hexsha
stringlengths 40
40
| size
int64 6
14.9M
| ext
stringclasses 1
value | lang
stringclasses 1
value | max_stars_repo_path
stringlengths 6
260
| max_stars_repo_name
stringlengths 6
119
| max_stars_repo_head_hexsha
stringlengths 40
41
| max_stars_repo_licenses
list | max_stars_count
int64 1
191k
⌀ | max_stars_repo_stars_event_min_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_stars_repo_stars_event_max_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_issues_repo_path
stringlengths 6
260
| max_issues_repo_name
stringlengths 6
119
| max_issues_repo_head_hexsha
stringlengths 40
41
| max_issues_repo_licenses
list | max_issues_count
int64 1
67k
⌀ | max_issues_repo_issues_event_min_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_issues_repo_issues_event_max_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_forks_repo_path
stringlengths 6
260
| max_forks_repo_name
stringlengths 6
119
| max_forks_repo_head_hexsha
stringlengths 40
41
| max_forks_repo_licenses
list | max_forks_count
int64 1
105k
⌀ | max_forks_repo_forks_event_min_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_forks_repo_forks_event_max_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | avg_line_length
float64 2
1.04M
| max_line_length
int64 2
11.2M
| alphanum_fraction
float64 0
1
| cells
list | cell_types
list | cell_type_groups
list |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
4ab88d08cfb12f66368debd9870c0f5b72fceaca
| 8,546 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
scriptbook/S5-convert-weburl-to-jekyll-url.ipynb
|
sorphwer/DPDS
|
ffea260c93f0a4f55bd068c19dd852c1705d4ed2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
scriptbook/S5-convert-weburl-to-jekyll-url.ipynb
|
sorphwer/DPDS
|
ffea260c93f0a4f55bd068c19dd852c1705d4ed2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
scriptbook/S5-convert-weburl-to-jekyll-url.ipynb
|
sorphwer/DPDS
|
ffea260c93f0a4f55bd068c19dd852c1705d4ed2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 36.678112 | 269 | 0.502691 |
[
[
[
"## Script S5\n\nConvert from jekyll title formato into origin url.\n\n**Target**: http://127.0.0.1:4000/2021/03/20/Fluid-Typography-with-CSS-Clamp()-is-My-New-Favorite-Thing-DEV-Community.html\n\n**File Path**: 2021-03-20-Fluid-Typography-with-CSS-Clamp()-is-My-New-Favorite Thing---DEV-Community.md\n\n\n**Title**: Fluid Typography with CSS-Clamp() is My New Favorite Thing",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from selenium import webdriver\nfrom bs4 import BeautifulSoup\nfrom neo4j import GraphDatabase, basic_auth\nfrom neo4j.exceptions import Neo4jError\nimport csv\nimport json\nimport time\nimport os\nimport re\nFOLDER_PATH = '../web/_posts/'\ntest_url = 'https://dev.to/cruip/50-free-tools-and-resources-to-create-awesome-user-interfaces-1c1b'\nDATA_FILE_PATH = 'dev-to-articles.csv'\nDATABASE_USERNAME=\"neo4j\"\nDATABASE_PASSWORD=\"spade-discounts-switch\"\nDATABASE_URL=\"bolt://localhost:7687\"\nDATA_FILE_PATH = 'dev-to-articles.csv'\ndriver = GraphDatabase.driver(DATABASE_URL, auth=basic_auth(DATABASE_USERNAME, str(DATABASE_PASSWORD)))\n\ndef cprint(content,module='DEBUG',*args):\n if args:\n print('\\033[1;32;43m ['+module+'] \\033[0m '+ content + '\\033[1;35m' +str(args) +' \\033[0m' + time.strftime(\" |%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S|\", time.localtime()) )\n else:\n print('\\033[1;32;43m ['+module+'] \\033[0m '+ content + time.strftime(\" |%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S|\", time.localtime()))\n\ndef remove_invalid_text(title):\n rstr = r\"[\\/\\\\\\:\\*\\?\\\"\\<\\>\\|]\" # '/ \\ : * ? \" < > |'\n new_title = re.sub(rstr, \"\", title) \n return new_title\ndef init_yaml_header(soup):\n '''\n Args: soup of source post\n Return: valid yaml for riinosite3\n '''\n title = soup.head.title.string\n date = soup.find(\"time\", {\"class\":\"date\"})['datetime'][:10]\n author = soup.find(\"a\",{\"class\":\"flex items-center mr-4 mb-4 s:mb-0 fw-medium crayons-link\"}).contents[-1].replace('\\n','').strip()\n yaml = ['---\\n',\n 'layout: post\\n'\n f'title: \"{title}\"\\n',\n f'author: \"{author}\"\\n',\n f'date: {date}\\n',\n 'toc: false\\n'\n 'tags:\\n'\n ]\n for tag in soup.find_all(\"a\",{\"class\":\"crayons-tag\"}):\n yaml.append(' - '+tag.text[1:]+'\\n')\n yaml.append('---\\n')\n return yaml\ndef generate_post_filename(published_at,title):\n '''\n Args: soup of source post\n Return: valid file name for riinosite3\n '''\n filename = published_at[:10]+'-'+title.replace(' ','-')+'---DEV-Community'+'.md'\n filename = remove_invalid_text(filename)\n filename = filename.replace('.','-')\n return filename\ndef save_markdown_file(soup,folder_path):\n '''\n Args: save markdown file from soup into target folder path\n Return: None\n '''\n with open(FOLDER_PATH+generate_post_filename(soup), mode='w',encoding=\"utf-8\") as file_w:\n #write yaml\n file_w.writelines(init_yaml_header(soup))\n #write body\n for i in soup.find(\"div\", {\"id\":\"article-body\"}).contents:\n file_w.write(str(i))\n cprint('Write file ssuccessfully ','FILE',FOLDER_PATH+generate_post_filename(soup))\n file_w.close()\n\ndef db_update_article_jekyll_path(session,id,value):\n '''\n Add a new value for article node with id\n Args:\n session: db session,driver.session()\n id: article id, in csv file.\n value: value of that key : reading_time\n '''\n def _cypher(tx,key,value):\n return list(tx.run(\n '''\n MATCH (n:Article { id: $id })\n SET n.jekyll_path = $value\n RETURN n\n '''\n ))\n result = session.write_transaction(_cypher,key,value)\n return result\n\narticle_props = []\n\nif os.path.exists(DATA_FILE_PATH):\n if not os.path.getsize(DATA_FILE_PATH):\n cprint(DATA_FILE_PATH +'is empty')\n else:\n with open(DATA_FILE_PATH, mode='r',encoding=\"utf-8\") as data_file_r:\n csv_reader = csv.DictReader(data_file_r)\n line_count = 0\n props=set()\n for row in csv_reader:\n if line_count == 0:\n cprint(f'Processing CSV header {\", \".join(row)}','CSV')\n line_count += 1\n article_prop = {\n 'id': row['id'],\n 'title': row['title'],\n 'url': row['url'],\n 'main_image_url': row['main_image_url'],\n 'reading_time': row['reading_time'],\n 'tag_names': row['tag_names'],\n 'published_at': row['published_at'],\n 'source_site':'dev.to',\n 'author_name':row['author_name'],\n 'count':row['public_reactions_count']\n }\n if article_prop in article_props:\n continue\n else:\n article_props.append(article_prop)\n line_count += 1\n cprint(f'File processed successfully with {line_count-1} ids.','CSV')\n data_file_r.close()\nelse:\n cprint(DATA_FILE_PATH +' does not exist')",
"\u001b[1;32;43m [CSV] \u001b[0m Processing CSV header id, title, url, main_image_url, reading_time, author_name, author_username, author_id, published_at, tag_names, keywords_for_search, comments_count, public_reactions_count, highlight |2021-05-09 20:31:52|\n\u001b[1;32;43m [CSV] \u001b[0m File processed successfully with 2375 ids. |2021-05-09 20:31:52|\n"
],
[
"generate_post_filename(article_props[1]['published_at'],article_props[1]['title'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"FOLDER_PATH+generate_post_filename(article_props[1]['published_at'],article_props[1]['title'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"'2020-10-06-ReactJS-Roadmap-🗺-For-Developers-💻---DEV-Community.md'",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4ab89b36a247faadc8bd03bfcad8a995013c4178
| 3,553 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
samples/lookup_attributes.ipynb
|
kbruxvoort/fetchbim
|
ce4bcb0b278834fc577a3f1d22cc6d33e8e96d29
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
samples/lookup_attributes.ipynb
|
kbruxvoort/fetchbim
|
ce4bcb0b278834fc577a3f1d22cc6d33e8e96d29
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
samples/lookup_attributes.ipynb
|
kbruxvoort/fetchbim
|
ce4bcb0b278834fc577a3f1d22cc6d33e8e96d29
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 38.204301 | 879 | 0.636645 |
[
[
[
"from fetchbim.query import SharedFile",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"shared_rule_id = 123",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"shared_rule = SharedFile.from_json(shared_rule_id)\r\nattrs = shared_rule.Attributes\r\nfor attr in attrs:\r\n print(f'[{attr.SharedAttributeId}] {attr.Name}\\n\\t{attr.Value}')",
"[8827] Manufacturer\n\tSouthwest Soltuions Group_PNC\n[8828] Info_Lead Time\n\tShips in 7-8 weeks\n[8829] Keynote\n\t12 31 00\n[8830] Assembly Code\n\tE20\n[8831] Includes Pricing\n\tYes\n[8832] ADA Compliant\n\tNo\n[8833] Has MEP Connectors\n\tNo\n[8834] Tags\n\tCasework, Blueprint, Shelving, 4 Post, 4-Post, Clipper\n[8835] Primary Material\n\tPowder coated steel\n[8836] BIMobject Category\n\tFurniture: Shelving & Storage\n[8837] Omniclass\n\t23-40-35-00\n[8838] IFC\n\tFurniture\n[8839] Family Design\n\t<p>This combination blueprint storage unit is a specially configured 4 post shelving system ideal for use in corporate settings and in design firms. Choose between two configuration options to select either the 48\" wide, 36\" deep combination shelves and cubbies configuration, or the 36\" wide, 24\" deep vertical cubbie configuration. All units are 7' 3\" tall and include a back panel. Optional double doors with lock are also included in this family.</p><p>Multiple units can be joined together by beginning with a unit with MODIFY_Starter checked. Uncheck ADD_Right Upright and align a unit with MODIFY_Adder checker. Repeat this process until the desired number of units is reached.</p><p>Download this families material library for access to all colors offered for this product, each with high quality textures and bump maps for photo realistic rendering</p>\n[8840] Technical Data\n\t<h2>Construction</h2><ul><li>Complies with SMA and ANSI MH 28.1-1982</li><li>Uprights made of 18 gauge steel.</li><li>Shelves and accessories are vertically adjustable on 1\" centers.</li><li>All shelves made of 18 gauge steel with a 1-3/16\" vertical face on all sides.</li><li>All corners and edges are welded and ground smooth</li><li>Optional doors are fully welded 116 gauge steel and equipped with three 5-knuckle hinges.</li><li>To finish, the steel is cleaned and primed, then coated with a high-grade polyester powder coat. See Finish Options for all available colors</li></ul>\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4ab89d2144994fdecf02bd776d508eda1eda4bb1
| 30,167 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks(colab)/Neural_network_models/Supervised_learning_models/curve_fitting_RU.ipynb
|
jswanglp/MyML
|
ea1510cc5c2dec9eb37e371a73234b3a228beca7
|
[
"MIT"
] | 7 |
2019-05-04T13:57:52.000Z
|
2021-12-31T03:39:58.000Z
|
notebooks(colab)/Neural_network_models/Supervised_learning_models/curve_fitting_RU.ipynb
|
jswanglp/MyML
|
ea1510cc5c2dec9eb37e371a73234b3a228beca7
|
[
"MIT"
] | 19 |
2020-09-26T01:16:10.000Z
|
2022-02-10T02:11:15.000Z
|
notebooks(colab)/Neural_network_models/Supervised_learning_models/curve_fitting_RU.ipynb
|
jswanglp/MyML
|
ea1510cc5c2dec9eb37e371a73234b3a228beca7
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2019-06-02T05:10:35.000Z
|
2020-09-19T07:24:43.000Z
| 30,167 | 30,167 | 0.878543 |
[
[
[
"# Инициализация",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#@markdown - **Монтирование GoogleDrive** \nfrom google.colab import drive\ndrive.mount('GoogleDrive')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# #@markdown - **Размонтирование**\n# !fusermount -u GoogleDrive",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Область кодов",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#@title Приближение с помощью кривых { display-mode: \"both\" }\n# Curve fitting\n# В программе реализовано приближение исходных данных с помощью нейронных сетей с одным скрытым слоем\n# Можно сравнить с результатами метода регуляризации Тихонова\n# conding: utf-8\nimport numpy as np\nimport tensorflow as tf\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport time",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#@markdown - **Настройка параметров**\nnum_epoch = 200 #@param {type: \"integer\"}\n# Предварительная обработка данных образца\ndata = np.array([[-2.95507616, 10.94533252],\n [-0.44226119, 2.96705822],\n [-2.13294087, 6.57336839],\n [1.84990823, 5.44244467],\n [0.35139795, 2.83533936],\n [-1.77443098, 5.6800407],\n [-1.8657203, 6.34470814],\n [1.61526823, 4.77833358],\n [-2.38043687, 8.51887713],\n [-1.40513866, 4.18262786]])\nx = data[:, 0]\ny = data[:, 1]\nX = x.reshape(-1, 1)\nY = y.reshape(-1, 1)\n# Более прогнозируемые данные, чем исходные данные\nx_pre = np.linspace(x.min(), x.max(), 30, endpoint=True).reshape(-1, 1)\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#@markdown - **Создание graph**\ngraph = tf.Graph()\nwith graph.as_default():\n with tf.name_scope('Input'):\n x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 1], name='x')\n y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 1], name='y')\n with tf.name_scope('FC'):\n w_1 = tf.get_variable('w_fc1', shape=[1, 32], initializer=tf.initializers.truncated_normal(stddev=0.1))\n b_1 = tf.get_variable('b_fc1', initializer=tf.constant(0.1, shape=[32]))\n layer_1 = tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.matmul(x, w_1) + b_1)\n with tf.name_scope('Output'):\n w_2 = tf.get_variable('w_fc2', shape=[32, 1], initializer=tf.initializers.truncated_normal(stddev=0.1))\n b_2 = tf.get_variable('b_fc2', initializer=tf.constant(0.1, shape=[1]))\n layer_2 = tf.matmul(layer_1, w_2) + b_2\n \n with tf.name_scope('Loss'):\n loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.pow(layer_2 - y, 2))\n with tf.name_scope('Train'):\n train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=3e-1).minimize(loss)",
"WARNING:tensorflow:From /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/tensorflow/python/framework/op_def_library.py:263: colocate_with (from tensorflow.python.framework.ops) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version.\nInstructions for updating:\nColocations handled automatically by placer.\n"
],
[
"#@markdown - **Обучение модели**\nwith tf.Session(graph=graph) as sess:\n sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())\n\n time_start = time.time()\n for num in range(num_epoch):\n _, ls = sess.run([train_op, loss], feed_dict={x: X, y: Y})\n print_list = [num+1, ls]\n if (num+1) % 10 == 0 or num == 0:\n print('Epoch {0[0]}, loss: {0[1]:.4f}.'.format(print_list))\n \n # time_start = time.time()\n y_pre = sess.run(layer_2, feed_dict={x: x_pre})\n sess.close()\n time_end = time.time()\n t = time_end - time_start\n print('Running time is: %.4f s.' % t)",
"Epoch 1, loss: 35.0321.\nEpoch 10, loss: 3.2330.\nEpoch 20, loss: 2.7602.\nEpoch 30, loss: 1.2835.\nEpoch 40, loss: 0.5167.\nEpoch 50, loss: 0.2306.\nEpoch 60, loss: 0.1536.\nEpoch 70, loss: 0.1228.\nEpoch 80, loss: 0.1032.\nEpoch 90, loss: 0.0929.\nEpoch 100, loss: 0.0843.\nEpoch 110, loss: 0.0788.\nEpoch 120, loss: 0.0755.\nEpoch 130, loss: 0.0733.\nEpoch 140, loss: 0.0717.\nEpoch 150, loss: 0.0703.\nEpoch 160, loss: 0.0690.\nEpoch 170, loss: 0.0678.\nEpoch 180, loss: 0.0667.\nEpoch 190, loss: 0.0657.\nEpoch 200, loss: 0.0647.\nRunning time is: 0.2594 s.\n"
],
[
"#@markdown - **Кривая прогнозирования**\ndata_pre = np.c_[x_pre, y_pre]\nDATA = [data, data_pre]\nNAME = ['Training data', 'Fitting curve']\nSTYLE = ['*r', 'b']\nfig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=1, figsize=(12, 6))\nfor dat, name, style in zip(DATA, NAME, STYLE):\n ax.plot(dat[:, 0], dat[:, 1], style, markersize=8, label=name)\n ax.legend(loc='upper right', fontsize=14)\n ax.tick_params(labelsize=14)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4ab8ae92f5ddff4266113957935b8737f13316ba
| 188,597 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Rafay notes/Samsung Course/Chapter 3/Class Work/Lecture-08-6th-Oct-2021-Wednesday/Lecture 08-06th-Oct-2021-Wednesday.ipynb
|
rafay99-epic/Ssmsunng-Innovation-Campus-Notes
|
19a2dfd125957d5a3d3458636d91747b48267689
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Rafay notes/Samsung Course/Chapter 3/Class Work/Lecture-08-6th-Oct-2021-Wednesday/Lecture 08-06th-Oct-2021-Wednesday.ipynb
|
rafay99-epic/Ssmsunng-Innovation-Campus-Notes
|
19a2dfd125957d5a3d3458636d91747b48267689
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Rafay notes/Samsung Course/Chapter 3/Class Work/Lecture-08-6th-Oct-2021-Wednesday/Lecture 08-06th-Oct-2021-Wednesday.ipynb
|
rafay99-epic/Ssmsunng-Innovation-Campus-Notes
|
19a2dfd125957d5a3d3458636d91747b48267689
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 27.882466 | 616 | 0.324586 |
[
[
[
"Lecture 8<br>\nDay: wednesday<br>\nDate: Oct 06th 2021",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Problem Solve:\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import os ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import random",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Quiz = np.random.randint(0,16,size =40)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(Quiz)",
"[ 6 14 8 9 13 14 15 8 11 7 2 0 0 7 8 6 14 0 1 14 7 2 0 10\n 13 11 13 13 7 14 7 6 1 8 1 11 13 14 12 11]\n"
],
[
"Assignment = np.random.randint(0,51, size = 50)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(Assignment)",
"[33 37 18 42 38 46 6 36 49 24 17 44 12 41 8 47 21 29 10 4 2 43 48 17\n 44 45 39 23 9 31 13 26 21 34 24 6 7 9 50 29 4 14 37 29 3 21 39 23\n 33 15]\n"
],
[
"Mid= np.random.randint(0,81, size= 80)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(Mid)",
"[59 10 51 60 36 62 75 41 66 44 41 56 3 63 29 15 27 54 22 74 1 71 74 51\n 22 59 74 11 26 74 8 21 50 53 71 59 51 34 41 33 4 78 53 76 36 6 49 9\n 8 28 31 37 12 8 25 6 50 37 10 14 62 30 8 52 32 5 69 74 42 35 0 65\n 42 8 22 51 41 16 36 12]\n"
],
[
"Final = np.random.randint(0, 151, size = 150 )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(Final)",
"[ 49 93 144 54 119 67 138 91 126 53 104 112 81 77 2 74 63 69\n 47 88 117 97 39 111 65 60 96 101 113 48 67 41 62 72 20 37\n 0 27 9 97 140 95 140 118 50 42 27 122 53 65 75 116 129 128\n 13 45 68 65 84 88 108 145 78 136 93 81 31 126 85 1 13 13\n 89 150 60 7 124 54 67 98 63 41 15 43 130 124 125 146 5 8\n 87 32 55 91 94 58 64 85 115 13 58 100 79 20 144 70 71 136\n 20 92 30 23 43 60 1 81 5 22 64 90 52 100 21 17 131 111\n 49 73 56 58 108 22 96 46 131 73 72 45 112 56 14 43 46 97\n 49 95 118 68 4 55]\n"
],
[
"Quiz_Sum = (Quiz/15) * 30",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(Quiz_Sum)",
"[12. 28. 16. 18. 26. 28. 30. 16. 22. 14. 4. 0. 0. 14. 16. 12. 28. 0.\n 2. 28. 14. 4. 0. 20. 26. 22. 26. 26. 14. 28. 14. 12. 2. 16. 2. 22.\n 26. 28. 24. 22.]\n"
],
[
"Final_Sum= (Final/150)* 40 ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(Final_Sum)",
"[13.06666667 24.8 38.4 14.4 31.73333333 17.86666667\n 36.8 24.26666667 33.6 14.13333333 27.73333333 29.86666667\n 21.6 20.53333333 0.53333333 19.73333333 16.8 18.4\n 12.53333333 23.46666667 31.2 25.86666667 10.4 29.6\n 17.33333333 16. 25.6 26.93333333 30.13333333 12.8\n 17.86666667 10.93333333 16.53333333 19.2 5.33333333 9.86666667\n 0. 7.2 2.4 25.86666667 37.33333333 25.33333333\n 37.33333333 31.46666667 13.33333333 11.2 7.2 32.53333333\n 14.13333333 17.33333333 20. 30.93333333 34.4 34.13333333\n 3.46666667 12. 18.13333333 17.33333333 22.4 23.46666667\n 28.8 38.66666667 20.8 36.26666667 24.8 21.6\n 8.26666667 33.6 22.66666667 0.26666667 3.46666667 3.46666667\n 23.73333333 40. 16. 1.86666667 33.06666667 14.4\n 17.86666667 26.13333333 16.8 10.93333333 4. 11.46666667\n 34.66666667 33.06666667 33.33333333 38.93333333 1.33333333 2.13333333\n 23.2 8.53333333 14.66666667 24.26666667 25.06666667 15.46666667\n 17.06666667 22.66666667 30.66666667 3.46666667 15.46666667 26.66666667\n 21.06666667 5.33333333 38.4 18.66666667 18.93333333 36.26666667\n 5.33333333 24.53333333 8. 6.13333333 11.46666667 16.\n 0.26666667 21.6 1.33333333 5.86666667 17.06666667 24.\n 13.86666667 26.66666667 5.6 4.53333333 34.93333333 29.6\n 13.06666667 19.46666667 14.93333333 15.46666667 28.8 5.86666667\n 25.6 12.26666667 34.93333333 19.46666667 19.2 12.\n 29.86666667 14.93333333 3.73333333 11.46666667 12.26666667 25.86666667\n 13.06666667 25.33333333 31.46666667 18.13333333 1.06666667 14.66666667]\n"
],
[
"Mid_Sum = (Mid / 10 )* 20",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(Mid_Sum)",
"[590. 100. 510. 600. 360. 620. 750. 410. 660. 440. 410. 560. 30. 630.\n 290. 150. 270. 540. 220. 740. 10. 710. 740. 510. 220. 590. 740. 110.\n 260. 740. 80. 210. 500. 530. 710. 590. 510. 340. 410. 330. 40. 780.\n 530. 760. 360. 60. 490. 90. 80. 280. 310. 370. 120. 80. 250. 60.\n 500. 370. 100. 140. 620. 300. 80. 520. 320. 50. 690. 740. 420. 350.\n 0. 650. 420. 80. 220. 510. 410. 160. 360. 120.]\n"
],
[
"Assignment_Sum = (Assignment / 50) * 30",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(Assignment_Sum)",
"[19.8 22.2 10.8 25.2 22.8 27.6 3.6 21.6 29.4 14.4 10.2 26.4 7.2 24.6\n 4.8 28.2 12.6 17.4 6. 2.4 1.2 25.8 28.8 10.2 26.4 27. 23.4 13.8\n 5.4 18.6 7.8 15.6 12.6 20.4 14.4 3.6 4.2 5.4 30. 17.4 2.4 8.4\n 22.2 17.4 1.8 12.6 23.4 13.8 19.8 9. ]\n"
],
[
"Final_Marks = Assignment_Sum + Mid_Sum+ Final_Sum + Quiz_Sum\nprint(Final_Marks)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import pandas as pd",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create a basic Series:\nx = pd.Series([1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8])\n# left side are the index \n# in Series ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(x)",
"0 1\n1 2\n2 3\n3 4\n4 5\n5 6\n6 7\n7 8\ndtype: int64\n"
],
[
"# in this we can also assign the index in series as well\ndata_new = [1,2,3,4]\nindex_new= ['a','b','c','d']\neye = pd.Series(data=data_new , index=index_new )\nprint(eye)",
"a 1\nb 2\nc 3\nd 4\ndtype: int64\n"
],
[
"# There are different attributies\n# All of the array function can be imported in the series as well,\nser.name\nser.index\nser.values\nser.sort_values()\nser.sort_index()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Splicaing the values and print data using range as well\nx = pd.Series([1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x[1]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# while adding the index must me same if index are not same then the operation will not be formed\n# the above will only be implmented when there are two series but if there is one series then you can add vales in the index\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# for One Series\nx[3]=x[1]+ x[2] ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x[3]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(x)",
"0 1\n1 2\n2 3\n3 5\n4 5\n5 6\n6 7\n7 8\ndtype: int64\n"
],
[
"# For Two Series:\nx = pd.Series([1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8])\ny = pd.Series([17,9,10,11,12,13,15,16])\nz = x+y ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# As you can see the same index values are sum.\nprint(z)",
"0 18\n1 11\n2 13\n3 15\n4 17\n5 19\n6 22\n7 24\ndtype: int64\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Exercise ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"my_index =['a','b','c']\nmy_values = [223,224,334]\nmy_dict = {'a':222, 'b':333, 'c':334}\nmy_arr = np.array(my_values)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.Series(my_values)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.Series(data= my_values, index= my_index)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.Series(my_arr)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.Series(my_dict)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"1.2. Series attributes and indexing:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"s = pd.Series(data =[111,222,333,444], index= ['a','b','c','d'], name= 'MySeries')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s.index",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s.name",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s.dtype",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s[1]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s['a']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s[['a','d']]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s1 = pd.Series(data=[1,2,3,4], index = ['d','b','c','a'])\ns2 = pd.Series(data=[1,2,3,4], index = ['a','b','d','e'])\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s1 + s2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s1-s2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s1* s2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s1/s2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"2*s1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s1.sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s1.mean()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s1.median()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s1.max()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s1.std()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s1.sort_values()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s1.sort_index()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ser_height = pd.Series([165.3, 170.1, 175.0, 182.1, 168.0, 162.0, 155.2, 176.9, 178.5, 176.1, 167.1, 180.0, 162.2, 176.1, 158.2, 168.6, 169.2],name='height')\nser_height ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ser_height.apply(lambda x : x/100)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Data Frame:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# it's s 2D array and it is used the most\n# the list of Numpy is that all of the data type must be same",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# to create a data frame",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Exercise 05",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport os",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data = {'Name': ['Jake','Jennifer', 'Rafay', 'Paul Walker', ' Jake Paul'], 'Age': [24,21,25,19,22], 'Gender': ['M','F','M','M','M']}",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# this will print data into the dataframe",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df=pd.DataFrame(data)\ndf",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Reading data from DataFrame:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df=pd.read_csv('data_studentlist.csv', header = 'infer')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.size",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.ndim",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.index",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"type(df)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.info()",
"<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>\nRangeIndex: 17 entries, 0 to 16\nData columns (total 8 columns):\n # Column Non-Null Count Dtype \n--- ------ -------------- ----- \n 0 name 17 non-null object \n 1 gender 17 non-null object \n 2 age 17 non-null int64 \n 3 grade 17 non-null int64 \n 4 absence 17 non-null object \n 5 bloodtype 17 non-null object \n 6 height 17 non-null float64\n 7 weight 17 non-null float64\ndtypes: float64(2), int64(2), object(4)\nmemory usage: 1.2+ KB\n"
],
[
"df.describe()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.head(6)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.tail(5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.columns = ['NAME', 'GENDER' , 'AGE', 'GRADE', 'ABSENCE', 'BLOODTYPE', 'HEIGHT', 'WEIGHT']\ndf.head(3)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.NAME",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"type(df.NAME)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df[['NAME']]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.loc[:,'NAME']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.loc[:,['NAME','GENDER']]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.iloc[:,[0,1]]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"header= df.columns\nheader",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.loc[:,(header =='NAME') | (header == 'GENDER')]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n\n# This is a row.\ndf.loc[2]\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n\ndf.loc[2:4]\n\ndf.iloc[2:4]\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.drop(columns=['NAME', 'GENDER'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.loc[:, (header!='NAME') & (header!='GENDER')]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df[df.GENDER=='M']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df[df.GENDER=='F']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n\ndf2 = df.drop(columns=['GRADE','ABSENCE'])\ndf2.to_csv('data_mine.csv',index=False)\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df3 = pd.read_csv('data_mine.csv',encoding='latin1',header='infer')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df3.head(3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dfx = pd.read_excel('StudentData.xlsx', sheet_name='Sheet1')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dfx.head(5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n\ndfx.to_excel('data_studentlist2.xlsx',sheet_name='NewSheet', index=False)\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Exercise 206",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport os\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = pd.read_csv('data_studentlist.csv', header='infer')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n\n# Replace the columns (header).\ndf.columns = ['NAME', 'GENDER' , 'AGE', 'GRADE', 'ABSENCE', 'BLOODTYPE', 'HEIGHT', 'WEIGHT']\ndf.head(3)\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.columns = ['NAME', 'GENDER' , 'AGE', 'GRADE', 'ABSENCE', 'BLOODTYPE', 'HEIGHT', 'WEIGHT']\ndf.head(3)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n\ndf['BMI'] = 10000*df['WEIGHT']/df['HEIGHT']**2\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.head(5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.drop('BMI',axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.head(5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.drop('BMI', axis=1, inplace=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.head(5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_left= df.loc[:,['NAME','AGE','GENDER','GRADE','ABSENCE']]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_left_small=df_left.loc[:10]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_left_small",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_right = df.loc[:,['NAME','BLOODTYPE','WEIGHT','HEIGHT']]\ndf_right_small = df_right.loc[7:,]\ndf_right_small",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_right = df.loc[:,['NAME','BLOODTYPE','WEIGHT','HEIGHT']]\ndf_right_small = df_right.loc[7:,]\ndf_right_small",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.merge(df_left_small,df_right_small,left_on='NAME', right_on = 'NAME', how='inner')\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.merge(df_left_small,df_right_small,left_on='NAME', right_on = 'NAME', how='left')\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.merge(df_left_small,df_right_small,left_on='NAME', right_on = 'NAME', how='right')\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.merge(df_left_small,df_right_small,left_on='NAME', right_on = 'NAME', how='outer')\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n\npd.concat([df_left_small,df_right_small],sort=True) \n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\npd.concat([df_left_small,df_right_small],axis=1,sort=True) \n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4ab8d7f87939deaf4c20e34cd40da194a91e83a6
| 82,720 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Food_recall.ipynb
|
mbuggus50/Food-Recall-Classifier-
|
5edde4fdf7814451213da4d8dd34ec411016ebbe
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Food_recall.ipynb
|
mbuggus50/Food-Recall-Classifier-
|
5edde4fdf7814451213da4d8dd34ec411016ebbe
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Food_recall.ipynb
|
mbuggus50/Food-Recall-Classifier-
|
5edde4fdf7814451213da4d8dd34ec411016ebbe
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 70.882605 | 16,780 | 0.775048 |
[
[
[
"# import project Libraries \nimport warnings\nwarnings.simplefilter(action='ignore', category=FutureWarning)\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn as sns\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Load the data and create pandas DataFrame. \ndf = pd.read_csv('./My_data/Food_enforcement_data.csv',encoding= 'unicode_escape')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Exploring the summary of our DataFrame\ndf.info()",
"<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>\nRangeIndex: 20677 entries, 0 to 20676\nData columns (total 12 columns):\n # Column Non-Null Count Dtype \n--- ------ -------------- ----- \n 0 FEI_Number 20677 non-null object\n 1 Product ID 20677 non-null int64 \n 2 Recalling_Firm 20677 non-null object\n 3 Product_Type 20677 non-null object\n 4 Status 20677 non-null object\n 5 Recalling_Firm_City 20677 non-null object\n 6 Recalling_Firm_State 20677 non-null object\n 7 Recalling_Firm_Country 20677 non-null object\n 8 Classification_Date 20677 non-null object\n 9 Recall_Reason 20677 non-null object\n 10 Product_Description 20677 non-null object\n 11 Classification 20677 non-null object\ndtypes: int64(1), object(11)\nmemory usage: 1.9+ MB\n"
],
[
"# get columns names( this works as week refrence once i start dropping columns not needed)\ndf.columns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# To identify any missing data (null value) and deal with with it. \ndf.isnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# LabelEncoder is used when Encoding Categorical features to numerical. \nlabel_encode = LabelEncoder()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Label encoding is performed on the target class \"Classification\" because its ordinal in nature\ndf[\"Classification\"] = label_encode.fit_transform(df['Classification'].astype('str'))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Source: https://maxhalford.github.io/blog/target-encoding-done-the-right-way/\ndef calc_smooth_mean(df1, df2, cat_name, target, weight):\n # Compute the global mean\n mean = df[target].mean()\n\n # Compute the number of values and the mean of each group\n agg = df.groupby(cat_name)[target].agg(['count', 'mean'])\n counts = agg['count']\n means = agg['mean']\n\n # Compute the \"smoothed\" means\n smooth = (counts * means + weight * mean) / (counts + weight)\n\n # Replace each value by the according smoothed mean\n if df2 is None:\n return df1[cat_name].map(smooth)\n else:\n return df1[cat_name].map(smooth),df2[cat_name].map(smooth.to_dict())\n\n\nWEIGHT = 5\ndf['Recall_Reason'] = calc_smooth_mean(df1=df, df2=None, cat_name='Recall_Reason', target='Classification', weight=WEIGHT)\ndf['Product_Description'] = calc_smooth_mean(df1=df, df2=None, cat_name='Product_Description', target='Classification', weight=WEIGHT)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import category_encoders as ce",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# here we are encoding \"Classification column\" which has ordinal data (ClassI, Class II, Class III)\n# Using LabelEncoder technique. \nencode = ce.OneHotEncoder(cols='Classification',handle_unknown='return_nan',return_df=True,use_cat_names=True)\ndata_encoded = encode.fit_transform(df)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Here we are Encoding 'Recalling_Firm_City' Column using binary Encoding technique\nencode_0 = ce.BinaryEncoder(cols=['Recalling_Firm_City'],return_df=True)\ndata_encoded = encode_0.fit_transform(data_encoded)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# encoding column \"status\" using One-Hot-Encode method\nenoder_1 = ce.OneHotEncoder(cols='Status',handle_unknown='return_nan',return_df=True,use_cat_names=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Trnsforming the encoded data. \ndata_encoded = enoder_1.fit_transform(data_encoded)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Here we are Encoding 'Recalling_Firm_Country' Column using binary Encoding technique\nencoder_2 = ce.BinaryEncoder(cols=['Recalling_Firm_Country'],return_df=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Trnsforming the encoded data. \ndata_encoded = encoder_2.fit_transform(data_encoded)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# drop unwanted columns \ndata_encoded = data_encoded.drop('Recalling_Firm_State',axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Dropping all Columns deemed unNecessary for the model performance \ndata_encoded = data_encoded.drop('Product_Type',axis=1)\ndata_encoded = data_encoded.drop('Recalling_Firm',axis=1)\ndata_encoded = data_encoded.drop('Product ID',axis=1)\ndata_encoded = data_encoded.drop('FEI_Number',axis=1)\ndata_encoded = data_encoded.drop('Classification_Date',axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\nX = data_encoded.iloc[:,:23].values\ny = data_encoded.iloc[:,23:].values",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Training test split\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(\n X, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=42)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"scaler = MinMaxScaler()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Feature scaling\nX_train = scaler.fit_transform(X_train)\nX_test = scaler.transform(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Import model frameworks and libraries \nfrom tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential\nfrom tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Activation, Dropout\nfrom tensorflow.keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# the model takes in 15507 records with 23 input features \nmodel = Sequential()\nmodel.add(Dense(24, input_dim=23, activation='relu', # rectified linear activation function is the function of choice \n kernel_initializer='random_normal')) #nitializer that generates tensors with a normal distribution.\nmodel.add(Dense(12,activation='relu',kernel_initializer='random_normal'))\nmodel.add(Dense(6,activation='relu',kernel_initializer='random_normal'))\n# softmax is the activation of choice for multiclass Classification problems\nmodel.add(Dense(3,activation='softmax'))\nmodel.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', \n optimizer='adam',\n metrics =['accuracy'])\nmonitor = EarlyStopping(monitor='val_loss', min_delta=1e-3, patience=5, \n verbose=1, mode='auto', restore_best_weights=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# model fiting \n# when trining the model, i have introduced Keras callbacks functions i.e early stopping to prevent overfitting \nmodel.fit(X_train,y_train,validation_data=(X_test,y_test),callbacks=[monitor],verbose=2,epochs=1000)",
"Train on 15507 samples, validate on 5170 samples\nEpoch 1/1000\n15507/15507 - 2s - loss: 0.7732 - accuracy: 0.6579 - val_loss: 0.3230 - val_accuracy: 0.9313\nEpoch 2/1000\n15507/15507 - 1s - loss: 0.2305 - accuracy: 0.9320 - val_loss: 0.1593 - val_accuracy: 0.9381\nEpoch 3/1000\n15507/15507 - 1s - loss: 0.1102 - accuracy: 0.9610 - val_loss: 0.0724 - val_accuracy: 0.9733\nEpoch 4/1000\n15507/15507 - 1s - loss: 0.0533 - accuracy: 0.9899 - val_loss: 0.0393 - val_accuracy: 0.9973\nEpoch 5/1000\n15507/15507 - 1s - loss: 0.0325 - accuracy: 0.9992 - val_loss: 0.0258 - val_accuracy: 0.9990\nEpoch 6/1000\n15507/15507 - 1s - loss: 0.0226 - accuracy: 0.9993 - val_loss: 0.0180 - val_accuracy: 0.9996\nEpoch 7/1000\n15507/15507 - 1s - loss: 0.0163 - accuracy: 0.9994 - val_loss: 0.0130 - val_accuracy: 0.9996\nEpoch 8/1000\n15507/15507 - 1s - loss: 0.0120 - accuracy: 0.9996 - val_loss: 0.0096 - val_accuracy: 0.9998\nEpoch 9/1000\n15507/15507 - 1s - loss: 0.0091 - accuracy: 0.9997 - val_loss: 0.0074 - val_accuracy: 0.9998\nEpoch 10/1000\n15507/15507 - 1s - loss: 0.0072 - accuracy: 0.9997 - val_loss: 0.0058 - val_accuracy: 0.9998\nEpoch 11/1000\n15507/15507 - 1s - loss: 0.0058 - accuracy: 0.9997 - val_loss: 0.0043 - val_accuracy: 0.9998\nEpoch 12/1000\n15507/15507 - 1s - loss: 0.0043 - accuracy: 0.9999 - val_loss: 0.0033 - val_accuracy: 1.0000\nEpoch 13/1000\n15507/15507 - 1s - loss: 0.0034 - accuracy: 0.9998 - val_loss: 0.0025 - val_accuracy: 1.0000\nEpoch 14/1000\n15507/15507 - 1s - loss: 0.0031 - accuracy: 0.9998 - val_loss: 0.0020 - val_accuracy: 1.0000\nEpoch 15/1000\n15507/15507 - 1s - loss: 0.0022 - accuracy: 0.9999 - val_loss: 0.0018 - val_accuracy: 1.0000\nEpoch 16/1000\n15507/15507 - 1s - loss: 0.0017 - accuracy: 0.9999 - val_loss: 0.0013 - val_accuracy: 1.0000\nEpoch 17/1000\n15507/15507 - 1s - loss: 0.0014 - accuracy: 0.9999 - val_loss: 0.0010 - val_accuracy: 1.0000\nEpoch 18/1000\n15507/15507 - 1s - loss: 0.0012 - accuracy: 0.9999 - val_loss: 8.7224e-04 - val_accuracy: 1.0000\nEpoch 19/1000\n15507/15507 - 1s - loss: 0.0011 - accuracy: 0.9999 - val_loss: 7.6955e-04 - val_accuracy: 1.0000\nEpoch 20/1000\n15507/15507 - 1s - loss: 9.4874e-04 - accuracy: 0.9999 - val_loss: 5.7037e-04 - val_accuracy: 1.0000\nEpoch 21/1000\nRestoring model weights from the end of the best epoch.\n15507/15507 - 1s - loss: 8.5084e-04 - accuracy: 0.9999 - val_loss: 4.6906e-04 - val_accuracy: 1.0000\nEpoch 00021: early stopping\n"
],
[
"#create a data frame of model metrics i.e losses and accuracy \ndf_loss = pd.DataFrame(model.history.history)\ndf_loss",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# ploting loss against validation loss and accuracy vas validation accuracy\ndf_loss.plot()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# predict unseen test data\npred = model.predict(X_test)\npred = np.argmax(pred,axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn import metrics\n\ny_compare = np.argmax(y_test,axis=1) \nscore = metrics.accuracy_score(y_compare, pred)\nprint(\"Accuracy score: {}\".format(score))",
"Accuracy score: 1.0\n"
],
[
"# define a confusion matrix\ndef plot_confusion_matrix(cm, names, title='Confusion matrix', \n cmap=plt.cm.Blues):\n plt.imshow(cm, interpolation='nearest', cmap=cmap)\n plt.title(title)\n plt.colorbar()\n tick_marks = np.arange(len(names))\n plt.xticks(tick_marks, names, rotation=45)\n plt.yticks(tick_marks, names)\n plt.tight_layout()\n plt.ylabel('True label')\n plt.xlabel('Predicted label')\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn import svm, datasets\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nfrom sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix\n\n# Compute confusion matrix\nMy_products = pd.DataFrame(data_encoded.iloc[:,23:])\nproducts = My_products.columns\ncm = confusion_matrix(y_compare, pred)\nnp.set_printoptions(precision=2)\nprint('Confusion matrix, without normalization')\nprint(cm)\nplt.figure()\nplot_confusion_matrix(cm, products)\n\n# Normalize the confusion matrix by row (i.e by the number of samples\n# in each class)\ncm_normalized = cm.astype('float') / cm.sum(axis=1)[:, np.newaxis]\nprint('Normalized confusion matrix')\nprint(cm_normalized)\nplt.figure()\nplot_confusion_matrix(cm_normalized, products, \n title='Normalized confusion matrix')\n\nplt.show()",
"Confusion matrix, without normalization\n[[2168 0 0]\n [ 0 2715 0]\n [ 0 0 287]]\nNormalized confusion matrix\n[[1. 0. 0.]\n [0. 1. 0.]\n [0. 0. 1.]]\n"
],
[
"pred[:30]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Evaluate the model performance \nmodel.evaluate(X_test,y_test,verbose=0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"epochs = len(df_loss)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# here we will scale the whole dataset without spliting \nscaled_X = scaler.fit_transform(X)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Second model but this time with all the 20677 dataset record (no splitting)\nmodel = Sequential()\nmodel.add(Dense(X.shape[1],input_dim=23, activation='relu',\n kernel_initializer='random_normal'))\nmodel.add(Dense(12,activation='relu',kernel_initializer='random_normal'))\nmodel.add(Dense(6,activation='relu',kernel_initializer='random_normal'))\nmodel.add(Dense(3,activation='softmax'))\nmodel.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', \n optimizer='adam',\n metrics =['accuracy'])\nmonitor = EarlyStopping(monitor='val_loss', min_delta=1e-3, patience=5, \n verbose=1, mode='auto', restore_best_weights=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model.fit(scaled_X,y,validation_data=(X_test,y_test),callbacks=[monitor],verbose=2,epochs=500)",
"Train on 20677 samples, validate on 5170 samples\nEpoch 1/500\n20677/20677 - 2s - loss: 0.8724 - accuracy: 0.5154 - val_loss: 0.8197 - val_accuracy: 0.5251\nEpoch 2/500\n20677/20677 - 1s - loss: 0.3644 - accuracy: 0.8624 - val_loss: 0.1008 - val_accuracy: 0.9375\nEpoch 3/500\n20677/20677 - 1s - loss: 0.0682 - accuracy: 0.9700 - val_loss: 0.0462 - val_accuracy: 0.9990\nEpoch 4/500\n20677/20677 - 1s - loss: 0.0329 - accuracy: 0.9989 - val_loss: 0.0146 - val_accuracy: 0.9998\nEpoch 5/500\n20677/20677 - 1s - loss: 0.0059 - accuracy: 0.9998 - val_loss: 0.0027 - val_accuracy: 1.0000\nEpoch 6/500\n20677/20677 - 1s - loss: 0.0016 - accuracy: 0.9999 - val_loss: 6.3667e-04 - val_accuracy: 1.0000\nEpoch 7/500\n20677/20677 - 1s - loss: 9.8296e-04 - accuracy: 1.0000 - val_loss: 3.3676e-04 - val_accuracy: 1.0000\nEpoch 8/500\n20677/20677 - 1s - loss: 7.0066e-04 - accuracy: 0.9999 - val_loss: 1.8019e-04 - val_accuracy: 1.0000\nEpoch 9/500\n20677/20677 - 1s - loss: 5.9281e-04 - accuracy: 1.0000 - val_loss: 1.3180e-04 - val_accuracy: 1.0000\nEpoch 10/500\n20677/20677 - 1s - loss: 5.7430e-04 - accuracy: 0.9999 - val_loss: 9.3424e-05 - val_accuracy: 1.0000\nEpoch 11/500\nRestoring model weights from the end of the best epoch.\n20677/20677 - 1s - loss: 5.1592e-04 - accuracy: 1.0000 - val_loss: 7.0276e-04 - val_accuracy: 1.0000\nEpoch 00011: early stopping\n"
],
[
"from tensorflow.keras.models import load_model",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Saving the model\nmodel.save('Food_racall_draft.h5')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"predictions = model.predict(X)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"predictions = np.argmax(predictions,axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import joblib",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Save the scaler\njoblib.dump(scaler, 'food_recall_scaler.pki')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# this list will hold all products classified as class I or II \nClass_I_and_II_products = []",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# In this prediction model the predicted items are at the same index as they were in the original dataframe\n# for example if product id 184301 was at position 44 in the original dataframe i.e df then it will be at the same\n# index position 44 in the predictions\n\nfor index in range(df.shape[0]):\n if predictions[index] ==0 | predictions[index] ==1:\n Class_I_and_II_products.append(df.loc[index,['Product ID']][0]) # get the preduct id if it's class I or II",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# A list of product classified as class I and II with potentital to be withdrawn. \nClass_I_and_II_products[:20]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Determine which countries whose recalled products are classified as Class I or II \nviolating_Countries = [df.loc[index,['Recalling_Firm_Country']][0] for index in range(df.shape[0]) if predictions[index] ==0 |predictions[index] ==1]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def High_Violating_countries(Country_list):\n \n country_dictionary = {} \n for country in Country_list:\n if country not in country_dictionary:\n country_dictionary[country] = violating_Countries.count(country)\n sorted(country_dictionary.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)\n return country_dictionary\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"high_riask_countries = High_Violating_countries(violating_Countries)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# return countries that appears at least five times in the violation list.\nfor key, value in high_riask_countries.items():\n if value >= 5:\n print(\"{:>10} has {:>5} food products in Violation \".format(key, value))",
"United States has 8508 food products in Violation \n Canada has 53 food products in Violation \n France has 5 food products in Violation \n Chile has 6 food products in Violation \n Mexico has 6 food products in Violation \n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4ab8ea447e271fa862a659fa478eab9dec06ee47
| 75,023 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
model_registery/notebooks/run_weather_forecast.ipynb
|
dmatrix/tmls-workshop
|
ff6a6e4a7fbd5227142816821bf8699289e6f405
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 26 |
2020-11-17T14:33:01.000Z
|
2021-11-16T15:22:57.000Z
|
model_registery/notebooks/run_weather_forecast.ipynb
|
dmatrix/tmls-workshop
|
ff6a6e4a7fbd5227142816821bf8699289e6f405
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2021-08-09T20:42:02.000Z
|
2021-08-09T20:42:14.000Z
|
model_registery/notebooks/run_weather_forecast.ipynb
|
dmatrix/tmls-workshop
|
ff6a6e4a7fbd5227142816821bf8699289e6f405
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 7 |
2020-12-07T19:50:42.000Z
|
2021-11-02T03:25:05.000Z
| 50.283512 | 26,404 | 0.671274 |
[
[
[
"# Machine Learning application: Forecasting wind power. Using alternative energy for social & enviromental Good\n\n<table>\n <tr><td>\n <img src=\"https://github.com/dmatrix/mlflow-workshop-part-3/raw/master/images/wind_farm.jpg\"\n alt=\"Keras NN Model as Logistic regression\" width=\"800\">\n </td></tr>\n</table>\n\nIn this notebook, we will use the MLflow Model Registry to build a machine learning application that forecasts the daily power output of a [wind farm](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wind_farm). \n\nWind farm power output depends on weather conditions: generally, more energy is produced at higher wind speeds. Accordingly, the machine learning models used in the notebook predicts power output based on weather forecasts with three features: `wind direction`, `wind speed`, and `air temperature`.\n\n* This notebook uses altered data from the [National WIND Toolkit dataset](https://www.nrel.gov/grid/wind-toolkit.html) provided by NREL, which is publicly available and cited as follows:*\n\n* Draxl, C., B.M. Hodge, A. Clifton, and J. McCaa. 2015. Overview and Meteorological Validation of the Wind Integration National Dataset Toolkit (Technical Report, NREL/TP-5000-61740). Golden, CO: National Renewable Energy Laboratory.*\n\n* Draxl, C., B.M. Hodge, A. Clifton, and J. McCaa. 2015. \"The Wind Integration National Dataset (WIND) Toolkit.\" Applied Energy 151: 355366.*\n\n* Lieberman-Cribbin, W., C. Draxl, and A. Clifton. 2014. Guide to Using the WIND Toolkit Validation Code (Technical Report, NREL/TP-5000-62595). Golden, CO: National Renewable Energy Laboratory.*\n\n* King, J., A. Clifton, and B.M. Hodge. 2014. Validation of Power Output for the WIND Toolkit (Technical Report, NREL/TP-5D00-61714). Golden, CO: National Renewable Energy Laboratory.*\n\nGoogle's DeepMind publised a [AI for Social Good: 7 Inspiring Examples](https://www.springboard.com/blog/ai-for-good/) blog. One of example was\nhow Wind Farms can predict expected power ouput based on wind conditions and temperature, hence mitigating the burden from consuming\nenergy from fossil fuels. \n\n\n<table>\n <tr><td>\n <img src=\"https://github.com/dmatrix/ds4g-workshop/raw/master/notebooks/images/deepmind_system-windpower.gif\"\n alt=\"Deep Mind ML Wind Power\" width=\"400\">\n <img src=\"https://github.com/dmatrix/ds4g-workshop/raw/master/notebooks/images/machine_learning-value_wind_energy.max-1000x1000.png\"\n alt=\"Deep Mind ML Wind Power\" width=\"400\">\n </td></tr>\n</table>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import warnings\nwarnings.filterwarnings(\"ignore\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import mlflow\nmlflow.__version__",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Run some class and utility notebooks \n\nThis defines and allows us to use some Python model classes and utility functions",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%run ./rfr_class.ipynb",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%run ./utils_class.ipynb",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Load our training data\n\nIdeally, you would load it from a Feature Store or Delta Lake table",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Load and print dataset\ncsv_path = \"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/dmatrix/olt-mlflow/master/model_registery/notebooks/data/windfarm_data.csv\"\n\n# Use column 0 (date) as the index\nwind_farm_data = Utils.load_data(csv_path, index_col=0)\nwind_farm_data.head(5)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Get Training and Validation data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"X_train, y_train = Utils.get_training_data(wind_farm_data)\nval_x, val_y = Utils.get_validation_data(wind_farm_data)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Initialize a set of hyperparameters for the training and try three runs",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Initialize our model hyperparameters\nparams_list = [{\"n_estimators\": 100},\n {\"n_estimators\": 200},\n {\"n_estimators\": 300}]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mlflow.set_tracking_uri(\"sqlite:///mlruns.db\")\nmodel_name = \"WindfarmPowerForecastingModel\"\nfor params in params_list:\n rfr = RFRModel.new_instance(params)\n print(\"Using paramerts={}\".format(params))\n runID = rfr.mlflow_run(X_train, y_train, val_x, val_y, model_name, register=True)\n print(\"MLflow run_id={} completed with MSE={} and RMSE={}\".format(runID, rfr.mse, rfr.rsme))",
"Using paramerts={'n_estimators': 100}\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Let's Examine the MLflow UI\n1. Let's examine some models and start comparing their metrics\n2. **mlflow ui --backend-store-uri sqlite:///mlruns.db**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Integrating Model Registry with CI/CD Forecasting Application\n\n<table>\n <tr><td>\n <img src=\"https://github.com/dmatrix/mlflow-workshop-part-3/raw/master/images/forecast_app.png\"\n alt=\"Keras NN Model as Logistic regression\" width=\"800\">\n </td></tr>\n</table>\n\n1. Use the model registry fetch different versions of the model\n2. Score the model\n3. Select the best scored model\n4. Promote model to production, after testing",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Define a helper function to load PyFunc model from the registry\n<table>\n <tr><td> Save a Built-in MLflow Model Flavor and load as PyFunc Flavor</td></tr>\n <tr><td>\n <img src=\"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/dmatrix/mlflow-workshop-part-2/master/images/models_2.png\"\n alt=\"\" width=\"600\">\n </td></tr>\n</table>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def score_model(data, model_uri):\n model = mlflow.pyfunc.load_model(model_uri)\n return model.predict(data)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Load scoring data\n\nAgain, ideally you would load it from on-line or off-line FeatureStore",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Load the score data\nscore_path = \"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/dmatrix/olt-mlflow/master/model_registery/notebooks/data/score_windfarm_data.csv\"\nscore_df = Utils.load_data(score_path, index_col=0)\nscore_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Drop the power column since we are predicting that value\nactual_power = pd.DataFrame(score_df.power.values, columns=['power'])\nscore = score_df.drop(\"power\", axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Score the version 1 of the model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Formulate the model URI to fetch from the model registery\nmodel_uri = \"models:/{}/{}\".format(model_name, 1)\n\n# Predict the Power output \npred_1 = pd.DataFrame(score_model(score, model_uri), columns=[\"predicted_1\"])\npred_1",
"INFO [alembic.runtime.migration] Context impl SQLiteImpl.\nINFO [alembic.runtime.migration] Will assume non-transactional DDL.\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### Combine with the actual power",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"actual_power[\"predicted_1\"] = pred_1[\"predicted_1\"]\nactual_power",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Score the version 2 of the model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Formulate the model URI to fetch from the model registery\nmodel_uri = \"models:/{}/{}\".format(model_name, 2)\n\n# Predict the Power output\npred_2 = pd.DataFrame(score_model(score, model_uri), columns=[\"predicted_2\"])\npred_2",
"INFO [alembic.runtime.migration] Context impl SQLiteImpl.\nINFO [alembic.runtime.migration] Will assume non-transactional DDL.\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### Combine with the actual power",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"actual_power[\"predicted_2\"] = pred_2[\"predicted_2\"]\nactual_power",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Score the version 3 of the model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Formulate the model URI to fetch from the model registery\nmodel_uri = \"models:/{}/{}\".format(model_name, 3)\n\n# Formulate the model URI to fetch from the model registery\npred_3 = pd.DataFrame(score_model(score, model_uri), columns=[\"predicted_3\"])\npred_3",
"INFO [alembic.runtime.migration] Context impl SQLiteImpl.\nINFO [alembic.runtime.migration] Will assume non-transactional DDL.\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### Combine the values into a single pandas DataFrame",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"actual_power[\"predicted_3\"] = pred_3[\"predicted_3\"]\nactual_power",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Plot the combined predicited results vs the actual power",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%matplotlib inline\n\nactual_power.plot.line()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4ab8ffe100dd8353d2d6cf31b6eb80edf6c036e1
| 115,041 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
train.ipynb
|
NewLuminous/Zalo-Vietnamese-Wiki-QA
|
77ebee07d4555c9ee91a65921eec4adeb86a24c0
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
train.ipynb
|
NewLuminous/Zalo-Vietnamese-Wiki-QA
|
77ebee07d4555c9ee91a65921eec4adeb86a24c0
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
train.ipynb
|
NewLuminous/Zalo-Vietnamese-Wiki-QA
|
77ebee07d4555c9ee91a65921eec4adeb86a24c0
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 103.361186 | 13,376 | 0.800654 |
[
[
[
"# Clone the repo",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# # Clone the entire repo.\n# !git clone -b master --single-branch https://github.com/NewLuminous/Zalo-Vietnamese-Wiki-QA.git zaloqa\n# %cd zaloqa",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Install & load libraries",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import modeling\nimport evaluation\n%matplotlib inline\n\nimport warnings\nwarnings.filterwarnings('ignore')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# To reload a module while in the interactive mode\nimport importlib\nimportlib.reload(modeling)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Load data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from utils import data_loading\n\nzalo_data = data_loading.load(['zaloai'])\nzalo_data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Train & evaluate",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\n\nX = zalo_data.drop(columns=['label'])\ny = zalo_data['label']\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 0.1, random_state=42)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## LogisticRegression + CountVectorizer",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model = modeling.get_model('logit')(vectorizer='bow-ngram', random_state=42)\nmodel.fit(X_train, y_train)\ny_pred = model.predict(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('Accuracy:', evaluation.get_accuracy(y_test, y_pred))\nevaluation.print_classification_report(y_test, y_pred)",
"Accuracy: 0.6234124792932082\nClassification report:\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n False 0.73 0.70 0.72 1234\n True 0.42 0.46 0.44 577\n\n accuracy 0.62 1811\n macro avg 0.58 0.58 0.58 1811\nweighted avg 0.63 0.62 0.63 1811\n\n"
],
[
"evaluation.plot_confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## LogisticRegression + TfidfVectorizer",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model = modeling.get_model('logit')(vectorizer='tfidf', random_state=42)\nmodel.fit(X_train, y_train)\ny_pred = model.predict(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('Accuracy:', evaluation.get_accuracy(y_test, y_pred))\nevaluation.print_classification_report(y_test, y_pred)",
"Accuracy: 0.620651573716179\nClassification report:\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n False 0.72 0.72 0.72 1234\n True 0.41 0.41 0.41 577\n\n accuracy 0.62 1811\n macro avg 0.56 0.57 0.56 1811\nweighted avg 0.62 0.62 0.62 1811\n\n"
],
[
"evaluation.plot_confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## LogisticRegression + Keras's Embedding",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model = modeling.get_model('logit-embedding')()\nmodel.fit(X_train, y_train)\ny_pred = model.predict(X_test)",
"Model: \"functional_1\"\n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nLayer (type) Output Shape Param # Connected to \n==================================================================================================\ninput_1 (InputLayer) [(None, 40)] 0 \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ninput_2 (InputLayer) [(None, 500)] 0 \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nembedding (Embedding) (None, 40, 64) 1920000 input_1[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nembedding_1 (Embedding) (None, 500, 64) 1920000 input_2[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nflatten (Flatten) (None, 2560) 0 embedding[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nflatten_1 (Flatten) (None, 32000) 0 embedding_1[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconcatenate (Concatenate) (None, 34560) 0 flatten[0][0] \n flatten_1[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndense (Dense) (None, 10) 345610 concatenate[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndense_1 (Dense) (None, 1) 11 dense[0][0] \n==================================================================================================\nTotal params: 4,185,621\nTrainable params: 4,185,621\nNon-trainable params: 0\n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nEpoch 1/50\n3931/3931 [==============================] - 1555s 396ms/step - loss: 0.5587 - acc: 0.6774 - val_loss: 0.5227 - val_acc: 0.6977\nEpoch 2/50\n3931/3931 [==============================] - 1363s 347ms/step - loss: 0.4575 - acc: 0.7430 - val_loss: 0.5275 - val_acc: 0.6938\nEpoch 3/50\n3931/3931 [==============================] - 1394s 355ms/step - loss: 0.3853 - acc: 0.7953 - val_loss: 0.5962 - val_acc: 0.6927\nEpoch 4/50\n3931/3931 [==============================] - 1374s 349ms/step - loss: 0.3134 - acc: 0.8414 - val_loss: 0.7231 - val_acc: 0.6900\nEpoch 5/50\n3931/3931 [==============================] - 1383s 352ms/step - loss: 0.2521 - acc: 0.8772 - val_loss: 0.8231 - val_acc: 0.6827\nEpoch 6/50\n3931/3931 [==============================] - 1380s 351ms/step - loss: 0.2109 - acc: 0.8994 - val_loss: 0.8791 - val_acc: 0.6815\nEpoch 7/50\n3931/3931 [==============================] - 1376s 350ms/step - loss: 0.1805 - acc: 0.9144 - val_loss: 0.8953 - val_acc: 0.6789\nEpoch 8/50\n3931/3931 [==============================] - 1405s 357ms/step - loss: 0.1554 - acc: 0.9263 - val_loss: 1.0633 - val_acc: 0.6845\n"
],
[
"print('Accuracy:', evaluation.get_accuracy(y_test, y_pred))\nevaluation.print_classification_report(y_test, y_pred)",
"Accuracy: 0.6570955273329652\nClassification report:\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n False 0.70 0.87 0.78 1234\n True 0.42 0.20 0.27 577\n\n accuracy 0.66 1811\n macro avg 0.56 0.54 0.52 1811\nweighted avg 0.61 0.66 0.62 1811\n\n"
],
[
"evaluation.plot_confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## LogisticRegression + Word2Vec",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model = modeling.get_model('logit')(vectorizer='word2vec', random_state=42)\nmodel.fit(X_train, y_train)\ny_pred = model.predict(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('Accuracy:', evaluation.get_accuracy(y_test, y_pred))\nevaluation.print_classification_report(y_test, y_pred)",
"Accuracy: 0.6515737161789067\nClassification report:\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n False 0.74 0.74 0.74 1234\n True 0.45 0.45 0.45 577\n\n accuracy 0.65 1811\n macro avg 0.60 0.60 0.60 1811\nweighted avg 0.65 0.65 0.65 1811\n\n"
],
[
"evaluation.plot_confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## CRNN",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model = modeling.get_model('crnn')()\nmodel.fit(X_train, y_train)",
"Model: \"functional_3\"\n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nLayer (type) Output Shape Param # Connected to \n==================================================================================================\ninput_4 (InputLayer) [(None, None, 50)] 0 \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconv1d_3 (Conv1D) (None, None, 400) 100400 input_4[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ninput_3 (InputLayer) [(None, None, 50)] 0 \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nmax_pooling1d_3 (MaxPooling1D) (None, None, 400) 0 conv1d_3[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconv1d_2 (Conv1D) (None, None, 200) 50200 input_3[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconv1d_4 (Conv1D) (None, None, 600) 1200600 max_pooling1d_3[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nmax_pooling1d_2 (MaxPooling1D) (None, None, 200) 0 conv1d_2[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nmax_pooling1d_4 (MaxPooling1D) (None, None, 600) 0 conv1d_4[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nbidirectional_2 (Bidirectional) (None, 40) 35360 max_pooling1d_2[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nbidirectional_3 (Bidirectional) (None, 140) 375760 max_pooling1d_4[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconcatenate_1 (Concatenate) (None, 180) 0 bidirectional_2[0][0] \n bidirectional_3[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndense_4 (Dense) (None, 128) 23168 concatenate_1[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndropout_1 (Dropout) (None, 128) 0 dense_4[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndense_5 (Dense) (None, 256) 33024 dropout_1[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndropout_2 (Dropout) (None, 256) 0 dense_5[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndense_6 (Dense) (None, 1) 257 dropout_2[0][0] \n==================================================================================================\nTotal params: 1,818,769\nTrainable params: 1,818,769\nNon-trainable params: 0\n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nEpoch 1/50\n 2/19317 [..............................] - ETA: 6:26:54 - loss: 0.6666 - acc: 0.5000WARNING:tensorflow:Callbacks method `on_train_batch_end` is slow compared to the batch time (batch time: 0.0930s vs `on_train_batch_end` time: 2.3098s). Check your callbacks.\n19317/19317 [==============================] - 320s 17ms/step - loss: 0.6978 - acc: 0.5976 - val_loss: 0.6734 - val_acc: 0.6017\nEpoch 2/50\n19317/19317 [==============================] - 263s 14ms/step - loss: 0.6833 - acc: 0.6285 - val_loss: 0.6600 - val_acc: 0.6323\nEpoch 3/50\n19317/19317 [==============================] - 265s 14ms/step - loss: 0.6843 - acc: 0.6356 - val_loss: 0.6816 - val_acc: 0.6498\nEpoch 4/50\n19317/19317 [==============================] - 264s 14ms/step - loss: 0.6797 - acc: 0.6381 - val_loss: 0.6847 - val_acc: 0.6421\nEpoch 5/50\n19317/19317 [==============================] - 270s 14ms/step - loss: 0.6797 - acc: 0.6387 - val_loss: 0.6654 - val_acc: 0.6498\nEpoch 6/50\n19317/19317 [==============================] - 265s 14ms/step - loss: 0.6803 - acc: 0.6465 - val_loss: 0.6709 - val_acc: 0.6365\nEpoch 7/50\n19317/19317 [==============================] - 265s 14ms/step - loss: 0.6792 - acc: 0.6429 - val_loss: 0.6505 - val_acc: 0.6592\nEpoch 8/50\n19317/19317 [==============================] - 265s 14ms/step - loss: 0.6760 - acc: 0.6460 - val_loss: 0.7021 - val_acc: 0.6214\nEpoch 9/50\n19317/19317 [==============================] - 261s 14ms/step - loss: 0.6785 - acc: 0.6446 - val_loss: 0.6749 - val_acc: 0.6512\nEpoch 10/50\n19317/19317 [==============================] - 262s 14ms/step - loss: 0.6815 - acc: 0.6450 - val_loss: 0.6611 - val_acc: 0.6477\nEpoch 11/50\n19317/19317 [==============================] - 266s 14ms/step - loss: 0.6796 - acc: 0.6460 - val_loss: 0.6654 - val_acc: 0.6567\nEpoch 12/50\n19317/19317 [==============================] - 264s 14ms/step - loss: 0.6747 - acc: 0.6472 - val_loss: 0.6645 - val_acc: 0.6486\nEpoch 13/50\n19317/19317 [==============================] - 263s 14ms/step - loss: 0.6750 - acc: 0.6495 - val_loss: 0.6897 - val_acc: 0.6411\nEpoch 14/50\n19317/19317 [==============================] - 263s 14ms/step - loss: 0.6728 - acc: 0.6508 - val_loss: 0.6914 - val_acc: 0.6140\nEpoch 15/50\n19317/19317 [==============================] - 261s 13ms/step - loss: 0.6812 - acc: 0.6489 - val_loss: 0.6722 - val_acc: 0.6478\n"
],
[
"y_pred = model.predict(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('Accuracy:', evaluation.get_accuracy(y_test, y_pred))\nevaluation.print_classification_report(y_test, y_pred)",
"Accuracy: 0.6212037548315847\nClassification report:\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n False 0.67 0.86 0.76 1234\n True 0.26 0.10 0.15 577\n\n accuracy 0.62 1811\n macro avg 0.47 0.48 0.45 1811\nweighted avg 0.54 0.62 0.56 1811\n\n"
],
[
"evaluation.plot_confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## CRNN + Attention",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model = modeling.get_model('crnn-attention')()\nmodel.fit(X_train, y_train)",
"Model: \"functional_1\"\n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nLayer (type) Output Shape Param # Connected to \n==================================================================================================\ninput_2 (InputLayer) [(None, None, 50)] 0 \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconv1d (Conv1D) (None, None, 128) 32128 input_2[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nmax_pooling1d (MaxPooling1D) (None, None, 128) 0 conv1d[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconv1d_1 (Conv1D) (None, None, 128) 82048 max_pooling1d[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ninput_1 (InputLayer) [(None, None, 50)] 0 \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nmax_pooling1d_1 (MaxPooling1D) (None, None, 128) 0 conv1d_1[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nbidirectional (Bidirectional) (None, 128) 58880 input_1[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nbidirectional_1 (Bidirectional) (None, 128) 98816 max_pooling1d_1[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndense (Dense) (None, 128) 16512 bidirectional[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndense_1 (Dense) (None, 128) 16512 bidirectional_1[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nmultiply (Multiply) (None, 128) 0 bidirectional[0][0] \n dense[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nmultiply_1 (Multiply) (None, 128) 0 bidirectional_1[0][0] \n dense_1[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconcatenate (Concatenate) (None, 256) 0 multiply[0][0] \n multiply_1[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndense_2 (Dense) (None, 128) 32896 concatenate[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndropout (Dropout) (None, 128) 0 dense_2[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndense_3 (Dense) (None, 1) 129 dropout[0][0] \n==================================================================================================\nTotal params: 337,921\nTrainable params: 337,921\nNon-trainable params: 0\n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nEpoch 1/50\n 1/125802 [..............................] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.6942 - acc: 0.0000e+00WARNING:tensorflow:From C:\\Users\\Admin\\AppData\\Roaming\\Python\\Python37\\site-packages\\tensorflow\\python\\ops\\summary_ops_v2.py:1277: stop (from tensorflow.python.eager.profiler) is deprecated and will be removed after 2020-07-01.\nInstructions for updating:\nuse `tf.profiler.experimental.stop` instead.\n125802/125802 [==============================] - 1597s 13ms/step - loss: 0.6472 - acc: 0.6396 - val_loss: 0.6302 - val_acc: 0.6613\nEpoch 2/50\n125802/125802 [==============================] - 1528s 12ms/step - loss: 0.6287 - acc: 0.6607 - val_loss: 0.6241 - val_acc: 0.6654\nEpoch 3/50\n125802/125802 [==============================] - 1532s 12ms/step - loss: 0.6192 - acc: 0.6689 - val_loss: 0.6283 - val_acc: 0.6672\nEpoch 4/50\n125802/125802 [==============================] - 1527s 12ms/step - loss: 0.6118 - acc: 0.6744 - val_loss: 0.6297 - val_acc: 0.6640\nEpoch 5/50\n125802/125802 [==============================] - 1525s 12ms/step - loss: 0.6077 - acc: 0.6792 - val_loss: 0.6330 - val_acc: 0.6708\nEpoch 6/50\n125802/125802 [==============================] - 1501s 12ms/step - loss: 0.6051 - acc: 0.6805 - val_loss: 0.6293 - val_acc: 0.6695\nEpoch 7/50\n125802/125802 [==============================] - 1505s 12ms/step - loss: 0.6028 - acc: 0.6821 - val_loss: 0.6393 - val_acc: 0.6682\nEpoch 8/50\n125802/125802 [==============================] - 1500s 12ms/step - loss: 0.6036 - acc: 0.6829 - val_loss: 0.6380 - val_acc: 0.6650\nEpoch 9/50\n125802/125802 [==============================] - 1579s 13ms/step - loss: 0.6022 - acc: 0.6828 - val_loss: 0.6436 - val_acc: 0.6633\nEpoch 10/50\n125802/125802 [==============================] - 1597s 13ms/step - loss: 0.6034 - acc: 0.6839 - val_loss: 0.6278 - val_acc: 0.6643\nEpoch 11/50\n125802/125802 [==============================] - 1555s 12ms/step - loss: 0.6038 - acc: 0.6840 - val_loss: 0.6300 - val_acc: 0.6656\nEpoch 12/50\n125802/125802 [==============================] - 1580s 13ms/step - loss: 0.6053 - acc: 0.6831 - val_loss: 0.6311 - val_acc: 0.6664\nEpoch 13/50\n125802/125802 [==============================] - 1608s 13ms/step - loss: 0.6088 - acc: 0.6807 - val_loss: 0.6276 - val_acc: 0.6673\n"
],
[
"y_pred = model.predict(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('Accuracy:', evaluation.get_accuracy(y_test, y_pred))\nevaluation.print_classification_report(y_test, y_pred)",
"Accuracy: 0.49088901159580345\nClassification report:\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n False 0.66 0.53 0.59 1234\n True 0.29 0.41 0.34 577\n\n accuracy 0.49 1811\n macro avg 0.47 0.47 0.46 1811\nweighted avg 0.54 0.49 0.51 1811\n\n"
],
[
"evaluation.plot_confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4ab900c5246256d3c3665382c1be4140e9938ba5
| 6,186 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
WebVisualizations/convert_to_html.ipynb
|
tpweste/Web-Design-Challenge
|
5da2edfc23907bacd794efd4a5b58d3988595f8b
|
[
"ADSL"
] | null | null | null |
WebVisualizations/convert_to_html.ipynb
|
tpweste/Web-Design-Challenge
|
5da2edfc23907bacd794efd4a5b58d3988595f8b
|
[
"ADSL"
] | null | null | null |
WebVisualizations/convert_to_html.ipynb
|
tpweste/Web-Design-Challenge
|
5da2edfc23907bacd794efd4a5b58d3988595f8b
|
[
"ADSL"
] | null | null | null | 27.0131 | 89 | 0.348367 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cities_df = pd.read_csv(\"cities.csv\")\ncities_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cities_HTML = cities_df.to_html()\nhtml = cities_HTML\nprint(html[0:500])",
"<table border=\"1\" class=\"dataframe\">\n <thead>\n <tr style=\"text-align: right;\">\n <th></th>\n <th>City_ID</th>\n <th>City</th>\n <th>Cloudiness</th>\n <th>Country</th>\n <th>Date</th>\n <th>Humidity</th>\n <th>Lat</th>\n <th>Lng</th>\n <th>Max Temp</th>\n <th>Wind Speed</th>\n </tr>\n </thead>\n <tbody>\n <tr>\n <th>0</th>\n <td>0</td>\n <td>jacareacanga</td>\n <td>0</td>\n <td>BR</td>\n <td>1528902000</td>\n <td>62</\n"
],
[
"with open(\"table_data.html\", \"w\") as file:\n file.write(html)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4ab90f632047bfa5772dd53253fdbf818d835f84
| 26,852 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/airr_c/SADIE_DEMO.ipynb
|
jwillis0720/pybody
|
2d7c68650ac1ef5f3003ccb67171898eac1f63eb
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/airr_c/SADIE_DEMO.ipynb
|
jwillis0720/pybody
|
2d7c68650ac1ef5f3003ccb67171898eac1f63eb
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/airr_c/SADIE_DEMO.ipynb
|
jwillis0720/pybody
|
2d7c68650ac1ef5f3003ccb67171898eac1f63eb
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 30.103139 | 401 | 0.581484 |
[
[
[
"<!--NAVIGATION-->\n<!--NAVIGATION-->\n<!-- markdownlint-disable -->\n<h2 align=\"center\" style=\"font-family:verdana;font-size:150%\"> <b>S</b>equencing <b>A</b>nalysis and <b>D</b>ata Library for <b>I</b>mmunoinformatics <b>E</b>xploration <br><br>Demonstration for AIRR-C 2022</h2>\n<div align=\"center\">\n <img src=\"https://sadiestaticcrm.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/Sadie.svg\" alt=\"SADIE\" style=\"margin:0.2em;width:50%\">\n</div>\n<br>\n\n<a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/jwillis0720/sadie/blob/airr_c/notebooks/airr_c/SADIE_DEMO.ipynb\"><img align=\"center\" src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open in Colab\" title=\"Open in Google Colaboratory\"></a>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Setup\n\nHere we will setup our files for the demo. If you are running the notebook locally, these files don't need to be pulled from the repository",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def install_packages() -> None:\n !pip -q install git+https://github.com/jwillis0720/sadie.git\n !pip -q install seaborn matplotlib\n\n\ndef get_demo_files() -> None:\n \"\"\"Get the demonstration files for AIRR-C 2022\"\"\"\n !wget -q -O input.tgz https://github.com/jwillis0720/sadie/raw/airr_c/notebooks/airr_c/input.tgz\n !tar -xf input.tgz\n\n\nimport sys\n\nif \"google.colab\" in sys.modules:\n install_packages()\n get_demo_files()\nelse:\n %load_ext lab_black",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 1. Low Level\n\nFirst, let's start at a very low level. These are pythonic objects that model the data we expect in an AIRR compliant data format. They are divided by [AIRR 1.3 Rearragment category](https://docs.airr-community.org/en/stable/datarep/rearrangements.html)\n\n* Input Sequence\n* Primay Annotations\n* Alignment Annotations\n* Alignment Positions\n* RegionSequences\n* RegionPositions\n\n\nAll of these are combined as a `Receptor Chain` Object. \n\nNow let's take a look how a person interested in low level programming could use these objects",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## First Model - Input Sequence",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sadie.receptor.rearrangment import InputSequence\nfrom Bio import SeqIO\nfrom pprint import pprint\n\nvrc01_heavy_sequecne = SeqIO.read(\"input/vrc01_heavy.fasta\", \"fasta\")\n\n# make an input sequence model\ninput_sequence_model = InputSequence(\n sequence_id=vrc01_heavy_sequecne.name,\n sequence=vrc01_heavy_sequecne.seq,\n raw_sequence=vrc01_heavy_sequecne.seq,\n)\n\n# Print out dictionary to see\npprint(input_sequence_model.__dict__)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Second Model - Primary Annotations",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sadie.receptor.rearrangment import PrimaryAnnotations\n\n# make a primary sequence model\nprimary_sequence_annotation_model = PrimaryAnnotations(\n rev_comp=False,\n productive=True,\n vj_in_frame=True,\n stop_codon=False,\n complete_vdj=True,\n locus=\"IGH\",\n v_call=\"IGHV1-2*02\",\n d_call=[\"IGHD3-16*01\", \"IGHD3-16*02\"],\n j_call=\"IGHJ1*01\",\n v_call_top=\"IGHV1-2*02\",\n d_call_top=\"IGHD3-16*01\",\n j_call_top=\"IGHJ1*01\",\n c_call=\"IGHG1*01\",\n)\n# pretty print the dictionary attribute\npprint(primary_sequence_annotation_model.__dict__)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Alignment Annotations",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sadie.receptor.rearrangment import AlignmentAnnotations\n\n# Model 3 - Alignment Annotations\nalignment_annotations_model = AlignmentAnnotations(\n sequence_alignment=\"CAGGTGCAGCTGGTGCAGTCTGGGGGTCAGATGAAGAAGCCTGGCGAGTCGATGAGAATTTCTTGTCGGGCTTCTGGATATGAATTTATTGATTGTACGCTAAATTGGATTCGTCTGGCCCCCGGAAAAAGGCCTGAGTGGATGGGATGGCTGAAGCCTCGGGGGGGGGCCGTCAACTACGCACGTCCACTTCAGGGCAGAGTGACCATGACTCGAGACGTTTATTCCGACACAGCCTTTTTGGAGCTGCGCTCGTTGACAGTAGACGACACGGCCGTCTACTTTTGTACTAGGGGAAAAAACTGTGATTACAATTGGGACTTCGAACACTGGGGCCGGGGCACCCCGGTCATCGTCTCATCAG\",\n sequence_alignment_aa=\"QVQLVQSGGQMKKPGESMRISCRASGYEFIDCTLNWIRLAPGKRPEWMGWLKPRGGAVNYARPLQGRVTMTRDVYSDTAFLELRSLTVDDTAVYFCTRGKNCDYNWDFEHWGRGTPVIVSS\",\n germline_alignment=\"CAGGTGCAGCTGGTGCAGTCTGGGGCTGAGGTGAAGAAGCCTGGGGCCTCAGTGAAGGTCTCCTGCAAGGCTTCTGGATACACCTTCACCGGCTACTATATGCACTGGGTGCGACAGGCCCCTGGACAAGGGCTTGAGTGGATGGGATGGATCAACCCTAACAGTGGTGGCACAAACTATGCACAGAAGTTTCAGGGCAGGGTCACCATGACCAGGGACACGTCCATCAGCACAGCCTACATGGAGCTGAGCAGGCTGAGATCTGACGACACGGCCGTGTATTACTGTGCGAGNNNNNNNNNNNNTGATTACGTTTGGGACTTCCAGCACTGGGGCCAGGGCACCCTGGTCACCGTCTCCTCAG\",\n germline_alignment_aa=\"QVQLVQSGAEVKKPGASVKVSCKASGYTFTGYYMHWVRQAPGQGLEWMGWINPNSGGTNYAQKFQGRVTMTRDTSISTAYMELSRLRSDDTAVYYCAXXXXXDYVWDFQHWGQGTLVTVSS\",\n v_score=168.2,\n d_score=17.8,\n j_score=52.6,\n v_identity=0.6825,\n d_identity=0.85,\n j_identity=0.86,\n v_cigar=\"6S293M76S3N\",\n d_cigar=\"311S6N14M50S17N\",\n j_cigar=\"325S7N45M5S\",\n v_support=6.796e-44,\n d_support=0.5755,\n j_support=5.727e-11,\n junction=\"TGTACTAGGGGAAAAAACTGTGATTACAATTGGGACTTCGAACACTGG\",\n junction_aa=\"CTRGKNCDYNWDFEHW\",\n np1=\"GGGAAAAAACTG\",\n c_score=100,\n c_identity=1,\n c_support=1e-44,\n c_cigar=\"6S293M76S3N\",\n)\n# alignment_sequence_annotation_model = AlignmentAnnotations(**alignment_dict)\npprint(alignment_annotations_model.__dict__)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Optional but recommended models\n\n## AlignmentPositions",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sadie.receptor.rearrangment import AlignmentPositions\n\nalignment_positions_dict = dict(\n v_sequence_start=7,\n v_sequence_end=299,\n v_germline_start=1,\n v_germline_end=293,\n v_alignment_start=1,\n v_alignment_end=293,\n d_sequence_start=312,\n d_sequence_end=325,\n d_germline_start=7,\n d_germline_end=20,\n d_alignment_start=306,\n d_alignment_end=319,\n j_sequence_start=326,\n j_sequence_end=370,\n j_germline_start=8,\n j_germline_end=52,\n j_alignment_start=320,\n j_alignment_end=364,\n)\nalignment_positions_model = AlignmentPositions(**alignment_positions_dict)\n# pretty print dictonary\npprint(alignment_positions_model.__dict__)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## RegionSequences",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sadie.receptor.rearrangment import RegionSequences\n\nregion_sequence_dict = dict(\n fwr=\"CAGGTGCAGCTGGTGCAGTCTGGGGGTCAGATGAAGAAGCCTGGCGAGTCGATGAGAATTTCTTGTCGGGCTTCT\",\n fwr1_aa=\"QVQLVQSGGQMKKPGESMRISCRAS\",\n cdr1=\"GGATATGAATTTATTGATTGTACG\",\n cdr1_aa=\"GYEFIDCT\",\n fwr2=\"CTAAATTGGATTCGTCTGGCCCCCGGAAAAAGGCCTGAGTGGATGGGATGG\",\n fwr2_aa=\"LNWIRLAPGKRPEWMGW\",\n cdr2=\"CTGAAGCCTCGGGGGGGGGCCGTC\",\n cdr2_aa=\"LKPRGGAV\",\n fwr3=\"AACTACGCACGTCCACTTCAGGGCAGAGTGACCATGACTCGAGACGTTTATTCCGACACAGCCTTTTTGGAGCTGCGCTCGTTGACAGTAGACGACACGGCCGTCTACTTTTGT\",\n fwr3_aa=\"NYARPLQGRVTMTRDVYSDTAFLELRSLTVDDTAVYFC\",\n cdr3=\"ACTAGGGGAAAAAACTGTGATTACAATTGGGACTTCGAACAC\",\n cdr3_aa=\"TRGKNCDYNWDFEH\",\n fwr4=\"TGGGGCCGGGGCACCCCGGTCATCGTCTCATCA\",\n fwr4_aa=\"WGRGTPVIVSS\",\n)\nregion_sequence_model = RegionSequences(**region_sequence_dict)\npprint(region_sequence_model.__dict__)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sadie.receptor.rearrangment import RegionPositions\n\nregion_positions_dict = dict(\n fwr1_start=7,\n fwr1_end=81,\n cdr1_start=82,\n cdr1_end=105,\n fwr2_start=106,\n fwr2_end=156,\n cdr2_start=157,\n cdr2_end=180,\n fwr3_start=181,\n fwr3_end=294,\n cdr3_start=295,\n cdr3_end=336,\n fwr4_start=337,\n fwr4_end=369,\n)\nregion_position_model = RegionPositions(**region_positions_dict)\npprint(region_position_model.__dict__)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Junction Lengths",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sadie.receptor.rearrangment import JunctionLengths\n\njunction_length_dict = dict(\n junction_length=48,\n junction_aa_length=None,\n np1_length=None,\n np2_length=None,\n np3_length=None,\n n1_length=None,\n n2_length=None,\n n3_length=None,\n p3v_length=None,\n p5d_length=None,\n p3d_length=None,\n p5d2_length=None,\n p3d2_length=None,\n p5j_length=None,\n)\njunction_length_model = JunctionLengths(**junction_length_dict)\npprint(junction_length_model.__dict__)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## ReceptorChain\n\nAll of those annotations can now be [composed](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0mcP8ZpUR38) into a ReceptorChain model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sadie.receptor.rearrangment import ReceptorChain\n\nreceptor_chain = ReceptorChain(\n input_sequence=input_sequence_model,\n primary_annotations=primary_sequence_annotation_model,\n alignment_annotations=alignment_annotations_model,\n alignment_positions=alignment_positions_model,\n region_sequences=region_sequence_model,\n region_positions=region_sequence_model,\n junction_lengths=junction_length_model,\n)\nprint(receptor_chain)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 2. Mid-level\n\nOkay, but maybe you don't even care about composing low level objects. You just have a sequence without the proper annotations. You can use convienience methods to quickly fill in the annotations in the model. How does it align and annotate? More on that later\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"receptor_chain = ReceptorChain.from_single(\"vrc01_heavy\", vrc01_heavy_sequecne.seq)\n# Same as before but from the `from_single` method\nprint(receptor_chain)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<h1><u> Using the SADIE AIRR module:</u></h1>\n\nSADIE AIRR will annotate sequences, verify fields, and return an AirrTable. The AirrTable is a subclass of a pandas dataframe so anything you can do on pandas, you can do on an AirrTable.\n\nThere are a variety of databases that ship with SADIE:\n\n<u>From IMGT</u>\n - CLK\n - Dog\n - Human\n - Mouse\n - Rabbit\n - Rat\n \n<u> Custom </u>\n - Macaque",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def plot_v_genes(df_one, df_two, colors=[\"red\", \"blue\"]):\n \"\"\"very simple function to plot v gene dataframes\"\"\"\n fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(15, 3))\n for df, axis, color in zip([df_one, df_two], axes, colors):\n df[\"v_call_top\"].str.split(\"*\").str.get(0).value_counts().plot(\n kind=\"bar\", color=color, ax=axis\n )\n axis.set_ylabel(\"Counts\")\n sns.despine()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sadie.airr import Airr\nimport seaborn as sns\nfrom matplotlib import pyplot as plt\nimport logging\n\n\nlogger = logging.getLogger()\nlogger.setLevel(\"INFO\")\n\nairr_api_human = Airr(\"human\", database=\"imgt\", adaptable=True)\ncatnap_heavy_base = airr_api_human.run_fasta(\"input/catnap_nt_heavy_sub.fasta\")\ncatnap_light_base = airr_api_human.run_fasta(\"input/catnap_nt_light_sub.fasta\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sadie.airr.airrtable import LinkedAirrTable\n\ncatnap_merged = LinkedAirrTable(\n catnap_heavy_base.merge(\n catnap_heavy_base, on=\"sequence_id\", how=\"inner\", suffixes=[\"_heavy\", \"_light\"]\n )\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# make a pretty plot of the V gene usage\nplot_v_genes(catnap_heavy_base, catnap_light_base)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Alternate species\n\nOkay, but what about a different species. Let's try the mouse repertoire as identified by IMGT",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"airr_api_mouse = Airr(\"mouse\", database=\"imgt\", adaptable=False)\ncatnap_heavy_mouse = airr_api_mouse.run_fasta(\"input/catnap_nt_heavy_sub.fasta\")\ncatnap_light_mouse = airr_api_mouse.run_fasta(\"input/catnap_nt_light_sub.fasta\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plot_v_genes(catnap_heavy_mouse, catnap_heavy_mouse)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Custom Databases - How about Watson/Karlsson-Hedestam?\n\nIn this instance, instead of calling things from IMGT, let's use a custom database we have in [G3](https://g3.jordanrwillis.com/docs) ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"airr_api_macaque = Airr(\"macaque\", database=\"custom\", adaptable=False)\ncatnap_heavy_macaque = airr_api_macaque.run_fasta(\"input/catnap_nt_heavy_sub.fasta\")\ncatnap_light_macaque = airr_api_macaque.run_fasta(\"input/catnap_nt_light_sub.fasta\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plot_v_genes(catnap_heavy_macaque, catnap_heavy_macaque)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<h1><u> Using the SADIE Reference module:</u></h1>\n\nSADIE uses a reference database. It uses a real time web API caled the *G*ermline *G*ene *G*ateway which provides realtime, currated genes avaialble via a RESTful API that conforms to [OpenAPI standards](https://swagger.io/specification/)\n\n[Let's take a look at the reference database](https://g3.jordanrwillis.com/docs)\n\nSince it's RESTful, we can gather database information programatically in real time!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import requests\nimport pandas as pd\n\n# We can just query our gene database progrmatically...this is super handy if you are changing reference databases on the fly\nresults_json = requests.get(\n \"https://g3.jordanrwillis.com/api/v1/genes?source=imgt&common=human&segment=V&limit=3\"\n).json()\n\n# turn the JSON into a dataframe\nresults_df = pd.json_normalize(results_json)\nresults_df",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Using reference objects to make custom/altered reference databaes",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import tempfile\nfrom sadie.reference import Reference\n\n# create empty reference object\nreference = Reference()\n\n# Add Genes one at a time, right in the program\nreference.add_gene(\n {\n \"species\": \"custom\",\n \"sub_species\": \"human\",\n \"gene\": \"IGHV1-2*01\",\n \"database\": \"imgt\",\n }\n)\nreference.add_gene(\n {\n \"species\": \"custom\",\n \"sub_species\": \"human\",\n \"gene\": \"IGHV3-15*01\",\n \"database\": \"imgt\",\n }\n)\nreference.add_gene(\n {\n \"species\": \"custom\",\n \"sub_species\": \"human\",\n \"gene\": \"IGHJ6*01\",\n \"database\": \"imgt\",\n }\n)\nreference.add_gene(\n {\n \"species\": \"custom\",\n \"sub_species\": \"mouse\",\n \"gene\": \"IGKJ5*01\",\n \"database\": \"imgt\",\n }\n)\nreference.add_gene(\n {\n \"species\": \"custom\",\n \"sub_species\": \"mouse\",\n \"gene\": \"IGKV10-96*04\",\n \"database\": \"imgt\",\n }\n)\nreference.add_gene(\n {\n \"species\": \"custom\",\n \"sub_species\": \"human\",\n \"gene\": \"IGHD3-3*01\",\n \"database\": \"imgt\",\n }\n)\n\n# Add a mouse gene in humans!\nreference.add_gene(\n {\n \"species\": \"custom\",\n \"sub_species\": \"mouse\",\n \"gene\": \"IGHV1-11*01\",\n \"database\": \"imgt\",\n }\n)\nlogger.setLevel(\"WARNING\")\nreference.get_dataframe()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# When we setup the API we can now pass a reference object we built\ncustom_airr_api = Airr(reference)\n\n# our custom results\noutput_custom_results_heavy = custom_airr_api.run_fasta(\n \"input/catnap_nt_heavy_sub.fasta\"\n)\noutput_custom_results_light = custom_airr_api.run_fasta(\n \"input/catnap_nt_light_sub.fasta\"\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plot_v_genes(output_custom_results_heavy, output_custom_results_light)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# SADIE Numbeing for AA sequences\n\nInspired from ANARCI, we can also renumber AA sequences in the following schemes:\n\n* Kabat\n* Chothia\n* IMGT\n* Martin\n* Aho\n\nAnd be able to deliniate CDR boundaries from \n\n* Kabat\n* Chothia\n* IMGT\n* SCDR",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sadie.hmmer import HMMER\n\n# setup numbering api\nhmmer_numbering_api = HMMER(\"imgt\", \"imgt\")\nresults = hmmer_numbering_api.run_dataframe(catnap_heavy_base, \"sequence_id\", \"vdj_aa\")\nresults_imgt = results.drop([\"domain_no\", \"hmm_species\", \"score\"], axis=1).rename(\n {\"Id\": \"sequence_id\"}, axis=1\n)\nresults_imgt",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Kabat numbering with Chothia boundaries\nhmmer_numbering_api = HMMER(\"kabat\", \"chothia\")\nresults = hmmer_numbering_api.run_dataframe(catnap_heavy_base, \"sequence_id\", \"vdj_aa\")\n\n\nchothia_results = results.drop([\"domain_no\", \"hmm_species\", \"score\"], axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"alignment_numbering = chothia_results.get_alignment_table()\nalignment_numbering",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
" Now it's super easy to change your sequencing data into a one hot vector for ML training",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"one_hot_encoded = pd.get_dummies(alignment_numbering.iloc[:, 3:])\n\nchothia_results[\"Id\"].to_frame().join(one_hot_encoded).reset_index(drop=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Sadie Mutational analysis\n\nThese methods can be used at a higher level to give specific mutations given a numbering scheme",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sadie.airr.methods import run_mutational_analysis\n\ncatnap_heavy_with_mutations = run_mutational_analysis(catnap_heavy_base, \"kabat\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Sadie Clustering \n\nAnd finally, we can use an agglomerative clustering approach (inspired from Briney Clonify)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sadie.cluster import Cluster\n\ncluster_api = Cluster(\n catnap_heavy_with_mutations,\n lookup=[\"cdr1_aa\", \"cdr2_aa\", \"cdr3_aa\"],\n pad_somatic=True,\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cluster_df = cluster_api.cluster(6)\ndistance_frame = cluster_api.distance_df",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from scipy.cluster import hierarchy as hc\nfrom scipy.spatial.distance import squareform\n\ndistance_frame = cluster_api.distance_df\ntotal_clusters = list(cluster_df[\"cluster\"].unique())\nclustuer_pal = sns.husl_palette(len(total_clusters), s=2)\ncluster_lut = dict(zip(map(int, total_clusters), clustuer_pal))\nrow_colors = pd.DataFrame(cluster_df)[\"cluster\"].apply(lambda x: cluster_lut[x])\n\nlinkage = hc.linkage(squareform(distance_frame), method=\"average\")\ng = sns.clustermap(\n distance_frame,\n method=\"complete\",\n row_linkage=linkage,\n col_linkage=linkage,\n row_colors=row_colors.to_numpy(),\n col_colors=row_colors.to_numpy(),\n dendrogram_ratio=(0.1, 0.1),\n cbar_pos=(1, 0.32, 0.03, 0.2),\n # linewidths=0.1,\n figsize=(7.6 * 0.9, 7.6 * 0.9),\n tree_kws={\"linewidths\": 1},\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# High level - command line apps\n\nbut what if you just want to use a command line app. We got you covered",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!sadie airr -s human --skip-mutation input/catnap_nt_heavy_sub.fasta test.tsv\npd.read_csv(\"test.tsv\", delimiter=\"\\t\", index_col=0)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4ab93f468affec1e60381fc180fb51ff8bf1c667
| 4,368 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
examples/lints_reproducibility/table_4/Analysis.ipynb
|
ncilfone/mabwiser
|
329125d4110312d6001e9486e1cb3490a90565c4
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 60 |
2020-06-10T11:20:52.000Z
|
2022-03-25T02:16:47.000Z
|
examples/lints_reproducibility/table_4/Analysis.ipynb
|
ncilfone/mabwiser
|
329125d4110312d6001e9486e1cb3490a90565c4
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 24 |
2020-06-04T18:40:21.000Z
|
2022-03-24T16:49:51.000Z
|
examples/lints_reproducibility/table_4/Analysis.ipynb
|
ncilfone/mabwiser
|
329125d4110312d6001e9486e1cb3490a90565c4
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 12 |
2020-11-30T10:37:05.000Z
|
2022-03-25T02:16:41.000Z
| 30.124138 | 425 | 0.490614 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport os",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Analysis\n\nHere, we analyze the discepancies between the environments and their rewards under different decomposition methods.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"results = []\nfor file in sorted(os.listdir('output')):\n df = pd.read_csv(os.path.join('output', file))\n results.append(df)\nresults = pd.concat(results).reset_index(drop=True)\nresults",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can see that the default implementation, which uses `np.random.multivariate_random`, leads to inconsistent results between environments. Note that this is the same as using `np.random.RandomState`, as the global seed sets the random state. We can also see that the new `Generator` class with default parameters, which internally uses SVD for decomposition, also leads to inconsistent results between environments.\n\nWhen using Cholesky decomposition with the new `Generator` class, our hypothesis is that this will produce reproducible results across different environments. As expected, using Cholesky decomposition leads to the same deterministic cumulative regret across all environments, alleviating the problem. In this case, the Cholesky results actually lead to higher reward.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4ab94897505ad4264cff4d366737c28ebbd6ccbc
| 18,001 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
site/en-snapshot/tutorials/keras/text_classification_with_hub.ipynb
|
ilyaspiridonov/docs-l10n
|
a061a44e40d25028d0a4458094e48ab717d3565c
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2021-09-23T09:56:29.000Z
|
2021-09-23T09:56:29.000Z
|
site/en-snapshot/tutorials/keras/text_classification_with_hub.ipynb
|
ilyaspiridonov/docs-l10n
|
a061a44e40d25028d0a4458094e48ab717d3565c
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
site/en-snapshot/tutorials/keras/text_classification_with_hub.ipynb
|
ilyaspiridonov/docs-l10n
|
a061a44e40d25028d0a4458094e48ab717d3565c
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2020-06-23T07:43:49.000Z
|
2020-06-23T07:43:49.000Z
| 39.475877 | 456 | 0.572413 |
[
[
[
"##### Copyright 2019 The TensorFlow Authors.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#@title Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the \"License\");\n# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.\n# You may obtain a copy of the License at\n#\n# https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0\n#\n# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software\n# distributed under the License is distributed on an \"AS IS\" BASIS,\n# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.\n# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and\n# limitations under the License.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#@title MIT License\n#\n# Copyright (c) 2017 François Chollet\n#\n# Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a\n# copy of this software and associated documentation files (the \"Software\"),\n# to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation\n# the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense,\n# and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the\n# Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:\n#\n# The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in\n# all copies or substantial portions of the Software.\n#\n# THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED \"AS IS\", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR\n# IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,\n# FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL\n# THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER\n# LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING\n# FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER\n# DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Text classification with TensorFlow Hub: Movie reviews",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<table class=\"tfo-notebook-buttons\" align=\"left\">\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/keras/text_classification_with_hub\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/tf_logo_32px.png\" />View on TensorFlow.org</a>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/tensorflow/docs/blob/master/site/en/tutorials/keras/text_classification_with_hub.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/colab_logo_32px.png\" />Run in Google Colab</a>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://github.com/tensorflow/docs/blob/master/site/en/tutorials/keras/text_classification_with_hub.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/GitHub-Mark-32px.png\" />View source on GitHub</a>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a href=\"https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow_docs/docs/site/en/tutorials/keras/text_classification_with_hub.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/download_logo_32px.png\" />Download notebook</a>\n </td>\n</table>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"This notebook classifies movie reviews as *positive* or *negative* using the text of the review. This is an example of *binary*—or two-class—classification, an important and widely applicable kind of machine learning problem.\n\nThe tutorial demonstrates the basic application of transfer learning with TensorFlow Hub and Keras.\n\nWe'll use the [IMDB dataset](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/datasets/imdb) that contains the text of 50,000 movie reviews from the [Internet Movie Database](https://www.imdb.com/). These are split into 25,000 reviews for training and 25,000 reviews for testing. The training and testing sets are *balanced*, meaning they contain an equal number of positive and negative reviews. \n\nThis notebook uses [tf.keras](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/keras), a high-level API to build and train models in TensorFlow, and [TensorFlow Hub](https://www.tensorflow.org/hub), a library and platform for transfer learning. For a more advanced text classification tutorial using `tf.keras`, see the [MLCC Text Classification Guide](https://developers.google.com/machine-learning/guides/text-classification/).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\n\nimport tensorflow as tf\n\n!pip install tensorflow-hub\n!pip install tfds-nightly\nimport tensorflow_hub as hub\nimport tensorflow_datasets as tfds\n\nprint(\"Version: \", tf.__version__)\nprint(\"Eager mode: \", tf.executing_eagerly())\nprint(\"Hub version: \", hub.__version__)\nprint(\"GPU is\", \"available\" if tf.config.experimental.list_physical_devices(\"GPU\") else \"NOT AVAILABLE\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Download the IMDB dataset\n\nThe IMDB dataset is available on [imdb reviews](https://www.tensorflow.org/datasets/catalog/imdb_reviews) or on [TensorFlow datasets](https://www.tensorflow.org/datasets). The following code downloads the IMDB dataset to your machine (or the colab runtime):",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Split the training set into 60% and 40%, so we'll end up with 15,000 examples\n# for training, 10,000 examples for validation and 25,000 examples for testing.\ntrain_data, validation_data, test_data = tfds.load(\n name=\"imdb_reviews\", \n split=('train[:60%]', 'train[60%:]', 'test'),\n as_supervised=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Explore the data \n\nLet's take a moment to understand the format of the data. Each example is a sentence representing the movie review and a corresponding label. The sentence is not preprocessed in any way. The label is an integer value of either 0 or 1, where 0 is a negative review, and 1 is a positive review.\n\nLet's print first 10 examples.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"train_examples_batch, train_labels_batch = next(iter(train_data.batch(10)))\ntrain_examples_batch",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's also print the first 10 labels.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"train_labels_batch",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Build the model\n\nThe neural network is created by stacking layers—this requires three main architectural decisions:\n\n* How to represent the text?\n* How many layers to use in the model?\n* How many *hidden units* to use for each layer?\n\nIn this example, the input data consists of sentences. The labels to predict are either 0 or 1.\n\nOne way to represent the text is to convert sentences into embeddings vectors. We can use a pre-trained text embedding as the first layer, which will have three advantages:\n\n* we don't have to worry about text preprocessing,\n* we can benefit from transfer learning,\n* the embedding has a fixed size, so it's simpler to process.\n\nFor this example we will use a **pre-trained text embedding model** from [TensorFlow Hub](https://www.tensorflow.org/hub) called [google/tf2-preview/gnews-swivel-20dim/1](https://tfhub.dev/google/tf2-preview/gnews-swivel-20dim/1).\n\nThere are three other pre-trained models to test for the sake of this tutorial:\n\n* [google/tf2-preview/gnews-swivel-20dim-with-oov/1](https://tfhub.dev/google/tf2-preview/gnews-swivel-20dim-with-oov/1) - same as [google/tf2-preview/gnews-swivel-20dim/1](https://tfhub.dev/google/tf2-preview/gnews-swivel-20dim/1), but with 2.5% vocabulary converted to OOV buckets. This can help if vocabulary of the task and vocabulary of the model don't fully overlap.\n* [google/tf2-preview/nnlm-en-dim50/1](https://tfhub.dev/google/tf2-preview/nnlm-en-dim50/1) - A much larger model with ~1M vocabulary size and 50 dimensions.\n* [google/tf2-preview/nnlm-en-dim128/1](https://tfhub.dev/google/tf2-preview/nnlm-en-dim128/1) - Even larger model with ~1M vocabulary size and 128 dimensions.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Let's first create a Keras layer that uses a TensorFlow Hub model to embed the sentences, and try it out on a couple of input examples. Note that no matter the length of the input text, the output shape of the embeddings is: `(num_examples, embedding_dimension)`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"embedding = \"https://tfhub.dev/google/tf2-preview/gnews-swivel-20dim/1\"\nhub_layer = hub.KerasLayer(embedding, input_shape=[], \n dtype=tf.string, trainable=True)\nhub_layer(train_examples_batch[:3])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's now build the full model:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model = tf.keras.Sequential()\nmodel.add(hub_layer)\nmodel.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(16, activation='relu'))\nmodel.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(1))\n\nmodel.summary()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The layers are stacked sequentially to build the classifier:\n\n1. The first layer is a TensorFlow Hub layer. This layer uses a pre-trained Saved Model to map a sentence into its embedding vector. The pre-trained text embedding model that we are using ([google/tf2-preview/gnews-swivel-20dim/1](https://tfhub.dev/google/tf2-preview/gnews-swivel-20dim/1)) splits the sentence into tokens, embeds each token and then combines the embedding. The resulting dimensions are: `(num_examples, embedding_dimension)`.\n2. This fixed-length output vector is piped through a fully-connected (`Dense`) layer with 16 hidden units.\n3. The last layer is densely connected with a single output node.\n\nLet's compile the model.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Loss function and optimizer\n\nA model needs a loss function and an optimizer for training. Since this is a binary classification problem and the model outputs logits (a single-unit layer with a linear activation), we'll use the `binary_crossentropy` loss function.\n\nThis isn't the only choice for a loss function, you could, for instance, choose `mean_squared_error`. But, generally, `binary_crossentropy` is better for dealing with probabilities—it measures the \"distance\" between probability distributions, or in our case, between the ground-truth distribution and the predictions.\n\nLater, when we are exploring regression problems (say, to predict the price of a house), we will see how to use another loss function called mean squared error.\n\nNow, configure the model to use an optimizer and a loss function:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model.compile(optimizer='adam',\n loss=tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(from_logits=True),\n metrics=['accuracy'])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Train the model\n\nTrain the model for 20 epochs in mini-batches of 512 samples. This is 20 iterations over all samples in the `x_train` and `y_train` tensors. While training, monitor the model's loss and accuracy on the 10,000 samples from the validation set:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"history = model.fit(train_data.shuffle(10000).batch(512),\n epochs=20,\n validation_data=validation_data.batch(512),\n verbose=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Evaluate the model\n\nAnd let's see how the model performs. Two values will be returned. Loss (a number which represents our error, lower values are better), and accuracy.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"results = model.evaluate(test_data.batch(512), verbose=2)\n\nfor name, value in zip(model.metrics_names, results):\n print(\"%s: %.3f\" % (name, value))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This fairly naive approach achieves an accuracy of about 87%. With more advanced approaches, the model should get closer to 95%.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Further reading\n\nFor a more general way to work with string inputs and for a more detailed analysis of the progress of accuracy and loss during training, see the [Text classification with preprocessed text](./text_classification.ipynb) tutorial.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4ab958f0938e4fc067144f1163b3fa65db2726dd
| 3,910 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
challenge.ipynb
|
mekijah/SQL
|
8c911f338671a41860bb225d5897f75d56f57af0
|
[
"CC-BY-3.0"
] | null | null | null |
challenge.ipynb
|
mekijah/SQL
|
8c911f338671a41860bb225d5897f75d56f57af0
|
[
"CC-BY-3.0"
] | null | null | null |
challenge.ipynb
|
mekijah/SQL
|
8c911f338671a41860bb225d5897f75d56f57af0
|
[
"CC-BY-3.0"
] | null | null | null | 26.598639 | 101 | 0.54399 |
[
[
[
" # Challenge\n\n ## Identifying Outliers using Standard Deviation",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# initial imports\nimport os\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport random\nfrom sqlalchemy import create_engine\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# create a connection to the database\nengine= ('postgresql://{username}:{password}@{ipaddress}:{port}/{dbname}'\n .format(username='mmassey',\n password=os.getenv('PGAdmin_PW'),\n ipaddress='localhost',\n port='5432',\n dbname='fraud_detection')\n )\n\nquery = \"select a.id, c.date, c.amount \\\nfrom card_holder a \\\ninner join credit_card b \\\non a.id = b.cardholder_id \\\ninner join transaction c \\\non b.card = c.card\"\n\ndf = pd.read_sql(query, engine)\ndf.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# code a function to identify outliers based on standard deviation\ndef card_transaction(input_id):\n return df.loc[df['id']==input_id, 'amount']\n\ndef outliers(input_id):\n df1 =card_transaction(input_id)\n return pd.DataFrame(df1[df1> df1.mean()+3*df1.std()])\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# find anomalous transactions for 3 random card holders\nrand_card_holders = np.random.randint(1,25,3)\n\nfor id in rand_card_holders:\n if len(outliers(id)) == 0:\n print(f\"Card holder {id} has no outlier transactions.\")\n else:\n print(f\"Card holder {id} has outlier transactions as below:\\n{outliers(id)}.\")\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
" ## Identifying Outliers Using Interquartile Range",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# code a function to identify outliers based on interquartile range\ndef outliers_iqr(input_id):\n df1 =card_transaction(input_id)\n IQR_threshold = np.quantile(df1, .75)+(np.quantile(df1, .75)-np.quantile(df1, .25))*1.5\n return pd.DataFrame(df1[df1> IQR_threshold])\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# find anomalous transactions for 3 random card holders\nfor id in rand_card_holders:\n if len(outliers_iqr(id)) == 0:\n print(f\"Card holder {id} has no outlier transactions.\")\n else:\n print(f\"Card holder {id} has outlier transactions as below:\\n{outliers_iqr(id)}.\")\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4ab9628fb3f813c3a6ac7842a9d8e8222746fde3
| 32,540 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
backend/cloud-run-api/notebooks/QuickStart-API.ipynb
|
tuxedocat/fast-annotation-tool
|
2e28e81bf5b383ac033eeae847921d68ed302556
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 2 |
2021-06-08T04:15:15.000Z
|
2021-06-08T06:20:50.000Z
|
backend/cloud-run-api/notebooks/QuickStart-API.ipynb
|
tuxedocat/fast-annotation-tool
|
2e28e81bf5b383ac033eeae847921d68ed302556
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
backend/cloud-run-api/notebooks/QuickStart-API.ipynb
|
tuxedocat/fast-annotation-tool
|
2e28e81bf5b383ac033eeae847921d68ed302556
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 40.17284 | 526 | 0.475753 |
[
[
[
"# TOC\n1. [Settings](#Settings)\n2. [Get the task list](#Get-the-task-list)\n3. [Upload annotations](#Upload-annotations)\n4. [Get annotation results](#Get-annotation-results)\n5. [Get annotation detail log](#Get-annotation-detail-log)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Settings",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import init\nimport pandas as pd\nimport json\nimport requests",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"host = 'http://api:5000'\nheaders = {}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Cloud Run API needs Authorization\nhost = 'https://******.a.run.app'\nheaders = {\n 'Authorization': 'Bearer <TOKEN>'\n}",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Get the task list",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"res = requests.get(f'{host}/tasks', headers=headers).json()\npd.DataFrame(res)[:3]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Upload annotations",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Card UI\n\n- [Task-dependent schema#card](https://github.com/CyberAgent/fast-annotation-tool/wiki/%E3%82%BF%E3%82%B9%E3%82%AF%E4%BE%9D%E5%AD%98%E3%81%AE%E3%82%B9%E3%82%AD%E3%83%BC%E3%83%9E#card)\n\n<img src=\"https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/17490886/101377448-2b53fe80-38f5-11eb-8f46-0b154fc60138.png\" alt=\"image\" />",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Make annotation data\nannotations_data = [\n {\n \"text\": f\"This is a test{i}.\", \n \"show_ambiguous_button\": True, \n \"hidden_data\": {\n \"desc\": \"Data for aggregation. It can be a dictionary or a string.\"\n }\n } for i in range(100)\n]\ndf_annotation = pd.DataFrame(annotations_data)\ndf_annotation[:3]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Post task data\npost_data = {\n \"task_id\": \"card-demo-20200602\",\n \"annotation_type\": \"card\",\n \"title\": \"Card Demo\",\n \"question\": \"This is card demo\",\n \"description\": \"This is a card demo, so feel free to annotate it as you wish.\",\n \"annotations_data\": annotations_data\n}\nres = requests.post(f'{host}/tasks', headers=headers, json=post_data).json()\nres",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Multi-Label UI\n\n- [Task-dependent schema#multilabel](https://github.com/CyberAgent/fast-annotation-tool/wiki/%E3%82%BF%E3%82%B9%E3%82%AF%E4%BE%9D%E5%AD%98%E3%81%AE%E3%82%B9%E3%82%AD%E3%83%BC%E3%83%9E#multilabel)\n\n\n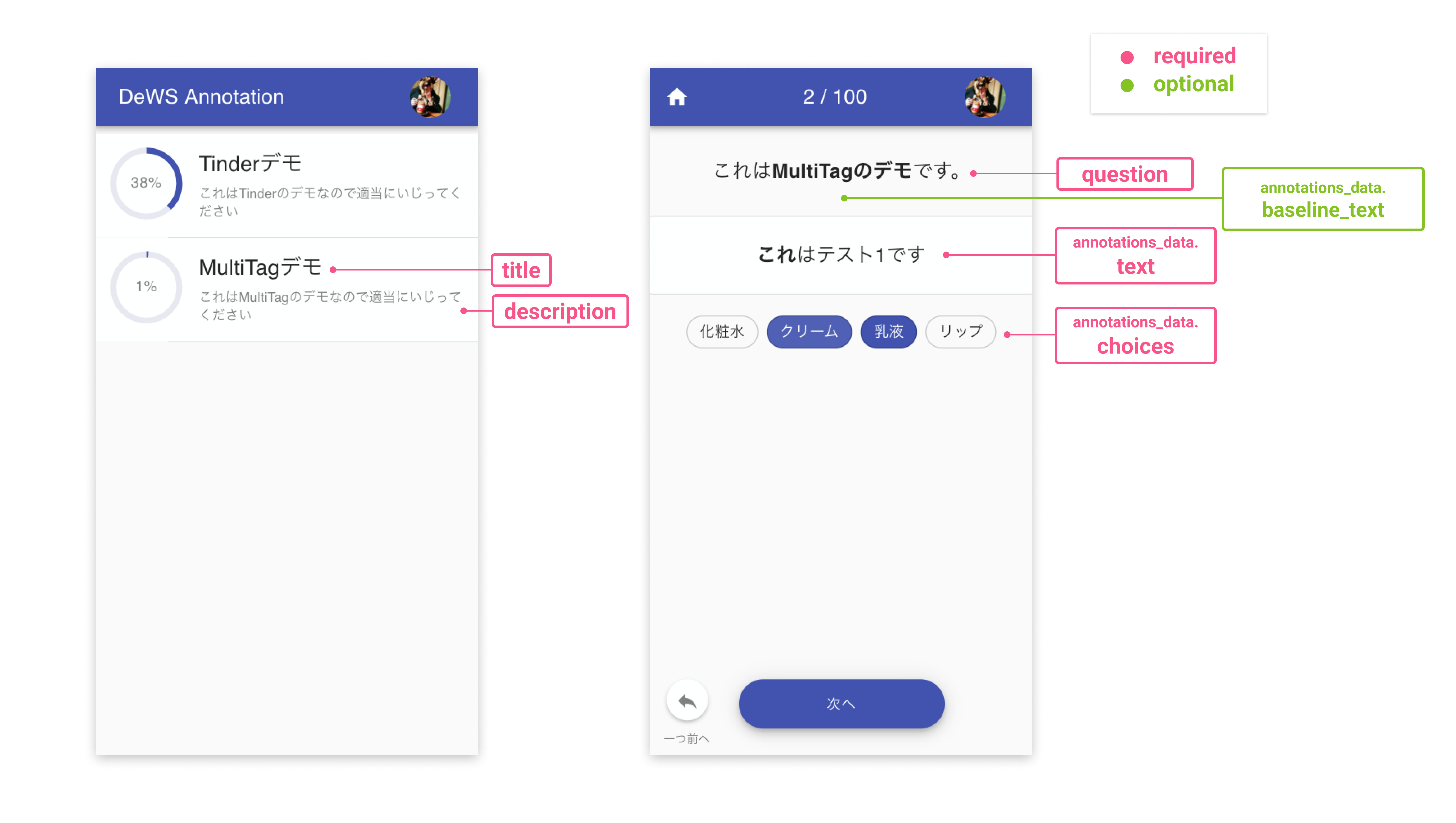",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Make annotation data\nannotation_data = [\n {\n \"text\": f\"This is a test{i}.\",\n \"choices\": [\"ChoiceA\", \"ChoiceB\", \"ChoiceC\", \"ChoiceD\"],\n \"baseline_text\": \"Baseline Text\",\n \"hidden_data\": {\n \"desc\": \"Data for aggregation. It can be a dictionary or a string.\"\n }\n }\n for i in range(100)\n]\ndf_annotation = pd.DataFrame(annotation_data)\ndf_annotation[:3]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Post task data\npost_data = {\n \"task_id\": \"multilabel-demo-20200602\",\n \"annotation_type\": \"multi_label\",\n \"title\": \"Multi-Label Demo\",\n \"question\": \"This is multi-label demo\",\n \"description\": \"This is a multi-label demo, so feel free to annotate it as you wish.\",\n \"annotations_data\": annotation_data\n}\nres = requests.post(f'{host}/tasks', headers=headers, json=post_data).json()\nres",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Get annotation results",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%time\ntask_id = \"card-demo-20200602\"\nres = requests.get(f'{host}/tasks/{task_id}', headers=headers).json()",
"CPU times: user 4.73 ms, sys: 2.57 ms, total: 7.3 ms\nWall time: 1.65 s\n"
],
[
"# Task Info\nres['task']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Annotation data and annotator responses\ndf_res = pd.DataFrame(res['annotations'])\ndf_res['name'] = '****'\ndf_res['email'] = '****'\ndf_res[~df_res.result_data.isna()][:3]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Get annotation detail log",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"task_id = \"card-demo-20200602\"\nres = requests.get(f'{host}/tasks/{task_id}/logs', headers=headers).json()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_res = pd.DataFrame(res['logs'])\ndf_res['name'] = '****'\ndf_res['email'] = '****'\ndf_res.sample(5)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4ab96439bc8eb12ddef0ee549381b126a07b67c0
| 23,321 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
webinars/gpu_bdb/GPU_BDB.ipynb
|
jacobtomlinson/Welcome_to_BlazingSQL_Notebooks
|
3f9eebff8a2d8edbc64b0da020340d287623a2c3
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 18 |
2020-03-17T21:15:35.000Z
|
2021-09-27T11:15:17.000Z
|
webinars/gpu_bdb/GPU_BDB.ipynb
|
jacobtomlinson/Welcome_to_BlazingSQL_Notebooks
|
3f9eebff8a2d8edbc64b0da020340d287623a2c3
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 9 |
2020-05-21T19:26:22.000Z
|
2021-08-29T19:23:06.000Z
|
webinars/gpu_bdb/GPU_BDB.ipynb
|
jacobtomlinson/Welcome_to_BlazingSQL_Notebooks
|
3f9eebff8a2d8edbc64b0da020340d287623a2c3
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 10 |
2020-04-21T10:01:24.000Z
|
2021-12-04T09:00:09.000Z
| 31.55751 | 470 | 0.631319 |
[
[
[
"# Real-world use-cases at scale!\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Imports\n\nLet's start with imports.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import sys\nsys.path.append(\"gpu_bdb_runner.egg\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import gpu_bdb_runner as gpubdb\nimport os\nimport inspect\nfrom highlight_code import print_code",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"config_options = {}\nconfig_options['JOIN_PARTITION_SIZE_THRESHOLD'] = os.environ.get(\"JOIN_PARTITION_SIZE_THRESHOLD\", 300000000)\nconfig_options['MAX_DATA_LOAD_CONCAT_CACHE_BYTE_SIZE'] = os.environ.get(\"MAX_DATA_LOAD_CONCAT_CACHE_BYTE_SIZE\", 400000000)\nconfig_options['BLAZING_DEVICE_MEM_CONSUMPTION_THRESHOLD'] = os.environ.get(\"BLAZING_DEVICE_MEM_CONSUMPTION_THRESHOLD\", 0.6)\nconfig_options['BLAZ_HOST_MEM_CONSUMPTION_THRESHOLD'] = os.environ.get(\"BLAZ_HOST_MEM_CONSUMPTION_THRESHOLD\", 0.6)\nconfig_options['MAX_KERNEL_RUN_THREADS'] = os.environ.get(\"MAX_KERNEL_RUN_THREADS\", 3)\nconfig_options['TABLE_SCAN_KERNEL_NUM_THREADS'] = os.environ.get(\"TABLE_SCAN_KERNEL_NUM_THREADS\", 1)\nconfig_options['MAX_NUM_ORDER_BY_PARTITIONS_PER_NODE'] = os.environ.get(\"MAX_NUM_ORDER_BY_PARTITIONS_PER_NODE\", 20)\nconfig_options['ORDER_BY_SAMPLES_RATIO'] = os.environ.get(\"ORDER_BY_SAMPLES_RATIO\", 0.0002)\nconfig_options['NUM_BYTES_PER_ORDER_BY_PARTITION'] = os.environ.get(\"NUM_BYTES_PER_ORDER_BY_PARTITION\", 400000000)\nconfig_options['MAX_ORDER_BY_SAMPLES_PER_NODE'] = os.environ.get(\"MAX_ORDER_BY_SAMPLES_PER_NODE\", 10000)\nconfig_options['MAX_SEND_MESSAGE_THREADS'] = os.environ.get(\"MAX_SEND_MESSAGE_THREADS\", 20)\nconfig_options['MEMORY_MONITOR_PERIOD'] = os.environ.get(\"MEMORY_MONITOR_PERIOD\", 50)\nconfig_options['TRANSPORT_BUFFER_BYTE_SIZE'] = os.environ.get(\"TRANSPORT_BUFFER_BYTE_SIZE\", 10485760) # 10 MBs\nconfig_options['TRANSPORT_POOL_NUM_BUFFERS'] = os.environ.get(\"TRANSPORT_POOL_NUM_BUFFERS\", 100)\nconfig_options['BLAZING_LOGGING_DIRECTORY'] = os.environ.get(\"BSQL_BLAZING_LOGGING_DIRECTORY\", 'blazing_log')\nconfig_options['BLAZING_CACHE_DIRECTORY'] = os.environ.get(\"BSQL_BLAZING_CACHE_DIRECTORY\", '/tmp/')\nconfig_options['LOGGING_LEVEL'] = os.environ.get(\"LOGGING_LEVEL\", \"trace\")\nconfig_options['MAX_JOIN_SCATTER_MEM_OVERHEAD'] = os.environ.get(\"MAX_JOIN_SCATTER_MEM_OVERHEAD\", 500000000)\nconfig_options['NETWORK_INTERFACE'] = os.environ.get(\"NETWORK_INTERFACE\", 'ens5')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Start the runner",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"runner = gpubdb.GPU_BDB_Runner(\n scale='SF1'\n , client_type='cluster'\n , bucket='bsql'\n , data_dir='s3://bsql/data/tpcx_bb/sf1/'\n , output_dir='tpcx-bb-runner/results'\n , **config_options\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Use cases for review",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Use case 2\n\n**Question:** Find the top 30 products that are mostly viewed together with a given product in online store. Note that the order of products viewed does not matter, and \"viewed together\" relates to a web_clickstreams, click_session of a known user with a session timeout of 60 min. If the duration between two click of a user is greater then the session timeout, a new session begins. With a session timeout of 60 min.\n\nLet's peek inside the code:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"q2_code = inspect.getsource(gpubdb.queries.gpu_bdb_queries.gpu_bdb_query_02).split('\\n')\nprint_code('\\n'.join(q2_code[92:-18]))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The `get_distinct_sessions` is defined as follows:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print_code('\\n'.join(q2_code[73:77]))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"It calls the `get_sessions`",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print_code('\\n'.join(q2_code[64:72]))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's have a look at the `get_session_id` method",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print_code('\\n'.join(q2_code[34:63]))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now that we know how this works - let's run the query",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"runner.run_query(2, repeat=1, validate_results=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Use case 23\n**Question:** This Query contains multiple, related iterations: \n1. Iteration 1: Calculate the coefficient of variation and mean of every item and warehouse of the given and the consecutive month. \n2. Iteration 2: Find items that had a coefficient of variation of 1.3 or larger in the given and the consecutive month",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"q23_code = inspect.getsource(gpubdb.queries.gpu_bdb_queries.gpu_bdb_query_23).split('\\n')\nprint_code('\\n'.join(q23_code[23:-12]))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"runner.run_query(23, repeat=1, validate_results=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Remaining usecases",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Use case 1\n\n**Question:** Find top ***100*** products that are sold together frequently in given stores. Only products in certain categories ***(categories 2 and 3)*** sold in specific stores are considered, and \"sold together frequently\" means at least ***50*** customers bought these products together in a transaction.\n\nIn ANSI-SQL code the solution would look somewhat similar to the one below.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"runner.run_query(1, repeat=1, validate_results=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Use case 3\n\n**Question:** For a given product get a top 30 list sorted by number of views in descending order of the last 5 products that are mostly viewed before the product was purchased online. For the viewed products, consider only products in certain item categories and viewed within 10 days before the purchase date.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"runner.run_query(3, repeat=1, validate_results=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Use case 4\n\n**Question:** Web_clickstream shopping cart abandonment analysis: For users who added products in their shopping carts but did not check out in the online store during their session, find the average number of pages they visited during their sessions. A \"session\" relates to a click_session of a known user with a session time-out of 60 min. If the duration between two clicks of a user is greater then the session time-out, a new session begins.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"runner.run_query(4, repeat=1, validate_results=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Use case 5\n\n**Question**: Build a model using logistic regression for a visitor to an online store: based on existing users online activities (interest in items of different categories) and demographics. This model will be used to predict if the visitor is interested in a given item category. Output the precision, accuracy and confusion matrix of model. *Note:* no need to actually classify existing users, as it will be later used to predict interests of unknown visitors.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"runner.run_query(5, repeat=1, validate_results=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Use case 6\n\nIdentifies customers shifting their purchase habit from store to web sales. Find customers who spend in relation more money in the second year following a given year in the web_sales channel then in the store sales channel. Report customers details: first name, last name, their country of origin, login name and email address, and identify if they are preferred customer, for the top 100 customers with the highest increase intheir second year web purchase ratio.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"runner.run_query(6, repeat=1, validate_results=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Use case 7\n**Question:** List top 10 states in descending order with at least 10 customers who during a given month bought products with the price tag at least 20% higher than the average price of products in the same category.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"runner.run_query(7, repeat=1, validate_results=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Use case 8\n**Question:** For online sales, compare the total sales monetary amount in which customers checked online reviews before making the purchase and that of sales in which customers did not read reviews. Consider only online sales for a specific category in a given year.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"runner.run_query(8, repeat=1, validate_results=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Use case 9\n\n**Question:** Aggregate total amount of sold items over different given types of combinations of customers based on selected groups of marital status, education status, sales price and different combinations of state and sales/profit.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"runner.run_query(9, repeat=1, validate_results=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Use case 10\n**Question:** For all products, extract sentences from its product reviews that contain positive or negative sentiment and display for each item the sentiment polarity of the extracted sentences (POS OR NEG) and the sentence and word in sentence leading to this classification.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"runner.run_query(10, repeat=1, validate_results=False, additional_resources_path='s3://bsql/data/tpcx_bb/additional_resources')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Use case 11\n**Question:** For a given product, measure the correlation of sentiments, including the number of reviews and average review ratings, on product monthly revenues within a given time frame.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"runner.run_query(11, repeat=1, validate_results=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Use case 12\n**Question:** Find all customers who viewed items of a given category on the web in a given month and year that was followed by an instore purchase of an item from the same category in the three consecutive months.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"runner.run_query(12, repeat=1, validate_results=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Use case 13\n**Question:** Display customers with both store and web sales in consecutive years for whom the increase in web sales exceeds the increase in store sales for a specified year.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"runner.run_query(13, repeat=1, validate_results=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Use case 14\n**Question:** What is the ratio between the number of items sold over the internet in the morning (7 to 8am) to the number of items sold in the evening (7 to 8pm) of customers with a specified number of dependents. Consider only websites with a high amount of content.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"runner.run_query(14, repeat=1, validate_results=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Use case 15\n**Question:** Find the categories with flat or declining sales for in store purchases during a given year for a given store.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"runner.run_query(15, repeat=1, validate_results=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Use case 16\n**Question:** Compute the impact of an item price change on the store sales by computing the total sales for items in a 30 day period before and after the price change. Group the items by location of warehouse where they were delivered from.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"runner.run_query(16, repeat=1, validate_results=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Use case 17\n**Question:** Find the ratio of items sold with and without promotions in a given month and year. Only items in certain categories sold to customers living in a specific time zone are considered.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"runner.run_query(17, repeat=1, validate_results=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Use case 18\n**Question:** Identify the stores with flat or declining sales in 4 consecutive months, check if there are any negative reviews regarding these stores available online.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"runner.run_query(18, repeat=1, validate_results=False, additional_resources_path='s3://bsql/data/tpcx_bb/additional_resources')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Use case 19\n**Question:** Retrieve the items with the highest number of returns where the number of returns was approximately equivalent across all store and web channels (within a tolerance of +/ 10%), within the week ending given dates. Analyse the online reviews for these items to see if there are any negative reviews.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"runner.run_query(19, repeat=1, validate_results=False, additional_resources_path='s3://bsql/data/tpcx_bb/additional_resources')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Use case 20\n**Question:** Customer segmentation for return analysis: Customers are separated along the following dimensions: \n1. return frequency, \n2. return order ratio (total number of orders partially or fully returned versus the totalnumber of orders), \n3. return item ratio (total number of items returned versus the number of itemspurchased), \n4. return amount ration (total monetary amount of items returned versus the amount purchased),\n5. return order ratio. \n\nConsider the store returns during a given year for the computation.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"runner.run_query(20, repeat=1, validate_results=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Use case 21\n**Question:** Get all items that were sold in stores in a given month and year and which were returned in the next 6 months and repurchased by the returning customer afterwards through the web sales channel in the following three years. For those items, compute the total quantity sold through the store, the quantity returned and the quantity purchased through the web. Group this information by item and store.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"runner.run_query(21, repeat=1, validate_results=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Use case 22\n**Question:** For all items whose price was changed on a given date, compute the percentage change in inventorybetween the 30 day period BEFORE the price change and the 30 day period AFTER the change. Group this information by warehouse.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"runner.run_query(22, repeat=1, validate_results=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Use case 24\n**Question:** For a given product, measure the effect of competitor's prices on products' in store and online sales.Compute the crossprice elasticity of demand for a given product.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"runner.run_query(24, repeat=1, validate_results=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Use case 25\n**Question:** Customer segmentation analysis: Customers are separated along the following key shopping dimensions: \n1. recency of last visit, \n2. frequency of visits and monetary amount. \n\nUse the store and online purchase data during a given year to compute. After model of separation is build, report for the analysed customers towhich \"group\" they where assigned.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"runner.run_query(25, repeat=1, validate_results=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Use case 26\n**Question:** Cluster customers into book buddies/club groups based on their in store book purchasing histories. Aftermodel of separation is build, report for the analysed customers to which \"group\" they where assigned.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"runner.run_query(26, repeat=1, validate_results=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Use case 27\n**Question:** For a given product, find \"competitor\" company names in the product reviews. Display review id, product id, \"competitor’s\" company name and the related sentence from the online review",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# runner.run_query(27, repeat=1, validate_results=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Use case 28\n**Question:** Build text classifier for online review sentiment classification (Positive, Negative, Neutral), using 90% of available reviews for training and the remaining 10% for testing. Display classifier accuracy on testing dataand classification result for the 10% testing data: \\<reviewSK\\>, \\<originalRating\\>, \\<classificationResult\\>.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"runner.run_query(28, repeat=1, validate_results=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Use case 29\n**Question:** Perform category affinity analysis for products purchased together online.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"runner.run_query(29, repeat=1, validate_results=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Use case 30\n**Question:** Perform category affinity analysis for products viewed together online. Note that the order of products viewed does not matter, and \"viewed together\" relates to a click_session of a user with a session timeout of 60 min. If the duration between two clicks of a user is greater then the session timeout, a new session begins.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"runner.run_query(30, repeat=1, validate_results=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4ab985271cc2c944744692044be0f4d930fee83e
