question_slug
stringlengths 3
77
| title
stringlengths 1
183
| slug
stringlengths 12
45
| summary
stringlengths 1
160
⌀ | author
stringlengths 2
30
| certification
stringclasses 2
values | created_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| updated_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| hit_count
int64 0
10.6M
| has_video
bool 2
classes | content
stringlengths 4
576k
| upvotes
int64 0
11.5k
| downvotes
int64 0
358
| tags
stringlengths 2
193
| comments
int64 0
2.56k
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
💢Faster✅💯 Lesser C++✅Python3🐍✅Java✅C✅Python🐍✅C#✅💥🔥💫Explained☠💥🔥 Beats 💯
|
faster-lesser-cpython3javacpythoncexplai-4zh8
|
IntuitionApproach
JavaScript Code --> https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn/submissions/1506106301
C++ Code --> https://leetcode.
|
Edwards310
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T11:18:05.472537+00:00
|
2025-01-13T08:37:30.857379+00:00
| 234 | false |

# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
- ***JavaScript Code -->*** https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn/submissions/1506106301
- ***C++ Code -->*** https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn/submissions/1506058939
- ***Python3 Code -->*** https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn/submissions/1506085036
- ***Java Code -->*** https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn/submissions/1506068518
- ***C Code -->*** https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn/submissions/1506106171
- ***Python Code -->*** https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn/submissions/1506085927
- ***C# Code -->*** https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn/submissions/1506106905
- ***Go Code -->*** https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn/submissions/1506106604
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(N∗M∗3)
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(N∗M∗3)
# Code

| 3 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C', 'Matrix', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'Go', 'Python3', 'JavaScript', 'C#']
| 2 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Memoization | 3D DP | Striver Based approach | T.C=(MxN ) S.C=(MxN)
|
memoization-3d-dp-striver-based-approach-frtg
|
EditInitialize your DP with -1e8 or (less than -1e3) because -1 could be
the possible solution in pathIntuitionApproachIn dp either you go top down(Memoization)
|
High_Codee
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T05:45:44.249876+00:00
|
2025-01-14T06:40:44.545626+00:00
| 264 | false |
# **Edit**
Initialize your DP with -1e8 or (less than -1e3) because -1 could be
the possible solution in path
# Intuition
<!-- -->After reading problem i realised this is dp question because i had done similar type question earlier
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
In dp either you go top down(Memoization) or bottom up(Tabulation)
I did this with Memo.. starting from index (m-1,n-1 )
Now i explore all path if coins>=0 else coins<0
Also you have to maintain count variable so 3d dp i used
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->O(M*N)
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->O(M*N)
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int solve(int row,int col, vector<vector<vector<int>>>&dp,vector<vector<int>>& coins,int count)
{
if(row==0 && col==0)
{
if(coins[row][col]>=0)
{
return coins[row][col];
}
else
{
if(count>0)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
return coins[row][col];
}
}
}
if(row<0 || col<0 )
{
return -1e8;
}
if(dp[row][col][count]!=-1e8)
{
return dp[row][col][count];
}
int up=0,left=0;
int ans=0;
if(coins[row][col]<0)
{
if(count>0)
{
int notneutralize=coins[row][col]; //either not neutralize
up=solve(row-1,col,dp,coins,count);
left=solve(row,col-1,dp,coins,count);
int neutralize=0; //or neutralize
int up1=solve(row-1,col,dp,coins,count-1);
int left1=solve(row,col-1,dp,coins,count-1);
ans=max(notneutralize+max(up,left),max(up1,left1));
}
else
{
int notneutralize=coins[row][col]; //either not neutralize
up=solve(row-1,col,dp,coins,count);
left=solve(row,col-1,dp,coins,count);
ans=notneutralize+max(up,left);
}
dp[row][col][count]=ans;
}
if(coins[row][col]>=0)
{
up=solve(row-1,col,dp,coins,count);
left=solve(row,col-1,dp,coins,count);
dp[row][col][count]=coins[row][col]+max(up,left);
}
return dp[row][col][count];
}
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int m=coins.size();
int n=coins[0].size();
vector<vector<vector<int>>>dp(m,vector<vector<int>>(n,vector<int>(3,-1e8)));
return solve(m-1,n-1,dp,coins,2);
}
};
```
| 3 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 2 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Check out Easy-to-Understand Simple Memoization Approach! 🚀
|
dont-miss-out-easy-to-understand-simple-ilfur
|
Code
|
yogesh_1___
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T04:56:22.235452+00:00
|
2025-01-12T04:58:54.520340+00:00
| 194 | false |
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
// Recursive helper function with memoization
int func(int i, int j, vector<vector<int>>& coins,
vector<vector<vector<int>>>& dp, int nutralize) {
// Base case: reached the starting cell (0,0)
if (i == 0 && j == 0) {
// If the starting cell is negative and neutralizations are
// available, neutralize it
if (coins[i][j] < 0 && nutralize > 0)
return 0;
return coins[i][j]; // Otherwise, take its value
}
// Out of bounds check
if (i < 0 || j < 0)
return INT_MIN;
// Return cached result if already computed
if (dp[i][j][nutralize] != -1)
return dp[i][j][nutralize];
// Option 1: Move from top or left, adding the current coin's value
int fc = coins[i][j] + max(func(i - 1, j, coins, dp, nutralize),
func(i, j - 1, coins, dp, nutralize));
// Option 2: Neutralize the current negative coin if possible
int sc = INT_MIN;
if (nutralize > 0 && coins[i][j] < 0)
sc = max(
func(i - 1, j, coins, dp, nutralize - 1),
func(i, j - 1, coins, dp,
nutralize - 1)); // Move without adding the negative coin
// Store and return the best option between
return dp[i][j][nutralize] = max(fc, sc);
}
// Main function to initiate the process
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int n = coins.size(); // Number of rows
int m = coins[0].size(); // Number of columns
// 3D DP array for memoization: dp[i][j][neutralize]
vector<vector<vector<int>>> dp(
n, vector<vector<int>>(m, vector<int>(3, -1)));
// Start from the bottom-right cell with 2 neutralizations allowed
return func(n - 1, m - 1, coins, dp, 2);
}
};
```

| 3 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 1 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Easy C++ solution || Leetcode Weekly Contest || Beats 95% ||
|
easy-c-solution-leetcode-weekly-contest-0z8ax
|
IntuitionThe code uses dynamic programming to find the maximum coins a robot can collect while moving from the top-left to the bottom-right of the grid. It main
|
Abhyanand_Sharma
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T04:33:10.668271+00:00
|
2025-01-12T04:33:10.668271+00:00
| 141 | false |
# Intuition
The code uses dynamic programming to find the maximum coins a robot can collect while moving from the top-left to the bottom-right of the grid. It maintains a 3D DP table, where `dp[i][j][k]` represents the maximum coins collected at cell `(i, j)` with `k` neutralizations used. At each cell, the robot can either move from the left or from above, and if the cell contains a robber (negative value), it may neutralize the robbery (if it has unused neutralizations). The solution iterates through the grid and tracks the maximum coins possible while considering neutralizations and path choices.<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
1. **🔍 Initialize the DP Table**:
Create a 3D DP table `dp[i][j][k]` to track the maximum coins collected at cell `(i, j)` with `k` neutralizations used.
2. **🚶♂️ Start from the Top-left**:
Set the starting point `(0, 0)` with the coins available or 0 if it's a robber. Initialize all other cells as negative infinity (`INT_MIN`).
3. **⬇️ Move Down and → Move Right**:
Iterate through each cell in the grid from left to right and top to bottom.
4. **💰 Update DP for Positive Coins**:
If the current cell has coins (positive value), update the DP table based on the maximum value from the top or left.
5. **💥 Neutralize Robbers**:
If the cell contains a robber (negative value), and you still have neutralizations left, use one to neutralize the robbery and update the DP table accordingly.
6. **🔄 Compare Results from Top & Left**:
For each cell, check the results from the previous cell in the row and column to choose the best path (with or without neutralization).
7. **🏁 Get the Maximum Coins**:
At the bottom-right cell `(m-1, n-1)`, get the maximum value considering all possible neutralization states (0, 1, or 2 neutralizations).<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
O(m * n)<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
O(m * n)<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int m = coins.size();
int n = coins[0].size();
vector<vector<vector<int>>> dp(m, vector<vector<int>>(n, vector<int>(3, INT_MIN)));
for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++) {
dp[0][0][k] = (coins[0][0] >= 0) ? coins[0][0] : ((k > 0) ? 0 : coins[0][0]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++) {
if (i == 0 && j == 0) continue;
int fromUp = (i > 0) ? dp[i-1][j][k] : INT_MIN;
int fromLeft = (j > 0) ? dp[i][j-1][k] : INT_MIN;
if (coins[i][j] >= 0) {
dp[i][j][k] = max(fromUp, fromLeft) + coins[i][j];
} else if (k > 0) {
int neutralize = max((i > 0 ? dp[i-1][j][k-1] : INT_MIN),
(j > 0 ? dp[i][j-1][k-1] : INT_MIN));
dp[i][j][k] = max(max(fromUp, fromLeft) + coins[i][j], neutralize);
} else {
dp[i][j][k] = max(fromUp, fromLeft) + coins[i][j];
}
}
}
}
return max({dp[m-1][n-1][0], dp[m-1][n-1][1], dp[m-1][n-1][2]});
}
};
```
| 3 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Depth-First Search', 'Memoization', 'Matrix', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Reccursive dp/ memoization/ Clean code
|
reccursive-dp-memoization-clean-code-by-orfpq
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity: O(m * n * 3)
Space complexity: O(m * n * 3)
UPVOTE if you found it helpfull :)
|
Ruturaj_720
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-14T10:12:20.792091+00:00
|
2025-01-14T10:12:20.792091+00:00
| 63 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->Keep calculating the maximum coins collected by going through the grid ans skip negative coins when allowed
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->use a 3D dynamic programming table to store the results for each cell and the remaining skips.
# Complexity
- Time complexity: O(m * n * 3)
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity: O(m * n * 3)
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# ___UPVOTE if you found it helpfull___ :)
```java []
class Solution {
public int solve(int[][] coins, int i, int j, int k, Integer dp[][][]) {
if (i >= coins.length || j >= coins[0].length) return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
if (i == coins.length-1 && j == coins[0].length-1) {
if (coins[i][j] < 0 && k > 0) return 0;
return coins[i][j];
}
if (dp[i][j][k] != null) return dp[i][j][k];
int skip = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int take = coins[i][j] + Math.max(solve(coins, i + 1, j, k, dp), solve(coins, i, j + 1, k, dp));
if (coins[i][j] < 0 && k > 0) {
skip = Math.max(solve(coins, i + 1, j, k - 1, dp), solve(coins, i, j + 1, k - 1, dp));
}
return dp[i][j][k] = Math.max(take, skip);
}
public int maximumAmount(int[][] coins) {
int n = coins.length, m = coins[0].length;
Integer dp[][][] = new Integer[n][m][3];
return solve(coins, 0, 0, 2, dp);
}
}
```
| 2 | 0 |
['Array', 'Math', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Depth-First Search', 'Memoization', 'Matrix', 'Java']
| 1 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Simple Solution || (Using Recursion + Memoization) ✅✅
|
simple-solution-using-recursion-memoizat-e216
|
Code
|
Abhi242
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-14T09:33:09.092199+00:00
|
2025-01-14T09:33:09.092199+00:00
| 117 | false |
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int helper(vector<vector<int>>& coins,int i,int j,int n,int m,int k,vector<vector<vector<int>>> &dp){
if(i==(n-1) && j==(m-1)){
if(k>0 && coins[i][j]<0){
return 0;
}else{
return coins[i][j];
}
}
if(dp[i][j][k]!=-pow(10,7)){
return dp[i][j][k];
}
int ans=-pow(10,7);
if(coins[i][j]<0 && k>0){
if((i+1)<n){
ans=max(ans,helper(coins,i+1,j,n,m,k-1,dp));
}
if((j+1)<m){
ans=max(ans,helper(coins,i,j+1,n,m,k-1,dp));
}
}
if((i+1)<n){
ans=max(ans,coins[i][j]+helper(coins,i+1,j,n,m,k,dp));
}
if((j+1)<m){
ans=max(ans,coins[i][j]+helper(coins,i,j+1,n,m,k,dp));
}
return dp[i][j][k]=ans;
}
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int n=coins.size();
int m=coins[0].size();
vector<vector<vector<int>>> dp(n,vector<vector<int>>(m,vector<int>(3,-pow(10,7))));
return helper(coins,0,0,n,m,2,dp);
}
};
```
| 2 | 0 |
['Recursion', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
3 approaches | Recursion -> Memoization (Top Down) -> Tabulation (Bottom Up) | RunTime Beats 100%
|
3-approaches-recursion-memoization-top-d-08gs
|
Code (Recursive)Code (Memoization) -577/578 Test cases Passed and 1 Test cases giving TLECode (Tabulation) - (All test cases passed 578/578) & Runtime 84 ms Bea
|
aayush209
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-13T19:42:33.579700+00:00
|
2025-01-13T19:45:27.248501+00:00
| 69 | false |
# Code (Recursive)
```java []
class Solution {
// RECURSIVE solution (will give TLE)
// method gives us the maximumAmount if we start at a certain row and col with 2 neutralizers
private int maximumAmountRecursive(int row, int col, int neutralizers, int[][] coins){
// out of bounds check
if(row >= coins.length || col >= coins[0].length)
return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
// bottom right corner reached
if(row == coins.length - 1 && col == coins[0].length - 1)
return coins[row][col];
int coinsAtCurrCell = coins[row][col];
// option 1 : don't neutralize
int dontNeutralize = coinsAtCurrCell +
Math.max(
maximumAmountRecursive(row, col + 1, neutralizers, coins), // move right
maximumAmountRecursive(row + 1, col, neutralizers, coins) // move down
);
// option 2 : neutralize (if possible)
int neutralize = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
if(coinsAtCurrCell < 0 && neutralizers > 0){
neutralize = Math.max(
maximumAmountRecursive(row, col + 1, neutralizers - 1, coins), // move right
maximumAmountRecursive(row + 1, col, neutralizers - 1, coins) // move down
);
}
return Math.max(dontNeutralize, neutralize);
}
public int maximumAmount(int[][] coins) {
// at every point the robot has a choice to either go right or down
// also it can neutralize atmost 2 robbers i.e. 2 neutralizations allowed
int neutralizers = 2; // given in question
// RECURSIVE
return maximumAmountRecursive(0, 0, 2, coins);
}
}
```
# Code (Memoization) -
577/578 Test cases Passed and 1 Test cases giving TLE
```java []
class Solution {
// MEMO solution
// method gives us the maximumAmount if we start at a certain row and col with 2 neutralizers
private int maximumAmountMemo(int row, int col, int neutralizers, int[][] coins, int [][][] dp){
// out of bounds check
if(row >= coins.length || col >= coins[0].length)
return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int coinsAtCurrCell = coins[row][col];
// bottom right corner reached
if(row == coins.length - 1 && col == coins[0].length - 1){
return dp[row][col][neutralizers] = (coinsAtCurrCell < 0 && neutralizers > 0) ? 0 : coinsAtCurrCell;
}
if(dp[row][col][neutralizers] != -1)
return dp[row][col][neutralizers];
// option 1 : don't neutralize
int dontNeutralize = coinsAtCurrCell +
Math.max(
maximumAmountMemo(row, col + 1, neutralizers, coins, dp), // move right
maximumAmountMemo(row + 1, col, neutralizers, coins, dp) // move down
);
// option 2 : neutralize (if possible)
int neutralize = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
if(coinsAtCurrCell < 0 && neutralizers > 0){
neutralize = Math.max(
maximumAmountMemo(row, col + 1, neutralizers - 1, coins, dp), // move right
maximumAmountMemo(row + 1, col, neutralizers - 1, coins, dp) // move down
);
}
return dp[row][col][neutralizers] = Math.max(dontNeutralize, neutralize);
}
public int maximumAmount(int[][] coins) {
// at every point the robot has a choice to either go right or down
// also it can neutralize atmost 2 robbers i.e. 2 neutralizations allowed
int neutralizers = 2; // given in question
// MEMO
int m = coins.length;
int n = coins[0].length;
// size = m * n * (neutralizers + 1) i.e m * n * 3
int dp[][][] = new int[m][n][neutralizers + 1];
// initialize all values to -1
for(int arr1 [][] : dp){
for(int arr2 [] : arr1){
Arrays.fill(arr2, -1);
}
}
return maximumAmountMemo(0, 0, neutralizers, coins, dp);
}
}
```
# Code (Tabulation) - (All test cases passed 578/578) & Runtime 84 ms Beats 78.11% & Memory 79.60 MB Beats 57.29%
```java []
class Solution {
// Tabulation solution
private int maximumAmountTabulation(int maxNeutralizers, int m, int n, int[][] coins){
// size = m * n * (neutralizers + 1) i.e m * n * 3
int dp[][][] = new int[m][n][maxNeutralizers + 1];
// incorporated in the dontNeutralize and neutralize cases
// out of bounds check
// if(row >= coins.length || col >= coins[0].length)
// return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
// bottom right corner reached
// if(row == coins.length - 1 && col == coins[0].length - 1){
// dp[row][col][neutralizers] = (coinsAtCurrCell < 0 && neutralizers > 0) ? 0 : coinsAtCurrCell;
// }
for(int neutralizers = maxNeutralizers; neutralizers >= 0; neutralizers--){
int coinsAtCurrCell = coins[m - 1][n - 1];
dp[m - 1][n - 1][neutralizers] = (coinsAtCurrCell < 0 && neutralizers > 0) ? 0 : coinsAtCurrCell;
}
for(int row = m - 1; row >= 0; row--){
for(int col = n - 1; col >= 0; col--){
int coinsAtCurrCell = coins[row][col];
for(int neutralizers = maxNeutralizers; neutralizers >= 0; neutralizers--){
// base case already covered, so skip
if(row == m - 1 && col == n - 1)
continue;
// option 1 : don't neutralize
int dontNeutralize = coinsAtCurrCell +
Math.max(
(col + 1 < n ? dp[row][col + 1][neutralizers] : Integer.MIN_VALUE), // move right
(row + 1 < m ? dp[row + 1][col][neutralizers] : Integer.MIN_VALUE) // move down
);
// option 2 : neutralize (if possible)
int neutralize = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
if(coinsAtCurrCell < 0 && neutralizers > 0){
neutralize = Math.max(
(col + 1 < n ? dp[row][col + 1][neutralizers - 1] : Integer.MIN_VALUE), // move right
(row + 1 < m ? dp[row + 1][col][neutralizers - 1] : Integer.MIN_VALUE) // move down
);
}
dp[row][col][neutralizers] = Math.max(dontNeutralize, neutralize);
}
}
}
return dp[0][0][maxNeutralizers];
}
public int maximumAmount(int[][] coins) {
// at every point the robot has a choice to either go right or down
// also it can neutralize atmost 2 robbers i.e. 2 neutralizations allowed
int neutralizers = 2; // given in question
int m = coins.length;
int n = coins[0].length;
// TABULATION
return maximumAmountTabulation(neutralizers, m, n, coins);
}
}
```
| 2 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization', 'Java']
| 1 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Maximum Amount of Money Robot Can Earn - Memoized Dynamic Programming Solution | Beats 100% 💰
|
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn-m-vlcc
|
IntuitionThe problem is a variation of the classic path-finding problem in a grid with constraints. The robot must maximize its profit while considering two key
|
PriyangDesai
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-13T06:39:22.660837+00:00
|
2025-01-13T06:39:22.660837+00:00
| 77 | false |
### Intuition
The problem is a variation of the classic path-finding problem in a grid with constraints. The robot must maximize its profit while considering two key rules:
1. Robbers (cells with negative values) decrease profit.
2. The robot can neutralize up to two robbers during its journey, turning their penalties into neutral cells.
The solution uses **recursive dynamic programming (DP)** to compute the maximum profit while traversing the grid.
### Key Insight:
- The robot has **two states** to track:
1. Its current position in the grid `(i, j)`.
2. The remaining number of robbers it can neutralize (`available`).
- Using a 3D DP array, `dp[i][j][available]`, we store the maximum profit the robot can achieve at each cell `(i, j)` with a specific number of neutralizations remaining.
### Approach
1. **Recursive Function (DFS):**
- Base Case:
- If the robot reaches the bottom-right corner `(m - 1, n - 1)`, return the value of the cell considering its neutralization state.
- Recursive Transition:
- At each cell `(i, j)`, calculate the profit for the next moves (`right` and `down`) under the following conditions:
1. If the cell has a robber and the robot can neutralize it.
2. If the cell has a robber and the robot cannot neutralize it.
3. If the cell has no robber.
- Use memoization to avoid redundant calculations.
2. **Initialization:**
- Start from the top-left corner `(0, 0)` with two available neutralizations.
3. **Result:**
- Return the maximum profit stored in `dp[0][0][2]`.
### Dry Run:
#### Problem:
Find the maximum profit for the robot while moving from the top-left `(0, 0)` to the bottom-right `(2, 2)` with at most two robber neutralizations available.
#### Input:
`coins = [[0, 1, -1], [1, -2, 3], [2, -3, 4]]`
`available = 2`
#### DP Table:
- A 3D DP table `dp[i][j][available]` is initialized to `INT_MIN` to store maximum profit for each cell `(i, j)` with a specific number of neutralizations remaining.
---
### Step-by-Step Dry Run:
**Start at `(0, 0)` with `available = 2`:**
1. Current cell value = `0` (neutral).
2. Move `Right (0, 1)` or `Down (1, 0)`.
---
**Move to `(0, 1)` with `available = 2`:**
1. Current cell value = `1` (neutral).
2. Add `1` to profit. Total profit so far = `1`.
3. Move `Right (0, 2)` or `Down (1, 1)`.
---
**Move to `(0, 2)` with `available = 2`:**
1. Current cell value = `-1` (robber).
2. Neutralize robber (`available = 1`), profit remains `1`.
- Move `Down (1, 2)`.
3. Do not neutralize robber (`available = 2`), profit = `0`.
- Move `Down (1, 2)`.
---
**Move to `(1, 2)` with `available = 1`:**
1. Current cell value = `3` (neutral).
2. Add `3` to profit. Total profit = `4`.
3. Move `Down (2, 2)`.
---
**Move to `(2, 2)` with `available = 1`:**
1. Current cell value = `4` (neutral).
2. Add `4` to profit. Total profit = `8`.
3. Reached the destination.
Backtrack to consider all possible paths.
---
**Move to `(1, 2)` with `available = 2`:**
1. Current cell value = `3` (neutral).
2. Add `3` to profit. Total profit = `3`.
3. Move `Down (2, 2)`.
---
**Move to `(2, 2)` with `available = 2`:**
1. Current cell value = `4` (neutral).
2. Add `4` to profit. Total profit = `7`.
---
**Move to `(1, 1)` with `available = 2`:**
1. Current cell value = `-2` (robber).
2. Neutralize robber (`available = 1`), profit remains `1`.
- Move `Right (1, 2)` or `Down (2, 1)`.
3. Do not neutralize robber (`available = 2`), profit = `-1`.
- Move `Right (1, 2)` or `Down (2, 1)`.
---
**Move to `(1, 1)` with `available = 1`:**
1. Repeating similar calculations, the maximum profit path is determined.
---
### Final DP Table:
After evaluating all paths, the DP table stores the following maximum profits:
`dp = [ [[8, 8, 8], [7, 7, 7], [6, 6, 6]], [[8, 8, 8], [7, 7, 7], [6, 6, 6]], [[8, 8, 8], [7, 7, 7], [6, 6, 6]] ]`
---
### Output:
The robot's maximum profit is `8`.
### Explanation of Optimal Path:
1. `(0, 0)` → `(0, 1)` → `(0, 2)` [Neutralize robber] → `(1, 2)` → `(2, 2)`.
2. Along this path, robbers were neutralized strategically to maximize the total profit.
3. Total profit: `0 + 1 + 0 (neutralized) + 3 + 4 = 8`.
---
### Complexity
- Time Complexity: `O(m * n * k)`
where \( m, n \) are the grid dimensions, and \( k = 3 \) (neutralization states).
- Space Complexity: `O(m * n * k)`
for the DP table.
---
### Code
```cpp
class Solution {
public:
int dfs(vector<vector<int>>& coins, int i, int j, int available,
vector<vector<vector<int>>>& dp) {
// Base case: Reached bottom-right corner
if (i == coins.size() - 1 && j == coins[0].size() - 1) {
if (coins[i][j] >= 0) return coins[i][j];
if (coins[i][j] < 0 && available > 0) return 0;
return coins[i][j];
}
// Out of bounds
if (i >= coins.size() || j >= coins[0].size()) return INT_MIN;
// Memoization
if (dp[i][j][available] != INT_MIN) return dp[i][j][available];
int profit = INT_MIN;
// Handle robbers and neutralization
if (coins[i][j] < 0) {
if (available > 0) {
// Neutralize robber
profit = max(profit, dfs(coins, i + 1, j, available - 1, dp));
profit = max(profit, dfs(coins, i, j + 1, available - 1, dp));
}
// Do not neutralize
profit = max(profit, coins[i][j] + dfs(coins, i + 1, j, available, dp));
profit = max(profit, coins[i][j] + dfs(coins, i, j + 1, available, dp));
} else {
// Normal cell
profit = max(profit, coins[i][j] + dfs(coins, i + 1, j, available, dp));
profit = max(profit, coins[i][j] + dfs(coins, i, j + 1, available, dp));
}
return dp[i][j][available] = profit;
}
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int m = coins.size(), n = coins[0].size();
int available = 2; // Robber neutralization limit
// 3D DP table: dp[i][j][available]
vector<vector<vector<int>>> dp(m, vector<vector<int>>(n, vector<int>(3, INT_MIN)));
return dfs(coins, 0, 0, available, dp);
}
};
| 2 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization', 'Matrix', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
💢Recursive ,Memoisation, Tabulation (Striver Based)💢✅💯 Clean Code Every Approach Explained💥🔥💫
|
recursive-memoisation-tabulation-striver-l3l6
|
Problem StatementGiven a 2D grid coins where each cell contains an integer representing coins (positive or negative), find the maximum amount of coins that can
|
Manaslc07
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T16:30:29.626979+00:00
|
2025-01-12T16:30:29.626979+00:00
| 55 | false |
## Problem Statement
Given a 2D grid `coins` where each cell contains an integer representing coins (positive or negative), find the maximum amount of coins that can be collected from the top-left corner `(0, 0)` to the bottom-right corner `(m-1, n-1)`. You are allowed to negate the value of at most 2 negative coins during the path.
---
## Recursive Approach
Gives TLE Because of high Time complexity
### Explanation
1. **Base Case**:
- If the current cell is `(m-1, n-1)` (destination):
- If the coin is negative:
- Negate it if `rem > 0`.
- Otherwise, take it as is.
- If the coin is positive, add its value.
- Return the computed value for the destination cell.
2. **Out of Bounds Check**:
- If the cell is out of bounds, return a large negative value (`-1e9`), representing an invalid path.
3. **Recursive Exploration**:
- From the current cell `(i, j)`, move **right** or **down**.
- If the current cell has a negative value and `rem > 0`, explore both:
- Negating the value and reducing `rem`.
- Keeping the value and retaining `rem`.
4. **Return the Maximum**:
- Return the maximum value between the paths explored.
### Code
```cpp
class Solution
{
public:
int helperF(int i, int j, int rem, int n, int m, vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
if (i == n - 1 && j == m - 1) { // Base Case
if (coins[i][j] < 0)
return (rem > 0) ? 0 : coins[i][j];
else
return coins[i][j];
}
if (i >= n || j >= m) // Out of Bounds
return -1e9;
int right = -1e9, down = -1e9;
// Handle negative coin
if (coins[i][j] < 0 && rem > 0) {
right = helperF(i, j + 1, rem - 1, n, m, coins);
down = helperF(i + 1, j, rem - 1, n, m, coins);
}
// Regular moves without negation
right = max(right, coins[i][j] + helperF(i, j + 1, rem, n, m, coins));
down = max(down, coins[i][j] + helperF(i + 1, j, rem, n, m, coins));
return max(right, down);
}
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int n = coins.size();
int m = coins[0].size();
return helperF(0, 0, 2, n, m, coins);
}
};
```
---
## Memoization Approach
### Explanation
1. **Base Case**:
- If the current cell is `(m-1, n-1)` (destination):
- If the coin is negative:
- Negate it if `rem > 0`.
- Otherwise, take it as is.
- If the coin is positive, add its value.
- Return the computed value for the destination cell.
2. **Out of Bounds Check**:
- If the cell is out of bounds, return a large negative value (`-1e9`), representing an invalid path.
3. **Memoization**:
- Use a 3D DP table `dp[i][j][rem]` to store intermediate results.
- Before computing the result for `(i, j)` with `rem` negations, check if the value is already computed.
- If computed, return the value. Otherwise, compute, store, and return.
4. **Recursive Exploration**:
- From the current cell `(i, j)`, move **right** or **down**.
- Handle negative values by optionally negating them if `rem > 0`.
5. **Return the Maximum**:
- Return the maximum value between the paths explored.
### Code
```cpp
class Solution
{
public:
int helperF(int i, int j, int rem, int n, int m, vector<vector<int>>& coins, vector<vector<vector<int>>>& dp) {
if (i == n - 1 && j == m - 1) { // Base Case
if (coins[i][j] < 0)
return (rem > 0) ? 0 : coins[i][j];
else
return coins[i][j];
}
if (i >= n || j >= m) // Out of Bounds
return -1e9;
if (dp[i][j][rem] != -1) // Return cached result
return dp[i][j][rem];
int right = -1e9, down = -1e9;
// Handle negative coin
if (coins[i][j] < 0 && rem > 0) {
right = helperF(i, j + 1, rem - 1, n, m, coins, dp);
down = helperF(i + 1, j, rem - 1, n, m, coins, dp);
}
// Regular moves without negation
right = max(right, coins[i][j] + helperF(i, j + 1, rem, n, m, coins, dp));
down = max(down, coins[i][j] + helperF(i + 1, j, rem, n, m, coins, dp));
return dp[i][j][rem] = max(right, down); // Store result
}
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int n = coins.size();
int m = coins[0].size();
vector<vector<vector<int>>> dp(n, vector<vector<int>>(m, vector<int>(3, -1)));
return helperF(0, 0, 2, n, m, coins, dp);
}
};
```
---
# Tabulation Approach
## Explanation
### 1. **DP Table Initialization**
- Use a 3D DP table `dp[i][j][rem]`:
- `dp[i][j][rem]` represents the maximum amount of coins collectable from cell `(i, j)` to the destination `(m-1, n-1)` with `rem` negations of negative coins left.
