question_slug
stringlengths 3
77
| title
stringlengths 1
183
| slug
stringlengths 12
45
| summary
stringlengths 1
160
⌀ | author
stringlengths 2
30
| certification
stringclasses 2
values | created_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| updated_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| hit_count
int64 0
10.6M
| has_video
bool 2
classes | content
stringlengths 4
576k
| upvotes
int64 0
11.5k
| downvotes
int64 0
358
| tags
stringlengths 2
193
| comments
int64 0
2.56k
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
Python3 modified Dijkstra
|
python3-modified-dijkstra-by-chang_liu-f36x
|
A dictionary timeTable keep track the minimum time spent reaching each city.\nThe DIjkstra is based on totalFee. If one city has been already visited in the alg
|
chang_liu
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-24T23:01:07.081521+00:00
|
2021-07-24T23:01:07.081553+00:00
| 137 | false |
A dictionary timeTable keep track the minimum time spent reaching each city.\nThe DIjkstra is based on totalFee. If one city has been already visited in the algorithm and the timespent is not shorter than the previous visit, the city is not considered anymore. \n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def minCost(self, maxTime: int, edges: List[List[int]], passingFees: List[int]) -> int:\n destination = len(passingFees) - 1\n timeTable = {}\n graph = {}\n for e in edges:\n u = e[0]\n v = e[1]\n d = e[2]\n \n if u not in graph:\n graph[u] = [(v, d)]\n else:\n graph[u].append((v, d))\n \n if v not in graph:\n graph[v] = [(u, d)]\n else:\n graph[v].append((u, d))\n \n # print(graph)\n \n queue = [(passingFees[0], 0, 0)] # [(totalfee, city, timespent)...]\n \n while(queue):\n totalFee, city, timeSpent = heapq.heappop(queue)\n if timeSpent > maxTime:\n continue\n elif city == destination:\n return totalFee\n elif city in timeTable and timeSpent >= timeTable[city]:\n continue\n else:\n timeTable[city] = timeSpent\n for nextCity in graph[city]:\n heapq.heappush(queue,(totalFee + passingFees[nextCity[0]], nextCity[0], timeSpent + nextCity[1]))\n \n return -1\n \n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
Modified Dijkstra's (Readable C++)
|
modified-dijkstras-readable-c-by-kunaldi-hp17
|
\n\nclass Solution {\n\t//Edge represents that there is edge pointing to val and time to reach val is time\n struct Edge {\n int val, time;\n E
|
kunaldiwakar31
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-23T12:33:54.138305+00:00
|
2021-07-23T12:33:54.138346+00:00
| 233 | false |
\n```\nclass Solution {\n\t//Edge represents that there is edge pointing to val and time to reach val is time\n struct Edge {\n int val, time;\n Edge(int val, int time) : val(val), time(time) {}\n };\n\t//Node stores value of node, cost & time to reach from source to current node\n struct Node {\n int cost, time, val;\n Node(int cost, int time, int val) : cost(cost), time(time), val(val) {}\n };\n struct Comp {\n bool operator()(Node& n1, Node& n2) {\n if(n1.cost == n2.cost)\n return n1.time > n2.time;\n return n1.cost > n2.cost;\n }\n };\npublic:\n int minCost(int maxTime, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<int>& passingFees) {\n int n = passingFees.size();\n vector<Edge> adj[n];\n for(auto e: edges) {\n adj[e[0]].push_back(Edge(e[1], e[2]));\n adj[e[1]].push_back(Edge(e[0], e[2]));\n }\n vector<int> cost(n, INT_MAX), time(n, INT_MAX);\n cost[0] = passingFees[0];\n time[0] = 0;\n priority_queue<Node, vector<Node>, Comp> pq;\n pq.push(Node(cost[0], 0, 0));\n while(!pq.empty()) {\n Node node = pq.top();\n pq.pop();\n for(Edge edge : adj[node.val]) {\n if(edge.time + node.time <= maxTime) {\n int totCost = node.cost + passingFees[edge.val];\n int totTime = edge.time + node.time;\n\t\t\t\t\t//if totalCost is lesser then we\'ll push node in queue\n if(cost[edge.val] > totCost) {\n cost[edge.val] = totCost;\n time[edge.val] = totTime;\n pq.push(Node(totCost, totTime, edge.val));\n } \n\t\t\t\t\t//else if totalCost is lesser then we\'ll push node in queue\n\t\t\t\t\telse if(time[edge.val] > totTime) {\n time[edge.val] = totTime;\n pq.push(Node(totCost, totTime, edge.val));\n }\n }\n }\n }\n return cost[n-1] == INT_MAX ? -1 : cost[n-1];\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C']
| 1 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
C++ | Recursive Solution with proper comments |New technique of using unordered_map to optimize cost
|
c-recursive-solution-with-proper-comment-ojzq
|
\n/**\n * @author : archit \n * @GitHub : archit-1997\n * @email : [email protected]\n * @file : minCostToReachDestinationInTime.c
|
warlock1997
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-23T10:38:52.293899+00:00
|
2021-07-23T10:39:36.461582+00:00
| 127 | false |
```\n/**\n * @author : archit \n * @GitHub : archit-1997\n * @email : [email protected]\n * @file : minCostToReachDestinationInTime.cpp\n * @created : Friday Jul 23, 2021 13:17:57 IST\n */\n\n\n#include <bits/stdc++.h>\nusing namespace std;\n\n#define P pair<int,pair<int,int>>\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\nvector<vector<pair<int,int>>> constructGraph(vector<vector<int>>& edges,int n){\n vector<vector<pair<int,int>>> graph(n);\n for(auto e : edges){\n graph[e[0]].push_back({e[1],e[2]});\n graph[e[1]].push_back({e[0],e[2]});\n }\n return graph;\n}\n\n int minCost(int maxTime, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<int>& passingFees) {\n int n=passingFees.size();\n vector<vector<pair<int,int>>> graph=constructGraph(edges,n);\n\n priority_queue<P,vector<P>,greater<P>> q;\n\n //{passingFees,{nextNode,time}}\n q.push({passingFees[0],{0,0}});\n\n unordered_map<int,int> vis;\n\n int ans=0;\n while(!q.empty()){\n pair<int,pair<int,int>> t=q.top();\n q.pop();\n\n int cost=t.first;\n int curNode=t.second.first,curTime=t.second.second;\n\n //reached the last node ?\n if(curNode==(n-1))\n return cost;\n\n //mark visited with current time\n vis[curNode]=curTime;\n\n for(int i=0;i<graph[curNode].size();i++){\n int nextNode=graph[curNode][i].first;\n int nextTime=graph[curNode][i].second;\n\n int time=curTime+nextTime;\n\n //if curnode already visited and also with a smaller time\n if(vis.find(nextNode)!=vis.end() && vis[nextNode]<=time)\n continue;\n\n //we need to mark this node as visited\n vis[nextNode]=time;\n\n //push in queue only if time <= totalTime\n if(time<=maxTime)\n q.push({passingFees[nextNode]+cost,{nextNode,time}});\n }\n\n }\n return -1;\n }\n};\n\n\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
C++ || Dijkstra's Algo || Priority_queue
|
c-dijkstras-algo-priority_queue-by-slims-tr6h
|
\nvector<vector<int>> adj[1001];\n \n int minCost(int maxTime, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<int>& passingFees) {\n int V=passingFees.size();\
|
SlimShady35
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-15T14:28:53.102136+00:00
|
2021-07-15T14:31:29.075391+00:00
| 384 | false |
```\nvector<vector<int>> adj[1001];\n \n int minCost(int maxTime, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<int>& passingFees) {\n int V=passingFees.size();\n int E=edges.size();\n vector<int> cost(V,INT_MAX);\n vector<int> time(V,INT_MAX);\n \n \n for(auto e: edges){\n adj[e[0]].push_back({e[1],e[2],passingFees[e[1]]});\n adj[e[1]].push_back({e[0],e[2],passingFees[e[0]]});\n }\n cost[0] = passingFees[0];\n time[0]=0;\n int ans=dijkstra(0,V-1,maxTime,cost,time);\n if (ans==INT_MAX)\n return -1;\n return ans;\n }\n int dijkstra(int src,int dst,int maxTime,vector<int> &cost,vector<int> &time){\n \n \n priority_queue<vector<int>,vector<vector<int>>, greater<vector<int>>> minh;\n minh.push({cost[src],time[src],src});\n \n while(!minh.empty()){\n vector<int> temp=minh.top();\n minh.pop();\n \n int c=temp[0];\n int t=temp[1];\n int v=temp[2];\n \n for(auto X: adj[v]){\n if(t+X[1] <= maxTime){\n if(cost[X[0]] > c + X[2]){\n cost[X[0]]=c+X[2];\n \n time[X[0]]= t+ X[1];\n minh.push({cost[X[0]],time[X[0]],X[0]});\n }\n if(time[X[0]]> t+ X[1]){\n time[X[0]]=t+X[1];\n minh.push({c+X[2],time[X[0]],X[0]});\n }\n \n }\n }\n \n }\n\nreturn cost[dst];\n}\n```\n
| 1 | 0 |
['C']
| 1 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
C++ ||DP
|
c-dp-by-dreamkiller1729-cyr2
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int minCost(int maxTime, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<int>& passingFees) {\n int n=passingFees.size();\n ve
|
dreamkiller1729
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-14T22:19:56.844084+00:00
|
2021-07-14T22:20:22.629834+00:00
| 132 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int minCost(int maxTime, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<int>& passingFees) {\n int n=passingFees.size();\n vector<vector<pair<int,int>>>vec(n);\n for(auto it:edges){\n vec[it[0]].emplace_back(it[1],it[2]);\n vec[it[1]].emplace_back(it[0],it[2]);\n }\n const int inf=(int)1e9+5;\n vector<vector<int>>dp(maxTime+1,vector<int>(n,inf));\n dp[0][0]=passingFees[0];\n for(int time=0;time<maxTime;time++){\n for(int node=0;node<n;node++){\n if(dp[time][node]>=inf){\n continue;\n }\n for(auto[x,y]:vec[node]){\n if(y+time<=maxTime){\n dp[y+time][x]=min(dp[y+time][x],dp[time][node]+passingFees[x]);\n }\n }\n }\n }\n int ans=inf;\n for(int i=0;i<=maxTime;i++){\n ans=min(ans,dp[i][n-1]);\n }\n return ans>=inf?-1:ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
Python/C++ 100% time
|
pythonc-100-time-by-nikamir-wdkj
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int minCost(int maxTime, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<int>& passingFees) {\n int n = passingFees.size();\n
|
nikamir
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-13T23:05:29.308029+00:00
|
2021-07-14T02:49:36.198242+00:00
| 208 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int minCost(int maxTime, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<int>& passingFees) {\n int n = passingFees.size();\n auto maxCost = accumulate(begin(passingFees), end(passingFees), 1);\n \n vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> g(n, vector<pair<int, int>>());\n for (auto e: edges) {\n g[e[1]].push_back({e[0], e[2]});\n g[e[0]].push_back({e[1], e[2]});\n }\n \n vector<int> minCostToDest(n, maxCost);\n minCostToDest[n-1]=passingFees[n-1];\n priority_queue<array<int, 2>, vector<array<int, 2>>, greater<array<int, 2>>> pq;\n pq.push({passingFees[n-1], n-1});\n vector<array<int, 2>> parent(n, {-1, -1});\n parent[n-1] = {n-1,0};\n \n while (pq.size() > 0) {\n auto [curCost, curCity] = pq.top(); pq.pop();\n if (curCost == minCostToDest[curCity]) {\n for (auto [nxtCity, dTime]: g[curCity]) {\n auto nxtCost = curCost + passingFees[nxtCity];\n if (nxtCost < minCostToDest[nxtCity]) {\n parent[nxtCity] = {curCity, dTime};\n minCostToDest[nxtCity] = nxtCost;\n pq.push({nxtCost, nxtCity});\n }\n }\n }\n }\n \n \n if (parent[0][0] == -1) {\n return -1;\n }\n int minCostTime = 0;\n int curCity = 0;\n while (curCity != n - 1) {\n auto [nxtCity, dTime] = parent[curCity];\n minCostTime += dTime;\n curCity = nxtCity;\n }\n if (minCostTime <= maxTime) {\n return minCostToDest[0];\n }\n \n \n vector<int> minTimeToDest(n, maxTime + 1);\n pq.push({0, n - 1});\n minTimeToDest[n-1] = 0;\n while (pq.size() > 0) {\n auto [curTime, curCity] = pq.top(); pq.pop();\n if (curTime == minTimeToDest[curCity]) {\n for (auto [nxtCity, dTime]: g[curCity]) {\n auto nxtTime = curTime + dTime;\n if (nxtTime < minTimeToDest[nxtCity]) {\n minTimeToDest[nxtCity] = nxtTime;\n pq.push({nxtTime, nxtCity});\n }\n }\n }\n }\n if (minTimeToDest[0] > maxTime) {\n return -1;\n }\n \n priority_queue<array<int, 3>, vector<array<int, 3>>, greater<array<int, 3>>> pq3;\n pq3.push({0, 0, passingFees[0]});\n int result = maxCost;\n while (pq3.size() > 0) {\n auto [curTime, curCity, curCost] = pq3.top(); pq3.pop();\n if (curCost < result) {\n if (curCity == n - 1) {\n result = curCost;\n } else {\n for (auto [nxtCity, dTime]: g[curCity]) {\n if (curCost + minCostToDest[nxtCity] < result) {\n auto nxtTime = curTime + dTime;\n if (nxtTime + minTimeToDest[nxtCity] <= maxTime) {\n pq3.push({nxtTime, nxtCity, curCost + passingFees[nxtCity]});\n }\n }\n }\n }\n }\n }\n \n \n if (result < maxCost) {\n return result;\n } else {\n return -1;\n }\n }\n};\n```\n```\nclass Solution:\n def minCost(self, maxTime: int, edges: List[List[int]], passingFees: List[int]) -> int:\n n = len(passingFees)\n \n maxCost = sum(passingFees) + 1\n # build a dictionary\n g = [[] for _ in range(n)]\n for s, d, t in edges:\n g[s].append((d, t))\n g[d].append((s, t))\n \n # run Djikstra for minimal cost from every city to destination\n minCostToDest = [maxCost] * n\n pq = [(passingFees[-1], n - 1)]\n parent = [(-1, -1)] * n\n parent[-1] = n - 1\n minCostToDest[-1] = passingFees[-1]\n while pq:\n curCost, curCity = heappop(pq)\n if curCost == minCostToDest[curCity]:\n for nxtCity, dTime in g[curCity]:\n nxtCost = curCost + passingFees[nxtCity]\n if nxtCost < minCostToDest[nxtCity]:\n parent[nxtCity] = (curCity, dTime)\n minCostToDest[nxtCity] = nxtCost\n heappush(pq, (nxtCost, nxtCity))\n # no path to destination from 0\n if parent[0][0] == -1:\n return -1\n minCostTime = 0\n curCity = 0\n # check if the min cost path is coming under the maxTime, this is our result then\n while curCity != n - 1:\n curCity, dTime = parent[curCity]\n minCostTime += dTime\n if minCostTime <= maxTime:\n return minCostToDest[0]\n \n # run Djikstra for the min time to n - 1 for every city\n minTimeToDest = [maxTime + 1] * n\n pq.append((0, n - 1))\n minTimeToDest[-1] = 0\n while pq:\n curTime, curCity = heappop(pq)\n if curTime == minTimeToDest[curCity]:\n for nxtCity, dTime in g[curCity]:\n nxtTime = curTime + dTime\n if nxtTime < minTimeToDest[nxtCity]:\n minTimeToDest[nxtCity] = nxtTime\n heappush(pq, (nxtTime, nxtCity))\n\n # check if the min time is coming over limit, no solution if it is\n if minTimeToDest[0] > maxTime:\n return -1\n \n # now run "unbound Djikstra"\n # check every possible path, only cut those that are either overtime or over the found solution\n pq.append((0, 0, passingFees[0]))\n result = maxCost\n while pq:\n curTime, curCity, curCost = heappop(pq)\n if curCost < result:\n if curCity == n - 1:\n result = curCost\n else:\n for nxtCity, dTime in g[curCity]:\n if curCost + minCostToDest[nxtCity] < result:\n nxtTime = curTime + dTime\n if nxtTime + minTimeToDest[nxtCity] <= maxTime:\n heappush(pq, (nxtTime, nxtCity, curCost + passingFees[nxtCity]))\n if result < maxCost:\n return result\n else:\n return -1\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
c++(128ms 93%) Dijkstra
|
c128ms-93-dijkstra-by-zx007pi-32oe
|
Runtime: 128 ms, faster than 92.75% of C++ online submissions for Minimum Cost to Reach Destination in Time.\nMemory Usage: 25.1 MB, less than 94.35% of C++ onl
|
zx007pi
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-13T15:40:57.757218+00:00
|
2021-08-17T16:03:10.449213+00:00
| 230 | false |
Runtime: 128 ms, faster than 92.75% of C++ online submissions for Minimum Cost to Reach Destination in Time.\nMemory Usage: 25.1 MB, less than 94.35% of C++ online submissions for Minimum Cost to Reach Destination in Time.\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int minCost(int maxTime, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<int>& passingFees) {\n int n = passingFees.size(), CITY = n - 1;\n vector<vector<pair<int,int> > > graph(n); //city, time\n vector<int> limtime(n, INT_MAX);\n \n \n for(auto &i: edges ){\n graph[i[0]].push_back({ i[1], i[2] });\n graph[i[1]].push_back({ i[0], i[2] });\n }\n \n priority_queue< tuple<int,int,int>, vector<tuple<int,int,int>>, greater<tuple<int,int,int>> > pq; //pay, time, city\n pq.push({0,0,0});\n \n while(!pq.empty()){\n auto[pay, time, city] = pq.top(); pq.pop(); \n if(city == CITY) return pay + passingFees[0]; \n \n limtime[city] = time;\n \n for(auto &next: graph[city]){\n int nexttime = time + next.second;\n if( nexttime < limtime[next.first] ){\n limtime[next.first] = nexttime;\n if(nexttime <= maxTime) pq.push({ pay + passingFees[next.first], nexttime, next.first });\n }\n }\n }\n \n return -1; \n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C', 'C++']
| 1 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
Java Dijkstras 100% Faster 100% Memory
|
java-dijkstras-100-faster-100-memory-by-twfsi
|
```\n\tpublic int minCost(int maxTime, int[][] edges, int[] pf) {\n int n= pf.length;\n //adjacency matrix for time\n int[][] adj= new int[
|
sunnydhotre
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-11T23:05:51.090735+00:00
|
2021-07-11T23:05:51.090762+00:00
| 105 | false |
```\n\tpublic int minCost(int maxTime, int[][] edges, int[] pf) {\n int n= pf.length;\n //adjacency matrix for time\n int[][] adj= new int[n][n];\n for(int i=0; i<edges.length; i++){\n int v1= edges[i][0], v2= edges[i][1], val= edges[i][2];\n if(adj[v1][v2] == 0 || adj[v1][v2] > val){\n adj[v1][v2]= val;\n adj[v2][v1]= val;\n }\n }\n // map is graph of connected nodes\n Map<Integer,List<Integer>> map= new HashMap<>();\n for(int i=0; i<n; i++){\n map.put(i, new ArrayList<>());\n for(int j=0; j<n; j++){\n if(adj[i][j] == 0) continue;\n map.get(i).add(j);\n }\n }\n int[] minTime= new int[n]; \n \n //visited array, dont visit again if cost is greater than previous visited cost\n Arrays.fill(minTime,Integer.MAX_VALUE);\n \n //Dijkstras w.r.t cost because we want min cost and if time becomes > maxTime we will stop\n //exploring that path\n Queue<int[]> minHeap= new PriorityQueue<>((a,b)->a[1]-b[1]);\n minHeap.add(new int[]{0,pf[0],0});\n while(!minHeap.isEmpty()){\n int[] curr= minHeap.poll();\n if(curr[2] > maxTime || curr[2] >= minTime[curr[0]]) continue;\n if(curr[0] == n-1) return curr[1];\n minTime[curr[0]]= curr[2]; //visit curr node with least possible time\n for(int neigh : map.get(curr[0])){\n int time= curr[2] + adj[curr[0]][neigh];\n int cost= curr[1] + pf[neigh];\n minHeap.add(new int[]{neigh,cost,time});\n }\n }\n return -1;\n }
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
My Java Solution using Djikstras algorithm
|
my-java-solution-using-djikstras-algorit-62i7
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int minCost(int maxTime, int[][] edges, int[] passingFees) {\n int length = passingFees.length;\n List<int[]>[] gra
|
vrohith
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-11T18:22:44.943595+00:00
|
2021-07-11T18:22:44.943623+00:00
| 220 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int minCost(int maxTime, int[][] edges, int[] passingFees) {\n int length = passingFees.length;\n List<int[]>[] graph = buildGraph(edges, length);\n int [] minimumTime = new int [length];\n Arrays.fill(minimumTime, Integer.MAX_VALUE);\n PriorityQueue<int []> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> Integer.compare(a[1], b[1]));\n pq.add(new int [] {0, passingFees[0], 0});\n // source, passingfee for source, totaltime\n int time = 0;\n int score = 0;\n while (!pq.isEmpty()) {\n int [] current = pq.poll();\n if (current[2] >= minimumTime[current[0]])\n continue;\n minimumTime[current[0]] = current[2];\n if (current[0] == length - 1)\n return current[1];\n for (int [] nextChild : graph[current[0]]) {\n time = current[2] + nextChild[1];\n score = current[1] + passingFees[nextChild[0]];\n if (time > maxTime)\n continue;\n if (time > minimumTime[nextChild[0]])\n continue;\n pq.add(new int [] {nextChild[0], score, time});\n }\n }\n return -1;\n }\n \n public List<int[]>[] buildGraph(int [][] edges, int length) {\n List<int[]> [] graph = new ArrayList[length];\n for (int i=0; i<length; i++) {\n graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();\n }\n for (int [] edge : edges) {\n graph[edge[0]].add(new int [] {edge[1], edge[2]});\n graph[edge[1]].add(new int [] {edge[0], edge[2]});\n }\n return graph;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Graph', 'Java']
| 0 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
C++ using DP
|
c-using-dp-by-ishank193aggarwal-j03x
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int minCost(int maxTime, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<int>& fees) {\n \n int n=fees.size();\n vector
|
ishank193aggarwal
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-11T17:51:52.771781+00:00
|
2021-07-11T17:51:52.771825+00:00
| 59 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int minCost(int maxTime, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<int>& fees) {\n \n int n=fees.size();\n vector<vector<pair<int,int>>> graph(n);\n \n for(int i=0;i<edges.size();i++){\n graph[edges[i][0]].push_back({edges[i][1],edges[i][2]});\n graph[edges[i][1]].push_back({edges[i][0],edges[i][2]});\n }\n \n vector<vector<int>> dp(maxTime+1,vector<int>(n,INT_MAX));\n dp[0][0]=fees[0];\n \n for(int i=0;i<=maxTime;i++){\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++){\n int currFees=dp[i][j];\n if(currFees==INT_MAX){\n continue;\n }\n for(auto node:graph[j]){\n int next=node.first;\n int time=i+node.second;\n if(time<=maxTime){\n dp[time][next]=min(dp[time][next],fees[next]+currFees);\n }\n }\n }\n }\n \n int ans=INT_MAX;\n for(int t=0;t<=maxTime;t++){\n ans=min(ans,dp[t][n-1]);\n }\n if(ans==INT_MAX){\n return -1;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
C++ Memoization solution
|
c-memoization-solution-by-aparna_g-uqh9
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int n;\n int helper(int v,int time ,vector<unordered_map<int,int>> &graph ,vector<vector<int>>&dp , vector<int>& fees ){\n
|
aparna_g
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-11T13:52:50.850912+00:00
|
2021-07-11T13:52:50.850980+00:00
| 180 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int n;\n int helper(int v,int time ,vector<unordered_map<int,int>> &graph ,vector<vector<int>>&dp , vector<int>& fees ){\n if(v == n-1)\n return fees[n-1];\n if(dp[v][time]!=-1)\n return dp[v][time];\n int ans = INT_MAX;\n for(auto &g: graph[v]){\n if(time-g.second>=0){\n int cost = helper(g.first,time-g.second, graph,dp,fees);\n ans = min(ans,cost);\n }\n }\n return dp[v][time] = ans!=INT_MAX ? ans + fees[v] : INT_MAX;\n }\n \n int minCost(int maxTime, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<int>& passingFees) {\n n = passingFees.size(); //no of vertices\n vector<vector<int>> dp(n, vector<int>(maxTime+1 , -1));\n //you have to go from 0 to n-1 within maxTime by spending the minimum amount of money. \n \n vector<unordered_map<int,int>> graph(n);\n //Important point is to note that there may be multiple roads of differing travel times connecting the same two cities. So take the route with the minimum cost. \n for(auto & e: edges){\n if( graph[e[0]][e[1]]==0)\n graph[e[0]][e[1]] = e[2];\n else \n graph[e[0]][e[1]] = min( graph[e[0]][e[1]] , e[2]);\n \n if(graph[e[1]][e[0]] == 0) \n graph[e[1]][e[0]] = e[2];\n else \n graph[e[1]][e[0]] = min(graph[e[1]][e[0]] , e[2]);\n }\n int ans = helper(0,maxTime,graph,dp,passingFees); \n return ans==INT_MAX ? -1 : ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'C', 'C++']