| 271,548 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
dashboards-examples/CatBoost-5-Fold-Stack-v0.1.9.ipynb
|
Cirice/4th-place-Home-Credit-Default-Risk
|
e120c98cb83b30b5c692d8ec40d3eb55060dc1ea
|
[
"MIT"
] | 26 |
2018-09-04T15:03:48.000Z
|
2022-03-06T08:11:23.000Z
|
dashboards-examples/CatBoost-5-Fold-Stack-v0.1.9.ipynb
|
Cirice/4th-place-Home-Credit-Default-Risk
|
e120c98cb83b30b5c692d8ec40d3eb55060dc1ea
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
dashboards-examples/CatBoost-5-Fold-Stack-v0.1.9.ipynb
|
Cirice/4th-place-Home-Credit-Default-Risk
|
e120c98cb83b30b5c692d8ec40d3eb55060dc1ea
|
[
"MIT"
] | 14 |
2018-09-06T01:36:49.000Z
|
2020-11-11T18:16:26.000Z
| 43.454633 | 455 | 0.440298 |
[
[
[
"import time\nnotebookstart= time.time()\nimport numpy as np # linear algebra\nimport pandas as pd # data processing, CSV file I/O (e.g. pd.read_csv)\nimport os\nimport gc\n# Models Packages\nfrom sklearn import metrics\nfrom sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error\nfrom sklearn import feature_selection\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nfrom sklearn import preprocessing\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import KFold\nfrom sklearn import preprocessing\nfrom sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score, roc_curve\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression\nimport category_encoders as ce\nfrom imblearn.under_sampling import RandomUnderSampler\nfrom catboost import CatBoostClassifier\n# Gradient Boosting\nimport lightgbm as lgb\nimport xgboost as xgb\nimport category_encoders as ce\n# Tf-Idf\nfrom sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer, TfidfVectorizer\nfrom sklearn.pipeline import FeatureUnion\nfrom scipy.sparse import hstack, csr_matrix\nfrom nltk.corpus import stopwords \nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler\nfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor \n# Viz\nimport seaborn as sns\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np # linear algebra\nimport pandas as pd # data processing, CSV file I/O (e.g. pd.read_csv)\nfrom scipy.cluster.vq import kmeans2, whiten\nfrom sklearn.neighbors import NearestNeighbors, KNeighborsRegressor\nfrom catboost import CatBoostRegressor\n%matplotlib inline\n# Input data files are available in the \"../input/\" directory.\n# For example, running this (by clicking run or pressing Shift+Enter) will list the files in the input directory\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"num_rows = None\nEPS = 1e-100",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"train = pd.read_csv('/media/limbo/Home-Credit/data/application_train.csv.zip')\ny = train['TARGET']\n\nn_train = train.shape[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"descretize = lambda x, n: list(map(str, list(pd.qcut(x, n, duplicates='drop'))))\n\ndef binary_encoder(df, n_train):\n original_columns = list(df.columns)\n categorical_columns = [col for col in df.columns if df[col].dtype == 'object']\n enc = ce.BinaryEncoder(impute_missing=True, cols=categorical_columns).fit(df[0:n_train], df[0:n_train]['TARGET'])\n df = enc.transform(df)\n new_columns = [c for c in df.columns if c not in original_columns]\n return df[new_columns]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def application_train_test(num_rows=num_rows, nan_as_category=False):\n # Read data and merge\n df = pd.read_csv('../data/application_train.csv.zip', nrows=num_rows)\n\n n_train = df.shape[0]\n\n test_df = pd.read_csv('../data/application_test.csv.zip', nrows=num_rows)\n print(\"Train samples: {}, test samples: {}\".format(len(df), len(test_df)))\n df = df.append(test_df).reset_index()\n\n df['CODE_GENDER'].replace('XNA', np.nan, inplace=True)\n df['DAYS_EMPLOYED'].replace(365243, np.nan, inplace=True)\n df['NAME_FAMILY_STATUS'].replace('Unknown', np.nan, inplace=True)\n df['ORGANIZATION_TYPE'].replace('XNA', np.nan, inplace=True)\n\n # Optional: Remove 4 applications with XNA CODE_GENDER (train set)\n df = df[df['CODE_GENDER'] != 'XNA']\n\n docs = [_f for _f in df.columns if 'FLAG_DOC' in _f]\n live = [_f for _f in df.columns if ('FLAG_' in _f) & ('FLAG_DOC' not in _f) & ('_FLAG_' not in _f)]\n\n # NaN values for DAYS_EMPLOYED: 365.243 -> nan\n df['DAYS_EMPLOYED'].replace(365243, np.nan, inplace=True)\n\n inc_by_org = df[['AMT_INCOME_TOTAL', 'ORGANIZATION_TYPE']].groupby('ORGANIZATION_TYPE').median()['AMT_INCOME_TOTAL']\n\n df['NEW_CREDIT_TO_ANNUITY_RATIO'] = df['AMT_CREDIT'] / df['AMT_ANNUITY']\n df['NEW_AMT_INCOME_TOTAL_RATIO'] = df['AMT_CREDIT'] / df['AMT_INCOME_TOTAL']\n df['NEW_CREDIT_TO_GOODS_RATIO'] = df['AMT_CREDIT'] / df['AMT_GOODS_PRICE']\n df['NEW_DOC_IND_AVG'] = df[docs].mean(axis=1)\n df['NEW_DOC_IND_STD'] = df[docs].std(axis=1)\n df['NEW_DOC_IND_KURT'] = df[docs].kurtosis(axis=1)\n df['NEW_LIVE_IND_SUM'] = df[live].sum(axis=1)\n df['NEW_LIVE_IND_STD'] = df[live].std(axis=1)\n df['NEW_LIVE_IND_KURT'] = df[live].kurtosis(axis=1)\n df['NEW_INC_PER_CHLD'] = df['AMT_INCOME_TOTAL'] / (1 + df['CNT_CHILDREN'])\n df['NEW_INC_BY_ORG'] = df['ORGANIZATION_TYPE'].map(inc_by_org)\n df['NEW_EMPLOY_TO_BIRTH_RATIO'] = df['DAYS_EMPLOYED'] / df['DAYS_BIRTH']\n df['NEW_ANNUITY_TO_INCOME_RATIO'] = df['AMT_ANNUITY'] / (1 + df['AMT_INCOME_TOTAL'])\n df['NEW_SOURCES_PROD'] = df['EXT_SOURCE_1'] * df['EXT_SOURCE_2'] * df['EXT_SOURCE_3']\n df['NEW_EXT_SOURCES_MEAN'] = df[['EXT_SOURCE_1', 'EXT_SOURCE_2', 'EXT_SOURCE_3']].mean(axis=1)\n df['NEW_SCORES_STD'] = df[['EXT_SOURCE_1', 'EXT_SOURCE_2', 'EXT_SOURCE_3']].std(axis=1)\n df['NEW_SCORES_STD'] = df['NEW_SCORES_STD'].fillna(df['NEW_SCORES_STD'].mean())\n df['NEW_CAR_TO_BIRTH_RATIO'] = df['OWN_CAR_AGE'] / df['DAYS_BIRTH']\n df['NEW_CAR_TO_EMPLOY_RATIO'] = df['OWN_CAR_AGE'] / df['DAYS_EMPLOYED']\n df['NEW_PHONE_TO_BIRTH_RATIO'] = df['DAYS_LAST_PHONE_CHANGE'] / df['DAYS_BIRTH']\n df['NEW_PHONE_TO_EMPLOY_RATIO'] = df['DAYS_LAST_PHONE_CHANGE'] / df['DAYS_EMPLOYED']\n df['NEW_CREDIT_TO_INCOME_RATIO'] = df['AMT_CREDIT'] / df['AMT_INCOME_TOTAL']\n\n# df['children_ratio'] = df['CNT_CHILDREN'] / df['CNT_FAM_MEMBERS']\n\n# df['NEW_EXT_SOURCES_MEDIAN'] = df[['EXT_SOURCE_1', 'EXT_SOURCE_2', 'EXT_SOURCE_3']].median(axis=1)\n\n# df['NEW_DOC_IND_SKEW'] = df[docs].skew(axis=1)\n# df['NEW_LIVE_IND_SKEW'] = df[live].skew(axis=1)\n\n# df['ind_0'] = df['DAYS_EMPLOYED'] - df['DAYS_EMPLOYED'].replace([np.inf, -np.inf], np.nan).fillna(\n# df['DAYS_EMPLOYED'].dropna().median()).mean()\n# df['ind_1'] = df['DAYS_EMPLOYED'] - df['DAYS_EMPLOYED'].replace([np.inf, -np.inf], np.nan).fillna(\n# df['DAYS_EMPLOYED'].dropna().median()).median()\n\n# df['ind_2'] = df['DAYS_BIRTH'] - df['DAYS_BIRTH'].replace([np.inf, -np.inf], np.nan).fillna(\n# df['DAYS_BIRTH'].dropna().median()).mean()\n# df['ind_3'] = df['DAYS_BIRTH'] - df['DAYS_BIRTH'].replace([np.inf, -np.inf], np.nan).fillna(\n# df['DAYS_BIRTH'].dropna().median()).median()\n\n# df['ind_4'] = df['AMT_INCOME_TOTAL'] - df['AMT_INCOME_TOTAL'].replace([np.inf, -np.inf], np.nan).fillna(\n# df['AMT_INCOME_TOTAL'].dropna().median()).mean()\n# df['ind_5'] = df['AMT_INCOME_TOTAL'] - df['AMT_INCOME_TOTAL'].replace([np.inf, -np.inf], np.nan).fillna(\n# df['AMT_INCOME_TOTAL'].dropna().median()).median()\n\n# df['ind_6'] = df['AMT_CREDIT'] - df['AMT_CREDIT'].replace([np.inf, -np.inf], np.nan).fillna(\n# df['AMT_CREDIT'].dropna().median()).mean()\n# df['ind_7'] = df['AMT_CREDIT'] - df['AMT_CREDIT'].replace([np.inf, -np.inf], np.nan).fillna(\n# df['AMT_CREDIT'].dropna().median()).median()\n\n# df['ind_8'] = df['AMT_ANNUITY'] - df['AMT_ANNUITY'].replace([np.inf, -np.inf], np.nan).fillna(\n# df['AMT_ANNUITY'].dropna().median()).mean()\n# df['ind_9'] = df['AMT_ANNUITY'] - df['AMT_ANNUITY'].replace([np.inf, -np.inf], np.nan).fillna(\n# df['AMT_ANNUITY'].dropna().median()).median()\n\n# df['ind_10'] = df['AMT_CREDIT'] - df['AMT_INCOME_TOTAL'].replace([np.inf, -np.inf], np.nan).fillna(\n# df['AMT_INCOME_TOTAL'].dropna().median()).mean()\n# df['ind_11'] = df['AMT_CREDIT'] - df['AMT_INCOME_TOTAL'].replace([np.inf, -np.inf], np.nan).fillna(\n# df['AMT_INCOME_TOTAL'].dropna().median()).median()\n\n# AGGREGATION_RECIPIES = [\n# (['CODE_GENDER', 'NAME_EDUCATION_TYPE'], [('AMT_ANNUITY', 'max'),\n# ('AMT_CREDIT', 'max'),\n# ('EXT_SOURCE_1', 'mean'),\n# ('EXT_SOURCE_2', 'mean'),\n# ('OWN_CAR_AGE', 'max'),\n# ('OWN_CAR_AGE', 'sum')]),\n# (['CODE_GENDER', 'ORGANIZATION_TYPE'], [('AMT_ANNUITY', 'mean'),\n# ('AMT_INCOME_TOTAL', 'mean'),\n# ('DAYS_REGISTRATION', 'mean'),\n# ('EXT_SOURCE_1', 'mean'),\n# ('NEW_CREDIT_TO_ANNUITY_RATIO', 'mean')]),\n# (['CODE_GENDER', 'REG_CITY_NOT_WORK_CITY'], [('AMT_ANNUITY', 'mean'),\n# ('CNT_CHILDREN', 'mean'),\n# ('DAYS_ID_PUBLISH', 'mean')]),\n# (['CODE_GENDER', 'NAME_EDUCATION_TYPE', 'OCCUPATION_TYPE', 'REG_CITY_NOT_WORK_CITY'], [('EXT_SOURCE_1', 'mean'),\n# ('EXT_SOURCE_2',\n# 'mean')]),\n# (['NAME_EDUCATION_TYPE', 'OCCUPATION_TYPE'], [('AMT_CREDIT', 'mean'),\n# ('AMT_REQ_CREDIT_BUREAU_YEAR', 'mean'),\n# ('APARTMENTS_AVG', 'mean'),\n# ('BASEMENTAREA_AVG', 'mean'),\n# ('EXT_SOURCE_1', 'mean'),\n# ('EXT_SOURCE_2', 'mean'),\n# ('EXT_SOURCE_3', 'mean'),\n# ('NONLIVINGAREA_AVG', 'mean'),\n# ('OWN_CAR_AGE', 'mean')]),\n# (['NAME_EDUCATION_TYPE', 'OCCUPATION_TYPE', 'REG_CITY_NOT_WORK_CITY'], [('ELEVATORS_AVG', 'mean'),\n# ('EXT_SOURCE_1', 'mean')]),\n# (['OCCUPATION_TYPE'], [('AMT_ANNUITY', 'mean'),\n# ('CNT_CHILDREN', 'mean'),\n# ('CNT_FAM_MEMBERS', 'mean'),\n# ('DAYS_BIRTH', 'mean'),\n# ('DAYS_EMPLOYED', 'mean'),\n# ('NEW_CREDIT_TO_ANNUITY_RATIO', 'median'),\n# ('DAYS_REGISTRATION', 'mean'),\n# ('EXT_SOURCE_1', 'mean'),\n# ('EXT_SOURCE_2', 'mean'),\n# ('EXT_SOURCE_3', 'mean')]),\n# ]\n\n# for groupby_cols, specs in AGGREGATION_RECIPIES:\n# group_object = df.groupby(groupby_cols)\n# for select, agg in specs:\n# groupby_aggregate_name = '{}_{}_{}'.format('_'.join(groupby_cols), agg, select)\n# df = df.merge(group_object[select]\n# .agg(agg)\n# .reset_index()\n# .rename(index=str,\n# columns={select: groupby_aggregate_name})\n# [groupby_cols + [groupby_aggregate_name]],\n# on=groupby_cols,\n# how='left')\n # ['DAYS_EMPLOYED', 'CNT_FAM_MEMBERS', 'CNT_CHILDREN', 'credit_per_person', 'cnt_non_child']\n df['retirement_age'] = (df['DAYS_BIRTH'] > -14000).astype(int)\n df['long_employment'] = (df['DAYS_EMPLOYED'] > -2000).astype(int)\n df['cnt_non_child'] = df['CNT_FAM_MEMBERS'] - df['CNT_CHILDREN']\n df['child_to_non_child_ratio'] = df['CNT_CHILDREN'] / df['cnt_non_child']\n df['income_per_non_child'] = df['AMT_INCOME_TOTAL'] / df['cnt_non_child']\n df['credit_per_person'] = df['AMT_CREDIT'] / df['CNT_FAM_MEMBERS']\n df['credit_per_child'] = df['AMT_CREDIT'] / (1 + df['CNT_CHILDREN'])\n df['credit_per_non_child'] = df['AMT_CREDIT'] / df['cnt_non_child']\n\n df['cnt_non_child'] = df['CNT_FAM_MEMBERS'] - df['CNT_CHILDREN']\n df['child_to_non_child_ratio'] = df['CNT_CHILDREN'] / df['cnt_non_child']\n df['income_per_non_child'] = df['AMT_INCOME_TOTAL'] / df['cnt_non_child']\n df['credit_per_person'] = df['AMT_CREDIT'] / df['CNT_FAM_MEMBERS']\n df['credit_per_child'] = df['AMT_CREDIT'] / (1 + df['CNT_CHILDREN'])\n df['credit_per_non_child'] = df['AMT_CREDIT'] / df['cnt_non_child']\n\n# df['p_0'] = descretize(df['credit_per_non_child'].values, 2 ** 5)\n# df['p_1'] = descretize(df['credit_per_person'].values, 2 ** 5)\n# df['p_2'] = descretize(df['credit_per_child'].values, 2 ** 5)\n# df['p_3'] = descretize(df['retirement_age'].values, 2 ** 5)\n# df['p_4'] = descretize(df['income_per_non_child'].values, 2 ** 5)\n# df['p_5'] = descretize(df['child_to_non_child_ratio'].values, 2 ** 5)\n\n# df['p_6'] = descretize(df['NEW_CREDIT_TO_ANNUITY_RATIO'].values, 2 ** 5)\n# df['p_7'] = descretize(df['NEW_CREDIT_TO_ANNUITY_RATIO'].values, 2 ** 6)\n# df['p_8'] = descretize(df['NEW_CREDIT_TO_ANNUITY_RATIO'].values, 2 ** 7)\n\n# df['pe_0'] = descretize(df['credit_per_non_child'].values, 2 ** 6)\n# df['pe_1'] = descretize(df['credit_per_person'].values, 2 ** 6)\n# df['pe_2'] = descretize(df['credit_per_child'].values, 2 ** 6)\n# df['pe_3'] = descretize(df['retirement_age'].values, 2 ** 6)\n# df['pe_4'] = descretize(df['income_per_non_child'].values, 2 ** 6)\n# df['pe_5'] = descretize(df['child_to_non_child_ratio'].values, 2 ** 6)\n\n c = df['NEW_CREDIT_TO_ANNUITY_RATIO'].replace([np.inf, -np.inf], np.nan).fillna(999).values\n a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 2, iter=333)\n df['x_0'] = b\n\n a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 4, iter=333)\n df['x_1'] = b\n\n a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 8, iter=333)\n df['x_2'] = b\n\n a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 16, iter=333)\n df['x_3'] = b\n\n a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 32, iter=333)\n df['x_4'] = b\n\n a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 64, iter=333)\n df['x_5'] = b\n\n a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 128, iter=333)\n df['x_6'] = b\n\n a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 150, iter=333)\n df['x_7'] = b\n\n a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 256, iter=333)\n df['x_8'] = b\n\n a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 512, iter=333)\n df['x_9'] = b\n\n a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 1024, iter=333)\n df['x_10'] = b\n \n \n# c = df['EXT_SOURCE_1'].replace([np.inf, -np.inf], np.nan).fillna(999).values\n# a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 2, iter=333)\n# df['ex1_0'] = b\n\n# a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 4, iter=333)\n# df['ex1_1'] = b\n\n# a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 8, iter=333)\n# df['ex1_2'] = b\n\n# a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 16, iter=333)\n# df['ex1_3'] = b\n\n# a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 32, iter=333)\n# df['ex1_4'] = b\n\n# a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 64, iter=333)\n# df['ex1_5'] = b\n\n# a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 128, iter=333)\n# df['ex1_6'] = b\n\n# a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 256, iter=333)\n# df['ex1_7'] = b \n \n \n# c = df['EXT_SOURCE_2'].replace([np.inf, -np.inf], np.nan).fillna(999).values\n# a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 2, iter=333)\n# df['ex2_0'] = b\n\n# a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 4, iter=333)\n# df['ex2_1'] = b\n\n# a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 8, iter=333)\n# df['ex2_2'] = b\n\n# a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 16, iter=333)\n# df['ex2_3'] = b\n\n# a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 32, iter=333)\n# df['ex2_4'] = b\n\n# a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 64, iter=333)\n# df['ex2_5'] = b\n\n# a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 128, iter=333)\n# df['ex2_6'] = b\n\n# a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 256, iter=333)\n# df['ex2_7'] = b \n \n# c = df['EXT_SOURCE_3'].replace([np.inf, -np.inf], np.nan).fillna(999).values\n# a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 2, iter=333)\n# df['ex3_0'] = b\n\n# a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 4, iter=333)\n# df['ex3_1'] = b\n\n# a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 8, iter=333)\n# df['ex3_2'] = b\n\n# a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 16, iter=333)\n# df['ex3_3'] = b\n\n# a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 32, iter=333)\n# df['ex3_4'] = b\n\n# a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 64, iter=333)\n# df['ex3_5'] = b\n\n# a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 128, iter=333)\n# df['ex3_6'] = b\n\n# a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 256, iter=333)\n# df['ex3_7'] = b \n \n\n# df['ex_1_0'] = descretize(df['EXT_SOURCE_1'].values, 2 ** 6)\n# df['ex_2_0'] = descretize(df['EXT_SOURCE_2'].values, 2 ** 6)\n# df['ex_3_0'] = descretize(df['EXT_SOURCE_3'].values, 2 ** 6)\n\n# df['ex_1_1'] = descretize(df['EXT_SOURCE_1'].values, 2 ** 4)\n# df['ex_2_1'] = descretize(df['EXT_SOURCE_2'].values, 2 ** 4)\n# df['ex_3_1'] = descretize(df['EXT_SOURCE_3'].values, 2 ** 4)\n\n# df['ex_1_2'] = descretize(df['EXT_SOURCE_1'].values, 2 ** 5)\n# df['ex_2_2'] = descretize(df['EXT_SOURCE_2'].values, 2 ** 5)\n# df['ex_3_2'] = descretize(df['EXT_SOURCE_3'].values, 2 ** 5)\n\n# df['ex_1_3'] = descretize(df['EXT_SOURCE_1'].values, 2 ** 3)\n# df['ex_2_4'] = descretize(df['EXT_SOURCE_2'].values, 2 ** 3)\n# df['ex_3_5'] = descretize(df['EXT_SOURCE_3'].values, 2 ** 3)\n\n# c = df['NEW_EXT_SOURCES_MEAN'].replace([np.inf, -np.inf], np.nan).fillna(999).values\n# a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 2, iter=333)\n# df['ex_mean_0'] = b\n\n# a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 4, iter=333)\n# df['ex_mean_1'] = b\n\n# a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 8, iter=333)\n# df['ex_mean_2'] = b\n\n# a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 16, iter=333)\n# df['ex_mean_3'] = b\n\n# a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 32, iter=333)\n# df['ex_mean_4'] = b\n\n# a, b = kmeans2(np.log1p(c), 64, iter=333)\n# df['ex_mean_5'] = b\n \n \n \n\n\n# df['NEW_SCORES_STD'] = df[['EXT_SOURCE_1', 'EXT_SOURCE_2', 'EXT_SOURCE_3']].std(axis=1)\n \n# df['ex1/ex2'] = df['EXT_SOURCE_1'] / df['EXT_SOURCE_2']\n# df['ex1/ex3'] = df['EXT_SOURCE_1'] / df['EXT_SOURCE_3']\n# df['ex2/ex3'] = df['EXT_SOURCE_3'] / df['EXT_SOURCE_3']\n \n# df['ex1*ex2'] = df['EXT_SOURCE_1'] * df['EXT_SOURCE_2']\n# df['ex1*ex3'] = df['EXT_SOURCE_1'] * df['EXT_SOURCE_3']\n# df['ex2*ex3'] = df['EXT_SOURCE_2'] * df['EXT_SOURCE_3']\n \n# df['cred*ex1'] = df['AMT_CREDIT'] * df['EXT_SOURCE_1']\n# df['cred*ex2'] = df['AMT_CREDIT'] * df['EXT_SOURCE_2']\n# df['cred*ex3'] = df['AMT_CREDIT'] * df['EXT_SOURCE_3']\n \n# df['cred/ex1'] = df['AMT_CREDIT'] / df['EXT_SOURCE_1']\n# df['cred/ex2'] = df['AMT_CREDIT'] / df['EXT_SOURCE_2']\n# df['cred/ex3'] = df['AMT_CREDIT'] / df['EXT_SOURCE_3']\n \n# df['cred*ex123'] = df['AMT_CREDIT'] * df['EXT_SOURCE_1'] * df['EXT_SOURCE_2'] * df['EXT_SOURCE_3']\n \n# del df['EXT_SOURCE_1']\n# del df['EXT_SOURCE_2']\n# del df['EXT_SOURCE_3']\n# del df['NEW_EXT_SOURCES_MEAN']\n\n # Categorical features with Binary encode (0 or 1; two categories)\n for bin_feature in ['CODE_GENDER', 'FLAG_OWN_CAR', 'FLAG_OWN_REALTY']:\n df[bin_feature], uniques = pd.factorize(df[bin_feature])\n \n del test_df\n gc.collect()\n return df",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = application_train_test(num_rows=num_rows, nan_as_category=False)",
"Train samples: 307511, test samples: 48744\n"
],
[
"df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"selected_features = ['AMT_ANNUITY', 'AMT_CREDIT', 'AMT_INCOME_TOTAL', 'NEW_CREDIT_TO_ANNUITY_RATIO', 'NEW_CREDIT_TO_GOODS_RATIO', 'NEW_CREDIT_TO_INCOME_RATIO'] + ['x_' + str(x) for x in range(11)] + \\\n['retirement_age', 'long_employment'] + ['EXT_SOURCE_1', 'EXT_SOURCE_2', 'EXT_SOURCE_3']\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"categorical_columns = [col for col in train.columns if train[col].dtype == 'object']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"numerical_columns = [col for col in df.columns if df[col].dtype != 'object']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"new_df = df.copy()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = new_df",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"encoder = preprocessing.LabelEncoder()\n\nfor f in categorical_columns:\n if df[f].dtype == 'object':\n df[f] = encoder.fit_transform(df[f].apply(str).values) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"categorical_columns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"gc.collect()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"train = pd.read_csv('../data/application_train.csv.zip', nrows=num_rows)\nn_train = train.shape[0]\ntest = pd.read_csv('../data/application_test.csv.zip', nrows=num_rows)\n \nnew_df = pd.concat([train, test], axis=0)\ngc.collect()",
"/home/kain/Workstation/PyEnv/lib/python3.5/site-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:5: FutureWarning: Sorting because non-concatenation axis is not aligned. A future version\nof pandas will change to not sort by default.\n\nTo accept the future behavior, pass 'sort=False'.\n\nTo retain the current behavior and silence the warning, pass 'sort=True'.\n\n \"\"\"\n"
],
[
"new_df.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"new_df[categorical_columns].head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"encoder = preprocessing.LabelEncoder()\n\nfor f in categorical_columns:\n if new_df[f].dtype == 'object':\n new_df[f] = encoder.fit_transform(new_df[f].apply(str).values) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"new_features = pd.read_csv('selected_features.csv', header=0, index_col=None)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"new_features.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"my_features = [f for f in selected_features if f not in new_features.columns]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"my_features",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"new_df[categorical_columns][0:n_train].shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"new_df[categorical_columns][n_train:].head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"suresh_august16 = pd.read_csv('../data/SureshFeaturesAug16.csv', header=0, index_col=None)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"suresh_august16.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"del suresh_august16['SK_ID_CURR']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"goran_features = pd.read_csv('../goran-data/goranm_feats_v3.csv', header=0, index_col=None)\ngoran_features.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"del goran_features['SK_ID_CURR']\ndel goran_features['IS_TRAIN']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"goran_features_19_8 = pd.read_csv('../data/goranm_feats_19_08.csv', header=0, index_col=None)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"goran_features_19_8.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"del goran_features_19_8['SK_ID_CURR']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.externals import joblib\n\nprevs_df = joblib.load('../data/prev_application_solution3_v2')\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"prevs_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"suresh_august16_2 = pd.read_csv('../data/SureshFeaturesAug16_2.csv', header=0, index_col=None)\nsuresh_august15 = pd.read_csv('../data/SureshFeaturesAug15.csv', header=0, index_col=None)\nsuresh_august16 = pd.read_csv('../data/SureshFeaturesAug16.csv', header=0, index_col=None)\nsuresh_august19 = pd.read_csv('../data/suresh_features_Aug19th.csv', header=0, index_col=None)\nsuresh_august19_2 = pd.read_csv('../data/SureshFeatures_19_2th.csv', header=0, index_col=None)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"suresh_august20 = pd.read_csv('../data/SureshFeatures3BestAgu20.csv', header=0, index_col=None)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"suresh_august20.head(100)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"del suresh_august15['SK_ID_CURR']\ndel suresh_august16_2['SK_ID_CURR']\ndel suresh_august19['SK_ID_CURR_SURESH']\ndel suresh_august16['SK_ID_CURR']\ndel suresh_august19_2['SK_ID_CURR']\nsuresh_august15.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"suresh_20 = pd.read_csv('../data/SureshFeatures20_2.csv', header=0, index_col=None)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\nsuresh_20.head(100)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"del suresh_20['SK_ID_CURR']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"goranm_8_20 = pd.read_csv('../data/goranm_08_20.csv', header=0, index_col=None)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"goranm_8_20.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"del goranm_8_20['SK_ID_CURR']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def do_countuniq( df, group_cols, counted, agg_name, agg_type='uint32', show_max=False, show_agg=True ):\n if show_agg:\n print( \"Counting unqiue \", counted, \" by \", group_cols , '...' )\n gp = df[group_cols+[counted]].groupby(group_cols)[counted].nunique().reset_index().rename(columns={counted:agg_name})\n df = df.merge(gp, on=group_cols, how='left')\n del gp\n if show_max:\n print( agg_name + \" max value = \", df[agg_name].max() )\n df[agg_name] = df[agg_name].astype(agg_type)\n gc.collect()\n return df \n\ndef do_mean(df, group_cols, counted, agg_name, agg_type='float32', show_max=False, show_agg=True ):\n if show_agg:\n print( \"Calculating mean of \", counted, \" by \", group_cols , '...' )\n gp = df[group_cols+[counted]].groupby(group_cols)[counted].mean().reset_index().rename(columns={counted:agg_name})\n df = df.merge(gp, on=group_cols, how='left')\n del gp\n if show_max:\n print( agg_name + \" max value = \", df[agg_name].max() )\n df[agg_name] = df[agg_name].astype(agg_type)\n gc.collect()\n return df \n\ndef do_count(df, group_cols, agg_name, agg_type='uint32', show_max=False, show_agg=True ):\n if show_agg:\n print( \"Aggregating by \", group_cols , '...' )\n gp = df[group_cols][group_cols].groupby(group_cols).size().rename(agg_name).to_frame().reset_index()\n df = df.merge(gp, on=group_cols, how='left')\n del gp\n if show_max:\n print( agg_name + \" max value = \", df[agg_name].max() )\n df[agg_name] = df[agg_name].astype(agg_type)\n gc.collect()\n return df ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"counts_columns = []\nfor f_0 in categorical_columns:\n for f_1 in [x for x in categorical_columns if x != f_0] :\n df = do_countuniq(df, [f_0], f_1,\n f_0 + '-' + f_1 + '_cunique', 'uint16', show_max=True); gc.collect()\n counts_columns.append(f_0 + '-' + f_1 + '_cunique')",
"Counting unqiue CODE_GENDER by ['NAME_CONTRACT_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_CONTRACT_TYPE-CODE_GENDER_cunique max value = 3\nCounting unqiue FLAG_OWN_CAR by ['NAME_CONTRACT_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_CONTRACT_TYPE-FLAG_OWN_CAR_cunique max value = 2\nCounting unqiue FLAG_OWN_REALTY by ['NAME_CONTRACT_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_CONTRACT_TYPE-FLAG_OWN_REALTY_cunique max value = 2\nCounting unqiue NAME_TYPE_SUITE by ['NAME_CONTRACT_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_CONTRACT_TYPE-NAME_TYPE_SUITE_cunique max value = 8\nCounting unqiue NAME_INCOME_TYPE by ['NAME_CONTRACT_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_CONTRACT_TYPE-NAME_INCOME_TYPE_cunique max value = 8\nCounting unqiue NAME_EDUCATION_TYPE by ['NAME_CONTRACT_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_CONTRACT_TYPE-NAME_EDUCATION_TYPE_cunique max value = 5\nCounting unqiue NAME_FAMILY_STATUS by ['NAME_CONTRACT_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_CONTRACT_TYPE-NAME_FAMILY_STATUS_cunique max value = 6\nCounting unqiue NAME_HOUSING_TYPE by ['NAME_CONTRACT_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_CONTRACT_TYPE-NAME_HOUSING_TYPE_cunique max value = 6\nCounting unqiue OCCUPATION_TYPE by ['NAME_CONTRACT_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_CONTRACT_TYPE-OCCUPATION_TYPE_cunique max value = 19\nCounting unqiue WEEKDAY_APPR_PROCESS_START by ['NAME_CONTRACT_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_CONTRACT_TYPE-WEEKDAY_APPR_PROCESS_START_cunique max value = 7\nCounting unqiue ORGANIZATION_TYPE by ['NAME_CONTRACT_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_CONTRACT_TYPE-ORGANIZATION_TYPE_cunique max value = 58\nCounting unqiue FONDKAPREMONT_MODE by ['NAME_CONTRACT_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_CONTRACT_TYPE-FONDKAPREMONT_MODE_cunique max value = 5\nCounting unqiue HOUSETYPE_MODE by ['NAME_CONTRACT_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_CONTRACT_TYPE-HOUSETYPE_MODE_cunique max value = 4\nCounting unqiue WALLSMATERIAL_MODE by ['NAME_CONTRACT_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_CONTRACT_TYPE-WALLSMATERIAL_MODE_cunique max value = 8\nCounting unqiue EMERGENCYSTATE_MODE by ['NAME_CONTRACT_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_CONTRACT_TYPE-EMERGENCYSTATE_MODE_cunique max value = 3\nCounting unqiue NAME_CONTRACT_TYPE by ['CODE_GENDER'] ...\nCODE_GENDER-NAME_CONTRACT_TYPE_cunique max value = 2\nCounting unqiue FLAG_OWN_CAR by ['CODE_GENDER'] ...\nCODE_GENDER-FLAG_OWN_CAR_cunique max value = 2\nCounting unqiue FLAG_OWN_REALTY by ['CODE_GENDER'] ...\nCODE_GENDER-FLAG_OWN_REALTY_cunique max value = 2\nCounting unqiue NAME_TYPE_SUITE by ['CODE_GENDER'] ...\nCODE_GENDER-NAME_TYPE_SUITE_cunique max value = 8\nCounting unqiue NAME_INCOME_TYPE by ['CODE_GENDER'] ...\nCODE_GENDER-NAME_INCOME_TYPE_cunique max value = 8\nCounting unqiue NAME_EDUCATION_TYPE by ['CODE_GENDER'] ...\nCODE_GENDER-NAME_EDUCATION_TYPE_cunique max value = 5\nCounting unqiue NAME_FAMILY_STATUS by ['CODE_GENDER'] ...\nCODE_GENDER-NAME_FAMILY_STATUS_cunique max value = 6\nCounting unqiue NAME_HOUSING_TYPE by ['CODE_GENDER'] ...\nCODE_GENDER-NAME_HOUSING_TYPE_cunique max value = 6\nCounting unqiue OCCUPATION_TYPE by ['CODE_GENDER'] ...\nCODE_GENDER-OCCUPATION_TYPE_cunique max value = 19\nCounting unqiue WEEKDAY_APPR_PROCESS_START by ['CODE_GENDER'] ...\nCODE_GENDER-WEEKDAY_APPR_PROCESS_START_cunique max value = 7\nCounting unqiue ORGANIZATION_TYPE by ['CODE_GENDER'] ...\nCODE_GENDER-ORGANIZATION_TYPE_cunique max value = 58\nCounting unqiue FONDKAPREMONT_MODE by ['CODE_GENDER'] ...\nCODE_GENDER-FONDKAPREMONT_MODE_cunique max value = 5\nCounting unqiue HOUSETYPE_MODE by ['CODE_GENDER'] ...\nCODE_GENDER-HOUSETYPE_MODE_cunique max value = 4\nCounting unqiue WALLSMATERIAL_MODE by ['CODE_GENDER'] ...\nCODE_GENDER-WALLSMATERIAL_MODE_cunique max value = 8\nCounting unqiue EMERGENCYSTATE_MODE by ['CODE_GENDER'] ...\nCODE_GENDER-EMERGENCYSTATE_MODE_cunique max value = 3\nCounting unqiue NAME_CONTRACT_TYPE by ['FLAG_OWN_CAR'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_CAR-NAME_CONTRACT_TYPE_cunique max value = 2\nCounting unqiue CODE_GENDER by ['FLAG_OWN_CAR'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_CAR-CODE_GENDER_cunique max value = 3\nCounting unqiue FLAG_OWN_REALTY by ['FLAG_OWN_CAR'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_CAR-FLAG_OWN_REALTY_cunique max value = 2\nCounting unqiue NAME_TYPE_SUITE by ['FLAG_OWN_CAR'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_CAR-NAME_TYPE_SUITE_cunique max value = 8\nCounting unqiue NAME_INCOME_TYPE by ['FLAG_OWN_CAR'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_CAR-NAME_INCOME_TYPE_cunique max value = 8\nCounting unqiue NAME_EDUCATION_TYPE by ['FLAG_OWN_CAR'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_CAR-NAME_EDUCATION_TYPE_cunique max value = 5\nCounting unqiue NAME_FAMILY_STATUS by ['FLAG_OWN_CAR'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_CAR-NAME_FAMILY_STATUS_cunique max value = 6\nCounting unqiue NAME_HOUSING_TYPE by ['FLAG_OWN_CAR'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_CAR-NAME_HOUSING_TYPE_cunique max value = 6\nCounting unqiue OCCUPATION_TYPE by ['FLAG_OWN_CAR'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_CAR-OCCUPATION_TYPE_cunique max value = 19\nCounting unqiue WEEKDAY_APPR_PROCESS_START by ['FLAG_OWN_CAR'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_CAR-WEEKDAY_APPR_PROCESS_START_cunique max value = 7\nCounting unqiue ORGANIZATION_TYPE by ['FLAG_OWN_CAR'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_CAR-ORGANIZATION_TYPE_cunique max value = 58\nCounting unqiue FONDKAPREMONT_MODE by ['FLAG_OWN_CAR'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_CAR-FONDKAPREMONT_MODE_cunique max value = 5\nCounting unqiue HOUSETYPE_MODE by ['FLAG_OWN_CAR'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_CAR-HOUSETYPE_MODE_cunique max value = 4\nCounting unqiue WALLSMATERIAL_MODE by ['FLAG_OWN_CAR'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_CAR-WALLSMATERIAL_MODE_cunique max value = 8\nCounting unqiue EMERGENCYSTATE_MODE by ['FLAG_OWN_CAR'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_CAR-EMERGENCYSTATE_MODE_cunique max value = 3\nCounting unqiue NAME_CONTRACT_TYPE by ['FLAG_OWN_REALTY'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_REALTY-NAME_CONTRACT_TYPE_cunique max value = 2\nCounting unqiue CODE_GENDER by ['FLAG_OWN_REALTY'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_REALTY-CODE_GENDER_cunique max value = 3\nCounting unqiue FLAG_OWN_CAR by ['FLAG_OWN_REALTY'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_REALTY-FLAG_OWN_CAR_cunique max value = 2\nCounting unqiue NAME_TYPE_SUITE by ['FLAG_OWN_REALTY'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_REALTY-NAME_TYPE_SUITE_cunique max value = 8\nCounting unqiue NAME_INCOME_TYPE by ['FLAG_OWN_REALTY'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_REALTY-NAME_INCOME_TYPE_cunique max value = 8\nCounting unqiue NAME_EDUCATION_TYPE by ['FLAG_OWN_REALTY'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_REALTY-NAME_EDUCATION_TYPE_cunique max value = 5\nCounting unqiue NAME_FAMILY_STATUS by ['FLAG_OWN_REALTY'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_REALTY-NAME_FAMILY_STATUS_cunique max value = 6\nCounting unqiue NAME_HOUSING_TYPE by ['FLAG_OWN_REALTY'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_REALTY-NAME_HOUSING_TYPE_cunique max value = 6\nCounting unqiue OCCUPATION_TYPE by ['FLAG_OWN_REALTY'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_REALTY-OCCUPATION_TYPE_cunique max value = 19\nCounting unqiue WEEKDAY_APPR_PROCESS_START by ['FLAG_OWN_REALTY'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_REALTY-WEEKDAY_APPR_PROCESS_START_cunique max value = 7\nCounting unqiue ORGANIZATION_TYPE by ['FLAG_OWN_REALTY'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_REALTY-ORGANIZATION_TYPE_cunique max value = 58\nCounting unqiue FONDKAPREMONT_MODE by ['FLAG_OWN_REALTY'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_REALTY-FONDKAPREMONT_MODE_cunique max value = 5\nCounting unqiue HOUSETYPE_MODE by ['FLAG_OWN_REALTY'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_REALTY-HOUSETYPE_MODE_cunique max value = 4\nCounting unqiue WALLSMATERIAL_MODE by ['FLAG_OWN_REALTY'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_REALTY-WALLSMATERIAL_MODE_cunique max value = 8\nCounting unqiue EMERGENCYSTATE_MODE by ['FLAG_OWN_REALTY'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_REALTY-EMERGENCYSTATE_MODE_cunique max value = 3\nCounting unqiue NAME_CONTRACT_TYPE by ['NAME_TYPE_SUITE'] ...\nNAME_TYPE_SUITE-NAME_CONTRACT_TYPE_cunique max value = 2\nCounting unqiue CODE_GENDER by ['NAME_TYPE_SUITE'] ...\nNAME_TYPE_SUITE-CODE_GENDER_cunique max value = 3\nCounting unqiue FLAG_OWN_CAR by ['NAME_TYPE_SUITE'] ...\nNAME_TYPE_SUITE-FLAG_OWN_CAR_cunique max value = 2\nCounting unqiue FLAG_OWN_REALTY by ['NAME_TYPE_SUITE'] ...\nNAME_TYPE_SUITE-FLAG_OWN_REALTY_cunique max value = 2\nCounting unqiue NAME_INCOME_TYPE by ['NAME_TYPE_SUITE'] ...\nNAME_TYPE_SUITE-NAME_INCOME_TYPE_cunique max value = 8\nCounting unqiue NAME_EDUCATION_TYPE by ['NAME_TYPE_SUITE'] ...\nNAME_TYPE_SUITE-NAME_EDUCATION_TYPE_cunique max value = 5\nCounting unqiue NAME_FAMILY_STATUS by ['NAME_TYPE_SUITE'] ...\nNAME_TYPE_SUITE-NAME_FAMILY_STATUS_cunique max value = 6\nCounting unqiue NAME_HOUSING_TYPE by ['NAME_TYPE_SUITE'] ...\nNAME_TYPE_SUITE-NAME_HOUSING_TYPE_cunique max value = 6\nCounting unqiue OCCUPATION_TYPE by ['NAME_TYPE_SUITE'] ...\nNAME_TYPE_SUITE-OCCUPATION_TYPE_cunique max value = 19\nCounting unqiue WEEKDAY_APPR_PROCESS_START by ['NAME_TYPE_SUITE'] ...\n"
],
[
"count_columns = []\nfor f_0 in categorical_columns:\n df = do_count(df, [f_0],\n f_0 + '_count', 'uint16', show_max=True); gc.collect()\n count_columns.append(f_0 + '_count')",
"Aggregating by ['NAME_CONTRACT_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_CONTRACT_TYPE_count max value = 326537\nAggregating by ['CODE_GENDER'] ...\nCODE_GENDER_count max value = 235126\nAggregating by ['FLAG_OWN_CAR'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_CAR_count max value = 235235\nAggregating by ['FLAG_OWN_REALTY'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_REALTY_count max value = 246970\nAggregating by ['NAME_TYPE_SUITE'] ...\nNAME_TYPE_SUITE_count max value = 288253\nAggregating by ['NAME_INCOME_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_INCOME_TYPE_count max value = 183307\nAggregating by ['NAME_EDUCATION_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_EDUCATION_TYPE_count max value = 252379\nAggregating by ['NAME_FAMILY_STATUS'] ...\nNAME_FAMILY_STATUS_count max value = 228715\nAggregating by ['NAME_HOUSING_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_HOUSING_TYPE_count max value = 316513\nAggregating by ['OCCUPATION_TYPE'] ...\nOCCUPATION_TYPE_count max value = 111996\nAggregating by ['WEEKDAY_APPR_PROCESS_START'] ...\nWEEKDAY_APPR_PROCESS_START_count max value = 63652\nAggregating by ['ORGANIZATION_TYPE'] ...\nORGANIZATION_TYPE_count max value = 78832\nAggregating by ['FONDKAPREMONT_MODE'] ...\nFONDKAPREMONT_MODE_count max value = 243092\nAggregating by ['HOUSETYPE_MODE'] ...\nHOUSETYPE_MODE_count max value = 177916\nAggregating by ['WALLSMATERIAL_MODE'] ...\nWALLSMATERIAL_MODE_count max value = 180234\nAggregating by ['EMERGENCYSTATE_MODE'] ...\nEMERGENCYSTATE_MODE_count max value = 185607\n"
],
[
"for f in ['AMT_ANNUITY', 'AMT_CREDIT', 'AMT_INCOME_TOTAL'] + ['EXT_SOURCE_1', 'EXT_SOURCE_2', 'EXT_SOURCE_3']:\n new_df[f] = new_df[f].replace([np.inf, -np.inf], np.nan).fillna(new_df[f].replace([np.inf, -np.inf], np.nan).dropna().median())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mean_columns = []\nfor f_0 in categorical_columns:\n for f_1 in ['AMT_ANNUITY', 'AMT_CREDIT', 'AMT_INCOME_TOTAL'] + ['EXT_SOURCE_1', 'EXT_SOURCE_2', 'EXT_SOURCE_3'] :\n new_df = do_mean(new_df, [f_0], f_1,\n f_0 + '-' + f_1 + '_mean', 'uint16', show_max=True); gc.collect()\n mean_columns.append(f_0 + '-' + f_1 + '_mean')",
"Calculating mean of AMT_ANNUITY by ['NAME_CONTRACT_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_CONTRACT_TYPE-AMT_ANNUITY_mean max value = 28439.780537886978\nCalculating mean of AMT_CREDIT by ['NAME_CONTRACT_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_CONTRACT_TYPE-AMT_CREDIT_mean max value = 611841.0087876718\nCalculating mean of AMT_INCOME_TOTAL by ['NAME_CONTRACT_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_CONTRACT_TYPE-AMT_INCOME_TOTAL_mean max value = 170440.64937227633\nCalculating mean of EXT_SOURCE_1 by ['NAME_CONTRACT_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_CONTRACT_TYPE-EXT_SOURCE_1_mean max value = 0.5045938349042247\nCalculating mean of EXT_SOURCE_2 by ['NAME_CONTRACT_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_CONTRACT_TYPE-EXT_SOURCE_2_mean max value = 0.5238536075754979\nCalculating mean of EXT_SOURCE_3 by ['NAME_CONTRACT_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_CONTRACT_TYPE-EXT_SOURCE_3_mean max value = 0.5141439408185883\nCalculating mean of AMT_ANNUITY by ['CODE_GENDER'] ...\nCODE_GENDER-AMT_ANNUITY_mean max value = 29000.096321981426\nCalculating mean of AMT_CREDIT by ['CODE_GENDER'] ...\nCODE_GENDER-AMT_CREDIT_mean max value = 597157.1490650155\nCalculating mean of AMT_INCOME_TOTAL by ['CODE_GENDER'] ...\nCODE_GENDER-AMT_INCOME_TOTAL_mean max value = 194571.8173129412\nCalculating mean of EXT_SOURCE_1 by ['CODE_GENDER'] ...\nCODE_GENDER-EXT_SOURCE_1_mean max value = 0.5245416016342868\nCalculating mean of EXT_SOURCE_2 by ['CODE_GENDER'] ...\nCODE_GENDER-EXT_SOURCE_2_mean max value = 0.5807519989440313\nCalculating mean of EXT_SOURCE_3 by ['CODE_GENDER'] ...\nCODE_GENDER-EXT_SOURCE_3_mean max value = 0.5165924181042661\nCalculating mean of AMT_ANNUITY by ['FLAG_OWN_CAR'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_CAR-AMT_ANNUITY_mean max value = 30372.967526028755\nCalculating mean of AMT_CREDIT by ['FLAG_OWN_CAR'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_CAR-AMT_CREDIT_mean max value = 652786.5696826971\nCalculating mean of AMT_INCOME_TOTAL by ['FLAG_OWN_CAR'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_CAR-AMT_INCOME_TOTAL_mean max value = 197857.94867699555\nCalculating mean of EXT_SOURCE_1 by ['FLAG_OWN_CAR'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_CAR-EXT_SOURCE_1_mean max value = 0.5082190806279482\nCalculating mean of EXT_SOURCE_2 by ['FLAG_OWN_CAR'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_CAR-EXT_SOURCE_2_mean max value = 0.5286760232098211\nCalculating mean of EXT_SOURCE_3 by ['FLAG_OWN_CAR'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_CAR-EXT_SOURCE_3_mean max value = 0.5162198834901489\nCalculating mean of AMT_ANNUITY by ['FLAG_OWN_REALTY'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_REALTY-AMT_ANNUITY_mean max value = 27461.07539003523\nCalculating mean of AMT_CREDIT by ['FLAG_OWN_REALTY'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_REALTY-AMT_CREDIT_mean max value = 608583.7058653978\nCalculating mean of AMT_INCOME_TOTAL by ['FLAG_OWN_REALTY'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_REALTY-AMT_INCOME_TOTAL_mean max value = 170749.11229934805\nCalculating mean of EXT_SOURCE_1 by ['FLAG_OWN_REALTY'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_REALTY-EXT_SOURCE_1_mean max value = 0.5092220106186647\nCalculating mean of EXT_SOURCE_2 by ['FLAG_OWN_REALTY'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_REALTY-EXT_SOURCE_2_mean max value = 0.51540622469143\nCalculating mean of EXT_SOURCE_3 by ['FLAG_OWN_REALTY'] ...\nFLAG_OWN_REALTY-EXT_SOURCE_3_mean max value = 0.5183504853018818\nCalculating mean of AMT_ANNUITY by ['NAME_TYPE_SUITE'] ...\nNAME_TYPE_SUITE-AMT_ANNUITY_mean max value = 29148.45088937432\nCalculating mean of AMT_CREDIT by ['NAME_TYPE_SUITE'] ...\nNAME_TYPE_SUITE-AMT_CREDIT_mean max value = 643037.7227726635\nCalculating mean of AMT_INCOME_TOTAL by ['NAME_TYPE_SUITE'] ...\nNAME_TYPE_SUITE-AMT_INCOME_TOTAL_mean max value = 175109.69087607806\nCalculating mean of EXT_SOURCE_1 by ['NAME_TYPE_SUITE'] ...\nNAME_TYPE_SUITE-EXT_SOURCE_1_mean max value = 0.5262607003656236\nCalculating mean of EXT_SOURCE_2 by ['NAME_TYPE_SUITE'] ...\nNAME_TYPE_SUITE-EXT_SOURCE_2_mean max value = 0.5252922826170473\nCalculating mean of EXT_SOURCE_3 by ['NAME_TYPE_SUITE'] ...\nNAME_TYPE_SUITE-EXT_SOURCE_3_mean max value = 0.5361407786862504\nCalculating mean of AMT_ANNUITY by ['NAME_INCOME_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_INCOME_TYPE-AMT_ANNUITY_mean max value = 67500.0\nCalculating mean of AMT_CREDIT by ['NAME_INCOME_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_INCOME_TYPE-AMT_CREDIT_mean max value = 1145454.5454545454\nCalculating mean of AMT_INCOME_TOTAL by ['NAME_INCOME_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_INCOME_TYPE-AMT_INCOME_TOTAL_mean max value = 634090.9090909091\nCalculating mean of EXT_SOURCE_1 by ['NAME_INCOME_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_INCOME_TYPE-EXT_SOURCE_1_mean max value = 0.6341488557633213\nCalculating mean of EXT_SOURCE_2 by ['NAME_INCOME_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_INCOME_TYPE-EXT_SOURCE_2_mean max value = 0.6630409655358898\nCalculating mean of EXT_SOURCE_3 by ['NAME_INCOME_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_INCOME_TYPE-EXT_SOURCE_3_mean max value = 0.5516909527186679\nCalculating mean of AMT_ANNUITY by ['NAME_EDUCATION_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_EDUCATION_TYPE-AMT_ANNUITY_mean max value = 33113.568292682925\nCalculating mean of AMT_CREDIT by ['NAME_EDUCATION_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_EDUCATION_TYPE-AMT_CREDIT_mean max value = 701045.143902439\nCalculating mean of AMT_INCOME_TOTAL by ['NAME_EDUCATION_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_EDUCATION_TYPE-AMT_INCOME_TOTAL_mean max value = 236260.9756097561\nCalculating mean of EXT_SOURCE_1 by ['NAME_EDUCATION_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_EDUCATION_TYPE-EXT_SOURCE_1_mean max value = 0.5292943146413936\nCalculating mean of EXT_SOURCE_2 by ['NAME_EDUCATION_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_EDUCATION_TYPE-EXT_SOURCE_2_mean max value = 0.5710050407765975\nCalculating mean of EXT_SOURCE_3 by ['NAME_EDUCATION_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_EDUCATION_TYPE-EXT_SOURCE_3_mean max value = 0.53028418406488\nCalculating mean of AMT_ANNUITY by ['NAME_FAMILY_STATUS'] ...\nNAME_FAMILY_STATUS-AMT_ANNUITY_mean max value = 31500.0\nCalculating mean of AMT_CREDIT by ['NAME_FAMILY_STATUS'] ...\nNAME_FAMILY_STATUS-AMT_CREDIT_mean max value = 631539.575576591\nCalculating mean of AMT_INCOME_TOTAL by ['NAME_FAMILY_STATUS'] ...\nNAME_FAMILY_STATUS-AMT_INCOME_TOTAL_mean max value = 326250.0\nCalculating mean of EXT_SOURCE_1 by ['NAME_FAMILY_STATUS'] ...\nNAME_FAMILY_STATUS-EXT_SOURCE_1_mean max value = 0.5673591913003326\nCalculating mean of EXT_SOURCE_2 by ['NAME_FAMILY_STATUS'] ...\nNAME_FAMILY_STATUS-EXT_SOURCE_2_mean max value = 0.6728929541405011\nCalculating mean of EXT_SOURCE_3 by ['NAME_FAMILY_STATUS'] ...\nNAME_FAMILY_STATUS-EXT_SOURCE_3_mean max value = 0.6020666915333535\nCalculating mean of AMT_ANNUITY by ['NAME_HOUSING_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_HOUSING_TYPE-AMT_ANNUITY_mean max value = 28752.020833333332\nCalculating mean of AMT_CREDIT by ['NAME_HOUSING_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_HOUSING_TYPE-AMT_CREDIT_mean max value = 610283.5074404762\nCalculating mean of AMT_INCOME_TOTAL by ['NAME_HOUSING_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_HOUSING_TYPE-AMT_INCOME_TOTAL_mean max value = 189062.63541666666\nCalculating mean of EXT_SOURCE_1 by ['NAME_HOUSING_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_HOUSING_TYPE-EXT_SOURCE_1_mean max value = 0.5092913350281945\nCalculating mean of EXT_SOURCE_2 by ['NAME_HOUSING_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_HOUSING_TYPE-EXT_SOURCE_2_mean max value = 0.5336724358336338\nCalculating mean of EXT_SOURCE_3 by ['NAME_HOUSING_TYPE'] ...\nNAME_HOUSING_TYPE-EXT_SOURCE_3_mean max value = 0.5168255532592988\nCalculating mean of AMT_ANNUITY by ['OCCUPATION_TYPE'] ...\nOCCUPATION_TYPE-AMT_ANNUITY_mean max value = 35493.331028262175\nCalculating mean of AMT_CREDIT by ['OCCUPATION_TYPE'] ...\nOCCUPATION_TYPE-AMT_CREDIT_mean max value = 768197.7732411305\nCalculating mean of AMT_INCOME_TOTAL by ['OCCUPATION_TYPE'] ...\nOCCUPATION_TYPE-AMT_INCOME_TOTAL_mean max value = 262478.3575688515\nCalculating mean of EXT_SOURCE_1 by ['OCCUPATION_TYPE'] ...\nOCCUPATION_TYPE-EXT_SOURCE_1_mean max value = 0.5583632483619353\nCalculating mean of EXT_SOURCE_2 by ['OCCUPATION_TYPE'] ...\nOCCUPATION_TYPE-EXT_SOURCE_2_mean max value = 0.5629814838441918\nCalculating mean of EXT_SOURCE_3 by ['OCCUPATION_TYPE'] ...\nOCCUPATION_TYPE-EXT_SOURCE_3_mean max value = 0.5311686985591276\nCalculating mean of AMT_ANNUITY by ['WEEKDAY_APPR_PROCESS_START'] ...\nWEEKDAY_APPR_PROCESS_START-AMT_ANNUITY_mean max value = 27687.385009066413\nCalculating mean of AMT_CREDIT by ['WEEKDAY_APPR_PROCESS_START'] ...\nWEEKDAY_APPR_PROCESS_START-AMT_CREDIT_mean max value = 594724.0061929758\nCalculating mean of AMT_INCOME_TOTAL by ['WEEKDAY_APPR_PROCESS_START'] ...\nWEEKDAY_APPR_PROCESS_START-AMT_INCOME_TOTAL_mean max value = 171331.74828850623\nCalculating mean of EXT_SOURCE_1 by ['WEEKDAY_APPR_PROCESS_START'] ...\n"
],
[
"# train_features = pd.DataFrame(np.concatenate([df[count_columns][0:n_train].values, train_stacked.values, df[my_features][0:n_train].values, goran_features[0:n_train].values, suresh_august16[:n_train].values, suresh_august15[0:n_train].values], axis=1), columns=\n# count_columns + ['y_' + str(i) for i in range(train_stacked.shape[1])] + my_features + list(goran_features.columns) + list(suresh_august16.columns) + list(suresh_august15.columns))\n# test_features = pd.DataFrame(np.concatenate([df[count_columns][n_train:].values, test_stacked.values, df[my_features][n_train:].values, goran_features[n_train:].values, suresh_august16[n_train:].values, suresh_august15[n_train:].values], axis=1), columns=\n# count_columns + ['y_' + str(i) for i in range(test_stacked.shape[1])] + my_features + list(goran_features.columns) + list(suresh_august16.columns) + list(suresh_august15.columns))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# train_features = np.concatenate([train_stacked.values, df[my_features][0:n_train].values, goran_features[0:n_train].values, suresh_august16[:n_train].values], axis=1)\n# test_features = np.concatenate([test_stacked.values, df[my_features][n_train:].values, goran_features[n_train:].values, suresh_august16[n_train:].values], axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# train_features = pd.DataFrame(np.concatenate([train_stacked.values, df[my_features][0:n_train].values, goran_features[0:n_train].values, suresh_august16[:n_train].values, suresh_august15[0:n_train].values, suresh_august16_2[0:n_train].values], axis=1), columns=\n# ['y_' + str(i) for i in range(train_stacked.shape[1])] + my_features + list(goran_features.columns) + list(suresh_august16.columns) + list(suresh_august15.columns) + list(suresh_august16_2.columns))\n# test_features = pd.DataFrame(np.concatenate([test_stacked.values, df[my_features][n_train:].values, goran_features[n_train:].values, suresh_august16[n_train:].values, suresh_august15[n_train:].values, suresh_august16_2[n_train:].values], axis=1), columns=\n# ['y_' + str(i) for i in range(test_stacked.shape[1])] + my_features + list(goran_features.columns) + list(suresh_august16.columns) + list(suresh_august15.columns) + list(suresh_august16_2.columns))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# train_features = pd.DataFrame(np.concatenate([train_stacked.values, df[my_features][0:n_train].values, goran_features[0:n_train].values, suresh_august19[:n_train].values, suresh_august15[0:n_train].values, prevs_df[0:n_train].values, suresh_august16[0:n_train].values, suresh_august16_2[0:n_train].values], axis=1), columns=\n# ['y_' + str(i) for i in range(train_stacked.shape[1])] + my_features + list(goran_features.columns) + list(suresh_august19.columns) + list(suresh_august15.columns) + list(prevs_df.columns) + list(suresh_august16.columns) + list(suresh_august16_2.columns))\n# test_features = pd.DataFrame(np.concatenate([test_stacked.values, df[my_features][n_train:].values, goran_features[n_train:].values, suresh_august19[n_train:].values, suresh_august15[n_train:].values, prevs_df[n_train:].values, suresh_august16[n_train:].values, suresh_august16_2[n_train:].values], axis=1), columns=\n# ['y_' + str(i) for i in range(test_stacked.shape[1])] + my_features + list(goran_features.columns) + list(suresh_august19.columns) + list(suresh_august15.columns) + list(prevs_df.columns) + list(suresh_august16.columns) + list(suresh_august16_2.columns))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# train_features = pd.DataFrame(np.concatenate([df[count_columns][0:n_train].values, train_stacked.values, df[my_features][0:n_train].values, suresh_august19[:n_train].values, suresh_august15[0:n_train].values, prevs_df[0:n_train].values, suresh_august16[0:n_train].values, suresh_august16_2[0:n_train].values], axis=1), columns=\n# count_columns + ['y_' + str(i) for i in range(train_stacked.shape[1])] + my_features + list(suresh_august19.columns) + list(suresh_august15.columns) + list(prevs_df.columns) + list(suresh_august16.columns) + list(suresh_august16_2.columns))\n# test_features = pd.DataFrame(np.concatenate([df[count_columns][n_train:].values, test_stacked.values, df[my_features][n_train:].values, suresh_august19[n_train:].values, suresh_august15[n_train:].values, prevs_df[n_train:].values, suresh_august16[n_train:].values, suresh_august16_2[n_train:].values], axis=1), columns=\n# count_columns + ['y_' + str(i) for i in range(test_stacked.shape[1])] + my_features + list(suresh_august19.columns) + list(suresh_august15.columns) + list(prevs_df.columns) + list(suresh_august16.columns) + list(suresh_august16_2.columns))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"new_df[mean_columns][0:n_train].values",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"new_df[mean_columns][n_train:].values",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"gc.collect()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# train_features = pd.DataFrame(np.concatenate([new_df[mean_columns][0:n_train].values, suresh_august16[0:n_train].values, df[count_columns][0:n_train].values , df[counts_columns][0:n_train].values, train_stacked.values, df[my_features][0:n_train].values], axis=1), columns=\n# mean_columns + list(suresh_august16.columns) + count_columns + counts_columns + ['y_' + str(i) for i in range(train_stacked.shape[1])] + my_features)\n# test_features = pd.DataFrame(np.concatenate([new_df[mean_columns][n_train:].values, suresh_august16[n_train:].values, df[count_columns][n_train:].values, df[counts_columns][n_train:].values, test_stacked.values, df[my_features][n_train:].values], axis=1), columns=\n# mean_columns + list(suresh_august16.columns) + count_columns + counts_columns + ['y_' + str(i) for i in range(test_stacked.shape[1])] + my_features)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# train_features = pd.DataFrame(np.concatenate([suresh_august16[0:n_train].values, df[count_columns][0:n_train].values , df[counts_columns][0:n_train].values, train_stacked.values, df[my_features][0:n_train].values], axis=1), columns=\n# list(suresh_august16.columns) + count_columns + counts_columns + ['y_' + str(i) for i in range(train_stacked.shape[1])] + my_features)\n# test_features = pd.DataFrame(np.concatenate([ suresh_august16[n_train:].values, df[count_columns][n_train:].values, df[counts_columns][n_train:].values, test_stacked.values, df[my_features][n_train:].values], axis=1), columns=\n# list(suresh_august16.columns) + count_columns + counts_columns + ['y_' + str(i) for i in range(test_stacked.shape[1])] + my_features)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# train_features = pd.DataFrame(np.concatenate([df[categorical_columns][0:n_train].values, goran_features_19_8[0:n_train].values, suresh_august16[0:n_train].values, df[count_columns][0:n_train].values , df[counts_columns][0:n_train].values, train_stacked.values, df[my_features][0:n_train].values], axis=1), columns=\n# categorical_columns + list(goran_features_19_8.columns) + list(suresh_august16.columns) + count_columns + counts_columns + ['y_' + str(i) for i in range(train_stacked.shape[1])] + my_features)\n# test_features = pd.DataFrame(np.concatenate([df[categorical_columns][n_train:].values, goran_features_19_8[n_train:].values, suresh_august16[n_train:].values, df[count_columns][n_train:].values, df[counts_columns][n_train:].values, test_stacked.values, df[my_features][n_train:].values], axis=1), columns=\n# categorical_columns + list(goran_features_19_8.columns) + list(suresh_august16.columns) + count_columns + counts_columns + ['y_' + str(i) for i in range(test_stacked.shape[1])] + my_features)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# train_features = pd.DataFrame(np.concatenate([goranm_8_20[0:n_train].values ,goran_features_19_8[0:n_train].values, suresh_august20[0:n_train].values, train_stacked.values, df[my_features][0:n_train].values, suresh_august16[:n_train].values, suresh_august15[0:n_train].values], axis=1), columns=\n# list(goranm_8_20.columns) + list(goran_features_19_8.columns) + list(suresh_august20.columns) + ['y_' + str(i) for i in range(train_stacked.shape[1])] + my_features + list(suresh_august16.columns) + list(suresh_august15.columns))\n# test_features = pd.DataFrame(np.concatenate([goranm_8_20[n_train:].values, goran_features_19_8[n_train:].values, suresh_august20[n_train:].values, test_stacked.values, df[my_features][n_train:].values, suresh_august16[n_train:].values, suresh_august15[n_train:].values], axis=1), columns=\n# list(goranm_8_20.columns) + list(goran_features_19_8.columns) + list(suresh_august20.columns) + ['y_' + str(i) for i in range(test_stacked.shape[1])] + my_features + list(suresh_august16.columns) + list(suresh_august15.columns))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# train_features = pd.DataFrame(np.concatenate([goranm_8_20[0:n_train].values ,goran_features_19_8[0:n_train].values, suresh_august20[0:n_train].values, train_stacked.iloc[:, selected_features].values, df[my_features][0:n_train].values, suresh_august16[:n_train].values, suresh_august15[0:n_train].values], axis=1), columns=\n# list(goranm_8_20.columns) + list(goran_features_19_8.columns) + list(suresh_august20.columns) + ['y_' + str(i) for i in selected_features] + my_features + list(suresh_august16.columns) + list(suresh_august15.columns))\n# test_features = pd.DataFrame(np.concatenate([goranm_8_20[n_train:].values, goran_features_19_8[n_train:].values, suresh_august20[n_train:].values, test_stacked.iloc[:, selected_features].values, df[my_features][n_train:].values, suresh_august16[n_train:].values, suresh_august15[n_train:].values], axis=1), columns=\n# list(goranm_8_20.columns) + list(goran_features_19_8.columns) + list(suresh_august20.columns) + ['y_' + str(i) for i in selected_features] + my_features + list(suresh_august16.columns) + list(suresh_august15.columns))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# train_features = pd.DataFrame(np.concatenate([goran_features_19_8[0:n_train].values, df[count_columns][0:n_train].values, train_stacked.values, df[my_features][0:n_train].values, goran_features[0:n_train].values, suresh_august16[:n_train].values, suresh_august15[0:n_train].values], axis=1), columns=\n# list(goran_features_19_8.columns) + count_columns + ['y_' + str(i) for i in range(train_stacked.shape[1])] + my_features + list(goran_features.columns) + list(suresh_august16.columns) + list(suresh_august15.columns))\n# test_features = pd.DataFrame(np.concatenate([goran_features_19_8[n_train:].values, df[count_columns][n_train:].values, test_stacked.values, df[my_features][n_train:].values, goran_features[n_train:].values, suresh_august16[n_train:].values, suresh_august15[n_train:].values], axis=1), columns=\n# list(goran_features_19_8.columns) + count_columns + ['y_' + str(i) for i in range(test_stacked.shape[1])] + my_features + list(goran_features.columns) + list(suresh_august16.columns) + list(suresh_august15.columns))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"train_features = pd.DataFrame(np.concatenate([df[counts_columns][0:n_train].values, df[count_columns][0:n_train].values ,new_df[mean_columns][0:n_train].values, prevs_df[0:n_train].values, suresh_20[0:n_train].values, goranm_8_20[0:n_train].values ,goran_features_19_8[0:n_train].values, suresh_august20[0:n_train].values, df[my_features][0:n_train].values, suresh_august16[:n_train].values, suresh_august15[0:n_train].values], axis=1), columns=\n counts_columns + count_columns + mean_columns + list(prevs_df.columns) + list(suresh_20.columns) + list(goranm_8_20.columns) + list(goran_features_19_8.columns) + list(suresh_august20.columns) + my_features + list(suresh_august16.columns) + list(suresh_august15.columns))\ntest_features = pd.DataFrame(np.concatenate([df[counts_columns][n_train:].values, df[count_columns][n_train:].values, new_df[mean_columns][n_train:].values, prevs_df[n_train:].values, suresh_20[n_train:].values, goranm_8_20[n_train:].values, goran_features_19_8[n_train:].values, suresh_august20[n_train:].values, df[my_features][n_train:].values, suresh_august16[n_train:].values, suresh_august15[n_train:].values], axis=1), columns=\n counts_columns + count_columns + mean_columns + list(prevs_df.columns) + list(suresh_20.columns) + list(goranm_8_20.columns) + list(goran_features_19_8.columns) + list(suresh_august20.columns) + my_features + list(suresh_august16.columns) + list(suresh_august15.columns))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"test_features.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"gc.collect()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cols_to_drop = [\n \n 'STCK_BERBAL_6_.', \n \"FLAG_DOCUMENT_2\",\n\n \"FLAG_DOCUMENT_7\",\n\n \"FLAG_DOCUMENT_10\",\n\n \"FLAG_DOCUMENT_12\",\n\n \"FLAG_DOCUMENT_13\",\n\n \"FLAG_DOCUMENT_14\",\n\n \"FLAG_DOCUMENT_15\",\n\n \"FLAG_DOCUMENT_16\",\n\n \"FLAG_DOCUMENT_17\",\n\n \"FLAG_DOCUMENT_18\",\n\n \"FLAG_DOCUMENT_19\",\n\n \"FLAG_DOCUMENT_20\",\n\n \"FLAG_DOCUMENT_21\",\n\n \"PREV_NAME_CONTRACT_TYPE_Consumer_loans\",\n\n \"PREV_NAME_CONTRACT_TYPE_XNA\",\n\n \"PB_CNT_NAME_CONTRACT_STATUS_Amortized_debt\",\n\n \"MAX_DATA_ALL\",\n\n \"MIN_DATA_ALL\",\n\n \"MAX_MIN_DURATION\",\n\n \"MAX_AMT_CREDIT_MAX_OVERDUE\",\n\n \"CC_AMT_DRAWINGS_ATM_CURRENT_MIN\",\n\n \"CC_AMT_DRAWINGS_OTHER_CURRENT_MAX\",\n\n \"CC_AMT_DRAWINGS_OTHER_CURRENT_MIN\",\n\n \"CC_CNT_DRAWINGS_ATM_CURRENT_MIN\",\n\n \"CC_CNT_DRAWINGS_OTHER_CURRENT_MAX\",\n\n \"CC_CNT_DRAWINGS_OTHER_CURRENT_MIN\",\n\n \"CC_SK_DPD_DEF_MIN\",\n\n \"CC_SK_DPD_MIN\",\n\n \"BERB_STATUS_CREDIT_TYPE_Loan_for_working_capital_replenishment\",\n\n \"BERB_STATUS_CREDIT_TYPE_Real_estate_loan\",\n\n \"BERB_STATUS_CREDIT_TYPE_Loan_for_the_purchase_of_equipment\",\n\n \"BERB_COMBO_CT_CA_COMBO_CT_CA_Loan_for_working_capital_replenishmentClosed\",\n\n \"BERB_COMBO_CT_CA_COMBO_CT_CA_Car_loanSold\",\n\n \"BERB_COMBO_CT_CA_COMBO_CT_CA_Another_type_of_loanActive\",\n\n \"BERB_COMBO_CT_CA_COMBO_CT_CA_Loan_for_working_capital_replenishmentSold\",\n\n \"BERB_COMBO_CT_CA_COMBO_CT_CA_MicroloanSold\",\n\n \"BERB_COMBO_CT_CA_COMBO_CT_CA_Another_type_of_loanSold\",\n\n \"FLAG_EMAIL\",\n\n \"APARTMENTS_AVG\",\n\n \"AMT_REQ_CREDIT_BUREAU_MON\",\n\n \"AMT_REQ_CREDIT_BUREAU_QRT\",\n\n \"AMT_REQ_CREDIT_BUREAU_YEAR\",\n\n \"STCK_BERBAL_6_\",\n\n \"STCK_CC_6_x\"]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"feats = [f for f in cols_to_drop if f in train_features.columns]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"train_features.drop(labels=feats, axis=1, inplace=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"test_features.drop(labels=feats, axis=1, inplace=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cat_features = [] # [i for i in range(len(categorical_columns))]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"gc.collect()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# train_stacked.to_csv('oofs/train_oofs-v0.1.0.csv', index=False)\n# test_stacked.to_csv('oofs/test_oofs-v0.1.0.csv', index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"test_features.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"train_features['nans'] = train_features.replace([np.inf, -np.inf], np.nan).isnull().sum(axis=1)\ntest_features['nans'] = test_features.replace([np.inf, -np.inf], np.nan).isnull().sum(axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"test_file_path = \"Level_1_stack/test_catb_xxx_0.csv\"\nvalidation_file_path = 'Level_1_stack/validation_catb_xxx_0.csv.csv'\nnum_folds = 5",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# train_features = train_features.replace([np.inf, -np.inf], np.nan).fillna(-999, inplace=False)\n# test_features = test_features.replace([np.inf, -np.inf], np.nan).fillna(-999, inplace=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"gc.collect()\nencoding = 'ohe'\n\ntrain_df = train_features\ntest_df = test_features\n\nprint(\"Starting LightGBM. Train shape: {}, test shape: {}\".format(train_df.shape, test_df.shape))\ngc.collect()\n# Cross validation model\nfolds = KFold(n_splits=num_folds, shuffle=True, random_state=1001)\n# Create arrays and dataframes to store results\noof_preds = np.zeros(train_df.shape[0])\nsub_preds = np.zeros(test_df.shape[0])\nfeature_importance_df = pd.DataFrame()\nfeats = [f for f in train_df.columns if f not in ['TARGET','SK_ID_CURR','SK_ID_BUREAU','SK_ID_PREV','index']]\n\n#feats = [col for col in feats_0 if df[col].dtype == 'object']\n\n\nprint(train_df[feats].shape)\nfor n_fold, (train_idx, valid_idx) in enumerate(folds.split(train_df[feats], train['TARGET'])):\n \n \n \n if encoding == 'ohe':\n x_train = train_df[feats].iloc[train_idx]\n #cat_features = [i for i, col in enumerate(x_train.columns) if col in categorical_cols]\n x_train = x_train.replace([np.inf, -np.inf], np.nan).fillna(-999).values\n x_valid = train_df[feats].iloc[valid_idx].replace([np.inf, -np.inf], np.nan).fillna(-999).values\n x_test = test_df[feats].replace([np.inf, -np.inf], np.nan).fillna(-999).values\n print(x_train.shape, x_valid.shape, x_test.shape)\n \n gc.collect()\n \n clf = CatBoostRegressor(learning_rate=0.05, iterations=2500, verbose=True, rsm=0.25,\n use_best_model=True, l2_leaf_reg=40, allow_writing_files=False, metric_period=50,\n random_seed=666, depth=6, loss_function='RMSE', od_wait=50, od_type='Iter')\n\n clf.fit(x_train, train['TARGET'].iloc[train_idx].values, eval_set=(x_valid, train['TARGET'].iloc[valid_idx].values)\n , cat_features=[], use_best_model=True, verbose=True)\n\n oof_preds[valid_idx] = clf.predict(x_valid)\n sub_preds += clf.predict(x_test) / folds.n_splits\n\n print('Fold %2d AUC : %.6f' % (n_fold + 1, roc_auc_score(train['TARGET'].iloc[valid_idx].values, oof_preds[valid_idx])))\n del clf\n gc.collect()\n \n \n \n\n",
"Starting LightGBM. Train shape: (307511, 423), test shape: (48744, 423)\n(307511, 421)\n(246008, 421) (61503, 421) (48744, 421)\nWarning: Parameter 'use_best_model' is true, thus evaluation metric iscalculated on every iteration. 'metric_period' is ignored for evaluation metric.\n0:\tlearn: 0.2813103\ttest: 0.2859832\tbest: 0.2859832 (0)\ttotal: 91.9ms\tremaining: 3m 49s\n50:\tlearn: 0.2600347\ttest: 0.2638970\tbest: 0.2638970 (50)\ttotal: 4.76s\tremaining: 3m 48s\n100:\tlearn: 0.2582922\ttest: 0.2622716\tbest: 0.2622716 (100)\ttotal: 9.58s\tremaining: 3m 47s\n150:\tlearn: 0.2574201\ttest: 0.2616139\tbest: 0.2616139 (150)\ttotal: 14.3s\tremaining: 3m 42s\n200:\tlearn: 0.2568222\ttest: 0.2612286\tbest: 0.2612286 (200)\ttotal: 19s\tremaining: 3m 37s\n250:\tlearn: 0.2563299\ttest: 0.2609930\tbest: 0.2609930 (250)\ttotal: 23.7s\tremaining: 3m 32s\n300:\tlearn: 0.2559197\ttest: 0.2608294\tbest: 0.2608294 (300)\ttotal: 28.5s\tremaining: 3m 27s\n350:\tlearn: 0.2555578\ttest: 0.2606731\tbest: 0.2606731 (350)\ttotal: 33.2s\tremaining: 3m 23s\n400:\tlearn: 0.2552333\ttest: 0.2605597\tbest: 0.2605597 (400)\ttotal: 38s\tremaining: 3m 18s\n450:\tlearn: 0.2549128\ttest: 0.2604635\tbest: 0.2604635 (450)\ttotal: 42.8s\tremaining: 3m 14s\n500:\tlearn: 0.2546064\ttest: 0.2603882\tbest: 0.2603882 (500)\ttotal: 47.5s\tremaining: 3m 9s\n550:\tlearn: 0.2543240\ttest: 0.2603104\tbest: 0.2603104 (550)\ttotal: 52.3s\tremaining: 3m 5s\n600:\tlearn: 0.2540642\ttest: 0.2602599\tbest: 0.2602599 (600)\ttotal: 57.1s\tremaining: 3m\n650:\tlearn: 0.2537940\ttest: 0.2601982\tbest: 0.2601982 (650)\ttotal: 1m 1s\tremaining: 2m 55s\n700:\tlearn: 0.2535374\ttest: 0.2601493\tbest: 0.2601493 (700)\ttotal: 1m 6s\tremaining: 2m 51s\n750:\tlearn: 0.2533019\ttest: 0.2601072\tbest: 0.2601072 (750)\ttotal: 1m 11s\tremaining: 2m 46s\n800:\tlearn: 0.2530568\ttest: 0.2600707\tbest: 0.2600707 (800)\ttotal: 1m 16s\tremaining: 2m 41s\n850:\tlearn: 0.2528092\ttest: 0.2600220\tbest: 0.2600220 (850)\ttotal: 1m 20s\tremaining: 2m 36s\n900:\tlearn: 0.2525877\ttest: 0.2600012\tbest: 0.2600012 (900)\ttotal: 1m 25s\tremaining: 2m 32s\n950:\tlearn: 0.2523627\ttest: 0.2599795\tbest: 0.2599795 (950)\ttotal: 1m 30s\tremaining: 2m 27s\n1000:\tlearn: 0.2521391\ttest: 0.2599747\tbest: 0.2599747 (1000)\ttotal: 1m 35s\tremaining: 2m 22s\nStopped by overfitting detector (50 iterations wait)\n\nbestTest = 0.2599746533\nbestIteration = 1000\n\nShrink model to first 1001 iterations.\nFold 1 AUC : 0.787449\n(246009, 421) (61502, 421) (48744, 421)\nWarning: Parameter 'use_best_model' is true, thus evaluation metric iscalculated on every iteration. 'metric_period' is ignored for evaluation metric.\n0:\tlearn: 0.2820776\ttest: 0.2829714\tbest: 0.2829714 (0)\ttotal: 85.7ms\tremaining: 3m 34s\n50:\tlearn: 0.2605657\ttest: 0.2616257\tbest: 0.2616257 (50)\ttotal: 4.57s\tremaining: 3m 39s\n100:\tlearn: 0.2588151\ttest: 0.2601365\tbest: 0.2601365 (100)\ttotal: 9.16s\tremaining: 3m 37s\n150:\tlearn: 0.2579496\ttest: 0.2595386\tbest: 0.2595386 (150)\ttotal: 13.7s\tremaining: 3m 33s\n200:\tlearn: 0.2573461\ttest: 0.2591925\tbest: 0.2591925 (200)\ttotal: 18.3s\tremaining: 3m 28s\n250:\tlearn: 0.2568440\ttest: 0.2589652\tbest: 0.2589652 (250)\ttotal: 22.8s\tremaining: 3m 24s\n300:\tlearn: 0.2564132\ttest: 0.2587661\tbest: 0.2587661 (300)\ttotal: 27.2s\tremaining: 3m 19s\n350:\tlearn: 0.2560571\ttest: 0.2586440\tbest: 0.2586440 (350)\ttotal: 31.8s\tremaining: 3m 14s\n400:\tlearn: 0.2557451\ttest: 0.2585332\tbest: 0.2585332 (400)\ttotal: 36.4s\tremaining: 3m 10s\n450:\tlearn: 0.2554310\ttest: 0.2584536\tbest: 0.2584536 (450)\ttotal: 41s\tremaining: 3m 6s\n500:\tlearn: 0.2551421\ttest: 0.2583958\tbest: 0.2583958 (500)\ttotal: 45.5s\tremaining: 3m 1s\n550:\tlearn: 0.2548587\ttest: 0.2583172\tbest: 0.2583172 (550)\ttotal: 50.1s\tremaining: 2m 57s\n600:\tlearn: 0.2546149\ttest: 0.2582586\tbest: 0.2582586 (600)\ttotal: 54.7s\tremaining: 2m 52s\n650:\tlearn: 0.2543415\ttest: 0.2582275\tbest: 0.2582275 (650)\ttotal: 59.2s\tremaining: 2m 48s\n700:\tlearn: 0.2540995\ttest: 0.2581889\tbest: 0.2581889 (700)\ttotal: 1m 3s\tremaining: 2m 43s\n750:\tlearn: 0.2538857\ttest: 0.2581722\tbest: 0.2581722 (750)\ttotal: 1m 8s\tremaining: 2m 39s\n800:\tlearn: 0.2536638\ttest: 0.2581435\tbest: 0.2581435 (800)\ttotal: 1m 12s\tremaining: 2m 34s\n850:\tlearn: 0.2534281\ttest: 0.2581086\tbest: 0.2581086 (850)\ttotal: 1m 17s\tremaining: 2m 30s\n900:\tlearn: 0.2531998\ttest: 0.2580936\tbest: 0.2580936 (900)\ttotal: 1m 22s\tremaining: 2m 25s\n950:\tlearn: 0.2529963\ttest: 0.2580630\tbest: 0.2580630 (950)\ttotal: 1m 26s\tremaining: 2m 20s\n1000:\tlearn: 0.2527993\ttest: 0.2580310\tbest: 0.2580310 (1000)\ttotal: 1m 31s\tremaining: 2m 16s\n1050:\tlearn: 0.2525840\ttest: 0.2579987\tbest: 0.2579987 (1050)\ttotal: 1m 35s\tremaining: 2m 11s\n1100:\tlearn: 0.2523778\ttest: 0.2579869\tbest: 0.2579869 (1100)\ttotal: 1m 40s\tremaining: 2m 7s\n1150:\tlearn: 0.2521834\ttest: 0.2579727\tbest: 0.2579727 (1150)\ttotal: 1m 44s\tremaining: 2m 2s\n1200:\tlearn: 0.2519831\ttest: 0.2579696\tbest: 0.2579696 (1200)\ttotal: 1m 49s\tremaining: 1m 58s\nStopped by overfitting detector (50 iterations wait)\n\nbestTest = 0.2579696417\nbestIteration = 1200\n\nShrink model to first 1201 iterations.\nFold 2 AUC : 0.788383\n(246009, 421) (61502, 421) (48744, 421)\nWarning: Parameter 'use_best_model' is true, thus evaluation metric iscalculated on every iteration. 'metric_period' is ignored for evaluation metric.\n0:\tlearn: 0.2828369\ttest: 0.2797438\tbest: 0.2797438 (0)\ttotal: 91.4ms\tremaining: 3m 48s\n50:\tlearn: 0.2610589\ttest: 0.2592571\tbest: 0.2592571 (50)\ttotal: 4.82s\tremaining: 3m 51s\n100:\tlearn: 0.2592691\ttest: 0.2580388\tbest: 0.2580388 (100)\ttotal: 9.64s\tremaining: 3m 49s\n150:\tlearn: 0.2584348\ttest: 0.2575508\tbest: 0.2575508 (150)\ttotal: 14.4s\tremaining: 3m 44s\n200:\tlearn: 0.2578273\ttest: 0.2572210\tbest: 0.2572210 (200)\ttotal: 19.1s\tremaining: 3m 38s\n250:\tlearn: 0.2573360\ttest: 0.2570073\tbest: 0.2570073 (250)\ttotal: 23.9s\tremaining: 3m 34s\n300:\tlearn: 0.2569029\ttest: 0.2568631\tbest: 0.2568631 (300)\ttotal: 28.6s\tremaining: 3m 29s\n350:\tlearn: 0.2565004\ttest: 0.2567196\tbest: 0.2567196 (350)\ttotal: 33.4s\tremaining: 3m 24s\n400:\tlearn: 0.2561677\ttest: 0.2566402\tbest: 0.2566402 (400)\ttotal: 38.2s\tremaining: 3m 19s\n450:\tlearn: 0.2558729\ttest: 0.2565718\tbest: 0.2565718 (450)\ttotal: 43s\tremaining: 3m 15s\n500:\tlearn: 0.2555797\ttest: 0.2565110\tbest: 0.2565110 (500)\ttotal: 47.7s\tremaining: 3m 10s\n550:\tlearn: 0.2553069\ttest: 0.2564554\tbest: 0.2564554 (550)\ttotal: 52.6s\tremaining: 3m 5s\n600:\tlearn: 0.2550320\ttest: 0.2564197\tbest: 0.2564197 (600)\ttotal: 57.4s\tremaining: 3m 1s\n650:\tlearn: 0.2547821\ttest: 0.2563751\tbest: 0.2563751 (650)\ttotal: 1m 2s\tremaining: 2m 56s\n700:\tlearn: 0.2545358\ttest: 0.2563253\tbest: 0.2563253 (700)\ttotal: 1m 6s\tremaining: 2m 51s\n750:\tlearn: 0.2542960\ttest: 0.2562744\tbest: 0.2562744 (750)\ttotal: 1m 11s\tremaining: 2m 46s\n800:\tlearn: 0.2540669\ttest: 0.2562341\tbest: 0.2562341 (800)\ttotal: 1m 16s\tremaining: 2m 42s\n850:\tlearn: 0.2538423\ttest: 0.2562182\tbest: 0.2562182 (850)\ttotal: 1m 21s\tremaining: 2m 37s\n900:\tlearn: 0.2536217\ttest: 0.2561972\tbest: 0.2561972 (900)\ttotal: 1m 26s\tremaining: 2m 32s\n950:\tlearn: 0.2534215\ttest: 0.2561639\tbest: 0.2561639 (950)\ttotal: 1m 30s\tremaining: 2m 28s\n1000:\tlearn: 0.2531914\ttest: 0.2561424\tbest: 0.2561424 (1000)\ttotal: 1m 35s\tremaining: 2m 23s\n1050:\tlearn: 0.2529902\ttest: 0.2561243\tbest: 0.2561243 (1050)\ttotal: 1m 40s\tremaining: 2m 18s\n1100:\tlearn: 0.2527805\ttest: 0.2561065\tbest: 0.2561065 (1100)\ttotal: 1m 45s\tremaining: 2m 13s\n1150:\tlearn: 0.2525628\ttest: 0.2560954\tbest: 0.2560954 (1150)\ttotal: 1m 49s\tremaining: 2m 8s\n1200:\tlearn: 0.2523590\ttest: 0.2560769\tbest: 0.2560769 (1200)\ttotal: 1m 54s\tremaining: 2m 4s\n1250:\tlearn: 0.2521731\ttest: 0.2560593\tbest: 0.2560593 (1250)\ttotal: 1m 59s\tremaining: 1m 59s\n1300:\tlearn: 0.2519732\ttest: 0.2560372\tbest: 0.2560372 (1300)\ttotal: 2m 4s\tremaining: 1m 54s\n1350:\tlearn: 0.2517694\ttest: 0.2560219\tbest: 0.2560219 (1350)\ttotal: 2m 9s\tremaining: 1m 49s\n1400:\tlearn: 0.2515749\ttest: 0.2560128\tbest: 0.2560128 (1400)\ttotal: 2m 14s\tremaining: 1m 45s\n1450:\tlearn: 0.2513860\ttest: 0.2559990\tbest: 0.2559990 (1450)\ttotal: 2m 18s\tremaining: 1m 40s\n1500:\tlearn: 0.2511968\ttest: 0.2559767\tbest: 0.2559767 (1500)\ttotal: 2m 23s\tremaining: 1m 35s\n1550:\tlearn: 0.2509983\ttest: 0.2559690\tbest: 0.2559690 (1550)\ttotal: 2m 28s\tremaining: 1m 30s\nStopped by overfitting detector (50 iterations wait)\n\nbestTest = 0.2559690303\nbestIteration = 1550\n\nShrink model to first 1551 iterations.\n"
],
[
"sub_df = test[['SK_ID_CURR']].copy()\nsub_df['TARGET'] = sub_preds\nsub_df[['SK_ID_CURR', 'TARGET']].to_csv(test_file_path, index= False)\n\n\nval_df = train[['SK_ID_CURR', 'TARGET']].copy()\nval_df['TARGET'] = oof_preds\nval_df[['SK_ID_CURR', 'TARGET']].to_csv(validation_file_path, index= False) \n\ngc.collect()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4ab9896d03aeff75773b335843b92e830844184b
| 63,414 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/factorize_linear_structure.ipynb
|
mederrata/spmf
|
f6fac4eb21d30221b7dc1ef06d7508b15b106a9d
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2020-08-11T10:42:15.000Z
|
2020-08-11T10:42:15.000Z
|
notebooks/factorize_linear_structure.ipynb
|
mederrata/spmf
|
f6fac4eb21d30221b7dc1ef06d7508b15b106a9d
|
[
"MIT"
] | 11 |
2020-09-29T19:17:23.000Z
|
2021-11-05T00:42:00.000Z
|
notebooks/factorize_linear_structure.ipynb
|
mederrata/spmf
|
f6fac4eb21d30221b7dc1ef06d7508b15b106a9d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 110.863636 | 27,112 | 0.816555 |
[
[
[
"%pylab inline\nimport sys\n\nimport numpy as np\nimport tensorflow as tf\nimport tensorflow_probability as tfp\nimport arviz as az\n\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom matplotlib import rcParams\nimport matplotlib.font_manager as fm\n\nrcParams['font.family'] = 'sans-serif'\n\nsys.path.append('../')\nfrom mederrata_spmf import PoissonMatrixFactorization\n",
"Populating the interactive namespace from numpy and matplotlib\n"
]
],
[
[
"In this notebook, we look at the $\\mathcal{M}$-open setting, where the generating process is in the span of models.\n\n# Generate a random matrices V, W\n\nFor V, assume that 10 variables share a factor structure and the other 20 are noise",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"N = 50000\nD_factor = 10\nD_noise = 20\nD = D_factor + D_noise\nP = 3\n\nV = np.abs(np.random.normal(1.5, 0.5, size=(P,D_factor)))\nZ = np.abs(np.random.normal(0, 1, size=(N,P)))\n\nZV = Z.dot(V)\n\nX = np.zeros((N, D_factor+D_noise))\nX = np.random.poisson(1.,size=(N,D_noise+D_factor))\nX[:, ::3] = np.random.poisson(ZV)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Test taking in from tf.dataset, don't pre-batch\ndata = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(\n {\n 'counts': X,\n 'indices': np.arange(N),\n 'normalization': np.ones(N)\n })\n\ndata = data.batch(1000)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# strategy = tf.distribute.MirroredStrategy()\nstrategy = None\nfactor = PoissonMatrixFactorization(\n data, latent_dim=P, strategy=strategy,\n u_tau_scale=1.0/np.sqrt(D*N),\n dtype=tf.float64)\n# Test to make sure sampling works\n",
"Looping through the entire dataset once to get some stats\nFeature dim: 30 -> Latent dim 3\n"
],
[
"losses = factor.calibrate_advi(\n num_epochs=200, learning_rate=.05)\n\n\n",
"Initial loss: 54.505081021975975\nEpoch 1: average-batch loss: 52.18392385770157 last batch loss: 51.61718268805165\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-1\nEpoch 2: average-batch loss: 51.47188594390579 last batch loss: 51.03566885862666\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-2\nEpoch 3: average-batch loss: 50.31910578335157 last batch loss: 48.42949112324473\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-3\nEpoch 4: average-batch loss: 48.07451143441375 last batch loss: 47.99966370839411\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-4\nEpoch 5: average-batch loss: 47.833077733383824 last batch loss: 47.80992648683104\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-5\nEpoch 6: average-batch loss: 47.69161720142685 last batch loss: 47.71099947714361\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-6\nEpoch 7: average-batch loss: 47.62094244183653 last batch loss: 47.6563286874736\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-7\nEpoch 8: average-batch loss: 47.579215780175545 last batch loss: 47.647523680647005\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-8\nEpoch 9: average-batch loss: 47.53866125945372 last batch loss: 47.56570832126065\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-9\nEpoch 10: average-batch loss: 47.48297395334625 last batch loss: 47.51862624415346\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-10\nEpoch 11: average-batch loss: 47.35230688738326 last batch loss: 47.34037544031407\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-11\nEpoch 12: average-batch loss: 47.21890694000364 last batch loss: 47.2554661382803\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-12\nEpoch 13: average-batch loss: 47.158276611546164 last batch loss: 47.20864556703984\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-13\nEpoch 14: average-batch loss: 47.12702272597266 last batch loss: 47.18551458777342\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-14\nEpoch 15: average-batch loss: 47.10720459159613 last batch loss: 47.15715400383067\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-15\nEpoch 16: average-batch loss: 47.0959257950597 last batch loss: 47.13338213311636\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-16\nEpoch 17: average-batch loss: 47.079558942657805 last batch loss: 47.15791856717731\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-17\nEpoch 18: average-batch loss: 47.07042002748222 last batch loss: 47.14061912527724\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-18\nEpoch 19: average-batch loss: 47.06566891385941 last batch loss: 47.119107827765035\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-19\nEpoch 20: average-batch loss: 47.05190996398477 last batch loss: 47.11818222826543\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-20\nEpoch 21: average-batch loss: 47.05153412228544 last batch loss: 47.11733987535518\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-21\nEpoch 22: average-batch loss: 47.03887309347601 last batch loss: 47.13689451476859\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-22\nEpoch 23: average-batch loss: 47.03655009266151 last batch loss: 47.11276770850706\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-23\nEpoch 24: average-batch loss: 47.032861837463386 last batch loss: 47.14294010827793\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-24\nEpoch 25: average-batch loss: 47.02867092632197 last batch loss: 47.0858444199787\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-25\nEpoch 26: average-batch loss: 47.033174592409424 last batch loss: 47.09241399892748\nWe are in a loss plateau learning rate: 0.0495 loss: 47.521406207410095\nRestoring from a checkpoint - loss: 47.53236321680261\nEpoch 27: average-batch loss: 47.02423601734153 last batch loss: 47.09452004816378\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-26\nEpoch 28: average-batch loss: 47.01921898969259 last batch loss: 47.08271128840423\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-27\nEpoch 29: average-batch loss: 47.02040865868162 last batch loss: 47.084653384651695\nEpoch 30: average-batch loss: 47.01784379414296 last batch loss: 47.11290833687907\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-28\nEpoch 31: average-batch loss: 47.01553037231474 last batch loss: 47.0726541619891\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-29\nEpoch 32: average-batch loss: 47.01298883596682 last batch loss: 47.09232939989718\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-30\nEpoch 33: average-batch loss: 47.01204748625219 last batch loss: 47.0844737676996\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-31\nEpoch 34: average-batch loss: 47.009409025352916 last batch loss: 47.060050621031586\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-32\nEpoch 35: average-batch loss: 47.01150784964856 last batch loss: 47.09444347378165\nEpoch 36: average-batch loss: 47.00822532356363 last batch loss: 47.0810419211081\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-33\nEpoch 37: average-batch loss: 47.0057957396057 last batch loss: 47.07875433833434\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-34\nEpoch 38: average-batch loss: 47.00686009195208 last batch loss: 47.068005138810996\nEpoch 39: average-batch loss: 47.004288022198644 last batch loss: 47.103238461226994\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-35\nEpoch 40: average-batch loss: 47.00282241059206 last batch loss: 47.063257223898894\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-36\nEpoch 41: average-batch loss: 47.00245256343075 last batch loss: 47.08323557787173\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-37\nEpoch 42: average-batch loss: 47.000343534488636 last batch loss: 47.05845064081246\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-38\nEpoch 43: average-batch loss: 46.994807536107366 last batch loss: 47.03851939533162\nSaved a checkpoint: ./.tf_ckpts/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b/f07d5462-d3a3-47d8-83f4-707d1007832b-39\nEpoch 44: average-batch loss: 46.999174711701045 last batch loss: 47.06109672917444\nEpoch 45: average-batch loss: 46.996518062914795 last batch loss: 47.04751144761156\nEpoch 46: average-batch loss: 46.99599139388867 last batch loss: 47.04822931698364\n"
],
[
"waic = factor.waic()\nprint(waic)",
"{'waic': 443250.7443048926, 'se': 2313.6626607298817, 'lppd': -41236.92593508755, 'pwaic': 180388.44621735875}\n"
],
[
"surrogate_samples = factor.surrogate_distribution.sample(1000)\nif 's' in surrogate_samples.keys():\n weights = surrogate_samples['s']/tf.reduce_sum(surrogate_samples['s'],-2,keepdims=True)\n intercept_data = az.convert_to_inference_data(\n {\n r\"$\\varphi_i/\\eta_i$\": \n (tf.squeeze(surrogate_samples['w'])*weights[:,-1,:]).numpy().T})\nelse:\n intercept_data = az.convert_to_inference_data(\n {\n r\"$\\varphi_i/\\eta_i$\": \n (tf.squeeze(surrogate_samples['w'])).numpy().T})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,2, figsize=(14,8))\nD = factor.feature_dim\npcm = ax[0].imshow(factor.encoding_matrix().numpy()[::-1,:], vmin=0, cmap=\"Blues\")\nax[0].set_yticks(np.arange(D))\nax[0].set_yticklabels(np.arange(D))\nax[0].set_ylabel(\"item\")\nax[0].set_xlabel(\"factor dimension\")\nax[0].set_xticks(np.arange(P))\nax[0].set_xticklabels(np.arange(P))\n\nfig.colorbar(pcm, ax=ax[0], orientation = \"vertical\")\naz.plot_forest(intercept_data, ax=ax[1])\nax[1].set_xlabel(\"background rate\")\nax[1].set_ylim((-0.014,.466))\nax[1].set_title(\"65% and 95% CI\")\n#plt.savefig('mix_nonlinear_factorization_sepmf.pdf', bbox_inches='tight')\nplt.show()\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4ab995c40f4cc119a3310f2ae194d3a353ab1ee1
| 14,898 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
MS-malware-suspectibility-detection/6-final-model/FinalModel2.ipynb
|
Semiu/malware-detector
|
3701c4bb7b4275a03f6d1c48dfab7303422b8d97
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2021-09-06T10:04:22.000Z
|
2021-09-06T17:49:45.000Z
|
MS-malware-suspectibility-detection/6-final-model/FinalModel2.ipynb
|
Semiu/malware-detector
|
3701c4bb7b4275a03f6d1c48dfab7303422b8d97
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
MS-malware-suspectibility-detection/6-final-model/FinalModel2.ipynb
|
Semiu/malware-detector
|
3701c4bb7b4275a03f6d1c48dfab7303422b8d97
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 36.876238 | 195 | 0.506578 |
[
[
[
"Final models with hyperparameters tuned for Logistics Regression and XGBoost with all features.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#Import the libraries \nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nfrom tqdm import tqdm\nfrom sklearn import linear_model, metrics, preprocessing, model_selection\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler\nimport xgboost as xgb",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Load the data\nmodeling_dataset = pd.read_csv('/content/drive/MyDrive/prediction/frac_cleaned_fod_data.csv', low_memory = False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#All columns - except 'HasDetections', 'kfold', and 'MachineIdentifier'\ntrain_features = [tf for tf in modeling_dataset.columns if tf not in ('HasDetections', 'kfold', 'MachineIdentifier')]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#The features selected based on the feature selection method earlier employed\ntrain_features_after_selection = ['AVProductStatesIdentifier', 'Processor','AvSigVersion', 'Census_TotalPhysicalRAM', 'Census_InternalPrimaryDiagonalDisplaySizeInInches', \n 'Census_IsVirtualDevice', 'Census_PrimaryDiskTotalCapacity', 'Wdft_IsGamer', 'Census_IsAlwaysOnAlwaysConnectedCapable', 'EngineVersion',\n 'Census_ProcessorCoreCount', 'Census_OSEdition', 'Census_OSInstallTypeName', 'Census_OSSkuName', 'AppVersion', 'OsBuildLab', 'OsSuite',\n 'Firewall', 'IsProtected', 'Census_IsTouchEnabled', 'Census_ActivationChannel', 'LocaleEnglishNameIdentifier','Census_SystemVolumeTotalCapacity',\n 'Census_InternalPrimaryDisplayResolutionHorizontal','Census_HasOpticalDiskDrive', 'OsBuild', 'Census_InternalPrimaryDisplayResolutionVertical',\n 'CountryIdentifier', 'Census_MDC2FormFactor', 'GeoNameIdentifier', 'Census_PowerPlatformRoleName', 'Census_OSWUAutoUpdateOptionsName', 'SkuEdition',\n 'Census_OSVersion', 'Census_GenuineStateName', 'Census_OSBuildRevision', 'Platform', 'Census_ChassisTypeName', 'Census_FlightRing', \n 'Census_PrimaryDiskTypeName', 'Census_OSBranch', 'Census_IsSecureBootEnabled', 'OsPlatformSubRelease']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Define the categorical features of the data\ncategorical_features = ['ProductName',\n 'EngineVersion',\n 'AppVersion',\n 'AvSigVersion',\n 'Platform',\n 'Processor',\n 'OsVer',\n 'OsPlatformSubRelease',\n 'OsBuildLab',\n 'SkuEdition',\n 'Census_MDC2FormFactor',\n 'Census_DeviceFamily',\n 'Census_PrimaryDiskTypeName',\n 'Census_ChassisTypeName',\n 'Census_PowerPlatformRoleName',\n 'Census_OSVersion',\n 'Census_OSArchitecture',\n 'Census_OSBranch',\n 'Census_OSEdition',\n 'Census_OSSkuName',\n 'Census_OSInstallTypeName',\n 'Census_OSWUAutoUpdateOptionsName',\n 'Census_GenuineStateName',\n 'Census_ActivationChannel',\n 'Census_FlightRing']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#XGBoost \ndef opt_run_xgboost(fold):\n for col in train_features:\n if col in categorical_features:\n #Initialize the Label Encoder\n lbl = preprocessing.LabelEncoder()\n #Fit on the categorical features\n lbl.fit(modeling_dataset[col])\n #Transform \n modeling_dataset.loc[:,col] = lbl.transform(modeling_dataset[col])\n \n #Get training and validation data using folds\n modeling_datasets_train = modeling_dataset[modeling_dataset.kfold != fold].reset_index(drop=True)\n modeling_datasets_valid = modeling_dataset[modeling_dataset.kfold == fold].reset_index(drop=True)\n \n #Get train data\n X_train = modeling_datasets_train[train_features].values\n #Get validation data\n X_valid = modeling_datasets_valid[train_features].values\n\n #Initialize XGboost model\n xgb_model = xgb.XGBClassifier(\n \talpha= 1.0,\n colsample_bytree= 0.6,\n eta= 0.05,\n gamma= 0.1,\n lamda= 1.0,\n max_depth= 9,\n min_child_weight= 5,\n subsample= 0.7,\n n_jobs=-1)\n \n #Fit the model on training data\n xgb_model.fit(X_train, modeling_datasets_train.HasDetections.values)\n\n #Predict on validation\n valid_preds = xgb_model.predict_proba(X_valid)[:,1]\n valid_preds_pc = xgb_model.predict(X_valid)\n\n #Get the ROC AUC score\n auc = metrics.roc_auc_score(modeling_datasets_valid.HasDetections.values, valid_preds)\n\n #Get the precision score\n pre = metrics.precision_score(modeling_datasets_valid.HasDetections.values, valid_preds_pc, average='binary')\n\n #Get the Recall score\n rc = metrics.recall_score(modeling_datasets_valid.HasDetections.values, valid_preds_pc, average='binary')\n\n return auc, pre, rc",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Function for Logistic Regression Classification\ndef opt_run_lr(fold):\n #Get training and validation data using folds\n cleaned_fold_datasets_train = modeling_dataset[modeling_dataset.kfold != fold].reset_index(drop=True)\n cleaned_fold_datasets_valid = modeling_dataset[modeling_dataset.kfold == fold].reset_index(drop=True)\n \n #Initialize OneHotEncoder from scikit-learn, and fit it on training and validation features\n ohe = preprocessing.OneHotEncoder()\n full_data = pd.concat(\n [cleaned_fold_datasets_train[train_features],cleaned_fold_datasets_valid[train_features]],\n axis = 0\n )\n ohe.fit(full_data[train_features])\n \n #transform the training and validation data\n x_train = ohe.transform(cleaned_fold_datasets_train[train_features])\n x_valid = ohe.transform(cleaned_fold_datasets_valid[train_features])\n\n #Initialize the Logistic Regression Model\n lr_model = linear_model.LogisticRegression(\n penalty= 'l2',\n C = 49.71967742639108,\n solver= 'lbfgs',\n max_iter= 300,\n n_jobs=-1\n )\n\n #Fit model on training data\n lr_model.fit(x_train, cleaned_fold_datasets_train.HasDetections.values)\n\n #Predict on the validation data using the probability for the AUC\n valid_preds = lr_model.predict_proba(x_valid)[:, 1]\n \n #For precision and Recall\n valid_preds_pc = lr_model.predict(x_valid)\n\n #Get the ROC AUC score\n auc = metrics.roc_auc_score(cleaned_fold_datasets_valid.HasDetections.values, valid_preds)\n\n #Get the precision score\n pre = metrics.precision_score(cleaned_fold_datasets_valid.HasDetections.values, valid_preds_pc, average='binary')\n\n #Get the Recall score \n rc = metrics.recall_score(cleaned_fold_datasets_valid.HasDetections.values, valid_preds_pc, average='binary')\n\n return auc, pre, rc",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#A list to hold the values of the XGB performance metrics\nxg = []\nfor fold in tqdm(range(10)):\n xg.append(opt_run_xgboost(fold))",
"100%|██████████| 10/10 [59:30<00:00, 357.04s/it]\n"
],
[
"#Run the Logistic regression model for all folds and hold their values\nlr = []\nfor fold in tqdm(range(10)):\n lr.append(opt_run_lr(fold))",
"100%|██████████| 10/10 [36:08<00:00, 216.81s/it]\n"
],
[
"xgb_auc = []\nxgb_pre = []\nxgb_rc = []\n\nlr_auc = []\nlr_pre = []\nlr_rc = []",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Loop to get each of the performance metric for average computation\nfor i in lr:\n lr_auc.append(i[0])\n lr_pre.append(i[1])\n lr_rc.append(i[2])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for j in xg:\n xgb_auc.append(i[0])\n xgb_pre.append(i[1])\n xgb_rc.append(i[2])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Dictionary to hold the basic model performance data\nfinal_model_performance2 = {\"logistic_regression\": {\"auc\":\"\", \"precision\":\"\", \"recall\":\"\"},\n \"xgb\": {\"auc\":\"\",\"precision\":\"\",\"recall\":\"\"}\n }",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Calculate average of each of the lists of performance metrics and update the dictionary\nfinal_model_performance2['logistic_regression'].update({'auc':sum(lr_auc)/len(lr_auc)})\nfinal_model_performance2['xgb'].update({'auc':sum(xgb_auc)/len(xgb_auc)})\n\nfinal_model_performance2['logistic_regression'].update({'precision':sum(lr_pre)/len(lr_pre)})\nfinal_model_performance2['xgb'].update({'precision':sum(xgb_pre)/len(xgb_pre)})\n\nfinal_model_performance2['logistic_regression'].update({'recall':sum(lr_rc)/len(lr_rc)})\nfinal_model_performance2['xgb'].update({'recall':sum(xgb_rc)/len(xgb_rc)})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"final_model_performance2",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4ab99d4da1a45161ee194822bf165bc5f82d4b59
| 482,430 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/Space ship classification sample.ipynb
|
Light4Code/tensorflow-research
|
392c2d7bc376f491fec68d479b130f883d6d028d
|
[
"MIT"
] | 5 |
2020-02-29T16:28:55.000Z
|
2021-11-24T07:47:36.000Z
|
notebooks/Space ship classification sample.ipynb
|
octumcore/tensorflow-research
|
ebb8e8243889f55affa354c49eb54db4fbcd2c87
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2020-11-13T18:41:57.000Z
|
2022-02-10T01:37:51.000Z
|
notebooks/Space ship classification sample.ipynb
|
octumcore/tensorflow-research
|
ebb8e8243889f55affa354c49eb54db4fbcd2c87
|
[
"MIT"
] | 4 |
2020-03-24T10:50:17.000Z
|
2020-06-02T13:07:28.000Z
| 1,098.929385 | 136,956 | 0.948689 |
[
[
[
"Imaging you are a metal toy producer and wan't to package your product automaticaly.\nIn this case it would be nice to categorise your products without much effort.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In this example we use a pretrained model ('Xception' with 'imagenet' dataset).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Import dependencies",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import warnings\nwarnings.filterwarnings('ignore')\nimport sys\nimport pathlib\ncurrent_path = pathlib.Path().absolute()\nroot_path = \"{0}/..\".format(current_path)\nsys.path.append(\"{0}/src\".format(root_path))\n\nimport numpy as np\nfrom tensorflow.keras import backend as K\nfrom tensorflow.keras.optimizers import SGD, Adam\nfrom tensorflow.keras.applications.xception import Xception\nfrom tensorflow.keras.layers import GlobalAveragePooling2D, Dense\nfrom tensorflow.keras.models import Model\n\nimport backbones\nimport utils.plots as plots\nfrom train_engine import TrainEngine\nfrom utils import load_dataset, ImageGeneratorConfig, setup_environment, export_util",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"setup_environment(enable_gpu=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Prepare training and evaluation",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"As we have only few images, we need to augment them to get more input for our neuronal network.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"train_files_path = \"{0}/img/space_ships/train\".format(root_path)\neval_files_path = \"{0}/img/space_ships/eval\".format(root_path)\n\ninput_shape = (138, 256, 3)\ngenerator_config = ImageGeneratorConfig()\ngenerator_config.loop_count = 10\ngenerator_config.horizontal_flip = True\ngenerator_config.zoom_range = 0.5\ngenerator_config.width_shift_range = 0.03\ngenerator_config.height_shift_range = 0.03\ngenerator_config.rotation_range = 180\n\ntrain_x, train_y, eval_x, eval_y = load_dataset(\n train_files_path, input_shape, validation_split=0.1\n)\n\nnumber_of_classes = 3",
"Using class indexes as train_y\nSplit dataset into 18 train and 3 test data\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Create model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"base_model = Xception(include_top=False, weights='imagenet', input_shape=input_shape)\nbase_layers_count = len(base_model.layers)\nx = base_model.output\nx = GlobalAveragePooling2D()(x)\nx = Dense(512, activation='relu')(x)\nx = Dense(number_of_classes, activation='softmax')(x)\nmodel = Model(inputs=base_model.input, outputs=x)\n\noptimizer = Adam(lr=0.001)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Train model",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"First we will teach the model the new classes.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for layer in base_model.layers:\n layer.trainable = False\n \ntrain_engine = TrainEngine(\n input_shape, \n model, \n optimizer, \n loss=\"sparse_categorical_crossentropy\"\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Train",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"loss, acc, val_loss, val_acc = train_engine.train(\n train_x,\n train_y,\n eval_x,\n eval_y,\n epochs=70,\n batch_size=32,\n image_generator_config=generator_config,\n is_augment_y_enabled=False,\n is_classification=True\n)",
"Epoch 10/70\tloss: 0.21795\tacc: 0.915\tval_loss: 0.04009\tval_acc: 1.0\nEpoch 20/70\tloss: 0.14248\tacc: 0.94778\tval_loss: 0.0203\tval_acc: 1.0\nEpoch 30/70\tloss: 0.1127\tacc: 0.95889\tval_loss: 0.02334\tval_acc: 0.98889\nEpoch 40/70\tloss: 0.09646\tacc: 0.965\tval_loss: 0.01755\tval_acc: 0.99167\nEpoch 50/70\tloss: 0.08477\tacc: 0.96933\tval_loss: 0.01404\tval_acc: 0.99333\nEpoch 60/70\tloss: 0.08154\tacc: 0.97083\tval_loss: 0.01171\tval_acc: 0.99444\nEpoch 70/70\tloss: 0.07685\tacc: 0.97246\tval_loss: 0.01004\tval_acc: 0.99524\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Show history",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plots.plot_history(loss, acc, val_loss, val_acc)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now we fine tune the convolutional layers from the base model.\nThis will remove connections between neurons that are not used and also create new ones.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for layer in base_model.layers[:base_layers_count]:\n layer.trainable = False\nfor layer in model.layers[base_layers_count:]:\n layer.trainable = True\n \noptimizer = SGD(lr=0.0001, momentum=0.9)\n\ntrain_engine = TrainEngine(\n input_shape, \n model, \n optimizer, \n loss=\"sparse_categorical_crossentropy\"\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"loss, acc, val_loss, val_acc = train_engine.train(\n train_x,\n train_y,\n eval_x,\n eval_y,\n epochs=20,\n batch_size=32,\n image_generator_config=generator_config,\n is_augment_y_enabled=False,\n is_classification=True\n)",
"Epoch 10/20\tloss: 0.01983\tacc: 0.99389\tval_loss: 0.0\tval_acc: 1.0\nEpoch 20/20\tloss: 0.02824\tacc: 0.99056\tval_loss: 0.0\tval_acc: 1.0\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Predict",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"classes = ['Millenium Falcon', 'Pelican', 'TIE Fighter']\n\nx, _, _, _ = load_dataset(\n eval_files_path, input_shape, validation_split=0\n) \n\nfor idx in range(len(x[:3])):\n predictions = train_engine.model.predict(\n np.array([x[idx]], dtype=np.float32), batch_size=1\n )\n plots.plot_classification(predictions, [x[idx]], input_shape, classes)",
"No classes detected, will continue without classes!\nUsing train_x as train_y\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Export model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"export_path = \"{0}/saved_models/space_ships\".format(root_path)\nexport_util.export_model(model, export_path)",
"WARNING:tensorflow:From /home/light/anaconda3/envs/tensorflow2/lib/python3.7/site-packages/tensorflow_core/python/ops/resource_variable_ops.py:1786: calling BaseResourceVariable.__init__ (from tensorflow.python.ops.resource_variable_ops) with constraint is deprecated and will be removed in a future version.\nInstructions for updating:\nIf using Keras pass *_constraint arguments to layers.\nINFO:tensorflow:Assets written to: /home/light/Source/tensorflow-research/notebooks/../saved_models/space_ships/assets\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Cleanup",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"K.clear_session()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4ab9bb66bdd6900b07e4cb653a7cbaa15942c5a1
| 4,496 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
0.12/_downloads/plot_linear_model_patterns.ipynb
|
drammock/mne-tools.github.io
|
5d3a104d174255644d8d5335f58036e32695e85d
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
0.12/_downloads/plot_linear_model_patterns.ipynb
|
drammock/mne-tools.github.io
|
5d3a104d174255644d8d5335f58036e32695e85d
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
0.12/_downloads/plot_linear_model_patterns.ipynb
|
drammock/mne-tools.github.io
|
5d3a104d174255644d8d5335f58036e32695e85d
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null | 49.955556 | 917 | 0.637456 |
[
[
[
"%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n# Linear classifier on sensor data with plot patterns and filters\n\n\nDecoding, a.k.a MVPA or supervised machine learning applied to MEG and EEG\ndata in sensor space. Fit a linear classifier with the LinearModel object\nproviding topographical patterns which are more neurophysiologically\ninterpretable [1] than the classifier filters (weight vectors).\nThe patterns explain how the MEG and EEG data were generated from the\ndiscriminant neural sources which are extracted by the filters.\nNote patterns/filters in MEG data are more similar than EEG data\nbecause the noise is less spatially correlated in MEG than EEG.\n\n[1] Haufe, S., Meinecke, F., Görgen, K., Dähne, S., Haynes, J.-D.,\nBlankertz, B., & Bießmann, F. (2014). On the interpretation of\nweight vectors of linear models in multivariate neuroimaging.\nNeuroImage, 87, 96–110. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.10.067\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Authors: Alexandre Gramfort <[email protected]>\n# Romain Trachel <[email protected]>\n#\n# License: BSD (3-clause)\n\nimport mne\nfrom mne import io\nfrom mne.datasets import sample\n\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression\n\n# import a linear classifier from mne.decoding\nfrom mne.decoding import LinearModel\n\nprint(__doc__)\n\ndata_path = sample.data_path()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Set parameters\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"raw_fname = data_path + '/MEG/sample/sample_audvis_filt-0-40_raw.fif'\nevent_fname = data_path + '/MEG/sample/sample_audvis_filt-0-40_raw-eve.fif'\ntmin, tmax = -0.2, 0.5\nevent_id = dict(aud_l=1, vis_l=3)\n\n# Setup for reading the raw data\nraw = io.read_raw_fif(raw_fname, preload=True)\nraw.filter(2, None, method='iir') # replace baselining with high-pass\nevents = mne.read_events(event_fname)\n\n# Read epochs\nepochs = mne.Epochs(raw, events, event_id, tmin, tmax, proj=True,\n decim=4, baseline=None, preload=True)\n\nlabels = epochs.events[:, -1]\n\n# get MEG and EEG data\nmeg_epochs = epochs.copy().pick_types(meg=True, eeg=False)\nmeg_data = meg_epochs.get_data().reshape(len(labels), -1)\neeg_epochs = epochs.copy().pick_types(meg=False, eeg=True)\neeg_data = eeg_epochs.get_data().reshape(len(labels), -1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Decoding in sensor space using a LogisticRegression classifier\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"clf = LogisticRegression()\nsc = StandardScaler()\n\n# create a linear model with LogisticRegression\nmodel = LinearModel(clf)\n\n# fit the classifier on MEG data\nX = sc.fit_transform(meg_data)\nmodel.fit(X, labels)\n# plot patterns and filters\nmodel.plot_patterns(meg_epochs.info, title='MEG Patterns')\nmodel.plot_filters(meg_epochs.info, title='MEG Filters')\n\n# fit the classifier on EEG data\nX = sc.fit_transform(eeg_data)\nmodel.fit(X, labels)\n# plot patterns and filters\nmodel.plot_patterns(eeg_epochs.info, title='EEG Patterns')\nmodel.plot_filters(eeg_epochs.info, title='EEG Filters')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4ab9c3434f29d933d45044733f43a15b399d82e8
| 17,055 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
src/Sodoku solver.ipynb
|
SpyrosDellas/software-testing
|
2bbe2d7cf6e45ee9e856be860bc7fa5027763d82
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
src/Sodoku solver.ipynb
|
SpyrosDellas/software-testing
|
2bbe2d7cf6e45ee9e856be860bc7fa5027763d82
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
src/Sodoku solver.ipynb
|
SpyrosDellas/software-testing
|
2bbe2d7cf6e45ee9e856be860bc7fa5027763d82
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 43.843188 | 284 | 0.482146 |
[
[
[
"# CHALLENGE PROBLEM: \n#\n# Use your check_sudoku function as the basis for solve_sudoku(): a\n# function that takes a partially-completed Sudoku grid and replaces\n# each 0 cell with an integer in the range 1..9 in such a way that the\n# final grid is valid.\n#\n# There are many ways to cleverly solve a partially-completed Sudoku\n# puzzle, but a brute-force recursive solution with backtracking is a\n# perfectly good option. The solver should return None for broken\n# input, False for inputs that have no valid solutions, and a valid\n# 9x9 Sudoku grid containing no 0 elements otherwise. In general, a\n# partially-completed Sudoku grid does not have a unique solution. You\n# should just return some member of the set of solutions.\n#\n# A solve_sudoku() in this style can be implemented in about 16 lines\n# without making any particular effort to write concise code.\n\n# solve_sudoku should return None\nill_formed = [[5,3,4,6,7,8,9,1,2],\n [6,7,2,1,9,5,3,4,8],\n [1,9,8,3,4,2,5,6,7],\n [8,5,9,7,6,1,4,2,3],\n [4,2,6,8,5,3,7,9], # <---\n [7,1,3,9,2,4,8,5,6],\n [9,6,1,5,3,7,2,8,4],\n [2,8,7,4,1,9,6,3,5],\n [3,4,5,2,8,6,1,7,9]]\n\n# solve_sudoku should return valid unchanged\nvalid = [[5,3,4,6,7,8,9,1,2],\n [6,7,2,1,9,5,3,4,8],\n [1,9,8,3,4,2,5,6,7],\n [8,5,9,7,6,1,4,2,3],\n [4,2,6,8,5,3,7,9,1],\n [7,1,3,9,2,4,8,5,6],\n [9,6,1,5,3,7,2,8,4],\n [2,8,7,4,1,9,6,3,5],\n [3,4,5,2,8,6,1,7,9]]\n\n# solve_sudoku should return False\ninvalid = [[5,3,4,6,7,8,9,1,2],\n [6,7,2,1,9,5,3,4,8],\n [1,9,8,3,8,2,5,6,7], # <------ 8 appears two times\n [8,5,9,7,6,1,4,2,3],\n [4,2,6,8,5,3,7,9,1],\n [7,1,3,9,2,4,8,5,6],\n [9,6,1,5,3,7,2,8,4],\n [2,8,7,4,1,9,6,3,5],\n [3,4,5,2,8,6,1,7,9]]\n\n# solve_sudoku should return a \n# sudoku grid which passes a \n# sudoku checker. There may be\n# multiple correct grids which \n# can be made from this starting \n# grid.\neasy = [[2,9,0,0,0,0,0,7,0],\n [3,0,6,0,0,8,4,0,0],\n [8,0,0,0,4,0,0,0,2],\n [0,2,0,0,3,1,0,0,7],\n [0,0,0,0,8,0,0,0,0],\n [1,0,0,9,5,0,0,6,0],\n [7,0,0,0,9,0,0,0,1],\n [0,0,1,2,0,0,3,0,6],\n [0,3,0,0,0,0,0,5,9]]\n\n# Note: this may timeout \n# in the Udacity IDE! Try running \n# it locally if you'd like to test \n# your solution with it.\n\nhard = [[1,0,0,0,0,7,0,9,0],\n [0,3,0,0,2,0,0,0,8],\n [0,0,9,6,0,0,5,0,0],\n [0,0,5,3,0,0,9,0,0],\n [0,1,0,0,8,0,0,0,2],\n [6,0,0,0,0,4,0,0,0],\n [3,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0],\n [0,4,0,0,0,0,0,0,7],\n [0,0,7,0,0,0,3,0,0]]\n\nimport copy\n\ndef columns(grid):\n '''Helper function that transposes grid and returns a list of columns'''\n return [[row[i] for row in grid] for i in range(9)]\n\ndef subgrids(grid):\n '''Helper function that returns a list of the nine 3x3 sub-grids in horizontal ordering'''\n return [[grid[i+m][j+k] for m in range(3) for k in range(3)] for i in range(0, 7, 3) for j in range(0, 7, 3)]\n\ndef check_sudoku(grid):\n \"\"\"Sudoku puzzle validity checker function. \n Returns None if input is not a 9x9 grid of the form [[int,..],... []] where int is an integer from 0 to 9. \n Returns False if the grid is not a valid Sudoku puzzle and True otherwise.\n Zeros are accepted as representing unsolved cells.\"\"\"\n # input validity checks\n if not isinstance(grid, list):\n return None\n elif not len(grid) == 9:\n return None\n elif not all([isinstance(row, list) for row in grid]):\n return None\n elif not all([len(row) == 9 for row in grid]):\n return None\n elif not all([isinstance(char, int) for row in grid for char in row]):\n return None\n elif not all([(0 <= char <= 9) for row in grid for char in row]):\n return None\n # create list of checks for rows, columns and sub_grinds\n checks = [grid, columns(grid), subgrids(grid)]\n for check in checks:\n if not all([row.count(num) <= 1 for row in check for num in range(1, 10)]):\n return False\n return True\n\ndef create_puzzle(grid):\n \"\"\"Helper function that takes an unsolved grid and replaces zeros with the set {1, ..., 9}.\n Solved cells are transformed to one element sets.\"\"\"\n puzzle = [[], [], [], [], [], [], [], [], []]\n for counter, row in enumerate(grid):\n for elem in row: \n if elem == 0:\n puzzle[counter].append(set(range(1, 10)))\n else:\n puzzle[counter].append(set([elem]))\n return puzzle\n\ndef convert_to_grid(puzzle):\n \"\"\"Helper function to convert a sudoku puuzle of the format [[{}, ...], ... , [{}, ...]]\n back to the original format of [[int, ..., int], ..., [int, ..., int]].\"\"\"\n grid = [[], [], [], [], [], [], [], [], []]\n for i, row in enumerate(puzzle):\n for j, elem in enumerate(row):\n if len(elem) == 1:\n grid[i].append(next(iter(elem)))\n else:\n grid[i].append(0)\n return grid\n\ndef solved_cells(puzzle):\n \"\"\"Helper function that counts solved cell in a sodoku grid, where each cell is a set\"\"\"\n return sum([1 for row in puzzle for elem in row if len(elem) == 1])\n\ndef first_stage_solve(puzzle):\n \"\"\"Helper function that eliminates possible values from unsolved cells, based on existing solved\n cells in corresponding row, column and subgrid and returns the result.\"\"\"\n result = [[], [], [], [], [], [], [], [], []] \n for i, row in enumerate(puzzle):\n for j, cell in enumerate(row):\n if len(cell) > 1:\n # construct a set of solved cell values in row i\n solved_row_values = set([]).union(*[elem for elem in row if len(elem) == 1])\n # construct a set of solved cell values in column j\n solved_column_values = set([]).union(*[elem for elem in columns(puzzle)[j] if len(elem) == 1])\n # construct a set of solved cell values in corresponding subgrid\n solved_subgrid_values = set([]).union(*[elem for elem in subgrids(puzzle)[3*(i//3) + j//3] if len(elem) == 1])\n # construct the set of not permitted values for cell\n not_permitted = solved_row_values | solved_column_values | solved_subgrid_values\n # eliminate not permitted values and append to result\n result[i].append(cell.difference(not_permitted))\n else:\n result[i].append(cell)\n return result\n\ndef second_stage_solve(puzzle):\n \"\"\"Helper function that solves unsolved cells, by checking for uniqueness of allowed values\n for the cell in corresponding row and column and returns the result.\"\"\"\n # check rows\n for i, row in enumerate(puzzle):\n for j, cell in enumerate(row):\n if len(cell) > 1:\n other_cell_values = set([]).union(*[elem for counter, elem in enumerate(row) if counter != j]) \n for value in cell:\n if not value in other_cell_values:\n puzzle[i][j] = set([value])\n break\n # check columns\n for j, column in enumerate(columns(puzzle)):\n for i, cell in enumerate(column):\n if len(cell) > 1:\n other_cell_values = set([]).union(*[elem for counter, elem in enumerate(column) if counter != i]) \n for value in cell:\n if not value in other_cell_values:\n puzzle[i][j] = set([value])\n break\n return puzzle\n\ndef pairs_of_two(row_column_subgrid):\n \"\"\"Helper function that returns the positions of the first pair of identical 2-sets found in input\n row, column or subgrid.\"\"\"\n for elem in row_column_subgrid:\n if len(elem) == 2 and row_column_subgrid.count(elem) == 2:\n i = row_column_subgrid.index(elem)\n j = i + 1 + row_column_subgrid[i+1: ].index(elem)\n return (i, j)\n else:\n return None\n\ndef third_stage_solve(puzzle):\n \"\"\"Helper function that scans each row, column and subgrid for pairs of cells with same 2-set\n of possible solutions and eliminates these values from remaining cells of the corresponding\n row, column or subgrid.\"\"\" \n # scan rows\n for i, row in enumerate(puzzle):\n pair_positions = pairs_of_two(row)\n if pair_positions:\n for j, cell in enumerate(row):\n if j not in pair_positions:\n puzzle[i][j] = cell.difference(row[pair_positions[0]])\n # scan columns\n for j, column in enumerate(columns(puzzle)):\n pair_positions = pairs_of_two(column)\n if pair_positions:\n for i, cell in enumerate(column):\n if i not in pair_positions:\n puzzle[i][j] = cell.difference(column[pair_positions[0]])\n # scan subgrids\n for i, subgrid in enumerate(subgrids(puzzle)):\n pair_positions = pairs_of_two(subgrid)\n if pair_positions:\n for j, cell in enumerate(subgrid):\n if j not in pair_positions:\n puzzle[3*(i//3) + j//3][3*(i%3) + j%3] = cell.difference(subgrid[pair_positions[0]])\n return puzzle\n\ndef logic_solve(puzzle):\n \"\"\"Helper function that attempts to solve the puzzle using logic\"\"\"\n while True:\n solved_cells_at_start = solved_cells(puzzle)\n puzzle = third_stage_solve(second_stage_solve(first_stage_solve(puzzle)))\n solved_cells_at_end = solved_cells(puzzle)\n if solved_cells_at_end == solved_cells_at_start:\n return puzzle \n\ndef backtracking_solve(puzzle):\n \"\"\"Helper function that solves the puzzle recursively using backtracking.\"\"\"\n for i, row in enumerate(puzzle):\n for j, cell in enumerate(row):\n if len(cell) > 1:\n for value in cell:\n # puzzle is a compound list, so a slice copy wouldn't work \n # here as the original puzzle would be affected\n possible_solution = copy.deepcopy(puzzle)\n possible_solution[i][j] = set([value])\n possible_solution = logic_solve(possible_solution)\n if solved_cells(possible_solution) == 81:\n if check_sudoku(convert_to_grid(possible_solution)):\n return possible_solution\n else:\n continue\n elif not all([len(elem) > 0 for row in possible_solution for elem in row]):\n continue\n else:\n possible_solution = backtracking_solve(possible_solution)\n if possible_solution is not None:\n return possible_solution\n else:\n continue\n # Possible values for cell exhausted. Either we backtrack or the cell examined\n # was the last one and the puzzle has no solution\n return None\n \ndef solve_sudoku(grid):\n if check_sudoku(grid) is None:\n return None\n elif not check_sudoku(grid):\n return False\n elif all([elem != 0 for row in grid for elem in row]):\n return grid\n \n puzzle = logic_solve(create_puzzle(grid))\n if solved_cells(puzzle) == 81:\n result = convert_to_grid(puzzle)\n assert check_sudoku(result)\n return result\n elif not all([len(elem) > 0 for row in puzzle for elem in row]):\n return False\n else:\n puzzle = backtracking_solve(puzzle)\n if puzzle is None:\n return False\n else: \n result = convert_to_grid(puzzle)\n assert check_sudoku(result)\n return result\n\n# print solve_sudoku(ill_formed) # --> None\n# print solve_sudoku(valid) # --> True\n# print solve_sudoku(invalid) # --> False\n\ntest1 = [[8,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0],\n [0,0,3,6,0,0,0,0,0],\n [0,7,0,0,9,0,2,0,0],\n [0,5,0,0,0,7,0,0,0],\n [0,0,0,0,4,5,7,0,0],\n [0,0,0,1,0,0,0,3,0],\n [0,0,1,0,0,0,0,6,8],\n [0,0,8,5,0,0,0,1,0],\n [0,9,0,0,0,0,4,0,0]]\n\ntest2 = [[7,0,0,2,0,0,0,0,0],\n [8,0,0,0,0,0,0,4,0],\n [0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0],\n [0,1,6,5,0,0,2,0,0],\n [0,0,0,0,0,0,0,7,0],\n [0,2,0,0,0,0,0,0,0],\n [0,0,0,0,0,0,6,0,1],\n [3,0,0,0,4,0,0,0,0],\n [0,5,0,0,8,0,0,0,0]]\n\n\nfor row in solve_sudoku(easy): # --> True\n print row\n \nprint ''\nfor row in solve_sudoku(test1): # --> True\n print row",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
]
] |
4ab9d0e85aed674b7f02d9776c0484a977c70e43
| 24,913 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Brownian Bridge.ipynb
|
Lonitch/stochastic-process
|
4631a7e453f96c40d1a135db108ad240a14f4f20
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Brownian Bridge.ipynb
|
Lonitch/stochastic-process
|
4631a7e453f96c40d1a135db108ad240a14f4f20
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Brownian Bridge.ipynb
|
Lonitch/stochastic-process
|
4631a7e453f96c40d1a135db108ad240a14f4f20
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 265.031915 | 22,996 | 0.926223 |
[
[
[
"Here we try to simulate Brownian Bridge by using the random variable\n$$X_t=B_t-tB_1$$\nwhere $0<t<1$, $B_t$ is standard Brownian process",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from scipy.stats import norm\nimport numpy as np\n\ndef bbsample(n):\n rv = norm(loc=0,scale=1/n)\n Xs = rv.rvs(size=n-1)\n ts = np.linspace(0,1,n)\n Bs = [0]\n for i in range(n-1):\n Bs.append(Bs[-1]+Xs[i])\n return ts, np.array(Bs)-ts*Bs[-1]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%matplotlib inline\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\nN = 10000\nx, y = bbsample(N)\nplt.plot(x,y,'-')\nplt.xlabel('T')\nplt.ylabel('Loc')\nplt.axhline(y=0.0,color='r')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4ab9e740ccb6902e4f4bb6a578afe8152cabb9e6
| 560,747 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
capstone/testing/librosa_poc.ipynb
|
ryanjmccall/sb_ml_eng_capstone
|
dfa87dcbd741c6f502b6cd0eb8f31203568c09a2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
capstone/testing/librosa_poc.ipynb
|
ryanjmccall/sb_ml_eng_capstone
|
dfa87dcbd741c6f502b6cd0eb8f31203568c09a2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
capstone/testing/librosa_poc.ipynb
|
ryanjmccall/sb_ml_eng_capstone
|
dfa87dcbd741c6f502b6cd0eb8f31203568c09a2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 1,381.150246 | 299,888 | 0.959939 |
[
[
[
"import librosa\n\nSAMPLE_1_FILE = 'data/sample1.wav'\nSAMPLE_2_FILE = 'data/sample2.wav'\n\nfilename = librosa.example('nutcracker')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(filename)",
"/Users/home/Library/Caches/librosa/Kevin_MacLeod_-_P_I_Tchaikovsky_Dance_of_the_Sugar_Plum_Fairy.ogg\n"
],
[
"# y, sr = librosa.load(filename)\ny, sr = librosa.load(SAMPLE_1_FILE)\n\nprint('waveform (y): ', type(y), len(y))\nprint(f'sampling rate {sr}')",
"waveform (y): <class 'numpy.ndarray'> 79460\nsampling rate 22050\n"
],
[
"# beat tracker\ntempo, beat_frames = librosa.beat.beat_track(y, sr)\nprint('Estimated tempo: {:.2f} beats per minute'.format(tempo))",
"Estimated tempo: 107.67 beats per minute\n"
],
[
"# 4. Convert the frame indices of beat events into timestamps\nbeat_times = librosa.frames_to_time(beat_frames, sr=sr)\nbeat_times",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# https://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2021/06/visualizing-sounds-librosa/\n\n%matplotlib inline\nimport matplotlib.pylab as plt\nimport numpy as np\nx = np.linspace(-np.pi, np.pi, 201)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.plot(x, np.sin(x))\nplt.xlabel('Angle [rad]')\nplt.ylabel('sin(x)')\nplt.axis('tight')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Short-Tiem Fourier Transform\nD = librosa.stft(y)\ns = np.abs(librosa.stft(y)**2) # Get magnitude of stft",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Chroma is a 12-element vector that measures energy from the sound pitch.\nchroma = librosa.feature.chroma_stft(S=s, sr=sr)\nchroma.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%matplotlib inline\n\n# increase figure size\nplt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [12, 8]\nplt.rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 100\n\nfeatures = chroma.shape[0]\n\nfig = plt.figure()\ngs = fig.add_gridspec(features, hspace=0)\naxs = gs.subplots(sharex=True, sharey=True)\n\nfor i in range(features):\n axs[i].plot(chroma[i].transpose()[:1000])\n\nplt.figure(figsize=(9,12))\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"chroma_sum = np.cumsum(chroma) \nchroma_sum.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%matplotlib inline\nx = np.linspace(-chroma_sum, chroma_sum)\nplt.plot(x, np.sin(x))\nplt.xlabel('Angle [rad]')\nplt.ylabel('sin(x)')\nplt.axis('tight')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from librosa.display import specshow",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# enhanced Chroma and Chroma variants\n\n# Constant-Q, type of graph to visualize chroma measurements, uses logartihmically spaced frquency axis\n# to display sound in decibels\nchroma_orig = librosa.feature.chroma_cqt(y=y, sr=sr)\nchroma_orig.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# For display purposes, let's zoom in on a 15-second chunk from the middle of the song\nstart = 0\nend = 2\nidx = tuple([slice(None), slice(*list(librosa.time_to_frames([start, end])))])\n# And for comparison, we'll show the CQT matrix as well.\nC = np.abs(librosa.cqt(y=y, sr=sr, bins_per_octave=12*3, n_bins=7*12*3))\nfig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=2, sharex=True)\nimg1 = specshow(librosa.amplitude_to_db(C, ref=np.max)[idx],\n y_axis='cqt_note', x_axis='time', bins_per_octave=12*3,\n ax=ax[0])\n\nfig.colorbar(img1, ax=[ax[0]], format=\"%+2.f dB\")\nax[0].label_outer()\nimg2 = specshow(chroma_orig[idx], y_axis='chroma', x_axis='time', ax=ax[1])\nfig.colorbar(img2, ax=[ax[1]])\nax[1].set(ylabel='Default chroma')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4ab9f47be0c5e3f27c89957f16025b1a229c7d1e
| 915,800 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/6AR_fig4_modelling_normal_cca.ipynb
|
mguo123/pan_omics
|
e1cacd543635b398fb08c0b31d08fa6b7c389658
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/6AR_fig4_modelling_normal_cca.ipynb
|
mguo123/pan_omics
|
e1cacd543635b398fb08c0b31d08fa6b7c389658
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/6AR_fig4_modelling_normal_cca.ipynb
|
mguo123/pan_omics
|
e1cacd543635b398fb08c0b31d08fa6b7c389658
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 3,768.72428 | 470,184 | 0.948316 |
[
[
[
