question_slug
stringlengths 3
77
| title
stringlengths 1
183
| slug
stringlengths 12
45
| summary
stringlengths 1
160
⌀ | author
stringlengths 2
30
| certification
stringclasses 2
values | created_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| updated_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| hit_count
int64 0
10.6M
| has_video
bool 2
classes | content
stringlengths 4
576k
| upvotes
int64 0
11.5k
| downvotes
int64 0
358
| tags
stringlengths 2
193
| comments
int64 0
2.56k
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
minimum-window-substring
|
✅☑Beats 97% Users || [C++/Java/Python/JavaScript] || EXPLAINED🔥
|
beats-97-users-cjavapythonjavascript-exp-g9af
|
PLEASE UPVOTE IF IT HELPED\n\n---\n\n\n---\n\n\n# Approaches\n(Also explained in the code)\n\n1. Problem Objective:\n\n - The goal is to find the minimum win
|
MarkSPhilip31
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-04T00:35:17.748122+00:00
|
2024-02-04T00:35:17.748153+00:00
| 33,043
| false
|
# PLEASE UPVOTE IF IT HELPED\n\n---\n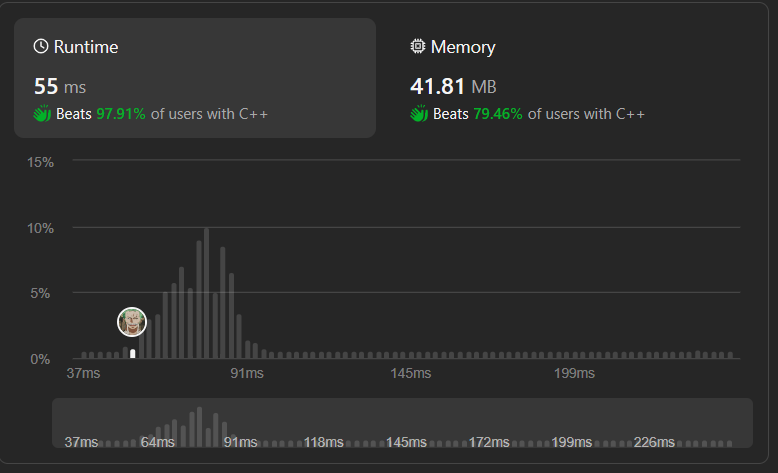\n\n---\n\n\n# Approaches\n(Also explained in the code)\n\n1. **Problem Objective:**\n\n - The goal is to find the minimum window in string `s` that contains all the characters in string `t` in any order.\n1. **Sliding Window Technique:**\n\n - Utilizes the sliding window technique where two pointers (`l` and `r`) represent the left and right ends of the current window.\n1. **Counting Characters:**\n\n - `dictT` is used to count the occurrences of characters in string `t`.\n - `windowCounts` keeps track of the characters within the current window.\n1. **Maintaining the Window:**\n\n - Move the right pointer `r` to expand the window.\n - Check if the characters in the current window satisfy the required counts from `t`.\n - If satisfied, increment `formed` (count of characters satisfying the required counts).\n1. **Shrinking the Window:**\n\n - Move the left pointer `l` to shrink the window.\n - Update the minimum window size (`ans`) if a smaller valid window is found.\n - Continue this process until a smaller valid window is not possible.\n - Repeat until the right pointer `r` reaches the end of the string.\n\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n $$O(s + t)$$\n*(where s and t are the lengths of strings s and t.)*\n \n\n- Space complexity:\n $$O(s + t)$$\n \n\n\n# Code\n```C++ []\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n if (s.empty() || t.empty()) {\n return "";\n }\n\n unordered_map<char, int> dictT;\n for (char c : t) {\n int count = dictT[c];\n dictT[c] = count + 1;\n }\n\n int required = dictT.size();\n int l = 0, r = 0;\n int formed = 0;\n\n unordered_map<char, int> windowCounts;\n int ans[3] = { -1, 0, 0 };\n\n while (r < s.length()) {\n char c = s[r];\n int count = windowCounts[c];\n windowCounts[c] = count + 1;\n\n if (dictT.find(c) != dictT.end() && windowCounts[c] == dictT[c]) {\n formed++;\n }\n\n while (l <= r && formed == required) {\n c = s[l];\n\n if (ans[0] == -1 || r - l + 1 < ans[0]) {\n ans[0] = r - l + 1;\n ans[1] = l;\n ans[2] = r;\n }\n\n windowCounts[c]--;\n if (dictT.find(c) != dictT.end() && windowCounts[c] < dictT[c]) {\n formed--;\n }\n\n l++;\n }\n\n r++;\n }\n\n return ans[0] == -1 ? "" : s.substr(ans[1], ans[0]);\n }\n};\n\n\n\n\n\n```\n```Java []\nclass Solution {\n public String minWindow(String s, String t) {\n if (s.isEmpty() || t.isEmpty()) {\n return "";\n }\n\n Map<Character, Integer> dictT = new HashMap<>();\n for (char c : t.toCharArray()) {\n int count = dictT.getOrDefault(c, 0);\n dictT.put(c, count + 1);\n }\n\n int required = dictT.size();\n int l = 0, r = 0;\n int formed = 0;\n\n Map<Character, Integer> windowCounts = new HashMap<>();\n int[] ans = { -1, 0, 0 };\n\n while (r < s.length()) {\n char c = s.charAt(r);\n int count = windowCounts.getOrDefault(c, 0);\n windowCounts.put(c, count + 1);\n\n if (dictT.containsKey(c) && windowCounts.get(c).intValue() == dictT.get(c).intValue()) {\n formed++;\n }\n\n while (l <= r && formed == required) {\n c = s.charAt(l);\n\n if (ans[0] == -1 || r - l + 1 < ans[0]) {\n ans[0] = r - l + 1;\n ans[1] = l;\n ans[2] = r;\n }\n\n windowCounts.put(c, windowCounts.get(c) - 1);\n if (dictT.containsKey(c) && windowCounts.get(c).intValue() < dictT.get(c).intValue()) {\n formed--;\n }\n\n l++;\n }\n\n r++;\n }\n\n return ans[0] == -1 ? "" : s.substring(ans[1], ans[2] + 1);\n }\n}\n\n\n```\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:\n if not s or not t:\n return ""\n\n dictT = defaultdict(int)\n for c in t:\n dictT[c] += 1\n\n required = len(dictT)\n l, r = 0, 0\n formed = 0\n\n windowCounts = defaultdict(int)\n ans = [-1, 0, 0]\n\n while r < len(s):\n c = s[r]\n windowCounts[c] += 1\n\n if c in dictT and windowCounts[c] == dictT[c]:\n formed += 1\n\n while l <= r and formed == required:\n c = s[l]\n\n if ans[0] == -1 or r - l + 1 < ans[0]:\n ans[0] = r - l + 1\n ans[1] = l\n ans[2] = r\n\n windowCounts[c] -= 1\n if c in dictT and windowCounts[c] < dictT[c]:\n formed -= 1\n\n l += 1\n\n r += 1\n\n return "" if ans[0] == -1 else s[ans[1]:ans[2] + 1]\n\n\n```\n```javascript []\nvar minWindow = function (s, t) {\n if (!s || !t) {\n return "";\n }\n\n let dictT = new Map();\n for (let c of t) {\n dictT.set(c, (dictT.get(c) || 0) + 1);\n }\n\n let required = dictT.size;\n let l = 0, r = 0;\n let formed = 0;\n\n let windowCounts = new Map();\n let ans = [-1, 0, 0];\n\n while (r < s.length) {\n let c = s.charAt(r);\n windowCounts.set(c, (windowCounts.get(c) || 0) + 1);\n\n if (dictT.has(c) && windowCounts.get(c) === dictT.get(c)) {\n formed++;\n }\n\n while (l <= r && formed === required) {\n c = s.charAt(l);\n\n if (ans[0] === -1 || r - l + 1 < ans[0]) {\n ans[0] = r - l + 1;\n ans[1] = l;\n ans[2] = r;\n }\n\n windowCounts.set(c, windowCounts.get(c) - 1);\n if (dictT.has(c) && windowCounts.get(c) < dictT.get(c)) {\n formed--;\n }\n\n l++;\n }\n\n r++;\n }\n\n return ans[0] === -1 ? "" : s.substring(ans[1], ans[2] + 1);\n};\n\n\n\n```\n---\n\n\n\n# PLEASE UPVOTE IF IT HELPED\n\n---\n---\n\n\n---
| 99
| 1
|
['Hash Table', 'String', 'Sliding Window', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'Python3', 'JavaScript']
| 11
|
minimum-window-substring
|
[C++] Short Sliding Window Solution with Explanation
|
c-short-sliding-window-solution-with-exp-dg4w
|
\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n unordered_map<char, int> letters; //unordered map for storing the characters in t that we need to check fo
|
hunarbatra
|
NORMAL
|
2020-01-17T18:09:43.980793+00:00
|
2020-01-17T18:09:43.980828+00:00
| 20,266
| false
|
```\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n unordered_map<char, int> letters; //unordered map for storing the characters in t that we need to check for in s\n for(auto c : t) letters[c]++; \n int count = 0; //counts number of t\'s letters in current window\n int low = 0, min_length = INT_MAX, min_start = 0; \n for(int high = 0; high<s.length(); high++) {\n if(letters[s[high]] > 0) count++; //means that this letter is in t \n letters[s[high]]--; //reduce the count for the letter on which we are currently \n if(count == t.length()) { //if current windows contains all of the letters in t\n while(low < high && letters[s[low]] < 0) letters[s[low]]++, low++; //move low ahead if its not of any significance\n if(min_length > high-low) min_length = high-(min_start=low)+1; //update the min length\n letters[s[low++]]++; //move low ahaead and also increment the value\n count--; //count-- as we are moving low ahead & low pointed to a char in t before\n }\n }\n return min_length == INT_MAX ? "" : s.substr(min_start, min_length); //check for edge case & return the result\n }\n```
| 97
| 8
|
['C', 'Sliding Window', 'C++']
| 15
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Python | My advice
|
python-my-advice-by-dev-josh-wp3w
|
My advice for solving this problem is to:\n Understand the intuition and what to do at a high level\n Try to implement your own solution WITHOUT copying anyone
|
dev-josh
|
NORMAL
|
2021-02-01T16:21:32.655771+00:00
|
2021-02-01T16:21:32.655817+00:00
| 6,294
| false
|
My advice for solving this problem is to:\n* Understand the intuition and what to do at a high level\n* Try to implement your own solution WITHOUT copying anyone elses\n* This is how you will learn\n* You will remember high level concepts, but never line for line code\n\nIntuition:\n* Two pointers, left and right\n* Both start from 0,0\n* Increase right pointer until valid window is found\n* Decrease left pointer until window is no longer valid\n* Add the minimum length window you\'ve found to your results\n* Continue increasing right pointer, pretty much repeating what we did above\n* Return the minimum length of your results\n\n\nMy code is AC but definitely not optimal, so I have some more learning & practice to do. I just wanted to share that by trying to implement & solve most of the problem yourself (after learning the high level concept), your learning is massive.\n\n\n```python\nfrom collections import Counter\n\n\nclass Solution:\n def minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:\n \n # Define variables\n s_count, t_count = Counter(), Counter(t)\n \n l, r = 0, 0\n \n results = []\n \n while r <= len(s)-1:\n \n # Find valid window\n s_count[s[r]] += 1 \n r += 1\n if s_count & t_count != t_count:\n continue\n \n # Minimize this window\n while l < r:\n s_count[s[l]] -= 1 \n l += 1\n if s_count & t_count == t_count:\n continue\n results.append(s[l-1:r])\n break\n \n \n # Return result\n if not results:\n return "" \n return min(results, key=len)\n```
| 76
| 0
|
['Python', 'Python3']
| 12
|
minimum-window-substring
|
✅🔥Sliding Window Approach with Explanation - C++/Java/Python
|
sliding-window-approach-with-explanation-tgop
|
\n# Intuition\nIn this problem, we need to find the minimum window substring of string s that contains all characters from string t. We can use a sliding window
|
dhruba-datta
|
NORMAL
|
2022-03-28T15:40:08.454696+00:00
|
2023-12-04T17:10:34.912935+00:00
| 10,133
| false
|
\n# Intuition\nIn this problem, we need to find the minimum window substring of string `s` that contains all characters from string `t`. We can use a sliding window approach to find the minimum window substring efficiently.\n\n# Approach 01\n1. Create an unordered_map `mp` to store the count of characters in string `t`.\n2. Initialize variables `ans`, `start`, and `count`.\n3. Use pointers `i` and `j` to iterate through string `s`.\n4. Decrement count of the current character in the map; if it becomes 0, decrement the `count` variable.\n5. Move pointer `i` to check if it is possible to remove more characters and get smaller substrings.\n6. Store the smaller length in `ans` and update the `start` variable.\n7. Add the current element to the map and increment the count if it becomes greater than 0.\n8. If `ans` has a length other than `INT_MAX`, return the substring from the `start` index to the length of `ans`; otherwise, return an empty string.\n\n# Complexity\n\n- Time complexity: The time complexity of this solution is O(m), where \'m\' is the length of string \'s\'. The algorithm iterates through the string once, and each iteration involves constant time operations.\n\n- Space complexity: The space complexity is O(n), where \'n\' is the length of string \'t\'. We use additional space for the unordered_map to store characters from \'t\'.\n\n# Code\n```C++ []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n int m = s.size(), n = t.size();\n unordered_map<char, int> mp;\n\n int ans = INT_MAX;\n int start = 0;\n\n for (auto x : t)\n mp[x]++;\n\n int count = mp.size();\n\n int i = 0, j = 0;\n\n while (j < s.length()) {\n mp[s[j]]--;\n if (mp[s[j]] == 0)\n count--;\n\n if (count == 0) {\n while (count == 0) {\n if (ans > j - i + 1) {\n ans = j - i + 1;\n start = i;\n }\n mp[s[i]]++;\n if (mp[s[i]] > 0)\n count++;\n\n i++;\n }\n }\n j++;\n }\n if (ans != INT_MAX)\n return s.substr(start, ans);\n else\n return "";\n }\n};\n```\n```Java []\nclass Solution {\n public String minWindow(String s, String t) {\n int m = s.length(), n = t.length();\n HashMap<Character, Integer> mp = new HashMap<>();\n\n int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;\n int start = 0;\n\n for (char x : t.toCharArray())\n mp.put(x, mp.getOrDefault(x, 0) + 1);\n\n int count = mp.size();\n\n int i = 0, j = 0;\n\n while (j < s.length()) {\n mp.put(s.charAt(j), mp.getOrDefault(s.charAt(j), 0) - 1);\n if (mp.get(s.charAt(j)) == 0)\n count--;\n\n if (count == 0) {\n while (count == 0) {\n if (ans > j - i + 1) {\n ans = j - i + 1;\n start = i;\n }\n mp.put(s.charAt(i), mp.getOrDefault(s.charAt(i), 0) + 1);\n if (mp.get(s.charAt(i)) > 0)\n count++;\n\n i++;\n }\n }\n j++;\n }\n if (ans != Integer.MAX_VALUE)\n return s.substring(start, start + ans);\n else\n return "";\n }\n}\n```\n```python []\nclass Solution(object):\n def minWindow(self, s, t):\n m, n = len(s), len(t)\n mp = {}\n\n ans = float(\'inf\')\n start = 0\n\n for x in t:\n mp[x] = mp.get(x, 0) + 1\n\n count = len(mp)\n\n i = 0\n j = 0\n\n while j < len(s):\n mp[s[j]] = mp.get(s[j], 0) - 1\n if mp[s[j]] == 0:\n count -= 1\n\n if count == 0:\n while count == 0:\n if ans > j - i + 1:\n ans = j - i + 1\n start = i\n mp[s[i]] = mp.get(s[i], 0) + 1\n if mp[s[i]] > 0:\n count += 1\n\n i += 1\n j += 1\n\n if ans != float(\'inf\'):\n return s[start:start + ans]\n else:\n return ""\n```\n\n\n---\n\n> **Please upvote this solution**\n>
| 75
| 1
|
['Two Pointers', 'Sliding Window', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'Python3']
| 10
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Share my neat java solution
|
share-my-neat-java-solution-by-tlj77-kd5z
|
public String minWindow(String S, String T) {\n if(S==null||S.isEmpty()||T==null||T.isEmpty()) return "";\n int i=0, j=0;\n int[] Tmap=new
|
tlj77
|
NORMAL
|
2015-04-22T02:58:02+00:00
|
2018-09-29T18:05:17.067477+00:00
| 33,284
| false
|
public String minWindow(String S, String T) {\n if(S==null||S.isEmpty()||T==null||T.isEmpty()) return "";\n int i=0, j=0;\n int[] Tmap=new int[256];\n int[] Smap=new int[256];\n for(int k=0; k< T.length(); k++){\n Tmap[T.charAt(k)]++;\n }\n int found=0;\n int length=Integer.MAX_VALUE;\n String res="";\n while(j<S.length()){\n if(found<T.length()){\n if(Tmap[S.charAt(j)]>0){\n Smap[S.charAt(j)]++;\n if(Smap[S.charAt(j)]<=Tmap[S.charAt(j)]){\n found++;\n }\n }\n j++;\n }\n while(found==T.length()){\n if(j-i<length){\n length=j-i; res=S.substring(i,j);\n }\n if(Tmap[S.charAt(i)]>0){\n Smap[S.charAt(i)]--;\n if(Smap[S.charAt(i)]<Tmap[S.charAt(i)]){\n found--;\n }\n }\n i++;\n }\n }\n return res;\n }
| 72
| 8
|
['Java']
| 11
|
minimum-window-substring
|
C++ Solution 68ms explanation
|
c-solution-68ms-explanation-by-leodicap9-a275
|
\nWe are going to use a two pointer approach to solve this.\n\nThe idea here is that \n1. We will store the characters of t in a map lets say mapt.\n2. We will
|
leodicap99
|
NORMAL
|
2020-05-07T05:31:08.846128+00:00
|
2020-05-07T05:31:08.846160+00:00
| 6,558
| false
|
```\nWe are going to use a two pointer approach to solve this.\n\nThe idea here is that \n1. We will store the characters of t in a map lets say mapt.\n2. We will have two pointers l and r.\n3. Whille we traverse through s we check if the character is found in mapt If so we will store the character into another hash map lets say maps.\n4. If the mapped charcter freq of s is less than or equal to mapt we increment a letter counter variable that will let us know when we have reached the t string size.\n5. We try to find the smallest substring which contains all chracters in t using a while loop.\n\n S = "ADOBECODEBANC" and T = "ABC"\n\n mapt\n A -> 1\n B -> 1\n C -> 1\n\n We keep l=0 and traverse S with r.\n\n "ADOBECODEBANC"\n ^\n |\n r \n\nas A is present in t we use another map for s to store A into the hashmap\n\nmaps\nA->1\nwe have another variable lettercounter that keeps track of the size.\nlettercounter\n1\n\n "ADOBECODEBANC"\n ^\n |\n r\nAs D isnt present in t we just continue traversing.\n\n "ADOBECODEBANC"\n ^\n |\n r\nSame as the above step.\n\n "ADOBECODEBANC"\n ^\n |\n r \nAs B is present in map t\n\nmaps\nA->1\nB->1\n\nlettercounter\n2\n\n "ADOBECODEBANC"\n ^\n |\n r\n "ADOBECODEBANC"\n ^\n |\n r\nC is present in mapt\n\nmaps\nA->1\nB->1\nC->1\n\nlettercounter\n3\nas lettercount is equal to t.size We will try shortening the substring\n\nAs there is only 1 A in s and t and A is the first character we cant reduce the size.\n\nSo out best bet currently would the substring\nans= "ADOBEC"\n\nWe continue traversing and checking the above steps.\n\n\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n unordered_map<char,int> map1;\n unordered_map<char,int> map2;\n int check=INT_MAX;\n string result;\n for(char &ch:t)map1[ch]++;\n int slow=0,fast=0,lettercounter=0;\n for(;fast<s.length();fast++)\n {\n char ch=s[fast];\n if(map1.find(ch)!=map1.end())\n {\n map2[ch]++;\n if(map2[ch]<=map1[ch])\n lettercounter++;\n }\n if(lettercounter>=t.length())\n {\n while(map1.find(s[slow])==map1.end()||map2[s[slow]]>map1[s[slow]])\n {\n map2[s[slow]]--;\n slow++;\n }\n if(fast-slow+1<check)\n {\n check=fast-slow+1;\n result=s.substr(slow,check);\n }\n }\n }\n return result;\n }\n```
| 53
| 2
|
['C', 'C++']
| 10
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Simple Java Solution | Sliding Window
|
simple-java-solution-sliding-window-by-g-f3s1
|
Kindly upvote, if it helps you!\n```\n public String minWindow(String s, String t) {\n String result = "";\n if(s.length() < t.length())\n
|
guptap151
|
NORMAL
|
2022-01-26T14:28:19.416146+00:00
|
2022-01-26T18:06:32.834936+00:00
| 4,902
| false
|
Kindly upvote, if it helps you!\n```\n public String minWindow(String s, String t) {\n String result = "";\n if(s.length() < t.length())\n return result;\n int minWindow = Integer.MAX_VALUE;\n\t\t//We will use two variables \'have\' & \'need\' to keep a track whether the characters \n\t\t//we need have been encountered.\n int need = t.length();\n int have = 0;\n\t\t//Two hashmaps are used to store the character count.\n Map<Character, Integer> sMap = new HashMap();\n Map<Character, Integer> tMap = new HashMap();\n for(int i=0; i<t.length(); i++){\n char ch = t.charAt(i);\n tMap.put(ch, tMap.getOrDefault(ch,0)+1);\n }\n int windowStart = 0;\n for(int windowEnd = 0; windowEnd<s.length(); windowEnd++){\n char ch = s.charAt(windowEnd);\n sMap.put(ch, sMap.getOrDefault(ch,0)+1);\n\t\t\t//if we have encountered a useful character, we will increment have variable.\n if(tMap.containsKey(ch) && sMap.get(ch)<=(tMap.get(ch))){\n have++;\n }\n\t\t\t//if have is equals to the need, means we got a substring in s having all the character of t\n while(have==need){\n\t\t\t\t//check if its the mimimum substring till now\n if(minWindow > windowEnd-windowStart+1){\n minWindow = windowEnd-windowStart+1;\n result = s.substring(windowStart, windowEnd+1);\n }\n\t\t\t\t//now we will check, can we do better\n\t\t\t\t//is there a shorter substring\n char charToRemove = s.charAt(windowStart);\n if(sMap.get(charToRemove) == 1){\n sMap.remove(charToRemove);\n }else{\n sMap.put(charToRemove, sMap.get(charToRemove)-1);\n }\n windowStart++;\n\t\t\t\t//if we remove a useful char, decrementing have varaible\n if(tMap.containsKey(charToRemove) && sMap.getOrDefault(charToRemove,0)<(tMap.get(charToRemove))){\n have--;\n }\n }\n }\n return result;\n }
| 45
| 1
|
['Sliding Window', 'Java']
| 6
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Java 4ms bit 97.6%
|
java-4ms-bit-976-by-huang593-liwd
|
Basically, there are two pointers for windows sliding. One for exploiting new matched substring, other pointer for expiring previous substring.\n\n public St
|
huang593
|
NORMAL
|
2016-03-30T03:10:24+00:00
|
2018-10-02T07:05:13.712462+00:00
| 12,670
| false
|
Basically, there are two pointers for windows sliding. One for exploiting new matched substring, other pointer for expiring previous substring.\n\n public String minWindow(String s, String t) {\n char[] s_array = s.toCharArray();\n char[] t_array = t.toCharArray();\n int[] map = new int[256];\n int end = 0;\n int start = 0;\n int min_length = Integer.MAX_VALUE;\n for(int i = 0; i < t_array.length; i++)\n map[t_array[i]] ++;\n int count = t_array.length;\n int min_start = 0;\n while(end < s_array.length)\n {\n if(map[s_array[end]] > 0)\n {\n count--;\n }\n map[s_array[end]] --;\n while(count == 0)\n {\n if((end - start + 1) < min_length)\n {\n min_length = end - start + 1;\n min_start = start;\n }\n map[s_array[start]] ++;\n if(map[s_array[start]] > 0){\n count ++;\n }\n start++;\n }\n end ++;\n \n }\n if( min_start+min_length > s_array.length)\n return "";\n return s.substring(min_start, min_start+min_length);\n }
| 45
| 1
|
[]
| 4
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Sliding Window | Beats 100% | Java | Python | C++ | JS | Go | Rust
|
sliding-window-beats-100-java-python-c-j-57n6
|
\n\n### INTUITION\n\n\nWe\u2019re given two strings: s, the large string, and t, the smaller one. Our job is to find the smallest substring of s that contains a
|
kartikdevsharma_
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-16T10:30:58.919549+00:00
|
2024-09-11T11:45:39.812527+00:00
| 7,533
| false
|
\n\n### INTUITION\n\n\nWe\u2019re given two strings: `s`, the large string, and `t`, the smaller one. Our job is to find the **smallest substring** of `s` that contains **all the characters** of `t`, and crucially, we need to consider duplicates. So, if `t` contains two `A`s, then any substring we pick from `s` needs to have **at least** two `A`s.\n\nLet\u2019s step back and simplify what this means in real terms. Imagine `t` as a kind of "recipe" that we need to find ingredients for inside `s`. For every character in `t`, we need to find those exact characters inside `s`\u2014and not just once, but exactly as many times as they appear in `t`.\n\n\n\nAt first it might seem like an easy task: just scan through `s`, looking for the characters in `t`, right? But the challenge lies in **how** we do this efficiently. Think about it: `s` could be **really** long\u2014thousands of characters long\u2014and if we simply checked every possible substring to see if it contains `t`, that could take a huge amount of time. Checking all possible substrings of `s` could get out of hand, especially with a string as long as 100,000 characters.\n\nSo, the tricky part is finding an approach that doesn\u2019t require us to check every substring one by one. Instead, we need a way to efficiently scan through `s` and pinpoint the smallest valid substring that includes all characters from `t`.\n\n\nWhat\u2019s the simplest approach that comes to mind? Maybe we just scan through `s` and mark where each character from `t` appears. That could be a good first step. But we need more than just knowing where the characters are\u2014we also need to group them together into a substring that includes **all** the characters from `t`, in the right quantities.\n\nSo, we need a strategy to **group** characters together and dynamically check whether they form a valid solution. This is where the idea of a **sliding window** comes into play.\n\n\nLet\u2019s talk about this concept of a "window." Imagine that `s` is like a long line of people, and we\u2019re trying to find the smallest group of people that contains certain key individuals from `t`. You start by focusing on a small group of people at the beginning of the line, then gradually expand your view to include more people. The moment your group contains everyone you need from `t`, you pause and check: \u201CIs this group the smallest one that works?\u201D If not, you start **shrinking** the group from the left to see if you can make it smaller while still keeping all the key people.\n\nThis idea of **expanding** and **shrinking** the window is at the heart of the solution. Instead of checking every possible group from scratch, you can adjust the group you\u2019re looking at by adding or removing people (characters) dynamically. This way, you\u2019re always refining your group, making it bigger when you need more characters and smaller when you have enough.\n\n\nOkay, so now we\u2019ve got this concept of a window in mind. But how do we actually make it work? How do we keep track of which characters we\u2019ve seen and how many we need?\n\n>Step 1: Expanding the Window\n\nLet\u2019s imagine we start at the very beginning of `s`. We\u2019ll have two pointers:\n- A **left** pointer that marks the beginning of the current window (the group of characters we\u2019re considering).\n- A **right** pointer that expands the window by moving to the right, adding more characters to the current window.\n\nWe begin by expanding the window by moving the right pointer. As we add each new character from `s` to the window, we check: is this character in `t`? If it is, and we still need more of that character (because `t` might have multiple copies of the same letter), we decrease a counter that tells us how many more of that character we need.\n\nFor example, say `t = "AAB"` and we\u2019re expanding the window in `s`. The first time we see an `A`, we note that we still need one more `A` (since `t` needs two). When we see a `B`, we note that we no longer need any more `B`s.\n\n>Step 2: Checking if the Window is Valid\n\nAs we keep expanding the window, we\u2019re keeping track of how many of each character from `t` we\u2019ve seen. The moment we\u2019ve seen **all** the characters in `t` (in the right quantities), the window becomes "valid." Now we know that this window contains everything `t` requires.\n\nBut just because the window is valid doesn\u2019t mean it\u2019s the **smallest** window. So, now we need to start **shrinking** it.\n\n> Step 3: Shrinking the Window\n\nOnce we\u2019ve found a valid window, we try to shrink it from the left. Why? Because even though the window contains all the characters we need, it might have some extra characters that aren\u2019t necessary. So, we move the left pointer to the right, one character at a time, trying to remove as many characters as possible while still keeping the window valid.\n\nFor example, if `t = "AAB"` and the current window contains `AABCC`, we can safely remove one `C` without making the window invalid. But the moment we try to remove one of the `A`s or the `B`, the window becomes invalid again because it no longer contains all the characters from `t`.\n\nAs we shrink the window, we keep track of the **smallest** valid window we\u2019ve seen so far.\n\n> Step 4: Continuing Until the End\n\nAfter shrinking the window as much as possible, we go back to expanding it by moving the right pointer further to the right. We repeat this process\u2014expanding the window, checking if it\u2019s valid, shrinking it, and updating the smallest valid window\u2014until the right pointer reaches the end of `s`.\n\n\n\nNow, how do we actually **keep track** of the characters we\u2019ve seen and still need? One efficient way is to use an array or a dictionary. We can create an array where each index represents a character (using the ASCII values of the characters as indices). This allows us to quickly update the count of each character in the window as we expand or shrink it.\n\nWe\u2019ll have two arrays:\n- One to store the counts of each character in `t` (this is our **target**).\n- Another to store the counts of each character in the current window of `s`.\n\nEvery time we add a character to the window by moving the right pointer, we update our current window\u2019s character count. When we remove a character by moving the left pointer, we adjust the count again. If the counts in the window match the counts in `t`, the window is valid.\n\n\nLet\u2019s go one step further. What if `s` is really long, but `t` only contains a few distinct characters? We might spend a lot of time checking characters in `s` that aren\u2019t even relevant to `t`. To optimize this, we can **pre-filter** `s` to remove any characters that don\u2019t appear in `t`.\n\nBy filtering `s` down to only the characters we care about, we reduce the amount of work the sliding window needs to do. This optimization is especially useful when `s` contains many irrelevant characters that don\u2019t appear in `t`.\n\n\n*So, to summarize:*\n1. We start with two pointers, left and right, both at the beginning of `s`.\n2. We use the right pointer to expand the window by adding characters from `s` and keeping track of which characters we\u2019ve seen and how many we still need.\n3. Once we have a valid window (i.e., a window that contains all characters from `t` in the right quantities), we shrink the window from the left to find the smallest possible valid window.\n4. We keep track of the smallest valid window we\u2019ve seen and return it at the end.\n\n\nThis approach is efficient because we only touch each character in `s` a limited number of times\u2014once when we add it to the window and once when we remove it. This gives us a time complexity of O(m + n), where `m` is the length of `s` and `n` is the length of `t`.\n\n### Algorithm:\n\n\n\n1. **Step 1: Initialize variables**:\n - Two pointers: `start` and `end`, both initialized to 0. These will represent the window\'s left and right boundaries, respectively.\n - A character frequency map for `t` (let\'s call it `target_freq`), which will store the count of each character in `t`.\n - A second frequency map (let\'s call it `window_freq`) to track the characters within the current window of `s`.\n - A counter variable `count` to keep track of how many characters from `t` have been fully matched in the current window.\n\n2. **Step 2: Populate the frequency map for `t`**:\n - For each character in `t`, increment its corresponding count in `target_freq`.\n\n3. **Step 3: Expand the window (Move the `end` pointer)**:\n - Start traversing `s` from left to right by moving the `end` pointer. For each character `s[end]`, increment its frequency in `window_freq`.\n - If the frequency of `s[end]` in `window_freq` matches the frequency in `target_freq` for that character, increment `count`.\n\n4. **Step 4: Check for valid windows**:\n - Once `count` equals the number of unique characters in `t` (i.e., the window contains all characters of `t`), move the `start` pointer to shrink the window.\n - For each valid window, compare its length with the minimum window length found so far. Update the minimum window length and its starting position if a smaller valid window is found.\n\n5. **Step 5: Shrink the window (Move the `start` pointer)**:\n - When the window is valid, try to shrink it by moving the `start` pointer to the right. After each move, update `window_freq` and check whether the window still contains all characters of `t`.\n - If the window becomes invalid (i.e., missing a required character), stop shrinking and continue expanding by moving the `end` pointer.\n\n6. **Step 6: Return the result**:\n - Once the `end` pointer reaches the end of `s`, return the smallest valid window substring found.\n\n\n\n```pseudo\nfunction minWindow(s, t):\n if length(s) < length(t):\n return ""\n \n # Step 1: Initialize variables\n target_freq = create empty map\n window_freq = create empty map\n \n for char in t:\n target_freq[char] += 1\n\n start = 0\n end = 0\n min_len = infinity\n min_start = 0\n count = 0 # Number of characters fully matched\n\n # Step 3: Expand the window by moving the `end` pointer\n while end < length(s):\n char_end = s[end]\n window_freq[char_end] += 1\n\n if char_end is in target_freq and window_freq[char_end] == target_freq[char_end]:\n count += 1\n\n # Step 4: When all characters are matched, try shrinking the window\n while count == number of unique characters in t:\n if (end - start + 1) < min_len:\n min_len = end - start + 1\n min_start = start\n\n char_start = s[start]\n window_freq[char_start] -= 1\n\n if char_start is in target_freq and window_freq[char_start] < target_freq[char_start]:\n count -= 1\n\n start += 1 # Shrink the window from the left\n\n end += 1 # Expand the window from the right\n\n if min_len == infinity:\n return ""\n\n return substring(s, min_start, min_start + min_len)\n```\n\n\n### Time Complexity (TC):$O( n)$\n\n- **Sliding Window Expansion (`end` pointer):**\n - The `end` pointer moves from the start of `s` to the end of `s`. Each character in `s` is processed once, so the time complexity of this is **O(m)**, where `m` is the length of `s`.\n\n- **Sliding Window Contraction (`start` pointer):**\n - The `start` pointer can also traverse the entire string `s`, but it only moves when the window contains all characters from `t`. The `start` pointer can move at most `m` times as well, since every character in `s` is processed once during contraction.\n - Therefore, the time complexity of shrinking the window is also **O(m)**.\n\n- **Checking and Updating Frequencies (`map` array):**\n - Checking whether the current window contains all characters from `t` requires constant time per operation because we are using an array of fixed size 128 (`int[] map = new int[128]`) to store the frequency of characters (based on ASCII values).\n - Therefore, all operations related to `map` (checking and updating character frequencies) take **O(1)** time per operation.\n\n- **Total Time Complexity:**\n - Since both `start` and `end` traverse the entire string `s` and the operations inside the loop are O(1), the overall time complexity is **O(m + n)**, where `m` is the length of `s` and `n` is the length of `t`but since n (the length of t) is smaller than or equal to m (the length of s), we can simplify the complexity to O(m), where m is the length of the string s.\n\n### Space Complexity (SC):$O(1)$\n\n- **Frequency Map (`map` array):**\n - The `map` array has a fixed size of 128 (since it stores the frequency of ASCII characters), regardless of the length of `s` or `t`.\n - The space complexity for the `map` array is **O(1)** (constant space).\n\n- **Other Variables:**\n - A few other integer variables like `count`, `start`, `end`, `minStart`, and `minLen` are used, but these take constant space.\n\n- **Total Space Complexity:**\n - The space complexity is **O(n)** because we need to store the characters in `t` in the `map` array and count the frequencies. However, since the `map` array is of constant size (128), it doesn\u2019t depend on the size of `s` or `t`. So, the overall space complexity is **O(1)**, or more accurately **O(128)**, which is effectively constant.\n\n\n\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public String minWindow(String s, String t) {\n if (s.length() < t.length()) return "";\n \n int[] map = new int[128];\n int count = t.length();\n int start = 0, end = 0, minStart = 0, minLen = Integer.MAX_VALUE;\n \n for (char c : t.toCharArray()) map[c]++;\n \n while (end < s.length()) {\n if (map[s.charAt(end++)]-- > 0) count--;\n \n while (count == 0) {\n if (end - start < minLen) {\n minStart = start;\n minLen = end - start;\n }\n \n if (map[s.charAt(start++)]++ == 0) count++;\n }\n }\n \n return minLen == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? "" : s.substring(minStart, minStart + minLen);\n }\n}\n```\n```python []\nclass Solution:\n def minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:\n if len(s) < len(t):\n return ""\n \n map = [0] * 128\n count = len(t)\n start = 0\n min_len = float(\'inf\')\n min_start = 0\n \n for c in t:\n map[ord(c)] += 1\n \n for end in range(len(s)):\n if map[ord(s[end])] > 0:\n count -= 1\n map[ord(s[end])] -= 1\n \n while count == 0:\n if end - start + 1 < min_len:\n min_start = start\n min_len = end - start + 1\n \n map[ord(s[start])] += 1\n if map[ord(s[start])] > 0:\n count += 1\n start += 1\n \n return "" if min_len == float(\'inf\') else s[min_start:min_start + min_len]\n```\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n if (s.length() < t.length()) return "";\n \n vector<int> map(128, 0);\n int count = t.length();\n int start = 0, minStart = 0, minLen = INT_MAX;\n \n for (char c : t) map[c]++;\n \n for (int end = 0; end < s.length(); end++) {\n if (map[s[end]]-- > 0) count--;\n \n while (count == 0) {\n if (end - start + 1 < minLen) {\n minStart = start;\n minLen = end - start + 1;\n }\n \n if (map[s[start++]]++ == 0) count++;\n }\n }\n \n return minLen == INT_MAX ? "" : s.substr(minStart, minLen);\n }\n};\n\n```\n```Rust []\nimpl Solution {\n pub fn min_window(s: String, t: String) -> String {\n if s.len() < t.len() {\n return String::new();\n }\n\n let s_bytes = s.as_bytes();\n let t_bytes = t.as_bytes();\n let mut map = [0; 128];\n let mut count = t.len();\n let mut start = 0;\n let mut min_start = 0;\n let mut min_len = usize::MAX;\n\n for &c in t_bytes {\n map[c as usize] += 1;\n }\n\n for end in 0..s.len() {\n if map[s_bytes[end] as usize] > 0 {\n count -= 1;\n }\n map[s_bytes[end] as usize] -= 1;\n\n while count == 0 {\n if end - start + 1 < min_len {\n min_start = start;\n min_len = end - start + 1;\n }\n\n map[s_bytes[start] as usize] += 1;\n if map[s_bytes[start] as usize] > 0 {\n count += 1;\n }\n start += 1;\n }\n }\n\n if min_len == usize::MAX {\n String::new()\n } else {\n s[min_start..min_start + min_len].to_string()\n }\n }\n}\n```\n```Go []\nfunc minWindow(s string, t string) string {\n if len(s) < len(t) {\n return ""\n }\n\n freqMap := [128]int{}\n count := len(t)\n start, minStart, minLen := 0, 0, math.MaxInt32\n\n // Initialize the frequency map with characters from t\n for _, c := range t {\n freqMap[c]++\n }\n\n // Start the sliding window\n for end := 0; end < len(s); end++ {\n if freqMap[s[end]] > 0 {\n count--\n }\n freqMap[s[end]]--\n\n // Try to minimize the window\n for count == 0 {\n if end-start+1 < minLen {\n minStart = start\n minLen = end - start + 1\n }\n\n freqMap[s[start]]++\n if freqMap[s[start]] > 0 {\n count++\n }\n start++\n }\n }\n\n if minLen == math.MaxInt32 {\n return ""\n }\n return s[minStart : minStart+minLen]\n}\n\n```\n\n```JavaScript []\n/**\n * @param {string} s\n * @param {string} t\n * @return {string}\n */\nvar minWindow = function(s, t) {\n if (s.length < t.length) return "";\n \n const map = new Array(128).fill(0);\n let count = t.length;\n let start = 0, minStart = 0, minLen = Infinity;\n \n for (let c of t) {\n map[c.charCodeAt(0)]++;\n }\n \n for (let end = 0; end < s.length; end++) {\n if (map[s.charCodeAt(end)]-- > 0) count--;\n \n while (count === 0) {\n if (end - start + 1 < minLen) {\n minStart = start;\n minLen = end - start + 1;\n }\n \n if (map[s.charCodeAt(start++)]++ === 0) count++;\n }\n }\n \n return minLen === Infinity ? "" : s.slice(minStart, minStart + minLen);\n};\n```\n---\n### Examples\nLet\'s go through some examples \n\nWe will focus on how the two pointers (`start` and `end`) work, how the `count` variable changes, and how the character frequency is managed in the `map` array.\n\n#### Explanation of Key Variables:\n\n- `start`: Beginning of the current window.\n- `end`: End of the current window.\n- `count`: Tracks how many characters from `t` are still missing from the window in `s`. When `count == 0`, it means all characters from `t` are currently in the window.\n- `map`: A frequency map for characters in `t`. It records how many times each character of `t` appears.\n- `minStart`: Keeps track of the starting index of the minimum window found so far.\n- `minLen`: Length of the minimum window substring found.\n\n### Example 1: Input: `s = "ADOBECODEBANC"`, `t = "ABC"`\n\n| Step | `start` | `end` | Current Window (`s[start:end]`) | `count` | Explanation (Character Operations) | `minStart` | `minLen` |\n|------|---------|-------|----------------------------------|---------|------------------------------------|------------|----------|\n| 1 | 0 | 1 | "A" | 2 | \'A\' is found (map[\'A\'] > 0), decrease `count` to 2 | - | \u221E |\n| 2 | 0 | 2 | "AD" | 2 | \'D\' is not in `t`, continue sliding `end` | - | \u221E |\n| 3 | 0 | 3 | "ADO" | 2 | \'O\' is not in `t`, continue sliding `end` | - | \u221E |\n| 4 | 0 | 4 | "ADOB" | 1 | \'B\' is found (map[\'B\'] > 0), decrease `count` to 1 | - | \u221E |\n| 5 | 0 | 5 | "ADOBE" | 1 | \'E\' is not in `t`, continue sliding `end` | - | \u221E |\n| 6 | 0 | 6 | "ADOBEC" | 0 | \'C\' is found (map[\'C\'] > 0), decrease `count` to 0. Window contains all characters from `t` | 0 | 6 |\n| 7 | 1 | 6 | "DOBEC" | 0 | Shrinking window by moving `start`. \'A\' removed, `count` remains 0 | 1 | 5 |\n| 8 | 2 | 6 | "OBEC" | 0 | Shrinking window by moving `start`. \'D\' removed, `count` remains 0 | 2 | 4 |\n| 9 | 3 | 6 | "BEC" | 0 | Shrinking window by moving `start`. \'O\' removed, `count` remains 0 | 3 | 3 |\n| 10 | 4 | 6 | "BEC" | 1 | Shrinking window by moving `start`. \'B\' removed, `count` increases to 1 (not valid window anymore) | 3 | 3 |\n| 11 | 4 | 7-10 | "CODEB" | 1 | Move `end` until all characters are found again. \'A\' is found again at `end = 10` | - | - |\n| 12 | 4 | 11 | "CODEBA" | 0 | \'A\' is found again (valid window) | 4 | 3 |\n| 13 | 4-7 | 11-13 | "BANC" | 0 | Shrink window to get minimum valid window ("BANC") | 9 | 4 |\n\n**Result:** The minimum window is `"BANC"`.\n\n---\n\n### Example 2: Input: `s = "a"`, `t = "a"`\n\n| Step | `start` | `end` | Current Window (`s[start:end]`) | `count` | Explanation (Character Operations) | `minStart` | `minLen` |\n|------|---------|-------|----------------------------------|---------|------------------------------------|------------|----------|\n| 1 | 0 | 1 | "a" | 0 | \'a\' found (map[\'a\'] > 0), `count` becomes 0, valid window found | 0 | 1 |\n| 2 | 1 | 1 | - | - | As `start` moves, no valid window remains | - | - |\n\n**Result:** The minimum window is `"a"`.\n\n---\n\n### Example 3: Input: `s = "a"`, `t = "aa"`\n\n| Step | `start` | `end` | Current Window (`s[start:end]`) | `count` | Explanation (Character Operations) | `minStart` | `minLen` |\n|------|---------|-------|----------------------------------|---------|------------------------------------|------------|----------|\n| 1 | 0 | 1 | "a" | 1 | \'a\' found, but only 1 \'a\' in `s`, `count` remains 1 | - | \u221E |\n| 2 | 1 | 1 | - | - | No valid window can be formed since `t` requires 2 \'a\'s but `s` only has 1 | - | - |\n\n**Result:** The minimum window is `""` (empty string).\n\n---\n\n\n\n- We traverse the string `s` using two pointers `start` and `end`.\n- We expand the window by moving `end`, and shrink the window by moving `start` when all characters from `t` are found in the window (i.e., `count == 0`).\n- The minimum valid window is updated by comparing the length of each valid window with `minLen`.\n- The algorithm ensures that even duplicate characters in `t` are taken care of by the frequency map `map`.\n\n\n\n
