aerosol = ACC\n Copying the file for mACC\n Appending mass_air\n Calculating the mass of ACC in each model level\n Summing over levels\n Renaming variable to cACC_LDG\n Setting units and long_name\n Calculating annual means\n Written marc_s2_1850_cACC_LDG_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_mACC.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_mass_ACC.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_column_ACC.nc\nFri Aug 17 15:27:41 +08 2018\n aerosol = SSLT01\n Copying the file for SSLT01\n Appending mass_air\n Calculating the mass of SSLT01 in each model level\n Summing over levels\n Renaming variable to cSSLT01_LDG\n Setting units and long_name\n Calculating annual means\n Written marc_s2_1850_cSSLT01_LDG_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_SSLT01.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_mass_SSLT01.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_column_SSLT01.nc\nFri Aug 17 15:28:48 +08 2018\n aerosol = SSLT02\n Copying the file for SSLT02\n Appending mass_air\n Calculating the mass of SSLT02 in each model level\n Summing over levels\n Renaming variable to cSSLT02_LDG\n Setting units and long_name\n Calculating annual means\n Written marc_s2_1850_cSSLT02_LDG_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_SSLT02.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_mass_SSLT02.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_column_SSLT02.nc\nFri Aug 17 15:29:56 +08 2018\n aerosol = SSLT03\n Copying the file for SSLT03\n Appending mass_air\n Calculating the mass of SSLT03 in each model level\n Summing over levels\n Renaming variable to cSSLT03_LDG\n Setting units and long_name\n Calculating annual means\n Written marc_s2_1850_cSSLT03_LDG_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_SSLT03.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_mass_SSLT03.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_column_SSLT03.nc\nFri Aug 17 15:31:05 +08 2018\n aerosol = SSLT04\n Copying the file for SSLT04\n Appending mass_air\n Calculating the mass of SSLT04 in each model level\n Summing over levels\n Renaming variable to cSSLT04_LDG\n Setting units and long_name\n Calculating annual means\n Written marc_s2_1850_cSSLT04_LDG_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_SSLT04.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_mass_SSLT04.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_column_SSLT04.nc\nFri Aug 17 15:32:13 +08 2018\n aerosol = DST01\n Copying the file for DST01\n Appending mass_air\n Calculating the mass of DST01 in each model level\n Summing over levels\n Renaming variable to cDST01_LDG\n Setting units and long_name\n Calculating annual means\n Written marc_s2_1850_cDST01_LDG_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_DST01.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_mass_DST01.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_column_DST01.nc\nFri Aug 17 15:33:24 +08 2018\n aerosol = DST02\n Copying the file for DST02\n Appending mass_air\n Calculating the mass of DST02 in each model level\n Summing over levels\n Renaming variable to cDST02_LDG\n Setting units and long_name\n Calculating annual means\n Written marc_s2_1850_cDST02_LDG_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_DST02.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_mass_DST02.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_column_DST02.nc\nFri Aug 17 15:34:39 +08 2018\n aerosol = DST03\n Copying the file for DST03\n Appending mass_air\n Calculating the mass of DST03 in each model level\n Summing over levels\n Renaming variable to cDST03_LDG\n Setting units and long_name\n Calculating annual means\n Written marc_s2_1850_cDST03_LDG_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_DST03.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_mass_DST03.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_column_DST03.nc\nFri Aug 17 15:35:52 +08 2018\n aerosol = DST04\n Copying the file for DST04\n Appending mass_air\n Calculating the mass of DST04 in each model level\n Summing over levels\n Renaming variable to cDST04_LDG\n Setting units and long_name\n Calculating annual means\n Written marc_s2_1850_cDST04_LDG_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_DST04.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_mass_DST04.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_column_DST04.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_PS.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_mass_air.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850.nco\nFri Aug 17 15:37:03 +08 2018\nyear = 2000\n Copying surface pressure file\n Calculating mass of air in each model level\nFri Aug 17 15:38:03 +08 2018\n aerosol = OC\n Copying the file for mOC\n Appending mass_air\n Calculating the mass of OC in each model level\n Summing over levels\n Renaming variable to cOC_LDG\n Setting units and long_name\n Calculating annual means\n Written marc_s2_2000_cOC_LDG_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_2000_mOC.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_2000_mass_OC.nc\n"
],
[
"# Compare cOC_LDG (calculated above) with standard OC_LDG\nfor year in ['1850', '2000']:\n # Input files\n in_filename_1 = '{}/marc_s2_{}_OC_LDG_ANN.nc'.format(out_dir, year)\n in_filename_2 = '{}/marc_s2_{}_cOC_LDG_ANN.nc'.format(out_dir, year)\n # Rename cOC_LDG to OC_LDG to enable comparison\n temp_filename = '{}/temp_marc_s2_{}_cOC_LDG_ANN.nc'.format(out_dir, year)\n ! ncrename -O -v cOC_LDG,OC_LDG {in_filename_2} {temp_filename} >/dev/null 2>/dev/null\n # Compare using CDO\n ! cdo diffv {in_filename_1} {temp_filename}\n # Remove temporary file\n for filename in [temp_filename, ]:\n print(' Removing {}'.format(filename.split('/')[-1]))\n os.remove(filename)\n! date",
" Date Time Level Gridsize Miss Diff : S Z Max_Absdiff Max_Reldiff : Parameter name\n 16 : 0001-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.4327e-08 0.0037840 : OC_LDG \n 28 : 0002-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.5460e-08 0.0035330 : OC_LDG \n 40 : 0003-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.0968e-08 0.0032956 : OC_LDG \n 52 : 0004-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.1714e-08 0.0038242 : OC_LDG \n 64 : 0005-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.3320e-08 0.0041843 : OC_LDG \n 76 : 0006-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 3.0619e-08 0.0045040 : OC_LDG \n 88 : 0007-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.0183e-08 0.0037437 : OC_LDG \n 100 : 0008-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.8374e-08 0.0036806 : OC_LDG \n 112 : 0009-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.1275e-08 0.0042557 : OC_LDG \n 124 : 0010-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.7931e-08 0.0042929 : OC_LDG \n 136 : 0011-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.1506e-08 0.0035773 : OC_LDG \n 148 : 0012-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.8109e-08 0.0035707 : OC_LDG \n 160 : 0013-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.0001e-08 0.0036887 : OC_LDG \n 172 : 0014-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.1386e-08 0.0031176 : OC_LDG \n 184 : 0015-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.5297e-08 0.0037429 : OC_LDG \n 196 : 0016-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.7497e-08 0.0036960 : OC_LDG \n 208 : 0017-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.4416e-08 0.0045443 : OC_LDG \n 220 : 0018-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.2629e-08 0.0037107 : OC_LDG \n 232 : 0019-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.6059e-08 0.0034830 : OC_LDG \n 244 : 0020-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.5165e-08 0.0038956 : OC_LDG \n 256 : 0021-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 1.6852e-08 0.0028722 : OC_LDG \n 268 : 0022-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.5914e-08 0.0046617 : OC_LDG \n 280 : 0023-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.5511e-08 0.0040788 : OC_LDG \n 292 : 0024-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.4578e-08 0.0036203 : OC_LDG \n 304 : 0025-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 1.8693e-08 0.0030742 : OC_LDG \n 316 : 0026-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.4101e-08 0.0032011 : OC_LDG \n 328 : 0027-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.1736e-08 0.0038488 : OC_LDG \n 340 : 0028-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.2724e-08 0.0038373 : OC_LDG \n 352 : 0029-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.2875e-08 0.0037878 : OC_LDG \n 364 : 0030-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.3477e-08 0.0036839 : OC_LDG \n 376 : 0031-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.2018e-08 0.0032665 : OC_LDG \n 388 : 0032-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.1149e-08 0.0039709 : OC_LDG \n 32 of 388 records differ\n 0 of 388 records differ more than 0.001\ncdo diffn: Processed 886206 values from 32 variables over 64 timesteps ( 0.14s )\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_cOC_LDG_ANN.nc\n Date Time Level Gridsize Miss Diff : S Z Max_Absdiff Max_Reldiff : Parameter name\n 16 : 0001-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 1.9382e-08 0.0033255 : OC_LDG \n 28 : 0002-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 1.7938e-08 0.0033809 : OC_LDG \n 40 : 0003-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 1.8225e-08 0.0030964 : OC_LDG \n 52 : 0004-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 1.9173e-08 0.0033514 : OC_LDG \n 64 : 0005-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 1.9805e-08 0.0031928 : OC_LDG \n 76 : 0006-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.4134e-08 0.0036310 : OC_LDG \n 88 : 0007-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 1.9865e-08 0.0032696 : OC_LDG \n 100 : 0008-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 1.9570e-08 0.0031486 : OC_LDG \n 112 : 0009-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.1547e-08 0.0030526 : OC_LDG \n 124 : 0010-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.0350e-08 0.0031322 : OC_LDG \n 136 : 0011-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 1.7894e-08 0.0030769 : OC_LDG \n 148 : 0012-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 1.4926e-08 0.0027383 : OC_LDG \n 160 : 0013-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.0861e-08 0.0036484 : OC_LDG \n 172 : 0014-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 1.7630e-08 0.0030775 : OC_LDG \n 184 : 0015-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 1.8540e-08 0.0029314 : OC_LDG \n 196 : 0016-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 1.7465e-08 0.0030326 : OC_LDG \n 208 : 0017-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 1.5098e-08 0.0033772 : OC_LDG \n 220 : 0018-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 1.9260e-08 0.0030257 : OC_LDG \n 232 : 0019-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.3571e-08 0.0033623 : OC_LDG \n 244 : 0020-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 1.5342e-08 0.0033874 : OC_LDG \n 256 : 0021-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 1.8648e-08 0.0029417 : OC_LDG \n 268 : 0022-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 1.3859e-08 0.0028956 : OC_LDG \n 280 : 0023-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 1.6703e-08 0.0027249 : OC_LDG \n 292 : 0024-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 1.3649e-08 0.0028630 : OC_LDG \n 304 : 0025-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 1.8532e-08 0.0031170 : OC_LDG \n 316 : 0026-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 1.8449e-08 0.0033111 : OC_LDG \n 328 : 0027-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 1.7149e-08 0.0030837 : OC_LDG \n 340 : 0028-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 1.7246e-08 0.0038835 : OC_LDG \n 352 : 0029-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.0369e-08 0.0030075 : OC_LDG \n 364 : 0030-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.0443e-08 0.0038447 : OC_LDG \n 376 : 0031-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.5351e-08 0.0036604 : OC_LDG \n 388 : 0032-07-16 22:00:00 0 13824 0 13824 : F F 2.1405e-08 0.0031861 : OC_LDG \n 32 of 388 records differ\n 0 of 388 records differ more than 0.001\ncdo diffn: Processed 886206 values from 32 variables over 64 timesteps ( 0.13s )\n Removing temp_marc_s2_2000_cOC_LDG_ANN.nc\nFri Aug 17 15:58:17 +08 2018\n"
]
],
[
[
"In results above, the maximum relative difference is less than 1%. This shows that the calculation of the column loadings is works as intended.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Derive additional atmosphere variables",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Derived variables that require *two* input variables\nderived_variable_dict = {'ctBURDENOM=BURDENPOM+BURDENSOA': ['mam3', 'mam7'], # total OM loading (MAM)\n 'ctOC_LDG=cOC_LDG+cOIM_LDG': ['marc_s2',], # total OC loading (MARC)\n 'ctBC_LDG=cBC_LDG+cBIM_LDG': ['marc_s2',], # total BC loading\n 'cSIMOS_LDG=cMOS_LDG-cOIM_LDG': ['marc_s2',], # SO4 in MOS loading\n 'cSIMBS_LDG=cMBS_LDG-cBIM_LDG': ['marc_s2',], # SO4 in MBS loading\n 'cPRECT=PRECC+PRECL': ['marc_s2', 'mam3', 'mam7'], # total precipitation rate\n 'cPRECST=PRECSC+PRECSL': ['marc_s2', 'mam3', 'mam7'], # total snow rate\n 'cFNTOA=FSNTOA+LWCF': ['marc_s2', 'mam3', 'mam7'], # net (SW + LW) radiative effect\n 'cDRE=FSNTOA-FSNTOANOA': ['marc_s2',], # direct radiative effect at TOA\n 'cDRE=FSNTOA-FSNTOA_d1': ['mam3', 'mam7'],\n 'cDREsurf=FSNS-FSNSNOA': ['marc_s2',], # direct radiative effect at surface\n 'cDREsurf=FSNS-FSNS_d1': ['mam3', 'mam7'],\n 'cAAA=cDRE-cDREsurf': ['marc_s2', 'mam3', 'mam7'], # absorption by aerosols in atmosphere\n }\nfor derived_variable, model_list in derived_variable_dict.items():\n for model in model_list:\n year_list = ['1850', '2000']\n for year in year_list:\n print('{}, {}, {}'.format(derived_variable, model, year))\n # Merge input files\n variable_list = re.split('\\=|\\+|\\-', derived_variable)\n in_filename_1 = '{}/{}_{}_{}_ANN.nc'.format(out_dir, model, year, variable_list[1])\n in_filename_2 = '{}/{}_{}_{}_ANN.nc'.format(out_dir, model, year, variable_list[2])\n merge_filename = '{}/temp_{}_{}_merge_ANN.nc'.format(out_dir, model, year)\n ! cdo -s merge {in_filename_1} {in_filename_2} {merge_filename} >/dev/null 2>/dev/null\n # Calculate derived variable\n out_filename = '{}/{}_{}_{}_ANN.nc'.format(out_dir, model, year, variable_list[0])\n ! cdo -s expr,'{derived_variable}' {merge_filename} {out_filename}\n if os.path.isfile(out_filename):\n print(' Written {}'.format(out_filename.split('/')[-1]))\n # Remove temporary file\n for filename in [merge_filename, ]:\n print(' Removing {}'.format(filename.split('/')[-1]))\n os.remove(filename)\n! date",
"ctBURDENOM=BURDENPOM+BURDENSOA, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_ctBURDENOM_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_1850_merge_ANN.nc\nctBURDENOM=BURDENPOM+BURDENSOA, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_ctBURDENOM_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_2000_merge_ANN.nc\nctBURDENOM=BURDENPOM+BURDENSOA, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_ctBURDENOM_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_1850_merge_ANN.nc\nctBURDENOM=BURDENPOM+BURDENSOA, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_ctBURDENOM_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_2000_merge_ANN.nc\nctOC_LDG=cOC_LDG+cOIM_LDG, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_ctOC_LDG_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_merge_ANN.nc\nctOC_LDG=cOC_LDG+cOIM_LDG, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_ctOC_LDG_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_2000_merge_ANN.nc\nctBC_LDG=cBC_LDG+cBIM_LDG, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_ctBC_LDG_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_merge_ANN.nc\nctBC_LDG=cBC_LDG+cBIM_LDG, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_ctBC_LDG_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_2000_merge_ANN.nc\ncSIMOS_LDG=cMOS_LDG-cOIM_LDG, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_cSIMOS_LDG_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_merge_ANN.nc\ncSIMOS_LDG=cMOS_LDG-cOIM_LDG, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_cSIMOS_LDG_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_2000_merge_ANN.nc\ncSIMBS_LDG=cMBS_LDG-cBIM_LDG, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_cSIMBS_LDG_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_merge_ANN.nc\ncSIMBS_LDG=cMBS_LDG-cBIM_LDG, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_cSIMBS_LDG_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_2000_merge_ANN.nc\ncPRECT=PRECC+PRECL, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_cPRECT_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_merge_ANN.nc\ncPRECT=PRECC+PRECL, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_cPRECT_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_2000_merge_ANN.nc\ncPRECT=PRECC+PRECL, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_cPRECT_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_1850_merge_ANN.nc\ncPRECT=PRECC+PRECL, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_cPRECT_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_2000_merge_ANN.nc\ncPRECT=PRECC+PRECL, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_cPRECT_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_1850_merge_ANN.nc\ncPRECT=PRECC+PRECL, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_cPRECT_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_2000_merge_ANN.nc\ncPRECST=PRECSC+PRECSL, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_cPRECST_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_merge_ANN.nc\ncPRECST=PRECSC+PRECSL, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_cPRECST_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_2000_merge_ANN.nc\ncPRECST=PRECSC+PRECSL, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_cPRECST_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_1850_merge_ANN.nc\ncPRECST=PRECSC+PRECSL, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_cPRECST_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_2000_merge_ANN.nc\ncPRECST=PRECSC+PRECSL, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_cPRECST_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_1850_merge_ANN.nc\ncPRECST=PRECSC+PRECSL, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_cPRECST_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_2000_merge_ANN.nc\ncFNTOA=FSNTOA+LWCF, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_cFNTOA_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_merge_ANN.nc\ncFNTOA=FSNTOA+LWCF, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_cFNTOA_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_2000_merge_ANN.nc\ncFNTOA=FSNTOA+LWCF, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_cFNTOA_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_1850_merge_ANN.nc\ncFNTOA=FSNTOA+LWCF, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_cFNTOA_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_2000_merge_ANN.nc\ncFNTOA=FSNTOA+LWCF, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_cFNTOA_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_1850_merge_ANN.nc\ncFNTOA=FSNTOA+LWCF, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_cFNTOA_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_2000_merge_ANN.nc\ncDRE=FSNTOA-FSNTOANOA, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_cDRE_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_merge_ANN.nc\ncDRE=FSNTOA-FSNTOANOA, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_cDRE_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_2000_merge_ANN.nc\ncDRE=FSNTOA-FSNTOA_d1, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_cDRE_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_1850_merge_ANN.nc\ncDRE=FSNTOA-FSNTOA_d1, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_cDRE_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_2000_merge_ANN.nc\ncDRE=FSNTOA-FSNTOA_d1, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_cDRE_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_1850_merge_ANN.nc\ncDRE=FSNTOA-FSNTOA_d1, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_cDRE_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_2000_merge_ANN.nc\ncDREsurf=FSNS-FSNSNOA, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_cDREsurf_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_merge_ANN.nc\ncDREsurf=FSNS-FSNSNOA, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_cDREsurf_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_2000_merge_ANN.nc\ncDREsurf=FSNS-FSNS_d1, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_cDREsurf_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_1850_merge_ANN.nc\ncDREsurf=FSNS-FSNS_d1, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_cDREsurf_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_2000_merge_ANN.nc\ncDREsurf=FSNS-FSNS_d1, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_cDREsurf_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_1850_merge_ANN.nc\ncDREsurf=FSNS-FSNS_d1, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_cDREsurf_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_2000_merge_ANN.nc\ncAAA=cDRE-cDREsurf, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_cAAA_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_merge_ANN.nc\ncAAA=cDRE-cDREsurf, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_cAAA_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_2000_merge_ANN.nc\ncAAA=cDRE-cDREsurf, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_cAAA_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_1850_merge_ANN.nc\ncAAA=cDRE-cDREsurf, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_cAAA_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_2000_merge_ANN.nc\ncAAA=cDRE-cDREsurf, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_cAAA_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_1850_merge_ANN.nc\ncAAA=cDRE-cDREsurf, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_cAAA_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_2000_merge_ANN.nc\nFri Aug 17 15:58:40 +08 2018\n"
],
[
"# ctSSLT_LDG and ctDST_LDG require *four* input variables\nfor sslt_or_dst in ['SSLT', 'DST']: # sea-salt or dust\n variable_list = ['ct{}_LDG'.format(sslt_or_dst), ]\n for size_bin in ['01', '02', '03', '04']:\n variable_list.append('c{}{}_LDG'.format(sslt_or_dst, size_bin))\n derived_variable = '{}={}+{}+{}+{}'.format(*variable_list)\n model = 'marc_s2' # MARC only\n year_list = ['1850', '2000']\n for year in year_list:\n print('{}, {}, {}'.format(derived_variable, model, year))\n # Merge input files\n in_filename_list = []\n for variable in variable_list[1:]:\n in_filename_list.append('{}/{}_{}_{}_ANN.nc'.format(out_dir, model,\n year, variable))\n merge_filename = '{}/temp_{}_{}_merge_ANN.nc'.format(out_dir, model, year)\n ! cdo -s merge {in_filename_list[0]} {in_filename_list[1]} \\\n {in_filename_list[2]} {in_filename_list[3]} {merge_filename} >/dev/null 2>/dev/null\n # Calculate derived variable\n out_filename = '{}/{}_{}_{}_ANN.nc'.format(out_dir, model, year, variable_list[0])\n ! cdo -s expr,'{derived_variable}' {merge_filename} {out_filename}\n if os.path.isfile(out_filename):\n print(' Written {}'.format(out_filename.split('/')[-1]))\n # Remove temporary file\n for filename in [merge_filename, ]:\n print(' Removing {}'.format(filename.split('/')[-1]))\n os.remove(filename)\n! date",
"ctSSLT_LDG=cSSLT01_LDG+cSSLT02_LDG+cSSLT03_LDG+cSSLT04_LDG, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_ctSSLT_LDG_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_merge_ANN.nc\nctSSLT_LDG=cSSLT01_LDG+cSSLT02_LDG+cSSLT03_LDG+cSSLT04_LDG, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_ctSSLT_LDG_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_2000_merge_ANN.nc\nctDST_LDG=cDST01_LDG+cDST02_LDG+cDST03_LDG+cDST04_LDG, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_ctDST_LDG_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_merge_ANN.nc\nctDST_LDG=cDST01_LDG+cDST02_LDG+cDST03_LDG+cDST04_LDG, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_ctDST_LDG_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_2000_merge_ANN.nc\nFri Aug 17 15:58:43 +08 2018\n"
],
[
"# ctSUL_LDG requires *seven* input variables\nderived_variable_dict = {'ctSUL_LDG=cACC_LDG+cAIT_LDG+cNUC_LDG+cMOS_LDG+cMBS_LDG-cOIM_LDG-cBIM_LDG':\n ['marc_s2',],} # total SO4 loading\nfor derived_variable, model_list in derived_variable_dict.items():\n for model in model_list:\n year_list = ['1850', '2000']\n for year in year_list:\n print('{}, {}, {}'.format(derived_variable, model, year))\n # Merge input files\n variable_list = re.split('\\=|\\+|\\-', derived_variable)\n in_filename_list = []\n for variable in variable_list[1:]:\n in_filename_list.append('{}/{}_{}_{}_ANN.nc'.format(out_dir, model, year, variable))\n merge_filename = '{}/temp_{}_{}_merge_ANN.nc'.format(out_dir, model, year)\n ! cdo -s merge {in_filename_list[0]} {in_filename_list[1]} {in_filename_list[2]} \\\n {in_filename_list[3]} {in_filename_list[4]} {in_filename_list[5]} \\\n {in_filename_list[6]} {merge_filename} >/dev/null 2>/dev/null\n # Calculate derived variable\n out_filename = '{}/{}_{}_{}_ANN.nc'.format(out_dir, model, year, variable_list[0])\n ! cdo -s expr,'{derived_variable}' {merge_filename} {out_filename}\n if os.path.isfile(out_filename):\n print(' Written {}'.format(out_filename.split('/')[-1]))\n # Remove temporary file\n for filename in [merge_filename, ]:\n print(' Removing {}'.format(filename.split('/')[-1]))\n os.remove(filename)\n! date",
"ctSUL_LDG=cACC_LDG+cAIT_LDG+cNUC_LDG+cMOS_LDG+cMBS_LDG-cOIM_LDG-cBIM_LDG, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_ctSUL_LDG_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_merge_ANN.nc\nctSUL_LDG=cACC_LDG+cAIT_LDG+cNUC_LDG+cMOS_LDG+cMBS_LDG-cOIM_LDG-cBIM_LDG, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_ctSUL_LDG_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_2000_merge_ANN.nc\nFri Aug 17 15:58:45 +08 2018\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Calculate annual means of land variables",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"variable_list = ['FSNO', # fraction of ground covered by snow\n 'SNOBCMSL', # mass of BC in top layer of snow\n 'BCDEP' # total BC deposition (dry+wet) from atmosphere\n ]\nfor variable in variable_list:\n for model in ['marc_s2', 'mam3', 'mam7']:\n for year in ['1850', '2000']:\n # Check if input file exists\n in_filename = '{}/p17c_{}_{}.clm2.h0.{}.nc'.format(in_dir, model, year, variable)\n if os.path.isfile(in_filename):\n print('{}, {}, {}'.format(variable, model, year))\n # Calculate annual means using NCO (with years starting in January)\n temp_filename = '{}/temp_{}_{}_{}_ANN.nc'.format(out_dir, model, year, variable)\n ! ncra -O --mro -d time,,,12,12 {in_filename} {temp_filename}\n # Replace missing values with zero\n out_filename = '{}/{}_{}_{}_ANN.nc'.format(out_dir, model, year, variable)\n ! cdo -s setmisstoc,0 {temp_filename} {out_filename}\n print(' Written {}'.format(out_filename.split('/')[-1]))\n # Remove temporary file\n for filename in [temp_filename, ]:\n print(' Removing {}'.format(filename.split('/')[-1]))\n os.remove(filename)\n! date",
"FSNO, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_FSNO_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_FSNO_ANN.nc\nFSNO, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_FSNO_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_2000_FSNO_ANN.nc\nFSNO, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_FSNO_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_1850_FSNO_ANN.nc\nFSNO, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_FSNO_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_2000_FSNO_ANN.nc\nFSNO, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_FSNO_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_1850_FSNO_ANN.nc\nFSNO, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_FSNO_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_2000_FSNO_ANN.nc\nSNOBCMSL, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_SNOBCMSL_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_SNOBCMSL_ANN.nc\nSNOBCMSL, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_SNOBCMSL_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_2000_SNOBCMSL_ANN.nc\nSNOBCMSL, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_SNOBCMSL_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_1850_SNOBCMSL_ANN.nc\nSNOBCMSL, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_SNOBCMSL_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_2000_SNOBCMSL_ANN.nc\nSNOBCMSL, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_SNOBCMSL_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_1850_SNOBCMSL_ANN.nc\nSNOBCMSL, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_SNOBCMSL_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_2000_SNOBCMSL_ANN.nc\nBCDEP, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_BCDEP_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_BCDEP_ANN.nc\nBCDEP, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_BCDEP_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_2000_BCDEP_ANN.nc\nBCDEP, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_BCDEP_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_1850_BCDEP_ANN.nc\nBCDEP, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_BCDEP_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_2000_BCDEP_ANN.nc\nBCDEP, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_BCDEP_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_1850_BCDEP_ANN.nc\nBCDEP, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_BCDEP_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_2000_BCDEP_ANN.nc\nFri Aug 17 15:59:00 +08 2018\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Calculate annual means of sea ice variables and remap to lonlat grid\nNote: the data are initially on a curvilinear grid.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create grid file\n# Note: this grid is only approximately the same as the land grid\ngrid_filename = '{}/grid.txt'.format(in_dir)\ngrid_file = open(grid_filename, 'w')\ngrid_file.writelines(['gridtype = lonlat\\n',\n 'xsize = 144\\n',\n 'ysize = 96\\n',\n 'xfirst = 0\\n',\n 'xinc = 2.5\\n',\n 'yfirst = -90\\n',\n 'yinc = 1.89473724\\n'])\ngrid_file.close()\nprint('Written {}'.format(grid_filename.split('/')[-1]))\n!date",
"Written grid.txt\nFri Aug 17 15:59:00 +08 2018\r\n"
],
[
"variable_list = ['fs', # grid-cell mean snow fraction over ice\n ]\nfor variable in variable_list:\n for model in ['marc_s2', 'mam3', 'mam7']:\n for year in ['1850', '2000']:\n # Check if input file exists\n in_filename = '{}/p17c_{}_{}.cice.h.{}.nc'.format(in_dir, model, year, variable)\n if os.path.isfile(in_filename):\n print('{}, {}, {}'.format(variable, model, year))\n # Calculate annual means using NCO (with years starting in January)\n annual_filename = '{}/temp_{}_{}_{}_ANN.nc'.format(out_dir, model, year, variable)\n ! ncra -O --mro -d time,,,12,12 {in_filename} {annual_filename}\n # Apply distance weighted remapping to new grid using CDO\n regrid_filename = '{}/temp_{}_{}_{}_ANN_regrid.nc'.format(out_dir, model, year, variable)\n ! cdo -s remapdis,{grid_filename} {annual_filename} {regrid_filename}\n # Replace missing values with zero\n out_filename = '{}/{}_{}_{}_ANN.nc'.format(out_dir, model, year, variable)\n ! cdo -s setmisstoc,0 {regrid_filename} {out_filename}\n print(' Written {}'.format(out_filename.split('/')[-1]))\n # Remove temporary file\n for filename in [annual_filename, regrid_filename]:\n print(' Removing {}'.format(filename.split('/')[-1]))\n os.remove(filename)\n! date",
"fs, marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_fs_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_fs_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_fs_ANN_regrid.nc\nfs, marc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_fs_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_2000_fs_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_2000_fs_ANN_regrid.nc\nfs, mam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_fs_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_1850_fs_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_1850_fs_ANN_regrid.nc\nfs, mam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_fs_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_2000_fs_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_2000_fs_ANN_regrid.nc\nfs, mam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_fs_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_1850_fs_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_1850_fs_ANN_regrid.nc\nfs, mam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_fs_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_2000_fs_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_2000_fs_ANN_regrid.nc\nFri Aug 17 16:02:18 +08 2018\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Combine snow cover over land and sea ice",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for model in ['marc_s2', 'mam3', 'mam7']:\n for year in ['1850', '2000']:\n # Check if input files exists\n lnd_filename = '{}/{}_{}_{}_ANN.nc'.format(out_dir, model, year, 'FSNO')\n ice_filename = '{}/{}_{}_{}_ANN.nc'.format(out_dir, model, year, 'fs')\n if os.path.isfile(lnd_filename) and os.path.isfile(lnd_filename):\n print('{}, {}'.format(model, year))\n # Remap land data to identical grid as was used for ice\n lnd_regrid_filename = '{}/temp_{}_{}_{}_ANN_regrid.nc'.format(out_dir, model, year, 'FSNO')\n ! cdo -s remapnn,{grid_filename} {lnd_filename} {lnd_regrid_filename}\n # Merge land and ice data into one file\n merge_filename = '{}/temp_{}_{}_merge_ANN.nc'.format(out_dir, model, year)\n ! cdo -s merge {lnd_regrid_filename} {ice_filename} {merge_filename}\n # Combine snow cover over land and ice, weighting by land fraction\n out_filename = '{}/{}_{}_{}_ANN.nc'.format(out_dir, model, year, 'cSnowCover')\n derivation_str = '_oceanfrac=1-landfrac;cSnowCover=landfrac*FSNO+_oceanfrac*fs'\n ! cdo -s expr,'{derivation_str}' {merge_filename} {out_filename}\n print(' Written {}'.format(out_filename.split('/')[-1]))\n # Remove temporary files\n for filename in [lnd_regrid_filename, merge_filename]:\n print(' Removing {}'.format(filename.split('/')[-1]))\n os.remove(filename)\n! date",
"marc_s2, 1850\n Written marc_s2_1850_cSnowCover_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_FSNO_ANN_regrid.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_1850_merge_ANN.nc\nmarc_s2, 2000\n Written marc_s2_2000_cSnowCover_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_2000_FSNO_ANN_regrid.nc\n Removing temp_marc_s2_2000_merge_ANN.nc\nmam3, 1850\n Written mam3_1850_cSnowCover_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_1850_FSNO_ANN_regrid.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_1850_merge_ANN.nc\nmam3, 2000\n Written mam3_2000_cSnowCover_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_2000_FSNO_ANN_regrid.nc\n Removing temp_mam3_2000_merge_ANN.nc\nmam7, 1850\n Written mam7_1850_cSnowCover_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_1850_FSNO_ANN_regrid.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_1850_merge_ANN.nc\nmam7, 2000\n Written mam7_2000_cSnowCover_ANN.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_2000_FSNO_ANN_regrid.nc\n Removing temp_mam7_2000_merge_ANN.nc\nFri Aug 17 16:02:22 +08 2018\n"
],
[
"! date",
"Fri Aug 17 16:02:23 +08 2018\r\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a768d7ecf3c30667bdace42e565e9e7ff818636
| 44,406 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Reinforcement Learning/Q-Learning.ipynb
|
vivekrathi14/Machine-Learning-with-Scikit-Learn-Python-3.x
|
16828cf26e4956166ec5c4cee7755a527ad27322
|
[
"MIT"
] | 39 |
2019-10-22T11:09:52.000Z
|
2022-03-01T11:30:26.000Z
|
Reinforcement Learning/Q-Learning.ipynb
|
gvbc42/scikit-learn-unsupervised_learning
|
beb5b58eae9290a417495b689e719fe03702c380
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2020-09-26T05:31:29.000Z
|
2020-09-26T06:16:01.000Z
|
Reinforcement Learning/Q-Learning.ipynb
|
gvbc42/scikit-learn-unsupervised_learning
|
beb5b58eae9290a417495b689e719fe03702c380
|
[
"MIT"
] | 16 |
2019-11-24T10:40:14.000Z
|
2022-02-27T04:57:53.000Z
| 43.450098 | 796 | 0.609873 |
[
[
[
"# A practical introduction to Reinforcement Learning\n\nMost of you have probably heard of AI learning to play computer games on their own, a very popular example being Deepmind. Deepmind hit the news when their AlphaGo program defeated the South Korean Go world champion in 2016. There had been many successful attempts in the past to develop agents with the intent of playing Atari games like Breakout, Pong, and Space Invaders.\n\nYou know what's common in most of these programs? A paradigm of Machine Learning known as **Reinforcement Learning**. For those of you that are new to RL, let's get some understand with few analogies.\n\n## Reinforcement Learning Analogy\nConsider the scenario of teaching a dog new tricks. The dog doesn't understand our language, so we can't tell him what to do. Instead, we follow a different strategy. We emulate a situation (or a cue), and the dog tries to respond in many different ways. If the dog's response is the desired one, we reward them with snacks. Now guess what, the next time the dog is exposed to the same situation, the dog executes a similar action with even more enthusiasm in expectation of more food. That's like learning \"what to do\" from positive experiences. Similarly, dogs will tend to learn what not to do when face with negative experiences. \n\nThat's exactly how Reinforcement Learning works in a broader sense:\n- Your dog is an \"agent\" that is exposed to the **environment**. The environment could in your house, with you.\n- The situations they encounter are analogous to a **state**. An example of a state could be your dog standing and you use a specific word in a certain tone in your living room\n- Our agents react by performing an **action** to transition from one \"state\" to another \"state,\" your dog goes from standing to sitting, for example.\n- After the transition, they may receive a **reward** or **penalty** in return. You give them a treat! Or a \"No\" as a penalty.\n- The **policy** is the strategy of choosing an action given a state in expectation of better outcomes.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Reinforcement Learning lies between the spectrum of Supervised Learning and Unsupervised Learning, and there's a few important things to note:\n\n 1. Being greedy doesn't always work \n\nThere are things that are easy to do for instant gratification, and there's things that provide long term rewards\nThe goal is to not be greedy by looking for the quick immediate rewards, but instead to optimize for maximum rewards over the whole training.\n\n 2. Sequence matters in Reinforcement Learning\n\nThe reward agent does not just depend on the current state, but the entire history of states. Unlike supervised and unsupervised learning, time is important here.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### The Reinforcement Process\n\nIn a way, Reinforcement Learning is the science of making optimal decisions using experiences. \nBreaking it down, the process of Reinforcement Learning involves these simple steps:\n\n1. Observation of the environment\n2. Deciding how to act using some strategy\n3. Acting accordingly\n4. Receiving a reward or penalty\n5. Learning from the experiences and refining our strategy\n6. Iterate until an optimal strategy is found\n\nLet's now understand Reinforcement Learning by actually developing an agent to learn to play a game automatically on its own.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Example Design: Self-Driving Cab\n\nLet's design a simulation of a self-driving cab. The major goal is to demonstrate, in a simplified environment, how you can use RL techniques to develop an efficient and safe approach for tackling this problem.\n\nThe Smartcab's job is to pick up the passenger at one location and drop them off in another. Here are a few things that we'd love our Smartcab to take care of:\n\n- Drop off the passenger to the right location.\n- Save passenger's time by taking minimum time possible to drop off\n- Take care of passenger's safety and traffic rules\n\nThere are different aspects that need to be considered here while modeling an RL solution to this problem: rewards, states, and actions.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 1. Rewards\n\nSince the agent (the imaginary driver) is reward-motivated and is going to learn how to control the cab by trial experiences in the environment, we need to decide the **rewards** and/or **penalties** and their magnitude accordingly. Here a few points to consider:\n\n- The agent should receive a high positive reward for a successful dropoff because this behavior is highly desired\n- The agent should be penalized if it tries to drop off a passenger in wrong locations\n- The agent should get a slight negative reward for not making it to the destination after every time-step. \"Slight\" negative because we would prefer our agent to reach late instead of making wrong moves trying to reach to the destination as fast as possible",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 2. State Space\n\nIn Reinforcement Learning, the agent encounters a state, and then takes action according to the state it's in. \n\nThe **State Space** is the set of all possible situations our taxi could inhabit. The state should contain useful information the agent needs to make the right action. \n\nLet's say we have a training area for our Smartcab where we are teaching it to transport people in a parking lot to four different locations (R, G, Y, B): \n\n\n\nLet's assume Smartcab is the only vehicle in this parking lot. We can break up the parking lot into a 5x5 grid, which gives us 25 possible taxi locations. These 25 locations are one part of our state space. Notice the current location state of our taxi is coordinate (3, 1).\n\nYou'll also notice there are four (4) locations that we can pick up and drop off a passenger: R, G, Y, B or `[(0,0), (0,4), (4,0), (4,3)] ` in (row, col) coordinates. Our illustrated passenger is in location **Y** and they wish to go to location **R**.\n\nWhen we also account for one (1) additional passenger state of being inside the taxi, we can take all combinations of passenger locations and destination locations to come to a total number of states for our taxi environment; there's four (4) destinations and five (4 + 1) passenger locations.\n\nSo, our taxi environment has $5 \\times 5 \\times 5 \\times 4 = 500$ total possible states.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 3. Action Space\n\nThe agent encounters one of the 500 states and it takes an action. The action in our case can be to move in a direction or decide to pickup/dropoff a passenger. \n\nIn other words, we have six possible actions:\n\n1. `south`\n2. `north`\n3. `east`\n4. `west`\n5. `pickup`\n6. `dropoff`\n\nThis is the **action space**: the set of all the actions that our agent can take in a given state.\n\nYou'll notice in the illustration above, that the taxi cannot perform certain actions in certain states due to walls. In environment's code, we will simply provide a -1 penalty for every wall hit and the taxi won't move anywhere. This will just rack up penalties causing the taxi to consider going around the wall.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Implementation with Python\n\nFortunately, [OpenAI Gym](https://gym.openai.com/) has this exact environment already built for us.\n\nGym provides different game environments which we can plug into our code and test an agent. The library takes care of API for providing all the information that our agent would require, like possible actions, score, and current state. We just need to focus just on the algorithm part for our agent.\n\nWe'll be using the Gym environment called `Taxi-V3`, which all of the details explained above were pulled from. The objectives, rewards, and actions are all the same.\n\n### Gym's interface\n\nWe need to install `gym` first. Executing the following in a Jupyter notebook should work:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!pip install cmake 'gym[atari]' scipy",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Once installed, we can load the game environment and render what it looks like:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import gym\n\nenv = gym.make(\"Taxi-v3\").env\n\nenv.render()",
"+---------+\n|R: | : :G|\n| : | : : |\n| :\u001b[43m \u001b[0m: : : |\n| | : | : |\n|\u001b[35mY\u001b[0m| : |\u001b[34;1mB\u001b[0m: |\n+---------+\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"The core gym interface is `env`, which is the unified environment interface. The following are the `env` methods that would be quite helpful to us:\n\n- `env.reset`: Resets the environment and returns a random initial state.\n- `env.step(action)`: Step the environment by one timestep. Returns\n + **observation**: Observations of the environment\n + **reward**: If your action was beneficial or not\n + **done**: Indicates if we have successfully picked up and dropped off a passenger, also called one *episode*\n + **info**: Additional info such as performance and latency for debugging purposes\n- `env.render`: Renders one frame of the environment (helpful in visualizing the environment)\n\nNote: We are using the `.env` on the end of `make` to avoid training stopping at 200 iterations, which is the default for the new version of Gym ([reference](https://stackoverflow.com/a/42802225)). ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Reminder of our problem\n\nHere's our restructured problem statement (from Gym docs):\n\n> There are 4 locations (labeled by different letters), and our job is to pick up the passenger at one location and drop him off at another. We receive +20 points for a successful drop-off and lose 1 point for every time-step it takes. There is also a 10 point penalty for illegal pick-up and drop-off actions.\n\nLet's dive more into the environment.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"env.reset() # reset environment to a new, random state\nenv.render()\n\nprint(\"Action Space {}\".format(env.action_space))\nprint(\"State Space {}\".format(env.observation_space))",
"+---------+\n|\u001b[34;1mR\u001b[0m: | : :\u001b[43mG\u001b[0m|\n| : | : : |\n| : : : : |\n| | : | : |\n|\u001b[35mY\u001b[0m| : |B: |\n+---------+\n\nAction Space Discrete(6)\nState Space Discrete(500)\n"
]
],
[
[
"- The **filled square** represents the taxi, which is yellow without a passenger and green with a passenger. \n- The **pipe (\"|\")** represents a wall which the taxi cannot cross. \n- **R, G, Y, B** are the possible pickup and destination locations. The **blue letter** represents the current passenger pick-up location, and the **purple letter** is the current destination. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"As verified by the prints, we have an **Action Space** of size 6 and a **State Space** of size 500. As you'll see, our RL algorithm won't need any more information than these two things. All we need is a way to identify a state uniquely by assigning a unique number to every possible state, and RL learns to choose an action number from 0-5 where:\n\n- 0 = south\n- 1 = north\n- 2 = east\n- 3 = west\n- 4 = pickup\n- 5 = dropoff\n\nRecall that the 500 states correspond to a encoding of the taxi's location, the passenger's location, and the destination location. \n\nReinforcement Learning will learn a mapping of **states** to the optimal **action** to perform in that state by *exploration*, i.e. the agent explores the environment and takes actions based off rewards defined in the environment.\n\nThe optimal action for each state is the action that has the **highest cumulative long-term reward**.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Back to our illustration\nWe can actually take our illustration above, encode its state, and give it to the environment to render in Gym. Recall that we have the taxi at row 3, column 1, our passenger is at location 2, and our destination is location 0. Using the Taxi-v2 state encoding method, we can do the following:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"state = env.encode(3, 1, 2, 0) # (taxi row, taxi column, passenger index, destination index)\nprint(\"State:\", state)\n\nenv.s = state\nenv.render()",
"State: 328\n+---------+\n|\u001b[35mR\u001b[0m: | : :G|\n| : | : : |\n| : : : : |\n| |\u001b[43m \u001b[0m: | : |\n|\u001b[34;1mY\u001b[0m| : |B: |\n+---------+\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"We are using our illustration's coordinates to generate a number corresponding to a state between 0 and 499, which turns out to be **328** for our illustration's state.\n\nThen we can set the environment's state manually with `env.env.s` using that encoded number. You can play around with the numbers and you'll see the taxi, passenger, and destination move around.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### The Reward Table\nWhen the Taxi environment is created, there is an initial Reward table that's also created, called `P`. We can think of it like a matrix that has the number of states as rows and number of actions as columns, i.e. a $states \\ \\times \\ actions$ matrix.\n\nSince every state is in this matrix, we can see the default reward values assigned to our illustration's state:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for I in range(10,20):\n print(env.P[I],'\\n')",
"{0: [(1.0, 110, -1, False)], 1: [(1.0, 10, -1, False)], 2: [(1.0, 30, -1, False)], 3: [(1.0, 10, -1, False)], 4: [(1.0, 10, -10, False)], 5: [(1.0, 10, -10, False)]} \n\n{0: [(1.0, 111, -1, False)], 1: [(1.0, 11, -1, False)], 2: [(1.0, 31, -1, False)], 3: [(1.0, 11, -1, False)], 4: [(1.0, 11, -10, False)], 5: [(1.0, 11, -10, False)]} \n\n{0: [(1.0, 112, -1, False)], 1: [(1.0, 12, -1, False)], 2: [(1.0, 32, -1, False)], 3: [(1.0, 12, -1, False)], 4: [(1.0, 12, -10, False)], 5: [(1.0, 12, -10, False)]} \n\n{0: [(1.0, 113, -1, False)], 1: [(1.0, 13, -1, False)], 2: [(1.0, 33, -1, False)], 3: [(1.0, 13, -1, False)], 4: [(1.0, 13, -10, False)], 5: [(1.0, 13, -10, False)]} \n\n{0: [(1.0, 114, -1, False)], 1: [(1.0, 14, -1, False)], 2: [(1.0, 34, -1, False)], 3: [(1.0, 14, -1, False)], 4: [(1.0, 14, -10, False)], 5: [(1.0, 14, -10, False)]} \n\n{0: [(1.0, 115, -1, False)], 1: [(1.0, 15, -1, False)], 2: [(1.0, 35, -1, False)], 3: [(1.0, 15, -1, False)], 4: [(1.0, 15, -10, False)], 5: [(1.0, 15, -10, False)]} \n\n{0: [(1.0, 116, -1, False)], 1: [(1.0, 16, -1, False)], 2: [(1.0, 36, -1, False)], 3: [(1.0, 16, -1, False)], 4: [(1.0, 16, -10, False)], 5: [(1.0, 0, 20, True)]} \n\n{0: [(1.0, 117, -1, False)], 1: [(1.0, 17, -1, False)], 2: [(1.0, 37, -1, False)], 3: [(1.0, 17, -1, False)], 4: [(1.0, 17, -10, False)], 5: [(1.0, 1, -1, False)]} \n\n{0: [(1.0, 118, -1, False)], 1: [(1.0, 18, -1, False)], 2: [(1.0, 38, -1, False)], 3: [(1.0, 18, -1, False)], 4: [(1.0, 18, -10, False)], 5: [(1.0, 2, -1, False)]} \n\n{0: [(1.0, 119, -1, False)], 1: [(1.0, 19, -1, False)], 2: [(1.0, 39, -1, False)], 3: [(1.0, 19, -1, False)], 4: [(1.0, 19, -10, False)], 5: [(1.0, 3, -1, False)]} \n\n"
]
],
[
[
"This dictionary has the structure `{action: [(probability, nextstate, reward, done)]}`.\n\nA few things to note:\n- The 0-5 corresponds to the actions (south, north, east, west, pickup, dropoff) the taxi can perform at our current state in the illustration. \n- In this env, `probability` is always 1.0. \n- The `nextstate` is the state we would be in if we take the action at this index of the dict\n- All the movement actions have a -1 reward and the pickup/dropoff actions have -10 reward in this particular state. If we are in a state where the taxi has a passenger and is on top of the right destination, we would see a reward of 20 at the dropoff action (5)\n- `done` is used to tell us when we have successfully dropped off a passenger in the right location. Each successfull dropoff is the end of an **episode**\n\nNote that if our agent chose to explore action two (2) in this state it would be going East into a wall. The source code has made it impossible to actually move the taxi across a wall, so if the taxi chooses that action, it will just keep acruing -1 penalties, which affects the **long-term reward**.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Solving the environment without Reinforcement Learning\n\nLet's see what would happen if we try to brute-force our way to solving the problem without RL.\n\nSince we have our `P` table for default rewards in each state, we can try to have our taxi navigate just using that.\n\nWe'll create an infinite loop which runs until one passenger reaches one destination (one **episode**), or in other words, when the received reward is 20. The `env.action_space.sample()` method automatically selects one random action from set of all possible actions.\n\nLet's see what happens:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"env.s = 328 # set environment to illustration's state\n\nepochs = 0\npenalties, reward = 0, 0\n\nframes = [] # for animation\n\ndone = False\n\nwhile not done:\n action = env.action_space.sample()\n state, reward, done, info = env.step(action)\n\n if reward == -10:\n penalties += 1\n \n # Put each rendered frame into dict for animation\n frames.append({\n 'frame': env.render(mode='ansi'),\n 'state': state,\n 'action': action,\n 'reward': reward\n }\n )\n\n epochs += 1\n \n \nprint(\"Timesteps taken: {}\".format(epochs))\nprint(\"Penalties incurred: {}\".format(penalties))",
"Timesteps taken: 591\nPenalties incurred: 198\n"
],
[
"from IPython.display import clear_output\nfrom time import sleep\n\ndef print_frames(frames):\n for i, frame in enumerate(frames):\n clear_output(wait=True)\n #print(frame['frame'].getvalue())\n print(f\"Timestep: {i + 1}\")\n print(f\"State: {frame['state']}\")\n print(f\"Action: {frame['action']}\")\n print(f\"Reward: {frame['reward']}\")\n sleep(.1)\n \nprint_frames(frames)",
"Timestep: 591\nState: 0\nAction: 5\nReward: 20\n"
]
],
[
[
"Not good. Our agent takes thousands of timesteps and makes lots of wrong drop offs to deliver just one passenger to the right destination.\n\nThis is because we aren't *learning* from past experience. We can run this over and over, and it will never optimize. The agent has no memory of which action was best for each state, which is exactly what Reinforcement Learning will do for us.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Enter Reinforcement Learning\n\nWe are going to use a simple RL algorithm called *Q-learning* which will give our agent some memory.\n\n#### Intro to Q-learning \n\nEssentially, Q-learning lets the agent use the environment's rewards to learn, over time, the best action to take in a given state. \n\nIn our Taxi environment, we have the reward table, `P`, that the agent will learn from. It does thing by looking receiving a reward for taking an action in the current state, then updating a *Q-value* to remember if that action was beneficial.\n\nThe values store in the Q-table are called a *Q-values*, and they map to a `(state, action)` combination.\n\nA Q-value for a particular state-action combination is representative of the \"quality\" of an action taken from that state. Better Q-values imply better chances of getting greater rewards. \n\nFor example, if the taxi is faced with a state that includes a passenger at its current location, it is highly likely that the Q-value for `pickup` is higher when compared to other actions, like `dropoff` or `north`.\n\nQ-values are initialized to an arbitrary value, and as the agent exposes itself to the environment and receives different rewards by executing different actions, the Q-values are updated using the equation:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"$$\\Large Q({\\small state}, {\\small action}) \\leftarrow (1 - \\alpha) Q({\\small state}, {\\small action}) + \\alpha \\Big({\\small reward} + \\gamma \\max_{a} Q({\\small next \\ state}, {\\small all \\ actions})\\Big)$$\n\nWhere:\n- $\\Large \\alpha$ (alpha) is the learning rate ($0 < \\alpha \\leq 1$) - Just like in supervised learning settings, $\\alpha$ is the extent to which our Q-values are being updated in every iteration.\n- $\\Large \\gamma$ (gamma) is the discount factor ($0 \\leq \\gamma \\leq 1$) - determines how much importance we want to give to future rewards. A high value for the discount factor (close to **1**) captures the long-term effective award, whereas, a discount factor of **0** makes our agent consider only immediate reward, hence making it greedy.\n\n**What is this saying?**\nWe are assigning ($\\leftarrow$), or updating, the Q-value of the agent's current *state* and *action* by first taking a weight ($1-\\alpha$) of the old Q-value, then adding the learned value. The learned value is a combination of the reward for taking the current action in the current state, and the discounted maximum reward from the next state we will be in once we take the current action.\n\nBasically, we are learning the proper action to take in the current state by looking at the reward for the current state/action combo, and the max rewards for the next state. This will eventually cause our taxi to consider the route with the best rewards strung together.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The Q-value of a state-action pair is the sum of the instant reward and the discounted future reward (of the resulting state). \nThe way we store the Q-values for each state and action is through a **Q-table**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"##### Q-Table\nThe Q-table is a matrix where we have a row for every state (500) and a column for every action (6). It's first initialized to 0, and then values are updated after training. Note that the Q-table has the same dimensions as the reward table, but it has a completely different purpose.\n\n<img src=\"assets/q-matrix-initialized-to-learned.png\" width=500px>\n\n#### Summing up the Q-Learning Process\nBreaking it down into steps, we get\n\n- Initialize the Q-table by all zeros. \n- Start exploring actions: For each state, select any one among all possible actions for the current state (S).\n- Travel to the next state (S') as a result of that action (a).\n- For all possible actions from the state (S') select the one with the highest Q-value.\n- Update Q-table values using the equation.\n- Set the next state as the current state.\n- If goal state is reached, then end and repeat the process.\n\n##### Exploiting learned values\nAfter enough random exploration of actions, the Q-values tend to converge serving our agent as an action-value function which it can exploit to pick the most optimal action from a given state.\n\nThere's a tradeoff between exploration (choosing a random action) and exploitation (choosing actions based on already learned Q-values). We want to prevent the action from always taking the same route, and possibly overfitting, so we'll be introducing another parameter called $\\Large \\epsilon$ \"epsilon\" to cater to this during training. \n\nInstead of just selecting the best learned Q-value action, we'll sometimes favor exploring the action space further. Lower epsilon value results in episodes with more penalties (on average) which is obvious because we are exploring and making random decisions.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Implementing Q-learning in python\n#### Training the Agent\n\nFirst, we'll initialize the Q-table to a $500 \\times 6$ matrix of zeros:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nq_table = np.zeros([env.observation_space.n, env.action_space.n])\nq_table",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can now create the training algorithm that will update this Q-table as the agent explores the environment over thousands of episodes.\n\nIn the first part of `while not done`, we decide whether to pick a random action or to exploit the already computed Q-values. This is done simply by using the `epsilon` value and comparing it to the `random.uniform(0, 1)` function, which returns an arbitrary number between 0 and 1.\n\nWe execute the chosen action in the environment to obtain the `next_state` and the `reward` from performing the action. After that, we calculate the maximum Q-value for the actions corresponding to the `next_state`, and with that, we can easily update our Q-value to the `new_q_value`:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%time\n\"\"\"Training the agent\"\"\"\n\nimport random\nfrom IPython.display import clear_output\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn as sns\nfrom time import sleep\n%matplotlib inline\n\n# Hyperparameters\nalpha = 0.1\ngamma = 0.6\nepsilon = 0.1\n\n# For plotting metrics\nall_epochs = []\nall_penalties = []\n\nfor i in range(1, 1000):\n state = env.reset()\n\n epochs, penalties, reward, = 0, 0, 0\n done = False\n \n while not done:\n if random.uniform(0, 1) < epsilon:\n action = env.action_space.sample() # Explore action space Sub sample\n else:\n action = np.argmax(q_table[state]) # Values Funcation\n\n next_state, reward, done, info = env.step(action) \n \n old_value = q_table[state, action] # Q-values Funcation\n next_max = np.max(q_table[next_state])\n \n new_value = (1 - alpha) * old_value + alpha * (reward + gamma * next_max)\n q_table[state, action] = new_value\n\n if reward == -10:\n penalties += 1\n\n state = next_state\n epochs += 1\n \n if i % 100 == 0:\n clear_output(wait=True)\n print(f\"Episode: {i}\")\n\nprint(\"Training finished.\\n\")",
"Episode: 900\nTraining finished.\n\nWall time: 14.2 s\n"
]
],
[
[
"Now that the Q-table has been established over 100,000 episodes, let's see what the Q-values are at our illustration's state:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"q_table[328]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The max Q-value is \"north\" (-1.971), so it looks like Q-learning has effectively learned the best action to take in our illustration's state!",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Evaluating the agent\nLet's evaluate the performance of our agent. We don't need to explore actions any further, so now the next action is always selected using the best Q-value:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\"\"\"Evaluate agent's performance after Q-learning\"\"\"\n\ntotal_epochs, total_penalties = 0, 0\nepisodes = 100\n\nfor _ in range(episodes):\n state = env.reset()\n epochs, penalties, reward = 0, 0, 0\n \n done = False\n \n while not done:\n action = np.argmax(q_table[state]) # Values\n Funcation\n state, reward, done, info = env.step(action)\n\n if reward == -10:\n penalties += 1\n\n epochs += 1\n\n total_penalties += penalties\n total_epochs += epochs\n\nprint(f\"Results after {episodes} episodes:\")\nprint(f\"Average timesteps per episode: {total_epochs / episodes}\")\nprint(f\"Average penalties per episode: {total_penalties / episodes}\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can see from the evaluation, the agent's performance improved significantly and it incurred no penalties, which means it performed the correct pickup/dropoff actions with 100 different passengers.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Comparing our Q-learning agent to no Reinforcement Learning\n\nWith Q-learning agent commits errors initially during exploration but once it has explored enough (seen most of the states), it can act wisely maximizing the rewards making smart moves. Let's see how much better our Q-learning solution is when compared to the agent making just random moves. \n\nWe evaluate our agents according to the following metrics,\n\n- **Average number of penalties per episode:** The smaller the number, the better the performance of our agent. Ideally, we would like this metric to be zero or very close to zero.\n- **Average number of timesteps per trip:** We want a small number of timesteps per episode as well since we want our agent to take minimum steps(i.e. the shortest path) to reach the destination.\n- **Average rewards per move:** The larger the reward means the agent is doing the right thing. That's why deciding rewards is a crucial part of Reinforcement Learning. In our case, as both timesteps and penalties are negatively rewarded, a higher average reward would mean that the agent reaches the destination as fast as possible with the least penalties\"\n\n| Measure \t| Random agent's performance \t| Q-learning agent's performance \t|\n|-----------------------------------------\t|--------------------------\t|--------------------------------\t|\n| Average rewards per move \t| -3.9012092102214075 \t| 0.6962843295638126 \t|\n| Average number of penalties per episode \t| 920.45 \t| 0.0 \t|\n| Average number of timesteps per trip \t| 2848.14 \t| 12.38 \t| |\n\nThese metrics were computed over 100 episodes. And as the results show, our Q-learning agent nailed it!",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Hyperparameters and optimizations\n\nThe values of `alpha`, `gamma`, and `epsilon` were mostly based on intuition and some \"hit and trial\", but there are better ways to come up with good values.\n\nIdeally, all three should decrease over time because as the agent continues to learn, it actually builds up more resilient priors;\n\n- $\\Large \\alpha$: (the learning rate) should decrease as you continue to gain a larger and larger knowledge base.\n- $\\Large \\gamma$: as you get closer and closer to the deadline, your preference for near-term reward should increase, as you won't be around long enough to get the long-term reward, which means your gamma should decrease.\n- $\\Large \\epsilon$: as we develop our strategy, we have less need of exploration and more exploitation to get more utility from our policy, so as trials increase, epsilon should decrease.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Tuning the hyperparameters\n\nA simple way to programmatically come up with the best set of values of the hyperparameter is to create a comprehensive search function (similar to [grid search](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hyperparameter_optimization#Grid_search)) that selects the parameters that would result in best `reward/time_steps` ratio. The reason for `reward/time_steps` is that we want to choose parameters which enable us to get the maximum reward as fast as possible. We may want to track the number of penalties corresponding to the hyperparameter value combination as well because this can also be a deciding factor (we don't want our smart agent to violate rules at the cost of reaching faster). A more fancy way to get the right combination of hyperparameter values would be to use Genetic Algorithms.\n\n## Conclusion and What's Ahead\n\nAlright! We began with understanding Reinforcement Learning with the help of real-world analogies. We then dived into the basics of Reinforcement Learning and framed a Self-driving cab as a Reinforcement Learning problem. We then used OpenAI's Gym in python to provide us with a related environment, where we can develop our agent and evaluate it. Then we observed how terrible our agent was without using any algorithm to play the game, so we went ahead to implement the Q-learning algorithm from scratch. The agent's performance improved significantly after Q-learning. Finally, we discussed better approaches for deciding the hyperparameters for our algorithm.\n\nQ-learning is one of the easiest Reinforcement Learning algorithms. The problem with Q-earning however is, once the number of states in the environment are very high, it becomes difficult to implement them with Q table as the size would become very, very large. State of the art techniques uses Deep neural networks instead of the Q-table (Deep Reinforcement Learning). The neural network takes in state information and actions to the input layer and learns to output the right action over the time. Deep learning techniques (like Convolutional Neural Networks) are also used to interpret the pixels on the screen and extract information out of the game (like scores), and then letting the agent control the game.\n\nWe have discussed a lot about Reinforcement Learning and games. But Reinforcement learning is not just limited to games. It is used for managing stock portfolios and finances, for making humanoid robots, for manufacturing and inventory management, to develop general AI agents, which are agents that can perform multiple things with a single algorithm, like the same agent playing multiple Atari games. Open AI also has a platform called universe for measuring and training an AI's general intelligence across myriads of games, websites and other general applications.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4a768e16af7dec82a91407b44c0bbcba0b00cd7f