"library(tidyverse)\nlibrary(pheatmap)\nsave_pheatmap_png <- function(x, filename, width=1200, height=1000, res = 200) {\n png(filename, width = width, height = height, res = res)\n grid::grid.newpage()\n grid::grid.draw(x$gtable)\n dev.off()\n}\nsave_pheatmap_pdf <- function(x, filename, width=7, height=7) {\n stopifnot(!missing(x))\n stopifnot(!missing(filename))\n pdf(filename, width=width, height=height)\n grid::grid.newpage()\n grid::grid.draw(x$gtable)\n dev.off()\n}",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 5. pairwise correlation heatmaps",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"GDSD6_tfcorr = read.csv('../data/processed/fig4_modelling/comb_tf_only_GDSD6_tfcorr.csv',row.names=1)\ndim(GDSD6_tfcorr)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"p = pheatmap(GDSD6_tfcorr)\nsave_pheatmap_pdf(p,'../data/processed/fig4_modelling/comb_tf_only_GDSD6_tfcorr.pdf', width=40, height=40) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"GDSD6_tfcorr_filt = GDSD6_tfcorr[rowSums(GDSD6_tfcorr)>0,]\nGDSD6_tfcorr_filt = GDSD6_tfcorr_filt[,colSums(GDSD6_tfcorr_filt)>0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dim(GDSD6_tfcorr_filt)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"p_filt = pheatmap(GDSD6_tfcorr_filt)\nsave_pheatmap_pdf(p_filt,'../data/processed/fig4_modelling/comb_tf_only_GDSD6_tfcorr_filt.pdf', width=30, height=30) ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4ab9fb34ddb80440130187c3a8dc3e744146c45f
| 51,800 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
experiments/Fig5.ipynb
|
ZhaozhiQIAN/Single-Cause-Perturbation-NeurIPS-2021
|
c1dd837bf4afc91d2a64a3afab759a21cbdc65cb
|
[
"MIT"
] | 8 |
2021-12-07T18:16:59.000Z
|
2022-03-08T02:17:06.000Z
|
experiments/Fig5.ipynb
|
ZhaozhiQIAN/Single-Cause-Perturbation-NeurIPS-2021
|
c1dd837bf4afc91d2a64a3afab759a21cbdc65cb
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
experiments/Fig5.ipynb
|
ZhaozhiQIAN/Single-Cause-Perturbation-NeurIPS-2021
|
c1dd837bf4afc91d2a64a3afab759a21cbdc65cb
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-12-03T16:25:41.000Z
|
2021-12-03T16:25:41.000Z
| 176.791809 | 27,158 | 0.897606 |
[
[
[
"import torch\nimport sim_data_gen\nimport numpy as np\nimport dr_crn\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"n_feat = 5",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def get_mmd(x_train):\n feat = x_train[:, :n_feat]\n causes = x_train[:, n_feat:]\n cause_ind = sim_data_gen.cause_to_num(causes)\n uniques, counts = np.unique(cause_ind, return_counts=True)\n uniques = uniques[counts > 1]\n mmd_sigma = 1\n mmd = 0\n for i in range(len(uniques)):\n x1 = torch.tensor(feat[cause_ind == uniques[i]])\n x2 = torch.tensor(feat[cause_ind != uniques[i]])\n mmd = mmd + torch.abs(dr_crn.mmd2_rbf(x1, x2, mmd_sigma))\n return mmd",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"scp_list = []\nscp_list_sd = []\n\nfor k in [1,2,3,4,5]:\n k = k * 2\n config_key = 'ea_balance_{}'.format(k)\n\n model_id='SCP'\n seed_list = []\n for seed in [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]:\n\n x_train = torch.load('model/simulation_overlap/{}_{}_{}_x.pth'.format(config_key, model_id, seed))\n x_train = x_train.cpu().numpy()\n m = get_mmd(x_train)\n seed_list.append(m)\n \n seed_list = np.array(seed_list)\n m = seed_list.mean()\n sd = seed_list.std()\n scp_list.append(m)\n scp_list_sd.append(sd)",
"0.028936246\n0.101032436\n0.1943626\n0.27979556\n0.34191176\n"
],
[
"base_line_list = []\nbase_line_list_sd = []\n\nfor k in [1,2,3,4,5]:\n k = k * 2\n config_key = 'ea_balance_{}'.format(k)\n\n model_id='IPW'\n seed_list = []\n for seed in [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]:\n\n x_train = torch.load('model/simulation_overlap/{}_{}_{}_x.pth'.format(config_key, model_id, seed))\n x_train = x_train.cpu().numpy()\n causes = x_train[:, n_feat:]\n m = get_mmd(x_train)\n seed_list.append(m)\n \n seed_list = np.array(seed_list)\n m = seed_list.mean()\n sd = seed_list.std()\n\n base_line_list.append(m)\n base_line_list_sd.append(sd)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"baseline = np.array(base_line_list)\nscp = np.array(scp_list)\n\nbaseline_sd = np.array(base_line_list_sd)\nscp_sd = np.array(scp_list_sd)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.style.use('tableau-colorblind10')\nplt.rcParams['font.size'] = '13'\n\ncolors = plt.rcParams['axes.prop_cycle'].by_key()['color']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(5,3))\nwidth = 0.4\nplt.bar(np.arange(1,6)-0.2, baseline,yerr=base_line_list_sd, color=colors[0], width=width, alpha=0.7, label='Observational')\nplt.bar(np.arange(1,6)+0.2, scp,yerr=scp_list_sd, color=colors[1], width=width, alpha=0.7, label = 'SCP Augmented')\nplt.xlabel(r'Confounding level $|v_m|$', fontsize=14) \nplt.ylabel('Distance: $b$', fontsize=16)\nplt.legend()\nplt.title(r'Balancing of the dataset (smaller better)', fontsize=14) \nplt.tight_layout(pad=0.2)\nplt.savefig(fname='Fig5_A.png', dpi=300)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import pandas as pds\nfrom scipy.special import comb",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.style.use('tableau-colorblind10')\nplt.rcParams['font.size'] = '13'\n\ncolors = plt.rcParams['axes.prop_cycle'].by_key()['color']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_base = pds.read_csv('results/results_ea_baseline.txt', sep=' ', header=None)\n\nweights = np.array([comb(5, i) for i in range(1, 6)])\nx_ref = np.sum(np.arange(1,6) * weights) / np.sum(weights)\ny_ref = np.interp(x_ref, np.arange(1, 6), df_base[2].values)\n\nx_ref_scp = 1 + 0.1 * (np.sum(np.arange(5))) / 5\nx_ref_scp\ny_ref_scp = np.interp(x_ref_scp, np.arange(1, 6), df_base[2].values)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"prefix=''\n\ndat = pds.read_csv('results{}/results_ea.txt'.format(prefix), sep=' ', header=None)\n\ndat[4] = dat[4] / np.sqrt(32)\ndat[5] = dat[5] / np.sqrt(32)\n\ndat = dat.sort_values(1)\ndat.tail(10)\ndat1 = dat[dat[0] == 'SCP']\ndat2 = dat[dat[0] == 'FB']\n\nz_ref_scp = np.interp(y_ref_scp, np.arange(7) / 10, dat1[4].values)\n\n\nplt.figure(figsize=(5,3))\n\nplt.fill_between(dat1[1], dat1[4] - 2 * dat1[5], dat1[4] + 2 * dat1[5], alpha=0.3, color=colors[0])\nplt.plot(dat1[1], dat1[4], '-o', color=colors[0], label='SCP')\n\n\nplt.plot([0, 0.6], [1.533/ np.sqrt(32), 1.533/ np.sqrt(32)], ls='--', c=colors[3], label='No Aug.', linewidth=3)\n\nplt.axvline(y_ref_scp, ymax=0.3, ls='--', c=colors[1], linewidth=3)\nplt.title(r'SCP Final Prediction Error (RMSE)', fontsize=14) \nplt.xlabel(r'Simulated Step One Error $\\xi$', fontsize=14) \nplt.ylabel('RMSE', fontsize=14) \n\nplt.text(0.1, 0.275, 'NN Baseline', fontsize=14)\nplt.text(0.21, 0.18, 'Actual step one error', fontsize=14, c=colors[1])\n\nplt.tight_layout(pad=0.1)\n\nplt.savefig(fname='Fig5_B.png', dpi=300)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4ab9fd888cbb44fe0fc2e3f36292ce981cd1f77a
| 10,507 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
End-to-End Machine Learning with TensorFlow on GCP/Labs/Solutions/4_preproc.ipynb
|
pablojgm/Coursera
|
3835dc774c91e567c477e1e956abbb582aef335c
|
[
"Unlicense"
] | null | null | null |
End-to-End Machine Learning with TensorFlow on GCP/Labs/Solutions/4_preproc.ipynb
|
pablojgm/Coursera
|
3835dc774c91e567c477e1e956abbb582aef335c
|
[
"Unlicense"
] | null | null | null |
End-to-End Machine Learning with TensorFlow on GCP/Labs/Solutions/4_preproc.ipynb
|
pablojgm/Coursera
|
3835dc774c91e567c477e1e956abbb582aef335c
|
[
"Unlicense"
] | null | null | null | 34.224756 | 553 | 0.58028 |
[
[
[
"<h1> Preprocessing using Dataflow </h1>\n\nThis notebook illustrates:\n<ol>\n<li> Creating datasets for Machine Learning using Dataflow\n</ol>\n<p>\nWhile Pandas is fine for experimenting, for operationalization of your workflow, it is better to do preprocessing in Apache Beam. This will also help if you need to preprocess data in flight, since Apache Beam also allows for streaming.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!sudo chown -R jupyter:jupyter /home/jupyter/training-data-analyst",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pip install --user apache-beam[gcp]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Run the command again if you are getting oauth2client error.\n\nNote: You may ignore the following responses in the cell output above:\n\nERROR (in Red text) related to: witwidget-gpu, fairing\n\nWARNING (in Yellow text) related to: hdfscli, hdfscli-avro, pbr, fastavro, gen_client\n\n<b>Restart</b> the kernel before proceeding further.\n\nMake sure the Dataflow API is enabled by going to this [link](https://console.developers.google.com/apis/api/dataflow.googleapis.com). Ensure that you've installed Beam by importing it and printing the version number.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Ensure the right version of Tensorflow is installed.\n!pip freeze | grep tensorflow==2.1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import apache_beam as beam\nprint(beam.__version__)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You may receive a `UserWarning` about the Apache Beam SDK for Python 3 as not being yet fully supported. Don't worry about this.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# change these to try this notebook out\nBUCKET = 'cloud-training-demos-ml'\nPROJECT = 'cloud-training-demos'\nREGION = 'us-central1'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import os\nos.environ['BUCKET'] = BUCKET\nos.environ['PROJECT'] = PROJECT\nos.environ['REGION'] = REGION",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%%bash\nif ! gsutil ls | grep -q gs://${BUCKET}/; then\n gsutil mb -l ${REGION} gs://${BUCKET}\nfi",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<h2> Create ML dataset using Dataflow </h2>\nLet's use Cloud Dataflow to read in the BigQuery data, do some preprocessing, and write it out as CSV files.\nIn this case, I want to do some preprocessing, modifying data so that we can simulate what is known if no ultrasound has been performed. \nNote that after you launch this, the actual processing is happening on the cloud. Go to the GCP webconsole to the Dataflow section and monitor the running job. It took about 20 minutes for me.\n<p>\nIf you wish to continue without doing this step, you can copy my preprocessed output:\n<pre>\ngsutil -m cp -r gs://cloud-training-demos/babyweight/preproc gs://your-bucket/\n</pre>\nBut if you do this, you also have to use my TensorFlow model since yours might expect the fields in a different order",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import datetime, os\n\ndef to_csv(rowdict):\n import hashlib\n import copy\n\n # TODO #1:\n # Pull columns from BQ and create line(s) of CSV input\n CSV_COLUMNS = None\n \n # Create synthetic data where we assume that no ultrasound has been performed\n # and so we don't know sex of the baby. Let's assume that we can tell the difference\n # between single and multiple, but that the errors rates in determining exact number\n # is difficult in the absence of an ultrasound.\n no_ultrasound = copy.deepcopy(rowdict)\n w_ultrasound = copy.deepcopy(rowdict)\n\n no_ultrasound['is_male'] = 'Unknown'\n if rowdict['plurality'] > 1:\n no_ultrasound['plurality'] = 'Multiple(2+)'\n else:\n no_ultrasound['plurality'] = 'Single(1)'\n\n # Change the plurality column to strings\n w_ultrasound['plurality'] = ['Single(1)', 'Twins(2)', 'Triplets(3)', 'Quadruplets(4)', 'Quintuplets(5)'][rowdict['plurality'] - 1]\n\n # Write out two rows for each input row, one with ultrasound and one without\n for result in [no_ultrasound, w_ultrasound]:\n data = ','.join([str(result[k]) if k in result else 'None' for k in CSV_COLUMNS])\n key = hashlib.sha224(data.encode('utf-8')).hexdigest() # hash the columns to form a key\n yield str('{},{}'.format(data, key))\n \ndef preprocess(in_test_mode):\n import shutil, os, subprocess\n job_name = 'preprocess-babyweight-features' + '-' + datetime.datetime.now().strftime('%y%m%d-%H%M%S')\n\n if in_test_mode:\n print('Launching local job ... hang on')\n OUTPUT_DIR = './preproc'\n shutil.rmtree(OUTPUT_DIR, ignore_errors=True)\n os.makedirs(OUTPUT_DIR)\n else:\n print('Launching Dataflow job {} ... hang on'.format(job_name))\n OUTPUT_DIR = 'gs://{0}/babyweight/preproc/'.format(BUCKET)\n try:\n subprocess.check_call('gsutil -m rm -r {}'.format(OUTPUT_DIR).split())\n except:\n pass\n\n options = {\n 'staging_location': os.path.join(OUTPUT_DIR, 'tmp', 'staging'),\n 'temp_location': os.path.join(OUTPUT_DIR, 'tmp'),\n 'job_name': job_name,\n 'project': PROJECT,\n 'region': REGION,\n 'teardown_policy': 'TEARDOWN_ALWAYS',\n 'no_save_main_session': True,\n 'num_workers': 4,\n 'max_num_workers': 5\n }\n opts = beam.pipeline.PipelineOptions(flags = [], **options)\n if in_test_mode:\n RUNNER = 'DirectRunner'\n else:\n RUNNER = 'DataflowRunner'\n p = beam.Pipeline(RUNNER, options = opts)\n \n query = \"\"\"\nSELECT\n weight_pounds,\n is_male,\n mother_age,\n plurality,\n gestation_weeks,\n FARM_FINGERPRINT(CONCAT(CAST(YEAR AS STRING), CAST(month AS STRING))) AS hashmonth\nFROM\n publicdata.samples.natality\nWHERE year > 2000\nAND weight_pounds > 0\nAND mother_age > 0\nAND plurality > 0\nAND gestation_weeks > 0\nAND month > 0\n \"\"\"\n\n if in_test_mode:\n query = query + ' LIMIT 100' \n\n for step in ['train', 'eval']:\n if step == 'train':\n selquery = 'SELECT * FROM ({}) WHERE ABS(MOD(hashmonth, 4)) < 3'.format(query)\n else:\n selquery = 'SELECT * FROM ({}) WHERE ABS(MOD(hashmonth, 4)) = 3'.format(query)\n\n (p \n ## TODO Task #2: Modify the Apache Beam pipeline such that the first part of the pipe reads the data from BigQuery\n | '{}_read'.format(step) >> None \n | '{}_csv'.format(step) >> beam.FlatMap(to_csv)\n | '{}_out'.format(step) >> beam.io.Write(beam.io.WriteToText(os.path.join(OUTPUT_DIR, '{}.csv'.format(step))))\n )\n\n job = p.run()\n if in_test_mode:\n job.wait_until_finish()\n print(\"Done!\")\n \n# TODO Task #3: Once you have verified that the files produced locally are correct, change in_test_mode to False\n# to execute this in Cloud Dataflow\npreprocess(in_test_mode = False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The above step will take 20+ minutes. Go to the GCP web console, navigate to the Dataflow section and <b>wait for the job to finish</b> before you run the following step.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%bash\ngsutil ls gs://${BUCKET}/babyweight/preproc/*-00000*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Copyright 2020 Google Inc. Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the \"License\"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an \"AS IS\" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4aba0465981299d98e5579a2daa06bca06a35132
| 10,236 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Python/Fundamentals/arcane_syntax.ipynb
|
Gjacquenot/training-material
|
16b29962bf5683f97a1072d961dd9f31e7468b8d
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | null | null | null |
Python/Fundamentals/arcane_syntax.ipynb
|
Gjacquenot/training-material
|
16b29962bf5683f97a1072d961dd9f31e7468b8d
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | null | null | null |
Python/Fundamentals/arcane_syntax.ipynb
|
Gjacquenot/training-material
|
16b29962bf5683f97a1072d961dd9f31e7468b8d
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | null | null | null | 20.804878 | 334 | 0.470496 |
[
[
[
"# Arcane Python syntax",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Python has a syntax with a few features that are quite unique.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**General advice:** don't use any of this unless you feel comfortable with it, since mistakes can lead to bugs that are hard to track down.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Interval checking",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In Python an expression such as `a < x <= b` is legal and well-defined.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"a, b = 1, 3\nfor x in range(-2, 5):\n if a < x <= b:\n print(f'{a} < {x} <= {b}: True')\n else:\n print(f'{a} < {x} <= {b}: False')",
"1 < -2 <= 3: False\n1 < -1 <= 3: False\n1 < 0 <= 3: False\n1 < 1 <= 3: False\n1 < 2 <= 3: True\n1 < 3 <= 3: True\n1 < 4 <= 3: False\n"
]
],
[
[
"The code above can be simplified to:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"a, b = 1, 3\nfor x in range(-2, 5):\n print(f'{a} < {x:2d} <= {b}: {a < x <= b}')",
"1 < -2 <= 3: False\n1 < -1 <= 3: False\n1 < 0 <= 3: False\n1 < 1 <= 3: False\n1 < 2 <= 3: True\n1 < 3 <= 3: True\n1 < 4 <= 3: False\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Multiple equality, inequality",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Along the same lines, `a == b == x` is also legal and well-defined.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for a in range(3):\n for b in range(3):\n print(f'{a} == {b} == 1: {a == b == 1}')",
"0 == 0 == 1: False\n0 == 1 == 1: False\n0 == 2 == 1: False\n1 == 0 == 1: False\n1 == 1 == 1: True\n1 == 2 == 1: False\n2 == 0 == 1: False\n2 == 1 == 1: False\n2 == 2 == 1: False\n"
]
],
[
[
"Although `a != b != x` is legal as well, it may, at least at first sight, not behave as expected.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for a in range(3):\n for b in range(3):\n print(f'{a} != {b} != 1: {a != b != 1}')",
"0 != 0 != 1: False\n0 != 1 != 1: False\n0 != 2 != 1: True\n1 != 0 != 1: True\n1 != 1 != 1: False\n1 != 2 != 1: True\n2 != 0 != 1: True\n2 != 1 != 1: False\n2 != 2 != 1: False\n"
]
],
[
[
"From the above, it is clear that `a != b != x` translates to `a != b and b != c`, which is true when `a == c and a != b`. From a mathematical point of view, bear in mind that `==` is transitive, while `!=` is not.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Iteration with `else`",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Iteration statements in Python, i.e., `for` and `while` can have an `else` block. The latter is executed when the iteration statement terminates normally, i.e., not by a `break` statement.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def illustrate_for_else(x):\n for i in range(10):\n if i == x:\n print('break')\n break\n else:\n print('no break')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"illustrate_for_else(12)",
"no break\n"
],
[
"illustrate_for_else(5)",
"break\n"
]
],
[
[
"Although naming this syntactic construct `else` feels awkward, it is quite useful, since it is a syntactic shortcut for the following reasonably common construct.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def illustrate_for_bool(x):\n completed_succesfully = True\n for i in range(10):\n if i == x:\n print('break')\n completed_succesfully = False\n break\n if completed_succesfully:\n print('no break')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"illustrate_for_bool(12)",
"no break\n"
],
[
"illustrate_for_bool(5)",
"break\n"
]
],
[
[
"The execution of `continue` has no influence on this.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for i in range(5):\n if i > -1:\n continue\n print(f'did something for {i}')\nelse:\n print('completed normally')",
"completed normally\n"
]
],
[
[
"The `while` statement can have an `else` with the same semantics.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Logical shortcircuits",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Boolean operators can be used directly as control statements. This is familiar to experience Bash programmers, but leads to code that is somewhat hard to understand.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import sys",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"output_file = None\nfh = output_file or sys.stdout\nprint('hello', file=fh)",
"hello\n"
]
],
[
[
"If the first operand to `or` is `False`, the value of the expression will be that of the second operand. The value `None` converts to Boolean `False`, hence the behavior above. However, if the first operand can be converted to `True`, the value of the expression is that of the first operand, a file handle in the example below.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"output_file = open('remove_me.txt', 'w')\nfh = output_file or sys.stdout\nprint('hello', file=fh)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!cat remove_me.txt",
"hello\r\n"
]
],
[
[
"The semantics of `and` expressions is similar. If the first operand converts to `True`, the expression will have the value of the second operand. If the first operand converts to `False`, that operand will be the value of the expression.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"a_list = []\nb_list = [3, 5, 7]\nmy_list = a_list and b_list\nprint(my_list)",
"[]\n"
],
[
"a_list = [3, 5, 7]\nb_list = [3, 5, 7, 9]\nmy_list = a_list and b_list\nprint(my_list)",
"[3, 5, 7, 9]\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4aba05ebfd8fb5fd86782e8c95eb954a7e78fbfc
| 20,191 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
pretrained-model/stt/conformer/evaluate/base-mixed.ipynb
|
dtx525942103/malaya-speech
|
212c4e890d0cbcbbca0037c89a698b68b05db393
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
pretrained-model/stt/conformer/evaluate/base-mixed.ipynb
|
dtx525942103/malaya-speech
|
212c4e890d0cbcbbca0037c89a698b68b05db393
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
pretrained-model/stt/conformer/evaluate/base-mixed.ipynb
|
dtx525942103/malaya-speech
|
212c4e890d0cbcbbca0037c89a698b68b05db393
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-08-19T02:34:41.000Z
|
2021-08-19T02:34:41.000Z
| 24.180838 | 300 | 0.460255 |
[
[
[
"import os\n\nos.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = ''",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import malaya_speech.train.model.conformer as conformer\nimport malaya_speech.train.model.transducer as transducer\nimport malaya_speech\nimport tensorflow as tf\nimport numpy as np\nimport json\nfrom glob import glob",
"WARNING:tensorflow:From /home/husein/malaya-speech/malaya_speech/train/optimizer/__init__.py:38: The name tf.train.AdagradOptimizer is deprecated. Please use tf.compat.v1.train.AdagradOptimizer instead.\n\nWARNING:tensorflow:From /home/husein/malaya-speech/malaya_speech/train/optimizer/__init__.py:39: The name tf.train.AdamOptimizer is deprecated. Please use tf.compat.v1.train.AdamOptimizer instead.\n\nWARNING:tensorflow:From /home/husein/malaya-speech/malaya_speech/train/optimizer/__init__.py:40: The name tf.train.FtrlOptimizer is deprecated. Please use tf.compat.v1.train.FtrlOptimizer instead.\n\nWARNING:tensorflow:From /home/husein/malaya-speech/malaya_speech/train/optimizer/__init__.py:42: The name tf.train.RMSPropOptimizer is deprecated. Please use tf.compat.v1.train.RMSPropOptimizer instead.\n\nWARNING:tensorflow:From /home/husein/malaya-speech/malaya_speech/train/optimizer/__init__.py:43: The name tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer is deprecated. Please use tf.compat.v1.train.GradientDescentOptimizer instead.\n\nWARNING:tensorflow:\nThe TensorFlow contrib module will not be included in TensorFlow 2.0.\nFor more information, please see:\n * https://github.com/tensorflow/community/blob/master/rfcs/20180907-contrib-sunset.md\n * https://github.com/tensorflow/addons\n * https://github.com/tensorflow/io (for I/O related ops)\nIf you depend on functionality not listed there, please file an issue.\n\n"
],
[
"subwords = malaya_speech.subword.load('transducer-mixed.subword')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"featurizer = malaya_speech.tf_featurization.STTFeaturizer(\n normalize_per_feature = True\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"n_mels = 80\nsr = 16000\nmaxlen = 18\nminlen_text = 1\n\ndef mp3_to_wav(file, sr = sr):\n audio = AudioSegment.from_file(file)\n audio = audio.set_frame_rate(sr).set_channels(1)\n sample = np.array(audio.get_array_of_samples())\n return malaya_speech.astype.int_to_float(sample), sr\n\n\ndef generate(file):\n with open(file) as fopen:\n dataset = json.load(fopen)\n audios, cleaned_texts = dataset['X'], dataset['Y']\n for i in range(len(audios)):\n try:\n if audios[i].endswith('.mp3'):\n # print('found mp3', audios[i])\n wav_data, _ = mp3_to_wav(audios[i])\n else:\n wav_data, _ = malaya_speech.load(audios[i], sr = sr)\n\n if (len(wav_data) / sr) > maxlen:\n # print(f'skipped audio too long {audios[i]}')\n continue\n\n if len(cleaned_texts[i]) < minlen_text:\n # print(f'skipped text too short {audios[i]}')\n continue\n\n t = malaya_speech.subword.encode(\n subwords, cleaned_texts[i], add_blank = False\n )\n\n yield {\n 'waveforms': wav_data,\n 'targets': t,\n 'targets_length': [len(t)],\n }\n except Exception as e:\n print(e)\n\n\ndef preprocess_inputs(example):\n s = featurizer.vectorize(example['waveforms'])\n mel_fbanks = tf.reshape(s, (-1, n_mels))\n length = tf.cast(tf.shape(mel_fbanks)[0], tf.int32)\n length = tf.expand_dims(length, 0)\n example['inputs'] = mel_fbanks\n example['inputs_length'] = length\n example.pop('waveforms', None)\n return example\n\n\ndef get_dataset(\n file,\n batch_size = 6,\n shuffle_size = 20,\n thread_count = 24,\n maxlen_feature = 1800,\n):\n def get():\n dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_generator(\n generate,\n {\n 'waveforms': tf.float32,\n 'targets': tf.int32,\n 'targets_length': tf.int32,\n },\n output_shapes = {\n 'waveforms': tf.TensorShape([None]),\n 'targets': tf.TensorShape([None]),\n 'targets_length': tf.TensorShape([None]),\n },\n args = (file,),\n )\n dataset = dataset.shuffle(shuffle_size)\n dataset = dataset.prefetch(tf.contrib.data.AUTOTUNE)\n dataset = dataset.map(\n preprocess_inputs, num_parallel_calls = thread_count\n )\n dataset = dataset.padded_batch(\n batch_size,\n padded_shapes = {\n 'inputs': tf.TensorShape([None, n_mels]),\n 'inputs_length': tf.TensorShape([None]),\n 'targets': tf.TensorShape([None]),\n 'targets_length': tf.TensorShape([None]),\n },\n padding_values = {\n 'inputs': tf.constant(0, dtype = tf.float32),\n 'inputs_length': tf.constant(0, dtype = tf.int32),\n 'targets': tf.constant(0, dtype = tf.int32),\n 'targets_length': tf.constant(0, dtype = tf.int32),\n },\n )\n return dataset\n\n return get",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dev_dataset = get_dataset('mixed-asr-test.json')()\nfeatures = dev_dataset.make_one_shot_iterator().get_next()\nfeatures",
"WARNING:tensorflow:From <ipython-input-6-6be0a8f0b815>:2: DatasetV1.make_one_shot_iterator (from tensorflow.python.data.ops.dataset_ops) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version.\nInstructions for updating:\nUse `for ... in dataset:` to iterate over a dataset. If using `tf.estimator`, return the `Dataset` object directly from your input function. As a last resort, you can use `tf.compat.v1.data.make_one_shot_iterator(dataset)`.\n"
],
[
"training = True",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"config = malaya_speech.config.conformer_base_encoder_config\nconformer_model = conformer.Model(\n kernel_regularizer = None, bias_regularizer = None, **config\n)\ndecoder_config = malaya_speech.config.conformer_base_decoder_config\ntransducer_model = transducer.rnn.Model(\n conformer_model, vocabulary_size = subwords.vocab_size, **decoder_config\n)\ntargets_length = features['targets_length'][:, 0]\nv = tf.expand_dims(features['inputs'], -1)\nz = tf.zeros((tf.shape(features['targets'])[0], 1), dtype = tf.int32)\nc = tf.concat([z, features['targets']], axis = 1)\n\nlogits = transducer_model([v, c, targets_length + 1], training = training)",
"WARNING:tensorflow:From /home/husein/.local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/tensorflow_core/python/ops/resource_variable_ops.py:1630: calling BaseResourceVariable.__init__ (from tensorflow.python.ops.resource_variable_ops) with constraint is deprecated and will be removed in a future version.\nInstructions for updating:\nIf using Keras pass *_constraint arguments to layers.\nWARNING:tensorflow:From /home/husein/malaya-speech/malaya_speech/train/model/transducer/layer.py:37: The name tf.get_variable is deprecated. Please use tf.compat.v1.get_variable instead.\n\nWARNING:tensorflow:From /home/husein/.local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/tensorflow_core/python/keras/backend.py:3994: where (from tensorflow.python.ops.array_ops) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version.\nInstructions for updating:\nUse tf.where in 2.0, which has the same broadcast rule as np.where\n"
],
[
"decoded = transducer_model.greedy_decoder(v, features['inputs_length'][:, 0], training = training)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sess = tf.Session()\nsess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())\nvar_list = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES)\nsaver = tf.train.Saver(var_list = var_list)\nsaver.restore(sess, 'asr-base-conformer-transducer-mixed/model.ckpt-1000000')",
"INFO:tensorflow:Restoring parameters from asr-base-conformer-transducer-mixed/model.ckpt-1000000\n"
],
[
"wer, cer = [], []\nindex = 0\nwhile True:\n try:\n r = sess.run([decoded, features['targets']])\n for no, row in enumerate(r[0]):\n d = malaya_speech.subword.decode(subwords, row[row > 0])\n t = malaya_speech.subword.decode(subwords, r[1][no])\n wer.append(malaya_speech.metrics.calculate_wer(t, d))\n cer.append(malaya_speech.metrics.calculate_cer(t, d))\n print(index)\n index += 1\n except:\n break",
"0\n1\n2\n3\n4\n5\n6\n7\n8\n9\n10\n11\n12\n13\n14\n15\n16\n17\n18\n19\n20\n21\n22\n23\n24\n25\n26\n27\n28\n29\n30\n31\n32\n33\n34\n35\n36\n37\n38\n39\n40\n41\n42\n43\n44\n45\n46\n47\n48\n49\n50\n51\n52\n53\n54\n55\n56\n57\n58\n59\n60\n61\n62\n63\n64\n65\n66\n67\n68\n69\n70\n71\n72\n73\n74\n75\n76\n77\n78\n79\n80\n81\n82\n83\n84\n85\n86\n87\n88\n89\n90\n91\n92\n93\n94\n95\n96\n97\n98\n99\n100\n101\n102\n103\n104\n105\n106\n107\n108\n109\n110\n111\n112\n113\n114\n115\n116\n117\n118\n119\n120\n121\n122\n123\n124\n125\n126\n127\n128\n129\n130\n131\n132\n133\n134\n135\n136\n137\n138\n139\n140\n141\n142\n143\n144\n145\n146\n147\n148\n149\n150\n151\n152\n153\n154\n155\n156\n157\n158\n159\n160\n161\n162\n163\n164\n165\n166\n167\n168\n169\n170\n171\n172\n173\n174\n175\n176\n177\n178\n179\n180\n181\n182\n183\n184\n185\n186\n187\n188\n189\n190\n191\n192\n193\n194\n195\n196\n197\n198\n199\n200\n201\n202\n203\n204\n205\n206\n207\n208\n209\n210\n211\n212\n213\n214\n215\n216\n217\n218\n219\n220\n221\n222\n223\n224\n225\n226\n227\n228\n229\n230\n231\n232\n233\n234\n235\n236\n237\n238\n239\n240\n241\n242\n243\n244\n245\n246\n247\n248\n249\n250\n251\n252\n253\n254\n255\n256\n257\n258\n259\n260\n261\n262\n263\n264\n265\n266\n267\n268\n269\n270\n271\n272\n273\n274\n275\n276\n277\n278\n279\n280\n281\n282\n283\n284\n285\n286\n287\n288\n289\n290\n291\n292\n293\n294\n295\n296\n297\n298\n299\n300\n301\n302\n303\n304\n305\n306\n307\n308\n309\n310\n311\n312\n313\n314\n315\n316\n317\n318\n319\n320\n321\n322\n323\n324\n325\n326\n327\n328\n329\n330\n331\n332\n333\n334\n335\n336\n337\n338\n339\n340\n341\n342\n343\n344\n345\n346\n347\n348\n349\n350\n351\n352\n353\n354\n355\n356\n357\n358\n359\n360\n361\n362\n363\n364\n365\n366\n367\n368\n369\n370\n371\n372\n373\n374\n375\n376\n377\n378\n379\n380\n381\n382\n383\n384\n385\n386\n387\n388\n389\n390\n391\n392\n393\n394\n395\n396\n397\n398\n399\n400\n401\n402\n403\n404\n405\n406\n407\n408\n409\n410\n411\n412\n413\n414\n415\n416\n417\n418\n419\n420\n421\n"
],
[
"np.mean(wer), np.mean(cer)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for no, row in enumerate(r[0]):\n d = malaya_speech.subword.decode(subwords, row[row > 0])\n t = malaya_speech.subword.decode(subwords, r[1][no])\n print(no, d)\n print(t)\n print()",
"0 okay is the is the is like your black door like\nokay is the is the is like your back door like\n\n1 ah um i used to read like those uh harry-potter series none and then after that i stopped any\nuh um i used to read like those uh harry potter series narnia and then after that i stopped and ya\n\n2 the new camera the ya\nthe digital camera ah the the\n\n3 okay okay okay okay\nbell okay okay okay okay\n\n4 and then there's like four seasons\nand then there's like four seasons\n\n5 if your human\nif you are human\n\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4aba185a6a6e04d6edf9ad336288261dda6c4504
| 69,360 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
dlaicourse-master/Course 1 - Part 2 - Lesson 2 - Notebook.ipynb
|
flight505/Google_TF_Certificate
|
b0ff1605b5159ea3dec33dbf2c9d112e5b30dd28
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
dlaicourse-master/Course 1 - Part 2 - Lesson 2 - Notebook.ipynb
|
flight505/Google_TF_Certificate
|
b0ff1605b5159ea3dec33dbf2c9d112e5b30dd28
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
dlaicourse-master/Course 1 - Part 2 - Lesson 2 - Notebook.ipynb
|
flight505/Google_TF_Certificate
|
b0ff1605b5159ea3dec33dbf2c9d112e5b30dd28
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 51.607143 | 435 | 0.335972 |
[
[
[
"<a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/lmoroney/dlaicourse/blob/master/Course%201%20-%20Part%202%20-%20Lesson%202%20-%20Notebook.ipynb\" target=\"_parent\"><img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open In Colab\"/></a>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"##### Copyright 2019 The TensorFlow Authors.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#@title Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the \"License\");\n# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.\n# You may obtain a copy of the License at\n#\n# https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0\n#\n# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software\n# distributed under the License is distributed on an \"AS IS\" BASIS,\n# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.\n# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and\n# limitations under the License.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# The Hello World of Deep Learning with Neural Networks",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Like every first app you should start with something super simple that shows the overall scaffolding for how your code works. \n\nIn the case of creating neural networks, the sample I like to use is one where it learns the relationship between two numbers. So, for example, if you were writing code for a function like this, you already know the 'rules' — \n\n\n```\nfloat hw_function(float x){\n float y = (2 * x) - 1;\n return y;\n}\n```\n\nSo how would you train a neural network to do the equivalent task? Using data! By feeding it with a set of Xs, and a set of Ys, it should be able to figure out the relationship between them. \n\nThis is obviously a very different paradigm than what you might be used to, so let's step through it piece by piece.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Imports\n\nLet's start with our imports. Here we are importing TensorFlow and calling it tf for ease of use.\n\nWe then import a library called numpy, which helps us to represent our data as lists easily and quickly.\n\nThe framework for defining a neural network as a set of Sequential layers is called keras, so we import that too.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import tensorflow as tf\nimport numpy as np\nfrom tensorflow import keras",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Define and Compile the Neural Network\n\nNext we will create the simplest possible neural network. It has 1 layer, and that layer has 1 neuron, and the input shape to it is just 1 value.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"xs = np.array([i**1 for i in range(50000,600000,50000)])\nprint(xs)\n",
"[ 50000 100000 150000 200000 250000 300000 350000 400000 450000 500000\n 550000]\n"
],
[
"model = tf.keras.Sequential([keras.layers.Dense(units=1, input_shape=[1])])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now we compile our Neural Network. When we do so, we have to specify 2 functions, a loss and an optimizer.\n\nIf you've seen lots of math for machine learning, here's where it's usually used, but in this case it's nicely encapsulated in functions for you. But what happens here — let's explain...\n\nWe know that in our function, the relationship between the numbers is y=2x-1. \n\nWhen the computer is trying to 'learn' that, it makes a guess...maybe y=10x+10. The LOSS function measures the guessed answers against the known correct answers and measures how well or how badly it did.\n\nIt then uses the OPTIMIZER function to make another guess. Based on how the loss function went, it will try to minimize the loss. At that point maybe it will come up with somehting like y=5x+5, which, while still pretty bad, is closer to the correct result (i.e. the loss is lower)\n\nIt will repeat this for the number of EPOCHS which you will see shortly. But first, here's how we tell it to use 'MEAN SQUARED ERROR' for the loss and 'STOCHASTIC GRADIENT DESCENT' for the optimizer. You don't need to understand the math for these yet, but you can see that they work! :)\n\nOver time you will learn the different and appropriate loss and optimizer functions for different scenarios. \n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model.compile(optimizer='sgd', loss='mean_squared_error')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Providing the Data\n\nNext up we'll feed in some data. In this case we are taking 6 xs and 6ys. You can see that the relationship between these is that y=2x-1, so where x = -1, y=-3 etc. etc. \n\nA python library called 'Numpy' provides lots of array type data structures that are a defacto standard way of doing it. We declare that we want to use these by specifying the values as an np.array[]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"xs = np.array([-1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0], dtype=float)\nys = np.array([-3.0, -1.0, 1.0, 3.0, 5.0, 7.0], dtype=float)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Training the Neural Network",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The process of training the neural network, where it 'learns' the relationship between the Xs and Ys is in the **model.fit** call. This is where it will go through the loop we spoke about above, making a guess, measuring how good or bad it is (aka the loss), using the opimizer to make another guess etc. It will do it for the number of epochs you specify. When you run this code, you'll see the loss on the right hand side.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model.fit(xs, ys, epochs=500)\n",
"Epoch 1/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 250ms/step - loss: 26.9468\nEpoch 2/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 7ms/step - loss: 21.4997\nEpoch 3/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 9ms/step - loss: 17.2080\nEpoch 4/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 13.8255\nEpoch 5/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 11.1585\nEpoch 6/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 6ms/step - loss: 9.0544\nEpoch 7/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 7ms/step - loss: 7.3933\nEpoch 8/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 6.0809\nEpoch 9/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 5.0430\nEpoch 10/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 6ms/step - loss: 4.2210\nEpoch 11/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 3.5692\nEpoch 12/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 10ms/step - loss: 3.0512\nEpoch 13/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 2.6387\nEpoch 14/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 2.3093\nEpoch 15/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 2.0454\nEpoch 16/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 1.8330\nEpoch 17/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 1.6613\nEpoch 18/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 1.5217\nEpoch 19/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 1.4075\nEpoch 20/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 1.3133\nEpoch 21/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 1.2350\nEpoch 22/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 1.1692\nEpoch 23/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 1.1134\nEpoch 24/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 1.0656\nEpoch 25/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 1.0240\nEpoch 26/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.9875\nEpoch 27/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.9550\nEpoch 28/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.9258\nEpoch 29/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.8993\nEpoch 30/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.8749\nEpoch 31/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.8522\nEpoch 32/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.8311\nEpoch 33/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.8111\nEpoch 34/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.7922\nEpoch 35/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.7741\nEpoch 36/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 0.7568\nEpoch 37/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.7402\nEpoch 38/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.7241\nEpoch 39/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.7085\nEpoch 40/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.6934\nEpoch 41/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.6788\nEpoch 42/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 0.6645\nEpoch 43/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 5ms/step - loss: 0.6506\nEpoch 44/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.6370\nEpoch 45/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.6238\nEpoch 46/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.6108\nEpoch 47/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.5982\nEpoch 48/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.5858\nEpoch 49/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 5ms/step - loss: 0.5737\nEpoch 50/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 0.5619\nEpoch 51/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 0.5503\nEpoch 52/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 0.5390\nEpoch 53/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 5ms/step - loss: 0.5279\nEpoch 54/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 5ms/step - loss: 0.5170\nEpoch 55/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 6ms/step - loss: 0.5064\nEpoch 56/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 10ms/step - loss: 0.4960\nEpoch 57/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 0.4858\nEpoch 58/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.4758\nEpoch 59/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 0.4660\nEpoch 60/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 11ms/step - loss: 0.4564\nEpoch 61/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 5ms/step - loss: 0.4470\nEpoch 62/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 6ms/step - loss: 0.4379\nEpoch 63/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4289\nEpoch 64/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.4201\nEpoch 65/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4114\nEpoch 66/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.4030\nEpoch 67/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.3947\nEpoch 68/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.3866\nEpoch 69/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.3786\nEpoch 70/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.3709\nEpoch 71/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.3632\nEpoch 72/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.3558\nEpoch 73/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 0.3485\nEpoch 74/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.3413\nEpoch 75/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.3343\nEpoch 76/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 7ms/step - loss: 0.3274\nEpoch 77/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 0.3207\nEpoch 78/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.3141\nEpoch 79/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 0.3077\nEpoch 80/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.3014\nEpoch 81/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.2952\nEpoch 82/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.2891\nEpoch 83/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 5ms/step - loss: 0.2832\nEpoch 84/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.2773\nEpoch 85/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.2717\nEpoch 86/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.2661\nEpoch 87/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 7ms/step - loss: 0.2606\nEpoch 88/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 0.2553\nEpoch 89/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 0.2500\nEpoch 90/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.2449\nEpoch 91/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.2398\nEpoch 92/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.2349\nEpoch 93/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.2301\nEpoch 94/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.2254\nEpoch 95/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.2207\nEpoch 96/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.2162\nEpoch 97/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.2118\nEpoch 98/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.2074\nEpoch 99/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.2032\nEpoch 100/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.1990\nEpoch 101/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.1949\nEpoch 102/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.1909\nEpoch 103/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.1870\nEpoch 104/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.1831\nEpoch 105/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.1794\nEpoch 106/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.1757\nEpoch 107/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.1721\nEpoch 108/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.1685\nEpoch 109/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.1651\nEpoch 110/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 7ms/step - loss: 0.1617\nEpoch 111/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.1584\nEpoch 112/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 5ms/step - loss: 0.1551\nEpoch 113/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 7ms/step - loss: 0.1519\nEpoch 114/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 6ms/step - loss: 0.1488\nEpoch 115/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 6ms/step - loss: 0.1457\nEpoch 116/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 0.1428\nEpoch 117/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.1398\nEpoch 118/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.1370\nEpoch 119/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 0.1341\nEpoch 120/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.1314\nEpoch 121/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.1287\nEpoch 122/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 5ms/step - loss: 0.1260\nEpoch 123/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 0.1235\nEpoch 124/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.1209\nEpoch 125/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.1184\nEpoch 126/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.1160\nEpoch 127/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.1136\nEpoch 128/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.1113\nEpoch 129/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.1090\nEpoch 130/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.1068\nEpoch 131/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.1046\nEpoch 132/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.1024\nEpoch 133/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.1003\nEpoch 134/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0983\nEpoch 135/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0962\nEpoch 136/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0943\nEpoch 137/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0923\nEpoch 138/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0904\nEpoch 139/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0886\nEpoch 140/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0867\nEpoch 141/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0850\nEpoch 142/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0832\nEpoch 143/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0815\nEpoch 144/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0798\nEpoch 145/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0782\nEpoch 146/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0766\nEpoch 147/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0750\nEpoch 148/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0735\nEpoch 149/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0720\nEpoch 150/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0705\nEpoch 151/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0690\nEpoch 152/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0676\nEpoch 153/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0662\nEpoch 154/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0649\nEpoch 155/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 0.0635\nEpoch 156/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0622\nEpoch 157/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0610\nEpoch 158/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0597\nEpoch 159/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0585\nEpoch 160/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0573\nEpoch 161/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0561\nEpoch 162/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 0.0550\nEpoch 163/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0538\nEpoch 164/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0527\nEpoch 165/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0516\nEpoch 166/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0506\nEpoch 167/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 0.0495\nEpoch 168/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 6ms/step - loss: 0.0485\nEpoch 169/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0475\nEpoch 170/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0465\nEpoch 171/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0456\nEpoch 172/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0447\nEpoch 173/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0437\nEpoch 174/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0428\nEpoch 175/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0420\nEpoch 176/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0411\nEpoch 177/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0403\nEpoch 178/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0394\nEpoch 179/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0386\nEpoch 180/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0378\nEpoch 181/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0370\nEpoch 182/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0363\nEpoch 183/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0355\nEpoch 184/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0348\nEpoch 185/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0341\nEpoch 186/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0334\nEpoch 187/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0327\nEpoch 188/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0320\nEpoch 189/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0314\nEpoch 190/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0307\nEpoch 191/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0301\nEpoch 192/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0295\nEpoch 193/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0289\nEpoch 194/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0283\nEpoch 195/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0277\nEpoch 196/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0271\nEpoch 197/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0266\nEpoch 198/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0260\nEpoch 199/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0255\nEpoch 200/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0250\nEpoch 201/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0245\nEpoch 202/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0240\nEpoch 203/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0235\nEpoch 204/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0230\nEpoch 205/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0225\nEpoch 206/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0220\nEpoch 207/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0216\nEpoch 208/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 0.0212\nEpoch 209/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0207\nEpoch 210/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0203\nEpoch 211/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0199\nEpoch 212/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0195\nEpoch 213/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0191\nEpoch 214/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0187\nEpoch 215/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0183\nEpoch 216/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0179\nEpoch 217/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0175\nEpoch 218/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0172\nEpoch 219/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0168\nEpoch 220/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0165\nEpoch 221/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 0.0161\nEpoch 222/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0158\nEpoch 223/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0155\nEpoch 224/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0152\nEpoch 225/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0149\nEpoch 226/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0146\nEpoch 227/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0143\nEpoch 228/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0140\nEpoch 229/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0137\nEpoch 230/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0134\nEpoch 231/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0131\nEpoch 232/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0129\nEpoch 233/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0126\nEpoch 234/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0123\nEpoch 235/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0121\nEpoch 236/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0118\nEpoch 237/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0116\nEpoch 238/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0113\nEpoch 239/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0111\nEpoch 240/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0109\nEpoch 241/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0107\nEpoch 242/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 7ms/step - loss: 0.0104\nEpoch 243/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0102\nEpoch 244/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0100\nEpoch 245/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0098\nEpoch 246/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0096\nEpoch 247/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0094\nEpoch 248/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 55ms/step - loss: 0.0092\nEpoch 249/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0090\nEpoch 250/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0088\nEpoch 251/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0087\nEpoch 252/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0085\nEpoch 253/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0083\nEpoch 254/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0081\nEpoch 255/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0080\nEpoch 256/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0078\nEpoch 257/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0077\nEpoch 258/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0075\nEpoch 259/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0073\nEpoch 260/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0072\nEpoch 261/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0070\nEpoch 262/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0069\nEpoch 263/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0068\nEpoch 264/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0066\nEpoch 265/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0065\nEpoch 266/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0063\nEpoch 267/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0062\nEpoch 268/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0061\nEpoch 269/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0060\nEpoch 270/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0058\nEpoch 271/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0057\nEpoch 272/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0056\nEpoch 273/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 6ms/step - loss: 0.0055\nEpoch 274/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0054\nEpoch 275/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0053\nEpoch 276/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0052\nEpoch 277/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0051\nEpoch 278/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0049\nEpoch 279/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0048\nEpoch 280/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0047\nEpoch 281/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0046\nEpoch 282/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0046\nEpoch 283/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0045\nEpoch 284/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0044\nEpoch 285/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0043\nEpoch 286/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0042\nEpoch 287/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0041\nEpoch 288/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0040\nEpoch 289/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0039\nEpoch 290/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 0.0039\nEpoch 291/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0038\nEpoch 292/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0037\nEpoch 293/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0036\nEpoch 294/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0035\nEpoch 295/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0035\nEpoch 296/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0034\nEpoch 297/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0033\nEpoch 298/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0033\nEpoch 299/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0032\nEpoch 300/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0031\nEpoch 301/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0031\nEpoch 302/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0030\nEpoch 303/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0029\nEpoch 304/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0029\nEpoch 305/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0028\nEpoch 306/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 0.0028\nEpoch 307/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0027\nEpoch 308/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 77ms/step - loss: 0.0027\nEpoch 309/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0026\nEpoch 310/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0025\nEpoch 311/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0025\nEpoch 312/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0024\nEpoch 313/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0024\nEpoch 314/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0023\nEpoch 315/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0023\nEpoch 316/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0022\nEpoch 317/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0022\nEpoch 318/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0022\nEpoch 319/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0021\nEpoch 320/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0021\nEpoch 321/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0020\nEpoch 322/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0020\nEpoch 323/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0019\nEpoch 324/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0019\nEpoch 325/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0019\nEpoch 326/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0018\nEpoch 327/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0018\nEpoch 328/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0018\nEpoch 329/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0017\nEpoch 330/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0017\nEpoch 331/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0016\nEpoch 332/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0016\nEpoch 333/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0016\nEpoch 334/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0015\nEpoch 335/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0015\nEpoch 336/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0015\nEpoch 337/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0015\nEpoch 338/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0014\nEpoch 339/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0014\nEpoch 340/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0014\nEpoch 341/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0013\nEpoch 342/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0013\nEpoch 343/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0013\nEpoch 344/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0013\nEpoch 345/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0012\nEpoch 346/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0012\nEpoch 347/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0012\nEpoch 348/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0012\nEpoch 349/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0011\nEpoch 350/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0011\nEpoch 351/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0011\nEpoch 352/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0011\nEpoch 353/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0010\nEpoch 354/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0010\nEpoch 355/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.0010\nEpoch 356/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 9.8024e-04\nEpoch 357/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 9.6011e-04\nEpoch 358/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 9.4039e-04\nEpoch 359/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 9.2107e-04\nEpoch 360/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 9.0215e-04\nEpoch 361/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 8.8363e-04\nEpoch 362/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 8.6547e-04\nEpoch 363/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 8.4769e-04\nEpoch 364/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 8.3029e-04\nEpoch 365/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 8.1323e-04\nEpoch 366/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 7.9653e-04\nEpoch 367/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 7.8017e-04\nEpoch 368/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 116ms/step - loss: 7.6414e-04\nEpoch 369/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 7.4844e-04\nEpoch 370/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 7.3307e-04\nEpoch 371/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 7.1801e-04\nEpoch 372/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 7.0326e-04\nEpoch 373/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 6.8882e-04\nEpoch 374/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 6.7467e-04\nEpoch 375/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 6.6081e-04\nEpoch 376/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 6.4724e-04\nEpoch 377/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 6.3395e-04\nEpoch 378/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 6.2092e-04\nEpoch 379/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 6.0817e-04\nEpoch 380/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 5.9568e-04\nEpoch 381/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 7ms/step - loss: 5.8344e-04\nEpoch 382/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 5ms/step - loss: 5.7146e-04\nEpoch 383/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 5ms/step - loss: 5.5972e-04\nEpoch 384/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 5ms/step - loss: 5.4822e-04\nEpoch 385/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 5ms/step - loss: 5.3696e-04\nEpoch 386/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 5.2593e-04\nEpoch 387/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 10ms/step - loss: 5.1513e-04\nEpoch 388/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 5ms/step - loss: 5.0455e-04\nEpoch 389/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 7ms/step - loss: 4.9418e-04\nEpoch 390/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 8ms/step - loss: 4.8403e-04\nEpoch 391/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 5ms/step - loss: 4.7409e-04\nEpoch 392/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 7ms/step - loss: 4.6435e-04\nEpoch 393/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 7ms/step - loss: 4.5481e-04\nEpoch 394/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 6ms/step - loss: 4.4547e-04\nEpoch 395/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 4.3632e-04\nEpoch 396/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 4.2736e-04\nEpoch 397/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 4.1858e-04\nEpoch 398/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 4.0998e-04\nEpoch 399/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 4.0156e-04\nEpoch 400/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 3.9331e-04\nEpoch 401/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 3.8523e-04\nEpoch 402/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 3.7732e-04\nEpoch 403/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 3.6957e-04\nEpoch 404/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 3.6198e-04\nEpoch 405/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 3.5454e-04\nEpoch 406/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 3.4726e-04\nEpoch 407/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 3.4013e-04\nEpoch 408/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 3.3314e-04\nEpoch 409/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 3.2630e-04\nEpoch 410/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 3.1960e-04\nEpoch 411/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 3.1303e-04\nEpoch 412/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 3.0660e-04\nEpoch 413/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 3.0030e-04\nEpoch 414/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 2.9414e-04\nEpoch 415/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 2.8809e-04\nEpoch 416/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 2.8218e-04\nEpoch 417/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 2.7638e-04\nEpoch 418/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 2.7070e-04\nEpoch 419/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 2.6514e-04\nEpoch 420/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 2.5970e-04\nEpoch 421/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 2.5436e-04\nEpoch 422/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 2.4914e-04\nEpoch 423/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 2.4402e-04\nEpoch 424/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 2.3901e-04\nEpoch 425/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 2.3410e-04\nEpoch 426/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 2.2929e-04\nEpoch 427/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 2.2458e-04\nEpoch 428/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 2.1997e-04\nEpoch 429/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 2.1545e-04\nEpoch 430/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 2.1102e-04\nEpoch 431/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 2.0669e-04\nEpoch 432/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 2.0244e-04\nEpoch 433/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 1.9829e-04\nEpoch 434/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 1.9422e-04\nEpoch 435/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 5ms/step - loss: 1.9023e-04\nEpoch 436/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 1.8632e-04\nEpoch 437/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 1.8249e-04\nEpoch 438/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 1.7874e-04\nEpoch 439/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 1.7507e-04\nEpoch 440/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 1.7148e-04\nEpoch 441/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 1.6795e-04\nEpoch 442/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 5ms/step - loss: 1.6450e-04\nEpoch 443/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 1.6113e-04\nEpoch 444/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 1.5781e-04\nEpoch 445/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 1.5457e-04\nEpoch 446/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 1.5140e-04\nEpoch 447/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 1.4829e-04\nEpoch 448/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 1.4524e-04\nEpoch 449/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 1.4226e-04\nEpoch 450/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 5ms/step - loss: 1.3934e-04\nEpoch 451/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 1.3647e-04\nEpoch 452/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 1.3367e-04\nEpoch 453/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 1.3093e-04\nEpoch 454/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 1.2824e-04\nEpoch 455/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 1.2560e-04\nEpoch 456/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 1.2302e-04\nEpoch 457/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 1.2050e-04\nEpoch 458/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 1.1802e-04\nEpoch 459/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 1.1560e-04\nEpoch 460/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 1.1322e-04\nEpoch 461/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 1.1090e-04\nEpoch 462/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 1.0862e-04\nEpoch 463/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 1.0639e-04\nEpoch 464/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 1.0420e-04\nEpoch 465/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 1.0206e-04\nEpoch 466/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 9.9964e-05\nEpoch 467/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 9.7912e-05\nEpoch 468/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 9.5900e-05\nEpoch 469/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 9.3930e-05\nEpoch 470/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 9.2001e-05\nEpoch 471/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 9.0110e-05\nEpoch 472/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 8.8259e-05\nEpoch 473/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 8.6446e-05\nEpoch 474/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 8.4670e-05\nEpoch 475/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 8.2933e-05\nEpoch 476/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 8.1229e-05\nEpoch 477/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 5ms/step - loss: 7.9560e-05\nEpoch 478/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 7.7927e-05\nEpoch 479/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 7.6326e-05\nEpoch 480/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 7.4758e-05\nEpoch 481/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 7.3222e-05\nEpoch 482/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 7.1719e-05\nEpoch 483/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 7.0246e-05\nEpoch 484/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 6.8803e-05\nEpoch 485/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 6.7390e-05\nEpoch 486/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 6.6005e-05\nEpoch 487/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 6.4650e-05\nEpoch 488/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 6.3322e-05\nEpoch 489/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 6.2022e-05\nEpoch 490/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 6.0747e-05\nEpoch 491/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 5.9499e-05\nEpoch 492/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 5.8278e-05\nEpoch 493/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 5.7081e-05\nEpoch 494/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 5.5909e-05\nEpoch 495/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 5.4759e-05\nEpoch 496/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 5.3635e-05\nEpoch 497/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 5.2533e-05\nEpoch 498/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 5.1455e-05\nEpoch 499/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 5.0398e-05\nEpoch 500/500\n1/1 [==============================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 4.9362e-05\n"
]
],
[
[
"Ok, now you have a model that has been trained to learn the relationship between X and Y. You can use the **model.predict** method to have it figure out the Y for a previously unknown X. So, for example, if X = 10, what do you think Y will be? Take a guess before you run this code:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(model.predict([10.0]))",
"[[18.979502]]\n"
]
],
[
[
"You might have thought 19, right? But it ended up being a little under. Why do you think that is? \n\nRemember that neural networks deal with probabilities, so given the data that we fed the NN with, it calculated that there is a very high probability that the relationship between X and Y is Y=2X-1, but with only 6 data points we can't know for sure. As a result, the result for 10 is very close to 19, but not necessarily 19. \n\nAs you work with neural networks, you'll see this pattern recurring. You will almost always deal with probabilities, not certainties, and will do a little bit of coding to figure out what the result is based on the probabilities, particularly when it comes to classification.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4aba2f6113181298f505a241d18ac7543f741619
| 9,078 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/1-welcome.ipynb
|
choldgraf/jupytercon_tutorial
|
5e0f433c4ae504867b0a36566c362b635a728385
|
[
"CC0-1.0"
] | 1 |
2020-09-23T01:06:12.000Z
|
2020-09-23T01:06:12.000Z
|
notebooks/1-welcome.ipynb
|
choldgraf/jupyterbook-with-turing-way
|
7f0b824bb6ccd29e2da825c7f0d75eed734f3af5
|
[
"CC0-1.0"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/1-welcome.ipynb
|
choldgraf/jupyterbook-with-turing-way
|
7f0b824bb6ccd29e2da825c7f0d75eed734f3af5
|
[
"CC0-1.0"
] | null | null | null | 51.874286 | 370 | 0.666006 |
[
[
[
"empty"
]
]
] |
[
"empty"
] |
[
[
"empty"
]
] |
4aba6e3af3b757e892dfe5ca0b51bf0305a0e5d7
| 31,111 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
.dev/GiNZA.ipynb
|
amenoyoya/ssl-rpa
|
16fa01ea688f1a51edff730fbd3ae332027950a2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
.dev/GiNZA.ipynb
|
amenoyoya/ssl-rpa
|
16fa01ea688f1a51edff730fbd3ae332027950a2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
.dev/GiNZA.ipynb
|
amenoyoya/ssl-rpa
|
16fa01ea688f1a51edff730fbd3ae332027950a2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 79.16285 | 12,972 | 0.726013 |
[
[
[
"import spacy\n\n# GiNZA日本語UDモデル を Spacy でロード\nnlp = spacy.load('ja_ginza')\n\n# 解析対象文字列を渡す\ndoc = nlp('今年の干支は庚子です。東京オリンピックたのしみだなあ。')\n\n# 形態素解析結果\nfor sent in doc.sents:\n for token in sent:\n print(token.i, token.orth_, token.lemma_, token.pos_, \n token.tag_, token.dep_, token.head.i)",
"0 今年 今年 NOUN 名詞-普通名詞-副詞可能 nmod 2\n1 の の ADP 助詞-格助詞 case 0\n2 干支 干支 NOUN 名詞-普通名詞-一般 nsubj 4\n3 は は ADP 助詞-係助詞 case 2\n4 庚子 庚子 NOUN 名詞-普通名詞-一般 ROOT 4\n5 です です AUX 助動詞 cop 4\n6 。 。 PUNCT 補助記号-句点 punct 4\n7 東京 東京 PROPN 名詞-固有名詞-地名-一般 compound 9\n8 オリンピック オリンピック NOUN 名詞-普通名詞-一般 compound 9\n9 たのしみ 楽しみ NOUN 名詞-普通名詞-一般 ROOT 9\n10 だ だ AUX 助動詞 cop 9\n11 なあ な PART 助詞-終助詞 aux 9\n12 。 。 PUNCT 補助記号-句点 punct 9\n"
],
[
"# 依存関係の可視化\nfrom spacy import displacy\n\ndisplacy.serve(doc, style='dep', options={'compact':True})\n## => Visualizer が localhost:5000 で稼働",
"/home/mint/anaconda3/envs/py36/lib/python3.6/runpy.py:193: UserWarning: [W011] It looks like you're calling displacy.serve from within a Jupyter notebook or a similar environment. This likely means you're already running a local web server, so there's no need to make displaCy start another one. Instead, you should be able to replace displacy.serve with displacy.render to show the visualization.\n \"__main__\", mod_spec)\n"
],
[
"# 単語のベクトル化\ndoc = nlp('あきらめたらそこで試合終了だ')\ntoken = doc[4]\n\nprint(token)\nprint(token.vector)\nprint(token.vector.shape)",
"試合\n[-1.7299166 1.3438352 0.51212436 0.8338855 0.42193085 -1.4436126\n 4.331309 -0.59857213 2.091658 3.1512427 -2.0446565 -0.41324708\n -1.6249566 2.0849636 -1.1432786 0.4402521 -0.2996736 -1.2537657\n -1.4408176 -3.61768 0.7704964 2.102502 2.0921223 0.04206143\n -1.8395482 0.18499917 -0.2579822 -1.4813038 -0.73962873 0.36772487\n -0.52210647 1.9044702 0.4267643 -0.80647945 -1.0729067 -0.11970597\n -0.6600776 -0.02893271 2.1134949 -0.9696921 0.06669673 0.17631757\n 1.333448 -0.19496314 -2.5899901 -0.08864212 -0.69199586 0.44197303\n -1.7922851 -0.6862237 0.3803087 0.53696775 1.1550635 0.79316735\n -0.45592362 1.8070105 -0.5869399 -1.923917 -1.1303633 0.5251339\n -1.8638126 -0.8316108 1.543806 -0.6436903 2.7160945 1.0952429\n 0.01095889 -0.7106281 0.33451897 -0.3829015 -2.5569937 2.485877\n 2.0016584 -0.3864923 1.1195239 -0.09876658 -1.4376799 1.3623239\n 0.82006216 0.6577988 -0.58017254 1.5773239 -0.8229859 -1.8199314\n -0.9141591 1.2801356 1.006551 -0.59739584 -1.7120061 0.12186961\n 2.480404 1.0830965 1.1604524 0.4160739 0.81988466 0.5288985\n 1.1213776 1.1430703 -1.231743 -2.3723211 ]\n(100,)\n"
],
[
"# 単語間の類似度\nword1 = nlp('おむすび')\nword2 = nlp('おにぎり')\nword3 = nlp('カレー')\n\nprint(word1.similarity(word2)) # おむすび と おにぎり の類似度は高い\nprint(word1.similarity(word3)) # おむすび と カレー の類似度は低い",
"0.8016603151410209\n0.5304326882294994\n"
],
[
"'''\n単語をベクトル空間に落とし込む\n'''\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom sklearn.decomposition import PCA\n\n#text2vector\nvec1 = nlp('あけましておめでとうございます').vector\nvec2 = nlp('昨日キャベツを買った').vector\nvec3 = nlp('映画を観に行こう').vector\nvec4 = nlp('カレーが食べたい').vector\nvec5 = nlp('買い物しようと町まで出かけた').vector\nvec6 = nlp('昨日食べたチョコレート').vector\n\n#pca\nvectors = np.vstack((vec1, vec2, vec3, vec4, vec5, vec6))\npca = PCA(n_components=2).fit(vectors)\ntrans = pca.fit_transform(vectors)\npc_ratio = pca.explained_variance_ratio_\n\n#plot\nplt.figure()\nplt.scatter(trans[:,0], trans[:,1])\n\ni = 0\nfor txt in ['text1','text2','text3','text4','text5','text6']:\n plt.text(trans[i,0]-0.2, trans[i,1]+0.1, txt)\n i += 1\n\nplt.hlines(0, min(trans[:,0]), max(trans[:,0]), linestyle='dashed', linewidth=1)\nplt.vlines(0, min(trans[:,1]), max(trans[:,1]), linestyle='dashed', linewidth=1)\nplt.xlabel('PC1 ('+str(round(pc_ratio[0]*100,2))+'%)')\nplt.ylabel('PC2 ('+str(round(pc_ratio[1]*100,2))+'%)')\nplt.tight_layout()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4aba89c31296fa77cc5d9ccf691ce2aea39f3816
| 27,191 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
ML-Capstone-Saudi-Stocks.ipynb
|
ageelg-mobile/ML-Capstone-Saudi-Stocks-Sub
|
0313203e4b127191ed30e14b56a7e4bf53397730
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
ML-Capstone-Saudi-Stocks.ipynb
|
ageelg-mobile/ML-Capstone-Saudi-Stocks-Sub
|
0313203e4b127191ed30e14b56a7e4bf53397730
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
ML-Capstone-Saudi-Stocks.ipynb
|
ageelg-mobile/ML-Capstone-Saudi-Stocks-Sub
|
0313203e4b127191ed30e14b56a7e4bf53397730
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 47.124783 | 501 | 0.456622 |
[
[
[
"empty"
]
]
] |
[
"empty"
] |
[
[
"empty"
]
] |
4aba9223dab785e87e4d706aed555cc656c0b85b
| 4,864 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
example.ipynb
|
dorianj/data-lineage
|
9116cfbc2771511adf23aff385d561e9c4427b5c
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
example.ipynb
|
dorianj/data-lineage
|
9116cfbc2771511adf23aff385d561e9c4427b5c
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
example.ipynb
|
dorianj/data-lineage
|
9116cfbc2771511adf23aff385d561e9c4427b5c
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 36.571429 | 268 | 0.547697 |
[
[
[
"queries = [\n \"\"\"\n INSERT INTO page_lookup_nonredirect \n SELECT page.page_id as redircet_id, page.page_title as redirect_title, page.page_title true_title, \n page.page_id, page.page_latest \n FROM page LEFT OUTER JOIN redirect ON page.page_id = redirect.rd_from\n WHERE redirect.rd_from IS NULL\n \"\"\",\n \"\"\"\n insert into page_lookup_redirect \n select original_page.page_id redirect_id, original_page.page_title redirect_title, \n final_page.page_title as true_title, final_page.page_id, final_page.page_latest \n from page final_page join redirect on (redirect.page_title = final_page.page_title) \n join page original_page on (redirect.rd_from = original_page.page_id)\n \"\"\",\n \"\"\"\n INSERT INTO page_lookup\n SELECT redirect_id, redirect_title, true_title, page_id, page_version\n FROM (\n SELECT redirect_id, redirect_title, true_title, page_id, page_version\n FROM page_lookup_nonredirect\n UNION ALL\n SELECT redirect_id, redirect_title, true_title, page_id, page_version\n FROM page_lookup_redirect) u\n \"\"\",\n \"\"\"\n INSERT INTO filtered_pagecounts \n SELECT regexp_replace (reflect ('java.net.URLDecoder','decode', reflect ('java.net.URLDecoder','decode',pvs.page_title)),'^\\s*([a-zA-Z0-9]+).*','$1') page_title \n ,SUM (pvs.views) AS total_views, SUM (pvs.bytes_sent) AS total_bytes_sent\n FROM pagecounts as pvs \n WHERE not pvs.page_title LIKE '(MEDIA|SPECIAL||Talk|User|User_talk|Project|Project_talk|File|File_talk|MediaWiki|MediaWiki_talk|Template|Template_talk|Help|Help_talk|Category|Category_talk|Portal|Wikipedia|Wikipedia_talk|upload|Special)\\:(.*)' and\n pvs.page_title LIKE '^([A-Z])(.*)' and\n not pvs.page_title LIKE '(.*).(jpg|gif|png|JPG|GIF|PNG|txt|ico)$' and\n pvs.page_title <> '404_error/' and \n pvs.page_title <> 'Main_Page' and \n pvs.page_title <> 'Hypertext_Transfer_Protocol' and \n pvs.page_title <> 'Favicon.ico' and \n pvs.page_title <> 'Search' and \n pvs.dt = '2020-01-01'\n GROUP BY \n regexp_replace (reflect ('java.net.URLDecoder','decode', reflect ('java.net.URLDecoder','decode',pvs.page_title)),'^\\s*([a-zA-Z0-9]+).*','$1')\n \"\"\",\n \"\"\"\n INSERT INTO normalized_pagecounts\n SELECT pl.page_id page_id, REGEXP_REPLACE(pl.true_title, '_', ' ') page_title, pl.true_title page_url, views, bytes_sent\n FROM page_lookup pl JOIN filtered_pagecounts fp \n ON fp.page_title = pl.redirect_title where fp.dt='2020-01-01'\n \"\"\"\n]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from data_lineage.catalog.query import Query\nfrom data_lineage.data_lineage import parse, get_dml_queries, create_graph\n\n\ngraph = create_graph(get_dml_queries(parse([Query(q) for q in queries])))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig = graph.fig()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import plotly\nplotly.offline.iplot(fig)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sub_graph = graph.sub_graph((None, 'page_lookup'))\nsub_fig = sub_graph.fig()\nplotly.offline.iplot(sub_fig)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4aba98e0a3e0765fef192aef56a5c94812c0ad2d
| 31,884 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
L08/code/softmax-regression-mnist.ipynb
|
ducdh1210/stat453-deep-learning-ss21
|
26e59b3c82c12e4dcd0d1a946a5634a77fddc8e0
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
L08/code/softmax-regression-mnist.ipynb
|
ducdh1210/stat453-deep-learning-ss21
|
26e59b3c82c12e4dcd0d1a946a5634a77fddc8e0
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
L08/code/softmax-regression-mnist.ipynb
|
ducdh1210/stat453-deep-learning-ss21
|
26e59b3c82c12e4dcd0d1a946a5634a77fddc8e0
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 62.517647 | 15,764 | 0.747177 |
[
[
[
"STAT 453: Deep Learning (Spring 2021) \nInstructor: Sebastian Raschka ([email protected]) \n\nCourse website: http://pages.stat.wisc.edu/~sraschka/teaching/stat453-ss2021/ \nGitHub repository: https://github.com/rasbt/stat453-deep-learning-ss21",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%load_ext watermark\n%watermark -a 'Sebastian Raschka' -v -p torch",
"Author: Sebastian Raschka\n\nPython implementation: CPython\nPython version : 3.8.5\nIPython version : 7.15.0\n\ntorch: 1.7.1\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"- Runs on CPU or GPU (if available)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Softmax Regression on MNIST",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Implementation of softmax regression (multinomial logistic regression).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Imports",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import time\nfrom torchvision import datasets\nfrom torchvision import transforms\nfrom torch.utils.data import DataLoader\nimport torch.nn.functional as F\nimport torch",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Settings and Dataset",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##########################\n### SETTINGS\n##########################\n\n# Device\ndevice = torch.device(\"cuda:0\" if torch.cuda.is_available() else \"cpu\")\n\n# Hyperparameters\nrandom_seed = 123\nlearning_rate = 0.1\nnum_epochs = 25\nbatch_size = 256\n\n# Architecture\nnum_features = 784\nnum_classes = 10\n\n\n##########################\n### MNIST DATASET\n##########################\n\ntrain_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root='data', \n train=True, \n transform=transforms.ToTensor(),\n download=True)\n\ntest_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root='data', \n train=False, \n transform=transforms.ToTensor())\n\n\ntrain_loader = DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset, \n batch_size=batch_size, \n shuffle=True)\n\ntest_loader = DataLoader(dataset=test_dataset, \n batch_size=batch_size, \n shuffle=False)\n\n\n# Checking the dataset\nfor images, labels in train_loader: \n print('Image batch dimensions:', images.shape) #NCHW\n print('Image label dimensions:', labels.shape)\n break",
"Downloading http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz to data/MNIST/raw/train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz\n"
],
[
"##########################\n### MODEL\n##########################\n\nclass SoftmaxRegression(torch.nn.Module):\n\n def __init__(self, num_features, num_classes):\n super(SoftmaxRegression, self).__init__()\n self.linear = torch.nn.Linear(num_features, num_classes)\n# print(self.linear.weight.shape)\n# print(self.linear.bias.shape)\n self.linear.weight.detach().zero_()\n self.linear.bias.detach().zero_()\n \n def forward(self, x):\n logits = self.linear(x)\n probas = F.softmax(logits, dim=1)\n\n return logits, probas\n\nmodel = SoftmaxRegression(num_features=num_features,\n num_classes=num_classes)\n\nmodel.to(device)\n\n##########################\n### COST AND OPTIMIZER\n##########################\n\noptimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Manual seed for deterministic data loader\ntorch.manual_seed(random_seed)\n\n\ndef compute_accuracy(model, data_loader):\n correct_pred, num_examples = 0, 0\n \n for features, targets in data_loader:\n features = features.view(-1, 28*28).to(device)\n targets = targets.to(device)\n logits, probas = model(features)\n _, predicted_labels = torch.max(probas, 1)\n num_examples += targets.size(0)\n correct_pred += (predicted_labels == targets).sum()\n \n return correct_pred.float() / num_examples * 100\n \n\nstart_time = time.time()\nepoch_costs = []\nfor epoch in range(num_epochs):\n avg_cost = 0.\n for batch_idx, (features, targets) in enumerate(train_loader):\n \n features = features.view(-1, 28*28).to(device)\n# print(\"features.shape: \", features.shape)\n targets = targets.to(device)\n \n ### FORWARD AND BACK PROP\n logits, probas = model(features)\n \n # note that the PyTorch implementation of\n # CrossEntropyLoss works with logits, not\n # probabilities\n cost = F.cross_entropy(logits, targets)\n \n optimizer.zero_grad()\n cost.backward()\n avg_cost += cost\n \n \n ### UPDATE MODEL PARAMETERS\n optimizer.step()\n \n ### LOGGING\n if not batch_idx % 50:\n print ('Epoch: %03d/%03d | Batch %03d/%03d | Cost: %.4f' \n %(epoch+1, num_epochs, batch_idx, \n len(train_dataset)//batch_size, cost))\n \n with torch.set_grad_enabled(False):\n avg_cost = avg_cost/len(train_dataset)\n epoch_costs.append(avg_cost)\n print('Epoch: %03d/%03d training accuracy: %.2f%%' % (\n epoch+1, num_epochs, \n compute_accuracy(model, train_loader)))\n print('Time elapsed: %.2f min' % ((time.time() - start_time)/60))",
"Epoch: 001/001 | Batch 000/234 | Cost: 0.3437\nEpoch: 001/001 | Batch 050/234 | Cost: 0.3712\nEpoch: 001/001 | Batch 100/234 | Cost: 0.4276\nEpoch: 001/001 | Batch 150/234 | Cost: 0.3654\nEpoch: 001/001 | Batch 200/234 | Cost: 0.3614\nEpoch: 001/001 training accuracy: 89.82%\nTime elapsed: 0.14 min\n"
],
[
"%matplotlib inline\nimport matplotlib\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\n\nplt.plot(epoch_costs)\nplt.ylabel('Avg Cross Entropy Loss\\n(approximated by averaging over minibatches)')\nplt.xlabel('Epoch')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('Test accuracy: %.2f%%' % (compute_accuracy(model, test_loader)))",
"Test accuracy: 90.41%\n"
],
[
"for features, targets in test_loader:\n break\n \nfig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 4)\nfor i in range(4):\n ax[i].imshow(features[i].view(28, 28), cmap=matplotlib.cm.binary)\n\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"_, predictions = model.forward(features[:4].view(-1, 28*28).to(device))\npredictions = torch.argmax(predictions, dim=1)\nprint('Predicted labels', predictions)",
"Predicted labels tensor([7, 2, 1, 0])\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4aba9aa6796643873c246a93f76df62d31451e31
| 8,129 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Zone Bars.ipynb
|
jbarratt/zonebars
|
75e03155593eb600c5df93352bb53e056d592b2f
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2015-06-03T16:32:20.000Z
|
2015-06-03T16:32:20.000Z
|
Zone Bars.ipynb
|
jbarratt/zonebars
|
75e03155593eb600c5df93352bb53e056d592b2f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Zone Bars.ipynb
|
jbarratt/zonebars
|
75e03155593eb600c5df93352bb53e056d592b2f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 29.136201 | 244 | 0.500062 |
[
[
[
"empty"
]
]
] |
[
"empty"
] |
[
[
"empty"
]
] |
4abaaef227c24f4d51606f7a0b96bdbfe401251c
| 725,683 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
eda-04-codes.ipynb
|
taudata-indonesia/elearning
|
6f9db8b829357cde1ae678255cc251629dfc25d2
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 3 |
2020-08-29T04:54:25.000Z
|
2021-12-12T08:25:48.000Z
|
eda-04-codes.ipynb
|
taudataid/eLearning
|
6f9db8b829357cde1ae678255cc251629dfc25d2
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
eda-04-codes.ipynb
|
taudataid/eLearning
|
6f9db8b829357cde1ae678255cc251629dfc25d2
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 6 |
2020-07-28T23:46:57.000Z
|
2021-09-27T02:22:01.000Z
| 1,358.956929 | 606,152 | 0.957266 |
[
[
[
"<center><img alt=\"\" src=\"images/Cover_EDA.jpg\"/></center> \n\n## <center><font color=\"blue\">EDA-04: Unsupervised Learning - Clustering Bagian ke-02</font></center>\n\n<h2 style=\"text-align: center;\">(C) Taufik Sutanto - 2020</h2>\n<h2 style=\"text-align: center;\">tau-data Indonesia ~ <a href=\"https://tau-data.id/eda-04/\" target=\"_blank\"><span style=\"color: #0009ff;\">https://tau-data.id/eda-04/</span></a></h2>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Run this cell ONLY if this notebook run from Google Colab\n# Kalau dijalankan lokal (Anaconda/WinPython) maka silahkan install di terminal/command prompt \n# Lalu unduh secara manual file yang dibutuhkan dan letakkan di folder Python anda.\n!pip install --upgrade umap-learn\n!wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/taudata-indonesia/eLearning/master/tau_unsup.py",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Importing Modules untuk Notebook ini\nimport warnings; warnings.simplefilter('ignore')\nimport time, umap, numpy as np, tau_unsup as tau, matplotlib.pyplot as plt, pandas as pd, seaborn as sns\nfrom matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap\nfrom sklearn import cluster, datasets\nfrom sklearn.metrics.pairwise import pairwise_distances_argmin\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler\nfrom itertools import cycle, islice\nfrom sklearn.metrics import silhouette_score as siluet\nfrom sklearn.metrics.cluster import homogeneity_score as purity\nfrom sklearn.metrics import normalized_mutual_info_score as NMI \n\nsns.set(style=\"ticks\", color_codes=True)\nrandom_state = 99",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Review\n\n## EDA-03\n* Pendahuluan Unsupervised Learning\n* k-Means, k-Means++, MiniBatch k-Means\n* internal & External Evaluation\n* Parameter Tunning\n\n## EDA-04\n* Hierarchical Clustering\n* Spectral Clustering\n* DBScan\n* Clustering Evaluation Revisited",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Linkages Comparisons\n\n* single linkage is fast, and can perform well on non-globular data, but it performs poorly in the presence of noise.\n* average and complete linkage perform well on cleanly separated globular clusters, but have mixed results otherwise.\n* Ward is the most effective method for noisy data.\n* http://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/cluster/plot_linkage_comparison.html#sphx-glr-auto-examples-cluster-plot-linkage-comparison-py",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tau.compare_linkages()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Pros\n* No assumption of a particular number of clusters (i.e. k-means)\n* May correspond to meaningful taxonomies\n\n### Cons\n* Once a decision is made to combine two clusters, it can’t be undone\n* Too slow for large data sets, O(𝑛2 log(𝑛))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Kita akan menggunakan data yang sama dengan EDA-03\ndf = sns.load_dataset(\"iris\")\nX = df[['sepal_length','sepal_width','petal_length','petal_width']].values\nC = df['species'].values\nprint(X.shape)\ndf.head()",
"(150, 4)\n"
],
[
"# Hierarchical http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.cluster.AgglomerativeClustering.html#sklearn.cluster.AgglomerativeClustering\nhierarchical = cluster.AgglomerativeClustering(n_clusters=3, linkage='average', affinity = 'euclidean')\nhierarchical.fit(X) # Lambat .... dan menggunakan banyak memori O(N^2 log(N))\nC_h = hierarchical.labels_.astype(np.int)\nC_h[:10]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Dendogram Example\n# http://seaborn.pydata.org/generated/seaborn.clustermap.html\ng = sns.clustermap(X, method=\"single\", metric=\"euclidean\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Scatter Plot of the hierarchical clustering results\nX2D = umap.UMAP(n_neighbors=5, min_dist=0.3, random_state=random_state).fit_transform(X)\nfig, ax = plt.subplots()\nax.scatter(X2D[:,0], X2D[:,1], c=C_h)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Evaluasi Hierarchical Clustering?\n\n* Silhoutte Coefficient, Dunn index, or Davies–Bouldin index\n* Domain knowledge - interpretability\n* External Evaluation\n\n### Read more here: https://www.ims.uni-stuttgart.de/document/team/schulte/theses/phd/algorithm.pdf",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Spectral : http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.cluster.SpectralClustering.html\n\nspectral = cluster.SpectralClustering(n_clusters=3)\nspectral.fit(X)\nC_spec = spectral.labels_.astype(np.int)\nsns.countplot(C_spec)\nC_spec[:10]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots()\nax.scatter(X2D[:,0], X2D[:,1], c=C_spec)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# DBSCAN http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.cluster.DBSCAN.html\n# tidak membutuhkan input parameter k!!!... sangat bermanfaat untuk clustering data yang besar\ndbscan = cluster.DBSCAN(eps=0.8, min_samples=5, metric='euclidean')\ndbscan.fit(X)\nC_db = dbscan.labels_.astype(np.int)\nsns.countplot(C_db)\nC_db[:10]\n# apa makna cluster label -1?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sum([1 for i in C_db if i==-1])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots()\nax.scatter(X2D[:,0], X2D[:,1], c=C_db)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"try:\n # Should work in Google Colab\n !wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/christopherjenness/DBCV/master/DBCV/DBCV.py\nexcept:\n pass # Download manually on windows\n\nimport dbcv",
"'wget' is not recognized as an internal or external command,\noperable program or batch file.\n"
],
[
"dbcv.DBCV(X, C_db)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Pelajari Studi Kasus Berikut (Customer Segmentation):\n## http://www.data-mania.com/blog/customer-profiling-and-segmentation-in-python/",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4abab2816a64e8a4addabf33cbec6f1751467a07
| 644,336 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
cirq-web/bloch_sphere_example.ipynb
|
anonymousr007/Cirq
|
fae0d85f79440e046ef365b58d86605ce35d4626
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 3,326 |
2018-07-18T23:17:21.000Z
|
2022-03-29T22:28:24.000Z
|
cirq-web/bloch_sphere_example.ipynb
|
anonymousr007/Cirq
|
fae0d85f79440e046ef365b58d86605ce35d4626
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 3,443 |
2018-07-18T21:07:28.000Z
|
2022-03-31T20:23:21.000Z
|
cirq-web/bloch_sphere_example.ipynb
|
anonymousr007/Cirq
|
fae0d85f79440e046ef365b58d86605ce35d4626
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 865 |
2018-07-18T23:30:24.000Z
|
2022-03-30T11:43:23.000Z
| 4,772.859259 | 641,013 | 0.721166 |
[
[
[
"#### Copyright 2021 The Cirq Developers",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#@title Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the \"License\");\n# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.\n# You may obtain a copy of the License at\n#\n# https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0\n#\n# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software\n# distributed under the License is distributed on an \"AS IS\" BASIS,\n# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.\n# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and\n# limitations under the License.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Cirq-web Bloch sphere visualization",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!pip install --quiet cirq",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from cirq_web import BlochSphere\nimport cirq\nimport math\n\n\nrandom_vector = cirq.testing.random_superposition(2)\n\nr2o2 = math.sqrt(2)/2\ni = (0 + 1j)\n\nzero_state = [1+0j, 0+0j]\none_state = [0+0j, 1+0j]\n\nplus_state = [r2o2+0j, r2o2+0j]\nminus_state = [r2o2+0j, -r2o2+0j]\n\ni_plus_state = [(r2o2+0j), i*(r2o2+0j)]\ni_minus_state = [(r2o2+0j), i*(-r2o2+0j)]\n\nstate_vector = cirq.to_valid_state_vector(plus_state)\nsphere=BlochSphere(state_vector=state_vector)\ndisplay(sphere)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4abadf6309abb387b24ff5d3c37cb33d21eda3fe
| 59,253 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
tensorflow_for_deep_learning/RoboND-DNN-Lab/DNN_lab.ipynb
|
mnbf9rca/nd209
|
12299549bc8621be055e0f544ba5c5666b81ee43
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2019-02-17T18:27:12.000Z
|
2019-02-17T18:27:12.000Z
|
tensorflow_for_deep_learning/RoboND-DNN-Lab/DNN_lab.ipynb
|
mnbf9rca/nd209
|
12299549bc8621be055e0f544ba5c5666b81ee43
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
tensorflow_for_deep_learning/RoboND-DNN-Lab/DNN_lab.ipynb
|
mnbf9rca/nd209
|
12299549bc8621be055e0f544ba5c5666b81ee43
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 77.252934 | 30,568 | 0.775488 |
[
[
[
"<h1 align=\"center\">TensorFlow Deep Neural Network Lab</h1>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<img src=\"image/notmnist.png\">\nIn this lab, you'll use all the tools you learned from the *Deep Neural Networks* lesson to label images of English letters! The data you are using, <a href=\"http://yaroslavvb.blogspot.com/2011/09/notmnist-dataset.html\">notMNIST</a>, consists of images of a letter from A to J in differents font.\n\nThe above images are a few examples of the data you'll be training on. After training the network, you will compare your prediction model against test data. While there is no predefined goal for this lab, we would like you to experiment and discuss with fellow students on what can improve such models to achieve the highest possible accuracy values.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"To start this lab, you first need to import all the necessary modules. Run the code below. If it runs successfully, it will print \"`All modules imported`\".",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import hashlib\nimport os\nimport pickle\nfrom urllib.request import urlretrieve\n\nimport numpy as np\nfrom PIL import Image\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import LabelBinarizer\nfrom sklearn.utils import resample\nfrom tqdm import tqdm\nfrom zipfile import ZipFile\n\nprint('All modules imported.')",
"All modules imported.\n"
]
],
[
[
"The notMNIST dataset is too large for many computers to handle. It contains 500,000 images for just training. You'll be using a subset of this data, 15,000 images for each label (A-J).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def download(url, file):\n \"\"\"\n Download file from <url>\n :param url: URL to file\n :param file: Local file path\n \"\"\"\n if not os.path.isfile(file):\n print('Downloading ' + file + '...')\n urlretrieve(url, file)\n print('Download Finished')\n\n# Download the training and test dataset.\ndownload('https://s3.amazonaws.com/udacity-sdc/notMNIST_train.zip', 'notMNIST_train.zip')\ndownload('https://s3.amazonaws.com/udacity-sdc/notMNIST_test.zip', 'notMNIST_test.zip')\n\n# Make sure the files aren't corrupted\nassert hashlib.md5(open('notMNIST_train.zip', 'rb').read()).hexdigest() == 'c8673b3f28f489e9cdf3a3d74e2ac8fa',\\\n 'notMNIST_train.zip file is corrupted. Remove the file and try again.'\nassert hashlib.md5(open('notMNIST_test.zip', 'rb').read()).hexdigest() == '5d3c7e653e63471c88df796156a9dfa9',\\\n 'notMNIST_test.zip file is corrupted. Remove the file and try again.'\n\n# Wait until you see that all files have been downloaded.\nprint('All files downloaded.')",
"Downloading notMNIST_train.zip...\nDownload Finished\nDownloading notMNIST_test.zip...\nDownload Finished\nAll files downloaded.\n"
],
[
"def uncompress_features_labels(file):\n \"\"\"\n Uncompress features and labels from a zip file\n :param file: The zip file to extract the data from\n \"\"\"\n features = []\n labels = []\n\n with ZipFile(file) as zipf:\n # Progress Bar\n filenames_pbar = tqdm(zipf.namelist(), unit='files')\n \n # Get features and labels from all files\n for filename in filenames_pbar:\n # Check if the file is a directory\n if not filename.endswith('/'):\n with zipf.open(filename) as image_file:\n image = Image.open(image_file)\n image.load()\n # Load image data as 1 dimensional array\n # We're using float32 to save on memory space\n feature = np.array(image, dtype=np.float32).flatten()\n\n # Get the the letter from the filename. This is the letter of the image.\n label = os.path.split(filename)[1][0]\n\n features.append(feature)\n labels.append(label)\n return np.array(features), np.array(labels)\n\n# Get the features and labels from the zip files\ntrain_features, train_labels = uncompress_features_labels('notMNIST_train.zip')\ntest_features, test_labels = uncompress_features_labels('notMNIST_test.zip')\n\n# Limit the amount of data to work with\nsize_limit = 150000\ntrain_features, train_labels = resample(train_features, train_labels, n_samples=size_limit)\n\n# Set flags for feature engineering. This will prevent you from skipping an important step.\nis_features_normal = False\nis_labels_encod = False\n\n# Wait until you see that all features and labels have been uncompressed.\nprint('All features and labels uncompressed.')",
"100%|██████████| 210001/210001 [00:34<00:00, 6148.87files/s]\n100%|██████████| 10001/10001 [00:01<00:00, 6334.02files/s]\n"
]
],
[
[
"<img src=\"image/mean_variance.png\" style=\"height: 75%;width: 75%; position: relative; right: 5%\">\n## Problem 1\nThe first problem involves normalizing the features for your training and test data.\n\nImplement Min-Max scaling in the `normalize()` function to a range of `a=0.1` and `b=0.9`. After scaling, the values of the pixels in the input data should range from 0.1 to 0.9.\n\nSince the raw notMNIST image data is in [grayscale](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Grayscale), the current values range from a min of 0 to a max of 255.\n\nMin-Max Scaling:\n$\nX'=a+{\\frac {\\left(X-X_{\\min }\\right)\\left(b-a\\right)}{X_{\\max }-X_{\\min }}}\n$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Problem 1 - Implement Min-Max scaling for grayscale image data\ndef normalize_grayscale(image_data):\n \"\"\"\n Normalize the image data with Min-Max scaling to a range of [0.1, 0.9]\n :param image_data: The image data to be normalized\n :return: Normalized image data\n \"\"\"\n # TODO: Implement Min-Max scaling for grayscale image data\n gray_min = 0\n gray_max = 255\n a = 0.1\n b = 0.9\n \n return a + ((image_data - gray_min) * (b - a)) / (gray_max - gray_min)\n\n\n### DON'T MODIFY ANYTHING BELOW ###\n# Test Cases\nnp.testing.assert_array_almost_equal(\n normalize_grayscale(np.array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 255])),\n [0.1, 0.103137254902, 0.106274509804, 0.109411764706, 0.112549019608, 0.11568627451, 0.118823529412, 0.121960784314,\n 0.125098039216, 0.128235294118, 0.13137254902, 0.9],\n decimal=3)\nnp.testing.assert_array_almost_equal(\n normalize_grayscale(np.array([0, 1, 10, 20, 30, 40, 233, 244, 254,255])),\n [0.1, 0.103137254902, 0.13137254902, 0.162745098039, 0.194117647059, 0.225490196078, 0.830980392157, 0.865490196078,\n 0.896862745098, 0.9])\n\nif not is_features_normal:\n train_features = normalize_grayscale(train_features)\n test_features = normalize_grayscale(test_features)\n is_features_normal = True\n\nprint('Tests Passed!')",
"Tests Passed!\n"
],
[
"if not is_labels_encod:\n # Turn labels into numbers and apply One-Hot Encoding\n encoder = LabelBinarizer()\n encoder.fit(train_labels)\n train_labels = encoder.transform(train_labels)\n test_labels = encoder.transform(test_labels)\n\n # Change to float32, so it can be multiplied against the features in TensorFlow, which are float32\n train_labels = train_labels.astype(np.float32)\n test_labels = test_labels.astype(np.float32)\n is_labels_encod = True\n\nprint('Labels One-Hot Encoded')",
"Labels One-Hot Encoded\n"
],
[
"assert is_features_normal, 'You skipped the step to normalize the features'\nassert is_labels_encod, 'You skipped the step to One-Hot Encode the labels'\n\n# Get randomized datasets for training and validation\ntrain_features, valid_features, train_labels, valid_labels = train_test_split(\n train_features,\n train_labels,\n test_size=0.05,\n random_state=832289)\n\nprint('Training features and labels randomized and split.')",
"Training features and labels randomized and split.\n"
],
[
"# Save the data for easy access\npickle_file = 'notMNIST.pickle'\nif not os.path.isfile(pickle_file):\n print('Saving data to pickle file...')\n try:\n with open('notMNIST.pickle', 'wb') as pfile:\n pickle.dump(\n {\n 'train_dataset': train_features,\n 'train_labels': train_labels,\n 'valid_dataset': valid_features,\n 'valid_labels': valid_labels,\n 'test_dataset': test_features,\n 'test_labels': test_labels,\n },\n pfile, pickle.HIGHEST_PROTOCOL)\n except Exception as e:\n print('Unable to save data to', pickle_file, ':', e)\n raise\n\nprint('Data cached in pickle file.')",
"Saving data to pickle file...\nData cached in pickle file.\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Checkpoint\nAll your progress is now saved to the pickle file. If you need to leave and comeback to this lab, you no longer have to start from the beginning. Just run the code block below and it will load all the data and modules required to proceed.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%matplotlib inline\n\n# Load the modules\nimport pickle\nimport math\n\nimport numpy as np\nimport tensorflow as tf\nfrom tqdm import tqdm\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\n# Reload the data\npickle_file = 'notMNIST.pickle'\nwith open(pickle_file, 'rb') as f:\n pickle_data = pickle.load(f)\n train_features = pickle_data['train_dataset']\n train_labels = pickle_data['train_labels']\n valid_features = pickle_data['valid_dataset']\n valid_labels = pickle_data['valid_labels']\n test_features = pickle_data['test_dataset']\n test_labels = pickle_data['test_labels']\n del pickle_data # Free up memory\n\n\nprint('Data and modules loaded.')",
"Data and modules loaded.\n"
]
],
[
[
"<img src=\"image/weight_biases.png\" style=\"height: 60%;width: 60%; position: relative; right: 10%\">\n## Problem 2\nFor the neural network to train on your data, you need the following <a href=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/resources/dims_types.html#data-types\">float32</a> tensors:\n - `features`\n - Placeholder tensor for feature data (`train_features`/`valid_features`/`test_features`)\n - `labels`\n - Placeholder tensor for label data (`train_labels`/`valid_labels`/`test_labels`)\n - `keep_prob`\n - Placeholder tensor for dropout's keep probability value\n - `weights`\n - List of Variable Tensors with random numbers from a truncated normal distribution for each list index.\n - See <a href=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/constant_op.html#truncated_normal\">`tf.truncated_normal()` documentation</a> for help.\n - `biases`\n - List of Variable Tensors with all zeros for each list index.\n - See <a href=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/constant_op.html#zeros\"> `tf.zeros()` documentation</a> for help.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"features_count = 784\nlabels_count = 10\n\n# TODO: Set the hidden layer width. You can try different widths for different layers and experiment.\nhidden_layer_width = 64\n\n# TODO: Set the features, labels, and keep_prob tensors\nfeatures = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)\nlabels = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)\nkeep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)\n\n\n# TODO: Set the list of weights and biases tensors based on number of layers\nweights = [ tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([features_count, hidden_layer_width])),\n tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([hidden_layer_width, labels_count]))]\n\nbiases = [ tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([hidden_layer_width])),\n tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([labels_count]))]\n\n\n\n### DON'T MODIFY ANYTHING BELOW ###\nfrom tensorflow.python.ops.variables import Variable\n\nassert features._op.name.startswith('Placeholder'), 'features must be a placeholder'\nassert labels._op.name.startswith('Placeholder'), 'labels must be a placeholder'\nassert all(isinstance(weight, Variable) for weight in weights), 'weights must be a TensorFlow variable'\nassert all(isinstance(bias, Variable) for bias in biases), 'biases must be a TensorFlow variable'\n\nassert features._shape == None or (\\\n features._shape.dims[0].value is None and\\\n features._shape.dims[1].value in [None, 784]), 'The shape of features is incorrect'\nassert labels._shape == None or (\\\n labels._shape.dims[0].value is None and\\\n labels._shape.dims[1].value in [None, 10]), 'The shape of labels is incorrect'\n\nassert features._dtype == tf.float32, 'features must be type float32'\nassert labels._dtype == tf.float32, 'labels must be type float32'",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n## Problem 3\nThis problem would help you implement the hidden and output layers of your model. As it was covered in the classroom, you will need the following:\n\n- [tf.add](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/add) and [tf.matmul](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/matmul) to create your hidden and output(logits) layers.\n- [tf.nn.relu](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/nn/relu) for your ReLU activation function.\n- [tf.nn.dropout](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/nn/dropout) for your dropout layer.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# TODO: Hidden Layers with ReLU Activation and dropouts. \"features\" would be the input to the first layer.\nhidden_layer_1 = tf.add(tf.matmul(features, weights[0]), biases[0])\nhidden_layer_1 = tf.nn.relu(hidden_layer_1)\nhidden_layer_1 = tf.nn.dropout(hidden_layer_1, keep_prob)\n\n# hidden_layer_2 = tf.add(tf.matmul(hidden_layer_1, weights[0]), biases[0])\n# hidden_layer_2 = tf.nn.relu(hidden_layer_2)\n# hidden_layer_2 = tf.nn.dropout(hidden_layer_2, keep_prob)\n\n# TODO: Output layer\nlogits = tf.add(tf.matmul(hidden_layer_1, weights[1]), biases[1])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### DON'T MODIFY ANYTHING BELOW ###\n\nprediction = tf.nn.softmax(logits)\n\n# Training loss\nloss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits, labels=labels))\n\n# Create an operation that initializes all variables\ninit = tf.global_variables_initializer()\n\n# Determine if the predictions are correct\nis_correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(prediction, 1), tf.argmax(labels, 1))\n# Calculate the accuracy of the predictions\naccuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(is_correct_prediction, tf.float32))\n\nprint('Accuracy function created.')",
"Accuracy function created.\n"
]
],
[
[
"<img src=\"image/learn_rate_tune.png\" style=\"height: 60%;width: 60%\">\n## Problem 4\nIn the previous lab for a single Neural Network, you attempted several different configurations for the hyperparameters given below. Try to first use the same parameters as the previous lab, and then adjust and finetune those values based on your new model if required. \n\nYou have another hyperparameter to tune now, however. Set the value for keep_probability and observe how it affects your results.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# TODO: Find the best parameters for each configuration\nepochs = 10\nbatch_size = 64\nlearning_rate = 0.01\nkeep_probability = 0.5\n\n\n\n### DON'T MODIFY ANYTHING BELOW ###\n# Gradient Descent\noptimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(loss) \n\n# The accuracy measured against the validation set\nvalidation_accuracy = 0.0\n\n# Measurements use for graphing loss and accuracy\nlog_batch_step = 50\nbatches = []\nloss_batch = []\ntrain_acc_batch = []\nvalid_acc_batch = []\n\nwith tf.Session() as session:\n session.run(init)\n batch_count = int(math.ceil(len(train_features)/batch_size))\n\n for epoch_i in range(epochs):\n \n # Progress bar\n batches_pbar = tqdm(range(batch_count), desc='Epoch {:>2}/{}'.format(epoch_i+1, epochs), unit='batches')\n \n # The training cycle\n for batch_i in batches_pbar:\n # Get a batch of training features and labels\n batch_start = batch_i*batch_size\n batch_features = train_features[batch_start:batch_start + batch_size]\n batch_labels = train_labels[batch_start:batch_start + batch_size]\n\n # Run optimizer and get loss\n _, l = session.run(\n [optimizer, loss],\n feed_dict={features: batch_features, labels: batch_labels, keep_prob: keep_probability})\n\n # Log every 50 batches\n if not batch_i % log_batch_step:\n # Calculate Training and Validation accuracy\n training_accuracy = session.run(accuracy, feed_dict={features: train_features, \n labels: train_labels, keep_prob: keep_probability})\n validation_accuracy = session.run(accuracy, feed_dict={features: valid_features, \n labels: valid_labels, keep_prob: 1.0})\n\n # Log batches\n previous_batch = batches[-1] if batches else 0\n batches.append(log_batch_step + previous_batch)\n loss_batch.append(l)\n train_acc_batch.append(training_accuracy)\n valid_acc_batch.append(validation_accuracy)\n\n # Check accuracy against Validation data\n validation_accuracy = session.run(accuracy, feed_dict={features: valid_features, \n labels: valid_labels, keep_prob: 1.0})\n\nloss_plot = plt.subplot(211)\nloss_plot.set_title('Loss')\nloss_plot.plot(batches, loss_batch, 'g')\nloss_plot.set_xlim([batches[0], batches[-1]])\nacc_plot = plt.subplot(212)\nacc_plot.set_title('Accuracy')\nacc_plot.plot(batches, train_acc_batch, 'r', label='Training Accuracy')\nacc_plot.plot(batches, valid_acc_batch, 'x', label='Validation Accuracy')\nacc_plot.set_ylim([0, 1.0])\nacc_plot.set_xlim([batches[0], batches[-1]])\nacc_plot.legend(loc=4)\nplt.tight_layout()\nplt.show()\n\nprint('Validation accuracy at {}'.format(validation_accuracy))",
"Epoch 1/10: 100%|██████████| 2227/2227 [00:14<00:00, 150.68batches/s]\nEpoch 2/10: 100%|██████████| 2227/2227 [00:15<00:00, 142.05batches/s]\nEpoch 3/10: 100%|██████████| 2227/2227 [00:15<00:00, 141.90batches/s]\nEpoch 4/10: 100%|██████████| 2227/2227 [00:15<00:00, 142.72batches/s]\nEpoch 5/10: 100%|██████████| 2227/2227 [00:15<00:00, 144.42batches/s]\nEpoch 6/10: 100%|██████████| 2227/2227 [00:15<00:00, 142.79batches/s]\nEpoch 7/10: 100%|██████████| 2227/2227 [00:15<00:00, 144.15batches/s]\nEpoch 8/10: 100%|██████████| 2227/2227 [00:16<00:00, 132.64batches/s]\nEpoch 9/10: 100%|██████████| 2227/2227 [00:16<00:00, 136.46batches/s]\nEpoch 10/10: 100%|██████████| 2227/2227 [00:16<00:00, 132.92batches/s]\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Test\nSet the epochs, batch_size, and learning_rate with the best learning parameters you discovered in problem 4. You're going to test your model against your hold out dataset/testing data. This will give you a good indicator of how well the model will do in the real world.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# TODO: Set the epochs, batch_size, and learning_rate with the best parameters from problem 4\nepochs = 10\nbatch_size = 64\nlearning_rate = .01\n\n\n\n### DON'T MODIFY ANYTHING BELOW ###\n# The accuracy measured against the test set\ntest_accuracy = 0.0\n\nwith tf.Session() as session:\n \n session.run(init)\n batch_count = int(math.ceil(len(train_features)/batch_size))\n\n for epoch_i in range(epochs):\n \n # Progress bar\n batches_pbar = tqdm(range(batch_count), desc='Epoch {:>2}/{}'.format(epoch_i+1, epochs), unit='batches')\n \n # The training cycle\n for batch_i in batches_pbar:\n # Get a batch of training features and labels\n batch_start = batch_i*batch_size\n batch_features = train_features[batch_start:batch_start + batch_size]\n batch_labels = train_labels[batch_start:batch_start + batch_size]\n\n # Run optimizer\n _ = session.run(optimizer, feed_dict={features: batch_features, labels: batch_labels, keep_prob: 1.0})\n\n # Check accuracy against Test data\n test_accuracy = session.run(accuracy, feed_dict={features: test_features, \n labels: test_labels, keep_prob: 1.0})\n\nprint('Nice Job! Test Accuracy is {}'.format(test_accuracy))",
"Epoch 1/10: 100%|██████████| 2227/2227 [00:01<00:00, 1276.68batches/s]\nEpoch 2/10: 100%|██████████| 2227/2227 [00:01<00:00, 1304.43batches/s]\nEpoch 3/10: 100%|██████████| 2227/2227 [00:01<00:00, 1284.55batches/s]\nEpoch 4/10: 100%|██████████| 2227/2227 [00:01<00:00, 1265.77batches/s]\nEpoch 5/10: 100%|██████████| 2227/2227 [00:01<00:00, 1292.97batches/s]\nEpoch 6/10: 100%|██████████| 2227/2227 [00:01<00:00, 1301.17batches/s]\nEpoch 7/10: 100%|██████████| 2227/2227 [00:01<00:00, 1278.88batches/s]\nEpoch 8/10: 100%|██████████| 2227/2227 [00:01<00:00, 1293.06batches/s]\nEpoch 9/10: 100%|██████████| 2227/2227 [00:01<00:00, 1295.32batches/s]\nEpoch 10/10: 100%|██████████| 2227/2227 [00:01<00:00, 1286.09batches/s]"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4abae6e290e9aaa7d32e612b910218b4e7369763
| 14,911 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
site/en/tutorials/distribute/training_loops.ipynb
|
aczzdx/docs
|
b115d0be1bfc505ed7b1219c06bd2ba81bc61b25
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
site/en/tutorials/distribute/training_loops.ipynb
|
aczzdx/docs
|
b115d0be1bfc505ed7b1219c06bd2ba81bc61b25
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
site/en/tutorials/distribute/training_loops.ipynb
|
aczzdx/docs
|
b115d0be1bfc505ed7b1219c06bd2ba81bc61b25
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 33.659142 | 331 | 0.526323 |
[
[
[
"##### Copyright 2019 The TensorFlow Authors.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#@title Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the \"License\");\n# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.\n# You may obtain a copy of the License at\n#\n# https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0\n#\n# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software\n# distributed under the License is distributed on an \"AS IS\" BASIS,\n# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.\n# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and\n# limitations under the License.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# tf.distribute.Strategy with Training Loops",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<table class=\"tfo-notebook-buttons\" align=\"left\">\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/alpha/tutorials/distribute/training_loops\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/tf_logo_32px.png\" />View on TensorFlow.org</a>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/tensorflow/docs/blob/master/site/en/r2/tutorials/distribute/training_loops.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/colab_logo_32px.png\" />Run in Google Colab</a>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://github.com/tensorflow/docs/blob/master/site/en/r2/tutorials/distribute/training_loops.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/GitHub-Mark-32px.png\" />View source on GitHub</a>\n </td>\n</table>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"This tutorial demonstrates how to use [`tf.distribute.Strategy`](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/distribute_strategy) with custom training loops. We will train a simple CNN model on the fashion MNIST dataset. The fashion MNIST dataset contains 60000 train images of size 28 x 28 and 10000 test images of size 28 x 28.\n\nWe are using custom training loops to train our model because they give us flexibility and a greater control on training. Moreover, it is easier to debug the model and the training loop.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals\n\n# Import TensorFlow\nimport tensorflow as tf\n\n# Helper libraries\nimport numpy as np\nimport os\n\nprint(tf.__version__)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Download the fashion mnist dataset",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"fashion_mnist = tf.keras.datasets.fashion_mnist\n\n(train_images, train_labels), (test_images, test_labels) = fashion_mnist.load_data()\n\n# Adding a dimension to the array -> new shape == (28, 28, 1)\n# We are doing this because the first layer in our model is a convolutional\n# layer and it requires a 4D input (batch_size, height, width, channels).\n# batch_size dimension will be added later on.\ntrain_images = train_images[..., None]\ntest_images = test_images[..., None]\n\n# Getting the images in [0, 1] range.\ntrain_images = train_images / np.float32(255)\ntest_images = test_images / np.float32(255)\n\ntrain_labels = train_labels.astype('int64')\ntest_labels = test_labels.astype('int64')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Create a strategy to distribute the variables and the graph",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"How does `tf.distribute.MirroredStrategy` strategy work?\n\n* All the variables and the model graph is replicated on the replicas.\n* Input is evenly distributed across the replicas.\n* Each replica calculates the loss and gradients for the input it received.\n* The gradients are synced across all the replicas by summing them.\n* After the sync, the same update is made to the copies of the variables on each replica.\n\nNote: You can put all the code below inside a single scope. We are dividing it into several code cells for illustration purposes.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# If the list of devices is not specified in the\n# `tf.distribute.MirroredStrategy` constructor, it will be auto-detected.\nstrategy = tf.distribute.MirroredStrategy()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print ('Number of devices: {}'.format(strategy.num_replicas_in_sync))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Setup input pipeline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"If a model is trained on multiple GPUs, the batch size should be increased accordingly so as to make effective use of the extra computing power. Moreover, the learning rate should be tuned accordingly.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"BUFFER_SIZE = len(train_images)\n\nBATCH_SIZE_PER_REPLICA = 64\nBATCH_SIZE = BATCH_SIZE_PER_REPLICA * strategy.num_replicas_in_sync\n\nEPOCHS = 10",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"`strategy.make_dataset_iterator` creates an iterator that evenly distributes the data across all the replicas.\n\n\nNote: This API is expected to change in the near future.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"with strategy.scope():\n train_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(\n (train_images, train_labels)).shuffle(BUFFER_SIZE).batch(BATCH_SIZE)\n train_iterator = strategy.make_dataset_iterator(train_dataset)\n\n test_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(\n (test_images, test_labels)).batch(BATCH_SIZE)\n test_iterator = strategy.make_dataset_iterator(test_dataset)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Model Creation\n\nCreate a model using `tf.keras.Sequential`. You can also use the Model Subclassing API to do this.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"with strategy.scope():\n model = tf.keras.Sequential([\n tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(32, 3, activation='relu',\n input_shape=(28, 28, 1)),\n tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(),\n tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64, 3, activation='relu'),\n tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(),\n tf.keras.layers.Flatten(),\n tf.keras.layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'),\n tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')\n ])\n optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.001)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Define the loss function\n\nNormally, on a single machine with 1 GPU/CPU, loss is divided by the number of examples in the batch of input.\n\n*So, how is the loss calculated when using a `tf.distribute.Strategy`?*\n\n> For an example, let's say you have 4 GPU's and a batch size of 64. One batch of input is distributed\nacross the replicas (4 GPUs), each replica getting an input of size 16.\n\n> The model on each replica does a forward pass with its respective input and calculates the loss. Now, instead of dividing the loss by the number of examples in its respective input (16), the loss is divided by the global input size (64).\n\n*Why is this done?*\n\n> This is done because after the gradients are calculated on each replica, they are synced across the replicas by **summing** them.\n\n*How to handle this in TensorFlow?*\n\n> `tf.keras.losses` handles this automatically.\n\n> If you distribute a custom loss function, don't implement it using `tf.reduce_mean` (which divides by the local batch size), divide the sum by the global batch size:\n\n```python\nscale_loss = tf.reduce_sum(loss) * (1. / global_batch_size)\n```\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Training loop",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"with strategy.scope():\n def train_step():\n def step_fn(inputs):\n images, labels = inputs\n logits = model(images)\n cross_entropy = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(\n logits=logits, labels=labels)\n loss = tf.reduce_sum(cross_entropy) * (1.0 / BATCH_SIZE)\n train_op = optimizer.minimize(loss)\n with tf.control_dependencies([train_op]):\n return tf.identity(loss)\n\n per_replica_losses = strategy.experimental_run(\n step_fn, train_iterator)\n mean_loss = strategy.reduce(\n tf.distribute.ReduceOp.SUM, per_replica_losses, axis=None)\n return mean_loss",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"with strategy.scope():\n iterator_init = train_iterator.initialize()\n var_init = tf.global_variables_initializer()\n loss = train_step()\n with tf.Session() as sess:\n sess.run([var_init])\n for epoch in range(EPOCHS):\n sess.run([iterator_init])\n for step in range(10000):\n if step % 1000 == 0:\n print('Epoch {} Step {} Loss {:.4f}'.format(epoch+1,\n step,\n sess.run(loss)))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Next Steps\n\nTry out the new `tf.distribute.Strategy` API on your models.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4abafae47d61b2a6a168d458a5d669108cc762c6