| 42
| 0
|
['Hash Table', 'String', 'Sliding Window', 'C++', 'Java', 'Go', 'Python3', 'Rust', 'JavaScript']
| 6
|
minimum-window-substring
|
C++/JAVA/Python | 🚀 ✅ Sliding Window | ✅ Fully Explained | ✅ Hash Table | ✅ String
|
cjavapython-sliding-window-fully-explain-ex0g
|
Intuition:\nThe problem asks to find the minimum window in s that contains all the characters of t. One way to approach this problem is to use a sliding window
|
devanshupatel
|
NORMAL
|
2023-04-14T18:05:53.116403+00:00
|
2023-04-24T20:23:28.926976+00:00
| 9,064
| false
|
# Intuition:\nThe problem asks to find the minimum window in s that contains all the characters of t. One way to approach this problem is to use a sliding window technique. We can maintain a window that starts from the beginning of s and moves forward until it contains all the characters of t. Once we have such a window, we can try to shrink it by moving the window\'s start pointer forward while still keeping all the characters of t in the window. This will give us the minimum window.\n\n#Approach:\n\n1. Check if s is shorter than t. If it is, there is no possible solution, and we return an empty string.\n2. Create a frequency map of characters in t.\n3. Initialize count, start, min_length, and min_start to 0.\n4. Traverse the string s using the end pointer.\n5. If the current character in s is present in the frequency map, increment the count.\n6. Decrement the frequency of the current character in the frequency map.\n7. If the count equals the length of t, it means we have found a window that contains all characters of t. Now we try to shrink the window by moving the start pointer forward until the window still contains all the characters of t.\n8. If the length of the current window is smaller than the minimum length so far, update the minimum length and the minimum start.\n9. Increment the frequency of the character at the start pointer and decrement the count.\n10. Return the minimum window or an empty string if no window exists.\n# Complexity:\n- Time complexity: O(N), where N is the length of the string s. We traverse the string s once.\n- Space complexity: O(M), where M is the length of the string t. We create a frequency map of characters in t.\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n if(s.size() < t.size()){\n return "";\n }\n unordered_map<char,int> map;\n for(int i=0;i<t.size();i++){\n map[t[i]]++;\n }\n int count=0,start=0,min_length = INT_MAX, min_start = 0;\n for(int end=0; end<s.size(); end++){\n if(map[s[end]]>0){\n count++;\n }\n map[s[end]]--; \n if(count == t.length()) { \n while(start < end && map[s[start]] < 0){\n map[s[start]]++, start++;\n } \n if(min_length > end-start){\n min_length = end-(min_start=start)+1; \n }\n map[s[start++]]++; \n count--;\n }\n }\n return min_length == INT_MAX ? "" : s.substr(min_start, min_length);\n }\n};\n```\n# JAVA\n```\nclass Solution {\n public String minWindow(String s, String t) {\n if(s.length() < t.length()){\n return "";\n }\n Map<Character,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();\n for(int i=0;i<t.length();i++){\n map.put(t.charAt(i), map.getOrDefault(t.charAt(i), 0) + 1);\n }\n int count=0,start=0,min_length = Integer.MAX_VALUE, min_start = 0;\n for(int end=0; end<s.length(); end++){\n if(map.containsKey(s.charAt(end))){\n if(map.get(s.charAt(end))>0){\n count++;\n }\n map.put(s.charAt(end), map.get(s.charAt(end))-1); \n }\n if(count == t.length()) { \n while(start < end && (!map.containsKey(s.charAt(start)) || map.get(s.charAt(start)) < 0)){\n if(map.containsKey(s.charAt(start))){\n map.put(s.charAt(start), map.get(s.charAt(start))+1);\n }\n start++;\n } \n if(min_length > end-start+1){\n min_length = end-(min_start=start)+1; \n }\n if(map.containsKey(s.charAt(start))){\n map.put(s.charAt(start), map.get(s.charAt(start))+1);\n }\n count--;\n start++;\n }\n }\n return min_length == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? "" : s.substring(min_start, min_start+min_length);\n }\n}\n\n```\n# Python\n```\nclass Solution(object):\n def minWindow(self, s, t):\n if len(s) < len(t):\n return ""\n map = {}\n for char in t:\n if char in map:\n map[char] += 1\n else:\n map[char] = 1\n count = 0\n start = 0\n min_length = float("inf")\n min_start = 0\n for end in range(len(s)):\n if s[end] in map:\n map[s[end]] -= 1\n if map[s[end]] >= 0:\n count += 1\n while count == len(t):\n if min_length > end - start + 1:\n min_length = end - start + 1\n min_start = start\n if s[start] in map:\n map[s[start]] += 1\n if map[s[start]] > 0:\n count -= 1\n start += 1\n return "" if min_length == float("inf") else s[min_start:min_start+min_length]\n\n```
| 38
| 0
|
['Hash Table', 'Sliding Window', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java']
| 4
|
minimum-window-substring
|
c++ || Advance || Sliding window || Fast
|
c-advance-sliding-window-fast-by-iam_sin-ckn3
|
Please upvote, your one upvote makes me happy\n\n^____^\n\nHere is the code\n\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n string minWindow(string str, string pat) {\n
|
Iam_SinghSunny
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-22T02:50:23.038629+00:00
|
2023-05-13T03:02:30.827669+00:00
| 6,945
| false
|
**Please upvote, your one upvote makes me happy**\n\n^____^\n\n**Here is the code**\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n string minWindow(string str, string pat) {\n \n int len1 = str.length();\n int len2 = pat.length();\n \n const int no_of_chars = 256;\n\n if (len1 < len2) {\n return "";\n }\n\n int hash_pat[no_of_chars] = { 0 };\n int hash_str[no_of_chars] = { 0 };\n\n \n for (int i = 0; i < len2; i++)\n hash_pat[pat[i]]++;\n\n int start = 0, start_index = -1, min_len = INT_MAX;\n\n int count = 0; \n for (int j = 0; j < len1; j++) {\n hash_str[str[j]]++;\n\n if (hash_str[str[j]] <= hash_pat[str[j]])\n count++;\n\n if (count == len2) {\n \n while (hash_str[str[start]]\n > hash_pat[str[start]]\n || hash_pat[str[start]] == 0) {\n\n if (hash_str[str[start]]\n > hash_pat[str[start]])\n hash_str[str[start]]--;\n start++;\n }\n\n int len_window = j - start + 1;\n if (min_len > len_window) {\n min_len = len_window;\n start_index = start;\n }\n }\n }\n\n if (start_index == -1) {\n \n return "";\n }\n\n return str.substr(start_index, min_len);\n\n }\n};\n```\n\n**Keep coding Keep upvoting**
| 38
| 1
|
['C', 'Sliding Window']
| 3
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Simple Python Solution Beats 99% with Detailed Explanation
|
simple-python-solution-beats-99-with-det-hp5w
|
The key idea is how you update the tracking variables. There are four essentials variables to track: 1. remaing length of a match 2. The position of previous ma
|
Brownian_motion
|
NORMAL
|
2018-09-15T20:12:14.414718+00:00
|
2018-10-09T05:15:57.640374+00:00
| 5,924
| false
|
The key idea is how you update the tracking variables. There are four essentials variables to track: 1. remaing length of a match 2. The position of previous matched first element 3. start_position of returned answer 4. end_position of returned answer. \n\nAnd a dictionary to count the occurrence of characters is useful.\n\n```\nclass Solution(object):\n def minWindow(self, s, t):\n """\n :type s: str\n :type t: str\n :rtype: str\n """\n # Defaultdict is very useful in this problem, though i don\'t like to import modules\n target_count_dict = collections.defaultdict(int)\n for ch in t:\n target_count_dict[ch] += 1\n remain_missing = len(t)\n start_pos, end_pos = 0, float(\'inf\')\n current_start = 0\n \n # Enumerate function makes current_end indexes from 1\n for current_end, ch in enumerate(s, 1):\n # Whenever we encounter a character, no matter ch in target or not, we minus 1 in count dictionary\n # But, only when ch is in target, we minus the length of remain_missing\n # When the remain_missing is 0, we find a potential solution.\n if target_count_dict[ch] > 0:\n remain_missing -= 1\n target_count_dict[ch] -= 1\n \n if remain_missing == 0:\n # Remove redundant character\n # Try to find the fist position in s that makes target_count_dict value equals 0\n # Which means we can\'t skip this character in s when returning answer\n while target_count_dict[s[current_start]] < 0:\n target_count_dict[s[current_start]] += 1\n current_start += 1\n if current_end - current_start < end_pos - start_pos:\n start_pos, end_pos = current_start, current_end\n \n # We need to add 1 to current_start, and the correspondence value in dictionary, is because\n # this is the first character of the potential answer. So, in future iteration, when we encounter this character,\n # We can remove this currently first character to try to find a shorter answer.\n target_count_dict[s[current_start]] += 1\n remain_missing += 1\n current_start += 1\n \n return s[start_pos:end_pos] if end_pos != float(\'inf\') else ""\n```
| 36
| 0
|
[]
| 2
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Java | TC: O(S+T) | SC: O(T) | Space-optimized Sliding Window using Two Pointers
|
java-tc-ost-sc-ot-space-optimized-slidin-kzl2
|
java\n/**\n * Space-optimized Sliding Window using Two Pointers\n *\n * Time Complexity: O(S + T)\n *\n * Space Complexity: O(T)\n *\n * S = length of String s.
|
NarutoBaryonMode
|
NORMAL
|
2021-10-01T06:46:46.340722+00:00
|
2021-10-07T07:56:11.751803+00:00
| 5,710
| false
|
```java\n/**\n * Space-optimized Sliding Window using Two Pointers\n *\n * Time Complexity: O(S + T)\n *\n * Space Complexity: O(T)\n *\n * S = length of String s. T = length of String t\n */\nclass Solution1 {\n public String minWindow(String s, String t) {\n if (s == null || t == null) {\n throw new IllegalArgumentException("Input string is null");\n }\n if (s.length() < t.length() || t.length() == 0) {\n return "";\n }\n\n HashMap<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();\n for (int i = 0; i < t.length(); i++) {\n map.put(t.charAt(i), map.getOrDefault(t.charAt(i), 0) + 1);\n }\n\n int start = 0;\n int end = 0;\n int charTLeft = t.length();\n int minStart = 0;\n int minLen = Integer.MAX_VALUE;\n\n while (end < s.length()) {\n char eChar = s.charAt(end);\n if (map.containsKey(eChar)) {\n int count = map.get(eChar);\n if (count > 0) {\n charTLeft--;\n }\n map.put(eChar, count - 1);\n }\n end++;\n\n while (charTLeft == 0) {\n if (minLen > end - start) {\n minLen = end - start;\n minStart = start;\n }\n char sChar = s.charAt(start);\n if (map.containsKey(sChar)) {\n int count = map.get(sChar);\n if (count == 0) {\n charTLeft++;\n }\n map.put(sChar, count + 1);\n }\n start++;\n }\n }\n\n return minLen == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? "" : s.substring(minStart, minStart + minLen);\n }\n}\n```\n\n---\n\nSolutions to other Sliding Window questions on LeetCode:\n- [340. Longest Substring with At Most K Distinct Characters](https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-substring-with-at-most-k-distinct-characters/discuss/1496838/Java-or-TC:-O(N)-or-SC:-O(K)-or-One-Pass-Sliding-Window-using-LinkedHashMap)\n- [159. Longest Substring with At Most Two Distinct Characters](https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-substring-with-at-most-two-distinct-characters/discuss/1496840/Java-or-TC:-O(N)-or-SC:-O(1)-or-One-Pass-Sliding-Window-using-LinkedHashMap)\n- [438. Find All Anagrams in a String](https://leetcode.com/problems/find-all-anagrams-in-a-string/discuss/1500039/Java-or-TC:-O(S+P)-or-SC:-O(1)-or-Sliding-window-solution)\n- [3. Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters](https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-substring-without-repeating-characters/discuss/1500874/Java-or-TC:-O(N)-or-SC:-O(1)-or-Sliding-Window-using-HashMap-and-Two-Pointers)\n- [209. Minimum Size Subarray Sum](https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-size-subarray-sum/discuss/1500877/Java-or-Both-O(N)-and-O(N-logN)-solutions-with-O(1)-space-or-Sliding-Window-and-Binary-Search-solutions)\n- [219. Contains Duplicate II](https://leetcode.com/problems/contains-duplicate-ii/discuss/1500887/Java-or-TC:-O(N)-or-SC:-O(min(N-K))-or-Sliding-Window-using-HashSet)\n- [220. Contains Duplicate III](https://leetcode.com/problems/contains-duplicate-iii/discuss/1500895/Java-or-TC:-O(N)-or-SC:-O(min(NK))-or-Sliding-Window-using-Buckets)\n- [567. Permutation in String](https://leetcode.com/problems/permutation-in-string/discuss/1500902/Java-or-TC:-O(S2)-or-SC:-O(1)-or-Constant-space-Sliding-Window-solution)\n- [239. Sliding Window Maximum](https://leetcode.com/problems/sliding-window-maximum/discuss/1506048/Java-or-TC:-O(N)-or-SC:-O(K)-or-Using-Deque-as-Sliding-Window)\n- [480. Sliding Window Median](https://leetcode.com/problems/sliding-window-median/discuss/1507981/Java-or-TC:-O(N*logK)-or-SC:-(K)-or-Optimized-sliding-window-using-TreeSet)\n- [487. Max Consecutive Ones II](https://leetcode.com/problems/max-consecutive-ones-ii/discuss/1508045/Java-or-TC:-O(N)-or-SC:-O(1)-or-Four-solutions-with-Follow-up-handled)\n- [1004. Max Consecutive Ones III](https://leetcode.com/problems/max-consecutive-ones-iii/discuss/1508044/Java-or-TC:-O(N)-or-SC:-O(1)-or-One-Pass-Optimized-Sliding-Window)\n
| 35
| 0
|
['Two Pointers', 'String', 'Sliding Window', 'Java']
| 3
|
minimum-window-substring
|
[Python3] Sliding window O(N+M)
|
python3-sliding-window-onm-by-yourick-us52
|
\n# Approach\nThis problem follows the Sliding Window pattern and has a lot of similarities with 567 Permutation in a String with one difference. In this proble
|
yourick
|
NORMAL
|
2023-11-09T17:11:24.818215+00:00
|
2024-06-27T19:59:25.410276+00:00
| 2,608
| false
|
\n# Approach\nThis problem follows the Sliding Window pattern and has a lot of similarities with [567 Permutation in a String](https://leetcode.com/problems/permutation-in-string/description/) with one difference. In this problem, we need to find a substring having all characters of the pattern which means that the required substring can have some additional characters and doesn\u2019t need to be a permutation of the pattern. Here is how we will manage these differences:\n\n1. We will keep a running count of every matching instance of a character.\n2. Whenever we have matched all the characters, we will try to shrink the window from the beginning, keeping track of the smallest substring that has all the matching characters.\n3. We will stop the shrinking process as soon as we remove a matched character from the sliding window. One thing to note here is that we could have redundant matching characters, e.g., we might have two \u2018a\u2019 in the sliding window when we only need one \u2018a\u2019. In that case, when we encounter the first \u2018a\u2019, we will simply shrink the window without decrementing the matched count. We will decrement the matched count when the second \u2018a\u2019 goes out of the window.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nThe time complexity of the above algorithm will be O(N+M) where \u2018N\u2019 and \u2018M\u2019 are the number of characters in the input string and the pattern respectively.\n\n- Space complexity:\nThe space complexity of the algorithm is O(M) since in the worst case, the whole pattern can have distinct characters which will go into the HashMap. In the worst case, we also need O(N) space for the resulting substring, which will happen when the input string is a permutation of the pattern.\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:\n if len(s) < len(t): return \'\'\n \n need, matchCnt, left, resStart, resLen = Counter(t), 0, 0, 0, len(s) + 1\n \n for right, ch in enumerate(s):\n if ch in need:\n need[ch] -= 1\n matchCnt += need[ch] == 0\n\n while matchCnt == len(need):\n # we found a smaller window, update result\n curWindowLen = right - left + 1\n if curWindowLen < resLen:\n resStart, resLen = left, curWindowLen\n \n removeCh = s[left]\n left += 1 \n if removeCh in need:\n matchCnt -= need[removeCh] == 0\n need[removeCh] += 1\n\n return s[resStart:resStart + resLen] if resLen <= len(s) else \'\'\n```
| 34
| 0
|
['Sliding Window', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 5
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Three O(N) concise implemetation according to leetcode oj discuss
|
three-on-concise-implemetation-according-ci60
|
// according to http://leetcode.com/2010/11/finding-minimum-window-in-s-which.html\n // finds the first window that satisfies the constraint\n // then con
|
shichaotan
|
NORMAL
|
2014-12-31T19:13:25+00:00
|
2014-12-31T19:13:25+00:00
| 9,563
| false
|
// according to http://leetcode.com/2010/11/finding-minimum-window-in-s-which.html\n // finds the first window that satisfies the constraint\n // then continue maintaining the constraint throughout\n // time complexity O(2N)\n string minWindow(string S, string T) {\n int m = S.size(), n = T.size();\n if (n <= 0 || m < n)\n return "";\n \n int require[128] = {0}, found[128] = {0};\n for (int k = 0; k < n; ++k) require[T[k]]++;\n \n int count = 0;\n int minLen = INT_MAX, minIndex = 0;\n for (int s = 0, e = 0; e < m; ++e) {\n // skip characters not in T\n if (require[S[e]] == 0) continue;\n if (++found[S[e]] <= require[S[e]]) count++;\n \n // windows constrain is sastisfied\n if (count == n) {\n // advance begin index as far as possible\n // stop when advancing breaks window constraint\n while (require[S[s]] == 0 || found[S[s]] > require[S[s]]) {\n if (found[S[s]] > require[S[s]]) found[S[s]]--;\n ++s;\n }\n // update minmum window\n if (e - s + 1 < minLen) {\n minLen = e - s + 1;\n minIndex = s;\n }\n }\n }\n \n if (minLen == INT_MAX) return "";\n return S.substr(minIndex, minLen); \n }\n \n string minWindow(string S, string T) {\n int m = S.size(), n = T.size();\n if (n <= 0 || m < n)\n return "";\n \n int require[128] = {0}, chSet[128] = {0};\n for (int k = 0; k < n; ++k) {\n require[T[k]]++;\n chSet[T[k]] = 1;\n }\n \n int minLen = INT_MAX, minIndex = 0;\n int i = -1, j = 0;\n while (i < m && j < m) {\n if (n) {\n ++i;\n require[S[i]]--;\n if (chSet[S[i]] && require[S[i]] >= 0) n--;\n }\n else {\n if (minLen > i - j + 1) {\n minLen = i - j + 1;\n minIndex = j;\n }\n require[S[j]]++;\n if (chSet[S[j]] && require[S[j]] > 0) n++;\n ++j;\n }\n }\n \n if (minLen == INT_MAX) return "";\n return S.substr(minIndex, minLen);\n }\n\n // the most concise one\n // maintain a window with two pointers (left side and right side)\n string minWindow(string S, string T) {\n int m = S.size(), n = T.size();\n if (n <= 0 || m < n) return "";\n \n int require[128] = {0};\n for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) require[T[i]]++;\n \n int count = 0;\n int minLen = INT_MAX, minIndex = 0;\n for (int s = 0, e = 0; e < m; ++e) {\n require[S[e]]--;\n if (require[S[e]] >= 0) count++;\n while (count == n) {\n if (e - s + 1 < minLen) {\n minLen = e - s + 1;\n minIndex = s;\n }\n require[S[s]]++;\n if (require[S[s]] > 0) count--;\n s++;\n }\n }\n \n if (minLen == INT_MAX) return "";\n return S.substr(minIndex, minLen); \n }
| 33
| 3
|
[]
| 2
|
minimum-window-substring
|
💡JavaScript Solution w/ Detailed Comments
|
javascript-solution-w-detailed-comments-jxrzs
|
javascript\nvar minWindowSlidingWindow = function (s, t) {\n\t// `right` is -1 since every loop, we start by expanding the right boundary\n\t// setting this to
|
aminick
|
NORMAL
|
2019-10-23T02:27:27.114250+00:00
|
2019-10-23T02:45:04.825380+00:00
| 6,620
| false
|
``` javascript\nvar minWindowSlidingWindow = function (s, t) {\n\t// `right` is -1 since every loop, we start by expanding the right boundary\n\t// setting this to -1 ensures that we will check the first char on the first time\n let min = "", left = 0, right = -1;\n let map = {};\n\t\n\t// this creates a map for the characters we need to include in the substring\n\t// we store the character and its count since it can be repeated\n\t// for example: "BAAC"\n t.split(\'\').forEach(element => {\n if (map[element]==null) map[element] = 1;\n else map[element] = map[element] + 1;\n });\n\t\n\t// sets how many different characters we still have\n\t// for example: given the input "BAAC", we still have 3 different characters need to check\n let count = Object.keys(map).length;\n\n while (right <= s.length) {\n\t\t// found a valid substring\n if (count == 0) {\n\t\t\n\t\t\t// try to shift left boudary to the right, this means the very left character will be removed\n\t\t\t// because of this, we need to check whats the affect by removing that character, \n let current = s[left];\n\t\t\t\n\t\t\t// if this chacter is in our map, it means we ll need to find another one in the future\n if (map[current] != null) map[current]++;\n\t\t\t\n\t\t\t// * we must have the condition `>0` because for case like "BBBA...", count for B could be negative\n if (map[current] > 0) count++; \n\t\t\t\n let temp = s.substring(left, right+1)\n if (min == "") min = temp;\n else min = min.length<temp.length?min:temp;\n\t\t\t\n left++;\n } else {\n right++;\n let current = s[right];\n\t\t\t\n\t\t\t// decrease the count for this character\n if (map[current] != null) map[current]--;\n\t\t\t\n if (map[current] == 0) count--;\n }\n }\n return min;\n}\n```
| 32
| 0
|
['JavaScript']
| 6
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Accepted Python solution using hashtable
|
accepted-python-solution-using-hashtable-0lno
|
class Solution:\n # @return a string\n def minWindow(self, S, T):\n indices = {}\n for char in T:\n indices[c
|
xiaoying10101
|
NORMAL
|
2015-01-03T04:14:51+00:00
|
2018-10-26T04:13:16.498421+00:00
| 9,739
| false
|
class Solution:\n # @return a string\n def minWindow(self, S, T):\n indices = {}\n for char in T:\n indices[char] = []\n miss = list(T)\n start = 0\n end = len(S)\n for i in range(len(S)):\n if S[i] in T:\n if S[i] not in miss and indices[S[i]] != []:\n indices[S[i]].pop(0)\n elif S[i] in miss:\n miss.remove(S[i])\n indices[S[i]].append(i)\n if miss == []:\n maximum = max([x[-1] for x in indices.values()])\n minimum = min([x[0] for x in indices.values()])\n if maximum-minimum+1 < end-start+1:\n start = minimum\n end = maximum\n if miss != []:\n return ""\n else:\n return S[start:end+1]\n\nBasically I kept a dictionary to record the index of each character of T. Each time I found a window, (when miss == []), I checked the length of this window by subtracting the maximum index and the minimum index of the characters. If this window is the smallest one so far, I record its beginning and ending index as "start" and "end."
| 31
| 1
|
[]
| 4
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Python easy to understand
|
python-easy-to-understand-by-clarketm-pgo7
|
python\ndef min_window(S: str, T: str) -> str:\n """\n Minimum Window Substring\n\n :param str S:\n :param str T:\n :return str:\n """\n Tc
|
clarketm
|
NORMAL
|
2019-05-05T01:41:24.979072+00:00
|
2019-05-05T01:41:24.979115+00:00
| 5,634
| false
|
```python\ndef min_window(S: str, T: str) -> str:\n """\n Minimum Window Substring\n\n :param str S:\n :param str T:\n :return str:\n """\n Tc = Counter(T)\n Sc = Counter()\n\n best_i = -sys.maxsize\n best_j = sys.maxsize\n\n i = 0\n\n for j, char in enumerate(S):\n Sc[char] += 1\n\n while Sc & Tc == Tc:\n if j - i < best_j - best_i:\n best_i, best_j = i, j\n\n Sc[S[i]] -= 1\n i += 1\n\n return S[best_i : best_j + 1] if best_j - best_i < len(S) else ""\n```
| 29
| 2
|
['Python']
| 9
|
minimum-window-substring
|
EXPLAINED | Easy to understand code with comments | 3ms
|
explained-easy-to-understand-code-with-c-s72w
|
\nclass Solution {\n public String minWindow(String s, String t) {\n int[] count = new int[128];\n\n // Count the characters in t\n for
|
heisenbergknocks
|
NORMAL
|
2020-11-13T08:02:12.571412+00:00
|
2022-10-25T08:54:03.558312+00:00
| 2,799
| false
|
```\nclass Solution {\n public String minWindow(String s, String t) {\n int[] count = new int[128];\n\n // Count the characters in t\n for (char ch : t.toCharArray()) count[ch]++;\n\n char[] sourceStr = s.toCharArray();\n String windowString = "";\n int windowLeft = 0, windowRight = 0, charsFoundInWindow = 0,\n totalCharsToFind = t.length(), minWindowLen = Integer.MAX_VALUE;\n while (windowRight < sourceStr.length) {\n int currentChar = sourceStr[windowRight];\n // Reduce the count of current character\n count[currentChar]--;\n // If current character\'s count is greater than or equal to 0 if it was also present in target string t\n // and we can say that we have found that character in current window so we increment charsFoundInWindow\n if (count[currentChar] >= 0) {\n charsFoundInWindow++;\n }\n\n // If we found a window containing all characters of t, find if it\'s smaller than the smallest window\n // If yes, store the window in windowString to return finally.\n while (charsFoundInWindow == totalCharsToFind) {\n int currentWindowLen = windowRight - windowLeft + 1;\n if(minWindowLen > currentWindowLen) {\n minWindowLen = currentWindowLen;\n windowString = s.substring(windowLeft, windowRight + 1);\n }\n // Now we need to reduce the window size from left to further look for smaller windows.\n // The current leftmost character was already visited by right pointer windowRight earlier\n // and we had reduced its count in count[]. So now we increment it because\n // we need the count of that character in the remaining window.\n count[sourceStr[windowLeft]]++;\n // Now if the last character is greater than 0, it means that character was present in t but\n // is not present in current window so we have to decrement charsFoundInWindow\n if (count[sourceStr[windowLeft]] > 0) {\n charsFoundInWindow--;\n }\n windowLeft++;\n }\n windowRight++;\n }\n return windowString;\n }\n}\n```
| 28
| 0
|
['Sliding Window', 'Java']
| 7
|
minimum-window-substring
|
[Python] O(n+m) sliding window, explained
|
python-onm-sliding-window-explained-by-d-0lmr
|
The idea of sliding window with 2 pointers: we create counter cnt_t is frequencies how many time s we need to take each symbol, for example for abca we have a:2
|
dbabichev
|
NORMAL
|
2021-08-15T07:52:22.792580+00:00
|
2021-08-15T07:52:22.792624+00:00
| 1,442
| false
|
The idea of sliding window with 2 pointers: we create counter `cnt_t` is frequencies how many time s we need to take each symbol, for example for `abca` we have `a:2, b:1, c:1`. We create also `cnt_s` as empty counter, which will keep information about frequencies is current window `[beg, end)` - not that we do not include `end`. To quickly understand how many symbols have good frequency, we have `found` variable. Now, we can have two options to change our window:\n\n1. If `found == len(cnt_t)`, it means that we have in our window all symbols we want: no need to extend it to the right: we will shrink it to the left. We need to update our `ans`, where we keep pair `(end - beg, beg)` , then we look at the first element `old = s[beg]` and if we have `cnt_s[old] == cnt_t[old]` it means that we have exactly the right frequency for this symbol. So, when we move `beg` one position to the right, we need to decrease `found by one. Finally, we decrease frequency by one and more `beg` to the right.\n2. In the opposite case, first we check if `end == len(s)` and if it is true, we break. Then we look at the new symbol `new = s[end]` (because it was not included, windows are `[beg, end)`. We check if `cnt_s[new] == cnt_t[new] - 1` and if it is the case, it means, that when we add new symbol we need to increase `found` by one. Then we increase frequency and move `end` one position to the right.\n\n#### Complexity\nTime complexity is `O(m + n)`, becuse on each step we move `beg` or `end` one point to the right. Space complexity is `O(A)`, where `A` is the size of alphabet.\n\n#### Code\n```python\nclass Solution:\n def minWindow(self, s, t):\n beg, end = 0, 0\n ans, found = (float("inf"), 0), 0\n cnt_t, cnt_s = Counter(t), Counter()\n while end <= len(s):\n if found == len(cnt_t):\n ans = min(ans, (end - beg, beg))\n old = s[beg]\n if cnt_s[old] == cnt_t[old]: found -= 1\n cnt_s[old] -= 1\n beg += 1\n else:\n if end == len(s): break\n new = s[end]\n if cnt_s[new] == cnt_t[new] - 1: found += 1\n cnt_s[new] += 1\n end += 1\n \n return s[ans[1]:ans[0]+ans[1]] if ans[0] != float("inf") else ""\n```\n\nIf you have any questions, feel free to ask. If you like solution and explanations, please **Upvote!**
| 27
| 3
|
['Sliding Window']
| 3
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Super Easy Java Solution or or 100% faster or or Easy to understand
|
super-easy-java-solution-or-or-100-faste-63p3
|
Looking for Contribution in Hacktoberfest\n## You are welcomed to contribute in my Repos:-\n# GITHUB LINK --> Yaduttam95\n# All PRs are getting accepted...\n\n#
|
Yaduttam_Pareek
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-22T01:41:11.734701+00:00
|
2022-10-22T01:41:11.734744+00:00
| 2,732
| false
|
# Looking for Contribution in Hacktoberfest\n## You are welcomed to contribute in my Repos:-\n# GITHUB LINK --> [Yaduttam95](https://github.com/Yaduttam95)\n# All PRs are getting accepted...\n\n# Please upvote if Helpful\n```\nclass Solution {\n public String minWindow(String s, String t) {\n \n \n if(s=="" || t=="")\n return "";\n if(s==null || t==null)\n return "";\n \n int n = s.length();\n int m = t.length();\n \n \n int freq[] = new int[128];\n int characters = 0;\n \n for(int i=0;i<m;i++){\n freq[t.charAt(i)]++;\n characters++;\n }\n \n int start =0, end = 0;\n int min_length = Integer.MAX_VALUE;\n int start_index = 0;\n \n while(end < n){\n \n if(freq[s.charAt(end)]>0)\n characters--;\n freq[s.charAt(end)]--;\n end++;\n \n while(characters==0){\n \n if(min_length>end-start){\n min_length = end-start;\n start_index = start;\n }\n freq[s.charAt(start)]++;\n if(freq[s.charAt(start)]>0){\n characters++;\n }\n start++;\n \n }\n \n }\n \n return min_length == Integer.MAX_VALUE? "" : s.substring(start_index,start_index+min_length);\n \n }\n}\n```\n\n
| 26
| 0
|
[]
| 3
|
minimum-window-substring
|
✅ Minimum Window Substring || Using Map w/ Explanation || C++ | Python | Java
|
minimum-window-substring-using-map-w-exp-4tlx
|
IDEA\nThe solution is a bit intuitive. We keep expanding the window by moving the right pointer. When the window has all the desired characters, we contract (if
|
Maango16
|
NORMAL
|
2021-08-15T07:58:11.255661+00:00
|
2021-08-15T07:58:11.255715+00:00
| 1,917
| false
|