- Initialize the DP table with a very small value `-1e9` to indicate unvisited states.
---
### 2. **Base Case**
- For the destination cell `(m-1, n-1)`:
- If the coin value is negative:
- Use the negation if `rem > 0` (set the value to `0`).
- Otherwise, take the coin value as it is.
- If the coin value is positive, add it directly to the DP table.
---
### 3. **Iterative Calculation**
- Traverse the grid from **bottom-right** to **top-left**.
- For each cell `(i, j)` and each possible value of `rem`:
- **Right Move**:
- If moving right `(i, j+1)` is within bounds:
- Add the coin value from the current cell to `dp[i][j+1][rem]`.
- If `rem > 0`, consider negating a negative coin (`dp[i][j+1][rem-1]`).
- **Down Move**:
- If moving down `(i+1, j)` is within bounds:
- Add the coin value from the current cell to `dp[i+1][j][rem]`.
- If `rem > 0`, consider negating a negative coin (`dp[i+1][j][rem-1]`).
- Store the maximum value between the two possible moves in `dp[i][j][rem]`.
---
### 4. **Result**
- The final result is stored in `dp[0][0][2]`, which represents the maximum coins collectable starting from `(0, 0)` with 2 negations allowed.
---
## Code
```cpp
class Solution
{
public:
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int m = coins.size();
int n = coins[0].size();
vector<vector<vector<int>>> dp(m, vector<vector<int>>(n, vector<int>(3, -1e9))); // Initialize DP table
for (int rem = 0; rem < 3; rem++) { // Iterate through remaining negations
for (int i = m - 1; i >= 0; i--) { // Bottom to top
for (int j = n - 1; j >= 0; j--) { // Right to left
if (i == m - 1 && j == n - 1) { // Base Case
dp[i][j][rem] = rem > 0 ? max(0, coins[i][j]) : coins[i][j];
continue;
}
int maxi = -1e9; // Initialize maximum value
// Move Down
if (i + 1 < m) {
maxi = max(maxi, coins[i][j] + dp[i + 1][j][rem]);
if (rem > 0) maxi = max(maxi, dp[i + 1][j][rem - 1]);
}
// Move Right
if (j + 1 < n) {
maxi = max(maxi, coins[i][j] + dp[i][j + 1][rem]);
if (rem > 0) maxi = max(maxi, dp[i][j + 1][rem - 1]);
}
dp[i][j][rem] = maxi; // Update DP table
}
}
}
return dp[0][0][2]; // Result stored in starting position with 2 negations
}
};
```
---
# Time and Space Complexities of All Approaches
| Approach | Time Complexity | Space Complexity | Explanation |
|----------------|-------------------------|-------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| **Recursive** | \(O(2^{(m+n)})\) | \(O(m + n)\) | Explores all possible paths with redundant computations, uses recursion stack. |
| **Memoization**| \(O(m*n*3)\) | \(O(m*n*3)\) + \(O(m + n)\) | Avoids redundant computations by storing results of subproblems, but requires extra space for memoization table. |
| **Tabulation** | \(O(m*n*3)\) | \(O(m*n*3)\) | Iterative approach that systematically fills the DP table, no recursion stack used. |
- **\(m\)**: Number of rows in the grid.
- **\(n\)**: Number of columns in the grid.
- **3**: Constant number of possible remaining negations (\(rem = 0, 1, 2\)).
### Key Notes:
1. **Recursive** approach is the least efficient due to exponential time complexity and lack of caching.
2. **Memoization** optimizes the recursive approach by reducing redundant calculations, but still uses recursion stack.
3. **Tabulation** is the most efficient and systematic approach with iterative computation and avoids stack overhead.
---

| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Iterative DP | Tabulation | Clear solution | Python | (Beats 100%)
|
iterative-dp-tabulation-clear-solution-p-v349
|
IntuitionSince the question contains that the cost needs to be calculated by moving right or bottom the hint can be taken that the question needs to be solved u
|
user8509BS
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T11:29:38.330319+00:00
|
2025-01-12T11:36:19.778698+00:00
| 70 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
Since the question contains that the cost needs to be calculated by moving right or bottom the hint can be taken that the question needs to be solved using Dp.
(Tip: same applies even if they give left and top, if it is all 4 directions then we can use dfs).
Now coming to dp we also need to decide the dimensions of dp array .If it was just finding the maximum coins without the extra feature of neutralizing, you can directly use a simple 2D dp array as that would be common 2d dp question. Since there is a neutralization thing that we need to do and it has to be done optimally, hence we need to use another dimension in the dp array which decides the number of neutralizations made untill now.
The final answer would be the maximum of
DP[m-1][n-1][0] , DP[m-1][n-1][1] , DP[m-1][n-1][2]
since maximum of 2 neutralizations can be made.
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
To solve any Dp problem no matter how many dimensions it may need,we do the following steps:
1. **Finding if it contains any overlapping subproblem or optimal sub-structure:**
We already saw the question contains going right and bottom which comes under optimal substructure hence we use dp
2. **Defining the DP state:**
DP[ i ][ j ][ k ] defines maximum coins required to reach (i,j) from (0,0) by moving either right or bottom only and neutralizing exactly k times along the path.
3. **Drawing state space tree:**
At every state check how the current state is depending on previous state. In this question the current cell cost depends on above cell and left cell with two cases (neutralize current cell and donot neutralize)
4. **Writing DP expression:**
from the state space tree we can easily write the dp expression
```
dp[i][j][k]=max(
dp[i][j-1][k]+cost[i][j],
dp[i][j-1][k-1],
dp[i-1][j][k]+cost[i][j],
dp[i-1][j][k-1]
)
```
5. **Base conditions:**
```
dp[0][0][k]=max(coins[i][j],0)
```
Wherever the expression can go list index out of range we check those using if else and write the code accordingly.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(M*N)
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(M*N*3)
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def maximumAmount(self, cost: List[List[int]]) -> int:
m=len(cost)
n=len(cost[0])
#Initializing DP array
dp=[]
for i in range(m):
l=[]
for j in range(n):
y=[0]*3
l.append(y)
dp.append(l)
#Constructing the DP array
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
for k in range(3):
if k==0:
if i-1<0 and j-1<0:# Top-left corner of the grid
dp[i][j][k]=cost[i][j]
elif i-1<0: # First row (no cell above)
dp[i][j][k]=dp[i][j-1][k]+cost[i][j]
elif j-1<0: # First column (no cell to the left)
dp[i][j][k]=dp[i-1][j][k]+cost[i][j]
else: # General case
dp[i][j][k]=max(dp[i][j-1][k]+cost[i][j],dp[i-1][j][k]+cost[i][j])
else:
if i-1<0 and j-1<0:# Top-left corner of the grid
dp[i][j][k]=max(cost[i][j],0)
elif i-1<0: # First row (no cell above)
dp[i][j][k]=max(dp[i][j-1][k]+cost[i][j],dp[i][j-1][k-1])
elif j-1<0: # First column (no cell to the left)
dp[i][j][k]=max(dp[i-1][j][k]+cost[i][j],dp[i-1][j][k-1])
else: # General case
dp[i][j][k]=max(dp[i][j-1][k]+cost[i][j],dp[i-1][j][k]+cost[i][j],dp[i][j-1][k-1],dp[i-1][j][k-1])
return max(dp[m-1][n-1][0],dp[m-1][n-1][1],dp[m-1][n-1][2])
```
| 2 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Matrix', 'Python3']
| 1 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Minimal Approach using DFS | Beats 💯
|
minimal-approach-using-dfs-beats-by-abh1-13qg
|
Intuition
Each step try to move right and down and keep the max returned value.
We can use recursion to achieve this.
Then we can use dp to optimize it.
We a
|
Abh15hek
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T07:19:54.104292+00:00
|
2025-01-12T07:19:54.104292+00:00
| 195 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
- Each step try to move right and down and keep the max returned value.
- We can use recursion to achieve this.
- Then we can use dp to optimize it.
- We also need to take care of negative values 2 times
- For this we can use variable $$k=2$$ to check how many times a negative value has been eliminated.
- If we encounter a -ve value
- We can choose to include it or exclude it while reducing k by 1 (only if k>0)
- and then return the max of two approaches.
- Since we are using 3 variables 1. for row, 2. for column and 3. k
- We will need a 3D DP to optimize.
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
public int maximumAmount(int[][] coins) {
int m=coins.length;
int n=coins[0].length;
Integer[][][] dp=new Integer[m][n][3];
return calc(coins,0,0,2,dp);
}
private int calc(int[][] coins,int i,int j,int k,Integer[][][] dp) {
int m=coins.length;
int n=coins[0].length;
if(i>=m||j>=n) {
return -(int)1e9;
}
if(i==m-1&&j==n-1)
return coins[i][j]>=0?coins[i][j]:(k>0?0:coins[i][j]);
if(dp[i][j][k]!=null)
return dp[i][j][k];
int d=coins[i][j]+calc(coins,i+1,j,k,dp);
if(coins[i][j]<0&&k>0)
d=Math.max(d,calc(coins,i+1,j,k-1,dp));
int r=coins[i][j]+calc(coins,i,j+1,k,dp);
if(coins[i][j]<0&&k>0)
r=Math.max(r,calc(coins,i,j+1,k-1,dp));
return dp[i][j][k]=Math.max(d,r);
}
}
```
| 2 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Depth-First Search', 'Java']
| 2 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Easy C++ Solution
|
easy-c-solution-by-bansalshreya904-4wf6
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:O(M*N)
Space complexity:O(M*N)
Code
|
bansalshreya904
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T07:17:14.834098+00:00
|
2025-01-12T07:17:14.834098+00:00
| 49 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:O(M*N)
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:O(M*N)
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int solve(int i,int j,vector<vector<int>>&coins,int cnt,vector<vector<vector<int>>>&dp){
int m=coins.size();
int n=coins[0].size();
if(i<0 || i>=m || j<0 || j>=n){
return -1e8;
}
if(i==m-1 && j==n-1){
if(coins[i][j]>=0) return coins[i][j];
else{
if(cnt>0) return 0;
return coins[i][j];
}
}
if(dp[i][j][cnt]!=INT_MIN){
return dp[i][j][cnt];
}
if(coins[i][j]>=0){
int right=coins[i][j]+solve(i,j+1,coins,cnt,dp);
int down=coins[i][j]+solve(i+1,j,coins,cnt,dp);
return dp[i][j][cnt]=max(right,down);
}else{
if(cnt>0){
int right=solve(i,j+1,coins,cnt-1,dp);
int down=solve(i+1,j,coins,cnt-1,dp);
int rightwithneg=coins[i][j]+solve(i,j+1,coins,cnt,dp);
int downwithneg=coins[i][j]+solve(i+1,j,coins,cnt,dp);
return dp[i][j][cnt] =max(max(right, down), max(rightwithneg, downwithneg));
}else{
int right=coins[i][j]+solve(i,j+1,coins,cnt,dp);
int down=coins[i][j]+solve(i+1,j,coins,cnt,dp);
return dp[i][j][cnt]= max(right,down);
}
}
}
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int m=coins.size();
int n=coins[0].size();
vector<vector<vector<int>>>dp(m+1,vector<vector<int>>(n+1,vector<int>(3,INT_MIN)));
return solve(0,0,coins,2,dp);
}
};
```
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
top-down DP Solution
|
top-down-dp-solution-by-vikas_verma-cz6w
|
Code
|
vikas_verma
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T05:28:12.968510+00:00
|
2025-01-12T05:28:12.968510+00:00
| 80 | false |
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int find(int r, int c, int nut, vector<vector<int>>& coins, vector<vector<vector<int>>>& dp){
// return if out of grid
if(r >= coins.size() || c >= coins[0].size()) return INT_MIN;
// if last cell
if(r==coins.size()-1 && c==coins[0].size()-1){
// if neutralizer avaliable, use it to return max value otherwise return cell value
if(nut<2) return max(0, coins[r][c]);
return coins[r][c];
}
// if already calculated for this cell with used neutralizers
if(dp[r][c][nut] != INT_MIN) return dp[r][c][nut];
int skip = INT_MIN;
// use newutralizer if available, do not add coins
if(coins[r][c] < 0 && nut<2){
skip = max(find(r, c+1, nut+1, coins, dp), find(r+1, c, nut+1, coins, dp));
}
// not use neutralizer, add the coins
int pick = coins[r][c] + max(find(r, c+1, nut, coins, dp), find(r+1, c, nut, coins, dp));
dp[r][c][nut] = max(skip, pick);
return dp[r][c][nut];
}
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
// dp[row][col][neut_used]
vector<vector<vector<int>>> dp(coins.size(), vector<vector<int>> (coins[0].size(), vector<int> (3, INT_MIN)));
// (curr_row, curr_col, neutralizers used, coins, dp)
return find(0, 0, 0, coins, dp);
}
};
```
| 2 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Easy Java Solution (✨Beats 100%) (Memoization)
|
easy-java-solution-beats-100-memoization-emx6
|
IntuitionThe robot can move only down or right at each step, and the grid cells contain either a positive value (coins gained) or a negative value (coins stolen
|
armaanaura
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T04:58:50.035937+00:00
|
2025-01-12T04:58:50.035937+00:00
| 305 | false |
### Intuition
The robot can move only down or right at each step, and the grid cells contain either a positive value (coins gained) or a negative value (coins stolen by robbers). **The robot can neutralize robbers in up to two cells** during its journey. This means we need to compute the maximum profit by considering both paths, as well as the use of neutralizing robbers, to ensure we make the best possible decisions.
### Approach
1. **Base Case**: If we reach the bottom-right corner `(m-1, n-1)`, we check if the current cell has a negative value (robber). If the robot still has neutralizations left, we neutralize the robber; otherwise, the robot loses coins equal to the absolute value of the cell.
2. **Recursive Case**: At each cell, we explore two possible moves: one to the cell below `(i+1, j)` and one to the cell to the right `(i, j+1)`. We choose the maximum profit from both moves.
3. **Negative Values**: If the cell has negative values, we should minimize the loss by using neutralize power. Either we can use our power at that point or save it for future. If we use it, save its case in `use` variable and wasting case in `waste` variable
4. **Max Value**: Now at the end, return the maximum possible value of all three cases.
3. **Dynamic Programming (DP) Setup**: We define a 3D DP array, `dp[i][j][n]`, where `i` and `j` represent the current cell in the grid, and `n` represents the number of neutralizations left. The value at `dp[i][j][n]` represents the maximum profit the robot can gain starting from cell `(i, j)` with `n` neutralizations remaining.
4. **Memoization**: To avoid recalculating the same state multiple times, we use memoization to store the results of subproblems in the `dp` array.
5. **Return Result**: Finally, the result of the problem is stored in `dp[0][0][2]`, which gives the maximum profit starting from the top-left corner with 2 neutralizations.
### Complexity
- **Time Complexity**: The time complexity is \(O(m \times n \times 3)\), where \(m\) is the number of rows and \(n\) is the number of columns in the grid. The factor of 3 accounts for the 3 possible states of neutralizations (0, 1, or 2) at each grid cell.
- **Space Complexity**: The space complexity is also \(O(m \times n \times 3)\) due to the 3D DP array storing the results of subproblems.
# Code Logic (No-DP)
```java []
class Solution {
private int helper(int [][]array, int i, int j, int n){
//if we go out of the grid
if(i>=array.length||j>=array[0].length){
return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
//if we reach at the end
if(i==array.length-1&&j==array[0].length-1){
//if we have negative value at the end
if(array[i][j]<0){
//if we have neutralize power, use it, else return the negative value
return n>0?0:array[i][j];
}else{
return array[i][j];
}
}
int value=array[i][j];
// further calls maximum solution (not handling curr values as of now)
int max=Math.max(helper(array,i+1,j,n),helper(array,i,j+1,n));
int use=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int waste=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
//if we have negative value at curr idx
if(value<0){
//if we have left with neutralize power
if(n>0){
//either use it
use=Math.max(helper(array,i+1,j,n-1),helper(array,i,j+1,n-1));
}
// or waste it
waste=max-Math.abs(value);
}
// max+value is the case when we have positive value, we need to add it.
//find max of all three conditions
return Math.max(max+value,Math.max(use,waste));
}
public int maximumAmount(int[][] coins) {
return helper(coins,0,0,2);
}
}
// 0 1 -1
// 1 -2 3
// 2 -3 4
// [4,-16,1,-11]
// [6,18,-17,14]
// [16,-10,9,3]
// [-11,17,0,-11]
```
# Code (Submitted)
```java []
class Solution {
private int helper(int [][]array, int i, int j, int n,Integer[][][] dp){
if(i>=array.length||j>=array[0].length){
return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
if(i==array.length-1&&j==array[0].length-1){
if(array[i][j]<0){
return n>0?0:array[i][j];
}else{
return array[i][j];
}
}
if (dp[i][j][n] != null) {
return dp[i][j][n];
}
int value=array[i][j];
int max=Math.max(helper(array,i+1,j,n,dp),helper(array,i,j+1,n,dp));
int use=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int waste=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
if(value<0){
if(n>0){
use=Math.max(helper(array,i+1,j,n-1,dp),helper(array,i,j+1,n-1,dp));
}
waste=max-Math.abs(value);
}
dp[i][j][n]= Math.max(max+value,Math.max(use,waste));
return dp[i][j][n];
}
public int maximumAmount(int[][] array) {
Integer[][][] dp = new Integer[array.length][array[0].length][3]; // Memoization
return helper(array,0,0,2,dp);
}
}
```
| 2 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization', 'Matrix', 'Java']
| 1 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Python solution
|
python-solution-by-ubitaperon-gxqv
|
IntuitionUsing Dynamic programming, we calculate all cases where after traversing a cell:
You must have 2 neutralizers remaining
You must have 1 neutralizer rem
|
ubitaperon
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T04:40:01.893038+00:00
|
2025-01-12T04:40:01.893038+00:00
| 106 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
Using Dynamic programming, we calculate all cases where after traversing a cell:
1. You must have 2 neutralizers remaining
2. You must have 1 neutralizer remaining
3. You have no neutralizer remaining
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
```
profits[i][j][k] = [
max(top[0], left[0]) + coins[i][j], # You must have 2 neutralizers at the end, so you have to be robbed at this cell
max(
max(top[0], left[0]), # You previously had 2 neutralizers left, now you use 1 on this cell
max(top[1], left[1]) + coins[i][j] # You have 1 neutralizer left, now you have to be robbed at this cell
),
max(
max(top[1], left[1]), # You previously had 1 neutralizer left, now you use 1 on this cell
max(top[2], left[2]) + coins[i][j] # You previously used all your neutralizers, now you have to be robbed at this cell
),
]
```
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(m*n)
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(m*n)
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def maximumAmount(self, coins: List[List[int]]) -> int:
m = len(coins)
n = len(coins[0])
profits = [[[-inf, -inf, -inf] for _ in range(n + 1)] for _ in range(m + 1)]
profits[0][1] = [0, 0, 0]
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
top = profits[i][j + 1]
left = profits[i + 1][j]
profit = coins[i][j]
profits[i + 1][j + 1] = [
max(top[0], left[0]) + profit,
max(
max(top[0], left[0]),
max(top[1], left[1]) + profit
),
max(
max(top[1], left[1]),
max(top[2], left[2]) + profit
),
]
return max(profits[m][n])
```
| 2 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 2 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Super Easy and least lines of code
|
super-easy-and-least-lines-of-code-by-ad-ts5z
|
IntuitionTry All possible cases to reach the end points with given constraints and movesApproachUsed memoization after running recursive solutionComplexity
Time
|
ad_gupta
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T04:35:28.465759+00:00
|
2025-01-12T04:35:28.465759+00:00
| 116 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
Try All possible cases to reach the end points with given constraints and moves
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
Used memoization after running recursive solution
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(m x n x 3)
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(m x n x 3)
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int n = coins.size(), m = coins[0].size();
vector<vector<vector<int>>> dp(n+1, vector<vector<int>>(m+1, vector<int>(3, -1)));
function<int(int, int, int)> f = [&](int i, int j, int rem) -> int{
if(i == n-1 && j == m-1) {
if(coins[i][j] < 0 && rem > 0) return 0;
return coins[i][j];
}
if(i >= n || j >= m) return -1e9;
if(dp[i][j][rem] != -1) return dp[i][j][rem];
int mx = coins[i][j] + max(f(i+1, j, rem), f(i, j+1, rem));
if(coins[i][j] < 0 && rem > 0) {
mx = max({mx, f(i+1, j, rem-1), f(i, j+1, rem-1)});
}
return dp[i][j][rem] = mx;
};
int ans = f(0, 0, 2);
return ans;
}
};
```
| 2 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
C++ | DP
|
c-dp-by-ahmedsayed1-96wm
|
Code
|
AhmedSayed1
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T04:27:21.971661+00:00
|
2025-01-12T04:27:21.971661+00:00
| 148 | false |
# Code
```cpp []
int n,m,dp[500][500][3] ,vis[500][500][3] ,id;
int rec(int i, int j ,int o ,vector<vector<int>>&coins){
if(i == coins.size() || j == coins[0].size())return -1e7;
if(i == coins.size() - 1 && j == coins[0].size()-1){
if(o < 2)return max(0, coins[i][j]);
else return coins[i][j];
}
int & ret = dp[i][j][o];
if(vis[i][j][o] == id)return ret;
vis[i][j][o] = id;
ret = -1e7;
if(o < 2)
ret = max(rec(i + 1 , j ,o + 1 ,coins), rec(i, j + 1 , o + 1, coins));
return ret = max(ret, coins[i][j] + max(rec(i + 1, j, o, coins) ,rec(i , j + 1, o, coins)));
}
class Solution {
public:
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
id++;
return rec(0 , 0 , 0, coins);
}
};
```
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
DP✅ | C++ | Beginner friendly💯
|
dp-c-beginner-friendly-by-procrastinator-51dw
|
Approachdp[i][j][k] = maximum coins you can earn from i,j to n-1,m-1 given you can still neutralise k robbersComplexity
Time complexity: O(N*M)
Space complexit
|
procrastinator_op
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T04:10:58.605741+00:00
|
2025-01-12T04:10:58.605741+00:00
| 51 | false |
# Approach
dp[i][j][k] = maximum coins you can earn from i,j to n-1,m-1 given you can still neutralise k robbers
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity: O(N*M)
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity: O(N*M)
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
#define ll long long
class Solution {
public:
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& c) {
int n = c.size();
int m = c[0].size();
ll dp[501][501][3];
for(int i=0; i<=500; i++){
for(int j=0; j<=500; j++){
for(int k=0; k<=2; k++){
dp[i][j][k] = -1e12;
}
}
}
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = m - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (i == n - 1 && j == m - 1) {
dp[i][j][0] = c[i][j];
for(int k=1; k<=2; k++){
dp[i][j][k] = max(0, c[i][j]);
}
continue;
}
dp[i][j][0] = c[i][j] + max(dp[i + 1][j][0], dp[i][j + 1][0]);
for(int k=1; k<=2; k++){
dp[i][j][k] = c[i][j] + max(dp[i + 1][j][k], dp[i][j + 1][k]);
dp[i][j][k] = max(dp[i][j][k], max(dp[i + 1][j][k - 1], dp[i][j + 1][k - 1]));
}
}
}
return dp[0][0][2];
}
};
```
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Beginner friendly easy to understand
|
beginner-friendly-easy-to-understand-by-yg6js
|
IntuitionSimple solution with just normal pick and nopick method.ApproachUsing memoizationComplexity
Time complexity:
O(n×m)
Space complexity:
O(n×m)
Code
|
Verdan_Shandilya
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-17T21:03:13.354240+00:00
|
2025-01-17T21:03:38.447747+00:00
| 45 | false |
# Intuition
Simple solution with just normal pick and nopick method.
# Approach
Using memoization
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
O(n×m)
- Space complexity:
O(n×m)
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int helper(vector<vector<int>>& coins,int k,int i,int j,vector<vector<vector<int>>> &dp){
if(i>=coins.size() || j>=coins[0].size()){
return -10000000;
}
if(i==coins.size()-1 && j==coins[0].size()-1){
if(k>0 && coins[i][j]<0){
return 0;
}
return coins[i][j];
}
if(dp[i][j][k]!=INT_MIN){
return dp[i][j][k];
}
int b=INT_MIN;
int a=coins[i][j]+max(helper(coins,k,i+1,j,dp),helper(coins,k,i,j+1,dp));
if(k>0 && coins[i][j]<0){
int down=helper(coins,k-1,i+1,j,dp);
int right=helper(coins,k-1,i,j+1,dp);
b=max(down,right);
}
return dp[i][j][k]=max(a,b);
}
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
vector<vector<vector<int>>> dp(coins.size(),vector<vector<int>> (coins[0].size(), vector<int> (3,INT_MIN)));
return helper(coins,2,0,0,dp);
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Depth-First Search', 'Memoization', 'Matrix', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Easy,Small,Well Explained, Beginner Friendly Solution , Recursive (memoization) , Top-down DP
|
easysmallwell-explained-beginner-friendl-jq0b
|
ApproachThis question was asked during my telephonic interview with Google three years back.(The initial question was similar; however, the interviewer later ad
|
lazybit
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-13T19:51:41.322791+00:00
|
2025-01-14T05:36:10.748589+00:00
| 52 | false |
# Approach
This question was asked during my telephonic interview with **Google** three years back.(The initial question was similar; however, the interviewer later adjusted the problem to make it more complex). That day I solved it via iterative approach, now this time using recursion:
Basic approach to select the value:
- **In case cell with positive value:**
- Select the value of the current cell and move to either down or right (↓ →).
- **In case cell with negative value:**
- If **Neutraliztion power is greater than 0:** we have option either use the neutraliztion power and reduce it by 1 (In this case we will add nothing) or don't use the power and let the power value same and select the value of the current cell and move ↓ → .
- If **Neutraliztion power is 0:** then no option left to select the value of the current cell and move ↓ → (down or right).
Do the max of all these cases and store it.
In general terms for negative value:
```
max(move i+1 with neutraliztion, move j+1 with neutraliztion , grid[i][j]+ move i+1 without neutraliztion, grid[i][j] + move j+1 without neutraliztion)
```
In general terms for positive value:
```
max(grid[i][j] + move i+1 without neutraliztion, grid[i][j] + move j+1 without neutraliztion)
```
**USED THE FLAT DP INSTEAD OF 3D DP.**
# Complexity
- Time complexity:$$O(m*n*k)$$
- Space complexity: $$O(m*n*k)$$ - worst case it will never take that much space
# Code
```python3 []
import sys
sys.setrecursionlimit(10**8)
class Solution:
def dpFunc(self,grid,dp,i,j,neutral):
if(i>=len(grid) or j>=len(grid[0])):
return -100000000
if(i==len(grid)-1 and j==len(grid[0])-1):
if(neutral > 0 and grid[i][j] < 0):
return 0
return grid[i][j]
if((i,j,neutral) in dp):
return dp[(i,j,neutral)]
val = -100000000
if(grid[i][j]<0 and neutral>0):
val = max(self.dpFunc(grid,dp,i+1,j,neutral-1),self.dpFunc(grid,dp,i,j+1,neutral-1))
dp[(i,j,neutral)] = max(grid[i][j]+self.dpFunc(grid,dp,i+1,j,neutral),grid[i][j]+self.dpFunc(grid,dp,i,j+1,neutral),val)
return dp[(i,j,neutral)]
def maximumAmount(self, coins: List[List[int]]) -> int:
m,n = len(coins), len(coins[0])
dp = {}
return(self.dpFunc(coins,dp,0,0,2))
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization', 'Python3']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Beat 100% || Very very easy solution || O(n*m)
|
beat-100-very-very-easy-solution-onm-by-cqgd0
|
Code
|
Rahul_Kantwa
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-13T19:01:01.418987+00:00
|
2025-01-13T19:01:01.418987+00:00
| 27 | false |
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def maximumAmount(self, coins: List[List[int]]) -> int:
n, m = len(coins), len(coins[0])
dp = []
for i in range(n+1):
raw_lst = []
for j in range(m+1):
lst = []
for k in range(3):
lst.append(float('-inf') if i == n or j == m else 0)
raw_lst.append(lst)
dp.append(raw_lst)
dp[-1][-2] = [0, 0, 0]
dp[-2][-1] = [0, 0, 0]
for i in range(n - 1, -1, -1):
for j in range(m - 1, -1, -1):
for k in range(2, 0, -1):
if coins[i][j] >= 0:
dp[i][j][k] = coins[i][j] + max(dp[i+1][j][k], dp[i][j+1][k])
else:
take = max(dp[i+1][j][k-1], dp[i][j+1][k-1])
not_take = coins[i][j] + max(dp[i+1][j][k], dp[i][j+1][k])
dp[i][j][k] = max(take, not_take)
dp[i][j][0] = coins[i][j] + max(dp[i+1][j][0], dp[i][j+1][0])
return dp[0][0][2]
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Java Recursive+Memoization
|
java-recursivememoization-by-abhishek_go-30rp
|
Intuition
It looks similar to classic 2D dp grid question of finding paths as per given constraint
Here constraint is given on robot, means another state variab
|
abhishek_goud
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-13T15:42:47.392677+00:00
|
2025-01-13T15:42:47.392677+00:00
| 30 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
1. It looks similar to classic 2D dp grid question of finding paths as per given constraint
2. Here constraint is given on robot, means another state variable has to be introduced
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
1. Step-1 On every step if coins array has negative value, you have 2 options either consider that coins and move to next step or skip that coin then move to next step. Remeber you skip atmost 2 times for a particular path
2. Step-2 If coins array value is positive you take that coin and consider make of right and down direction
3. Step-3 Finally take maximum of step1 and step2 , save and return
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(m*n)
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(m*n)
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
static int dp[][][];
public int rec(int level, int j, int skip, int coins[][]){
if(level == 0 && j == 0){
System.out.println("here");
int val = coins[0][0];
if(skip > 0 && val < 0) return 0;
System.out.println("this");
return val;
}
if(level < 0 || j < 0) return (int)-1e9;
if(dp[level][j][skip] != -3303) return dp[level][j][skip];
int ans = (int) -1e9;
if(coins[level][j] < 0 && skip > 0){
ans = rec(level - 1, j, skip - 1, coins); //skip
ans = Math.max(ans, rec(level, j - 1, skip - 1, coins)); //skip
}
ans = Math.max(ans, coins[level][j] + rec(level - 1, j, skip, coins));
ans = Math.max(ans, coins[level][j] + rec(level, j - 1, skip, coins));
return dp[level][j][skip] = ans;
}
public int maximumAmount(int[][] coins) {
// if(coins.length == 1 && coins[0].length == 1) return 0;
dp = new int[coins.length][coins[0].length][3];
for(int arr[][] : dp){
for(int a[] : arr) Arrays.fill(a, -3303);
}
System.out.println((coins.length - 1)+" "+(coins[0].length - 1));
return rec(coins.length - 1, coins[0].length - 1, 2, coins);
}
}
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'Java']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
[C++][Bottom up DP solution]
|
cbottom-up-dp-solution-by-mumrocks-8mu6
|
Code
|
MumRocks
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-13T14:43:39.961181+00:00
|
2025-01-13T14:43:39.961181+00:00
| 22 | false |
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int m = coins.size(), n=coins[0].size(), ans=0;
vector<vector<vector<int>>> dp(m+1, vector<vector<int>>(n+1,vector<int>(3, -500000)));
dp[0][1][0]=0;
for (int i=0;i<m;i++){
for (int j=0;j<n;j++){
dp[i+1][j+1][0] = max(dp[i][j+1][0],dp[i+1][j][0])+coins[i][j];
dp[i+1][j+1][1] = max(max(max(dp[i][j+1][1],dp[i+1][j][1]) +coins[i][j], max(dp[i][j+1][0],dp[i+1][j][0])),dp[i+1][j+1][0]);
dp[i+1][j+1][2] = max(max(max(dp[i][j+1][2],dp[i+1][j][2]) +coins[i][j], max(dp[i][j+1][1],dp[i+1][j][1])),dp[i+1][j+1][1]);
//cout << i << " " << j << " " << dp[i+1][j+1][0] << " " << dp[i+1][j+1][1] << " " << dp[i+1][j+1][2] << endl;
}
}
return dp.back().back()[2];
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Memoize Code || Best Solution
|
memoize-code-best-solution-by-algoace200-qne5
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
AlgoAce2004
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-13T12:59:44.452226+00:00
|
2025-01-13T13:00:44.935413+00:00
| 22 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
static Integer dp[][][];// imp Integer dp lena tha becz negative value is also present; so we cant take int dp and intialize with -1
public static int solve(int i,int j,int k,int coins[][]){
if(i>=coins.length || j>=coins[0].length)return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
if(i==coins.length-1 && j==coins[0].length-1){
if(coins[i][j]<0 && k>0)return 0;
return coins[i][j];
}
if(dp[i][j][k]!=null)return dp[i][j][k];
int take=Integer.MIN_VALUE,nottake=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
take=coins[i][j]+Math.max(solve(i+1,j,k,coins),solve(i,j+1,k,coins));
if(coins[i][j]<0 && k>0)nottake=Math.max(solve(i+1,j,k-1,coins),solve(i,j+1,k-1,coins));
return dp[i][j][k]=Math.max(take,nottake);
}
public int maximumAmount(int[][] coins) {
int n=coins.length;
int m=coins[0].length;
dp=new Integer[n][m][3];
return solve(0,0,2,coins);
}
}
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
3418
|
3418-by-sandeep_27-0gj5
|
IntuitionTop down intutionApproachRecursion+DPComplexity
Time complexity:
O(mn3);
Space complexity:
O(mn3);Code
|
SANDEEP_27
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-13T08:17:35.520414+00:00
|
2025-01-13T08:17:35.520414+00:00
| 10 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
Top down intution
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
Recursion+DP
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(m*n*3);
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(m*n*3);
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
Integer dp[][][];
public int dfs(int[][] coins,int i,int j,int move){
if(i>=coins.length || j>=coins[0].length || move<0){
return -(int)1e9;
}
if(i==coins.length-1 && j==coins[0].length-1){
int val=coins[i][j]<0?move>0?0:coins[i][j]:coins[i][j];
return val;
}
if(dp[i][j][move]!=null)return dp[i][j][move];
int val=coins[i][j];
int right=val+dfs(coins,i,j+1,move);
int down=val+dfs(coins,i+1,j,move);
int skip1=dfs(coins,i,j+1,move-1);
int skip2=dfs(coins,i+1,j,move-1);
return dp[i][j][move]=Math.max(Math.max(right,down),Math.max(skip1,skip2));
}
public int maximumAmount(int[][] coins) {
dp=new Integer[coins.length][coins[0].length][3];
return dfs(coins,0,0,2);
}
}
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Recursive Approach || Tabulation Method || and Top 100% Solution✅🔥
|
recursive-approach-tabulation-method-and-zq43
|
IntuitionThe problem involves finding the maximum amount you can collect from a grid of coins, starting from the bottom-right corner (target) and moving to the
|
raj_961
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-13T07:06:17.723389+00:00
|
2025-01-13T07:06:17.723389+00:00
| 20 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
The problem involves finding the maximum amount you can collect from a grid of coins, starting from the bottom-right corner (target) and moving to the top-left corner. You have three chances to neutralize negative values if you encounter any. The goal is to maximize the collected value while considering these opportunities to "overwrite" negative coins.