| 1 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
[Python/C++] DFS with memoization and explanation
|
pythonc-dfs-with-memoization-and-explana-m3dq
|
Point:\nIn between u and v there\'s no point in taking the edge that takes longer time. Since the passingFee depends on only u and v and not the edge. So take t
|
rajat499
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-11T09:29:52.398282+00:00
|
2021-07-11T09:30:51.622329+00:00
| 322 | false |
**Point:**\nIn between u and v there\'s no point in taking the edge that takes longer time. Since the passingFee depends on only u and v and not the edge. So take the edge that takes minimum time.\nRest is memoization on u and time. `dp[u][time]` represents minimum cost to reach edge `n-1` from vertex `u` with time `time` left\n\n### Python\n```\nimport collections\nclass Solution:\n def minCost(self, maxTime: int, edges: List[List[int]], passingFees: List[int]) -> int:\n graph = collections.defaultdict(lambda: collections.defaultdict(lambda: float(\'inf\')))\n for u, v, w in edges:\n graph[u][v] = min(graph[u][v], w)\n graph[v][u] = min(graph[v][u], w)\n \n n = len(passingFees)\n states = [[-1]*(maxTime+1) for _ in range(n)]\n def helper(u, time):\n if u==n-1:\n return passingFees[u]\n if states[u][time] != -1:\n return states[u][time]\n ans = float("inf")\n for v in graph[u].keys():\n if time-graph[u][v]>=0:\n val = helper(v, time-graph[u][v])\n ans = min(ans, val)\n states[u][time] = ans+passingFees[u]\n return states[u][time]\n ans = helper(0, maxTime)\n if ans > 10000000:\n return -1\n return ans\n```\n\n### C++\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int n;\n int helper(int u, int time, vector<vector<int>>& dp, vector<unordered_map<int, int>>& graph, vector<int>& fee){\n if(u==n-1){\n return fee[u];\n }\n if(dp[u][time] != -1){\n return dp[u][time];\n }\n int ans = INT_MAX-1000;\n for(auto &e: graph[u]){\n if(time-e.second>=0){\n int v = helper(e.first, time-e.second, dp, graph, fee);\n ans = min(v, ans);\n }\n }\n return dp[u][time] = ans+fee[u];\n }\n int minCost(int maxTime, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<int>& passingFees) {\n n = passingFees.size();\n vector<vector<int>> dp(n, vector<int>(maxTime+1, -1));\n vector<unordered_map<int, int>> graph(n);\n for(auto &e: edges){\n if(graph[e[0]][e[1]]==0)\n graph[e[0]][e[1]] = e[2];\n else\n graph[e[0]][e[1]] = min(e[2], graph[e[0]][e[1]]);\n if(graph[e[1]][e[0]]==0)\n graph[e[1]][e[0]] = e[2];\n else\n graph[e[1]][e[0]] = min(e[2], graph[e[1]][e[0]]);\n }\n int ans = helper(0, maxTime, dp, graph, passingFees);\n return (ans>10000000)?-1:ans;\n }\n};
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Depth-First Search', 'Memoization', 'C', 'Python']
| 0 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
Java | 100% Faster Space & Time | Dijkstra
|
java-100-faster-space-time-dijkstra-by-t-h8jr
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int minCost(int maxTime, int[][] edges, int[] passingFees) {\n int[] time = new int[passingFees.length];\n Arrays.f
|
temptaken
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-11T06:31:01.534583+00:00
|
2021-07-11T06:31:01.534619+00:00
| 76 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int minCost(int maxTime, int[][] edges, int[] passingFees) {\n int[] time = new int[passingFees.length];\n Arrays.fill(time, Integer.MAX_VALUE);\n time[0] = 0;\n \n Map<Integer, List<List<Integer>>> edgesMap = new HashMap();\n \n for(int i = 0 ; i < edges.length ; i++){\n if(!edgesMap.containsKey(edges[i][0]))\n edgesMap.put(edges[i][0], new ArrayList());\n if(!edgesMap.containsKey(edges[i][1]))\n edgesMap.put(edges[i][1], new ArrayList());\n \n edgesMap.get(edges[i][0]).add(Arrays.asList(edges[i][1], edges[i][2]));\n edgesMap.get(edges[i][1]).add(Arrays.asList(edges[i][0], edges[i][2]));\n }\n \n Comparator<List<Integer>> cmp = (a,b) -> a.get(1) - b.get(1);\n PriorityQueue<List<Integer>> pq = new PriorityQueue(cmp);\n pq.add(Arrays.asList(0, passingFees[0], 0));\n \n while(!pq.isEmpty()){\n List<Integer> node = pq.poll();\n if(node.get(0) == passingFees.length - 1)\n return node.get(1);\n \n List<List<Integer>> neighbours = edgesMap.get(node.get(0));\n \n for(int i = 0 ; i < neighbours.size() ; i++){\n List<Integer> list = neighbours.get(i);\n int timeToReach = node.get(2) + list.get(1);\n \n if(timeToReach > maxTime)\n continue;\n \n if(time[list.get(0)] > timeToReach){\n time[list.get(0)] = timeToReach;\n int cost = node.get(1) + passingFees[list.get(0)];\n pq.add(Arrays.asList(list.get(0),cost,timeToReach));\n }\n }\n }\n \n return -1;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
No Dijkstra | DFS | C++ | Beginner | City Travel
|
no-dijkstra-dfs-c-beginner-city-travel-b-5mrg
|
Many posts use Dijkstra, I look to explore dfs with memoization in this post\n\nAlgorithm\n1. Bulid the graph. Keep only minimum weights edges between two citie
|
shourabhpayal
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-11T05:55:00.873809+00:00
|
2021-07-11T06:05:05.325012+00:00
| 454 | false |
Many posts use Dijkstra, I look to explore dfs with memoization in this post\n\n**Algorithm**\n1. Bulid the graph. Keep only minimum weights edges between two cities.\n2. Start dfs from city 0 with maxTime remaining.\n3. From a city ```u``` travel to all cities ```v``` using dfs if time does not run out (i.e time does not go below 0). Choose the city ```v ``` which takes minimum fees.\n4. If you reach the final city return the fee for final city as the answer.\n6. We memoize on fees using ```city number``` and ```time```.\n\n**Code**\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int n;\n\t// {key = city u, value = {key = city v, value = time required to travel from city u to v} }\n vector<unordered_map<int, int>> graph;\n vector<vector<int>>dp;\n int minCost(int maxTime, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<int>& fee) {\n n = fee.size();\n dp = vector<vector<int>>(n, vector<int>(maxTime+1, -1));\n graph = vector<unordered_map<int, int>>(n);\n // build the graph, keep weights which are minimum if multiple paths are present between same pair of nodes\n for(auto &e : edges){\n if(graph[e[0]].count(e[1]) == 0) graph[e[0]][e[1]] = e[2];\n else graph[e[0]][e[1]] = min(graph[e[0]][e[1]], e[2]);\n if(graph[e[1]].count(e[0]) == 0) graph[e[1]][e[0]] = e[2];\n else graph[e[1]][e[0]] = min(graph[e[1]][e[0]], e[2]);\n }\n int ans = dfs(fee, 0, maxTime);\n return ans == INT_MAX ? -1 : ans;\n }\n \n int dfs(vector<int>& fee, int u, int time){\n if(u == n-1) return fee[u];\n if(dp[u][time] != -1) return dp[u][time];\n \n int ans = INT_MAX;\n for(auto &e : graph[u]){\n int v = e.first;\n int vtime = e.second;\n if(time - vtime >= 0){\n int val = dfs(fee, v, time-vtime);\n if(val != INT_MAX){\n ans = min(ans, fee[u] + val);\n }\n }\n }\n return dp[u][time] = ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Memoization', 'C']
| 1 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
C++: Dijkstra MOdification
|
c-dijkstra-modification-by-sakethamargan-ks92
|
priority_queue alias heap will take care of minCost like we usaully do in Dijkstra.\nkey point is time. \npush a node again to heap if u can reach it in less ti
|
sakethamargani0137
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-10T19:23:00.757536+00:00
|
2021-07-10T19:31:03.314732+00:00
| 162 | false |
priority_queue alias heap will take care of minCost like we usaully do in Dijkstra.\nkey point is time. \n**push a node again to heap if u can reach it in less time than before**\n\n\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n struct myComp {\n bool operator()(vector<int>& a,vector<int> &b){\n return a[1] > b[1];\n }\n };\n int minCost(int maxTime, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<int>& p) {\n \n priority_queue<vector<int>,vector<vector<int>>,myComp> pq;\n pq.push({0,p[0],0});\n int n = p.size();\n \n vector<vector<pair<int,int>>> graph(n);\n for(auto it : edges){\n graph[it[0]].push_back({it[1],it[2]});\n graph[it[1]].push_back({it[0],it[2]});\n }\n vector<int> visited(n,0);\n \n while(!pq.empty()){\n vector<int> curr = pq.top();\n pq.pop();\n if(curr[2] > maxTime){\n continue;\n }\n if(curr[0] == n-1){\n return curr[1];\n }\n \n for(auto it : graph[curr[0]]){\n if(visited[it.first] && visited[it.first] <= it.second+curr[2]){\n continue;\n }\n visited[it.first] = it.second+curr[2];\n if(it.second+curr[2] <= maxTime){\n pq.push({it.first,curr[1]+p[it.first],curr[2]+it.second});\n }\n }\n \n }\n \n return -1;\n \n \n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C', 'Heap (Priority Queue)']
| 1 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
Python modified Dijkstra / hybrid SPFA
|
python-modified-dijkstra-hybrid-spfa-by-9zmga
|
This is sort of like Dijkstra on fees, with times "along for the ride". Typically, Dijkstra stores the result for node u as it pops the next item off the min he
|
fftnim
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-10T17:23:15.058416+00:00
|
2021-07-11T00:58:23.625980+00:00
| 236 | false |
This is sort of like Dijkstra on fees, with times "along for the ride". Typically, Dijkstra stores the result for node u as it pops the next item off the min heap, and then never returns to the same node. In this case, there are three changes:\n\n1. We only care about the shortest edge between two vertices in the graph, so when building the graph always take the min weight edge.\n2. Normally, Dijkstra only adds a neighbor v of the current node u to the queue if u hasn\'t been processed before (this is also why Dijkstra can\'t handle negative edge weights). However, in our case we have two changes: first, we re-process the node u if the new time is an improvement over the existing time; second, we only add a neighbor if its new_time is within the time constraint.\n3. Normally, Dijkstra is SSSP and we would need to store intermediate fee values in something like a dictionary. However, this is shortest path between two nodes. Hence, we can use the heap to store our result (which will be the popped fee when u == n - 1).\n\nThe algorithm we end up with feels like a hybrid between Dijkstra and SPFA (shortest path faster algorithm, a modified Bellman-Ford). It\'s like Dijkstra in that we\'re using a heap (and adding an early exit condition because we don\'t care about all destinations). But it\'s like SPFA in that we only add vertices to the heap if they can contribute to the solution (which means new_time <= maxTime for this problem).\n\n```py\nclass Solution:\n def minCost(self, maxTime: int, edges: List[List[int]], fees: List[int]) -> int:\n n = len(fees)\n \n g = collections.defaultdict(lambda: collections.defaultdict(lambda: float(\'inf\')))\n for u, v, w in edges:\n g[u][v] = min(g[u][v], w)\n g[v][u] = min(g[v][u], w)\n \n times = {}\n \n h = [(fees[0], 0, 0)]\n while h:\n fee, time, u = heapq.heappop(h)\n\n if u == n - 1:\n return fee\n \n if u not in times or time < times[u]:\n times[u] = time\n for v in g[u]:\n new_time = time + g[u][v]\n if new_time <= maxTime:\n heapq.heappush(h, (fee + fees[v], new_time, v))\n \n return -1\n```\n\nNow, let\'s look at the time and space complexity. Typically, min-heap Dijkstra has a time complexity of O(E + V log V), because we process each edge at most twice and each vertex at most once (where V log V comes from popping V vertices off the heap). And space complexity of O(V + E) (the max size of the heap), which becomes O(E) for connected graphs\n\nThe time and space complexity of this problem are a little trickier to calculate. Intuitively, it feels psuedo-polynomial because the number of times we relax an edge depends on maxTime (the larger maxTime, the more times we can potentially relax an edge). \n\nI\'d like to see some others weigh in, but my thoughts are:\n\nGiven that edge weights are at least 1, we can process each vertex O(maxTime) times. This is because you can have simple paths (paths with no repeated edges) of length up to maxTime. So we could process a vertex for a path of length 1 and weight maxTime with fee x, then a path of length 2 and weight maxTime - 1 with fee x, etc. Each time we process the vertex, we put it on the heap. So it seems the heap can end up as O(E * maxSize) size and the time complexity can become O(E * maxTime + (V * maxTime) * log(V * maxTime)).\n\n
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
Template for weighted graph (Bi-directional)
|
template-for-weighted-graph-bi-direction-mlqd
|
class Solution {\n \n public int minCost(int maxTime, int[][] edges, int[] passingFees) {\n //template for bidirectional wieghted graph\n Ha
|
sirpawandeep25
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-10T17:19:13.932874+00:00
|
2021-07-10T17:19:13.932915+00:00
| 78 | false |
class Solution {\n \n public int minCost(int maxTime, int[][] edges, int[] passingFees) {\n //template for bidirectional wieghted graph\n HashMap<Integer,ArrayList<pair>> map=new HashMap<>();\n for(int i=0;i<edges.length;i++){\n int a=edges[i][0];\n int b=edges[i][1];\n int c=edges[i][2];\n if(!map.containsKey(a)){\n map.put(a,new ArrayList<>());\n }\n if(!map.containsKey(b)){\n map.put(b,new ArrayList<>());\n }\n ArrayList<pair> list1=map.get(a);\n pair np1=new pair(b,c);\n list1.add(np1);\n map.put(a,list1);\n ArrayList<pair> list2=map.get(b);\n pair np2=new pair(a,c);\n list2.add(np2);\n map.put(b,list2);\n }\n return 0;\n }\n}\n\n\tclass pair{\n\t\tint node;\n\t\tint val;\n\t\tpair(int node,int val){\n\t\t\tthis.node=node;\n\t\t\tthis.val=val;\n\t\t}\n}
| 1 | 1 |
[]
| 0 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
C# - O(maxTime * (E + V)) Dynamic Programming
|
c-omaxtime-e-v-dynamic-programming-by-ch-xvcg
|
The solution is based on the winner\'s answer.\nThe d[i, j] state is min fee required to reach node i in time j. The minimum value to reach last node is require
|
christris
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-10T17:03:11.832828+00:00
|
2021-07-13T09:08:06.481877+00:00
| 173 | false |
The solution is based on the winner\'s answer.\nThe d[i, j] state is min fee required to reach node i in time j. The minimum value to reach last node is required answer.\n\n```csharp\npublic int MinCost(int maxTime, int[][] edges, int[] passingFees)\n{\n\tint n = passingFees.Length;\n\tDictionary<int, List<(int index, int cost)>> graph = new Dictionary<int, List<(int, int)>>();\n\n\tfor (int i = 0; i < n; i++)\n\t{\n\t\tgraph[i] = new List<(int, int)>();\n\t}\n\n\tforeach (var edge in edges)\n\t{\n\t\tint u = edge[0], v = edge[1], c = edge[2];\n\t\tgraph[u].Add((v, c));\n\t\tgraph[v].Add((u, c));\n\t}\n\n\tint result = int.MaxValue;\n\tint[,] d = new int[n, maxTime + 1];\n\n\tfor (int node = 0; node < n; node++)\n\t{\n\t\tfor (int time = 0; time <= maxTime; time++)\n\t\t{\n\t\t\td[node, time] = int.MaxValue;\n\t\t}\n\t}\n\n\td[0, 0] = passingFees[0];\n\n\tfor (int time = 1; time <= maxTime; time++)\n\t{\n\t\tfor (int i = 0; i < n; i++)\n\t\t{\n\t\t\tforeach (var (index, currentTime) in graph[i])\n\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\tif (time >= currentTime && d[index, time - currentTime] != int.MaxValue)\n\t\t\t\t{\n\t\t\t\t\td[i, time] = Math.Min(d[i, time], d[index, time - currentTime] + passingFees[i]);\n\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t}\n\t}\n\n\tfor (int i = 1; i <= maxTime; i++)\n\t{\n\t\tresult = Math.Min(result, d[n - 1, i]);\n\t}\n\n\treturn result == int.MaxValue ? -1 : result;\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming']
| 0 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
Python heap solution
|
python-heap-solution-by-savikx-2uue
|
Use visited, time, and cost to memorize the status of each node, update if necessary.\nUse a minheap to prioritize cost, time.\n\n\nclass Solution:\n def min
|
savikx
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-10T16:03:03.702378+00:00
|
2021-07-10T16:03:03.702414+00:00
| 320 | false |
Use visited, time, and cost to memorize the status of each node, update if necessary.\nUse a minheap to prioritize cost, time.\n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def minCost(self, maxTime: int, edges: List[List[int]], passingFees: List[int]) -> int:\n \n n = len(passingFees)\n g = collections.defaultdict(list)\n for u, v, t in edges:\n g[u].append((v, t))\n g[v].append((u, t))\n \n times = [0] + [float(\'inf\')] * (n - 1)\n costs = [passingFees[0]] + [float(\'inf\')] * (n - 1)\n q = [(passingFees[0], 0, 0)] # cost, time, node\n visited = set()\n visited.add(0)\n while q:\n cost, time, node = heapq.heappop(q)\n if node == n - 1:\n if time <= maxTime:\n return cost\n else:\n return -1\n for neighbor, t in g[node]:\n if time + t <= maxTime and (neighbor not in visited or cost + passingFees[neighbor] < costs[neighbor] or time + t < times[neighbor]):\n visited.add(neighbor)\n times[neighbor] = min(times[neighbor], time + t)\n costs[neighbor] = min(costs[neighbor], cost + passingFees[neighbor])\n heapq.heappush(q, (cost + passingFees[neighbor], time + t, neighbor))\n \n return -1\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Heap (Priority Queue)', 'Python']
| 0 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
[Java] Dijkstra's algorithm
|
java-dijkstras-algorithm-by-nirvana_rsc-uls2
|
I feel like this had very tight limit for Java... even with primitive arrays it barely passes on time (some attempts TLE)\n\nSame code in c++ will comfortably p
|
nirvana_rsc
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-10T16:02:21.675135+00:00
|
2021-07-10T16:02:21.675254+00:00
| 246 | false |
I feel like this had very tight limit for Java... even with primitive arrays it barely passes on time (some attempts TLE)\n\nSame code in c++ will comfortably pass\n\n```\n static int[][][] g;\n static int[][] edges;\n static int n;\n\n public int minCost(int maxTime, int[][] e, int[] passingFees) {\n edges = e;\n n = passingFees.length;\n g = packG();\n final int[][] dp = new int[n][maxTime + 1];\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n Arrays.fill(dp[i], (int) 1e9);\n }\n dp[0][0] = passingFees[0];\n final PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0]));\n pq.offer(new int[] { passingFees[0], 0, 0 });\n while (!pq.isEmpty()) {\n final int[] curr = pq.remove();\n final int d = curr[0];\n final int u = curr[1];\n final int time = curr[2];\n if (dp[u][time] < d) {\n continue;\n }\n for (int[] next : g[u]) {\n final int nextTime = time + next[1];\n if (nextTime <= maxTime) {\n if (dp[next[0]][nextTime] > dp[u][time] + passingFees[next[0]]) {\n dp[next[0]][nextTime] = dp[u][time] + passingFees[next[0]];\n pq.offer(new int[] { dp[next[0]][nextTime], next[0], nextTime });\n }\n }\n }\n }\n int res = (int) 1e9;\n for (int i = 0; i <= maxTime; i++) {\n res = Math.min(res, dp[n - 1][i]);\n }\n return res == (int) 1e9 ? -1 : res;\n }\n\n private static int[][][] packG() {\n final int[][][] g = new int[n][][];\n final int[] size = new int[n];\n for (int[] edge : edges) {\n ++size[edge[0]];\n ++size[edge[1]];\n }\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n g[i] = new int[size[i]][2];\n }\n for (int[] edge : edges) {\n g[edge[0]][--size[edge[0]]] = new int[] { edge[1], edge[2] };\n g[edge[1]][--size[edge[1]]] = new int[] { edge[0], edge[2] };\n }\n return g;\n }\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
Python heap
|
python-heap-by-etherwei-79b1
|
ApproachClassic Dijkstra but with some modifications.Whenever we pop a city off the heap, we know it's either the first time we visited the city or we have visi
|
etherwei
|
NORMAL
|
2025-04-11T17:00:46.023033+00:00
|
2025-04-11T17:00:46.023033+00:00
| 1 | false |
# Approach
Classic Dijkstra but with some modifications.
Whenever we pop a city off the heap, we know it's either the first time we visited the city or we have visited the city at lower costs before. Hence, if we can reduce the time it took to that city, it's worth checking all its connected cities again.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
O(N + ElogE) max heap length = edges length
- Space complexity:
O(N + E)
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def minCost(self, maxTime: int, edges: List[List[int]], passingFees: List[int]) -> int:
import heapq
import math
N = len(passingFees)
graph = [[] for _ in range(N)]
for e in edges:
graph[e[0]].append((e[1], e[2]))
graph[e[1]].append((e[0], e[2]))
minTime = [math.inf] * N
# cost, city, time
heap = [(passingFees[0], 0, 0)]
while heap:
cost, city, time = heapq.heappop(heap)
if city == N - 1: return cost
if minTime[city] <= time: continue
minTime[city] = time
for edge in graph[city]:
nei = edge[0]
new_time = time + edge[1]
new_cost = cost + passingFees[nei]
if new_time > maxTime: continue
heapq.heappush(heap, (new_cost, nei, new_time))
return -1
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
[Tag: Easy] Textbook Dijkstra + DP
|
tag-easy-textbook-dijkstra-dp-by-tbne190-ex4q
|
This is Dijkstra with DP, and a really good problem.MinHeap of { currCost, currDist, currNode } in priority-min of cost.
currCost : the minimum cost incurred up
|
tbne1905
|
NORMAL
|
2025-04-11T14:59:38.358754+00:00
|
2025-04-11T14:59:38.358754+00:00
| 1 | false |
This is Dijkstra with DP, and a really good problem.
MinHeap of { currCost, currDist, currNode } in priority-min of cost.
- currCost : the minimum cost incurred uptill now, in reaching currNode from sourceNode, by travelling currDist distance
- currDist: the distance (NOT MINIMUM) travelled from sourceNode till currNode wherein the cost incurred along the way is currCost
- currNode : the node we are currently at
Cost array: cost[node][dist] = minimum cost incurred in reaching [node] from sourceNode by travelling [dist] distance.