**IDEA**\nThe solution is a bit intuitive. We keep expanding the window by moving the right pointer. When the window has all the desired characters, we contract (if possible) and save the smallest window till now.\n`The answer is the smallest desirable window.`\n\n**EXAMPLE**\nFor eg. `S = "ABAACBAB" T = "ABC"`. Then our answer window is `"ACB"` and shown below is one of the possible desirable windows.\n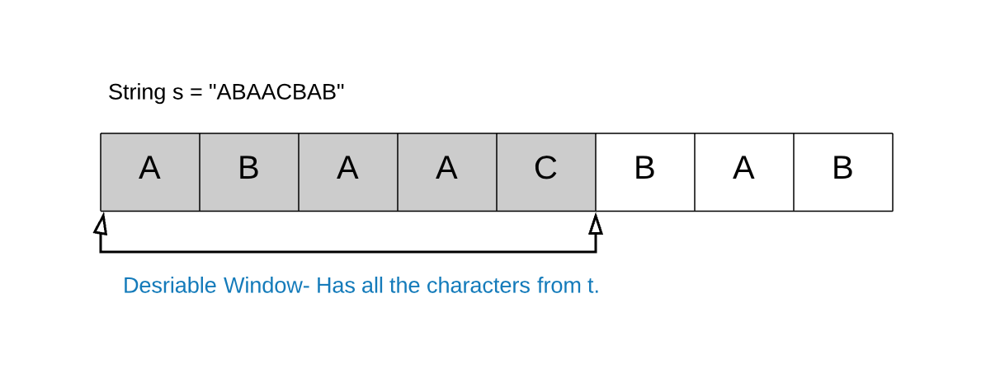\n\n**ALGORITHM**\n*BASE CASE-*\nIf either s or t is null then we can\u2019t find any common window between them.\n\n*ELSE-*\n* We start with two pointers, `leftleft` and `rightright` initially pointing to the first element of the string SS.\n* We use the `rightright pointer` to expand the window until we get a desirable window i.e. a window that contains all of the characters of TT.\n* Once we have a window with all the characters, we can move the left pointer ahead one by one. \n\t* \tIf the window is still a desirable one we keep on updating the minimum window size.\n\t* \tIf the window is not desirable any more, we repeat step 2 onwards.\n\n**SOLUTION**\n`In C++`\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n unordered_map<char,int> mp;\n for(auto ch:t)\n {\n mp[ch]++;\n }\n int dist=mp.size() ;\n unordered_map<char,int> window;\n int count = 0 , ll = 0 , rr = 0 ;\n int l = 0 , r = 0 , ans = INT_MAX ;\n while(r<s.length())\n {\n window[s[r]]++ ;\n if(mp.count(s[r]) and mp[s[r]]==window[s[r]])\n {\n count++;\n }\n r++;\n while(count == dist and l < r)\n {\n if(ans > r-l)\n {\n ans= r - l ;\n ll = l ;\n rr = r ;\n }\n window[s[l]]-- ;\n if(mp.count(s[l]) and window[s[l]] < mp[s[l]])\n {\n count--;\n }\n l++;\n }\n }\n return s.substr(ll,rr-ll);\n }\n};\n```\n`In Python`\n```\nclass Solution(object):\n def minWindow(self, s, t):\n """\n :type s: str\n :type t: str\n :rtype: str\n """\n if not t or not s:\n return ""\n\n dict_t = Counter(t)\n required = len(dict_t)\n l, r = 0, 0\n formed = 0\n window_counts = {}\n ans = float("inf"), None, None\n while r < len(s):\n character = s[r]\n window_counts[character] = window_counts.get(character, 0) + 1\n if character in dict_t and window_counts[character] == dict_t[character]:\n formed += 1\n while l <= r and formed == required:\n character = s[l]\n\n # Save the smallest window until now.\n if r - l + 1 < ans[0]:\n ans = (r - l + 1, l, r)\n\n window_counts[character] -= 1\n if character in dict_t and window_counts[character] < dict_t[character]:\n formed -= 1\n l += 1 \n\n r += 1 \n return "" if ans[0] == float("inf") else s[ans[1] : ans[2] + 1]\n\n```\n`In JAVA`\n```\nclass Solution {\n public String minWindow(String s, String t) {\n if(s==null || t==null)\n {\n return "";\n }\n HashMap<Character,Integer> map = new HashMap<Character,Integer>();\n for(char c : t.toCharArray())\n {\n if(map.containsKey(c))\n {\n map.put(c,map.get(c)+1);\n }\n else\n {\n map.put(c,1);\n }\n }\n int left = 0 , minLeft = 0, minLen = s.length() + 1 ;\n int count = 0;\n for(int right = 0; right < s.length(); right++)\n {\n if(map.containsKey(s.charAt(right)))\n {\n map.put(s.charAt(right),map.get(s.charAt(right))-1);\n if(map.get(s.charAt(right)) >= 0)\n {\n count ++;\n }\n while(count == t.length())\n {\n if(right-left+1 < minLen)\n {\n minLeft = left;\n minLen = right-left+1;\n }\n if(map.containsKey(s.charAt(left)))\n {\n map.put(s.charAt(left),map.get(s.charAt(left))+1);\n if(map.get(s.charAt(left)) > 0)\n {\n count --;\n }\n }\n left++ ;\n }\n }\n }\n return minLen > s.length() ? "" : s.substring(minLeft,minLeft+minLen);\n }\n}\n```\n
| 26
| 2
|
[]
| 9
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Sliding Windows||Hash tables->Freq Array||0ms Beats 100%
|
sliding-windowshash-tables-freq-array0ms-4tes
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n2 kinds of solutions. the main idea is the the sliding windows. but for implementation
|
anwendeng
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-04T00:46:24.152403+00:00
|
2024-02-04T06:54:34.247401+00:00
| 6,243
| false
|
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n2 kinds of solutions. the main idea is the the sliding windows. but for implementation it needs the info of frequencies of alphabets.\n1 is just using hash tables (map or unordered_map) which is slow & done many months ago.\nOther is using the frequency arrays to speed up the code; different languages C, C++ & python are used for implementations.\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n[Please turn on English subtitles if necessary]\n[https://youtu.be/pi1XpQU_Yxo?si=dsD4W9WVMckv_Rka](https://youtu.be/pi1XpQU_Yxo?si=dsD4W9WVMckv_Rka)\nNote that `s and t consist of uppercase and lowercase English letters`.\nIt is known that \'A\'=65, \'z\'=122. using bitmask with `& 0x3f` to fit in a 64-elemented array.\n\nThe main structure is roughly presented as follows:\n```\n1. Count the frequency table for `t` & store in `tmp`\n2. loop of moving `right` from 0 to end of of `s`:\n If substring is found which containing `t`:\n using while-loop compare 2 freq tables moving `left`\n update min window\n3. return min window if found otherwise ""\n```\nThe process for finding substrings for testcase `s="ADOBECODEBANC", t="ABC"` which is done by adding some output to the submitted code\n```\n[0,5]:ADOBEC\n[0,9]:ADOBECODEB\n[5,10]:CODEBA\n[9,12]:BANC\n```\n|Method| elapsed time| Time record | Space |\n|---|---|---|---|\n|C++ SW freq arrays|0ms|100%|9.21MB|\n|C++ SW unordered_map|28ms|21.43%|10.43MB|\n|C++ SW map|33ms|16.94%|10.50MB|\n|Python SW freq arrays|65ms|99.48%|17.26MB|\n|C SW freq arrays|2ms|81.82%|6.44MB|\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(|s|+|t|)$$\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(|s|+|t|)$$\n# Codes using freq arrays||C++ 0ms Beats 100%||Python beats 99.48%|| C 2ms\n```C []\n#pragma GCC optimize("O3", "unroll-loops")\nchar* minWindow(char* s, char* t) {\n int n=strlen(s), tn=0;\n int left=0;\n int mp[64]={0}, tmp[64]={0};\n\n // Count the characters in string t\n for(char* p=t; *p!=\'\\0\'; p++){\n int idx=0x3f &(*p);\n // printf("%c", *p);\n tmp[idx]++;\n tn++;// Count strlen for t\n }\n // printf(s);\n\n int count=0; // Counter for matching characters\n int minLength=INT_MAX, minLeft = 0; \n\n for (register right=0; right<n; right++) {\n int idx = 0x3f & s[right];\n \n if (tmp[idx] == 0) continue;\n mp[idx]++;\n\n // Check if the current character count matches the required count\n if (mp[idx] <= tmp[idx]) count++;\n\n // If all characters of t are found in the current window\n if (count == tn) {\n // Try to minimize the window by moving the left pointer\n int idx_left;// compute idx_left=0x3f&s[left] only once\n while (tmp[(idx_left= 0x3f & s[left])]==0 || mp[idx_left]>tmp[idx_left]) {\n if (mp[idx_left]!=0) mp[idx_left]--;\n left++;\n }\n\n // Update the minimum window if necessary\n if (right-left+1 < minLength) {\n minLength=right-left+1;\n minLeft=left;\n }\n }\n }\n\n // If no valid window found\n if (minLength == INT_MAX) return "";\n\n // Return the minimum window substring\n s[minLeft+minLength] = \'\\0\';\n return s+minLeft;// substring for C-string\n}\n```\n```python []\nclass Solution:\n def minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:\n n, tn= len(s), len(t)\n left=0\n mp=[0]*64\n tmp=[0]*64\n\n for c in t:\n idx=ord(c)& 63\n tmp[idx]+=1\n # print(tmp)\n count=0\n minLength=2**31\n minLeft=0\n\n for right, c in enumerate(s):\n idx=ord(c)& 63\n if tmp[idx]==0: continue\n mp[idx]+=1\n if mp[idx]<=tmp[idx]: count+=1\n if count==tn:\n while tmp[ll:=(63& ord(s[left]))]==0 or mp[ll]>tmp[ll]:\n if mp[ll]!=0: mp[ll]-=1\n left+=1\n # print("[", left,",", right,"]:",str(s[left:right+1]))\n if right-left+1<minLength:\n minLength=right-left+1\n minLeft=left\n if minLength==2**31: return ""\n return str(s[minLeft:minLeft+minLength])\n \n```\n```C++ []\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string& s, string& t) {//call by reference\n int n = s.size(), tn= t.size();\n int left = 0, right;\n int mp[64]={0}, tmp[64]={0};\n \n // Count the characters in string t\n for (char c : t){\n int idx=0x3f &c;\n tmp[idx]++;\n }\n \n int count = 0; // Counter for matching characters\n \n int minLength = INT_MAX; // Length of the minimum window\n int minLeft = 0; // Start index of the minimum window\n \n for (right = 0; right < n; right++) {\n char c = s[right];\n int idx= 0x3f & c;\n // Skip characters not present in string t\n if (tmp[idx] == 0) continue;\n \n // Increment the count of matching characters\n mp[idx]++;\n \n // Check if the current character count matches the required count\n if (mp[idx] <= tmp[idx]) count++;\n \n // If all characters of t are found in the current window\n if (count == tn) {\n // Try to minimize the window by moving the left pointer\n while (tmp[0x3f& s[left]]==0|| mp[0x3f& s[left]]>tmp[0x3f& s[left]]) {\n if (mp[0x3f&s[left]]!=0) mp[0x3f&s[left]]--;\n left++;\n }\n \n // Update the minimum window if necessary\n if (right - left + 1 < minLength) {\n minLength = right - left + 1;\n minLeft = left;\n }\n }\n }\n \n // If no valid window found, return an empty string\n if (minLength == INT_MAX) return "";\n \n // Return the minimum window substring\n return s.substr(minLeft, minLength);\n }\n};\n\n```\n# C++ code with unordered_map done before\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n int n = s.size();\n int tn= t.size();\n int left = 0, right;\n unordered_map<char, int> mp, tmp;\n \n // Count the characters in string t\n for (char c : t)\n tmp[c]++;\n \n int count = 0; // Counter for matching characters\n \n int minLength = INT_MAX; // Length of the minimum window\n int minLeft = 0; // Start index of the minimum window\n \n for (right = 0; right < n; right++) {\n char c = s[right];\n \n // Skip characters not present in string t\n if (tmp.count(c) == 0) continue;\n \n // Increment the count of matching characters\n mp[c]++;\n \n // Check if the current character count matches the required count\n if (mp[c] <= tmp[c]) count++;\n \n // If all characters of t are found in the current window\n if (count == tn) {\n // Try to minimize the window by moving the left pointer\n while (tmp.count(s[left])==0|| mp[s[left]]>tmp[s[left]]) {\n if (mp.count(s[left])!=0) mp[s[left]]--;\n left++;\n }\n \n // Update the minimum window if necessary\n if (right - left + 1 < minLength) {\n minLength = right - left + 1;\n minLeft = left;\n }\n }\n }\n \n // If no valid window found, return an empty string\n if (minLength == INT_MAX) return "";\n \n // Return the minimum window substring\n return s.substr(minLeft, minLength);\n }\n};\n```
| 24
| 0
|
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'String', 'Bit Manipulation', 'C', 'Sliding Window', 'C++', 'Python3']
| 8
|
minimum-window-substring
|
A visualized first principles approach for better understanding
|
a-visualized-first-principles-approach-f-xfis
|
Heres a visualization techinque that might help you get a better idea of the solution. \n\nImagine the strings (henceforth S and T) as a long chain of character
|
principled_man
|
NORMAL
|
2020-07-20T22:58:48.675684+00:00
|
2020-07-21T16:42:00.081153+00:00
| 1,141
| false
|
Heres a visualization techinque that might help you get a better idea of the solution. \n\nImagine the strings (henceforth **S** and **T**) as a long chain of characters\n\nFirst we will build a tool that will help us extract information about the target string **T**\n\nWe will extract 2 pieces of info from **T** - \nfirst how many characters there are in T and what is the frequency of each character. \n\nWe focus on these 2 pieces of information because any substring in S that must contain T should satisfy 2 criteria: a. Have all the characters in T, b. Match the character frequency of T \n\n\n\nSo Rem is the total number of characters remaining, and each characters frequency is the count of each char that is required. \n\nNext we will use this "tool" and run a sliding window over **S** to get to point where REM is 0. The points where REM is 0 are our windows where we have found all the characters that are present in T and match the same frequency. \n\nWe will continue expanding our window as long as REM is postive.\nAt a step when Rem is <=0 we will start shrinking our window from the start until REM stays below or equal to 0. This will help us find our minimum length substring \n\n\n\nIt is important to note that the variable REM is changed **ONLY** when we see a character in **S** that is present in our tool. Then it can be that either: \n\na. We are expanding our window and the frequency of the matching character is postive in our tool. In this case required character frequency and REM are decreased **OR**\nb. We are shirinking our window and the frequency of the matching character is negative in our tool. In this case character frequency is increased and REM is increased. \n \n A run of the two steps above is shown below: \n \n \n \n 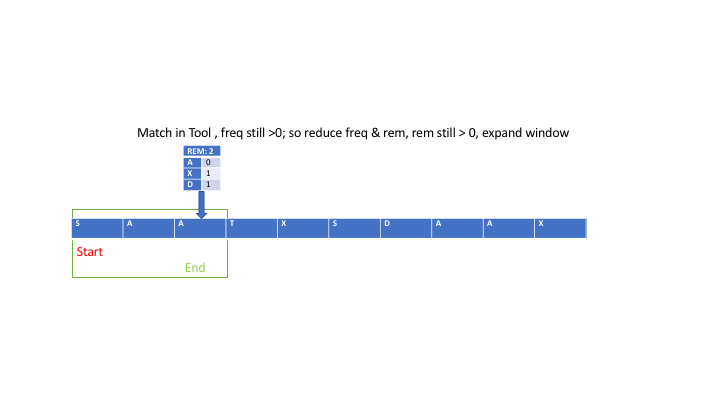\n 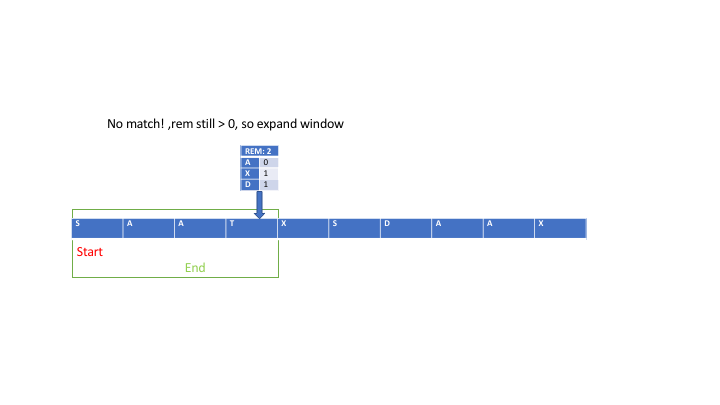\n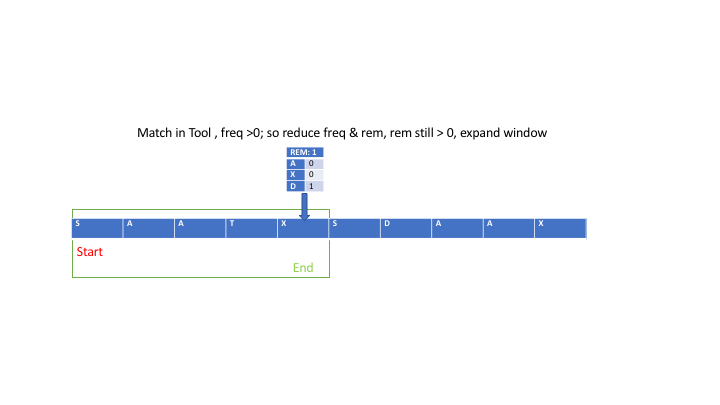\n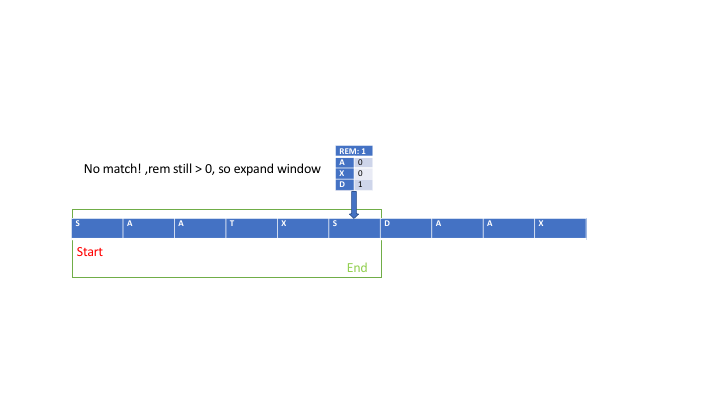\n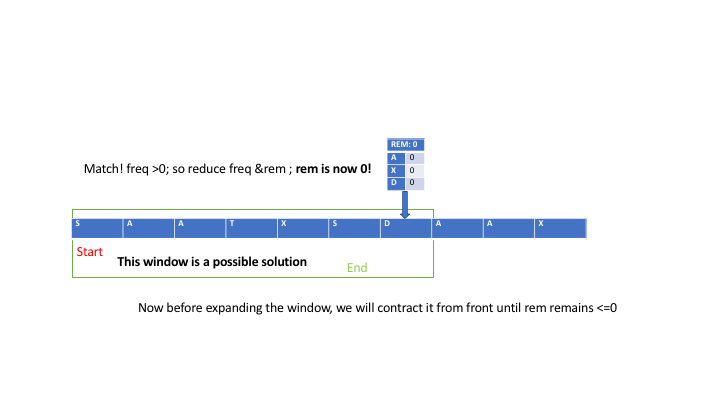\n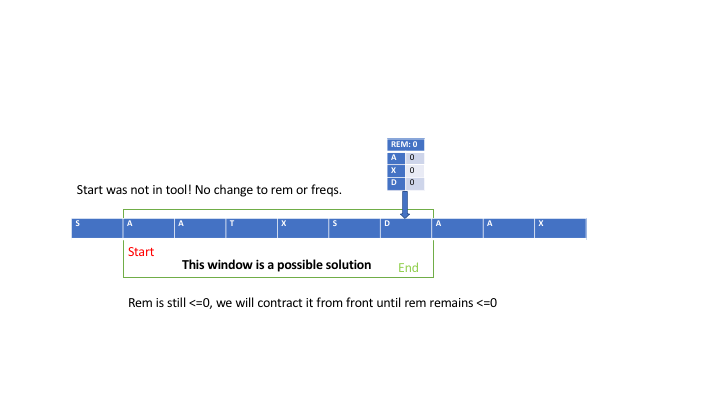\n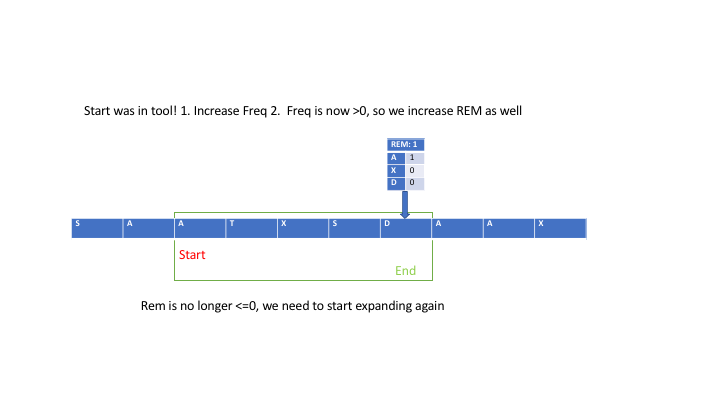\n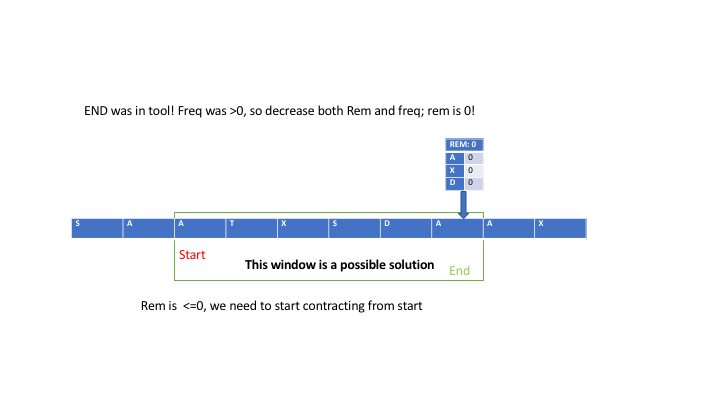\n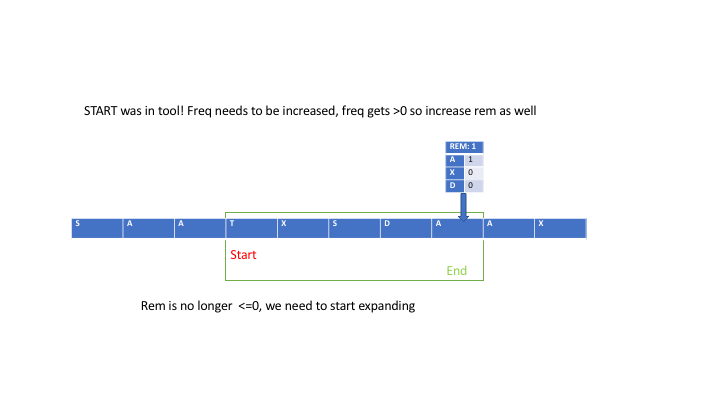\n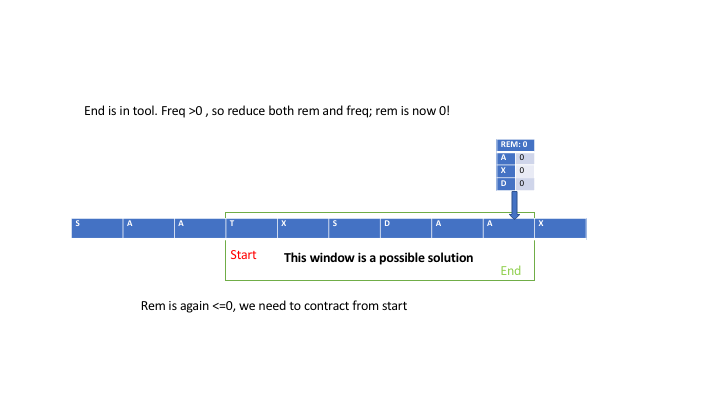\n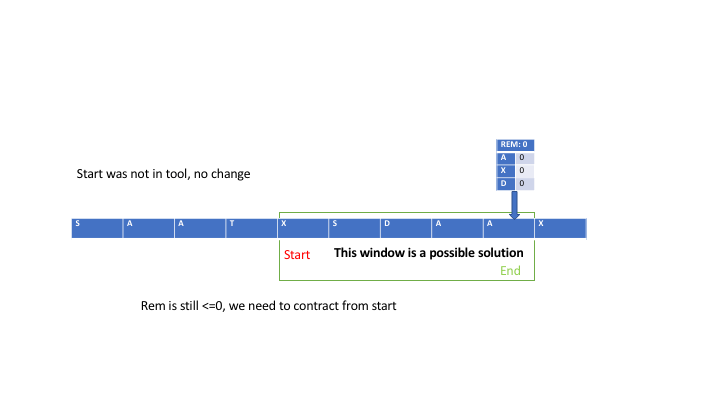\n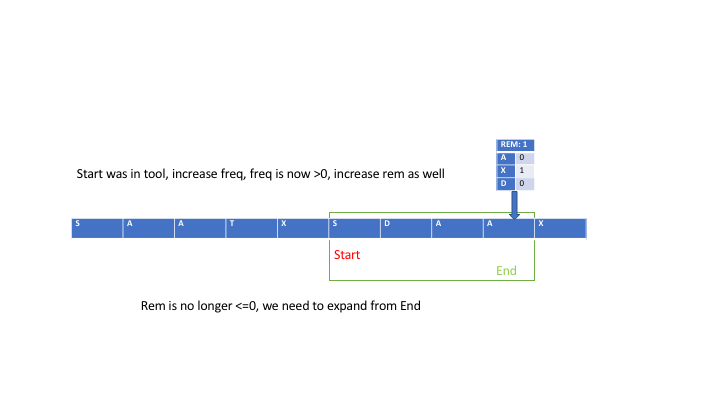\n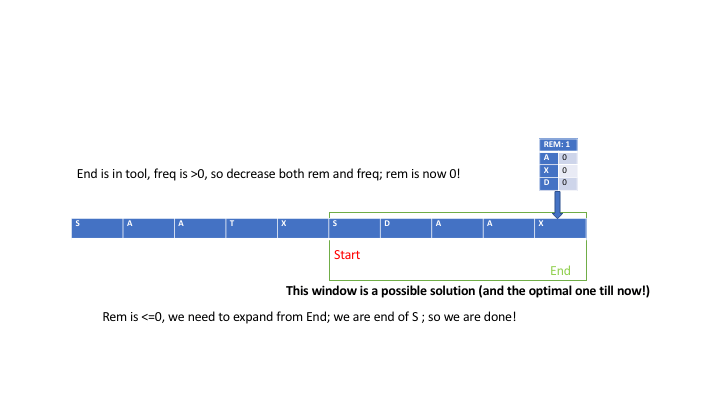\n\nHeres a corresponding AC solution in golang\n```\nfunc minWindow(s string, t string) string {\n rem := 0\n counter := make(map[byte]int)\n for i := range t {\n rem++\n counter[t[i]]++\n }\n if rem > len(s) {\n return ""\n }\n var ret = string(make([]byte, len(s)))\n start, end := 0,0\n for end < len(s){\n if v,ok := counter[s[end]] ;ok {\n if v>0 {\n rem--\n }\n counter[s[end]]--\n }\n for rem <= 0 {\n if len(ret) >= len(s[start:end+1]) {\n ret = s[start:end+1]\n }\n if _,ok := counter[s[start]] ;ok {\n counter[s[start]]++\n if counter[s[start]] > 0 {\n rem++ \n } \n }\n start++\n }\n end++\n }\n \n if ret == string(make([]byte, len(s))) {\n return ""\n }\n return ret\n}\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n
| 24
| 0
|
['Go']
| 3
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Here is my C++ code with line by line Explanation as comments
|
here-is-my-c-code-with-line-by-line-expl-7zrv
|
Please Upvote if you find it useful\n\n\nstring minWindow(string s, string t) {\n \n //This result variable will store the string which we will return\n
|
yvrjprshr
|
NORMAL
|
2021-10-15T07:24:10.931891+00:00
|
2021-10-15T07:24:10.931931+00:00
| 3,128
| false
|
Please **Upvote** if you find it useful\n\n```\nstring minWindow(string s, string t) {\n \n //This result variable will store the string which we will return\n string result;\n\n //It will check if any of the two string is empty and return empty string result\n if(s.empty() || t.empty()){\n return result;\n }\n\n //These 2 unorders maps will store frequency of characters in t string and windows\n unordered_map<char, int> map;\n unordered_map<char, int> window;\n\n //It will update the frequency of each charater of string t int map;\n for(int i = 0; i < t.length(); i++){\n map[t[i]]++;\n }\n\n //variable to store minimum length of result string\n int minLength = INT_MAX;\n\n //counter\n int letterCounter = 0;\n \n for(int slow = 0, fast = 0; fast < s.length(); fast++){\n \n //This c variable will store each character of string s according to the fast pointer movement starting from 0\n char c = s[fast];\n\n //If current character of "s" is available in map that consists of string "t" characters\n if(map.find(c) != map.end()){\n //store that character in current window and increase the counter by 1\n window[c]++;\n //This if condition will execute only if there is need to fulfill required charters from map to window and increase the letter counter\n if(window[c] <= map[c]){\n letterCounter++;\n }\n }\n\n //This condition we have found the result in current window\n if(letterCounter >= t.length()){\n while (map.find(s[slow]) == map.end() || window[s[slow]] > map[s[slow]])\n {\n //This will start decreasing frequency of extra character in window\n window[s[slow]]--;\n\n //and move slow pointer\n slow++;\n }\n\n //It will update the minimum required substring\n if(fast-slow + 1 < minLength){\n minLength = fast - slow + 1;\n //It will update the result string\n result = s.substr(slow, minLength);\n }\n }\n }\n return result;\n}\n```
| 22
| 1
|
['Two Pointers', 'C', 'Sliding Window']
| 2
|
minimum-window-substring
|
✅ One Line Solution
|
one-line-solution-by-mikposp-ptcs
|
(Disclaimer: this is not an example to follow in a real project - it is written for fun and training mostly)\n\n# Code #1.1 - Oneliner\nTime complexity: O(n). S
|
MikPosp
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-04T12:00:50.308006+00:00
|
2024-02-04T21:23:19.893242+00:00
| 4,474
| false
|
(Disclaimer: this is not an example to follow in a real project - it is written for fun and training mostly)\n\n# Code #1.1 - Oneliner\nTime complexity: $$O(n)$$. Space complexity: $$O(n)$$.\n```\nclass Solution:\n def minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:\n return (g:={\'s\':s,\'t\':t,\'a\':0,\'c\':Counter(),\'d\':Counter(t),\'r\':[inf,\'\']}) and \\\n all([setitem(g,\'b\',b),exec(\'c[s[b]]+=1\',g),exec(\'while c>=d:r=min(r,[b-a+1,s[a:b+1]]);c[s[a]]-=1;a+=1\',g)] for b in range(len(s))) and g[\'r\'][1]\n```\n\n# Code #1.2 - Unwrapped\n```\nclass Solution:\n def minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:\n a, c, d, r = 0, Counter(), Counter(t), [inf, \'\']\n for b in range(len(s)):\n c[s[b]] += 1\n while c >= d:\n r = min(r, [b-a+1, s[a:b+1]])\n c[s[a]] -= 1\n a += 1\n \n return r[1]\n```\n\n(Disclaimer 2: all code above is just a product of fantasy, it is not claimed to be pure impeccable oneliners - please, remind about drawbacks only if you know how to make it better. PEP 8 is violated intentionally)
| 21
| 0
|
['Hash Table', 'String', 'Sliding Window', 'Counting', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 10
|
minimum-window-substring
|
O(N) JAVA Sliding Window solution with explanation
|
on-java-sliding-window-solution-with-exp-t6ci
|
Sliding Window Solution:\n\n 1) Spread the right pointer until it satisfies the requirement \n 2) Shrink the left pointer to get the minimum range \n
|
cheng_zhang
|
NORMAL
|
2015-10-06T03:26:07+00:00
|
2015-10-06T03:26:07+00:00
| 6,765
| false
|
**Sliding Window Solution:**\n\n 1) Spread the right pointer until it satisfies the requirement \n 2) Shrink the left pointer to get the minimum range \n 3) Keep the above steps.\n\n**Time complexity = O(2n) = O(n)**\n\nThere're 2 loops: for loop of i, while loop of j. As j only steps forward, never steps backward. So time complexity = O(n) + O(n) = O(2n) = O(n)\n\n**JAVA Code:** \n \nA little trick is using two arrays to count the characters in s and t, instead of HashMap, to avoid TLE.\n\n boolean sContainsT(int mapS[], int mapT[]) {// Runtime = O(256) = O(1)\n for (int i = 0; i < mapT.length; i++) {// s should cover all characters in t\n if (mapT[i] > mapS[i])\n return false; \n } \n return true;\n }\n \n public String minWindow(String s, String t) { \n int mapS[] = new int[256];// Count characters in s\n int mapT[] = new int[256];// Count characters in t \n for (char ch : t.toCharArray())\n mapT[ch]++;\n \n String res = "";\n int right = 0, min = Integer.MAX_VALUE; \n for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {// Two pointers of the sliding window: i(left), right\n while (right < s.length() && !sContainsT(mapS, mapT)) {// Extend the right pointer of the sliding window\n mapS[s.charAt(right)]++;\n right++;\n }\n if (sContainsT(mapS, mapT) && min > right - i + 1) {\n res = s.substring(i, right);\n min = right - i + 1;\n }\n mapS[s.charAt(i)]--;// Shrink the left pointer from i to i + 1\n }\n return res;\n }
| 21
| 4
|
[]
| 7
|
minimum-window-substring
|
[JavaScript] Simple Sliding Window + Hash Map Solution
|
javascript-simple-sliding-window-hash-ma-7r40
|
Time Complexity: O(S + T) where S and T are the respective lengths of strings s and t\nSpace Complexity: O(S + T)\n\nIntuition\n\nThis is actually very similar
|
ryangdev
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-18T23:48:27.856387+00:00
|
2022-07-18T23:48:27.856420+00:00
| 2,733
| false
|
Time Complexity: O(S + T) where S and T are the respective lengths of strings `s` and `t`\nSpace Complexity: O(S + T)\n\n**Intuition**\n\nThis is actually very similar to the [Permutation in String](https://leetcode.com/problems/permutation-in-string/) problem. The difference is that we don\'t match based on string length since we aren\'t finding an exact permutation/anagram. Instead, we want the minimal substring which means that we move our window based on finding the smallest possible solution that takes care of the counts of all the characters in `t`. However, instead of keeping track of checking the exact count of each character each time we encounter a matching a character in `s`, we instead only need to keep track of how many unique characters there are in `t` and when a unique character goes down to 0 (or less, since having more characters than we need is okay too). Since the length only goes down each time a character reaches exactly 0, we will never reach the count of all unique characters until every unique character has reached 0.\n\nThe key insight is that once we find the first substring that satisfies the condition, we need to start moving the left part of the window until we have the minimal substring that satisfies it since we don\'t necessarily need all the characters on the left. In the test case provided:\n\n`s = "ADOBECODEBANC"`\n`t = "ABC"`\n\nThe minimal substring is just `BANC`, but we won\'t encounter it until we\'ve covered all of s. At that point, we need to trim our substring from the left until we get to the minimal substring which can be accomplished with a while loop that moves the left pointer while the substring condition is true.\n\n```\n/**\n * @param {string} s\n * @param {string} t\n * @return {string}\n */\nvar minWindow = function(s, t) {\n if (t.length > s.length) return \'\';\n \n const neededChars = {};\n \n for (let char of t) {\n neededChars[char] = (neededChars[char] || 0) + 1;\n }\n \n let left = 0;\n let right = 0;\n let neededLength = Object.keys(neededChars).length;\n let substring = \'\';\n \n while (right < s.length) {\n const rightChar = s[right];\n neededChars[rightChar]--;\n if (neededChars[rightChar] === 0) neededLength--;\n \n while (neededLength === 0) {\n if (!substring || substring.length > right - left + 1) {\n substring = s.slice(left, right + 1);\n }\n \n const leftChar = s[left];\n // If the leftChar in charMap is at exactly 0 before being \n // incremented, we now need more leftChars so that its count\n // in charMap goes down to exactly 0\n if (neededChars[leftChar] === 0) {\n neededLength++;\n }\n neededChars[leftChar]++;\n left++;\n \n }\n \n right++;\n }\n \n return substring;\n};\n```\n\n\n
| 20
| 0
|
['Sliding Window', 'JavaScript']
| 3
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Java 100% 2ms | Clean Code w/ Video Explanation
|
java-100-2ms-clean-code-w-video-explanat-j6g2
|
Please Upvote if you find the explanation helpful\n\nVideo Explanation\nMinimum Window Substring | YouTube\n\nJava Solution\n\n//2ms\n\nclass Solution {\n pu
|
sagnik_20
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-22T02:37:39.148739+00:00
|
2022-10-22T02:37:39.148777+00:00
| 2,844
| false
|
*Please **Upvote** if you find the explanation helpful*\n\n**Video Explanation**\n[Minimum Window Substring | YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vVSEJuN6BHA&feature=youtu.be)\n\n**Java Solution**\n```\n//2ms\n\nclass Solution {\n public String minWindow(String s, String t) {\n int [] map = new int[128];\n for (char c : t.toCharArray()) {\n map[c]++;\n }\n int start = 0, end = 0, minStart = 0, minLen = Integer.MAX_VALUE, counter = t.length();\n while (end < s.length()) {\n final char c1 = s.charAt(end);\n if (map[c1] > 0) counter--;\n map[c1]--;\n end++;\n while (counter == 0) {\n if (minLen > end - start) {\n minLen = end - start;\n minStart = start;\n }\n final char c2 = s.charAt(start);\n map[c2]++;\n if (map[c2] > 0) counter++;\n start++;\n }\n }\n\n return minLen == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? "" : s.substring(minStart, minStart + minLen);\n }\n}\n```
| 18
| 1
|
['Two Pointers', 'Sliding Window', 'Java']
| 6
|
minimum-window-substring
|
easy peasy python [comments] solution
|
easy-peasy-python-comments-solution-by-l-ieto
|
\tdef minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:\n ln_s = len(s)\n ln_t = len(t)\n if ln_s == 0 or ln_t == 0 or ln_t > ln_s:\n retu
|
lostworld21
|
NORMAL
|
2019-09-25T03:17:23.733874+00:00
|
2019-09-25T03:17:23.733931+00:00
| 5,029
| false
|
\tdef minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:\n ln_s = len(s)\n ln_t = len(t)\n if ln_s == 0 or ln_t == 0 or ln_t > ln_s:\n return ""\n dct = {}\n for ch in t:\n dct[ch] = dct.get(ch, 0) + 1\n \n i = j = 0\n minWindow = ln_s + 1\n output = ""\n \n #ln_t will act as my counter.\n while i < ln_s:\n if s[i] in dct:\n # count how many needed chars are decremented\n if dct[s[i]] > 0:\n ln_t -= 1\n \n # decrement from the dict even if it leads to negative\n # so that I can take care of cases such as "AZBBCA" where I\n # need to find "ABC"\n dct[s[i]] -= 1\n \n # shrink the window size\n # and get the result and make it non-valid window\n # so that I can look forward\n while ln_t == 0:\n if i - j + 1 < minWindow:\n minWindow = i - j + 1\n output = s[j: i+1]\n \n if s[j] in dct:\n dct[s[j]] += 1\n \n # I added a char from shrinking window\n # which is needed for me to get "T"\n if dct[s[j]] > 0:\n ln_t += 1\n \n j += 1\n \n i += 1\n \n return "" if minWindow == ln_s + 1 else output
| 18
| 2
|
['Sliding Window', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 2
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Java | Beats 100 %
|
java-beats-100-by-beingbmc12-r2l1
|
java\nclass Solution {\n public String minWindow(String s, String t) {\n if(s.isEmpty()) return "";\n int[] need = new int[128];\n for(c
|
beingbmc12
|
NORMAL
|
2019-06-09T07:06:31.863273+00:00
|
2019-06-09T07:06:31.863306+00:00
| 1,488
| false
|
```java\nclass Solution {\n public String minWindow(String s, String t) {\n if(s.isEmpty()) return "";\n int[] need = new int[128];\n for(char c : t.toCharArray()) need[c]++;\n char[] a = s.toCharArray();\n int r = 0, l = 0, missing = t.length(), i = 0, j = 0;\n while(r < s.length()){\n if(need[a[r]] > 0) missing --;\n need[a[r]]--;\n r ++;\n while(missing == 0){\n if(j == 0 || (r - l) < (j - i)){\n j = r;\n i = l;\n }\n need[a[l]]++;\n if(need[a[l]] > 0) missing++;\n l++;\n }\n }\n return s.substring(i, j);\n }\n}\n```
| 18
| 0
|
[]
| 5
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Python, easy to understand, no weird tricks
|
python-easy-to-understand-no-weird-trick-rww4
|
\nimport collections\nclass Solution(object):\n def minWindow(self, s, t):\n """\n :type s: str\n :type t: str\n :rtype: str\n
|
frankli92
|
NORMAL
|
2019-03-26T20:56:14.265147+00:00
|
2019-03-26T20:56:14.265204+00:00
| 1,086
| false
|
```\nimport collections\nclass Solution(object):\n def minWindow(self, s, t):\n """\n :type s: str\n :type t: str\n :rtype: str\n """\n if len(s) < len(t):\n return ""\n \n hashmap = collections.Counter(t)\n counter = len(t)\n min_window = ""\n start, end = 0, 0\n \n \n for end in range(len(s)):\n if hashmap[s[end]] > 0:\n counter -= 1\n hashmap[s[end]] -= 1\n \n while counter == 0:\n length = end - start + 1\n \n if not min_window or len(min_window) > length:\n min_window = s[start:end+1]\n \n hashmap[s[start]] += 1\n\n if hashmap[s[start]] > 0:\n counter += 1\n \n start += 1\n return min_window\n \n \n \n```
| 18
| 0
|
[]
| 5
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Simple JavaScript solution with comments
|
simple-javascript-solution-with-comments-ssxg
|
function minWindow(s, t) {\n var ans = '';\n \n // 1. process hashmap\n var map = {};\n t.split('').forEach(ch => map[ch] = (
|
linfongi
|
NORMAL
|
2016-05-16T03:39:09+00:00
|
2016-05-16T03:39:09+00:00
| 4,167
| false
|
function minWindow(s, t) {\n var ans = '';\n \n // 1. process hashmap\n var map = {};\n t.split('').forEach(ch => map[ch] = (map[ch] || 0) + 1);\n var count = Object.keys(map).length;\n \n // 2. traverse s to find boundaries\n // both l & r are inclusive\n var l = 0;\n var r = -1;\n \n while (r < s.length) {\n if (count === 0) {\n // good condition\n // l~r contains t\n \n // update ans\n if (!ans || r - l + 1 < ans.length) {\n ans = s.slice(l, r + 1);\n }\n \n // get rid of curr ch and then move l\n if (map[s[l]] !== undefined) {\n map[s[l]]++;\n }\n if (map[s[l]] > 0) {\n count++;\n }\n l++;\n \n } else {\n // bad condition\n // l~r doesn't contain t\n \n // move r and add new ch\n r++;\n if (map[s[r]] !== undefined) {\n map[s[r]]--;\n }\n if (map[s[r]] === 0) {\n count--;\n }\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }
| 18
| 0
|
[]
| 9
|
minimum-window-substring
|
C++ - Easiest Beginner Friendly Sol || Sliding Window
|
c-easiest-beginner-friendly-sol-sliding-f1qv2
|
Intuition of this Problem:\nReference - https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-window-substring/solutions/26808/here-is-a-10-line-template-that-can-solve-most-su
|
singhabhinash
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-05T09:21:51.345562+00:00
|
2023-02-05T09:21:51.345594+00:00
| 2,501
| false
|
# Intuition of this Problem:\nReference - https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-window-substring/solutions/26808/here-is-a-10-line-template-that-can-solve-most-substring-problems/?orderBy=hot\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n**NOTE - PLEASE READ APPROACH FIRST THEN SEE THE CODE. YOU WILL DEFINITELY UNDERSTAND THE CODE LINE BY LINE AFTER SEEING THE APPROACH.**\n\n# Approach for this Problem:\n1. Initialize a map of size 128 to store the frequency of each character in string t.\n2. Use a counter to keep track of the number of characters in t that have not been found in s yet.\n3. Use two pointers, begin and end, to traverse the string s.\n4. Increment the end pointer until a character is found in t and decrement the frequency of that character in the map. If the frequency of the character in the map becomes zero, decrement the counter.\n5. When the counter reaches zero, it means that all the characters in t have been found in s. Start incrementing the begin pointer until the frequency of the character in the map becomes greater than zero.\n6. Increment the counter when this happens.\n7. Update the minimum window length and starting position if a new minimum window is found.\n8. Repeat steps 3-5 until the end pointer has reached the end of string s.\n9. Return the minimum window substring or an empty string if no such window exists.\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Humble Request:\n- If my solution is helpful to you then please **UPVOTE** my solution, your **UPVOTE** motivates me to post such kind of solution.\n- Please let me know in comments if there is need to do any improvement in my approach, code....anything.\n- **Let\'s connect on** https://www.linkedin.com/in/abhinash-singh-1b851b188\n\n\n\n# Code:\n```C++ []\n//shorter version\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n vector<int> map(128,0);\n for (auto c : t) map[c]++;\n int counter = t.size(), begin = 0, end = 0, d = INT_MAX, head = 0;\n while (end < s.size()){\n if (map[s[end++]]-- > 0) counter--; //in t\n while (counter == 0){ //valid\n if (end - begin<d) d = end - (head = begin);\n if (map[s[begin++]]++ == 0) counter++; //make it invalid\n } \n }\n return d == INT_MAX ? "" : s.substr(head, d);\n }\n};\n```\n```C++ []\n//detailed version\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n\t vector<int> m(128, 0);\n\t // Statistic for count of char in t\n\t for (auto c : t) \n m[c]++;\n\t // counter represents the number of chars of t to be found in s.\n\t int start = 0, end = 0, counter = t.size(), minStart = 0, minLen = INT_MAX;\n\t int size = s.size(); \n\t\n\t // Move end to find a valid window.\n\t while (end < size) {\n\t\t // If char in s exists in t, decrease counter\n\t\t if (m[s[end]] > 0)\n\t\t\t counter--;\n\t\t // Decrease m[s[end]]. If char does not exist in t, m[s[end]] will be negative.\n\t\t m[s[end]]--;\n\t\t end++;\n\t\t // When we found a valid window, move start to find smaller window.\n\t\t while (counter == 0) {\n\t\t\t if (end - start < minLen) {\n\t\t\t\t minStart = start;\n\t\t\t\t minLen = end - start;\n\t\t\t }\n\t\t\t m[s[start]]++;\n\t\t\t // When char exists in t, increase counter.\n\t\t\t if (m[s[start]] > 0)\n\t\t\t\t counter++;\n\t\t\t start++;\n\t\t }\n\t }\n\t if (minLen != INT_MAX)\n\t\t return s.substr(minStart, minLen);\n\t return "";\n }\n};\n```\n\n# Time Complexity and Space Complexity:\n- Time complexity: **O(|s| + |t|)**\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: **O(1)**, as the size of the map is constant and the space required is independent of the size of s and t.\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
| 17
| 0
|
['Hash Table', 'String', 'Sliding Window', 'C++']
| 2
|
minimum-window-substring
|
[C++] [Sliding Window] - Simple and easy to understand with explanation | O(n) time complexity
|
c-sliding-window-simple-and-easy-to-unde-p3vv
|
Make two frequency count array and store the frequency of t initially\n2. If character match with the characters of t, increment the count variable\n3. if count
|
morning_coder
|
NORMAL
|
2020-10-11T09:21:10.403538+00:00
|
2020-10-11T09:25:22.376006+00:00
| 4,905
| false
|
1. Make two frequency count array and store the frequency of t initially\n2. If character match with the characters of t, increment the count variable\n3. if count==length of t (t_len) => we found a window with all characters of t\n4. Minimize the window size by removing extra characters from the start of window (using win_left for this).\n5. Keep updating window of smaller length \n6. Print substring of the smallest window found.\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n int s_len=s.length();\n int t_len=t.length();\n \n vector<int> freq_t(256,0);\n vector<int> freq_s(256,0);\n for(int i=0;i<t_len;i++)\n freq_t[t[i]]++;\n \n int win_left=0; //Current window will always be [win_left,i]\n int ans=INT_MAX,ans_left; //Track smallest window\n int count=0; //For tracking number of characters encountered of string t in string s\n\t\t\n\t\t\n for(int i=0;i<s_len;i++){\n if(freq_t[s[i]]>0 && freq_t[s[i]]>freq_s[s[i]])\n count++;\n freq_s[s[i]]++;\n if(count==t_len){ \n /*\n\t\t\t\tAll characters required are in current window\n Now , try to minimize window by removing extra character at the start of window\n */\n\t\t\t\t\n while(win_left<i && //Extra frequency or zero frequency characters\n (freq_t[s[win_left]]<freq_s[s[win_left]] || freq_t[s[win_left]]==0)){\n \n if(freq_t[s[win_left]]<freq_s[s[win_left]])\n freq_s[s[win_left]]--;\n win_left++;\n }\n if(ans>(i-win_left+1)){\n ans=(i-win_left+1);\n ans_left=win_left; \n }\n }\n }\n if(ans==INT_MAX)\n return "";\n return s.substr(ans_left,ans);\n }\n};\n```
| 17
| 2
|
['C', 'Sliding Window', 'C++']
| 4
|
minimum-window-substring
|
C++ || Sliding Window || Map || String || Easy Explanation || Simple
|
c-sliding-window-map-string-easy-explana-iewz
|
Approach \n- Sliding Window Technique!!\n- Map for storing Frequency\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(m+n)\n Add your time complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n\n-
|
yashgaherwar2002
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-22T05:39:05.234493+00:00
|
2022-10-22T05:39:05.234538+00:00
| 2,541
| false
|
# Approach \n- Sliding Window Technique!!\n- Map for storing Frequency\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(m+n)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(n)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n // Sliding Window Approach\n // Time Complexity:- O(m+n)\n // Space Complexity:- O(n)\n \n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n vector<string> ans;\n map<char,int> mp;\n\n // Storing frequency of each character resent in t string\n for(auto i: t){\n mp[i]++;\n }\n\n // Starting Point of window\n int i=0;\n // Ending Point of window\n int j=0;\n int count=mp.size();\n // st and mini for storing starting and ending point of our resultant substring\n int st=0;\n int mini=INT_MAX;\n\n // Actual Approach\n while(j<s.size()){\n mp[s[j]]--;\n\n if(mp[s[j]]==0){\n count--;\n }\n\n if(count==0){\n while(count==0){\n if((j-i+1)<mini){\n mini=j-i+1;\n st=i;\n }\n\n mp[s[i]]++;\n\n if(mp[s[i]]>0){\n count++;\n }\n\n i++;\n }\n }\n \n j++;\n }\n \n // If No valid ans possible return empty string else return the final substring \n if(mini==INT_MAX){\n return "";\n }\n else{\n return s.substr(st,mini);\n }\n\n }\n};\n```
| 15
| 0
|
['String', 'Ordered Map', 'Sliding Window', 'C++']
| 3
|
minimum-window-substring
|
[Python] O(N) and O(T) with explanation
|
python-on-and-ot-with-explanation-by-unk-n3b0
|
\nTime Complexity: O(N)\nSpace Complexity: O(T)\n\n\n\nfrom collections import Counter\nclass Solution:\n def minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:\n\t\t#
|
Unkn0wnPerson
|
NORMAL
|
2021-01-08T06:43:17.396055+00:00
|
2021-01-08T08:07:58.167722+00:00
| 1,693
| false
|
```\nTime Complexity: O(N)\nSpace Complexity: O(T)\n```\n\n```\nfrom collections import Counter\nclass Solution:\n def minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:\n\t\t# Count number of occurrences of each character from target string.\n t=Counter(t) \n\t\t\n #This will store number of unique characters in target string e.g "aba": 2, "abc": 3\n\t\tcount=len(t) \n\t\t\n\t\t# Sliding window initialization\n\t\ti, j=0, 0 \n\t\t\n\t\t# Minimum size of the window where all characters from target string are found\n mini_window=float(\'inf\') \n\t\t\n\t\t# Return answer\n mini_word=""\n \n while j < len(s):\n\t\t\n\t\t\t# The following loop will run till we get all occourences of target characters in the window\n\t\t\t# size of s[i: j], this is indicated if the count hits 0.\n while j < len(s) and count != 0: \n if s[j] in t:\n t[s[j]] -= 1\n if t[s[j]] == 0:\n count -= 1\n j += 1\n \n\t\t\t# Now since we have a window from s[i: j] containing all characters from target string.\n\t\t\t# We will try to reduce the string until one character goes missing\n\t\t\t# And concurrently store the minimum string containing all characters from traget string.\n while i <= j and count==0:\n if mini_window > j-i:\n mini_word=s[i: j]\n mini_window = j-i # j-i is minimum window size.\n\n if s[i] in t:\n t[s[i]] += 1\n \n if t[s[i]] >=1:\n count += 1 \n i += 1\n\t\t\n\t\t# Finally return the answer we received\n return mini_word\n```\n\n**UPVOTE IF YOU LIKED THE EXPLANATION OR COMMENT THE EDIT IF ANY**