| 188,118 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Accuracy and Misclassification.ipynb
|
Garima13a/Accuracy-and-Misclassification
|
ab457b0691569196ef0c285ce410ddca55235ae5
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2019-07-05T18:34:18.000Z
|
2022-02-05T16:14:48.000Z
|
Accuracy and Misclassification.ipynb
|
Garima13a/Accuracy-and-Misclassification
|
ab457b0691569196ef0c285ce410ddca55235ae5
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Accuracy and Misclassification.ipynb
|
Garima13a/Accuracy-and-Misclassification
|
ab457b0691569196ef0c285ce410ddca55235ae5
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 389.478261 | 87,324 | 0.937321 |
[
[
[
"# Day and Night Image Classifier\n---\n\nThe day/night image dataset consists of 200 RGB color images in two categories: day and night. There are equal numbers of each example: 100 day images and 100 night images.\n\nWe'd like to build a classifier that can accurately label these images as day or night, and that relies on finding distinguishing features between the two types of images!\n\n*Note: All images come from the [AMOS dataset](http://cs.uky.edu/~jacobs/datasets/amos/) (Archive of Many Outdoor Scenes).*\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Import resources\n\nBefore you get started on the project code, import the libraries and resources that you'll need.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import cv2 # computer vision library\nimport helpers\n\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport matplotlib.image as mpimg\n\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Training and Testing Data\nThe 200 day/night images are separated into training and testing datasets. \n\n* 60% of these images are training images, for you to use as you create a classifier.\n* 40% are test images, which will be used to test the accuracy of your classifier.\n\nFirst, we set some variables to keep track of some where our images are stored:\n\n image_dir_training: the directory where our training image data is stored\n image_dir_test: the directory where our test image data is stored",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Image data directories\nimage_dir_training = \"day_night_images/training/\"\nimage_dir_test = \"day_night_images/test/\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Load the datasets\n\nThese first few lines of code will load the training day/night images and store all of them in a variable, `IMAGE_LIST`. This list contains the images and their associated label (\"day\" or \"night\"). \n\nFor example, the first image-label pair in `IMAGE_LIST` can be accessed by index: \n``` IMAGE_LIST[0][:]```.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Using the load_dataset function in helpers.py\n# Load training data\nIMAGE_LIST = helpers.load_dataset(image_dir_training)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Construct a `STANDARDIZED_LIST` of input images and output labels.\n\nThis function takes in a list of image-label pairs and outputs a **standardized** list of resized images and numerical labels.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Standardize all training images\nSTANDARDIZED_LIST = helpers.standardize(IMAGE_LIST)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Visualize the standardized data\n\nDisplay a standardized image from STANDARDIZED_LIST.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Display a standardized image and its label\n\n# Select an image by index\nimage_num = 0\nselected_image = STANDARDIZED_LIST[image_num][0]\nselected_label = STANDARDIZED_LIST[image_num][1]\n\n# Display image and data about it\nplt.imshow(selected_image)\nprint(\"Shape: \"+str(selected_image.shape))\nprint(\"Label [1 = day, 0 = night]: \" + str(selected_label))\n",
"Shape: (600, 1100, 3)\nLabel [1 = day, 0 = night]: 1\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Feature Extraction\n\nCreate a feature that represents the brightness in an image. We'll be extracting the **average brightness** using HSV colorspace. Specifically, we'll use the V channel (a measure of brightness), add up the pixel values in the V channel, then divide that sum by the area of the image to get the average Value of the image.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"---\n### Find the average brightness using the V channel\n\nThis function takes in a **standardized** RGB image and returns a feature (a single value) that represent the average level of brightness in the image. We'll use this value to classify the image as day or night.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Find the average Value or brightness of an image\ndef avg_brightness(rgb_image):\n # Convert image to HSV\n hsv = cv2.cvtColor(rgb_image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2HSV)\n\n # Add up all the pixel values in the V channel\n sum_brightness = np.sum(hsv[:,:,2])\n area = 600*1100.0 # pixels\n \n # find the avg\n avg = sum_brightness/area\n \n return avg",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Testing average brightness levels\n# Look at a number of different day and night images and think about \n# what average brightness value separates the two types of images\n\n# As an example, a \"night\" image is loaded in and its avg brightness is displayed\nimage_num = 190\ntest_im = STANDARDIZED_LIST[image_num][0]\n\navg = avg_brightness(test_im)\nprint('Avg brightness: ' + str(avg))\nplt.imshow(test_im)",
"Avg brightness: 119.6223\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Classification and Visualizing Error\n\nIn this section, we'll turn our average brightness feature into a classifier that takes in a standardized image and returns a `predicted_label` for that image. This `estimate_label` function should return a value: 0 or 1 (night or day, respectively).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"---\n### TODO: Build a complete classifier \n\nComplete this code so that it returns an estimated class label given an input RGB image.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# This function should take in RGB image input\ndef estimate_label(rgb_image):\n \n # TO-DO: Extract average brightness feature from an RGB image \n avg = avg_brightness(rgb_image)\n \n # Use the avg brightness feature to predict a label (0, 1)\n predicted_label = 0\n # TO-DO: Try out different threshold values to see what works best!\n threshold = 98.999999\n if(avg > threshold):\n # if the average brightness is above the threshold value, we classify it as \"day\"\n predicted_label = 1\n # else, the predicted_label can stay 0 (it is predicted to be \"night\")\n \n return predicted_label \n ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Testing the classifier\n\nHere is where we test your classification algorithm using our test set of data that we set aside at the beginning of the notebook!\n\nSince we are using a pretty simple brightess feature, we may not expect this classifier to be 100% accurate. We'll aim for around 75-85% accuracy usin this one feature.\n\n\n### Test dataset\n\nBelow, we load in the test dataset, standardize it using the `standardize` function you defined above, and then **shuffle** it; this ensures that order will not play a role in testing accuracy.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import random\n\n# Using the load_dataset function in helpers.py\n# Load test data\nTEST_IMAGE_LIST = helpers.load_dataset(image_dir_test)\n\n# Standardize the test data\nSTANDARDIZED_TEST_LIST = helpers.standardize(TEST_IMAGE_LIST)\n\n# Shuffle the standardized test data\nrandom.shuffle(STANDARDIZED_TEST_LIST)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Determine the Accuracy\n\nCompare the output of your classification algorithm (a.k.a. your \"model\") with the true labels and determine the accuracy.\n\nThis code stores all the misclassified images, their predicted labels, and their true labels, in a list called `misclassified`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Constructs a list of misclassified images given a list of test images and their labels\ndef get_misclassified_images(test_images):\n # Track misclassified images by placing them into a list\n misclassified_images_labels = []\n\n # Iterate through all the test images\n # Classify each image and compare to the true label\n for image in test_images:\n\n # Get true data\n im = image[0]\n true_label = image[1]\n\n # Get predicted label from your classifier\n predicted_label = estimate_label(im)\n\n # Compare true and predicted labels \n if(predicted_label != true_label):\n # If these labels are not equal, the image has been misclassified\n misclassified_images_labels.append((im, predicted_label, true_label))\n \n # Return the list of misclassified [image, predicted_label, true_label] values\n return misclassified_images_labels\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Find all misclassified images in a given test set\nMISCLASSIFIED = get_misclassified_images(STANDARDIZED_TEST_LIST)\n\n# Accuracy calculations\ntotal = len(STANDARDIZED_TEST_LIST)\nnum_correct = total - len(MISCLASSIFIED)\naccuracy = num_correct/total\n\nprint('Accuracy: ' + str(accuracy))\nprint(\"Number of misclassified images = \" + str(len(MISCLASSIFIED)) +' out of '+ str(total))",
"Accuracy: 0.9375\nNumber of misclassified images = 10 out of 160\n"
]
],
[
[
"---\n<a id='task9'></a>\n### TO-DO: Visualize the misclassified images\n\nVisualize some of the images you classified wrong (in the `MISCLASSIFIED` list) and note any qualities that make them difficult to classify. This will help you identify any weaknesses in your classification algorithm.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Visualize misclassified example(s)\nnum = 0\ntest_mis_im = MISCLASSIFIED[num][0]\n\n## TODO: Display an image in the `MISCLASSIFIED` list \n## TODO: Print out its predicted label - \n## to see what the image *was* incorrectly classified as",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"---\n<a id='question2'></a>\n## (Question): After visualizing these misclassifications, what weaknesses do you think your classification algorithm has?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Answer:** Write your answer, here.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 5. Improve your algorithm!\n\n* (Optional) Tweak your threshold so that accuracy is better.\n* (Optional) Add another feature that tackles a weakness you identified!\n---\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4abafc7a397829d805fbd806d0797f27c36e40f6
| 104,950 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Course2-Build Better Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)/week3/C2W3_Assignment.ipynb
|
shreyansh26/GANs-Specialization-Deeplearning.ai
|
1c9f5324f67360209a76e0040c607991bd8f4655
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2020-12-30T13:50:59.000Z
|
2020-12-30T13:50:59.000Z
|
Course2-Build Better Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)/week3/C2W3_Assignment.ipynb
|
shreyansh26/GANs-Specialization-Deeplearning.ai
|
1c9f5324f67360209a76e0040c607991bd8f4655
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Course2-Build Better Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)/week3/C2W3_Assignment.ipynb
|
shreyansh26/GANs-Specialization-Deeplearning.ai
|
1c9f5324f67360209a76e0040c607991bd8f4655
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 115.5837 | 67,480 | 0.830672 |
[
[
[
"# Components of StyleGAN\n\n### Goals\nIn this notebook, you're going to implement various components of StyleGAN, including the truncation trick, the mapping layer, noise injection, adaptive instance normalization (AdaIN), and progressive growing. \n\n### Learning Objectives\n\n1. Understand the components of StyleGAN that differ from the traditional GAN.\n2. Implement the components of StyleGAN.\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Getting Started\nYou will begin by importing some packages from PyTorch and defining a visualization function which will be useful later.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import torch\nimport torch.nn as nn\nimport torch.nn.functional as F\n\ndef show_tensor_images(image_tensor, num_images=16, size=(3, 64, 64), nrow=3):\n '''\n Function for visualizing images: Given a tensor of images, number of images,\n size per image, and images per row, plots and prints the images in an uniform grid.\n '''\n image_tensor = (image_tensor + 1) / 2\n image_unflat = image_tensor.detach().cpu().clamp_(0, 1)\n image_grid = make_grid(image_unflat[:num_images], nrow=nrow, padding=0)\n plt.imshow(image_grid.permute(1, 2, 0).squeeze())\n plt.axis('off')\n plt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Truncation Trick\nThe first component you will implement is the truncation trick. Remember that this is done after the model is trained and when you are sampling beautiful outputs. The truncation trick resamples the noise vector $z$ from a truncated normal distribution which allows you to tune the generator's fidelity/diversity. The truncation value is at least 0, where 1 means there is little truncation (high diversity) and 0 means the distribution is all truncated except for the mean (high quality/fidelity). This trick is not exclusive to StyleGAN. In fact, you may recall playing with it in an earlier GAN notebook.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# UNQ_C1 (UNIQUE CELL IDENTIFIER, DO NOT EDIT)\n# GRADED CELL: get_truncated_noise\n\nfrom scipy.stats import truncnorm\ndef get_truncated_noise(n_samples, z_dim, truncation):\n '''\n Function for creating truncated noise vectors: Given the dimensions (n_samples, z_dim)\n and truncation value, creates a tensor of that shape filled with random\n numbers from the truncated normal distribution.\n Parameters:\n n_samples: the number of samples to generate, a scalar\n z_dim: the dimension of the noise vector, a scalar\n truncation: the truncation value, a non-negative scalar\n '''\n #### START CODE HERE ####\n truncated_noise = truncnorm.rvs(-truncation, truncation, size=(n_samples, z_dim))\n #### END CODE HERE ####\n return torch.Tensor(truncated_noise)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Test the truncation sample\nassert tuple(get_truncated_noise(n_samples=10, z_dim=5, truncation=0.7).shape) == (10, 5)\nsimple_noise = get_truncated_noise(n_samples=1000, z_dim=10, truncation=0.2)\nassert simple_noise.max() > 0.199 and simple_noise.max() < 2\nassert simple_noise.min() < -0.199 and simple_noise.min() > -0.2\nassert simple_noise.std() > 0.113 and simple_noise.std() < 0.117\nprint(\"Success!\")",
"Success!\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Mapping $z$ → $w$\n\nThe next component you need to implement is the mapping network. It takes the noise vector, $z$, and maps it to an intermediate noise vector, $w$. This makes it so $z$ can be represented in a more disentangled space which makes the features easier to control later.\n\nThe mapping network in StyleGAN is composed of 8 layers, but for your implementation, you will use a neural network with 3 layers. This is to save time training later.\n\n<details>\n<summary>\n<font size=\"3\" color=\"green\">\n<b>Optional hints for <code><font size=\"4\">MappingLayers</font></code></b>\n</font>\n</summary>\n\n1. This code should be five lines.\n2. You need 3 linear layers and should use ReLU activations.\n3. Your linear layers should be input -> hidden_dim -> hidden_dim -> output.\n</details>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# UNQ_C2 (UNIQUE CELL IDENTIFIER, DO NOT EDIT)\n# GRADED CELL: MappingLayers\n\nclass MappingLayers(nn.Module):\n '''\n Mapping Layers Class\n Values:\n z_dim: the dimension of the noise vector, a scalar\n hidden_dim: the inner dimension, a scalar\n w_dim: the dimension of the intermediate noise vector, a scalar\n '''\n \n def __init__(self, z_dim, hidden_dim, w_dim):\n super().__init__()\n self.mapping = nn.Sequential(\n # Please write a neural network which takes in tensors of \n # shape (n_samples, z_dim) and outputs (n_samples, w_dim)\n # with a hidden layer with hidden_dim neurons\n #### START CODE HERE ####\n nn.Linear(z_dim, hidden_dim),\n nn.ReLU(),\n nn.Linear(hidden_dim, hidden_dim),\n nn.ReLU(),\n nn.Linear(hidden_dim, w_dim)\n #### END CODE HERE ####\n )\n\n def forward(self, noise):\n '''\n Function for completing a forward pass of MappingLayers: \n Given an initial noise tensor, returns the intermediate noise tensor.\n Parameters:\n noise: a noise tensor with dimensions (n_samples, z_dim)\n '''\n return self.mapping(noise)\n \n #UNIT TEST COMMENT: Required for grading\n def get_mapping(self):\n return self.mapping",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Test the mapping function\nmap_fn = MappingLayers(10,20,30)\nassert tuple(map_fn(torch.randn(2, 10)).shape) == (2, 30)\nassert len(map_fn.mapping) > 4\noutputs = map_fn(torch.randn(1000, 10))\nassert outputs.std() > 0.05 and outputs.std() < 0.3\nassert outputs.min() > -2 and outputs.min() < 0\nassert outputs.max() < 2 and outputs.max() > 0\nlayers = [str(x).replace(' ', '').replace('inplace=True', '') for x in map_fn.get_mapping()]\nassert layers == ['Linear(in_features=10,out_features=20,bias=True)', \n 'ReLU()', \n 'Linear(in_features=20,out_features=20,bias=True)', \n 'ReLU()', \n 'Linear(in_features=20,out_features=30,bias=True)']\nprint(\"Success!\")",
"Success!\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Random Noise Injection\nNext, you will implement the random noise injection that occurs before every AdaIN block. To do this, you need to create a noise tensor that is the same size as the current feature map (image).\n\nThe noise tensor is not entirely random; it is initialized as one random channel that is then multiplied by learned weights for each channel in the image. For example, imagine an image has 512 channels and its height and width are (4 x 4). You would first create a random (4 x 4) noise matrix with one channel. Then, your model would create 512 values—one for each channel. Next, you multiply the (4 x 4) matrix by each one of these values. This creates a \"random\" tensor of 512 channels and (4 x 4) pixels, the same dimensions as the image. Finally, you add this noise tensor to the image. This introduces uncorrelated noise and is meant to increase the diversity in the image.\n\nNew starting weights are generated for every new layer, or generator, where this class is used. Within a layer, every following time the noise injection is called, you take another step with the optimizer and the weights that you use for each channel are optimized (i.e. learned).\n\n<details>\n\n<summary>\n<font size=\"3\" color=\"green\">\n<b>Optional hint for <code><font size=\"4\">InjectNoise</font></code></b>\n</font>\n</summary>\n\n1. The weight should have the shape (1, channels, 1, 1).\n</details>\n\n<!-- <details>\n\n<summary>\n<font size=\"3\" color=\"green\">\n<b>Optional hint for <code><font size=\"4\">InjectNoise</font></code></b>\n</font>\n</summary>\n\n1. Remember that you only make the noise for one channel (it is then multiplied by random values to create ones for the other channels).\n</details> -->\n\n<!-- (not sure how??) You'll find the get_noise function from before helpful here -->",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# UNQ_C3 (UNIQUE CELL IDENTIFIER, DO NOT EDIT)\n# GRADED CELL: InjectNoise\n\nclass InjectNoise(nn.Module):\n '''\n Inject Noise Class\n Values:\n channels: the number of channels the image has, a scalar\n '''\n def __init__(self, channels):\n super().__init__()\n self.weight = nn.Parameter( # You use nn.Parameter so that these weights can be optimized\n # Initiate the weights for the channels from a random normal distribution\n #### START CODE HERE ####\n torch.randn(1, channels, 1, 1)\n #### END CODE HERE ####\n )\n\n def forward(self, image):\n '''\n Function for completing a forward pass of InjectNoise: Given an image, \n returns the image with random noise added.\n Parameters:\n image: the feature map of shape (n_samples, channels, width, height)\n '''\n # Set the appropriate shape for the noise!\n \n #### START CODE HERE ####\n noise_shape = (image.shape[0], 1, image.shape[2], image.shape[3])\n #### END CODE HERE ####\n \n noise = torch.randn(noise_shape, device=image.device) # Creates the random noise\n return image + self.weight * noise # Applies to image after multiplying by the weight for each channel\n \n #UNIT TEST COMMENT: Required for grading\n def get_weight(self):\n return self.weight\n \n #UNIT TEST COMMENT: Required for grading\n def get_self(self):\n return self\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# UNIT TEST\ntest_noise_channels = 3000\ntest_noise_samples = 20\nfake_images = torch.randn(test_noise_samples, test_noise_channels, 10, 10)\ninject_noise = InjectNoise(test_noise_channels)\nassert torch.abs(inject_noise.weight.std() - 1) < 0.1\nassert torch.abs(inject_noise.weight.mean()) < 0.1\nassert type(inject_noise.get_weight()) == torch.nn.parameter.Parameter\n\nassert tuple(inject_noise.weight.shape) == (1, test_noise_channels, 1, 1)\ninject_noise.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.ones_like(inject_noise.weight))\n# Check that something changed\nassert torch.abs((inject_noise(fake_images) - fake_images)).mean() > 0.1\n# Check that the change is per-channel\nassert torch.abs((inject_noise(fake_images) - fake_images).std(0)).mean() > 1e-4\nassert torch.abs((inject_noise(fake_images) - fake_images).std(1)).mean() < 1e-4\nassert torch.abs((inject_noise(fake_images) - fake_images).std(2)).mean() > 1e-4\nassert torch.abs((inject_noise(fake_images) - fake_images).std(3)).mean() > 1e-4\n# Check that the per-channel change is roughly normal\nper_channel_change = (inject_noise(fake_images) - fake_images).mean(1).std()\nassert per_channel_change > 0.9 and per_channel_change < 1.1\n# Make sure that the weights are being used at all\ninject_noise.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros_like(inject_noise.weight))\nassert torch.abs((inject_noise(fake_images) - fake_images)).mean() < 1e-4\nassert len(inject_noise.weight.shape) == 4\nprint(\"Success!\")",
"Success!\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Adaptive Instance Normalization (AdaIN)\nThe next component you will implement is AdaIN. To increase control over the image, you inject $w$ — the intermediate noise vector — multiple times throughout StyleGAN. This is done by transforming it into a set of style parameters and introducing the style to the image through AdaIN. Given an image ($x_i$) and the intermediate vector ($w$), AdaIN takes the instance normalization of the image and multiplies it by the style scale ($y_s$) and adds the style bias ($y_b$). You need to calculate the learnable style scale and bias by using linear mappings from $w$.\n\n# $ \\text{AdaIN}(\\boldsymbol{\\mathrm{x}}_i, \\boldsymbol{\\mathrm{y}}) = \\boldsymbol{\\mathrm{y}}_{s,i} \\frac{\\boldsymbol{\\mathrm{x}}_i - \\mu(\\boldsymbol{\\mathrm{x}}_i)}{\\sigma(\\boldsymbol{\\mathrm{x}}_i)} + \\boldsymbol{\\mathrm{y}}_{b,i} $\n\n<details>\n\n<summary>\n<font size=\"3\" color=\"green\">\n<b>Optional hints for <code><font size=\"4\">forward</font></code></b>\n</font>\n</summary>\n\n1. Remember the equation for AdaIN.\n2. The instance normalized image, style scale, and style shift have already been calculated for you.\n</details>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# UNQ_C4 (UNIQUE CELL IDENTIFIER, DO NOT EDIT)\n# GRADED CELL: AdaIN\n\nclass AdaIN(nn.Module):\n '''\n AdaIN Class\n Values:\n channels: the number of channels the image has, a scalar\n w_dim: the dimension of the intermediate noise vector, a scalar\n '''\n\n def __init__(self, channels, w_dim):\n super().__init__()\n\n # Normalize the input per-dimension\n self.instance_norm = nn.InstanceNorm2d(channels)\n\n # You want to map w to a set of style weights per channel.\n # Replace the Nones with the correct dimensions - keep in mind that \n # both linear maps transform a w vector into style weights \n # corresponding to the number of image channels.\n #### START CODE HERE ####\n self.style_scale_transform = nn.Linear(w_dim, channels)\n self.style_shift_transform = nn.Linear(w_dim, channels)\n #### END CODE HERE ####\n\n def forward(self, image, w):\n '''\n Function for completing a forward pass of AdaIN: Given an image and intermediate noise vector w, \n returns the normalized image that has been scaled and shifted by the style.\n Parameters:\n image: the feature map of shape (n_samples, channels, width, height)\n w: the intermediate noise vector\n '''\n normalized_image = self.instance_norm(image)\n style_scale = self.style_scale_transform(w)[:, :, None, None]\n style_shift = self.style_shift_transform(w)[:, :, None, None]\n \n # Calculate the transformed image\n #### START CODE HERE ####\n transformed_image = style_scale * normalized_image + style_shift\n #### END CODE HERE ####\n return transformed_image\n \n #UNIT TEST COMMENT: Required for grading\n def get_style_scale_transform(self):\n return self.style_scale_transform\n \n #UNIT TEST COMMENT: Required for grading\n def get_style_shift_transform(self):\n return self.style_shift_transform\n \n #UNIT TEST COMMENT: Required for grading\n def get_self(self):\n return self \n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"w_channels = 50\nimage_channels = 20\nimage_size = 30\nn_test = 10\nadain = AdaIN(image_channels, w_channels)\ntest_w = torch.randn(n_test, w_channels)\nassert adain.style_scale_transform(test_w).shape == adain.style_shift_transform(test_w).shape\nassert adain.style_scale_transform(test_w).shape[-1] == image_channels\nassert tuple(adain(torch.randn(n_test, image_channels, image_size, image_size), test_w).shape) == (n_test, image_channels, image_size, image_size)\n\nw_channels = 3\nimage_channels = 2\nimage_size = 3\nn_test = 1\nadain = AdaIN(image_channels, w_channels)\n\nadain.style_scale_transform.weight.data = torch.ones_like(adain.style_scale_transform.weight.data) / 4\nadain.style_scale_transform.bias.data = torch.zeros_like(adain.style_scale_transform.bias.data)\nadain.style_shift_transform.weight.data = torch.ones_like(adain.style_shift_transform.weight.data) / 5\nadain.style_shift_transform.bias.data = torch.zeros_like(adain.style_shift_transform.bias.data)\ntest_input = torch.ones(n_test, image_channels, image_size, image_size)\ntest_input[:, :, 0] = 0\ntest_w = torch.ones(n_test, w_channels)\ntest_output = adain(test_input, test_w)\nassert(torch.abs(test_output[0, 0, 0, 0] - 3 / 5 + torch.sqrt(torch.tensor(9 / 8))) < 1e-4)\nassert(torch.abs(test_output[0, 0, 1, 0] - 3 / 5 - torch.sqrt(torch.tensor(9 / 32))) < 1e-4)\nprint(\"Success!\")",
"Success!\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Progressive Growing in StyleGAN\nThe final StyleGAN component that you will create is progressive growing. This helps StyleGAN to create high resolution images by gradually doubling the image's size until the desired size.\n\nYou will start by creating a block for the StyleGAN generator. This is comprised of an upsampling layer, a convolutional layer, random noise injection, an AdaIN layer, and an activation.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# UNQ_C5 (UNIQUE CELL IDENTIFIER, DO NOT EDIT)\n# GRADED CELL: MicroStyleGANGeneratorBlock\n\nclass MicroStyleGANGeneratorBlock(nn.Module):\n '''\n Micro StyleGAN Generator Block Class\n Values:\n in_chan: the number of channels in the input, a scalar\n out_chan: the number of channels wanted in the output, a scalar\n w_dim: the dimension of the intermediate noise vector, a scalar\n kernel_size: the size of the convolving kernel\n starting_size: the size of the starting image\n '''\n\n def __init__(self, in_chan, out_chan, w_dim, kernel_size, starting_size, use_upsample=True):\n super().__init__()\n self.use_upsample = use_upsample\n # Replace the Nones in order to:\n # 1. Upsample to the starting_size, bilinearly (https://pytorch.org/docs/master/generated/torch.nn.Upsample.html)\n # 2. Create a kernel_size convolution which takes in \n # an image with in_chan and outputs one with out_chan (https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.Conv2d.html)\n # 3. Create an object to inject noise\n # 4. Create an AdaIN object\n # 5. Create a LeakyReLU activation with slope 0.2\n \n #### START CODE HERE ####\n if self.use_upsample:\n self.upsample = nn.Upsample((starting_size), mode='bilinear')\n self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_chan, out_chan, kernel_size, padding=1) # Padding is used to maintain the image size\n self.inject_noise = InjectNoise(out_chan)\n self.adain = AdaIN(out_chan, w_dim)\n self.activation = nn.LeakyReLU(0.2)\n #### END CODE HERE ####\n\n def forward(self, x, w):\n '''\n Function for completing a forward pass of MicroStyleGANGeneratorBlock: Given an x and w, \n computes a StyleGAN generator block.\n Parameters:\n x: the input into the generator, feature map of shape (n_samples, channels, width, height)\n w: the intermediate noise vector\n '''\n if self.use_upsample:\n x = self.upsample(x)\n x = self.conv(x)\n x = self.inject_noise(x)\n x = self.activation(x)\n x = self.adain(x, w)\n return x\n \n #UNIT TEST COMMENT: Required for grading\n def get_self(self):\n return self;",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"test_stylegan_block = MicroStyleGANGeneratorBlock(in_chan=128, out_chan=64, w_dim=256, kernel_size=3, starting_size=8)\ntest_x = torch.ones(1, 128, 4, 4)\ntest_x[:, :, 1:3, 1:3] = 0\ntest_w = torch.ones(1, 256)\ntest_x = test_stylegan_block.upsample(test_x)\nassert tuple(test_x.shape) == (1, 128, 8, 8)\nassert torch.abs(test_x.mean() - 0.75) < 1e-4\ntest_x = test_stylegan_block.conv(test_x)\nassert tuple(test_x.shape) == (1, 64, 8, 8)\ntest_x = test_stylegan_block.inject_noise(test_x)\ntest_x = test_stylegan_block.activation(test_x)\nassert test_x.min() < 0\nassert -test_x.min() / test_x.max() < 0.4\ntest_x = test_stylegan_block.adain(test_x, test_w) \nfoo = test_stylegan_block(torch.ones(10, 128, 4, 4), torch.ones(10, 256))\n\nprint(\"Success!\")",
"Success!\n"
]
],
[
[
"Now, you can implement progressive growing. \n\nStyleGAN starts with a constant 4 x 4 (x 512 channel) tensor which is put through an iteration of the generator without upsampling. The output is some noise that can then be transformed into a blurry 4 x 4 image. This is where the progressive growing process begins. The 4 x 4 noise can be further passed through a generator block with upsampling to produce an 8 x 8 output. However, this will be done gradually.\n\nYou will simulate progressive growing from an 8 x 8 image to a 16 x 16 image. Instead of simply passing it to the generator block with upsampling, StyleGAN gradually trains the generator to the new size by mixing in an image that was only upsampled. By mixing an upsampled 8 x 8 image (which is 16 x 16) with increasingly more of the 16 x 16 generator output, the generator is more stable as it progressively trains. As such, you will do two separate operations with the 8 x 8 noise:\n\n1. Pass it into the next generator block to create an output noise, that you will then transform to an image.\n2. Transform it into an image and then upsample it to be 16 x 16.\n\nYou will now have two images that are both double the resolution of the 8 x 8 noise. Then, using an alpha ($\\alpha$) term, you combine the higher resolution images obtained from (1) and (2). You would then pass this into the discriminator and use the feedback to update the weights of your generator. The key here is that the $\\alpha$ term is gradually increased until eventually, only the image from (1), the generator, is used. That is your final image or you could continue this process to make a 32 x 32 image or 64 x 64, 128 x 128, etc. \n\nThis micro model you will implement will visualize what the model outputs at a particular stage of training, for a specific value of $\\alpha$. However to reiterate, in practice, StyleGAN will slowly phase out the upsampled image by increasing the $\\alpha$ parameter over many training steps, doing this process repeatedly with larger and larger alpha values until it is 1—at this point, the combined image is solely comprised of the image from the generator block. This method of gradually training the generator increases the stability and fidelity of the model.\n\n<!-- by passing a random noise vector in $z$ through the mapping function you wrote to get $w$. $w$ is then passed through the first block of the generator to create your first output noise. -->\n\n<details>\n\n<summary>\n<font size=\"3\" color=\"green\">\n<b>Optional hint for <code><font size=\"4\">forward</font></code></b>\n</font>\n</summary>\n\n1. You may find [torch.lerp](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.lerp.html) helpful.\n\n</details>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# UNQ_C6 (UNIQUE CELL IDENTIFIER, DO NOT EDIT)\n# GRADED CELL: MicroStyleGANGenerator\n\nclass MicroStyleGANGenerator(nn.Module):\n '''\n Micro StyleGAN Generator Class\n Values:\n z_dim: the dimension of the noise vector, a scalar\n map_hidden_dim: the mapping inner dimension, a scalar\n w_dim: the dimension of the intermediate noise vector, a scalar\n in_chan: the dimension of the constant input, usually w_dim, a scalar\n out_chan: the number of channels wanted in the output, a scalar\n kernel_size: the size of the convolving kernel\n hidden_chan: the inner dimension, a scalar\n '''\n\n def __init__(self, \n z_dim, \n map_hidden_dim,\n w_dim,\n in_chan,\n out_chan, \n kernel_size, \n hidden_chan):\n super().__init__()\n self.map = MappingLayers(z_dim, map_hidden_dim, w_dim)\n # Typically this constant is initiated to all ones, but you will initiate to a\n # Gaussian to better visualize the network's effect\n self.starting_constant = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1, in_chan, 4, 4))\n self.block0 = MicroStyleGANGeneratorBlock(in_chan, hidden_chan, w_dim, kernel_size, 4, use_upsample=False)\n self.block1 = MicroStyleGANGeneratorBlock(hidden_chan, hidden_chan, w_dim, kernel_size, 8)\n self.block2 = MicroStyleGANGeneratorBlock(hidden_chan, hidden_chan, w_dim, kernel_size, 16)\n # You need to have a way of mapping from the output noise to an image, \n # so you learn a 1x1 convolution to transform the e.g. 512 channels into 3 channels\n # (Note that this is simplified, with clipping used in the real StyleGAN)\n self.block1_to_image = nn.Conv2d(hidden_chan, out_chan, kernel_size=1)\n self.block2_to_image = nn.Conv2d(hidden_chan, out_chan, kernel_size=1)\n self.alpha = 0.2\n\n def upsample_to_match_size(self, smaller_image, bigger_image):\n '''\n Function for upsampling an image to the size of another: Given a two images (smaller and bigger), \n upsamples the first to have the same dimensions as the second.\n Parameters:\n smaller_image: the smaller image to upsample\n bigger_image: the bigger image whose dimensions will be upsampled to\n '''\n return F.interpolate(smaller_image, size=bigger_image.shape[-2:], mode='bilinear')\n\n def forward(self, noise, return_intermediate=False):\n '''\n Function for completing a forward pass of MicroStyleGANGenerator: Given noise, \n computes a StyleGAN iteration.\n Parameters:\n noise: a noise tensor with dimensions (n_samples, z_dim)\n return_intermediate: a boolean, true to return the images as well (for testing) and false otherwise\n '''\n x = self.starting_constant\n w = self.map(noise)\n x = self.block0(x, w)\n x_small = self.block1(x, w) # First generator run output\n x_small_image = self.block1_to_image(x_small)\n x_big = self.block2(x_small, w) # Second generator run output \n x_big_image = self.block2_to_image(x_big)\n x_small_upsample = self.upsample_to_match_size(x_small_image, x_big_image) # Upsample first generator run output to be same size as second generator run output \n # Interpolate between the upsampled image and the image from the generator using alpha\n \n #### START CODE HERE ####\n interpolation = ((1 - self.alpha) * x_small_upsample) + (self.alpha * x_big_image)\n #### END CODE HERE #### \n \n if return_intermediate:\n return interpolation, x_small_upsample, x_big_image\n return interpolation\n \n #UNIT TEST COMMENT: Required for grading\n def get_self(self):\n return self;",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"z_dim = 128\nout_chan = 3\ntruncation = 0.7\n\nmu_stylegan = MicroStyleGANGenerator(\n z_dim=z_dim, \n map_hidden_dim=1024,\n w_dim=496,\n in_chan=512,\n out_chan=out_chan, \n kernel_size=3, \n hidden_chan=256\n)\n\ntest_samples = 10\ntest_result = mu_stylegan(get_truncated_noise(test_samples, z_dim, truncation))\n\n# Check if the block works\nassert tuple(test_result.shape) == (test_samples, out_chan, 16, 16)\n\n# Check that the interpolation is correct\nmu_stylegan.alpha = 1.\ntest_result, _, test_big = mu_stylegan(\n get_truncated_noise(test_samples, z_dim, truncation), \n return_intermediate=True)\nassert torch.abs(test_result - test_big).mean() < 0.001\nmu_stylegan.alpha = 0.\ntest_result, test_small, _ = mu_stylegan(\n get_truncated_noise(test_samples, z_dim, truncation), \n return_intermediate=True)\nassert torch.abs(test_result - test_small).mean() < 0.001\nprint(\"Success!\")",
"Success!\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Running StyleGAN\nFinally, you can put all the components together to run an iteration of your micro StyleGAN!\n\nYou can also visualize what this randomly initiated generator can produce. The code will automatically interpolate between different values of alpha so that you can intuitively see what it means to mix the low-resolution and high-resolution images using different values of alpha. In the generated image, the samples start from low alpha values and go to high alpha values.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nfrom torchvision.utils import make_grid\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nplt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [15, 15]\n\nviz_samples = 10\n# The noise is exaggerated for visual effect\nviz_noise = get_truncated_noise(viz_samples, z_dim, truncation) * 10\n\nmu_stylegan.eval()\nimages = []\nfor alpha in np.linspace(0, 1, num=5):\n mu_stylegan.alpha = alpha\n viz_result, _, _ = mu_stylegan(\n viz_noise, \n return_intermediate=True)\n images += [tensor for tensor in viz_result]\nshow_tensor_images(torch.stack(images), nrow=viz_samples, num_images=len(images))\nmu_stylegan = mu_stylegan.train()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4abafe70665995c088e3586df74badbe633907f2
| 1,495 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
May21/investment_calulator/investment.ipynb
|
pythonbykhaja/intesivepython
|
d3074f35bf36a04d4d1d9b4ff4631733d40b5817
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 2 |
2021-05-29T18:21:50.000Z
|
2021-07-24T13:03:30.000Z
|
May21/investment_calulator/investment.ipynb
|
pythonbykhaja/intesivepython
|
d3074f35bf36a04d4d1d9b4ff4631733d40b5817
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
May21/investment_calulator/investment.ipynb
|
pythonbykhaja/intesivepython
|
d3074f35bf36a04d4d1d9b4ff4631733d40b5817
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 2 |
2021-05-25T10:19:54.000Z
|
2021-09-21T12:20:48.000Z
| 24.112903 | 99 | 0.598662 |
[
[
[
"principal = 1000000\nfd_rate_of_intrest = 5.5\nmf_rate_of_intrest = 7.5\nperiod_in_years = 2\nfd_after_period = principal * (1+ fd_rate_of_intrest/100)** period_in_years\nmf_after_period = principal * (1+ mf_rate_of_intrest/100)** period_in_years\n\nprint(f\"FD after {period_in_years} years is {fd_after_period}\")\nprint(f\"MF after {period_in_years} years is {mf_after_period}\")",
"FD after 2 years is 1113025.0\nMF after 2 years is 1155625.0\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
]
] |
4abb07fb02cc29f4a1fcd98cc3c2f797a8f098f4
| 125,747 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
tests/test.ipynb
|
nivlekp/abjad-ext-ipython
|
dc3fbae6ec54b9ba1cf9af7e8ae97def33555151
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
tests/test.ipynb
|
nivlekp/abjad-ext-ipython
|
dc3fbae6ec54b9ba1cf9af7e8ae97def33555151
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
tests/test.ipynb
|
nivlekp/abjad-ext-ipython
|
dc3fbae6ec54b9ba1cf9af7e8ae97def33555151
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 1,093.452174 | 117,495 | 0.971634 |
[
[
[
"import abjad",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%load_ext abjadext.ipython",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"staff = abjad.Staff(\"c'4 d'4 e'4 f'4\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"abjad.show(staff)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"abjad.graph(staff)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"abjad.play(staff)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4abb1069e9de1de04138bfbbc65e7d0fd28efe4e
| 1,259 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
cw1_22.03.2022.ipynb
|
K4cp3rski/Julia_Lang
|
8bffd583a208207da1c458a56d70be294fbc0219
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
cw1_22.03.2022.ipynb
|
K4cp3rski/Julia_Lang
|
8bffd583a208207da1c458a56d70be294fbc0219
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
cw1_22.03.2022.ipynb
|
K4cp3rski/Julia_Lang
|
8bffd583a208207da1c458a56d70be294fbc0219
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 19.075758 | 76 | 0.520254 |
[
[
[
"empty"
]
]
] |
[
"empty"
] |
[
[
"empty"
]
] |
4abb11e4c275afb21d2d6e9ffdc5cfde57a700cb
| 55,542 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
lect01_git_basic_types/2021_DPO_1_1_Data_types.ipynb
|
weqrwer/Python_DPO_2021_fall
|
8558ed2c1a744638f693ad036cfafccd1a05f392
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
lect01_git_basic_types/2021_DPO_1_1_Data_types.ipynb
|
weqrwer/Python_DPO_2021_fall
|
8558ed2c1a744638f693ad036cfafccd1a05f392
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
lect01_git_basic_types/2021_DPO_1_1_Data_types.ipynb
|
weqrwer/Python_DPO_2021_fall
|
8558ed2c1a744638f693ad036cfafccd1a05f392
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 22.94176 | 621 | 0.52526 |
[
[
[
"Центр непрерывного образования\n\n# Программа «Python для автоматизации и анализа данных»\n\nНеделя 1 - 1\n\n*Татьяна Рогович, НИУ ВШЭ*\n\n## Введение в Python. Целые и вещественные числа. Логические переменные.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Функция print()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"С помощью Python можно решать огромное количество задач. Мы начнем с очень простых и постепенно будем их усложнять, закончив наш курс небольшим проектом. Если вы уже сталкивались с программированием, то вы помните, что обычно самой первой программой становится вывод \"Hello, world\". Попробуем сделать это в Python.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"a = 1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a = 2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a + 2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a = a + 2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a += 2 # a = a + 2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a -= 2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a *= 2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"b = a",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"c",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(a)",
"28\n"
],
[
"print('Hello, world!')\nprint(1)",
"Hello, world!\n1\n"
]
],
[
[
"Обратите внимание, что \"Hello, world!\" мы написали в кавычках, а единицу - нет. Это связанно с тем,\nчто в программировании мы имеем дело с разными типами данных. И Python будет воспринимать текст как текст (строковую переменную), только в том случае, если мы его возьмем в кавычки (неважно, одинарные или двойные). А при выводе эти кавычки отображаться уже не будут (они служат знаком для Python, что внутри них - текст).\n\nprint() - это функция, которая выводит то, что мы ей передадим. В других IDE это был бы вывод в терминал, а в Jupyter вывод напечатается под запускаемой ячейкой. Распознать функцию в питоне можно по скобкам после слова, внутри которых мы передаем аргумент, к которому эту функцию нужно применить (текст \"Hello, world\" или 1 в нашем случае). ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(Hello, world)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Написали без кавычек - получили ошибку. Кстати, обратите внимание, что очень часто в тексте ошибки есть указание на то, что именно произошло, и можно попробовать догадаться, что же нужно исправить. Текст без кавычек Python воспринимает как название переменной, которую еще не задали. Кстати, если забыть закрыть или открыть кавычку (или поставить разные), то тоже поймаем ошибку.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\nИногда мы хотим комментировать наш код, чтобы я-будущий или наши коллеги поменьше задавались вопросами, а что вообще имелось ввиду. Комментарии можно писать прямо в коде, они не повлияют на работу программы, если их правильно оформить.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Обратите внимание: так выглядит комментарий - часть скрипта, которая не будет исполнена \n# при запуске программы.\n# Каждую строку комментария мы начинаем со знака хэштега.\n\n'''\nЭто тоже комментарий - обычно выделение тремя апострофами мы используем для тех случаев, \nкогда хотим написать длинный, развернутый текст.\n'''\n\nprint('Hello, world')",
"Hello, world\n"
]
],
[
[
"Обратите внимание, что в отличие от других IDE (например, PyCharm) в Jupyter Notebook не всегда обязательно использовать print(), чтобы что-то вывести. Но не относитесь к этому как к стандарту для любых IDE.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\"Hello, world\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Выше рядом с выводом появилась подпись Out[]. В данном случае Jupyter показывает нам последнее значение, лежащее в буфере ячейки. Например, в PyCharm такой вывод всегда будет скрыт, пока мы его не \"напечатаем\" с помощью print(). Но эта особенность Jupyter помогает нам быстро проверить, что, например, находится внутри переменной, когда мы отлаживаем наш код.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Следующая вещь, которую нужно знать про язык программирования - как в нем задаются переменные. Переменные - это \nконтейнеры, которые хранят в себе информацию (текстовую, числовую, какие-то более сложные виды данных). В Python\nзнаком присвоения является знак =. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x = 'Hello, world!'\nprint(x) # Обратите внимание, что результат вызова этой функции такой же, как выше, \n # только текст теперь хранится внутри переменной.",
"Hello, world!\n"
]
],
[
[
"Python - язык чувствительный к регистру. Поэтому, когда создаете/вызываете переменные или функции, обязательно используйте правильный регистр. Так, следующая строка выдаст ошибку.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(X) # мы создали переменную x, а X не существует",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Еще раз обратим внимание на ошибку. *NameError: name 'X' is not defined* означает, что переменная с таким названием не была создана в этой программе. Кстати, обратите внимание, что переменные в Jupyter хранятся на протяжении всей сессии (пока вы работаете с блокнотом и не закрыли его), и могут быть созданы в одной ячейке, а вызваны в другой. Давайте опять попробуем обратиться к x.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(x) # работает!",
"Hello, world!\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Типы данных: целочисленные переменные (integer)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Знакомство с типа данных мы начнем с целых чисел. Если вы вдруг знакомы с другими языками программирования, то стоит отметить, что типизация в Python - динамическая. Это значит, что вам не нужно говорить какой тип данных вы хотите положить в переменную - Python сам все определит. Проверить тип данных можно с помощью функции type(), передав ей в качестве аргумента сами данные или переменную.\n\n**ЦЕЛЫЕ ЧИСЛА (INT, INTEGER):** 1, 2, 592, 1030523235 - любое целое число без дробной части. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"10",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"100",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"type(100)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"5 / 2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"type(2.5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"type(1.0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"int(1.0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"type(int(1.0))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"float(2)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"y = 2\nprint(type(2))\nprint(type(y))",
"<class 'int'>\n<class 'int'>\n"
]
],
[
[
"Обратите внимание - выше мы вызвали функцию внутри функции. \ntype(2) возвращает скрытое значение типа переменной (int для integer). \nЧтобы вывести это скрытое значение - мы должны его \"напечатать\".\n\nСамое элементарное, что можно делать в Python - использовать его как калькулятор. Давайте посмотрим, как\nон вычитает, складывает и умножает.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(2 + 2)\nprint(18 - 9)\nprint(4 * 3)",
"4\n9\n12\n"
]
],
[
[
"С делением нужно быть немного осторожней. Существует два типа деления - привычное нам, которое даст в ответе дробь при делении 5 на 2, и целочисленное деление, в результате которого мы получим только целую часть частного.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(5 / 2) # в результате такого деления получается другой тип данных (float), подробнее о нем поговорим позже.\nprint(5 // 2)",
"2.5\n2\n"
]
],
[
[
"А если нам надо как раз найти остаток от деления, то мы можем воспользоваться оператором модуло %\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(5 % 2)",
"1\n"
]
],
[
[
"Еще одна математическая операция, которую мы можем выполнять без загрузки специальных математических библиотек - это\nвозведение в степень.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(5**2)",
"25\n"
]
],
[
[
"Все то же самое работает и с переменными, содержащими числа.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"a = 2\nb = 3\nprint(a ** b)\n# изменится ли результат, если мы перезапишем переменную a?\na = 5\nprint(a ** b)",
"8\n125\n"
]
],
[
[
"Часто возникает ситуация, что мы считали какие-то данные в формате текста, и у нас не работают арифметические операции. Тогда мы можем с помощью функции int() преобразовать строковую переменную (о них ниже) в число, если эта строка может быть переведена в число в десятичной системе.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(2 + '5') # ошибка, не сможем сложить целое число и строку",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(2 + int('5')) # преобразовали строку в число и все заработало",
"7\n"
],
[
"int('текст') # здесь тоже поймаем ошибку, потому что строка не представляет собой число",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## (∩`-´)⊃━☆゚.*・。゚ Задача\n\n### Сумма цифр трехзначного числа\n\nДано трехзначное число 179. Найдите сумму его цифр.\n\n**Формат вывода** \nВыведите ответ на задачу.\n\n**Ответ** \nВывод программы: \n17",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# (∩`-´)⊃━☆゚.*・。゚\n\nx = int(input())\nx_1 = x // 100\nx_2 = x // 10 % 10\nx_3 = x % 10\n# print(x_1, x_2, x_3) # тестовый вывод, проверяем, что правильно \"достали\" цифры из числа\nprint(x_1 + x_2 + x_3) # ответ на задачу",
"2 8 3\n13\n"
],
[
"x = int(input())",
"12\n"
],
[
"int(12.5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"type(x)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"179 // 100",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"179 // 10",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"17 % 10 ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## (∩`-´)⊃━☆゚.*・。゚ Задача\n\n### Электронные часы\n\nДано число N. С начала суток прошло N минут. Определите, сколько часов и минут будут показывать электронные часы в этот момент.\n\n**Формат ввода** \n\nВводится число N — целое, положительное, не превышает 10⁷.\n\n**Формат вывода**\n\nПрограмма должна вывести два числа: количество часов (от 0 до 23) и количество минут (от 0 до 59).\n\nУчтите, что число N может быть больше, чем количество минут в сутках.\n\n#### Примеры\n\nТест 1 \n**Входные данные:** \n150\n\n**Вывод программы:** \n2 30",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# (∩`-´)⊃━☆゚.*・。゚\n\nminutes = int(input())\n\nprint(minutes // 60 % 24, minutes % 60)",
"1000\n16 40\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Типы данных: логические или булевы переменные (boolean)\n\nСледующий тип данных - это логические переменные. Логические переменные могут принимать всего два значения - **истина (True)** или **ложь (False)**. В Python тип обознчается **bool**.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(type(True), type(False))",
"<class 'bool'> <class 'bool'>\n"
],
[
"type(True)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Логические переменные чаще всего используется в условных операторах if-else и в цикле с остановкой по условию while. В части по анализу данных еще увидим одно частое применение - создание булевых масок для фильтрации данных (например, вывести только те данные, где возраст больше 20).\n\nОбратите внимание, что True и False обязательно пишутся с большой буквы и без кавычек, иначе можно получить ошибку.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(type('True')) # тип str - строковая переменная\nprint(true) # ошибка, Python думает, что это название переменной",
"<class 'str'>\n"
]
],
[
[
"Как и в случае чисел и строк, с логическими переменными работает преобразование типов. Превратить что-либо в логическую переменную можно с помощью функции bool().\n\nПреобразование чисел работает следующим образом - 0 превращается в False, все остальное в True.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"int(2.45)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"float(3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"float('2.5')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"bool(0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"bool(1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(bool(0))\nprint(bool(23))\nprint(bool(-10))",
"False\nTrue\nTrue\n"
]
],
[
[
"Пустая строка преобразуется в False, все остальные строки в True.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(bool(''))\nprint(bool('Hello'))\nprint(bool(' ')) # даже строка из одного пробела - это True\nprint(bool('False')) # и даже строка 'False' - это True",
"False\nTrue\nTrue\nTrue\n"
]
],
[
[
"И при необходимости булеву переменную можно конвертировать в int. Тут все без сюрпризов - ноль и единица.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(int(True))\nprint(int(False))",
"1\n0\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Логические выражения\n\nДавайте посмотрим, где используется новый тип данных.\n\nМы поработаем с логическими выражениями, результат которых - булевы переменные.\n\nЛогические выражения выполняют проверку на истинность, то есть выражение равно True, если оно истинно, и False, если ложно.\n\nВ логических выражениях используются операторы сравнения:\n* == (равно)\n* != (не равно)\n* \\> (больше)\n* < (меньше)\n* \\>= (больше или равно)\n* <= (меньше или равно)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"5 == 5",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a = 5",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a == 5",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"5 != 5",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"1 < 3 < 5 == 7",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"1 < 3 < 5 < 7",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(1 == 1)\nprint(1 != '1') \nc = 1 > 3\nprint(c)\nprint(type(c))\nx = 5\nprint(1 < x <= 5) # можно писать связки цепочкой",
"True\nTrue\nFalse\n<class 'bool'>\nTrue\n"
]
],
[
[
"Логические выражения можно комбинировать с помощью следующих логических операторов:\n\n* логическое И (and) - выражение истинно, только когда обе части истинны, иначе оно ложно\n* логическое ИЛИ (or) - выражение ложно, только когда обе части ложны, иначе оно истинно\n* логическое отрицание (not) - превращает True в False и наоборот",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print((1 == 1) and ('1' == 1))\nprint((1 == 1) or ('1' == 1))\nprint(not(1 == 1))\nprint(((1 == 1) or ('1' == 1)) and (2 == 2))",
"False\nTrue\nFalse\nTrue\n"
]
],
[
[
"## (∩`-´)⊃━☆゚.*・。゚ Задача\n## Вася в Италии\n\nВася уехал учиться по обмену на один семестр в Италию. Единственный магазин в городе открыт с 6 до 8 утра и с 16 до 17 вечера (включительно). Вася не мог попасть в магазин уже несколько дней и страдает от голода. Он может прийти в магазин в X часов. Если магазин открыт в X часов, то выведите True, а если закрыт - выведите False.\n\nВ единственной строке входных данных вводится целое число X, число находится в пределах от 0 до 23\n\n**Формат ввода** \n\nЦелое число X, число находится в пределах от 0 до 23\n\n**Формат вывода**\n\nTrue или False\n\n#### Примеры\n\nТест 1 \n**Входные данные:** \n16\n\n**Вывод программы:** \nTrue",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## (∩`-´)⊃━☆゚.*・。゚ \n\ntime = 16\ncan_visit = 6 <= time <= 8\ncan_visit2 = 16 <= time <= 17\nprint(can_visit or can_visit2)",
"True\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Типы данных: вещественные числа (float)\n\nПо сути, вещественные числа это десятичные дроби, записанные через точку. Вещественные числа в питоне обозначаются словом float (от \"плавающей\" точки в них). Также могут быть представлены в виде инженерной записи: 1/10000 = 1e-05\n\n**ВЕЩЕСТВЕННЫЕ ЧИСЛА (FLOAT):** 3.42, 2.323212, 3.0, 1e-05 - число с дробной частью (в том числе целое с дробной частью равной 0)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"4.5 + 5",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Если у нас было действие с участие целого и вещественного числа, то ответ всегда будет в виде вещественного числа (см. выше).\n\nТакже давайте вспомним про \"обычное\" деление, в результате которого получается вещественное число.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(11 / 2)\nprint(type(11 / 2))\nprint(11 // 2)\nprint(type(11 // 2))",
"5.5\n<class 'float'>\n5\n<class 'int'>\n"
]
],
[
[
"С вещественными числами нужно быть осторожными со сравнениями. В связи с особенностями устройства памяти компьютера дробные числа хранятся там весьма хитро и не всегда условные 0.2 то, чем кажутся. Это связано с проблемой точности представления чисел.\n\nПодробнее можно прочитать [здесь](https://pythoner.name/documentation/tutorial/floatingpoint).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"0.2 + 0.1 == 0.3",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"0.4 - 0.3 == 0.1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x = 0.4 - 0.3\nx",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x == 0.10000000000000003",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"0 <= x - 0.1 < 0.0001",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Наверняка, от такого равенства мы ожидали результат True, но нет. Поэтому будьте аккуратны и старайтесь не \"завязывать\" работу вашей программы на условия, связанные с вычислением вещественных чисел. Давайте посмотрим, как на самом деле выглядят эти числа в памяти компьютера.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(0.2 + 0.1)\nprint(0.3)",
"0.30000000000000004\n0.3\n"
]
],
[
[
"Числа с плавающей точкой представлены в компьютерном железе как дроби с основанием 2 (двоичная система счисления). Например, десятичная дробь\n\n0.125 \nимеет значение 1/10 + 2/100 + 5/1000, и таким же образом двоичная дробь\n\n0.001 \nимеет значение 0/2 + 0/4 + 1/8. Эти две дроби имеют одинаковые значения, отличаются только тем, что первая записана в дробной нотации по основанию 10, а вторая по основанию 2.\n\nК сожалению, большинство десятичных дробей не могут быть точно представлены в двоичной записи. Следствием этого является то, что в основном десятичные дробные числа вы вводите только приближенными к двоичным, которые и сохраняются в компьютере.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Если вам совсем не обойтись без такого сравнения, то можно сделать так: сравнивать не результат сложения и числа, а разность эти двух чисел с каким-то очень маленьким числом (с таким, размер которого будет точно не критичен для нашего вычисления). Например, порог это числа будет разным для каких-то физических вычислений, где важна высокая точность, и сравнения доходов граждан.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"0.2 + 0.1 - 0.3 < 0.000001",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"0.2 + 0.1 - 0.3 < 1e-16",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Следующая проблема, с которой можно столкнуться - вместо результата вычисления получить ошибку 'Result too large'. Cвязано это с ограничением выделяемой памяти на хранение вещественного числа.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"1.5 ** 100000",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"1.5 ** 1000",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"А если все получилось, то ответ еще может выглядеть вот так. Такая запись числа называется научной и экономит место - она хранит целую часть числа (мантисса) и степень десятки на которую это число нужно умножить (экспонента). Здесь результатом возведения 1.5 в степень 1000 будет число 1.2338405969061735, умноженное на 10 в степень 176. Понятно, что это число очень большое. Если бы вместо знакак + стоял -, то и степень десятки была бы отрицательная (10 в -176 степени), и такое число было бы очень, очень маленьким.\n\nКак и в случае с целыми числами, вы можете перевести строку в вещественное число, если это возможно. Сделать это можно фукнцией float()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(2.5 + float('2.4'))",
"4.9\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Округление вещественных чисел",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"У нас часто возникает необходимость превратить вещественное число в целое (\"округлить\"). В питоне есть несколько способов это сделать, но, к сожалению, ни один из них не работает как наше привычное округление и про это всегда нужно помнить.\n\nБольшинство этих функций не реализованы в базовом наборе команд питона и для того, чтобы ими пользоваться, нам придется загрузить дополнительную библиотеку math, которая содержит всякие специальные функции для математических вычислений.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import math # команда import загружает модуль под названием math",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"math.ceil(2.3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import math as mh",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mh.ceil(2.1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from math import ceil",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ceil(3.1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"math.floor(3.8)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# !pip install math",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Модуль math устанавливается в рамках дистрибутива Anaconda, который мы использовали, чтобы установить Jupyter Notebook, поэтому его не нужно отдельно скачивать, а можно просто импортировать (загрузить в оперативную память текущей сессии). Иногда нужную библиотеку придется сначала установить на компьютер с помощью команды !pip install -название модуля- и только потом импортировать.\n\nСамый простой способ округлить число - применить к нему функцию int.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"int(2.6)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"int(2.1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Обратите внимание, что такой метод просто обрубает дробную часть (значения выше 0.5 не округляются в сторону большего числа).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(int(2.6))\nprint(int(-2.6))",
"2\n-2\n"
]
],
[
[
"Округление \"в пол\" из модуля math округляет до ближайшего меньшего целого числа.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(math.floor(2.6)) # чтобы использовать функцю из дополнительного модуля - \n # нужно сначала написать название этого модуля и через точку название функции\nprint(math.floor(-2.6))",
"2\n-3\n"
]
],
[
[
"Округление \"в потолок\" работает ровно наоброт - округляет до ближайшего большего числа, независимо от значения дробной части.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(math.ceil(2.6))\nprint(math.ceil(-2.6))",
"3\n-2\n"
]
],
[
[
"В самом питоне есть еще функция round(). Вот она работает почти привычно нам, если бы не одно \"но\"...",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(round(2.2))\nprint(round(2.7))\nprint(round(2.5)) # внимание на эту строку\nprint(round(3.5))",
"2\n3\n2\n4\n"
]
],
[
[
"Неожиданно? Тут дело в том, что в питоне реализованы не совсем привычные нам правила округления чисел с вещественной частью 0.5 - такое число округляется до ближайшего четного числа: 2 для 2.5 и 4 для 3.5.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Замечание по импорту функций\nИногда нам не нужна вся библиотека, а только одна функция из-за нее. Скажите, странно же хранить в опреативной памяти всю \"Войну и мир\", если нас интересует только пятое предложение на восьмой странице.\nДля этого можно воспользоваться импортом функции из библиотеки и тогда не нужно будет писать ее название через точку. Подводный камень здесь только тот, что если среди базовых команд питона есть функция с таким же именем, то она перезапишется и придется перезапускать свой блокнот, чтобы вернуть все как было.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from math import ceil\nceil(2.6) # теперь работает без math.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## (∩`-´)⊃━☆゚.*・。゚ Задача\n## Дробная часть\n\nДано вещественное число. Выведите его дробную часть.\n\n**Формат ввода** \n\nВещественное число\n\n**Формат вывода**\n\nВещественное число (ответ на задачу)\n\n#### Примеры\n\nТест 1 \n**Входные данные:** \n4.0\n\n**Вывод программы:** \n0.0",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# (∩`-´)⊃━☆゚.*・。゚\nx = 4.0\nprint(x - int(x))\n\nx = 5.2\nprint(x - int(x))",
"0.0\n0.20000000000000018\n"
],
[
"!pip install wikipedia",
"Requirement already satisfied: wikipedia in /Users/a18509896/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.8/site-packages (1.4.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: beautifulsoup4 in /Users/a18509896/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.8/site-packages (from wikipedia) (4.9.3)\nRequirement already satisfied: requests<3.0.0,>=2.0.0 in /Users/a18509896/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.8/site-packages (from wikipedia) (2.25.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: soupsieve>1.2; python_version >= \"3.0\" in /Users/a18509896/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.8/site-packages (from beautifulsoup4->wikipedia) (2.0.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: certifi>=2017.4.17 in /Users/a18509896/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.8/site-packages (from requests<3.0.0,>=2.0.0->wikipedia) (2020.6.20)\nRequirement already satisfied: urllib3<1.27,>=1.21.1 in /Users/a18509896/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.8/site-packages (from requests<3.0.0,>=2.0.0->wikipedia) (1.26.4)\nRequirement already satisfied: idna<3,>=2.5 in /Users/a18509896/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.8/site-packages (from requests<3.0.0,>=2.0.0->wikipedia) (2.10)\nRequirement already satisfied: chardet<5,>=3.0.2 in /Users/a18509896/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.8/site-packages (from requests<3.0.0,>=2.0.0->wikipedia) (3.0.4)\n"
],
[
"import wikipedia",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"wikipedia.search(\"Barack\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a = input()",
"\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4abb18d07ff853291e468efbcc505aef4232fc98
| 9,833 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
BatchNorm_from_scratch.ipynb
|
poodarchu/gluon_step_by_step
|
5c98a057f1ef0b30dfbe47fa7b6bc7e667e0bb3b
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2018-04-03T07:03:01.000Z
|
2018-04-03T07:03:01.000Z
|
BatchNorm_from_scratch.ipynb
|
poodarchu/gluon_step_by_step
|
5c98a057f1ef0b30dfbe47fa7b6bc7e667e0bb3b
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
BatchNorm_from_scratch.ipynb
|
poodarchu/gluon_step_by_step
|
5c98a057f1ef0b30dfbe47fa7b6bc7e667e0bb3b
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 29.528529 | 95 | 0.497915 |
[
[
[
"from mxnet import nd",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def pure_batch_norm(X, gamma, beta, eps=1e-5):\n assert len(X.shape) in (2, 4)\n # 全连接: batch_size x feature\n if len(X.shape) == 2:\n # 每个输入维度在样本上的平均和方差\n mean = X.mean(axis=0)\n variance = ((X - mean)**2).mean(axis=0)\n # 2D卷积: batch_size x channel x height x width\n else:\n # 对每个通道算均值和方差,需要保持4D形状使得可以正确地广播\n mean = X.mean(axis=(0,2,3), keepdims=True)\n variance = ((X - mean)**2).mean(axis=(0,2,3), keepdims=True)\n\n # 均一化\n X_hat = (X - mean) / nd.sqrt(variance + eps)\n # 拉升和偏移\n print(X_hat.shape)\n print(mean.shape)\n return gamma.reshape(mean.shape) * X_hat + beta.reshape(mean.shape)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"A = nd.arange(6).reshape((3,2))\npure_batch_norm(A, gamma=nd.array([1, 1]), beta=nd.array([0, 0]))",
"(3, 2)\n(2,)\n"
],
[
"B = nd.arange(18).reshape((1,2,3,3))\npure_batch_norm(B, gamma=nd.array([1,1]), beta=nd.array([0,0]))",
"(1, 2, 3, 3)\n(1, 2, 1, 1)\n"
],
[
"# 在训练时,计算整个 batch 上的均值和方差\n# 在测试时,计算整个数据集的均值方差,当训练数据量极大时,使用 moving average 近似计算\ndef batch_norm(X, gamma, beta, is_training, moving_mean, moving_variance,\n eps = 1e-5, moving_momentum = 0.9):\n assert len(X.shape) in (2, 4)\n # 全连接: batch_size x feature\n if len(X.shape) == 2:\n # 每个输入维度在样本上的平均和方差\n mean = X.mean(axis=0)\n variance = ((X - mean)**2).mean(axis=0)\n # 2D卷积: batch_size x channel x height x width\n else:\n # 对每个通道算均值和方差,需要保持4D形状使得可以正确的广播\n mean = X.mean(axis=(0,2,3), keepdims=True)\n variance = ((X - mean)**2).mean(axis=(0,2,3), keepdims=True)\n # 变形使得可以正确的广播\n moving_mean = moving_mean.reshape(mean.shape)\n moving_variance = moving_variance.reshape(mean.shape)\n\n # 均一化\n if is_training:\n X_hat = (X - mean) / nd.sqrt(variance + eps)\n #!!! 更新全局的均值和方差\n moving_mean[:] = moving_momentum * moving_mean + (\n 1.0 - moving_momentum) * mean\n moving_variance[:] = moving_momentum * moving_variance + (\n 1.0 - moving_momentum) * variance\n else:\n #!!! 测试阶段使用全局的均值和方差\n X_hat = (X - moving_mean) / nd.sqrt(moving_variance + eps)\n\n # 拉升和偏移\n return gamma.reshape(mean.shape) * X_hat + beta.reshape(mean.shape)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 定义模型",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import sys\nsys.path.append('..')\nimport utils\nctx = utils.try_gpu()\nctx",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"weight_scale = 0.01\n\n# 输出通道 = 20, 卷积核 = (5,5)\nc1 = 20\nW1 = nd.random.normal(shape=(c1,1,5,5), scale=weight_scale, ctx=ctx)\nb1 = nd.zeros(c1, ctx=ctx)\n\n# 第1层批量归一化\ngamma1 = nd.random.normal(shape=c1, scale=weight_scale, ctx=ctx)\nbeta1 = nd.random.normal(shape=c1, scale=weight_scale, ctx=ctx)\nmoving_mean1 = nd.zeros(c1, ctx=ctx)\nmoving_variance1 = nd.zeros(c1, ctx=ctx)\n\n# 输出通道 = 50, 卷积核 = (3,3)\nc2 = 50\nW2 = nd.random_normal(shape=(c2,c1,3,3), scale=weight_scale, ctx=ctx)\nb2 = nd.zeros(c2, ctx=ctx)\n\n# 第2层批量归一化\ngamma2 = nd.random.normal(shape=c2, scale=weight_scale, ctx=ctx)\nbeta2 = nd.random.normal(shape=c2, scale=weight_scale, ctx=ctx)\nmoving_mean2 = nd.zeros(c2, ctx=ctx)\nmoving_variance2 = nd.zeros(c2, ctx=ctx)\n\n# 输出维度 = 128\no3 = 128\nW3 = nd.random.normal(shape=(1250, o3), scale=weight_scale, ctx=ctx)\nb3 = nd.zeros(o3, ctx=ctx)\n\n# 输出维度 = 10\nW4 = nd.random_normal(shape=(W3.shape[1], 10), scale=weight_scale, ctx=ctx)\nb4 = nd.zeros(W4.shape[1], ctx=ctx)\n\n# 注意这里moving_*是不需要更新的\nparams = [W1, b1, gamma1, beta1,\n W2, b2, gamma2, beta2,\n W3, b3, W4, b4]\n\nfor param in params:\n param.attach_grad()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# BatchNorm 添加的位置: 卷积层之后,激活函数之前\ndef net(X, is_training=False, verbose=False):\n X = X.as_in_context(W1.context)\n # 第一层卷积\n h1_conv = nd.Convolution(\n data=X, weight=W1, bias=b1, kernel=W1.shape[2:], num_filter=c1)\n ### 添加了批量归一化层\n h1_bn = batch_norm(h1_conv, gamma1, beta1, is_training,\n moving_mean1, moving_variance1)\n h1_activation = nd.relu(h1_bn)\n h1 = nd.Pooling(\n data=h1_activation, pool_type=\"max\", kernel=(2,2), stride=(2,2))\n # 第二层卷积\n h2_conv = nd.Convolution(\n data=h1, weight=W2, bias=b2, kernel=W2.shape[2:], num_filter=c2)\n ### 添加了批量归一化层\n h2_bn = batch_norm(h2_conv, gamma2, beta2, is_training,\n moving_mean2, moving_variance2)\n h2_activation = nd.relu(h2_bn)\n h2 = nd.Pooling(data=h2_activation, pool_type=\"max\", kernel=(2,2), stride=(2,2))\n h2 = nd.flatten(h2)\n # 第一层全连接\n h3_linear = nd.dot(h2, W3) + b3\n h3 = nd.relu(h3_linear)\n # 第二层全连接\n h4_linear = nd.dot(h3, W4) + b4\n if verbose:\n print('1st conv block:', h1.shape)\n print('2nd conv block:', h2.shape)\n print('1st dense:', h3.shape)\n print('2nd dense:', h4_linear.shape)\n print('output:', h4_linear)\n return h4_linear",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from mxnet import autograd\nfrom mxnet import gluon\n\nbatch_size = 256\ntrain_data, test_data = utils.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size)\n\nsoftmax_cross_entropy = gluon.loss.SoftmaxCrossEntropyLoss()\n\nlearning_rate = 0.2\n\nfor epoch in range(5):\n train_loss = 0.\n train_acc = 0.\n for data, label in train_data:\n label = label.as_in_context(ctx)\n with autograd.record():\n output = net(data, is_training=True)\n loss = softmax_cross_entropy(output, label)\n loss.backward()\n utils.SGD(params, learning_rate/batch_size)\n\n train_loss += nd.mean(loss).asscalar()\n train_acc += utils.accuracy(output, label)\n\n test_acc = utils.evaluate_accuracy(test_data, net, ctx)\n print(\"Epoch %d. Loss: %f, Train acc %f, Test acc %f\" % (\n epoch, train_loss/len(train_data), train_acc/len(train_data), test_acc))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4abb21b0b452ffa4c3c249c3a57595a2de46b989
| 587,638 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Data_Science_projects/Blog_Google_Analytics/Report.ipynb
|
wguesdon/Data_Science_portfolio
|
7530fe3841c948c1c021c6061803195e5f9873c9
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-02-11T08:34:23.000Z
|
2021-02-11T08:34:23.000Z
|
Data_Science_projects/Blog_Google_Analytics/Report.ipynb
|
wguesdon/Data_Science_portfolio
|
7530fe3841c948c1c021c6061803195e5f9873c9
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-02-11T06:41:59.000Z
|
2021-02-11T09:51:47.000Z
|
Data_Science_projects/Blog_Google_Analytics/Report.ipynb
|
wguesdon/Data_Science_portfolio
|
7530fe3841c948c1c021c6061803195e5f9873c9
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 520.955674 | 230,778 | 0.929788 |
[
[
[
"<a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/wguesdon/BrainPost_google_analytics/blob/master/Report_v01_02.ipynb\" target=\"_parent\"><img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open In Colab\"/></a>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Project Presentation",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## About BrainPost\n\nKasey Hemington runs BrainPost with a fellow PhD friend, Leigh Christopher as a way to keep in touch with her scientific roots while working as a data scientist! Every Tuesday since we started in early 2018, we publish our e-newsletter which is three short summaries of new neuroscience studies that have just come out. After publishing on our website each Tuesday, we typically post on Twitter (@brainpostco) and Facebook (@brainpostco) once to announce the release of the e-newsletter and three times (once for each of the three summaries) to highlight each summary. There are a few exceptions to our publishing schedule. Sometimes we post extra articles here: https://www.brainpost.co/brainpost-life-hacks, and also a few weeks we've only been able to publish two summaries instead of three. At around the same time as we publish the e-newsletter on the website each Tuesday, we also send it to our ~1700 email subscribers directly (via mailchimp).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## About the Challenge\n\nWe're always wondering if we should change what type of content we're publishing, and how people are finding us. From some small surveys we've done for example, we find people would be interested in more casual/applicable to daily life content (like we publish on this tab https://www.brainpost.co/brainpost-life-hacks) than more technical summaries of complex articles, but we also aren't really sure if that's just a subgroup of people who get the e-newsletter to their email inbox filling out the survey. We also might have two audiences - academics and non-academics (?) who like different things.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## About the data\n\nIn the remaining tabs of this workbook there is weekly pageview data for each page on the website (I think..according to our google analytics). Each tab represents pageview data for two one week periods, split up by the page name/URL and the source/medium (first two columns). My general idea was people can look at the data at a weekly cadence and figure out stats about different pages/content, BUT with google analytics a huge problem is that it doesn't really take into account that different content is published on different days (for example, a stat about 'only 2 pageviews' to a page is meaningless to me if it is because the page was only published an hour ago). Our content is published weekly so it should approximately match that I extracted the data weekly. My apologies for the formatting... Google analytics was a nightmare to extract from - a very manual process. But, I guess data cleaning is a part of the process! So, we've been publishing ~3 new pages a week since 2018, but I've only included data starting in July 2020 because the data extraction process is so manual. The date of publication can be extracted from the URL.\n\nWe've noticed some pages seem really popular possibly for strange reasons (maybe they come up on the first page of google because people are searching for something really similar?) and those anomalies might not reflect what people like overall about the site.\n\nThere is also a tab with a page (URL) to page title lookup",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## The questions we'd like to ask\n\nWhat content (or types of content) is most popular (what are patterns we see in popular content) and is different content popular amongst different subgroups (e.g. by source/medium)?\n\nAny question that will help us to take action to better tailor our content to our audience(s) or understand how traffic comes to the site.\n\nWhere are people visiting from (source-wise)?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## How this challenge works:\n\nJust like the last challenge, you can submit an entry by posting a github link to your analysis on the signup page (second tab). Use any combination of reports/visuals/code/presentation you think is best - just make sure your code is accessible!\n\nLet's have a few days for people to review the data and ask any questions and then we can discuss what everyone thinks is a reasonable deadline/timeline and set the timeline from there. If you have any further data requests you think would help answer the questions I might be able to get it (google analytics or mailchimp).\n\nAfter the deadline I'll choose the first and second place submission. The criteria will be whatever submission provides the most compelling evidence that gives me a clear idea of what actions we could take next to improve the site.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Initialize",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Load libraries\n# https://stackoverflow.com/questions/58667299/google-colab-why-matplotlib-has-a-behaviour-different-then-default-after-import\n# Panda profilling alter seaborn plotting style\n\nfrom google.colab import drive # to load data from google drive\nimport numpy as np # linear algebra\nimport pandas as pd # data processing, CSV file I/O (e.g. pd.read_csv)\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt # ploting the data\nimport seaborn as sns # ploting the data\n%matplotlib inline\nimport math # calculation",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"drive.mount(\"/content/drive\")",
"Mounted at /content/drive\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Data Cleaning",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Load the Pages Titles\npages_tiltes = pd.read_excel(r'/content/drive/MyDrive/DSS/BrainPost_blog/Data/DSS BrainPost Web Analytics Challenge!.xlsx', sheet_name='Page to Page Title lookup', skiprows=6)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Load the content-pages oct 4-17\n# Skip the first 6 rows with headers\n# Skip the last 18 rows with total view\n# See https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/reference/api/pandas.read_excel.html\n# See https://stackoverflow.com/questions/49876077/pandas-reading-excel-file-starting-from-the-row-below-that-with-a-specific-valu\n\n#content-pages july 12-25\njuly12_25 = pd.read_excel(r'/content/drive/MyDrive/DSS/BrainPost_blog/Data/DSS BrainPost Web Analytics Challenge!.xlsx', \n sheet_name='content-pages july 12-25', \n skiprows=6, skipfooter=20)\n#july12_25\n\n#content-pages jul 26 - aug 8\njul26_aug8 = pd.read_excel(r'/content/drive/MyDrive/DSS/BrainPost_blog/Data/DSS BrainPost Web Analytics Challenge!.xlsx', \n sheet_name='content-pages jul 26 - aug 8', \n skiprows=6, skipfooter=20)\n#jul26_aug8\n\n#content-pages aug 9-22\naug9_22 = pd.read_excel(r'/content/drive/MyDrive/DSS/BrainPost_blog/Data/DSS BrainPost Web Analytics Challenge!.xlsx', \n sheet_name='content-pages aug 9-22', \n skiprows=6, skipfooter=20)\n#aug9_22\n\n#content-pages aug23-sept5\naug23_sept5 = pd.read_excel(r'/content/drive/MyDrive/DSS/BrainPost_blog/Data/DSS BrainPost Web Analytics Challenge!.xlsx', \n sheet_name='content-pages aug23-sept5', \n skiprows=6, skipfooter=20)\n#aug23_sept5\n\n#content-pages sept 6-19\nsept6_19 = pd.read_excel(r'/content/drive/MyDrive/DSS/BrainPost_blog/Data/DSS BrainPost Web Analytics Challenge!.xlsx', \n sheet_name='content-pages sept 6-19', \n skiprows=6, skipfooter=20)\n#sept6_19\n\n#content-pages sept 20-oct3\nsept20_oct3 = pd.read_excel(r'/content/drive/MyDrive/DSS/BrainPost_blog/Data/DSS BrainPost Web Analytics Challenge!.xlsx', \n sheet_name='content-pages sept 20-oct3', \n skiprows=6, skipfooter=20)\n#sept20_oct3\n\n#content-pages oct 4-17\nOct4_17 = pd.read_excel(r'/content/drive/MyDrive/DSS/BrainPost_blog/Data/DSS BrainPost Web Analytics Challenge!.xlsx', \n sheet_name='content-pages oct 4-17', \n skiprows=6, skipfooter=20)\n#Oct4_17\n\n#content-pages oct 18-31\nOct18_31 = pd.read_excel(r'/content/drive/MyDrive/DSS/BrainPost_blog/Data/DSS BrainPost Web Analytics Challenge!.xlsx', \n sheet_name='content-pages oct 18-31', \n skiprows=6, skipfooter=20)\n#Oct18_31\n\n# Combine data frame\n# https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/reference/api/pandas.DataFrame.combine.html\n# https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/merging.html\n\nframes = [july12_25,\n jul26_aug8,\n aug9_22,\n aug23_sept5,\n sept6_19,\n sept20_oct3,\n Oct4_17,\n Oct18_31]\ndf = pd.concat(frames)\ndf",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_outer = pd.merge(df, pages_tiltes, how='outer', on='Page')\ndf = df_outer.copy()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Determine the number of missing values for every column\ndf.isnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Filter entries with Pageviews >= 0\n# https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/reference/api/pandas.DataFrame.filter.html\n# https://cmdlinetips.com/2018/02/how-to-subset-pandas-dataframe-based-on-values-of-a-column/\n\ndf_Pageviews_filtered = df[df['Pageviews'] > 0]\ndf_Pageviews_filtered.isnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create a value count column\n# https://stackoverflow.com/questions/29791785/python-pandas-add-a-column-to-my-dataframe-that-counts-a-variable\n\ndf_Pageviews_filtered['Page_count'] = df_Pageviews_filtered.groupby('Page')['Page'].transform('count')\ndf_Pageviews_filtered['Source_count'] = df_Pageviews_filtered.groupby('Source / Medium')['Source / Medium'].transform('count')\ndf_Pageviews_filtered['Page_Title_count'] = df_Pageviews_filtered.groupby('Page Title')['Page Title'].transform('count')\n\ndf = df_Pageviews_filtered.copy()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Merge all facebook\n# https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/reference/api/pandas.DataFrame.replace.html\n\n# I chose to combine all facebook referal \n# m.facebook indicate mobile trafic. \n# There is no equivalent for the other Source so I will ignnore this for this part of the analysis.\n\ndf = df.replace(to_replace = [\"l.facebook.com / referral\", \"m.facebook.com / referral\", \"facebook.com / referral\"], \n value = \"facebook\")\ndf = df.replace( to_replace = \"google / organic\", value = \"google\")\ndf = df.replace( to_replace = \"(direct) / (none)\", value = \"direct\")\n# t.co is twitter\n# https://analypedia.carloseo.com/t-co-referral/\ndf = df.replace( to_replace = \"t.co / referral\", value = \"twitter\")\ndf = df.replace( to_replace = \"bing / organic\", value = \"bing\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Deal with time data\ndf['time'] = pd.to_datetime(df['Avg. Time on Page'], format='%H:%M:%S')\ndf['time'] = pd.to_datetime(df['time'], unit='s')\ndf[['time0']] = pd.to_datetime('1900-01-01 00:00:00')\ndf['time_diff'] = df['time'] - df['time0']\ndf['time_second'] = df['time_diff'].dt.total_seconds().astype(int)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Data Visualization",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# https://stackoverflow.com/questions/42528921/how-to-prevent-overlapping-x-axis-labels-in-sns-countplot\n# https://stackoverflow.com/questions/46623583/seaborn-countplot-order-categories-by-count\n# https://stackoverflow.com/questions/25328003/how-can-i-change-the-font-size-using-seaborn-facetgrid\n\ndata = df.copy()\ndata = data[data['Page_count'] >= 60]\n\nplt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))\nsns.set(font_scale=1.25)\nsns.set_style(\"white\")\ntitle = 'Top 5 Pages visited'\nsns.countplot(y = data['Page'], \n order = data['Page'].value_counts().index)\nplt.title(title)\nplt.ioff()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Figure: Top 5 pages visited all time**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data = df.copy()\ndata = data[data['Page_count'] >= 25]\n\nplt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))\nsns.set(font_scale=1.25)\nsns.set_style(\"white\")\ntitle = 'Top Pages visited more than 25 times'\nsns.countplot(y = data['Page'], \n order = data['Page'].value_counts().index,\n color='#2b7bba')\nplt.title(title)\nplt.ioff()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Figure: Top pages visited at least 25 times**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# https://www.statology.org/pandas-filter-multiple-conditions/\n\ndata = df.copy()\ndata = data[(data['Source_count'] >= 270)]\n\nsns.displot(data, x=\"time_second\", kind=\"kde\", hue='Source / Medium')\nplt.ioff()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Figure: Average time spent on page for the top sources**\n\nThe 0 second trafic is not restricted to google.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"See this [discussion](https://support.google.com/google-ads/thread/1455669?hl=en) related to 0 second visits on Google Analytics.\n\nThe issue seems related to bounce rate preventing Google Analytic to accuralely measure the time spent on the page.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Time spend on page\n\n# https://www.statology.org/pandas-filter-multiple-conditions/\ndata = df.copy()\ndata = data[(data['Source_count'] >= 270)]\n\nsns.set(font_scale=1.25)\nsns.set_style(\"white\")\n\nsns.displot(data, x=\"Bounce Rate\", kind=\"kde\", hue='Source / Medium')\nplt.ioff()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Figure: Average Bounce Rate on page for the top sources**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The bounce rate correspond to users that take no other action after landing on the site such as visiting another page. \nFrom the figure above this seems to be frequent on the blog which make sense if the user are interested in a particular article.\n\nIt also potentially means that for most traffic on the site the average time spend on a page can't be calculated.\n\nThere seems to be way to work around this as seen in this [discussion](https://support.google.com/google-ads/thread/1455669?hl=en).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data = df.copy()\ndata = data[data['Source_count'] >= 100]\n\nplt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))\nsns.set(font_scale=1.25)\nsns.set_style(\"white\")\n\ntitle = 'Top 5 Source for Pages visited more than 100 time'\nsns.countplot(y = data['Source / Medium'], \n order = data['Source / Medium'].value_counts().index)\nplt.title(title)\nplt.ioff()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Figure: Top 5 Source for Pages visited more than 100 time**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# https://www.statology.org/pandas-filter-multiple-conditions/\n\ndata = df.copy()\ndata = data[data['Source_count'] >= 100]\ndata = data[data['time_second'] > 5]\n\ny=\"Source / Medium\"\nx=\"time_second\"\n\ntitle = 'Top 5 Source for Pages visited more than 100 time and viewed more than 5 seconds'\n\nplt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))\nsns.set(font_scale=1.25)\nsns.set_style(\"white\")\n\nsns.boxplot(x=x, y=y, data=data, notch=True, showmeans=False,\n meanprops={\"marker\":\"s\",\"markerfacecolor\":\"white\", \"markeredgecolor\":\"black\"})\n\nplt.title(title)\nplt.ioff()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# https://www.statology.org/pandas-filter-multiple-conditions/\n\ndata = df.copy()\ndata = data[(data['Page_count'] >= 60) & (data['Source_count'] >= 100)]\ndata = data[data['time_second'] > 5]\n\ntitle = \"\"\n\ny=\"Page\"\nx=\"time_second\"\n\nplt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))\nsns.set(font_scale=1.25)\nsns.set_style(\"white\")\n\nsns.boxplot(x=x, y=y, data=data, notch=False, showmeans=False,\n meanprops={\"marker\":\"s\",\"markerfacecolor\":\"white\", \"markeredgecolor\":\"black\"},\n hue='Source / Medium')\nplt.title(title)\nplt.ioff()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# https://www.statology.org/pandas-filter-multiple-conditions/\n\ndata = df.copy()\ndata = data[(data['Page_count'] >= 61) & (data['Source_count'] >= 100)]\ndata = data[data['time_second'] > 5]\ndata = data[data['time_second'] < 600]\n\ntitle = \"\"\n\ny=\"Page\"\nx=\"time_second\"\n\nplt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))\nsns.set(font_scale=1.25)\nsns.set_style(\"white\")\n\nsns.boxplot(x=x, y=y, data=data, notch=False, showmeans=False,\n meanprops={\"marker\":\"s\",\"markerfacecolor\":\"white\", \"markeredgecolor\":\"black\"},\n hue='Source / Medium')\nplt.title(title)\nplt.ioff()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# https://stackoverflow.com/questions/42528921/how-to-prevent-overlapping-x-axis-labels-in-sns-countplot\n# https://stackoverflow.com/questions/46623583/seaborn-countplot-order-categories-by-count\n# https://stackoverflow.com/questions/25328003/how-can-i-change-the-font-size-using-seaborn-facetgrid\n\ndata = df.copy()\ndata = data[data['Page_count'] >= 50]\ndata = data[data['Source_count'] >= 100]\n#data = data[data['time_second'] > 5]\n\nplt.figure(figsize=(15, 10))\nsns.set(font_scale=1.25)\nsns.set_style(\"white\")\ntitle = 'Average View for page visited more than 50 times from top source'\nsns.countplot(data = data, y = 'Page', hue='Source / Medium')\n\n# Put the legend out of the figure\n# https://stackoverflow.com/questions/30490740/move-legend-outside-figure-in-seaborn-tsplot\nplt.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.05, 1), loc=2, borderaxespad=0.)\n\nplt.title(title)\nplt.ioff()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Conclusion\n\n* **What content (or types of content) is most popular (what are patterns we see in popular content) and is different content popular amongst different subgroups (e.g. by source/medium)?**\n\nThe homepage, weekly-brainpost, and archive are the most popular pages on the website.\nWe would need more information to analyze trends in page popularity by sources. The user with direct access, possibly via a mailing list, tend to visit the weekly brain posts pages more. \n\n* **Any question that will help us to take action to better tailor our content to our audience(s) or understand how traffic comes to the site.**\n\nWhat is causing the high bounce rate in the analytics?\n\nA large number of visitors are registered as spending 0 seconds on the page. This, combined with the high bounce rate, could indicate an issue in measuring the site traffic. This Google support [page](https://www.brainpost.co/about-brainpost) offers suggestions to solve this problem. \n\n* **Where are people visiting from (source-wise)?**\n\nGoogle, Facebook and direct access are the three most common traffic sources. \n\n# Final remarks\nI put this together as a quick and modest analysis. I appreciate real-life projects, so I plan to investigate this further. Any feedback is welcome. \n\n* E-mail: [email protected]\n* Twitter: williamguesdon\n* LinkedIn: william-guesdon",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4abb2c152e58e4c67e1386d65fd1215f1f2ca2f6
| 15,637 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
HolidayGreetings/MerryChristmasandHappyHolidays_Python.ipynb
|
sptennak/ComputingIsFun
|
bff1d46c178a5456ec8653f735711041997d4727
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
HolidayGreetings/MerryChristmasandHappyHolidays_Python.ipynb
|
sptennak/ComputingIsFun
|
bff1d46c178a5456ec8653f735711041997d4727
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
HolidayGreetings/MerryChristmasandHappyHolidays_Python.ipynb
|
sptennak/ComputingIsFun
|
bff1d46c178a5456ec8653f735711041997d4727
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 32.645094 | 265 | 0.394449 |
[
[
[
"# Merry Christmas and Happy Holidays !\n## Using Python\nAuthor: Sumudu Tennakoon\\\nCreated Date: 2020-12-24",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Goal\nTo create a Greeting Card in the console output with \n* An illustration of a Christmas tree using characters.\n* Randomly distributed Ornaments and Decorations.\n* a start in the top of of the tree\n* A border at the bottom of the leaves\n* A base attached to the tree\n* Greeting message \"MERRY CHRISTMAS AND HAPPY HOLIDAYS\"\n* Colors: red star green tree, a blue border at the bottom, magenta base, and the message in red.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Task 1: Setup Tree Parameters (width, body height, and full hight with the base)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"width = 25 # Tree width\nbody_height = 25 # Height without stand\nfull_height = 31 # Total height",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Task 2: Print Basic Tree Body",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tree = ''\nfor x in range(1, full_height, 2):\n s = ''\n if x == 1 :\n s='*'\n print(s.center(width)) \n elif x < body_height: \n for y in range(0,x): \n s = s + '^'\n print(s.center(width)) ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Task 3: Add Bottom Border Ribbon, Base, and Ground",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tree = ''\nfor x in range(1, full_height, 2):\n s = ''\n if x == 1 :\n s='*'\n print(s.center(width)) \n elif x < body_height: \n for y in range(0,x): \n s = s + '^'\n print(s.center(width)) \n elif x == body_height:\n s = s + '#'*width\n print(s) \n elif x > body_height and x < full_height:\n s = s + 'II'\n print(s.center(width)) \n\nprint(('~'*width).center(width))",
" * \n ^^^ \n ^^^^^ \n ^^^^^^^ \n ^^^^^^^^^ \n ^^^^^^^^^^^ \n ^^^^^^^^^^^^^ \n ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ \n ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ \n ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ \n ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ \n ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ \n#########################\n II \n II \n~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Task 4: Add Ornaments",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from random import randint\n\ntree = ''\nfor x in range(1, full_height, 2):\n s = ''\n if x == 1 :\n s='*'\n print(s.center(width)) \n elif x < body_height: \n for y in range(0,x): \n b = randint(0, width) # Location to add random decoration 1\n a = randint(0, width) # Add random decoration 2\n c = randint(0, width) # Add random decoration 3\n if y==b:\n s = s + 'o'\n elif y==a:\n s = s + '@'\n elif y==c:\n s = s + '+'\n else:\n s = s + '^'\n print(s.center(width)) \n elif x == body_height:\n s = s + '#'*width\n print(s) \n elif x > body_height and x < full_height:\n s = s + 'II'\n print(s.center(width)) \n\nprint(('~'*width).center(width))",
" * \n @o^ \n o^^o^ \n ^^^^^^^ \n ^^^+^^^^^ \n ^^^^^^^^^^^ \n ^+^^^^^^^^^^^ \n ^o^^^@^^^^^^^o^ \n ^^^^^^^^^^^+^^^^^ \n ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^@ \n ^^^^^^^^+^^oo^^^^^^^^ \n +^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^o^o^ \n#########################\n II \n II \n~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Task 5: Add Greeting Message",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from random import randint\n\ntree = ''\nfor x in range(1, full_height, 2):\n s = ''\n if x == 1 :\n s='*'\n print(s.center(width)) \n elif x < body_height: \n for y in range(0,x): \n b = randint(0, width) # Location to add random decoration 1\n a = randint(0, width) # Add random decoration 2\n c = randint(0, width) # Add random decoration 3\n if y==b:\n s = s + 'o'\n elif y==a:\n s = s + '@'\n elif y==c:\n s = s + '+'\n else:\n s = s + '^'\n print(s.center(width)) \n elif x == body_height:\n s = s + '#'*width\n print(s) \n elif x > body_height and x < full_height:\n s = s + 'II'\n print(s.center(width)) \n\nprint(('~'*width).center(width))\nprint('MERRY CHRISTMAS'.center(width)) \nprint('AND'.center(width))\nprint('HAPPY HOLIDAYS !'.center(width))\nprint(('~'*width).center(width)) ",
" * \n ^^o \n ^^^^^ \n ^^^^oo^ \n ^^^^^^^o^ \n ^^^^^^^^^oo \n ^^^^^^^@^^^^^ \n ^^^^^^^o^^^^^^^ \n ^^^^^^^^^^+^^^o^^ \n ^^^@+^^^^^^^+^^^+@^ \n ^^^^+^^^^+^^o^^^^^^^^ \n ^o^^@^^^^^^^^^^^^o^^^^^ \n#########################\n II \n II \n~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~\n MERRY CHRISTMAS \n AND \n HAPPY HOLIDAYS ! \n~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Task 6: Add colors",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from colorama import * # To change font colors (https://github.com/tartley/colorama)\nfrom random import randint\n\nwidth = 25 # Tree width\nbody_height = 25 # Height without stand\nfull_height = 31 # Total height\n\ntree = ''\nfor x in range(1, full_height, 2):\n s = ''\n if x == 1 :\n s='*'\n print(Fore.RED + s.center(width)) \n elif x < body_height: \n for y in range(0,x):\n b = randint(0, width) # Location to add random decoration 1\n a = randint(0, width) # Add random decoration 2\n c = randint(0, width) # Add random decoration 3\n if y==b:\n s = s + 'o'\n elif y==a:\n s = s + '@'\n elif y==c:\n s = s + '+'\n else:\n s = s + '^'\n print(Fore.GREEN + s.center(width)) \n elif x == body_height:\n s = s + '#'*width\n print(Fore.BLUE + s.center(width)) \n elif x > body_height and x < full_height:\n s = s + 'II'\n print(Fore.MAGENTA + s.center(width)) \n\nprint(('~'*width).center(width)) \nprint(Fore.RED + 'MERRY CHRISTMAS'.center(width)) \nprint(Fore.RED + 'AND'.center(width))\nprint(Fore.RED + 'HAPPY HOLIDAYS !'.center(width))\nprint(('~'*width).center(width)) ",
"\u001b[31m * \n\u001b[32m ^^^ \n\u001b[32m ^^^^^ \n\u001b[32m ^^^^^^^ \n\u001b[32m ^^^^^^^^^ \n\u001b[32m ^^^^^^+^^+^ \n\u001b[32m ^^^^^^^@^^^^^ \n\u001b[32m +^^@^^^^^^^^^^^ \n\u001b[32m ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^o \n\u001b[32m ^^^^^^o@^^^o^^^^^^^ \n\u001b[32m ^^^@+^^^^o^^^++^^^^^^ \n\u001b[32m ^^^+o@^^^^^@^^^^^^^@^^@ \n\u001b[34m#########################\n\u001b[35m II \n\u001b[35m II \n~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~\n\u001b[31m MERRY CHRISTMAS \n\u001b[31m AND \n\u001b[31m HAPPY HOLIDAYS ! \n~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Bonus \n* Add new Ornament\n* Add Colors to Ornaments (printing characters individually)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from colorama import * # To change font colors (https://github.com/tartley/colorama)\nfrom random import randint\n\nwidth = 25 # Tree width\nbody_height = 25 # Height without stand\nfull_height = 31 # Total height\n\ntree = ''\nfor x in range(1, full_height, 2):\n s = ''\n center = int((width-1)/2)\n padding = center-int((x-1)/2)\n \n print('\\n', end='') \n \n if x == 1 :\n print(' '*padding, end='') \n print(Fore.RED + '*', end='') \n elif x < body_height: \n print(' '*padding, end='')\n for y in range(0,x):\n b = randint(0, width) # Location to add random decoration 1\n a = randint(0, width) # Add random decoration 2\n c = randint(0, width) # Add random decoration 3\n if y==b:\n print(Fore.YELLOW + 'o', end='') \n elif y==a:\n print(Fore.CYAN + '@', end='') \n elif y==c:\n print(Fore.RED + '+', end='') \n else:\n print(Fore.GREEN + '^', end='') \n \n \n elif x == body_height:\n print(' '*padding, end='') \n print(Fore.BLUE + '#'*width, end='') \n elif x > body_height and x < full_height:\n print(' '*center, end='') \n print(Fore.MAGENTA + 'II', end='') \n \nprint('\\n', end='') \nprint(('~'*width).center(width)) \nprint(Fore.RED + 'MERRY CHRISTMAS'.center(width)) \nprint(Fore.RED + 'AND'.center(width))\nprint(Fore.RED + 'HAPPY HOLIDAYS !'.center(width))\nprint(('~'*width).center(width)) ",
"\n \u001b[31m*\n \u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\n \u001b[33mo\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\n \u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\n \u001b[33mo\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[36m@\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\n \u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\n \u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[36m@\n \u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\n \u001b[36m@\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[31m+\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\n \u001b[31m+\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[36m@\u001b[36m@\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[36m@\u001b[32m^\n \u001b[33mo\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[33mo\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\n \u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\u001b[32m^\n\u001b[34m#########################\n \u001b[35mII\n \u001b[35mII\n~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~\n\u001b[31m MERRY CHRISTMAS \n\u001b[31m AND \n\u001b[31m HAPPY HOLIDAYS ! \n~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~\n"
]
],
[
[
"<hr>\n©2020 Sumudu Tennakoon",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4abb31794f8fea1c687f9569baf1fc01e16ae063
| 8,755 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/trees_regression.ipynb
|
Imarcos/scikit-learn-mooc
|
69a7a7e891c5a4a9bce8983d7c92326674fda071
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/trees_regression.ipynb
|
Imarcos/scikit-learn-mooc
|
69a7a7e891c5a4a9bce8983d7c92326674fda071
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/trees_regression.ipynb
|
Imarcos/scikit-learn-mooc
|
69a7a7e891c5a4a9bce8983d7c92326674fda071
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | null | null | null | 31.492806 | 101 | 0.609252 |
[
[
[
"# Decision tree for regression\n\nIn this notebook, we present how decision trees are working in regression\nproblems. We show differences with the decision trees previously presented in\na classification setting.\n\nFirst, we load the penguins dataset specifically for solving a regression\nproblem.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<div class=\"admonition note alert alert-info\">\n<p class=\"first admonition-title\" style=\"font-weight: bold;\">Note</p>\n<p class=\"last\">If you want a deeper overview regarding this dataset, you can refer to the\nAppendix - Datasets description section at the end of this MOOC.</p>\n</div>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\n\npenguins = pd.read_csv(\"../datasets/penguins_regression.csv\")\n\nfeature_name = \"Flipper Length (mm)\"\ntarget_name = \"Body Mass (g)\"\ndata_train, target_train = penguins[[feature_name]], penguins[target_name]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"To illustrate how decision trees are predicting in a regression setting, we\nwill create a synthetic dataset containing all possible flipper length from\nthe minimum to the maximum of the original data.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\n\ndata_test = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(data_train[feature_name].min(),\n data_train[feature_name].max()),\n columns=[feature_name])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Using the term \"test\" here refers to data that was not used for training.\nIt should not be confused with data coming from a train-test split, as it\nwas generated in equally-spaced intervals for the visual evaluation of the\npredictions.\n\nNote that this is methodologically valid here because our objective is to get\nsome intuitive understanding on the shape of the decision function of the\nlearned decision trees.\n\nHowever computing an evaluation metric on such a synthetic test set would\nbe meaningless since the synthetic dataset does not follow the same\ndistribution as the real world data on which the model will be deployed.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn as sns\n\nsns.scatterplot(data=penguins, x=feature_name, y=target_name,\n color=\"black\", alpha=0.5)\n_ = plt.title(\"Illustration of the regression dataset used\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We will first illustrate the difference between a linear model and a decision\ntree.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression\n\nlinear_model = LinearRegression()\nlinear_model.fit(data_train, target_train)\ntarget_predicted = linear_model.predict(data_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sns.scatterplot(data=penguins, x=feature_name, y=target_name,\n color=\"black\", alpha=0.5)\nplt.plot(data_test[feature_name], target_predicted, label=\"Linear regression\")\nplt.legend()\n_ = plt.title(\"Prediction function using a LinearRegression\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"On the plot above, we see that a non-regularized `LinearRegression` is able\nto fit the data. A feature of this model is that all new predictions\nwill be on the line.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"ax = sns.scatterplot(data=penguins, x=feature_name, y=target_name,\n color=\"black\", alpha=0.5)\nplt.plot(data_test[feature_name], target_predicted, label=\"Linear regression\",\n linestyle=\"--\")\nplt.scatter(data_test[::3], target_predicted[::3], label=\"Predictions\",\n color=\"tab:orange\")\nplt.legend()\n_ = plt.title(\"Prediction function using a LinearRegression\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Contrary to linear models, decision trees are non-parametric models:\nthey do not make assumptions about the way data is distributed.\nThis will affect the prediction scheme. Repeating the above experiment\nwill highlight the differences.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor\n\ntree = DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=1)\ntree.fit(data_train, target_train)\ntarget_predicted = tree.predict(data_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sns.scatterplot(data=penguins, x=feature_name, y=target_name,\n color=\"black\", alpha=0.5)\nplt.plot(data_test[feature_name], target_predicted, label=\"Decision tree\")\nplt.legend()\n_ = plt.title(\"Prediction function using a DecisionTreeRegressor\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We see that the decision tree model does not have an *a priori* distribution\nfor the data and we do not end-up with a straight line to regress flipper\nlength and body mass.\n\nInstead, we observe that the predictions of the tree are piecewise constant.\nIndeed, our feature space was split into two partitions. Let's check the\ntree structure to see what was the threshold found during the training.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.tree import plot_tree\n\n_, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 6))\n_ = plot_tree(tree, feature_names=feature_name, ax=ax)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The threshold for our feature (flipper length) is 206.5 mm. The predicted\nvalues on each side of the split are two constants: 3683.50 g and 5023.62 g.\nThese values corresponds to the mean values of the training samples in each\npartition.\n\nIn classification, we saw that increasing the depth of the tree allowed us to\nget more complex decision boundaries.\nLet's check the effect of increasing the depth in a regression setting:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tree = DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=3)\ntree.fit(data_train, target_train)\ntarget_predicted = tree.predict(data_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sns.scatterplot(data=penguins, x=feature_name, y=target_name,\n color=\"black\", alpha=0.5)\nplt.plot(data_test[feature_name], target_predicted, label=\"Decision tree\")\nplt.legend()\n_ = plt.title(\"Prediction function using a DecisionTreeRegressor\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Increasing the depth of the tree will increase the number of partition and\nthus the number of constant values that the tree is capable of predicting.\n\nIn this notebook, we highlighted the differences in behavior of a decision\ntree used in a classification problem in contrast to a regression problem.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4abb3f0e262011d9882c23e65e39c5efdfd1c91b
| 172,291 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
lectures/correlation/Linear Correlation Analysis.ipynb
|
johnmathews/quant1
|
77030f5de646ca21e951d81d823f265bef87445e
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | null | null | null |
lectures/correlation/Linear Correlation Analysis.ipynb
|
johnmathews/quant1
|
77030f5de646ca21e951d81d823f265bef87445e
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | null | null | null |
lectures/correlation/Linear Correlation Analysis.ipynb
|
johnmathews/quant1
|
77030f5de646ca21e951d81d823f265bef87445e
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | null | null | null | 322.039252 | 42,664 | 0.921714 |
[
[
[
"# The Correlation Coefficient\nBy Evgenia \"Jenny\" Nitishinskaya and Delaney Granizo-Mackenzie with example algorithms by David Edwards\n\nPart of the Quantopian Lecture Series:\n\n* [www.quantopian.com/lectures](https://www.quantopian.com/lectures)\n* [github.com/quantopian/research_public](https://github.com/quantopian/research_public)\n\nNotebook released under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License. Please do not remove this attribution.\n\n---\n\nThe correlation coefficient measures the extent to which the relationship between two variables is linear. Its value is always between -1 and 1. A positive coefficient indicates that the variables are directly related, i.e. when one increases the other one also increases. A negative coefficient indicates that the variables are inversely related, so that when one increases the other decreases. The closer to 0 the correlation coefficient is, the weaker the relationship between the variables.\n\nThe correlation coefficient of two series $X$ and $Y$ is defined as\n$$r = \\frac{Cov(X,Y)}{std(X)std(Y)}$$\nwhere $Cov$ is the covariance and $std$ is the standard deviation.\n\nTwo random sets of data will have a correlation coefficient close to 0:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"##Correlation vs. Covariance\n\nCorrelation is simply a normalized form of covariance. They are otherwise the same and are often used semi-interchangeably in everyday conversation. It is obviously important to be precise with language when discussing the two, but conceptually they are almost identical.\n\n###Covariance isn't that meaningful by itself\n\nLet's say we have two variables $X$ and $Y$ and we take the covariance of the two.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X = np.random.rand(50)\nY = 2 * X + np.random.normal(0, 0.1, 50)\n\nnp.cov(X, Y)[0, 1]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"So now what? What does this mean? Correlation uses information about the variance of X and Y to normalize this metric. Once we've normalized the metric to the -1 to 1 scale, we can make meaningful statements and compare correlations.\n\nTo see how this is done consider the formula.\n\n$$\\frac{Cov(X, Y)}{std(X)std(Y)}$$\n\n$$= \\frac{Cov(X, Y)}{\\sqrt{var(X)}\\sqrt{var(Y)}}$$\n\n$$= \\frac{Cov(X, Y)}{\\sqrt{Cov(X, X)}\\sqrt{Cov(Y, Y)}}$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"To demonstrate this let's compare the correlation and covariance of two series.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"X = np.random.rand(50)\nY = 2 * X + 4\n\nprint 'Covariance of X and Y: \\n' + str(np.cov(X, Y))\nprint 'Correlation of X and Y: \\n' + str(np.corrcoef(X, Y))",
"Covariance of X and Y: \n[[ 0.07290409 0.14580818]\n [ 0.14580818 0.29161635]]\nCorrelation of X and Y: \n[[ 1. 1.]\n [ 1. 1.]]\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Why do both `np.cov` and `np.corrcoef` return matricies?\n\nThe covariance matrix is an important concept in statistics. Often people will refer to the covariance of two variables $X$ and $Y$, but in reality that is just one entry in the covariance matrix of $X$ and $Y$. For each input variable we have one row and one column. The diagonal is just the variance of that variable, or $Cov(X, X)$, entries off the diagonal are covariances between different variables. The matrix is symmetric across the diagonal. Let's check that this is true.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cov_matrix = np.cov(X, Y)\n\n# We need to manually set the degrees of freedom on X to 1, as numpy defaults to 0 for variance\n# This is usually fine, but will result in a slight mismatch as np.cov defaults to 1\nerror = cov_matrix[0, 0] - X.var(ddof=1)\n\nprint 'error: ' + str(error)",
"error: -2.77555756156e-17\n"
],
[
"X = np.random.rand(50)\nY = np.random.rand(50)\n\nplt.scatter(X,Y)\nplt.xlabel('X Value')\nplt.ylabel('Y Value')\n\n# taking the relevant value from the matrix returned by np.cov\nprint 'Correlation: ' + str(np.cov(X,Y)[0,1]/(np.std(X)*np.std(Y)))\n# Let's also use the builtin correlation function\nprint 'Built-in Correlation: ' + str(np.corrcoef(X, Y)[0, 1])",
"Correlation: 0.0435685025905\nBuilt-in Correlation: 0.0426971325387\n"
]
],
[
[
"Now let's see what two correlated sets of data look like.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"X = np.random.rand(50)\nY = X + np.random.normal(0, 0.1, 50)\n\nplt.scatter(X,Y)\nplt.xlabel('X Value')\nplt.ylabel('Y Value')\n\nprint 'Correlation: ' + str(np.corrcoef(X, Y)[0, 1])",
"Correlation: 0.947346247257\n"
]
],
[
[
"Let's dial down the relationship by introducing more noise.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"X = np.random.rand(50)\nY = X + np.random.normal(0, .2, 50)\n\nplt.scatter(X,Y)\nplt.xlabel('X Value')\nplt.ylabel('Y Value')\n\nprint 'Correlation: ' + str(np.corrcoef(X, Y)[0, 1])",
"Correlation: 0.83001059779\n"
]
],
[
[
"Finally, let's see what an inverse relationship looks like.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"X = np.random.rand(50)\nY = -X + np.random.normal(0, .1, 50)\n\nplt.scatter(X,Y)\nplt.xlabel('X Value')\nplt.ylabel('Y Value')\n\nprint 'Correlation: ' + str(np.corrcoef(X, Y)[0, 1])",
"Correlation: -0.942559986469\n"
]
],
[
[
"We see a little bit of rounding error, but they are clearly the same value.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## How is this useful in finance?\n\n### Determining related assets\n\nOnce we've established that two series are probably related, we can use that in an effort to predict future values of the series. For example. let's loook at the price of Apple and a semiconductor equipment manufacturer, Lam Research Corporation.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Pull the pricing data for our two stocks and S&P 500\nstart = '2013-01-01'\nend = '2015-01-01'\nbench = get_pricing('SPY', fields='price', start_date=start, end_date=end)\na1 = get_pricing('LRCX', fields='price', start_date=start, end_date=end)\na2 = get_pricing('AAPL', fields='price', start_date=start, end_date=end)\n\nplt.scatter(a1,a2)\nplt.xlabel('LRCX')\nplt.ylabel('AAPL')\nplt.title('Stock prices from ' + start + ' to ' + end)\nprint \"Correlation coefficients\"\nprint \"LRCX and AAPL: \", np.corrcoef(a1,a2)[0,1]\nprint \"LRCX and SPY: \", np.corrcoef(a1,bench)[0,1]\nprint \"AAPL and SPY: \", np.corrcoef(bench,a2)[0,1]",
"Correlation coefficients\nLRCX and AAPL: 0.954684674528\nLRCX and SPY: 0.935191172334\nAAPL and SPY: 0.89214568707\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Constructing a portfolio of uncorrelated assets\n\nAnother reason that correlation is useful in finance is that uncorrelated assets produce the best portfolios. The intuition for this is that if the assets are uncorrelated, a drawdown in one will not correspond with a drawdown in another. This leads to a very stable return stream when many uncorrelated assets are combined.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Limitations\n\n## Significance\n\nIt's hard to rigorously determine whether or not a correlation is significant, especially when, as here, the variables are not normally distributed. Their correlation coefficient is close to 1, so it's pretty safe to say that the two stock prices are correlated over the time period we use, but is this indicative of future correlation? If we examine the correlation of each of them with the S&P 500, we see that it is also quite high. So, AAPL and LRCX are slightly more correlated with each other than with the average stock.\n\nOne fundamental problem is that it is easy to datamine correlations by picking the right time period. To avoid this, one should compute the correlation of two quantities over many historical time periods and examine the distibution of the correlation coefficient. More details on why single point estimates are bad will be covered in future notebooks.\n\nAs an example, remember that the correlation of AAPL and LRCX from 2013-1-1 to 2015-1-1 was 0.95. Let's take the rolling 60 day correlation between the two to see how that varies.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"rolling_correlation = pd.rolling_corr(a1, a2, 60)\nplt.plot(rolling_correlation)\nplt.xlabel('Day')\nplt.ylabel('60-day Rolling Correlation')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Non-Linear Relationships\n\nThe correlation coefficient can be useful for examining the strength of the relationship between two variables. However, it's important to remember that two variables may be associated in different, predictable ways which this analysis would not pick up. For instance, one variable might precisely follow the behavior of a second, but with a delay. There are techniques for dealing with this lagged correlation. Alternatively, a variable may be related to the rate of change of another. Neither of these relationships are linear, but can be very useful if detected.\n\nAdditionally, the correlation coefficient can be very sensitive to outliers. This means that including or excluding even a couple of data points can alter your result, and it is not always clear whether these points contain information or are simply noise.\n\nAs an example, let's make the noise distribution poisson rather than normal and see what happens.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"X = np.random.rand(100)\nY = X + np.random.poisson(size=100)\n\nplt.scatter(X, Y)\n\nnp.corrcoef(X, Y)[0, 1]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"In conclusion, correlation is a powerful technique, but as always in statistics, one should be careful not to interpret results where there are none.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4abb4a612214b1aefb81bae52cd95cfbead3ac3f
| 9,720 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
_notebooks/2022-05-23-aws-sagemaker-wrangler-p2.ipynb
|
hassaanbinaslam/myblog
|
6b8b7e3631bbc52cccafd03e6b18273aba2652f4
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
_notebooks/2022-05-23-aws-sagemaker-wrangler-p2.ipynb
|
hassaanbinaslam/myblog
|
6b8b7e3631bbc52cccafd03e6b18273aba2652f4
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
_notebooks/2022-05-23-aws-sagemaker-wrangler-p2.ipynb
|
hassaanbinaslam/myblog
|
6b8b7e3631bbc52cccafd03e6b18273aba2652f4
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 46.956522 | 486 | 0.664198 |
[
[
[
"# Data Preparation with SageMaker Data Wrangler (Part 2)\n> A detailed guide on AWS SageMaker Data Wrangler to prepare data for machine learning models. This is a five parts series where we will prepare, import, explore, process, and export data using AWS Data Wrangler. You are reading **Part 2:Import data from multiple sources using Data Wrangler**.\n\n- toc: true \n- badges: true\n- comments: true\n- categories: [aws, ml, sagemaker]\n- keyword: [aws, ml, sagemaker, wrangler]\n- image: images/copied_from_nb/images/2022-05-23-aws-sagemaker-wrangler-p2.jpeg",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Enviornment\n\nThis notebook is prepared with Amazon SageMaker Studio using `Python 3 (Data Science)` Kernel and `ml.t3.medium` instance.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# About\nThis is a detailed guide on using **AWS SageMaker Data Wrangler** service to prepare data for machine learning models. SageMaker Data Wrangler is a multipurpose tool with which you can\n* import data from multiple sources\n* explore data with visualizations\n* apply transformations\n* export data for ml training\n\nThis guide is divided into five parts\n* [Part 1: Prepare synthetic data and place it on multiple sources](https://hassaanbinaslam.github.io/myblog/aws/ml/sagemaker/2022/05/17/aws-sagemaker-wrangler-p1.html)\n* **Part 2: Import data from multiple sources using Data Wrangler (You are here)**\n* [Part 3: Explore data with Data Wrangler visualizations](https://hassaanbinaslam.github.io/myblog/aws/ml/sagemaker/2022/05/24/aws-sagemaker-wrangler-p3.html)\n* [Part 4: Preprocess data using Data Wrangler](https://hassaanbinaslam.github.io/myblog/aws/ml/sagemaker/2022/05/25/aws-sagemaker-wrangler-p4.html)\n* [Part 5: Export data for ML training](https://hassaanbinaslam.github.io/myblog/aws/ml/sagemaker/2022/05/26/aws-sagemaker-wrangler-p5.html)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Part 2: Import data from multiple sources using Data Wrangler\n\nIn this post, we will create SageMaker Data Wrangler Flow pipeline to import data from multiple sources. Once data is imported, we will then add a step to join the data into a single dataset that can be used for training ML models.\n\n## Launch SageMaker Data Wrangler Flow\nCreate a new Data Wrangler flow by clicking on the main menu tabs `File > New > Data Wrangler Flow`.\n\n\n\nOnce launched SageMaker may take a minute to initialize a new flow. The reason for this is SageMaker will launch a separate machine in the background `ml.m5.4xlarge` with 16vCPU and 64 GiB memory for processing flow files. A flow file is a JSON file that just captures all the steps performed from the Flow UI console. When you execute the flow, the Flow engine parses this file and performs all the steps. Once a new flow file is available, rename it to `customer-churn.flow`.\n\n\n\n## Import data from sources\n\nFirst, we will create a flow to import data (created in the part-1 post) from S3 bucket. For this from the flow UI click on **Amazon S3 bucket**. From the next window select the bucket name **S3://sagemaker-us-east-1-801598032724**. In your case, it could be different where you have stored the data. From the UI select the filename \"telco_churn_customer_info.csv\" and click **Import**\n\n\n\nOnce the data is imported repeat the steps for the filename \"telco_churn_account_info.csv\". If you are not seeing the \"import from S3 bucket\" option on the UI then check the flow UI and click on the 'Import' tab option. Once both files are imported, your **Data Flow** tab will look similar to this\n\n\n\nNow that we have imported data from S3, we can now work on importing data from the Athena database. For this from the Flow UI Import tab click on **Amazon Athena** option. From the next UI select `AwsDataCatalog` Data catalog option. For Databases drop down select `telco_db` and in the query pane write the below query.\n```\nselect * from telco_churn_utility\n```\nYou can also preview the data by clicking on the table preview option. Once satisfied with the results click 'Import'. When asked about the database name write `telco_churn_utility`\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"At this point, you will find all three tables imported in Data Flow UI. Against each table, a plus sign (+) will appear that you can use to add any transformations you want to apply on each table. \n\n\n\nfor `telco_churn_customer_info` click on the plus sign and then select 'Edit' to change data types.\n\n\n\nWe will add the following transformations\n* Change **Area Code** from Long to String\n* Click **Preview**\n* Then click **Apply**\n\n\n\nSimilarly for `telco_churn_account_info.csv` edit data types as\n* Change **Account Length** to Long\n* Change **Int'l Plan** and **VMail Plan** to Bool\n* Click **Preview** and then click **Apply**\n\nFor `telco_churn_utility.csv` edit data types as\n* Change **custserv_calls** to Long\n* Click **Preview** and then click **Apply**\n\nAt this point, we have imported the data from all three sources and have also properly transformed their column types.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Joining Tables\n\nNow we will join all three tables to get a full dataset. For this from the Flow UI Data flow click on the plus sign next to **customer_info** data type and this time select 'Join'. From the new window select **account_info** as the right dataset and click **Configure**\n\n\n\nFrom the next screen select\n* Join Type = Full Outer\n* Columns Left = CustomerID\n* Columns Right = CustomerID\n* Click Preview and then Add\n\n\n\nA new join step will appear on the Data Flow UI. Click on the plus sign next to it and repeat the steps for **utility** table\n\n\n\n* Join Type = Full Outer\n* Columns Left = CustomerID_0\n* Columns Right = CustomerID\n* Click Preview and then Add\n\n\n\n# Summary\n\nAt this point, we have all the tables joined together. The `customer-churn.flow` created is available on the GitHub [here](https://github.com/hassaanbinaslam/myblog/blob/master/_notebooks/datasets/2022-05-23-aws-sagemaker-wrangler-p2/customer-churn.flow). In the next post, we will clean duplicate columns and create some visualizations to analyze the data.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4abb6793c0f7f703d43bbb28b2dd8fc1ba377d9b
| 5,047 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
B_URLs.ipynb
|
mrrgeresez/my-python-approach
|
fdd4671fe3e2498720a93b96bbc39c6597260d37
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
B_URLs.ipynb
|
mrrgeresez/my-python-approach
|
fdd4671fe3e2498720a93b96bbc39c6597260d37
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
B_URLs.ipynb
|
mrrgeresez/my-python-approach
|
fdd4671fe3e2498720a93b96bbc39c6597260d37
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 42.411765 | 1,269 | 0.609471 |
[
[
[
"### URL\n\nAny Internet content has an identifier with which it can be located through the network protocols. Several python libraries are available to interact with these elements and especially with their content. Let's check the content of any url and search every line that contains a specified keyword",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import sys\nimport requests\n\ndef keywordURL(searchWord,URLp):\n r = requests.get(URLp)\n for line in r.text.split('\\n'): # split lines when return\n if searchWord in line:\n print(''.join([line.strip(),'\\n']))\nkeywordURL('IDN','https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/URL')",