Base Case:
The bottom-right corner of the grid has either a positive or negative value. Depending on whether it’s negative, you either store the value itself if you have no more chances left (k == 0) or you store 0 if you have remaining chances.
Recursive Relation:
From each cell, you can move right or down. If you encounter a negative value, you can either:
Use one of your remaining chances to overwrite it and continue, or
Ignore it if you have no chances left.
The approach is to calculate the maximum possible value you can collect by making these choices recursively.
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
The approach to solving this problem involves using dynamic programming (DP) to keep track of the maximum amount of coins that can be collected starting from the bottom-right corner and moving towards the top-left corner of the grid. The DP table is a 3D matrix, where each cell dp[i][j][k] represents the maximum coins collected at position (i, j) with k chances left to overwrite negative values. We iterate through the grid in a bottom-up fashion, filling the DP table by considering the possible moves to the right or down from each cell. The base case is handled at the bottom-right corner, where we either take the coin value directly or ignore it based on the availability of chances. For cells with negative coins, if we have available chances, we can overwrite the negative value; otherwise, we skip it. Finally, the result is found at dp[0][0][2], which gives the maximum coins that can be collected starting from the top-left corner with two chances remaining.
# Complexity
**- Time complexity:**
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- The DP table has dimensions m x n x 3, where m is the number of rows and n is the number of columns.
- The table will be filled in O(m * n * 3), leading to O(m * n) time co
**- Space complexity:**
- The DP table consumes O(m * n * 3) space, leading to O(m * n) space complexity.
# Code
**Memorizarion**
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int m = coins.size();
int n = coins[0].size();
int const NEG_INF = -1e9;
vector<vector<vector<int>>> dp(m, vector<vector<int>>(n, vector<int>(3, NEG_INF)));
for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++) { // Iterate over chances
for (int i = m - 1; i >= 0; i--) { // Iterate rows in reverse
for (int j = n - 1; j >= 0; j--) { // Iterate columns in reverse
// Base case: Bottom-right cell
if (i == m - 1 && j == n - 1) {
if (coins[i][j] < 0) {
dp[i][j][k] = (k == 0) ? coins[i][j] : 0; // Use chance if available
} else {
dp[i][j][k] = coins[i][j];
}
continue;
}
int right = NEG_INF, down = NEG_INF;
// Neutralize negatives if chances are available
if (coins[i][j] < 0 && k > 0) {
right = (j + 1 < n) ? dp[i][j + 1][k - 1] : NEG_INF;
down = (i + 1 < m) ? dp[i + 1][j][k - 1] : NEG_INF;
}
// Add current cell value for positive cases
right = max(right, (j + 1 < n) ? coins[i][j] + dp[i][j + 1][k] : NEG_INF);
down = max(down, (i + 1 < m) ? coins[i][j] + dp[i + 1][j][k] : NEG_INF);
dp[i][j][k] = max(right, down); // Corrected this line
}
}
}
return dp[0][0][2]; // Return the result from the top-left corner
}
};
```
# Code
**Recursive approach**
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int f(vector<vector<int>> &coins,int chances,int row,int col,int m,int n,vector<vector<vector<int>>> &dp){
if (row == m - 1 && col == n - 1) {
if (coins[row][col] < 0 )
if( chances <= 0)
return coins[row][col]; // No chance left to handle negative
else
return 0;
return coins[row][col];
}
// Out-of-bounds condition
if (row >= m || col >= n) return -1e9;
if (dp[row][col][chances] != INT_MIN)
return dp[row][col][chances];
int right=-1e9,down=-1e9;
if (coins[row][col] < 0 && chances > 0) {
right = f(coins, chances - 1, row, col + 1, m, n,dp);
down = f(coins, chances - 1, row + 1, col, m, n,dp);
}
right = max(right, coins[row][col] + f(coins, chances, row, col + 1, m, n,dp));
down = max(down, coins[row][col] + f(coins, chances, row + 1, col, m, n,dp));
return dp[row][col][chances]=max(right, down);
}
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int m=coins.size();
int n=coins[0].size();
vector<vector<vector<int>>> dp(m,vector<vector<int>>(n,vector<int>(3,INT_MIN)));
return f(coins,2,0,0,m,n,dp);
}
};
```
please upvote 😊
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Idk - I'm just a Chill Guy
|
idk-im-just-a-chill-guy-by-jay_1410-8gt0
|
Code
|
Jay_1410
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T19:47:11.024329+00:00
|
2025-01-12T19:47:11.024329+00:00
| 18 | false |
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution{
public:
int DP[500][500][3];
int getmaxProfit(int R , int C , int T , vector<vector<int>> &A){
if(R == 0 && C == 0) return T ? max(0 , A[R][C]) : A[R][C];
if(DP[R][C][T] != -8e8) return DP[R][C][T];
int ans = -8e8;
for(int D : {0 , -1}){
int NR = R + D;
int NC = C - 1 - D;
if(min(NR , NC) >= 0){
ans = max(ans , A[R][C] + getmaxProfit(NR , NC , T , A));
if(T > 0 && A[R][C] < 0) ans = max(ans , getmaxProfit(NR , NC , T - 1 , A));
}
}
return DP[R][C][T] = ans;
}
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>> &A){
int N = A.size() , M = A[0].size();
for(int R = 0 ; R < N ; R++)
for(int C = 0 ; C < M ; C++)
DP[R][C][0] = DP[R][C][1] = DP[R][C][2] = -8e8;
return getmaxProfit(N - 1 , M - 1 , 2 , A);
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Top down approach - memoization - beats 100% - python3
|
top-down-approach-memoization-beats-100-jdu2j
|
IntuitionThe problem requires us to maximize the coins collected along a path from the top-left to the bottom-right of a grid. Multiple paths are possible, and
|
UCJTBKG5qL
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T18:46:35.988541+00:00
|
2025-01-12T19:36:17.673489+00:00
| 68 | false |
## Intuition
The problem requires us to maximize the coins collected along a path from the top-left to the bottom-right of a grid. Multiple paths are possible, and we can neutralize up to two negative cells, which adds complexity to the problem.
This means we need to explore all paths and compute the maximum coins collected. To efficiently solve this, we use a **top-down dynamic programming (DP)** approach with memoization. This approach allows us to avoid redundant calculations by caching results for overlapping subproblems.
## Approach
We define a recursive function `dfs(i, j, k)`:
- `i`: Row index of the current cell.
- `j`: Column index of the current cell.
- `k`: Remaining neutralizations available.
### Steps:
1. **Base Cases**:
- If `(i, j)` is out of bounds, return a very small value (e.g., `-inf`) since the path is invalid.
- If `(i, j)` is the bottom-right corner, return the value of the cell, considering whether neutralization is needed.
2. **Recursive Step**:
- At each cell, we have two choices:
1. Move **down**: Explore the path starting at `(i+1, j)`.
2. Move **right**: Explore the path starting at `(i, j+1)`.
- For each choice, we also decide whether to use a neutralization if the cell's value is negative (`coins[i][j] < 0`).
3. **Memoization**:
- Store the result of `dfs(i, j, k)` in a cache to avoid recalculating results for the same state `(i, j, k)`.
4. **Initial Call**:
- Start the recursion with `dfs(0, 0, 2)`, representing the top-left cell with 2 neutralizations available.
### Key Idea:
The DP function computes the maximum coins that can be collected starting from cell `(i, j)` with `k` neutralizations remaining. The results are cached to optimize performance.
## Complexity
### Time Complexity:
- Each cell `(i, j)` is visited for all possible values of `k` (0, 1, 2).
- Total number of states: \(O(m \* n \* 3)\).
- Each state is computed in \(O(1)\), so the overall time complexity is: O(m \* n)
### Space Complexity:
1. **Memoization Table**:
- Stores \(O(m \* n \*times* 3)\) states.
2. **Recursion Stack**:
- The maximum recursion depth is \(O(m + n - 1)\).
3. **Total Space Complexity**:
O(m \* n \* 3 + m + n - 1) = O(m \times n)
---
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def maximumAmount(self, coins: List[List[int]]) -> int:
m = len(coins)
n = len(coins[0])
cache = {}
def dfs(i, j, k):
if i >= m or j >= n:
return float('-inf')
if i == m-1 and j == n-1:
# print(i, j)
return max(0, coins[i][j]) if coins[i][j] < 0 and k > 0 else coins[i][j]
if (i, j, k) in cache:
return cache[(i, j,k)]
val = coins[i][j]
d = dfs(i+1, j, k)
r = dfs(i, j+1, k)
max_coins = max(d, r) + val
if val < 0 and k > 0:
neturalized = max(dfs(i+1, j, k-1), dfs(i, j+1, k-1))
max_coins = max(max_coins, neturalized)
cache[(i, j, k)] = max_coins
# print(i, j, k, max_coins)
return max_coins
return dfs(0, 0, 2)
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Memoization', 'Python3']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Weekly Contest Problem 2 using DP
|
weekly-contest-problem-2-using-dp-by-pra-0k84
|
Complexity
Time complexity:
O(M * N * 3)
Space complexity:
O(M * N * 3)Code
|
PradyumnaPrahas2_2
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T16:34:03.144579+00:00
|
2025-01-12T16:34:03.144579+00:00
| 28 | false |
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(M * N * 3)
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(M * N * 3)
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
public int maximumAmount(int[][] coins) {
int r=coins.length,c=coins[0].length;
int[][][] dp=new int[r][c][3];
for(int i=0;i<r;i++){
for(int j=0;j<c;j++){
Arrays.fill(dp[i][j],Integer.MIN_VALUE);
}
}
if(coins[0][0]<0){
Arrays.fill(dp[0][0],0);
dp[0][0][0]=coins[0][0];
}
else{
Arrays.fill(dp[0][0],coins[0][0]);
}
for(int i=0;i<coins.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<coins[0].length;j++){
if(i!=0 || j!=0){
for(int k=0;k<3;k++){
int MAX=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
if(i-1>=0){
MAX=Math.max(dp[i-1][j][k],MAX);
}
if(j-1>=0){
MAX=Math.max(dp[i][j-1][k],MAX);
}
if(coins[i][j]<0){
if(k==0){
dp[i][j][0]=Math.max(MAX+coins[i][j],dp[i][j][0]);
dp[i][j][1]=Math.max(MAX,dp[i][j][1]);
}
else if(k==1){
dp[i][j][1]=Math.max(MAX+coins[i][j],dp[i][j][1]);
dp[i][j][2]=Math.max(MAX,dp[i][j][2]);
}
else{
dp[i][j][2]=Math.max(dp[i][j][2],MAX+coins[i][j]);
}
}
else{
dp[i][j][k]=Math.max(dp[i][j][k],MAX+coins[i][j]);
}
}
}
}
}
return Math.max(Math.max(dp[r-1][c-1][0],dp[r-1][c-1][1]),dp[r-1][c-1][2]);
}
}
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Greedy', 'Java']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
c++ solution
|
c-solution-by-dilipsuthar60-9nr0
|
Code
|
dilipsuthar17
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T13:51:03.802944+00:00
|
2025-01-12T13:51:03.802944+00:00
| 16 | false |
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int n,m;
long long dp[510][510][3];
int find(vector<vector<int>>&mat,int i,int j,int rem){
if((i==n-1)&&(j==m-1)){
if(rem>0&&mat[i][j]<0){
return 0;
}
return mat[i][j];
}
if(i>=n||j>=m){
return -1e8;
}
if(dp[i][j][rem]!=-1e8){
return dp[i][j][rem];
}
int ans = mat[i][j]+max(find(mat,i,j+1,rem),find(mat,i+1,j,rem));
if(rem>0&&mat[i][j]<0){
ans=max({ans,find(mat,i,j+1,rem-1),find(mat,i+1,j,rem-1)});
}
return dp[i][j][rem]= ans;
}
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
n=coins.size();
m=coins[0].size();
for(int i=0;i<505;i++){
for(int j=0;j<505;j++){
for(int k=0;k<3;k++){
dp[i][j][k]=-1e8;
}
}
}
return find(coins,0,0,2);
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Easy C++ || Memoization Soln
|
easy-c-memoization-soln-by-riteshthakare-dy33
|
Code
|
riteshthakare1191
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T13:30:57.966946+00:00
|
2025-01-12T13:32:09.293436+00:00
| 52 | false |
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int dp[501][501][3];
int f(int r, int c, int neu, vector<vector<int>>& grid, int n, int m) {
if (neu > 2 || r >= n || c >= m) return -1e8;
if (r == n - 1 && c == m - 1) {
if (grid[r][c] > 0) return grid[r][c];
return neu < 2 ? 0 : grid[r][c];
}
if (dp[r][c][neu] != -1) return dp[r][c][neu];
// All different ways
int right = grid[r][c] + f(r, c + 1, neu, grid, n, m);
int down = grid[r][c] + f(r + 1, c, neu, grid, n, m);
int neuR = -1e8;
if (grid[r][c] < 0 && neu < 2) neuR = f(r + 1, c, neu + 1, grid, n, m);
int neuD = -1e8;
if (grid[r][c] < 0 && neu < 2) neuD = f(r, c + 1, neu + 1, grid, n, m);
if (grid[r][c] > 0) return dp[r][c][neu] = max(right, down);
else return dp[r][c][neu] = max({right, down, neuD, neuR});
}
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int n = grid.size(), m = grid[0].size();
memset(dp, -1, sizeof(dp));
return f(0, 0, 0, grid, n, m);
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Easy Recursive solution with DP Memoization || Beginner Friendly || 3-D DP Solution ||
|
easy-recursive-solution-with-dp-memoizat-7srq
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
abhishek_manglani_--05
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T12:13:30.054347+00:00
|
2025-01-12T12:13:30.054347+00:00
| 29 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int f(int row,int col,int cur,vector<vector<int>>&coins,vector<vector<vector<int>>>&dp){
if(row==coins.size()-1 && col==coins[0].size()-1){
if(coins[row][col]>=0){
return coins[row][col];
}
else if(cur>0){
return 0;
}
else{
return coins[row][col];
}
}
if(row>=coins.size() || col>=coins[0].size()){
return -250000000;
}
if(dp[row][col][cur]!=-1){
return dp[row][col][cur];
}
int one=0;
int two=0;
if(cur>0){
if(coins[row][col]>=0){
one=coins[row][col]+f(row+1,col,cur,coins,dp);
two=coins[row][col]+f(row,col+1,cur,coins,dp);
}
else{
one=max(coins[row][col]+f(row+1,col,cur,coins,dp),f(row+1,col,cur-1,coins,dp));
two=max(coins[row][col]+f(row,col+1,cur,coins,dp),f(row,col+1,cur-1,coins,dp));
// three=0+f(row+1,col,cur-1,coins);
// four=0+f(row,col+1,cur-1,coins);
}
}
else{
if(coins[row][col]>=0){
one=coins[row][col]+f(row+1,col,cur,coins,dp);
two=coins[row][col]+f(row,col+1,cur,coins,dp);
}
else{
one=coins[row][col]+f(row+1,col,cur,coins,dp);
two=coins[row][col]+f(row,col+1,cur,coins,dp);
}
}
return dp[row][col][cur]=max(one,two);
}
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
vector<vector<vector<int>>>dp(coins.size(),vector<vector<int>>(coins[0].size(),vector<int>(3,-1)));
return f(0,0,2,coins,dp);
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Traditional DP Approach || Easy to understand ✅✅
|
traditional-dp-approach-easy-to-understa-bqw6
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
Harshsharma08
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T10:54:58.764774+00:00
|
2025-01-12T10:57:27.611744+00:00
| 69 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->Try All Possible Ways using DP.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
Integer dp[][][];
int maxCoins(int nums[][],int row,int col,int k){
int n = nums.length; int m = nums[0].length;
if(row>=n || row<0 || col>=m || col<0) return Integer.MIN_VALUE/2;
if(row==n-1 && col==m-1){
if(nums[row][col]>=0) return nums[row][col];
if(nums[row][col]<0){
if(k>0) return 0;
return nums[row][col];
}
}
if(dp[row][col][k]!=null) return dp[row][col][k];
int right = Integer.MIN_VALUE/2, down = Integer.MIN_VALUE/2;
if(nums[row][col]>=0){
right = nums[row][col] + maxCoins(nums,row,col+1,k);
down = nums[row][col] + maxCoins(nums,row+1,col,k);
}
else{
if(k>0){
right = maxCoins(nums,row,col+1,k-1);
down = maxCoins(nums,row+1,col,k-1);
}
right = Math.max(right,nums[row][col] + maxCoins(nums,row,col+1,k));
down = Math.max(down,nums[row][col] + maxCoins(nums,row+1,col,k));
}
return dp[row][col][k] = Math.max(right,down);
}
public int maximumAmount(int[][] coins) {
int n = coins.length; int m = coins[0].length;
dp = new Integer[n][m][3];
return maxCoins(coins,0,0,2);
}
}
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Depth-First Search', 'Memoization', 'C++', 'Java']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Dynammic programming | memoization
|
dynammic-programming-memoization-by-prad-znzl
|
IntuitionStandard grid problem.Since maximising profit is asked for. We can think of recursion.BFS is not thought of as shortest or longest path is not asked. H
|
pradygup
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T07:55:23.026209+00:00
|
2025-01-12T07:55:23.026209+00:00
| 41 | false |
# Intuition
Standard grid problem.Since maximising profit is asked for. We can think of recursion.BFS is not thought of as shortest or longest path is not asked. Here all possible paths need to be explored.
# Approach
- Go from 0,0 cell to m-1,n-1 cell. Paths only right and down.
- if coins[i][j]>=0 just pick the value normally.
- when <0 just pick value once by subtracting the neutral, other keeping neutral the same and select the maxpath.
- Do same for down path.
- Select max of both paths and return at the end.
- Optimise using 3d dp.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
O(N*M*2)
- Space complexity:
O(N*M*2)
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(int row,int col,vector<vector<int>>& coins,int neutral,vector<vector<vector<int>>>&dp){
int m=coins.size();
int n=coins[0].size();
if(row>=m || col>=n)return -1e9;
if(row==m-1 && col==n-1){
if(coins[row][col]>=0)return coins[row][col];
else{
if(neutral>0){
return 0;
}
else{
return coins[row][col];
}
}
}
if(dp[row][col][neutral]!=-1)return dp[row][col][neutral];
//move right
int right=-1e9;
if(coins[row][col]>=0)right=coins[row][col] + maxProfit(row,col+1,coins,neutral,dp);
else {
if(neutral>0)right=maxProfit(row,col+1,coins,neutral-1,dp);
right=max(right,maxProfit(row,col+1,coins,neutral,dp)+(coins[row][col]));
}
//move down
int down=-1e9;
if(coins[row][col]>=0)down=coins[row][col] + maxProfit(row+1,col,coins,neutral,dp);
else {
if(neutral>0)down=maxProfit(row+1,col,coins,neutral-1,dp);
down=max(down,maxProfit(row+1,col,coins,neutral,dp)+(coins[row][col]));
}
return dp[row][col][neutral]=max(right,down);
}
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int m=coins.size();
int n=coins[0].size();
vector<vector<vector<int>>>dp(m+1,vector<vector<int>>(n+1,vector<int>(3,-1)));
return maxProfit(0,0,coins,2,dp);
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 1 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
DP || Recursion + Memoization || Super Simple || C++
|
dp-recursion-memoization-super-simple-c-equzx
|
Code
|
lotus18
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T06:07:06.989135+00:00
|
2025-01-12T06:07:06.989135+00:00
| 68 | false |
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution
{
public:
int m, n;
int dp[501][501][3];
int f(int r, int c, int rem, vector<vector<int>>& coins)
{
if(r>=m || c>=n) return INT_MIN;
if(r==m-1 && c==n-1)
{
if(rem>0 && coins[r][c]<0) return 0;
return coins[r][c];
}
if(dp[r][c][rem]!=-1) return dp[r][c][rem];
int ans=coins[r][c]+max(f(r,c+1,rem,coins), f(r+1,c,rem,coins));
if(rem>0 && coins[r][c]<0)
{
ans=max(ans,max(f(r,c+1,rem-1,coins), f(r+1,c,rem-1,coins)));
}
return dp[r][c][rem]=ans;
}
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins)
{
memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp));
m=coins.size(), n=coins[0].size();
return f(0,0,2,coins);
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
🌟🧠💡O(n*m) Striver Style DP on GRID SOLUTION 🌟🧠💡
|
onm-striver-style-dp-on-grid-solution-by-av7j
|
Complexity
Time complexity:
O(n∗m)
Space complexity:
O(n∗m)
Code
|
Dynamic_Dishank
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T06:06:03.062512+00:00
|
2025-01-12T06:06:03.062512+00:00
| 29 | false |
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
$$O(n*m)$$
- Space complexity:
$$O(n*m)$$
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int n,m;
int solve(int x,int y,int power_left,vector<vector<int>> &arr,vector<vector<vector<long long>>> &dp)
{
if(x>=n || y>=m || x<0 || y<0 || power_left<0) return -1e9;
if(x==n-1 && y==m-1)
{
if(arr[x][y]>=0) return arr[x][y];
else if(power_left) return 0;
else return arr[x][y];
}
if(dp[x][y][power_left]!=LLONG_MIN) return dp[x][y][power_left];
long long right=-1e9;
long long down=-1e9;
right=max(right,0LL+arr[x][y]+solve(x,y+1,power_left,arr,dp));
down=max(down,0LL+arr[x][y]+solve(x+1,y,power_left,arr,dp));
if(power_left && arr[x][y]<0)
{
right=max(right,0LL+solve(x,y+1,power_left-1,arr,dp));
down=max(down,0LL+solve(x+1,y,power_left-1,arr,dp));
}
return dp[x][y][power_left]=max(right,down);
}
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& arr)
{
n=arr.size();
m=arr[0].size();
vector<vector<vector<long long>>> dp(n+1,vector<vector<long long>>(m+1,vector<long long>(3,LLONG_MIN)));
return solve(0,0,2,arr,dp);
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C++']
| 1 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
C++ || Recursion + Memoization || Easy to understand ||
|
c-recursion-memoization-easy-to-understa-u7t0
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
gourav_raghuwanshi_1_2
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T05:12:43.391659+00:00
|
2025-01-12T05:12:43.391659+00:00
| 47 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
int n,m;
long long dp[501][501][3];
int solve(int i,int j,int k,vector<vector<int>>& coins){
if(i==n-1 && j==m-1) {
if(coins[i][j]>=0) return coins[i][j];
else if(k>0) return 0;
else return coins[i][j];
}
if(i>=n || j>=m) return -1e9;
if(dp[i][j][k]!=LLONG_MIN) return dp[i][j][k];
int take=-1e9;
int ntake=-1e9;
int useK=-1e9;
if(coins[i][j]>=0){
take=coins[i][j]+max(solve(i+1,j,k,coins),solve(i,j+1,k,coins));
}else{
ntake=coins[i][j]+max(solve(i+1,j,k,coins),solve(i,j+1,k,coins));
if(k>0){
useK=max(solve(i+1,j,k-1,coins),solve(i,j+1,k-1,coins));
}
}
return dp[i][j][k] = max({take,useK,ntake});
}
public:
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
for(int i=0;i<501;i++){
for(int j=0;j<501;j++){
for(int k=0;k<3;k++){
dp[i][j][k]=LLONG_MIN;
}
}
}
n=coins.size();
m=coins[0].size();
return solve(0,0,2,coins);
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Python Solution Using Memoization with simple Explanation | Beats 100% in Time Complexity
|
python-solution-using-memoization-with-s-pkhf
|
IntuitionThis problem either can be solved using tabulation or memoization.
This solution uses memoization technique to solve this problem.Approach
Let declare
|
Mohamed_Hamdan_A
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T05:00:29.789601+00:00
|
2025-01-12T05:00:29.789601+00:00
| 59 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
This problem either can be solved using tabulation or memoization.
This solution uses memoization technique to solve this problem.
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
1. Let declare a dictionary to store the calculated results of the functon.
2. Check if the index is in the last row and col.
3. Check out of bound row or col
4. Check ans present in dictionary
5. Moving through right and left of the grid without applying any neutralize.
``` right = helper(i+1,j,neutralize); down = helper(i,j+1,neutralize)```
6. Moving through right and left of the grid appliying neutralize if available.
7. store the result in dictionary.
8. return the result.
# Complexity
- Time complexity: O(m×n)
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity: O(m×n)
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def maximumAmount(self, coins: List[List[int]]) -> int:
dic = {}
def helper(i: int,j: int,neutralize: int) ->int:
#check if the index is in the last row and col
if i==len(coins)-1 and j==len(coins[0])-1:
ans = coins[i][j]
if ans<0 and neutralize>0:
return 0
else:
return ans
#check out of bound row or col
if i>=len(coins) or j>=len(coins[0]):
return -float('inf')
#check ans present in dictionary
if (i,j,neutralize) in dic:
return dic[i,j,neutralize]
#moving through right and left of the grid without applying any neutralize
down_row = helper(i+1,j,neutralize)
right_col = helper(i,j+1,neutralize)
ans = max(down_row,right_col) + coins[i][j]
#moving through right and left of the grid appliying neutralize if available
if coins[i][j]<0 and neutralize>0:
ans = max(helper(i+1,j,neutralize-1),helper(i,j+1,neutralize-1),ans)
#storing the ans in dictionary
dic[i,j,neutralize]=ans
return ans
return helper(0,0,2) #start at [0,0] with neutralize = 2
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Max Path Sum with small twist | DP | Top Down
|
max-path-sum-with-small-twist-dp-top-dow-agbf
|
This is just standard max path sum problem with a small twist that we can ignore upto k negative cells along the path. everything else remains same.Codeyou can
|
karna001
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T04:42:08.933310+00:00
|
2025-01-12T04:42:08.933310+00:00
| 45 | false |
This is just standard max path sum problem with a small twist that we can ignore upto k negative cells along the path. everything else remains same.