| 15
| 0
|
['Sliding Window', 'Python3']
| 2
|
minimum-window-substring
|
⭐✅ LOGICAL COMMENTS || EASY C++ CODE || Including logical comments
|
logical-comments-easy-c-code-including-l-9odz
|
Easy to understand code with complete comments:\n\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n unordered_map<char, int>mp;\
|
SachinSahu
|
NORMAL
|
2022-06-22T05:24:18.500542+00:00
|
2022-11-08T13:54:19.178848+00:00
| 909
| false
|
# Easy to understand code with complete comments:\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n unordered_map<char, int>mp;\n \n // keeping track of common char b/w s ans t\n for(auto i : t)\n mp[i]++;\n \n int start = 0,end =0; // starting and ending of window\n int minlen = INT_MAX, minstart = 0;\n int count = t.size(); // variable to track when our window becomes valid\n int s_size = s.size();\n \n while(end<s_size)\n {\n \n if(mp[s[end]]>0) // possible only for char common b/w s and t\n count--;\n \n mp[s[end]]--; // adding char to window and decreasing the mapping\n end++; //move end forward\n \n while(count==0) // possible answer only here\n {\n if(end - start < minlen) // window length minimization\n {\n minlen = end - start;\n minstart = start;\n }\n \n mp[s[start]]++; // removing char from window and increasing the mapping\n \n if(mp[s[start]]>0) // possible only for the common chars and hence increase its count to make window invalid\n count++;\n \n start++; // move start forward\n }\n \n }\n \n if (minlen != INT_MAX)\n\t\t return s.substr(minstart, minlen);\n\t return ""; // happens when s.size() < t.size()\n }\n};\n```
| 14
| 0
|
['Two Pointers', 'C', 'Sliding Window', 'C++']
| 1
|
minimum-window-substring
|
C++ 😊 ADITYA VERMA SOLUTION 💖
|
c-aditya-verma-solution-by-sayan_11_mait-zoqn
|
\nclass Solution\n{\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t)\n {\n unordered_map<char, int> mp;\n for (int i = 0; i < t.size(); i++)\
|
sayan_11_maitra
|
NORMAL
|
2022-01-14T16:41:51.422347+00:00
|
2022-09-17T10:08:58.417616+00:00
| 999
| false
|
```\nclass Solution\n{\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t)\n {\n unordered_map<char, int> mp;\n for (int i = 0; i < t.size(); i++)\n {\n mp[t[i]]++;\n }\n int count = mp.size();\n string ans;\n\n int mini = INT_MAX;\n\n int i = 0;\n int j = 0;\n\n while (j < s.size())\n {\n\n if (mp.find(s[j]) != mp.end())\n {\n mp[s[j]]--;\n if (mp[s[j]] == 0)\n {\n count--;\n }\n }\n\n while (count == 0)\n {\n if (mini > j - i + 1)\n {\n mini = min(mini, j - i + 1);\n ans = s.substr(i, j - i + 1);\n }\n if (mp.find(s[i]) != mp.end())\n {\n mp[s[i]]++;\n if (mp[s[i]] == 1)\n {\n count++;\n }\n }\n i++;\n }\n j++;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n\t```
| 14
| 1
|
['C']
| 4
|
minimum-window-substring
|
C++ - 2 approaches for hashmap - way too much commenting and explanation
|
c-2-approaches-for-hashmap-way-too-much-9ptw2
|
The idea of sliding window is this:\n1. Start two pointers - begin and end, both at 0.\n2. Keep begin constant. Move end (i.e., do end++) till the condition is
|
kiyosaanb
|
NORMAL
|
2020-09-14T17:34:46.595961+00:00
|
2020-09-14T17:35:25.490167+00:00
| 1,932
| false
|
**The idea of sliding window is this:**\n1. Start two pointers - begin and end, both at 0.\n2. Keep begin constant. Move end (i.e., do end++) till the condition is satisfied.\n3. Once the condition is satisfied, move the begin pointer (do begin++) for as long as the condition is still satisfied. Update the minLength and keep a track of where the start pointer is at for that particular length. If its smaller than a previous length, update it. If not, continue with resizing the window as below:\n4. Move end pointer to the right till the condition is satisfied again.\n5. Once the entire string is traversed, use the minStart pointer and minlength to get the substring.\n\n**Checking the condition:**\n* Now, the condition to satisfy here is - all chars (including duplicates) of string t are in the substring of s that we are processing. How do we check this? We need something like a hashcode. So build a hashtable/hashmap for t with it\'s chars and their respective frequencies. \n* Okay, now we need something similar for the substring we are processing so we can compare them both. Two ways to do this - create a plain vanilla hashmap for the substring or, use the map of t and use a counter to indicate number of chars to be matched. The second one is troubling for me. Its a bit too much to wrap my head around. nevertheless, code for both approaches are below:\n\n**WITH TWO HASHMAPS**\n```\nclass Solution {\nprivate:\n bool isMatchingHashCode(map<char,int>& smap,map<char,int>& tmap){\n for(auto it = tmap.begin(); it != tmap.end(); ++it){\n char c= it->first; int freq = it->second;\n if(smap[c] <freq)\n return false;\n }\n return true;\n }\n \npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n \n map<char,int> tmap,smap;\n for(char c : t) tmap[c]++;\n //tmap is the hashcode\n \n int start=0,end=0,counter=t.size(),minStart=0,minLen=INT_MAX;\n // counter represents the number of chars of t to be found in s.\n int size = s.size();\n \n while(end<size){\n smap[s[end]]++;; //add the freq of the char to smap \n end++; //window to the right\n \n //by this time, if we have reached the matching substring, we will start resizing. If not, then the window has been expanded on the right size and its proceeding\n while(isMatchingHashCode(smap,tmap)){\n if(end-start<minLen){\n minStart=start;\n minLen = end-start;\n } //update the head and tail and length if needed, else, continue resizing\n smap[s[start]]--; //going left \n start++;\n }\n \n }\n \n if(minLen!=INT_MAX){\n return s.substr(minStart,minLen);\n }\n return "";\n \n }\n};\n```\n\nThis one is super slow. Comparing the two maps over and over takes time. \nHere is the second approach:\n\n**USING ONE HASHMAP**\n(Though i do understand this now, i dont think this comes to me intuitively. How does one develop this intuition? Please help me understand this. Thanks in advance!)\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n vector<int> tfreq(128,0);\n for(char c : t) tfreq[c]++;\n //tfreq is the hashcode\n \n int start=0,end=0,counter=t.size(),minStart=0,minLen=INT_MAX;\n // counter represents the number of chars of t to be found in s.\n int size = s.size();\n \n while(end<size){\n //if character in s exists in t => i.e., if char exists in t, the freq would be positive. (0if non-existent, -ve never happens)\n if(tfreq[s[end]]>0){\n counter--; //no.of chars to be found is 1 less now\n }\n tfreq[s[end]]--; //reduce the freq of that char regardless of its presence in t\n //if the char is not in t, it will result in negative frequency. later as we move the start pointer to the left, we will increase the freq of this char. So we will essentially cancel out all the subtractions we do on the char \n end++; //window to the right\n \n //by this time, if we have reached the matching substring, we will start resizing. If not, then the window has been expanded on the right size and its proceeding\n //when counter=0, tfreq should have all 0s\n while(counter==0){\n if(end-start<minLen){\n minStart=start;\n minLen = end-start;\n } //update the head and tail and length if needed, and then continue resizing\n tfreq[s[start]]++; \n /*if the char existed in t already, then freq would be greater than 0. Otherwise it will be 0 or less than 0as we reduced the frequency of the char earlier regardless of it being in t or not*/\n if(tfreq[s[start]]>0) counter++;\n start++;\n }\n \n }\n if(minLen!=INT_MAX){\n return s.substr(minStart,minLen);\n }\n return "";\n \n }\n};\n```
| 14
| 1
|
['C', 'C++']
| 5
|
minimum-window-substring
|
O( n )✅ | C++ (Step by step explanation)✅
|
o-n-c-step-by-step-explanation-by-monste-o5g2
|
Intuition\nThe problem requires finding the minimum window in string \'s\' that contains all characters from string \'t\'. We can use a sliding window approach
|
monster0Freason
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-27T17:43:52.444678+00:00
|
2023-10-27T17:43:52.444710+00:00
| 1,673
| false
|
# Intuition\nThe problem requires finding the minimum window in string \'s\' that contains all characters from string \'t\'. We can use a sliding window approach to solve this problem efficiently.\n\n# Approach\n1. First, we handle the edge case: if \'t\' is an empty string, we return an empty string as the result.\n\n2. We initialize two dictionaries, \'t_counter\' and \'window\', to keep track of character counts in \'t\' and the current window, respectively.\n\n3. We populate \'t_counter\' by iterating through the characters of \'t\' and incrementing their counts. It helps us keep track of the characters we need to match in \'s\'.\n\n4. We define \'have\' to track how many required characters we have in our current window and \'need\' to represent the total number of characters required. We also initialize \'ans\' and \'ans_size\' to store the minimum window and its size. \'ans\' starts as [-1, -1] to represent an invalid window, and \'ans_size\' starts as positive infinity.\n\n5. We set \'left\' to 0 as the start of our sliding window.\n\n6. We iterate through \'s\' using a \'right\' pointer to expand the window:\n - Update \'window\' to keep track of character counts in the current window.\n - If the character at \'right\' is in \'t_counter\' and its count in \'window\' matches its count in \'t_counter\', we increment \'have\'.\n\n7. We enter a while loop as long as we have all required characters in our window:\n - If the current window size is smaller than \'ans_size\', we update \'ans\' and \'ans_size\' to record this as a potential minimum window.\n - We decrement the count of the character at \'left\' in \'window\'.\n - If the character at \'left\' is in \'t_counter\' and its count in \'window\' is less than its count in \'t_counter\', we decrement \'have\'.\n - We move \'left\' to the right to shrink the window.\n\n8. After the loop, we have found the minimum window. We return the substring of \'s\' from \'ans[0]\' to \'ans[1]\' if \'ans_size\' is not still equal to positive infinity. Otherwise, we return an empty string.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(s + t), where \'s\' is the length of string \'s\' and \'t\' is the length of string \'t\'.\n- Space complexity: O(s + t) due to the dictionaries \'t_counter\' and \'window\'.\n\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n if(t == ""){\n return "";\n }\n\n unordered_map<char , int> t_counter , window ;\n\n for(auto x : t){\n t_counter[x] = 1 + t_counter[x];\n }\n\n int have = 0 , need = t_counter.size() , ans_size = INT_MAX;\n vector<int> ans;\n int left = 0 ;\n\n for(int right = 0 ; right < s.size() ; right++){\n window[s[right]] = 1 + window[s[right]] ;\n\n if(t_counter.find(s[right]) != t_counter.end() && window[s[right]] == t_counter[s[right]]){\n have++;\n }\n\n while(have == need){\n if((right - left + 1) < ans_size){\n ans = {left , right} ;\n ans_size = right - left + 1 ;\n }\n \n window[s[left]] -= 1 ;\n if(t_counter.find(s[left]) != t_counter.end() && window[s[left]] < t_counter[s[left]]){\n have--;\n }\n left++ ;\n } \n }\n\n return ans_size != INT_MAX ? s.substr(ans[0] , ans[1]-ans[0]+1) : "" ;\n \n \n }\n};\n```\n\n# Please upvote the solution if you understood it.\n\n
| 13
| 0
|
['Sliding Window', 'C++']
| 1
|
minimum-window-substring
|
✅ [Python/Rust/C++] fast & concise using two-pointer sliding window (with detailed comments)
|
pythonrustc-fast-concise-using-two-point-3djq
|
\u2705 IF YOU LIKE THIS SOLUTION, PLEASE UPVOTE.\n*\nThis solution employs a two-pointer sliding window approach to search for the minimum substring. Time compl
|
stanislav-iablokov
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-22T11:49:45.391794+00:00
|
2022-10-23T11:15:05.703121+00:00
| 1,639
| false
|
**\u2705 IF YOU LIKE THIS SOLUTION, PLEASE UPVOTE.**\n****\nThis solution employs a two-pointer sliding window approach to search for the minimum substring. Time complexity is linear: **O(n+m)**. Space complexity is linear: **O(n)**. \n\n| Language | Runtime | Memory |\n|---|---|---|\n| [**Python**](https://leetcode.com/submissions/detail/827879845/) | **105 ms (92.26%)** | **14.6 MB (83.90%)** |\n| [**Rust**](https://leetcode.com/submissions/detail/827849495/) | **0 ms (100.00%)** | **2.2 MB (69.33%)** |\n| [**C++**](https://leetcode.com/submissions/detail/827877701/) | **0 ms (100.00%)** | **7.8 MB (68.10%)** |\n\n<iframe src="https://leetcode.com/playground/gqPFE9ur/shared" frameBorder="0" width="800" height="600"></iframe>\n
| 13
| 1
|
['C', 'Python', 'Rust']
| 1
|
minimum-window-substring
|
JavaScript - 96.66 % better - used char Array instead if Hash Map
|
javascript-9666-better-used-char-array-i-u0sl
|
```\nvar minWindow = function(s, t) {\n \n let arr = new Array(128).fill(0); // Ascii charSet array to store count\n let result = [-Infinity, Infinity]
|
varungowde
|
NORMAL
|
2020-03-28T07:50:01.342088+00:00
|
2020-03-28T07:50:01.342126+00:00
| 3,396
| false
|
```\nvar minWindow = function(s, t) {\n \n let arr = new Array(128).fill(0); // Ascii charSet array to store count\n let result = [-Infinity, Infinity] // result not yet known\n let missing = t.length; // missing words initially\n \n for(let i=0; i < t.length; i++){ // increase the count in arr\n arr[t.charCodeAt(i)]++\n }\n \n let start = 0;\n \n for(let end = 0; end < s.length; end++){ // start from 0 and then expand\n if(arr[s.charCodeAt(end)] > 0){ // element present in t then decrese missing\n missing--\n }\n \n arr[s.charCodeAt(end)]-- // if not present in t then make it negative\n \n while(missing == 0){ // start decrementing start to check the best option\n if(result[1]-result[0] > end - start){ // store the best answer always\n result[1] = end; result[0] = start\n }\n \n \n arr[s.charCodeAt(start)]++ \n if(arr[s.charCodeAt(start)] > 0){ // if the char is present in t\n missing++\n }\n \n start++ \n }\n \n \n }\n \n return result[1] == Infinity ? "" : s.slice(result[0], result[1]+1);\n \n};
| 13
| 0
|
['Array', 'Sliding Window', 'JavaScript']
| 2
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Simple Python two-pointer solution
|
simple-python-two-pointer-solution-by-ot-on6e
|
Please see and vote for my solutions for these similar problems.\n1208. Get Equal Substrings Within Budget\n3. Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters\n1
|
otoc
|
NORMAL
|
2019-07-27T07:03:54.464836+00:00
|
2019-09-29T04:19:38.236871+00:00
| 1,345
| false
|
Please see and vote for my solutions for these similar problems.\n[1208. Get Equal Substrings Within Budget](https://leetcode.com/problems/get-equal-substrings-within-budget/discuss/392901/Simple-Python-moving-window)\n[3. Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters](https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-substring-without-repeating-characters/discuss/348137/Simple-Python-two-pointer-solution-(52ms-beat-97.94))\n[159. Longest Substring with At Most Two Distinct Characters](https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-substring-with-at-most-two-distinct-characters/discuss/348157/Simple-Python-two-pointer-solution)\n[340. Longest Substring with At Most K Distinct Characters](https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-substring-with-at-most-k-distinct-characters/discuss/348216/Simple-Python-two-pointer-solution-(72-ms-beat-94.93))\n[992. Subarrays with K Different Integers](https://leetcode.com/problems/subarrays-with-k-different-integers/discuss/348984/Different-Python-two-pointer-solutions)\n[424. Longest Repeating Character Replacement](https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-repeating-character-replacement/discuss/363071/Simple-Python-two-pointer-solution)\n[209. Minimum Size Subarray Sum](https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-size-subarray-sum/discuss/344476/Simple-Python-two-pointer-solution)\n[713. Subarray Product Less Than K](https://leetcode.com/problems/subarray-product-less-than-k/discuss/344245/Simple-Python-solution-(beat-94.59))\n[76. Minimum Window Substring](https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-window-substring/discuss/344533/Simple-Python-two-pointer-solution)\n\nSolution 1:\nKeep a moving window expand while curr_freqs < freqs , then shrink while curr_freqs >= freqs.\nEach time after shrinking, update the minimal window.\nWhere curr_freqs >= freqs means all([curr_freqs[c] >= freqs[c] for c in freqs]).\n```\n def minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:\n freqs = collections.Counter(t)\n curr_freqs = {c: 0 for c in freqs}\n res, res_len = "", float(\'inf\')\n left = 0\n for right in range(len(s)):\n if s[right] in freqs:\n curr_freqs[s[right]] += 1\n while all([curr_freqs[c] >= freqs[c] for c in freqs]):\n if right - left + 1 < res_len:\n res_len = right - left + 1\n res = s[left:right+1]\n if s[left] in freqs:\n curr_freqs[s[left]] -= 1\n left += 1\n return res\n```\n\nSolution 2: improve the efficiency of all([curr_freqs[c] >= freqs[c] for c in freqs])\n```\n def minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:\n need = collections.Counter(t)\n missing = sum(need.values())\n res, res_len = "", float(\'inf\')\n left = 0\n for right in range(len(s)):\n if s[right] in need:\n missing -= need[s[right]] > 0\n need[s[right]] -= 1\n while missing == 0:\n if right - left + 1 < res_len:\n res_len = right - left + 1\n res = s[left:right+1]\n if s[left] in need:\n missing += need[s[left]] >= 0\n need[s[left]] += 1\n left += 1\n return res\n```
| 13
| 0
|
[]
| 1
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Simple 2 pointer approach || Beats 100% 🔥🔥 || Python & CPP || T.C. : O(n) & S.C. : O(1)
|
simple-2-pointer-approach-beats-100-pyth-l7z8
|
IntuitionThe problem is about finding the smallest substring of s that contains all the characters of string t (including duplicates). The task can be efficient
|
devilshiv_07
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-25T19:03:52.111077+00:00
|
2025-02-08T11:42:12.211457+00:00
| 2,060
| false
|
---
# Intuition
The problem is about finding the smallest substring of s that contains all the characters of string t (including duplicates). The task can be efficiently solved using the sliding window technique with a frequency map to count characters.
The goal is to:
1. Expand the window to include characters until all characters of t are covered.
2. Shrink the window while maintaining the condition that all characters of t are still covered to minimize the substring length.
---
# Approach
1. Frequency Map for t:
• Create a frequency map (Hash) to store the count of each character in t. This helps us keep track of which characters and how many of each are still needed.
2. Sliding Window:
• Use two pointers (l and r) to define the current window in s.
• Expand the window by moving the right pointer (r) and updating the frequency map for the characters in the current window.
• Maintain a count (cnt) of how many characters from t are currently satisfied in the window.
3. Check for Valid Window:
• When all characters of t are covered (cnt == len(t)), try shrinking the window from the left (l) to see if a smaller valid window exists.
• If the current window is smaller than the previously recorded minimum window, update the result.
4. Move Left Pointer:
• Increment the count of the character at l in the frequency map.
• If it causes a character from t to fall below its required count, decrement cnt.
5. Output the Result:
• After iterating through s, return the smallest valid window substring. If no such substring exists, return an empty string.
---
# Complexity
1. Time complexity:
• Building the Frequency Map: O(m), where m is the length of t.
• Sliding Window Process: The right pointer (r) iterates through the string s once, and the left pointer (l) moves independently. Both pointers combined move at most times, where n is the length of s. Thus, this part is O(n).
• Overall: (n+m).
2. Space complexity:
• Frequency Map: A fixed size array of size 256 is used to store character frequencies. This takes O(1) space.
• Additional Variables: A few integers are used for tracking indices and counts.
• Overall: O(1) additional space.
---
# Code
```python3 []
# If it's helpful, Please upvote my solution🙏.
class Solution:
def minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:
n, m = len(s), len(t)
l, r, cnt = 0, 0, 0
maxLen = 10**9
sIndex = n
Hash = [0]*256
for c in t:
Hash[ord(c)] += 1
while(r < n):
if Hash[ord(s[r])] > 0: cnt += 1
Hash[ord(s[r])] -= 1
while(cnt == m):
if (r-l+1) < maxLen:
maxLen = r -l+1
sIndex = l
Hash[ord(s[l])] += 1
if Hash[ord(s[l])] > 0: cnt -= 1
l += 1
r += 1
return s[sIndex:sIndex+maxLen]
```
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
string minWindow(string s, string t) {
int n = s.length(), m = t.length();
int l = 0, r = 0, cnt = 0;
int maxLen = INT_MAX;
int sIndex = n;
vector<int> hash(256, 0);
for (char c : t) {
hash[c]++;
}
while (r < n) {
if (hash[s[r]] > 0) cnt++;
hash[s[r]]--;
while (cnt == m) {
if (r - l + 1 < maxLen) {
maxLen = r - l + 1;
sIndex = l;
}
hash[s[l]]++;
if (hash[s[l]] > 0) cnt--;
l++;
}
r++;
}
return maxLen == INT_MAX ? "" : s.substr(sIndex, maxLen);
}
};
```
---

| 12
| 0
|
['Hash Table', 'Two Pointers', 'Sliding Window', 'C++', 'Python3']
| 1
|
minimum-window-substring
|
C++ - Easiest Beginner Friendly Sol || Sliding window
|
c-easiest-beginner-friendly-sol-sliding-t54i5
|
Intuition of this Problem:\nReference - https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-window-substring/solutions/26808/here-is-a-10-line-template-that-can-solve-most-su
|
singhabhinash
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-04T13:34:44.302376+00:00
|
2023-02-04T13:34:44.302403+00:00
| 2,963
| false
|
# Intuition of this Problem:\nReference - https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-window-substring/solutions/26808/here-is-a-10-line-template-that-can-solve-most-substring-problems/?orderBy=hot\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n**NOTE - PLEASE READ APPROACH FIRST THEN SEE THE CODE. YOU WILL DEFINITELY UNDERSTAND THE CODE LINE BY LINE AFTER SEEING THE APPROACH.**\n\n# Approach for this Problem:\n1. Create a vector of size 128, m, to store the count of characters in string t.\n2. Initialize start and end pointers, counter and variables minStart and minLen to store the starting position and length of the minimum window substring.\n3. Traverse the string s from the end pointer and increase the end pointer until you find a valid window:\n4. If the current character in s exists in t, decrease the counter.\n5. Decrease the value of the current character in m.\n6. If a valid window is found, move the start pointer to find a smaller window:\n7. If the current window size is smaller than the minimum length found so far, update the minimum length and start position.\n8. Increase the value of the current character in m.\n9. If the current character exists in t, increase the counter.\n10. Repeat steps 3 and 4 until the end pointer reaches the end of the string s.\n11. If the minimum length is not equal to INT_MAX, return the minimum window substring, otherwise return an empty string.\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Humble Request:\n- If my solution is helpful to you then please **UPVOTE** my solution, your **UPVOTE** motivates me to post such kind of solution.\n- Please let me know in comments if there is need to do any improvement in my approach, code....anything.\n- **Let\'s connect on** https://www.linkedin.com/in/abhinash-singh-1b851b188\n\n\n\n# Code:\n```C++ []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n\t vector<int> m(128, 0);\n\t // Statistic for count of char in t\n\t for (auto c : t) \n m[c]++;\n\t // counter represents the number of chars of t to be found in s.\n\t int start = 0, end = 0, counter = t.size(), minStart = 0, minLen = INT_MAX;\n\t int size = s.size();\n\t\n\t // Move end to find a valid window.\n\t while (end < size) {\n\t\t // If char in s exists in t, decrease counter\n\t\t if (m[s[end]] > 0)\n\t\t\t counter--;\n\t\t // Decrease m[s[end]]. If char does not exist in t, m[s[end]] will be negative.\n\t\t m[s[end]]--;\n\t\t end++;\n\t\t // When we found a valid window, move start to find smaller window.\n\t\t while (counter == 0) {\n\t\t\t if (end - start < minLen) {\n\t\t\t\t minStart = start;\n\t\t\t\t minLen = end - start;\n\t\t\t }\n\t\t\t m[s[start]]++;\n\t\t\t // When char exists in t, increase counter.\n\t\t\t if (m[s[start]] > 0)\n\t\t\t\t counter++;\n\t\t\t start++;\n\t\t }\n\t }\n\t if (minLen != INT_MAX)\n\t\t return s.substr(minStart, minLen);\n\t return "";\n }\n};\n```\n```Java []\nclass Solution {\n public String minWindow(String s, String t) {\n int[] m = new int[128];\n for (char c : t.toCharArray()) \n m[c]++;\n int start = 0, end = 0, counter = t.length(), minStart = 0, minLen = Integer.MAX_VALUE;\n int size = s.length();\n while (end < size) {\n if (m[s.charAt(end++)]-- > 0) \n counter--;\n while (counter == 0) {\n if (end - start < minLen) {\n minStart = start;\n minLen = end - start;\n }\n if (m[s.charAt(start++)]++ == 0) \n counter++;\n }\n }\n return minLen == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? "" : s.substring(minStart, minStart + minLen);\n }\n}\n\n```\n```Python []\nclass Solution:\n def minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:\n m = [0] * 128\n for c in t:\n m[ord(c)] += 1\n start = 0\n end = 0\n counter = len(t)\n minStart = 0\n minLen = float(\'inf\')\n size = len(s)\n while end < size:\n if m[ord(s[end])] > 0:\n counter -= 1\n m[ord(s[end])] -= 1\n end += 1\n while counter == 0:\n if end - start < minLen:\n minStart = start\n minLen = end - start\n m[ord(s[start])] += 1\n if m[ord(s[start])] > 0:\n counter\n\n```\n\n# Time Complexity and Space Complexity:\n- Time complexity: **O(n)**, where n is the length of the input string s. This is because the while loop runs at most 2n times in the worst case (when all characters of s are different from t).\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: **O(1)**, as the size of the frequency vector is fixed at 128. This is because the ASCII character set has only 128 characters. The size of other variables used in the algorithm is constant and does not grow with the input size.\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
| 12
| 0
|
['Hash Table', 'Sliding Window', 'C++', 'Java', 'Python3']
| 3
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Simple c++ solution | Sliding Window | Hashmap | Explained clearly with comments
|
simple-c-solution-sliding-window-hashmap-wz1x
|
\n\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n // Initialize minl as INT_MAX\n int minl = INT_MAX;\n \n // Map to keep count of all c
|
maitreyeepaliwal
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-24T19:49:59.753700+00:00
|
2021-07-24T19:49:59.753745+00:00
| 1,329
| false
|
\n```\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n // Initialize minl as INT_MAX\n int minl = INT_MAX;\n \n // Map to keep count of all characters of t \n unordered_map <int, int> mp;\n for(auto ch: t) mp[ch]++;\n \n // Sliding Window Approach\n // Let c be the count of chars of t in a particular window. Initialize as 0\n // start be the start of the current window\n // end be the end of current window\n // minstart be the start for the minimum window found yet.\n \n int c = 0;\n \n int start = 0;\n int minstart = 0;\n \n for(int end = 0; end<s.length(); end++)\n {\n if(mp[s[end]]>0) c++;\n mp[s[end]]--; \n \n // continue untill c equals length of t or when current window has all characters of t in it\n if(c==t.length())\n {\n // Note that negative values in map indicate the key char is not present in t, but present in s. And hence leading chars in s with negative values are insignificant.\n \n while(start<end && mp[s[start]]<0){\n mp[s[start]]++;\n start++;\n }\n \n if(end-start+1<minl)\n {\n minl = end-start+1;\n minstart = start;\n }\n \n // reduce the window size by incrementing start, reducing mp[s[start]] value, and reducing c\n \n mp[s[start]]++;\n start++;\n c--;\n }\n }\n \n if(minl==INT_MAX) return "";\n return s.substr(minstart, minl);\n```
| 12
| 0
|
['Two Pointers', 'C', 'Sliding Window']
| 1
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Sliding Window Thinking Process
|
sliding-window-thinking-process-by-grace-4ti5
|
For example\n\ne.g. S = "ADOBECODEBANC", T = "ABC"\n ADOBEC \n\t BECODEBA \n CODEBA\n BANC\nThe substrings abov
|
gracemeng
|
NORMAL
|
2018-06-23T13:13:00.025631+00:00
|
2018-06-23T13:13:00.025631+00:00
| 1,064
| false
|
> For example\n```\ne.g. S = "ADOBECODEBANC", T = "ABC"\n ADOBEC \n\t BECODEBA \n CODEBA\n BANC\nThe substrings above are candidates for the result.\n```\n> In Brute Force, \n```\nfor left in [0: sLen - 1]\n for right in [left*: sLen - 1]\n if (canCover()) \n\t update minLen and minStr\n\t break\n```\n> After observation, there is no need to reset right to left here*\n> If canCover, we move left forward until !canCover, we move right forward\n```\nfor left in [0: sLen - 1]\n while (right < sLen && !canCover()) \n\tright++\n update minLen and minStr\n left++\n```\n> So we use the Sliding Window technique to generate these candidates. \n****\n```\n private int[] charToFreqT; // Map char to freq in t\n \n public String minWindow(String s, String t) {\n // Corner case\n if (s.isEmpty() || t.isEmpty()) return "";\n \n buildCharToFreqT(t);\n \n int sLen = s.length(), minLen = Integer.MAX_VALUE, left = 0, right = 0;\n String minStr = ""; // Final result\n \n charToFreqT[s.charAt(0)]--;\n \n while (left <= right) { \n while (right < sLen && !canCover()) { \n right++;\n if (right < sLen) charToFreqT[s.charAt(right)]--;\n }\n if (right == sLen) break;\n // Update min by current window [left, right]\n if (right - left + 1 < minLen) {\n minLen = right - left + 1;\n minStr = s.substring(left, right + 1);\n }\n charToFreqT[s.charAt(left)]++;\n left++;\n }\n \n return minStr;\n }\n \n private void buildCharToFreqT(String t) {\n charToFreqT = new int[256];\n for (char ch : t.toCharArray()) {\n charToFreqT[ch]++;\n }\n }\n \n private boolean canCover() {\n // For each key in charToFreqT, charToFreqS contains and value >= T\n for (int freq : charToFreqT) {\n if (freq > 0) return false;\n }\n return true;\n }\n```\n**(\u4EBA \u2022\u0348\u1D17\u2022\u0348)** Thanks for voting!
| 12
| 1
|
[]
| 3
|
minimum-window-substring
|
My 12ms simple C++ code (O(1) space, O(N) time)
|
my-12ms-simple-c-code-o1-space-on-time-b-rslz
|
Just used an array dict to count the occurence of the letters in t. To distinguish the letters that are not in t, we initialize dict with -slen and for those le
|
lejas
|
NORMAL
|
2015-08-05T03:24:49+00:00
|
2015-08-05T03:24:49+00:00
| 3,697
| false
|
Just used an array dict to count the occurence of the letters in t. To distinguish the letters that are not in t, we initialize dict with -slen and for those letters that are not in t, their corresponding elements in dict will be -slen. For example, t="abc", then dict['a']= dict['b']=dict['c']=1, while the others, such as dict['d'] = -slen. so if dict[x] == -slen, we know x is not in t. Of course, you can use an unordered_map to simplify the logic, but it is much slower.\nAfter building dict, we scan the string s, we use start to track the starting point of the current window and move i forward: we decrease dict[s[i]], if s[i] is a letter in t and in the current window we don't find all the occurence of s[i] (i.e. (--dict[s[i]]>=0) ), then s[i] will be counted as one letter of t. we decrease count by 1 and if count ==0 (i.e. --count ==0), it means we find all the letters of t in the current window. Then we move start to find the minium window, if s[start] is not in t (dict[s[start]]<= -slen ) or if we have more than enough such letters in the current window (i.e. (++dict[s[start]] <= 0, for example, s= aaab, t= ab, say start = 0, i=3, then in that case dict[s[0]] = -1, so we can move start to 1 (so dict[s[0]] = 0), and stop at 2 (dict[s[0]] = 1)). After while, we find start of the minium window ending at i, then we compare such window with the one we found so far (with length minL and starts at minS). If it is shorter than minL, update minL and minS. At last, we increase start and count, and continue the search. \nSince we have to move i and start through s, the complexity is O(N) \n\n class Solution {\n public:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n int slen = s.size(), tlen = t.size(), i, start=0, count, minL = INT_MAX, minS;\n int dict[128];\n fill_n(dict,128,-slen);\n for(i=0;i<tlen;++i) dict[t[i]] = dict[t[i]]>0? (dict[t[i]]+1):1;\n \n for(i=0, count = tlen; i<slen;++i)\n {\n if( (--dict[s[i]]>=0) && (--count == 0) )\n {\n while(dict[s[start]]<=-slen || (++dict[s[start]] <= 0) ) ++start;\n if(minL>i-start+1)\n {\n minL = i-start+1;\n minS = start; \n }\n count=1;\n ++start;\n }\n }\n return minL==INT_MAX? "":s.substr(minS, minL);\n }\n };
| 12
| 1
|
[]
| 1
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Java, SlidingWindow, HashMap, TwoPointer Solution
|
java-slidingwindow-hashmap-twopointer-so-3hi4
|
plz... upvote! if you find my solution helpful.\n\nStatus: Accepted*\nRuntime: 4 ms\nMemory Usage: 43.9 MB\nAll test cases passed.\n\n
|
kumar-rinku0
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-25T09:50:36.379176+00:00
|
2022-07-25T09:52:12.730683+00:00
| 2,272
| false
|
***plz... upvote! if you find my solution helpful.***\n\nStatus: **Accepted***\nRuntime: 4 ms\nMemory Usage: 43.9 MB\nAll test cases passed.\n\n[<iframe src="https://leetcode.com/playground/jpJPCeKg/shared" frameBorder="0" width="800" height="600"></iframe>](http://)
| 11
| 0
|
['Sliding Window', 'Java']
| 3
|
minimum-window-substring
|
O(n) 5ms Java Solution Beats 93.18%
|
on-5ms-java-solution-beats-9318-by-longs-gr7t
|
This solution adopts the idea described in this [LeetCode article][1]. It explains this O(n) solution very well. Because of that article, I kept the comments si
|
longstation
|
NORMAL
|
2016-03-04T23:53:48+00:00
|
2016-03-04T23:53:48+00:00
| 5,275
| false
|
This solution adopts the idea described in this [LeetCode article][1]. It explains this O(n) solution very well. Because of that article, I kept the comments simple. I highly suggest you to read it before trying this code.\n\n public class Solution {\n public String minWindow(String s, String t) {\n char[] needToFind = new char[256];\n char[] hasFound = new char[256];\n int sLen = s.length();\n int tLen = t.length();\n int count = 0;\n int optLen = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // opt stands for optimal\n int optBegin = 0;\n int optEnd = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < tLen; i++) { // gives a counter for each character in t\n needToFind[t.charAt(i)]++;\n }\n for (int begin = 0, end = 0; end < sLen; end++) {\n if (needToFind[s.charAt(end)] == 0) { // skips irrelevant char\n continue;\n }\n char currEnd = s.charAt(end); // the char at the end\n hasFound[currEnd]++;\n if (hasFound[currEnd] <= needToFind[currEnd]) {\n count++;\n }\n if (count == tLen) { // pauses end, moves beginning to the right as much as possible\n char currBegin = s.charAt(begin); // char at begin\n while (hasFound[currBegin] > needToFind[currBegin] || needToFind[currBegin] == 0) {\n if (hasFound[currBegin] > needToFind[currBegin]) {\n hasFound[currBegin]--;\n }\n begin++;\n currBegin = s.charAt(begin);\n }\n if (optLen > end - begin + 1) { // if current length is smaller, update our optimum solution\n optLen = end - begin + 1;\n optBegin = begin;\n optEnd = end;\n }\n }\n }\n if (count != tLen) {\n return "";\n }\n return s.substring(optBegin, optEnd + 1);\n }\n }\n\n [1]: http://articles.leetcode.com/finding-minimum-window-in-s-which/
| 11
| 0
|
['Java']
| 4
|
minimum-window-substring
|
[Animated Video] Sliding Window Template + Visualization
|
animated-video-sliding-window-template-v-q06l
|
CodeInMotion ResourcesEvery Leetcode Pattern You Need To Knowhttps://www.blog.codeinmotion.io/p/leetcode-patternsBlind 75 Animated Playlisthttps://www.youtube.c
|
codeinmotion
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-03T22:03:54.784433+00:00
|
2025-01-03T22:03:54.784433+00:00
| 624
| false
|

# *CodeInMotion Resources*
## Every Leetcode Pattern You Need To Know
https://www.blog.codeinmotion.io/p/leetcode-patterns
## Blind 75 Animated Playlist
https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLHm8nzcbp3_19DiTlDg8QYvR-hN5jzPCp
## Subscribe to YouTube
https://www.youtube.com/@CodeInMotion-IO?sub_confirmation=1
---
## Animated Video
https://youtu.be/OjskLohz_Nw
## Pre-reqs
Before starting a hard problem like this one, it is important to have foundational knowledge from previous LeetCode questions. I highly recommend you first solve the following 2 questions to understand the **sliding window technique** and **how to find anagrams**.