"</p><p>The domain name in the IRI is known as an <a href=\"/wiki/Internationalized_Domain_Name\" class=\"mw-redirect\" title=\"Internationalized Domain Name\">Internationalized Domain Name</a> (IDN). Web and Internet software automatically convert the domain name into <a href=\"/wiki/Punycode\" title=\"Punycode\">punycode</a> usable by the Domain Name System; for example, the Chinese URL <code>http://例子.卷筒纸</code> becomes <code>http://xn--fsqu00a.xn--3lr804guic/</code>. The <code>xn--</code> indicates that the character was not originally ASCII.<sup id=\"cite_ref-FOOTNOTEIANA2003_26-0\" class=\"reference\"><a href=\"#cite_note-FOOTNOTEIANA2003-26\">[22]</a></sup>\n\n<li><link rel=\"mw-deduplicated-inline-style\" href=\"mw-data:TemplateStyles:r999302996\"/><cite id=\"CITEREFIANA2003\" class=\"citation web cs1\"><a href=\"/wiki/Internet_Assigned_Numbers_Authority\" title=\"Internet Assigned Numbers Authority\">Internet Assigned Numbers Authority</a> (2003-02-14). <a rel=\"nofollow\" class=\"external text\" href=\"https://web.archive.org/web/20041208124351/http://www.atm.tut.fi/list-archive/ietf-announce/msg13572.html\">\"Completion of IANA Selection of IDNA Prefix\"</a>. <i>IETF-Announce mailing list</i>. Archived from <a rel=\"nofollow\" class=\"external text\" href=\"http://www.atm.tut.fi/list-archive/ietf-announce/msg13572.html\">the original</a> on 2004-12-08<span class=\"reference-accessdate\">. Retrieved <span class=\"nowrap\">2015-09-03</span></span>.</cite><span title=\"ctx_ver=Z39.88-2004&rft_val_fmt=info%3Aofi%2Ffmt%3Akev%3Amtx%3Ajournal&rft.genre=unknown&rft.jtitle=IETF-Announce+mailing+list&rft.atitle=Completion+of+IANA+Selection+of+IDNA+Prefix&rft.date=2003-02-14&rft.au=Internet+Assigned+Numbers+Authority&rft_id=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.atm.tut.fi%2Flist-archive%2Fietf-announce%2Fmsg13572.html&rfr_id=info%3Asid%2Fen.wikipedia.org%3AURL\" class=\"Z3988\"></span></li>\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"To download a binary or any file from internet and assign a certain name is as easy as:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-\n\n\"\"\"Ejemplo de uso:\n\n$ python3 bajaArch.py https://is.gd/1D3s1F bop_hoy.pdf\n\nbajará el pdf enlazado, poniéndole como nombre 'bop_hoy.pdf'.\n\n$ python3 bajaArch.py https://is.gd/1D3s1F \n\ny esto bajará el bop enlazado a la url, poniéndole como nombre 'bop'\nseguido de la fecha del día del uso del script y concluyendo con la extensión '.pdf'\n\n\"\"\"\n\nimport sys, requests\nfrom datetime import date\n\ndef downloadFrom(URLp,*rename):\n \"\"\"\n provide the downloading url and the new name if desired, otherwise renamed with date\n \"\"\"\n\n if URLp[-4] == '.':\n exten = URLp[-4:]\n else:\n exten = ''\n\n if rename:\n name = ''.join([rename[0],exten])\n else:\n today = date.today()\n d1 = today.strftime(\"%Y_%m_%d\")\n name = ''.join(['file_',d1,exten])\n\n req = requests.get(URLp)\n myfile = open(name,'wb')\n myfile.write(req.content)\ndownloadFrom('http://www.africau.edu/images/default/sample.pdf','samplefile')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4abb68d73cb0a6a2a2ec642c8bb218df0ad4eb39
| 73,761 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
data/spotify_suggester_app.ipynb
|
build-week-spoitify-1-mp/ML
|
e0bdfef1a2d32b8df673f8a04419bc5549aa7857
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
data/spotify_suggester_app.ipynb
|
build-week-spoitify-1-mp/ML
|
e0bdfef1a2d32b8df673f8a04419bc5549aa7857
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
data/spotify_suggester_app.ipynb
|
build-week-spoitify-1-mp/ML
|
e0bdfef1a2d32b8df673f8a04419bc5549aa7857
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 41.438764 | 6,937 | 0.424113 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Load and Read In Dataframes",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from google.colab import files\nuploaded = files.upload()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df1 = pd.read_csv('base_api_df (7).csv')\ndf2 = pd.read_csv('data-2.csv')\ndf3 = pd.read_csv('featuresdf.csv')\ndf4 = pd.read_csv('SpotifyFeatures.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Cut Dataframes Down to Track Ids and Music Features",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df1.head(1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df1 = df1.drop(columns=['albums', 'artists', 'tracks'])\ndf1.head(1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df2.head(1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df2 = df2.drop(columns=['explicit', 'key', 'popularity', 'release_date', 'year', 'artists', 'duration_ms', 'name', 'mode'])\ndf2.head(1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df3.head(1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df3 = df3.drop(columns=['key', 'name', 'artists', 'key', 'mode', 'duration_ms', 'time_signature'])\ndf3.head(1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df4.head(1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df4 = df4.drop(columns=['genre', 'popularity', 'key', 'artist_name', 'track_name', 'duration_ms', 'mode', 'time_signature'])\ndf4.head(1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Merge Dataframes",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Rename id columns so that columns from every dataframe are the same\ndf4 = df4.rename(columns={'track_id':'id'})\ndf1 = df1.rename(columns={'tracks_id':'id'})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"spotify_df = df1.merge(df2, how='outer')\nspotify_df = spotify_df.merge(df3, how='outer')\nspotify_df = spotify_df.merge(df4, how='outer')\nspotify_df.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"spotify_df = spotify_df.drop_duplicates()\nspotify_df['id'] = spotify_df['id'].drop_duplicates()\nspotify_df = spotify_df.dropna()\nspotify_df.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"spotify_df = spotify_df.rename(columns={'track_key':'id'})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"spotify_df.sample(10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"track_key = []\nfor i in range(spotify_df.shape[0]):\n\n track_key.append(i)\n\nlen(track_key)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"spotify_df['track_key'] = track_key\nspotify_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"spotify_df.to_csv('spotify_song_data.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Let's Create a Baseline Predictive Model Now",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\ntrain, test = train_test_split(spotify_df)\ntrain, test",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_train, X_test = train.drop(columns='id'), test.drop(columns='id')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler, OneHotEncoder\n\n# Instantiate Standard Scaler\nscaler = StandardScaler()\n\n# Fit_transform train data\nX_train_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(X_train)\n\n# Transform test data\nX_test_scaled = scaler.transform(X_test)\n\nX_train_scaled",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(X_train_scaled), len(X_test_scaled)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Reshape data\nimport numpy as np\nX_train = X_train_scaled.reshape((len(X_train), np.prod(X_train_scaled.shape[1:])))\nX_test = X_test_scaled.reshape((len(X_test), np.prod(X_test_scaled.shape[1:])))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(X_train),len(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create our baseline model\nfrom tensorflow import keras\nfrom tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential\nfrom tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Flatten\n\n# Important hyperparameters\ninputs = X_train.shape[1]\nepochs = 75\nbatch_size = 10\n\n# Create model\nmodel = Sequential([\n Dense(64, activation='relu', input_dim=inputs),\n Dense(64, activation='relu'),\n Dense(10, activation='softmax')\n ])\n\n# Compile model\nmodel.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='categorical_crossentropy')\n\n# Fit model\nmodel.fit(X_train, X_train,\n validation_data=(X_test, X_test),\n epochs=epochs,\n batch_size=batch_size\n )",
"Epoch 1/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 67s 2ms/step - loss: -175811424.0000 - val_loss: -626918464.0000\nEpoch 2/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 69s 3ms/step - loss: -2034432384.0000 - val_loss: -4077159936.0000\nEpoch 3/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 67s 2ms/step - loss: -7878820352.0000 - val_loss: -12598508544.0000\nEpoch 4/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 67s 2ms/step - loss: -19934423040.0000 - val_loss: -28449884160.0000\nEpoch 5/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 70s 3ms/step - loss: -40561459200.0000 - val_loss: -53766463488.0000\nEpoch 6/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 70s 3ms/step - loss: -71658807296.0000 - val_loss: -90689929216.0000\nEpoch 7/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 72s 3ms/step - loss: -115748831232.0000 - val_loss: -141680427008.0000\nEpoch 8/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 67s 2ms/step - loss: -175036612608.0000 - val_loss: -208814424064.0000\nEpoch 9/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 66s 2ms/step - loss: -251529576448.0000 - val_loss: -294075170816.0000\nEpoch 10/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 67s 2ms/step - loss: -347439497216.0000 - val_loss: -399721562112.0000\nEpoch 11/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 67s 2ms/step - loss: -465428086784.0000 - val_loss: -528631234560.0000\nEpoch 12/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 66s 2ms/step - loss: -607116918784.0000 - val_loss: -681960603648.0000\nEpoch 13/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 66s 2ms/step - loss: -774927876096.0000 - val_loss: -862095605760.0000\nEpoch 14/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 66s 2ms/step - loss: -971111202816.0000 - val_loss: -1071708897280.0000\nEpoch 15/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 66s 2ms/step - loss: -1197462388736.0000 - val_loss: -1312970506240.0000\nEpoch 16/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 68s 2ms/step - loss: -1457238441984.0000 - val_loss: -1587442614272.0000\nEpoch 17/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 66s 2ms/step - loss: -1751786848256.0000 - val_loss: -1897581641728.0000\nEpoch 18/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 66s 2ms/step - loss: -2083363618816.0000 - val_loss: -2245992382464.0000\nEpoch 19/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 67s 2ms/step - loss: -2453270429696.0000 - val_loss: -2634661494784.0000\nEpoch 20/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 68s 2ms/step - loss: -2867319275520.0000 - val_loss: -3066961068032.0000\nEpoch 21/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 67s 2ms/step - loss: -3323302772736.0000 - val_loss: -3542307569664.0000\nEpoch 22/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 70s 3ms/step - loss: -3825658232832.0000 - val_loss: -4064723861504.0000\nEpoch 23/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 71s 3ms/step - loss: -4377654591488.0000 - val_loss: -4636090564608.0000\nEpoch 24/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 68s 2ms/step - loss: -4975995387904.0000 - val_loss: -5257761914880.0000\nEpoch 25/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 65s 2ms/step - loss: -5629288644608.0000 - val_loss: -5933635731456.0000\nEpoch 26/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 64s 2ms/step - loss: -6338748350464.0000 - val_loss: -6665633529856.0000\nEpoch 27/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 63s 2ms/step - loss: -7105576173568.0000 - val_loss: -7457264893952.0000\nEpoch 28/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 64s 2ms/step - loss: -7929382567936.0000 - val_loss: -8306160041984.0000\nEpoch 29/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 64s 2ms/step - loss: -8817807982592.0000 - val_loss: -9218408054784.0000\nEpoch 30/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 66s 2ms/step - loss: -9767329202176.0000 - val_loss: -10192709222400.0000\nEpoch 31/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 64s 2ms/step - loss: -10784145932288.0000 - val_loss: -11235778101248.0000\nEpoch 32/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 64s 2ms/step - loss: -11864154046464.0000 - val_loss: -12345525927936.0000\nEpoch 33/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 68s 2ms/step - loss: -13019768684544.0000 - val_loss: -13527494426624.0000\nEpoch 34/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 68s 2ms/step - loss: -14244367040512.0000 - val_loss: -14780275359744.0000\nEpoch 35/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 67s 2ms/step - loss: -15543909220352.0000 - val_loss: -16107875336192.0000\nEpoch 36/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 65s 2ms/step - loss: -16920557387776.0000 - val_loss: -17515137728512.0000\nEpoch 37/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 65s 2ms/step - loss: -18379538694144.0000 - val_loss: -19004286566400.0000\nEpoch 38/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 64s 2ms/step - loss: -19919808757760.0000 - val_loss: -20575722405888.0000\nEpoch 39/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 65s 2ms/step - loss: -21544484995072.0000 - val_loss: -22232703172608.0000\nEpoch 40/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 65s 2ms/step - loss: -23255446454272.0000 - val_loss: -23972177510400.0000\nEpoch 41/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 64s 2ms/step - loss: -25050998636544.0000 - val_loss: -25800216674304.0000\nEpoch 42/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 65s 2ms/step - loss: -26936606720000.0000 - val_loss: -27721251946496.0000\nEpoch 43/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 66s 2ms/step - loss: -28916848787456.0000 - val_loss: -29728824098816.0000\nEpoch 44/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 68s 2ms/step - loss: -30987048189952.0000 - val_loss: -31838502387712.0000\nEpoch 45/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 66s 2ms/step - loss: -33156291887104.0000 - val_loss: -34039683612672.0000\nEpoch 46/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 66s 2ms/step - loss: -35426547007488.0000 - val_loss: -36341630894080.0000\nEpoch 47/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 66s 2ms/step - loss: -37789303308288.0000 - val_loss: -38742937042944.0000\nEpoch 48/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 66s 2ms/step - loss: -40264332738560.0000 - val_loss: -41248077381632.0000\nEpoch 49/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 67s 2ms/step - loss: -42838951723008.0000 - val_loss: -43866161938432.0000\nEpoch 50/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 65s 2ms/step - loss: -45527966154752.0000 - val_loss: -46587527036928.0000\nEpoch 51/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 64s 2ms/step - loss: -48329887055872.0000 - val_loss: -49425195991040.0000\nEpoch 52/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 65s 2ms/step - loss: -51237374394368.0000 - val_loss: -52372025901056.0000\nEpoch 53/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 65s 2ms/step - loss: -54266416857088.0000 - val_loss: -55432085241856.0000\nEpoch 54/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 68s 2ms/step - loss: -57403278098432.0000 - val_loss: -58612802125824.0000\nEpoch 55/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 66s 2ms/step - loss: -60656791322624.0000 - val_loss: -61905049747456.0000\nEpoch 56/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 67s 2ms/step - loss: -64043234623488.0000 - val_loss: -65327681503232.0000\nEpoch 57/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 67s 2ms/step - loss: -67543674912768.0000 - val_loss: -68872325562368.0000\nEpoch 58/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 69s 3ms/step - loss: -71190332833792.0000 - val_loss: -72548163256320.0000\nEpoch 59/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 67s 2ms/step - loss: -74946206236672.0000 - val_loss: -76341860892672.0000\nEpoch 60/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 67s 2ms/step - loss: -78831750742016.0000 - val_loss: -80271370092544.0000\nEpoch 61/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 67s 2ms/step - loss: -82855069745152.0000 - val_loss: -84336338534400.0000\nEpoch 62/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 69s 3ms/step - loss: -87014510690304.0000 - val_loss: -88531816939520.0000\nEpoch 63/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 69s 3ms/step - loss: -91308387467264.0000 - val_loss: -92865824817152.0000\nEpoch 64/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 67s 2ms/step - loss: -95742261723136.0000 - val_loss: -97341465952256.0000\nEpoch 65/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 66s 2ms/step - loss: -100310932520960.0000 - val_loss: -101955124854784.0000\nEpoch 66/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 67s 2ms/step - loss: -105038181564416.0000 - val_loss: -106710165356544.0000\nEpoch 67/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 68s 2ms/step - loss: -109901393166336.0000 - val_loss: -111621619843072.0000\nEpoch 68/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 68s 2ms/step - loss: -114913141850112.0000 - val_loss: -116671511527424.0000\nEpoch 69/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 66s 2ms/step - loss: -120080088170496.0000 - val_loss: -121879343923200.0000\nEpoch 70/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 67s 2ms/step - loss: -125397802942464.0000 - val_loss: -127236820697088.0000\nEpoch 71/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 67s 2ms/step - loss: -130874154680320.0000 - val_loss: -132755056754688.0000\nEpoch 72/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 67s 2ms/step - loss: -136505418842112.0000 - val_loss: -138431619399680.0000\nEpoch 73/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 68s 3ms/step - loss: -142306342600704.0000 - val_loss: -144267783700480.0000\nEpoch 74/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 66s 2ms/step - loss: -148256365477888.0000 - val_loss: -150257736351744.0000\nEpoch 75/75\n27362/27362 [==============================] - 66s 2ms/step - loss: -154377381740544.0000 - val_loss: -156423463895040.0000\n"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4abb774c57a0c23357219ead54f59dc5f0de4646
| 28,717 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
DataFrame_7.ipynb
|
heejinADP/TIL
|
6f9a95c9a21e38d641f69152271b98700941f7ca
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
DataFrame_7.ipynb
|
heejinADP/TIL
|
6f9a95c9a21e38d641f69152271b98700941f7ca
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
DataFrame_7.ipynb
|
heejinADP/TIL
|
6f9a95c9a21e38d641f69152271b98700941f7ca
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 24.481671 | 179 | 0.371627 |
[
[
[
"# Functions of DataFrame 7",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**이산화**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nfrom pandas import DataFrame\nnp.random.seed(777)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df=DataFrame({'c1':np.random.randn(20),\n 'c2':['a','a','a','a','a','a','a','a','a','a',\n 'b','b','b','b','b','b','b','b','b','b']})\nprint(df)",
" c1 c2\n0 -0.468209 a\n1 -0.822825 a\n2 -0.065380 a\n3 -0.713362 a\n4 0.906351 a\n5 0.766237 a\n6 0.826054 a\n7 -1.323683 a\n8 -1.752445 a\n9 1.002449 a\n10 0.544809 b\n11 1.895161 b\n12 -0.769357 b\n13 -1.403096 b\n14 -0.632468 b\n15 -0.558874 b\n16 -1.233231 b\n17 -0.439504 b\n18 0.914787 b\n19 0.265041 b\n"
],
[
"bins=np.linspace(df.c1.min(),df.c1.max(),10)\ndf['c1_bin']=np.digitize(df['c1'],bins)\nprint(df)",
" c1 c2 c1_bin\n0 -0.468209 a 4\n1 -0.822825 a 3\n2 -0.065380 a 5\n3 -0.713362 a 3\n4 0.906351 a 7\n5 0.766237 a 7\n6 0.826054 a 7\n7 -1.323683 a 2\n8 -1.752445 a 1\n9 1.002449 a 7\n10 0.544809 b 6\n11 1.895161 b 10\n12 -0.769357 b 3\n13 -1.403096 b 1\n14 -0.632468 b 3\n15 -0.558874 b 3\n16 -1.233231 b 2\n17 -0.439504 b 4\n18 0.914787 b 7\n19 0.265041 b 5\n"
],
[
"print(df.groupby('c1_bin')['c1'].size())",
"c1_bin\n1 2\n2 2\n3 5\n4 2\n5 2\n6 1\n7 5\n10 1\nName: c1, dtype: int64\n"
],
[
"print(df.groupby('c1_bin')['c1'].mean())",
"c1_bin\n1 -1.577770\n2 -1.278457\n3 -0.699377\n4 -0.453856\n5 0.099830\n6 0.544809\n7 0.883176\n10 1.895161\nName: c1, dtype: float64\n"
],
[
"print(df.groupby('c1_bin')['c1'].std())",
"c1_bin\n1 0.247027\n2 0.063959\n3 0.105535\n4 0.020298\n5 0.233643\n6 NaN\n7 0.090416\n10 NaN\nName: c1, dtype: float64\n"
],
[
"print(df.groupby('c1_bin')['c2'].value_counts())",
"c1_bin c2\n1 a 1\n b 1\n2 a 1\n b 1\n3 b 3\n a 2\n4 a 1\n b 1\n5 a 1\n b 1\n6 b 1\n7 a 4\n b 1\n10 b 1\nName: c2, dtype: int64\n"
],
[
"print(df[df['c1_bin']==2])",
" c1 c2 c1_bin\n7 -1.323683 a 2\n16 -1.233231 b 2\n"
],
[
"print(pd.get_dummies(df['c1_bin'],prefix='c1'))",
" c1_1 c1_2 c1_3 c1_4 c1_5 c1_6 c1_7 c1_10\n0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0\n1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0\n2 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0\n3 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0\n4 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0\n5 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0\n6 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0\n7 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0\n8 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0\n9 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0\n10 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0\n11 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1\n12 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0\n13 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0\n14 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0\n15 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0\n16 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0\n17 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0\n18 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0\n19 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0\n"
],
[
"print(df.c1.mean())",
"-0.15307715643591518\n"
],
[
"df['high_low']=np.where(df['c1']>=df.c1.mean(),'high','low')\nprint(df)",
" c1 c2 c1_bin high_low\n0 -0.468209 a 4 low\n1 -0.822825 a 3 low\n2 -0.065380 a 5 high\n3 -0.713362 a 3 low\n4 0.906351 a 7 high\n5 0.766237 a 7 high\n6 0.826054 a 7 high\n7 -1.323683 a 2 low\n8 -1.752445 a 1 low\n9 1.002449 a 7 high\n10 0.544809 b 6 high\n11 1.895161 b 10 high\n12 -0.769357 b 3 low\n13 -1.403096 b 1 low\n14 -0.632468 b 3 low\n15 -0.558874 b 3 low\n16 -1.233231 b 2 low\n17 -0.439504 b 4 low\n18 0.914787 b 7 high\n19 0.265041 b 5 high\n"
],
[
"print(df.groupby('high_low')['c1'].size())",
"high_low\nhigh 9\nlow 11\nName: c1, dtype: int64\n"
],
[
"print(df.groupby('high_low')['c1'].mean())",
"high_low\nhigh 0.783945\nlow -0.919732\nName: c1, dtype: float64\n"
],
[
"print(df.groupby('high_low')['c1'].std())",
"high_low\nhigh 0.543661\nlow 0.437074\nName: c1, dtype: float64\n"
],
[
"Q1=np.percentile(df['c1'],25)\nQ3=np.percentile(df['c1'],75)\ndf['h_m_l']=np.where(df['c1']>=Q3, '01_high',np.where(df['c1']>=Q1, '02_median', '03_low'))\nprint(df)",
" c1 c2 c1_bin high_low h_m_l\n0 -0.468209 a 4 low 02_median\n1 -0.822825 a 3 low 03_low\n2 -0.065380 a 5 high 02_median\n3 -0.713362 a 3 low 02_median\n4 0.906351 a 7 high 01_high\n5 0.766237 a 7 high 02_median\n6 0.826054 a 7 high 01_high\n7 -1.323683 a 2 low 03_low\n8 -1.752445 a 1 low 03_low\n9 1.002449 a 7 high 01_high\n10 0.544809 b 6 high 02_median\n11 1.895161 b 10 high 01_high\n12 -0.769357 b 3 low 02_median\n13 -1.403096 b 1 low 03_low\n14 -0.632468 b 3 low 02_median\n15 -0.558874 b 3 low 02_median\n16 -1.233231 b 2 low 03_low\n17 -0.439504 b 4 low 02_median\n18 0.914787 b 7 high 01_high\n19 0.265041 b 5 high 02_median\n"
]
],
[
[
"**재구조화 : reshaping**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data=DataFrame({'cust_id': ['c1', 'c1', 'c1', 'c2', 'c2', 'c2', 'c3', 'c3', 'c3'],\n 'prod_cd': ['p1', 'p2', 'p3', 'p1', 'p2', 'p3', 'p1', 'p2', 'p3'],\n 'grade' : ['A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'B', 'B', 'B'],\n 'pch_amt': [30, 10, 0, 40, 15, 30, 0, 0, 10]})\nprint(data)",
" cust_id prod_cd grade pch_amt\n0 c1 p1 A 30\n1 c1 p2 A 10\n2 c1 p3 A 0\n3 c2 p1 A 40\n4 c2 p2 A 15\n5 c2 p3 A 30\n6 c3 p1 B 0\n7 c3 p2 B 0\n8 c3 p3 B 10\n"
],
[
"dp=data.pivot(index='cust_id',columns='prod_cd',values='pch_amt')\nprint(dp)",
"prod_cd p1 p2 p3\ncust_id \nc1 30 10 0\nc2 40 15 30\nc3 0 0 10\n"
],
[
"dp=pd.pivot_table(data,index='cust_id',columns='prod_cd',values='pch_amt')\nprint(dp)",
"prod_cd p1 p2 p3\ncust_id \nc1 30 10 0\nc2 40 15 30\nc3 0 0 10\n"
],
[
"dp=pd.pivot_table(data,index=['cust_id','grade'],columns='prod_cd',\n values='pch_amt')\nprint(dp)",
"prod_cd p1 p2 p3\ncust_id grade \nc1 A 30 10 0\nc2 A 40 15 30\nc3 B 0 0 10\n"
]
],
[
[
"=======================================================",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mul_index=pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples([('cust_1', '2018'),\n ('cust_1', '2019'),\n ('cust_2', '2018'),\n ('cust_2', '2019'),])\nprint(mul_index)",
"MultiIndex(levels=[['cust_1', 'cust_2'], ['2018', '2019']],\n labels=[[0, 0, 1, 1], [0, 1, 0, 1]])\n"
],
[
"data=DataFrame(data=np.arange(16).reshape(4,4),index=mul_index,\n columns=['prd_1','prd_2','prd_3','prd_4'],dtype='int')\nprint(data)",
" prd_1 prd_2 prd_3 prd_4\ncust_1 2018 0 1 2 3\n 2019 4 5 6 7\ncust_2 2018 8 9 10 11\n 2019 12 13 14 15\n"
],
[
"data_stacked=data.stack()\nprint(data_stacked)",
"cust_1 2018 prd_1 0\n prd_2 1\n prd_3 2\n prd_4 3\n 2019 prd_1 4\n prd_2 5\n prd_3 6\n prd_4 7\ncust_2 2018 prd_1 8\n prd_2 9\n prd_3 10\n prd_4 11\n 2019 prd_1 12\n prd_2 13\n prd_3 14\n prd_4 15\ndtype: int32\n"
],
[
"print(data_stacked.index)",
"MultiIndex(levels=[['cust_1', 'cust_2'], ['2018', '2019'], ['prd_1', 'prd_2', 'prd_3', 'prd_4']],\n labels=[[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1], [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1], [0, 1, 2, 3, 0, 1, 2, 3, 0, 1, 2, 3, 0, 1, 2, 3]])\n"
],
[
"print(data_stacked['cust_2']['2018'][['prd_1','prd_2']])",
"prd_1 8\nprd_2 9\ndtype: int32\n"
],
[
"data.loc['cust_2','prd_4']=np.nan\nprint(data)",
" prd_1 prd_2 prd_3 prd_4\ncust_1 2018 0 1 2 3.0\n 2019 4 5 6 7.0\ncust_2 2018 8 9 10 NaN\n 2019 12 13 14 NaN\n"
],
[
"print(data.stack())",
"cust_1 2018 prd_1 0.0\n prd_2 1.0\n prd_3 2.0\n prd_4 3.0\n 2019 prd_1 4.0\n prd_2 5.0\n prd_3 6.0\n prd_4 7.0\ncust_2 2018 prd_1 8.0\n prd_2 9.0\n prd_3 10.0\n 2019 prd_1 12.0\n prd_2 13.0\n prd_3 14.0\ndtype: float64\n"
],
[
"print(data.stack(dropna=False))",
"cust_1 2018 prd_1 0.0\n prd_2 1.0\n prd_3 2.0\n prd_4 3.0\n 2019 prd_1 4.0\n prd_2 5.0\n prd_3 6.0\n prd_4 7.0\ncust_2 2018 prd_1 8.0\n prd_2 9.0\n prd_3 10.0\n prd_4 NaN\n 2019 prd_1 12.0\n prd_2 13.0\n prd_3 14.0\n prd_4 NaN\ndtype: float64\n"
],
[
"print(data_stacked)",
"cust_1 2018 prd_1 0\n prd_2 1\n prd_3 2\n prd_4 3\n 2019 prd_1 4\n prd_2 5\n prd_3 6\n prd_4 7\ncust_2 2018 prd_1 8\n prd_2 9\n prd_3 10\n prd_4 11\n 2019 prd_1 12\n prd_2 13\n prd_3 14\n prd_4 15\ndtype: int32\n"
],
[
"print(data_stacked.unstack(level=-1))",
" prd_1 prd_2 prd_3 prd_4\ncust_1 2018 0 1 2 3\n 2019 4 5 6 7\ncust_2 2018 8 9 10 11\n 2019 12 13 14 15\n"
],
[
"print(data_stacked.unstack(level=0))",
" cust_1 cust_2\n2018 prd_1 0 8\n prd_2 1 9\n prd_3 2 10\n prd_4 3 11\n2019 prd_1 4 12\n prd_2 5 13\n prd_3 6 14\n prd_4 7 15\n"
],
[
"print(data_stacked.unstack(level=1))",
" 2018 2019\ncust_1 prd_1 0 4\n prd_2 1 5\n prd_3 2 6\n prd_4 3 7\ncust_2 prd_1 8 12\n prd_2 9 13\n prd_3 10 14\n prd_4 11 15\n"
],
[
"data_stacked_unstacked=data_stacked.unstack(level=-1)\nprint(data_stacked_unstacked)",
" prd_1 prd_2 prd_3 prd_4\ncust_1 2018 0 1 2 3\n 2019 4 5 6 7\ncust_2 2018 8 9 10 11\n 2019 12 13 14 15\n"
],
[
"print(type(data_stacked_unstacked))",
"<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>\n"
],
[
"dsu_df=data_stacked_unstacked.reset_index()\nprint(dsu_df)",
" level_0 level_1 prd_1 prd_2 prd_3 prd_4\n0 cust_1 2018 0 1 2 3\n1 cust_1 2019 4 5 6 7\n2 cust_2 2018 8 9 10 11\n3 cust_2 2019 12 13 14 15\n"
],
[
"dsu_df=dsu_df.rename(columns={'level_0':'custID',\n 'level_1':'year'})\nprint(dsu_df)",
" custID year prd_1 prd_2 prd_3 prd_4\n0 cust_1 2018 0 1 2 3\n1 cust_1 2019 4 5 6 7\n2 cust_2 2018 8 9 10 11\n3 cust_2 2019 12 13 14 15\n"
]
],
[
[
"=======================================================",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data=DataFrame({'cust_id': ['c1', 'c1', 'c2', 'c2'],\n 'prod_cd': ['p1', 'p2', 'p1', 'p2'],\n 'pch_cnt' : [1,2,3,4],\n 'pch_amt': [100,200,300,400]})\nprint(data)",
" cust_id prod_cd pch_cnt pch_amt\n0 c1 p1 1 100\n1 c1 p2 2 200\n2 c2 p1 3 300\n3 c2 p2 4 400\n"
],
[
"print(pd.melt(data))",
" variable value\n0 cust_id c1\n1 cust_id c1\n2 cust_id c2\n3 cust_id c2\n4 prod_cd p1\n5 prod_cd p2\n6 prod_cd p1\n7 prod_cd p2\n8 pch_cnt 1\n9 pch_cnt 2\n10 pch_cnt 3\n11 pch_cnt 4\n12 pch_amt 100\n13 pch_amt 200\n14 pch_amt 300\n15 pch_amt 400\n"
],
[
"print(pd.melt(data,id_vars=['cust_id','prod_cd']))",
" cust_id prod_cd variable value\n0 c1 p1 pch_cnt 1\n1 c1 p2 pch_cnt 2\n2 c2 p1 pch_cnt 3\n3 c2 p2 pch_cnt 4\n4 c1 p1 pch_amt 100\n5 c1 p2 pch_amt 200\n6 c2 p1 pch_amt 300\n7 c2 p2 pch_amt 400\n"
],
[
"data_melt=pd.melt(data,id_vars=['cust_id','prod_cd'],\n var_name='pch_cd',\n value_name='pch_value')\nprint(data_melt)",
" cust_id prod_cd pch_cd pch_value\n0 c1 p1 pch_cnt 1\n1 c1 p2 pch_cnt 2\n2 c2 p1 pch_cnt 3\n3 c2 p2 pch_cnt 4\n4 c1 p1 pch_amt 100\n5 c1 p2 pch_amt 200\n6 c2 p1 pch_amt 300\n7 c2 p2 pch_amt 400\n"
],
[
"print(data_melt.index)",
"RangeIndex(start=0, stop=8, step=1)\n"
],
[
"print(data_melt.columns)",
"Index(['cust_id', 'prod_cd', 'pch_cd', 'pch_value'], dtype='object')\n"
]
],
[
[
"=======================================================",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data_melt_pivot=pd.pivot_table(data_melt,index=['cust_id','prod_cd'],\n columns='pch_cd',values='pch_value')\nprint(data_melt_pivot)",
"pch_cd pch_amt pch_cnt\ncust_id prod_cd \nc1 p1 100 1\n p2 200 2\nc2 p1 300 3\n p2 400 4\n"
],
[
"print(data_melt_pivot.index)",
"MultiIndex(levels=[['c1', 'c2'], ['p1', 'p2']],\n labels=[[0, 0, 1, 1], [0, 1, 0, 1]],\n names=['cust_id', 'prod_cd'])\n"
],
[
"print(data_melt_pivot.columns)",
"Index(['pch_amt', 'pch_cnt'], dtype='object', name='pch_cd')\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4abb8d1ad133ae0d56145c90129876375fe96a61
| 86,468 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
code/supplementary/assessing_architecture_and_performance.ipynb
|
t-davidson/ffc-socius
|
6f023fcd04efc14ad3b41b7091afe01ff9d35cf9
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
code/supplementary/assessing_architecture_and_performance.ipynb
|
t-davidson/ffc-socius
|
6f023fcd04efc14ad3b41b7091afe01ff9d35cf9
|
[
"MIT"
] | 12 |
2020-01-28T22:32:13.000Z
|
2022-03-11T23:33:25.000Z
|
code/supplementary/assessing_architecture_and_performance.ipynb
|
t-davidson/ffc-socius
|
6f023fcd04efc14ad3b41b7091afe01ff9d35cf9
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 77.758993 | 14,484 | 0.651756 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport statsmodels.formula.api as smf\nfrom statsmodels.iolib.summary2 import summary_col\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n%matplotlib inline\n#%config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'retina' # Uncomment if using a retina display\nplt.rc('pdf', fonttype=42)\nplt.rcParams['ps.useafm'] = True\nplt.rcParams['pdf.use14corefonts'] = True\n#plt.rcParams['text.usetex'] = True # Uncomment if LaTeX installed to render plots in LaTeX\nplt.rcParams['font.serif'] = 'Times'\nplt.rcParams['font.family'] = 'serif'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = pd.read_csv('../output/model_params_and_results.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Score is defined as the absolute value of the mean of the negative MSE on the test sets across all k-folds used in training. Other variables are renamed.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df['score'] = abs(df['mean_test_score'])\ndf['num_hidden_layers'] = df['param_num_hidden_layers']\ndf['hidden_layer_size'] = df['param_hidden_layer_size']\ndf['activation_function'] = df['param_activation_function']",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can now look at some descriptive statistics for different parameters.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pd.DataFrame.hist(data=df, column='score',bins=50)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.scatter(x=df.num_hidden_layers, y=df.score)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.scatter(x=df.hidden_layer_size, y=df.score)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"activation_dummies = pd.get_dummies(df.activation_function)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df['layers_and_size_interaction'] = df.num_hidden_layers + df.hidden_layer_size",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = pd.concat([df,activation_dummies],axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.columns",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Basic OLS model:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model1 = smf.ols(formula='score ~ num_hidden_layers + hidden_layer_size\\\n + relu + sigmoid + tanh', data=df)\n\nresults1 = model1.fit()\nprint(results1.summary())",
" OLS Regression Results \n==============================================================================\nDep. Variable: score R-squared: 0.384\nModel: OLS Adj. R-squared: 0.293\nMethod: Least Squares F-statistic: 4.240\nDate: Tue, 06 Nov 2018 Prob (F-statistic): 0.00420\nTime: 14:35:30 Log-Likelihood: -60.205\nNo. Observations: 40 AIC: 132.4\nDf Residuals: 34 BIC: 142.5\nDf Model: 5 \nCovariance Type: nonrobust \n=====================================================================================\n coef std err t P>|t| [0.025 0.975]\n-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\nIntercept 2.1931 0.541 4.052 0.000 1.093 3.293\nnum_hidden_layers -0.6496 0.201 -3.235 0.003 -1.058 -0.242\nhidden_layer_size -0.0042 0.002 -1.865 0.071 -0.009 0.000\nrelu 0.5912 0.529 1.118 0.271 -0.483 1.666\nsigmoid 0.0697 0.529 0.132 0.896 -1.005 1.144\ntanh 0.0880 0.529 0.166 0.869 -0.987 1.162\n==============================================================================\nOmnibus: 44.789 Durbin-Watson: 1.227\nProb(Omnibus): 0.000 Jarque-Bera (JB): 220.162\nSkew: 2.537 Prob(JB): 1.56e-48\nKurtosis: 13.313 Cond. No. 721.\n==============================================================================\n\nWarnings:\n[1] Standard Errors assume that the covariance matrix of the errors is correctly specified.\n"
]
],
[
[
"OLS model with interaction between layer number and size:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model2 = smf.ols(formula='score ~ num_hidden_layers + hidden_layer_size + layers_and_size_interaction \\\n + relu + sigmoid + tanh', data=df)\n\nresults2 = model2.fit()\nprint(results2.summary())",
" OLS Regression Results \n==============================================================================\nDep. Variable: score R-squared: 0.384\nModel: OLS Adj. R-squared: 0.293\nMethod: Least Squares F-statistic: 4.240\nDate: Tue, 06 Nov 2018 Prob (F-statistic): 0.00420\nTime: 14:35:34 Log-Likelihood: -60.205\nNo. Observations: 40 AIC: 132.4\nDf Residuals: 34 BIC: 142.5\nDf Model: 5 \nCovariance Type: nonrobust \n===============================================================================================\n coef std err t P>|t| [0.025 0.975]\n-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\nIntercept 2.1931 0.541 4.052 0.000 1.093 3.293\nnum_hidden_layers -0.4317 0.134 -3.219 0.003 -0.704 -0.159\nhidden_layer_size 0.2138 0.067 3.171 0.003 0.077 0.351\nlayers_and_size_interaction -0.2179 0.067 -3.267 0.002 -0.354 -0.082\nrelu 0.5912 0.529 1.118 0.271 -0.483 1.666\nsigmoid 0.0697 0.529 0.132 0.896 -1.005 1.144\ntanh 0.0880 0.529 0.166 0.869 -0.987 1.162\n==============================================================================\nOmnibus: 44.789 Durbin-Watson: 1.227\nProb(Omnibus): 0.000 Jarque-Bera (JB): 220.162\nSkew: 2.537 Prob(JB): 1.56e-48\nKurtosis: 13.313 Cond. No. 8.25e+15\n==============================================================================\n\nWarnings:\n[1] Standard Errors assume that the covariance matrix of the errors is correctly specified.\n[2] The smallest eigenvalue is 3.06e-26. This might indicate that there are\nstrong multicollinearity problems or that the design matrix is singular.\n"
]
],
[
[
"None of the coefficients are significant, making it difficult to interpret the results of the model. Overall it appears that all of the activation functions have a stronger negative effect on mean squared error (thus improving the predictions) than the reference category, the linear activation function. The number of hidden layers and the interaction between this and the hidden layer size (the number of neurons in the layer) are both also negative, which hidden layer size alone is positive.\n\nAn issue with the current data is that the outliers with extremely high MSE, where the model was never able to converge towards sensible predictions, may be biasing the results. To assess whether this is the case I can re-run the models excluding these outliers.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_ = df[df['score'] <= 1.0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Basic model without outliers:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model3 = smf.ols(formula='score ~ num_hidden_layers + hidden_layer_size \\\n + relu + sigmoid + tanh', data=df_)\n\nresults3 = model3.fit()\nprint(results3.summary())",
" OLS Regression Results \n==============================================================================\nDep. Variable: score R-squared: 0.223\nModel: OLS Adj. R-squared: 0.093\nMethod: Least Squares F-statistic: 1.718\nDate: Tue, 06 Nov 2018 Prob (F-statistic): 0.161\nTime: 14:35:46 Log-Likelihood: 24.291\nNo. Observations: 36 AIC: -36.58\nDf Residuals: 30 BIC: -27.08\nDf Model: 5 \nCovariance Type: nonrobust \n=====================================================================================\n coef std err t P>|t| [0.025 0.975]\n-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\nIntercept 0.2789 0.083 3.374 0.002 0.110 0.448\nnum_hidden_layers -0.0399 0.028 -1.450 0.157 -0.096 0.016\nhidden_layer_size 0.0006 0.000 2.106 0.044 1.78e-05 0.001\nrelu -0.0022 0.064 -0.035 0.972 -0.132 0.128\nsigmoid -0.0741 0.064 -1.165 0.253 -0.204 0.056\ntanh -0.0538 0.064 -0.845 0.405 -0.184 0.076\n==============================================================================\nOmnibus: 50.759 Durbin-Watson: 2.121\nProb(Omnibus): 0.000 Jarque-Bera (JB): 292.579\nSkew: 3.113 Prob(JB): 2.93e-64\nKurtosis: 15.502 Cond. No. 794.\n==============================================================================\n\nWarnings:\n[1] Standard Errors assume that the covariance matrix of the errors is correctly specified.\n"
]
],
[
[
"Including interactions:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model4 = smf.ols(formula='score ~ num_hidden_layers + hidden_layer_size + layers_and_size_interaction \\\n + relu + sigmoid + tanh', data=df_)\n\nresults4 = model4.fit()\nprint(results4.summary())",
" OLS Regression Results \n==============================================================================\nDep. Variable: score R-squared: 0.223\nModel: OLS Adj. R-squared: 0.093\nMethod: Least Squares F-statistic: 1.718\nDate: Tue, 06 Nov 2018 Prob (F-statistic): 0.161\nTime: 14:35:50 Log-Likelihood: 24.291\nNo. Observations: 36 AIC: -36.58\nDf Residuals: 30 BIC: -27.08\nDf Model: 5 \nCovariance Type: nonrobust \n===============================================================================================\n coef std err t P>|t| [0.025 0.975]\n-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\nIntercept 0.2789 0.083 3.374 0.002 0.110 0.448\nnum_hidden_layers -0.0268 0.018 -1.461 0.155 -0.064 0.011\nhidden_layer_size 0.0137 0.009 1.493 0.146 -0.005 0.032\nlayers_and_size_interaction -0.0131 0.009 -1.428 0.164 -0.032 0.006\nrelu -0.0022 0.064 -0.035 0.972 -0.132 0.128\nsigmoid -0.0741 0.064 -1.165 0.253 -0.204 0.056\ntanh -0.0538 0.064 -0.845 0.405 -0.184 0.076\n==============================================================================\nOmnibus: 50.759 Durbin-Watson: 2.121\nProb(Omnibus): 0.000 Jarque-Bera (JB): 292.579\nSkew: 3.113 Prob(JB): 2.93e-64\nKurtosis: 15.502 Cond. No. 7.99e+16\n==============================================================================\n\nWarnings:\n[1] Standard Errors assume that the covariance matrix of the errors is correctly specified.\n[2] The smallest eigenvalue is 3.27e-28. This might indicate that there are\nstrong multicollinearity problems or that the design matrix is singular.\n"
]
],
[
[
"Here we see that the overall model fit has improved, with the R-squared value increasing from 0.079 to 0.374. The coefficient for the ReLU activation is also positive now, consistent with the observation that its performance tends to fluctuate more than the other functions.\n\nOverall these results show that there are no clear, statistically significant, effects of basic architecture on model performance. Nonetheless the observed differences in the results elsewhere provide some evidence that models with more layers and node and non-linear activation are better able to generalize to out-of-sample data. The small number of observations may also be preventing us from seeing statistically significant relationships. Future work should assess the performance of models over a greater range of architectures to better assess how these choices affect predictive performance.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"info = {'N': lambda x: str(int(x.nobs)),\n 'R2': lambda x: '%.3f' % x.rsquared,\n 'R2-adj': lambda x: '%.3f' % x.rsquared_adj,\n 'F': lambda x: '%.3f' % x.fvalue} \n\ntbl = summary_col([results1, results2, results3, results4],\n model_names=['Model 1', 'Model 2', 'Model 3', 'Model 4'],\n info_dict = info,\n stars=True, \n float_format='%0.4f',\n regressor_order=['num_hidden_layers', 'hidden_layer_size', 'layer_and_size_interaction',\n 'relu', 'sigmoid', 'tanh', 'Intercept'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tbl # Order is incorrect here even though specified above. Manually changed for paper.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4abb8df44b2f38de9fbeac49cb79d062346481f6
| 6,063 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Data_processing/Data_processing_scripts/Proximity_to_points.ipynb
|
uwescience/DSSG2017-Equity
|
b48247017824629be57df35661fda89f8ab07e3e
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2017-06-27T21:43:51.000Z
|
2018-10-11T16:50:50.000Z
|
Data_processing/Data_processing_scripts/Proximity_to_points.ipynb
|
uwescience/DSSG2017-Equity
|
b48247017824629be57df35661fda89f8ab07e3e
|
[
"MIT"
] | 28 |
2017-06-27T18:29:17.000Z
|
2017-08-18T21:37:11.000Z
|
Data_processing/Data_processing_scripts/Proximity_to_points.ipynb
|
uwescience/DSSG2017-Equity
|
b48247017824629be57df35661fda89f8ab07e3e
|
[
"MIT"
] | 5 |
2017-06-27T18:20:17.000Z
|
2020-03-21T21:04:57.000Z
| 25.47479 | 107 | 0.454396 |
[
[
[
"#for a list of points of interest, find the shortest distance from all BG centroids to nearest poi\n\nimport pandas\nimport math",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#load in the POIs\ninputs = pandas.read_csv('food_banks.csv')[['long','lat']]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# function to find the (straight line) distance between 2 lat,long points\ndef distance(lon1,lat1,lon2,lat2):\n radius = 6371 # km\n\n dlat = math.radians(lat2-lat1)\n dlon = math.radians(lon2-lon1)\n a = math.sin(dlat/2) * math.sin(dlat/2) + math.cos(math.radians(lat1)) \\\n * math.cos(math.radians(lat2)) * math.sin(dlon/2) * math.sin(dlon/2)\n c = 2 * math.atan2(math.sqrt(a), math.sqrt(1-a))\n d = radius * c\n\n return d",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#load the BG centroids\nBG_centroids = pandas.read_csv('BG_centroids.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def get_shortest_distance(long1,lat1,inputs):\n dist = 100000000000\n \n #find the closest point (straight distance)\n for index, row in inputs.iterrows():\n long1_fl = float(long1)\n lat1_fl = float(lat1)\n long2_fl = float(row['long'])\n lat2_fl = float(row['lat'])\n dist_test = distance(long1_fl,lat1_fl,long2_fl,lat2_fl)\n if dist_test < dist:\n dist = dist_test\n \n return dist",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for index, row in BG_centroids.iterrows():\n long1 = str(row['long'])\n lat1 = str(row['lat'])\n #print(long1,lat1)\n distance_value = get_shortest_distance(long1,lat1,inputs)\n BG_centroids.set_value(index, 'distance', distance_value)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#distance value are in km\nBG_centroids.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#save to an appropriate file\nBG_centroids.to_csv('BG_dist_food_banks.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4abba6284ec33950a84f79d1326528ae74afc72a
| 19,894 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
03-fundamentals-of-python/03-lists.ipynb
|
noushinkarim/rcsc18_lessons
|
f7eafc5b0f2d601e5cf0da63cc857c7d02827d5a
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | null | null | null |
03-fundamentals-of-python/03-lists.ipynb
|
noushinkarim/rcsc18_lessons
|
f7eafc5b0f2d601e5cf0da63cc857c7d02827d5a
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | null | null | null |
03-fundamentals-of-python/03-lists.ipynb
|
noushinkarim/rcsc18_lessons
|
f7eafc5b0f2d601e5cf0da63cc857c7d02827d5a
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | null | null | null | 22.840413 | 408 | 0.529557 |
[
[
[
"# Storing Multiple Values in Lists",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Just as a `for` loop is a way to do operations many times,\na list is a way to store many values.\nUnlike NumPy arrays,\nlists are built into the language (so we don't have to load a library\nto use them).\nWe create a list by putting values inside square brackets and separating the values with commas:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"odds = [1,3,5,7]\nodds",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We select individual elements from lists by indexing them:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"weird = [\"bob\",5,5.8,[1,2,3],sum]\nodds",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"and if we loop over a list,\nthe loop variable is assigned elements one at a time:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"odds = [1,3,5,7]\nodds[2]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"There is one important difference between lists and strings:\nwe can change the values in a list,\nbut we cannot change individual characters in a string.\nFor example:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for o in weird:\n print(o)",
"bob\n5\n5.8\n[1, 2, 3]\n<built-in function sum>\n"
]
],
[
[
"works, but:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"odds[2] = 17",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"does not.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"odds",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Ch-Ch-Ch-Ch-Changes\n\nData which can be modified in place is called mutable,\nwhile data which cannot be modified is called immutable.\nStrings and numbers are immutable. This does not mean that variables with string or number values\nare constants, but when we want to change the value of a string or number variable, we can only\nreplace the old value with a completely new value.\nLists and arrays, on the other hand, are mutable: we can modify them after they have been\ncreated. We can change individual elements, append new elements, or reorder the whole list. For\nsome operations, like sorting, we can choose whether to use a function that modifies the data\nin-place or a function that returns a modified copy and leaves the original unchanged.\nBe careful when modifying data in-place. If two variables refer to the same list, and you modify\nthe list value, it will change for both variables!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"evens = odds",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"If you want variables with mutable values to be independent, you\nmust make a copy of the value when you assign it.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"evens[1] = 200",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Because of pitfalls like this, code which modifies data in place can be more difficult to\nunderstand. However, it is often far more efficient to modify a large data structure in place\nthan to create a modified copy for every small change. You should consider both of these aspects\nwhen writing your code.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"evens",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"odds",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Nested Lists\nSince lists can contain any Python variable, it can even contain other lists.\nFor example, we could represent the products in the shelves of a small grocery shop:\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Here is a visual example of how indexing a list of lists `x` works:\n[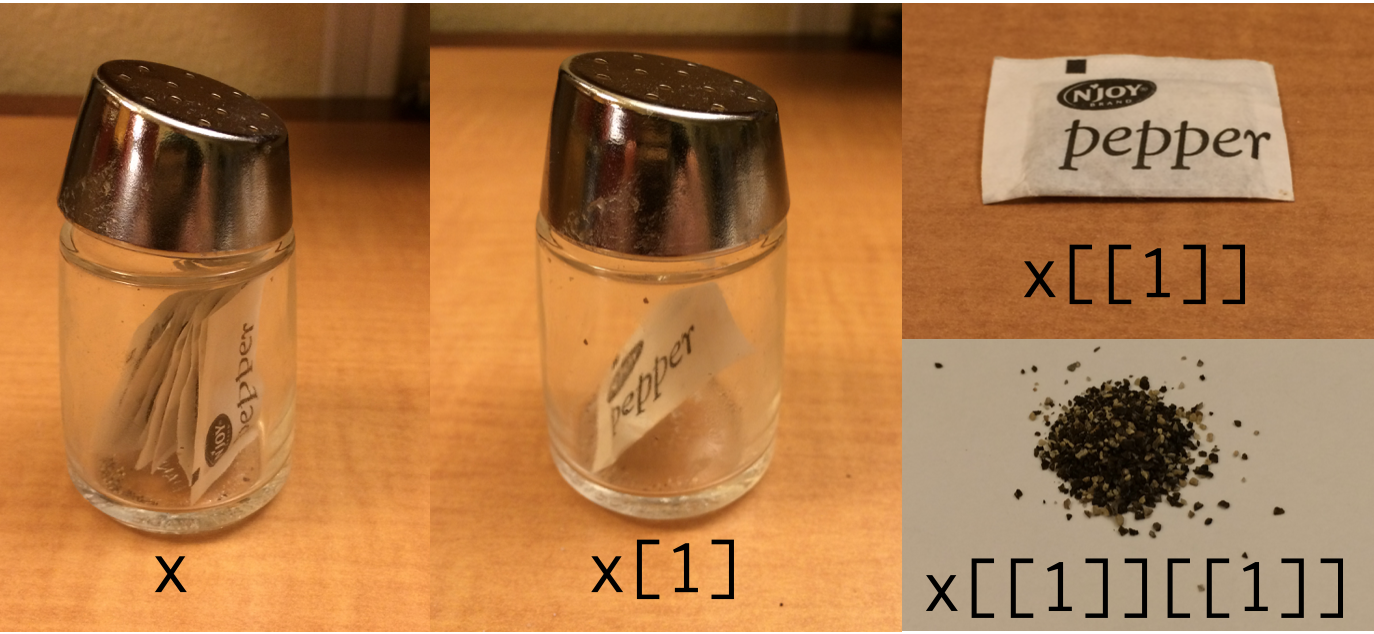](https://twitter.com/hadleywickham/status/643381054758363136)\n\nUsing the previously declared list `x`, these would be the results of the\nindex operations shown in the image:\n\n*Thanks to [Hadley Wickham](https://twitter.com/hadleywickham/status/643381054758363136) for the image above.*",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Heterogeneous Lists\n\nLists in Python can contain elements of different types. Example:\n```python\nsample_ages = [10, 12.5, 'Unknown']\n```\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"There are many ways to change the contents of lists besides assigning new values to\nindividual elements:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"While modifying in place, it is useful to remember that Python treats lists in a slightly\ncounter-intuitive way.\n\nIf we make a list and (attempt to) copy it then modify in place, we can cause all sorts of trouble:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"This is because Python stores a list in memory, and then can use multiple names to refer to the\nsame list. If all we want to do is copy a (simple) list, we can use the `list` function, so we do\nnot modify a list we did not mean to:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"This is different from how variables worked in lesson 1, and more similar to how a spreadsheet\nworks.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n<section class=\"challenge panel panel-success\">\n<div class=\"panel-heading\">\n<h2><span class=\"fa fa-pencil\"></span> Challenge: Turn a String Into a List</h2>\n</div>\n\n\n<div class=\"panel-body\">\n\n<p>Use a for-loop to convert the string \"hello\" into a list of letters:</p>\n<div class=\"codehilite\"><pre><span></span><span class=\"p\">[</span><span class=\"s2\">"h"</span><span class=\"p\">,</span> <span class=\"s2\">"e"</span><span class=\"p\">,</span> <span class=\"s2\">"l"</span><span class=\"p\">,</span> <span class=\"s2\">"l"</span><span class=\"p\">,</span> <span class=\"s2\">"o"</span><span class=\"p\">]</span>\n</pre></div>\n\n\n<p>Hint: You can create an empty list like this:</p>\n<div class=\"codehilite\"><pre><span></span><span class=\"n\">my_list</span> <span class=\"o\">=</span> <span class=\"p\">[]</span>\n</pre></div>\n\n</div>\n\n</section>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n<section class=\"solution panel panel-primary\">\n<div class=\"panel-heading\">\n<h2><span class=\"fa fa-eye\"></span> Solution</h2>\n</div>\n\n</section>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Subsets of lists and strings can be accessed by specifying ranges of values in brackets,\nsimilar to how we accessed ranges of positions in a NumPy array.\nThis is commonly referred to as \"slicing\" the list/string.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n<section class=\"challenge panel panel-success\">\n<div class=\"panel-heading\">\n<h2><span class=\"fa fa-pencil\"></span> Challenge: Slicing From the End</h2>\n</div>\n\n\n<div class=\"panel-body\">\n\n<p>Use slicing to access only the last four characters of the following string and the last four entries of the following list.</p>\n\n</div>\n\n</section>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Would your solution work regardless of whether you knew beforehand\nthe length of the string or list\n(e.g. if you wanted to apply the solution to a set of lists of different lengths)?\nIf not, try to change your approach to make it more robust.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n<section class=\"solution panel panel-primary\">\n<div class=\"panel-heading\">\n<h2><span class=\"fa fa-eye\"></span> Solution</h2>\n</div>\n\n\n<div class=\"panel-body\">\n\n<p>Use negative indices to count elements from the end of a container (such as list or string):</p>\n\n</div>\n\n</section>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Non-Continuous Slices\nSo far we've seen how to use slicing to take single blocks\nof successive entries from a sequence.\nBut what if we want to take a subset of entries\nthat aren't next to each other in the sequence?\n\nYou can achieve this by providing a third argument\nto the range within the brackets, called the _step size_.\nThe example below shows how you can take every third entry in a list:\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Notice that the slice taken begins with the first entry in the range,\nfollowed by entries taken at equally-spaced intervals (the steps) thereafter.\nIf you wanted to begin the subset with the third entry,\nyou would need to specify that as the starting point of the sliced range:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n<section class=\"challenge panel panel-success\">\n<div class=\"panel-heading\">\n<h2><span class=\"fa fa-pencil\"></span> Challenge:</h2>\n</div>\n\n\n<div class=\"panel-body\">\n\n<p>Use the step size argument to create a new string\nthat contains only every other character in the string\n\"In an octopus's garden in the shade\"</p>\n\n</div>\n\n</section>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n<section class=\"solution panel panel-primary\">\n<div class=\"panel-heading\">\n<h2><span class=\"fa fa-eye\"></span> Solution</h2>\n</div>\n\n\n<div class=\"panel-body\">\n\n<p>To obtain every other character you need to provide a slice with the step\nsize of 2:</p>\n\n</div>\n\n</section>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"You can also leave out the beginning and end of the slice to take the whole string\nand provide only the step argument to go every second\nelement:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"If you want to take a slice from the beginning of a sequence, you can omit the first index in the\nrange:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"And similarly, you can omit the ending index in the range to take a slice to the very end of the\nsequence:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Overloading\n\n`+` usually means addition, but when used on strings or lists, it means \"concatenate\".\nGiven that, what do you think the multiplication operator `*` does on lists?\nIn particular, what will be the output of the following code?\n\n```python\ncounts = [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]\nrepeats = counts * 2\nprint(repeats)\n```\n\n1. `[2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10]`\n2. `[4, 8, 12, 16, 20]`\n3. `[[2, 4, 6, 8, 10],[2, 4, 6, 8, 10]]`\n4. `[2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 4, 8, 12, 16, 20]`\n\nThe technical term for this is *operator overloading*:\na single operator, like `+` or `*`,\ncan do different things depending on what it's applied to.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Solution\n\nThe multiplication operator `*` used on a list replicates elements of the list and concatenates\nthem together:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"counts = [2,4,6,8,10]\nrepeats = counts*2\nrepeats",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"It's equivalent to:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"repeats = counts + counts\nrepeats",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"---\nThe material in this notebook is derived from the Software Carpentry lessons\n© [Software Carpentry](http://software-carpentry.org/) under the terms\nof the [CC-BY 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/) license.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"col = [\"c0\",\"c1\",\"c3\"]\nfor colour in col*2:\n print(colour)",
"c0\nc1\nc3\nc0\nc1\nc3\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4abbaae8780d454018c9d94a61b2976c9b0208e1
| 483,823 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
projects/ms-learn-ml-crash-course/04. Polynomial Regression - Python.ipynb
|
Code360In/data-science
|
cb6093e898ccb860e76914057a52f751d6b8a4d2
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2020-02-04T20:10:26.000Z
|
2021-04-01T08:38:55.000Z
|
projects/ms-learn-ml-crash-course/04. Polynomial Regression - Python.ipynb
|
Code360In/data-science
|
cb6093e898ccb860e76914057a52f751d6b8a4d2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
projects/ms-learn-ml-crash-course/04. Polynomial Regression - Python.ipynb
|
Code360In/data-science
|
cb6093e898ccb860e76914057a52f751d6b8a4d2
|
[
"MIT"
] | 5 |
2021-04-01T08:40:22.000Z
|
2022-03-25T03:52:36.000Z
| 892.662362 | 110,005 | 0.949021 |
[
[
[
"Exercise 4 - Polynomial Regression\n========\n\nSometimes our data doesn't have a linear relationship, but we still want to predict an outcome.\n\nSuppose we want to predict how satisfied people might be with a piece of fruit, we would expect satisfaction would be low if the fruit was under ripened or over ripened. Satisfaction would be high in between underripened and overripened.\n\nThis is not something linear regression will help us with, so we can turn to polynomial regression to help us make predictions for these more complex non-linear relationships!",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Step 1\n------\n\nIn this exercise we will look at a dataset analysing internet traffic over the course of the day. Observations were made every hour over the course of several days. Suppose we want to predict the level of traffic we might see at any time during the day, how might we do this?\n\nLet's start by opening up our data and having a look at it.\n\n#### In the cell below replace the text `<printDataHere>` with `print(dataset.head())`, and __run the code__ to see the data.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# This sets up the graphing configuration\nimport warnings\nwarnings.filterwarnings(\"ignore\")\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as graph\n%matplotlib inline\ngraph.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (15,5)\ngraph.rcParams[\"font.family\"] = \"DejaVu Sans\"\ngraph.rcParams[\"font.size\"] = \"12\"\ngraph.rcParams['image.cmap'] = 'rainbow'\ngraph.rcParams['axes.facecolor'] = 'white'\ngraph.rcParams['figure.facecolor'] = 'white'\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\n\ndataset = pd.read_csv('Data/traffic_by_hour.csv')\n\n###\n# BELOW, REPLACE <printDataHere> WITH print(dataset.head()) TO PREVIEW THE DATASET ---###\n###\nprint(dataset.head())\n###",
" 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 \\\n0 43.606554 24.714152 9.302911 3.694417 9.324995 9.837653 7.960157 \n1 44.584835 19.604348 9.480832 13.476905 14.465224 6.014083 22.679671 \n2 33.208561 29.584181 27.207633 11.243233 12.229805 5.072605 6.111838 \n3 35.026655 20.367550 21.445285 7.449592 2.232115 8.104623 9.095805 \n4 40.163194 19.936328 18.066480 12.109940 10.878539 9.766027 19.504761 \n\n 07 08 09 ... 14 15 \\\n0 21.292098 27.714126 46.709211 ... 41.714860 38.130357 \n1 18.192898 28.783762 40.113972 ... 51.364457 35.819379 \n2 26.176792 35.246483 38.220432 ... 37.738029 42.104013 \n3 19.499463 37.689567 33.907093 ... 32.354274 36.112366 \n4 10.313875 28.509128 30.809746 ... 37.509431 54.416484 \n\n 16 17 18 19 20 21 \\\n0 42.779751 41.304179 49.499137 43.566211 43.339814 64.096617 \n1 53.243056 49.910267 45.219895 52.002619 56.817581 61.359132 \n2 54.642667 49.656174 34.779641 45.305791 41.818246 61.140163 \n3 53.821508 35.869990 41.830910 46.922595 42.676526 60.139054 \n4 36.801343 49.216991 43.927595 40.657175 44.350371 51.909886 \n\n 22 23 \n0 59.582208 42.819702 \n1 50.287926 40.383544 \n2 61.446353 58.811576 \n3 61.639772 44.670988 \n4 61.674395 46.727170 \n\n[5 rows x 24 columns]\n"
]
],
[
[
"Step 2\n-----\n\nNext we're going to flip the data with the transpose method - our rows will become columns and our columns will become rows. Transpose is commonly used to reshape data so we can use it. Let's try it out.\n\n#### In the cell below find the text `<addCallToTranspose>` and replace it with `transpose`",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### \n# REPLACE THE <addCallToTranspose> BELOW WITH transpose\n###\ndataset_T = np.transpose(dataset)\n###\nprint(dataset_T.shape)\n\nprint(dataset_T)",
"(24, 6)\n 0 1 2 3 4 5\n00 43.606554 44.584835 33.208561 35.026655 40.163194 49.169391\n01 24.714152 19.604348 29.584181 20.367550 19.936328 24.455188\n02 9.302911 9.480832 27.207633 21.445285 18.066480 12.391360\n03 3.694417 13.476905 11.243233 7.449592 12.109940 10.705337\n04 9.324995 14.465224 12.229805 2.232115 10.878539 6.511395\n05 9.837653 6.014083 5.072605 8.104623 9.766027 21.785345\n06 7.960157 22.679671 6.111838 9.095805 19.504761 19.257321\n07 21.292098 18.192898 26.176792 19.499463 10.313875 23.273782\n08 27.714126 28.783762 35.246483 37.689567 28.509128 29.661006\n09 46.709211 40.113972 38.220432 33.907093 30.809746 34.608582\n10 39.111999 46.149334 30.902951 31.018349 36.326509 38.679585\n11 47.428745 43.753611 50.462422 43.379814 45.893941 48.254502\n12 43.459394 45.312618 41.865849 40.330625 31.512743 44.585404\n13 39.046579 34.654569 43.628736 41.798041 37.239437 33.561915\n14 41.714860 51.364457 37.738029 32.354274 37.509431 39.392238\n15 38.130357 35.819379 42.104013 36.112366 54.416484 54.708007\n16 42.779751 53.243056 54.642667 53.821508 36.801343 48.042698\n17 41.304179 49.910267 49.656174 35.869990 49.216991 36.682722\n18 49.499137 45.219895 34.779641 41.830910 43.927595 47.843339\n19 43.566211 52.002619 45.305791 46.922595 40.657175 45.872196\n20 43.339814 56.817581 41.818246 42.676526 44.350371 41.636422\n21 64.096617 61.359132 61.140163 60.139054 51.909886 54.049169\n22 59.582208 50.287926 61.446353 61.639772 61.674395 53.708731\n23 42.819702 40.383544 58.811576 44.670988 46.727170 55.473724\n"
]
],
[
[
"Now lets visualize the data. \n\n#### Replace the text `<addSampleHere>` with `sample` and then __run the code__.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Let's visualise the data!\n\n###\n# REPLACE <addSampleHere> BELOW WITH sample\n###\nfor sample in range(0, dataset_T.shape[1]):\n graph.plot(dataset.columns.values, dataset_T[sample])\n###\n\ngraph.xlabel('Time of day')\ngraph.ylabel('Internet traffic (Gbps)')\ngraph.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Step 3\n-----\n\nThis all looks a bit busy, let's see if we can draw out a clearer pattern by taking the __average values__ for each hour.\n\n#### In the cell below find all occurances of `<replaceWithHour>` and replace them with `hour` and then __run the code__.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# We want to look at the mean values for each hour.\n\nhours = dataset.columns.values\n\n###\n# REPLACE THE <replaceWithHour>'s BELOW WITH hour\n###\ntrain_Y = [dataset[hour].mean() for hour in hours] # This will be our outcome we measure (label) - amount of internet traffic\ntrain_X = np.transpose([int(hour) for hour in hours]) # This is our feature - time of day\n###\n\n# This makes our graph, don't edit!\ngraph.scatter(train_X, train_Y)\nfor sample in range(0,dataset_T.shape[1]):\n graph.plot(hours, dataset_T[sample], alpha=0.25)\ngraph.xlabel('Time of day')\ngraph.ylabel('Internet traffic (Gbps)')\ngraph.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This alone could help us make a prediction if we wanted to know the expected traffic exactly on the hour.\n\nBut, we'll need to be a bit more clever if we want to make a __good__ prediction of times in between.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Step 4\n------\n\nLet's use the midpoints in between the hours to analyse the relationship between the __time of day__ and the __amount of internet traffic__.\n\nNumpy's `polyfit(x,y,d)` function allows us to do polynomial regression, or more precisely least squares polynomial fit.\n\nWe specify a __feature $x$ (time of day)__, our __label $y$ (the amount of traffic)__, and the __degree $d$ of the polynomial (how curvy the line is)__.\n\n#### In the cell below find the text `<replaceWithDegree>`, replace it with the value `1` then __run the code__.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Polynomials of degree 1 are linear!\n# Lets include this one just for comparison\n\n###\n# REPLACE THE <replaceWithDegree> BELOW WITH 1\n###\npoly_1 = np.polyfit(train_X, train_Y, 1)\n###",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's also compare a few higher-degree polynomials.\n\n#### Replace the `<replaceWithDegree>`'s below with numbers, as directed in the comments.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"###\n# REPLACE THE <replaceWithDegree>'s BELOW WITH 2, 3, AND THEN 4\n###\npoly_2 = np.polyfit(train_X, train_Y, 2)\npoly_3 = np.polyfit(train_X, train_Y, 3)\npoly_4 = np.polyfit(train_X, train_Y, 4)\n###\n\n# Let's plot it!\ngraph.scatter(train_X, train_Y)\nxp = np.linspace(0, 24, 100)\n\n# black dashed linear degree 1\ngraph.plot(xp, np.polyval(poly_1, xp), 'k--')\n# red degree 2\ngraph.plot(xp, np.polyval(poly_2, xp), 'r-')\n# blue degree 3\ngraph.plot(xp, np.polyval(poly_3, xp), 'b-') \n# yellow degree 4\ngraph.plot(xp, np.polyval(poly_4, xp), 'y-') \n\ngraph.xticks(train_X, dataset.columns.values)\ngraph.xlabel('Time of day')\ngraph.ylabel('Internet traffic (Gbps)')\ngraph.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"None of these polynomials do a great job of generalising the data. Let's try a few more.\n\n#### Follow the instructions in the comments to replace the `<replaceWithDegree>`'s and then __run the code__.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"###\n# REPLACE THE <replaceWithDegree>'s 5, 6, AND 7\n###\npoly_5 = np.polyfit(train_X, train_Y, 5)\npoly_6 = np.polyfit(train_X, train_Y, 6)\npoly_7 = np.polyfit(train_X, train_Y, 7)\n###\n\n# Let's plot it!\ngraph.scatter(train_X, train_Y)\nxp = np.linspace(0, 24, 100)\n\n# black dashed linear degree 1\ngraph.plot(xp, np.polyval(poly_1, xp), 'k--')\n# red degree 5\ngraph.plot(xp, np.polyval(poly_5, xp), 'r-') \n# blue degree 6\ngraph.plot(xp, np.polyval(poly_6, xp), 'b-') \n# yellow degree 7\ngraph.plot(xp, np.polyval(poly_7, xp), 'y-') \n\ngraph.xticks(train_X, dataset.columns.values)\ngraph.xlabel('Time of day')\ngraph.ylabel('Internet traffic (Gbps)')\ngraph.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"It looks like the 5th and 6th degree polynomials have an identical curve. This looks like a good curve to use.\n\nWe could perhaps use an even higher degree polynomial to fit it even more tightly, but we don't want to overfit the curve, since we want just a generalisation of the relationship.\n\nLet's see how our degree 6 polynomial compares to the real data.\n\n#### Replace the text `<replaceWithPoly6>` with `poly_6` and __run the code__.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for row in range(0,dataset_T.shape[1]):\n graph.plot(dataset.columns.values, dataset_T[row], alpha = 0.5)\n\n###\n# REPLACE <replaceWithPoly6> BELOW WITH poly_6 - THE POLYNOMIAL WE WISH TO VISUALIZE\n### \ngraph.plot(xp, np.polyval(poly_6, xp), 'k-')\n###\n\ngraph.xlabel('Time of day')\ngraph.ylabel('Internet traffic (Gbps)')\ngraph.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Step 5\n------\n\nNow let's try using this model to make a prediction for a time between 00 and 24.\n\n#### In the cell below follow the instructions in the code to replace `<replaceWithTime>` and `<replaceWithPoly6>` then __run the code__.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"###\n# REPLACE <replaceWithTime> BELOW WITH 12.5 (this represents the time 12:30)\n###\ntime = 12.5\n###\n\n###\n# REPLACE <replaceWithPoly6> BELOW WITH poly_6 SO WE CAN VISUALIZE THE 6TH DEGREE POLYNOMIAL MODEL\n###\npred = np.polyval(poly_6, time)\n###\n\nprint(\"at t=%s, predicted internet traffic is %s Gbps\"%(time,pred))\n\n# Now let's visualise it\ngraph.plot(xp, np.polyval(poly_6, xp), 'y-')\n\ngraph.plot(time, pred, 'ko') # result point\ngraph.plot(np.linspace(0, time, 2), np.full([2], pred), dashes=[6, 3], color='black') # dashed lines (to y-axis)\ngraph.plot(np.full([2], time), np.linspace(0, pred, 2), dashes=[6, 3], color='black') # dashed lines (to x-axis)\n\ngraph.xticks(train_X, dataset.columns.values)\ngraph.ylim(0, 60)\ngraph.title('expected traffic throughout the day')\ngraph.xlabel('time of day')\ngraph.ylabel('internet traffic (Gbps)')\n\ngraph.show()",
"at t=12.5, predicted internet traffic is 43.70388389312018 Gbps\n"
]
],
[
[
"Conclusion\n-----\n\nAnd there we have it! You have made a polynomial regression model and used it for analysis! This models gives us a prediction for the level of internet traffic we should expect to see at any given time of day.\n\nYou can go back to the course and either click __'Next Step'__ to start an optional step with tips on how to better work with AI models, or you can go to the next module where instead of predicting numbers we predict categories.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4abbbc763a5337715722b09e515c32b19da869ce
| 888,765 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
iclub-DefaultPrediction9.ipynb
|
georgetown-analytics/lending-club
|
ea1141b4d71e23c2d91e2f59859f0d84c7502f6a
|
[
"MIT"
] | 4 |
2016-11-16T07:53:47.000Z
|
2020-02-26T21:10:29.000Z
|
iclub-DefaultPrediction9.ipynb
|
georgetown-analytics/lending-club
|
ea1141b4d71e23c2d91e2f59859f0d84c7502f6a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
iclub-DefaultPrediction9.ipynb
|
georgetown-analytics/lending-club
|
ea1141b4d71e23c2d91e2f59859f0d84c7502f6a
|
[
"MIT"
] | 5 |
2017-04-02T13:53:29.000Z
|
2020-03-04T01:20:49.000Z
| 198.075552 | 490,422 | 0.868025 |
[
[
[
"# Building a Classifier from Lending Club Data\n**An end-to-end machine learning example using Pandas and Scikit-Learn** \n\n\n\n\n## Data Ingestion\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%matplotlib inline\nimport os \nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn as sns\nfrom pandas.tools.plotting import scatter_matrix",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"names = [\n#Lending Club features\n \"funded_amnt\",\n \"term\",\n \"int_rate\",\n \"emp_length\",\n \"home_ownership\",\n \"annual_inc\",\n \"verification_status\",\n \"purpose\",\n \"dti\",\n \"delinq_2yrs\",\n \"inq_last_6mths\",\n \"open_acc\",\n \"pub_rec\",\n \"revol_bal\",\n \"revol_util\",\n# Macroeconomical data\n \"ilc_mean\",\n \"ilc_LSFT\",\n \"gdp_mean\",\n \"gdp_LSFT\",\n \"Tbill_mean\",\n \"Tbill_LSFT\",\n \"cc_rate\",\n \"unemp\",\n \"unemp_LSFT\",\n \"spread\",\n# Label\n \"loan_status\"\n]\n\nFnames = names[:-1]\n\nlabel = names[-1]\n\n# Open up the earlier CSV to determine how many different types ofentries there are in the column 'loan_status'\ndata_with_all_csv_features = pd.read_csv(\"./data/dfaWR4F.csv\")\nfull_data = data_with_all_csv_features[names];\ndata = full_data.copy()[names]\ndata.head(3)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Data Exploration\n\nThe very first thing to do is to explore the dataset and see what's inside. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Shape of the full dataset\nprint data.shape",
"(84795, 26)\n"
],
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n%matplotlib inline\ndata.boxplot(column=\"annual_inc\",by=\"loan_status\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from pandas.tools.plotting import radviz\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\nfig = plt.figure()\nradviz(data, 'loan_status')\n\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"areas = full_data[['funded_amnt','term','int_rate', 'loan_status']]\nscatter_matrix(areas, alpha=0.2, figsize=(18,18), diagonal='kde')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sns.set_context(\"poster\")\nsns.countplot(x='home_ownership', hue='loan_status', data=full_data,)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sns.set_context(\"poster\")\nsns.countplot(x='emp_length', hue='loan_status', data=full_data,)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sns.set_context(\"poster\")\nsns.countplot(x='term', hue='loan_status', data=full_data,)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sns.set_context(\"poster\")\nsns.countplot(y='purpose', hue='loan_status', data=full_data,)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sns.set_context(\"poster\", font_scale=0.8) \nplt.figure(figsize=(15, 15)) \nplt.ylabel('Loan Originating State')\nsns.countplot(y='verification_status', hue='loan_status', data=full_data)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.crosstab(data[\"term\"],data[\"loan_status\"],margins=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def percConvert(ser):\n return ser/float(ser[-1])\n\npd.crosstab(data[\"term\"],data[\"loan_status\"],margins=True).apply(percConvert, axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.hist(column=\"annual_inc\",by=\"loan_status\",bins=30)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Balancing the data so that we have 50/50 class balancing (underbalancing reducing one class)\npaid_data = data.loc[(data['loan_status'] == \"Paid\")]\ndefault_data = data.loc[(data['loan_status'] == \"Default\")]\n\n# Reduce the Fully Paid data to the same number as Defaulted\nnum_of_paid = default_data.shape[0]\nreduce_paid_data = paid_data.sample(num_of_paid)\n\n# This is the smaller sample data with 50-50 Defaulted and Fully aod loan\nbalanced_data = reduce_paid_data.append(default_data,ignore_index = True )\n\n#Now shuffle several times\ndata = balanced_data.sample(balanced_data.shape[0])\ndata = data.sample(balanced_data.shape[0])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print \"Fully Paid data size was {}\".format(paid_data.shape[0])\nprint \"Default data size was {}\".format(default_data.shape[0])\nprint \"Updated new Data size is {}\".format(data.shape[0])",
"Fully Paid data size was 73355\nDefault data size was 11440\nUpdated new Data size is 22880\n"
],
[
"pd.crosstab(data[\"term\"],data[\"loan_status\"],margins=True).apply(percConvert, axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig = plt.figure()\nax = fig.add_subplot(111)\nax.hist(paid_data['int_rate'], bins = 50, alpha = 0.4, label='Fully_Paid', color = 'blue', range = (paid_data['int_rate'].min(),reduce_paid_data['int_rate'].max()))\nax.hist(default_data['int_rate'], bins = 50, alpha = 0.4, label='Default', color = 'red', range = (default_data['int_rate'].min(),default_data['int_rate'].max()))\nplt.title('Interest Rate vs Number of Loans')\nplt.legend(loc='upper right')\nplt.xlabel('Interest Rate')\nplt.axis([0, 25, 0, 8000])\nplt.ylabel('Number of Loans')\nplt.show()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The countplot function accepts either an x or a y argument to specify if this is a bar plot or a column plot. I chose to use the y argument so that the labels were readable. The hue argument specifies a column for comparison; in this case we're concerned with the relationship of our categorical variables to the target income.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n## Data Management \n\nIn order to organize our data on disk, we'll need to add the following files:\n\n- `README.md`: a markdown file containing information about the dataset and attribution. Will be exposed by the `DESCR` attribute.\n- `meta.json`: a helper file that contains machine readable information about the dataset like `target_names` and `feature_names`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import json \n\nmeta = {\n 'target_names': list(full_data.loan_status.unique()),\n 'feature_names': list(full_data.columns),\n 'categorical_features': {\n column: list(full_data[column].unique())\n for column in full_data.columns\n if full_data[column].dtype == 'object'\n },\n}\n\nwith open('data/ls_meta.json', 'wb') as f:\n json.dump(meta, f, indent=2)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This code creates a `meta.json` file by inspecting the data frame that we have constructued. The `target_names` column, is just the two unique values in the `data.loan_status` series; by using the `pd.Series.unique` method - we're guarenteed to spot data errors if there are more or less than two values. The `feature_names` is simply the names of all the columns. \n\nThen we get tricky — we want to store the possible values of each categorical field for lookup later, but how do we know which columns are categorical and which are not? Luckily, Pandas has already done an analysis for us, and has stored the column data type, `data[column].dtype`, as either `int64` or `object`. Here I am using a dictionary comprehension to create a dictionary whose keys are the categorical columns, determined by checking the object type and comparing with `object`, and whose values are a list of unique values for that field. \n\nNow that we have everything we need stored on disk, we can create a `load_data` function, which will allow us to load the training and test datasets appropriately from disk and store them in a `Bunch`: ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn import cross_validation\nfrom sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split\nfrom sklearn.datasets.base import Bunch\n\ndef load_data(root='data'):\n # Load the meta data from the file \n with open(os.path.join(root, 'meta.json'), 'r') as f:\n meta = json.load(f) \n \n names = meta['feature_names']\n \n # Load the readme information \n with open(os.path.join(root, 'README.md'), 'r') as f:\n readme = f.read() \n \n X = data[Fnames]\n \n # Remove the target from the categorical features \n meta['categorical_features'].pop(label)\n \n y = data[label]\n \n X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = cross_validation.train_test_split(X,y,test_size = 0.2,random_state=10)\n\n \n # Return the bunch with the appropriate data chunked apart\n return Bunch(\n #data = train[names[:-1]],\n data = X_train,\n #target = train[names[-1]], \n target = y_train, \n #data_test = test[names[:-1]], \n data_test = X_test, \n #target_test = test[names[-1]], \n target_test = y_test, \n target_names = meta['target_names'],\n feature_names = meta['feature_names'], \n categorical_features = meta['categorical_features'], \n DESCR = readme,\n )\n\ndataset = load_data()\nprint meta['target_names']",
"['Paid', 'Default']\n"
],
[
"dataset.data_test.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The primary work of the `load_data` function is to locate the appropriate files on disk, given a root directory that's passed in as an argument (if you saved your data in a different directory, you can modify the root to have it look in the right place). The meta data is included with the bunch, and is also used split the train and test datasets into `data` and `target` variables appropriately, such that we can pass them correctly to the Scikit-Learn `fit` and `predict` estimator methods. \n\n## Feature Extraction \n\nNow that our data management workflow is structured a bit more like Scikit-Learn, we can start to use our data to fit models. Unfortunately, the categorical values themselves are not useful for machine learning; we need a single instance table that contains _numeric values_. In order to extract this from the dataset, we'll have to use Scikit-Learn transformers to transform our input dataset into something that can be fit to a model. In particular, we'll have to do the following:\n\n- encode the categorical labels as numeric data \n- impute missing values with data (or remove)\n\nWe will explore how to apply these transformations to our dataset, then we will create a feature extraction pipeline that we can use to build a model from the raw input data. This pipeline will apply both the imputer and the label encoders directly in front of our classifier, so that we can ensure that features are extracted appropriately in both the training and test datasets. \n\n### Label Encoding \n\nOur first step is to get our data out of the object data type land and into a numeric type, since nearly all operations we'd like to apply to our data are going to rely on numeric types. Luckily, Sckit-Learn does provide a transformer for converting categorical labels into numeric integers: [`sklearn.preprocessing.LabelEncoder`](http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.preprocessing.LabelEncoder.html). Unfortunately it can only transform a single vector at a time, so we'll have to adapt it in order to apply it to multiple columns. \n\nLike all Scikit-Learn transformers, the `LabelEncoder` has `fit` and `transform` methods (as well as a special all-in-one, `fit_transform` method) that can be used for stateful transformation of a dataset. In the case of the `LabelEncoder`, the `fit` method discovers all unique elements in the given vector, orders them lexicographically, and assigns them an integer value. These values are actually the indices of the elements inside the `LabelEncoder.classes_` attribute, which can also be used to do a reverse lookup of the class name from the integer value. \n\nFor example, if we were to encode the `home_ownership` column of our dataset as follows:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder \n\nownership = LabelEncoder() \nownership.fit(dataset.data.home_ownership)\nprint(ownership.classes_)",
"[1 2 3 4]\n"
],
[
"from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder \n\npurpose = LabelEncoder() \npurpose.fit(dataset.data.purpose)\nprint(purpose.classes_)",
"[ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14]\n"
]
],
[
[
"Obviously this is very useful for a single column, and in fact the `LabelEncoder` really was intended to encode the target variable, not necessarily categorical data expected by the classifiers.\n\nIn order to create a multicolumn LabelEncoder, we'll have to extend the `TransformerMixin` in Scikit-Learn to create a transformer class of our own, then provide `fit` and `transform` methods that wrap individual `LabelEncoders` for our columns. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.base import BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin\n\nclass EncodeCategorical(BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin):\n \"\"\"\n Encodes a specified list of columns or all columns if None. \n \"\"\"\n \n def __init__(self, columns=None):\n self.columns = columns \n self.encoders = None\n \n def fit(self, data, target=None):\n \"\"\"\n Expects a data frame with named columns to encode. \n \"\"\"\n # Encode all columns if columns is None\n if self.columns is None:\n self.columns = data.columns \n \n # Fit a label encoder for each column in the data frame\n self.encoders = {\n column: LabelEncoder().fit(data[column])\n for column in self.columns \n }\n return self\n\n def transform(self, data):\n \"\"\"\n Uses the encoders to transform a data frame. \n \"\"\"\n output = data.copy()\n for column, encoder in self.encoders.items():\n output[column] = encoder.transform(data[column])\n \n return output\n\nencoder = EncodeCategorical(dataset.categorical_features.keys())\n\n#data = encoder.fit_transform(dataset.data)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This specialized transformer now has the ability to label encode multiple columns in a data frame, saving information about the state of the encoders. It would be trivial to add an `inverse_transform` method that accepts numeric data and converts it to labels, using the `inverse_transform` method of each individual `LabelEncoder` on a per-column basis. \n\n### Imputation \n\nScikit-Learn provides a transformer for dealing with missing values at either the column level or at the row level in the `sklearn.preprocessing` library called the [Imputer](http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.preprocessing.Imputer.html).\n\nThe `Imputer` requires information about what missing values are, either an integer or the string, `Nan` for `np.nan` data types, it then requires a strategy for dealing with it. For example, the `Imputer` can fill in the missing values with the mean, median, or most frequent values for each column. If provided an axis argument of 0 then columns that contain only missing data are discarded; if provided an axis argument of 1, then rows which contain only missing values raise an exception. Basic usage of the `Imputer` is as follows:\n\n```python\nimputer = Imputer(missing_values='Nan', strategy='most_frequent')\nimputer.fit(dataset.data)\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.preprocessing import Imputer \n\nclass ImputeCategorical(BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin):\n \"\"\"\n Encodes a specified list of columns or all columns if None. \n \"\"\"\n \n def __init__(self, columns=None):\n self.columns = columns \n self.imputer = None\n \n def fit(self, data, target=None):\n \"\"\"\n Expects a data frame with named columns to impute. \n \"\"\"\n # Encode all columns if columns is None\n if self.columns is None:\n self.columns = data.columns \n \n # Fit an imputer for each column in the data frame\n #self.imputer = Imputer(strategy='most_frequent')\n self.imputer = Imputer(strategy='mean')\n self.imputer.fit(data[self.columns])\n\n return self\n\n def transform(self, data):\n \"\"\"\n Uses the encoders to transform a data frame. \n \"\"\"\n output = data.copy()\n output[self.columns] = self.imputer.transform(output[self.columns])\n \n return output\n\nimputer = ImputeCategorical(Fnames)\n \n#data = imputer.fit_transform(data)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.head(5)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Our custom imputer, like the `EncodeCategorical` transformer takes a set of columns to perform imputation on. In this case we only wrap a single `Imputer` as the `Imputer` is multicolumn — all that's required is to ensure that the correct columns are transformed. \n\nI had chosen to do the label encoding first, assuming that because the `Imputer` required numeric values, I'd be able to do the parsing in advance. However, after requiring a custom imputer, I'd say that it's probably best to deal with the missing values early, when they're still a specific value, rather than take a chance. \n\n## Model Build \n\nTo create classifier, we're going to create a [`Pipeline`](http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.pipeline.Pipeline.html) that uses our feature transformers and ends in an estimator that can do classification. We can then write the entire pipeline object to disk with the `pickle`, allowing us to load it up and use it to make predictions in the future. \n\nA pipeline is a step-by-step set of transformers that takes input data and transforms it, until finally passing it to an estimator at the end. Pipelines can be constructed using a named declarative syntax so that they're easy to modify and develop. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# PCA",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder \nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler\nfrom sklearn.decomposition import PCA\nimport pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import scale\n%matplotlib inline\n\n# we need to encode our target data as well. \n\nyencode = LabelEncoder().fit(dataset.target)\n#print yencode\n\n# construct the pipeline \npca = Pipeline([\n ('encoder', EncodeCategorical(dataset.categorical_features.keys())),\n ('imputer', ImputeCategorical(Fnames)), \n ('scalar', StandardScaler()), \n #('classifier', PCA(n_components=20))\n ('classifier', PCA())\n ])\n\n# fit the pipeline \npca.fit(dataset.data, yencode.transform(dataset.target))\n#print dataset.target",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import numpy as np\n\n#The amount of variance that each PC explains\nvar= pca.named_steps['classifier'].explained_variance_ratio_\n\n#Cumulative Variance explains\nvar1=np.cumsum(np.round(pca.named_steps['classifier'].explained_variance_ratio_, decimals=4)*100)\n\nprint var1\nplt.plot(var1)",
"[ 14.47 25.55 34.34 41.42 47.73 52.61 57.19 61.45 65.67 69.65\n 73.51 77.03 80.47 83.49 86.3 88.88 90.93 92.78 94.57 96.15\n 97.47 98.74 99.44 99.94 99.99]\n"
]
],
[
[
"# LDA",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder \nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler\nfrom sklearn.decomposition import PCA\nfrom sklearn.lda import LDA\nimport pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import scale\n%matplotlib inline\n\n# we need to encode our target data as well. \n\nyencode = LabelEncoder().fit(dataset.target)\n#print yencode\n\n# construct the pipeline \nlda = Pipeline([\n ('encoder', EncodeCategorical(dataset.categorical_features.keys())),\n ('imputer', ImputeCategorical(Fnames)), \n ('scalar', StandardScaler()), \n ('classifier', LDA())\n\n ])\n\n# fit the pipeline \nlda.fit(dataset.data, yencode.transform(dataset.target))\n#print dataset.target",
"C:\\Users\\ArchangeGiscard\\Anaconda2\\lib\\site-packages\\sklearn\\lda.py:4: DeprecationWarning: lda.LDA has been moved to discriminant_analysis.LinearDiscriminantAnalysis in 0.17 and will be removed in 0.19\n \"in 0.17 and will be removed in 0.19\", DeprecationWarning)\n"
],
[
"import numpy as np\n\n#The amount of variance that each PC explains\nvar= lda.named_steps['classifier']\nprint var\n\n#Cumulative Variance explains\n#var1=np.cumsum(np.round(lda.named_steps['classifier'], decimals=4)*100)\n\nprint var1\nplt.plot(var1)",
"LinearDiscriminantAnalysis(n_components=None, priors=None, shrinkage=None,\n solver='svd', store_covariance=False, tol=0.0001)\n[ 14.47 25.55 34.34 41.42 47.73 52.61 57.19 61.45 65.67 69.65\n 73.51 77.03 80.47 83.49 86.3 88.88 90.93 92.78 94.57 96.15\n 97.47 98.74 99.44 99.94 99.99]\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Logistic Regression\n\nFits a logistic model to data and makes predictions about the probability of a categorical event (between 0 and 1). Logistic regressions make predictions between 0 and 1, so in order to classify multiple classes a one-vs-all scheme is used (one model per class, winner-takes-all).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder \nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import Normalizer\n\nfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, f1_score, precision_score, recall_score, roc_auc_score\n\n# we need to encode our target data as well. \nyencode = LabelEncoder().fit(dataset.target)\n\n#normalizer = Normalizer(copy=False)\n\n# construct the pipeline \nlr = Pipeline([\n ('encoder', EncodeCategorical(dataset.categorical_features.keys())),\n ('imputer', ImputeCategorical(Fnames)), \n ('scalar', StandardScaler()),\n #('normalizer', Normalizer(copy=False)),\n #('classifier', LogisticRegression(class_weight='{0:.5, 1:.3}'))\n ('classifier', LogisticRegression())\n ])\n\n# fit the pipeline \nlr.fit(dataset.data, yencode.transform(dataset.target))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.metrics import classification_report \nfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, f1_score, precision_score, recall_score, roc_auc_score\nimport collections\n\n\nprint collections.Counter(dataset.target_test)\nprint collections.Counter(dataset.target)\nprint collections.Counter(full_data[label])\n\n\nprint \"Test under TEST DATASET\"\n\n# encode test targets\ny_true = yencode.transform(dataset.target_test)\n# use the model to get the predicted value\ny_pred = lr.predict(dataset.data_test)\n# execute classification report \nprint classification_report(y_true, y_pred, target_names=dataset.target_names)\n\nprint \"Test under TRAIN DATASET\"\n# encode test targets\ny_true = yencode.transform(dataset.target)\n# use the model to get the predicted value\ny_pred = lr.predict(dataset.data)\n# execute classification report \nprint classification_report(y_true, y_pred, target_names=dataset.target_names)\n\nprint \"Test under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\"\n\n#lr.fit(full_data[Fnames], yencode.transform(full_data[label]))\n# encode test targets\ny_true = yencode.transform(full_data[label])\n# use the model to get the predicted value\ny_pred = lr.predict(full_data[Fnames])\n# execute classification report \nprint classification_report(y_true, y_pred, target_names=dataset.target_names)",
"Counter({'Default': 2319, 'Paid': 2257})\nCounter({'Paid': 9183, 'Default': 9121})\nCounter({'Paid': 73355, 'Default': 11440})\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n Paid 0.63 0.61 0.62 2319\n Default 0.61 0.62 0.62 2257\n\navg / total 0.62 0.62 0.62 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n Paid 0.61 0.61 0.61 9121\n Default 0.62 0.61 0.61 9183\n\navg / total 0.61 0.61 0.61 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n Paid 0.20 0.61 0.30 11440\n Default 0.91 0.62 0.74 73355\n\navg / total 0.82 0.62 0.68 84795\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Chaining PCA and Logistic Regression\nThe PCA does an unsupervised dimensionality reduction, while the logistic regression does the prediction.\nHere we are using default values for all component of the pipeline.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split\nfrom sklearn.grid_search import GridSearchCV\nfrom sklearn.metrics import classification_report\nfrom sklearn import linear_model, decomposition\n\nyencode = LabelEncoder().fit(dataset.target)\nlogistic = linear_model.LogisticRegression()\npca = decomposition.PCA()\n\npipe = Pipeline(steps=[\n ('encoder', EncodeCategorical(dataset.categorical_features.keys())),\n ('imputer', ImputeCategorical(Fnames)),\n ('scalar', StandardScaler()),\n ('pca', pca),\n ('logistic', logistic)\n ])\n\n# we need to encode our target data as well. \nyencode = LabelEncoder().fit(dataset.target)\n\n#print yencode\n\n# construct the pipeline \nlda = Pipeline([\n ('encoder', EncodeCategorical(dataset.categorical_features.keys())),\n ('imputer', ImputeCategorical(Fnames)), \n ('scalar', StandardScaler()), \n ('classifier', LDA())\n\n ])\n\n# fit the pipeline \nlda.fit(dataset.data, yencode.transform(dataset.target))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Running the test\nfrom sklearn.metrics import classification_report \nfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, f1_score, precision_score, recall_score, roc_auc_score\nimport collections\n\n\nprint collections.Counter(dataset.target_test)\nprint collections.Counter(dataset.target)\nprint collections.Counter(full_data[label])\n\n\nprint \"Test under TEST DATASET\"\n\n# encode test targets\ny_true = yencode.transform(dataset.target_test)\n# use the model to get the predicted value\ny_pred = lda.predict(dataset.data_test)\n# execute classification report \nprint classification_report(y_true, y_pred, target_names=dataset.target_names)\n\nprint \"Test under TRAIN DATASET\"\n# encode test targets\ny_true = yencode.transform(dataset.target)\n# use the model to get the predicted value\ny_pred = lda.predict(dataset.data)\n# execute classification report \nprint classification_report(y_true, y_pred, target_names=dataset.target_names)\n\nprint \"Test under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\"\n\n#lda.fit(full_data[Fnames], yencode.transform(full_data[label]))\n# encode test targets\ny_true = yencode.transform(full_data[label])\n# use the model to get the predicted value\ny_pred = lda.predict(full_data[Fnames])\n# execute classification report \nprint classification_report(y_true, y_pred, target_names=dataset.target_names)",
"Counter({'Default': 2319, 'Paid': 2257})\nCounter({'Paid': 9183, 'Default': 9121})\nCounter({'Paid': 73355, 'Default': 11440})\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n Paid 0.62 0.61 0.62 2319\n Default 0.61 0.62 0.62 2257\n\navg / total 0.62 0.62 0.62 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n Paid 0.61 0.62 0.61 9121\n Default 0.62 0.61 0.61 9183\n\navg / total 0.61 0.61 0.61 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n Paid 0.20 0.62 0.30 11440\n Default 0.91 0.62 0.73 73355\n\navg / total 0.82 0.62 0.68 84795\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Random Forest",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier\nfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor\nfrom sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline\nfrom sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error as mse\nfrom sklearn.metrics import r2_score\n\n# we need to encode our target data as well. \nyencode = LabelEncoder().fit(dataset.target)\n\n# construct the pipeline \nrf = Pipeline([\n ('encoder', EncodeCategorical(dataset.categorical_features.keys())),\n ('imputer', ImputeCategorical(Fnames)),\n ('scalar', StandardScaler()),\n ('classifier', RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=20, oob_score=True, max_depth=7))\n ])\n\n# ...and then run the 'fit' method to build a forest of trees\nrf.fit(dataset.data, yencode.transform(dataset.target))",
"C:\\Users\\ArchangeGiscard\\Anaconda2\\lib\\site-packages\\sklearn\\ensemble\\forest.py:403: UserWarning: Some inputs do not have OOB scores. This probably means too few trees were used to compute any reliable oob estimates.\n warn(\"Some inputs do not have OOB scores. \"\n"
],
[
"# Running the test\nfrom sklearn.metrics import classification_report \nfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, f1_score, precision_score, recall_score, roc_auc_score\nimport collections\n\n\nprint collections.Counter(dataset.target_test)\nprint collections.Counter(dataset.target)\nprint collections.Counter(full_data[label])\n\n\nprint \"Test under TEST DATASET\"\n\n# encode test targets\ny_true = yencode.transform(dataset.target_test)\n# use the model to get the predicted value\ny_pred = rf.predict(dataset.data_test)\n# execute classification report \nprint classification_report(y_true, y_pred, target_names=dataset.target_names)\n\nprint \"Test under TRAIN DATASET\"\n# encode test targets\ny_true = yencode.transform(dataset.target)\n# use the model to get the predicted value\ny_pred = rf.predict(dataset.data)\n# execute classification report \nprint classification_report(y_true, y_pred, target_names=dataset.target_names)\n\nprint \"Test under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\"\n\n#rf.fit(full_data[Fnames], yencode.transform(full_data[label]))\n# encode test targets\ny_true = yencode.transform(full_data[label])\n# use the model to get the predicted value\ny_pred = rf.predict(full_data[Fnames])\n# execute classification report \nprint classification_report(y_true, y_pred, target_names=dataset.target_names)",
"Counter({'Default': 2319, 'Paid': 2257})\nCounter({'Paid': 9183, 'Default': 9121})\nCounter({'Paid': 73355, 'Default': 11440})\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n Paid 0.62 0.66 0.64 2319\n Default 0.62 0.58 0.60 2257\n\navg / total 0.62 0.62 0.62 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n Paid 0.64 0.70 0.67 9121\n Default 0.67 0.61 0.64 9183\n\navg / total 0.65 0.65 0.65 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n Paid 0.20 0.69 0.31 11440\n Default 0.92 0.57 0.71 73355\n\navg / total 0.83 0.59 0.65 84795\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"## ElasticNet",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import ElasticNet\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder \nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler\n\n# we need to encode our target data as well. \n\nyencode = LabelEncoder().fit(dataset.target)\n\n\n# construct the pipeline \nlelastic = Pipeline([\n ('encoder', EncodeCategorical(dataset.categorical_features.keys())),\n ('imputer', ImputeCategorical(Fnames)), \n ('scalar', StandardScaler()),\n ('classifier', ElasticNet(alpha=0.01, l1_ratio =0.1))\n ])\n\n# fit the pipeline \nlelastic.fit(dataset.data, yencode.transform(dataset.target))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#A helper method for pretty-printing linear models\ndef pretty_print_linear(coefs, names = None, sort = False):\n if names == None:\n names = [\"X%s\" % x for x in range(len(coefs))]\n lst = zip(coefs[0], names)\n if sort:\n lst = sorted(lst, key = lambda x:-np.abs(x[0]))\n return \" + \".join(\"%s * %s\" % (round(coef, 3), name)\n for coef, name in lst)\n\ncoefs = lelastic.named_steps['classifier'].coef_\nprint coefs\n#print \"Linear model:\", pretty_print_linear(coefs, Fnames)",
"[-0.00186761 -0.02403045 -0.09010096 0. -0.01103339 0.04294196\n 0.00211798 -0.01513696 -0.01334734 -0. -0.04200854 0.00208419\n -0.0115911 -0.00422037 -0.01563444 -0.00311538 0.02072409 0.01096682\n 0.00114683 -0.01717843 0.00408832 0. -0.02759456 -0.00485918\n 0.01712018]\n"
],
[
"#Naive Bayes\n\nfrom sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB\nfrom sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB\nfrom sklearn.naive_bayes import BernoulliNB\nfrom sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline\nfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, f1_score, precision_score, recall_score, roc_auc_score\n\n\n# we need to encode our target data as well. \nyencode = LabelEncoder().fit(dataset.target)\n\n\n# construct the pipeline \nnb = Pipeline([\n ('encoder', EncodeCategorical(dataset.categorical_features.keys())),\n ('imputer', ImputeCategorical(Fnames)), \n ('scalar', StandardScaler()),\n# ('classifier', GaussianNB())\n# ('classifier', MultinomialNB(alpha=0.7, class_prior=[0.5, 0.5], fit_prior=True))\n ('classifier', BernoulliNB(alpha=1.0, binarize=0.0, fit_prior=False))\n ])\n\n\n\n# Next split up the data with the 'train test split' method in the Cross Validation module\n#X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X,y, test_size=0.2)\n\n# ...and then run the 'fit' method to build a model\nnb.fit(dataset.data, yencode.transform(dataset.target))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Running the test\nfrom sklearn.metrics import classification_report \nfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, f1_score, precision_score, recall_score, roc_auc_score\nimport collections\n\n\nprint collections.Counter(dataset.target_test)\nprint collections.Counter(dataset.target)\nprint collections.Counter(full_data[label])\n\n\nprint \"Test under TEST DATASET\"\n\n# encode test targets\ny_true = yencode.transform(dataset.target_test)\n# use the model to get the predicted value\ny_pred = nb.predict(dataset.data_test)\n# execute classification report \nprint classification_report(y_true, y_pred, target_names=dataset.target_names)\n\nprint \"Test under TRAIN DATASET\"\n# encode test targets\ny_true = yencode.transform(dataset.target)\n# use the model to get the predicted value\ny_pred = nb.predict(dataset.data)\n# execute classification report \nprint classification_report(y_true, y_pred, target_names=dataset.target_names)\n\nprint \"Test under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\"\n\n#rf.fit(full_data[Fnames], yencode.transform(full_data[label]))\n# encode test targets\ny_true = yencode.transform(full_data[label])\n# use the model to get the predicted value\ny_pred = nb.predict(full_data[Fnames])\n# execute classification report \nprint classification_report(y_true, y_pred, target_names=dataset.target_names)",
"Counter({'Default': 2319, 'Paid': 2257})\nCounter({'Paid': 9183, 'Default': 9121})\nCounter({'Paid': 73355, 'Default': 11440})\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n Paid 0.61 0.60 0.60 2319\n Default 0.59 0.61 0.60 2257\n\navg / total 0.60 0.60 0.60 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n Paid 0.60 0.60 0.60 9121\n Default 0.60 0.60 0.60 9183\n\navg / total 0.60 0.60 0.60 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n Paid 0.19 0.60 0.29 11440\n Default 0.91 0.61 0.73 73355\n\navg / total 0.81 0.61 0.67 84795\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Gradient Boosting Classifier",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingClassifier\n\nclf = GradientBoostingClassifier(n_estimators=100, learning_rate=1.0,\n max_depth=1, random_state=0).fit(dataset.data, dataset.target)\n\n# encode test targets\ny_true = yencode.transform(dataset.target_test)\n# use the model to get the predicted value\ny_pred = clf.predict(dataset.data_test)\n# execute classification report \nclf.score(dataset.data_test, y_true) \n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Voting Classifier \n1xLogistic, 4xRandom Forest, 1xgNB, 1xDecisionTree, 2xkNeighbors",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression\nfrom sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB\nfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier\nfrom sklearn.ensemble import VotingClassifier\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder \nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler\nfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, f1_score, precision_score, recall_score, roc_auc_score\nfrom sklearn import linear_model, decomposition\nfrom sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier\nfrom sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier\nfrom sklearn.svm import SVC\n\n\n# we need to encode our target data as well. \n\nyencode = LabelEncoder().fit(dataset.target)\n\nclf1 = LogisticRegression(random_state=12)\nclf2 = RandomForestClassifier(max_features=5, min_samples_leaf=4, min_samples_split=9, \n bootstrap=False, criterion='entropy', max_depth=None, n_estimators=24, random_state=12) \nclf3 = GaussianNB()\nclf4 = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=4)\nclf5 = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=7)\n#clf6 = SVC(kernel='rbf', probability=True)\n\npca = decomposition.PCA(n_components=24)\n\n# construct the pipeline \npipe = Pipeline([\n ('encoder', EncodeCategorical(dataset.categorical_features.keys())),\n ('imputer', ImputeCategorical(Fnames)),\n ('scalar', StandardScaler()),\n ('pca', pca),\n ('eclf_classifier', VotingClassifier(estimators=[('lr', clf1), ('rf', clf2), ('gnb', clf3),\n ('dtc', clf4),('knc', clf5)],\n voting='soft',\n weights=[1, 4, 1, 1, 2])),\n ])\n\n# fit the pipeline \npipe.fit(dataset.data, yencode.transform(dataset.target))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.metrics import classification_report \nfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, f1_score, precision_score, recall_score, roc_auc_score\nimport collections\n\n\nprint collections.Counter(dataset.target_test)\nprint collections.Counter(dataset.target)\nprint collections.Counter(full_data[label])\n\n\nprint \"Test under TEST DATASET\"\ny_true, y_pred = yencode.transform(dataset.target_test), pipe.predict(dataset.data_test)\nprint(classification_report(y_true, y_pred))\n\nprint \"Test under TRAIN DATASET\"\ny_true, y_pred = yencode.transform(dataset.target), pipe.predict(dataset.data)\nprint(classification_report(y_true, y_pred))\n\nprint \"Test under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\"\ny_true, y_pred = yencode.transform(full_data[label]), pipe.predict(full_data[Fnames])\nprint(classification_report(y_true, y_pred))",
"Counter({'Default': 2319, 'Paid': 2257})\nCounter({'Paid': 9183, 'Default': 9121})\nCounter({'Paid': 73355, 'Default': 11440})\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.62 0.62 0.62 2319\n 1 0.61 0.62 0.61 2257\n\navg / total 0.62 0.62 0.62 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.98 0.98 0.98 9121\n 1 0.98 0.98 0.98 9183\n\navg / total 0.98 0.98 0.98 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.29 0.90 0.44 11440\n 1 0.98 0.66 0.79 73355\n\navg / total 0.88 0.69 0.74 84795\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Parameter Tuning for Logistic regression inside pipeline\nA grid search or feature analysis may lead to a higher scoring model than the one we quickly put together.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split\nfrom sklearn.grid_search import GridSearchCV\nfrom sklearn.metrics import classification_report\nfrom sklearn import linear_model, decomposition\n\nyencode = LabelEncoder().fit(dataset.target)\n\nlogistic = LogisticRegression(penalty='l2', dual=False, solver='newton-cg')\nclf2 = RandomForestClassifier(max_features=5, min_samples_leaf=4, min_samples_split=9, \n bootstrap=False, criterion='entropy', max_depth=None, n_estimators=24, random_state=12) \nclf3 = GaussianNB()\nclf4 = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=4)\nclf5 = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=7)\n#clf6 = SVC(kernel='rbf', probability=True)\n\npca = decomposition.PCA(n_components=24)\n\n# construct the pipeline \npipe = Pipeline([\n ('encoder', EncodeCategorical(dataset.categorical_features.keys())),\n ('imputer', ImputeCategorical(Fnames)),\n ('scalar', StandardScaler()),\n ('pca', pca),\n ('logistic', logistic),\n ])\n\n\ntuned_parameters = {\n #'pca__n_components':[5, 7, 13, 24],\n 'logistic__fit_intercept':(False, True),\n #'logistic__C':(0.1, 1, 10),\n 'logistic__class_weight':({0:.5, 1:.5},{0:.7, 1:.3},{0:.6, 1:.4},{0:.55, 1:.45},None),\n }\n\nscores = ['precision', 'recall', 'f1']\n\nfor score in scores:\n print(\"# Tuning hyper-parameters for %s\" % score)\n print()\n \n clf = GridSearchCV(pipe, tuned_parameters, scoring='%s_weighted' % score)\n clf.fit(dataset.data, yencode.transform(dataset.target))\n\n print(\"Best parameters set found on development set:\")\n print()\n print(clf.best_params_)\n print()\n print(\"Grid scores on development set:\")\n print()\n for params, mean_score, scores in clf.grid_scores_:\n print(\"%0.3f (+/-%0.03f) for %r\"\n % (mean_score, scores.std() * 2, params))\n print()\n\n print(\"Detailed classification report:\")\n print()\n print(\"The model is trained on the full development set.\")\n print(\"The scores are computed on the full evaluation set.\")\n print()\n \n print \"Test under TEST DATASET\"\n y_true, y_pred = yencode.transform(dataset.target_test), clf.predict(dataset.data_test)\n print(classification_report(y_true, y_pred))\n print \"Test under TRAIN DATASET\"\n y_true, y_pred = yencode.transform(dataset.target), clf.predict(dataset.data)\n print(classification_report(y_true, y_pred))\n print \"Test under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\"\n y_true, y_pred = yencode.transform(full_data[label]), clf.predict(full_data[Fnames])\n print(classification_report(y_true, y_pred))\n \n",
"# Tuning hyper-parameters for precision\n()\nBest parameters set found on development set:\n()\n{'logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.7, 1: 0.3}, 'logistic__fit_intercept': True}\n()\nGrid scores on development set:\n()\n0.612 (+/-0.002) for {'logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.5, 1: 0.5}, 'logistic__fit_intercept': False}\n0.612 (+/-0.000) for {'logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.5, 1: 0.5}, 'logistic__fit_intercept': True}\n0.613 (+/-0.004) for {'logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.7, 1: 0.3}, 'logistic__fit_intercept': False}\n0.654 (+/-0.010) for {'logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.7, 1: 0.3}, 'logistic__fit_intercept': True}\n0.612 (+/-0.003) for {'logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.6, 1: 0.4}, 'logistic__fit_intercept': False}\n0.625 (+/-0.014) for {'logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.6, 1: 0.4}, 'logistic__fit_intercept': True}\n0.612 (+/-0.003) for {'logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.55, 1: 0.45}, 'logistic__fit_intercept': False}\n0.617 (+/-0.011) for {'logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.55, 1: 0.45}, 'logistic__fit_intercept': True}\n0.612 (+/-0.002) for {'logistic__class_weight': None, 'logistic__fit_intercept': False}\n0.612 (+/-0.001) for {'logistic__class_weight': None, 'logistic__fit_intercept': True}\n()\nDetailed classification report:\n()\nThe model is trained on the full development set.\nThe scores are computed on the full evaluation set.\n()\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.54 0.96 0.69 2319\n 1 0.78 0.15 0.25 2257\n\navg / total 0.66 0.56 0.47 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.53 0.96 0.68 9121\n 1 0.78 0.14 0.24 9183\n\navg / total 0.65 0.55 0.46 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.15 0.96 0.26 11440\n 1 0.96 0.14 0.25 73355\n\navg / total 0.85 0.25 0.25 84795\n\n# Tuning hyper-parameters for recall\n()\nBest parameters set found on development set:\n()\n{'logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.7, 1: 0.3}, 'logistic__fit_intercept': False}\n()\nGrid scores on development set:\n()\n0.612 (+/-0.002) for {'logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.5, 1: 0.5}, 'logistic__fit_intercept': False}\n0.612 (+/-0.000) for {'logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.5, 1: 0.5}, 'logistic__fit_intercept': True}\n0.613 (+/-0.004) for {'logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.7, 1: 0.3}, 'logistic__fit_intercept': False}\n0.549 (+/-0.004) for {'logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.7, 1: 0.3}, 'logistic__fit_intercept': True}\n0.612 (+/-0.004) for {'logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.6, 1: 0.4}, 'logistic__fit_intercept': False}\n0.594 (+/-0.012) for {'logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.6, 1: 0.4}, 'logistic__fit_intercept': True}\n0.612 (+/-0.003) for {'logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.55, 1: 0.45}, 'logistic__fit_intercept': False}\n0.608 (+/-0.010) for {'logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.55, 1: 0.45}, 'logistic__fit_intercept': True}\n0.612 (+/-0.002) for {'logistic__class_weight': None, 'logistic__fit_intercept': False}\n0.612 (+/-0.001) for {'logistic__class_weight': None, 'logistic__fit_intercept': True}\n()\nDetailed classification report:\n()\nThe model is trained on the full development set.\nThe scores are computed on the full evaluation set.\n()\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.62 0.62 0.62 2319\n 1 0.61 0.61 0.61 2257\n\navg / total 0.61 0.61 0.61 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.61 0.63 0.62 9121\n 1 0.62 0.61 0.61 9183\n\navg / total 0.62 0.62 0.62 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.20 0.63 0.30 11440\n 1 0.91 0.61 0.73 73355\n\navg / total 0.82 0.61 0.67 84795\n\n# Tuning hyper-parameters for f1\n()\nBest parameters set found on development set:\n()\n{'logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.7, 1: 0.3}, 'logistic__fit_intercept': False}\n()\nGrid scores on development set:\n()\n0.612 (+/-0.002) for {'logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.5, 1: 0.5}, 'logistic__fit_intercept': False}\n0.612 (+/-0.000) for {'logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.5, 1: 0.5}, 'logistic__fit_intercept': True}\n0.613 (+/-0.004) for {'logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.7, 1: 0.3}, 'logistic__fit_intercept': False}\n0.457 (+/-0.006) for {'logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.7, 1: 0.3}, 'logistic__fit_intercept': True}\n0.612 (+/-0.004) for {'logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.6, 1: 0.4}, 'logistic__fit_intercept': False}\n0.568 (+/-0.013) for {'logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.6, 1: 0.4}, 'logistic__fit_intercept': True}\n0.612 (+/-0.003) for {'logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.55, 1: 0.45}, 'logistic__fit_intercept': False}\n0.601 (+/-0.011) for {'logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.55, 1: 0.45}, 'logistic__fit_intercept': True}\n0.612 (+/-0.002) for {'logistic__class_weight': None, 'logistic__fit_intercept': False}\n0.612 (+/-0.001) for {'logistic__class_weight': None, 'logistic__fit_intercept': True}\n()\nDetailed classification report:\n()\nThe model is trained on the full development set.\nThe scores are computed on the full evaluation set.\n()\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.62 0.62 0.62 2319\n 1 0.61 0.61 0.61 2257\n\navg / total 0.61 0.61 0.61 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.61 0.63 0.62 9121\n 1 0.62 0.61 0.61 9183\n\navg / total 0.62 0.62 0.62 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.20 0.63 0.30 11440\n 1 0.91 0.61 0.73 73355\n\navg / total 0.82 0.61 0.67 84795\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Parameter Tuning for classifiers inside VotingClassifier\nA grid search or feature analysis may lead to a higher scoring model than the one we quickly put together.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split\nfrom sklearn.grid_search import GridSearchCV\nfrom sklearn.metrics import classification_report\nfrom sklearn import linear_model, decomposition\n\nyencode = LabelEncoder().fit(dataset.target)\n\nlogistic = LogisticRegression(penalty='l2', dual=False, solver='newton-cg')\nclf2 = RandomForestClassifier(max_features=5, min_samples_leaf=4, min_samples_split=9, \n bootstrap=False, criterion='entropy', max_depth=None, n_estimators=24, random_state=12) \nclf3 = GaussianNB()\nclf4 = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=4)\nclf5 = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=7)\n#clf6 = SVC(kernel='rbf', probability=True)\n\npca = decomposition.PCA(n_components=24)\n\n# construct the pipeline \npipe = Pipeline([\n ('encoder', EncodeCategorical(dataset.categorical_features.keys())),\n ('imputer', ImputeCategorical(Fnames)),\n ('scalar', StandardScaler()),\n ('pca', pca),\n ('eclf_classifier', VotingClassifier(estimators=[('logistic', logistic), ('randomf', clf2), ('nb', clf3),\n ('decisiontree', clf4),('kn', clf5)],\n voting='soft',\n weights=[1, 4, 1, 1, 2])),\n ])\n\n\ntuned_parameters = {\n #'pca__n_components':[5, 7, 13, 20, 24],\n #'eclf_classifier__logistic__fit_intercept':(False, True),\n #'logistic__C':(0.1, 1, 10),\n 'eclf_classifier__logistic__class_weight':({0:.5, 1:.5},{0:.7, 1:.3},{0:.6, 1:.4},{0:.55, 1:.45},None),\n #'randomf__max_depth': [3, None],\n #'randomf__max_features': sp_randint(1, 11),\n #'randomf__min_samples_split': sp_randint(1, 11),\n #'randomf__min_samples_leaf': sp_randint(1, 11),\n #'randomf__bootstrap': [True, False],\n #'randomf__criterion': ['gini', 'entropy']\n\n }\n\nscores = ['precision', 'recall', 'f1']\n\nfor score in scores:\n print(\"# Tuning hyper-parameters for %s\" % score)\n print()\n \n clf = GridSearchCV(pipe, tuned_parameters, scoring='%s_weighted' % score)\n clf.fit(dataset.data, yencode.transform(dataset.target))\n\n print(\"Best parameters set found on development set:\")\n print()\n print(clf.best_params_)\n print()\n print(\"Grid scores on development set:\")\n print()\n for params, mean_score, scores in clf.grid_scores_:\n print(\"%0.3f (+/-%0.03f) for %r\"\n % (mean_score, scores.std() * 2, params))\n print()\n\n print(\"Detailed classification report:\")\n print()\n print(\"The model is trained on the full development set.\")\n print(\"The scores are computed on the full evaluation set.\")\n print()\n \n print \"Test under TEST DATASET\"\n y_true, y_pred = yencode.transform(dataset.target_test), clf.predict(dataset.data_test)\n print(classification_report(y_true, y_pred))\n\n print \"Test under TRAIN DATASET\"\n y_true, y_pred = yencode.transform(dataset.target), clf.predict(dataset.data)\n print(classification_report(y_true, y_pred))\n\n print \"Test under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\"\n y_true, y_pred = yencode.transform(full_data[label]), clf.predict(full_data[Fnames])\n print(classification_report(y_true, y_pred))\n \n",
"# Tuning hyper-parameters for precision\n()\nBest parameters set found on development set:\n()\n{'eclf_classifier__logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.7, 1: 0.3}}\n()\nGrid scores on development set:\n()\n0.597 (+/-0.007) for {'eclf_classifier__logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.5, 1: 0.5}}\n0.600 (+/-0.012) for {'eclf_classifier__logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.7, 1: 0.3}}\n0.598 (+/-0.011) for {'eclf_classifier__logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.6, 1: 0.4}}\n0.597 (+/-0.009) for {'eclf_classifier__logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.55, 1: 0.45}}\n0.597 (+/-0.007) for {'eclf_classifier__logistic__class_weight': None}\n()\nDetailed classification report:\n()\nThe model is trained on the full development set.\nThe scores are computed on the full evaluation set.\n()\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.62 0.67 0.64 2319\n 1 0.63 0.57 0.60 2257\n\navg / total 0.62 0.62 0.62 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.97 0.98 0.98 9121\n 1 0.98 0.97 0.98 9183\n\navg / total 0.98 0.98 0.98 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.27 0.92 0.41 11440\n 1 0.98 0.61 0.75 73355\n\navg / total 0.88 0.65 0.70 84795\n\n# Tuning hyper-parameters for recall\n()\nBest parameters set found on development set:\n()\n{'eclf_classifier__logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.7, 1: 0.3}}\n()\nGrid scores on development set:\n()\n0.597 (+/-0.007) for {'eclf_classifier__logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.5, 1: 0.5}}\n0.598 (+/-0.011) for {'eclf_classifier__logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.7, 1: 0.3}}\n0.598 (+/-0.011) for {'eclf_classifier__logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.6, 1: 0.4}}\n0.597 (+/-0.009) for {'eclf_classifier__logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.55, 1: 0.45}}\n0.597 (+/-0.007) for {'eclf_classifier__logistic__class_weight': None}\n()\nDetailed classification report:\n()\nThe model is trained on the full development set.\nThe scores are computed on the full evaluation set.\n()\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.62 0.67 0.64 2319\n 1 0.63 0.57 0.60 2257\n\navg / total 0.62 0.62 0.62 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.97 0.98 0.98 9121\n 1 0.98 0.97 0.98 9183\n\navg / total 0.98 0.98 0.98 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.27 0.92 0.41 11440\n 1 0.98 0.61 0.75 73355\n\navg / total 0.88 0.65 0.70 84795\n\n# Tuning hyper-parameters for f1\n()\nBest parameters set found on development set:\n()\n{'eclf_classifier__logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.6, 1: 0.4}}\n()\nGrid scores on development set:\n()\n0.597 (+/-0.007) for {'eclf_classifier__logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.5, 1: 0.5}}\n0.596 (+/-0.010) for {'eclf_classifier__logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.7, 1: 0.3}}\n0.597 (+/-0.010) for {'eclf_classifier__logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.6, 1: 0.4}}\n0.597 (+/-0.009) for {'eclf_classifier__logistic__class_weight': {0: 0.55, 1: 0.45}}\n0.597 (+/-0.007) for {'eclf_classifier__logistic__class_weight': None}\n()\nDetailed classification report:\n()\nThe model is trained on the full development set.\nThe scores are computed on the full evaluation set.\n()\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.62 0.65 0.63 2319\n 1 0.62 0.60 0.61 2257\n\navg / total 0.62 0.62 0.62 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.98 0.98 0.98 9121\n 1 0.98 0.98 0.98 9183\n\navg / total 0.98 0.98 0.98 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.28 0.91 0.43 11440\n 1 0.98 0.63 0.77 73355\n\navg / total 0.88 0.67 0.72 84795\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Tuning the weights in the VotingClassifier",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.base import BaseEstimator\nfrom sklearn.base import ClassifierMixin\nimport numpy as np\nimport operator\n\nclass EnsembleClassifier(BaseEstimator, ClassifierMixin):\n \"\"\"\n Ensemble classifier for scikit-learn estimators.\n\n Parameters\n ----------\n\n clf : `iterable`\n A list of scikit-learn classifier objects.\n weights : `list` (default: `None`)\n If `None`, the majority rule voting will be applied to the predicted class labels.\n If a list of weights (`float` or `int`) is provided, the averaged raw probabilities (via `predict_proba`)\n will be used to determine the most confident class label.\n\n \"\"\"\n def __init__(self, clfs, weights=None):\n self.clfs = clfs\n self.weights = weights\n\n def fit(self, X, y):\n \"\"\"\n Fit the scikit-learn estimators.\n\n Parameters\n ----------\n\n X : numpy array, shape = [n_samples, n_features]\n Training data\n y : list or numpy array, shape = [n_samples]\n Class labels\n\n \"\"\"\n for clf in self.clfs:\n clf.fit(X, y)\n\n def predict(self, X):\n \"\"\"\n Parameters\n ----------\n\n X : numpy array, shape = [n_samples, n_features]\n\n Returns\n ----------\n\n maj : list or numpy array, shape = [n_samples]\n Predicted class labels by majority rule\n\n \"\"\"\n\n self.classes_ = np.asarray([clf.predict(X) for clf in self.clfs])\n if self.weights:\n avg = self.predict_proba(X)\n\n maj = np.apply_along_axis(lambda x: max(enumerate(x), key=operator.itemgetter(1))[0], axis=1, arr=avg)\n\n else:\n maj = np.asarray([np.argmax(np.bincount(self.classes_[:,c])) for c in range(self.classes_.shape[1])])\n\n return maj\n\n def predict_proba(self, X):\n\n \"\"\"\n Parameters\n ----------\n\n X : numpy array, shape = [n_samples, n_features]\n\n Returns\n ----------\n\n avg : list or numpy array, shape = [n_samples, n_probabilities]\n Weighted average probability for each class per sample.\n\n \"\"\"\n self.probas_ = [clf.predict_proba(X) for clf in self.clfs]\n avg = np.average(self.probas_, axis=0, weights=self.weights)\n\n return avg",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"y_true = yencode.transform(full_data[label])\n\ndf = pd.DataFrame(columns=('w1', 'w2', 'w3','w4','w5', 'mean', 'std'))\n\ni = 0\nfor w1 in range(0,2):\n for w2 in range(0,2):\n for w3 in range(0,2):\n for w4 in range(0,2):\n for w5 in range(0,2):\n if len(set((w1,w2,w3,w4,w5))) == 1: # skip if all weights are equal\n continue\n\n eclf = EnsembleClassifier(clfs=[clf1, clf2, clf3, clf4, clf5], weights=[w1,w2,w3,w4,w5])\n eclf.fit(dataset.data, yencode.transform(dataset.target))\n print \"w1\"\n print w1\n print \"w2\"\n print w2\n print \"w3\"\n print w3\n print \"w4\"\n print w4\n print \"w5\"\n print w5\n print \"Test under TEST DATASET\"\n y_true, y_pred = yencode.transform(dataset.target_test), eclf.predict(dataset.data_test)\n print(classification_report(y_true, y_pred))\n\n print \"Test under TRAIN DATASET\"\n y_true, y_pred = yencode.transform(dataset.target), eclf.predict(dataset.data)\n print(classification_report(y_true, y_pred))\n\n print \"Test under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\"\n y_true, y_pred = yencode.transform(full_data[label]), eclf.predict(full_data[Fnames])\n print(classification_report(y_true, y_pred))\n \n #scores = cross_validation.cross_val_score(\n # estimator=eclf,\n # X=full_data[Fnames],\n # y=y_true,\n # cv=5,\n # scoring='f1',\n # n_jobs=1)\n\n #df.loc[i] = [w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, scores.mean(), scores.std()]\n i += 1\n #print i\n #print scores.mean()\n#df.sort(columns=['mean', 'std'], ascending=False)",
