hexsha
stringlengths 40
40
| size
int64 6
14.9M
| ext
stringclasses 1
value | lang
stringclasses 1
value | max_stars_repo_path
stringlengths 6
260
| max_stars_repo_name
stringlengths 6
119
| max_stars_repo_head_hexsha
stringlengths 40
41
| max_stars_repo_licenses
list | max_stars_count
int64 1
191k
⌀ | max_stars_repo_stars_event_min_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_stars_repo_stars_event_max_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_issues_repo_path
stringlengths 6
260
| max_issues_repo_name
stringlengths 6
119
| max_issues_repo_head_hexsha
stringlengths 40
41
| max_issues_repo_licenses
list | max_issues_count
int64 1
67k
⌀ | max_issues_repo_issues_event_min_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_issues_repo_issues_event_max_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_forks_repo_path
stringlengths 6
260
| max_forks_repo_name
stringlengths 6
119
| max_forks_repo_head_hexsha
stringlengths 40
41
| max_forks_repo_licenses
list | max_forks_count
int64 1
105k
⌀ | max_forks_repo_forks_event_min_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_forks_repo_forks_event_max_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | avg_line_length
float64 2
1.04M
| max_line_length
int64 2
11.2M
| alphanum_fraction
float64 0
1
| cells
list | cell_types
list | cell_type_groups
list |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
c501b4417a98938a2ae600b4d838796b29b5c5d9
| 33,976 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
kaggle_notebooks/humanpro-classifier-training-nocrop.ipynb
|
qAp/kgl_humanprotein
|
05dc0a493c7545b59c4a20547f885b13d9ea1a6a
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
kaggle_notebooks/humanpro-classifier-training-nocrop.ipynb
|
qAp/kgl_humanprotein
|
05dc0a493c7545b59c4a20547f885b13d9ea1a6a
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
kaggle_notebooks/humanpro-classifier-training-nocrop.ipynb
|
qAp/kgl_humanprotein
|
05dc0a493c7545b59c4a20547f885b13d9ea1a6a
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 34.319192 | 208 | 0.595715 |
[
[
[
"# Classifier Training",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Make image size and crop size the same.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"! rsync -a /kaggle/input/mmdetection-v280/mmdetection /\n! pip install /kaggle/input/mmdetection-v280/src/mmpycocotools-12.0.3/mmpycocotools-12.0.3/\n! pip install /kaggle/input/hpapytorchzoo/pytorch_zoo-master/\n! pip install /kaggle/input/hpacellsegmentation/HPA-Cell-Segmentation/\n! pip install /kaggle/input/iterative-stratification/iterative-stratification-master/\n\n! cp -r /kaggle/input/kgl-humanprotein-data/kgl_humanprotein_data /\n! cp -r /kaggle/input/humanpro/kgl_humanprotein /\n\nimport sys\nsys.path.append('/kgl_humanprotein/')",
"Processing /kaggle/input/mmdetection-v280/src/mmpycocotools-12.0.3/mmpycocotools-12.0.3\r\nRequirement already satisfied: setuptools>=18.0 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages (from mmpycocotools==12.0.3) (49.6.0.post20201009)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: cython>=0.27.3 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages (from mmpycocotools==12.0.3) (0.29.21)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: matplotlib>=2.1.0 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages (from mmpycocotools==12.0.3) (3.3.3)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: kiwisolver>=1.0.1 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages (from matplotlib>=2.1.0->mmpycocotools==12.0.3) (1.3.1)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: pillow>=6.2.0 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages (from matplotlib>=2.1.0->mmpycocotools==12.0.3) (7.2.0)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: cycler>=0.10 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages (from matplotlib>=2.1.0->mmpycocotools==12.0.3) (0.10.0)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: python-dateutil>=2.1 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages (from matplotlib>=2.1.0->mmpycocotools==12.0.3) (2.8.1)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: pyparsing!=2.0.4,!=2.1.2,!=2.1.6,>=2.0.3 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages (from matplotlib>=2.1.0->mmpycocotools==12.0.3) (2.4.7)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: numpy>=1.15 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages (from matplotlib>=2.1.0->mmpycocotools==12.0.3) (1.19.5)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: six in /opt/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages (from cycler>=0.10->matplotlib>=2.1.0->mmpycocotools==12.0.3) (1.15.0)\r\nBuilding wheels for collected packages: mmpycocotools\r\n Building wheel for mmpycocotools (setup.py) ... \u001b[?25l-\b \b\\\b \b|\b \b/\b \b-\b \b\\\b \b|\b \b/\b \b-\b \b\\\b \bdone\r\n\u001b[?25h Created wheel for mmpycocotools: filename=mmpycocotools-12.0.3-cp37-cp37m-linux_x86_64.whl size=272915 sha256=21c802f514d5c4968fc959af7f5dda7204a64111a6d78ae9fdfb0787dc48bf21\r\n Stored in directory: /root/.cache/pip/wheels/80/e0/da/3288fdf3965b5c9090f368462db9d28be2c82013f51821090a\r\nSuccessfully built mmpycocotools\r\nInstalling collected packages: mmpycocotools\r\nSuccessfully installed mmpycocotools-12.0.3\r\nProcessing /kaggle/input/hpapytorchzoo/pytorch_zoo-master\r\nBuilding wheels for collected packages: pytorch-zoo\r\n Building wheel for pytorch-zoo (setup.py) ... \u001b[?25l-\b \b\\\b \bdone\r\n\u001b[?25h Created wheel for pytorch-zoo: filename=pytorch_zoo-0.0.0-py3-none-any.whl size=30139 sha256=569f1c4d21b90403367fe780a0f7a4235526fecd6f1ca0b195293135627d6f19\r\n Stored in directory: /root/.cache/pip/wheels/7f/18/21/aff5a8914e22461b2b025a9629c2b70464c36183caaf12bc09\r\nSuccessfully built pytorch-zoo\r\nInstalling collected packages: pytorch-zoo\r\nSuccessfully installed pytorch-zoo-0.0.0\r\nProcessing /kaggle/input/hpacellsegmentation/HPA-Cell-Segmentation\r\nBuilding wheels for collected packages: hpacellseg\r\n Building wheel for hpacellseg (setup.py) ... \u001b[?25l-\b \b\\\b \bdone\r\n\u001b[?25h Created wheel for hpacellseg: filename=hpacellseg-0.1.8-py3-none-any.whl size=14815 sha256=46f6c5187b355c1659f49219f0455a8daa980d34330451a50e3bdd2419e1a1d1\r\n Stored in directory: /root/.cache/pip/wheels/50/41/15/9f15b23726cf96bdbc26670ce1c7526c719d4bce49418c1a20\r\nSuccessfully built hpacellseg\r\nInstalling collected packages: hpacellseg\r\nSuccessfully installed hpacellseg-0.1.8\r\nProcessing /kaggle/input/iterative-stratification/iterative-stratification-master\r\nRequirement already satisfied: numpy in /opt/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages (from iterative-stratification==0.1.6) (1.19.5)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: scipy in /opt/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages (from iterative-stratification==0.1.6) (1.5.4)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: scikit-learn in /opt/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages (from iterative-stratification==0.1.6) (0.24.1)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: joblib>=0.11 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages (from scikit-learn->iterative-stratification==0.1.6) (1.0.0)\r\nRequirement already satisfied: threadpoolctl>=2.0.0 in /opt/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages (from scikit-learn->iterative-stratification==0.1.6) (2.1.0)\r\nBuilding wheels for collected packages: iterative-stratification\r\n Building wheel for iterative-stratification (setup.py) ... \u001b[?25l-\b \b\\\b \bdone\r\n\u001b[?25h Created wheel for iterative-stratification: filename=iterative_stratification-0.1.6-py3-none-any.whl size=8401 sha256=cac582c2c75cf5ac446b5c08978230188ab060d814be4e035181904078e89cec\r\n Stored in directory: /root/.cache/pip/wheels/b8/47/3f/eb4af42d124f37d23d6f13a4c8bbc32c1d70140e6e1cecb4aa\r\nSuccessfully built iterative-stratification\r\nInstalling collected packages: iterative-stratification\r\nSuccessfully installed iterative-stratification-0.1.6\r\n"
],
[
"import os\nimport time\nfrom pathlib import Path\nimport shutil\nimport zipfile\nimport functools\nimport multiprocessing\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport cv2\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import KFold,StratifiedKFold\nfrom iterstrat.ml_stratifiers import MultilabelStratifiedKFold\nimport torch\nfrom torch.backends import cudnn\nfrom torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader, RandomSampler, SequentialSampler\nfrom torch.nn import DataParallel\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom tqdm import tqdm\n\nfrom kgl_humanprotein.utils.common_util import *\nfrom kgl_humanprotein.config.config import *\nfrom kgl_humanprotein.data_process import *\nfrom kgl_humanprotein.datasets.tool import image_to_tensor\nfrom kgl_humanprotein.networks.imageclsnet import init_network\nfrom kgl_humanprotein.layers.loss import *\nfrom kgl_humanprotein.layers.scheduler import *\nfrom kgl_humanprotein.utils.augment_util import train_multi_augment2\nfrom kgl_humanprotein.utils.log_util import Logger\nfrom kgl_humanprotein.run.train import *",
"run on 52b0d1eadd16\n"
],
[
"%cd /kaggle",
"/kaggle\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Write out 6 image-level samples from each subset for testing on laptop",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# import shutil",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# def generate_testing_samples(isubset, n_images=6, sz_img=384, dir_out=None):\n# dir_subset = Path(f'/kaggle/input/humanpro-train-cells-subset{isubset}')\n# dir_subset = dir_subset / f'humanpro_train_cells_subset{isubset}/train'\n \n# df = pd.read_feather(dir_subset / 'train.feather')\n# imgids = df['Id'].apply(lambda o: o.split('_')[0])\n# sample_imgids = np.random.choice(imgids.unique(), n_images)\n# df_sample = df[imgids.isin(sample_imgids)].reset_index(drop=True)\n \n# if dir_out is not None:\n# dir_subset_out = dir_out/'train'\n# dir_subset_out.mkdir(exist_ok=True, parents=True)\n# df_sample.to_feather(dir_subset_out/'train.feather')\n \n# dir_img = dir_subset/f'images_{sz_img}'\n# dir_img_out = dir_subset_out/f'images_{sz_img}'\n# dir_img_out.mkdir(exist_ok=True, parents=True)\n# for _, row in df_sample.iterrows():\n# srcs = list(dir_img.glob(f\"{row['Id']}*.png\"))\n# for src in srcs:\n# shutil.copy(src, dir_img_out/src.name)\n \n# return df_sample",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# n_subsets = 5\n\n# for isubset in range(n_subsets):\n# print(f'\\rProcessing subset {isubset}...', end='', flush=True)\n# dir_out = Path(f'/kaggle/working/humanpro_train_cells_subset{isubset}')\n# generate_testing_samples(isubset, dir_out=dir_out)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# ! zip -qr humanpro_train_cells_subset0.zip humanpro_train_cells_subset0/\n# ! zip -qr humanpro_train_cells_subset1.zip humanpro_train_cells_subset1/\n# ! zip -qr humanpro_train_cells_subset2.zip humanpro_train_cells_subset2/\n# ! zip -qr humanpro_train_cells_subset3.zip humanpro_train_cells_subset3/\n# ! zip -qr humanpro_train_cells_subset4.zip humanpro_train_cells_subset4/",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Combine subsets' meta data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dir_data = Path('/kaggle/input')\ndir_mdata = Path('/kaggle/mdata')\nn_subsets = 5\n# sz_img = 384",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%%time\ndf_cells = combine_subsets_metadata(dir_data, n_subsets)",
"Processing subset 4...CPU times: user 1.83 s, sys: 1.09 s, total: 2.92 s\nWall time: 8.27 s\n"
],
[
"dir_mdata_raw = dir_mdata/'raw'\ndir_mdata_raw.mkdir(exist_ok=True, parents=True)\n\ndf_cells.to_feather(dir_mdata_raw/'train.feather')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"del df_cells",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Filter samples",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Keep single labels\ndf_cells = pd.read_feather(dir_mdata_raw/'train.feather')\ndf_cells = (df_cells[df_cells['Target'].apply(lambda o: len(o.split('|'))==1)]\n .reset_index(drop=True))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Limit number of samples per label\n\ndef cap_number_per_label(df_cells, cap=10_000, idx_start=0):\n df_cells_cap = pd.DataFrame()\n for label in df_cells.Target.unique():\n df = df_cells[df_cells.Target==label]\n if len(df) > cap:\n df = df.iloc[idx_start:idx_start + cap]\n df_cells_cap = df_cells_cap.append(df, ignore_index=True)\n return df_cells_cap",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_cells = cap_number_per_label(df_cells, cap=10_000, idx_start=0) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_cells.Target.value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_cells.to_feather(dir_mdata_raw/'train.feather')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## One-hot encode labels",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%time\ngenerate_meta(dir_mdata, 'train.feather')",
"CPU times: user 59.8 s, sys: 662 ms, total: 1min\nWall time: 1min\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Split generation",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%time\ntrain_meta = pd.read_feather(dir_mdata/'meta'/'train_meta.feather')\ncreate_random_split(dir_mdata, train_meta, n_splits=5, alias='random')\ndel train_meta",
"Nucleoplasm 8000 2000\nNuclear membrane 3876 969\nNucleoli 8000 2000\nNucleoli fibrillar center 8000 2000\nNuclear speckles 8000 2000\nNuclear bodies 8000 2000\nEndoplasmic reticulum 8000 2000\nGolgi apparatus 8000 2000\nIntermediate filaments 8000 2000\nActin filaments 4258 1064\nMicrotubules 6232 1557\nMitotic spindle 8 2\nCentrosome 8000 2000\nPlasma membrane 8000 2000\nMitochondria 8000 2000\nAggresome 1820 455\nCytosol 8000 2000\nVesicles and punctate cytosolic patterns 4495 1124\nNegative 761 191\ncreate split file: /kaggle/mdata/split/random_folds5/random_train_cv0.feather, shape: (117450, 26)\ncreate split file: /kaggle/mdata/split/random_folds5/random_valid_cv0.feather, shape: (29362, 26)\ncreate split file: /kaggle/mdata/split/random_folds5/random_train_cv1.feather, shape: (117450, 26)\ncreate split file: /kaggle/mdata/split/random_folds5/random_valid_cv1.feather, shape: (29362, 26)\ncreate split file: /kaggle/mdata/split/random_folds5/random_train_cv2.feather, shape: (117449, 26)\ncreate split file: /kaggle/mdata/split/random_folds5/random_valid_cv2.feather, shape: (29363, 26)\ncreate split file: /kaggle/mdata/split/random_folds5/random_train_cv3.feather, shape: (117449, 26)\ncreate split file: /kaggle/mdata/split/random_folds5/random_valid_cv3.feather, shape: (29363, 26)\ncreate split file: /kaggle/mdata/split/random_folds5/random_train_cv4.feather, shape: (117450, 26)\ncreate split file: /kaggle/mdata/split/random_folds5/random_valid_cv4.feather, shape: (29362, 26)\nCPU times: user 12.1 s, sys: 1.58 s, total: 13.7 s\nWall time: 13.4 s\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Training",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model_multicell = (\n '../../kgl_humanprotein_data/result/models/'\n 'external_crop512_focal_slov_hardlog_class_densenet121_dropout_i768_aug2_5folds/'\n 'fold0/final.pth')\ngpu_id = '0' # '0,1,2,3'\narch = 'class_densenet121_dropout'\nnum_classes = len(LABEL_NAME_LIST)\nscheduler = 'Adam55'\nepochs = 10 #55\nresume = Path('/kaggle/input/humanpro-classifier/results/models/'\n 'external_crop384_focal_slov_hardlog_class_densenet121_dropout_i384_aug2_5folds/fold0/final.pth')\nsz_img = 384\ncrop_size = 384\nbatch_size = 32\nsplit_name = 'random_folds5'\nfold = 0\nworkers = 3\npin_memory = True\n\ndir_results = Path('results')\ndir_results.mkdir(exist_ok=True, parents=True)\n\nout_dir = Path(f'external_crop{crop_size}_focal_slov_hardlog_class_densenet121_dropout_i{sz_img}_aug2_5folds')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"main_training(dir_data, dir_mdata, dir_results, out_dir, \n split_name=split_name, fold=fold,\n arch=arch, model_multicell=model_multicell, scheduler=scheduler,\n epochs=epochs, resume=resume,\n img_size=sz_img, crop_size=crop_size, batch_size=batch_size, \n gpu_id=gpu_id, workers=workers, pin_memory=pin_memory)",
">> Creating directory if it does not exist:\n>> 'results/models/external_crop384_focal_slov_hardlog_class_densenet121_dropout_i384_aug2_5folds/fold0'\n>> Using pre-trained model.\n>> Loading multi-cell model.\n>> Loading checkpoint:\n>> '/kaggle/input/humanpro-classifier/results/models/external_crop384_focal_slov_hardlog_class_densenet121_dropout_i384_aug2_5folds/fold0/final.pth'\n>> Loading checkpoint:\n>> '/kaggle/input/humanpro-classifier/results/models/external_crop384_focal_slov_hardlog_class_densenet121_dropout_i384_aug2_5folds/fold0/final_optim.pth'\n>>>> loaded checkpoint:\n>>>> '/kaggle/input/humanpro-classifier/results/models/external_crop384_focal_slov_hardlog_class_densenet121_dropout_i384_aug2_5folds/fold0/final.pth' (epoch 3)\n** start training here! **\n\nepoch iter rate | train_loss/acc | valid_loss/acc/focal/kaggle |best_epoch/best_focal| min \n-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n 4.0 3670 0.000300 | 0.7664 0.9664 | 28.6586 0.9636 42.4583 0.5449 | 3.0 1.3889 | 65.0 min \n 5.0 3670 0.000300 | 0.7011 0.9688 | 32.2796 0.9671 43.2645 0.5660 | 3.0 1.3889 | 64.4 min \n 6.0 3670 0.000300 | 0.6479 0.9709 | 0.9893 0.9695 1.2439 0.6035 | 6.0 1.2439 | 62.7 min \n 7.0 3670 0.000300 | 0.6058 0.9722 | 37.5953 0.9701 48.5047 0.6168 | 6.0 1.2439 | 62.2 min \n 8.0 3670 0.000300 | 0.5603 0.9740 | 4.5893 0.9716 6.2746 0.6413 | 6.0 1.2439 | 62.2 min \n 9.0 3670 0.000300 | 0.5274 0.9751 | 0.4417 0.9736 0.4278 0.7100 | 9.0 0.4278 | 62.9 min \n 10.0 3670 0.000300 | 0.4961 0.9766 | 0.4350 0.9738 0.4207 0.7111 | 10.0 0.4207 | 63.8 min \n"
],
[
"! cp -r results/ /kaggle/working/.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c501ce6693e292724f4aa02c00b6261a49d59bf9
| 230,991 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
MassSpectrometer/.ipynb_checkpoints/BackgroundSubstract-checkpoint.ipynb
|
fraksuh/QLab
|
ac6984e30623c4023ade2f4f53d5326463c6059e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
MassSpectrometer/.ipynb_checkpoints/BackgroundSubstract-checkpoint.ipynb
|
fraksuh/QLab
|
ac6984e30623c4023ade2f4f53d5326463c6059e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
MassSpectrometer/.ipynb_checkpoints/BackgroundSubstract-checkpoint.ipynb
|
fraksuh/QLab
|
ac6984e30623c4023ade2f4f53d5326463c6059e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 493.570513 | 33,416 | 0.933768 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom scipy.optimize import curve_fit # import the curve fitting function\nimport pandas as pd\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Argon",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Argon = pd.read_table('Ar.txt',delimiter=', ',engine='python', header=None)\n\nAmu = Argon[0] #These are the values of amu that the mass spec searches for\n\nArgon = np.array([entry[:-1] for entry in Argon[1]],dtype='float')*1e6",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Raw Argon Data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(9,4))\nplt.scatter(Amu, Argon);\nax = plt.gca()\n#ax.set_yscale('log')\nplt.xlim(12,45);\nplt.ylim(0,4)\nplt.xlabel('Particle Mass [Amu]',size=18);\nplt.ylabel('Pressure [Torr]$\\cdot 10^{-6}$',size=18);\nplt.xticks(size = 11);\nplt.yticks(size = 11);\nplt.savefig('RawArgon.png')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Substract Argon Background",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Arbkd = pd.read_table('Background_Ar.txt',delimiter=', ',engine='python', header=None)\n\nArbkd = np.array([entry[:-1] for entry in Arbkd[1]],dtype='float')*1e6",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(9,4))\nplt.scatter(Amu, Argon - Arbkd);\nax = plt.gca()\n#ax.set_yscale('log')\nplt.xlim(12,45);\nplt.ylim(0,4)\nplt.xlabel('Particle Mass [Amu]',size=18);\nplt.ylabel('Pressure [Torr]$\\cdot 10^{-6}$',size=18);\nplt.xticks(size = 11);\nplt.yticks(size = 11);\nplt.savefig('TrueArgon.png')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Upon close inspection, background substraction has removed a single peak near 19 amu.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Kyrpton",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Krypton = pd.read_table('Kr.txt',delimiter=', ',engine='python', header=None)\n\nKrypton = np.array([entry[:-1] for entry in Krypton[1]],dtype='float')*1e6\n\nKrbkd = pd.read_table('Background_Kr.txt',delimiter=', ',engine='python', header=None)\n\nKrbkd = np.array([entry[:-1] for entry in Krbkd[1]],dtype='float')*1e6",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(9,4))\nplt.scatter(Amu, Krypton - Krbkd);\nax = plt.gca()\nplt.xlim(12,45);\nplt.ylim(0,6)\nplt.xlabel('Particle Mass [Amu]',size=18);\nplt.ylabel('Pressure [Torr]$\\cdot 10^{-6}$',size=18);\nplt.xticks(size = 11);\nplt.yticks(size = 11);\nplt.savefig('Krypton.png')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Here, and for all subsequent measurements on this day, there is a slight peak at 40 amu, which is to be some residual from the Argon test.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Neon",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Neon = pd.read_table('Ne.txt',delimiter=', ',engine='python', header=None)\n\nNeon = np.array([entry[:-1] for entry in Neon[1]],dtype='float')*1e6\n\nNebkd = pd.read_table('Background_Ne.txt',delimiter=', ',engine='python', header=None)\n\nNebkd = np.array([entry[:-1] for entry in Nebkd[1]],dtype='float')*1e6\n\nplt.figure(figsize=(9,4))\nplt.scatter(Amu, Neon - Nebkd);\nax = plt.gca()\nplt.xlim(12,35);\nplt.ylim(0,3.2)\nplt.xlabel('Particle Mass [Amu]',size=18);\nplt.ylabel('Pressure [Torr]$\\cdot 10^{-6}$',size=18);\nplt.xticks(size = 11);\nplt.yticks(size = 11);\nplt.savefig('Neon.png')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Air",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Air = pd.read_table('Air.txt',delimiter=', ',engine='python', header=None)\n\nAir = np.array([entry[:-1] for entry in Air[1]],dtype='float')*1e6\n\nplt.figure(figsize=(9,4))\nplt.scatter(Amu, Air - Nebkd);\nax = plt.gca()\nplt.xlim(12,35);\nplt.ylim(0,3.2)\nplt.xlabel('Particle Mass [Amu]',size=18);\nplt.ylabel('Pressure [Torr]$\\cdot 10^{-6}$',size=18);\nplt.xticks(size = 11);\nplt.yticks(size = 11);\nplt.savefig('Air.png')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Day 2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Quick Exhale vs Hold Breath",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Quick = pd.read_table('QuickExhale.txt',delimiter=', ',engine='python', header=None)\n\nQuick = np.array([entry[:-1] for entry in Quick[1]],dtype='float')*1e6\n\nQuickbkd = pd.read_table('Background_Breath.txt',delimiter=', ',engine='python', header=None)\n\nQuickbkd = np.array([entry[:-1] for entry in Quickbkd[1]],dtype='float')*1e6\n\nHold = pd.read_table('HoldBreath30s.txt',delimiter=', ',engine='python', header=None)\n\nHold = np.array([entry[:-1] for entry in Hold[1]],dtype='float')*1e6\n\nplt.figure(figsize=(9,4))\nplt.scatter(Amu, Quick - Quickbkd,color='blue',label='Quick Exhale');\nplt.scatter(Amu, Hold - Quickbkd,color='red',label = 'Hold Breath');\nax = plt.gca()\nplt.xlim(12,35);\nplt.ylim(0,8.5)\nplt.xlabel('Particle Mass [Amu]',size=18);\nplt.ylabel('Pressure [Torr]$\\cdot 10^{-6}$',size=18);\nplt.xticks(size = 11);\nplt.yticks(size = 11);\nplt.legend(loc='upper left')\nplt.savefig('Breath.png')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Compressed Air Comparison",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Can1 = pd.read_table('CompressedAir_Tetrafluoroethane.txt',delimiter=', ',engine='python', header=None)\n\nCan1 = np.array([entry[:-1] for entry in Can1[1]],dtype='float')*1e6\n\nCan2 = pd.read_table('CompressedAir_Difluoroethane.txt',delimiter=', ',engine='python', header=None)\n\nCan2 = np.array([entry[:-1] for entry in Can2[1]],dtype='float')*1e6\n\nplt.figure(figsize=(9,4))\nplt.scatter(Amu, Can1 - Quickbkd,color='blue',label='Tetrafluoroethane');\nplt.scatter(Amu, Can2 - Quickbkd,color='red',label = 'Difluoroethane');\nax = plt.gca()\nplt.xlim(10,65);\nplt.ylim(0,8.5)\nplt.xlabel('Particle Mass [Amu]',size=18);\nplt.ylabel('Pressure [Torr]$\\cdot 10^{-6}$',size=18);\nplt.xticks(size = 11);\nplt.yticks(size = 11);\nplt.legend(loc='upper right')\nplt.savefig('CompressedAir.png')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Volcano = pd.read_table('Volcano.txt',delimiter=', ',engine='python', header=None)\n\nVolcano = np.array([entry[:-1] for entry in Volcano[1]],dtype='float')*1e6\n\nVolcanoBackground = pd.read_table('VolcanoBackground.txt',delimiter=', ',engine='python', header=None)\n\nVolcanoBackground = np.array([entry[:-1] for entry in VolcanoBackground[1]],dtype='float')*1e6\n\nplt.figure(figsize=(9,4))\nplt.scatter(Amu, Volcano - VolcanoBackground);\nax = plt.gca()\nplt.xlim(10,35);\nplt.ylim(0,8.5)\nplt.xlabel('Particle Mass [Amu]',size=18);\nplt.ylabel('Pressure [Torr]$\\cdot 10^{-6}$',size=18);\nplt.xticks(size = 11);\nplt.yticks(size = 11);\nplt.savefig('Volcano.png')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c501cf3bbc9b6c60dcc0aefb2960832280d7a338
| 13,761 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
code/notebooks/collision.ipynb
|
nzw0301/Understanding-Negative-Samples-in-Instance-Discriminative-Self-supervised-Representation-Learning
|
957173bd8ec5b5e00994099d8b4467c74b802303
|
[
"MIT"
] | 4 |
2021-10-06T07:04:43.000Z
|
2022-01-28T09:31:29.000Z
|
code/notebooks/collision.ipynb
|
nzw0301/Understanding-Negative-Samples
|
957173bd8ec5b5e00994099d8b4467c74b802303
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
code/notebooks/collision.ipynb
|
nzw0301/Understanding-Negative-Samples
|
957173bd8ec5b5e00994099d8b4467c74b802303
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 38.76338 | 114 | 0.569726 |
[
[
[
"import json\nimport pathlib\n\nimport numpy as np\nimport sklearn\nimport yaml\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import normalize\nfrom numba import jit\n\n\nfrom utils import get_weight_path_in_current_system\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def load_features() -> dict:\n datasets = (\"cifar10\", \"cifar100\", \"ag_news\")\n epochs = (500, 500, 100)\n\n features = {}\n for dataset, epoch in zip(datasets, epochs):\n\n base_dir = pathlib.Path(\"../results/{}/analysis/save_unnormalised_feature/\".format(dataset))\n\n for config_path in base_dir.glob(\"**/config.yaml\"):\n \n with open(config_path) as f:\n config = yaml.load(f, Loader=yaml.FullLoader)\n \n seed = config[\"experiment\"][\"seed\"]\n\n if config[\"experiment\"][\"use_projection_head\"]:\n extractor = \"Head\"\n else:\n extractor = \"Without Head\"\n\n self_sup_path = pathlib.Path(\n get_weight_path_in_current_system(config[\"experiment\"][\"target_weight_file\"])).parent\n\n with open(self_sup_path / \".hydra\" / \"config.yaml\") as f:\n config = yaml.load(f, Loader=yaml.FullLoader)\n num_mini_batches = config[\"experiment\"][\"batches\"]\n\n\n path = config_path.parent.parent\n\n d = dataset.replace(\"100\", \"\").replace(\"10\", \"\")\n y_train = np.load(path / \"epoch_{}-{}.pt.label.train.npy\".format(epoch, d))\n\n X_train_0 = np.load(path / \"epoch_{}-{}.pt.feature.0.train.npy\".format(epoch, d))\n X_train_1 = np.load(path / \"epoch_{}-{}.pt.feature.1.train.npy\".format(epoch, d))\n \n d_name = dataset\n\n if \"augmentation_type\" in config[\"dataset\"]:\n d_name = \"{}-{}\".format(dataset, config[\"dataset\"][\"augmentation_type\"])\n \n if d_name not in features:\n features[d_name] = {} \n\n if extractor not in features[d_name]:\n features[d_name][extractor] = {}\n\n if seed not in features[d_name][extractor]:\n features[d_name][extractor][seed] = {}\n\n features[d_name][extractor][seed][num_mini_batches] = (\n X_train_0,\n X_train_1,\n y_train\n )\n\n return features\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"features = load_features()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"@jit(nopython=True, parallel=True)\ndef compute_bound(c, y_train, X_train_0, X_train_1):\n target_ids = y_train == c\n X_train_0_c = X_train_0[target_ids]\n X_train_1_c = X_train_1[target_ids]\n cos_sim = X_train_0_c.dot(X_train_1_c.T)\n n = np.sum(target_ids)\n\n bounds_by_sample = np.abs(cos_sim - np.diag(cos_sim)).sum(axis=0) / (n - 1)\n return bounds_by_sample",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"upper_bound_collision = {}\nfor dataset, f_d in features.items():\n upper_bound_collision[dataset] = {}\n\n for head_info, f_d_h in f_d.items():\n\n upper_bound_collision[dataset][head_info] = {}\n for seed, f_d_h_s in f_d_h.items():\n negs = list(sorted(f_d_h_s))\n\n for i, neg in enumerate(negs):\n if neg not in upper_bound_collision[dataset][head_info]:\n upper_bound_collision[dataset][head_info][neg] = []\n\n X_train_0, X_train_1, y_train = f_d_h[seed][neg]\n\n C = len(np.unique(y_train))\n\n X_train_0 = sklearn.preprocessing.normalize(X_train_0, axis=1)\n X_train_1 = sklearn.preprocessing.normalize(X_train_1, axis=1)\n\n upper_bounds = []\n\n for c in range(C):\n upper_bounds.append(\n compute_bound(c, y_train, X_train_0, X_train_1)\n )\n\n upper_bound = np.array(upper_bounds).flatten().mean()\n print(dataset, head_info, seed, neg, upper_bound)\n upper_bound_collision[dataset][head_info][neg].append(float(upper_bound))\n",
"cifar10 Without Head 13 32 0.20344003\ncifar10 Without Head 13 64 0.20893289\ncifar10 Without Head 13 128 0.21950303\ncifar10 Without Head 13 256 0.23831828\ncifar10 Without Head 13 512 0.37764415\ncifar10 Without Head 11 32 0.20120734\ncifar10 Without Head 11 64 0.21036161\ncifar10 Without Head 11 128 0.21415293\ncifar10 Without Head 11 256 0.24843346\ncifar10 Without Head 11 512 0.3816658\ncifar10 Without Head 7 32 0.2020581\ncifar10 Without Head 7 64 0.20859843\ncifar10 Without Head 7 128 0.21780524\ncifar10 Without Head 7 256 0.24569704\ncifar10 Without Head 7 512 0.37573105\ncifar10 Head 13 32 0.6004361\ncifar10 Head 13 64 0.60644984\ncifar10 Head 13 128 0.6113785\ncifar10 Head 13 256 0.6158205\ncifar10 Head 13 512 0.62248313\ncifar10 Head 11 32 0.60062814\ncifar10 Head 11 64 0.6057505\ncifar10 Head 11 128 0.60984033\ncifar10 Head 11 256 0.6150309\ncifar10 Head 11 512 0.6226506\ncifar10 Head 7 32 0.60107994\ncifar10 Head 7 64 0.60679954\ncifar10 Head 7 128 0.6118673\ncifar10 Head 7 256 0.6146793\ncifar10 Head 7 512 0.6232999\ncifar100 Head 13 128 0.5233955\ncifar100 Head 13 256 0.5195236\ncifar100 Head 13 384 0.5152851\ncifar100 Head 13 512 0.5130686\ncifar100 Head 13 640 0.51149356\ncifar100 Head 13 768 0.5096279\ncifar100 Head 13 896 0.5117583\ncifar100 Head 13 1024 0.5077058\ncifar100 Head 11 128 0.5218632\ncifar100 Head 11 256 0.5186\ncifar100 Head 11 384 0.51519334\ncifar100 Head 11 512 0.51290786\ncifar100 Head 11 640 0.51123\ncifar100 Head 11 768 0.5095178\ncifar100 Head 11 896 0.5113434\ncifar100 Head 11 1024 0.50731766\ncifar100 Head 7 128 0.524001\ncifar100 Head 7 256 0.5196578\ncifar100 Head 7 384 0.516787\ncifar100 Head 7 512 0.51445174\ncifar100 Head 7 640 0.5122713\ncifar100 Head 7 768 0.5109851\ncifar100 Head 7 896 0.5112811\ncifar100 Head 7 1024 0.508517\ncifar100 Without Head 13 128 0.21599847\ncifar100 Without Head 13 256 0.23525405\ncifar100 Without Head 13 384 0.29480755\ncifar100 Without Head 13 512 0.33783492\ncifar100 Without Head 13 640 0.35608903\ncifar100 Without Head 13 768 0.37021708\ncifar100 Without Head 13 896 0.37402523\ncifar100 Without Head 13 1024 0.38472536\ncifar100 Without Head 11 128 0.21888873\ncifar100 Without Head 11 256 0.23722278\ncifar100 Without Head 11 384 0.29888344\ncifar100 Without Head 11 512 0.34190804\ncifar100 Without Head 11 640 0.3611424\ncifar100 Without Head 11 768 0.37094355\ncifar100 Without Head 11 896 0.3727542\ncifar100 Without Head 11 1024 0.38792542\ncifar100 Without Head 7 128 0.21592535\ncifar100 Without Head 7 256 0.23009011\ncifar100 Without Head 7 384 0.29627556\ncifar100 Without Head 7 512 0.33912125\ncifar100 Without Head 7 640 0.35595816\ncifar100 Without Head 7 768 0.3714959\ncifar100 Without Head 7 896 0.37216112\ncifar100 Without Head 7 1024 0.3892289\nag_news-erase Without Head 13 16 0.6802308\nag_news-erase Without Head 13 32 0.6587549\nag_news-erase Without Head 13 64 0.63992685\nag_news-erase Without Head 13 128 0.65759057\nag_news-erase Without Head 13 256 0.64326227\nag_news-erase Without Head 13 512 0.6576946\nag_news-erase Without Head 11 16 0.6827846\nag_news-erase Without Head 11 32 0.662171\nag_news-erase Without Head 11 64 0.65594393\nag_news-erase Without Head 11 128 0.63299924\nag_news-erase Without Head 11 256 0.6398547\nag_news-erase Without Head 11 512 0.65171695\nag_news-erase Without Head 7 16 0.6807822\nag_news-erase Without Head 7 32 0.6148044\nag_news-erase Without Head 7 64 0.6550175\nag_news-erase Without Head 7 128 0.67127097\nag_news-erase Without Head 7 256 0.64912045\nag_news-erase Without Head 7 512 0.6506703\nag_news-erase Head 13 16 0.86198103\nag_news-erase Head 13 32 0.8943226\nag_news-erase Head 13 64 0.91088486\nag_news-erase Head 13 128 0.92450774\nag_news-erase Head 13 256 0.925273\nag_news-erase Head 13 512 0.93130946\nag_news-erase Head 11 16 0.86617124\nag_news-erase Head 11 32 0.89477706\nag_news-erase Head 11 64 0.9158056\nag_news-erase Head 11 128 0.91711986\nag_news-erase Head 11 256 0.9255694\nag_news-erase Head 11 512 0.9333389\nag_news-erase Head 7 16 0.87013197\nag_news-erase Head 7 32 0.89149624\nag_news-erase Head 7 64 0.91662204\nag_news-erase Head 7 128 0.9259806\nag_news-erase Head 7 256 0.92472786\nag_news-erase Head 7 512 0.9320492\nag_news-replace Without Head 13 16 0.32230434\nag_news-replace Without Head 13 32 0.28970602\nag_news-replace Without Head 13 64 0.3194761\nag_news-replace Without Head 13 128 0.3062203\nag_news-replace Without Head 13 256 0.3199254\nag_news-replace Without Head 13 512 0.3080308\nag_news-replace Without Head 11 16 0.32226416\nag_news-replace Without Head 11 32 0.2853236\nag_news-replace Without Head 11 64 0.31568468\nag_news-replace Without Head 11 128 0.3090292\nag_news-replace Without Head 11 256 0.30611002\nag_news-replace Without Head 11 512 0.30035335\nag_news-replace Without Head 7 16 0.3209531\nag_news-replace Without Head 7 32 0.3675287\nag_news-replace Without Head 7 64 0.30311224\nag_news-replace Without Head 7 128 0.29802865\nag_news-replace Without Head 7 256 0.31011763\nag_news-replace Without Head 7 512 0.29626855\nag_news-replace Head 13 16 0.93805754\nag_news-replace Head 13 32 0.95574975\nag_news-replace Head 13 64 0.95955634\nag_news-replace Head 13 128 0.96328974\nag_news-replace Head 13 256 0.962719\nag_news-replace Head 13 512 0.96368074\nag_news-replace Head 11 16 0.93933964\nag_news-replace Head 11 32 0.95231324\nag_news-replace Head 11 64 0.9602895\nag_news-replace Head 11 128 0.96412253\nag_news-replace Head 11 256 0.963571\nag_news-replace Head 11 512 0.96288466\nag_news-replace Head 7 16 0.9399904\nag_news-replace Head 7 32 0.9520399\nag_news-replace Head 7 64 0.9599813\nag_news-replace Head 7 128 0.96250224\nag_news-replace Head 7 256 0.96397954\nag_news-replace Head 7 512 0.9660967\n"
],
[
"with open(\"upper_bound_collision.json\", \"w\") as f:\n json.dump(upper_bound_collision, f)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c501d12fa141897203ad26a7d15c1808f4ac0f75