1. *Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters teaches you the Sliding Window Technique*
https://youtu.be/aHwl6PMDWJ8
2. *Valid Anagram teaches you how to determine if two strings share the same characters and frequency of those characters efficiently*
https://youtu.be/C-hRcCGLUak?si=mV4r3obr2cpq64nK
## Intuition
One approach to break down a complicated problem like this is to **split** it into multiple steps.
**Step 1**: First, recognize that you need to find the **smallest substring** which is a key indicator to use the **Sliding Window Technique** to scan the substrings in $$O(n)$$ instead of $$O(n^2)$$.
**If you are not familiar with the sliding window technique, see my blog post https://www.blog.codeinmotion.io/i/151790118/sliding-window**
**Step 2**: To use the sliding window, we must have a condition that tells us when to shrink the window (move the i pointer closer to j). **We need a condition that represents the current substring s[i:j] contains all characters in string t**. We can use an Anagram-style solution to solve this by creating a hashmap `FreqT` that keeps track of all the letters and their frequencies of T.
As you move the right pointer, you **decrement the frequency** in `FreqT`. Once all characters in `FreqT` have **frequency \<= 0** (meaning the current window has all of them), start moving the left pointer to see if you can shrink the window further. If removing a character causes the frequency count to go above zero again, you know the substring no longer contains all of **t**, so you stop shrinking and move the right pointer again.
The **key** to knowing when to shrink the window is to check if you have **satisfied all needed characters**. You can do this by keeping a **count** of how many unique characters are left to satisfy. When **this count** is zero, it means your current window contains all of **t**.
## Approach
1. **Build a frequency map** for all characters in **t**.
2. **Maintain a count** of how many distinct characters from **t** are still needed.
3. **Use two pointers**: an **outer** pointer (**j**) that moves through **s** and an **inner** pointer (**i**) that shrinks the window whenever the window is valid.
4. Each time you **move j** to the right and encounter a character in **freqT**, **decrement** its count. If the count of that character reaches **0**, it means you've satisfied one more character requirement.
5. **When the window contains** all characters of **t** (i.e., the needed character count is **0**), try shrinking from the left (**i** pointer) to find the smallest valid window in that range.
6. Track the **minimum** window size during this process.
## Example Walkthrough
s="ADOBECODEBANC"
t="ABC"
- Initialize a frequency map for **t**: { 'A':1, 'B':1, 'C':1 } and **lettersToSatisfy = 3**
- Expand **j** and decrement frequency counts whenever you encounter a char in **t**.
- Once **lettersToSatisfy** becomes **0**, try moving **i** up to shorten the window.
- Track every valid window’s size; keep the minimum.
Eventually, your minimum window is **"BANC"**.
## Complexity
- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$, where **n** is the length of **s**
- Space complexity: $$O(m)$$, where **m** is the length of **t**
## Code
```Python []
from collections import defaultdict
class Solution:
def minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:
freqT = defaultdict(int)
for letter in t:
freqT[letter] += 1
lettersToSatisfy = len(freqT)
left, right = float('-inf'), float('inf')
i = 0
for j, char in enumerate(s):
if char in freqT:
freqT[char] -= 1
if freqT[char] == 0:
lettersToSatisfy -= 1
while lettersToSatisfy == 0:
if j - i < right - left:
left, right = i, j
if s[i] in freqT:
freqT[s[i]] += 1
if freqT[s[i]] > 0:
lettersToSatisfy += 1
i += 1
return '' if right == float('inf') else s[left:right+1]
```
```Java []
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
class Solution {
public String minWindow(String s, String t) {
if (s.length() == 0 || t.length() == 0) return "";
Map<Character, Integer> freqT = new HashMap<>();
for (char c : t.toCharArray()) {
freqT.put(c, freqT.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1);
}
int lettersToSatisfy = freqT.size();
int left = 0, right = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int i = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < s.length(); j++) {
char c = s.charAt(j);
if (freqT.containsKey(c)) {
freqT.put(c, freqT.get(c) - 1);
if (freqT.get(c) == 0) {
lettersToSatisfy--;
}
}
while (lettersToSatisfy == 0) {
if (j - i < right - left) {
left = i;
right = j;
}
char leftChar = s.charAt(i);
if (freqT.containsKey(leftChar)) {
freqT.put(leftChar, freqT.get(leftChar) + 1);
if (freqT.get(leftChar) > 0) {
lettersToSatisfy++;
}
}
i++;
}
}
return right == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? "" : s.substring(left, right + 1);
}
}
```
```JavaScript []
/**
* @param {string} s
* @param {string} t
* @return {string}
*/
var minWindow = function(s, t) {
if (!s.length || !t.length) return "";
let freqT = new Map();
for (let char of t) {
freqT.set(char, (freqT.get(char) || 0) + 1);
}
let lettersToSatisfy = freqT.size;
let left = 0, right = Infinity;
let i = 0;
for (let j = 0; j < s.length; j++) {
let c = s[j];
if (freqT.has(c)) {
freqT.set(c, freqT.get(c) - 1);
if (freqT.get(c) === 0) {
lettersToSatisfy--;
}
}
while (lettersToSatisfy === 0) {
if ((j - i) < (right - left)) {
left = i;
right = j;
}
let leftChar = s[i];
if (freqT.has(leftChar)) {
freqT.set(leftChar, freqT.get(leftChar) + 1);
if (freqT.get(leftChar) > 0) {
lettersToSatisfy++;
}
}
i++;
}
}
return right === Infinity ? "" : s.substring(left, right + 1);
};
```
```C# []
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class Solution {
public string MinWindow(string s, string t) {
if (s.Length == 0 || t.Length == 0) return "";
Dictionary<char, int> freqT = new Dictionary<char, int>();
foreach (char c in t) {
if (!freqT.ContainsKey(c)) {
freqT[c] = 0;
}
freqT[c]++;
}
int lettersToSatisfy = freqT.Count;
int left = 0, right = int.MaxValue;
int i = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < s.Length; j++) {
char c = s[j];
if (freqT.ContainsKey(c)) {
freqT[c]--;
if (freqT[c] == 0) {
lettersToSatisfy--;
}
}
while (lettersToSatisfy == 0) {
if (j - i < right - left) {
left = i;
right = j;
}
char leftChar = s[i];
if (freqT.ContainsKey(leftChar)) {
freqT[leftChar]++;
if (freqT[leftChar] > 0) {
lettersToSatisfy++;
}
}
i++;
}
}
return right == int.MaxValue ? "" : s.Substring(left, right - left + 1);
}
}
```
```C++ []
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
string minWindow(string s, string t) {
if (s.empty() || t.empty()) return "";
unordered_map<char, int> freqT;
for (char c : t) {
freqT[c]++;
}
int lettersToSatisfy = freqT.size();
int left = 0;
int minLeft = 0, minSize = INT_MAX;
for (int j = 0; j < (int)s.size(); j++) {
char c = s[j];
if (freqT.find(c) != freqT.end()) {
freqT[c]--;
if (freqT[c] == 0) {
lettersToSatisfy--;
}
}
while (lettersToSatisfy == 0) {
if (j - left + 1 < minSize) {
minSize = j - left + 1;
minLeft = left;
}
char leftChar = s[left];
if (freqT.find(leftChar) != freqT.end()) {
freqT[leftChar]++;
if (freqT[leftChar] > 0) {
lettersToSatisfy++;
}
}
left++;
}
}
return (minSize == INT_MAX) ? "" : s.substr(minLeft, minSize);
}
};
```
```Go []
func minWindow(s string, t string) string {
if len(s) == 0 || len(t) == 0 {
return ""
}
freqT := make(map[rune]int)
for _, c := range t {
freqT[c]++
}
lettersToSatisfy := len(freqT)
left := 0
minLeft, minSize := 0, math.MaxInt32
sRunes := []rune(s)
for j := 0; j < len(sRunes); j++ {
c := sRunes[j]
if _, exists := freqT[c]; exists {
freqT[c]--
if freqT[c] == 0 {
lettersToSatisfy--
}
}
for lettersToSatisfy == 0 {
if j-left+1 < minSize {
minSize = j - left + 1
minLeft = left
}
leftChar := sRunes[left]
if _, exists := freqT[leftChar]; exists {
freqT[leftChar]++
if freqT[leftChar] > 0 {
lettersToSatisfy++
}
}
left++
}
}
if minSize == math.MaxInt32 {
return ""
}
return string(sRunes[minLeft : minLeft+minSize])
}
```
### Please thumbs up on the bottom-left corner!<br>It motivates me to create more solutions and videos for you!

| 10
| 0
|
['Hash Table', 'String', 'Sliding Window', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'Go', 'Python3', 'JavaScript', 'C#']
| 0
|
minimum-window-substring
|
C++ STL SOLUTION | | 2 APPROACHES | | EASY TO UNDERSTAND
|
c-stl-solution-2-approaches-easy-to-unde-338v
|
APPROACH 1\n\n## Approach\nSteps:\n1. We first create a hashmap for the characters of the string \'t\'.\n\n\nfor (auto value:t){\n m[value]++;\n}\n\n\n2. The
|
ALANT535
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-04T07:36:02.503088+00:00
|
2024-02-04T07:36:02.503120+00:00
| 1,493
| false
|
# APPROACH 1\n\n## Approach\nSteps:\n1. We first create a hashmap for the characters of the string \'t\'.\n\n```\nfor (auto value:t){\n m[value]++;\n}\n```\n\n2. Then we use two pointers, left and right to iterate through the string \'s\'. For each index, we do the following-\n\n\n2.1. If s[i] is inside m, the hashmap of t, then we reduce m[s[i]] by 1 and check if its 0; if so, we remove it from the hashmap, because that character requirement has been achieved.\n\n~~~\nif (temp.find(s[right]) != temp.end()){\n\n // cout<<"found the element\\t"<<temp[s[right]]<<"\\n";\n\n if (temp[s[right]] == 1){\n temp.erase(s[right]);\n }\n else{\n temp[s[right]]--;\n }\n}\n~~~\n\nNote, that these changes are being done to a copy of the hashmap, \'temp\'.\n\n2.2 Similarly, if all elements from the hashmap \'m\' are removed, that means that all the characters have been found in the substring and so we can consider this a valid substring.\n\nIn that case, we calculate the current length = right - left + 1 and compare it with the global minimum and make the necessary changes.\n~~~\nif (temp.size() == 0){\n // cout<<"temp is empty now\\t";\n curr_len = right - left + 1;\n \n // cout<<"curr_len and min_len is "<<curr_len<<"\\t"<<min_len<<endl;\n if (curr_len < min_len){\n min_len = min(min_len,curr_len);\n res = s.substr(left,curr_len);\n }\n temp = m;\n left++;\n right = left - 1;\n}\n~~~\n\nNow that we have found the substring, We then reset temp to the original hashmap value, move left by 1 and reset right also.\n\nThe reason why we are doing left++ and not left = right + 1, is because; for example, we can have "ABAODCHJIBC" as s and "ABC" as t.\n\nWe find substring "ABAODC" and then start from left = 0 to find "BAODC" which is a shorter length substring.\n\n\n2.3 If s[i] is not inside the hashmap, then we have two cases, when we are looking to start a substring and when we have already started.\n\nFor example, for "AOBC" with t = "ABC", we have already started the substring at "A" and "O" is not present in the hashmap, so should be ignored. NO CHANGES TO THE LEFT POINTER. When we find the substring "AOBC", left = 0, right = 3, length = right - left + 1 = 4.\n\n\nBut for "OAOBC", we have not started the substring ye, so left should also be moved because it represents the starting point of the substring.\nSo here, left should be incremented from 0 to 1, then when substring "AOBC" is found, left = 1, right = 4, length = 4 - 1 + 1 = 4.\nThe same is implemented here.\n\n~~~\nelse{\n if (temp == m){\n left++;\n }\n // left++;\n // cout<<"not found the element so keep going\\n";\n }\n\n right++;\n}\n~~~\n\nAfter the whole string has been iterated through, we use substring operator.\n\n## Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(n^2)\n\nsince we have to take multiple runs of the string s with size n.\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(m)\n\nwhere m is the size of the string \'t\'. This is because in the worst case where t completely consists of new characters, the hashmap would be of size = n.(worst case being all 26 aphabets present in t).\n\n## Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n unordered_map<char,int> m;\n\n if (s.size() < t.size()){\n return "";\n }\n\n for (auto value:t){\n m[value]++;\n }\n\n unordered_map<char,int> temp = m;\n int left = 0;\n int right = 0;\n int min_len = INT_MAX;\n int curr_len;\n string res;\n\n while (right < s.size()){\n \n // cout<<"current\\t"<<s[right]<<"\\t";\n\n //found the element\n if (temp.find(s[right]) != temp.end()){\n\n // cout<<"found the element\\t"<<temp[s[right]]<<"\\n";\n\n if (temp[s[right]] == 1){\n temp.erase(s[right]);\n }\n else{\n temp[s[right]]--;\n }\n // cout<<"temp is now of size "<<temp.size()<<endl;\n if (temp.size() == 0){\n // cout<<"temp is empty now\\t";\n curr_len = right - left + 1;\n \n // cout<<"curr_len and min_len is "<<curr_len<<"\\t"<<min_len<<endl;\n if (curr_len < min_len){\n min_len = min(min_len,curr_len);\n res = s.substr(left,curr_len);\n }\n temp = m;\n right = left;\n left++;\n }\n\n \n\n }\n\n //not found the element\n else{\n if (temp == m){\n left++;\n }\n // left++;\n // cout<<"not found the element so keep going\\n";\n }\n\n right++;\n\n }\n \n return res;\n\n }\n};\n```\n\n\n# APPROACH 2\n\n## Approach\nSteps:\n1. We first create a hashmap for the characters of the string \'t\'.\n\n```\nfor (auto value:t){\n m[value]++;\n}\n```\nSame as APPROACH 1.\n\n2. Initialise set<int> unique to store the unique indexes of caught elements. map<char,deque<int>> position to access the initial positions of characters.\n\n\n3. Then for each index, we do the following-\n\n\n3.1. If s[i] is inside m, the hashmap of t, then we add the index to the deque of that character in position. Also add it to the set<int>. We use a set to sort the indexes directly.\n\n3.2 Now, suppose \'t\' has 2 \'A\', but we got 3 \'A\', what we do is check the deque of \'A\', remove that index from the map and the set and then add the latest index, \'i\' in this case.\n\n~~~\nif (m[s[i]] < position[s[i]].size()){\n int temp = position[s[i]].front();\n position[s[i]].pop_front();\n sorted.erase(temp);\n}\n~~~\n\n3.3 If all the required elements are present; which we can do by checking if size of the set is size of t; then we have a valid substring. We then calculate the length and then make changes if current minimum is lesser than the global minimum.\n\n~~~\nif (sorted.size() == t.size()){\n if (res.second - res.first > i - *sorted.begin()){\n res = {*sorted.begin(),i};\n cout<<"res being updated\\t"<<res.first<<"\\t"<<res.second<<endl;\n }\n}\n~~~\n\nAll credit for the APPROACH 2 solution to - https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-window-substring/solutions/4673661/easy-o-n-m-sliding-window-detailed-explanation/?envType=daily-question&envId=2024-02-04\n\n## Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(n+m)\n\n(where n and m are the sizes of the \'s\' and \'t\' strings)\nSince we have to iterate through s and t once each.\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(m)\n\n\n## Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n unordered_map<char,int> m;\n\n if (s.size() < t.size()){\n return "";\n }\n\n for (auto value:t){\n m[value]++;\n }\n\n unordered_map<char,deque<int> > position;\n set<int> sorted;\n pair<int,int> res = {0,INT_MAX},initial;\n initial = {0,INT_MAX};\n for (int i = 0 ; i < s.size() ; i++){\n if (m.find(s[i]) != m.end()){\n \n position[s[i]].push_back(i);\n sorted.insert(i);\n\n //we have too much so remove stuff\n if (m[s[i]] < position[s[i]].size()){\n int temp = position[s[i]].front();\n position[s[i]].pop_front();\n sorted.erase(temp);\n }\n\n if (sorted.size() == t.size()){\n if (res.second - res.first > i - *sorted.begin()){\n res = {*sorted.begin(),i};\n cout<<"res being updated\\t"<<res.first<<"\\t"<<res.second<<endl;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n cout<<res.first<<"\\t"<<res.second<<endl;\n string ans;\n if (res != initial){\n ans = s.substr(res.first,res.second - res.first + 1);\n }\n\n else{\n ans = "";\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n\n};\n```
| 10
| 0
|
['Hash Table', 'String', 'Sliding Window', 'C++']
| 6
|
minimum-window-substring
|
✔️ Python's Simple and Easy to Understand Solution Using Sliding Window | 99% Faster 🔥
|
pythons-simple-and-easy-to-understand-so-wvv7
|
\uD83D\uDD3C IF YOU FIND THIS POST HELPFUL PLEASE UPVOTE \uD83D\uDC4D\n\n\nclass Solution:\n def minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:\n lookup = Co
|
pniraj657
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-22T05:27:11.294594+00:00
|
2022-10-31T05:28:42.546285+00:00
| 2,337
| false
|
**\uD83D\uDD3C IF YOU FIND THIS POST HELPFUL PLEASE UPVOTE \uD83D\uDC4D**\n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:\n lookup = Counter(t)\n mx = float("inf")\n output = ""\n S = len(s)\n start, end = 0, 0\n count = len(lookup)\n \n while end < S:\n \n # End Pointer\n while end < S and count != 0:\n if s[end] in lookup:\n lookup[s[end]] -= 1\n if lookup[s[end]] == 0:\n count -=1\n end += 1\n \n # Start Pointer\n while start <= end and count == 0:\n \n if end-start < mx:\n mx = end - start\n output = s[start:end]\n \n if s[start] in lookup:\n lookup[s[start]] += 1\n if lookup[s[start]] > 0:\n count += 1\n \n start += 1\n \n return output\n```\n**If you\'re interested in learning Python, check out my blog. https://www.python-techs.com/**\n\n**Thank you for reading! \uD83D\uDE04 Comment if you have any questions or feedback.**
| 10
| 0
|
['Sliding Window', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 2
|
minimum-window-substring
|
✔️ 100% Fastest Swift Solution
|
100-fastest-swift-solution-by-sergeylesc-cfcp
|
\nclass Solution {\n func minWindow(_ s: String, _ t: String) -> String {\n guard s.count >= t.count else { return "" }\n \n let sChars
|
sergeyleschev
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-06T05:43:40.603423+00:00
|
2022-04-06T05:43:40.603468+00:00
| 1,271
| false
|
```\nclass Solution {\n func minWindow(_ s: String, _ t: String) -> String {\n guard s.count >= t.count else { return "" }\n \n let sChars = Array(s)\n let tChars = Array(t)\n \n let indexs = validIndexs(sChars, tChars)\n guard s.count >= t.count else { return "" }\n \n let target = targetChars(tChars)\n let firstMatchIndex = firstMatch(sChars, indexs, target) \n var start = firstMatchIndex.0\n var end = firstMatchIndex.1\n \n if end == -1 {\n return ""\n }\n \n var tmp: [Character: Int] = [:]\n for i in indexs {\n if i < indexs[start] {\n continue\n }\n \n if i > indexs[end] {\n break\n }\n \n let c = sChars[i]\n if let _ = tmp[c] {\n tmp[c]! += 1 \n \n } else {\n tmp[c] = 1\n }\n }\n \n var minLength = indexs[end] - indexs[start]\n var minStart = start\n \n while end < indexs.count {\n // start +1\n let c = sChars[indexs[start]]\n \n if tmp[c]! > target[c]! {\n start += 1\n tmp[c]! -= 1\n let currentLength = indexs[end] - indexs[start]\n minLength = minLength < currentLength ? minLength : currentLength\n minStart = minLength < currentLength ? minStart : start\n continue\n \n } else {\n start += 1\n tmp[c]! -= 1\n end += 1\n while end < indexs.count {\n let e = sChars[indexs[end]]\n tmp[e]! += 1\n if e == c {\n let currentLength = indexs[end] - indexs[start]\n minLength = minLength < currentLength ? minLength : currentLength\n minStart = minLength < currentLength ? minStart : start\n break\n }\n end += 1\n } \n }\n }\n \n return Array(sChars[indexs[minStart]...indexs[minStart] + minLength]).join("")\n }\n\n \n func firstMatch(_ s: [Character], _ indexs: [Int], _ target: [Character: Int]) -> (Int, Int) {\n var target = target\n var tmp = -1\n \n func reachTarget() -> Bool {\n var res = true\n for (_, value) in target {\n if value > 0 {\n res = false\n break\n }\n }\n return res\n }\n \n for (i, index) in indexs.enumerated() {\n target[s[index]]! -= 1\n if reachTarget() {\n tmp = i\n break\n }\n }\n \n return (0, tmp)\n }\n \n\n func validIndexs(_ s: [Character], _ t: [Character]) -> [Int] {\n var res: [Int] = []\n \n for (i, c) in s.enumerated() {\n if t.contains(c) { res.append(i) }\n }\n \n return res\n }\n\n \n func targetChars(_ t: [Character]) -> [Character: Int] {\n var map: [Character: Int] = [:]\n \n for c in t {\n if let _ = map[c] { map[c]! += 1 } else { map[c] = 1 }\n }\n \n return map\n }\n\n}\n\n\nextension Array {\n func join(_ s: String) -> String {\n guard self.count > 0 else { return "" }\n if self.count == 1 { return "\\(self[0])" }\n var string = ""\n\n for i in 0..<self.count - 1 { string += "\\(self[i])\\(s)" }\n \n string += "\\(self[self.count - 1])"\n return string\n }\n}\n```\n\nLet me know in comments if you have any doubts. I will be happy to answer.\n\nPlease upvote if you found the solution useful.
| 10
| 0
|
['Swift']
| 3
|
minimum-window-substring
|
C++|| Sliding Window|| Using arrays
|
c-sliding-window-using-arrays-by-hiteshc-650u
|
Runtime: 8 ms\n\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n \n //frequency mapping\n int FP[256]={0};\n
|
hiteshcmonga
|
NORMAL
|
2021-06-09T15:28:27.804483+00:00
|
2021-06-09T15:29:01.647947+00:00
| 720
| false
|
Runtime: 8 ms\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n \n //frequency mapping\n int FP[256]={0};\n int FS[256]={0};\n int cnt=0;\n int start=0; //left contraction\n int start_idx=-1 ;//for best window\n int min_so_far=INT_MAX;\n \n for(int i=0;i<t.length();i++){\n FP[t[i]]++;\n }\n \n //sliding window algo\n for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){\n //expand window by including current character\n \n char ch=s[i];\n FS[ch]++;\n //count how many characters have been matched till now\n if(FP[ch]!=0 and FS[ch]<=FP[ch]){\n cnt+=1;\n }\n //if all characters are found in current window then start contracting\n \n if(cnt==t.length()){\n \n //start contracting \n while(FP[s[start]]==0 or FS[s[start]]>FP[s[start]]){\n FS[s[start]]--;\n start++;\n }\n \n int window_size=i-start+1;\n if(window_size<min_so_far){\n min_so_far=window_size;\n start_idx=start;\n }\n }\n \n }\n if(start_idx==-1){\n return "";\n }\n return s.substr(start_idx,min_so_far);\n }\n};\n```
| 10
| 3
|
['C', 'Sliding Window']
| 0
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Minimum window substring
|
minimum-window-substring-by-r9n-zyb4
|
\n\nusing System;\nusing System.Collections.Generic;\n\npublic class Solution\n{\n public string MinWindow(string s, string t)\n {\n if (s.Length =
|
r9n
|
NORMAL
|
2024-08-15T01:48:27.810142+00:00
|
2024-08-15T01:48:27.810165+00:00
| 261
| false
|
\n```\nusing System;\nusing System.Collections.Generic;\n\npublic class Solution\n{\n public string MinWindow(string s, string t)\n {\n if (s.Length == 0 || t.Length == 0)\n return "";\n\n var required = new Dictionary<char, int>();\n var window = new Dictionary<char, int>();\n \n foreach (char c in t)\n {\n if (required.ContainsKey(c))\n required[c]++;\n else\n required[c] = 1;\n }\n\n int left = 0;\n int right = 0;\n int minLength = int.MaxValue;\n int start = 0;\n int requiredChars = required.Count;\n int formedChars = 0;\n\n while (right < s.Length)\n {\n char c = s[right];\n window[c] = window.GetValueOrDefault(c, 0) + 1;\n\n if (required.ContainsKey(c) && window[c] == required[c])\n formedChars++;\n\n while (left <= right && formedChars == requiredChars)\n {\n if (right - left + 1 < minLength)\n {\n minLength = right - left + 1;\n start = left;\n }\n\n char leftChar = s[left];\n window[leftChar]--;\n if (required.ContainsKey(leftChar) && window[leftChar] < required[leftChar])\n formedChars--;\n\n left++;\n }\n\n right++;\n }\n\n return minLength == int.MaxValue ? "" : s.Substring(start, minLength);\n }\n}\n\n```
| 9
| 0
|
['C#']
| 0
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Sliding Window 🪟 | Python 🐍 | CLEAR EXPLANATION 📒
|
sliding-window-python-clear-explanation-iumlu
|
Efficiency\n\n\n\n# Approach\nSliding Window algorithm: Create 2 pointers to identify the start and end points of the output string.\n1. First, we create a Hash
|
kcp_1410
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-04T19:30:55.437579+00:00
|
2024-02-04T19:31:35.777700+00:00
| 149
| false
|
# Efficiency\n\n\n\n# Approach\n**Sliding Window algorithm**: Create 2 pointers to identify the start and end points of the output string.\n1. First, we create a HashMap `t_chars` and count the occurrences of characters of string `t` using the `Counter` method.\n2. We move the left & right pointers of `s` following 2 phases:\n * 2.1. Moving right pointer: Keep the left pointer at the start of string `s` (`left = 0`). We expand the range of `s` by moving the right pointer to the right, but when to stop? The answer is when our range consists of all characters in HashMap `t_chars` (all characters in `t`) including duplicates. So how can we achieve this? We use the right pointer `right` to traverse through `s` and whenever we see a char that is in `t_chars`, we decrement its occurrence by 1. If the occurrence of a char reaches 0 that means we\'ve moved `right`to a point where our current range includes a sufficient occurrence of that char. But that\'s only one char, what about the others? That is when `count = len(t_chars)` comes into play. This counts the number of unique chars in `t_chars` (ignore the occurrences). This line `if t_chars[s[right]] == 0: count -= 1` essentially says if the occurrence of char has reached 0 then we decrement the number of unique chars by 1 to indicate that we\'ve finished searching for all occurrences of that char. If `count > 0` means we still need to move `right` further to search for the remaining occurrences (by `continue` to the next loop immediately), otherwise our range has encompassed enough of occurrences of all chars in `t` and we can move on to the next phase.\n * 2.2. Moving left pointer: This is to remove the redundant characters to minimize the length of our range. So, starting at index 0, as we move `left` to the right, if we see a char that is not in `t_chars` then that is the redundant char and we don\'t even need to care about it, we\'re just going to move the left pointer (increment `left` by 1) to leave that char out of our range. But if we see a char that is in `t_chars` then we\'ll have to consider whether to leave it out or not. `t_chars[s[left]] < 0` means the occurrence of a char has gone to a negative value. Well if it\'s negative then we must have subtracted more than enough from it in *phase 2.1*, indicating that we\'ve not only included enough of occurrence of that char but also have included redundant occurrences. So what do we do with redundancy? We leave it out, but before we do that, we must increment the occurrence of it by 1 to say that we\'ve left it out and out range doesn\'t include it anymore (the opposite of when we added it into our range in *phase 2.1* before). Else if the value is non-negative (precisely 0) then we know that our range consists of just enough occurrences of it and so we cannot leave it out since our range will be missing chars if we do that, thus we\'ll `break` the loop to say that "Okay stop here, don\'t move the left pointer any further".\n3. We\'ll keep moving the two pointers to the end of `s`.\n4. For the first time of sufficient occurrences of characters, we\'re just going to set `output` as the current range which our current left & right pointers determine `output == "": output = s[left : right + 1]`. For the remaining iterations, we check if the length of current range is shorter than the previous or not (`if right - left + 1 < len(output)`), if yes then assign the current range to output. By doing this, we ensure to get the shortest possible partition of `s` that includes all characters of `t`.\n5. Finally, return the `output` and enjoy!\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(M+N)$$ with M is the length of `t` because we used `Counter` on `t` & N is the length of `s` since we use the pointers to traverse through `s`.\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(K)$$ with K is the number of unique values in the HashMap `t_chars`.\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str: # Sliding Window\n if len(s) < len(t): return ""\n if t in s: return t\n t_chars = Counter(t) # Count occurrences of `t`\n count = len(t_chars) # Number of unique chars of `t`\n output = ""\n left = 0 # Left pointer\n \n for right in range(len(s)):\n if s[right] in t_chars:\n t_chars[s[right]] -= 1 # Saw the char we\'re searching for\n if t_chars[s[right]] == 0: # Enough occurrence of a char\n count -= 1 # Finished searching for a char\n \n if count > 0: # Still remaining occurrences to search for\n continue\n else: # Completed searching - Sufficient\n while True:\n if s[left] in t_chars:\n if t_chars[s[left]] < 0: # Redundancy\n t_chars[s[left]] += 1 # Leave out\n else:\n break # Don\'t leave out\n left += 1 # Reduce the range\n \n if right - left + 1 < len(output) or output == "": # Minimize\n output = s[left : right + 1]\n \n return output\n```\n## Upvote if you find this solution helpful, thank you \uD83E\uDD0D
| 9
| 0
|
['Hash Table', 'String', 'Sliding Window', 'Python3']
| 2
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Beats 100% 🚀➡️Detailed Explanation 💯➡️[Java/C++/Python3/JavaScript]
|
beats-100-detailed-explanation-javacpyth-yh81
|
Intuition\n1. Window Creation with Two Pointers:\n - Use two pointers, one for the left end of the window and another for the right end, to create a window o
|
Shivansu_7
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-04T09:52:18.108292+00:00
|
2024-02-04T09:52:18.108325+00:00
| 3,014
| false
|
# Intuition\n1. **Window Creation with Two Pointers:**\n - Use two pointers, one for the left end of the window and another for the right end, to create a window of letters in string `s`.\n - This window should aim to contain all the characters present in string `t`.\n2. **Expanding the Window:**\n - Start by expanding the right pointer until all the characters from string t are included in the window.\n3. **Shrinking the Window:**\n - Once all characters from t are covered, start moving the left pointer to minimize the size of the window while still ensuring all characters from t are present.\n - This ensures the smallest possible window containing all characters from t is achieved.\n4. **Continued Adjustment of Pointers:**\n - Continue the process of expanding the right pointer and shrinking the left pointer until reaching the end of string `s`.\n - This ensures thorough coverage and minimizes the size of the window containing all characters from `t`.\n\n# Approach\n1. **Initialization:**\n - Initialize an empty string `ans` to store the minimum window substring.\n - Initialize two HashMaps: `mapT` to store the frequency of characters in string `t`, and `mapS` to store the frequency of characters in the current window of string `s`.\n - Initialize `mct` to track the number of characters matched so far and `dmct` to represent the desired match count, which is the length of string `t`.\n2. **Iterating through the string:**\n - Use two pointers, `i` and `j`, to represent the window boundaries. Start both pointers at `-1`.\n - `i` will be moved forward to expand the window, and `j` will be moved forward to shrink the window.\n3. **Expanding the window (while loop):**\n - Increment `i` until either the end of string `s` is reached or all characters from string `t` are found (`mct` reaches `dmct`).\n - Update mapS with the frequency of characters encountered. If a character is found which is present in t, increment mct.\n4. **Shrinking the window (`nested while loop`):**\n - After expanding the window, increment `j` until the minimum window containing all characters from `t` is found (`mct` equals `dmct`).\n - Update the ans if the current window is smaller than the previous minimum.\n - Update `mapS` accordingly and decrement `mct` if a character is no longer in the window.\n5. **Check for completion:**\n - Break the loop if neither `flag1` (expanding) nor `flag2` (shrinking) flags are set. This indicates that both pointer movements did not happen, implying that the windows cannot be expanded or shrunk further.\n6. **Return the minimum window substring found:**\n - Return the `ans` after the while loop exits, which contains the minimum window substring.\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$ *n is length of string s*\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(n)$$ *n is length of string s*\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```Java []\nclass Solution {\n public String minWindow(String s, String t) {\n if(s.equals(t)){\n return s;\n } \n String ans = "";\n HashMap<Character, Integer> mapT = new HashMap<>(); //frequecny of t\n for(char ch : t.toCharArray()) {\n mapT.put(ch, mapT.getOrDefault(ch,0)+1);\n }\n\n int mct = 0; //match count\n int dmct = t.length(); //desired match count\n HashMap<Character, Integer> mapS = new HashMap<>();\n int i = -1;\n int j = -1;\n\n while(true) {\n boolean flag1 = false;\n boolean flag2 = false;\n\n //acquire the character\n while(i < s.length()-1 && mct < dmct) {\n i++;\n char ch = s.charAt(i);\n mapS.put(ch, mapS.getOrDefault(ch, 0)+1);\n\n if(mapS.getOrDefault(ch, 0) <= mapT.getOrDefault(ch,0)){\n mct++;\n }\n flag1=true;\n }\n\n // Collect answers and release\n while(j < i && mct == dmct) {\n j++;\n String pans = s.substring(j, i+1); //pans = potential answer\n if(ans.length()==0 || pans.length() < ans.length()) {\n ans = pans;\n }\n\n char ch = s.charAt(j);\n if(mapS.get(ch)==1) {\n mapS.remove(ch);\n }\n else {\n mapS.put(ch, mapS.get(ch)-1);\n }\n\n if(mapS.getOrDefault(ch, 0) < mapT.getOrDefault(ch, 0)) {\n mct--;\n }\n flag2=true;\n }\n if(f1==false && f2==false) {\n break;\n } \n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```\n```C++ []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n if(s == t) {\n return s;\n } \n string ans = "";\n unordered_map<char, int> mapT; // frequency of t\n for(char ch : t) {\n mapT[ch]++;\n }\n\n int mct = 0; // match count\n int dmct = t.length(); // desired match count\n unordered_map<char, int> mapS;\n int i = -1;\n int j = -1;\n\n while(true) {\n bool f1 = false;\n bool f2 = false;\n\n // Acquire the character\n while(i < s.length()-1 && mct < dmct) {\n i++;\n char ch = s[i];\n mapS[ch]++;\n\n if(mapS[ch] <= mapT[ch]) {\n mct++;\n }\n f1 = true;\n }\n\n // Collect answers and release\n while(j < i && mct == dmct) {\n j++;\n string pans = s.substr(j, i-j+1); // pans = potential answer\n if(ans.length() == 0 || pans.length() < ans.length()) {\n ans = pans;\n }\n\n char ch = s[j];\n if(mapS[ch] == 1) {\n mapS.erase(ch);\n } else {\n mapS[ch]--;\n }\n\n if(mapS[ch] < mapT[ch]) {\n mct--;\n }\n f2 = true;\n }\n if(!f1 && !f2) {\n break;\n } \n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\n```Python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:\n if s == t:\n return s\n ans = ""\n mapT = {} # frequency of t\n for ch in t:\n mapT[ch] = mapT.get(ch, 0) + 1\n\n mct = 0 # match count\n dmct = len(t) # desired match count\n mapS = {}\n i = -1\n j = -1\n\n while True:\n f1 = False\n f2 = False\n\n # Acquire the character\n while i < len(s) - 1 and mct < dmct:\n i += 1\n ch = s[i]\n mapS[ch] = mapS.get(ch, 0) + 1\n\n if mapS.get(ch, 0) <= mapT.get(ch, 0):\n mct += 1\n f1 = True\n\n # Collect answers and release\n while j < i and mct == dmct:\n j += 1\n pans = s[j:i + 1] # pans = potential answer\n if not ans or len(pans) < len(ans):\n ans = pans\n\n ch = s[j]\n if mapS[ch] == 1:\n del mapS[ch]\n else:\n mapS[ch] -= 1\n\n if mapS.get(ch, 0) < mapT.get(ch, 0):\n mct -= 1\n f2 = True\n\n if not f1 and not f2:\n break\n return ans\n```\n```JavaScript []\n/**\n * @param {string} s\n * @param {string} t\n * @return {string}\n */\nvar minWindow = function(s, t) {\n if (s === t) {\n return s;\n } \n let ans = "";\n const mapT = new Map(); // frequency of t\n for (const ch of t) {\n mapT.set(ch, (mapT.get(ch) || 0) + 1);\n }\n\n let mct = 0; // match count\n const dmct = t.length; // desired match count\n const mapS = new Map();\n let i = -1;\n let j = -1;\n\n while (true) {\n let f1 = false;\n let f2 = false;\n\n // Acquire the character\n while (i < s.length - 1 && mct < dmct) {\n i++;\n const ch = s[i];\n mapS.set(ch, (mapS.get(ch) || 0) + 1);\n\n if (mapS.get(ch) <= mapT.get(ch) || 0) {\n mct++;\n }\n f1 = true;\n }\n\n // Collect answers and release\n while (j < i && mct === dmct) {\n j++;\n const pans = s.substring(j, i + 1); // pans = potential answer\n if (ans.length === 0 || pans.length < ans.length) {\n ans = pans;\n }\n\n const ch = s[j];\n if (mapS.get(ch) === 1) {\n mapS.delete(ch);\n } else {\n mapS.set(ch, mapS.get(ch) - 1);\n }\n\n if ((mapS.get(ch) || 0) < (mapT.get(ch) || 0)) {\n mct--;\n }\n f2 = true;\n }\n if (!f1 && !f2) {\n break;\n } \n }\n return ans;\n};\n```
| 9
| 0
|
['Sliding Window', 'C++', 'Java', 'Python3', 'JavaScript']
| 6
|
minimum-window-substring
|
🚀🚀 Beats 100% | Optimized Approach 🔥🔥 | Fully Explained 💎
|
beats-100-optimized-approach-fully-expla-xrvg
|
Intuition \uD83E\uDD14:\nWe are given two strings, s and t, and we need to find the minimum window substring in s that contains all characters of t. To approach
|
The_Eternal_Soul
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-04T01:29:13.091631+00:00
|
2024-02-04T01:29:13.091660+00:00
| 2,351
| false
|