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int dp[500][500][3];
int done[500][500][3];
int rec(int lx, int ly, int k, vector<vector<int>>&c){
int n = c.size();
int m = c[0].size();
// pruning
if(lx>=n|| ly>=m){
return -1e9;
}
// base case
if(lx==n-1&& ly==m-1){
if(c[lx][ly]>=0){
return c[lx][ly];
}
else{
// if it is not positive
int notrob = k<2?0:-1e9;
int rob = c[lx][ly];
return max(rob,notrob);
}
}
// cache check
if(done[lx][ly][k]!=-1){
return dp[lx][ly][k];
}
// compute and transition
// current state = lx,ly ,k
int right = rec(lx+1,ly,k,c);
int down = rec(lx,ly+1,k,c);
int nolifeline = max(right,down)+c[lx][ly];
int lifeline = -1e9;
if(c[lx][ly]<0 && k<2){
int fromleft = rec(lx+1,ly,k+1,c);
int fromtop = rec(lx,ly+1,k+1,c);
lifeline = max(fromleft,fromtop);
}
dp[lx][ly][k] = max(nolifeline,lifeline);
done[lx][ly][k] =1;
return dp[lx][ly][k];
// save and return
}
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& c) {
// maximum oath sum in grid , either right or down
// small variation - if current cell is negative , max two times you can avoid adding in the ur total sum
// return total sum
// top down approach
int n = c.size();
int m = c[0].size();
memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp));
memset(done,-1,sizeof(done));
// return rec(n-1,m-1,2,c);
return rec(0,0,0,c);
}
};
```
you can find my detailed solution here
https://youtu.be/7oTFJDGVQPM
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Easy Recursive Solution using four options available
|
easy-recursive-solution-using-four-optio-41ao
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
shubhraj625
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T04:39:31.979605+00:00
|
2025-01-12T04:39:31.979605+00:00
| 31 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
long long dfs(int i, int j, vector<vector<int>>& coins, int neu,
vector<vector<vector<long long>>>& dp) {
int m = coins.size();
int n = coins[0].size();
if (i > m - 1 || j > n - 1) {
return INT_MIN;
}
if (i == m - 1 && j == n - 1) {
if(coins[i][j]<0 && neu>0){
return 0;
}
return coins[i][j];
}
if (dp[i][j][neu] != -1)
return dp[i][j][neu];
long long opt1 = coins[i][j] + dfs(i, j + 1, coins, neu, dp);
long long opt2 = coins[i][j] + dfs(i + 1, j, coins, neu, dp);
long long result = max(opt1, opt2);
if (coins[i][j] < 0 && neu > 0) {
long long opt3 = dfs(i, j + 1, coins, neu - 1, dp);
long long opt4 = dfs(i + 1, j, coins, neu - 1, dp);
result = max(result, max(opt3, opt4));
}
return dp[i][j][neu] = result;
}
public:
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int m = coins.size(), n = coins[0].size();
int neu = 2;
vector<vector<vector<long long>>> dp(
m, vector<vector<long long>>(n, vector<long long>(neu + 1, -1)));
return dfs(0, 0, coins, neu, dp);
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
beginner friendly easy maximising path sum problem(pattern dp)
|
beginner-friendly-easy-maximising-path-s-iyzx
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
nishant2526
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T04:37:56.916505+00:00
|
2025-01-12T04:37:56.916505+00:00
| 32 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
int m,n;
vector<vector<vector<int>>> dp;
int find(int i,int j,vector<vector<int>>& coins,int k){
if(i>=m||j>=n){
return INT_MIN;
}
if(i==m-1 && j==n-1){
if(coins[i][j]<0 && k>0){
return 0;
}
else{
return coins[i][j];
}
}
if(dp[i][j][k]!=INT_MIN){
return dp[i][j][k];
}
long long count=INT_MIN;
if(coins[i][j]<0 && k>0)
{
count=max(count,1LL*0+find(i,j+1,coins,k-1));
count=max(count,1LL*0+find(i+1,j,coins,k-1));
}
count=max(count,1LL*(coins[i][j])+find(i,j+1,coins,k));
count=max(count,1LL*(coins[i][j])+find(i+1,j,coins,k));
return dp[i][j][k]=count;
}
public:
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
m=coins.size();
n=coins[0].size();
dp=vector<vector<vector<int>>>(m+1, vector<vector<int>>(n+1, vector<int>(3, INT_MIN)));
return find(0,0,coins,2);
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Easy understanding python solution 100% beats solution
|
easy-understanding-python-solution-100-b-ip6h
|
Complexity
Time complexity: O(n∗m∗2)
Space complexity: O(n∗m∗2)
Code
|
osoba_mask
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T04:22:37.040563+00:00
|
2025-01-12T04:22:37.040563+00:00
| 29 | false |
# Complexity
- Time complexity: $$O(n*m*2)$$
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity: $$O(n*m*2)$$
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def maximumAmount(self, coins: List[List[int]]) -> int:
n = len(coins)
m = len(coins[0])
memo = {}
def recur(i,j, sac):
if i >= n or j >= m:
return -float('inf')
if i==n-1 and j == m-1:
if sac > 0 and coins[i][j] < 0:
return 0
return coins[i][j]
if (i,j,sac) in memo:
return memo[(i,j,sac)]
right = -float('inf')
if coins[i][j] < 0 and sac > 0:
right = max(right,recur(i,j+1,sac-1))
right = max(right,coins[i][j] + recur(i,j+1,sac))
down = -float('inf')
if coins[i][j] < 0 and sac > 0:
down = max(down,recur(i+1,j,sac-1))
down = max(down,coins[i][j]+recur(i+1,j,sac))
memo[(i,j,sac)] = max(right,down)
return max(right,down)
return recur(0,0,2)
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Java DynamicProgramming using Memoization
|
java-dynamicprogramming-using-memoizatio-wdjq
|
IntuitionApproachJust to avoid passing m & n values everytime in function ,
Traversed in Reverse direction .i.e., Start at position = (m-1,n-1) to reach posit
|
Naveen_Kumar_Marupalli
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T04:19:19.815651+00:00
|
2025-01-12T04:19:19.815651+00:00
| 134 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
Just to avoid passing m & n values everytime in function ,
Traversed in Reverse direction .
i.e., Start at position = (m-1,n-1) to reach position (0,0)
dp[i][j] --> indicates maximum amount of money robot can earn starting from position(i,j) to reach (0,0) .
Additionally consider neutralization count parameter .
<!-- # Complexity -->
<!-- - Time complexity: -->
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
<!-- - Space complexity: -->
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
public int f( int[][] coins , int[][][] dp , int i , int j , int neutrals ){
if( i==0 && j==0 ){
if( coins[i][j] < 0 && neutrals<2 ){
dp[i][j][neutrals] = 0 ;
}
else{
dp[i][j][neutrals] = coins[i][j] ;
}
return dp[i][j][neutrals] ;
}
if( i<0 || j<0 ) return -(int)1e9;
if(dp[i][j][neutrals] != -(int)1e9 ) return dp[i][j][neutrals];
int up = -(int)1e9 ;
int left = -(int)1e9 ;
if(i>0){
if( coins[i][j] < 0 && neutrals<2 ){
// Neutralize
up = Math.max( up , f( coins, dp, i-1, j , neutrals+1 ) );
}
// NO neutralize
up = Math.max( up, coins[i][j] + f( coins, dp, i-1, j , neutrals ) );
}
if(j>0){
if( coins[i][j] < 0 && neutrals<2 ){
// Neutralize
left = Math.max( left , f( coins, dp, i, j-1, neutrals+1 ) ) ;
}
// NO neutralize
left = Math.max( left , coins[i][j] + f( coins, dp, i, j-1, neutrals ) );
}
return dp[i][j][neutrals] = Math.max(up,left) ;
}
public int maximumAmount(int[][] coins) {
int m = coins.length ;
int n = coins[0].length ;
int[][][] dp = new int[m][n][3] ;
for(int i=0 ; i<m ; i++){
for(int j=0 ; j<n ; j++){
for(int k=0 ; k<3 ; k++){
dp[i][j][k] = -(int)1e9 ;
}
}
}
f( coins , dp , m-1 , n-1 , 0 );
return Math.max( dp[m-1][n-1][0] , Math.max( dp[m-1][n-1][1] , dp[m-1][n-1][2] ) ) ;
}
}
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Java']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Recursive + Memo | C++
|
recursive-memo-c-by-iamnishthavan-j5bw
|
Code
|
nishsolvesalgo
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T04:18:03.326246+00:00
|
2025-01-12T04:18:03.326246+00:00
| 14 | false |
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int dp[501][501][3];
memset(dp, -1, sizeof(dp));
function<int(int, int, int)> dfs = [&](int row, int col, int robber){
if(row == coins.size() - 1 && col == coins[0].size() - 1 && robber <= 2){
if(robber < 2 && coins[row][col] < 0) return 0;
return coins[row][col];
}
if(robber > 2) return -99999999;
if(row >= coins.size()) return -99999999;
if(col >= coins[0].size()) return -99999999;
if(dp[row][col][robber] != -1) return dp[row][col][robber];
int total = coins[row][col] + max(dfs(row + 1, col, robber), dfs(row, col + 1, robber));
int possible = -99999999; // Pruning
if(coins[row][col] < 0) possible = max(dfs(row + 1, col, robber + 1), dfs(row, col + 1, robber + 1));
return dp[row][col][robber] = max(total, possible);
};
return dfs(0, 0, 0);
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
LEETCODE WEEKLY 432 | Q-2
|
leetcode-weekly-432-q-2-by-priyabratam-h1z4
|
IntuitionThe problem requires us to maximize the amount we can collect while traversing a grid. We are allowed to move either right or down at each step, and we
|
priyabratam
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T04:17:10.961955+00:00
|
2025-01-12T04:17:10.961955+00:00
| 7 | false |
# Intuition
The problem requires us to maximize the amount we can collect while traversing a grid. We are allowed to move either right or down at each step, and we can only ignore a limited number of negative values during the traversal. We will need a dynamic programming (DP) approach to track the maximum sum at each cell, while also managing the number of negative values that can be skipped.
# Approach
1. **Grid Setup**: We have a grid where each cell contains either a positive or negative value. We need to keep track of the maximum sum we can accumulate while traversing the grid, considering that we are allowed to skip at most two negative values.
2. **DP Initialization**:
- Initialize a 3D DP array `dp[i][j][k]` where `i` and `j` are the row and column indices of the grid, and `k` represents how many negative values have been skipped (0, 1, or 2).
- For the starting cell, if the value is negative, initialize `dp[0][0][0]` to the value of the cell and `dp[0][0][1]` to 0.
3. **DP Transition**:
- For each cell `(i, j)` and each possible number of skipped negative values (`k`), propagate the value to the neighboring cells `(i+1, j)` and `(i, j+1)`.
- If the value in the neighboring cell is negative and we haven't skipped two negatives yet, allow skipping it and transition to `dp[ni][nj][k+1]`.
4. **Final Answer**: After filling the DP table, the final answer will be the maximum value among the three possibilities in the bottom-right cell: `dp[m-1][n-1][0]`, `dp[m-1][n-1][1]`, and `dp[m-1][n-1][2]`.
# Complexity
- Time complexity: \(O(m * n * 3)\), where `m` and `n` are the number of rows and columns of the grid, and the factor of 3 comes from the three possible states of negative values that can be skipped.
- Space complexity: \(O(m * n * 3)\), due to the 3D DP table that stores the results for each state.
# Code
```cpp
class Solution {
public:
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int m = coins.size();
int n = coins[0].size();
int dp[505][505][3];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++) {
dp[i][j][k] = INT_MIN;
}
}
}
if (coins[0][0] >= 0) {
dp[0][0][0] = coins[0][0];
} else {
dp[0][0][0] = coins[0][0];
dp[0][0][1] = 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++) {
if (dp[i][j][k] == INT_MIN)
continue;
for (auto& it : vector<pair<int, int>>{{1, 0}, {0, 1}}) {
int ni = i + it.first, nj = j + it.second;
if (ni >= m || nj >= n)
continue;
int val = dp[i][j][k];
int c = coins[ni][nj];
dp[ni][nj][k] = max(dp[ni][nj][k], val + c);
if (c < 0 && k < 2) {
dp[ni][nj][k + 1] = max(dp[ni][nj][k + 1], val);
}
}
}
}
}
int ans = max(
{dp[m - 1][n - 1][0], dp[m - 1][n - 1][1], dp[m - 1][n - 1][2]});
return ans;
}
};
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
DP using memoization
|
dp-using-memoization-by-ashwani5009-qjz2
|
IntuitionStandard DP Question (top left to right bottom , down or right)
using memoizationApproachCase 1) coins[i][j] >= 0
a) take and move to right column
b) t
|
ashwani5009
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T04:14:52.672560+00:00
|
2025-01-12T04:15:52.427291+00:00
| 51 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
Standard DP Question (top left to right bottom , down or right)
using memoization
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
Case 1) coins[i][j] >= 0
a) take and move to right column
b) take and move to bottom row
Case 2) coins[i][j] < 0
a) don't neutralize(we will save for maybe future as we can at max neutralize 2 negative coins[i][j]) and move right.
b) don't neutralize and move down.
c) neutralize and move to right(only 1 neutralizing option remains so decreament the cnt).
d) neutralize and move to down.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
TC: O(n * m * 3) ~ O(n*m)
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
SC : O(n * m * 3) + O(n) (stack space)
# Code
```cpp []
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <cinttypes>
#include <climits>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdint>
#include <cstring>
#include <cwchar>
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <numeric>
#include <ostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <queue>
#include <set>
#include <stack>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
template <typename a, typename B>
ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, const pair<a, B> &p) {
return os << '(' << p.first << ", " << p.second << ')';
}
template <typename T_container, typename T = typename enable_if<
!is_same<T_container, string>::value,
typename T_container::value_type>::type>
ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, const T_container &v) {
os << '{';
string sep;
for (const T &x : v)
os << sep << x, sep = ", ";
return os << '}';
}
void dbg_out() { cerr << endl; }
template <typename Head, typename... Tail> void dbg_out(Head H, Tail... T) {
cerr << ' ' << H;
dbg_out(T...);
}
#ifdef LOCAL
#define dbg(...) cerr << "(" << #__VA_ARGS__ << "):", dbg_out(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define dbg(...)
#endif
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define vi vector<int>
#define pb push_back
#define ppb pop_back
#define mp make_pair
#define ff first
#define ss second
#define rep(i, m, n) for (ll i = m; i < n; i++)
#define vll vector<ll>
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef long double lld;
class Solution {
private:
int f(int i, int j, int cnt, vector<vector<int>>& coins, int n, int m, vector<vector<vector<int>>>& dp) {
if (i == n - 1 && j == m - 1) {
if (cnt < 2) {
if(coins[i][j] >= 0) return coins[i][j];
else return 0;
} else {
return coins[i][j];
}
}
if (i >= n || j >= m) return -1e8;
if (dp[i][j][cnt] != -1) return dp[i][j][cnt];
if (coins[i][j] >= 0) {
int take1 = coins[i][j] + f(i, j + 1, cnt, coins, n, m, dp);
int take2 = coins[i][j] + f(i + 1, j, cnt, coins, n, m, dp);
return dp[i][j][cnt] = max({take1, take2});
}
int neutralize1 = -1e8 , neutralize2 = -1e8;
if (coins[i][j] < 0) {
int notNeutralize1 = coins[i][j] + f(i, j + 1, cnt, coins, n, m, dp);
int notNeutralize2 = coins[i][j] + f(i + 1, j, cnt, coins, n, m, dp);
if(cnt < 2) neutralize1 = 0 + f(i, j + 1, cnt + 1, coins, n, m, dp);
if(cnt < 2) neutralize2 = 0 + f(i + 1, j, cnt + 1, coins, n, m, dp);
return dp[i][j][cnt] = max({notNeutralize1, notNeutralize2, neutralize1, neutralize2});
}
return dp[i][j][cnt] = 0;
}
public:
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int n = coins.size();
int m = coins[0].size();
vector<vector<vector<int>>> dp(n, vector<vector<int>>(m, vector<int>(3, -1)));
return f(0, 0, 0, coins, n, m, dp);
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
JAVA || 3D DP
|
java-3d-dp-by-ganesh_dandekar-bwju
|
Code
|
ganesh_dandekar
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T04:05:25.759263+00:00
|
2025-01-12T04:05:25.759263+00:00
| 42 | false |
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
static int n;
static int m;
public int maximumAmount(int[][] coins) {
n = coins.length;
m = coins[0].length;
int dp[][][] = new int[n][m][3];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<m; j++) {
Arrays.fill(dp[i][j], Integer.MIN_VALUE);
}
}
return findMaxAns(coins, 0, 0, 2, dp);
}
int findMaxAns(int coins[][], int i, int j, int limit, int dp[][][]) {
if(i == n-1 && j == m-1) {
if(limit > 0) return Math.max(0, coins[n-1][m-1]);
return coins[n-1][m-1];
}
if(dp[i][j][limit] != Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
return dp[i][j][limit];
}
int left = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int right = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
if(i+1 < n) {
if(coins[i][j] < 0 && limit > 0) {
left = findMaxAns(coins, i+1, j, limit-1, dp);
}
left = Math.max(findMaxAns(coins, i+1, j, limit, dp)+coins[i][j], left);
}
if(j+1 < m) {
if(coins[i][j] < 0 && limit > 0) {
right = findMaxAns(coins, i, j+1, limit-1, dp);
right = Math.max(findMaxAns(coins, i, j+1, limit, dp)+coins[i][j], right);
}
right = Math.max(findMaxAns(coins, i, j+1, limit, dp)+coins[i][j], right);
}
return dp[i][j][limit] = Math.max(right, left);
}
}
// [0,1,-1]
// [1,-2,3]
// [2,-3,4]
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 1 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
DP store remaining moves
|
dp-store-remaining-moves-by-theabbie-udo7
| null |
theabbie
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T04:03:23.193825+00:00
|
2025-01-12T04:03:23.193825+00:00
| 116 | false |
```python3 []
class Solution:
def maximumAmount(self, coins: List[List[int]]) -> int:
m = len(coins)
n = len(coins[0])
dp = [[[float('-inf'), float('-inf'), float('-inf')] for _ in range(n + 1)] for _ in range(m + 1)]
dp[m][n - 1] = [0, 0, 0]
dp[m - 1][n] = [0, 0, 0]
for i in range(m - 1, -1, -1):
for j in range(n - 1, -1, -1):
for rem in range(3):
if rem > 0:
dp[i][j][rem] = max(dp[i][j][rem], dp[i][j][rem - 1])
dp[i][j][rem] = max(dp[i][j][rem], dp[i + 1][j][rem - 1], dp[i][j + 1][rem - 1])
dp[i][j][rem] = max(dp[i][j][rem], coins[i][j] + max(dp[i + 1][j][rem], dp[i][j + 1][rem]))
return dp[0][0][2]
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Recursion || Memoization || Top Down approach || C++
|
recursion-memoization-top-down-approach-fww2b
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
Aditya560
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T04:01:53.347830+00:00
|
2025-01-12T13:38:23.927341+00:00
| 146 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int tr(vector<vector<int>>&coins,int i,int j,int t,vector<vector<vector<int>>>&dp){
if(i>=coins.size() || j>=coins[0].size()){
// cout<<endl;
return INT_MIN+1010;
}
if(i==coins.size()-1 && j==coins[0].size()-1){
// cout<<endl;
if(coins[i][j]<0 && t>=1){
return 0;
}
return dp[i][j][t+1] = coins[i][j];
}
if(dp[i][j][t+1]!=INT_MIN){
return dp[i][j][t+1];
}
int left = INT_MIN+1000;
int right = INT_MIN+1000;
// cout<<coins[i][j]<<" ";
if(coins[i][j]>=0){
left = coins[i][j] + tr(coins,i+1,j,t,dp);
left = max(left,coins[i][j]+tr(coins,i,j+1,t,dp));
}
else{
if(t<=0){
right = coins[i][j] + tr(coins,i+1,j,t,dp);
right = max(right,coins[i][j] +tr(coins,i,j+1,t,dp));
}
else{
right = coins[i][j] + tr(coins,i+1,j,t,dp);
right = max(right,coins[i][j] +tr(coins,i,j+1,t,dp));
// cout<<t<<" ";
// cout<<right<<" ";
right = max(right,tr(coins,i+1,j,t-1,dp));
right = max(right,tr(coins,i,j+1,t-1,dp));
// cout<<right<<" ";
}
}
return dp[i][j][t+1] = max(left,right);
}
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
vector<vector<vector<int>>>dp(coins.size()+1,vector<vector<int>>(coins[0].size()+1,vector<int>(4,INT_MIN)));
return tr(coins,0,0,2,dp);
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization', 'Matrix', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Brief and precise Explanation
|
brief-and-precise-explanation-by-chetan_-anns
|
IntuitionApproachif robot is at (i, j) then either it will come from (i-1, j) or (i, j-1)
so we need to know the maximum score at this 2 cellswe will store 3 va
|
Chetan_496_
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T04:01:47.643673+00:00
|
2025-01-12T04:01:47.643673+00:00
| 41 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
if robot is at (i, j) then either it will come from (i-1, j) or (i, j-1)
so we need to know the maximum score at this 2 cells
we will store 3 value in each cell i.e.
score of :
1. robot hasn't used special ability (dp[i][j][0])
2. robot used special ability 1 time (dp[i][j][1])
3. robot used special ability 2 times (dp[i][j][2])
For this we will use 3D DP array -> size:m*n*3
dp[i][j][0] will store prev cell calue + current cell value as it is
dp[i][j][1] will store maximum of (previousl cell used 1 ability value + current value as it is , previous cell value as it it + Use 1 ability in this cell)
dp[i][j][2] will store maximum of (previousl cell used 2 ability value + current value as it is , previous cell used 1 ability value + Use 1 ability in this cell)
in this previos cells for (i,j) are : (i-1, j) and (i, j-1)
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
O(M*N)
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
O(M*N)
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& v) {
int m = v.size(), n = v[0].size();
vector<vector<vector<int>>> ans(m, vector<vector<int>>(n, vector<int>(3, INT_MIN)));
ans[0][0][0] = v[0][0];
ans[0][0][1] = 0;
ans[0][0][2] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){
ans[0][i][0] = ans[0][i-1][0] + v[0][i];
ans[0][i][1] = ans[0][i-1][1] + v[0][i];
ans[0][i][2] = ans[0][i-1][2] + v[0][i];
if(v[0][i] < 0){
ans[0][i][1] = max(ans[0][i][1], ans[0][i-1][0]);
ans[0][i][2] = max(ans[0][i-1][1], ans[0][i][2]);
}
}
for(int i = 1; i < m; i++){
ans[i][0][0] = ans[i-1][0][0] + v[i][0];
ans[i][0][1] = ans[i-1][0][1] + v[i][0];
ans[i][0][2] = ans[i-1][0][2] + v[i][0];
if(v[i][0] < 0){
ans[i][0][1] = max(ans[i][0][1], ans[i-1][0][0]);
ans[i][0][2] = max(ans[i-1][0][1], ans[i][0][2]);
}
}
for(int i = 1; i < m; i++){
for(int j = 1; j < n; j++){
ans[i][j][0] = max({ans[i-1][j][0], ans[i][j-1][0]}) + v[i][j];
ans[i][j][1] = max(ans[i-1][j][1] + v[i][j], ans[i][j-1][1] + v[i][j]);
ans[i][j][2] = max(ans[i-1][j][2]+ v[i][j], ans[i][j-1][2]+ v[i][j]);
if(v[i][j] < 0){
ans[i][j][1] = max({ans[i][j][1], ans[i][j-1][0], ans[i-1][j][0]});
ans[i][j][2] = max({ans[i-1][j][1], ans[i][j-1][1], ans[i][j][2]});
}
}
}
int total = max({ans[m-1][n-1][0], ans[m-1][n-1][1], ans[m-1][n-1][2]});
return total;
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
C++ DP Memo
|
c-dp-memo-by-tristan232-79al
|
We use x and y and rem as our parameters. Since rem can only be 2, our overall complexity will not exceed O(n*m)TIME COMPLEXITY: O(n*m)Code
|
Tristan232
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T04:01:25.256200+00:00
|
2025-01-12T04:01:25.256200+00:00
| 62 | false |
We use x and y and rem as our parameters. Since rem can only be 2, our overall complexity will not exceed O(n*m)
TIME COMPLEXITY: O(n*m)
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int recur(vector<vector<int>>& coins, int x, int y, int remain,vector<vector<vector<int>>>& dp) {
if (x==coins.size()-1&&y==coins[x].size()-1) {
if (coins[x][y]<0&&remain>0) {
return 0;
}
return coins[x][y];
}
if (x<0||y<0||x>=coins.size()||y>=coins[x].size()) {
return -INT_MAX+10000;
}
if (dp[x][y][remain]!=-1) {
return dp[x][y][remain];
}
int use = -INT_MAX+10000;
int lose = -INT_MAX+10000;
if (coins[x][y]<0&&remain>0) {
use = max(recur(coins,x+1,y,remain-1,dp),recur(coins,x,y+1,remain-1,dp));
}
lose = max(recur(coins,x+1,y,remain,dp)+coins[x][y],recur(coins,x,y+1,remain,dp)+coins[x][y]);
return dp[x][y][remain]=max(use,lose);
}
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
vector<vector<vector<int>>> dp(coins.size()+1,vector<vector<int>>(coins[0].size()+1,vector<int>(3,-1)));
return recur(coins,0,0,2,dp);
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Python3: Top-down approach, T.C: O(M*N*2)
|
python3-top-down-approach-tc-omn2-by-nik-tanu
|
Code
|
Nikhil_Gunne_05
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T04:01:20.569494+00:00
|
2025-01-12T04:01:20.569494+00:00
| 101 | false |
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def maximumAmount(self, coins: List[List[int]]) -> int:
dp = {}
rows = len(coins)
cols = len(coins[0])
def solve(r,c,cnt):
if r==rows-1 and c == cols-1:
return 0 if coins[r][c]<0 and cnt<2 else coins[r][c]
if r==rows:
return float('-inf')
if c==cols:
return float('-inf')
if (r,c,cnt) in dp:
return dp[(r,c,cnt)]
res = float('-inf')
res = coins[r][c] + max(solve(r,c+1,cnt), solve(r+1,c,cnt))
if cnt<2 and coins[r][c] < 0:
res = max(res,solve(r,c+1,cnt+1),solve(r+1,c,cnt+1))
# print(r,c,res)
dp[(r,c,cnt)] = res
return res
return solve(0,0,0)
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Python3']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
C++ DP Tabulation (row, col, neutralized)
|
c-dp-tabulation-row-col-neutralized-by-b-igxn
|
Complexity
Time complexity: O(n∗m)
Space complexity: O(n∗m)
Code
|
bramar2
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-12T03:38:16.256279+00:00
|
2025-01-12T03:38:47.751134+00:00
| 124 | false |
# Complexity
- Time complexity: $O(n*m)$
- Space complexity: $O(n*m)$
# Code
```cpp []
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const vector<vector<int>> directions {{1, 0}, {0, 1}};
int dp[501][501][3];
class Solution {
public:
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int n = coins.size(), m = coins[0].size();
for(int neutralized = 2; neutralized >= 0; neutralized--) {
for(int i = n-1; i >= 0; i--) {
for(int j = m-1; j >= 0; j--) {
if(i == n-1 && j == m-1) {
if(neutralized < 2 && coins[i][j] < 0) dp[i][j][neutralized] = 0;
else dp[i][j][neutralized] = coins[i][j];
}else {
dp[i][j][neutralized] = INT_MIN;
for(const auto& dir : directions) {
int ni = i + dir[0], nj = j + dir[1];
if(0 <= ni && ni < n && 0 <= nj && nj < m) {
if(neutralized < 2 && coins[i][j] < 0) dp[i][j][neutralized] = max(dp[i][j][neutralized], dp[ni][nj][neutralized + 1]);
dp[i][j][neutralized] = max(dp[i][j][neutralized], coins[i][j] + dp[ni][nj][neutralized]);
}
}
}
}
}
}
return dp[0][0][0];
}
};
```
| 1 | 1 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Memoization from recursion
|
memoization-from-recursion-by-gitgetmons-2ugc
|
IntuitionSo we can think that if coins[i][j] >= 0 then pick it up else if its negative then we can choose to use power(if powerCount > 0) else not use power. An
|
gitgetmonster
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-25T20:03:50.687685+00:00
|
2025-03-25T20:03:50.687685+00:00
| 1 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
So we can think that if coins[i][j] >= 0 then pick it up else if its negative then we can choose to use power(if powerCount > 0) else not use power. And take the maximum answer from right and down. We can use memoization to reduce unecessary calls to things that are getting called again and again.