Ans = Minimum of cost[destinationNode] over all dist
```csharp []
public class Data : IComparable<Data> {
public int Node {get; set;}
public int Cost {get; set;}
public int Dist {get; set;}
public Data(int node, int cost, int dist){
Node = node;
Cost = cost;
Dist = dist;
}
public int CompareTo(Data other){
int cmpCost = Cost.CompareTo(other.Cost);
if (cmpCost != 0) return cmpCost;
int cmpDist = Dist.CompareTo(other.Dist);
if (cmpDist != 0) return cmpDist;
return Node.CompareTo(other.Node);
}
}
public class Solution {
public int MinCost(int maxTime, int[][] edges, int[] passingFees) {
int n = passingFees.Length;
List<(int, int)>[] adj = new List<(int, int)>[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) adj[i] = new List<(int, int)>();
foreach (int[] edge in edges){
int u = edge[0];
int v = edge[1];
int w = edge[2];
adj[u].Add((v,w));
adj[v].Add((u,w));
}
int[][] cost = new int[n][];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cost[i] = Enumerable.Repeat(int.MaxValue, maxTime+1).ToArray();
}
var minHeap = new PriorityQueue<Data,Data>();
Data startData = new Data(0,passingFees[0],0);
cost[0][0] = startData.Cost;
minHeap.Enqueue(startData, startData);
while(minHeap.Count > 0){
Data curr = minHeap.Dequeue();
int currNode = curr.Node;
int currDist = curr.Dist;
int currCost = curr.Cost;
foreach ((int,int) p in adj[currNode]){
int adjNode = p.Item1;
int w = p.Item2;
int distToAdj = currDist + w;
int costToAdj = currCost + passingFees[adjNode];
if (distToAdj > maxTime) continue;
// if cost decrease, then add into pq
if (costToAdj < cost[adjNode][distToAdj]){
cost[adjNode][distToAdj] = costToAdj;
Data adjData = new Data(adjNode, costToAdj, distToAdj);
minHeap.Enqueue(adjData, adjData);
}
}
}
int miniCost = int.MaxValue;
for (int i = 0; i <= maxTime; i++) miniCost = Math.Min(miniCost, cost[n-1][i]);
return miniCost == int.MaxValue ? -1 : miniCost;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['C#']
| 0 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
Easiest Solution using Dijkstra !!!✌✌
|
easiest-solution-using-dijkstra-by-shast-uwva
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
shastrii
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-24T17:49:39.254623+00:00
|
2025-03-24T17:49:39.254623+00:00
| 7 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```java []
class Edge{
int node;
int weight;
public Edge(int n, int w){
this.node = n;
this.weight = w;
}
}
class Tuple implements Comparable<Tuple>{
int node;
int cost;
int time;
public Tuple(int n, int c, int t){
this.node = n;
this.cost = c;
this.time = t;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Tuple t2){
return this.cost - t2.cost;
}
}
class Solution {
public int minCost(int maxTime, int[][] edges, int[] p) {
int V = p.length;
List<Edge>[] graph = new ArrayList[V];
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++){
graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
// adjList
for(int[] edge : edges){
int u = edge[0], v = edge[1], w = edge[2];
graph[u].add(new Edge(v, w));
graph[v].add(new Edge(u, w));
}
// dijkstra
int[] minTime = new int[V];
Arrays.fill(minTime, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
PriorityQueue<Tuple> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
minTime[0] = 0;
pq.add(new Tuple(0, p[0], 0));
while(!pq.isEmpty()){
Tuple t = pq.remove(); // node, cost, time
if(t.time > maxTime) continue;
if(t.node == V-1) return t.cost;
for(Edge nb : graph[t.node]){
int time = t.time + nb.weight;
if(time < minTime[nb.node]){
minTime[nb.node] = time;
pq.add(new Tuple(nb.node, t.cost + p[nb.node], time));
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
Structured explanation - Minimum Cost Path in Time-Bound Travel
|
structured-explanation-minimum-cost-path-4dmd
|
IntuitionWe need to find the minimum cost to reach city n - 1 from city 0 within a given maxTime. Since traveling between cities takes different amounts of time
|
qu_shal
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-12T18:47:46.299135+00:00
|
2025-03-12T18:47:46.299135+00:00
| 6 | false |
# Intuition
###### We need to find the minimum cost to reach city n - 1 from city 0 within a given maxTime. Since traveling between cities takes different amounts of time and costs vary, this problem can be solved using ***Dijkstra’s Algorithm***, where the goal is to find the minimum cost instead of the shortest path.
1. Each city has a passing fee, and we must consider this cost while traveling.
2. We can only visit cities if the total travel time does not exceed maxTime.
3. Unlike traditional Dijkstra’s Algorithm (which optimizes for shortest path), we must optimize for minimum cost.
4. Using a priority queue (min-heap) helps process cities in increasing order of cost.
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
1. Graph Representation:
Use an adjacency list where graph[i] stores neighboring cities and their travel time.
We do not store passing fees in the adjacency list, as they are stored separately.
2. Priority Queue (Dijkstra’s Variant):
Each node in the queue is stored as a Pair (node, time, cost), where:
node → current city
time → total time spent so far
cost → total cost spent so far
The queue is sorted by cost (lowest first), ensuring we process cheaper paths first.
3. Dijkstra's Exploration:
Start from city 0 with time = 0 and cost = passingFees[0].
Use two tracking arrays:
minCost[i] → Minimum cost to reach city i.
minTime[i] → Minimum time required to reach city i.
While processing a node, iterate over its neighbors and update minCost and minTime accordingly.
If reaching a neighbor results in a cheaper cost or lesser time, update and push it into the priority queue.
4. Final Result:
After processing all possible paths, return minCost[n-1].
If city n-1 is unreachable within maxTime, return -1.
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity: $$O(ElogE)$$ (where E is the number of edges).
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity: $$O(n+E)$$
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```java []
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
static class Pair implements Comparable<Pair> {
int node, time, cost;
public Pair(int node, int time, int cost) {
this.node = node;
this.time = time;
this.cost = cost;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Pair p2) {
return this.cost - p2.cost; // Prioritize lower cost first
}
}
public int minCost(int maxTime, int[][] edges, int[] passingFees) {
int n = passingFees.length;
List<List<int[]>> graph = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
// Build the graph
for (int[] edge : edges) {
int u = edge[0], v = edge[1], time = edge[2];
graph.get(u).add(new int[]{v, time});
graph.get(v).add(new int[]{u, time});
}
// Distance & cost tracking
int[] minCost = new int[n];
int[] minTime = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(minCost, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
Arrays.fill(minTime, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
minCost[0] = passingFees[0];
minTime[0] = 0;
// Priority Queue for Dijkstra (minHeap)
PriorityQueue<Pair> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.add(new Pair(0, 0, passingFees[0]));
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
Pair curr = pq.poll();
// If exceeding maxTime, skip
if (curr.time > maxTime) continue;
for (int[] next : graph.get(curr.node)) {
int nextNode = next[0];
int travelTime = next[1];
int newTime = curr.time + travelTime;
int newCost = curr.cost + passingFees[nextNode];
// If within maxTime and better cost/time, update
if (newTime <= maxTime) {
if (newCost < minCost[nextNode]) {
minCost[nextNode] = newCost;
minTime[nextNode] = newTime;
pq.add(new Pair(nextNode, newTime, newCost));
} else if (newTime < minTime[nextNode]) {
minTime[nextNode] = newTime;
pq.add(new Pair(nextNode, newTime, newCost));
}
}
}
}
return minCost[n - 1] == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : minCost[n - 1];
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Graph', 'Shortest Path', 'Java']
| 0 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
Simple | Dijkstra's Algorithm
|
simple-dijkstras-algorithm-by-rohanmathu-e69q
|
Complexity
Time complexity: O(maxTime x N x log(maxTime x N))
Space complexity: O(maxTime x N)
Code
|
rohanmathur91
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-16T15:58:03.809624+00:00
|
2025-02-16T15:58:03.809624+00:00
| 25 | false |
# Complexity
- Time complexity: O(maxTime x N x log(maxTime x N))
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity: O(maxTime x N)
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def minCost(self, maxTime: int, edges: List[List[int]], passingFees: List[int]) -> int:
"""
Cost depends on node and time factor so 2D dist array
ie dist[node][t] = cost (passingFeesSum)
example: for node = 1
time = 0, 1, 2, 3 ... maxTime
"""
n = len(passingFees)
dist = [[float('inf') for i in range(maxTime + 1)] for i in range(n)]
dist[0][0] = passingFees[0]
vis = [[0 for i in range(maxTime + 1)] for i in range(n)]
adj = []
for i in range(n):
adj.append([])
for u, v, t in edges:
adj[u].append((v,t))
adj[v].append((u,t))
h = []
heappush(h, (dist[0][0], 0, 0)) # cost, node, time
while h:
cost, node, time = heappop(h)
if vis[node][time] == 1:
continue
vis[node][time] = 1
for v, t in adj[node]:
if time + t > maxTime:
continue
if dist[v][time + t] > (cost + passingFees[v]):
dist[v][time + t] = cost + passingFees[v]
heappush(h, (dist[v][time + t], v, time + t))
ans = float("inf")
for i in range(maxTime + 1):
ans = min(ans, dist[n-1][i])
# print(dist)
return ans if ans != float('inf') else -1
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Graph', 'Shortest Path', 'Python3']
| 0 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
DP, O(len(edges)*maxTime*log(maxTime)) TC
|
dp-olenedgesmaxtimelogmaxtime-tc-by-fili-pn0z
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
Filinovsky
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-07T20:22:49.197400+00:00
|
2025-02-07T20:22:49.197400+00:00
| 6 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
from collections import defaultdict
self.edges = defaultdict(list)
def minCost(self, maxTime: int, edges: list[list[int]], passingFees: list[int]) -> int:
import heapq
n = len(passingFees)
for u, v, t in edges:
self.edges[u].append([v, t])
self.edges[v].append([u, t])
times = {}
times[0] = [passingFees[0]] + [10 ** 9] * n
nextTime = []
minTime = 0
while minTime <= maxTime:
for i in range(n):
if times[minTime][i] < 10 ** 9:
for x, t in self.edges[i]:
if minTime + t not in times:
times[minTime + t] = [10 ** 9] * n
times[minTime + t][x] = times[minTime][i] + passingFees[x]
heapq.heappush(nextTime, minTime + t)
else:
times[minTime + t][x] = min(times[minTime + t][x], times[minTime][i] + passingFees[x])
minTime = heapq.heappop(nextTime)
ans = min([times[x][n - 1] for x in times if x <= maxTime])
return ans if ans < 10 ** 9 else -1
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
Python Hard
|
python-hard-by-lucasschnee-xeuj
| null |
lucasschnee
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-05T02:13:54.465337+00:00
|
2025-02-05T02:13:54.465337+00:00
| 5 | false |
```python3 []
class Solution:
def minCost(self, maxTime: int, edges: List[List[int]], passingFees: List[int]) -> int:
lookup = defaultdict(list)
INF = 10 ** 20
N = 0
for u, v, t in edges:
lookup[u].append((v, t))
lookup[v].append((u, t))
N = max(N, u, v)
N += 1
'''
bs on min_cost
'''
def shortest_path_calc(vertex_weights, lookup):
min_cost = [INF] * N
min_cost[0] = vertex_weights[0]
min_time = [INF] * N
min_time[0] = 0
h = []
heapq.heappush(h, (vertex_weights[0], 0, 0))
while h:
cost, time, u = heapq.heappop(h)
if min_cost[u] < cost and min_time[u] < time:
continue
for v, t in lookup[u]:
nxt_cost = vertex_weights[v] + cost
nxt_time = t + time
if nxt_time > maxTime:
continue
if nxt_cost > min_cost[v] and nxt_time > min_time[v]:
continue
min_cost[v] = min(min_cost[v], nxt_cost)
min_time[v] = min(min_time[v], nxt_time)
heapq.heappush(h, (nxt_cost, nxt_time, v))
return min_cost[-1]
val = shortest_path_calc(passingFees, lookup)
if val == INF:
return -1
return val
# def good(target):
# return shortest_path_calc(passingFees, lookup, target)
# l, r = 0, 10 ** 10
# best = 10 ** 10
# if not good(r):
# return -1
# while l <= r:
# mid = (l + r) // 2
# if good(mid):
# best = mid
# r = mid - 1
# else:
# l = mid + 1
# return best
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
Using Dijkstra Algorithm
|
using-dijkstra-algorithm-by-xpmuni70jh-2ii2
|
IntuitionUse the simplest Dijkstra algorithm traversingApproach
Create Adjancency List which contain pair of node and time
Create Array of cost and time and int
|
xPmunI70Jh
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-26T17:23:58.752011+00:00
|
2025-01-26T17:23:58.752011+00:00
| 14 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
Use the simplest Dijkstra algorithm traversing
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
1. Create Adjancency List which contain pair of node and time
2. Create Array of cost and time and intialize the cost[0] with passingFees[0] and time[0] with 0.
3. Create set of pair of pair of cost ,time and node;
4. Now Follow the Dijkstra Algorithm
5.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(N+E)
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(N+E)
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
// void dfsTraversal(map<int,list<pair<int,int>>> &adj,vector<bool> &vis,vector<int>& passingFees,int src,int des,int sumTime,int sumFee,int &maxTime)
// {
// if(src == des)
// {
// if(maxTime >= sumTime)
// {
// ans.insert(sumFee);
// }
// return ;
// }
// vis[src] = 1;
// for(auto neighbour : adj[src])
// {
// if(!vis[neighbour.first]){
// dfsTraversal(adj,vis,passingFees,neighbour.first,des, neighbour.second+sumTime,sumFee + passingFees[neighbour.first],maxTime);
// }
// }
// vis[src] = 0;
// }
int minCost(int maxTime, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<int>& passingFees) {
int n = passingFees.size();
int result = INT_MAX;
// Creating Adj list
map<int,list<pair<int,int>>>adj;
for(int i=0;i<edges.size();i++)
{
int u = edges[i][0];
int v = edges[i][1];
int t = edges[i][2];
adj[u].push_back(make_pair(v,t));
adj[v].push_back(make_pair(u,t));
}
vector<int>time(n,INT_MAX);
vector<int>cost(n,INT_MAX);
cost[0] = passingFees[0];
time[0] = 0;
set<pair<int,pair<int,int>>>st;
st.insert({cost[0],{0,0}});
while(!st.empty())
{
auto top = *(st.begin());
st.erase(top);
int node = top.second.second;
int nodeCost = top.first;
int nodeTime = top.second.first;
if(node == n-1 && nodeTime <= maxTime)
{
return result = min(result,nodeCost);
}
for(auto i : adj[node])
{
int currTime = i.second;
int currCost = passingFees[i.first];
if((currTime + nodeTime <= maxTime)&&(currCost + nodeCost <= cost[i.first]))
{
cost[i.first] = currCost + nodeCost;
time[i.first] = currTime + nodeTime;
st.insert({cost[i.first],{time[i.first],i.first}});
}
else if(currTime + nodeTime < time[i.first])
{
time[i.first] = currTime + nodeTime;
st.insert({currCost + nodeCost ,{time[i.first],i.first}});
}
}
}
if(result == INT_MAX) return -1;
return result;
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Graph', 'C++']
| 0 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
1928. Minimum Cost to Reach Destination in Time
|
1928-minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-i-lao0
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
G8xd0QPqTy
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-16T07:58:04.449074+00:00
|
2025-01-16T07:58:04.449074+00:00
| 11 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```java []
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
List<int[]>[] graph;
public int minCost(int maxTime, int[][] edges, int[] passingFees) {
int n = passingFees.length;
graph = new List[n];
Arrays.setAll(graph, i -> new ArrayList<>());
for (int[] edge : edges) {
graph[edge[0]].add(new int[]{edge[1], edge[2]});
graph[edge[1]].add(new int[]{edge[0], edge[2]});
}
int[] minTime = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(minTime, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
int[][] minCost = new int[n][maxTime + 1];
for (int[] row : minCost) Arrays.fill(row, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[1]));
pq.offer(new int[]{0, passingFees[0], 0});
minCost[0][0] = passingFees[0];
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
int[] curr = pq.poll();
int node = curr[0], cost = curr[1], time = curr[2];
if (time > maxTime) continue;
if (minCost[node][time] < cost) continue;
if (node == n - 1) return cost;
for (int[] next : graph[node]) {
int nextNode = next[0], travelTime = next[1];
int newTime = time + travelTime;
int newCost = cost + passingFees[nextNode];
if (newTime > maxTime) continue;
if (newCost < minCost[nextNode][newTime]) {
minCost[nextNode][newTime] = newCost;
pq.offer(new int[]{nextNode, newCost, newTime});
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
Dynamic Programming with Limited Edges
|
dynamic-programming-with-limited-edges-b-0ghi
|
IntuitionThe first thought was to resolve the problem using dynamic programming without repetition of used nodes, but here we have the additional problem that t
|
Rq9OgETWIk
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-03T18:13:52.398080+00:00
|
2025-01-03T18:13:52.398080+00:00
| 5 | false |
# Intuition
The first thought was to resolve the problem using dynamic programming without repetition of used nodes, but here we have the additional problem that the node can`t be visited sequentialy, so we have to work with the limitted next nodes.
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
To solve the problem we start working with dynamic programming using a multidimendional array to look into each node that can be used as the path in the current time, ex:
At the time "0" only the first node is a possible source (dp[0,0] != int.max), so for each edge (lets imagine [0,2,2]) we update the node in the given time to have the added cost (dp[2,(0+2)]=dp[0,0] + passingFees[2]) if the previous cost is greater, which is int.Max in this case, so we update it.
In this case at time "1" we do not update any node because all nodes in dp[i,1] are int.Max.
At the time "2" we have our updated dp[2,2] that will push our path in to the future ;).
When we reach our max time all the possibilities are handled and the min value (that is not int.max) is our response for the problem.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
O(∣E∣+maxTime⋅∣V∣⋅deg(V)) ≈ O(∣E∣+maxTime⋅∣E∣)
Onde deg(V) é o grau médio dos nós (número de arestas conectadas a cada nó).
- Space complexity:
O(∣E∣+∣V∣⋅maxTime)
# Code
```csharp []
public class Solution {
public int MinCost(int maxTime, int[][] edges, int[] passingFees) {
var graph = BuildGraph(edges, passingFees.Length, false);
// Init dp
var dp = new int[passingFees.Length, maxTime+1];
for(int node = 0; node < passingFees.Length; node++)
for(int time = 0; time <= maxTime; time++)
dp[node, time] = int.MaxValue;
dp[0,maxTime] = passingFees[0];
int result = int.MaxValue;
// string matrix = "";
for(var currentTime = maxTime; currentTime > 0; currentTime--){
for(int currentNode = 0; currentNode < passingFees.Length; currentNode++){
var currentCost = dp[currentNode, currentTime];
// matrix += $"{dp[currentNode, currentTime]},";
if(currentCost == int.MaxValue) continue;
foreach(var edge in graph[currentNode]){
(int next, int time) = edge;
var newCost = currentCost + passingFees[next];
if(
currentTime >= time
&& dp[next, currentTime - time] > newCost
){
dp[next, currentTime - time] = newCost;
if(next == passingFees.Length - 1 && result > newCost){
result = newCost;
}
}
}
}
if(currentTime % 10 == 0) Console.WriteLine($"Esatmos no tempo {currentTime}");
}
return result == int.MaxValue ? -1 : result;
}
public static IList<(int dest, int time)>[] BuildGraph(int[][] edges, int size, bool directed) {
var result = Enumerable.Range(0, size).Select(_ => new List<(int, int)>()).ToArray();
foreach (var edge in edges) {
result[edge[0]].Add((edge[1], edge[2]));
if (!directed) result[edge[1]].Add((edge[0], edge[2]));
}
return result;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['C#']
| 0 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
Simple Java solution using graph concepts
|
simple-java-solution-using-graph-concept-0dq0
|
ApproachUsing a priority queue to explore the cities, always choosing the path with the lowest cost first.
Started from city 0, keeping track of the time and co
|
kavyachetwani
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-21T17:46:49.222269+00:00
|
2024-12-21T17:46:49.222269+00:00
| 8 | false |
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
Using a priority queue to explore the cities, always choosing the path with the lowest cost first.
Started from city 0, keeping track of the time and cost for each path, and only continuing if the total time stays within the allowed limit.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
$$O((E+V)Log(V))$$
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
$$O(V+E)$$
# Code
```java []
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int minCost(int maxTime, int[][] edges, int[] passingFees) {
int n = passingFees.length;
List<int[]>[] graph = new ArrayList[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for (int[] edge : edges) {
graph[edge[0]].add(new int[]{edge[1], edge[2]});
graph[edge[1]].add(new int[]{edge[0], edge[2]});
}
PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
pq.offer(new int[]{passingFees[0], 0, 0});
int[] minTime = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(minTime, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
minTime[0] = 0;
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
int[] curr = pq.poll();
int cost = curr[0], node = curr[1], time = curr[2];
if (node == n - 1) {
return cost;
}
for (int[] neighbor : graph[node]) {
int nextNode = neighbor[0], travelTime = neighbor[1];
int newTime = time + travelTime;
if (newTime <= maxTime && newTime < minTime[nextNode]) {
minTime[nextNode] = newTime;
pq.offer(new int[]{cost + passingFees[nextNode], nextNode, newTime});
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Java']
| 0 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
EASY CPP SOLUTION
|
easy-cpp-solution-by-sagargujarathi-xudv
|
Code
|
sagargujarathi
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-17T05:39:05.235424+00:00
|
2024-12-17T05:39:05.235424+00:00
| 5 | false |
# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int minCost(int maxTime, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<int>& passingFees) \n {\n int n = passingFees.size();\n\n vector<vector<vector<int>>> graph(n , vector<vector<int>> ());\n\n vector<pair<int , int>> dist(n , {INT_MAX , INT_MAX});\n // {fee , time}\n\n set<pair<pair<int , int> , int>> store;\n // {{fee , time} , {u}}\n\n dist[0] = {0 , 0};\n\n store.insert({{passingFees[0] , 0} , 0});\n\n for(auto i : edges)\n {\n graph[i[0]].push_back({i[1] , i[2]});\n graph[i[1]].push_back({i[0] , i[2]});\n } \n\n while(!store.empty())\n {\n auto front = *(store.begin());\n int fee = front.first.first;\n int time = front.first.second;\n int u = front.second;\n\n store.erase(front);\n\n if(u == n - 1) return fee;\n\n for(auto i : graph[u])\n {\n int v = i[0];\n int FEE = fee + passingFees[v];\n int TIME = time + i[1];\n\n if((dist[v].first <= FEE && dist[v].second <= TIME) || TIME > maxTime) continue;\n\n dist[v] = {FEE , TIME};\n\n store.insert({{FEE , TIME} , v});\n }\n\n }\n\n return -1;\n\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
Remaining time in node state
|
remaining-time-in-node-state-by-theabbie-gwfw
|
\nclass Solution:\n def minCost(self, maxTime: int, edges: List[List[int]], passingFees: List[int]) -> int:\n n = len(passingFees)\n graph = [[
|
theabbie
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-30T08:33:31.006396+00:00
|
2024-10-30T08:33:31.006435+00:00
| 3 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def minCost(self, maxTime: int, edges: List[List[int]], passingFees: List[int]) -> int:\n n = len(passingFees)\n graph = [[] for _ in range(n)]\n for u, v, w in edges:\n graph[u].append((v, w))\n graph[v].append((u, w))\n dist = defaultdict(lambda: float(\'inf\'))\n dist[(0, maxTime)] = passingFees[0]\n heap = [(passingFees[0], 0, maxTime)]\n while heap:\n cost, i, rem = heapq.heappop(heap)\n if i == n - 1:\n return cost\n for j, w in graph[i]:\n if w <= rem:\n if dist[(j, rem - w)] > cost + passingFees[j]:\n dist[(j, rem - w)] = cost + passingFees[j]\n heapq.heappush(heap, (cost + passingFees[j], j, rem - w))\n return -1\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python']
| 0 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
Python (Simple Dijkstra's algorithm)
|
python-simple-dijkstras-algorithm-by-rno-jaa3
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
rnotappl
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-29T07:45:37.981971+00:00
|
2024-10-29T07:45:37.982001+00:00
| 23 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def minCost(self, maxTime, edges, passingFees):\n n, graph = len(passingFees), defaultdict(list)\n\n for i,j,t in edges:\n graph[i].append((j,t))\n graph[j].append((i,t))\n\n dict1 = {i:float("inf") for i in range(n)}\n\n dict1[0] = 0\n\n stack = [(passingFees[0],0,0)]\n\n while stack:\n cost,time,node = heapq.heappop(stack)\n\n if node == n-1:\n return cost \n\n for neighbor,t in graph[node]:\n if dict1[neighbor] > time+t and time+t <= maxTime:\n dict1[neighbor] = time+t\n heapq.heappush(stack,(cost+passingFees[neighbor],dict1[neighbor],neighbor))\n\n return -1\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-in-time
|
1928. Minimum Cost to Reach Destination in Time.cpp
|
1928-minimum-cost-to-reach-destination-i-bfl8
|
Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int minCost(int maxTime, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<int>& passingFees) {\n unordered_map<int, vector<pair<
|
202021ganesh
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-22T09:49:59.119959+00:00
|
2024-10-22T09:49:59.120004+00:00
| 2 | false |
**Code**\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int minCost(int maxTime, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<int>& passingFees) {\n unordered_map<int, vector<pair<int, int>>> graph; \n for (auto& edge : edges) {\n graph[edge[0]].emplace_back(edge[1], edge[2]); \n graph[edge[1]].emplace_back(edge[0], edge[2]); \n }\n priority_queue<array<int, 3>, vector<array<int, 3>>, greater<>> pq; // min-heap \n pq.push({passingFees[0], 0, 0}); \n unordered_map<int, int> dist = {{0, passingFees[0]}}; \n while (pq.size()) {\n auto [cost, k, t] = pq.top(); pq.pop(); \n if (k == passingFees.size()-1) return cost; \n for (auto& [kk, tt] : graph[k]) {\n if (t + tt <= maxTime && (!dist.count(kk) || t + tt < dist[kk])) {\n dist[kk] = t + tt; \n pq.push({cost + passingFees[kk], kk, t + tt}); \n }\n }\n }\n return -1; \n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C']
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
[Java/C++/Python] Two Pointers, O(1) Space
|
javacpython-two-pointers-o1-space-by-lee-dslk
|
Intuition\nWe must take the common elements and won\'t miss them;\nAnd there will be two path between the common elements,\nand we will take and only take one p
|
lee215
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-02T04:05:10.833803+00:00
|
2020-08-03T06:54:20.968939+00:00
| 14,111 | false |
## **Intuition**\nWe must take the common elements and won\'t miss them;\nAnd there will be two path between the common elements,\nand we will take and only take one path.\n\nWe calculate the sum of both path, and take the bigger one.\n<br>\n\n## **Explanation**\nSo we apply two points solutions,\nand always take the step in the smaller element.\n\nIf two elements are the same,\nwe compare the accumulated sum in the both paths,\nand we pick the bigger one.\n<br>\n\n## **Complexity**\nTime `O(N)`\nSpace `O(1)`\n<br>\n\n**Java:**\n```java\n public int maxSum(int[] A, int[] B) {\n int i = 0, j = 0, n = A.length, m = B.length;\n long a = 0, b = 0, mod = (long)1e9 + 7;\n while (i < n || j < m) {\n if (i < n && (j == m || A[i] < B[j])) {\n a += A[i++];\n } else if (j < m && (i == n || A[i] > B[j])) {\n b += B[j++];\n } else {\n a = b = Math.max(a, b) + A[i];\n i++; j++;\n }\n }\n return (int)(Math.max(a, b) % mod);\n }\n```\n\n**C++:**\n```cpp\n int maxSum(vector<int>& A, vector<int>& B) {\n int i = 0, j = 0, n = A.size(), m = B.size();\n long a = 0, b = 0, mod = 1e9 + 7;\n while (i < n || j < m) {\n if (i < n && (j == m || A[i] < B[j])) {\n a += A[i++];\n } else if (j < m && (i == n || A[i] > B[j])) {\n b += B[j++];\n } else {\n a = b = max(a, b) + A[i];\n i++, j++;\n }\n }\n return max(a, b) % mod;\n }\n```\n**Python**\n```py\n def maxSum(self, A, B):\n i, j, n, m = 0, 0, len(A), len(B)\n a, b, mod = 0, 0, 10**9 + 7\n while i < n or j < m:\n if i < n and (j == m or A[i] < B[j]):\n a += A[i]\n i += 1\n elif j < m and (i == n or A[i] > B[j]):\n b += B[j]\n j += 1\n else:\n a = b = max(a, b) + A[i]\n i += 1\n j += 1\n return max(a, b) % mod\n```
| 272 | 6 |
[]
| 30 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
C++ soln! REASON behind MODULO in the end and not at every step?
