question_slug
stringlengths 3
77
| title
stringlengths 1
183
| slug
stringlengths 12
45
| summary
stringlengths 1
160
⌀ | author
stringlengths 2
30
| certification
stringclasses 2
values | created_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| updated_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| hit_count
int64 0
10.6M
| has_video
bool 2
classes | content
stringlengths 4
576k
| upvotes
int64 0
11.5k
| downvotes
int64 0
358
| tags
stringlengths 2
193
| comments
int64 0
2.56k
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
maximal-rectangle
|
My O(n^3) solution for your reference
|
my-on3-solution-for-your-reference-by-un-v9ye
|
class Solution {\n public:\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char> > &matrix) {\n int num_i=matrix.size();\n if (num_i==0) re
|
uniqueness
|
NORMAL
|
2014-03-07T21:00:10+00:00
|
2018-08-16T13:28:01.682321+00:00
| 7,452 | false |
class Solution {\n public:\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char> > &matrix) {\n int num_i=matrix.size();\n if (num_i==0) return 0;\n int num_j=matrix[0].size();\n if (num_j==0) return 0;\n vector<vector<int>> max_x(num_i,vector<int>(num_j,0)); //number of consecutive 1s to the left of matrix[i][j], including itself\n \n int area=0;\n for (int i=0;i<num_i;i++){\n for (int j=0;j<num_j;j++){\n if (matrix[i][j]=='1'){\n if (j==0) max_x[i][j]=1;\n else max_x[i][j]=max_x[i][j-1]+1;\n int y=1;\n int x=num_j;\n while((i-y+1>=0)&&(matrix[i-y+1][j]=='1')){\n x=min(x, max_x[i-y+1][j]);\n area=max(area,x*y);\n y++;\n } \n }\n }\n }\n \n \n \n return area;\n \n \n }\n };
| 30 | 1 |
[]
| 5 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Pyrhon O(n^2) solution based on Largest Rectangle in Histogram
|
pyrhon-on2-solution-based-on-largest-rec-09ls
|
class Solution:\n # @param matrix, a list of lists of 1 length string\n # @return an integer\n def maximalRectangle(self, matrix):\n if not matr
|
tusizi
|
NORMAL
|
2015-03-05T16:07:37+00:00
|
2018-09-08T00:31:58.759388+00:00
| 9,682 | false |
class Solution:\n # @param matrix, a list of lists of 1 length string\n # @return an integer\n def maximalRectangle(self, matrix):\n if not matrix:\n return 0\n h, w = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])\n m = [[0]*w for _ in range(h)]\n for j in range(h):\n for i in range(w):\n if matrix[j][i] == '1':\n m[j][i] = m[j-1][i] + 1\n return max(self.largestRectangleArea(row) for row in m)\n\n def largestRectangleArea(self, height):\n height.append(0)\n stack, size = [], 0\n for i in range(len(height)):\n while stack and height[stack[-1]] > height[i]:\n h = height[stack.pop()]\n w = i if not stack else i-stack[-1]-1\n size = max(size, h*w)\n stack.append(i)\n return size\n\nm is every row height, it is easy to convert this to Largest Rectangle in Histogram
| 30 | 0 |
['Python']
| 8 |
maximal-rectangle
|
【Video】Simple Solution
|
video-simple-solution-by-niits-k0sn
|
---\n\n# Solution Video\n\nhttps://youtu.be/A-yig8nSmT0\n\n### \u2B50\uFE0F\u2B50\uFE0F Don\'t forget to subscribe to my channel! \u2B50\uFE0F\u2B50\uFE0F\n\n\u
|
niits
|
NORMAL
|
2023-04-12T03:14:31.018661+00:00
|
2024-04-13T06:32:46.421500+00:00
| 4,427 | false |
---\n\n# Solution Video\n\nhttps://youtu.be/A-yig8nSmT0\n\n### \u2B50\uFE0F\u2B50\uFE0F Don\'t forget to subscribe to my channel! \u2B50\uFE0F\u2B50\uFE0F\n\n**\u25A0 Subscribe URL**\nhttp://www.youtube.com/channel/UC9RMNwYTL3SXCP6ShLWVFww?sub_confirmation=1\n\nSubscribers: 4,382\nThank you for your support!\n\n---\n\n\n\n# Approach\n1. Check if the input matrix is empty, if it is return 0.\n\n2. Determine the number of columns in the matrix (n) by getting the length of the first row of the matrix.\n\n3. Create a list called heights, with n+1 elements, and initialize each element to 0.\n\n4. Create a variable called max_area and initialize it to 0.\n\n5. For each row in the matrix, do the following:\n - Iterate through each column in the row, and update the corresponding height in the "heights" list.\n - If the character in the matrix is "1", increment the corresponding height in the "heights" list by 1, otherwise set it to 0.\n\n6. Create an empty stack and add -1 to it.\n\n7. For each element in the "heights" list, do the following:\n - Compare the current height to the height of the top element in the stack.\n - If the current height is less than the height of the top element of the stack, do the following:\n - Pop the top element of the stack and calculate the area of the rectangle formed by the popped height.\n - Calculate the width of the rectangle by subtracting the index of the current element from the index of the new top element of the stack.\n - Calculate the area of the rectangle by multiplying the height and width.\n - Update the maximum area seen so far if the area of the current rectangle is larger than the current maximum.\n - Append the index of the current element to the stack.\n\n8. Return the maximum area seen so far.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(m*n)\nm is the number of rows in the input matrix and n is the number of columns. This is because we have to iterate through each element in the matrix at least once, and the time it takes to process each element is constant.\n\n- Space complexity: O(n)\nn is the number of columns in the matrix. This is because we are creating a "heights" list with n+1 elements, and a stack that could have up to n+1 elements. The rest of the variables used in the algorithm are constants and do not contribute significantly to the space complexity.\n\n# Python\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maximalRectangle(self, matrix: List[List[str]]) -> int:\n if not matrix:\n return 0\n \n n = len(matrix[0])\n heights = [0] * (n + 1)\n max_area = 0\n\n for row in matrix:\n for i in range(n):\n heights[i] = heights[i] + 1 if row[i] == "1" else 0\n \n stack = [-1]\n for i in range(n + 1):\n while heights[i] < heights[stack[-1]]:\n h = heights[stack.pop()]\n w = i - stack[-1] - 1\n max_area = max(max_area, h * w)\n \n stack.append(i)\n \n return max_area\n```\n\n# JavaScript\n```\n/**\n * @param {character[][]} matrix\n * @return {number}\n */\nvar maximalRectangle = function(matrix) {\n if (!matrix.length) {\n return 0;\n }\n \n const n = matrix[0].length;\n const heights = new Array(n + 1).fill(0);\n let maxArea = 0;\n \n for (let row of matrix) {\n for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n heights[i] = row[i] === \'1\' ? heights[i] + 1 : 0;\n }\n \n const stack = [-1];\n for (let i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) {\n while (heights[i] < heights[stack[stack.length - 1]]) {\n const h = heights[stack.pop()];\n const w = i - stack[stack.length - 1] - 1;\n maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, h * w);\n }\n stack.push(i);\n }\n }\n \n return maxArea; \n};\n```\n\n# Java\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) {\n if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0) {\n return 0;\n }\n \n int n = matrix[0].length;\n int[] heights = new int[n + 1];\n int maxArea = 0;\n \n for (char[] row : matrix) {\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n heights[i] = row[i] == \'1\' ? heights[i] + 1 : 0;\n }\n \n Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();\n stack.push(-1);\n for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) {\n while (stack.peek() != -1 && heights[i] < heights[stack.peek()]) {\n int h = heights[stack.pop()];\n int w = i - stack.peek() - 1;\n maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, h * w);\n }\n stack.push(i);\n }\n }\n \n return maxArea; \n }\n}\n```\n\n# C++\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n if (matrix.empty()) {\n return 0;\n }\n \n int n = matrix[0].size();\n vector<int> heights(n + 1);\n int maxArea = 0;\n \n for (auto row : matrix) {\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n heights[i] = row[i] == \'1\' ? heights[i] + 1 : 0;\n }\n \n stack<int> st;\n st.push(-1);\n for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) {\n while (st.top() != -1 && heights[i] < heights[st.top()]) {\n int h = heights[st.top()];\n st.pop();\n int w = i - st.top() - 1;\n maxArea = max(maxArea, h * w);\n }\n st.push(i);\n }\n }\n \n return maxArea; \n }\n};\n```
| 28 | 0 |
['C++', 'Java', 'Python3', 'JavaScript']
| 6 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Monotonic stack|DP+count successive '1's||16ms Beats 99.62%
|
monotonic-stackdpcount-successive-1s16ms-3j71
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nSimilar to solving 84. Largest Rectangle in Histogram.\n\n2nd approach uses the old DP
|
anwendeng
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-13T02:14:35.029296+00:00
|
2024-04-13T15:39:31.076269+00:00
| 11,061 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nSimilar to solving 84. Largest Rectangle in Histogram.\n\n2nd approach uses the old DP solution for LC 84.\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nIn this question, one has to build the histogram (`h` in code) for each row.\nThe part for monotonic stack is almost the same like in solving Leetcode 84. Largest Rectangle in Histogram\n\nThe pattern for monotonic stack is used for many Leetcode\'s hard questions for which the variant is applied to LC 84 & LC 85 as follows\n```\nst={-1}; //let stack contain an element -1\ntop=0;\nfor (r=0; r<=col; r++){//Moving right index\n // Count the successive \'1\'s & store in h[j]\n h[j]=compute_for_h(j);\n\n // monotonic stack has at least element -1\n while(st has more than -1 and (j==col or h[j]<h[st[top]])){\n m=st[top--];//pop\n l=st[top];//left index\n w=r-l-1;\n area=h[m]*w;\n maxArea=max(maxArea, area);\n }\n st[++top]=j;//push\n}\n```\n\nThe following is generated by random data to show the maxArea for the histogram `h`. The green area is in fact the cells with \'1\' which are connected to the cells \'1\' in the row for considering.\n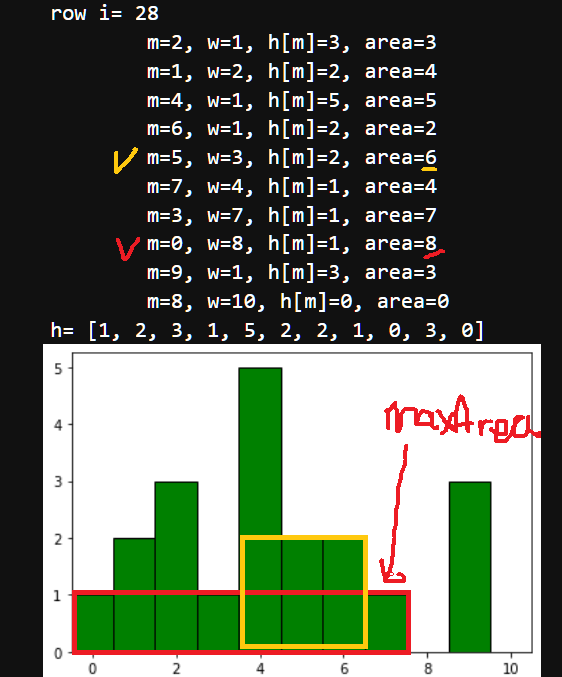\n[Please turn on english subtitles. Solving [42. Trapping Rain Water](https://leetcode.com/problems/trapping-rain-water/solutions/5010020/monotonic-stack-vs-priority-queueusing-pyplot-explain3ms-beats-9910/) use a similar way of monotonic stack, in the film is shown how to use pyplot.bar to visualize the data, especially for the area computing.]\n[https://youtu.be/IERpc-YJIT0?si=HaXCPOHz83goH3yf](https://youtu.be/IERpc-YJIT0?si=HaXCPOHz83goH3yf)\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(row\\times col)$$\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(col)$$\n# Code||C++ 16ms Beats 99.62%\n```\n#pragma GCC optimize("O3", "unroll-loops")\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n const unsigned short row=matrix.size(), col=matrix[0].size();\n if (row==1 && col==1) return matrix[0][0]==\'1\';\n vector<unsigned short> h(col+1);//height \n int maxArea=0;\n\n for(int i=0; i<row; i++){\n vector<int> st={-1}; //stack will not be empty\n for (int j=0; j<=col; j++){\n // Count the successive \'1\'s & store in h[j]\n h[j]=(j==col||matrix[i][j]==\'0\')?0:h[j]+1;\n\n // monotonic stack has at least element -1\n while(st.size()>1 && (j==col||h[j]<h[st.back()])){\n const int m=st.back();\n st.pop_back();\n const int w=j-st.back()-1;\n const int area=h[m]*w;\n maxArea=max(maxArea, area);\n }\n st.push_back(j);\n }\n }\n return maxArea;\n }\n};\n\n\nauto init = []() {\n ios::sync_with_stdio(false);\n cin.tie(nullptr);\n cout.tie(nullptr);\n return \'c\';\n}();\n```\n# Python Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maximalRectangle(self, matrix: List[List[str]]) -> int:\n r, c=len(matrix), len(matrix[0])\n if r==1 and c==1:\n if matrix[0][0]==\'1\': return 1\n else: return 0\n h=[0]*(c+1)\n maxArea=0\n\n for i, row in enumerate(matrix):\n st=[-1] \n row.append(\'0\')\n for j, x in enumerate(row):\n # build h\n if x==\'1\': h[j]+=1\n else: h[j]=0\n # mononotonic stack has at leat element -1\n while len(st)>1 and (j==c or h[j]<h[st[-1]]):\n m=st[-1]\n st.pop()\n w=j-st[-1]-1\n area=h[m]*w\n maxArea=max(maxArea, area)\n st.append(j)\n return maxArea\n\n \n```\n# C++ using DP solution for LC 84||19ms beats 99.01%\n```\n#pragma GCC optimize("O3", "unroll-loops")\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n //l: the x-coordinate of the bar to the left with height h[l] < h[i].\n //r: the x-coordinate of the bar to the right with height h[r] < h[i].\n int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights, int n) {\n //adopt from leetcode 84 which is a 2-pass solution using DP\n if (n==0) return 0;\n vector<int> l(n), r(n);\n r[n-1]=n, l[0]=-1;\n\n for(int i=1; i<n; i++){\n int p=i-1;\n while(p>=0 && heights[p]>=heights[i])\n p=l[p];\n l[i]=p;\n }\n\n int maxA=heights[n-1]*(r[n-1]-l[n-1]-1);\n for(int i=n-2; i>=0; i--){\n int p=i+1;\n while(p<n && heights[p]>=heights[i])\n p=r[p];\n r[i]=p;\n maxA=max(maxA, heights[i]*(r[i]-l[i]-1));\n }\n // cout<<maxA<<endl;\n return maxA;\n }\n\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n const unsigned short row=matrix.size(), col=matrix[0].size();\n if (row==1 && col==1) return matrix[0][0]==\'1\';\n vector<int> h(col);//height \n int maxArea=0;\n\n for(int i=0; i<row; i++){\n for (int j=0; j<col; j++){\n // Count the successive \'1\'s & store in h[j]\n h[j]=(matrix[i][j]==\'0\')?0:h[j]+1;\n }\n maxArea=max(maxArea, largestRectangleArea(h, col));\n }\n return maxArea;\n }\n};\n\n```
| 25 | 1 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Monotonic Stack', 'C++', 'Python3']
| 3 |
maximal-rectangle
|
C++ 2 Solutions | Better to Optimal with Explanation | Easy to Understand
|
c-2-solutions-better-to-optimal-with-exp-0ar7
|
Approach 1\n\n\nint maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n//base cases\n int n = matrix.size();\n if(n == 0) return 0;\n int m
|
rishabh_devbanshi
|
NORMAL
|
2021-11-30T08:59:36.378659+00:00
|
2021-11-30T11:25:24.578465+00:00
| 3,914 | false |
## Approach 1\n\n```\nint maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n//base cases\n int n = matrix.size();\n if(n == 0) return 0;\n int m = matrix[0].size();\n if(n + m == 2) return matrix.front().front() == \'1\';\n\t\t\n\t\t//dp to store max number of adjacent 1s on left for each matrix[ i ][ j ]\n vector<vector<int>> dp(n+1,vector<int>(m+1,0));\n for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)\n {\n for(int j=1;j<=m;j++)\n {\n if(matrix[i-1][j-1] != \'0\')\n dp[i][j] = 1 + dp[i][j-1];\n // cout<<dp[i][j]<<" ";\n }\n // cout<<endl;\n }\n \n\t\t\n\t\t//variable to store answer\n int area = 0;\n\t\t\n for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)\n {\n for(int j=1;j<=m;j++)\n {\n\t\t\t//variable to store current width of rectangle of size 1 * dp[i][j]\n int width = dp[i][j];\n int k = i-1;\n int height = 1;\n area = max(area,width * height);\n\t\t\t\t\n\t\t\t\t//now we\'ll start moving upwards as long as we are inside the matrix\n\t\t\t\t//ans change the height ans width accordingly to find the largest\n\t\t\t\t//area which can be achieved including current element\n\t\t\t\t//height always increases as we go up, width of rectangle till that height changes\n\t\t\t\t//to minimum no. of left 1s for every upward element\n while(k > 0 and dp[k][j] > 0)\n {\n height++;\n width = min(width,dp[k--][j]);\n\t\t\t\t\t//for every acceptable height, we check if it can be our answer\n area = max(width * height,area);\n }\n }\n }\n \n return area;\n }\n```\n\n**Time Complexity :** O(n * m * n)\n**Space Complexity :** O(n * m)\n\n## Approach 2\n\nThe second method utilizes the concept of the [Largest Reactangle in Histogram](https://leetcode.com/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/) to compute the largest rectangle for a given row efficiently.\n\n```\n//code to find largest rectangle in histogram\nint largestRectangle(vector<int> &dp)\n {\n stack<int> st;\n st.push(-1);\n int max_area = 0;\n for(int i=0;i<=dp.size();i++)\n {\n int val = (i == dp.size()) ? -1 : dp[i];\n while(st.top() != -1 and dp[st.top()] > val)\n {\n int height = dp[st.top()];\n st.pop();\n int width = i - st.top() - 1;\n max_area = max(max_area,width * height);\n }\n st.push(i);\n }\n return max_area;\n }\n\t\n\tint maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n\t\t//base cases\n int n = matrix.size();\n if(n == 0) return 0;\n int m = matrix[0].size();\n if(n + m == 2) return matrix[0][0] == \'1\';\n \n\t\t//program to calculate maximum height for current element\n vector<int> dp(m,0);\n \n int res = 0;\n \n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<m;j++)\n {\n\t\t\t\t//if current 0 then total height is 0 else increase the previous height\n if(matrix[i][j] == \'0\') dp[j] = 0;\n else dp[j]++;\n }\n res = max(res,largestRectangle(dp));\n }\n \n return res;\n }\n```\n\n**Time Complexity :** O(n * (m + n) )\n**Space Complexity :** O(n + n) [dp array + stack to find largest rectangle]\n\nDO upvote, if it helped you :)
| 25 | 3 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Stack']
| 3 |
maximal-rectangle
|
📢Stack and DP: Unveiling the Secrets to Count Maximal Rectangles || Full Explanation || Mr. Robot
|
stack-and-dp-unveiling-the-secrets-to-co-eokh
|
Unlocking the Power of Algorithms: Solving the Maximal Rectangle Problem\n\nIf you\'re a coding enthusiast or a budding programmer, you\'ve probably heard about
|
LakshayBrejwal_1_0
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-15T21:20:54.388073+00:00
|
2023-10-15T21:20:54.388105+00:00
| 3,885 | false |
# Unlocking the Power of Algorithms: Solving the Maximal Rectangle Problem\n\nIf you\'re a coding enthusiast or a budding programmer, you\'ve probably heard about the Maximal Rectangle Problem. This fascinating problem is a classic in the world of computer science and is often used to demonstrate the power of dynamic programming and efficient algorithm design.\n\nIn this blog post, we\'ll dive deep into the problem and explore a solution using a clever algorithm. We\'ll provide code examples in multiple programming languages to ensure that you can follow along regardless of your coding preferences. So, whether you\'re a C++ aficionado, a Java enthusiast, a Python pro, or a JavaScript wizard, you\'re in the right place!\n\n## Understanding the Maximal Rectangle Problem\n\nThe Maximal Rectangle Problem can be defined as follows: Given a binary matrix, find the largest rectangle containing only ones and return its area. This might sound a bit complex at first, but with the right algorithm, it becomes a manageable challenge.\n\n## The Algorithm: Dynamic Programming to the Rescue\n\nThe key to solving the Maximal Rectangle Problem lies in dynamic programming. Dynamic programming is a powerful technique that involves breaking down a complex problem into smaller subproblems and reusing solutions to subproblems to avoid redundant computations. \n\n### Step 1: The `largestRectangleArea` Function\n\nFirst, let\'s take a look at the `largestRectangleArea` function. This function, written in C++, Java, Python, and JavaScript, calculates the largest rectangle area in a histogram. The idea is to use a stack to efficiently find the maximum area.\n\nHere\'s a simplified overview of the algorithm:\n\n1. Create an empty stack to store indices.\n2. Iterate through the histogram from left to right.\n3. While the stack is not empty and the current histogram value is less than the value at the index stored in the stack\'s top element, pop elements from the stack and calculate the maximum area for each popped element.\n4. Keep track of the maximum area as you iterate through the histogram.\n\nThis algorithm efficiently finds the largest rectangle area in the histogram, which we\'ll use in the next step.\n\n### Step 2: The `maximalAreaOfSubMatrixOfAll1` Function\n\nIn this step, we adapt the `largestRectangleArea` function to solve the Maximal Rectangle Problem for a binary matrix. We create a vector to store the height of each column and use dynamic programming to find the maximum rectangle area for each row.\n\n### Step 3: Bringing It All Together\n\nIn the final step, we create the `maximalRectangle` function, which takes a binary matrix as input and returns the maximum rectangle area containing only ones.\n\n\n## Dry Run of `maximalRectangle` Function\n\nWe\'ll perform a dry run of the `maximalRectangle` function using the following matrix:\n\n```python\nmatrix = [\n [\'1\', \'0\', \'1\', \'0\', \'0\'],\n [\'1\', \'0\', \'1\', \'1\', \'1\'],\n [\'1\', \'1\', \'1\', \'1\', \'1\'],\n [\'1\', \'0\', \'0\', \'1\', \'0\']\n]\n```\n\n### Step 1: Initializing Variables\n\nWe start with the given matrix:\n\n```\n1 0 1 0 0\n1 0 1 1 1\n1 1 1 1 1\n1 0 0 1 0\n```\n\nWe have two helper functions, `largestRectangleArea` and `maximalAreaOfSubMatrixOfAll1`, which are used within the `maximalRectangle` function.\n\n### Step 2: `maximalAreaOfSubMatrixOfAll1`\n\nWe enter the `maximalAreaOfSubMatrixOfAll1` function, which computes the maximal area of submatrices containing only \'1\'s. \n\n**Matrix and `height` after each row iteration:**\n\n1. Process Row 1:\n - Matrix:\n ```\n 1 0 1 0 0\n ```\n - Height: `[1, 0, 1, 0, 0]`\n\n2. Process Row 2:\n - Matrix:\n ```\n 1 0 1 1 1\n ```\n - Height: `[2, 0, 2, 1, 1]`\n\n3. Process Row 3:\n - Matrix:\n ```\n 1 1 1 1 1\n ```\n - Height: `[3, 1, 3, 2, 2]`\n\n4. Process Row 4:\n - Matrix:\n ```\n 1 0 0 1 0\n ```\n - Height: `[4, 1, 1, 3, 1]`\n\n**Maximal Area of Histogram (`largestRectangleArea`):**\n\nFor each `height`, we calculate the maximal area of the histogram using the `largestRectangleArea` function.\n\n- For the height `[1, 0, 1, 0, 0]`, the maximal area is `1`.\n- For the height `[2, 0, 2, 1, 1]`, the maximal area is `4`.\n- For the height `[3, 1, 3, 2, 2]`, the maximal area is `6`.\n- For the height `[4, 1, 1, 3, 1]`, the maximal area is `4`.\n\nThe maximal area of submatrices for each row is `[1, 4, 6, 4]`.\n\n### Step 3: `maximalRectangle`\n\nFinally, we return the maximum value from the array `[1, 4, 6, 4]`, which is `6`.\n\nThe maximal area of a submatrix containing only \'1\'s in the given matrix is `6`.\n\nThis concludes the dry run of the `maximalRectangle` function with the provided matrix.\n\n### **Code C++ Java Python JS C#**\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\nint largestRectangleArea(vector < int > & histo) {\n stack < int > st;\n int maxA = 0;\n int n = histo.size();\n for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {\n while (!st.empty() && (i == n || histo[st.top()] >= histo[i])) {\n int height = histo[st.top()];\n st.pop();\n int width;\n if (st.empty())\n width = i;\n else\n width = i - st.top() - 1;\n maxA = max(maxA, width * height);\n }\n st.push(i);\n }\n return maxA;\n}\nint maximalAreaOfSubMatrixOfAll1(vector<vector<char>> &mat, int n, int m) {\n \n int maxArea = 0;\n vector<int> height(m, 0);\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {\n if (mat[i][j] == \'1\') height[j]++;\n else height[j] = 0;\n }\n int area = largestRectangleArea(height);\n maxArea = max(maxArea, area);\n }\n return maxArea;\n}\n\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n return maximalAreaOfSubMatrixOfAll1(matrix,matrix.size(),matrix[0].size());\n }\n};\n```\n\n**Java:**\n```java []\nimport java.util.Stack;\n\npublic class Solution {\n\n public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {\n Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();\n int maxArea = 0;\n int n = heights.length;\n for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {\n while (!stack.isEmpty() && (i == n || heights[stack.peek()] >= heights[i])) {\n int height = heights[stack.pop()];\n int width = stack.isEmpty() ? i : i - stack.peek() - 1;\n maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, width * height);\n }\n stack.push(i);\n }\n return maxArea;\n }\n\n public int maximalAreaOfSubMatrixOfAll1(char[][] matrix, int n, int m) {\n int maxArea = 0;\n int[] height = new int[m];\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {\n if (matrix[i][j] == \'1\') {\n height[j]++;\n } else {\n height[j] = 0;\n }\n }\n int area = largestRectangleArea(height);\n maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, area);\n }\n return maxArea;\n }\n\n public int maximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) {\n return maximalAreaOfSubMatrixOfAll1(matrix, matrix.length, matrix[0].length);\n }\n}\n```\n\n**Python:**\n```python []\nclass Solution:\n def largestRectangleArea(self, heights):\n stack = []\n max_area = 0\n n = len(heights)\n \n for i in range(n + 1):\n while stack and (i == n or heights[stack[-1]] >= heights[i]):\n height = heights[stack.pop()]\n width = i if not stack else i - stack[-1] - 1\n max_area = max(max_area, height * width)\n \n stack.append(i)\n \n return max_area\n\n def maximalAreaOfSubMatrixOfAll1(self, mat, n, m):\n max_area = 0\n height = [0] * m\n\n for i in range(n):\n for j in range(m):\n if mat[i][j] == \'1\':\n height[j] += 1\n else:\n height[j] = 0\n\n area = self.largestRectangleArea(height)\n max_area = max(max_area, area)\n \n return max_area\n\n def maximalRectangle(self, matrix):\n if not matrix:\n return 0\n n, m = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])\n return self.maximalAreaOfSubMatrixOfAll1(matrix, n, m)\n\n```\n\n**JavaScript:**\n```javascript []\nfunction largestRectangleArea(heights) {\n const stack = [];\n let maxArea = 0;\n const n = heights.length;\n for (let i = 0; i <= n; i++) {\n while (stack.length > 0 && (i === n || heights[stack[stack.length - 1]] >= heights[i])) {\n const height = heights[stack.pop()];\n const width = stack.length === 0 ? i : i - stack[stack.length - 1] - 1;\n maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, width * height);\n }\n stack.push(i);\n }\n return maxArea;\n}\n\nfunction maximalAreaOfSubMatrixOfAll1(matrix, n, m) {\n let maxArea = 0;\n const height = new Array(m).fill(0);\n for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n for (let j = 0; j < m; j++) {\n if (matrix[i][j] === \'1\') {\n height[j]++;\n } else {\n height[j] = 0;\n }\n }\n const area = largestRectangleArea(height);\n maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, area);\n }\n return maxArea;\n}\n\nfunction maximalRectangle(matrix) {\n return maximalAreaOfSubMatrixOfAll1(matrix, matrix.length, matrix[0].\n\nlength);\n}\n``` \n**C#**\n\n``` csharp []\nusing System;\nusing System.Collections.Generic;\n\nclass Solution\n{\n public int MaximalRectangle(char[][] matrix)\n {\n if (matrix == null || matrix.Length == 0 || matrix[0].Length == 0)\n {\n return 0;\n }\n\n int numRows = matrix.Length;\n int numCols = matrix[0].Length;\n\n int maxArea = 0;\n int[] height = new int[numCols];\n\n for (int row = 0; row < numRows; row++)\n {\n for (int col = 0; col < numCols; col++)\n {\n if (matrix[row][col] == \'1\')\n {\n height[col]++;\n }\n else\n {\n height[col] = 0;\n }\n }\n\n int area = LargestRectangleArea(height);\n maxArea = Math.Max(maxArea, area);\n }\n\n return maxArea;\n }\n\n private int LargestRectangleArea(int[] heights)\n {\n Stack<int> stack = new Stack<int>();\n int maxArea = 0;\n int n = heights.Length;\n\n for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)\n {\n while (stack.Count > 0 && (i == n || heights[stack.Peek()] >= heights[i]))\n {\n int h = heights[stack.Pop()];\n int w = stack.Count == 0 ? i : i - stack.Peek() - 1;\n maxArea = Math.Max(maxArea, h * w);\n }\n\n stack.Push(i);\n }\n\n return maxArea;\n }\n}\n```\n---\n## Analysis\n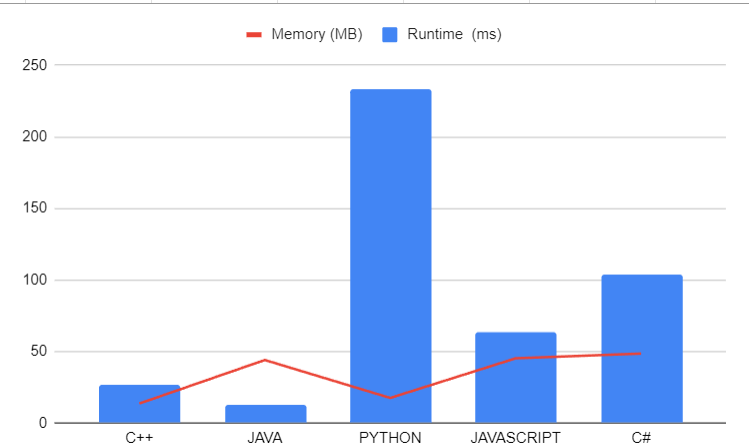\n\n---\n| Language | Runtime (ms) | Memory (MB) |\n|------------|--------------|-------------|\n| C++ | 27 | 13.6 |\n| Java | 13 | 44 |\n| Python | 233 | 17.5 |\n| JavaScript | 63 | 45.2 |\n| C# | 104 | 48.5 |\n\n---\n# Consider UPVOTING\u2B06\uFE0F\n\n\n\n\n# DROP YOUR SUGGESTIONS IN THE COMMENT\n\n## Keep Coding\uD83E\uDDD1\u200D\uD83D\uDCBB\n\n -- *MR.ROBOT SIGNING OFF*\n
| 24 | 0 |
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Stack', 'Matrix', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'Python3', 'JavaScript', 'C#']
| 2 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Easy Solution || C++
|
easy-solution-c-by-vishal_k78-4j41
|
Tabulation code : Dynamic Programming : Idea behind this\nTaking a small refernce from largest rectangle area Question , where we have to calculate largest area
|
vishal_k78
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-27T17:31:45.751515+00:00
|
2022-10-27T17:31:45.751563+00:00
| 3,466 | false |
**Tabulation code : Dynamic Programming** : Idea behind this\nTaking a small refernce from largest rectangle area Question , where we have to calculate largest area possible by using stack approach. We can boil down this problem in sub - problem that are related to the largest rectangle area problem . where in this we traverse this matrix for every value of j from 0 to m , if the matrix value at that particular is 1 then we just increment the height vector that we have consider. at each traversal of i we calculate the area at the last from the refrence question . calculate the max at the last.\n\n```\n// Maximal Rectangle\n // tab\n class Solution {\n public:\n int largestRectangleArea(vector < int > & histo) {\n stack < int > st;\n int maxA = 0;\n int n = histo.size();\n for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {\n while (!st.empty() && (i == n || histo[st.top()] >= histo[i])) {\n int height = histo[st.top()];\n st.pop();\n int width;\n if (st.empty())\n width = i;\n else\n width = i - st.top() - 1;\n maxA = max(maxA, width * height);\n }\n st.push(i);\n }\n return maxA;\n }\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n int maxiArea = 0, n = matrix.size(), m = matrix[0].size();\n vector<int> height(m,0);\n \n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<m;j++){\n if(matrix[i][j] == \'1\') height[j]++;\n else height[j] = 0;\n } \n int area = largestRectangleArea(height);\n maxiArea = max(maxiArea,area);\n }\n return maxiArea;\n }\n };\n```\n<br>\n<div>Happy Coding</div>\nPlease do upvote this post. \n\n
| 21 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Stack', 'C', 'Monotonic Stack', 'C++']
| 1 |
maximal-rectangle
|
[Python3] DYNAMIC PROGRAMMING, Explained
|
python3-dynamic-programming-explained-by-dgt7
|
First, we form an auxiliary matrix dp storing the number of consecutive "1"s on the left side of the corresponding slot at the input matrix. Then we iterate slo
|
artod
|
NORMAL
|
2021-11-30T04:37:08.359665+00:00
|
2021-11-30T05:22:22.842890+00:00
| 3,918 | false |
First, we form an auxiliary matrix `dp` storing the number of consecutive "1"s on the left side of the corresponding slot at the input matrix. Then we iterate slots of the `dp` upwards and find all possible rectangles that can be formed having the current slot as the right bottom angle. The first possible rectangle area is equal to `dp[i][j] * 1`. We go up and check whether the above slot can form a rectangle with the current one and if yes, the rectangle area will be equal to `min(dp[i][j], dp[i - 1][j]) * 2`, and so on. The maximum value is our result.\n\nTime: **O(rows*cols * rows)** - because when searching for a max rectangle using our `dp`, in worst case we have to scan all rows up to the first one for every slot\nSpace: **O(rows*cols)** - for an aux matrix\n\nRuntime: 420 ms, faster than **20.81%** of Python3 online submissions for Maximal Rectangle.\nMemory Usage: 15.6 MB, less than **21.06%** of Python3 online submissions for Maximal Rectangle.\n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maximalRectangle(self, m: List[List[str]]) -> int:\n rows = len(m)\n if not rows:\n return 0\n \n cols = len(m[0])\n \n dp = [[0] * cols for _ in range(rows)]\n\n for i in range(rows): # fill dp, value = number of 1s on the left side\n acc = 0\n \n for j in range(cols):\n if m[i][j] == "1":\n acc += 1\n else:\n acc = 0\n \n dp[i][j] = acc\n \n res = 0\n \n for i in reversed(range(rows)):\n for j in reversed(range(cols)):\n bSide, rSide = dp[i][j], 0 # bottom and right side\n k = i\n \n while k > -1 and dp[k][j]: # iterate all possible rectangles\n bSide = min(bSide, dp[k][j])\n rSide += 1\n\n res = max(res, bSide * rSide)\n \n k -= 1\n \n return res\n```