| 901,135 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
x5gonlamtools/tools/wikifier/test_wikification.ipynb
|
X5GON/lamapi
|
0558c3b7af520ab83bdbd29e1b1b9b87bdc147b0
|
[
"BSD-2-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
x5gonlamtools/tools/wikifier/test_wikification.ipynb
|
X5GON/lamapi
|
0558c3b7af520ab83bdbd29e1b1b9b87bdc147b0
|
[
"BSD-2-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
x5gonlamtools/tools/wikifier/test_wikification.ipynb
|
X5GON/lamapi
|
0558c3b7af520ab83bdbd29e1b1b9b87bdc147b0
|
[
"BSD-2-Clause"
] | null | null | null | 46.049108 | 166 | 0.460596 |
[
[
[
"from wikification import wikification, wikification_filter",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"TEST_PATH = \"test.txt\"\nwith open(TEST_PATH, \"r\") as f:\n text = \"\\n\".join(f.readlines())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(text)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"res = wikification(text[:10000],\n wikification_type=\"FULL\",\n long_text_method_name=\"sum_classic_page_rank\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(res[\"words\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"res[\"concepts\"] # attention chunk 0 ?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"wikification_filter(res, \"SIMPLE\", in_place=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"wikification_filter(res, \"CLASSIC\", in_place=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"res",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Test SAHAN",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"PATH = \"/home/benromdhane-w/Bureau/ls2n/projects/X5GON/hackaton/x5gon_hackathon_materials/x5gon_materials_catelogue.tsv\"\nPATHOUT = \"/home/benromdhane-w/Bureau/ls2n/projects/X5GON/hackaton/x5gon_hackathon_materials/comparewiki.tsv\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import psycopg2\n\nPGCred = dict(PGHOST='127.0.0.1',\n PGDATABASE='x5gon',\n PGUSER='developernantestest',\n PGPASSWORD='devntes#51!&#test',\n PGPORT='5555')\n\ndef db_connect(PGHOST:str,PGDATABASE:str,PGUSER:str,PGPASSWORD:str,PGPORT:str):\n # Set up a connection to the postgres server.\n conn_string = \"host=\"+ PGHOST +\" port=\"+ PGPORT +\" dbname=\"+ PGDATABASE +\" user=\" + PGUSER +\" password=\"+ PGPASSWORD\n conn=psycopg2.connect(conn_string)\n conn.set_session(autocommit=True)\n cursor = conn.cursor()\n return {'connexion': conn, 'cursor': cursor}\nconnexion = db_connect(PGCred['PGHOST'],\n PGCred['PGDATABASE'],\n PGCred['PGUSER'],\n PGCred['PGPASSWORD'],\n PGCred['PGPORT'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def get_data_generator(rid, *, verbose=True):\n query = \"SELECT value FROM material_contents WHERE material_id=\" + rid + \" AND language='en' AND extension='plain';\" \n # query exec\n if verbose: print(\"Sending query...\")\n try:\n cursor = connexion[\"cursor\"]\n cursor.execute(query)\n except:\n print(\"Error when executing the query: verify it !\")\n if verbose: print(\"Query processed!\")\n return cursor",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import csv \nimport spacy\nimport time\nnlp = spacy.load(\"en\")\nfrom wikification import LONG_TEXT_METHODS, wikification\n\n# del LONG_TEXT_METHODS[\"sum_page_rank\"]\nnb = 0\nwith open(PATH, \"r\") as csvfile:\n with open(PATHOUT, \"w\") as csvout:\n csv_reader = csv.reader(csvfile, delimiter=\"\\t\", quotechar='\"', quoting=csv.QUOTE_ALL)\n fields = next(csv_reader)\n print(fields)\n csv_writer = csv.writer(csvout, delimiter=\"\\t\", quotechar='\"')\n csv_writer.writerow(fields + [\"concepts sum_classic_page_rank cos\",\n \"concepts sum_classic_page_rank pk\",\n \"concepts sum_classic_page_rank cos top10\",\n \"concepts sum_classic_page_rank pk top10\",\n \"concepts recompute_on_anchor_text cos\",\n \"concepts recompute_on_anchor_text pk\",\n \"concepts recompute_on_anchor_text cos top10\",\n \"concepts recompute_on_anchor_text pk top10\",\n \"concepts sum_classic_page time\",\n \"concepts recompute_on_anchor_text time\"])\n for row in csv_reader:\n nb += 1\n print(nb)\n rid = row[1]\n try:\n text = next(get_data_generator(rid, verbose=False))[0][\"value\"]\n except StopIteration:\n print(row, \" has no en version in db!\")\n wikifications = []\n runtime = []\n for m in LONG_TEXT_METHODS:\n print(f\"Wikification {m}...\")\n start = time.time()\n res = [(c['url'], c['title'], c['pageRank'], c['cosine']) for c in wikification(text, long_text_method_name=m)]\n end = time.time()\n ccos = sorted(res, key=lambda x: x[3], reverse=True)\n cpr = sorted(res, key=lambda x: x[2], reverse=True)\n top10cos = [c[1] for c in ccos[:10]]\n top10pr = [c[1] for c in cpr[:10]]\n wikifications.extend([ccos, cpr, top10cos, top10pr])\n runtime.append(end - start)\n print(f\"{m} elapsed time: %f ms\" % (1000*(end - start)))\n csv_writer.writerow(row + wikifications + runtime)\n if nb > 100: break",
"['#', 'id', 'title', 'language', 'type']\n1\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 4190.375566 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 8254.183769 ms\n2\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 3578.340292 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 8418.923378 ms\n3\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 2747.653961 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 7196.440458 ms\n4\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 2763.147116 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 11080.199003 ms\n5\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 3670.319080 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 5206.295490 ms\n6\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 3784.085274 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 5991.353512 ms\n7\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 2846.351624 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 9089.615107 ms\n8\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 3796.042681 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 6004.167557 ms\n9\n['9', '82541', '45 let Nacionalnega inštituta za biologijo | 45th anniversary of the National Institute of Biology', 'sl', 'mp4'] has no en version in db!\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 4462.502956 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 6124.587536 ms\n10\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 4266.768217 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 4998.503208 ms\n11\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 6037.398815 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 7818.226337 ms\n12\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 2886.986971 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 6915.290117 ms\n13\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 2892.765999 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 2512.521267 ms\n14\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 1263.699532 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 2032.653809 ms\n15\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 5002.927542 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 7293.339252 ms\n16\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 5289.523840 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 11738.499403 ms\n17\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 2473.007441 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 5093.167305 ms\n18\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 2886.327744 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 7596.126795 ms\n19\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 2401.640892 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 5860.953808 ms\n20\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 1877.862930 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 8925.778151 ms\n21\n['21', '82579', 'Živo srebro: od pomembne surovine do nevarnega odpadka', 'sl', 'pdf'] has no en version in db!\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 2124.764204 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 9786.525249 ms\n22\n['22', '82580', 'Dizajn molekulskega origamija za nove molekulske stroje in uravnavanje delovanja celic', 'sl', 'pdf'] has no en version in db!\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 2172.121286 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 4819.957733 ms\n23\n['23', '82581', 'Modifikacija površin z neravnovesno plazmo', 'sl', 'pdf'] has no en version in db!\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 3164.249659 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 3829.174519 ms\n24\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 8584.124327 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 9390.389919 ms\n25\n['25', '82596', 'Življenje in smrt v Hudi jami', 'sl', 'mp4'] has no en version in db!\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 10494.590044 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 9300.315857 ms\n26\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 4669.770479 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 8112.838984 ms\n27\n['27', '82599', 'Saksofon, ali te poznam?', 'sl', 'mp4'] has no en version in db!\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 4585.075140 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 9393.514395 ms\n28\n['28', '82600', 'Od ideje do izdelka', 'sl', 'mp4'] has no en version in db!\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 3858.740091 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 8063.073397 ms\n29\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 1623.477459 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 1916.675329 ms\n30\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 6891.006470 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 9217.612028 ms\n31\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 1943.078756 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 4896.094561 ms\n32\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 5783.622742 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 7704.862356 ms\n33\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 6089.389086 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 8050.746441 ms\n34\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 5695.441008 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 11082.671404 ms\n35\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 1803.220272 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 2986.572027 ms\n36\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 2037.798643 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 4502.619267 ms\n37\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 906.926632 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 1022.077322 ms\n38\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 2668.114185 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 4623.667717 ms\n39\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 1869.882345 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\nrecompute_on_anchor_text elapsed time: 1995.677233 ms\n40\nWikification sum_classic_page_rank...\nsum_classic_page_rank elapsed time: 631.375313 ms\nWikification recompute_on_anchor_text...\n"
],
[
"times",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"wikifications = {k: sorted(v, key=lambda x: x[2], reverse=True)[:20] for k, v in wikifications.items()}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"wikifications[\"sum_classic_page_rank\"]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"wikifications[\"recompute_on_anchor_text\"]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c501d566ca0070c6faf9f2f408fbf74c5ef96416
| 17,381 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
HASAA/arjun/Challenge_qctrls_code_p2.ipynb
|
arjundavis/qchack
|
ffad92c969bf62fd23c338487dc1aa41d07171a8
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 7 |
2021-04-10T14:26:36.000Z
|
2022-02-02T17:11:17.000Z
|
HASAA/arjun/Challenge_qctrls_code_p2.ipynb
|
arjundavis/qchack
|
ffad92c969bf62fd23c338487dc1aa41d07171a8
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 4 |
2021-04-11T03:29:12.000Z
|
2021-04-11T14:13:06.000Z
|
HASAA/arjun/Challenge_qctrls_code_p2.ipynb
|
arjundavis/qchack
|
ffad92c969bf62fd23c338487dc1aa41d07171a8
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 41 |
2021-04-10T14:43:08.000Z
|
2021-11-01T05:40:05.000Z
| 34.971831 | 335 | 0.557851 |
[
[
[
"\"\"\"\ncreated by Arj at 16:28 BST\n\n#Section\nInvestigating the challenge notebook and running it's code. \n\n#Subsection\nRunning a simulated qubit with errors\n\"\"\"\n\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\n\nfrom qctrlvisualizer import get_qctrl_style, plot_controls\nfrom qctrl import Qctrl\n\nplt.style.use(get_qctrl_style())\n\nqctrl = Qctrl()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def simulate_more_realistic_qubit(\n duration=1, values=np.array([np.pi]), shots=1024, repetitions=1\n):\n\n # 1. Limits for drive amplitudes\n assert np.amax(values) <= 1.0\n assert np.amin(values) >= -1.0\n max_drive_amplitude = 2 * np.pi * 20 # MHz\n\n # 2. Dephasing error\n dephasing_error = -2 * 2 * np.pi # MHz\n\n # 3. Amplitude error\n amplitude_i_error = 0.98\n amplitude_q_error = 1.03\n\n # 4. Control line bandwidth limit\n cut_off_frequency = 2 * np.pi * 10 # MHz\n resample_segment_count = 1000\n\n # 5. SPAM error confusion matrix\n confusion_matrix = np.array([[0.99, 0.01], [0.02, 0.98]])\n\n # Lowering operator\n b = np.array([[0, 1], [0, 0]])\n # Number operator\n n = np.diag([0, 1])\n # Initial state\n initial_state = np.array([[1], [0]])\n\n with qctrl.create_graph() as graph:\n # Apply 1. max Rabi rate.\n values = values * max_drive_amplitude\n\n # Apply 3. amplitude errors.\n values_i = np.real(values) * amplitude_i_error\n values_q = np.imag(values) * amplitude_q_error\n values = values_i + 1j * values_q\n\n # Apply 4. bandwidth limits\n drive_unfiltered = qctrl.operations.pwc_signal(duration=duration, values=values)\n drive_filtered = qctrl.operations.convolve_pwc(\n pwc=drive_unfiltered,\n kernel_integral=qctrl.operations.sinc_integral_function(cut_off_frequency),\n )\n drive = qctrl.operations.discretize_stf(\n drive_filtered, duration=duration, segments_count=resample_segment_count\n )\n\n # Construct microwave drive\n drive_term = qctrl.operations.pwc_operator_hermitian_part(\n qctrl.operations.pwc_operator(signal=drive, operator=b)\n )\n\n # Construct 2. dephasing term.\n dephasing_term = qctrl.operations.constant_pwc_operator(\n operator=dephasing_error * n,\n duration=duration,\n )\n\n # Construct Hamiltonian.\n hamiltonian = qctrl.operations.pwc_sum(\n [\n drive_term,\n dephasing_term,\n ]\n )\n\n # Solve Schrodinger's equation and get total unitary at the end\n unitary = qctrl.operations.time_evolution_operators_pwc(\n hamiltonian=hamiltonian,\n sample_times=np.array([duration]),\n )[-1]\n unitary.name = \"unitary\"\n\n # Repeat final unitary\n repeated_unitary = np.eye(2)\n for _ in range(repetitions):\n repeated_unitary = repeated_unitary @ unitary\n repeated_unitary.name = \"repeated_unitary\"\n\n # Calculate final state.\n state = repeated_unitary @ initial_state\n\n # Calculate final populations.\n populations = qctrl.operations.abs(state[:, 0]) ** 2\n # Normalize populations\n norm = qctrl.operations.sum(populations)\n populations = populations / norm\n populations.name = \"populations\"\n\n # Evaluate graph.\n result = qctrl.functions.calculate_graph(\n graph=graph,\n output_node_names=[\"unitary\", \"repeated_unitary\", \"populations\"],\n )\n\n # Extract outputs.\n unitary = result.output[\"unitary\"][\"value\"]\n repeated_unitary = result.output[\"repeated_unitary\"][\"value\"]\n populations = result.output[\"populations\"][\"value\"]\n\n # Sample projective measurements.\n true_measurements = np.random.choice(2, size=shots, p=populations)\n measurements = np.array(\n [np.random.choice(2, p=confusion_matrix[m]) for m in true_measurements]\n )\n\n results = {\"unitary\": unitary, \"measurements\": measurements}\n\n return results\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"max_rabi_rate = 20 * 2 * np.pi # MHz\nnot_duration = np.pi / (max_rabi_rate) # us\nh_duration = np.pi / (2 * max_rabi_rate) # us\nshots = 1024\n\nvalues = np.array([1.0])\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"not_results = simulate_more_realistic_qubit(\n duration=not_duration, values=values, shots=shots\n)\nh_results = simulate_more_realistic_qubit(\n duration=h_duration, values=values, shots=shots\n)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"error_norm = (\n lambda operate_a, operator_b: 1\n - np.abs(np.trace((operate_a.conj().T @ operator_b)) / 2) ** 2\n)\n\ndef estimate_probability_of_one(measurements):\n size = len(measurements)\n probability = np.mean(measurements)\n standard_error = np.std(measurements) / np.sqrt(size)\n return (probability, standard_error)\n\n\nrealised_not_gate = not_results[\"unitary\"]\nideal_not_gate = np.array([[0, -1j], [-1j, 0]])\nnot_error = error_norm(realised_not_gate, ideal_not_gate)\nrealised_h_gate = h_results[\"unitary\"]\nideal_h_gate = (1 / np.sqrt(2)) * np.array([[1, -1j], [-1j, 1]])\nh_error = error_norm(realised_h_gate, ideal_h_gate)\n\nnot_measurements = not_results[\"measurements\"]\nh_measurements = h_results[\"measurements\"]\nnot_probability, not_standard_error = estimate_probability_of_one(not_measurements)\nh_probability, h_standard_error = estimate_probability_of_one(h_measurements)\n\nprint(\"Realised NOT Gate:\")\nprint(realised_not_gate)\nprint(\"Ideal NOT Gate:\")\nprint(ideal_not_gate)\nprint(\"NOT Gate Error:\" + str(not_error))\nprint(\"NOT estimated probability of getting 1:\" + str(not_probability))\nprint(\"NOT estimate standard error:\" + str(not_standard_error) + \"\\n\")\n\nprint(\"Realised H Gate:\")\nprint(realised_h_gate)\nprint(\"Ideal H Gate:\")\nprint(ideal_h_gate)\nprint(\"H Gate Error:\" + str(h_error))\nprint(\"H estimated probability of getting 1:\" + str(h_probability))\nprint(\"H estimate standard error:\" + str(h_standard_error))",
"Realised NOT Gate:\n[[0.75412104-0.02524955j 0.1026601 -0.64817036j]\n [0.1026601 -0.64817036j 0.70940919+0.25704996j]]\nIdeal NOT Gate:\n[[ 0.+0.j -0.-1.j]\n [-0.-1.j 0.+0.j]]\nNOT Gate Error:0.5693360860922008\nNOT estimated probability of getting 1:0.453125\nNOT estimate standard error:0.015556183908275381\n\nRealised H Gate:\n[[0.98219782-0.00092913j 0.01473832-0.18726817j]\n [0.01473832-0.18726817j 0.96995998+0.15456728j]]\nIdeal H Gate:\n[[0.70710678+0.j 0. -0.70710678j]\n [0. -0.70710678j 0.70710678+0.j ]]\nH Gate Error:0.31912041750757547\nH estimated probability of getting 1:0.046875\nH estimate standard error:0.006605346317611662\n"
],
[
"# Now using the CLHO",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Define standard matrices.\nsigma_x = np.array([[0, 1], [1, 0]], dtype=np.complex)\nsigma_y = np.array([[0, -1j], [1j, 0]], dtype=np.complex)\nsigma_z = np.array([[1, 0], [0, -1]], dtype=np.complex)\n\n# Define control parameters.\nduration = 1e-6 # s\n\n# Define standard deviation of the errors in the experimental results.\nsigma = 0.01\n\n# Create a random unknown operator.\nrng = np.random.default_rng(seed=10)\nphi = rng.uniform(-np.pi, np.pi)\nu = rng.uniform(-1, 1)\nQ_unknown = (\n u * sigma_z + np.sqrt(1 - u ** 2) * (np.cos(phi) * sigma_x + np.sin(phi) * sigma_y)\n) / 4\n\n\ndef run_experiments(omegas):\n \"\"\"\n Simulates a series of experiments where controls `omegas` attempt to apply\n an X gate to a system. The result of each experiment is the infidelity plus\n a Gaussian error.\n\n In your actual implementation, this function would run the experiment with\n the parameters passed. Note that the simulation handles multiple test points,\n while your experimental implementation might need to queue the test point\n requests to obtain one at a time from the apparatus.\n \"\"\"\n # Create the graph with the dynamics of the system.\n with qctrl.create_graph() as graph:\n signal = qctrl.operations.pwc_signal(values=omegas, duration=duration)\n\n hamiltonian = qctrl.operations.pwc_operator(\n signal=signal,\n operator=0.5 * (sigma_x + Q_unknown),\n )\n\n qctrl.operations.infidelity_pwc(\n hamiltonian=hamiltonian,\n target_operator=qctrl.operations.target(operator=sigma_x),\n name=\"infidelities\",\n )\n\n # Run the simulation.\n result = qctrl.functions.calculate_graph(\n graph=graph,\n output_node_names=[\"infidelities\"],\n )\n\n # Add error to the measurement.\n error_values = rng.normal(loc=0, scale=sigma, size=len(omegas))\n infidelities = result.output[\"infidelities\"][\"value\"] + error_values\n\n # Return only infidelities between 0 and 1.\n return np.clip(infidelities, 0, 1)\n",
"/opt/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:2: DeprecationWarning: `np.complex` is a deprecated alias for the builtin `complex`. To silence this warning, use `complex` by itself. Doing this will not modify any behavior and is safe. If you specifically wanted the numpy scalar type, use `np.complex128` here.\nDeprecated in NumPy 1.20; for more details and guidance: https://numpy.org/devdocs/release/1.20.0-notes.html#deprecations\n \n/opt/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:3: DeprecationWarning: `np.complex` is a deprecated alias for the builtin `complex`. To silence this warning, use `complex` by itself. Doing this will not modify any behavior and is safe. If you specifically wanted the numpy scalar type, use `np.complex128` here.\nDeprecated in NumPy 1.20; for more details and guidance: https://numpy.org/devdocs/release/1.20.0-notes.html#deprecations\n This is separate from the ipykernel package so we can avoid doing imports until\n/opt/conda/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:4: DeprecationWarning: `np.complex` is a deprecated alias for the builtin `complex`. To silence this warning, use `complex` by itself. Doing this will not modify any behavior and is safe. If you specifically wanted the numpy scalar type, use `np.complex128` here.\nDeprecated in NumPy 1.20; for more details and guidance: https://numpy.org/devdocs/release/1.20.0-notes.html#deprecations\n after removing the cwd from sys.path.\n"
],
[
"# Define the number of test points obtained per run.\ntest_point_count = 20\n\n# Define number of segments in the control.\nsegment_count = 10\n\n# Define parameters as a set of controls with piecewise constant segments.\nparameter_set = (\n np.pi\n / duration\n * (np.linspace(-1, 1, test_point_count)[:, None])\n * np.ones((test_point_count, segment_count))\n)\n\n# Obtain a set of initial experimental results.\nexperiment_results = run_experiments(parameter_set)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Define initialization object for the automated closed-loop optimization.\nlength_scale_bound = qctrl.types.closed_loop_optimization_step.BoxConstraint(\n lower_bound=1e-5,\n upper_bound=1e5,\n)\nbound = qctrl.types.closed_loop_optimization_step.BoxConstraint(\n lower_bound=-5 * np.pi / duration,\n upper_bound=5 * np.pi / duration,\n)\ninitializer = qctrl.types.closed_loop_optimization_step.GaussianProcessInitializer(\n length_scale_bounds=[length_scale_bound] * segment_count,\n bounds=[bound] * segment_count,\n rng_seed=0,\n)\n\n# Define state object for the closed-loop optimization.\noptimizer = qctrl.types.closed_loop_optimization_step.Optimizer(\n gaussian_process_initializer=initializer,\n)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c501d8a2589704b6716f012354c336016889208f
| 7,941 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/1-jc-process-text-280117.ipynb
|
joaeechew/toxic
|
22beaea0ef2ad0ca519797c846cb5e42a5926b6a
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2017-12-29T02:31:55.000Z
|
2017-12-29T02:31:55.000Z
|
notebooks/1-jc-process-text-280117.ipynb
|
joaeechew/toxic
|
22beaea0ef2ad0ca519797c846cb5e42a5926b6a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/1-jc-process-text-280117.ipynb
|
joaeechew/toxic
|
22beaea0ef2ad0ca519797c846cb5e42a5926b6a
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2018-09-03T08:27:47.000Z
|
2018-09-03T08:27:47.000Z
| 25.699029 | 115 | 0.496159 |
[
[
[
"import os\nimport pandas as pd",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def load_data(path):\n full_path = os.path.join(os.path.realpath('..'), path)\n df = pd.read_csv(full_path, header=0, index_col=0)\n print(\"Dataset has {} rows, {} columns.\".format(*df.shape))\n return df",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_train = load_data('data/raw/train.csv')\ndf_test = load_data('data/raw/test.csv')",
"Dataset has 159571 rows, 7 columns.\nDataset has 153164 rows, 1 columns.\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Data cleaning",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# fill NaN with string \"unknown\"\ndf_train.fillna('unknown',inplace=True)\ndf_test.fillna('unknown',inplace=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Create features",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def create_features(df):\n \"Create features as seen in EDA\"\n print(\"Dataframe as {} rows and {} columns.\".format(*df.shape))\n # Uppercase count\n df['processed'] = df['comment_text'].str.split()\n print(\"Counting uppercases...\")\n df['uppercase_count'] = df['processed'].apply(lambda x: sum(1 for t in x if t.isupper() and len(t)>2))\n print(\"Dataframe as {} rows and {} columns.\".format(*df.shape))\n \n # Bad words\n print(\"Counting bad words...\")\n path = 'data/external/badwords.txt'\n bad_words = []\n f = open(os.path.join(os.path.realpath('..'), path), mode='rt', encoding='utf-8')\n for line in f:\n words = line.split(', ')\n for word in words:\n word = word.replace('\\n', '')\n bad_words.append(word)\n f.close()\n\n df['bad_words'] = df['processed'].apply(lambda x: sum(1 for t in x if t in bad_words))\n print(\"Dataframe as {} rows and {} columns.\".format(*df.shape))\n \n # Count of typos\n from enchant.checker import SpellChecker\n\n def typo_count(corpus):\n \"Count the number of errors found by pyenchant\"\n count = []\n for row in corpus:\n chkr = SpellChecker(\"en_US\")\n chkr.set_text(row)\n i = 0\n for err in chkr:\n i += 1\n count.append(i)\n return count\n \n print(\"Counting typos...\")\n df['typos'] = typo_count(df.comment_text)\n print(\"Dataframe as {} rows and {} columns.\".format(*df.shape))\n \n # Doc length\n print(\"Counting length of each comment...\")\n df['length'] = [len(t) for t in df['processed']]\n print(\"Dataframe as {} rows and {} columns.\".format(*df.shape))\n \n # Drop processed (helper column)\n df = df.drop(['processed'], axis=1)\n print(\"Dataframe as {} rows and {} columns.\".format(*df.shape))\n return df",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_train = create_features(df_train)\ndf_test = create_features(df_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Spell check - TBC",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import enchant\nfrom enchant.checker import SpellChecker",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from enchant.checker import SpellChecker\n\ndef spellcheck(corpus):\n \"Spellcheck using pyenchant\"\n for row in corpus:\n chkr = SpellChecker(\"en_US\")\n chkr.set_text(row)\n for err in chkr:\n sug = err.suggest()[0]\n err.replace(sug)\n print(err.word, sug)\n row = chkr.get_text()\n return corpus",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"spellcheck(df_train.comment_text[:5])",
"username user name\nMetallica Metallic\nGAs Gas\nFAC AC\nD'aww D'art\ncolour color\nUTC CUT\nie IE\neg g\nWikipedia Pediatric\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Output",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# save list to file\ndef save_list(lines, filename):\n # convert lines to a single blob of text data = '\\n'.join(lines)\n data = '\\n'.join(lines)\n # open file\n file = open(filename, 'w')\n # write text\n file.write(data)\n # close file\n file.close()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def save_df(df, path):\n full_path = os.path.join(os.path.realpath('..'), path)\n df.to_csv(full_path, header=True, index=True)\n print('Dataframe ({}, {}) saved as csv.'.format(*df.shape))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"save_df(df_train, 'data/processed/train.csv')\nsave_df(df_test, 'data/processed/test.csv')",
"Dataframe (159571, 11) saved as csv.\nDataframe (153164, 5) saved as csv.\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c501da7d9da6cef18cf507a1bd9f230ba8d4ac85
| 7,885 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
sagemaker-python-sdk/mxnet_gluon_sentiment/mxnet_sentiment_analysis_with_gluon.ipynb
|
dleen/amazon-sagemaker-examples
|
8edd462adf37b5b173098ffea729b7198ce8d41c
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 2 |
2019-11-17T08:00:42.000Z
|
2021-04-08T11:01:47.000Z
|
sagemaker-python-sdk/mxnet_gluon_sentiment/mxnet_sentiment_analysis_with_gluon.ipynb
|
lokeshinumpudi/amazon-sagemaker-examples
|
bb0a5fcafac9e1735672e72c263f017edebecaaa
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
sagemaker-python-sdk/mxnet_gluon_sentiment/mxnet_sentiment_analysis_with_gluon.ipynb
|
lokeshinumpudi/amazon-sagemaker-examples
|
bb0a5fcafac9e1735672e72c263f017edebecaaa
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2019-08-25T22:45:27.000Z
|
2019-08-25T22:45:27.000Z
| 34.432314 | 557 | 0.619911 |
[
[
[
"## Sentiment Analysis with MXNet and Gluon\n\nThis tutorial will show how to train and test a Sentiment Analysis (Text Classification) model on SageMaker using MXNet and the Gluon API.\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import os\nimport boto3\nimport sagemaker\nfrom sagemaker.mxnet import MXNet\nfrom sagemaker import get_execution_role\n\nsagemaker_session = sagemaker.Session()\n\nrole = get_execution_role()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Download training and test data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In this notebook, we will train the **Sentiment Analysis** model on [SST-2 dataset (Stanford Sentiment Treebank 2)](https://nlp.stanford.edu/sentiment/index.html). The dataset consists of movie reviews with one sentence per review. Classification involves detecting positive/negative reviews. \nWe will download the preprocessed version of this dataset from the links below. Each line in the dataset has space separated tokens, the first token being the label: 1 for positive and 0 for negative.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%bash\nmkdir data\ncurl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/saurabh3949/Text-Classification-Datasets/master/stsa.binary.phrases.train > data/train\ncurl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/saurabh3949/Text-Classification-Datasets/master/stsa.binary.test > data/test ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Uploading the data\n\nWe use the `sagemaker.Session.upload_data` function to upload our datasets to an S3 location. The return value `inputs` identifies the location -- we will use this later when we start the training job.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"inputs = sagemaker_session.upload_data(path='data', key_prefix='data/DEMO-sentiment')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Implement the training function\n\nWe need to provide a training script that can run on the SageMaker platform. The training scripts are essentially the same as one you would write for local training, except that you need to provide a `train` function. When SageMaker calls your function, it will pass in arguments that describe the training environment. Check the script below to see how this works.\n\nThe script here is a simplified implementation of [\"Bag of Tricks for Efficient Text Classification\"](https://arxiv.org/abs/1607.01759), as implemented by Facebook's [FastText](https://github.com/facebookresearch/fastText/) for text classification. The model maps each word to a vector and averages vectors of all the words in a sentence to form a hidden representation of the sentence, which is inputted to a softmax classification layer. Please refer to the paper for more details.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!cat 'sentiment.py'",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Run the training script on SageMaker\n\nThe ```MXNet``` class allows us to run our training function on SageMaker infrastructure. We need to configure it with our training script, an IAM role, the number of training instances, and the training instance type. In this case we will run our training job on a single c4.2xlarge instance. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"m = MXNet('sentiment.py',\n role=role,\n train_instance_count=1,\n train_instance_type='ml.c4.xlarge',\n framework_version='1.4.0',\n py_version='py2',\n distributions={'parameter_server': {'enabled': True}},\n hyperparameters={'batch-size': 8,\n 'epochs': 2,\n 'learning-rate': 0.01,\n 'embedding-size': 50, \n 'log-interval': 1000})",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"After we've constructed our `MXNet` object, we can fit it using the data we uploaded to S3. SageMaker makes sure our data is available in the local filesystem, so our training script can simply read the data from disk.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"m.fit(inputs)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"As can be seen from the logs, we get > 80% accuracy on the test set using the above hyperparameters.\n\nAfter training, we use the MXNet object to build and deploy an MXNetPredictor object. This creates a SageMaker endpoint that we can use to perform inference. \n\nThis allows us to perform inference on json encoded string array. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"predictor = m.deploy(initial_instance_count=1, instance_type='ml.c4.xlarge')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The predictor runs inference on our input data and returns the predicted sentiment (1 for positive and 0 for negative).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data = [\"this movie was extremely good .\",\n \"the plot was very boring .\",\n \"this film is so slick , superficial and trend-hoppy .\",\n \"i just could not watch it till the end .\",\n \"the movie was so enthralling !\"]\n\nresponse = predictor.predict(data)\nprint(response)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Cleanup\n\nAfter you have finished with this example, remember to delete the prediction endpoint to release the instance(s) associated with it.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"predictor.delete_endpoint()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c501e17f07865aa9d26bfba54cc973479ff8e30b
| 28,932 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Lessons/Lesson04b_Dictionaries.ipynb
|
GeoPythonVT/geosf21
|
a1cf6f9b370afa73e83e78d70fbef5db140f9322
|
[
"CC0-1.0"
] | null | null | null |
Lessons/Lesson04b_Dictionaries.ipynb
|
GeoPythonVT/geosf21
|
a1cf6f9b370afa73e83e78d70fbef5db140f9322
|
[
"CC0-1.0"
] | null | null | null |
Lessons/Lesson04b_Dictionaries.ipynb
|
GeoPythonVT/geosf21
|
a1cf6f9b370afa73e83e78d70fbef5db140f9322
|
[
"CC0-1.0"
] | null | null | null | 29.342799 | 416 | 0.570614 |
[
[
[