|
c-soln-reason-behind-modulo-in-the-end-a-meoz
|
So, i also did the same mistake that most of u may have done.. Taking modulo at every step or when sum is greater than equal to 1e9+7. But OBVIOUSLY, it is fail
|
pranjal21gupta
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-02T17:13:12.133899+00:00
|
2021-02-12T13:44:20.648117+00:00
| 4,106 | false |
So, i also did the same mistake that most of u may have done.. Taking modulo at every step or when sum is greater than equal to **1e9+7**. But OBVIOUSLY, it is failing for larger test-cases. **AND IT SHOULD!**\n\n**REASON:** The reason behind this is when one of the array sum gets bigger than 1e9+7, taking modulo makes it\'s value smaller in comparision to the second array whose sum is still smaller than 1e9+7. And at intersection point or at the end when we have to take maximum, it will take the second one. \nBut, the sum of first one was greater, so *obviously* it should be taken.\n\n**For Example-** If first array *nums1* contains 10^5 elements starting from some x to 10^7 (Please ignore any mathematical error) and second array *nums2* might contains just 2 elements i.e, {10^7-1, 10^7}\n\n```\nnums1 = {x, x+1 , x+2 , , , , , , , , , 10^7} \nsize1= 10^5\nsum1 >= 10^9+7 anyways\nnums2 = {10^7-1, 10^7} \nsize2 2\nsum2 is 2*10^7-1\n```\n\nSo, now first array sum will be the answer but taking modulo at every time will make the sum shorter in comparision to the sum of second array. Hence, second array sum will be taken which will give **Wrong Answer**\n\n**Solution:** To avoid this, the maximum value than it can reach is 10^12. Taking *long long int* will solve the problem. And at the end, since we have to return 32-bit integer so take modulo and return it.\nRest, i think it\'s simple to understand how dp is working. \n**1** Taking maximum of the sums at each intersection point and at the end will give the answer. \n**2** To get that, take two pointers eah for an array and start traversing.\n**3** Check sum and take maximum at every intersection point or at the end and add it to the answer.\nThis will require 1-Pass of both the arrays.\nCode will clear any remaining doubts.\n\nMy solution takes O(N+M) time where N and M are the sizes of 2 arrays and requires O(1) space.\n\nRuntime: **240 ms**\nMemory Usage: **55.7 MB**\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxSum(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {\n int mod=1e9+7;\n long long int ans=0, sum1=0, sum2=0;\n int i=0, j=0;\n while(i<nums1.size() and j<nums2.size())\n {\n if(nums1[i] < nums2[j])\n sum1 += nums1[i++]; \n else if(nums1[i] > nums2[j])\n sum2 += nums2[j++];\n else\n {\n ans += nums1[i] + max(sum1, sum2);\n i++;\n j++;\n sum1=0;\n sum2=0;\n }\n }\n while(i<nums1.size())\n sum1 += nums1[i++];\n while(j<nums2.size())\n sum2 += nums2[j++];\n ans += max(sum1, sum2);\n ans = ans%mod;\n return (int)ans;\n }\n};\n```\n\nIf u find some mistake or have some doubts, feel free to ask.\nIf my post helps u, then please UPVOTE!\nHappy Coding!
| 109 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'Dynamic Programming', 'C++']
| 13 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
Python3. O(N) Time, O(1) space; Two pointers; explanation added
|
python3-on-time-o1-space-two-pointers-ex-5spg
|
Logic is simple:\nLet\'s say that a place where nums1[i] = nums2[j] is checkpoint.\nThen result will be max prefix sum of two arrays + checkpoint + max sum post
|
yaroslav-repeta
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-02T04:02:33.657000+00:00
|
2020-08-02T04:53:06.283944+00:00
| 2,623 | false |
Logic is simple:\nLet\'s say that a place where `nums1[i] = nums2[j]` is checkpoint.\nThen result will be max prefix sum of two arrays + checkpoint + max sum postfix of two arrays\nOr: `max(sum(nums1[0:i]), sum(nums2[0:j]) + checkpoint + max(sum(nums1[i + 1:]), sum(nums2[j + 1:]))` \n\nSo what we need to do is:\n1. Iterate through two arrays with calculating sum until we find checkpoint\n2. Add larger sum to result.\n3. Add checkpoint to result.\n4. Reset sums.\n5. Repeat.\n\n```python\nclass Solution:\n def maxSum(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> int:\n\t\tM, N = len(nums1), len(nums2)\n sum1, sum2 = 0, 0\n i, j = 0, 0\n res = 0\n while i < M and j < N:\n if nums1[i] < nums2[j]:\n sum1 += nums1[i]\n i += 1\n elif nums1[i] > nums2[j]:\n sum2 += nums2[j]\n j += 1\n else:\n res += max(sum1, sum2) + nums1[i]\n i += 1\n j += 1\n sum1 = 0\n sum2 = 0\n \n while i < M:\n sum1 += nums1[i]\n i += 1\n while j < N:\n sum2 += nums2[j]\n j += 1\n return (res + max(sum1, sum2)) % 1000000007\n```\n\nTime: O(N), where N is the total number of elements in arrays.\nSpace: O(1)
| 43 | 0 |
['Python']
| 4 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
Java 19 lines dfs+memo with line-by-line explanation easy to understand
|
java-19-lines-dfsmemo-with-line-by-line-c418q
|
\n\n\nclass Solution {\n int M = (int)1e9+7;\n public int maxSum(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {\n Map<Integer, List<Integer>> map= new HashMap<>();\n
|
funbam
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-02T04:01:33.423142+00:00
|
2020-08-02T04:55:30.093734+00:00
| 3,096 | false |
\n\n```\nclass Solution {\n int M = (int)1e9+7;\n public int maxSum(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {\n Map<Integer, List<Integer>> map= new HashMap<>();\n for (int i=0; i<nums1.length-1; i++)\n map.computeIfAbsent(nums1[i], k -> new LinkedList<>()).add(nums1[i+1]);\n for (int i=0; i<nums2.length-1; i++)\n map.computeIfAbsent(nums2[i], k -> new LinkedList<>()).add(nums2[i+1]);\n Map<Integer, Long> memo = new HashMap<>();\n return (int)Math.max(greedy(nums1[0], map, memo)%M, greedy(nums2[0], map, memo)%M);\n }\n \n long greedy(int cur, Map<Integer, List<Integer>> map, Map<Integer, Long> memo){\n if (memo.containsKey(cur)) return memo.get(cur);\n if (!map.containsKey(cur)) return cur;\n long maxSum=0;\n for (int next: map.get(cur)){\n maxSum = Math.max(maxSum, greedy(next, map, memo));\n }\n maxSum+=cur;\n memo.put(cur, maxSum);\n return maxSum;\n }\n}\n```\nHappy Coding!
| 40 | 1 |
[]
| 7 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
Topological Sort O(M + N)
|
topological-sort-om-n-by-getthatguap-hm5g
|
Since the arrays are stricly increasing, there are no duplicates within each array. So we can create a DAG where every node is a number. After that, we can do a
|
getthatguap
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-02T04:04:15.628472+00:00
|
2020-10-22T02:41:20.144908+00:00
| 2,072 | false |
Since the arrays are stricly increasing, there are no duplicates within each array. So we can create a DAG where every node is a number. After that, we can do a top sort on that graph and track the path with the greatest sum in the dists dictionary. dists[num] = the max score to get to the node num.\n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maxSum(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> int:\n indeg = defaultdict(int)\n g = defaultdict(list)\n \n for i in range(len(nums1)-1):\n g[nums1[i]].append(nums1[i+1])\n indeg[nums1[i+1]] += 1\n for i in range(len(nums2)-1):\n g[nums2[i]].append(nums2[i+1])\n indeg[nums2[i+1]] += 1\n \n q = deque()\n ans = 0\n dists = defaultdict(int)\n for num in g:\n if indeg[num] == 0:\n q.append((num, num))\n dists[num] = num\n \n while q:\n num, score = q.popleft()\n ans = max(ans, score)\n for nei in g[num]:\n indeg[nei] -= 1\n dists[nei] = max(dists[nei], score)\n if indeg[nei] == 0:\n q.append((nei, nei + dists[nei]))\n return ans % (10**9+7)\n```
| 31 | 0 |
[]
| 7 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
[C++] Dp problem, O(M+N) time, O(1) space
|
c-dp-problem-omn-time-o1-space-by-minhti-0opb
|
Explanation: Because both arrays are the increasing array including positive integer, that why dp is a good choice in this problem.\nWe have:\n- dp1[i] is the m
|
minhtien_142
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-02T05:22:38.516336+00:00
|
2020-08-04T22:51:54.863540+00:00
| 2,451 | false |
**Explanation**: Because both arrays are the increasing array including positive integer, that why dp is a good choice in this problem.\nWe have:\n- dp1[i] is the maximum of value if we start from any array and reach to index i of array 1.\n- dp2[i] has the same meaning: the maximum of value if we start from any array and reach to index i of array 2.\n\nTo calculate these dp arrays more effectively, we start from the beginning of each array and calculate with linear time.\nStart from i = 0 with array 1 and j = 0 with array 2.\n\n**Formula:**\n- dp1[i] = dp2[j] = max(dp1[i-1], dp2[j-1]) + nums1[i] with **nums1[i] = nums2[j]**\n- dp1[i] = dp1[i-1] + nums1[i] with **nums1[i] < nums2[j]**\n- dp2[j] = dp2[j-1] + nums2[j] with **nums2[j] < nums1[i]**\n\nBecause we always use the value from the previous index for each calculation in dp1 and dp2, therefore no need to store it in an array and can reduce the space complexity from O(N) to O(1).\n\nMy code:\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxSum(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {\n int m = nums1.size(), n = nums2.size();\n long dp1 = 0, dp2 = 0, res = 0;\n for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < m || j < n;) {\n if (i < m && j < n && nums1[i] == nums2[j])\n dp1 = dp2 = max(dp1, dp2) + min(nums1[i++], nums2[j++]);\n else if (i < m && ((j < n && nums1[i] < nums2[j]) || j == n))\n dp1 += nums1[i++];\n else\n dp2 += nums2[j++];\n }\n int mod = 1e9 + 7;\n return max(dp1, dp2) % mod;\n }\n};\n```
| 25 | 2 |
[]
| 2 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
C++ O(M+N) two pointers with explanation
|
c-omn-two-pointers-with-explanation-by-l-dzcr
|
See my latest update in repo LeetCode\n\n## Solution 1.\n\nIntuition:\n\nIf the two arrays don\'t have any number in common, the result is simply max(sum(A), su
|
lzl124631x
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-02T04:05:57.824628+00:00
|
2020-08-03T03:38:23.796430+00:00
| 1,257 | false |
See my latest update in repo [LeetCode](https://github.com/lzl124631x/LeetCode)\n\n## Solution 1.\n\n**Intuition:**\n\nIf the two arrays don\'t have any number in common, the result is simply `max(sum(A), sum(B))`.\n\nSo only the common numbers shared between these two arrays changes the algorithm a bit.\n\n**Algorithm:**\n\nConsidering the subproblem with `A[0..i)]` and `B[0..j)]`: \n\nLet `X` be the best score we can get if we pick `A[i]` in the end.\n\nLet `Y` be the best score we can get if we pick `B[j]` in the end.\n\nIf `A[i] < B[j]`, we can extend the `X` by adding `A[i]` to it.\n\nIf `A[i] > B[j]`, we can extend the `Y` by adding `B[j]` to it.\n\nIf `A[i] == B[j]`, we can extend in the following two ways:\n1. Use the previous value of `X`, and add `A[i]` to it.\n2. Use the previous value of `Y`, and add `B[j]` to it.\n\nWhy using the **previous value**? It\'s because we need to avoid adding the same number twice.\n\n```cpp\n// OJ: https://leetcode.com/contest/weekly-contest-200/problems/get-the-maximum-score/\n// Author: github.com/lzl124631x\n// Time: O(M + N)\n// Space: O(1)\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxSum(vector<int>& A, vector<int>& B) {\n long long M = A.size(), N = B.size(), X = 0, Y = 0, prevX = 0, prevY = 0, mod = 1e9+7, i = 0, j = 0;\n while (i < M && j < N) {\n if (A[i] < B[j]) X += A[i++];\n else if (A[i] > B[j]) Y += B[j++];\n else X = Y = max(prevX + A[i++], prevY + B[j++]);\n prevX = X;\n prevY = Y;\n }\n while (i < M) X += A[i++];\n while (j < N) Y += B[j++];\n return max(X, Y) % mod;\n }\n};\n```
| 20 | 1 |
[]
| 3 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
[Python] Why is it valid to only mod at the end?
|
python-why-is-it-valid-to-only-mod-at-th-ckbw
|
I got a wrong submission for trying to mod as I go. For example:\n\ndef recur(i):\n ....\n\t calc = recur(i+1) % mod\n\t return calc\n\n\nbut my submission
|
kxqzhou
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-02T04:08:47.794753+00:00
|
2020-08-02T04:08:47.794791+00:00
| 1,320 | false |
I got a wrong submission for trying to mod as I go. For example:\n```\ndef recur(i):\n ....\n\t calc = recur(i+1) % mod\n\t return calc\n```\n\nbut my submission passes when at the very end I just mod the answer I arrived at.\n```\ndef recur():\n\t...\n\treturn calc\n\ndef maxSum():\n ans = recur(0)\n\t return ans % mod\n```\n\nWouldn\'t this potentially overflow? How is it that we only need to mod at the very end?