| 19 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming']
| 5 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Java | TC: O(RC) | SC: O(min(R,C)) | Optimal Stack solution
|
java-tc-orc-sc-ominrc-optimal-stack-solu-1m2o
|
java\n/**\n * This solution is converting the input matrix row by row (OR column by column)\n * to Largest Rectangle in a Histogram.\n *\n * For each row (OR co
|
NarutoBaryonMode
|
NORMAL
|
2021-10-13T10:06:21.348216+00:00
|
2021-10-13T10:09:22.220297+00:00
| 1,539 | false |
```java\n/**\n * This solution is converting the input matrix row by row (OR column by column)\n * to Largest Rectangle in a Histogram.\n *\n * For each row (OR column) cumulative height is calculated. Then use stack to\n * save the increasing height index.\n *\n * Time Complexity: O(R * C). Each element is added to stack once and popped\n * from stack once.\n *\n * Space Complexity: O(min(R,C)). We will either store a row or a column\n *\n * R = Number of rows in the matrix. C = Number of columns in the matrix.\n */\nclass Solution {\n public int maximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) {\n if (matrix == null) {\n throw new IllegalArgumentException("Input matrix is null");\n }\n if (matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {\n return 0;\n }\n\n int rows = matrix.length;\n int cols = matrix[0].length;\n\n if (cols < rows) {\n return maximalRectangleHelper(matrix, rows, cols, true);\n } else {\n return maximalRectangleHelper(matrix, cols, rows, false);\n }\n }\n\n private int maximalRectangleHelper(char[][] matrix, int big, int small, boolean isColsSmall) {\n int[] heights = new int[small];\n int largestRectangle = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < big; i++) {\n Deque<Integer> stack = new ArrayDeque<>();\n for (int j = 0; j <= small; j++) {\n if (j < small) {\n if (isColsSmall) {\n heights[j] = matrix[i][j] == \'0\' ? 0 : heights[j] + 1;\n } else {\n heights[j] = matrix[j][i] == \'0\' ? 0 : heights[j] + 1;\n }\n\n }\n while (!stack.isEmpty() && (j == small || heights[stack.peek()] >= heights[j])) {\n int h = heights[stack.pop()];\n int left = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek();\n largestRectangle = Math.max(largestRectangle, (j - 1 - left) * h);\n }\n stack.push(j);\n }\n }\n return largestRectangle;\n }\n}\n```\n\n---\n\nSolutions to other similar question on LeetCode:\n- [84. Largest Rectangle in Histogram](https://leetcode.com/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/discuss/1519257/Java-or-TC:-O(N)-or-SC:-O(N)-or-Optimal-Stack-solution)\n
| 17 | 0 |
['Array', 'Stack', 'Matrix', 'Java']
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
using max area of histofgram
|
using-max-area-of-histofgram-by-ranjeetk-i6xn
|
This guy deserves an appluase for a fabulous explanation ! (video in Hindi)\n\nhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=St0Jf_VmG_g&list=PL_z_8CaSLPWdeOezg68SKkeLN4-T_jN
|
ranjeetkgupta
|
NORMAL
|
2020-05-21T18:04:14.346644+00:00
|
2020-05-21T18:04:14.346685+00:00
| 1,664 | false |
This guy deserves an appluase for a fabulous explanation ! (video in Hindi)\n\nhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=St0Jf_VmG_g&list=PL_z_8CaSLPWdeOezg68SKkeLN4-T_jNHd&index=8\n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maximalRectangle(self, matrix: List[List[str]]) -> int:\n \n if not matrix:\n return 0\n \n prev = [0]*len(matrix[0])\n max_area = 0\n for row in matrix:\n curr_row = [int(i) for i in row]\n for j in range (len(curr_row)):\n curr_row[j] = curr_row[j] + prev[j] if curr_row[j] !=0 else 0\n max_area = max(max_area, self.largestRectangleArea(curr_row))\n prev = curr_row\n \n return max_area\n \n \n \n #largest ares of a histogram !!\n def largestRectangleArea(self, heights): \n\n def get_small_r(heights):\n stack_r = []\n sm_r = [0] * len(heights)\n for j in range(len(heights) - 1, -1 , -1):\n\n while stack_r and heights[stack_r[-1]] >= heights[j]:\n stack_r.pop()\n\n if(not stack_r):\n sm_r[j] = -1\n else:\n sm_r[j] = stack_r[-1]\n stack_r.append(j) \n return sm_r\n\n def get_small_l(heights):\n stack_l = []\n sm_l = [None] * len(heights)\n for j in range(len(heights)):\n while stack_l and heights[stack_l[-1]] >= heights[j]:\n stack_l.pop()\n if(not stack_l):\n sm_l[j] = -1\n else:\n sm_l[j] = stack_l[-1]\n stack_l.append(j) \n return sm_l\n\n max_area = 0\n stack_l = get_small_l(heights)\n stack_r = get_small_r(heights)\n \n for j in range (len(heights)):\n l = j - stack_l[j] -1 if stack_l[j] != -1 else j\n r = stack_r[j] -1 -j if stack_r[j] != -1 else len(heights) - j -1\n t = 1 + l + r \n max_area = max(max_area, heights[j] *t )\n return max_area\n\n```
| 16 | 1 |
[]
| 1 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Variation of MAH [C++] || A bit long but easy solution
|
variation-of-mah-c-a-bit-long-but-easy-s-xt90
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\t\tvector<int> NSL(vector<int> heights){ // Function to find indices of next smallest left element\n vector<int> left;\n
|
anshika_28
|
NORMAL
|
2021-08-05T17:50:53.737908+00:00
|
2021-08-05T17:50:53.737976+00:00
| 1,386 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\t\tvector<int> NSL(vector<int> heights){ // Function to find indices of next smallest left element\n vector<int> left;\n stack<pair<int,int>> st;\n for(int i=0;i<heights.size();i++){\n if(st.empty())\n left.push_back(-1);\n else if(!st.empty() && st.top().first<heights[i])\n left.push_back(st.top().second);\n else if(!st.empty() && st.top().first>=heights[i]){\n while(!st.empty() && st.top().first>=heights[i])\n st.pop();\n if(st.empty())\n left.push_back(-1);\n else \n left.push_back(st.top().second);\n }\n st.push({heights[i],i});\n }\n return left;\n }\n vector<int> NSR(vector<int> heights){ // Function to find indices of next smallest right element\n vector<int> right;\n stack<pair<int,int>> st;\n for(int i=heights.size()-1;i>=0;i--){\n if(st.empty())\n right.push_back(heights.size());\n else if(!st.empty() && st.top().first<heights[i])\n right.push_back(st.top().second);\n else if(!st.empty() && st.top().first>=heights[i]){\n while(!st.empty() && st.top().first>=heights[i])\n st.pop();\n if(st.empty())\n right.push_back(heights.size());\n else \n right.push_back(st.top().second);\n }\n st.push({heights[i],i});\n }\n reverse(right.begin(),right.end());\n return right;\n }\n int MAH(vector<int>& heights) { //Function to find maximum area of histogram\n vector<int> right;\n vector<int> left;\n \n right=NSR(heights);\n left=NSL(heights);\n \n vector<int> width;\n int mx=0;\n for(int i=0;i<left.size();i++){\n width.push_back(right[i]-left[i]-1);\n }\n \n for(int i=0;i<heights.size();i++){\n mx=max(mx,heights[i]*width[i]);\n }\n \n return mx;\n }\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) { // Finally......our required Maximal Rectangle Function\n int n=matrix.size();\n if(n == 0){\n return 0;\n }\n int m=matrix[0].size();\n vector<int> v;\n for(int j=0;j<m;j++){\n v.push_back(matrix[0][j]-\'0\');\n }\n int mx= MAH(v);\n for(int i=1;i<n;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<m;j++){\n if(matrix[i][j]==\'0\')\n v[j]=0;\n else\n v[j]=v[j]+(matrix[i][j]-\'0\');\n }\n mx=max(mx,MAH(v));\n }\n return mx;\n }\n};\n```
| 14 | 1 |
['Stack', 'C', 'C++']
| 5 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Java | Simple | Detailed Explanation | Histogram Approach | O(n^2)
|
java-simple-detailed-explanation-histogr-x1xk
|
Note:\nIf you haven\'t solved the Largest Rectangle in Histogram problem, I\'d highly recommend to solve that first. You can check my detailed explanation for t
|
ud240
|
NORMAL
|
2021-06-06T16:48:36.899845+00:00
|
2021-06-06T16:49:17.937718+00:00
| 1,230 | false |
**Note:**\nIf you haven\'t solved the [Largest Rectangle in Histogram](https://leetcode.com/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram) problem, I\'d highly recommend to solve that first. You can check my detailed explanation for the same [here](https://leetcode.com/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/discuss/1255567/Java-or-Explanation-or-Stack-approach).\n\nApproach:\n1. The idea here is to break the problem in parts. We see each set of rows as a histogram, and evaluate the height of the building considering row in consideration/iteration currently as the base, and evaluating the maximum area using above mentioned **Histogram** approach.\n2. Then we continue to next row and consider the imaginary histogram with this row as base, and again evaluate the maximum area in this histogram.\n3. Similarly, we do the above at each row, and keep updating the **maxArea** and have the max. rectangle area at the end.\n\nFor example, if the matrix is:\n1 0 1 0 0\n1 0 1 1 1\n1 1 1 1 1\n1 0 0 1 0\n\n**Round-1:**\nWe consider row-1. Histogram at this point is, `1 0 1 0 0`.\nHere, `heights[0] = [1,0,1,0,0]`.\n\n**Round-2:**\nWe consider row-1 and row-2.\nSo now, histogram is of max. height 2, and buildings are like:\n`1 0 1 0 0`\n`1 0 1 1 1`\nSo, here, `heights[1] = [2 0 2 1 1]`.\n\nSimilarly, at next levels,\n`heights[3] = [3 1 3 2 2]`\n`heights[4] = [4 0 0 3 0]`\n\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) {\n if (matrix.length == 0)\n return 0;\n int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;\n int[] heights = new int[n];\n int maxArea = 0;\n\n for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {\n if (matrix[i][j] == \'0\')\n heights[j] = 0;\n if (matrix[i][j] == \'1\')\n heights[j] += 1;\n }\n maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, largestRectangleArea(heights));\n }\n return maxArea;\n }\n\n private int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {\n Stack<int[]> stack = new Stack<>();\n int maxArea = 0;\n\n for (int i = 0; i < heights.length; i++) {\n int[] block = new int[]{i, heights[i]};\n while (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek()[1] > heights[i]) {\n block = stack.pop();\n maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, block[1] * (i - block[0]));\n block[1] = heights[i];\n }\n stack.push(block);\n }\n while (!stack.isEmpty()) {\n int[] block = stack.pop();\n maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, block[1] * (heights.length - block[0]));\n }\n return maxArea;\n }\n}\n```\n\n-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\nHope this helps! Please let me know if something isn\'t clear/missing. I\'ll try to improve.\n\nAlso, please upvote this if you find this useful. Happy Coding!!
| 14 | 0 |
['Stack', 'Java']
| 1 |
maximal-rectangle
|
~0ms🔰we have to beat 🥲100% of java Users 🦾 🔰Height-Based Dynamic Programming Approach🔰
|
0mswe-have-to-beat-100-of-java-users-hei-2nzs
|
The method used to solve this problem involves iterating through each row of the matrix and updating arrays to keep track of heights, left boundaries, and right
|
YOGENDRARAJPUT
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-13T00:25:20.667762+00:00
|
2024-04-13T00:41:42.002103+00:00
| 5,809 | false |
1. > The method used to solve this problem involves iterating through each row of the matrix and updating arrays to keep track of heights, left boundaries, and right boundaries of each column. Then, for each row, calculate the maximum rectangle area using the updated arrays. Finally, return the maximum rectangle area found. This method efficiently finds the maximal rectangle in the given matrix\n\nThe code starts by checking if the input matrix is valid (not null and non-empty), returning 0 if it\'s not.\nIt initializes variables for the number of rows (m) and columns (n) in the matrix.\nThree arrays are created to keep track of heights, left boundaries, and right boundaries of each column.\nThe right boundaries array is initialized to be the length of the matrix\'s columns.\nThe main loop iterates through each row of the matrix.\nFor each row, it updates the heights and left boundaries arrays using the updateHeightsAndLeftBoundaries method.\nIt then updates the right boundaries array using the updateRightBoundaries method.\nAfter updating the boundaries, it calculates the maximum rectangle area for the current row using the calculateMaxRectangle method.\nFinally, it returns the maximum rectangle area found.\nAdditional methods are defined to update heights and boundaries and calculate the maximum rectangle area based on the updated boundaries.\n\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) {\n if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {\n return 0;\n }\n\n int m = matrix.length;\n int n = matrix[0].length;\n\n int[] heights = new int[n];\n int[] leftBoundaries = new int[n];\n int[] rightBoundaries = new int[n];\n Arrays.fill(rightBoundaries, n);\n\n int maxRectangle = 0;\n\n for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {\n int left = 0;\n int right = n;\n\n updateHeightsAndLeftBoundaries(matrix[i], heights, leftBoundaries, left);\n\n updateRightBoundaries(matrix[i], rightBoundaries, right);\n\n maxRectangle = calculateMaxRectangle(heights, leftBoundaries, rightBoundaries, maxRectangle);\n }\n\n return maxRectangle;\n }\n\n private void updateHeightsAndLeftBoundaries(char[] row, int[] heights, int[] leftBoundaries, int left) {\n for (int j = 0; j < heights.length; j++) {\n if (row[j] == \'1\') {\n heights[j]++;\n leftBoundaries[j] = Math.max(leftBoundaries[j], left);\n } else {\n heights[j] = 0;\n leftBoundaries[j] = 0;\n left = j + 1;\n }\n }\n }\n\n private void updateRightBoundaries(char[] row, int[] rightBoundaries, int right) {\n for (int j = rightBoundaries.length - 1; j >= 0; j--) {\n if (row[j] == \'1\') {\n rightBoundaries[j] = Math.min(rightBoundaries[j], right);\n } else {\n rightBoundaries[j] = right;\n right = j;\n }\n }\n }\n\n private int calculateMaxRectangle(int[] heights, int[] leftBoundaries, int[] rightBoundaries, int maxRectangle) {\n for (int j = 0; j < heights.length; j++) {\n int width = rightBoundaries[j] - leftBoundaries[j];\n int area = heights[j] * width;\n maxRectangle = Math.max(maxRectangle, area);\n }\n return maxRectangle;\n }\n}\n```
| 13 | 1 |
['Java']
| 10 |
maximal-rectangle
|
c++(20ms 99%) simple, easy, small (commented)
|
c20ms-99-simple-easy-small-commented-by-nzh01
|
\n\n\n\nGeneral idea : do precalculating contigious ones (vertical and horizontal)\n\nRuntime: 20 ms, faster than 98.92% of C++ online submissions for Maximal R
|
zx007pi
|
NORMAL
|
2021-11-18T08:40:49.427904+00:00
|
2021-11-18T08:42:31.324570+00:00
| 2,349 | false |
\n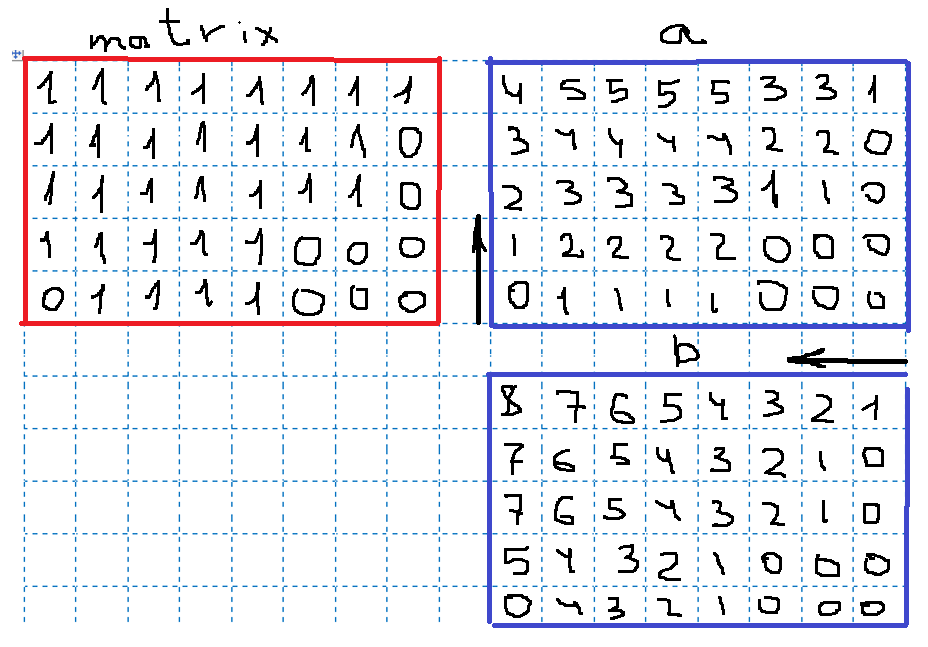\n\n\n**General idea : do precalculating contigious ones (vertical and horizontal)**\n\nRuntime: 20 ms, faster than 98.92% of C++ online submissions for Maximal Rectangle.\nMemory Usage: 12.1 MB, less than 53.69% of C++ online submissions for Maximal Rectangle.\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n if(matrix.empty()) return 0;\n int y = matrix.size(), x = matrix[0].size(), answer = 0;\n vector<vector<int>> a(y,vector<int>(x)), b(y,vector<int>(x));\n \n for(int j = 0; j != x; j++)\n for(int i = y - 1, k = 0; i >= 0; i--)\n if(matrix[i][j] == \'1\') a[i][j] = ++k;\n else a[i][j] = k = 0;\n \n for(int i = 0; i != y; i++)\n for(int j = x - 1, k = 0; j >= 0; j--)\n if(matrix[i][j] == \'1\') b[i][j] = ++k;\n else b[i][j] = k = 0;\n \n for(int i = 0; i != y; i++)\n for(int j = 0; j != x; j++){\n int Y = a[i][j], X = b[i][j];\n for(int w = j + 1, lim = j + X; w < lim; w++)\n if(Y > a[i][w]) {answer = max(answer, Y * (w - j)); Y = a[i][w];}\n \n answer = max(answer, Y * X);\n }\n \n return answer;\n }\n};\n```
| 13 | 0 |
['C', 'C++']
| 4 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Java Simple DP Solution with state table
|
java-simple-dp-solution-with-state-table-6xzg
|
DP State\n\n1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0\n1 0 1 1 1 => 2 0 2 1 1\n1 1 1 1 1 => 3 1 3 2 2\n1 0 0 1 0 4 0 0 3 0\n\nFind the max area row by row, as we can se
|
edwardleejan
|
NORMAL
|
2019-10-12T09:22:13.850093+00:00
|
2019-10-13T06:50:52.442888+00:00
| 2,544 | false |
DP State\n```\n1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0\n1 0 1 1 1 => 2 0 2 1 1\n1 1 1 1 1 => 3 1 3 2 2\n1 0 0 1 0 4 0 0 3 0\n```\nFind the **max area** row by row, as we can see `3 1 3 2 2` contains the **max area**.\n\n```java\nclass Solution {\n public int maximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) {\n if (matrix.length <= 0) return 0;\n int n = matrix.length;\n int m = matrix[0].length;\n int[][] dp = new int[n][m];\n int maxArea = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {\n if (i == 0)\n\t\t dp[i][j] = matrix[i][j] == \'1\' ? 1 : 0;\n else\n\t\t dp[i][j] = matrix[i][j] == \'1\' ? (dp[i-1][j] + 1) : 0;\n int min = dp[i][j];\n for (int k = j; k >= 0; k--) {\n if (min == 0) break;\n if (dp[i][k] < min) min = dp[i][k];\n maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, min * (j - k + 1));\n }\n }\n }\n return maxArea;\n }\n}\n```
| 13 | 1 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Java']
| 4 |
maximal-rectangle
|
My solution on Java using DP
|
my-solution-on-java-using-dp-by-yauheni-smvz
|
Open matrix from top to the bottom line by line, counting height of each column. Then check for each column (only if it wasn't counted already) how many times
|
yauheni
|
NORMAL
|
2015-08-07T19:55:10+00:00
|
2015-08-07T19:55:10+00:00
| 6,835 | false |
Open matrix from top to the bottom line by line, counting height of each column. Then check for each column (only if it wasn't counted already) how many times it appears to the right and to the left. Area = (left+right)*height. Just pick the max one. Pretty fast\n\n public class Solution {\n public int maximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) {\n int area = 0, new_area, r, l;\n if(matrix.length > 0){\n int[] line = new int[matrix[0].length];\n boolean[] is_processed = new boolean[matrix[0].length];\n for(int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++){\n for(int j = 0; j < matrix[i].length; j++){\n if (matrix[i][j] == '1') {\n line[j]++;\n is_processed[j] = false;\n } else {\n line[j] = 0;\n is_processed[j] = true;\n }\n }\n for(int j = 0; j < matrix[i].length; j++){\n if(is_processed[j]) continue;\n r = l = 1;\n while((j + r < line.length)&&(line[j + r] >= line[j])){\n if(line[j + r] == line[j]) is_processed[j + r] = true;\n r++;\n }\n while((j - l >= 0)&&(line[j - l] >= line[j])) l++;\n new_area = (r + l - 1)*line[j];\n if (new_area > area) area = new_area;\n }\n }\n } return area;\n }\n }
| 13 | 1 |
[]
| 2 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Easy Solution using Stacks✅💯
|
easy-solution-using-stacks-by-aditiadya1-blbm
|
\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(nm) + O(n2m)\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(n*m) + O(n)\n\n\n# Code\ncpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int largestRectan
|
aditiadya1211
|
NORMAL
|
2024-08-25T17:51:55.686193+00:00
|
2024-08-25T17:51:55.686223+00:00
| 1,132 | false |
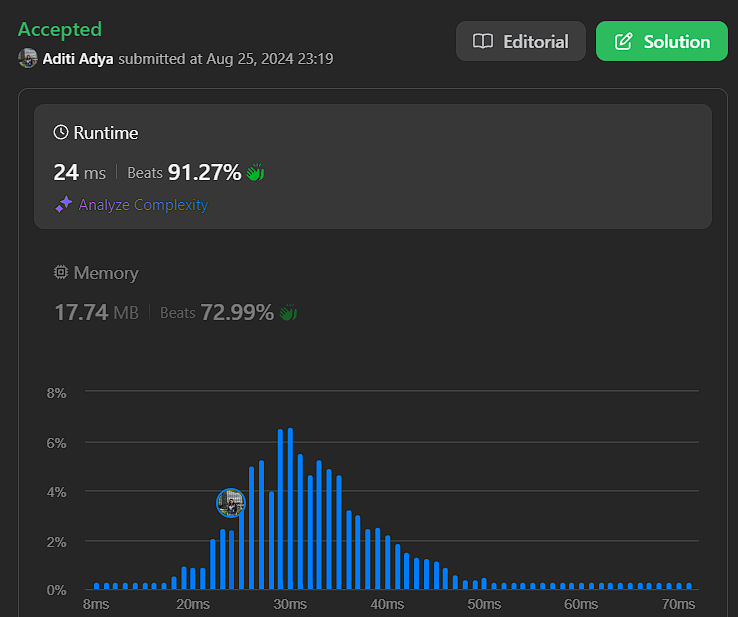\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n$$O(n*m) + O(n*2m)$$\n\n- Space complexity:\n$$O(n*m) + O(n)$$\n\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {\n stack<int> st;\n int maxArea=0;\n int n=heights.size();\n int nse;\n int pse;\n int ele;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n while(!st.empty() && heights[st.top()]>=heights[i]){\n ele=st.top();\n st.pop();\n nse=i;\n pse=st.empty()?-1:st.top();\n maxArea=max(maxArea, heights[ele]*(nse-pse-1));\n }\n st.push(i);\n }\n while(!st.empty()){\n nse=n;\n ele=st.top();\n st.pop();\n pse=st.empty()?-1:st.top();\n maxArea=max(maxArea, heights[ele]*(nse-pse-1));\n }\n return maxArea;\n }\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n int r = matrix.size();\n if(r == 0) return 0;\n int c = matrix[0].size();\n\n vector<int> ps(c,0);\n int maxi = 0;\n\n for(int i = 0; i < r; ++i){\n for(int j = 0; j < c; ++j){\n if(matrix[i][j] == \'1\') ps[j]++;\n if(matrix[i][j] == \'0\') ps[j] = 0;\n }\n maxi = max(maxi, largestRectangleArea(ps));\n }\n return maxi;\n }\n};\n```
| 12 | 0 |
['C++']
| 1 |
maximal-rectangle
|
✔️ 100% Fastest Swift Solution
|
100-fastest-swift-solution-by-sergeylesc-854k
|
\nclass Solution {\n\tfunc maximalRectangle(_ matrix: [[Character]]) -> Int {\n if matrix.count == 0 || matrix[0].count == 0 { return 0 }\n var ma
|
sergeyleschev
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-07T05:46:32.911164+00:00
|
2022-04-07T05:47:42.895837+00:00
| 415 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n\tfunc maximalRectangle(_ matrix: [[Character]]) -> Int {\n if matrix.count == 0 || matrix[0].count == 0 { return 0 }\n var max = 0\n\n for i in 0..<matrix.count {\n for j in 0..<matrix[0].count {\n let area = helper(matrix, i, j, matrix.count, matrix[0].count)\n max = max > area ? max : area\n }\n }\n \n return max\n }\n\n\n func helper(_ matrix: [[Character]], _ i: Int, _ j: Int, _ maxI: Int, _ maxJ: Int) -> Int {\n if matrix[i][j] == "0" || maxI == i || maxJ == j { return 0 }\n var x = -1\n var y = -1\n\n loop: \n for row in i..<maxI {\n for col in j..<maxJ {\n if matrix[row][col] == "0" {\n x = row\n y = col\n break loop\n }\n }\n }\n \n if x >= 0 {\n return max(helper(matrix, i, j, x, maxJ), helper(matrix, i, j, maxI, y))\n } else {\n return (maxI - i) * (maxJ - j)\n } \n }\n \n}\n```\n\nLet me know in comments if you have any doubts. I will be happy to answer.\n\nPlease upvote if you found the solution useful.
| 12 | 0 |
['Swift']
| 3 |
maximal-rectangle
|
C++ | DP | STACK | O(n) | Faster than 90%
|
c-dp-stack-on-faster-than-90-by-baiskhiy-sjul
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int getarea(vector<vector<int>>&dp , int row , int n)\n {\n \n vector<int> pre(n) ; \n pre[0] = -1 ;\n
|
baiskhiyar
|
NORMAL
|
2022-01-20T16:04:44.677716+00:00
|
2022-02-01T07:10:01.782323+00:00
| 684 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int getarea(vector<vector<int>>&dp , int row , int n)\n {\n \n vector<int> pre(n) ; \n pre[0] = -1 ;\n vector<int> next(n) ;\n next[n-1] = n ; \n stack<int> s ; \n s.push(0) ; \n \n for(int i = 1 ; i<n ; i++)\n {\n if(dp[row][s.top()] < dp[row][i]) \n {\n pre[i] = s.top() ; \n s.push(i) ; \n }\n else\n {\n while(!s.empty() && dp[row][s.top()] >= dp[row][i]) \n {\n s.pop() ; \n }\n if(s.empty())\n {\n pre[i] = -1 ; \n s.push(i) ;\n }\n else\n {\n pre[i] = s.top() ; \n s.push(i) ; \n }\n }\n }\n // s.clear() ; \n while(!s.empty()) s.pop() ; \n \n s.push(n-1) ; \n for(int i = n-2 ; i>=0 ; i--)\n {\n if(dp[row][s.top()] < dp[row][i]) \n {\n next[i] = s.top() ; \n s.push(i) ; \n }\n else\n {\n while(!s.empty() && dp[row][s.top()] >= dp[row][i]) \n {\n s.pop() ; \n }\n if(s.empty())\n {\n s.push(i) ;\n next[i] = n ; \n }\n else\n {\n next[i] = s.top() ; \n s.push(i) ; \n }\n }\n }\n int ans = INT_MIN ; \n int area ; \n for(int i = 0 ; i<n ; i++)\n {\n area = ( next[i] - pre[i] - 1) * dp[row][i] ; \n ans = max(ans , area) ; \n }\n return ans ; \n }\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n \n int n = matrix.size() ; \n int m = matrix[0].size() ; \n vector<vector<int>> dp(n , vector<int> (m)) ; \n for(int i = 0 ; i<n ; i++)\n {\n for(int j = 0 ; j < m ; j++)\n {\n if(i == 0)\n {\n if(matrix[i][j] == \'0\') dp[i][j] = 0 ;\n else dp[i][j] = 1 ; \n continue ; \n }\n if(matrix[i][j] == \'0\') dp[i][j] = 0 ; \n else dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + 1 ; \n }\n }\n int ans = INT_MIN ; \n \n for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++)\n {\n int area = getarea(dp , i , m ) ; \n ans = max(ans , area) ;\n }\n return ans ; \n }\n};\n```
| 11 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Stack']
| 3 |
maximal-rectangle
|
C++ || Based on Largest Rectangle in Histogram
|
c-based-on-largest-rectangle-in-histogra-ra30
|
\nint maxHistogram(vector<int>& heights)\n {\n heights.push_back(0);\n int n = heights.size();\n stack<int> st;\n int res = 0;\n
|
suniti0804
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-29T23:52:24.308815+00:00
|
2021-05-29T23:52:34.227992+00:00
| 1,273 | false |
```\nint maxHistogram(vector<int>& heights)\n {\n heights.push_back(0);\n int n = heights.size();\n stack<int> st;\n int res = 0;\n \n int i = 0;\n while(i < n)\n {\n if(st.empty() || heights[i] >= heights[st.top()])\n st.push(i++);\n else\n {\n int top = st.top();\n st.pop();\n res = max(res, heights[top] * (st.empty() ? i : i - st.top() - 1));\n }\n }\n \n return res;\n }\n \n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) \n {\n if(matrix.empty())\n return 0;\n \n int m = matrix.size();\n int n = matrix[0].size();\n int res = 0;\n \n vector<int> height(n, 0);\n \n for(int i = 0; i < m; i++)\n {\n for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)\n {\n if(matrix[i][j] == \'1\')\n height[j]++;\n else\n height[j] = 0;\n }\n \n res = max(res, maxHistogram(height));\n }\n \n return res;\n \n }\n```
| 10 | 0 |
['Stack', 'C', 'C++']
| 4 |
maximal-rectangle
|
DP concise explanation 97% faster Javascript JS ES6
|
dp-concise-explanation-97-faster-javascr-p7fm
|
\nALGORITHM: \n- Initiate an aux-matrix with zeroes to begin with.\n- The first row of aux-matrix is same as matrix\'s first row.\n- Values in aux-matrix reflec
|
mp3393
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-24T15:06:21.657607+00:00
|
2021-05-24T15:50:43.948697+00:00
| 1,330 | false |
\n`ALGORITHM:` \n- Initiate an aux-matrix with zeroes to begin with.\n- The first row of aux-matrix is same as matrix\'s first row.\n- Values in aux-matrix reflect the height for that column, like this:\n```\n["1","0","1","0","0"]\n["1","0","1","1","1"]\n["1","1","1","1","1"]\n["1","0","0","1","0"]\nbecomes\n["1","0","1","0","0"]\n["2","0","2","1","1"]\n["3","1","3","2","2"]\n["4","0","0","3","0"]]\n```\n- Another for-loop moves the column-pointer backwards, while updating the maxArea \n\n`CODE:`\n```\nconst maximalRectangle = function(matrix) {\n if (!matrix.length) return 0;\n const ROWS = matrix.length;\n const COLS = matrix[0].length;\n const dp = Array.from({length:ROWS}, ()=> Array(COLS).fill(0));\n let maxArea = 0;\n \n for (let row = 0; row < ROWS; row++) {\n for (let col = 0; col < COLS; col++) {\n\t\n\t //update height\n if(row === 0) dp[row][col] = matrix[row][col] == \'1\' ? 1 : 0;\n else dp[row][col] = matrix[row][col] == \'1\' ? (dp[row-1][col] + 1) : 0;\n\t \n //update area \n\t let minHeight = dp[row][col];\n\t for(let pointer = col; pointer >= 0; pointer--) {\n\t\t if (minHeight === 0) break;\n\t\t if (dp[row][pointer] < minHeight) minHeight = dp[row][pointer];\n\t\t maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, minHeight * (col - pointer + 1));\n\t }\n }\n }\n return maxArea; \n};\n```\n\n
| 10 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'JavaScript']
| 1 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Simple Solution using Monotonic Stack | C++ | With Diagram Explaination ✅
|
simple-solution-using-monotonic-stack-c-gauqp
|
Better to solve https://leetcode.com/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram first.\n\nApproach\n\n1. Initialize: Start by creating a histogram array with one e
|
garima_singh_gryffindor
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-13T12:34:13.624606+00:00
|
2024-04-13T12:34:13.624638+00:00
| 1,173 | false |
Better to solve `https://leetcode.com/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram` first.\n\n**Approach**\n\n1. **Initialize**: Start by creating a histogram array with one extra element initialized to 0. This extra element acts as a sentinel.\n2. **Iterate Through Rows**: Traverse each row of the matrix.\n3. **Update Histogram**: For each row, update the histogram by incrementing the height if the corresponding element in the matrix is \'1\', otherwise reset it to 0.\n4. **Calculate Maximum Rectangle Area**: Utilize a monotonic stack to find the maximum area of rectangles. For each histogram bar, if it\'s smaller than the top of the stack, pop the stack and calculate the area using the popped element as height and the difference between the current position and the previous popped element\'s position as width. Update the maximum area accordingly.\n5. **Return Maximum Area**: After processing all rows, return the maximum area found.\n\n<br/><br/>\n\n##### For Row = 1, the maximum area is 1\n<img src="https://assets.leetcode.com/users/images/28767c2e-7d14-492e-8405-a275050831cf_1713010966.420261.png" alt="closed_paren" title="Closed Parenthesis" width="250"/>\n\n<br/><br/>\n\n##### For Row = 2, the maximum area is 3\n<img src="https://assets.leetcode.com/users/images/e492b807-1c94-4490-aa52-d205f8678293_1713011208.7472572.png" alt="closed_paren" title="Closed Parenthesis" width="250"/>\n\n<br/><br/>\n\n##### For Row = 3, the maximum area is 6\n<img src="https://assets.leetcode.com/users/images/d5016a31-b5d3-43af-a22f-c0b98d3db28f_1713011245.4743698.png" alt="closed_paren" title="Closed Parenthesis" width="250"/>\n\n<br/><br/>\n\n##### For Row = 4, the maximum area is 4\n<img src="https://assets.leetcode.com/users/images/348cb5b6-c124-4b32-bd69-8a1b01f4b2cb_1713011254.0632894.png" alt="closed_paren" title="Closed Parenthesis" width="250"/>\n\n\n<br/><br/>\n## Implementation\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n int maxArea = 0;\n \n if(matrix.size() == 0 || matrix[0].size() == 0) return 0;\n int cols = matrix[0].size();\n int rows = matrix.size();\n vector<int>histogram(cols+1, 0);\n histogram[cols] = -1;\n stack<pair<int,int>>monotonic;\n \n for(auto row: matrix) {\n for(int i = 0; i < cols; i++) {\n if(row[i] == \'1\') {\n histogram[i]++;\n } else {\n histogram[i] = 0;\n } \n }\n \n for(int i = 0; i < cols+1; i++) {\n int x = 0;\n while(!monotonic.empty() && monotonic.top().first >= histogram[i]) {\n auto tp = monotonic.top(); monotonic.pop();\n int h = tp.first, steps = tp.second;\n x += steps;\n maxArea = max(maxArea, h*x);\n }\n monotonic.push({histogram[i], x+1});\n }\n }\n \n return maxArea;\n }\n};\n```
| 9 | 0 |
['Array', 'C', 'Matrix', 'Monotonic Stack', 'C++']
| 2 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Python 3 || 10 lines, histogram || T/S: 99% / 80%
|
python-3-10-lines-histogram-ts-99-80-by-fbxip
|
\nclass Solution:\n def maximalRectangle(self, matrix: list[list[str]], ans = 0) -> int:\n\n m, n = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])\n dp = [0]*(n+1
|
Spaulding_
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-13T01:00:11.034982+00:00
|
2024-05-24T18:32:02.981649+00:00
| 489 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def maximalRectangle(self, matrix: list[list[str]], ans = 0) -> int:\n\n m, n = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])\n dp = [0]*(n+1)\n \n for i in range(m):\n stk = deque([-1])\n\n for j in range(n+1):\n if j < n and matrix[i][j] == \'1\': dp[j]+= 1\n else: dp[j] = 0\n\n while(dp[stk[0]] > dp[j]):\n ans = max(ans,dp[stk.popleft()]*(j-stk[0]-1))\n\n stk.appendleft(j)\n\n return ans\n \n```\n[https://leetcode.com/problems/maximal-rectangle/submissions/1266891831/](https://leetcode.com/problems/maximal-rectangle/submissions/1266891831/\n)\n\n\n\nI could be wrong, but I think that time complexity is *O*(*MN*) and space complexity is *O*(*N*), in which *M* ~ `m` and *N* ~ `n`.