"\"Geo Data Science with Python\" \n### Notebook Lesson 3\n \n# Object Type: Dictionaries\n\nThis lesson discusses the Python object type **Dictionaries**. Carefully study the content of this Notebook and use the chance to reflect the material through the interactive examples.\n\n### Sources\nThis lesson is an adaption of the lesson [Understanding Dictionaries in Python 3](https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/understanding-dictionaries-in-python-3) of the [Digital Ocean Community](https://www.digitalocean.com/community).\n\n---",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Part A: Introduction",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Table 1 provides a comprehensive overview of Python object classifications. The table gives information about their mutability and their category. The sequential character of strings and lists was emphasized in the last notebooks. Now we want to look at another type of objects in Python that provides the most flexibility: *Dictionaries*. Tuples, Sets and Files will be discussed in the upcoming notebooks.\n\nTable 1. *Object Cassifications* (Lutz, 2013)\n\n| Object Type | Category | Mutable? | \n| :---------: | :-------: | :-------: |\n| Numbers (all) | Numeric | No | \n| Strings | Sequence | No | \n| Lists | Sequence | Yes | \n| Dictionaries | Mapping | Yes | \n| Files | Extention | N/A | \n| Tuples | Sequence | No | \n| Sets | Set | Yes | \n| `frozenset` | Set | No | ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The dictionary is Python’s built-in *mapping* type. Dictionaries map *keys* to *values* and these key-value pairs provide a useful way to store data in Python. Since dictionaries are mutable, they allow **mutable data mapping**. \n\n<div class=\"alert alert-info\">\n\n**Note**\nDictionaries are an unordered collection of arbritrary objects (no sequences) of variable length. They are similar to lists, but provide more general data access, since accessing the content is not limited to index numbers and it can be achieved by other types of indices. \n</div>\n\nDictionaries are typically used to hold data that are related, such as the information contained in an ID or a user profile. They are constructed with curly braces on either side `{` `}`.\n\nA simple example for a dictionary looks like this:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sammy = {'username': 'sammy-shark', 'online': True, 'followers': 987}\ntype(sammy)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"In addition to the curly braces, there are also colons (`:`) throughout the dictionary.\n\nThe words to the left of the colons are the keys. *Keys* can be made up of any immutable data type. The keys in the dictionary above are: \n\n* `'username'`\n* `'online'`\n* `'followers'`\n\nKeys have to be of immutable object type, like numbers or strings. Each of the keys in the above example are string values.\n\nThe words to the right of the colons are the values. Values can be comprised of any data type. The values in the dictionary above are:\n\n* `'sammy-shark'`\n* `True`\n* `987`\n\nEach of these values is either a string, Boolean, or integer. \n\nLet’s print out the dictionary `sammy`:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(sammy)",
"{'username': 'sammy-shark', 'online': False, 'followers': 987}\n"
]
],
[
[
"Looking at the output, the order of the key-value pairs may have shifted. In Python version 3.5 and earlier, the dictionary data type is unordered. However, in Python version 3.6 and later, the dictionary data type remains ordered. Regardless of whether the dictionary is ordered or not, the key-value pairs will remain intact, enabling us to access data based on their relational meaning. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Part B: Accessing Dictionary Elements\n\nWe can call the values of a dictionary by referencing the related keys.\n\n### Accessing Data Items with Keys\n\nBecause dictionaries offer key-value pairs for storing data, they can be important elements in your Python program.\n\nIf we want to isolate Sammy’s username, we can do so by calling `sammy['username']`. Let’s print that out:\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(sammy['username'])",
"sammy-shark\n"
]
],
[
[
"Dictionaries behave like a database in that instead of calling an integer to get a particular index value as you would with a list, you assign a value to a key and can call that key to get its related value. \n\nBy invoking the key `'username'` we receive the value of that key, which is `'sammy-shark'`.\n\nThe remaining values in the `sammy` dictionary can similarly be called using the same format:\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sammy['followers']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sammy['online']",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"By making use of dictionaries’ key-value pairs, we can reference keys to retrieve values.\n\n### Using Methods to Access Elements\n\nIn addition to using keys to access values, we can also work with some type-specific methods is a placeholder for the name of a dictionary):\n\n* `.keys()` isolates keys\n* `.values()` isolates values\n* `.items()` returns items in a list format of `(key, value)` tuple pairs\n\nTo return the keys, we would use the `.keys()` method. In our example, that would use the variable name and be `sammy.keys()`. Let’s pass that to a `print()` method and look at the output:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(sammy.keys())",
"dict_keys(['username', 'online', 'followers'])\n"
],
[
"type(sammy.keys())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We receive output that places the keys within an iterable view object of the `dict_keys` class. The keys are then printed within a list format.\n\nThis method can be used to query across dictionaries. For example, we could take a look at the common keys shared between two dictionary data structures:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sammy = {'username': 'sammy-shark', 'online': True, 'followers': 987}\njesse = {'username': 'JOctopus', 'online': False, 'points': 723}",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The dictionary `sammy` and the dictionary `jesse` are each a user profile dictionary. \n\nTheir profiles have different keys, however, because Sammy has a social profile with associated followers, and Jesse has a gaming profile with associated points. The two keys they have in common are `username` and `online` status, which we can find when we run this small program:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for common_key in sammy.keys() & jesse.keys():\n print(sammy[common_key], jesse[common_key])",
"sammy-shark JOctopus\nTrue False\n"
]
],
[
[
"We could certainly improve on the program to make the output more user-readable, but this illustrates that the method `.keys()` can be used to check across various dictionaries to see what they share in common or not. This is especially useful for large dictionaries.\n\nSimilarly, we can use the `.values()` method to query the values in the `sammy` dictionary, which would be constructed as `sammy.values()`. Let’s print those out:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sammy = {'username': 'sammy-shark', 'online': True, 'followers': 987}\nprint(sammy.values())",
"dict_values(['sammy-shark', True, 987])\n"
]
],
[
[
"Both the methods `keys()` and `values()` return unsorted lists of the keys and values present in the `sammy` dictionary with the view objects of `dict_keys` and `dict_values` respectively.\n\nIf we are interested in all of the items in a dictionary, we can access them with the `items()` method:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(sammy.items())",
"dict_items([('username', 'sammy-shark'), ('online', True), ('followers', 987)])\n"
]
],
[
[
"The returned format of this is a list made up of `(key, value)` tuple pairs with the `dict_items` view object. We will discuss tuples in the next notebook lesson.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We can iterate over the returned list format with a `for` loop. For example, we can print out both at the same time keys and values of a given dictionary, and then make it more human-readable by adding a string:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for key, value in sammy.items():\n print(key, 'is the key for the value', value)",
"username is the key for the value sammy-shark\nonline is the key for the value True\nfollowers is the key for the value 987\n"
]
],
[
[
"The `for` loop above iterated over the items within the sammy dictionary and printed out the keys and values line by line, with information to make it easier to understand by humans.\n\nWe can use built-in methods to access items, values, and keys from dictionary data structures.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Part C: Modifying Dictionaries\n\nDictionaries are a mutable data structure, so you are able to modify them. In this section, we’ll go over adding and deleting dictionary elements.\n\n### Adding and Changing Dictionary Elements\n\nWithout using a method or function, you can add key-value pairs to dictionaries by using the following syntax:\n\n`dict[key] = value`.\n\nWe’ll look at how this works in practice by adding a key-value pair to a dictionary called `usernames`:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"usernames = {'Sammy': 'sammy-shark', 'Jamie': 'mantisshrimp54'}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"usernames['Drew'] = 'squidly'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(usernames)",
"{'Sammy': 'sammy-shark', 'Jamie': 'mantisshrimp54', 'Drew': 'squidly'}\n"
]
],
[
[
"We see now that the dictionary has been updated with the `'Drew': 'squidly'` key-value pair. Because dictionaries may be unordered, this pair may occur anywhere in the dictionary output. If we use the `usernames` dictionary later in our program file, it will include the additional key-value pair.\n\nAdditionally, this syntax can be used for modifying the value assigned to a key. In this case, we’ll reference an existing key and pass a different value to it.\n\nLet’s consider a dictionary `drew` that is one of the users on a given network. We’ll say that this user got a bump in followers today, so we need to update the integer value passed to the `'followers'` key. We’ll use the `print()` function to check that the dictionary was modified.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"drew = {'username': 'squidly', 'online': True, 'followers': 305}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"drew['followers'] = 342",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(drew)",
"{'username': 'squidly', 'online': True, 'followers': 342}\n"
]
],
[
[
"In the output, we see that the number of followers jumped from the integer value of 305 to 342.\n\nWe can also add and modify dictionaries by using the `.update()` method. This varies from the `append()` method available in lists.\n\nIn the `jesse` dictionary below, let’s add the key `'followers'` and give it an integer value with `jesse.update()`. Following that, let’s `print()` the updated dictionary.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"jesse = {'username': 'JOctopus', 'online': False, 'points': 723}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"jesse.update({'followers': 481})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(jesse)",
"{'username': 'JOctopus', 'online': False, 'points': 723, 'followers': 481}\n"
]
],
[
[
"From the output, we can see that we successfully added the `'followers': 481` key-value pair to the dictionary `jesse`.\n\nWe can also use the `.update()` method to modify an existing key-value pair by replacing a given value for a specific key.\n\nLet’s change the online status of Sammy from `True` to `False` in the sammy dictionary:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sammy = {'username': 'sammy-shark', 'online': True, 'followers': 987}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sammy.update({'online': False})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(sammy)",
"{'username': 'sammy-shark', 'online': False, 'followers': 987}\n"
]
],
[
[
"The line `sammy.update({'online': False})` references the existing key `'online'` and modifies its Boolean value from `True` to `False`. When we call to `print()` the dictionary, we see the update take place in the output.\n\nTo add items to dictionaries or modify values, we can use wither the `dict[key] = value` syntax or the method `.update()`.\n\n### Deleting Dictionary Elements\n\nJust as you can add key-value pairs and change values within the dictionary data type, you can also delete items within a dictionary.\n\nTo remove a key-value pair from a dictionary, we’ll use the following syntax:\n\n`del dict[key]`\n\nLet’s take the `jesse` dictionary that represents one of the users. We’ll say that Jesse is no longer using the online platform for playing games, so we’ll remove the item associated with the `'points'` key. Then, we’ll print the dictionary out to confirm that the item was deleted:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"jesse = {'username': 'JOctopus', 'online': False, 'points': 723, 'followers': 481}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"del jesse['points']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(jesse)",
"{'username': 'JOctopus', 'online': False, 'followers': 481}\n"
]
],
[
[
"The line `del jesse['points']` removes the key-value pair `'points': 723` from the jesse dictionary.\n\nIf we would like to clear a dictionary of all of its values, we can do so with the `.clear()` method. This will keep a given dictionary in case we need to use it later in the program, but it will no longer contain any items.\n\nLet’s remove all the items within the `jesse` dictionary:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"jesse = {'username': 'JOctopus', 'online': False, 'points': 723, 'followers': 481}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"jesse.clear()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(jesse)",
"{}\n"
]
],
[
[
"The output shows that we now have an empty dictionary devoid of key-value pairs.\n\nIf we no longer need a specific dictionary, we can use `del` to get rid of it entirely:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"del jesse",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"When we run a call to `print()` after deleting the jesse dictionary, we’ll receive the `NameError`:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(jesse)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Because dictionaries are mutable data types, they can be added to, modified, and have items removed and cleared.\n\n### Nested Dictionaries and Lists\n\nA for-loop on a dictionary in the syntax of *list comprehensions* iterates over its keys by default. This returns the keys saved in a list object (in contrast to the `keys()` method). The keys will appear in an arbitrary order.\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"[ key for key in jesse ]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"In addition to that, lists and dictionaries can be combined, i.e. nested in order to design various useful data structures. For example, instead of saving the user information of `sammy`, `jesse` and `drew` in three different dictionaries, ...",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sammy = {'username': 'sammy-shark', 'online': True, 'points': 120, 'followers': 987}\njesse = {'username': 'JOctopus' , 'online': False, 'points': 723, 'followers': 481}\ndrew = {'username': 'squidly' , 'online': False, 'points': 652, 'followers': 532}",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"... we coul simply feed the data into a nested dictionary - a dictionary of dictionaries:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"AppUsers_dictDict = {\n 'sammy': {'username': 'sammy-shark', 'online': True, 'points': 120, 'followers': 987},\n 'jesse': {'username': 'JOctopus' , 'online': False, 'points': 723, 'followers': 481},\n 'drew' : {'username': 'squidly' , 'online': False, 'points': 652, 'followers': 532}\n}",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"... or we coul generate a dictionary nesting information in lists:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"AppUsers_dictList = {\n 'names' : ['sammy', 'jesse', 'drew' ] ,\n 'usernames': ['sammy-shark', 'JOctopus', 'squidly' ] ,\n 'online' : [True, False, False] ,\n 'points' : [120, 723, 652 ] ,\n 'followers': [987, 481, 532 ]\n}",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"... alternatively, dictionaries in a list:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"AppUsers_listDict = [\n {'name': 'sammy', 'username': 'sammy-shark', 'online': True, 'points': 120, 'followers': 987},\n {'name': 'jesse', 'username': 'JOctopus' , 'online': False, 'points': 723, 'followers': 481},\n {'name': 'drew' , 'username': 'squidly' , 'online': False, 'points': 652, 'followers': 532}\n]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"To access the individual elements of such nested objects, the syntax has to follow the hierarchy of the nested elements. For example, referencing a nested list-dictionary combination is has to be achieved through a combination of dictionary keys and list indexes. \n\nLet's retrieve the username of jesse from the three nested objects. Elements in nested dictionaries can be referenced through keys of the various nesting levels:\n\n`dictname[‘keyLevel1’][‘keyLevel2’][...]`\n\nFor the example `AppUsers_dictDict`, the respective literal is:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"AppUsers_dictDict['jesse']['username']",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"If lists and dictionaries were combined, keys and indexes have to be combined respectively:\n\n`dictname[‘key’][indexnumber]` or `dictname[indexnumber][‘key’]`\n\nFor the examples `AppUsers_dictList` and `AppUsers_listDict` above:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"AppUsers_dictList['usernames'][1]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"AppUsers_listDict[1]['username']",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Summary\n\nDictionaries are made up of key-value pairs and provide a way to store data without relying on indexing. This allows us to retrieve values based on their meaning and relation to other data types. \n\n* Elements in dictionaries are directly accessible by keys.\n* Keys have to be of immutable object type, like numbers or strings.\n* Lists are mutable, they can't be used as keys, but they can be used as nested values.\n* A list comprehension performed on a dictionary iterates over its keys by default. The keys will appear in an arbitrary order.\n\nMost common specific operations (methods) are: `pop`, `keys`, `values`, `items`, `get`. A comprehensive overview of built-in dictionary operations, functions and methods is provided here: https://www.tutorialspoint.com/python/python_dictionary.htm\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
c501e1f5a4e2469e06eb878edc9c3cf0cf27e033
| 797,720 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/binary_notebook.ipynb
|
afeinstein20/flares_soc
|
b120b6174c6a5b305823dc5bef668fe17ea2e9c0
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/binary_notebook.ipynb
|
afeinstein20/flares_soc
|
b120b6174c6a5b305823dc5bef668fe17ea2e9c0
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/binary_notebook.ipynb
|
afeinstein20/flares_soc
|
b120b6174c6a5b305823dc5bef668fe17ea2e9c0
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 1,106.407767 | 393,232 | 0.946694 |
[
[
[
"import numpy as np\nfrom astropy import units as u\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom astroquery.gaia import Gaia\nfrom astropy.coordinates import SkyCoord\nfrom gaiadr2ruwetools import ruwetools\nfrom astropy.table import Table, Column\nfrom tqdm import tqdm_notebook\nfrom ffd_tools import *\n\nplt.rcParams['font.size'] = 16",
"WARNING: leap-second auto-update failed due to the following exception: ValueError(\"Malformed URL: '//anaconda3/lib/python3.7/site-packages/astropy/utils/iers/data/Leap_Second.dat'\") [astropy.time.core]\n"
],
[
"#flares = Table.read('all_flares_param_catalog_ruwe.tab', format='csv')\ncatalog= Table.read('all_star_param_catalog_ruwe.tab', format='csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from matplotlib.colors import LinearSegmentedColormap\n\nclist0 = np.array(['EA8F3C', 'EB6A41', '69469D', '241817'])\nclist1 = np.array(['66C6C6', '2B8D9D', '19536C', '123958', '121422'])\n\ndef hex_to_rgb(h):\n if '#' in h:\n h = h.lstrip('#') \n hlen = int(len(h))\n rgb = tuple(int(h[i:int(i+hlen/3)], 16) / 255.0 for i in range(0, hlen, int(hlen/3)))\n return rgb\n\ndef make_cmap(clist):\n rgb_tuples = []\n\n for c in clist:\n rgb_tuples.append(hex_to_rgb(c))\n\n cm = LinearSegmentedColormap.from_list(\n 'sequential', rgb_tuples, N=2048)\n return cm",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cm = make_cmap(clist0)\ncm1 = make_cmap(clist1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"uwe = np.sqrt( catalog['astrometric_chi2_al'] / (catalog['astrometric_n_good_obs_al']-5) )\nu0fit = ruwetools.U0Interpolator()\nu0 = u0fit.get_u0(catalog['phot_g_mean_mag'], \n catalog['bp_rp'])\nruwe = uwe/u0\ncatalog.add_column(Column(ruwe, 'RUWE'))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"catalog.write('all_star_param_catalog_ruwe.tab', format='csv')",
"WARNING: AstropyDeprecationWarning: all_star_param_catalog_ruwe.tab already exists. Automatically overwriting ASCII files is deprecated. Use the argument 'overwrite=True' in the future. [astropy.io.ascii.ui]\n"
],
[
"fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(ncols=2, figsize=(14,10), \n sharex=True, sharey=True)\nruwe_cutoff = 2.0\nfig.set_facecolor('w')\nax1.plot(catalog['teff'], catalog['lum'], '.', \n c='#b3b3b3', ms=2, alpha=0.3, zorder=0)\nim = ax1.scatter(catalog['teff'][catalog['RUWE']>=ruwe_cutoff], \n catalog['lum'][catalog['RUWE']>=ruwe_cutoff], \n c=catalog['RUWE'][catalog['RUWE']>=ruwe_cutoff], s=10, \n vmin=ruwe_cutoff, vmax=5, zorder=3,\n cmap=cm1.reversed())\nfig.colorbar(im, ax=ax1, label='RUWE')\n#ax1.colorbar(label='RUWE')\n\ninds = np.where((catalog['teff'] > 6000) & \n (catalog['lum']>3) & \n (catalog['N_flares_per_day']>2) &\n (catalog['RUWE'] < ruwe_cutoff))[0]\ngood_inds = np.delete(np.arange(0,len(catalog),1,dtype=int), inds)\nax2.plot(catalog['teff'][good_inds], catalog['lum'][good_inds], '.',\n c='#b3b3b3', ms=2, alpha=0.3, zorder=0)\n\ngood_inds = catalog['RUWE'] > ruwe_cutoff\nim = ax2.scatter(catalog['teff'][good_inds], catalog['lum'][good_inds], \n c=catalog['N_flares_per_day'][good_inds], s=10, vmin=0, vmax=1,\n cmap=cm.reversed(), zorder=3)\nfig.colorbar(im, ax=ax2, label='Flare Rate [day$^{-1}$]')\n#ax2.colorbar(label='Flare Rate')\n\nplt.xlim(12000,2300)\nplt.yscale('log')\nplt.ylim(10**-3.5, 10**3)\nax1.set_xlabel('$T_{eff}$ [K]')\nax2.set_xlabel('$T_{eff}$ [K]')\nax1.set_ylabel('Luminosity [L/L$_\\odot$]')\nax1.set_rasterized(True)\nax2.set_rasterized(True)\nplt.savefig('ruwe_hr.pdf', dpi=250, rasterize=True, bbox_inches='tight')",
"//anaconda3/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:38: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning: savefig() got unexpected keyword argument \"rasterize\" which is no longer supported as of 3.3 and will become an error two minor releases later\n"
],
[
"catalog",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(ncols=2, figsize=(14,10), \n sharex=True, sharey=True)\n\nabsmag = catalog['phot_g_mean_mag'] - 5*np.log10(catalog['TICv8_d']/10)\n\nruwe_cutoff = 1.4\nfig.set_facecolor('w')\nax1.plot(catalog['bp_rp'], absmag, '.', \n c='#b3b3b3', ms=2, alpha=0.3, zorder=0)\nim = ax1.scatter(catalog['bp_rp'][catalog['RUWE']>=ruwe_cutoff], \n absmag[catalog['RUWE']>=ruwe_cutoff], \n c=catalog['RUWE'][catalog['RUWE']>=ruwe_cutoff], s=10, \n vmin=ruwe_cutoff, vmax=5, zorder=3,\n cmap=cm1.reversed())\nfig.colorbar(im, ax=ax1, label='RUWE')\n#ax1.colorbar(label='RUWE')\n\ninds = np.where((catalog['teff'] > 6000) & \n (catalog['lum']>3) & \n (catalog['N_flares_per_day']>2) &\n (catalog['RUWE'] < ruwe_cutoff))[0]\ngood_inds = np.delete(np.arange(0,len(catalog),1,dtype=int), inds)\nax2.plot(catalog['bp_rp'][good_inds], \n absmag[good_inds], '.',\n c='#b3b3b3', ms=2, alpha=0.3, zorder=0)\n\ngood_inds = catalog['RUWE'] > ruwe_cutoff\nim = ax2.scatter(catalog['bp_rp'][good_inds], \n absmag[good_inds], \n c=catalog['N_flares_per_day'][good_inds], s=10, \n vmin=0, vmax=0.5,\n cmap=cm.reversed(), zorder=3)\nfig.colorbar(im, ax=ax2, label='Flare Rate [day$^{-1}$]')\n#ax2.colorbar(label='Flare Rate')\n\nplt.xlim(-1,5)\n#plt.yscale('log')\nplt.ylim(17,-5)\nax1.set_xlabel('Gaia B$_p$ - R$_p$')\nax2.set_xlabel('Gaia B$_p$ - R$_p$')\nax1.set_ylabel('Gaia G Mag')\nax1.set_rasterized(True)\nax2.set_rasterized(True)\nplt.savefig('ruwe_hr.pdf', dpi=250, rasterize=True, bbox_inches='tight')",
"//anaconda3/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:4: RuntimeWarning: divide by zero encountered in log10\n after removing the cwd from sys.path.\n//anaconda3/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:44: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning: savefig() got unexpected keyword argument \"rasterize\" which is no longer supported as of 3.3 and will become an error two minor releases later\n"
],
[
"def amp_slope_fit(data, bins, i=0, j=-1):\n \n n, _ = np.histogram(data['amp']*100, bins=bins)\n y, binedges, _ = plt.hist(data['amp']*100, \n bins=bins,\n weights=np.full(len(data['amp']),\n 1.0/np.nansum(data['weights'])),\n alpha=0.4)\n plt.yscale('log')\n plt.show()\n plt.close()\n\n x = binedges[1:] + 0.0\n logx = np.log10(x)\n logn = np.log10(n)\n q = logn > 0\n\n plt.plot(logx[i:j], np.log10(n[i:j]), '.', c='k')\n plt.plot(logx[i:j], linear([-2.5, 7], logx[i:j]), '--', c='w', linewidth=3)\n plt.show()\n\n results = minimize(linear_fit, x0=[-2.5, 7],\n args=(logx[q][i:j-1]-np.diff(logx[q][i:j])/2., \n logn[q][i:j-1], np.sqrt(logn[q][i:j-1]) ), \n bounds=( (-10.0, 10.0), (-100, 100)),\n method='L-BFGS-B', tol=1e-8)\n \n results.x[1] = 10**results.x[1]\n\n results2 = leastsq(power_law_resid, results.x,\n args=(x[q][i:j-1]-np.diff(x[q][i:j])/2., \n n[q][i:j-1], \n np.sqrt(n[q][i:j-1]) ),\n full_output=True)\n\n fit_params = results2[0]\n \n slope_err = np.sqrt(results2[1][0][0])\n\n model = linear([fit_params[0], np.log10(fit_params[1])], logx)\n #plt.plot(logx, model, c='r')\n #plt.show()\n\n #print(fit_params[0], slope_err)\n\n return fit_params[0], slope_err, binedges, y",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"temp_bins = [2300,4500, 6000, 12000]\nslopes_high = np.zeros(len(temp_bins)-1)\nerrs_high = np.zeros(len(temp_bins)-1)\nslopes_low = np.zeros(len(temp_bins)-1)\nerrs_low = np.zeros(len(temp_bins)-1)\nlogx_high = []\nlogx_low = []\n\nruwe_cutoff = 2.0\n\nbins = np.linspace(1,300,30)\n\nfor i in range(len(temp_bins)-1):\n dat = flares[(flares['teff']>=temp_bins[i]) &\n (flares['teff']<=temp_bins[i+1]) &\n (flares['RUWE']>=ruwe_cutoff)]\n\n slope, err, x, n = amp_slope_fit(dat, bins=bins)\n slopes_high[i] = slope\n errs_high[i] = err\n logx_high.append([x, n])\n\n \n dat = flares[(flares['teff']>=temp_bins[i]) &\n (flares['teff']<=temp_bins[i+1]) &\n (flares['RUWE']<ruwe_cutoff)]\n\n slope, err, x, n = amp_slope_fit(dat, bins=bins, i=0, j=-1)\n slopes_low[i] = slope\n errs_low[i] = err\n logx_low.append([x, n])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, (ax1, ax2, ax3) = plt.subplots(ncols=3, figsize=(14,4), sharex=True, sharey=True)\nfig.set_facecolor('w')\naxes = [ax1, ax2, ax3]\n\nfor i in range(len(axes)):\n dat = flares[(flares['teff']>=temp_bins[i]) &\n (flares['teff']<=temp_bins[i+1]) &\n (flares['RUWE']<ruwe_cutoff)]\n axes[i].hist(dat['amp']*100, bins=bins, weights=np.full(len(dat['amp']),\n 1.0/np.nansum(dat['weights'])),\n color='deepskyblue', alpha=0.6)\n \n dat = flares[(flares['teff']>=temp_bins[i]) &\n (flares['teff']<=temp_bins[i+1]) &\n (flares['RUWE']>=ruwe_cutoff)]\n axes[i].hist(dat['amp']*100, bins=bins, weights=np.full(len(dat['amp']),\n 1.0/np.nansum(dat['weights'])),\n color='k', alpha=0.7)\n axes[i].set_title('{0}-{1} K'.format(temp_bins[i], temp_bins[i+1]))\nplt.yscale('log')\nax2.set_xlabel('Flare Amplitude [%]')\nax1.set_ylabel('Flare Rate [day$^{-1}$]')\nplt.savefig('ruwe_hists.pdf', dpi=250, rasterize=True, bbox_inches='tight')",
"//anaconda3/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:23: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning: savefig() got unexpected keyword argument \"rasterize\" which is no longer supported as of 3.3 and will become an error two minor releases later\n"
],
[
"fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8,4))\nfig.set_facecolor('w')\nfor i in range(len(slopes_high)):\n plt.errorbar((temp_bins[i]+temp_bins[i+1])/2.0, \n slopes_high[i], yerr=errs_high[i], marker='o', color='k')\n plt.errorbar((temp_bins[i]+temp_bins[i+1])/2.0, \n slopes_low[i], yerr=errs_low[i], marker='o', color='deepskyblue')\n \nplt.plot(1,1,'ko', label='RUWE >= {}'.format(ruwe_cutoff))\nplt.plot(1,1,'o', c='deepskyblue', label='RUWE < 2.0')\nplt.legend()\nplt.ylim(-2.5,-5)\nplt.ylabel('FFD Slope')\nplt.xlim(3000,9500)\nplt.xlabel('Median of T$_{eff}$ Bin [K]')\nplt.savefig('ruwe.png', dpi=250, rasterize=True, bbox_inches='tight')",
"//anaconda3/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:16: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning: savefig() got unexpected keyword argument \"rasterize\" which is no longer supported as of 3.3 and will become an error two minor releases later\n app.launch_new_instance()\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c501ec470159a531c5cf3bc8c97cd0b3de111897
| 550,127 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Notebooks/brri-dataset/dataset_preprocessing/brri-dataset_exploration.ipynb
|
ferdouszislam/Weather-WaterLevel-Prediction-ML
|
9ab40b0a6661d3885dc77497048fcb9e7d4b00f6
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Notebooks/brri-dataset/dataset_preprocessing/brri-dataset_exploration.ipynb
|
ferdouszislam/Weather-WaterLevel-Prediction-ML
|
9ab40b0a6661d3885dc77497048fcb9e7d4b00f6
|
[
"MIT"
] | 14 |
2021-11-07T13:36:51.000Z
|
2021-12-22T17:16:20.000Z
|
Notebooks/brri-dataset/dataset_preprocessing/brri-dataset_exploration.ipynb
|
ferdouszislam/Weather-Prediction-ML
|
9ab40b0a6661d3885dc77497048fcb9e7d4b00f6
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2022-01-28T14:19:41.000Z
|
2022-01-28T14:19:41.000Z
| 238.356586 | 181,992 | 0.892398 |
[
[
[
"# required for jupyter notebook\n%matplotlib inline \n\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\nimport seaborn as sns\nsns.set(rc={'figure.figsize':(8,6)}) # set sns figure size\n\nimport os\nimport math",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def show_corr_heatmap(df):\n # https://medium.com/@szabo.bibor/how-to-create-a-seaborn-correlation-heatmap-in-python-834c0686b88e\n\n plt.figure(figsize=(20, 10))\n\n corr_matrix = df.corr()\n\n # mask to hide the upper triangle of the symmetric corr-matrix\n # mask = np.triu(np.ones_like(corr_matrix, dtype=np.bool))\n\n heatmap = sns.heatmap(\n\n # correlation matrix\n corr_matrix,\n\n # mask the top triangle of the matrix\n # mask=mask,\n\n # two-contrast color, different color for + -\n cmap=\"PiYG\",\n\n # color map range\n vmin=-1, vmax=1,\n\n # show corr values in the cells\n annot=True\n )\n\n # set a title\n heatmap.set_title('Correlation Heatmap', fontdict={'fontsize':20}, pad=16);\n\n plt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# read raw csv by marking dropping missing values\nmissing_values = ['NIL', 'nil', '']\nraw_df = pd.read_csv(os.path.join('..', '..', 'Datasets', 'brri-datasets', 'all-station_raw.csv'), \n na_values=missing_values)\n\nraw_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"raw_df.info()",
"<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>\nRangeIndex: 4954 entries, 0 to 4953\nData columns (total 13 columns):\n # Column Non-Null Count Dtype \n--- ------ -------------- ----- \n 0 Station 4954 non-null object \n 1 Year 4954 non-null int64 \n 2 Month 4954 non-null int64 \n 3 Day 4954 non-null int64 \n 4 Max Temp. (degree Celcius) 4948 non-null float64\n 5 Min Temp. (degree Celcius) 4948 non-null float64\n 6 Rainfall (mm) 4820 non-null float64\n 7 Actual Evaporation (mm) 4436 non-null float64\n 8 Relative Humidity (morning, %) 4950 non-null float64\n 9 Relative Humidity (afternoon, %) 4918 non-null float64\n 10 Sunshine (hour/day) 4939 non-null float64\n 11 Cloudy (hour/day) 4767 non-null float64\n 12 Solar Radiation (cal/cm^2/day) 4948 non-null float64\ndtypes: float64(9), int64(3), object(1)\nmemory usage: 503.3+ KB\n"
],
[
"def show_max_min(_df):\n df = _df.copy()\n for column in df.columns:\n print(f'{column}: max={raw_df[column].max()}, min={raw_df[column].min()}\\n')\n \n# show_max_min(raw_df)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Drop invalid datas**\n- Drop Max/Min Temp > 50 \n- Relative Humidity (afternoon, %) > 100, \n- Sunshine/Cloudy (hour/day) > 24, \n- Solar Radiation (cal/cm^2/day) > 20000 (from the box plot)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# _=raw_df.boxplot(column=['Solar Radiation (cal/cm^2/day)'], vert=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"raw_df.drop(raw_df.index[raw_df['Max Temp. (degree Celcius)'] > 50], inplace=True)\nraw_df.drop(raw_df.index[raw_df['Min Temp. (degree Celcius)'] > 50], inplace=True)\nraw_df.drop(raw_df.index[raw_df['Relative Humidity (afternoon, %)'] > 100], inplace=True)\nraw_df.drop(raw_df.index[raw_df['Sunshine (hour/day)'] > 24], inplace=True)\nraw_df.drop(raw_df.index[raw_df['Cloudy (hour/day)'] > 24], inplace=True)\nraw_df.drop(raw_df.index[raw_df['Solar Radiation (cal/cm^2/day)'] > 20000], inplace=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# show_max_min(raw_df)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# _=raw_df.boxplot(column=['Solar Radiation (cal/cm^2/day)'], vert=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# len(raw_df[raw_df['Solar Radiation (cal/cm^2/day)']>1000])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Drop 'Solar Radiation (cal/cm^2/day)' > 1000**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"raw_df.drop(raw_df.index[raw_df['Solar Radiation (cal/cm^2/day)'] > 1000], inplace=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# show_max_min(raw_df)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# _=raw_df.boxplot(column=['Solar Radiation (cal/cm^2/day)'], vert=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Get station-wise dataframes",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# read Gazipur raw csv by marking dropping missing values\ngazipur_raw_df = raw_df[raw_df['Station']=='Gazipur']\n\ngazipur_raw_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# read Rangpur raw csv by marking dropping missing values\nrangpur_raw_df = raw_df[raw_df['Station']=='Rangpur']\n\nrangpur_raw_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# read Barisal raw csv by marking dropping missing values\nbarisal_raw_df = raw_df[raw_df['Station']=='Barisal']\n\nbarisal_raw_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# read Habiganj raw csv by marking dropping missing values\nhabiganj_raw_df = raw_df[raw_df['Station']=='Habiganj']\n\nhabiganj_raw_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def get_val_freq_map(df, column):\n '''\n get map of value counts of a dataframe for a particular column\n '''\n mp = {}\n for val in raw_df[column]:\n if val in mp:\n mp[val]+=1\n else:\n mp[val]=1\n return mp",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Analyze all station Rainfall data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"rainfall_column = 'Rainfall (mm)'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"rainfall_df = raw_df[[rainfall_column]].copy()\nrainfall_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"rainfall_df.value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(rainfall_df.max())",