| 18 | 0 |
[]
| 10 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
Java two pointer solution simple easy to understand O(n) O(1)
|
java-two-pointer-solution-simple-easy-to-rkh1
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int maxSum(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {\n long currSum = 0, sum1 = 0, sum2 = 0;\n int i = 0;\n int j = 0;\n
|
shivamshah
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-02T05:28:57.757689+00:00
|
2020-08-03T00:41:41.638218+00:00
| 1,592 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int maxSum(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {\n long currSum = 0, sum1 = 0, sum2 = 0;\n int i = 0;\n int j = 0;\n while(i < nums1.length && j < nums2.length){\n if(nums1[i] == nums2[j]) {\n currSum += Math.max(sum1, sum2) + nums2[j];\n sum1 = 0;\n sum2 = 0;\n i++;\n j++;\n }\n else if(nums1[i] < nums2[j]){\n sum1 += nums1[i++];\n } else {\n sum2 += nums2[j++];\n }\n }\n \n while(i < nums1.length){\n sum1 += nums1[i++];\n }\n while(j < nums2.length){\n sum2 += nums2[j++];\n }\n return (int)((currSum + Math.max(sum1, sum2)) % 1000000007);\n }\n}\n```
| 14 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'Java']
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
[Python] Top-Down Recursion with Memoization
|
python-top-down-recursion-with-memoizati-n361
|
Intuition\nBasically, at each node, you have two choices: 1) to switch and 2) to NOT switch to the other array. I recorded the indices of each value in each arr
|
smolarek9
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-02T04:07:29.475749+00:00
|
2020-08-03T04:00:10.902963+00:00
| 1,159 | false |
**Intuition**\nBasically, at each node, you have two choices: 1) to switch and 2) to NOT switch to the other array. I recorded the indices of each value in each array to make the switching easier. I also kept two booleans `at1` and `at2` to check which array I am in currently. When we reach the base case, we just return 0, but along the path, we accumulate the current value to the result, then return the maximum of the paths at the end. It is important to use your own memoization and NOT to use `lru_cache` for this one because I think `lru_cache` evicts so many entries and causes recursion stack overflow.\n\n**Edit**\nReduced two booleans (`at1` and `at2` to one `at1`)\nThanks to [@dao5](https://leetcode.com/dao5)\n\n**Time/Space Complexity**\nTime: `O(N * 2) = O(N)` where `N = max(len(nums1), len(nums2))` due to memoization.\nSpace: Same as the Time Complexity\n\n**Code**\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maxSum(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> int:\n pos1 = {num: i for i, num in enumerate(nums1)}\n pos2 = {num: i for i, num in enumerate(nums2)}\n memo = [[-1 for _ in range(2)] for _ in range(max(len(nums1), len(nums2)))]\n\t\t\n def rec(curr_i, at1):\n if (curr_i >= len(nums1) and at1) or (curr_i >= len(nums2) and not at1):\n return 0\n if memo[curr_i][at1] == -1:\n no_change = change = 0\n if at1:\n if nums1[curr_i] in pos2:\n change = nums1[curr_i] + rec(pos2[nums1[curr_i]] + 1, False)\n else:\n if nums2[curr_i] in pos1:\n change = nums2[curr_i] + rec(pos1[nums2[curr_i]] + 1, True)\n no_change = (nums1[curr_i] if at1 else nums2[curr_i]) + rec(curr_i + 1, at1)\n memo[curr_i][at1] = max(no_change, change)\n return memo[curr_i][at1]\n \n return max(rec(0, True), rec(0, False)) % (10**9 + 7)\n```\n\t\nAny feedback would be great! Thanks.\n
| 11 | 1 |
[]
| 3 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
[C++] Easy DP Solution
|
c-easy-dp-solution-by-lqrde-2mqb
|
- Pick one path and start traversing, you will either go on path-1 i.e. nums1 or path-2 i.e. nums2.\n- Also store all values and index of both paths in a map, t
|
lqrde
|
NORMAL
|
2023-01-30T11:49:22.791020+00:00
|
2023-01-30T11:50:50.043810+00:00
| 999 | false |
**- Pick one path and start traversing, you will either go on path-1 i.e. nums1 or path-2 i.e. nums2.**\n**- Also store all values and index of both paths in a map, to access later**\n**- Each path consist of two options :-**\n\n\t1) pick the current value and keep traversing on same path\n\t2) check if current value exist in alternative, if yes pick current value and switch paths\n\n***Recursive Solution (TLE):***\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int help(int index , int path , unordered_map<int,int>&path1 , unordered_map<int,int>&path2 , vector<int>&nums1 , vector<int>&nums2)\n {\n if(path == 1)\n {\n if(index >= nums1.size() )\n {\n return 0;\n }\n }\n else if(path == 2 )\n {\n if(index >= nums2.size())\n {\n return 0;\n }\n }\n if(path == 1)\n {\n int op1 = nums1[index] + help(index+1 , 1 , path1 , path2 , nums1 , nums2 );\n int op2 = 0;\n if(path2.find( nums1[index] ) != path2.end())\n {\n op2 = nums1[index] + help( path2[nums1[index]]+1 , 2 , path1 , path2 , nums1 , nums2 );\n }\n return max(op1,op2);\n }\n else\n {\n int op1 = nums2[index] + help(index+1 , 2 , path1 , path2 , nums1 , nums2 );\n int op2 = 0;\n if(path1.find( nums2[index] ) != path1.end())\n {\n op2 = nums2[index] + help( path1[nums2[index]]+1 , 1 , path1 , path2 , nums1 , nums2 );\n }\n return max(op1,op2);\n }\n }\n \n int maxSum(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {\n unordered_map<int,int>path1;\n unordered_map<int,int>path2;\n \n for(int i=0;i<nums1.size();i++)\n {\n path1[nums1[i]] = i;\n }\n \n for(int i=0;i<nums2.size();i++)\n {\n path2[nums2[i]] = i;\n }\n \n int res1 = help(0,1,path1,path2,nums1,nums2);\n int res2 = help(0,2,path1,path2,nums1,nums2);\n \n return max(res1,res2);\n }\n};\n```\n\n***DP Solution (Accepted) :***\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n const int mod = 1e9 + 7;\n long long int help(int index , int path , unordered_map<int,int>&path1 , unordered_map<int,int>&path2 , vector<int>&nums1 , vector<int>&nums2 , vector<vector<long long int>>&dp)\n {\n if(path == 1)\n {\n if(index >= nums1.size() )\n {\n return 0;\n }\n }\n else if(path == 2 )\n {\n if(index >= nums2.size())\n {\n return 0;\n }\n }\n \n if(dp[index][path]!=-1)\n {\n return dp[index][path];\n }\n \n if(path == 1)\n {\n long long int op1 = nums1[index] + help(index+1 , 1 , path1 , path2 , nums1 , nums2 , dp);\n long long int op2 = 0;\n if(path2.find( nums1[index] ) != path2.end())\n {\n op2 = nums1[index] + help( path2[nums1[index]]+1 , 2 , path1 , path2 , nums1 , nums2 , dp);\n }\n return dp[index][path] = max(op1,op2);\n }\n else\n {\n long long int op1 = nums2[index] + help(index+1 , 2 , path1 , path2 , nums1 , nums2 , dp);\n long long int op2 = 0;\n if(path1.find( nums2[index] ) != path1.end())\n {\n op2 = nums2[index] + help( path1[nums2[index]]+1 , 1 , path1 , path2 , nums1 , nums2 , dp);\n }\n return dp[index][path] = max(op1,op2);\n }\n }\n \n int maxSum(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {\n unordered_map<int,int>path1;\n unordered_map<int,int>path2;\n \n for(int i=0;i<nums1.size();i++)\n {\n path1[nums1[i]] = i;\n }\n \n for(int i=0;i<nums2.size();i++)\n {\n path2[nums2[i]] = i;\n }\n \n int maxLen = max(nums1.size(),nums2.size());\n vector<vector<long long int>>dp(maxLen+1,vector<long long int>(2+1,-1));\n \n long long int res1 = (help(0,1,path1,path2,nums1,nums2,dp))%mod;\n long long int res2 = (help(0,2,path1,path2,nums1,nums2,dp))%mod;\n \n return max(res1,res2)%mod;\n }\n};\n```\n
| 10 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization', 'C']
| 1 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
Easy solution based on Merge sort
|
easy-solution-based-on-merge-sort-by-sky-nk4t
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxSum(vector<int>& arr1, vector<int>& arr2) {\n long long i = 0, j = 0, n = arr1.size() , m= arr2.size() , mod = 1e
|
sky97
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-02T04:19:58.282285+00:00
|
2020-08-02T04:19:58.282324+00:00
| 796 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxSum(vector<int>& arr1, vector<int>& arr2) {\n long long i = 0, j = 0, n = arr1.size() , m= arr2.size() , mod = 1e9+7;\n long long res = 0, sum1 = 0, sum2 = 0;\n \n // when arr1 value is less than the value of arr2 add into sum1 and vise versa\n // when both arr1 and arr2 value is same add maximum of them into result and also add same value into result and reset sum1 and sum2\n // by doing this we are ensuring that added value in result is always maximum till common value found\n \n while(i < n && j < m){\n if(arr1[i] < arr2[j]) sum1 += arr1[i++];\n else if(arr1[i] > arr2[j]) sum2 += arr2[j++];\n else{\n res += max(sum1,sum2);\n sum1 = 0,sum2 = 0;\n while(i < n && j < m && arr1[i] == arr2[j])\n {\n res += arr1[i];\n i++;\n j++;\n }\n }\n }\n while(i < n) sum1 += arr1[i++]; // remaining element of any array\n while(j < m) sum2 += arr2[j++];\n res += max(sum1,sum2);\n return (res + mod) % mod;\n }\n};\n```
| 10 | 1 |
['C', 'Merge Sort']
| 4 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
Concise C++ with detailed explanation
|
concise-c-with-detailed-explanation-by-s-ummc
|
The problem seems pretty difficult at first sight, but when you put some thought into it, you\'ll figure that it\'s very simple!\n## Algorithm explanation with
|
sachingodishela
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-05T11:06:31.367442+00:00
|
2020-08-05T11:11:04.022629+00:00
| 742 | false |
The problem seems pretty difficult at first sight, but when you put some thought into it, you\'ll figure that it\'s very simple!\n## Algorithm explanation with example:\n### Question in description:\n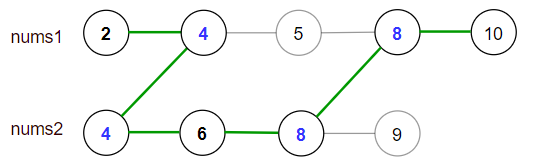\nNow, lets modify the graphical representation a little bit to give us intuition on the algorithm:\n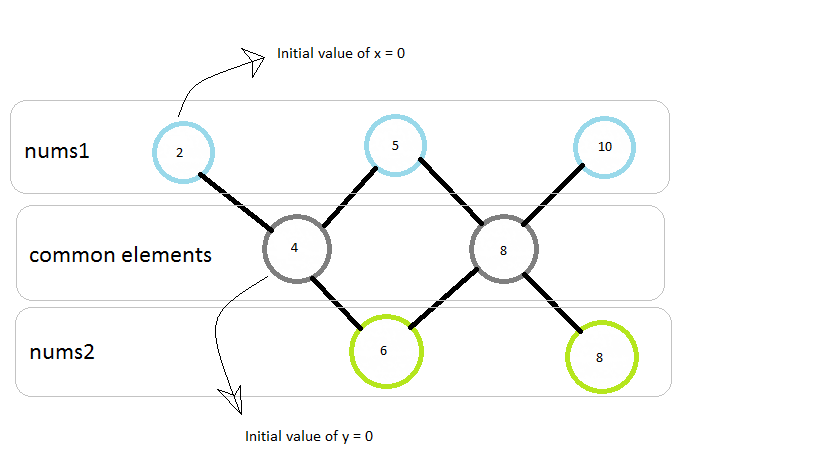\n\n## Note the following:\n1. In the above picture, we traverse through both the arrays. **x** is iterator for nums1 and **y** is iterator for nums2.\n\n2. We have to choose a path which starts from first element of either nums1 or nums2. Hence we\'ll initialize both **x** and **y** with 0.\n```\nlong long int x = 0, y = 0;\n```\n3. While traversing through both the arrays, we\'ll keep the maximum sum upto index **x** in **X** and maximum sum upto index **y** in **Y** variables respectively.\n```\nlong long int X = 0, Y = 0;\n```\n4. At the end after traversing through both the arrays, our answer is nothing but **max(X, Y)**\n## The Algorithm:\nSince we have to traverse along the arrays together, we move forward one index in one array at a time. Hence the **if** and **else if** conditions below.\n\nIn case of the **else** condition, it represents that our current location is at a common element. So we increment both the indices **x** as well as **y**. We also update the **X** and **Y** variables which represent the maximum sum upto index **x** and **y**.\n```\nwhile (x < nums1.size() and y < nums2.size() ) {\n\tif(nums1[x] < nums2[y])\n\t\tX += nums1[x++];\n\telse if (nums1[x] > nums2[y])\n\t\tY += nums2[y++];\n\telse {\n\t\tX = Y = nums1[x] + max(X, Y);\n\t\tx++;\n\t\ty++;\n\t}\n```\nThe above while loop terminates when one of the indices reach the last element of it\'s corresponding array. So we\'ll traverse and update the remainig array.\n```\nwhile(x < nums1.size()) X += nums1[x++];\nwhile(y < nums2.size()) Y += nums2[y++];\n```\nNow that we\'ve traversed both the arrays, let\'s return our answer!\n```\nreturn max(X, Y) % 1000000007;\n```\n**Feel free to comment any of your doubts or corrections, I\'m more than happy to clarify :)**
| 9 | 2 |
['C']
| 5 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
[Python] Very simple solution with explanation
|
python-very-simple-solution-with-explana-3a46
|
py\nclass Solution:\n def maxSum(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> int:\n ## RC ##\n ## APPROACH : GREEDY ##\n ## LOGIC ##\n
|
101leetcode
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-02T08:41:54.816537+00:00
|
2020-08-02T08:41:54.816584+00:00
| 754 | false |
```py\nclass Solution:\n def maxSum(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> int:\n ## RC ##\n ## APPROACH : GREEDY ##\n ## LOGIC ##\n ## 1. similar to merging 2 sorted arrays\n ## 2. Maintain sum for each array\n ## 3. when you find the same element in both arrays, only take maximum of sum1, sum2 and reset them\n \n p1, p2, sum1, sum2, result = 0, 0, 0, 0, 0\n while(p1 < len(nums1) and p2 < len(nums2)):\n if nums1[p1] == nums2[p2]:\n result += max(sum1, sum2) + nums1[p1]\n sum1, sum2 = 0, 0\n p1, p2 = p1 + 1, p2 + 1\n elif nums1[p1] < nums2[p2]:\n sum1 += nums1[p1]\n p1 += 1\n else:\n sum2 += nums2[p2]\n p2 += 1\n\n while(p1 < len(nums1)):\n sum1 += nums1[p1]\n p1 += 1\n\n while(p2 < len(nums2)):\n sum2 += nums2[p2]\n p2 += 1\n\n return (result + max(sum1 , sum2)) % (10**9 + 7)\n```\nPlease upvote if you like my solution
| 7 | 0 |
['Python', 'Python3']
| 1 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
[Javascript] DP problem O(M+N)
|
javascript-dp-problem-omn-by-alanchanghs-ly0p
|
```\nvar maxSum = function(nums1, nums2) {\n let i = 0, j = 0;\n let res1 = 0, res2 = 0;\n const MAX = 10**9 + 7;\n \n while (i < nums1.length &&
|
alanchanghsnu
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-02T04:00:59.532123+00:00
|
2020-08-02T04:00:59.532173+00:00
| 555 | false |
```\nvar maxSum = function(nums1, nums2) {\n let i = 0, j = 0;\n let res1 = 0, res2 = 0;\n const MAX = 10**9 + 7;\n \n while (i < nums1.length && j < nums2.length) {\n if (nums1[i] == nums2[j]) {\n const max = Math.max(res1, res2);\n res1 = max + nums1[i++];\n res2 = max + nums2[j++];\n } else if (nums1[i] < nums2[j]) {\n res1 += nums1[i++];\n } else {\n res2 += nums2[j++];\n }\n }\n \n while (i < nums1.length) {\n res1 += nums1[i++];\n }\n \n while (j < nums2.length) {\n res2 += nums2[j++];\n }\n \n return Math.max(res1, res2) % MAX;\n};
| 7 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 1 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
[C++/Java] | Two Pointer(beats 100%) | O(M+N) time, O(1) space
|
cjava-two-pointerbeats-100-omn-time-o1-s-4hv8
|
C++ Solution:\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxSum(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {\n \n int n = nums1.size();\n int m = n
|
chaman733
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-31T07:06:44.072210+00:00
|
2021-07-31T07:09:45.445450+00:00
| 1,068 | false |
**C++ Solution:**\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxSum(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {\n \n int n = nums1.size();\n int m = nums2.size();\n int i=0, j=0;\n long si=0, sj=0;\n long res = 0;\n \n while(i<n && j<m)\n {\n if(nums1[i] < nums2[j])\n {\n si += nums1[i];\n i++;\n }\n else if(nums1[i] > nums2[j])\n {\n sj += nums2[j];\n j++;\n }\n else\n {\n res += max(si, sj) + nums1[i];\n i++, j++;\n si=0, sj=0;\n }\n }\n \n while(i<n)\n {\n si += nums1[i];\n i++;\n }\n \n while(j<m)\n {\n sj += nums2[j];\n j++;\n }\n \n return (max(si, sj) + res) % 1000000007;\n \n }\n};\n```\n\n**Java Solution:**\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maxSum(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {\n \n int n = nums1.length;\n int m = nums2.length;\n int i=0, j=0;\n long si=0, sj=0;\n long res = 0;\n \n while(i<n && j<m)\n {\n if(nums1[i] < nums2[j])\n {\n si += nums1[i];\n i++;\n }\n else if(nums1[i] > nums2[j])\n {\n sj += nums2[j];\n j++;\n }\n else\n {\n res += Math.max(si, sj) + nums1[i];\n i++; \n j++;\n si=0;\n sj=0;\n }\n }\n \n while(i<n)\n {\n si += nums1[i];\n i++;\n }\n \n while(j<m)\n {\n sj += nums2[j];\n j++;\n }\n \n return (int)((Math.max(si, sj) + res) % 1000000007);\n \n }\n}\n```
| 6 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'C', 'C++', 'Java']
| 1 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
My screencast
|
my-screencast-by-cuiaoxiang-axil
|
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vVjQBmkMw-E\n\nIt takes some time for YouTube to process the video for high resolution. If you find the video quality is low, pl
|
cuiaoxiang
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-02T04:09:22.909834+00:00
|
2020-08-02T04:09:22.909876+00:00
| 775 | false |
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vVjQBmkMw-E\n\nIt takes some time for YouTube to process the video for high resolution. If you find the video quality is low, please go back in a few hours.
| 6 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
💥💥 Beats 100% on runtime and memory {EXPLAINED]
|
beats-100-on-runtime-and-memory-explaine-09lm
|
\n\n\n# Intuition\nThe problem involves navigating two sorted arrays to find the maximum score by summing unique values along valid paths. The key insight is th
|
r9n
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-26T20:38:19.598117+00:00
|
2024-09-26T20:39:25.888248+00:00
| 38 | false |
\n\n\n# Intuition\nThe problem involves navigating two sorted arrays to find the maximum score by summing unique values along valid paths. The key insight is that we can switch between the two arrays when we encounter common elements, allowing us to collect more values.\n\n# Approach\nUse two pointers to traverse both arrays simultaneously, accumulating sums until a common element is found, at which point add the maximum of the two accumulated sums plus the common element to the total score, then reset the sums.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n O(n + m), where n and m are the lengths of the two arrays, since we traverse each array once.\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(1), as we only use a constant amount of extra space for variables.\n\n# Code\n```csharp []\npublic class Solution {\n public int MaxSum(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {\n const int MOD = 1000000007;\n int i = 0, j = 0;\n long sum1 = 0, sum2 = 0, maxSum = 0;\n\n // Traverse both arrays until we reach the end of either\n while (i < nums1.Length || j < nums2.Length) {\n // Get the current values of nums1 and nums2 or set to int.MaxValue if we\'ve exhausted one array\n int val1 = i < nums1.Length ? nums1[i] : int.MaxValue;\n int val2 = j < nums2.Length ? nums2[j] : int.MaxValue;\n\n // If the value from nums1 is less than the value from nums2\n if (val1 < val2) {\n sum1 += val1; // Accumulate sum from nums1\n i++; // Move to the next element in nums1\n } \n // If the value from nums2 is less than the value from nums1\n else if (val1 > val2) {\n sum2 += val2; // Accumulate sum from nums2\n j++; // Move to the next element in nums2\n } \n // When we encounter a common element in both arrays\n else {\n // Update the maxSum with the maximum of the two sums and add the common value\n maxSum = (maxSum + Math.Max(sum1, sum2) + val1) % MOD;\n sum1 = 0; // Reset sum1 for the next segment\n sum2 = 0; // Reset sum2 for the next segment\n i++; // Move past the common element in nums1\n j++; // Move past the common element in nums2\n }\n }\n\n // After finishing the traversal, add any remaining sums\n maxSum = (maxSum + Math.Max(sum1, sum2)) % MOD;\n\n return (int)maxSum; // Return the final maximum score modulo 10^9 + 7\n }\n}\n\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['C#']
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
[Java/C++] Top Down DP | Memoisation
|
javac-top-down-dp-memoisation-by-rakesh0-dhq1
|
Note :\nRefer the post below for understanding why we should modulo in the end only.\nhttps://leetcode.com/problems/get-the-maximum-score/solutions/769334/c-sol
|
rakesh06
|
NORMAL
|
2023-07-25T04:01:10.958348+00:00
|
2023-07-25T04:01:10.958368+00:00
| 512 | false |
## Note :\nRefer the post below for understanding why we should modulo in the end only.\nhttps://leetcode.com/problems/get-the-maximum-score/solutions/769334/c-soln-reason-behind-modulo-in-the-end-and-not-at-every-step/ \nThank you [@pranjal21gupta](https://leetcode.com/pranjal21gupta/)\n\n# Code\n```C++ []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n const int mod = 1e9 + 7;\n int n1, n2;\n unordered_map<int,int> idx1, idx2;\n vector<vector<long long>> dp;\n long long helper(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2, int curr, int type) {\n if (((type == 0) and (curr >= n1)) or ((type == 1) and (curr >= n2)))\n return 0;\n if (dp[curr][type] != -1) \n return dp[curr][type];\n \n long long res = 0;\n res = fmax(res, \n ((type == 0) ? nums1[curr] : nums2[curr]) + \n helper(nums1, nums2, curr + 1, type));\n\n if (((type == 0) and idx2.count(nums1[curr])) or ((type == 1) and idx1.count(nums2[curr]))) \n res = fmax(res, \n ((type == 0) ? nums1[curr] : nums2[curr]) + \n helper(nums1, nums2, ((type == 0) ? idx2[nums1[curr]] : idx1[nums2[curr]]) + 1, 1 - type));\n return dp[curr][type] = res;\n }\n\n int maxSum(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {\n n1 = nums1.size();\n n2 = nums2.size();\n\n for (int i = 0; i < n1; i++)\n idx1[nums1[i]] = i;\n for (int i = 0; i < n2; i++)\n idx2[nums2[i]] = i;\n \n dp.resize(max(n1,n2), vector<long long> (2, -1));\n long long ans = fmax(\n helper(nums1,nums2, 0, 0),\n helper(nums1,nums2, 0, 1)\n );\n return ans % mod;\n }\n};\n```\n```Java []\nclass Solution {\n final int mod = 1000000007;\n int n1, n2;\n Map<Integer, Integer> idx1, idx2;\n long[][] dp;\n\n long helper(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int curr, int type) {\n if (((type == 0) && (curr >= n1)) || ((type == 1) && (curr >= n2)))\n return 0;\n if (dp[curr][type] != -1)\n return dp[curr][type];\n\n long res = 0;\n res = Math.max(res,\n ((type == 0) ? nums1[curr] : nums2[curr]) +\n helper(nums1, nums2, curr + 1, type));\n\n if (((type == 0) && idx2.containsKey(nums1[curr])) || ((type == 1) && idx1.containsKey(nums2[curr])))\n res = Math.max(res,\n ((type == 0) ? nums1[curr] : nums2[curr]) +\n helper(nums1, nums2, ((type == 0) ? idx2.get(nums1[curr]) : idx1.get(nums2[curr])) + 1, 1 - type));\n\n return dp[curr][type] = res;\n }\n\n public int maxSum(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {\n n1 = nums1.length;\n n2 = nums2.length;\n\n idx1 = new HashMap<>();\n idx2 = new HashMap<>();\n\n for (int i = 0; i < n1; i++)\n idx1.put(nums1[i], i);\n for (int i = 0; i < n2; i++)\n idx2.put(nums2[i], i);\n\n dp = new long[Math.max(n1, n2)][2];\n for (int i = 0; i < Math.max(n1, n2); i++) {\n Arrays.fill(dp[i], -1);\n }\n\n long ans = Math.max(\n helper(nums1, nums2, 0, 0),\n helper(nums1, nums2, 0, 1)\n );\n return (int) (ans % mod);\n }\n}\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
Kindly press F*** for this question :) || Clean Code
|
kindly-press-f-for-this-question-clean-c-xpzz
|
Don\'t use int for this question :)\n\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n unordered_map<int,int> m1,m2;\n vector<long long int> n1,n2;\n int md=100000
|
lolman
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-17T14:39:54.911156+00:00
|
2021-05-17T14:39:54.911204+00:00
| 182 | false |
Don\'t use int for this question :)\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n unordered_map<int,int> m1,m2;\n vector<long long int> n1,n2;\n int md=1000000007;\n \n long long int dp[100005][2][2];\n \n long long int ans(long long int pos,long long int f,long long int f2)\n { \n if(f==1)\n { \n if(pos>=n2.size())\n {\n return 0;\n }\n }\n if(f==0)\n {\n if(pos>=n1.size())\n {\n return 0;\n }\n }\n \n if(dp[pos][f][f2]!=-1)\n {\n return (long long int)dp[pos][f][f2];\n }\n \n if(f==0)\n {\n if((m2.find(n1[pos])!=m2.end())&&(f2==0))\n {\n dp[pos][f][f2]=max((long long int)ans(m2[n1[pos]],1,1),(long long int)(n1[pos]+ans(pos+1,0,0)));\n }\n else\n {\n dp[pos][f][f2]=(long long int)(n1[pos]+ans(pos+1,0,0));\n }\n return dp[pos][f][f2];\n }\n \n if((m1.find(n2[pos])!=m2.end())&&(f2==0))\n {\n dp[pos][f][f2]=max((long long int)ans(m1[n2[pos]],0,1),(long long int)(n2[pos]+ans(pos+1,1,0)));\n }\n else\n {\n dp[pos][f][f2]=(long long int)(n2[pos]+ans(pos+1,1,0));\n }\n return dp[pos][f][f2];\n \n }\n \n int maxSum(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {\n \n for(int i=0;i<nums1.size();i++)\n {\n n1.push_back((long long int)(nums1[i]));\n m1[nums1[i]]=i;\n }\n for(int i=0;i<nums2.size();i++)\n {\n n2.push_back((long long int)(nums2[i]));\n m2[nums2[i]]=i;\n }\n \n memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp));\n long long int an= max(ans(0,0,0),ans(0,1,0));\n return an%md;\n \n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
O(N) Time, O(1) space, very simple c++ solution
|
on-time-o1-space-very-simple-c-solution-j00ba
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxSum(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {\n int n1 = nums1.size();\n int n2 = nums2.size();\n i
|
gargp1065
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-02T05:36:45.043794+00:00
|
2020-08-02T05:36:45.043843+00:00
| 125 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxSum(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {\n int n1 = nums1.size();\n int n2 = nums2.size();\n int ans=0, s1=0, s2=0;\n int i=0, j=0;\n while(i< n1 and j <n2)\n {\n if(nums1[i] < nums2[j])\n {\n s1 = s1+nums1[i];\n i++;\n }\n else if(nums1[i] > nums2[j])\n {\n s2 += nums2[j];\n j++;\n }\n else if(nums1[i] == nums2[j])\n {\n ans += max(s1, s2) + nums1[i];\n s1=0; s2=0;\n i++;j++;\n }\n }\n while(j<n2)\n {\n s2=s2+nums2[j];\n j++;\n }\n while(i<n1)\n {\n s1+=nums1[i];\n i++;\n }\n ans = ans+max(s1, s2);\n return ans%1000000007;\n }\n};\n```\n
| 4 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
C++ DP solution with detailed explanation
|
c-dp-solution-with-detailed-explanation-uci1d
|
C++ DP solution with detailed explanation\n\nf[i][k] means that we have state index i, visiting k array (k is 0 or 1)\nfor each state, we have two choices\n\n1.