| 9 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
C++ solution\uff0c simple and clean code
|
c-solutionuff0c-simple-and-clean-code-by-mysf
|
int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n const int row = matrix.size();\n if (0 == row) return 0;\n const int col = matrix[0
|
lchen77
|
NORMAL
|
2015-08-09T19:50:25+00:00
|
2015-08-09T19:50:25+00:00
| 2,437 | false |
int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n const int row = matrix.size();\n if (0 == row) return 0;\n const int col = matrix[0].size();\n vector<vector<int>> ones(row, vector<int>(col+1, 0));\n for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) \n for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {\n if (matrix[i][j] == '1') {\n ones[i][j] = 1 + (i > 0 ? ones[i-1][j] : 0);\n }\n }\n int i = 0, max_a = 0;\n for (i; i < row; i++) {\n stack<int> stk;\n vector<int> cur = ones[i];\n int idx = 0;\n while (idx < cur.size()) {\n if (stk.empty() || cur[idx] >= cur[stk.top()]) {\n stk.push(idx++);\n } else {\n int h = stk.top();\n stk.pop();\n max_a = max(max_a, cur[h] *(stk.empty() ? idx : idx - stk.top() - 1));\n }\n }\n }\n return max_a;\n }
| 9 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
maximal-rectangle
|
[step by step]thoughts on the problem
|
step-by-stepthoughts-on-the-problem-by-r-n1ex
|
Just like my previous post of the largest area under the histogram.\n\nWe can solve this problem by solve level by level and the sub-problem is just the largest
|
rainbowsecret
|
NORMAL
|
2016-02-05T16:27:53+00:00
|
2016-02-05T16:27:53+00:00
| 3,282 | false |
Just like my previous post of the largest area under the histogram.\n\nWe can solve this problem by solve level by level and the sub-problem is just the largest rectangle under the histogram.\n\nCode:\n\n class Solution {\n public:\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n /** largest rectangle based solution **/\n if(matrix.size()<=0 || matrix[0].size()<=0)\n return 0;\n int m=matrix.size();\n int n=matrix[0].size()+1;\n int h=0, w=0, result=0;\n vector<int> height(n, 0);\n for(int i=0; i<m; i++){\n stack<int> s;\n for(int j=0; j<n; j++){\n /** update the current row ended height array **/\n if(j<n-1){\n if(matrix[i][j]=='1') height[j]+=1;\n else height[j]=0;\n }\n /** use the histogram-max-rectangle-module **/\n while(!s.empty() && height[s.top()]>=height[j]){\n h=height[s.top()];\n s.pop();\n w=s.empty() ? j:j-s.top()-1;\n if(h*w>result) result=h*w;\n }\n s.push(j);\n }\n }\n return result;\n }\n };
| 9 | 0 |
[]
| 3 |
maximal-rectangle
|
C++ | Easiest Solution | Basic Maths | Commented Code for Understanding
|
c-easiest-solution-basic-maths-commented-rl8r
|
\n\n\n# IF YOU WANT ANOTHER MORE OPTIMIZED SOLUTION, YOU CAN CHECK THIS SOLUTION OUT: \nIt is 100% Faster using Stacks:\nhttps://leetcode.com/problems/maximal-r
|
VYOM_GOYAL
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-13T03:59:51.586278+00:00
|
2024-04-13T05:45:27.843376+00:00
| 3,373 | false |
\n\n\n# IF YOU WANT ANOTHER MORE OPTIMIZED SOLUTION, YOU CAN CHECK THIS SOLUTION OUT: \nIt is 100% Faster using Stacks:\nhttps://leetcode.com/problems/maximal-rectangle/solutions/5014969/c-100-faster-easy-stacks-basic-maths-easy-step-by-step-explanation/\n\n# THIS IS NOT THE MOST EFFECIENT SOLUTION, BUT IS THE EASIEST POSSIBLE CODE\n\n# THE BASIC IDEA IS TO CALCULATE THE LARGEST RECTANGLE FOR HISTOGRAM\nYOU CAN REFER TO STRIVER YT VIDEO FOR LARGEST RECTANGLE FOR HISTOGRAM : https://youtu.be/X0X6G-eWgQ8?si=cCUSmjz96Dx9lkGk\n\n# AFTER THIS CREATE ROW-WISE HISTOGRAM AND THEN FIND THE LARGEST RECTANGLE FOR EACH OF THEM AND RETURN THE LARGEST RECTANGLE AREA AS THE ANSWER\n\n# REFER TO CODE FOR COMMENTS AND EXPLANATION LINE BY LINE\n\n# Intuition\nThe problem asks us to find the rectangle with the largest area that consists entirely of 1s in a binary matrix. Here\'s an intuitive approach:\n\n1. **Think horizontally:** For each row, imagine stacking 1s vertically. We can treat this as a histogram where the height of each bar represents the number of consecutive 1s in the current row.\n2. **Find maximal area in a histogram:** We know efficient algorithms (like the stack-based approach) to find the largest rectangle within a histogram.\n\n# Approach\n1. **Build row-wise histograms:** Iterate through the matrix. For each row, create a new histogram array to keep track of the number of consecutive 1s encountered so far for each column. If a 0 is encountered, reset the count to 0.\n2. **Process each histogram:** For each row\'s histogram, apply the findLargestAreaInHistogram function to determine the maximum rectangle area that can be formed using the heights in that row.\n3. **Track global maximum:** Maintain a variable area to keep track of the largest rectangle area found so far across all rows. Update area with the maximum area calculated for each row\'s histogram.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: **O(n*m)**\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: **O(m)**\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\n#pragma GCC optimize("O3", "unroll-loops")\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int findLargestAreaInHistogram(int n, vector<int>& rowHistogram) {\n int area = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n int breadth = 1;\n // first find only this area\n area = max(area, rowHistogram[i] * breadth);\n // now start checking for other lengths as well\n // as we might need other heights for more area\n\n // first check for heights behind it\n for (int j = i - 1; j >= 0; j--) {\n if (rowHistogram[j] >= rowHistogram[i]) {\n breadth++;\n } else {\n break;\n }\n }\n\n // now check for heights after it\n for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {\n if (rowHistogram[j] >= rowHistogram[i]) {\n breadth++;\n } else {\n break;\n }\n }\n\n // now compute the area\n area = max(area, rowHistogram[i] * breadth);\n }\n return area;\n }\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n int n = matrix.size();\n int m = matrix[0].size();\n int area = 0;\n // first make the histogram row wise\n vector<int> rowHistogram(m, 0);\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {\n if (matrix[i][j] == \'1\') {\n rowHistogram[j]++;\n } else {\n rowHistogram[j] = 0;\n }\n }\n // now I have created the histogram for the particular level\n // now find the largest area in that level\n area = max(area, findLargestAreaInHistogram(m, rowHistogram));\n }\n return area;\n }\n};\nauto init = []() {\n ios::sync_with_stdio(false);\n cin.tie(nullptr);\n cout.tie(nullptr);\n return \'c\';\n}();\n```
| 8 | 0 |
['Array', 'Matrix', 'C++']
| 2 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Using DP | Python
|
using-dp-python-by-pragya_2305-5p12
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(m(n^2))\n\n- Space complexity: O(mn)\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution:\n def maximalRectangle(self, matrix: List[List[str]]) -> i
|
pragya_2305
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-13T03:45:14.374967+00:00
|
2024-04-13T03:45:14.374997+00:00
| 2,153 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(m(n^2))\n\n- Space complexity: O(mn)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maximalRectangle(self, matrix: List[List[str]]) -> int:\n m,n = len(matrix),len(matrix[0])\n ans = 0\n dp = {}\n\n for i in range(m):\n for j in range(n):\n if matrix[i][j]==\'0\':\n dp[(i,j)]=(0,0)\n else:\n x = dp[(i,j-1)][0]+1 if j>0 else 1\n y = dp[(i-1,j)][1]+1 if i>0 else 1\n dp[(i,j)] = (x,y)\n ans = max(x,y,ans)\n minWidth = x\n # verical max possible\n for r in range(i-1,i-y,-1):\n minWidth = min(minWidth,dp[(r,j)][0])\n ans = max(ans,minWidth*(i-r+1))\n \n \n return ans\n```
| 8 | 0 |
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Matrix', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
✅Easy solution || ✅Short & Simple || ✅Best Method || ✅Easy-To-Understand
|
easy-solution-short-simple-best-method-e-1y5d
|
\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {\n stack<int> st;\n int n=heights.size();\n vect
|
sanjaydwk8
|
NORMAL
|
2022-12-26T14:59:23.126998+00:00
|
2022-12-26T14:59:23.127029+00:00
| 1,818 | false |
\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {\n stack<int> st;\n int n=heights.size();\n vector<int> left(n);\n vector<int> ryt(n);\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n while(!st.empty() && heights[i]<=heights[st.top()])\n st.pop();\n if(st.empty())\n left[i]=0;\n else\n left[i]=st.top()+1;\n st.push(i);\n }\n while(!st.empty())\n st.pop();\n for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--)\n {\n while(!st.empty() && heights[i]<=heights[st.top()])\n st.pop();\n if(st.empty())\n ryt[i]=n-1;\n else\n ryt[i]=st.top()-1;\n st.push(i);\n }\n int ans=0;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n int area=heights[i]*(ryt[i]-left[i]+1);\n ans=max(ans, area);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n int m=matrix.size();\n int n=matrix[0].size();\n vector<vector<int>> dp(m, vector<int>(n));\n for(int i=0;i<m;i++)\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++)\n dp[i][j]=matrix[i][j]-\'0\';\n \n for(int i=1;i<m;i++)\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++)\n if(dp[i][j]!=0)\n dp[i][j]+=dp[i-1][j];\n int ans=0;\n for(int i=0;i<m;i++)\n ans=max(ans, largestRectangleArea(dp[i]));\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\nPlease **UPVOTE** if it helps \u2764\uFE0F\uD83D\uDE0A\nThank You and Happy To Help You!!
| 8 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
JAVA Solution Explained in HINDI
|
java-solution-explained-in-hindi-by-the_-mvfa
|
https://youtu.be/PyJ3zsCghZ0\n\nFor explanation, please watch the above video and do like, share and subscribe the channel. \u2764\uFE0F Also, please do upvote
|
The_elite
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-13T12:40:06.130236+00:00
|
2024-04-13T12:40:06.130262+00:00
| 598 | false |
https://youtu.be/PyJ3zsCghZ0\n\nFor explanation, please watch the above video and do like, share and subscribe the channel. \u2764\uFE0F Also, please do upvote the solution if you liked it.\n\nSubscribe link:- [ReelCoding](https://www.youtube.com/@reelcoding?sub_confirmation=1)\n\nSubscribe Goal:- 400\nCurrent Subscriber:- 312\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(m*n)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(n)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) {\n if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {\n return 0;\n }\n \n int n = matrix[0].length;\n int[] curRow = new int[n];\n int maxAns = 0; // Initialize the maximum answer\n \n for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {\n if (matrix[i][j] == \'1\') {\n curRow[j] += 1;\n } else {\n curRow[j] = 0;\n }\n }\n \n // Calculate the largest area in histogram for the current row\n int curAns = largestAreaHistogram(curRow);\n \n // Update maxAns with the maximum of maxAns and curAns\n maxAns = Math.max(maxAns, curAns);\n }\n \n return maxAns;\n }\n\n private int largestAreaHistogram(int a[]) {\n int n = a.length;\n ArrayDeque<Integer> st = new ArrayDeque<>();\n int[] leftSmall = new int[n];\n int[] rightSmall = new int[n];\n \n // Calculate leftSmalls\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n while (!st.isEmpty() && a[st.peek()] >= a[i]) {\n st.pop();\n }\n leftSmall[i] = st.isEmpty() ? 0 : st.peek() + 1;\n st.push(i);\n }\n\n // Clear the stack\n st.clear();\n \n // Calculate rightSmalls\n for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {\n while (!st.isEmpty() && a[st.peek()] >= a[i]) {\n st.pop();\n }\n rightSmall[i] = st.isEmpty() ? n - 1 : st.peek() - 1;\n st.push(i);\n }\n\n // Calculate the maximum area\n int maxA = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n maxA = Math.max(maxA, a[i] * (rightSmall[i] - leftSmall[i] + 1));\n }\n return maxA;\n }\n}\n\n```
| 7 | 0 |
['Java']
| 1 |
maximal-rectangle
|
easy solution with dp.
|
easy-solution-with-dp-by-meliodasmc-1ogp
|
Intuition\nfind all squares (n * n) and sum n by each the squares that are adjacent to the right and to the down with the same size of my current square, the an
|
meliodasmc
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-13T02:28:04.587320+00:00
|
2024-04-13T23:25:58.366516+00:00
| 2,399 | false |
# Intuition\nfind all squares (n * n) and sum n by each the squares that are adjacent to the right and to the down with the same size of my current square, the answer is the max of these sums.\n# Approach\n- find alls squares (n * n):\nfor this, we movent from left to right for alls row in my square, if my current cell is one, the max square (n * n) is the min between (left cell in this row, up cell in this colum, and left cell in the up row) + 1. \n\n- find alls rectangle (n * m) where m>=n:\nafter find the squares (n * n), we need to find alls squares that are contiguos and after sum ths, the second n in the operation (n * n) augmenter to m or the first n in the operation (n * n) augmenter.\nfor this, we have to travel for all cells in my tablet, if this cells have an one, we have to move to the maximal right cell, where alls cells in this range if the same square (n * n) and the sum is (n * n)+n * (range) move to the maximal down cell where alls cells in this range if the same square (n * n) and the sum is (n * n)+n * (range) for this cell the answer is the maximal betwen this two case, and the answer of this problem is the maximal the alls maximal found.\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(N * M * max(N, M))\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(N*M)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n \n vector<vector<int>>table(matrix.size(), vector<int>(matrix[0].size()));\n\n int i, j, k, l, maxi = 0, counter1, counter2;\n\n for(i = 0; i<matrix.size(); i++){\n table[i][0] = (matrix[i][0] == \'1\');\n }\n for(i = 0; i<matrix[0].size(); i++){\n table[0][i] = (matrix[0][i] == \'1\');\n }\n\n for(i = 1; i<matrix.size(); i++){\n for(j = 1; j<matrix[0].size(); j++){\n if(matrix[i][j] == \'1\'){\n table[i][j] = min({table[i][j-1], table[i-1][j], table[i-1][j-1]})+1;\n }\n }\n }\n\n for(i = 0; i<matrix.size(); i++){\n for(j = 0; j<matrix[0].size(); j++){\n if(matrix[i][j] == \'1\'){\n counter1 = table[i][j] * table[i][j];\n counter2 = table[i][j] * table[i][j];\n for(k = i+1; k<matrix.size() && table[i][j] <= table[k][j] && table[k][j]; k++){\n counter1+=table[i][j];\n }\n for(l = j+1; l<matrix[0].size() && table[i][j] <= table[i][l] && table[i][l]; l++){\n counter2+=table[i][j];\n }\n maxi = max({counter1, counter2, maxi});\n }\n }\n }\n\n return maxi;\n }\n};\n```
| 7 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C++']
| 2 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Maximal Rectangle with step by step explanation
|
maximal-rectangle-with-step-by-step-expl-py9w
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\nThis solution uses the concept of histogram to solve the problem. For eac
|
Marlen09
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-14T14:14:40.388274+00:00
|
2023-02-14T14:14:40.388318+00:00
| 1,132 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\nThis solution uses the concept of histogram to solve the problem. For each row, it converts the binary values into heights of the bars and then calculates the largest rectangle in the histogram using the stack data structure. The solution has a time complexity of O(n * m) and a space complexity of O(m).\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n89.51%\n\n- Space complexity:\n85%\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maximalRectangle(self, matrix: List[List[str]]) -> int:\n if not matrix or not matrix[0]:\n return 0\n \n n, m = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])\n height = [0] * (m + 1)\n ans = 0\n \n for row in matrix:\n for i in range(m):\n height[i] = height[i] + 1 if row[i] == \'1\' else 0\n stack = [-1]\n for i in range(m + 1):\n while height[i] < height[stack[-1]]:\n h = height[stack.pop()]\n w = i - stack[-1] - 1\n ans = max(ans, h * w)\n stack.append(i)\n \n return ans\n\n```
| 7 | 0 |
['Python', 'Python3']
| 1 |
maximal-rectangle
|
✅ [c++] || stack solution
|
c-stack-solution-by-xor09-jr1x
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n int row = matrix.size(); \n if(row==0) return 0;\n
|
xor09
|
NORMAL
|
2021-11-30T03:38:37.705692+00:00
|
2021-11-30T03:38:37.708017+00:00
| 1,167 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n int row = matrix.size(); \n if(row==0) return 0;\n int col = matrix[0].size();\n vector<vector<int>> grid(row,vector<int> (col,0));\n int area=0;\n for(int i=0; i<row; ++i){\n for(int j=0; j<col; ++j){\n if(i==0){\n grid[i][j]=matrix[i][j]-\'0\';\n }else{\n if(matrix[i][j]==\'0\') grid[i][j]=0;\n else grid[i][j] = 1+grid[i-1][j];\n }\n }\n \n vector<int> left(col), right(col);\n stack<int> stk;\n for(int j=0; j<col; ++j){\n int cur = grid[i][j];\n while(!stk.empty() && grid[i][stk.top()]>=cur) stk.pop();\n if(stk.empty()) left[j]=-1 ;\n else left[j]=stk.top();\n stk.push(j);\n }\n \n while(!stk.empty()) stk.pop();\n \n for(int j=col-1; j>=0; --j){\n int cur = grid[i][j];\n while(!stk.empty() && grid[i][stk.top()]>=cur) stk.pop();\n if(stk.empty()) right[j]=col;\n else right[j]=stk.top();\n stk.push(j);\n }\n \n for(int j=0;j<col;++j){\n area=max(area, (grid[i][j]*(right[j]-left[j]-1)));\n }\n }\n return area;\n }\n};\n```\nPlease **UPVOTE**
| 7 | 1 |
['Stack', 'C', 'Monotonic Stack', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Python solution built off of Maximal Square [Time complexity: O(n^3)]
|
python-solution-built-off-of-maximal-squ-nxig
|
```class Solution:\n def maximalRectangle(self, matrix: List[List[str]]) -> int:\n \n if not matrix or not matrix[0]:\n return 0\n
|
optimusmersenne
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-12T16:17:37.529503+00:00
|
2020-08-12T17:18:34.670800+00:00
| 399 | false |
```class Solution:\n def maximalRectangle(self, matrix: List[List[str]]) -> int:\n \n if not matrix or not matrix[0]:\n return 0\n \n m = len(matrix)\n n = len(matrix[0])\n \n #prepping max squares array and finding largest value in array (max_num)\n\t\tmax_num = 1\n for i in range(m):\n matrix[i][0] = int(matrix[i][0])\n\n for j in range(n):\n matrix[0][j] = int(matrix[0][j])\n \n for i in range(1, m):\n for j in range(1, n):\n if matrix[i][j] == \'1\':\n tmp = min(matrix[i - 1][j], matrix[i][j - 1], matrix[i - 1][j - 1]) + 1\n matrix[i][j] = tmp\n max_num = max(max_num, tmp)\n else:\n matrix[i][j] = 0\n \n\t\t#initialize array for global longest chain of each number\n max_values = [0 for i in range(max_num)]\n \n #iterate through rows to find longest chain of each value\n\t\tfor step in range(max_num):\n for i in range(m):\n curr_value = 0\n for j in range(n):\n if matrix[i][j] > step:\n curr_value += 1\n else:\n if curr_value > max_values[step]:\n max_values[step] = curr_value\n curr_value = 0\n if curr_value > max_values[step]:\n max_values[step] = curr_value\n \n #iterate through columns to find largest chain of each value\n for step in range(max_num):\n for j in range(n):\n curr_value = 0\n for i in range(m):\n if matrix[i][j] > step:\n curr_value += 1\n else:\n if curr_value > max_values[step]:\n max_values[step] = curr_value\n curr_value = 0\n if curr_value > max_values[step]:\n max_values[step] = curr_value \n \n res = 0\n \n\t\t#area of the rectangle can be calculated from neigboring squares\n for s, count in enumerate(max_values):\n if count != 0:\n res = max(res, (s + 1) ** 2 + (s + 1) * (count - 1))\n \n return res
| 7 | 1 |
[]
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
[Python] Similar to Leetcode 84. Explained.
|
python-similar-to-leetcode-84-explained-et5lq
|
\nclass Solution:\n def maximalRectangle(self, matrix: List[List[str]]) -> int:\n \n ## RC ##\n ## APPROACH : DP ##\n ## SIMILAR
|
101leetcode
|
NORMAL
|
2020-06-15T11:00:17.207812+00:00
|
2020-06-15T11:00:17.207845+00:00
| 2,415 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def maximalRectangle(self, matrix: List[List[str]]) -> int:\n \n ## RC ##\n ## APPROACH : DP ##\n ## SIMILAR TO LEETCODE 84. LARGEST RECTANGLE IN A HISTOGRAM ##\n \n # 1. we will create heights matrix, just like below (to imagine line histogram)\n # 2. on each heights matrix row, we find the maxArea\n # 3. return maxArea\n # Ex :\n # [\n # ["1","0","1","0","0"],\n # ["1","0","1","1","1"],\n # ["1","1","1","1","1"],\n # ["1","0","0","1","0"]\n # ]\n # [\n # ["1","0","1","0","0"],\n # ["2","0","2","1","1"],\n # ["3","1","3","2","2"],\n # ["4","0","0","3","0"]\n # ]\n \n if(not matrix) : return 0\n \n for i in range(0, len(matrix)):\n for j in range(len(matrix[0])):\n if( matrix[i][j] == \'1\' ):\n matrix[i][j] = int(matrix[i][j]) + int(matrix[i-1][j] if(i>0) else 0 )\n else:\n matrix[i][j] = 0\n \n def findLargestArea(heights):\n if(not heights): return 0\n heights.append(0)\n stack = [-1]\n ans = 0\n for i in range(len(heights)):\n while( heights[i] < heights[stack[-1]] ):\n h = heights[stack.pop()]\n w = i - stack[-1] - 1\n ans = max( ans, h*w )\n stack.append(i)\n return ans\n \n maxArea = 0\n for row in matrix:\n maxArea = max( maxArea, findLargestArea(row) )\n return maxArea \n```
| 7 | 1 |
['Python', 'Python3']
| 1 |
maximal-rectangle
|
JavaScript DP O(n) Time & Space
|
javascript-dp-on-time-space-by-stevenkin-obng
|
\n/**\n * @param {character[][]} matrix\n * @return {number}\n */\nconst maximalRectangle = (matrix) => {\n if (!matrix.length || !matrix[0].length) return 0;\
|
stevenkinouye
|
NORMAL
|
2019-12-16T03:41:40.167979+00:00
|
2019-12-16T03:41:40.168033+00:00
| 1,173 | false |
```\n/**\n * @param {character[][]} matrix\n * @return {number}\n */\nconst maximalRectangle = (matrix) => {\n if (!matrix.length || !matrix[0].length) return 0;\n const height = matrix.length;\n const width = matrix[0].length;\n const lefts = matrix[0].map(() => 0);\n const rights = matrix[0].map(() => width);\n const heights = lefts.slice();\n let max = 0;\n for (let row = 0; row < height; row++) {\n let left = 0;\n let right = width;\n for (let i = 0; i < width; i++) {\n if (matrix[row][i] === \'1\') {\n lefts[i] = Math.max(left, lefts[i]);\n heights[i]++;\n } else {\n lefts[i] = heights[i] = 0;\n left = i + 1\n }\n\n const rightIdx = width - 1 - i;\n if (matrix[row][rightIdx] === \'1\') {\n rights[rightIdx] = Math.min(right, rights[rightIdx])\n } else {\n rights[rightIdx] = width;\n right = rightIdx;\n }\n }\n for (let i = 0; i < width; i++) {\n max = Math.max(max,(rights[i] - lefts[i]) * heights[i]);\n }\n }\n return max\n}\n```
| 7 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 1 |
maximal-rectangle
|
DP solution faster than 99.8% w/ description, example & analysis - O(nm + n³) time / O(1) space
|
dp-solution-faster-than-998-w-descriptio-ome4
|
Solution:\n\n/* Leetcode speedup */\nstatic vector<vector<char>> mat {[](){\n std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);\n std::cin.tie(NULL);\n std::cout.tie(N
|
dd0rz
|
NORMAL
|
2019-01-13T23:16:23.086968+00:00
|
2019-01-13T23:16:23.087038+00:00
| 1,679 | false |
# Solution:\n```\n/* Leetcode speedup */\nstatic vector<vector<char>> mat {[](){\n std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);\n std::cin.tie(NULL);\n std::cout.tie(NULL);\n return NULL;\n}()};\n\n/* Solution */\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>> &mat) {\n\t\t// Iterate over mat and count the number of contiguous 1\'s to the left of each position\n for (int i {0}; i < mat.size(); ++i) {\n for (int j {1}; j < mat.front().size(); ++j) {\n mat[i][j] = mat[i][j] != \'0\' ? mat[i][j-1] + 1 : mat[i][j];\n }\n }\n\n\t\t// Return value -- area of maximal 1\'s rectangle \n int ret {0};\n\t\t\n\t\t// Iterate over new values and calculate/find area of maximal 1\'s rectangle\n for (int i {0}; i < mat.size(); ++i) { \n for (int j {0}; j < mat.front().size(); ++j) {\n for (int k {i}, minw {mat[i][j] - \'0\'}; k < mat.size() && minw; ++k) {\n ret = max(ret, (k - i + 1) * (minw= min(minw, mat[k][j] - \'0\')));\n\t\t\t\t\tmat[k][j] = mat[k][j] - \'0\' <= minw ? \'0\' : mat[k][j];\n }\n }\n }\n \n\t\t// Return area of maximal rectangle\n return ret;\n }\n};\n```\n\n\n# Description:\nFirst, the algorithm iterates over the elements in the matrix and counts the number of horizontally contiguous 1\u2019s to the left of each position. Starting at the 2nd element (1th position) of each row, if the current element, ```mat[i][j]```, is ```\u20181\u2019```, then its value is set to that of the previous element in the same row plus one.\n\ni.e., if ```mat[i][j] == \u20181\u2019``` then ```mat[i][j] = mat[i][j-1] + 1```, else ```mat[i][j]``` remains ```\'0\'```. \n\nHere there\'s one iteration for each element, and the original matrix is modified to count horizontally contiguous 1\u2019s. Hence, the time complexity for this portion is O(nm), and the space complexity is O(1).\n \n*Note: since the matrix holds char types and not ints, it\u2019s necessary to subtract \u20180\u2019 from elements to obtain an accurate numerical value for the number of horizontally contiguous 1\u2019s counted. Alternatively, you could use an identical 2d vector of ints for counting, but this would change the space complexity from O(1) to O(nm).*\n \nTake the following example matrix: \n\n ```\nvector<vector<char>> mat {\n { \'0\', \'1\', \'1\', \'1\', \'0\' },\n { \'0\', \'1\', \'1\', \'0\', \'0\' }, \n { \'0\', \'0\', \'0\', \'0\', \'1\' },\n { \'1\', \'1\', \'0\', \'0\', \'0\' } \n};\n```\n\nAfter iterating over the elements and counting the number of horizontally contiguous 1\u2019s for each position, the values (after having subtracted \u20180\u2019 from them) for each element would be:\n \n ```\n0 1 2 3 0 \n0 1 2 0 0 \n0 0 0 0 1 \n1 2 0 0 0 \n ```\n \nNext, the new values are iterated over and used to calculate areas of rectangles in the matrix originally, and the maximal area calculated is kept track of with the return variable ```ret```.\n \nThis is done using three nested loops:\n1. The outermost loop iterates vertically over the rows of the matrix, from ```i = 0``` to ```i = n-1```. \n2. The second loop iterates horizontally over the columns, from ```j = 0``` to ```j = m-1```. \n3. The innermost loop also iterates over the rows, from```k = i``` to ```k = n-1```, but only while the value of ```mat[k][j]``` is not ```\'0\'``` (i.e., non-zero).\n \nAs we iterate vertically over elements in the innermost loop, we keep track of the minimum (non-zero) value encountered for ```mat[k][j]```. This value represents the largest width for which the elements iterated over by ```k``` form a rectangle without any gaps or holes. Moreover, since these elements make up one side of the rectangle, the number of elements iterated over consecutively in this loop, ```k - i + 1```, represents the height of the rectangle they form.\n\nUsing these values for width and height, each iteration we calculate the area of the largest possible rectangle and keep track of the overall maximal area found. \n\nAdditionally, an optimization is made by setting ```mat[k][j] = \'0\'``` when its numerical value (```mat[k][j] - \'0\'```) is not greater than ```minw```. This allows duplicate iterations over elements we know will not produce a larger area to be avoided. \n \n# Example:\n\nGiven the following example input matrix:\n \n ```\nvector<vector<char>> mat {\n { \'0\', \'1\', \'1\', \'1\', \'0\' },\n { \'0\', \'1\', \'1\', \'0\', \'0\' }, \n { \'0\', \'0\', \'0\', \'0\', \'1\' },\n { \'1\', \'1\', \'0\', \'0\', \'0\' } \n};\n```\n\n\nAfter iterating over the matrix the first time and recording the number of contiguous 1\'s to the left of each position the values become:\n\n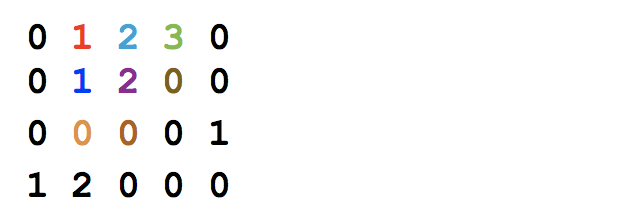\n\n\n*Note: integer values shown for mat, i.e., mat[][] - \'0\'*\n\nNext, the new values are iterated over and used to calculate the area of 1\'s rectangles in the matrix originally. The first several iterations where area calculations are performed are as follows (note that the innermost loop does not execute and no calculations are performed when ```mat[i][j] == \'0\'```, thus these iterations are not shown):\n\n\n\nAfter completion, the maximal rectangle returned for the given matrix is ```ret = 4```.\n\n# Computational Complexity\n**Worst-case Space Complexity**\nSince our solution modifies the original input matrix and uses a constant amount of memory rather than some amount based on the input size, our space complexity is constant time, O(1). \n\n**Worst-case Time Complexity**\nTo analyze the worst-case runtime complexity, consider a 5x5 matrix with the worst-case configuration:\n\n```\n0, 0, 0, 0, 1\n0, 0, 0, 1, 1\n0, 0, 1, 1, 1\n0, 1, 1, 1, 1\n1, 1, 1, 1, 1\n```\n\nWhen counting horizontally contiguous 1\'s in the first set of loops, there\'s one iteration for each element in the matrix. Hence the runtime complexity for this part is O(nm), where where n = height and w = width. Next, we consider the now modified worst-case 5x5 matrix to determine the runtime complexity of the second set of loops:\n\n```\n0, 0, 0, 0, 1\n0, 0, 0, 1, 2\n0, 0, 1, 2, 3\n0, 1, 2, 3, 4\n1, 2, 3, 4, 5\n```\n\nIt\'s now apparent this is the worst-case configuration because when calculating areas smaller widths are always checked before larger ones. This prevents duplicate iterations from being avoided by setting elements to 0. \n\nSince the two outer loops in the second part will produce one iteration for each element in the matrix, we\'ll always have nm iterations plus any additional duplicate iterations over elements performed by the innermost loop. If we can find an expression, X, for the number of extra iterations over elements performed by the innermost loop, then we\'ll know the runtime complexity for this part is O(nm + X).\n\nStart by considering elements in the rightmost column, ```j=4```. When ```i=0``` and the innermost loop is entered, all elements in the column from [```k=0``` to ```k=4```] will be iterated over for 5 iterations total. This is the first time iterating over any element in the column, so none of the iterations are extra iterations. When ```i=1``` elements in the column from [```k=1``` to ```k=4```] (from the value 2 downwards) will be iterated over for 4 iterations total. This time these will all be duplicate iterations since all elements in the column have been iterated over already. When ```i=2```, elements in the column from [```k=2``` to ```k=4```] are iterated over for 3 iterations total, which again are all duplicate iterations. For all values of ```i``` the number of duplicate iterations over elements in rightmost column, ```j=4```, will be:\n\n*4 + 3 + 2 + 1 = 10*\n\nFor the preceding column, ```j=3```, the first element is 0, so there are no iterations over elements in the column when ```i=0```. Starting at ```i=1```, however, we can see the same pattern as before will occur. This means the total number of duplicate iterations over elements in the column for all values of ```i``` will be:\n\n*3 + 2 + 1 = 6*\n\nThe same pattern occurs for all columns in the matrix, and the number of duplicate iterations over elements in each will be:\n\n*1st column (```j=0```): 0 = 0\n2nd column (```j=1```): 1 + 0 = 1\n3rd column (```j=2```): 2 + 1 + 0 = 3\n4th column (```j=3```): 3 + 2 + 1 + 0 = 6\n5th column (```j=4```): 4 + 3 + 2 + 1 + 0 = 10*\n\nIt can be seen for the worst-case configuration, in each column the number of duplicate iterations over elements will be the sum of the first n-1 natural numbers, where n is the largest value in the column. Putting n-1 into the equation n(n+1)/2 (sum of natural numbers up to n), for each column we have:\n\n*(n-1)(n-1+1)/2 = n(n-1)/2 duplicate iterations*\n\nThus, for all columns in the matrix, the total number duplicate iterations is:\n\n*\u03A3n(n-1)/2 [1 => n]*, or equivalently, *n\xB3/6 - n/6*\n\nThis means for our worst-case 5x5 matrix we should have nm iterations + n\xB3/6 - n/6 duplicate iterations:\n\n*5 * 5 + 125/6 - 5/6 = 25 iterations + 20 duplicate iterations = 45 total iterations*, which is accurate.\n\nCombining both the first and second parts, our overall worst-case time is:\n\n*O(nm) + O(nm + n\xB3/6 - n/6) = O(2nm + n\xB3/6 - n/6) =*\n\n*O(nm + n\xB3)*, where n = height and m = width.