| 14,491 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Section 2/Digging Deeper into Dask Arrays.ipynb
|
akashmavle5/-Scalable-Data-Analysis-in-Python-with-Dask
|
43b85fc295ed0857e0ce9b57213ec0c85ac45233
|
[
"MIT"
] | 9 |
2019-10-30T12:35:39.000Z
|
2021-10-01T22:06:06.000Z
|
Section 2/Digging Deeper into Dask Arrays.ipynb
|
solly0702/-Scalable-Data-Analysis-in-Python-with-Dask
|
d5fc4a858a13ed0877a7383d3d770afa6dd25c5a
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2020-01-15T18:02:00.000Z
|
2020-01-15T18:02:00.000Z
|
Section 2/Digging Deeper into Dask Arrays.ipynb
|
solly0702/-Scalable-Data-Analysis-in-Python-with-Dask
|
d5fc4a858a13ed0877a7383d3d770afa6dd25c5a
|
[
"MIT"
] | 6 |
2019-06-09T20:08:16.000Z
|
2021-04-13T11:53:01.000Z
| 19.34713 | 86 | 0.411359 |
[
[
[
"## Scalar operations ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import dask.array as da",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"my_arr = da.random.randint(10, size=20, chunks=3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"my_arr.compute()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"my_hundred_arr = my_arr + 100\nmy_hundred_arr.compute()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"(my_arr * (-1)).compute()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Reductions",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dask_sum = my_arr.sum()\ndask_sum",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"my_arr.compute()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dask_sum.compute()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"my_ones_arr = da.ones((10,10), chunks=2, dtype=int)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"my_ones_arr.compute()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"my_ones_arr.mean(axis=0).compute()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"my_custom_array = da.random.randint(10, size=(4,4), chunks=(1,4))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"my_custom_array.compute()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"my_custom_array.mean(axis=0).compute()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"my_custom_array.mean(axis=1).compute()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Slicing",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"my_custom_array[1:3, 2:4]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"my_custom_array[1:3, 2:4].compute()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Broadcasting",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"my_custom_array.compute()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"my_small_arr = da.ones(4, chunks=2)\nmy_small_arr.compute()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"brd_example1 = da.add(my_custom_array, my_small_arr)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# [[7, 1, 4, 4], + [[1, 1, 1, 1]\n# [1, 5, 5, 5], [1, 1, 1, 1]\n# [9, 0, 2, 8], [1, 1, 1, 1]\n# [1, 8, 8, 0]] [1, 1, 1, 1]]\nbrd_example1.compute()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ten_arr = da.full_like(my_small_arr, 10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ten_arr.compute()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"brd_example2 = da.add(my_custom_array, ten_arr)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"brd_example2.compute()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Reshaping",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"my_custom_array.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"custom_arr_1d = my_custom_array.reshape(16)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"custom_arr_1d",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"custom_arr_1d.compute()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Stacking",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"stacked_arr = da.stack([brd_example1, brd_example2])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"stacked_arr.compute()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"another_stacked = da.stack([brd_example1, brd_example2], axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"another_stacked.compute()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Concatenate",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"concate_arr = da.concatenate([brd_example1, brd_example2])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"concate_arr.compute()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"another_concate_arr = da.concatenate([brd_example1, brd_example2],axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"another_concate_arr.compute()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a769b42f441c01760fdd3a21b619bcf3d90d9bf
| 218,392 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Informe 5/Datos/Work Temrmo.ipynb
|
maps16/LabTermo
|
d2f38955e78457cb748f52f31bdace15d7c6c4f9
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | null | null | null |
Informe 5/Datos/Work Temrmo.ipynb
|
maps16/LabTermo
|
d2f38955e78457cb748f52f31bdace15d7c6c4f9
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | null | null | null |
Informe 5/Datos/Work Temrmo.ipynb
|
maps16/LabTermo
|
d2f38955e78457cb748f52f31bdace15d7c6c4f9
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | null | null | null | 307.594366 | 38,464 | 0.922795 |
[
[
[
"#install.packages(\"caTools\", repo=\"http://cran.itam.mx\")\n#R.version",
"package 'caTools' successfully unpacked and MD5 sums checked\n\nThe downloaded binary packages are in\n\tC:\\Users\\Martin\\AppData\\Local\\Temp\\RtmpCgTKdo\\downloaded_packages\n"
],
[
"path<- \"C:/Users/Martin/Documents/Tareas UNISON/Termodinamica/Laboratorio/Informe 5/Datos\"\nsetwd(path)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"library(\"ggplot2\")\nlibrary(\"reshape2\")\nlibrary(\"dplyr\")\nlibrary(\"plotly\")",
"\nAttaching package: 'dplyr'\n\nThe following objects are masked from 'package:stats':\n\n filter, lag\n\nThe following objects are masked from 'package:base':\n\n intersect, setdiff, setequal, union\n\n\nAttaching package: 'plotly'\n\nThe following object is masked from 'package:ggplot2':\n\n last_plot\n\nThe following object is masked from 'package:stats':\n\n filter\n\nThe following object is masked from 'package:graphics':\n\n layout\n\n"
],
[
"D1 <- read.csv(\"Datos1.csv\" ,header=TRUE, sep=\",\" , stringsAsFactors=FALSE)\n#head(D1,8)\nD2 <- read.csv(\"Datos2.csv\" ,header=TRUE, sep=\",\" , stringsAsFactors=FALSE)\n#head(D1,8)\nD3 <- read.csv(\"Datos3.csv\" ,header=TRUE, sep=\",\" , stringsAsFactors=FALSE)\n#head(D1,8)\nD4 <- read.csv(\"Datos4-1.csv\" ,header=TRUE, sep=\",\" , stringsAsFactors=FALSE)\n#head(D1,8)\nD5 <- read.csv(\"Datos5-1.csv\" ,header=TRUE, sep=\",\" , stringsAsFactors=FALSE)\n#head(D1,8)\nD6 <- read.csv(\"Datos6-1.csv\" ,header=TRUE, sep=\",\" , stringsAsFactors=FALSE)\n#head(D1,8)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"names(D1)[names(D1)==\"Tiempo...s..\"] <- \"Tiempo\"\nnames(D1)[names(D1)==\"T...K..\"] <- \"T\"\nnames(D1)[names(D1)==\"V...m3..\"] <- \"V\"\nnames(D1)[names(D1)==\"P...kPa..\"] <- \"P\"\n#head(D1); tail(D1)\nnames(D2)[names(D2)==\"Tiempo...s..\"] <- \"Tiempo\"\nnames(D2)[names(D2)==\"T...K..\"] <- \"T\"\nnames(D2)[names(D2)==\"V...m3..\"] <- \"V\"\nnames(D2)[names(D2)==\"P...kPa..\"] <- \"P\"\n#head(D2); tail(D2)\nnames(D3)[names(D3)==\"Tiempo...s..\"] <- \"Tiempo\"\nnames(D3)[names(D3)==\"T...K..\"] <- \"T\"\nnames(D3)[names(D3)==\"V...m3..\"] <- \"V\"\nnames(D3)[names(D3)==\"P...kPa..\"] <- \"P\"\n#head(D3); tail(D3)\nnames(D4)[names(D4)==\"Tiempo...s..\"] <- \"Tiempo\"\nnames(D4)[names(D4)==\"T...K..\"] <- \"T\"\nnames(D4)[names(D4)==\"V...m3..\"] <- \"V\"\nnames(D4)[names(D4)==\"P...kPa..\"] <- \"P\"\n#head(D4); tail(D4)\nnames(D5)[names(D5)==\"Tiempo...s..\"] <- \"Tiempo\"\nnames(D5)[names(D5)==\"T...K..\"] <- \"T\"\nnames(D5)[names(D5)==\"V...m3..\"] <- \"V\"\nnames(D5)[names(D5)==\"P...kPa..\"] <- \"P\"\n#head(D5); tail(D5)\nnames(D6)[names(D6)==\"Tiempo...s..\"] <- \"Tiempo\"\nnames(D6)[names(D6)==\"T...K..\"] <- \"T\"\nnames(D6)[names(D6)==\"V...m3..\"] <- \"V\"\nnames(D6)[names(D6)==\"P...kPa..\"] <- \"P\"\n#head(D6); tail(D6)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"k1<-ggplot(D1, aes(x=Tiempo,y=T)) +\n#theme_bw() +\ngeom_point(col=\"blue\") + \ngeom_line(col=\"black\")+\n#stat_smooth(method = \"loess\", span=0.1,colour=\"black\")+\n#geom_hline(aes(yintercept = MT), linetype= \"dashed\", size =1.25)+\nlabs( x=\"Tiempo(s)\", y=\"Temperatura (K)\", title= \"Datos 1\")\n#ggplotly(k)\nk1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"k2<-ggplot(D2, aes(x=Tiempo,y=T)) +\n#theme_bw() +\ngeom_point(col=\"blue\") + \ngeom_line(col=\"black\")+\n#stat_smooth(method = \"loess\", span=0.1,colour=\"black\")+\n#geom_hline(aes(yintercept = MT), linetype= \"dashed\", size =1.25)+\nlabs( x=\"Tiempo(s)\", y=\"Temperatura (K)\", title= \"Datos 2\")\n#ggplotly(k)\nk2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"k3<-ggplot(D3, aes(x=Tiempo,y=T)) +\n#theme_bw() +\ngeom_point(col=\"blue\") + \ngeom_line(col=\"black\")+\n#stat_smooth(method = \"loess\", span=0.1,colour=\"black\")+\n#geom_hline(aes(yintercept = MT), linetype= \"dashed\", size =1.25)+\nlabs( x=\"Tiempo(s)\", y=\"Temperatura (K)\", title= \"Datos 3\")\n#ggplotly(k)\nk3",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"k4<-ggplot(D4, aes(x=Tiempo,y=T)) +\n#theme_bw() +\ngeom_point(col=\"blue\", size = 0.5) + \n#geom_line(col=\"black\")+\n#stat_smooth(method = \"loess\", span=0.1,colour=\"black\")+\n#geom_hline(aes(yintercept = MT), linetype= \"dashed\", size =1.25)+\nlabs( x=\"Tiempo(s)\", y=\"Temperatura (K)\", title= \"Datos 4\")\n#ggplotly(k4)\nk4",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"k5<-ggplot(D5, aes(x=Tiempo,y=T)) +\n#theme_bw() +\ngeom_point(col=\"blue\") + \ngeom_line(col=\"black\")+\n#stat_smooth(method = \"loess\", span=0.1,colour=\"black\")+\n#geom_hline(aes(yintercept = MT), linetype= \"dashed\", size =1.25)+\nlabs( x=\"Tiempo(s)\", y=\"Temperatura (K)\", title= \"Datos 5\")\n#ggplotly(k)\nk5",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"k6<-ggplot(D6, aes(x=Tiempo,y=T)) +\n#theme_bw() +\ngeom_point(col=\"blue\") + \ngeom_line(col=\"black\")+\n#stat_smooth(method = \"loess\", span=0.1,colour=\"black\")+\n#geom_hline(aes(yintercept = MT), linetype= \"dashed\", size =1.25)+\nlabs( x=\"Tiempo(s)\", y=\"Temperatura (K)\", title= \"Datos 6\")\n#ggplotly(k)\nk6",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ggplot() + theme_bw() +\ngeom_point(data=D1, aes(x=Tiempo, y=T), color='blue', size =1) + \ngeom_point(data=D2, aes(x=Tiempo, y=T), color='green', size =1) + \ngeom_point(data=D3, aes(x=Tiempo, y=T), color='red', size =1)+\ngeom_line(data=D1, aes(x=Tiempo, y=T), color=' dark blue', size =0.75) + \ngeom_line(data=D2, aes(x=Tiempo, y=T), color='dark green', size =0.75) + \ngeom_line(data=D3, aes(x=Tiempo, y=T), color='dark red', size =0.75)+\nlabs( x=\"Tiempo(s)\", y=\"Temperatura (K)\", title= \"Proceso Isotermicos\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ggplot() + theme_bw() +\ngeom_point(data=D4, aes(x=Tiempo, y=T), color='blue', size =1) + \ngeom_point(data=D5, aes(x=Tiempo, y=T), color='green', size =1) + \ngeom_point(data=D6, aes(x=Tiempo, y=T), color='red', size =1)+\ngeom_line(data=D4, aes(x=Tiempo, y=T), color=' dark blue', size =0.75) + \ngeom_line(data=D5, aes(x=Tiempo, y=T), color='dark green', size =0.75) + \ngeom_line(data=D6, aes(x=Tiempo, y=T), color='dark red', size =0.75)+\nlabs( x=\"Tiempo(s)\", y=\"Temperatura (K)\", title= \"ProcesoAdiabaticos\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"iso<-ggplot() + theme_bw() +\ngeom_point(data = D1, aes(x=V,y=P), color = 1, size = 0.75) +\ngeom_point(data = D2, aes(x=V,y=P), color = 2, size = 0.75) +\ngeom_point(data = D3, aes(x=V,y=P), color = 3, size = 0.75) +\nscale_x_log10() +\nscale_y_log10() +\nlabs( x=\"Volumen ( m3 )\", y=\"Presion ( kPa )\", title= \"Proceso Isotermico\")\n#ggplotly(iso)\niso",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"require(caTools)\nx <- trapz(D1$V, D1$P)\ny <- trapz(D2$V, D2$P)\nz <- trapz(D3$V, D3$P)\nx;y;z\n(x+y+z)/3\n",
"Loading required package: caTools\n"
],
[
"adb<-ggplot() + theme_bw() +\ngeom_point(data = D4, aes(x=V,y=P), color = 1, size = 0.75) +\ngeom_point(data = D5, aes(x=V,y=P), color = 2, size = 0.75) +\ngeom_point(data = D6, aes(x=V,y=P), color = 3, size = 0.75) +\nscale_x_log10() +\nscale_y_log10() +\nlabs( x=\"Volumen ( m3 )\", y=\"Presion ( kPa )\", title= \"Proceso Adiabatico\")\n#ggplotly(adb)\nadb",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"require(caTools)\na <- trapz(D4$V, D4$P)\nb <- trapz(D5$V, D5$P)\nc <- trapz(D6$V, D6$P)\na;b;c\n(a+b+c)/3",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a769e26bf9be4de3e628e59f62f6da47180a4fc
| 14,595 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
bs_tags.ipynb
|
hakdj/test_webscraping
|
aa661256a6ecb1bb6a07df4b279354ab3d948c57
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
bs_tags.ipynb
|
hakdj/test_webscraping
|
aa661256a6ecb1bb6a07df4b279354ab3d948c57
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
bs_tags.ipynb
|
hakdj/test_webscraping
|
aa661256a6ecb1bb6a07df4b279354ab3d948c57
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 17.584337 | 82 | 0.435971 |
[
[
[
"from bs4 import BeautifulSoup",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"html = '''\n<html>\n <head>\n </head>\n <body>\n <h1> 우리동네시장</h1>\n <div class = 'sale'>\n <p id='fruits1' class='fruits'>\n <span class = 'name'> 바나나 </span>\n <span class = 'price'> 3000원 </span>\n <span class = 'inventory'> 500개 </span>\n <span class = 'store'> 가나다상회 </span>\n <a href = 'http://bit.ly/forPlaywithData' > 홈페이지 </a>\n </p>\n </div>\n <div class = 'prepare'>\n <p id='fruits2' class='fruits'>\n <span class ='name'> 파인애플 </span>\n </p>\n </div>\n </body>\n</html>\n'''",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"soup=BeautifulSoup(html,'html.parser')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"span=soup.select('span')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"type(span),span",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"span[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"span[4]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fruits=soup.select('#fruits1')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"type(fruits), fruits",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(fruits)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"re=soup.select('.inventory')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"type(re),re",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(re)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pri=soup.select('span.price')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"type(pri), pri",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(pri)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dt1=soup.select('p#fruits1 > span.name')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"type(dt1), dt1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(dt1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dt2=soup.select('div.sale > p > .name')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dt2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(dt2)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dt3=soup.select('.name')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dt3",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(dt3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dt3[0].text",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dt3[1].text",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s=dt3[0].text",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s.strip()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dt3[0].text.strip()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for tag in dt3:\n print(tag.text.strip())",
"바나나\n파인애플\n"
],
[
"cls=dt3[0]['class']\ncls",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dt3[0]['class'][0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cls[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"type(cls)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for tag in dt3:\n print(tag.text.strip(),tag['class'][0])",
"바나나 name\n파인애플 name\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a76ba0cf4dcc2a2571d44ed8f73f262a11a75fe
| 527,841 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
archive_dog_app.ipynb
|
lalit527/dog-project
|
a17a287a9f0036f2a757ab4a2ba020ea5e1181ac
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
archive_dog_app.ipynb
|
lalit527/dog-project
|
a17a287a9f0036f2a757ab4a2ba020ea5e1181ac
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
archive_dog_app.ipynb
|
lalit527/dog-project
|
a17a287a9f0036f2a757ab4a2ba020ea5e1181ac
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 266.048891 | 205,840 | 0.889722 |
[
[
[
"## Convolutional Neural Networks\n\n## Project: Write an Algorithm for a Dog Identification App \n\n---\n\nIn this notebook, some template code has already been provided for you, and you will need to implement additional functionality to successfully complete this project. You will not need to modify the included code beyond what is requested. Sections that begin with **'(IMPLEMENTATION)'** in the header indicate that the following block of code will require additional functionality which you must provide. Instructions will be provided for each section, and the specifics of the implementation are marked in the code block with a 'TODO' statement. Please be sure to read the instructions carefully! \n\n> **Note**: Once you have completed all of the code implementations, you need to finalize your work by exporting the iPython Notebook as an HTML document. Before exporting the notebook to html, all of the code cells need to have been run so that reviewers can see the final implementation and output. You can then export the notebook by using the menu above and navigating to \\n\",\n \"**File -> Download as -> HTML (.html)**. Include the finished document along with this notebook as your submission.\n\nIn addition to implementing code, there will be questions that you must answer which relate to the project and your implementation. Each section where you will answer a question is preceded by a **'Question X'** header. Carefully read each question and provide thorough answers in the following text boxes that begin with **'Answer:'**. Your project submission will be evaluated based on your answers to each of the questions and the implementation you provide.\n\n>**Note:** Code and Markdown cells can be executed using the **Shift + Enter** keyboard shortcut. Markdown cells can be edited by double-clicking the cell to enter edit mode.\n\nThe rubric contains _optional_ \"Stand Out Suggestions\" for enhancing the project beyond the minimum requirements. If you decide to pursue the \"Stand Out Suggestions\", you should include the code in this IPython notebook.\n\n\n\n---\n### Why We're Here \n\nIn this notebook, you will make the first steps towards developing an algorithm that could be used as part of a mobile or web app. At the end of this project, your code will accept any user-supplied image as input. If a dog is detected in the image, it will provide an estimate of the dog's breed. If a human is detected, it will provide an estimate of the dog breed that is most resembling. The image below displays potential sample output of your finished project (... but we expect that each student's algorithm will behave differently!). \n\n\n\nIn this real-world setting, you will need to piece together a series of models to perform different tasks; for instance, the algorithm that detects humans in an image will be different from the CNN that infers dog breed. There are many points of possible failure, and no perfect algorithm exists. Your imperfect solution will nonetheless create a fun user experience!\n\n### The Road Ahead\n\nWe break the notebook into separate steps. Feel free to use the links below to navigate the notebook.\n\n* [Step 0](#step0): Import Datasets\n* [Step 1](#step1): Detect Humans\n* [Step 2](#step2): Detect Dogs\n* [Step 3](#step3): Create a CNN to Classify Dog Breeds (from Scratch)\n* [Step 4](#step4): Use a CNN to Classify Dog Breeds (using Transfer Learning)\n* [Step 5](#step5): Create a CNN to Classify Dog Breeds (using Transfer Learning)\n* [Step 6](#step6): Write your Algorithm\n* [Step 7](#step7): Test Your Algorithm\n\n---\n<a id='step0'></a>\n## Step 0: Import Datasets\n\n### Import Dog Dataset\n\nIn the code cell below, we import a dataset of dog images. We populate a few variables through the use of the `load_files` function from the scikit-learn library:\n- `train_files`, `valid_files`, `test_files` - numpy arrays containing file paths to images\n- `train_targets`, `valid_targets`, `test_targets` - numpy arrays containing onehot-encoded classification labels \n- `dog_names` - list of string-valued dog breed names for translating labels",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.datasets import load_files \nfrom keras.utils import np_utils\nimport numpy as np\nfrom glob import glob\n\n# define function to load train, test, and validation datasets\ndef load_dataset(path):\n data = load_files(path)\n dog_files = np.array(data['filenames'])\n dog_targets = np_utils.to_categorical(np.array(data['target']), 133)\n return dog_files, dog_targets\n\n# load train, test, and validation datasets\ntrain_files, train_targets = load_dataset('/data/dog_images/train')\nvalid_files, valid_targets = load_dataset('/data/dog_images/valid')\ntest_files, test_targets = load_dataset('/data/dog_images/test')\n\n# load list of dog names\ndog_names = [item[20:-1] for item in sorted(glob(\"/data/dog_images/train/*/\"))]\n\n# print statistics about the dataset\nprint('There are %d total dog categories.' % len(dog_names))\nprint('There are %s total dog images.\\n' % len(np.hstack([train_files, valid_files, test_files])))\nprint('There are %d training dog images.' % len(train_files))\nprint('There are %d validation dog images.' % len(valid_files))\nprint('There are %d test dog images.'% len(test_files))",
"There are 133 total dog categories.\nThere are 8351 total dog images.\n\nThere are 6680 training dog images.\nThere are 835 validation dog images.\nThere are 836 test dog images.\n"
],
[
"!ls /data/lfw/Monica_Bellucci/Monica_Bellucci_0002.jpg",
"Monica_Bellucci_0001.jpg Monica_Bellucci_0003.jpg\r\nMonica_Bellucci_0002.jpg Monica_Bellucci_0004.jpg\r\n"
],
[
"train_files.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Import Human Dataset\n\nIn the code cell below, we import a dataset of human images, where the file paths are stored in the numpy array `human_files`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import random\nrandom.seed(8675309)\n\n# load filenames in shuffled human dataset\nhuman_files = np.array(glob(\"/data/lfw/*/*\"))\nrandom.shuffle(human_files)\n\n# print statistics about the dataset\nprint('There are %d total human images.' % len(human_files))",
"There are 13233 total human images.\n"
]
],
[
[
"---\n<a id='step1'></a>\n## Step 1: Detect Humans\n\nWe use OpenCV's implementation of [Haar feature-based cascade classifiers](http://docs.opencv.org/trunk/d7/d8b/tutorial_py_face_detection.html) to detect human faces in images. OpenCV provides many pre-trained face detectors, stored as XML files on [github](https://github.com/opencv/opencv/tree/master/data/haarcascades). We have downloaded one of these detectors and stored it in the `haarcascades` directory.\n\nIn the next code cell, we demonstrate how to use this detector to find human faces in a sample image.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import cv2 \nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt \n%matplotlib inline \n\n# extract pre-trained face detector\nface_cascade = cv2.CascadeClassifier('haarcascades/haarcascade_frontalface_alt.xml')\n\n# load color (BGR) image\nimg = cv2.imread(human_files[3])\n# convert BGR image to grayscale\ngray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)\n\n# find faces in image\nfaces = face_cascade.detectMultiScale(gray)\n\n# print number of faces detected in the image\nprint('Number of faces detected:', len(faces))\n\n# get bounding box for each detected face\nfor (x,y,w,h) in faces:\n # add bounding box to color image\n cv2.rectangle(img,(x,y),(x+w,y+h),(255,0,0),2)\n \n# convert BGR image to RGB for plotting\ncv_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)\n\n# display the image, along with bounding box\nplt.imshow(cv_rgb)\nplt.show()",
"Number of faces detected: 1\n"
]
],
[
[
"Before using any of the face detectors, it is standard procedure to convert the images to grayscale. The `detectMultiScale` function executes the classifier stored in `face_cascade` and takes the grayscale image as a parameter. \n\nIn the above code, `faces` is a numpy array of detected faces, where each row corresponds to a detected face. Each detected face is a 1D array with four entries that specifies the bounding box of the detected face. The first two entries in the array (extracted in the above code as `x` and `y`) specify the horizontal and vertical positions of the top left corner of the bounding box. The last two entries in the array (extracted here as `w` and `h`) specify the width and height of the box.\n\n### Write a Human Face Detector\n\nWe can use this procedure to write a function that returns `True` if a human face is detected in an image and `False` otherwise. This function, aptly named `face_detector`, takes a string-valued file path to an image as input and appears in the code block below.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# returns \"True\" if face is detected in image stored at img_path\ndef face_detector(img_path):\n img = cv2.imread(img_path)\n gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)\n faces = face_cascade.detectMultiScale(gray)\n return len(faces) > 0",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### (IMPLEMENTATION) Assess the Human Face Detector\n\n__Question 1:__ Use the code cell below to test the performance of the `face_detector` function. \n- What percentage of the first 100 images in `human_files` have a detected human face? \n- What percentage of the first 100 images in `dog_files` have a detected human face? \n\nIdeally, we would like 100% of human images with a detected face and 0% of dog images with a detected face. You will see that our algorithm falls short of this goal, but still gives acceptable performance. We extract the file paths for the first 100 images from each of the datasets and store them in the numpy arrays `human_files_short` and `dog_files_short`.\n\n__Answer:__ ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"human_files_short = human_files[:100]\ndog_files_short = train_files[:100]\n# Do NOT modify the code above this line.\n\n## TODO: Test the performance of the face_detector algorithm \nhuman_correct_label = 0\ndog_incorrect_label = 0\nfor human, dog in zip(human_files_short, dog_files_short):\n human_correct_label += int(face_detector(human))\n dog_incorrect_label += int(face_detector(dog))\nhuman_correct_label, dog_incorrect_label\n## on the images in human_files_short and dog_files_short.\nprint(f'Total correctly labeled human out of 100 is {human_correct_label}')\nprint(f'Total incorrectly labeled dog as human out of 100 is {dog_incorrect_label}')",
"Total correctly labeled human out of 100 is 100\nTotal incorrectly labeled dog as human out of 100 is 11\n"
]
],
[
[
"__Question 2:__ This algorithmic choice necessitates that we communicate to the user that we accept human images only when they provide a clear view of a face (otherwise, we risk having unneccessarily frustrated users!). In your opinion, is this a reasonable expectation to pose on the user? If not, can you think of a way to detect humans in images that does not necessitate an image with a clearly presented face?\n\n__Answer:__\n\nWe suggest the face detector from OpenCV as a potential way to detect human images in your algorithm, but you are free to explore other approaches, especially approaches that make use of deep learning :). Please use the code cell below to design and test your own face detection algorithm. If you decide to pursue this _optional_ task, report performance on each of the datasets.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## (Optional) TODO: Report the performance of another \n## face detection algorithm on the LFW dataset\n### Feel free to use as many code cells as needed.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%ls data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"---\n<a id='step2'></a>\n## Step 2: Detect Dogs\n\nIn this section, we use a pre-trained [ResNet-50](http://ethereon.github.io/netscope/#/gist/db945b393d40bfa26006) model to detect dogs in images. Our first line of code downloads the ResNet-50 model, along with weights that have been trained on [ImageNet](http://www.image-net.org/), a very large, very popular dataset used for image classification and other vision tasks. ImageNet contains over 10 million URLs, each linking to an image containing an object from one of [1000 categories](https://gist.github.com/yrevar/942d3a0ac09ec9e5eb3a). Given an image, this pre-trained ResNet-50 model returns a prediction (derived from the available categories in ImageNet) for the object that is contained in the image.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from keras.applications.resnet50 import ResNet50\n\n# define ResNet50 model\nResNet50_model = ResNet50(weights='imagenet')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Pre-process the Data\n\nWhen using TensorFlow as backend, Keras CNNs require a 4D array (which we'll also refer to as a 4D tensor) as input, with shape\n\n$$\n(\\text{nb_samples}, \\text{rows}, \\text{columns}, \\text{channels}),\n$$\n\nwhere `nb_samples` corresponds to the total number of images (or samples), and `rows`, `columns`, and `channels` correspond to the number of rows, columns, and channels for each image, respectively. \n\nThe `path_to_tensor` function below takes a string-valued file path to a color image as input and returns a 4D tensor suitable for supplying to a Keras CNN. The function first loads the image and resizes it to a square image that is $224 \\times 224$ pixels. Next, the image is converted to an array, which is then resized to a 4D tensor. In this case, since we are working with color images, each image has three channels. Likewise, since we are processing a single image (or sample), the returned tensor will always have shape\n\n$$\n(1, 224, 224, 3).\n$$\n\nThe `paths_to_tensor` function takes a numpy array of string-valued image paths as input and returns a 4D tensor with shape \n\n$$\n(\\text{nb_samples}, 224, 224, 3).\n$$\n\nHere, `nb_samples` is the number of samples, or number of images, in the supplied array of image paths. It is best to think of `nb_samples` as the number of 3D tensors (where each 3D tensor corresponds to a different image) in your dataset!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from keras.preprocessing import image \nfrom tqdm import tqdm\n\ndef path_to_tensor(img_path):\n # loads RGB image as PIL.Image.Image type\n img = image.load_img(img_path, target_size=(224, 224))\n # convert PIL.Image.Image type to 3D tensor with shape (224, 224, 3)\n x = image.img_to_array(img)\n # convert 3D tensor to 4D tensor with shape (1, 224, 224, 3) and return 4D tensor\n return np.expand_dims(x, axis=0)\n\ndef paths_to_tensor(img_paths):\n list_of_tensors = [path_to_tensor(img_path) for img_path in tqdm(img_paths)]\n return np.vstack(list_of_tensors)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Making Predictions with ResNet-50\n\nGetting the 4D tensor ready for ResNet-50, and for any other pre-trained model in Keras, requires some additional processing. First, the RGB image is converted to BGR by reordering the channels. All pre-trained models have the additional normalization step that the mean pixel (expressed in RGB as $[103.939, 116.779, 123.68]$ and calculated from all pixels in all images in ImageNet) must be subtracted from every pixel in each image. This is implemented in the imported function `preprocess_input`. If you're curious, you can check the code for `preprocess_input` [here](https://github.com/fchollet/keras/blob/master/keras/applications/imagenet_utils.py).\n\nNow that we have a way to format our image for supplying to ResNet-50, we are now ready to use the model to extract the predictions. This is accomplished with the `predict` method, which returns an array whose $i$-th entry is the model's predicted probability that the image belongs to the $i$-th ImageNet category. This is implemented in the `ResNet50_predict_labels` function below.\n\nBy taking the argmax of the predicted probability vector, we obtain an integer corresponding to the model's predicted object class, which we can identify with an object category through the use of this [dictionary](https://gist.github.com/yrevar/942d3a0ac09ec9e5eb3a). ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from keras.applications.resnet50 import preprocess_input, decode_predictions\n\ndef ResNet50_predict_labels(img_path):\n # returns prediction vector for image located at img_path\n img = preprocess_input(path_to_tensor(img_path))\n return np.argmax(ResNet50_model.predict(img))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Write a Dog Detector\n\nWhile looking at the [dictionary](https://gist.github.com/yrevar/942d3a0ac09ec9e5eb3a), you will notice that the categories corresponding to dogs appear in an uninterrupted sequence and correspond to dictionary keys 151-268, inclusive, to include all categories from `'Chihuahua'` to `'Mexican hairless'`. Thus, in order to check to see if an image is predicted to contain a dog by the pre-trained ResNet-50 model, we need only check if the `ResNet50_predict_labels` function above returns a value between 151 and 268 (inclusive).\n\nWe use these ideas to complete the `dog_detector` function below, which returns `True` if a dog is detected in an image (and `False` if not).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### returns \"True\" if a dog is detected in the image stored at img_path\ndef dog_detector(img_path):\n prediction = ResNet50_predict_labels(img_path)\n return ((prediction <= 268) & (prediction >= 151)) ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### (IMPLEMENTATION) Assess the Dog Detector\n\n__Question 3:__ Use the code cell below to test the performance of your `dog_detector` function. \n- What percentage of the images in `human_files_short` have a detected dog? \n- What percentage of the images in `dog_files_short` have a detected dog?\n\n__Answer:__ ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### TODO: Test the performance of the dog_detector function\n### on the images in human_files_short and dog_files_short.\nhuman_correct_label = 0\ndog_incorrect_label = 0\nfor human, dog in zip(human_files_short, dog_files_short):\n human_correct_label += int(dog_detector(human))\n dog_incorrect_label += int(dog_detector(dog))\nhuman_correct_label, dog_incorrect_label",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"---\n<a id='step3'></a>\n## Step 3: Create a CNN to Classify Dog Breeds (from Scratch)\n\nNow that we have functions for detecting humans and dogs in images, we need a way to predict breed from images. In this step, you will create a CNN that classifies dog breeds. You must create your CNN _from scratch_ (so, you can't use transfer learning _yet_!), and you must attain a test accuracy of at least 1%. In Step 5 of this notebook, you will have the opportunity to use transfer learning to create a CNN that attains greatly improved accuracy.\n\nBe careful with adding too many trainable layers! More parameters means longer training, which means you are more likely to need a GPU to accelerate the training process. Thankfully, Keras provides a handy estimate of the time that each epoch is likely to take; you can extrapolate this estimate to figure out how long it will take for your algorithm to train. \n\nWe mention that the task of assigning breed to dogs from images is considered exceptionally challenging. To see why, consider that *even a human* would have great difficulty in distinguishing between a Brittany and a Welsh Springer Spaniel. \n\nBrittany | Welsh Springer Spaniel\n- | - \n<img src=\"images/Brittany_02625.jpg\" width=\"100\"> | <img src=\"images/Welsh_springer_spaniel_08203.jpg\" width=\"200\">\n\nIt is not difficult to find other dog breed pairs with minimal inter-class variation (for instance, Curly-Coated Retrievers and American Water Spaniels). \n\nCurly-Coated Retriever | American Water Spaniel\n- | -\n<img src=\"images/Curly-coated_retriever_03896.jpg\" width=\"200\"> | <img src=\"images/American_water_spaniel_00648.jpg\" width=\"200\">\n\n\nLikewise, recall that labradors come in yellow, chocolate, and black. Your vision-based algorithm will have to conquer this high intra-class variation to determine how to classify all of these different shades as the same breed. \n\nYellow Labrador | Chocolate Labrador | Black Labrador\n- | -\n<img src=\"images/Labrador_retriever_06457.jpg\" width=\"150\"> | <img src=\"images/Labrador_retriever_06455.jpg\" width=\"240\"> | <img src=\"images/Labrador_retriever_06449.jpg\" width=\"220\">\n\nWe also mention that random chance presents an exceptionally low bar: setting aside the fact that the classes are slightly imabalanced, a random guess will provide a correct answer roughly 1 in 133 times, which corresponds to an accuracy of less than 1%. \n\nRemember that the practice is far ahead of the theory in deep learning. Experiment with many different architectures, and trust your intuition. And, of course, have fun! \n\n### Pre-process the Data\n\nWe rescale the images by dividing every pixel in every image by 255.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from PIL import ImageFile \nImageFile.LOAD_TRUNCATED_IMAGES = True \n\n# pre-process the data for Keras\ntrain_tensors = paths_to_tensor(train_files).astype('float32')/255\nvalid_tensors = paths_to_tensor(valid_files).astype('float32')/255\ntest_tensors = paths_to_tensor(test_files).astype('float32')/255",
"100%|██████████| 6680/6680 [01:27<00:00, 49.11it/s] \n100%|██████████| 835/835 [00:13<00:00, 63.28it/s]\n100%|██████████| 836/836 [00:11<00:00, 72.82it/s]\n"
],
[
"train_tensors.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### (IMPLEMENTATION) Model Architecture\n\nCreate a CNN to classify dog breed. At the end of your code cell block, summarize the layers of your model by executing the line:\n \n model.summary()\n\nWe have imported some Python modules to get you started, but feel free to import as many modules as you need. If you end up getting stuck, here's a hint that specifies a model that trains relatively fast on CPU and attains >1% test accuracy in 5 epochs:\n\n\n \n__Question 4:__ Outline the steps you took to get to your final CNN architecture and your reasoning at each step. If you chose to use the hinted architecture above, describe why you think that CNN architecture should work well for the image classification task.\n\n__Answer:__ ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from keras.layers import Conv2D, MaxPooling2D, GlobalAveragePooling2D\nfrom keras.layers import Dropout, Flatten, Dense\nfrom keras.models import Sequential\n\nmodel = Sequential()\n\n### TODO: Define your architecture.\nmodel.add(Conv2D(filters=16, kernel_size=(2, 2), strides=(1, 1), padding='same',\n activation='relu', input_shape=(224, 224, 3)))\nmodel.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))\n\nmodel.add(Conv2D(filters=32, kernel_size=(2, 2), strides=(1, 1), activation='relu'))\nmodel.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))\n\nmodel.add(Conv2D(filters=64, kernel_size=(2, 2), strides=(1, 1), activation='relu'))\nmodel.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))\n\nmodel.add(Dropout(0.5))\nmodel.add(Flatten())\nmodel.add(Dense(512, activation='relu'))\nmodel.add(Dropout(0.5))\nmodel.add(Dense(232, activation='relu'))\nmodel.add(Dropout(0.5))\nmodel.add(Dense(133, activation='softmax'))\n\nmodel.summary()",
"_________________________________________________________________\nLayer (type) Output Shape Param # \n=================================================================\nconv2d_4 (Conv2D) (None, 224, 224, 16) 208 \n_________________________________________________________________\nmax_pooling2d_6 (MaxPooling2 (None, 112, 112, 16) 0 \n_________________________________________________________________\nconv2d_5 (Conv2D) (None, 111, 111, 32) 2080 \n_________________________________________________________________\nmax_pooling2d_7 (MaxPooling2 (None, 55, 55, 32) 0 \n_________________________________________________________________\nconv2d_6 (Conv2D) (None, 54, 54, 64) 8256 \n_________________________________________________________________\nmax_pooling2d_8 (MaxPooling2 (None, 27, 27, 64) 0 \n_________________________________________________________________\ndropout_5 (Dropout) (None, 27, 27, 64) 0 \n_________________________________________________________________\nflatten_4 (Flatten) (None, 46656) 0 \n_________________________________________________________________\ndense_7 (Dense) (None, 512) 23888384 \n_________________________________________________________________\ndropout_6 (Dropout) (None, 512) 0 \n_________________________________________________________________\ndense_8 (Dense) (None, 232) 119016 \n_________________________________________________________________\ndropout_7 (Dropout) (None, 232) 0 \n_________________________________________________________________\ndense_9 (Dense) (None, 133) 30989 \n=================================================================\nTotal params: 24,048,933\nTrainable params: 24,048,933\nNon-trainable params: 0\n_________________________________________________________________\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Compile the Model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop', loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### (IMPLEMENTATION) Train the Model\n\nTrain your model in the code cell below. Use model checkpointing to save the model that attains the best validation loss.\n\nYou are welcome to [augment the training data](https://blog.keras.io/building-powerful-image-classification-models-using-very-little-data.html), but this is not a requirement. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from keras.callbacks import ModelCheckpoint \n\n### TODO: specify the number of epochs that you would like to use to train the model.\n\nepochs = 10\n\n### Do NOT modify the code below this line.\n\ncheckpointer = ModelCheckpoint(filepath='saved_models/weights.best.from_scratch.hdf5', \n verbose=1, save_best_only=True)\n\nmodel.fit(train_tensors, train_targets, \n validation_data=(valid_tensors, valid_targets),\n epochs=epochs, batch_size=20, callbacks=[checkpointer], verbose=1)",
"Train on 6680 samples, validate on 835 samples\nEpoch 1/10\n6660/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 4.8820 - acc: 0.0125Epoch 00001: val_loss improved from inf to 4.70474, saving model to saved_models/weights.best.from_scratch.hdf5\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 34s 5ms/step - loss: 4.8814 - acc: 0.0124 - val_loss: 4.7047 - val_acc: 0.0311\nEpoch 2/10\n6660/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 4.6402 - acc: 0.0284Epoch 00002: val_loss improved from 4.70474 to 4.46172, saving model to saved_models/weights.best.from_scratch.hdf5\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 30s 5ms/step - loss: 4.6403 - acc: 0.0284 - val_loss: 4.4617 - val_acc: 0.0443\nEpoch 3/10\n6660/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 4.4352 - acc: 0.0386Epoch 00003: val_loss improved from 4.46172 to 4.34023, saving model to saved_models/weights.best.from_scratch.hdf5\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 30s 5ms/step - loss: 4.4350 - acc: 0.0386 - val_loss: 4.3402 - val_acc: 0.0599\nEpoch 4/10\n6660/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 4.3023 - acc: 0.0520Epoch 00004: val_loss improved from 4.34023 to 4.22692, saving model to saved_models/weights.best.from_scratch.hdf5\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 30s 5ms/step - loss: 4.3010 - acc: 0.0521 - val_loss: 4.2269 - val_acc: 0.0635\nEpoch 5/10\n6660/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 4.1449 - acc: 0.0647Epoch 00005: val_loss improved from 4.22692 to 4.13647, saving model to saved_models/weights.best.from_scratch.hdf5\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 30s 5ms/step - loss: 4.1456 - acc: 0.0647 - val_loss: 4.1365 - val_acc: 0.0695\nEpoch 6/10\n6660/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 3.9826 - acc: 0.0803Epoch 00006: val_loss improved from 4.13647 to 4.07064, saving model to saved_models/weights.best.from_scratch.hdf5\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 30s 5ms/step - loss: 3.9825 - acc: 0.0805 - val_loss: 4.0706 - val_acc: 0.0826\nEpoch 7/10\n6660/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 3.7948 - acc: 0.1047Epoch 00007: val_loss improved from 4.07064 to 4.00788, saving model to saved_models/weights.best.from_scratch.hdf5\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 30s 5ms/step - loss: 3.7957 - acc: 0.1045 - val_loss: 4.0079 - val_acc: 0.0862\nEpoch 8/10\n6660/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 3.5915 - acc: 0.1312Epoch 00008: val_loss did not improve\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 30s 4ms/step - loss: 3.5926 - acc: 0.1311 - val_loss: 4.0428 - val_acc: 0.0982\nEpoch 9/10\n6660/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 3.3908 - acc: 0.1637Epoch 00009: val_loss did not improve\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 30s 4ms/step - loss: 3.3897 - acc: 0.1638 - val_loss: 4.0623 - val_acc: 0.0958\nEpoch 10/10\n6660/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 3.1863 - acc: 0.2002Epoch 00010: val_loss did not improve\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 30s 4ms/step - loss: 3.1868 - acc: 0.2000 - val_loss: 4.0193 - val_acc: 0.1114\n"
],
[
"# from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator\n\n# batch_size = 16\n\n# train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(\n# shear_range=0.2,\n# zoom_range=0.2,\n# horizontal_flip=True)\n\n# validation_datagen = ImageDataGenerator()\n\n# test_datagen = ImageDataGenerator()\n\n# # this is a generator that will read pictures found in\n# # subfolers of 'data/train', and indefinitely generate\n# # batches of augmented image data\n# train_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory(\n# '/data/dog_images/train',\n# target_size=(224, 224),\n# batch_size=batch_size,\n# class_mode='categorical')\n\n# validation_generator = validation_datagen.flow_from_directory(\n# '/data/dog_images/valid/',\n# target_size=(224, 224),\n# batch_size=batch_size,\n# class_mode='categorical')\n\n# test_generator = test_datagen.flow_from_directory(\n# '/data/dog_images/test/',\n# target_size=(224, 224),\n# batch_size=batch_size,\n# class_mode='categorical')\n\n# ### TODO: specify the number of epochs that you would like to use to train the model.\n\n# epochs = 10\n\n# ### Do NOT modify the code below this line.\n\n# checkpointer = ModelCheckpoint(filepath='saved_models/weights.best.from_scratch_aug.hdf5', \n# verbose=1, save_best_only=True)\n\n# model.fit_generator(\n# train_generator,\n# steps_per_epoch=2000 // batch_size,\n# epochs=epochs,\n# validation_data=validation_generator,\n# validation_steps=800 // batch_size,\n# callbacks=[checkpointer], verbose=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Load the Model with the Best Validation Loss",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model.load_weights('saved_models/weights.best.from_scratch.hdf5')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Test the Model\n\nTry out your model on the test dataset of dog images. Ensure that your test accuracy is greater than 1%.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# get index of predicted dog breed for each image in test set\ndog_breed_predictions = [np.argmax(model.predict(np.expand_dims(tensor, axis=0))) for tensor in test_tensors]\n\n# report test accuracy\ntest_accuracy = 100*np.sum(np.array(dog_breed_predictions)==np.argmax(test_targets, axis=1))/len(dog_breed_predictions)\nprint('Test accuracy: %.4f%%' % test_accuracy)",
"Test accuracy: 8.7321%\n"
]
],
[
[
"---\n<a id='step4'></a>\n## Step 4: Use a CNN to Classify Dog Breeds\n\nTo reduce training time without sacrificing accuracy, we show you how to train a CNN using transfer learning. In the following step, you will get a chance to use transfer learning to train your own CNN.\n\n### Obtain Bottleneck Features",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"bottleneck_features = np.load('/data/bottleneck_features/DogVGG16Data.npz')\ntrain_VGG16 = bottleneck_features['train']\nvalid_VGG16 = bottleneck_features['valid']\ntest_VGG16 = bottleneck_features['test']",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Model Architecture\n\nThe model uses the the pre-trained VGG-16 model as a fixed feature extractor, where the last convolutional output of VGG-16 is fed as input to our model. We only add a global average pooling layer and a fully connected layer, where the latter contains one node for each dog category and is equipped with a softmax.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"VGG16_model = Sequential()\nVGG16_model.add(GlobalAveragePooling2D(input_shape=train_VGG16.shape[1:]))\nVGG16_model.add(Dense(133, activation='softmax'))\n\nVGG16_model.summary()",
"_________________________________________________________________\nLayer (type) Output Shape Param # \n=================================================================\nglobal_average_pooling2d_3 ( (None, 512) 0 \n_________________________________________________________________\ndense_10 (Dense) (None, 133) 68229 \n=================================================================\nTotal params: 68,229\nTrainable params: 68,229\nNon-trainable params: 0\n_________________________________________________________________\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Compile the Model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"VGG16_model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='rmsprop', metrics=['accuracy'])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Train the Model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"checkpointer = ModelCheckpoint(filepath='saved_models/weights.best.VGG16.hdf5', \n verbose=1, save_best_only=True)\n\nVGG16_model.fit(train_VGG16, train_targets, \n validation_data=(valid_VGG16, valid_targets),\n epochs=20, batch_size=20, callbacks=[checkpointer], verbose=1)",
"Train on 6680 samples, validate on 835 samples\nEpoch 1/20\n6660/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 12.7903 - acc: 0.1137Epoch 00001: val_loss improved from inf to 11.51199, saving model to saved_models/weights.best.VGG16.hdf5\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 3s 379us/step - loss: 12.7857 - acc: 0.1138 - val_loss: 11.5120 - val_acc: 0.1856\nEpoch 2/20\n6520/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 10.9745 - acc: 0.2376Epoch 00002: val_loss improved from 11.51199 to 10.72079, saving model to saved_models/weights.best.VGG16.hdf5\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 270us/step - loss: 10.9453 - acc: 0.2386 - val_loss: 10.7208 - val_acc: 0.2647\nEpoch 3/20\n6480/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 10.2602 - acc: 0.3029Epoch 00003: val_loss improved from 10.72079 to 10.35028, saving model to saved_models/weights.best.VGG16.hdf5\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 271us/step - loss: 10.2384 - acc: 0.3043 - val_loss: 10.3503 - val_acc: 0.2838\nEpoch 4/20\n6640/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 9.9084 - acc: 0.3395Epoch 00004: val_loss improved from 10.35028 to 10.16675, saving model to saved_models/weights.best.VGG16.hdf5\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 272us/step - loss: 9.9106 - acc: 0.3392 - val_loss: 10.1667 - val_acc: 0.3018\nEpoch 5/20\n6660/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 9.7679 - acc: 0.3632Epoch 00005: val_loss improved from 10.16675 to 10.02383, saving model to saved_models/weights.best.VGG16.hdf5\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 271us/step - loss: 9.7798 - acc: 0.3624 - val_loss: 10.0238 - val_acc: 0.3090\nEpoch 6/20\n6540/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 9.6144 - acc: 0.3766Epoch 00006: val_loss improved from 10.02383 to 9.97352, saving model to saved_models/weights.best.VGG16.hdf5\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 268us/step - loss: 9.6245 - acc: 0.3757 - val_loss: 9.9735 - val_acc: 0.3162\nEpoch 7/20\n6540/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 9.4813 - acc: 0.3919Epoch 00007: val_loss improved from 9.97352 to 9.90103, saving model to saved_models/weights.best.VGG16.hdf5\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 276us/step - loss: 9.5111 - acc: 0.3901 - val_loss: 9.9010 - val_acc: 0.3269\nEpoch 8/20\n6560/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 9.4656 - acc: 0.3962Epoch 00008: val_loss improved from 9.90103 to 9.81394, saving model to saved_models/weights.best.VGG16.hdf5\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 269us/step - loss: 9.4331 - acc: 0.3981 - val_loss: 9.8139 - val_acc: 0.3401\nEpoch 9/20\n6540/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 9.2276 - acc: 0.4086Epoch 00009: val_loss improved from 9.81394 to 9.60822, saving model to saved_models/weights.best.VGG16.hdf5\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 270us/step - loss: 9.2183 - acc: 0.4094 - val_loss: 9.6082 - val_acc: 0.3509\nEpoch 10/20\n6480/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 9.0585 - acc: 0.4181Epoch 00010: val_loss improved from 9.60822 to 9.39389, saving model to saved_models/weights.best.VGG16.hdf5\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 270us/step - loss: 9.0457 - acc: 0.4178 - val_loss: 9.3939 - val_acc: 0.3425\nEpoch 11/20\n6500/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 8.8150 - acc: 0.4323Epoch 00011: val_loss improved from 9.39389 to 9.34619, saving model to saved_models/weights.best.VGG16.hdf5\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 269us/step - loss: 8.8198 - acc: 0.4322 - val_loss: 9.3462 - val_acc: 0.3569\nEpoch 12/20\n6520/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 8.6776 - acc: 0.4449Epoch 00012: val_loss improved from 9.34619 to 9.16199, saving model to saved_models/weights.best.VGG16.hdf5\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 268us/step - loss: 8.6814 - acc: 0.4449 - val_loss: 9.1620 - val_acc: 0.3509\nEpoch 13/20\n6660/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 8.5195 - acc: 0.4568Epoch 00013: val_loss improved from 9.16199 to 9.01265, saving model to saved_models/weights.best.VGG16.hdf5\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 270us/step - loss: 8.5085 - acc: 0.4575 - val_loss: 9.0126 - val_acc: 0.3760\nEpoch 14/20\n6500/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 8.4067 - acc: 0.4643Epoch 00014: val_loss improved from 9.01265 to 8.97603, saving model to saved_models/weights.best.VGG16.hdf5\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 271us/step - loss: 8.4389 - acc: 0.4624 - val_loss: 8.9760 - val_acc: 0.3784\nEpoch 15/20\n6660/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 8.3739 - acc: 0.4712Epoch 00015: val_loss did not improve\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 269us/step - loss: 8.3722 - acc: 0.4713 - val_loss: 9.0046 - val_acc: 0.3820\nEpoch 16/20\n6520/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 8.3383 - acc: 0.4742Epoch 00016: val_loss improved from 8.97603 to 8.95344, saving model to saved_models/weights.best.VGG16.hdf5\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 271us/step - loss: 8.3516 - acc: 0.4734 - val_loss: 8.9534 - val_acc: 0.3844\nEpoch 17/20\n6600/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 8.2428 - acc: 0.4773Epoch 00017: val_loss improved from 8.95344 to 8.74847, saving model to saved_models/weights.best.VGG16.hdf5\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 274us/step - loss: 8.2303 - acc: 0.4778 - val_loss: 8.7485 - val_acc: 0.3916\nEpoch 18/20\n6460/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 8.0881 - acc: 0.4915Epoch 00018: val_loss improved from 8.74847 to 8.74220, saving model to saved_models/weights.best.VGG16.hdf5\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 277us/step - loss: 8.0974 - acc: 0.4909 - val_loss: 8.7422 - val_acc: 0.3916\nEpoch 19/20\n6600/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 8.0585 - acc: 0.4923Epoch 00019: val_loss improved from 8.74220 to 8.73121, saving model to saved_models/weights.best.VGG16.hdf5\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 272us/step - loss: 8.0486 - acc: 0.4927 - val_loss: 8.7312 - val_acc: 0.4048\nEpoch 20/20\n6460/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 7.9193 - acc: 0.4997Epoch 00020: val_loss improved from 8.73121 to 8.50872, saving model to saved_models/weights.best.VGG16.hdf5\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 271us/step - loss: 7.9138 - acc: 0.4999 - val_loss: 8.5087 - val_acc: 0.4132\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Load the Model with the Best Validation Loss",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"VGG16_model.load_weights('saved_models/weights.best.VGG16.hdf5')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Test the Model\n\nNow, we can use the CNN to test how well it identifies breed within our test dataset of dog images. We print the test accuracy below.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# get index of predicted dog breed for each image in test set\nVGG16_predictions = [np.argmax(VGG16_model.predict(np.expand_dims(feature, axis=0))) for feature in test_VGG16]\n\n# report test accuracy\ntest_accuracy = 100*np.sum(np.array(VGG16_predictions)==np.argmax(test_targets, axis=1))/len(VGG16_predictions)\nprint('Test accuracy: %.4f%%' % test_accuracy)",
"Test accuracy: 42.9426%\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Predict Dog Breed with the Model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from extract_bottleneck_features import *\n\ndef VGG16_predict_breed(img_path):\n # extract bottleneck features\n bottleneck_feature = extract_VGG16(path_to_tensor(img_path))\n # obtain predicted vector\n predicted_vector = VGG16_model.predict(bottleneck_feature)\n # return dog breed that is predicted by the model\n return dog_names[np.argmax(predicted_vector)]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"---\n<a id='step5'></a>\n## Step 5: Create a CNN to Classify Dog Breeds (using Transfer Learning)\n\nYou will now use transfer learning to create a CNN that can identify dog breed from images. Your CNN must attain at least 60% accuracy on the test set.\n\nIn Step 4, we used transfer learning to create a CNN using VGG-16 bottleneck features. In this section, you must use the bottleneck features from a different pre-trained model. To make things easier for you, we have pre-computed the features for all of the networks that are currently available in Keras. These are already in the workspace, at /data/bottleneck_features. If you wish to download them on a different machine, they can be found at:\n- [VGG-19](https://s3-us-west-1.amazonaws.com/udacity-aind/dog-project/DogVGG19Data.npz) bottleneck features\n- [ResNet-50](https://s3-us-west-1.amazonaws.com/udacity-aind/dog-project/DogResnet50Data.npz) bottleneck features\n- [Inception](https://s3-us-west-1.amazonaws.com/udacity-aind/dog-project/DogInceptionV3Data.npz) bottleneck features\n- [Xception](https://s3-us-west-1.amazonaws.com/udacity-aind/dog-project/DogXceptionData.npz) bottleneck features\n\nThe files are encoded as such:\n\n Dog{network}Data.npz\n \nwhere `{network}`, in the above filename, can be one of `VGG19`, `Resnet50`, `InceptionV3`, or `Xception`. \n\nThe above architectures are downloaded and stored for you in the `/data/bottleneck_features/` folder.\n\nThis means the following will be in the `/data/bottleneck_features/` folder:\n\n`DogVGG19Data.npz`\n`DogResnet50Data.npz`\n`DogInceptionV3Data.npz`\n`DogXceptionData.npz`\n\n\n\n### (IMPLEMENTATION) Obtain Bottleneck Features\n\nIn the code block below, extract the bottleneck features corresponding to the train, test, and validation sets by running the following:\n\n bottleneck_features = np.load('/data/bottleneck_features/Dog{network}Data.npz')\n train_{network} = bottleneck_features['train']\n valid_{network} = bottleneck_features['valid']\n test_{network} = bottleneck_features['test']",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### TODO: Obtain bottleneck features from another pre-trained CNN.\nbottleneck_features = np.load('/data/bottleneck_features/DogResnet50Data.npz')\ntrain_res50 = bottleneck_features['train']\nvalid_res50 = bottleneck_features['valid']\ntest_res50 = bottleneck_features['test']",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### (IMPLEMENTATION) Model Architecture\n\nCreate a CNN to classify dog breed. At the end of your code cell block, summarize the layers of your model by executing the line:\n \n <your model's name>.summary()\n \n__Question 5:__ Outline the steps you took to get to your final CNN architecture and your reasoning at each step. Describe why you think the architecture is suitable for the current problem.\n\n__Answer:__ \n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### TODO: Define your architecture.\nres50_model = Sequential()\nres50_model.add(GlobalAveragePooling2D(input_shape=train_res50.shape[1:]))\nres50_model.add(Dense(512, activation='relu'))\nres50_model.add(Dropout(0.5))\nres50_model.add(Dense(133, activation='softmax'))\n\nres50_model.summary()",
"_________________________________________________________________\nLayer (type) Output Shape Param # \n=================================================================\nglobal_average_pooling2d_4 ( (None, 2048) 0 \n_________________________________________________________________\ndense_11 (Dense) (None, 512) 1049088 \n_________________________________________________________________\ndropout_8 (Dropout) (None, 512) 0 \n_________________________________________________________________\ndense_12 (Dense) (None, 133) 68229 \n=================================================================\nTotal params: 1,117,317\nTrainable params: 1,117,317\nNon-trainable params: 0\n_________________________________________________________________\n"
]
],
[
[
"### (IMPLEMENTATION) Compile the Model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### TODO: Compile the model.\nres50_model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='rmsprop', metrics=['accuracy'])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### (IMPLEMENTATION) Train the Model\n\nTrain your model in the code cell below. Use model checkpointing to save the model that attains the best validation loss. \n\nYou are welcome to [augment the training data](https://blog.keras.io/building-powerful-image-classification-models-using-very-little-data.html), but this is not a requirement. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### TODO: Train the model.\n### TODO: specify the number of epochs that you would like to use to train the model.\n\nepochs = 100\n\n### Do NOT modify the code below this line.\n\ncheckpointer = ModelCheckpoint(filepath='saved_models/weights.best.res50.hdf5', \n verbose=1, save_best_only=True)\n\nres50_model.fit(train_res50, train_targets, \n validation_data=(valid_res50, valid_targets),\n epochs=epochs, batch_size=20, callbacks=[checkpointer], verbose=1)",
"Train on 6680 samples, validate on 835 samples\nEpoch 1/100\n6620/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1814 - acc: 0.9707Epoch 00001: val_loss improved from inf to 1.60747, saving model to saved_models/weights.best.res50.hdf5\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 343us/step - loss: 0.1798 - acc: 0.9710 - val_loss: 1.6075 - val_acc: 0.8395\nEpoch 2/100\n6600/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1700 - acc: 0.9697Epoch 00002: val_loss did not improve\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 349us/step - loss: 0.1696 - acc: 0.9696 - val_loss: 1.6496 - val_acc: 0.8335\nEpoch 3/100\n6580/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1637 - acc: 0.9696Epoch 00003: val_loss did not improve\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 348us/step - loss: 0.1624 - acc: 0.9696 - val_loss: 1.6981 - val_acc: 0.8287\nEpoch 4/100\n6540/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1502 - acc: 0.9732Epoch 00004: val_loss improved from 1.60747 to 1.51754, saving model to saved_models/weights.best.res50.hdf5\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 354us/step - loss: 0.1487 - acc: 0.9734 - val_loss: 1.5175 - val_acc: 0.8431\nEpoch 5/100\n6580/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1668 - acc: 0.9723Epoch 00005: val_loss did not improve\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 349us/step - loss: 0.1682 - acc: 0.9719 - val_loss: 1.5714 - val_acc: 0.8371\nEpoch 6/100\n6600/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1768 - acc: 0.9723Epoch 00006: val_loss did not improve\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 336us/step - loss: 0.1764 - acc: 0.9725 - val_loss: 1.6625 - val_acc: 0.8395\nEpoch 7/100\n6660/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1674 - acc: 0.9724Epoch 00007: val_loss improved from 1.51754 to 1.51150, saving model to saved_models/weights.best.res50.hdf5\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 341us/step - loss: 0.1669 - acc: 0.9725 - val_loss: 1.5115 - val_acc: 0.8419\nEpoch 8/100\n6540/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1592 - acc: 0.9702Epoch 00008: val_loss did not improve\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 336us/step - loss: 0.1623 - acc: 0.9699 - val_loss: 1.5601 - val_acc: 0.8431\nEpoch 9/100\n6640/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1434 - acc: 0.9733Epoch 00009: val_loss did not improve\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 341us/step - loss: 0.1426 - acc: 0.9735 - val_loss: 1.6559 - val_acc: 0.8287\nEpoch 10/100\n6580/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1690 - acc: 0.9720Epoch 00010: val_loss did not improve\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 345us/step - loss: 0.1678 - acc: 0.9720 - val_loss: 1.6863 - val_acc: 0.8371\nEpoch 11/100\n6580/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1837 - acc: 0.9701Epoch 00011: val_loss did not improve\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 342us/step - loss: 0.1839 - acc: 0.9699 - val_loss: 1.6700 - val_acc: 0.8311\nEpoch 12/100\n6660/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1371 - acc: 0.9751Epoch 00012: val_loss did not improve\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 342us/step - loss: 0.1373 - acc: 0.9750 - val_loss: 1.7853 - val_acc: 0.8216\nEpoch 13/100\n6520/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1602 - acc: 0.9730Epoch 00013: val_loss did not improve\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 337us/step - loss: 0.1648 - acc: 0.9725 - val_loss: 1.5298 - val_acc: 0.8299\nEpoch 14/100\n6600/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1577 - acc: 0.9744Epoch 00014: val_loss did not improve\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 342us/step - loss: 0.1559 - acc: 0.9747 - val_loss: 1.6987 - val_acc: 0.8371\nEpoch 15/100\n6500/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1439 - acc: 0.9754Epoch 00015: val_loss did not improve\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 339us/step - loss: 0.1402 - acc: 0.9760 - val_loss: 1.6427 - val_acc: 0.8299\nEpoch 16/100\n6640/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1410 - acc: 0.9758Epoch 00016: val_loss did not improve\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 342us/step - loss: 0.1403 - acc: 0.9757 - val_loss: 1.7021 - val_acc: 0.8311\nEpoch 17/100\n6600/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1380 - acc: 0.9748Epoch 00017: val_loss did not improve\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 342us/step - loss: 0.1380 - acc: 0.9750 - val_loss: 1.5215 - val_acc: 0.8515\nEpoch 18/100\n6540/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1750 - acc: 0.9735Epoch 00018: val_loss did not improve\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 340us/step - loss: 0.1761 - acc: 0.9732 - val_loss: 1.6210 - val_acc: 0.8431\nEpoch 19/100\n6620/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1907 - acc: 0.9693Epoch 00019: val_loss did not improve\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 342us/step - loss: 0.1910 - acc: 0.9692 - val_loss: 1.8077 - val_acc: 0.8240\nEpoch 20/100\n6640/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1391 - acc: 0.9742Epoch 00020: val_loss did not improve\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 341us/step - loss: 0.1383 - acc: 0.9744 - val_loss: 1.7288 - val_acc: 0.8419\nEpoch 21/100\n6640/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1495 - acc: 0.9739Epoch 00021: val_loss did not improve\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 340us/step - loss: 0.1500 - acc: 0.9738 - val_loss: 1.5973 - val_acc: 0.8383\nEpoch 22/100\n6540/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1419 - acc: 0.9769Epoch 00022: val_loss did not improve\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 341us/step - loss: 0.1423 - acc: 0.9766 - val_loss: 1.6384 - val_acc: 0.8407\nEpoch 23/100\n6540/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1592 - acc: 0.9720Epoch 00023: val_loss did not improve\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 339us/step - loss: 0.1605 - acc: 0.9720 - val_loss: 1.7714 - val_acc: 0.8407\nEpoch 24/100\n6600/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1885 - acc: 0.9697Epoch 00024: val_loss did not improve\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 342us/step - loss: 0.1926 - acc: 0.9693 - val_loss: 1.6809 - val_acc: 0.8407\nEpoch 25/100\n6580/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1692 - acc: 0.9729Epoch 00025: val_loss did not improve\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 336us/step - loss: 0.1685 - acc: 0.9732 - val_loss: 1.5992 - val_acc: 0.8335\nEpoch 26/100\n6520/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1668 - acc: 0.9730Epoch 00026: val_loss did not improve\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 333us/step - loss: 0.1635 - acc: 0.9734 - val_loss: 1.6659 - val_acc: 0.8323\nEpoch 27/100\n6520/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1603 - acc: 0.9733Epoch 00027: val_loss did not improve\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 339us/step - loss: 0.1583 - acc: 0.9734 - val_loss: 1.7411 - val_acc: 0.8216\nEpoch 28/100\n6640/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1489 - acc: 0.9730Epoch 00028: val_loss did not improve\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 335us/step - loss: 0.1488 - acc: 0.9729 - val_loss: 1.5866 - val_acc: 0.8455\nEpoch 29/100\n6500/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1579 - acc: 0.9752Epoch 00029: val_loss did not improve\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 341us/step - loss: 0.1585 - acc: 0.9749 - val_loss: 1.5851 - val_acc: 0.8371\nEpoch 30/100\n6520/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1533 - acc: 0.9727Epoch 00030: val_loss did not improve\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 331us/step - loss: 0.1578 - acc: 0.9720 - val_loss: 1.6160 - val_acc: 0.8263\nEpoch 31/100\n6520/6680 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1547 - acc: 0.9732Epoch 00031: val_loss did not improve\n6680/6680 [==============================] - 2s 332us/step - loss: 0.1611 - acc: 0.9723 - val_loss: 1.6212 - val_acc: 0.8347\n"