"w1\n0\nw2\n0\nw3\n0\nw4\n0\nw5\n1\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.54 0.55 0.55 2319\n 1 0.53 0.51 0.52 2257\n\navg / total 0.53 0.53 0.53 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.67 0.67 0.67 9121\n 1 0.67 0.67 0.67 9183\n\navg / total 0.67 0.67 0.67 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.18 0.64 0.28 11440\n 1 0.91 0.55 0.68 73355\n\navg / total 0.81 0.56 0.63 84795\n\nw1\n0\nw2\n0\nw3\n0\nw4\n1\nw5\n0\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.62 0.63 0.62 2319\n 1 0.61 0.60 0.60 2257\n\navg / total 0.61 0.61 0.61 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.60 0.63 0.62 9121\n 1 0.61 0.59 0.60 9183\n\navg / total 0.61 0.61 0.61 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.19 0.63 0.29 11440\n 1 0.91 0.59 0.71 73355\n\navg / total 0.81 0.59 0.66 84795\n\nw1\n0\nw2\n0\nw3\n0\nw4\n1\nw5\n1\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.58 0.61 0.59 2319\n 1 0.57 0.54 0.56 2257\n\navg / total 0.58 0.58 0.57 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.68 0.71 0.70 9121\n 1 0.70 0.67 0.68 9183\n\navg / total 0.69 0.69 0.69 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.20 0.69 0.31 11440\n 1 0.92 0.56 0.70 73355\n\navg / total 0.82 0.58 0.65 84795\n\nw1\n0\nw2\n0\nw3\n1\nw4\n0\nw5\n0\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.64 0.40 0.49 2319\n 1 0.55 0.77 0.64 2257\n\navg / total 0.60 0.58 0.57 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.63 0.40 0.49 9121\n 1 0.56 0.77 0.65 9183\n\navg / total 0.60 0.58 0.57 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.21 0.40 0.28 11440\n 1 0.89 0.77 0.83 73355\n\navg / total 0.80 0.72 0.75 84795\n\nw1\n0\nw2\n0\nw3\n1\nw4\n0\nw5\n1\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.61 0.50 0.55 2319\n 1 0.57 0.68 0.62 2257\n\navg / total 0.59 0.58 0.58 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.71 0.58 0.64 9121\n 1 0.65 0.76 0.70 9183\n\navg / total 0.68 0.67 0.67 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.22 0.56 0.32 11440\n 1 0.91 0.69 0.78 73355\n\navg / total 0.82 0.67 0.72 84795\n\nw1\n0\nw2\n0\nw3\n1\nw4\n1\nw5\n0\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.63 0.51 0.57 2319\n 1 0.58 0.70 0.63 2257\n\navg / total 0.61 0.60 0.60 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.62 0.51 0.56 9121\n 1 0.59 0.69 0.64 9183\n\navg / total 0.61 0.60 0.60 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.21 0.51 0.30 11440\n 1 0.90 0.69 0.78 73355\n\navg / total 0.81 0.67 0.72 84795\n\nw1\n0\nw2\n0\nw3\n1\nw4\n1\nw5\n1\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.61 0.54 0.58 2319\n 1 0.58 0.65 0.61 2257\n\navg / total 0.60 0.59 0.59 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.69 0.61 0.65 9121\n 1 0.65 0.73 0.69 9183\n\navg / total 0.67 0.67 0.67 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.22 0.60 0.32 11440\n 1 0.91 0.67 0.77 73355\n\navg / total 0.82 0.66 0.71 84795\n\nw1\n0\nw2\n1\nw3\n0\nw4\n0\nw5\n0\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.61 0.63 0.62 2319\n 1 0.61 0.59 0.60 2257\n\navg / total 0.61 0.61 0.61 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 1.00 1.00 1.00 9121\n 1 1.00 1.00 1.00 9183\n\navg / total 1.00 1.00 1.00 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.28 0.92 0.44 11440\n 1 0.98 0.64 0.77 73355\n\navg / total 0.89 0.68 0.73 84795\n\nw1\n0\nw2\n1\nw3\n0\nw4\n0\nw5\n1\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.60 0.61 0.60 2319\n 1 0.59 0.57 0.58 2257\n\navg / total 0.59 0.59 0.59 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.97 0.97 0.97 9121\n 1 0.97 0.97 0.97 9183\n\navg / total 0.97 0.97 0.97 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.27 0.90 0.42 11440\n 1 0.98 0.63 0.76 73355\n\navg / total 0.88 0.66 0.72 84795\n\nw1\n0\nw2\n1\nw3\n0\nw4\n1\nw5\n0\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.62 0.65 0.64 2319\n 1 0.62 0.59 0.61 2257\n\navg / total 0.62 0.62 0.62 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.97 0.96 0.97 9121\n 1 0.96 0.97 0.97 9183\n\navg / total 0.97 0.97 0.97 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.28 0.90 0.42 11440\n 1 0.98 0.63 0.77 73355\n\navg / total 0.88 0.67 0.72 84795\n\nw1\n0\nw2\n1\nw3\n0\nw4\n1\nw5\n1\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.61 0.63 0.62 2319\n 1 0.60 0.59 0.59 2257\n\navg / total 0.61 0.61 0.61 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.93 0.94 0.94 9121\n 1 0.94 0.93 0.93 9183\n\navg / total 0.94 0.94 0.94 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.27 0.88 0.41 11440\n 1 0.97 0.63 0.76 73355\n\navg / total 0.88 0.66 0.72 84795\n\nw1\n0\nw2\n1\nw3\n1\nw4\n0\nw5\n0\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.64 0.52 0.57 2319\n 1 0.58 0.69 0.63 2257\n\navg / total 0.61 0.61 0.60 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.93 0.88 0.90 9121\n 1 0.89 0.93 0.91 9183\n\navg / total 0.91 0.91 0.91 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.31 0.81 0.45 11440\n 1 0.96 0.72 0.83 73355\n\navg / total 0.87 0.73 0.77 84795\n\nw1\n0\nw2\n1\nw3\n1\nw4\n0\nw5\n1\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.63 0.55 0.59 2319\n 1 0.59 0.66 0.62 2257\n\navg / total 0.61 0.61 0.61 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.92 0.88 0.90 9121\n 1 0.89 0.92 0.91 9183\n\navg / total 0.90 0.90 0.90 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.29 0.81 0.43 11440\n 1 0.96 0.70 0.81 73355\n\navg / total 0.87 0.71 0.76 84795\n\nw1\n0\nw2\n1\nw3\n1\nw4\n1\nw5\n0\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.63 0.56 0.60 2319\n 1 0.60 0.67 0.63 2257\n\navg / total 0.62 0.61 0.61 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.89 0.84 0.87 9121\n 1 0.85 0.90 0.88 9183\n\navg / total 0.87 0.87 0.87 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.28 0.79 0.42 11440\n 1 0.95 0.69 0.80 73355\n\navg / total 0.86 0.70 0.75 84795\n\nw1\n0\nw2\n1\nw3\n1\nw4\n1\nw5\n1\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.63 0.58 0.60 2319\n 1 0.60 0.65 0.62 2257\n\navg / total 0.61 0.61 0.61 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.89 0.85 0.87 9121\n 1 0.86 0.89 0.87 9183\n\navg / total 0.87 0.87 0.87 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.28 0.80 0.41 11440\n 1 0.96 0.68 0.80 73355\n\navg / total 0.86 0.70 0.74 84795\n\nw1\n1\nw2\n0\nw3\n0\nw4\n0\nw5\n0\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.62 0.61 0.61 2319\n 1 0.60 0.62 0.61 2257\n\navg / total 0.61 0.61 0.61 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.61 0.61 0.61 9121\n 1 0.61 0.61 0.61 9183\n\navg / total 0.61 0.61 0.61 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.20 0.61 0.30 11440\n 1 0.91 0.62 0.74 73355\n\navg / total 0.81 0.62 0.68 84795\n\nw1\n1\nw2\n0\nw3\n0\nw4\n0\nw5\n1\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.59 0.60 0.60 2319\n 1 0.58 0.58 0.58 2257\n\navg / total 0.59 0.59 0.59 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.69 0.70 0.69 9121\n 1 0.70 0.69 0.69 9183\n\navg / total 0.69 0.69 0.69 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.21 0.68 0.32 11440\n 1 0.92 0.60 0.72 73355\n\navg / total 0.83 0.61 0.67 84795\n\nw1\n1\nw2\n0\nw3\n0\nw4\n1\nw5\n0\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.62 0.62 0.62 2319\n 1 0.61 0.60 0.61 2257\n\navg / total 0.61 0.61 0.61 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.61 0.63 0.62 9121\n 1 0.62 0.60 0.61 9183\n\navg / total 0.61 0.61 0.61 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.20 0.63 0.30 11440\n 1 0.91 0.60 0.72 73355\n\navg / total 0.82 0.60 0.67 84795\n\nw1\n1\nw2\n0\nw3\n0\nw4\n1\nw5\n1\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.61 0.62 0.61 2319\n 1 0.60 0.59 0.59 2257\n\navg / total 0.60 0.60 0.60 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.68 0.70 0.69 9121\n 1 0.69 0.68 0.68 9183\n\navg / total 0.69 0.69 0.69 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.21 0.68 0.32 11440\n 1 0.92 0.60 0.73 73355\n\navg / total 0.83 0.61 0.68 84795\n\nw1\n1\nw2\n0\nw3\n1\nw4\n0\nw5\n0\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.63 0.50 0.56 2319\n 1 0.58 0.70 0.63 2257\n\navg / total 0.60 0.60 0.60 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.62 0.51 0.56 9121\n 1 0.59 0.69 0.64 9183\n\navg / total 0.60 0.60 0.60 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.21 0.51 0.29 11440\n 1 0.90 0.70 0.79 73355\n\navg / total 0.81 0.67 0.72 84795\n\nw1\n1\nw2\n0\nw3\n1\nw4\n0\nw5\n1\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.62 0.53 0.57 2319\n 1 0.58 0.67 0.62 2257\n\navg / total 0.60 0.60 0.60 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.69 0.60 0.64 9121\n 1 0.65 0.73 0.69 9183\n\navg / total 0.67 0.66 0.66 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.22 0.58 0.32 11440\n 1 0.91 0.68 0.78 73355\n\navg / total 0.82 0.67 0.72 84795\n\nw1\n1\nw2\n0\nw3\n1\nw4\n1\nw5\n0\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.64 0.56 0.59 2319\n 1 0.60 0.67 0.63 2257\n\navg / total 0.62 0.61 0.61 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.62 0.55 0.58 9121\n 1 0.60 0.67 0.63 9183\n\navg / total 0.61 0.61 0.61 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.21 0.55 0.30 11440\n 1 0.91 0.67 0.77 73355\n\navg / total 0.81 0.65 0.71 84795\n\nw1\n1\nw2\n0\nw3\n1\nw4\n1\nw5\n1\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.63 0.57 0.60 2319\n 1 0.60 0.65 0.62 2257\n\navg / total 0.61 0.61 0.61 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.68 0.62 0.65 9121\n 1 0.65 0.71 0.68 9183\n\navg / total 0.67 0.66 0.66 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.22 0.61 0.32 11440\n 1 0.92 0.66 0.77 73355\n\navg / total 0.82 0.65 0.71 84795\n\nw1\n1\nw2\n1\nw3\n0\nw4\n0\nw5\n0\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.62 0.63 0.63 2319\n 1 0.62 0.60 0.61 2257\n\navg / total 0.62 0.62 0.62 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.96 0.97 0.97 9121\n 1 0.97 0.96 0.97 9183\n\navg / total 0.97 0.97 0.97 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.28 0.90 0.43 11440\n 1 0.98 0.65 0.78 73355\n\navg / total 0.88 0.68 0.73 84795\n\nw1\n1\nw2\n1\nw3\n0\nw4\n0\nw5\n1\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.61 0.62 0.62 2319\n 1 0.61 0.59 0.60 2257\n\navg / total 0.61 0.61 0.61 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.93 0.94 0.93 9121\n 1 0.94 0.93 0.93 9183\n\navg / total 0.93 0.93 0.93 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.27 0.87 0.42 11440\n 1 0.97 0.64 0.77 73355\n\navg / total 0.88 0.67 0.72 84795\n\nw1\n1\nw2\n1\nw3\n0\nw4\n1\nw5\n0\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.62 0.64 0.63 2319\n 1 0.62 0.60 0.61 2257\n\navg / total 0.62 0.62 0.62 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.90 0.91 0.90 9121\n 1 0.91 0.89 0.90 9183\n\navg / total 0.90 0.90 0.90 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.26 0.85 0.40 11440\n 1 0.97 0.63 0.76 73355\n\navg / total 0.87 0.66 0.71 84795\n\nw1\n1\nw2\n1\nw3\n0\nw4\n1\nw5\n1\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.62 0.64 0.63 2319\n 1 0.62 0.59 0.61 2257\n\navg / total 0.62 0.62 0.62 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.89 0.90 0.89 9121\n 1 0.90 0.89 0.89 9183\n\navg / total 0.89 0.89 0.89 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.26 0.85 0.40 11440\n 1 0.96 0.63 0.76 73355\n\navg / total 0.87 0.66 0.72 84795\n\nw1\n1\nw2\n1\nw3\n1\nw4\n0\nw5\n0\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.63 0.56 0.59 2319\n 1 0.60 0.67 0.63 2257\n\navg / total 0.62 0.61 0.61 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.88 0.82 0.85 9121\n 1 0.83 0.89 0.86 9183\n\navg / total 0.85 0.85 0.85 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.28 0.76 0.41 11440\n 1 0.95 0.70 0.80 73355\n\navg / total 0.86 0.71 0.75 84795\n\nw1\n1\nw2\n1\nw3\n1\nw4\n0\nw5\n1\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.63 0.57 0.60 2319\n 1 0.60 0.65 0.62 2257\n\navg / total 0.61 0.61 0.61 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.88 0.84 0.86 9121\n 1 0.85 0.89 0.87 9183\n\navg / total 0.87 0.86 0.86 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.28 0.78 0.41 11440\n 1 0.95 0.69 0.80 73355\n\navg / total 0.86 0.70 0.75 84795\n\nw1\n1\nw2\n1\nw3\n1\nw4\n1\nw5\n0\nTest under TEST DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.63 0.58 0.60 2319\n 1 0.60 0.65 0.62 2257\n\navg / total 0.62 0.61 0.61 4576\n\nTest under TRAIN DATASET\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.84 0.79 0.81 9121\n 1 0.80 0.85 0.83 9183\n\navg / total 0.82 0.82 0.82 18304\n\nTest under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.26 0.75 0.39 11440\n 1 0.95 0.67 0.79 73355\n\navg / total 0.85 0.68 0.73 84795\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"The pipeline first passes data through our encoder, then to the imputer, and finally to our classifier. In this case, I have chosen a `LogisticRegression`, a regularized linear model that is used to estimate a categorical dependent variable, much like the binary target we have in this case. We can then evaluate the model on the test data set using the same exact pipeline. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The last step is to save our model to disk for reuse later, with the `pickle` module:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Model Pickle",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pickle \n\ndef dump_model(model, path='data', name='classifier.pickle'):\n with open(os.path.join(path, name), 'wb') as f:\n pickle.dump(model, f)\n \ndump_model(lr)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import pickle \n\ndef dump_model(model, path='data', name='encodert.pickle'):\n with open(os.path.join(path, name), 'wb') as f:\n pickle.dump(model, f)\n \ndump_model(yencode)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# SVMs\n\nSupport Vector Machines (SVM) uses points in transformed problem space that separates the classes into groups.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline\nfrom sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error as mse\nfrom sklearn.metrics import r2_score\nfrom sklearn.svm import SVC\n\n# we need to encode our target data as well. \n\nyencode = LabelEncoder().fit(dataset.target)\n\n\n# construct the pipeline \nsvm = Pipeline([\n ('encoder', EncodeCategorical(dataset.categorical_features.keys())),\n ('imputer', ImputeCategorical(Fnames)),\n ('scalar', StandardScaler()),\n ('classifier', SVC(kernel='linear'))\n ])\n\nsvm.fit(dataset.data, yencode.transform(dataset.target))\n\nprint \"Test under TEST DATASET\"\ny_true, y_pred = yencode.transform(dataset.target_test), svm.predict(dataset.data_test)\nprint(classification_report(y_true, y_pred))\nprint \"Test under TRAIN DATASET\"\ny_true, y_pred = yencode.transform(dataset.target), svm.predict(dataset.data)\nprint(classification_report(y_true, y_pred))\nprint \"Test under FULL IMBALANCED DATASET without new fit call\"\ny_true, y_pred = yencode.transform(full_data[label]), svm.predict(full_data[Fnames])\nprint(classification_report(y_true, y_pred))\n\n#kernels = ['linear', 'poly', 'rbf']\n\n\n#for kernel in kernels:\n# if kernel != 'poly':\n# model = SVC(kernel=kernel)\n# else:\n# model = SVC(kernel=kernel, degree=3)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can also dump meta information about the date and time your model was built, who built the model, etc. But we'll skip that step here. \n\n## Model Operation \n\nNow it's time to explore how to use the model. To do this, we'll create a simple function that gathers input from the user on the command line, and returns a prediction with the classifier model. Moreover, this function will load the pickled model into memory to ensure the latest and greatest saved model is what's being used. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def load_model(path='data/classifier.pickle'):\n with open(path, 'rb') as f:\n return pickle.load(f) \n\n\ndef predict(model, meta=meta):\n data = {} # Store the input from the user\n \n for column in meta['feature_names'][:-1]:\n # Get the valid responses\n valid = meta['categorical_features'].get(column)\n \n # Prompt the user for an answer until good \n while True:\n val = \"\" + raw_input(\"enter {} >\".format(column))\n print val\n# if valid and val not in valid:\n# print \"Not valid, choose one of {}\".format(valid)\n# else:\n data[column] = val\n break\n \n # Create prediction and label \n# yhat = model.predict(pd.DataFrame([data]))\n yhat = model.predict_proba(pd.DataFrame([data]))\n print yhat\n return yencode.inverse_transform(yhat)\n \n \n# Execute the interface \n#model = load_model()\n#predict(model)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#print data\n#yhat = model.predict_proba(pd.DataFrame([data]))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n## Conclusion \n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4abbe528a000ab28317fdeb4501207087e2273ee
| 35,985 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
price_promos2.ipynb
|
ericschulman/drills
|
918afe7a966422671e76705c1e30d9d27a0d596c
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
price_promos2.ipynb
|
ericschulman/drills
|
918afe7a966422671e76705c1e30d9d27a0d596c
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
price_promos2.ipynb
|
ericschulman/drills
|
918afe7a966422671e76705c1e30d9d27a0d596c
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 57.392344 | 10,172 | 0.731722 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd #package for reading data\nimport numpy as np \nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt #package for creating plots",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Import data into the notebook",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data_folder = \"data/\"\nprices = pd.read_csv(data_folder + \"clean_prices.csv\")\nprint(prices.columns)",
"Index(['platform', 'website', 'date', 'zipcode', 'rank', 'page', 'query',\n 'prod_id', 'upc', 'product', 'manufacturer', 'model', 'price',\n 'list_price', 'in_stock', 'max_qty', 'seller', 'arrives', 'shipping',\n 'shipping_price', 'shipping_options', 'store_stock', 'store_address',\n 'store_zip', 'store_price', 'weight', 'reviews', 'rating', 'quantity1',\n 'quantity2', 'quantity3', 'quantity4', 'quantity5', 'ads', 'calc_rank',\n 'calc_inven', 'calc_promo', 'calc_ship'],\n dtype='object')\n"
]
],
[
[
"How many unique models of drill are in the data?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"prices['label'] = prices['manufacturer'].astype(str) + \" \" + prices['model']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"prices['label'].nunique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"prices.groupby('platform')['label'].nunique()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"How many unique manufacturers of drills are in the data? ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"prices['manufacturer'].nunique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"prices.groupby('platform')['manufacturer'].nunique()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Are ads correlated with the rankings and inventory? Create a scatter plot with the two variables.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"prices['label'] = prices['manufacturer'].astype(str) + \" \" + prices['model']\nprice_ads = prices.groupby('label')['ads'].mean()\nprice_ads = price_ads[price_ads >0].index\nads_select = np.zeros(len(prices),dtype=bool)\nfor label in price_ads:\n ads_select = (prices['label']==label) | ads_select\nprices_ads = prices[ads_select]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# correlation\nprint( round(prices_ads['calc_rank'].corr(prices_ads['ads']), 4))\nprint(round(prices_ads['calc_inven'].corr(prices_ads['ads']), 4))",
"0.0612\n0.3057\n"
],
[
"# scatterplot\nplt.title(\"rank vs ads\")\nplt.scatter(prices_ads['calc_rank'], prices_ads['ads'],alpha=.05)\nplt.show()\nplt.title(\"inventory vs ads\")\nplt.scatter(prices_ads['calc_inven'], prices_ads['ads'],alpha=.05)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"How do average prices differ between products that are sponsored/advertised in the search results versus products that are not. i.e. report the average price for products that are advertised against those that are not.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"avg_price_ads = pd.DataFrame(prices.groupby('ads')['price'].mean())\navg_price_ads",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"If a product stops being sponsored, does the price change?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"avg_price_ads = pd.DataFrame(prices_ads.groupby('ads')['price'].mean())\navg_price_ads",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Create a variance, covariance matrix, separate for each platform, for the following variables:\n* Weight\n* Reviews\n* Rating\n* Rank\n* Price\n* Shipping times\n* Inventory",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"price_columns = ['weight', 'reviews', 'rating', 'calc_rank', 'price','calc_ship','calc_inven']\nprices[price_columns].mean()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"prices[price_columns].max()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"prices[price_columns].cov()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4abbed041cd08aad73f5bcfcf9d30c131df9d742
| 273,147 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Improving Deep Neural Networks: Hyperparameter tuning, Regularization and Optimization/Regularization-v2.ipynb
|
NishantBhavsar/deep-learning-coursera
|
933ba342c8206265490101e9fb034ee01cdda5f0
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2018-11-15T04:06:12.000Z
|
2018-11-15T04:06:12.000Z
|
Improving Deep Neural Networks: Hyperparameter tuning, Regularization and Optimization/Regularization-v2.ipynb
|
NishantBhavsar/deep-learning-coursera
|
933ba342c8206265490101e9fb034ee01cdda5f0
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Improving Deep Neural Networks: Hyperparameter tuning, Regularization and Optimization/Regularization-v2.ipynb
|
NishantBhavsar/deep-learning-coursera
|
933ba342c8206265490101e9fb034ee01cdda5f0
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 240.65815 | 56,104 | 0.891355 |
[
[
[
"# Regularization\n\nWelcome to the second assignment of this week. Deep Learning models have so much flexibility and capacity that **overfitting can be a serious problem**, if the training dataset is not big enough. Sure it does well on the training set, but the learned network **doesn't generalize to new examples** that it has never seen!\n\n**You will learn to:** Use regularization in your deep learning models.\n\nLet's first import the packages you are going to use.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# import packages\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom reg_utils import sigmoid, relu, plot_decision_boundary, initialize_parameters, load_2D_dataset, predict_dec\nfrom reg_utils import compute_cost, predict, forward_propagation, backward_propagation, update_parameters\nimport sklearn\nimport sklearn.datasets\nimport scipy.io\nfrom testCases import *\n\n%matplotlib inline\nplt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (7.0, 4.0) # set default size of plots\nplt.rcParams['image.interpolation'] = 'nearest'\nplt.rcParams['image.cmap'] = 'gray'",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Problem Statement**: You have just been hired as an AI expert by the French Football Corporation. They would like you to recommend positions where France's goal keeper should kick the ball so that the French team's players can then hit it with their head. \n\n<img src=\"images/field_kiank.png\" style=\"width:600px;height:350px;\">\n<caption><center> <u> **Figure 1** </u>: **Football field**<br> The goal keeper kicks the ball in the air, the players of each team are fighting to hit the ball with their head </center></caption>\n\n\nThey give you the following 2D dataset from France's past 10 games.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"train_X, train_Y, test_X, test_Y = load_2D_dataset()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Each dot corresponds to a position on the football field where a football player has hit the ball with his/her head after the French goal keeper has shot the ball from the left side of the football field.\n- If the dot is blue, it means the French player managed to hit the ball with his/her head\n- If the dot is red, it means the other team's player hit the ball with their head\n\n**Your goal**: Use a deep learning model to find the positions on the field where the goalkeeper should kick the ball.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Analysis of the dataset**: This dataset is a little noisy, but it looks like a diagonal line separating the upper left half (blue) from the lower right half (red) would work well. \n\nYou will first try a non-regularized model. Then you'll learn how to regularize it and decide which model you will choose to solve the French Football Corporation's problem. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 1 - Non-regularized model\n\nYou will use the following neural network (already implemented for you below). This model can be used:\n- in *regularization mode* -- by setting the `lambd` input to a non-zero value. We use \"`lambd`\" instead of \"`lambda`\" because \"`lambda`\" is a reserved keyword in Python. \n- in *dropout mode* -- by setting the `keep_prob` to a value less than one\n\nYou will first try the model without any regularization. Then, you will implement:\n- *L2 regularization* -- functions: \"`compute_cost_with_regularization()`\" and \"`backward_propagation_with_regularization()`\"\n- *Dropout* -- functions: \"`forward_propagation_with_dropout()`\" and \"`backward_propagation_with_dropout()`\"\n\nIn each part, you will run this model with the correct inputs so that it calls the functions you've implemented. Take a look at the code below to familiarize yourself with the model.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def model(X, Y, learning_rate = 0.3, num_iterations = 30000, print_cost = True, lambd = 0, keep_prob = 1):\n \"\"\"\n Implements a three-layer neural network: LINEAR->RELU->LINEAR->RELU->LINEAR->SIGMOID.\n \n Arguments:\n X -- input data, of shape (input size, number of examples)\n Y -- true \"label\" vector (1 for blue dot / 0 for red dot), of shape (output size, number of examples)\n learning_rate -- learning rate of the optimization\n num_iterations -- number of iterations of the optimization loop\n print_cost -- If True, print the cost every 10000 iterations\n lambd -- regularization hyperparameter, scalar\n keep_prob - probability of keeping a neuron active during drop-out, scalar.\n \n Returns:\n parameters -- parameters learned by the model. They can then be used to predict.\n \"\"\"\n \n grads = {}\n costs = [] # to keep track of the cost\n m = X.shape[1] # number of examples\n layers_dims = [X.shape[0], 20, 3, 1]\n \n # Initialize parameters dictionary.\n parameters = initialize_parameters(layers_dims)\n\n # Loop (gradient descent)\n\n for i in range(0, num_iterations):\n\n # Forward propagation: LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID.\n if keep_prob == 1:\n a3, cache = forward_propagation(X, parameters)\n elif keep_prob < 1:\n a3, cache = forward_propagation_with_dropout(X, parameters, keep_prob)\n \n # Cost function\n if lambd == 0:\n cost = compute_cost(a3, Y)\n else:\n cost = compute_cost_with_regularization(a3, Y, parameters, lambd)\n \n # Backward propagation.\n assert(lambd==0 or keep_prob==1) # it is possible to use both L2 regularization and dropout, \n # but this assignment will only explore one at a time\n if lambd == 0 and keep_prob == 1:\n grads = backward_propagation(X, Y, cache)\n elif lambd != 0:\n grads = backward_propagation_with_regularization(X, Y, cache, lambd)\n elif keep_prob < 1:\n grads = backward_propagation_with_dropout(X, Y, cache, keep_prob)\n \n # Update parameters.\n parameters = update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate)\n \n # Print the loss every 10000 iterations\n if print_cost and i % 10000 == 0:\n print(\"Cost after iteration {}: {}\".format(i, cost))\n if print_cost and i % 1000 == 0:\n costs.append(cost)\n \n # plot the cost\n plt.plot(costs)\n plt.ylabel('cost')\n plt.xlabel('iterations (x1,000)')\n plt.title(\"Learning rate =\" + str(learning_rate))\n plt.show()\n \n return parameters",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's train the model without any regularization, and observe the accuracy on the train/test sets.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"parameters = model(train_X, train_Y)\nprint (\"On the training set:\")\npredictions_train = predict(train_X, train_Y, parameters)\nprint (\"On the test set:\")\npredictions_test = predict(test_X, test_Y, parameters)",
"Cost after iteration 0: 0.6557412523481002\nCost after iteration 10000: 0.16329987525724216\nCost after iteration 20000: 0.13851642423255986\n"
]
],
[
[
"The train accuracy is 94.8% while the test accuracy is 91.5%. This is the **baseline model** (you will observe the impact of regularization on this model). Run the following code to plot the decision boundary of your model.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plt.title(\"Model without regularization\")\naxes = plt.gca()\naxes.set_xlim([-0.75,0.40])\naxes.set_ylim([-0.75,0.65])\nplot_decision_boundary(lambda x: predict_dec(parameters, x.T), train_X, train_Y)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The non-regularized model is obviously overfitting the training set. It is fitting the noisy points! Lets now look at two techniques to reduce overfitting.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 2 - L2 Regularization\n\nThe standard way to avoid overfitting is called **L2 regularization**. It consists of appropriately modifying your cost function, from:\n$$J = -\\frac{1}{m} \\sum\\limits_{i = 1}^{m} \\large{(}\\small y^{(i)}\\log\\left(a^{[L](i)}\\right) + (1-y^{(i)})\\log\\left(1- a^{[L](i)}\\right) \\large{)} \\tag{1}$$\nTo:\n$$J_{regularized} = \\small \\underbrace{-\\frac{1}{m} \\sum\\limits_{i = 1}^{m} \\large{(}\\small y^{(i)}\\log\\left(a^{[L](i)}\\right) + (1-y^{(i)})\\log\\left(1- a^{[L](i)}\\right) \\large{)} }_\\text{cross-entropy cost} + \\underbrace{\\frac{1}{m} \\frac{\\lambda}{2} \\sum\\limits_l\\sum\\limits_k\\sum\\limits_j W_{k,j}^{[l]2} }_\\text{L2 regularization cost} \\tag{2}$$\n\nLet's modify your cost and observe the consequences.\n\n**Exercise**: Implement `compute_cost_with_regularization()` which computes the cost given by formula (2). To calculate $\\sum\\limits_k\\sum\\limits_j W_{k,j}^{[l]2}$ , use :\n```python\nnp.sum(np.square(Wl))\n```\nNote that you have to do this for $W^{[1]}$, $W^{[2]}$ and $W^{[3]}$, then sum the three terms and multiply by $ \\frac{1}{m} \\frac{\\lambda}{2} $.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# GRADED FUNCTION: compute_cost_with_regularization\n\ndef compute_cost_with_regularization(A3, Y, parameters, lambd):\n \"\"\"\n Implement the cost function with L2 regularization. See formula (2) above.\n \n Arguments:\n A3 -- post-activation, output of forward propagation, of shape (output size, number of examples)\n Y -- \"true\" labels vector, of shape (output size, number of examples)\n parameters -- python dictionary containing parameters of the model\n \n Returns:\n cost - value of the regularized loss function (formula (2))\n \"\"\"\n m = Y.shape[1]\n W1 = parameters[\"W1\"]\n W2 = parameters[\"W2\"]\n W3 = parameters[\"W3\"]\n \n cross_entropy_cost = compute_cost(A3, Y) # This gives you the cross-entropy part of the cost\n \n ### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 1 line)\n L2_regularization_cost = (lambd / (2 * m)) * (np.sum(np.square(W1)) + np.sum(np.square(W2)) + np.sum(np.square(W3)))\n ### END CODER HERE ###\n \n cost = cross_entropy_cost + L2_regularization_cost\n \n return cost",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"A3, Y_assess, parameters = compute_cost_with_regularization_test_case()\n\nprint(\"cost = \" + str(compute_cost_with_regularization(A3, Y_assess, parameters, lambd = 0.1)))",
"cost = 1.78648594516\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Expected Output**: \n\n<table> \n <tr>\n <td>\n **cost**\n </td>\n <td>\n 1.78648594516\n </td>\n \n </tr>\n\n</table> ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Of course, because you changed the cost, you have to change backward propagation as well! All the gradients have to be computed with respect to this new cost. \n\n**Exercise**: Implement the changes needed in backward propagation to take into account regularization. The changes only concern dW1, dW2 and dW3. For each, you have to add the regularization term's gradient ($\\frac{d}{dW} ( \\frac{1}{2}\\frac{\\lambda}{m} W^2) = \\frac{\\lambda}{m} W$).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# GRADED FUNCTION: backward_propagation_with_regularization\n\ndef backward_propagation_with_regularization(X, Y, cache, lambd):\n \"\"\"\n Implements the backward propagation of our baseline model to which we added an L2 regularization.\n \n Arguments:\n X -- input dataset, of shape (input size, number of examples)\n Y -- \"true\" labels vector, of shape (output size, number of examples)\n cache -- cache output from forward_propagation()\n lambd -- regularization hyperparameter, scalar\n \n Returns:\n gradients -- A dictionary with the gradients with respect to each parameter, activation and pre-activation variables\n \"\"\"\n \n m = X.shape[1]\n (Z1, A1, W1, b1, Z2, A2, W2, b2, Z3, A3, W3, b3) = cache\n \n dZ3 = A3 - Y\n \n ### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 1 line)\n dW3 = 1./m * np.dot(dZ3, A2.T) + (lambd/m) * W3\n ### END CODE HERE ###\n db3 = 1./m * np.sum(dZ3, axis=1, keepdims = True)\n \n dA2 = np.dot(W3.T, dZ3)\n dZ2 = np.multiply(dA2, np.int64(A2 > 0))\n ### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 1 line)\n dW2 = 1./m * np.dot(dZ2, A1.T) + (lambd/m) * W2\n ### END CODE HERE ###\n db2 = 1./m * np.sum(dZ2, axis=1, keepdims = True)\n \n dA1 = np.dot(W2.T, dZ2)\n dZ1 = np.multiply(dA1, np.int64(A1 > 0))\n ### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 1 line)\n dW1 = 1./m * np.dot(dZ1, X.T) + (lambd/m) * W1\n ### END CODE HERE ###\n db1 = 1./m * np.sum(dZ1, axis=1, keepdims = True)\n \n gradients = {\"dZ3\": dZ3, \"dW3\": dW3, \"db3\": db3,\"dA2\": dA2,\n \"dZ2\": dZ2, \"dW2\": dW2, \"db2\": db2, \"dA1\": dA1, \n \"dZ1\": dZ1, \"dW1\": dW1, \"db1\": db1}\n \n return gradients",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_assess, Y_assess, cache = backward_propagation_with_regularization_test_case()\n\ngrads = backward_propagation_with_regularization(X_assess, Y_assess, cache, lambd = 0.7)\nprint (\"dW1 = \"+ str(grads[\"dW1\"]))\nprint (\"dW2 = \"+ str(grads[\"dW2\"]))\nprint (\"dW3 = \"+ str(grads[\"dW3\"]))",
"dW1 = [[-0.25604646 0.12298827 -0.28297129]\n [-0.17706303 0.34536094 -0.4410571 ]]\ndW2 = [[ 0.79276486 0.85133918]\n [-0.0957219 -0.01720463]\n [-0.13100772 -0.03750433]]\ndW3 = [[-1.77691347 -0.11832879 -0.09397446]]\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Expected Output**:\n\n<table> \n <tr>\n <td>\n **dW1**\n </td>\n <td>\n [[-0.25604646 0.12298827 -0.28297129]\n [-0.17706303 0.34536094 -0.4410571 ]]\n </td>\n </tr>\n <tr>\n <td>\n **dW2**\n </td>\n <td>\n [[ 0.79276486 0.85133918]\n [-0.0957219 -0.01720463]\n [-0.13100772 -0.03750433]]\n </td>\n </tr>\n <tr>\n <td>\n **dW3**\n </td>\n <td>\n [[-1.77691347 -0.11832879 -0.09397446]]\n </td>\n </tr>\n</table> ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Let's now run the model with L2 regularization $(\\lambda = 0.7)$. The `model()` function will call: \n- `compute_cost_with_regularization` instead of `compute_cost`\n- `backward_propagation_with_regularization` instead of `backward_propagation`",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"parameters = model(train_X, train_Y, lambd = 0.7)\nprint (\"On the train set:\")\npredictions_train = predict(train_X, train_Y, parameters)\nprint (\"On the test set:\")\npredictions_test = predict(test_X, test_Y, parameters)",
"Cost after iteration 0: 0.6974484493131264\nCost after iteration 10000: 0.2684918873282239\nCost after iteration 20000: 0.2680916337127301\n"
]
],
[
[
"Congrats, the test set accuracy increased to 93%. You have saved the French football team!\n\nYou are not overfitting the training data anymore. Let's plot the decision boundary.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plt.title(\"Model with L2-regularization\")\naxes = plt.gca()\naxes.set_xlim([-0.75,0.40])\naxes.set_ylim([-0.75,0.65])\nplot_decision_boundary(lambda x: predict_dec(parameters, x.T), train_X, train_Y)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Observations**:\n- The value of $\\lambda$ is a hyperparameter that you can tune using a dev set.\n- L2 regularization makes your decision boundary smoother. If $\\lambda$ is too large, it is also possible to \"oversmooth\", resulting in a model with high bias.\n\n**What is L2-regularization actually doing?**:\n\nL2-regularization relies on the assumption that a model with small weights is simpler than a model with large weights. Thus, by penalizing the square values of the weights in the cost function you drive all the weights to smaller values. It becomes too costly for the cost to have large weights! This leads to a smoother model in which the output changes more slowly as the input changes. \n\n<font color='blue'>\n**What you should remember** -- the implications of L2-regularization on:\n- The cost computation:\n - A regularization term is added to the cost\n- The backpropagation function:\n - There are extra terms in the gradients with respect to weight matrices\n- Weights end up smaller (\"weight decay\"): \n - Weights are pushed to smaller values.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 3 - Dropout\n\nFinally, **dropout** is a widely used regularization technique that is specific to deep learning. \n**It randomly shuts down some neurons in each iteration.** Watch these two videos to see what this means!\n\n<!--\nTo understand drop-out, consider this conversation with a friend:\n- Friend: \"Why do you need all these neurons to train your network and classify images?\". \n- You: \"Because each neuron contains a weight and can learn specific features/details/shape of an image. The more neurons I have, the more featurse my model learns!\"\n- Friend: \"I see, but are you sure that your neurons are learning different features and not all the same features?\"\n- You: \"Good point... Neurons in the same layer actually don't talk to each other. It should be definitly possible that they learn the same image features/shapes/forms/details... which would be redundant. There should be a solution.\"\n!--> \n\n\n<center>\n<video width=\"620\" height=\"440\" src=\"images/dropout1_kiank.mp4\" type=\"video/mp4\" controls>\n</video>\n</center>\n<br>\n<caption><center> <u> Figure 2 </u>: Drop-out on the second hidden layer. <br> At each iteration, you shut down (= set to zero) each neuron of a layer with probability $1 - keep\\_prob$ or keep it with probability $keep\\_prob$ (50% here). The dropped neurons don't contribute to the training in both the forward and backward propagations of the iteration. </center></caption>\n\n<center>\n<video width=\"620\" height=\"440\" src=\"images/dropout2_kiank.mp4\" type=\"video/mp4\" controls>\n</video>\n</center>\n\n<caption><center> <u> Figure 3 </u>: Drop-out on the first and third hidden layers. <br> $1^{st}$ layer: we shut down on average 40% of the neurons. $3^{rd}$ layer: we shut down on average 20% of the neurons. </center></caption>\n\n\nWhen you shut some neurons down, you actually modify your model. The idea behind drop-out is that at each iteration, you train a different model that uses only a subset of your neurons. With dropout, your neurons thus become less sensitive to the activation of one other specific neuron, because that other neuron might be shut down at any time. \n\n### 3.1 - Forward propagation with dropout\n\n**Exercise**: Implement the forward propagation with dropout. You are using a 3 layer neural network, and will add dropout to the first and second hidden layers. We will not apply dropout to the input layer or output layer. \n\n**Instructions**:\nYou would like to shut down some neurons in the first and second layers. To do that, you are going to carry out 4 Steps:\n1. In lecture, we dicussed creating a variable $d^{[1]}$ with the same shape as $a^{[1]}$ using `np.random.rand()` to randomly get numbers between 0 and 1. Here, you will use a vectorized implementation, so create a random matrix $D^{[1]} = [d^{[1](1)} d^{[1](2)} ... d^{[1](m)}] $ of the same dimension as $A^{[1]}$.\n2. Set each entry of $D^{[1]}$ to be 0 with probability (`1-keep_prob`) or 1 with probability (`keep_prob`), by thresholding values in $D^{[1]}$ appropriately. Hint: to set all the entries of a matrix X to 0 (if entry is less than 0.5) or 1 (if entry is more than 0.5) you would do: `X = (X < 0.5)`. Note that 0 and 1 are respectively equivalent to False and True.\n3. Set $A^{[1]}$ to $A^{[1]} * D^{[1]}$. (You are shutting down some neurons). You can think of $D^{[1]}$ as a mask, so that when it is multiplied with another matrix, it shuts down some of the values.\n4. Divide $A^{[1]}$ by `keep_prob`. By doing this you are assuring that the result of the cost will still have the same expected value as without drop-out. (This technique is also called inverted dropout.)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# GRADED FUNCTION: forward_propagation_with_dropout\n\ndef forward_propagation_with_dropout(X, parameters, keep_prob = 0.5):\n \"\"\"\n Implements the forward propagation: LINEAR -> RELU + DROPOUT -> LINEAR -> RELU + DROPOUT -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID.\n \n Arguments:\n X -- input dataset, of shape (2, number of examples)\n parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters \"W1\", \"b1\", \"W2\", \"b2\", \"W3\", \"b3\":\n W1 -- weight matrix of shape (20, 2)\n b1 -- bias vector of shape (20, 1)\n W2 -- weight matrix of shape (3, 20)\n b2 -- bias vector of shape (3, 1)\n W3 -- weight matrix of shape (1, 3)\n b3 -- bias vector of shape (1, 1)\n keep_prob - probability of keeping a neuron active during drop-out, scalar\n \n Returns:\n A3 -- last activation value, output of the forward propagation, of shape (1,1)\n cache -- tuple, information stored for computing the backward propagation\n \"\"\"\n \n np.random.seed(1)\n \n # retrieve parameters\n W1 = parameters[\"W1\"]\n b1 = parameters[\"b1\"]\n W2 = parameters[\"W2\"]\n b2 = parameters[\"b2\"]\n W3 = parameters[\"W3\"]\n b3 = parameters[\"b3\"]\n \n # LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID\n Z1 = np.dot(W1, X) + b1\n A1 = relu(Z1)\n ### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 4 lines) # Steps 1-4 below correspond to the Steps 1-4 described above. \n D1 = np.random.rand(A1.shape[0], A1.shape[1]) # Step 1: initialize matrix D1 = np.random.rand(..., ...)\n D1 = D1 < keep_prob # Step 2: convert entries of D1 to 0 or 1 (using keep_prob as the threshold)\n A1 = A1 * D1 # Step 3: shut down some neurons of A1\n A1 = A1 / keep_prob # Step 4: scale the value of neurons that haven't been shut down\n ### END CODE HERE ###\n Z2 = np.dot(W2, A1) + b2\n A2 = relu(Z2)\n ### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 4 lines)\n D2 = np.random.rand(A2.shape[0], A2.shape[1]) # Step 1: initialize matrix D2 = np.random.rand(..., ...)\n D2 = D2 < keep_prob # Step 2: convert entries of D2 to 0 or 1 (using keep_prob as the threshold)\n A2 = A2 * D2 # Step 3: shut down some neurons of A2\n A2 = A2 / keep_prob # Step 4: scale the value of neurons that haven't been shut down\n ### END CODE HERE ###\n Z3 = np.dot(W3, A2) + b3\n A3 = sigmoid(Z3)\n \n cache = (Z1, D1, A1, W1, b1, Z2, D2, A2, W2, b2, Z3, A3, W3, b3)\n \n return A3, cache",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_assess, parameters = forward_propagation_with_dropout_test_case()\n\nA3, cache = forward_propagation_with_dropout(X_assess, parameters, keep_prob = 0.7)\nprint (\"A3 = \" + str(A3))",
"A3 = [[ 0.36974721 0.00305176 0.04565099 0.49683389 0.36974721]]\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Expected Output**: \n\n<table> \n <tr>\n <td>\n **A3**\n </td>\n <td>\n [[ 0.36974721 0.00305176 0.04565099 0.49683389 0.36974721]]\n </td>\n \n </tr>\n\n</table> ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 3.2 - Backward propagation with dropout\n\n**Exercise**: Implement the backward propagation with dropout. As before, you are training a 3 layer network. Add dropout to the first and second hidden layers, using the masks $D^{[1]}$ and $D^{[2]}$ stored in the cache. \n\n**Instruction**:\nBackpropagation with dropout is actually quite easy. You will have to carry out 2 Steps:\n1. You had previously shut down some neurons during forward propagation, by applying a mask $D^{[1]}$ to `A1`. In backpropagation, you will have to shut down the same neurons, by reapplying the same mask $D^{[1]}$ to `dA1`. \n2. During forward propagation, you had divided `A1` by `keep_prob`. In backpropagation, you'll therefore have to divide `dA1` by `keep_prob` again (the calculus interpretation is that if $A^{[1]}$ is scaled by `keep_prob`, then its derivative $dA^{[1]}$ is also scaled by the same `keep_prob`).\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# GRADED FUNCTION: backward_propagation_with_dropout\n\ndef backward_propagation_with_dropout(X, Y, cache, keep_prob):\n \"\"\"\n Implements the backward propagation of our baseline model to which we added dropout.\n \n Arguments:\n X -- input dataset, of shape (2, number of examples)\n Y -- \"true\" labels vector, of shape (output size, number of examples)\n cache -- cache output from forward_propagation_with_dropout()\n keep_prob - probability of keeping a neuron active during drop-out, scalar\n \n Returns:\n gradients -- A dictionary with the gradients with respect to each parameter, activation and pre-activation variables\n \"\"\"\n \n m = X.shape[1]\n (Z1, D1, A1, W1, b1, Z2, D2, A2, W2, b2, Z3, A3, W3, b3) = cache\n \n dZ3 = A3 - Y\n dW3 = 1./m * np.dot(dZ3, A2.T)\n db3 = 1./m * np.sum(dZ3, axis=1, keepdims = True)\n dA2 = np.dot(W3.T, dZ3)\n ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)\n dA2 = dA2 * D2 # Step 1: Apply mask D2 to shut down the same neurons as during the forward propagation\n dA2 = dA2 / keep_prob # Step 2: Scale the value of neurons that haven't been shut down\n ### END CODE HERE ###\n dZ2 = np.multiply(dA2, np.int64(A2 > 0))\n dW2 = 1./m * np.dot(dZ2, A1.T)\n db2 = 1./m * np.sum(dZ2, axis=1, keepdims = True)\n \n dA1 = np.dot(W2.T, dZ2)\n ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)\n dA1 = dA1 * D1 # Step 1: Apply mask D1 to shut down the same neurons as during the forward propagation\n dA1 = dA1 / keep_prob # Step 2: Scale the value of neurons that haven't been shut down\n ### END CODE HERE ###\n dZ1 = np.multiply(dA1, np.int64(A1 > 0))\n dW1 = 1./m * np.dot(dZ1, X.T)\n db1 = 1./m * np.sum(dZ1, axis=1, keepdims = True)\n \n gradients = {\"dZ3\": dZ3, \"dW3\": dW3, \"db3\": db3,\"dA2\": dA2,\n \"dZ2\": dZ2, \"dW2\": dW2, \"db2\": db2, \"dA1\": dA1, \n \"dZ1\": dZ1, \"dW1\": dW1, \"db1\": db1}\n \n return gradients",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_assess, Y_assess, cache = backward_propagation_with_dropout_test_case()\n\ngradients = backward_propagation_with_dropout(X_assess, Y_assess, cache, keep_prob = 0.8)\n\nprint (\"dA1 = \" + str(gradients[\"dA1\"]))\nprint (\"dA2 = \" + str(gradients[\"dA2\"]))",
"dA1 = [[ 0.36544439 0. -0.00188233 0. -0.17408748]\n [ 0.65515713 0. -0.00337459 0. -0. ]]\ndA2 = [[ 0.58180856 0. -0.00299679 0. -0.27715731]\n [ 0. 0.53159854 -0. 0.53159854 -0.34089673]\n [ 0. 0. -0.00292733 0. -0. ]]\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Expected Output**: \n\n<table> \n <tr>\n <td>\n **dA1**\n </td>\n <td>\n [[ 0.36544439 0. -0.00188233 0. -0.17408748]\n [ 0.65515713 0. -0.00337459 0. -0. ]]\n </td>\n \n </tr>\n <tr>\n <td>\n **dA2**\n </td>\n <td>\n [[ 0.58180856 0. -0.00299679 0. -0.27715731]\n [ 0. 0.53159854 -0. 0.53159854 -0.34089673]\n [ 0. 0. -0.00292733 0. -0. ]]\n </td>\n \n </tr>\n</table> ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Let's now run the model with dropout (`keep_prob = 0.86`). It means at every iteration you shut down each neurons of layer 1 and 2 with 14% probability. The function `model()` will now call:\n- `forward_propagation_with_dropout` instead of `forward_propagation`.\n- `backward_propagation_with_dropout` instead of `backward_propagation`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"parameters = model(train_X, train_Y, keep_prob = 0.86, learning_rate = 0.3)\n\nprint (\"On the train set:\")\npredictions_train = predict(train_X, train_Y, parameters)\nprint (\"On the test set:\")\npredictions_test = predict(test_X, test_Y, parameters)",
"Cost after iteration 0: 0.6543912405149825\n"
]
],
[
[
"Dropout works great! The test accuracy has increased again (to 95%)! Your model is not overfitting the training set and does a great job on the test set. The French football team will be forever grateful to you! \n\nRun the code below to plot the decision boundary.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plt.title(\"Model with dropout\")\naxes = plt.gca()\naxes.set_xlim([-0.75,0.40])\naxes.set_ylim([-0.75,0.65])\nplot_decision_boundary(lambda x: predict_dec(parameters, x.T), train_X, train_Y)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Note**:\n- A **common mistake** when using dropout is to use it both in training and testing. You should use dropout (randomly eliminate nodes) only in training. \n- Deep learning frameworks like [tensorflow](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/nn/dropout), [PaddlePaddle](http://doc.paddlepaddle.org/release_doc/0.9.0/doc/ui/api/trainer_config_helpers/attrs.html), [keras](https://keras.io/layers/core/#dropout) or [caffe](http://caffe.berkeleyvision.org/tutorial/layers/dropout.html) come with a dropout layer implementation. Don't stress - you will soon learn some of these frameworks.\n\n<font color='blue'>\n**What you should remember about dropout:**\n- Dropout is a regularization technique.\n- You only use dropout during training. Don't use dropout (randomly eliminate nodes) during test time.\n- Apply dropout both during forward and backward propagation.\n- During training time, divide each dropout layer by keep_prob to keep the same expected value for the activations. For example, if keep_prob is 0.5, then we will on average shut down half the nodes, so the output will be scaled by 0.5 since only the remaining half are contributing to the solution. Dividing by 0.5 is equivalent to multiplying by 2. Hence, the output now has the same expected value. You can check that this works even when keep_prob is other values than 0.5. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 4 - Conclusions",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Here are the results of our three models**: \n\n<table> \n <tr>\n <td>\n **model**\n </td>\n <td>\n **train accuracy**\n </td>\n <td>\n **test accuracy**\n </td>\n\n </tr>\n <td>\n 3-layer NN without regularization\n </td>\n <td>\n 95%\n </td>\n <td>\n 91.5%\n </td>\n <tr>\n <td>\n 3-layer NN with L2-regularization\n </td>\n <td>\n 94%\n </td>\n <td>\n 93%\n </td>\n </tr>\n <tr>\n <td>\n 3-layer NN with dropout\n </td>\n <td>\n 93%\n </td>\n <td>\n 95%\n </td>\n </tr>\n</table> ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Note that regularization hurts training set performance! This is because it limits the ability of the network to overfit to the training set. But since it ultimately gives better test accuracy, it is helping your system. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Congratulations for finishing this assignment! And also for revolutionizing French football. :-) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<font color='blue'>\n**What we want you to remember from this notebook**:\n- Regularization will help you reduce overfitting.\n- Regularization will drive your weights to lower values.\n- L2 regularization and Dropout are two very effective regularization techniques.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4abbfb7b7ca11502aace62a1232edb8195766419
| 124,444 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Datasets.ipynb
|
antolouis/learn-julia
|
0a32a7723cb7f7d8dedf81f413048b7c84dde8b3
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Datasets.ipynb
|
antolouis/learn-julia
|
0a32a7723cb7f7d8dedf81f413048b7c84dde8b3
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Datasets.ipynb
|
antolouis/learn-julia
|
0a32a7723cb7f7d8dedf81f413048b7c84dde8b3
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 27.076588 | 2,186 | 0.435794 |
[
[
[
"empty"
]
]
] |
[
"empty"
] |
[
[
"empty"
]
] |
4abbfd4480218aaecdd7a51555d2fcb6ae3f81db
| 7,106 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
misc/aoc/day4.ipynb
|
mmolnar0/sgillen_research
|
752e09fdf7a996c832e71b0a8296322fe77e9ae3
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
misc/aoc/day4.ipynb
|
mmolnar0/sgillen_research
|
752e09fdf7a996c832e71b0a8296322fe77e9ae3
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
misc/aoc/day4.ipynb
|
mmolnar0/sgillen_research
|
752e09fdf7a996c832e71b0a8296322fe77e9ae3
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 25.021127 | 74 | 0.495497 |
[
[
[
"import datetime as dt\nimport copy\n\nwith open('day4_input.txt') as f:\n inp_raw = f.readlines()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"inp = [None for _ in range(len(inp_raw))]\ntime_list = [None for _ in range(len(inp_raw))]\nfor i,event in enumerate(inp_raw):\n inter = event.split(']')\n timestamp = inter[0].strip('[')\n \n (date, time) = timestamp.split(' ')\n (year, month, day) = map(int, date.split('-'))\n (hour, minute) = map(int, time.split(':'))\n\n time = dt.datetime(year, month, day, hour, minute)\n \n if 'Guard' in inter[1]:\n action = int(inter[1][8:12])\n elif 'asleep' in inter[1]:\n action = 'asleep'\n elif 'wake' in inter[1]:\n action = 'wake'\n \n inp[i] = (time, action)\n time_list[i] = time\n \n \ninp.sort() # These seems to magically work",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"(date, time) = test.split(' ')\n(year, month, day) = map(int, date.split('-'))\n(hour, minute) = map(int, time.split(':'))\n\ntest_dt = dt.datetime(year, month, day, hour, minute)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class worker:\n def __init__(self, gid):\n self.minute_dict = {x:0 for x in range(0,60)}\n self.total_mins = 0\n self.gid = gid\n \nworker_dict = {}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cur_worker = None\nfor event in inp:\n if type(event[1]) is int:\n gid = event[1]\n \n if gid not in worker_dict:\n worker_dict[gid] = worker(gid)\n \n cur_worker = worker_dict[gid]\n \n if event[1] == 'asleep':\n sleep_time = event[0]\n if event[1] == 'wake':\n wake_time = event[0]\n total_time = wake_time - sleep_time\n worker_dict[gid].total_mins += (total_time.seconds/60)\n \n for minute in range(sleep_time.minute, wake_time.minute):\n worker_dict[gid].minute_dict[minute] += 1\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"max_minutes = 0\nmax_worker = None\nfor worker in worker_dict.values():\n \n if worker.total_mins > max_minutes:\n max_worker = worker\n max_minutes = worker.total_mins",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"max_minutes = 0\nmax_bin = None\n\nfor minute_bin, total_mins in max_worker.minute_dict.items():\n if total_mins > max_minutes:\n max_bin = minute_bin\n max_minutes = total_minutes\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"max_minute*max_worker.gid",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"max_minutes = 0\nmax_bin = None\nmax_worker2 = None\n\nfor worker in worker_dict.values():\n for minute_bin, total_mins in worker.minute_dict.items():\n if total_mins > max_minutes:\n max_bin = minute_bin\n max_minutes = total_mins\n max_worker2 = worker",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"max_worker2.gid*max_bin",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(max_worker2.gid)\nprint(max_bin)",
"1993\n50\n"
],
[
"worker_dict",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4abc15339d550dd3f3d2f699cfcaf49cf8a02d13
| 205,514 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
masters_of_information/YieldData.ipynb
|
oostendo/2022-SI699-011
|
26aecb2a9d28b7d9e0ba2ff0b6a0fb1b3cf28375
|
[
"MIT"
] | 4 |
2022-01-04T15:21:45.000Z
|
2022-01-06T23:50:27.000Z
|
masters_of_information/YieldData.ipynb
|
oostendo/2022-SI699-011
|
26aecb2a9d28b7d9e0ba2ff0b6a0fb1b3cf28375
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2022-02-03T23:01:09.000Z
|
2022-02-10T02:43:11.000Z
|
masters_of_information/YieldData.ipynb
|
oostendo/2022-SI699-011
|
26aecb2a9d28b7d9e0ba2ff0b6a0fb1b3cf28375
|
[
"MIT"
] | 4 |
2022-02-01T15:18:47.000Z
|
2022-02-03T23:08:33.000Z
| 45.578621 | 14,746 | 0.432146 |
[
[
[
"## Yield Data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport altair as alt\nimport os\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pwd\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"vegetables = pd.read_csv('MichiganVegetableData.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"commodity_list1 = vegetables['Commodity'].unique().tolist()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for commodity in commodity_list1:\n commoditydf = vegetables[vegetables['Commodity'] == commodity]\n mi_commodity_YIELD = commoditydf[commoditydf['Data Item'].str.contains(\"YIELD\")]\n year_length = len(mi_commodity_YIELD.Year.unique().tolist())\n if year_length > 15:\n print(commodity)",
"BEANS\nCABBAGE\nCARROTS\nCELERY\nONIONS\nPEPPERS\nPOTATOES\nSQUASH\nSWEET CORN\nTOMATOES\nASPARAGUS\nCUCUMBERS\nPUMPKINS\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Cucumbers",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mi_cucumbers = vegetables[vegetables['Commodity'] == 'CUCUMBERS']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mi_cucumbers['Data Item'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mi_cucumbers_yield = mi_cucumbers[mi_cucumbers['Data Item'] \n == 'CUCUMBERS, PROCESSING, PICKLES - YIELD, MEASURED IN TONS / ACRE']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mi_cucumbers_yield.Year.unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#mi_cucumbers_yield",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#cucumbers_ordered",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cucumbers_yield_stripped_data = mi_cucumbers_yield[['Year', 'Value']]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cucumbers_yield_stripped_data['Value'] = pd.to_numeric(\n cucumbers_yield_stripped_data['Value'].str.replace(',', ''), errors='coerce')",
"<ipython-input-14-be056347f78d>:1: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy\n cucumbers_yield_stripped_data['Value'] = pd.to_numeric(\n"
],
[
"cucumbers_yield_stripped_data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Pumpkin\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mi_pumpkins = vegetables[vegetables['Commodity'] == 'PUMPKINS']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mi_pumpkins_yield = mi_pumpkins[mi_pumpkins['Data Item'] == 'PUMPKINS - YIELD, MEASURED IN CWT / ACRE']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mi_pumpkins_yield.Year.unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pumpkins_yield_stripped_data = mi_pumpkins_yield[['Year', 'Value']]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pumpkins_yield_stripped_data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Cabbage",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mi_cabbage = vegetables[vegetables['Commodity'] == 'CABBAGE']\n#mi_cabbage['Data Item'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mi_cabbage_yield = mi_cabbage[mi_cabbage['Data Item'] == 'CABBAGE, FRESH MARKET - YIELD, MEASURED IN CWT / ACRE']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#mi_cabbage_yield",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mi_cabbage_yield.Year.unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cabbage_yield_stripped_data = mi_cabbage_yield[['Year', 'Value']]\ncabbage_yield_stripped_data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Potatoes",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mi_potatoes = vegetables[vegetables['Commodity'] == 'POTATOES']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#mi_potatoes['Data Item'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"potatoes_yield = mi_potatoes[mi_potatoes['Data Item'] == 'POTATOES - YIELD, MEASURED IN CWT / ACRE']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"potatoes_yield.Year.unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"potatoes_year_only = potatoes_yield[potatoes_yield['Period'] == 'YEAR']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"potatoes_yield_stripped_data = potatoes_year_only[['Year', 'Value']]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"potatoes_yield_stripped_data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Squash",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mi_squash = vegetables[vegetables['Commodity'] == 'SQUASH']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"squash_yield = mi_squash[mi_squash['Data Item'] == \"SQUASH - YIELD, MEASURED IN CWT / ACRE\"]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"squash_yield.Year.unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"squash_yield_stripped_data = squash_yield[['Year', 'Value']]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"squash_yield_stripped_data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Carrots",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mi_carrots = vegetables[vegetables['Commodity'] == 'CARROTS']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#mi_carrots['Data Item'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"carrots_yield = mi_carrots[mi_carrots['Data Item'] == \"CARROTS, FRESH MARKET - YIELD, MEASURED IN CWT / ACRE\"]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"carrots_yield.Year.unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"carrots_yield_stripped_data = carrots_yield[['Year', 'Value']]\ncarrots_yield_stripped_data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Celery",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mi_celery = vegetables[vegetables['Commodity'] == 'CELERY']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#mi_celery['Data Item'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"celery_yield = mi_celery[mi_celery['Data Item'] == \"CELERY - YIELD, MEASURED IN CWT / ACRE\"]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"celery_yield.Year.unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"celery_yield_stripped_data = celery_yield[['Year', 'Value']]\ncelery_yield_stripped_data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Onions",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mi_onions = vegetables[vegetables['Commodity'] == 'ONIONS']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#mi_onions['Data Item'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"onion_yield = mi_onions[mi_onions['Data Item'] == \"ONIONS, DRY, SUMMER, STORAGE - YIELD, MEASURED IN CWT / ACRE\"]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"onion_yield.Year.nunique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"onion_yield_stripped_data = onion_yield[['Year', 'Value']]\nonion_yield_stripped_data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"onion_yield_stripped_data.to_csv('onions.csv', index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Peppers",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mi_peppers = vegetables[vegetables['Commodity'] == 'PEPPERS']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#mi_peppers['Data Item'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pepper_yield = mi_peppers[mi_peppers['Data Item'] == \"PEPPERS, BELL - YIELD, MEASURED IN CWT / ACRE\"]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pepper_yield.Year.unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"peppers_yield_stripped_data = pepper_yield[['Year', 'Value']]\npeppers_yield_stripped_data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"peppers_yield_stripped_data.to_csv('peppers.csv', index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Corn",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mi_corn = vegetables[vegetables['Commodity'] == 'SWEET CORN']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#mi_corn['Data Item'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"corn_yield = mi_corn[mi_corn['Data Item'] == \"SWEET CORN, FRESH MARKET - YIELD, MEASURED IN CWT / ACRE\"]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"corn_yield.Year.unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"corn_yield_stripped_data = corn_yield[['Year', 'Value']]\ncorn_yield_stripped_data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"corn_yield_stripped_data.to_csv('corn.csv', index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Tomatoes",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mi_tomatoes = vegetables[vegetables['Commodity'] == 'TOMATOES'] ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#mi_tomatoes['Data Item'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tomatoes_yield = mi_tomatoes[mi_tomatoes['Data Item'] == \"TOMATOES, IN THE OPEN, FRESH MARKET - YIELD, MEASURED IN CWT / ACRE\"]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tomatoes_yield.Year.unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tomatoes_yield_stripped_data = tomatoes_yield[['Year', 'Value']]\ntomatoes_yield_stripped_data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tomatoes_yield_stripped_data.to_csv('tomatoes.csv', index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Asparagus",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mi_asparagus = vegetables[vegetables['Commodity'] == 'ASPARAGUS'] ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#mi_asparagus['Data Item'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"asparagus_yield = mi_asparagus[mi_asparagus['Data Item'] == \"ASPARAGUS - YIELD, MEASURED IN CWT / ACRE\"]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"asparagus_yield.Year.unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"asparagus_yield_stripped_data = asparagus_yield[['Year', 'Value']]\nasparagus_yield_stripped_data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"asparagus_yield_stripped_data.to_csv('asparagus.csv', index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Merging DataFrames",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#cucumbers carrots onions corn tomatoes asparagus",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cucumbers_yield_stripped_data['Crop'] = 'Cucumbers'",
"<ipython-input-79-e6774d2b0e9e>:1: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy\n cucumbers_yield_stripped_data['Crop'] = 'Cucumbers'\n"
],
[
"cucumbers_yield_stripped_data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"carrots_yield_stripped_data ['Crop'] = 'Carrots'",
"<ipython-input-81-a4120013d2f4>:1: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy\n carrots_yield_stripped_data ['Crop'] = 'Carrots'\n"
],
[
"cucumbers_and_carrots = cucumbers_yield_stripped_data.merge(carrots_yield_stripped_data, on='Year')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"carrots_cucumbers = pd.concat([carrots_yield_stripped_data, cucumbers_yield_stripped_data])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"onion_yield_stripped_data['Crop'] = 'Onions'",
"<ipython-input-84-08a6b29d4b04>:1: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy\n onion_yield_stripped_data['Crop'] = 'Onions'\n"
],
[
"corn_yield_stripped_data['Crop'] = 'Corn'",
"<ipython-input-85-0324135952a8>:1: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy\n corn_yield_stripped_data['Crop'] = 'Corn'\n"
],
[
"asparagus_yield_stripped_data['Crop'] = 'Asparagus'",
"<ipython-input-86-d9ba4fe9a65b>:1: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy\n asparagus_yield_stripped_data['Crop'] = 'Asparagus'\n"
],
[
"tomatoes_yield_stripped_data['Crop'] = 'Tomatoes'",
"<ipython-input-87-d3002c82ea85>:1: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy\n tomatoes_yield_stripped_data['Crop'] = 'Tomatoes'\n"
],
[
"squash_yield_stripped_data['Crop'] = 'Squash'",
"<ipython-input-88-c8501a222bda>:1: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy\n squash_yield_stripped_data['Crop'] = 'Squash'\n"
],
[
"celery_yield_stripped_data['Crop'] = 'Celery'",
"<ipython-input-89-62f48d199caf>:1: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy\n celery_yield_stripped_data['Crop'] = 'Celery'\n"
],
[
"peppers_yield_stripped_data['Crop'] = 'Peppers'",
"<ipython-input-90-a6820c68629c>:1: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy\n peppers_yield_stripped_data['Crop'] = 'Peppers'\n"
],
[
"pumpkins_yield_stripped_data['Crop'] = 'Pumpkins'",
"<ipython-input-91-817cd81763bd>:1: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy\n pumpkins_yield_stripped_data['Crop'] = 'Pumpkins'\n"
],
[
"cabbage_yield_stripped_data['Crop'] = 'Cabbage'",
"<ipython-input-92-1681bf6066e7>:1: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy\n cabbage_yield_stripped_data['Crop'] = 'Cabbage'\n"
],
[
"carrots_cucumbers_asparagus = pd.concat([carrots_cucumbers, asparagus_yield_stripped_data])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"carrots_cucumbers_asparagus",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"carrots_cucumbers_asparagus_tomatoes = pd.concat([carrots_cucumbers_asparagus, tomatoes_yield_stripped_data])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"carrots_cucumbers_asparagus_tomatoes_onions = pd.concat([carrots_cucumbers_asparagus_tomatoes, onion_yield_stripped_data])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"carrots_cucumbers_asparagus_tomatoes_onions.Crop.unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"carrots_cucumbers_asparagus_tomatoes_onions_cabbage = pd.concat([carrots_cucumbers_asparagus_tomatoes_onions, cabbage_yield_stripped_data])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"carrots_cucumbers_asparagus_tomatoes_onions_cabbage_pumpkins = pd.concat([carrots_cucumbers_asparagus_tomatoes_onions_cabbage, pumpkins_yield_stripped_data])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"carrots_cucumbers_asparagus_tomatoes_onions_cabbage_pumpkins_squash = pd.concat([carrots_cucumbers_asparagus_tomatoes_onions_cabbage_pumpkins, squash_yield_stripped_data])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"carrots_cucumbers_asparagus_tomatoes_onions_cabbage_pumpkins_squash_peppers = pd.concat([carrots_cucumbers_asparagus_tomatoes_onions_cabbage_pumpkins_squash, peppers_yield_stripped_data])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"vegetable_yield = pd.concat([carrots_cucumbers_asparagus_tomatoes_onions_cabbage_pumpkins_squash_peppers, celery_yield_stripped_data])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from vega_datasets import data\n\nsource = data.stocks()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"vegetable_yield",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"all_crops = alt.Chart(vegetable_yield).mark_line().encode(\n x='Year:N',\n y=alt.Y('Value:Q', title = 'Yield (CWT/ACRE)'),\n color='Crop',\n strokeDash='Crop',\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"asparagus_and_cucumbers = pd.concat([asparagus_yield_stripped_data, cucumbers_yield_stripped_data])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"alt.Chart(asparagus_and_cucumbers).mark_line().encode(\n x='Year:N',\n y=alt.Y('Value:Q', title = 'Yield (CWT/ACRE)'),\n color='Crop',\n strokeDash='Crop',\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"crops=list(vegetable_yield['Crop'].unique())\ncrops.sort()\ncrops",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"selectCrops =alt.selection_multi(\n fields=['Crop'],\n init={\"Crop\":crops[0]},\n # notice the binding_radio\n bind=alt.binding_radio(options=crops, name=\"Crop\"),#edit this line\n name=\"Crop\"\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"radio_chart = all_crops.encode(\n opacity=alt.condition(selectCrops, alt.value(1.0), alt.value(0.0))\n).add_selection(selectCrops)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"radio_chart",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
" hover = alt.selection_single(\n fields=[\"Year\"],\n nearest=True,\n on=\"mouseover\",\n empty=\"none\",\n clear=\"mouseout\",\n )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"selectors = all_crops.mark_point(filled = True, color = 'grey', size = 100).encode(\n x=alt.X(\n 'Year'), \n opacity=alt.condition(hover, alt.value(1), alt.value(0)))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"selectors",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tooltips = alt.Chart(vegetable_yield).mark_rule(strokeWidth=2, color=\"grey\").encode(\n x='Year:T',\n opacity=alt.condition(hover, alt.value(1), alt.value(0)),\n tooltip=['Value:Q','Year:N', 'Crop']\n \n \n ).add_selection(hover)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tooltips",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"alt.layer(radio_chart, tooltips, selectors)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\nbase = (\n alt.Chart(vegetable_yield)\n .encode(\n x=alt.X(\n \"Year:T\",\n axis=alt.Axis(title=None, format=(\"%b %Y\"), labelAngle=0, tickCount=6),\n ),\n y=alt.Y(\n \"Value:Q\", axis=alt.Axis(title='Yield (CWT/ACRE)')\n ),\n )\n .properties(width=500, height=400)\n )\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\nradio_select = alt.selection_multi(\n fields=[\"Crop\"], name=\"Crop\", \n )\n\ncrop_color_condition = alt.condition(\n radio_select, alt.Color(\"Crop:N\", legend=None), alt.value(\"lightgrey\")\n )\n\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\nmake_selector = (\n alt.Chart(vegetable_yield)\n .mark_circle(size=200)\n .encode(\n y=alt.Y(\"Crop:N\", axis=alt.Axis(title=\"Pick Crop\", titleFontSize=15)),\n color=crop_color_condition,\n )\n .add_selection(radio_select)\n )\n\n \n\nhighlight_crops = (\n base.mark_line(strokeWidth=2)\n .add_selection(radio_select)\n .encode(color=crop_color_condition)\n ).properties(title=\"Crop Yield by Year\")\n\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# nearest = alt.selection(\n# type=\"single\", nearest=True, on=\"mouseover\", fields=[\"Year\"], empty=\"none\"\n# )\n\n# # Transparent selectors across the chart. This is what tells us\n# # the x-value of the cursor\n# selectors = (\n# alt.Chart(vegetable_yield)\n# .mark_point()\n# .encode(\n# x=\"Year:T\",\n# opacity=alt.value(0),\n# )\n# .add_selection(nearest)\n# )\n\n\n \n# points = base.mark_point(size=5, dy=-10).encode(\n# opacity=alt.condition(nearest, alt.value(1), alt.value(0))\n# ).transform_filter(radio_select)\n \n\n# tooltip_text = base.mark_text(\n# align=\"left\",\n# dx=-60,\n# dy=-15,\n# fontSize=10,\n# fontWeight=\"bold\",\n# lineBreak = \"\\n\",\n# ).encode(\n# text=alt.condition(\n# nearest, \n# alt.Text(\"Value:Q\", format=\".2f\"), \n# alt.value(\" \"),\n \n# ),\n# ).transform_filter(radio_select)\n\n\n# # Draw a rule at the location of the selection\n# rules = (\n# alt.Chart(vegetable_yield)\n# .mark_rule(color=\"black\", strokeWidth=2)\n# .encode(\n# x=\"Year:T\",\n# )\n# .transform_filter(nearest)\n# )\n \n\n\n\n\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\nhover = alt.selection_single(\n fields=[\"Year\"],\n nearest=True,\n on=\"mouseover\",\n empty=\"none\",\n clear=\"mouseout\",\n )\ntooltips2 = alt.Chart(vegetable_yield).transform_pivot(\n \"Crop\", \"Value\", groupby=[\"Year\"]\n ).mark_rule(strokeWidth=2, color=\"red\").encode(\n x='Year:T',\n opacity=alt.condition(hover, alt.value(1), alt.value(0)),\n tooltip=[\"Year\", \"Asparagus:Q\", \"Cabbage:Q\", \"Carrots:Q\",\n \"Celery:Q\", \"Cucumbers:Q\", \"Onions:Q\", \"Peppers:Q\", \"Pumpkins:Q\", \"Squash:Q\", \"Tomatoes:Q\"]\n ).add_selection(hover)\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n(make_selector | alt.layer(highlight_crops, tooltips2 ))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4abc25c8e25de011869e79d94d7c54c7279f8c89
| 92,845 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
quanteconomics/ddp_ex_MF_7_6_5_py.ipynb
|
AadityaGupta/Artificial-Intelligence-Deep-Learning-Machine-Learning-Tutorials
|
352dd6d9a785e22fde0ce53a6b0c2e56f4964950
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 3,266 |
2017-08-06T16:51:46.000Z
|
2022-03-30T07:34:24.000Z
|
quanteconomics/ddp_ex_MF_7_6_5_py.ipynb
|
AadityaGupta/Artificial-Intelligence-Deep-Learning-Machine-Learning-Tutorials
|
352dd6d9a785e22fde0ce53a6b0c2e56f4964950
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 150 |
2017-08-28T14:59:36.000Z
|
2022-03-11T23:21:35.000Z
|
quanteconomics/ddp_ex_MF_7_6_5_py.ipynb
|
AadityaGupta/Artificial-Intelligence-Deep-Learning-Machine-Learning-Tutorials
|
352dd6d9a785e22fde0ce53a6b0c2e56f4964950
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1,449 |
2017-08-06T17:40:59.000Z
|
2022-03-31T12:03:24.000Z
| 162.885965 | 39,266 | 0.887178 |
[
[
[
"# DiscreteDP Example: Water Management",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Daisuke Oyama**\n\n*Faculty of Economics, University of Tokyo*",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"From Miranda and Fackler, <i>Applied Computational Economics and Finance</i>, 2002,\nSection 7.6.5",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import itertools\nimport numpy as np\nfrom scipy import sparse\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom quantecon.markov import DiscreteDP",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"maxcap = 30\nn = maxcap + 1 # Number of states\nm = n # Number of actions\n\na1, b1 = 14, 0.8\na2, b2 = 10, 0.4\nF = lambda x: a1 * x**b1 # Benefit from irrigation\nU = lambda c: a2 * c**b2 # Benefit from recreational consumption c = s - x\n\nprobs = [0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.2, 0.1]\nsupp_size = len(probs)\n\nbeta = 0.9",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Product formulation",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Reward array\nR = np.empty((n, m))\nfor s, x in itertools.product(range(n), range(m)):\n R[s, x] = F(x) + U(s-x) if x <= s else -np.inf",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Transition probability array\nQ = np.zeros((n, m, n))\nfor s, x in itertools.product(range(n), range(m)):\n if x <= s:\n for j in range(supp_size):\n Q[s, x, np.minimum(s-x+j, n-1)] += probs[j]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create a DiscreteDP\nddp = DiscreteDP(R, Q, beta)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Solve the dynamic optimization problem (by policy iteration)\nres = ddp.solve()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Number of iterations\nres.num_iter",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Optimal policy\nres.sigma",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Optimal value function\nres.v",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Simulate the controlled Markov chain for num_rep times\n# and compute the average\ninit = 0\nnyrs = 50\nts_length = nyrs + 1\nnum_rep = 10**4\nave_path = np.zeros(ts_length)\nfor i in range(num_rep):\n path = res.mc.simulate(ts_length, init=init)\n ave_path = (i/(i+1)) * ave_path + (1/(i+1)) * path",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ave_path",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Stationary distribution of the Markov chain\nstationary_dist = res.mc.stationary_distributions[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"stationary_dist",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Plot sigma, v, ave_path, stationary_dist\nhspace = 0.3\nfig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(12, 8+hspace))\nfig.subplots_adjust(hspace=hspace)\n\naxes[0, 0].plot(res.sigma, '*')\naxes[0, 0].set_xlim(-1, 31)\naxes[0, 0].set_ylim(-0.5, 5.5)\naxes[0, 0].set_xlabel('Water Level')\naxes[0, 0].set_ylabel('Irrigation')\naxes[0, 0].set_title('Optimal Irrigation Policy')\n\naxes[0, 1].plot(res.v)\naxes[0, 1].set_xlim(0, 30)\ny_lb, y_ub = 300, 700\naxes[0, 1].set_ylim(y_lb, y_ub)\naxes[0, 1].set_yticks(np.linspace(y_lb, y_ub, 5, endpoint=True))\naxes[0, 1].set_xlabel('Water Level')\naxes[0, 1].set_ylabel('Value')\naxes[0, 1].set_title('Optimal Value Function')\n\naxes[1, 0].plot(ave_path)\naxes[1, 0].set_xlim(0, nyrs)\ny_lb, y_ub = 0, 15\naxes[1, 0].set_ylim(y_lb, y_ub)\naxes[1, 0].set_yticks(np.linspace(y_lb, y_ub, 4, endpoint=True))\naxes[1, 0].set_xlabel('Year')\naxes[1, 0].set_ylabel('Water Level')\naxes[1, 0].set_title('Average Optimal State Path')\n\naxes[1, 1].bar(range(n), stationary_dist, align='center')\naxes[1, 1].set_xlim(-1, n)\ny_lb, y_ub = 0, 0.15\naxes[1, 1].set_ylim(y_lb, y_ub+0.01)\naxes[1, 1].set_yticks(np.linspace(y_lb, y_ub, 4, endpoint=True))\naxes[1, 1].set_xlabel('Water Level')\naxes[1, 1].set_ylabel('Probability')\naxes[1, 1].set_title('Stationary Distribution')\n\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## State-action pairs formulation",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Arrays of state and action indices\nS = np.arange(n)\nX = np.arange(m)\nS_left = S.reshape(n, 1) - X.reshape(1, n)\ns_indices, a_indices = np.where(S_left >= 0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Reward vector\nS_left = S_left[s_indices, a_indices]\nR = F(X[a_indices]) + U(S_left)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Transition probability array\nL = len(S_left)\nQ = sparse.lil_matrix((L, n))\nfor i, s_left in enumerate(S_left):\n for j in range(supp_size):\n Q[i, np.minimum(s_left+j, n-1)] += probs[j]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create a DiscreteDP\nddp = DiscreteDP(R, Q, beta, s_indices, a_indices)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Solve the dynamic optimization problem (by policy iteration)\nres = ddp.solve()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Number of iterations\nres.num_iter",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Simulate the controlled Markov chain for num_rep times\n# and compute the average\ninit = 0\nnyrs = 50\nts_length = nyrs + 1\nnum_rep = 10**4\nave_path = np.zeros(ts_length)\nfor i in range(num_rep):\n path = res.mc.simulate(ts_length, init=init)\n ave_path = (i/(i+1)) * ave_path + (1/(i+1)) * path",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Stationary distribution of the Markov chain\nstationary_dist = res.mc.stationary_distributions[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Plot sigma, v, ave_path, stationary_dist\nhspace = 0.3\nfig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(12, 8+hspace))\nfig.subplots_adjust(hspace=hspace)\n\naxes[0, 0].plot(res.sigma, '*')\naxes[0, 0].set_xlim(-1, 31)\naxes[0, 0].set_ylim(-0.5, 5.5)\naxes[0, 0].set_xlabel('Water Level')\naxes[0, 0].set_ylabel('Irrigation')\naxes[0, 0].set_title('Optimal Irrigation Policy')\n\naxes[0, 1].plot(res.v)\naxes[0, 1].set_xlim(0, 30)\ny_lb, y_ub = 300, 700\naxes[0, 1].set_ylim(y_lb, y_ub)\naxes[0, 1].set_yticks(np.linspace(y_lb, y_ub, 5, endpoint=True))\naxes[0, 1].set_xlabel('Water Level')\naxes[0, 1].set_ylabel('Value')\naxes[0, 1].set_title('Optimal Value Function')\n\naxes[1, 0].plot(ave_path)\naxes[1, 0].set_xlim(0, nyrs)\ny_lb, y_ub = 0, 15\naxes[1, 0].set_ylim(y_lb, y_ub)\naxes[1, 0].set_yticks(np.linspace(y_lb, y_ub, 4, endpoint=True))\naxes[1, 0].set_xlabel('Year')\naxes[1, 0].set_ylabel('Water Level')\naxes[1, 0].set_title('Average Optimal State Path')\n\naxes[1, 1].bar(range(n), stationary_dist, align='center')\naxes[1, 1].set_xlim(-1, n)\ny_lb, y_ub = 0, 0.15\naxes[1, 1].set_ylim(y_lb, y_ub+0.01)\naxes[1, 1].set_yticks(np.linspace(y_lb, y_ub, 4, endpoint=True))\naxes[1, 1].set_xlabel('Water Level')\naxes[1, 1].set_ylabel('Probability')\naxes[1, 1].set_title('Stationary Distribution')\n\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4abc3343692383e5681557fae5d2933b31b438db
| 2,315 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Google_automation_course/Lab_assessment_problems_solutions/usefull_notes.ipynb
|
Akshaychdev/Python-Scripts-Notebooks
|
f4246c0d7310abaf0b88c4e0f45807d5ab004d88
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Google_automation_course/Lab_assessment_problems_solutions/usefull_notes.ipynb
|
Akshaychdev/Python-Scripts-Notebooks
|
f4246c0d7310abaf0b88c4e0f45807d5ab004d88
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Google_automation_course/Lab_assessment_problems_solutions/usefull_notes.ipynb
|
Akshaychdev/Python-Scripts-Notebooks
|
f4246c0d7310abaf0b88c4e0f45807d5ab004d88
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 24.368421 | 79 | 0.519222 |
[
[
[
"Solution from officials - for the efficiant path copy lab",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#!/usr/bin/env python3\n\nfrom multiprocessing import Pool\nimport multiprocessing\nimport subprocess\nimport os\n\nhome_path = os.path.expanduser('~')\n\nsrc = home_path + \"/data/prod/\"\ndest = home_path + \"/data/prod_backup/\"\n\nif __name__ == \"__main__\":\n pool = Pool(multiprocessing.cpu_count())\n pool.apply(subprocess.call, args=([\"rsync\", \"-arq\", src, dest]))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from multiprocessing import Pool\nimport subprocess\nimport os\n\ndef run(dir):\n dest = \"./data/prod_backup\"\n print(\"transfer from {} to {}\".format(dir, dest))\n subprocess.call([\"rsync\", \"-arq\", dir, dest])\n\nif __name__ == \"__main__\":\n listOffiles = os.listdir(\"./data/prod\")\n # Empty List\n allFiles = [];\n for entry in listOffiles:\n fullpath = os.path.join(\"./data/prod\", entry)\n if os.path.isdir(fullpath):\n allFiles.append(fullpath)\n\n p = Pool(len(allFiles))\n p = map(run, allFiles)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4abc43b2b9dfe19123a31c32ef4d99daffbb14f3
| 114,403 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/sample.ipynb
|
iJKos/MAB
|
551e420844aa29a1a303e47391cd28ee8f2a3b84
|
[
"MIT"
] | 6 |
2017-09-04T13:10:26.000Z
|
2019-05-21T09:15:29.000Z
|
notebooks/sample.ipynb
|
iJKos/MAB
|
551e420844aa29a1a303e47391cd28ee8f2a3b84
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/sample.ipynb
|
iJKos/MAB
|
551e420844aa29a1a303e47391cd28ee8f2a3b84
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 468.864754 | 46,470 | 0.932589 |
[
[
[
"from MAB import GameEngine,ActionRewardAgents as Agents,SimpleMAB\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn as sns\nimport pandas as pd\nsns.set()\n\n%matplotlib inline \n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Max_steps = 5000\nRepeats_count = 20\n\nEnviroment = SimpleMAB.BernoulliEnviroment([0.1,0.1,0.1,0.1,0.6,0.6,0.6,0.9])\n#Enviroment = SimpleMAB.GaussianEnviroment(10,-3,3,1,1)\nagents = {\n#\"Optimistic\" : Agents.SimpleAgent(optimistic=1),\n#\"Simple\" : Agents.SimpleAgent(optimistic=0),\n#\"Random\" : Agents.RandomAgent(),\n\"enGreedy\" : Agents.enGreedyAgent(c=0.5,d=0.9),\n\"UCB\" : Agents.UCB1Agent()\n}\n\ngame = GameEngine.Game(Enviroment, agents,verbose=0)\ngame.Reset()\nlogs = game.Play(Max_steps,Repeats_count)\n\nlogs.columns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Max_steps = 2000\nRepeats_count = 250\n\nEnviroment = SimpleMAB.GaussianEnviroment(10,-3,3,1,1)\n\nagents = {\n\"Greedy 0\" : Agents.SimpleAgent(),\n\"Greedy 0.01\" : Agents.GreedyAgent(greedy=0.01),\n\"Greedy 0.1\" : Agents.GreedyAgent(greedy=0.1)\n}\n\ngame = GameEngine.Game(Enviroment, agents,verbose=0)\ngame.Reset()\nlogs = game.Play(Max_steps,Repeats_count)\n\nlogs.columns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Max_steps = 2000\nRepeats_count = 10\n\nEnviroment = SimpleMAB.BernoulliEnviroment(10)\n\nagents = {\n\"UCB 0\" : Agents.UCBAgent(c=0),\n\"UCB 0.1\" : Agents.UCBAgent(c=0.1),\n\"UCB 0.5\" : Agents.UCBAgent(c=0.5),\n\"UCB 1\" : Agents.UCBAgent(c=1)\n}\n\ngame = GameEngine.Game(Enviroment, agents,verbose=0)\ngame.Reset()\nlogs = game.Play(Max_steps,Repeats_count)\n\nlogs.columns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#sns.boxplot(data=Enviroment.getRewardSample())\nsns.barplot(data=Enviroment.getRewardSample())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(15, 5))\nsns.tsplot(data=logs, time=\"Iter\", unit=\"N_repeat\",\n condition=\"Agent\", value=\"Sum_regret\", ci=[50,100])\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(15, 5))\n\nsns.tsplot(data=logs, time=\"Iter\", unit=\"N_repeat\",\n condition=\"Agent\", value=\"Avg_pseudo_regret\", ci=[50])\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(15, 5))\n\nsns.tsplot(data=logs, time=\"Iter\", unit=\"N_repeat\",\n condition=\"Agent\", value=\"Avg_best_action\", ci=[50])\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4abc451e31b5d80acc68d3c13619969d72488b9a
| 146,361 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
stats-newtextbook-python/samples/3-5-標本の統計量の性質.ipynb
|
sota0121/datascience-exercise
|
f27fe3b0a053a9253bcacc181cf5813933a43035
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
stats-newtextbook-python/samples/3-5-標本の統計量の性質.ipynb
|
sota0121/datascience-exercise
|
f27fe3b0a053a9253bcacc181cf5813933a43035
|
[
"MIT"
] | 15 |
2020-04-14T07:28:39.000Z
|
2021-03-31T19:54:03.000Z
|
stats-newtextbook-python/samples/3-5-標本の統計量の性質.ipynb
|
sota0121/datascience-exercise
|
f27fe3b0a053a9253bcacc181cf5813933a43035
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 169.399306 | 23,362 | 0.895888 |
[
[
[
"# 第3部 Pythonによるデータ分析|Pythonで学ぶ統計学入門\n\n## 5章 標本の統計量の性質",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### ライブラリのインポート",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 数値計算に使うライブラリ\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport scipy as sp\nfrom scipy import stats\n\n# グラフを描画するライブラリ\nfrom matplotlib import pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn as sns\nsns.set()\n\n# 表示桁数の指定\n%precision 3\n# グラフをjupyter Notebook内に表示させるための指定\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 平均4、標準偏差0.8の正規分布を使いまわす\npopulation = stats.norm(loc = 4, scale = 0.8)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 標本平均を何度も計算してみる",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 平均値を格納する入れ物\nsample_mean_array = np.zeros(10000)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 「データを10個選んで平均値を求める」試行を10000回繰り返す\nnp.random.seed(1)\nfor i in range(0, 10000):\n sample = population.rvs(size = 10)\n sample_mean_array[i] = sp.mean(sample)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sample_mean_array",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 標本平均の平均値は、母平均に近い",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 標本平均の平均値\nsp.mean(sample_mean_array)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 標本平均の標準偏差\nsp.std(sample_mean_array, ddof = 1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 標本平均の分布\nsns.distplot(sample_mean_array, color = 'black')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### サンプルサイズ大なら、標本平均は母平均に近い",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# サンプルサイズを10~100010までの範囲で100区切りで変化させる\nsize_array = np.arange(\n start = 10, stop = 100100, step = 100)\nsize_array",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 「標本平均」を格納する入れ物\nsample_mean_array_size = np.zeros(len(size_array))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 「標本平均を求める」試行を、サンプルサイズを変えながら何度も実行\nnp.random.seed(1)\nfor i in range(0, len(size_array)):\n sample = population.rvs(size = size_array[i])\n sample_mean_array_size[i] = sp.mean(sample)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.plot(size_array, sample_mean_array_size, \n color = 'black')\nplt.xlabel(\"sample size\")\nplt.ylabel(\"sample mean\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 標本平均を何度も計算する関数を作る",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 標本平均を何度も計算する関数\ndef calc_sample_mean(size, n_trial):\n sample_mean_array = np.zeros(n_trial)\n for i in range(0, n_trial):\n sample = population.rvs(size = size)\n sample_mean_array[i] = sp.mean(sample)\n return(sample_mean_array)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 動作確認。\n# 「データを10個選んで平均値を求める」試行を10000回繰り返した結果をさらに平均する\nnp.random.seed(1)\nsp.mean(calc_sample_mean(size = 10, n_trial = 10000))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### サンプルサイズを変えた時の標本平均の分布",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.random.seed(1)\n# サンプルサイズ10\nsize_10 = calc_sample_mean(size = 10, n_trial = 10000)\nsize_10_df = pd.DataFrame({\n \"sample_mean\":size_10,\n \"size\" :np.tile(\"size 10\", 10000)\n})\n# サンプルサイズ20\nsize_20 = calc_sample_mean(size = 20, n_trial = 10000)\nsize_20_df = pd.DataFrame({\n \"sample_mean\":size_20,\n \"size\" :np.tile(\"size 20\", 10000)\n})\n# サンプルサイズ30\nsize_30 = calc_sample_mean(size = 30, n_trial = 10000)\nsize_30_df = pd.DataFrame({\n \"sample_mean\":size_30,\n \"size\" :np.tile(\"size 30\", 10000)\n})\n\n# 結合\nsim_result = pd.concat(\n [size_10_df, size_20_df, size_30_df])\n\n# 結果の表示\nprint(sim_result.head())",
" sample_mean size\n0 3.922287 size 10\n1 3.864329 size 10\n2 4.069530 size 10\n3 3.857140 size 10\n4 4.184654 size 10\n"
],
[
"sns.violinplot(x = \"size\", y = \"sample_mean\", \n data = sim_result, color = 'gray')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 標本平均の標準偏差は母標準偏差よりも小さくなる",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# サンプルサイズを2~100までの範囲で2区切りで変化させる\nsize_array = np.arange(\n start = 2, stop = 102, step = 2)\nsize_array",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 「標本平均の標準偏差」を格納する入れ物\nsample_mean_std_array = np.zeros(len(size_array))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 「標本平均の標準偏差を計算する」試行を、サンプルサイズを変えながら何度も実行\nnp.random.seed(1)\nfor i in range(0, len(size_array)):\n sample_mean = calc_sample_mean(size =size_array[i], \n n_trial = 100)\n sample_mean_std_array[i] = sp.std(sample_mean, \n ddof = 1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.plot(size_array, sample_mean_std_array, \n color = 'black')\nplt.xlabel(\"sample size\")\nplt.ylabel(\"mean_std value\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 標準誤差",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 標本平均の理論上の値:標準誤差\nstandard_error = 0.8 / np.sqrt(size_array)\nstandard_error",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.plot(size_array, sample_mean_std_array, \n color = 'black')\nplt.plot(size_array, standard_error, \n color = 'black', linestyle = 'dotted')\nplt.xlabel(\"sample size\")\nplt.ylabel(\"mean_std value\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 標本分散の平均値は、母分散からずれている",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 「標本分散」を格納する入れ物\nsample_var_array = np.zeros(10000)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 「データを10個選んで標本分散を求める」試行を10000回繰り返す\nnp.random.seed(1)\nfor i in range(0, 10000):\n sample = population.rvs(size = 10)\n sample_var_array[i] = sp.var(sample, ddof = 0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 標本分散の平均値\nsp.mean(sample_var_array)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 不偏分散を使うと、バイアスがなくなる",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 「不偏分散」を格納する入れ物\nunbias_var_array = np.zeros(10000)\n# 「データを10個選んで不偏分散を求める」試行を\n# 10000回繰り返す\nnp.random.seed(1)\nfor i in range(0, 10000):\n sample = population.rvs(size = 10)\n unbias_var_array[i] = sp.var(sample, ddof = 1)\n# 不偏分散の平均値\nsp.mean(unbias_var_array)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### サンプルサイズを増やすと、不偏分散は母分散に近づく",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# サンプルサイズを10~100010までの範囲で100区切りで変化させる\nsize_array = np.arange(\n start = 10, stop = 100100, step = 100)\nsize_array",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 「不偏分散」を格納する入れ物\nunbias_var_array_size = np.zeros(len(size_array))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 「不偏分散を求める」試行を、サンプルサイズを変えながら何度も実行\nnp.random.seed(1)\nfor i in range(0, len(size_array)):\n sample = population.rvs(size = size_array[i])\n unbias_var_array_size[i] = sp.var(sample, ddof = 1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.plot(size_array, unbias_var_array_size, \n color = 'black')\nplt.xlabel(\"sample size\")\nplt.ylabel(\"unbias var\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 補足:中心極限定理",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# サンプルサイズと試行回数\nn_size = 10000\nn_trial = 50000\n# 表ならば1、裏ならば0を表す\ncoin = np.array([0,1])\n# 表が出た回数\ncount_coin = np.zeros(n_trial)\n# コインをn_size回投げる試行をn_trial回行う\nnp.random.seed(1)\nfor i in range(0, n_trial):\n count_coin[i] = sp.sum(\n np.random.choice(coin, size = n_size, \n replace = True))\n# ヒストグラムを描く\nsns.distplot(count_coin, color = 'black')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4abc4719747674d0764110b60d3ac54f49b45b08
| 1,315 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
09/9.7.ipynb
|
XXG-Lab/Dragon
|
741b36f8836d8a1d7a6912021ac3e54d57784124
|
[
"MIT"
] | 4 |
2019-09-14T13:46:18.000Z
|
2022-01-11T22:05:41.000Z
|
09/9.7.ipynb
|
XGG-Lab/Dragon
|
741b36f8836d8a1d7a6912021ac3e54d57784124
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
09/9.7.ipynb
|
XGG-Lab/Dragon
|
741b36f8836d8a1d7a6912021ac3e54d57784124
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2019-09-14T13:46:19.000Z
|
2022-01-11T22:34:55.000Z
| 20.546875 | 135 | 0.486692 |
[
[
[
"## 9.7 Region-Based Analysis",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 9.7.1\n\n> For the flow graph of Fig. 9.10:\n\n> i. Find all the possible regions.\n\n> ii. Give the set of nested regions constructed by Algorithm 9.52.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* $R_7 = \\{ R_3, R_4 \\}$\n* $R_8 = \\{ R_7 \\}$\n* $R_9 = \\{ R_2, R_8, R_5 \\}$\n* $R_{10} = \\{ R_9 \\}$\n* $R_{11} = \\{ R_1, B_{10}, B_6 \\}$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"> iii. Give a $T_1-T_2$ reduction of the flow graph as described in the box on \"Where 'Reducible' Comes From\" in Section 9.7.2.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4abc7b098f8b0db64205933be1596e5b8cdca2e3
| 14,547 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
11_stream/archive/11_stream.orig/01_Setup_IAM.ipynb
|
NRauschmayr/workshop
|
c890e38a5f4a339540697206ebdea479e66534e5
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2021-02-20T14:55:02.000Z
|
2021-02-20T14:55:02.000Z
|
11_stream/archive/11_stream.orig/01_Setup_IAM.ipynb
|
NRauschmayr/workshop
|
c890e38a5f4a339540697206ebdea479e66534e5
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
11_stream/archive/11_stream.orig/01_Setup_IAM.ipynb
|
NRauschmayr/workshop
|
c890e38a5f4a339540697206ebdea479e66534e5
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 25.211438 | 139 | 0.483536 |
[
[
[
"# Setup IAM for Kinesis",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import boto3\nimport sagemaker\nimport pandas as pd\n\nsess = sagemaker.Session()\nbucket = sess.default_bucket()\nrole = sagemaker.get_execution_role()\nregion = boto3.Session().region_name\n\nsts = boto3.Session().client(service_name=\"sts\", region_name=region)\niam = boto3.Session().client(service_name=\"iam\", region_name=region)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create Kinesis Role",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"iam_kinesis_role_name = \"DSOAWS_Kinesis\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"iam_kinesis_role_passed = False",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"assume_role_policy_doc = {\n \"Version\": \"2012-10-17\",\n \"Statement\": [\n {\"Effect\": \"Allow\", \"Principal\": {\"Service\": \"kinesis.amazonaws.com\"}, \"Action\": \"sts:AssumeRole\"},\n {\"Effect\": \"Allow\", \"Principal\": {\"Service\": \"firehose.amazonaws.com\"}, \"Action\": \"sts:AssumeRole\"},\n {\"Effect\": \"Allow\", \"Principal\": {\"Service\": \"kinesisanalytics.amazonaws.com\"}, \"Action\": \"sts:AssumeRole\"},\n ],\n}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import json\nimport time\n\nfrom botocore.exceptions import ClientError\n\ntry:\n iam_role_kinesis = iam.create_role(\n RoleName=iam_kinesis_role_name,\n AssumeRolePolicyDocument=json.dumps(assume_role_policy_doc),\n Description=\"DSOAWS Kinesis Role\",\n )\n print(\"Role succesfully created.\")\n iam_kinesis_role_passed = True\nexcept ClientError as e:\n if e.response[\"Error\"][\"Code\"] == \"EntityAlreadyExists\":\n iam_role_kinesis = iam.get_role(RoleName=iam_kinesis_role_name)\n print(\"Role already exists. That is OK.\")\n iam_kinesis_role_passed = True\n else:\n print(\"Unexpected error: %s\" % e)\n\ntime.sleep(30)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"iam_role_kinesis_name = iam_role_kinesis[\"Role\"][\"RoleName\"]\nprint(\"Role Name: {}\".format(iam_role_kinesis_name))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"iam_role_kinesis_arn = iam_role_kinesis[\"Role\"][\"Arn\"]\nprint(\"Role ARN: {}\".format(iam_role_kinesis_arn))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"account_id = sts.get_caller_identity()[\"Account\"]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Specify Stream Name",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"stream_name = \"dsoaws-kinesis-data-stream\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Specify Firehose Name",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"firehose_name = \"dsoaws-kinesis-data-firehose\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Specify Lambda Function Name",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"lambda_fn_name = \"DeliverKinesisAnalyticsToCloudWatch\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create Policy",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"kinesis_policy_doc = {\n \"Version\": \"2012-10-17\",\n \"Statement\": [\n {\n \"Effect\": \"Allow\",\n \"Action\": [\n \"s3:AbortMultipartUpload\",\n \"s3:GetBucketLocation\",\n \"s3:GetObject\",\n \"s3:ListBucket\",\n \"s3:ListBucketMultipartUploads\",\n \"s3:PutObject\",\n ],\n \"Resource\": [\n \"arn:aws:s3:::{}/kinesis-data-firehose\".format(bucket),\n \"arn:aws:s3:::{}/kinesis-data-firehose/*\".format(bucket),\n ],\n },\n {\n \"Effect\": \"Allow\",\n \"Action\": [\"logs:PutLogEvents\"],\n \"Resource\": [\"arn:aws:logs:{}:{}:log-group:/*\".format(region, account_id)],\n },\n {\n \"Effect\": \"Allow\",\n \"Action\": [\n \"kinesis:Get*\",\n \"kinesis:DescribeStream\",\n \"kinesis:Put*\",\n \"kinesis:List*\",\n ],\n \"Resource\": [\"arn:aws:kinesis:{}:{}:stream/{}\".format(region, account_id, stream_name)],\n },\n {\n \"Effect\": \"Allow\",\n \"Action\": [\n \"firehose:*\",\n ],\n \"Resource\": [\"arn:aws:firehose:{}:{}:deliverystream/{}\".format(region, account_id, firehose_name)],\n },\n {\n \"Effect\": \"Allow\",\n \"Action\": [\n \"kinesisanalytics:*\",\n ],\n \"Resource\": [\"*\"],\n },\n {\n \"Sid\": \"UseLambdaFunction\",\n \"Effect\": \"Allow\",\n \"Action\": [\"lambda:InvokeFunction\", \"lambda:GetFunctionConfiguration\"],\n \"Resource\": \"arn:aws:lambda:{}:{}:function:{}:$LATEST\".format(region, account_id, lambda_fn_name),\n },\n {\n \"Effect\": \"Allow\",\n \"Action\": \"iam:PassRole\",\n \"Resource\": \"arn:aws:iam::*:role/service-role/kinesis-analytics*\",\n },\n ],\n}\n\nprint(json.dumps(kinesis_policy_doc, indent=4, sort_keys=True, default=str))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Update Policy",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import time\n\nresponse = iam.put_role_policy(\n RoleName=iam_role_kinesis_name, PolicyName=\"DSOAWS_KinesisPolicy\", PolicyDocument=json.dumps(kinesis_policy_doc)\n)\n\ntime.sleep(30)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(json.dumps(response, indent=4, sort_keys=True, default=str))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create AWS Lambda IAM Role",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"iam_lambda_role_name = \"DSOAWS_Lambda\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"iam_lambda_role_passed = False",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"assume_role_policy_doc = {\n \"Version\": \"2012-10-17\",\n \"Statement\": [\n {\"Effect\": \"Allow\", \"Principal\": {\"Service\": \"lambda.amazonaws.com\"}, \"Action\": \"sts:AssumeRole\"},\n {\"Effect\": \"Allow\", \"Principal\": {\"Service\": \"kinesisanalytics.amazonaws.com\"}, \"Action\": \"sts:AssumeRole\"},\n ],\n}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import time\n\nfrom botocore.exceptions import ClientError\n\ntry:\n iam_role_lambda = iam.create_role(\n RoleName=iam_lambda_role_name,\n AssumeRolePolicyDocument=json.dumps(assume_role_policy_doc),\n Description=\"DSOAWS Lambda Role\",\n )\n print(\"Role succesfully created.\")\n iam_lambda_role_passed = True\nexcept ClientError as e:\n if e.response[\"Error\"][\"Code\"] == \"EntityAlreadyExists\":\n iam_role_lambda = iam.get_role(RoleName=iam_lambda_role_name)\n print(\"Role already exists. This is OK.\")\n iam_lambda_role_passed = True\n else:\n print(\"Unexpected error: %s\" % e)\n\ntime.sleep(30)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"iam_role_lambda_name = iam_role_lambda[\"Role\"][\"RoleName\"]\nprint(\"Role Name: {}\".format(iam_role_lambda_name))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"iam_role_lambda_arn = iam_role_lambda[\"Role\"][\"Arn\"]\nprint(\"Role ARN: {}\".format(iam_role_lambda_arn))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create AWS Lambda IAM Policy",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"lambda_policy_doc = {\n \"Version\": \"2012-10-17\",\n \"Statement\": [\n {\n \"Sid\": \"UseLambdaFunction\",\n \"Effect\": \"Allow\",\n \"Action\": [\"lambda:InvokeFunction\", \"lambda:GetFunctionConfiguration\"],\n \"Resource\": \"arn:aws:lambda:{}:{}:function:*\".format(region, account_id),\n },\n {\"Effect\": \"Allow\", \"Action\": \"cloudwatch:*\", \"Resource\": \"*\"},\n {\n \"Effect\": \"Allow\",\n \"Action\": \"logs:CreateLogGroup\",\n \"Resource\": \"arn:aws:logs:{}:{}:*\".format(region, account_id),\n },\n {\n \"Effect\": \"Allow\",\n \"Action\": [\"logs:CreateLogStream\", \"logs:PutLogEvents\"],\n \"Resource\": \"arn:aws:logs:{}:{}:log-group:/aws/lambda/*\".format(region, account_id),\n },\n ],\n}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(json.dumps(lambda_policy_doc, indent=4, sort_keys=True, default=str))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import time\n\nresponse = iam.put_role_policy(\n RoleName=iam_role_lambda_name, PolicyName=\"DSOAWS_LambdaPolicy\", PolicyDocument=json.dumps(lambda_policy_doc)\n)\n\ntime.sleep(30)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(json.dumps(response, indent=4, sort_keys=True, default=str))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Store Variables for Next Notebooks",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%store stream_name",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%store firehose_name",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%store iam_kinesis_role_name",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%store iam_role_kinesis_arn",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%store iam_lambda_role_name",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%store iam_role_lambda_arn",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%store lambda_fn_name",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%store iam_kinesis_role_passed",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%store iam_lambda_role_passed",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%store",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%%javascript\nJupyter.notebook.save_checkpoint()\nJupyter.notebook.session.delete();",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4abc8f5026e6e25412c5d4906d62c4191ac36e0f
| 6,342 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
docs/examples/Plot-Units.ipynb
|
atomicateam/atomica
|
de05daf15088e315b89fd62319fa11529d43f8cf
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2019-04-16T17:56:01.000Z
|
2019-09-02T15:53:18.000Z
|
docs/examples/Plot-Units.ipynb
|
atomicateam/atomica
|
de05daf15088e315b89fd62319fa11529d43f8cf
|
[
"MIT"
] | 93 |
2018-09-20T16:45:22.000Z
|
2021-11-15T21:59:38.000Z
|
docs/examples/Plot-Units.ipynb
|
atomicateam/atomica
|
de05daf15088e315b89fd62319fa11529d43f8cf
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2018-09-22T08:12:53.000Z
|
2018-09-22T08:12:53.000Z
| 28.3125 | 194 | 0.601861 |
[
[
[
"# Plot unit conversions\n\nThis notebook demonstrates some examples of different kinds of units, and the circumstances under which they are converted and displayed.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%matplotlib inline\nimport sys\nimport atomica as at\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport sciris as sc\nfrom IPython.display import display, HTML",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"testdir = at.parent_dir()\nP = at.Project(framework='unit_demo_framework.xlsx',databook='unit_demo_databook.xlsx')\nP.load_progbook('unit_demo_progbook.xlsx')\nres = P.run_sim('default','default',at.ProgramInstructions(start_year=2018))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This test example has examples of parameters with different timescales, and different types of programs.\n\n##### Parameters\n\n- `recrate` - Duration in months\n- `infdeath` - Weekly probability\n- `susdeath` - Daily probability\n- `foi` - Annual probability",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"d = at.PlotData(res,outputs=['recrate','infdeath','susdeath','foi','sus:inf','susdeath:flow','dead'],pops='adults')\nat.plot_series(d,axis='pops');",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Notice that parameters are plotted in their native units. For example, a probability per day is shown as probability per day, matching the numbers that were entered in the databook.\n\nAggregating these units without specifying the aggregation method will result in either integration or averaging as most appropriate for the units of the underlying quantity:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for output in ['recrate','infdeath','susdeath','foi','sus:inf','susdeath:flow','dead']:\n d = at.PlotData(res,outputs=output,pops='adults',t_bins=10)\n at.plot_bars(d);",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Accumulation will result in the units and output name being updated appropriately:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"d = at.PlotData(res,outputs='sus:inf',pops='adults',accumulate='integrate',project=P)\nat.plot_series(d);\nd = at.PlotData(res,outputs='sus',pops='adults',accumulate='integrate',project=P)\nat.plot_series(d);",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### Programs\n\n - `Risk avoidance` - Continuous\n - `Harm reduction 1` - Continuous\n - `Harm reduction 2` - Continuous\n - `Treatment 1` - One-off\n - `Treatment 2` - One-off\n \n Programs with continuous coverage cover a certain number of people every year:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"d = at.PlotData.programs(res,outputs='Risk avoidance',quantity='coverage_number')\nat.plot_series(d);",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Programs with one-off coverage cover a number of people at each time step. This is the number that gets returned by `Result.get_coverage()` but it is automatically annualized for plotting:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"annual_coverage = res.model.progset.programs['Treatment 1'].spend_data.vals[0]/res.model.progset.programs['Treatment 1'].unit_cost.vals[0]\ntimestep_coverage = res.get_coverage('number')['Treatment 1'][0]\nprint('Annual coverage = %g, Timestep coverage = %g' % (annual_coverage, timestep_coverage))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"d = at.PlotData.programs(res,outputs='Treatment 1',quantity='coverage_number')\nat.plot_series(d)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"These units are handled automatically when aggregating. For example, consider computing the number of people covered over a period of time:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"d = at.PlotData.programs(res,outputs='Treatment 1',quantity='coverage_number',t_bins=[2000,2000.5])\nat.plot_bars(d);\n\nd = at.PlotData.programs(res,outputs='Treatment 1',quantity='coverage_number',t_bins=[2000,2002])\nat.plot_bars(d);",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"d = at.PlotData.programs(res,outputs='Treatment 1',quantity='coverage_eligible',t_bins=[2000,2000.5])\nat.plot_bars(d);\n\nd = at.PlotData.programs(res,outputs='Treatment 1',quantity='coverage_number',t_bins=[2000,2002])\nat.plot_bars(d);",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4abcb4831a7bf1d55019fccdc489a19f078c1116
| 213,973 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
centralms/notebooks/true_starforming.ipynb
|
changhoonhahn/centralMS
|
39b4509ea99e47ab5cf1f9be8775d53eee6de80f
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2018-05-30T23:43:52.000Z
|
2018-05-30T23:43:52.000Z
|
centralms/notebooks/true_starforming.ipynb
|
changhoonhahn/centralMS
|
39b4509ea99e47ab5cf1f9be8775d53eee6de80f
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2017-04-24T22:58:40.000Z
|
2017-04-24T22:59:28.000Z
|
centralms/notebooks/true_starforming.ipynb
|
changhoonhahn/centralMS
|
39b4509ea99e47ab5cf1f9be8775d53eee6de80f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 388.335753 | 65,670 | 0.91827 |
[
[
[
"# Using the model and best-fit parameters from CenQue, we measure the following values:\nThe \"true\" SF fraction\n$$f_{True SF}(\\mathcal{M}_*)$$\n\nThe \"true\" SF SMF\n$$\\Phi_{True SF}(\\mathcal{M}_*)$$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np \nimport pickle\nimport util as UT\nimport observables as Obvs\nfrom scipy.interpolate import interp1d\n# plotting\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n%matplotlib inline\nfrom ChangTools.plotting import prettyplot\nfrom ChangTools.plotting import prettycolors",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"prettyplot()\npretty_colors = prettycolors()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## import output from CenQue model with best-fit parameters\n\n$$ F_{cenque} ({\\bf \\theta_{best-fit}}) $$\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cenque = pickle.load(open(''.join([UT.dat_dir(), 'Descendant.ABC_posterior.RHOssfrfq_TinkerFq_Std.updated_prior.p']), 'rb'))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print cenque.keys()\nfor k in cenque.keys(): \n if cenque[k] is not None: \n print k\n print cenque[k][:10]",
"['t_quench', 'quenched', 'sfr_class', 'sfr', 'mass', 'sham_mass', 'halo_mass', 'ssfr', 'gal_type']\nt_quench\n[ 12.45486937 999. 12.78196255 999. 999. 999.\n 999. 999. 999. 999. ]\nquenched\n[0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]\nsfr_class\n['quiescent' 'star-forming' 'quiescent' 'star-forming' 'star-forming'\n 'star-forming' 'star-forming' 'star-forming' 'star-forming' 'star-forming']\nsfr\n[-0.43487979 -1.89122474 -0.2471175 -1.69143443 -1.20001857 -1.21875458\n -0.49085328 -0.66988371 -0.56843078 -0.77496214]\nmass\n[ 9.78588867 7.72811699 10.52382469 7.77867794 8.11984444\n 8.61879349 10.26619911 9.27050591 9.2674427 9.11982822]\nhalo_mass\n[ 11.69618893 10.57685661 12.53023911 10.79275322 10.76711559\n 10.96514034 11.54843426 11.19728184 11.24716091 11.19564438]\nssfr\n[-10.22076847 -9.61934173 -10.77094219 -9.47011237 -9.31986301\n -9.83754807 -10.7570524 -9.94038961 -9.83587348 -9.89479037]\n"
],
[
"print cenque['sfr_class'][np.where(cenque['quenched'] != 0)]\nprint cenque['t_quench'][np.where(cenque['quenched'] != 0)]\nprint cenque['t_quench'][np.where((cenque['quenched'] != 0) & (cenque['sfr_class'] == 'star-forming'))]",
"['quiescent' 'quiescent' 'quiescent' ..., 'quiescent' 'quiescent'\n 'quiescent']\n[ 8.30266693 5.88093758 6.07194362 ..., 6.28075036 7.36811249\n 7.2392411 ]\n[ 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999.\n 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999.\n 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999.\n 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999.\n 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999.\n 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999.\n 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999.\n 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999.\n 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999.\n 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999.\n 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999.\n 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999.\n 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999.\n 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999. 999.\n 999. 999. 999.]\n"
],
[
"# Star-forming only\nisSF = np.where((cenque['sfr_class'] == 'star-forming') & (cenque['quenched'] == 0))\n\n# quenching \n#isQing = np.where((cenque['quenched'] == 0) & (cenque['t_quench'] != 999))\nisQing = np.where((cenque['quenched'] == 0) & (cenque['sfr_class'] == 'quiescent'))\n\n# quiescent\nisQ = np.where(cenque['quenched'] != 0)\n\nassert len(cenque['sfr_class']) == len(isSF[0]) + len(isQing[0]) + len(isQ[0])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Lets examine SSFRs of each galaxy class",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"esef = Obvs.Ssfr()\n\nbin_pssfr_tot, pssfr_tot = esef.Calculate(cenque['mass'], cenque['ssfr'])\n\nbin_pssfr_sf, pssfr_sf = esef.Calculate(cenque['mass'][isSF], cenque['ssfr'][isSF])\n\nbin_pssfr_qing, pssfr_qing = esef.Calculate(cenque['mass'][isQing], cenque['ssfr'][isQing])\n\nbin_pssfr_q, pssfr_q = esef.Calculate(cenque['mass'][isQ], cenque['ssfr'][isQ])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig = plt.figure(figsize=(20, 5))\nbkgd = fig.add_subplot(111, frameon=False)\n\nfor i_m, mass_bin in enumerate(esef.mass_bins): \n sub = fig.add_subplot(1, 4, i_m+1)\n\n in_mbin = (cenque['mass'] >= mass_bin[0]) & (cenque['mass'] < mass_bin[1])\n also_sf = (cenque['sfr_class'] == 'star-forming') & (cenque['quenched'] == 0)\n also_q = cenque['quenched'] != 0\n also_qing = (cenque['quenched'] == 0) & (cenque['sfr_class'] == 'quiescent')\n \n N_tot = np.float(len(np.where(in_mbin)[0]))\n f_sf = np.float(len(np.where(in_mbin & also_sf)[0])) / N_tot\n f_q = np.float(len(np.where(in_mbin & also_q)[0])) / N_tot\n f_qing = np.float(len(np.where(in_mbin & also_qing)[0])) / N_tot \n assert f_sf + f_q + f_qing == 1.\n \n # Star-forming\n sub.fill_between(bin_pssfr_sf[i_m], f_sf * pssfr_sf[i_m], np.repeat(0., len(bin_pssfr_sf[i_m])), \n color='b', edgecolor=None)\n # Quiescent\n sub.fill_between(bin_pssfr_q[i_m], f_q * pssfr_q[i_m], np.repeat(0., len(bin_pssfr_q[i_m])), \n color='r', edgecolor=None)\n # quienching\n sub.fill_between(bin_pssfr_qing[i_m], f_qing * pssfr_qing[i_m] + f_q * pssfr_q[i_m] + f_sf * pssfr_sf[i_m], \n f_q * pssfr_q[i_m] + f_sf * pssfr_sf[i_m], \n color='g', edgecolor=None)\n \n sub.plot(bin_pssfr_tot[i_m], pssfr_tot[i_m], color='k', lw=3, ls='--')\n \n massbin_str = ''.join([r'$\\mathtt{log \\; M_{*} = [', \n str(mass_bin[0]), ',\\;', str(mass_bin[1]), ']}$'])\n sub.text(-12., 1.4, massbin_str, fontsize=20)\n \n # x-axis\n sub.set_xlim([-13., -9.])\n # y-axis \n sub.set_ylim([0.0, 1.7])\n sub.set_yticks([0.0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5])\n if i_m == 0: \n sub.set_ylabel(r'$\\mathtt{P(log \\; SSFR)}$', fontsize=25) \n else: \n sub.set_yticklabels([])\nbkgd.tick_params(labelcolor='none', top='off', bottom='off', left='off', right='off')\nbkgd.set_xlabel(r'$\\mathtt{log \\; SSFR \\;[yr^{-1}]}$', fontsize=25) \nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig = plt.figure(figsize=(20, 5))\nbkgd = fig.add_subplot(111, frameon=False)\n\nfor i_m, mass_bin in enumerate(esef.mass_bins): \n sub = fig.add_subplot(1, 4, i_m+1)\n\n in_mbin = (cenque['mass'] >= mass_bin[0]) & (cenque['mass'] < mass_bin[1])\n also_sf = (cenque['sfr_class'] == 'star-forming') & (cenque['quenched'] == 0)\n also_q = cenque['quenched'] != 0\n also_qing = (cenque['quenched'] == 0) & (cenque['sfr_class'] == 'quiescent')\n \n N_tot = np.float(len(np.where(in_mbin)[0]))\n f_sf = np.float(len(np.where(in_mbin & also_sf)[0])) / N_tot\n f_q = np.float(len(np.where(in_mbin & also_q)[0])) / N_tot\n f_qing = np.float(len(np.where(in_mbin & also_qing)[0])) / N_tot \n assert f_sf + f_q + f_qing == 1.\n \n # quienching\n sub.fill_between(bin_pssfr_qing[i_m], f_qing * pssfr_qing[i_m], np.zeros(len(bin_pssfr_qing[i_m])), \n color='g', edgecolor=None)\n \n # Star-forming\n sub.fill_between(bin_pssfr_sf[i_m], f_sf * pssfr_sf[i_m] + f_qing * pssfr_qing[i_m], f_qing * pssfr_qing[i_m], \n color='b', edgecolor=None)\n # Quiescent\n sub.fill_between(bin_pssfr_q[i_m], f_q * pssfr_q[i_m] + f_sf * pssfr_sf[i_m] + f_qing * pssfr_qing[i_m], \n f_sf * pssfr_sf[i_m] + f_qing * pssfr_qing[i_m], \n color='r', edgecolor=None)\n \n sub.plot(bin_pssfr_tot[i_m], pssfr_tot[i_m], color='k', lw=3, ls='--')\n \n massbin_str = ''.join([r'$\\mathtt{log \\; M_{*} = [', \n str(mass_bin[0]), ',\\;', str(mass_bin[1]), ']}$'])\n sub.text(-12., 1.4, massbin_str, fontsize=20)\n \n # x-axis\n sub.set_xlim([-13., -9.])\n # y-axis \n sub.set_ylim([0.0, 1.7])\n sub.set_yticks([0.0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5])\n if i_m == 0: \n sub.set_ylabel(r'$\\mathtt{P(log \\; SSFR)}$', fontsize=25) \n else: \n sub.set_yticklabels([])\nbkgd.tick_params(labelcolor='none', top='off', bottom='off', left='off', right='off')\nbkgd.set_xlabel(r'$\\mathtt{log \\; SSFR \\;[yr^{-1}]}$', fontsize=25) \nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Calculate $f_{True SF}$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"effq = Obvs.Fq()\ntheta_sfms = {'name': 'linear', 'zslope': 1.14}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"qf = effq.Calculate(mass=cenque['mass'], sfr=cenque['sfr'], z=UT.z_nsnap(1), theta_SFMS=theta_sfms)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# calculate true SF fraction \nm_low = np.arange(8.0, 12.0, 0.1)\nm_high = m_low + 0.1\n\nm_mid, f_truesf = np.zeros(len(m_low)), np.zeros(len(m_low))\n\nalso_sf = (cenque['sfr_class'] == 'star-forming') & (cenque['quenched'] == 0)\nfor i_m in range(len(m_low)): \n in_mbin = (cenque['mass'] >= m_low[i_m]) & (cenque['mass'] < m_high[i_m])\n \n N_tot = np.float(len(np.where(in_mbin)[0]))\n N_sf = np.float(len(np.where(in_mbin & also_sf)[0]))\n \n m_mid[i_m] = 0.5 * (m_low[i_m] + m_high[i_m]) \n f_truesf[i_m] = N_sf/N_tot",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Comparison of $f_{SF} = 1 - f_Q$ versus $f_{True SF}$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"fig = plt.figure(figsize=(7,7))\nsub = fig.add_subplot(111)\n\nsub.plot(qf[0], 1. - qf[1], c='k', ls='--', lw=2, label='$f_{SF} = 1 - f_Q$')\nsub.plot(m_mid, f_truesf, c='b', ls='-', lw=2, label='$f_{True\\;SF}$')\n\nf_truesf_interp = interp1d(m_mid, f_truesf)\nsub.fill_between(qf[0], (1. - qf[1]) - f_truesf_interp(qf[0]), np.zeros(len(qf[0])), color='k', edgecolor=None, label='$\\Delta$')\n# x-axis\nsub.set_xlim([9., 12.])\nsub.set_xlabel('Stellar Mass $(\\mathcal{M}_*)$', fontsize=25)\nsub.set_ylim([0., 1.])\nsub.set_ylabel('Star-forming Fraction', fontsize=25)\nsub.legend(loc = 'upper right', prop={'size': 25})",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Calculate SMF of (only) star-forming galaxies",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# total SMF\nsmf_tot = Obvs.getMF(cenque['mass'])\n\n# SMF of true SF\nsmf_truesf = Obvs.getMF(cenque['mass'][isSF])\n\n# SMF of galaxies *classified* as SF\ngal_class = effq.Classify(cenque['mass'], cenque['sfr'], UT.z_nsnap(1), theta_SFMS=theta_sfms)\nsmf_sfclass = Obvs.getMF(cenque['mass'][np.where(gal_class == 'star-forming')])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig = plt.figure(figsize=(7,7))\nsub = fig.add_subplot(111)\n\nsub.plot(smf_tot[0], smf_tot[1], c='k', lw=3, label='Total')\nsub.plot(smf_truesf[0], smf_truesf[1], c='b', lw=3, label='True SF')\nsub.plot(smf_sfclass[0], smf_sfclass[1], c='k', ls='--')\n\nsub.set_xlim([9., 12.])\nsub.set_xlabel('Stellar Masses $(\\mathcal{M}_*)$', fontsize=25)\nsub.set_ylim([1e-5, 10**-1.5])\nsub.set_yscale('log')\nsub.set_ylabel('$\\Phi$', fontsize=25)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4abcc8503d5368a877c105a13c61459eab919fcf
| 7,388 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
simulation.ipynb
|
Christian-Hirsch/extremal_linkage
|
dea32732b2b8ec53d5b356f38c215de1381fa35f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
simulation.ipynb
|
Christian-Hirsch/extremal_linkage
|
dea32732b2b8ec53d5b356f38c215de1381fa35f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
simulation.ipynb
|
Christian-Hirsch/extremal_linkage
|
dea32732b2b8ec53d5b356f38c215de1381fa35f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 28.972549 | 349 | 0.458446 |
[
[
[
"# Extremal linkage networks",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"This notebook contains code accompanying the paper [extremal linkage networks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.01817). ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We first implement the network dynamics and then rely on [TikZ](https://github.com/pgf-tikz/pgf) for visualization.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## The Model",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We define a random network on an infinite set of layers, each consisting of $N \\ge 1$ nodes. The node $i \\in \\{0, \\dots, N - 1\\}$ in layer $h \\in \\mathbb Z$ has a fitness $F_{i, h}$, where we assume the family $\\{F_{i, h}\\}_{i \\in \\{0, \\dots, N - 1\\}, h \\in \\mathbb Z}$ to be independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.).\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Then, the number of nodes on layer $h+1$ that are visible for the $i$th node in layer $h$, which we call the *scope* of $(i,h)$, is given by $\\varphi(F_{i, h}) \\wedge N$, where\n\\begin{equation}\\label{eqPhiDef}\n \\varphi(f) = 1 + 2 \\lceil f \\rceil.\n\\end{equation}\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Now, $(i, h)$ connects to precisely one visible node $(j, h+1)$ in layer $h+1$, namely the one of maximum fitness. In other words,\n$$F_{j, h+1} = \\max_{j':\\, d_N(i, j') \\le \\lceil F_{i, h}\\rceil}F_{j', h+1}.$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\nHenceforth, we assume the fitnesses to follow a Fréchet distribution with tail index 1. That is,\n$$\\mathbb P(F \\le s) = \\exp(-s^{-1}).$$\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Simulation of Network Dynamics",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def simulate_network(hrange = 250,\n layers = 6):\n \"\"\"Simulation of the network model\n # Arguments\n hrange: horizontal range of the network\n layers: number of layers\n \n # Result\n fitnesses and selected edge\n \"\"\"\n #generate fréchet distribution\n fits = np.array([1/np.log(1/np.random.rand(hrange)) for _ in range(layers)]) \n fits_int = 1+ np.array(fits, dtype = np.int)\n \n #determine possible neighbors\n neighbs = [[(idx + np.arange(-fit, fit + 1)) % hrange \n for idx, fit in enumerate(layer) ] \n for layer in fits_int]\n\n #determine selected neighbor\n sel_edge = [[neighb[np.argmax(fit[neighb])] \n for neighb in nb] \n for (fit, nb) in zip(np.roll(fits, -1, 0), neighbs)]\n \n return fits, sel_edge",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now, we simulate the random network model as described above.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\n\n#seed\nseed = 56\nnp.random.seed(seed)\n\nfits, edges = simulate_network()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Visualization",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Now, plot the network in tikz.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def plot_synapses(edges,\n idxs = np.arange(102, 131),\n layers = 4,\n x_scale = .15,\n node_scale = .5):\n \"\"\"Plot relevant synapses\n # Arguments\n idxs: indexes of layer-0 node\n edges: edges in the linkage graph\n layers: number of layers to be plotted\n x_scale: scaling in x-direction\n node_scale: scaling of nodes\n \n # Result\n tikz representation of graph\n \"\"\"\n result = []\n\n #horizontal range\n hrange = len(edges[0])\n\n #plot layer by layer\n for layer in range(layers):\n #plot points \n result +=[\"\\\\fill ({0:1.2f}, {1:1.2f}) circle ({2:1.1f}pt);\\n\".format((idx % hrange) * x_scale, \n layer,\n node_scale * np.log(fits)[layer, idx]) \n for idx in idxs] \n \n #plot edges\n string = \"\\\\draw[line width = .5pt]\"\n string += \" ({0:1.2f}, {1:1.2f})--({2:1.2f}, {3:1.2f});\\n\"\n path_unordered = [string.format(idx * x_scale,\n layer,\n edges[layer][idx] * x_scale,\n layer + 1) for idx in idxs]\n result += path_unordered\n\n #update indexes\n idxs = np.unique([edges[layer][idx] for idx in idxs])\n\n\n #plot points \n result +=[\"\\\\fill ({0:1.2f}, {1:1.2f}) circle ({2:1.1f}pt);\\n\".format((idx % hrange) * x_scale, \n layers,\n node_scale * np.log(fits)[layer + 1, idx]) \n for idx in idxs] \n\n \n\n tikz = ''.join(result)\n\n return '\\\\begin{tikzpicture}\\n' + tikz + '\\\\end{tikzpicture}\\n'",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Finally, we write to a file.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"fname = 'coalesc.tex'\n\nf = open(fname, \"w\")\nf.write(plot_synapses(idxs,\n edges))\nf.close()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!pdflatex evolFig.tex\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4abcd24a57c278994e9613a3eceb5a1f6b114b4f
| 58,599 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
3DBPP/ActorCritic/state_Cnn_Test.ipynb
|
kidrabit/Data-Visualization-Lab-RND
|
baa19ee4e9f3422a052794e50791495632290b36
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2022-01-18T01:53:34.000Z
|
2022-01-18T01:53:34.000Z
|
3DBPP/ActorCritic/state_Cnn_Test.ipynb
|
kidrabit/Data-Visualization-Lab-RND
|
baa19ee4e9f3422a052794e50791495632290b36
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
3DBPP/ActorCritic/state_Cnn_Test.ipynb
|
kidrabit/Data-Visualization-Lab-RND
|
baa19ee4e9f3422a052794e50791495632290b36
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 65.989865 | 26,728 | 0.721941 |
[
[
[