| 7 | 1 |
[]
| 3 |
maximal-rectangle
|
O(n^2) dp java solution
|
on2-dp-java-solution-by-timemachine-x8ir
|
public int maximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) {\n if (matrix.length == 0) return 0;\n int m = matrix.length;\n int n = matrix[0]
|
timemachine
|
NORMAL
|
2016-02-02T23:11:20+00:00
|
2016-02-02T23:11:20+00:00
| 2,672 | false |
public int maximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) {\n if (matrix.length == 0) return 0;\n int m = matrix.length;\n int n = matrix[0].length;\n int[] left = new int[n]; // left boundary of histogram columns.\n int[] right = new int[n]; // right boundary of histogram columns.\n int[] height = new int[n]; // height of histogram columns.\n Arrays.fill(right, n);\n int area = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {\n int l = 0, r = n;\n for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {\n if (matrix[i][j] == '1') {\n height[j]++;\n left[j] = Math.max(l, left[j]);\n }\n else {\n l = j + 1;\n height[j] = 0;\n left[j] = 0;\n right[j] = n;\n }\n }\n for (int j = n - 1; j >= 0; j--) {\n if (matrix[i][j] == '1') {\n right[j] = Math.min(r, right[j]);\n area = Math.max(area, height[j] * (right[j] - left[j]));\n }\n else {\n r = j;\n }\n }\n }\n return area;\n }
| 7 | 1 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Java']
| 1 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Java Clean Solution || Multiple Approaches and Detail Explanation
|
java-clean-solution-multiple-approaches-axtno
|
Intuition And Approach\nIf you\'re a coding enthusiast or a budding programmer, you\'ve probably heard about the Maximal Rectangle Problem. This fascinating pro
|
Shree_Govind_Jee
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-13T05:38:02.644321+00:00
|
2024-04-13T05:38:02.644362+00:00
| 1,080 | false |
# Intuition And Approach\nIf you\'re a coding enthusiast or a budding programmer, you\'ve probably heard about the Maximal Rectangle Problem. This fascinating problem is a classic in the world of computer science and is often used to demonstrate the power of dynamic programming and efficient algorithm design.\n\nIn this blog post, we\'ll dive deep into the problem and explore a solution using a clever algorithm. We\'ll provide code examples in multiple programming languages to ensure that you can follow along regardless of your coding preferences. So, whether you\'re a C++ aficionado, a Java enthusiast, a Python pro, or a JavaScript wizard, you\'re in the right place!\n\n# Understanding the Maximal Rectangle Problem\nThe Maximal Rectangle Problem can be defined as follows: Given a binary matrix, find the largest rectangle containing only ones and return its area. This might sound a bit complex at first, but with the right algorithm, it becomes a manageable challenge.\n\n# The Algorithm: Dynamic Programming to the Rescue\nThe key to solving the Maximal Rectangle Problem lies in dynamic programming. Dynamic programming is a powerful technique that involves breaking down a complex problem into smaller subproblems and reusing solutions to subproblems to avoid redundant computations.\n\n# Step 1: The `largestRectangleArea` Function\nFirst, let\'s take a look at the `largestRectangleArea` function. This function, written in C++, Java, Python, and JavaScript, calculates the largest rectangle area in a histogram. The idea is to use a stack to efficiently find the maximum area.\n\nHere\'s a simplified overview of the algorithm:\n\n1. Create an empty stack to store indices.\n1. Iterate through the histogram from left to right.\n1. While the stack is not empty and the current histogram value is less than the value at the index stored in the stack\'s top element, pop elements from the stack and calculate the maximum area for each popped element.\n1. Keep track of the maximum area as you iterate through the histogram.\n1. This algorithm efficiently finds the largest rectangle area in the histogram, which we\'ll use in the next step.\n\n# Step 2: The `maximalAreaOfSubMatrixOfAll1` Function\nIn this step, we adapt the `largestRectangleArea` function to solve the Maximal Rectangle Problem for a binary matrix. We create a vector to store the height of each column and use dynamic programming to find the maximum rectangle area for each row.\n\n# Step 3: Bringing It All Together\nIn the final step, we create the maximalRectangle function, which takes a binary matrix as input and returns the maximum rectangle area containing only ones.\n\n# Dry Run of **`maximalRectangle`** Function\nWe\'ll perform a dry run of the `maximalRectangle` function using the following matrix:\n\n```\nmatrix = [\n [\'1\', \'0\', \'1\', \'0\', \'0\'],\n [\'1\', \'0\', \'1\', \'1\', \'1\'],\n [\'1\', \'1\', \'1\', \'1\', \'1\'],\n [\'1\', \'0\', \'0\', \'1\', \'0\']\n]\n```\n**Step 1: Initializing Variables**\nWe start with the given matrix:\n\n```\n1 0 1 0 0\n1 0 1 1 1\n1 1 1 1 1\n1 0 0 1 0\n```\nWe have two helper functions, largestRectangleArea and maximalAreaOfSubMatrixOfAll1, which are used within the `maximalRectangle` function.\n\nStep 2: maximalAreaOfSubMatrixOfAll1\nWe enter the maximalAreaOfSubMatrixOfAll1 function, which computes the maximal area of submatrices containing only \'1\'s.\n\nMatrix and height after each row iteration:\n\n1. Process Row 1:\n\n - Matrix:\n```\n 1 0 1 0 0\n```\n - Height: `[1, 0, 1, 0, 0]`\n1. Process Row 2:\n\n - Matrix:\n``````\n1 0 1 1 1\n``````\n - Height: `[2, 0, 2, 1, 1]`\n1. Process Row 3:\n\n - Matrix:\n```\n1 1 1 1 1\n```\n - Height: `[3, 1, 3, 2, 2]`\n1. Process Row 4:\n\n - Matrix:\n```\n1 0 0 1 0\n```\n - Height: `[4, 1, 1, 3, 1]`\n# Maximal Area of Histogram `(largestRectangleArea)`:\n\nFor each height, we calculate the maximal area of the histogram using the `largestRectangleArea` function.\n\nFor the height `[1, 0, 1, 0, 0]`, the maximal area is `1`.\nFor the height `[2, 0, 2, 1, 1]`, the maximal area is `4`.\nFor the height `[3, 1, 3, 2, 2]`, the maximal area is `6`.\nFor the height `[4, 1, 1, 3, 1]`, the maximal area is `4`.\nThe maximal area of submatrices for each row is `[1, 4, 6, 4]`.\n\n# Step 3: `maximalRectangle`\nFinally, we return the maximum value from the array `[1, 4, 6, 4],` which is `6`.\n\nThe maximal area of a submatrix containing only \'1\'s in the given matrix is `6`.\n\nThis concludes the dry run of the `maximalRectangle` function with the provided matrix.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:$$O(n*m)$$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:$$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n private int getMaximumArea(int[] height) {\n Stack<Integer> stck = new Stack<>();\n int area = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i <= height.length; i++) {\n while (!stck.isEmpty() && (i == height.length || height[stck.peek()] >= height[i])) {\n int newHeight = height[stck.pop()];\n int width = stck.isEmpty() ? i : i - stck.peek() - 1;\n area = Math.max(area, width * newHeight);\n }\n stck.push(i);\n }\n return area;\n }\n\n public int maximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) {\n int area = 0;\n int[] height = new int[matrix[0].length];\n for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < matrix[0].length; j++) {\n if (matrix[i][j] == \'0\') {\n height[j] = 0;\n } else if (matrix[i][j] == \'1\') {\n height[j]++;\n }\n }\n\n int currentMaximumArea = getMaximumArea(height);\n area = Math.max(area, currentMaximumArea);\n }\n return area;\n }\n}\n```\n\n---\n\n\n```\nclass Solution {\n private void getLeftBound(char[] matrix, int[] leftBound, int[] height, int left) {\n for (int i = 0; i < height.length; i++) {\n if (matrix[i] == \'1\') {\n height[i]++;\n leftBound[i] = Math.max(leftBound[i], left);\n } else {\n height[i] = 0;\n leftBound[i] = 0;\n left = i + 1;\n }\n }\n }\n\n private void getRightBound(char[] matrix, int[] rightBound, int right) {\n for (int i = rightBound.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {\n if (matrix[i] == \'1\') {\n rightBound[i] = Math.min(rightBound[i], right);\n } else {\n rightBound[i] = right;\n right = i;\n }\n }\n }\n\n private int getMaximumArea(int[] height, int[] leftBound, int[] rightBound, int area) {\n for (int i = 0; i < height.length; i++) {\n int width = rightBound[i] - leftBound[i];\n area = Math.max(area, height[i] * width);\n }\n return area;\n }\n\n public int maximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) {\n if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {\n return 0;\n }\n\n\n int[] leftBound = new int[matrix[0].length];\n int[] rightBound = new int[matrix[0].length];\n int[] height = new int[matrix[0].length];\n\n Arrays.fill(rightBound, matrix[0].length);\n int area = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {\n int left = 0;\n int right = matrix[0].length;\n\n getLeftBound(matrix[i], leftBound, height, left);\n getRightBound(matrix[i], rightBound, right);\n\n area = getMaximumArea(height, leftBound, rightBound, area);\n }\n return area;\n }\n}\n```
| 6 | 0 |
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Stack', 'Matrix', 'Monotonic Stack', 'Java']
| 1 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Python | Easy
|
python-easy-by-khosiyat-vkkd
|
see the Successfully Accepted Submission\n\n# Code\n\nfrom collections import deque\n\nclass Solution:\n def histogram(self, heights):\n n = len(heigh
|
Khosiyat
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-13T05:23:51.306221+00:00
|
2024-04-13T05:23:51.306255+00:00
| 844 | false |
[see the Successfully Accepted Submission](https://leetcode.com/problems/maximal-rectangle/submissions/1230875459/?source=submission-ac)\n\n# Code\n```\nfrom collections import deque\n\nclass Solution:\n def histogram(self, heights):\n n = len(heights)\n st1 = deque()\n st2 = deque()\n left = [0] * n\n right = [0] * n\n\n # Previous smaller element\n for i in range(n):\n num = heights[i]\n\n while st1 and heights[st1[-1]] > num:\n st1.pop()\n\n if not st1:\n left[i] = -1\n else:\n left[i] = st1[-1]\n\n st1.append(i)\n\n # Next greater element\n for i in range(n - 1, -1, -1):\n num = heights[i]\n\n while st2 and heights[st2[-1]] >= num:\n st2.pop()\n\n if not st2:\n right[i] = n\n else:\n right[i] = st2[-1]\n\n st2.append(i)\n\n max_area = 0\n for i in range(n):\n area = (right[i] - left[i] - 1) * heights[i]\n max_area = max(max_area, area)\n\n return max_area\n\n def maximalRectangle(self, matrix):\n if not matrix:\n return 0\n\n n = len(matrix)\n m = len(matrix[0])\n curr_row = [0] * len(matrix[0])\n max_area = 0\n\n for i in range(n):\n for j in range(m):\n if matrix[i][j] == \'1\':\n curr_row[j] += 1\n else:\n curr_row[j] = 0\n\n curr_max = self.histogram(curr_row)\n max_area = max(max_area, curr_max)\n\n return max_area\n\n```\n\n
| 6 | 0 |
['Python']
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
C++|| Easy to understand clean solution || Mono Stack
|
c-easy-to-understand-clean-solution-mono-0mbi
|
\n\n# Approach\n\nQuestion is similar to LC 84 : Largest Rectangle in Histogram. \n\nIn that question we had only one row and all the heights were column.\nHere
|
prajnanam
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-13T04:44:34.774815+00:00
|
2024-04-13T05:10:51.295571+00:00
| 827 | false |
\n\n# Approach\n\nQuestion is similar to LC 84 : Largest Rectangle in Histogram. \n\nIn that question we had only one row and all the heights were column.\nHere we have n rows and m columns. simply we apply that logic here for each row. but here we need to take care of one condition if my current cell (matrix[i][j] == 0) then my height will be zero as the vertical length chain will be disrupted. and if matrix[i][j] != 0 that means the vertical length chain will continue without any disruption so we add height[j]+=1;\n \nLogic for LC 84\n\nArea = length*breadth\nNow for each height which is equivalent to my length in this case.\nI will try to find its maximum breadth both in left and right direction from that height[i]. \nTake 4 5 6 6 1\n\nfor height[1] = 5;\nin left direction: next smallest is 4.\nin right direction: next smallest is 1.\n\nfor heights[2] =6;\nin left direction: next smallest is 5.\nin right direction: next smallest is 1.\n\n**Now if my height is constant and lets say h = 6 then on right if its 5, then it cannot be included in the rectangle of height =6 as heights are different. but if my constant height is 5 and on right my height is 6 then this 6 can be included because i can take length 5 from 6.** \n\nWe can use stack to find the NEXT SMALLEST ELEMENT FROM LEFT AND NEXT SMALLEST ELEMENT FROM RIGHT. We will store the indexes in the stack. \n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(n^2)\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(n)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n int solve(vector<int> &heights){\n int n = heights.size();\n vector<int> nslr(n),nsrl(n);\n stack<int> st;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n while(!st.empty() && heights[st.top()] >= heights[i]) st.pop();\n if(st.empty()) nslr[i] = -1;\n else nslr[i] = st.top();\n st.push(i);\n }\n while(!st.empty()) st.pop();\n for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--){\n while(!st.empty() && heights[st.top()] >= heights[i]) st.pop();\n if(st.empty()) nsrl[i] = n;\n else nsrl[i] = st.top();\n st.push(i);\n }\n\n int ans = 0;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n ans = max(ans,heights[i]*(nsrl[i]-nslr[i]-1));\n }\n return ans;\n }\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(NULL);\n int ans = 0;\n int n = matrix.size();\n int m = matrix[0].size();\n vector<int> heights(m,0);\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<m;j++){\n if(matrix[i][j] == \'0\'){\n heights[j] = 0;\n }else{\n heights[j]+=1;\n }\n }\n ans = max(ans,solve(heights));\n }\n return ans;\n \n }\n};\n```\n
| 6 | 1 |
['Monotonic Stack', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
C++ Very Easy Solution Using Stack + 84. Largest Rectangle in Histogram
|
c-very-easy-solution-using-stack-84-larg-781f
|
\nint largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {\n int n=heights.size();\n stack<int> s;\n s.push(-1);\n int maxArea=0;\n i
|
jaigupta2210
|
NORMAL
|
2021-11-30T03:42:20.293366+00:00
|
2021-11-30T03:42:20.293396+00:00
| 894 | false |
```\nint largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {\n int n=heights.size();\n stack<int> s;\n s.push(-1);\n int maxArea=0;\n int rm=0,lm=0;\n for(int i=0;i<=n;i++)\n {\n int val = (i==n ? 0 : heights[i]);\n while(s.top() != -1 and heights[s.top()]>=val)\n {\n rm = i;\n int h = heights[s.top()];\n s.pop();\n lm = s.top();\n maxArea = max(maxArea, h*(rm-lm-1));\n }\n s.push(i);\n }\n return maxArea;\n }\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix){\n int row = matrix.size();\n if(row == 0) return 0;\n int col = matrix[0].size();\n \n vector<int> v(col);\n for(int i=0;i<col;i++)\n {\n v[i] = matrix[0][i] - \'0\';\n }\n int maxArea = 0;\n maxArea = max(maxArea, largestRectangleArea(v));\n for(int i=1;i<row;i++)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<col;j++)\n {\n if(matrix[i][j]==\'1\')\n {\n v[j]++;\n }\n else\n {\n v[j]=0;\n }\n }\n maxArea = max(maxArea, largestRectangleArea(v));\n }\n return maxArea;\n }\n```
| 6 | 1 |
[]
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Maximal Rectangle||using Max area Histogram||Aditya Verma ||C++
|
maximal-rectangleusing-max-area-histogra-qa46
|
\'\'\'\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n /\n \n 1.> for every row consider as 1 block of height \n 2.> write maximum are in histogram\n 3.> for MAH \n
|
bevkuff_786
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-11T12:03:43.614581+00:00
|
2021-07-11T12:03:43.614619+00:00
| 390 | false |
\'\'\'\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n /*\n \n 1.> for every row consider as 1 block of height \n 2.> write maximum are in histogram\n 3.> for MAH \n a> create a left array of next smaller element to left\n b> create a right array of next smaller to right\n c> create a width array\n d>make area array \n e> take max area\n 4> for all row it return a max area\n 5> take maximu of all returned value\n 6> which is our answer\n \n \n \n */\n int MAH(int*arr,int n)\n { // next smaller to right side\n stack<pair<int,int>>stk1;\n vector<int>right;\n for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--)\n {\n while(!stk1.empty() and stk1.top().first>=arr[i])\n {\n stk1.pop();\n }\n if(stk1.empty())\n {\n right.push_back(n);\n }\n else\n right.push_back(stk1.top().second);\n \n stk1.push({arr[i],i});\n }\n reverse(right.begin(),right.end());\n // next smaller to left side of array\n \n stack<pair<int,int>>stk2;\n vector<int>left;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n while(!stk2.empty() and stk2.top().first>=arr[i])\n {\n stk2.pop();\n }\n if(stk2.empty())\n {\n left.push_back(-1);\n }\n else\n {\n left.push_back(stk2.top().second);\n }\n stk2.push({arr[i],i});\n }\n \n // make width array and area area;\n vector<int>area;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n area.push_back((right[i]-left[i]-1)*arr[i]);\n }\n int no=*max_element(area.begin(),area.end());\n return no;\n \n }\n \n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) \n { if(matrix.empty())\n return 0;\n int n=matrix[0].size();\n \n \n int arr[200];\n vector<int>check;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n arr[i]=0;\n }\n for(int i=0;i<matrix.size();i++)\n { int k=0;\n for(int j=0;j<matrix[0].size();j++)\n {\n if(matrix[i][j]==\'1\')\n {\n arr[k]=arr[k]+1;\n k++;\n \n }\n else\n {\n arr[k]=0;\n k++;\n }\n \n }\n \n int no=MAH(arr,n);\n \n check.push_back(no);\n }\n int ans=0;\n ans=*max_element(check.begin(),check.end());\n return ans;\n }\n};
| 6 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Python monotone stack solution with comments and explanation.
|
python-monotone-stack-solution-with-comm-rj7o
|
This problem can be visualised as an extension to largest rectangle in histogram\nIn the above problem you can use Next Smallest Element (NSE) logic on a monoto
|
shootingstaradil
|
NORMAL
|
2021-04-09T07:29:14.461169+00:00
|
2021-04-09T07:29:14.461199+00:00
| 299 | false |
This problem can be visualised as an extension to [largest rectangle in histogram](https://leetcode.com/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/)\nIn the above problem you can use Next Smallest Element (NSE) logic on a monotonically increasing stack to find the maximum rectangle possible in the histogram given.\n\nYou can easily extend that concept on this 2D matrix by constructing/updating histogram row by row and processing on the histogram. \n1. For the first row the whole row is a histogram with bar heights either 1 or 0\n2. For the next row we update the histogram as\n => If the value of current grid is \'0\' then histogram height is reset to 0 (as the continuation of the rectangle breaks here)\n\t\t=> If the value of the current grid is \'1\' then histogram height can be increased by 1 vertically\n3. So on for rest of the rows...\n**Note:** As we are processing row by row so rectangle continuity in horizontal direction is handled in histogram automatically while the vertical continuity is handled by updating the histogram as in step 2.\n4. Now after updating the histogram for each row, we calculate the maximum area of rectangle possible.\n5. Once we have maximum from all the rows, we pick the maximum of the maximums to get our final answer. \n\nExample:\n**Input:** \n```\n[\n ["1","0","1","0","0"],\n ["1","0","1","1","1"],\n ["1","1","1","1","1"],\n ["1","0","0","1","0"]\n]\n```\n\n**Histogram creation and updation for each row of matrix:**\n```\nRow 1 => [1, 0, 1, 0, 0] [current max = 1 and overall max = 1]\nRow 2 => [2, 0, 2, 1, 1] [current max = 3 and overall max = 3]\nRow 3 => [3, 1, 3, 2, 2] [current max = 6 and overall max = 6]\nRow 4 => [4, 0, 0, 3, 0] [current max = 4 and overall max = 6]\n```\nAs you can see the final answer will be picked as 6\n\n**Code:**\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maximalRectangle(self, matrix: List[List[str]]) -> int:\n if not matrix:\n return 0 # To handle `matrix = []` case\n\t\t\n\t\t# Prepare histogram for the first row of input matrix and find maximum area.\n histogram = list(map(int, matrix[0]))\n histogram.append(0)\n current_max = self.max_rect_histogram(histogram)\n\t\t\n\t\t# Process on the remaining rows of matrix\n for row in matrix[1:]:\n for i in range(len(row)):\n\t\t\t # update histogram, if grid is a \'0\' reset histogram height else increase height by one\n if row[i] == \'0\':\n histogram[i] = 0\n else:\n histogram[i] += int(row[i])\n\t\t\t# Once histogram is updated for current row find the maximum rectangle area in current histogram\n current_max = max(current_max, self.max_rect_histogram(histogram))\n return current_max\n \n def max_rect_histogram(self, histogram):\n stack = [-1]\n mx = 0\n for i,v in enumerate(histogram):\n\t\t\t# As long as the stack has increasing value keep adding the index of histogram\n\t\t\t# If the insertion to stack will result in a decreasing stack, then keep poping till it becomes increasing again\n\t\t\t# For each pop, calculate the area of the rectangle\n while(stack[-1] != -1 and histogram[stack[-1]] > v):\n height = histogram[stack.pop()]\n\t\t\t\t# i is right limit, stack[-1] is left limit so width of rectangle in consideration is r-l-1\n width = i - stack[-1] - 1\n mx = max(mx, height*width)\n stack.append(i)\n return mx\n```
| 6 | 0 |
[]
| 3 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Simple solution Using NSR and NSL | stack based solution
|
simple-solution-using-nsr-and-nsl-stack-h0cxt
|
\nSame approach as to find maximum area histogram using Nearest smaller to left and Nearest smaller to right, only difference is that maximum area histogram is
|
neil028
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-02T13:10:30.122892+00:00
|
2020-08-02T13:10:30.122929+00:00
| 590 | false |
``\nSame approach as to find maximum area histogram using Nearest smaller to left and Nearest smaller to right, only difference is that maximum area histogram is 1D and this is 2D so we start taking by one row at a time and find its area and keep max_area variable which keep track of max and then add it to second row and find again and so on and just keep in mind one thing while you are at current row and adding values to previous check if current level ith value is 0 or 1 if 0 then put 0 because if base is zero which is not possible means bulding can\'t be in air and if 1 then add it...\n``\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int pseudoIndex;\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n int rows = matrix.size();\n if (rows == 0) {\n return 0;\n }\n int cols = matrix[0].size();\n if (cols == 0) {\n return 0;\n }\n vector<int>histogram(cols,0);\n \n int res = 0;\n \n for (int i = 0; i< rows; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j< cols; j++) {\n if (matrix[i][j] == \'0\') {\n histogram[j] = 0;\n }\n else {\n histogram[j] += (matrix[i][j] - \'0\');\n }\n }\n int area = largestRectangleArea(histogram);\n \n res = max(area, res);\n }\n return res;\n }\n \n int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {\n \n if(heights.size() == 0)\n return 0;\n //we store index of nearest smaller to left of i\n vector<int> nsl = NearestSmallerToLeft(heights);\n //we store index of nearest smaller to right of i\n vector<int> nsr = NearestSmallerToRight(heights);\n \n //find the max area possible\n int max_area = INT_MIN,area;\n for(int i = 0; i < heights.size(); i++)\n {\n area = (nsr[i]-nsl[i]-1)*heights[i];\n max_area = max(area,max_area);\n }\n return max_area;\n }\n \n vector<int> NearestSmallerToLeft(vector<int> temp)\n {\n stack<pair<int,int>> st;\n vector<int> left;\n pseudoIndex = -1;\n for(int i = 0; i < temp.size();i++)\n {\n if(st.empty())\n left.push_back(pseudoIndex);\n else if(!st.empty() && st.top().first < temp[i])\n left.push_back(st.top().second);\n else if(!st.empty() && st.top().first >= temp[i])\n {\n while(!st.empty() && st.top().first >= temp[i])\n {\n st.pop();\n }\n if(st.empty())\n {\n left.push_back(-1);\n }\n else left.push_back(st.top().second);\n }\n st.push({temp[i],i});\n }\n return left;\n }\n\n vector<int> NearestSmallerToRight(vector<int> temp)\n {\n stack<pair<int,int>> st;\n vector<int> right;\n pseudoIndex = temp.size(); \n for(int i = temp.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--)\n {\n if(st.empty())\n {\n right.push_back(pseudoIndex);\n }\n else if(!st.empty() && st.top().first < temp[i])\n right.push_back(st.top().second);\n else if(!st.empty() && st.top().first >= temp[i])\n {\n while(!st.empty() && st.top().first >= temp[i])\n st.pop();\n if(st.empty())\n right.push_back(pseudoIndex);\n else \n right.push_back(st.top().second);\n }\n st.push({temp[i],i});\n }\n reverse(right.begin(),right.end());\n return right;\n }\n};\n```
| 6 | 0 |
['Stack']
| 1 |
maximal-rectangle
|
A simple C++ Approach with explanation
|
a-simple-c-approach-with-explanation-by-ylgs6
|
This is a mixture of two problems that is\n1. Finding the largest rectangle in an Histogram.\n2. Then finding the answer for the particular problem\n\nI hereby
|
akshay4570
|
NORMAL
|
2020-07-13T06:39:58.794393+00:00
|
2020-07-13T06:39:58.794424+00:00
| 492 | false |
This is a mixture of two problems that is\n1. Finding the largest rectangle in an Histogram.\n2. Then finding the answer for the particular problem\n\nI hereby assume that u know how to find the largest Rectangle in a Histogram,if not check this out\nhttps://leetcode.com/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/\nSolve it first before jumping to it as the intuition behind that problem is the base for this and those who have solve that here is the explanation..\n\nThe function find answer is the snippet which simply finds the maximum area rectangle in an histogram but before that the main function requires some preprocessing..\nIf given the Input\n1 0 1 0 0 \n1 0 1 1 1\n1 1 1 1 1\n1 0 0 1 0\n\n**We can assume each row as potential input for histogram but for every row we have to take the cummulative sum with the above row inorder to get how many 1\'s are there in the above row**\n\nOnce u get the above where each cummulative sum vector is an input for the function **find_ans** which calculates largest are rectangle we can extend it to 2D as well,Once u get the above then it is down hill from there..\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int find_ans(vector<int>& h)\n {\n h.push_back(0);\n int n = h.size();\n stack<int> s;\n int sum = 0;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n while(!s.empty() && h[i] < h[s.top()])\n {\n int idx = s.top();\n s.pop();\n int l = s.empty() ? 0 : s.top() + 1;\n sum = max(sum,h[idx]*(i-l));\n }\n s.push(i);\n }\n return sum;\n }\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n if(matrix.empty())\n return 0;\n int n = matrix.size();\n int m = matrix[0].size();\n int max_ans = 0;\n vector<int> h(m,0);\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<m;j++)\n if(matrix[i][j] == \'0\')\n h[j] = 0;\n else\n h[j]++;\n max_ans = max(max_ans,find_ans(h));\n }\n return max_ans;\n }\n};\n```\n\n**Upvotes are appreciated**
| 6 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
maximal-rectangle
|
C++ Dynamic programming, not so fast, but easy with explanation.