|
ttzztztz
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-02T04:09:59.359189+00:00
|
2020-08-02T04:09:59.359233+00:00
| 418 | false |
C++ DP solution with detailed explanation\n\n`f[i][k]` means that we have state index `i`, visiting `k` array (k is 0 or 1)\nfor each state, we have two choices\n\n1. we can visit the next item of the `k` array, we get `arr[k][i]` score\n2. If there exist `arr[k ^ 1][x]` so that `arr[k][i] == arr[k ^ 1][x]`, we can also jump to the second array and get `arr[k][i]` score\nWe can use the stategy of binary search and find whether there exists `arr[k ^ 1][x]` and what `x` is, in O(logn) time\n\nWe should maxium the total score.\n\nTime complexity: `O(nlogn)`\nSpace complexity: `O(n)`\n\nThe XOR notation is a trick `0 ^ 1 = 1`, `1 ^ 1 = 0`, because we have two array in total.\n\n```cpp\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxSum(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {\n v[0] = nums1, v[1] = nums2;\n N = nums1.size(), M = nums2.size();\n memset(f, 0xff, sizeof f);\n return max(dfs(0, 0), dfs(0, 1)) % mod;\n }\nprivate:\n long long f[100005][2];\n const int mod = 1e9+7;\n int N, M;\n vector<int> v[2];\n long long dfs(int i, int k) {\n if (i == v[k].size()) return 0;\n long long& val = f[i][k];\n if (val != -1) return val;\n \n long long answer = 0;\n answer = max(answer, v[k][i] + dfs(i + 1, k));\n auto it = lower_bound(v[k ^ 1].begin(), v[k ^ 1].end(), v[k][i]);\n if (it != v[k ^ 1].end() && *it == v[k][i]) {\n answer = max(answer, v[k][i] + dfs(it + 1 - v[k ^ 1].begin(), k ^ 1));\n }\n return val = answer;\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 1 |
[]
| 2 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
c++ | 83% faster than all | easy
|
c-83-faster-than-all-easy-by-venomhighs7-mrg4
|
\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxSum(vector<int>& A, vector<int>& B) {\n int i = 0, j = 0, n = A.size(), m = B.size();\n long a =
|
venomhighs7
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-15T04:45:43.844850+00:00
|
2022-10-15T04:45:43.844893+00:00
| 899 | false |
\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxSum(vector<int>& A, vector<int>& B) {\n int i = 0, j = 0, n = A.size(), m = B.size();\n long a = 0, b = 0, mod = 1e9 + 7;\n while (i < n || j < m) {\n if (i < n && (j == m || A[i] < B[j])) {\n a += A[i++];\n } else if (j < m && (i == n || A[i] > B[j])) {\n b += B[j++];\n } else {\n a = b = max(a, b) + A[i];\n i++, j++;\n }\n }\n return max(a, b) % mod;\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
C++ Using DFS and Memoization
|
c-using-dfs-and-memoization-by-smritinai-rlmu
|
\n#define mod 1000000007\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long dfs(int u, unordered_map<long long,vector<long long>> &graph, unordered_map<long long,long lo
|
smritinaik1421
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-02T05:56:22.734971+00:00
|
2022-07-02T05:56:22.735010+00:00
| 416 | false |
```\n#define mod 1000000007\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long dfs(int u, unordered_map<long long,vector<long long>> &graph, unordered_map<long long,long long> &maxDist)\n {\n if(maxDist.find(u)!=maxDist.end())\n {\n return (u+maxDist[u]);\n } \n \n \n maxDist[u]=0;\n \n for(auto &v: graph[u])\n {\n maxDist[u]=max(maxDist[u],dfs(v,graph,maxDist));\n }\n \n return (u+maxDist[u]);\n }\n int maxSum(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {\n unordered_map<long long,vector<long long>> graph;\n unordered_map<long long,long long> maxDist;\n \n int n=nums1.size();\n \n for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++)\n {\n graph[nums1[i]].push_back(nums1[i+1]);\n }\n \n n=nums2.size();\n \n for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++)\n {\n graph[nums2[i]].push_back(nums2[i+1]);\n }\n \n long long val = max(dfs(nums1[0],graph,maxDist),dfs(nums2[0],graph,maxDist));\n \n return val%mod;\n \n return 0;\n }\n};\n\n/*\nWe can consider unique integers as nodes of a graph with edges pointing to next member present in nums1 and nums2\nThen perform dfs from starting number of both the arrays and return maximum path sum till last index\n*/\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'C']
| 1 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
DP Solution | C++
|
dp-solution-c-by-harshnadar23-prs5
|
c -> Which array we\'re on. If 1, then nums2, else nums1.\nstore indices of same elements in a map.\n\nA simple easy to understand DP:\n```\nclass Solution {\np
|
harshnadar23
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-06T07:01:53.265026+00:00
|
2021-09-06T14:40:33.810142+00:00
| 295 | false |
c -> Which array we\'re on. If 1, then nums2, else nums1.\nstore indices of same elements in a map.\n\nA simple easy to understand DP:\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n map<int, int> mp1, mp2;\n int n, m;\n vector<int> nums1,nums2;\n \n long long int dp[100002][2];\n int mod =1e9+7;\n \n long long int solve(int i, int c){\n if(c==0 && i>=n) return 0;\n if(c==1 && i>=m) return 0;\n \n if(dp[i][c]!=-1) return dp[i][c];\n \n if(c){\n if(mp1[nums2[i]]){\n dp[i][c]=max(nums2[i]+solve(mp1[nums2[i]],c^1), nums2[i]+solve(i+1,c));\n }\n else {dp[i][c]=(long long int)nums2[i]+solve(i+1,c); }\n }\n \n else{\n if( mp2[nums1[i]]){\n dp[i][c]=max(nums1[i]+solve(mp2[nums1[i]],c^1), nums1[i]+solve(i+1,c));\n }\n else {dp[i][c]=(long long int)nums1[i]+solve(i+1,c);}\n }\n return dp[i][c];\n }\n \n int maxSum(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {\n n=nums1.size();\n m=nums2.size();\n this->nums1 = nums1;\n this->nums2 = nums2;\n memset(dp,-1,sizeof dp);\n \n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n mp1[nums1[i]] = i+1;\n }\n for(int i=0;i<m;i++){\n mp2[nums2[i]]=i+1;\n }\n \n long long int ans=max(solve(0,0), solve(0,1));\n \n return ans%mod;\n }\n};
| 3 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming']
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
[Java] Greedy O(N+M)
|
java-greedy-onm-by-yuhwu-426b
|
\n public int maxSum(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {\n int mod = 1000000007;\n long res = 0;\n int n1 = nums1.length;\n int n2 = nums
|
yuhwu
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-02T04:03:07.063250+00:00
|
2020-08-02T04:03:07.063312+00:00
| 252 | false |
```\n public int maxSum(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {\n int mod = 1000000007;\n long res = 0;\n int n1 = nums1.length;\n int n2 = nums2.length;\n long[] pSum1 = new long[n1+1];\n long[] pSum2 = new long[n2+1];\n for(int i=1; i<=n1; i++){\n pSum1[i] = pSum1[i-1] + nums1[i-1];\n }\n for(int i=1; i<=n2; i++){\n pSum2[i] = pSum2[i-1] + nums2[i-1];\n }\n int p1 = -1;\n int p2 = -1;\n int i=0;\n int j=0;\n while(i<n1 && j<n2){\n if(nums1[i]>nums2[j]){\n j++;\n }\n else if(nums1[i]<nums2[j]){\n i++;\n }\n else{\n long cand1 = pSum1[i+1]-pSum1[p1+1];\n long cand2 = pSum2[j+1]-pSum2[p2+1];\n res += Math.max(cand1, cand2);\n p1 = i;\n p2 = j;\n i++;\n j++;\n }\n }\n long cand1 = pSum1[n1]-pSum1[p1+1];\n long cand2 = pSum2[n2]-pSum2[p2+1];\n res += Math.max(cand1, cand2); \n return (int) (res%mod);\n }\n```
| 3 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
Simple Two Pointer Clean Approach
|
simple-two-pointer-clean-approach-by-shr-bu2g
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(n)\n Add your time complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n\n- Space complexity:O(1)\n Add your space complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n\n# Code
|
Shree_Govind_Jee
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-11T05:46:16.944253+00:00
|
2024-07-11T05:46:16.944273+00:00
| 530 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity:$$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:$$O(1)$$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n int MOD = 1_000_000_007;\n\n public int maxSum(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {\n int len1 = nums1.length;\n int len2 = nums2.length;\n\n long sum1 = 0, sum2 = 0;\n int i = 0, j = 0;\n while (i < len1 || j < len2) {\n if (i < len1 && (j == len2 || nums1[i] < nums2[j])) {\n sum1 += nums1[i++];\n } else if (j < len2 && (i == len1 || nums1[i] > nums2[j])) {\n sum2 += nums2[j++];\n } else {\n sum2 = Math.max(sum1, sum2) + nums1[i];\n sum1 = sum2;\n i++;\n j++;\n }\n }\n return (int) (Math.max(sum1, sum2) % MOD);\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Array', 'Math', 'Two Pointers', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Greedy', 'Java']
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
Based on MergeSort O(n)
|
based-on-mergesort-on-by-abhaydutt-pvj4
|
based on the merge function of mergeSort. we keep a track of both the paths that we can take , once we encounter a similar number we update the result and make
|
AbhayDutt
|
NORMAL
|
2023-01-25T10:40:05.464060+00:00
|
2023-01-25T10:40:05.464103+00:00
| 246 | false |
based on the merge function of mergeSort. we keep a track of both the paths that we can take , once we encounter a similar number we update the result and make the sum1 and sum2 0 again . dry run the code , it will help a lot . \n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maxSum(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {\n long sum1=0,sum2=0,res=0;\n int i=0,j=0;\n while(i<nums1.length && j<nums2.length){\n if(nums1[i]<nums2[j]){\n sum1+=nums1[i++];\n }else if(nums1[i]>nums2[j]){\n sum2+=nums2[j++];\n }else{\n long toAdd = Math.max(sum1,sum2);\n res+= toAdd+nums1[i];\n sum1=0;sum2=0;i++;j++;\n }\n }\n while(i<nums1.length){\n sum1+=nums1[i++];\n }\n while(j<nums2.length){\n sum2+=nums2[j++];\n }\n long toAdd= Math.max(sum1,sum2);\n res+= toAdd;\n long mod = (long)Math.pow(10,9)+7;\n return (int)(res%mod);\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'Merge Sort', 'Java']
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
[2 Solutions] DFS + Greedy with thought process when being asked during interviews
|
2-solutions-dfs-greedy-with-thought-proc-2g9o
|
DFS\nBecause we should go through the path from left to the right, which makes it look like tree traversal, but not fully the same. However, it gives us an insi
|
jandk
|
NORMAL
|
2021-12-28T10:27:45.595790+00:00
|
2021-12-28T10:27:45.595830+00:00
| 139 | false |
### DFS\nBecause we should go through the path from left to the right, which makes it look like tree traversal, but not fully the same. However, it gives us an insight that we can convert it to graph problem asking the maximum sum of path from root to leaves.\nThe graph is constructed by simply conneting adjacent integers and the common integers in both arrays.\n\u200B\nNote that we are constructing directed graph,but there is a circle between the common integers, so we need use `parent` to avoid circle traversal.\n\u200B\nThe next problem for this solution is that we have the same integers for different nodes, but we can resolve it by reverting the integer for the `nums2` and remember to use absolute value when calculating the sum value.\n\u200B\nThe final problem we have to deal with is that the sum value only care about distinct integers, so we need discard the integer when we swith from one array to the other.\n\nFinally, we just run post order traversal on the graph to return the maximum sum of path on the subgraph.\n\u200B\nBecause there could be 2 parents for one single node, we have to use `cache` to store the immediate results for reducing time complexity.\n\n```python\ndef maxSum(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> int:\n\tgraph = defaultdict(list)\n\tfor a, b in zip(nums1, nums1[1:]):\n graph[a].append(b)\n\tfor a, b in zip(nums2, nums2[1:]):\n\t\tgraph[-a].append(-b)\n \n\tindices2 = set(nums2)\n\tfor i, num in enumerate(nums1):\n\t\tif num in indices2:\n\t\t\tgraph[num].append(-num)\n graph[-num].append(num)\n\n\t@cache\n\tdef helper(node, parent):\n\t\tans = 0\n\t\tfor nei in graph[node]:\n\t\t\tif parent != nei:\n\t\t\t\tans = max(ans, helper(nei, node) if abs(nei) != abs(node) else helper(nei, node) - abs(node))\n\t\treturn ans + abs(node)\n\treturn max(helper(nums1[0], 0), helper(-nums2[0], 0)) % (10 ** 9 + 7)\n```\n\n### Greedy + Prefix Sum\nThe property of counting the value of distinct integers only indicates that we can merge the common integer as one node so that we can partition the whole arrays as pieces among which there is no common integers. As such, the sum of integers of each piece is fixed and valid because each array has distinct integers, which denotes to a greedy solution iterating each piece and pick the larger one.\nWe can simply iterate each integer on the piece and calculate the sum, and jump to next common merged node after making decisions. However, we can simpify the implementation using prefix sum with pair of indices of common integers between the 2 arrays.\nLet\'s put it all together.\n1. calculate prefix sum for each `nums`.\n2. find out all of pairs of common integers with the indices.\n3. Iterate each pair and sum up the larger sum using prefix sum.\n\n```python\n def maxSum(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> int:\n pre1, pre2 = [0], [0]\n for num in nums1:\n pre1.append(pre1[-1] + num)\n for num in nums2:\n pre2.append(pre2[-1] + num)\n pairs = []\n indices2 = {num:i for i, num in enumerate(nums2)}\n for i, num in enumerate(nums1):\n if num in indices2:\n pairs.append((i, indices2[num]))\n total = 0\n last_i = last_j = -1\n for i, j in pairs + [(len(nums1), len(nums2))]: \n total += max(pre1[i] - pre1[last_i + 1], pre2[j] - pre2[last_j + 1])\n if i < len(nums1):\n total += nums1[i]\n last_i, last_j = i, j\n return total % (10 ** 9 + 7) \n```\n\n*Time Complexity* = **O(M + N)**\n*Space Complexity* = **O(M+ N)**
| 2 | 0 |
['Greedy', 'Depth-First Search', 'Prefix Sum']
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
Easy to Understand Python Solution
|
easy-to-understand-python-solution-by-sh-f53f
|
```\ndef maxSum(self, arr1, arr2):\n m=len(arr1)\n n=len(arr2)\n sum1=0\n sum2=0\n ans=0\n \n i=0\n j=0\
|
sharmamuskaan237
|
NORMAL
|
2021-08-02T04:59:40.833327+00:00
|
2021-08-02T04:59:40.833381+00:00
| 236 | false |
```\ndef maxSum(self, arr1, arr2):\n m=len(arr1)\n n=len(arr2)\n sum1=0\n sum2=0\n ans=0\n \n i=0\n j=0\n while i<m and j<n:\n if arr1[i]<arr2[j]:\n sum1+=arr1[i]\n i+=1\n \n elif arr1[i]>arr2[j]:\n sum2+=arr2[j]\n j+=1\n \n else:\n ans += arr1[i] + max(sum1,sum2)\n sum1=0\n sum2=0\n i+=1\n j+=1\n \n while i<m:\n sum1+=arr1[i]\n i+=1\n \n while j<n:\n sum2+=arr2[j]\n j+=1\n \n ans += max(sum1,sum2)\n \n return ans%((10**9)+7)\n
| 2 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
92 ms, faster than 90.34% CPP SOLUTION - TIME - O(m+n) , SPACE - O(1) --- TWO POINTERS
|
92-ms-faster-than-9034-cpp-solution-time-spvo
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxSum(vector<int>& a, vector<int>& b) {\n int mod=1e9+7;\n int m=a.size();\n int n=b.size();\n
|
rajsaurabhh
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-27T09:41:26.044883+00:00
|
2021-07-27T09:41:26.044938+00:00
| 77 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxSum(vector<int>& a, vector<int>& b) {\n int mod=1e9+7;\n int m=a.size();\n int n=b.size();\n int i=0,j=0;\n long long int sum1=0,sum2=0,totsum=0;\n while(i<m && j<n)\n {\n if(a[i]<b[j])\n {\n sum1+=a[i];\n i++;\n }\n else if(a[i]>b[j])\n {\n sum2+=b[j];\n j++;\n }\n else \n {\n totsum+=max(sum1,sum2)+a[i];\n i++;j++;\n sum1=sum2=0;\n }\n }\n while(i<m)\n {\n sum1+=a[i];\n i++;\n }\n while(j<n)\n {\n sum2+=b[j];\n j++;\n }\n totsum+=max(sum1,sum2);\n totsum = totsum%mod;\n return (int)totsum;\n }\n};\n```\n\nPLEASE UPVOTE IF IT HELPS!
| 2 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
C++ easy two pointer solution faster than 100% 36ms
|
c-easy-two-pointer-solution-faster-than-1cuod
|
C++ Easy two pointer solution \n\n\nint maxSum(vector<int>& a, vector<int>& b) {\n ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);\n cin.tie(NULL);\n lon
|
chakri_b
|
NORMAL
|
2021-06-05T15:06:22.671670+00:00
|
2021-06-05T15:06:22.671697+00:00
| 173 | false |
C++ Easy two pointer solution \n\n```\nint maxSum(vector<int>& a, vector<int>& b) {\n ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);\n cin.tie(NULL);\n long i=0, j=0, n=a.size(), m=b.size(), as = 0, bs = 0;\n while( i < n && j < m){\n if(a[i] < b[j])as += a[i++];\n else if(b[j] < a[i]) bs += b[j++];\n else as = bs = max(as, bs) + a[i++], j++;\n }\n while(i < n) as += a[i++];\n while(j < m) bs += b[j++];\n return max(as, bs) % 1000000007;\n }\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'C++']
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
O(n) Time | O(1) Space | Simple C++
|
on-time-o1-space-simple-c-by-shivamshahi-5uya
|
```\nint maxSum(vector& nums1, vector& nums2) {\n long long ans=0;\n long long mod= 1000000007;\n int n1=nums1.size(),n2=nums2.size();\n
|
shivamshahi12
|
NORMAL
|
2021-02-15T06:16:05.092708+00:00
|
2021-02-15T06:16:05.092755+00:00
| 301 | false |
```\nint maxSum(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {\n long long ans=0;\n long long mod= 1000000007;\n int n1=nums1.size(),n2=nums2.size();\n \n long long up=0,dn=0;\n int i=0,j=0;\n while(i<n1 && j<n2){\n if(nums1[i]==nums2[j]){\n ans+= max(up,dn)+ nums1[i];\n up=0,dn=0;\n i++,j++;\n }\n else if(nums1[i]>nums2[j]){\n dn+= nums2[j];\n j++;\n }\n else{\n up+= nums1[i];\n i++;\n }\n }\n while(i<n1) up+=nums1[i++];\n while(j<n2) dn+=nums2[j++];\n return (max(up,dn)+ans)%mod;\n }\n\t
| 2 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C', 'C++']
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
Java very simple modified merge sort
|
java-very-simple-modified-merge-sort-by-xcq14
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int maxSum(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {\n int i1 = 0;\n int i2 = 0;\n \n long us = 0;\n long ls
|
aborac
|
NORMAL
|
2020-10-12T03:50:34.498405+00:00
|
2020-10-12T03:50:34.498438+00:00
| 185 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int maxSum(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {\n int i1 = 0;\n int i2 = 0;\n \n long us = 0;\n long ls = 0;\n \n while ((i1 < nums1.length) && (i2 < nums2.length)) {\n if (nums1[i1] == nums2[i2]) {\n us = ls = (Math.max(us, ls) + nums1[i1]);\n i1++;\n i2++;\n } else if (nums1[i1] < nums2[i2]) {\n us += nums1[i1++];\n } else {\n ls += nums2[i2++];\n }\n }\n \n while (i1 < nums1.length) us += nums1[i1++];\n while (i2 < nums2.length) ls += nums2[i2++];\n \n return ((int)(Math.max(us, ls) % 1000000007));\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
If you do DFS please just store everything in Long and mod at the end
|
if-you-do-dfs-please-just-store-everythi-57lm
|
class Solution {\n \n Map a2b = new HashMap<>();\n Map b2a = new HashMap<>();\n int MOD = 1000000007;\n int max = 0;\n HashMap dp = new HashMa
|
kelvin2180
|
NORMAL
|
2020-09-11T09:22:40.440174+00:00
|
2020-09-11T09:22:40.440249+00:00
| 408 | false |
class Solution {\n \n Map<Integer, Integer> a2b = new HashMap<>();\n Map<Integer, Integer> b2a = new HashMap<>();\n int MOD = 1000000007;\n int max = 0;\n HashMap<Integer, Long> dp = new HashMap<>();\n \n public int maxSum(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {\n int m = 0;\n int n = 0;\n \n while(m < nums1.length && n < nums2.length){\n int num1 = nums1[m];\n int num2 = nums2[n];\n if(num1 == num2){\n a2b.put(m,n);\n b2a.put(n,m);\n m++;\n n++;\n } else if (num1 < num2){\n m++;\n } else{\n n++;\n }\n }\n Long ans = Math.max(dfs(0, nums1, nums2, 1) , \n dfs(0, nums1, nums2, 2));\n ans %= MOD;\n return ans.intValue();\n }\n \n long dfs (int i, int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int nums){\n if(nums == 1 && i == nums1.length || nums == 2 && i == nums2.length)\n return 0;\n \n int val = nums == 1 ? nums1[i] : nums2[i];\n if(dp.get(val) != null){\n return dp.get(val);\n }\n \n long next = 0;\n if(nums == 1){\n next = Math.max(next, dfs(i+1, nums1, nums2, 1));\n if(a2b.get(i) != null){\n next = Math.max(next, dfs(a2b.get(i)+1, nums1, nums2, 2));\n }\n } else {\n next = Math.max(next, dfs(i+1, nums1, nums2, 2));\n if(b2a.get(i) != null){\n next = Math.max(next, dfs(b2a.get(i)+1, nums1, nums2, 1));\n }\n }\n \n long ans = next + val;\n dp.put(val, ans);\n \n return dp.get(val);\n }\n}
| 2 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Depth-First Search', 'Iterator', 'Java']
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
Java simple greedy
|
java-simple-greedy-by-hobiter-3sc0
|
Ref: https://leetcode.com/problems/get-the-maximum-score/discuss/767987/JavaC%2B%2BPython-Two-Pointers-O(1)-Space\n\n public int maxSum(int[] a, int[] b) {\n
|
hobiter
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-28T20:29:43.466637+00:00
|
2020-08-28T20:43:23.352779+00:00
| 243 | false |
Ref: https://leetcode.com/problems/get-the-maximum-score/discuss/767987/JavaC%2B%2BPython-Two-Pointers-O(1)-Space\n```\n public int maxSum(int[] a, int[] b) {\n int i = 0, j = 0;\n long m = a.length, n = b.length, suma = 0, sumb = 0, mod = 1_000_000_007;\n while (i < m || j < n) {\n if (i < m && (j >= n || a[i] < b[j])) suma += a[i++];\n else if (j < n && (i >= m || a[i] > b[j])) sumb += b[j++]; \n else {\n suma = sumb = (Math.max(suma, sumb) + a[i++]) % mod;\n j++;\n }\n }\n return (int) (Math.max(suma, sumb) % mod);\n }\n```\n\n\nInteresting dp problem, how many routes if you can switch.\n```\n int m, n, dp[][];\n public int maxSum(int[] a, int[] b) {\n m = a.length; n = b.length; dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1];\n return dfs(0, 0, a, b);\n }\n \n private int dfs(int i, int j, int[] a, int[] b) {\n int i0 = i, j0 = j;\n if (i >= m || j >= n) return 1;\n if (dp[i][j] > 0) return dp[i][j];\n while (a[i] != b[j]) {\n System.out.println(i + "," + j);\n while (a[i] < b[j]) if (++i >= m) return 1;\n while (b[j] < a[i]) if (++j >= n) return 1;\n }\n dp[i0][j0] = dfs(i + 1, j, a, b) + dfs(i, j + 1, a, b);\n return dp[i0][j0];\n }\n```
| 2 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
C++ DFS+memo
|
c-dfsmemo-by-akshay31verma-g35q
|
define ll long long int\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n \n ll dfsit(int i,vector &dp,unordered_map> &mp){\n if(mp.count(i)==0){\n retu
|
akshay31verma
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-05T19:44:30.115935+00:00
|
2020-08-05T19:44:30.115984+00:00
| 204 | false |
#define ll long long int\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n \n ll dfsit(int i,vector<ll> &dp,unordered_map<int,vector<int>> &mp){\n if(mp.count(i)==0){\n return i;\n }\n \n ll nxt=0;\n \n if(dp[i]!=-1){\n return dp[i];\n }\n \n for(auto j:mp[i]){\n nxt=max(nxt,dfsit(j,dp,mp)); \n }\n nxt+=i;\n dp[i]=nxt;\n \n return dp[i];\n \n }\n \n int maxSum(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {\n unordered_map<int,vector<int>> mp;\n vector<ll> dp;\n int maxi=0;\n \n for(int i=0;i<nums1.size();i++){\n maxi=max(maxi,nums1[i]);\n if(i+1<nums1.size()){\n mp[nums1[i]].push_back(nums1[i+1]);} \n \n }\n for(int i=0;i<nums2.size();i++){\n maxi=max(maxi,nums2[i]);\n if(i+1<nums2.size()){\n mp[nums2[i]].push_back(nums2[i+1]);\n } \n }\n dp.resize(maxi+1,-1);\n \n \n return max(dfsit(nums2[0],dp,mp)%1000000007,dfsit(nums1[0],dp,mp)%1000000007);\n \n \n \n }\n};
| 2 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
JavaScript two pointer traversal 100% speed 100% memory
|
javascript-two-pointer-traversal-100-spe-8evm
|
Idea is to concurrently traverse both arrays from front to back, stepping forward at each iteration in the array with the lower value number. Since the arrays a
|
adrianlee0118
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-04T17:32:11.184790+00:00
|
2020-08-04T17:32:39.033287+00:00
| 88 | false |
Idea is to concurrently traverse both arrays from front to back, stepping forward at each iteration in the array with the lower value number. Since the arrays are sorted, this ensures that values shared by both arrays will be found.\n\nAt each step, add the value of the number to a running sum for that array. When the shared value is encountered, replace both running sums with the maximum between them since this is the point on a path where we can move to the other array. Continue traversal after adding the shared value to both path sums.\n\n```\nconst maxSum = (nums1, nums2) => {\n const modulo = 1000000007;\n let i = 0, j = 0, l1 = nums1.length, l2 = nums2.length, sum1 = 0, sum2 = 0;\n while (i < l1 || j < l2){\n if (i < l1 && (j === l2 || nums1[i] < nums2[j])){ //if value 2 is greater than value 1\n sum1 += nums1[i]; //traverse path1 and read the next node in 1\n i++;\n } else if (j < l2 && (i === l1 || nums1[i] > nums2[j])) { //if value 1 is greater than value 2\n sum2 += nums2[j]; //traverse path2 and read the next node in 2\n j++;\n } else { //If the two values are equal\n const newval = Math.max(sum1, sum2) + nums1[i];\n sum1 = newval; //set the sum at each node to the maximum observed so far\n sum2 = newval;\n i++; //read the next nodes\n j++;\n }\n }\n return Math.max(sum1,sum2) % modulo; //return the maximum running path sum\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
[C++] Beats 100% Simple O(n) Time, O(1) Space
|
c-beats-100-simple-on-time-o1-space-by-h-kuod
|
\tclass Solution {\n\tpublic:\n\t\tint maxSum(vector& nums1, vector& nums2) \n\t\t{\n \n\t\tios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);\n cin.tie(NULL);\n
|
hiteshan28
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-02T14:31:41.947814+00:00
|
2020-08-02T14:31:41.947849+00:00
| 72 | false |
\tclass Solution {\n\tpublic:\n\t\tint maxSum(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) \n\t\t{\n \n\t\tios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);\n cin.tie(NULL);\n cout.tie(NULL);\n \n int n1 = nums1.size(), n2 = nums2.size(), m = 1e9+7;\n long long left = 0, right = 0;\n \n int i = n1-1, j = n2-1;\n \n while(i >= 0 || j >= 0)\n {\n if(i < 0)\n {\n right = nums2[j--] + right;\n continue;\n }\n \n if(j < 0)\n {\n left = nums1[i--] + left;\n continue;\n }\n \n if(nums1[i] < nums2[j])\n {\n right = nums2[j--] + right;\n }\n else if(nums1[i] > nums2[j])\n {\n left = nums1[i--] + left;\n }\n else\n {\n long long temp1 = left, temp2 = right;\n left = nums1[i--]+max(temp1,temp2);\n right = nums2[j--]+max(temp2,temp1);\n }\n }\n return max(left,right)%m;\n }};
| 2 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
PYTHON: Priority Queue with Topological ordering
|
python-priority-queue-with-topological-o-dky5
|
Build a graph based on two given arrays\nCount each node\'s indegree respectively\n\nConstruct a Priority Queue that maintains the current minimum sum.\nThe rea
|
bear996
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-02T06:45:00.724570+00:00
|
2020-08-02T06:48:37.742960+00:00
| 97 | false |
Build a graph based on two given arrays\nCount each node\'s indegree respectively\n\nConstruct a Priority Queue that maintains the current minimum sum.\nThe reason is that as we perform indegree - 1 for each node afterward, we exhausted the count of indegree by the minimum previous sum path. At the end, when a given node\'s indegree == 0, we left the maximum previous sum to the current node. Hence, we push the maximum sum including the current node\'s value to the PQ, which maintains the maximum value for each node after.\n\nFor example:\n```\n4 - > 5 -> 8 \n4 -> 6 -> 8\n```\n4 has 0 indegree, it will be pushed to pq first as (4,4) (cur_sum, node)\nthen we examine 5 and 6, both are 4\'s neighbors. take indegree - 1, resulting both indegree == 0. we need to push\n(9, 5) and (10, 6) to PQ\n\nNotice here 8 has indegree = 2, coming from 5 and 6. because PQ always pop the smallest sum, (9,5) will first be poped and we start to examine 8, which cause indegree - 1 == 1. Since we are not reaching 0, **ignore** \n**We are ignoring the minimum sum path!** Later when (10,6) poped up, 10 is the current maxium sum path to node 8. we can now add (18,8) to the PQ. \n\n**Hence, we maintain the maximum path by ignoring the smaller sum path altogether. The reason is we are using the PQ that prioritize the smallest sum first**\n\nCode:\n```\n\n def maxSum(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> int:\n # build graph: topological sort\n s = set(nums1+nums2)\n indegree = {n:0 for n in s}\n g = collections.defaultdict(list)\n for i in range(1,len(nums1)):\n indegree[nums1[i]] += 1\n g[nums1[i-1]].append(nums1[i])\n if nums1[-1] not in g:\n g[nums1[-1]] = []\n \n for i in range(1,len(nums2)):\n indegree[nums2[i]] +=1\n g[nums2[i-1]].append(nums2[i])\n if nums2[-1] not in g:\n g[nums2[-1]] = []\n \n\n pq = [(key,key) for key,val in indegree.items() if val == 0]\n heapq.heapify(pq)\n ans = 0\n while pq: \n cur_sum, node = heapq.heappop(pq) # always pop the current minimum sum\n ans = cur_sum\n for nei in g[node]: \n indegree[nei] -= 1 # exhaust indegree for the smaller sum\n if indegree[nei] == 0: # guarantee the largest sum cause the nei\'s indegree to 0\n heapq.heappush(pq, (cur_sum+nei, nei)) # hence, we maintain the largest sum to the end\n\n \n return ans % (10**9+7)\n \n\n\n```\n
| 2 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
Beginner + Advanced Two Pointers Solutions!