"Rainfall (mm) 265.0\ndtype: float64\n"
],
[
"rainfall_df[rainfall_column].hist(bins=10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def group_column_vals(df, column, diff=10):\n group_labels = []\n group_freqs = []\n\n length = math.ceil(df[column].max()/diff)\n\n for i in range(length+1):\n group_freqs.append(0)\n if i==0:\n group_labels.append('0')\n else:\n group_labels.append(str(1+(i-1)*diff) + '-' + str(i*diff))\n\n for val in df[column]:\n if math.isnan(val):\n continue\n group_freqs[math.ceil(val/diff)]+=1\n \n mp = {}\n total_freq = sum(group_freqs)\n for i in range(length+1):\n # store percantage of each group\n mp[group_labels[i]] = round((group_freqs[i]/total_freq) * 100, 2) \n \n return mp",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"group_column_vals(df=rainfall_df, column=rainfall_column, diff=20)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Analyze Staion-wise Rainfall",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Gazipur",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"gazipur_rainfall_df = gazipur_raw_df[[rainfall_column]].copy()\n# gazipur_rainfall_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"gazipur_rainfall_df[rainfall_column].hist(bins=10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"group_column_vals(gazipur_rainfall_df, rainfall_column, 20)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Rangpur",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"rangpur_rainfall_df = rangpur_raw_df[[rainfall_column]].copy()\n# rangpur_rainfall_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"rangpur_rainfall_df[rainfall_column].hist(bins=10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"group_column_vals(rangpur_rainfall_df, rainfall_column, 20)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Barisal",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"barisal_rainfall_df = barisal_raw_df[[rainfall_column]].copy()\n# barisal_rainfall_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"barisal_rainfall_df[rainfall_column].hist(bins=10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"group_column_vals(barisal_rainfall_df, rainfall_column, 20)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Habiganj",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"habiganj_rainfall_df = habiganj_raw_df[[rainfall_column]].copy()\n# habiganj_rainfall_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"habiganj_rainfall_df[rainfall_column].hist(bins=10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"group_column_vals(habiganj_rainfall_df, rainfall_column, 20)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Analyze Rainfall Per Year",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"raw_df_2016 = raw_df[raw_df['Year']==2016]\nraw_df_2017 = raw_df[raw_df['Year']==2017]\nraw_df_2018 = raw_df[raw_df['Year']==2018]\nraw_df_2019 = raw_df[raw_df['Year']==2019]\nraw_df_2020 = raw_df[raw_df['Year']==2020]\n\n# raw_df_2020.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Year 2016",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# raw_df_2016[rainfall_column].hist(bins=10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"group_column_vals(raw_df_2016, rainfall_column, 20)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Year 2017",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# raw_df_2017[rainfall_column].hist(bins=10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"group_column_vals(raw_df_2017, rainfall_column, 20)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Year 2018",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# raw_df_2018[rainfall_column].hist(bins=10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"group_column_vals(raw_df_2018, rainfall_column, 20)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Year 2019",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# raw_df_2019[rainfall_column].hist(bins=10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"group_column_vals(raw_df_2019, rainfall_column, 20)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Year 2020",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# raw_df_2020[rainfall_column].hist(bins=10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"group_column_vals(raw_df_2020, rainfall_column, 20)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Monthly Rainfall Analysis",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"raw_df_month = raw_df[raw_df['Month'].isin([5,6,7,8])] \nraw_df_month.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# raw_df_month[rainfall_column].hist(bins=10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"group_column_vals(raw_df_month, rainfall_column, 15)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Correlation Heatmap",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Whole dataset",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"show_corr_heatmap(raw_df)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Monthly dataset",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"show_corr_heatmap(raw_df_month)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Scatter plots",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"_=sns.scatterplot(data=raw_df, x='Month', y=rainfall_column, hue='Station')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"_=sns.scatterplot(data=raw_df, x='Year', y=rainfall_column, hue='Station')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# sns.pairplot(raw_df[['Rainfall (mm)', 'Month', 'Station']], hue = 'Station', height = 5)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c501ed647a27708d5b3dbc0320b8769cff8d1920
| 359,324 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
1-Machine Learning with Python/ML0108EN-Clus-K-Means-Customer-Seg-py-v1.ipynb
|
bcosta12/ibm-ai-engineering
|
35599281eb3662aeb8cc943f149289fa0b43c072
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
1-Machine Learning with Python/ML0108EN-Clus-K-Means-Customer-Seg-py-v1.ipynb
|
bcosta12/ibm-ai-engineering
|
35599281eb3662aeb8cc943f149289fa0b43c072
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
1-Machine Learning with Python/ML0108EN-Clus-K-Means-Customer-Seg-py-v1.ipynb
|
bcosta12/ibm-ai-engineering
|
35599281eb3662aeb8cc943f149289fa0b43c072
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 224.858573 | 135,148 | 0.900822 |
[
[
[
"<a href=\"https://www.bigdatauniversity.com\"><img src=\"https://ibm.box.com/shared/static/cw2c7r3o20w9zn8gkecaeyjhgw3xdgbj.png\" width=\"400\" align=\"center\"></a>\n\n<h1><center>K-Means Clustering</center></h1>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Introduction\n\nThere are many models for **clustering** out there. In this notebook, we will be presenting the model that is considered one of the simplest models amongst them. Despite its simplicity, the **K-means** is vastly used for clustering in many data science applications, especially useful if you need to quickly discover insights from **unlabeled data**. In this notebook, you will learn how to use k-Means for customer segmentation.\n\nSome real-world applications of k-means:\n- Customer segmentation\n- Understand what the visitors of a website are trying to accomplish\n- Pattern recognition\n- Machine learning\n- Data compression\n\n\nIn this notebook we practice k-means clustering with 2 examples:\n- k-means on a random generated dataset\n- Using k-means for customer segmentation",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<h1>Table of contents</h1>\n\n<div class=\"alert alert-block alert-info\" style=\"margin-top: 20px\">\n <ul>\n <li><a href=\"#random_generated_dataset\">k-Means on a randomly generated dataset</a></li>\n <ol>\n <li><a href=\"#setting_up_K_means\">Setting up K-Means</a></li>\n <li><a href=\"#creating_visual_plot\">Creating the Visual Plot</a></li>\n </ol>\n <li><a href=\"#customer_segmentation_K_means\">Customer Segmentation with K-Means</a></li>\n <ol>\n <li><a href=\"#pre_processing\">Pre-processing</a></li>\n <li><a href=\"#modeling\">Modeling</a></li>\n <li><a href=\"#insights\">Insights</a></li>\n </ol>\n </ul>\n</div>\n<br>\n<hr>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Import libraries\nLets first import the required libraries.\nAlso run <b> %matplotlib inline </b> since we will be plotting in this section.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import random \nimport numpy as np \nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt \nfrom sklearn.cluster import KMeans \nfrom sklearn.datasets.samples_generator import make_blobs \n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<h1 id=\"random_generated_dataset\">k-Means on a randomly generated dataset</h1>\nLets create our own dataset for this lab!\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"First we need to set up a random seed. Use <b>numpy's random.seed()</b> function, where the seed will be set to <b>0</b>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.random.seed(0)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Next we will be making <i> random clusters </i> of points by using the <b> make_blobs </b> class. The <b> make_blobs </b> class can take in many inputs, but we will be using these specific ones. <br> <br>\n<b> <u> Input </u> </b>\n<ul>\n <li> <b>n_samples</b>: The total number of points equally divided among clusters. </li>\n <ul> <li> Value will be: 5000 </li> </ul>\n <li> <b>centers</b>: The number of centers to generate, or the fixed center locations. </li>\n <ul> <li> Value will be: [[4, 4], [-2, -1], [2, -3],[1,1]] </li> </ul>\n <li> <b>cluster_std</b>: The standard deviation of the clusters. </li>\n <ul> <li> Value will be: 0.9 </li> </ul>\n</ul>\n<br>\n<b> <u> Output </u> </b>\n<ul>\n <li> <b>X</b>: Array of shape [n_samples, n_features]. (Feature Matrix)</li>\n <ul> <li> The generated samples. </li> </ul> \n <li> <b>y</b>: Array of shape [n_samples]. (Response Vector)</li>\n <ul> <li> The integer labels for cluster membership of each sample. </li> </ul>\n</ul>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"X, y = make_blobs(n_samples=5000, centers=[[4,4], [-2, -1], [2, -3], [1, 1]], cluster_std=0.9)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Display the scatter plot of the randomly generated data.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], marker='.')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<h2 id=\"setting_up_K_means\">Setting up K-Means</h2>\nNow that we have our random data, let's set up our K-Means Clustering.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The KMeans class has many parameters that can be used, but we will be using these three:\n<ul>\n <li> <b>init</b>: Initialization method of the centroids. </li>\n <ul>\n <li> Value will be: \"k-means++\" </li>\n <li> k-means++: Selects initial cluster centers for k-mean clustering in a smart way to speed up convergence.</li>\n </ul>\n <li> <b>n_clusters</b>: The number of clusters to form as well as the number of centroids to generate. </li>\n <ul> <li> Value will be: 4 (since we have 4 centers)</li> </ul>\n <li> <b>n_init</b>: Number of time the k-means algorithm will be run with different centroid seeds. The final results will be the best output of n_init consecutive runs in terms of inertia. </li>\n <ul> <li> Value will be: 12 </li> </ul>\n</ul>\n\nInitialize KMeans with these parameters, where the output parameter is called <b>k_means</b>.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"k_means = KMeans(init = \"k-means++\", n_clusters = 4, n_init = 12)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now let's fit the KMeans model with the feature matrix we created above, <b> X </b>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"k_means.fit(X)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now let's grab the labels for each point in the model using KMeans' <b> .labels\\_ </b> attribute and save it as <b> k_means_labels </b> ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"k_means_labels = k_means.labels_\nk_means_labels",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We will also get the coordinates of the cluster centers using KMeans' <b> .cluster_centers_ </b> and save it as <b> k_means_cluster_centers </b>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"k_means_cluster_centers = k_means.cluster_centers_\nk_means_cluster_centers",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<h2 id=\"creating_visual_plot\">Creating the Visual Plot</h2>\nSo now that we have the random data generated and the KMeans model initialized, let's plot them and see what it looks like!",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Please read through the code and comments to understand how to plot the model.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Initialize the plot with the specified dimensions.\nfig = plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4))\n\n# Colors uses a color map, which will produce an array of colors based on\n# the number of labels there are. We use set(k_means_labels) to get the\n# unique labels.\ncolors = plt.cm.Spectral(np.linspace(0, 1, len(set(k_means_labels))))\n\n# Create a plot\nax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)\n\n# For loop that plots the data points and centroids.\n# k will range from 0-3, which will match the possible clusters that each\n# data point is in.\nfor k, col in zip(range(len([[4,4], [-2, -1], [2, -3], [1, 1]])), colors):\n\n # Create a list of all data points, where the data poitns that are \n # in the cluster (ex. cluster 0) are labeled as true, else they are\n # labeled as false.\n my_members = (k_means_labels == k)\n \n # Define the centroid, or cluster center.\n cluster_center = k_means_cluster_centers[k]\n \n # Plots the datapoints with color col.\n ax.plot(X[my_members, 0], X[my_members, 1], 'w', markerfacecolor=col, marker='.')\n \n # Plots the centroids with specified color, but with a darker outline\n ax.plot(cluster_center[0], cluster_center[1], 'o', markerfacecolor=col, markeredgecolor='k', markersize=6)\n\n# Title of the plot\nax.set_title('KMeans')\n\n# Remove x-axis ticks\nax.set_xticks(())\n\n# Remove y-axis ticks\nax.set_yticks(())\n\n# Show the plot\nplt.show()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Practice\nTry to cluster the above dataset into 3 clusters. \nNotice: do not generate data again, use the same dataset as above.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"k_means3 = KMeans(init = \"k-means++\", n_clusters = 3, n_init = 12)\nk_means3.fit(X)\nfig = plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4))\ncolors = plt.cm.Spectral(np.linspace(0, 1, len(set(k_means3.labels_))))\nax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)\nfor k, col in zip(range(len(k_means3.cluster_centers_)), colors):\n my_members = (k_means3.labels_ == k)\n cluster_center = k_means3.cluster_centers_[k]\n ax.plot(X[my_members, 0], X[my_members, 1], 'w', markerfacecolor=col, marker='.')\n ax.plot(cluster_center[0], cluster_center[1], 'o', markerfacecolor=col, markeredgecolor='k', markersize=6)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Double-click __here__ for the solution.\n\n<!-- Your answer is below:\n\nk_means3 = KMeans(init = \"k-means++\", n_clusters = 3, n_init = 12)\nk_means3.fit(X)\nfig = plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4))\ncolors = plt.cm.Spectral(np.linspace(0, 1, len(set(k_means3.labels_))))\nax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)\nfor k, col in zip(range(len(k_means3.cluster_centers_)), colors):\n my_members = (k_means3.labels_ == k)\n cluster_center = k_means3.cluster_centers_[k]\n ax.plot(X[my_members, 0], X[my_members, 1], 'w', markerfacecolor=col, marker='.')\n ax.plot(cluster_center[0], cluster_center[1], 'o', markerfacecolor=col, markeredgecolor='k', markersize=6)\nplt.show()\n\n\n-->",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<h1 id=\"customer_segmentation_K_means\">Customer Segmentation with K-Means</h1>\nImagine that you have a customer dataset, and you need to apply customer segmentation on this historical data.\nCustomer segmentation is the practice of partitioning a customer base into groups of individuals that have similar characteristics. It is a significant strategy as a business can target these specific groups of customers and effectively allocate marketing resources. For example, one group might contain customers who are high-profit and low-risk, that is, more likely to purchase products, or subscribe for a service. A business task is to retaining those customers. Another group might include customers from non-profit organizations. And so on.\n\nLets download the dataset. To download the data, we will use **`!wget`** to download it from IBM Object Storage. \n__Did you know?__ When it comes to Machine Learning, you will likely be working with large datasets. As a business, where can you host your data? IBM is offering a unique opportunity for businesses, with 10 Tb of IBM Cloud Object Storage: [Sign up now for free](http://cocl.us/ML0101EN-IBM-Offer-CC)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!wget -O Cust_Segmentation.csv https://s3-api.us-geo.objectstorage.softlayer.net/cf-courses-data/CognitiveClass/ML0101ENv3/labs/Cust_Segmentation.csv",
"--2020-02-25 02:58:58-- https://s3-api.us-geo.objectstorage.softlayer.net/cf-courses-data/CognitiveClass/ML0101ENv3/labs/Cust_Segmentation.csv\nResolving s3-api.us-geo.objectstorage.softlayer.net (s3-api.us-geo.objectstorage.softlayer.net)... 67.228.254.196\nConnecting to s3-api.us-geo.objectstorage.softlayer.net (s3-api.us-geo.objectstorage.softlayer.net)|67.228.254.196|:443... connected.\nHTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK\nLength: 34276 (33K) [text/csv]\nSaving to: ‘Cust_Segmentation.csv’\n\nCust_Segmentation.c 100%[===================>] 33.47K --.-KB/s in 0.02s \n\n2020-02-25 02:58:58 (1.50 MB/s) - ‘Cust_Segmentation.csv’ saved [34276/34276]\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Load Data From CSV File \nBefore you can work with the data, you must use the URL to get the Cust_Segmentation.csv.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\ncust_df = pd.read_csv(\"Cust_Segmentation.csv\")\ncust_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<h2 id=\"pre_processing\">Pre-processing</h2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"As you can see, __Address__ in this dataset is a categorical variable. k-means algorithm isn't directly applicable to categorical variables because Euclidean distance function isn't really meaningful for discrete variables. So, lets drop this feature and run clustering.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df = cust_df.drop('Address', axis=1)\ndf.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Normalizing over the standard deviation\nNow let's normalize the dataset. But why do we need normalization in the first place? Normalization is a statistical method that helps mathematical-based algorithms to interpret features with different magnitudes and distributions equally. We use __StandardScaler()__ to normalize our dataset.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler\nX = df.values[:,1:]\nX = np.nan_to_num(X)\nClus_dataSet = StandardScaler().fit_transform(X)\nClus_dataSet",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<h2 id=\"modeling\">Modeling</h2>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In our example (if we didn't have access to the k-means algorithm), it would be the same as guessing that each customer group would have certain age, income, education, etc, with multiple tests and experiments. However, using the K-means clustering we can do all this process much easier.\n\nLets apply k-means on our dataset, and take look at cluster labels.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"clusterNum = 3\nk_means = KMeans(init = \"k-means++\", n_clusters = clusterNum, n_init = 12)\nk_means.fit(X)\nlabels = k_means.labels_\nprint(labels)",
"[0 2 0 0 1 2 0 2 0 2 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 2 2 2 0 0 2 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0\n 0 0 2 0 2 0 1 0 2 0 0 0 2 2 0 0 2 2 0 0 0 2 0 2 0 2 2 0 0 2 0 0 0 2 2 2 0\n 0 0 0 0 2 0 2 2 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0\n 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 2 0\n 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 2 2 0 2 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 2 0\n 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 2 0 2 0 0 2 1 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 2 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 2 2 0 2 0 2\n 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0\n 0 0 2 0 0 2 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 2 0 2 0 2 0 2 2 0 0 0 0 0 0\n 0 0 0 2 2 2 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 2 2 0\n 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 2 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 2 0 2 2 2 0\n 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0\n 0 2 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 1\n 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 2 0 1 0 0 0 0 2 0 2 2 2 0 0 2 2 0 0 0 0 0 0\n 0 2 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 2 0 2 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 2 2 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0\n 0 2 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 2 0 0 1 0 1 0\n 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 2 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 2\n 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 2 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2\n 2 0 0 2 0 2 0 0 2 0 2 0 0 1 0 2 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 2 2 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 2 2 0 0\n 2 0 0 0 2 0 1 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0\n 0 0 2 0 0 2 0 2 0 2 2 0 0 0 2 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 2 2 0 0 2 2 0 0 0 0\n 0 2 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 2 2 0 2 0 2 2 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 2 2\n 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 2 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0\n 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2]\n"
]
],
[
[
"<h2 id=\"insights\">Insights</h2>\nWe assign the labels to each row in dataframe.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df[\"Clus_km\"] = labels\ndf.head(5)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can easily check the centroid values by averaging the features in each cluster.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df.groupby('Clus_km').mean()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now, lets look at the distribution of customers based on their age and income:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"area = np.pi * ( X[:, 1])**2 \nplt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 3], s=area, c=labels.astype(np.float), alpha=0.5)\nplt.xlabel('Age', fontsize=18)\nplt.ylabel('Income', fontsize=16)\n\nplt.show()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D \nfig = plt.figure(1, figsize=(8, 6))\nplt.clf()\nax = Axes3D(fig, rect=[0, 0, .95, 1], elev=48, azim=134)\n\nplt.cla()\n# plt.ylabel('Age', fontsize=18)\n# plt.xlabel('Income', fontsize=16)\n# plt.zlabel('Education', fontsize=16)\nax.set_xlabel('Education')\nax.set_ylabel('Age')\nax.set_zlabel('Income')\n\nax.scatter(X[:, 1], X[:, 0], X[:, 3], c= labels.astype(np.float))\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"k-means will partition your customers into mutually exclusive groups, for example, into 3 clusters. The customers in each cluster are similar to each other demographically.\nNow we can create a profile for each group, considering the common characteristics of each cluster. \nFor example, the 3 clusters can be:\n\n- AFFLUENT, EDUCATED AND OLD AGED\n- MIDDLE AGED AND MIDDLE INCOME\n- YOUNG AND LOW INCOME",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<h2>Want to learn more?</h2>\n\nIBM SPSS Modeler is a comprehensive analytics platform that has many machine learning algorithms. It has been designed to bring predictive intelligence to decisions made by individuals, by groups, by systems – by your enterprise as a whole. A free trial is available through this course, available here: <a href=\"http://cocl.us/ML0101EN-SPSSModeler\">SPSS Modeler</a>\n\nAlso, you can use Watson Studio to run these notebooks faster with bigger datasets. Watson Studio is IBM's leading cloud solution for data scientists, built by data scientists. With Jupyter notebooks, RStudio, Apache Spark and popular libraries pre-packaged in the cloud, Watson Studio enables data scientists to collaborate on their projects without having to install anything. Join the fast-growing community of Watson Studio users today with a free account at <a href=\"https://cocl.us/ML0101EN_DSX\">Watson Studio</a>\n\n<h3>Thanks for completing this lesson!</h3>\n\n<h4>Author: <a href=\"https://ca.linkedin.com/in/saeedaghabozorgi\">Saeed Aghabozorgi</a></h4>\n<p><a href=\"https://ca.linkedin.com/in/saeedaghabozorgi\">Saeed Aghabozorgi</a>, PhD is a Data Scientist in IBM with a track record of developing enterprise level applications that substantially increases clients’ ability to turn data into actionable knowledge. He is a researcher in data mining field and expert in developing advanced analytic methods like machine learning and statistical modelling on large datasets.</p>\n\n<hr>\n\n<p>Copyright © 2018 <a href=\"https://cocl.us/DX0108EN_CC\">Cognitive Class</a>. This notebook and its source code are released under the terms of the <a href=\"https://bigdatauniversity.com/mit-license/\">MIT License</a>.</p>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
c501f79f9b9b5357fca35e360b018ed6d5a426d2
| 146,996 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
unit1/Unit1-simple-regression.ipynb
|
areding/6420-pymc
|
181ee40b8bf4a2c9fb237c4d388c4f62ea41bfeb
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 2 |
2022-01-23T00:16:39.000Z
|
2022-02-26T23:44:38.000Z
|
unit1/Unit1-simple-regression.ipynb
|
areding/6420-pymc
|
181ee40b8bf4a2c9fb237c4d388c4f62ea41bfeb
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2022-01-11T03:31:11.000Z
|
2022-01-11T03:31:11.000Z
|
unit1/Unit1-simple-regression.ipynb
|
areding/6420-pymc
|
181ee40b8bf4a2c9fb237c4d388c4f62ea41bfeb
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 273.735568 | 106,944 | 0.918562 |
[
[
[
"from warnings import filterwarnings\n\nimport arviz as az\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport pymc as pm\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression\n\n%load_ext lab_black\n%load_ext watermark",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"filterwarnings(\"ignore\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# A Simple Regression\n\nFrom [Codes for Unit 1](https://www2.isye.gatech.edu/isye6420/supporting.html).\n\nAssociated lecture video: Unit 1 Lesson 4\n\nYou don't usually need to set inits in PyMC. The default method of generating inits is 'jitter+adapt_diag', which chooses them based on the model and input data while adding some randomness.\n\nIf you do want to set an initial value, pass a dictionary to the start parameter of pm.sample.\n\n```python\ninits = {\n \"alpha\": np.array(0.0),\n \"beta\": np.array(0.0)\n}\n\ntrace = pm.sample(2000, start=inits)\n```\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"X = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])\ny = np.array([1, 3, 3, 3, 5])\nx_bar = np.mean(X)\n\nwith pm.Model() as m:\n # priors\n alpha = pm.Normal(\"alpha\", sigma=100)\n beta = pm.Normal(\"beta\", sigma=100)\n # using precision for direct comparison with BUGS output\n tau = pm.Gamma(\"tau\", alpha=0.001, beta=0.001)\n sigma = 1 / pm.math.sqrt(tau)\n\n mu = alpha + beta * (X - x_bar)\n likelihood = pm.Normal(\"likelihood\", mu=mu, sigma=sigma, observed=y)\n\n # start sampling\n trace = pm.sample(\n 3000, # samples\n chains=4,\n tune=500,\n init=\"jitter+adapt_diag\",\n random_seed=1,\n cores=4, # parallel processing of chains\n return_inferencedata=True, # return arviz inferencedata object\n )",
"Auto-assigning NUTS sampler...\nInitializing NUTS using jitter+adapt_diag...\nMultiprocess sampling (4 chains in 4 jobs)\nNUTS: [alpha, beta, tau]\n"
]
],
[
[
"PyMC3 uses the tuning step specified in the pm.sample call to adjust various parameters in the No-U-Turn Sampler [(NUTS) algorithm](https://arxiv.org/abs/1111.4246), which is a form of Hamiltonian Monte Carlo. BUGS also silently uses different types of tuning depending on the algorithm it [chooses](https://www.york.ac.uk/depts/maths/histstat/pml1/bayes/winbugsinfo/cowles_winbugs.pdf). The professor often burns some number of samples in his examples. Note that this is separate from the tuning phase for both programs!\n\nFor some more detail on tuning, see [this post](https://colcarroll.github.io/hmc_tuning_talk/).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# this burns the first 500 samples\ntrace_burned = trace.sel(draw=slice(500, None))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Arviz has a variety of functions to view the results of the model. One of the most useful is az.summary. Professor Vidakovic arbitrarily asks for the 95% credible set (also called the highest density interval), so we can specify hdi_prob=.95 to get that. This is the HPD, or minimum-width, credible set.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"az.summary(trace_burned, hdi_prob=0.95)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You can also get the HDIs directly:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"az.hdi(trace_burned, hdi_prob=0.95)[\"beta\"].values",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"There are a variety of plots available. Commonly used to diagnose problems are the trace (see [When Traceplots go Bad](https://jpreszler.rbind.io/post/2019-09-28-bad-traceplots/)) and rank plots (see the Maybe it's time to let traceplots die section from [this post](https://statmodeling.stat.columbia.edu/2019/03/19/maybe-its-time-to-let-the-old-ways-die-or-we-broke-r-hat-so-now-we-have-to-fix-it/)).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"az.plot_trace(trace_burned)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"az.plot_rank(trace_burned)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"There are many ways to manipulate Arviz [InferenceData](https://arviz-devs.github.io/arviz/api/generated/arviz.InferenceData.html) objects to calculate statistics after sampling is complete.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# alpha - beta * x.bar\nintercept = (\n trace_burned.posterior.alpha.mean() - trace_burned.posterior.beta.mean() * x_bar\n)\nintercept.values",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"OpenBugs results:\n\n| | mean | sd | MC_error | val2.5pc | median | val97.5pc | start | sample |\n|-------|--------|--------|----------|----------|--------|-----------|-------|--------|\n| alpha | 2.995 | 0.5388 | 0.005863 | 1.947 | 3.008 | 4.015 | 1000 | 9001 |\n| beta | 0.7963 | 0.3669 | 0.003795 | 0.08055 | 0.7936 | 1.526 | 1000 | 9001 |\n| tau | 1.88 | 1.524 | 0.02414 | 0.1416 | 1.484 | 5.79 | 1000 | 9001 |\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Sometimes you might want to do a sanity check with classical regression. If your Bayesian regression has noninformative priors, the results should be close.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"reg = LinearRegression().fit(X.reshape(-1, 1), y)\n# compare with intercept and beta from above\nreg.intercept_, reg.coef_",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%watermark --iversions -v",
"Python implementation: CPython\nPython version : 3.10.4\nIPython version : 8.4.0\n\narviz : 0.12.1\nmatplotlib: 3.5.2\nnumpy : 1.22.4\npymc : 4.0.0\n\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c501f933821ee58fd21467dd9e1a5af8e02c1c07
| 209,123 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
content/teaching/2021-solving-problems/Tutorials/Fermions_in_double_well_qiskit.ipynb
|
mr128254/synqs.github.io
|
eff6b488472320b08af458e0ae5b3456c91c78f7
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
content/teaching/2021-solving-problems/Tutorials/Fermions_in_double_well_qiskit.ipynb
|
mr128254/synqs.github.io
|
eff6b488472320b08af458e0ae5b3456c91c78f7
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
content/teaching/2021-solving-problems/Tutorials/Fermions_in_double_well_qiskit.ipynb
|
mr128254/synqs.github.io
|
eff6b488472320b08af458e0ae5b3456c91c78f7
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 323.219474 | 40,004 | 0.933025 |
[
[
[
"# Example Notebook for the tunneling Fermions\n\nThis Notebook is based on the following [paper](https://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.114.080402) from the Jochim group. In these experiments two fermions of different spins are put into a single tweezer and then coupled to a second tweezer. The dynamics is then controlled by two competing effects. The interactions and the tunneling. \n\nLet us first start by looking at the data, then look how the can be described in the Hamiltonian language and finally in the gate language.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\n\nimport pandas as pd",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data_murmann_no_int = pd.read_csv('Data/Murmann_No_Int.csv', names = ['time', \"nR\"])\ndata_murmann_with_int = pd.read_csv('Data/Murmann_With_Int.csv', names = ['time', \"nR\"])\n\n#plt.figure(dpi=96)\nf, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(2,1, sharex = True, sharey = True);\nax1.plot(data_murmann_no_int.time, data_murmann_no_int.nR, 'ro', label=\"U = 0\", markersize=4)\nax2.plot(data_murmann_with_int.time, data_murmann_with_int.nR, 'bo', label=\"U = J\", markersize=4)\nax1.set_ylabel(r'atoms in right valley')\nax2.set_ylabel(r'atoms in right valley')\nax2.set_xlabel(r'time (ms)')\nax1.legend()\nax2.legend()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Analytical prediction\n\nFor the two atoms the Hamiltonian can be written down in the basis $\\{LL, LR, RL, RR\\}$ as:\n \n$$\nH = \\left(\\begin{array}{cccc}\nU & -J & -J & 0\\\\\n-J & 0 & 0 &-J\\\\\n-J & 0 & 0 &-J\\\\\n0 & -J & -J & U\n \\end{array}\n \\right)\n$$\n\nAnd we start out in the basis state $|LL\\rangle$. So we can write",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from scipy.sparse.linalg import expm",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"J = np.pi*134; # in units of hbar\nU = 0.7*J;",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Nt_an = 50;\nt_analytical = np.linspace(0, 20, Nt_an)*1e-3;\nH_With_Int = np.array([[U, -J,-J,0],[-J,0,0,-J],[-J,0,0,-J],[0, -J,-J,U]])\nH_Wo_Int = np.array([[0, -J,-J,0],[-J,0,0,-J],[-J,0,0,-J],[0, -J,-J,0]])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"psi0 = np.zeros(4)*1j\npsi0[0] = 1.+0j\nprint(psi0)",