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(3*nm)
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(3*mn)
# Recursion-
```java[]
class Solution {
public int maximumAmount(int[][] coins) {
return getMaximumCoins(0, 0, coins, 2);
}
private int getMaximumCoins(int row, int col, int[][] coins, int powerCount) {
int n = coins.length, m = coins[0].length;
if(row >= n || col >= m) {
return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
} else if(row == n-1 && col == m-1) {
if(coins[n-1][m-1] >= 0) return coins[n-1][m-1];
else {
return powerCount > 0 ? 0 : coins[row][col];
}
} else {
if(coins[row][col] >= 0) {
int positiveTotal = coins[row][col] + Math.max(getMaximumCoins(row+1, col, coins, powerCount), getMaximumCoins(row, col+1, coins, powerCount));
return positiveTotal;
} else {
int total = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
if(powerCount > 0) {
int negativeTotalWithPowerUse = 0 + Math.max(getMaximumCoins(row+1, col, coins, powerCount-1), getMaximumCoins(row, col+1, coins, powerCount-1));
total = Math.max(total, negativeTotalWithPowerUse);
}
int negativeTotalWithoutPowerUse = coins[row][col] +
Math.max(
getMaximumCoins(row+1, col, coins, powerCount),
getMaximumCoins(row, col+1, coins, powerCount)
);
total = Math.max(total, negativeTotalWithoutPowerUse);
return total;
}
}
}
}
```
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
public int maximumAmount(int[][] coins) {
int n = coins.length, m=coins[0].length;
int[][][] dp = new int[n][m][3];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<m;j++) {
for(int k=0;k<3;k++) {
dp[i][j][k] = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
}
}
return getMaximumCoins(0, 0, coins, 2, dp);
}
private int getMaximumCoins(int row, int col, int[][] coins, int powerCount, int[][][] dp) {
int n = coins.length, m = coins[0].length;
// Base case if it goes out of bound return Minimum value and not 0(this could give wrong path answer)
if(row >= n || col >= m) {
return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
// If we already have the answer then return that no need to calculate
if(dp[row][col][powerCount] != Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
return dp[row][col][powerCount];
}
// base case if row, col == n-1, m-1 then check the cell value only
if(row == n-1 && col == m-1) {
if(coins[n-1][m-1] >= 0) {
return dp[n-1][m-1][powerCount] = coins[n-1][m-1];
}
return dp[n-1][m-1][powerCount] = (powerCount > 0 ? 0 : coins[row][col]);
}
int maxDownWithoutPowerUse = getMaximumCoins(row+1, col, coins, powerCount, dp);
int maxRightWithoutPowerUse = getMaximumCoins(row, col+1, coins, powerCount, dp);
if(coins[row][col] >= 0) {
return dp[row][col][powerCount] = coins[row][col]+Math.max(maxDownWithoutPowerUse, maxRightWithoutPowerUse);
} else {
int maxWithoutPowerUse = coins[row][col] + Math.max(maxDownWithoutPowerUse, maxRightWithoutPowerUse);
int maxWithPowerUse = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
if(powerCount > 0) {
int maxDownWithPowerUse = getMaximumCoins(row+1, col, coins, powerCount-1, dp);
int maxRightWithPowerUse = getMaximumCoins(row, col+1, coins, powerCount-1, dp);
maxWithPowerUse = Math.max(maxDownWithPowerUse, maxRightWithPowerUse);
}
return dp[row][col][powerCount] = Math.max(maxWithoutPowerUse, maxWithPowerUse);
}
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
My solution
|
my-solution-by-kkanra-1ag6
|
Code
|
KKanra
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-02T05:18:28.134405+00:00
|
2025-03-02T05:18:28.134405+00:00
| 6 | false |
# Code
```rust []
impl Solution {
pub fn maximum_amount(coins: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let rows = coins.len();
let cols = coins[0].len();
let mut memory = vec![[i32::MIN; 3]; rows];
memory[rows - 1] = [0; 3];
*(0..cols).rev().fold(memory, |mut mem, col| {
for row in (0..rows).rev() {
let pos_mon = coins[row][col];
for neu_rem in 0..=2 {
if neu_rem == 2 {
mem[row][neu_rem] = pos_mon
+ mem[row][neu_rem]
.max(mem.get(row + 1).map(|v| v[neu_rem]).unwrap_or(i32::MIN));
} else {
mem[row][neu_rem] = (pos_mon
+ mem[row][neu_rem]
.max(mem.get(row + 1).map(|v| v[neu_rem]).unwrap_or(i32::MIN)))
.max(
pos_mon.max(0)
+ mem[row][neu_rem + 1]
.max(mem.get(row + 1).map(|v| v[neu_rem + 1]).unwrap_or(i32::MIN)),
);
}
}
}
mem
})[0]
.iter()
.max()
.unwrap()
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Rust']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
C++ | Recursive DP
|
c-recursive-dp-by-kena7-y376
|
Code
|
kenA7
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-28T19:24:13.218307+00:00
|
2025-02-28T19:24:13.218307+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<vector<int>>>dp;
int m,n;
int find(int i,int j, int power, vector<vector<int>>& coins)
{
if(i==m-1 && j==n-1)
{
if(coins[i][j]>=0 || power==0)
return coins[i][j];
return 0;
}
if(dp[i][j][power]!=INT_MIN)
return dp[i][j][power];
int res=INT_MIN;
if(i+1<m)
{
res=max(res,coins[i][j]+find(i+1,j,power,coins));
if(coins[i][j]<0 && power>0)
res=max(res,find(i+1,j,power-1,coins));
}
if(j+1<n)
{
res=max(res,coins[i][j]+find(i,j+1,power,coins));
if(coins[i][j]<0 && power>0)
res=max(res,find(i,j+1,power-1,coins));
}
return dp[i][j][power]=res;
}
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins)
{
m=coins.size(),n=coins[0].size();
dp.resize(m,vector<vector<int>>(n,vector<int>(3,INT_MIN)));
return find(0,0,2,coins);
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Python
|
python-by-noobmaster696969-nu0t
| null |
noobmaster696969
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-14T02:33:36.647713+00:00
|
2025-02-14T02:33:36.647713+00:00
| 5 | false |
```python3 []
class Solution:
def maximumAmount(self, coins: List[List[int]]) -> int:
m, n = len(coins), len(coins[0])
@cache
def dfs(i,j,k) :
if i == m - 1 and j == n - 1 :
return max(0, coins[i][j]) if k else coins[i][j]
if i >= m or j >= n :
return -float("inf")
else :
skip = -float(inf)
if k and coins[i][j] < 0 :
skip = max(dfs(i + 1,j, k - 1), dfs(i, j + 1, k - 1))
take = coins[i][j] + max(dfs(i + 1, j, k), dfs(i, j + 1, k))
return max(skip,take)
return dfs(0,0,2)
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
scala dp
|
scala-dp-by-vititov-3gui
| null |
vititov
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-06T21:31:06.934178+00:00
|
2025-02-06T21:31:06.934178+00:00
| 2 | false |
```scala []
object Solution {
def maximumAmount(coins: Array[Array[Int]]): Int = {
val dp = Array.fill(coins.size,coins.head.size,4)(-250_000_001)
dp(0)(0)(0) = coins(0)(0); dp(0)(0)(1) = coins(0)(0) max 0
for{
k <- (0 to 2).iterator
i <- coins.indices.iterator
j <- coins.head.indices.iterator
} {
if(i>0) dp(i)(j)(k) = (dp(i-1)(j)(k)+coins(i)(j)) max dp(i)(j)(k)
if(j>0) dp(i)(j)(k) = (dp(i)(j-1)(k)+coins(i)(j)) max dp(i)(j)(k)
if(coins(i)(j)<0 && k<2) {
if(i>0) dp(i)(j)(k+1) = (dp(i-1)(j)(k)) max dp(i)(j)(k+1)
if(j>0) dp(i)(j)(k+1) = (dp(i)(j-1)(k)) max dp(i)(j)(k+1)
}
}
(0 to 2).map(dp(coins.size-1)(coins.head.size-1)).max
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Matrix', 'Scala']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
[Beats 100%]Very Simple C++ Solution with O(N) space
|
beats-100very-simple-c-solution-with-on-jmrxq
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity: O(2*M*N)
Space complexity:O(2*N)
Code
|
zyx5256
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-03T05:14:29.769064+00:00
|
2025-02-03T05:14:29.769064+00:00
| 10 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity: *O(2\*M\*N)*
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:*O(2\*N)*
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int m = coins.size();
int n = coins[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> prev(3, vector<int>(n + 1, -1000000));
vector<vector<int>> curr(3, vector<int>(n + 1, -1000000));
for (int k = 0; k < 3; ++k) {
prev[k][0] = 0;
prev[k][1] = 0;
curr[k][0] = 0;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
for (int k = 0; k < 3; ++k) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
curr[k][j] = max(prev[k][j], curr[k][j - 1]) + coins[i - 1][j - 1];
if (coins[i - 1][j - 1] < 0 && k > 0) {
curr[k][j] = max(max(curr[k - 1][j - 1], prev[k - 1][j]), curr[k][j]);
}
}
}
prev = curr;
curr = vector<vector<int>>(3, vector<int>(n + 1, -1000000));
}
return max(prev[0].back(), max(prev[1].back(), prev[2].back()));
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Clever python solution based on iterables
|
clever-python-solution-based-on-iterable-kc0z
|
Code
|
skookumchoocher
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-25T19:07:54.746172+00:00
|
2025-01-25T19:07:54.746172+00:00
| 7 | false |
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def maximumAmount(self, coins: List[List[int]]) -> int:
dp_0 = chain([(0,) * 3], repeat((-inf,) * 3))
dp_n = reduce(next_dp, coins, dp_0)
last = deque(dp_n, maxlen=1)[0]
return max(*last)
def next_dp(dp, row):
h0 = h1 = h2 = -inf
for (v0, v1, v2), coins in zip(dp, row):
h2 = max(v2 + coins, h2 + coins, v1, h1)
h1 = max(v1 + coins, h1 + coins, v0, h0)
h0 = max(v0 + coins, h0 + coins)
yield h0, h1, h2
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Bottom-Up & Top-Down
|
bottom-up-top-down-by-pabloteclado-77qs
|
Bottom-UpTop-Down
|
PabloTeclado
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-25T14:22:28.060156+00:00
|
2025-01-25T14:22:28.060156+00:00
| 10 | false |
# Bottom-Up
```python3 []
class Solution:
def maximumAmount(self, coins: List[List[int]]) -> int:
m,n = len(coins),len(coins[0])
dp = [[[float('-inf')] * 3 for _ in range(n)] for _ in range(m)]
dp[0][0][2] = coins[0][0]
if coins[0][0] < 0: dp[0][0][0] = dp[0][0][1] = 0
for x in range(m):
for y in range(n):
for neutralize in range(2,-1,-1):
if x > 0:
dp[x][y][neutralize] = max(dp[x][y][neutralize], coins[x][y] + dp[x-1][y][neutralize])
if neutralize < 2 and coins[x][y] < 0:
dp[x][y][neutralize] = max(dp[x][y][neutralize], dp[x-1][y][neutralize+1])
if y > 0:
dp[x][y][neutralize] = max(dp[x][y][neutralize], coins[x][y] + dp[x][y-1][neutralize])
if neutralize < 2 and coins[x][y] < 0:
dp[x][y][neutralize] = max(dp[x][y][neutralize], dp[x][y-1][neutralize+1])
return max(dp[m-1][n-1])
```
# Top-Down
```python3 []
class Solution:
def maximumAmount(self, coins: List[List[int]]) -> int:
m,n = len(coins),len(coins[0])
memo = [[[None] * 3 for _ in range(n)] for _ in range(m)]
def dfs(x,y,neutralize):
if x == m: return float('-inf')
if y == n: return float('-inf')
if (x,y) == (m-1,n-1):
return 0 if coins[x][y] < 0 and neutralize > 0 else coins[x][y]
if memo[x][y][neutralize] is None:
ans = coins[x][y]+max(dfs(x+1,y,neutralize),dfs(x,y+1,neutralize))
if neutralize > 0 and coins[x][y] < 0:
ans = max(ans,dfs(x+1,y,neutralize-1),dfs(x,y+1,neutralize-1))
memo[x][y][neutralize] = ans
return memo[x][y][neutralize]
return dfs(0,0,2)
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Python3']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
solved
|
solved-by-0mis-0b46
|
IntuitionThe problem requires the robot to collect the maximum coins while potentially neutralizing up to two robbers. The key challenge is deciding when to use
|
0mis
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-25T09:08:39.970764+00:00
|
2025-01-25T09:08:39.970764+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition
The problem requires the robot to collect the maximum coins while potentially neutralizing up to two robbers. The key challenge is deciding when to use the neutralizations to avoid the largest losses. Dynamic Programming (DP) is suitable here as it allows tracking the maximum coins collected at each cell while considering the remaining neutralizations.
# Approach
We use a 3D DP array dp[i][j][k], where i and j represent the current cell, and k (0, 1, or 2) tracks the remaining neutralizations. For each cell:
If the cell has coins (coins[i][j] >= 0), add them to the current total without changing k.
If the cell has a robber (coins[i][j] < 0), choose between:
Taking the loss (subtracting its absolute value) and keeping k unchanged.
Neutralizing it (adding 0 coins) and reducing k by 1 (if k > 0).
The DP transitions consider paths from the top and left cells, updating the maximum coins for each possible k.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
O(m * n)
The algorithm iterates through each cell of the grid once, and for each cell, it checks two directions (top and left) and three possible values of k. This results in O(m * n * 3 * 2) operations, which simplifies to O(m * n).
- Space complexity:
O(m * n)
The 3D DP array uses O(m * n * 3) space. Since k is bounded by a constant (2), the space complexity simplifies to O(m * n).
# Code
```python3 []
from typing import List
from math import inf
class Solution:
def maximumAmount(self, coins: List[List[int]]) -> int:
m = len(coins)
n = len(coins[0]) if m else 0
if m == 0 or n == 0:
return 0
# Initialize DP table with -infinity
dp = [[[-inf] * 3 for _ in range(n)] for __ in range(m)]
# Handle the starting cell (0, 0)
current_coin = coins[0][0]
if current_coin >= 0:
dp[0][0][2] = current_coin
else:
# Option 1: Do not neutralize, k remains 2
dp[0][0][2] = current_coin
# Option 2: Neutralize, k becomes 1, coins added 0
dp[0][0][1] = 0
# Iterate through each cell in row-major order
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if i == 0 and j == 0:
continue # already initialized
# Check both possible directions (up and left)
for di, dj in [(-1, 0), (0, -1)]:
pi, pj = i + di, j + dj
if pi < 0 or pj < 0:
continue # invalid previous cell
# Iterate through all possible k values for the previous cell
for prev_k in range(3):
prev_val = dp[pi][pj][prev_k]
if prev_val == -inf:
continue # no valid path through this previous state
current_coin_val = coins[i][j]
if current_coin_val >= 0:
# Add the current coin value, no change to k
new_val = prev_val + current_coin_val
new_k = prev_k
if new_val > dp[i][j][new_k]:
dp[i][j][new_k] = new_val
else:
# Option 1: Do not neutralize, subtract the absolute value
new_val1 = prev_val + current_coin_val
new_k1 = prev_k
if new_val1 > dp[i][j][new_k1]:
dp[i][j][new_k1] = new_val1
# Option 2: Neutralize if possible
if prev_k >= 1:
new_val2 = prev_val + 0
new_k2 = prev_k - 1
if new_val2 > dp[i][j][new_k2]:
dp[i][j][new_k2] = new_val2
# The result is the maximum value in the bottom-right cell for all k
max_result = max(dp[m-1][n-1][k] for k in range(3))
return max_result if max_result != -inf else 0
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
[Python] recursion + @cache = DP
|
python-dfs-cache-by-pbelskiy-t1ok
| null |
pbelskiy
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-23T16:06:58.715427+00:00
|
2025-01-23T16:07:36.646166+00:00
| 6 | false |
```python3
class Solution:
def maximumAmount(self, coins: List[List[int]]) -> int:
@cache
def dfs(y, x, r):
# we reach the final position
if y == h - 1 and x == w - 1:
return 0
m = float('-inf')
# go right
if x + 1 < w:
m = max(m, dfs(y, x + 1, r) + coins[y][x + 1])
if r > 0:
m = max(m, dfs(y, x + 1, r - 1))
# go down
if y + 1 < h:
m = max(m, dfs(y + 1, x, r) + coins[y + 1][x])
if r > 0:
m = max(m, dfs(y + 1, x, r - 1))
return m
h, w = len(coins), len(coins[0])
return max(dfs(0, 0, 1), dfs(0, 0, 2) + coins[0][0])
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Easy 3 d dp solution
|
easy-3-d-dp-solution-by-ejjvu4zego-f7nu
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
EJJVU4zeGO
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-23T09:25:59.567048+00:00
|
2025-01-23T09:25:59.567048+00:00
| 8 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int dp[501][501][3];
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int n = coins.size();
int m = coins[0].size();
for (int i = 0; i < 501; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < 501; ++j)
for (int k = 0; k < 3; ++k)
dp[i][j][k] = INT_MIN;
for(int k = 0; k < 3; k++){
for(int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--){
for(int j = m - 1; j >= 0; j--){
if( i == n-1 && j == m-1){
if(k > 0){
dp[i][j][k] = max(0, coins[i][j]);
}
else{
dp[i][j][k] = coins[i][j];
}
continue;
}
if(coins[i][j] >= 0){
int right = j + 1 < m ? dp[i][j + 1][k] : INT_MIN;
int down = i + 1 < n ? dp[i + 1][j][k] : INT_MIN;
dp[i][j][k] = coins[i][j] + max(right, down);
}else{
//take
int tright = INT_MIN;
int tdown = INT_MIN;
int take = INT_MIN;
if(k > 0){
tright = j + 1 < m ? dp[i][j + 1][k - 1] : INT_MIN;
tdown = i + 1 < n ? dp[i + 1][j][k - 1] : INT_MIN;
take = max(tright, tdown);
}
int nright = j + 1 < m ? dp[i][j + 1][k] : INT_MIN;
int ndown = i + 1 < n ? dp[i + 1][j][k] : INT_MIN;
int ntake = coins[i][j] + max(nright, ndown);
dp[i][j][k] = max(take, ntake);
}
}
}
}
return dp[0][0][2];
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Baring Accepted Solution But Easy To Understand | Memoization | O(m*n*2)
|
baring-accepted-solution-but-easy-to-und-nx98
|
Code
|
NinzaRJ01
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-22T04:07:55.176706+00:00
|
2025-01-22T04:07:55.176706+00:00
| 8 | false |
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
Integer[][][] memo;
private int process(int[][] coins, int i, int j, int count) {
if (memo[i][j][count] != null) return memo[i][j][count];
if (i == coins.length - 1 && j == coins[0].length - 1) {
if (coins[i][j] < 0 && count > 0)return memo[i][j][count] = 0;
return memo[i][j][count]=coins[i][j];
}
int max1 = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int max2 = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int[][] dirt = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}};
// Try normal moves
for (int[] d : dirt) {
int x = i + d[0];
int y = j + d[1];
if (x < coins.length && y < coins[0].length) {
max1 = Math.max(max1, process(coins, x, y, count));
if (coins[i][j] < 0 && count > 0) {
max2 = Math.max(max2, process(coins, x, y, count - 1));
}
}
}
// Store the result in the memo table
return memo[i][j][count] = Math.max(coins[i][j] + max1, max2);
}
public int maximumAmount(int[][] coins) {
int m = coins.length, n = coins[0].length;
memo = new Integer[m][n][3];
// for (int[][] mem : memo) for (int[] me : mem) Arrays.fill(me, -1);
return process(coins, 0, 0, 2);
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Easy Java Solution || Dynamic Programing || Top Down || Bottom Up
|
easy-java-solution-dynamic-programing-to-43iy
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
ravikumar50
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-21T20:17:29.283172+00:00
|
2025-01-21T20:17:29.283172+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
static int dp[][][];
static int findMaxProfitTopDown(int arr[][], int i, int j, int power){
int n = arr.length;
int m = arr[0].length;
if(i>=n || j>=m) return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
if(i==n-1 && j==m-1){
if(power>0 && arr[i][j]<0) return 0;
else return arr[i][j];
}
if(dp[i][j][power]!=Integer.MIN_VALUE) return dp[i][j][power];
int a = findMaxProfitTopDown(arr,i+1,j,power);
int b = findMaxProfitTopDown(arr,i,j+1,power);
int take = arr[i][j]+Math.max(a,b);
int notTake = -(int)1e9;
if(power>0 && arr[i][j]<0){
int c = findMaxProfitTopDown(arr,i+1,j,power-1);
int d = findMaxProfitTopDown(arr,i,j+1,power-1);
notTake = Math.max(c,d);
}
return dp[i][j][power] = Math.max(take,notTake);
}
static int findMaxProfitBottomUp(int arr[][]){
int n = arr.length;
int m = arr[0].length;
int dp[][][] = new int[n+1][m+1][3];
for (int p = 0; p < 3; p++) {
dp[n-1][m-1][p] = (p > 0 && arr[n-1][m-1] < 0) ? 0 : arr[n-1][m-1];
}
for(int p=0; p<3; p++){
for(int i=0; i<n+1; i++){
dp[i][m][p] = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
}
for(int p=0; p<3; p++){
for(int j=0; j<m+1; j++){
dp[n][j][p] = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
}
for(int i=n-1; i>=0; i--){
for(int j=m-1; j>=0; j--){
for(int power=0; power<3; power++){
if (i == n - 1 && j == m - 1) continue; // Skip
int a = dp[i+1][j][power];
int b = dp[i][j+1][power];
int take = arr[i][j]+Math.max(a,b);
int notTake = -(int)1e9;
if(power>0 && arr[i][j]<0){
int c = dp[i+1][j][power-1];
int d = dp[i][j+1][power-1];
notTake = Math.max(c,d);
}
dp[i][j][power] = Math.max(take,notTake);
}
}
}
return dp[0][0][2];
}
public int maximumAmount(int[][] coins) {
int n = coins.length;
int m = coins[0].length;
dp = new int[n+1][m+1][4];
for(var a : dp) for(var b : a) Arrays.fill(b,Integer.MIN_VALUE);
return findMaxProfitBottomUp(coins);
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
3D DP solution
|
3d-dp-solution-by-rickeypandya-gtn6
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
rickeypandya
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-19T18:41:08.288018+00:00
|
2025-01-19T18:41:08.288018+00:00
| 12 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& a) {
int m = a.size() ;
int n = a[0].size() ;
vector<vector<vector<int>>> dp ;
dp.resize(m , vector<vector<int>>(n , vector<int>(3, -1))) ;
if(a[0][0] >= 0){
dp[0][0][0] = a[0][0] ;
dp[0][0][1] = a[0][0] ;
dp[0][0][2] = a[0][0] ;
}else{
dp[0][0][0] = 0 ;
dp[0][0][1] = 0 ;
dp[0][0][2] = a[0][0];
}
for(int i = 1 ; i < n ; i++){
if(a[0][i] >= 0){
dp[0][i][0] = dp[0][i-1][0] + a[0][i] ;
dp[0][i][1] = dp[0][i-1][1] + a[0][i] ;
dp[0][i][2] = dp[0][i-1][2] + a[0][i] ;
}
else{
dp[0][i][0] = max({dp[0][i-1][0] + a[0][i] , dp[0][i-1][1]}) ;
dp[0][i][1] = max({dp[0][i-1][1] + a[0][i] , dp[0][i-1][2]}) ;
dp[0][i][2] = dp[0][i-1][2] + a[0][i] ;
}
}
for(int i = 1 ; i < m ; i++){
if(a[i][0] >= 0){
dp[i][0][0] = dp[i-1][0][0] + a[i][0] ;
dp[i][0][1] = dp[i-1][0][1] + a[i][0] ;
dp[i][0][2] = dp[i-1][0][2] + a[i][0] ;
}
else{
dp[i][0][0] = max({dp[i-1][0][0] + a[i][0] , dp[i-1][0][1]}) ;
dp[i][0][1] = max({dp[i-1][0][1] + a[i][0] , dp[i-1][0][2]}) ;
dp[i][0][2] = dp[i-1][0][2] + a[i][0] ;
}
}
for(int i = 1 ; i < m ; i++){
for(int j = 1 ; j < n ; j++){
if(a[i][j] >= 0){
dp[i][j][0] = max({dp[i-1][j][0] , dp[i][j-1][0]}) + a[i][j] ;
dp[i][j][1] = max({dp[i-1][j][1] , dp[i][j-1][1]}) + a[i][j] ;
dp[i][j][2] = max({dp[i-1][j][2] , dp[i][j-1][2]}) + a[i][j] ;
}
else{
dp[i][j][0] = max({dp[i-1][j][1] ,
dp[i][j-1][1] ,
dp[i-1][j][0] + a[i][j] ,
dp[i][j-1][0] + a[i][j]});
dp[i][j][1] = max({dp[i-1][j][2] ,
dp[i][j-1][2] ,
dp[i-1][j][1] + a[i][j] ,
dp[i][j-1][1] + a[i][j]});
dp[i][j][2] = max({dp[i-1][j][2] + a[i][j] ,
dp[i][j-1][2] + a[i][j]});
}
}
}
return max({dp[m-1][n-1][0] , dp[m-1][n-1][1] , dp[m-1][n-1][2]}) ;
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Can anyone explain why my solution is giving TLE,
|
can-anyone-explain-why-my-solution-is-gi-ciap
|
IntuitionCan anyone explain why my code is giving TLE, maybe if I convert it into tabularization it might work but i want to find out the reason.PS : i tried wi
|
niti_n_n_itin
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-19T13:59:09.909442+00:00
|
2025-01-19T13:59:09.909442+00:00
| 9 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
Can anyone explain why my code is giving TLE, maybe if I convert it into tabularization it might work but i want to find out the reason.
PS : i tried with adding fast i/o line too.
# Approach
3D Dp -> i , j, k where i and j are the coordinate of the cell and k represent the power of the robot to neutralize robber.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
O ( n * m * k) which is basically O(n * m) because k is constant.
- Space complexity:
O ( N * M * K)
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int traverse(vector<vector< vector<int> > > &dp, int i, int j, vector<vector<int>> & ar, int k, int n, int m){
if(i >= n || j >= m){
return -1000000;
}
if(i == (n - 1) && j == (m - 1) ){
if (ar[i][j] >= 0 || k <= 0)
return ar[i][j];
return 0;
}
if(dp[i][j][k] != -1) return dp[i][j][k];
int ans = traverse(dp, i + 1, j, ar, k, n, m) + ar[i][j];
ans = max(ans, traverse(dp, i, j + 1, ar, k, n, m) + ar[i][j] );
if(k > 0 && ar[i][j] < 0){
ans = max(ans, traverse(dp, i , j + 1, ar, k -1, n, m));
ans = max(ans, traverse(dp, i + 1, j, ar, k - 1, n, m));
}
return dp[i][j][k] = ans;
}
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& ar) {
int n = ar.size();
int m = ar[0].size();
vector<vector< vector<int> > > dp(n, vector<vector<int>> (m, vector<int>(3, -1)));
return traverse(dp, 0, 0, ar, 2, n, m);
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Java based solution || 3D DP
|
java-based-solution-3d-dp-by-ankurdwived-p4f0
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
once u understand the state dp[i][j][k]=max coins robot can take from cell (i,j) -> cell (n-1,m-
|
ankurdwivedy
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-19T09:15:28.342236+00:00
|
2025-01-19T09:15:28.342236+00:00
| 0 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->O(n*m)
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->O(n*m)
once u understand the state dp[i][j][k]=max coins robot can take from cell (i,j) -> cell (n-1,m-1) while neutralizing upto k robbers the transition follows.
Code has comments for base case and transition.
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
public int maximumAmount(int[][] coins) {
return maxProfit(coins);
}
public int maxProfit(int[][] coins) {
int m = coins.length;
int n = coins[0].length;
int maxNeutralize = 2;
int[][][] dp = new int[m][n][maxNeutralize + 1];
// Initialize with MIN_VALUE
for (int[][] grid : dp) {
for (int[] row : grid) {
Arrays.fill(row, Integer.MIN_VALUE);
}
}
// Initialize bottom-right corner
for (int k = 0; k <= maxNeutralize; k++) {
if (coins[m-1][n-1] >= 0) {
dp[m-1][n-1][k] = coins[m-1][n-1];
} else if (k > 0) {
dp[m-1][n-1][k] = 0;
} else {
dp[m-1][n-1][k] = coins[m-1][n-1];
}
}
for (int i = m - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = n - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (i == m-1 && j == n-1) continue;
for (int k = 0; k <= maxNeutralize; k++) {
// Try all possible moves from current position
if (coins[i][j] >= 0) {
// For positive or zero values, just add them
if (j + 1 < n && dp[i][j+1][k] != Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
dp[i][j][k] = Math.max(dp[i][j][k], coins[i][j] + dp[i][j+1][k]);
}
if (i + 1 < m && dp[i+1][j][k] != Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
dp[i][j][k] = Math.max(dp[i][j][k], coins[i][j] + dp[i+1][j][k]);
}
} else {
// For negative values (robbers)
// Option 1: Neutralize the robber if we have neutralizations left
if (k > 0) {
if (j + 1 < n && dp[i][j+1][k-1] != Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
dp[i][j][k] = Math.max(dp[i][j][k], dp[i][j+1][k-1]);
}
if (i + 1 < m && dp[i+1][j][k-1] != Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
dp[i][j][k] = Math.max(dp[i][j][k], dp[i+1][j][k-1]);
}
}
// Option 2: Don't neutralize and take the penalty
if (j + 1 < n && dp[i][j+1][k] != Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
dp[i][j][k] = Math.max(dp[i][j][k], coins[i][j] + dp[i][j+1][k]);
}
if (i + 1 < m && dp[i+1][j][k] != Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
dp[i][j][k] = Math.max(dp[i][j][k], coins[i][j] + dp[i+1][j][k]);
}
}
}
}
}
int result = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int k = 0; k <= maxNeutralize; k++) {
result = Math.max(result, dp[0][0][k]);
}
return result == Integer.MIN_VALUE ? 0 : result;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Java']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Java based solution || 3D DP
|
java-based-solution-3d-dp-by-ankurdwived-gfcc
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
once u understand the state dp[i][j][k]=max coins robot can take from cell (i,j) -> cell (n-1,m-
|
ankurdwivedy
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-19T09:15:25.010163+00:00
|
2025-01-19T09:15:25.010163+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->O(n*m)
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->O(n*m)
once u understand the state dp[i][j][k]=max coins robot can take from cell (i,j) -> cell (n-1,m-1) while neutralizing upto k robbers the transition follows.
Code has comments for base case and transition.
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
public int maximumAmount(int[][] coins) {
return maxProfit(coins);
}
public int maxProfit(int[][] coins) {
int m = coins.length;
int n = coins[0].length;
int maxNeutralize = 2;
int[][][] dp = new int[m][n][maxNeutralize + 1];
// Initialize with MIN_VALUE
for (int[][] grid : dp) {
for (int[] row : grid) {
Arrays.fill(row, Integer.MIN_VALUE);
}
}
// Initialize bottom-right corner
for (int k = 0; k <= maxNeutralize; k++) {
if (coins[m-1][n-1] >= 0) {
dp[m-1][n-1][k] = coins[m-1][n-1];
} else if (k > 0) {
dp[m-1][n-1][k] = 0;
} else {
dp[m-1][n-1][k] = coins[m-1][n-1];
}
}
for (int i = m - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = n - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (i == m-1 && j == n-1) continue;
for (int k = 0; k <= maxNeutralize; k++) {
// Try all possible moves from current position
if (coins[i][j] >= 0) {
// For positive or zero values, just add them
if (j + 1 < n && dp[i][j+1][k] != Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
dp[i][j][k] = Math.max(dp[i][j][k], coins[i][j] + dp[i][j+1][k]);
}
if (i + 1 < m && dp[i+1][j][k] != Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
dp[i][j][k] = Math.max(dp[i][j][k], coins[i][j] + dp[i+1][j][k]);
}
} else {
// For negative values (robbers)
// Option 1: Neutralize the robber if we have neutralizations left
if (k > 0) {
if (j + 1 < n && dp[i][j+1][k-1] != Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
dp[i][j][k] = Math.max(dp[i][j][k], dp[i][j+1][k-1]);
}
if (i + 1 < m && dp[i+1][j][k-1] != Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
dp[i][j][k] = Math.max(dp[i][j][k], dp[i+1][j][k-1]);
}
}
// Option 2: Don't neutralize and take the penalty
if (j + 1 < n && dp[i][j+1][k] != Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
dp[i][j][k] = Math.max(dp[i][j][k], coins[i][j] + dp[i][j+1][k]);
}
if (i + 1 < m && dp[i+1][j][k] != Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
dp[i][j][k] = Math.max(dp[i][j][k], coins[i][j] + dp[i+1][j][k]);
}
}
}
}
}
int result = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int k = 0; k <= maxNeutralize; k++) {
result = Math.max(result, dp[0][0][k]);
}
return result == Integer.MIN_VALUE ? 0 : result;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Java']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
C++ DP :)
|
c-dp-by-asmitpapney-lj0z
|
Code
|
asmitpapney
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-18T15:48:32.957107+00:00
|
2025-01-18T15:48:32.957107+00:00
| 12 | false |
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int t[502][502][3];
int Solve(vector<vector<int>>&A, int i, int j, int powerUsed){
int N = A.size(), M = A[0].size();
if(i >= N || j>= M) return -1e9;
if(i==N-1 && j==M-1){
if(A[i][j] >= 0 ) return A[i][j];
if(powerUsed < 2) return 0;
return A[i][j];
}
if(t[i][j][powerUsed]!=-1)
return t[i][j][powerUsed];
int Ans = -1e9;
if(A[i][j] >= 0) {
Ans = max(Ans, A[i][j] +
max(Solve(A, i+1, j, powerUsed), Solve(A, i, j+1, powerUsed))
);
} else{
if(powerUsed < 2){
Ans = 0 + max(Ans,
max(Solve(A, i+1, j, powerUsed+1), Solve(A, i, j+1, powerUsed+1))
);
}
Ans = max(Ans, A[i][j] + max(Solve(A, i+1, j, powerUsed), Solve(A, i, j+1, powerUsed)) );
}
return t[i][j][powerUsed] = Ans;
}
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
memset(t, -1, sizeof(t));
return Solve(coins, 0, 0, 0);
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Dynamic Programming Solution | C++
|
dynamic-programming-solution-c-by-predat-3dfd
|
IntuitionApproachDefine a state and recurrence relation that accounts for the robot's ability to neutralize robbers in at most two cells.Complexity
Time complex
|
Predator21X
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-18T11:26:51.088136+00:00
|
2025-01-18T11:26:51.088136+00:00
| 11 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
Define a state and recurrence relation that accounts for the robot's ability to neutralize robbers in at most two cells.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(m×n×3)=O(m×n), we compute the DP table for each cell and each robber-neutralization state.