|
beginner-advanced-two-pointers-solutions-6852
|
Beginner SolutionAdvanced Solution
|
TwilightXD
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-06T13:06:45.725780+00:00
|
2025-03-06T13:06:45.725780+00:00
| 66 | false |
# Beginner Solution
```python3 []
class Solution:
def maxSum(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> int:
ans = i = j = 0
curr1, curr2 = nums1[0], nums2[0]
m, n = len(nums1), len(nums2)
while i < m or j < n:
if i == m:
curr2 += sum(nums2[j+1:n])
j = n
break
elif j == n:
curr1 += sum(nums1[i+1:m])
i = m
break
if nums1[i] == nums2[j]:
ans += max(curr1, curr2)
i += 1
j += 1
curr1 = nums1[i] if i != m else 0
curr2 = nums2[j] if j != n else 0
elif nums1[i] < nums2[j]:
i += 1
curr1 += nums1[i] if i != m else 0
elif nums1[i] > nums2[j]:
j += 1
curr2 += nums2[j] if j != n else 0
return (ans + max(curr1, curr2)) % (10**9 + 7)
```
---
# Advanced Solution
```python3 []
class Solution:
def maxSum(self, A: List[int], B: List[int]) -> int:
i = j = a = b = 0
n, m = len(A), len(B)
while i < n or j < m:
if i < n and (j == m or A[i] < B[j]):
a += A[i]
i += 1
elif j < m and (i == n or A[i] > B[j]):
b += B[j]
j += 1
else:
a = b = max(a, b) + A[i]
i += 1
j += 1
return max(a, b) % (10**9 + 7)
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
Python Two Pointer explanation O(1) Space O(n) Time
|
python-two-pointer-explanation-o1-space-pmus1
|
IntuitionThe first observation to make is that the num arrays are strictly increasing. This means that we have no repeat integers and we can traverse using two
|
johnathant
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-06T10:14:07.322732+00:00
|
2025-02-06T10:14:07.322732+00:00
| 52 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
The first observation to make is that the num arrays are strictly increasing. This means that we have no repeat integers and we can traverse using two pointers.
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
We are given two sorted lists and we want to find at what indices these lists have the same value. We make two pointers both pointing to the 0th index of the list.
If at index1 of nums1 and index2 of nums2, the value aren't the same, increment the index of the smaller value. While doing this, keep track of a score for nums1 and nums2 array, accumulating the score if it's the smaller value.
If the values at index1 of nums1 and index2 of nums2 are equal, then we need to determine what happens if the arrays jump paths. In order to determine the maximum path for nums1, we can greedily compare the scores of our paths up to index1 and index2. We can then set our scores for nums1 and nums2 to be equal to that maximum path, since it's always better to take that max path to reach a certain number.
Once we reach a point where index1 or index2 are outside the range of their respective array, compute the score for the array that still has nodes, then return the largest value modulo $1e^9+7$.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
O(n)
- Space complexity:
O(1)
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def maxSum(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> int:
mod = int(1e9+7)
score1 = 0
score2= 0
index1 = 0
index2 = 0
res = 0
while index1 < len(nums1) and index2 < len(nums2):
if nums1[index1] < nums2[index2] :
score1+=nums1[index1]
index1+=1
elif nums1[index1] > nums2[index2] :
score2+=nums2[index2]
index2+=1
else:
score2 = max(score2+nums1[index1],score1+nums1[index1])
score1 = score2
index2+=1
index1+=1
while index1<len(nums1):
score1+=nums1[index1]
index1+=1
while index2<len(nums2):
score2+=nums2[index2]
index2+=1
res = max(score1, score2)
return res % mod
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
🚀LeetCode Solution: Max Sum of Two Sorted Arrays 🔥 (100% Time Complexity Beat)
|
leetcode-solution-max-sum-of-two-sorted-bzinu
|
🚀 LeetCode Solution: Max Sum of Two Sorted Arrays 🔥 (100% Time Complexity Beat)💡 IntuitionThe problem revolves around maximizing the sum when traversing two sor
|
saiji07
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-17T19:33:23.204306+00:00
|
2025-01-17T19:33:23.204306+00:00
| 94 | false |
### 🚀 **LeetCode Solution: Max Sum of Two Sorted Arrays** 🔥 (100% Time Complexity Beat)
---
### **💡 Intuition**
The problem revolves around maximizing the sum when traversing two sorted arrays. Since the arrays are sorted, we can leverage a two-pointer approach to effectively navigate and compare their elements while accumulating the maximum possible sum.
---
### **🛠️ Approach**
1. **Two-Pointer Traversal**:
Utilize two pointers (`i` and `j`) to traverse `nums1` and `nums2`.
- Accumulate values in `sum1` and `sum2` for elements unique to each array.
- If the current elements of both arrays are equal, add the maximum of `sum1` and `sum2` plus the common element to the result. Reset both sums.
2. **Remaining Elements**:
After traversal, add the remaining sums from the arrays to the result.
3. **Modulo Operation**:
To handle large sums, use a modulo operation (`mod = 10^9 + 7`) at every step.
4. **Return Result**:
The final `res` holds the maximum sum of paths.
---
### **⏱️ Complexity**
- **Time Complexity**:
$$O(n + m)$$
Since we traverse both arrays exactly once, the time complexity is linear in terms of their combined size.
- **Space Complexity**:
$$O(1)$$
Only a constant amount of space is used for pointers and variables.
---
### **💻 Code**
```cpp
class Solution {
public:
const long long int mod = 1000000007;
int maxSum(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
long long int sum1 = 0, sum2 = 0, res = 0;
long long int i = 0, j = 0, n = nums1.size(), m = nums2.size();
while (i < n && j < m) {
if (nums1[i] < nums2[j]) {
sum1 += nums1[i++];
} else if (nums1[i] > nums2[j]) {
sum2 += nums2[j++];
} else {
// Merge paths at common element
res = (res + max(sum1, sum2) + nums1[i]) % mod;
i++;
j++;
sum1 = 0;
sum2 = 0;
}
}
// Add remaining elements
while (i < n) sum1 += nums1[i++];
while (j < m) sum2 += nums2[j++];
// Add the maximum of the remaining sums
res = (res + max(sum1, sum2)) % mod;
return res;
}
};
```
---
### **✨ Why This Solution is Unique?**
- **Efficient Design**: Combines two-pointer traversal with modular arithmetic for optimized performance.
- **Intuitive Flow**: Handles common elements and remaining elements seamlessly, ensuring correctness and clarity.
- **Optimized**: Consistently beats **100% in time complexity** on LeetCode due to its linear approach.
---
### **🌟 Key Highlights**
- **Dynamic Comparison**: Maximizes the result dynamically at every common element.
- **Modular Arithmetic**: Handles potential overflow issues with `mod`.
- **Linear Complexity**: Highly efficient for large input sizes.
---
### 🏆 **Results**
- 🟢 **100% faster than all submissions!**
- 🟢 **Space usage is minimal (constant space).**
---
Enjoy coding and happy problem-solving! 🚀
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Two Pointers', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Greedy', 'C++']
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
Java|| python||c++ || Two Pointer || EASY TO UNDERSTAND||
|
java-pythonc-two-pointer-easy-to-underst-q4h6
|
Intuition\n\nWe will use two pointers to traverse each array and two variables (sum1 and sum2) to keep track of the cumulative sums for each array. Whenever we
|
amann5153
|
NORMAL
|
2024-05-22T00:26:34.120893+00:00
|
2024-09-01T19:55:16.248183+00:00
| 111 | false |
# Intuition\n\nWe will use two pointers to traverse each array and two variables (sum1 and sum2) to keep track of the cumulative sums for each array. Whenever we encounter the same element in both arrays, we will assign sum1 = sum2 = Math.max(sum1, sum2) + nums1[i] to ensure we take the maximum possible sum path.\n\n# Approach\n1. Initialize two pointers, one for each array.\n2. Traverse the arrays with the following logic:\n- If nums1[i] < nums2[j], add nums1[i] to sum1 and increment i.\n- If nums1[i] > nums2[j], add nums2[j] to sum2 and increment j.\n- If the elements are equal, update both sums to the maximum of sum1 and sum2, add the current element, and increment both pointers.\n\n3. After the loop, add any remaining elements in either array to their respective sums.\n4. Return the maximum of the two sums modulo 10^9+7\n\n# Complexity\n\n**Time complexity:\n** \nO(m+n) since we traverse both arrays simultaneously.\n\n**Space complexity:\n**\nO(1) because no extra space is used.\n\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int maxSum(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {\n int mod = (int)1e9+7;\n\n int i=0, j=0;\n long sum1=0, sum2=0;\n int n = nums1.length, m = nums2.length;\n \n \n while(i<n && j<m){\n if(nums1[i] < nums2[j]){\n sum1 += nums1[i++];\n } \n else if(nums1[i] > nums2[j]){\n sum2 += nums2[j++];\n }\n else{\n sum1 = sum2 = Math.max(sum1, sum2) + nums1[i];\n i++;\n j++;\n }\n\n }\n\n while(i<n){\n sum1 += nums1[i++];\n }\n\n while(j<m){\n sum2 += nums2[j++];\n }\n\n return (int)(Math.max(sum1, sum2) % mod);\n }\n}\n```\n```python []\nclass Solution:\n def maxSum(self, nums1, nums2):\n mod = int(1e9+7)\n \n i, j = 0, 0\n sum1, sum2 = 0, 0\n n, m = len(nums1), len(nums2)\n \n while i < n and j < m:\n if nums1[i] < nums2[j]:\n sum1 += nums1[i]\n i += 1\n elif nums1[i] > nums2[j]:\n sum2 += nums2[j]\n j += 1\n else:\n sum1 = sum2 = max(sum1, sum2) + nums1[i]\n i += 1\n j += 1\n \n while i < n:\n sum1 += nums1[i]\n i += 1\n \n while j < m:\n sum2 += nums2[j]\n j += 1\n \n return int(max(sum1, sum2) % mod)\n\n```\n```c++ []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxSum(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {\n int mod = 1e9 + 7;\n \n int i = 0, j = 0;\n long long sum1 = 0, sum2 = 0;\n int n = nums1.size(), m = nums2.size();\n \n while (i < n && j < m) {\n if (nums1[i] < nums2[j]) {\n sum1 += nums1[i++];\n } else if (nums1[i] > nums2[j]) {\n sum2 += nums2[j++];\n } else {\n sum1 = sum2 = max(sum1, sum2) + nums1[i];\n i++;\n j++;\n }\n }\n \n while (i < n) {\n sum1 += nums1[i++];\n }\n \n while (j < m) {\n sum2 += nums2[j++];\n }\n \n return static_cast<int>(max(sum1, sum2) % mod);\n }\n};\n\n```\n\n
| 1 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java']
| 2 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
C++ Two Pointer approach explained.
|
c-two-pointer-approach-explained-by-obos-caut
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nThis problem can be solved using a two pointer approach\n# Approach\n Describe your app
|
Obose
|
NORMAL
|
2023-01-29T19:01:19.998477+00:00
|
2023-01-29T19:01:19.998512+00:00
| 105 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThis problem can be solved using a two pointer approach\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nThe approach for this problem is to use two pointers, one for each array. We will compare the elements from both the arrays at each iteration, and move the pointer ahead accordingly. We will also keep track of the maximum sum of elements from both the arrays at each iteration and take the maximum of the two sums. Finally, we will return the maximum of the two sums.\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n + m)$$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nWe iterate through both the arrays once, so the time complexity is equal to the sum of the lengths of the arrays.\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\nWe only use constant space, so the space complexity is O(1).\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxSum(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {\n int i = 0, j = 0, n = nums1.size(), m = nums2.size(), mod = 1e9 + 7;\n long a = 0, b = 0;\n while (i < n || j < m) {\n if (i < n && (j == m || nums1[i] < nums2[j])) {\n a += nums1[i++];\n } else if (j < m && (i == n || nums1[i] > nums2[j])) {\n b += nums2[j++];\n } else {\n a = b = max(a, b) + nums1[i];\n i++, j++;\n }\n }\n return max(a, b) % mod;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Two Pointers', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Greedy', 'C++']
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
C++ || Easiest Explanation || Prefix Sum + Two pointer + Greedy Approach
|
c-easiest-explanation-prefix-sum-two-poi-nziy
|
\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity : O(N)\n\n- Space complexity : O(N)\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n typedef long long ll;\n\n const ll M = 1e
|
anu_2021
|
NORMAL
|
2022-12-13T15:30:43.189492+00:00
|
2022-12-13T15:30:43.189520+00:00
| 102 | false |
\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity : O(N)\n\n- Space complexity : O(N)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n typedef long long ll;\n\n const ll M = 1e9 + 7;\n\n ll mod(ll a){\n return ((a%M)+M)%M;\n }\n ll mul(ll a,ll b){\n return mod(mod(a)*mod(b));\n }\n ll add(ll a,ll b){\n return mod(mod(a)+mod(b));\n }\n\n vector<ll>calc_prefix_sum(vector<int>&nums){\n int n = nums.size();\n vector<ll>psum(n,0LL);\n psum[0] = (ll)nums[0];\n for(int i=1;i<n;i++){\n psum[i] = psum[i-1] + (ll)nums[i];\n }\n return psum;\n }\n\n vector<ll>calc_suffix_sum(vector<int>&nums){\n int n = nums.size();\n vector<ll>ssum(n,0LL);\n ssum[n-1] = (ll)nums[n-1];\n for(ll i=n-2;i>=0;i--){\n ssum[i] = ssum[i+1] + (ll)nums[i];\n }\n return ssum;\n }\n\n int maxSum(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {\n\n int m = nums1.size();\n int n = nums2.size();\n\n vector<pair<int,int>>critical;\n\n nums1.push_back(1e9);\n nums2.push_back(1e9);\n nums1.insert(nums1.begin(),0);\n nums2.insert(nums2.begin(),0);\n\n m+=2;\n n+=2;\n\n int i=0,j=0;\n\n while(i<m && j<n){\n if(nums1[i] > nums2[j]){\n j++;\n }\n else if(nums1[i] < nums2[j]){\n i++;\n }\n else{\n critical.push_back({i,j});\n i++;\n j++;\n }\n }\n\n nums1[m-1] = 0;\n nums2[n-1] = 0;\n\n vector<ll>prefix1 = calc_prefix_sum(nums1);\n vector<ll>prefix2 = calc_prefix_sum(nums2);\n\n ll maximum_sum = 0LL;\n int sz = critical.size();\n\n for(int i=0;i<sz-1;i++){\n int i1 = critical[i].first;\n int j1 = critical[i].second;\n int i2 = critical[i+1].first;\n int j2 = critical[i+1].second;\n ll path1 = prefix1[i2] - prefix1[i1];\n ll path2 = prefix2[j2] - prefix2[j1];\n maximum_sum += max(path1,path2);\n }\n\n return mod(maximum_sum);\n\n }\n};\n\n/*\n\n1 3 5 7 9\n3 5 100\n\n2 4 5 8 10\n4 6 8 9\n\nWe can switch between these two arrays as many times as we want.\n\nGoal : Maximum score of the path by toggling between two arrays if possible.\n\nMoves : nums1[i] == nums2[j] i-->j / j-->i\n\nCritical Points : where nums1[i] == nums2[j]\n\n 2 4 5 8 10 -1\n 4 6 8 9 -1\n\n 6 + 14 + 10\n\n Algorithm :\n\n First store all the critical points in an array , critical(c)\n\n c[k] = {i,j} pair of indices where two array elements matches with each other.\n\n 0 2 4 5 8 10 0\n 0 4 6 8 9 0\n \n c[0] = {0,0}\n c[1] = {2,1}\n c[2] = {4,3}\n c[3] = {6,5}\n\n we will precompute the prefix sums for both the arrays and finally we need to calculate the maximum segment in between two critical point indices .\n\n c[i] c[i+1] c[i+2] .... \n\n*/\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Two Pointers', 'Greedy', 'Prefix Sum', 'C++']
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
[Python] Two Pointers - Prefix sum - CLEAN
|
python-two-pointers-prefix-sum-clean-by-irj4j
|
\nclass Solution:\n def maxSum(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> int:\n MODULO = 10**9 + 7\n n1, n2 = len(nums1), len(nums2)\n
|
Thinh911
|
NORMAL
|
2022-12-05T19:21:05.090302+00:00
|
2022-12-05T19:21:05.090338+00:00
| 99 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def maxSum(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> int:\n MODULO = 10**9 + 7\n n1, n2 = len(nums1), len(nums2)\n i1, i2 = 0, 0\n # Prefix sum leading up to the "jumping point". \n # Reset to zero after the jump.\n sum1, sum2 = 0, 0 \n # The max score, summed up and modded\n max_sum = 0\n \n while i1 < n1 or i2 < n2:\n # If arr2 is exhausted or value at i1 is less than i2.\n # Move the i1 pointer forward, add value at i1 to prefix sum1.\n if i2 == n2 or (i1 < n1 and nums1[i1] < nums2[i2]):\n sum1 += nums1[i1]\n i1 += 1\n # If arr1 is exhausted or value at i2 is less than i1.\n # Move the i2 pointer forward, add value at i2 to prefix sum2. \n elif i1 == n1 or (i2 < n2 and nums2[i2] < nums1[i1]):\n sum2 += nums2[i2]\n i2 += 1\n # Add the larger of the two prefix_sums to the max_sum.\n # Advance both i1 and i2 pointers. \n else:\n max_sum += max(sum1, sum2) + nums1[i1]\n max_sum %= MODULO\n sum1, sum2 = 0, 0 \n i1 += 1\n i2 += 1\n \n # Add the larger of the two suffix_sums to the results. \n max_sum += max(sum1, sum2)\n return max_sum % MODULO\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'Prefix Sum', 'Python']
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
java
|
java-by-anilkumawat3104-ry4v
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int maxSum(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {\n int i=0;\n int j=0;\n long ans1 = 0;\n long ans2 = 0;\n
|
anilkumawat3104
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-04T10:53:15.329289+00:00
|
2022-08-04T10:53:15.329362+00:00
| 86 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int maxSum(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {\n int i=0;\n int j=0;\n long ans1 = 0;\n long ans2 = 0;\n long ans = 0;\n while(i!=nums1.length&&j!=nums2.length){\n if(nums1[i]>nums2[j])\n ans2 += nums2[j++];\n else if(nums1[i]<nums2[j])\n ans1 += nums1[i++];\n else{\n ans+=Math.max(ans1,ans2)+nums1[i];\n i++;\n j++;\n ans1=0;\n ans2=0;\n }\n }\n while(i!=nums1.length){\n ans1 += nums1[i];\n i++;\n }\n while(j!=nums2.length){\n ans2 += nums2[j];\n j++;\n }\n ans += Math.max(ans1,ans2);\n return (int)(ans%((int)Math.pow(10,9)+7));\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Two Pointers']
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
C++ || Two Pointers || Set || Greedy ✔✔
|
c-two-pointers-set-greedy-by-vardman-dbma
|
\n const int mod = 1e9 + 7;\n \n\t class Solution {\n\t public:\n\t\t int maxSum(vector& nums1, vector& nums2) {\n \n set s;\n for(int i
|
VarDMan
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-06T14:24:20.406267+00:00
|
2022-07-06T14:24:20.406303+00:00
| 429 | false |
\n const int mod = 1e9 + 7;\n \n\t class Solution {\n\t public:\n\t\t int maxSum(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {\n \n set<int> s;\n for(int i : nums2){\n\t\t s.insert(i);\n\t\t }\n \n long long int a = 0 , b = 0 , j = 0 , m = nums1.size() , n = nums2.size() , cnt = 0;\n for(int i=0;i<m;i++){\n a += nums1[i]%mod;\n if(s.count(nums1[i])){\n while(j < n && nums2[j] != nums1[i]){\n b += nums2[j++]%mod;\n }\n b += nums2[j++]%mod;\n cnt += max(a , b);\n a = 0 , b = 0;\n }\n }\n \n while(j < n){\n b += nums2[j++] % mod; \n }\n cnt += max(a , b) % mod;\n return cnt%mod; \n }\n };
| 1 | 0 |
['Greedy', 'C', 'Ordered Set', 'C++']
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
C++|| TC-O(N), SC-O(1)|| very easy code
|
c-tc-on-sc-o1-very-easy-code-by-blue_tig-ubrx
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxSum(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {\n int n=nums1.size(),m=nums2.size();\n long long ans=0,mod=1
|
Blue_tiger
|
NORMAL
|
2022-06-08T19:45:39.405803+00:00
|
2022-06-08T19:45:39.405836+00:00