"[1.+0.j 0.+0.j 0.+0.j 0.+0.j]\n"
],
[
"psis_wo_int = 1j*np.zeros((4,Nt_an))\npsis_w_int = 1j*np.zeros((4,Nt_an))\n\nfor ii in np.arange(Nt_an):\n\n U_wo = expm(-1j*t_analytical[ii]*H_Wo_Int);\n psis_wo_int[:,ii] = np.dot(U_wo,psi0);\n \n U_w = expm(-1j*t_analytical[ii]*H_With_Int);\n psis_w_int[:,ii] = np.dot(U_w,psi0);\n\nps_wo = np.abs(psis_wo_int)**2\nps_w = np.abs(psis_w_int)**2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"nR_wo = ps_wo[1,:]+ps_wo[2,:]+2*ps_wo[3,:];\nnR_w = ps_w[1,:]+ps_w[2,:]+2*ps_w[3,:];",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"f, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(2,1, sharex = True, sharey = True);\nax1.plot(t_analytical*1e3, nR_wo, 'r-', label=\"U = 0\", linewidth=4, alpha = 0.5)\nax1.plot(data_murmann_no_int.time, data_murmann_no_int.nR, 'ro', label=\"U = 0\", markersize=4)\n\nax2.plot(t_analytical*1e3, nR_w, 'b-', label=\"U = 0\", linewidth=4, alpha = 0.5)\nax2.plot(data_murmann_with_int.time, data_murmann_with_int.nR, 'bo', label=\"U = J\", markersize=4)\nax1.set_ylabel(r'atoms in right valley')\nax2.set_ylabel(r'atoms in right valley')\nax2.set_xlabel(r'time (ms)')\nax2.set_xlim(0,20)\nax1.legend()\nax2.legend()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from qiskit_cold_atom.providers import ColdAtomProvider\n\nprovider = ColdAtomProvider()\nbackend = provider.get_backend(\"fermionic_tweezer_simulator\")\n\n# give initial occupations separated by spin species\nqc = backend.initialize_circuit([[1, 0,0,0], [1, 0,0,0]])\n\nqc.draw(output='mpl')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from qiskit_cold_atom.providers import ColdAtomProvider\n\nprovider = ColdAtomProvider()\nbackend = provider.get_backend(\"fermionic_tweezer_simulator\")\n\n# give initial occupations separated by spin species\nqc = backend.initialize_circuit([[1, 0,0,0], [1, 0,0,0]])\n\nqc.draw(output='mpl')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"initialize the full dynamics",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"time =3*1e-3;\n\nfrom qiskit_cold_atom.fermions.fermion_gate_library import FermiHubbard\n\nqc = backend.initialize_circuit([[1, 0,0,0], [1, 0,0,0]])\nall_modes=range(8)\n\nqc.append(FermiHubbard(num_modes=8, j=[J*time,0,0], u=U*time, mu=[0*time,0,0,0]), qargs=all_modes)\nqc.measure_all()\n# alternatively append the FH gate directly:\n# qc.FH(j=[0.5, 1., -1.], u=5., mu=[0., -1., 1., 0.], modes=all_modes)\n\nqc.draw(output='mpl')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"job = backend.run(qc, shots=100)\n\nprint(\"counts: \", job.result().get_counts())",
"counts: {'01000100': 82, '10000100': 7, '01001000': 6, '10001000': 5}\n"
],
[
"def get_left_right_occupation(counts):\n sum_counts = 0;\n nL = 0;\n nR = 0;\n for k, v in counts.items():\n # look for lefties\n sum_counts += v;\n if int(k[0]):\n nL += v\n if int(k[4]):\n nL += v\n if int(k[1]):\n nR += v\n if int(k[5]):\n nR += v\n return nL/sum_counts, nR/sum_counts",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"get_left_right_occupation(job.result().get_counts())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## No interaction\nIn a first set of experiments there are no interactions and the two atoms are simply allowed to hop. The experiment is then described by the following very simple circuit.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"now let us simulate the time evolution",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Ntimes = 25;\ntimes = np.linspace(0, 20, Ntimes)*1e-3;\nmeans = np.zeros(Ntimes);\nfor i in range(Ntimes):\n time = times[i]\n qc = backend.initialize_circuit([[1, 0,0,0], [1, 0,0,0]])\n all_modes=range(8)\n\n qc.append(FermiHubbard(num_modes=8, j=[J*time,0,0], u=0*time, mu=[0*time,0,0,0]), qargs=all_modes)\n qc.measure_all()\n job = backend.run(qc, shots=100)\n counts = job.result().get_counts()\n _, means[i] = get_left_right_occupation(counts)\n if i%10==0:\n print(\"step\", i)\n # Calculate the resulting states after each rotation\n ",
"step 0\nstep 10\nstep 20\n"
]
],
[
[
"and compare to the data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"f, ax1 = plt.subplots(1,1, sharex = True, sharey = True);\nax1.plot(times*1e3, means, 'r-', label=\"U = 0\", linewidth=4, alpha = 0.5)\nax1.plot(data_murmann_no_int.time, data_murmann_no_int.nR, 'ro', label=\"U = 0\", markersize=4)\nax1.set_xlim(0,20)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Hopping with interactions\n\nIn a next step the atoms are interacting. The circuit description of the experiment is the application of the hopping gate and the interaction gate. It can be written as",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Ntimes = 25;\ntimes = np.linspace(0, 20, Ntimes)*1e-3;\nmeans_int = np.zeros(Ntimes);\nfor i in range(Ntimes):\n time = times[i]\n qc = backend.initialize_circuit([[1, 0,0,0], [1, 0,0,0]])\n all_modes=range(8)\n\n qc.append(FermiHubbard(num_modes=8, j=[J*time,0,0], u=U*time, mu=[0*time,0,0,0]), qargs=all_modes)\n qc.measure_all()\n job = backend.run(qc, shots=100)\n counts = job.result().get_counts()\n _, means_int[i] = get_left_right_occupation(counts)\n if i%10==0:\n print(\"step\", i)\n # Calculate the resulting states after each rotation\n ",
"step 0\nstep 10\nstep 20\n"
]
],
[
[
"And we compare to the data to obtain",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"f, ax2 = plt.subplots(1,1, sharex = True, sharey = True);\n\nax2.plot(times*1e3, means_int, 'b-', label=\"simulation\", linewidth=4, alpha = 0.5)\nax2.plot(data_murmann_with_int.time, data_murmann_with_int.nR, 'bo', label=\"U = J\", markersize=4)\nax2.set_ylabel(r'atoms in right valley')\nax2.set_xlabel(r'time (ms)')\nax2.legend()\nax2.set_xlim(0,20)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Summary\n\nAnd finally we can compare the experimental data with all the descriptions.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"f, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(2,1, sharex = True, sharey = True);\n\n\nax1.plot(times*1e3, means, 'r-', label=\"qiskit\", linewidth=4, alpha = 0.5)\nax1.plot(t_analytical*1e3, nR_wo, 'r-.', label=\"analytical\", linewidth=4, alpha = 0.5)\nax1.plot(data_murmann_no_int.time, data_murmann_no_int.nR, 'ro', label=\"experiment\", markersize=4)\n\nax2.plot(times*1e3, means_int, 'b-', label=\"qiskit\", linewidth=4, alpha = 0.5)\nax2.plot(t_analytical*1e3, nR_w, 'b-.', label=\"analytical\", linewidth=4, alpha = 0.5)\nax2.plot(data_murmann_with_int.time, data_murmann_with_int.nR, 'bo', label=\"experiment\", markersize=4)\nax1.set_ylabel(r'atoms in right valley')\nax2.set_ylabel(r'atoms in right valley')\nax2.set_xlabel(r'time (ms)')\nax1.legend(loc='upper right')\nax2.legend(loc='upper right')\nax1.set_xlim(-1,20)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c501fac2c671bd06d999858d10d8a9a70b50e766
| 13,882 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
lessons/CRISP_DM/Removing Values - Solution.ipynb
|
ZacksAmber/Udacity-Data-Scientist
|
b21595413f21a1200fe0b46f47e747ca9bff8d1f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
lessons/CRISP_DM/Removing Values - Solution.ipynb
|
ZacksAmber/Udacity-Data-Scientist
|
b21595413f21a1200fe0b46f47e747ca9bff8d1f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
lessons/CRISP_DM/Removing Values - Solution.ipynb
|
ZacksAmber/Udacity-Data-Scientist
|
b21595413f21a1200fe0b46f47e747ca9bff8d1f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 24.311734 | 293 | 0.366878 |
[
[
[
"#### Removing Values\n\nYou have seen:\n\n1. sklearn break when introducing missing values\n2. reasons for dropping missing values\n\nIt is time to make sure you are comfortable with the methods for dropping missing values in pandas. You can drop values by row or by column, and you can drop based on whether **any** value is missing in a particular row or column or **all** are values in a row or column are missing.\n\nA useful set of many resources in pandas is available [here](https://chrisalbon.com/). Specifically, Chris takes a close look at missing values [here](https://chri}salbon.com/python/data_wrangling/pandas_dropping_column_and_rows/).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport RemovingValues as t\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n%matplotlib inline\n\nsmall_dataset = pd.DataFrame({'col1': [1, 2, np.nan, np.nan, 5, 6], \n 'col2': [7, 8, np.nan, 10, 11, 12],\n 'col3': [np.nan, 14, np.nan, 16, 17, 18]})\n\nsmall_dataset",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Question 1\n\n**1.** Drop any row with a missing value.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"all_drop = small_dataset.dropna()\n\n\n#print result\nall_drop",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"t.all_drop_test(all_drop) #test",
"Nice job! That looks right!\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### Question 2\n\n**2.** Drop only the row with all missing values.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"all_row = small_dataset.dropna(axis=0, how='all') #axis 0 specifies you drop, how all specifies that you \n\n\n#print result\nall_row",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"t.all_row_test(all_row) #test",
"Nice job! That looks right!\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### Question 3\n\n**3.** Drop only the rows with missing values in column 3.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"only3_drop = small_dataset.dropna(subset=['col3'], how='any')\n\n\n#print result\nonly3_drop",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"t.only3_drop_test(only3_drop) #test",
"Nice job! That looks right!\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### Question 4\n\n**4.** Drop only the rows with missing values in column 3 or column 1.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"only3or1_drop = small_dataset.dropna(subset=['col1', 'col3'], how='any')\n\n\n#print result\nonly3or1_drop",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"t.only3or1_drop_test(only3or1_drop) #test",
"Nice job! That looks right!\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c5020b851abfbdf9f34d062ed3ea9807f80ade12
| 805,565 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
enumeration.ipynb
|
seaneberhard/sassy
|
08762146edecd08df868c0e9a79969f7bea8cf3e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
enumeration.ipynb
|
seaneberhard/sassy
|
08762146edecd08df868c0e9a79969f7bea8cf3e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
enumeration.ipynb
|
seaneberhard/sassy
|
08762146edecd08df868c0e9a79969f7bea8cf3e
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 27.468374 | 120 | 0.475823 |
[
[
[
"Goal: Find a non-Schurian coherent set configuration / set association scheme\n\nVia a Hamming-type construction this would give a non-Schurian PCC with large automorphism group.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sassy import SAS",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## basic unit test\nX = SAS(6)\nX.separate([{1, 2}, {3, 4}, {5, 6}])\nX.wl_full(log_progress=True)\nX.summary()",
"WL step:\n"
]
],
[
[
"expected: $\\texttt{(6, 10, [1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 1, 1], True, True, 'C2 x S4')}$\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## $n \\leq 5$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"all_sas = []\nfor n in [1..5]:\n all_sas.extend(SAS.find_all(n, verbosity=2))",
"Searching for coherent refinements of <SAS of degree 1 and ranks [1, 1]>\nSummary: (1, 2, [1, 1], True, True, '1')\n"
],
[
"table([s.summary() for s in all_sas],\n header_row=('n', 'total rank', 'ranks', 'homogeneous?', 'schurian?', r'$\\mathrm{Aut}(\\mathfrak{X})$'))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"missing_schurians = [\n sch\n for n in [1..5]\n for gp in (SymmetricGroup(n).conjugacy_classes_subgroups() if n > 1 else [SymmetricGroup(1)])\n for sch in [SAS.orbital_scheme(gp)]\n if sch.automorphism_group() == gp\n if not(any(map(sch.is_isomorphic_to, all_sas)))\n]\nlen(missing_schurians)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## $n = 6$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"n = 6",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"all_sas = []\nall_sas.extend(SAS.find_all(n, verbosity=2))",
"Searching for coherent refinements of <SAS of degree 6 and ranks [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]>\nSummary: (6, 7, [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1], True, True, 'S6')\n"
],
[
"table([s.summary() for s in all_sas],\n header_row=('n', 'total rank', 'ranks', 'homogeneous?', 'schurian?', r'$\\mathrm{Aut}(\\mathfrak{X})$'))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"missing_schurians = [\n sch\n for gp in (SymmetricGroup(n).conjugacy_classes_subgroups() if n > 1 else [SymmetricGroup(1)])\n for sch in [SAS.orbital_scheme(gp)]\n if sch.automorphism_group() == gp\n if not(any(map(sch.is_isomorphic_to, all_sas)))\n]\nlen(missing_schurians)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## $n = 7$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"n = 7",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"all_sas = []\nall_sas.extend(SAS.find_all(n, verbosity=2))",
"Searching for coherent refinements of <SAS of degree 7 and ranks [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]>\nSummary: (7, 8, [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1], True, True, 'S7')\n"
],
[
"table([s.summary() for s in all_sas],\n header_row=('n', 'total rank', 'ranks', 'homogeneous?', 'schurian?', r'$\\mathrm{Aut}(\\mathfrak{X})$'))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"missing_schurians = [\n sch\n for gp in SymmetricGroup(n).conjugacy_classes_subgroups()\n for sch in [SAS.orbital_scheme(gp)]\n if sch.automorphism_group() == gp\n if not(any(map(sch.is_isomorphic_to, all_sas)))\n]\nlen(missing_schurians)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## $n = 8$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"n = 8",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"all_sas = []\nall_sas.extend(SAS.find_all(n, verbosity=2))",
"Searching for coherent refinements of <SAS of degree 8 and ranks [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]>\nSummary: (8, 9, [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1], True, True, 'S8')\n"
],
[
"table([s.summary() for s in all_sas])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"table([s.summary() for s in all_sas if not s.is_schurian()])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c5021ad0f8f59f29196249e1bcac3c45107e47ad
| 2,941 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
BCN activa 2- exploratory analytics.ipynb
|
katakulcsar/data_visualization_python
|
e58c6d71f72bce452a0225a4aada07f74a025715
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
BCN activa 2- exploratory analytics.ipynb
|
katakulcsar/data_visualization_python
|
e58c6d71f72bce452a0225a4aada07f74a025715
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
BCN activa 2- exploratory analytics.ipynb
|
katakulcsar/data_visualization_python
|
e58c6d71f72bce452a0225a4aada07f74a025715
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 18.042945 | 99 | 0.49915 |
[
[
[
"##Datos:\n ### https://www.kaggle.com/arjunprasadsarkhel/2021-olympics-in-tokyo?select=Medals.xlsx\n####https://www.kaggle.com/arjunprasadsarkhel/2021-olympics-in-tokyo?select=Athletes.xlsx",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import pandas as pd\n\nfrom pandas import read_excel\ndf_medals=read_excel('Medals.xlsx')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c502211479a89a82b5e746b6b1f498f155ab7426
| 43,289 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
PythonDataScienceHandbook-master/notebooks/02.06-Boolean-Arrays-and-Masks.ipynb
|
BioCogito/sagemakertest
|
76733c23287959f5080404b7db3ef53a80cdd83a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
PythonDataScienceHandbook-master/notebooks/02.06-Boolean-Arrays-and-Masks.ipynb
|
BioCogito/sagemakertest
|
76733c23287959f5080404b7db3ef53a80cdd83a
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2021-06-08T21:31:36.000Z
|
2022-01-13T01:42:22.000Z
|
PythonDataScienceHandbook-master/notebooks/02.06-Boolean-Arrays-and-Masks.ipynb
|
BioCogito/sagemakertest
|
76733c23287959f5080404b7db3ef53a80cdd83a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 30.832621 | 7,376 | 0.607429 |
[
[
[
"<!--BOOK_INFORMATION-->\n<img align=\"left\" style=\"padding-right:10px;\" src=\"figures/PDSH-cover-small.png\">\n\n*This notebook contains an excerpt from the [Python Data Science Handbook](http://shop.oreilly.com/product/0636920034919.do) by Jake VanderPlas; the content is available [on GitHub](https://github.com/jakevdp/PythonDataScienceHandbook).*\n\n*The text is released under the [CC-BY-NC-ND license](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/us/legalcode), and code is released under the [MIT license](https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT). If you find this content useful, please consider supporting the work by [buying the book](http://shop.oreilly.com/product/0636920034919.do)!*",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<!--NAVIGATION-->\n< [Computation on Arrays: Broadcasting](02.05-Computation-on-arrays-broadcasting.ipynb) | [Contents](Index.ipynb) | [Fancy Indexing](02.07-Fancy-Indexing.ipynb) >\n\n<a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/jakevdp/PythonDataScienceHandbook/blob/master/notebooks/02.06-Boolean-Arrays-and-Masks.ipynb\"><img align=\"left\" src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open in Colab\" title=\"Open and Execute in Google Colaboratory\"></a>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Comparisons, Masks, and Boolean Logic",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"This section covers the use of Boolean masks to examine and manipulate values within NumPy arrays.\nMasking comes up when you want to extract, modify, count, or otherwise manipulate values in an array based on some criterion: for example, you might wish to count all values greater than a certain value, or perhaps remove all outliers that are above some threshold.\nIn NumPy, Boolean masking is often the most efficient way to accomplish these types of tasks.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Example: Counting Rainy Days\n\nImagine you have a series of data that represents the amount of precipitation each day for a year in a given city.\nFor example, here we'll load the daily rainfall statistics for the city of Seattle in 2014, using Pandas (which is covered in more detail in [Chapter 3](03.00-Introduction-to-Pandas.ipynb)):",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\n\n# use pandas to extract rainfall inches as a NumPy array\nrainfall = pd.read_csv('data/Seattle2014.csv')['PRCP'].values\ninches = rainfall / 254.0 # 1/10mm -> inches\ninches.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The array contains 365 values, giving daily rainfall in inches from January 1 to December 31, 2014.\n\nAs a first quick visualization, let's look at the histogram of rainy days, which was generated using Matplotlib (we will explore this tool more fully in [Chapter 4](04.00-Introduction-To-Matplotlib.ipynb)):",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%matplotlib inline\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn; seaborn.set() # set plot styles",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.hist(inches, 40);",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This histogram gives us a general idea of what the data looks like: despite its reputation, the vast majority of days in Seattle saw near zero measured rainfall in 2014.\nBut this doesn't do a good job of conveying some information we'd like to see: for example, how many rainy days were there in the year? What is the average precipitation on those rainy days? How many days were there with more than half an inch of rain?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Digging into the data\n\nOne approach to this would be to answer these questions by hand: loop through the data, incrementing a counter each time we see values in some desired range.\nFor reasons discussed throughout this chapter, such an approach is very inefficient, both from the standpoint of time writing code and time computing the result.\nWe saw in [Computation on NumPy Arrays: Universal Functions](02.03-Computation-on-arrays-ufuncs.ipynb) that NumPy's ufuncs can be used in place of loops to do fast element-wise arithmetic operations on arrays; in the same way, we can use other ufuncs to do element-wise *comparisons* over arrays, and we can then manipulate the results to answer the questions we have.\nWe'll leave the data aside for right now, and discuss some general tools in NumPy to use *masking* to quickly answer these types of questions.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Comparison Operators as ufuncs\n\nIn [Computation on NumPy Arrays: Universal Functions](02.03-Computation-on-arrays-ufuncs.ipynb) we introduced ufuncs, and focused in particular on arithmetic operators. We saw that using ``+``, ``-``, ``*``, ``/``, and others on arrays leads to element-wise operations.\nNumPy also implements comparison operators such as ``<`` (less than) and ``>`` (greater than) as element-wise ufuncs.\nThe result of these comparison operators is always an array with a Boolean data type.\nAll six of the standard comparison operations are available:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x < 3 # less than",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x > 3 # greater than",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x <= 3 # less than or equal",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x >= 3 # greater than or equal",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x != 3 # not equal",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x == 3 # equal",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"It is also possible to do an element-wise comparison of two arrays, and to include compound expressions:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"(2 * x) == (x ** 2)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"As in the case of arithmetic operators, the comparison operators are implemented as ufuncs in NumPy; for example, when you write ``x < 3``, internally NumPy uses ``np.less(x, 3)``.\n A summary of the comparison operators and their equivalent ufunc is shown here:\n\n| Operator\t | Equivalent ufunc || Operator\t | Equivalent ufunc |\n|---------------|---------------------||---------------|---------------------|\n|``==`` |``np.equal`` ||``!=`` |``np.not_equal`` |\n|``<`` |``np.less`` ||``<=`` |``np.less_equal`` |\n|``>`` |``np.greater`` ||``>=`` |``np.greater_equal`` |",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Just as in the case of arithmetic ufuncs, these will work on arrays of any size and shape.\nHere is a two-dimensional example:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"rng = np.random.RandomState(0)\nx = rng.randint(10, size=(3, 4))\nx",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x < 6",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"In each case, the result is a Boolean array, and NumPy provides a number of straightforward patterns for working with these Boolean results.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Working with Boolean Arrays\n\nGiven a Boolean array, there are a host of useful operations you can do.\nWe'll work with ``x``, the two-dimensional array we created earlier.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(x)",
"[[5 0 3 3]\n [7 9 3 5]\n [2 4 7 6]]\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Counting entries\n\nTo count the number of ``True`` entries in a Boolean array, ``np.count_nonzero`` is useful:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# how many values less than 6?\nnp.count_nonzero(x < 6)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We see that there are eight array entries that are less than 6.\nAnother way to get at this information is to use ``np.sum``; in this case, ``False`` is interpreted as ``0``, and ``True`` is interpreted as ``1``:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.sum(x < 6)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The benefit of ``sum()`` is that like with other NumPy aggregation functions, this summation can be done along rows or columns as well:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# how many values less than 6 in each row?\nnp.sum(x < 6, axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This counts the number of values less than 6 in each row of the matrix.\n\nIf we're interested in quickly checking whether any or all the values are true, we can use (you guessed it) ``np.any`` or ``np.all``:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# are there any values greater than 8?\nnp.any(x > 8)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# are there any values less than zero?\nnp.any(x < 0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# are all values less than 10?\nnp.all(x < 10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# are all values equal to 6?\nnp.all(x == 6)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"``np.all`` and ``np.any`` can be used along particular axes as well. For example:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# are all values in each row less than 8?\nnp.all(x < 8, axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Here all the elements in the first and third rows are less than 8, while this is not the case for the second row.\n\nFinally, a quick warning: as mentioned in [Aggregations: Min, Max, and Everything In Between](02.04-Computation-on-arrays-aggregates.ipynb), Python has built-in ``sum()``, ``any()``, and ``all()`` functions. These have a different syntax than the NumPy versions, and in particular will fail or produce unintended results when used on multidimensional arrays. Be sure that you are using ``np.sum()``, ``np.any()``, and ``np.all()`` for these examples!",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Boolean operators\n\nWe've already seen how we might count, say, all days with rain less than four inches, or all days with rain greater than two inches.\nBut what if we want to know about all days with rain less than four inches and greater than one inch?\nThis is accomplished through Python's *bitwise logic operators*, ``&``, ``|``, ``^``, and ``~``.\nLike with the standard arithmetic operators, NumPy overloads these as ufuncs which work element-wise on (usually Boolean) arrays.\n\nFor example, we can address this sort of compound question as follows:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.sum((inches > 0.5) & (inches < 1))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"So we see that there are 29 days with rainfall between 0.5 and 1.0 inches.\n\nNote that the parentheses here are important–because of operator precedence rules, with parentheses removed this expression would be evaluated as follows, which results in an error:\n\n``` python\ninches > (0.5 & inches) < 1\n```\n\nUsing the equivalence of *A AND B* and *NOT (NOT A OR NOT B)* (which you may remember if you've taken an introductory logic course), we can compute the same result in a different manner:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.sum(~( (inches <= 0.5) | (inches >= 1) ))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Combining comparison operators and Boolean operators on arrays can lead to a wide range of efficient logical operations.\n\nThe following table summarizes the bitwise Boolean operators and their equivalent ufuncs:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"| Operator\t | Equivalent ufunc || Operator\t | Equivalent ufunc |\n|---------------|---------------------||---------------|---------------------|\n|``&`` |``np.bitwise_and`` ||| |``np.bitwise_or`` |\n|``^`` |``np.bitwise_xor`` ||``~`` |``np.bitwise_not`` |",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Using these tools, we might start to answer the types of questions we have about our weather data.\nHere are some examples of results we can compute when combining masking with aggregations:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(\"Number days without rain: \", np.sum(inches == 0))\nprint(\"Number days with rain: \", np.sum(inches != 0))\nprint(\"Days with more than 0.5 inches:\", np.sum(inches > 0.5))\nprint(\"Rainy days with < 0.2 inches :\", np.sum((inches > 0) &\n (inches < 0.2)))",
"Number days without rain: 215\nNumber days with rain: 150\nDays with more than 0.5 inches: 37\nRainy days with < 0.2 inches : 75\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Boolean Arrays as Masks\n\nIn the preceding section we looked at aggregates computed directly on Boolean arrays.\nA more powerful pattern is to use Boolean arrays as masks, to select particular subsets of the data themselves.\nReturning to our ``x`` array from before, suppose we want an array of all values in the array that are less than, say, 5:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can obtain a Boolean array for this condition easily, as we've already seen:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x < 5",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now to *select* these values from the array, we can simply index on this Boolean array; this is known as a *masking* operation:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x[x < 5]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"What is returned is a one-dimensional array filled with all the values that meet this condition; in other words, all the values in positions at which the mask array is ``True``.\n\nWe are then free to operate on these values as we wish.\nFor example, we can compute some relevant statistics on our Seattle rain data:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# construct a mask of all rainy days\nrainy = (inches > 0)\n\n# construct a mask of all summer days (June 21st is the 172nd day)\ndays = np.arange(365)\nsummer = (days > 172) & (days < 262)\n\nprint(\"Median precip on rainy days in 2014 (inches): \",\n np.median(inches[rainy]))\nprint(\"Median precip on summer days in 2014 (inches): \",\n np.median(inches[summer]))\nprint(\"Maximum precip on summer days in 2014 (inches): \",\n np.max(inches[summer]))\nprint(\"Median precip on non-summer rainy days (inches):\",\n np.median(inches[rainy & ~summer]))",
"Median precip on rainy days in 2014 (inches): 0.194881889764\nMedian precip on summer days in 2014 (inches): 0.0\nMaximum precip on summer days in 2014 (inches): 0.850393700787\nMedian precip on non-summer rainy days (inches): 0.200787401575\n"
]
],
[
[
"By combining Boolean operations, masking operations, and aggregates, we can very quickly answer these sorts of questions for our dataset.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Aside: Using the Keywords and/or Versus the Operators &/|\n\nOne common point of confusion is the difference between the keywords ``and`` and ``or`` on one hand, and the operators ``&`` and ``|`` on the other hand.\nWhen would you use one versus the other?\n\nThe difference is this: ``and`` and ``or`` gauge the truth or falsehood of *entire object*, while ``&`` and ``|`` refer to *bits within each object*.\n\nWhen you use ``and`` or ``or``, it's equivalent to asking Python to treat the object as a single Boolean entity.\nIn Python, all nonzero integers will evaluate as True. Thus:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"bool(42), bool(0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"bool(42 and 0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"bool(42 or 0)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"When you use ``&`` and ``|`` on integers, the expression operates on the bits of the element, applying the *and* or the *or* to the individual bits making up the number:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"bin(42)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"bin(59)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"bin(42 & 59)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"bin(42 | 59)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Notice that the corresponding bits of the binary representation are compared in order to yield the result.\n\nWhen you have an array of Boolean values in NumPy, this can be thought of as a string of bits where ``1 = True`` and ``0 = False``, and the result of ``&`` and ``|`` operates similarly to above:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"A = np.array([1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0], dtype=bool)\nB = np.array([1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1], dtype=bool)\nA | B",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Using ``or`` on these arrays will try to evaluate the truth or falsehood of the entire array object, which is not a well-defined value:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"A or B",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Similarly, when doing a Boolean expression on a given array, you should use ``|`` or ``&`` rather than ``or`` or ``and``:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x = np.arange(10)\n(x > 4) & (x < 8)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Trying to evaluate the truth or falsehood of the entire array will give the same ``ValueError`` we saw previously:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"(x > 4) and (x < 8)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"So remember this: ``and`` and ``or`` perform a single Boolean evaluation on an entire object, while ``&`` and ``|`` perform multiple Boolean evaluations on the content (the individual bits or bytes) of an object.\nFor Boolean NumPy arrays, the latter is nearly always the desired operation.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<!--NAVIGATION-->\n< [Computation on Arrays: Broadcasting](02.05-Computation-on-arrays-broadcasting.ipynb) | [Contents](Index.ipynb) | [Fancy Indexing](02.07-Fancy-Indexing.ipynb) >\n\n<a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/jakevdp/PythonDataScienceHandbook/blob/master/notebooks/02.06-Boolean-Arrays-and-Masks.ipynb\"><img align=\"left\" src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open in Colab\" title=\"Open and Execute in Google Colaboratory\"></a>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
c502270bf70aac7b09531d3de965d6a508700e52
| 841,303 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
single_cell_analysis.ipynb
|
calt-laboratory/scRNAseq-analysis-using-Tabula-Muris-data-
|
e0da13494e2c823e4abca1087a1b41fb497affc7
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
single_cell_analysis.ipynb
|
calt-laboratory/scRNAseq-analysis-using-Tabula-Muris-data-
|
e0da13494e2c823e4abca1087a1b41fb497affc7
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
single_cell_analysis.ipynb
|
calt-laboratory/scRNAseq-analysis-using-Tabula-Muris-data-
|
e0da13494e2c823e4abca1087a1b41fb497affc7
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 314.505794 | 87,064 | 0.903402 |
[
[
[