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(m×n×3) for the DP table.
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int m = coins.size();
int n = coins[0].size();
vector<vector<vector<int>>> dp(m, vector<vector<int>>(n, vector<int>(3, INT_MIN)));
// Base case
for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++) {
dp[0][0][k] = coins[0][0] >= 0 ? coins[0][0] : (k > 0 ? 0 : coins[0][0]);
}
// DP Transition
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++) {
if (i == 0 && j == 0) continue;
int currentValue = coins[i][j];
int neutralizeValue = (currentValue < 0 && k > 0) ? 0 : currentValue;
if (j > 0) { // From the left
dp[i][j][k] = max(dp[i][j][k], dp[i][j - 1][k] + currentValue);
if (currentValue < 0 && k > 0) {
dp[i][j][k] = max(dp[i][j][k], dp[i][j - 1][k - 1] + neutralizeValue);
}
}
if (i > 0) { // From above
dp[i][j][k] = max(dp[i][j][k], dp[i - 1][j][k] + currentValue);
if (currentValue < 0 && k > 0) {
dp[i][j][k] = max(dp[i][j][k], dp[i - 1][j][k - 1] + neutralizeValue);
}
}
}
}
}
// Find the maximum profit at the bottom-right corner
return max({dp[m - 1][n - 1][0], dp[m - 1][n - 1][1], dp[m - 1][n - 1][2]});
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Java
|
java-by-atulraju-4pfb
|
Understanding the Problem StatementThis problem involves a grid of integers (coins), where each cell contains a value representing coins you can collect or a pe
|
atulraju
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-18T08:52:38.786603+00:00
|
2025-01-18T08:52:38.786603+00:00
| 6 | false |
### Understanding the Problem Statement
This problem involves a grid of integers (`coins`), where each cell contains a value representing coins you can collect or a penalty (negative value). Starting from the top-left corner, the goal is to reach the bottom-right corner while maximizing the coins collected. You may move either **down** or **right**. Additionally, you are allowed to "ignore" negative penalties up to **two times** (`k=2`) during your journey.
---
### Code Breakdown and Explanation
The provided code solves the problem using **dynamic programming (DP)** and recursion. Let’s break down the solution step by step:
---
#### 1. **Initial Setup**
The class `Solution` includes:
- A 3D array `dp` to store intermediate results and avoid redundant calculations (memoization).
- Variables `m` and `n` to store the dimensions of the grid.
```java
Integer [][][] dp;
int m, n;
```
---
#### 2. **Core Functionality**
The key methods are:
1. **`maximumAmount(int[][] coins)`**:
- Initializes `m`, `n`, and the `dp` array.
- Calls the recursive helper function `solve` starting from the top-left cell `(0, 0)` with `k=2` remaining skips.
2. **`solve(int i, int j, int k, int[][] coins)`**:
- A recursive function that explores all possible paths to maximize the coin collection.
- Accounts for grid boundaries and skips penalties intelligently.
---
#### 3. **Recursive Logic**
**Base Case:**
- If the current position is out of bounds, return a large negative value (`Integer.MIN_VALUE`), as it is not a valid path.
- If we are at the bottom-right corner (`i == m - 1 && j == n - 1`):
- If the value is positive or zero, return it.
- If it’s negative, reduce it to 0 only if `k > 0` (i.e., a skip is available).
```java
if (i == m - 1 && j == n - 1) {
int c = coins[i][j];
if (c >= 0) dp[i][j][k] = c;
else dp[i][j][k] = (k > 0) ? Math.max(c, 0) : c;
return dp[i][j][k];
}
```
---
#### 4. **Recursive Transitions**
For each cell `(i, j)`:
1. Compute the maximum coins collected by moving **down** and **right**:
```java
int down = solve(i + 1, j, k, coins);
int right = solve(i, j + 1, k, coins);
int best = Math.max(right, down);
```
2. Handle two cases for the current cell value `c = coins[i][j]`:
- If `c >= 0`, add it to the `best` value.
- If `c < 0`, decide between:
- Paying the penalty: `c + best`.
- Skipping the penalty (if `k > 0`), exploring the remaining paths with `k - 1` skips:
```java
int skipDown = solve(i + 1, j, k - 1, coins);
int skipRight = solve(i, j + 1, k - 1, coins);
not = Math.max(skipDown, skipRight);
dp[i][j][k] = Math.max(pay, not);
```
---
#### 5. **Memoization**
To avoid redundant calculations, the results for each state `(i, j, k)` are stored in the `dp` array. Before computing a result, the function checks if the value is already cached.
```java
if (dp[i][j][k] != null) {
return dp[i][j][k];
}
```
---
### Example Walkthrough
For the input grid:
```
coins = [[ 0, 1, -1],
[ 1, -2, 3],
[ 2, -3, 4]]
```
1. Starting at `(0, 0)` with `k = 2`:
- Possible moves: `(1, 0)` or `(0, 1)`.
2. At `(1, 0)`, compute:
- Maximum coins collected by going down or right.
- Handle the penalty `-2` at `(1, 1)` using one of the skips (`k - 1`).
3. Continue recursively until reaching the bottom-right corner `(2, 2)`.
---
### Output for Example Input
The optimal path is:
`(0, 0) -> (0, 1) -> (1, 1) -> (1, 2) -> (2, 2)`, with `k=1` skip used at `(1, 1)`.
The maximum coins collected = **9**.
---
### Key Points
- **Dynamic Programming** ensures efficiency by storing previously computed results.
- **Penalty Skipping** (`k > 0`) is critical to finding the optimal path.
- The solution explores all valid paths and handles negative penalties intelligently.
This approach ensures the problem is solved within acceptable time limits for large grids.
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
Integer [][][] dp;
int m,n;
public int maximumAmount(int[][] coins) {
m=coins.length;
n=coins[0].length;
dp = new Integer[m][n][3];
return solve(0,0,2,coins);
}
private int solve(int i,int j,int k,int[][] coins){
if(i<0 || j<0 || j>=n ||i>=m) return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
if (dp[i][j][k] != null) {
return dp[i][j][k];
}
if (i == m- 1 && j == n - 1){
int c= coins[i][j];
if(c>=0) dp[i][j][k]=c;
else{
if(k>0) dp[i][j][k] =Math.max(c,0);
else dp[i][j][k]=c;
}
return dp[i][j][k];
}
int c=coins[i][j];
int down = solve(i + 1, j, k,coins);
int right = solve(i, j + 1, k, coins);
int best=Math.max(right,down);
if(c>=0){
dp[i][j][k]=c+best;
}else{
int pay= c+best;
int not = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
if (k>0) {
int skipDown = solve(i + 1, j, k - 1, coins);
int skipRight = solve(i, j + 1, k - 1, coins);
not = Math.max(skipDown, skipRight);
}
dp[i][j][k]= Math.max(pay,not);
}
return dp[i][j][k];
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 1 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
C++ || Dynamic Programming || Memoization || Simple Code
|
c-dynamic-programming-memoization-simple-x2hp
|
Complexity
Time complexity: O (M * N * 3)
Space complexity: O (M * N * 3)
Code
|
Thangakumaran
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-18T06:15:01.425115+00:00
|
2025-01-18T06:15:01.425115+00:00
| 13 | false |
# Complexity
- Time complexity: O (M * N * 3)
- Space complexity: O (M * N * 3)
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int fun(int i , int j, int pass, vector<vector<int>>& coins, vector<vector<vector<int>>>& dp)
{
if(i == 0 && j == 0)
{
return (coins[i][j] >= 0) ? coins[i][j] : (pass >= 1) ? 0 : coins[i][j];
}
if(i < 0 || j < 0) return -1e8;
if(dp[i][j][pass] != 1e9 ) return dp[i][j][pass];
int one , two;
if(coins[i][j] >= 0){
one = coins[i][j] + fun(i - 1, j, pass, coins, dp);
two = coins[i][j] + fun(i, j - 1, pass, coins, dp);
}else{
one = INT_MIN, two = INT_MIN;
if(pass >= 1){
one = fun(i - 1, j, pass - 1, coins, dp);
two = fun(i , j - 1, pass - 1, coins, dp);
}
one = max(one, fun(i - 1, j, pass, coins, dp) - abs(coins[i][j]));
two = max(two, fun(i, j - 1, pass, coins, dp) - abs(coins[i][j]));
}
return dp[i][j][pass] = max(one, two);
}
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins)
{
int m = coins.size(), n = coins[0].size(), ans;
vector<vector<vector<int>>> dp(m, vector<vector<int>>(n, vector<int>(3, 1e9)));
ans = fun(m - 1, n - 1, 2, coins, dp);
return ans;
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Iterative Solution
|
iterative-solution-by-dnanper-81wc
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
dnanper
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-18T04:20:42.958922+00:00
|
2025-01-18T04:20:42.958922+00:00
| 6 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int n = coins.size(), m = coins[0].size();
vector<vector<vector<int>>> dp(n, vector<vector<int>>(m, vector<int>(3, INT_MIN)));
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j) {
for (int k = 0; k <= 2; ++k) {
if (i == 0 && j == 0)
{
dp[i][j][k] = k < 2 ? max(0, coins[i][j]) : coins[i][j];
continue;
}
if (i > 0)
{
dp[i][j][k] = max(dp[i][j][k], coins[i][j] + dp[i-1][j][k]);
if (coins[i][j] < 0 && k < 2)
dp[i][j][k] = max(dp[i][j][k], dp[i-1][j][k+1]);
}
if (j > 0)
{
dp[i][j][k] = max(dp[i][j][k], coins[i][j] + dp[i][j-1][k]);
if (coins[i][j] < 0 && k < 2)
dp[i][j][k] = max(dp[i][j][k], dp[i][j-1][k+1]);
}
}
}
}
return *max_element(dp[n-1][m-1].begin(), dp[n-1][m-1].end());
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Dynamic Programming with a 3D Matrix
|
dynamic-programming-with-a-3d-matrix-by-xnyyj
|
IntuitionWe will create a matrix, where each cell contains the maximum possible coins which the robot can obtain by starting its jounrney from that cell.Approac
|
AbhayRajpootIndia
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-17T20:16:03.761812+00:00
|
2025-02-23T13:13:30.496408+00:00
| 22 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
We will create a matrix, where each cell contains the maximum possible coins which the robot can obtain by starting its jounrney from that cell.
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
Each cell has three dimensions:-
1. First (0) - The row of that cell.
2. Second (1) - The column of that cell.
3. Third (2) - Number of remaining neutralizations when arriving at that cell.
We start from the last cell, and calculate the values of all cells in reverse, untill we reach the first cell.
#### The formula I came up with is given below:
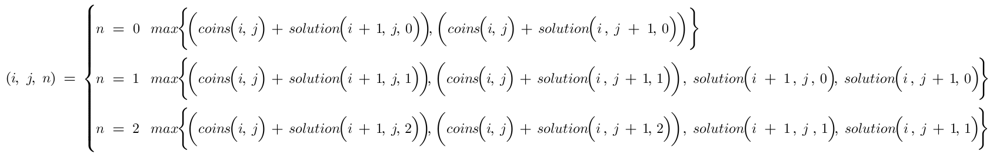
##### Where: i = row, j = column, n = no. of neutralizations left
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
$$O(n^2)$$
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
$$O(n^2)$$
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
public int maximumAmount(int[][] coins) {
// Number of rows
int m = coins.length;
// Number of columns
int n = coins[0].length;
// 3D Matrix for storing all posible steps
int[][][] solution = new int[m][n][3];
// Iteration variables
int row = 0, col = 0;
int currentBlock = 0;
// For -ve current value
int[] neutralizeRobber = new int[3];
int[] dontNeutralizeRobber = new int[3];
// For +ve current value
int[] currentBlockMax = new int[3];
// Booleans for validating whether the robot can
// move Right or move Down
boolean canRobotMoveRight = false;
boolean canRobotMoveDown = false;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
// Iterate each row
row = m - 1 - i;
// Calculate posible down movements
canRobotMoveDown = row + 1 < m;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// Iterate each column
col = n - 1 - j;
// Value of the current block
currentBlock = coins[row][col];
// Calculate posible right movements
canRobotMoveRight = col + 1 < n;
if (currentBlock < 0) {
// If current block is a Robber
// Initialize with MIN integer value
neutralizeRobber[0] = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
neutralizeRobber[1] = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
// Initialize with MIN integer value
dontNeutralizeRobber[0] = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
dontNeutralizeRobber[1] = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
dontNeutralizeRobber[2] = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
if (!canRobotMoveRight && !canRobotMoveDown) {
// Current block is the last block
neutralizeRobber[0] = 0;
neutralizeRobber[1] = 0;
dontNeutralizeRobber[0] = currentBlock;
dontNeutralizeRobber[1] = currentBlock;
dontNeutralizeRobber[2] = currentBlock;
}
if (canRobotMoveRight) {
// Calculate values for possible steps when moving right
// and neutralizing the robber
neutralizeRobber[0] = solution[row][col + 1][0];
neutralizeRobber[1] = max(solution[row][col + 1][0], solution[row][col + 1][1]);
// Calculate values for possible steps when moving right
// and not neutralizing the robber
dontNeutralizeRobber[0] = currentBlock + solution[row][col + 1][0];
dontNeutralizeRobber[1] = currentBlock + max(solution[row][col + 1][0], solution[row][col + 1][1]);
dontNeutralizeRobber[2] = currentBlock + max(solution[row][col + 1][1], solution[row][col + 1][2]);
}
if (canRobotMoveDown) {
// Calculate values for possible steps when moving down
// and neutralizing the robber
neutralizeRobber[0] = max(neutralizeRobber[0], solution[row + 1][col][0]);
neutralizeRobber[1] = max(neutralizeRobber[1], max(solution[row + 1][col][0], solution[row + 1][col][1]));
// Calculate values for possible steps when moving down
// and not neutralizing the robber
dontNeutralizeRobber[0] = max(dontNeutralizeRobber[0], currentBlock + solution[row + 1][col][0]);
dontNeutralizeRobber[1] = max(dontNeutralizeRobber[1], currentBlock + max(solution[row + 1][col][0], solution[row + 1][col][1]));
dontNeutralizeRobber[2] = max(dontNeutralizeRobber[2], currentBlock + max(solution[row + 1][col][1], solution[row + 1][col][2]));
}
// Calculate the overall solution for the current block
// for all posibilities
solution[row][col][0] = dontNeutralizeRobber[0];
solution[row][col][1] = max(dontNeutralizeRobber[1], neutralizeRobber[0]);
solution[row][col][2] = max(dontNeutralizeRobber[2], neutralizeRobber[1]);
}
else {
// Initialize with MIN integer value
currentBlockMax[0] = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
currentBlockMax[1] = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
currentBlockMax[2] = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
if (!canRobotMoveRight && !canRobotMoveDown) {
// Current block is the last block
currentBlockMax[0] = currentBlock;
currentBlockMax[1] = currentBlock;
currentBlockMax[2] = currentBlock;
}
if (canRobotMoveRight) {
// Calculate values for possible steps when moving right
currentBlockMax[0] = currentBlock + solution[row][col + 1][0];
currentBlockMax[1] = currentBlock + solution[row][col + 1][1];
currentBlockMax[2] = currentBlock + solution[row][col + 1][2];
}
if (canRobotMoveDown) {
// Calculate values for possible steps when moving down
currentBlockMax[0] = max(currentBlockMax[0], currentBlock + solution[row + 1][col][0]);
currentBlockMax[1] = max(currentBlockMax[1], currentBlock + solution[row + 1][col][1]);
currentBlockMax[2] = max(currentBlockMax[2], currentBlock + solution[row + 1][col][2]);
}
// Calculate the overall solution for the current block
// for all posibilities
solution[row][col][0] = currentBlockMax[0];
solution[row][col][1] = currentBlockMax[1];
solution[row][col][2] = currentBlockMax[2];
}
}
}
return max(solution[0][0][0], max(solution[0][0][1], solution[0][0][2]));
}
public static int max(int firstNumber, int secondNumber) {
// Return the largest number
return firstNumber > secondNumber ? firstNumber : secondNumber;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
DP recursion with Memoization
|
dp-recursion-with-memoization-by-prateek-r2o6
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
prateekrai2602
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-17T16:48:03.485022+00:00
|
2025-01-17T16:48:03.485022+00:00
| 8 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
int f(int[][] coins , int i , int j , int k , Integer[][][] dp){
int n = coins.length;
int m = coins[0].length;
if(i == n-1 && j == m-1){
if(coins[i][j] > 0 ){
return coins[i][j];
}
else{
if(k > 0) return 0;
else return coins[i][j];
}
}
if(i == coins.length || j == coins[0].length) return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
if(dp[i][j][k]!=null) return dp[i][j][k];
if(coins[i][j] > 0 ){
return dp[i][j][k] =coins[i][j] + Math.max(f(coins , i +1 , j , k , dp) , f(coins , i , j+1 , k , dp));
}
else{
if(k > 0){
int skip = Math.max(f(coins , i +1 , j , k-1 , dp) , f(coins , i , j+1 , k-1 , dp));
int give = coins[i][j] + Math.max(f(coins , i +1 , j , k ,dp) , f(coins , i , j+1 , k, dp));
return dp[i][j][k]= Math.max(skip , give);
}
else{
return dp[i][j][k]= coins[i][j] + Math.max(f(coins , i +1 , j , k , dp) , f(coins , i , j+1 , k , dp));
}
}
}
public int maximumAmount(int[][] coins) {
int n = coins.length;
int m = coins[0].length;
return f(coins , 0 , 0 , 2 , new Integer[n+1][m+1][3]);
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
489 ms Beats 54.37% || All Test Case Passed
|
489-ms-beats-5437-all-test-case-passed-b-6b8m
|
IntuitionThe intuition behind the solution is to track the maximum coins the robot can collect while considering the two key factors: the robot's ability to neu
|
shashwatt1
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-17T10:45:37.108361+00:00
|
2025-01-17T10:45:37.108361+00:00
| 8 | false |
# Intuition
The intuition behind the solution is to **track the maximum coins** the robot can collect while **considering the two key factors**: the robot's ability to neutralize robbers and the path it takes through the grid. We use **dynamic programming** to break the problem down into manageable subproblems.
### Key Ideas:
1. **State Representation**:
- At any cell `(i, j)`, we need to remember:
- The **maximum coins** collected so far.
- The number of **neutralizations** used so far (since the robot can neutralize up to 2 robbers).
2. **Transitions**:
- From any cell, the robot can either move **right** or **down**.
- If the robot encounters a **robber** (negative coins), it has two choices:
1. **Neutralize** the robber (if it hasn't used both neutralizations).
2. **Take the penalty** and lose coins.
- If there's no robber, the robot just **gains coins**.
3. **Goal**:
- Maximize the **total coins** collected when reaching the bottom-right corner of the grid.
### Intuition:
- The robot needs to consider **all possible paths** to reach the destination while deciding when to **neutralize robbers**.
- It uses a **3D DP table** to track:
- The maximum coins collected.
- The number of neutralizations used (0, 1, or 2).
- The result is the maximum value from the last cell `(m-1, n-1)` considering all neutralizations (0, 1, or 2).
By breaking down the problem into these subproblems and considering neutralization as an optional decision at each step, the robot can ensure it makes the **optimal decisions** at each point to maximize its profit.
# Approach
To solve the problem efficiently, we use a **Dynamic Programming (DP)** approach that keeps track of the maximum coins the robot can collect while considering all possible paths and the option to neutralize robbers. Here's the approach in detail:
### 1. **State Representation**:
We define a 3D DP array `dp[i][j][k]`:
- `i` represents the row index.
- `j` represents the column index.
- `k` represents the number of robbers neutralized up to that point (0, 1, or 2).
The value of `dp[i][j][k]` holds the maximum coins collected at cell `(i, j)` with exactly `k` neutralizations used.
### 2. **Initialization**:
- **Starting Point**: The robot begins at the top-left corner of the grid `(0, 0)`. We initialize the DP table based on whether the starting cell contains a robber or not:
- If `coins[0][0] < 0`, we initialize `dp[0][0][1] = 0` (since neutralizing the first robber would avoid the coin loss).
- If `coins[0][0] >= 0`, we initialize `dp[0][0][0] = coins[0][0]` (the robot gains coins at the start).
### 3. **Transitions**:
From each cell `(i, j)`, the robot can move either **right** or **down**:
- **Moving Right**: If the robot moves to cell `(i, j+1)`:
- If the cell contains a **non-negative number** (coins), the robot simply collects those coins.
- If the cell contains a **negative number** (robber), the robot can either:
- **Neutralize** the robber (if it has neutralizations left).
- **Take the penalty** (losing the coins).
- **Moving Down**: The same logic applies when moving down to cell `(i+1, j)`.
For each move, the DP value is updated considering both options: neutralize or take the penalty.
### 4. **Final Result**:
The robot reaches the bottom-right corner `(m-1, n-1)`. We check the maximum value of `dp[m-1][n-1][0]`, `dp[m-1][n-1][1]`, and `dp[m-1][n-1][2]` because the robot could have neutralized 0, 1, or 2 robbers on the path.
### 5. **Time and Space Complexity**:
- **Time Complexity**: \(O(m \times n \times 3)\), where `m` is the number of rows, `n` is the number of columns, and `3` is the number of possible neutralization states.
- **Space Complexity**: \(O(m \times n \times 3)\), as we need to store the DP table with 3 possible neutralization states for each cell.
### Conclusion:
By maintaining a dynamic programming table that considers the maximum coins collected and the number of neutralizations used, we can efficiently compute the maximum profit the robot can make while traversing the grid. This approach ensures that the robot makes the optimal decision at each step, balancing the trade-off between neutralizing robbers and collecting coins.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
The time complexity depends on the size of the grid and the number of states (neutralizations) we are tracking.
Grid size: The grid has m rows and n columns, so there are a total of m * n cells in the grid.
States: For each cell (i, j), we track 3 possible states based on the number of neutralizations used (0, 1, and 2).
Thus, for each of the m * n cells, we are considering 3 possible neutralization states. For each state, the robot can move either right or down, and we are updating the DP table based on the conditions (whether to neutralize a robber or not, and the coins gained or lost).
For each cell: We are updating the value for 3 states, and each update takes constant time
𝑂(1).
Total cells: There are m * n cells.
States per cell: There are 3 possible neutralization states for each cell.
Therefore, the overall time complexity is:
𝑂(𝑚×𝑛×3) = 𝑂(𝑚×𝑛)
Since the factor of 3 is constant, it doesn't affect the overall complexity.
- Space complexity:
Space Complexity:
𝑂(𝑚×𝑛)
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int m = coins.size();
int n = coins[0].size();
// DP array: dp[i][j][k] stores the max coins at (i, j) with k neutralizations used
vector<vector<vector<int>>> dp(m, vector<vector<int>>(n, vector<int>(3, INT_MIN)));
// Initialization for the starting cell
dp[0][0][0] = coins[0][0]; // Start without neutralization
if (coins[0][0] < 0) dp[0][0][1] = 0; // Neutralize if starting with a robber
// Fill the DP table
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
for (int k = 0; k <= 2; ++k) {
if (dp[i][j][k] == INT_MIN) continue;
// Move right
if (j + 1 < n) {
int nextCell = coins[i][j + 1];
// Case 1: Don't neutralize
dp[i][j + 1][k] = max(dp[i][j + 1][k], dp[i][j][k] + nextCell);
// Case 2: Neutralize if it's a robber
if (nextCell < 0 && k + 1 <= 2) {
dp[i][j + 1][k + 1] = max(dp[i][j + 1][k + 1], dp[i][j][k]);
}
}
// Move down
if (i + 1 < m) {
int nextCell = coins[i + 1][j];
// Case 1: Don't neutralize
dp[i + 1][j][k] = max(dp[i + 1][j][k], dp[i][j][k] + nextCell);
// Case 2: Neutralize if it's a robber
if (nextCell < 0 && k + 1 <= 2) {
dp[i + 1][j][k + 1] = max(dp[i + 1][j][k + 1], dp[i][j][k]);
}
}
}
}
}
// Get the maximum value at the bottom-right corner considering all neutralization states
return max({dp[m - 1][n - 1][0], dp[m - 1][n - 1][1], dp[m - 1][n - 1][2]});
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Easy Tabulation with simple explanation
|
easy-tabulation-with-simple-explanation-lmee7
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
Ritwick1467
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-17T08:13:44.516791+00:00
|
2025-01-17T08:13:44.516791+00:00
| 7 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int row=coins.size();
int col=coins[0].size();
//think about last col, from down comes negative and right 0 then you take 0 which is wrong
// so we take -1e9
vector<vector<vector<int>>> dp(row+1,vector<vector<int>>(col+1,vector<int>(3,-1e9)));
for(int i=row-1;i>=0;i--)
{
for(int j=col-1;j>=0;j--)
{
for(int k=0;k<=2;k++)
{
int c = max(dp[i+1][j][k],dp[i][j+1][k]);
if(c<-1e8) c=0; //if both are -1e9 so take 0;
if(coins[i][j] > 0 || k==0) //you must take
{
dp[i][j][k]=coins[i][j]+c;
}
else //neg coins and you can neutrslize
{
//c means no neutralize
// caclulate d neutralize
int d = max(dp[i+1][j][k-1],dp[i][j+1][k-1]);
if(d<-1e8) d=0;
dp[i][j][k]=max( coins[i][j]+c, d);
}
}
}
}
return dp[0][0][2];
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Matrix', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
[CODE ONLY] PYTHON DP
|
code-only-python-dp-by-greg_savage-7ein
|
Code
|
greg_savage
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-17T05:50:51.920075+00:00
|
2025-01-17T05:50:51.920075+00:00
| 8 | false |
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def maximumAmount(self, coins: List[List[int]]) -> int:
n = len(coins)
m = len(coins[0])
end = (n - 1, m - 1)
best_subs = [
[
[] for _ in range(m)
] for _ in range(n)
]
first_value = coins[0][0]
first_option = [
(0, 0),
(0, 1),
(first_value, 2 )
]
best_subs[0][0] = first_option
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if i == 0 and j == 0:
continue
prev_row = i - 1
prev_row_options = []
if prev_row >= 0 and prev_row < n:
prev_row_options = best_subs[prev_row][j]
prev_col = j - 1
prev_col_options = []
if prev_col >= 0 and prev_col < m:
prev_col_options = best_subs[i][prev_col]
all_options = prev_row_options + prev_col_options
current_coin = coins[i][j]
current_best = [
(-inf, 0),
(-inf, 1),
(-inf, 2)
]
is_robber = current_coin < 0
for each_option in all_options:
option_total, neutralize_remaining = each_option
if is_robber and neutralize_remaining:
used = neutralize_remaining - 1
current_total, _ = current_best[used]
current_best[used] = (max(current_total, option_total), used)
option_total += current_coin
current_total, _ = current_best[neutralize_remaining]
current_best[neutralize_remaining] = (max(current_total, option_total), neutralize_remaining)
best_subs[i][j] = current_best
last_choices = [ each_choice for each_choice, _ in best_subs[-1][-1]]
return max(last_choices)
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Two same solution one is working others is not
|
two-same-solution-one-is-working-others-yxq5x
|
IntuitionDifference is In first solution, I initialize the DP dynamica
and In the second one static.Kindly anybody help, why this is happeningCode
|
yadavankit8969
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-17T05:40:04.250677+00:00
|
2025-01-17T05:40:04.250677+00:00
| 8 | false |
# Intuition
Difference is In first solution, I initialize the DP dynamica
and In the second one static.