]
],
[
[
"### (IMPLEMENTATION) Load the Model with the Best Validation Loss",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### TODO: Load the model weights with the best validation loss.\nres50_model.load_weights('saved_models/weights.best.res50.hdf5')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### (IMPLEMENTATION) Test the Model\n\nTry out your model on the test dataset of dog images. Ensure that your test accuracy is greater than 60%.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### TODO: Calculate classification accuracy on the test dataset.\nresnet50_predictions = [np.argmax(res50_model.predict(np.expand_dims(feature, axis=0))) for feature in test_res50]\n\ntest_accuracy = 100 * np.sum(np.array(resnet50_predictions) == np.argmax(test_targets, axis=1))/len(resnet50_predictions)\nprint('Test accuracy: %.4f' % test_accuracy)",
"Test accuracy: 83.1340\n"
]
],
[
[
"### (IMPLEMENTATION) Predict Dog Breed with the Model\n\nWrite a function that takes an image path as input and returns the dog breed (`Affenpinscher`, `Afghan_hound`, etc) that is predicted by your model. \n\nSimilar to the analogous function in Step 5, your function should have three steps:\n1. Extract the bottleneck features corresponding to the chosen CNN model.\n2. Supply the bottleneck features as input to the model to return the predicted vector. Note that the argmax of this prediction vector gives the index of the predicted dog breed.\n3. Use the `dog_names` array defined in Step 0 of this notebook to return the corresponding breed.\n\nThe functions to extract the bottleneck features can be found in `extract_bottleneck_features.py`, and they have been imported in an earlier code cell. To obtain the bottleneck features corresponding to your chosen CNN architecture, you need to use the function\n\n extract_{network}\n \nwhere `{network}`, in the above filename, should be one of `VGG19`, `Resnet50`, `InceptionV3`, or `Xception`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### TODO: Write a function that takes a path to an image as input\n### and returns the dog breed that is predicted by the model.\ndef Resnet50_predict_breed(img_path):\n bottleneck_feature = extract_Resnet50(path_to_tensor(img_path))\n predicted_vector = res50_model.predict(bottleneck_feature)\n return dog_names[np.argmax(predicted_vector)]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"---\n<a id='step6'></a>\n## Step 6: Write your Algorithm\n\nWrite an algorithm that accepts a file path to an image and first determines whether the image contains a human, dog, or neither. Then,\n- if a __dog__ is detected in the image, return the predicted breed.\n- if a __human__ is detected in the image, return the resembling dog breed.\n- if __neither__ is detected in the image, provide output that indicates an error.\n\nYou are welcome to write your own functions for detecting humans and dogs in images, but feel free to use the `face_detector` and `dog_detector` functions developed above. You are __required__ to use your CNN from Step 5 to predict dog breed. \n\nSome sample output for our algorithm is provided below, but feel free to design your own user experience!\n\n\n\n\n### (IMPLEMENTATION) Write your Algorithm",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### TODO: Write your algorithm.\n### Feel free to use as many code cells as needed.\ndef prediction_maker(img_path):\n img = cv2.imread(img_path)\n cv_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)\n plt.imshow(cv_rgb)\n if dog_detector(img_path):\n print(\"Dog\")\n print(\"Gussed Breed is {}\".format(Resnet50_predict_breed(img_path)))\n elif face_detector(img_path):\n print(\"Human\")\n print(\"Expected Breed is {}\".format(Resnet50_predict_breed(img_path)))\n else:\n print(\"Not a Human or a Dog\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"---\n<a id='step7'></a>\n## Step 7: Test Your Algorithm\n\nIn this section, you will take your new algorithm for a spin! What kind of dog does the algorithm think that __you__ look like? If you have a dog, does it predict your dog's breed accurately? If you have a cat, does it mistakenly think that your cat is a dog?\n\n### (IMPLEMENTATION) Test Your Algorithm on Sample Images!\n\nTest your algorithm at least six images on your computer. Feel free to use any images you like. Use at least two human and two dog images. \n\n__Question 6:__ Is the output better than you expected :) ? Or worse :( ? Provide at least three possible points of improvement for your algorithm.\n\n__Answer:__ ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## TODO: Execute your algorithm from Step 6 on\n## at least 6 images on your computer.\n## Feel free to use as many code cells as needed.\ntest_samples = glob(\"images/\");\ntest_samples",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!ls images",
"American_water_spaniel_00648.jpg Labrador_retriever_06457.jpg\r\nBrittany_02625.jpg\t\t sample_cnn.png\r\nCurly-coated_retriever_03896.jpg sample_dog_output.png\r\nLabrador_retriever_06449.jpg\t sample_human_output.png\r\nLabrador_retriever_06455.jpg\t Welsh_springer_spaniel_08203.jpg\r\n"
],
[
"prediction_maker('images/American_water_spaniel_00648.jpg')",
"Dog\nDownloading data from https://github.com/fchollet/deep-learning-models/releases/download/v0.2/resnet50_weights_tf_dim_ordering_tf_kernels_notop.h5\n94658560/94653016 [==============================] - 7s 0us/step\nGussed Breed is in/035.Boykin_spaniel\n"
],
[
"prediction_maker('images/sample_human_output.png')",
"Human\nExpected Breed is in/064.English_toy_spaniel\n"
],
[
"prediction_maker('/data/lfw/Monica_Bellucci/Monica_Bellucci_0002.jpg')",
"Human\nExpected Breed is in/064.English_toy_spaniel\n"
],
[
"/data/lfw/Monica_Bellucci/Monica_Bellucci_0002.jpg",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Please download your notebook to submit\n\nIn order to submit, please do the following:\n1. Download an HTML version of the notebook to your computer using 'File: Download as...'\n2. Click on the orange Jupyter circle on the top left of the workspace.\n3. Navigate into the dog-project folder to ensure that you are using the provided dog_images, lfw, and bottleneck_features folders; this means that those folders will *not* appear in the dog-project folder. If they do appear because you downloaded them, delete them.\n4. While in the dog-project folder, upload the HTML version of this notebook you just downloaded. The upload button is on the top right.\n5. Navigate back to the home folder by clicking on the two dots next to the folder icon, and then open up a terminal under the 'new' tab on the top right\n6. Zip the dog-project folder with the following command in the terminal:\n `zip -r dog-project.zip dog-project`\n7. Download the zip file by clicking on the square next to it and selecting 'download'. This will be the zip file you turn in on the next node after this workspace!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a76ba61455a97ebacfd401ea0b32de9f2ea1e37
| 12,580 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebook/operator_usage.ipynb
|
puyopop/python-snippets
|
9d70aa3b2a867dd22f5a5e6178a5c0c5081add73
|
[
"MIT"
] | 174 |
2018-05-30T21:14:50.000Z
|
2022-03-25T07:59:37.000Z
|
notebook/operator_usage.ipynb
|
puyopop/python-snippets
|
9d70aa3b2a867dd22f5a5e6178a5c0c5081add73
|
[
"MIT"
] | 5 |
2019-08-10T03:22:02.000Z
|
2021-07-12T20:31:17.000Z
|
notebook/operator_usage.ipynb
|
puyopop/python-snippets
|
9d70aa3b2a867dd22f5a5e6178a5c0c5081add73
|
[
"MIT"
] | 53 |
2018-04-27T05:26:35.000Z
|
2022-03-25T07:59:37.000Z
| 15.60794 | 63 | 0.422655 |
[
[
[
"import operator",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(2 + 3)",
"5\n"
],
[
"print(operator.add(2, 3))",
"5\n"
],
[
"print(operator.sub(2, 3)) # 2 - 3",
"-1\n"
],
[
"print(operator.mul(2, 3)) # 2 * 3",
"6\n"
],
[
"print(operator.truediv(2, 3)) # 2 / 3",
"0.6666666666666666\n"
],
[
"print(operator.floordiv(2, 3)) # 2 // 3",
"0\n"
],
[
"print(operator.lt(2, 3)) # 2 < 3",
"True\n"
],
[
"print(operator.le(2, 3)) # 2 <= 3",
"True\n"
],
[
"print(operator.gt(2, 3)) # 2 > 3",
"False\n"
],
[
"print(operator.ge(2, 3)) # 2 >= 3",
"False\n"
],
[
"print(operator.eq(2, 3)) # 2 == 3",
"False\n"
],
[
"print(operator.ne(2, 3)) # 2 != 3",
"True\n"
],
[
"print(bin(0b1100 & 0b1010))",
"0b1000\n"
],
[
"print(bin(operator.and_(0b1100, 0b1010)))",
"0b1000\n"
],
[
"print(bin(0b1100 | 0b1010))",
"0b1110\n"
],
[
"print(bin(operator.or_(0b1100, 0b1010)))",
"0b1110\n"
],
[
"print(bin(0b1100 ^ 0b1010))",
"0b110\n"
],
[
"print(bin(operator.xor(0b1100, 0b1010)))",
"0b110\n"
],
[
"print(bin(0b1100 and 0b1010))",
"0b1010\n"
],
[
"print(bin(0b1100 or 0b1010))",
"0b1100\n"
],
[
"l = [0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(l[3])",
"30\n"
],
[
"f = operator.itemgetter(3)\nprint(f(l))",
"30\n"
],
[
"print(operator.itemgetter(3)(l))",
"30\n"
],
[
"print(l[-1])",
"50\n"
],
[
"print(operator.itemgetter(-1)(l))",
"50\n"
],
[
"print(l[1:4])",
"[10, 20, 30]\n"
],
[
"print(operator.itemgetter(slice(1, 4))(l))",
"[10, 20, 30]\n"
],
[
"print(l[1::2])",
"[10, 30, 50]\n"
],
[
"print(operator.itemgetter(slice(1, None, 2))(l))",
"[10, 30, 50]\n"
],
[
"print(operator.itemgetter(0, slice(1, 4), -1)(l))",
"(0, [10, 20, 30], 50)\n"
],
[
"print(type(operator.itemgetter(0, slice(1, 4), -1)(l)))",
"<class 'tuple'>\n"
],
[
"d = {'k1': 0, 'k2': 10, 'k3': 20}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(d['k2'])",
"10\n"
],
[
"print(operator.itemgetter('k2')(d))",
"10\n"
],
[
"print(operator.itemgetter('k2', 'k1')(d))",
"(10, 0)\n"
],
[
"import datetime",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dt = datetime.date(2001, 10, 20)\nprint(dt)",
"2001-10-20\n"
],
[
"print(type(dt))",
"<class 'datetime.date'>\n"
],
[
"print(dt.year)",
"2001\n"
],
[
"f = operator.attrgetter('year')\nprint(f(dt))",
"2001\n"
],
[
"print(operator.attrgetter('year', 'month', 'day')(dt))",
"(2001, 10, 20)\n"
],
[
"s = 'xxxAyyyAzzz'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(s.upper())",
"XXXAYYYAZZZ\n"
],
[
"f = operator.methodcaller('upper')\nprint(f(s))",
"XXXAYYYAZZZ\n"
],
[
"print(s.split('A', maxsplit=1))",
"['xxx', 'yyyAzzz']\n"
],
[
"print(operator.methodcaller('split', 'A', maxsplit=1)(s))",
"['xxx', 'yyyAzzz']\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a76bdc28e8ad05bec8890f403a7e4f26d540e07
| 243,482 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
l4e_notebooks/.ipynb_checkpoints/4(optional)_model_evaluation-checkpoint.ipynb
|
dast1/aws-iot-sitewise-with-amazon-lookout-for-equipment
|
e77823eabf811e06b8a7f5cb31316b4449071651
|
[
"MIT-0"
] | null | null | null |
l4e_notebooks/.ipynb_checkpoints/4(optional)_model_evaluation-checkpoint.ipynb
|
dast1/aws-iot-sitewise-with-amazon-lookout-for-equipment
|
e77823eabf811e06b8a7f5cb31316b4449071651
|
[
"MIT-0"
] | null | null | null |
l4e_notebooks/.ipynb_checkpoints/4(optional)_model_evaluation-checkpoint.ipynb
|
dast1/aws-iot-sitewise-with-amazon-lookout-for-equipment
|
e77823eabf811e06b8a7f5cb31316b4449071651
|
[
"MIT-0"
] | null | null | null | 339.584379 | 127,452 | 0.923629 |
[
[
[
"empty"
]
]
] |
[
"empty"
] |
[
[
"empty"
]
] |
4a76cc08eae228d376060d1bc636506ed2ed0683
| 5,734 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
_numpy_pandas/pd_to_datetime.ipynb
|
aixpact/data-science
|
f04a54595fbc2d797918d450b979fd4c2eabac15
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2020-07-22T23:12:39.000Z
|
2020-07-25T02:30:48.000Z
|
_numpy_pandas/pd_to_datetime.ipynb
|
aixpact/data-science
|
f04a54595fbc2d797918d450b979fd4c2eabac15
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
_numpy_pandas/pd_to_datetime.ipynb
|
aixpact/data-science
|
f04a54595fbc2d797918d450b979fd4c2eabac15
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 17.697531 | 122 | 0.479421 |
[
[
[
"# Time",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Date Functionality in Pandas\n\nhttps://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/timeseries.html",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Timestamp",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pd.Timestamp('9/1/2016 10:05AM')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Period",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pd.Period('1/2016')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.Period('3/5/2016')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### DatetimeIndex",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"t1 = pd.Series(list('abc'), [pd.Timestamp('2016-09-01'), pd.Timestamp('2016-09-02'), pd.Timestamp('2016-09-03')])\nt1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"type(t1.index)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### PeriodIndex",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"t2 = pd.Series(list('def'), [pd.Period('2016-09'), pd.Period('2016-10'), pd.Period('2016-11')])\nt2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"type(t2.index)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Converting to Datetime",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"d1 = ['2 June 2013', 'Aug 29, 2014', '2015-06-26', '7/12/16']\nts3 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(10, 100, (4,2)), index=d1, columns=list('ab'))\nts3",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ts3.index = pd.to_datetime(ts3.index)\nts3",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.to_datetime('4.7.12', dayfirst=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Timedeltas",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pd.Timestamp('9/3/2016') - pd.Timestamp('9/1/2016')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.Timestamp('9/2/2016 8:10AM') + pd.Timedelta('12D 3H')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Working with Dates in a Dataframe",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dates = np.arange('2017-01-01', '2017-01-09', dtype='datetime64[D]')\ndates = pd.to_datetime(dates).strftime('%Y-%m-%d')\ndates",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"type(pd.to_datetime(dates))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dates = pd.date_range('10-01-2016', periods=9, freq='2W-SUN')\ndates",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = pd.DataFrame({'Count 1': 100 + np.random.randint(-5, 10, 9).cumsum(),\n 'Count 2': 120 + np.random.randint(-5, 10, 9)}, index=dates)\ndf",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.index.weekday_name",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.diff()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.resample('M').mean()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df['2017']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df['2016-12']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df['2016-12':]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.asfreq('W', method='ffill')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Plot",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n%matplotlib inline\n\ndf.plot()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a771165a58e71352a8e00a17a8456526fe27a9e
| 295,086 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
AAAI/Interpretability/complexity/5D_elliptical_blob_data/zeroth_layer/zeroth_layer_50_200.ipynb
|
lnpandey/DL_explore_synth_data
|
0a5d8b417091897f4c7f358377d5198a155f3f24
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2019-08-24T07:20:35.000Z
|
2020-03-27T08:16:59.000Z
|
AAAI/Interpretability/complexity/5D_elliptical_blob_data/zeroth_layer/zeroth_layer_50_200.ipynb
|
lnpandey/DL_explore_synth_data
|
0a5d8b417091897f4c7f358377d5198a155f3f24
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
AAAI/Interpretability/complexity/5D_elliptical_blob_data/zeroth_layer/zeroth_layer_50_200.ipynb
|
lnpandey/DL_explore_synth_data
|
0a5d8b417091897f4c7f358377d5198a155f3f24
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2019-06-21T09:34:32.000Z
|
2019-09-19T10:43:07.000Z
| 189.888031 | 25,770 | 0.862945 |
[
[
[
"from google.colab import drive\ndrive.mount('/content/drive')",
"Drive already mounted at /content/drive; to attempt to forcibly remount, call drive.mount(\"/content/drive\", force_remount=True).\n"
],
[
"path = '/content/drive/MyDrive/Research/AAAI/complexity/50_200/'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\n\nimport torch\nimport torchvision\nfrom torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader\nfrom torchvision import transforms, utils\nimport torch.nn as nn\nimport torch.nn.functional as F\nimport torch.optim as optim\n\nfrom matplotlib import pyplot as plt\n%matplotlib inline\n\ntorch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True\ntorch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Generate dataset",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mu1 = np.array([3,3,3,3,0])\nsigma1 = np.array([[1,1,1,1,1],[1,16,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1]])\n\nmu2 = np.array([4,4,4,4,0])\nsigma2 = np.array([[16,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1]])\n\nmu3 = np.array([10,5,5,10,0])\nsigma3 = np.array([[1,1,1,1,1],[1,16,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1]])\n\nmu4 = np.array([-10,-10,-10,-10,0])\nsigma4 = np.array([[1,1,1,1,1],[1,16,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1]])\n\nmu5 = np.array([-21,4,4,-21,0])\nsigma5 = np.array([[16,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1]])\n\nmu6 = np.array([-10,18,18,-10,0])\nsigma6 = np.array([[1,1,1,1,1],[1,16,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1]])\n\nmu7 = np.array([4,20,4,20,0])\nsigma7 = np.array([[16,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1]])\n\nmu8 = np.array([4,-20,-20,4,0])\nsigma8 = np.array([[16,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1]])\n\nmu9 = np.array([20,20,20,20,0])\nsigma9 = np.array([[1,1,1,1,1],[1,16,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1]])\n\nmu10 = np.array([20,-10,-10,20,0])\nsigma10 = np.array([[1,1,1,1,1],[1,16,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1]])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.random.seed(12)\nsample1 = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean=mu1,cov= sigma1,size=500)\nsample2 = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean=mu2,cov= sigma2,size=500)\nsample3 = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean=mu3,cov= sigma3,size=500)\nsample4 = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean=mu4,cov= sigma4,size=500)\nsample5 = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean=mu5,cov= sigma5,size=500)\nsample6 = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean=mu6,cov= sigma6,size=500)\nsample7 = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean=mu7,cov= sigma7,size=500)\nsample8 = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean=mu8,cov= sigma8,size=500)\nsample9 = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean=mu9,cov= sigma9,size=500)\nsample10 = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean=mu10,cov= sigma10,size=500)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X = np.concatenate((sample1,sample2,sample3,sample4,sample5,sample6,sample7,sample8,sample9,sample10),axis=0)\nY = np.concatenate((np.zeros((500,1)),np.ones((500,1)),2*np.ones((500,1)),3*np.ones((500,1)),4*np.ones((500,1)),\n 5*np.ones((500,1)),6*np.ones((500,1)),7*np.ones((500,1)),8*np.ones((500,1)),9*np.ones((500,1))),axis=0).astype(int)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(X[0], Y[0])",
"[ 2.20218134 1.32290141 2.20218134 2.20218134 -0.79781866] [0]\n"
],
[
"print(X[500], Y[500])",
"[12.65418869 5.7937588 5.7937588 5.7937588 1.7937588 ] [1]\n"
],
[
"class SyntheticDataset(Dataset):\n \"\"\"MosaicDataset dataset.\"\"\"\n def __init__(self, x, y):\n \"\"\"\n Args:\n x: list of instance\n y: list of instance label\n \"\"\"\n self.x = x\n self.y = y\n #self.fore_idx = fore_idx\n \n def __len__(self):\n return len(self.y)\n\n def __getitem__(self, idx):\n return self.x[idx] , self.y[idx] #, self.fore_idx[idx]\n\ntrainset = SyntheticDataset(X,Y)\n\nclasses = ('zero','one','two','three','four','five','six','seven','eight','nine')\n\nforeground_classes = {'zero','one','two'}\nfg_used = '012'\nfg1, fg2, fg3 = 0,1,2\n\nall_classes = {'zero','one','two','three','four','five','six','seven','eight','nine'}\nbackground_classes = all_classes - foreground_classes\nprint(\"background classes \",background_classes)\n\ntrainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(trainset, batch_size=100, shuffle=False)\n\ndataiter = iter(trainloader)\nbackground_data=[]\nbackground_label=[]\nforeground_data=[]\nforeground_label=[]\nbatch_size=100\n\nfor i in range(50):\n images, labels = dataiter.next()\n for j in range(batch_size):\n if(classes[labels[j]] in background_classes):\n img = images[j].tolist()\n background_data.append(img)\n background_label.append(labels[j])\n else:\n img = images[j].tolist()\n foreground_data.append(img)\n foreground_label.append(labels[j])\n \nforeground_data = torch.tensor(foreground_data)\nforeground_label = torch.tensor(foreground_label)\nbackground_data = torch.tensor(background_data)\nbackground_label = torch.tensor(background_label)",
"background classes {'six', 'three', 'five', 'seven', 'eight', 'nine', 'four'}\n"
],
[
"print(foreground_data[0], foreground_label[0] )",
"tensor([ 2.2022, 1.3229, 2.2022, 2.2022, -0.7978]) tensor(0)\n"
],
[
"def create_mosaic_img(bg_idx,fg_idx,fg): \n \"\"\"\n bg_idx : list of indexes of background_data[] to be used as background images in mosaic\n fg_idx : index of image to be used as foreground image from foreground data\n fg : at what position/index foreground image has to be stored out of 0-8\n \"\"\"\n image_list=[]\n j=0\n for i in range(9):\n if i != fg:\n image_list.append(background_data[bg_idx[j]])\n j+=1\n else: \n image_list.append(foreground_data[fg_idx])\n label = foreground_label[fg_idx] - fg1 # minus fg1 because our fore ground classes are fg1,fg2,fg3 but we have to store it as 0,1,2\n #image_list = np.concatenate(image_list ,axis=0)\n image_list = torch.stack(image_list) \n return image_list,label",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"desired_num = 6000\nmosaic_list_of_images =[] # list of mosaic images, each mosaic image is saved as list of 9 images\nfore_idx =[] # list of indexes at which foreground image is present in a mosaic image i.e from 0 to 9 \nmosaic_label=[] # label of mosaic image = foreground class present in that mosaic\nlist_set_labels = [] \nfor i in range(desired_num):\n set_idx = set()\n np.random.seed(i)\n bg_idx = np.random.randint(0,3500,8)\n set_idx = set(background_label[bg_idx].tolist())\n fg_idx = np.random.randint(0,1500)\n set_idx.add(foreground_label[fg_idx].item())\n fg = np.random.randint(0,9)\n fore_idx.append(fg)\n image_list,label = create_mosaic_img(bg_idx,fg_idx,fg)\n mosaic_list_of_images.append(image_list)\n mosaic_label.append(label)\n list_set_labels.append(set_idx)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(mosaic_list_of_images), mosaic_list_of_images[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# load mosaic data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class MosaicDataset(Dataset):\n \"\"\"MosaicDataset dataset.\"\"\"\n\n def __init__(self, mosaic_list, mosaic_label,fore_idx):\n \"\"\"\n Args:\n csv_file (string): Path to the csv file with annotations.\n root_dir (string): Directory with all the images.\n transform (callable, optional): Optional transform to be applied\n on a sample.\n \"\"\"\n self.mosaic = mosaic_list\n self.label = mosaic_label\n self.fore_idx = fore_idx\n \n def __len__(self):\n return len(self.label)\n\n def __getitem__(self, idx):\n return self.mosaic[idx] , self.label[idx] , self.fore_idx[idx]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"batch = 250\nmsd1 = MosaicDataset(mosaic_list_of_images[0:3000], mosaic_label[0:3000] , fore_idx[0:3000])\ntrain_loader = DataLoader( msd1 ,batch_size= batch ,shuffle=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"batch = 250\nmsd2 = MosaicDataset(mosaic_list_of_images[3000:6000], mosaic_label[3000:6000] , fore_idx[3000:6000])\ntest_loader = DataLoader( msd2 ,batch_size= batch ,shuffle=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# models",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class Focus_deep(nn.Module):\n '''\n deep focus network averaged at zeroth layer with input-50-output architecture\n input : elemental data\n '''\n \n def __init__(self,inputs,output,K,d):\n super(Focus_deep,self).__init__()\n self.inputs = inputs\n self.output = output\n self.K = K\n self.d = d\n self.linear1 = nn.Linear(self.inputs,50, bias=False) #,self.output)\n self.linear2 = nn.Linear(50,self.output, bias=False) \n\n torch.nn.init.xavier_normal_(self.linear1.weight)\n torch.nn.init.xavier_normal_(self.linear2.weight)\n\n def forward(self,z):\n batch = z.shape[0]\n x = torch.zeros([batch,self.K],dtype=torch.float64)\n y = torch.zeros([batch,self.d], dtype=torch.float64)\n x,y = x.to(\"cuda\"),y.to(\"cuda\")\n for i in range(self.K):\n x[:,i] = self.helper(z[:,i] )[:,0] # self.d*i:self.d*i+self.d\n log_x = F.log_softmax(x,dim=1)\n x = F.softmax(x,dim=1) # alphas\n x1 = x[:,0]\n for i in range(self.K):\n x1 = x[:,i] \n y = y+torch.mul(x1[:,None],z[:,i]) # self.d*i:self.d*i+self.d\n return y , x , log_x\n def helper(self,x):\n x = F.relu(self.linear1(x))\n x = self.linear2(x)\n return x",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class Classification_deep(nn.Module):\n '''\n input : elemental data\n deep classification module data averaged at zeroth layer with input-50-output architecture\n '''\n def __init__(self,inputs,output):\n super(Classification_deep,self).__init__()\n self.inputs = inputs\n self.output = output\n self.linear1 = nn.Linear(self.inputs,200)\n self.linear2 = nn.Linear(200,self.output)\n \n torch.nn.init.xavier_normal_(self.linear1.weight)\n torch.nn.init.zeros_(self.linear1.bias)\n torch.nn.init.xavier_normal_(self.linear2.weight)\n torch.nn.init.zeros_(self.linear2.bias)\n\n def forward(self,x):\n x = F.relu(self.linear1(x))\n x = self.linear2(x)\n return x",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"torch.manual_seed(12)\nfocus_net = Focus_deep(2,1,9,2).double()\nfocus_net = focus_net.to(\"cuda\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"focus_net.linear1.weight.shape,focus_net.linear2.weight.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"focus_net.linear1.weight.data[25:,:] = focus_net.linear1.weight.data[:25,:] #torch.nn.Parameter(torch.tensor([last_layer]) )\n(focus_net.linear1.weight[:25,:]== focus_net.linear1.weight[25:,:] )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"focus_net.linear2.weight.data[:,25:] = -focus_net.linear2.weight.data[:,:25] #torch.nn.Parameter(torch.tensor([last_layer]) )\nfocus_net.linear2.weight",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"focus_net.helper( torch.randn((1,5,2)).double().to(\"cuda\") )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()\ndef my_cross_entropy(x, y,alpha,log_alpha,k):\n # log_prob = -1.0 * F.log_softmax(x, 1)\n # loss = log_prob.gather(1, y.unsqueeze(1))\n # loss = loss.mean()\n loss = criterion(x,y)\n \n #alpha = torch.clamp(alpha,min=1e-10) \n \n b = -1.0* alpha * log_alpha\n b = torch.mean(torch.sum(b,dim=1))\n closs = loss\n entropy = b \n loss = (1-k)*loss + ((k)*b)\n return loss,closs,entropy",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def calculate_attn_loss(dataloader,what,where,criter,k):\n what.eval()\n where.eval()\n r_loss = 0\n cc_loss = 0\n cc_entropy = 0\n alphas = []\n lbls = []\n pred = []\n fidices = []\n with torch.no_grad():\n for i, data in enumerate(dataloader, 0):\n inputs, labels,fidx = data\n lbls.append(labels)\n fidices.append(fidx)\n inputs = inputs.double()\n inputs, labels = inputs.to(\"cuda\"),labels.to(\"cuda\")\n avg,alpha,log_alpha = where(inputs)\n outputs = what(avg)\n _, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)\n pred.append(predicted.cpu().numpy())\n alphas.append(alpha.cpu().numpy())\n\n #ent = np.sum(entropy(alpha.cpu().detach().numpy(), base=2, axis=1))/batch\n # mx,_ = torch.max(alpha,1)\n # entropy = np.mean(-np.log2(mx.cpu().detach().numpy()))\n # print(\"entropy of batch\", entropy)\n\n #loss = (1-k)*criter(outputs, labels) + k*ent\n loss,closs,entropy = my_cross_entropy(outputs,labels,alpha,log_alpha,k)\n r_loss += loss.item()\n cc_loss += closs.item()\n cc_entropy += entropy.item()\n\n alphas = np.concatenate(alphas,axis=0)\n pred = np.concatenate(pred,axis=0)\n lbls = np.concatenate(lbls,axis=0)\n fidices = np.concatenate(fidices,axis=0)\n #print(alphas.shape,pred.shape,lbls.shape,fidices.shape) \n analysis = analyse_data(alphas,lbls,pred,fidices)\n return r_loss/i,cc_loss/i,cc_entropy/i,analysis",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def analyse_data(alphas,lbls,predicted,f_idx):\n '''\n analysis data is created here\n '''\n batch = len(predicted)\n amth,alth,ftpt,ffpt,ftpf,ffpf = 0,0,0,0,0,0\n for j in range (batch):\n focus = np.argmax(alphas[j])\n if(alphas[j][focus] >= 0.5):\n amth +=1\n else:\n alth +=1\n if(focus == f_idx[j] and predicted[j] == lbls[j]):\n ftpt += 1\n elif(focus != f_idx[j] and predicted[j] == lbls[j]):\n ffpt +=1\n elif(focus == f_idx[j] and predicted[j] != lbls[j]):\n ftpf +=1\n elif(focus != f_idx[j] and predicted[j] != lbls[j]):\n ffpf +=1\n #print(sum(predicted==lbls),ftpt+ffpt)\n return [ftpt,ffpt,ftpf,ffpf,amth,alth]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# training",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"number_runs = 10\nfull_analysis =[]\nFTPT_analysis = pd.DataFrame(columns = [\"FTPT\",\"FFPT\", \"FTPF\",\"FFPF\"])\nk = 0\nfor n in range(number_runs):\n print(\"--\"*40)\n \n # instantiate focus and classification Model\n torch.manual_seed(n)\n where = Focus_deep(5,1,9,5).double()\n where.linear1.weight.data[25:,:] = where.linear1.weight.data[:25,:]\n where.linear2.weight.data[:,25:] = -where.linear2.weight.data[:,:25]\n where = where.double().to(\"cuda\")\n\n print(where.helper( torch.randn((1,5,9)).double().to(\"cuda\")))\n\n what = Classification_deep(5,3).double()\n where = where.to(\"cuda\")\n what = what.to(\"cuda\")\n\n # instantiate optimizer\n optimizer_where = optim.Adam(where.parameters(),lr =0.001)\n optimizer_what = optim.Adam(what.parameters(), lr=0.001)\n #criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()\n acti = []\n analysis_data = []\n loss_curi = []\n epochs = 2000\n\n\n # calculate zeroth epoch loss and FTPT values\n running_loss ,_,_,anlys_data= calculate_attn_loss(train_loader,what,where,criterion,k)\n loss_curi.append(running_loss)\n analysis_data.append(anlys_data)\n\n print('epoch: [%d ] loss: %.3f' %(0,running_loss)) \n\n # training starts \n for epoch in range(epochs): # loop over the dataset multiple times\n ep_lossi = []\n running_loss = 0.0\n what.train()\n where.train()\n for i, data in enumerate(train_loader, 0):\n # get the inputs\n inputs, labels,_ = data\n inputs = inputs.double()\n inputs, labels = inputs.to(\"cuda\"),labels.to(\"cuda\")\n\n # zero the parameter gradients\n optimizer_where.zero_grad()\n optimizer_what.zero_grad()\n \n # forward + backward + optimize\n avg, alpha,log_alpha = where(inputs)\n outputs = what(avg)\n\n my_loss,_,_ = my_cross_entropy(outputs,labels,alpha,log_alpha,k)\n\n # print statistics\n running_loss += my_loss.item()\n my_loss.backward()\n optimizer_where.step()\n optimizer_what.step()\n #break\n running_loss,ccloss,ccentropy,anls_data = calculate_attn_loss(train_loader,what,where,criterion,k)\n analysis_data.append(anls_data)\n\n if(epoch % 200==0):\n print('epoch: [%d] loss: %.3f celoss: %.3f entropy: %.3f' %(epoch + 1,running_loss,ccloss,ccentropy)) \n loss_curi.append(running_loss) #loss per epoch\n if running_loss<=0.01:\n print('breaking in epoch: ', epoch)\n break\n print('Finished Training run ' +str(n))\n #break\n analysis_data = np.array(analysis_data)\n FTPT_analysis.loc[n] = analysis_data[-1,:4]/30\n full_analysis.append((epoch, analysis_data))\n correct = 0\n total = 0\n with torch.no_grad():\n for data in test_loader:\n images, labels,_ = data\n images = images.double()\n images, labels = images.to(\"cuda\"), labels.to(\"cuda\")\n avg, alpha,log_alpha = where(images)\n outputs = what(avg)\n _, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)\n total += labels.size(0)\n correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item()\n\n print('Accuracy of the network on the 3000 test images: %f %%' % ( 100 * correct / total))\n ",
"--------------------------------------------------------------------------------\ntensor([[[-3.4694e-17],\n [-1.7944e-17],\n [ 0.0000e+00],\n [-8.6736e-17],\n [ 0.0000e+00]]], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.float64,\n grad_fn=<UnsafeViewBackward>)\nepoch: [0 ] loss: 1.685\nepoch: [1] loss: 1.251 celoss: 1.251 entropy: 2.354\nbreaking in epoch: 100\nFinished Training run 0\nAccuracy of the network on the 3000 test images: 99.966667 %\n--------------------------------------------------------------------------------\ntensor([[[-6.9389e-18],\n [-3.4694e-18],\n [ 0.0000e+00],\n [-1.7347e-17],\n [ 8.6736e-18]]], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.float64,\n grad_fn=<UnsafeViewBackward>)\nepoch: [0 ] loss: 1.470\nepoch: [1] loss: 1.205 celoss: 1.205 entropy: 2.217\nbreaking in epoch: 98\nFinished Training run 1\nAccuracy of the network on the 3000 test images: 100.000000 %\n--------------------------------------------------------------------------------\ntensor([[[ 4.3368e-18],\n [-4.1633e-17],\n [ 6.9389e-18],\n [-3.4261e-17],\n [ 1.8648e-17]]], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.float64,\n grad_fn=<UnsafeViewBackward>)\nepoch: [0 ] loss: 1.537\nepoch: [1] loss: 1.214 celoss: 1.214 entropy: 2.218\nbreaking in epoch: 99\nFinished Training run 2\nAccuracy of the network on the 3000 test images: 99.966667 %\n--------------------------------------------------------------------------------\ntensor([[[-1.5613e-17],\n [-3.4694e-18],\n [-2.7756e-17],\n [ 1.0755e-16],\n [ 1.7889e-17]]], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.float64,\n grad_fn=<UnsafeViewBackward>)\nepoch: [0 ] loss: 1.415\nepoch: [1] loss: 1.213 celoss: 1.213 entropy: 2.102\nbreaking in epoch: 101\nFinished Training run 3\nAccuracy of the network on the 3000 test images: 100.000000 %\n--------------------------------------------------------------------------------\ntensor([[[ 4.1633e-17],\n [ 5.5511e-17],\n [-2.7756e-17],\n [-5.5511e-17],\n [ 0.0000e+00]]], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.float64,\n grad_fn=<UnsafeViewBackward>)\nepoch: [0 ] loss: 1.444\nepoch: [1] loss: 1.216 celoss: 1.216 entropy: 2.305\nbreaking in epoch: 93\nFinished Training run 4\nAccuracy of the network on the 3000 test images: 100.000000 %\n--------------------------------------------------------------------------------\ntensor([[[ 0.0000e+00],\n [-2.0817e-17],\n [ 2.4937e-17],\n [ 1.3878e-17],\n [ 1.4854e-17]]], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.float64,\n grad_fn=<UnsafeViewBackward>)\nepoch: [0 ] loss: 1.260\nepoch: [1] loss: 1.207 celoss: 1.207 entropy: 2.172\nbreaking in epoch: 88\nFinished Training run 5\nAccuracy of the network on the 3000 test images: 100.000000 %\n--------------------------------------------------------------------------------\ntensor([[[-1.3010e-18],\n [-1.3878e-17],\n [ 2.7756e-17],\n [ 4.1633e-17],\n [ 2.7756e-17]]], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.float64,\n grad_fn=<UnsafeViewBackward>)\nepoch: [0 ] loss: 1.683\nepoch: [1] loss: 1.215 celoss: 1.215 entropy: 1.759\nbreaking in epoch: 104\nFinished Training run 6\nAccuracy of the network on the 3000 test images: 100.000000 %\n--------------------------------------------------------------------------------\ntensor([[[ 0.0000e+00],\n [-2.7756e-17],\n [-6.9389e-18],\n [-1.1102e-16],\n [ 0.0000e+00]]], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.float64,\n grad_fn=<UnsafeViewBackward>)\nepoch: [0 ] loss: 1.551\nepoch: [1] loss: 1.233 celoss: 1.233 entropy: 2.219\nbreaking in epoch: 91\nFinished Training run 7\nAccuracy of the network on the 3000 test images: 100.000000 %\n--------------------------------------------------------------------------------\ntensor([[[ 1.3878e-17],\n [ 5.2042e-18],\n [-8.1532e-17],\n [ 6.9389e-18],\n [-5.5511e-17]]], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.float64,\n grad_fn=<UnsafeViewBackward>)\nepoch: [0 ] loss: 1.259\nepoch: [1] loss: 1.203 celoss: 1.203 entropy: 2.374\nbreaking in epoch: 83\nFinished Training run 8\nAccuracy of the network on the 3000 test images: 100.000000 %\n--------------------------------------------------------------------------------\ntensor([[[ 6.9389e-18],\n [ 0.0000e+00],\n [ 2.4286e-17],\n [-4.8572e-17],\n [ 4.5103e-17]]], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.float64,\n grad_fn=<UnsafeViewBackward>)\nepoch: [0 ] loss: 1.384\nepoch: [1] loss: 1.224 celoss: 1.224 entropy: 2.149\nbreaking in epoch: 95\nFinished Training run 9\nAccuracy of the network on the 3000 test images: 100.000000 %\n"
],
[
"print(np.mean(np.array(FTPT_analysis),axis=0)) ",
"[9.99933333e+01 6.66666667e-03 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]\n"
],
[
"FTPT_analysis",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"FTPT_analysis[FTPT_analysis['FTPT']+FTPT_analysis['FFPT'] > 90 ]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(np.mean(np.array(FTPT_analysis[FTPT_analysis['FTPT']+FTPT_analysis['FFPT'] > 90 ]),axis=0))",
"[9.99933333e+01 6.66666667e-03 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00]\n"
],
[
"cnt=1\nfor epoch, analysis_data in full_analysis:\n analysis_data = np.array(analysis_data)\n # print(\"=\"*20+\"run \",cnt,\"=\"*20)\n \n plt.figure(figsize=(6,5))\n plt.plot(np.arange(0,epoch+2,1),analysis_data[:,0]/30,label=\"FTPT\")\n plt.plot(np.arange(0,epoch+2,1),analysis_data[:,1]/30,label=\"FFPT\")\n plt.plot(np.arange(0,epoch+2,1),analysis_data[:,2]/30,label=\"FTPF\")\n plt.plot(np.arange(0,epoch+2,1),analysis_data[:,3]/30,label=\"FFPF\")\n\n plt.title(\"Training trends for run \"+str(cnt))\n plt.grid()\n # plt.legend(loc='center left', bbox_to_anchor=(1, 0.5))\n plt.legend()\n plt.xlabel(\"epochs\", fontsize=14, fontweight = 'bold')\n plt.ylabel(\"percentage train data\", fontsize=14, fontweight = 'bold')\n plt.savefig(path + \"run\"+str(cnt)+\".png\",bbox_inches=\"tight\")\n plt.savefig(path + \"run\"+str(cnt)+\".pdf\",bbox_inches=\"tight\")\n cnt+=1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"FTPT_analysis.to_csv(path+\"synthetic_zeroth.csv\",index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a771df08305ef0cdb812dd0fdd758149ff97a60
| 102,574 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Circuit_Basics.ipynb
|
MonitSharma/Quantum-Computing
|
9bcb70ac6afd46ee606e4bc2ae10657b803369b8
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2020-12-25T15:05:53.000Z
|
2020-12-25T15:05:53.000Z
|
Circuit_Basics.ipynb
|
MonitSharma/Quantum-Computing
|
9bcb70ac6afd46ee606e4bc2ae10657b803369b8
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Circuit_Basics.ipynb
|
MonitSharma/Quantum-Computing
|
9bcb70ac6afd46ee606e4bc2ae10657b803369b8
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 200.731898 | 39,402 | 0.89085 |
[
[
[
"<a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/MonitSharma/Learn-Quantum-Computing/blob/main/Circuit_Basics.ipynb\" target=\"_parent\"><img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open In Colab\"/></a>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!pip install qiskit",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Qiskit Basics",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nfrom qiskit import QuantumCircuit",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# building a circuit\n\nqc = QuantumCircuit(3)\n\n\n# adding gates\n\nqc.h(0)\nqc.cx(0,1)\n\nqc.cx(0,2)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"qc.draw('mpl')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Simulating the Circuits",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from qiskit.quantum_info import Statevector\n# setting the initial state to 0\nstate = Statevector.from_int(0,2**3)\n\nstate = state.evolve(qc)\n\nstate.draw('latex')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from qiskit.quantum_info import Statevector\n# setting the initial state to 1\nstate = Statevector.from_int(1,2**3)\n\nstate = state.evolve(qc)\n\nstate.draw('latex')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Below we use the visualization function to plot the bloch sphere and a hinton representing the real and the imaginary components of the state density matrix $\\rho$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"state.draw('qsphere')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"state.draw('hinton')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Unitary Representation of a Circuit\nThe quant_info module of qiskit has an operator method that can be used to make unitary operator for the circuit.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from qiskit.quantum_info import Operator\nU = Operator(qc)\n\nU.data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Open QASM backend\nThe simulators above are useful, as they help us in providing information about the state output and matrix representation of the circuit.\nHere we would learn about more simulators that will help us in measuring the circuit",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"qc2 = QuantumCircuit(3,3)\nqc2.barrier(range(3))\n\n# do the measurement\nqc2.measure(range(3), range(3))\nqc2.draw('mpl')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# now, if we want to add both the qc and qc2 circuit\n\ncirc = qc2.compose(qc, range(3), front = True)\n\ncirc.draw('mpl')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This circuit adds a classical register , and three measurement that are used to map the outcome of qubits to the classical bits.\n\nTo simulate this circuit we use the 'qasm_simulator' in Qiskit Aer. Each single run will yield a bit string $000$ or $111$. To build up the statistics about the distribution , we need to repeat the circuit many times.\n\nThe number of times the circuit is repeated is specified in the 'execute' function via the 'shots' keyword. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from qiskit import transpile \n\n# import the qasm simulator\n\nfrom qiskit.providers.aer import QasmSimulator\n\nbackend = QasmSimulator()\n\n# first transpile the quantum circuit to low level QASM instructions\n\nqc_compiled = transpile(circ, backend)\n\n# execute the circuit\n\njob_sim = backend.run(qc_compiled, shots=1024)\n\n# get the result\n\nresult_sim = job_sim.result()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Since, the code has run, we can count the number of specific ouputs it recieved and plot it too.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"counts = result_sim.get_counts(qc_compiled)\nprint(counts)",
"{'111': 479, '000': 545}\n"
],
[
"from qiskit.visualization import plot_histogram\nplot_histogram(counts)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a77242b009492d664136f3c8e1d38ab326e8b8e
| 282,238 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/bitcoinabuse data analysis.ipynb
|
manula2004/ChainKeeper-Analytics
|
e9f959129b99ec66368eb1f45ea41adeeeec57d1
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/bitcoinabuse data analysis.ipynb
|
manula2004/ChainKeeper-Analytics
|
e9f959129b99ec66368eb1f45ea41adeeeec57d1
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/bitcoinabuse data analysis.ipynb
|
manula2004/ChainKeeper-Analytics
|
e9f959129b99ec66368eb1f45ea41adeeeec57d1
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 54.910117 | 1,928 | 0.548466 |
[
[
[
"import pandas\nimport json\nimport glob",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"files = glob.glob('../data/bitcoinabuse crawler data/json/*')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"DATA = list()\nerr = list()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for file in files:\n data = open(file,'r').read()\n for con in data.split('\\n'):\n con = con.replace(\"\\'\", \"\\\"\")\n con = con.replace('u\"', '\"')\n try:\n DATA.append(json.loads(con))\n except:\n err.append(file)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"DATA",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a7729c66bbec122d33971c264f18b5d3369baa0
| 33,033 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/02_fmri.ipynb
|
Yu-Group/veridical-flow
|
2c26f3eae23fa85a43fa3c3b3aa13c7aaedc8c71
|
[
"MIT"
] | 25 |
2021-09-10T20:50:25.000Z
|
2022-03-02T19:35:40.000Z
|
notebooks/02_fmri.ipynb
|
Yu-Group/veridical-flow
|
2c26f3eae23fa85a43fa3c3b3aa13c7aaedc8c71
|
[
"MIT"
] | 32 |
2021-10-05T23:38:20.000Z
|
2022-03-08T01:42:50.000Z
|
notebooks/02_fmri.ipynb
|
Yu-Group/veridical-flow
|
2c26f3eae23fa85a43fa3c3b3aa13c7aaedc8c71
|
[
"MIT"
] | 5 |
2021-09-25T02:19:19.000Z
|
2022-01-13T09:54:58.000Z
| 34.992585 | 161 | 0.382617 |
[
[
[
"%load_ext autoreload\n%autoreload 2\nimport numpy as np\nfrom vflow import Vset, init_args, dict_to_df, perturbation_stats\nfrom functools import partial\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import LassoCV\nfrom sklearn.metrics import r2_score, explained_variance_score\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nfrom sklearn.decomposition import PCA",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# fMRI Voxel Prediction",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"This `vflow` pipeline predicts using fMRI voxels.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"ind = {}\n\ndef top_n_features(X, Y, n, i):\n if i not in ind:\n corr = np.abs(np.apply_along_axis(lambda x: np.corrcoef(x, Y[:, i])[0, 1], 0, X))\n ind[i] = np.argsort(corr[~np.isnan(corr)])[::-1][:n]\n return X[:, ind[i]]\n\n\ndef pca(X, n):\n return PCA(n_components=n, copy=True).fit(X).transform(X)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# load data\ndata_dir = \"./data/fmri/\"\nX = np.load(data_dir + \"fit_feat.npy\")\nY = np.load(data_dir + \"resp_dat.npy\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.random.seed(14)\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.33, random_state=14)\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = init_args((X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test),\n names=['X_train', 'X_test', 'y_train', 'y_test'])\n\n# split y_train by voxel and extract top 500 correlated features per voxel\nvoxel_extract_funcs = [partial(lambda x, y, i: (top_n_features(x, y, 20, i), y[:, i]), i=i) for i in range(20)]\nvoxel_extract_set = Vset(name='voxel_extract', modules=voxel_extract_funcs, output_matching=True)\nX_trains, y_trains = voxel_extract_set(X_train, y_train)\nX_tests, y_tests = voxel_extract_set(X_test, y_test)",
"/Users/rush/anaconda3/envs/vflow/lib/python3.6/site-packages/numpy/lib/function_base.py:2534: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in true_divide\n c /= stddev[:, None]\n/Users/rush/anaconda3/envs/vflow/lib/python3.6/site-packages/numpy/lib/function_base.py:2535: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in true_divide\n c /= stddev[None, :]\n"
],
[
"# modeling\nmodeling_set = Vset(name='modeling', modules=[LassoCV()], module_keys=[\"Lasso\"])\nmodeling_set.fit(X_trains, y_trains)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"preds = modeling_set.predict(X_trains)\n\nhard_metrics_set = Vset(name='hard_metrics', modules=[r2_score, explained_variance_score],\n module_keys=[\"R2\", \"EV\"])\nhard_metrics = hard_metrics_set.evaluate(y_trains, preds)\n\ndf = dict_to_df(hard_metrics)\ndf",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"metrics_stats = perturbation_stats(df, 'voxel_extract')\nmetrics_stats",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a7731f31a16d6828a23aae95e4ef934a7f2d4b6
| 7,718 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
python/.ipynb_checkpoints/ephys_criterion_check-checkpoint.ipynb
|
int-brain-lab/analysis
|
a8bf474815cb6ed690b3da07ff2f501459375b75
|
[
"MIT"
] | 7 |
2018-11-22T17:36:02.000Z
|
2020-10-17T10:59:59.000Z
|
python/.ipynb_checkpoints/ephys_criterion_check-checkpoint.ipynb
|
int-brain-lab/tmp_analysis_matlab
|
effedfd0b5997411f576b4ebcc747c8613715c24
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2020-01-13T17:47:14.000Z
|
2020-05-21T18:31:47.000Z
|
python/.ipynb_checkpoints/ephys_criterion_check-checkpoint.ipynb
|
int-brain-lab/tmp_analysis_matlab
|
effedfd0b5997411f576b4ebcc747c8613715c24
|
[
"MIT"
] | 4 |
2019-05-30T17:55:32.000Z
|
2021-01-06T18:45:48.000Z
| 34 | 180 | 0.583441 |
[
[
[
"This script performs analyses to check how many mice pass the currenty set criterion for ephys.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import datajoint as dj\ndj.config['database.host'] = 'datajoint.internationalbrainlab.org'\n\nfrom ibl_pipeline import subject, acquisition, action, behavior, reference, data\nfrom ibl_pipeline.analyses.behavior import PsychResults, SessionTrainingStatus\nfrom ibl_pipeline.utils import psychofit as psy\nfrom ibl_pipeline.analyses import behavior as behavior_analysis\n\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport pandas as pd",
"Connecting [email protected]:3306\nConnected to https://alyx.internationalbrainlab.org as lacerbi\n"
],
[
"# Get list of subjects associated to the repeated site probe trajectory from ONE (original snippet from Gaelle Chapuis)\nfrom oneibl.one import ONE\n\none = ONE()\ntraj = one.alyx.rest('trajectories', 'list', provenance='Planned',\n x=-2243, y=-2000, # repeated site coordinate\n project='ibl_neuropixel_brainwide_01')\nsess = [p['session'] for p in traj]\n\nfirst_pass_map_repeated = [(s['subject'],s['start_time'][0:10]) for s in sess]",
"Connected to https://alyx.internationalbrainlab.org as lacerbi\n"
],
[
"# Download all ephys sessions from DataJoint\nsess_ephys = (acquisition.Session * subject.Subject * behavior_analysis.SessionTrainingStatus ) & 'task_protocol LIKE \"%ephys%\"'\n# & 'task_protocol LIKE \"%biased%\"' & 'session_start_time < \"2019-09-30\"')\ndf = pd.DataFrame(sess_ephys)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The following code computes how many `ephys` sessions are considered `good_enough_for_brainwide_map`:\n- across *all* ephys sessions;\n- across the ephys sessions in the first-pass map for the repeated site.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"session_dates = df['session_start_time'].apply(lambda x : x.strftime(\"%Y-%m-%d\"))\n\n# First, count all mice\n\ntotal = len(df.index)\ngood_enough = np.sum(df['good_enough_for_brainwide_map'])\nprc = good_enough / total * 100\nprint('Total # of ephys sessions: '+ str(total))\nprint('Total # of sessions good_enough_for_brainwide_map: ' + str(good_enough) + ' (' + \"{:.1f}\".format(prc) + ' %)')\n\n# Now, consider only mice in the first pass map, repeated site\n\ncount = 0\nfor (mouse_name,session_date) in first_pass_map_repeated:\n tmp = df[(df['subject_nickname'] == mouse_name) & (session_dates == session_date)]\n count = count + np.sum(tmp['good_enough_for_brainwide_map'])\n \ntotal = len(first_pass_map_repeated)\ngood_enough = count\nprc = good_enough / total * 100\nprint('Total # of ephys sessions in first pass map, repeated site: '+ str(total))\nprint('Total # of sessions good_enough_for_brainwide_map in first pass map, repeated site: ' + str(good_enough) + ' (' + \"{:.1f}\".format(prc) + ' %)')\n",
"Total # of ephys sessions: 208\nTotal # of sessions good_enough_for_brainwide_map: 120 (57.7 %)\nTotal # of ephys sessions in first pass map, repeated site: 20\nTotal # of sessions good_enough_for_brainwide_map in first pass map, repeated site: 11 (55.0 %)\n"
]
],
[
[
"The following code computes how many sessions are required for a mouse to reach certain levels of training or protocols, in particular:\n- from `trained` status to `biased` protocol\n- from `biased` protocol to `ready4ephys` status",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mice_list = set(df['subject_nickname'])\n\ntrained2biased = []\nbiased2ready4ephys = []\n\nfor mouse_name in mice_list:\n subj_string = 'subject_nickname LIKE \"' + mouse_name + '\"'\n sess_mouse = (acquisition.Session * subject.Subject * behavior_analysis.SessionTrainingStatus ) & subj_string\n df1 = pd.DataFrame(sess_mouse)\n \n # Find first session of training\n trained_start = np.argmax(df1['training_status'].apply(lambda x: 'trained' in x))\n if 'trained' not in df1['training_status'][trained_start]:\n trained_start = None\n \n # Find first session of biased protocol\n biased_start = np.argmax(df1['task_protocol'].apply(lambda x: 'biased' in x))\n if 'biased' not in df1['task_protocol'][biased_start]:\n biased_start = None\n \n # Find first session of ephys\n ready4ephys_start = np.argmax(df1['training_status'].apply(lambda x: 'ready4ephys' in x))\n if 'ready4ephys' not in df1['training_status'][ready4ephys_start]:\n ready4ephys_start = None\n \n if ready4ephys_start != None:\n trained2biased.append(biased_start - trained_start)\n biased2ready4ephys.append(ready4ephys_start - biased_start)\n \ntrained2biased = np.array(trained2biased)\nbiased2ready4ephys = np.array(biased2ready4ephys)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\nflag = trained2biased > 0\nprint('# Mice: ' + str(np.sum(flag)))\nprint('# Sessions from \"trained\" to \"biased\": ' + \"{:.2f}\".format(np.mean(trained2biased[flag])) + ' +/- '+ \"{:.2f}\".format(np.std(trained2biased[flag])))\nprint('# Sessions from \"biased\" to \"ready4ephys\": ' + \"{:.2f}\".format(np.mean(biased2ready4ephys[flag])) + ' +/- '+ \"{:.2f}\".format(np.std(biased2ready4ephys[flag])))",
"# Mice: 41\n# Sessions from \"trained\" to \"biased\": 6.20 +/- 10.86\n# Sessions from \"biased\" to \"ready4ephys\": 7.85 +/- 8.90\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a7733f4ef18979ab1d091e1020c1444884fc04a
| 12,904 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Capstone 2/src/eda.ipynb
|
0xd5dc/amazon-review-validator
|
44f9386fda51a3abaa90a6474fb4e4cbd456031a
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
Capstone 2/src/eda.ipynb
|
0xd5dc/amazon-review-validator
|
44f9386fda51a3abaa90a6474fb4e4cbd456031a
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
Capstone 2/src/eda.ipynb
|
0xd5dc/amazon-review-validator
|
44f9386fda51a3abaa90a6474fb4e4cbd456031a
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null | 32.422111 | 342 | 0.407393 |
[
[
[
"# %load ../../templates/load_libs.py\nimport sys\nfrom pyspark.ml.classification import LogisticRegression, NaiveBayes, DecisionTreeClassifier, GBTClassifier, \\\n RandomForestClassifier\n# set project directory for shared library\nPROJECT_DIR='/home/jovyan/work/amazon-review-validator'\nif PROJECT_DIR not in sys.path:\n sys.path.insert(0, PROJECT_DIR)\n \nfrom libs.utils import hello\nhello()",
"hello works\n"
],
[
"# %load ../../templates/load_data.py\nimport pyspark as ps\nfrom pyspark.sql.types import StructField, StructType, StringType, IntegerType\n\nDATA_FILE = '../../data/amazon_reviews_us_Camera_v1_00.tsv.gz'\nAPP_NAME = 'EDA'\nFEATURES = ['star_rating', 'review_body', 'helpful_votes', 'total_votes', 'verified_purchase', 'review_date']\nSAMPLE_SIZE = 10000\n\nreview_schema = StructType(\n [StructField('marketplace', StringType(), True),\n StructField('customer_id', StringType(), True),\n StructField('review_id', StringType(), True),\n StructField('product_id', StringType(), True),\n StructField('product_parent', StringType(), True),\n StructField('product_title', StringType(), True),\n StructField('product_category', StringType(), True),\n StructField('star_rating', IntegerType(), True),\n StructField('helpful_votes', IntegerType(), True),\n StructField('total_votes', IntegerType(), True),\n StructField('vine', StringType(), True),\n StructField('verified_purchase', StringType(), True),\n StructField('review_headline', StringType(), True),\n StructField('review_body', StringType(), True),\n StructField('review_date', StringType(), True)])\n\nspark = (ps.sql.SparkSession.builder\n .master(\"local[1]\")\n .appName(APP_NAME)\n .getOrCreate()\n )\nsc = spark.sparkContext\n\ndf = spark.read.format(\"csv\") \\\n .option(\"header\", \"true\") \\\n .option(\"sep\", \"\\t\") \\\n .schema(review_schema) \\\n .load(DATA_FILE)\ndf.createOrReplaceTempView(\"dfTable\")\n\nreview_all = df.select(FEATURES)\nreview_sample = df.select(FEATURES).limit(SAMPLE_SIZE).cache()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"spark.sql(\n \"select customer_id, count(if (star_rating==1,1,NULL)) as one_star, count(if (star_rating==2,1,NULL)) as two_star, count(if (star_rating==3,1,NULL)) as tre_star, count(if (star_rating==4,1,NULL)) as qua_star, count(if (star_rating==5,1,NULL)) as cin_star from eda_sql_view group by customer_id order by one_star desc \").show()",
"+-----------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+\n|customer_id|one_star|two_star|tre_star|qua_star|cin_star|\n+-----------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+\n| 11298115| 28| 2| 0| 0| 2|\n| 12572844| 26| 0| 0| 0| 0|\n| 49010601| 24| 0| 0| 0| 0|\n| 47129351| 24| 1| 0| 0| 0|\n| 35955273| 21| 0| 5| 1| 45|\n| 25109130| 20| 0| 0| 0| 3|\n| 10430957| 19| 0| 0| 0| 0|\n| 50350415| 19| 8| 5| 18| 27|\n| 45420831| 17| 0| 0| 0| 0|\n| 36814878| 16| 2| 5| 2| 19|\n| 52614016| 16| 15| 7| 8| 23|\n| 12761652| 16| 0| 0| 0| 0|\n| 8199747| 16| 1| 2| 1| 16|\n| 13027341| 14| 3| 0| 0| 0|\n| 52482526| 13| 0| 0| 0| 7|\n| 20865812| 13| 0| 0| 0| 0|\n| 23372436| 13| 3| 4| 12| 16|\n| 36410465| 13| 3| 13| 7| 2|\n| 29233410| 12| 0| 1| 1| 0|\n| 1260834| 12| 0| 0| 2| 12|\n+-----------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+\nonly showing top 20 rows\n\n"
],
[
"spark.sql(\n \"select customer_id, count(if (star_rating==1,1,NULL)) as one_star, count(if (star_rating==2,1,NULL)) as two_star, count(if (star_rating==3,1,NULL)) as tre_star, count(if (star_rating==4,1,NULL)) as qua_star, count(if (star_rating==5,1,NULL)) as cin_star from eda_sql_view group by customer_id order by cin_star desc \").show()",
"+-----------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+\n|customer_id|one_star|two_star|tre_star|qua_star|cin_star|\n+-----------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+\n| 31588426| 4| 2| 7| 59| 213|\n| 9115336| 0| 0| 1| 17| 122|\n| 45371561| 0| 1| 3| 6| 116|\n| 38681283| 0| 1| 3| 6| 104|\n| 52340667| 11| 7| 9| 16| 103|\n| 40109303| 0| 0| 0| 20| 103|\n| 50820654| 1| 2| 15| 70| 103|\n| 52859210| 9| 2| 10| 13| 95|\n| 52764559| 9| 10| 12| 49| 91|\n| 48640632| 0| 0| 4| 10| 90|\n| 44777060| 1| 1| 11| 45| 90|\n| 16255502| 1| 0| 2| 1| 89|\n| 2840168| 0| 0| 1| 0| 89|\n| 53017806| 0| 0| 0| 6| 87|\n| 50854611| 2| 4| 3| 5| 86|\n| 24550970| 4| 0| 7| 30| 85|\n| 52904056| 0| 2| 1| 10| 84|\n| 51865210| 2| 6| 5| 26| 81|\n| 20096217| 0| 0| 0| 8| 77|\n| 2383044| 1| 1| 1| 9| 75|\n+-----------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+\nonly showing top 20 rows\n\n"
],
[
"spark.sql(\n \"SELECT (COUNT(IF (verified_purchase == 'Y', 1, NULL))/COUNT(*)) as percentage_verified_purchase FROM eda_sql_view\").show()",
"+----------------------------+\n|percentage_verified_purchase|\n+----------------------------+\n| 0.8293132975281552|\n+----------------------------+\n\n"
],
[
"spark.sql(\n \"SELECT (COUNT(IF (star_rating >3, 1, NULL))/COUNT(*)) as percentage_star_rating FROM eda_sql_view\").show()",
"+----------------------+\n|percentage_star_rating|\n+----------------------+\n| 0.7765961107096995|\n+----------------------+\n\n"
],
[
"spark.sql(\n \"select verified_purchase, count(verified_purchase) as counts from EDA_sql_view group by verified_purchase order by counts desc \").show()",
"+-----------------+-------+\n|verified_purchase| counts|\n+-----------------+-------+\n| Y|1494401|\n| N| 307571|\n| null| 0|\n+-----------------+-------+\n\n"
],
[
"spark.sql(\n \"select star_rating, count(star_rating) as counts from EDA_sql_view group by star_rating order by counts desc \").show()",
"+-----------+-------+\n|star_rating| counts|\n+-----------+-------+\n| 5|1062706|\n| 4| 336700|\n| 1| 170157|\n| 3| 141460|\n| 2| 90949|\n| null| 0|\n+-----------+-------+\n\n"
],
[
"spark.sql(\"select avg(helpful_votes) as average, min(helpful_votes) as min, max(helpful_votes) as max from eda_sql_view\").show()\n",
"+-----------------+---+----+\n| average|min| max|\n+-----------------+---+----+\n|2.905414179576597| 0|5132|\n+-----------------+---+----+\n\n"
],
[
"spark.sql(\"select avg(review_body) as average, min(review_body) as min, max(review_body) as max from eda_sql_view\").show()",
"+------------------+---+------+\n| average|min| max|\n+------------------+---+------+\n|16.515151515151516| \u001a\u001a|🚘🎥👍|\n+------------------+---+------+\n\n"
],
[
"spark.sql(\n \"select avg(length(review_body)) as average, min(length(review_body)) as min, max(length(review_body)) as max from eda_sql_view\").show()",
"+-----------------+---+-----+\n| average|min| max|\n+-----------------+---+-----+\n|420.7652951133557| 1|48929|\n+-----------------+---+-----+\n\n"
],
[
"len(df.columns)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"spark.sql(\n \"Select count( distinct product_id) from eda_sql_view\").show()",
"+--------------------------+\n|count(DISTINCT product_id)|\n+--------------------------+\n| 168675|\n+--------------------------+\n\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a773505eb8c32675cb7fd6e3d8b82c050c9869a
| 6,589 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Object_oriented/Objectoriented.ipynb
|
lkatsouri/pystarters-assignments
|
4620d931cd9708a08079a59a4aa5122f4afe55bf
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Object_oriented/Objectoriented.ipynb
|
lkatsouri/pystarters-assignments
|
4620d931cd9708a08079a59a4aa5122f4afe55bf
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Object_oriented/Objectoriented.ipynb
|
lkatsouri/pystarters-assignments
|
4620d931cd9708a08079a59a4aa5122f4afe55bf
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 41.968153 | 413 | 0.623463 |
[
[
[
"Link for exercises\n\nhttps://python-textbok.readthedocs.io/en/1.0/Classes.html\n\n Classes and types are themselves objects, and they are of type type. You can find out the type of any object using the type function:\ntype(any_object)\nThe data values which we store inside an object are called attributes, and the functions which are associated with the object are called methods. We have already used the methods of some built-in objects, like strings and lists.\n\nimport datetime # we will use this for date objects\nclass Person:\ndef __init__(self, name, surname, birthdate, address, telephone, email): # The first instance is the selfwhich is a conventional way of writing, and then you can call self.anything that is defined in your parenthesis and it will make sense of it)\n\nSee below how they define the methods of this class by self.name/surname.etc\n\n self.name = name\n self.surname = surname\n self.birthdate = birthdate\nself.address = address\n self.telephone = telephone\n self.email = email\n\n\nSOS: SELF HELPS RETURN AN ERROR IF YOUR OBECT DOESN'T HAVE THAT VALUE OTHERWISE IF IT WAS ONLY THE NAME OF THE FUNCTION THEN YOUR CODE WOULD HAVE A PROBLEM (AND YOU WOULDN'T BE ABLE TO DETECT IT AS IT WILL UNLIKELY RETURN AN ERROR)\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import datetime # we will use this for date objects\n\nclass Person:\n\n def __init__(self, name, surname, birthdate, address, telephone, email): #_init_ is everything that it wil try to run \n self.name = name\n self.surname = surname\n self.birthdate = birthdate\n\n self.address = address\n self.telephone = telephone\n self.email = email\n\n def age(self):\n today = datetime.date.today()\n age = today.year - self.birthdate.year\n\n if today < datetime.date(today.year, self.birthdate.month, self.birthdate.day):\n age -= 1\n\n return age\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"person = Person(\n \"Jane\",\n \"Doe\",\n datetime.date(1981, 10, 12), # year, month, day\n \"No. 12 Short Street, Greenville\",\n \"555 456 0987\",\n \"[email protected]\"\n)\n\nprint(person.name)\nprint(person.email)\nprint(person.age())",
"Jane\[email protected]\n37\n"
]
],
[
[
"INFORMATION\n\n1. Explain what the following variables refer to, and their scope:\n2. Person # It's the name of the class \n3. person # It's the definition of your object \n4. surname # one of the attributes of your object (data values) that will be passed when calling the Class\n5. self #SOS: SELF HELPS RETURN AN ERROR IF YOUR OBECT DOESN'T HAVE THAT VALUE OTHERWISE IF IT WAS ONLY THE NAME OF THE FUNCTION THEN YOUR CODE WOULD HAVE A PROBLEM (AND YOU WOULDN'T BE ABLE TO DETECT IT AS IT WILL UNLIKELY RETURN AN ERROR)\nYou may have noticed that both of these method definitions have self as the first parameter, and we use this variable inside the method bodies – but we don’t appear to pass this parameter in. This is because whenever we call a method on an object, the object itself is automatically passed in as the first parameter. This gives us a way to access the object’s properties from inside the object’s methods.\n6. age (the function name) # is defining the age \n7. age (the variable used inside the function) # this \n8. self.email # this is the \n9. person.email #\n\nSOS:\nnum - 1: produce the result of subtracting one from num; num is not changed\nnum -= 1: subtract one from num and store that result (equivalent to num = num - 1 when numis a number)\nNote that you can use num - 1 as an expression since it produces a result, e.g. foo = num - 1, or print(num - 1), but you cannot use num -= 1 as an expression in Python.\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"CLASS DEFINITION\n\nWe start the class definition with the class keyword, followed by the class name and a colon. We would list any parent classes in between round brackets before the colon, but this class doesn’t have any, so we can leave them out.\n\nInside the class body, we define two functions – these are our object’s methods. \n\nThe first is called __init__, which is a special method. When we call the class object, a new instance of the class is created, and the __init__ method on this new object is immediately executed with all the parameters that we passed to the class object. The purpose of this method is thus to set up a new object using data that we have provided.\n\nThe second method is a custom method which calculates the age of our person using the birthdate and the current date.\n\nYou may have noticed that both of these method definitions have self as the first parameter, and we use this variable inside the method bodies – but we don’t appear to pass this parameter in. This is because whenever we call a method on an object, the object itself is automatically passed in as the first parameter. This gives us a way to access the object’s properties from inside the object’s methods.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4a773d77007c08d24953ea3e77b6a4d0cc76fcd3