|
c-dynamic-programming-not-so-fast-but-ea-bdxs
|
The key to the question is that, in each row, we can compute the area subtended by each column to its right. The maximum value will eventually be computed. The
|
varkey98
|
NORMAL
|
2020-05-19T18:22:07.197119+00:00
|
2020-05-19T18:22:34.741714+00:00
| 1,732 | false |
The key to the question is that, in each row, we can compute the area subtended by each column to its right. The maximum value will eventually be computed. The complexity is O(n*m*m). The dynamic programming comes from just memoizing the height of column row by row.\n```\nvector<vector<int>> memo;\nint maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) \n{\n\tint n=matrix.size(),m;\n if(n)\n m=matrix[0].size();\t\n\tmemo.resize(n,vector<int>(m,0));\n if(n>0)\n for(int j=0;j<m;++j)\n if(matrix[0][j]==\'1\')\n memo[0][j]=1;\n \tfor(int i=1;i<n;++i)//finding height of each cloumn in each row.\n\t\tfor(int j=0;j<m;++j)\n\t\t\tif(matrix[i][j]==\'1\')\n\t\t\t\tmemo[i][j]=1+memo[i-1][j];\n\tint ret=0;\n\tfor(int i=0;i<n;++i)\n\t\tfor(int j=0;j<m;++j)\n\t\t{\n\t\t\tint h=memo[i][j];\n\t\t\tfor(int k=j;k<m;++k)\n\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\th=min(h,memo[i][k]);\n\t\t\t\tret=max(ret,(k-j+1)*h);\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t}\n\treturn ret;\n}\n```
| 6 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C++']
| 2 |
maximal-rectangle
|
javascript 100.00% 72 ms
|
javascript-10000-72-ms-by-gaponov-x36r
|
\nvar maximalRectangle = function (matrix) {\n const n = matrix.length;\n if (n === 0) return 0;\n const m = matrix[0].length;\n\n const h = new Arr
|
gaponov
|
NORMAL
|
2018-04-21T17:21:01.544314+00:00
|
2019-06-06T08:17:55.242824+00:00
| 1,123 | false |
```\nvar maximalRectangle = function (matrix) {\n const n = matrix.length;\n if (n === 0) return 0;\n const m = matrix[0].length;\n\n const h = new Array(n).fill(0);\n\n let max = 0;\n for (let j = 0; j < m; j++) {\n for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n if (matrix[i][j] === \'1\') h[i]++;\n else h[i] = 0;\n }\n for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n let k1 = i - 1;\n while (k1 >= 0 && h[i] <= h[k1]) k1--;\n let k2 = i + 1;\n while (k2 < n && h[i] <= h[k2]) k2++;\n max = Math.max(max, h[i] * (k2 - k1 - 1));\n }\n }\n return max;\n}\n```
| 6 | 1 |
['JavaScript']
| 1 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Using Histogram Approach || Stack
|
using-histogram-approach-stack-by-prayas-fwq9
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nThe problem requires finding the largest rectangle containing only 1\'s in a binary mat
|
prayashbhuria931
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-07T23:41:28.167506+00:00
|
2024-09-07T23:41:28.167538+00:00
| 375 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThe problem requires finding the largest rectangle containing only 1\'s in a binary matrix. To solve this, the key idea is to treat each row as the base of a histogram and compute the largest rectangle in that histogram.\n\nFor each row, we create a height array where each element represents the number of consecutive 1\'s encountered in that column (from the top of the matrix to the current row). Once the height array is built for a row, the problem is reduced to finding the largest rectangle in a histogram, which is a classic problem that can be efficiently solved using a monotonic stack.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1. Building the Height Array:\n For each row in the matrix:\n - If the current element is \'1\', we increment the corresponding column in the height array.\n - If the current element is \'0\', we reset the corresponding column in the height array to 0.\n2. Largest Rectangle in Histogram:\nOnce we have the height array for a row, we compute the largest rectangle in that histogram using the concept of next smaller element and previous smaller element:\n\n - Next Smaller Element (NSE): For each bar, we find the next bar that is smaller to the right.\n - Previous Smaller Element (PSE): For each bar, we find the previous bar that is smaller to the left. Using these, we can determine the width of the largest rectangle for each bar in the histogram, and then compute the area.\n3. Maximal Rectangle:\nFor each row, we compute the largest rectangle in the histogram built from the height array and update the maximum area encountered so far.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n\xD7m) , where n is the number of rows and m is the number of columns in the matrix\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(m)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\nprivate:\n vector<int> nextSmallerElement(vector<int> &arr, int n)\n{\n // Write your code here.\n\n stack<int> s;\n s.push(-1);\n vector<int> ans(n);\n\n for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--)\n {\n int curr=arr[i];\n while(s.top()!=-1 && arr[s.top()]>=curr)\n {\n s.pop();\n }\n //ans stack ka top\n ans[i]=s.top();\n s.push(i);\n }\n return ans;\n}\nvector<int> prevSmallerElement(vector<int> &arr, int n)\n{\n // Write your code here.\n\n stack<int> s;\n s.push(-1);\n vector<int> ans(n);\n\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n int curr=arr[i];\n while(s.top()!=-1 && arr[s.top()]>=curr)\n {\n s.pop();\n }\n //ans stack ka top\n ans[i]=s.top();\n s.push(i);\n }\n return ans;\n}\n\nint largestArea(vector<int> &arr)\n{\n int n=arr.size();\n vector<int> next(n);\n next=nextSmallerElement(arr,n);\n\n vector<int> prev(n);\n prev=prevSmallerElement(arr,n);\n\n int area=INT_MIN;\n\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n int l=arr[i];\n\n\n if(next[i]==-1)\n {\n next[i]=n;\n }\n int b=next[i]-prev[i]-1;\n\n int newArr=l*b;\n area=max(area,newArr);\n\n\n }\n return area;\n}\npublic:\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n vector<int> height(matrix[0].size(),0);\n\n int maxi=INT_MIN;\n for(int i=0;i<matrix.size();i++)\n {\n //to create height array\n for(int j=0;j<height.size();j++)\n {\n if(matrix[i][j]==\'1\')\n {\n height[j]++;\n }\n else height[j]=0;\n }\n maxi=max(maxi,largestArea(height));\n }\n\n return maxi;\n }\n\n};\n```\n\n
| 5 | 0 |
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Stack', 'Matrix', 'Monotonic Stack', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
[EXPLANATION] Runtime beats 92.59%
|
explanation-runtime-beats-9259-by-r9n-ktgt
|
Intuition\nConvert each row of the matrix into a histogram of heights, where each height represents the count of consecutive 1s up to that row. This allows us t
|
r9n
|
NORMAL
|
2024-08-22T19:45:23.634185+00:00
|
2024-08-26T19:52:03.253797+00:00
| 37 | false |
# Intuition\nConvert each row of the matrix into a histogram of heights, where each height represents the count of consecutive 1s up to that row. This allows us to apply the largest rectangle in a histogram technique to find the maximal rectangle of 1s in the matrix.\n\n# Approach\nFor each row, update histogram heights based on consecutive 1s.\n\nUse a stack to find the largest rectangle in the histogram for each row, updating the maximum area as you go.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(rows * cols): We update the histogram and compute the maximal rectangle area for each row.\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(cols): We use an array for heights and a stack, both proportional to the number of columns.\n\n# Code\n```typescript []\nfunction maximalRectangle(matrix: string[][]): number {\n if (matrix.length === 0) return 0;\n \n const rows = matrix.length;\n const cols = matrix[0].length;\n const heights = new Array(cols).fill(0);\n let maxArea = 0;\n \n for (let i = 0; i < rows; i++) {\n for (let j = 0; j < cols; j++) {\n // Update heights array\n heights[j] = matrix[i][j] === \'1\' ? heights[j] + 1 : 0;\n }\n // Calculate the maximal rectangle area for the current row (histogram)\n maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, largestRectangleArea(heights));\n }\n \n return maxArea;\n}\n\nfunction largestRectangleArea(heights: number[]): number {\n const stack: number[] = [];\n let maxArea = 0;\n heights.push(0); // Sentinel to ensure all heights are processed\n \n for (let i = 0; i < heights.length; i++) {\n while (stack.length > 0 && heights[i] < heights[stack[stack.length - 1]]) {\n const height = heights[stack.pop()!];\n const width = stack.length === 0 ? i : i - stack[stack.length - 1] - 1;\n maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, height * width);\n }\n stack.push(i);\n }\n \n return maxArea;\n}\n\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['TypeScript']
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
hope
|
hope-by-doaaosamak-w5ic
|
\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\n public int maximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) {\n if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {\n
|
DoaaOsamaK
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-13T17:31:08.513596+00:00
|
2024-04-13T17:31:08.513616+00:00
| 83 | false |
\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) {\n if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {\n return 0;\n }\n\n int m = matrix.length;\n int n = matrix[0].length;\n\n int[] heights = new int[n];\n int[] leftBoundaries = new int[n];\n int[] rightBoundaries = new int[n];\n Arrays.fill(rightBoundaries, n);\n\n int maxRectangle = 0;\n\n for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {\n int left = 0;\n int right = n;\n\n updateHeightsAndLeftBoundaries(matrix[i], heights, leftBoundaries, left);\n\n updateRightBoundaries(matrix[i], rightBoundaries, right);\n\n maxRectangle = calculateMaxRectangle(heights, leftBoundaries, rightBoundaries, maxRectangle);\n }\n\n return maxRectangle;\n }\n\n private void updateHeightsAndLeftBoundaries(char[] row, int[] heights, int[] leftBoundaries, int left) {\n for (int j = 0; j < heights.length; j++) {\n if (row[j] == \'1\') {\n heights[j]++;\n leftBoundaries[j] = Math.max(leftBoundaries[j], left);\n } else {\n heights[j] = 0;\n leftBoundaries[j] = 0;\n left = j + 1;\n }\n }\n }\n\n private void updateRightBoundaries(char[] row, int[] rightBoundaries, int right) {\n for (int j = rightBoundaries.length - 1; j >= 0; j--) {\n if (row[j] == \'1\') {\n rightBoundaries[j] = Math.min(rightBoundaries[j], right);\n } else {\n rightBoundaries[j] = right;\n right = j;\n }\n }\n }\n\n private int calculateMaxRectangle(int[] heights, int[] leftBoundaries, int[] rightBoundaries, int maxRectangle) {\n for (int j = 0; j < heights.length; j++) {\n int width = rightBoundaries[j] - leftBoundaries[j];\n int area = heights[j] * width;\n maxRectangle = Math.max(maxRectangle, area);\n }\n return maxRectangle;\n }\n}\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Python3 and C++ || Largest Rectangle in Histogram Concept || Simple and Optimal
|
python3-and-c-largest-rectangle-in-histo-ns5g
|
\n# Code\nPython3 []\nclass Solution:\n def largestRectangleArea(self, heights: List[int]) -> int:\n stack = []\n maxArea = 0\n heights.
|
meurudesu
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-13T05:16:02.978342+00:00
|
2024-04-13T05:16:02.978371+00:00
| 692 | false |
> \n# Code\n```Python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def largestRectangleArea(self, heights: List[int]) -> int:\n stack = []\n maxArea = 0\n heights.append(0)\n for i, h in enumerate(heights):\n start = i\n while stack and stack[-1][1] > h:\n idx, height = stack.pop()\n maxArea = max(maxArea, height * (i - idx))\n start = idx\n stack.append((start, h))\n return maxArea\n\n def maximalRectangle(self, matrix: List[List[str]]) -> int:\n maxArea = 0\n height = [0] * len(matrix[0])\n for i in range(len(matrix)):\n for j in range(len(matrix[0])):\n if matrix[i][j] == \'1\':\n height[j] += 1\n else:\n height[j] = 0\n area = self.largestRectangleArea(height)\n maxArea = max(maxArea, area)\n return maxArea\n```\n```C++ []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {\n stack <pair <int, int>> st;\n heights.push_back(0);\n int maxArea = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < heights.size(); i++) {\n int start = i;\n while (!st.empty() && st.top().second > heights[i]) {\n auto [idx, height] = st.top();\n st.pop();\n maxArea = max(maxArea, height * (i - idx));\n start = idx;\n }\n st.push({start, heights[i]});\n }\n return maxArea;\n }\n\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n int maxArea = 0;\n vector <int> height(matrix[0].size(), 0);\n for (int i = 0; i < matrix.size(); i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < matrix[0].size(); j++) {\n if (matrix[i][j] == \'1\') height[j]++;\n else height[j] = 0;\n }\n int area = largestRectangleArea(height);\n maxArea = max(maxArea, area);\n }\n return maxArea;\n }\n};\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['Array', 'Stack', 'Monotonic Stack', 'C++', 'Python3']
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Fully Explained C++ solution using largest rectangle in histogram problem
|
fully-explained-c-solution-using-largest-auit
|
Similar to Problem No.84 \n# Intuition\nTo solve this problem, we can utilize the concept of histograms and the largest rectangle in histogram problem. We\'ll t
|
vanshwari
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-20T07:12:02.425254+00:00
|
2024-06-28T12:03:09.124199+00:00
| 405 | false |
Similar to Problem No.84 \n# Intuition\nTo solve this problem, we can utilize the concept of histograms and the largest rectangle in histogram problem. We\'ll treat each row of the matrix as the base of a histogram, where the height of each bar represents the number of consecutive \'1\'s in the corresponding column. Then, we\'ll find the largest rectangle in each histogram and return the maximum area.\n\n# Approach\n1. Define a helper function `largestRectangle()` that calculates the largest rectangle in a histogram represented by a vector of heights.\n2. Define two helper functions `nextsmaller()` and `prevsmaller()` that find the indices of the next smaller and previous smaller elements for each element in a vector.\n3. Iterate through each row of the matrix.\n4. For each row, update the heights vector to represent the histogram.\n5. Calculate the largest rectangle in the histogram using the `largestRectangle()` function and update the maximum area.\n6. Return the maximum area.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: \n - For each row, we perform operations to update the heights vector and find the largest rectangle in the histogram, both of which take O(m) time, where m is the number of columns. Therefore, the overall time complexity is O(n * m), where n is the number of rows and m is the number of columns.\n- Space complexity:\n - We use additional space to store vectors for heights, next smaller indices, and previous smaller indices, each of size m (the number of columns). Therefore, the space complexity is O(m).\n\n# Code\n```cpp\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> nextsmaller(vector<int>&v , int n){\n vector<int>ans(n,n);\n stack<int>st;\n for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--){\n while(!st.empty() && v[st.top()]>=v[i]){\n st.pop();\n }\n if(!st.empty()) ans[i]=st.top();\n st.push(i);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n\n vector<int> prevsmaller(vector<int>&v , int n){\n vector<int>ans(n,-1);\n stack<int>st;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n while(!st.empty() && v[st.top()]>=v[i]){\n st.pop();\n }\n if(!st.empty()) ans[i]=st.top();\n st.push(i);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n\n int largestRectangle(vector<int>& heights) {\n int n = heights.size();\n int ans = 0;\n vector<int> next(n), prev(n);\n next = nextsmaller(heights, n);\n prev = prevsmaller(heights, n);\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n int l = heights[i];\n int b = next[i] - prev[i] - 1;\n int area = l * b;\n ans = max(ans, area);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& mat) {\n int n = mat.size();\n int m = mat[0].size();\n vector<int> h(m,0);\n int ans = 0;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n vector<int> he;\n for(int j=0;j<m;j++){\n if(mat[i][j]==\'1\') he.push_back(1 + h[j]);\n else he.push_back(0);\n }\n ans = max(ans, largestRectangle(he));\n h = he;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\n\nThis code efficiently calculates the area of the largest rectangle in a binary matrix by treating each row as a histogram and finding the largest rectangle in each histogram. The time complexity is proportional to the number of rows times the number of columns, making it an efficient solution for large matrices.
| 5 | 0 |
['Stack', 'Matrix', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Easiest Java Solution|| Beats 100%
|
easiest-java-solution-beats-100-by-nish_-qje8
|
\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \nWe can solve this question using the "Largest Rectangle in Histogram" question approach. consider every row
|
Nish_03
|
NORMAL
|
2023-08-01T07:02:46.150562+00:00
|
2023-08-01T07:02:46.150594+00:00
| 948 | false |
\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nWe can solve this question using the "Largest Rectangle in Histogram" question approach. consider every row as a histogram and for every row find the max rectangle area. \n\nYou can check the histogram approach [here](https://leetcode.com/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/solutions/3845893/best-simple-java-solution-beats-85/).\n\nAlso, if the current row has an element with 0 value, then the height will be 0. for the rest where matrix[i][j] == 0, just add the previous value + 1, \n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(n^2)\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(n)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n\n public static int histogram(int[] heights){\n int n = heights.length;\n\n ArrayDeque<Integer> st1 = new ArrayDeque<>();\n ArrayDeque<Integer> st2 = new ArrayDeque<>();\n\n int left[] = new int[n];\n int right[] = new int[n];\n\n //previous smaller element\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){\n\n int num = heights[i] ;\n\n while(!st1.isEmpty() && heights[st1.peek()] > num)\n st1.pop();\n\n if(st1.isEmpty())\n left[i] = -1;\n else \n left[i] = st1.peek();\n\n st1.push(i); \n\n }\n \n\n //next greater element\n for(int i = n-1; i >= 0; i--){\n\n int num = heights[i];\n\n while(!st2.isEmpty() && heights[st2.peek()] >= num)\n st2.pop();\n\n if(st2.isEmpty())\n right[i] = n;\n else \n right[i] = st2.peek();\n\n st2.push(i); \n\n }\n\n int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){\n\n int sum = (right[i] - left[i] - 1) * (heights[i]);\n max = Math.max(max, sum); \n\n }\n\n System.out.println("Max"+ max);\n return max;\n }\n\n public int maximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) {\n \n int n = matrix.length;\n int m = matrix[0].length;\n int[] currRow = new int[matrix[0].length];\n int max = 0;\n\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){\n\n for(int j = 0; j < m; j++){\n\n if(matrix[i][j] == \'1\')\n currRow[j]++;\n else \n currRow[j] = 0; \n }\n\n int currMax = histogram(currRow);\n max = Math.max(max, currMax);\n\n }\n\n return max;\n \n }\n}\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Stack', 'Monotonic Stack', 'Java']
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Easy Stack Solution using C++
|
easy-stack-solution-using-c-by-2005115-9v90
|
PLS UPVOTE MY SOLUTION IF YOPU LIKE AND COMMENT FOR ANY DISCUSSION\n\n# Approach\nThe nextelement function takes a vector heights and its size n as input. It in
|
2005115
|
NORMAL
|
2023-07-27T08:47:53.773030+00:00
|
2023-07-27T08:47:53.773048+00:00
| 941 | false |
# PLS UPVOTE MY SOLUTION IF YOPU LIKE AND COMMENT FOR ANY DISCUSSION\n\n# Approach\nThe nextelement function takes a vector heights and its size n as input. It initializes an empty stack and a vector ans of size n to store the indices of the next smaller elements. It then iterates through the heights vector from right to left (from the last element to the first).\n\nFor each element in the heights vector, it compares its height with the elements at the top of the stack (using st.top()), and if the element at the top of the stack is greater than or equal to the current element, it pops elements from the stack (until the top element is smaller than the current element).\n\nAfter the while loop, it stores the index of the next smaller element in the ans vector for the current element (ans[i] = st.top()). If there is no smaller element, it stores the value n (one greater than the last index) to indicate that there is no next smaller element for that element.\n\nThe prevelement function works similarly to nextelement but iterates from left to right to find the previous smaller elements for each element in the heights vector.\n\nThe largestRectangleArea function calculates the largest rectangle area in a histogram. It takes a vector heights as input and uses the nextelement and prevelement functions to find the indices of the next smaller and previous smaller elements for each element in the histogram.\n\nIt then iterates through the heights vector and calculates the area of the rectangle for each bar, considering the bar as the height and the width as the difference between the indices of the next smaller and previous smaller elements for that bar.\n\nThe function returns the maximum area found.\n\nThe maximalRectangle function takes a 2D matrix matrix as input. It initializes a vector histogram of size equal to the number of columns in the matrix, and maxi variable to store the maximum area.\n\nIt iterates through each row of the matrix and populates the histogram vector based on the \'1\'s encountered in each column. When a \'0\' is encountered, the height of the histogram for that column is reset to 0.\n\nFor each row, it calculates the largest rectangle area in the histogram (representing the consecutive \'1\'s encountered so far) using the largestRectangleArea function.\n\nThe function updates maxi with the maximum area found.\n\nFinally, the function returns the maximum area, which represents the largest rectangle area formed by \'1\'s in the binary matrix.\n\nThe approach efficiently uses the concept of histograms and the largest rectangle area calculation to solve the maximalRectangle problem for a binary matrix, resulting in an overall time complexity of O(M * N), where M is the number of rows and N is the number of columns in the matrix.\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:0(N*(M+N)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:0(N)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\nvector<int> nextelement(vector<int>& heights, int n )\n{\n stack<int>st;\n st.push(-1);\n vector<int>ans(n);\n for(int i =n-1;i>=0;i--)\n {\n int curr= heights[i];\n while(st.top()!=-1 && heights[st.top()]>=curr)\n {\n st.pop();\n }\n if(st.top()==-1)\n {\n ans[i]=n;\n }\n else\n {\n ans[i]=st.top();\n }\n st.push(i);\n }\n return ans;\n}\n\nvector<int> prevelement(vector<int>& heights, int n )\n{\n stack<int>st;\n st.push(-1);\n vector<int>ans(n);\n for(int i =0;i<n;i++)\n {\n int curr= heights[i];\n while(st.top()!=-1 && heights[st.top()]>=curr)\n {\n st.pop();\n }\n ans[i]=st.top();\n st.push(i);\n }\n return ans;\n}\n\n int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {\n int n =heights.size();\n int area= INT_MIN;\n vector<int>next=nextelement(heights,n); \n vector<int>prev=prevelement(heights,n); \n for(int i =0;i<n;i++)\n {\n int l = heights[i];\n int b = next[i]-prev[i]-1;\n int newarea= l*b;\n area=max(area,newarea);\n }\n return area;\n }\n\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n vector<int>histogram(matrix[0].size(),0);\n int maxi= INT_MIN;\n \n for(int i = 0;i<matrix.size();i++)\n {\n for(int j= 0 ;j<histogram.size();j++)\n {\n if (matrix[i][j]==\'1\')\n {\n histogram[j]++;\n }\n else\n {\n histogram[j]=0;\n }\n }\n maxi=max(maxi,largestRectangleArea(histogram));\n }\n return maxi;\n }\n};\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Stack', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Super Similar problem like Histogram
|
super-similar-problem-like-histogram-by-t1d62
|
https://leetcode.com/problems/maximal-rectangle/discuss/3544364/Super-Similar-problem-like-Histogram-------------------------->Histogram problem\n# Similar to H
|
GANJINAVEEN
|
NORMAL
|
2023-05-20T09:27:19.493214+00:00
|
2023-05-20T09:33:03.049424+00:00
| 3,665 | false |
https://leetcode.com/problems/maximal-rectangle/discuss/3544364/Super-Similar-problem-like-Histogram-------------------------->Histogram problem\n# Similar to Histogram Problem\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maximalRectangle(self, matrix: List[List[str]]) -> int:\n if not matrix:\n return 0\n maxarea=0\n height=[0]*(len(matrix[0]))\n for i in range(len(matrix)):\n for j in range(len(matrix[0])):\n if matrix[i][j]=="1":\n height[j]+=1\n else:\n height[j]=0\n\t\t\t\tstack=[]\n for i,h in enumerate(height):\n start=i\n while stack and h<stack[-1][1]:\n index,hi=stack.pop()\n start=index\n maxarea=max(maxarea,(i-index)*hi)\n stack.append([start,h])\n for i,h in stack:\n maxarea=max(maxarea,(len(height)-i)*h)\n return maxarea\n ```\n # please upvote me it would encourage me alot\n
| 5 | 0 |
['Stack', 'Python3']
| 1 |
maximal-rectangle
|
illustrated explanation
|
illustrated-explanation-by-wilmerkrisp-33sg
|
<-- please vote\n\n\n\n def maximalRectangle(self, matrix: List[List[str]]) -> int:\n """ O(NM)TS """\n ans = []\n prefix = [zip(([itert
|
wilmerkrisp
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-01T21:31:11.301680+00:00
|
2022-04-01T21:31:11.301721+00:00
| 597 | false |
<-- please vote\n\n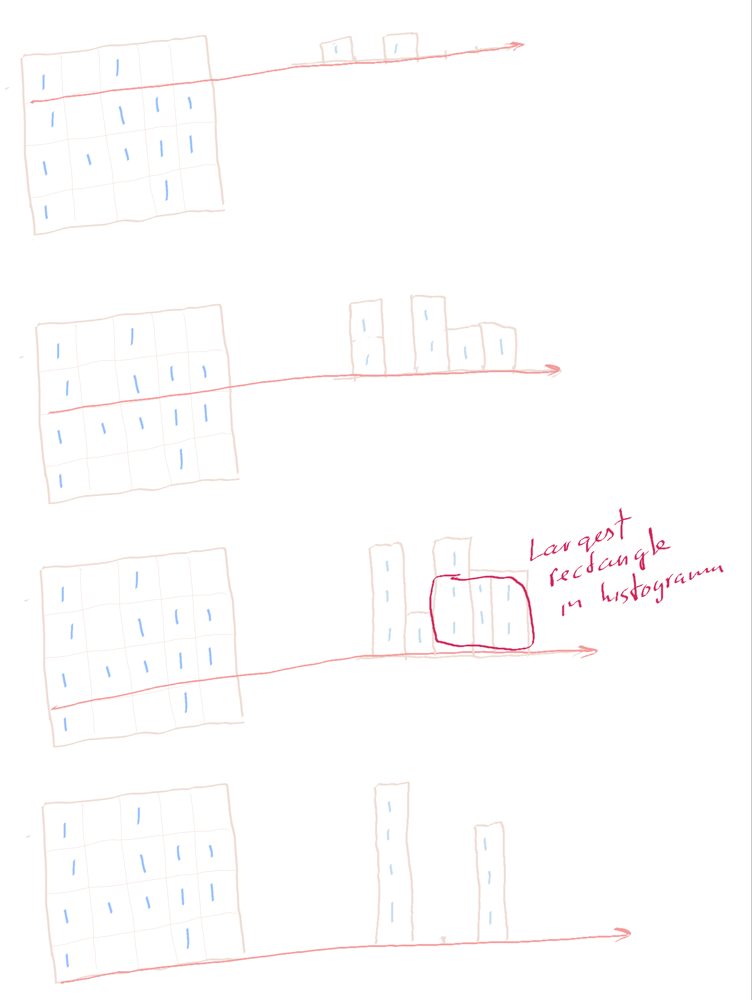\n\n def maximalRectangle(self, matrix: List[List[str]]) -> int:\n """ O(NM)TS """\n ans = []\n prefix = [*zip(*([*itertools.accumulate(map(int, col), lambda x, y: x + y if y == 1 else 0)] for col in zip(*matrix)))]\n\n for row in prefix:\n stack = [-1]\n for i, n in enumerate(row):\n while len(stack) > 1 and row[stack[-1]] >= n:\n ans += row[stack.pop()] * (i - stack[-1] - 1),\n stack += i,\n while len(stack) > 1:\n ans += row[stack.pop()] * (len(row) - stack[-1] - 1),\n\n return max(ans)\n\t\t\n\nsee the problem 84\n\n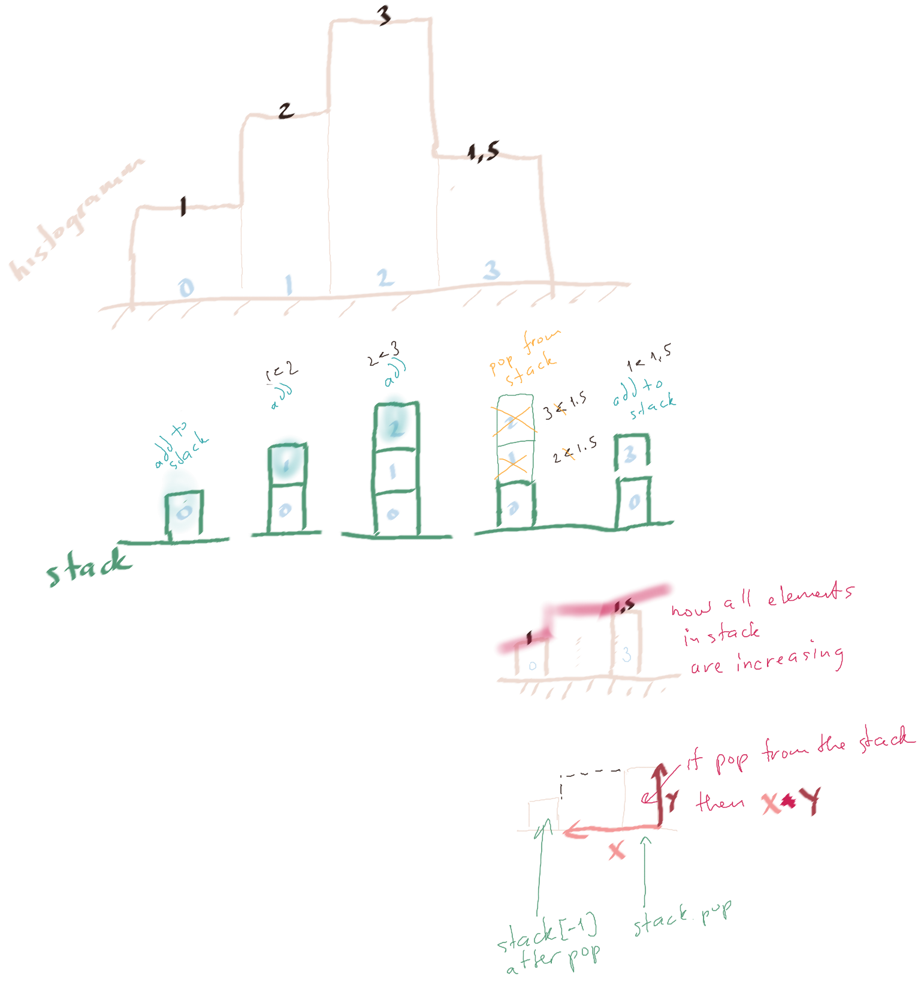\n\nhow to use pref summ\n\n\n\n\n\n
| 5 | 1 |
['Python']
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Simple Explanation | O(n^2) | C++ | Derived from Maximum Area in Histogram
|
simple-explanation-on2-c-derived-from-ma-mjam
|
Prerequisite : Please solve this problem first for better understanding Maximum Area in Histogram\n\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n\t// This function accep
|
av1shek
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-25T13:35:08.638150+00:00
|
2021-05-25T13:35:08.638193+00:00
| 582 | false |
**Prerequisite** : Please solve this problem first for better understanding [Maximum Area in Histogram](https://leetcode.com/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/)\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n\t// This function accepts height of histograms and calculates the maximum area of reactange\n\t// i.e this function is the solution of problem mentioned in the above link\n int maxAreaHistogram(vector<int> &arr)\n {\n int n = arr.size();\n vector<int> rig(n, n), lef(n, -1); // rig and lef vectors stores the first index in right and left whose height is less\n stack<int> s;\n \n\t\t// storing the right index\n for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--)\n {\n while(!s.empty() && arr[s.top()]>=arr[i]) s.pop();\n \n if(!s.empty()) rig[i] = s.top();\n s.push(i);\n }\n\t\t\n while(!s.empty()) s.pop();\n \n\t\t// storing the left index\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n while(!s.empty() && arr[s.top()]>=arr[i]) s.pop();\n if(!s.empty()) lef[i] = s.top();\n s.push(i);\n }\n \n int ans = 0;\n\t\t// area = width x height = ( rig[i] - lef[i]-1 ) x ( arr[i] )\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n ans = max(ans, arr[i]*(rig[i]-lef[i]-1));\n \n return ans;\n }\n \n\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n int n = matrix.size();\n if(n==0) return 0;\n int m = matrix[0].size();\n \n vector<vector<int> > mat(n, vector<int>(m));\n \n\t\t// Converting char matrix to integer matrix\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n for(int j=0;j<m;j++)\n mat[i][j] = int(matrix[i][j]-\'0\');\n \n\t\t// Calculating height of histogram for each row, but note that whenever we encounter zero height will become zero\n for(int i=1;i<n;i++)\n for(int j=0;j<m;j++)\n if(mat[i][j])\n mat[i][j] += mat[i-1][j];\n\n int ans = 0;\n\t\t\n\t\t// now solving maxAreaHistogram for considering each row, and maximum of each level will be our ans\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n ans = max(ans, maxAreaHistogram(mat[i]) );\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['Stack', 'C']
| 1 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Maximal Rectangle [C++]
|
maximal-rectangle-c-by-moveeeax-kqvk
|
IntuitionTo solve the problem of finding the maximal rectangle in a binary matrix, we can leverage the concept of histogram area calculation. The idea is to tre
|
moveeeax
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-22T15:33:20.687729+00:00
|
2025-01-22T15:33:20.687729+00:00
| 1,037 | false |
# Intuition
To solve the problem of finding the maximal rectangle in a binary matrix, we can leverage the concept of histogram area calculation. The idea is to treat each row of the matrix as the base of a histogram and calculate the largest rectangle that can be formed under that histogram. By iterating through each row and updating the heights of the histogram based on the presence of '1's, we can find the maximal rectangle in the entire matrix.
# Approach
1. **Initialize Heights**: Start by initializing a vector `heights` with the same number of columns as the matrix, setting all values to 0. This vector will keep track of the height of the histogram at each column.
2. **Update Heights**: For each row in the matrix, update the `heights` vector. If the current cell contains '1', increment the height at that column. If it contains '0', reset the height to 0.
3. **Calculate Largest Rectangle**: After updating the heights for each row, use the `largestRectangleArea` function to calculate the largest rectangle that can be formed under the current histogram. This function uses a stack-based approach to efficiently compute the maximum area.
4. **Track Maximum Area**: Keep track of the maximum area found across all rows.
5. **Return Result**: After processing all rows, return the maximum area found.
# Complexity
- **Time Complexity**: The time complexity is \(O(n \times m)\), where \(n\) is the number of rows and \(m\) is the number of columns in the matrix. This is because we process each cell in the matrix once and for each row, we compute the largest rectangle area in \(O(m)\) time.
- **Space Complexity**: The space complexity is \(O(m)\), where \(m\) is the number of columns. This is due to the additional space used by the `heights` vector and the stack in the `largestRectangleArea` function.
# Code
```cpp
class Solution {
public:
int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {
if (matrix.empty()) return 0;
int n = matrix.size(), m = matrix[0].size();
vector<int> heights(m, 0);
int maxArea = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
heights[j] = matrix[i][j] == '1' ? heights[j] + 1 : 0;
}
maxArea = max(maxArea, largestRectangleArea(heights));
}
return maxArea;
}
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {
stack<int> s;
heights.push_back(0);
int maxArea = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < heights.size(); ++i) {
while (!s.empty() && heights[s.top()] > heights[i]) {
int h = heights[s.top()];
s.pop();
int w = s.empty() ? i : i - s.top() - 1;
maxArea = max(maxArea, h * w);
}
s.push(i);
}
heights.pop_back();
return maxArea;
}
};
```
### Explanation
- **Initialization**: We start by checking if the matrix is empty. If it is, we return 0. Otherwise, we initialize the `heights` vector to keep track of the histogram heights.
- **Updating Heights**: For each row, we update the `heights` vector based on the current cell value. If the cell is '1', we increment the height; otherwise, we reset it to 0.
- **Calculating Largest Rectangle**: The `largestRectangleArea` function calculates the largest rectangle under the histogram using a stack. It iterates through the heights, using the stack to keep track of indices and calculating the area whenever a smaller height is encountered.
- **Tracking Maximum Area**: We keep updating the `maxArea` with the largest area found for each row.