"# scRNAseq Analysis of Tabula muris data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport pandas as pd\n\nimport scanpy as sc\nfrom sklearn.cluster import KMeans\nfrom sklearn.metrics import adjusted_rand_score\nfrom scipy.stats import ttest_ind",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#\nbrain_counts = pd.read_csv(\"data/brain_counts.csv\", index_col=0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# check the data\nbrain_counts\n# rows: cell names (unique identifiers)\n# columns: genes",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#\nbrain_counts.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# load metadata\nmetadata = pd.read_csv(\"data/brain_metadata.csv\", index_col=0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# check the metadata\nmetadata",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#\nmetadata.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# check value counts for each column\ncol = 0\nfor i in metadata.columns.values:\n print(\"*** \" + metadata.columns[col] + \" ***\")\n print(metadata[i].value_counts())\n print(\"-\"*50)\n col+=1",
"*** cell_ontology_class ***\noligodendrocyte 1574\nendothelial cell 715\nastrocyte 432\nneuron 281\noligodendrocyte precursor cell 203\nbrain pericyte 156\nBergmann glial cell 40\nName: cell_ontology_class, dtype: int64\n--------------------------------------------------\n*** subtissue ***\nCortex 1149\nHippocampus 976\nStriatum 723\nCerebellum 553\nName: subtissue, dtype: int64\n--------------------------------------------------\n*** mouse.sex ***\nM 2694\nF 707\nName: mouse.sex, dtype: int64\n--------------------------------------------------\n*** mouse.id ***\n3_10_M 980\n3_9_M 871\n3_8_M 590\n3_38_F 355\n3_11_M 253\n3_39_F 241\n3_56_F 111\nName: mouse.id, dtype: int64\n--------------------------------------------------\n*** plate.barcode ***\nMAA000560 287\nMAA000926 263\nMAA000581 190\nMAA000944 184\nMAA000932 174\nMAA001894 147\nMAA000564 143\nMAA000942 136\nMAA000935 131\nMAA000941 125\nMAA000930 111\nMAA000923 108\nMAA000947 107\nB003290 98\nMAA000561 97\nMAA000615 95\nB003275 93\nMAA000641 67\nB003728 66\nMAA000940 63\nMAA001895 60\nMAA000563 57\nMAA000925 55\nB003277 52\nMAA000638 51\nMAA000902 40\nMAA000424 39\nMAA000553 39\nMAA000578 38\nMAA000928 36\nMAA000550 34\nMAA001845 33\nB001688 32\nB003274 27\nB000621 24\nMAA001854 23\nMAA001853 22\nB000404 21\nMAA000924 14\nMAA000538 10\nMAA001856 9\nName: plate.barcode, dtype: int64\n--------------------------------------------------\n"
],
[
"# build a AnnData object (=annotated data)\nannotated_data = sc.AnnData(X=brain_counts, obs=metadata)\nannotated_data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# check the AnnData obj\nprint(\"Gene names: \")\nprint(annotated_data.var_names)",
"Gene names: \nIndex(['0610005C13Rik', '0610007C21Rik', '0610007L01Rik', '0610007N19Rik',\n '0610007P08Rik', '0610007P14Rik', '0610007P22Rik', '0610008F07Rik',\n '0610009B14Rik', '0610009B22Rik',\n ...\n 'Zxdb', 'Zxdc', 'Zyg11a', 'Zyg11b', 'Zyx', 'Zzef1', 'Zzz3', 'a',\n 'l7Rn6', 'zsGreen_transgene'],\n dtype='object', length=23433)\n"
],
[
"# find spike-ins\nspike_ins = {}\nnum_spike_ins = 0\n\nfor gene in annotated_data.var_names:\n if 'ERCC' in gene:\n spike_ins[gene] = True\n num_spike_ins += 1\n else:\n spike_ins[gene] = False\n \nannotated_data.var['ERCC'] = pd.Series(spike_ins)\nprint('Number of spike-ins: ', num_spike_ins)",
"Number of spike-ins: 92\n"
],
[
"#\nannotated_data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# save AnnData\n#annotated_data.write(\"../data/brain_annotated_data_obj.h5ad\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Data Preprocessing - Quality control",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# load annotated AnnData object\n#annotated_data = sc.read(\"../data/brain_annotated_data_obj.h5ad\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# computation of qc metrics (for cells and for genes)\n# \nquality_ctrl = sc.pp.calculate_qc_metrics(annotated_data)\nprint(type(quality_ctrl))\nquality_ctrl",
"<class 'tuple'>\n"
],
[
"# get additional information about the spike-ins\nquality_ctrl = sc.pp.calculate_qc_metrics(annotated_data, qc_vars=[\"ERCC\"])\nquality_ctrl",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# store the cell quality ctrl and the gene quality ctrl in extra vars\ncell_quality = quality_ctrl[0]\ngene_quality = quality_ctrl[1]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# check cell quality\ncell_quality",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# check gene quality\ngene_quality",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### QC for cells",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# plot total number of reads per cell and check for existing cell with less than 50.000 reads\nplt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))\nplt.hist(cell_quality['total_counts'], bins=5000)\nplt.axvline(50.000, color='red')\nplt.title('Total Number of Reads per Cell')\nplt.xlabel('Total Counts')\nplt.ylabel('Number of Cells')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# plot number of unique genes per cell\nplt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))\nplt.hist(cell_quality['n_genes_by_counts'], bins=1000)\nplt.title('Number of Unique Genes per Cell')\nplt.xlabel('Number of Genes')\nplt.ylabel('Number of Cells')\nplt.axvline(1000, color='red')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# plot percentage of spike-ins\nplt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))\nplt.hist(cell_quality['pct_counts_ERCC'], bins=1000)\nplt.title('Percentage Distribution of Spike-ins')\nplt.xlabel('Percentage of Spike-ins')\nplt.ylabel('Number of Cells')\nplt.axvline(10, color='red')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# remove cells with more than 10 % spike-ins\nless_10_spike_ins = cell_quality['pct_counts_ERCC'] < 10\nannotated_data = annotated_data[less_10_spike_ins]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### QC for genes",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"annotated_data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# reserve only cells with minimum of 750 genes\nsc.pp.filter_cells(annotated_data, min_genes=750)",
"Trying to set attribute `.obs` of view, copying.\n"
],
[
"# plot number of cells vs number of genes\nplt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))\nplt.hist(gene_quality['n_cells_by_counts'], bins=1000)\n# \"n_cells_by_counts\": number of cells containing genes with an expression > 0\nplt.title('Number of Cells vs Number of Genes where expression > 0')\nplt.xlabel('Number of Cells')\nplt.ylabel('log(Number of Genes)')\nplt.yscale('log')\nplt.axvline(2, color='red')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# plot total expression in genes\nplt.figure(figsize=(12, 9))\nplt.hist(gene_quality['total_counts'], bins=1000)\n# \"total_counts\": sum of expression values for a given gene\nplt.title('Total Expression of Genes')\nplt.xlabel('Total Expression')\nplt.ylabel('log(Number of Genes)')\nplt.yscale('log')\nplt.axvline(10, color='red')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# check number of genes before filtering\nannotated_data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# filter genes\n# Definition of a detectable gene:\n# 2 cells need to contain > 5 reads from the gene\nsc.pp.filter_genes(annotated_data, min_cells=2)\nsc.pp.filter_genes(annotated_data, min_counts=10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# check number of genes after filtering\nannotated_data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# store annotated data\n#annotated_data.write(\"../data/brain_annotated_data_quality.h5ad\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Data Preprocessing - PCA",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# apply PCA on data\nsc.pp.pca(annotated_data)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# plot PCA results\nplt.figure(figsize=(12, 12))\nsc.pl.pca_overview(annotated_data, color='mouse.id', return_fig=False)\n# 1st) PC1 vs PC2 diagram\n# 2nd) Loadings = how much contributes a variable to a PC\n# 3rd) how much contributes a PC to the variation of the data",
"... storing 'cell_ontology_class' as categorical\n... storing 'subtissue' as categorical\n... storing 'mouse.sex' as categorical\n... storing 'mouse.id' as categorical\n... storing 'plate.barcode' as categorical\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Data preprocessing - Normalization",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Normalization using CPM (counts per million)\n- convert data to counts per million by dividing each cell (row) by a size factor (= sum of all counts in the row) and then multiply by 1x10⁶",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# apply CPM\ndata_cpm = annotated_data.copy()\ndata_cpm.raw = data_cpm\nsc.pp.normalize_per_cell(data_cpm, counts_per_cell_after=1e6)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# apply PCA on normalized data\nsc.pp.pca(data_cpm)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# show PCA results\nsc.pl.pca_overview(data_cpm, color='mouse.id')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# apply normalization using CPM and exclude highly expressed genes from the size factor calculation\ndata_cpm_ex_high_expressed = data_cpm.copy()\nsc.pp.normalize_total(data_cpm_ex_high_expressed, target_sum=1e6, exclude_highly_expressed=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# apply PCA\nsc.pp.pca(data_cpm_ex_high_expressed)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# show PCA results\nsc.pl.pca_overview(data_cpm, color='mouse.id')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### Normalizing gene expression",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# remove gene Rn45s and apply PCA again\nmask_Rn45s = data_cpm.var.index != 'Rn45s'\ndata_without_Rn45s = data_cpm[:, mask_Rn45s]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# apply PCA\nsc.pp.pca(data_without_Rn45s)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# show PCA results\nsc.pl.pca_overview(data_without_Rn45s, color='mouse.id')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### Scaling the expression values",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# log(1+x) of each value\nsc.pp.log1p(data_cpm)\n\n# scaling each value using z-score\nsc.pp.scale(data_cpm)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# PCA\nsc.pp.pca(data_cpm)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# PCA results\nsc.pl.pca_overview(data_cpm, color='plate.barcode')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# store normalized data\n#data_cpm.write(\"../data/brain_annotated_data_normalized.h5ad\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Data Analysis - Dimensionality Reduction",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### tSNE (t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# apply tSNE and show results\nsc.tl.tsne(data_cpm, perplexity=45, learning_rate=800, random_state=42)\nsc.pl.tsne(data_cpm, color='cell_ontology_class')",
"WARNING: Consider installing the package MulticoreTSNE (https://github.com/DmitryUlyanov/Multicore-TSNE). Even for n_jobs=1 this speeds up the computation considerably and might yield better converged results.\n"
],
[
"# store tSNE results\n#data_cpm.write('data/brain_annotated_data_tsne.h5ad')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Data Analysis - Clustering",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### k-Means Clustering",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# extract coordinates of the tSNE data\ntsne_data = data_cpm\ntsne_coords = tsne_data.obsm['X_tsne']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# apply kmeans\nkmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=4, random_state=42)\nkmeans.fit(tsne_coords)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# add labels to meta data column\ntsne_data.obs['kmeans'] = kmeans.labels_\ntsne_data.obs['kmeans'] = tsne_data.obs['kmeans'].astype(str)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# plot results\nsc.pl.tsne(tsne_data, color='kmeans')",
"... storing 'kmeans' as categorical\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Adjusted Rand Index",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# evalutate the clustering results using the adj rand idx\nadj_rand_idx = adjusted_rand_score(labels_true=tsne_data.obs['cell_ontology_class'],\n labels_pred=tsne_data.obs['kmeans'])\nround(adj_rand_idx, 2)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# store cluster results\ntsne_data.write('data/brain_cluster_results.h5ad')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Data Analysis - Differential Expression",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# load/store cluster data\n#cluster_data = sc.read('data/brain_cluster_results.h5ad')\ncluster_data = tsne_data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# store raw data\nraw_data = pd.DataFrame(data=cluster_data.raw.X, index=cluster_data.raw.obs_names,\n columns=cluster_data.raw.var_names)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# define a gene of interest\nastrocyte_marker = 'Gja1'\n\n# astrocyte are cluster 2\ncluster_2 = raw_data[cluster_data.obs['kmeans'] == '2']\nwithout_cluster_2 = raw_data[cluster_data.obs['kmeans'] != '2']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# histograms\ncluster_2_marker = cluster_2[astrocyte_marker]\nplt.hist(cluster_2_marker.values, bins=100, color='purple',\n label='Cluster 2', alpha=.5)\n\nwithout_cluster_2_marker = without_cluster_2[astrocyte_marker]\nplt.hist(without_cluster_2_marker.values, bins=1000, color='black', label='Other Clusters')\n\nplt.xlabel(f'{astrocyte_marker} Expression')\nplt.ylabel('Number of Cells')\nplt.yscale('log')\nplt.legend()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# use independent t-test to check whether clusters reveal statistical significant difference\nttest = ttest_ind(cluster_2_marker, without_cluster_2_marker, equal_var=False, nan_policy='omit')\n\nprint(ttest)\nprint(round(ttest.statistic, 2))\nprint(round(ttest.pvalue, 2))",
"Ttest_indResult(statistic=10.447316348816619, pvalue=2.6049876880394232e-23)\n10.45\n0.0\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c502296faf0a1f6ca9c1563422099a5b1ed23917
| 31,483 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
class06_bfs_python3_template.ipynb
|
curiositymap/Networks-in-Computational-Biology
|
c7734cf2c03c7a794ab6990d433b1614c1837b58
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 11 |
2020-09-17T14:59:30.000Z
|
2022-03-29T16:35:39.000Z
|
class06_bfs_python3_template.ipynb
|
curiositymap/Networks-in-Computational-Biology
|
c7734cf2c03c7a794ab6990d433b1614c1837b58
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
class06_bfs_python3_template.ipynb
|
curiositymap/Networks-in-Computational-Biology
|
c7734cf2c03c7a794ab6990d433b1614c1837b58
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 5 |
2020-03-12T19:21:56.000Z
|
2022-03-28T08:23:58.000Z
| 64.382413 | 1,880 | 0.628244 |
[
[
[
"# CSX46\n## Class session 6: BFS\n\nObjective: write and test a function that can compute single-vertex shortest paths in an unweighted simple graph. Compare to the results that we get using `igraph.Graph.get_shortest_paths()`.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We're going to need several packages for this notebook; let's import them first",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import random\nimport igraph\nimport numpy as np\nimport math\nimport collections",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's set the random number seed using `random.seed` and with seed value 1337, so that we are all starting with the same graph structure. Make a simple 10-vertex random (Barabasi-Albert model) graph. Set the random number seed so that the graph is always the same, for purposes of reproducibility (we want to know that the \"hub\" vertex will be vertex 2, and we will test your BFS function starting at that \"hub\" vertex).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Let's plot the graph, using `bbox=[0,0,200,200]` so it is not huge, and using `vertex_label=` to display the vertex IDs.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Let's look at an adjacency list representation of the graph, using the method `igraph.Graph.get_adjlist`",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Let's look at the degrees of the vertices using the `igraph.Graph.degree` method and the `enumerate` built-in function and list comprehension: ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"OK, let's implement a function to compute shortest-path (geodesic path) distances to all vertices in the graph, starting at a single vertex `p_vertex`. We'll implement the \nbreadth-first search (BFS) algorithm in order to compute these geodesic path distances. \n\nWe'll start by implementing the queue data structure \"by hand\" with our own `read_ptr` and `write_ptr` exactly as described on page 320 of Newman's book. Newman says to use an \"array\" to implement the queue. As it turns out, Python's native `list` data type is internally implemented as a (resizeable) array, so we can just use a `list` here. We'll call our function `bfs_single_vertex_newman`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# compute N, the number of vertices by calling len() on the VertexSet obtained from graph.vs()\n# initialize \"queue\" array (length N, containing np.nan)\n# initialize distances array (length N, containing np.nan)\n# set \"p_vertex\" entry of distances array to be 0\n# while write_ptr is gerater than read_ptr:\n# obtain the vertex ID of the entry at index \"read_ptr\" in the queue array, as cur_vertex_num\n# increment read_ptr\n# get the distance to cur_vertex_num, from the \"distances\" array\n# get the neighbors of vertex cur_vertex_num in the graph, using the igraph \"neighbors\" func\n# for each vertex_neighbor in the array vertex_neighbors\n# if the distances[vertex_neighbor] is nan:\n# (1) set the distance to vertex_neighbor (in \"distances\" vector) to the distance to\n# cur_vertex_num, plus one\n# (2) add neighbor to the queue\n# put vertex_neighbor at position write_ptr in the queue array\n# increment write_ptr\n# end-while\n# return \"distances\"\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's test out our implementation of `bfs_single_vertex_newman`, on vertex 0 of the graph. Do the results make sense?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Now let's re-implement the single-vertex BFS distance function using a convenient queue data structure, `collections.deque` (note, `deque` is actually a *double-ended* queue, so it is a bit more fancy than we need, but that's OK, we just will only be using its methods `popleft` and `append`)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# compute N, the number of vertices by calling len() on the VertexSet obtained from graph.vs()\n# create a deque data structure called \"queue\" and initialize it to contain p_vertex\n# while the queue is not empty:\n# pop vertex_id off of the left of the queue\n# get the vertex_id entry of the distances vector, call it \"vertex_dist\"\n# for each neighbor_id of vertex_id:\n# if the neighbor_id entry of the distances vector is nan:\n# set the neighbor_id entry of the distances vector to vertex_dist + 1\n# append neighbor_id to the queue\n# return \"distances\"\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Compare the code implementations of `bfs_single_vertex_newman` and `bfs_single_vertex`. Which is easier to read and understand?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Test out your function `bfs_single_vertex` on vertex 0. Do we get the same result as when we used `bfs_single_vertex_newman`?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"If the graph was a lot bigger, how could we systematically check that the results of `bfs_single_vertex` (from vertex 0) are correctly calculated? We can use the `igraph.Graph.get_shortest_paths` method, and specify `v=0`. Let's look at the results of calling `get_shortest_paths` with `v=0`:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"So, clearly, we need to calculate the length of the list of vertices in each entry of this ragged list. But the *path* length is one less than the length of the list of vertices, so we have to subtract one in order to get the correct path length. Now we are ready to compare our BFS-based single-vertex geodesic distances with the results from calling `igraph.Graph.get_shortest_paths`:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Now let's implement a function that can compute a numpy.matrix of geodesic path distances for all pairs of vertices. The pythonic way to do this is probably to use the list-of-lists constructor for np.array, and to use list comprehension.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def sp_matrix(p_graph):\n return FILL IN HERE",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"How about if we want to implement it using a plain old for loop?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def sp_matrix_forloop(p_graph):\n N = FILL IN HERE\n geo_dists = FILL IN HERE\n FILL IN HERE\n return geo_dists",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's run it on our little ten-vertex graph:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
c50232dcd051a6aae8ee8d7a99a7618571dcf482
| 37,102 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
docs/tutorials/mlmd/mlmd_tutorial.ipynb
|
fanszoro/tfx
|
b1acab7bf89ec1364c96b9b4e2cc41594407b86c
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
docs/tutorials/mlmd/mlmd_tutorial.ipynb
|
fanszoro/tfx
|
b1acab7bf89ec1364c96b9b4e2cc41594407b86c
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2020-11-10T02:21:30.000Z
|
2020-11-10T02:21:30.000Z
|
docs/tutorials/mlmd/mlmd_tutorial.ipynb
|
fanszoro/tfx
|
b1acab7bf89ec1364c96b9b4e2cc41594407b86c
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 33.790528 | 552 | 0.536305 |
[
[
[
"##### Copyright 2020 The TensorFlow Authors.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#@title Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the \"License\");\n# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.\n# You may obtain a copy of the License at\n#\n# https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0\n#\n# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software\n# distributed under the License is distributed on an \"AS IS\" BASIS,\n# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.\n# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and\n# limitations under the License.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Better ML Engineering with ML Metadata\n\n\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<table class=\"tfo-notebook-buttons\" align=\"left\">\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/tfx/tutorials/mlmd_tutorial\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/tf_logo_32px.png\" />View on TensorFlow.org</a>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/tensorflow/tfx/blob/master/docs/tutorials/mlmd_tutorial.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/colab_logo_32px.png\" />Run in Google Colab</a>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://github.com/tensorflow/docs/blob/master/tools/templates/notebook.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/GitHub-Mark-32px.png\" />View source on GitHub</a>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a href=\"https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow_docs/docs/tools/templates/notebook.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/download_logo_32px.png\" />Download notebook</a>\n </td>\n</table>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Assume a scenario where you set up a production ML pipeline to classify pictures of iris flowers. The pipeline ingests your training data, trains and evaluates a model, and pushes it to production. \n\nHowever, when you later try using this model with a larger dataset that contains images of different kinds of flowers, you observe that your model does not behave as expected and starts classifying roses and lilies as types of irises.\n\nAt this point, you are interested in knowing:\n\n* What is the most efficient way to debug the model when the only available artifact is the model in production?\n* Which training dataset was used to train the model?\n* Which training run led to this erroneous model?\n* Where are the model evaluation results?\n* Where to begin debugging?\n\n[ML Metadata (MLMD)](https://github.com/google/ml-metadata) is a library that leverages the metadata associated with ML models to help you answer these questions and more. A helpful analogy is to think of this metadata as the equivalent of logging in software development. MLMD enables you to reliably track the artifacts and lineage associated with the various components of your ML pipeline.\n\nIn this tutorial, you set up a TFX Pipeline to create a model that classifies Iris flowers into three species - Iris setosa, Iris virginica, and Iris versicolor based on the length and width measurements of their petals and sepals. You then use MLMD to track the lineage of pipeline components.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## TFX Pipelines in Colab\n\nColab is a lightweight development environment which differs significantly from a production environment. In production, you may have various pipeline components like data ingestion, transformation, model training, run histories, etc. across multiple, distributed systems. For this tutorial, you should be aware that siginificant differences exist in Orchestration and Metadata storage - it is all handled locally within Colab. Learn more about TFX in Colab [here](https://www.tensorflow.org/tfx/tutorials/tfx/components_keras#background).\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Setup\n\nImport all required libraries.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Install and import TFX",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
" !pip install --quiet tfx==0.23.0",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You must restart the Colab runtime after installing TFX. Select **Runtime > Restart runtime** from the Colab menu.\n\nDo not proceed with the rest of this tutorial without first restarting the runtime.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Import other libraries",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import base64\nimport csv\nimport json\nimport os\nimport requests\nimport tempfile\nimport urllib\nimport pprint\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\n\npp = pprint.PrettyPrinter()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import tensorflow as tf\nimport tfx",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Import [TFX component](https://tensorflow.google.cn/tfx/tutorials/tfx/components_keras) classes.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from tfx.components.evaluator.component import Evaluator\nfrom tfx.components.example_gen.csv_example_gen.component import CsvExampleGen\nfrom tfx.components.pusher.component import Pusher\nfrom tfx.components.schema_gen.component import SchemaGen\nfrom tfx.components.statistics_gen.component import StatisticsGen\nfrom tfx.components.trainer.component import Trainer\nfrom tfx.components.base import executor_spec\nfrom tfx.components.trainer.executor import GenericExecutor\nfrom tfx.orchestration.experimental.interactive.interactive_context import InteractiveContext\nfrom tfx.proto import evaluator_pb2\nfrom tfx.proto import pusher_pb2\nfrom tfx.proto import trainer_pb2\nfrom tfx.utils.dsl_utils import external_input\n\nfrom tensorflow_metadata.proto.v0 import anomalies_pb2\nfrom tensorflow_metadata.proto.v0 import schema_pb2\nfrom tensorflow_metadata.proto.v0 import statistics_pb2\n\nimport tensorflow_model_analysis as tfma\n\nfrom tfx.components import ResolverNode\nfrom tfx.dsl.experimental import latest_blessed_model_resolver\nfrom tfx.types import Channel\nfrom tfx.types.standard_artifacts import Model\nfrom tfx.types.standard_artifacts import ModelBlessing",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Import the MLMD library.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import ml_metadata as mlmd\nfrom ml_metadata.proto import metadata_store_pb2",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Download the dataset\n\nDownload the [Iris dataset](https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/iris) dataset to use in this tutorial. The dataset contains data about the length and width measurements of sepals and petals for 150 Iris flowers. You use this data to classify irises into one of three species - Iris setosa, Iris virginica, and Iris versicolor.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"DATA_PATH = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tensorflow/tfx/master/tfx/examples/iris/data/iris.csv'\n_data_root = tempfile.mkdtemp(prefix='tfx-data')\n_data_filepath = os.path.join(_data_root, \"iris.csv\")\nurllib.request.urlretrieve(DATA_PATH, _data_filepath)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Create an InteractiveContext\n\nTo run TFX components interactively in this notebook, create an `InteractiveContext`. The `InteractiveContext` uses a temporary directory with an ephemeral MLMD database instance. Note that calls to `InteractiveContext` are no-ops outside the Colab environment.\n\nIn general, it is a good practice to group similar pipeline runs under a `Context`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"interactive_context = InteractiveContext()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Construct the TFX Pipeline\n\nA TFX pipeline consists of several components that perform different aspects of the ML workflow. In this notebook, you create and run the `ExampleGen`, `StatisticsGen`, `SchemaGen`, and `TrainerGen` components and use the `Evaluator` and `Pusher` component to evaluate and push the trained model. \n\nRefer to the [components tutorial](https://www.tensorflow.org/tfx/tutorials/tfx/components_keras) for more information on TFX pipeline components.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Note: Constructing a TFX Pipeline by setting up the individual components involves a lot of boilerplate code. For the purpose of this tutorial, it is alright if you do not fully understand every line of code in the pipeline setup. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Instantiate and run the ExampleGen Component",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"input_data = external_input(_data_root)\nexample_gen = CsvExampleGen(input=input_data)\n\n# Run the ExampleGen component using the InteractiveContext\ninteractive_context.run(example_gen)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Instantiate and run the StatisticsGen Component",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"statistics_gen = StatisticsGen(examples=example_gen.outputs['examples'])\n\n# Run the StatisticsGen component using the InteractiveContext\ninteractive_context.run(statistics_gen)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Instantiate and run the SchemaGen Component",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"infer_schema = SchemaGen(statistics=statistics_gen.outputs['statistics'],\n infer_feature_shape = True)\n\n# Run the SchemaGen component using the InteractiveContext\ninteractive_context.run(infer_schema)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Instantiate and run the Trainer Component\n\n\n\n\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Define the module file for the Trainer component\ntrainer_module_file = 'iris_trainer.py'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%%writefile {trainer_module_file}\n\n# Define the training algorithm for the Trainer module file\nimport os\nfrom typing import List, Text\n\nimport tensorflow as tf\nfrom tensorflow import keras\n\nfrom tfx.components.trainer.executor import TrainerFnArgs\nfrom tfx.components.trainer.fn_args_utils import FnArgs\n\n# The iris dataset has 150 records, and is split into training and evaluation \n# datasets in a 2:1 split\n\n_TRAIN_DATA_SIZE = 100\n_EVAL_DATA_SIZE = 50\n_TRAIN_BATCH_SIZE = 100\n_EVAL_BATCH_SIZE = 50\n\n# Features used for classification - sepal length and width, petal length and\n# width, and variety (species of flower)\n\n_FEATURES = {\n 'sepal_length': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([], dtype=tf.float32, default_value=0),\n 'sepal_width': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([], dtype=tf.float32, default_value=0),\n 'petal_length': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([], dtype=tf.float32, default_value=0),\n 'petal_width': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([], dtype=tf.float32, default_value=0),\n 'variety': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([], dtype=tf.int64, default_value=0)\n}\n\n_LABEL_KEY = 'variety'\n\n_FEATURE_KEYS = ['sepal_length', 'sepal_width', 'petal_length', 'petal_width']\n\ndef _gzip_reader_fn(filenames):\n return tf.data.TFRecordDataset(filenames, compression_type='GZIP')\n\ndef _input_fn(file_pattern: List[Text],\n batch_size: int = 200):\n dataset = tf.data.experimental.make_batched_features_dataset(\n file_pattern=file_pattern,\n batch_size=batch_size,\n features=_FEATURES,\n reader=_gzip_reader_fn,\n label_key=_LABEL_KEY)\n \n return dataset\n \ndef _build_keras_model():\n inputs = [keras.layers.Input(shape = (1,), name = f) for f in _FEATURE_KEYS]\n d = keras.layers.concatenate(inputs)\n d = keras.layers.Dense(8, activation = 'relu')(d)\n d = keras.layers.Dense(8, activation = 'relu')(d)\n outputs = keras.layers.Dense(3, activation = 'softmax')(d)\n model = keras.Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs)\n model.compile(optimizer = 'adam',\n loss = 'sparse_categorical_crossentropy',\n metrics= [keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy()])\n return model\n\ndef run_fn(fn_args: TrainerFnArgs):\n train_dataset = _input_fn(fn_args.train_files, batch_size=_TRAIN_BATCH_SIZE)\n eval_dataset = _input_fn(fn_args.eval_files, batch_size=_EVAL_BATCH_SIZE)\n \n model = _build_keras_model()\n\n steps_per_epoch = _TRAIN_DATA_SIZE / _TRAIN_BATCH_SIZE\n\n model.fit(train_dataset, \n epochs=int(fn_args.train_steps / steps_per_epoch),\n steps_per_epoch=steps_per_epoch,\n validation_data=eval_dataset,\n validation_steps=fn_args.eval_steps)\n model.save(fn_args.serving_model_dir, save_format='tf')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Run the `Trainer` component.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"trainer = Trainer(\n module_file=os.path.abspath(trainer_module_file),\n custom_executor_spec=executor_spec.ExecutorClassSpec(GenericExecutor),\n examples=example_gen.outputs['examples'],\n schema=infer_schema.outputs['schema'],\n train_args=trainer_pb2.TrainArgs(num_steps=100),\n eval_args=trainer_pb2.EvalArgs(num_steps=50))\n\ninteractive_context.run(trainer)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Evaluate and push the model\n\nUse the `Evaluator` component to evaluate and 'bless' the model before using the `Pusher` component to push the model to a serving directory.