### Intuition \uD83E\uDD14:\nWe are given two strings, `s` and `t`, and we need to find the minimum window substring in `s` that contains all characters of `t`. To approach this problem, we\'ll use two hash maps to keep track of characters in `s` and `t`, and then we\'ll use a sliding window technique to find the minimum window substring.\n\n### Approach \uD83D\uDE0E:\n1. Initialize variables: \n - `len1` and `len2` store the lengths of strings `s` and `t` respectively.\n - `start` indicates the start index of the current window.\n - `ansIndex` holds the index of the minimum window substring.\n - `ansLen` stores the length of the minimum window substring.\n2. Handle edge cases: If the length of `s` is less than the length of `t`, return an empty string.\n3. Create two unordered maps, `m1` and `m2`, to count the occurrences of characters in strings `s` and `t` respectively.\n4. Iterate through the characters of `s`:\n - Increment the count of the current character in `m1`.\n - Check if the count of the current character in `m1` is less than or equal to the count of the same character in `m2`. If so, increment `count`.\n - Once `count` equals the length of `t`, it means we have found a window that contains all characters of `t`.\n - Shrink the window by moving `start` forward while maintaining the window validity.\n - Update the minimum window substring if the current window is smaller than the previous minimum.\n5. Finally, return the minimum window substring.\n\n### Time Complexity \uD83D\uDE80:\n- The time complexity of this solution is O(m + n), where m is the length of string `s` and n is the length of string `t`. \n- The solution iterates through string `s` once and does constant-time operations within each iteration.\n\n### Space Complexity \uD83D\uDC8E:\n- The space complexity is O(n), where n is the length of string `t`. \n- This is because we use two hash maps of constant size to store the counts of characters in `s` and `t`.\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);\n cin.tie(0);\n cout.tie(0);\n \n int len1 = s.length();\n int len2 = t.length();\n int start = 0;\n int ansIndex = -1;\n int ansLen = INT_MAX;\n \n if(len1 < len2) {\n return "";\n }\n \n unordered_map<char, int> m1;\n unordered_map<char, int> m2;\n //to keep track of all characters of P string\n for(auto x : t) {\n m2[x]++;\n }\n \n int count = 0;\n for(int i = 0; i < len1; i++) {\n char ch = s[i];\n \n m1[ch]++;\n \n //valid character -> jo character tumhare pattern me bhi ho \n if(m1[ch] <= m2[ch]) {\n count++;\n }\n \n if(count == len2) {\n \n //window is ready\n \n //minimise the window -> freq decrement, ans update , start ko aage badhana h \n char temp = s[start];\n while(m1[temp] > m2[temp] or m2[temp] == 0 ) {\n \n if(m1[temp] > m2[temp])\n m1[temp]--;\n \n start++;\n temp = s[start];\n }\n \n //ans update\n int lengthOfWindow = i - start + 1;\n if(lengthOfWindow < ansLen ) {\n ansLen = lengthOfWindow;\n ansIndex = start;\n }\n \n \n }\n }\n \n if(ansIndex == -1)\n return "";\n else\n return s.substr(ansIndex, ansLen);\n }\n};\n```\n\n
| 9
| 1
|
['Hash Table', 'String', 'C', 'Sliding Window', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'JavaScript']
| 3
|
minimum-window-substring
|
SUPER EASY SOLUTION
|
super-easy-solution-by-himanshu__mehra-jfc9
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_t8kq_RpiPU\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n
|
himanshu__mehra__
|
NORMAL
|
2023-07-11T18:00:27.491009+00:00
|
2023-07-11T18:00:27.491029+00:00
| 1,811
| false
|
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_t8kq_RpiPU\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n unordered_map<char,int> hast_s;\n unordered_map<char,int> hast_t;\n if(s.length()<t.length()) return "";\n\n for(int i=0;i<t.length();i++){\n hast_t[t[i]]++;\n }\n \n int count=0, start=0,start_ind=-1,min_length=INT_MAX;\n for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){\n hast_s[s[i]]++;\n if(hast_s[s[i]] <= hast_t[s[i]])count++;\n\n if(count==t.length()){\n while(hast_s[s[start]]>hast_t[s[start]]){\n hast_s[s[start]]--;\n start++; \n }\n if(min_length>i-start+1){\n min_length= i-start+1;\n start_ind=start;\n }\n }\n }\n if(start_ind == -1)return "";\n else return s.substr(start_ind , min_length);\n }\n};\n```
| 9
| 0
|
['Hash Table', 'Sliding Window', 'C++']
| 1
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Brute force to Optimal | Sliding Window | C++
|
brute-force-to-optimal-sliding-window-c-l91j6
|
Brute Force\n\nclass Solution {\n bool check(unordered_map<char, int> &mp, unordered_map<char, int> &m) {\n if(m.size() < mp.size()) return false;\n
|
TusharBhart
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-22T05:19:36.454471+00:00
|
2022-10-22T05:19:36.454511+00:00
| 2,074
| false
|
# Brute Force\n```\nclass Solution {\n bool check(unordered_map<char, int> &mp, unordered_map<char, int> &m) {\n if(m.size() < mp.size()) return false;\n for(auto i : m) {\n if(i.second < mp[i.first]) return false;\n }\n return true;\n }\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n unordered_map<char, int> mp, m;\n for(char c : t) mp[c]++;\n\n int i = 0, d = INT_MAX;\n string ans;\n for(int j=0; j<s.size(); j++) {\n if(mp.find(s[j]) != mp.end()) m[s[j]]++;\n while(check(mp, m)) {\n if(j - i + 1 < d) d = j - i + 1, ans = s.substr(i, j - i + 1);\n if(m.find(s[i]) != m.end()) m[s[i]]--;\n i++;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\n\n# Optimal\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n unordered_map<char, int> m;\n for(char c : t) m[c]++;\n\n int i = 0, d = INT_MAX, cnt = m.size();\n string ans;\n for(int j=0; j<s.size(); j++) {\n if(m.find(s[j]) != m.end()) {\n m[s[j]]--;\n if(!m[s[j]]) cnt--;\n }\n while(!cnt) {\n if(j - i + 1 < d) d = j - i + 1, ans = s.substr(i, j - i + 1);\n if(m.find(s[i]) != m.end()) {\n m[s[i]]++;\n if(m[s[i]] > 0) cnt++;\n }\n i++;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\n\n\n
| 9
| 0
|
['Hash Table', 'Sliding Window', 'C++']
| 2
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Simple Python O(N) Sliding Window Explained with Example
|
simple-python-on-sliding-window-explaine-n2wn
|
O(N) Sliding Window Python Solution with Counter\n\ndef minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:\n\ttCounter = Counter(t) # counter for t to check with\n\twindow
|
bloomh
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-22T03:54:39.488692+00:00
|
2022-10-23T04:38:53.947778+00:00
| 2,228
| false
|
**O(N) Sliding Window Python Solution with Counter**\n```\ndef minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:\n\ttCounter = Counter(t) # counter for t to check with\n\twindow = Counter() # sliding window\n\tans = "" # answer\n\tlast = 0 # last index in our window\n\tfor i,char in enumerate(s):\n\t\twindow[char] = window.get(char,0)+1 # add this character to our window\n\t\twhile window >= tCounter: # while we have all the necessary characters in our window\n\t\t\tif ans == "" or i - last < len(ans): # if the answer is better than our last one\n\t\t\t\tans = s[last:i+1] # update ans\n\t\t\twindow[s[last]] -= 1 # remove the last element from our counter\n\t\t\tlast += 1 # move the last index forward\n\treturn ans # return answer\n```\n**Explanation**\nThe basic idea of this solution is to use a sliding window, ```window```, to keep track of the elements we are looking at (from ```last``` to ```i```, inclusive). While this window has all the necessary counters (```window >= tCounter```), we update the answer if the length of our window, ```i - last```, is less than the length of the answer. We remove the last character when this is true to see if we can use a shorter window.\n\n**Example**\nTo help understand how this algorithm works, let\'s consider the first example given in the problem:\n```\ns = "ADOBECODEBANC", t = "ABC"\ntCounter = Counter({\'A\': 1, \'B\': 1, \'C\': 1})\n\ni = 0, char = A\nwindow = Counter({\'A\': 1}), from "A"\nwe don\'t have all the characters in tCounter!\n\ni = 1, char = D\nwindow = Counter({\'A\': 1, \'D\': 1}), from "AD"\nwe don\'t have all the characters in tCounter!\n\ni = 2, char = O\nwindow = Counter({\'A\': 1, \'D\': 1, \'O\': 1}), from "ADO"\nwe don\'t have all the characters in tCounter!\n\ni = 3, char = B\nwindow = Counter({\'A\': 1, \'D\': 1, \'O\': 1, \'B\': 1}), from "ADOB"\nwe don\'t have all the characters in tCounter!\n\ni = 4, char = E\nwindow = Counter({\'A\': 1, \'D\': 1, \'O\': 1, \'B\': 1, \'E\': 1}), from "ADOBE"\nwe don\'t have all the characters in tCounter!\n\ni = 5, char = C\nwindow = Counter({\'A\': 1, \'D\': 1, \'O\': 1, \'B\': 1, \'E\': 1, \'C\': 1}), from "ADOBEC"\nthe window contains all necessary elements\nwe need to update our answer now! \u2013\u2013> ans = "ADOBEC"\nremove the last element, "A"\nnow window = Counter({\'D\': 1, \'O\': 1, \'B\': 1, \'E\': 1, \'C\': 1, \'A\': 0}), from "DOBEC"\n\ni = 6, char = O\nwindow = Counter({\'O\': 2, \'D\': 1, \'B\': 1, \'E\': 1, \'C\': 1, \'A\': 0}), from "DOBECO"\nwe don\'t have all the characters in tCounter!\n\ni = 7, char = D\nwindow = Counter({\'D\': 2, \'O\': 2, \'B\': 1, \'E\': 1, \'C\': 1, \'A\': 0}), from "DOBECOD"\nwe don\'t have all the characters in tCounter!\n\ni = 8, char = E\nwindow = Counter({\'D\': 2, \'O\': 2, \'E\': 2, \'B\': 1, \'C\': 1, \'A\': 0}), from "DOBECODE"\nwe don\'t have all the characters in tCounter!\n\ni = 9, char = B\nwindow = Counter({\'D\': 2, \'O\': 2, \'B\': 2, \'E\': 2, \'C\': 1, \'A\': 0}), from "DOBECODEB"\nwe don\'t have all the characters in tCounter!\n\ni = 10, char = A\nwindow = Counter({\'D\': 2, \'O\': 2, \'B\': 2, \'E\': 2, \'A\': 1, \'C\': 1}), from "DOBECODEBA"\nthe window contains all necessary elements\nhowever, the window length is longer than our answer so we don\'t update it\nremove the last element, "D"\nnow window = Counter({\'O\': 2, \'B\': 2, \'E\': 2, \'A\': 1, \'D\': 1, \'C\': 1}), from "OBECODEBA"\n\nthe window contains all necessary elements\nhowever, the window length is longer than our answer so we don\'t update it\nremove the last element, "O"\nnow window = Counter({\'B\': 2, \'E\': 2, \'A\': 1, \'D\': 1, \'O\': 1, \'C\': 1}), from "BECODEBA"\n\nthe window contains all necessary elements\nhowever, the window length is longer than our answer so we don\'t update it\nremove the last element, "B"\nnow window = Counter({\'E\': 2, \'A\': 1, \'D\': 1, \'O\': 1, \'B\': 1, \'C\': 1}), from "ECODEBA"\n\nthe window contains all necessary elements\nhowever, the window length is longer than our answer so we don\'t update it\nremove the last element, "E"\nnow window = Counter({\'A\': 1, \'D\': 1, \'O\': 1, \'B\': 1, \'E\': 1, \'C\': 1}), from "CODEBA"\n\nthe window contains all necessary elements\nwe need to update our answer now! \u2013\u2013> ans = "CODEBA"\nremove the last element, "C"\nnow window = Counter({\'A\': 1, \'D\': 1, \'O\': 1, \'B\': 1, \'E\': 1, \'C\': 0}), from "ODEBA"\n\ni = 11, char = N\nwindow = Counter({\'A\': 1, \'D\': 1, \'O\': 1, \'B\': 1, \'E\': 1, \'N\': 1, \'C\': 0}), from "ODEBAN"\nwe don\'t have all the characters in tCounter!\n\ni = 12, char = C\nwindow = Counter({\'A\': 1, \'D\': 1, \'O\': 1, \'B\': 1, \'E\': 1, \'C\': 1, \'N\': 1}), from "ODEBANC"\nthe window contains all necessary elements\nhowever, the window length is longer than our answer so we don\'t update it\nremove the last element, "O"\nnow window = Counter({\'A\': 1, \'D\': 1, \'B\': 1, \'E\': 1, \'C\': 1, \'N\': 1, \'O\': 0}), from "DEBANC"\n\nthe window contains all necessary elements\nwe need to update our answer now! \u2013\u2013> ans = "DEBANC"\nremove the last element, "D"\nnow window = Counter({\'A\': 1, \'B\': 1, \'E\': 1, \'C\': 1, \'N\': 1, \'D\': 0, \'O\': 0}), from "EBANC"\n\nthe window contains all necessary elements\nwe need to update our answer now! \u2013\u2013> ans = "EBANC"\nremove the last element, "E"\nnow window = Counter({\'A\': 1, \'B\': 1, \'C\': 1, \'N\': 1, \'D\': 0, \'O\': 0, \'E\': 0}), from "BANC"\n\nthe window contains all necessary elements\nwe need to update our answer now! \u2013\u2013> ans = "BANC"\nremove the last element, "B"\nnow window = Counter({\'A\': 1, \'C\': 1, \'N\': 1, \'D\': 0, \'O\': 0, \'B\': 0, \'E\': 0}), from "ANC"\n\nreturn "BANC"\n```
| 9
| 0
|
['Sliding Window', 'Python']
| 3
|
minimum-window-substring
|
The most easy sliding window solution
|
the-most-easy-sliding-window-solution-by-7xtz
|
\nstring minWindow(string s, string t) {\n string res = "";\n if(s.size() < t.size()) return res;\n unordered_map<char, int> umap;\n
|
codingGuy2016
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-11T18:04:52.697989+00:00
|
2022-05-11T18:04:52.698090+00:00
| 913
| false
|
```\nstring minWindow(string s, string t) {\n string res = "";\n if(s.size() < t.size()) return res;\n unordered_map<char, int> umap;\n for(auto it: t) umap[it]++;\n int i=0, j=0;\n int length = INT_MAX, count = umap.size();\n while(j<s.size()){\n if(umap.find(s[j])!=umap.end()){\n umap[s[j]]--;\n if(umap[s[j]]==0) count--;\n }\n if(count > 0) j++;\n else if(count == 0){\n while(count==0){\n if(umap.find(s[i])!=umap.end()){\n if(j-i+1 < length){\n length = j-i+1;\n res = s.substr(i, j-i+1);\n }\n umap[s[i]]++;\n if(umap[s[i]] > 0) count++;\n }\n i++;\n }\n j++;\n }\n }\n return res;\n }\n```
| 9
| 0
|
['C', 'Sliding Window', 'C++']
| 2
|
minimum-window-substring
|
[Python 3] From Brute Force to Sliding Window - 3 solutions - O(N)
|
python-3-from-brute-force-to-sliding-win-8wx9
|
Solution 1: Brute force\npython\nclass Solution:\n def minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:\n def isCover(cnt1, cnt2): # return True if all charact
|
hiepit
|
NORMAL
|
2021-08-16T16:09:46.569921+00:00
|
2023-08-21T13:51:12.776208+00:00
| 459
| false
|
**Solution 1: Brute force**\n```python\nclass Solution:\n def minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:\n def isCover(cnt1, cnt2): # return True if all characters in cnt2 is covered by cnt1\n for k, v in cnt2.items():\n if cnt1[k] < v:\n return False\n return True\n\n n = len(s)\n cntT = Counter(t)\n ansStartIdx = 0\n ansSize = math.inf\n for i in range(n):\n cnt = Counter()\n for j in range(i, n):\n cnt[s[j]] += 1\n if isCover(cnt, cntT):\n if ansSize > j - i + 1:\n ansSize = j - i + 1\n ansStartIdx = i\n break\n\n if ansSize == math.inf:\n return ""\n return s[ansStartIdx:ansStartIdx+ansSize]\n```\n**Complexity**\n- Time: `O(N^2 + M)`, where `N <= 10^5` is length of string `s`, `M <= 10^5` is length of string `t`.\n- Space: `O(1)`\n\n----\n**Solution 2: Sliding Window**\n```python\nclass Solution:\n def minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:\n def isCover(cnt1, cnt2): # return True if all characters in cnt2 is covered by cnt1\n for k, v in cnt2.items():\n if cnt1[k] < v:\n return False\n return True\n\n cntT = Counter(t)\n cnt = Counter()\n l = 0\n ansSize = math.inf\n ansStartIdx = 0\n for r, c in enumerate(s):\n cnt[c] += 1\n while isCover(cnt, cntT):\n if ansSize > r - l + 1:\n ansSize = r - l + 1\n ansStartIdx = l\n cnt[s[l]] -= 1\n l += 1\n if ansSize == math.inf:\n return ""\n return s[ansStartIdx : ansStartIdx + ansSize]\n```\n\n**Complexity**\n- Time: `O(26 * N + M)`, where `N <= 10^5` is length of string `s`, `M <= 10^5` is length of string `t`.\n- Space: `O(1)`\n\n----\n**Solution 3: Sliding Window (Optimized)**\n```python\nclass Solution:\n def minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:\n cnt = Counter(t)\n consumedTarget = len(cnt)\n consumed = 0\n\n l = 0\n ansSize = math.inf\n ansStartIdx = 0\n for r, c in enumerate(s):\n cnt[c] -= 1\n if cnt[c] == 0:\n consumed += 1\n\n while consumed == consumedTarget: # check if conver all chars of string `t`\n if ansSize > r - l + 1:\n ansSize = r - l + 1\n ansStartIdx = l\n if cnt[s[l]] == 0:\n consumed -= 1\n cnt[s[l]] += 1\n l += 1\n\n if ansSize == math.inf:\n return ""\n return s[ansStartIdx : ansStartIdx + ansSize]\n```\n\n**Complexity**\n- Time: `O(N + M)`, where `N <= 10^5` is length of string `s`, `M <= 10^5` is length of string `t`.\n- Space: `O(1)`
| 9
| 1
|
['Sliding Window']
| 0
|
minimum-window-substring
|
[C++] Sliding Window || Easy To Understand
|
c-sliding-window-easy-to-understand-by-m-k9dp
|
IDEA\nWe keep expanding the window by moving the right pointer. When the window has all the desired characters, we contract (if possible) and save the smallest
|
Maango16
|
NORMAL
|
2021-08-15T08:52:17.480608+00:00
|
2021-08-15T08:52:17.480634+00:00
| 559
| false
|
**IDEA**\nWe keep expanding the window by moving the right pointer. When the window has all the desired characters, we contract (if possible) and save the smallest window till now.\n`The answer is the smallest desirable window.`\n\u200B\n**EXAMPLE**\nFor eg. `S = "ABAACBAB" T = "ABC"`. Then our answer window is `"ACB"` and shown below is one of the possible desirable windows.\n\n\n\u200B**ALGORITHM**\n* We start with two pointers, `leftleft` and `rightright` initially pointing to the first element of the string S.\n* We use the `rightright pointer` to expand the window until we get a desirable window i.e. a window that contains all of the characters of T.\n* Once we have a window with all the characters, we can move the left pointer ahead one by one. \n\t* \tIf the window is still a desirable one we keep on updating the minimum window size.\n\t* \tIf the window is not desirable any more, we repeat step 2 onwards.\n\n**SOLUTION**\n`In C++`\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n unordered_map<char,int> mp;\n for(auto ch:t)\n {\n mp[ch]++;\n }\n int dist=mp.size() ;\n unordered_map<char,int> window;\n int count = 0 , ll = 0 , rr = 0 ;\n int l = 0 , r = 0 , ans = INT_MAX ;\n while(r<s.length())\n {\n window[s[r]]++ ;\n if(mp.count(s[r]) and mp[s[r]]==window[s[r]])\n {\n count++;\n }\n r++;\n while(count == dist and l < r)\n {\n if(ans > r-l)\n {\n ans= r - l ;\n ll = l ;\n rr = r ;\n }\n window[s[l]]-- ;\n if(mp.count(s[l]) and window[s[l]] < mp[s[l]])\n {\n count--;\n }\n l++;\n }\n }\n return s.substr(ll,rr-ll);\n }\n};\n```\n
| 9
| 4
|
[]
| 2
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Share my neat and easy-understand python solution in O(n)
|
share-my-neat-and-easy-understand-python-vprw
|
class Solution(object):\n '''\n b -- begin index of window; e -- end index of window.\n example: S="acbbaca", T="aba"\n \n 0
|
mach7
|
NORMAL
|
2015-10-14T23:03:52+00:00
|
2015-10-14T23:03:52+00:00
| 2,662
| false
|
class Solution(object):\n '''\n b -- begin index of window; e -- end index of window.\n example: S="acbbaca", T="aba"\n \n 0 1 2 3 4 5 6\n a c b b a c a\n \n initially, b=e=0\n a:2\n b:1\n pc=2 (positive count. pc>0 indicates that there are element in T yet to find, that is, current window is not legit.)\n \n expanding:\n b=0,e=0 b=0,e=2 b=0,e=3 b=0,e=4 b=0,e=6\n a:1 a:1 a:1 a:0 a:-1 \n b:1 b:0 b:-1(more b than need) b:-1 b:-1\n pc=2 pc=1 pc=1 pc=0 pc=0\n [0:4] [0:6]\n \n shrinking:\n b=2,e=6 b=3,e=6 \n a:0 a:0\n b:-1 b:0\n pc=0 pc=0\n [2:6] [3:6]\n \n then expanding... and so on.\n '''\n def minWindow(self, s, t):\n """\n :type s: str\n :type t: str\n :rtype: str\n """\n m = {}\n pc = 0 # positive count\n for c in t:\n if not c in m:\n m[c] = 1\n pc += 1\n else:\n m[c] += 1\n \n b = e = 0\n w = [-1, -1] # ret str = [w[0], w[1]), left inclusive, right not.\n while True:\n if e<len(s) and b<=e and pc>0: # expand\n if s[e] in m: # what if including char @ index e?\n m[s[e]] -= 1\n if m[s[e]]==0: # previously m[s[e]]==1, of course pc-=1\n pc -= 1\n e += 1\n elif b<=e and pc==0: # shrink\n if w[0]==-1 or e-b<w[1]-w[0]:\n w[0], w[1] = b, e\n if s[b] in m: # what if excluding char @ index b?\n m[s[b]] += 1\n if m[s[b]] == 1: # previously m[s[b]]==0, of course pc+=1\n pc += 1\n b += 1\n else:\n break\n \n if w[0]==-1:\n return ""\n else:\n return s[w[0]:w[1]]
| 9
| 0
|
['Python']
| 1
|
minimum-window-substring
|
The fast 7ms O(N) Java solution use only one array without map
|
the-fast-7ms-on-java-solution-use-only-o-tni3
|
public String minWindow(String s, String t) {\n if (t.length() <= 0 || s.length() < t.length()) return "";\n int start = 0, end = 0, i = 0, j = 0,
|
alpenliebe
|
NORMAL
|
2016-01-13T21:26:57+00:00
|
2016-01-13T21:26:57+00:00
| 3,471
| false
|
public String minWindow(String s, String t) {\n if (t.length() <= 0 || s.length() < t.length()) return "";\n int start = 0, end = 0, i = 0, j = 0, count = t.length(), min = s.length()+1;\n int[] table = new int[256];\n \n for(int k = 0; k<count; k++){\n char c = t.charAt(k);\n table[c]++;\n }\n for(int k = 0; k<256; k++){\n if(table[k]<1)\n table[k]=Integer.MIN_VALUE;\n }\n while(end<s.length()){\n while(end<s.length()&&count>0){\n char c = s.charAt(end++);\n if(table[c]!=Integer.MIN_VALUE){\n if(table[c]>0)\n count--;\n table[c]--;\n }\n }\n if(count>0) break;\n while(start<s.length()&&count<=0){\n char c = s.charAt(start++);\n if(table[c]!=Integer.MIN_VALUE){\n if(table[c]>=0)\n count++;\n table[c]++;\n }\n }\n if(end-start+1<min){\n min = end-start+1;\n i = start-1;\n j = end;\n }\n }\n return min==s.length()+1 ? "" : s.substring(i,j);\n }
| 9
| 2
|
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Java']
| 1
|
minimum-window-substring
|
C++ post referred to top voted post
|
c-post-referred-to-top-voted-post-by-rai-bakx
|
First, thanks the post from @vinceyuan\n\nHere I just try explain it carefully so to help some beginners to better understand the inspiring ideas behind the sol
|
rainbowsecret
|
NORMAL
|
2016-02-20T11:06:22+00:00
|
2016-02-20T11:06:22+00:00
| 3,525
| false
|
First, thanks the post from @vinceyuan\n\nHere I just try explain it carefully so to help some beginners to better understand the inspiring ideas behind the solution.\n\nPreprocessing step:\n\nstore the condition variable in the unordered_map\n\nWhile loop step:\n\n check sub-conditions, update global variable\n\n for the satisfying condition, we can move the start pointer \n forward to calculate all the possible solution.\n\nI do think this solution is really not easy to us to implement all by our self. \n\nThe only way to better grasp this solution is to write it many times by yourself.\n\nHere is the C++ implementation:\n\n\n class Solution {\n public:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n vector<int> v(128, 0);\n for(auto c:t) v[c]++;\n int start=0, end=0, counter=t.size();\n int minStart=0, minLen=INT_MAX;\n int len=s.size();\n while(end<len){\n if(v[s[end]]>0) counter--;\n v[s[end]]--;\n end++;\n while(counter==0){\n if(end-start<minLen){\n minStart=start;\n minLen=end-start;\n }\n v[s[start]]++;\n if(v[s[start]]>0) counter++;\n start++;\n }\n }\n if(minLen!=INT_MAX)\n return s.substr(minStart, minLen);\n return "";\n }\n };
| 9
| 1
|
[]
| 6
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Minimum Window Substring - Solution Explanation and Code (Video Solution Available)
|
minimum-window-substring-solution-explan-2t72
|
Video SolutionIntuitionThe problem involves finding the minimum window in the string s that contains all the characters of string t. My first thought was to use
|
CodeCrack7
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-25T03:40:16.974122+00:00
|
2025-01-25T03:40:16.974122+00:00
| 979
| false
|
# Video Solution
[https://youtu.be/OoLytq4DRro?si=agfFSpEcxAEablx_]()
# Intuition
The problem involves finding the minimum window in the string `s` that contains all the characters of string `t`. My first thought was to use a sliding window approach with a frequency map to track the required characters and their counts.
# Approach
1. Create a frequency map for all characters in string `t`.
2. Use two pointers (`left` and `right`) to define a sliding window in `s`.
3. Maintain a `formed` variable to count how many characters in the current window satisfy the required frequency.
4. Expand the `right` pointer to include characters in the window and check if the condition is satisfied.
5. When all required characters are present (`formed == required`), shrink the window by moving the `left` pointer to find the minimum window.
6. Keep track of the smallest window size and its starting index.
7. Return the substring corresponding to the smallest window size. If no such window exists, return an empty string.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
The algorithm traverses the string `s` using two pointers, so the time complexity is $$O(n)$$, where `n` is the length of `s`.
- Space complexity:
Two hash maps are used to store the frequency of characters in `t` and the window. The space complexity is $$O(|t|)$$, where `|t|` is the number of unique characters in `t`.
# Code
```java
class Solution {
public String minWindow(String s, String t) {
if (s.length() < t.length()) {
return "";
}
// Frequency map for characters in `t`
HashMap<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < t.length(); i++) {
map.put(t.charAt(i), map.getOrDefault(t.charAt(i), 0) + 1);
}
int left = 0, right = 0, start = 0, minLength = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
HashMap<Character, Integer> ans = new HashMap<>();
int required = map.size();
int formed = 0;
while (right < s.length()) {
char c = s.charAt(right);
ans.put(c, ans.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1);
if (map.containsKey(c) && ans.get(c).equals(map.get(c))) {
formed++;
}
// Contract the window
while (left <= right && formed == required) {
c = s.charAt(left);
// Update the minimum length window
if (right - left + 1 < minLength) {
minLength = right - left + 1;
start = left;
}
ans.put(c, ans.get(c) - 1);
if (map.containsKey(c) && ans.get(c) < map.get(c)) {
formed--;
}
left++;
}
right++;
}
return minLength == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? "" : s.substring(start, start + minLength);
}
}
| 8
| 0
|
['Java']
| 1
|
minimum-window-substring
|
🔥🔥🔥 Easy Sliding Window Solution | Explained 🔥🔥🔥
|
easy-sliding-window-solution-explained-b-0u59
|
Intuition\nThe main problem is finding the smallest substring in s that contains all the characters in t. Use the sliding window concept to solve this problem.\
|
pratamandiko
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-04T02:43:51.157837+00:00
|
2024-02-04T02:43:51.157866+00:00
| 1,406
| false
|
# Intuition\nThe main problem is finding the **smallest** substring in **s** that contains all the characters in **t**. Use the sliding window concept to solve this problem.\n\n# Approach\n**Character Frequency t:** We start by counting the frequency of each character in **t** using a hashmap.\n\n**Sliding Window Expansion:** We use two pointers (**left** and **right**) to represent our current window in **s**. Initially, our window is empty. We expand our window by moving end to the right, thereby including more characters of s into our window.\n\n**Tracking Character Frequencies in the Window:** As we include more characters in our window, we use another hashmap to keep track of the frequency of each character within the window.\n\n**Valid Window Check:** Our goal is to adjust the window to include at least as many of each character as are found in t. Once our window includes enough of each required character, we have a valid window.\n\n**Window Minimization:** reduce its size from the left, maintaining validity (is it still contains all characters from t) while seeking the minimum length. We do this by incrementally moving start to the right, reducing the window size until it no longer meets the criteria.\n\n**Result Update and Repeat:** Each time a valid minimum window is found, we compare its size to the smallest found so far and update our result accordingly. We continue this process until end has reached the end of s.\n\nTermination: If we find a valid window, we return it. If no such window exists, we return an empty string.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n**$$O(n)$$**\n\n- Space complexity:\n**$$O(n)$$**\n\n# Code\n```javascript []\nvar minWindow = function(s, t) {\n if (s.length < t.length) return ""\n const tCount = {}\n for (let char of t){\n tCount[char] = (tCount[char] || 0) + 1\n }\n let needCount = Object.keys(tCount).length\n let haveCount = 0\n let left = 0\n let idxResultWindow = [0, Infinity] // Store the start and end of the minimum window\n const windowCount = {}\n\n for (let right = 0 ; right < s.length ; right++){\n const char = s[right]\n windowCount[char] = (windowCount[char] || 0) + 1\n\n if (windowCount[char] === tCount[char]){\n haveCount++\n }\n\n // when the current window satisfy the needs, try to shrink the window\n while (haveCount === needCount){\n // Update result if this window is smaller than the previous one\n if (right - left < idxResultWindow[1] - idxResultWindow[0]){\n idxResultWindow = [left, right]\n }\n\n // slide the left window pointer to minimize the solution\n windowCount[s[left]]--\n if (windowCount[s[left]] < tCount[s[left]]){\n haveCount--\n }\n left++\n }\n }\n console.log(idxResultWindow)\n return idxResultWindow[1] === Infinity ? "" : s.slice(idxResultWindow[0], idxResultWindow[1] + 1)\n};\n```\n```python3 []\nfrom collections import defaultdict\n\nclass Solution:\n def minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:\n if len(s) < len(t):\n return ""\n\n t_count = defaultdict(int)\n for char in t:\n t_count[char] += 1\n\n need_count = len(t_count)\n have_count = 0\n left = 0\n idx_result_window = [0, float(\'inf\')]\n window_count = defaultdict(int)\n\n for right in range(len(s)):\n char = s[right]\n window_count[char] += 1\n\n if window_count[char] == t_count[char]:\n have_count += 1\n\n while have_count == need_count:\n if right - left < idx_result_window[1] - idx_result_window[0]:\n idx_result_window = [left, right]\n\n window_count[s[left]] -= 1\n if window_count[s[left]] < t_count[s[left]]:\n have_count -= 1\n\n left += 1\n\n return "" if idx_result_window[1] == float(\'inf\') else s[idx_result_window[0]:idx_result_window[1] + 1]\n\n```\n```Go []\nfunc minWindow(s string, t string) string {\n\tif len(s) < len(t) {\n\t\treturn ""\n\t}\n\n\ttCount := make(map[byte]int)\n\tfor i := 0; i < len(t); i++ {\n\t\ttCount[t[i]]++\n\t}\n\n\tneedCount := len(tCount)\n\thaveCount := 0\n\tleft := 0\n\tidxResultWindow := [2]int{0, math.MaxInt64}\n\twindowCount := make(map[byte]int)\n\n\tfor right := 0; right < len(s); right++ {\n\t\tchar := s[right]\n\t\twindowCount[char]++\n\n\t\tif windowCount[char] == tCount[char] {\n\t\t\thaveCount++\n\t\t}\n\n\t\tfor haveCount == needCount {\n\t\t\tif right-left < idxResultWindow[1]-idxResultWindow[0] {\n\t\t\t\tidxResultWindow = [2]int{left, right}\n\t\t\t}\n\n\t\t\twindowCount[s[left]]--\n\t\t\tif windowCount[s[left]] < tCount[s[left]] {\n\t\t\t\thaveCount--\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t\tleft++\n\t\t}\n\t}\n\n\tif idxResultWindow[1] == math.MaxInt64 {\n\t\treturn ""\n\t}\n\treturn s[idxResultWindow[0] : idxResultWindow[1]+1]\n}\n```\n```Java []\nclass Solution {\n public String minWindow(String s, String t) {\n if (s.length() < t.length()) return "";\n HashMap<Character, Integer> tCount = new HashMap<>();\n for (char c : t.toCharArray()) {\n tCount.put(c, tCount.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1);\n }\n int needCount = tCount.size();\n int haveCount = 0;\n int left = 0;\n int[] idxResultWindow = {0, Integer.MAX_VALUE};\n HashMap<Character, Integer> windowCount = new HashMap<>();\n\n for (int right = 0; right < s.length(); right++) {\n char c = s.charAt(right);\n windowCount.put(c, windowCount.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1);\n\n if (windowCount.get(c).equals(tCount.get(c))) {\n haveCount++;\n }\n\n while (haveCount == needCount) {\n if (right - left < idxResultWindow[1] - idxResultWindow[0]) {\n idxResultWindow[0] = left;\n idxResultWindow[1] = right;\n }\n\n windowCount.put(s.charAt(left), windowCount.get(s.charAt(left)) - 1);\n if (windowCount.get(s.charAt(left)) < tCount.getOrDefault(s.charAt(left), 0)) {\n haveCount--;\n }\n left++;\n }\n }\n\n return idxResultWindow[1] == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? "" : s.substring(idxResultWindow[0], idxResultWindow[1] + 1);\n }\n}\n\n```\n```C++ []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n std::string minWindow(std::string s, std::string t) {\n if (s.length() < t.length()) return "";\n \n std::unordered_map<char, int> tCount;\n for (char c : t) {\n tCount[c]++;\n }\n\n int needCount = tCount.size();\n int haveCount = 0;\n int left = 0;\n std::pair<int, int> idxResultWindow = {0, INT_MAX};\n std::unordered_map<char, int> windowCount;\n\n for (int right = 0; right < s.length(); right++) {\n char currentChar = s[right];\n windowCount[currentChar]++;\n\n if (windowCount[currentChar] == tCount[currentChar]) {\n haveCount++;\n }\n\n while (haveCount == needCount) {\n if (right - left < idxResultWindow.second - idxResultWindow.first) {\n idxResultWindow = {left, right};\n }\n\n // Slide the left window pointer to minimize the solution\n windowCount[s[left]]--;\n if (windowCount[s[left]] < tCount[s[left]]) {\n haveCount--;\n }\n left++;\n }\n }\n\n std::cout << "[" << idxResultWindow.first << ", " << idxResultWindow.second << "]" << std::endl;\n\n return idxResultWindow.second == INT_MAX ? "" : s.substr(idxResultWindow.first, idxResultWindow.second - idxResultWindow.first + 1);\n }\n};\n```\n# PLEASE UPVOTE IF ITS HELP!!!!!\uD83D\uDE4F\uD83D\uDE4F\uD83D\uDE4F\uD83D\uDE09
| 8
| 0
|
['Hash Table', 'String', 'Sliding Window', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'Go', 'Python3', 'JavaScript']
| 0
|
minimum-window-substring
|
[Python] ✅ || Easy Mind Map Diagram || Two Pointer + Sliding Window [Dynamic Size] || Space O(m+n)
|
python-easy-mind-map-diagram-two-pointer-r7jt
|
Intuition\nThe "Minimum Window Substring" problem requires finding the smallest substring in s that contains all the characters of t. Initially, the challenge s
|
chitralpatil
|
NORMAL
|
2024-01-08T19:57:07.765945+00:00
|
2024-01-08T19:57:07.765972+00:00
| 944
| false
|
# Intuition\nThe "Minimum Window Substring" problem requires finding the smallest substring in `s` that contains all the characters of `t`. Initially, the challenge seems to lie in efficiently checking if a substring contains all required characters, and then minimizing this substring. The key is realizing the dynamic nature of the problem, where a \'sliding window\' can expand and contract to encapsulate the required characters.\n\n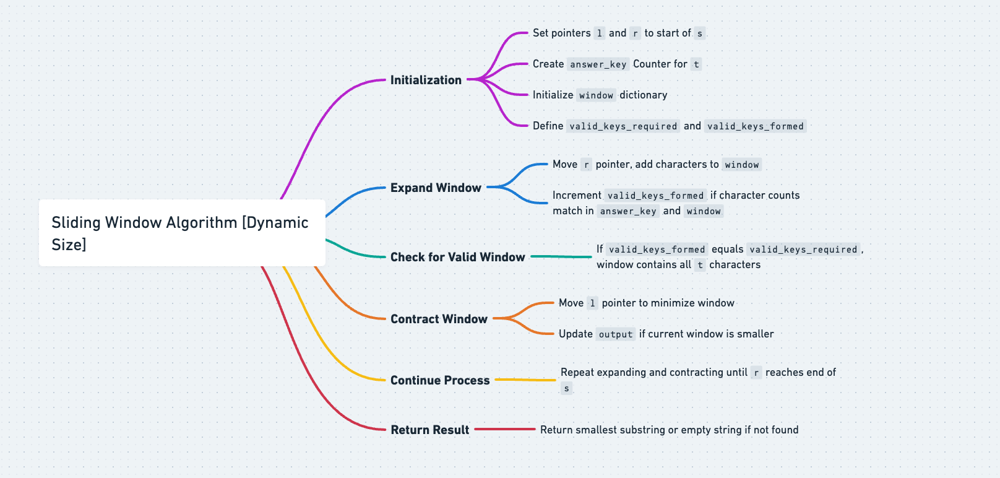\n\n\n# Approach\nThe approach involves two main phases: window expansion and window contraction. The expansion phase keeps extending the window until it encompasses a valid substring that contains all characters of `t`. Once a valid window is found, the contraction phase begins, shrinking the window from the left while ensuring the window still contains all characters of `t`. The condition `l <= r` in the contraction loop is essential to handle edge cases, particularly when both `s` and `t` are single characters. This rhythm of expanding and contracting continues, always checking for and updating the minimum window found.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: The time complexity is $$O(m + n)$$, where `m` is the length of `s` and `n` is the length of `t`. This is because each character in `s` is visited at most twice, once by the right pointer and once by the left pointer.\n- Space complexity: The space complexity is $$O(m + n)$$, mainly due to the extra space used for two hash maps (or Counters) for `t` and the current window.\n\n# Code\n```python\nfrom collections import Counter\n\nclass Solution:\n def minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:\n \n answer_key = Counter(t)\n window = {}\n \n valid_keys_required = len(answer_key)\n valid_keys_formed = 0\n\n output = float(\'inf\'), 0, 0 \n l, r = 0, 0\n\n # Keep expanding the window until we find a valid substring\n while r < len(s):\n char = s[r] \n window[char] = window.get(char, 0) + 1 \n\n if char in answer_key and window[char] == answer_key[char]:\n valid_keys_formed += 1\n\n while l <= r and valid_keys_formed == valid_keys_required:\n prev_char = s[l]\n\n # Make sure to update the value of output before incrementing "l"\n if output[0] > (r-l+1):\n output = (r-l+1), l, r\n \n window[prev_char] -= 1\n\n if prev_char in answer_key and window[prev_char] < answer_key[prev_char]:\n valid_keys_formed -= 1\n \n l += 1\n \n r += 1\n \n \n return "" if output[0] == float(\'inf\') else s[output[1]:output[2]+1]\n```\n
| 8
| 0
|
['Hash Table', 'Two Pointers', 'String', 'Sliding Window', 'Python3']
| 0
|
minimum-window-substring
|
🙎C++ || Easy || Daily LeetCoding Challenge (22nd October 2022)
|
c-easy-daily-leetcoding-challenge-22nd-o-dfrh
|
Easy to Understand\nIf understand the sol^n then Please Upvote\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n if (s.size() <
|
spyder_master
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-22T04:36:54.298965+00:00
|
2022-10-22T04:36:54.298993+00:00
| 5,674
| false
|
# Easy to Understand\n**If understand the sol^n then Please Upvote**\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n if (s.size() < t.size() or s.empty()) {\n return "";\n }\n \n int i = 0, j = 0;\n int start = -1, len = INT_MAX;\n std::vector<int> m(128, 0);\n \n // Push elements of t into hash table.\n for (auto c : t) {\n m[c]++;\n }\n \n while (j < s.size()) {\n if (isFound(m)) {\n // Current string contains all characters of t,\n // then we start to shrink it from left.\n if (j - i < len) {\n start = i;\n len = j - i;\n }\n m[s[i++]]++;\n continue;\n }\n // Current string doesn\'t contain all characters of t,\n // so we need to extend it and do checking in the next iteration.\n m[s[j++]]--;\n }\n \n // Try to shrink the last found string.\n while (isFound(m)) {\n if (j - i < len) {\n start = i;\n len = j - i;\n }\n m[s[i++]]++;\n }\n \n if (start != -1) {\n return s.substr(start, len);\n }\n return "";\n }\n\nprivate:\n // If all values of hash table are <= 0,\n // it means all characters of t are included in current string\n bool isFound(const std::vector<int>& m) {\n return std::all_of(m.begin(), m.end(), [](int i) { return i <= 0; });\n }\n};\n```\n\n
| 8
| 0
|
['Hash Table', 'C', 'Sliding Window']
| 2
|
minimum-window-substring
|
[Java] Sliding window | Aditya Verma
|
java-sliding-window-aditya-verma-by-naga-0gxp
|
\nclass Solution {\n public String minWindow(String s, String t) {\n \n Map<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();\n for(char ch: t.