- **Returning Result**: Finally, we return the `maxArea` which holds the largest rectangle area found in the entire matrix.
| 4 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Easy Approach✅| CPP| Java| C| Python
|
easy-approach-cpp-java-c-python-by-vaib8-bdgo
|
Intuition\nTo find the largest rectangle of 1\'s in a binary matrix, we can learn the concept used in the "largest rectangle in histogram" problem. Essentially,
|
vaib8557
|
NORMAL
|
2024-06-29T13:34:16.764607+00:00
|
2024-06-29T13:34:16.764641+00:00
| 1,031 | false |
# Intuition\nTo find the largest rectangle of 1\'s in a binary matrix, we can learn the concept used in the "largest rectangle in histogram" problem. Essentially, we can treat each row of the matrix as the base of a histogram where each column contributes to the height of the histogram bars.\n\n# Prerequisite\n84. Largest Rectangle in Histogram\nhttps://leetcode.com/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/solutions/5287725/simplest-and-easiest-solution-on-c/\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(rows * cols)\n\n- Space complexity: O(cols)\n\n# CPP Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n // Return 0 if the matrix is empty\n if (matrix.empty()) return 0;\n\n int numRows = matrix.size();\n int numCols = matrix[0].size();\n vector<int> heights(numCols, 0);\n int maxArea = 0;\n\n for (int i = 0; i < numRows; i++) {\n // Update the heights array\n for (int j = 0; j < numCols; j++) {\n if (matrix[i][j] == \'0\') {\n heights[j] = 0;\n } else {\n heights[j] += 1;\n }\n }\n\n // Vectors to store the next and previous smaller elements\' indices\n vector<int> nextSmaller(numCols, numCols);\n vector<int> prevSmaller(numCols, -1);\n stack<int> s;\n\n // Find the next smaller element for each position\n for (int j = numCols - 1; j >= 0; j--) {\n while (!s.empty() && heights[s.top()] >= heights[j]) s.pop();\n if (!s.empty()) nextSmaller[j] = s.top();\n s.push(j);\n }\n\n // Clear the stack for the next computation\n while (!s.empty()) s.pop();\n\n // Find the previous smaller element for each position\n for (int j = 0; j < numCols; j++) {\n while (!s.empty() && heights[s.top()] >= heights[j]) s.pop();\n if (!s.empty()) prevSmaller[j] = s.top();\n s.push(j);\n }\n\n // Calculate the area for each position and update maxArea\n for (int j = 0; j < numCols; j++) {\n int width = nextSmaller[j] - prevSmaller[j] - 1;\n int area = heights[j] * width;\n maxArea = max(maxArea, area);\n }\n }\n return maxArea;\n }\n};\n```\n# Java Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) {\n // Return 0 if the matrix is empty\n if (matrix.length == 0) return 0;\n \n int numRows = matrix.length;\n int numCols = matrix[0].length;\n int[] heights = new int[numCols]; // Array to store the heights of histograms\n int maxArea = 0;\n\n for (int i = 0; i < numRows; i++) {\n // Update the heights array for the current row\n for (int j = 0; j < numCols; j++) {\n if (matrix[i][j] == \'0\') {\n heights[j] = 0;\n } else {\n heights[j] += 1;\n }\n }\n\n Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();\n int[] nextSmaller = new int[numCols];\n int[] prevSmaller = new int[numCols];\n \n for (int j = 0; j < numCols; j++) prevSmaller[j] = -1;\n for (int j = 0; j < numCols; j++) nextSmaller[j] = numCols;\n\n // Find the next smaller element for each position\n for (int j = numCols - 1; j >= 0; j--) {\n while (!stack.isEmpty() && heights[stack.peek()] >= heights[j]) stack.pop();\n if (!stack.isEmpty()) nextSmaller[j] = stack.peek();\n stack.push(j);\n }\n\n stack.clear(); // Clear the stack for the next computation\n\n // Find the previous smaller element for each position\n for (int j = 0; j < numCols; j++) {\n while (!stack.isEmpty() && heights[stack.peek()] >= heights[j]) stack.pop();\n if (!stack.isEmpty()) prevSmaller[j] = stack.peek();\n stack.push(j);\n }\n\n // Calculate the area for each position and update maxArea\n for (int j = 0; j < numCols; j++) {\n int width = nextSmaller[j] - prevSmaller[j] - 1;\n int area = heights[j] * width;\n maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, area);\n }\n }\n return maxArea;\n }\n}\n```\n\n# C Code\n```\nint maximalRectangle(char** matrix, int matrixSize, int* matrixColSize) {\n // Return 0 if the matrix is empty\n if (matrixSize == 0) return 0;\n\n int numCols = matrixColSize[0];\n int* heights = (int*)calloc(numCols, sizeof(int)); // Array to store the heights of histograms\n int maxArea = 0;\n\n for (int i = 0; i < matrixSize; i++) {\n // Update the heights array for the current row\n for (int j = 0; j < numCols; j++) {\n if (matrix[i][j] == \'0\') {\n heights[j] = 0;\n } else {\n heights[j] += 1;\n }\n }\n\n int* nextSmaller = (int*)malloc(numCols * sizeof(int));\n int* prevSmaller = (int*)malloc(numCols * sizeof(int));\n for (int j = 0; j < numCols; j++) prevSmaller[j] = -1;\n for (int j = 0; j < numCols; j++) nextSmaller[j] = numCols;\n\n int* stack = (int*)malloc(numCols * sizeof(int));\n int top = -1;\n\n // Find the next smaller element for each position\n for (int j = numCols - 1; j >= 0; j--) {\n while (top != -1 && heights[stack[top]] >= heights[j]) top--;\n if (top != -1) nextSmaller[j] = stack[top];\n stack[++top] = j;\n }\n\n top = -1;\n\n // Find the previous smaller element for each position\n for (int j = 0; j < numCols; j++) {\n while (top != -1 && heights[stack[top]] >= heights[j]) top--;\n if (top != -1) prevSmaller[j] = stack[top];\n stack[++top] = j;\n }\n\n // Calculate the area for each position and update maxArea\n for (int j = 0; j < numCols; j++) {\n int width = nextSmaller[j] - prevSmaller[j] - 1;\n int area = heights[j] * width;\n if (area > maxArea) maxArea = area;\n }\n\n free(nextSmaller);\n free(prevSmaller);\n free(stack);\n }\n\n free(heights);\n return maxArea;\n}\n```\n\n\n# Python Code\n```\nclass Solution(object):\n def maximalRectangle(self, matrix):\n """\n :type matrix: List[List[str]]\n :rtype: int\n """\n # Return 0 if the matrix is empty\n if not matrix:\n return 0\n \n numRows = len(matrix)\n numCols = len(matrix[0])\n heights = [0] * numCols # Array to store the heights of histograms\n maxArea = 0\n\n for i in range(numRows):\n # Update the heights array for the current row\n for j in range(numCols):\n if matrix[i][j] == \'0\':\n heights[j] = 0\n else:\n heights[j] += 1\n\n nextSmaller = [numCols] * numCols\n prevSmaller = [-1] * numCols\n stack = []\n\n # Find the next smaller element for each position\n for j in range(numCols - 1, -1, -1):\n while stack and heights[stack[-1]] >= heights[j]:\n stack.pop()\n if stack:\n nextSmaller[j] = stack[-1]\n stack.append(j)\n\n # Clear the stack for the next computation\n stack = []\n\n # Find the previous smaller element for each position\n for j in range(numCols):\n while stack and heights[stack[-1]] >= heights[j]:\n stack.pop()\n if stack:\n prevSmaller[j] = stack[-1]\n stack.append(j)\n\n # Calculate the area for each position and update maxArea\n for j in range(numCols):\n width = nextSmaller[j] - prevSmaller[j] - 1\n area = heights[j] * width\n maxArea = max(maxArea, area)\n\n return maxArea\n\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Stack', 'C', 'Monotonic Stack', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java']
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Leetcode POTD
|
leetcode-potd-by-user9105lu-6sf2
|
Approach :\n\n1. Here we will use the logic of largest rectangular area in a histogram .\n2. In this logic we will find the next and prev smallest element from
|
user9105Lu
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-13T15:57:44.247466+00:00
|
2024-04-13T15:58:19.831348+00:00
| 444 | false |
Approach :\n\n1. Here we will use the logic of largest rectangular area in a histogram .\n2. In this logic we will find the next and prev smallest element from the array by traversing it using stack .\n3. Now we will find the max rectangle area by converting it into largest rectangular histogram row by row and update te max rectangle area.\n\n\nThis approach is inspired by Love babbar.\n\nCode in C++\n\n```\nclass Solution {\n \n vector<int>next_small(vector<int>&arr){\n int n=arr.size();\n stack<int>st;\n \n st.push(-1);\n \n vector<int>ans(n);\n \n for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--){\n int curr=arr[i];\n \n while(st.top()!=-1 && arr[st.top()]>=curr){\n st.pop();\n }\n \n \n // smaller element found\n \n ans[i]=st.top();\n \n st.push(i);\n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n \n vector<int>prev_small(vector<int>&arr ){\n int n=arr.size();\n stack<int>st;\n \n st.push(-1);\n \n vector<int>ans(n);\n \n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n int curr=arr[i];\n \n while(st.top()!=-1 && arr[st.top()]>=curr){\n st.pop();\n }\n \n \n // smaller element found\n \n ans[i]=st.top();\n \n st.push(i);\n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n \n int largest_area(vector<int>&heights){\n int n=heights.size();\n \n vector<int>next(n);\n next=next_small(heights);\n \n vector<int>prev(n);\n prev=prev_small(heights);\n int maxi=0;\n \n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n int length=heights[i];\n \n if(next[i]==-1){\n next[i]=n;\n }\n int breadth=next[i]-prev[i]-1;\n \n \n int area=length*breadth;\n maxi=max(maxi,area);\n \n }\n \n return maxi;\n }\npublic:\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n \n int maxi=0;\n \n vector<int>height(matrix[0].size(),0);\n \n for(int i=0;i<matrix.size();i++){\n for(int j=0;j<height.size();j++){\n if(matrix[i][j]==\'1\'){\n height[j]++;\n }\n else{\n height[j]=0;\n }\n \n }\n maxi=max(maxi,largest_area(height));\n }\n \n return maxi;\n }\n};\n\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Stack', 'C', 'Monotonic Stack']
| 3 |
maximal-rectangle
|
C# Solution for Maximal Rectangle Problem
|
c-solution-for-maximal-rectangle-problem-2dwd
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nThe intuition behind the C# solution is still to treat each row of the matrix as the ba
|
Aman_Raj_Sinha
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-13T04:48:30.380349+00:00
|
2024-04-13T04:48:30.380374+00:00
| 646 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThe intuition behind the C# solution is still to treat each row of the matrix as the base of a histogram and then apply the largest rectangle in histogram algorithm to find the maximum area rectangle that can be formed using that row as the base. However, instead of using nested loops, it uses a single loop for iterating through the matrix and updating the heights array.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1.\tIterate through each row of the matrix.\n2.\tUpdate the heights array by incrementing the height if the corresponding matrix element is \u20181\u2019, or resetting it to 0 if it\u2019s \u20180\u2019.\n3.\tCalculate the maximum area using the largest rectangle in histogram algorithm for each updated heights array.\n4.\tUpdate and return the maximum area found.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\u2022\tLet n be the number of rows and m be the number of columns in the matrix.\n\u2022\tUpdating the heights array for each row takes O(m) time.\n\u2022\tCalculating the maximum area for each row takes O(m) time using the largest rectangle in histogram algorithm.\n\u2022\tTherefore, the total time complexity is O(n*m).\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\u2022\tWe use an additional heights array of length m to store the heights of the histogram.\n\u2022\tTherefore, the space complexity is O(m) since we only need to store the heights array.\n\n# Code\n```\npublic class Solution {\n public int MaximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) {\n if (matrix == null || matrix.Length == 0 || matrix[0].Length == 0) {\n return 0;\n }\n \n int rows = matrix.Length;\n int cols = matrix[0].Length;\n int maxArea = 0;\n int[] heights = new int[cols];\n \n for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {\n heights[j] = matrix[i][j] == \'1\' ? heights[j] + 1 : 0;\n }\n maxArea = Math.Max(maxArea, LargestRectangleArea(heights));\n }\n \n return maxArea;\n }\n\n private int LargestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {\n Stack<int> stack = new Stack<int>();\n int maxArea = 0;\n int i = 0;\n \n while (i < heights.Length) {\n if (stack.Count == 0 || heights[stack.Peek()] <= heights[i]) {\n stack.Push(i++);\n } else {\n int top = stack.Pop();\n int area = heights[top] * (stack.Count == 0 ? i : i - stack.Peek() - 1);\n maxArea = Math.Max(maxArea, area);\n }\n }\n \n while (stack.Count > 0) {\n int top = stack.Pop();\n int area = heights[top] * (stack.Count == 0 ? i : i - stack.Peek() - 1);\n maxArea = Math.Max(maxArea, area);\n }\n \n return maxArea;\n }\n}\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['C#']
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Easy || C++ Solution || Using stack || Most Optimised
|
easy-c-solution-using-stack-most-optimis-jgr6
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Jr_Murphy_05
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-13T04:38:30.695494+00:00
|
2024-04-13T04:38:30.695518+00:00
| 1,383 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int largestRectangleArea(vector < int > & histo) {\n stack < int > st;\n int maxA = 0;\n int n = histo.size();\n for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {\n while (!st.empty() && (i == n || histo[st.top()] >= histo[i])) {\n int height = histo[st.top()];\n st.pop();\n int width;\n if (st.empty())\n width = i;\n else\n width = i - st.top() - 1;\n maxA = max(maxA, width * height);\n }\n st.push(i);\n }\n return maxA;\n }\n\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n int maxArea = 0;\n int n = matrix.size();\n int m = matrix[0].size();\n vector<int> height(m, 0);\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {\n if (matrix[i][j] == \'1\') height[j]++;\n else height[j] = 0;\n }\n int area = largestRectangleArea(height);\n maxArea = max(maxArea, area);\n }\n return maxArea;\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Stack', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Easy C++ Solution Based on Largest Stack || Stack
|
easy-c-solution-based-on-largest-stack-s-xogq
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity:\no(n^3)\n\n- Space complexity:\no(n)\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\nint largestRectangleArea(vector < int > & histo) {
|
ayushsachan123
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-29T05:01:56.880590+00:00
|
2024-02-29T05:01:56.880608+00:00
| 1,053 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\no(n^3)\n\n- Space complexity:\no(n)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\nint largestRectangleArea(vector < int > & histo) {\n\tstack < int > st;\n\tint maxA = 0;\n\tint n = histo.size();\n\tfor (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {\n\t\twhile (!st.empty() && (i == n || histo[st.top()] >= histo[i])) {\n\t\t\tint height = histo[st.top()];\n\t\t\tst.pop();\n\t\t\tint width;\n\t\t\tif (st.empty())\n\t\t\t\twidth = i;\n\t\t\telse\n\t\t\t\twidth = i - st.top() - 1;\n\t\t\tmaxA = max(maxA, width * height);\n\t\t}\n\t\tst.push(i);\n\t}\n\treturn maxA;\n}\n\nint solve(vector<vector<char>>&mat, int n, int m) {\n\tint maxArea = 0;\n\tvector<int> height(m, 0);\n\tfor (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n\t\tfor (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {\n\t\t\tif (mat[i][j] == \'1\') height[j]++;\n\t\t\telse height[j] = 0;\n\t\t}\n\t\tint area = largestRectangleArea(height);\n\t\tmaxArea = max(area, maxArea);\n\t}\n\n\treturn maxArea;\n}\n\n\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n int n = matrix.size();\n int m = matrix[0].size();\n\n return solve(matrix, n, m);\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Array', 'Stack', 'Matrix', 'Monotonic Stack', 'C++']
| 1 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Easy understandable C++ solution || Similar to Leetcode 84 - Largest Rectangle in Histogram
|
easy-understandable-c-solution-similar-t-3bs4
|
\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> nextSmallerElement(vector<int> &arr){\n int n = arr.size();\n vector<int> ans(n);\n
|
bharathgowda29
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-09T07:18:53.295285+00:00
|
2024-02-09T07:18:53.295323+00:00
| 1,271 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> nextSmallerElement(vector<int> &arr){\n int n = arr.size();\n vector<int> ans(n);\n stack<int> st;\n st.push(-1);\n\n for(int i=n-1; i>=0; i--){\n while(st.top() != -1 && arr[st.top()] >= arr[i]){\n st.pop();\n }\n ans[i] = st.top();\n st.push(i);\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n\n\n vector<int> previousSmallerElement(vector<int> &arr){\n int n = arr.size();\n vector<int> ans(n);\n stack<int> st;\n st.push(-1);\n \n for(int i=0; i<n; i++){\n while(st.top() != -1 && arr[st.top()] >= arr[i]){\n st.pop();\n }\n ans[i] = st.top();\n st.push(i);\n }\n \n return ans;\n } \n\n\n int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {\n vector<int> nextSmaller;\n vector<int> previousSmaller;\n int n = heights.size();\n\n nextSmaller = nextSmallerElement(heights);\n previousSmaller = previousSmallerElement(heights);\n int maxi = 0;\n\n for(int i=0; i<n; i++){\n if(nextSmaller[i] == -1){\n nextSmaller[i] = n;\n }\n int width = nextSmaller[i] - previousSmaller[i] - 1;\n int area = heights[i] * width;\n maxi = max(maxi, area);\n }\n\n return maxi;\n }\n\n\n\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n int m = matrix.size();\n int n = matrix[0].size();\n vector<vector<int>> v;\n\n //convert the matrix to int for our shortcut\n for(int i=0; i<m; i++){\n vector<int> temp;\n for(int j=0; j<n; j++){\n temp.push_back(matrix[i][j] - \'0\');\n }\n v.push_back(temp);\n }\n\n int area = largestRectangleArea(v[0]);\n for(int i=1; i<m; i++){\n for(int j=0; j<n; j++){\n if(v[i][j] == 0){\n v[i][j] = 0;\n }\n else{\n v[i][j] += v[i-1][j];\n }\n }\n area = max(area, largestRectangleArea(v[i]));\n }\n\n return area;\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Array', 'Stack', 'Matrix', 'Monotonic Stack', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Java Solution for Maximal Rectangle Problem
|
java-solution-for-maximal-rectangle-prob-4sfp
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nThe above solution uses a dynamic programming approach to calculate the height of the l
|
Aman_Raj_Sinha
|
NORMAL
|
2023-05-01T05:00:05.746487+00:00
|
2023-05-01T05:00:05.746522+00:00
| 1,358 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThe above solution uses a dynamic programming approach to calculate the height of the largest rectangle that can be formed with the current cell at the bottom of the rectangle. It then applies a modified version of the algorithm for finding the maximum area of a histogram on each row of the matrix to find the maximum area of a rectangle that can be formed using that row as the bottom edge.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nThe approach first creates a new matrix height where height[i][j] represents the height of the largest rectangle that can be formed with cell (i,j) as the bottom cell. If matrix[i][j] is \'0\', then height[i][j] is set to 0, since no rectangle can be formed with a bottom cell of \'0\'. Otherwise, height[i][j] is set to height[i-1][j] + 1 if i > 0, since we can extend a rectangle from the cell above it, or to 1 if i == 0, since the current cell is the topmost cell of the rectangle.\n\nOnce the height matrix has been constructed, the solution applies the modified histogram algorithm to each row of the height matrix to find the maximum area of a rectangle that can be formed using that row as the bottom edge. The modified histogram algorithm maintains a stack of indices of increasing heights of bars seen so far. When a bar with height smaller than the bar at the top of the stack is encountered, the bars in the stack are popped and their maximum area is calculated based on the height of the popped bar and the width of the rectangle, which is the difference between the current index and the index of the bar at the top of the stack (or the entire length of the stack if it is empty). The maximum area seen so far is updated if the current area is greater than it. Finally, the function returns the maximum area of a rectangle that can be formed using the heights of the bars in the given input array.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(m * n)\nThe code iterates over every cell in the input matrix once to calculate the height array, where m and n are the dimensions of the input matrix. It then calls the maxAreaInHist method once for each row in the matrix, which has a time complexity of O(n) for each row. Thus, the total time complexity is O(m * n) for the two nested loops and the maxAreaInHist method.\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(m * n)\nThe code creates a 2D array height with m rows and n+1 columns to store the height of the histogram. Each row of the height array has n+1 elements, which increases the space complexity by an extra n elements per row. Thus, the space complexity is O(m * (n+1)), which can be simplified to O(m * n) asymptotically. Additionally, the code uses a stack to store indices, which can have a worst-case space complexity of O(n) if all elements are strictly decreasing in height\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) {\n int m = matrix.length;\n int n = m == 0 ? 0 : matrix[0].length;\n int[][] height = new int[m][n + 1];\n int maxArea = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) \n {\n for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) \n {\n if (matrix[i][j] == \'0\') \n {\n height[i][j] = 0;\n } \n else \n {\n height[i][j] = i == 0 ? 1 : height[i - 1][j] + 1;\n }\n }\n }\n for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) \n {\n int area = maxAreaInHist(height[i]);\n if (area > maxArea) \n {\n maxArea = area;\n }\n }\n return maxArea;\n }\n private int maxAreaInHist(int[] height) {\n Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();\n int i = 0;\n int max = 0;\n while (i < height.length) \n {\n if (stack.isEmpty() || height[stack.peek()] <= height[i]) \n {\n stack.push(i++);\n } \n else \n {\n int t = stack.pop();\n max = Math.max(max, height[t] * (stack.isEmpty() ? i : i - stack.peek() - 1));\n }\n }\n return max;\n }\n\n}\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
stack || cpp || similar to max area in histogram
|
stack-cpp-similar-to-max-area-in-histogr-1jzp
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n# Please upvote the solution if you like it.\n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to
|
evilshadow01
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-23T19:03:01.952539+00:00
|
2023-03-23T19:03:01.952579+00:00
| 1,049 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n# **Please upvote the solution if you like it.**\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nThe solution uses the concept of histogram where the heights of each column are taken as bars of the histogram. Then, the problem is reduced to finding the largest rectangle area in the histogram.\n\nThe code first defines two helper functions nextSmaller() and prevSmaller() that return the indices of the next smaller and previous smaller element to each element of a given array. These functions use a stack to store the indices of the elements in a decreasing order of their values. The top of the stack always stores the index of the next smaller or previous smaller element.\n\nThen, the maxAreaHistogram() function takes an array and returns the maximum area of the rectangle that can be formed using the histogram of the heights of the bars of the histogram. It uses the nextSmaller() and prevSmaller() functions to calculate the next and previous smaller elements\' indices for each element in the array and then calculates the maximum area of the rectangle using the formula area = length * width, where length is the height of the current element, and width is the distance between the next smaller and previous smaller element indices.\n\nFinally, the maximalRectangle() function takes the binary matrix as input, converts it into an array of integers, and calculates the maximum area of the rectangle by iterating over each row of the matrix and updating the array of heights for each row. The maximum area is returned as the output.\n\nOverall, the code is an implementation of the histogram-based approach to find the maximal rectangle area in a binary matrix.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(m*n) where m and n are the dimensions of the input matrix.\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(m*n)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\nprivate:\n vector<int> nextSmaller(vector<int> &arr,int n){\n stack<int> st;\n vector<int> ans(n);\n st.push(-1);\n for(int i=arr.size()-1;i>=0;i--){\n while(st.top()!=-1 && arr[st.top()]>=arr[i]){\n st.pop();\n }\n ans[i]=st.top();\n st.push(i);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n vector<int> prevSmaller(vector<int> &arr,int n){\n stack<int> st;\n vector<int> ans(n);\n st.push(-1);\n for(int i=0;i<arr.size();i++){\n while(st.top()!=-1 && arr[st.top()]>=arr[i]){\n st.pop();\n }\n ans[i]=st.top();\n st.push(i);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n int maxAreaHistogram(vector<int> &arr){\n int n = arr.size();\n vector<int> next(n);\n vector<int> prev(n);\n next = nextSmaller(arr,n);\n prev = prevSmaller(arr,n);\n int area = 0;\n for(int i=0;i<arr.size();i++){\n int length = arr[i];\n if(next[i]==-1){\n next[i]=n;\n }\n int width = next[i]-prev[i]-1;\n area = max(area,(length*width));\n }\n return area;\n }\npublic:\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);\n vector<vector<int>> mat;\n for(int i=0;i<matrix.size();i++){\n vector<int> v;\n for(int j=0;j<matrix[i].size();j++){\n if(matrix[i][j]==\'1\'){\n v.push_back(1);\n }\n else{\n v.push_back(0);\n }\n }\n mat.push_back(v);\n }\n int n = mat.size();\n int area = maxAreaHistogram(mat[0]);\n for(int i=1;i<n;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<mat[i].size();j++){\n if(mat[i][j]!=0){\n mat[i][j]+=mat[i-1][j];\n }\n }\n area=max(area,maxAreaHistogram(mat[i]));\n }\n return area;\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
EASY C++ CODE || zarur dkhooo
|
easy-c-code-zarur-dkhooo-by-sadhana_om14-2vjh
|
Intuition\nThis question links the concept of several questions, for example: \n- Finding next smaller element\n- Finding Previous smaller element\n- Histogram
|
sadhana_om142003
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-17T17:56:57.956011+00:00
|
2023-03-17T18:01:13.664296+00:00
| 7,184 | false |
# Intuition\nThis question links the concept of several questions, for example: \n- Finding next smaller element\n- Finding Previous smaller element\n- Histogram area problem.\nSo we will be just writting 3 seperate functions for each set of problem mentioned above and use these functions in our current working function.\n\n---\n\n# Complexity\n\n- Time complexity:\nO(NXN)\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(N), since we have created vectors.\n\n---\n\n\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> prev(vector<int> v,int n){\n vector<int> ans(n);\n stack<int> s;\n s.push(-1);\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n int curr=v[i];\n while(s.top()!=-1 && v[s.top()]>=curr){\n s.pop();\n }\n //top me hi ans h;\n ans[i]=s.top();\n s.push(i);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n\n vector<int> next(vector<int> v,int n){\n vector<int> ans(n);\n stack<int> s;\n s.push(-1);\n for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--){\n int curr=v[i];\n while(s.top()!=-1 && v[s.top()]>=curr){\n s.pop();\n }\n //top me hi ans h;\n ans[i]=s.top();\n s.push(i);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n\n int maxHisto(vector<int> v){\n int nt=v.size();\n vector<int> p(nt);\n p=prev(v,nt);\n vector<int> n(nt);\n n=next(v,nt);\n int sum=INT_MIN;\n for(int i=0;i<nt;i++){\n if(n[i]==-1){\n n[i]=nt;\n }\n int a= v[i]*(n[i]-p[i]-1);\n sum=max(a,sum);\n }\n return sum;\n }\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n vector<vector<int>> v(matrix.size());\n for(int i=0;i<matrix.size();i++){\n for(int j=0;j<matrix[i].size();j++){\n if(matrix[i][j]==\'0\')\n v[i].push_back(0);\n else v[i].push_back(1);\n }\n } \n int first= maxHisto(v[0]);\n for(int i=1;i<v.size();i++){\n for(int j=0;j<v[i].size();j++){\n if(v[i][j]!=0){\n v[i][j]=v[i-1][j]+v[i][j];\n }\n else v[i][j]=0;\n }\n int a= maxHisto(v[i]);\n first= max(first,a);\n }\nreturn first;\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Stack', 'C++']
| 2 |
maximal-rectangle
|
[JavaScript] 85. Maximal Rectangle
|
javascript-85-maximal-rectangle-by-pgmre-axen
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n- 1-dimensional: https://leetcode.com/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histo
|
pgmreddy
|
NORMAL
|
2023-03-13T15:59:11.955373+00:00
|
2023-03-14T18:36:04.425685+00:00
| 3,666 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n- 1-dimensional: https://leetcode.com/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/\n\nSolution: https://leetcode.com/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/solutions/3297538/javascript-84-largest-rectangle-in-histogram/\n\n- 2-dimensional: https://leetcode.com/problems/maximal-rectangle/\n\nSolution: below\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n\nGood one\n\n1\n```\nvar maximalRectangle = function (aa) {\n let m = aa.length,\n n = aa[0].length;\n\n let widthOnLeftTillHere = Array.from({ length: m }, () =>\n new Array(n).fill(0)\n );\n for (let r = 0; r < m; r++)\n for (let c = 0; c < n; c++)\n if (aa[r][c] === "1") {\n widthOnLeftTillHere[r][c] =\n (widthOnLeftTillHere[r][c - 1] || 0) + 1;\n }\n\n let maxArea = 0;\n for (let r = 0; r < m; r++)\n for (let c = 0; c < n; c++)\n if (aa[r][c] === "1") {\n let minWidthGoingUp = Infinity;\n let increasingHeight = 1;\n for (let r2 = r; r2 >= 0; r2--, increasingHeight++) {\n minWidthGoingUp = Math.min(\n minWidthGoingUp,\n widthOnLeftTillHere[r2][c]\n );\n maxArea = Math.max(\n maxArea,\n minWidthGoingUp * increasingHeight\n );\n }\n }\n return maxArea;\n};\n```\n\n2 - Optimized, a bit difficult to understand at begin\n```\nfunction maximalRectangle(aa) {\n let m = aa.length,\n n = aa[0].length;\n\n let heights = new Array(n + 1).fill(0), // this row heights, last col is 0\n maxArea = 0;\n\n for (let r = 0; r < m; r++) {\n let cols = []; // prev increasing columns - stack\n cols.top = () => cols[cols.length - 1]; // get column left on top of stack\n\n for (let c = 0; c <= n; c++) {\n if (c < n) {\n if (aa[r][c] === "1") heights[c]++;\n else heights[c] = 0;\n }\n\n while (cols.length && heights[cols.top()] > heights[c]) {\n let height = heights[cols.pop()]; // prev column height\n let width = cols.length ? c - cols.top() - 1 : c; // prev prev column to cur column width\n maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, width * height);\n }\n cols.push(c);\n }\n }\n return maxArea;\n}\n```\n
| 4 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Aditya verma Solution | C++ | Maximal Rectangle
|
aditya-verma-solution-c-maximal-rectangl-bolc
|
Aditya Verma Solutions\n\nQ1.\n85. Maximal Rectangle\nhttps://leetcode.com/problems/maximal-rectangle/\n\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\nint largestRectangleArea(
|
Lokesh_Kumar_Kumawat
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-28T11:17:31.391204+00:00
|
2022-08-28T11:17:31.391246+00:00
| 736 | false |
# Aditya Verma Solutions\n\n**Q1.**\n***85. Maximal Rectangle***\nhttps://leetcode.com/problems/maximal-rectangle/\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\nint largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {\n int n= heights.size();\n vector<int> left,right;\n stack<pair<int,int>> s1,s2;\n int pseudo_index =-1;\n int pseudo_index1 =n;\n for (int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n if (s1.size()==0)\n {\n left.push_back(pseudo_index);\n }\n else if (s1.size()>0 && s1.top().first<heights[i])\n {\n left.push_back(s1.top().second);\n }\n else if (s1.size()>0 && s1.top().first>=heights[i])\n {\n while(s1.size()>0 && s1.top().first>=heights[i])\n {\n s1.pop();\n }\n if (s1.size()==0)\n {\n left.push_back(pseudo_index);\n }\n else\n {\n left.push_back(s1.top().second);\n }\n }\n s1.push({heights[i],i});\n }\n for (int i=n-1;i>=0;i--)\n {\n if (s2.size()==0)\n {\n right.push_back(pseudo_index1);\n }\n else if (s2.size()>0 && s2.top().first<heights[i])\n {\n right.push_back(s2.top().second);\n }\n else if (s2.size()>0 && s2.top().first >= heights[i])\n {\n while(s2.size()>0 && s2.top().first >= heights[i])\n {\n s2.pop();\n }\n if (s2.size()==0)\n {\n right.push_back(pseudo_index1);\n }\n else\n {\n right.push_back(s2.top().second);\n }\n }\n s2.push({heights[i],i});\n }\n reverse(right.begin(),right.end());\n int m=INT_MIN;\n for (long long i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n m=max(m,(right[i]-left[i]-1)*heights[i]);// taking max after finding area\n }\n return m;\n }\n\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n int m=matrix.size();\n if(m==0) return 0;\n int n=matrix[0].size(), result=0;\n vector<int> histogram(n, 0);\n \n for(int i=0; i<m; i++){\n for(int j=0; j<n; j++){\n if(matrix[i][j]==\'1\')\n histogram[j]+=1;\n else\n histogram[j]=0;\n }\n \n result = max(result, largestRectangleArea(histogram));\n // cout<<result<<" ";\n }\n return result;\n }\n};\n\n```\n\n**Q2.**\n***84. Largest Rectangle in Histogram***\nhttps://leetcode.com/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/\n\n```\nclass Solution\n{\n\tpublic:\n\t\tint getMaxArea(vector<int> &arr, int n)\n\t\t{\n\t\t\tvector<int> left, right;\n\t\t\tstack<pair<int, int>> s1, s2;\n\t\t\tint pseudo_index = -1;\n\t\t\tint pseudo_index1 = n;\n\t\t\tfor (int i = 0; i < n; i++)\n\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\tif (s1.size() == 0)\n\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\tleft.push_back(pseudo_index);\n\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\telse if (s1.size() > 0 && s1.top().first < arr[i])\n\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\tleft.push_back(s1.top().second);\n\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\telse if (s1.size() > 0 && s1.top().first >= arr[i])\n\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\twhile (s1.size() > 0 && s1.top().first >= arr[i])\n\t\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\t\ts1.pop();\n\t\t\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\t\t\tif (s1.size() == 0)\n\t\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\t\tleft.push_back(pseudo_index);\n\t\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\t\telse\n\t\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\t\tleft.push_back(s1.top().second);\n\t\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\t\ts1.push({ arr[i], i });\n\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\tfor (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--)\n\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\tif (s2.size() == 0)\n\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\tright.push_back(pseudo_index1);\n\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\telse if (s2.size() > 0 && s2.top().first < arr[i])\n\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\tright.push_back(s2.top().second);\n\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\telse if (s2.size() > 0 && s2.top().first >= arr[i])\n\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\twhile (s2.size() > 0 && s2.top().first >= arr[i])\n\t\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\t\ts2.pop();\n\t\t\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\t\t\tif (s2.size() == 0)\n\t\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\t\tright.push_back(pseudo_index1);\n\t\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\t\telse\n\t\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\t\tright.push_back(s2.top().second);\n\t\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\t\ts2.push({ arr[i], i });\n\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\treverse(right.begin(), right.end());\n\t\t\tint m = INT_MIN;\n\t\t\tfor (int i = 0; i < n; i++)\n\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\tint s = (right[i] - left[i] - 1) *arr[i];\n\t\t\t\tm = max(m, s);\t// taking max after finding area\n\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\treturn m;\n\t\t}\n\n\tint largestRectangleArea(vector<int> &heights)\n\t{\n\t\tint n = heights.size();\n\t\treturn getMaxArea(heights, n);\n\n\t}\n};\n
| 4 | 0 |