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"_serving_model_dir = os.path.join(tempfile.mkdtemp(), 'serving_model/iris_classification')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"eval_config = tfma.EvalConfig(model_specs=[tfma.ModelSpec(label_key ='variety')],\n metrics_specs =[tfma.MetricsSpec(metrics = \n [tfma.MetricConfig(class_name='ExampleCount'),\n tfma.MetricConfig(class_name='BinaryAccuracy',\n threshold=tfma.MetricThreshold(\n value_threshold=tfma.GenericValueThreshold(\n lower_bound={'value': 0.5}),\n change_threshold=tfma.GenericChangeThreshold(\n direction=tfma.MetricDirection.HIGHER_IS_BETTER,\n absolute={'value': -1e-10})))])],\n slicing_specs = [tfma.SlicingSpec(),\n tfma.SlicingSpec(feature_keys=['sepal_length'])])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model_resolver = ResolverNode(\n instance_name='latest_blessed_model_resolver',\n resolver_class=latest_blessed_model_resolver.LatestBlessedModelResolver,\n model=Channel(type=Model),\n model_blessing=Channel(type=ModelBlessing))\ninteractive_context.run(model_resolver)\n\nevaluator = Evaluator(\n examples=example_gen.outputs['examples'],\n model=trainer.outputs['model'],\n baseline_model=model_resolver.outputs['model'],\n eval_config=eval_config)\ninteractive_context.run(evaluator)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pusher = Pusher(\n model=trainer.outputs['model'],\n model_blessing=evaluator.outputs['blessing'],\n push_destination=pusher_pb2.PushDestination(\n filesystem=pusher_pb2.PushDestination.Filesystem(\n base_directory=_serving_model_dir)))\ninteractive_context.run(pusher)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Running the TFX pipeline populates the MLMD Database. In the next section, you use the MLMD API to query this database for metadata information. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Query the MLMD Database\n\nThe MLMD database stores three types of metadata: \n\n* Metadata about the pipeline and lineage information associated with the pipeline components\n* Metadata about artifacts that were generated during the pipeline run\n* Metadata about the executions of the pipeline\n\nA typical production environment pipeline serves multiple models as new data arrives. When you encounter erroneous results in served models, you can query the MLMD database to isolate the erroneous models. You can then trace the lineage of the pipeline components that correspond to these models to debug your models",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Set up the metadata (MD) store with the `InteractiveContext` defined previously to query the MLMD database.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#md_store = mlmd.MetadataStore(interactive_context.metadata_connection_config)\nstore = mlmd.MetadataStore(interactive_context.metadata_connection_config)\n\n# All TFX artifacts are stored in the base directory\nbase_dir = interactive_context.metadata_connection_config.sqlite.filename_uri.split('metadata.sqlite')[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Create some helper functions to view the data from the MD store.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def display_types(types):\n # Helper function to render dataframes for the artifact and execution types\n table = {'id': [], 'name': []}\n for a_type in types:\n table['id'].append(a_type.id)\n table['name'].append(a_type.name)\n return pd.DataFrame(data=table)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def display_artifacts(store, artifacts):\n # Helper function to render dataframes for the input artifacts\n table = {'artifact id': [], 'type': [], 'uri': []}\n for a in artifacts:\n table['artifact id'].append(a.id)\n artifact_type = store.get_artifact_types_by_id([a.type_id])[0]\n table['type'].append(artifact_type.name)\n table['uri'].append(a.uri.replace(base_dir, './'))\n return pd.DataFrame(data=table)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def display_properties(store, node):\n # Helper function to render dataframes for artifact and execution properties\n table = {'property': [], 'value': []}\n for k, v in node.properties.items():\n table['property'].append(k)\n table['value'].append(\n v.string_value if v.HasField('string_value') else v.int_value)\n for k, v in node.custom_properties.items():\n table['property'].append(k)\n table['value'].append(\n v.string_value if v.HasField('string_value') else v.int_value)\n return pd.DataFrame(data=table)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"First, query the MD store for a list of all its stored `ArtifactTypes`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"display_types(store.get_artifact_types())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Next, query all `PushedModel` artifacts.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pushed_models = store.get_artifacts_by_type(\"PushedModel\")\ndisplay_artifacts(store, pushed_models)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Query the MD store for the latest pushed model. This tutorial has only one pushed model. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pushed_model = pushed_models[-1]\ndisplay_properties(store, pushed_model)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"One of the first steps in debugging a pushed model is to look at which trained model is pushed and to see which training data is used to train that model. \n\nMLMD provides traversal APIs to walk through the provenance graph, which you can use to analyze the model provenance. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def get_one_hop_parent_artifacts(store, artifacts):\n # Get a list of artifacts within a 1-hop neighborhood of the artifacts of interest\n artifact_ids = [artifact.id for artifact in artifacts]\n executions_ids = set(\n event.execution_id\n for event in store.get_events_by_artifact_ids(artifact_ids)\n if event.type == metadata_store_pb2.Event.OUTPUT)\n artifacts_ids = set(\n event.artifact_id\n for event in store.get_events_by_execution_ids(executions_ids)\n if event.type == metadata_store_pb2.Event.INPUT) \n return [artifact for artifact in store.get_artifacts_by_id(artifacts_ids)]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Query the parent artifacts for the pushed model.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"parent_artifacts = get_one_hop_parent_artifacts(store, [pushed_model])\ndisplay_artifacts(store, parent_artifacts)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Query the properties for the model.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"exported_model = parent_artifacts[0]\ndisplay_properties(store, exported_model)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Query the upstream artifacts for the model.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model_parents = get_one_hop_parent_artifacts(store, [exported_model])\ndisplay_artifacts(store, model_parents)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Get the training data the model trained with.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"used_data = model_parents[0]\ndisplay_properties(store, used_data)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now that you have the training data that the model trained with, query the database again to find the training step (execution). Query the MD store for a list of the registered execution types.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"display_types(store.get_execution_types())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The training step is the `ExecutionType` named `tfx.components.trainer.component.Trainer`. Traverse the MD store to get the trainer run that corresponds to the pushed model.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def find_producer_execution(store, artifact):\n executions_ids = set(\n event.execution_id\n for event in store.get_events_by_artifact_ids([artifact.id])\n if event.type == metadata_store_pb2.Event.OUTPUT) \n return store.get_executions_by_id(executions_ids)[0]\n\ntrainer = find_producer_execution(store, exported_model)\ndisplay_properties(store, trainer)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Summary\n\nIn this tutorial, you learned about how you can leverage MLMD to trace the lineage of your TFX pipeline components and resolve issues.\n\nTo learn more about how to use MLMD, check out these additional resources:\n\n* [MLMD API documentation](https://www.tensorflow.org/tfx/ml_metadata/api_docs/python/mlmd)\n* [MLMD guide](https://www.tensorflow.org/tfx/guide/mlmd)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
c5023801ea9421da474a30d2799b299abd3a8a76
| 1,912 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
task/sumo.ipynb
|
RobInLabUJI/mindstorms-nb
|
70613d3f60958a1691fbc55042f38093534290d0
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
task/sumo.ipynb
|
RobInLabUJI/mindstorms-nb
|
70613d3f60958a1691fbc55042f38093534290d0
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
task/sumo.ipynb
|
RobInLabUJI/mindstorms-nb
|
70613d3f60958a1691fbc55042f38093534290d0
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2018-07-16T13:04:11.000Z
|
2021-12-16T07:46:00.000Z
| 24.831169 | 171 | 0.585774 |
[
[
[
"# Combat de sumo\n\n[<img src=\"img/lego_sumo.jpg\" align=\"right\" width=200>](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3tguWcKTXQI)\nEls combats de sumo són una competició molt popular entre els robots mòbils. Dos robots han de lluitar per traure al contrincant del tatami.\n\nEn esta pàgina fareu un programa per a que el robot de Lego puga lluitar contra un*sparring*, una caixa que farà de contrincant, a la què ha de traure del tatami.\n\nCom sempre, connectem el robot.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from functions import connect\nconnect() ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Una possible estratègia\n\nS'admeten idees alternatives ;-)\n\n1. Localitzar la caixa: el robot girar sobre ell mateix fins que detecta un objecte a distància\n2. Atacar: el robot avança en la direcció de l'objecte, fins que detecta la línia del tatami\n3. Recuperar: el robot retrocedeix, i torna a intentar-ho\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
c5023da749cd253a5d74386c988cee0a0ab9f383
| 39,286 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
P3-landmark-detection-and-tracking/1. Robot Moving and Sensing.ipynb
|
aliabid2243/CV_ND
|
fdad3bb29ed7b12de038b5d6aa57719b0154c37d
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2020-04-27T14:55:34.000Z
|
2021-01-19T14:05:07.000Z
|
P3-landmark-detection-and-tracking/1. Robot Moving and Sensing.ipynb
|
aliabid2243/CV_ND
|
fdad3bb29ed7b12de038b5d6aa57719b0154c37d
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2021-09-08T01:56:12.000Z
|
2022-03-12T00:26:13.000Z
|
P3-landmark-detection-and-tracking/1. Robot Moving and Sensing.ipynb
|
aliabid2243/CV_ND
|
fdad3bb29ed7b12de038b5d6aa57719b0154c37d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 81.506224 | 7,552 | 0.781372 |
[
[
[
"# Robot Class\n\nIn this project, we'll be localizing a robot in a 2D grid world. The basis for simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) is to gather information from a robot's sensors and motions over time, and then use information about measurements and motion to re-construct a map of the world.\n\n### Uncertainty\n\nAs you've learned, robot motion and sensors have some uncertainty associated with them. For example, imagine a car driving up hill and down hill; the speedometer reading will likely overestimate the speed of the car going up hill and underestimate the speed of the car going down hill because it cannot perfectly account for gravity. Similarly, we cannot perfectly predict the *motion* of a robot. A robot is likely to slightly overshoot or undershoot a target location.\n\nIn this notebook, we'll look at the `robot` class that is *partially* given to you for the upcoming SLAM notebook. First, we'll create a robot and move it around a 2D grid world. Then, **you'll be tasked with defining a `sense` function for this robot that allows it to sense landmarks in a given world**! It's important that you understand how this robot moves, senses, and how it keeps track of different landmarks that it sees in a 2D grid world, so that you can work with it's movement and sensor data.\n\n---\n\nBefore we start analyzing robot motion, let's load in our resources and define the `robot` class. You can see that this class initializes the robot's position and adds measures of uncertainty for motion. You'll also see a `sense()` function which is not yet implemented, and you will learn more about that later in this notebook.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# import some resources\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport random\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# the robot class\nclass robot:\n\n # --------\n # init: \n # creates a robot with the specified parameters and initializes \n # the location (self.x, self.y) to the center of the world\n #\n def __init__(self, world_size = 100.0, measurement_range = 30.0,\n motion_noise = 1.0, measurement_noise = 1.0):\n self.measurement_noise = 0.0\n self.world_size = world_size\n self.measurement_range = measurement_range\n self.x = world_size / 2.0\n self.y = world_size / 2.0\n self.motion_noise = motion_noise\n self.measurement_noise = measurement_noise\n self.landmarks = []\n self.num_landmarks = 0\n\n\n # returns a positive, random float\n def rand(self):\n return random.random() * 2.0 - 1.0\n\n\n # --------\n # move: attempts to move robot by dx, dy. If outside world\n # boundary, then the move does nothing and instead returns failure\n #\n def move(self, dx, dy):\n\n x = self.x + dx + self.rand() * self.motion_noise\n y = self.y + dy + self.rand() * self.motion_noise\n\n if x < 0.0 or x > self.world_size or y < 0.0 or y > self.world_size:\n return False\n else:\n self.x = x\n self.y = y\n return True\n \n\n # --------\n # sense: returns x- and y- distances to landmarks within visibility range\n # because not all landmarks may be in this range, the list of measurements\n # is of variable length. Set measurement_range to -1 if you want all\n # landmarks to be visible at all times\n #\n \n ## TODO: complete the sense function\n def sense(self):\n ''' This function does not take in any parameters, instead it references internal variables\n (such as self.landamrks) to measure the distance between the robot and any landmarks\n that the robot can see (that are within its measurement range).\n This function returns a list of landmark indices, and the measured distances (dx, dy)\n between the robot's position and said landmarks.\n This function should account for measurement_noise and measurement_range.\n One item in the returned list should be in the form: [landmark_index, dx, dy].\n '''\n \n measurements = []\n \n ## TODO: iterate through all of the landmarks in a world\n for i, lm in enumerate(self.landmarks):\n ## 1. compute dx and dy, the distances between the robot and the landmark\n\n dx = lm[0] - self.x\n dy = lm[1] - self.y\n ## TODO: For each landmark\n ## 2. account for measurement noise by *adding* a noise component to dx and dy\n dx += self.rand() * self.measurement_noise\n dy += self.rand() * self.measurement_noise\n ## - The noise component should be a random value between [-1.0, 1.0)*measurement_noise\n ## - Feel free to use the function self.rand() to help calculate this noise component\n ## - It may help to reference the `move` function for noise calculation\n ## 3. If either of the distances, dx or dy, fall outside of the internal var, measurement_range\n ## then we cannot record them; if they do fall in the range, then add them to the measurements list\n ## as list.append([index, dx, dy]), this format is important for data creation done later\n if abs(dx) <= self.measurement_range and abs(dy) <= self.measurement_range:\n measurements.append([i, dx, dy])\n ## TODO: return the final, complete list of measurements\n return measurements\n\n \n # --------\n # make_landmarks: \n # make random landmarks located in the world\n #\n def make_landmarks(self, num_landmarks):\n self.landmarks = []\n for i in range(num_landmarks):\n self.landmarks.append([round(random.random() * self.world_size),\n round(random.random() * self.world_size)])\n self.num_landmarks = num_landmarks\n \n \n # called when print(robot) is called; prints the robot's location\n def __repr__(self):\n return 'Robot: [x=%.5f y=%.5f]' % (self.x, self.y)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Define a world and a robot\n\nNext, let's instantiate a robot object. As you can see in `__init__` above, the robot class takes in a number of parameters including a world size and some values that indicate the sensing and movement capabilities of the robot.\n\nIn the next example, we define a small 10x10 square world, a measurement range that is half that of the world and small values for motion and measurement noise. These values will typically be about 10 times larger, but we ust want to demonstrate this behavior on a small scale. You are also free to change these values and note what happens as your robot moves!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"world_size = 10.0 # size of world (square)\nmeasurement_range = 5.0 # range at which we can sense landmarks\nmotion_noise = 0.2 # noise in robot motion\nmeasurement_noise = 0.2 # noise in the measurements\n\n# instantiate a robot, r\nr = robot(world_size, measurement_range, motion_noise, measurement_noise)\n\n# print out the location of r\nprint(r)",
"Robot: [x=5.00000 y=5.00000]\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Visualizing the World\n\nIn the given example, we can see/print out that the robot is in the middle of the 10x10 world at (x, y) = (5.0, 5.0), which is exactly what we expect!\n\nHowever, it's kind of hard to imagine this robot in the center of a world, without visualizing the grid itself, and so in the next cell we provide a helper visualization function, `display_world`, that will display a grid world in a plot and draw a red `o` at the location of our robot, `r`. The details of how this function wors can be found in the `helpers.py` file in the home directory; you do not have to change anything in this `helpers.py` file.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# import helper function\nfrom helpers import display_world\n\n# define figure size\nplt.rcParams[\"figure.figsize\"] = (5,5)\n\n# call display_world and display the robot in it's grid world\nprint(r)\ndisplay_world(int(world_size), [r.x, r.y])",
"Robot: [x=5.00000 y=5.00000]\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Movement\n\nNow you can really picture where the robot is in the world! Next, let's call the robot's `move` function. We'll ask it to move some distance `(dx, dy)` and we'll see that this motion is not perfect by the placement of our robot `o` and by the printed out position of `r`. \n\nTry changing the values of `dx` and `dy` and/or running this cell multiple times; see how the robot moves and how the uncertainty in robot motion accumulates over multiple movements.\n\n#### For a `dx` = 1, does the robot move *exactly* one spot to the right? What about `dx` = -1? What happens if you try to move the robot past the boundaries of the world?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# choose values of dx and dy (negative works, too)\ndx = 1\ndy = 2\nr.move(dx, dy)\n\n# print out the exact location\nprint(r)\n\n# display the world after movement, not that this is the same call as before\n# the robot tracks its own movement\ndisplay_world(int(world_size), [r.x, r.y])",
"Robot: [x=6.10027 y=7.08510]\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Landmarks\n\nNext, let's create landmarks, which are measurable features in the map. You can think of landmarks as things like notable buildings, or something smaller such as a tree, rock, or other feature.\n\nThe robot class has a function `make_landmarks` which randomly generates locations for the number of specified landmarks. Try changing `num_landmarks` or running this cell multiple times to see where these landmarks appear. We have to pass these locations as a third argument to the `display_world` function and the list of landmark locations is accessed similar to how we find the robot position `r.landmarks`. \n\nEach landmark is displayed as a purple `x` in the grid world, and we also print out the exact `[x, y]` locations of these landmarks at the end of this cell.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# create any number of landmarks\nnum_landmarks = 3\nr.make_landmarks(num_landmarks)\n\n# print out our robot's exact location\nprint(r)\n\n# display the world including these landmarks\ndisplay_world(int(world_size), [r.x, r.y], r.landmarks)\n\n# print the locations of the landmarks\nprint('Landmark locations [x,y]: ', r.landmarks)",
"Robot: [x=6.10027 y=7.08510]\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Sense\n\nOnce we have some landmarks to sense, we need to be able to tell our robot to *try* to sense how far they are away from it. It will be up t you to code the `sense` function in our robot class.\n\nThe `sense` function uses only internal class parameters and returns a list of the the measured/sensed x and y distances to the landmarks it senses within the specified `measurement_range`. \n\n### TODO: Implement the `sense` function \n\nFollow the `##TODO's` in the class code above to complete the `sense` function for the robot class. Once you have tested out your code, please **copy your complete `sense` code to the `robot_class.py` file in the home directory**. By placing this complete code in the `robot_class` Python file, we will be able to refernce this class in a later notebook.\n\nThe measurements have the format, `[i, dx, dy]` where `i` is the landmark index (0, 1, 2, ...) and `dx` and `dy` are the measured distance between the robot's location (x, y) and the landmark's location (x, y). This distance will not be perfect since our sense function has some associated `measurement noise`.\n\n---\n\nIn the example in the following cell, we have a given our robot a range of `5.0` so any landmarks that are within that range of our robot's location, should appear in a list of measurements. Not all landmarks are guaranteed to be in our visibility range, so this list will be variable in length.\n\n*Note: the robot's location is often called the **pose** or `[Pxi, Pyi]` and the landmark locations are often written as `[Lxi, Lyi]`. You'll see this notation in the next notebook.*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# try to sense any surrounding landmarks\nmeasurements = r.sense()\n\n# this will print out an empty list if `sense` has not been implemented\nprint(measurements)",
"[[0, -0.002076982491630186, -3.2404268776117666], [1, 2.8326846395317338, 2.0600127473930523], [2, -2.0576181732593706, -2.2140868325481606]]\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Refer back to the grid map above. Do these measurements make sense to you? Are all the landmarks captured in this list (why/why not)?**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"---\n## Data\n\n#### Putting it all together\n\nTo perform SLAM, we'll collect a series of robot sensor measurements and motions, in that order, over a defined period of time. Then we'll use only this data to re-construct the map of the world with the robot and landmar locations. You can think of SLAM as peforming what we've done in this notebook, only backwards. Instead of defining a world and robot and creating movement and sensor data, it will be up to you to use movement and sensor measurements to reconstruct the world!\n\nIn the next notebook, you'll see this list of movements and measurements (which you'll use to re-construct the world) listed in a structure called `data`. This is an array that holds sensor measurements and movements in a specific order, which will be useful to call upon when you have to extract this data and form constraint matrices and vectors.\n\n`data` is constructed over a series of time steps as follows:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data = []\n\n# after a robot first senses, then moves (one time step)\n# that data is appended like so:\ndata.append([measurements, [dx, dy]])\n\n# for our example movement and measurement\nprint(data)",
"[[[[0, -0.002076982491630186, -3.2404268776117666], [1, 2.8326846395317338, 2.0600127473930523], [2, -2.0576181732593706, -2.2140868325481606]], [1, 2]]]\n"
],
[
"# in this example, we have only created one time step (0)\ntime_step = 0\n\n# so you can access robot measurements:\nprint('Measurements: ', data[time_step][0])\n\n# and its motion for a given time step:\nprint('Motion: ', data[time_step][1])",
"Measurements: [[0, -0.002076982491630186, -3.2404268776117666], [1, 2.8326846395317338, 2.0600127473930523], [2, -2.0576181732593706, -2.2140868325481606]]\nMotion: [1, 2]\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Final robot class\n\nBefore moving on to the last notebook in this series, please make sure that you have copied your final, completed `sense` function into the `robot_class.py` file in the home directory. We will be using this file in the final implementation of slam!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
c502423226b61c976222aab976e680e416dfe421
| 190,036 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
site/notebooks/matrix-solutions.ipynb
|
rpi-techfundamentals/ms-website-fall-2020
|
517b24801286140af5f1e10ee9099cf5d0a28b7c
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
site/notebooks/matrix-solutions.ipynb
|
rpi-techfundamentals/ms-website-fall-2020
|
517b24801286140af5f1e10ee9099cf5d0a28b7c
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
site/notebooks/matrix-solutions.ipynb
|
rpi-techfundamentals/ms-website-fall-2020
|
517b24801286140af5f1e10ee9099cf5d0a28b7c
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 358.558491 | 102,092 | 0.936696 |
[
[
[
"# Matrix Solutions \n## Introduction to Linear Programming\n\nThis gives some foundational methods of working with arrays to do matrix multiplication\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\n#Let's put in a m(rows) x n(columns)\nquant = np.array([[8, 5, 8, 0], \n [8, 2, 4, 0],\n [8, 7, 7, 5]]) \n\nprice = np.array([75,50,10,105])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#This prints a 3 x 4 matrix\nquant ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Price is a 1 x 4\nprice",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#This performance the transpose operation on the matrix.\n#This turns a 3 x 4 matrix to a 4 x 3 matrix\nquant.T",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"If vectors are identified with row matrices, the dot product can also be written as a matrix product\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#Remember that the dot product is the same as the sumproduct here.\n#Here multipying a 3 x 4 by a 1 x 4 matrix. \n#The 1 x 4 matrix is really a 4 x 1 because the dot product involves the \n#The transpose of the matrix.\n\nsum_cost= quant.dot(price)\nsum_cost",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Notice when multiplying we have to keep the inner numbers the same.\n# 1 x 4 by a 4 x 3\nprice.dot(quant.T)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!pip install pulp",
"Requirement already satisfied: pulp in /Users/jasonkuruzovich/anaconda3/envs/tf2/lib/python3.7/site-packages (2.3)\nRequirement already satisfied: amply>=0.1.2 in /Users/jasonkuruzovich/anaconda3/envs/tf2/lib/python3.7/site-packages (from pulp) (0.1.2)\nRequirement already satisfied: docutils>=0.3 in /Users/jasonkuruzovich/anaconda3/envs/tf2/lib/python3.7/site-packages (from amply>=0.1.2->pulp) (0.15.2)\nRequirement already satisfied: pyparsing in /Users/jasonkuruzovich/anaconda3/envs/tf2/lib/python3.7/site-packages (from amply>=0.1.2->pulp) (2.4.7)\n"
],
[
"#Import some required packages. \nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#Initialize the model as a minimization problem. \nimport pulp as pl\nopt_model = pl.LpProblem(\"MIPModel\", pl.LpMinimize)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Set the variables. Notice this is where we put \n# the \"non-negativity\" constraint\nfor x in range(1,4):\n for y in range(1,4):\n var='x'+str(x)+str(y)\n print(var)\n #this systematically creates all the variables. \n exec(var +' = pl.LpVariable(cat=pl.LpInteger, lowBound=0, name=\"$'+var+'$\")')\n#x1 =pl.LpVariable(cat=pl.LpInteger, lowBound=0, name=\"$x_{1}$\") \n#x2 =pl.LpVariable(cat=pl.LpInteger, lowBound=0, name=\"$x_{2}$\") ",
"x11\nx12\nx13\nx21\nx22\nx23\nx31\nx32\nx33\n"
],
[
"#Set the objective function\nopt_model += np.array([x11, x12, x13], \\\n [x21, x22, x23],\\\n [x11, x12, x13]]) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Set the Constraints\nopt_model += 2 * x1 + 4* x2 >= 16\n\nopt_model += 4 * x1 + 3 * x2 >= 24",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Review Model\n\nNow that we have created the model we can review it. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"opt_model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Markdown of output\nIf we copy the above text into a markdown cell you will see the implications of the varous models. \n\n\nMIPModel:\n\nMINIMIZE\n\n6*$x_{1}$ + 3*$x_{2}$ + 0\n\nSUBJECT TO\n\n_C1: 2 $x_{1}$ + 4 $x_{2}$ >= 16\n\n_C2: 4 $x_{1}$ + 3 $x_{2}$ >= 24\n\nVARIABLES\n\n0 <= $x_{1}$ Integer\n\n0 <= $x_{2}$ Integer\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Solve\n\nWe now solve the system of equations with the solve command. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#Solve the program\nopt_model.solve()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Check the Status\n\nHere are 5 status codes:\n* **Not Solved**: Status prior to solving the problem.\n* **Optimal**: An optimal solution has been found.\n* **Infeasible**: There are no feasible solutions (e.g. if you set the constraints x <= 1 and x >=2).\n* **Unbounded**: The constraints are not bounded, maximising the solution will tend towards infinity (e.g. if the only constraint was x >= 3).\n* **Undefined**: The optimal solution may exist but may not have been found.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pl.LpStatus[opt_model.status]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for variable in opt_model.variables():\n print(variable.name,\" = \", variable.varValue)",
"$x_{1}$ = 0.0\n$x_{2}$ = 8.0\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Hurray! \nWe got the same answer as we did before. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Exercise\n\nSolve the LP problem for Beaver Creek Pottery using the maximization model type (`pl.LpMaximize`).\n\n\n### Product mix problem - Beaver Creek Pottery Company\nHow many bowls and mugs should be produced to maximize profits given labor and materials constraints?\n\nProduct resource requirements and unit profit:\n\nDecision Variables:\n\n$x_{1}$ = number of bowls to produce per day\n\n$x_{2}$ = number of mugs to produce per day\n\n\nProfit (Z) Mazimization\n\nZ = 40$x_{1}$ + 50$x_{2}$\n\nLabor Constraint Check\n\n1$x_{1}$ + 2$x_{2}$ <= 40\n\nClay (Physicial Resource) Constraint Check\n\n4$x_{1}$ + 3$x_{2}$ <= 120\n\nNegative Production Constaint Check\n\n$x_{1}$ > 0\n\n$x_{2}$ > 0\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Sensitivity Analysis",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for name, c in opt_model.constraints.items():\n print (name, \":\", c, \"\\t\", c.pi, \"\\t\\t\", c.slack)",
"_C1 : 2*$x_{1}$ + 4*$x_{2}$ >= 16 \t 0.0 \t\t -16.0\n_C2 : 4*$x_{1}$ + 3*$x_{2}$ >= 24 \t 0.0 \t\t -0.0\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c5024316e933f752dc9171c3c83c5a0c51d99097
| 1,835 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
hello.ipynb
|
Ferrandino/github-tutorial
|
e1f83d54f597ed06e111c5dfc1969fc490ba0f00
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
hello.ipynb
|
Ferrandino/github-tutorial
|
e1f83d54f597ed06e111c5dfc1969fc490ba0f00
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
hello.ipynb
|
Ferrandino/github-tutorial
|
e1f83d54f597ed06e111c5dfc1969fc490ba0f00
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 31.637931 | 549 | 0.547684 |
[
[
[
" def hello(name): \n print(\"Hello \" + name)\n\n if __name__ == \"__main__\":\n hello()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
]
] |
c502638433753d173f99628e12f1be46fb5caa09
| 67,693 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
EDyA_II/2_search/Iterative binary search.ipynb
|
jrg-sln/academy
|
498c11dcfeab78dbbbb77045a13d7d6675c0d150
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
EDyA_II/2_search/Iterative binary search.ipynb
|
jrg-sln/academy
|
498c11dcfeab78dbbbb77045a13d7d6675c0d150
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
EDyA_II/2_search/Iterative binary search.ipynb
|
jrg-sln/academy
|
498c11dcfeab78dbbbb77045a13d7d6675c0d150
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 170.082915 | 19,076 | 0.882661 |
[
[
[
"## Binary search",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"El método de búsqueda binaria funciona, únicamente, sobre conjunto de datos ordenados.\n\nEl método consiste en dividir el intervalo de búsqueda en dos partes y compara el elemento que ocupa la posición central del conjunto. Si el elemento del conjunto no es igual al elemento buscado se redefinen los extremos del intervalo, dependiendo de si el elemento central es mayor o menor que el elemento buscado, reduciendo así el espacio de búsqueda.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%pylab inline\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D\nimport random",
"Populating the interactive namespace from numpy and matplotlib\n"
],
[
"def binary_iterative_search(intList, intValue):\n lowIndex = 0\n highIndex = len(intList)-1\n while lowIndex != highIndex:\n medium = (highIndex + lowIndex)//2\n if intList[medium] == intValue:\n return medium\n else:\n if intValue < intList[medium]:\n highIndex = medium\n else:\n lowIndex = medium + 1\n if intList[lowIndex] == intValue:\n return lowIndex\n else:\n return -1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"TAM_LIST = 2001\nTAM_RANDOM_INT = 1000\n#val = random.randint(1, TAM_RANDOM_INT)\nval = 2000\ncont = 0\n\nl = []\nfor i in range(1, TAM_LIST, 1):\n l.append(random.randint(1, TAM_RANDOM_INT))\nl.sort()\n\nres = binary_iterative_search(l, val)\n\nif res == -1:\n print('La llave', val,'no se encuentra en el conjunto')\nelse:\n print('El valor', val,'se encuentra en la posición', res)",
"La llave 2000 no se encuentra en el conjunto\n"
],
[
"class Node:\n def __init__(self, number, name, lastname, email, sex):\n self.identifier = number\n self.name = name\n self.last_name = lastname\n self.email = email\n self.sex = sex[0]\n \n def __str__(self):\n return self.name + \": \" + self.email",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def bubble_sort_node(nodeList):\n times = 0\n cont = 0\n comp = 0\n aux = 0\n while cont < len(nodeList)-1:\n times += 1\n comp = len(nodeList)-1\n while comp > cont:\n times += 1\n if nodeList[comp-1].name > nodeList[comp].name:\n aux = nodeList[comp-1]\n nodeList[comp-1] = nodeList[comp]\n nodeList[comp] = aux\n comp = comp - 1\n cont = cont + 1\n return times",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def binary_iterative_node_search(nodeList, nodeValue):\n lowIndex = 0\n highIndex = len(nodeList)-1\n while lowIndex != highIndex:\n medium = (highIndex + lowIndex)//2\n if nodeList[medium].name == nodeValue.name:\n return medium\n else:\n if nodeValue.name < nodeList[medium].name:\n highIndex = medium\n else:\n lowIndex = medium + 1\n if nodeList[lowIndex].name == nodeValue.name:\n return lowIndex\n else:\n return -1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"nodeList = []\nfile = open(\"DATA_10.csv\", \"r\")\nfor line in file:\n fields = line.split(\",\")\n nodeList.append(Node(fields[0], fields[1], fields[2], fields[3], fields[4]))\n \nprint(\"List\")\nfor node in nodeList:\n print(node)\n\nbubble_sort_node(nodeList)\nprint(\"\\nBubble sort\")\nfor node in nodeList:\n print(node)\n \nvalue = nodeList[random.randint(0, len(nodeList)-1)]\nprint(\"\\nSearch \", value.name)\nprint(binary_iterative_node_search(nodeList, value))",