Kindly anybody help, why this is happening
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int recur(int x, int y, int row, int col, int chance,vector<vector<int>>& coins, vector<vector<vector<int>>>&dp) {
if((x == row-1 && y == col-1)) {
if(coins[x][y] < 0 && chance > 0) return 0;
return coins[x][y];
}
if(x>=row || y>=row) return -999999;
if(dp[x][y][chance] != -999999) return dp[x][y][chance];
int t1 = -999999, t2 = -999999;
if(coins[x][y] < 0 && chance > 0){
t1 = max(recur(x+1, y, row, col, chance-1, coins, dp),
recur(x, y+1, row, col, chance-1, coins, dp));
}
t2 = coins[x][y] + max(recur(x+1, y, row, col, chance, coins, dp),
recur(x, y+1, row, col, chance, coins, dp));
return dp[x][y][chance] = max({t1, t2});
}
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int n = coins.size();
int m = coins[0].size();
vector<vector<vector<int>>> dp(n+1, vector<vector<int>>(m+1, vector<int>(3, -999999)));
return recur(0, 0, n, m, 2, coins, dp);
}
};
```
```
class Solution {
public:
int dp[501][501][3];
int recur(int x, int y, int row, int col, int chance,vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
if((x == row-1 && y == col-1)) {
if(coins[x][y] < 0 && chance > 0) return 0;
return coins[x][y];
}
if(x>=row || y>=row) return -999999;
if(dp[x][y][chance] != -1) return dp[x][y][chance];
int t1 = -999999, t2 = -999999;
if(coins[x][y] < 0 && chance > 0){
t1 = max(recur(x+1, y, row, col, chance-1, coins),
recur(x, y+1, row, col, chance-1, coins));
}
t2 = coins[x][y] + max(recur(x+1, y, row, col, chance, coins),
recur(x, y+1, row, col, chance, coins));
return dp[x][y][chance] = max({t1, t2});
}
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int row = coins.size();
int col = coins[0].size();
memset(dp, -1, sizeof(dp));
return recur(0, 0, row, col, 2, coins);
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Both Recursive and DP Solution
|
both-recursive-and-dp-solution-by-aakash-h51y
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
aakashg1999
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-16T19:43:54.988493+00:00
|
2025-01-16T19:43:54.988493+00:00
| 11 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
private int Traverse(int[][] coin, int[][][] dp, int i, int j, int robber){
if(i < 0 || j<0){
return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
if(i == 0 && j == 0){
if(coin[i][j] < 0 && robber > 0){
return 0;
}else{
return coin[i][j];
}
}
if(dp[i][j][robber] != Integer.MIN_VALUE)return dp[i][j][robber];
if(coin[i][j] < 0 && robber > 0){
return dp[i][j][robber] = Math.max(Traverse(coin, dp, i-1, j, robber-1), Math.max(Traverse(coin, dp, i, j-1, robber-1), coin[i][j] + Math.max(Traverse(coin, dp, i-1, j, robber), Traverse(coin, dp, i, j - 1, robber))));
}else{
return dp[i][j][robber] = coin[i][j] + Math.max( Traverse(coin, dp, i-1,j,robber),Traverse(coin, dp, i,j-1,robber));
}
}
private int recursiveTraverse(int[][] coin, int i, int j, int robber){
if(i < 0 || j<0){
return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
if(i == 0 && j == 0){
if(coin[i][j] < 0 && robber > 0){
return 0;
}else{
return coin[i][j];
}
}
if(coin[i][j] < 0 && robber > 0){
return Math.max(recursiveTraverse(coin, i-1, j, robber-1), Math.max(recursiveTraverse(coin, i, j-1, robber-1), coin[i][j] + Math.max(recursiveTraverse(coin,i-1, j, robber), recursiveTraverse(coin, i, j - 1, robber))));
}else{
return coin[i][j] + Math.max( recursiveTraverse(coin,i-1,j,robber),recursiveTraverse(coin,i,j-1,robber));
}
}
public int maximumAmount(int[][] coins) {
int m = coins.length;
int n = coins[0].length;
if(m == 1 && n == 1){
return Math.max(0, coins[0][0]);
}
int[][][] dp = new int[m][n][3];
for(int i=0; i<m; i++){
for(int j = 0; j<n; j++){
for(int k = 0; k<3; k++){
dp[i][j][k] = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
}
}
Traverse(coins,dp,m-1,n-1,2);
int max_coins = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for(int i=0; i<3; i++)max_coins = Math.max(max_coins, dp[m-1][n-1][i]);
return max_coins == Integer.MIN_VALUE ? 0 : max_coins;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
BEATS100%||C++
|
beats100c-by-spidee180-lmnq
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
spidee180
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-16T16:07:24.624775+00:00
|
2025-01-16T16:07:24.624775+00:00
| 5 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maximumAmount(vector<vector<int>>& coins) {
int constant = -300000;
int m = coins.size();
int n = coins[0].size();
// cout<<m<<" "<<n<<endl;
vector<vector<vector<int>>>dp(3 , vector<vector<int>>(m , vector<int>(
n , constant)));
for(int i=0; i<m; i++)
{
for(int j =0; j<n; j++)
{
if(i == 0 && j == 0)
{
if(coins[0][0] >= 0)
{
dp[0][0][0] = coins[0][0];
}
else
{
dp[0][0][0] = coins[0][0];
dp[1][0][0] = 0;
}
}
else if(i ==0)
{
if(coins[i][j] >= 0)
{
for(int k =0; k<3; k++)
{
dp[k][i][j] = dp[k][i][j-1] + coins[i][j];
}
}
else
{
dp[0][i][j] = dp[0][i][j-1] + coins[i][j];
dp[1][i][j] = max(dp[0][i][j-1], dp[1][i][j-1]+ coins[i][j]);
dp[2][i][j] = max(dp[2][i][j-1] + coins[i][j] , dp[1][i][j-1]);
}
}
else if(j == 0)
{
if(coins[i][j] >= 0)
{
for(int k =0; k<3; k++)
{
dp[k][i][j] = coins[i][j] + dp[k][i-1][j];
}
}
else
{
dp[0][i][j] = coins[i][j] + dp[0][i-1][j];
dp[1][i][j] = max(dp[0][i-1][j] , dp[1][i-1][j] + coins[i][j]);
dp[2][i][j] = max(dp[1][i-1][j] , dp[2][i-1][j] + coins[i][j]);
}
}
else
{
if(coins[i][j] >= 0)
{
for(int k = 0; k < 3; k++)
{
dp[k][i][j] = coins[i][j] + max(dp[k][i-1][j] , dp[k][i][j-1]);
}
}
else
{
dp[0][i][j] = max(coins[i][j] + dp[0][i-1][j] ,dp[0][i][j-1] + coins[i][j]);
dp[1][i][j] = max(max(dp[0][i][j-1], dp[1][i][j-1] + coins[i][j]),
max(dp[0][i-1][j] , dp[1][i-1][j] + coins[i][j]));
dp[2][i][j] = max(max(dp[1][i-1][j] , dp[2][i-1][j] + coins[i][j]),
max(dp[2][i][j-1] + coins[i][j] , dp[1][i][j-1]));
}
}
}
}
return max(dp[1][m-1][n-1] , max(dp[0][m-1][n-1] , dp[2][m-1][n-1]));
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Python DFS Solution
|
python-dfs-solution-by-bhargav_1122-va9g
|
Intuition for the ProblemThe goal is to maximize the total amount collected from a grid of coins, with the ability to neutralize up to 2 negative coins. This is
|
bhargav_1122
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-16T03:36:53.503446+00:00
|
2025-01-16T03:36:53.503446+00:00
| 10 | false |
# Intuition for the Problem
The goal is to maximize the total amount collected from a grid of coins, with the ability to neutralize up to 2 negative coins. This is achieved by using a recursive Depth-First Search (DFS) approach with memoization to efficiently explore all possible paths from the top-left to the bottom-right corner.
## Key Observations
1. **Path Constraints:**
- At each step, you can move either **down** or **right** within the grid.
- The recursion ends when we reach the bottom-right corner or go out of bounds.
2. **Handling Negative Coins:**
- If a cell contains a negative coin, we can either:
- **Neutralize it** (if we haven't already neutralized 2 coins).
- **Take it as is** without neutralizing.
- If neutralization is chosen, it counts as one of the two neutralization opportunities.
3. **Decision-Making:**
- At each cell, we calculate the maximum coins we can collect by considering:
- The value obtained if the current coin is **not neutralized**.
- The value obtained if the current coin is **neutralized** (if allowed).
- We take the maximum of these two values.
4. **Dynamic Programming with Memoization:**
- To avoid redundant calculations, we use `lru_cache` to memoize the results of subproblems.
- The state of our recursion is defined by `(row, column, k)`, where:
- `row` and `column` represent the current position in the grid.
- `k` represents the number of coins already neutralized.
## Base Cases
1. If we move out of the grid bounds (`r >= rowLen` or `c >= colLen`), the result is `0`.
2. If we are at the bottom-right corner:
- If the coin is negative and can be neutralized, decide accordingly.
- Otherwise, simply take the coin's value.
## Recursive Relation
At each position `(r, c)`:
- Let `notNeutralized` be the result of taking the coin as is.
- Let `neutralized` be the result of neutralizing the coin (if it's negative and `k < 2`).
- The result for `(r, c, k)` is:max(notNeutralized, neutralized)
## Complexity Analysis
1. **Time Complexity:**
- Since there are `rowLen * colLen` cells and `k` can take at most 3 states (`0, 1, 2`), the number of unique states is `O(rowLen * colLen * 3)`.
- Each state is computed once due to memoization, making the time complexity approximately `O(rowLen * colLen)`.
2. **Space Complexity:**
- The memoization cache and the recursive call stack take up `O(rowLen * colLen * 3)` space.
## Conclusion
The solution efficiently explores all possible paths in the grid using recursion and memoization, while carefully managing the use of neutralizations to maximize the total coins collected.
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def maximumAmount(self, coins: List[List[int]]) -> int:
rowLen = len(coins)
colLen = len(coins[0])
@lru_cache(None)
def dfs(r,c,k):
if r>= rowLen or c >=colLen:
return float('-inf')
if r == rowLen -1 and c == colLen -1:
if coins[r][c] < 0:
if k < 2:
return 0
return coins[r][c]
notNeutralized = coins[r][c] + max(dfs(r+1,c,k),dfs(r,c+1,k))
neutralized = float('-inf')
if coins[r][c] < 0 and k < 2:
neutralized = 0 + max(dfs(r+1,c,k+1),dfs(r,c+1,k+1))
else:
neutralized = coins[r][c] + max(dfs(r+1,c,k),dfs(r,c+1,k))
return max(neutralized,notNeutralized)
return dfs(0,0,0)
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Memoization', 'Python3']
| 0 |
maximum-amount-of-money-robot-can-earn
|
Simple DP Solution
|
simple-dp-solution-by-jsharmz-xrdd
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
jsharmz
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-15T21:36:35.555751+00:00
|
2025-01-15T21:36:35.555751+00:00
| 11 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def maximumAmount(self, coins: List[List[int]]) -> int:
dp = {}
def dfs(i, j, num):
if i == len(coins) - 1 and j == len(coins[0]) - 1:
if num > 0:
return max(coins[i][j], 0)
return coins[i][j]
if i >= len(coins) or j >= len(coins[0]):
return float("-inf")
if (i,j,num) in dp:
return dp[(i,j,num)]
if coins[i][j] >= 0:
dp[(i,j,num)] = coins[i][j] + max(dfs(i,j+1, num), dfs(i+1,j, num))
return dp[(i,j,num)]
val = coins[i][j] + max(dfs(i,j+1, num), dfs(i+1,j, num))
if num > 0:
val = max(val, max(dfs(i,j+1, num-1), dfs(i+1,j, num-1)))
dp[(i,j,num)] = val
return dp[(i,j,num)]
return dfs(0,0,2)
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
cut-off-trees-for-golf-event
|
Java solution, PriorityQueue + BFS
|
java-solution-priorityqueue-bfs-by-shawn-ya2j
|
Since we have to cut trees in order of their height, we first put trees (int[] {row, col, height}) into a priority queue and sort by height.\n2. Poll each tree
|
shawngao
|
NORMAL
|
2017-09-10T05:46:01.021000+00:00
|
2018-10-24T14:50:23.651021+00:00
| 37,621 | false |
1. Since we have to cut trees in order of their height, we first put trees (int[] {row, col, height}) into a priority queue and sort by height.\n2. Poll each tree from the queue and use BFS to find out steps needed.\n\nThe worst case time complexity could be O(m^2 * n^2) (m = number of rows, n = number of columns) since there are m * n trees and for each BFS worst case time complexity is O(m * n) too.\n```\nclass Solution {\n static int[][] dir = {{0,1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};\n\n public int cutOffTree(List<List<Integer>> forest) {\n if (forest == null || forest.size() == 0) return 0;\n int m = forest.size(), n = forest.get(0).size();\n\n PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> a[2] - b[2]);\n\n for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {\n if (forest.get(i).get(j) > 1) {\n pq.add(new int[] {i, j, forest.get(i).get(j)});\n }\n }\n }\n\n int[] start = new int[2];\n int sum = 0;\n while (!pq.isEmpty()) {\n int[] tree = pq.poll();\n int step = minStep(forest, start, tree, m, n);\n\n if (step < 0) return -1;\n sum += step;\n\n start[0] = tree[0];\n start[1] = tree[1];\n }\n\n return sum;\n }\n\n private int minStep(List<List<Integer>> forest, int[] start, int[] tree, int m, int n) {\n int step = 0;\n boolean[][] visited = new boolean[m][n];\n Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();\n queue.add(start);\n visited[start[0]][start[1]] = true;\n\n while (!queue.isEmpty()) {\n int size = queue.size();\n for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {\n int[] curr = queue.poll();\n if (curr[0] == tree[0] && curr[1] == tree[1]) return step;\n\n for (int[] d : dir) {\n int nr = curr[0] + d[0];\n int nc = curr[1] + d[1];\n if (nr < 0 || nr >= m || nc < 0 || nc >= n \n || forest.get(nr).get(nc) == 0 || visited[nr][nc]) continue;\n queue.add(new int[] {nr, nc});\n visited[nr][nc] = true;\n }\n }\n step++;\n }\n\n return -1;\n }\n}\n```
| 211 | 2 |
[]
| 35 |
cut-off-trees-for-golf-event
|
Logical Thinking with Java Code Beats 98.04%
|
logical-thinking-with-java-code-beats-98-f78k
|
Logical Thinking\nSince we always cut off the tree with lowest height first, we collect all trees and sort them by heights. \nIf we make sure we walk the minimu
|
gracemeng
|
NORMAL
|
2018-07-12T07:11:07.225457+00:00
|
2018-09-25T03:49:20.511733+00:00
| 9,792 | false |
**Logical Thinking**\nSince we always cut off the tree with lowest height first, we collect all trees and sort them by heights. \nIf we **make sure we walk the minimum steps to cut off each tree**, the sum of these minimum steps will be the final answer.\nFor cutting each tree `(aimX, aimY)`, we implement BFS once:\n**Start point**: `(curX, curY)`\n**Aim point**: `(aimX, aimY)`\n**End point**: `(aimX, aimY)` or `we have no way out`.\n**Transition**: we try advancing by one step in 4 directions.\n\n**Clear Java Code**\n```\n private static int[][] directions = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};\n\n public int cutOffTree(List<List<Integer>> forest) {\n\n List<int[]> treeHeights = getAllTreeHights(forest);\n Collections.sort(treeHeights, new Comparator<int[]>() {\n @Override\n public int compare(int[] o1, int[] o2) {\n return o1[2] - o2[2];\n }\n });\n int minSteps = 0;\n int curX = 0, curY = 0;\n while (!treeHeights.isEmpty()) {\n int[] curTree = treeHeights.remove(0);\n int steps = getMinimumSteps(forest, curX, curY, curTree[0], curTree[1]);\n if (steps == -1) {\n return -1;\n }\n minSteps += steps;\n curX = curTree[0];\n curY = curTree[1];\n forest.get(curX).set(curY, 1);\n }\n return minSteps;\n }\n\n private int getMinimumSteps(List<List<Integer>> forest, int curX, int curY, int aimX, int aimY) {\n\n int minSteps = 0;\n int rows = forest.size(), cols = forest.get(0).size();\n boolean[][] visited = new boolean[forest.size()][forest.get(0).size()];\n Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();\n int startVal = forest.get(curX).get(curY);\n queue.offer(new int[]{curX, curY});\n visited[curX][curY] = true;\n\n while (!queue.isEmpty()) {\n int size = queue.size();\n for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {\n int[] curCell = queue.poll();\n if (curCell[0] == aimX && curCell[1] == aimY) {\n return minSteps;\n }\n for (int[] direction : directions) {\n int nx = curCell[0] + direction[0];\n int ny = curCell[1] + direction[1];\n if (nx >= 0 && nx < rows && ny >= 0 && ny < cols && !visited[nx][ny] && forest.get(nx).get(ny) != 0) {\n queue.add(new int[]{nx, ny});\n visited[nx][ny] = true;\n }\n }\n }\n minSteps++;\n }\n return -1;\n }\n\n private List<int[]> getAllTreeHights(List<List<Integer>> forest) {\n List<int[]> treeHeights = new LinkedList<>();\n for (int i = 0; i < forest.size(); i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < forest.get(0).size(); j++) {\n int tmpVal = forest.get(i).get(j);\n if (tmpVal > 1) {\n int[] element = new int[3];\n element[0] = i;\n element[1] = j;\n element[2] = tmpVal;\n treeHeights.add(element);\n }\n }\n }\n return treeHeights;\n }\n```\n**I would appreciate your VOTE UP ;)**
| 106 | 1 |
[]
| 8 |
cut-off-trees-for-golf-event
|
Python solution based on wufangjie's (Hadlock's algorithm?)
|
python-solution-based-on-wufangjies-hadl-abw9
|
Just my own very similar implementation of @wufangjie's solution (and some terminology from the Hadlock algorithm which @awice mentioned to me), with some more
|
stefanpochmann
|
NORMAL
|
2017-09-13T20:39:53.189000+00:00
|
2018-10-23T17:33:49.547532+00:00
| 12,821 | false |
Just my own very similar implementation of @wufangjie's [solution](https://discuss.leetcode.com/topic/103532/my-python-solution-inspired-by-a-algorithm) (and some terminology from the Hadlock algorithm which @awice mentioned to me), with some more explanation. Gets accepted in about 700 ms.\n\nBasically find the trees, sort them by order, find the distance from each tree to the next, and sum those distances. But how to find the distance from one cell to some other cell? BFS is far to slow for the current test suite. Instead use what's apparently known as "Hadlock's Algorithm" (though I've only seen high-level descriptions of that). First try paths with no detour (only try steps in the direction towards the goal), then if necessary try paths with one detour step, then paths with two detour steps, etc. The distance then is the Manhattan distance plus twice the number of detour steps (twice because you'll have to make up for a detour step with a later step back towards the goal).\n\nHow to implement that?\n- Round 1: Run a DFS only on cells that you can reach from the start cell with no detour towards the goal, i.e., only walking in the direction towards the goal. If this reaches the goal, we're done. Otherwise...\n- Round 2: Try again, but this time try starting from all those cells reachable with one detour step. Collect these in round 1.\n- Round 3: If round 2 fails, try again but start from all those cells reachable with two detour steps. Collect these in round 2.\n- And so on...\n\nIf there are no obstacles, then this directly walks a shortest path towards the goal, which is of course very fast. Much better than BFS which would waste time looking in all directions. With only a few obstacles, it's still close to optimal.\n\nMy `distance` function does this searching algorithm. I keep the current to-be-searched cells in my `now` stack. When I move to a neighbor that's closer to the goal, I also put it in `now`. If it's not closer, then that's a detour step so I just remember it on my `soon` stack for the next round.\n\n def cutOffTree(self, forest):\n\n # Add sentinels (a border of zeros) so we don't need index-checks later on.\n forest.append([0] * len(forest[0]))\n for row in forest:\n row.append(0)\n\n # Find the trees.\n trees = [(height, i, j)\n for i, row in enumerate(forest)\n for j, height in enumerate(row)\n if height > 1]\n\n # Can we reach every tree? If not, return -1 right away.\n queue = [(0, 0)]\n reached = set()\n for i, j in queue:\n if (i, j) not in reached and forest[i][j]:\n reached.add((i, j))\n queue += (i+1, j), (i-1, j), (i, j+1), (i, j-1)\n if not all((i, j) in reached for (_, i, j) in trees):\n return -1\n\n # Distance from (i, j) to (I, J).\n def distance(i, j, I, J):\n now, soon = [(i, j)], []\n expanded = set()\n manhattan = abs(i - I) + abs(j - J)\n detours = 0\n while True:\n if not now:\n now, soon = soon, []\n detours += 1\n i, j = now.pop()\n if (i, j) == (I, J):\n return manhattan + 2 * detours\n if (i, j) not in expanded:\n expanded.add((i, j))\n for i, j, closer in (i+1, j, i < I), (i-1, j, i > I), (i, j+1, j < J), (i, j-1, j > J):\n if forest[i][j]:\n (now if closer else soon).append((i, j))\n\n # Sum the distances from one tree to the next (sorted by height).\n trees.sort()\n return sum(distance(i, j, I, J) for (_, i, j), (_, I, J) in zip([(0, 0, 0)] + trees, trees))
| 79 | 0 |
[]
| 15 |
cut-off-trees-for-golf-event
|
C++, Sort + BFS with explanation
|
c-sort-bfs-with-explanation-by-zestypand-8ebp
|
The solution has two steps:\n\n1) Sort tree positions based on tree height; \n2) BFS to find shortest path between two points; \n\nThe end point of current path
|
zestypanda
|
NORMAL
|
2017-09-10T03:02:38.741000+00:00
|
2018-10-26T17:24:54.405828+00:00
| 11,476 | false |
The solution has two steps:\n```\n1) Sort tree positions based on tree height; \n2) BFS to find shortest path between two points; \n```\nThe end point of current path is the starting point of next path. Priority_queue also works, but may be slower than simple sort due to both push and pop operations.\n\nThe run time is up to O(m^2 n^2) where m and n is the matrix size. \n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int cutOffTree(vector<vector<int>>& forest) {\n if (forest.empty() || forest[0].empty()) return 0;\n int m = forest.size(), n = forest[0].size();\n vector<vector<int>> trees;\n // get all the tree positions and sort based on height\n // trees[i][0] is height. The default comparison of vector compare first element before other elements.\n for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {\n if (forest[i][j] > 1) trees.push_back({forest[i][j], i, j});\n }\n }\n sort(trees.begin(), trees.end());\n int ans = 0;\n // accumulate all the paths\n for (int i = 0, cur_row = 0, cur_col = 0; i < trees.size(); i++) {\n int step = next_step(forest, cur_row, cur_col, trees[i][1], trees[i][2]);\n // if next tree cannot be reached, step = -1;\n if (step == -1) return -1;\n ans += step;\n cur_row = trees[i][1];\n cur_col = trees[i][2];\n }\n return ans;\n }\nprivate:\n // BFS to find shortest path to next tree; if cannot reach next tree, return -1\n int next_step(vector<vector<int>>& forest, int sr, int sc, int er, int ec) {\n if (sr == er && sc == ec) return 0;\n int m = forest.size(), n = forest[0].size();\n queue<pair<int, int>> myq;\n myq.push({sr, sc}); \n vector<vector<int>> visited(m, vector<int>(n, 0));\n visited[sr][sc] = 1;\n int step = 0;\n vector<int> dir = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};\n while (!myq.empty()) {\n step++;\n int sz = myq.size();\n for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {\n int row = myq.front().first, col = myq.front().second;\n myq.pop();\n for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {\n int r = row + dir[i], c = col + dir[i+1];\n if (r < 0 || r >= m || c < 0 || c >= n || visited[r][c] == 1 || forest[r][c] == 0) continue;\n if (r == er && c == ec) return step;\n visited[r][c] = 1;\n myq.push({r, c});\n }\n }\n }\n return -1;\n }\n};\n```
| 67 | 2 |
[]
| 12 |
cut-off-trees-for-golf-event
|
Very simple Python BFS, But Why TLE??