['Stack', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Using Kadane's Algorithm
|
using-kadanes-algorithm-by-coding_sprint-vqfa
|
Just Replace 0 with negative of MAX possible sum in array. And proceed as in the question of finding maximum sum rectangle.\n\nclass Solution {\n public int
|
Coding_sprint
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-27T14:50:11.797687+00:00
|
2022-08-27T14:57:50.156994+00:00
| 1,470 | false |
Just Replace 0 with negative of MAX possible sum in array. And proceed as in the question of finding maximum sum rectangle.\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) {\n int ans = 0, m=matrix.length,n = matrix[0].length,INF = -m*n;\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++){\n int[] temp = new int[m];\n for(int z=j;z<n;z++){\n for(int c=0;c<m;c++) temp[c]+= matrix[c][z]==\'0\'?INF:1;\n \n ans = Math.max(ans,kadaneAlgo(temp));\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n private int kadaneAlgo(int[] arr){\n int max = arr[0], local_max = arr[0];\n for(int i=1;i<arr.length;i++){\n local_max = Math.max(arr[i],local_max+arr[i]);\n max = Math.max(local_max,max);\n }\n return max;\n }\n}\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
[Java] Same as Maximum Rectangle in Histogram | NSL | NSR | Aditya Verma
|
java-same-as-maximum-rectangle-in-histog-9g5r
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int maximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) {\n int m = matrix.length;\n int n = matrix[0].length;\n int[] heights
|
nagato19
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-21T21:10:38.805266+00:00
|
2022-08-21T21:10:38.805302+00:00
| 564 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int maximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) {\n int m = matrix.length;\n int n = matrix[0].length;\n int[] heights = new int[n];\n \n int ans = Integer.MIN_VALUE;\n \n for(int i=0; i<m; i++) {\n for(int j=0; j<n; j++) {\n heights[j] = matrix[i][j] == \'1\' ? heights[j] + 1: 0;\n }\n ans = Math.max(ans, getMAH(heights, n));\n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n \n private int getMAH(int[] heights, int n) {\n int maxArea = Integer.MIN_VALUE;\n List<Integer> nsl = NSL(heights, n);\n List<Integer> nsr = NSR(heights, n);\n int[] width = new int[n];\n \n for(int i=0; i<n; i++)\n width[i] = nsr.get(i) - nsl.get(i) - 1;\n \n for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {\n int area = heights[i] * width[i];\n maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, area);\n }\n return maxArea;\n }\n \n \n private List<Integer> NSL(int[] heights, int n) {\n \n List<Integer> nsl = new ArrayList<>();\n Stack<int[]> st = new Stack<>();\n \n for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {\n int curr = heights[i];\n while(!st.isEmpty() && st.peek()[0] >= curr) { st.pop(); }\n if(st.isEmpty()) nsl.add(-1);\n else nsl.add(st.peek()[1]);\n st.add(new int[] { curr, i });\n }\n \n return nsl;\n }\n \n \n private List<Integer> NSR(int[] heights, int n) {\n \n List<Integer> nsr = new ArrayList<>();\n Stack<int[]> st = new Stack<>();\n \n for(int i=n-1; i>=0; i--) {\n int curr = heights[i];\n while(!st.isEmpty() && st.peek()[0] >= curr) { st.pop(); }\n if(st.isEmpty()) nsr.add(n);\n else nsr.add(st.peek()[1]);\n st.add(new int[] { curr, i });\n }\n \n Collections.reverse(nsr);\n return nsr;\n }\n \n}\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Stack', 'Java']
| 1 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Easy C++ Solution | DP + Stack
|
easy-c-solution-dp-stack-by-ahanavish-q7bz
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxarea(vector<int> &v){\n stack<int> s;\n int ans=0;\n for(int i=0; i<=v.size(); i++){\n w
|
ahanavish
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-14T14:48:46.526431+00:00
|
2022-07-14T14:49:24.876426+00:00
| 576 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxarea(vector<int> &v){\n stack<int> s;\n int ans=0;\n for(int i=0; i<=v.size(); i++){\n while(!s.empty() && (i==v.size() || v[s.top()]>v[i])){\n int cur=s.top();\n s.pop();\n int width = s.empty()? i:i-s.top()-1;\n ans = max(ans, width*v[cur]);\n }\n s.push(i);\n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n \n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size();\n vector<int> curr(n, 0);\n \n int ans=0;\n for(int i=0; i<m; i++){\n for(int j=0; j<n; j++){\n if(matrix[i][j]==\'1\') curr[j]++;\n else curr[j]=0;\n }\n int area = maxarea(curr);\n ans=max(ans, area);\n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Stack', 'C', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Explanation with diagram
|
explanation-with-diagram-by-abhinav_sing-zzom
|
\n\n\n1. Every row can be converted into a histogram very easily. Total time taken for this operation will be O(rows * cols).\n2. Then for every histogram we ca
|
abhinav_singh22
|
NORMAL
|
2022-03-22T16:19:04.568768+00:00
|
2022-03-23T07:21:32.079684+00:00
| 269 | false |
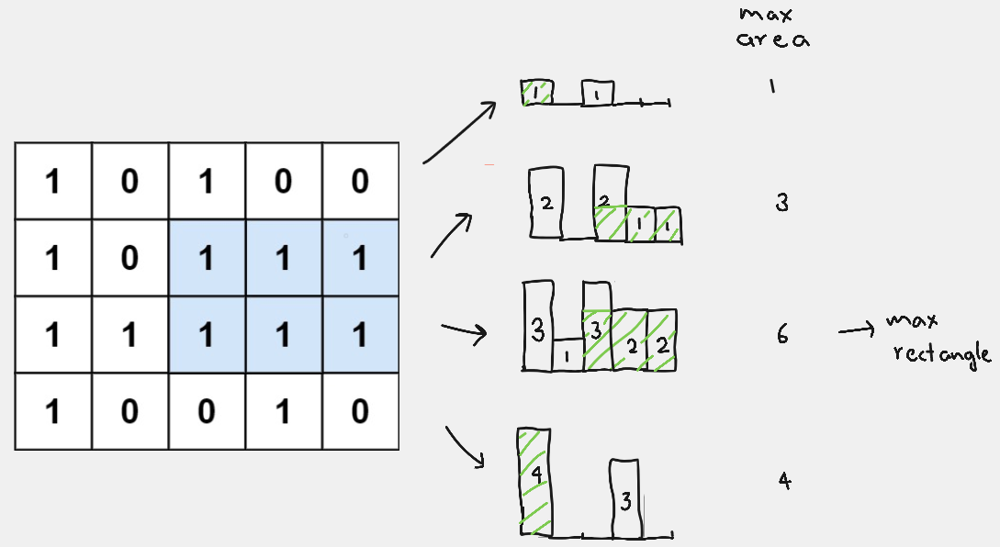\n\n\n1. Every row can be converted into a histogram very easily. Total time taken for this operation will be **O(rows * cols)**.\n2. Then for every histogram we can find the largest area of rectangle in it. We can find the largest area of rectangle in histogram in **O(cols)** time using monotonous stack. So the total time complexity for finding largest area of reactangle in every histogram will be **O(rows * cols)**.\n3. Max rectangle will be the largest area of histogram among all histograms.\n\nTime Complexity: O(rows * cols)\nSpace Complexity: O(rows * cols)\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n int rows = matrix.size(), cols = matrix[0].size();\n\n vector<vector<int>> rowHeights(rows, vector(cols, 0));\n \n\t\t// convert every row into a histogram\n for(int row = 0; row < rows; row++) {\n for(int col = 0; col < cols; col++) {\n if (row == 0) {\n rowHeights[row][col] = matrix[row][col] - \'0\';\n } else {\n if (matrix[row][col] == \'0\') rowHeights[row][col] = 0;\n else rowHeights[row][col] = 1 + rowHeights[row-1][col];\n }\n }\n }\n \n int maxRectangle = 0;\n \n for(auto &heights: rowHeights) {\n int area = getMaxArea(heights);\n maxRectangle = max(area, maxRectangle);\n }\n \n return maxRectangle;\n }\n \n // return the maximum area of rectangle in histogram\n int getMaxArea(vector<int> &heights) {\n int n = heights.size();\n vector<int> areas(n);\n stack<int> stk;\n stk.push(n);\n \n // nearest smaller element to right\n for(int i = n-1; i >= 0; i--) {\n int height = heights[i];\n\n while (stk.top() != n && heights[stk.top()] >= height) stk.pop();\n \n areas[i] = stk.top();\n \n stk.push(i);\n }\n\n stk.push(-1);\n // nearest smaller element to left\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n int height = heights[i];\n\n while (stk.top() != -1 && heights[stk.top()] >= height) stk.pop();\n \n // width = right - left - 1\n // width = right - (left + 1)\n areas[i] -= stk.top() + 1;\n\n areas[i] *= height;\n \n stk.push(i);\n }\n \n return *max_element(areas.begin(), areas.end());\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Stack', 'Monotonic Stack']
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
C++ || two stacks solution || simple
|
c-two-stacks-solution-simple-by-ritamsad-12qb
|
leetcode 84-> same approach\n https://leetcode.com/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/discuss/1825607/C++-oror-two-stack-solution-oror-simple-oror-previous
|
ritamsadhu
|
NORMAL
|
2022-03-06T17:27:14.972749+00:00
|
2022-03-06T17:28:40.050104+00:00
| 183 | false |
leetcode 84-> same approach\n https://leetcode.com/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/discuss/1825607/C++-oror-two-stack-solution-oror-simple-oror-previous-smaller-element-oror-next-smaller-element\n \n ```\n class Solution {\n int fun(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n = nums.size();\n vector<int> nsl,nsr;\n stack<pair<int,int>> s1,s2;\n\n for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++)\n {\n if(s1.empty())\n nsl.push_back(-1);\n else{\n while(!s1.empty() && s1.top().first>=nums[i])\n s1.pop();\n if(s1.empty())\n nsl.push_back(-1);\n else\n nsl.push_back(s1.top().second);\n }\n s1.push({nums[i],i});\n }\n\t\t\n for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--)\n {\n if(s2.empty())\n nsr.push_back(n);\n else{\n while(!s2.empty() && s2.top().first>=nums[i])\n s2.pop();\n if(s2.empty())\n nsr.push_back(n);\n else\n nsr.push_back(s2.top().second);\n }\n s2.push({nums[i],i});\n }\n reverse(nsr.begin(),nsr.end());\n\t\t\n int res = INT_MIN;\n int val=0;\n for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++)\n {\n val = (nsr[i]-nsl[i]-1)*nums[i];\n res = max(res,val);\n }\n return res;\n }\npublic:\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n int row = matrix.size();\n int column = matrix[0].size();\n vector<int> arr(column,0);\n int res = INT_MIN;\n for(int i = 0;i<row;i++)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<column;j++)\n {\n if(matrix[i][j]==\'0\')\n arr[j]=0;\n else\n arr[j]++;\n }\n res = max(res,fun(arr));\n }\n return res;\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
C++ solution
|
c-solution-by-anchal2907-zb6v
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic: \n vector<int> nextSmallerElement(int *arr,int n)\n {\n stack<int>s;\n s.push(-1);\n vector<int> ans(n);\
|
anchal2907
|
NORMAL
|
2022-02-22T11:39:37.329180+00:00
|
2022-02-22T11:39:37.329224+00:00
| 120 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic: \n vector<int> nextSmallerElement(int *arr,int n)\n {\n stack<int>s;\n s.push(-1);\n vector<int> ans(n);\n for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--)\n {\n int curr=arr[i];\n while(s.top()!=-1 && arr[s.top()]>=curr)\n {\n s.pop();\n }\n ans[i]=s.top();\n s.push(i);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n vector<int> prevSmallerElement(int *arr,int n)\n {\n stack<int>s;\n s.push(-1);\n vector<int> ans(n);\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n int curr=arr[i];\n while(s.top()!=-1 && arr[s.top()]>=curr)\n {\n s.pop();\n }\n ans[i]=s.top();\n s.push(i);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n \n int largestRectangleArea(int *heights,int n) {\n //int n=heights.size();\n \n vector<int> next(n);\n next=nextSmallerElement(heights,n);\n \n vector<int> prev(n);\n prev=prevSmallerElement(heights,n);\n \n int area=INT_MIN;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n int l=heights[i];\n \n if(next[i]==-1)\n next[i]=n;\n int b=next[i]-prev[i]-1;\n int newArea=l*b;\n area= max(area,newArea);\n }\n return area;\n \n }\n \n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n int rows=matrix.size();\n int cols=matrix[0].size();\n int mat[rows][cols];\n for(int i=0;i<rows;i++)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<cols;j++)\n {\n mat[i][j]=matrix[i][j]-\'0\';\n }\n }\n int area=largestRectangleArea(mat[0],cols);\n for(int i=1;i<rows;i++)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<cols;j++)\n {\n if(mat[i][j]!=0)\n mat[i][j]=mat[i][j]+mat[i-1][j];\n else\n mat[i][j]=0;\n }\n int newArea=largestRectangleArea(mat[i],cols);\n area=max(area,newArea);\n }\n \n return area;\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
C++ Solution
|
c-solution-by-brooklynzhang-1o2v
|
class Solution {\npublic:\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n vector<int> dp (matrix[0].size(), 0);\n int res = 0;\n
|
brooklynzhang
|
NORMAL
|
2022-01-25T08:07:09.437133+00:00
|
2022-01-25T08:07:09.437161+00:00
| 438 | false |
```class Solution {\npublic:\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n vector<int> dp (matrix[0].size(), 0);\n int res = 0;\n \n for (int i = 0; i < matrix.size(); i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < matrix[0].size(); j++) {\n if (matrix[i][j] == \'1\') {\n dp[j] ++;\n int row_len = dp[j];\n int k = j;\n while (k >= 0) {\n row_len = min(row_len, dp[k]);\n res = max(res, row_len * (j - k + 1));\n k--;\n }\n } else {\n dp[j] = 0;\n }\n }\n } \n return res;\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C']
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Easy to Understand in C++ || Histogram Approach || D.p
|
easy-to-understand-in-c-histogram-approa-lcpl
|
class Solution {\npublic:\n \n int maxAreaHistogram(vector& heights)\n {\n int n = heights.size();\n vector nsl(n),psl(n);\n \n
|
luciferraturi
|
NORMAL
|
2021-12-15T16:28:53.023690+00:00
|
2021-12-15T17:00:17.156235+00:00
| 153 | false |
class Solution {\npublic:\n \n int maxAreaHistogram(vector<int>& heights)\n {\n int n = heights.size();\n vector<int> nsl(n),psl(n);\n \n stack<int> s;\n \n for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--){\n while(!s.empty() && heights[s.top()]>=heights[i]){\n s.pop();\n }\n nsl[i] = s.empty() ? n : s.top();\n s.push(i);\n }\n \n while(!s.empty()){\n s.pop();\n }\n \n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n while(!s.empty() && heights[s.top()]>=heights[i]){\n s.pop();\n }\n psl[i] = s.empty() ? -1: s.top();\n s.push(i);\n }\n \n int ans = INT_MIN;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n ans = max(ans,(nsl[i]-psl[i]-1)*(heights[i]));\n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n \n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n \n if( matrix.empty() ) return 0;\n \n int rowSize = matrix.size();\n int colSize = matrix[0].size();\n int maxArea = 0;\n \n vector<vector<int>>grid(rowSize,vector<int>(colSize,0));\n \n for( int i = 0; i < rowSize; i++ )\n {\n for( int j = 0; j < colSize; j++ )\n {\n grid[i][j] = ( matrix[i][j] == \'1\' ? 1 : 0 );\n if( i != 0 && grid[i][j] == 1 ) grid[i][j] += grid[i-1][j];\n }\n \n int tmpAns = maxAreaHistogram(grid[i]);\n maxArea = max(maxArea,tmpAns);\n }\n\n return maxArea;\n \n }\n};
| 4 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming']
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
python | from n^4 to n^3 to n^2
|
python-from-n4-to-n3-to-n2-by-sid00-8xp2
|
Goal: explain approach from n^4 to n^3 to n^2\n\nn^4\n- we start creating a rectangle at any given point in matrix -> o(n^2)\n- so at this given point we check
|
sid00
|
NORMAL
|
2021-11-11T22:01:56.902150+00:00
|
2021-11-11T22:01:56.902184+00:00
| 754 | false |
**Goal**: explain approach from n^4 to n^3 to n^2\n\n**n^4**\n- we start creating a rectangle at any given point in matrix -> o(n^2)\n- so at this given point we check each row below it and see if the # of consecutive \'1\'s in each row gives us a new `minWidth` to consider\n- then update `maxArea` according to this `minWidth`\n- this approach has ideas similar to max stock price profit problem\n```\nclass Solution(object):\n def maximalRectangle(self, matrix):\n maxVal = 0\n out = 0\n minWidth = defaultdict(int)\n for i in range(len(matrix)-1,-1,-1):\n for j in range(len(matrix[0])-1, -1, -1):\n minW = len(matrix[0])-j\n maxArea = 0\n for di in range(i, len(matrix)):\n currW = len(matrix[0])-j\n for dj in range(j,len(matrix[0])):\n if matrix[di][dj] != "1":\n currW=dj-j\n break\n minW = min(minW, currW)\n maxArea = max(maxArea, (di-i+1)*minW)\n out = max(out, maxArea)\n return out\n```\n\n**n^3**\n- we can preprocess the `minWidth` beforehand\n- if the `matrix[i][j+1]` is "1" and `matrix[i][j]` is \'1\' then just add `minWidth[i][j+1] + 1` to `matrix[i][j]` else it remains 0\n```\nclass Solution(object):\n def maximalRectangle(self, matrix): \n maxVal = 0\n out = 0\n minWidth = defaultdict(int)\n for di in range(len(matrix)):\n currW = len(matrix[0])\n for dj in range(len(matrix[0])-1, -1, -1):\n if matrix[di][dj] != "1":\n minWidth[(di,dj)] = 0\n else:\n minWidth[(di,dj)] = 1\n minWidth[(di,dj)] += minWidth[(di,dj+1)] if dj+1!=len(matrix[0]) else 0\n\n \n for i in range(len(matrix)-1,-1,-1):\n for j in range(len(matrix[0])-1, -1, -1):\n minW = len(matrix[0])-j\n maxArea = 0\n for di in range(i, len(matrix)):\n minW = min(minW, minWidth[(di,j)])\n maxArea = max(maxArea, (di-i+1)*minW)\n out = max(out, maxArea)\n return out\n```\n\n**n^2**\n- the last optimization to consider is that instead of using the o(1) extra space `maxArea`, we can use o(n) extra space with `maxLeft`, `maxRight`, and `stack` to do one less loop\n- we consider that at each column `j`:\n- one row\'s `maxWidth[i][j]` to be the max width\n\t- that means anything greater than this can still be considered in the rectangle\'s area\n\t- anything less than this will bound the rectangle we\'re considering\n\t- area = `minWidth[i][j]` * distance btwn the two bounding rows\n- this operation can be implemented using the `stack` data structure\n- this approach is very similar to the largest rectangle in histogram problem\n```\nclass Solution(object):\n def maximalRectangle(self, matrix):\n maxVal = 0\n out = 0\n if matrix==[]:\n return 0\n minWidth = defaultdict(lambda: defaultdict(int))\n for di in range(len(matrix)):\n currW = len(matrix[0])\n for dj in range(len(matrix[0])-1, -1, -1):\n if matrix[di][dj] != "1":\n minWidth[di][dj] = 0\n else:\n minWidth[di][dj] = 1\n minWidth[di][dj] += minWidth[di][dj+1] if dj+1!=len(matrix[0]) else 0\n\t\t\t\t\t\n maxArea = 0\n for j in range(len(matrix[0])):\n maxLeft = [-1]*len(matrix)\n maxRight = [len(matrix)]*len(matrix)\n stack = []\n for i in range(len(matrix)):\n while stack and minWidth[i][j] < minWidth[stack[-1]][j]:\n maxRight[stack.pop()] = i\n maxLeft[i] = stack[-1] if stack else -1\n stack.append(i)\n area = [(maxRight[i] - maxLeft[i] - 1)*minWidth[i][j] for i in range(len(matrix))]\n maxArea = max(maxArea, max(area))\n return maxArea\n``` \n \n
| 4 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Stack', 'Python']
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Based on Largest Rectangle in Histogram
|
based-on-largest-rectangle-in-histogram-iw63q
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {\n \n \n int[] left = new int[heights.length]; \n int[] right = new int[
|
iashi_g
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-23T13:02:00.667631+00:00
|
2021-09-23T13:02:00.667666+00:00
| 125 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {\n \n \n int[] left = new int[heights.length]; \n int[] right = new int[heights.length];\n int[] width = new int[heights.length];\n Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack();\n \n \n //width --- left\n for(int i=0;i<heights.length;i++){\n \n while(!stack.isEmpty() && heights[i]<=heights[stack.peek()]){\n stack.pop();\n }\n \n if(stack.isEmpty()){\n left[i] = -1;\n }else{\n left[i] = stack.peek();\n }\n \n stack.add(i);\n }\n stack.clear();\n //width --- right\n for(int i=heights.length-1;i>=0;i--){\n \n while(!stack.isEmpty() && heights[i]<=heights[stack.peek()]){\n stack.pop();\n }\n \n if(stack.isEmpty()){\n right[i] = heights.length;\n }else{\n right[i] = stack.peek();\n }\n \n stack.add(i);\n }\n \n int area = 0;\n \n for(int i=0;i<heights.length;i++){\n width[i] = right[i]-left[i]-1;\n area = Math.max(heights[i]* width[i] ,area);\n }\n \n return area;\n }\n public int maximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) {\n if(matrix.length==0) return 0;\n // for each cell with value=1, we look upward (north), the number of continuous \'1\' is the height of cell\n int[] heights = new int[matrix[0].length];\n int maxArea=-1;\n for(int i=0; i<matrix.length; i++){\n for(int j=0; j<matrix[0].length; j++){\n if(matrix[i][j]==\'0\'){\n heights[j] = 0;\n } else {\n heights[j] ++;\n }\n } \n int area = largestRectangleArea(heights);\n maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, area);\n }\n return maxArea;\n }\n}\n```
| 4 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
maximal-rectangle
|
C++ || dp
|
c-dp-by-priyanka1230-58tj
|
\n\npublic:\n int maximalRectangle(vector>& matrix) {\n int i,j,k,n,m,minn,res=0;\n n=matrix.size();\n if(n==0)\n {\n
|
priyanka1230
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-31T12:17:44.472105+00:00
|
2021-07-31T12:17:44.472137+00:00
| 332 | false |
```\n\n```public:\n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n int i,j,k,n,m,minn,res=0;\n n=matrix.size();\n if(n==0)\n {\n return 0;\n }\n m=matrix[0].size();\n vector<vector<int>>dp(n,vector<int>(m,0));\n for(i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n dp[i][m-1]=(int)matrix[i][m-1]-\'0\';\n for(j=m-2;j>=0;j--)\n {\n if(matrix[i][j]==\'1\')\n {\n dp[i][j]=dp[i][j+1]+1;\n }\n }\n }\n for(i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n for(j=0;j<m;j++)\n {\n k=i;\n minn=dp[i][j];\n while(k<n&&dp[k][j])\n {\n minn=min(minn,dp[k][j]);\n res=max(res,minn*(k-i+1));\n k++;\n }\n }\n }\n return res;\n }\n};
| 4 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Python | DP
|
python-dp-by-pvkcse-cf8o
|
\nclass Solution(object):\n def maximalRectangle(self, matrix):\n if len(matrix) == 0: return 0\n matrix, rows, cols=[map(int, i) for i in matr
|
pvkcse
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-21T23:39:08.554489+00:00
|
2021-07-21T23:39:26.563244+00:00
| 926 | false |
```\nclass Solution(object):\n def maximalRectangle(self, matrix):\n if len(matrix) == 0: return 0\n matrix, rows, cols=[map(int, i) for i in matrix], len(matrix), len(matrix[0])\n max_area, dp = float("-inf"), [[0 for __ in range(cols+1)] for _ in range(rows+1)]\n for i in range(0, rows):\n for j in range(cols):\n dp[i][j]=matrix[i][j] if i==0 else matrix[i][j]+dp[i-matrix[i][j]][j]\n for i in range(rows):\n for j in range(cols):\n current_height = dp[i][j]\n for k in range(j, cols):\n current_height = min(current_height, dp[i][k])\n max_area = max(max_area, current_height * (k-j+1))\n return max_area\n```
| 4 | 1 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Python']
| 1 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Python O(row*col) using histogram
|
python-orowcol-using-histogram-by-in_sid-f8i9
|
\n\n\nclass Solution:\n def maximalRectangle(self, matrix: List[List[str]]) -> int:\n if not matrix:\n return 0\n row=len(matrix)\n
|
iN_siDious
|
NORMAL
|
2021-06-29T06:14:25.541206+00:00
|
2021-06-29T06:20:57.757899+00:00
| 781 | false |
\n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maximalRectangle(self, matrix: List[List[str]]) -> int:\n if not matrix:\n return 0\n row=len(matrix)\n col=len(matrix[0])\n histograms=[[0]*col for _ in range(row)]\n for i in range(row):\n for j in range(col):\n if i==0:\n histograms[i][j]=int(matrix[i][j])\n else:\n if int(matrix[i][j])==0:\n histograms[i][j]=0\n else:\n histograms[i][j]=histograms[i-1][j]+int(matrix[i][j])\n def maxArea(arr):\n stack=[]\n i=0\n Max=0\n while i<len(arr):\n if not stack or arr[i]>=arr[stack[-1]]:\n stack.append(i)\n i+=1\n else:\n a=stack.pop()\n area=arr[a]*((i-stack[-1]-1) if stack else i)\n Max=max(area,Max)\n pre=stack[-1]\n while stack:\n a=stack.pop()\n area=arr[a]*((pre-stack[-1]) if stack else pre+1)\n Max=max(area,Max)\n return Max\n k=0\n for i in histograms:\n k=max(k,maxArea(i))\n return k\n \n \n \n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Python', 'Python3']
| 1 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Largest Histogram + Bottom Up filling O(n^2) solution
|
largest-histogram-bottom-up-filling-on2-11bnl
|
\nBased on Largest area rectangle in Histogram ...\n\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n int hist(vector<int> &height){\n \n if(height.size()
|
o_hades_o
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-31T20:03:44.334845+00:00
|
2021-07-04T13:39:04.392967+00:00
| 113 | false |
\nBased on Largest area rectangle in Histogram ...\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n int hist(vector<int> &height){\n \n if(height.size()==0){return 0;}\n if(height.size()==1){return height[0];}\n int ans=0;\n stack<int> s;\n for(int i=0;i<height.size();i++){\n if(s.empty()||height[i]>=height[s.top()]){\n s.push(i);\n }\n else {\n int temp=s.top();\n s.pop();\n if(s.empty()){\n ans=max(ans,height[temp]*i);\n }\n else{\n ans=max(ans,height[temp]*(i-s.top()-1));\n }\n i--;\n }\n }\n int i=height.size();\n while(!s.empty()){\n int temp=s.top();\n s.pop();\n if(s.empty()){\n ans=max(ans,height[temp]*i);\n }\n else{\n ans=max(ans,height[temp]*(i-s.top()-1));\n }\n }\n return ans;\n \n }\n \n \n int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {\n if(matrix.size()==0){return 0;}\n vector<vector<int>> heights(matrix.size(),vector<int> (matrix[0].size(),0));\n int n=matrix.size();\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n heights[i][matrix[i].size()-1]= matrix[i][matrix[i].size()-1]==\'0\'?0:1;\n \n for(int j=matrix[i].size()-2;j>=0;j--){\n if(matrix[i][j]==\'0\'){heights[i][j]=0;}\n else{\n heights[i][j]=heights[i][j+1]+1;\n }\n }\n }\n \n int ans=0;\n \n for(int j=0;j<matrix[0].size();j++){\n vector<int> temp;\n int mini =INT_MAX;\n for(int i=0;i<matrix.size();i++){\n mini=min(mini,heights[i][j]);\n temp.push_back(heights[i][j]);\n }\n ans=max(ans,hist(temp));\n j+=mini;\n }\n return ans;\n \n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Java || Stack || O(n*m) time || Largest area in Histogram
|
java-stack-onm-time-largest-area-in-hist-02k7
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int maximalRectangle(char[][] M) {\n \n int m = M.length;\n if( m == 0) return 0;\n int n = M[0].length;
|
hemant_sood
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-20T07:26:21.374087+00:00
|
2020-08-20T07:26:21.374136+00:00
| 852 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int maximalRectangle(char[][] M) {\n \n int m = M.length;\n if( m == 0) return 0;\n int n = M[0].length;\n int ans = 0;\n int a[] = new int[n];\n \n for(int i = 0;i<n;i++)\n a[i] = M[0][i]-\'0\';\n \n for(int i = 0;i<m;i++){\n if( i == 0){\n \n ans = Math.max(ans, maximumAreaInHistogram(a));\n continue;\n }\n \n for(int j = 0; j<n;j++){\n a[j] += M[i][j]-\'0\' ;\n if( M[i][j] == \'0\')\n a[j] = 0;\n } \n \n \n ans = Math.max(ans, maximumAreaInHistogram(a));\n \n }\n \n return ans;\n \n \n }\n \n \n \n int maximumAreaInHistogram(int h[]){\n \n int n = h.length;\n \n Stack<Integer> st = new Stack();\n \n int l[] = new int[n];\n int r[] = new int[n];\n \n \n for(int i = 0;i<n;i++){\n if( st.isEmpty()){\n l[i] = -1;\n st.push(i);\n continue;\n }\n \n while( !st.isEmpty() && h[st.peek()] >= h[i] ){\n st.pop();\n \n }\n \n int p = st.isEmpty() ? -1 : st.peek() ;\n \n l[i] = p;\n st.push(i);\n\n }\n \n st.clear();\n \n for(int i = n-1; i>=0; i--){\n if( st.isEmpty()){\n r[i] = n;\n st.push(i);\n continue;\n }\n \n while( !st.isEmpty() && h[st.peek()] >= h[i] ){\n st.pop();\n \n }\n \n int p = st.isEmpty() ? n : st.peek() ;\n \n r[i] = p;\n st.push(i);\n\n }\n \n \n \n int m = 0;\n \n for(int i = 0;i<n;i++){\n m = Math.max(m, h[i]*(r[i]-l[i]-1) );\n }\n \n \n return m;\n \n }\n \n}\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Stack', 'Java']
| 0 |
maximal-rectangle
|
Detailed explanation (code + video) with best time complexity
|
detailed-explanation-code-video-with-bes-c76s
|
Please refer this video for detailed explanation - \n[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q39oYu4p9gY]\n\n\n\nclass Solution {\n public int maximalRectangle(char
|
jayatitiwari
|
NORMAL
|
2020-05-28T19:14:12.059302+00:00
|
2020-05-31T20:07:01.227122+00:00
| 340 | false |
Please refer this video for detailed explanation - \n[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q39oYu4p9gY]\n\n\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) {\n if(matrix.length == 0)\n return 0;\n int max = 0;\n int[] height = new int[matrix[0].length];\n for(int i=0; i<matrix.length; i++){\n for(int j=0; j<matrix[0].length; j++){\n if(matrix[i][j] == \'0\'){\n height[j] = 0;\n } else {\n height[j]+=1;\n }\n }\n max = Math.max(max, findTheArea(height));\n }\n return max;\n }\n \n public int findTheArea(int[] h){\n int max = 0;\n Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();\n stack.add(0);\n for(int i=1; i<h.length; i++){\n int curr = h[i];\n if(stack.isEmpty() || curr >= h[stack.peek()]){\n stack.add(i);\n } else {\n while(!stack.isEmpty() && curr < h[stack.peek()]){\n int temp = h[stack.pop()];\n if(stack.isEmpty()){\n max = Math.max(max, temp*i);\n } else {\n max = Math.max(max, temp*(i-stack.peek()-1));\n }\n }\n stack.add(i);\n }\n }\n \n if(!stack.isEmpty()){\n while(!stack.isEmpty()){\n int i = h.length;\n int temp = h[stack.pop()];\n if(stack.isEmpty()){\n max = Math.max(max, temp*i);\n } else {\n max = Math.max(max, temp*(i-stack.peek()-1));\n }\n }\n }\n return max;\n }\n}\n```
| 4 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Iterative dp/ Reccursive dp/ memoization/ Clean code
|
iterative-dp-reccursive-dp-memoization-b-9acn
|
For this we can use either Reccurision with memoization or iterative dp
We Have a 3 state dp/cache
[x][y][k]
x = i y = j and k = the robbers we can dodge from i
|
bluetwoblue
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T04:01:36.818002+00:00
|
2025-01-14T08:39:23.806159+00:00
| 5,621 | false |
For this we can use either Reccurision with memoization or iterative dp
- We Have a 3 state dp/cache
- `[x][y][k]`
- x = i y = j and k = the robbers we can dodge from `i, j -> n - 1, m - 1`
Reccursive code:
```
class Solution {
private:
int cache[501][501][3];
int f(vector<vector<int>>& coins, int i, int j, int neu){
int n = coins.size();
int m = coins[0].size();
if(i == n - 1 && j == m - 1){
if(neu > 0 && coins[i][j] < 0){
return 0;
}else{
return coins[i][j];
}
}
if(i >= n || j>= m){
return INT_MIN;
}
if (cache[i][j][neu] != INT_MIN) {
return cache[i][j][neu];
}
int take = INT_MIN;int nottake = INT_MIN;
take = coins[i][j] + max(f(coins, i + 1, j, neu), f(coins, i, j + 1, neu));
if(neu > 0 && coins[i][j] < 0)
nottake = max(f(coins, i + 1, j, neu - 1), f(coins, i, j + 1, neu - 1));
return cache[i][j][neu] = max(take, nottake);
}
public:
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
for (int i = 0; i < 501; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < 501; ++j)
for (int k = 0; k < 3; ++k)
cache[i][j][k] = INT_MIN;
return f(coins, 0, 0, 2);
}
};
```
Iterative:
```
class Solution {
public:
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int m=coins.size();
int n=coins[0].size();
vector<vector<vector<int>>> dp(m, vector<vector<int>>(n, vector<int>(3, INT_MIN)));
dp[0][0][0]=coins[0][0];
if (coins[0][0]<0) {
dp[0][0][1]=0;
dp[0][0][2]=0;
} else {
dp[0][0][1]=dp[0][0][2]=coins[0][0];
}
for (int i=0; i<m; ++i) {
for (int j=0; j<n; ++j) {
// if(k==2) break;
for (int k=0; k<3; ++k) {
if (i==0 && j==0) continue;
// int coins[i][j]=coins[i][j];
// cout<<dp[i][j][k];
// cout<<coins[i][j];
if (i>0) {
dp[i][j][k]=max(dp[i][j][k], dp[i-1][j][k]+coins[i][j]);
if (coins[i][j]<0 && k>0) {
dp[i][j][k]=max(dp[i][j][k],dp[i-1][j][k-1]);
// cout<<dp[i][j][k];
}
}
if (j>0) {
// cout<<dp[i][j][k];
dp[i][j][k]=max(dp[i][j][k], dp[i][j-1][k]+coins[i][j]);
if (coins[i][j]<0 && k>0)
{
dp[i][j][k]=max(dp[i][j][k], dp[i][j-1][k-1]);
}
}
}
}
}
// cout<<dp[n-1][m-1];
return max({dp[m-1][n-1][0], dp[m-1][n-1][1], dp[m-1][n-1][2]});
}
};
```
Credits for iterative solution : Het_modi_25
| 33 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 14 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
DP | Tabulation | C++ | Easy
|
dp-tabulation-c-easy-by-gavnish_kumar-4mxw
|
IntuitionThe problem involves finding the maximum amount the robot can collect while neutralizing up to two robbers on its path from the top-left corner to the
|
gavnish_kumar
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T04:11:45.111314+00:00
|
2025-01-12T04:54:00.748648+00:00
| 3,030 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
The problem involves finding the maximum amount the robot can collect while neutralizing up to two robbers on its path from the top-left corner to the bottom-right corner. This can be solved using a bottom-up dynamic programming approach. The grid is traversed from the bottom-right corner to the top-left corner, and the dp array keeps track of the maximum profit the robot can gain at each cell with a certain number of robber neutralizations left.
# Approach:
**Dynamic Programming State**
Use a 3D dp array where dp[i][j][count] stores the maximum coins the robot can collect at cell (i, j) with count neutralizations remaining.
count ranges from 0 to 2, representing the number of robber neutralizations left.
**Base Case**
At the bottom-right corner (m-1, n-1), the profit is either:
coins[i][j] if no neutralization is used (count = 0).
max(0, coins[i][j]) if neutralizations are available (count > 0).
**For each cell (i, j):**
Consider moving down (i+1, j) or right (i, j+1).
If neutralizations are available (count > 0), check the maximum profit obtained by neutralizing the robber at the current cell.
**Result**
The maximum profit is stored in dp[0][0][2] (starting from the top-left corner with 2 neutralizations available).
**Edge Cases**
Small grids (e.g., 1x1 or 1xN).
Grids with only positive or only negative values.
Neutralizations may not always be beneficial.
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity: $$O(M*N)$$
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity: $$O(M*N)$$
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int m = coins.size(); // Number of rows
int n = coins[0].size(); // Number of columns
// 3D DP array initialized to INT_MIN to represent unvisited states
vector<vector<vector<int>>> dp(m, vector<vector<int>>(n, vector<int>(3, INT_MIN)));
// Iterate over the number of neutralizations (0, 1, 2)
for (int count = 0; count < 3; ++count) {
// Traverse the grid from bottom-right to top-left
for (int i = m - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
for (int j = n - 1; j >= 0; --j) {
// Base case: Bottom-right corner
if (i == m - 1 && j == n - 1) {
dp[i][j][count] = count > 0 ? max(0, coins[i][j]) : coins[i][j];
continue;
}
int ans = INT_MIN; // Store the maximum profit for this cell
// Check the cell below (down movement)
if (i + 1 < m) {
ans = max(ans, coins[i][j] + dp[i + 1][j][count]); // No neutralization
if (count > 0) ans = max(ans, dp[i + 1][j][count - 1]); // With neutralization
}
// Check the cell to the right (right movement)
if (j + 1 < n) {
ans = max(ans, coins[i][j] + dp[i][j + 1][count]); // No neutralization
if (count > 0) ans = max(ans, dp[i][j + 1][count - 1]); // With neutralization
}
// Update dp array for the current cell
dp[i][j][count] = ans;
}
}
}
// The answer is stored at the starting cell with 2 neutralizations available
return dp[0][0][2];
}
};
```
| 21 | 0 |
['C++']
| 5 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
[C++|Java|JavaScript|Python3] bottom-up dp
|
python3-dp-by-ye15-ci1n
|
IntuitionUse DP. Let's define dp[i][j][k] as the maximum coins collected at i, j with k ops remaining. Then,dp[i][j][k] = max(dp[i-1][j][k] + coins[i][j], dp[i]
|
ye15
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T06:17:53.038576+00:00
|
2025-01-12T22:35:44.354248+00:00
| 1,157 | false |
# Intuition
Use DP. Let's define `dp[i][j][k]` as the maximum coins collected at `i, j` with `k` ops remaining. Then,
`dp[i][j][k] = max(dp[i-1][j][k] + coins[i][j], dp[i][j-1][k] + coins[i][j], dp[i-1][j][k+1], dp[i][j-1][k+1])`
Assuming indices are all within reasonable range.