| 24,411 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/2.0 - Datasets.ipynb
|
collab-uniba/Benchmark_sentimentAnalysis_ITA
|
450e22074d5bb07c8a8ad6d3cd028bb3385eecfd
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/2.0 - Datasets.ipynb
|
collab-uniba/Benchmark_sentimentAnalysis_ITA
|
450e22074d5bb07c8a8ad6d3cd028bb3385eecfd
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/2.0 - Datasets.ipynb
|
collab-uniba/Benchmark_sentimentAnalysis_ITA
|
450e22074d5bb07c8a8ad6d3cd028bb3385eecfd
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2022-03-15T19:00:33.000Z
|
2022-03-15T19:00:33.000Z
| 35.532751 | 301 | 0.480562 |
[
[
[
"# Datasets processing",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Import and preprocessing",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\npd.set_option('display.max_colwidth', None)\nimport warnings\nwarnings.filterwarnings(\"ignore\")\n\n#INPS\nht_inps=pd.read_csv('../data/raw/Enti/INPS/Hashtags.csv')\nht_inps['type'] = 'hashtag'\nmn_inps=pd.read_csv('../data/raw/Enti/INPS/Mentions.csv')\nmn_inps['type']='mention'\n\n#INAIL\nht_inail=pd.read_csv('../data/raw/Enti/INAIL/Hashtags.csv')\nht_inail['type'] = 'hashtag'\nmn_inail=pd.read_csv('../data/raw/Enti/INAIL/Mentions.csv')\nmn_inail['type']='mention'\n\n#Protezione Civile\nht_pc=pd.read_csv('../data/raw/Enti/Protezione Civile/Hashtags.csv')\nht_pc['type'] = 'hashtag'\nmn_pc=pd.read_csv('../data/raw/Enti/Protezione Civile/Mentions.csv')\nmn_pc['type']='mention'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import numpy as np\n\n#INPS\n#concatenation of hashtags and mentions dataframes indicating the type of tweet in a column\nframes_inps = [ht_inps, mn_inps]\ndf_inps = pd.concat(frames_inps)\n#column definition to identify retweets\ndf_inps['retweet'] = np.where(df_inps['tweet'].str.contains('RT @'), True, False)\n\n#INAIL\n#concatenation of hashtags and mentions dataframes indicating the type of tweet in a column\nframes_inail = [ht_inail, mn_inail]\ndf_inail = pd.concat(frames_inail)\n#column definition to identify retweets\ndf_inail['retweet'] = np.where(df_inail['tweet'].str.contains('RT @'), True, False)\n\n#Protezione Civile\n#concatenation of hashtags and mentions dataframes indicating the type of tweet in a column\nframes_pc = [ht_pc, mn_pc]\ndf_pc = pd.concat(frames_pc)\n#column definition to identify retweets\ndf_pc['retweet'] = np.where(df_pc['tweet'].str.contains('RT @'), True, False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Dataset infos\ndef get_stats(df):\n print(\"Dataset Shape: \",df.shape)\n print(\"\\t Mentions - Hashtags\")\n print(\"#Mentions:\",df.loc[df['type'] == 'mention'].shape)\n print(\"#Hashtags:\",df.loc[df['type'] == 'hashtag'].shape)\n print(df['type'].value_counts(normalize=True) * 100)\n if \"retweet\" in df:\n print(\"\\t Retweet\")\n print(\"#Retweet:\",df.loc[df['retweet'] == True].shape)\n print(df['retweet'].value_counts(normalize=True) * 100)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"get_stats(df_inps)",
"Dataset Shape: (64373, 13)\n\t Mentions - Hashtags\n#Mentions: (36460, 13)\n#Hashtags: (27913, 13)\nmention 56.638653\nhashtag 43.361347\nName: type, dtype: float64\n\t Retweet\n#Retweet: (25214, 13)\nFalse 60.831404\nTrue 39.168596\nName: retweet, dtype: float64\n"
],
[
"df_inps.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Removing retweets and unnecessary columns\n\n#INPS\ndf_inps=df_inps.loc[df_inps['retweet'] == False]\ndf_inps=df_inps[['created_at','tweet_id','tweet','type']]\n\n#INAIL\ndf_inail=df_inail.loc[df_inail['retweet'] == False]\ndf_inail=df_inail[['created_at','tweet_id','tweet','type']]\n\n#Protezione Civile\ndf_pc=df_pc.loc[df_pc['retweet'] == False]\ndf_pc=df_pc[['created_at','tweet_id','tweet','type']]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"get_stats(df_inps)",
"Dataset Shape: (39159, 4)\n\t Mentions - Hashtags\n#Mentions: (23133, 4)\n#Hashtags: (16026, 4)\nmention 59.074542\nhashtag 40.925458\nName: type, dtype: float64\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Silver labelling",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#Emoji lists\npositive_emoticons=[\"😀\",\"😃\",\"😄\",\"😁\",\"😆\",\"🤣\",\"😂\",\"🙂\",\"😊\",\"😍\",\"🥰\",\"🤩\",\"☺\",\"🥳\"]\nnegative_emoticons=[\"😒\",\"😔\",\"😟\",\"🙁\",\"☹\",\"😥\",\"😢\",\"😭\",\"😱\",\"😞\",\"😓\",\"😩\",\"😫\",\"😡\",\"😠\",\"🤬\"]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Definition of silver labels based on the presence / absence of emojis within the entire tweet\n\n#INPS\npos_df_inps = df_inps.loc[df_inps['tweet'].str.contains('|'.join(positive_emoticons))]\nneg_df_inps = df_inps.loc[df_inps['tweet'].str.contains('|'.join(negative_emoticons))]\nneutral_df_inps = pd.concat([df_inps, pos_df_inps, neg_df_inps]).drop_duplicates(keep=False)\n\n#INAIL\npos_df_inail = df_inail.loc[df_inail['tweet'].str.contains('|'.join(positive_emoticons))]\nneg_df_inail = df_inail.loc[df_inail['tweet'].str.contains('|'.join(negative_emoticons))]\nneutral_df_inail = pd.concat([df_inail, pos_df_inail, neg_df_inail]).drop_duplicates(keep=False)\n\n#Protezione Civile\npos_df_pc = df_pc.loc[df_pc['tweet'].str.contains('|'.join(positive_emoticons))]\nneg_df_pc = df_pc.loc[df_pc['tweet'].str.contains('|'.join(negative_emoticons))]\nneutral_df_pc = pd.concat([df_pc, pos_df_pc, neg_df_pc]).drop_duplicates(keep=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"get_stats(neutral_df_pc)",
"Dataset Shape: (15104, 4)\n\t Mentions - Hashtags\n#Mentions: (8130, 4)\n#Hashtags: (6974, 4)\nmention 53.826801\nhashtag 46.173199\nName: type, dtype: float64\n"
],
[
"#tweets containing both positive and negative emoticons\nint_df_inps = pd.merge(pos_df_inps, neg_df_inps, how ='inner')\nint_df_inail = pd.merge(pos_df_inail, neg_df_inail, how ='inner')\nint_df_pc = pd.merge(pos_df_pc, neg_df_pc, how ='inner')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"int_df_inps.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Sampling neutral datasets to balance classes\n\n#INPS\nsample_neutral_df_inps = neutral_df_inps.sample(frac=0.015)\n\n#INAIL\nsample_neutral_df_inail = neutral_df_inail.sample(frac=0.015)\n\n#Protezione Civile\nsample_neutral_df_pc = neutral_df_pc.sample(frac=0.015)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"neg_df_inail.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Added polarity and topic column\n\n#INPS\npos_df_inps['polarity']='positive'\npos_df_inps['topic']='inps'\nneg_df_inps['polarity']='negative'\nneg_df_inps['topic']='inps'\nsample_neutral_df_inps['polarity']='neutral'\nsample_neutral_df_inps['topic']='inps'\n\n#INAIL\npos_df_inail['polarity']='positive'\npos_df_inail['topic']='inail'\nneg_df_inail['polarity']='negative'\nneg_df_inail['topic']='inail'\nsample_neutral_df_inail['polarity']='neutral'\nsample_neutral_df_inail['topic']='inail'\n\n#Protezione civile\npos_df_pc['polarity']='positive'\npos_df_pc['topic']='pc'\nneg_df_pc['polarity']='negative'\nneg_df_pc['topic']='pc'\nsample_neutral_df_pc['polarity']='neutral'\nsample_neutral_df_pc['topic']='pc'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#concatenation of all dataframes\ndf_total = pd.concat([pos_df_inps, pos_df_inail, pos_df_pc,neg_df_inps,neg_df_inail,neg_df_pc,sample_neutral_df_inps,sample_neutral_df_inail,sample_neutral_df_pc])\ndf_total.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Dataset shuffling\ndf_total_shuffle = df_total.sample(frac=1)\n#Duplicate removal\ndf_total_shuffle = df_total_shuffle.drop_duplicates(keep='first',subset=['tweet_id'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#First round annotation file\nann_1 = df_total_shuffle.sample(n=322,random_state=1)\nann_1.to_csv(\"../data/interim/Annotazione_1.csv\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Second round annotation file\nann_2 = pd.concat([df_total_shuffle,ann_1]).drop_duplicates(keep=False,subset=['tweet_id'])\nann_2.to_csv(\"../data/interim/Annotazione_2\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a7749d64369d863100662f556796a39386b7746
| 936,423 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/impulse response of lti models/0.1-pipeline_analysis.ipynb
|
ncsl/virtual_cortical_stim_epilepsy
|
638c54aa0c5330bf57cb20c4925973ea33917c14
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2021-01-12T03:59:11.000Z
|
2021-01-12T03:59:11.000Z
|
notebooks/impulse response of lti models/0.1-pipeline_analysis.ipynb
|
ncsl/virtual_cortical_stim_epilepsy
|
638c54aa0c5330bf57cb20c4925973ea33917c14
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/impulse response of lti models/0.1-pipeline_analysis.ipynb
|
ncsl/virtual_cortical_stim_epilepsy
|
638c54aa0c5330bf57cb20c4925973ea33917c14
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 537.247849 | 197,948 | 0.938706 |
[
[
[
"# Pipeline Analysis for CSM Model\n\n- Plot Heatmaps of the model results using Z-normalization\n- CEZ/OEZ Pooled Patient Analysis\n- CEZ/OEZ IRR Metric",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import os\nimport sys\nimport collections\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport warnings\nwarnings.filterwarnings(\"ignore\")\nimport scipy.stats\nfrom sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, auc, precision_recall_curve, \\\n average_precision_score, confusion_matrix, accuracy_score\nfrom pprint import pprint\nimport copy\n\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression\n\nfrom scipy.cluster.hierarchy import linkage\nfrom scipy.cluster.hierarchy import dendrogram\n\nsys.path.append(\"../../\")\n\n%matplotlib inline\nimport matplotlib as mp\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn as sns\nimport dabest\n\nfrom eztrack.edm.classifiers.evaluate.dataset import Dataset, Patient\nfrom eztrack.edm.classifiers.evaluate.pipeline import EvaluationFramework\nfrom eztrack.edm.classifiers.evaluate.model_selection import get_clinical_split, compute_category_regression, \\\n compute_splits_train, large_scale_train\n\nfrom eztrack.edv.results.plot_distributions import PlotDistributions\nfrom eztrack.edv.base.utils import plot_baseline, plot_boxplot, plot_pr, \\\n plot_roc, plot_confusion_matrix, plot_boxplot_withdf\nfrom eztrack.base.utils.data_science_utils import cutoff_youdens, split_inds_engel, \\\n split_inds_clindiff, split_inds_outcome, get_numerical_outcome, compute_minmaxfragilitymetric, compute_fragilitymetric,\\\n compute_znormalized_fragilitymetric, split_inds_modality\nfrom eztrack.edm.classifiers.model.cez_oez_analyzer import FragilitySplitAnalyzer\nfrom eztrack.pipeline.experiments.cez_vs_oez.center_cezvsoez import plot_results\nfrom eztrack.edp.objects.clinical.master_clinical import MasterClinicalSheet\nfrom eztrack.edp.loaders.dataset.clinical.excel_meta import ExcelReader\n\n# Import magic commands for jupyter notebook \n# - autoreloading a module\n# - profiling functions for memory usage and scripts\n%load_ext autoreload\n%autoreload 2",
"The autoreload extension is already loaded. To reload it, use:\n %reload_ext autoreload\n"
],
[
"def get_per_patient_results(timewarpdict_dataset):\n # reorder them into patients\n timewarp_patient = collections.defaultdict(list)\n datasetids = []\n for datasetid in sorted(timewarpdict_dataset.keys()):\n # extract the patient id\n patid = datasetid.split(\"_\")[0]\n _datasetid = datasetid.split(\"_\")[0]\n datasetids.append(_datasetid)\n\n # extract the data from each dataset and the corresponding cez/oez matrix\n data = timewarpdict_dataset[datasetid]\n cezmat = data['cezmat']\n oezmat = data['oezmat']\n if oezmat.shape[0] == 0 or cezmat.shape[0] == 0:\n print(cezmat.shape, oezmat.shape)\n print(patid, datasetid)\n continue\n\n # add to patient's list of datasets\n timewarp_patient[patid].append((cezmat, oezmat))\n\n totaldatasets = 0\n for pat in timewarp_patient.keys():\n totaldatasets += len(timewarp_patient[pat])\n\n return timewarp_patient, datasetids, totaldatasets",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"datadir = \"/Users/adam2392/Dropbox/phd_research/Fragility_Analysis_Project/\"\n# datadir = \"/home/adam2392/Documents/Dropbox/phd_research/Fragility_Analysis_Project/\"\n\nexcelfilename = \"organized_clinical_datasheet_raw.xlsx\"\nexcelfilepath = os.path.join(datadir, excelfilename)\n\noutputexcelfilename = \"organized_clinical_datasheet_formatted.xlsx\"\noutputexcelfilepath = os.path.join(datadir, outputexcelfilename)\nprint(os.path.exists(excelfilepath))\nprint(excelfilepath)",
"True\n/Users/adam2392/Dropbox/phd_research/Fragility_Analysis_Project/organized_clinical_datasheet_raw.xlsx\n"
],
[
"clinreader = ExcelReader(excelfilepath)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ieegdf, datasetdf, scalpdf = clinreader.read_formatted_df()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mastersheet = MasterClinicalSheet(ieegdf, datasetdf, scalpdf)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"figdir = \"/Users/adam2392/Downloads/journalfigs/\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Load In Data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"modality = 'ieeg'\n# modality = 'scalp'\nreference = \"common_avg\"\nreference = \"monopolar\"\n\nmodelname = \"impulse\"\nnetworkmodelname = \"\"\nfreqband = \"\"\nexpname = \"trimmed\"\n\ndatadir = f\"/Users/adam2392/Downloads/output_new/{expname}/{modelname}{networkmodelname}/{reference}/{modality}/\"\n\nresultfilepath = os.path.join(datadir, f\"{modelname}_responses.npz\")\nif not os.path.exists(resultfilepath):\n resultfilepath = os.path.join(datadir, f\"networkstatic_responses.npz\")\nallfiles = os.listdir(datadir)\nprint(allfiles)\n \n# data that is only timewarped, but without threshold applied yet\n# datadir = \"/Users/adam2392/Downloads/output_new/joined_results/timewarp_nothreshold/\"\n# datadir = \"/Users/adam2392/Downloads/output_new/common_avg_timewarp_nothresh/\"",
"['jhu', 'nih', 'ummc', 'cleveland']\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Create Plots of Data\n\nFirst create for successful patients, then for failure patients.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"COMBINE_SEPARATE_PATS = [\n 'pt11',\n 'nl22',\n 'ummc007',\n 'tvb7',\n 'nl02', 'nl06', 'nl11', # no resection\n]\n\nignore_pats = [\n# 'pt11',\n# 'jh107'\n 'la01-2','la01',\n 'la03', 'la05', \n# 'la09', \n 'la23',\n 'nl22',\n]\n\ncenter = 'nih'\n\ndict_dataset = dict()\ncenterdir = os.path.join(datadir, center)\nif freqband != \"\":\n centerdir = os.path.join(centerdir, freqband)\nresultfilepath = os.path.join(centerdir, f\"{modelname}_responses.npz\")\nif not os.path.exists(resultfilepath):\n resultfilepath = os.path.join(centerdir, f\"networkstatic_responses.npz\")\nif not os.path.exists(resultfilepath):\n resultfilepath = os.path.join(centerdir, f\"impulsemodel_magnitude1_responses.npz\")\nallfiles = os.listdir(os.path.join(centerdir))\n\n# load in the dataset\ntrainresult = np.load(resultfilepath, allow_pickle=True)\ndict_dataset.update(**trainresult['timewarpdict'].item())\n\ndataset_patient, datasetids, numdatasets = get_per_patient_results(dict_dataset)\nprint(dataset_patient.keys())\nprint(numdatasets)",
"dict_keys(['pt10', 'pt11', 'pt12', 'pt13', 'pt14', 'pt15', 'pt16', 'pt1', 'pt2', 'pt3', 'pt6', 'pt7', 'pt8'])\n41\n"
],
[
"dict_dataset = dict()\ncenters = [\n# 'clevelandnl', \n 'cleveland',\n 'nih',\n 'jhu',\n 'ummc'\n]\n\nfor center in centers:\n centerdir = os.path.join(datadir, center)\n if freqband != \"\":\n centerdir = os.path.join(centerdir, freqband)\n resultfilepath = os.path.join(centerdir, f\"{modelname}_responses.npz\")\n# print(resultfilepath)\n if not os.path.exists(resultfilepath):\n resultfilepath = os.path.join(centerdir, f\"networkstatic_responses.npz\")\n if not os.path.exists(resultfilepath):\n resultfilepath = os.path.join(centerdir, f\"impulsemodel_magnitude1_responses.npz\")\n allfiles = os.listdir(os.path.join(centerdir))\n # load in the datasete\n result = np.load(resultfilepath, allow_pickle=True)\n dict_dataset.update(**result['timewarpdict'].item())\n\nprint(dict_dataset.keys())\ndataset_patient, datasetids, totaldatasets = get_per_patient_results(dict_dataset)\nprint(totaldatasets)\n",
"dict_keys(['la22_sz_5p', 'la11_sz', 'la01_sz', 'la13_sz_1', 'la08_sz', 'la02_sz', 'la06_sz', 'la04_sz', 'la07_sz_1', 'la17_sz', 'la22_sz_6p', 'la08_sz_1pg', 'la22_sz_7p', 'la06_sz_1p', 'pt1_sz_2', 'pt1_sz_6', 'pt1_sz_4', 'pt1_sz_3', 'pt12_sz_2', 'pt15_sz_1', 'pt10_sz_2', 'pt15_sz_2', 'pt16_sz_1', 'pt16_sz_3', 'pt10_sz_1', 'pt15_sz_3', 'pt2_sz_4', 'pt6_sz_5', 'pt6_sz_4', 'pt10_sz_3', 'pt12_sz_1', 'pt6_sz_3', 'pt7_sz_22', 'pt2_sz_3', 'pt15_sz_4', 'pt16_sz_2', 'pt3_sz_2', 'pt2_sz_1', 'pt14_sz_1', 'pt3_sz_4', 'pt14_sz_2', 'pt7_sz_21', 'pt14_sz_3', 'pt11_sz_2', 'pt11_sz_4', 'pt11_sz_3', 'pt7_sz_19', 'pt8_sz_1', 'pt8_sz_2', 'pt11_sz_1', 'pt8_sz_3', 'pt13_sz_3', 'pt13_sz_5', 'pt13_sz_2', 'pt13_sz_1', 'jh107_sz_8', 'jh107_sz_7', 'jh107_sz_9', 'jh107_sz_1', 'jh107_sz_2', 'jh107_sz_4', 'jh102_sz_3', 'jh102_sz_6', 'jh104_sz_1', 'jh103_sz_3', 'jh103_sz_1', 'jh108_sz_3', 'jh105_sz_5', 'jh105_sz_1', 'jh108_sz_4', 'jh108_sz_6', 'jh105_sz_2', 'jh105_sz_3', 'jh105_sz_4', 'jh108_sz_5', 'jh108_sz_7', 'jh108_sz_2', 'ummc008_sz_2', 'ummc007_sz_3', 'ummc007_sz_1', 'ummc005_sz_3', 'ummc009_sz_3', 'ummc007_sz_2', 'ummc008_sz_3', 'ummc005_sz_2', 'ummc009_sz_2', 'ummc009_sz_1', 'ummc002_sz_2', 'ummc002_sz_3', 'ummc006_sz_1', 'ummc001_sz_3', 'ummc001_sz_2', 'ummc001_sz_1', 'ummc003_sz_3', 'ummc002_sz_1', 'ummc004_sz_2', 'ummc006_sz_2', 'ummc003_sz_1', 'ummc004_sz_1', 'ummc008_sz_1', 'ummc003_sz_2'])\n101\n"
],
[
"plotter = PlotDistributions(figdir)\n\nprint(dataset_patient.keys())\n\njhcount = 0\numcount = 0\nnihcount = 0\ncccount = 0\n\nfor key in dataset_patient.keys():\n if 'jh' in key:\n jhcount += 1\n elif 'ummc' in key:\n umcount += 1\n elif 'pt' in key:\n nihcount += 1\n elif 'la' in key:\n cccount += 1\nprint(jhcount)\nprint(umcount, nihcount, cccount)\nprint(6+9+13+10)",
"dict_keys(['jh102', 'jh103', 'jh104', 'jh105', 'jh107', 'jh108', 'la01', 'la02', 'la04', 'la06', 'la07', 'la08', 'la11', 'la13', 'la17', 'la22', 'pt10', 'pt11', 'pt12', 'pt13', 'pt14', 'pt15', 'pt16', 'pt1', 'pt2', 'pt3', 'pt6', 'pt7', 'pt8', 'ummc001', 'ummc002', 'ummc003', 'ummc004', 'ummc005', 'ummc006', 'ummc007', 'ummc008', 'ummc009'])\n6\n9 13 10\n38\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Dataset Summary",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"failcount = 0\nsuccesscount = 0\n\nengel_count_dict = dict()\nfor patient in patientlist:\n if patient.outcome == 'nr':\n continue\n elif patient.outcome == 'f':\n failcount += 1\n else:\n successcount += 1\n \n if str(patient.engelscore) not in engel_count_dict.keys():\n engel_count_dict[str(patient.engelscore)] = 0\n engel_count_dict[str(patient.engelscore)] += 1\n \nprint(failcount, successcount)\nprint(engel_count_dict)",
"14 19\n{'4.0': 4, '1.0': 19, '2.0': 8, '3.0': 2}\n"
],
[
"print(4+19+8+2)",
"33\n"
],
[
"cez_chs = []\nother_chs = []\nallpats = []\n\nfor pat in dataset_patient.keys():\n datasets = dataset_patient[pat]\n \n if pat in ignore_pats:\n continue\n \n cezs = []\n oezs = []\n print(pat)\n \n # normalize\n print(len(datasets))\n# for i in range(len(datasets)):\n# cezmat, oezmat = datasets[i]\n# # print(cezmat.shape, oezmat.shape)\n# mat = np.concatenate((cezmat, oezmat), axis=0)\n# mat = compute_minmaxfragilitymetric(mat)\n# cezmat = mat[:cezmat.shape[0], :]\n# oezmat = mat[cezmat.shape[0]:, :]\n# print(cezmat.shape, oezmat.shape)\n \n for i in range(len(datasets)):\n cezmat, oezmat = datasets[i]\n \n mat = np.concatenate((cezmat, oezmat), axis=0)\n# mat = compute_fragilitymetric(mat)\n cezmat = mat[:cezmat.shape[0], :]\n oezmat = mat[cezmat.shape[0]:, :]\n \n if pat in joinseppats:\n cezs.append(np.mean(cezmat, axis=0))\n oezs.append(np.mean(oezmat, axis=0))\n else:\n cezs.append(cezmat)\n oezs.append(oezmat)\n \n if pat not in joinseppats:\n cezs = np.nanmedian(np.array(cezs), axis=0)\n oezs = np.nanmedian(np.array(oezs), axis=0)\n \n# print(np.array(cezs).shape)\n \n # store the entire patient concatenated vector\n cez_chs.append(np.mean(cezs, axis=0))\n other_chs.append(np.mean(oezs, axis=0))\n allpats.append(pat)\n \ncez_chs = np.array(cez_chs)\nother_chs = np.array(other_chs)",
"jh102\n2\n"
],
[
"print(cez_chs.shape, other_chs.shape)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# split by outcome\nsucc_inds, fail_inds = split_inds_outcome(allpats, mastersheet)\n\nprint(len(succ_inds), len(fail_inds))\nprint(totaldatasets)\ncenter = \", \".join(centers)\nprint(center)",
"19 14\n101\ncleveland, nih, jhu, ummc\n"
],
[
"sns.set(font_scale=1.75)\n\ncez_mat_fail = cez_chs[fail_inds,...]\noez_mat_fail = other_chs[fail_inds,...]\n\n# take the average across all patients\nmean_onset = np.nanmean(cez_mat_fail, axis=0)\nmean_other = np.nanmean(oez_mat_fail, axis=0)\nstderr_onset = scipy.stats.sem(cez_mat_fail, nan_policy='omit', axis=0)\nstderr_other = scipy.stats.sem(oez_mat_fail, nan_policy='omit', axis=0)\n\n# mean_onset[mean_onset > 3] = 5\n# mean_other[mean_other > 3] = 5\n# stderr_onset[np.abs(stderr_onset) > 3] = 3\n# stderr_other[np.abs(stderr_other) > 3] = 3\n\nxs = [np.arange(len(mean_onset)), np.arange(len(mean_other))]\nys = [mean_onset, mean_other]\nerrors = [stderr_onset, stderr_other]\nlabels = ['clinez (n={})'.format(len(cez_mat_fail)), \n 'others (n={})'.format(len(oez_mat_fail))]\nthreshstr = \"\\n Thresh=0.7\"\n# threshstr = \"\"\ntitlestr=\"{center} {reference} Failure Fragile Channels\".format(center=center, \n reference=reference)\nxlabel = \"Normalized Window Around Seizure Onset (+/- 10 secs)\"\nvertline = [30,130]\n# vertline = [offsetwin]\nfig, ax = plotter.plot_comparison_distribution(xs, ys, labels=labels, alpha=0.5,\n save=True, \n# ylim=[0,7.5],\n figure_name=titlestr,\n errors=errors, \n titlestr=titlestr, \n ylabel=\"DOA +/- stderr\",\n xlabel=\"Time (a.u.)\",\n vertlines=vertline)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(cez_chs.shape, other_chs.shape)\ncez_mat = cez_chs[succ_inds,...]\noez_mat = other_chs[succ_inds,...]\n\n# take the average across all patients\nmean_onset = np.mean(cez_mat, axis=0)\nmean_other = np.mean(oez_mat, axis=0)\nstderr_onset = scipy.stats.sem(cez_mat, axis=0)\nstderr_other = scipy.stats.sem(oez_mat, axis=0)\n\n# mean_onset[mean_onset>5] = 5\n# mean_other[mean_other>5] = 5\n# stderr_onset[stderr_onset > 5] = 5\n# stderr_other[stderr_other > 5] = 5\n\nxs = [np.arange(len(mean_onset)), np.arange(len(mean_other))]\nys = [mean_onset, mean_other]\nerrors = [stderr_onset, stderr_other]\nlabels = ['clinez (n={})'.format(len(cez_mat)), \n 'others (n={})'.format(len(oez_mat))]\nthreshstr = \"\\n Thresh=0.7\"\n# threshstr = \"\"\ntitlestr=\"{center} {reference} Success Fragile Channels\".format(center=center, \n reference=reference)\nxlabel = \"Normalized Window Around Seizure Onset (+/- 10 secs)\"\nvertline = [30,130]\n# vertline = [offsetwin]\nfig, ax = plotter.plot_comparison_distribution(xs, ys, labels=labels, \n save=True,\n# ylim=[0, 7],\n figure_name=titlestr,\n errors=errors, \n titlestr=titlestr, \n ylabel=\"DOA +/- stderr\",\n xlabel=\"Time (a.u.)\",\n vertlines=vertline)",
"(37, 160) (37, 160)\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Create Pipeline Object",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def plot_summary(succ_ezratios, fail_ezratios, clinical_baseline,\n engelscore_box, clindiff_box,\n fpr, tpr, precision, recall, average_precision,\n youdenind, youdenpred, titlestr, clf_auc,\n Y_pred_engel, Y_pred_clindiff):\n ylabel = \"DOA Metric\"\n\n # plotting for baselines\n baselinex_roc = [0, 1-(clinical_baseline-0.5)]\n baseliney_roc = [0+(clinical_baseline-0.5), 1]\n baselinex_pr = [0, 1]\n baseliney_pr = [clinical_baseline, clinical_baseline]\n\n # make box plot\n plt.style.use(\"classic\")\n sns.set_style(\"white\")\n fix, axs = plt.subplots(2,3, figsize=(25,15))\n axs = axs.flatten()\n ax = axs[0]\n titlestr = f\"Outcome Split N={numdatasets} P={numpats}\"\n boxdict = [\n [fail_ezratios, succ_ezratios],\n [ 'Fail', 'Success']\n ]\n plot_boxplot(ax, boxdict, titlestr, ylabel)\n\n outcome_df = create_df_from_outcome(succ_ezratios, fail_ezratios)\n outcome_dabest = dabest.load(data=outcome_df, \n x='outcome', y=\"ezr\",\n idx=('failure','success')\n )\n # Produce a Cumming estimation plot.\n outcome_dabest.mean_diff.plot();\n \n ax = axs[1]\n titlestr = f\"Engel Score Split N={numdatasets} P={numpats}\"\n plot_boxplot(ax, engelscore_box, \n titlestr, ylabel=\"\")\n xticks = ax.get_xticks()\n ax.plot(xticks, Y_pred_engel, \n color='red',\n label=f\"y={engel_intercept:.2f} + {engel_slope:.2f}x\"\n )\n ax.legend()\n\n ax = axs[2]\n titlestr = f\"Clin Difficulty Split N={numdatasets} P={numpats}\"\n plot_boxplot(ax, clindiff_box, titlestr, \n ylabel=\"\")\n ax.plot(xticks, Y_pred_clindiff, color='red', \n label=f\"y={clindiff_intercept:.2f} + {clindiff_slope:.2f}x\")\n ax.legend()\n\n # make ROC Curve plot\n ax = axs[3]\n titlestr = f\"ROC Curve N={numdatasets} P={numpats}\"\n label = \"ROC Curve (AUC = %0.2f)\" % (clf_auc)\n plot_roc(ax, fpr, tpr, label, titlestr)\n plot_baseline(ax, baselinex_roc, baseliney_roc)\n ax.legend(loc='lower right')\n ax.plot(np.mean(baselinex_roc).squeeze(), np.mean(baseliney_roc).squeeze(), \n 'k*', linewidth=4, markersize=12, \n label=f\"Clinical-Baseline {np.round(clinical_baseline, 2)}\"\n )\n ax.plot(fpr[youdenind], tpr[youdenind], \n 'r*', linewidth=4, markersize=12, \n label=f\"Youden-Index {np.round(youdenacc, 2)}\")\n ax.legend(loc='lower right')\n\n # make PR Curve\n ax = axs[4]\n label = 'PR Curve (AP = %0.2f)' % (average_precision)\n titlestr = f\"PR-Curve N={numdatasets} P={numpats}\"\n plot_pr(ax, recall, precision, label, titlestr)\n plot_baseline(ax, baselinex_pr, baseliney_pr)\n ax.legend(loc='lower right')\n\n # Confusion Matrix\n ax = axs[5]\n titlestr = f\"Confusion matrix Youdens-cutoff\"\n plot_confusion_matrix(ax, ytrue, youdenpred, classes=[0.,1.],\n title=titlestr, normalize=True)\n\n# titlestr = f\"{modelname}{networkmodelname}-{freqband} {center} N={numdatasets} P={numpats}\"\n # plt.savefig(os.path.join(figdir, normname, titlestr+\".png\"), \n # box_inches='tight')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%%time\n\n# create patient list for all datasets\npatientlist = []\n\nfor patientid in dataset_patient.keys():\n # initialize empty list to store datasets per patient\n datasetlist = []\n \n if patientid in ignore_pats:\n continue\n \n # get metadata for patient\n center = mastersheet.get_patient_center(patientid)\n outcome = mastersheet.get_patient_outcome(patientid)\n engelscore = mastersheet.get_patient_engelscore(patientid)\n clindiff = mastersheet.get_patient_clinicaldiff(patientid)\n modality = mastersheet.get_patient_modality(patientid)\n \n for datasetname, result in dict_dataset.items():\n # get the patient/dataset id\n patid = datasetname.split(\"_\")[0]\n datasetid = datasetname.split(patid + \"_\")[1]\n \n# print(patid, datasetid)\n if patid != patientid:\n continue\n # format the matrix and the indices\n mat = np.concatenate((result['cezmat'], result['oezmat']), axis=0)\n cezinds = np.arange(0, result['cezmat'].shape[0])\n\n # create dataset object\n dataset_obj = Dataset(mat=mat, \n patientid=patid,\n name=datasetid,\n datatype='ieeg', \n cezinds=cezinds, \n markeron=30, \n markeroff=130)\n datasetlist.append(dataset_obj)\n\n if patientid == 'pt2':\n print(mat.shape)\n ax = sns.heatmap(mat,cmap='inferno',\n yticklabels=[],\n# vmax=3, \n# vmin=-3\n )\n ax.axhline(len(cezinds), linewidth=5, color='white')\n ax.set_ylabel(\"CEZ vs OEZ Map\")\n ax.axvline(30, linewidth=4, linestyle='--', color='red')\n ax.axvline(130, linewidth=4, linestyle='--', color='black')\n \n # create patient object\n patient_obj = Patient(datasetlist, \n name=patientid,\n center=center,\n outcome=outcome,\n engelscore=engelscore,\n clindiff=clindiff,\n modality=modality)\n patientlist.append(patient_obj)\n# print(patient_obj, len(datasetlist))\nevalpipe = EvaluationFramework(patientlist)",
"(64, 160)\nCPU times: user 413 ms, sys: 71.8 ms, total: 485 ms\nWall time: 362 ms\n"
],
[
"print(patient_obj)\nprint(evalpipe.centers, evalpipe.modalities)\nprint(evalpipe)\n\nCOMBINE_SEPARATE_PATS = [\n 'pt11',\n# 'nl22',\n 'ummc007',\n# 'tvb7',\n# 'nl02', 'nl06', 'nl11', # no resection\n]\n\nignore_pats = [\n# 'pt11',\n# 'jh107'\n# 'jh102', 'jh104',\n 'la01-2','la01',\n 'la03', 'la05', \n# 'la09', \n 'la23',\n 'nl22',\n]",
"ummc009 (ecog, s, 1.0, 1.0) - ummc w/ 3 datasets\n['cc' 'jhh' 'nih' 'ummc'] ['ecog' 'seeg']\n37 Patients - 100 Data Snapshots\n"
],
[
"# evalpipe.apply_normalization(normalizemethod=None)\nezr_list = evalpipe.compute_ezratios(\n# threshold=0.5,\n ignore_pats=ignore_pats, \n combine_sep_pats=COMBINE_SEPARATE_PATS\n )\nnr_inds = evalpipe.remove_nr_inds()\nsurgery_inds = evalpipe.get_surgery_inds()",
"jh102\njh103\njh104\njh105\njh107\njh108\nla02\nla04\nla06\nla07\nla08\nla11\nla13\nla17\nla22\npt10\npt11\npt12\npt13\npt14\npt15\npt16\npt1\npt2\npt3\npt6\npt7\npt8\nummc001\nummc002\nummc003\nummc004\nummc005\nummc006\nummc007\nummc008\nummc009\n"
],
[
"ezratios = ezr_list[surgery_inds]\npatlist = evalpipe.patientlist[surgery_inds]\n\n# split by outcome\nsucc_inds, fail_inds = split_inds_outcome(patlist, mastersheet)\nytrue = get_numerical_outcome(patlist, mastersheet)\nengel_inds_dict = split_inds_engel(patlist, mastersheet)\nclindiff_inds_dict = split_inds_clindiff(patlist, mastersheet)\n\nroc_dict, cm = evalpipe.evaluate_roc_performance(ezratios, ytrue, \n normalize=True)\n\npr_dict = evalpipe.evaluate_pr_performance(ezratios, ytrue, pos_label=1)\n\n# extract data from dictionaries\nfpr = roc_dict['fpr']\ntpr = roc_dict['tpr']\nclf_auc = roc_dict['auc']\nyoudenthreshold = roc_dict['youdenthresh']\nyoudenacc = roc_dict['youdenacc']\nyoudenind = roc_dict['youdenind']\nprecision = pr_dict['prec']\nrecall = pr_dict['recall']\naverage_precision = pr_dict['avgprec']\nclinical_baseline = pr_dict['baseline']\n\n# youden prediction\nyoudenpred = ezratios >= youdenthreshold\nyoudenpred = [int(y == True) for y in youdenpred]\n# evaluate box plot separation using wilcoxon rank-sum\nsucc_ezratios, fail_ezratios, \\\n stat, pval = evalpipe.evaluate_metric_separation(ytrue, ezratios, pos_label=1, neg_label=0)\n\nprint(\"Wilcoxon Rank-sum: \", stat, pval)\nprint(\"Clinical baseline: \", clinical_baseline)\nprint(sum(ytrue))\n# pprint(pr_dict)",
"Normalized confusion matrix\nWilcoxon Rank-sum: 2.0398506592577563 0.04136520236222277\nClinical baseline: 0.5757575757575758\n19\n"
],
[
"engelscore_box = {}\nfor i in sorted(engel_inds_dict.keys()):\n if i == -1:\n continue\n if np.isnan(i):\n continue\n this_fratio = ezratios[engel_inds_dict[i]]\n engelscore_box[f\"ENG{int(i)}\"] = this_fratio\n \nclindiff_box = {}\nfor i in sorted(clindiff_inds_dict.keys()):\n this_fratio = ezratios[clindiff_inds_dict[i]]\n clindiff_box[f\"CD{int(i)}\"] = this_fratio\nprint(\"Total amount of data: \", len(ezratios), len(patlist))",
"Total amount of data: 33 33\n"
],
[
"\nlinear_regressor = LinearRegression() # create object for the class\n\nX = []\ny = []\nfor idx, engelscore in enumerate(engelscore_box.keys()):\n print(engelscore)\n y.append(np.mean(engelscore_box[engelscore]))\n X.append(idx+1)\nX = np.array(X)[:, np.newaxis]\nlinear_regressor.fit(X, y) # perform linear regression\nengel_intercept = linear_regressor.intercept_\nengel_slope = linear_regressor.coef_[0]\nY_pred_engel = linear_regressor.predict(X) # make predictions\n\nX = []\ny = []\nfor idx, clindiff in enumerate(clindiff_box.keys()):\n print(clindiff)\n y.append(np.mean(clindiff_box[clindiff]))\n X.append(idx+1)\nX = np.array(X)[:, np.newaxis]\nlinear_regressor.fit(X, y) # perform linear regression\nclindiff_intercept = linear_regressor.intercept_\nclindiff_slope = linear_regressor.coef_[0]\nY_pred_clindiff = linear_regressor.predict(X) # make predictions\n\nprint(X, y)\nprint(\"Slope and intercept: \", clindiff_slope, clindiff_intercept)",
"ENG1\nENG2\nENG3\nENG4\nCD1\nCD2\nCD3\nCD4\n[[1]\n [2]\n [3]\n [4]] [0.5392008014783284, 0.5469054273374603, 0.5455448985873456, 0.4966586046210598]\nSlope and intercept: -0.012898711932192044 0.5643242128365286\n"
],
[
"sns.set(font_scale=2.5)\ncenternames = \"UMMC, JHH, CC\"\nnumpats = len(patlist)\nnumdatasets = totaldatasets\n# titlestr = f\"{modelname}{networkmodelname}-{freqband} {center} N={numdatasets} P={numpats}\"\ntitlestr= f\"{modelname}{networkmodelname}-{freqband} {centernames} N={numdatasets} P={numpats}\"\ntitlestr = \"\"\nplot_summary(succ_ezratios, fail_ezratios, clinical_baseline,\n engelscore_box, clindiff_box,\n fpr, tpr, precision, recall, average_precision,\n youdenind, youdenpred, titlestr, clf_auc,\n Y_pred_engel, Y_pred_clindiff)",
"Normalized confusion matrix\n"
],
[
"print(\"Outlier min on fratio_succ: \", \n patlist[ezratios==min(succ_ezratios)])\nprint(\"Outlier max oon fratio_fail: \", \n patlist[ezratios==max(fail_ezratios)])\n\nargsort_succ = np.sort(succ_ezratios)\ntopinds = [ezratios.tolist().index(argsort_succ[i]) for i in range(10)]\nsucc_bad_pats = patlist[topinds]\n\nprint(\"\\n\\n Outlier of success patients:\")\nprint(succ_bad_pats)\n\nargsort_fail = np.sort(fail_ezratios)[::-1]\ntopinds = [ezratios.tolist().index(argsort_fail[i]) for i in range(10)]\nfail_bad_pats = patlist[topinds]\n\nprint(\"\\n\\n Outlier of failed patients:\")\nprint(fail_bad_pats)",
"Outlier min on fratio_succ: ['jh107']\nOutlier max oon fratio_fail: ['pt6']\n\n\n Outlier of success patients:\n['jh107' 'pt16' 'pt15' 'la07' 'pt11' 'ummc005' 'pt8' 'pt2' 'pt3' 'ummc008']\n\n\n Outlier of failed patients:\n['pt6' 'la13' 'pt7' 'pt14' 'jh108' 'la22' 'la04' 'la06' 'la17' 'pt12']\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Train/Test Split",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# traininds, testinds = train_test_split(np.arange(len(y)), test_size=0.6, random_state=98765)\ntraininds, testinds = evalpipe.train_test_split(method='engel', \n trainsize=0.50)\n\nprint(len(traininds), len(testinds))\n\n''' RUN TRAINING '''\nezratios = ezr_list[surgery_inds]\n# ezratios = ezratios[traininds]\npatlist = evalpipe.patientlist[surgery_inds]\n# patlist = patlist[traininds]\n\nnumpats = len(patlist)\nprint(len(patlist), len(ezratios))\n# split by outcome\nsucc_inds, fail_inds = split_inds_outcome(patlist, mastersheet)\nytrue = get_numerical_outcome(patlist, mastersheet)\nengel_inds_dict = split_inds_engel(patlist, mastersheet)\nclindiff_inds_dict = split_inds_clindiff(patlist, mastersheet)\n\nsucc_ezratios = ezratios[succ_inds]\nfail_ezratios = ezratios[fail_inds]\n\n# engel / clindiff metric split into dictionary\nengel_metric_dict = get_clinical_split(ezratios, 'engel', engel_inds_dict)\nclindiff_metric_dict = get_clinical_split(ezratios, 'clindiff', clindiff_inds_dict)\n\n# create dictionary split engel and clindiff classes\nengel_metric_dict = get_clinical_split(ezratios, 'engel', engel_inds_dict)\nclindiff_metric_dict = get_clinical_split(ezratios, 'clindiff', clindiff_inds_dict)\n\nY_pred_engel, engel_intercept, engel_slope = compute_category_regression(engel_metric_dict)\nY_pred_clindiff, clindiff_intercept, clindiff_slope = compute_category_regression(clindiff_metric_dict)\n",
"18 22\n33 33\nENG_1\nENG_2\nENG_3\nENG_4\nCD_1\nCD_2\nCD_3\nCD_4\n"
],
[
"ezrcolvals = np.concatenate((succ_ezratios, fail_ezratios), axis=-1)[:, np.newaxis]\nscorevals = np.array(['Success']*len(succ_ezratios) + ['Failure']*len(fail_ezratios))[:, np.newaxis]\noutcome_df = pd.DataFrame(data=ezrcolvals, columns=['ezr'])\noutcome_df['Outcome'] = scorevals\n\nezrcolvals = []\nscorevals = []\nfor key, vals in engel_metric_dict.items():\n scorevals.extend([key] * len(vals))\n ezrcolvals.extend(vals)\nengel_df = pd.DataFrame(data=ezrcolvals, columns=['ezr'])\nengel_df['Engel Score'] = scorevals\n\nezrcolvals = []\nscorevals = []\nfor key, vals in clindiff_metric_dict.items():\n scorevals.extend([key] * len(vals))\n ezrcolvals.extend(vals)\nclindiff_df = pd.DataFrame(data=ezrcolvals, columns=['ezr'])\nclindiff_df['Epilepsy Category'] = scorevals\n\nprint(\"converted clinical categorizations into dataframes!\")\ndisplay(outcome_df.head())\ndisplay(engel_df.head())\ndisplay(clindiff_df.head())",
"converted clinical categorizations into dataframes!\n"
],
[
"outcome_df.to_csv(\"/Users/adam2392/Downloads/outcome_impulsemodel.csv\")\nengel_df.to_csv(\"/Users/adam2392/Downloads/engel_impulsemodel.csv\")\nclindiff_df.to_csv(\"/Users/adam2392/Downloads/clindiff_impulsemodel.csv\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ylabel = \"Degree of Agreement (CEZ)\"\n\noutcome_dabest = dabest.load(data=outcome_df, x='Outcome', y=\"ezr\", \n idx=outcome_df['Outcome'].unique()\n )\nengel_dabest = dabest.load(data=engel_df, x='Engel Score', y=\"ezr\", \n idx=engel_df['Engel Score'].unique()\n )\nclindiff_dabest = dabest.load(data=clindiff_df, x='Epilepsy Category', y=\"ezr\", \n idx=clindiff_df['Epilepsy Category'].unique()\n )\n\n# make box plot\nplt.style.use(\"classic\")\nsns.set(font_scale=1.75)\nsns.set_style(\"white\")\ncols = 3\nrows = 1\nylim = [0.3, 0.7]\nylim = None\n\nfig, axs = plt.subplots(rows, cols, figsize=(24,8), constrained_layout=True)\n# ax1 = fig.add_subplot(cols, rows, 1)\naxs = axs.flatten()\nax = axs[0]\ntitlestr = f\"Outcome Split N={numdatasets} P={numpats}\"\ntitlestr = \"\"\nplot_boxplot_withdf(ax, outcome_df, df_xlabel='Outcome', df_ylabel='ezr', color='black',\n ylabel=ylabel, titlestr=titlestr, ylim=ylim, yticks=np.linspace(0.3, 0.7, 5))\n\nax = axs[1]\ntitlestr = f\"Engel Score Split N={numdatasets} P={numpats}\"\ntitlestr = \"\"\nplot_boxplot_withdf(ax, engel_df, df_xlabel='Engel Score', df_ylabel='ezr', color='black',\n ylabel=\"\", titlestr=titlestr, ylim=ylim, yticks=np.linspace(0.3, 0.7, 5))\nxticks = ax.get_xticks()\nax.plot(xticks, Y_pred_engel, color='red', label=f\"y={engel_intercept:.2f} + {engel_slope:.2f}x\")\nax.legend()\n\nax = axs[2]\ntitlestr = f\"Clin Difficulty Split N={numdatasets} P={numpats}\"\ntitlestr = \"\"\nplot_boxplot_withdf(ax, clindiff_df, df_xlabel='Epilepsy Category', df_ylabel='ezr',color='black', \n ylabel=\"\", titlestr=titlestr, ylim=ylim, yticks=np.linspace(0.3, 0.7, 5))\nxticks = ax.get_xticks()\nax.plot(xticks, Y_pred_clindiff, color='red', label=f\"y={clindiff_intercept:.2f} + {clindiff_slope:.2f}x\")\nax.legend()\n\n# fig.tight_layout()\nsuptitle = f\"Clinical Categories Split N={numdatasets}, P={numpats}\"\nst = fig.suptitle(suptitle)\nfigpath = os.path.join(figdir, suptitle+\".png\")\nplt.savefig(figpath, bbox_extra_artists=[st], bbox_inches='tight')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Produce a Cumming estimation plot.\nfig1 = outcome_dabest.median_diff.plot()\nax1_list = fig1.axes\nax1 = ax1_list[0]\nfig1.suptitle(\"SRR of Success vs Failure Outcomes\", fontsize=20)\nfig1.tight_layout()\n# print(fig1, ax1)\n# print(ax1.)\nfig2 = engel_dabest.median_diff.plot()\nax2_list = fig2.axes\nax2 = ax2_list[0]\nfig2.suptitle(\"SRR of Outcomes Stratified By Engel Class\", fontsize=20)\nfig2.tight_layout()\nprint(\"Done\")\n# clindiff_dabest.mean_diff.plot()",
"Done\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Load in Previous Analysis",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from eztrack.edv.plot_fragility_heatmap import PlotFragilityHeatmap\nfrom eztrack.edv.baseplot import BasePlotter",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plotter = BasePlotter(figdir)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"trimmed_dataset_dict = np.load(f\"/Users/adam2392/Downloads/improved_allmap_embc_datasets.npy\", allow_pickle=True)\ntrimmed_dataset_ids = np.load(f\"/Users/adam2392/Downloads/improved_allmap_embc_datasetids.npy\", allow_pickle=True)\ntrimmed_patient_ids = np.load(f\"/Users/adam2392/Downloads/improved_allmap_embc_patientids.npy\", allow_pickle=True)\ntrimmed_chanlabels = np.load(f\"/Users/adam2392/Downloads/improved_allmap_embc_chanlabels.npy\", allow_pickle=True)\ntrimmed_cezcontacts = np.load(f\"/Users/adam2392/Downloads/improved_allmap_embc_cezcontacts.npy\", allow_pickle=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(trimmed_dataset_dict.shape)\nprint(len(trimmed_patient_ids))\n# print(trimmed_cezcontacts[0])",
"(60,)\n60\n['pd1', 'pd2', 'pd3', 'pd4', 'ad1', 'ad2', 'ad3', 'ad4', 'att1', 'att2']\n"
],
[
"for i, dataset in enumerate(trimmed_dataset_dict):\n patient_id = trimmed_patient_ids[i]\n dataset_id = trimmed_dataset_ids[i]\n print(dataset.shape)\n \n break",
"(925, 86, 86)\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a774b5aec47b75250434058d5a95ca542597c51
| 52,724 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
recurrent-neural-networks/time-series/Simple_RNN.ipynb
|
steventango/deep-learning-v2-pytorch
|
856b63ad0652a3f49b110cc63dd48d585fa2bd94
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
recurrent-neural-networks/time-series/Simple_RNN.ipynb
|
steventango/deep-learning-v2-pytorch
|
856b63ad0652a3f49b110cc63dd48d585fa2bd94
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
recurrent-neural-networks/time-series/Simple_RNN.ipynb
|
steventango/deep-learning-v2-pytorch
|
856b63ad0652a3f49b110cc63dd48d585fa2bd94
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 145.646409 | 32,276 | 0.669809 |
[
[
[
"# Simple RNN\n\nIn this notebook, we're going to train a simple RNN to do **time-series prediction**. Given some set of input data, it should be able to generate a prediction for the next time step!\n<img src='assets/time_prediction.png' width=40% />\n\n> * First, we'll create our data\n* Then, define an RNN in PyTorch\n* Finally, we'll train our network and see how it performs",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Import resources and create data ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import torch\nfrom torch import nn\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(8,5))\n\n# how many time steps/data pts are in one batch of data\nseq_length = 20\n\n# generate evenly spaced data pts\ntime_steps = np.linspace(0, np.pi, seq_length + 1)\ndata = np.sin(time_steps)\ndata.resize((seq_length + 1, 1)) # size becomes (seq_length+1, 1), adds an input_size dimension\n\nx = data[:-1] # all but the last piece of data\ny = data[1:] # all but the first\n\n# display the data\nplt.plot(time_steps[1:], x, 'r.', label='input, x') # x\nplt.plot(time_steps[1:], y, 'b.', label='target, y') # y\n\nplt.legend(loc='best')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"---\n## Define the RNN\n\nNext, we define an RNN in PyTorch. We'll use `nn.RNN` to create an RNN layer, then we'll add a last, fully-connected layer to get the output size that we want. An RNN takes in a number of parameters:\n* **input_size** - the size of the input\n* **hidden_dim** - the number of features in the RNN output and in the hidden state\n* **n_layers** - the number of layers that make up the RNN, typically 1-3; greater than 1 means that you'll create a stacked RNN\n* **batch_first** - whether or not the input/output of the RNN will have the batch_size as the first dimension (batch_size, seq_length, hidden_dim)\n\nTake a look at the [RNN documentation](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html#rnn) to read more about recurrent layers.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class RNN(nn.Module):\n def __init__(self, input_size, output_size, hidden_dim, n_layers):\n super(RNN, self).__init__()\n \n self.hidden_dim=hidden_dim\n\n # define an RNN with specified parameters\n # batch_first means that the first dim of the input and output will be the batch_size\n self.rnn = nn.RNN(input_size, hidden_dim, n_layers, batch_first=True)\n \n # last, fully-connected layer\n self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, output_size)\n\n def forward(self, x, hidden):\n # x (batch_size, seq_length, input_size)\n # hidden (n_layers, batch_size, hidden_dim)\n # r_out (batch_size, time_step, hidden_size)\n batch_size = x.size(0)\n \n # get RNN outputs\n r_out, hidden = self.rnn(x, hidden)\n # shape output to be (batch_size*seq_length, hidden_dim)\n r_out = r_out.view(-1, self.hidden_dim) \n \n # get final output \n output = self.fc(r_out)\n \n return output, hidden\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Check the input and output dimensions\n\nAs a check that your model is working as expected, test out how it responds to input data.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# test that dimensions are as expected\ntest_rnn = RNN(input_size=1, output_size=1, hidden_dim=10, n_layers=2)\n\n# generate evenly spaced, test data pts\ntime_steps = np.linspace(0, np.pi, seq_length)\ndata = np.sin(time_steps)\ndata.resize((seq_length, 1))\n\ntest_input = torch.Tensor(data).unsqueeze(0) # give it a batch_size of 1 as first dimension\nprint('Input size: ', test_input.size())\n\n# test out rnn sizes\ntest_out, test_h = test_rnn(test_input, None)\nprint('Output size: ', test_out.size())\nprint('Hidden state size: ', test_h.size())",
"Input size: torch.Size([1, 20, 1])\nOutput size: torch.Size([20, 1])\nHidden state size: torch.Size([2, 1, 10])\n"
]
],
[
[
"---\n## Training the RNN\n\nNext, we'll instantiate an RNN with some specified hyperparameters. Then train it over a series of steps, and see how it performs.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# decide on hyperparameters\ninput_size=1 \noutput_size=1\nhidden_dim=32\nn_layers=1\n\n# instantiate an RNN\nrnn = RNN(input_size, output_size, hidden_dim, n_layers)\nprint(rnn)",
"RNN(\n (rnn): RNN(1, 32, batch_first=True)\n (fc): Linear(in_features=32, out_features=1, bias=True)\n)\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Loss and Optimization\n\nThis is a regression problem: can we train an RNN to accurately predict the next data point, given a current data point?\n\n>* The data points are coordinate values, so to compare a predicted and ground_truth point, we'll use a regression loss: the mean squared error.\n* It's typical to use an Adam optimizer for recurrent models.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# MSE loss and Adam optimizer with a learning rate of 0.01\ncriterion = nn.MSELoss()\noptimizer = torch.optim.Adam(rnn.parameters(), lr=0.01) ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Defining the training function\n\nThis function takes in an rnn, a number of steps to train for, and returns a trained rnn. This function is also responsible for displaying the loss and the predictions, every so often.\n\n#### Hidden State\n\nPay close attention to the hidden state, here:\n* Before looping over a batch of training data, the hidden state is initialized\n* After a new hidden state is generated by the rnn, we get the latest hidden state, and use that as input to the rnn for the following steps",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# train the RNN\ndef train(rnn, n_steps, print_every):\n \n # initialize the hidden state\n hidden = None \n \n for batch_i, step in enumerate(range(n_steps)):\n # defining the training data \n time_steps = np.linspace(step * np.pi, (step+1)*np.pi, seq_length + 1)\n data = np.sin(time_steps)\n data.resize((seq_length + 1, 1)) # input_size=1\n\n x = data[:-1]\n y = data[1:]\n \n # convert data into Tensors\n x_tensor = torch.Tensor(x).unsqueeze(0) # unsqueeze gives a 1, batch_size dimension\n y_tensor = torch.Tensor(y)\n\n # outputs from the rnn\n prediction, hidden = rnn(x_tensor, hidden)\n\n ## Representing Memory ##\n # make a new variable for hidden and detach the hidden state from its history\n # this way, we don't backpropagate through the entire history\n hidden = hidden.data\n\n # calculate the loss\n loss = criterion(prediction, y_tensor)\n # zero gradients\n optimizer.zero_grad()\n # perform backprop and update weights\n loss.backward()\n optimizer.step()\n\n # display loss and predictions\n if batch_i % print_every == 0: \n print('Loss: ', loss.item())\n plt.plot(time_steps[1:], x, 'r.') # input\n plt.plot(time_steps[1:], prediction.data.numpy().flatten(), 'b.') # predictions\n plt.show()\n \n return rnn\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# train the rnn and monitor results\nn_steps = 75\nprint_every = 15\n\ntrained_rnn = train(rnn, n_steps, print_every)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Time-Series Prediction\n\nTime-series prediction can be applied to many tasks. Think about weather forecasting or predicting the ebb and flow of stock market prices. You can even try to generate predictions much further in the future than just one time step!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a774c2e0baed43ce06d464af7136a6df6d78bbd
| 436 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
novice/01-01/Untitled.ipynb
|
blackjokie/praxis-academy
|
594d24fcf18cea4f76c9889030eba4aa3f834b7a
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2019-08-11T16:58:04.000Z
|
2019-08-27T17:01:40.000Z
|
novice/01-01/Untitled.ipynb
|
blackjokie/praxis-academy
|
594d24fcf18cea4f76c9889030eba4aa3f834b7a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
novice/01-01/Untitled.ipynb
|
blackjokie/praxis-academy
|
594d24fcf18cea4f76c9889030eba4aa3f834b7a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 14.533333 | 30 | 0.486239 |
[
[
[
"print (\"hello world\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
]
] |
4a775095f9298c63582998014e76d3009ad3ab67
| 23,706 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
learntools/python/nbs/tut5.ipynb
|
bkmalayC/learntools
|
c739a1ee131caebcb9bbd8b138d51cff75152f3a
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
learntools/python/nbs/tut5.ipynb
|
bkmalayC/learntools
|
c739a1ee131caebcb9bbd8b138d51cff75152f3a
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
learntools/python/nbs/tut5.ipynb
|
bkmalayC/learntools
|
c739a1ee131caebcb9bbd8b138d51cff75152f3a
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 27.154639 | 368 | 0.540412 |
[
[
[
"Welcome to day 5 of the Python Challenge! If you missed any of the previous days, here are the links:\n\n- [Day 1 (syntax, variable assignment, numbers)](https://www.kaggle.com/colinmorris/learn-python-challenge-day-1)\n- [Day 2 (functions and getting help)](https://www.kaggle.com/colinmorris/learn-python-challenge-day-2)\n- [Day 3 (booleans and conditionals)](https://www.kaggle.com/colinmorris/learn-python-challenge-day-3)\n- [Day 4 (lists and objects)](https://www.kaggle.com/colinmorris/learn-python-challenge-day-4)\n\nToday we'll be talking about **loops**.\n\n\nLoops are a way to repeatedly execute some code statement.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"planets = ['Mercury', 'Venus', 'Earth', 'Mars', 'Jupiter', 'Saturn', 'Uranus', 'Neptune']\nfor planet in planets:\n print(planet, end=' ') # print all on same line",
"Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune "
]
],
[
[
"Notice the simplicity of the ``for`` loop: we specify the variable we want to use, the sequence we want to loop over, and use the \"``in``\" keyword to link them together in an intuitive and readable way.\n\nThe object to the right of the \"``in``\" can be any object that supports iteration. Basically, if it can be thought of as a sequence or collection of things, you can probably loop over it. In addition to lists, we can iterate over the elements of a tuple:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"multiplicands = (2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 5)\nproduct = 1\nfor mult in multiplicands:\n product = product * mult\nproduct",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"And even iterate over each character in a string:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"s = 'steganograpHy is the practicE of conceaLing a file, message, image, or video within another fiLe, message, image, Or video.'\nmsg = ''\n# print all the uppercase letters in s, one at a time\nfor char in s:\n if char.isupper():\n print(char, end='') ",
"HELLO"
]
],
[
[
"### range()\n\n`range()` is a function that returns a sequence of numbers. It turns out to be very useful for writing loops.\n\nFor example, if we want to repeat some action 5 times:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for i in range(5):\n print(\"Doing important work. i =\", i)",
"Doing important work. i = 0\nDoing important work. i = 1\nDoing important work. i = 2\nDoing important work. i = 3\nDoing important work. i = 4\n"
]
],
[
[
"You might assume that `range(5)` returns the list `[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]`. The truth is a little bit more complicated:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"r = range(5)\nr",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"`range` returns a \"range object\". It acts a lot like a list (it's iterable), but doesn't have all the same capabilities. As we saw yesterday, we can call `help()` on an object like `r` to see Python's documentation on that object, including all of its methods. Click the 'output' button if you're curious about what the help page for a range object looks like.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"help(range)",
"Help on class range in module builtins:\n\nclass range(object)\n | range(stop) -> range object\n | range(start, stop[, step]) -> range object\n | \n | Return an object that produces a sequence of integers from start (inclusive)\n | to stop (exclusive) by step. range(i, j) produces i, i+1, i+2, ..., j-1.\n | start defaults to 0, and stop is omitted! range(4) produces 0, 1, 2, 3.\n | These are exactly the valid indices for a list of 4 elements.\n | When step is given, it specifies the increment (or decrement).\n | \n | Methods defined here:\n | \n | __contains__(self, key, /)\n | Return key in self.\n | \n | __eq__(self, value, /)\n | Return self==value.\n | \n | __ge__(self, value, /)\n | Return self>=value.\n | \n | __getattribute__(self, name, /)\n | Return getattr(self, name).\n | \n | __getitem__(self, key, /)\n | Return self[key].\n | \n | __gt__(self, value, /)\n | Return self>value.\n | \n | __hash__(self, /)\n | Return hash(self).\n | \n | __iter__(self, /)\n | Implement iter(self).\n | \n | __le__(self, value, /)\n | Return self<=value.\n | \n | __len__(self, /)\n | Return len(self).\n | \n | __lt__(self, value, /)\n | Return self<value.\n | \n | __ne__(self, value, /)\n | Return self!=value.\n | \n | __new__(*args, **kwargs) from builtins.type\n | Create and return a new object. See help(type) for accurate signature.\n | \n | __reduce__(...)\n | helper for pickle\n | \n | __repr__(self, /)\n | Return repr(self).\n | \n | __reversed__(...)\n | Return a reverse iterator.\n | \n | count(...)\n | rangeobject.count(value) -> integer -- return number of occurrences of value\n | \n | index(...)\n | rangeobject.index(value, [start, [stop]]) -> integer -- return index of value.\n | Raise ValueError if the value is not present.\n | \n | ----------------------------------------------------------------------\n | Data descriptors defined here:\n | \n | start\n | \n | step\n | \n | stop\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"Just as we can use `int()`, `float()`, and `bool()` to convert objects to another type, we can use `list()` to convert a list-like thing into a list, which shows a more familiar (and useful) representation:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"list(range(5))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Note that the range starts at zero, and that by convention the top of the range is not included in the output. `range(5)` gives the numbers from 0 up to *but not including* 5. \n\nThis may seem like a strange way to do things, but the documentation (accessed via `help(range)`) alludes to the reasoning when it says:\n\n> `range(4)` produces 0, 1, 2, 3. These are exactly the valid indices for a list of 4 elements. \n\nSo for any list `L`, `for i in range(len(L)):` will iterate over all its valid indices.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"nums = [1, 2, 4, 8, 16]\nfor i in range(len(nums)):\n nums[i] = nums[i] * 2\nnums",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This is the classic way of iterating over the indices of a list or other sequence.\n\n> **Aside**: `for i in range(len(L)):` is analogous to constructs like `for (int i = 0; i < L.length; i++)` in other languages.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### `enumerate`\n\n`for foo in x` loops over the elements of a list and `for i in range(len(x))` loops over the indices of a list. What if you want to do both?\n\nEnter the `enumerate` function, one of Python's hidden gems:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def double_odds(nums):\n for i, num in enumerate(nums):\n if num % 2 == 1:\n nums[i] = num * 2\n\nx = list(range(10))\ndouble_odds(x)\nx",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Given a list, `enumerate` returns an object which iterates over the indices *and* the values of the list.\n\n(Like the `range()` function, it returns an iterable object. To see its contents as a list, we can call `list()` on it.)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"list(enumerate(['a', 'b']))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can see that that the things we were iterating over are tuples. This helps explain that `for i, num` syntax. We're \"unpacking\" the tuple, just like in this example from yesterday:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x = 0.125\nnumerator, denominator = x.as_integer_ratio()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can use this unpacking syntax any time we iterate over a collection of tuples.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"nums = [\n ('one', 1, 'I'),\n ('two', 2, 'II'),\n ('three', 3, 'III'),\n ('four', 4, 'IV'),\n]\n\nfor word, integer, roman_numeral in nums:\n print(integer, word, roman_numeral, sep=' = ', end='; ')",
"1 = one = I; 2 = two = II; 3 = three = III; 4 = four = IV; "
]
],
[
[
"This is equivalent to the following (more tedious) code:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for tup in nums:\n word = tup[0]\n integer = tup[1]\n roman_numeral = tup[2]\n print(integer, word, roman_numeral, sep=' = ', end='; ')",
"1 = one = I; 2 = two = II; 3 = three = III; 4 = four = IV; "
]
],
[
[
"## ``while`` loops\nThe other type of loop in Python is a ``while`` loop, which iterates until some condition is met:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"i = 0\nwhile i < 10:\n print(i, end=' ')\n i += 1",
"0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 "
]
],
[
[
"The argument of the ``while`` loop is evaluated as a boolean statement, and the loop is executed until the statement evaluates to False.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## List comprehensions\n\nList comprehensions are one of Python's most beloved and unique features. The easiest way to understand them is probably to just look at a few examples:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"squares = [n**2 for n in range(10)]\nsquares",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Here's how we would do the same thing without a list comprehension:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"squares = []\nfor n in range(10):\n squares.append(n**2)\nsquares",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can also add an `if` condition:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"short_planets = [planet for planet in planets if len(planet) < 6]\nshort_planets",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"(If you're familiar with SQL, you might think of this as being like a \"WHERE\" clause)\n\nHere's an example of filtering with an `if` condition *and* applying some transformation to the loop variable:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# str.upper() returns an all-caps version of a string\nloud_short_planets = [planet.upper() + '!' for planet in planets if len(planet) < 6]\nloud_short_planets",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"People usually write these on a single line, but you might find the structure clearer when it's split up over 3 lines:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"[\n planet.upper() + '!' \n for planet in planets \n if len(planet) < 6\n]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"(Continuing the SQL analogy, you could think of these three lines as SELECT, FROM, and WHERE)\n\nThe expression on the left doesn't technically have to involve the loop variable (though it'd be pretty unusual for it not to). What do you think the expression below will evaluate to? Press the 'output' button to check.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"[32 for planet in planets]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"List comprehensions combined with some of the functions we've seen like `min`, `max`, `sum`, `len`, and `sorted`, can lead to some pretty impressive one-line solutions for problems that would otherwise require several lines of code. \n\nFor example, yesterday's exercise included a brainteaser asking you to write a function to count the number of negative numbers in a list *without using loops* (or any other syntax we hadn't seen). Here's how we might solve the problem now that we have loops in our arsenal:\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def count_negatives(nums):\n \"\"\"Return the number of negative numbers in the given list.\n \n >>> count_negatives([5, -1, -2, 0, 3])\n 2\n \"\"\"\n n_negative = 0\n for num in nums:\n if num < 0:\n n_negative = n_negative + 1\n return n_negative",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Here's a solution using a list comprehension:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def count_negatives(nums):\n return len([num for num in nums if num < 0])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Much better, right?\n\nWell if all we care about is minimizing the length of our code, this third solution is better still!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def count_negatives(nums):\n # Reminder: in the day 3 exercise we learned about a quirk of Python where it calculates\n # something like True + True + False + True to be equal to 3.\n return sum([num < 0 for num in nums])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Which of these solutions is the \"best\" is entirely subjective. Solving a problem with less code is always nice, but it's worth keeping in mind the following lines from [The Zen of Python](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zen_of_Python):\n\n> Readability counts. \n> Explicit is better than implicit.\n\nThe last definition of `count_negatives` might be the shortest, but will other people reading your code understand how it works? \n\nWriting Pythonic code doesn't mean never using for loops!",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Your turn\n\nHead over to [the Exercises notebook](https://www.kaggle.com/kernels/fork/961955) to get some hands-on practice working with loops and list comprehensions.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4a77590dc3c87842180dce770f50f580053bd2ff
| 7,677 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/protocol_examples.ipynb
|
OrthoDex/seldon-core
|
1c2b511d1b14cbdae64ebde2e67f20aa18e6554e
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2020-03-29T18:56:31.000Z
|
2020-03-29T18:56:31.000Z
|
notebooks/protocol_examples.ipynb
|
OrthoDex/seldon-core
|
1c2b511d1b14cbdae64ebde2e67f20aa18e6554e
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/protocol_examples.ipynb
|
OrthoDex/seldon-core
|
1c2b511d1b14cbdae64ebde2e67f20aa18e6554e
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2020-03-29T18:56:33.000Z
|
2020-03-29T18:56:33.000Z
| 24.605769 | 174 | 0.535886 |
[
[
[
"# Basic Examples with Different Protocols\n\n## Prerequisites\n\n * A kubernetes cluster with kubectl configured\n * curl\n * grpcurl\n * pygmentize\n \n\n## Setup Seldon Core\n\nUse the setup notebook to [Setup Cluster](seldon_core_setup.ipynb) to setup Seldon Core with an ingress - either Ambassador or Istio.\n\nThen port-forward to that ingress on localhost:8003 in a separate terminal either with:\n\n * Ambassador: `kubectl port-forward $(kubectl get pods -n seldon -l app.kubernetes.io/name=ambassador -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') -n seldon 8003:8080`\n * Istio: `kubectl port-forward $(kubectl get pods -l istio=ingressgateway -n istio-system -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') -n istio-system 8003:80`",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!kubectl create namespace seldon",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!kubectl config set-context $(kubectl config current-context) --namespace=seldon",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import json",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Seldon Protocol REST Model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!pygmentize resources/model_seldon_rest.yaml",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!kubectl apply -f resources/model_seldon_rest.yaml",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!kubectl rollout status deploy/$(kubectl get deploy -l seldon-deployment-id=rest-seldon \\\n -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X=!curl -s -d '{\"data\": {\"ndarray\":[[1.0, 2.0, 5.0]]}}' \\\n -X POST http://localhost:8003/seldon/seldon/rest-seldon/api/v1.0/predictions \\\n -H \"Content-Type: application/json\"\nd=json.loads(X[0])\nprint(d)\nassert(d[\"data\"][\"ndarray\"][0][0] > 0.4)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!kubectl delete -f resources/model_seldon_rest.yaml",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Seldon Protocol GRPC Model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!pygmentize resources/model_seldon_grpc.yaml",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!kubectl apply -f resources/model_seldon_grpc.yaml",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!kubectl rollout status deploy/$(kubectl get deploy -l seldon-deployment-id=grpc-seldon \\\n -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X=!cd ../executor/proto && grpcurl -d '{\"data\":{\"ndarray\":[[1.0,2.0,5.0]]}}' \\\n -rpc-header seldon:grpc-seldon -rpc-header namespace:seldon \\\n -plaintext \\\n -proto ./prediction.proto 0.0.0.0:8003 seldon.protos.Seldon/Predict\nd=json.loads(\"\".join(X))\nprint(d)\nassert(d[\"data\"][\"ndarray\"][0][0] > 0.4)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!kubectl delete -f resources/model_seldon_grpc.yaml",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Tensorflow Protocol REST Model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!pygmentize resources/model_tfserving_rest.yaml",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!kubectl apply -f resources/model_tfserving_rest.yaml",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!kubectl rollout status deploy/$(kubectl get deploy -l seldon-deployment-id=rest-tfserving \\\n -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X=!curl -s -d '{\"instances\": [1.0, 2.0, 5.0]}' \\\n -X POST http://localhost:8003/seldon/seldon/rest-tfserving/v1/models/halfplustwo/:predict \\\n -H \"Content-Type: application/json\"\nd=json.loads(\"\".join(X))\nprint(d)\nassert(d[\"predictions\"][0] == 2.5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!kubectl delete -f resources/model_tfserving_rest.yaml",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Tensorflow Protocol GRPC Model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!pygmentize resources/model_tfserving_grpc.yaml",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!kubectl apply -f resources/model_tfserving_grpc.yaml",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!kubectl rollout status deploy/$(kubectl get deploy -l seldon-deployment-id=grpc-tfserving \\\n -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X=!cd ../executor/proto && grpcurl \\\n -d '{\"model_spec\":{\"name\":\"halfplustwo\"},\"inputs\":{\"x\":{\"dtype\": 1, \"tensor_shape\": {\"dim\":[{\"size\": 3}]}, \"floatVal\" : [1.0, 2.0, 3.0]}}}' \\\n -rpc-header seldon:grpc-tfserving -rpc-header namespace:seldon \\\n -plaintext -proto ./prediction_service.proto \\\n 0.0.0.0:8003 tensorflow.serving.PredictionService/Predict\nd=json.loads(\"\".join(X))\nprint(d)\nassert(d[\"outputs\"][\"x\"][\"floatVal\"][0] == 2.5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!kubectl delete -f resources/model_tfserving_grpc.yaml",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a775be591f2a24a51ea0dd62d12ebf6e784d2ec