|
very-simple-python-bfs-but-why-tle-by-an-qs4y
|
I thought it is a straightforward BFS search, so I write it like the following. \nActually, I have the same question with Number of Island problem:\nhttps://dis
|
andrinux
|
NORMAL
|
2017-09-10T03:23:34.548000+00:00
|
2018-10-20T21:53:21.203365+00:00
| 11,620 | false |
I thought it is a straightforward BFS search, so I write it like the following. \nActually, I have the same question with `Number of Island` problem:\nhttps://discuss.leetcode.com/topic/88586/why-python-bfs-get-time-exceed-error\n\n\n```\nimport collections\nclass Solution(object):\n def cutOffTree(self, G):\n """\n :type forest: List[List[int]]\n :rtype: int\n """\n if not G or not G[0]: return -1\n m, n = len(G), len(G[0])\n trees = []\n for i in xrange(m):\n for j in xrange(n):\n if G[i][j] > 1:\n trees.append((G[i][j], i, j))\n trees = sorted(trees)\n count = 0\n cx, cy = 0, 0\n for h, x, y in trees:\n step = self.BFS(G, cx, cy, x, y)\n if step == -1:\n return -1\n else:\n count += step\n G[x][y] = 1\n cx, cy = x, y\n return count\n\n def BFS(self, G, cx, cy, tx, ty):\n m, n = len(G), len(G[0])\n visited = [[False for j in xrange(n)] for i in xrange(m)]\n Q = collections.deque()\n step = -1\n Q.append((cx, cy))\n while len(Q) > 0:\n size = len(Q)\n step += 1\n for i in xrange(size):\n x, y = Q.popleft()\n visited[x][y] = True\n if x == tx and y == ty:\n return step\n for nx, ny in [(x + 1, y), (x - 1, y), (x, y-1), (x, y + 1)]:\n if nx < 0 or nx >= m or ny < 0 or ny >= n or G[nx][ny] == 0 or visited[nx][ny]:\n continue\n Q.append((nx, ny))\n return -1\n```
| 34 | 1 |
[]
| 9 |
cut-off-trees-for-golf-event
|
my python solution, inspired by A* algorithm
|
my-python-solution-inspired-by-a-algorit-mj8x
|
The expected min distance between p1 and p2 is d = abs(p1[0] - p2[0]) + abs(p1[1] - p2[1]). \nFrom p1 (or the following positions), we may have two choices, mov
|
wufangjie
|
NORMAL
|
2017-09-13T14:27:17.322000+00:00
|
2017-09-13T14:27:17.322000+00:00
| 6,304 | false |
The expected min distance between p1 and p2 is d = abs(p1[0] - p2[0]) + abs(p1[1] - p2[1]). \nFrom p1 (or the following positions), we may have two choices, move a step towards p2 or a step far away from p2 (if we do this, the min distance we can expect is d + 2, so we needn't think about them until all the expected min distance way are blocked). \nAnd I use stack to find the possible way greedily. \nHere is my code:\n```\nclass Solution(object):\n def cutOffTree(self, forest):\n """\n :type forest: List[List[int]]\n :rtype: int\n """\n nrow, ncol = len(forest), len(forest[0])\n forest.append([0] * ncol)\n for row in forest:\n row.append(0)\n\n trees = {(i, j) for i in range(nrow) for j in range(ncol)\n if forest[i][j] > 1}\n\n canReach = {(0, 0)}\n stack = [(0, 0)]\n while stack:\n i, j = stack.pop()\n for i2, j2 in ((i - 1, j), (i + 1, j), (i, j - 1), (i, j + 1)):\n if forest[i2][j2] != 0 and (i2, j2) not in canReach:\n canReach.add((i2, j2))\n stack.append((i2, j2))\n\n if trees.difference(canReach):\n return -1\n\n def get_sp(p1, p2):\n theMin = abs(p1[0] - p2[0]) + abs(p1[1] - p2[1])\n stack1, stack2 = [p1], []\n used, visited = {p1}, {p1}\n\n while 1:\n if not stack1:\n stack1, stack2 = stack2, stack1\n used.update(stack1)\n theMin += 2\n\n p = stack1.pop()\n if p == p2:\n break\n\n i, j = p\n add1, add2 = [], []\n\n if i == p2[0]:\n add2.append((i - 1, j))\n add2.append((i + 1, j))\n elif i < p2[0]:\n add2.append((i - 1, j))\n add1.append((i + 1, j))\n else:\n add1.append((i - 1, j))\n add2.append((i + 1, j))\n\n if j == p2[1]:\n add2.append((i, j - 1))\n add2.append((i, j + 1))\n elif j < p2[1]:\n add2.append((i, j - 1))\n add1.append((i, j + 1))\n else:\n add1.append((i, j - 1))\n add2.append((i, j + 1))\n\n for v in add1:\n if forest[v[0]][v[1]] != 0 and v not in used:\n visited.add(v)\n used.add(v)\n stack1.append(v)\n for v in add2:\n if forest[v[0]][v[1]] != 0 and v not in visited:\n visited.add(v)\n stack2.append(v)\n\n return theMin\n\n seq = sorted(trees, key=lambda x: forest[x[0]][x[1]])\n if seq[0] != (0, 0):\n seq.insert(0, (0, 0))\n return sum(get_sp(seq[i], seq[i + 1]) for i in range(len(seq) - 1))\n```
| 23 | 0 |
[]
| 10 |
cut-off-trees-for-golf-event
|
[Java/C++] Straightforward solution - sorted array + BFS
|
javac-straightforward-solution-sorted-ar-xmst
|
My idea to solve this problem is by two steps:\n1. Save each {tree height, tree position} into an array heights, and then sort this array based on its tree hei
|
caihao0727mail
|
NORMAL
|
2017-09-10T06:42:46.861000+00:00
|
2018-10-16T13:04:15.367532+00:00
| 5,759 | false |
My idea to solve this problem is by two steps:\n1. Save each ```{tree height, tree position}``` into an array ```heights```, and then sort this array based on its ```tree height```. (You can also do this by using ```TreeMap``` or ```PriorityQueue```);\n2. Accumulate the shortest steps between each two adajacent points in ```heights[]```.\n\nJava version:\n```\nclass Solution {\n int[][] dir = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};\n \n public int cutOffTree(List<List<Integer>> forest) {\n if (forest == null || forest.size() == 0) return -1;\n int m = forest.size(), n = forest.get(0).size(), res = 0;\n //first step: sort the tree position based on its height\n List<int[]> heights = new ArrayList<>();\n for(int i = 0; i<m; i++){\n for(int j = 0; j<n; j++){\n if(forest.get(i).get(j) > 1)heights.add( new int[]{forest.get(i).get(j), i, j} );\n }\n }\n Collections.sort(heights, new Comparator<int[]>() {\n public int compare(int[] arr1, int[] arr2) {\n return Integer.compare(arr1[0], arr2[0]);\n }\n });\n //second step: accumulate the shortest steps between each two adajacent points in heights[].\n int start_x = 0, start_y = 0; \n for(int i = 0; i<heights.size(); i++){\n int cnt_steps = BFS(forest, m, n, start_x, start_y, heights.get(i)[1], heights.get(i)[2]); \n if(cnt_steps == -1)return -1;\n res += cnt_steps;\n start_x = heights.get(i)[1]; \n start_y = heights.get(i)[2];\n }\n return res;\n }\n \n public int BFS(List<List<Integer>> forest, int m, int n, int start_x, int start_y, int des_x, int des_y){\n if(start_x == des_x && start_y == des_y)return 0;\n int steps = 0;\n Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();\n q.add(new int[]{start_x, start_y});\n int[][] visited = new int[m][n];\n visited[start_x][start_y] = 1;\n while(!q.isEmpty()){\n int qsize = q.size();\n steps++;\n while(qsize-- >0 ){\n int[] cur = q.poll();\n int cur_x = cur[0], cur_y = cur[1];\n for(int k = 0; k<4; k++){\n int x = cur_x + dir[k][0], y = cur_y + dir[k][1];\n if(x>=0 && x<m && y>=0 && y<n && forest.get(x).get(y) > 0 && visited[x][y] == 0){\n if(x == des_x && y == des_y)return steps;\n visited[x][y] = 1;\n q.add(new int[]{x,y});\n }\n }\n }\n }\n return -1;\n }\n}\n```\n\nC++ version:\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic: \n vector<vector<int>> dir = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};\n int cutOffTree(vector<vector<int>>& forest) {\n int m = forest.size(), n , res = 0;\n if(m == 0)return -1;\n n = forest[0].size();\n //first step: sort the tree position based on its height\n vector<vector<int>> heights;\n for(int i = 0; i<m; i++){\n for(int j = 0; j<n; j++){\n if(forest[i][j] > 1)heights.push_back({forest[i][j], i, j});\n }\n }\n sort(heights.begin(), heights.end());\n //second step: accumulate the shortest steps between each two adajacent points in heights[].\n int start_x = 0, start_y = 0; \n for(int i = 0; i<heights.size(); i++){\n int cnt_steps = BFS(forest, m, n, start_x, start_y, heights[i][1], heights[i][2]); \n if(cnt_steps == -1)return -1;\n res += cnt_steps;\n start_x = heights[i][1], start_y = heights[i][2];\n }\n return res;\n }\n \n int BFS(vector<vector<int>>& forest, int m, int n, int start_x, int start_y, int des_x, int des_y){\n if(start_x == des_x && start_y == des_y)return 0;\n int steps = 0;\n queue<pair<int, int>> q;\n q.push({start_x, start_y});\n vector<vector<int>> visited(m, vector<int>(n, 0));\n visited[start_x][start_y] = 1;\n while(!q.empty()){\n int qsize = q.size();\n steps++;\n while(qsize-- >0 ){\n int cur_x = q.front().first, cur_y = q.front().second;\n q.pop();\n for(int k = 0; k<4; k++){\n int x = cur_x + dir[k][0], y = cur_y + dir[k][1];\n if(x>=0 && x<m && y>=0 && y<n && forest[x][y] > 0 && visited[x][y] == 0){\n if(x == des_x && y == des_y)return steps;\n visited[x][y] = 1;\n q.push({x,y});\n }\n }\n }\n }\n return -1;\n }\n};\n```
| 19 | 3 |
[]
| 5 |
cut-off-trees-for-golf-event
|
A-Star Search Algorithm in Python 3, (Faster than 90% solutions)
|
a-star-search-algorithm-in-python-3-fast-71fw
|
1) Sort the trees by height.\n2) Sum up the distance between successive trees. I have used A star search algorithm to find the distance between two trees.\n\nWh
|
barracoda
|
NORMAL
|
2021-06-25T01:03:16.361368+00:00
|
2021-06-25T01:05:12.760515+00:00
| 2,822 | false |
1) Sort the trees by height.\n2) Sum up the distance between successive trees. I have used A star search algorithm to find the distance between two trees.\n\n**Why Astar?**\nWith BFS you circularly expand the explored area. With DFS, you pick a specific direction and explore in that direction until you reach the end, and then repeat the process. In Astar however, you move in the direction of the destination. The choice of the direction is based on two things. The distance g(n) from the source to current node, and h(n) a heuristic distance between current node and destination. Heuristic is a rough estimate, which can lead to a better solution. Here manhattan distance is used as the heuristic. \n\nMathematically, f(n) = g(n) + h(n)\n\nUse a priority queue (heap) to keep track of neighbouring nodes with smallest f(n) value and explore in that direction.\n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def cutOffTree(self, forest: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n m,n = len(forest), len(forest[0])\n tree_order = []\n for i in range(m):\n for j in range(n):\n if(forest[i][j] > 1):\n tree_order.append((forest[i][j],(i,j))) # (tree height, cordinates)\n tree_order.sort()\n \n def manhattan(s,t):\n return abs(s[0] - t[0]) + abs(s[1] - t[1])\n \n def astar_search_distance(source, target):\n pq = [(manhattan(source, target), 0, source)] # Tuple content: (f= g+h, g, cordinates)\n seen = set()\n while(pq):\n f,d,cur = heapq.heappop(pq)\n if(cur == target):\n return d\n i,j = cur\n # Using for loop here will make the code cleaner, but will have extra boundary checks.\n # Adding the cords into seen node while offering to pq, is much faster than adding after polling.\n if(j+1<n and (i,j+1) not in seen and forest[i][j+1]!= 0): \n heapq.heappush(pq, (manhattan((i,j+1),target)+d+1, d+1, (i,j+1)))\n seen.add((i,j+1))\n if(i+1<m and (i+1,j) not in seen and forest[i+1][j]!= 0): \n heapq.heappush(pq, (manhattan((i+1,j),target)+d+1, d+1, (i+1,j)))\n seen.add((i+1,j))\n if(j-1>=0 and (i,j-1) not in seen and forest[i][j-1]!= 0): \n heapq.heappush(pq, (manhattan((i,j-1),target)+d+1, d+1, (i,j-1)))\n seen.add((i,j-1))\n if(i-1>=0 and (i-1,j) not in seen and forest[i-1][j]!= 0): \n heapq.heappush(pq, (manhattan((i-1,j),target)+d+1, d+1, (i-1,j)))\n seen.add((i-1,j))\n \n return -1\n\t\t\t\n prev = (0,0)\n res = 0\n for tree in tree_order:\n d = astar_search_distance(prev, tree[1])\n if(d == -1): break\n res += d\n prev = tree[1]\n \n return res if d != -1 else -1\n```
| 16 | 0 |
[]
| 4 |
cut-off-trees-for-golf-event
|
Briefly Explained Approach
|
briefly-explained-approach-by-anshul_07-30hp
|
EXPLANATION:-\n We can only visit the whole tree if we can go from lower to higher value cells.\n Therefore we have to do something like we can go from cu
|
Anshul_07
|
NORMAL
|
2021-11-30T17:03:08.915275+00:00
|
2023-06-06T11:07:41.255414+00:00
| 632 | false |
# EXPLANATION:-\n* We can only visit the whole tree if we can go from lower to higher value cells.\n* Therefore we have to do something like we can go from current cell to next greater cell.\n* So we will do something like \n 1) Sort tree positions based on height of the tree \n 2) Aplly BFS to find shortest path between two points \n* i.e we will first store all the cells in a 2D vector and sort them so that next cell to visit\n will be next greater of current cell. \n* And then we will apply bfs in evry 2 pair of sorted new vector to see if we can reach to every current\'s next greater or not. \n* \tIf in any of the case we cant then return -1 from there only, otherwise keep going.\n* \tAnd if we are able to finish all pairs then return total number of steps calculated from every pair.\n* Note:- All cell values stored in new array which was sorted after soring all cells values should be greater than 1 (should be a tree).\n\n* Example which may help:- [[1,2,3],[9,10,4],[7,6,5]]\n\n# CODE:-\n```\nclass Solution {\n int Solve(vector<vector<int>> &forest, int src_row, int src_col, int dst_row, int dst_col){\n int n = forest.size(), m = forest[0].size();\n \n if(src_row == dst_row && src_col == dst_col) {\n return 0;\n }\n \n queue<pair<int, int>> q;\n q.push({src_row, src_col});\n \n vector<vector<int>> vis(n, vector<int>(m, 0));\n vis[src_row][src_col] = 1;\n \n int step = 0;\n while(!q.empty()){\n int size = q.size();\n while(size--){\n int x = q.front().first, y = q.front().second;\n q.pop();\n \n if(x == dst_row && y == dst_col){\n return step;\n }\n \n int dx[] = {0, -1, 0, 1}, dy[] = {1, 0, -1, 0};\n \n for(int k=0; k<4; k++){\n int newx = x+dx[k], newy = y+dy[k];\n if(newx>=0 && newy>=0 && newx<n && newy<m){\n if(vis[newx][newy] || !forest[newx][newy]) {\n continue;\n }\n vis[newx][newy] = 1;\n q.push({newx, newy});\n }\n }\n }\n step+=1;\n }\n return -1;\n }\npublic:\n int cutOffTree(vector<vector<int>>& forest) {\n int n = forest.size();\n int m = forest[0].size();\n \n vector<vector<int>> trees;\n \n //storing all trees in a vector and sorting it\n //storing in the format of {tree height, position} --> {forest[i], i, j}\n for(int i=0; i<n; i++){\n for(int j=0; j<m; j++){\n if(forest[i][j] > 1) \n\t\t\t\t\ttrees.push_back({forest[i][j], i, j});\n }\n }\n \n sort(trees.begin(), trees.end());\n \n int total_steps = 0;\n int src_row = 0, src_col = 0;\n for(int i=0; i<trees.size(); i++){\n int dst_row = trees[i][1], dst_col = trees[i][2];\n \n //now bfs to find shorest distance from src to dst\n int steps = Solve(forest, src_row, src_col, dst_row, dst_col);\n \n // if next tree cannot be reached\n if(steps == -1) return -1;\n \n total_steps += steps;\n \n src_row = trees[i][1];\n src_col = trees[i][2];\n }\n return total_steps;\n }\n};\n```
| 10 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
cut-off-trees-for-golf-event
|
BFS & PriorityQueue - w/ comments and prints for visualization
|
python-bfs-priorityqueue-w-comments-and-qcyqs
|
ApproachHave priority queue that stores (height,x,y) for each tree in order of min to max.
Use BFS to find the next available smallest height in priority queue.
|
vikktour
|
NORMAL
|
2021-01-24T18:14:49.862880+00:00
|
2025-03-02T03:13:30.564779+00:00
| 2,335 | false |
## Approach
Have priority queue that stores (height,x,y) for each tree in order of min to max.
Use BFS to find the next available smallest height in priority queue.
## Complexity
Let m=len(forest), n=len(forest[0]), N=m*n
Time: O(N^2) - 692ms (45.50%)
- N^2: N for each BFS search between two elements. The priority queue can have N elements. In total, this is N^2.
- NlogN for building the priority queue, but it gets dominated by N^2.
Space: O(N) - 14.9MB (56.88%)
For storing elements in the priority queue.
## Code
```Python []
from typing import List
import heapq
import collections
import numpy as np #for printing
class Solution:
def cutOffTree(self, forest: List[List[int]]) -> int:
#print("forest at start: \n{}".format(np.array(forest)))
m = len(forest)
n = len(forest[0])
# Store all trees in priority queue in (height,x,y) format
pq = []
for x in range(m):
for y in range(n):
height = forest[x][y]
if height > 1:
heapq.heappush(pq,(height,x,y))
#print("heap: {}".format(pq))
# Takes in starting position and next tree position, returns min steps to get to that next tree position
def bfs(x,y,nextX,nextY) -> int:
queue = collections.deque([(x,y,0)])
seen = {(x,y)}
#print("starting at: ({},{})".format(x,y))
# Keep BFS searching until we find target tree or tried all paths
while queue:
x,y,steps = queue.popleft()
if x == nextX and y == nextY:
# Found the next tree, chop it down and return depth
forest[x][y] = 1
#print("ending at: ({},{}) after {} steps".format(x,y,steps))
return steps
# Append adjacent nodes (if they are a valid position i.e. height >= 1, within bounds of forest, and not already used)
for dx,dy in [(-1,0),(0,1),(0,-1),(1,0)]:
adjX,adjY = x+dx, y+dy
if (0 <= adjX < m and 0 <= adjY < n) and (forest[adjX][adjY] >= 1) and ((adjX,adjY) not in seen):
# if (nextX,nextY) == (0,0):
# #print("seen for reaching {},{}: {}".format(nextX,nextY,seen))
# print("queue: {}".format(queue))
queue.append((adjX,adjY,steps+1))
seen.add((adjX,adjY))
#print("seen: {}".format(seen))
# No such path exists
return -1
# Start from 0,0 and have next be the first smallest tree, and use BFS for the others
x,y = 0,0
steps = 0
# While there are still trees to cut
while pq:
_,nextX,nextY = heapq.heappop(pq)
# Find the shortest path to the next tree
shortestPath = bfs(x,y,nextX,nextY)
if shortestPath == -1:
#print("forest: \n{}".format(np.array(forest)))
return -1
steps += shortestPath
#print("total steps taken: {}".format(steps))
x,y = nextX,nextY
#print("forest at end: \n{}".format(np.array(forest)))
return steps
```
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int cutOffTree(vector<vector<int>>& forest) {
int m = forest.size();
int n = forest[0].size();
priority_queue<tuple<int, int, int>, vector<tuple<int, int, int>>, greater<>> pq;
// Store all trees in priority queue as (height, x, y)
for (int x = 0; x < m; ++x) {
for (int y = 0; y < n; ++y) {
if (forest[x][y] > 1) {
pq.emplace(forest[x][y], x, y);
}
}
}
// BFS to find shortest path between two points
auto bfs = [&](int startX, int startY, int targetX, int targetY) -> int {
deque<tuple<int, int, int>> queue;
queue.emplace_back(startX, startY, 0);
set<pair<int, int>> seen;
seen.insert({startX, startY});
// cout << "Starting BFS from: (" << startX << ", " << startY << ")\n";
while (!queue.empty()) {
auto [x, y, steps] = queue.front();
queue.pop_front();
if (x == targetX && y == targetY) {
forest[x][y] = 1;
// cout << "Ending at: (" << targetX << ", " << targetY << ") after " << steps << " steps\n";
return steps;
}
vector<pair<int, int>> directions = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
for (auto [dx, dy] : directions) {
int adjX = x + dx, adjY = y + dy;
if (adjX >= 0 && adjX < m && adjY >= 0 && adjY < n && forest[adjX][adjY] >= 1 && seen.find({adjX, adjY}) == seen.end()) {
queue.emplace_back(adjX, adjY, steps + 1);
seen.insert({adjX, adjY});
}
}
}
// cout << "No path exists to target: (" << targetX << ", " << targetY << ")\n";
return -1;
};
int x = 0, y = 0, totalSteps = 0;
while (!pq.empty()) {
auto [height, nextX, nextY] = pq.top();
pq.pop();
// cout << "Processing tree at: (" << nextX << ", " << nextY << ") with height: " << height << "\n";
int shortestPath = bfs(x, y, nextX, nextY);
if (shortestPath == -1) {
// cout << "Forest after failure:\n";
// for (const auto& row : forest) {
// for (int val : row) cout << val << " ";
// cout << "\n";
// }
return -1;
}
totalSteps += shortestPath;
// cout << "Total steps taken: " << totalSteps << "\n";
x = nextX;
y = nextY;
}
// cout << "Forest at end:\n";
// for (const auto& row : forest) {
// for (int val : row) cout << val << " ";
// cout << "\n";
// }
return totalSteps;
}
};
```
```Java []
class Solution {
public int cutOffTree(List<List<Integer>> forest) {
int m = forest.size();
int n = forest.get(0).size();
PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0]));
// Store all trees in priority queue as [height, x, y]
for (int x = 0; x < m; x++) {
for (int y = 0; y < n; y++) {
int height = forest.get(x).get(y);
if (height > 1) {
pq.offer(new int[]{height, x, y});
}
}
}
// BFS to find shortest path between two points
int bfs(int startX, int startY, int targetX, int targetY) {
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(new int[]{startX, startY, 0});
Set<String> seen = new HashSet<>();
seen.add(startX + "," + startY);
// System.out.println("Starting BFS from: (" + startX + ", " + startY + ")");
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] node = queue.poll();
int x = node[0], y = node[1], steps = node[2];
if (x == targetX && y == targetY) {
forest.get(x).set(y, 1);
// System.out.println("Ending at: (" + targetX + ", " + targetY + ") after " + steps + " steps");
return steps;
}
int[][] directions = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
for (int[] dir : directions) {
int adjX = x + dir[0], adjY = y + dir[1];
if (adjX >= 0 && adjX < m && adjY >= 0 && adjY < n && forest.get(adjX).get(adjY) >= 1 && !seen.contains(adjX + "," + adjY)) {
queue.offer(new int[]{adjX, adjY, steps + 1});
seen.add(adjX + "," + adjY);
}
}
}
// System.out.println("No path exists to target: (" + targetX + ", " + targetY + ")");
return -1;
}
int x = 0, y = 0, totalSteps = 0;
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
int[] tree = pq.poll();
int nextX = tree[1], nextY = tree[2];
// System.out.println("Processing tree at: (" + nextX + ", " + nextY + ") with height: " + tree[0]);
int shortestPath = bfs(x, y, nextX, nextY);
if (shortestPath == -1) {
// System.out.println("Forest after failure:");
// for (List<Integer> row : forest) {
// System.out.println(row);
// }
return -1;
}
totalSteps += shortestPath;
// System.out.println("Total steps taken: " + totalSteps);
x = nextX;
y = nextY;
}
// System.out.println("Forest at end:");
// for (List<Integer> row : forest) {
// System.out.println(row);
// }
return totalSteps;
}
}
```
| 10 | 1 |
['Breadth-First Search', 'Heap (Priority Queue)', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'Python3']
| 3 |
cut-off-trees-for-golf-event
|
Simple Java Solution using BFS with comments and explanation
|
simple-java-solution-using-bfs-with-comm-7yem
|
The idea is: \n1. Create a list of int[] which contains x_coordinate, y_coordinate, and height of tree\n2. Add all the trees which have height >1 to the list.
|
jayrt
|
NORMAL
|
2019-03-10T05:54:26.234707+00:00
|
2019-03-10T05:54:26.234791+00:00
| 2,245 | false |
The idea is: \n1. Create a list of int[] which contains ```x_coordinate, y_coordinate, and height of tree```\n2. Add all the trees which have height >1 to the list.\n3. Sort the given list based on their height, by using the Comparator class(or simply using Lambda expression from Java8)\n4. Then traverse through each tree by using a BFS\n5. In the BFS we are checking the distance needed to go to the tree from the current source coordinates(Since we have sorted the trees based on their height, our source coordinates will be different from the tree coordinates)\nFor eg: Our input is like this [[1,0,0],[1,0,0],[1,1,5]], then\ni) We have only 1 entry to be traversed, which is ```{x,y,height} = {2,2,5}```\nii) Once we have sorted the input trees, we are going to apply BFS\niii) Our source coordinates are (0,0) and our tree coordinates are (2,2) and then using BFS we are going to find out the shortest distance needed to to go from source to destination. \n\n\n```\nclass Solution {\n int[][] dirs = new int[][]{{-1,0},{1,0},{0,-1},{0,1}};\n public int cutOffTree(List<List<Integer>> forest) {\n \n //create a list of int[] {x, y, Height}\n List<int[]> trees = new ArrayList<>();\n for (int i = 0; i < forest.size(); i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < forest.get(0).size(); j++) {\n int height = forest.get(i).get(j);\n if (height > 1)\n trees.add(new int[]{i, j, height});\n }\n }\n \n //Sort all the trees based on their height\n Collections.sort(trees, (a, b)->(a[2]-b[2]));\n \n //Run thru each test tree given to us\n int res = 0, x = 0, y = 0;\n for (int[] tree: trees) {\n //Do a BFS traversal from current location(x,y) to that tree location(tree[0], tree[1])\n int dist = bfs(forest, x, y, tree[0], tree[1]);\n if (dist < 0) \n return -1;\n else\n {\n res = res + dist;\n x = tree[0];\n y = tree[1];\n }\n }\n return res;\n }\n \n private int bfs(List<List<Integer>> forest, int x, int y, int tx, int ty) \n {\n //A typical BFS approach that we use\n int m = forest.size(), n = forest.get(0).size();\n Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();\n boolean[][] visited = new boolean[m][n];\n \n //Add the current source coordinates to the queue and mark it as visited\n queue.add(new int[]{x, y});\n visited[x][y] = true;\n \n int dist = 0;\n \n while (!queue.isEmpty()) {\n int size = queue.size();\n \n for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) {\n int[] cur = queue.poll();\n \n //If we have reached the tree at (tx,ty) through traversal then that means we can return the distance covered from (x,y) to (tx,ty)\n if (cur[0] == tx && cur[1] == ty) \n return dist;\n \n //Traverse in all 4 directions and then process it if it meets the conditions\n for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) \n {\n int nx = cur[0]+dirs[i][0];\n int ny = cur[1]+dirs[i][1];\n \n if (nx >= 0 && nx < m && ny >= 0 && ny < n && \n !visited[nx][ny] && forest.get(nx).get(ny) >= 1)\n {\n visited[nx][ny] = true;\n queue.add(new int[]{nx, ny});\n }\n }\n }\n dist++;\n }\n return -1;\n }\n}\n```
| 10 | 0 |
['Breadth-First Search', 'Java']
| 2 |
cut-off-trees-for-golf-event
|
How come same Python solution got TLE again? Again? Are you kidding me?
|
how-come-same-python-solution-got-tle-ag-j9sf
|
Just translated https://leetcode.com/problems/cut-off-trees-for-golf-event/discuss/107404/Java-solution-PriorityQueue-+-BFS into Python. Same time complexity I
|
whglamrock
|
NORMAL
|
2018-06-30T23:16:20.602829+00:00
|
2018-10-20T21:52:20.996407+00:00
| 1,771 | false |
Just translated https://leetcode.com/problems/cut-off-trees-for-golf-event/discuss/107404/Java-solution-PriorityQueue-+-BFS into Python. Same time complexity I believe. How come I got TLE again? If you admins really hate python, you should ban python from available languages. \n\nremember, I pay 100+ dollars per year not for getting TLE for working out the optimal solution that will pass the actual interview.\n\n\'\'\'\n\t\n\tfrom collections import deque\n\n\tclass Solution(object):\n\t def cutOffTree(self, forest):\n\n\t if not forest or not forest[0]:\n\t return -1\n\t \n\t # cut the tree in reverse order of tree\'s height\n\t treeList = []\n\t for i in xrange(len(forest)):\n\t for j in xrange(len(forest[0])):\n\t if forest[i][j] > 1:\n\t treeList.append([forest[i][j], [i, j]])\n\t treeList.sort()\n\t \n\t totalSteps = self.minStep(forest, [0, 0], treeList[0][1])\n\t k = 0\n\t while k < len(treeList) - 1:\n\t step = self.minStep(forest, treeList[k][1], treeList[k + 1][1])\n\t if step == -1:\n\t return -1\n\t totalSteps += step\n\t k += 1\n\t \n\t return totalSteps\n\t \n\t # do BFS to see if we can find a path from start to end\n\t def minStep(self, forest, start, end):\n\t directions = [(0, -1), (0, 1), (-1, 0), (1, 0)]\n\t step = 0\n\t m, n = len(forest), len(forest[0])\n\t visited = [[False for x in xrange(n)] for _ in xrange(m)]\n\t visited[start[0]][start[1]] = True\n\t queue = deque()\n\t queue.append(start)\n\t \n\t while queue:\n\t size = len(queue)\n\t for i in xrange(size):\n\t curr = queue.popleft()\n\t if curr == end:\n\t return step\n\t for direction in directions:\n\t nextRow = curr[0] + direction[0]\n\t nextCol = curr[1] + direction[1]\n\t if nextRow < 0 or nextRow >= m or nextCol < 0 or nextCol >= n or visited[nextRow][nextCol] or forest[nextRow][nextCol] == 0:\n\t continue\n\t queue.append([nextRow, nextCol])\n\t visited[nextRow][nextCol] = True\n\t step += 1\n\t \n\t # here, it means we can never find the destination\n\t return -1\n\'\'\'
| 10 | 0 |
[]
| 5 |
cut-off-trees-for-golf-event
|
Python 3 Solution using BFS
|
python-3-solution-using-bfs-by-manideep8-msgz
|
The Idea behind this is to \nStep 1 :\nGet all the trees from a matrix in sorted order. \nStep 2 :\nThen for every tree let\'s know how many number of steps it
|
manideep8
|
NORMAL
|
2020-04-14T11:36:29.727798+00:00
|
2020-04-14T11:37:14.803277+00:00
| 1,152 | false |
The Idea behind this is to \n**Step 1 :**\nGet all the trees from a matrix in sorted order. \n**Step 2 :**\nThen for every tree let\'s know how many number of steps it takes from the previous node\n(Initially for first tree we will start from (0,0)) \nIf steps < 0 then we are unable to move further due to obstacle so return -1 else add these steps to the totalSteps. \n**Step 3 :**\nIn order to get steps we use bfs \n\nThanks to @CrisaGazzola for video explanation.\nReference : https://youtu.be/HlBnTBLOPOw\n\n```class Solution:\n def cutOffTree(self, forest: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n noOfRows = len(forest)\n noOfColumns = len(forest[0])\n\t\t\n\t\t#step 1 \n\t\t\n trees = [ (forest[i][j], i, j) for i in range(noOfRows) for j in range(noOfColumns) if forest[i][j] > 1 ]\n trees = sorted(trees)\n\t\t\n\t\t#Implementation of step 3 BFS\n\t\t\n def bfs(row,col,treeX,treeY) :\n visited = [ [False for j in range(noOfColumns)] for i in range(noOfRows)]\n queue = deque([])\n queue.append( (row,col,0) )\n while queue :\n currX,currY,currSteps = queue.popleft()\n if (currX == treeX) and (currY == treeY) :\n return currSteps \n for r,c in [ (currX + 1,currY), (currX - 1,currY), (currX,currY + 1), (currX,currY - 1) ] : \n if (r >= 0) and (r < noOfRows) and (c >= 0) and (c < noOfColumns) and (not visited[r][c]) and (forest[r][c] > 0) :\n visited[r][c] = True \n queue.append( ( r, c, currSteps + 1) )\n return -1 \n \n x = 0\n y = 0 \n totalSteps = 0 \n\t\t\n\t\t#step 2 \n\t\t\n for tree in trees :\n steps = bfs(x,y,tree[1],tree[2]) #step 3 \n if steps < 0 :\n return -1 \n totalSteps += steps \n x = tree[1]\n y = tree[2]\n \n return totalSteps \n```\n
| 9 | 1 |
[]
| 2 |
cut-off-trees-for-golf-event
|
Python 3 || 19 lines bfs || T/S: 88% / 44%
|
python-3-19-lines-bfs-ts-88-44-by-spauld-mnp2
|
This code is similar to those in other posts, with one exception. We use unseen to prune out the zero cells initially, and then keep track of the cells not visi
|
Spaulding_
|
NORMAL
|
2023-08-18T20:38:55.995533+00:00
|
2024-05-29T17:18:10.709871+00:00
| 985 | false |
This code is similar to those in other posts, with one exception. We use `unseen` to prune out the zero cells initially, and then keep track of the cells *not* visited.\n```\nclass Solution:\n\n def cutOffTree(self, forest: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n\n def bfs(beg, end):\n queue, uns = deque([(beg,0)]), unseen.copy()\n uns.discard(beg)\n\n while queue:\n (r,c), steps = queue.popleft()\n\n if (r,c) == end: return steps\n\n for R,C in ((r-1,c), (r,c-1), (r+1,c), (r,c+1)):\n\n if (R,C) not in uns: continue\n\n queue.append(((R,C),steps+1))\n uns.discard((R,C))\n\n return -1\n \n m, n, ans = len(forest), len(forest[0]), 0\n start, trees = (0,0), []\n\n grid = tuple(product(range(m), range(n)))\n unseen = set(filter(lambda x: forest[x[0]][x[1]] != 0, grid))\n\n for r,c in grid:\n if forest[r][c] > 1: heappush(trees,(forest[r][c], (r,c)))\n\n while trees:\n if (res:= bfs(start,(pos:= heappop(trees)[1]))) < 0: return -1\n\n ans += res\n start = pos\n\n return ans\n```\n[https://leetcode.com/problems/cut-off-trees-for-golf-event/submissions/1271625830/](https://leetcode.com/problems/cut-off-trees-for-golf-event/submissions/1271625830/)\n\nI could be wrong, but I think that time complexity is *O*(*N*) and space complexity is *O*(*N*log*N*), in which *N* ~ number of cells in the 2D array`forest` (which is `len(forest)*len(forest[0])`).
| 8 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
cut-off-trees-for-golf-event
|
C++ Simple (BFS+ PriorityQueue) Solution With Explanation
|
c-simple-bfs-priorityqueue-solution-with-usyy
|
Approach:\nWhat we are being told is we want to cut trees in such a manner:\n1. We want to cut the trees in increasing order of their heights\n2. We can travers
|
harshseta003
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-11T06:27:45.554182+00:00
|
2022-08-11T06:28:13.229156+00:00
| 837 | false |
Approach:\nWhat we are being told is we want to cut trees in such a manner:\n1. We want to cut the trees in increasing order of their heights\n2. We can traverse through nodes with value > 1 \n\nAnd we want to minimise the number of steps to cut all trees.\nMin no. of steps to cut all trees = (min. no of steps from (0,0) to smallest tree + min. no of steps from smallest tree to second smallest tree+.... )\n\nIn order to find the next smallest tree, we use priority queue and\nin order to find min. no. of steps from (i,j) to (u,v) we use BFS.\n```\n#define p pair<int,pair<int,int>>\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int m,n;\n int bfs(int &i,int &j,int &u,int &v,vector<vector<int>>& nums){\n vector<vector<bool>>explored(m,vector<bool>(n,false));\n bool found=false;\n queue<pair<int,int>>q;\n q.push({i,j});\n explored[i][j]=true;\n int cnt=0;\n while(!q.empty()){\n int l=q.size();\n while(l--){\n pair<int,int>a=q.front();\n int x=a.first,y=a.second;\n q.pop();\n if(x==u && y==v){\n found=true;\n break;\n }\n if(x>0 && nums[x-1][y] && !explored[x-1][y]){\n explored[x-1][y]=true;\n q.push({x-1,y});\n }\n if(y>0 && nums[x][y-1] && !explored[x][y-1]){\n explored[x][y-1]=true;\n q.push({x,y-1});\n }\n if(x<m-1 && nums[x+1][y] && !explored[x+1][y]){\n explored[x+1][y]=true;\n q.push({x+1,y});\n }\n if(y<n-1 && nums[x][y+1] && !explored[x][y+1]){\n explored[x][y+1]=true;\n q.push({x,y+1});\n }\n }\n if(found)\n break;\n cnt++;\n }\n return found?cnt:-1;\n }\n int cutOffTree(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {\n m=nums.size(),n=nums[0].size();\n priority_queue<p,vector<p>,greater<p>>q;\n for(int i=0;i<m;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++){\n if(nums[i][j]>1)\n q.push({nums[i][j],{i,j}});\n }\n }\n int i=0,j=0,ans=0;\n while(!q.empty()){\n p a=q.top();\n int u=a.second.first,v=a.second.second;\n q.pop();\n int b=bfs(i,j,u,v,nums);\n if(b==-1)\n return -1;\n i=u,j=v;\n ans+=b;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 7 | 0 |
['Breadth-First Search', 'C', 'Heap (Priority Queue)']
| 1 |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.