# Approach
Run DP and check the maximum of `dp[m-1][n-1][0..2]`.
# Complexity
- Time complexity: `O(MN)`
- Space complexity: `O(MN)`
# Code
```C++ []
class Solution {
public:
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int m = coins.size(), n = coins[0].size();
vector<vector<vector<int>>> dp(m, vector<vector<int>>(n, vector<int>(4, -1'000'000'000)));
dp[0][0][2] = coins[0][0];
if (coins[0][0] < 0) dp[0][0][1] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
for (int k = 0; k <= 2; ++k) {
if (i) dp[i][j][k] = max({dp[i][j][k], dp[i-1][j][k] + coins[i][j], dp[i-1][j][k+1]});
if (j) dp[i][j][k] = max({dp[i][j][k], dp[i][j-1][k] + coins[i][j], dp[i][j-1][k+1]});
}
return *max_element(dp[m-1][n-1].begin(), dp[m-1][n-1].end());
}
};
```
```Java []
class Solution {
public int maximumAmount(int[][] coins) {
int m = coins.length, n = coins[0].length;
int[][][] dp = new int[m][n][4];
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
Arrays.fill(dp[i][j], -1_000_000_000);
dp[0][0][2] = coins[0][0];
if (coins[0][0] < 0) dp[0][0][1] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
for (int k = 0; k <= 2; ++k) {
if (i > 0) dp[i][j][k] = Math.max(dp[i][j][k], Math.max(dp[i-1][j][k] + coins[i][j], dp[i-1][j][k+1]));
if (j > 0) dp[i][j][k] = Math.max(dp[i][j][k], Math.max(dp[i][j-1][k] + coins[i][j], dp[i][j-1][k+1]));
}
return Math.max(dp[m-1][n-1][0], Math.max(dp[m-1][n-1][1], dp[m-1][n-1][2]));
}
}
```
```JavaScript []
var maximumAmount = function(coins) {
const m = coins.length, n = coins[0].length;
const dp = Array(m).fill(0).map(() => Array(n).fill(0).map(() => Array(4).fill(-Infinity)));
dp[0][0][2] = coins[0][0];
if (coins[0][0] < 0) dp[0][0][1] = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i)
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j)
for (let k = 0; k <= 2; ++k) {
if (i) dp[i][j][k] = Math.max(dp[i][j][k], dp[i-1][j][k] + coins[i][j], dp[i-1][j][k+1]);
if (j) dp[i][j][k] = Math.max(dp[i][j][k], dp[i][j-1][k] + coins[i][j], dp[i][j-1][k+1]);
}
return Math.max(...dp[m-1][n-1]);
};
```
```python3 []
class Solution:
def maximumAmount(self, coins: List[List[int]]) -> int:
m, n = len(coins), len(coins[0])
dp = [[[-inf]*4 for _ in range(n)] for _ in range(m)]
dp[0][0][2] = coins[0][0]
if coins[0][0] < 0: dp[0][0][1] = 0
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
for k in range(3):
if i: dp[i][j][k] = max(dp[i][j][k], dp[i-1][j][k] + coins[i][j], dp[i-1][j][k+1])
if j: dp[i][j][k] = max(dp[i][j][k], dp[i][j-1][k] + coins[i][j], dp[i][j-1][k+1])
return max(dp[m-1][n-1][k] for k in range(3))
```
| 13 | 0 |
['C++', 'Java', 'Python3', 'JavaScript']
| 2 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Python3 || 13 lines, top-down dp, w/ example || 99% / 91%
|
python3-13-lines-top-down-dp-w-example-9-5byc
|
Here's an explanation by example.The plan is to use dynamic programming by overwriting coins with tuples each of length three, representing the the best values
|
Spaulding_
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-15T17:41:59.265723+00:00
|
2025-01-15T17:49:12.423370+00:00
| 127 | false |
Here's an explanation by example.
The plan is to use dynamic programming by overwriting *coins* with tuples each of length three, representing the the best values for each of three states, in which the number of unused *neutralizations* is zero, one, or two, respectively.
We use Problem 1 in the description:
```
[[0, 1, -1],
coins = [1, -2, 3],
[2, -3, 4]]
```
1. We initialize the upper-left corner with its tuple:
```
[[(0, 0, 0), 1, -1],
coins = [ 1, -2, 3],
[ 2, -3, 4]]
```
2. We complete the first row using the function *dp*:
```
[[(0, 0, 0), (1, 1, 1), (1, 1, 0)],
coins = [ 1, -2, 3 ],
[ 2, -3, 4]]
```
3. We use *dp* to complete the modification of *coins*
```
[[(0, 0, 0), (1, 1, 1), (1, 1, 0)],
coins = [(1, 1, 1), (1, 1, -1), (4, 4, 3)],
[(3, 3, 3), (3, 3, 0), (8, 8, 7) <-- coins[-1][-1]]]
```
4. We return the maximum value of `coins[-1][-1]`.
```
return max((8, 8, 7)) = 8
```
____
Here's the code:
```python3 []
class Solution:
def maximumAmount(self, coins: List[List[int]]) -> int:
dp = lambda v, x: (max(v + x[0], x[1]), max(v + x[1], x[2]), v + x[2])
m, n = len(coins), len(coins[0])
coins[0][0] = (0, 0, coins[0][0]) # <-- 1)
for col in range(1,n): # <-- 2)
coins[0][col] = dp(coins[0][col], coins[0][col-1])
for row in range(1,m): # <-- 3)
coins[row][0] = dp(coins[row][0], coins[row-1][0])
for col in range(1,n):
uppr0, uppr1, uppr2 = coins[row-1][col]
left0, left1, left2 = coins[row][col-1]
best = (max(uppr0, left0), max(uppr1, left1), max(uppr2, left2))
coins[row][col] = dp(coins[row][col], best)
return max(coins[-1][-1]) # <-- 4)
```
[https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn/submissions/1509589747/](https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn/submissions/1509589747/)
I could be wrong, but I think that time complexity is *O*(*MN*) and space complexity is *O*(*MN*), in which *M, N* ~ `m, n`.
| 10 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Memoization, Simple Approach
|
memoization-simple-approach-by-arpan_bar-f138
|
IntuitionMoving right or down and returning max from them gives intuition for DP.Complexity
Time complexity:O(nxm)
Space complexity:O(nxm)
Code
|
arpan_bareja
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T04:02:12.963997+00:00
|
2025-01-12T04:02:12.963997+00:00
| 2,331 | false |
# Intuition
Moving right or down and returning max from them gives intuition for DP.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:O(nxm)
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:O(nxm)
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
long long dp[501][501][3] ;
bool visited[501][501][3] ;
long long helper(int i , int j , int count , vector<vector<int>> &coins) {
int n = coins.size() , m = coins[0].size() ;
if( i == coins.size()-1 && j == coins[0].size()-1 ) {
if( coins[i][j] < 0 && count > 0 ) return 0 ;
return coins[i][j] ;
}
if( i >= coins.size() || j >= coins[0].size() ) return INT_MIN ;
if( visited[i][j][count] ) return dp[i][j][count] ;
long long right = INT_MIN , down = INT_MIN;
right = coins[i][j] + helper(i , j+1 , count , coins) ;
if( count > 0 && coins[i][j] < 0 ) {
right = max(right , helper(i , j +1 , count-1 , coins)) ;
}
down = helper(i+1 , j , count , coins) + coins[i][j] ;
if( count > 0 && coins[i][j] < 0 )
down = max(down , helper(i+1 , j , count -1 , coins)) ;
visited[i][j][count] = 1 ;
return dp[i][j][count] = max(right , down) ;
}
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
memset(dp , -1 , sizeof(dp)) ;
memset(visited , 0 , sizeof(visited)) ;
return helper(0 , 0 , 2 , coins) ;
}
};
```
| 10 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 2 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
C++ Solution Beats 100%
|
c-solution-beats-100-by-fjaksfjklds-bmfa
|
IntuitionThis solution uses a 3D dynamic programming (DP) approach to maximize the amount of coins the robot can collect while neutralizing at most 2 cells with
|
fjaksfjklds
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T14:43:54.291206+00:00
|
2025-01-12T14:52:36.201771+00:00
| 570 | false |
# Intuition
This solution uses a 3D dynamic programming (DP) approach to maximize the amount of coins the robot can collect while neutralizing at most 2 cells with negative coins.
States:
dp[k][i][j] represents the maximum coins collected when reaching cell (i, j) with k remaining neutralizations available.
k = 2: The robot hasn't neutralized any cells yet.
k = 1: The robot has neutralized 1 cell.
k = 0: The robot has exhausted its neutralization ability.
Transitions:
Either to the right or bottom
From the top (dp[k][i-1][j]) or left (dp[k][i][j-1]) cells, add the coins at (i, j).
If the current cell has negative coins and k > 0, use a neutralization to keep the value unchanged.
Base Case:
At the starting point (0, 0):
dp[0][0][0] = coins[0][0] (if no neutralization is used).
Adjust states for negative coins accordingly.
Result:
The answer is the maximum value among dp[0][n-1][m-1], dp[1][n-1][m-1], and dp[2][n-1][m-1], which represent all possible scenarios of neutralization usage.
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int n = (int)coins.size(), m = (int)coins[0].size();
long dp[3][n][m];
for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
dp[k][i][j] = -1e9;
}
}
}
dp[0][0][0] = coins[0][0];
if (coins[0][0] < 0) {
dp[1][0][0] = 0;
dp[2][0][0] = 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
for (int k = 2; k >= 0; k--) {
if (i == 0 && j == 0) continue;
if (i > 0) {
dp[k][i][j] = max(dp[k][i][j], dp[k][i - 1][j] + coins[i][j]);
if (coins[i][j] < 0 && k > 0) {
dp[k][i][j] = max(dp[k][i][j], dp[k - 1][i - 1][j]);
}
}
if (j > 0) {
dp[k][i][j] = max(dp[k][i][j], dp[k][i][j - 1] + coins[i][j]);
if (coins[i][j] < 0 && k > 0) {
dp[k][i][j] = max(dp[k][i][j], dp[k - 1][i][j - 1]);
}
}
}
}
}
return max({dp[0][n - 1][m - 1], dp[1][n - 1][m - 1], dp[2][n - 1][m - 1]});
}
};
```
| 7 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C++']
| 2 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
3418. Maximum Amount of Money Robot Can Earn | DP - Memoization Approach Explained ✨✅
|
3418-maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-e-re89
|
Navigate the Coin Grid: Maximize Profits with Smart Moves!Problem IntuitionThe problem involves navigating an n X m grid where each cell contains coins (positiv
|
ayushkumar08032003
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T04:49:41.139576+00:00
|
2025-01-12T16:53:51.251931+00:00
| 1,402 | false |
# **Navigate the Coin Grid: Maximize Profits with Smart Moves!**
### **Problem Intuition**
The problem involves navigating an n X m grid where each cell contains coins (positive or negative). The robot starts from the **top-left corner** and must reach the **bottom-right corner**, moving **either right or down**. Key challenges include:
1. **Maximizing total coins** while traveling through the grid.
2. **Neutralizing robbers** in at most 2 cells to avoid losing coins.
3. Using **Dynamic Programming (DP)** to systematically explore and optimize paths.
The solution requires us to carefully decide:
- **When to neutralize robbers**, using the two opportunities available.
- **Which path (down/right)** gives the maximum total coins.
---
### **Approach**
To solve the problem efficiently, we use **Dynamic Programming with recursion**. Let's break this approach into clear steps:
#### **Step 1: State Representation**
Define a function `help(i, j, rem, n, m, coins, dp)`:
- \(i, j\): Current cell position.
- \(rem\): Remaining opportunities to neutralize robbers.
- \(n, m\): Grid dimensions.
- `coins`: The grid with coin values.
- `dp[i][j][rem]`: Memoization table that stores the maximum coins obtainable from position \((i, j)\) with `rem` robber-neutralization opportunities left.
#### **Step 2: Recursive Formula**
1. **Base Case:**
- If \((i, j) = (n-1, m-1)\) (bottom-right corner):
- Return the coin value of the cell, adjusting for robbers if needed.
- If out of bounds, return \(-\infty\) to indicate an invalid path.
2. **Recursive Cases:**
- Explore **right** and **down** paths from the current cell:
- **If the cell has a robber (\(coins[i][j] < 0\))**, decide:
- Use one neutralization opportunity (if available) and ignore the loss.
- Accept the loss without neutralizing.
- Add the current cell value to the results of the right or down path.
- Store and return the maximum of the two options.
#### **Step 3: DP Table Initialization**
Use a 3D DP table, `dp[n][m][3]`:
- \(n, m\): Grid dimensions.
- 3 layers for `rem` values (0, 1, or 2 neutralizations available).
#### **Step 4: Optimization**
- **Memoization:** Avoid recomputing states by caching results in the DP table.
- **Iterate efficiently** through valid paths, minimizing redundant checks.
---
### **Code Explanation**
```cpp []
#define vi vector<int>
#define vvi vector<vi>
class Solution {
public:
// Helper function to calculate max coins from (i, j) with 'rem' neutralizations left
int help(int i, int j, int rem, int n, int m, vvi& coins, vector<vvi>& dp) {
// Base case: reached bottom-right corner
if (i == n - 1 && j == m - 1) {
if (coins[i][j] < 0) {
// If this is a robber cell, neutralize if rem > 0
return (rem > 0) ? 0 : coins[i][j];
} else {
return coins[i][j];
}
}
// Boundary check: If out of bounds, return -infinity
if (i >= n || j >= m)
return -1e9;
// If already computed, return cached result
if (dp[i][j][rem] != INT_MIN)
return dp[i][j][rem];
int right = -1e9, down = -1e9;
// If current cell is a robber, consider neutralization options
if (coins[i][j] < 0) {
if (rem > 0) { // Neutralize the robber
right = help(i, j + 1, rem - 1, n, m, coins, dp);
down = help(i + 1, j, rem - 1, n, m, coins, dp);
}
}
// Take the current cell value + max of right/down without neutralization
right = max(right, coins[i][j] + help(i, j + 1, rem, n, m, coins, dp));
down = max(down, coins[i][j] + help(i + 1, j, rem, n, m, coins, dp));
// Store and return the result
return dp[i][j][rem] = max(right, down);
}
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int n = coins.size(), m = coins[0].size();
// Initialize 3D DP table with INT_MIN
vector<vvi> dp(n + 1, vvi(m + 1, vi(3, INT_MIN)));
// Start recursion from the top-left corner with 2 neutralizations available
return help(0, 0, 2, n, m, coins, dp);
}
};
```
---
### **Complexity Analysis**
1. **Time Complexity:**
- O(n⋅m⋅3)=O(n⋅m): We compute for every cell (n⋅m) and for 3 neutralization states.
- Memoization avoids redundant calculations.
2. **Space Complexity:**
- O(n⋅m⋅3)=O(n⋅m): Space for the 3D DP table.
---
## **PLEASE UPVOTE IF YOU LIKED IT ✅**
| 6 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java']
| 4 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
DP on Grid (3D) | Recursive | Memoization | Tabulation | Clean and Concise
|
dp-on-grid-3d-recursive-memoization-by-l-2s6f
|
CodeEdit : My python solution was AC at first but later turned TLE for using -1. So i changed it to inf
|
lokeshwar777
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T04:03:48.190237+00:00
|
2025-01-15T17:53:42.003362+00:00
| 1,029 | false |
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def maximumAmount(self, coins: List[List[int]]) -> int:
m=len(coins)
n=len(coins[0])
inf=float('inf')
dp=[[[inf]*3 for _ in range(n)]for _ in range(m)]
def solve(i,j,k):
if i>=m or j>=n or k<0:return -inf
if i==m-1 and j==n-1:
if coins[i][j]<0 and k>0:dp[i][j][k]=0
else: dp[i][j][k]=coins[i][j]
return dp[i][j][k]
if dp[i][j][k]!=inf:return dp[i][j][k]
ans=coins[i][j]+max(solve(i+1,j,k),solve(i,j+1,k))
if coins[i][j]<0:
ans=max(ans,max(solve(i+1,j,k-1),solve(i,j+1,k-1)))
dp[i][j][k]=ans
return dp[i][j][k]
return solve(0,0,2)
```
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
const int inf=1e9;
int m,n;
vector<vector<int>>vec;
// int dp[501][501][3]={inf};
// bottom up (recursion and memoisation)
// // using array for memoisation
// int solve(int i,int j,int k){
// if(i>=m||j>=n||k<0)return -inf;
// if(i==m-1&&j==n-1)return dp[i][j][k]=(vec[i][j]<0&&k>0)?0:vec[i][j];
// if(dp[i][j][k]!=inf)return dp[i][j][k];
// int ans=vec[i][j]+max(solve(i+1,j,k),solve(i,j+1,k));
// if(vec[i][j]<0)ans=max(ans,max(solve(i+1,j,k-1),solve(i,j+1,k-1)));
// return dp[i][j][k]=ans;
// };
// // using vector for memoisation
// int solve(int i,int j,int k,vector<vector<vector<int>>>&dp){
// if(i>=m||j>=n||k<0)return -inf;
// if(i==m-1&&j==n-1)return dp[i][j][k]=(vec[i][j]<0&&k>0)?0:vec[i][j];
// if(dp[i][j][k]!=inf)return dp[i][j][k];
// int ans=vec[i][j]+max(solve(i+1,j,k,dp),solve(i,j+1,k,dp));
// if(vec[i][j]<0)ans=max(ans,max(solve(i+1,j,k-1,dp),solve(i,j+1,k-1,dp)));
// return dp[i][j][k]=ans;
// };
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
m=coins.size();n=coins[0].size();vec=coins;
vector<vector<vector<int>>>dp(m+1,vector<vector<int>>(n+1,vector<int>(3,-inf)));
// vector<vector<vector<int>>>dp(m+1,vector<vector<int>>(n+1,vector<int>(3,inf)));
// for(int i=0;i<m;++i)for(int j=0;j<n;++j)for(int k=0;k<3;++k)dp[i][j][k]=inf;
// return solve(0,0,2);
// top down (tabulation)
for(int i=m-1;i>=0;--i){
for(int j=n-1;j>=0;--j){
for(int k=0;k<3;++k){
if(i==m-1&&j==n-1){dp[i][j][k]=(coins[i][j]<0&&k>0)?0:coins[i][j];continue;}
int ans=coins[i][j]+max(dp[i+1][j][k],dp[i][j+1][k]);
if(coins[i][j]<0&&k>0)ans=max(ans,max(dp[i+1][j][k-1],dp[i][j+1][k-1]));
dp[i][j][k]=ans;
}
}
}
return dp[0][0][2];
}
};
```
Edit : My python solution was AC at first but later turned TLE for using `-1`. So i changed it to `inf`
| 6 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization', 'C++', 'Python3']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
✅ ⟣ | Memoization | 3D DP | Top Down Approach | CPP Solution | Simple Approach | Clean Code
|
memoization-3d-dp-top-down-approach-cpp-gfq0n
|
IntuitionBasic Recursion according to stepsApproachUsed Top Down ApproachCode
|
MinavKaria
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T04:12:48.692892+00:00
|
2025-01-12T04:12:48.692892+00:00
| 157 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
Basic Recursion according to steps
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
Used Top Down Approach
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int solve(vector<vector<int>>& coins, int row, int col, int neutralize,
vector<vector<vector<int>>>& dp) {
int n = coins.size();
int m = coins[0].size();
if (row >= n || col >= m) {
return INT_MIN;
}
if (row == n - 1 && col == m - 1) {
if (coins[row][col] < 0 && neutralize > 0) {
return 0;
}
return coins[row][col];
}
if (dp[row][col][neutralize] != INT_MIN) {
return dp[row][col][neutralize];
}
int moveRight = solve(coins, row, col + 1, neutralize, dp);
int moveDown = solve(coins, row + 1, col, neutralize, dp);
int profit = coins[row][col] + max(moveRight, moveDown);
if (coins[row][col] < 0 && neutralize > 0) {
profit =
max(profit,
0 + max(solve(coins, row, col + 1, neutralize - 1, dp),
solve(coins, row + 1, col, neutralize - 1, dp)));
}
return dp[row][col][neutralize] = profit;
}
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int n = coins.size();
int m = coins[0].size();
int neutralize = 2;
vector<vector<vector<int>>> dp(
n, vector<vector<int>>(m, vector<int>(neutralize + 1, INT_MIN)));
return solve(coins, 0, 0, neutralize, dp);
}
};
```
| 5 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
DP Approach || 3DP Problem
|
dp-approach-3dp-problem-by-movazed-aimb
|
IntuitionThe problem involves finding the maximum amount of coins that can be collected while moving through a 2D grid. The grid contains positive and negative
|
Movazed
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T04:06:45.751884+00:00
|
2025-01-12T04:06:45.751884+00:00
| 418 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
The problem involves finding the maximum amount of coins that can be collected while moving through a 2D grid. The grid contains positive and negative values, and we are allowed to skip up to two negative values. The goal is to maximize the sum of the collected coins while adhering to the constraints.
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
1. **Dynamic Programming (DP) Setup**:
- Use a 3D DP array `dp[i][j][k]` where:
- `i` and `j` represent the current cell in the grid.
- `k` represents the number of negative values skipped so far (0, 1, or 2).
- Initialize the DP array with `INT_MIN` to represent unreachable states.
2. **Base Case**:
- Start at the top-left corner of the grid. If the cell contains a positive value, initialize `dp[0][0][0]` with that value. If it contains a negative value, initialize `dp[0][0][1]` with 0 (indicating one skip).
3. **DP Transition**:
- Traverse the grid row-wise and column-wise.
- For each cell, update the DP values based on the values from the left cell (`dp[i][j-1][k]`) and the top cell (`dp[i-1][j][k]`).
- If the current cell contains a positive value, add it to the DP value.
- If the current cell contains a negative value, update the DP value for the next skip count (`k + 1`).
4. **Result Extraction**:
- The result is the maximum value among `dp[m-1][n-1][k]` for `k = 0, 1, 2`.
# Complexity
- **Time complexity**: $$O(m \times n \times 3)$$
- We traverse the entire grid of size `m x n` and update the DP array for 3 possible skip counts.
- **Space complexity**: $$O(m \times n \times 3)$$
- The DP array requires space proportional to `m x n x 3`.
# Code
```cpp
#define ll long long
#define vvvi vector<vector<vector<int>>>
#define vvi vector<vector<int>>
#define vi vector<int>
#define ll long long
class Solution {
public:
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
ll m = coins.size();
ll n = coins[0].size();
// Initialize DP array with INT_MIN
vvvi dp(m, vvi(n, vi(3, INT_MIN)));
// Base case: starting cell
dp[0][0][0] = coins[0][0];
if (coins[0][0] < 0) {
dp[0][0][1] = 0;
}
// Fill the first row
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k <= 2; k++) {
if (dp[0][j - 1][k] == INT_MIN) continue;
if (coins[0][j] >= 0) {
dp[0][j][k] = max(dp[0][j][k], dp[0][j - 1][k] + coins[0][j]);
} else {
dp[0][j][k] = max(dp[0][j][k], dp[0][j - 1][k] + coins[0][j]);
}
if (k < 2 && coins[0][j] < 0) {
dp[0][j][k + 1] = max(dp[0][j][k + 1], dp[0][j - 1][k]);
}
}
}
// Fill the first column
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
for (int k = 0; k <= 2; k++) {
if (dp[i - 1][0][k] == INT_MIN) continue;
if (coins[i][0] >= 0) {
dp[i][0][k] = max(dp[i][0][k], dp[i - 1][0][k] + coins[i][0]);
} else {
dp[i][0][k] = max(dp[i][0][k], dp[i - 1][0][k] + coins[i][0]);
}
if (k < 2 && coins[i][0] < 0) {
dp[i][0][k + 1] = max(dp[i][0][k + 1], dp[i - 1][0][k]);
}
}
}
// Fill the rest of the grid
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k <= 2; k++) {
if (dp[i][j - 1][k] != INT_MIN) {
if (coins[i][j] >= 0) {
dp[i][j][k] = max(dp[i][j][k], dp[i][j - 1][k] + coins[i][j]);
} else {
dp[i][j][k] = max(dp[i][j][k], dp[i][j - 1][k] + coins[i][j]);
}
if (k < 2 && coins[i][j] < 0) {
dp[i][j][k + 1] = max(dp[i][j][k + 1], dp[i][j - 1][k]);
}
}
if (dp[i - 1][j][k] != INT_MIN) {
if (coins[i][j] >= 0) {
dp[i][j][k] = max(dp[i][j][k], dp[i - 1][j][k] + coins[i][j]);
} else {
dp[i][j][k] = max(dp[i][j][k], dp[i - 1][j][k] + coins[i][j]);
}
if (k < 2 && coins[i][j] < 0) {
dp[i][j][k + 1] = max(dp[i][j][k + 1], dp[i - 1][j][k]);
}
}
}
}
}
// Find the maximum result among the last cell's DP values
int result = INT_MIN;
for (int k = 0; k <= 2; k++) {
result = max(result, dp[m - 1][n - 1][k]);
}
return result;
}
};
| 5 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
✅ ⟣ Java Solution ⟢
|
java-solution-by-harsh__005-bwa0
|
Code
|
Harsh__005
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T04:02:00.140274+00:00
|
2025-01-12T04:02:00.140274+00:00
| 728 | false |
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
private int solve(int[][] coins, int r, int c, int i, int j, int skip, int[][][] dp) {
if(i==r-1 && j == c-1) {
if(coins[i][j] < 0 && skip > 0) return 0;
return coins[i][j];
}else if(dp[i][j][skip] != Integer.MIN_VALUE) return dp[i][j][skip];
int val1 = Integer.MIN_VALUE, val2 = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
if(i < r-1) {
if(coins[i][j] < 0 && skip>0) {
val1 = Math.max(solve(coins, r, c, i+1, j, skip-1, dp), coins[i][j] + solve(coins, r, c, i+1, j, skip, dp));
} else {
val1 = coins[i][j] + solve(coins, r, c, i+1, j, skip, dp);
}
}
if(j < c-1) {
if(coins[i][j] < 0 && skip>0) {
val2 = Math.max(solve(coins, r, c, i, j+1, skip-1, dp), coins[i][j] + solve(coins, r, c, i, j+1, skip, dp));
} else {
val2 = coins[i][j] + solve(coins, r, c, i, j+1, skip, dp);
}
}
return dp[i][j][skip] = Math.max(val1, val2);
}
public int maximumAmount(int[][] coins) {
int r = coins.length, c = coins[0].length;
int dp[][][] = new int[r][c][3];
for(int arr1[][]: dp) {
for(int arr2[] : arr1) Arrays.fill(arr2, Integer.MIN_VALUE);
}
return solve(coins, r, c, 0, 0, 2, dp);
}
}
```
| 5 | 0 |
['Java']
| 1 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Java Solution | Easy to Understand | Beats 100% | Clean Code
|
java-solution-easy-to-understand-beats-1-s786
|
IntuitionKeep calculating the maximum coins collected by going through the grid ans skip negative coins when allowed.Approachuse a 3D dynamic programming table
|
rizbanul08
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-13T01:04:19.912386+00:00
|
2025-01-13T01:08:30.595294+00:00
| 338 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
Keep calculating the maximum coins collected by going through the grid ans skip negative coins when allowed.
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
use a 3D dynamic programming table to store the results for each cell and the remaining skips.
# Complexity
- Time complexity: O(m * n * 3)
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity: O(m * n * 3)
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
public int solve(int i, int j, int k, Integer[][][] dp, int[][] coins) {
if (i == coins.length || j == coins[0].length) {
return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
if (i == coins.length - 1 && j == coins[0].length - 1) {
if(coins[i][j] < 0 && k < 2){
return 0;
}
return coins[i][j];
}
if (dp[i][j][k] != null) {
return dp[i][j][k];
}
int down = solve(i + 1, j, k, dp, coins);
int right = solve(i, j + 1, k, dp, coins);
int take = coins[i][j] + Math.max(down, right);
int not = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
if (coins[i][j] < 0 && k < 2) {
int skipDown = solve(i + 1, j, k + 1, dp, coins);
int skipRight = solve(i, j + 1, k + 1, dp, coins);
not = Math.max(skipDown, skipRight);
}
return dp[i][j][k] = Math.max(take, not);
}
public int maximumAmount(int[][] coins) {
int m = coins.length;
int n = coins[0].length;
Integer dp[][][] = new Integer[m][n][3];
return solve(0, 0, 0, dp, coins);
}
}
```
| 4 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'Java']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
3D DP with clean and short code
|
3d-dp-with-clean-and-short-code-by-andy0-3ev6
|
Intuitiondp[i][j][k] means maximum coins robot can get at position (i, j) with status k neutralize left.ApproachComplexity
Time complexity: O(mn)
Space complex
|
andy022419942004
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T09:02:47.385258+00:00
|
2025-01-12T09:02:47.385258+00:00
| 205 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
dp[i][j][k] means maximum coins robot can get at position (i, j) with status k neutralize left.
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity: O(mn)
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity: O(mn)
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def maximumAmount(self, coins: List[List[int]]) -> int:
dp = [[[float('-inf') for i in range(3)] for _ in range(len(coins[0])+1)] for _ in range(len(coins)+1)]
dp[0][1][0] = 0
dp[0][1][1] = 0
dp[0][1][2] = 0
dp[1][0][0] = 0
dp[1][0][1] = 0
dp[1][0][2] = 0
for i in range(1, len(dp)):
for j in range(1, len(dp[0])):
dp[i][j][2] = max(dp[i][j-1][2], dp[i-1][j][2]) + coins[i-1][j-1] # no use neutralize
dp[i][j][1] = max(dp[i][j-1][1] + coins[i-1][j-1], dp[i-1][j][1] + coins[i-1][j-1], # no use neutralize
dp[i][j-1][2], dp[i-1][j][2]) # use neutralize
dp[i][j][0] = max(dp[i][j-1][0] + coins[i-1][j-1], dp[i-1][j][0] + coins[i-1][j-1], # no use neutralize
dp[i][j-1][1], dp[i-1][j][1]) # use neutralize
return max(dp[-1][-1])
```
| 4 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 1 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Maximizing Coin Collection in a Grid with Limited Negative Neutralization | Recursion + Memoization
|
maximizing-coin-collection-in-a-grid-wit-8x53
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
O(m * n * k)
m, n are the dimensions of the grid.
k is the maximum value of canNeutralize (here, 2).
Space complexi
|
Utsav_K
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T04:49:58.967432+00:00
|
2025-01-12T04:49:58.967432+00:00
| 600 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(m * n * k)
m, n are the dimensions of the grid.
k is the maximum value of canNeutralize (here, 2).
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
Space for the 3D DP table = O(m * n * k).
Recursion stack space = O(m + n) (in the worst case for the grid traversal).
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int solve(int i, int j, int canNeutralize, vector<vector<int>>& coins, vector<vector<vector<int>>>& dp) {
int m = coins.size();
int n = coins[0].size();
if (i >= m || j >= n) return -1000000;
if (i == m - 1 && j == n - 1) {
return (coins[i][j] < 0 && canNeutralize > 0) ? 0 : coins[i][j];
}
if (dp[i][j][canNeutralize] != -1) {
return dp[i][j][canNeutralize];
}
int right = -1000000, down = -1000000;
if (coins[i][j] < 0) {
if (canNeutralize > 0) {
right = solve(i, j + 1, canNeutralize - 1, coins, dp);
down = solve(i + 1, j, canNeutralize - 1, coins, dp);
}
right = max(right, solve(i, j + 1, canNeutralize, coins, dp) + coins[i][j]);
down = max(down, solve(i + 1, j, canNeutralize, coins, dp) + coins[i][j]);
} else {
right = solve(i, j + 1, canNeutralize, coins, dp) + coins[i][j];
down = solve(i + 1, j, canNeutralize, coins, dp) + coins[i][j];
}
dp[i][j][canNeutralize] = max(right, down);
return dp[i][j][canNeutralize];
}
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int m = coins.size();
int n = coins[0].size();
vector<vector<vector<int>>> dp(m, vector<vector<int>>(n, vector<int>(3, -1)));
return solve(0, 0, 2, coins, dp);
}
};
```
| 4 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 2 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Simple Python solution
|
simple-python-solution-by-baaqar-007-4jon
|
IntuitionImagine a robot that wants to collect the maximum coins while moving from the top-left to the bottom-right of a grid. Some cells have robbers that stea
|
Baaqar-007
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T04:08:14.985787+00:00
|
2025-01-14T16:53:53.288559+00:00
| 641 | false |
# Intuition
Imagine a robot that wants to collect the maximum coins while moving from the top-left to the bottom-right of a grid. Some cells have robbers that steal coins, but the robot can neutralize up to two robbers during its journey. We need a way to track the robot's path and decide when to neutralize robbers to get the best outcome.
# Approach
1. Use a dynamic programming (DP) table where `dp[i][j][k]` represents the maximum coins collected when reaching cell `(i, j)` with `k` neutralizations used.
2. Start at the top-left corner, initializing the DP table based on whether the starting cell has a robber.
3. Fill the DP table by considering two possible moves to each cell: coming from the top or from the left.
- If the current cell is positive, add its value to the previous best path.
- If the cell is negative (a robber), decide whether to neutralize it (if neutralizations are left) or not.
4. At the end, look at the bottom-right corner of the grid and find the maximum coins collected with up to 2 neutralizations.
# Complexity
- Time complexity: $$O(m \times n \times 3)$$, where $$m$$ is the number of rows, $$n$$ is the number of columns, and we check up to 3 neutralizations for each cell.
- Space complexity: $$O(m \times n \times 3)$$, as we store the DP table with 3 states for each cell.
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def maximumAmount(self, coins: List[List[int]]) -> int:
m, n = len(coins), len(coins[0])
dp = [[[float('-inf')] * 3 for _ in range(n)] for _ in range(m)]
for k in range(3):
dp[0][0][k] = 0 if coins[0][0] < 0 and k > 0 else coins[0][0]
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
for k in range(3):
if i == 0 and j == 0:
continue
gain = coins[i][j]
if i > 0:
dp[i][j][k] = max(dp[i][j][k], dp[i - 1][j][k] + gain)
if k > 0 and gain < 0:
dp[i][j][k] = max(dp[i][j][k], dp[i - 1][j][k - 1])
if j > 0:
dp[i][j][k] = max(dp[i][j][k], dp[i][j - 1][k] + gain)
if k > 0 and gain < 0:
dp[i][j][k] = max(dp[i][j][k], dp[i][j - 1][k - 1])
return max(dp[m - 1][n - 1])
```
As pointed out by [Jojo](https://leetcode.com/u/wxy0925/), the return statement could be updated to `dp[-1][-1][-1]` or `dp[m-1][n-1][2]`.
| 4 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Python3']
| 1 |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.