| 483,813 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
examples/notebooks/etf_cointegration/ETF Cointegration.ipynb
|
gsamarakoon/Odin
|
e2e9d638c68947d24f1260d35a3527dd84c2523f
|
[
"MIT"
] | 103 |
2017-01-14T19:38:14.000Z
|
2022-03-10T12:52:09.000Z
|
examples/notebooks/etf_cointegration/ETF Cointegration.ipynb
|
gsamarakoon/Odin
|
e2e9d638c68947d24f1260d35a3527dd84c2523f
|
[
"MIT"
] | 6 |
2017-01-19T01:38:53.000Z
|
2020-03-09T19:03:18.000Z
|
examples/notebooks/etf_cointegration/ETF Cointegration.ipynb
|
JamesBrofos/Odin
|
e2e9d638c68947d24f1260d35a3527dd84c2523f
|
[
"MIT"
] | 33 |
2017-02-05T21:51:17.000Z
|
2021-12-22T20:38:30.000Z
| 817.251689 | 228,952 | 0.934239 |
[
[
[
"import fund\nimport settings\nimport handlers",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from odin.metrics import Visualizer",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%matplotlib inline\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fund.fund.trade()",
"FILL\t2012-01-03 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t2650\t50749.41\nFILL\t2012-01-03 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t1897\t48967.07\nFILL\t2012-01-26 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t2650\t58716.73\nFILL\t2012-01-26 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t1897\t43229.97\nFILL\t2012-02-21 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t1989\t43590.62\nFILL\t2012-02-21 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t1945\t42457.56\nFILL\t2012-02-24 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t1989\t44136.09\nFILL\t2012-02-24 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1945\t41663.27\nFILL\t2012-03-02 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t2017\t43733.41\nFILL\t2012-03-02 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t2222\t43906.44\nFILL\t2012-03-22 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t2017\t43008.39\nFILL\t2012-03-22 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t2222\t40109.25\nFILL\t2012-03-30 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t1969\t41922.10\nFILL\t2012-03-30 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t2596\t41842.47\nFILL\t2012-04-10 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1969\t39525.00\nFILL\t2012-04-10 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t2596\t40036.25\nFILL\t2012-04-12 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t2009\t42922.49\nFILL\t2012-04-12 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t2815\t42837.56\nFILL\t2012-04-24 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t2009\t41178.75\nFILL\t2012-04-24 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t2815\t41908.46\nFILL\t2012-05-01 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t2079\t43317.90\nFILL\t2012-05-01 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t2553\t42715.85\nFILL\t2012-05-29 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t2079\t38982.61\nFILL\t2012-05-29 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t2553\t45108.52\nFILL\t2012-06-08 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t2195\t39340.88\nFILL\t2012-06-08 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t2486\t39808.32\nFILL\t2012-06-15 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t2195\t40732.55\nFILL\t2012-06-15 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t2486\t42688.13\nFILL\t2012-06-19 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t2169\t40664.78\nFILL\t2012-06-19 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t2235\t39428.03\nFILL\t2012-06-20 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t2169\t41038.44\nFILL\t2012-06-20 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t2235\t39411.57\nFILL\t2012-06-22 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t2219\t40447.23\nFILL\t2012-06-22 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t2255\t40851.44\nFILL\t2012-07-09 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t2219\t40830.65\nFILL\t2012-07-09 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t2255\t44129.86\nFILL\t2012-07-13 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t2194\t38919.51\nFILL\t2012-07-13 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t2011\t39385.84\nFILL\t2012-07-30 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t2194\t39066.86\nFILL\t2012-07-30 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t2011\t43922.08\nFILL\t2012-08-09 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t1959\t36883.97\nFILL\t2012-08-09 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t1832\t37794.73\nFILL\t2012-08-23 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1959\t36419.68\nFILL\t2012-08-23 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t1832\t34488.47\nFILL\t2012-09-05 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t1962\t35450.63\nFILL\t2012-09-05 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t1851\t35003.41\nFILL\t2012-09-07 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t1962\t37462.80\nFILL\t2012-09-07 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1851\t33584.67\nFILL\t2012-09-10 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t1909\t37284.32\nFILL\t2012-09-10 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t2003\t37304.49\nFILL\t2012-09-12 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1909\t37952.46\nFILL\t2012-09-12 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t2003\t40540.47\nFILL\t2012-09-17 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t1845\t38018.79\nFILL\t2012-09-17 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t1963\t38248.54\nFILL\t2012-09-21 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1845\t36326.08\nFILL\t2012-09-21 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t1963\t38386.89\nFILL\t2012-09-26 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t2088\t39240.82\nFILL\t2012-09-26 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t1932\t39547.58\nFILL\t2012-10-17 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t2088\t40446.80\nFILL\t2012-10-17 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1932\t43337.10\nFILL\t2012-11-05 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t2055\t37969.66\nFILL\t2012-11-05 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t1795\t37686.91\nFILL\t2012-11-09 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t2055\t37128.35\nFILL\t2012-11-09 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t1795\t37164.83\nFILL\t2012-11-14 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t2130\t37503.66\nFILL\t2012-11-14 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t1718\t38154.87\nFILL\t2012-11-27 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t2130\t38012.46\nFILL\t2012-11-27 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1718\t37969.60\nFILL\t2012-11-30 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t2127\t38118.03\nFILL\t2012-11-30 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t1828\t37684.77\nFILL\t2012-12-21 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t2127\t39066.27\nFILL\t2012-12-21 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t1828\t35938.78\nFILL\t2013-01-03 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t1923\t37195.27\nFILL\t2013-01-03 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t2043\t36843.49\nFILL\t2013-01-14 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1923\t36841.65\nFILL\t2013-01-14 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t2043\t38930.32\nFILL\t2013-02-04 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t1997\t37965.04\nFILL\t2013-02-04 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t2058\t38462.66\nFILL\t2013-02-06 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1997\t38259.59\nFILL\t2013-02-06 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t2058\t39750.97\nFILL\t2013-02-11 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t2020\t38531.60\nFILL\t2013-02-11 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t2126\t38967.80\nFILL\t2013-02-21 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t2020\t37767.97\nFILL\t2013-02-21 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t2126\t38886.35\nFILL\t2013-02-26 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t2137\t38648.13\nFILL\t2013-02-26 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t2040\t38801.79\nFILL\t2013-04-04 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t2137\t38013.74\nFILL\t2013-04-04 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t2040\t43585.98\nFILL\t2013-04-08 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t2031\t36207.92\nFILL\t2013-04-08 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t1597\t35762.89\nFILL\t2013-04-10 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t2031\t36520.16\nFILL\t2013-04-10 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1597\t35798.68\nFILL\t2013-04-12 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t2037\t36052.53\nFILL\t2013-04-12 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t1585\t36381.33\nFILL\t2013-04-25 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t2037\t36780.94\nFILL\t2013-04-25 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1585\t36251.22\nFILL\t2013-05-03 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t2007\t37013.96\nFILL\t2013-05-03 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t1673\t36498.00\nFILL\t2013-05-15 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t2007\t36744.45\nFILL\t2013-05-15 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t1673\t36670.55\nFILL\t2013-05-24 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t2014\t36937.68\nFILL\t2013-05-24 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t1610\t36754.01\nFILL\t2013-05-31 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t2014\t36987.43\nFILL\t2013-05-31 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1610\t34527.60\nFILL\t2013-06-10 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t2117\t37854.11\nFILL\t2013-06-10 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t1857\t37892.45\nFILL\t2013-06-18 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t2117\t37208.02\nFILL\t2013-06-18 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t1857\t38643.41\nFILL\t2013-07-12 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t2224\t38666.72\nFILL\t2013-07-12 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t1997\t38781.15\nFILL\t2013-07-19 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t2224\t38968.87\nFILL\t2013-07-19 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t1997\t39989.89\nFILL\t2013-07-29 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t2255\t38963.08\nFILL\t2013-07-29 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t2141\t39232.02\nFILL\t2013-08-16 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t2255\t39174.93\nFILL\t2013-08-16 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t2141\t38272.64\nFILL\t2013-08-22 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t2250\t38844.83\nFILL\t2013-08-22 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t2063\t38486.64\nFILL\t2013-09-06 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t2250\t38392.92\nFILL\t2013-09-06 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t2063\t38370.34\nFILL\t2013-09-19 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t2060\t37998.52\nFILL\t2013-09-19 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t1955\t38405.62\nFILL\t2013-09-23 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t2060\t37012.13\nFILL\t2013-09-23 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t1955\t37253.44\nFILL\t2013-09-25 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t2123\t38289.35\nFILL\t2013-09-25 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t2075\t38126.43\nFILL\t2013-10-02 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t2123\t36629.31\nFILL\t2013-10-02 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t2075\t38243.87\nFILL\t2013-10-09 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t2214\t39228.56\nFILL\t2013-10-09 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t2051\t38908.51\nFILL\t2013-10-11 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t2214\t39834.94\nFILL\t2013-10-11 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t2051\t39737.48\nFILL\t2013-10-22 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t2084\t41119.50\nFILL\t2013-10-22 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t1978\t36690.46\nFILL\t2013-11-08 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t2084\t40360.76\nFILL\t2013-11-08 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t1978\t34894.25\nFILL\t2013-12-04 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t1896\t38755.19\nFILL\t2013-12-04 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t1954\t38015.59\nFILL\t2013-12-18 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t1896\t40092.58\nFILL\t2013-12-18 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1954\t40937.22\nFILL\t2013-12-27 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t1668\t38126.28\nFILL\t2013-12-27 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t1728\t36971.76\nFILL\t2014-01-14 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1668\t37133.44\nFILL\t2014-01-14 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t1728\t36477.11\nFILL\t2014-01-21 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t1482\t38659.00\nFILL\t2014-01-21 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t1724\t36955.17\nFILL\t2014-01-27 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1482\t37267.40\nFILL\t2014-01-27 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t1724\t40821.14\nFILL\t2014-01-30 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t1549\t40144.82\nFILL\t2014-01-30 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t1585\t39858.66\nFILL\t2014-01-31 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t1549\t39013.98\nFILL\t2014-01-31 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1585\t37868.72\nFILL\t2014-02-05 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t1648\t40045.56\nFILL\t2014-02-05 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t1507\t39094.63\nFILL\t2014-02-10 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t1648\t39593.84\nFILL\t2014-02-10 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1507\t34753.72\nFILL\t2014-02-24 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t1680\t42832.33\nFILL\t2014-02-24 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t1539\t41009.22\nFILL\t2014-02-25 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t1680\t42607.05\nFILL\t2014-02-25 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1539\t39810.74\nFILL\t2014-03-24 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t1651\t43342.01\nFILL\t2014-03-24 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t1813\t43225.39\nFILL\t2014-03-27 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1651\t44516.23\nFILL\t2014-03-27 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t1813\t45338.58\nFILL\t2014-03-28 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t1586\t43323.80\nFILL\t2014-03-28 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t1735\t43570.28\nFILL\t2014-04-07 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1586\t43384.38\nFILL\t2014-04-07 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t1735\t43361.98\nFILL\t2014-05-07 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t1504\t43495.98\nFILL\t2014-05-07 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t1643\t43197.51\nFILL\t2014-05-09 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t1504\t43485.11\nFILL\t2014-05-09 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1643\t41185.95\nFILL\t2014-05-13 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t1473\t44368.68\nFILL\t2014-05-13 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t1817\t44238.80\nFILL\t2014-05-21 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1473\t42422.75\nFILL\t2014-05-21 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t1817\t45284.24\nFILL\t2014-06-10 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t1482\t45882.01\nFILL\t2014-06-10 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t1814\t45799.18\nFILL\t2014-06-13 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1482\t46234.75\nFILL\t2014-06-13 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t1814\t47566.49\nFILL\t2014-06-19 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t1458\t46234.12\nFILL\t2014-06-19 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t1810\t46449.71\nFILL\t2014-08-01 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1458\t52127.00\nFILL\t2014-08-01 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t1810\t38180.95\nFILL\t2014-08-08 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t1155\t40032.98\nFILL\t2014-08-08 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t1819\t39416.20\nFILL\t2014-08-14 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t1155\t40849.51\nFILL\t2014-08-14 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1819\t38955.16\nFILL\t2014-09-03 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t1106\t40612.16\nFILL\t2014-09-03 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t1891\t39759.23\nFILL\t2014-09-15 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1106\t39807.63\nFILL\t2014-09-15 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t1891\t40456.62\nFILL\t2014-09-17 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t1166\t41292.54\nFILL\t2014-09-17 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t1861\t40679.72\nFILL\t2014-10-07 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t1166\t40729.90\nFILL\t2014-10-07 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1861\t39268.11\nFILL\t2014-10-13 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t1274\t41320.37\nFILL\t2014-10-13 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t2002\t41740.84\nFILL\t2014-10-20 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t1274\t43279.81\nFILL\t2014-10-20 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t2002\t39589.32\nFILL\t2014-10-22 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t1213\t43086.03\nFILL\t2014-10-22 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t2208\t43519.35\nFILL\t2014-10-31 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1213\t43698.54\nFILL\t2014-10-31 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t2208\t44855.16\nFILL\t2014-11-07 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t1216\t43527.06\nFILL\t2014-11-07 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t1941\t44533.38\nFILL\t2014-11-13 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t1216\t44719.11\nFILL\t2014-11-13 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1941\t41286.29\nFILL\t2014-12-02 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t1228\t46193.49\nFILL\t2014-12-02 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t2290\t45628.15\nFILL\t2014-12-10 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1228\t42640.45\nFILL\t2014-12-10 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t2290\t42961.81\nFILL\t2014-12-15 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t1409\t46521.51\nFILL\t2014-12-15 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t2384\t45738.00\nFILL\t2014-12-19 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t1409\t48907.29\nFILL\t2014-12-19 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t2384\t42539.90\nFILL\t2015-01-13 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t1366\t48101.26\nFILL\t2015-01-13 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t3413\t50076.67\nFILL\t2015-01-14 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1366\t44847.80\nFILL\t2015-01-14 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t3413\t55041.22\nFILL\t2015-01-15 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t1607\t52953.51\nFILL\t2015-01-15 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t3220\t52121.83\nFILL\t2015-01-21 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t1607\t55235.72\nFILL\t2015-01-21 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t3220\t47760.37\nFILL\t2015-02-04 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t1567\t56616.77\nFILL\t2015-02-04 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t4067\t55786.45\nFILL\t2015-02-10 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1567\t54029.46\nFILL\t2015-02-10 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t4067\t55893.29\nFILL\t2015-02-26 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t1751\t57802.97\nFILL\t2015-02-26 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t4070\t56951.51\nFILL\t2015-03-04 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t1751\t55445.35\nFILL\t2015-03-04 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t4070\t56906.69\nFILL\t2015-03-05 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t1794\t56431.36\nFILL\t2015-03-05 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t4041\t57535.26\nFILL\t2015-03-27 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t1794\t50071.80\nFILL\t2015-03-27 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t4041\t53570.02\nFILL\t2015-04-07 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t1877\t55531.69\nFILL\t2015-04-07 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t4152\t55893.09\nFILL\t2015-04-17 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1877\t55155.39\nFILL\t2015-04-17 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t4152\t55214.74\nFILL\t2015-04-21 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t1847\t54805.86\nFILL\t2015-04-21 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t4273\t55298.89\nFILL\t2015-04-24 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1847\t53545.33\nFILL\t2015-04-24 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t4273\t54346.74\nFILL\t2015-04-28 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t1868\t55592.56\nFILL\t2015-04-28 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t4420\t55189.18\nFILL\t2015-05-01 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1868\t56835.23\nFILL\t2015-05-01 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t4420\t60457.46\nFILL\t2015-05-04 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t1854\t57347.23\nFILL\t2015-05-04 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t4205\t57931.80\nFILL\t2015-05-05 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t1854\t56795.22\nFILL\t2015-05-05 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t4205\t57978.97\nFILL\t2015-05-13 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t1933\t58284.00\nFILL\t2015-05-13 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t4015\t57807.16\nFILL\t2015-05-29 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t1933\t53200.44\nFILL\t2015-05-29 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t4015\t51779.23\nFILL\t2015-06-09 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t2157\t58003.73\nFILL\t2015-06-09 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t4282\t58484.27\nFILL\t2015-07-30 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t2157\t47629.57\nFILL\t2015-07-30 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t4282\t57600.28\nFILL\t2015-08-10 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t2542\t54596.94\nFILL\t2015-08-10 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t3820\t51849.66\nFILL\t2015-08-11 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t2542\t53591.38\nFILL\t2015-08-11 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t3820\t51748.66\nFILL\t2015-08-12 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t2556\t53039.56\nFILL\t2015-08-12 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t3804\t53020.26\nFILL\t2015-08-18 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t2556\t52311.56\nFILL\t2015-08-18 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t3804\t49400.61\nFILL\t2015-08-24 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t3005\t54644.91\nFILL\t2015-08-24 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t4296\t54424.57\nFILL\t2015-08-28 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t3005\t60244.40\nFILL\t2015-08-28 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t4296\t55059.28\nFILL\t2015-09-18 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t2615\t56943.13\nFILL\t2015-09-18 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t4556\t56431.48\nFILL\t2015-09-23 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t2615\t54091.05\nFILL\t2015-09-23 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t4556\t55373.26\nFILL\t2015-10-06 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t2507\t59142.95\nFILL\t2015-10-06 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t4979\t56440.28\nFILL\t2015-10-13 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t2507\t55446.76\nFILL\t2015-10-13 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t4979\t57627.99\nFILL\t2015-11-03 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t2961\t61154.23\nFILL\t2015-11-03 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t6224\t59344.38\nFILL\t2015-11-09 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t2961\t57256.65\nFILL\t2015-11-09 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t6224\t60124.88\nFILL\t2015-11-11 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t3364\t61518.17\nFILL\t2015-11-11 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t6366\t61369.37\nFILL\t2015-11-19 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t3364\t64167.46\nFILL\t2015-11-19 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t6366\t61048.62\nFILL\t2015-11-27 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t3094\t64072.00\nFILL\t2015-11-27 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t7249\t63097.83\nFILL\t2015-12-09 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t3094\t59110.52\nFILL\t2015-12-09 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t7249\t58832.45\nFILL\t2015-12-16 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t3139\t63548.57\nFILL\t2015-12-16 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t8975\t63664.57\nFILL\t2015-12-31 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t3139\t68641.47\nFILL\t2015-12-31 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t8975\t78043.46\nFILL\t2016-01-06 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t3450\t66979.26\nFILL\t2016-01-06 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t7928\t67750.51\nFILL\t2016-01-27 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t3450\t54078.25\nFILL\t2016-01-27 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t7928\t63257.41\nFILL\t2016-02-04 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t3795\t67652.89\nFILL\t2016-02-04 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t8381\t61253.82\nFILL\t2016-02-12 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t3795\t63761.79\nFILL\t2016-02-12 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t8381\t60480.56\nFILL\t2016-02-17 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t3605\t67143.37\nFILL\t2016-02-17 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t9257\t65526.02\nFILL\t2016-03-14 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t3605\t76652.03\nFILL\t2016-03-14 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t9257\t59909.11\nFILL\t2016-04-05 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t2823\t58928.11\nFILL\t2016-04-05 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t8537\t56657.34\nFILL\t2016-04-07 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t2823\t60183.68\nFILL\t2016-04-07 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t8537\t57482.74\nFILL\t2016-04-15 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t2635\t58687.97\nFILL\t2016-04-15 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t8956\t58332.71\nFILL\t2016-04-26 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t2635\t60969.06\nFILL\t2016-04-26 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t8956\t62257.84\nFILL\t2016-04-27 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t2500\t61030.35\nFILL\t2016-04-27 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t8293\t57333.28\nFILL\t2016-05-04 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t2500\t57373.62\nFILL\t2016-05-04 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t8293\t57275.98\nFILL\t2016-05-10 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t2861\t60499.96\nFILL\t2016-05-10 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t8756\t60911.29\nFILL\t2016-05-25 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t2861\t60948.45\nFILL\t2016-05-25 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t8756\t57073.86\nFILL\t2016-06-13 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t2987\t62931.70\nFILL\t2016-06-13 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t7987\t62626.69\nFILL\t2016-06-20 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t2987\t65326.42\nFILL\t2016-06-20 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t7987\t64767.00\nFILL\t2016-06-28 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t3029\t62602.94\nFILL\t2016-06-28 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t7519\t63503.78\nFILL\t2016-07-08 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t3029\t65066.24\nFILL\t2016-07-08 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t7519\t62175.61\nFILL\t2016-07-12 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t2724\t64299.32\nFILL\t2016-07-12 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t8017\t64488.91\nFILL\t2016-07-25 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t2724\t63514.77\nFILL\t2016-07-25 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t8017\t65025.43\nFILL\t2016-08-02 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t2789\t64626.82\nFILL\t2016-08-02 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t7954\t65309.44\nFILL\t2016-08-08 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t2789\t65341.37\nFILL\t2016-08-08 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t7954\t64937.09\nFILL\t2016-08-25 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t2932\t66174.87\nFILL\t2016-08-25 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t7835\t66055.18\nFILL\t2016-09-06 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t2932\t66828.01\nFILL\t2016-09-06 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t7835\t62907.31\nFILL\t2016-09-12 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t3192\t68515.70\nFILL\t2016-09-12 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t7911\t67407.55\nFILL\t2016-09-23 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t3192\t69728.60\nFILL\t2016-09-23 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t7911\t69612.03\nFILL\t2016-09-30 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t3020\t67823.48\nFILL\t2016-09-30 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t7913\t66185.76\nFILL\t2016-10-12 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t3020\t61284.19\nFILL\t2016-10-12 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t7913\t73119.11\nFILL\t2016-10-13 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t3761\t74362.03\nFILL\t2016-10-13 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t8006\t74818.67\nFILL\t2016-10-25 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t3761\t76524.45\nFILL\t2016-10-25 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t8006\t68365.38\nFILL\t2016-11-01 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t3543\t72713.40\nFILL\t2016-11-01 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t10061\t78565.37\nFILL\t2016-11-02 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t3543\t64362.72\nFILL\t2016-11-02 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t10061\t76324.81\nFILL\t2016-12-01 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t4208\t82048.85\nFILL\t2016-12-01 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t9259\t81068.29\nFILL\t2016-12-08 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tEXIT\t4208\t88301.02\nFILL\t2016-12-08 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tEXIT\t9259\t85225.39\nFILL\t2016-12-13 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tBUY\t3818\t81201.95\nFILL\t2016-12-13 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tBUY\t9198\t81120.91\nFILL\t2016-12-15 00:00:00\tARNC\tSHORT\tEXIT\t3818\t78940.14\nFILL\t2016-12-15 00:00:00\tUNG\tLONG\tEXIT\t9198\t80901.93\nFILL\t2016-12-27 00:00:00\tARNC\tLONG\tBUY\t4208\t83476.51\nFILL\t2016-12-27 00:00:00\tUNG\tSHORT\tBUY\t8924\t83219.29\n"
],
[
"fund.fund.performance_summary()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"v = Visualizer()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(17, 8))\nax1 = plt.subplot(211)\nax1 = v.equity(fund.fund, ax=ax1)\nax2 = plt.subplot(212, sharex=ax1)\nax2 = v.positions(fund.fund, ax=ax2)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(17, 6))\nax1 = plt.subplot(111)\nax1 = v.long_short_equity(fund.fund, ax=ax1)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a77af26ce8f1bb1ae86e2e7649735a18f57e44f
| 4,196 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebook/sequencing_process.ipynb
|
kberkey/ccal
|
92aa8372997dccec2908928f71a11b6c8327d7aa
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebook/sequencing_process.ipynb
|
kberkey/ccal
|
92aa8372997dccec2908928f71a11b6c8327d7aa
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebook/sequencing_process.ipynb
|
kberkey/ccal
|
92aa8372997dccec2908928f71a11b6c8327d7aa
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 23.054945 | 88 | 0.580315 |
[
[
[
"%load_ext autoreload\n%autoreload 2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import os\nimport sys\n\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport plotly as pl",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sys.path.insert(0, \"..\")\n\nnp.random.random(20121020)\n\npl.offline.init_notebook_mode(connected=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sequencing_process.support.support.path import clean_path\n\nGRCH_DIRECTORY_PATH = clean_path(\"~/sequencing_process_grch\")\n\nassert os.path.isdir(GRCH_DIRECTORY_PATH)\n\nPEOPLE_DIRECTORY_PATH = clean_path(\"~/sequencing_process_people\")\n\nassert os.path.isdir(PEOPLE_DIRECTORY_PATH)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sequencing_process.download_clinvar_vcf_gz import download_clinvar_vcf_gz\n\nvcf_gz_file_path = download_clinvar_vcf_gz(GRCH_DIRECTORY_PATH, overwrite=True)\n\nvcf_gz_file_path",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sequencing_process.support.support.compression import gzip_decompress_file\n\nvcf_file_path = gzip_decompress_file(vcf_gz_file_path)\n\nvcf_file_path",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sequencing_process.bgzip_and_tabix import bgzip_and_tabix\n\nvcf_gz_file_path = bgzip_and_tabix(vcf_file_path, overwrite=True)\n\nvcf_gz_file_path",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sequencing_process.make_reference_genome import make_reference_genome\n\nfasta_gz_file_path = make_reference_genome(GRCH_DIRECTORY_PATH, overwrite=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sequencing_process.simulate_sequences_using_dwgsim import (\n simulate_sequences_using_dwgsim,\n)\n\nsimulate_sequences_using_dwgsim(\n fasta_gz_file_path[:-3],\n \"{}/simulation\".format(PEOPLE_DIRECTORY_PATH),\n n_sequence=int(1e6),\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a77b12744b36daa4a78c733537d252caec0dc62
| 38,667 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Labs/Lab 03 - Machine Learning/src/.ipynb_checkpoints/Untitled-checkpoint.ipynb
|
caiobarretta/ED1L3
|
19e5afe73391388b06ac238169e40fcdbbe45268
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Labs/Lab 03 - Machine Learning/src/.ipynb_checkpoints/Untitled-checkpoint.ipynb
|
caiobarretta/ED1L3
|
19e5afe73391388b06ac238169e40fcdbbe45268
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Labs/Lab 03 - Machine Learning/src/.ipynb_checkpoints/Untitled-checkpoint.ipynb
|
caiobarretta/ED1L3
|
19e5afe73391388b06ac238169e40fcdbbe45268
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 30.785828 | 129 | 0.50053 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nfrom sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier\nfrom scipy.spatial import distance\nimport scipy\nimport math\nimport scipy.spatial\nfrom collections import Counter",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"treino = pd.read_csv(\"dados/3.fit\", sep=\" \")\ntreino.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"teste = pd.read_csv(\"dados/3.test\", sep=\" \")\nteste.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"m, n, k = 30, 10, 3",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"neigh = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=k)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def create_2D_array_from_1d_array(n, a, b):\n array = []\n for i in range(n):\n array.append([a[i], b[i]])\n return array",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_train = create_2D_array_from_1d_array(m, treino.horas.to_numpy(), treino.media.to_numpy())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_test = create_2D_array_from_1d_array(n, teste.horas.to_numpy(), teste.media.to_numpy())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"y_train = treino.aprovado.array",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"y_test = []",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"neigh.fit(X_train, y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"predict = neigh.predict(X_test)\npredict",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for i in range(n):\n media = teste.media.array[i]\n horas = teste.horas.array[i]\n aprovacao = (\"Aprovado\" if predict[i] == 1 else \"Reprovado\")\n print(\"Aluno {}: ({}, {}) = {}\".format(i, media, horas, aprovacao))",
"Aluno 0: (5.5, 2.5) = Aprovado\nAluno 1: (8.3, 4.25) = Aprovado\nAluno 2: (6.8, 7.2) = Aprovado\nAluno 3: (7.5, 9.5) = Aprovado\nAluno 4: (9.0, 1.0) = Reprovado\nAluno 5: (3.8, 1.0) = Reprovado\nAluno 6: (7.0, 0.5) = Reprovado\nAluno 7: (6.3, 2.0) = Reprovado\nAluno 8: (4.0, 3.0) = Aprovado\nAluno 9: (2.0, 4.0) = Reprovado\n"
],
[
"def dist_euclidiana(v1, v2):\n dim, soma = len(v1), 0\n for i in range(dim):\n soma += math.pow(v1[i] - v2[i], 2)\n #print(\"v1[{}]:{} - v2[{}]:{}\".format(i, v1[i], i, v2[i]))\n return math.sqrt(soma)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#float p1 = dadosTreino[i].notaMediaNaEscola;\n#float p2 = dadoTeste.notaMediaNaEscola;\n\n#float q1 = dadosTreino[i].horasDeEstudosSemanais;\n#float q2 = dadoTeste.horasDeEstudosSemanais;\nfor i in range(n):\n for j in range(m):\n p1 = treino.media.array[j]\n p2 = teste.media.array[i]\n a = [p1, p2]\n q1 = treino.horas.array[j]\n q2 = teste.horas.array[i]\n b = [q1, q2]\n d = distance.euclidean(a, b)\n d1 = dist_euclidiana(a, b)\n #print(\"distance.euclidean: p1: {:.2f} p2: {:.2f} q1: {:.2f} q2: {:.2f} d: {:.6f}\".format(p1, p2, q1, q2, d));\n #print(\"dist_euclidiana: p1: {:.2f} p2: {:.2f} q1: {:.2f} q2: {:.2f} d: {:.6f}\".format(p1, p2, q1, q2, d1));\n media = teste.media.array[i]\n horas = teste.horas.array[i]\n aprovacao = (\"Aprovado\" if predict[i] == 1 else \"Reprovado\")\n print(\"Aluno {}: ({}, {}) = {}\".format(i, media, horas, aprovacao))",
"Aluno 0: (5.5, 2.5) = Aprovado\nAluno 1: (8.3, 4.25) = Aprovado\nAluno 2: (6.8, 7.2) = Aprovado\nAluno 3: (7.5, 9.5) = Aprovado\nAluno 4: (9.0, 1.0) = Reprovado\nAluno 5: (3.8, 1.0) = Reprovado\nAluno 6: (7.0, 0.5) = Reprovado\nAluno 7: (6.3, 2.0) = Reprovado\nAluno 8: (4.0, 3.0) = Aprovado\nAluno 9: (2.0, 4.0) = Reprovado\n"
],
[
"i=4\nfor j in range(m):\n p1 = treino.media.array[j]\n p2 = teste.media.array[i]\n a = [p1, p2]\n q1 = treino.horas.array[j]\n q2 = teste.horas.array[i]\n b = [q1, q2]\n d = distance.euclidean(a, b)\n d1 = dist_euclidiana(a, b)\n #print(\"distance.euclidean: p1: {:.2f} p2: {:.2f} q1: {:.2f} q2: {:.2f} d: {:.6f}\".format(p1, p2, q1, q2, d));\n #print(\"dist_euclidiana: p1: {:.2f} p2: {:.2f} q1: {:.2f} q2: {:.2f} d: {:.6f}\".format(p1, p2, q1, q2, d1));\nmedia = teste.media.array[i]\nhoras = teste.horas.array[i]\naprovacao = (\"Aprovado\" if predict[i] == 1 else \"Reprovado\")\nprint(\"Aluno {}: ({}, {}) = {}\".format(i, media, horas, aprovacao))",
"Aluno 4: (9.0, 1.0) = Reprovado\n"
],
[
"\ndef classificacao(i):\n lista = list()\n for j in range(m):\n p1 = treino.media.array[j]\n p2 = teste.media.array[i]\n a = [p1, p2]\n q1 = treino.horas.array[j]\n q2 = teste.horas.array[i]\n b = [q1, q2]\n d = distance.euclidean(a, b)\n d1 = dist_euclidiana(a, b)\n a = treino.aprovado.array[j]\n lista.append({\"i\":j, \"d\": d, \"a\": a})\n\n lista_ordenada = sorted(lista, key=lambda k: k['d'])\n lista_k = lista_ordenada[0:k]\n count_aprovados = 0\n count_reprovados = 0\n for i in range(k):\n if(lista_k[i]['a'] == 1):\n count_aprovados = count_aprovados + 1\n else:\n count_reprovados = count_reprovados + 1\n #print(\"Aprovados:{}\".format(count_aprovados))\n #print(\"Reprovados:{}\".format(count_reprovados))\n if(count_aprovados > count_reprovados):\n return \"Aprovado\"\n else:\n return \"Reprovado\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for i in range(n):\n aprovacao = classificacao(i)\n media = teste.media.array[i]\n horas = teste.horas.array[i]\n print(\"Aluno {}: ({}, {}) = {}\".format(i, media, horas, aprovacao))",
"Aluno 0: (5.5, 2.5) = Aprovado\nAluno 1: (8.3, 4.25) = Aprovado\nAluno 2: (6.8, 7.2) = Aprovado\nAluno 3: (7.5, 9.5) = Aprovado\nAluno 4: (9.0, 1.0) = Aprovado\nAluno 5: (3.8, 1.0) = Aprovado\nAluno 6: (7.0, 0.5) = Aprovado\nAluno 7: (6.3, 2.0) = Aprovado\nAluno 8: (4.0, 3.0) = Aprovado\nAluno 9: (2.0, 4.0) = Aprovado\n"
],
[
"class KNN:\n def __init__(self, k):\n self.k = k\n \n def fit(self, X, y):\n self.X_train = X\n self.y_train = y\n \n def distance(self, X1, X2):\n distance = scipy.spatial.distance.euclidean(X1, X2)\n \n def predict(self, X_test):\n final_output = []\n for i in range(len(X_test)):\n d = []\n votes = []\n for j in range(len(X_train)):\n dist = scipy.spatial.distance.euclidean(X_train[j] , X_test[i])\n d.append([dist, j])\n #print(\"antes:\")\n #for dist, j in d:\n # print(\"d:{} j:{}\".format(dist, j))\n \n d.sort()\n #print(\"depois:\")\n #for s in d:\n # print(\"d:{} j:{}\".format(s[0], s[1]))\n \n d = d[0:self.k]\n #print(\"com k:\")\n #for s in d:\n # print(\"d:{} j:{}\".format(s[0], s[1]))\n for d, j in d:\n votes.append(y_train[j])\n ans = Counter(votes).most_common(1)[0][0]\n final_output.append(ans)\n \n return final_output\n \n def score(self, X_test, y_test):\n predictions = self.predict(X_test)\n return (predictions == y_test).sum() / len(y_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"clf = KNN(3)\nclf.fit(X_train, y_train)\nprediction = clf.predict(X_test)\nfor i in range(n):\n media = teste.media.array[i]\n horas = teste.horas.array[i]\n aprovacao = (\"Aprovado\" if prediction[i] == 1 else \"Reprovado\")\n print(\"Aluno {}: ({}, {}) = {}\".format(i, media, horas, aprovacao))",
"antes:\nd:4.924428900898052 j:0\nd:4.366062299143245 j:1\nd:4.301162633521313 j:2\nd:3.3541019662496847 j:3\nd:2.7950849718747373 j:4\nd:3.1011127035307826 j:5\nd:2.596998267230843 j:6\nd:2.462214450449026 j:7\nd:2.0615528128088303 j:8\nd:0.6200000000000001 j:9\nd:1.8200274723201295 j:10\nd:1.8027756377319946 j:11\nd:1.6770509831248424 j:12\nd:3.5355339059327378 j:13\nd:6.103277807866851 j:14\nd:7.516648189186454 j:15\nd:6.380000000000001 j:16\nd:0.7071067811865476 j:17\nd:5.024937810560445 j:18\nd:5.5901699437494745 j:19\nd:1.0 j:20\nd:2.9154759474226504 j:21\nd:4.038873605350878 j:22\nd:5.385164807134504 j:23\nd:3.5355339059327378 j:24\nd:3.3541019662496847 j:25\nd:4.301162633521313 j:26\nd:5.942432162002357 j:27\nd:1.9525624189766635 j:28\nd:4.301162633521313 j:29\ndepois:\nd:0.6200000000000001 j:9\nd:0.7071067811865476 j:17\nd:1.0 j:20\nd:1.6770509831248424 j:12\nd:1.8027756377319946 j:11\nd:1.8200274723201295 j:10\nd:1.9525624189766635 j:28\nd:2.0615528128088303 j:8\nd:2.462214450449026 j:7\nd:2.596998267230843 j:6\nd:2.7950849718747373 j:4\nd:2.9154759474226504 j:21\nd:3.1011127035307826 j:5\nd:3.3541019662496847 j:3\nd:3.3541019662496847 j:25\nd:3.5355339059327378 j:13\nd:3.5355339059327378 j:24\nd:4.038873605350878 j:22\nd:4.301162633521313 j:2\nd:4.301162633521313 j:26\nd:4.301162633521313 j:29\nd:4.366062299143245 j:1\nd:4.924428900898052 j:0\nd:5.024937810560445 j:18\nd:5.385164807134504 j:23\nd:5.5901699437494745 j:19\nd:5.942432162002357 j:27\nd:6.103277807866851 j:14\nd:6.380000000000001 j:16\nd:7.516648189186454 j:15\ncom k:\nd:0.6200000000000001 j:9\nd:0.7071067811865476 j:17\nd:1.0 j:20\nantes:\nd:8.206856889211606 j:0\nd:7.647875521999558 j:1\nd:7.599506562928939 j:2\nd:6.648496070541067 j:3\nd:6.090155991434046 j:4\nd:6.325693637855062 j:5\nd:5.785058340241696 j:6\nd:5.517245689653489 j:7\nd:4.995247741604015 j:8\nd:3.6683647583085306 j:9\nd:4.1880783182743855 j:10\nd:3.715171597651985 j:11\nd:2.8178005607210745 j:12\nd:4.260575078554537 j:13\nd:3.3245300419758577 j:14\nd:6.629668166658117 j:15\nd:5.4108132475627 j:16\nd:2.6177280225416855 j:17\nd:3.9815198103236913 j:18\nd:4.159627387158615 j:19\nd:2.510478042126639 j:20\nd:1.500833101980364 j:21\nd:2.385372088375313 j:22\nd:3.3470135942359125 j:23\nd:0.8077747210701759 j:24\nd:0.320156211871642 j:25\nd:1.025914226434159 j:26\nd:9.213576938409968 j:27\nd:5.243090691567332 j:28\nd:6.344485794766981 j:29\ndepois:\nd:0.320156211871642 j:25\nd:0.8077747210701759 j:24\nd:1.025914226434159 j:26\nd:1.500833101980364 j:21\nd:2.385372088375313 j:22\nd:2.510478042126639 j:20\nd:2.6177280225416855 j:17\nd:2.8178005607210745 j:12\nd:3.3245300419758577 j:14\nd:3.3470135942359125 j:23\nd:3.6683647583085306 j:9\nd:3.715171597651985 j:11\nd:3.9815198103236913 j:18\nd:4.159627387158615 j:19\nd:4.1880783182743855 j:10\nd:4.260575078554537 j:13\nd:4.995247741604015 j:8\nd:5.243090691567332 j:28\nd:5.4108132475627 j:16\nd:5.517245689653489 j:7\nd:5.785058340241696 j:6\nd:6.090155991434046 j:4\nd:6.325693637855062 j:5\nd:6.344485794766981 j:29\nd:6.629668166658117 j:15\nd:6.648496070541067 j:3\nd:7.599506562928939 j:2\nd:7.647875521999558 j:1\nd:8.206856889211606 j:0\nd:9.213576938409968 j:27\ncom k:\nd:0.320156211871642 j:25\nd:0.8077747210701759 j:24\nd:1.025914226434159 j:26\nantes:\nd:8.86171540955813 j:0\nd:8.348203399534537 j:1\nd:8.653323061113575 j:2\nd:7.545197147855052 j:3\nd:7.059922095887461 j:4\nd:7.802236858747625 j:5\nd:7.372408019093897 j:6\nd:7.320689858203256 j:7\nd:6.937578828380979 j:8\nd:5.476531749200401 j:9\nd:6.499423051317709 j:10\nd:6.2072538211353985 j:11\nd:5.453668490108287 j:12\nd:7.299315036357864 j:13\nd:2.220360331117452 j:14\nd:3.3286633954186473 j:15\nd:2.1242410409367394 j:16\nd:4.27551166528639 j:17\nd:0.8544003745317529 j:18\nd:0.8544003745317529 j:19\nd:4.709564735726647 j:20\nd:2.209072203437452 j:21\nd:0.9708243919473801 j:22\nd:0.7615773105863909 j:23\nd:2.505992817228334 j:24\nd:3.623534186398688 j:25\nd:3.111269837220809 j:26\nd:9.723296766015116 j:27\nd:6.575902979819578 j:28\nd:5.280151512977634 j:29\ndepois:\nd:0.7615773105863909 j:23\nd:0.8544003745317529 j:18\nd:0.8544003745317529 j:19\nd:0.9708243919473801 j:22\nd:2.1242410409367394 j:16\nd:2.209072203437452 j:21\nd:2.220360331117452 j:14\nd:2.505992817228334 j:24\nd:3.111269837220809 j:26\nd:3.3286633954186473 j:15\nd:3.623534186398688 j:25\nd:4.27551166528639 j:17\nd:4.709564735726647 j:20\nd:5.280151512977634 j:29\nd:5.453668490108287 j:12\nd:5.476531749200401 j:9\nd:6.2072538211353985 j:11\nd:6.499423051317709 j:10\nd:6.575902979819578 j:28\nd:6.937578828380979 j:8\nd:7.059922095887461 j:4\nd:7.299315036357864 j:13\nd:7.320689858203256 j:7\nd:7.372408019093897 j:6\nd:7.545197147855052 j:3\nd:7.802236858747625 j:5\nd:8.348203399534537 j:1\nd:8.653323061113575 j:2\nd:8.86171540955813 j:0\nd:9.723296766015116 j:27\ncom k:\nd:0.7615773105863909 j:23\nd:0.8544003745317529 j:18\nd:0.8544003745317529 j:19\nantes:\nd:11.10180165558726 j:0\nd:10.609547586961472 j:1\nd:10.977249200050075 j:2\nd:9.86154146165801 j:3\nd:9.39747306460625 j:4\nd:10.188076364064022 j:5\nd:9.768541344540647 j:6\nd:9.724325169388361 j:7\nd:9.340770846134703 j:8\nd:7.878096216726475 j:9\nd:8.877640452282352 j:10\nd:8.558621384311845 j:11\nd:7.766112283504533 j:12\nd:9.513148795220223 j:13\nd:2.5 j:14\nd:2.5495097567963922 j:15\nd:2.0938958904396365 j:16\nd:6.670832032063167 j:17\nd:2.5 j:18\nd:1.8027756377319946 j:19\nd:7.0710678118654755 j:20\nd:4.527692569068709 j:21\nd:3.2882366094914763 j:22\nd:2.0 j:23\nd:4.527692569068709 j:24\nd:5.5901699437494745 j:25\nd:4.743416490252569 j:26\nd:11.908505363814553 j:27\nd:8.96172416446746 j:28\nd:7.106335201775948 j:29\ndepois:\nd:1.8027756377319946 j:19\nd:2.0 j:23\nd:2.0938958904396365 j:16\nd:2.5 j:14\nd:2.5 j:18\nd:2.5495097567963922 j:15\nd:3.2882366094914763 j:22\nd:4.527692569068709 j:21\nd:4.527692569068709 j:24\nd:4.743416490252569 j:26\nd:5.5901699437494745 j:25\nd:6.670832032063167 j:17\nd:7.0710678118654755 j:20\nd:7.106335201775948 j:29\nd:7.766112283504533 j:12\nd:7.878096216726475 j:9\nd:8.558621384311845 j:11\nd:8.877640452282352 j:10\nd:8.96172416446746 j:28\nd:9.340770846134703 j:8\nd:9.39747306460625 j:4\nd:9.513148795220223 j:13\nd:9.724325169388361 j:7\nd:9.768541344540647 j:6\nd:9.86154146165801 j:3\nd:10.188076364064022 j:5\nd:10.609547586961472 j:1\nd:10.977249200050075 j:2\nd:11.10180165558726 j:0\nd:11.908505363814553 j:27\ncom k:\nd:1.8027756377319946 j:19\nd:2.0 j:23\nd:2.0938958904396365 j:16\nantes:\nd:8.0156097709407 j:0\nd:7.504165509901817 j:1\nd:7.0710678118654755 j:2\nd:6.5 j:3\nd:6.005206074732157 j:4\nd:5.568383966645978 j:5\nd:5.03829336184387 j:6\nd:4.562071897723665 j:7\nd:4.031128874149275 j:8\nd:3.6089333604265956 j:9\nd:3.010398644698074 j:10\nd:2.5 j:11\nd:2.1360009363293826 j:12\nd:1.4142135623730951 j:13\nd:6.5 j:14\nd:9.848857801796104 j:15\nd:8.622319873444734 j:16\nd:3.605551275463989 j:17\nd:7.158910531638177 j:18\nd:7.433034373659253 j:19\nd:2.9154759474226504 j:20\nd:4.47213595499958 j:21\nd:5.618051263561058 j:22\nd:6.670832032063167 j:23\nd:4.123105625617661 j:24\nd:3.0413812651491097 j:25\nd:4.0 j:26\nd:9.031195934094221 j:27\nd:5.006246098625197 j:28\nd:8.06225774829855 j:29\ndepois:\nd:1.4142135623730951 j:13\nd:2.1360009363293826 j:12\nd:2.5 j:11\nd:2.9154759474226504 j:20\nd:3.010398644698074 j:10\nd:3.0413812651491097 j:25\nd:3.605551275463989 j:17\nd:3.6089333604265956 j:9\nd:4.0 j:26\nd:4.031128874149275 j:8\nd:4.123105625617661 j:24\nd:4.47213595499958 j:21\nd:4.562071897723665 j:7\nd:5.006246098625197 j:28\nd:5.03829336184387 j:6\nd:5.568383966645978 j:5\nd:5.618051263561058 j:22\nd:6.005206074732157 j:4\nd:6.5 j:3\nd:6.5 j:14\nd:6.670832032063167 j:23\nd:7.0710678118654755 j:2\nd:7.158910531638177 j:18\nd:7.433034373659253 j:19\nd:7.504165509901817 j:1\nd:8.0156097709407 j:0\nd:8.06225774829855 j:29\nd:8.622319873444734 j:16\nd:9.031195934094221 j:27\nd:9.848857801796104 j:15\ncom k:\nd:1.4142135623730951 j:13\nd:2.1360009363293826 j:12\nd:2.5 j:11\nantes:\nd:2.844292530665578 j:0\nd:2.313547060251855 j:1\nd:2.0591260281974 j:2\nd:1.2999999999999998 j:3\nd:0.8381527307120104 j:4\nd:0.920271699010678 j:5\nd:0.6514598989960932 j:6\nd:1.0259142264341596 j:7\nd:1.3000000000000003 j:8\nd:1.914262259984248 j:9\nd:2.214158982548453 j:10\nd:2.7 j:11\nd:3.2867156859089595 j:12\nd:4.317406628984581 j:13\nd:8.324061508662703 j:14\nd:9.079647570252934 j:15\nd:8.061290219313532 j:16\nd:2.973213749463701 j:17\nd:6.862215385719105 j:18\nd:7.502666192761078 j:19\nd:3.0886890422961004 j:20\nd:5.122499389946279 j:21\nd:6.148373768729419 j:22\nd:7.4793047805260615 j:23\nd:5.8 j:24\nd:5.57584074378026 j:25\nd:6.56048778674269 j:26\nd:3.873306081372862 j:27\nd:0.32015621187164256 j:28\nd:4.386342439892261 j:29\ndepois:\nd:0.32015621187164256 j:28\nd:0.6514598989960932 j:6\nd:0.8381527307120104 j:4\nd:0.920271699010678 j:5\nd:1.0259142264341596 j:7\nd:1.2999999999999998 j:3\nd:1.3000000000000003 j:8\nd:1.914262259984248 j:9\nd:2.0591260281974 j:2\nd:2.214158982548453 j:10\nd:2.313547060251855 j:1\nd:2.7 j:11\nd:2.844292530665578 j:0\nd:2.973213749463701 j:17\nd:3.0886890422961004 j:20\nd:3.2867156859089595 j:12\nd:3.873306081372862 j:27\nd:4.317406628984581 j:13\nd:4.386342439892261 j:29\nd:5.122499389946279 j:21\nd:5.57584074378026 j:25\nd:5.8 j:24\nd:6.148373768729419 j:22\nd:6.56048778674269 j:26\nd:6.862215385719105 j:18\nd:7.4793047805260615 j:23\nd:7.502666192761078 j:19\nd:8.061290219313532 j:16\nd:8.324061508662703 j:14\nd:9.079647570252934 j:15\ncom k:\nd:0.32015621187164256 j:28\nd:0.6514598989960932 j:6\nd:0.8381527307120104 j:4\nantes:\nd:6.0 j:0\nd:5.50567888638631 j:1\nd:5.024937810560445 j:2\nd:4.527692569068709 j:3\nd:4.0697051490249265 j:4\nd:3.5195028057951596 j:5\nd:3.0023990407672327 j:6\nd:2.5124689052802225 j:7\nd:2.0 j:8\nd:2.0382345301755636 j:9\nd:1.0307764064044151 j:10\nd:0.7071067811865476 j:11\nd:1.25 j:12\nd:1.118033988749895 j:13\nd:7.280109889280518 j:14\nd:9.7082439194738 j:15\nd:8.51318976647414 j:16\nd:2.692582403567252 j:17\nd:7.0710678118654755 j:18\nd:7.516648189186454 j:19\nd:2.0615528128088303 j:20\nd:4.5 j:21\nd:5.75 j:22\nd:7.0178344238090995 j:23\nd:4.6097722286464435 j:24\nd:3.8078865529319543 j:25\nd:4.924428900898052 j:26\nd:7.00446286306095 j:27\nd:3.092329219213245 j:28\nd:6.726812023536855 j:29\ndepois:\nd:0.7071067811865476 j:11\nd:1.0307764064044151 j:10\nd:1.118033988749895 j:13\nd:1.25 j:12\nd:2.0 j:8\nd:2.0382345301755636 j:9\nd:2.0615528128088303 j:20\nd:2.5124689052802225 j:7\nd:2.692582403567252 j:17\nd:3.0023990407672327 j:6\nd:3.092329219213245 j:28\nd:3.5195028057951596 j:5\nd:3.8078865529319543 j:25\nd:4.0697051490249265 j:4\nd:4.5 j:21\nd:4.527692569068709 j:3\nd:4.6097722286464435 j:24\nd:4.924428900898052 j:26\nd:5.024937810560445 j:2\nd:5.50567888638631 j:1\nd:5.75 j:22\nd:6.0 j:0\nd:6.726812023536855 j:29\nd:7.00446286306095 j:27\nd:7.0178344238090995 j:23\nd:7.0710678118654755 j:18\nd:7.280109889280518 j:14\nd:7.516648189186454 j:19\nd:8.51318976647414 j:16\nd:9.7082439194738 j:15\ncom k:\nd:0.7071067811865476 j:11\nd:1.0307764064044151 j:10\nd:1.118033988749895 j:13\nantes:\nd:5.508175741568165 j:0\nd:4.960090724976712 j:1\nd:4.742362280551751 j:2\nd:3.9293765408777 j:3\nd:3.384154251803543 j:4\nd:3.3670313333855386 j:5\nd:2.813254343282882 j:6\nd:2.510478042126638 j:7\nd:1.9849433241279206 j:8\nd:0.8089499366462672 j:9\nd:1.285496013218244 j:10\nd:1.019803902718557 j:11\nd:0.7433034373659254 j:12\nd:2.6248809496813377 j:13\nd:6.126989472816156 j:14\nd:8.104936767180853 j:15\nd:6.926355463012277 j:16\nd:1.044030650891055 j:17\nd:5.508175741568165 j:18\nd:6.003332407921453 j:19\nd:0.5385164807134505 j:20\nd:3.0805843601498726 j:21\nd:4.307261310856354 j:22\nd:5.629387178015028 j:23\nd:3.448187929913334 j:24\nd:2.973213749463701 j:25\nd:4.036087214122113 j:26\nd:6.538539592294291 j:27\nd:2.419194080680589 j:28\nd:5.243090691567332 j:29\ndepois:\nd:0.5385164807134505 j:20\nd:0.7433034373659254 j:12\nd:0.8089499366462672 j:9\nd:1.019803902718557 j:11\nd:1.044030650891055 j:17\nd:1.285496013218244 j:10\nd:1.9849433241279206 j:8\nd:2.419194080680589 j:28\nd:2.510478042126638 j:7\nd:2.6248809496813377 j:13\nd:2.813254343282882 j:6\nd:2.973213749463701 j:25\nd:3.0805843601498726 j:21\nd:3.3670313333855386 j:5\nd:3.384154251803543 j:4\nd:3.448187929913334 j:24\nd:3.9293765408777 j:3\nd:4.036087214122113 j:26\nd:4.307261310856354 j:22\nd:4.742362280551751 j:2\nd:4.960090724976712 j:1\nd:5.243090691567332 j:29\nd:5.508175741568165 j:0\nd:5.508175741568165 j:18\nd:5.629387178015028 j:23\nd:6.003332407921453 j:19\nd:6.126989472816156 j:14\nd:6.538539592294291 j:27\nd:6.926355463012277 j:16\nd:8.104936767180853 j:15\ncom k:\nd:0.5385164807134505 j:20\nd:0.7433034373659254 j:12\nd:0.8089499366462672 j:9\nantes:\nd:3.905124837953327 j:0\nd:3.3634060117684275 j:1\nd:3.605551275463989 j:2\nd:2.5 j:3\nd:2.0155644370746373 j:4\nd:2.9132284496757204 j:5\nd:2.62 j:6\nd:2.7950849718747373 j:7\nd:2.692582403567252 j:8\nd:1.8720042734993956 j:9\nd:3.010398644698074 j:10\nd:3.2015621187164243 j:11\nd:3.25 j:12\nd:5.0 j:13\nd:6.726812023536855 j:14\nd:7.0710678118654755 j:15\nd:6.068311132432154 j:16\nd:2.0 j:17\nd:4.924428900898052 j:18\nd:5.5901699437494745 j:19\nd:2.5495097567963922 j:20\nd:3.605551275463989 j:21\nd:4.422951503238533 j:22\nd:5.70087712549569 j:23\nd:4.47213595499958 j:24\nd:4.6097722286464435 j:25\nd:5.385164807134504 j:26\nd:4.8541219597369 j:27\nd:1.75 j:28\nd:2.8284271247461903 j:29\ndepois:\nd:1.75 j:28\nd:1.8720042734993956 j:9\nd:2.0 j:17\nd:2.0155644370746373 j:4\nd:2.5 j:3\nd:2.5495097567963922 j:20\nd:2.62 j:6\nd:2.692582403567252 j:8\nd:2.7950849718747373 j:7\nd:2.8284271247461903 j:29\nd:2.9132284496757204 j:5\nd:3.010398644698074 j:10\nd:3.2015621187164243 j:11\nd:3.25 j:12\nd:3.3634060117684275 j:1\nd:3.605551275463989 j:2\nd:3.605551275463989 j:21\nd:3.905124837953327 j:0\nd:4.422951503238533 j:22\nd:4.47213595499958 j:24\nd:4.6097722286464435 j:25\nd:4.8541219597369 j:27\nd:4.924428900898052 j:18\nd:5.0 j:13\nd:5.385164807134504 j:26\nd:5.5901699437494745 j:19\nd:5.70087712549569 j:23\nd:6.068311132432154 j:16\nd:6.726812023536855 j:14\nd:7.0710678118654755 j:15\ncom k:\nd:1.75 j:28\nd:1.8720042734993956 j:9\nd:2.0 j:17\nantes:\nd:3.640054944640259 j:0\nd:3.2882366094914763 j:1\nd:4.0 j:2\nd:3.0413812651491097 j:3\nd:2.9261749776799064 j:4\nd:4.15053008662749 j:5\nd:4.13574660732497 j:6\nd:4.5069390943299865 j:7\nd:4.6097722286464435 j:8\nd:4.0919921798556755 j:9\nd:5.153882032022076 j:10\nd:5.408326913195984 j:11\nd:5.482928049865327 j:12\nd:7.211102550927978 j:13\nd:7.826237921249264 j:14\nd:6.708203932499369 j:15\nd:6.005364268718427 j:16\nd:4.123105625617661 j:17\nd:5.315072906367325 j:18\nd:6.020797289396148 j:19\nd:4.743416490252569 j:20\nd:5.0990195135927845 j:21\nd:5.482928049865327 j:22\nd:6.519202405202649 j:23\nd:6.082762530298219 j:24\nd:6.5 j:25\nd:7.0710678118654755 j:26\nd:4.25 j:27\nd:3.400367627183861 j:28\nd:1.0 j:29\ndepois:\nd:1.0 j:29\nd:2.9261749776799064 j:4\nd:3.0413812651491097 j:3\nd:3.2882366094914763 j:1\nd:3.400367627183861 j:28\nd:3.640054944640259 j:0\nd:4.0 j:2\nd:4.0919921798556755 j:9\nd:4.123105625617661 j:17\nd:4.13574660732497 j:6\nd:4.15053008662749 j:5\nd:4.25 j:27\nd:4.5069390943299865 j:7\nd:4.6097722286464435 j:8\nd:4.743416490252569 j:20\nd:5.0990195135927845 j:21\nd:5.153882032022076 j:10\nd:5.315072906367325 j:18\nd:5.408326913195984 j:11\nd:5.482928049865327 j:12\nd:5.482928049865327 j:22\nd:6.005364268718427 j:16\nd:6.020797289396148 j:19\nd:6.082762530298219 j:24\nd:6.5 j:25\nd:6.519202405202649 j:23\nd:6.708203932499369 j:15\nd:7.0710678118654755 j:26\nd:7.211102550927978 j:13\nd:7.826237921249264 j:14\ncom k:\nd:1.0 j:29\nd:2.9261749776799064 j:4\nd:3.0413812651491097 j:3\nAluno 0: (5.5, 2.5) = Aprovado\nAluno 1: (8.3, 4.25) = Aprovado\nAluno 2: (6.8, 7.2) = Aprovado\nAluno 3: (7.5, 9.5) = Aprovado\nAluno 4: (9.0, 1.0) = Reprovado\nAluno 5: (3.8, 1.0) = Reprovado\nAluno 6: (7.0, 0.5) = Reprovado\nAluno 7: (6.3, 2.0) = Reprovado\nAluno 8: (4.0, 3.0) = Aprovado\nAluno 9: (2.0, 4.0) = Reprovado\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a77bb5e18ec2904b870b5ce90a53107416d1aff
| 17,438 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
deep-learning-keras/d4p2-sentiment-analysis-deep-learning.ipynb
|
Abed-AlRahman/spark-demos
|
53034ff711fec31e0da50ce051459d9760c31d10
|
[
"Apache-1.1"
] | 3 |
2020-09-17T08:29:14.000Z
|
2021-11-20T09:42:57.000Z
|
deep-learning-keras/d4p2-sentiment-analysis-deep-learning.ipynb
|
Abed-AlRahman/spark-demos
|
53034ff711fec31e0da50ce051459d9760c31d10
|
[
"Apache-1.1"
] | null | null | null |
deep-learning-keras/d4p2-sentiment-analysis-deep-learning.ipynb
|
Abed-AlRahman/spark-demos
|
53034ff711fec31e0da50ce051459d9760c31d10
|
[
"Apache-1.1"
] | 18 |
2020-07-04T13:08:07.000Z
|
2021-12-27T05:20:23.000Z
| 31.763206 | 180 | 0.437149 |
[
[
[
"Configurations:\n* install tensorflow 2.1\n* install matplotlib\n* install pandas\n* install scjkit-learn\n* install nltk",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport tensorflow as tf\nimport re\n\nfrom tensorflow import keras\nfrom keras.models import Sequential\nfrom keras.layers import Dense, Activation, Dropout\nfrom keras.preprocessing import text, sequence\nfrom keras import utils\nfrom keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences\n\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\n\nfrom keras.layers.embeddings import Embedding\nfrom keras.layers.core import SpatialDropout1D\nfrom keras.layers import LSTM\nfrom keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping\n\nfrom numpy.random import seed",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Load Data\ndf_train = pd.read_csv('../data/deep-learning-datasets/twitter-sentiment-analysis/train_E6oV3lV.csv')\ndf_train.columns = [\"id\", \"label\", \"text\"]\n\ndf_test = pd.read_csv('../data/deep-learning-datasets/twitter-sentiment-analysis/test_tweets_anuFYb8.csv')\ndf_test.columns = [\"id\",\"text\"]\ndf_train",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# clean data\nREPLACE_BY_SPACE_RE = re.compile('[/(){}\\[\\]\\|@,;]')\nBAD_SYMBOLS_RE = re.compile('[^0-9a-z #+_]')\n\ndef clean_text(text):\n \"\"\"\n text: a string\n return: modified initial string\n \"\"\"\n text = text.lower() # lowercase text\n text = REPLACE_BY_SPACE_RE.sub(' ', text) # replace REPLACE_BY_SPACE_RE symbols by space in text. substitute the matched string in REPLACE_BY_SPACE_RE with space.\n text = BAD_SYMBOLS_RE.sub('', text) # remove symbols which are in BAD_SYMBOLS_RE from text. substitute the matched string in BAD_SYMBOLS_RE with nothing.\n text = ' '.join(word for word in text.split() if len(word) > 2) # remove stopwors from text\n return text\n\ndef preprocess_text(df):\n df = df.reset_index(drop=True)\n df['text'] = df['text'].apply(clean_text)\n df['text'] = df['text'].str.replace('\\d+', '')\n return df\n\ndf_train = preprocess_text(df_train)\ndf_test = preprocess_text(df_test)\n\ndf_train",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# The maximum number of words to be used. (most frequent)\nMAX_NB_WORDS = 30000\n\n# Max number of words in each complaint.\nMAX_SEQUENCE_LENGTH = 50\n\n# This is fixed.\nEMBEDDING_DIM = 100\ntokenizer = text.Tokenizer(num_words=MAX_NB_WORDS, filters='#!\"$%&()*+,-./:;<=>?@[\\]^_`{|}~', lower=True, split= ' ')\n\ntokenizer.fit_on_texts((df_train['text'].append(df_test['text'])).values)\nword_index = tokenizer.word_index\nword_index['study']\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def fromTextToFeatures(df_text):\n # gives you a list of integer sequences encoding the words in your sentence\n X = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(df_text.values)\n # split the X 1-dimensional sequence of word indexes into a 2-d listof items\n # Each item is split is a sequence of 50 value left-padded with zeros\n X = pad_sequences(X, maxlen=MAX_SEQUENCE_LENGTH)\n return X\nX = fromTextToFeatures(df_train['text'])\nprint('Shape of data tensor:', X.shape)\n#X",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_test_ex = fromTextToFeatures(df_test['text'])\n\nprint('Shape of data tensor:', X_test_ex.shape)",
"Shape of data tensor: (17197, 50)\n"
],
[
"Y = pd.get_dummies(df_train['label']).values\n# asdas dasda sd asd asd asd [0, 1]\n# dfsdf asd sd fdsf sdf [1, 0]\n\nprint('Shape of label tensor:', Y.shape)",
"Shape of label tensor: (31962, 2)\n"
],
[
"X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(X,Y, test_size = 0.10, random_state = 42)\nprint(X_train.shape,Y_train.shape)\nprint(X_test.shape,Y_test.shape)",
"(28765, 50) (28765, 2)\n(3197, 50) (3197, 2)\n"
],
[
"seed(100)\n\nmodel = Sequential()\n# The Embedding layer is used to create word vectors for incoming words. \n# It sits between the input and the LSTM layer, i.e. \n# the output of the Embedding layer is the input to the LSTM layer.\nmodel.add(Embedding(MAX_NB_WORDS, EMBEDDING_DIM, input_length=X.shape[1]))\nmodel.add(LSTM(100, dropout=0.2, recurrent_dropout=0.2))\nmodel.add(Dense(2, activation='softmax'))\nmodel.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])\n\nepochs = 3\nbatch_size = 64\n\nhistory = model.fit(X_train, Y_train, epochs=epochs, batch_size=batch_size,validation_split=0.1,callbacks=[EarlyStopping(monitor='val_loss', patience=3, min_delta=0.0001)])\n",
"Train on 25888 samples, validate on 2877 samples\nEpoch 1/3\n25888/25888 [==============================] - 97s 4ms/step - loss: 0.1743 - acc: 0.9453 - val_loss: 0.1204 - val_acc: 0.9566\nEpoch 2/3\n25888/25888 [==============================] - 104s 4ms/step - loss: 0.0649 - acc: 0.9781 - val_loss: 0.1266 - val_acc: 0.9607\nEpoch 3/3\n25888/25888 [==============================] - 105s 4ms/step - loss: 0.0304 - acc: 0.9892 - val_loss: 0.1497 - val_acc: 0.9593\n"
],
[
"accr = model.evaluate(X_test,Y_test)\nprint('Test set\\n Loss: {:0.3f}\\n Accuracy: {:0.3f}'.format(accr[0],accr[1]))\n\npred_y = model.predict(X_test)\n",
"3197/3197 [==============================] - 9s 3ms/step\nTest set\n Loss: 0.127\n Accuracy: 0.962\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a77c0b04deeca6a920e7e8ee886a37637288bdc
| 949,909 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
simple_test.ipynb
|
quolc/keras-OpenSlideGenerator
|
27479f3568ffe239f57192bef70b2ee65c2444f2
|
[
"MIT"
] | 8 |
2018-04-18T00:59:28.000Z
|
2021-07-20T17:08:23.000Z
|
simple_test.ipynb
|
quolc/keras-OpenSlideGenerator
|
27479f3568ffe239f57192bef70b2ee65c2444f2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
simple_test.ipynb
|
quolc/keras-OpenSlideGenerator
|
27479f3568ffe239f57192bef70b2ee65c2444f2
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2018-10-16T14:47:51.000Z
|
2020-11-04T23:20:14.000Z
| 6,689.5 | 691,308 | 0.966867 |
[
[
[
"from matplotlib import pyplot as plt\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import openslide_generator\nimport importlib\nimportlib.reload(openslide_generator)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"gen = openslide_generator.SimpleOpenSlideGenerator(color_matching=\"test_slides/desert1.jpg\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ret = gen.fetch_patches_from_slide(\"../test_images/TCGA-VD-AA8N-01Z-00-DX1.svs\",\n count=3, blur=30, he_augmentation=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(9,3))\nfor i, img in enumerate(ret):\n plt.subplot(1,3,i+1)\n plt.imshow(img.transpose((1,2,0)))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ret = gen.fetch_patches_from_slide(\"../test_images/TCGA-VD-AA8N-01Z-00-DX1.svs\",\n count=3, rotations=[30,60,90],\n blur=30, he_augmentation=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(12,9))\nfor i, elem in enumerate(ret):\n for j, img in enumerate(elem):\n plt.subplot(3,4,i*4+j+1)\n plt.imshow(img.transpose((1,2,0)))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a77d2d8b608ff10826ba7614a63da1b81cda3a4
| 39,055 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
examples/notebooks/Getting Started/Tutorial 4 - Setting parameter values.ipynb
|
dalbamont/PyBaMM
|
23b29273806f514e3725c67c30d25cc50b57a4f4
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
examples/notebooks/Getting Started/Tutorial 4 - Setting parameter values.ipynb
|
dalbamont/PyBaMM
|
23b29273806f514e3725c67c30d25cc50b57a4f4
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
examples/notebooks/Getting Started/Tutorial 4 - Setting parameter values.ipynb
|
dalbamont/PyBaMM
|
23b29273806f514e3725c67c30d25cc50b57a4f4
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null | 39.094094 | 351 | 0.487313 |
[
[
[
"# Tutorial 4 - Setting parameter values",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In [Tutorial 1](./Tutorial%201%20-%20How%20to%20run%20a%20model.ipynb) and [Tutorial 2](./Tutorial%202%20-%20Compare%20models.ipynb), we saw how to run a PyBaMM model with all the default settings. However, PyBaMM also allows you to tweak these settings for your application. In this tutorial, we will see how to change the parameters in PyBaMM.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%pip install pybamm -q # install PyBaMM if it is not installed\nimport pybamm",