|
nagato19
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-14T19:15:15.550855+00:00
|
2022-08-14T19:15:15.550907+00:00
| 807
| false
|
```\nclass Solution {\n public String minWindow(String s, String t) {\n \n Map<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();\n for(char ch: t.toCharArray())\n map.put(ch, map.getOrDefault(ch, 0) + 1);\n \n int count = map.size(), ansLength = Integer.MAX_VALUE;\n String ans = "";\n \n int i = 0, j = 0;\n while(j < s.length()) {\n \n char cur = s.charAt(j);\n if(map.containsKey(cur)) {\n map.put(cur, map.get(cur) - 1);\n if(map.get(cur) == 0) count--;\n }\n \n if(count > 0)\n j++;\n \n else if(count == 0) { \n \n while(count == 0) {\n \n if(j-i+1 < ansLength) {\n ansLength = j-i+1;\n ans = s.substring(i, j+1);\n }\n \n char rm = s.charAt(i);\n if(map.containsKey(rm)) {\n map.put(rm, map.get(rm) + 1);\n if(map.get(rm) == 1) count++;\n } \n \n i++; \n } \n \n j++; \n }\n }\n \n return ans;\n \n }\n}\n```
| 8
| 0
|
['Sliding Window', 'Java']
| 0
|
minimum-window-substring
|
🔥 JAVA 2️⃣-pointer sliding window || Simple Explanation 👀😄
|
java-2-pointer-sliding-window-simple-exp-jkc8
|
\uD83D\uDCCC 2 pointer Sliding window with 2 Hashmaps \uD83D\uDC49\uD83C\uDFFB \'Acquired\' and \'Required\' \n\n ## \u2705 At any point of time we will find
|
Yash_kr
|
NORMAL
|
2022-06-13T09:55:10.298019+00:00
|
2022-06-22T05:02:02.859113+00:00
| 882
| false
|
# \uD83D\uDCCC 2 pointer Sliding window with 2 Hashmaps \uD83D\uDC49\uD83C\uDFFB \'Acquired\' and \'Required\' \n\n ## \u2705 At any point of time we will find : Minimum window substring starting from ith index (i.e. first pointer )\n \n \u270D\uD83C\uDFFB **Notations** : \n1. acquired -> Hashmap containing details of current window elements\n2. required -> HashMap containing details of required no. of elements\n3. i -> left / back pointer\n4. j -> right / front pointer\n \n \uD83C\uDFAF **Logic** :\n \n step 1 : Keep moving the front pointer (j) until your window do not contains all the required elements\n step 2 : Note the current window size and update the ans ( if required )\n step 3 : Once your window contain all the required elements, keep moving the back pointer (i) till your window contains all the req. elements and keep on updating the ans and \'acquired\' hashmap accordingly.\n step 4 : repeat step 1\n \n \n \n \n```\nclass Solution {\n public String minWindow(String s, String t) {\n int l = s.length();\n int m = t.length();\n \n HashMap<Character,Integer> required = new HashMap<>();\n for(char c : t.toCharArray())\n {\n int ov = required.getOrDefault(c, 0);\n required.put(c, ov+1);\n }\n \n HashMap<Character,Integer> acquired = new HashMap<>();\n int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;\n String ans="";\n int i = 0;\n int j=0;\n int found = 0;\n while(i<l)\n {\n while(j<l && found!=m)\n {\n char cc = s.charAt(j);\n if(required.containsKey(cc)) // one useful character we have found\n {\n int ov = acquired.getOrDefault(cc, 0);\n acquired.put(cc, ov+1);\n if(acquired.get(cc) > required.get(cc)){} // character was found more than its requirement\n else found += 1;\n } \n j++;\n }\n \n int window_size = j-i;\n if(found==m && window_size<min)\n {\n min = window_size;\n ans = s.substring(i,j);\n }\n \n if(required.containsKey(s.charAt(i))) // useful character we might loose\n {\n int ov = acquired.get(s.charAt(i));\n acquired.put(s.charAt(i), ov-1);\n if(acquired.get(s.charAt(i)) < required.get(s.charAt(i))) found -= 1; // we lost one useful character\n }\n \n i++;\n \n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n}\n```\n\n\uD83D\uDCCC Please upvote if you lked the approach \uD83D\uDE0A\uD83D\uDE42
| 8
| 0
|
['Two Pointers', 'Sliding Window', 'Java']
| 0
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Sliding window C++ solution
|
sliding-window-c-solution-by-workday-rzkr
|
Using a sliding window to increase the right boundary to include more elements. Once the sliding window includes all elements in the target array, try to increa
|
workday
|
NORMAL
|
2022-03-15T04:12:48.371258+00:00
|
2022-03-15T04:12:48.371327+00:00
| 542
| false
|
Using a sliding window to increase the right boundary to include more elements. Once the sliding window includes all elements in the target array, try to increase the left boundary to decrease the size of the window until the window doesn\'t include all elements in the target array. Repeat the previous steps till the right boundary of the window reaches the end of the original array.\n\nThe mistake I had in my submission:\n1. when updating the minimum length of the window, I used right - left + 1, but actually I increased right before when updating the right boundary of the window.\n2. when updating the left boundary, I used valid == t.size(). I forgot the target array could have repeated elements. I should use need.size(), which is the size of the map. All keys are unique.\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n unordered_map<char, int> need, window;\n \n for(char c : t)\n need[c]++;\n \n int left = 0, right = 0, valid = 0;\n int start = 0, len = INT_MAX;\n \n while(right < s.size())\n {\n char c = s[right];\n right++;\n \n if(need.count(c))\n {\n window[c]++;\n if(window[c] == need[c])\n valid++;\n }\n \n while(valid == need.size())\n {\n if(right - left < len)\n {\n start = left;\n len = right - left;\n }\n \n char c = s[left];\n \n if(need.count(c))\n {\n if(window[c] == need[c])\n valid--;\n window[c]--;\n }\n left++;\n }\n }\n \n return len == INT_MAX ? "" : s.substr(start, len);\n }\n};\n```
| 8
| 0
|
['C', 'Sliding Window']
| 2
|
minimum-window-substring
|
JS optimized solution with explanations O(t+s) time O(t+s) space
|
js-optimized-solution-with-explanations-c6554
|
Note\n- Should be pretty straight forward if you did these problems before: 567-permutation-in-string, 438. Find All Anagrams in a String\n- Do those first.\n-
|
inxela
|
NORMAL
|
2022-02-17T00:04:44.457157+00:00
|
2022-02-17T17:25:31.038455+00:00
| 1,497
| false
|
# Note\n- Should be pretty straight forward if you did these problems before: [567-permutation-in-string](https://leetcode.com/problems/permutation-in-string/), [438. Find All Anagrams in a String](https://leetcode.com/problems/find-all-anagrams-in-a-string/)\n- Do those first.\n- Here is the idea:\n1. create a hashmap that counts character frequency of t\n2. use two pointers to define your window size\n3. whenever you encounter a character in s that is in your hashmap, decrease the count. When the count is 0, it means that you used up the required amount of this character. Therefore you increase your "match" count.\n4. When match is equal to numbers of keys in your hashmap, it means that you have a solution. Notice that "uniqueChars" is the number of keys in the hashmap.\n5. when you have a solution, try to decrease your window size by increasing the left pointer until the window is no longer a solution.\n6. record the solution you had before\n\n# Big O Analysis\n- Time: O(t) time to build the hashmap. O(s+s) for window sliding since in the worst case the right and left pointer loop through the entire string s once. Therefore overall time complexity is O(t + s)\n- Space: O(t) for the hashmap in the worst case. O(s) for the answer in the worst case if s is a permutation of t. Therefore overall space complexity is O(t+s)\n\n```javascript\n/**\n * @param {string} s\n * @param {string} t\n * @return {string}\n */\nvar minWindow = function(s, t) {\n // count t\'s frequency of its characters\n let map = {}, uniqueChars = 0;\n for (let char of t) {\n if (char in map) {\n map[char] += 1;\n } else {\n map[char] = 1;\n uniqueChars += 1;\n }\n }\n \n let ans = \'\';\n let left = 0, match = 0;\n for (let right = 0; right < s.length; right++) {\n let rightChar = s[right];\n if (rightChar in map) {\n map[rightChar] -= 1;\n if (map[rightChar] === 0) match += 1;\n }\n \n if (match === uniqueChars) { // there is a solution\n // try to shrink the window from the left\n while (match === uniqueChars) {\n let leftChar = s[left++];\n if (map[leftChar] === 0) match -= 1;\n map[leftChar] += 1;\n }\n \n // record the solution, notice that you need to use left-1 instead of left when slicing\n let solution = s.slice(left-1, right+1);\n ans = (ans === \'\')? solution: (ans.length > solution.length)? solution: ans;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n}\n```
| 8
| 0
|
['Two Pointers', 'Sliding Window', 'JavaScript']
| 0
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Aditya Verma Approach || Easy Hashmap with Sliding Window || Minimum Window Substring
|
aditya-verma-approach-easy-hashmap-with-h77av
|
\nif (t.length() > s.length()) {\n return "";\n}\n\nif (s == t)\n return s;\nunordered_map < char, int > m;\n\nfor (auto it: t) {\n m[it]++;\n}\n\nint cnt =
|
akshansh773
|
NORMAL
|
2021-10-01T06:39:55.185780+00:00
|
2023-03-20T06:22:11.087501+00:00
| 1,025
| false
|
```\nif (t.length() > s.length()) {\n return "";\n}\n\nif (s == t)\n return s;\nunordered_map < char, int > m;\n\nfor (auto it: t) {\n m[it]++;\n}\n\nint cnt = m.size();\nint i = 0;\nint j = 0;\nint ans = INT_MAX;\nint start = -1;\nint end = -1;\nwhile (j < s.length()) {\n if (m.find(s[j]) != m.end()) {\n m[s[j]]--;\n if (m[s[j]] == 0)\n cnt--;\n }\n\n if (cnt == 0) {\n if (j - i + 1 < ans) {\n start = i;\n end = j;\n ans = j - i + 1;\n }\n\n while (cnt == 0) {\n if (m.find(s[i]) != m.end()) {\n\n m[s[i]]++;\n if (m[s[i]] > 0)\n cnt++;\n\n }\n i++;\n if (j - i + 1 < ans && cnt == 0) {\n start = i;\n end = j;\n ans = j - i + 1;\n }\n }\n }\n\n j++;\n}\n\nstring sans = "";\nif (start == -1 && end == -1) {\n\n return sans;\n}\n\nfor (int i = start; i <= end; i++) {\n\n sans += s[i];\n}\n\nreturn sans;\n```
| 8
| 0
|
['C++']
| 1
|
minimum-window-substring
|
C++|| Commented || Easy to Understand || Sliding Window|| Map
|
c-commented-easy-to-understand-sliding-w-i7a9
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t)\n {\n unordered_map<char, int> mapt; // For frequency of characters of string t\
|
pragyatewary24
|
NORMAL
|
2021-08-15T18:22:13.661135+00:00
|
2021-08-15T18:22:13.661179+00:00
| 815
| false
|
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t)\n {\n unordered_map<char, int> mapt; // For frequency of characters of string t\n for(auto ch : t)\n {\n mapt[ch]++;\n }\n unordered_map<char, int> maps; // For frequency of characters of string s\n int n = s.length();\n string ans = "";\n int k = 0;\n int counter = 0; // To count whether we have got all the characters of string t in string s\n int i= -1;\n int j = -1;\n while(k<n)\n {\n \n // Acquire\n while(i < n-1 && counter != t.size())\n {\n i++;\n maps[s[i]]++;\n \n if(maps[s[i]] <= mapt[s[i]]) // If the acquired character is matched, increased the count\n {\n counter++;\n }\n \n }\n \n //Store ans and Release\n while(j < i && counter == t.size())\n {\n j++;\n string pans = s.substr(j, i-j+1); // Potential answer\n \n if(ans.size()== 0 || ans.size() > pans.size())\n { \n ans = pans; // If size of potential answer is less than answer, update the answer\n }\n \n if(maps[s[j]] == 1)\n {\n maps.erase(s[j]);\n }\n else maps[s[j]]--;\n \n if(maps[s[j]] < mapt[s[j]]) // If the released character is matched, decreased the count\n {\n counter--;\n } \n }\n k++;\n }\n return ans;\n \n \n \n }\n};\n```
| 8
| 0
|
['C', 'Sliding Window']
| 2
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Easy to understand C++ sliding window technique
|
easy-to-understand-c-sliding-window-tech-090u
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n int mm = s.size(), n = t.size();\n unordered_map<char, int> m;\n
|
tejas702
|
NORMAL
|
2021-08-15T14:56:23.037338+00:00
|
2021-08-15T14:57:01.438480+00:00
| 588
| false
|
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n int mm = s.size(), n = t.size();\n unordered_map<char, int> m;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)m[t[i]]++;\n int l = 0, r = 0;\n int res = INT_MAX;\n string st = "";\n string ryan = s.substr(l,r-l+1);\n array<int,2> ff = {-1,-1};\n unordered_map<char, int> m2;\n for(char c : ryan)m2[c]++;\n while(l<mm&&r<mm){\n int rr = 0;\n bool done = 0;\n for(auto it : m){\n if(m2.find(it.first)!=m2.end()){\n if(m2[it.first]<it.second){\n done=1;break;\n } \n }else{\n done=1;break;\n }\n }\n if(done==1){\n r+=1;\n m2[s[r]]++;\n }else{\n if((r-l+1)<res){\n res = r-l+1;\n ff[0]=l;ff[1]=r;\n }\n m2[s[l]]--;\n l+=1;\n }\n }\n if(ff[0]==-1)return st;\n st = s.substr(ff[0],ff[1]-ff[0]+1);\n return st;\n }\n};\n```\n**Feel free to share improvements/suggestions. Questions/Discussions are welcome.**
| 8
| 6
|
['C', 'Sliding Window']
| 0
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Template for sliding window problems
|
template-for-sliding-window-problems-by-ex624
|
Inspired by the top post, I create my own template for sliding window problems. I feel it is more generic and is good for all the sliding window problems I stud
|
yu6
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-26T01:22:23.091984+00:00
|
2021-01-03T19:27:33.267840+00:00
| 678
| false
|
Inspired by the top post, I create my own template for sliding window problems. I feel it is more generic and is good for all the sliding window problems I studied so far.\n\n**The template**\n```\nwhile(r<n) {\n\t//process r\n\twhile(r cannot move) {\n\t\t//process l to free r\n\t\tl++;\n\t}\n\t//process r\n\tr++;\n}\n```\n[**3. Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters**](https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-substring-without-repeating-characters/discuss/950438/Sliding-window-template)\n```\n\tpublic int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {\n int l=0, r=0, max = 0;\n boolean[] window = new boolean[256];\n while(r<s.length()) {\n char c = s.charAt(r);\n while(window[c]) {\n max = Math.max(max, r-l);\n window[s.charAt(l)]=false;\n l++; \n }\n window[c] = true;\n r++;\n }\n return Math.max(max,r-l);\n }\n```\n**76. Minimum Window Substring**\n```\n\tpublic String minWindow(String s, String t) {\n int l=0, r=0, tn=t.length(), sn=s.length(), start=0, len=sn+1;\n int[] count=new int[256];\n for(int i=0;i<tn;i++) \n count[t.charAt(i)]++; \n while(r<sn) {\n if(count[s.charAt(r)]-->0) tn--;\n while(tn==0) { //count[] all neg or 0, r at last element in window\n if(count[s.charAt(l)]++==0) {\n tn=1;\n if(r-l+1<len) { //l at 1st element in window\n start=l;\n len=r-l+1;\n }\n }\n l++; \n }\n r++;\n }\n return len==sn+1?"":s.substring(start,start+len);\n }\n```\n**159. Longest Substring with At Most Two Distinct Characters**\n```\n\tpublic int lengthOfLongestSubstringTwoDistinct(String s) {\n int l=0, r=0, types=0, len=0;\n int[] count = new int[256];\n while(r<s.length()) {\n if(count[s.charAt(r)]++==0) {\n types++; \n }\n while(types==3) {\n len = Math.max(len, r-l);\n if(count[s.charAt(l)]--==1) {\n types--;\n }\n l++;\n }\n r++;\n }\n return Math.max(len, r-l);\n }\n```\n **[209. Minimum Size Subarray Sum](https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-size-subarray-sum/discuss/59141/Evolve-from-brute-force-to-optimal)**\n```\n\tpublic int minSubArrayLen(int s, int[] nums) {\n int l=0,r=0,n=nums.length,res=n+1,sum=0;\n while(r<n) {\n sum+=nums[r];\n while(sum>=s) {\n res=Math.min(res,r-l+1); //can be here or outside depdending on the context \n sum-=nums[l];\n l++;\n }\n r++;\n }\n return res==n+1?0:res;\n }\n```\n**340. Longest Substring with At Most K Distinct Characters**\n```\n\tpublic int lengthOfLongestSubstringKDistinct(String s, int k) {\n int l=0, r=0, types=0, len=0;\n int[] count = new int[256];\n while(r<s.length()) {\n if(count[s.charAt(r)]++==0) {\n types++; \n }\n while(types==k+1) {\n len = Math.max(len, r-l);\n if(count[s.charAt(l)]--==1) {\n types--;\n }\n l++;\n }\n r++;\n }\n return Math.max(len, r-l);\n }\n```\n**[904. Fruit Into Baskets](https://leetcode.com/problems/fruit-into-baskets/discuss/1000442/Sliding-window-template)**\n```\n\tpublic int totalFruit(int[] tree) {\n int l=0, r=0, n = tree.length, types=0, len=0;\n int[] count = new int[n];\n while(r<n) {\n if(count[tree[r]]++==0) {\n types++; \n }\n while(types==3) {\n len = Math.max(len, r-l);\n if(count[tree[l]]--==1) {\n types--;\n }\n l++;\n }\n r++;\n }\n return Math.max(len, r-l);\n }\n```\n**[1004. Max Consecutive Ones III](https://leetcode.com/problems/max-consecutive-ones-iii/discuss/929117/Evolve-from-brute-force-to-optimal)**\n```\n\tpublic int longestOnes(int[] A, int K) {\n int l=0,r=0,sum=0,max=-1;\n while(r<A.length) {\n sum+=A[r];\n while(sum+K<r-l+1) {\n max=Math.max(max,r-l);\n sum-=A[l];\n l++;\n }\n r++;\n }\n return Math.max(max,r-l);\n }\n```\n[**1610. Maximum Number of Visible Points**](https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-number-of-visible-points/discuss/926504/Template-for-sliding-window-problems)\n```\n\tpublic int visiblePoints(List<List<Integer>> points, int angle, List<Integer> location) {\n List<Double> arcs=new ArrayList<>();\n int ovlp=0;\n for(List<Integer> point:points) {\n int dx=point.get(0)-location.get(0), dy=point.get(1)-location.get(1);\n if(dx==0&&dy==0) ovlp++;\n else arcs.add(Math.atan2(dx,dy));\n }\n Collections.sort(arcs);\n int n=arcs.size();\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n arcs.add(arcs.get(i)+2*Math.PI);\n double arc=Math.PI*angle/180;\n int l=0, r=0, max=0;\n while(r<n*2) {\n while(arcs.get(r)-arcs.get(l)>arc) {\n max=Math.max(r-l,max);\n l++; \n }\n r++;\n }\n return max+ovlp;\n }\n```\n\n
| 8
| 0
|
[]
| 1
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Python 20 lines AC O(n) solution
|
python-20-lines-ac-on-solution-by-round1-bcxy
|
Idea is pretty simple, keep two pointers left and right.\n\n If s[left:right] has all chars in T, calculate distance and keep answer, then move left pointer.\n\
|
round1lc
|
NORMAL
|
2015-05-12T06:48:28+00:00
|
2015-05-12T06:48:28+00:00
| 4,858
| false
|
Idea is pretty simple, keep two pointers left and right.\n\n If s[left:right] has all chars in T, calculate distance and keep answer, then move left pointer.\n\n If s[left:right] doesn't have all chars in T, move right pointer.\n\n\n class Solution:\n # @param {string} s\n # @param {string} t\n # @return {string}\n # sliding window problem\n # count all chars in string T\n # left pointer point to string which has been processed\n # right pointer point to string, which has not been processed\n # 1.if all window from left to right contains all string T(counter values all less then or equal to 0)\n # calculate min window length, and keep answer\n # then move left pointer\n # 2.else there are missing string in current answer\n # move right pointer\n # update counter\n # repeat 1, 2 steps until right is equal to len(s), then break it\n def minWindow(self, s, t):\n left, right = 0, 0\n # count T chars\n counter = collections.defaultdict(int)\n for a in t:\n counter[a] += 1\n \n minwindow = len(s) + 1\n answer = None\n \n while right <= len(s):\n # check all chars in T are in the current answer\n if all(map(lambda x: True if x<=0 else False, counter.values())):\n if minwindow > right-left:\n minwindow = right-left\n answer = s[left:right]\n char = s[left]\n if char in counter:\n counter[char] += 1\n left += 1\n else:\n if right == len(s):\n break\n char = s[right]\n if char in counter:\n counter[char] -= 1\n right += 1\n \n return answer if answer else ''
| 8
| 0
|
['Python']
| 3
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Sliding Window Explained || Beginner-friendly
|
sliding-window-explained-beginner-friend-ojis
|
IntuitionAs we need to check for substring, window would be the best approach to handle this. The only issue was deciding when to shrink. Once we find all the e
|
Bulba_Bulbasar
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-26T08:23:14.219517+00:00
|
2025-01-26T08:30:42.968145+00:00
| 1,107
| false
|
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
As we need to check for substring, window would be the best approach to handle this. The only issue was deciding when to shrink. Once we find all the elements we will shrink the window from left till the next element and then look for the missing element while moving to right. By doing so we will find a window with the minimum length having all the elements for second string
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
1. Input Check
- check is the input strings are valid and if not return an empty string
2. Frequency counts
- Initiate a frequency array to accomodate both lower and uppercase characters(ie-len:58)
- Iterate over the characters in string t and increment the frequency count for each character encountered.
3. Variable Initiation
- left & right pointers : Sliding window
- count : no. of characters in string t
- minLen & result : for smaller subString
4. Sliding Window
- Initiate while loop for sliding window till right is less than length of string s
- if current element if part of the string t, that is freq of current character is greater than 0, then decrement the count
- decrement the frequency of the current character in string s
- if count is 0 that is all elements are encountered from string t,
- start shrinking the window by moving the left pointer till one of the characters from string t is removed from the window
- parallely while count is 0, check if current window is smaller than the previous one and update the result string and minLen accordingly
5. Return result once sliding window is completed
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(n)
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(1)
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
public String minWindow(String s, String t) {
if (s == null || t == null || s.length() < t.length()) {
return "";
}
// Frequency array to count characters in `t`
int[] freq = new int[58]; // 58 to account for both uppercase and lowercase letters
// Fill frequency array for characters in `t`
for (char c : t.toCharArray()) {
freq[c - 'A']++;
}
// Variables for the sliding window
int left = 0, right = 0, count = t.length();
int minLen = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
String result = "";
// Start sliding window
while (right < s.length()) {
char rightChar = s.charAt(right);
// If character is needed, reduce its count
if (freq[rightChar - 'A'] > 0) {
count--;
}
// Decrement the frequency array for the current character
freq[rightChar - 'A']--;
right++;
// When all characters from `t` are in the current window
while (count == 0) {
// Update result if the current window is smaller
if (right - left < minLen) {
minLen = right - left;
result = s.substring(left, right);
}
char leftChar = s.charAt(left);
// Restore the count in the frequency array
freq[leftChar - 'A']++;
// If the restored character was part of `t`, increment `count`
if (freq[leftChar - 'A'] > 0) {
count++;
}
left++; // Shrink the window
}
}
return result;
}
}
```
# Possible Optimization
Instead of using a frequency array of size 58 to account for all possible characters, we can utilize a HashMap to store the frequency of only the characters present in string t. This approach reduces unnecessary space usage for characters that aren't relevant to the problem. Additionally, instead of reconstructing the substring multiple times, we can keep track of the start and end indices of the minimum window and construct the result substring only once, after determining the optimal window
# Space Complexity
O(k), k being the no. of unique characters in string t
# Code
```Java []
class Solution {
public String minWindow(String s, String t) {
if (s == null || t == null || s.length() < t.length()) {
return "";
}
// Use a HashMap to track the frequency of characters in `t`
HashMap<Character, Integer> freqMap = new HashMap<>();
for (char c : t.toCharArray()) {
freqMap.put(c, freqMap.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1);
}
int left = 0, right = 0, count = freqMap.size();
int minLen = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int start = 0; // To store the start index of the smallest window
// Sliding window
while (right < s.length()) {
char rightChar = s.charAt(right);
// If the character is part of `t`, decrement its count in the map
if (freqMap.containsKey(rightChar)) {
freqMap.put(rightChar, freqMap.get(rightChar) - 1);
if (freqMap.get(rightChar) == 0) {
count--; // All occurrences of this character are satisfied
}
}
right++; // Expand the window
// When the current window satisfies all characters in `t`
while (count == 0) {
// Update the result if this window is smaller
if (right - left < minLen) {
minLen = right - left;
start = left;
}
char leftChar = s.charAt(left);
// If the character is part of `t`, restore its count
if (freqMap.containsKey(leftChar)) {
freqMap.put(leftChar, freqMap.get(leftChar) + 1);
if (freqMap.get(leftChar) > 0) {
count++; // This character is no longer satisfied
}
}
left++; // Shrink the window
}
}
return minLen == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? "" : s.substring(start, start + minLen);
}
}
```
---
---

| 7
| 0
|
['Hash Table', 'Two Pointers', 'Sliding Window', 'Java']
| 1
|
minimum-window-substring
|
✅HARD MADE EASY | SLIDING WINDOW | JAVA | Explained🔥🔥🔥
|
hard-made-easy-sliding-window-java-expla-3mx4
|
Problem: Find the minimum window substring in string S which will contain all the characters in string T in inclusion and order.\n\nApproach:\n\nWe employ a sli
|
AdnanNShaikh
|
NORMAL
|
2024-08-16T16:41:58.405132+00:00
|
2024-08-16T16:41:58.405173+00:00
| 730
| false
|
**Problem**: Find the minimum window substring in string S which will contain all the characters in string T in inclusion and order.\n\n**Approach**:\n\nWe employ a sliding window technique, where we maintain a window of characters in string S.\nA HashMap is used to keep track of the characters in string T and their required frequencies.\nA count variable is used to keep track of the number of characters from T found in the current window.\n\n**Code** **Breakdown**:\n\n**Initialization**:\n\n**i and j**: Pointers representing the start and end of the sliding window.\nminLen: Stores the minimum length of the valid substring found so far.\nmap: A HashMap to store characters and their frequencies from string T.\ncount: To keep track of the number of characters from T found in the current window.\n**startInd:** Stores the starting index of the minimum window.\n\n**Preprocessing:**\n\nPopulate the map with characters from string T and their frequencies.\n\n**Sliding Window:**\n\nWhile j is less than the length of string S:\nIf the current character at index j is in the map and its frequency is greater than 0, increment count.\nDecrement the frequency of the current character in the map.\nIf count equals the length of string T, it means we found a valid window.\nUpdate minLen and startInd if the current window is smaller.\nIncrement the frequency of the character at index i in the map.\nIf the increased frequency becomes greater than 0, it means we can remove this character from the window without affecting the validity. Decrement count.\nIncrement i to shrink the window.\nIncrement j to expand the window.\n\n**Return the result:**\n\nIf a valid window was found, return the substring starting at startInd with length minLen. Otherwise, return an empty string.\n\n**Key Points:**\n\nThe sliding window efficiently explores all possible substrings.\nThe HashMap keeps track of character frequencies from string T.\nThe count variable helps identify valid windows.\nThe code optimizes the process by shrinking the window when possible.\n\n# Code\n```\n// Algo Used: Slinding Window , 2 pounters, Hashing\n// TC: O N , SC : O N\nclass Solution {\n public String minWindow(String s, String t) {\n int i= 0;\n int j= 0;\n int n= s.length();\n int m= t.length();\n int minLen= Integer.MAX_VALUE;;\n HashMap<Character , Integer> map = new HashMap<>();\n int count= 0; // for counting if we have got all the chars from t in our substring\n int startInd= -1;\n\n for(int ind = 0 ; ind< m; ind++){ // add all the chars from t in our map\n map.put(t.charAt(ind) , map.getOrDefault(t.charAt(ind) ,0)+1);\n }\n while(j < n){\n if(map.getOrDefault(s.charAt(j) ,0)>0){ // if curr sbubstring has one of the char from t then increase count by 1 (Note: Imp : In our curr substring only the char which are equal from the t will be > 0 , other then t will be in negative value)\n count++;\n }\n map.put(s.charAt(j) , map.getOrDefault(s.charAt(j),0)-1); // adding in map (which ever value we put , we will reduce it freq)\n \n while(count == m){ // jab tak count == k hai chalega, jaisi count < k hoga toh break hojayga\n if(j - i + 1 < minLen){\n minLen= j - i + 1;\n startInd= i;\n }\n\n map.put(s.charAt(i) , map.get(s.charAt(i))+1); // found one of the ans so now shrinking left pointer, so now increase the freq\n if(map.get(s.charAt(i))>0){ // updating count\n count--;\n }\n i++;\n }\n j++;\n }\n if(startInd == -1){\n return "";\n }\n return s.substring(startInd, startInd+minLen);\n }\n}\n```
| 7
| 0
|
['Java']
| 1
|
minimum-window-substring
|
Easy to Understand, C++ solution Sliding Window's Most Important Question
|
easy-to-understand-c-solution-sliding-wi-8z8q
|
Intuition\nAs we see the problems of String and Array, in which we have to optimise the solution and we have to perform sequential operations on those problems.
|
sribhargav1345
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-04T06:26:29.617144+00:00
|
2024-02-04T06:26:29.617174+00:00
| 1,288
| false
|
# Intuition\nAs we see the problems of String and Array, in which we have to optimise the solution and we have to perform sequential operations on those problems. We need to think of **Sliding Window**\n\n# Approach\nStore the elements of string \'t\' in a map, and compare that with the elements of string \'s\', and if they matches, then decrease the string \'s\' from the starting to get the minimum string.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$ \n\n- Space complexity: $$O(n)$$\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n int n = s.size();\n int m = t.size();\n\n // This is the common sliding window problem\n\n unordered_map<char,int> mp2; // Storing values of string \'t\'\n string ans;\n for(auto x:t)\n {\n mp2[x]++;\n }\n\n unordered_map<char,int> mp;\n int mini = INT_MAX;\n\n int i=0,j=0;\n while(j<n)\n {\n mp[s[j]]++;\n \n int flag = 0;\n for(auto x:mp2) // Checking if all values of mp2 are in mp1.\n {\n if(mp2[x.first]>mp[x.first])\n {\n flag = 1;\n break;\n }\n }\n\n if(flag==0) // If matches, then find min by decreasing the string \'s\'\n {\n while(mp[s[i]]>mp2[s[i]])\n {\n mp[s[i]]--;\n\n if(mp[s[i]]==0) mp.erase(s[i]);\n i++;\n }\n if(mini>j-i+1)\n {\n mini = min(mini,j-i+1);\n ans = s.substr(i,j-i+1);\n }\n }\n\n j++;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 7
| 0
|
['Ordered Map', 'Sliding Window', 'C++']
| 1
|
minimum-window-substring
|
✔️ ✔️Beat 97.97%|| Sliding Window Approach with Clear Comments and Explanation
|
beat-9797-sliding-window-approach-with-c-ww6s
|
Please upvote if you find the solution helpful.\n\n\n## Explanation\n\n1. Initialization:\n - Create a character frequency map mp1 for string t.\n - Initial
|
Inam_28_06
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-04T01:10:30.818487+00:00
|
2024-02-04T03:37:43.827510+00:00
| 1,311
| false
|
Please **upvote** if you find the solution helpful.\n\n\n## Explanation\n\n1. **Initialization**:\n - Create a character frequency map `mp1` for string `t`.\n - Initialize sliding window pointers `i` and `j`, and counters `count`, `mini`, and `start`.\n\n2. **Sliding Window Approach**:\n - Move the end pointer `j` through string `s`.\n - Adjust character counts and window size based on character occurrences.\n - Shrink the window when all characters from `t` are found.\n\n3. **Return Minimum Window**:\n - Return the minimum window substring of `s` if found, else return an empty string.\n\nThe algorithm efficiently identifies the minimum window in `s` containing all characters of `t`.\n\n**Time Complexity: O(S + T)**\n**Space Complexity: O(T)**\n**C++**\n```\n **Here\'s the code with concise comments:**\n\n```c++\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n string minWindow(string s, string t) {\n // Store character frequencies in t\n unordered_map<char, int> mp1;\n for (char c : t) {\n mp1[c]++;\n }\n\n // Sliding window variables\n int i = 0, j = 0, count = t.size(), mini = s.size() + 1, start = 0;\n\n while (j < s.size()) {\n // Decrement count if a required character is found\n if (mp1.count(s[j]) && mp1[s[j]] > 0) {\n count--;\n }\n mp1[s[j]]--; // Update character count in map\n\n // Shrink window while all characters in t are found\n while (count == 0) {\n if (mini > j - i + 1) {\n mini = j - i + 1;\n start = i;\n }\n mp1[s[i]]++; // Re-adjust character count\n if (mp1[s[i]] > 0) { // If a required character is removed, increment count\n count++;\n }\n i++; // Move start pointer\n }\n j++; // Move end pointer\n }\n\n return mini == s.size() + 1 ? "" : s.substr(start, mini);\n }\n};\n```\n**Java**\n```\nclass Solution {\n public String minWindow(String s, String t) {\n HashMap<Character, Integer> mp1 = new HashMap<>();\n int count = t.length();\n for (char i : t.toCharArray()) {\n mp1.put(i, mp1.getOrDefault(i, 0) + 1);\n }\n int i = 0, j = 0, mini = s.length() + 1, start = 0;\n while (j < s.length()) {\n if (mp1.containsKey(s.charAt(j)) && mp1.get(s.charAt(j)) > 0) {\n count--;\n }\n if (mp1.containsKey(s.charAt(j))) {\n mp1.put(s.charAt(j), mp1.get(s.charAt(j)) - 1);\n }\n while (count == 0) {\n if (mini > j - i + 1) {\n mini = j - i + 1;\n start = i;\n }\n if (mp1.containsKey(s.charAt(i))) {\n mp1.put(s.charAt(i), mp1.get(s.charAt(i)) + 1);\n if (mp1.get(s.charAt(i)) > 0) {\n count++;\n }\n }\n i++;\n }\n j++;\n }\n if (mini == s.length() + 1) {\n return "";\n }\n return s.substring(start, start + mini);\n }\n}\n```\n**python**\n```\nclass Solution(object):\n def minWindow(self, s, t):\n mp1 = defaultdict(int)\n count = len(t)\n for i in t:\n mp1[i] += 1\n\n i, j, mini, start = 0, 0, len(s) + 1, 0\n while j < len(s):\n if s[j] in mp1 and mp1[s[j]] > 0:\n count -= 1\n if s[j] in mp1:\n mp1[s[j]] -= 1\n\n while count == 0:\n if mini > j - i + 1:\n mini = j - i + 1\n start = i\n if s[i] in mp1:\n mp1[s[i]] += 1\n if mp1[s[i]] > 0:\n count += 1\n i += 1\n j += 1\n\n if mini == len(s) + 1:\n return ""\n return s[start:start + mini]\n \n```\n\n\n
| 7
| 0
|
['C', 'Sliding Window', 'Python', 'Java']
| 0
|
minimum-window-substring
|
O( n )✅ | Python (Step by step explanation)✅
|
o-n-python-step-by-step-explanation-by-m-q7j2
|
Intuition\nThe problem requires finding the minimum window in string \'s\' that contains all characters from string \'t\'. We can use a sliding window approach
|
monster0Freason
|
NORMAL
|
2023-10-27T07:34:54.036360+00:00
|
2023-10-27T07:34:54.036381+00:00
| 485
| false
|
# Intuition\nThe problem requires finding the minimum window in string \'s\' that contains all characters from string \'t\'. We can use a sliding window approach to solve this problem efficiently.\n\n# Approach\n1. First, we handle the edge case: if \'t\' is an empty string, we return an empty string as the result.\n\n2. We initialize two dictionaries, \'t_counter\' and \'window\', to keep track of character counts in \'t\' and the current window, respectively.\n\n3. We populate \'t_counter\' by iterating through the characters of \'t\' and incrementing their counts. It helps us keep track of the characters we need to match in \'s\'.\n\n4. We define \'have\' to track how many required characters we have in our current window and \'need\' to represent the total number of characters required. We also initialize \'ans\' and \'ans_size\' to store the minimum window and its size. \'ans\' starts as [-1, -1] to represent an invalid window, and \'ans_size\' starts as positive infinity.\n\n5. We set \'left\' to 0 as the start of our sliding window.\n\n6. We iterate through \'s\' using a \'right\' pointer to expand the window:\n - Update \'window\' to keep track of character counts in the current window.\n - If the character at \'right\' is in \'t_counter\' and its count in \'window\' matches its count in \'t_counter\', we increment \'have\'.\n\n7. We enter a while loop as long as we have all required characters in our window:\n - If the current window size is smaller than \'ans_size\', we update \'ans\' and \'ans_size\' to record this as a potential minimum window.\n - We decrement the count of the character at \'left\' in \'window\'.\n - If the character at \'left\' is in \'t_counter\' and its count in \'window\' is less than its count in \'t_counter\', we decrement \'have\'.\n - We move \'left\' to the right to shrink the window.\n\n8. After the loop, we have found the minimum window. We return the substring of \'s\' from \'ans[0]\' to \'ans[1]\' if \'ans_size\' is not still equal to positive infinity. Otherwise, we return an empty string.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(s + t), where \'s\' is the length of string \'s\' and \'t\' is the length of string \'t\'.\n- Space complexity: O(s + t) due to the dictionaries \'t_counter\' and \'window\'.\n\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:\n if t=="" : return ""\n\n t_counter , window = {} , {}\n\n for x in t:\n t_counter[x] = 1 + t_counter.get(x , 0)\n\n have , need = 0 , len(t_counter)\n ans , ans_size = [-1 , -1] , float("infinity") \n left = 0\n\n for right in range(len(s)):\n window[s[right]] = 1 + window.get(s[right] , 0)\n\n if s[right] in t_counter and window[s[right]] == t_counter[s[right]] :\n have += 1\n\n while have == need :\n if (right - left + 1) < ans_size:\n ans = [left , right] \n ans_size = (right - left + 1)\n\n window[s[left]] -= 1\n if s[left] in t_counter and window[s[left]] < t_counter[s[left]] :\n have -= 1\n left += 1\n\n return s[ans[0] : ans[1]+1] if ans_size != float("infinity") else "" \n \n```\n\n# Please upvote the solution if you understood it.\n\n
| 7
| 0
|
['Sliding Window', 'Python3']
| 0
|
apply-operations-to-an-array
|
🚀 Beats 100% | In-Place Processing + Zero Shifting | Apply Operations on Array
|
beats-100-in-place-processing-zero-shift-p3w7
|
Youtube🚀 Beats 100% | In-Place Processing + Zero Shifting | Apply Operations on Array🔼 Please Upvote🔼 Please Upvote🔼 Please Upvote🔼 Please Upvote💡 If this helpe
|
rahulvijayan2291
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-01T03:38:56.513541+00:00
|
2025-03-01T03:38:56.513541+00:00
| 18,214
| false
|
# Youtube
https://youtu.be/81UhXYJOz1g
---
# 🚀 Beats 100% | In-Place Processing + Zero Shifting | Apply Operations on Array
---
# **🔼 Please Upvote**
# **🔼 Please Upvote**
# **🔼 Please Upvote**
# **🔼 Please Upvote**
💡 **If this helped, don’t forget to upvote! 🚀🔥**
---
## **💡 Problem Breakdown**
Given an array `nums`, perform the following operations:
1. If `nums[i] == nums[i+1]`, double `nums[i]` and set `nums[i+1] = 0`.
2. Shift all nonzero elements to the left, keeping the order the same.
### **Example:**
#### **Input:**
```plaintext
nums = [2,2,0,4,4,8]
```
#### **Output:**
```plaintext
[4,8,8,0,0,0]
```
#### **Explanation:**
- `2 + 2 = 4`, `nums[1] = 0`.