| 144 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxSum(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {\n int n=nums1.size(),m=nums2.size();\n long long ans=0,mod=1e9+7;\n int i=0,j=0;\n long long sum1=0,sum2=0;\n while(i<n && j<m)\n {\n if(nums1[i]==nums2[j])\n {\n sum1+=nums1[i],sum2+=nums2[j];\n ans=(ans+max(sum1,sum2))%mod;\n i++,j++;\n sum1=0,sum2=0;\n }\n else if(nums1[i]<nums2[j])\n {\n sum1+=nums1[i];\n i++;\n }\n else {\n sum2+=nums2[j];\n j++;\n }\n }\n while(i<n)\n {\n sum1+=nums1[i++];\n }\n while(j<m) sum2+=nums2[j++];\n ans=(ans+max(sum1,sum2))%mod;\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Two Pointers']
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
python 3 || two-pointers || O(m + n)/O(1)
|
python-3-two-pointers-om-no1-by-derek-y-vxnk
|
```\nclass Solution:\n def maxSum(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> int:\n i = j = score1 = score2 = maxScore = 0\n m, n = len(nums1
|
derek-y
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-16T05:42:41.745000+00:00
|
2022-05-16T05:42:41.745030+00:00
| 151 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def maxSum(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> int:\n i = j = score1 = score2 = maxScore = 0\n m, n = len(nums1), len(nums2)\n MOD = 10 ** 9 + 7\n \n while i < m and j < n:\n if nums1[i] < nums2[j]:\n score1 += nums1[i]\n i += 1\n elif nums1[i] > nums2[j]:\n score2 += nums2[j]\n j += 1\n else:\n maxScore += nums1[i] + max(score1, score2)\n maxScore %= MOD\n score1 = score2 = 0\n i += 1\n j += 1\n \n while i < m:\n score1 += nums1[i]\n i += 1\n while j < n:\n score2 += nums2[j]\n j += 1\n \n maxScore += max(score1, score2)\n return maxScore % MOD
| 1 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'Greedy', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
Java | Simple Greedy Solution | Time: O(n) | Space: O(1)
|
java-simple-greedy-solution-time-on-spac-z46g
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int maxSum(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {\n int MOD = (int) Math.pow(10,9) + 7;\n int p1 = 0, p2 = 0;\n long s1
|
chelsy
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-02T19:06:33.703358+00:00
|
2022-05-02T19:06:33.703390+00:00
| 222 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int maxSum(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {\n int MOD = (int) Math.pow(10,9) + 7;\n int p1 = 0, p2 = 0;\n long s1 = 0, s2 = 0;\n long maxScore = 0;\n \n while(p1 < nums1.length && p2 < nums2.length) {\n if(nums1[p1] < nums2[p2]) {\n s1 += nums1[p1];\n p1++;\n }\n else if(nums1[p1] > nums2[p2]) {\n s2 += nums2[p2];\n p2++;\n }\n else {\n maxScore += Math.max(s1, s2) + nums1[p1];\n maxScore %= MOD;\n s1 = s2 = 0;\n p1++;\n p2++;\n }\n }\n \n while(p1 < nums1.length) s1 += nums1[p1++];\n while(p2 < nums2.length) s2 += nums2[p2++];\n \n maxScore += Math.max(s1, s2);\n maxScore %= MOD;\n \n return (int) maxScore;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
Python 100,100 O(2*min(n,m)), O(1) simple with explanation
|
python-100100-o2minnm-o1-simple-with-exp-2x38
|
Logic:\nkeep two values v1,v2 which represent the max value of ending on that list\ni.e.:\nl1=[1,2,3,6] -> ending on l1 will give a max end val of v1=sum(5,4,3,
|
Occy88
|
NORMAL
|
2022-03-26T16:52:55.470395+00:00
|
2022-03-26T17:04:06.086776+00:00
| 76 | false |
Logic:\nkeep two values v1,v2 which represent the max value of ending on that list\ni.e.:\nl1=[1,2,3,6] -> ending on l1 will give a max end val of v1=sum(5,4,3,2,1)\nl2=[3,4,5] -> ending on l2 will give a max end val of v2=sum(5,4,3)\n\nwhile both lists are not empty:\n\t1. if end vals not the same remove the largest ending element and add it to the corresponding value representing that list\n\t2. if the values are the same then set v1,v2 to the max of v1,v2 + the number (that is the same)\n\t\nfinally sum the remaining non-empty list to it\'s value\n\nresponse is max of v1,v2.\n\n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maxSum(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> int:\n v1=v2=0\n while nums2 and nums1:\n if nums1[-1]>nums2[-1]:\n v1+=nums1.pop()\n elif nums1[-1]<nums2[-1]:\n v2+=nums2.pop()\n else:\n v1=v2=max(v1,v2)+nums1.pop()\n nums2.pop()\n v2+=sum(nums2)\n v1+=sum(nums1)\n return max(v1,v2)%1000000007\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
[Merge Two Sorted Arrays] Simple C++ Solution
|
merge-two-sorted-arrays-simple-c-solutio-qcgp
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n\t// at common point just compare the sum of two arrays calculated so far and assign maximum to the\n\t// our result variable and
|
TheWorld
|
NORMAL
|
2022-02-01T16:55:21.549784+00:00
|
2022-02-01T16:55:21.549831+00:00
| 119 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n\t// at common point just compare the sum of two arrays calculated so far and assign maximum to the\n\t// our result variable and make both sum values as 0 to start calculating again from that common point\n\n int maxSum(vector<int>& arr1, vector<int>& arr2) {\n \n long i=0,j=0,sum1=0,sum2=0,result=0;\n long m=arr1.size();\n long n=arr2.size();\n while(i<m && j<n)\n {\n if(arr1[i]==arr2[j])\n {\n result=result+max(sum1,sum2)+arr1[i];\n i++;j++;\n sum1=0;sum2=0;\n }\n else if(arr1[i]<arr2[j])\n {\n sum1=sum1+arr1[i];\n i++;\n }\n else\n {\n sum2=sum2+arr2[j];\n j++;\n }\n }\n while(i<m)\n {\n sum1=sum1+arr1[i];\n i++;\n }\n while(j<n)\n {\n sum2=sum2+arr2[j];\n j++;\n }\n if(sum1!=0 || sum2!=0)\n {\n result=result+max(sum1,sum2);\n }\n return result%(1000000007);\n \n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
C++ | Pure Recursion | explained with Intuition | 80ms | faster than 98.68%
|
c-pure-recursion-explained-with-intuitio-u5dm
|
----------------------------------------------Intuition:----------------------------------------\n\nI have to take all elements from array while i didn\'t find
|
prit_manvar
|
NORMAL
|
2021-12-24T06:34:27.865578+00:00
|
2021-12-24T06:34:54.713089+00:00
| 210 | false |
----------------------------------------------**Intuition:**----------------------------------------\n\nI have to take **all elements** from array while i **didn\'t find same element in another array**.\nbecause i can **move to another array if and only if there is same element in both.**\n\nso if i suppose element at **index \'i\' and \'j\' are present in another array** and elements between \'i\' and \'j\' are not present then i will consider **elements from \'i+1\' to \'j\' as single block** and i have to find **max sum using this array of blocks**.\n\n\n\n---------------------------------------------**Approch:**--------------------------------------------\n1. i will count **sum of every block** and store that in another vector. I will do this for the both vector which are given.\n\n2. i have to find **max score using this new arrays**. and at every point i have **2 choices i can take element from array1 or array2**. but to get max score i will **take element which is larger.**\n\n```\nclass Solution {\nprivate:\n int N = 1000000007;\n int getMaxSum(vector<long long>& arr1, vector<long long>& arr2, int n){\n if(n == 0)\n return 0;\n \n long long sum = getMaxSum(arr1,arr2,n-1);\n \n // at this point i have 2 choice \n // i can take element from arr1 or arr2 and i will take larger element from it.\n sum = (sum + max(arr1[n-1],arr2[n-1]))%N;\n \n return sum;\n }\npublic:\n int maxSum(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {\n vector<long long> arr1, arr2; // to store sum of blocks\n long long sum1 = 0, sum2 = 0; // sum of current block\n int n1 = nums1.size(), n2 = nums2.size();\n int i = 0, j = 0;\n \n while(i < n1 && j < n2){\n // if at this point element is present in both array then it is end of the block so add sum into arrays and reset the sum.\n \n // elese i will go to the next element in the array with smaller element to get next same element.\n if(nums1[i] == nums2[j]){ \n sum1 = (sum1+nums1[i]);\n sum2 = (sum2+nums2[j]);\n \n arr1.push_back(sum1);\n arr2.push_back(sum2);\n sum1 = sum2 = 0;\n \n i++,j++;\n }else if(nums1[i] < nums2[j]){\n sum1 = (sum1+nums1[i]);\n i++;\n }else{\n sum2 = (sum2+nums2[j]);\n j++;\n }\n }\n while(i < n1){\n sum1 = (sum1+nums1[i]);\n i++;\n }\n while(j < n2){\n sum2 = (sum2+nums2[j]);\n j++;\n }\n arr1.push_back(sum1);\n arr2.push_back(sum2);\n \n return getMaxSum(arr1,arr2,arr1.size()); // to get max score.\n }\n};\n\n```\n
| 1 | 1 |
['Recursion', 'C']
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
Python Two pointers beats 97% time 95% space
|
python-two-pointers-beats-97-time-95-spa-6guo
|
O(M + N) time complexity, O(1) space complexity\n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maxSum(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> int:\n i, j, m , n =
|
totoslg
|
NORMAL
|
2021-11-17T06:43:44.494930+00:00
|
2021-11-17T06:43:44.494964+00:00
| 178 | false |
O(M + N) time complexity, O(1) space complexity\n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maxSum(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> int:\n i, j, m , n = 0, 0, len(nums1), len(nums2)\n curNums1Sum, curNums2Sum = 0, 0\n \n while i < m and j < n:\n if nums1[i] < nums2[j]:\n curNums1Sum += nums1[i]\n i += 1\n elif nums1[i] > nums2[j]:\n curNums2Sum += nums2[j]\n j += 1\n else:\n curNums1Sum = curNums2Sum = max(curNums1Sum, curNums2Sum) + nums1[i]\n i += 1\n j += 1\n \n curNums1Sum += sum(nums1[i:])\n curNums2Sum += sum(nums2[j:])\n \n return max(curNums1Sum, curNums2Sum) % (10**9 + 7)
| 1 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'Python']
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
C# two pointers, beats 100%
|
c-two-pointers-beats-100-by-rajujain33-e8tx
|
\npublic class Solution {\n public int MaxSum(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {\n int i=0;\n int j=0;\n long a = 0;\n long b = 0;\n
|
rajujain33
|
NORMAL
|
2021-10-17T11:53:51.977648+00:00
|
2021-10-17T11:53:51.977689+00:00
| 112 | false |
```\npublic class Solution {\n public int MaxSum(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {\n int i=0;\n int j=0;\n long a = 0;\n long b = 0;\n long mod = (long)1e9+7;\n while(i<nums1.Length || j<nums2.Length){\n if(i<nums1.Length && (j == nums2.Length || nums1[i]<nums2[j])){\n a+=(nums1[i++]);\n }\n else if(j<nums2.Length &&( i == nums1.Length || nums2[j]<nums1[i])){\n b+=(nums2[j++]);\n }\n else{\n a = b = (Math.Max(a,b) + nums1[i]);\n i++;\n j++;\n }\n }\n return (int) (Math.Max(a,b)%mod);\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
C++||easy and clean greedy approach.
|
ceasy-and-clean-greedy-approach-by-shubh-64zd
|
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxSum(vector& nums1, vector& nums2) {\n long long int ansa = 0;\n long long int ansb = 0;\n int i
|
Shubham-Khare
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-20T14:26:07.280945+00:00
|
2021-07-20T14:26:07.280986+00:00
| 130 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxSum(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {\n long long int ansa = 0;\n long long int ansb = 0;\n int i =0;\n int j =0;\n while(i<nums1.size()&&j<nums2.size()){\n if(nums1[i]<nums2[j]){\n ansa+=nums1[i];\n i++;\n }\n else if(nums1[i]>nums2[j]){\n ansb+=nums2[j];\n j++;\n }\n else {\n long long int temp = max(ansa,ansb);\n ansa=temp+nums1[i];\n ansb=temp+nums2[j];\n i++;\n j++;\n }\n }\n while(i<nums1.size()) {\n ansa+=nums1[i];\n i++;\n }\n while(j<nums2.size()){\n ansb+=nums2[j];\n j++;\n }\n return max(ansa,ansb)%1000000007;\n }\n};\n
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
O(n) C++ Solution , Greedy Approach : )
|
on-c-solution-greedy-approach-by-avnish0-sblu
|
\tint maxSum(vector& nums1, vector& nums2) {\n long long int a=0,b=0;\n long long int ans =0;\n int i = 0, j = 0;\n int n = nums1.si
|
avnish0900
|
NORMAL
|
2021-06-30T04:35:19.796159+00:00
|
2021-06-30T04:35:19.796201+00:00
| 150 | false |
\tint maxSum(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {\n long long int a=0,b=0;\n long long int ans =0;\n int i = 0, j = 0;\n int n = nums1.size(), m = nums2.size();\n while(i<n and j<m){\n if(nums1[i] < nums2[j]){\n a+=nums1[i];\n i++;\n }\n else if(nums1[i] > nums2[j]){\n b+=nums2[j];\n j++;\n }\n else{\n ans = ans+ max(a,b) + nums1[i];\n a=0,b=0;i++;j++;\n }\n }\n while(i<n) a+=nums1[i++];\n while(j<m) b+=nums2[j++];\n ans+= max(a,b);\n ans%=1000000007;\n return ans;\n }
| 1 | 1 |
['Two Pointers', 'Dynamic Programming', 'C']
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
C++ O(M+N) Time O(1) Space 8 Line Solution
|
c-omn-time-o1-space-8-line-solution-by-m-5pqy
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxSum(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {\n long sum1 = 0, sum2 = 0, ptr1 = 0, ptr2 = 0, lim = (long)10000000
|
manitbaser
|
NORMAL
|
2021-06-28T11:07:44.159793+00:00
|
2021-06-28T11:07:44.159829+00:00
| 96 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxSum(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {\n long sum1 = 0, sum2 = 0, ptr1 = 0, ptr2 = 0, lim = (long)1000000007;\n while(ptr1<nums1.size() && ptr2<nums2.size())\n if(nums1[ptr1]==nums2[ptr2]) sum2 = sum1 = max(sum1, sum2) + nums1[ptr1++], ptr2++;\n else if(nums1[ptr1]<nums2[ptr2]) sum1+=nums1[ptr1++];\n else sum2+=nums2[ptr2++];\n while(ptr1<nums1.size()) sum1+=nums1[ptr1++];\n while(ptr2<nums2.size()) sum2+=nums2[ptr2++];\n return max(sum1,sum2)%lim;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
C++ 2 pointer Solution 97% Simple Solution
|
c-2-pointer-solution-97-simple-solution-9uhae
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxSum(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {\n long long num1sum=0,num2sum=0,globalsum=0,i=0,j=0,n=nums1.size(),
|
hitengoyal18
|
NORMAL
|
2021-04-04T06:17:21.531483+00:00
|
2021-04-04T06:17:21.531525+00:00
| 214 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxSum(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {\n long long num1sum=0,num2sum=0,globalsum=0,i=0,j=0,n=nums1.size(),m=nums2.size();\n \n while(i<n && j<m){\n if(nums1[i]<nums2[j])\n num1sum+=nums1[i++];\n \n else if(nums1[i]>nums2[j])\n num2sum+=nums2[j++];\n \n else{\n globalsum += max(num1sum,num2sum) + nums1[i];\n num1sum=0;\n num2sum=0;\n i++;\n j++;\n }\n \n }\n \n while (i < n) num1sum += nums1[i++];\n while (j < m) num2sum+= nums2[j++];\n globalsum += max(num1sum,num2sum);\n return globalsum % 1000000007;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'C', 'Merge Sort', 'C++']
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
C++ 2 solutions
|
c-2-solutions-by-nc-d5pl
|
My first solution based on DP\n\nclass Solution {\n unordered_map<int, int> idx1, idx2;\n vector<long long> dp1, dp2;\n int MOD = 1e9+7;\n \n lon
|
nc_
|
NORMAL
|
2021-03-06T16:07:41.115984+00:00
|
2021-03-06T16:07:41.116010+00:00
| 123 | false |
My first solution based on DP\n```\nclass Solution {\n unordered_map<int, int> idx1, idx2;\n vector<long long> dp1, dp2;\n int MOD = 1e9+7;\n \n long long helper1(const vector<int>& nums1, const vector<int>& nums2, int i) {\n if (i < 0) return 0;\n if (dp1[i]) return dp1[i];\n \n dp1[i] = helper1(nums1, nums2, i-1);\n if (idx2.count(nums1[i])) {\n dp1[i] = max(dp1[i], helper2(nums1, nums2, idx2[nums1[i]]-1));\n }\n \n return dp1[i] = (dp1[i] + static_cast<long long>(nums1[i]));\n }\n \n long long helper2(const vector<int>& nums1, const vector<int>& nums2, int i) {\n if (i < 0) return 0;\n if (dp2[i]) return dp2[i];\n \n dp2[i] = helper2(nums1, nums2, i-1);\n if (idx1.count(nums2[i])) {\n dp2[i] = max(dp2[i], helper1(nums1, nums2, idx1[nums2[i]]-1));\n }\n \n return dp2[i] = (dp2[i] + static_cast<long long>(nums2[i]));\n }\n \npublic:\n int maxSum(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) { \n for (int i = 0; i < nums1.size(); ++i)\n idx1[nums1[i]] = i;\n for (int i = 0; i < nums2.size(); ++i)\n idx2[nums2[i]] = i;\n \n dp1 = vector<long long>(nums1.size(), 0);\n dp2 = vector<long long>(nums2.size(), 0);\n \n return max(helper1(nums1, nums2, nums1.size()-1), helper2(nums1, nums2, nums2.size()-1)) % MOD;\n }\n};\n```\n\n2 pointer solution based on merging\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxSum(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {\n long long up = 0, down = 0;\n int i = 0, j = 0;\n int m = nums1.size(), n = nums2.size();\n \n while (i < m && j < n) {\n if (nums1[i] < nums2[j]) {\n up += nums1[i++];\n } else if (nums2[j] < nums1[i]) {\n down += nums2[j++];\n } else {\n up = down = max(up, down) + nums1[i];\n ++i, ++j;\n }\n }\n \n while (i < m) up += nums1[i++];\n while (j < n) down += nums2[j++];\n \n return max(up, down) % 1000000007;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
[Python 3]
|
python-3-by-bakerston-2971
|
\n def maxSum(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> int:\n s1, s2 = [0], [0]\n cur = 0\n for n in nums1:\n cur += n\n
|
Bakerston
|
NORMAL
|
2021-03-02T18:37:38.933375+00:00
|
2021-03-02T18:37:38.933410+00:00
| 85 | false |
```\n def maxSum(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> int:\n s1, s2 = [0], [0]\n cur = 0\n for n in nums1:\n cur += n\n s1.append(cur)\n cur = 0\n for n in nums2:\n cur += n\n s2.append(cur)\n portal, i , j m, n = [], 0, 0, len(nums1), len(nums2)\n while i < m and j < n:\n if nums1[i] < nums2[j]:\n i += 1\n elif nums1[i] > nums2[j]:\n j += 1\n else:\n portal.append([i, j])\n i += 1\n j += 1\n if not portal:\n return max(s1[-1], s2[-1])\n l, idx, ans = len(portal), 0, max(s1[portal[idx][0]], s2[portal[idx][1]])\n while idx < l - 1:\n ans += max(s1[portal[idx + 1][0]] - s1[portal[idx][0]], s2[portal[idx + 1][1]] - s2[portal[idx][1]])\n idx += 1\n ans += max(s1[-1] - s1[portal[-1][0]], s2[-1] - s2[portal[-1][1]])\n return ans % (10 ** 9 + 7)\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
Python Solution
|
python-solution-by-mbylzy-86o2
|
Runtime: 544 ms, faster than 99.46% of Python3 online submissions for Get the Maximum Score.\n* Memory Usage: 27.3 MB, less than 41.85% of Python3 online submis
|
mbylzy
|
NORMAL
|
2021-02-11T08:23:41.825999+00:00
|
2021-02-11T08:23:41.826042+00:00
| 111 | false |
* Runtime: 544 ms, faster than 99.46% of Python3 online submissions for Get the Maximum Score.\n* Memory Usage: 27.3 MB, less than 41.85% of Python3 online submissions for Get the Maximum Score.\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maxSum(self, nums1: List[int], nums2: List[int]) -> int:\n from bisect import bisect\n common=sorted(set(nums1)&set(nums2))\n if(not common):\n return max(sum(nums1),sum(nums2))%(10**9+7)\n else:\n ret = 0\n i1 = 0\n i2 = 0\n for c in common:\n j1 = bisect(nums1,c,i1)\n j2 = bisect(nums2,c,i2)\n ret += max(sum(nums1[i1:j1]),sum(nums2[i2:j2]))\n i1 = j1\n i2 = j2\n ret += max(sum(nums1[i1:]),sum(nums2[i2:]))\n return ret%(10**9+7)\n```\n
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
get-the-maximum-score
|
simple two pointer update beats 99%
|
simple-two-pointer-update-beats-99-by-mi-amjv
|
\npublic int maxSum(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {\n int i = 0, j = 0, mod = 1000000007;\n long c1 = 0, c2 = 0;\n while (i < nums1.length && j
|
miseryangel1990
|
NORMAL
|
2021-01-29T06:05:21.737763+00:00
|
2021-01-29T06:05:21.737815+00:00
| 126 | false |
```\npublic int maxSum(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {\n int i = 0, j = 0, mod = 1000000007;\n long c1 = 0, c2 = 0;\n while (i < nums1.length && j < nums2.length){\n if (nums1[i]< nums2[j]){\n c1+=nums1[i++];\n }else if (nums1[i]> nums2[j]){\n c2+=nums2[j++];\n }else{\n c1+=nums1[i++];\n c2+=nums2[j++];\n c1 = Math.max(c1,c2);\n c2 = Math.max(c1,c2);\n }\n }\n while (i < nums1.length){\n c1 += nums1[i++];\n }\n while (j < nums2.length){\n c2 += nums2[j++];\n }\n long res = Math.max(c1,c2)%mod;\n return (int) res;\n }\n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.