"Note: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Change the whole parameter set",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"PyBaMM has a number of in-built parameter sets (check the list [here](https://pybamm.readthedocs.io/en/latest/source/parameters/parameter_sets.html)), which can be selected doing",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"chemistry = pybamm.parameter_sets.Chen2020",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This variable is a dictionary with the corresponding parameter subsets for each component.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"chemistry",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"More details on each subset can be found [here](https://github.com/pybamm-team/PyBaMM/tree/master/pybamm/input/parameters).\n\nNow we can pass `'chemistry'` into `ParameterValues` to create the dictionary of parameter values",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"parameter_values = pybamm.ParameterValues(chemistry=chemistry)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can see all the parameters stored in the dictionary",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"parameter_values",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"or we can search for a particular parameter",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"parameter_values.search(\"electrolyte\")",
"EC initial concentration in electrolyte [mol.m-3]\t4541.0\nElectrolyte conductivity [S.m-1]\t<function electrolyte_conductivity_Nyman2008 at 0x7f234684e1e0>\nElectrolyte diffusivity [m2.s-1]\t<function electrolyte_diffusivity_Nyman2008 at 0x7f2391b5a268>\nInitial concentration in electrolyte [mol.m-3]\t1000.0\nNegative electrode Bruggeman coefficient (electrolyte)\t1.5\nPositive electrode Bruggeman coefficient (electrolyte)\t1.5\nSeparator Bruggeman coefficient (electrolyte)\t1.5\nTypical electrolyte concentration [mol.m-3]\t1000.0\n"
]
],
[
[
"To run a simulation with this parameter set, we can proceed as usual but passing the parameters as a keyword argument",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model = pybamm.lithium_ion.DFN()\nsim = pybamm.Simulation(model, parameter_values=parameter_values)\nsim.solve([0, 3600])\nsim.plot()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Change individual parameters",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We often want to quickly change a small number of parameter values to investigate how the behaviour or the battery changes. In such cases, we can change parameter values without having to leave the notebook or script you are working in. \n\nWe start initialising the model and the parameter values",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model = pybamm.lithium_ion.DFN()\nparameter_values = pybamm.ParameterValues(chemistry=pybamm.parameter_sets.Chen2020)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"In this example we will change the current to 10 A",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"parameter_values[\"Current function [A]\"] = 10",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now we just need to run the simulation with the new parameter values",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sim = pybamm.Simulation(model, parameter_values=parameter_values)\nsim.solve([0, 3600])\nsim.plot()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Note that we still passed the interval `[0, 3600]` to `sim.solve()`, but the simulation terminated early as the lower voltage cut-off was reached.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"You can also simulate drive cycles by passing the data directly",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"parameter_values[\"Current function [A]\"] = \"[current data]US06\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Then we can just define the model and solve it",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model = pybamm.lithium_ion.SPMe()\nsim = pybamm.Simulation(model, parameter_values=parameter_values)\nsim.solve()\nsim.plot([\"Current [A]\", \"Terminal voltage [V]\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Alternatively, we can define the current to be an arbitrary function of time",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\n\ndef my_current(t):\n return pybamm.sin(2 * np.pi * t / 60)\n\nparameter_values[\"Current function [A]\"] = my_current",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"and we can now solve the model again. In this case, we can pass `t_eval` to the solver to make sure we have enough time points to resolve the function in our output.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model = pybamm.lithium_ion.SPMe()\nsim = pybamm.Simulation(model, parameter_values=parameter_values)\nt_eval = np.arange(0, 121, 1)\nsim.solve(t_eval=t_eval)\nsim.plot([\"Current [A]\", \"Terminal voltage [V]\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"In this notebook we have seen how we can change the parameters of our model. In [Tutorial 5](./Tutorial%205%20-%20Run%20experiments.ipynb) we show how can we define and run experiments.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a77d756189cff4c51da7c23a095e15ac9069d05
| 80,988 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
lab1/solutions/Part2_Music_Generation_Solution.ipynb
|
sbcyr/introtodeeplearning
|
604f7a437d09d06599c9c2881c7b36bc86fbd412
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
lab1/solutions/Part2_Music_Generation_Solution.ipynb
|
sbcyr/introtodeeplearning
|
604f7a437d09d06599c9c2881c7b36bc86fbd412
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
lab1/solutions/Part2_Music_Generation_Solution.ipynb
|
sbcyr/introtodeeplearning
|
604f7a437d09d06599c9c2881c7b36bc86fbd412
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 59.946706 | 15,644 | 0.737961 |
[
[
[
"<table align=\"center\">\n <td align=\"center\"><a target=\"_blank\" href=\"http://introtodeeplearning.com\">\n <img src=\"http://introtodeeplearning.com/images/colab/mit.png\" style=\"padding-bottom:5px;\" />\n Visit MIT Deep Learning</a></td>\n <td align=\"center\"><a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/aamini/introtodeeplearning/blob/master/lab1/solutions/Part2_Music_Generation_Solution.ipynb\">\n <img src=\"http://introtodeeplearning.com/images/colab/colab.png?v2.0\" style=\"padding-bottom:5px;\" />Run in Google Colab</a></td>\n <td align=\"center\"><a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://github.com/aamini/introtodeeplearning/blob/master/lab1/solutions/Part2_Music_Generation_Solution.ipynb\">\n <img src=\"http://introtodeeplearning.com/images/colab/github.png\" height=\"70px\" style=\"padding-bottom:5px;\" />View Source on GitHub</a></td>\n</table>\n\n# Copyright Information",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Copyright 2020 MIT 6.S191 Introduction to Deep Learning. All Rights Reserved.\n# \n# Licensed under the MIT License. You may not use this file except in compliance\n# with the License. Use and/or modification of this code outside of 6.S191 must\n# reference:\n#\n# © MIT 6.S191: Introduction to Deep Learning\n# http://introtodeeplearning.com\n#",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Lab 1: Intro to TensorFlow and Music Generation with RNNs\n\n# Part 2: Music Generation with RNNs\n\nIn this portion of the lab, we will explore building a Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) for music generation. We will train a model to learn the patterns in raw sheet music in [ABC notation](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ABC_notation) and then use this model to generate new music. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 2.1 Dependencies \nFirst, let's download the course repository, install dependencies, and import the relevant packages we'll need for this lab.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import Tensorflow 2.0\nimport tensorflow as tf \n\n# Download and import the MIT 6.S191 package\n!pip install mitdeeplearning\nimport mitdeeplearning as mdl\n\n# Import all remaining packages\nimport numpy as np\nimport os\nimport time\nimport functools\nfrom IPython import display as ipythondisplay\nfrom tqdm import tqdm\n!apt-get install abcmidi timidity > \"C:\\Users\\Shaun Cyr\\GitHub\\introtodeeplearning\\lab2\" 2>&1\n\n# Check that we are using a GPU, if not switch runtimes\n# using Runtime > Change Runtime Type > GPU\nassert len(tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU')) > 0",
"Requirement already satisfied: mitdeeplearning in c:\\users\\shaun cyr\\.conda\\envs\\machinelearning\\lib\\site-packages (0.1.2)\nRequirement already satisfied: numpy in c:\\users\\shaun cyr\\.conda\\envs\\machinelearning\\lib\\site-packages (from mitdeeplearning) (1.18.5)\nRequirement already satisfied: tqdm in c:\\users\\shaun cyr\\.conda\\envs\\machinelearning\\lib\\site-packages (from mitdeeplearning) (4.46.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: regex in c:\\users\\shaun cyr\\.conda\\envs\\machinelearning\\lib\\site-packages (from mitdeeplearning) (2020.6.8)\nRequirement already satisfied: gym in c:\\users\\shaun cyr\\.conda\\envs\\machinelearning\\lib\\site-packages (from mitdeeplearning) (0.17.2)\nRequirement already satisfied: pyglet<=1.5.0,>=1.4.0 in c:\\users\\shaun cyr\\.conda\\envs\\machinelearning\\lib\\site-packages (from gym->mitdeeplearning) (1.5.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: scipy in c:\\users\\shaun cyr\\.conda\\envs\\machinelearning\\lib\\site-packages (from gym->mitdeeplearning) (1.5.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: cloudpickle<1.4.0,>=1.2.0 in c:\\users\\shaun cyr\\.conda\\envs\\machinelearning\\lib\\site-packages (from gym->mitdeeplearning) (1.3.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: future in c:\\users\\shaun cyr\\.conda\\envs\\machinelearning\\lib\\site-packages (from pyglet<=1.5.0,>=1.4.0->gym->mitdeeplearning) (0.18.2)\n"
]
],
[
[
"## 2.2 Dataset\n\n\n\nWe've gathered a dataset of thousands of Irish folk songs, represented in the ABC notation. Let's download the dataset and inspect it: \n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Download the dataset\nsongs = mdl.lab1.load_training_data()\n\n# Print one of the songs to inspect it in greater detail!\nexample_song = songs[0]\nprint(\"\\nExample song: \")\nprint(example_song)",
"Found 816 songs in text\n\nExample song: \nX:2\nT:An Buachaill Dreoite\nZ: id:dc-hornpipe-2\nM:C|\nL:1/8\nK:G Major\nGF|DGGB d2GB|d2GF Gc (3AGF|DGGB d2GB|dBcA F2GF|!\nDGGB d2GF|DGGF G2Ge|fgaf gbag|fdcA G2:|!\nGA|B2BG c2cA|d2GF G2GA|B2BG c2cA|d2DE F2GA|!\nB2BG c2cA|d^cde f2 (3def|g2gf gbag|fdcA G2:|!\n"
]
],
[
[
"We can easily convert a song in ABC notation to an audio waveform and play it back. Be patient for this conversion to run, it can take some time.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Convert the ABC notation to audio file and listen to it\nmdl.lab1.play_song(example_song)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"One important thing to think about is that this notation of music does not simply contain information on the notes being played, but additionally there is meta information such as the song title, key, and tempo. How does the number of different characters that are present in the text file impact the complexity of the learning problem? This will become important soon, when we generate a numerical representation for the text data.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Join our list of song strings into a single string containing all songs\nsongs_joined = \"\\n\\n\".join(songs) \n\n# Find all unique characters in the joined string\nvocab = sorted(set(songs_joined))\nprint(\"There are\", len(vocab), \"unique characters in the dataset\")",
"There are 83 unique characters in the dataset\n"
]
],
[
[
"## 2.3 Process the dataset for the learning task\n\nLet's take a step back and consider our prediction task. We're trying to train a RNN model to learn patterns in ABC music, and then use this model to generate (i.e., predict) a new piece of music based on this learned information. \n\nBreaking this down, what we're really asking the model is: given a character, or a sequence of characters, what is the most probable next character? We'll train the model to perform this task. \n\nTo achieve this, we will input a sequence of characters to the model, and train the model to predict the output, that is, the following character at each time step. RNNs maintain an internal state that depends on previously seen elements, so information about all characters seen up until a given moment will be taken into account in generating the prediction.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Vectorize the text\n\nBefore we begin training our RNN model, we'll need to create a numerical representation of our text-based dataset. To do this, we'll generate two lookup tables: one that maps characters to numbers, and a second that maps numbers back to characters. Recall that we just identified the unique characters present in the text.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Define numerical representation of text ###\n\n# Create a mapping from character to unique index.\n# For example, to get the index of the character \"d\", \n# we can evaluate `char2idx[\"d\"]`. \nchar2idx = {u:i for i, u in enumerate(vocab)}\n\n# Create a mapping from indices to characters. This is\n# the inverse of char2idx and allows us to convert back\n# from unique index to the character in our vocabulary.\nidx2char = np.array(vocab)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This gives us an integer representation for each character. Observe that the unique characters (i.e., our vocabulary) in the text are mapped as indices from 0 to `len(unique)`. Let's take a peek at this numerical representation of our dataset:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print('{')\nfor char,_ in zip(char2idx, range(20)):\n print(' {:4s}: {:3d},'.format(repr(char), char2idx[char]))\nprint(' ...\\n}')",
"{\n '\\n': 0,\n ' ' : 1,\n '!' : 2,\n '\"' : 3,\n '#' : 4,\n \"'\" : 5,\n '(' : 6,\n ')' : 7,\n ',' : 8,\n '-' : 9,\n '.' : 10,\n '/' : 11,\n '0' : 12,\n '1' : 13,\n '2' : 14,\n '3' : 15,\n '4' : 16,\n '5' : 17,\n '6' : 18,\n '7' : 19,\n ...\n}\n"
],
[
"### Vectorize the songs string ###\n\n'''TODO: Write a function to convert the all songs string to a vectorized\n (i.e., numeric) representation. Use the appropriate mapping\n above to convert from vocab characters to the corresponding indices.\n\n NOTE: the output of the `vectorize_string` function \n should be a np.array with `N` elements, where `N` is\n the number of characters in the input string\n'''\ndef vectorize_string(string):\n vectorized_output = np.array([char2idx[char] for char in string])\n return vectorized_output\n\n# def vectorize_string(string):\n # TODO\n\nvectorized_songs = vectorize_string(songs_joined)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can also look at how the first part of the text is mapped to an integer representation:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print ('{} ---- characters mapped to int ----> {}'.format(repr(songs_joined[:10]), vectorized_songs[:10]))\n# check that vectorized_songs is a numpy array\nassert isinstance(vectorized_songs, np.ndarray), \"returned result should be a numpy array\"",
"'X:2\\nT:An B' ---- characters mapped to int ----> [49 22 14 0 45 22 26 69 1 27]\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Create training examples and targets\n\nOur next step is to actually divide the text into example sequences that we'll use during training. Each input sequence that we feed into our RNN will contain `seq_length` characters from the text. We'll also need to define a target sequence for each input sequence, which will be used in training the RNN to predict the next character. For each input, the corresponding target will contain the same length of text, except shifted one character to the right.\n\nTo do this, we'll break the text into chunks of `seq_length+1`. Suppose `seq_length` is 4 and our text is \"Hello\". Then, our input sequence is \"Hell\" and the target sequence is \"ello\".\n\nThe batch method will then let us convert this stream of character indices to sequences of the desired size.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Batch definition to create training examples ###\n\ndef get_batch(vectorized_songs, seq_length, batch_size):\n # the length of the vectorized songs string\n n = vectorized_songs.shape[0] - 1\n # randomly choose the starting indices for the examples in the training batch\n idx = np.random.choice(n-seq_length, batch_size)\n\n '''TODO: construct a list of input sequences for the training batch'''\n input_batch = [vectorized_songs[i : i+seq_length] for i in idx]\n # input_batch = # TODO\n '''TODO: construct a list of output sequences for the training batch'''\n output_batch = [vectorized_songs[i+1 : i+seq_length+1] for i in idx]\n # output_batch = # TODO\n\n # x_batch, y_batch provide the true inputs and targets for network training\n x_batch = np.reshape(input_batch, [batch_size, seq_length])\n y_batch = np.reshape(output_batch, [batch_size, seq_length])\n return x_batch, y_batch\n\n\n# Perform some simple tests to make sure your batch function is working properly! \ntest_args = (vectorized_songs, 10, 2)\nif not mdl.lab1.test_batch_func_types(get_batch, test_args) or \\\n not mdl.lab1.test_batch_func_shapes(get_batch, test_args) or \\\n not mdl.lab1.test_batch_func_next_step(get_batch, test_args): \n print(\"======\\n[FAIL] could not pass tests\")\nelse: \n print(\"======\\n[PASS] passed all tests!\")",
"[PASS] test_batch_func_types\n[PASS] test_batch_func_shapes\n[PASS] test_batch_func_next_step\n======\n[PASS] passed all tests!\n"
]
],
[
[
"For each of these vectors, each index is processed at a single time step. So, for the input at time step 0, the model receives the index for the first character in the sequence, and tries to predict the index of the next character. At the next timestep, it does the same thing, but the RNN considers the information from the previous step, i.e., its updated state, in addition to the current input.\n\nWe can make this concrete by taking a look at how this works over the first several characters in our text:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x_batch, y_batch = get_batch(vectorized_songs, seq_length=5, batch_size=1)\n\nfor i, (input_idx, target_idx) in enumerate(zip(np.squeeze(x_batch), np.squeeze(y_batch))):\n print(\"Step {:3d}\".format(i))\n print(\" input: {} ({:s})\".format(input_idx, repr(idx2char[input_idx])))\n print(\" expected output: {} ({:s})\".format(target_idx, repr(idx2char[target_idx])))",
"Step 0\n input: 20 ('8')\n expected output: 15 ('3')\nStep 1\n input: 15 ('3')\n expected output: 0 ('\\n')\nStep 2\n input: 0 ('\\n')\n expected output: 38 ('M')\nStep 3\n input: 38 ('M')\n expected output: 22 (':')\nStep 4\n input: 22 (':')\n expected output: 28 ('C')\n"
]
],
[
[
"## 2.4 The Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) model",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Now we're ready to define and train a RNN model on our ABC music dataset, and then use that trained model to generate a new song. We'll train our RNN using batches of song snippets from our dataset, which we generated in the previous section.\n\nThe model is based off the LSTM architecture, where we use a state vector to maintain information about the temporal relationships between consecutive characters. The final output of the LSTM is then fed into a fully connected [`Dense`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/layers/Dense) layer where we'll output a softmax over each character in the vocabulary, and then sample from this distribution to predict the next character. \n\nAs we introduced in the first portion of this lab, we'll be using the Keras API, specifically, [`tf.keras.Sequential`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/models/Sequential), to define the model. Three layers are used to define the model:\n\n* [`tf.keras.layers.Embedding`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/layers/Embedding): This is the input layer, consisting of a trainable lookup table that maps the numbers of each character to a vector with `embedding_dim` dimensions.\n* [`tf.keras.layers.LSTM`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/layers/LSTM): Our LSTM network, with size `units=rnn_units`. \n* [`tf.keras.layers.Dense`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/layers/Dense): The output layer, with `vocab_size` outputs.\n\n\n<img src=\"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/aamini/introtodeeplearning/2019/lab1/img/lstm_unrolled-01-01.png\" alt=\"Drawing\"/>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Define the RNN model\n\nNow, we will define a function that we will use to actually build the model.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def LSTM(rnn_units): \n return tf.keras.layers.LSTM(\n rnn_units, \n return_sequences=True, \n recurrent_initializer='glorot_uniform',\n recurrent_activation='sigmoid',\n stateful=True,\n )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The time has come! Fill in the `TODOs` to define the RNN model within the `build_model` function, and then call the function you just defined to instantiate the model!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Defining the RNN Model ###\n\n'''TODO: Add LSTM and Dense layers to define the RNN model using the Sequential API.'''\ndef build_model(vocab_size, embedding_dim, rnn_units, batch_size):\n model = tf.keras.Sequential([\n # Layer 1: Embedding layer to transform indices into dense vectors \n # of a fixed embedding size\n tf.keras.layers.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim, batch_input_shape=[batch_size, None]),\n\n # Layer 2: LSTM with `rnn_units` number of units. \n # TODO: Call the LSTM function defined above to add this layer.\n LSTM(rnn_units), \n # LSTM('''TODO'''),\n\n # Layer 3: Dense (fully-connected) layer that transforms the LSTM output\n # into the vocabulary size. \n # TODO: Add the Dense layer.\n tf.keras.layers.Dense(vocab_size)\n # '''TODO: DENSE LAYER HERE'''\n ])\n\n return model\n\n# Build a simple model with default hyperparameters. You will get the \n# chance to change these later.\nmodel = build_model(len(vocab), embedding_dim=256, rnn_units=1024, batch_size=32)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Test out the RNN model\n\nIt's always a good idea to run a few simple checks on our model to see that it behaves as expected. \n\nFirst, we can use the `Model.summary` function to print out a summary of our model's internal workings. Here we can check the layers in the model, the shape of the output of each of the layers, the batch size, etc.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model.summary()",
"Model: \"sequential\"\n_________________________________________________________________\nLayer (type) Output Shape Param # \n=================================================================\nembedding (Embedding) (32, None, 256) 21248 \n_________________________________________________________________\nlstm (LSTM) (32, None, 1024) 5246976 \n_________________________________________________________________\ndense (Dense) (32, None, 83) 85075 \n=================================================================\nTotal params: 5,353,299\nTrainable params: 5,353,299\nNon-trainable params: 0\n_________________________________________________________________\n"
]
],
[
[
"We can also quickly check the dimensionality of our output, using a sequence length of 100. Note that the model can be run on inputs of any length.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x, y = get_batch(vectorized_songs, seq_length=100, batch_size=32)\npred = model(x)\nprint(\"Input shape: \", x.shape, \" # (batch_size, sequence_length)\")\nprint(\"Prediction shape: \", pred.shape, \"# (batch_size, sequence_length, vocab_size)\")",
"Input shape: (32, 100) # (batch_size, sequence_length)\nPrediction shape: (32, 100, 83) # (batch_size, sequence_length, vocab_size)\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Predictions from the untrained model\n\nLet's take a look at what our untrained model is predicting.\n\nTo get actual predictions from the model, we sample from the output distribution, which is defined by a `softmax` over our character vocabulary. This will give us actual character indices. This means we are using a [categorical distribution](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Categorical_distribution) to sample over the example prediction. This gives a prediction of the next character (specifically its index) at each timestep.\n\nNote here that we sample from this probability distribution, as opposed to simply taking the `argmax`, which can cause the model to get stuck in a loop.\n\nLet's try this sampling out for the first example in the batch.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sampled_indices = tf.random.categorical(pred[0], num_samples=1)\nsampled_indices = tf.squeeze(sampled_indices,axis=-1).numpy()\nsampled_indices",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can now decode these to see the text predicted by the untrained model:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(\"Input: \\n\", repr(\"\".join(idx2char[x[0]])))\nprint()\nprint(\"Next Char Predictions: \\n\", repr(\"\".join(idx2char[sampled_indices])))",
"Input: \n '3efg|a2ab ageg|agab a2ge|dega gedB|c2A2 A2:|!\\n[2 cB|AGAB AGEG|AGAB cBcd|(3efg fa gedB|c2A2 A2|]!\\n\\nX:'\n\nNext Char Predictions: \n '.>UTv0fSVyfP(na\\'jS5JmnogSH]q2q7B5Z7n)!2Z\"XKnbUfDAT[8|NC_o1-U#GPU0rg!HURYJm|9XGWKaqAn[\\'[:VA8QmXBjriwv'\n"
]
],
[
[
"As you can see, the text predicted by the untrained model is pretty nonsensical! How can we do better? We can train the network!",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 2.5 Training the model: loss and training operations\n\nNow it's time to train the model!\n\nAt this point, we can think of our next character prediction problem as a standard classification problem. Given the previous state of the RNN, as well as the input at a given time step, we want to predict the class of the next character -- that is, to actually predict the next character. \n\nTo train our model on this classification task, we can use a form of the `crossentropy` loss (negative log likelihood loss). Specifically, we will use the [`sparse_categorical_crossentropy`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/backend/sparse_categorical_crossentropy) loss, as it utilizes integer targets for categorical classification tasks. We will want to compute the loss using the true targets -- the `labels` -- and the predicted targets -- the `logits`.\n\nLet's first compute the loss using our example predictions from the untrained model: ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Defining the loss function ###\n\n'''TODO: define the loss function to compute and return the loss between\n the true labels and predictions (logits). Set the argument from_logits=True.'''\ndef compute_loss(labels, logits):\n loss = tf.keras.losses.sparse_categorical_crossentropy(labels, logits, from_logits=True)\n # loss = tf.keras.losses.sparse_categorical_crossentropy('''TODO''', '''TODO''', from_logits=True) # TODO\n return loss\n\n'''TODO: compute the loss using the true next characters from the example batch \n and the predictions from the untrained model several cells above'''\nexample_batch_loss = compute_loss(y, pred)\n# example_batch_loss = compute_loss('''TODO''', '''TODO''') # TODO\n\nprint(\"Prediction shape: \", pred.shape, \" # (batch_size, sequence_length, vocab_size)\") \nprint(\"scalar_loss: \", example_batch_loss.numpy().mean())",
"Prediction shape: (32, 100, 83) # (batch_size, sequence_length, vocab_size)\nscalar_loss: 4.419714\n"
]
],
[
[
"Let's start by defining some hyperparameters for training the model. To start, we have provided some reasonable values for some of the parameters. It is up to you to use what we've learned in class to help optimize the parameter selection here!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Hyperparameter setting and optimization ###\n\n# Optimization parameters:\nnum_training_iterations = 2000 # Increase this to train longer\nbatch_size = 4 # Experiment between 1 and 64\nseq_length = 100 # Experiment between 50 and 500\nlearning_rate = 5e-3 # Experiment between 1e-5 and 1e-1\n\n# Model parameters: \nvocab_size = len(vocab)\nembedding_dim = 256 \nrnn_units = 1024 # Experiment between 1 and 2048\n\n# Checkpoint location: \ncheckpoint_dir = './training_checkpoints'\ncheckpoint_prefix = os.path.join(checkpoint_dir, \"my_ckpt\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now, we are ready to define our training operation -- the optimizer and duration of training -- and use this function to train the model. You will experiment with the choice of optimizer and the duration for which you train your models, and see how these changes affect the network's output. Some optimizers you may like to try are [`Adam`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/optimizers/Adam?version=stable) and [`Adagrad`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/optimizers/Adagrad?version=stable).\n\nFirst, we will instantiate a new model and an optimizer. Then, we will use the [`tf.GradientTape`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/GradientTape) method to perform the backpropagation operations. \n\nWe will also generate a print-out of the model's progress through training, which will help us easily visualize whether or not we are minimizing the loss.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Define optimizer and training operation ###\n\n'''TODO: instantiate a new model for training using the `build_model`\n function and the hyperparameters created above.'''\nmodel = build_model(vocab_size, embedding_dim, rnn_units, batch_size)\n# model = build_model('''TODO: arguments''')\n\n'''TODO: instantiate an optimizer with its learning rate.\n Checkout the tensorflow website for a list of supported optimizers.\n https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/optimizers/\n Try using the Adam optimizer to start.'''\noptimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate)\n# optimizer = # TODO\n\[email protected]\ndef train_step(x, y): \n # Use tf.GradientTape()\n with tf.GradientTape() as tape:\n \n '''TODO: feed the current input into the model and generate predictions'''\n y_hat = model(x) # TODO\n # y_hat = model('''TODO''')\n \n '''TODO: compute the loss!'''\n loss = compute_loss(y, y_hat) # TODO\n # loss = compute_loss('''TODO''', '''TODO''')\n\n # Now, compute the gradients \n '''TODO: complete the function call for gradient computation. \n Remember that we want the gradient of the loss with respect all \n of the model parameters. \n HINT: use `model.trainable_variables` to get a list of all model\n parameters.'''\n grads = tape.gradient(loss, model.trainable_variables) # TODO\n # grads = tape.gradient('''TODO''', '''TODO''')\n \n # Apply the gradients to the optimizer so it can update the model accordingly\n optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, model.trainable_variables))\n return loss\n\n##################\n# Begin training!#\n##################\n\nhistory = []\nplotter = mdl.util.PeriodicPlotter(sec=2, xlabel='Iterations', ylabel='Loss')\nif hasattr(tqdm, '_instances'): tqdm._instances.clear() # clear if it exists\n\nfor iter in tqdm(range(num_training_iterations)):\n\n # Grab a batch and propagate it through the network\n x_batch, y_batch = get_batch(vectorized_songs, seq_length, batch_size)\n loss = train_step(x_batch, y_batch)\n\n # Update the progress bar\n history.append(loss.numpy().mean())\n plotter.plot(history)\n\n # Update the model with the changed weights!\n if iter % 100 == 0: \n model.save_weights(checkpoint_prefix)\n \n# Save the trained model and the weights\nmodel.save_weights(checkpoint_prefix)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 2.6 Generate music using the RNN model\n\nNow, we can use our trained RNN model to generate some music! When generating music, we'll have to feed the model some sort of seed to get it started (because it can't predict anything without something to start with!).\n\nOnce we have a generated seed, we can then iteratively predict each successive character (remember, we are using the ABC representation for our music) using our trained RNN. More specifically, recall that our RNN outputs a `softmax` over possible successive characters. For inference, we iteratively sample from these distributions, and then use our samples to encode a generated song in the ABC format.\n\nThen, all we have to do is write it to a file and listen!",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Restore the latest checkpoint\n\nTo keep this inference step simple, we will use a batch size of 1. Because of how the RNN state is passed from timestep to timestep, the model will only be able to accept a fixed batch size once it is built. \n\nTo run the model with a different `batch_size`, we'll need to rebuild the model and restore the weights from the latest checkpoint, i.e., the weights after the last checkpoint during training:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"'''TODO: Rebuild the model using a batch_size=1'''\nmodel = build_model(vocab_size, embedding_dim, rnn_units, batch_size=1) # TODO\n# model = build_model('''TODO''', '''TODO''', '''TODO''', batch_size=1)\n\n# Restore the model weights for the last checkpoint after training\nmodel.load_weights(tf.train.latest_checkpoint(checkpoint_dir))\nmodel.build(tf.TensorShape([1, None]))\n\nmodel.summary()",
"Model: \"sequential_2\"\n_________________________________________________________________\nLayer (type) Output Shape Param # \n=================================================================\nembedding_2 (Embedding) (1, None, 256) 21248 \n_________________________________________________________________\nlstm_2 (LSTM) (1, None, 1024) 5246976 \n_________________________________________________________________\ndense_2 (Dense) (1, None, 83) 85075 \n=================================================================\nTotal params: 5,353,299\nTrainable params: 5,353,299\nNon-trainable params: 0\n_________________________________________________________________\n"
]
],
[
[
"Notice that we have fed in a fixed `batch_size` of 1 for inference.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### The prediction procedure\n\nNow, we're ready to write the code to generate text in the ABC music format:\n\n* Initialize a \"seed\" start string and the RNN state, and set the number of characters we want to generate.\n\n* Use the start string and the RNN state to obtain the probability distribution over the next predicted character.\n\n* Sample from multinomial distribution to calculate the index of the predicted character. This predicted character is then used as the next input to the model.\n\n* At each time step, the updated RNN state is fed back into the model, so that it now has more context in making the next prediction. After predicting the next character, the updated RNN states are again fed back into the model, which is how it learns sequence dependencies in the data, as it gets more information from the previous predictions.\n\n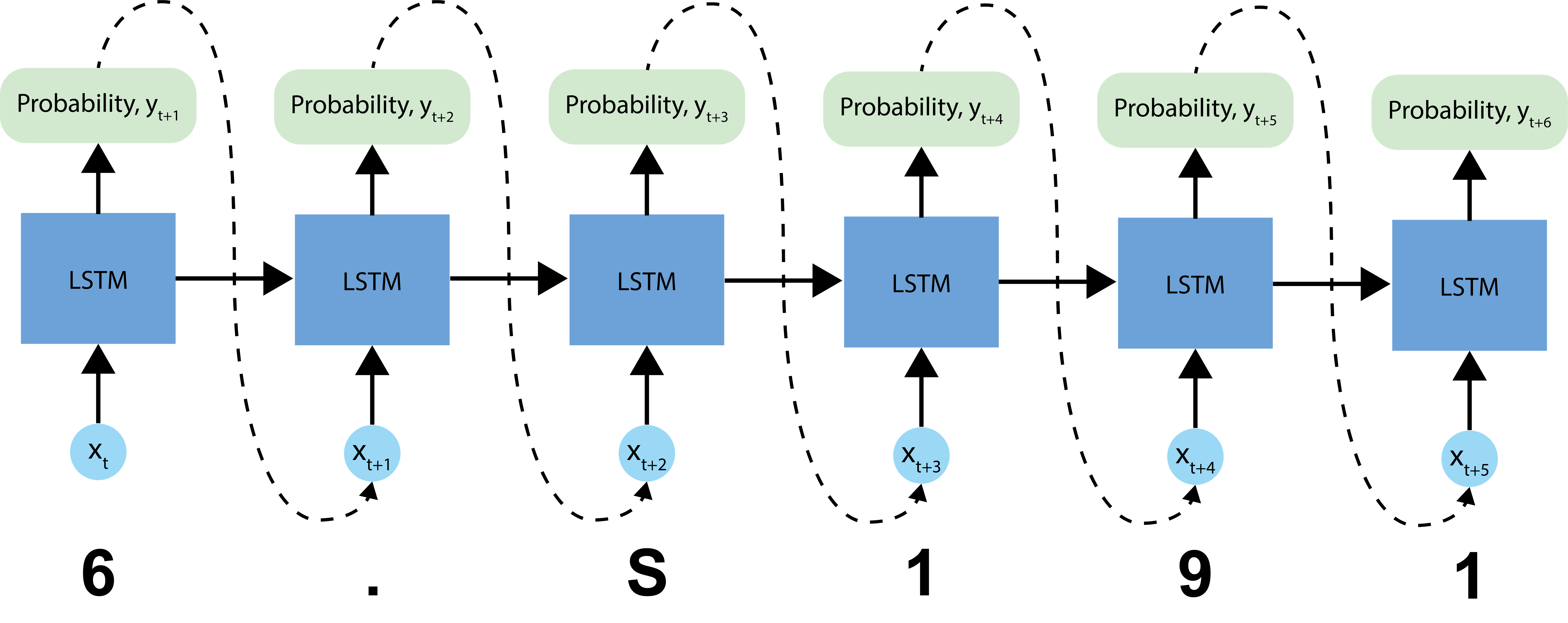\n\nComplete and experiment with this code block (as well as some of the aspects of network definition and training!), and see how the model performs. How do songs generated after training with a small number of epochs compare to those generated after a longer duration of training?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Prediction of a generated song ###\n\ndef generate_text(model, start_string, generation_length=1000):\n # Evaluation step (generating ABC text using the learned RNN model)\n\n '''TODO: convert the start string to numbers (vectorize)'''\n input_eval = [char2idx[s] for s in start_string] # TODO\n # input_eval = ['''TODO''']\n input_eval = tf.expand_dims(input_eval, 0)\n\n # Empty string to store our results\n text_generated = []\n\n # Here batch size == 1\n model.reset_states()\n tqdm._instances.clear()\n\n for i in tqdm(range(generation_length)):\n '''TODO: evaluate the inputs and generate the next character predictions'''\n predictions = model(input_eval)\n # predictions = model('''TODO''')\n \n # Remove the batch dimension\n predictions = tf.squeeze(predictions, 0)\n \n '''TODO: use a multinomial distribution to sample'''\n predicted_id = tf.random.categorical(predictions, num_samples=1)[-1,0].numpy()\n # predicted_id = tf.random.categorical('''TODO''', num_samples=1)[-1,0].numpy()\n \n # Pass the prediction along with the previous hidden state\n # as the next inputs to the model\n input_eval = tf.expand_dims([predicted_id], 0)\n \n '''TODO: add the predicted character to the generated text!'''\n # Hint: consider what format the prediction is in vs. the output\n text_generated.append(idx2char[predicted_id]) # TODO \n # text_generated.append('''TODO''')\n \n return (start_string + ''.join(text_generated))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"'''TODO: Use the model and the function defined above to generate ABC format text of length 1000!\n As you may notice, ABC files start with \"X\" - this may be a good start string.'''\ngenerated_text = generate_text(model, start_string=\"X\", generation_length=1000) # TODO\n# generated_text = generate_text('''TODO''', start_string=\"X\", generation_length=1000)",
"100%|██████████| 1000/1000 [00:08<00:00, 112.33it/s]\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Play back the generated music!\n\nWe can now call a function to convert the ABC format text to an audio file, and then play that back to check out our generated music! Try training longer if the resulting song is not long enough, or re-generating the song!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Play back generated songs ###\n\ngenerated_songs = mdl.lab1.extract_song_snippet(generated_text)\n\nfor i, song in enumerate(generated_songs): \n # Synthesize the waveform from a song\n waveform = mdl.lab1.play_song(song)\n\n # If its a valid song (correct syntax), lets play it! \n if waveform:\n print(\"Generated song\", i)\n ipythondisplay.display(waveform)",
"Found 0 songs in text\n"
]
],
[
[
"## 2.7 Experiment and **get awarded for the best songs**!!\n\nCongrats on making your first sequence model in TensorFlow! It's a pretty big accomplishment, and hopefully you have some sweet tunes to show for it.\n\nIf you want to go further, try to optimize your model and submit your best song! Tweet us at [@MITDeepLearning](https://twitter.com/MITDeepLearning) or [email us](mailto:[email protected]) a copy of the song (if you don't have Twitter), and we'll give out prizes to our favorites! \n\nConsider how you may improve your model and what seems to be most important in terms of performance. Here are some ideas to get you started:\n\n* How does the number of training epochs affect the performance?\n* What if you alter or augment the dataset? \n* Does the choice of start string significantly affect the result? \n\nHave fun and happy listening!\n\n\n\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Example submission by a previous 6.S191 student (credit: Christian Adib) \n\n%%html\n<blockquote class=\"twitter-tweet\"><a href=\"https://twitter.com/AdibChristian/status/1090030964770783238?ref_src=twsrc%5Etfw\">January 28, 2019</a></blockquote> \n<script async src=\"https://platform.twitter.com/widgets.js\" charset=\"utf-8\"></script>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a77e15dcf5c67d2bb33b8e3f846fb2e43bf82e1
| 10,167 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Notebooks/Untitled.ipynb
|
ambo2020/Anna-Borowska
|
607ee5c60f5042a6aa7a3aa518b13da3c8cf7967
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Notebooks/Untitled.ipynb
|
ambo2020/Anna-Borowska
|
607ee5c60f5042a6aa7a3aa518b13da3c8cf7967
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Notebooks/Untitled.ipynb
|
ambo2020/Anna-Borowska
|
607ee5c60f5042a6aa7a3aa518b13da3c8cf7967
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 55.557377 | 1,332 | 0.63411 |
[
[
[
"#import pylab\nimport re\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn as sns\n\nimport requests\nimport urllib\nfrom bs4 import BeautifulSoup as bs\n\n%matplotlib inline\n#%matplotlib notebook",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"url2 = 'https://ge.globo.com/futebol/brasileirao-serie-a/' \ncontent = requests.get(url2)\nprint(content.status_code)",
"200\n"
],
[
"soup = bs(content.text,'html5lib')\nprint(type(soup))",
"<class 'bs4.BeautifulSoup'>\n"
],
[
"soup.find_all('div', attrs={'class':'classificacao_pontos-corridos'})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"table = soup.find_all(class_=\"medium-centered\")[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from selenium import webdriver\ndriver = webdriver.PhantomJS()\ndriver.get(my_url)\np_element = driver.find_element_by_id(id_='intro-text')\nprint(p_element.text)",
"/opt/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages/selenium/webdriver/phantomjs/webdriver.py:49: UserWarning: Selenium support for PhantomJS has been deprecated, please use headless versions of Chrome or Firefox instead\n warnings.warn('Selenium support for PhantomJS has been deprecated, please use headless '\n"
],
[
"! pip install selenium",
"Collecting selenium\n Downloading selenium-3.141.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl (904 kB)\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 904 kB 4.7 MB/s eta 0:00:01\n\u001b[?25hRequirement already satisfied: urllib3 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages (from selenium) (1.25.7)\nInstalling collected packages: selenium\nSuccessfully installed selenium-3.141.0\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a7822e23d3f67145a179254b0488cc3e60d2d7a
| 9,196 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
code/neural_networks/train_rbergomi_extended_3.ipynb
|
steefeen/rough_volatility
|
7b3f7c05dce33a3823ba16589c23b45cf3498838
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
code/neural_networks/train_rbergomi_extended_3.ipynb
|
steefeen/rough_volatility
|
7b3f7c05dce33a3823ba16589c23b45cf3498838
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
code/neural_networks/train_rbergomi_extended_3.ipynb
|
steefeen/rough_volatility
|
7b3f7c05dce33a3823ba16589c23b45cf3498838
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 32.725979 | 162 | 0.570574 |
[
[
[
"# Training the extended rough Bergomi model part 3\n\nIn this notebook we train a neural network for the extended rough Bergomi model for expiries in the range (0.03,0.12].\n\nBe aware that the datasets are rather large.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Load, split and scale the datasets",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import os, pandas as pd, numpy as np\nwd = os.getcwd()\n\n# Load contract grid:\nlogMoneyness = pd.read_csv(wd + '\\\\data\\\\logMoneyness.txt', delimiter=\",\", header = None).values\nexpiries = pd.read_csv(wd + '\\\\data\\\\expiries.txt', delimiter=\",\", header = None).values\n\n# Set useful parameters:\nnIn = 17\nnOut = 275\nnXi = 13\n\n# Load training data:\ndata_train = pd.read_csv(wd + '\\\\data\\\\training_and_test_data\\\\rbergomi_extended\\\\rbergomi_extended_training_data_3.csv', delimiter=\",\").values\nx_train = data_train[:,:nIn]\ny_train = data_train[:,nIn:nIn+nOut]\ndata_train = None\n\n# Load test data:\ndata_test = pd.read_csv(wd + '\\\\data\\\\training_and_test_data\\\\rbergomi_extended\\\\rbergomi_extended_test_data_3.csv', delimiter=\",\").values\nx_valid = data_test[:,:nIn]\ny_valid = data_test[:,nIn:nIn+nOut]\ndata_test = None\n\n# Normalise data:\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler\n\ntmp1 = np.reshape(np.array([3.50,0.00,0.50,0.50]), (1, 4))\ntmp2 = np.reshape(np.array([0.75,-1.00,-0.50,-0.50]), (1, 4))\nub = np.concatenate((tmp1,np.tile(1,(1,nXi))),1)\nlb = np.concatenate((tmp2,np.tile(0.0025,(1,nXi))),1)\n\ndef myscale(x):\n res=np.zeros(nIn)\n for i in range(nIn):\n res[i]=(x[i] - (ub[0,i] + lb[0,i])*0.5) * 2 / (ub[0,i] - lb[0,i])\n \n return res\n\ndef myinverse(x):\n res=np.zeros(nIn)\n for i in range(nIn):\n res[i]=x[i]*(ub[0,i] - lb[0,i]) *0.5 + (ub[0,i] + lb[0,i])*0.5\n \n return res\n\n# Scale inputs:\nx_train_mod = np.array([myscale(x) for x in x_train])\nx_valid_mod = np.array([myscale(x) for x in x_valid])\n\n# Scale and normalise output:\nscale_y = StandardScaler()\ny_train_mod = scale_y.fit_transform(y_train)\ny_valid_mod = scale_y.transform(y_valid)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Define utility functions",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import keras\nfrom keras.layers import Activation\nfrom keras import backend as K\nfrom keras.utils.generic_utils import get_custom_objects\nkeras.backend.set_floatx('float64')\n\ndef GetNetwork(nIn,nOut,nNodes,nLayers,actFun):\n # Description: Creates a neural network of a specified structure\n input1 = keras.layers.Input(shape=(nIn,))\n layerTmp = keras.layers.Dense(nNodes,activation = actFun)(input1) \n for i in range(nLayers-1):\n layerTmp = keras.layers.Dense(nNodes,activation = actFun)(layerTmp) \n output1 = keras.layers.Dense(nOut,activation = 'linear')(layerTmp)\n return(keras.models.Model(inputs=input1, outputs=output1))\n\ndef TrainNetwork(nn,batchsize,numEpochs,objFun,optimizer,xTrain,yTrain,xTest,yTest):\n # Description: Trains a neural network and returns the network including the history\n # of the training process.\n nn.compile(loss = objFun, optimizer = optimizer)\n history = nn.fit(xTrain, yTrain, batch_size = batchsize,\n validation_data = (xTest,yTest),\n epochs = numEpochs, verbose = True, shuffle=1) \n return nn,history.history['loss'],history.history['val_loss']\n\ndef root_mean_squared_error(y_true, y_pred):\n return K.sqrt(K.mean(K.square( y_pred - y_true )))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Define and train neural network\n<span style=\"color:red\">This section can be skipped! Just go straight to \"Load network\" and load the already trained model</span>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Define model:\nmodel = GetNetwork(nIn,nOut,200,3,'elu')\n\n# Set seed\nimport random\nrandom.seed(455165)\n\n# Train network\nmodel,loss1,vloss1 = TrainNetwork(model,32,500,root_mean_squared_error,'adam',x_train_mod,y_train_mod,x_valid_mod,y_valid_mod)\nmodel,loss2,vloss2 = TrainNetwork(model,5000,200,root_mean_squared_error,'adam',x_train_mod,y_train_mod,x_valid_mod,y_valid_mod)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Save network\n<span style=\"color:red\">This section can be skipped! Just go straight to \"Load network\" and load the already trained model</span>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Save model:\nmodel.save(wd + '\\\\data\\\\neural_network_weights\\\\rbergomi_extended\\\\rbergomi_extended_model_3.h5')\n\n# Save weights (and scalings) in JSON format:\n# - You need to install 'json-tricks' first.\n# - We need this file for proper import into Matlab, R... etc.\nweights_and_more = model.get_weights()\nweights_and_more.append(0.5*(ub + lb))\nweights_and_more.append(np.power(0.5*(ub - lb),2))\nweights_and_more.append(scale_y.mean_)\nweights_and_more.append(scale_y.var_)\n\nimport codecs, json \nfor idx, val in enumerate(weights_and_more):\n weights_and_more[idx] = weights_and_more[idx].tolist()\n\njson_str = json.dumps(weights_and_more)\n\ntext_file = open(wd + \"\\\\data\\\\neural_network_weights\\\\rbergomi_extended\\\\rbergomi_extended_weights_3.json\", \"w\")\ntext_file.write(json_str)\ntext_file.close()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Load network",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Load already trained neural network:\nmodel = keras.models.load_model(wd + '\\\\data\\\\neural_network_weights\\\\rbergomi_extended\\\\rbergomi_extended_model_3.h5', \n custom_objects={'root_mean_squared_error': root_mean_squared_error})",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Validate approximation",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Specify test sample to plot:\nsample_ind = 5006\n\n# Print parameters of test sample:\nprint(\"Model Parameters (eta,rho,alpha,beta,xi1,xi2,...): \",myinverse(x_valid_mod[sample_ind,:]))\n\nimport scipy, matplotlib.pyplot as plt \nnpts = 25\nx_sample = x_valid_mod[sample_ind,:]\ny_sample = y_valid_mod[sample_ind,:]\n\nprediction = scale_y.inverse_transform(model.predict(x_valid_mod))\nplt.figure(1,figsize=(14,12))\nj = -1\nfor i in range(0,13):\n j = j + 1\n plt.subplot(4,4,j+1)\n \n plt.plot(logMoneyness[i*npts:(i+1)*npts],y_valid[sample_ind,i*npts:(i+1)*npts],'b',label=\"True\")\n plt.plot(logMoneyness[i*npts:(i+1)*npts],prediction[sample_ind,i*npts:(i+1)*npts],'--r',label=\" Neural network\")\n\n plt.title(\"Maturity=%1.3f \"%expiries[i*npts])\n plt.xlabel(\"log-moneyness\")\n plt.ylabel(\"Implied volatility\")\n \n plt.legend()\nplt.tight_layout()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a7827e89db15e6821286e5c59ada16ae75b3b83
| 153,975 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
data-science/practical-exercises/ICD20191-Lista06/Lista06.ipynb
|
ramongonze/ufmg-practical-assignments
|
d85821e330a0f089a7601168bbbf8b4aef174f27
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
data-science/practical-exercises/ICD20191-Lista06/Lista06.ipynb
|
ramongonze/ufmg-practical-assignments
|
d85821e330a0f089a7601168bbbf8b4aef174f27
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
data-science/practical-exercises/ICD20191-Lista06/Lista06.ipynb
|
ramongonze/ufmg-practical-assignments
|
d85821e330a0f089a7601168bbbf8b4aef174f27
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 177.186421 | 132,660 | 0.902692 |
[
[
[
"# Lista 06 - Gradiente Descendente e Regressão Multivariada",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\n\nfrom numpy.testing import *\n\nplt.ion()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Hoje vamos fazer um gradiente descendente para uma regressão linear com múltiplas variáveis.\n\nPara isso, utilizaremos a base de dados carros, ``hybrid.csv``. As colunas são definidas da seguinte forma:\n\n* veículo (vehicle): modelo do carro\n\n* ano (year): ano de fabricação\n\n* msrp: preço de varejo em dólar sugerido pelo fabricante em 2013.\n\n* aceleração (acceleration): taxa de aceleração em km por hora por segundo\n\n* mpg: economia de combustível em milhas por galão\n\n* classe (class): a classe do modelo.\n\nNosso objetivo será estimar o valor de preço sugerido dos carros a partir dos demais atributos (exluindo o nome do veículo e a classe).\nPortanto, teremos a regressão definida pela fórmula:\n\n$$ Y = X\\Theta + \\epsilon $$\n\nEm que, Y corresponde à coluna ``msrp`` dos dados, e X corresponde às colunas ``year,acceleration,mpg``.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df = pd.read_csv('./hybrid.csv')\ndf.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import seaborn as sns\nsns.pairplot(df, diag_kws={'edgecolor':'k'}, plot_kws={'alpha':0.5, 'edgecolor':'k'})",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Selecionamos apenas as colunas que serão utilizadas.\n\nNormalizamos os dados para que o gradiente descendente rode sem problemas.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"y = df['msrp']\nX = df[['year','acceleration','mpg']]\n\nX -= X.mean()\nX /= X.std(ddof=1)\ny -= y.mean()\ny /= y.std(ddof=1)\n\nX.insert(0, 'intercept', 1.0)\n\nX = X.values\ny = y.values",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"__IMPORTANTE:__\nNão crie ou utilize qualquer variável ou função com nome iniciado por ``_teste_``.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"A) Implemente a função de gradiente dos parâmetros da regressão, retornando um array com os valores dos gradientes para cada parâmetro theta.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def gradients(theta, X, y):\n # x : matriz nxm\n # y : array nx1\n # theta : array mx1\n theta = np.array(theta)\n X = np.array(X)\n y = np.array(y)\n \n return -2 * ((y - X@theta) * X.T).mean(axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"B) Implemente a função de gradiente descendente para os parâmetros da regressão linear. \n\nRetorne uma lista com o valor de alpha e os valores de beta para cada coluna, nessa ordem.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def descent(theta0, X, y, learning_rate=0.005, tolerance=0.0000001):\n theta = theta0.copy()\n oldError, error = np.inf, 0\n \n while abs(error - oldError) > tolerance:\n dTheta = gradients(theta, X, y)\n theta -= (learning_rate * dTheta)\n \n oldError = error\n error = ((X.dot(theta) - y) ** 2).mean()\n \n return theta",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"C) Agora vamos tentar avaliar o modelo de regressão linear obtido com o gradiente descendente.\n\nPrimeiro implementem uma função que calcule o valor da soma total dos quadrados (SST) a partir dos dados.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def sst(y):\n y = np.array(y)\n return sum((y - y.mean())**2)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"D) Para calcular a soma total de erros (SSE), primeiro precisamos ter uma previsão para os valores de\n preço dos apartamentos.\nImplementem uma função que obtenha os valores estimativa de preço a partir dos demais atributos, de acordo com o modelo de regressão linear.\n\nA função deve retornar uma lista com os valores previstos.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def predict(X, theta):\n return [sum(x_i * theta) for x_i in X]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"E) Agora implemente a função de cálculo da soma total de erros (SSE).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def sse(X, y, theta):\n yPredict = predict(X, theta)\n return sum((yPredict - y)**2)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"F) Finalmente, implemente a função que calcula o coeficiente de determinação (R2).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def r2(X, y, theta):\n return 1 - sse(X, y, theta)/sst(y)\nr2(X,y,descent([1,1,1,1], X, y))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"G) Se observarmos os dados pelos gráficos gerados no começo do notebook, podemos perceber que nem todos possuem uma relação linear. Vamos tentar transformar os dados de um dos atributos dos carros, para que uma regressão linear possa ser aplicada com melhores resultados.\n\nTire o logaritmo dos dados do atributo ```mpg```, antes de z-normalizar.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"y = df['msrp']\nX = df[['year','acceleration','mpg']]\n\nfrom math import log\nX['mpg'] = X['mpg'].apply(lambda p: log(p))\n\nX -= X.mean()\nX /= X.std(ddof=1)\ny -= y.mean()\ny /= y.std(ddof=1)\n\nX.insert(0, 'intercept', 1.0)\n\nX = X.values\ny = y.values",
"/home/ramon/anaconda3/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:5: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#indexing-view-versus-copy\n \"\"\"\n"
]
],
[
[
"Note que o código do gradiente descendente pode ser executado sem alterações.\n\nVerifique se o R2 da regressão melhorou ou piorou ao se transformar os dados.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"r2(X,y,descent([1,1,1,1], X, y))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a782999c47526a66a26618e05705e78679aac54
| 134,758 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
MultipleLinearRegression_python.ipynb
|
linocondor/Concrete-Slump-Data-Analysis
|
ebc0a27425b237bbd59fd97bdbe0edcd61260924
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-06-15T03:36:07.000Z
|
2021-06-15T03:36:07.000Z
|
MultipleLinearRegression_python.ipynb
|
linocondor/Concrete-Slump-Data-Analysis
|
ebc0a27425b237bbd59fd97bdbe0edcd61260924
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
MultipleLinearRegression_python.ipynb
|
linocondor/Concrete-Slump-Data-Analysis
|
ebc0a27425b237bbd59fd97bdbe0edcd61260924
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 469.54007 | 92,736 | 0.679396 |
[
[
[
"## Multiple Linear Regression with python\nThis is a Multiple Linear Regression analysis using Concrete Slump Data.\n\nThe UCI Machine Learning Repository has this dataset containing diferent variables (Cement, Slag, Fly ash, Water, SP, Coarse Aggr., Fine Aggr., SLUMP, FLOW, 28-day Compressive Strength). \n\nThe dataset is maintained on their site, where it can be found by the title \"Concrete Slump Test Data Set\".\n\n<b>Citation:</b>\nYeh, I-Cheng, \"Modeling slump flow of concrete using second-order regressions and artificial neural networks,\" Cement and Concrete Composites, Vol.29, No. 6, 474-480, 2007.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#importing libraries\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport pandas as pd",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#importing data\ndataset = pd.read_excel('Concrete_Data.xls')\ndataset",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#We are going to use the Cement and Concrete compressive Strength for this\nX = dataset.iloc[:,:-1].values\ny = dataset.iloc[:,-1].values\n#X = X.reshape(-1, 1)\ny = y.reshape(-1,1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(X)",
"[[ 540. 0. 0. ... 1040. 676. 28. ]\n [ 540. 0. 0. ... 1055. 676. 28. ]\n [ 332.5 142.5 0. ... 932. 594. 270. ]\n ...\n [ 148.5 139.4 108.6 ... 892.4 780. 28. ]\n [ 159.1 186.7 0. ... 989.6 788.9 28. ]\n [ 260.9 100.5 78.3 ... 864.5 761.5 28. ]]\n"
],
[
"print(y)",
"[[79.98611076]\n [61.88736576]\n [40.26953526]\n ...\n [23.69660064]\n [32.76803638]\n [32.40123514]]\n"
],
[
"#Splitting the data\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 0.2)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#print(X_train,y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#print(X_test,y_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Training the simple Linear Regression model on training set\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression\nregressor = LinearRegression()\nregressor.fit(X_train, y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Predicting the test set results\ny_pred = regressor.predict(X_test)\nnp.set_printoptions(precision=2) #two decimals\nprint(np.concatenate((y_pred.reshape(len(y_pred),1),y_test.reshape(len(y_test),1)),1)) #reshape vertically, and join prediction and real",
"71]\n [39.84 57.22]\n [23.21 22.53]\n [51.02 35.3 ]\n [36.47 31.38]\n [49.5 28.8 ]\n [37.59 37.72]\n [33.65 41.2 ]\n [42.53 39.38]\n [30.13 31.12]\n [33.94 28.99]\n [27.73 32.72]\n [31.15 26.23]\n [23.08 17.44]\n [19.78 8. ]\n [16.7 18.75]\n [50.87 60.28]\n [24.26 37.27]\n [30.66 14.94]\n [24.31 33.06]\n [56.77 60.29]\n [16.5 17.34]\n [27. 26.77]\n [25.45 13.09]\n [26.25 32.25]\n [28.14 19.11]\n [53.97 56.34]\n [51.4 76.24]\n [35.83 42.14]\n [20.26 17.17]\n [48.87 49.9 ]\n [29.91 27.92]\n [42.27 55.02]\n [49. 29.55]\n [49.1 56.83]\n [53.32 33.69]\n [30.66 30.12]\n [31.79 33.42]\n [32.07 35.17]\n [46.36 35.1 ]\n [49.97 41.84]\n [35.28 38.77]\n [53.78 33.4 ]\n [53. 69.84]\n [29.07 23.22]\n [24.87 27.22]\n [20.63 24.45]\n [33.61 19.54]\n [20.85 13.36]\n [25.64 13.54]\n [64.19 73.3 ]\n [13.99 11.17]\n [41.16 33.76]\n [48.7 41.64]\n [26.03 31.97]\n [40.3 56.85]\n [60.89 60.2 ]\n [31.89 39.05]\n [60.92 59.09]\n [35.87 47.4 ]\n [21.73 21.65]\n [44.67 50.53]\n [19.32 11.58]\n [30.22 31.72]\n [26.53 23.7 ]\n [21.88 8.49]\n [24.68 30.23]\n [49.16 40.76]\n [32.41 12.37]\n [40.34 41.94]\n [50.74 54.1 ]\n [18.4 19.69]\n [39.87 55.83]\n [28.41 19.2 ]\n [33.3 34.67]\n [43. 50.73]\n [32.89 35.85]\n [28.68 39.66]\n [26.94 9.62]\n [52.09 55.55]\n [60.73 43.01]\n [40.11 29.59]\n [24.38 6.9 ]\n [37.55 24.4 ]\n [24.19 15.34]\n [21.54 27.87]\n [59.04 33.7 ]\n [33.6 37.43]\n [38.32 45.08]\n [34.7 44.61]\n [24.79 18.29]\n [22.59 24.28]\n [54.58 67.57]\n [21.94 25.18]\n [22.54 25.73]\n [30.41 34.24]\n [47.21 81.75]\n [34.47 7.75]\n [40.75 41.05]\n [35.43 36.8 ]\n [28.5 44.87]\n [16.96 8.54]\n [31.77 37.96]\n [40.41 46.23]\n [20.34 18.91]\n [27.36 33.95]\n [38.31 46.64]\n [47.08 28.1 ]\n [19.79 11.41]\n [38.02 48.72]\n [25.68 15.44]\n [37.23 42.92]\n [25.69 29.93]\n [56.77 60.29]\n [35.85 42.13]\n [59.58 53.69]\n [35.43 48.59]\n [29.07 37.4 ]\n [17.35 11.65]\n [25.71 26.92]\n [72.89 41.93]\n [24.51 18. ]\n [48.07 46.23]\n [40.8 41.05]\n [33.19 46.25]\n [33.34 46.24]\n [22.62 16.26]\n [44.47 56.74]\n [53.96 51.02]\n [28.41 31.35]\n [35.78 17.82]\n [37.53 32.33]\n [55.89 29.79]\n [29.42 32.92]]\n"
],
[
"median_error = sum(abs(y_pred - y_test))/len(y_pred)\nprint(f\"Median error = {median_error}\")",
"Median error = [7.92]\n"
],
[
"#Visualising the Trainin set results\nplt.scatter(range(0,len(y_pred)),y_pred, color = 'red', s=10) #predictions result\nplt.scatter(range(0,len(y_pred)),y_test, color = 'blue', s=10) #real result\n\nplt.title('Concrete compressive strength (Mpa) [red = predictions, blue = real] vs. Count')\nplt.xlabel('Count')\nplt.ylabel('Concrete compressive strength (Mpa)')\nplt.grid(True)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a7836d07e57212a73b01301946baf955804b0df
| 580,746 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
2010-2018 (2).ipynb
|
helenhc/Crime-Hate-Crime
|
e3d673a24c9372b99fd143ccd128461a54fcb746
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
2010-2018 (2).ipynb
|
helenhc/Crime-Hate-Crime
|
e3d673a24c9372b99fd143ccd128461a54fcb746
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
2010-2018 (2).ipynb
|
helenhc/Crime-Hate-Crime
|
e3d673a24c9372b99fd143ccd128461a54fcb746
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 39.37261 | 896 | 0.238936 |
[
[
[