- `4 + 4 = 8`, `nums[4] = 0`.
- Shift nonzero elements left.
---
## **🚀 Approach Overview**
### 🔹 **Key Observations:**
1. **Iterate through `nums`** and check adjacent elements.
2. **If equal, double the value** and set the next to `0`.
3. **Use a new array** to place nonzero elements sequentially.
### 🔹 **Strategy:**
1. Traverse `nums`, applying the doubling rule.
2. Store the results in `newNums`, ensuring order is preserved.
3. Return the modified array.
---
## **⏳ Complexity Analysis**
- **Time Complexity:** `O(N)`, since we traverse the array once.
- **Space Complexity:** `O(N)`, for storing results.
---
## **📝 Code Implementation**
### **🔵 Java Solution**
```java
class Solution {
public int[] applyOperations(int[] nums) {
int[] result = new int[nums.length];
int count = 0;
int i;
for(i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; i++){
if(nums[i] != 0){
if(nums[i] == nums[i + 1]){
result[count] = nums[i] * 2;
i++;
}
else{
result[count] = nums[i];
}
count++;
}
}
if(i != nums.length){
result[count] = nums[nums.length - 1];
}
return result;
}
}
```
---
### **🟢 C++ Solution**
```cpp
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> applyOperations(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
vector<int> newNums(n, 0);
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
if (nums[i] != 0) {
if (nums[i] == nums[i + 1]) {
newNums[count] = nums[i] * 2;
nums[i + 1] = 0;
i++;
} else {
newNums[count] = nums[i];
}
count++;
}
}
if (nums[n - 1] != 0) {
newNums[count++] = nums[n - 1];
}
return newNums;
}
};
```
---
### **🟣 Python3 Solution**
```python
from typing import List
class Solution:
def applyOperations(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:
new_nums = [0] * len(nums)
count = 0
i = 0
while i < len(nums) - 1:
if nums[i] != 0:
if nums[i] == nums[i + 1]:
new_nums[count] = nums[i] * 2
i += 1
else:
new_nums[count] = nums[i]
count += 1
i += 1
if i < len(nums) and nums[i] != 0:
new_nums[count] = nums[i]
return new_nums
```
---
### **🔴 C Solution**
```c
int* applyOperations(int* nums, int numsSize, int* returnSize) {
int* newNums = (int*)calloc(numsSize, sizeof(int));
int count = 0;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < numsSize - 1; i++) {
if (nums[i] != 0) {
if (nums[i] == nums[i + 1]) {
newNums[count] = nums[i] * 2;
i++;
} else {
newNums[count] = nums[i];
}
count++;
}
}
if (i < numsSize && nums[i] != 0) {
newNums[count] = nums[i];
}
*returnSize = numsSize;
return newNums;
}
```
---
### **🟠 C# Solution**
```csharp
using System;
public class Solution {
public int[] ApplyOperations(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.Length;
int[] newNums = new int[n];
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
if (nums[i] != 0) {
if (nums[i] == nums[i + 1]) {
newNums[count] = nums[i] * 2;
nums[i + 1] = 0;
i++;
} else {
newNums[count] = nums[i];
}
count++;
}
}
if (nums[n - 1] != 0) {
newNums[count++] = nums[n - 1];
}
return newNums;
}
}
```
---
### **🟡 JavaScript Solution**
```js
var applyOperations = function(nums) {
let n = nums.length;
let newNums = new Array(n).fill(0);
let count = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
if (nums[i] !== 0) {
if (nums[i] === nums[i + 1]) {
newNums[count] = nums[i] * 2;
nums[i + 1] = 0;
i++;
} else {
newNums[count] = nums[i];
}
count++;
}
}
if (nums[n - 1] !== 0) {
newNums[count++] = nums[n - 1];
}
return newNums;
};
```
---
### **🟣 TypeScript Solution**
```ts
function applyOperations(nums: number[]): number[] {
let n = nums.length;
let newNums: number[] = new Array(n).fill(0);
let count = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
if (nums[i] !== 0) {
if (nums[i] === nums[i + 1]) {
newNums[count] = nums[i] * 2;
nums[i + 1] = 0;
i++;
} else {
newNums[count] = nums[i];
}
count++;
}
}
if (nums[n - 1] !== 0) {
newNums[count++] = nums[n - 1];
}
return newNums;
}
```
---
# **🔼 Please Upvote**
# **🔼 Please Upvote**
# **🔼 Please Upvote**
# **🔼 Please Upvote**
💡 **If this helped, don’t forget to upvote! 🚀🔥**
| 74
| 3
|
['Array', 'C', 'C++', 'Java', 'TypeScript', 'Python3', 'JavaScript', 'C#']
| 6
|
apply-operations-to-an-array
|
✅✅✅ C++ & Java || O(n) time & O(1) space || Very Simple and Easy to Understand
|
c-solution-on-time-o1-space-very-simple-2l5hy
|
Approach:
Simply change the value of nums[i] to 2 times & set nums[i+1] to zero when nums[i] == nums[i+1].
Then take a pointer and keep on accumulating non zero
|
kreakEmp
|
NORMAL
|
2022-11-06T04:00:38.429018+00:00
|
2025-03-01T07:13:05.365924+00:00
| 6,232
| false
|
# Approach:
- Simply change the value of nums[i] to 2 times & set nums[i+1] to zero when nums[i] == nums[i+1].
- Then take a pointer and keep on accumulating non zero value at the front.
- Set all remaining values to zero, utill pointer is less then size of the array.
```cpp []
vector<int> applyOperations(vector<int>& nums) {
for(int i = 0; i+1 < nums.size(); ++i){
if(nums[i] == nums[i+1]){ //update values of ith and (i+1)th value
nums[i] = 2*nums[i];
nums[i+1] = 0;
}
}
int i = 0;
for(auto n: nums){ // collect all noon zero values at front
if(n != 0) nums[i++] = n;
}
while(i < nums.size()) nums[i++] = 0; //set values to zero for remainintg ith element
return nums;
}
```
```java []
int[] applyOperations(int[] nums) {
for(int i = 0; i+1 < nums.length; ++i){
if(nums[i] == nums[i+1]){ //update values of ith and (i+1)th value
nums[i] = 2*nums[i];
nums[i+1] = 0;
}
}
int i = 0;
for(int n: nums){ // collect all noon zero values at front
if(n != 0) nums[i++] = n;
}
while(i < nums.length) nums[i++] = 0; //set values to zero for remainintg ith element
return nums;
}
```
# Single pass solution :
```cpp []
vector<int> applyOperations(vector<int>& nums) {
for(int i = 0, j = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i){
if(i + 1 < nums.size() && nums[i] == nums[i+1]) {
nums[i] = nums[i]*2;
nums[i+1] = 0;
}
if(nums[i] != 0) nums[j++] = nums[i];
if(j <= i) nums[i] = 0;
}
return nums;
}
```
```Java []
int[] applyOperations(int[] nums) {
for(int i = 0, j = 0; i < nums.length; ++i){
if(i + 1 < nums.length && nums[i] == nums[i+1]) {
nums[i] = nums[i]*2;
nums[i+1] = 0;
}
if(nums[i] != 0) nums[j++] = nums[i];
if(j <= i) nums[i] = 0;
}
return nums;
}
```
---
<b>Here is an article of my interview experience - A Journey to FAANG Company, I recomand you to go through this to know which all resources I have used & how I cracked interview at Amazon:
https://leetcode.com/discuss/interview-experience/3171859/Journey-to-a-FAANG-Company-Amazon-or-SDE2-(L5)-or-Bangalore-or-Oct-2022-Accepted
---
| 65
| 9
|
['C++', 'Java']
| 11
|
apply-operations-to-an-array
|
One Pass [C++/Java/Python3]
|
one-pass-cjavapython3-by-xxvvpp-za84
|
Just do Operation and Swapping of non-zeroes at front of array simultaneously.\n# C++\n vector applyOperations(vector& A) {\n for (int i = 0, j = 0; i
|
xxvvpp
|
NORMAL
|
2022-11-06T04:01:46.657909+00:00
|
2022-11-06T08:15:39.924890+00:00
| 2,977
| false
|
Just do `Operation` and `Swapping of non-zeroes at front` of array simultaneously.\n# C++\n vector<int> applyOperations(vector<int>& A) {\n for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < size(A); ++i){\n if (i + 1 < size(A) and A[i] == A[i + 1]){\n A[i] *= 2;\n A[i + 1] = 0;\n }\n if (A[i]) swap(A[j++], A[i]);\n } \n return A;\n }\n# Java\n void swap(int[] A, int i, int j){\n int temp = A[i];\n A[i] = A[j];\n A[j] = temp;\n }\n \n public int[] applyOperations(int[] A) {\n for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < A.length; ++i){\n if (i + 1 < A.length && A[i] == A[i + 1]){\n A[i] *= 2;\n A[i + 1] = 0;\n }\n if (A[i] != 0){\n swap(A,i,j);\n j++;\n }\n } \n return A;\n }\n# Python3\n def applyOperations(self, A: List[int]) -> List[int]:\n j = 0\n for i in range(len(A)):\n if i + 1 < len(A) and A[i] == A[i + 1]:\n A[i] *= 2\n A[i + 1] = 0 \n if A[i]:\n A[j], A[i] = A[i], A[j]\n j += 1 \n return A
| 56
| 2
|
['C']
| 5
|
apply-operations-to-an-array
|
✅ Two Pointers | Python | C++ | Java | C# | JS | Go | Swift | PHP | Rust | Kotlin | Dart | Ruby
|
two-pointers-python-by-otabek_kholmirzae-kumt
|
IntuitionThe problem involves two distinct operations: first, we need to perform a series of comparisons and modifications on adjacent elements, and then we nee
|
otabek_kholmirzaev
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-01T08:44:49.113410+00:00
|
2025-03-01T10:30:19.084090+00:00
| 6,009
| false
|
# Intuition
**The problem involves two distinct operations:** first, we need to perform a series of comparisons and modifications on adjacent elements, and then we need to move all zeros to the end of the array. A natural way to approach this is to follow the instructions step by step.
# Approach
1. **Apply Operations:** Iterate through the array from index 0 to n-2 and apply the given rule:
- If current element equals the next element, multiply the current element by 2 and set the next element to 0
- Otherwise, skip and continue
2. **Shift Zeros:** After applying all operations, we need to move all zeros to the end while preserving the order of non-zero elements. We can do this in-place using a *two-pointer technique*:
- Use a pointer to keep track of where the next non-zero element should go
- Iterate through the array, moving non-zero elements to their correct positions
- Fill the remaining positions with zeros
This approach follows the exact requirements of the problem and **manipulates the array in-place**, which is more efficient in terms of space.
# Complexity
- Time complexity: O(n)
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity: O(1)
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def applyOperations(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:
n = len(nums)
# Apply operations
for i in range(n - 1):
if nums[i] == nums[i + 1]:
nums[i] *= 2
nums[i + 1] = 0
# Shift zeros to the end (in-place)
non_zero_idx = 0
# Move all non-zero elements to the front
for i in range(n):
if nums[i] != 0:
nums[non_zero_idx] = nums[i]
non_zero_idx += 1
# Fill the remaining positions with zeros
for i in range(non_zero_idx, n):
nums[i] = 0
return nums
```
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> applyOperations(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
// Apply operations
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
if (nums[i] == nums[i + 1]) {
nums[i] *= 2;
nums[i + 1] = 0;
}
}
// Shift zeros to the end (in-place)
int nonZeroIdx = 0;
// Move all non-zero elements to the front
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (nums[i] != 0) {
nums[nonZeroIdx++] = nums[i];
}
}
// Fill the remaining positions with zeros
while (nonZeroIdx < n) {
nums[nonZeroIdx++] = 0;
}
return nums;
}
};
```
```java []
class Solution {
public int[] applyOperations(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
// Apply operations
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
if (nums[i] == nums[i + 1]) {
nums[i] *= 2;
nums[i + 1] = 0;
}
}
// Shift zeros to the end (in-place)
int nonZeroIdx = 0;
// Move all non-zero elements to the front
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (nums[i] != 0) {
nums[nonZeroIdx++] = nums[i];
}
}
// Fill the remaining positions with zeros
while (nonZeroIdx < n) {
nums[nonZeroIdx++] = 0;
}
return nums;
}
}
```
```csharp []
class Solution {
public int[] ApplyOperations(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.Length;
// Apply operations
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
if (nums[i] == nums[i + 1]) {
nums[i] *= 2;
nums[i + 1] = 0;
}
}
// Shift zeros to the end (in-place)
int nonZeroIdx = 0;
// Move all non-zero elements to the front
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (nums[i] != 0) {
nums[nonZeroIdx++] = nums[i];
}
}
// Fill the remaining positions with zeros
while (nonZeroIdx < n) {
nums[nonZeroIdx++] = 0;
}
return nums;
}
}
```
```javascript []
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {number[]}
*/
var applyOperations = function(nums) {
const n = nums.length;
// Apply operations
for (let i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
if (nums[i] === nums[i + 1]) {
nums[i] *= 2;
nums[i + 1] = 0;
}
}
// Shift zeros to the end (in-place)
let nonZeroIdx = 0;
// Move all non-zero elements to the front
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (nums[i] !== 0) {
nums[nonZeroIdx++] = nums[i];
}
}
// Fill the remaining positions with zeros
while (nonZeroIdx < n) {
nums[nonZeroIdx++] = 0;
}
return nums;
};
```
```go []
func applyOperations(nums []int) []int {
n := len(nums)
// Apply operations
for i := 0; i < n-1; i++ {
if nums[i] == nums[i+1] {
nums[i] *= 2
nums[i+1] = 0
}
}
// Shift zeros to the end (in-place)
nonZeroIdx := 0
// Move all non-zero elements to the front
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
if nums[i] != 0 {
nums[nonZeroIdx] = nums[i]
nonZeroIdx++
}
}
// Fill the remaining positions with zeros
for i := nonZeroIdx; i < n; i++ {
nums[i] = 0
}
return nums
}
```
```swift []
class Solution {
func applyOperations(_ nums: [Int]) -> [Int] {
var result = nums // Create a mutable copy
let n = result.count
// Apply operations
for i in 0..<(n-1) {
if result[i] == result[i+1] {
result[i] *= 2
result[i+1] = 0
}
}
// Shift zeros to the end
var nonZeroIdx = 0
// Move all non-zero elements to the front
for i in 0..<n {
if result[i] != 0 {
result[nonZeroIdx] = result[i]
nonZeroIdx += 1
}
}
// Fill the remaining positions with zeros
for i in nonZeroIdx..<n {
result[i] = 0
}
return result
}
}
```
```php []
class Solution {
/**
* @param Integer[] $nums
* @return Integer[]
*/
function applyOperations($nums) {
$n = count($nums);
// Apply operations
for ($i = 0; $i < $n - 1; $i++) {
if ($nums[$i] == $nums[$i + 1]) {
$nums[$i] *= 2;
$nums[$i + 1] = 0;
}
}
// Shift zeros to the end (in-place)
$nonZeroIdx = 0;
// Move all non-zero elements to the front
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++) {
if ($nums[$i] != 0) {
$nums[$nonZeroIdx++] = $nums[$i];
}
}
// Fill the remaining positions with zeros
while ($nonZeroIdx < $n) {
$nums[$nonZeroIdx++] = 0;
}
return $nums;
}
}
```
```rust []
impl Solution {
pub fn apply_operations(mut nums: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<i32> {
let n = nums.len();
// Apply operations
for i in 0..n - 1 {
if nums[i] == nums[i + 1] {
nums[i] *= 2;
nums[i + 1] = 0;
}
}
// Shift zeros to the end (in-place)
let mut non_zero_idx = 0;
// Move all non-zero elements to the front
for i in 0..n {
if nums[i] != 0 {
nums[non_zero_idx] = nums[i];
non_zero_idx += 1;
}
}
// Fill the remaining positions with zeros
for i in non_zero_idx..n {
nums[i] = 0;
}
nums
}
}
```
```kotlin []
class Solution {
fun applyOperations(nums: IntArray): IntArray {
val n = nums.size
// Apply operations
for (i in 0 until n - 1) {
if (nums[i] == nums[i + 1]) {
nums[i] *= 2
nums[i + 1] = 0
}
}
// Shift zeros to the end (in-place)
var nonZeroIdx = 0
// Move all non-zero elements to the front
for (i in nums.indices) {
if (nums[i] != 0) {
nums[nonZeroIdx] = nums[i]
nonZeroIdx++
}
}
// Fill the remaining positions with zeros
for (i in nonZeroIdx until n) {
nums[i] = 0
}
return nums
}
}
```
```dart []
class Solution {
List<int> applyOperations(List<int> nums) {
int n = nums.length;
// Apply operations
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
if (nums[i] == nums[i + 1]) {
nums[i] *= 2;
nums[i + 1] = 0;
}
}
// Shift zeros to the end (in-place)
int nonZeroIdx = 0;
// Move all non-zero elements to the front
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (nums[i] != 0) {
nums[nonZeroIdx++] = nums[i];
}
}
// Fill the remaining positions with zeros
for (int i = nonZeroIdx; i < n; i++) {
nums[i] = 0;
}
return nums;
}
}
```
```ruby []
# @param {Integer[]} nums
# @return {Integer[]}
def apply_operations(nums)
n = nums.length
# Apply operations
(0...n - 1).each do |i|
if nums[i] == nums[i + 1]
nums[i] *= 2
nums[i + 1] = 0
end
end
# Shift zeros to the end (in-place)
non_zero_idx = 0
# Move all non-zero elements to the front
(0...n).each do |i|
if nums[i] != 0
nums[non_zero_idx] = nums[i]
non_zero_idx += 1
end
end
# Fill the remaining positions with zeros
(non_zero_idx...n).each do |i|
nums[i] = 0
end
nums
end
```
---

| 49
| 0
|
['Swift', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'Go', 'Python3', 'Rust', 'Kotlin', 'JavaScript', 'C#']
| 3
|
apply-operations-to-an-array
|
✅ [Python/C++] use the NOT trick to move zeros (explained)
|
pythonc-use-the-not-trick-to-move-zeros-e54cc
|
\u2705 IF YOU LIKE THIS SOLUTION, PLEASE UPVOTE.\n*\nThis solution employs a brute force approach to perform operations along with (stable-)sorting using a *log
|
stanislav-iablokov
|
NORMAL
|
2022-11-06T04:00:48.478990+00:00
|
2022-11-06T05:19:33.054526+00:00
| 2,892
| false
|
**\u2705 IF YOU LIKE THIS SOLUTION, PLEASE UPVOTE.**\n****\nThis solution employs a brute force approach to perform operations along with (stable-)sorting using a **logical not** trick to move zeros to the end of array. Time complexity is linear: **O(N\\*logN)**. Space complexity is linear: **O(N)**.\n\n\n**Python.**\n```\nclass Solution:\n def applyOperations(self, n):\n\n # apply the first part of operations\n for i in range(1,len(n)):\n if n[i] == n[i-1]:\n n[i-1], n[i] = n[i-1]*2, 0 \n \n # \'not\' of any non-zero number is equal to 0, i.e.,\n # less than \'not 0\' which is 1 (here, sorting is stable)\n return sorted(n, key=lambda x: not x)\n```\n\n**C++.**\n```\nclass Solution \n{\npublic:\n vector<int> applyOperations(vector<int>& nums) \n {\n for (int i = 1; i < nums.size(); ++i)\n if (nums[i] == nums[i-1])\n nums[i-1] *= 2, nums[i] = 0;\n \n\t\t// stable sort is important, it keeps the original order of non-zero numbers\n stable_sort(nums.begin(), nums.end(), [](int a, int b) { return !a < !b; });\n return nums;\n }\n};\n```
| 37
| 1
|
[]
| 10
|
apply-operations-to-an-array
|
✅2 Method's ||🌟JAVA||🧑💻 BEGINNER FREINDLY||C++||Python3
|
2-methods-java-beginner-freindlycpython3-gdqh
|
Approach 1: Two-Pass1.Apply Operations and Shift Zeros in a Single Pass:
. Use a pointer index to track the position where the next non-zero element should be
|
Varma5247
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-01T00:41:28.990563+00:00
|
2025-03-01T05:42:01.649157+00:00
| 2,847
| false
|
# Approach 1: Two-Pass
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
**1.Apply Operations and Shift Zeros in a Single Pass:**
. Use a pointer ```index``` to track the position where the next non-zero element should be placed.
.Iterate through the array:
.If the current element (```nums[i]```) is equal to the next element (```nums[i + 1]```):
.Double the value of``` nums[i]```.
Set ```nums[i + 1]``` to 0.
.If the current element ```(nums[i])``` is not zero, move it to ```nums[index] ```and increment index.
.After processing all elements, fill the remaining positions from ```index``` to ```nums.length - 1``` with zeros.
**2.Return the Modified Array:**
.The array is modified in place, so return ```nums``` as the result.
# ⏳Complexity Analysis
- Time complexity:$$ O(n)$$
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:$$O(1)$$
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
### Step-by-Step Table
### nums = [1, 2, 2, 1, 1, 0]
# 💻Code Implementation
```java []
class Solution {
public int[] applyOperations(int[] nums) {
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; i++) {
if (nums[i] == nums[i + 1]) {
nums[i] *= 2;
nums[i + 1] = 0;
}
}
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] != 0) {
nums[index++] = nums[i];
}
}
while (index < nums.length) {
nums[index++] = 0;
}
return nums;
}
}
```
```c++ []
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> applyOperations(vector<int>& nums) {
// Step 1: Merge adjacent equal elements
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size() - 1; i++) {
if (nums[i] == nums[i + 1]) {
nums[i] *= 2;
nums[i + 1] = 0;
}
}
// Step 2: Shift non-zero elements to the front
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if (nums[i] != 0) {
nums[index++] = nums[i];
}
}
// Step 3: Fill the rest of the array with zeros
while (index < nums.size()) {
nums[index++] = 0;
}
return nums;
}
};
```
```python []
class Solution:
def applyOperations(self, nums):
# Step 1: Merge adjacent equal elements
for i in range(len(nums) - 1):
if nums[i] == nums[i + 1]:
nums[i] *= 2
nums[i + 1] = 0
# Step 2: Shift non-zero elements to the front
index = 0
for i in range(len(nums)):
if nums[i] != 0:
nums[index] = nums[i]
index += 1
# Step 3: Fill the rest of the array with zeros
while index < len(nums):
nums[index] = 0
index += 1
return nums
```
___
# Approach 2: Two-Pointer
**1.Merging and Shifting:**
.We iterate through the array with a single loop.
.If two adjacent elements are equal, we double the first one and place it at the current ```index```, then increment ```i``` to skip the next element since it has been merged.
.If the current element is non-zero and not part of a merge, we place it at the current ```index```.
**2.Filling Zeros:**
After processing all elements, we fill the remaining positions in the array with zeros.
# ⏳Complexity Analysis
- Time complexity:$$ O(n)$$
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:$$O(1)$$
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# 💻Code Implementation
```java []
class Solution {
public int[] applyOperations(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
// Step 1: Apply the operations and shift non-zero elements to the front
int index = 0; // Pointer to track the position for non-zero elements
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (i < n - 1 && nums[i] == nums[i + 1]) {
nums[i] *= 2; // Double the current element
nums[i + 1] = 0; // Set the next element to 0
}
// Shift non-zero elements to the front
if (nums[i] != 0) {
nums[index] = nums[i]; // Place non-zero element at the current index
if (index != i) {
nums[i] = 0; // Set the original position to 0 if it was moved
}
index++; // Move the index forward
}
}
return nums;
}
}
```
```c++ []
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> applyOperations(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
int index = 0; // Pointer to track the position for non-zero elements
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (i < n - 1 && nums[i] == nums[i + 1]) {
nums[i] *= 2; // Double the current element
nums[i + 1] = 0; // Set the next element to 0
}
// Shift non-zero elements to the front
if (nums[i] != 0) {
nums[index] = nums[i]; // Place non-zero element at the current index
if (index != i) {
nums[i] = 0; // Set the original position to 0 if it was moved
}
index++; // Move the index forward
}
}
// Fill the remaining positions with zeros
while (index < n) {
nums[index++] = 0;
}
return nums;
}
};
```
```python []
class Solution:
def applyOperations(self, nums):
n = len(nums)
index = 0 # Pointer to track the position for non-zero elements
for i in range(n):
if i < n - 1 and nums[i] == nums[i + 1]:
nums[i] *= 2 # Double the current element
nums[i + 1] = 0 # Set the next element to 0
# Shift non-zero elements to the front
if nums[i] != 0:
nums[index] = nums[i] # Place non-zero element at the current index
if index != i:
nums[i] = 0 # Set the original position to 0 if it was moved
index += 1 # Move the index forward
# Fill the remaining positions with zeros
while index < n:
nums[index] = 0
index += 1
return nums
```
**If you found my solution helpful, I would greatly appreciate your upvote, as it would motivate me to continue sharing more solutions.**
🔼 **Please Upvote**
🔼 **Please Upvote**
🔼 **Please Upvote**
| 22
| 0
|
['Array', 'Two Pointers', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'TypeScript', 'Python3', 'JavaScript']
| 1
|
apply-operations-to-an-array
|
2 pointers O(1) space vs 1 loop||C++ Py3 beats 100%
|
2-passes-2-pointers-o1-spacec-beats-100-gs9qz
|
Intuition1st pass is for applying operations
2nd pass use 2 pointers to reuse the array nums for the answer
Both C++ & Python are made.a 1 loop solution is also
|
anwendeng
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-01T00:17:41.882187+00:00
|
2025-03-01T02:56:39.007387+00:00
| 2,249
| false
|
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
1st pass is for applying operations
2nd pass use 2 pointers to reuse the array nums for the answer
Both C++ & Python are made.
a 1 loop solution is also made.
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
1. Use a loop to proceed the operation to the adjacent pair `(nums[i], nums[i+1])` to get `(nums[i]*2, 0)` for i satisfying `nums[i]==nums[i+1]`
2. 2nd pass uses 2 pointers `i, j` to set `nums[j]=nums[i]; j++` for i with `nums[i]>0`
3. The subarray `nums[j:]` is filled with `0` & return `nums`
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
$$O(n)$$
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
Extra: $$O(1)$$ for C++
# Code||C++ Python 0ms 100%
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> applyOperations(vector<int>& nums) {
const int n=nums.size();
for(int i=0; i<n-1; i++){
if (nums[i]==nums[i+1]){
nums[i]<<=1;
nums[i+1]=0;
i++;// 0 needs no operation
}
}
int j=0;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
if (nums[i]>0) nums[j++]=nums[i];
}
fill(nums.begin()+j, nums.end(), 0);
return nums;
}
};
```
```Python []
class Solution:
def applyOperations(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:
n, i=len(nums), 0
while i<n-1:
if nums[i]==nums[i+1]:
nums[i], nums[i+1]=nums[i]<<1, 0
i+=1
i+=1
j=0
for x in nums:
if x>0:
nums[j]=x
j+=1
nums[j:]=[0]*(n-j)
return nums
```
# C++ 1 loop ||0ms
```
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> applyOperations(vector<int>& nums) {
const int n=nums.size();
vector<int> ans(n, 0);
int j=0;
for(int i=0; i<n-1; i++){
if (nums[i]==nums[i+1]){
nums[i]<<=1;
nums[i+1]=0;
}
if (nums[i]) ans[j++]=nums[i];
}
if (nums.back()) ans[j++]=nums.back();
return ans;
}
};
```
| 17
| 0
|
['Two Pointers', 'C++', 'Python3']
| 5
|
apply-operations-to-an-array
|
✅✅🔥BEATS 96.37% SIMPLEST PROGRAM | JAVA 🔥 Python 🔥 C++ 🔥 JS 🔥 | Simplest Program | O(n) & O(1)
|
beats-9637-simplest-program-java-python-zotsv
|
IntuitionThis method modifies the given array based on certain operations:
If two consecutive elements are equal, double the first one and set the second one to
|
peEAWW4Y33
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-01T12:12:23.310810+00:00
|
2025-03-01T12:12:23.310810+00:00
| 596
| false
|
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
This method modifies the given array based on certain operations:
- If two consecutive elements are equal, double the first one and set the second one to 0.
- Shift all non-zero elements to the left while maintaining their relative order.
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
- This loop iterates through the array from index 0 to nums.length - 2.
- It checks if two consecutive elements (nums[i] and nums[i+1]) are equal.
- If true, it doubles nums[i] and sets nums[i+1] to 0.
- If false, it continues to the next iteration.
# Complexity
- Time complexity: **O(n)**
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity: **O(1)**
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# ⬆️PLS UPVOTE
# ⬆️PLS UPVOTE
# ⬆️PLS UPVOTE
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
public int[] applyOperations(int[] nums) {
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length-1; i++) {
if(nums[i] == nums[i+1]) {
nums[i] *= 2;
nums[i+1] = 0;
} else {
continue;
}
}
int index = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(nums[i] != 0) {
int temp = nums[index];
nums[index] = nums[i];
nums[i] = temp;
index++;
}
}
return nums;
}
}
```
```Python []
class Solution:
def applyOperations(self, nums):
n = len(nums)
for i in range(n - 1):
if nums[i] == nums[i + 1]:
nums[i] *= 2
nums[i + 1] = 0
index = 0
for i in range(n):
if nums[i] != 0:
nums[index], nums[i] = nums[i], nums[index]
index += 1
return nums
```
```C++ []
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> applyOperations(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
if (nums[i] == nums[i + 1]) {
nums[i] *= 2;
nums[i + 1] = 0;
}
}
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (nums[i] != 0) {
swap(nums[index], nums[i]);
index++;
}
}
return nums;
}
};
```
```JavaScript []
var applyOperations = function(nums) {
let n = nums.length;
for (let i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
if (nums[i] === nums[i + 1]) {
nums[i] *= 2;
nums[i + 1] = 0;
}
}
let index = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (nums[i] !== 0) {
[nums[index], nums[i]] = [nums[i], nums[index]];
index++;
}
}
return nums;
};
```
| 15
| 0
|
['Two Pointers', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'JavaScript']
| 0
|
apply-operations-to-an-array
|
Python 3 || 6 lines, iteration || T/S: 99% / 52%
|
python-3-6-lines-iteration-ts-99-52-by-s-bsbl
|
[https://leetcode.com/problems/apply-operations-to-an-array/submissions/1166861606/?submissionId=1166861050)updateI could be wrong, but I think that time comple
|
Spaulding_
|
NORMAL
|
2022-11-06T07:05:15.846795+00:00
|
2025-03-01T01:28:10.872483+00:00
| 945
| false
|
```Python3 []
class Solution:
def applyOperations(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:
for i in range(len(nums)-1):
if nums[i] == nums[i+1]:
nums[i]*= 2
nums[i + 1] = 0 # <-- performing the "operation."
nums.sort(key=lambda x: x == 0) # Sorting on a boolean key: False, then True
return nums
```
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
std::vector<int> applyOperations(std::vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
// Perform the operation
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
if (nums[i] == nums[i + 1]) {
nums[i] *= 2;
nums[i + 1] = 0;
}
}
// Move all zeros to the end while maintaining order
std::stable_partition(nums.begin(), nums.end(), [](int x) { return x != 0; });
return nums;
}
};
```
```java []
class Solution {
public int[] applyOperations(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
// Perform the operation
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
if (nums[i] == nums[i + 1]) {
nums[i] *= 2;
nums[i + 1] = 0;
}
}
// Move all zeros to the end while maintaining order
int[] result = new int[n];
int index = 0;
// First, copy non-zero elements
for (int num : nums) {
if (num != 0) {
result[index++] = num;
}
}
// Remaining elements will be zeros (no need to explicitly set them)
return result;
}
}
```
[https://leetcode.com/problems/apply-operations-to-an-array/submissions/1166861606/?submissionId=1166861050)
[update](https://leetcode.com/problems/apply-operations-to-an-array/submissions/1558649597/?submissionId=1166861050)
I could be wrong, but I think that time complexity is *O*(*N* log *N*) and space complexity is *O*(1), in which *N* ~ `len(nums)`.
| 14
| 0
|
['C++', 'Java', 'Python3']
| 5
|
apply-operations-to-an-array
|
✅c++|| Simple solution|| Move Zeroes problem extension || O(1) space
|
c-simple-solution-move-zeroes-problem-ex-dgec
|
The idea is super simple go through all n - 1 elements and see if condition satisifies\nthen the problem is move all zeroes to end \nwe solve it using two point
|
dinesh55
|
NORMAL
|
2022-11-06T04:02:37.108295+00:00
|
2022-11-06T06:49:57.678610+00:00
| 941
| false
|
The idea is super simple go through all n - 1 elements and see if condition satisifies\nthen the problem is move all zeroes to end \nwe solve it using two pointers \n\nLink to move zeroes to end problem :- <b>[Move Zeroes Problem](https://leetcode.com/problems/move-zeroes/)</b>\n\n```c++\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> applyOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n = nums.size();\n\t\t// checking for the n- 1 conditions \n for(int i = 0; i < n - 1 ; i++){\n if(nums[i] == nums[i+1]){\n nums[i] *= 2;\n nums[i+1] = 0;\n }\n }\n\t\t// using two pointers to push numbers to end\n int sp = 0;\n for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){\n if(nums[i]){\n swap(nums[i] , nums[sp++]);\n }\n }\n return nums;\n }\n};\n```
| 11
| 1
|
['C']
| 0
|
apply-operations-to-an-array
|
✅Simple Java Solutions in O(N) || ✅Runtime 0ms || ✅ Beats 100%
|
simple-java-solutions-in-on-runtime-0ms-t5v1y
|
\n# Intuition\nDescribe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n\n\nThis code defines a `Solution` class with a method called `applyOperations`,
|
ahmedna126
|
NORMAL
|
2023-09-27T16:28:12.413227+00:00
|
2023-11-07T11:36:10.517206+00:00
| 398
| false
|
<!-- \n# Intuition\nDescribe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n\n\nThis code defines a `Solution` class with a method called `applyOperations`, which takes an integer array `nums` as input and returns another integer array as output. The goal of this code is to perform certain operations on the input array `nums` and return the result in a new array.\n-->\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n1. It first determines the length of the input array `nums` and creates a new integer array `arr` of the same length to store the result.\n\n2. The code uses two pointers, `i` and `j`, to iterate through the input array `nums` and the result array `arr`, respectively. Initially, both pointers are set to 0.\n\n3. The code enters a loop that iterates over the elements of the input array `nums`.\n\n4. Inside the loop, it checks the current element `nums[i]`:\n - If `nums[i]` is equal to 0, it continues to the next iteration (skips the current element).\n - If `nums[i]` is not equal to 0, it checks whether the next element (`nums[i+1]`) is equal to the current element (`nums[i]`) and whether it\'s within the bounds of the array (`i < length-1`).\n \n - If both conditions are true, it means there\'s a pair of consecutive elements with the same value. In this case, it performs the following actions:\n - It doubles the value of the current element and stores the result in the corresponding position of the result array `arr` (i.e., `arr[j++] = 2 * nums[i]`).\n - It sets the next element (`nums[i+1]`) to 0 to indicate that it has been used in the operation.\n - It increments both `i` and `j` to move to the next elements in both arrays.\n \n - If the conditions are not met, it means the current element is not part of a pair with the next element, so it simply stores the current element\'s value in the result array `arr` (i.e., `arr[j++] = nums[i]`).\n\n5. After processing all elements in the input array `nums`, the loop ends, and the result array `arr` contains the values after applying the specified operations.\n\n6. The code returns the result array `arr` as the output of the `applyOperations` method.\n\nIn summary, this code processes an input array, doubles the values of consecutive equal elements, and returns a new array with the result of these operations, eliminating the intermediate zeros generated by the doubling operation.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(N)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(N)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code1\n```Java\nclass Solution {\n public int[] applyOperations(int[] nums) {\n int length = nums.length;\n int [] arr = new int[length];\n\n for (int i = 0 , j = 0; i < length; i++)\n {\n if(nums[i] == 0) continue;\n \n if (i < length-1 && nums[i] == nums[i+1])\n {\n arr[j++] = 2 * nums[i];\n nums[++i] = 0; // or i++; only\n }else{\n arr[j++] = nums[i];\n }\n }\n return arr;\n }\n}\n```\n\n# Code2\nin Runtime 1ms\nCheck out the `moveZeroes` method [here](https://leetcode.com/problems/move-zeroes/solutions/3960034/three-simple-java-solutions-runtime-0ms-beats100/) for a solution to efficiently move all zeros to the end of an array\n```Java\nclass Solution {\n public int[] applyOperations(int[] nums) {\n for (int i = 0; i < nums.length-1; i++)\n {\n if (nums[i] == nums[i+1])\n {\n nums[i] = 2 * nums[i];\n nums[++i] = 0;\n }\n }\n\n moveZeroes(nums);\n \n return nums;\n }\n\n public static void moveZeroes(int[] nums) \n {\n int i = 0;\n for (int num : nums)\n {\n if (num != 0)\n {\n nums[i++] = num;\n }\n }\n\n while (i <= nums.length - 1)\n {\n nums[i++] = 0;\n }\n\n }\n}\n```\n\n\n## For additional problem-solving solutions, you can explore my repository on GitHub: [GitHub Repository](https://github.com/ahmedna126/java_leetcode_challenges)\n\n\n\n\n
| 10
| 0
|
['Java']
| 0
|
apply-operations-to-an-array
|
✅C++|| Simple Traversal || Easy Solution
|
c-simple-traversal-easy-solution-by-indr-i7k6
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> applyOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n=nums.size();\n\n vector<int>ans;\n \n for(
|
indresh149
|
NORMAL
|
2022-11-06T04:04:07.403275+00:00
|
2022-11-06T04:04:07.403318+00:00
| 1,264
| false
|
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<int> applyOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n=nums.size();\n\n vector<int>ans;\n \n for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++)\n {\n if(nums[i]==nums[i+1])\n {\n nums[i]=2*nums[i];\n \n nums[i+1]=0;\n }\n }\n \n int cntt=0;\n \n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n if(nums[i]==0) {\n cntt++;\n }\n else {\n ans.push_back(nums[i]);\n }\n }\n while(cntt--)\n {\n \n ans.push_back(0);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\n**Please upvote if it was helpful for you, thank you!**
| 10
| 0
|
['C']
| 1
|
apply-operations-to-an-array
|
JavaScript easy and fast solution (93.71% faster)
|
javascript-easy-and-fast-solution-9371-f-8oag
|
\n\n\n\n* only sort the zeros: nums.sort((a,b)=> !a - !b)\n\n\n# Code\n\n/**\n * @param {number[]} nums\n * @return {number[]}\n */\nvar applyOperations = func
|
fahim_ash
|
NORMAL
|
2022-11-14T08:34:31.993881+00:00
|
2022-11-14T08:35:15.490547+00:00
| 496
| false
|
\n\n\n\n* only sort the zeros: nums.sort((a,b)=> !a - !b)\n\n\n# Code\n```\n/**\n * @param {number[]} nums\n * @return {number[]}\n */\nvar applyOperations = function(nums) {\n for (let i=0;i<nums.length;i++){\n if (nums[i]==nums[i+1]){\n [nums[i],nums[i+1]]=[nums[i]*2,0];\n }\n }return nums.sort((a,b)=> !a - !b );\n};\n \n\n```
| 9
| 0
|
['JavaScript']
| 0
|
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.