"import os\nimport random\nimport math\nimport time\nimport numpy as np\nimport tensorflow as tf\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\nfrom tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam\nfrom tensorflow.keras import Sequential\nfrom tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Conv1D, MaxPooling1D, Flatten, concatenate, Conv2D, MaxPooling2D\n\nfrom libs.utils import *\nfrom libs.generate_boxes import *",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '0'\ntf.get_logger().setLevel('INFO')\ntf.keras.backend.floatx()\n\nplt.style.use('fivethirtyeight')\nplt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (20,10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class StateCNN(tf.keras.Model):\n def __init__(self, state_size, selected_size, remain_size):\n super(StateCNN, self).__init__()\n \n self.case_cnn1 = Conv2D(filters=16, kernel_size=3, activation='relu',\n padding='valid', input_shape = selected_size)\n self.case_cnn2 = Conv2D(filters=16, kernel_size=3, activation='relu',\n padding='valid')\n \n self.select_cnn1 = Conv2D(filters=16, kernel_size=3, activation='relu',\n padding='valid', input_shape=selected_size)\n self.select_cnn2 = Conv2D(filters=16, kernel_size=3, activation='relu',\n padding='valid')\n \n self.remain_cnn1 = Conv1D(filters=32, kernel_size=2, activation='relu',\n padding='same', input_shape = remain_size)\n self.remain_cnn2 = Conv1D(filters=32, kernel_size=2, activation='relu',\n padding='same')\n \n def call(self, cb_list):\n c,s,r = cb_list[0], cb_list[1], cb_list[2]\n \n c = self.case_cnn1(c)\n c = MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2))(c)\n c = self.case_cnn2(c)\n c = MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2))(c)\n c = Flatten()(c)\n \n s = self.select_cnn1(s)\n s = MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2))(s)\n s = self.select_cnn2(s)\n s = MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2))(s)\n s = Flatten()(s)\n \n r = self.remain_cnn1(r)\n r = self.remain_cnn2(r)\n r = MaxPooling1D(pool_size=1)(r)\n r = Flatten()(r)\n \n x = concatenate([c,s,r])\n return x",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class Actor(tf.keras.Model):\n def __init__(self, output_size):\n super(Actor, self).__init__()\n self.d1 = Dense(2048, activation='relu')\n self.d2 = Dense(1024, activation='relu')\n self.actor = Dense(output_size)\n \n def call(self, inputs):\n x = self.d1(inputs)\n x = self.d2(x)\n actor = self.actor(x)\n return actor",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class Critic(tf.keras.Model):\n def __init__(self, output_size):\n super(Critic, self).__init__()\n self.d1 = Dense(2048, activation='relu')\n self.d2 = Dense(1024, activation='relu')\n self.critic = Dense(output_size)\n \n def call(self, inputs):\n x = self.d1(inputs)\n x = self.d2(x)\n critic = self.critic(x)\n return critic",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class ActorCriticAgent:\n def __init__(self, L=20, B=20, H=20, n_remains=5, lr=1e-8, gamma=0.99):\n \n self.state_size = (L,B,1)\n self.selected_size = (L,B,H)\n self.remain_size = (n_remains, 3)\n self.output_size = 1\n \n self.lr = lr\n self.gamma = gamma\n \n self.state_cnn = StateCNN(self.state_size, self.selected_size, self.remain_size)\n self.actor = Actor(self.output_size)\n self.critic = Critic(self.output_size)\n \n self.actor_optimizer = Adam(learning_rate=self.lr)\n self.critic_optimizer = Adam(learning_rate=self.lr)\n \n self.avg_actor_loss = 0\n self.avg_critic_loss = 0\n \n def get_action(self, state, s_locs, r_boxes):\n sc = self.state_cnn([state, s_locs, r_boxes])\n actor = self.actor(sc)\n argmax_idx = np.where(actor == tf.math.reduce_max(actor))\n action_idx = argmax_idx[0][0]\n return action_idx\n \n def actor_loss():\n pass\n \n def critic_loss():\n pass\n \n def train():\n state_params = self.\n actor_params = self.\n critic_params = self.\n \n for \n with tf.GradientTape() as tape:\n state_cnn = self.state_cnn([state, s_boxes, remains])\n actor = self.actor()\n values = self.critic()\n next_values = self.critic()\n \n expect_reward = \n \n actor_loss = \n critic_loss = \n \n self.avg_actor_loss += \n self.avg_critic_loss += \n \n actor_grads = actor_tape.gradient(actor_loss, actor_params)\n critic_grads = critic_tape.gradient(critic_loss, critic_params)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"max_episode = 2000\nN_MDD = 5\nK = 3\nN_Candidates = 4",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"boxes, gt_pos = generation_3dbox_random(case_size=[[20,20,20,]],min_s = 1,\n N_mdd = N_MDD)\nboxes = boxes[0]\ngt_pos = gt_pos[0]\n\nnum_max_boxes = len(boxes)\nnum_max_remain = num_max_boxes - K\n\nnum_max_boxes, num_max_remain",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"env = Bpp3DEnv()\nagent = ActorCriticAgent(L=20, B=20, H=20, n_remains=num_max_remain, \n lr=1e-6, gamma=0.99)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"frac_l, avg_actor_loss, avg_critic_loss = [],[],[]\nfor episode in range(max_episode):\n st = time.time()\n env.reset()\n done = False\n step = 0\n \n used_boxes, pred_pos = [], []\n r_boxes = np.array(np.array(boxes).copy())\n \n while not done:\n state = env.container.copy()\n k = min(K, len(r_boxes))\n step += 1\n \n selected = cbn_select_boxes(r_boxes[:N_Candidates], k)\n s_order = get_selected_order(selected, k)\n \n state_h = env.update_h().copy()\n in_state, in_r_boxes = raw_to_input(state_h, s_order, r_boxes, num_max_remain)\n s_loc_c, pred_pos_c, used_boxes_c, next_state_c , num_loaded_box_c, next_cube_c = get_selected_location(s_order, pred_pos, used_boxes, state)\n \n action_idx = agent.get_action(in_state, s_loc_c, in_r_boxes)\n num_loaded_box = num_loaded_box_c[action_idx]\n if num_loaded_box != 0:\n new_used_boxes = get_remain(used_boxes, used_boxes_c[action_idx])\n r_boxes = get_remain(new_used_boxes, r_boxes)\n \n used_boxes = used_boxes_c[action_idx]\n pred_pos = pred_pos_c[action_idx]\n \n env.convert_state(next_cube_c[action_idx])\n \n if len(r_boxes) == 0:\n done = True\n else:\n r_boxes = get_remain(s_order[action_idx], r_boxes)\n if len(r_boxes) == 0:\n done = True\n \n if done:\n avg_frac = 0 if len(frac_l) == 0 else np.mean(frac_l)\n frac_l.append(env.terminal_reward())\n \n agent.train_model()\n \n avg_actor_loss.append(agent.avg_actor_loss / float(step))\n avg_critic_loss.append(agent.avg_critic_loss / float(step))\n \n log = \"=====episode: {:5d} | \".format(e)\n log += \"env.terminal_reward(): {:.3f} | \".format(env.terminal_reward())\n log += \"actor avg loss : {:6f} \".format(agent.avg_actor_loss / float(step))\n log += \"critic avg loss : {:6f} \".format(agent.avg_critic_loss / float(step))\n log += \"time: {:.3f}\".format(time.time()-st)\n print(log)\n \n agent.avg_actor_loss, agent.avg_critic_loss = 0, 0",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"env.reset()\ndone = False\nstep = 0\n\nr_boxes = np.array(np.array(boxes).copy())\nstate = env.container.copy()\nk = min(K, len(r_boxes))\nstep += 1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"vis_box(boxes, gt_pos)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"selected = cbn_select_boxes(r_boxes[:N_Candidates], k)\nselected",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s_order = get_selected_order(selected, k)\ns_order",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"state_h = env.update_h().copy()\nin_state, in_r_boxes = raw_to_input(state_h, s_order, r_boxes, num_max_remain)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pred_pos, used_boxes = [], []",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s_loc_c, pred_pos_c, used_boxes_c, next_state_c, num_loaded_box_c, next_cube_c = get_selected_location(s_order, pred_pos, used_boxes, state)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"action_idx = agent.get_action(in_state, s_loc_c, in_r_boxes)\naction_idx",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"num_loaded_box_c",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"num_loaded_box = num_loaded_box_c[action_idx]\nnum_loaded_box",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"new_used_boxes = get_remain(used_boxes, used_boxes_c[action_idx])\nnew_used_boxes",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"r_boxes",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"r_boxes = get_remain(new_used_boxes, r_boxes)\nr_boxes",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"used_boxes = used_boxes_c[action_idx]\npred_pos = pred_pos_c[action_idx]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"env.convert_state(next_cube_c[action_idx])\nt_state = env.container.copy()\nt_state_h = env.container_h.copy()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"k = min",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4abcd41528600a0dbe46155f47eb694ce7df8e74
| 141,650 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
labs/lab1.6.ipynb
|
shevkunov/workout
|
d36b84f4341d36a6c45553a1c7fa7d147370fba8
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
labs/lab1.6.ipynb
|
shevkunov/workout
|
d36b84f4341d36a6c45553a1c7fa7d147370fba8
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
labs/lab1.6.ipynb
|
shevkunov/workout
|
d36b84f4341d36a6c45553a1c7fa7d147370fba8
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null | 377.733333 | 65,158 | 0.915814 |
[
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport math \nimport random\nfrom math import sqrt",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def sciPrintR(val, relErr, name=None):\n if name != None:\n print name, val, \"+-\", val * relErr, \"(\", relErr * 100., \"%)\"\n else:\n print val, \"+-\", val * relErr, \"(\", relErr * 100., \"%)\"\n \ndef sciPrintD(val, dErr, name=None):\n if name != None:\n print name, val, \"+-\", dErr, \"(\", (dErr/val) * 100., \"%)\"\n else:\n print val, \"+-\", dErr, \"(\", (dErr/val) * 100., \"%)\"\n \ndef prodErrorR(errors):\n errors = np.array(errors)\n return np.sqrt((errors**2).sum())\n\ndef stdPlt(X, Y, title=None):\n fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 16))\n if title != None:\n plt.title(title)\n\n ax = fig.add_subplot(111)\n k_off = 1.05\n x_minor_ticks = np.linspace(0, X.max() * k_off + 0.0001, 125) # 104 \n x_major_ticks = np.array([x_minor_ticks[i] for i in range(0, x_minor_ticks.size, 20)])\n y_minor_ticks = np.linspace(0, Y.max() * k_off + 0.0001, 248) # 4822\n y_major_ticks = np.array([y_minor_ticks[i] for i in range(0, y_minor_ticks.size, 20)])\n\n\n ax.set_xticks(x_major_ticks)\n ax.set_xticks(x_minor_ticks, minor=True)\n ax.set_yticks(y_major_ticks)\n ax.set_yticks(y_minor_ticks, minor=True)\n ax.grid(which='minor', alpha=0.4, linestyle='-')\n ax.grid(which='major', alpha=0.7, linestyle='-')\n\n\n plt.xlim((0, X.max() * k_off))\n plt.ylim((0, Y.max() * k_off))\n\n \n k = Y.max() / Y.mean()\n plt.plot([0, X.mean() * k], [0, Y.mean()* k])\n #plt.plot(X, Y)\n plt.scatter(X, Y, s=5, color=\"black\")\n plt.show()\n\n \nprint(math.sqrt(0.1*0.1 + 0.6*0.6 + 0.4*0.4))\nprodErrorR([0.1,0.6,0.4])\n",
"0.728010988928\n"
],
[
"L = 501 * 1e-3\nDL = 1 * 1e-3\n\nam = (50.695 + 2.573 + 2.571 + 0.740) * 1e-3\nm1 = 492.7 * 1e-3\nm2 = 494.6 * 1e-3\nm3 = 491.5 * 1e-3 # 491.5 * 1e-3\nDm = 0.5 * 1e-3\n\ng = 9.815\n\nprint(am)",
"0.056579\n"
],
[
"freqs = np.array([0, 134.4, 403.0, 675.7, 949.4, 1229.6, 1513.5, 1790.9]) # ! corrr\nns = np.array([0, 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13])\n\ndef pl_works(freqs, ns, m_sum_1):\n print \"freq :\"\n sciPrintD((freqs[1:] / ns[1:]).mean(), (freqs[1:] / ns[1:]).std(ddof=1) / np.size(freqs.size))\n # tables\n wave_lengths = (2. * L) / ns[1:]\n us = freqs[1:] * wave_lengths # u = lambda * freq\n print \"us :\"\n otd_freq_err = (freqs[1:] / ns[1:]).std(ddof=1)\n for i in range(us.size):\n sciPrintR(us[i], prodErrorR([otd_freq_err / (freqs[i + 1] / ns[i + 1]), DL / L]))\n \n us_mean = us.mean()\n Dus_mean = us.std(ddof=1)/np.sqrt(us.size)\n sciPrintD(us_mean, Dus_mean, \"us_mean = \")\n\n T = g * m_sum_1 \n pl = T / (us * us ) # u = sqrt(T / pl)\n pls = pl\n print \"pls :\"\n for i in range(pl.size):\n sciPrintR(pl[i], pl.std(ddof=1) / pl[i], \"pl[%d]\" % (i))\n\n print \"pls mean after =\"\n sciPrintR(pl.mean(), prodErrorR([(pl.std(ddof=1) / math.sqrt(pl.size) / pl.mean()), 1 / 501]), \"pl_mean_after\")\n\n # mean\n freq_base = freqs[1:] / ns[1:]\n freq_mean = freq_base.mean()\n Dfreq_mean = freq_base.std(ddof=1) / np.sqrt(freq_base.size)\n Rfreq_mean = Dfreq_mean / freq_mean\n sciPrintR(freq_mean, Rfreq_mean, \"lambda_1 = \")\n\n wave_length = 2. * L / ns[1]\n Rwave_length = DL / wave_length\n\n u = freq_mean * wave_length\n Ru = prodErrorR([Rwave_length, Rfreq_mean])\n\n Rm_sum_1 = (Dm * 2) / m_sum_1\n T = g * m_sum_1 \n RT = Rm_sum_1\n\n pl = T / (u * u)\n Rpl = prodErrorR([RT, Ru, Ru])\n\n sciPrintR(pl, Rpl, \"pl_mean = \")\n return pls, us_mean, Dus_mean\n\ngreat_pl_1, us_mean_1, Dus_mean1 = pl_works(freqs, ns, am + m1 + m2)\nstdPlt(ns, freqs, title=r\"$\\nu(n) [m = %f]$\" % (am + m1 + m2))",
"freq :\n135.925224934 +- 1.42579613834 ( 1.04895624711 %)\nus :\n134.6688 +- 1.45371516405 ( 1.07947435787 %)\n134.602 +- 1.45369051588 ( 1.07999176527 %)\n135.41028 +- 1.45398955175 ( 1.0737660034 %)\n135.899828571 +- 1.45417150837 ( 1.07003189309 %)\n136.895466667 +- 1.45454352448 ( 1.06252132368 %)\n137.866090909 +- 1.45490871578 ( 1.05530570004 %)\n138.037061538 +- 1.45497330014 ( 1.05404540195 %)\nus_mean = 136.197075384 +- 0.539978086618 ( 0.396468195148 %)\npls :\npl[0] 0.00056494540974 +- 1.15592677133e-05 ( 2.0460857835 %)\npl[1] 0.000565506288742 +- 1.15592677133e-05 ( 2.04405643993 %)\npl[2] 0.000558775289906 +- 1.15592677133e-05 ( 2.06867911342 %)\npl[3] 0.000554756816139 +- 1.15592677133e-05 ( 2.08366393651 %)\npl[4] 0.000546716689393 +- 1.15592677133e-05 ( 2.11430672184 %)\npl[5] 0.000539045644718 +- 1.15592677133e-05 ( 2.14439497407 %)\npl[6] 0.000537711163999 +- 1.15592677133e-05 ( 2.14971689025 %)\npls mean after =\npl_mean_after 0.000552493900377 +- 4.36899252961e-06 ( 0.79077660887 %)\nlambda_1 = 135.925224934 +- 0.538900286046 ( 0.396468195148 %)\npl_mean = 0.000552337971977 +- 3.23705525864e-06 ( 0.586064225687 %)\n"
],
[
"print(\"New start freq = \", freqs[1] * sqrt((m1 + m2 + m3)/(m1 + m2)))",
"('New start freq = ', 164.48618243331526)\n"
],
[
"freq2 = np.array([0, 161.1, 484.6, 806.7, 1130.5, 1457.55, 1790.7, 2128.0])\nns2 = np.array([0, 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13])\n\ngreat_pl_2, us_mean_2, Dus_mean2 = pl_works(freq2, ns2, am + m1 + m2 + m3 )\nstdPlt(ns2, freq2, title=r\"$\\nu(n) [m = %f]$\" % (am + m1 + m2 + m3))",
"freq :\n161.986650017 +- 0.931313833509 ( 0.574932461048 %)\nus :\n161.4222 +- 0.987234089613 ( 0.611585079136 %)\n161.8564 +- 0.987517280256 ( 0.610119389938 %)\n161.66268 +- 0.987390849711 ( 0.610772288144 %)\n161.823 +- 0.98749547224 ( 0.61023184111 %)\n162.2739 +- 0.987790219477 ( 0.608717864966 %)\n163.116490909 +- 0.988342970848 ( 0.605912354624 %)\n164.019692308 +- 0.988938316623 ( 0.602938770771 %)\nus_mean = 162.310623317 +- 0.352707549373 ( 0.217304044656 %)\npls :\npl[0] 0.0005783348673 +- 6.52812298848e-06 ( 1.12877907897 %)\npl[1] 0.000575236118306 +- 6.52812298848e-06 ( 1.13485971773 %)\npl[2] 0.000576615552407 +- 6.52812298848e-06 ( 1.13214479929 %)\npl[3] 0.000575473598381 +- 6.52812298848e-06 ( 1.13439139638 %)\npl[4] 0.000572279978903 +- 6.52812298848e-06 ( 1.14072188948 %)\npl[5] 0.000566382935758 +- 6.52812298848e-06 ( 1.15259881192 %)\npl[6] 0.000560162348902 +- 6.52812298848e-06 ( 1.16539838875 %)\npls mean after =\npl_mean_after 0.000572069342851 +- 2.46739856508e-06 ( 0.431311098194 %)\nlambda_1 = 161.986650017 +- 0.352003542289 ( 0.217304044656 %)\npl_mean = 0.000572021047713 +- 1.96998199708e-06 ( 0.344389774635 %)\n"
],
[
"all_pl = np.append(great_pl_1, great_pl_2)\n# print(all_pl)\n\nPL_VAL = all_pl.mean()\nR_PL_VAL = all_pl.std(ddof=1)/np.sqrt(all_pl.size) / PL_VAL\n\nR_PL_VAL = prodErrorR([R_PL_VAL, Dm / (am + m1+ m2+m3), 1. / 501.])\n\nsciPrintR(PL_VAL * 1e6, R_PL_VAL)",
"562.281621614 +- 3.80423450194 ( 0.676571019879 %)\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4abce297bf24a08c5e5bdf4e1c74491e652f0b35
| 305,253 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
algo-dev/India Rainfall Gold Price Linear Correlation.ipynb
|
joseph97git/alpha-learn
|
3ab6339e60f0ca0194f2e32b575d28c57ac0aeb4
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
algo-dev/India Rainfall Gold Price Linear Correlation.ipynb
|
joseph97git/alpha-learn
|
3ab6339e60f0ca0194f2e32b575d28c57ac0aeb4
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
algo-dev/India Rainfall Gold Price Linear Correlation.ipynb
|
joseph97git/alpha-learn
|
3ab6339e60f0ca0194f2e32b575d28c57ac0aeb4
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 376.390875 | 90,320 | 0.927093 |
[
[
[
"# libraries\nfrom pandas_datareader import data\nfrom datetime import datetime\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn as sns\nimport os",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# configure\n%matplotlib inline\nsns.set(style = 'whitegrid')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# path\nos.getcwd()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# import india rain data\nindia_rain = pd.read_csv('C:\\\\Users\\\\Joseph\\\\Desktop\\\\AlphaLearn\\\\Data\\\\rainfall-india.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# summary\nprint(india_rain.head())\nprint(india_rain.info())\nprint(india_rain.columns)",
" Rainfall - (MM) Year Month Country ISO3\n0 11.8792 1991 Jan India IND\n1 12.3276 1991 Feb India IND\n2 13.4113 1991 Mar India IND\n3 41.9814 1991 Apr India IND\n4 55.3486 1991 May India IND\n<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>\nRangeIndex: 312 entries, 0 to 311\nData columns (total 5 columns):\nRainfall - (MM) 312 non-null float64\n Year 312 non-null int64\n Month 312 non-null object\n Country 312 non-null object\n ISO3 312 non-null object\ndtypes: float64(1), int64(1), object(3)\nmemory usage: 12.3+ KB\nNone\nIndex(['Rainfall - (MM)', ' Year', ' Month', ' Country', ' ISO3'], dtype='object')\n"
],
[
"## data preprocessing\n\n# get time\nmonth = list(pd.Series(list(india_rain[' Month'])).apply(lambda t: t.split(' ')[1]))\nyear = [str(time) for time in list(india_rain[' Year'])]\nzipped_dates = zip(month, year)\n\n# combine and cast to datetime object\nstring_dates = [str(t[0]) + \"-\" + str(t[1]) for t in list(zipped_dates)]\nobj_dates = pd.Series([datetime.strptime(sd, '%b-%Y') for sd in string_dates], name='Date')\n\n# rename rainfall, create dataframe\ndf_india_rainfall = pd.DataFrame(india_rain['Rainfall - (MM)'])\n\nstart_date = '2013-01-01'\nend_date = '2016-01-01'\n\n# set index to date time\ndf_india_rainfall = df_india_rainfall.set_index(obj_dates)\ndf_india_rainfall = df_india_rainfall.loc[start_date:end_date]\ndf_india_rainfall = df_india_rainfall[0:36]\n\ndf_india_rainfall.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# plot data over time\ndf_india_rainfall.plot(figsize = (30, 10), linewidth = 3, fontsize = 20)\nplt.legend(labels = ['rainfall (mm)'], loc = 'upper left', fontsize = 20)\nplt.xlabel('Year', fontsize = 20, labelpad = 20);",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# get gold data\nstart_date = '2013-01-01'\nend_date = '2016-01-01'\n\ngld_price = data.DataReader('GLD', 'yahoo', start_date, end_date)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"gld_price.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"gld_price.max()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"gld_price.info()",
"<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>\nDatetimeIndex: 756 entries, 2013-01-02 to 2015-12-31\nData columns (total 6 columns):\nHigh 756 non-null float64\nLow 756 non-null float64\nOpen 756 non-null float64\nClose 756 non-null float64\nVolume 756 non-null int64\nAdj Close 756 non-null float64\ndtypes: float64(5), int64(1)\nmemory usage: 41.3 KB\n"
],
[
"gld_monthly = gld_price.resample('MS').mean()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"gld_monthly.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_gld_price = pd.DataFrame(gld_monthly['Adj Close'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_gld_price.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# plot gld price over time\ndf_gld_price.plot(figsize = (30, 10), linewidth = 3, fontsize = 20)\nplt.legend(labels = ['price'], loc = 'upper left', fontsize = 20)\nplt.xlabel('Year', fontsize = 20, labelpad = 20);",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize = (10, 8))\nsns.jointplot(x = df_india_rainfall['Rainfall - (MM)'], y = df_gld_price['Adj Close'], s = 60)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"rain = df_india_rainfall['Rainfall - (MM)']\ngld = df_gld_price['Adj Close']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# check overall correlation\nnp.corrcoef(rain, gld)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# check rolling \ndf_rolling_corr = pd.DataFrame(rain.rolling(3).corr(gld))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# plot 6 month rolling correlation\ndf_rolling_corr.plot(figsize = (20, 10), linewidth = 3, fontsize = 20)\nplt.legend(labels = ['correlation'], loc = 'upper left', fontsize = 20)\nplt.xlabel('Year', fontsize = 20, labelpad = 20);",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize = (10, 8))\nsns.distplot(df_rolling_corr.dropna(), bins = len(df_rolling_corr))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Summary:\nThe point estimate showed a negative correlation of ~ 0.1 between the price of gold and rainfall in India. Further exploration of a 3 month rolling correlation revealed a non-normal distribution of correlations with widely varying oscillations in the correlation values over time. There is no signal found in the relationship between GLD and India's rainfall.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4abd257a1c309978bcc102769607e9d2f1b75ff2
| 91,848 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
MT5 Small Model.ipynb
|
tomiyee/6.806-Card-Translation
|
9286b232f60ec53fabbbcbeca23ddd71cd6c3483
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
MT5 Small Model.ipynb
|
tomiyee/6.806-Card-Translation
|
9286b232f60ec53fabbbcbeca23ddd71cd6c3483
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
MT5 Small Model.ipynb
|
tomiyee/6.806-Card-Translation
|
9286b232f60ec53fabbbcbeca23ddd71cd6c3483
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 32.88507 | 1,386 | 0.567394 |
[
[
[
"# MT5 Small Model\n\nIn this notebook, we will be fine tuning the MT5 Sequence-to-Sequence Transformer model to take a Natural Language structured card specification to Java code.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Check for Cuda Compatibility.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import torch\nimport torch.nn as nn\ntorch.cuda.is_available()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"using_google_drive = True\n\nif using_google_drive:\n from google.colab import drive\n drive.mount('/content/gdrive')\n mahmoud_path = '/content/gdrive/MyDrive/Final Project/'\n tommy_path = '/content/gdrive/MyDrive/Colab Notebooks/Final Project/'\n path = mahmoud_path\n PATH = path",
"Mounted at /content/gdrive\n"
],
[
"%%bash\npip -q install transformers\npip -q install tqdm\npip -q install sentencepiece \npip -q install sacrebleu",
"Collecting sacrebleu\n Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/7e/57/0c7ca4e31a126189dab99c19951910bd081dea5bbd25f24b77107750eae7/sacrebleu-1.5.1-py3-none-any.whl (54kB)\nCollecting portalocker==2.0.0\n Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/89/a6/3814b7107e0788040870e8825eebf214d72166adf656ba7d4bf14759a06a/portalocker-2.0.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl\nInstalling collected packages: portalocker, sacrebleu\nSuccessfully installed portalocker-2.0.0 sacrebleu-1.5.1\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Tokenizer for the MT5 Model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Tokenizers\nimport transformers\n#from transformers import MT5ForConditionalGeneration, T5Tokenizer\npretrained_model_name = 'google/mt5-small'\n\ntokenizer = transformers.AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(pretrained_model_name)\ncontext_ids = tokenizer.encode(\"When this creature enters the battle field, target creature loses 2 life.\")\nprint(tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(context_ids))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ctx_list = [\n \"You can protect yourself by wearing an N95 mask.\", \n \"wearing an N95 mask\"\n]\n\ntokenizer_output = tokenizer.batch_encode_plus(\n ctx_list,\n max_length = 12,\n truncation=True,\n padding='longest',\n return_attention_mask=True,\n return_tensors='pt'\n)\n\nfor key, value in tokenizer_output.items():\n print(key)\n print(value)\n print('-------------------------')",
"input_ids\ntensor([[ 1662, 738, 36478, 23191, 455, 25972, 347, 461, 441, 4910,\n 6408, 1],\n [25972, 347, 461, 441, 4910, 6408, 1, 0, 0, 0,\n 0, 0]])\n-------------------------\nattention_mask\ntensor([[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],\n [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])\n-------------------------\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Dataset Collection and Processing\n\nLoad the dataset. The framework for making changes to individual points in the dataset is set in the `preprocess_datapoint` method, which at the moment does nothing to our dataset.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"with open(PATH + 'datasets/train_magic.in') as f:\n train_x = f.readlines()\nwith open(PATH + 'datasets/train_magic.out') as f:\n train_y = f.readlines()\nwith open(PATH + 'datasets/test_magic.in') as f:\n test_x = f.readlines()\nwith open(PATH + 'datasets/test_magic.out') as f:\n test_y = f.readlines()\n# Structure the dataset somewhat similarly to the dataset objects\ntraining_dataset = [{ 'card': x, 'code': y } for x, y in zip(train_x, train_y)]\ntesting_dataset = [{ 'card': x, 'code': y } for x, y in zip(test_x, test_y )]\n\ndataset = {\n \"train\": training_dataset,\n \"test\": testing_dataset\n}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import json\nimport random\nfrom multiprocessing import Pool\nfrom tqdm import tqdm, trange\n\n\ndef preproc_init(tokenizer_for_model):\n \"\"\" \n Use this to assign global variables within a new thread \n \n Parameters\n ----------\n tokenizer_for_mode: fn\n The tokenizer for the pretrained transformer model\n \"\"\"\n global tokenizer\n tokenizer = tokenizer_for_model\n\ndef preprocess_datapoint (datapoint):\n \"\"\"\n Is effectively an identity function, but is here if we do preprocessing later\n \n This method will preprocess a single datapoint loaded above. This can involve\n replacing characters, removing parts of the input or output, etc. The current\n implementation applies no change to the dict. It can return None if we want to \n remove this datapoint as well.\n\n Parameters\n ----------\n datapoint: dict\n The dict containing the initial value of each data in the dataset.\n Each datapoint has the following two datapoints\n \"card\": the string for the card description and meta data\n \"code\": the string for the card implementation in Java\n \n Returns\n -------\n dict\n A new representation for this individual datapoint.\n \"\"\"\n \n # We have access to global vars defined in preproc_init\n return datapoint\n \n \ndef preprocess_dataset(dataset_list, threads, tokenizer):\n \"\"\"\n Preprocesses the entire dataset in `threads` threads\n \n This method opens `threads` new threads in\n\n Parameters\n ----------\n dataset_list: dict[]\n A list of datapoints, where each datapoint is in the shape:\n \"card\": the string for the card description and meta data\n \"code\": the string for the card implementation in Java\n threads: int\n The number of threads to run the preprocessing on\n tokenizer: fn\n The tokenizer for the particular pretrained model\n \n Returns\n -------\n dict\n A new representation for every datapoint in the dataset_list\n \"\"\"\n \n # Open new threads and map tasks between them\n with Pool(threads, initializer=preprocess_datapoint, initargs=(tokenizer,)) as p:\n processed_dataset = list(tqdm(p.imap(preprocess_datapoint, dataset_list), total=len(dataset_list)))\n # Remove None values in the list\n processed_dataset = [x for x in processed_dataset if x]\n \n json.dump(processed_dataset, open(PATH + \"/processed_dataset.json\", 'w'))\n return processed_dataset\n\nprocessed_dataset = preprocess_dataset(dataset['train'], 16, tokenizer)\n",
"100%|██████████| 11969/11969 [00:01<00:00, 9925.69it/s] \n"
]
],
[
[
"# Building the Model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\nclass ModelOutputs:\n def __init__(self, output_logits=None, loss=None):\n \"\"\"\n An object containing the output of the CardTranslationModel\n \n Parameters\n ----------\n output_logits : torch.tensor\n shape (batch_size, ans_len)\n loss : torch.tensor\n shape (1) The loss of the output\n\n \"\"\"\n self.output_logits = output_logits\n self.loss = loss\n \nclass CardTranslationModel(nn.Module):\n\n def __init__(self, lm=None):\n \"\"\"\n Initializes the CardTranslationModel with the provided learning mdoel\n\n Parameters\n ----------\n lm : pretrained transformer\n Description of arg1\n\n \"\"\"\n super(CardTranslationModel, self).__init__()\n self.lm = lm\n \n def forward(self, input_ids=None, attention_mask=None, label_ids=None):\n \"\"\"\n Summary line.\n\n Extended description of function.\n\n Parameters\n ----------\n input_ids : torch.tensor\n shape (batch_size, seq_len) ids of the concatenated input tokens\n attention_mask : torch.tensor\n shape (batch_size, seq_len) concatenated attention masks\n label_ids: torch.tensor\n shape (batch_size, ans_len) the expected code output\n\n Returns\n -------\n ModelOutputs\n Description of return value\n\n \"\"\"\n # Feed our input ids into the pretrained transformer\n lm_output = self.lm(\n input_ids=input_ids,\n attention_mask=attention_mask,\n labels=label_ids,\n use_cache=False\n )\n \n # Compute Loss from the output of the learning model\n total_loss = lm_output['loss']\n if False and label_ids is not None:\n loss_fct = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()\n total_loss = loss_fct(label_ids, lm_output['logits'])\n \n return ModelOutputs(\n output_logits=lm_output['logits'],\n loss=total_loss)\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from transformers import MT5ForConditionalGeneration, T5Tokenizer\n\ntokenizer = T5Tokenizer.from_pretrained(pretrained_model_name)\n# Create the CardTranslationModel using the MT5 Conditional Generation model\nlm_pretrained = MT5ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(pretrained_model_name)\nmodel = CardTranslationModel(lm_pretrained).cuda()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Up Next Training:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import torch\n\n# Hyper-parameters: you could try playing with different settings\nnum_epochs = 5\nlearning_rate = 3e-5\nweight_decay = 1e-5\neps = 1e-6\nbatch_size = 2\nwarmup_rate = 0.05\ncard_max_length = 448\ncode_max_length = 448\n\n# Calculating the number of warmup steps\nnum_training_cases = len(processed_dataset)\nt_total = (num_training_cases // batch_size + 1) * num_epochs\next_warmup_steps = int(warmup_rate * t_total)\n\n# Initializing an AdamW optimizer\next_optim = torch.optim.AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate,\n eps=eps, weight_decay=weight_decay)\n\n# Initializing the learning rate scheduler [details are in the BERT paper]\n# ext_sche = transformers.get_linear_schedule_with_warmup(\n# ext_optim, num_warmup_steps=ext_warmup_steps, num_training_steps=t_total\n# )\n\nprint(\"***** Training Info *****\")\nprint(\" Num examples = %d\" % t_total)\nprint(\" Num Epochs = %d\" % num_epochs)\nprint(\" Batch size = %d\" % batch_size)\nprint(\" Total optimization steps = %d\" % t_total)",
"***** Training Info *****\n Num examples = 29925\n Num Epochs = 5\n Batch size = 2\n Total optimization steps = 29925\n"
],
[
"def vectorize_batch(batch, tokenizer):\n \"\"\"\n Converts the batch of processed datapoints into separate tensors of token ids\n \n Converts the batch of processed datapoints into separate tensors of token ids\n hosted on the GPU. \n \n Parameters\n ----------\n batch: str[]\n shape (batch_size, 1)\n tokenizer: fn\n Converts the batch to a tensor of input and output ids\n \n Returns\n -------\n input_ids: torch.tensor\n shape (batch_size, max_input_len)\n input_attn_mask: torch.tensor\n shape (batch_size, max_input_len)\n label_ids: torch.tensor\n shape (batch_size, max_output_len)\n \"\"\"\n \n # Separate the batch into input and output\n card_batch = [card_data['card'] for card_data in batch]\n code_batch = [code_data['code'] for code_data in batch]\n \n # Encode the card's natural language representation\n card_encode = tokenizer.batch_encode_plus(\n card_batch,\n max_length = card_max_length,\n truncation = True,\n padding = 'longest',\n return_attention_mask = True,\n return_tensors = 'pt'\n )\n\n # Encode the card's java code representation\n code_encode = tokenizer.batch_encode_plus(\n code_batch,\n max_length = code_max_length,\n truncation = True,\n padding = 'longest',\n return_attention_mask = True,\n return_tensors = 'pt'\n )\n \n # Move the training batch to GPU\n card_ids = card_encode['input_ids'].cuda()\n card_attn_mask = card_encode['attention_mask'].cuda()\n code_ids = code_encode['input_ids'].cuda()\n \n return card_ids, card_attn_mask, code_ids\n \n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import gc\n\nmodel.train()\nmax_grad_norm = 1\n\ntraining_dataset = processed_dataset[:6000]\nnum_training_cases = len(training_dataset)\n\nstep_id = 0\nfor _ in range(num_epochs):\n\n random.shuffle(training_dataset)\n\n for i in range(0, num_training_cases, batch_size):\n gc.collect()\n torch.cuda.empty_cache()\n\n batch = training_dataset[i: i + batch_size]\n input_ids, input_attn_mask, label_ids = vectorize_batch(batch, tokenizer)\n\n gc.collect()\n torch.cuda.empty_cache()\n\n model.zero_grad() # Does the same as ext_optim.zero_grad()\n\n # Get the model outputs, including (start, end) logits and losses\n # stored as a ModelOutput object\n outputs = model( \n input_ids=input_ids,\n attention_mask=input_attn_mask,\n label_ids=label_ids\n )\n \n gc.collect()\n torch.cuda.empty_cache()\n\n # Back-propagate the loss signal and clip the gradients\n loss = outputs.loss.mean()\n loss.backward()\n torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), max_grad_norm)\n\n # Update neural network parameters and the learning rate\n ext_optim.step()\n # ext_sche.step() # Update learning rate for better convergence\n\n if step_id % 100 == 0:\n print(f'At step {step_id}, the extraction loss = {loss}')\n \n step_id += 1\n\n input_ids.detach()\n input_attn_mask.detach()\n label_ids.detach()\n outputs.loss.detach()\n \n del input_ids\n del input_attn_mask\n del label_ids\n del outputs\n\n torch.cuda.empty_cache()\n\nprint('Finished Training')",
"At step 0, the extraction loss = 27.42669105529785\nAt step 100, the extraction loss = 23.36913299560547\nAt step 200, the extraction loss = 20.11041831970215\nAt step 300, the extraction loss = 11.491966247558594\nAt step 400, the extraction loss = 10.240728378295898\nAt step 500, the extraction loss = 7.24114465713501\nAt step 600, the extraction loss = 4.9385986328125\nAt step 700, the extraction loss = 3.3570027351379395\nAt step 800, the extraction loss = 3.2423012256622314\nAt step 900, the extraction loss = 2.9838950634002686\nAt step 1000, the extraction loss = 3.0114777088165283\nAt step 1100, the extraction loss = 2.369136095046997\nAt step 1200, the extraction loss = 1.9337669610977173\nAt step 1300, the extraction loss = 2.0089476108551025\nAt step 1400, the extraction loss = 1.0087634325027466\nAt step 1500, the extraction loss = 0.9787460565567017\nAt step 1600, the extraction loss = 1.4310035705566406\nAt step 1700, the extraction loss = 1.3666661977767944\nAt step 1800, the extraction loss = 1.1607486009597778\nAt step 1900, the extraction loss = 1.5134541988372803\nAt step 2000, the extraction loss = 1.7148966789245605\nAt step 2100, the extraction loss = 1.0815958976745605\nAt step 2200, the extraction loss = 1.8246418237686157\nAt step 2300, the extraction loss = 1.1198770999908447\nAt step 2400, the extraction loss = 1.1242128610610962\nAt step 2500, the extraction loss = 0.9191697835922241\nAt step 2600, the extraction loss = 0.8780674338340759\nAt step 2700, the extraction loss = 0.7124984264373779\nAt step 2800, the extraction loss = 0.5556655526161194\nAt step 2900, the extraction loss = 1.1693847179412842\nAt step 3000, the extraction loss = 0.756405234336853\nAt step 3100, the extraction loss = 0.9293815493583679\nAt step 3200, the extraction loss = 0.7856726050376892\nAt step 3300, the extraction loss = 1.0267770290374756\nAt step 3400, the extraction loss = 1.2203233242034912\nAt step 3500, the extraction loss = 0.7437225580215454\nAt step 3600, the extraction loss = 0.9773829579353333\nAt step 3700, the extraction loss = 1.0819579362869263\nAt step 3800, the extraction loss = 1.0005775690078735\nAt step 3900, the extraction loss = 0.4275340735912323\nAt step 4000, the extraction loss = 0.6523104310035706\nAt step 4100, the extraction loss = 0.8234095573425293\nAt step 4200, the extraction loss = 0.6025868654251099\nAt step 4300, the extraction loss = 1.2854207754135132\nAt step 4400, the extraction loss = 0.4090226888656616\nAt step 4500, the extraction loss = 0.6668330430984497\nAt step 4600, the extraction loss = 0.7071539759635925\nAt step 4700, the extraction loss = 0.6531234383583069\nAt step 4800, the extraction loss = 0.9471729397773743\nAt step 4900, the extraction loss = 0.5031733512878418\nAt step 5000, the extraction loss = 1.4180824756622314\nAt step 5100, the extraction loss = 0.7825360894203186\nAt step 5200, the extraction loss = 0.6495810747146606\nAt step 5300, the extraction loss = 0.5521975159645081\nAt step 5400, the extraction loss = 0.3334417939186096\nAt step 5500, the extraction loss = 0.6853172183036804\nAt step 5600, the extraction loss = 0.34593647718429565\nAt step 5700, the extraction loss = 0.8152886033058167\nAt step 5800, the extraction loss = 0.21945123374462128\nAt step 5900, the extraction loss = 0.7279553413391113\nAt step 6000, the extraction loss = 0.5015457272529602\nAt step 6100, the extraction loss = 0.752597987651825\nAt step 6200, the extraction loss = 0.7410480380058289\nAt step 6300, the extraction loss = 0.2949809432029724\nAt step 6400, the extraction loss = 1.2870599031448364\nAt step 6500, the extraction loss = 0.24797122180461884\nAt step 6600, the extraction loss = 0.6508302092552185\nAt step 6700, the extraction loss = 0.6074438095092773\nAt step 6800, the extraction loss = 0.21315844357013702\nAt step 6900, the extraction loss = 0.3965783715248108\nAt step 7000, the extraction loss = 0.5654870867729187\nAt step 7100, the extraction loss = 0.3093186616897583\nAt step 7200, the extraction loss = 0.7512523531913757\nAt step 7300, the extraction loss = 0.7772887349128723\nAt step 7400, the extraction loss = 0.472146213054657\nAt step 7500, the extraction loss = 0.20111046731472015\nAt step 7600, the extraction loss = 0.40833866596221924\nAt step 7700, the extraction loss = 0.6478528380393982\nAt step 7800, the extraction loss = 0.33955439925193787\nAt step 7900, the extraction loss = 0.4507996439933777\nAt step 8000, the extraction loss = 0.4340634047985077\nAt step 8100, the extraction loss = 0.2934355139732361\nAt step 8200, the extraction loss = 0.16092024743556976\nAt step 8300, the extraction loss = 0.3186894655227661\nAt step 8400, the extraction loss = 0.5291315317153931\nAt step 8500, the extraction loss = 0.7034416198730469\nAt step 8600, the extraction loss = 0.6836539506912231\nAt step 8700, the extraction loss = 0.5104719400405884\nAt step 8800, the extraction loss = 0.5264183282852173\nAt step 8900, the extraction loss = 0.512683629989624\nAt step 9000, the extraction loss = 0.2742081582546234\nAt step 9100, the extraction loss = 0.30157485604286194\nAt step 9200, the extraction loss = 0.7200645804405212\nAt step 9300, the extraction loss = 0.44359642267227173\nAt step 9400, the extraction loss = 0.32372450828552246\nAt step 9500, the extraction loss = 0.6433591246604919\nAt step 9600, the extraction loss = 0.598628580570221\nAt step 9700, the extraction loss = 0.5018230676651001\nAt step 9800, the extraction loss = 0.5383405089378357\nAt step 9900, the extraction loss = 0.5042721033096313\nAt step 10000, the extraction loss = 0.5362268686294556\nAt step 10100, the extraction loss = 0.6742969751358032\nAt step 10200, the extraction loss = 0.21474777162075043\nAt step 10300, the extraction loss = 0.5609588623046875\nAt step 10400, the extraction loss = 0.3987993597984314\nAt step 10500, the extraction loss = 0.1262146383523941\nAt step 10600, the extraction loss = 0.7390260100364685\nAt step 10700, the extraction loss = 0.21857938170433044\nAt step 10800, the extraction loss = 0.38800469040870667\nAt step 10900, the extraction loss = 0.23982185125350952\nAt step 11000, the extraction loss = 0.42909422516822815\nAt step 11100, the extraction loss = 0.6600440144538879\nAt step 11200, the extraction loss = 0.504970133304596\nAt step 11300, the extraction loss = 0.4201797544956207\nAt step 11400, the extraction loss = 0.20326006412506104\nAt step 11500, the extraction loss = 0.20859761536121368\nAt step 11600, the extraction loss = 0.34249743819236755\nAt step 11700, the extraction loss = 0.2430625706911087\nAt step 11800, the extraction loss = 0.6703437566757202\nAt step 11900, the extraction loss = 0.7071929574012756\nAt step 12000, the extraction loss = 0.41943737864494324\nAt step 12100, the extraction loss = 0.30614808201789856\nAt step 12200, the extraction loss = 0.4945047199726105\nAt step 12300, the extraction loss = 0.6519198417663574\nAt step 12400, the extraction loss = 0.3450867235660553\nAt step 12500, the extraction loss = 0.11693011224269867\nAt step 12600, the extraction loss = 0.4378349781036377\nAt step 12700, the extraction loss = 0.36536529660224915\nAt step 12800, the extraction loss = 0.30169081687927246\nAt step 12900, the extraction loss = 0.4471839964389801\nAt step 13000, the extraction loss = 0.2306031733751297\nAt step 13100, the extraction loss = 0.5430821180343628\nAt step 13200, the extraction loss = 0.2801911532878876\nAt step 13300, the extraction loss = 0.4989015758037567\nAt step 13400, the extraction loss = 0.5380953550338745\nAt step 13500, the extraction loss = 0.3418399393558502\nAt step 13600, the extraction loss = 0.7957169413566589\nAt step 13700, the extraction loss = 0.40531831979751587\nAt step 13800, the extraction loss = 0.4823487401008606\nAt step 13900, the extraction loss = 0.4548686146736145\nAt step 14000, the extraction loss = 0.399920791387558\nAt step 14100, the extraction loss = 0.1869756430387497\nAt step 14200, the extraction loss = 0.5262470841407776\nAt step 14300, the extraction loss = 0.3174189329147339\nAt step 14400, the extraction loss = 0.3589947819709778\nAt step 14500, the extraction loss = 0.1567850112915039\nAt step 14600, the extraction loss = 0.3813924193382263\nAt step 14700, the extraction loss = 0.1728142648935318\nAt step 14800, the extraction loss = 0.5704279541969299\nAt step 14900, the extraction loss = 0.3548668920993805\nFinished Training\n"
],
[
"torch.save(model.state_dict(), '/content/gdrive/MyDrive/MT5_checkpoint/MT5.pt')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import torch\nimport gc\ngc.collect()\ntorch.cuda.empty_cache()\nprint(torch.cuda.memory_summary(device=None, abbreviated=False))",
"|===========================================================================|\n| PyTorch CUDA memory summary, device ID 0 |\n|---------------------------------------------------------------------------|\n| CUDA OOMs: 0 | cudaMalloc retries: 0 |\n|===========================================================================|\n| Metric | Cur Usage | Peak Usage | Tot Alloc | Tot Freed |\n|---------------------------------------------------------------------------|\n| Allocated memory | 4586 MB | 9114 MB | 145854 GB | 145850 GB |\n| from large pool | 4298 MB | 8755 MB | 134476 GB | 134472 GB |\n| from small pool | 288 MB | 545 MB | 11377 GB | 11377 GB |\n|---------------------------------------------------------------------------|\n| Active memory | 4586 MB | 9114 MB | 145854 GB | 145850 GB |\n| from large pool | 4298 MB | 8755 MB | 134476 GB | 134472 GB |\n| from small pool | 288 MB | 545 MB | 11377 GB | 11377 GB |\n|---------------------------------------------------------------------------|\n| GPU reserved memory | 5062 MB | 9412 MB | 49461 GB | 49456 GB |\n| from large pool | 4666 MB | 8946 MB | 48081 GB | 48076 GB |\n| from small pool | 396 MB | 614 MB | 1380 GB | 1379 GB |\n|---------------------------------------------------------------------------|\n| Non-releasable memory | 486854 KB | 1585 MB | 87248 GB | 87247 GB |\n| from large pool | 376607 KB | 1471 MB | 74575 GB | 74575 GB |\n| from small pool | 110247 KB | 118 MB | 12672 GB | 12672 GB |\n|---------------------------------------------------------------------------|\n| Allocations | 761 | 1311 | 50847 K | 50846 K |\n| from large pool | 200 | 580 | 17036 K | 17036 K |\n| from small pool | 561 | 1025 | 33810 K | 33810 K |\n|---------------------------------------------------------------------------|\n| Active allocs | 761 | 1311 | 50847 K | 50846 K |\n| from large pool | 200 | 580 | 17036 K | 17036 K |\n| from small pool | 561 | 1025 | 33810 K | 33810 K |\n|---------------------------------------------------------------------------|\n| GPU reserved segments | 221 | 339 | 955 K | 955 K |\n| from large pool | 23 | 62 | 249 K | 249 K |\n| from small pool | 198 | 307 | 706 K | 706 K |\n|---------------------------------------------------------------------------|\n| Non-releasable allocs | 252 | 371 | 21213 K | 21213 K |\n| from large pool | 19 | 26 | 10981 K | 10981 K |\n| from small pool | 233 | 353 | 10231 K | 10231 K |\n|===========================================================================|\n\n"
],
[
"\n#model.load_state_dict(torch.load(PATH + 'checkpoint.pt'))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#---Sandbox code---#\n\nimport random\nbatch_size = 2\ni = random.randint(0, num_training_cases-1)\n\ndatapoint = training_dataset[i:i + batch_size]\n#print(datapoint)\ncard_ids, card_attn_masks, code_ids = vectorize_batch(datapoint, tokenizer)\n\noutput = model(card_ids, card_attn_masks, code_ids)\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#---Sandbox code---#\nimport sacrebleu\n\n\n#print(output.output_logits)\nsoftmax = torch.nn.Softmax(dim=1)(output.output_logits)\n\ninput_id = tokenizer([datapoint[_]['card'] for _ in range(2)], padding=True, return_tensors='pt').input_ids.cuda()\nprint('Card: ' + datapoint[0]['card'])\n#print(input_id)\noutputs = model.lm.generate(input_id, max_length=1000)\n#print(outputs.squeeze(0))\n#print(outputs[0])\noutputs = outputs[0][1:] # remove first pad\n#print(outputs)\n#print('wat:',(outputs == 0).nonzero(as_tuple=True))\n#print((outputs == 0).nonzero(as_tuple=True)[0][0])\noutputs = outputs[:int((outputs == 1).nonzero(as_tuple=True)[0][0])]\ncode = tokenizer.decode(outputs)#[6:]\nprint('Generated code:')\nprint(code)\n#print(end)\nprint('Ground-truth code: ')\nprint(datapoint[0]['code'])\nprint(type(datapoint[0]['code']))\nprint(len(code))\n# how to sacrebleu: first arg is list of outputs, second arg is list of lists of allowable translations\nprint('BLEU:', sacrebleu.raw_corpus_bleu([code], [[datapoint[0]['code']]]).score)\n#print(type(tokenizer))\n#print(type(code))\n",
"Card: Filigree Fracture NAME_END NIL ATK_END NIL DEF_END {2}{G} COST_END NIL DUR_END Instant TYPE_END Conflux PLAYER_CLS_END 82 RACE_END U RARITY_END Destroy target artifact or enchantment . If that permanent was blue or black , draw a card .\n\nGenerated code:\npublic class FiligreeCommute extends CardImpl {§public FiligreeCommute(UUID ownerId) {§super(ownerId, 82, \"Filgree Fracture\", Rarity.UNCOMMON, new CardType[]{CardType.INSTANT}, \"{2}{G}\");§this.expansionSetCode = \"CON\";§this.getSpellAbility().addEffect(new ConditionalTriggeredAbility(new DestroyTargetEffect());§this.getSpellAbility().addEffect(new DrawCardSourceControllerEffect(new FilterPermanent(\"artifact or enchantment\")), \"\"));§}§public FiligreeCommute(final FiligreeCommute card) {§super(card);§}§@Override§public FiligreeCommute copy() {§return new FiligreeCommute(this);§}§}§class FiligreeCommute(final FiligreeCommute card) {§super(card);§}§@Override§public FiligreeCommute copy() {§return new FiligreeCommute(this);§}§}§\nGround-truth code: \npublic class FiligreeFracture extends CardImpl {§public FiligreeFracture(UUID ownerId) {§super(ownerId, 82, \"Filigree Fracture\", Rarity.UNCOMMON, new CardType[]{CardType.INSTANT}, \"{2}{G}\");§this.expansionSetCode = \"CON\";§this.getSpellAbility().addTarget(new TargetPermanent(new FilterArtifactOrEnchantmentPermanent()));§this.getSpellAbility().addEffect(new DestroyTargetEffect());§this.getSpellAbility().addEffect(new FiligreeFractureEffect());§}§public FiligreeFracture(final FiligreeFracture card) {§super(card);§}§@Override§public FiligreeFracture copy() {§return new FiligreeFracture(this);§}§}§class FiligreeFractureEffect extends OneShotEffect {§public FiligreeFractureEffect() {§super(Outcome.DrawCard);§this.staticText = \"If that permanent was blue or black, draw a card\";§}§public FiligreeFractureEffect(final FiligreeFractureEffect effect) {§super(effect);§}§@Override§public FiligreeFractureEffect copy() {§return new FiligreeFractureEffect(this);§}§@Override§public boolean apply(Game game, Ability source) {§Player player = game.getPlayer(source.getControllerId());§Permanent permanent = (Permanent) game.getLastKnownInformation(source.getFirstTarget(), Zone.BATTLEFIELD);§if (player != null && permanent != null§&& (permanent.getColor(game).isBlack() || permanent.getColor(game).isBlue())) {§player.drawCards(1, game);§return true;§}§return false;§}§}§\n\n<class 'str'>\n732\nBLEU: 8.750712728100327\n"
],
[
"def autoregressive_generate(model, tokenizer, card_desc):\n '''\n Applies autoregressive generation on a card description to generate its corresponding code\n\n Parameters\n ----------\n model: CardTranslationModel\n Model used for autoregressive generation\n tokenizer: transformers.models.tokenizer.PreTrainedTokenizer\n Tokenizer for encoding the card description\n card_desc: str or list[str] (batch_size length)\n card description\n\n Returns\n ---------\n torch.Tensor containing the sequence of code ids generated from the card description\n shape: (batch_size, max_seq_len)\n'''\n card_inputs = tokenizer(card_desc, padding=True, return_tensors='pt').input_ids.cuda()\n return model.lm.generate(card_inputs)\n\ndef decode(tokenizer, code_ids):\n '''\n Translates code ids into tokens\n\n Parameters\n ----------\n tokenizer: transformers.models.tokenizer.PreTrainedTokenizer\n Tokenizer for decoding\n code_ids: torch.Tensor\n shape: (batch_size, max_seq_len)\n\n Returns\n ---------\n list containing the token seq for each id sequence in the batch\n shape (batch_size, max_seq_len)\n '''\n decode_output = tokenizer.batch_decode(code_ids)\n return decode_output\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"test_data = testing_dataset[:200]\nbleu = 0\nfor pt in test_data:\n input_id = tokenizer([pt['card']], padding=True, return_tensors='pt').input_ids.cuda()\n outputs = model.lm.generate(input_id, max_length=2000)\n outputs = outputs[0][1:] # remove first pad\n try:\n outputs = outputs[:int((outputs == 1).nonzero(as_tuple=True)[0][0])] # truncate at end token\n except:\n print('huh', pt['card'])\n code = tokenizer.decode(outputs)\n #print('Generated code:')\n #print(code) \n #print('Ground-truth code: ')\n #print(pt['code'])\n bleu += sacrebleu.raw_corpus_bleu([code], [[pt['code']]]).score\n #print('baby bleu:', bleu)\nprint(\"BLEU:\", bleu/len(test_data))",
"huh Tibalt, the Fiend-Blooded NAME_END NIL ATK_END NIL DEF_END {R}{R} COST_END NIL DUR_END Planeswalker - Tibalt TYPE_END Avacyn Restored PLAYER_CLS_END 161 RACE_END M RARITY_END +1 : Draw a card , then discard a card at random . $-4 : Tibalt , the Fiend-Blooded deals damage equal to the number of cards in target player's hand to that player . $-6 : Gain control of all creatures until end of turn . Untap them . They gain haste until end of turn .\n\nBLEU: 34.91172539461733\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4abd3a448147ce5c290c452c229579a8e2f551c1
| 3,664 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/ungraded/fncpy/Untitled.ipynb
|
data301-2021-winter1/solo-sei-wiese
|
b365a8aad9ae992f49052e09e84867010e0b361c
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/ungraded/fncpy/Untitled.ipynb
|
data301-2021-winter1/solo-sei-wiese
|
b365a8aad9ae992f49052e09e84867010e0b361c
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/ungraded/fncpy/Untitled.ipynb
|
data301-2021-winter1/solo-sei-wiese
|
b365a8aad9ae992f49052e09e84867010e0b361c
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 25.622378 | 164 | 0.552948 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nfrom sklearn.datasets import load_wine\n\ndata = load_wine() # this a data file that gets loaded\n\n# Method chaining begins\n\ndf = ( \n pd.DataFrame(data.data,columns=data.feature_names)\n .rename(columns={\"color_intensity\": \"ci\"})\n .assign(color_filter=lambda x: np.where((x.hue > 1) & (x.ci > 7), 1, 0))\n .loc[lambda x: x['alcohol']>14]\n .sort_values(\"alcohol\", ascending=False)\n .reset_index(drop=True)\n .loc[:, [\"alcohol\", \"ci\", \"hue\"]]\n)\n\ndf",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# First, Import the libraries\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nfrom pandas import DataFrame, Series\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn as sns\n\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"missing_columns = ['10/50 Ratio', 'Pop', 'Unnamed: 12']\n\ndf_country_variables = pd.read_csv('../data/raw/cpi_variable_data/country_variable.csv', header=1).drop(missing_columns, axis=1, inplace=True)\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_mc = pd.read_csv('data/src/sample_pandas_normal.csv', index_col=0).assign(point_ratio=df['point'] / 100).drop(columns='state').sort_values('age').head(3)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\ndf_data =(pd.read_csv('../data/raw/archive/data.csv')\n .replace(['-'], np.nan)\n .mean(numeric_only=True)\n)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"path_data = '../data/raw/archive/data.csv'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def load_and_process(url_or_path_to_csv_file):\n df_data =(pd.read_csv('../data/raw/archive/data.csv')\n .replace(['-'], np.nan)\n .mean(numeric_only=True)\n )\n \n return df_data\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4abd4da8b5791d3c512dea7c4e247733710adfef
| 449,300 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
proto/setpoint_analysis/pymc_insulation_change_detection.ipynb
|
pjkundert/wikienergy
|
ac3a13780bccb001c81d6f8ee27d3f5706cfa77e
|
[
"MIT"
] | 29 |
2015-01-08T19:20:37.000Z
|
2021-04-20T08:25:56.000Z
|
proto/setpoint_analysis/pymc_insulation_change_detection.ipynb
|
pjkundert/wikienergy
|
ac3a13780bccb001c81d6f8ee27d3f5706cfa77e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
proto/setpoint_analysis/pymc_insulation_change_detection.ipynb
|
pjkundert/wikienergy
|
ac3a13780bccb001c81d6f8ee27d3f5706cfa77e
|
[
"MIT"
] | 17 |
2015-02-01T18:12:04.000Z
|
2020-06-15T14:13:04.000Z
| 49.254549 | 38,393 | 0.625059 |
[
[
[
"empty"
]
]
] |
[
"empty"
] |
[
[
"empty"
]
] |
4abd59003b73f34d59e81f7d4159f19182533869
| 101,210 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Forecasting/Solar_energy_forecasting.ipynb
|
subramanyakrishna/solarenergypredictionproject
|
317e4f6afc286ccb281bc798aaa4e4bbbbab6f84
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2021-11-22T14:14:24.000Z
|
2021-11-22T16:04:29.000Z
|
Forecasting/Solar_energy_forecasting.ipynb
|
subramanyakrishna/solarenergypredictionproject
|
317e4f6afc286ccb281bc798aaa4e4bbbbab6f84
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Forecasting/Solar_energy_forecasting.ipynb
|
subramanyakrishna/solarenergypredictionproject
|
317e4f6afc286ccb281bc798aaa4e4bbbbab6f84
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 48.682059 | 16,444 | 0.677621 |
[
[
[
"%config Completer.use_jedi = False",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn as sns\nimport tensorflow as tf\nimport sklearn \n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df=pd.read_excel('hourly-dataset_without-night-hrs.xlsx')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"se=df.reset_index()['Solar energy']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"se",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"se.plot()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"se.value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.plot(se)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler\nscaler=MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(0,1))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"se=scaler.fit_transform(np.array(se).reshape(-1,1))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"se",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"se.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"trs=int(len(se)*0.75)\nts=len(se)-trs",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"trs,ts",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"train=se[0:trs]\ntest=se[trs:]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"train.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"test.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import numpy\n\ndef create_dataset(dataset, time_step=1):\n\tdataX, dataY = [], []\n\tfor i in range(len(dataset)-time_step-1):\n\t\ta = dataset[i:(i+time_step), 0] \n\t\tdataX.append(a)\n\t\tdataY.append(dataset[i + time_step, 0])\n\treturn numpy.array(dataX), numpy.array(dataY)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_train,Y_train=create_dataset(train,9)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_train[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Y_train[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_test,Y_test=create_dataset(test,9)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_test.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_train.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Y_test.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Y_train.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Adding extra column which is required for LSTM",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"X_train =X_train.reshape(X_train.shape[0],X_train.shape[1] , 1)\nX_test = X_test.reshape(X_test.shape[0],X_test.shape[1] , 1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_train.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_test.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Model Definition",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense,LSTM\nfrom tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\nmodel=Sequential()\nmodel.add(LSTM(50,return_sequences=True,input_shape=(9,1)))\nmodel.add(LSTM(50,return_sequences=True))\nmodel.add(LSTM(50))\nmodel.add(Dense(1))\nmodel.compile(loss='mean_squared_error',optimizer='adam')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model.summary()",
"Model: \"sequential\"\n_________________________________________________________________\nLayer (type) Output Shape Param # \n=================================================================\nlstm (LSTM) (None, 9, 50) 10400 \n_________________________________________________________________\nlstm_1 (LSTM) (None, 9, 50) 20200 \n_________________________________________________________________\nlstm_2 (LSTM) (None, 50) 20200 \n_________________________________________________________________\ndense (Dense) (None, 1) 51 \n=================================================================\nTotal params: 50,851\nTrainable params: 50,851\nNon-trainable params: 0\n_________________________________________________________________\n"
],
[
"\nmodel.fit(X_train,Y_train,validation_data=(X_test,Y_test),epochs=100,batch_size=32,verbose=1)",
"Epoch 1/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 37s 15ms/step - loss: 0.1139 - val_loss: 0.0384\nEpoch 2/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0265 - val_loss: 0.0187\nEpoch 3/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0169 - val_loss: 0.0151\nEpoch 4/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0164 - val_loss: 0.0171\nEpoch 5/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 9ms/step - loss: 0.0170 - val_loss: 0.0137\nEpoch 6/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0154 - val_loss: 0.0143\nEpoch 7/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0155 - val_loss: 0.0161\nEpoch 8/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0153 - val_loss: 0.0139\nEpoch 9/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0149 - val_loss: 0.0133\nEpoch 10/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0149 - val_loss: 0.0124\nEpoch 11/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0129 - val_loss: 0.0123\nEpoch 12/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0145 - val_loss: 0.0124\nEpoch 13/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0141 - val_loss: 0.0120\nEpoch 14/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0135 - val_loss: 0.0125\nEpoch 15/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0136 - val_loss: 0.0116\nEpoch 16/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0131 - val_loss: 0.0115\nEpoch 17/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0135 - val_loss: 0.0114\nEpoch 18/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0131 - val_loss: 0.0112\nEpoch 19/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0123 - val_loss: 0.0115\nEpoch 20/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0126 - val_loss: 0.0111\nEpoch 21/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 9ms/step - loss: 0.0131 - val_loss: 0.0113\nEpoch 22/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 9ms/step - loss: 0.0122 - val_loss: 0.0124\nEpoch 23/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 9ms/step - loss: 0.0125 - val_loss: 0.0111\nEpoch 24/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0124 - val_loss: 0.0111\nEpoch 25/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0125 - val_loss: 0.0109\nEpoch 26/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 9ms/step - loss: 0.0127 - val_loss: 0.0109\nEpoch 27/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0124 - val_loss: 0.0111\nEpoch 28/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 9ms/step - loss: 0.0119 - val_loss: 0.0104\nEpoch 29/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0124 - val_loss: 0.0115\nEpoch 30/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0119 - val_loss: 0.0105\nEpoch 31/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0124 - val_loss: 0.0108\nEpoch 32/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 9ms/step - loss: 0.0118 - val_loss: 0.0103\nEpoch 33/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0119 - val_loss: 0.0106\nEpoch 34/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0119 - val_loss: 0.0105\nEpoch 35/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0113 - val_loss: 0.0106\nEpoch 36/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 9ms/step - loss: 0.0121 - val_loss: 0.0104\nEpoch 37/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0118 - val_loss: 0.0111\nEpoch 38/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0124 - val_loss: 0.0105\nEpoch 39/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0118 - val_loss: 0.0106\nEpoch 40/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0112 - val_loss: 0.0105\nEpoch 41/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0112 - val_loss: 0.0110\nEpoch 42/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0117 - val_loss: 0.0112\nEpoch 43/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0119 - val_loss: 0.0107\nEpoch 44/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0115 - val_loss: 0.0103\nEpoch 45/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0119 - val_loss: 0.0109\nEpoch 46/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0114 - val_loss: 0.0100\nEpoch 47/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0115 - val_loss: 0.0107\nEpoch 48/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0115 - val_loss: 0.0103\nEpoch 49/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 9ms/step - loss: 0.0114 - val_loss: 0.0106\nEpoch 50/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0119 - val_loss: 0.0102\nEpoch 51/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0110 - val_loss: 0.0106\nEpoch 52/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 9ms/step - loss: 0.0118 - val_loss: 0.0116\nEpoch 53/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 9ms/step - loss: 0.0114 - val_loss: 0.0101\nEpoch 54/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 9ms/step - loss: 0.0113 - val_loss: 0.0102\nEpoch 55/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0112 - val_loss: 0.0100\nEpoch 56/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0114 - val_loss: 0.0102\nEpoch 57/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0118 - val_loss: 0.0101\nEpoch 58/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0118 - val_loss: 0.0097\nEpoch 59/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0110 - val_loss: 0.0099\nEpoch 60/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0111 - val_loss: 0.0100\nEpoch 61/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0108 - val_loss: 0.0099\nEpoch 62/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 9ms/step - loss: 0.0106 - val_loss: 0.0100\nEpoch 63/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0110 - val_loss: 0.0099\nEpoch 64/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0109 - val_loss: 0.0100\nEpoch 65/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 9ms/step - loss: 0.0109 - val_loss: 0.0099\nEpoch 66/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 9ms/step - loss: 0.0112 - val_loss: 0.0103\nEpoch 67/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 9ms/step - loss: 0.0115 - val_loss: 0.0098\nEpoch 68/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 9ms/step - loss: 0.0109 - val_loss: 0.0097\nEpoch 69/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0105 - val_loss: 0.0102\nEpoch 70/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 9ms/step - loss: 0.0104 - val_loss: 0.0097\nEpoch 71/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0108 - val_loss: 0.0098\nEpoch 72/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 9ms/step - loss: 0.0111 - val_loss: 0.0100\nEpoch 73/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0105 - val_loss: 0.0098\nEpoch 74/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 9ms/step - loss: 0.0108 - val_loss: 0.0097\nEpoch 75/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0103 - val_loss: 0.0098\nEpoch 76/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 9ms/step - loss: 0.0103 - val_loss: 0.0098\nEpoch 77/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0102 - val_loss: 0.0099\nEpoch 78/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0106 - val_loss: 0.0101\nEpoch 79/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 9ms/step - loss: 0.0110 - val_loss: 0.0097\nEpoch 80/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 9ms/step - loss: 0.0105 - val_loss: 0.0098\nEpoch 81/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 9ms/step - loss: 0.0105 - val_loss: 0.0099\nEpoch 82/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 9ms/step - loss: 0.0105 - val_loss: 0.0097\nEpoch 83/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0100 - val_loss: 0.0095\nEpoch 84/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0106 - val_loss: 0.0096\nEpoch 85/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0113 - val_loss: 0.0099\nEpoch 86/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0098 - val_loss: 0.0105\nEpoch 87/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0105 - val_loss: 0.0098\nEpoch 88/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0101 - val_loss: 0.0101\nEpoch 89/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0101 - val_loss: 0.0100\nEpoch 90/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 9ms/step - loss: 0.0105 - val_loss: 0.0095\nEpoch 91/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 9ms/step - loss: 0.0104 - val_loss: 0.0097\nEpoch 92/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 9ms/step - loss: 0.0107 - val_loss: 0.0100\nEpoch 93/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0106 - val_loss: 0.0103\nEpoch 94/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0105 - val_loss: 0.0096\nEpoch 95/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 2s 9ms/step - loss: 0.0098 - val_loss: 0.0098\nEpoch 96/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0100 - val_loss: 0.0095\nEpoch 97/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0100 - val_loss: 0.0097\nEpoch 98/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0096 - val_loss: 0.0099\nEpoch 99/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0092 - val_loss: 0.0100\nEpoch 100/100\n177/177 [==============================] - 1s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0093 - val_loss: 0.0106\n"
],
[
"train_predict=model.predict(X_train)\ntest_predict=model.predict(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"train_predict=scaler.inverse_transform(train_predict)\ntest_predict=scaler.inverse_transform(test_predict)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import math\nfrom sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error\nmath.sqrt(mean_squared_error(Y_train,train_predict))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"math.sqrt(mean_squared_error(Y_test,test_predict))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"inp=test[-9:].reshape(1,-1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"inp",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"inp.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"inp[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"temp=list(inp)\ntemp",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"temp=temp[0].tolist()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"temp",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"t=np.array(temp)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"t.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"t=t.reshape(-1,9)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"t.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"t=t.reshape(1,9,1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"t.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pr=model.predict(t,verbose=0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pr[0][0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"temp=temp[0:9]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"temp.append(pr[0][0])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"temp",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"n=np.array(temp)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"n=n.reshape(-1,1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"n.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"p=scaler.inverse_transform(n)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"p",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"day_new=np.arange(1,9)\nday_pred=np.arange(9,10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.plot(p[0:9])\nplt.plot(p[9])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4abd67fe70afce4432c77d0978ba4218ff2451c0
| 22,171 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
forecasting.ipynb
|
mcknn/exp
|
1712a94694e5bf439091110fe9ec456b3a1f61f3
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
forecasting.ipynb
|
mcknn/exp
|
1712a94694e5bf439091110fe9ec456b3a1f61f3
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
forecasting.ipynb
|
mcknn/exp
|
1712a94694e5bf439091110fe9ec456b3a1f61f3
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 96.816594 | 17,091 | 0.865816 |
[
[
[
"from sklearn.multioutput import MultiOutputRegressor\nfrom sklearn.pipeline import FeatureUnion\n\nfrom skits.feature_extraction import AutoregressiveTransformer\nfrom skits.pipeline import ForecasterPipeline\nfrom skits.preprocessing import ReversibleImputer\nfrom skits.preprocessing import HorizonTransformer\nfrom xgboost import XGBRegressor\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression\nfrom sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostRegressor\nimport numpy as np\nimport seaborn as sns\nimport pandas as pd",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x = np.arange(1200)\n\ny = np.array([np.sin(x)+0.1*x for x in range(1200)])\n\npipe = ForecasterPipeline([\n ('pre_horizon', HorizonTransformer(horizon=12)),\n ('pre_reversible_imputer', ReversibleImputer(y_only=True)),\n ('features', FeatureUnion([('ar_features', AutoregressiveTransformer(num_lags=120)),])),\n ('post_feature_imputer', ReversibleImputer()),\n ('regressor', MultiOutputRegressor(XGBRegressor(n_estimators=64)))\n])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lin_model = LinearRegression()\nlin_model.fit(x.reshape(-1,1), y)\ntrend = lin_model.predict(x.reshape(-1,1))\ndetrended = [y[i] - trend[i] for i in range(y.shape[0])]\n\ny_transformed = np.nan_to_num(np.array(detrended))\nX = y_transformed.reshape(-1,1).copy()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"test_shape = 20\ntrain_shape = x.shape[0] - test_shape\npipe = pipe.fit(X, y)",
"/home/amckann/.conda/envs/django_env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/xgboost/data.py:104: UserWarning: Use subset (sliced data) of np.ndarray is not recommended because it will generate extra copies and increase memory consumption\n warnings.warn(\n"
],
[
"#sns.lineplot(X.flatten(), np.arange(X.shape[0]))\npred = pipe.predict(X, start_idx=0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pred.flatten()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = pd.DataFrame({\n 'actual': y_transformed[1100:1120],\n 'predicted': pred.flatten()[1100:1120]\n})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sns.lineplot(data=df).plot()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4abd6a5e19df54a0d1b2ad7e560a87d407b561bb
| 31,694 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
workshop/3-Experimentation/3.3-Interleaving-Experiment.ipynb
|
xtrim-serverless/retail-demo-store
|
5746a25983821ab45430b28ea023fb350ff7c528
|
[
"MIT-0"
] | null | null | null |
workshop/3-Experimentation/3.3-Interleaving-Experiment.ipynb
|
xtrim-serverless/retail-demo-store
|
5746a25983821ab45430b28ea023fb350ff7c528
|
[
"MIT-0"
] | null | null | null |
workshop/3-Experimentation/3.3-Interleaving-Experiment.ipynb
|
xtrim-serverless/retail-demo-store
|
5746a25983821ab45430b28ea023fb350ff7c528
|
[
"MIT-0"
] | null | null | null | 43.179837 | 939 | 0.639395 |
[
[
[
"# Retail Demo Store Experimentation Workshop - Interleaving Recommendation Exercise\n\nIn this exercise we will define, launch, and evaluate the results of an experiment using recommendation interleaving using the experimentation framework implemented in the Retail Demo Store project. If you have not already stepped through the **[3.1-Overview](./3.1-Overview.ipynb)** workshop notebook, please do so now as it provides the foundation built upon in this exercise. It is also recommended, but not required, to complete the **[3.2-AB-Experiment](./3.2-AB-Experiment.ipynb)** workshop notebook.\n\nRecommended Time: 30 minutes\n\n## Prerequisites\n\nSince this module uses the Retail Demo Store's Recommendation microservice to run experiments across variations that depend on the personalization features of the Retail Demo Store, it is assumed that you have either completed the [Personalization](../1-Personalization/Lab-1-Introduction-and-data-preparation.ipynb) workshop or those resources have been pre-provisioned in your AWS environment. If you are unsure and attending an AWS managed event such as a workshop, check with your event lead.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Exercise 2: Interleaving Recommendations Experiment\n\nFor the first exercise, **[3.2-AB-Experiment](./3.2-AB-Experiment.ipynb)**, we demonstrated how to create and run an A/B experiment using two different variations for making product recommendations. We calculated the sample sizes of users needed to reach a statistically significant result comparing the two variations. Then we ran the experiment using a simulation until the sample sizes were reached for both variations. In real-life, depending on the baseline and minimum detectable effect rate combined with your site's user traffic, the amount of time necessary to complete an experiment can take several days to a few weeks. This can be expensive from both an opportunity cost perspective as well as negatively impacting the pace at which experiments and changes can be rolled out to your site.\n\nIn this exercise we will look at an alternative approach to evaluating product recommendation variations that requires a smaller sample size and shorter experiment durations. This technique is often used as a preliminary step before formal A/B testing to reduce a larger number of variations to just the top performers. Traditional A/B testing is then done against the best performing variations, significantly reducing the overall time necessary for experimentation.\n\nWe will use the same two variations as the last exercise. The first variation will represent our current implementation using the [**Default Product Resolver**](https://github.com/aws-samples/retail-demo-store/blob/master/src/recommendations/src/recommendations-service/experimentation/resolvers.py) and the second variation will use the [**Personalize Recommendation Resolver**](https://github.com/aws-samples/retail-demo-store/blob/master/src/recommendations/src/recommendations-service/experimentation/resolvers.py). The scenario we are simulating is adding product recommendations powered by Amazon Personalize to the home page and measuring the impact/uplift in click-throughs for products as a result of deploying a personalization strategy. We will use the same hypothesis from our A/B test where the conversion rate of our existing approach is 15% and we expect a 25% lift in this rate by adding personalized recommendations.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### What is Interleaving Recommendation Testing?\n\nThe approach of interleaving recommendations is to take the recommendations from two or more variations and interleave, or blend, them into a single set of recommendations for *every user in the experiment*. Because each user in the sample is exposed to recommendations from all variations, we gain some key benefits. First, the sample size can be smaller since we don't need separate groups of users for each variation. This also results in a shorter experiment duration. Additionally, this approach is less susceptible to variances in user type and behavior that could throw off the results of an experiment. For example, it's not uncommon to have power users who shop/watch/listen/read much more than a typical user. With multiple sample groups, the behavior of these users can throw off results for their group, particularly with smaller sample sizes.\n\nCare must be taken in how recommendations are interleaved, though, to account for position bias in the recommendations and to track variation attribution. There are two common methods to interleaving recommendations. First is a balanced approach where recommendations are taken from each variation in an alternating style where the starting variation is selected randomly. The other approach follows the team-draft analogy where team captains select their \"best player\" (recommendation) from the variations in random selection order. Both methods can result in different interleaving outputs.\n\nInterleaving recommendations as an approach to experimenation got its start with information retrieval systems and search engines (Yahoo! & Bing) where different approaches to ranking results could be measured concurrently. More recently, [Netflix has adopted the interleaving technique](https://medium.com/netflix-techblog/interleaving-in-online-experiments-at-netflix-a04ee392ec55) to rapidly evaluate different approaches to making movie recommendations to its users. The image below depicts the recommendations from two different recommenders/variations (Ranker A and Ranker B) and examples of how they are interleaved.\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### InterleavingExperiment Class\n\nBefore stepping through creating and executing our interleaving test, let's look at the relevant source code for the [**InterleavingExperiment**](https://github.com/aws-samples/retail-demo-store/blob/master/src/recommendations/src/recommendations-service/experimentation/experiment_interleaving.py) class that implements this experiment type in the Retail Demo Store project.\n\nAs noted in the **[3.1-Overview](./3.1-Overview.ipynb)** notebook, all experiment types are subclasses of the abstract **Experiment** class. See **[3.1-Overview](./3.1-Overview.ipynb)** for more details on the experimentation framework.\n\nThe `InterleavingExperiment.get_items()` method is where item recommendations are retrieved for the experiment. This method will retrieve recommendations from the resolvers for all variations and then use the configured interleaving method (balanced or team-draft) to interleave the recommendations to produce the final result. Exposure tracking is also implemented to facilitate measuring the outcome of an experiment. The implementations for the balanced and team-draft interleaving methods are not included below but are available in the source code for the Recommendations service.\n\n```python\n# from src/recommendations/src/recommendations-service/experimentation/experiment_interleaving.py\n\nclass InterleavingExperiment(Experiment):\n \"\"\" Implements interleaving technique described in research paper by \n Chapelle et al http://olivier.chapelle.cc/pub/interleaving.pdf\n \"\"\"\n METHOD_BALANCED = 'balanced'\n METHOD_TEAM_DRAFT = 'team-draft'\n\n def __init__(self, table, **data):\n super(InterleavingExperiment, self).__init__(table, **data)\n self.method = data.get('method', InterleavingExperiment.METHOD_BALANCED)\n\n def get_items(self, user_id, current_item_id = None, item_list = None, num_results = 10, tracker = None):\n ...\n \n # Initialize array structure to hold item recommendations for each variation\n variations_data = [[] for x in range(len(self.variations))]\n\n # Get recomended items for each variation\n for i in range(len(self.variations)):\n resolve_params = {\n 'user_id': user_id,\n 'product_id': current_item_id,\n 'product_list': item_list,\n 'num_results': num_results * 3 # account for overlaps\n }\n variation = self.variations[i]\n items = variation.resolver.get_items(**resolve_params)\n variations_data[i] = items\n\n # Interleave items to produce result\n interleaved = []\n if self.method == InterleavingExperiment.METHOD_TEAM_DRAFT:\n interleaved = self._interleave_team_draft(user_id, variations_data, num_results)\n else:\n interleaved = self._interleave_balanced(user_id, variations_data, num_results)\n\n # Increment exposure for each variation (can be optimized)\n for i in range(len(self.variations)):\n self._increment_exposure_count(i)\n\n ...\n\n return interleaved\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Setup - Import Dependencies\n\nThrougout this workshop we will need access to some common libraries and clients for connecting to AWS services. Let's set those up now.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import boto3\nimport json\nimport uuid\nimport numpy as np\nimport requests\nimport pandas as pd\nimport random\nimport scipy.stats as scs\nimport time\nimport decimal\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\nfrom boto3.dynamodb.conditions import Key\nfrom random import randint\n\n# import custom scripts for plotting results\nfrom src.plot import *\nfrom src.stats import *\n\n%matplotlib inline\nplt.style.use('ggplot')\n\n# We will be using a DynamoDB table to store configuration info for our experiments.\ndynamodb = boto3.resource('dynamodb')\n\n# Service discovery will allow us to dynamically discover Retail Demo Store resources\nservicediscovery = boto3.client('servicediscovery')\n# Retail Demo Store config parameters are stored in SSM\nssm = boto3.client('ssm')\n\n# Utility class to convert types for printing as JSON.\nclass CompatEncoder(json.JSONEncoder):\n def default(self, obj):\n if isinstance(obj, decimal.Decimal):\n if obj % 1 > 0:\n return float(obj)\n else:\n return int(obj)\n else:\n return super(CompatEncoder, self).default(obj)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Experiment Strategy Datastore\n\nLet's create an experiment using the interleaving technique.\n\nA DynamoDB table was created by the Retail Demo Store CloudFormation template that we will use to store the configuration information for our experiments. The table name can be found in a system parameter.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"response = ssm.get_parameter(Name='retaildemostore-experiment-strategy-table-name')\n\ntable_name = response['Parameter']['Value'] # Do Not Change\nprint('Experiments DDB table: ' + table_name)\ntable = dynamodb.Table(table_name)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Next we need to lookup the Amazon Personalize campaign ARN for product recommendations. This is the campaign that was created in the Personalization workshop.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"response = ssm.get_parameter(Name = '/retaildemostore/personalize/recommended-for-you-arn')\n\ncampaign_arn = response['Parameter']['Value'] # Do Not Change\nprint('Personalize product recommendations ARN: ' + campaign_arn)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Create Interleaving Experiment\n\nThe Retail Demo Store supports running multiple experiments concurrently. For this workshop we will create a single interleaving test/experiment that will expose users of a single group to recommendations from the default behavior and recommendations from Amazon Personalize. The [Recommendations](https://github.com/aws-samples/retail-demo-store/tree/master/src/recommendations) microservice already has logic that supports interleaving experiments when an active experiment is detected.\n\nExperiment configurations are stored in a DynamoDB table where each item in the table represents an experiment and has the following fields.\n\n- **id** - Uniquely identified this experience (UUID).\n- **feature** - Identifies the Retail Demo Store feature where the experiment should be applied. The name for the home page product recommendations feature is `home_product_recs`.\n- **name** - The name of the experiment. Keep the name short but descriptive. It will be used in the UI for demo purposes and when logging events for experiment result tracking.\n- **status** - The status of the experiment (`ACTIVE`, `EXPIRED`, or `PENDING`).\n- **type** - The type of test (`ab` for an A/B test, `interleaving` for interleaved recommendations, or `mab` for multi-armed bandit test)\n- **method** - The interleaving method (`balanced` or `team-draft`)\n- **variations** - List of configurations representing variations for the experiment. For example, for interleaving tests of the `home_product_recs` feature, the `variations` can be two Amazon Personalize campaign ARNs (variation type `personalize-recommendations`) or a single Personalize campaign ARN and the default product behavior.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"feature = 'home_product_recs'\nexperiment_name = 'home_personalize_interleaving'\n\n# First, make sure there are no other active experiments so we can isolate\n# this experiment for the exercise.\nresponse = table.scan(\n ProjectionExpression='#k', \n ExpressionAttributeNames={'#k' : 'id'},\n FilterExpression=Key('status').eq('ACTIVE')\n)\nfor item in response['Items']:\n response = table.update_item(\n Key=item,\n UpdateExpression='SET #s = :inactive',\n ExpressionAttributeNames={\n '#s' : 'status'\n },\n ExpressionAttributeValues={\n ':inactive' : 'INACTIVE'\n }\n )\n\n# Query the experiment strategy table to see if our experiment already exists\nresponse = table.query(\n IndexName='feature-name-index',\n KeyConditionExpression=Key('feature').eq(feature) & Key('name').eq(experiment_name),\n FilterExpression=Key('status').eq('ACTIVE')\n)\n\nif response.get('Items') and len(response.get('Items')) > 0:\n print('Experiment already exists')\n home_page_experiment = response['Items'][0]\nelse:\n print('Creating experiment')\n \n # Default product resolver\n variation_0 = {\n 'type': 'product'\n }\n \n # Amazon Personalize resolver\n variation_1 = {\n 'type': 'personalize-recommendations',\n 'campaign_arn': campaign_arn\n }\n\n home_page_experiment = { \n 'id': uuid.uuid4().hex,\n 'feature': feature,\n 'name': experiment_name,\n 'status': 'ACTIVE',\n 'type': 'interleaving',\n 'method': 'team-draft',\n 'analytics': {},\n 'variations': [ variation_0, variation_1 ]\n }\n \n response = table.put_item(\n Item=home_page_experiment\n )\n\n print(json.dumps(response, indent=4))\n \nprint(json.dumps(home_page_experiment, indent=4, cls=CompatEncoder))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Load Users\n\nFor our experiment simulation, we will load all Retail Demo Store users and run the experiment until the sample size has been met.\n\nFirst, let's discover the IP address for the Retail Demo Store's [Users](https://github.com/aws-samples/retail-demo-store/tree/master/src/users) service.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"response = servicediscovery.discover_instances(\n NamespaceName='retaildemostore.local',\n ServiceName='users',\n MaxResults=1,\n HealthStatus='HEALTHY'\n)\n\nusers_service_instance = response['Instances'][0]['Attributes']['AWS_INSTANCE_IPV4']\nprint('Users Service Instance IP: {}'.format(users_service_instance))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Next, let's load all users into a local data frame.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Load all users so we have enough to satisfy our sample size requirements.\nresponse = requests.get('http://{}/users/all?count=10000'.format(users_service_instance))\nusers = response.json()\nusers_df = pd.DataFrame(users)\npd.set_option('display.max_rows', 5)\n\nusers_df",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Discover Recommendations Service\n\nNext, let's discover the IP address for the Retail Demo Store's [Recommendations](https://github.com/aws-samples/retail-demo-store/tree/master/src/recommendations) service.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"response = servicediscovery.discover_instances(\n NamespaceName='retaildemostore.local',\n ServiceName='recommendations',\n MaxResults=1,\n HealthStatus='HEALTHY'\n)\n\nrecommendations_service_instance = response['Instances'][0]['Attributes']['AWS_INSTANCE_IPV4']\nprint('Recommendation Service Instance IP: {}'.format(recommendations_service_instance))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Simulate Experiment\n\nNext we will simulate our interleaving recommendation experiment by making calls to the [Recommendations](https://github.com/aws-samples/retail-demo-store/tree/master/src/recommendations) service across the users we just loaded.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Simulation Function\n\nThe following `simulate_experiment` function is supplied with the number of trials we want to run and the probability of conversion for each variation for our simulation. It runs the simulation long enough to satisfy the number of trials and calls the Recommendations service for each trial in the experiment.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def simulate_experiment(n_trials, probs):\n \"\"\"Simulates experiment based on pre-determined probabilities\n\n Example:\n\n Parameters:\n n_trials (int): number of trials to run for experiment\n probs (array float): array of floats containing probability/conversion \n rate for each variation\n\n Returns:\n df (df) - data frame of simulation data/results\n \"\"\"\n\n # will hold exposure/outcome data\n data = []\n\n print('Simulating experiment for {} users... this may take a few minutes'.format(n_trials))\n\n for idx in range(n_trials):\n if idx > 0 and idx % 500 == 0:\n print('Simulated experiment for {} users so far'.format(idx))\n \n row = {}\n\n # Get random user\n user = users[randint(0, len(users)-1)]\n\n # Call Recommendations web service to get recommendations for the user\n response = requests.get('http://{}/recommendations?userID={}&feature={}'.format(recommendations_service_instance, user['id'], feature))\n\n recommendations = response.json()\n recommendation = recommendations[randint(0, len(recommendations)-1)]\n \n variation = recommendation['experiment']['variationIndex']\n row['variation'] = variation\n \n # Conversion based on probability of variation\n row['converted'] = np.random.binomial(1, p=probs[variation])\n\n if row['converted'] == 1:\n # Update experiment with outcome/conversion\n correlation_id = recommendation['experiment']['correlationId']\n requests.post('http://{}/experiment/outcome'.format(recommendations_service_instance), data={'correlationId':correlation_id})\n \n data.append(row)\n \n # convert data into pandas dataframe\n df = pd.DataFrame(data)\n \n print('Done')\n\n return df",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Run Simulation\n\nNext we run the simulation by defining our simulation parameters for the number of trials and probabilities and then call `simulate_experiment`. This will take a few minutes to run.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%time\n\n# Number of trials to run\nN = 2000\n\n# bcr: baseline conversion rate\np_A = 0.15\n# d_hat: difference in a metric between the two groups, sometimes referred to as minimal detectable effect or lift depending on the context\np_B = 0.1875\n\nab_data = simulate_experiment(N, [p_A, p_B])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ab_data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Inspect Experiment Summary Statistics\n\nSince the **Experiment** class updates statistics on the experiment in the experiment strategy table when a user is exposed to an experiment (\"exposure\") and when a user converts (\"outcome\"), we should see updated counts on our experiment. Let's reload our experiment and inspect the exposure and conversion counts for our simulation.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"response = table.get_item(Key={'id': home_page_experiment['id']})\n\nprint(json.dumps(response['Item'], indent=4, cls=CompatEncoder))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Note the `conversions` and `exposures` counts for each variation above. These counts were incremented by the experiment class each time a trial was run (exposure) and a user converted in the `simulate_experiment` function above.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Analyze Simulation Results\n\nTo wrap up, let's analyze some of the results from our simulated interleaving experiment by inspecting the actual conversion rate and verifying our target confidence interval and power.\n\nFirst, let's take a closer look at the results of our simulation. We'll start by calculating some summary statistics.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"ab_summary = ab_data.pivot_table(values='converted', index='variation', aggfunc=np.sum)\n# add additional columns to the pivot table\nab_summary['total'] = ab_data.pivot_table(values='converted', index='variation', aggfunc=lambda x: len(x))\nab_summary['rate'] = ab_data.pivot_table(values='converted', index='variation')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ab_summary",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Next let's isolate data for each variation.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"A_group = ab_data[ab_data['variation'] == 0]\nB_group = ab_data[ab_data['variation'] == 1]\nA_converted, B_converted = A_group['converted'].sum(), B_group['converted'].sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"A_converted, B_converted",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Determine the actual sample size for each variation.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"A_total, B_total = len(A_group), len(B_group)\nA_total, B_total",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Calculate the actual conversion rates and uplift from our simulation.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"p_A, p_B = A_converted / A_total, B_converted / B_total\np_A, p_B",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"p_B - p_A",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Determining Statistical Significance\n\nFor simplicity we will use the same approach as our A/B test to determine statistical significance. \n\nLet's plot the data from both groups as binomial distributions.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12,6))\nxA = np.linspace(A_converted-49, A_converted+50, 100)\nyA = scs.binom(A_total, p_A).pmf(xA)\nax.scatter(xA, yA, s=10)\nxB = np.linspace(B_converted-49, B_converted+50, 100)\nyB = scs.binom(B_total, p_B).pmf(xB)\nax.scatter(xB, yB, s=10)\nplt.xlabel('converted')\nplt.ylabel('probability')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Based the probabilities from our hypothesis, we should see that the test group in blue (B) converted more users than the control group in red (A). However, the plot above is not a plot of the null and alternate hypothesis. The null hypothesis is a plot of the difference between the probability of the two groups.\n\n> Given the randomness of our user selection, group hashing, and probabilities, your simulation results should be different for each simulation run and therefore may or may not be statistically significant.\n\nIn order to calculate the difference between the two groups, we need to standardize the data. Because the number of samples can be different between the two groups, we should compare the probability of successes, p.\n\nAccording to the central limit theorem, by calculating many sample means we can approximate the true mean of the population from which the data for the control group was taken. The distribution of the sample means will be normally distributed around the true mean with a standard deviation equal to the standard error of the mean.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"SE_A = np.sqrt(p_A * (1-p_A)) / np.sqrt(A_total)\nSE_B = np.sqrt(p_B * (1-p_B)) / np.sqrt(B_total)\nSE_A, SE_B",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12,6))\nxA = np.linspace(0, .3, A_total)\nyA = scs.norm(p_A, SE_A).pdf(xA)\nax.plot(xA, yA)\nax.axvline(x=p_A, c='red', alpha=0.5, linestyle='--')\n\nxB = np.linspace(0, .3, B_total)\nyB = scs.norm(p_B, SE_B).pdf(xB)\nax.plot(xB, yB)\nax.axvline(x=p_B, c='blue', alpha=0.5, linestyle='--')\n\nplt.xlabel('Converted Proportion')\nplt.ylabel('PDF')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Next Steps\n\nYou have completed the exercise for implementing an A/B test using the experimentation framework in the Retail Demo Store. Close this notebook and open the notebook for the next exercise, **[3.4-Multi-Armed-Bandit-Experiment](./3.4-Multi-Armed-Bandit-Experiment.ipynb)**.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### References and Further Reading\n\n- [Large Scale Validation and Analysis of Interleaved Search Evaluation](http://olivier.chapelle.cc/pub/interleaving.pdf), Chapelle et al\n- [Innovating Faster on Personalization Algorithms at Netflix Using Interleaving](https://medium.com/netflix-techblog/interleaving-in-online-experiments-at-netflix-a04ee392ec55), Netflix Technology Blog",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4abd6e1c5b52820b00c1e83e2a9b8bc84aa5257d
| 154,631 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Pymaceuticals/pymaceuticals_starter.ipynb
|
kb4dive/matplotlib-challenge
|
8c1ede86e84b3a9137c06de83fd07462087318b1
|
[
"ADSL"
] | null | null | null |
Pymaceuticals/pymaceuticals_starter.ipynb
|
kb4dive/matplotlib-challenge
|
8c1ede86e84b3a9137c06de83fd07462087318b1
|
[
"ADSL"
] | null | null | null |
Pymaceuticals/pymaceuticals_starter.ipynb
|
kb4dive/matplotlib-challenge
|
8c1ede86e84b3a9137c06de83fd07462087318b1
|
[
"ADSL"
] | null | null | null | 101.864954 | 33,340 | 0.791316 |
[
[
[
"# Dependencies and Setup\n%matplotlib inline\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\n\n# Hide warning messages in notebook\nimport warnings\nwarnings.filterwarnings('ignore')\n\n# File to Load (Remember to Change These)\nmouse_drug_data_to_load = \"data/mouse_drug_data.csv\"\nclinical_trial_data_to_load = \"data/clinicaltrial_data.csv\"\n\n# Read the Mouse and Drug Data and the Clinical Trial Data\nmouse_data = pd.read_csv(mouse_drug_data_to_load)\nclinical_data = pd.read_csv(clinical_trial_data_to_load)\n\n# Combine the data into a single dataset\ndatamerge = mouse_data.merge(clinical_data, on=\"Mouse ID\", how=\"left\")\n\n# Display the data table for preview\ndatamerge.head()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#summary stats\ndatamerge.describe()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Tumor Response to Treatment",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Store the Mean Tumor Volume Data Grouped by Drug and Timepoint \n\n\ntumor_response = datamerge.groupby(['Drug','Timepoint']).mean()['Tumor Volume (mm3)'] \n\n# Convert to DataFrame\ndf_tumor_response = (pd.DataFrame(data = tumor_response)).reset_index()\n\n# Preview DataFrame\ndf_tumor_response.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Store the Standard Error of Tumor Volumes Grouped by Drug and Timepoint\nstandard_error = datamerge.groupby(['Drug','Timepoint']).sem()['Tumor Volume (mm3)'] \n\n# Convert to DataFrame\ndf_standard_error = (pd.DataFrame(standard_error)).reset_index()\n\n# Preview DataFrame\ndf_standard_error.head()\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Minor Data Munging to Re-Format the Data Frames\ndf_tumor_pvt = df_tumor_response.pivot(index='Timepoint', columns='Drug')['Tumor Volume (mm3)']\ndf_stderr_pvt = df_standard_error.pivot(index='Timepoint', columns='Drug')['Tumor Volume (mm3)']\n\n\n# Preview that Reformatting worked\ndf_tumor_pvt\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Create list of drugs to chart\ndrug_list = [('Capomulin','o','red', 'Capomulin'),('Infubinol','^','blue', 'Infubinol'),\n ('Ketapril','s','green', 'Ketapril'),('Placebo','d','black', 'Placebo')]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#loop through drug list to plot\nfor drug,marker,colors, label in drug_list:\n stderr = df_stderr_pvt[drug]\n tumor_plt = plt.errorbar(df_tumor_pvt.index,df_tumor_pvt[drug],stderr,\n fmt=marker,ls='--',color=colors,linewidth=0.5, label = label)\nplt.legend(loc='best')\nplt.title('Tumor Response to Treatment')\nplt.xlabel('Time (Days)')\nplt.ylabel('Tumor Volume (mm3)')\nplt.grid()\nplt.show()\n\n# Save the Figure\nplt.savefig('Response_to_Treatment.png')\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Metastatic Response to Treatment",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Store the Mean Met. Site Data Grouped by Drug and Timepoint \nmetastic_site_mean = datamerge.groupby(['Drug','Timepoint']).mean()['Metastatic Sites']\n# Convert to DataFrame\ndf_metastic_site_mean = (pd.DataFrame(data = metastic_site_mean)).reset_index()\n\n# Preview DataFrame\ndf_metastic_site_mean.head()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Store the Standard Error associated with Met. Sites Grouped by Drug and Timepoint \nmetastic_site_sem = datamerge.groupby(['Drug','Timepoint']).sem()['Metastatic Sites']\n\n# Convert to DataFrame\ndf_metastic_site_sem = (pd.DataFrame(data = metastic_site_sem)).reset_index()\n\n# Preview DataFrame\ndf_metastic_site_sem.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Minor Data Munging to Re-Format the Data Frames\ndf_metastic_mean_pvt = df_metastic_site_mean.pivot(index='Timepoint', columns='Drug')['Metastatic Sites']\ndf_metastic_sem_pvt = df_metastic_site_sem.pivot(index='Timepoint', columns='Drug')['Metastatic Sites']\n\n# Preview that Reformatting worked\ndf_metastic_mean_pvt.head()\n#df_metastic_sem_pvt.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for drug,marker,colors, label in drug_list:\n metaerr = df_metastic_sem_pvt[drug]\n metastatic_plt = plt.errorbar(df_metastic_mean_pvt.index,df_metastic_mean_pvt[drug],metaerr,\n fmt=marker,ls='--',color=colors,linewidth=0.5, label = label)\n \nplt.legend(loc = 'best')\nplt.title('Metastatic Spread During Treatment')\nplt.xlabel('Treatment Duration(Days)')\nplt.ylabel('Metastatic Sites')\nx_lim = len(df_metastic_mean_pvt.index)\nplt.grid()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Survival Rates",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Store the Count of Mice Grouped by Drug and Timepoint (W can pass any metric)\nmice_count_grp = datamerge.groupby(['Drug', 'Timepoint'])['Mouse ID']\nmice_count = mice_count_grp.nunique()\n\n# Convert to DataFrame\ndf_mice_count = (pd.DataFrame(data = mice_count)).reset_index()\ndf_mice_count = df_mice_count.rename(columns={'Mouse ID':'Mouse Count'})\n\n# Preview DataFrame\ndf_mice_count.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Minor Data Munging to Re-Format the Data Frames\ndf_mice_count_pvt = df_mice_count.pivot(index='Timepoint', columns='Drug')['Mouse Count']\n\n# Preview the Data Frame\ndf_mice_count_pvt.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Generate the Plot (Accounting for percentages)\nfor drug,marker,colors, label in drug_list:\n micetotal = df_mice_count_pvt[drug][0]\n Survival_plt = plt.plot(df_mice_count_pvt.index,df_mice_count_pvt[drug]/micetotal * 100,\n color = colors, marker=marker, markersize = 5, ls='--',linewidth=0.5, label = label)\n\n \nplt.legend(loc = 'best')\nplt.title('Survival During Treatment')\nplt.xlabel('Treatment Duration(Days)')\nplt.ylabel('Survival Rate(%)')\n\nplt.grid()\nplt.show()\n\n# Save the Figure\nplt.savefig('Survival During Treatment.png')\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Summary Bar Graph",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Calculate the percent changes for each drug\npercent_change = (df_tumor_pvt.iloc[-1]/(df_tumor_pvt.iloc[0])-1)*100\n\n# Display the data to confirm\npercent_change",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Store all Relevant Percent Changes into a Tuple\ndrug_list = ['Capomulin','Infubinol','Ketapril','Placebo']\n\n# Splice the data between passing and failing drugs\npassing = percent_change < 0\n\n# Orient widths. Add labels, tick marks, etc. \nchange_list = [(percent_change[drug]) for drug in drug_list]\nchange_plt = plt.bar(drug_list, change_list, width = -1, align = 'edge', color = passing.map({True:'g', False:'r'}))\nplt.grid()\nplt.ylim(-30,70)\nplt.ylabel('% Tumor Volume Change')\nplt.title('Tumor Change over 45 Day Treatment')\n\n# Use functions to label the percentages of changes\ndef label (changes):\n for change in changes:\n height = change.get_height()\n if height > 0:\n label_position = 2\n else:\n label_position = -8\n plt.text(change.get_x() + change.get_width()/2., label_position,\n '%d' % int(height)+'%',color='white',\n ha='center', va='bottom')\n\n# Call functions to implement the function calls\nlabel(change_plt)\n\n# Save the Figure\nplt.savefig('Tumor Change over Treatment.png')\n\n# Show the Figure\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Observations\nCapomulin seems to be most effective\n1. Tumor Volume decreased over treatment period whereas there was an increase with the other drugs.\n2. Metastatic sites had a lower increase rate from the other drugs.\n3. Tumor change over a 45 day treatment was positive (decrease).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4abd788a1848c61ba42b872ae26e6012a273003c
| 7,926 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Recipes/SBPLAT/projects_listAll.ipynb
|
sbg/okAPI
|
4dbf9e917e2a53241fc2a58ddb51ccc9a990b348
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | 23 |
2016-04-03T13:44:35.000Z
|
2020-11-19T13:18:33.000Z
|
Recipes/SBPLAT/projects_listAll.ipynb
|
sbg/okAPI
|
4dbf9e917e2a53241fc2a58ddb51ccc9a990b348
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | 8 |
2016-07-06T21:42:35.000Z
|
2022-03-05T01:06:32.000Z
|
Recipes/SBPLAT/projects_listAll.ipynb
|
sbg/okAPI
|
4dbf9e917e2a53241fc2a58ddb51ccc9a990b348
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | 17 |
2016-03-23T12:36:24.000Z
|
2021-10-30T17:35:21.000Z
| 30.602317 | 248 | 0.59677 |
[
[
[
"# What _projects_ am I a member of?\n### Overview\nThere are a number of API calls related to projects. Here we focus on listing projects. As with any **list**-type call, we will get minimal information about each project. There are two versions of this call:\n\n 1. (default) **paginated** call that will return 50 projects\n 2. **all-records** call that will page through and return all projects \n\n### Prerequisites\n 1. You need to be a member (or owner) of _at least one_ project.\n 2. You need your _authentication token_ and the API needs to know about it. See <a href=\"Setup_API_environment.ipynb\">**Setup_API_environment.ipynb**</a> for details.\n \n## Imports\nWe import the _Api_ class from the official sevenbridges-python bindings below.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import sevenbridges as sbg",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Initialize the object\nThe `Api` object needs to know your **auth\\_token** and the correct path. Here we assume you are using the credentials file in your home directory. For other options see <a href=\"Setup_API_environment.ipynb\">Setup_API_environment.ipynb</a>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# [USER INPUT] specify credentials file profile {cgc, sbg, default}\nprof = 'default'\n\nconfig_file = sbg.Config(profile=prof)\napi = sbg.Api(config=config_file)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Get _some_ projects\nWe will start with the basic list call. A **list**-call for projects returns the following *attributes*:\n* **id** _Unique_ identifier for the project, generated based on Project Name\n* **name** Name of project specified by the user, maybe _non-unique_\n* **href** Address<sup>1</sup> of the project.\n\nA **detail**-call for projects returns the following *attributes*:\n* **description** The user specified project description\n* **id** _Unique_ identifier for the project, generated based on Project Name\n* **name** Name of project specified by the user, maybe _non-unique_\n* **href** Address<sup>1</sup> of the project.\n* **tags** List of tags\n* **created_on** Project creation time\n* **modified_on** Project modification time\n* **created_by** User that created the project\n* **root_folder** ID of the root folder for that project\n* **billing_group** ID of the billing group for the project\n* **settings** Dictionary with project settings for storage and task execution\n\nAll list API calls will feature pagination, by _default_ 50 items will be returned. We will also show how to specify a different limit and page forward and backwards. \n\n<sup>1</sup> This is the address where, by using API you can get this resource",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# list (up to) 50 (this is the default for 'limit') projects\nmy_projects = api.projects.query()\n\nprint(' List of project ids and names:')\nfor project in my_projects:\n print('{} \\t {}'.format(project.id, project.name))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# use a short query to highlight pagination\nmy_projects = api.projects.query(limit=3)\n\nprint(' List of first 3 project ids and names:')\nfor project in my_projects:\n print('{} \\t {}'.format(project.id, project.name))\n \n# method to retrieve the next page of results\nnext_page_of_projects = my_projects.next_page()\n\nprint('\\n List of next 3 project ids and names:')\nfor project in next_page_of_projects:\n print('{} \\t {}'.format(project.id, project.name))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Note\nFor the pagination above, we used the **.next_page()** and could have also used the **.prior_page()** methods. These will return another list with an limit equal to the prior call and a offset based on the prior call",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Get _all_ projects\nIt's probably most useful to know all of your projects. Regardless of the query limit, the project object knows the actual total number of projects. We only need to use the **.all** attribute to get all projects.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"existing_projects = my_projects.all()\n\nprint(' List of all project ids and names:')\nfor project in existing_projects:\n print('{} \\t {}'.format(project.id, project.name))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Note\nEach time you do **anything** with this _generator object_, it will become exhausted. The next call will be an empty list",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# NOTE, after each time you operate on the existing_projects generator object, \n# it will become an empty list\n\nexisting_projects = my_projects.all()\nprint(existing_projects)\nprint('\\n For the first list() operation, there are %i projects in the generator' \\\n % (len(list(existing_projects))))\nprint(' For the next list() operation, there are %i projects in the generator' % \\\n (len(list(existing_projects))))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Additional Information\nDetailed documentation of this particular REST architectural style request is available [here](http://docs.sevenbridges.com/docs/list-all-your-projects)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4abd805948eaf7534ce8894f232bebd70e123ba8
| 12,211 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
dementia_optima/preprocessing/dataAnalysis_and_preparation.ipynb
|
SDM-TIB/dementia_mmse
|
bf22947aa06350edd454794eb2b926f082d2dcf2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
dementia_optima/preprocessing/dataAnalysis_and_preparation.ipynb
|
SDM-TIB/dementia_mmse
|
bf22947aa06350edd454794eb2b926f082d2dcf2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
dementia_optima/preprocessing/dataAnalysis_and_preparation.ipynb
|
SDM-TIB/dementia_mmse
|
bf22947aa06350edd454794eb2b926f082d2dcf2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 33.182065 | 245 | 0.605929 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport pickle\n\npd.set_option('display.max_columns', None) \npd.set_option('display.max_rows', None)\npd.set_option('display.max_colwidth', -1)\n\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Remove unrelated columns form data and get their name\n\nfolder_path = '../../../datalcdem/data/optima/dementia_18July/'\n\npatient_df = pd.read_csv(folder_path + 'optima_patients.csv')\ndisplay(patient_df.head(5))\n\n#patient_df[['MMS1', 'MMS2']].hist()\n\npatient_com_df = pd.read_csv(folder_path + 'optima_patients_comorbidities.csv').groupby(by=['patient_id', 'EPISODE_DATE'], as_index=False).agg(lambda x: x.tolist())[['patient_id', 'EPISODE_DATE', 'Comorbidity_cui']]\ndisplay(patient_com_df.head(10))\n\npatient_filt_df = pd.read_csv(folder_path + 'optima_patients_filtered.csv')\n#display(patient_filt_df.head(5))\n\n\npatient_treat_df = pd.read_csv(folder_path + 'optima_patients_treatments.csv').groupby(by=['patient_id', 'EPISODE_DATE'], as_index=False).agg(lambda x: x.tolist())[['patient_id', 'EPISODE_DATE', 'Medication_cui']]\ndisplay(patient_treat_df.head(5))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(set(patient_com_df['patient_id'].tolist())), len(set(patient_treat_df['patient_id'].tolist()))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"patient_treat_df['EPISODE_DATE'] = pd.to_datetime(patient_treat_df['EPISODE_DATE'])\npatient_com_df['EPISODE_DATE'] = pd.to_datetime(patient_com_df['EPISODE_DATE'])\n\npatient_com_treat_df = pd.merge(patient_com_df, patient_treat_df,on=['patient_id', 'EPISODE_DATE'], how='outer')\n#pd.concat([patient_com_df, patient_treat_df], keys=['patient_id', 'EPISODE_DATE'], ignore_index=True, sort=False) #patient_com_df.append(patient_treat_df, sort=False) #pd.concat([patient_com_df, patient_treat_df], axis=0, sort=False)\n#patient_treat_com_df = patient_treat_df.join(patient_com_df, on=['patient_id', 'EPISODE_DATE'], how='outer')\nprint (patient_com_treat_df.shape)\nprint (len(set(patient_com_treat_df['patient_id'].tolist())))\npatient_com_treat_df.sort_values(by=['patient_id', 'EPISODE_DATE'],axis=0, inplace=True, ascending=True)\npatient_com_treat_df.reset_index(drop=True, inplace=True)\npatient_com_treat_df.head(10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"patient_com_treat_df.to_csv('../../../datalcdem/data/optima/optima_ahmad/patient_com_treat_df.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"folder_path = '../../../datalcdem/data/optima/dementia_18July/'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_datarequest = pd.read_excel(folder_path+'Data_Request_Jan_2019_final.xlsx')\ndf_datarequest.head(5)\ndf_datarequest_mmse = df_datarequest[['GLOBAL_PATIENT_DB_ID', 'Age At Episode', 'EPISODE_DATE', 'CAMDEX SCORES: MINI MENTAL SCORE']]\ndf_datarequest_mmse_1 = df_datarequest_mmse.rename(columns={'GLOBAL_PATIENT_DB_ID':'patient_id'})\ndf_datarequest_mmse_1.head(10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#patient_com_treat_df.astype('datetime')\npatient_com_treat_df['EPISODE_DATE'] = pd.to_datetime(patient_com_treat_df['EPISODE_DATE'])\nprint (df_datarequest_mmse_1.dtypes, patient_com_treat_df.dtypes)\npatient_com_treat_df = pd.merge(patient_com_treat_df,df_datarequest_mmse_1,on=['patient_id', 'EPISODE_DATE'], how='left')\npatient_com_treat_df.shape, patient_com_treat_df.head(10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(set (patient_com_treat_df['patient_id'].tolist()))\npatient_com_treat_df.sort_values(by=['patient_id', 'EPISODE_DATE'],axis=0, inplace=True, ascending=True)\npatient_com_treat_df.head(20)\npatient_com_treat_df.reset_index(inplace=True, drop=True)\npatient_com_treat_df.head(5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def setLineNumber(lst):\n lst_dict = {ide:0 for ide in lst}\n lineNumber_list = []\n \n for idx in lst:\n if idx in lst_dict:\n lst_dict[idx] = lst_dict[idx] + 1 \n lineNumber_list.append(lst_dict[idx])\n \n return lineNumber_list\n \n\npatient_com_treat_df['lineNumber'] = setLineNumber(patient_com_treat_df['patient_id'].tolist())\npatient_com_treat_df.tail(20)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = patient_com_treat_df\n\nid_dict = {i:0 for i in df['patient_id'].tolist()}\nfor x in df['patient_id'].tolist():\n if x in id_dict:\n id_dict[x]=id_dict[x]+1\n\nline_updated = [int(j) for i in id_dict.values() for j in range(1,i+1)]\nprint (line_updated[0:10])\ndf.update(pd.Series(line_updated, name='lineNumber'),errors='ignore')\ndisplay(df.head(20))\n\n\n#patients merging based on id and creating new columns\nr = df['lineNumber'].max()\nprint ('Max line:',r)\nl = [df[df['lineNumber']==i] for i in range(1, int(r+1))]\nprint('Number of Dfs to merge: ',len(l))\ndf_new = pd.DataFrame()\ntmp_id = []\nfor i, df_l in enumerate(l):\n df_l = df_l[~df_l['patient_id'].isin(tmp_id)]\n for j, df_ll in enumerate(l[i+1:]):\n #df_l = df_l.merge(df_ll, on='id', how='left', suffix=(str(j), str(j+1))) #suffixe is not working\n #print (j)\n df_l = df_l.join(df_ll.set_index('patient_id'), on='patient_id', rsuffix='_'+str(j+1))\n tmp_id = tmp_id + df_l['patient_id'].tolist()\n #display(df_l)\n df_new = df_new.append(df_l, ignore_index=True, sort=False)\ndisplay(df_new.head(20))\ndisplay(df_new[['patient_id']+[col for col in df_new.columns if 'line' in col or 'DATE' in col]].head(10))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fltr_linnum = ['_'+str(i) for i in range(10, 27)]\nprint (fltr_linnum)\ndf_new.drop(columns=[col for col in df_new.columns for i in fltr_linnum if i in col],inplace=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_new.to_csv(folder_path+'dementialTreatmentLine_preData_line_episode.csv', index=False)\ndf_new = df_new.drop([col for col in df_new.columns if 'lineNumber' in col], axis=1).reset_index(drop=True)\ndf_new.to_csv(folder_path+'dementialTreatmentLine_preData.csv', index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Calculate matching intial episode in the data\n\n''' df_episode= pd.read_csv('../../../datalcdem/data/optima/dementialTreatmentLine_preData_line_episode.csv')\ndf_patients = pd.read_csv('../../../datalcdem/data/optima/patients.csv')\ndisplay(df_episode.columns, df_patients.columns)\n\ndf_pat_ep = pd.merge(df_episode[['patient_id', 'EPISODE_DATE']], df_patients[['patient_id', 'epDateInicial', 'mmseInicial']])\n\ndf_episode.shape, df_patients.shape, df_pat_ep.shape\n\ndf_pat_ep['dateEqual']=df_pat_ep['EPISODE_DATE']==df_pat_ep['epDateInicial']\ndisplay(sum(df_pat_ep['dateEqual'].tolist()))\ndf_pat_ep.head(10)\ndisplay(sum(df_pat_ep['mmseInicial']<24))'''",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_new.head(10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Calculate differnce beween patient API & Ahmad data\ndf_diff = df_new[['patient_id']]\n\ndf_patient_api = pd.read_csv(folder_path+'patients.csv')\n\ndf_diff['patient_id_1'] = df_patient_api['patient_id']\n\ndf_diff.head(10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"set_ahmad = set(df_new['patient_id'].tolist()) \ndf_patient_api = pd.read_csv(folder_path+'patients_df.csv') \nset_api = set(df_patient_api['patient_id'].tolist()) \nprint (set_ahmad.difference(set_api)) \nprint (sorted(set_api.difference(set_ahmad)))\nlist_val= sorted(set_api.difference(set_ahmad))\n\ndf_patient_api[df_patient_api['patient_id'].isin(list_val)].head(10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Take Some other features from API\ndf_patient_api = pd.read_csv(folder_path+'patients.csv')\ndisplay(df_patient_api.head(10))\ndf_patient_api = df_patient_api[['patient_id', 'gender', 'dementia', 'smoker', 'alcohol', 'education',\n 'bmi', 'weight', 'apoe']]\ndisplay(df_patient_api.head(10))\ndisplay(df_new.head(10))\ndf_patient_new = df_patient_api.merge(df_new, on=['patient_id'], how='inner')\ndf_patient_new.head(10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_patient_new.to_csv(folder_path+'patients_new.csv', index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def removeNANvalues(lst):\n return lst[~pd.isnull(lst)]\n\ncomorbidity_cui_lst = list(set([y for x in removeNANvalues(df_patient_new[[col for col in df_patient_new.columns if 'Comorbidity_cui' in col]].values.flatten()) for y in x]))\nmedication_cui_lst = list(set([y for x in removeNANvalues(df_patient_new[[col for col in df_patient_new.columns if 'Medication_cui' in col]].values.flatten()) for y in x]))\n\nwith open(folder_path+'comorbidity_cui_lst.pkl', 'wb') as f:\n pickle.dump(comorbidity_cui_lst, f)\n \nwith open(folder_path+'medication_cui_lst.pkl', 'wb') as f:\n pickle.dump(medication_cui_lst, f)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4abd822c467875ed9475f20abd0d155358e7c82e
| 76,076 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
50-unsupervised/PCA.ipynb
|
zunio/python-recipes
|
c932db459fae2c9e189b50f45d78d9fb918e7cb9
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
50-unsupervised/PCA.ipynb
|
zunio/python-recipes
|
c932db459fae2c9e189b50f45d78d9fb918e7cb9
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
50-unsupervised/PCA.ipynb
|
zunio/python-recipes
|
c932db459fae2c9e189b50f45d78d9fb918e7cb9
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 227.772455 | 29,828 | 0.91402 |
[
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nfrom matplotlib import pyplot as plt\nfrom sklearn import datasets\nfrom sklearn.decomposition import PCA\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler\nfrom sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"iris=datasets.load_iris()\nX=iris.data\ny=iris.target",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model = PCA()\nmodel.fit(X)\ntransformed = model.transform(X)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.scatter(transformed[:,0],transformed[:,1], c=y)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model.explained_variance_ratio_",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model.singular_values_",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model.components_ #Direction of variance",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Explained variance\nplt.bar(range(model.n_components_), model.explained_variance_)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#mean of the features\nprint(model.mean_)\nmean=model.mean_\n#first principal components\nfirst_pc=model.components_[0,:]\nprint(first_pc)",
"[ 5.84333333 3.054 3.75866667 1.19866667]\n[ 0.36158968 -0.08226889 0.85657211 0.35884393]\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Scaling",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"scaler = StandardScaler()\npca = PCA()\npipeline = make_pipeline(scaler,pca)\npipeline.fit(X)\ntransformed = pipeline.transform(X)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Explained variance\nplt.bar(range(pca.n_components_), pca.explained_variance_)\nplt.xlabel('PCA feature')\nplt.ylabel('variance')\nplt.xticks(range(pca.n_components_))\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#mean of the features\nprint(pca.mean_)\nmean=pca.mean_\n#first principal components\nfirst_pc=pca.components_[0,:]\nprint(first_pc)\nsecond_pc=pca.components_[1,:]",
"[ -1.69031455e-15 -1.63702385e-15 -1.48251781e-15 -1.62314606e-15]\n[ 0.52237162 -0.26335492 0.58125401 0.56561105]\n"
],
[
"pca.components_",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.scatter(transformed[:,0],transformed[:,1], c=y)\nplt.arrow(mean[0], mean[1], first_pc[0], first_pc[1], color='red', width=0.11)\nplt.arrow(mean[0], mean[1], second_pc[0], second_pc[1], color='red', width=0.11)\nplt.axis('equal')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"first_pc",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4abd93a004ba90a4e8ce2a37dd884fc7585aadd1
| 18,742 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Aspect Extraction Laptop.ipynb
|
Mphasis-ML-Marketplace/Product-Review-Aspect-Detection-Laptops
|
ea0d7e16064e9ed8870fef1f057da616b3f5ca5b
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Aspect Extraction Laptop.ipynb
|
Mphasis-ML-Marketplace/Product-Review-Aspect-Detection-Laptops
|
ea0d7e16064e9ed8870fef1f057da616b3f5ca5b
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Aspect Extraction Laptop.ipynb
|
Mphasis-ML-Marketplace/Product-Review-Aspect-Detection-Laptops
|
ea0d7e16064e9ed8870fef1f057da616b3f5ca5b
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 37.710262 | 1,096 | 0.619251 |
[
[
[
"## Product Review Aspect Detection: Laptop\n\n\n### This is a Natural Language Processing based solution which can detect up to 8 aspects from online product reviews for laptops.\n\nThis sample notebook shows you how to deploy Product Review Aspect Detection: Laptop using Amazon SageMaker.\n\n> **Note**: This is a reference notebook and it cannot run unless you make changes suggested in the notebook.\n\n#### Pre-requisites:\n1. **Note**: This notebook contains elements which render correctly in Jupyter interface. Open this notebook from an Amazon SageMaker Notebook Instance or Amazon SageMaker Studio.\n1. Ensure that IAM role used has **AmazonSageMakerFullAccess**\n1. To deploy this ML model successfully, ensure that:\n 1. Either your IAM role has these three permissions and you have authority to make AWS Marketplace subscriptions in the AWS account used: \n 1. **aws-marketplace:ViewSubscriptions**\n 1. **aws-marketplace:Unsubscribe**\n 1. **aws-marketplace:Subscribe** \n 2. or your AWS account has a subscription to Product Review Aspect Detection: Laptop. If so, skip step: [Subscribe to the model package](#1.-Subscribe-to-the-model-package)\n\n#### Contents:\n1. [Subscribe to the model package](#1.-Subscribe-to-the-model-package)\n2. [Create an endpoint and perform real-time inference](#2.-Create-an-endpoint-and-perform-real-time-inference)\n 1. [Create an endpoint](#A.-Create-an-endpoint)\n 2. [Create input payload](#B.-Create-input-payload)\n 3. [Perform real-time inference](#C.-Perform-real-time-inference)\n 4. [Visualize output](#D.-Visualize-output)\n 5. [Delete the endpoint](#E.-Delete-the-endpoint)\n3. [Perform batch inference](#3.-Perform-batch-inference) \n4. [Clean-up](#4.-Clean-up)\n 1. [Delete the model](#A.-Delete-the-model)\n 2. [Unsubscribe to the listing (optional)](#B.-Unsubscribe-to-the-listing-(optional))\n \n\n#### Usage instructions\nYou can run this notebook one cell at a time (By using Shift+Enter for running a cell).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 1. Subscribe to the model package",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"To subscribe to the model package:\n1. Open the model package listing page Product Review Aspect Detection: Laptop. \n1. On the AWS Marketplace listing, click on the **Continue to subscribe** button.\n1. On the **Subscribe to this software** page, review and click on **\"Accept Offer\"** if you and your organization agrees with EULA, pricing, and support terms. \n1. Once you click on **Continue to configuration button** and then choose a **region**, you will see a **Product Arn** displayed. This is the model package ARN that you need to specify while creating a deployable model using Boto3. Copy the ARN corresponding to your region and specify the same in the following cell.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model_package_arn='arn:aws:sagemaker:us-east-2:786796469737:model-package/laptop-aspect-extraction'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import base64\nimport json \nimport uuid\nfrom sagemaker import ModelPackage\nimport sagemaker as sage\nfrom sagemaker import get_execution_role\nfrom sagemaker import ModelPackage\nfrom urllib.parse import urlparse\nimport boto3\nfrom IPython.display import Image\nfrom PIL import Image as ImageEdit\nimport urllib.request\nimport numpy as np",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"role = get_execution_role()\n\nsagemaker_session = sage.Session()\n\nbucket=sagemaker_session.default_bucket()\nbucket",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 2. Create an endpoint and perform real-time inference",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"If you want to understand how real-time inference with Amazon SageMaker works, see [Documentation](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/sagemaker/latest/dg/how-it-works-hosting.html).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model_name='laptop-aspect-extraction'\n\ncontent_type='text/plain'\n\nreal_time_inference_instance_type='ml.m5.large'\nbatch_transform_inference_instance_type='ml.m5.large'",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### A. Create an endpoint",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\ndef predict_wrapper(endpoint, session):\n return sage.predictor.Predictor(endpoint, session,content_type)\n\n#create a deployable model from the model package.\nmodel = ModelPackage(role=role,\n model_package_arn=model_package_arn,\n sagemaker_session=sagemaker_session,\n predictor_cls=predict_wrapper)\n\n#Deploy the model\npredictor = model.deploy(1, real_time_inference_instance_type, endpoint_name=model_name)",
"----!"