"import pandas\nimport re \ntable_5_2018 = pandas.read_excel('Table_5_Offenses_Known_Offenders_Race_and_Ethnicity_by_Bias_Motivation_2018.xls')\nnew_5_2018 =table_5_2018.rename(columns = {'Table 5' : 'Bias Motivation'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 1' : 'Total Offenses'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 2' : \"White\"}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 3' : 'Black or African American'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 4' : 'American Indian or Alaska Native'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 5' : 'Asian'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 6' : 'Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 7': 'Group of Multiple Races'}).rename(columns= {'Unnamed: 8': 'Unknown Race'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 9' : 'Hispanic or Latino'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 10' : 'Not Hispanic or Latino'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 11' : 'Group of multiple ethnicites'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 12' : 'Unknown Ethnicity'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 13' : 'Unknown Offender'}).drop(0).drop(1).drop(2).drop(3).drop(4).drop(48).drop(49)\nnew_5_2018 = new_5_2018.reset_index(drop=True)\nhold= new_5_2018['Bias Motivation'][42][:-2]\nnew_5_2018['Bias Motivation'][42] = hold\nnew_5_2018",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"table_9_2018 =pandas.read_excel('Table_9_Known_Offenders_Known_Offenders_Race_Ethnicity_and_Age_2018.xls')\ntable_2018_9 = table_9_2018.drop(['Unnamed: 2', 'Unnamed: 3', 'Unnamed: 4', 'Unnamed: 5', 'Unnamed: 6'], axis =1).rename(columns = {'Table 9':'Known Offenders'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 1' : 'Total'}).drop(0).drop(1).drop(2).drop(19).drop(20).drop(21).drop(22).drop(23).drop(24)\ntable_2018_9\n\nhold= table_2018_9['Bias Motivation'][42][:-2]\ntable_2018_9['Bias Motivation'][42] = hold\nnew_5_2018",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"table_10_2018 =pandas.read_excel('Table_10_Incidents_Bias_Motivation_by_Location_2018.xls')\ntable_10_2018.rename(columns ={'Table 10': 'Location'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 1' : 'Total Incidents'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 2' : 'Race/Ethnicity/Ancestry'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 3' : 'Religion'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 4' : 'Sexual Orientation'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 5' : 'Disability'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 6' : 'Gender'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 7' : 'Gender Identity'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 8' : 'Multiple Bias Incidents'}).drop(0).drop(1).drop(2).drop(53).drop(54).drop(3).drop(4).drop(columns =['Unnamed: 9', 'Unnamed: 10', 'Unnamed: 11'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"table_10_2017 = pandas.read_excel('Table_10_Incidents_Bias_Motivation_by_Location_2017.xls')\nnew_table_10_2017 = table_10_2017.drop(0).drop(1).drop(2).rename(columns ={'Table 10': 'Location'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 1' : 'Total Incidents'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 2' : 'Race/Ethnicity/Ancestry'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 3' : 'Religion'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 4' : 'Sexual Orientation'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 5' : 'Disability'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 6' : 'Gender'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 7' : 'Gender Identity'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 8' : 'Multiple Bias Incidents'})\nnew_table_10_2017.drop(3).drop(4).drop(52).drop(53)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"table_5_2017 = pandas.read_excel('Table_5_Offenses_Known_Offenders_Race_and_Ethnicity_by_Bias_Motivation_2017.xls')\nnew_table_5_2017 = table_5_2017.drop(0).drop(1).drop(2).drop(48).drop(49)\nnew_2017_5 = new_table_5_2017.rename(columns = {'Table 5' : 'Bias Motivation'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 1' : 'Total Offenses'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 2' : \"White\"}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 3' : 'Black or African American'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 4' : 'American Indian or Alaska Native'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 5' : 'Asian'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 6' : 'Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 7': 'Group of Multiple Races'}).rename(columns= {'Unnamed: 8': 'Unknown Race'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 9' : 'Hispanic or Latino'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 10' : 'Not Hispanic or Latino'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 11' : 'Group of multiple ethnicites'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 12' : 'Unknown Ethnicity'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 13' : 'Unknown Offender'}).drop(3).drop(4)\n\nnew_2017_5 = new_2017_5.reset_index(drop=True)\nhold= new_2017_5['Bias Motivation'][42][:-2]\nnew_2017_5['Bias Motivation'][42] = hold\nnew_2017_5",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"table_9_2017 = pandas.read_excel('Table_9_Known_Offenders_Known_Offenders_Race_Ethnicity_and_Age_2017.xls')\ntable_9_2017.drop(0).drop(1).rename(columns = {'Table 9' : 'Race/Ethnicity/Age'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 1' : 'Total'}).drop(2).drop(19).drop(20).drop(21).drop(22).drop(23).drop(24)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"table_10_2016 = pandas.read_excel('Table_10_Incidents_Bias_Motivation_by_Location_2016.xls')\nnew_10_2016 = table_10_2016.drop(0).drop(1).drop(2).rename(columns = {'Table 10' : 'Location'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 1' : 'Total Incidents'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 2': 'Race/Ethnicity/Ancestry'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 3': 'Religion'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 4': 'Sexual Orientation'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 5': 'Disability'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 6': 'Gender'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 7': 'Gender Identity'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 8': 'Multiple Bias Incidents'}).drop(3).drop(4)\nnew_10_2016.drop(['Unnamed: 9', 'Unnamed: 10', 'Unnamed: 11', 'Unnamed: 12'], axis =1).drop(52).drop(53)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"table_5_2016 = pandas.read_excel('Table_5_Offenses_Known_Offenders_Race_and_Ethnicity_by_Bias_Motivation_2016.xls')\nnew_5_2016 =table_5_2016.drop(0).drop(1).drop(2).drop(['Unnamed: 14', 'Unnamed: 15', 'Unnamed: 16'], axis= 1)\nnew_2016_5 = new_5_2016.rename(columns = {'Table 5': 'Bias Motivation'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 1': 'Total Offenses'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 2': 'White'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 3': 'Black or African American'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 4': 'American Indian or Alaska Native'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 5': 'Asian'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 6': 'Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 7': 'Group of Multiple races'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 8': 'Unknown Race'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 9': 'Hispanic or Latino'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 10': 'Not Hispanic or Latino'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 11':'Group of multiple ethnicities'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 12': 'Unknown Ethnicity'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 13': 'Unknown Offender'}).drop(3).drop(4).drop(48).drop(49)\n\nnew_2016_5 = new_2016_5.reset_index(drop=True)\nhold= new_2016_5['Bias Motivation'][42][:-2]\nnew_2016_5['Bias Motivation'][42] = hold\nnew_2016_5",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"table_9_2016 = pandas.read_excel('Table_9_Known_Offenders_Known_Offenders_Race_Ethnicity_and_Age_2016.xls')\ntable_9_2016.drop(0).drop(1).drop(['Unnamed: 2'], axis=1).rename(columns = {'Table 9':'Race/Ethnicity/Age'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 1':'Total'}).drop(2).drop(19).drop(20).drop(21).drop(22).drop(23).drop(24)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"table_10_2015 = pandas.read_excel('Table_10_Incidents_Bias_Motivation_by_Location_2015.xls')\ntable_10_2015.rename(columns ={'Table 10': 'Location'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 1' : 'Total Incidents'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 2' : 'Race/Ethnicity/Ancestry'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 3' : 'Religion'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 4' : 'Sexual Orientation'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 5' : 'Disability'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 6' : 'Gender'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 7' : 'Gender Identity'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 8' : 'Multiple Bias Incidents'}).drop(0).drop(1).drop(2).drop(51).drop(52).drop(3).drop(4)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"table_5_2015 = pandas.read_excel('Table_5_Offenses_Known_Offenders_Race_and_Ethnicity_by_Bias_Motivation_2015.xls')\ntable_5_2015.rename(columns = {'Table 5': 'Bias Motivation'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 1': 'Total Offenses'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 2': 'White'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 3': 'Black or African American'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 4': 'American Indian or Alaska Native'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 5': 'Asian'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 6': 'Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 7': 'Group of Multiple races'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 8': 'Unknown Race'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 9': 'Hispanic or Latino'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 10': 'Not Hispanic or Latino'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 11':'Group of multiple ethnicities'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 12': 'Unknown Ethnicity'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 13': 'Unknown Offender'}).drop(3).drop(48).drop(49).drop(0).drop(1).drop(2).drop(4)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"table_9_2015 = pandas.read_excel('Table_9_Known_Offenders_Known_Offenders_Race_Ethnicity_and_Age_2015.xls')\ntable_9_2015.drop(0).drop(1).rename(columns = {'Table 9':'Race/Ethnicity/Age'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 1':'Total'}).drop(2).drop(19).drop(20).drop(21).drop(22).drop(23).drop(24)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"table_10_2014 = pandas.read_excel('Table_10_Incidents_Bias_Motivation_by_Location_2014.xls')\nnew_2014_10 = table_10_2014.rename(columns = {'Table 10' : 'Location'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 1' : 'Total Incidents'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 2': 'Race'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 3': 'Religion'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 4': 'Sexual Orientation'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 5': 'Ethnicity'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 6': 'Disability'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 7': 'Gender'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 8': 'Gender Identity'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 9':'Multiple Bias Incidents'})\nnew_2014_10.drop(0).drop(1).drop(2).drop(48).drop(49).drop(3).drop(4)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"table_5_2014 = pandas.read_excel('Table_5_Offenses_Known_Offenders_Race_and_Ethnicity_by_Bias_Motivation_2014.xls')\nnew_5_2014 = table_5_2014.rename(columns = {'Table 5': 'Bias Motivation'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 1': 'Total Offenses'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 2': 'White'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 3': 'Black or African American'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 4': 'American Indian or Alaska Native'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 5': 'Asian'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 6': 'Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 7': 'Group of Multiple races'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 8': 'Unknown Race'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 9': 'Hispanic or Latino'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 10': 'Not Hispanic or Latino'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 11':'Group of multiple ethnicities'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 12': 'Unknown Ethnicity'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 13': 'Unknown Offender'})\nnew_5_2014.drop(0).drop(1).drop(2).drop(3).drop(41).drop(42).drop(43).drop(4)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"table_9_2014 = pandas.read_excel('Table_9_Known_Offenders_Known_Offenders_Race_Ethnicity_and_Age_2014.xls')\ntable_9_2014.drop(['Unnamed: 2', 'Unnamed: 3', 'Unnamed: 4', 'Unnamed: 5', 'Unnamed: 6'], axis =1).rename(columns = {'Table 9':'Race/Ethnicity/Age'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 1':'Total'}).drop(0).drop(1).drop(2).drop(19).drop(20).drop(21).drop(22).drop(23).drop(24)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"table_10_2013 = pandas.read_excel('Table_10_Incidents_Bias_Motivation_by_Location_2013.xls')\ntable_10_2013.rename(columns = {'Table 10' : 'Location'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 1' : 'Total Incidents'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 2': 'Race'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 3': 'Religion'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 4': 'Sexual Orientation'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 5': 'Ethnicity'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 6': 'Disability'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 7': 'Gender'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 8': 'Gender Identity'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 9':'Multiple Bias Incidents'}).drop(0).drop(1).drop(2).drop(3).drop(4).drop(48).drop(49)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"table_9_2013 = pandas.read_excel('Table_9_Known_Offenders_Known_Offenders_Race_2013.xls')\ntable_9_2013.rename(columns = {'Table 9' : 'Race/Ethnicity/Age'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 1' : 'Total'}).drop(2).drop(19).drop(20).drop(21).drop(22).drop(23).drop(24).drop(['Unnamed: 2', 'Unnamed: 3', 'Unnamed: 4', 'Unnamed: 5', 'Unnamed: 6'], axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"table_5_2013 = pandas.read_excel('Table_5_Offenses_Known_Offenders_Race_by_Bias_Motivation_2013.xls')\ntable_5_2013.rename(columns = {'Table 5': 'Bias Motivation'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 1': 'Total Offenses'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 2': 'White'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 3': 'Black or African American'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 4': 'American Indian or Alaska Native'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 5': 'Asian'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 6': 'Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 7': 'Group of Multiple races'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 8': 'Unknown Race'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 9': 'Hispanic or Latino'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 10': 'Not Hispanic or Latino'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 11':'Group of multiple ethnicities'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 12': 'Unknown Ethnicity'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 13': 'Unknown Offender'}).drop(0).drop(1).drop(2).drop(3).drop(4).drop(41).drop(42).drop(43)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"table_10_2012 = pandas.read_excel('Table_10_Incidents_Bias_Motivation_by_Location_2012.xls')\ntable_10_2012.rename(columns = {'Table 10' : 'Location'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 1' : 'Total Incidents'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 2': 'Race'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 3': 'Religion'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 4': 'Sexual Orientation'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 5': 'Ethnicity'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 6': 'Disability'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 7': 'Gender'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 8': 'Gender Identity'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 9':'Multiple Bias Incidents'}).drop(0).drop(1).drop(2).drop(3).drop(4).drop(48).drop(49)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"table_9_2012 = pandas.read_excel('Table_9_Known_Offenders_Known_Offenders_Race_2012.xls')\ntable_9_2012.drop(9).drop(10).rename(columns = {'Table 9': \"Known Offenders\"}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 1': 'Total'}).drop(0).drop(1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"table_5_2012.rename(columns = {'Table 5': 'Bias Motivation'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 1': 'Total Offenses'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 2': 'White'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 3': 'Black or African American'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 4': 'American Indian or Alaska Native'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 5': 'Asian and Pacific Islander'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 6': 'Multiple Races'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 7': 'Unknown Race'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 8': 'Unknown Offender'}).drop(0).drop(1).drop(2).drop(3).drop(4).drop(34)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"table_10_2011 = pandas.read_excel('Table_10_Incidents_Bias_Motivation_by_Location_2011.xls')\ntable_10_2011.rename(columns = {'Table 10': 'Location'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 1': 'Total Incidents'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 2':'Race'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 3':'Religion'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 4':'Sexual Orientation'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 5': 'Ethnicity'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 6':'Disability'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 7': 'Multiple Bias Incidents'}).drop(0).drop(1).drop(2).drop(3).drop(48).drop(49)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"table_9_2011 = pandas.read_excel('Table_9_Known_Offenders_Known_Offenders_Race_2011.xls')\ntable_9_2011.rename(columns = {'Table 9':'Known Offender Race'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 1':'Total'}).drop(0).drop(1).drop(9).drop(10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"table_5_2011 = pandas.read_excel('Table_5_Offenses_Known_Offenders_Race_by_Bias_Motivation_2011.xls')\ntable_5_2011.rename(columns = {'Table 5':'Bias Motivation'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 1':'Total Offenses'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 2':'White'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 3':'Black'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 4': 'American Indian or Alaska Native'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 5': 'Asian or Pacific Islander'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 6': 'Multiple Race Groups'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 7': 'Unknown Race'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 8': 'Unknown Offender'}).drop(0).drop(1).drop(2).drop(3).drop(33)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"table_10_2010 = pandas.read_excel('Table 10-Incidents-Bias Motivation-by Location 2010.xls')\ntable_10_2010.drop(0).drop(1).drop(2).drop(35).rename(columns = {'Table 10': 'Location'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 1': 'Total Incidents'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 2':'Race'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 3':'Religion'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 4':'Sexual Orientation'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 5': 'Ethnicity'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 6':'Disability'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 7': 'Multiple Bias Incidents'}).rename(columns = { 'Table 10': 'Location'})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"table_9_2010 = pandas.read_excel('Table 9-Known Offenders-Known Offenders Race 2010.xls')\ntable_9_2010.rename(columns = {'Table 9': 'Known Offender Race'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 1': 'Total'}).drop(0).drop(8).drop(9)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"table_5_2010 = pandas.read_excel('Table 5-Offenses-Known Offenders Race-by Bias Motivation 2010.xls')\ntable_5_2010.rename(columns = {'Table 5':'Bias Motivation'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 1':'Total Offenses'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 2':'White'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 3':'Black'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 4': 'American Indian and Alaska Native'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 5': 'Asian and Pacific Islander'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 6': 'Multiple Race Groups'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 7': 'Unknown Race'}).rename(columns = {'Unnamed: 8': 'Unknown Offender'}).drop(0).drop(1).drop(2).drop(32)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a78396932d45dd0616ac47502df2112f144b2a5
| 13,628 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
intro.ipynb
|
SpartanTan/aima-python
|
2a53507729929a9b6f805e33667e814ab472a939
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
intro.ipynb
|
SpartanTan/aima-python
|
2a53507729929a9b6f805e33667e814ab472a939
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
intro.ipynb
|
SpartanTan/aima-python
|
2a53507729929a9b6f805e33667e814ab472a939
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 89.071895 | 2,916 | 0.70157 |
[
[
[
"# An Introduction To `aima-python` \n \nThe [aima-python](https://github.com/aimacode/aima-python) repository implements, in Python code, the algorithms in the textbook *[Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach](http://aima.cs.berkeley.edu)*. A typical module in the repository has the code for a single chapter in the book, but some modules combine several chapters. See [the index](https://github.com/aimacode/aima-python#index-of-code) if you can't find the algorithm you want. The code in this repository attempts to mirror the pseudocode in the textbook as closely as possible and to stress readability foremost; if you are looking for high-performance code with advanced features, there are other repositories for you. For each module, there are three/four files, for example:\n\n- [**`nlp.py`**](https://github.com/aimacode/aima-python/blob/master/nlp.py): Source code with data types and algorithms for natural language processing; functions have docstrings explaining their use.\n- [**`nlp.ipynb`**](https://github.com/aimacode/aima-python/blob/master/nlp.ipynb): A notebook like this one; gives more detailed examples and explanations of use.\n- [**`nlp_apps.ipynb`**](https://github.com/aimacode/aima-python/blob/master/nlp_apps.ipynb): A Jupyter notebook that gives example applications of the code.\n- [**`tests/test_nlp.py`**](https://github.com/aimacode/aima-python/blob/master/tests/test_nlp.py): Test cases, used to verify the code is correct, and also useful to see examples of use.\n\nThere is also an [aima-java](https://github.com/aimacode/aima-java) repository, if you prefer Java.\n \n## What version of Python?\n \nThe code is tested in Python [3.4](https://www.python.org/download/releases/3.4.3/) and [3.5](https://www.python.org/downloads/release/python-351/). If you try a different version of Python 3 and find a problem, please report it as an [Issue](https://github.com/aimacode/aima-python/issues).\n \nWe recommend the [Anaconda](https://www.anaconda.com/download/) distribution of Python 3.5. It comes with additional tools like the powerful IPython interpreter, the Jupyter Notebook and many helpful packages for scientific computing. After installing Anaconda, you will be good to go to run all the code and all the IPython notebooks. \n\n## IPython notebooks \n \nThe IPython notebooks in this repository explain how to use the modules, and give examples of usage. \nYou can use them in three ways: \n\n1. View static HTML pages. (Just browse to the [repository](https://github.com/aimacode/aima-python) and click on a `.ipynb` file link.)\n2. Run, modify, and re-run code, live. (Download the repository (by [zip file](https://github.com/aimacode/aima-python/archive/master.zip) or by `git` commands), start a Jupyter notebook server with the shell command \"`jupyter notebook`\" (issued from the directory where the files are), and click on the notebook you want to interact with.)\n3. Binder - Click on the binder badge on the [repository](https://github.com/aimacode/aima-python) main page to open the notebooks in an executable environment, online. This method does not require any extra installation. The code can be executed and modified from the browser itself. Note that this is an unstable option; there is a chance the notebooks will never load.\n\n \nYou can [read about notebooks](https://jupyter-notebook-beginner-guide.readthedocs.org/en/latest/) and then [get started](https://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/jupyter/notebook/blob/master/docs/source/examples/Notebook/Running%20Code.ipynb).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Helpful Tips\n\nMost of these notebooks start by importing all the symbols in a module:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from logic import *",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"From there, the notebook alternates explanations with examples of use. You can run the examples as they are, and you can modify the code cells (or add new cells) and run your own examples. If you have some really good examples to add, you can make a github pull request.\n\nIf you want to see the source code of a function, you can open a browser or editor and see it in another window, or from within the notebook you can use the IPython magic function `%psource` (for \"print source\") or the function `psource` from `notebook.py`. Also, if the algorithm has pseudocode available, you can read it by calling the `pseudocode` function with the name of the algorithm passed as a parameter.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%psource WalkSAT",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from notebook import psource, pseudocode\n\npsource(WalkSAT)\npseudocode(\"WalkSAT\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Or see an abbreviated description of an object with a trailing question mark:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"WalkSAT?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Authors\n\nThis notebook is written by [Chirag Vertak](https://github.com/chiragvartak) and [Peter Norvig](https://github.com/norvig).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a783a41cdd639827a43bb71837272d1cba7a147
| 2,047 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Plus-One.ipynb
|
AllenTom/Algorithm
|
0c327211ce914f7b356d45856dc940cf3feafe85
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Plus-One.ipynb
|
AllenTom/Algorithm
|
0c327211ce914f7b356d45856dc940cf3feafe85
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Plus-One.ipynb
|
AllenTom/Algorithm
|
0c327211ce914f7b356d45856dc940cf3feafe85
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 24.662651 | 150 | 0.504152 |
[
[
[
"# Plus One\n\nGiven a non-empty array of digits representing a non-negative integer, increment one to the integer.\n\nThe digits are stored such that the most significant digit is at the head of the list, and each element in the array contains a single digit.\n\nYou may assume the integer does not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 解析\n题目来源:[LeetCode - Plus One - 66](https://leetcode.com/problems/plus-one/)\n\n题目非常简单,处理好进位的情况就好,类似于计算机组成原理`CU`加法运算的步骤",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def plusOne(digits):\n idx = len(digits) - 1\n add = True\n while idx > -1:\n if (add == True):\n value = digits[idx] + 1\n if value >= 10:\n value -= 10\n add = True\n else:\n add = False\n digits[idx] = value\n if idx == 0 and add:\n digits.insert(0,1)\n idx -= 1\n return digits",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(plusOne([9,9,9,9,9,9,9,9,9,9]))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a784cedeec45688c18dd14c804aa0f8d3b411f9
| 2,853 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Assets/Noedify/Demos/TensorflowImport_MNIST_Drawing/Tensorflow/Jupyter/TrainMNIST.ipynb
|
JinguMastery/My-Unity-Project-OSMCity
|
3540a8f2b46f7f1182cd533e9958499f3bf0800f
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2020-09-09T04:10:46.000Z
|
2020-09-09T04:10:46.000Z
|
Assets/Noedify/Demos/TensorflowImport_MNIST_Drawing/Tensorflow/Jupyter/TrainMNIST.ipynb
|
JinguMastery/My-Unity-Project-OSMCity
|
3540a8f2b46f7f1182cd533e9958499f3bf0800f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Assets/Noedify/Demos/TensorflowImport_MNIST_Drawing/Tensorflow/Jupyter/TrainMNIST.ipynb
|
JinguMastery/My-Unity-Project-OSMCity
|
3540a8f2b46f7f1182cd533e9958499f3bf0800f
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2020-03-31T04:09:49.000Z
|
2020-03-31T04:09:49.000Z
| 25.473214 | 80 | 0.564669 |
[
[
[
"import tensorflow as tf\nimport tensorflow.keras as keras\nfrom tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist\nfrom tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential\nfrom tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Dropout, Activation, Flatten\nfrom tensorflow.keras.callbacks import TensorBoard\nimport numpy as np\n\nbatch_size = 128\nnum_classes = 10",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Import Training Data\nimg_rows, img_cols = 28, 28\n\n(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()\n\nx_train = x_train.reshape(x_train.shape[0], img_rows*img_cols*1)\nx_test = x_test.reshape(x_test.shape[0],img_rows*img_cols*1)\n\nx_train = x_train.astype('float32')\nx_test = x_test.astype('float32')\nx_train /= 255\nx_test /= 255\n\ny_train = keras.utils.to_categorical(y_train, num_classes)\ny_test = keras.utils.to_categorical(y_test, num_classes)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Build Network\nmodel = Sequential()\nmodel.add(Dense(600, activation='sigmoid'))\nmodel.add(Dense(300, activation='sigmoid'))\nmodel.add(Dense(140, activation='sigmoid'))\n\nmodel.add(Dense(num_classes, activation='sigmoid'))\n\nmodel.compile(loss = \"categorical_crossentropy\", \n optimizer=\"adam\",\n metrics=['accuracy'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Train Network\nepochs = 10\nmodel.fit(x_train, y_train,\n batch_size=batch_size,\n epochs=epochs,\n verbose=1,\n validation_data=(x_test, y_test))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Export Network Parameters\nimport NoedifyPython\nNoedifyPython.ExportModel(model, \"FC_mnist_600x300x140_parameters.txt\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a78592e4ef8d5e5a2a7f8bc9c165ed8b8a0a17f
| 229,721 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
examples/screen_new_reactions.ipynb
|
andrewtarzia/enzyme_screen
|
c7f9291e5e29b51dd28193f46e1a2ac377dafa9e
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2020-09-11T15:29:18.000Z
|
2020-09-11T15:29:18.000Z
|
examples/screen_new_reactions.ipynb
|
andrewtarzia/enzyme_screen
|
c7f9291e5e29b51dd28193f46e1a2ac377dafa9e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
examples/screen_new_reactions.ipynb
|
andrewtarzia/enzyme_screen
|
c7f9291e5e29b51dd28193f46e1a2ac377dafa9e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 179.609851 | 87,836 | 0.876276 |
[
[
[
"# A case study in screening for new enzymatic reactions\n\nIn this example, we show how to search the KEGG database for a reaction of interest based on user requirements. At specific points we highlight how our code could be used for arbitrary molecules that the user is interested in. This is crucial because the KEGG database is not exhaustive, and we only accessed a portion of the database that has no ambiguities (to avoid the need for manual filtering).\n\nRequirements to run this script:\n* rdkit (2019.09.2.0)\n* matplotlib (3.1.1)\n* numpy (1.17.4)\n* enzyme_screen\n * Clone source code and run this notebook in its default directory.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# This notebook requires data from screening, which is not uploaded!",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## The idea:\n\nWe want to screen all collected reactions for a reaction that fits these constraints (automatic or manual application is noted):\n\n1. Maximum component size within 5-7 Angstrom (automatic)\n2. *One* component on *one* side of the reaction contains a nitrile group (automatic)\n3. Value added from reactant to product (partially manual) e.g.:\n - cost of the reactants being much less than the products\n - products being unpurchasable and reactants being purchasable\n\nConstraint *2* affords potential reaction monitoring through the isolated FT-IR signal of the nitrile group.\n\nConstraint *3* is vague, but generally aims to determine some value-added by using an enzyme for a given reaction. This is often based on overcoming the cost of purchasing/synthesising the product through some non-enzymatic pathway by using an encapsulate enzyme. In this case, we use the primary literature on a selected reaction and some intuition to guide our efforts (i.e. we select a reaction (directionality determined from KEGG) where a relatively cheap (fair assumption) amino acid is the reactant). \n\nThe alternative to this process would be to select a target reactant or product and search all reactions that include that target and apply similar constraints to test the validity of those reactions.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Provide directory to reaction data and molecule data, and parameter file.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport pandas as pd\nimport os\nimport sys\n\nreaction_dir = (\n '/data/atarzia/projects/psp_phd/production/rxn_collection'\n)\nmolecule_dir = (\n '/data/atarzia/projects/psp_phd/molecules/molecule_DBs/production'\n)\n\n# Handle import directories.\nmodule_path = os.path.abspath(os.path.join('../src'))\nif module_path not in sys.path:\n sys.path.append(module_path)\nimport utilities\nparam_file = '../data/param_file.txt'\nparams = utilities.read_params(param_file)",
"---------------------------------------------------------\nrun parameters:\nVDW scale: 0.9\nBox Margin: 4.0 Angstrom\nGrid spacing: 0.5 Angstrom\nshow VDW?: False\nPlot Ellipsoid?: False\nNo Conformers: 100.0\nMW threshold: 500.0 g/mol\npI threshold: 6.0\nDiffusion threshold: 4.2 Angstrom\nDBs: KEGG\n---------------------------------------------------------\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Find reaction systems with max component sizes within threshold\n\nUsing a threshold of 5 to 7 angstrom.\n\nResults in a plot of reaction distributions.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import plotting_fn as pfn",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"threshold_min = 5\nthreshold_max = 7",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Read in reaction collection CSV: rs_properties.csv \n# from running RS_analysis.py.\nrs_properties = pd.read_csv(\n os.path.join(reaction_dir, 'rs_properties.csv')\n)\nrs_within_threshold = rs_properties[\n rs_properties['max_mid_diam'] < threshold_max\n]\nrs_within_threshold = rs_within_threshold[\n rs_within_threshold['max_mid_diam'] >= threshold_min\n]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(f'{len(rs_within_threshold)} reactions in threshold')",
"989 reactions in threshold\n"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots()\n\nalpha = 1.0\nwidth = 0.25\nX_bins = np.arange(0, 20, width)\n\n# All reactions.\nhist, bin_edges = np.histogram(\n a=list(rs_properties['max_mid_diam']), \n bins=X_bins\n)\nax.bar(\n bin_edges[:-1],\n hist,\n align='edge',\n alpha=alpha,\n width=width,\n color='lightgray',\n edgecolor='lightgray',\n label='all reactions'\n)\n\n# Within threshold.\nhist, bin_edges = np.histogram(\n a=list(rs_within_threshold['max_mid_diam']), \n bins=X_bins\n)\nax.bar(\n bin_edges[:-1],\n hist,\n align='edge',\n alpha=alpha,\n width=width,\n color='firebrick',\n edgecolor='firebrick',\n label='within threshold'\n)\n\npfn.define_standard_plot(\n ax,\n xtitle='$d$ of largest component [$\\mathrm{\\AA}$]',\n ytitle='count',\n xlim=(0, 20),\n ylim=None\n)\nfig.legend(fontsize=16)\nfig.savefig(\n os.path.join(reaction_dir, 'screen_example_distribution.pdf'),\n dpi=720,\n bbox_inches='tight'\n)\n\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Find reaction systems with at least one nitrile functionality on one side of the reaction",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import reaction",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from rdkit.Chem import AllChem as rdkit\nfrom rdkit.Chem import Fragments\n# Handle some warnings for flat molecules.\nfrom rdkit import RDLogger\nRDLogger.DisableLog('rdApp.*') \n# Needed to show molecules\nfrom rdkit.Chem import Draw\nfrom rdkit.Chem.Draw import IPythonConsole \n\ndef has_nitrile(mol_file):\n \"\"\"\n Returns False if nitrile fragment is not found using RDKIT.\n\n \"\"\"\n\n mol = rdkit.MolFromMolFile(mol_file)\n no_frag = Fragments.fr_nitrile(mol)\n if no_frag > 0:\n return True\n else:\n return False",
"RDKit WARNING: [21:33:05] Enabling RDKit 2019.09.2 jupyter extensions\n"
],
[
"# Define generator over reactions.\ngenerator = reaction.yield_rxn_syst(\n output_dir=reaction_dir, \n pars=params,\n)\n\n# Iterate over reactions, checking for validity.\ntarget_reaction_ids = []\nmolecules_with_nitriles = []\nfor i, (count, rs) in enumerate(generator):\n if 'KEGG' not in rs.pkl:\n continue\n if rs.skip_rxn:\n continue\n if rs.components is None:\n continue\n \n # Check components for nitrile groups.\n reactants_w_nitriles = 0\n products_w_nitriles = 0\n for m in rs.components:\n mol_file = os.path.join(\n molecule_dir,\n m.name+'_opt.mol'\n )\n if has_nitrile(mol_file):\n if mol_file not in molecules_with_nitriles:\n molecules_with_nitriles.append(mol_file)\n if m.role == 'reactant':\n reactants_w_nitriles += 1\n elif m.role == 'product':\n products_w_nitriles += 1\n\n # Get both directions.\n if products_w_nitriles == 1 and reactants_w_nitriles == 0:\n target_reaction_ids.append(rs.DB_ID)\n if products_w_nitriles == 0 and reactants_w_nitriles == 1:\n target_reaction_ids.append(rs.DB_ID)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Draw nitrile containing molecules",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(\n f'There are {len(molecules_with_nitriles)} molecules '\n f'with nitrile groups, corresponding to '\n f'{len(target_reaction_ids)} reactions '\n 'out of all.'\n)",
"There are 40 molecules with nitrile groups, corresponding to 35 reactions out of all.\n"
],
[
"molecules = [\n rdkit.MolFromSmiles(rdkit.MolToSmiles(rdkit.MolFromMolFile(i)))\n for i in molecules_with_nitriles\n]\nmol_names = [\n i.replace(molecule_dir+'/', '').replace('_opt.mol', '')\n for i in molecules_with_nitriles\n]\n\nimg = Draw.MolsToGridImage(\n molecules,\n molsPerRow=6,\n subImgSize=(100, 100),\n legends=mol_names,\n)\nimg",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Update dataframe to have target reaction ids only.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"target_reactions = rs_within_threshold[\n rs_within_threshold['db_id'].isin(target_reaction_ids)\n]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(\n f'There are {len(target_reactions)} reactions '\n 'that fit all constraints so far.'\n)",
"There are 19 reactions that fit all constraints so far.\n"
],
[
"target_reactions",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Select reaction based on bertzCT and SAScore, plus intuition from visualisation\n\nPlotting the measures of reaction productivity is useful, but so is looking manually through the small subset.\n\nBoth methods highlight R02846 (https://www.genome.jp/dbget-bin/www_bget?rn:R02846) as a good candidate:\n\n- High deltaSA and deltaBertzCT\n- The main reactant is a natural amino acid (cysteine). Note that the chirality is not defined in this specific KEGG Reaction, however, the chirality is defined as L-cysteine in the Enzyme entry (https://www.genome.jp/dbget-bin/www_bget?ec:4.4.1.9)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots()\n\nax.scatter(\n target_reactions['deltasa'], \n target_reactions['deltabct'],\n alpha=1.0,\n c='#ff3b3b',\n edgecolor='none',\n label='target reactions',\n s=100,\n)\n\npfn.define_standard_plot(\n ax,\n xtitle=r'$\\Delta$ SAscore',\n ytitle=r'$\\Delta$ BertzCT',\n xlim=(-10, 10),\n ylim=None,\n)\nfig.legend(fontsize=16)\nfig.savefig(\n os.path.join(\n reaction_dir, \n 'screen_example_complexity_targets.pdf'\n ),\n dpi=720,\n bbox_inches='tight'\n)\n\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots()\n\nax.scatter(\n rs_properties['deltasa'], \n rs_properties['deltabct'],\n alpha=1.0,\n c='lightgray',\n edgecolor='none',\n label='all reactions',\n s=40,\n)\nax.scatter(\n rs_within_threshold['deltasa'], \n rs_within_threshold['deltabct'],\n alpha=1.0,\n c='#2c3e50',\n edgecolor='none',\n label='within threshold',\n s=40,\n)\nax.scatter(\n target_reactions['deltasa'], \n target_reactions['deltabct'],\n alpha=1.0,\n c='#ff3b3b',\n edgecolor='k',\n label='target reactions',\n marker='P',\n s=60,\n)\n\npfn.define_standard_plot(\n ax,\n xtitle=r'$\\Delta$ SAscore',\n ytitle=r'$\\Delta$ BertzCT',\n xlim=(-10, 10),\n ylim=(-850, 850),\n)\nfig.legend(fontsize=16)\nfig.savefig(\n os.path.join(\n reaction_dir, \n 'screen_example_complexity_all.pdf'\n ),\n dpi=720,\n bbox_inches='tight'\n)\n\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Visualise properties of chosen reaction\n\nReaction: R02846 (https://www.genome.jp/dbget-bin/www_bget?rn:R02846)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Read in reaction system.\nrs = reaction.get_RS(\n filename=os.path.join(\n reaction_dir, 'sRS-4_4_1_9-KEGG-R02846.gpkl'\n ),\n output_dir=reaction_dir,\n pars=params,\n verbose=True\n)\n\n# Print properties and collate components.\nprint(rs)\nif rs.skip_rxn:\n print(f'>>> {rs.skip_reason}')\n\nprint(\n f'max intermediate diameter = {rs.max_min_mid_diam} angstrom'\n)\nprint(\n f'deltaSA = {rs.delta_SA}'\n)\nprint(\n f'deltaBertzCT = {rs.delta_bCT}'\n)\nprint('--------------------------\\n')\nprint('Components:')\n\n# Output molecular components and their properties.\nreacts = []\nreactstr = []\nprodstr = []\nprods = []\nfor rsc in rs.components:\n prop_dict = rsc.read_prop_file()\n print(rsc)\n print(f\"SA = {round(prop_dict['Synth_score'], 3)}\")\n print(f\"BertzCT = {round(prop_dict['bertzCT'], 3)}\")\n print('\\n')\n if rsc.role == 'product':\n prods.append(\n rdkit.MolFromMolFile(rsc.structure_file)\n )\n prodstr.append(f'{rsc.name}')\n if rsc.role == 'reactant':\n reacts.append(\n rdkit.MolFromMolFile(rsc.structure_file)\n )\n reactstr.append(f'{rsc.name}')\n",
"loading: sRS-4_4_1_9-KEGG-R02846.gpkl\nKEGG_Reaction(EC=4.4.1.9, DB=KEGG, ID=R02846, pkl=sRS-4_4_1_9-KEGG-R02846.gpkl)\nmax intermediate diameter = 6.080380383824703 angstrom\ndeltaSA = 1.716078234896762\ndeltaBertzCT = 51.15506614568605\n--------------------------\n\nComponents:\nMolecule(name=C00736, role=reactant, DB=KEGG, ID=C00736)\nSA = 2.979\nBertzCT = 75.335\n\n\nMolecule(name=C00177, role=reactant, DB=KEGG, ID=C00177)\nSA = 5.248\nBertzCT = 6.755\n\n\nMolecule(name=C00283, role=product, DB=KEGG, ID=C00283)\nSA = 6.964\nBertzCT = 0\n\n\nMolecule(name=C02512, role=product, DB=KEGG, ID=C02512)\nSA = 3.243\nBertzCT = 126.49\n\n\n"
],
[
"img = Draw.MolsToGridImage(\n reacts,\n molsPerRow=2,\n subImgSize=(300, 300),\n legends=reactstr,\n)\nimg.save(\n os.path.join(\n reaction_dir, \n 'screen_example_reactants.png'\n )\n)\nimg",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"img = Draw.MolsToGridImage(\n prods,\n molsPerRow=2,\n subImgSize=(300, 300),\n legends=prodstr,\n)\nimg.save(\n os.path.join(\n reaction_dir, \n 'screen_example_products.png'\n )\n)\nimg",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Manually obtaining the cost of molecules\n\nIn this example, we will assume C00283 and C00177 are obtainable/purchasable through some means and that only C00736 and C02512 are relevant to the productivity of the reaction.\n\nNote that the synthetic accessibility is 'large' for these molecules due to the two small molecules, while the change in BertzCT comes from the two larger molecules.\n\n- Get CAS number from KEGG Compound pages:\n - KEGG: C00736, CAS: 3374-22-9\n - KEGG: C02512, CAS: 6232-19-5\n- Use CAS number in some supplier website (using http://astatechinc.com/ here for no particular reason) \n - KEGG: C00736, Price: \\\\$69 for 10 gram = \\\\$6.9 per gram\n - KEGG: C02512, Price: \\\\$309 for 1 gram = \\\\$309 per gram",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4a7859b4c4472ea06c4fb84e38fb23e16f85b0fd
| 69,969 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
machine-learning-ex3/ex3/ex3.ipynb
|
Dream74/coursera-ml-py
|
b8cfe21024ca9aa61def952e00576c25ecd8076b
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
machine-learning-ex3/ex3/ex3.ipynb
|
Dream74/coursera-ml-py
|
b8cfe21024ca9aa61def952e00576c25ecd8076b
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
machine-learning-ex3/ex3/ex3.ipynb
|
Dream74/coursera-ml-py
|
b8cfe21024ca9aa61def952e00576c25ecd8076b
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 163.861827 | 57,440 | 0.88049 |
[
[
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport scipy.io as scio\n\nimport displayData as dd\nimport lrCostFunction as lCF\nimport oneVsAll as ova\nimport predictOneVsAll as pova\nimport scipy.optimize as opt",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Setup the parameters you will use for this part of the exercise\ninput_layer_size = 400 # 20x20 input images of Digits\nnum_labels = 10 # 10 labels, from 0 to 9\n # Note that we have mapped \"0\" to label 10",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# ===================== Part 1: Loading and Visualizing Data =====================\n# We start the exercise by first loading and visualizing the dataset.\n# You will be working with a dataset that contains handwritten digits.\n#\n\n# Load Training Data\nprint('Loading and Visualizing Data ...')\n\ndata = scio.loadmat('ex3data1.mat')\nX = data['X']\ny = data['y'].flatten()\nm = y.size",
"Loading and Visualizing Data ...\n"
],
[
"def display_data(x):\n (m, n) = x.shape\n\n # Set example_width automatically if not passed in\n example_width = np.round(np.sqrt(n)).astype(int)\n example_height = (n / example_width).astype(int)\n\n # Compute the number of items to display\n display_rows = np.floor(np.sqrt(m)).astype(int)\n display_cols = np.ceil(m / display_rows).astype(int)\n\n # Between images padding\n pad = 1\n\n # Setup blank display\n display_array = - np.ones((pad + display_rows * (example_height + pad),\n pad + display_rows * (example_height + pad)))\n\n # Copy each example into a patch on the display array\n curr_ex = 0\n for j in range(display_rows):\n for i in range(display_cols):\n if curr_ex > m:\n break\n\n # Copy the patch\n # Get the max value of the patch\n max_val = np.max(np.abs(x[curr_ex]))\n display_array[pad + j * (example_height + pad) + np.arange(example_height),\n pad + i * (example_width + pad) + np.arange(example_width)[:, np.newaxis]] = \\\n x[curr_ex].reshape((example_height, example_width)) / max_val\n curr_ex += 1\n\n if curr_ex > m:\n break\n\n # Display image\n plt.figure()\n plt.imshow(display_array, cmap='gray', extent=[-1, 1, -1, 1])\n plt.axis('off')\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"rand_indices = np.random.permutation(range(m))\nselected = X[rand_indices[0:100], :]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"display_data(selected)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# ===================== Part 2-a: Vectorize Logistic Regression =====================\n# In this part of the exercise, you will reuse your logistic regression\n# code from the last exercise. Your task here is to make sure that your\n# regularized logistic regression implementation is vectorized. After\n# that, you will implement one-vs-all classification for the handwritten\n# digit dataset\n#\n\n# Test case for lrCostFunction\nprint('Testing lrCostFunction()')",
"Testing lrCostFunction()\n"
],
[
"theta_t = np.array([-2, -1, 1, 2])\nX_t = np.c_[np.ones(5), np.arange(1, 16).reshape((3, 5)).T/10]\ny_t = np.array([1, 0, 1, 0, 1])\nlmda_t = 3",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# sigmoid function\nsigmoid_func = lambda x: 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))\n# sigmoid_func = lambda x: np.exp(x) / (np.exp(x)+1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# hypothesis function \nh_func = lambda theta, X: sigmoid_func(theta @ X.transpose()) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def lr_cost_function(theta, X, y, lmd):\n m = y.size\n\n # You need to return the following values correctly\n cost = 0\n grad = np.zeros(theta.shape)\n\n # ===================== Your Code Here =====================\n # Instructions : Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta\n # You should set cost and grad correctly.\n #\n\n cost = (-y @ np.log(h_func(theta, X)) - (1-y) @ np.log((1-h_func(theta, X)))) / m + (theta[1:] @ theta[1:]) * lmd / (2*m) \n for idx in range(theta.size):\n grad[idx] += ((h_func(theta, X) - y) @ X[:, idx]) / m + (0 if idx == 0 else lmd * theta[idx] / m)\n # =========================================================\n \n return cost, grad\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\ncost, grad = lr_cost_function(theta_t, X_t, y_t, lmda_t)\n\nnp.set_printoptions(formatter={'float': '{: 0.6f}'.format})\nprint('Cost: {:0.7f}'.format(cost))\nprint('Expected cost: 2.534819')\nprint('Gradients:\\n{}'.format(grad))\nprint('Expected gradients:\\n[ 0.146561 -0.548558 0.724722 1.398003]')\n",
"Cost: 2.5348194\nExpected cost: 2.534819\nGradients:\n[ 0.146561 -0.548558 0.724722 1.398003]\nExpected gradients:\n[ 0.146561 -0.548558 0.724722 1.398003]\n"
],
[
"def one_vs_all(X, y, num_labels, lmd):\n # Some useful variables\n (m, n) = X.shape\n\n # You need to return the following variables correctly\n all_theta = np.zeros((num_labels, n + 1))\n\n # Add ones to the X data 2D-array\n X = np.c_[np.ones(m), X]\n\n # Optimize\n def cost_func(t):\n return lr_cost_function(t, X, y_flag, lmd)[0]\n\n def grad_func(t):\n return lr_cost_function(t, X, y_flag, lmd)[1]\n\n for i in range(num_labels):\n print('Optimizing for handwritten number {}...'.format(i))\n # ===================== Your Code Here =====================\n # Instructions : You should complete the following code to train num_labels\n # logistic regression classifiers with regularization\n # parameter lambda\n #\n #\n # Hint: you can use y == c to obtain a vector of True(1)'s and False(0)'s that tell you\n # whether the ground truth is true/false for this class\n #\n # Note: For this assignment, we recommend using opt.fmin_cg to optimize the cost\n # function. It is okay to use a for-loop (for c in range(num_labels) to\n # loop over the different classes\n #\n y_flag = (y == (i+1)) * 1\n\n theta = all_theta[i]\n theta, cost, *unused = opt.fmin_bfgs(f=cost_func, fprime=grad_func, x0=theta, maxiter=400, full_output=True, disp=False)\n all_theta[i] = theta\n # ============================================================ \n print('Done')\n\n return all_theta\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lmd = 0.1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# ===================== Part 2-b: One-vs-All Training =====================\nprint('Training One-vs-All Logistic Regression ...')\n\nlmd = 0.1\nall_theta = one_vs_all(X, y, num_labels, lmd)",
"Training One-vs-All Logistic Regression ...\nOptimizing for handwritten number 0...\nDone\nOptimizing for handwritten number 1...\nDone\nOptimizing for handwritten number 2...\nDone\nOptimizing for handwritten number 3...\nDone\nOptimizing for handwritten number 4...\nDone\nOptimizing for handwritten number 5...\nDone\nOptimizing for handwritten number 6...\nDone\nOptimizing for handwritten number 7...\nDone\nOptimizing for handwritten number 8...\nDone\nOptimizing for handwritten number 9...\nDone\n"
],
[
"def predict_one_vs_all(theta, X):\n m = X.shape[0]\n\n # Return the following variable correctly\n p = np.zeros(m)\n \n # Add ones to the X data 2D-array\n X = np.c_[np.ones(m), X]\n\n # ===================== Your Code Here =====================\n # Instructions : Complete the following code to make predictions using\n # your learned logistic regression parameters.\n # You should set p to a 1D-array of 0's and 1's\n #\n p = np.argmax((X @ all_theta.T), axis=1)+1\n \n # ===========================================================\n\n return p\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# ===================== Part 3: Predict for One-Vs-All =====================\n\npred = predict_one_vs_all(all_theta, X)\n\nprint('Training set accuracy: {}'.format(np.mean(pred == y)*100))\n\nprint('ex3 Finished. Press ENTER to exit')\n",
"Training set accuracy: 96.48\nex3 Finished. Press ENTER to exit\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a78a71498e804615e52a5323a99c4d4d2262627
| 159,056 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Learn ML 2021 challange/learn_ml_2021.ipynb
|
harry418/Hackathons-participated
|
d1c9e169bc0e9f4f1054f2b2770ea2ee4364bb7f
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Learn ML 2021 challange/learn_ml_2021.ipynb
|
harry418/Hackathons-participated
|
d1c9e169bc0e9f4f1054f2b2770ea2ee4364bb7f
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Learn ML 2021 challange/learn_ml_2021.ipynb
|
harry418/Hackathons-participated
|
d1c9e169bc0e9f4f1054f2b2770ea2ee4364bb7f
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 159,056 | 159,056 | 0.849688 |
[
[
[
"# Get the data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from google.colab import drive\ndrive.mount('/content/gdrive')",
"Drive already mounted at /content/gdrive; to attempt to forcibly remount, call drive.mount(\"/content/gdrive\", force_remount=True).\n"
],
[
"from sklearn.linear_model import ElasticNet, Lasso, Ridge\nfrom sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import RobustScaler,MinMaxScaler,StandardScaler\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import KFold, cross_val_score, train_test_split,GridSearchCV\nfrom sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error,mean_absolute_error\nimport numpy as np\nimport warnings\ndef ignore_warn(*args, **kwargs):\n pass\nwarnings.warn = ignore_warn \n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import pandas as pd\ndataset = pd.read_csv('/content/gdrive/MyDrive/Dockship/learn_ml_2021_grand_ai_challenge-dataset/new_train.csv')\n#dataset.tail()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dataset.corr()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# for stock-1\n\n\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"inp1= dataset[[\"Open-Stock-1\",\"High-Stock-1\",\"Low-Stock-1\",\"VWAP-Stock-1\"]]\nop1 = dataset['Close-Stock-1']\ninp2 = dataset[[\"Open-Stock-2\",\"High-Stock-2\",\"Low-Stock-2\",\"VWAP-Stock-2\"]]\nop2 = dataset['Close-Stock-2']\ninp3 = dataset[[\"Open-Stock-3\",\"High-Stock-3\",\"Low-Stock-3\",\"VWAP-Stock-3\"]]\nop3 = dataset['Close-Stock-3']\ninp4 = dataset[[\"Open-Stock-4\",\"High-Stock-4\",\"Low-Stock-4\",\"VWAP-Stock-4\"]]\nop4 = dataset['Close-Stock-4']\ninp5 = dataset[[\"Open-Stock-5\",\"High-Stock-5\",\"Low-Stock-5\",\"VWAP-Stock-5\"]]\nop5 = dataset['Close-Stock-5']\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"n_folds = 5\n\ndef rmsle_cv(model):\n kf = KFold(n_folds, shuffle=True, random_state=42).get_n_splits(x_train.values)\n rmse= np.sqrt(-cross_val_score(model, x_train,y_train, scoring=\"neg_mean_squared_error\", cv = kf,n_jobs=-1))\n return(rmse)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x,y = inp5,op5\nx_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size = 0.2, random_state = 101)\n\nlasso = make_pipeline(RobustScaler(), Lasso(alpha =0.0005, random_state=1,normalize=True,max_iter=100000))\nENet = make_pipeline(RobustScaler(), ElasticNet(alpha=0.0005, l1_ratio=.99, random_state=3,max_iter=100000))\n\nscore = rmsle_cv(lasso)\nprint(\"\\nLasso score: {:.4f} ({:.4f})\\n\".format(score.mean(), score.std()))\nscore = rmsle_cv(ENet)\nprint(\"ElasticNet score: {:.4f} ({:.4f})\\n\".format(score.mean(), score.std()))\nl1 = make_pipeline(RobustScaler(),ElasticNet(alpha=0.000001, l1_ratio=0.5, random_state=3,max_iter=100000,selection='random'))\nscore = rmsle_cv(l1)\nprint(\"\\nUpdated-Enet score: {:.4f} ({:.4f})\\n\".format(score.mean(), score.std()))\nl2 = make_pipeline(StandardScaler(), Lasso(alpha =0.0001, random_state=1,normalize=True,max_iter=100000))\nscore = rmsle_cv(l2)\nprint(\"\\nUpdated-lasso score: {:.4f} ({:.4f})\\n\".format(score.mean(), score.std()))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"l3 = make_pipeline(RobustScaler(),ElasticNet(alpha=0.0000001, l1_ratio=0.000009, random_state=1,max_iter=1000000,selection='random',normalize=True))\nscore = rmsle_cv(l3)\nprint(\"\\nUpdated-Enet score: {:.4f} ({:.4f})\\n\".format(score.mean(), score.std()))\nl4 = make_pipeline(RobustScaler(),Lasso(alpha =0.0035, random_state=1,max_iter=10000000))\nscore = rmsle_cv(l4)\nprint(\"\\nUpdated-lasso score: {:.4f} ({:.4f})\\n\".format(score.mean(), score.std()))\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(rmsle_cv(Lasso(alpha =0.0035, random_state=1,max_iter=10000000)))",
"None\n"
],
[
"from sklearn.linear_model import SGDRegressor\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures\nl5 = make_pipeline(RobustScaler(),SGDRegressor(max_iter=1000000,alpha=0.000001))\nscore = rmsle_cv(l5)\nprint(\"\\nUpdated-lasso score: {:.4f} ({:.4f})\\n\".format(score.mean(), score.std()))",
"\nUpdated-lasso score: 1.7323 (0.5460)\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Prediction for Test data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dataset2 = pd.read_csv('/content/gdrive/MyDrive/Dockship/learn_ml_2021_grand_ai_challenge-dataset/new_test.csv')\n#dataset2.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model = l4\nmodel.fit(x_train, y_train)\npred = model.predict(dataset2[list(x.columns)])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"id_sv = dataset2['Date']\nsol = pd.DataFrame()\nsol['Date']=id_sv\n#sol[\"Close-Stock-1\"]=pred\n#sol.to_csv('sol.csv',index = False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sol['Close-Stock-5'] = pred",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#pred2 = pred\nsol['Close-Stock-1'] = sol['Close-Stock-1'].apply(lambda x:'%.2f'%x)\nsol['Close-Stock-2'] = sol['Close-Stock-2'].apply(lambda x:'%.2f'%x)\nsol['Close-Stock-3'] = sol['Close-Stock-3'].apply(lambda x:'%.2f'%x)\nsol['Close-Stock-4'] = sol['Close-Stock-4'].apply(lambda x:'%.2f'%x)\nsol['Close-Stock-5'] = sol['Close-Stock-5'].apply(lambda x:'%.2f'%x)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sol.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sol.to_csv('sol.csv',index = False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# LSTM",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#Create a new dataframe with only the 'Close column\ndata = dataset.filter(['Close-Stock-3'])\n#Convert the dataframe to a numpy array\ndataset_new = data.values\n#Get the number of rows to train the model on\ntraining_data_len = int(np.ceil( len(dataset_new) * .8 ))\n\ntraining_data_len",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Scale the data\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler\n\nscaler = StandardScaler()\nscaled_data = scaler.fit_transform(dataset_new)\n\n#scaled_data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Create the scaled training data set\ntrain_data = scaled_data[0:int(training_data_len), :]\n#Split the data into x_train and y_train data sets\nx_train = []\ny_train = []\n\nfor i in range(120, len(train_data)):\n x_train.append(train_data[i-120:i, 0])\n y_train.append(train_data[i, 0])\n if i<= 61:\n print(x_train)\n print(y_train)\n print()\n \n# Convert the x_train and y_train to numpy arrays \nx_train, y_train = np.array(x_train), np.array(y_train)\n\n#Reshape the data\nx_train = np.reshape(x_train, (x_train.shape[0], x_train.shape[1], 1))\n# x_train.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from keras.models import Sequential\nfrom keras.layers import Dense, LSTM,Dropout\n\n#Defining the LSTM Recurrent Model\n#Step 2 Build Model\nregressor = Sequential()\nregressor.add(LSTM(units = 50, return_sequences = True, input_shape = (x_train.shape[1], 1)))\nregressor.add(Dropout(0.2))\nregressor.add(LSTM(units = 50, return_sequences = True))\nregressor.add(Dropout(0.2))\nregressor.add(LSTM(units = 50, return_sequences = True))\nregressor.add(Dropout(0.2))\nregressor.add(LSTM(units = 50))\nregressor.add(Dropout(0.2))\nregressor.add(Dense(units = 1))\n\n\nregressor.compile(optimizer = 'rmsprop', loss = 'mean_squared_error')\nregressor.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs = 15, batch_size = 32)",
"Epoch 1/15\n4/4 [==============================] - 7s 218ms/step - loss: 0.2953\nEpoch 2/15\n4/4 [==============================] - 1s 219ms/step - loss: 0.2113\nEpoch 3/15\n4/4 [==============================] - 1s 223ms/step - loss: 0.1602\nEpoch 4/15\n4/4 [==============================] - 1s 217ms/step - loss: 0.1620\nEpoch 5/15\n4/4 [==============================] - 1s 219ms/step - loss: 0.1217\nEpoch 6/15\n4/4 [==============================] - 1s 217ms/step - loss: 0.1356\nEpoch 7/15\n4/4 [==============================] - 1s 220ms/step - loss: 0.1035\nEpoch 8/15\n4/4 [==============================] - 1s 215ms/step - loss: 0.0894\nEpoch 9/15\n4/4 [==============================] - 1s 222ms/step - loss: 0.1138\nEpoch 10/15\n4/4 [==============================] - 1s 217ms/step - loss: 0.1166\nEpoch 11/15\n4/4 [==============================] - 1s 216ms/step - loss: 0.0862\nEpoch 12/15\n4/4 [==============================] - 1s 220ms/step - loss: 0.0849\nEpoch 13/15\n4/4 [==============================] - 1s 253ms/step - loss: 0.1141\nEpoch 14/15\n4/4 [==============================] - 1s 260ms/step - loss: 0.0961\nEpoch 15/15\n4/4 [==============================] - 1s 322ms/step - loss: 0.0815\n"
],
[
"#Create the testing data set\n#Create a new array containing scaled values from index 1543 to 2002 \ntest_data = scaled_data[training_data_len - 120: , :]\n#Create the data sets x_test and y_test\nx_test = []\ny_test = dataset_new[training_data_len:, :]\nfor i in range(120, len(test_data)):\n x_test.append(test_data[i-120:i, 0])\n \n# Convert the data to a numpy array\nx_test = np.array(x_test)\n\n# Reshape the data\nx_test = np.reshape(x_test, (x_test.shape[0], x_test.shape[1], 1 ))\n\n# Get the models predicted price values \npredictions = regressor.predict(x_test)\npredictions = scaler.inverse_transform(predictions)\n\n# Get the root mean squared error (RMSE)\nrmse = np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(predictions, y_test))\nrmse",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Get the root mean squared error (RMSE)\nimport math\nrmse = math.sqrt(mean_squared_error(predictions, y_test))\nrmse",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Plot the data\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\ntrain = data[:training_data_len]\nvalid = data[training_data_len:]\nvalid['Predictions'] = predictions\n# Visualize the data\nplt.figure(figsize=(16,8))\nplt.title('Model')\nplt.xlabel('Date', fontsize=18)\nplt.ylabel('Close Price USD ($)', fontsize=18)\nplt.plot(train['Close-Stock-3'])\nplt.plot(valid[['Close-Stock-3', 'Predictions']])\nplt.legend(['Train', 'Val', 'Predictions'], loc='lower right')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Create the prediction data set\n#Create a new array containing scaled values \npred_data = scaled_data[len(scaled_data)-97 - 120: , :]\n#Create the data sets x_test and y_test\nx_pred = []\n#y_test = dataset_new[training_data_len:, :]\nfor i in range(120, len(pred_data)):\n x_pred.append(pred_data[i-120:i, 0])\n \n# Convert the data to a numpy array\nx_pred = np.array(x_pred)\n\n# Reshape the data\nx_pred = np.reshape(x_pred, (x_pred.shape[0], x_pred.shape[1], 1 ))\n\n# Get the models predicted price values \npredictions = model.predict(x_pred)\npredictions = scaler.inverse_transform(predictions)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"id_sv = dataset2['Date']\nsol = pd.DataFrame()\nsol['Date']=id_sv\nsol[\"Close-Stock-1\"]=predictions\n#sol.to_csv('sol.csv',index = False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sol[\"Close-Stock-5\"]=predictions",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sol.to_csv('sol.csv',index = False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# New Section",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dataset.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = dataset.iloc[:,[0,18]]\ndf['pred'] = lasso.predict(x)\ndf.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.corr()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x = dataset[[\"Open-Stock-3\",\"High-Stock-3\",\"Low-Stock-3\",\"VWAP-Stock-3\"]]\ny = dataset['Close-Stock-3']\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.neighbors import LocalOutlierFactor\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression\nfor i in range(1,6):\n x = dataset[[\"Open-Stock-\"+str(i),\"High-Stock-\"+str(i),\"Low-Stock-\"+str(i),\"VWAP-Stock-\"+str(i)]]\n #x = df\n y = dataset['Close-Stock-'+str(i)]\n x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x.values, y.values, test_size = 0.2, random_state = 101)\n lof = LocalOutlierFactor(n_neighbors=25,n_jobs=-1)\n yhat = lof.fit_predict(x_train)\n mask = yhat != -1\n x_train, y_train = x_train[mask, :], y_train[mask] \n lasso = Lasso(alpha =0.0005, random_state=1,normalize=True,max_iter=100000)\n lasso.fit(x,y)\n print(np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_test,lasso.predict(x_test))))\n sol['Close-Stock-'+str(i)] = lasso.predict(dataset2[list(x.columns)])",
"10.315221953200108\n1.1220376956066076\n17.709211358832636\n5.932154450678855\n8.409034759109726\n"
],
[
"x = dataset[[\"Open-Stock-3\",\"High-Stock-3\",\"Low-Stock-3\",\"VWAP-Stock-3\"]]\ny = dataset['Close-Stock-3']\nimport statsmodels.api as sm\n\nx_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x.values, y.values, test_size = 0.2, random_state = 101)\n\nX_train_lm = sm.add_constant(x_train)\n\nlr_1 = sm.OLS(y_train, X_train_lm).fit()\n\nlr_1.summary()\n#print(x_train.shape, y_train.shape)\n#lasso = Lasso(alpha =0.0005, random_state=1,normalize=True,max_iter=100000)\n#lasso.fit(x,y)\n#print(np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_test,lasso.predict(x_test))))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nplt.plot(y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sol.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a78b2e1107d6c29fe6f7f237d4ead237bfc7df2
| 133,358 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
assignments/assignment1/KNN.ipynb
|
DANTEpolaris/dlcourse_ai
|
66604c9c7182c46e5b38d3650410c69ce85d931a
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2019-04-05T17:48:15.000Z
|
2020-01-09T12:41:45.000Z
|
assignments/assignment1/KNN.ipynb
|
DANTEpolaris/dlcourse_ai
|
66604c9c7182c46e5b38d3650410c69ce85d931a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
assignments/assignment1/KNN.ipynb
|
DANTEpolaris/dlcourse_ai
|
66604c9c7182c46e5b38d3650410c69ce85d931a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 240.718412 | 115,592 | 0.91762 |
[
[
[
"# Задание 1.1 - Метод К-ближайших соседей (K-neariest neighbor classifier)\n\nВ первом задании вы реализуете один из простейших алгоритмов машинного обучения - классификатор на основе метода K-ближайших соседей.\nМы применим его к задачам\n- бинарной классификации (то есть, только двум классам)\n- многоклассовой классификации (то есть, нескольким классам)\n\nТак как методу необходим гиперпараметр (hyperparameter) - количество соседей, мы выберем его на основе кросс-валидации (cross-validation).\n\nНаша основная задача - научиться пользоваться numpy и представлять вычисления в векторном виде, а также ознакомиться с основными метриками, важными для задачи классификации.\n\nПеред выполнением задания:\n- запустите файл `download_data.sh`, чтобы скачать данные, которые мы будем использовать для тренировки\n- установите все необходимые библиотеки, запустив `pip install -r requirements.txt` (если раньше не работали с `pip`, вам сюда - https://pip.pypa.io/en/stable/quickstart/)\n\nЕсли вы раньше не работали с numpy, вам может помочь tutorial. Например этот: \nhttp://cs231n.github.io/python-numpy-tutorial/",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\n%matplotlib inline\n\n%load_ext autoreload\n%autoreload 2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from dataset import load_svhn\nfrom knn import KNN\nfrom metrics import binary_classification_metrics, multiclass_accuracy",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Загрузим и визуализируем данные\n\nВ задании уже дана функция `load_svhn`, загружающая данные с диска. Она возвращает данные для тренировки и для тестирования как numpy arrays.\n\nМы будем использовать цифры из датасета Street View House Numbers (SVHN, http://ufldl.stanford.edu/housenumbers/), чтобы решать задачу хоть сколько-нибудь сложнее MNIST.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"train_X, train_y, test_X, test_y = load_svhn(\"data\", max_train=1000, max_test=100)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"samples_per_class = 5 # Number of samples per class to visualize\nplot_index = 1\nfor example_index in range(samples_per_class):\n for class_index in range(10):\n plt.subplot(5, 10, plot_index)\n image = train_X[train_y == class_index][example_index]\n plt.imshow(image.astype(np.uint8))\n plt.axis('off')\n plot_index += 1",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Сначала реализуем KNN для бинарной классификации\n\nВ качестве задачи бинарной классификации мы натренируем модель, которая будет отличать цифру 0 от цифры 9.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# First, let's prepare the labels and the source data\n\n# Only select 0s and 9s\nbinary_train_mask = (train_y == 0) | (train_y == 9)\nbinary_train_X = train_X[binary_train_mask]\nbinary_train_y = train_y[binary_train_mask] == 0\n\nbinary_test_mask = (test_y == 0) | (test_y == 9)\nbinary_test_X = test_X[binary_test_mask]\nbinary_test_y = test_y[binary_test_mask] == 0\n\n# Reshape to 1-dimensional array [num_samples, 32*32*3]\nbinary_train_X = binary_train_X.reshape(binary_train_X.shape[0], -1)\nbinary_test_X = binary_test_X.reshape(binary_test_X.shape[0], -1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create the classifier and call fit to train the model\n# KNN just remembers all the data\nknn_classifier = KNN(k=1)\nknn_classifier.fit(binary_train_X, binary_train_y)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Пришло время написать код! \n\nПоследовательно реализуйте функции `compute_distances_two_loops`, `compute_distances_one_loop` и `compute_distances_no_loops`\nв файле `knn.py`.\n\nЭти функции строят массив расстояний между всеми векторами в тестовом наборе и в тренировочном наборе. \nВ результате они должны построить массив размера `(num_test, num_train)`, где координата `[i][j]` соотвествует расстоянию между i-м вектором в test (`test[i]`) и j-м вектором в train (`train[j]`).\n\n**Обратите внимание** Для простоты реализации мы будем использовать в качестве расстояния меру L1 (ее еще называют [Manhattan distance](https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/%D0%A0%D0%B0%D1%81%D1%81%D1%82%D0%BE%D1%8F%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%B5_%D0%B3%D0%BE%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B4%D1%81%D0%BA%D0%B8%D1%85_%D0%BA%D0%B2%D0%B0%D1%80%D1%82%D0%B0%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%B2)).\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# TODO: implement compute_distances_two_loops in knn.py\ndists = knn_classifier.compute_distances_two_loops(binary_test_X)\nassert np.isclose(dists[0, 10], np.sum(np.abs(binary_test_X[0] - binary_train_X[10])))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# TODO: implement compute_distances_one_loop in knn.py\ndists = knn_classifier.compute_distances_one_loop(binary_test_X)\nassert np.isclose(dists[0, 10], np.sum(np.abs(binary_test_X[0] - binary_train_X[10])))\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# TODO: implement compute_distances_no_loops in knn.py\ndists = knn_classifier.compute_distances_no_loops(binary_test_X)\nassert np.isclose(dists[0, 10], np.sum(np.abs(binary_test_X[0] - binary_train_X[10])))\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Lets look at the performance difference\n%timeit knn_classifier.compute_distances_two_loops(binary_test_X)\n%timeit knn_classifier.compute_distances_one_loop(binary_test_X)\n%timeit knn_classifier.compute_distances_no_loops(binary_test_X)",
"14.2 ms ± 81.4 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100 loops each)\n21.9 ms ± 1.33 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10 loops each)\n21.2 ms ± 146 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10 loops each)\n"
],
[
"# TODO: implement predict_labels_binary in knn.py\nprediction = knn_classifier.predict(binary_test_X)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# TODO: implement binary_classification_metrics in metrics.py\nprecision, recall, f1, accuracy = binary_classification_metrics(prediction, binary_test_y)\nprint(\"KNN with k = %s\" % knn_classifier.k)\nprint(\"Accuracy: %4.2f, Precision: %4.2f, Recall: %4.2f, F1: %4.2f\" % (accuracy, precision, recall, f1)) ",
"KNN with k = 1\nAccuracy: 0.56, Precision: 0.73, Recall: 0.67, F1: 0.70\n"
],
[
"# Let's put everything together and run KNN with k=3 and see how we do\nknn_classifier_3 = KNN(k=3)\nknn_classifier_3.fit(binary_train_X, binary_train_y)\nprediction = knn_classifier_3.predict(binary_test_X)\n\nprecision, recall, f1, accuracy = binary_classification_metrics(prediction, binary_test_y)\nprint(\"KNN with k = %s\" % knn_classifier_3.k)\nprint(\"Accuracy: %4.2f, Precision: %4.2f, Recall: %4.2f, F1: %4.2f\" % (accuracy, precision, recall, f1)) ",
"KNN with k = 3\nAccuracy: 0.56, Precision: 0.73, Recall: 0.67, F1: 0.70\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Кросс-валидация (cross-validation)\n\nПопробуем найти лучшее значение параметра k для алгоритма KNN! \n\nДля этого мы воспользуемся k-fold cross-validation (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cross-validation_(statistics)#k-fold_cross-validation). Мы разделим тренировочные данные на 5 фолдов (folds), и по очереди будем использовать каждый из них в качестве проверочных данных (validation data), а остальные -- в качестве тренировочных (training data).\n\nВ качестве финальной оценки эффективности k мы усредним значения F1 score на всех фолдах.\nПосле этого мы просто выберем значение k с лучшим значением метрики.\n\n*Бонус*: есть ли другие варианты агрегировать F1 score по всем фолдам? Напишите плюсы и минусы в клетке ниже.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Find the best k using cross-validation based on F1 score\nnum_folds = 5\ntrain_folds_X = []\ntrain_folds_y = []\n\n# TODO: split the training data in 5 folds and store them in train_folds_X/train_folds_y\ntrain_indexes = range(0, binary_train_X.shape[0])\ntest_size = np.floor_divide(binary_train_X.shape[0], num_folds)\n\nk_choices = [1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 10, 15, 20, 25, 50]\nk_to_f1 = {} # dict mapping k values to mean F1 scores (int -> float)\n\nfor k in k_choices:\n # TODO: perform cross-validation\n # Go through every fold and use it for testing and all other folds for training\n # Perform training and produce F1 score metric on the validation dataset\n # Average F1 from all the folds and write it into k_to_f1\n f1_arr = []\n \n for i_fold in range(num_folds):\n #split indexes \n if (i_fold == 0):\n test_slice, remainder = np.split(train_indexes, [test_size], axis=0)\n else:\n remainder[(i_fold-1)*test_size:i_fold*test_size], test_slice = test_slice, remainder[(i_fold-1)*test_size:i_fold*test_size].copy()\n \n # Reshape to 1-dimensional array [num_samples, 32*32*3]\n train_folds_X = binary_train_X[remainder]\n train_folds_y = binary_train_y[remainder]\n validation_folds_X = binary_train_X[test_slice]\n validation_folds_y = binary_train_y[test_slice]\n \n # train & predict\n knn_classifier = KNN(k=k)\n knn_classifier.fit(train_folds_X, train_folds_y)\n prediction = knn_classifier.predict(validation_folds_X)\n\n precision, recall, f1, accuracy = binary_classification_metrics(prediction, validation_folds_y)\n #print(precision, recall, f1, accuracy) \n \n f1_arr = np.append(f1_arr, f1)\n\n k_to_f1[k] = np.mean(f1_arr)\n\nprint('----')\nfor k in sorted(k_to_f1):\n print('k = %d, f1 = %f' % (k, k_to_f1[k]))",
"----\nk = 1, f1 = 0.673180\nk = 2, f1 = 0.533228\nk = 3, f1 = 0.683108\nk = 5, f1 = 0.611453\nk = 8, f1 = 0.580125\nk = 10, f1 = 0.620342\nk = 15, f1 = 0.632905\nk = 20, f1 = 0.651463\nk = 25, f1 = 0.647727\nk = 50, f1 = 0.626737\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Проверим, как хорошо работает лучшее значение k на тестовых данных (test data)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# TODO Set the best k to the best value found by cross-validation\nbest_k = 1\n\nbest_knn_classifier = KNN(k=best_k)\nbest_knn_classifier.fit(binary_train_X, binary_train_y)\nprediction = best_knn_classifier.predict(binary_test_X)\n\nprecision, recall, f1, accuracy = binary_classification_metrics(prediction, binary_test_y)\nprint(\"Best KNN with k = %s\" % best_k)\nprint(\"Accuracy: %4.2f, Precision: %4.2f, Recall: %4.2f, F1: %4.2f\" % (accuracy, precision, recall, f1)) ",
"Best KNN with k = 1\nAccuracy: 0.56, Precision: 0.73, Recall: 0.67, F1: 0.70\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Многоклассовая классификация (multi-class classification)\n\nПереходим к следующему этапу - классификации на каждую цифру.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Now let's use all 10 classes\ntrain_X = train_X.reshape(train_X.shape[0], -1)\ntest_X = test_X.reshape(test_X.shape[0], -1)\n\nknn_classifier = KNN(k=1)\nknn_classifier.fit(train_X, train_y)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# TODO: Implement predict_labels_multiclass\npredict = knn_classifier.predict(test_X)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# TODO: Implement multiclass_accuracy\naccuracy = multiclass_accuracy(predict, test_y)\nprint(\"Accuracy: %4.2f\" % accuracy)",
"Accuracy: 0.21\n"
]
],
[
[
"Снова кросс-валидация. Теперь нашей основной метрикой стала точность (accuracy), и ее мы тоже будем усреднять по всем фолдам.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Find the best k using cross-validation based on accuracy\nnum_folds = 5\ntrain_folds_X = []\ntrain_folds_y = []\n\n# TODO: split the training data in 5 folds and store them in train_folds_X/train_folds_y\n\nk_choices = [1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 10, 15, 20, 25, 50]\nk_to_accuracy = {}\n\nfor k in k_choices:\n # TODO: perform cross-validation\n # Go through every fold and use it for testing and all other folds for validation\n # Perform training and produce accuracy metric on the validation dataset\n # Average accuracy from all the folds and write it into k_to_accuracy\n pass\n\nfor k in sorted(k_to_accuracy):\n print('k = %d, accuracy = %f' % (k, k_to_accuracy[k]))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Финальный тест - классификация на 10 классов на тестовой выборке (test data)\n\nЕсли все реализовано правильно, вы должны увидеть точность не менее **0.2**.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# TODO Set the best k as a best from computed\nbest_k = 1\n\nbest_knn_classifier = KNN(k=best_k)\nbest_knn_classifier.fit(train_X, train_y)\nprediction = best_knn_classifier.predict(test_X)\n\n# Accuracy should be around 20%!\naccuracy = multiclass_accuracy(prediction, test_y)\nprint(\"Accuracy: %4.2f\" % accuracy)",
"Accuracy: 0.21\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a78bee63d61804ff2303ebe74d7cca1e534dcbf
| 1,029 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
examples/reference/pandas/step.ipynb
|
ppwadhwa/hvplot
|
35481575ed16e40e82f5768e0bf096163b65ffc9
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 338 |
2019-11-13T17:17:23.000Z
|
2022-03-30T13:28:54.000Z
|
examples/reference/pandas/step.ipynb
|
ppwadhwa/hvplot
|
35481575ed16e40e82f5768e0bf096163b65ffc9
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 368 |
2019-11-13T15:43:50.000Z
|
2022-03-31T17:06:06.000Z
|
examples/reference/pandas/step.ipynb
|
ppwadhwa/hvplot
|
35481575ed16e40e82f5768e0bf096163b65ffc9
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 55 |
2019-12-01T17:17:14.000Z
|
2022-03-30T13:53:40.000Z
| 21 | 118 | 0.546161 |
[
[
[
"import hvplot.pandas # noqa",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"`step` can be used pretty much anytime line might be used and has many of the same options available. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from bokeh.sampledata.degrees import data as deg\ndeg.sample(n=5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"deg.hvplot.step(x='Year', y=['Art and Performance', 'Business', 'Biology', 'Education', 'Computer Science'], \n value_label='% of Degrees Earned by Women', legend='top', height=500, width=620)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a78c00de7948e26478819f51436172accac0641
| 21,017 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Chapter02/Chapter 2 - Implementing a single-layer neural network.ipynb
|
ShubhInfotech-Bhilai/PythonDeep-Learning
|
2183de8a1c8a050a07e2cb8e8dab01bacbd237f2
|
[
"MIT"
] | 143 |
2017-10-27T22:39:27.000Z
|
2022-02-10T19:05:07.000Z
|
Chapter02/Chapter 2 - Implementing a single-layer neural network.ipynb
|
ShubhInfotech-Bhilai/PythonDeep-Learning
|
2183de8a1c8a050a07e2cb8e8dab01bacbd237f2
|
[
"MIT"
] | 7 |
2017-12-31T18:26:59.000Z
|
2020-12-01T19:48:08.000Z
|
Chapter02/Chapter 2 - Implementing a single-layer neural network.ipynb
|
ShubhInfotech-Bhilai/PythonDeep-Learning
|
2183de8a1c8a050a07e2cb8e8dab01bacbd237f2
|
[
"MIT"
] | 110 |
2017-10-27T05:33:48.000Z
|
2022-01-21T13:54:43.000Z
| 106.146465 | 15,418 | 0.842175 |
[
[
[
"import numpy as np \nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n# We will be using make_circles from scikit-learn\nfrom sklearn.datasets import make_circles\n\nSEED = 2017",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# We create an inner and outer circle\nX, y = make_circles(n_samples=400, factor=.3, noise=.05, random_state=2017)\nouter = y == 0\ninner = y == 1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.title(\"Two Circles\")\nplt.plot(X[outer, 0], X[outer, 1], \"ro\")\nplt.plot(X[inner, 0], X[inner, 1], \"bo\")\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X = X+1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=SEED)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def sigmoid(x):\n return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"n_hidden = 50 # number of hidden units\nn_epochs = 1000\nlearning_rate = 1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Initialise weights\nweights_hidden = np.random.normal(0.0, size=(X_train.shape[1], n_hidden))\nweights_output = np.random.normal(0.0, size=(n_hidden))\n\nhist_loss = []\nhist_accuracy = []",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for e in range(n_epochs):\n del_w_hidden = np.zeros(weights_hidden.shape)\n del_w_output = np.zeros(weights_output.shape)\n\n # Loop through training data in batches of 1\n for x_, y_ in zip(X_train, y_train):\n # Forward computations\n hidden_input = np.dot(x_, weights_hidden)\n hidden_output = sigmoid(hidden_input)\n output = sigmoid(np.dot(hidden_output, weights_output))\n\n # Backward computations\n error = y_ - output\n output_error = error * output * (1 - output)\n hidden_error = np.dot(output_error, weights_output) * hidden_output * (1 - hidden_output)\n del_w_output += output_error * hidden_output\n del_w_hidden += hidden_error * x_[:, None]\n\n # Update weights\n weights_hidden += learning_rate * del_w_hidden / X_train.shape[0]\n weights_output += learning_rate * del_w_output / X_train.shape[0]\n\n # Print stats (validation loss and accuracy)\n if e % 100 == 0:\n hidden_output = sigmoid(np.dot(X_val, weights_hidden))\n out = sigmoid(np.dot(hidden_output, weights_output))\n loss = np.mean((out - y_val) ** 2)\n # Final prediction is based on a threshold of 0.5\n predictions = out > 0.5\n accuracy = np.mean(predictions == y_val)\n print(\"Epoch: \", '{:>4}'.format(e), \n \"; Validation loss: \", '{:>6}'.format(loss.round(4)), \n \"; Validation accuracy: \", '{:>6}'.format(accuracy.round(4)))",
"Epoch: 0 ; Validation loss: 0.2532 ; Validation accuracy: 0.65\nEpoch: 100 ; Validation loss: 0.207 ; Validation accuracy: 0.75\nEpoch: 200 ; Validation loss: 0.1707 ; Validation accuracy: 0.8\nEpoch: 300 ; Validation loss: 0.1428 ; Validation accuracy: 0.825\nEpoch: 400 ; Validation loss: 0.1211 ; Validation accuracy: 0.8625\nEpoch: 500 ; Validation loss: 0.1043 ; Validation accuracy: 0.9125\nEpoch: 600 ; Validation loss: 0.0914 ; Validation accuracy: 0.925\nEpoch: 700 ; Validation loss: 0.0813 ; Validation accuracy: 0.95\nEpoch: 800 ; Validation loss: 0.0733 ; Validation accuracy: 0.9875\nEpoch: 900 ; Validation loss: 0.0669 ; Validation accuracy: 1.0\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a78c4c6056f545542b596471930caeb78f22756
| 19,292 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
10_Missing_Values/1_Imputation_Pandas/4_Detecting_NaN/1_How_to_detect_other_than_NaN.ipynb
|
sureshmecad/Pandas
|
128091e7021158f39eb0ff97e0e63d76e778a52c
|
[
"CNRI-Python"
] | null | null | null |
10_Missing_Values/1_Imputation_Pandas/4_Detecting_NaN/1_How_to_detect_other_than_NaN.ipynb
|
sureshmecad/Pandas
|
128091e7021158f39eb0ff97e0e63d76e778a52c
|
[
"CNRI-Python"
] | null | null | null |
10_Missing_Values/1_Imputation_Pandas/4_Detecting_NaN/1_How_to_detect_other_than_NaN.ipynb
|
sureshmecad/Pandas
|
128091e7021158f39eb0ff97e0e63d76e778a52c
|
[
"CNRI-Python"
] | null | null | null | 27.918958 | 108 | 0.338327 |
[
[
[
"https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GBZTd6NXHrE",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# PANDAS detects only NaN's\n\n# How to detect other than NaN's",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<img src=\"NaN.JPG\" height=\"700\" width=\"600\" align=\"left\" />",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"url = \"C:/Users/deepusuresh/Documents/Data Science/10. Missing Values\"\n\ndf = pd.read_csv('NaN_missing values.csv')\ndf",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.isnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(df['ST_NUM'].isnull())",
"0 False\n1 False\n2 True\n3 False\n4 False\n5 False\n6 True\n7 False\n8 False\nName: ST_NUM, dtype: bool\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### blank cell ----> Recognised as NaN\n#### n/a & NA ----> Recognised as NaN\n#### na ----> Not Recognised as NaN",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(df['NUM_BEDROOMS'].isnull())",
"0 False\n1 False\n2 True\n3 False\n4 False\n5 True\n6 False\n7 False\n8 False\nName: NUM_BEDROOMS, dtype: bool\n"
],
[
"missing_value = [\"n/a\",\"na\",\"--\"]\ndf = pd.read_csv('NaN_missing values.csv', na_values=missing_value)\ndf",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.isnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(df['OWN_OCCUPIED'].isnull())",
"0 False\n1 False\n2 False\n3 False\n4 False\n5 False\n6 True\n7 False\n8 False\nName: OWN_OCCUPIED, dtype: bool\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### OWN_OCCUPIED -----> text column; but one cell have value of 12 (may be by mistake entered)\n#### Need to follow below code to replace \"12\" by \"NaN\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"count = 0\nfor row in df['OWN_OCCUPIED']:\n try:\n int(row)\n df.loc[count,'OWN_OCCUPIED'] = np.nan\n except ValueError:\n pass\n count+=1 ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"raw",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"raw"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a78c8ce18fe1ec2baeb1fa88eb9597a5194dd5e
| 58,822 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
doc/example_usage.ipynb
|
maximskorik/RIAssigner
|
6ac249298859290c1ffa209258102cf1e4ca065c
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2021-04-20T12:44:15.000Z
|
2021-06-29T14:24:57.000Z
|
doc/example_usage.ipynb
|
maximskorik/RIAssigner
|
6ac249298859290c1ffa209258102cf1e4ca065c
|
[
"MIT"
] | 53 |
2021-04-09T14:09:41.000Z
|
2022-03-10T08:24:16.000Z
|
doc/example_usage.ipynb
|
maximskorik/RIAssigner
|
6ac249298859290c1ffa209258102cf1e4ca065c
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2021-04-09T14:06:05.000Z
|
2021-07-15T10:18:29.000Z
| 54.213825 | 206 | 0.610775 |
[
[
[
"from RIAssigner.compute import Kovats\nfrom RIAssigner.data import MatchMSData, PandasData\n\n# Load test data and init computation method\nquery = PandasData(\"../tests/data/csv/aplcms_aligned_peaks.csv\", \"csv\", rt_unit=\"seconds\")\nreference = MatchMSData(\"../tests/data/msp/Alkanes_20210325.msp\", \"msp\", rt_unit=\"min\")\nmethod = Kovats()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Compute and print retention indices\r\nretention_indices = method.compute(query, reference)\r\nretention_indices",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Write modified data back to disk\r\nquery.retention_indices = retention_indices\r\nquery.write(\"peaks_with_rt.csv\")",
"C:\\Users\\473355\\Miniconda3\\envs\\riassigner-dev\\lib\\site-packages\\pandas\\core\\dtypes\\cast.py:1638: UnitStrippedWarning: The unit of the quantity is stripped when downcasting to ndarray.\n result[:] = values\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a78d0834cd0f2571d871e5444da4ebc2f2fd489
| 259,506 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
VQC_NEW.ipynb
|
Gitter39/Quantum_dissertation
|
00c0b88c59a5db11eb0a145dffd3cb51a972ffbf
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
VQC_NEW.ipynb
|
Gitter39/Quantum_dissertation
|
00c0b88c59a5db11eb0a145dffd3cb51a972ffbf
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
VQC_NEW.ipynb
|
Gitter39/Quantum_dissertation
|
00c0b88c59a5db11eb0a145dffd3cb51a972ffbf
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 507.83953 | 48,248 | 0.943038 |
[
[
[
"This notebook was created to convert the original VQC notebook to follow the routines of the new Qiskit version.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import logging\nimport numpy as np\nfrom sklearn.metrics import f1_score\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nplt.style.use('dark_background')\n\nimport qiskit\nfrom qiskit import IBMQ, Aer, QuantumCircuit\nfrom qiskit.circuit import ParameterVector\nfrom qiskit.providers.aer import AerSimulator\nfrom qiskit.providers.aer.noise import NoiseModel\nfrom qiskit.utils import QuantumInstance\nfrom qiskit.circuit.library import TwoLocal, ZZFeatureMap\nfrom qiskit.algorithms.optimizers import COBYLA, L_BFGS_B\n\nfrom qiskit_machine_learning.algorithms.classifiers import VQC, NeuralNetworkClassifier\nfrom qiskit_machine_learning.neural_networks import CircuitQNN\nfrom qiskit_machine_learning.datasets import breast_cancer\n\n# provider = IBMQ.load_account() # Load account to use cloud-simulator.\nfrom IPython.display import clear_output",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Load data. PCA reduced to four dimensions.\nXtrain, Ytrain, Xtest, Ytest = breast_cancer(training_size=4,\n test_size=40, n = 4, plot_data=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# We create the feature map and ansatz to be used.\nfeature_map = ZZFeatureMap(4, reps=2, \n entanglement=\"linear\") # Our data is two dimensional, hence, two qubits.\n\nparameters = ParameterVector('θ', 16)\nansatz = QuantumCircuit(4)\nfor i in range(4):\n ansatz.ry(parameters[i], i)\n \nansatz.crx(parameters[4], 3, 0)\nansatz.crx(parameters[5], 2, 3)\nansatz.crx(parameters[6], 1, 2)\nansatz.crx(parameters[7], 0, 1)\nansatz.barrier()\n\nfor ii in range(8,12):\n ansatz.ry(parameters[ii], ii-8)\n\nansatz.crx(parameters[12], 3, 2)\nansatz.crx(parameters[13], 0, 3)\nansatz.crx(parameters[14], 1, 0)\nansatz.crx(parameters[15], 2, 1)\n\ntotal = feature_map.compose(ansatz)\ntotal.draw(output='mpl', filename=\"full_expressive_circuit.png\")\n# ansatz.draw(output='mpl', filename='circ14.png')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# # Build a noisy simulator\n# quantum_backend = provider.get_backend(\"ibmq_manila\")\n# # Generate a noise model based of a real quantum computer.\n# noise_model = NoiseModel.from_backend(quantum_backend)\n# # Get coupling map from backend\n# coupling_map = quantum_backend.configuration().coupling_map\n# # Get basis gates from noise model\n# basis_gates = noise_model.basis_gates\n\n# cloud_simulator = provider.get_backend('simulator_statevector') # Use cloud-basesd-simulator.\n\n# quantum_instance = QuantumInstance(backend=simulator, coupling_map=coupling_map, \n# basis_gates=basis_gates, noise_model=noise_model)\n\n# Noiseless simulator.\nquantum_instance = Aer.get_backend(\"aer_simulator\")\n\n# Quantum computer\n# quantum_instance = QuantumInstance(quantum_backend)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# callback function that draws a live plot when the .fit() method is called\ndef callback_graph(weights, obj_func_eval):\n clear_output(wait=True)\n objective_func_vals.append(obj_func_eval)\n plt.title(\"Objective function value against iteration\")\n plt.xlabel(\"Iteration\")\n plt.ylabel(\"Objective function value\")\n plt.plot(range(len(objective_func_vals)), objective_func_vals)\n plt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create our VQC instance.\nvqc = VQC(feature_map=feature_map,\n ansatz=ansatz,\n loss='cross_entropy',\n optimizer=COBYLA(),\n quantum_instance=quantum_instance,\n callback=callback_graph)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# create empty list for callback to store evaluations of the objective function\nobjective_func_vals = []\nplt.rcParams[\"figure.figsize\"] = (12, 6)\n\n# fit classifier to data\nvqc.fit(Xtrain, Ytrain)\n\n# return to default figsize\nplt.rcParams[\"figure.figsize\"] = (6, 4)\n\n# score classifier\n# vqc.score(Xtest, Ytest)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# with open('barren_model.npy', 'wb') as f:\n# np.save(f, np.array(objective_func_vals))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"with open('barren_model.npy', 'rb') as f:\n qc_expressive_results = np.load(f)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# plt.rcdefaults()\nwith plt.style.context('seaborn-colorblind'):\n plt.title(\"Convergence with an expressive ansatz on a QC\")\n plt.xlabel(\"Epochs\")\n plt.ylabel(\"Loss\")\n plt.plot(range(len(qc_expressive_results)), qc_expressive_results)\n plt.xticks(range(0,len(qc_expressive_results),2))\n# plt.savefig(\"qc_expressive.png\", dpi=200)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def reverse_one_hot(x):\n return x[:,0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# predictions = vqc.predict(Xtest)\n\nf1_score(reverse_one_hot(Ytest), reverse_one_hot(predictions))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"0.46153846153846156 F1 score for expressive setup executed on quantum computer.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Cross entropy loss, COBYLA and circuit 14 from Sim et al. gives a score of 0.6 :(.\n# 0.675 with cross entropy loss and AQGD and the same circuit as the first example. BOTH ENDED UP\n# IN A BARREN PLATEAU!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We also perform a simulated run to see what we can expect without noise.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"with plt.style.context('seaborn-colorblind'):\n plt.title(\"Convergence with an expressive ansatz on an ideal simulator\")\n plt.xlabel(\"Epochs\")\n plt.ylabel(\"Loss\")\n plt.plot(range(len(objective_func_vals)), objective_func_vals, label=\"Ideal Simulator\")\n plt.plot(range(len(qc_expressive_results)), qc_expressive_results, '--', label=\"QC\")\n plt.xticks(range(0,len(qc_expressive_results),2))\n plt.legend()\n# plt.savefig(\"expressive_comparison.png\", dpi=200)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"predictions = vqc.predict(Xtest)\nf1_score(reverse_one_hot(Ytest), reverse_one_hot(predictions))\n# 0.6410256410256411 f1 score with ideal simulator.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Since we ended up in a barren plateau, we will now try much simpler conditions to see whether we can escape it. We now run the simple circuit for many qubtits to show that we get better results but also the variance in the gradient drops as we increase the number of qubits.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"all_loss_values = [] # Store loss values for each iteration.\nf1_scores = [] # Store respective f1 score for each iteration.\n\nfor i in range(2,10,2):\n objective_func_vals = [] # Callback function expects a list with this name.\n # Scale dimension and data size with ratio defined in paper.\n Xtrain, Ytrain, Xtest, Ytest = breast_cancer(training_size=i,\n test_size=40, n = i, one_hot=True)\n # Redefine circuit to match larger dimension size.\n feature_map = ZZFeatureMap(feature_dimension=i, reps=2, entanglement='linear')\n ansatz = TwoLocal(num_qubits=i, rotation_blocks='ry', entanglement_blocks='cx', \n entanglement='linear', reps=2)\n # Define our vqc.\n vqc = VQC(feature_map=feature_map,\n ansatz=ansatz,\n loss='cross_entropy',\n optimizer=L_BFGS_B(),\n quantum_instance=quantum_instance,\n callback=callback_graph)\n \n vqc.fit(Xtrain, Ytrain)\n \n predicitons = vqc.predict(Xtest) \n \n all_loss_values.append(objective_func_vals)\n f1_scores.append(f1_score(reverse_one_hot(Ytest), reverse_one_hot(predicitons)))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"epochs = range(0,21,2)\nlabels = range(2,10,2)\n\nwith plt.style.context('seaborn-colorblind'):\n plt.title(\"Convergence with an expressive ansatz on an ideal simulator\")\n plt.xlabel(\"Epochs\")\n plt.ylabel(\"Loss\")\n \n for i in range(len(all_loss_values)):\n plt.plot(range(len(all_loss_values[i])), all_loss_values[i],\n label=\"{} qubits\".format(labels[i]))\n \n plt.xticks(range(0,len(all_loss_values[-1]),2)) # last run was the longest.\n plt.yticks(range(0,17,2))\n plt.legend()\n# plt.savefig(\"vanishing_loss.png\", dpi=200)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"[0.6486486486486486,\n 0.5555555555555556,\n 0.5238095238095238,\n 0.5569620253164557] F1 scores for the above evaluations.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"0.7 score with zzfeaturemap, reps=2, and TwoLocal with ry and cx blocks with reps=2 also. Could be a noise induced barren-plateau. Going to try reps=1 now. Better now, 0.725 but have that loss issue so can't see what is happening. Actually seems to be working, possibly, going to try without noise now. See: https://quantumcomputing.stackexchange.com/questions/15166/callback-function-in-vqe-do-not-return-the-intermediate-values-of-the-parameters for what was attempted to check if its working. We saw that print matched final list. Without noise 0.5 for reps=1. 0.725 with reps=2.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Random test with 2 and 4 qubits with reps=1, for simple configuration returns better results for 2 qubit. Worse for 4 qubits and reps=2. Same performance for 2 qubits.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# For dissertaion.\nqc = QuantumCircuit(2)\nparameters = ParameterVector('θ', 4)\nqc.ry(parameters[0], 0)\nqc.ry(parameters[1], 1)\nqc.cx(0,1)\nqc.ry(parameters[2], 0)\nqc.ry(parameters[3], 1)\n\nqc.draw(output='mpl', scale=2, filename='simplecirc.png')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a78d78a1965fd11ecdf93ecd5d9c3d67638d3d6
| 56,324 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
PSO-function maximum.ipynb
|
AndyRay1998/Bio-inspired-AI
|
c01e620f7cc6c582031b5f0eeaee56049aa1d52d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
PSO-function maximum.ipynb
|
AndyRay1998/Bio-inspired-AI
|
c01e620f7cc6c582031b5f0eeaee56049aa1d52d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
PSO-function maximum.ipynb
|
AndyRay1998/Bio-inspired-AI
|
c01e620f7cc6c582031b5f0eeaee56049aa1d52d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 190.283784 | 15,248 | 0.914903 |
[
[
[
"Find maximal value of a single-parameter function",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport random\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def obj_func(x):\n return - x ** 4 + 2 * x + 3",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def update_best(val, x_max_his, x):\n # update val\n val = obj_func(x)\n \n # global max\n maxindex = np.argmax(val)\n max_x = x[maxindex]\n \n # local max\n for i in range(len(val)):\n if(obj_func(x_max_his[i]) < val[i]):\n x_max_his[i] = x[i]\n \n return max_x, x_max_his, val",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# initialization",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"num_par = 100\nmax_x = 50\nmin_x = -50\nx = np.random.uniform(min_x, max_x, size=(num_par))\nv = np.zeros(num_par)\nx_max_his = np.zeros((num_par))\nval = obj_func(x)\nw = 0.8\nc1 = 2\nc2 = 2\nmax_x, x_max_his, val = update_best(val, x_max_his, x)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# main ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"if __name__ == '__main__':\n fittest = []\n for j in range(100):\n for i in range(len(val)):\n v[i] = w * v[i] + c1 * random.random() * (x_max_his[i] - x[i]) + c2 * random.random() * (max_x - x[i])\n x[i] += v[i]\n max_x, x_max_his, val = update_best(val, x_max_his, x)\n # print(x, v)\n # print(np.mean(x))\n fittest.append(obj_func(max_x))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.plot(fittest)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.plot(x)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.max(val)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.plot(val)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"result = [obj_func(x/10) for x in np.arange(-50,50,0.1)]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.plot(result)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a78f344f1879f4e0d1ef54213672669b70603f7
| 2,386 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/Pipeline.ipynb
|
BeautyOfWeb/OPP_Analysis
|
59b2dbc91e07fc14b3a130bff6fadaa19cd36b42
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/Pipeline.ipynb
|
BeautyOfWeb/OPP_Analysis
|
59b2dbc91e07fc14b3a130bff6fadaa19cd36b42
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/Pipeline.ipynb
|
BeautyOfWeb/OPP_Analysis
|
59b2dbc91e07fc14b3a130bff6fadaa19cd36b42
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 25.934783 | 139 | 0.571668 |
[
[
[
"import sys, warnings\npkg_path = '/home/jupyter/code'\nif pkg_path not in sys.path:\n sys.path.append(pkg_path)\nwarnings.filterwarnings(\"ignore\")\n\nimport torch\n\nfrom optical_electrophysiology import entire_pipeline\n\nuse_gpu = True\nif use_gpu and torch.cuda.is_available():\n device = torch.device('cuda')\nelse:\n device = torch.device('cpu')\n \n%load_ext autoreload\n%autoreload 2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"bucket = 'gs://broad-opp-voltage/2020-07-23_VoltageMovies_SCDN011'\nbin_files = ['153316_1992_NR_d4inf_freezethaw_D32_FOV1']\nresult_folder = 'results4'\nentire_pipeline(bucket, result_folder=result_folder, \n bin_files=bin_files, \n delete_local_data=True, \n apply_spectral_clustering=True, spectral_soft_threshold=True, spectral_cor_threshold=None,\n denoise=False, denoise_model_config=None, denoise_loss_threshold=0, denoise_num_epochs=10, denoise_num_iters=500, \n display=False, verbose=False, half_precision=False, device=device)",
"Process 153316_1992_NR_d4inf_freezethaw_D32_FOV1\nTime spent: 162.0614573955536\n"
],
[
"torch.cuda.empty_cache()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a790f0e91d53816603906a49b9fff534101865a
| 25,796 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
asgjove/asg1/Asg1_Q10_hints.ipynb
|
Thanhson89/JA
|
baa32b5964a3d8f30badae35486b7281ab2fed04
|
[
"Unlicense"
] | null | null | null |
asgjove/asg1/Asg1_Q10_hints.ipynb
|
Thanhson89/JA
|
baa32b5964a3d8f30badae35486b7281ab2fed04
|
[
"Unlicense"
] | null | null | null |
asgjove/asg1/Asg1_Q10_hints.ipynb
|
Thanhson89/JA
|
baa32b5964a3d8f30badae35486b7281ab2fed04
|
[
"Unlicense"
] | null | null | null | 30.276995 | 175 | 0.483951 |
[
[
[
"*Hints on Solving Asg1's Q10*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import sys\nsys.path[0:0] = ['../..','../../3rdparty'] # Put these at the head of the search path\n\nfrom jove.DotBashers import *\nfrom jove.Def_md2mc import *\nfrom jove.Def_DFA import *\nfrom jove.LangDef import *",
"You may use any of these help commands:\nhelp(ResetStNum)\nhelp(NxtStateStr)\n\nYou may use any of these help commands:\nhelp(md2mc)\n.. and if you want to dig more, then ..\nhelp(default_line_attr)\nhelp(length_ok_input_items)\nhelp(union_line_attr_list_fld)\nhelp(extend_rsltdict)\nhelp(form_delta)\nhelp(get_machine_components)\n\nYou may use any of these help commands:\nhelp(mkp_dfa)\nhelp(mk_dfa)\nhelp(totalize_dfa)\nhelp(addtosigma_delta)\nhelp(step_dfa)\nhelp(run_dfa)\nhelp(accepts_dfa)\nhelp(comp_dfa)\nhelp(union_dfa)\nhelp(intersect_dfa)\nhelp(pruneUnreach)\nhelp(iso_dfa)\nhelp(langeq_dfa)\nhelp(same_status)\nhelp(h_langeq_dfa)\nhelp(fixptDist)\nhelp(min_dfa)\nhelp(pairFR)\nhelp(state_combos)\nhelp(sepFinNonFin)\nhelp(bash_eql_classes)\nhelp(listminus)\nhelp(bash_1)\nhelp(mk_rep_eqc)\nhelp(F_of)\nhelp(rep_of_s)\nhelp(q0_of)\nhelp(Delta_of)\nhelp(mk_state_eqc_name)\n\nYou may use any of these help commands:\nhelp(lphi)\nhelp(lunit)\nhelp(lcat)\nhelp(lexp)\nhelp(lunion)\nhelp(lstar)\nhelp(srev)\nhelp(lrev)\nhelp(shomo)\nhelp(lhomo)\nhelp(powset)\nhelp(lint)\nhelp(lsymdiff)\nhelp(lminus)\nhelp(lissubset)\nhelp(lissuperset)\nhelp(lcomplem)\nhelp(product)\nhelp(nthnumeric)\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"*Problem-1*\n\nDesign a DFA with alphabet {0,1} such that\n\n* it accepts all even length strings",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Accept even-length strings over {0,1}\n\nDEven = md2mc('''\nDFA !! IMPORTANT: this is required to tell the markdown converter \n !! the expected machine type\n\nIF: 0|1 -> S\nS : 0|1 -> IF\n''')\n\n#..use the right dotObj command of the DFA with the right FuseEdges boolean value..\ndotObj_dfa(DEven, FuseEdges=True)",
"Generating LALR tables\n"
],
[
"DEven",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*Show it accepts only the requested strings*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"help(accepts_dfa)",
"Help on function accepts_dfa in module jove.Def_DFA:\n\naccepts_dfa(D, s)\n In : D (consistent DFA)\n s (string over D's sigma, including \"\")\n Out: Boolean (if state after s-run is in D's final).\n\n"
],
[
"TestStrs = lstar({'0','1'}, 6)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"TestStrs",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Test the DFA\n\n# ..Write some Python code that prints the strings the DFA accepts..\n# ..End this printout with a statement saying \"All other strings are rejected\"..\n\nfor w in TestStrs:\n if accepts_dfa(DEven, w):\n print(w, \" is accepted\")\nprint(\"All other strings rejected\")",
" is accepted\n000011 is accepted\n100000 is accepted\n101101 is accepted\n000111 is accepted\n001101 is accepted\n1000 is accepted\n11 is accepted\n111001 is accepted\n110111 is accepted\n111111 is accepted\n001100 is accepted\n01 is accepted\n10 is accepted\n0000 is accepted\n011001 is accepted\n000110 is accepted\n011110 is accepted\n101110 is accepted\n101111 is accepted\n101010 is accepted\n111010 is accepted\n011011 is accepted\n1010 is accepted\n000101 is accepted\n010010 is accepted\n0101 is accepted\n011100 is accepted\n000100 is accepted\n1101 is accepted\n000010 is accepted\n100100 is accepted\n111101 is accepted\n110100 is accepted\n001001 is accepted\n010110 is accepted\n100001 is accepted\n100011 is accepted\n0011 is accepted\n100101 is accepted\n000000 is accepted\n001010 is accepted\n101000 is accepted\n001000 is accepted\n111000 is accepted\n0001 is accepted\n110110 is accepted\n010001 is accepted\n110001 is accepted\n011101 is accepted\n111110 is accepted\n101011 is accepted\n1011 is accepted\n010111 is accepted\n0010 is accepted\n110011 is accepted\n011000 is accepted\n010100 is accepted\n100111 is accepted\n001011 is accepted\n110101 is accepted\n110010 is accepted\n001111 is accepted\n0111 is accepted\n010000 is accepted\n011010 is accepted\n001110 is accepted\n010011 is accepted\n1001 is accepted\n010101 is accepted\n101100 is accepted\n000001 is accepted\n100110 is accepted\n00 is accepted\n111011 is accepted\n1111 is accepted\n0110 is accepted\n011111 is accepted\n111100 is accepted\n1110 is accepted\n1100 is accepted\n0100 is accepted\n100010 is accepted\n110000 is accepted\n101001 is accepted\nAll other strings rejected\n"
]
],
[
[
"*Let us do another exercise*",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\nDesign a DFA with alphabet {0,1} such that\n\n* it accepts all odd-length strings which begin with a 1\n* it rejects all other strings",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"*Solution outline*:\n\nDescribe your solution in a few sentences. This helps you form your design\nstrategy. Then you can incrementally code-up and test the machine.\n\n* I will call my machine D1Odd to signify that it is a DFA for strings that are odd in length when starting with a 1.\n* All other cases are separately handled:\n - starting with a 0 \n * reject\n - starting with a 1, but even length\n * reject",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Odd len when starting with 1\n# Reject all others\n\nD1Odd = md2mc('''\nDFA !! IMPORTANT: this is required to tell the markdown converter \n !! the expected machine type\n\nI : 1 -> F\nF : 0|1 -> B\nB : 0|1 -> F\nI : 0 -> BH\nBH: 0|1 -> BH\n''')\n\n#..use the right dotObj command of the DFA with the right FuseEdges boolean value..\ndotObj_dfa_w_bh(D1Odd, FuseEdges=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Test the DFA\n\n# ..Write some Python code that prints the strings the DFA accepts..\n# ..End this printout with a statement saying \"All other strings are rejected\"..\n\nfor w in TestStrs:\n if accepts_dfa(D1Odd, w):\n print(w, \" is accepted\")\nprint(\"All other strings rejected\")",
"11000 is accepted\n10011 is accepted\n101 is accepted\n11011 is accepted\n10000 is accepted\n11110 is accepted\n10010 is accepted\n111 is accepted\n10111 is accepted\n11100 is accepted\n10110 is accepted\n10100 is accepted\n1 is accepted\n11001 is accepted\n10101 is accepted\n100 is accepted\n11010 is accepted\n10001 is accepted\n11111 is accepted\n110 is accepted\n11101 is accepted\nAll other strings rejected\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4a792205791bd23001fa92d292f4542cb76bfe2a
| 24,822 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
examples/Paper_v1.0/gt_and_use_case.ipynb
|
nicolahunfeld/CLMM
|
a431649713e56b907a7366bdf21693c30851dee7
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 20 |
2018-02-23T22:28:39.000Z
|
2022-03-24T07:03:47.000Z
|
examples/Paper_v1.0/gt_and_use_case.ipynb
|
nicolahunfeld/CLMM
|
a431649713e56b907a7366bdf21693c30851dee7
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 446 |
2018-06-01T17:43:41.000Z
|
2022-03-31T13:29:23.000Z
|
examples/Paper_v1.0/gt_and_use_case.ipynb
|
nicolahunfeld/CLMM
|
a431649713e56b907a7366bdf21693c30851dee7
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 20 |
2019-01-18T08:16:11.000Z
|
2022-03-29T05:27:00.000Z
| 37.27027 | 346 | 0.572718 |
[
[
[
"# API demonstration for paper of v1.0\n\n_the LSST-DESC CLMM team_\n\n\nHere we demonstrate how to use `clmm` to estimate a WL halo mass from observations of a galaxy cluster when source galaxies follow a given distribution (The LSST DESC Science Requirements Document - arXiv:1809.01669, implemented in `clmm`). It uses several functionalities of the support `mock_data` module to produce mock datasets.\n\n- Setting things up, with the proper imports.\n- Computing the binned reduced tangential shear profile, for the 2 datasets, using logarithmic binning.\n- Setting up a model accounting for the redshift distribution.\n- Perform a simple fit using `scipy.optimize.curve_fit` included in `clmm` and visualize the results.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Setup",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"First, we import some standard packages.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\nplt.rcParams['font.family'] = ['gothambook','gotham','gotham-book','serif']",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Generating mock data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"`clmm` has a support code to generate a mock catalog given a input cosmology and cluster parameters. We will use this to generate a data sample to be used in this example:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from clmm import Cosmology\nimport clmm.support.mock_data as mock",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.random.seed(14) # For reproducibility\n\n# Set cosmology of mock data\ncosmo = Cosmology(H0=70.0, Omega_dm0=0.27-0.045, Omega_b0=0.045, Omega_k0=0.0)\n\n# Cluster info\ncluster_m = 1.e15 # Cluster mass - ($M200_m$) [Msun]\nconcentration = 4 # Cluster concentration\ncluster_z = 0.3 # Cluster redshift\ncluster_ra = 0. # Cluster Ra in deg\ncluster_dec = 0. # Cluster Dec in deg\n\n# Catalog info\nfield_size = 10 # i.e. 10 x 10 Mpc field at the cluster redshift, cluster in the center\n\n# Make mock galaxies\nmock_galaxies = mock.generate_galaxy_catalog(\n cluster_m=cluster_m, cluster_z=cluster_z, cluster_c=concentration, # Cluster data\n cosmo=cosmo, # Cosmology object\n zsrc='desc_srd', # Galaxy redshift distribution, \n zsrc_min=0.4, # Minimum redshift of the galaxies\n shapenoise=0.05, # Gaussian shape noise to the galaxy shapes\n photoz_sigma_unscaled=0.05, # Photo-z errors to source redshifts\n field_size=field_size,\n ngal_density=20 # number of gal/arcmin2 for z in [0, infty]\n)['ra', 'dec', 'e1', 'e2', 'z', 'ztrue', 'pzbins', 'pzpdf', 'id']\nprint(f'Catalog table with the columns: {\", \".join(mock_galaxies.colnames)}')\n\nngals_init = len(mock_galaxies)\nprint(f'Initial number of galaxies: {ngals_init:,}')\n\n# Keeping only galaxies with \"measured\" redshift greater than cluster redshift\nmock_galaxies = mock_galaxies[(mock_galaxies['z']>cluster_z)]\nngals_good = len(mock_galaxies)\n\nif ngals_good < ngals_init:\n print(f'Number of excluded galaxies (with photoz < cluster_z): {ngals_init-ngals_good:,}')\n # reset galaxy id for later use\n mock_galaxies['id'] = np.arange(ngals_good)\n\n# Check final density\nfrom clmm.utils import convert_units\nfield_size_arcmin = convert_units(field_size, 'Mpc', 'arcmin', redshift=cluster_z, cosmo=cosmo)\nprint(f'Background galaxy density = {ngals_good/field_size_arcmin**2:.2f} gal/arcmin2\\n')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can extract the column of this mock catalog to show explicitely how the quantities can be used on `clmm` functionality and how to add them to a `GalaxyCluster` object: ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Put galaxy values on arrays\ngal_ra = mock_galaxies['ra'] # Galaxies Ra in deg\ngal_dec = mock_galaxies['dec'] # Galaxies Dec in deg\ngal_e1 = mock_galaxies['e1'] # Galaxies elipticipy 1\ngal_e2 = mock_galaxies['e2'] # Galaxies elipticipy 2\ngal_z = mock_galaxies['z'] # Galaxies observed redshift\ngal_ztrue = mock_galaxies['ztrue'] # Galaxies true redshift\ngal_pzbins = mock_galaxies['pzbins'] # Galaxies P(z) bins \ngal_pzpdf = mock_galaxies['pzpdf'] # Galaxies P(z)\ngal_id = mock_galaxies['id'] # Galaxies ID",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Measuring shear profiles ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"From the source galaxy quantities, we can compute the elepticities and corresponding radial profile usimg `clmm.dataops` functions:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import clmm.dataops as da",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Convert elipticities into shears\ngal_ang_dist, gal_gt, gal_gx = da.compute_tangential_and_cross_components(cluster_ra, cluster_dec,\n gal_ra, gal_dec,\n gal_e1, gal_e2,\n geometry=\"flat\")\n\n# Measure profile\nprofile = da.make_radial_profile([gal_gt, gal_gx, gal_z],\n gal_ang_dist, \"radians\", \"Mpc\",\n bins=da.make_bins(0.01, field_size/2., 50),\n cosmo=cosmo,\n z_lens=cluster_z,\n include_empty_bins=False)\nprint(f'Profile table has columns: {\", \".join(profile.colnames)},')\nprint('where p_(0, 1, 2) = (gt, gx, z)')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The other possibility is to use the `GalaxyCluster` object. This is the main approach to handle data with `clmm`, and also the simpler way. For that you just have to provide the following information of the cluster:\n\n* Ra, Dec [deg]\n* Mass - ($M200_m$) [Msun]\n* Concentration\n* Redshift\n\n\nand the source galaxies:\n\n* Ra, Dec [deg]\n* 2 axis of eliptticities\n* Redshift\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import clmm",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create a GCData with the galaxies\ngalaxies = clmm.GCData([gal_ra, gal_dec, gal_e1, gal_e2, gal_z,\n gal_ztrue, gal_pzbins, gal_pzpdf, gal_id],\n names=['ra', 'dec', 'e1', 'e2', 'z',\n 'ztrue', 'pzbins', 'pzpdf', 'id'])\n\n# Create a GalaxyCluster\ncluster = clmm.GalaxyCluster(\"Name of cluster\", cluster_ra, cluster_dec,\n cluster_z, mock_galaxies)\n\n# Convert elipticities into shears for the members\ncluster.compute_tangential_and_cross_components(geometry=\"flat\")\nprint(cluster.galcat.colnames)\n\n# Measure profile and add profile table to the cluster\nseps = convert_units(cluster.galcat['theta'], 'radians', 'mpc',cluster.z, cosmo)\n\ncluster.make_radial_profile(bins=da.make_bins(0.1, field_size/2., 25, method='evenlog10width'),\n bin_units=\"Mpc\",\n cosmo=cosmo,\n include_empty_bins=False,\n gal_ids_in_bins=True,\n )\nprint(cluster.profile.colnames)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This results in an attribute `table` added to the `cluster` object.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from paper_formating import prep_plot\nprep_plot(figsize=(9, 9))\nerrorbar_kwargs = dict(linestyle='', marker='o',\n markersize=1, elinewidth=.5, capthick=.5)\nplt.errorbar(cluster.profile['radius'], cluster.profile['gt'],\n cluster.profile['gt_err'], c='k', **errorbar_kwargs)\nplt.xlabel('r [Mpc]', fontsize = 10)\nplt.ylabel(r'$g_t$', fontsize = 10)\nplt.xscale('log')\nplt.yscale('log')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Theoretical predictions\n\nWe consider 3 models:\n1. One model where all sources are considered at the same redshift\n2. One model using the overall source redshift distribution to predict the reduced tangential shear\n3. A more accurate model, relying on the fact that we have access to the individual redshifts of the sources, where the average reduced tangential shear is averaged independently in each bin, accounting for the acutal population of sources in each bin.\n\nAll models rely on `clmm.predict_reduced_tangential_shear` to make a prediction that accounts for the redshift distribution of the galaxies in each radial bin:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Model considering all sources located at the average redshift\n\\begin{equation}\n g_{t,i}^{\\rm{avg(z)}} = g_t(R_i, \\langle z \\rangle)\\;,\n \\label{eq:wrong_gt_model}\n \\end{equation} ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def predict_reduced_tangential_shear_mean_z(profile, logm):\n return clmm.compute_reduced_tangential_shear(\n r_proj=profile['radius'], # Radial component of the profile\n mdelta=10**logm, # Mass of the cluster [M_sun]\n cdelta=4, # Concentration of the cluster\n z_cluster=cluster_z, # Redshift of the cluster\n z_source=np.mean(cluster.galcat['z']), # Mean value of source galaxies redshift\n cosmo=cosmo,\n delta_mdef=200,\n halo_profile_model='nfw'\n )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Model relying on the overall redshift distribution of the sources N(z), not using individual redshift information (eq. (6) from Applegate et al. 2014, MNRAS, 439, 48) \n\\begin{equation}\n g_{t,i}^{N(z)} = \\frac{\\langle\\beta_s\\rangle \\gamma_t(R_i, z\\rightarrow\\infty)}{1-\\frac{\\langle\\beta_s^2\\rangle}{\\langle\\beta_s\\rangle}\\kappa(R_i, z\\rightarrow\\infty)}\n \\label{eq:approx_model}\n \\end{equation}",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"z_inf = 1000\ndl_inf = cosmo.eval_da_z1z2(cluster_z, z_inf)\nd_inf = cosmo.eval_da(z_inf)\n\ndef betas(z):\n dls = cosmo.eval_da_z1z2(cluster_z, z)\n ds = cosmo.eval_da(z)\n return dls * d_inf / (ds * dl_inf)\n\ndef predict_reduced_tangential_shear_approx(profile, logm):\n\n bs_mean = np.mean(betas(cluster.galcat['z'])) \n bs2_mean = np.mean(betas(cluster.galcat['z'])**2)\n\n gamma_t_inf = clmm.compute_tangential_shear(\n r_proj=profile['radius'], # Radial component of the profile\n mdelta=10**logm, # Mass of the cluster [M_sun]\n cdelta=4, # Concentration of the cluster\n z_cluster=cluster_z, # Redshift of the cluster\n z_source=z_inf, # Redshift value at infinity\n cosmo=cosmo,\n delta_mdef=200,\n halo_profile_model='nfw')\n convergence_inf = clmm.compute_convergence(\n r_proj=profile['radius'], # Radial component of the profile\n mdelta=10**logm, # Mass of the cluster [M_sun]\n cdelta=4, # Concentration of the cluster\n z_cluster=cluster_z, # Redshift of the cluster\n z_source=z_inf, # Redshift value at infinity\n cosmo=cosmo,\n delta_mdef=200,\n halo_profile_model='nfw')\n \n return bs_mean*gamma_t_inf/(1-(bs2_mean/bs_mean)*convergence_inf) ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Model using individual redshift and radial information, to compute the averaged shear in each radial bin, based on the galaxies actually present in that bin.\n\\begin{equation}\n g_{t,i}^{z, R} = \\frac{1}{N_i}\\sum_{{\\rm gal\\,}j\\in {\\rm bin\\,}i} g_t(R_j, z_j)\n \\label{eq:exact_model}\n \\end{equation}",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cluster.galcat['theta_mpc'] = convert_units(cluster.galcat['theta'], 'radians', 'mpc',cluster.z, cosmo)\n\ndef predict_reduced_tangential_shear_exact(profile, logm):\n return np.array([np.mean(\n clmm.compute_reduced_tangential_shear(\n # Radial component of each source galaxy inside the radial bin\n r_proj=cluster.galcat[radial_bin['gal_id']]['theta_mpc'],\n mdelta=10**logm, # Mass of the cluster [M_sun]\n cdelta=4, # Concentration of the cluster\n z_cluster=cluster_z, # Redshift of the cluster\n # Redshift value of each source galaxy inside the radial bin\n z_source=cluster.galcat[radial_bin['gal_id']]['z'],\n cosmo=cosmo,\n delta_mdef=200,\n halo_profile_model='nfw'\n )) for radial_bin in profile])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Mass fitting",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We estimate the best-fit mass using `scipy.optimize.curve_fit`. The choice of fitting $\\log M$ instead of $M$ lowers the range of pre-defined fitting bounds from several order of magnitude for the mass to unity. From the associated error $\\sigma_{\\log M}$ we calculate the error to mass as $\\sigma_M = M_{fit}\\ln(10)\\sigma_{\\log M}$.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### First, identify bins with sufficient galaxy statistics to be kept for the fit\nFor small samples, error bars should not be computed using the simple error on the mean approach available so far in CLMM)\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mask_for_fit = cluster.profile['n_src'] > 5\ndata_for_fit = cluster.profile[mask_for_fit]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Perform the fits\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from clmm.support.sampler import fitters\ndef fit_mass(predict_function):\n popt, pcov = fitters['curve_fit'](predict_function,\n data_for_fit, \n data_for_fit['gt'], \n data_for_fit['gt_err'], bounds=[10.,17.])\n logm, logm_err = popt[0], np.sqrt(pcov[0][0])\n return {'logm':logm, 'logm_err':logm_err,\n 'm': 10**logm, 'm_err': (10**logm)*logm_err*np.log(10)}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fit_mean_z = fit_mass(predict_reduced_tangential_shear_mean_z)\nfit_approx = fit_mass(predict_reduced_tangential_shear_approx)\nfit_exact = fit_mass(predict_reduced_tangential_shear_exact)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(f'Input mass = {cluster_m:.2e} Msun\\n')\n\nprint(f'Best fit mass for average redshift = {fit_mean_z[\"m\"]:.3e} +/- {fit_mean_z[\"m_err\"]:.3e} Msun')\nprint(f'Best fit mass for N(z) model = {fit_approx[\"m\"]:.3e} +/- {fit_approx[\"m_err\"]:.3e} Msun')\nprint(f'Best fit mass for individual redshift and radius = {fit_exact[\"m\"]:.3e} +/- {fit_exact[\"m_err\"]:.3e} Msun')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"As expected, the reconstructed mass is biased when the redshift distribution is not accounted for in the model",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Visualization of the results",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"For visualization purpose, we calculate the reduced tangential shear predicted by the model with estimated masses for noisy and ideal data.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def get_predicted_shear(predict_function, fit_values):\n gt_est = predict_function(data_for_fit, fit_values['logm'])\n gt_est_err = [predict_function(data_for_fit, fit_values['logm']+i*fit_values['logm_err'])\n for i in (-3, 3)]\n return gt_est, gt_est_err",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"gt_mean_z, gt_err_mean_z = get_predicted_shear(predict_reduced_tangential_shear_mean_z, fit_mean_z)\ngt_approx, gt_err_approx = get_predicted_shear(predict_reduced_tangential_shear_approx, fit_approx)\ngt_exact, gt_err_exact = get_predicted_shear(predict_reduced_tangential_shear_exact, fit_exact)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Check reduced chi2 values of the best-fit model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"chi2_mean_z_dof = np.sum((gt_mean_z-data_for_fit['gt'])**2/(data_for_fit['gt_err'])**2)/(len(data_for_fit)-1)\nchi2_approx_dof = np.sum((gt_approx-data_for_fit['gt'])**2/(data_for_fit['gt_err'])**2)/(len(data_for_fit)-1)\nchi2_exact_dof = np.sum((gt_exact-data_for_fit['gt'])**2/(data_for_fit['gt_err'])**2)/(len(data_for_fit)-1)\n\nprint(f'Reduced chi2 (mean z model) = {chi2_mean_z_dof}')\nprint(f'Reduced chi2 (N(z) model) = {chi2_approx_dof}')\nprint(f'Reduced chi2 (individual (R,z) model) = {chi2_exact_dof}')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We compare to tangential shear obtained with theoretical mass. We plot the reduced tangential shear models first when redshift distribution is accounted for in the model then for the naive approach, with respective best-fit masses.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from matplotlib.ticker import MultipleLocator\nprep_plot(figsize=(9 , 9))\ngt_ax = plt.axes([.25, .42, .7, .55])\ngt_ax.errorbar(data_for_fit['radius'],data_for_fit['gt'], data_for_fit['gt_err'],\n c='k', label=rf'$M_{{input}} = {cluster_m*1e-15}\\times10^{{{15}}} M_\\odot$',\n **errorbar_kwargs)\n\n# Points in grey have not been used for the fit\ngt_ax.errorbar(cluster.profile['radius'][~mask_for_fit], cluster.profile['gt'][~mask_for_fit],\n cluster.profile['gt_err'][~mask_for_fit], \n c='grey',**errorbar_kwargs)\n\npow10 = 15\nmlabel = lambda name, fits: fr'$M_{{fit}}^{{{name}}} = {fits[\"m\"]/10**pow10:.3f}\\pm{fits[\"m_err\"]/10**pow10:.3f}\\times 10^{{{pow10}}} M_\\odot$'\n# Avg z\ngt_ax.loglog(data_for_fit['radius'], gt_mean_z,'-C0', \n label=mlabel('avg(z)', fit_mean_z),lw=.5)\ngt_ax.fill_between(data_for_fit['radius'], *gt_err_mean_z, lw=0, color='C0', alpha=.2)\n# Approx model\ngt_ax.loglog(data_for_fit['radius'], gt_approx,'-C1', \n label=mlabel('N(z)', fit_approx),\n lw=.5)\ngt_ax.fill_between(data_for_fit['radius'], *gt_err_approx, lw=0, color='C1', alpha=.2)\n# Exact model\ngt_ax.loglog(data_for_fit['radius'], gt_exact,'-C2', \n label=mlabel('z,R', fit_exact),\n lw=.5)\ngt_ax.fill_between(data_for_fit['radius'], *gt_err_exact, lw=0, color='C2', alpha=.2)\n\n\ngt_ax.set_ylabel(r'$g_t$', fontsize = 8)\ngt_ax.legend(fontsize=6)\ngt_ax.set_xticklabels([])\ngt_ax.tick_params('x', labelsize=8)\ngt_ax.tick_params('y', labelsize=8)\n\n#gt_ax.set_yscale('log')\nerrorbar_kwargs2 = {k:v for k, v in errorbar_kwargs.items() if 'marker' not in k}\nerrorbar_kwargs2['markersize'] = 3\nerrorbar_kwargs2['markeredgewidth'] = .5\nres_ax = plt.axes([.25, .2, .7, .2])\ndelta = (cluster.profile['radius'][1]/cluster.profile['radius'][0])**.25\nres_err = data_for_fit['gt_err']/data_for_fit['gt']\nres_ax.errorbar(data_for_fit['radius']/delta, gt_mean_z/data_for_fit['gt']-1,\n yerr=res_err, marker='.', c='C0', **errorbar_kwargs2)\nerrorbar_kwargs2['markersize'] = 1.5\nres_ax.errorbar(data_for_fit['radius'], gt_approx/data_for_fit['gt']-1,\n yerr=res_err, marker='s', c='C1', **errorbar_kwargs2)\nerrorbar_kwargs2['markersize'] = 3\nerrorbar_kwargs2['markeredgewidth'] = .5\nres_ax.errorbar(data_for_fit['radius']*delta, gt_exact/data_for_fit['gt']-1,\n yerr=res_err, marker='*', c='C2', **errorbar_kwargs2)\nres_ax.set_xlabel(r'$R$ [Mpc]', fontsize = 8)\n\nres_ax.set_ylabel(r'$g_t^{mod.}/g_t^{data}-1$', fontsize = 8)\nres_ax.set_xscale('log')\nres_ax.set_xlim(gt_ax.get_xlim())\nres_ax.set_ylim(-0.65,0.65)\nres_ax.yaxis.set_minor_locator(MultipleLocator(.1))\n\nres_ax.tick_params('x', labelsize=8)\nres_ax.tick_params('y', labelsize=8)\n\nfor p in (gt_ax, res_ax):\n p.xaxis.grid(True, which='major', lw=.5)\n p.yaxis.grid(True, which='major', lw=.5)\n p.xaxis.grid(True, which='minor', lw=.1)\n p.yaxis.grid(True, which='minor', lw=.1)\n\nplt.savefig('r_gt.png')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4a792d4512ce336f9284f1630763dc2f3aa87a47
| 19,596 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
dev/32_text_models_awdlstm.ipynb
|
dejanbatanjac/fastai_dev
|
a923fa0d148513e0bc77aa269bf678df69a4e2dd
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
dev/32_text_models_awdlstm.ipynb
|
dejanbatanjac/fastai_dev
|
a923fa0d148513e0bc77aa269bf678df69a4e2dd
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
dev/32_text_models_awdlstm.ipynb
|
dejanbatanjac/fastai_dev
|
a923fa0d148513e0bc77aa269bf678df69a4e2dd
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 36.288889 | 358 | 0.565575 |
[
[
[
"#export\nfrom local.torch_basics import *\nfrom local.test import *\nfrom local.core import *\nfrom local.layers import *\nfrom local.data.all import *\nfrom local.text.core import *\nfrom local.notebook.showdoc import show_doc",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#default_exp text.models.awdlstm\n#default_cls_lvl 3",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# AWD-LSTM\n\n> AWD LSTM from [Smerity et al.](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1708.02182.pdf) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Basic NLP modules",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"On top of the pytorch or the fastai [`layers`](/layers.html#layers), the language models use some custom layers specific to NLP.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#export\ndef dropout_mask(x, sz, p):\n \"Return a dropout mask of the same type as `x`, size `sz`, with probability `p` to cancel an element.\"\n return x.new(*sz).bernoulli_(1-p).div_(1-p)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"t = dropout_mask(torch.randn(3,4), [4,3], 0.25)\ntest_eq(t.shape, [4,3])\nassert ((t == 4/3) + (t==0)).all()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#export\nclass RNNDropout(Module):\n \"Dropout with probability `p` that is consistent on the seq_len dimension.\"\n def __init__(self, p=0.5): self.p=p\n\n def forward(self, x):\n if not self.training or self.p == 0.: return x\n return x * dropout_mask(x.data, (x.size(0), 1, x.size(2)), self.p)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dp = RNNDropout(0.3)\ntst_inp = torch.randn(4,3,7)\ntst_out = dp(tst_inp)\nfor i in range(4):\n for j in range(7):\n if tst_out[i,0,j] == 0: assert (tst_out[i,:,j] == 0).all()\n else: test_close(tst_out[i,:,j], tst_inp[i,:,j]/(1-0.3))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#export\nimport warnings",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#export\nclass WeightDropout(Module):\n \"A module that warps another layer in which some weights will be replaced by 0 during training.\"\n\n def __init__(self, module, weight_p, layer_names='weight_hh_l0'):\n self.module,self.weight_p,self.layer_names = module,weight_p,L(layer_names)\n for layer in self.layer_names:\n #Makes a copy of the weights of the selected layers.\n w = getattr(self.module, layer)\n self.register_parameter(f'{layer}_raw', nn.Parameter(w.data))\n self.module._parameters[layer] = F.dropout(w, p=self.weight_p, training=False)\n\n def _setweights(self):\n \"Apply dropout to the raw weights.\"\n for layer in self.layer_names:\n raw_w = getattr(self, f'{layer}_raw')\n self.module._parameters[layer] = F.dropout(raw_w, p=self.weight_p, training=self.training)\n\n def forward(self, *args):\n self._setweights()\n with warnings.catch_warnings():\n #To avoid the warning that comes because the weights aren't flattened.\n warnings.simplefilter(\"ignore\")\n return self.module.forward(*args)\n\n def reset(self):\n for layer in self.layer_names:\n raw_w = getattr(self, f'{layer}_raw')\n self.module._parameters[layer] = F.dropout(raw_w, p=self.weight_p, training=False)\n if hasattr(self.module, 'reset'): self.module.reset()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"module = nn.LSTM(5,7).cuda()\ndp_module = WeightDropout(module, 0.4)\nwgts = getattr(dp_module.module, 'weight_hh_l0')\ntst_inp = torch.randn(10,20,5).cuda()\nh = torch.zeros(1,20,7).cuda(), torch.zeros(1,20,7).cuda()\nx,h = dp_module(tst_inp,h)\nnew_wgts = getattr(dp_module.module, 'weight_hh_l0')\ntest_eq(wgts, getattr(dp_module, 'weight_hh_l0_raw'))\nassert 0.2 <= (new_wgts==0).sum().float()/new_wgts.numel() <= 0.6",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#export\nclass EmbeddingDropout(Module):\n \"Apply dropout with probabily `embed_p` to an embedding layer `emb`.\"\n\n def __init__(self, emb, embed_p):\n self.emb,self.embed_p = emb,embed_p\n\n def forward(self, words, scale=None):\n if self.training and self.embed_p != 0:\n size = (self.emb.weight.size(0),1)\n mask = dropout_mask(self.emb.weight.data, size, self.embed_p)\n masked_embed = self.emb.weight * mask\n else: masked_embed = self.emb.weight\n if scale: masked_embed.mul_(scale)\n return F.embedding(words, masked_embed, ifnone(self.emb.padding_idx, -1), self.emb.max_norm,\n self.emb.norm_type, self.emb.scale_grad_by_freq, self.emb.sparse)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"enc = nn.Embedding(10, 7, padding_idx=1)\nenc_dp = EmbeddingDropout(enc, 0.5)\ntst_inp = torch.randint(0,10,(8,))\ntst_out = enc_dp(tst_inp)\nfor i in range(8):\n assert (tst_out[i]==0).all() or torch.allclose(tst_out[i], 2*enc.weight[tst_inp[i]])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#export\nfrom torch.nn.utils.rnn import pack_padded_sequence, pad_packed_sequence",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#export\nclass AWD_LSTM(Module):\n \"AWD-LSTM inspired by https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.02182\"\n initrange=0.1\n\n def __init__(self, vocab_sz, emb_sz, n_hid, n_layers, pad_token=1, hidden_p=0.2, input_p=0.6, embed_p=0.1,\n weight_p=0.5, bidir=False, packed=False):\n store_attr(self, 'emb_sz,n_hid,n_layers,pad_token,packed')\n self.bs = 1\n self.n_dir = 2 if bidir else 1\n self.encoder = nn.Embedding(vocab_sz, emb_sz, padding_idx=pad_token)\n self.encoder_dp = EmbeddingDropout(self.encoder, embed_p)\n self.rnns = nn.ModuleList([self._one_rnn(emb_sz if l == 0 else n_hid, (n_hid if l != n_layers - 1 else emb_sz)//self.n_dir,\n bidir, weight_p, l) for l in range(n_layers)])\n self.encoder.weight.data.uniform_(-self.initrange, self.initrange)\n self.input_dp = RNNDropout(input_p)\n self.hidden_dps = nn.ModuleList([RNNDropout(hidden_p) for l in range(n_layers)])\n\n def forward(self, inp, from_embeds=False):\n bs,sl = inp.shape[:2] if from_embeds else inp.shape\n if bs!=self.bs:\n self.bs=bs\n self.reset()\n if self.packed: inp,lens = self._pack_sequence(inp, sl)\n \n raw_output = self.input_dp(inp if from_embeds else self.encoder_dp(inp))\n new_hidden,raw_outputs,outputs = [],[],[]\n for l, (rnn,hid_dp) in enumerate(zip(self.rnns, self.hidden_dps)):\n if self.packed: raw_output = pack_padded_sequence(raw_output, lens, batch_first=True)\n raw_output, new_h = rnn(raw_output, self.hidden[l])\n if self.packed: raw_output = pad_packed_sequence(raw_output, batch_first=True)[0]\n new_hidden.append(new_h)\n raw_outputs.append(raw_output)\n if l != self.n_layers - 1: raw_output = hid_dp(raw_output)\n outputs.append(raw_output)\n self.hidden = to_detach(new_hidden, cpu=False)\n return raw_outputs, outputs\n\n def _one_rnn(self, n_in, n_out, bidir, weight_p, l):\n \"Return one of the inner rnn\"\n rnn = nn.LSTM(n_in, n_out, 1, batch_first=True, bidirectional=bidir)\n return WeightDropout(rnn, weight_p)\n\n def _one_hidden(self, l):\n \"Return one hidden state\"\n nh = (self.n_hid if l != self.n_layers - 1 else self.emb_sz) // self.n_dir\n return (one_param(self).new_zeros(self.n_dir, self.bs, nh), one_param(self).new_zeros(self.n_dir, self.bs, nh))\n\n def reset(self):\n \"Reset the hidden states\"\n [r.reset() for r in self.rnns if hasattr(r, 'reset')]\n self.hidden = [self._one_hidden(l) for l in range(self.n_layers)]\n \n def _pack_sequence(self, inp, sl):\n mask = (inp == self.pad_token)\n lens = sl - mask.long().sum(1)\n n_empty = (lens == 0).sum()\n if n_empty > 0:\n inp,lens = inp[:-n_empty],lens[:-n_empty]\n self.hidden = [(h[0][:,:inp.size(0)], h[1][:,:inp.size(0)]) for h in self.hidden]\n return (inp,lens)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This is the core of an AWD-LSTM model, with embeddings from `vocab_sz` and `emb_sz`, `n_layers` LSTMs potentialy `bidir` stacked, the first one going from `emb_sz` to `n_hid`, the last one from `n_hid` to `emb_sz` and all the inner ones from `n_hid` to `n_hid`. `pad_token` is passed to the PyTorch embedding layer. The dropouts are applied as such:\n- the embeddings are wrapped in `EmbeddingDropout` of probability `embed_p`;\n- the result of thise embedding layer goes through an `RNNDropout` of probability `input_p`;\n- each LSTM has `WeightDropout` applied with probability `weight_p`;\n- between two of the inner LSTM, an `RNNDropout` is applied with probabilith `hidden_p`.\n\nTHe module returns two lists: the raw outputs (without being applied the dropout of `hidden_p`) of each inner LSTM and the list of outputs with dropout. Since there is no dropout applied on the last output, those two lists have the same last element, which is the output that should be fed to a decoder (in the case of a language model).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tst = AWD_LSTM(100, 20, 10, 2)\nx = torch.randint(0, 100, (10,5))\nr = tst(x)\ntest_eq(tst.bs, 10)\ntest_eq(len(tst.hidden), 2)\ntest_eq([h_.shape for h_ in tst.hidden[0]], [[1,10,10], [1,10,10]])\ntest_eq([h_.shape for h_ in tst.hidden[1]], [[1,10,20], [1,10,20]])\ntest_eq(len(r), 2)\ntest_eq(r[0][-1], r[1][-1]) #No dropout for last output\nfor i in range(2): test_eq([h_.shape for h_ in r[i]], [[10,5,10], [10,5,20]])\nfor i in range(2): test_eq(r[0][i][:,-1], tst.hidden[i][0][0]) #hidden state is the last timestep in raw outputs",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#test packed with padding\ntst = AWD_LSTM(100, 20, 10, 2, packed=True)\nx = torch.randint(2, 100, (10,5))\nx[9,3:] = 1\nr = tst(x)\ntest_eq(tst.bs, 10)\ntest_eq(len(tst.hidden), 2)\ntest_eq([h_.shape for h_ in tst.hidden[0]], [[1,10,10], [1,10,10]])\ntest_eq([h_.shape for h_ in tst.hidden[1]], [[1,10,20], [1,10,20]])\ntest_eq(len(r), 2)\ntest_eq(r[0][-1], r[1][-1]) #No dropout for last output\nfor i in range(2): test_eq([h_.shape for h_ in r[i]], [[10,5,10], [10,5,20]])\n#hidden state is the last timestep in raw outputs\nfor i in range(2): test_eq(r[0][i][:,-1][:9], tst.hidden[i][0][0][:9])\nfor i in range(2): test_eq(r[0][i][:,-3][9], tst.hidden[i][0][0][9])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#export\ndef awd_lstm_lm_split(model):\n \"Split a RNN `model` in groups for differential learning rates.\"\n groups = [nn.Sequential(rnn, dp) for rnn, dp in zip(model[0].rnns, model[0].hidden_dps)]\n groups = L(groups + [nn.Sequential(model[0].encoder, model[0].encoder_dp, model[1])])\n return groups.mapped(trainable_params)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"splits = awd_lstm_lm_split",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#export\nawd_lstm_lm_config = dict(emb_sz=400, n_hid=1152, n_layers=3, pad_token=1, bidir=False, output_p=0.1, packed=False,\n hidden_p=0.15, input_p=0.25, embed_p=0.02, weight_p=0.2, tie_weights=True, out_bias=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#export\ndef awd_lstm_clas_split(model):\n \"Split a RNN `model` in groups for differential learning rates.\"\n groups = [nn.Sequential(model[0].module.encoder, model[0].module.encoder_dp)]\n groups += [nn.Sequential(rnn, dp) for rnn, dp in zip(model[0].module.rnns, model[0].module.hidden_dps)]\n groups = L(groups + [model[1]])\n return groups.mapped(trainable_params)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#export\nawd_lstm_clas_config = dict(emb_sz=400, n_hid=1152, n_layers=3, pad_token=1, bidir=False, output_p=0.4,\n hidden_p=0.3, input_p=0.4, embed_p=0.05, weight_p=0.5, packed=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## QRNN",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#export\nclass AWD_QRNN(AWD_LSTM):\n \"Same as an AWD-LSTM, but using QRNNs instead of LSTMs\"\n def _one_rnn(self, n_in, n_out, bidir, weight_p, l):\n from local.text.models.qrnn import QRNN\n rnn = QRNN(n_in, n_out, 1, save_prev_x=True, zoneout=0, window=2 if l == 0 else 1, output_gate=True, bidirectional=bidir)\n rnn.layers[0].linear = WeightDropout(rnn.layers[0].linear, weight_p, layer_names='weight')\n return rnn\n\n def _one_hidden(self, l):\n \"Return one hidden state\"\n nh = (self.n_hid if l != self.n_layers - 1 else self.emb_sz) // self.n_dir\n return one_param(self).new_zeros(self.n_dir, self.bs, nh)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#export\nawd_qrnn_lm_config = dict(emb_sz=400, n_hid=1552, n_layers=4, pad_token=1, bidir=False, output_p=0.1,\n hidden_p=0.15, input_p=0.25, embed_p=0.02, weight_p=0.2, tie_weights=True, out_bias=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#export\nawd_qrnn_clas_config = dict(emb_sz=400, n_hid=1552, n_layers=4, pad_token=1, bidir=False, output_p=0.4,\n hidden_p=0.3, input_p=0.4, embed_p=0.05, weight_p=0.5)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Export -",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#hide\nfrom local.notebook.export import notebook2script\nnotebook2script(all_fs=True)",
"Converted 00_test.ipynb.\nConverted 01_core.ipynb.\nConverted 01a_torch_core.ipynb.\nConverted 02_script.ipynb.\nConverted 03_dataloader.ipynb.\nConverted 04_transform.ipynb.\nConverted 05_data_core.ipynb.\nConverted 06_data_transforms.ipynb.\nConverted 07_vision_core.ipynb.\nConverted 08_pets_tutorial.ipynb.\nConverted 09_vision_augment.ipynb.\nConverted 11_layers.ipynb.\nConverted 11a_vision_models_xresnet.ipynb.\nConverted 12_optimizer.ipynb.\nConverted 13_learner.ipynb.\nConverted 14_callback_schedule.ipynb.\nConverted 15_callback_hook.ipynb.\nConverted 16_callback_progress.ipynb.\nConverted 17_callback_tracker.ipynb.\nConverted 18_callback_fp16.ipynb.\nConverted 19_callback_mixup.ipynb.\nConverted 20_metrics.ipynb.\nConverted 21_tutorial_imagenette.ipynb.\nConverted 22_vision_learner.ipynb.\nConverted 23_tutorial_transfer_learning.ipynb.\nConverted 30_text_core.ipynb.\nConverted 31_text_data.ipynb.\nConverted 32_text_models_awdlstm.ipynb.\nConverted 33_text_models_core.ipynb.\nConverted 34_callback_rnn.ipynb.\nConverted 35_tutorial_wikitext.ipynb.\nConverted 36_text_models_qrnn.ipynb.\nConverted 40_tabular_core.ipynb.\nConverted 41_tabular_model.ipynb.\nConverted 42_tabular_rapids.ipynb.\nConverted 50_data_block.ipynb.\nConverted 90_notebook_core.ipynb.\nConverted 91_notebook_export.ipynb.\nConverted 92_notebook_showdoc.ipynb.\nConverted 93_notebook_export2html.ipynb.\nConverted 94_index.ipynb.\nConverted 95_utils_test.ipynb.\nConverted 96_data_external.ipynb.\nConverted notebook2jekyll.ipynb.\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.