]
],
[
[
"Once endpoint has been created, you would be able to perform real-time inference.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### B. Create input payload",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"file_name = 'sample.txt'",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<Add code snippet that shows the payload contents>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### C. Perform real-time inference",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!aws sagemaker-runtime invoke-endpoint \\\n --endpoint-name $model_name \\\n --body fileb://$file_name \\\n --content-type $content_type \\\n --region $sagemaker_session.boto_region_name \\\n output.txt",
"{\r\n \"ContentType\": \"application/json\",\r\n \"InvokedProductionVariant\": \"AllTraffic\"\r\n}\r\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### D. Visualize output",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import json\nwith open('output.txt', 'r') as f:\n output = json.load(f)\nprint(output)",
"{'review': \"The screen doesn't lift keyboard Build & Looks are awesome. Performance is just awesome, Boots in seconds (5 - 6 sec) & same way it shuts down Apps opens in no time Gestures works perfectly All thanks to 11th Gen i5, 16GB Ram & 512 NvMe SSD. Didn't checked in daylight but at home it is very bright Watching videos in FHD IPS display is a pleasure. Only drawback I noticed was charging pin is too tight to push & pull out and battery life is low\", 'topics': [{'aspect': {'build': 0.3893656460066695, 'hardware - keyboard and mouse': 0.3455548403269604}, 'sentence': 'screen lift keyboard build look awesome'}, {'aspect': {'processor': 0.46793959907425536}, 'sentence': 'performance awesome boot second sec way shuts opens time gesture work perfectly thanks th gen gb ram nvme ssd'}, {'aspect': {'display quality': 0.5265764379448377, 'processor': 0.4274929887240397}, 'sentence': 'check daylight home bright watch video fhd ip display pleasure'}, {'aspect': {'battery life': 0.3337075096010938}, 'sentence': 'drawback notice charge pin tight push pull battery life low'}]}\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### E. Delete the endpoint",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Now that you have successfully performed a real-time inference, you do not need the endpoint any more. You can terminate the endpoint to avoid being charged.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"predictor=sage.predictor.Predictor(model_name, sagemaker_session,content_type)\npredictor.delete_endpoint(delete_endpoint_config=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 3. Perform batch inference",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In this section, you will perform batch inference using multiple input payloads together. If you are not familiar with batch transform, and want to learn more, see these links:\n1. [How it works](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/sagemaker/latest/dg/ex1-batch-transform.html)\n2. [How to run a batch transform job](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/sagemaker/latest/dg/how-it-works-batch.html)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#upload the batch-transform job input files to S3\ntransform_input_folder = \"input\"\ntransform_input = sagemaker_session.upload_data(transform_input_folder, key_prefix=model_name) \nprint(\"Transform input uploaded to \" + transform_input)",
"Transform input uploaded to s3://sagemaker-us-east-2-786796469737/laptop-aspect-extraction\n"
],
[
"\n#Run the batch-transform job\ntransformer = model.transformer(1, batch_transform_inference_instance_type)\ntransformer.transform(transform_input, content_type=content_type)\ntransformer.wait()",
".....................\n\u001b[34m/usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/sklearn/base.py:315: UserWarning: Trying to unpickle estimator CountVectorizer from version 0.20.2 when using version 0.24.2. This might lead to breaking code or invalid results. Use at your own risk.\n UserWarning)\n * Serving Flask app 'serve' (lazy loading)\n * Environment: production\n WARNING: This is a development server. Do not use it in a production deployment.\n Use a production WSGI server instead.\n * Debug mode: off\n * Running on all addresses.\n WARNING: This is a development server. Do not use it in a production deployment.\n * Running on http://169.254.255.131:8080/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)\u001b[0m\n\u001b[34m169.254.255.130 - - [24/Nov/2021 09:57:56] \"GET /ping HTTP/1.1\" 200 -\u001b[0m\n\u001b[34m169.254.255.130 - - [24/Nov/2021 09:57:56] \"#033[33mGET /execution-parameters HTTP/1.1#033[0m\" 404 -\u001b[0m\n\u001b[34m169.254.255.130 - - [24/Nov/2021 09:57:57] \"POST /invocations HTTP/1.1\" 200 -\u001b[0m\n\u001b[35m169.254.255.130 - - [24/Nov/2021 09:57:57] \"POST /invocations HTTP/1.1\" 200 -\u001b[0m\n\u001b[32m2021-11-24T09:57:56.088:[sagemaker logs]: MaxConcurrentTransforms=1, MaxPayloadInMB=6, BatchStrategy=MULTI_RECORD\u001b[0m\n\u001b[34m/usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/sklearn/base.py:315: UserWarning: Trying to unpickle estimator CountVectorizer from version 0.20.2 when using version 0.24.2. This might lead to breaking code or invalid results. Use at your own risk.\n UserWarning)\n * Serving Flask app 'serve' (lazy loading)\n * Environment: production\n WARNING: This is a development server. Do not use it in a production deployment.\n Use a production WSGI server instead.\n * Debug mode: off\n * Running on all addresses.\n WARNING: This is a development server. Do not use it in a production deployment.\n * Running on http://169.254.255.131:8080/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)\u001b[0m\n\u001b[35m/usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/sklearn/base.py:315: UserWarning: Trying to unpickle estimator CountVectorizer from version 0.20.2 when using version 0.24.2. This might lead to breaking code or invalid results. Use at your own risk.\n UserWarning)\n * Serving Flask app 'serve' (lazy loading)\n * Environment: production\n WARNING: This is a development server. Do not use it in a production deployment.\n Use a production WSGI server instead.\n * Debug mode: off\n * Running on all addresses.\n WARNING: This is a development server. Do not use it in a production deployment.\n * Running on http://169.254.255.131:8080/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)\u001b[0m\n\u001b[34m169.254.255.130 - - [24/Nov/2021 09:57:56] \"GET /ping HTTP/1.1\" 200 -\u001b[0m\n\u001b[34m169.254.255.130 - - [24/Nov/2021 09:57:56] \"#033[33mGET /execution-parameters HTTP/1.1#033[0m\" 404 -\u001b[0m\n\u001b[35m169.254.255.130 - - [24/Nov/2021 09:57:56] \"GET /ping HTTP/1.1\" 200 -\u001b[0m\n\u001b[35m169.254.255.130 - - [24/Nov/2021 09:57:56] \"#033[33mGET /execution-parameters HTTP/1.1#033[0m\" 404 -\u001b[0m\n\u001b[34m169.254.255.130 - - [24/Nov/2021 09:57:57] \"POST /invocations HTTP/1.1\" 200 -\u001b[0m\n\u001b[35m169.254.255.130 - - [24/Nov/2021 09:57:57] \"POST /invocations HTTP/1.1\" 200 -\u001b[0m\n\u001b[32m2021-11-24T09:57:56.088:[sagemaker logs]: MaxConcurrentTransforms=1, MaxPayloadInMB=6, BatchStrategy=MULTI_RECORD\u001b[0m\n"
],
[
"import os\ns3_conn = boto3.client(\"s3\")\nwith open('output.txt', 'wb') as f:\n s3_conn.download_fileobj(bucket, os.path.basename(transformer.output_path)+'/sample.txt.out', f)\n print(\"Output file loaded from bucket\")",
"Output file loaded from bucket\n"
],
[
"with open('output.txt', 'r') as f:\n output = json.load(f)\nprint(output)",
"{'review': \"The screen doesn't lift keyboard Build & Looks are awesome. Performance is just awesome, Boots in seconds (5 - 6 sec) & same way it shuts down Apps opens in no time Gestures works perfectly All thanks to 11th Gen i5, 16GB Ram & 512 NvMe SSD. Didn't checked in daylight but at home it is very bright Watching videos in FHD IPS display is a pleasure. Only drawback I noticed was charging pin is too tight to push & pull out and battery life is low\", 'topics': [{'aspect': {'build': 0.3893656460066695, 'hardware - keyboard and mouse': 0.3455548403269604}, 'sentence': 'screen lift keyboard build look awesome'}, {'aspect': {'processor': 0.46793959907425536}, 'sentence': 'performance awesome boot second sec way shuts opens time gesture work perfectly thanks th gen gb ram nvme ssd'}, {'aspect': {'display quality': 0.5265764379448377, 'processor': 0.4274929887240397}, 'sentence': 'check daylight home bright watch video fhd ip display pleasure'}, {'aspect': {'battery life': 0.3337075096010938}, 'sentence': 'drawback notice charge pin tight push pull battery life low'}]}\n"
]
],
[
[
"### 4. Clean-up",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### A. Delete the model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model.delete_model()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### B. Unsubscribe to the listing (optional)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"If you would like to unsubscribe to the model package, follow these steps. Before you cancel the subscription, ensure that you do not have any [deployable model](https://console.aws.amazon.com/sagemaker/home#/models) created from the model package or using the algorithm. Note - You can find this information by looking at the container name associated with the model. \n\n**Steps to unsubscribe to product from AWS Marketplace**:\n1. Navigate to __Machine Learning__ tab on [__Your Software subscriptions page__](https://aws.amazon.com/marketplace/ai/library?productType=ml&ref_=mlmp_gitdemo_indust)\n2. Locate the listing that you want to cancel the subscription for, and then choose __Cancel Subscription__ to cancel the subscription.\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4abd9d7d243619b405758366ab269017abe7c3f0
| 39,943 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
02 Pandas/pivot_tables_pandas.ipynb
|
ketangangal/Ml_Projects
|
4ee0415ce12a95b0eb2abaacf2286a84405c01a2
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
02 Pandas/pivot_tables_pandas.ipynb
|
ketangangal/Ml_Projects
|
4ee0415ce12a95b0eb2abaacf2286a84405c01a2
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
02 Pandas/pivot_tables_pandas.ipynb
|
ketangangal/Ml_Projects
|
4ee0415ce12a95b0eb2abaacf2286a84405c01a2
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 33.965136 | 170 | 0.316676 |
[
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = pd.read_csv(\"C:\\\\Users\\\\Ketan Gangal\\\\OneDrive\\\\Desktop\\\\python_basic\\\\Untitled Folder\\\\machine_learning\\\\03-Pandas\\\\Sales_Funnel_CRM.csv\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"exa = df.pivot(index='Company',columns='Product',values= 'Licenses')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"exa.fillna(value=0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.pivot_table(index='Company',aggfunc=\"sum\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# milti level index ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.pivot_table(index=['Account Manager','Contact'],columns=['Product'],\n values=['Sale Price'],aggfunc='sum',fill_value=0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.pivot_table(index=['Account Manager','Contact'],columns=['Product'],\n values=['Sale Price'],aggfunc=[np.sum],fill_value=0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.pivot_table(index=['Account Manager','Contact','Company'],columns=['Product'],\n values=['Sale Price'],aggfunc=[np.sum,np.mean],fill_value=0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.pivot_table(index=['Account Manager','Contact','Company','Product'],\n values=['Sale Price'],aggfunc=[np.sum],fill_value=0,margins=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4abd9e86c816590bb99ed4ca465e9e8e9c59cf2c
| 114,180 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
examples/jupyter_notebooks/plot_roc_curve.ipynb
|
moritzschaefer/scikit-plot
|
00e75e1de6af736cb5b5a9e875269087d9180fc0
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2,360 |
2017-02-12T01:43:09.000Z
|
2022-03-31T10:06:31.000Z
|
examples/jupyter_notebooks/plot_roc_curve.ipynb
|
moritzschaefer/scikit-plot
|
00e75e1de6af736cb5b5a9e875269087d9180fc0
|
[
"MIT"
] | 79 |
2017-02-12T21:42:08.000Z
|
2022-02-28T03:00:44.000Z
|
examples/jupyter_notebooks/plot_roc_curve.ipynb
|
moritzschaefer/scikit-plot
|
00e75e1de6af736cb5b5a9e875269087d9180fc0
|
[
"MIT"
] | 302 |
2017-02-17T19:36:33.000Z
|
2022-01-28T16:22:06.000Z
| 1,130.49505 | 111,810 | 0.945796 |
[
[
[
"### An example showing the plot_roc_curve method used by a scikit-learn classifier\n\nIn this example, we'll be plotting the ROC curve for our Naive Bayes classifier on the digits dataset. First, we're going\nto fit our model with the data, then obtain the predicted probabilities `y_probas`. Afterwhich, we can then pass the ground-truth values `y` and `y_probas` into `scikitplot.metrics.plot_roc_curve` method.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from __future__ import absolute_import\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB\nfrom sklearn.datasets import load_digits as load_data\n\n# Import scikit-plot\nimport scikitplot as skplt\n\n%pylab inline\npylab.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (14, 14)",
"Populating the interactive namespace from numpy and matplotlib\n"
],
[
"# Load the data\nX, y = load_data(return_X_y=True)\n\n# Create classifier instance then fit\nnb = GaussianNB()\nnb.fit(X,y)\n\n# Get y_probabilities\ny_probas = nb.predict_proba(X)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Plot!\nskplt.metrics.plot_roc_curve(y, y_probas, cmap='nipy_spectral')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4abda0c58819cd24d690f57783d8177969578733
| 5,916 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
3. DP/Value Iteration.ipynb
|
josungbae/dennybritz-reinforcement-learning
|
0732cb512abe38cdec04966883baef84854e4a59
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2022-02-21T03:58:26.000Z
|
2022-02-21T03:58:26.000Z
|
3. DP/Value Iteration.ipynb
|
josungbae/dennybritz-reinforcement-learning
|
0732cb512abe38cdec04966883baef84854e4a59
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
3. DP/Value Iteration.ipynb
|
josungbae/dennybritz-reinforcement-learning
|
0732cb512abe38cdec04966883baef84854e4a59
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 29.142857 | 108 | 0.469743 |
[
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pprint\nimport sys\nif \"../\" not in sys.path:\n sys.path.append(\"../\") \nfrom lib.envs.gridworld import GridworldEnv",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pp = pprint.PrettyPrinter(indent=2)\nenv = GridworldEnv()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def value_iteration(env, theta=0.0001, discount_factor=1.0):\n \"\"\"\n Value Iteration Algorithm.\n \n Args:\n env: OpenAI env. env.P represents the transition probabilities of the environment.\n env.P[s][a] is a list of transition tuples (prob, next_state, reward, done).\n env.nS is a number of states in the environment. \n env.nA is a number of actions in the environment.\n theta: We stop evaluation once our value function change is less than theta for all states.\n discount_factor: Gamma discount factor.\n \n Returns:\n A tuple (policy, V) of the optimal policy and the optimal value function. \n \"\"\"\n \n\n V = np.zeros(env.nS)\n policy = np.zeros([env.nS, env.nA])\n \n # Implement!\n # policy evaluation using Bellman optimality equation\n while True:\n threshold = 0\n for s in range(env.nS):\n action_value_list = []\n old_value = V[s]\n for action, action_prob in enumerate(policy[s]):\n state_action_value = 0\n for prob, next_state, reward, done in env.P[s][action]:\n state_action_value += prob * (reward + discount_factor * V[next_state])\n \n action_value_list.append(state_action_value)\n \n # Bellman optimality equation\n V[s] = np.max(action_value_list)\n threshold = max(threshold, np.abs(old_value-V[s]))\n \n if threshold < theta:\n break\n\n # Policy improvement\n for s in range(env.nS):\n action_value_list = []\n for action, action_prob in enumerate(policy[s]):\n state_action_value = 0\n for prob, next_state, reward, done in env.P[s][action]:\n state_action_value += prob * (reward + discount_factor * V[next_state])\n\n action_value_list.append(state_action_value)\n \n greedy_action = np.argmax(action_value_list)\n policy[s] = np.eye(env.nA)[greedy_action]\n\n return policy, V",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"policy, v = value_iteration(env)\n\nprint(\"Policy Probability Distribution:\") \nprint(policy)\nprint(\"\")\n\nprint(\"Reshaped Grid Policy (0=up, 1=right, 2=down, 3=left):\")\nprint(np.reshape(np.argmax(policy, axis=1), env.shape))\nprint(\"\")\n\nprint(\"Value Function:\")\nprint(v)\nprint(\"\")\n\nprint(\"Reshaped Grid Value Function:\")\nprint(v.reshape(env.shape))\nprint(\"\")",
"Policy Probability Distribution:\n[[1. 0. 0. 0.]\n [0. 0. 0. 1.]\n [0. 0. 0. 1.]\n [0. 0. 1. 0.]\n [1. 0. 0. 0.]\n [1. 0. 0. 0.]\n [1. 0. 0. 0.]\n [0. 0. 1. 0.]\n [1. 0. 0. 0.]\n [1. 0. 0. 0.]\n [0. 1. 0. 0.]\n [0. 0. 1. 0.]\n [1. 0. 0. 0.]\n [0. 1. 0. 0.]\n [0. 1. 0. 0.]\n [1. 0. 0. 0.]]\n\nReshaped Grid Policy (0=up, 1=right, 2=down, 3=left):\n[[0 3 3 2]\n [0 0 0 2]\n [0 0 1 2]\n [0 1 1 0]]\n\nValue Function:\n[ 0. -1. -2. -3. -1. -2. -3. -2. -2. -3. -2. -1. -3. -2. -1. 0.]\n\nReshaped Grid Value Function:\n[[ 0. -1. -2. -3.]\n [-1. -2. -3. -2.]\n [-2. -3. -2. -1.]\n [-3. -2. -1. 0.]]\n\n"
],
[
"# Test the value function\nexpected_v = np.array([ 0, -1, -2, -3, -1, -2, -3, -2, -2, -3, -2, -1, -3, -2, -1, 0])\nnp.testing.assert_array_almost_equal(v, expected_v, decimal=2)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4abda4576aab7c0ebc67a5c27455224c2fdf8652
| 1,938 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Code/13.Introduction_to_Unsupervised_Learning.ipynb
|
Eurus-Holmes/Statistics-Base
|
a84f9bd0089b8b462e8ee88ee541be19a92d5687
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 3 |
2019-12-28T12:55:46.000Z
|
2021-06-18T01:55:52.000Z
|
Code/13.Introduction_to_Unsupervised_Learning.ipynb
|
Eurus-Holmes/Statistics-Base
|
a84f9bd0089b8b462e8ee88ee541be19a92d5687
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Code/13.Introduction_to_Unsupervised_Learning.ipynb
|
Eurus-Holmes/Statistics-Base
|
a84f9bd0089b8b462e8ee88ee541be19a92d5687
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2021-06-18T01:55:54.000Z
|
2021-06-18T01:55:54.000Z
| 24.531646 | 143 | 0.609391 |
[
[
[
"# 第13章 无监督学习概论",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"1.机器学习或统计学习一般包括监督学习、无监督学习、强化学习。\n\n无监督学习是指从无标注数据中学习模型的机器学习问题。无标注数据是自然得到的数据,模型表示数据的类别、转换或概率无监督学习的本质是学习数据中的统计规律或潜在结构,主要包括聚类、降维、概率估计。\n\n2.无监督学习可以用于对已有数据的分析,也可以用于对未来数据的预测。学习得到的模型有函数$z=g(x)$,条件概率分布$P(z|x)$,或条件概率分布$P(x|z)$。\n\n无监督学习的基本想法是对给定数据(矩阵数据)进行某种“压缩”,从而找到数据的潜在结构,假定损失最小的压缩得到的结果就是最本质的结构。可以考虑发掘数据的纵向结构,对应聚类。也可以考虑发掘数据的横向结构,对应降维。还可以同时考虑发掘数据的纵向与横向结构,对应概率模型估计。\n\n3.聚类是将样本集合中相似的样本(实例)分配到相同的类,不相似的样本分配到不同的类。聚类分硬聚类和软聚类。聚类方法有层次聚类和$k$均值聚类。\n\n4.降维是将样本集合中的样本(实例)从高维空间转换到低维空间。假设样本原本存在于低维空间,或近似地存在于低维空间,通过降维则可以更好地表示样本数据的结构,即更好地表示样本之间的关系。降维有线性降维和非线性降维,降维方法有主成分分析。\n\n5.概率模型估计假设训练数据由一个概率模型生成,同时利用训练数据学习概率模型的结构和参数。概率模型包括混合模型、率图模型等。概率图模型又包括有向图模型和无向图模型。\n\n6.话题分析是文本分析的一种技术。给定一个文本集合,话题分析旨在发现文本集合中每个文本的话题,而话题由单词的集合表示。话题分析方法有潜在语义分析、概率潜在语义分析和潜在狄利克雷分配。\n\n7.图分析的目的是发掘隐藏在图中的统计规律或潜在结构。链接分析是图分析的一种,主要是发现有向图中的重要结点,包括 **PageRank**算法。",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"----\n\n中文注释制作:机器学习初学者\n\n微信公众号:ID:ai-start-com\n\n配置环境:python 3.5+\n\n代码全部测试通过。\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4abda74532e124549848c57c9ce1cf3b65d0b785
| 36,858 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
storage_utilization_by_firecloud_workspaces.ipynb
|
cbirger/firecloud-ws-stats
|
03963a2eadcb26940ee542339cb10ae12c002bde
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
storage_utilization_by_firecloud_workspaces.ipynb
|
cbirger/firecloud-ws-stats
|
03963a2eadcb26940ee542339cb10ae12c002bde
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
storage_utilization_by_firecloud_workspaces.ipynb
|
cbirger/firecloud-ws-stats
|
03963a2eadcb26940ee542339cb10ae12c002bde
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 44.94878 | 401 | 0.469613 |
[
[
[
"# Obtaining Storage Statistics For all of Workspaces Associated with a single FireCloud Billing Project ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import json\nimport os\nimport csv\nimport subprocess\nfrom fisswrapper.workspace_functions import list_workspaces\nfrom fisswrapper.workspace_functions import get_workspace_info\nimport pandas as pd\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"project = \"broad-firecloud-testing\"\noutputFile = \"broad-firecloud-testing.tsv\"\ntmpFile = \"tmp.txt\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"workspaceList = list_workspaces(project=project)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"with open(outputFile, 'w') as out:\n for workspaceListEntry in workspaceList:\n entryFields = workspaceListEntry.split(sep='\\t')\n project = entryFields[0]\n workspace = entryFields[1]\n workspaceInfo = json.loads(get_workspace_info(project, workspace))\n owners = workspaceInfo['owners']\n bucketName = workspaceInfo['workspace']['bucketName'] \n out.write(\"{0}\\t{1}\\t{2}\\n\".format(workspace, owners, bucketName))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# IMPORTANT!\nBefore going further, execute the get_bucket_sizes.sh script, which will create a tmp.txt file with file sizes. I'm doing it this way because I was having trouble running gsutil from within my python notebook. The bash script creates a list of bucket sizes, one integer per line in the file tmp.txt. The nth line in tmp.txt corresponds to the nth line in the broad-firecloud-testing.tsv file.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In the following cell we combine the contents of broad-firecloud-testing.tsv and tmp.txt into a list object, and then create a pandas data frame from that list.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"combinedTable = []\nwith open(outputFile) as tsvfile, open(tmpFile) as tmpfile:\n reader1 = csv.reader(tsvfile, delimiter='\\t')\n reader2 = csv.reader(tmpfile, delimiter='\\t')\n for row1, row2 in zip(reader1, reader2):\n combinedTable.append(row1+row2)\nlabels = ['workspace_name', 'workspace_owners', 'workspace_bucket', 'bucket_size']\nmyDataFrame = pd.DataFrame.from_records(combinedTable,columns=labels)\n# need to change the bucket_size column data from strong to numeric\nmyDataFrame[['bucket_size']] = myDataFrame[['bucket_size']].apply(pd.to_numeric)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"myDataFrame.sort_values(by=['bucket_size'], ascending=False, inplace=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"myDataFrame",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now write sorted dataframe as a TSV file.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"finalFilename = 'broad-firecloud-testing-complete.tsv'\nmyDataFrame.to_csv(finalFilename,sep='\\t')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4abdb0a79b7a2816e11a828b9989c28924d172a4
| 29,149 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
_posts/python-v3/databases/bigquery/BigQuery-Plotly.ipynb
|
bmb804/documentation
|
57826d25e0afea7fff6a8da9abab8be2f7a4b48c
|
[
"CC-BY-3.0"
] | 2 |
2019-06-24T23:55:53.000Z
|
2019-07-08T12:22:56.000Z
|
_posts/python-v3/databases/bigquery/BigQuery-Plotly.ipynb
|
bmb804/documentation
|
57826d25e0afea7fff6a8da9abab8be2f7a4b48c
|
[
"CC-BY-3.0"
] | 15 |
2020-06-30T21:21:30.000Z
|
2021-08-02T21:16:33.000Z
|
_posts/python-v3/databases/bigquery/BigQuery-Plotly.ipynb
|
bmb804/documentation
|
57826d25e0afea7fff6a8da9abab8be2f7a4b48c
|
[
"CC-BY-3.0"
] | 1 |
2019-11-10T04:01:48.000Z
|
2019-11-10T04:01:48.000Z
| 27.629384 | 316 | 0.533638 |
[
[
[
"#### New to Plotly?\nPlotly's Python library is free and open source! [Get started](https://plot.ly/python/getting-started/) by downloading the client and [reading the primer](https://plot.ly/python/getting-started/).\n<br>You can set up Plotly to work in [online](https://plot.ly/python/getting-started/#initialization-for-online-plotting) or [offline](https://plot.ly/python/getting-started/#initialization-for-offline-plotting) mode, or in [jupyter notebooks](https://plot.ly/python/getting-started/#start-plotting-online).\n<br>We also have a quick-reference [cheatsheet](https://images.plot.ly/plotly-documentation/images/python_cheat_sheet.pdf) (new!) to help you get started!\n#### Version Check\nPlotly's python package is updated frequently. Run `pip install plotly --upgrade` to use the latest version.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import plotly\nplotly.__version__",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### What is BigQuery?\nIt's a service by Google, which enables analysis of massive datasets. You can use the traditional SQL-like language to query the data. You can host your own data on BigQuery to use the super fast performance at scale.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Google BigQuery Public Datasets\n\nThere are [a few datasets](https://cloud.google.com/bigquery/public-data/) stored in BigQuery, available for general public to use. Some of the publicly available datasets are:\n- Hacker News (stories and comments)\n- USA Baby Names\n- GitHub activity data\n- USA disease surveillance",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We will use the [Hacker News](https://cloud.google.com/bigquery/public-data/hacker-news) dataset for our analysis.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Imports",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import plotly.plotly as py\nimport plotly.graph_objs as go\nimport plotly.figure_factory as ff\n\nimport pandas as pd\nfrom pandas.io import gbq # to communicate with Google BigQuery",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Prerequisites\n\nYou need to have the following libraries:\n* [python-gflags](http://code.google.com/p/python-gflags/)\n* httplib2\n* google-api-python-client\n\n#### Create Project\n\nA project can be created on the [Google Developer Console](https://console.developers.google.com/iam-admin/projects).\n\n#### Enable BigQuery API\n\nYou need to activate the BigQuery API for the project.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"You will have find the `Project ID` for your project to get the queries working.\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"project_id = 'bigquery-plotly'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Top 10 Most Active Users on Hacker News (by total stories submitted)\n\nWe will select the top 10 high scoring `author`s and their respective `score` values.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"top10_active_users_query = \"\"\"\nSELECT\n author AS User,\n count(author) as Stories\nFROM\n [fh-bigquery:hackernews.stories]\nGROUP BY\n User\nORDER BY\n Stories DESC\nLIMIT\n 10\n\"\"\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The `pandas.gbq` module provides a method `read_gbq` to query the BigQuery stored dataset and stores the result as a `DataFrame`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"try:\n top10_active_users_df = gbq.read_gbq(top10_active_users_query, project_id=project_id)\nexcept:\n print 'Error reading the dataset'",
"Requesting query... ok.\nQuery running...\n Elapsed 8.74 s. Waiting...\nQuery done.\nCache hit.\n\nRetrieving results...\n Got page: 1; 100.0% done. Elapsed 9.36 s.\nGot 10 rows.\n\nTotal time taken 9.37 s.\nFinished at 2016-07-19 17:28:38.\n"
]
],
[
[
"Using the `create_table` method from the `FigureFactory` module, we can generate a table from the resulting `DataFrame`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"top_10_users_table = ff.create_table(top10_active_users_df)\npy.iplot(top_10_users_table, filename='top-10-active-users')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Top 10 Hacker News Submissions (by score)\n\nWe will select the `title` and `score` columns in the descending order of their `score`, keeping only top 10 stories among all.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"top10_story_query = \"\"\"\nSELECT\n title,\n score,\n time_ts AS timestamp\nFROM\n [fh-bigquery:hackernews.stories]\nORDER BY\n score DESC\nLIMIT\n 10\n\"\"\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"try:\n top10_story_df = gbq.read_gbq(top10_story_query, project_id=project_id)\nexcept:\n print 'Error reading the dataset'",
"Requesting query... ok.\nQuery running...\n Elapsed 13.54 s. Waiting...\nQuery done.\nCache hit.\n\nRetrieving results...\n Got page: 1; 100.0% done. Elapsed 14.34 s.\nGot 10 rows.\n\nTotal time taken 14.34 s.\nFinished at 2016-07-19 17:28:57.\n"
],
[
"# Create a table figure from the DataFrame\ntop10_story_figure = FF.create_table(top10_story_df)\n\n# Scatter trace for the bubble chart timeseries\nstory_timeseries_trace = go.Scatter(\n x=top10_story_df['timestamp'],\n y=top10_story_df['score'],\n xaxis='x2',\n yaxis='y2',\n mode='markers',\n text=top10_story_df['title'],\n marker=dict(\n color=[80 + i*5 for i in range(10)],\n size=top10_story_df['score']/50,\n showscale=False\n )\n)\n\n# Add the trace data to the figure\ntop10_story_figure['data'].extend(go.Data([story_timeseries_trace]))\n\n# Subplot layout\ntop10_story_figure.layout.yaxis.update({'domain': [0, .45]})\ntop10_story_figure.layout.yaxis2.update({'domain': [.6, 1]})\n\n# Y-axis of the graph should be anchored with X-axis\ntop10_story_figure.layout.yaxis2.update({'anchor': 'x2'})\ntop10_story_figure.layout.xaxis2.update({'anchor': 'y2'})\n\n# Add the height and title attribute\ntop10_story_figure.layout.update({'height':900})\ntop10_story_figure.layout.update({'title': 'Highest Scoring Submissions on Hacker News'})\n\n# Update the background color for plot and paper\ntop10_story_figure.layout.update({'paper_bgcolor': 'rgb(243, 243, 243)'})\ntop10_story_figure.layout.update({'plot_bgcolor': 'rgb(243, 243, 243)'})\n\n# Add the margin to make subplot titles visible\ntop10_story_figure.layout.margin.update({'t':75, 'l':50})\ntop10_story_figure.layout.yaxis2.update({'title': 'Upvote Score'})\ntop10_story_figure.layout.xaxis2.update({'title': 'Post Time'})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"py.image.save_as(top10_story_figure, filename='top10-posts.png')\npy.iplot(top10_story_figure, filename='highest-scoring-submissions')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You can see that the lists consist of the stories involving some big names.\n* \"Death of Steve Jobs and Aaron Swartz\"\n* \"Announcements of the Hyperloop and the game 2048\".\n* \"Microsoft open sourcing the .NET\"\n\nThe story title is visible when you `hover` over the bubbles.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### From which Top-level domain (TLD) most of the stories come?\nHere we have used the url-function [TLD](https://cloud.google.com/bigquery/query-reference#tld) from BigQuery's query syntax. We collect the domain for all URLs with their respective count, and group them by it.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tld_share_query = \"\"\"\nSELECT\n TLD(url) AS domain,\n count(score) AS stories\nFROM\n [fh-bigquery:hackernews.stories]\nGROUP BY\n domain\nORDER BY\n stories DESC\nLIMIT 10\n\"\"\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"try:\n tld_share_df = gbq.read_gbq(tld_share_query, project_id=project_id)\nexcept:\n print 'Error reading the dataset'",
"Requesting query... ok.\nQuery running...\nQuery done.\nCache hit.\n\nRetrieving results...\n Got page: 1; 100.0% done. Elapsed 7.09 s.\nGot 10 rows.\n\nTotal time taken 7.09 s.\nFinished at 2016-07-19 17:29:10.\n"
],
[
"labels = tld_share_df['domain']\nvalues = tld_share_df['stories']\n\ntld_share_trace = go.Pie(labels=labels, values=values)\ndata = [tld_share_trace]\n\nlayout = go.Layout(\n title='Submissions shared by Top-level domains'\n)\n\nfig = go.Figure(data=data, layout=layout)\npy.iplot(fig)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can notice that the **.com** top-level domain contributes to most of the stories on Hacker News.\n#### Public response to the \"Who Is Hiring?\" posts\nThere is an account on Hacker News by the name [whoishiring](https://news.ycombinator.com/user?id=whoishiring). This account automatically submits a 'Who is Hiring?' post at 11 AM Eastern time on the first weekday of every month.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"wih_query = \"\"\"\nSELECT\n id,\n title,\n score,\n time_ts\nFROM\n [fh-bigquery:hackernews.stories]\nWHERE\n author == 'whoishiring' AND\n LOWER(title) contains 'who is hiring?'\nORDER BY\n time\n\"\"\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"try:\n wih_df = gbq.read_gbq(wih_query, project_id=project_id)\nexcept:\n print 'Error reading the dataset'",
"Requesting query... ok.\nQuery running...\nQuery done.\nCache hit.\n\nRetrieving results...\nGot 52 rows.\n\nTotal time taken 4.73 s.\nFinished at 2016-07-19 17:29:19.\n"
],
[
"trace = go.Scatter(\n x=wih_df['time_ts'],\n y=wih_df['score'],\n mode='markers+lines',\n text=wih_df['title'],\n marker=dict(\n size=wih_df['score']/50\n )\n)\n\nlayout = go.Layout(\n title='Public response to the \"Who Is Hiring?\" posts',\n xaxis=dict(\n title=\"Post Time\"\n ),\n yaxis=dict(\n title=\"Upvote Score\"\n )\n)\n\ndata = [trace]\n\nfig = go.Figure(data=data, layout=layout)\npy.iplot(fig, filename='whoishiring-public-response')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Submission Traffic Volume in a Week",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"week_traffic_query = \"\"\"\nSELECT\n DAYOFWEEK(time_ts) as Weekday,\n count(DAYOFWEEK(time_ts)) as story_counts\nFROM\n [fh-bigquery:hackernews.stories]\nGROUP BY\n Weekday\nORDER BY\n Weekday\n\"\"\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"try:\n week_traffic_df = gbq.read_gbq(week_traffic_query, project_id=project_id)\nexcept:\n print 'Error reading the dataset'",
"Requesting query... ok.\nQuery running...\nQuery done.\nCache hit.\n\nRetrieving results...\nGot 8 rows.\n\nTotal time taken 5.26 s.\nFinished at 2016-07-19 17:29:29.\n"
],
[
"week_traffic_df['Day'] = ['NULL', 'Sunday', 'Monday', 'Tuesday', 'Wednesday', 'Thursday', 'Friday', 'Saturday']\nweek_traffic_df = week_traffic_df.drop(week_traffic_df.index[0])\n\ntrace = go.Scatter(\n x=week_traffic_df['Day'],\n y=week_traffic_df['story_counts'],\n mode='lines',\n text=week_traffic_df['Day']\n)\n\nlayout = go.Layout(\n title='Submission Traffic Volume (Week Days)',\n xaxis=dict(\n title=\"Day of the Week\"\n ),\n yaxis=dict(\n title=\"Total Submissions\"\n )\n)\n\ndata = [trace]\n\nfig = go.Figure(data=data, layout=layout)\npy.iplot(fig, filename='submission-traffic-volume')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can observe that the Hacker News faces fewer submissions during the weekends.\n#### Programming Language Trend on HackerNews\nWe will compare the trends for the Python and PHP programming languages, using the Hacker News post titles.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"python_query = \"\"\"\nSELECT\n YEAR(time_ts) as years,\n COUNT(YEAR(time_ts )) as trends\nFROM\n [fh-bigquery:hackernews.stories]\nWHERE\n LOWER(title) contains 'python'\nGROUP BY\n years\nORDER BY\n years\n\"\"\"\n\nphp_query = \"\"\"\nSELECT\n YEAR(time_ts) as years,\n COUNT(YEAR(time_ts )) as trends\nFROM\n [fh-bigquery:hackernews.stories]\nWHERE\n LOWER(title) contains 'php'\nGROUP BY\n years\nORDER BY\n years\n\"\"\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"try:\n python_df = gbq.read_gbq(python_query, project_id=project_id)\nexcept:\n print 'Error reading the dataset'",
"Requesting query... ok.\nQuery running...\n Elapsed 10.07 s. Waiting...\nQuery done.\nCache hit.\n\nRetrieving results...\n Got page: 1; 100.0% done. Elapsed 10.92 s.\nGot 9 rows.\n\nTotal time taken 10.93 s.\nFinished at 2016-07-19 17:29:44.\n"
],
[
"try:\n php_df = gbq.read_gbq(php_query, project_id=project_id)\nexcept:\n print 'Error reading the dataset'",
"Requesting query... ok.\nQuery running...\n Elapsed 9.28 s. Waiting...\nQuery done.\nCache hit.\n\nRetrieving results...\n Got page: 1; 100.0% done. Elapsed 9.91 s.\nGot 9 rows.\n\nTotal time taken 9.92 s.\nFinished at 2016-07-19 17:29:54.\n"
],
[
"trace1 = go.Scatter(\n x=python_df['years'],\n y=python_df['trends'],\n mode='lines',\n line=dict(color='rgba(115,115,115,1)', width=4),\n connectgaps=True,\n)\n\ntrace2 = go.Scatter(\n x=[python_df['years'][0], python_df['years'][8]],\n y=[python_df['trends'][0], python_df['trends'][8]],\n mode='markers',\n marker=dict(color='rgba(115,115,115,1)', size=8)\n)\n\ntrace3 = go.Scatter(\n x=php_df['years'],\n y=php_df['trends'],\n mode='lines',\n line=dict(color='rgba(189,189,189,1)', width=4),\n connectgaps=True,\n)\n\ntrace4 = go.Scatter(\n x=[php_df['years'][0], php_df['years'][8]],\n y=[php_df['trends'][0], php_df['trends'][8]],\n mode='markers',\n marker=dict(color='rgba(189,189,189,1)', size=8)\n)\n\ntraces = [trace1, trace2, trace3, trace4]\n\nlayout = go.Layout(\n xaxis=dict(\n showline=True,\n showgrid=False,\n showticklabels=True,\n linecolor='rgb(204, 204, 204)',\n linewidth=2,\n autotick=False,\n ticks='outside',\n tickcolor='rgb(204, 204, 204)',\n tickwidth=2,\n ticklen=5,\n tickfont=dict(\n family='Arial',\n size=12,\n color='rgb(82, 82, 82)',\n ),\n ),\n yaxis=dict(\n showgrid=False,\n zeroline=False,\n showline=False,\n showticklabels=False,\n ),\n autosize=False,\n margin=dict(\n autoexpand=False,\n l=100,\n r=20,\n t=110,\n ),\n showlegend=False,\n)\n\nannotations = []\n\nannotations.append(\n dict(xref='paper', x=0.95, y=python_df['trends'][8],\n xanchor='left', yanchor='middle',\n text='Python',\n font=dict(\n family='Arial',\n size=14,\n color='rgba(49,130,189, 1)'\n ),\n showarrow=False)\n)\n\nannotations.append(\n dict(xref='paper', x=0.95, y=php_df['trends'][8],\n xanchor='left', yanchor='middle',\n text='PHP',\n font=dict(\n family='Arial',\n size=14,\n color='rgba(49,130,189, 1)'\n ),\n showarrow=False)\n)\n\nannotations.append(\n dict(xref='paper', yref='paper', x=0.5, y=-0.1,\n xanchor='center', yanchor='top',\n text='Source: Hacker News submissions with the title containing Python/PHP',\n font=dict(\n family='Arial',\n size=12,\n color='rgb(150,150,150)'\n ),\n showarrow=False)\n)\n\nlayout['annotations'] = annotations\n\nfig = go.Figure(data=traces, layout=layout)\npy.iplot(fig, filename='programming-language-trends')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"As we already know about this trend, Python is dominating PHP throughout the timespan.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Reference \nSee https://plot.ly/python/getting-started/ for more information about Plotly's Python Open Source Graphing Library!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from IPython.display import display, HTML\n\ndisplay(HTML('<link href=\"//fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Open+Sans:600,400,300,200|Inconsolata|Ubuntu+Mono:400,700\" rel=\"stylesheet\" type=\"text/css\" />'))\ndisplay(HTML('<link rel=\"stylesheet\" type=\"text/css\" href=\"http://help.plot.ly/documentation/all_static/css/ipython-notebook-custom.css\">'))\n\n! pip install git+https://github.com/plotly/publisher.git --upgrade\nimport publisher\npublisher.publish(\n 'BigQuery-Plotly.ipynb', 'python/google_big_query/', 'Google Big-Query',\n 'How to make your-tutorial-chart plots in Python with Plotly.',\n title = 'Google Big Query | plotly',\n has_thumbnail='true', thumbnail='thumbnail/bigquery2.jpg', \n language='python', page_type='example_index',\n display_as='databases', order=7) ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4abdbc957714ecebcd7a7a29c53870b2deeca7f2
| 568,114 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
nbs/03b_asymmetric_loss.ipynb
|
discipleOfExperience/timmdocs
|
6697f36a5d3c8c4cea17f160c1133bc8ec5fb370
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 117 |
2021-01-19T20:42:39.000Z
|
2022-03-21T19:07:42.000Z
|
nbs/03b_asymmetric_loss.ipynb
|
discipleOfExperience/timmdocs
|
6697f36a5d3c8c4cea17f160c1133bc8ec5fb370
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 37 |
2021-01-27T03:03:53.000Z
|
2022-03-20T03:08:04.000Z
|
nbs/03b_asymmetric_loss.ipynb
|
discipleOfExperience/timmdocs
|
6697f36a5d3c8c4cea17f160c1133bc8ec5fb370
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 11 |
2021-01-22T09:18:54.000Z
|
2022-03-03T07:03:24.000Z
| 1,409.712159 | 525,144 | 0.958346 |
[
[
[
"# Asymmetric Loss",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"This documentation is based on the paper \"[Asymmetric Loss For Multi-Label Classification](https://arxiv.org/abs/2009.14119)\".",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Asymetric Single-Label Loss",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import timm\nimport torch\nimport torch.nn.functional as F\nfrom timm.loss import AsymmetricLossMultiLabel, AsymmetricLossSingleLabel\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom PIL import Image\nfrom pathlib import Path",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's create a example of the `output` of a model, and our `labels`. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"output = F.one_hot(torch.tensor([0,9,0])).float()\nlabels=torch.tensor([0,0,0])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"labels, output",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"If we set all the parameters to 0, the loss becomes `F.cross_entropy` loss. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"asl = AsymmetricLossSingleLabel(gamma_pos=0,gamma_neg=0,eps=0.0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"asl(output,labels)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"F.cross_entropy(output,labels)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now lets look at the asymetric part. ASL is Asymetric in how it handles positive and negative examples. Positive examples being the labels that are present in the image, and negative examples being labels that are not present in the image. The idea being that an image has a lot of easy negative examples, few hard negative examples and very few positive examples. Getting rid of the influence of easy negative examples, should help emphasize the gradients of the positive examples.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Image.open(Path()/'images/cat.jpg')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Notice this image contains a cat, that would be a positive label. This images does not contain a dog, elephant bear, giraffe, zebra, banana or many other of the labels found in the coco dataset, those would be negative examples. It is very easy to see that a giraffe is not in this image. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"output = (2*F.one_hot(torch.tensor([0,9,0]))-1).float()\nlabels=torch.tensor([0,9,0])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"losses=[AsymmetricLossSingleLabel(gamma_neg=i*0.04+1,eps=0.1,reduction='mean')(output,labels) for i in range(int(80))]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.plot([ i*0.04+1 for i,l in enumerate(losses)],[loss for loss in losses])\nplt.ylabel('Loss')\nplt.xlabel('Change in gamma_neg')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"$$L_- = (p)^{\\gamma-}\\log(1-p) $$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The contibution of small negative examples quickly decreases as gamma_neg is increased as $\\gamma-$ is an exponent and $p$ should be a small number close to 0. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Below we set `eps=0`, this has the effect of completely flattening out the above graph, we are no longer applying label smoothing, so negative examples end up not contributing to the loss. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"losses=[AsymmetricLossSingleLabel(gamma_neg=0+i*0.02,eps=0.0,reduction='mean')(output,labels) for i in range(100)]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.plot([ i*0.04 for i in range(len(losses))],[loss for loss in losses])\nplt.ylabel('Loss')\nplt.xlabel('Change in gamma_neg')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## AsymmetricLossMultiLabel",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"`AsymmetricLossMultiLabel` allows for working on multi-label problems. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"labels=F.one_hot(torch.LongTensor([0,0,0]),num_classes=10)+F.one_hot(torch.LongTensor([1,9,1]),num_classes=10)\nlabels",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"AsymmetricLossMultiLabel()(output,labels)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"For `AsymmetricLossMultiLabel` another parameter exists called `clip`. This clamps smaller inputs to 0 for negative examples. This is called Asymmetric Probability Shifting. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"losses=[AsymmetricLossMultiLabel(clip=i/100)(output,labels) for i in range(100)]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.plot([ i/100 for i in range(len(losses))],[loss for loss in losses])\nplt.ylabel('Loss')\nplt.xlabel('Clip')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4abddcd3ee148882c0b113e143c366f29b09893b
| 767 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
docs/example.ipynb
|
arunprakash16/code-2021-11-27-arunprakash
|
67f23d88f0cbd7803fe7ed90210d36495e1d5335
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
docs/example.ipynb
|
arunprakash16/code-2021-11-27-arunprakash
|
67f23d88f0cbd7803fe7ed90210d36495e1d5335
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
docs/example.ipynb
|
arunprakash16/code-2021-11-27-arunprakash
|
67f23d88f0cbd7803fe7ed90210d36495e1d5335
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 17.044444 | 34 | 0.509778 |
[
[
[
"# Example usage\n\nTo use `pybmi` in a project:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pybmi\n\nprint(pybmi.__version__)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
4abdeefb607d031871da9617cca29da270f51d58
| 123,005 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
PCA.ipynb
|
Jovania/Machine_Learning
|
d65f5dfff47ca7772966a83bc7e61c94b7f86e28
|
[
"MIT"
] | 199 |
2017-05-17T22:48:16.000Z
|
2022-03-31T21:01:37.000Z
|
PCA.ipynb
|
Jovania/Machine_Learning
|
d65f5dfff47ca7772966a83bc7e61c94b7f86e28
|
[
"MIT"
] | 4 |
2018-10-13T20:13:35.000Z
|
2019-03-19T00:19:44.000Z
|
PCA.ipynb
|
Jovania/Machine_Learning
|
d65f5dfff47ca7772966a83bc7e61c94b7f86e28
|
[
"MIT"
] | 75 |
2018-04-17T12:11:57.000Z
|
2022-02-24T10:36:35.000Z
| 123.251503 | 28,032 | 0.830495 |
[
[
[
"# 0. Dependências",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom sklearn.datasets import load_iris\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler\nfrom sklearn.decomposition import PCA\n\n%matplotlib inline\npd.options.display.max_rows = 10",
"/Users/arnaldo/miniconda3/envs/ml/lib/python3.5/site-packages/sklearn/utils/fixes.py:313: FutureWarning: numpy not_equal will not check object identity in the future. The comparison did not return the same result as suggested by the identity (`is`)) and will change.\n _nan_object_mask = _nan_object_array != _nan_object_array\n"
]
],
[
[
"# 1. Introdução ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**O objetivo principal do PCA é analisar os dados para identificar padrões visando reduzir a dimensionalidade dos dados com uma perda mínima de informação**. Uma possível aplicação seria o reconhecimento de padrões, onde queremos reduzir os custos computacionais e o erro da estimação de parâmetros pela redução da dimensionalidade do nosso espaço de atributos extraindo um subespaço que descreve os nosso dados \"de forma satisfatória\". **A redução de dimensionalidade se torna importante quando temos um número de atributos significativamente maior que o número de amostras de treinamento**.\n\nNós aplicamos o PCA para projetar todos os nossos dados (sem rótulos de classe) em um subespaço diferente, procurando encontrar os eixos com a máxima variância onde os dados são mais distribuídos. A questão principal é: **\"Qual o subespaço que representa *bem* os nossos dados?\"**.\n\n**Primeiramente, calculamos os autovetores (componentes principais) dos nossos dados e organizamos em uma matriz de projeção. Cada autovetor (*eigenvector*) é associada a um autovalor (*eigenvalue*) que pode ser interpretado como o \"tamanho\" ou \"magnitude\" do autovetor correspondente**. Em geral, consideramos apenas o autovalores que tem uma magnitude significativamente maior que os outros e desconsideramos os autopares (autovetores-autovalores) que consideramos *menos informativos*. \n\nSe observamos que todos os autovalores tem uma magnitude similar, isso pode ser um bom indicador que nossos dados já estão em um *bom* subespaço. Por outro lado, **se alguns autovalores tem a magnitude muito maior que a dos outros, devemos escolher seus autovetores já que eles contém mais informação sobre a distribuição dos nossos dados**. Da mesma forma, autovalores próximos a zero são menos informativos e devemos desconsiderá-los na construção do nosso subespaço.\n\nEm geral, a aplicação do PCA envolve os seguintes passos:\n \n1. Padronização dos dados\n2. Obtenção dos autovetores e autovalores através da:\n - Matriz de Covariância; ou\n - Matriz de Correlação; ou\n - *Singular Vector Decomposition*\n3. Construção da matriz de projeção a partir dos autovetores selecionados\n4. Transformação dos dados originais X via a matriz de projeção para obtenção do subespaço Y\n\n## 1.1 PCA vs LDA\n\nAmbos PCA e LDA (*Linear Discrimant Analysis*) são métodos de transformação linear. Por uma lado, o PCA fornece as direções (autovetores ou componentes principais) que maximiza a variância dos dados, enquanto o LDA visa as direções que maximizam a separação (ou discriminação) entre classes diferentes. Maximizar a variância, no caso do PCA, também significa reduzir a perda de informação, que é representada pela soma das distâncias de projeção dos dados nos eixos dos componentes principais.\n\nEnquanto o PCA projeta os dados em um subespaço diferente, o LDA tenta determinar um subespaço adequado para distinguir os padrões pertencentes as classes diferentes.\n\n<img src=\"images/PCAvsLDA.png\" width=600>\n\n## 1.2 Autovetores e autovalores\n\nOs autovetores e autovalores de uma matriz de covariância (ou correlação) representam a base do PCA: os autovetores (componentes principais) determinam a direção do novo espaço de atributos, e os autovalores determinam sua magnitude. Em outras palavras, os autovalores explicam a variância dos dados ao longo dos novos eixos de atributos.\n\n### 1.2.1 Matriz de Covariância\n\nA abordagem clássica do PCA calcula a matriz de covariância, onde cada elemento representa a covariância entre dois atributos. A covariância entre dois atributos é calculada da seguinte forma:\n\n$$\\sigma_{jk} = \\frac{1}{n-1}\\sum_{i=1}^N(x_{ij}-\\overline{x}_j)(x_{ik}-\\overline{x}_k)$$\n\nQue podemos simplificar na forma vetorial através da fórmula:\n\n$$S=\\frac{1}{n-1}((x-\\overline{x})^T(x-\\overline{x}))$$\n\nonde $\\overline{x}$ é um vetor d-dimensional onde cada valor representa a média de cada atributo, e $n$ representa o número de atributos por amostra. Vale ressaltar ainda que x é um vetor onde cada amostra está organizada em linhas e cada coluna representa um atributo. Caso se tenha um vetor onde as amostras estão organizadas em colunas e cada linha representa um atributo, a transposta passa para o segundo elemento da multiplicação.\n\nNa prática, o resultado da matriz de covariância representa basicamente a seguinte estrutura:\n\n$$\\begin{bmatrix}var(1) & cov(1,2) & cov(1,3) & cov(1,4) \n\\\\ cov(1,2) & var(2) & cov(2,3) & cov(2,4)\n\\\\ cov(1,3) & cov(2,3) & var(3) & cov(3,4)\n\\\\ cov(1,4) & cov(2,4) & cov(3,4) & var(4)\n\\end{bmatrix}$$\n\nOnde a diagonal principal representa a variância em cada dimensão e os demais elementos são a covariância entre cada par de dimensões.\n\nPara se calcular os autovalores e autovetores, só precisamos chamar a função *np.linalg.eig*, onde cada autovetor estará representado por uma coluna.\n\n> Uma propriedade interessante da matriz de covariância é que **a soma da diagonal principal da matriz (variância para cada dimensão) é igual a soma dos autovalores**.\n \n### 1.2.2 Matriz de Correlação\n\nOutra maneira de calcular os autovalores e autovetores é utilizando a matriz de correlação. Apesar das matrizes serem diferentes, elas vão resultar nos mesmos autovalores e autovetores (mostrado mais a frente) já que a matriz de correlação é dada pela normalização da matriz de covariância.\n\n$$corr(x,y) = \\frac{cov(x,y)}{\\sigma_x \\sigma_y}$$\n\n\n### 1.2.3 Singular Vector Decomposition\n\nApesar da autodecomposição (cálculo dos autovetores e autovalores) efetuada pelas matriz de covariância ou correlação ser mais intuitiva, a maior parte das implementações do PCA executam a *Singular Vector Decomposition* (SVD) para melhorar o desempenho computacional. Para calcular a SVD, podemos utilizar a biblioteca numpy, através do método *np.linalg.svd*.\n\nNote que a autodecomposição resulta nos mesmos autovalores e autovetores utilizando qualquer uma das matrizes abaixo:\n\n- Matriz de covariânca após a padronização dos dados\n- Matriz de correlação\n- Matriz de correlação após a padronização dos dados\n\nMas qual a relação entre a SVD e o PCA? Dado que a matriz de covariância $C = \\frac{X^TX}{n-1}$ é uma matriz simétrica, ela pode ser diagonalizada da seguinte forma:\n\n$$C = VLV^T$$\n\nonde $V$ é a matriz de autovetores (cada coluna é um autovetor) e $L$ é a matriz diagonal com os autovalores $\\lambda_i$ na ordem decrescente na diagonal. Se executarmos o SVD em X, nós obtemos a seguinte decomposição:\n\n$$X = USV^T$$\n\nonde $U$ é a matriz unitária e $S$ é a matriz diagonal de *singular values* $s_i$. A partir disso, pode-se calcular que:\n\n$$C = VSU^TUSV^T = V\\frac{S^2}{n-1}V^T$$\n\nIsso significa que os *right singular vectors* V são as *principal directions* e que os *singular values* estão relacionados aos autovalores da matriz de covariância via $\\lambda_i = \\frac{s_i^2}{n-1}$. Os componentes principais são dados por $XV = USV^TV = US$\n\nResumindo:\n\n1. Se $X = USV^T$, então as colunas de V são as direções/eixos principais;\n2. As colunas de $US$ são os componentes principais;\n3. *Singular values* estão relacionados aos autovalores da matriz de covariância via $\\lambda_i = \\frac{s_i^2}{n-1}$;\n4. Scores padronizados (*standardized*) são dados pelas colunas de $\\sqrt{n-1}U$ e *loadings* são dados pelas colunas de $\\frac{VS}{\\sqrt{n-1}}$. Veja [este link](https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/125684) e [este](https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/143905) para entender as diferenças entre *loadings* e *principal directions*;\n5. As fórmulas acima só são válidas se $X$ está centralizado, ou seja, somente quando a matriz de covariância é igual a $\\frac{X^TX}{n-1}$;\n6. As proposições acima estão corretas somente quando $X$ for representado por uma matriz onde as linhas são amostras e as colunas são atributos. Caso contrário, $U$ e $V$ tem interpretações contrárias. Isto é, $U, V = V, U$;\n7. Para reduzir a dimensionalidade com o PCA baseado no SVD, selecione as *k*-ésimas primeiras colunas de U, e $k\\times k$ parte superior de S. O produto $U_kS_k$ é a matriz $n \\times k$ necessária para conter os primeiros $k$ PCs.\n8. Para reconstruir os dados originais a partir dos primeiros $k$ PCs, multiplicá-los pelo eixos principais correspondentes $V_k^T$ produz a matriz $X_k = U_kS_kV_k^T$ que tem o tamanho original $n \\times p$. Essa forma gera a matriz reconstruída com o menor erro de reconstrução possível dos dados originais. [Veja esse link](https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/130721);\n9. Estritamente falando, $U$ é de tamanho $n \\times n$ e $V$ é de tamanho $p \\times p$. Entretanto, se $n > p$ então as últimas $n-p$ colunas de $U$ são arbitrárias (e as linhas correspondentes de $S$ são constantes e iguais a zero).\n\n### 1.2.4 Verificação dos autovetores e autovalores\n\nPara verificar se os autovetores e autovalores calculados na autodecomposição estão corretos, devemos verificar se eles satisfazem a equação para cada autovetor e autovalor correspondente:\n\n$$\\Sigma \\overrightarrow{v} = \\lambda \\overrightarrow{v}$$\n\nonde:\n$$\\Sigma = Matriz\\,de\\,Covariância$$\n$$\\overrightarrow{v} = autovetor$$\n$$\\lambda = autovalor$$\n\n### 1.2.5 Escolha dos autovetores e autovalores\n\nComo dito, o objetivo típico do PCA é reduzir a dimensionalidade dos dados pela projeção em um subespaço menor, onde os autovetores formam os eixos. Entretando, os autovetores definem somente as direções dos novos eixos, já que todos eles tem tamanho 1. Logo, para decidir qual(is) autovetor(es) podemos descartar sem perder muita informação na construção do nosso subespaço, precisamos verificar os autovalores correspondentes. **Os autovetores com os maiores valores são os que contém mais informação sobre a distribuição dos nossos dados**. Esse são os autovetores que queremos.\n\nPara fazer isso, devemos ordenar os autovalores em ordem decrescente para escolher o top k autovetores.\n\n### 1.2.6 Cálculo da Informação\n\nApós ordenar os autovalores, o próximo passo é **definir quantos componentes principais serão escolhidos para o nosso novo subespaço**. Para fazer isso, podemos utilizar o método da *variância explicada*, que calcula quanto de informação (variância) é atribuida a cada componente principal.\n\n## 1. 3 Matriz de Projeção\n\nNa prática, a matriz de projeção nada mais é que os top k autovetores concatenados. Portanto, se queremos reduzir o nosso espaço 4-dimensional para um espaço 2-dimensional, devemos escolher os 2 autovetores com os 2 maiores autovalores para construir nossa matriz W (d$\\times$k).\n\n## 1.4 Projeção no novo subespaço\n\nO último passo do PCA é utilizar a nossa matriz de projeção dimensional W (4x2, onde cada coluna representa um autovetor) para transformar nossas amostras em um novo subespaço. Para isso, basta aplicar a seguinte equação:\n\n$$S = (X-\\mu_X) \\times W$$\n\nOnde cada linha em S contém os pesos para cada atributo (coluna da matriz) no novo subespaço.\n\nA título de curiosidade, repare que se W representasse todos os autovetores - e não somente os escolhidos -, poderíamos recompor cada instância em X pela seguinte fórmula:\n\n$$X = (S \\times W^{-1}) + \\mu_X$$\n\nNovamente, cada linha em S representa os pesos para cada atributo, só que dessa vez seria possível representar X pela soma de cada autovetor multiplicado por um peso.\n\n## 1.5 Recomendações\n\n- Sempre normalize os atributos antes de aplicar o PCA (StandarScaler);\n- Lembre-se de armazenar a média para efetuar a ida e volta;\n- Não aplique o PCA após outros algoritmos de seleção de atributos ([fonte](https://www.quora.com/Should-I-apply-PCA-before-or-after-feature-selection));\n- O número de componentes principais que você quer manter deve ser escolhido através da análise entre o número de componentes e a precisão do sistema. Nem sempre mais componentes principais ocasionam em melhor precisão!",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 2. Dados",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"iris = load_iris()\n\ndf = pd.DataFrame(data=iris.data, columns=iris.feature_names)\ndf['class'] = iris.target\ndf",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.describe()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x = df.drop(labels='class', axis=1).values\ny = df['class'].values\n\nprint(x.shape, y.shape)",
"(150, 4) (150,)\n"
]
],
[
[
"# 3. Implementação ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class MyPCACov():\n def __init__(self, n_components=None):\n self.n_components = n_components\n self.eigen_values = None\n self.eigen_vectors = None\n \n def fit(self, x):\n self.n_components = x.shape[1] if self.n_components is None else self.n_components\n self.mean_ = np.mean(x, axis=0)\n \n cov_matrix = np.cov(x - self.mean_, rowvar=False)\n \n self.eigen_values, self.eigen_vectors = np.linalg.eig(cov_matrix)\n self.eigen_vectors = self.eigen_vectors.T\n \n self.sorted_components_ = np.argsort(self.eigen_values)[::-1]\n \n self.projection_matrix_ = self.eigen_vectors[self.sorted_components_[:self.n_components]]\n\n self.explained_variance_ = self.eigen_values[self.sorted_components_]\n self.explained_variance_ratio_ = self.explained_variance_ / self.eigen_values.sum()\n \n def transform(self, x):\n return np.dot(x - self.mean_, self.projection_matrix_.T)\n \n def inverse_transform(self, x):\n return np.dot(x, self.projection_matrix_) + self.mean_",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class MyPCASVD():\n def __init__(self, n_components=None):\n self.n_components = n_components\n self.eigen_values = None\n self.eigen_vectors = None\n \n def fit(self, x):\n self.n_components = x.shape[1] if self.n_components is None else self.n_components\n self.mean_ = np.mean(x, axis=0)\n \n U, s, Vt = np.linalg.svd(x - self.mean_, full_matrices=False) # a matriz s já retorna ordenada\n# S = np.diag(s)\n \n self.eigen_vectors = Vt\n self.eigen_values = s\n \n self.projection_matrix = self.eigen_vectors[:self.n_components]\n\n self.explained_variance_ = (self.eigen_values ** 2) / (x.shape[0] - 1)\n self.explained_variance_ratio_ = self.explained_variance_ / self.explained_variance_.sum()\n \n def transform(self, x):\n return np.dot(x - self.mean_, self.projection_matrix.T)\n \n def inverse_transform(self, x):\n return np.dot(x, self.projection_matrix) + self.mean_",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 4. Teste ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"std = StandardScaler()\nx_std = StandardScaler().fit_transform(x)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### PCA implementado pela matriz de covariância",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pca_cov = MyPCACov(n_components=2)\npca_cov.fit(x_std)\n\nprint('Autovetores: \\n', pca_cov.eigen_vectors)\nprint('Autovalores: \\n', pca_cov.eigen_values)\nprint('Variância explicada: \\n', pca_cov.explained_variance_)\nprint('Variância explicada (ratio): \\n', pca_cov.explained_variance_ratio_)\nprint('Componentes ordenados: \\n', pca_cov.sorted_components_)",
"Autovetores: \n [[ 0.52106591 -0.26934744 0.5804131 0.56485654]\n [-0.37741762 -0.92329566 -0.02449161 -0.06694199]\n [-0.71956635 0.24438178 0.14212637 0.63427274]\n [ 0.26128628 -0.12350962 -0.80144925 0.52359713]]\nAutovalores: \n [ 2.93808505 0.9201649 0.14774182 0.02085386]\nVariância explicada: \n [ 2.93808505 0.9201649 0.14774182 0.02085386]\nVariância explicada (ratio): \n [ 0.72962445 0.22850762 0.03668922 0.00517871]\nComponentes ordenados: \n [0 1 2 3]\n"
],
[
"x_std_proj = pca_cov.transform(x_std)\n\nplt.figure()\nplt.scatter(x_std_proj[:, 0], x_std_proj[:, 1], c=y)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x_std_back = pca_cov.inverse_transform(x_std_proj)\n\nprint(x_std[:5])\nprint(x_std_back[:5])",
"[[-0.90068117 1.01900435 -1.34022653 -1.3154443 ]\n [-1.14301691 -0.13197948 -1.34022653 -1.3154443 ]\n [-1.38535265 0.32841405 -1.39706395 -1.3154443 ]\n [-1.50652052 0.09821729 -1.2833891 -1.3154443 ]\n [-1.02184904 1.24920112 -1.34022653 -1.3154443 ]]\n[[-0.99888895 1.05319838 -1.30270654 -1.24709825]\n [-1.33874781 -0.06192302 -1.22432772 -1.22057235]\n [-1.36096129 0.32111685 -1.38060338 -1.35833824]\n [-1.42359795 0.0677615 -1.34922386 -1.33881298]\n [-1.00113823 1.24091818 -1.37125365 -1.30661752]]\n"
]
],
[
[
"### PCA implementado pela SVD",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pca_svd = MyPCASVD(n_components=2)\npca_svd.fit(x_std)\n\nprint('Autovetores: \\n', pca_svd.eigen_vectors)\nprint('Autovalores: \\n', pca_svd.eigen_values)\nprint('Variância explicada: \\n', pca_svd.explained_variance_)\nprint('Variância explicada (ratio): \\n', pca_svd.explained_variance_ratio_)",
"Autovetores: \n [[ 0.52106591 -0.26934744 0.5804131 0.56485654]\n [-0.37741762 -0.92329566 -0.02449161 -0.06694199]\n [ 0.71956635 -0.24438178 -0.14212637 -0.63427274]\n [ 0.26128628 -0.12350962 -0.80144925 0.52359713]]\nAutovalores: \n [ 20.92306556 11.7091661 4.69185798 1.76273239]\nVariância explicada: \n [ 2.93808505 0.9201649 0.14774182 0.02085386]\nVariância explicada (ratio): \n [ 0.72962445 0.22850762 0.03668922 0.00517871]\n"
],
[
"x_std_proj = pca_svd.transform(x_std)\n\nplt.figure()\nplt.scatter(x_std_proj[:, 0], x_std_proj[:, 1], c=y)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x_std_back = pca_svd.inverse_transform(x_std_proj)\n\nprint(x_std[:5])\nprint(x_std_back[:5])",
"[[-0.90068117 1.01900435 -1.34022653 -1.3154443 ]\n [-1.14301691 -0.13197948 -1.34022653 -1.3154443 ]\n [-1.38535265 0.32841405 -1.39706395 -1.3154443 ]\n [-1.50652052 0.09821729 -1.2833891 -1.3154443 ]\n [-1.02184904 1.24920112 -1.34022653 -1.3154443 ]]\n[[-0.99888895 1.05319838 -1.30270654 -1.24709825]\n [-1.33874781 -0.06192302 -1.22432772 -1.22057235]\n [-1.36096129 0.32111685 -1.38060338 -1.35833824]\n [-1.42359795 0.0677615 -1.34922386 -1.33881298]\n [-1.00113823 1.24091818 -1.37125365 -1.30661752]]\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Comparação com o Scikit-learn",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pca_sk = PCA(n_components=2)\npca_sk.fit(x_std)\n\nprint('Autovetores: \\n', pca_sk.components_)\nprint('Autovalores: \\n', pca_sk.singular_values_)\nprint('Variância explicada: \\n', pca_sk.explained_variance_)\nprint('Variância explicada (ratio): \\n', pca_sk.explained_variance_ratio_)",
"Autovetores: \n [[ 0.52106591 -0.26934744 0.5804131 0.56485654]\n [ 0.37741762 0.92329566 0.02449161 0.06694199]]\nAutovalores: \n [ 20.92306556 11.7091661 ]\nVariância explicada: \n [ 2.93808505 0.9201649 ]\nVariância explicada (ratio): \n [ 0.72962445 0.22850762]\n"
],
[
"x_std_proj_sk = pca_sk.transform(x_std)\n\nplt.figure()\nplt.scatter(x_std_proj_sk[:, 0], x_std_proj_sk[:, 1], c=y)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x_std_back_sk = pca_sk.inverse_transform(x_std_proj_sk)\n\nprint(x_std[:5])\nprint(x_std_back_sk[:5])",
"[[-0.90068117 1.01900435 -1.34022653 -1.3154443 ]\n [-1.14301691 -0.13197948 -1.34022653 -1.3154443 ]\n [-1.38535265 0.32841405 -1.39706395 -1.3154443 ]\n [-1.50652052 0.09821729 -1.2833891 -1.3154443 ]\n [-1.02184904 1.24920112 -1.34022653 -1.3154443 ]]\n[[-0.99888895 1.05319838 -1.30270654 -1.24709825]\n [-1.33874781 -0.06192302 -1.22432772 -1.22057235]\n [-1.36096129 0.32111685 -1.38060338 -1.35833824]\n [-1.42359795 0.0677615 -1.34922386 -1.33881298]\n [-1.00113823 1.24091818 -1.37125365 -1.30661752]]\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Observação sobre a implementação do Scikit-learn\n\nPor algum motivo (que não sei qual), a [implementação do scikit-learn](https://github.com/scikit-learn/scikit-learn/blob/master/sklearn/decomposition/pca.py) inverte os sinais de alguns valores na matriz de autovetores. Na implementação, as matrizes $U$ e $V$ são passada para um método ```svd_flip``` (implementada [nesse arquivo](https://github.com/scikit-learn/scikit-learn/blob/master/sklearn/utils/extmath.py)):\n\n```py\nU, V = svd_flip(U[:, ::-1], V[::-1])\n```\n\nRepare que isso muda apenas os dados projetados. No gráfico, isso inverte os eixos correspondentes apenas. No entanto, os **autovalores**, a ```explained_variance```, ```explained_variance_ratio``` e os dados reprojetados ao espaço original são exatamente iguais.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 5. Referências",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"- [Antigo notebook do PCA com explicações passo-a-passo](https://github.com/arnaldog12/Machine_Learning/blob/62b628bd3c37ec2fa52e349f38da24751ef67313/PCA.ipynb)\n- [Principal Component Analysis in Python](https://plot.ly/ipython-notebooks/principal-component-analysis/)\n- [Implementing a Principal Component Analysis (PCA)](https://sebastianraschka.com/Articles/2014_pca_step_by_step.html)\n- [Relationship between SVD and PCA. How to use SVD to perform PCA?](https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/134282/relationship-between-svd-and-pca-how-to-use-svd-to-perform-pca)\n- [How to reverse PCA and reconstruct original variables from several principal components?](https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/229092/how-to-reverse-pca-and-reconstruct-original-variables-from-several-principal-com)\n- [Everything you did and didn't know about PCA](http://alexhwilliams.info/itsneuronalblog/2016/03/27/pca/)\n- [Unpacking (** PCA )](https://towardsdatascience.com/unpacking-pca-b5ea8bec6aa5)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4abdf54819cf1ddee09952c1a07adce622b18724
| 12,755 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
array_strings/ipynb/add_binary.ipynb
|
PRkudupu/Algo-python
|
a0b9c3e19e4ece48f5dc47e34860510565ab2f38
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2019-05-04T00:43:52.000Z
|
2019-05-04T00:43:52.000Z
|
array_strings/ipynb/add_binary.ipynb
|
PRkudupu/Algo-python
|
a0b9c3e19e4ece48f5dc47e34860510565ab2f38
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
array_strings/ipynb/add_binary.ipynb
|
PRkudupu/Algo-python
|
a0b9c3e19e4ece48f5dc47e34860510565ab2f38
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 24.912109 | 119 | 0.39851 |
[
[
[
"## Given two binary strings, return their sum (also a binary string).\n\nThe input strings are both non-empty and contains only characters 1 or 0.\n\n### Example 1:\n\nInput: a = \"11\", b = \"1\"\nOutput: \"100\"\n### Example 2:\n\nInput: a = \"1010\", b = \"1011\"\nOutput: \"10101\"\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def add_binary(a,b):\n return '{0:b}'.format(int(a, 2) + int(b, 2))\n\nprint(add_binary('11','11'))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This method has quite low performance in the case of large input numbers.\n\nOne could use Bit Manipulation approach to speed up the solution.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
" ### Logic\n \n \n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### 1.Find the maxlength\n#### 2.Based on the length fill with zero\n#### 3.Create a variable for carry and result\n#### 4.Loop through tail, check if value is \"1\" .If yes then increment carry\n#### 5.if Carry % 2 == 1 then append 1 else zero\n#### 6. Divide carry by 2 (Keep doing this for all the elements in the array)\n#### 7. Outside the loop if carry is 1 then append 1\n#### 8. Reverse the string and join all the values\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Program with comments\ndef add_binary(a,b):\n n = max(len(a), len(b))\n print('\\nlength',n)\n a, b = a.zfill(n), b.zfill(n)\n print('zfill a,b',a,b)\n carry = 0\n result = []\n for i in range(n - 1, -1, -1):\n print('\\ni',i)\n print('carry on top',carry)\n if a[i] == '1':\n carry += 1\n if b[i] == '1':\n carry += 1\n\n if carry % 2 == 1:\n result.append('1')\n else:\n result.append('0')\n print('\\a[i]',a[i])\n print('\\b[i]',b[i])\n print('carry after increement',carry)\n print('carry % 2',carry % 2)\n print('answer',result)\n #carry =cary//2\n print(\"Carry=carry// 2\", carry)\n carry //= 2\n print(\"After division carry\", carry)\n if carry == 1:\n result.append('1')\n print('result',result)\n result.reverse()\n\n return ''.join(result)\nprint(add_binary('01','11'))",
"\nlength 2\nzfill a,b 01 11\n\ni 1\ncarry on top 0\n\u0007[i] 1\n\b[i] 1\ncarry after increement 2\ncarry % 2 0\nanswer ['0']\nCarry=carry// 2 2\nAfter division carry 1\n\ni 0\ncarry on top 1\n\u0007[i] 0\n\b[i] 1\ncarry after increement 2\ncarry % 2 0\nanswer ['0', '0']\nCarry=carry// 2 2\nAfter division carry 1\nresult ['0', '0', '1']\n100\n"
],
[
"# Program without comments\ndef add_binary(a,b):\n n = max(len(a), len(b))\n a, b = a.zfill(n), b.zfill(n)\n carry = 0\n result = []\n for i in range(n - 1, -1, -1):\n if a[i] == '1':\n carry += 1\n if b[i] == '1':\n carry += 1\n\n if carry % 2 == 1:\n result.append('1')\n else:\n result.append('0')\n carry //= 2\n if carry == 1:\n result.append('1')\n result.reverse()\n return ''.join(result) \nprint(add_binary('10','110'))",
"1000\n"
]
],
[
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def addBinary(a, b) -> str:\n x, y = int(a, 2), int(b, 2)\n while y:\n answer = x ^ y\n carry = (x & y) << 1\n x, y = answer, carry\n return bin(x)[2:]\nprint(addBinary('001','101'))",
"110\n"
]
],
[
[
" def addBinary( a, b):\n if len(a)==0: return b\n if len(b)==0: return a\n if a[-1] == '1' and b[-1] == '1':\n return addBinary(addBinary(a[0:-1],b[0:-1]),'1')+'0' \n if a[-1] == '0' and b[-1] == '0':\n return addBinary(a[0:-1],b[0:-1])+'0'\n else:\n return addBinary(a[0:-1],b[0:-1])+'1'",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# addBinary(addBinary(1,[]),1)+'0' \n# addBinary(addBinary(1,[]),1) + '0' ==> addBinary(1,[]) return a =1 B\n# addBinary(1,1)+'0' \n# return {addBinary(addBinary(a[0:-1],b[0:-1]),'1')+'0' } +'0' ==> addBinary(a[0:-1],b[0:-1]) return empty A\n# return {addBinary(empty,'1')+'0' } +'0' ===> addBinary(empty,'1') return 1 A\n#1 +'0' +'0' ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"addBinary(\"11\",\"1\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def add_binary(a,b):\n print(\"len(a) {}\".format(len(a)))\n print(\"len(b) {}\".format(len(b)))\n print(\"a[-1] {}\".format(a[-1])) \n print(\"b[-1] {}\".format(b[-1]))\n print(\"a[0:-1]) {}\".format(a[0:-1])) \n print(\"b[0:-1]) {}\".format(b[0:-1]))\n if len(a)==0:\n print(\"len a==0\")\n return b\n if len(b)==0:\n print(\"len b==0\")\n return a\n if a[-1] == '1' and b[-1] == '1':\n print(\"First if condition 1,1\")\n return addBinary(addBinary(a[0:-1],b[0:-1]),'1')+'0'\n if a[-1] == '0' and b[-1] == '0':\n print(\"Second if condition 0,0\")\n return add_binary(a[0:-1],b[0:-1])+'0'\n else:\n print(\"Else\")\n return add_binary(a[0:-1],b[0:-1])+'1'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"add_binary(\"1010\",\"1011\")",
"len(a) 4\nlen(b) 4\na[-1] 0\nb[-1] 1\na[0:-1]) 101\nb[0:-1]) 101\nElse\nlen(a) 3\nlen(b) 3\na[-1] 1\nb[-1] 1\na[0:-1]) 10\nb[0:-1]) 10\nFirst if condition 1,1\n"
],
[
"def add_binary_nums(x, y):\n print((len(x)))\n print((len(x)))\n max_len = max(len(x), len(y)) \n print(\"max_len {}\".format(max_len))\n \n print()\n #Fill it with zeros\n x = x.zfill(max_len) \n print(\"x {}\".format(x))\n y = y.zfill(max_len)\n print(\"y {}\".format(y))\n print(y)\n \n # initialize the result \n result = '' \n \n # initialize the carry \n carry = 0\n \n # Traverse the string \n for i in range(max_len - 1, -1, -1): \n r = carry \n r += 1 if x[i] == '1' else 0\n r += 1 if y[i] == '1' else 0\n result = ('1' if r % 2 == 1 else '0') + result \n carry = 0 if r < 2 else 1 # Compute the carry. \n \n if carry !=0 : result = '1' + result \n \n return result.zfill(max_len) \n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"add_binary_nums('100','10')",
"3\n3\nmax_len 3\n\nx 100\ny 010\n010\n"
],
[
"\"\"\"\nThis is the same solution with print\nNote: carry //=2\n This step is needed to carry the current unit\n\"\"\"\ndef add_binary(a,b):\n n = max(len(a), len(b))\n a, b = a.zfill(n), b.zfill(n)\n carry = 0\n result = []\n for i in range(n - 1, -1, -1):\n if a[i] == '1':\n carry += 1\n if b[i] == '1':\n carry += 1\n print('\\na',a[i])\n print('b',b[i])\n \n if carry % 2 == 1:\n result.append('1')\n else:\n result.append('0')\n print('carry',carry % 2 == 1)\n print('result',result)\n print('\\nb4 carry',carry)\n carry //= 2\n print('out carry',carry)\n if carry == 1:\n result.append('1')\n print('result',result)\n result.reverse()\n return ''.join(result) \n\nprint(add_binary('10','111'))\nprint(0//2)\nprint(1//2)\n",
"\na 0\nb 1\ncarry True\nresult ['1']\n\nb4 carry 1\nout carry 0\n\na 1\nb 1\ncarry False\nresult ['1', '0']\n\nb4 carry 2\nout carry 1\n\na 0\nb 1\ncarry False\nresult ['1', '0', '0']\n\nb4 carry 2\nout carry 1\nresult ['1', '0', '0', '1']\n1001\n0\n0\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
4abe0be6d5e04c8f521f9229a02ab99a2a7dd6c1
| 6,606 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
chap4-solutions.ipynb
|
dominhhai/rl-intro
|
9967ac93af34d6104ea0e0a2abb1127f1426a156
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2018-07-26T07:46:09.000Z
|
2018-08-02T12:51:40.000Z
|
chap4-solutions.ipynb
|
dominhhai/rl-intro
|
9967ac93af34d6104ea0e0a2abb1127f1426a156
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
chap4-solutions.ipynb
|
dominhhai/rl-intro
|
9967ac93af34d6104ea0e0a2abb1127f1426a156
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2018-08-28T04:16:59.000Z
|
2018-11-16T14:29:09.000Z
| 30.027273 | 202 | 0.480775 |
[
[
[
"# Chapter 3: Dynamic Programming",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 1. Exercise 4.1\n$\\pi$ is equiprobable random policy, so all actions equally likely.\n\n- $q_\\pi(11, down)$\n\nWith current state $s=11$ and action $a=down$, we have next is the terminal state $s'=end$, which have reward $R'=0$\n\n$$\n\\begin{aligned}\nq_\\pi(11, down) &= \\sum_{s',r}p(s',r | s,a)\\big[r+\\gamma v_\\pi(s')\\big]\n\\cr &= 1 * (-1 + 0)\n\\cr &= -1\n\\end{aligned}\n$$\n\n- $q_\\pi(7, down)$\n\nWith current state $s=7$ and action $a=down$, we have next is the terminal state $s'=11$, which have state-value function $v_\\pi(s)$\n\n$$\n\\begin{aligned}\nq_\\pi(7, down) &= \\sum_{s',r}p(s',r | s,a)\\big[r+\\gamma v_\\pi(s')\\big]\n\\cr &= 1 * \\big[-1 + \\gamma v_\\pi(s')\\big]\n\\cr &= -1 + \\gamma v_\\pi(s')\n\\end{aligned}\n$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 2. Exercise 4.2\n- Transitions from the original states are unchanged\n$$\n\\begin{aligned}\nv_\\pi(15) &= \\sum_a \\pi(a|s=15)\\sum_{s',r}p(s',r|s,a)\\big[r+\\gamma v_\\pi(s')\\big]\n\\cr &= 0.25\\big[1*\\big(-1+\\gamma v_\\pi(12)\\big)+1*\\big(-1+\\gamma v_\\pi(13)\\big)+1*\\big(-1+\\gamma v_\\pi(14)\\big)+1*\\big(-1+\\gamma v_\\pi(15)\\big)\\big]\n\\cr &= -1 + 0.25\\gamma\\sum_{s=12}^{15}v_\\pi(s)\n\\end{aligned}\n$$\n\nIn which, $\\displaystyle v_\\pi(13)=-1 + 0.25\\gamma\\sum_{s\\in\\{9,12,13,14\\}}v_\\pi(s)$ \n- Add action **down** to state 13, to go to state 15\n\nCompute Fomular is similar to above:\n$$v_\\pi(15)=-1 + 0.25\\gamma\\sum_{s=12}^{15}v_\\pi(s)$$\n\nBut, $\\displaystyle v_\\pi(13)=-1 + 0.25\\gamma\\sum_{s\\in\\{9,12,14,15\\}}v_\\pi(s)$ ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 3. Exercise 4.3\n- $q_\\pi$ evaluation\n$$\n\\begin{aligned}\nq_\\pi(s, a) &= E[G_t | S_t=s, A_t=a]\n\\cr &= E[R_{t+1}+\\gamma G_{t+1} | S_t=s, A_t=a]\n\\cr &= E[R_{t+1}+\\gamma V_\\pi(S_{t+1}) | S_t=s, A_t=a]\n\\cr &= \\sum_{s',r}p(s',r | s,a)\\big[r+\\gamma v_\\pi(s')\\big]\n\\end{aligned}\n$$\n\n- Update rule for $q_\\pi$\n$$\n\\begin{aligned}\nq_{k+1}(s, a) &= E_\\pi[R_{t+1} + \\gamma v_k(S_{t+1}) | S_t=s, A_t=a]\n\\cr &= \\sum_{s',r}p(s',r | s,a)\\big[r+\\gamma v_k(s')\\big]\n\\cr &= \\sum_{s',r}p(s',r | s,a)\\Big[r+\\gamma \\sum_{a'\\in\\mathcal A(s')}\\pi(a' | s')q_k(s', a')\\Big]\n\\end{aligned}\n$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 4. Exercise 4.4\nWhen, the policy continually switches between two or more policies that are equally good, the difference between switches is small, so policy evaluation loop will be breaked before convergence.\n\n$$\\Delta = \\max\\big(\\Delta, | v-V(s) |\\big)$$\n\nSo, in this case, it maybe useful if we talk the sum of all differences\n$$\\Delta = \\Delta + | v-V(s) |$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 5. Exercise 4.5\n\nPolicy Iteration algorithm for action values\n\n### 1. Initialization\n$\\quad \\pi(s)\\in\\mathcal A(s)$ and $Q(s,a)\\in\\mathbb R$ arbitrarily for all $s\\in\\mathcal S$ and $a\\in\\mathcal A(s)$\n\n### 2. Policy Evaluation\n$\\quad$Loop:\n \n$\\quad\\quad \\Delta\\gets0$\n\n$\\quad\\quad$ Loop for each $s\\in\\mathcal S$\n\n$\\quad\\quad\\quad$ Loop for each $a\\in\\mathcal A(s)$\n\n$\\quad\\quad\\quad\\quad q\\gets Q(s,a)$\n\n$\\quad\\quad\\quad\\quad \\displaystyle Q(s,a)\\gets \\sum_{s',r}p(s',r | s,a)\\Big[r+\\gamma \\sum_{a'\\in\\mathcal A(s')}\\pi(a' | s')Q(s', a')\\Big]$\n\n$\\quad\\quad\\quad\\quad \\Delta\\gets \\Delta+\\big| q- Q(s,a)\\big|$\n\n$\\quad\\quad \\text{until }\\Delta<\\theta$ a small positive number determining the accuracy of estimation\n\n\n### 3. Policy Improvement\n$\\quad\\textit{policy-stable}\\gets\\textit{true}$\n\n$\\quad$For each $s\\in\\mathcal S$\n\n$\\quad\\quad \\textit{old-aciton}\\gets\\pi(s)$\n\n$\\quad\\quad \\pi(s)\\gets\\arg\\max_a Q(s,a)$\n\n$\\quad\\quad$If $\\textit{old-aciton}\\neq\\pi(s)$, then $\\textit{policy-stable}\\gets\\textit{false}$\n\n$\\quad$If $\\textit{policy-stable}$, then stop and return $Q\\approx q_*$ and $\\pi\\approx\\pi_*$; else go to $2$\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 6. Exercise 4.6\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 7. Exercise 4.7",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 8. Exercise 4.8",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 9. Exercise 4.9",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 10. Exercise 4.10\nValue iteration update for action values, $q_{k+1}(s,a)$\n\n$$\n\\begin{aligned}\nq_{k+1}(s,a) &= \\max E\\big[R_{t+1}+\\gamma v_k(S_{t+1}) | S_t=s,A_t=a\\big]\n\\cr &= \\max\\sum_{s',r}p(s',r | s,a)\\big[r+\\gamma v_k(s')\\big]\n\\cr &= \\max\\sum_{s',r}p(s',r | s,a)\\big[r+\\gamma\\sum_{a'\\in\\mathcal A(s')}\\pi(a' | s')q_k(s', a')\\big]\n\\end{aligned}\n$$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
4abe1a04776afb0a0a5e4fe8bf5bb2c7be979362
| 33,420 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
examples/07_Pyro_Integration/Pyro_GPyTorch_High_Level.ipynb
|
wecacuee/gpytorch
|
cd7c19bcf853d91b8b30eead99cffc9efe933c43
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2021-10-30T03:50:28.000Z
|
2022-02-22T22:01:14.000Z
|
examples/07_Pyro_Integration/Pyro_GPyTorch_High_Level.ipynb
|
francescovaroli/gpytorch
|
273536b5620f65308ad0875d6ab4d1ac900555c2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
examples/07_Pyro_Integration/Pyro_GPyTorch_High_Level.ipynb
|
francescovaroli/gpytorch
|
273536b5620f65308ad0875d6ab4d1ac900555c2
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2020-09-18T18:58:12.000Z
|
2021-05-27T15:39:00.000Z
| 107.459807 | 17,372 | 0.851466 |
[
[
[
"\n# Predictions with Pyro + GPyTorch (High-Level Interface)\n\n## Overview\n\nIn this example, we will give an overview of the high-level Pyro-GPyTorch integration - designed for predictive models.\nThis will introduce you to the key GPyTorch objects that play with Pyro. Here are the key benefits of the integration:\n\n**Pyro provides:**\n\n- The engines for performing approximate inference or sampling\n- The ability to define additional latent variables\n\n**GPyTorch provides:**\n\n- A library of kernels/means/likelihoods\n- Mechanisms for efficient GP computations",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import math\nimport torch\nimport pyro\nimport tqdm\nimport gpytorch\nfrom matplotlib import pyplot as plt\n\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"In this example, we will be doing simple variational regression to learn a monotonic function. This example is doing the exact same thing as [GPyTorch's native approximate inference](../04_Variational_and_Approximate_GPs/SVGP_Regression_CUDA.ipynb), except we're now using Pyro's variational inference engine.\n\nIn general - if this was your dataset, you'd be better off using GPyTorch's native exact or approximate GPs.\n(We're just using a simple example to introduce you to the GPyTorch/Pyro integration).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"train_x = torch.linspace(0., 1., 21)\ntrain_y = torch.pow(train_x, 2).mul_(3.7)\ntrain_y = train_y.div_(train_y.max())\ntrain_y += torch.randn_like(train_y).mul_(0.02)\n\nfig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(3, 2))\nax.plot(train_x.numpy(), train_y.numpy(), 'bo')\nax.set_xlabel('x')\nax.set_ylabel('y')\nax.legend(['Training data'])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## The PyroGP model\n\nIn order to use Pyro with GPyTorch, your model must inherit from `gpytorch.models.PyroGP` (rather than `gpytorch.modelks.ApproximateGP`). The `PyroGP` extends the `ApproximateGP` class and differs in a few key ways:\n\n- It adds the `model` and `guide` functions which are used by Pyro's inference engine.\n- It's constructor requires two additional arguments beyond the variational strategy:\n - `likelihood` - the model's likelihood\n - `num_data` - the total amount of training data (required for minibatch SVI training)\n - `name_prefix` - a unique identifier for the model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class PVGPRegressionModel(gpytorch.models.PyroGP):\n def __init__(self, train_x, train_y, likelihood):\n # Define all the variational stuff\n variational_distribution = gpytorch.variational.CholeskyVariationalDistribution(\n num_inducing_points=train_y.numel(),\n )\n variational_strategy = gpytorch.variational.VariationalStrategy(\n self, train_x, variational_distribution\n )\n \n # Standard initializtation\n super(PVGPRegressionModel, self).__init__(\n variational_strategy,\n likelihood,\n num_data=train_y.numel(),\n name_prefix=\"simple_regression_model\"\n )\n self.likelihood = likelihood\n \n # Mean, covar\n self.mean_module = gpytorch.means.ConstantMean()\n self.covar_module = gpytorch.kernels.ScaleKernel(\n gpytorch.kernels.MaternKernel(nu=1.5)\n )\n\n def forward(self, x):\n mean = self.mean_module(x) # Returns an n_data vec\n covar = self.covar_module(x)\n return gpytorch.distributions.MultivariateNormal(mean, covar)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model = PVGPRegressionModel(train_x, train_y, gpytorch.likelihoods.GaussianLikelihood())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Performing inference with Pyro\n\nUnlike all the other examples in this library, `PyroGP` models use Pyro's inference and optimization classes (rather than the classes provided by PyTorch).\n\nIf you are unfamiliar with Pyro's inference tools, we recommend checking out the [Pyro SVI tutorial](http://pyro.ai/examples/svi_part_i.html).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# this is for running the notebook in our testing framework\nimport os\nsmoke_test = ('CI' in os.environ)\nnum_iter = 2 if smoke_test else 200\nnum_particles = 1 if smoke_test else 256\n\n\ndef train(lr=0.01):\n optimizer = pyro.optim.Adam({\"lr\": 0.1})\n elbo = pyro.infer.Trace_ELBO(num_particles=num_particles, vectorize_particles=True, retain_graph=True)\n svi = pyro.infer.SVI(model.model, model.guide, optimizer, elbo)\n model.train()\n\n iterator = tqdm.tqdm_notebook(range(num_iter))\n for i in iterator:\n model.zero_grad()\n loss = svi.step(train_x, train_y)\n iterator.set_postfix(loss=loss)\n \n%time train()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"In this example, we are only performing inference over the GP latent function (and its associated hyperparameters). In later examples, we will see that this basic loop also performs inference over any additional latent variables that we define.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Making predictions\n\nFor some problems, we simply want to use Pyro to perform inference over latent variables. However, we can also use the models' (approximate) predictive posterior distribution. Making predictions with a PyroGP model is exactly the same as for standard GPyTorch models.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(4, 3))\ntrain_data, = ax.plot(train_x.cpu().numpy(), train_y.cpu().numpy(), 'bo')\n\nmodel.eval()\nwith torch.no_grad():\n output = model.likelihood(model(train_x))\n \nmean = output.mean\nlower, upper = output.confidence_region()\nline, = ax.plot(train_x.cpu().numpy(), mean.detach().cpu().numpy())\nax.fill_between(train_x.cpu().numpy(), lower.detach().cpu().numpy(),\n upper.detach().cpu().numpy(), color=line.get_color(), alpha=0.5)\nax.set_xlabel('x')\nax.set_ylabel('y')\nax.legend([train_data, line], ['Train data', 'Prediction'])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Next steps\n\nThis was a pretty boring example, and it wasn't really all that different from GPyTorch's native SVGP implementation! The real power of the Pyro integration comes when we have additional latent variables to infer over. We will see an example of this in the [next example](./Clustered_Multitask_GP_Regression.ipynb), which learns a clustering over multiple time series using multitask GPs and Pyro.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
4abe21e8093bd48a22817716082c06143ccd9398
| 2,465 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Chapter07/Exercise07_01/Test_Exercise07_01.ipynb
|
vishwesh5/The-Pandas-Workshop
|
60772d780e6015150715393b91a2e4b70c0e9eb3
|
[
"MIT"
] | 11 |
2020-05-11T17:03:15.000Z
|
2022-03-08T04:39:20.000Z
|
Chapter07/Exercise07_01/Test_Exercise07_01.ipynb
|
vishwesh5/The-Pandas-Workshop
|
60772d780e6015150715393b91a2e4b70c0e9eb3
|
[
"MIT"
] | 5 |
2021-04-06T18:40:18.000Z
|
2022-03-12T00:56:07.000Z
|
Chapter07/Exercise07_01/Test_Exercise07_01.ipynb
|
vishwesh5/The-Pandas-Workshop
|
60772d780e6015150715393b91a2e4b70c0e9eb3
|
[
"MIT"
] | 20 |
2020-05-19T11:39:43.000Z
|
2022-02-04T11:55:36.000Z
| 29.698795 | 145 | 0.530223 |
[
[
[
"import unittest\nimport pandas as pd\nimport import_ipynb\nimport pandas.testing as pd_testing\n\nclass Test(unittest.TestCase):\n def setUp(self):\n import Exercise06_01\n self.exercises = Exercise06_01\n\n self.file_url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/PacktWorkshops/The-Pandas-Workshop/master/Chapter06/Data/messy_addresses.csv'\n self.data_frame = pd.read_csv(self.file_url, header=None)\n\n def test_file_url(self):\n self.assertEqual(self.exercises.file_url, self.file_url)\n \n def test_df(self):\n self.data_frame.drop([2,3], axis=1, inplace=True)\n self.column_names = [\"full_name\", \"address\"]\n self.data_frame.columns = [\"full_name\", \"address\"]\n self.data_frame[['first_name','last_name']]=self.data_frame.full_name.str.split(expand=True)\n self.data_frame.drop('full_name', axis=1, inplace=True)\n self.data_frame[['street', 'city','state']] = self.data_frame.address.str.split(pat = \", \", expand=True)\n self.data_frame.drop('address', axis=1, inplace=True)\n pd_testing.assert_frame_equal(self.exercises.data_frame, self.data_frame)\n \n \n\nif __name__ == '__main__':\n unittest.main(argv=['first-arg-is-ignored'], exit=False)\n",
"importing Jupyter notebook from Exercise06_01.ipynb\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
]
] |
4abe38f03e671841f6fff0ee56dfb0d896fe95ab
| 98,495 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Notebook Exercises/Course 3 Lesson 5 Introduction to Data Lakes/Exercise 1 - Schema On Read.ipynb
|
senthilvel-dev/UD_DE
|
536cb92f47743b7a52fd62b91845992943965411
|
[
"MIT"
] | 42 |
2020-05-22T01:24:33.000Z
|
2022-03-28T14:51:13.000Z
|
Notebook Exercises/Course 3 Lesson 5 Introduction to Data Lakes/Exercise 1 - Schema On Read.ipynb
|
senthilvel-dev/UD_DE
|
536cb92f47743b7a52fd62b91845992943965411
|
[
"MIT"
] | 9 |
2020-12-17T21:21:08.000Z
|
2022-03-29T22:29:16.000Z
|
Notebook Exercises/Course 3 Lesson 5 Introduction to Data Lakes/Exercise 1 - Schema On Read.ipynb
|
vineeths96/Data-Engineering-Nanodegree
|
4b588607ca654db7e8a2469ab113d4323a1fc079
|
[
"MIT"
] | 30 |
2020-05-22T01:19:31.000Z
|
2022-03-13T20:06:28.000Z
| 43.562583 | 226 | 0.425808 |
[
[
[
"# Exercise 1: Schema on Read",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from pyspark.sql import SparkSession\nimport pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"spark = SparkSession.builder.getOrCreate()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dfLog = spark.read.text(\"data/NASA_access_log_Jul95.gz\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Load the dataset",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#Data Source: http://ita.ee.lbl.gov/traces/NASA_access_log_Jul95.gz\ndfLog = spark.read.text(\"data/NASA_access_log_Jul95.gz\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Quick inspection of the data set",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# see the schema\ndfLog.printSchema()",
"root\n |-- value: string (nullable = true)\n\n"
],
[
"# number of lines\ndfLog.count()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#what's in there? \ndfLog.show(5)",
"+--------------------+\n| value|\n+--------------------+\n|199.72.81.55 - - ...|\n|unicomp6.unicomp....|\n|199.120.110.21 - ...|\n|burger.letters.co...|\n|199.120.110.21 - ...|\n+--------------------+\nonly showing top 5 rows\n\n"
],
[
"#a better show?\ndfLog.show(5, truncate=False)",
"+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+\n|value |\n+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+\n|199.72.81.55 - - [01/Jul/1995:00:00:01 -0400] \"GET /history/apollo/ HTTP/1.0\" 200 6245 |\n|unicomp6.unicomp.net - - [01/Jul/1995:00:00:06 -0400] \"GET /shuttle/countdown/ HTTP/1.0\" 200 3985 |\n|199.120.110.21 - - [01/Jul/1995:00:00:09 -0400] \"GET /shuttle/missions/sts-73/mission-sts-73.html HTTP/1.0\" 200 4085 |\n|burger.letters.com - - [01/Jul/1995:00:00:11 -0400] \"GET /shuttle/countdown/liftoff.html HTTP/1.0\" 304 0 |\n|199.120.110.21 - - [01/Jul/1995:00:00:11 -0400] \"GET /shuttle/missions/sts-73/sts-73-patch-small.gif HTTP/1.0\" 200 4179|\n+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+\nonly showing top 5 rows\n\n"
],
[
"#pandas to the rescue\npd.set_option('max_colwidth', 200)\ndfLog.limit(5).toPandas()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Let' try simple parsing with split",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from pyspark.sql.functions import split\n\n# TODO\ndfArrays = dfLog.withColumn(\"tokenized\", split(\"value\",\" \"))\ndfArrays.limit(10).toPandas()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Second attempt, let's build a custom parsing UDF ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from pyspark.sql.functions import udf\n\n# TODO\n@udf\ndef parseUDF(line):\n import re\n PATTERN = '^(\\S+) (\\S+) (\\S+) \\[([\\w:/]+\\s[+\\-]\\d{4})\\] \"(\\S+) (\\S+)\\s*(\\S*)\" (\\d{3}) (\\S+)'\n match = re.search(PATTERN, line)\n if match is None:\n return (line, 0)\n size_field = match.group(9)\n if size_field == '-':\n size = 0\n else:\n size = match.group(9)\n return {\n \"host\" : match.group(1), \n \"client_identd\" : match.group(2), \n \"user_id\" : match.group(3), \n \"date_time\" : match.group(4), \n \"method\" : match.group(5),\n \"endpoint\" : match.group(6),\n \"protocol\" : match.group(7),\n \"response_code\" : int(match.group(8)),\n \"content_size\" : size\n }",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# TODO\ndfParsed= dfLog.withColumn(\"parsed\", parseUDF(\"value\"))\ndfParsed.limit(10).toPandas()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dfParsed.printSchema()",
"root\n |-- value: string (nullable = true)\n |-- parsed: string (nullable = true)\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Third attempt, let's fix our UDF",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#from pyspark.sql.functions import udf # already imported\nfrom pyspark.sql.types import MapType, StringType\n\n# TODO\n@udf(MapType(StringType(),StringType()))\ndef parseUDFbetter(line):\n import re\n PATTERN = '^(\\S+) (\\S+) (\\S+) \\[([\\w:/]+\\s[+\\-]\\d{4})\\] \"(\\S+) (\\S+)\\s*(\\S*)\" (\\d{3}) (\\S+)'\n match = re.search(PATTERN, line)\n if match is None:\n return (line, 0)\n size_field = match.group(9)\n if size_field == '-':\n size = 0\n else:\n size = match.group(9)\n return {\n \"host\" : match.group(1), \n \"client_identd\" : match.group(2), \n \"user_id\" : match.group(3), \n \"date_time\" : match.group(4), \n \"method\" : match.group(5),\n \"endpoint\" : match.group(6),\n \"protocol\" : match.group(7),\n \"response_code\" : int(match.group(8)),\n \"content_size\" : size\n }",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# TODO\ndfParsed= dfLog.withColumn(\"parsed\", parseUDFbetter(\"value\"))\ndfParsed.limit(10).toPandas()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# TODO\ndfParsed= dfLog.withColumn(\"parsed\", parseUDFbetter(\"value\"))\ndfParsed.limit(10).toPandas()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Bingo!! we'got a column of type map with the fields parsed\ndfParsed.printSchema()",
"root\n |-- value: string (nullable = true)\n |-- parsed: map (nullable = true)\n | |-- key: string\n | |-- value: string (valueContainsNull = true)\n\n"
],
[
"dfParsed.select(\"parsed\").limit(10).toPandas()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Let's build separate columns",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dfParsed.selectExpr(\"parsed['host'] as host\").limit(5).show(5)",
"+--------------------+\n| host|\n+--------------------+\n| 199.72.81.55|\n|unicomp6.unicomp.net|\n| 199.120.110.21|\n| burger.letters.com|\n| 199.120.110.21|\n+--------------------+\n\n"
],
[
"dfParsed.selectExpr([\"parsed['host']\", \"parsed['date_time']\"]).show(5)",
"+--------------------+--------------------+\n| parsed[host]| parsed[date_time]|\n+--------------------+--------------------+\n| 199.72.81.55|01/Jul/1995:00:00...|\n|unicomp6.unicomp.net|01/Jul/1995:00:00...|\n| 199.120.110.21|01/Jul/1995:00:00...|\n| burger.letters.com|01/Jul/1995:00:00...|\n| 199.120.110.21|01/Jul/1995:00:00...|\n+--------------------+--------------------+\nonly showing top 5 rows\n\n"
],
[
"fields = [\"host\", \"client_identd\",\"user_id\", \"date_time\", \"method\", \"endpoint\", \"protocol\", \"response_code\", \"content_size\"]\nexprs = [ \"parsed['{}'] as {}\".format(field,field) for field in fields]\nexprs",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dfClean = dfParsed.selectExpr(*exprs)\ndfClean.limit(5).toPandas()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Popular hosts",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from pyspark.sql.functions import desc\n\ndfClean.groupBy(\"host\").count().orderBy(desc(\"count\")).limit(10).toPandas()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Popular content",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from pyspark.sql.functions import desc\n\ndfClean.groupBy(\"endpoint\").count().orderBy(desc(\"count\")).limit(10).toPandas()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Large Files",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dfClean.createOrReplaceTempView(\"cleanlog\")\nspark.sql(\"\"\"\nselect endpoint, content_size\nfrom cleanlog \norder by content_size desc\n\"\"\").limit(10).toPandas()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from pyspark.sql.functions import expr\n\ndfCleanTyped = dfClean.withColumn(\"content_size_bytes\", expr(\"cast(content_size as int)\"))\ndfCleanTyped.limit(5).toPandas()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dfCleanTyped.createOrReplaceTempView(\"cleantypedlog\")\nspark.sql(\"\"\"\nselect endpoint, content_size\nfrom cleantypedlog \norder by content_size_bytes desc\n\"\"\").limit(10).toPandas()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from pyspark.sql.functions import col, unix_timestamp\n\nparsedDateDf = dfCleanTyped.withColumn(\n 'parsed_date_time',\n unix_timestamp(col('date_time'), \"dd/MMM/yyyy:HH:mm:ss Z\").cast(\"timestamp\")\n)\nparsedDateDf.limit(20).toPandas()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.