"List\nCori: [email protected]\nBarri: [email protected]\nElyssa: [email protected]\nMendie: [email protected]\nFaulkner: [email protected]\nFarr: [email protected]\nTy: [email protected]\nStephenie: [email protected]\nAngil: [email protected]\nSorcha: [email protected]\n\nBubble sort\nAngil: [email protected]\nBarri: [email protected]\nCori: [email protected]\nElyssa: [email protected]\nFarr: [email protected]\nFaulkner: [email protected]\nMendie: [email protected]\nSorcha: [email protected]\nStephenie: [email protected]\nTy: [email protected]\n\nSearch Angil\n0\n"
],
[
"def binary_iterative_node_search_graph(nodeList, nodeValue):\n cont = 0\n lowIndex = 0\n highIndex = len(nodeList)-1\n while lowIndex != highIndex:\n cont += 1\n medium = (highIndex + lowIndex)//2\n if nodeList[medium].name == nodeValue.name:\n return cont\n else:\n if nodeValue.name < nodeList[medium].name:\n highIndex = medium\n else:\n lowIndex = medium + 1\n cont += 1\n if nodeList[lowIndex].name == nodeValue.name:\n return cont\n else:\n return cont",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"TAM = 101\nx = list(range(1,TAM,1))\ny_omega = []\ny_efedeene = []\ny_omicron = []\nL = []\nfor num in x:\n iter = 1\n file = open(\"DATA_10000.csv\", \"r\")\n L = []\n for line in file:\n fields = line.split(\",\")\n L.append(Node(fields[0], fields[1], fields[2], fields[3], fields[4]))\n \n if iter == num:\n break\n iter += 1\n \n res = bubble_sort_node(L)\n \n # average case\n value = L[random.randint(0, len(L)-1)]\n\n y_efedeene.append(binary_iterative_node_search_graph(L, value)+res)\n\n # best case\n value = L[(len(L)-1)//2]\n y_omega.append(binary_iterative_node_search_graph(L, value)+res)\n\n # worst case\n value = Node(0, \"zzzzzzzzzzzz\", \"zzzzzzzzzzzz\", \"zzzzzzzzzzzz\", \"zzzzzzzzzzzz\")\n y_omicron.append(binary_iterative_node_search_graph(L, value)+res)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(facecolor='w', edgecolor='k')\nax.plot(x, y_omega, marker=\"o\",color=\"b\", linestyle='None')\nax.set_xlabel('x')\nax.set_ylabel('y')\nax.grid(True)\nax.legend([\"Binary iterative search\"])\nplt.title('Binary iterative search (best case)')\nplt.show()\n\nfig, ax = plt.subplots(facecolor='w', edgecolor='k')\nax.plot(x, y_efedeene, marker=\"o\",color=\"b\", linestyle='None')\nax.set_xlabel('x')\nax.set_ylabel('y')\nax.grid(True)\nax.legend([\"Binary iterative search\"])\nplt.title('Binary iterative search (average case)')\nplt.show()\n\nfig, ax = plt.subplots(facecolor='w', edgecolor='k')\nax.plot(x, y_omicron, marker=\"o\",color=\"b\", linestyle='None')\nax.set_xlabel('x')\nax.set_ylabel('y')\nax.grid(True)\nax.legend([\"Binary iterative search\"])\nplt.title('Binary iterative search (worst case)')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50275ce462e73009de4a8a92837acfa534b32a2
| 11,041 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
prac12/solution.ipynb
|
mathmechterver/stat2022
|
c5a26ef47a880641755788cd788c974a8f2390e3
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 5 |
2022-01-13T12:09:34.000Z
|
2022-02-14T13:50:08.000Z
|
prac12/solution.ipynb
|
mathmechterver/stat2022
|
c5a26ef47a880641755788cd788c974a8f2390e3
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
prac12/solution.ipynb
|
mathmechterver/stat2022
|
c5a26ef47a880641755788cd788c974a8f2390e3
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 2 |
2022-02-15T03:50:23.000Z
|
2022-03-29T04:44:14.000Z
| 48.004348 | 420 | 0.548954 |
[
[
[
"## Классная работа\n\nЯвляется ли процесс ($X_n$) мартингалом по отношению к фильтрации $\\mathcal{F}_n$?\n\n1. $z_1,z_2,\\ldots,z_n$ — независимы и $z_i\\sim N(0,49)$, $X_n=\\sum_{i=1}^n z_i$. Фильтрация: $\\mathcal{F}_n=\\sigma(z_1,z_2,\\ldots,z_n);$\n\n2. $z_1,z_2,\\ldots,z_n$ — независимы и $z_i\\sim U[0,1]$, $X_n=\\sum_{i=1}^n z_i$. Фильтрация: $\\mathcal{F}_n=\\sigma(z_1,z_2,\\ldots,z_n);$\n\n3. Есть колода карт. Всего 52 карты, 4 масти. Я открываю одну карту за другой и смотрю, какую карту я открыла. Пусть $X_n$ — доля тузов в оставшейся колоде после открытия $n$ карт. $\\mathcal{F}_n$ — знаю те карты, которые открыты. Рассмотрим, какие значения могут принимать $X_0$ и $X_{51}.$\n\n$X_0=\\dfrac4{52}.$ \n\nПосле открытия 51-ой карты, получим, что значения, которые принимает $X_{51}$ будет либо 1 (последняя карта — туз), либо 0 (последняя карта — не туз). Тогда вероятность того, что последняя карта окажется тузом, равна $\\dfrac4{52}$, так как всего 4 туза, а количество карт равно 52.\n\n| Исход | Не туз | Туз |\n|----------|----------------|-------------|\n| $X_{51}$ | $0$ | $1$ |\n| $p$ |$\\dfrac{48}{52}$|$\\dfrac4{52}$|\n\nd) Сколько элементов в $\\mathcal{F_1}$ и $\\mathcal{F_2}$? Понять, что больше: число элементарных частиц во Вселенной или число элементов в $\\mathcal{F_2}$?\n\n### Решение:\nДля всех случаев нужно проверить выполнение двух условий из определения мартингала.\n\n**a) Рассмотрим 1-ый случай:**\n\n 1-ое условие: Я знаю $z_1,z_2,\\ldots,z_n$ и так как $X_n=\\sum_{i=1}^n z_i$, то я знаю $X_n$.\n\n 2-ое условие: $E(X_{n+1}|\\mathcal{F}_n) = E(z_1+z_2+\\ldots+z_{n+1}|z_1,z_2,\\ldots,z_n) =$ (знаю $z_1,z_2,\\ldots,z_n$, поэтому могу их вынести) $= z_1+z_2+\\ldots+z_n + E(z_{n+1}|z_1,z_2,\\ldots,z_n) = z_1+z_2+\\ldots+z_n+E (z_{n+1})=z_1+z_2+\\ldots+z_n=X_n.$\n \nПояснения ко 2-ому условию: ($E (z_{n+1}) = 0$ так как $z_i \\sim N(0,1).$\n \n $E (z_{n+1}|z_1,z_2,\\ldots,z_n)=E (z_{n+1})$, так как случайные величины $z_1,z_2,\\ldots,z_{n+1}$ — независимы).\n \n Оба условия выполняются, а значит, процесс ($X_n$) — мартингал по отношению к фильтрации $\\mathcal{F}_n.$\n\n**b) Рассмотрим 2-ой случай:**\n\n 1-ое условие: Я знаю $z_1,z_2,\\ldots,z_n$ и так как $X_n=\\sum_{i=1}^n z_i$, то я знаю $X_n.$\n\n 2-ое условие: $E (X_{n+1}|\\mathcal{F}_n)=E (z_1+z_2+\\ldots+z_{n+1}|z_1,z_2,\\ldots,z_n) =$ (знаю $z_1,z_2,\\ldots,z_n$, поэтому могу их вынести) $= z_1+z_2+\\ldots+z_n+E (z_{n+1}|z_1,z_2,\\ldots,z_n) = z_1+z_2+\\ldots+z_n+E (z_{n+1}) = z_1+z_2+\\ldots+z_n+\\dfrac{0+1}{2}=X_n+\\dfrac12 \\ne X_n.$ \n\n2-ое условие не выполняется, а значит, в этом случае процесс ($X_n$) — не является мартингалом.\n\n**c) Рассмотрим 3-ий случай:**\n\n 1-ое условие: выполнено, так как если я вижу открытые карты, то могу посчитать долю тузов среди неоткрытых, то есть могу посчитать $X_n.$\n \n 2-ое условие:\n Спрогнозируем долю тузов, когда открою следующую карту : $E (X_{n+1}|\\mathcal{F}_n).$\n \n Сейчас: открыто $n$, закрыто $52-n.$\n \n Доля тузов среди закрытых карт: $X_n.$\n \n Количество закрытых тузов: $X_n(52-n).$\n \n Тогда вероятность того, что при открытии $n+1$ карты будет туз, равна доле тузов среди закрытых карт или $X_n$. Если карта — туз, то после её открытия доля тузов будет равна $X_{n+1}=\\dfrac{(52-n)X_n-1}{51-n}$. Если же при открытии карта окажется не тузом, то $X_{n+1}=\\dfrac{(52-n)X_n}{51-n}$. Ниже представлена таблица с долями тузов и вероятностями исходов.\n \n| Исход | Туз | Не туз |\n|---------|---------------------------|-------------------------|\n|$X_{n+1}$|$\\dfrac{(52-n)X_n-1}{51-n}$|$\\dfrac{(52-n)X_n}{51-n}$|\n| $p$ | $X_n$ | $1-X_n$ |\n \n \n \n\n$E (X_{n+1}|\\mathcal{F}_n) = X_n\\dfrac{(52-n)X_n-1}{51-n}+(1-X_n)\\dfrac{(52-n)X_n}{51-n} = \\dfrac{52X_n^2-nX_n^2-X_n+52X_n-52X_n^2-nX_n+nX_n^2}{51-n}=\\dfrac{51X_n-nX_n}{51-n}=X_n$ \n\n2-ое условие выполняется.\n\nОба условия выполняются, а значит, процесс ($X_n$) — мартингал по отношению к фильтрации $\\mathcal{F}_n.$\n\n**d) Последнее задание**\n\n$\\mathcal{F_1}$ содержит 52 элементарных события (например, карта №1 — дама $\\clubsuit$, карта №2 — туз $\\spadesuit$ и т.д.). Каждое событие либо включаем либо не включаем, поэтому получим $card\\mathcal{F_1}=2^{52}.$\n\n$card\\mathcal{F_2}=2^{C_{52}^1C_{51}^1}=2^{52\\cdot51} \\approx (4 \\cdot 10^{15})^{51}=4^{51} \\cdot 10^{15\\cdot51}$ \n\nЧисло элементарных частиц во Вселенной $\\approx 10^{81}$\n\n$4^{51}\\cdot 10^{15\\cdot51} \\gg 10^{81}$\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Упражнение**\n\n$z_1,z_2,\\ldots,z_n$ — независимы и $z_i\\sim U[0,1]$, $X_n=\\sum_{i=1}^n z_i.$ Фильтрация: $\\mathcal{F}_n=\\sigma(X_1,X_2,\\ldots,X_n).$ Возьмём процесс $M_n=a^{X_n}$. Нужно подобрать число $a$ так, чтобы $(M_n)$ был мартингалом относительно фильтрации $\\mathcal{F}_n$.\n\n**Решение**\n\nПростой случай: $a = 1$. Действительно, $(M_n) = (1,1,1,1,\\ldots)$. Тогда $E (M_{n+1}|\\mathcal{F}_n)=1=M_n$, а значит, $(M_n)$ — мартингал. \n\nТеперь попробуем найти $a \\ne 1$. Для этого проверим выполнимость двух условий из определения мартингала.\n\n1-ое условие: $M_n$ измерим относительно $\\mathcal{F}_n$ при известном $a.$\n\n2-ое условие: $E (M_{n+1}|\\mathcal{F}_n)=E (a^{X_{n+1}}|\\mathcal{F}_n)=E (a^{z_1+z_2+\\ldots+z_{n+1}}|\\mathcal{F}_n) =$ (знаю $z_1,z_2,\\ldots,z_n$, поэтому могу их вынести) $= a^{z_1+z_2+\\ldots+z_n}E (a^{z_{n+1}}|\\mathcal{F}_n)=a^{X_n}E (a^{z_{n+1}}|\\mathcal{F}_n) =$ (так как случайная величина $z_{n+1}$ не зависит от $z_1,z_2,\\ldots,z_n$) $= M_nE (a^{z_{n+1}}) =$ (по определению мартингала) $= M_n.$\n\nТогда\n\n$E (a^{z_{n+1}})=1$\n\n$E (a^{z_{n+1}})=\\int\\limits_0^1 a^t\\,dt=1$\n\n$\\int\\limits_0^1 e^{t\\cdot\\ln a}\\,dt=\\left. \\dfrac{e^{t\\cdot\\ln a}}{\\ln a}\\right|_0^1=\\dfrac{e^{\\ln a}}{\\ln a}-\\dfrac1{\\ln a}=\\dfrac{e^{\\ln a}-1}{\\ln a}=\\dfrac{a-1}{\\ln a} = 1$ $\\Rightarrow$\n\n$\\Rightarrow a-1=\\ln a$\n\nЭто уравнение имеет единственное решение $a = 1.$\n\nПолучаем:\n\nПроцесс $M_n=a^{X_n}$ является мартингалом относительно фильтрации $\\mathcal{F}_n$ только при $a = 1.$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Мартингалы (продолжение). Момент остановки.{#12 Martingals. Stopping time}\n\n## Мартингалы (продолжение) \n### Задачка\n### Упражнение:\n\nИзвестно, что $M_t$ — мартингал. Чему равняется $E(M_{t+1}|\\mathcal{F_{t+1}})$, $E(M_{t+2}|\\mathcal{F_t}),$\n а также $E(M_{t+k}|\\mathcal{F_t}),$ (при $k \\geqslant 0$)?\n \n### Решение:\n\n1) По определению мартингала: $E(M_{t+1}|\\mathcal{F_{t+1}})=M_{t+1}.$\n\n**Важное свойство:** $\\mathcal{F_t} \\leqslant \\mathcal{F_{t+1}}.$\n\n2) $E(M_{t+2}|\\mathcal{F_t})=E[E(M_{t+2}|\\mathcal{F_{t+1}})|\\mathcal{F_t}]=$ (по свойству повторного математического ожидания) $=E(M_{t+1}|\\mathcal{F_t})=M_t.$\n3) $E(M_{t+k}|\\mathcal{F_t})=M_t, k \\geqslant 0.$\n\n## Момент остановки \n\n**Определение:**\nСлучайная величина $T$ называется моментом остановки (stopping time) по отношению к фильтрации $\\mathcal{F_t}$, если:\n1) Интуитивно: когда $T$ наступит, это можно понять;\n2) Формально:\n2.1) $T$ принимает значения $({0,1,2,3,\\ldots }) U (+\\infty)$;\n2.2)Событие $(T=k)$ содержится в $\\mathcal{F_k}$ для любого k.\n\n### Задачки:\n\n#### Задача №1:\n\nПусть $X_t$ — симметричное случайное блуждание,\n$X_t=D_1+D_2+\\ldots+D_t$, где $D_i$ — независимы и равновероятно принимают значения $(\\pm 1)$\nФильтрация:\n$\\mathcal{F_t}=\\sigma(X_1,X_2,\\ldots,X_t)$ (мы видим значения случайного блуждания).\nИмеются случайные величины:\n$T_1=min\\{t|X_t=100\\}$,\n$T_2=T_1+1$,\n$T_3=T_1-1.$\nЧто из этого является моментом остановки?\n\n#### Решение: \n\n$T_1=min\\{t|X_t=100\\}$ — Да, момент остановки. В тот момент, когда он наступает, мы можем точно сказать был он или не был.\n$T_2=T_1+1$ — Да, момент остановки. Если $T_1$ — произошло, то мы сможем сказать, что на следующем шаге наступит $T_2.$\n$T_3=T_1-1$ — Нет.\n\nИнтуитивное объяснение: Бабушка говорит внуку: \"Приходи ко мне в гости, когда наступит момент $T$\", а внук видит значения $X$. Прийдет ли внук вовремя в гости к бабушке? \n\nОтвет: $T_1$, $T_2.$\n\n#### Задача №2:\nИзвлекаем карты из коллоды по одной и видим извлечённые значения.\n$T_1$ — извлечение второго туза, является моментом остановки,\n$T_1/2$ — не является моментом остановки. \n\n## Остановленный процесс\n\n**Определение:**\nПусть $X_t$ — случайный процесс, а $t$ — момент остановки.\nПроцесс $Y_t=X_{min\\{t,T\\}}$ называется остановленным процессом $X_t$.\n\n### Примеры:\n\n#### Пример №1:\nПусть $X_t$ — симметричное случайное блуждание,\n$\\tau=min\\{t|X_t=20\\}.$\nПостроить две траектории $X_t$ и соответствующие траектории $Y_t=X_{\\tau}.$\n\n\n\nКогда $min\\{t,\\tau\\}=t$ и $t \\leqslant \\tau$ то $Y_t = X_t$,\nкогда $t > \\tau$ то $Y_t < X_t.$\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
c502781ac8cfc5b97fc79dd16d4574b1f3001aac
| 354,657 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
modules/ai-codes/modules/recommender-system/surpriselib.ipynb
|
drigols/Studies
|
9c293156935b491ded24be6b511daac67fd43538
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
modules/ai-codes/modules/recommender-system/surpriselib.ipynb
|
drigols/Studies
|
9c293156935b491ded24be6b511daac67fd43538
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
modules/ai-codes/modules/recommender-system/surpriselib.ipynb
|
drigols/Studies
|
9c293156935b491ded24be6b511daac67fd43538
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 46.800871 | 7,900 | 0.418382 |
[
[
[
"# Sistema de Recomendação com a biblioteca Surprise\nAqui nós vamos implementar um simples **Sistema de Recomendação** com a biblioteca **[Surprise](http://surpriselib.com/)**. O objetivo principal é testar alguns dos recursos básico da biblioteca.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 01 - Preparando o Ambiente & Conjunto de dados",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 01.1 - Baixando a biblioteca \"surprise\"\nA primeira coisa que nós vamos fazer é baixar a biblioteca **[Surprise](http://surpriselib.com/)** que é uma biblioteca especifica para **Sistemas de Recomendação**.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#conda install -c conda-forge scikit-surprise\n#!pip install scikit-surprise",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 01.2 - Importando as bibliotecas necessárias\nAgora vamos importar as bibliotecas necessárias para criar nosso **Sistema de Recomendação**.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport datetime\nimport surprise\n\nfrom datetime import datetime",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 01.3 - Pegando o conjunto de dados\nAgora nós vamos pegar o conjunto de dados **[FilmTrust](https://guoguibing.github.io/librec/datasets.html)** que basicamente vai ter:\n\n - ID dos usuários;\n - ID do filme;\n - Nota (rating) que foi dado ao filme.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df = pd.read_csv(\n \"datasets/ratings.txt\", # Get dataset.\n sep=\" \", # Separate data by space.\n names=[\"user_id\", \"movie_id\", \"rating\"] # Set columns names.\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.info()\ndf.head(20)",
"<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>\nRangeIndex: 35497 entries, 0 to 35496\nData columns (total 3 columns):\n # Column Non-Null Count Dtype \n--- ------ -------------- ----- \n 0 user_id 35497 non-null int64 \n 1 movie_id 35497 non-null int64 \n 2 rating 35497 non-null float64\ndtypes: float64(1), int64(2)\nmemory usage: 832.1 KB\n"
]
],
[
[
"**NOTE:** \nVejam que nós temos **35.497** amostras e 3 colunas (features).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"---",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 02 - Análise Exploratória dos dados (EDA)\nAgora nós vamos fazer uma breve **Análise Exploratória dos dados (EDA)** no nosso conjunto de dados a fim de tirar insights dos mesmos.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 02.1 - Contabilizando o número total de filmes (movies), usuários (users) e amostras (samples)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"movies = len(df[\"movie_id\"].unique())\nusers = len(df[\"user_id\"].unique())\nsamples = df.shape[0]\n\nprint(\"Total movies:\", movies)\nprint(\"Total users:\", users)\nprint(\"Total samples:\", samples)",
"Total movies: 2071\nTotal users: 1508\nTotal samples: 35497\n"
]
],
[
[
"**NOTE:** \nComo podem ver nós temos apenas **35.497** amostras, mas as combinações entre **filmes (movies)** e **usuários (users)** é bem maior que isso:\n\n```python\n2.071 x 1.508 = 3.123.068\n```\n\nOu seja, temos muitos dados faltantes (missing) e isso pode ocorrer porque alguns usuários apenas não viram determinados filmes. Por isso, vai ser interessante tentar ***prever*** esses valores.\n\nPor exemplo, vamos olhar as 20 primeiras amostras:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df.head(20)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**NOTE:** \nCom apenas 20 amostras já da para tirar algumas concluções:\n - O usuário 1 viu apenas 12 filmes:\n - Ou seja, teremos que fazer inúmeras previsões de notas (rating) de filmes para esse usuário.\n - O usuário 2 viu apenas 2 filme:\n - Pior ainda, podemos ter até um problema de underfitting para prever notas (rating) para esse usuário visto que o nosso Algoritmo não vai generalizar o suficiente.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 02.2 - Contabilizando o número de notas (rating)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df['rating'].value_counts().plot(kind=\"bar\")\nplt.xlabel(\"User Rating\")\nplt.ylabel(\"Frequency\")\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**NOTE:** \nOlhando para o gráfico acima nós temos que:\n - A nota (rating) mínima foi 0.5;\n - A nota (rating) máxima foi 4.0;\n - A nota (rating) mais frequente foi 4.0.\n\nVamos ver esse mesmo resultado, porém, utilizando outra abordagem, apenas para fins de ensino.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"max_rating = df[\"rating\"].max()\nmin_rating = df[\"rating\"].min()\nprint(\"Max rating: {0} \\nMin rating: {1}\".format(max_rating, min_rating))",
"Max rating: 4.0 \nMin rating: 0.5\n"
]
],
[
[
"---",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 03 - Preparando & Treinando um modelo para Sistema de Recomendação",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 03.1 - Redefinindo o range (escala) do ratings\nPor padrão a classe **surprise.Reader** tem o range (escala) de rating de **rating_scale=(1, 5)**, então, vamos redefinir esse parâmetro para se ajustar a nossa necessidade, ou seja, de **0.5** até **4.0**.\n\nPara utilizar um conjunto de dados externos da biblioteca Surprise (visto que ela também tem conjuntos de dados prontos para testes) você antes tem que utilizar a classe [Reader](https://github.com/NicolasHug/Surprise/blob/fa7455880192383f01475162b4cbd310d91d29ca/surprise/reader.py). Essa classe, tem o seguinte construtor por padrão (default):\n\n```python\ndef __init__(\n self,\n name=None,\n line_format='user item rating',\n sep=None,\n rating_scale=(1, 5),\n skip_lines=0\n):\n```\n\nVamos criar uma instância dessa classe apenas passando como argumento o que nos interessa - **rating_scale = (0.5, 4.0)**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"reader = surprise.Reader(rating_scale = (0.5, 4.0))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 03.2 - Passando o nosso conjunto de dados (DataFrame Pandas) para o Surprise\nA biblioteca Surprise tem uma abordagem um pouco diferente de se trabalhar. Uma delas é na hora de passar dados externos para a biblioteca, por exemplo, para passar um DataFrame Pandas nós podemos utilizar o método **load_from_df()** da classe **Dataset**.\n\nEsse método recebe os seguintes argumentos:\n - **df (Dataframe):**\n - O dataframe que contém as classificações. Ele deve ter três colunas, correspondentes aos:\n - ids do usuário;\n - aos ids do item (filmes no nosso caso);\n - e às classificações (ratings), nesta ordem.\n - **leitor (Reader):**\n - Um leitor (Reader) para ler o arquivo. Apenas o campo **rating_scale** precisa ser especificado.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Load df to surprise library + Pass rating_scale by Reader class.\ndf_surprise = surprise.Dataset.load_from_df(df, reader)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 03.3 - Criando um conjunto de dados de treinamento a partir de \"df_surprise\"\nComo nós vimos no passo anterior, nós passamos nosso conjunto de dados para a biblioteca Surprise e salvamos isso na variável **df_surprise**. Agora nós vamos pegar todo esse conjunto de dados e criar um conjunto de dados de treinamento (isso mesmo, sem dados de validação/teste).\n\nPara isso nós vamos utilizar o método **build_full_trainset()** da classe **[Dataset](https://surprise.readthedocs.io/en/stable/dataset.html#surprise.dataset.DatasetAutoFolds.build_full_trainset)**:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_without_missing = df_surprise.build_full_trainset()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**NOTE:** \nEu deixei bem explicito a partir do nome da variável (df_without_missing) que esse conjunto de dados de treinamento não vai conter valores **faltantes/missing**.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 03.4 - Criando uma instância do Algoritmo SVD++\nComo nós sabemos uma das abordagens para fazer previsões em Sistemas de Recomendações é utilizando **Matrix Factorization** que é uma abordagem baseada em **Filtragem Colaborativa**.\n\n**NOTE:** \nEsse Algoritmo vai criar *características (features)* para os usuários e itens (filmes no nosso caso) e a partir dessas *características (features)* nós podemos fazer previsões futuras.\n\nA primeira coisa que nós vamos fazer aqui é criar uma instância do Algoritmo SVD++:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"algo_svdpp = surprise.SVDpp(n_factors=20) # SVD++ instance.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 03.5 - Criando as características (features) a partir do Algoritmo SVD++\nPara criar as *características (features)* é muito simples, basta treinar nosso modelo com o método **fit()** passando como argumento um conjunto de dados.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"algo_svdpp.fit(df_without_missing)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**NOTE:** \nA parte do código acima nada mais do que utilizar o algoritmo **SVD++** para criar as *features* para o nosso conjunto de dados. Por padrão, o algoritmo criar 20 features (n_factors=20). Outra observação é que ele está utilizando o método **Matrix Factorization** como pode ser visto na saída acima.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 03.6 - Criando um DataFrame com os dados faltantes/missing\nComo nós sabemos, nós temos:\n\n```python\nTotal movies: 2071\nTotal users: 1508\nTotal samples: 35497\n```\n\nO que nos resultaria em:\n\n```python\n2.071 x 1.508 = 3.123.068\n```\n\nOu seja, ainda faltam milhões de combinações de usuários e notas (rating) para filmes. Como nós criamos as *features* para esse conjunto de dados agora vamos ***prever*** as combinações faltantes.\n\nPara isso primeiro nós vamos utilizar o método **build_anti_testset()** a partir da nossa variável **df_without_missing (nosso conjunto de dados sem dados missing)**. Esse método retorna uma lista de classificações (ratings) que podem ser usadas como um conjunto de testes.\n\nPor exemplo, primeiro vamos pegar as combinações que faltam para o nosso conjunto de dados, ou seja, os dados faltantea/missing:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_missing_values = df_without_missing.build_anti_testset()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Se você utilizar a função **len(df_missing_values)** vai ver que existem milhões de combinações que estavam faltando e agora nosso algoritmo **SVD++** *preveu (estimou)*.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"len(df_missing_values)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Ué, mas essa saída é menos do que o tamanho máximo de combinações possíveis!** \nLembrem, que essa saída são apenas os faltantes/missing. Nós devemo subtrair to número total às **35.497** amostras que nós já temos:\n\n```python\n(Total movies: 2071) * (Total users: 1508)\n2.071 x 1.508 = 3.123.068\n\n(Total combinations: 3.123.068) - (Samples we already had: 35497) = 3.087.574\n```\n\nÓtimo agora nós já temos as combinações que faltavam salvos na variável **df_missing_values**. Só para estudos mesmo, vou criar uma mecanismo abaixo que **printa()** as 10 primeiras combinações que faltavam, isso porque se a gente tinha toda a variável **df_missing_values** vai dar uma saída muito grande.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"count = 0\nwhile count < 10:\n print(df_missing_values[count])\n count += 1",
"(1, 13, 3.0028030537791928)\n(1, 14, 3.0028030537791928)\n(1, 15, 3.0028030537791928)\n(1, 16, 3.0028030537791928)\n(1, 17, 3.0028030537791928)\n(1, 18, 3.0028030537791928)\n(1, 19, 3.0028030537791928)\n(1, 20, 3.0028030537791928)\n(1, 21, 3.0028030537791928)\n(1, 22, 3.0028030537791928)\n"
]
],
[
[
"**NOTE:** \nSe vocês compararem essa saída com a do nosso conjunto de dados originais (sem previsões alguma) vai ver que o primeiro usuário só deu notas (rating) até o filme com ID 12. Ou seja, o nosso Algoritmo SVD++ fez as previsões para as combinações que faltavam.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 03.7 - Relacionando todos os dados em um único objeto\nAgora nós vamos utilizar o método **test()** do modelo SVD++ (objeto) para fazer uma relação entre os dados que os usuários já tinham passado e os que nós prevemos (estimamos), onde, vamos ter:\n - **uid:**\n - ID do usuário.\n - **iid:**\n - ID do filme.\n - **r_ui:**\n - A resposta real. Ou seja, o valor passado pelo usuário.\n - **est:**\n - O valora/nota (rating) previsto/estimado.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_complete = algo_svdpp.test(df_missing_values)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Agora que nós já temos um objeto com todos os valores possíveis vamos dar uma olhada na primeira previsão:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_complete[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**NOTE:** \nVejam que tem uma pequena diferença entre o valor que o usuário passou **r_ui** e o valor estimado pelo Algoritmo SVD++ **est**:\n - r_ui=3.0028030537791928\n - est=3.530673400436856",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 03.8 - Pegando as TOP recomendações por usuário\nAgora nós vamos criar uma função que retorne o top-N recomendações para cada usuário. Essa função retorna um **dicionário**, onde, as chaves são os usuários e os valores são listas de tuplas.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from collections import defaultdict\n\ndef get_top_recommendations(predicts, n=5):\n top_n = defaultdict(list) # Create a dictionary where lists are empty.\n for user, movie, _, predict, _ in predicts:\n top_n[user].append((movie, predict)) # Add key-value\n for user, user_predicts in top_n.items():\n user_predicts.sort(key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True) # Order predicts rating from high to less.\n top_n[user] = user_predicts[:n] # Save only the first values.\n return top_n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Vamos começar pegando as top 5 recomendações (que é o valor default da função get_top_recommendations) para cada usuário:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"top_five = get_top_recommendations(df_complete)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"top_five",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Olhando para a saída acima nós temos:\n - Um dicionário onde:\n - A chave é o ID do usuário\n - E os valores são uma lista de duplas, onde:\n - O primeiro elemento da tupla representa o ID do filme;\n - O segundo elemento da tupla representa a nota (rating) do filme.\n - Isso tudo em ordem decrescente, ou seja, da maior nota (rating) para a menor.\n\n**NOTE:** \nAgora você pode pegar essa saída e trabalhar com ela da maneira que você desejar, por exemplo, passar para uma API e etc. Só por questão didática vamos pegar essa saída (dicionário) e criar uma mecanismo, onde, nós vamos ter o ID do usuário e uma lista com os top 5 filmes por ID e não por nota (rating).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for user, user_predicts in top_five.items():\n print(user, [movie for (movie, _) in user_predicts])",
"1 [286, 805, 335, 728, 307]\n2 [805, 286, 335, 658, 675]\n3 [253, 797, 5, 7, 2]\n4 [286, 805, 391, 2, 318]\n5 [286, 805, 335, 705, 414]\n6 [286, 805, 689, 318, 335]\n7 [286, 805, 218, 335, 675]\n8 [335, 286, 805, 705, 658]\n9 [286, 805, 335, 705, 563]\n10 [805, 286, 335, 363, 689]\n11 [286, 805, 335, 675, 705]\n12 [286, 805, 335, 218, 307]\n13 [286, 805, 335, 705, 689]\n14 [286, 805, 689, 705, 307]\n15 [286, 805, 335, 563, 307]\n16 [286, 335, 805, 425, 299]\n17 [286, 805, 318, 335, 689]\n18 [286, 805, 335, 705, 728]\n19 [286, 805, 335, 563, 689]\n20 [805, 286, 335, 307, 705]\n21 [52, 126, 144, 189, 218]\n22 [52, 68, 96, 126, 167]\n23 [286, 805, 318, 218, 335]\n24 [335, 286, 805, 658, 705]\n25 [335, 805, 286, 689, 446]\n26 [286, 805, 335, 696, 318]\n27 [805, 286, 335, 563, 705]\n28 [286, 335, 805, 705, 563]\n29 [335, 705, 675, 658, 702]\n30 [286, 805, 335, 1091, 307]\n31 [286, 805, 335, 705, 728]\n32 [286, 335, 805, 705, 728]\n33 [286, 805, 689, 335, 728]\n34 [286, 318, 805, 218, 563]\n35 [286, 805, 363, 335, 689]\n36 [24, 43, 52, 68, 69]\n37 [24, 43, 52, 68, 69]\n38 [286, 805, 278, 689, 1091]\n39 [286, 805, 335, 218, 705]\n40 [286, 805, 335, 728, 705]\n41 [286, 335, 805, 658, 446]\n42 [286, 318, 658, 391, 805]\n43 [286, 805, 335, 675, 297]\n44 [286, 335, 805, 689, 728]\n45 [286, 805, 335, 689, 299]\n46 [286, 335, 805, 299, 728]\n47 [286, 335, 805, 689, 728]\n48 [286, 805, 335, 689, 363]\n49 [286, 335, 318, 728, 689]\n50 [218, 286, 297, 299, 307]\n51 [286, 335, 805, 299, 638]\n52 [286, 805, 335, 675, 696]\n53 [218, 286, 299, 318, 335]\n54 [286, 805, 335, 705, 391]\n55 [286, 805, 335, 675, 705]\n56 [286, 675, 805, 705, 465]\n57 [805, 286, 335, 689, 728]\n58 [286, 318, 805, 335, 218]\n59 [335, 805, 286, 307, 705]\n60 [335, 286, 805, 658, 299]\n61 [286, 805, 335, 705, 675]\n62 [286, 805, 335, 689, 728]\n63 [189, 286, 335, 398, 658]\n64 [286, 805, 335, 675, 705]\n65 [286, 805, 335, 299, 705]\n66 [805, 286, 335, 689, 658]\n67 [805, 286, 335, 307, 658]\n68 [16, 18, 19, 23, 24]\n69 [286, 805, 335, 658, 770]\n70 [286, 335, 658, 705, 805]\n71 [286, 307, 335, 805, 705]\n72 [52, 68, 96, 126, 144]\n73 [286, 335, 805, 689, 425]\n74 [805, 286, 696, 335, 363]\n75 [286, 805, 335, 689, 318]\n76 [286, 335, 805, 318, 658]\n77 [805, 286, 335, 705, 218]\n78 [689, 805, 286, 1694, 335]\n79 [253, 211, 705, 1068, 299]\n80 [286, 335, 391, 696, 299]\n81 [805, 286, 689, 335, 1173]\n82 [286, 805, 335, 705, 307]\n83 [286, 805, 335, 658, 689]\n84 [144, 189, 197, 218, 279]\n85 [5, 27, 35, 43, 52]\n86 [16, 19, 24, 27, 33]\n87 [286, 805, 335, 689, 705]\n88 [286, 335, 805, 705, 299]\n89 [286, 805, 335, 307, 318]\n90 [286, 335, 805, 363, 307]\n91 [335, 286, 805, 705, 297]\n92 [805, 335, 286, 218, 675]\n93 [286, 805, 335, 307, 658]\n94 [335, 286, 805, 705, 728]\n95 [286, 318, 335, 805, 1118]\n96 [805, 335, 286, 1091, 307]\n97 [805, 335, 286, 307, 728]\n98 [68, 216, 242, 286, 297]\n99 [286, 805, 563, 705, 218]\n100 [286, 805, 335, 675, 218]\n101 [286, 335, 805, 658, 705]\n102 [286, 805, 335, 658, 770]\n103 [286, 675, 805, 696, 335]\n104 [286, 335, 805, 299, 391]\n105 [286, 805, 335, 705, 675]\n106 [286, 805, 335, 705, 728]\n107 [286, 318, 335, 563, 805]\n108 [286, 805, 689, 218, 1118]\n109 [43, 68, 69, 126, 144]\n110 [335, 286, 805, 658, 689]\n111 [805, 286, 335, 675, 658]\n112 [805, 286, 335, 689, 658]\n113 [286, 805, 335, 689, 705]\n114 [286, 805, 218, 675, 563]\n115 [286, 805, 335, 705, 658]\n116 [286, 335, 805, 689, 363]\n117 [286, 805, 335, 675, 563]\n118 [286, 805, 335, 689, 728]\n119 [286, 335, 805, 705, 299]\n120 [286, 335, 805, 689, 363]\n121 [335, 307, 286, 805, 318]\n122 [286, 805, 335, 705, 658]\n123 [286, 805, 335, 307, 705]\n124 [286, 805, 307, 1091, 696]\n125 [43, 68, 96, 126, 167]\n126 [805, 689, 286, 335, 299]\n127 [286, 805, 689, 218, 335]\n128 [286, 805, 218, 335, 68]\n129 [5, 43, 52, 68, 69]\n130 [286, 805, 335, 398, 689]\n131 [286, 335, 805, 299, 705]\n132 [286, 335, 658, 299, 675]\n133 [286, 805, 689, 391, 363]\n134 [286, 805, 335, 363, 675]\n135 [286, 335, 805, 299, 689]\n136 [126, 167, 189, 197, 218]\n137 [286, 805, 307, 363, 335]\n138 [805, 335, 286, 705, 307]\n139 [218, 286, 318, 335, 805]\n140 [286, 805, 335, 689, 318]\n141 [218, 286, 293, 299, 307]\n142 [286, 805, 335, 705, 728]\n143 [286, 805, 335, 689, 675]\n144 [286, 335, 805, 689, 705]\n145 [805, 286, 335, 689, 705]\n146 [805, 335, 286, 307, 218]\n147 [286, 805, 335, 318, 658]\n148 [805, 335, 286, 689, 363]\n149 [286, 805, 335, 675, 696]\n150 [286, 805, 335, 307, 563]\n151 [286, 805, 335, 658, 299]\n152 [286, 335, 705, 805, 689]\n153 [286, 335, 705, 805, 728]\n154 [197, 218, 286, 299, 307]\n155 [335, 805, 307, 1091, 286]\n156 [805, 286, 307, 335, 563]\n157 [286, 805, 335, 689, 728]\n158 [286, 335, 805, 705, 318]\n159 [286, 805, 335, 705, 218]\n160 [189, 286, 307, 335, 400]\n161 [363, 805, 563, 940, 213]\n162 [286, 805, 335, 658, 316]\n163 [286, 705, 335, 675, 299]\n164 [286, 805, 335, 563, 307]\n165 [335, 286, 363, 307, 689]\n166 [286, 805, 335, 705, 299]\n167 [286, 335, 446, 689, 805]\n168 [805, 335, 286, 563, 307]\n169 [286, 805, 335, 563, 218]\n170 [286, 805, 335, 299, 658]\n171 [35, 43, 44, 52, 68]\n172 [16, 18, 19, 23, 24]\n173 [286, 805, 335, 658, 318]\n174 [286, 805, 318, 335, 307]\n175 [805, 286, 335, 658, 705]\n176 [286, 335, 805, 446, 728]\n177 [286, 675, 805, 705, 335]\n178 [286, 805, 335, 318, 307]\n179 [286, 805, 335, 398, 658]\n180 [286, 805, 689, 335, 318]\n181 [286, 318, 335, 689, 805]\n182 [286, 335, 805, 689, 318]\n183 [286, 335, 805, 299, 658]\n184 [5, 52, 96, 126, 181]\n185 [286, 335, 805, 658, 696]\n186 [286, 805, 335, 218, 728]\n187 [286, 805, 705, 675, 335]\n188 [446, 335, 215, 434, 805]\n189 [218, 286, 299, 307, 335]\n190 [805, 286, 307, 335, 1091]\n191 [189, 286, 318, 335, 658]\n192 [286, 805, 335, 705, 675]\n193 [286, 805, 705, 335, 689]\n194 [286, 218, 689, 805, 335]\n195 [286, 805, 335, 705, 728]\n196 [286, 805, 689, 335, 705]\n197 [805, 335, 286, 307, 318]\n198 [286, 335, 805, 307, 728]\n199 [805, 705, 307, 5, 408]\n200 [286, 299, 335, 425, 689]\n201 [286, 335, 805, 728, 689]\n202 [805, 335, 286, 689, 391]\n203 [286, 805, 689, 728, 318]\n204 [16, 18, 19, 23, 24]\n205 [286, 297, 299, 318, 335]\n206 [805, 335, 286, 689, 363]\n207 [286, 805, 335, 563, 307]\n208 [286, 689, 805, 335, 705]\n209 [286, 805, 689, 335, 400]\n210 [286, 335, 805, 689, 705]\n211 [286, 335, 805, 299, 675]\n212 [286, 805, 335, 1091, 675]\n213 [286, 805, 335, 689, 318]\n214 [286, 805, 335, 675, 658]\n215 [286, 805, 318, 335, 68]\n216 [286, 318, 218, 770, 805]\n217 [286, 335, 675, 705, 805]\n218 [689, 335, 286, 414, 805]\n219 [335, 805, 286, 658, 705]\n220 [286, 335, 705, 805, 728]\n221 [286, 335, 675, 805, 318]\n222 [335, 805, 286, 689, 705]\n223 [286, 335, 805, 705, 563]\n224 [68, 189, 286, 318, 335]\n225 [805, 335, 286, 563, 218]\n226 [286, 805, 335, 689, 728]\n227 [43, 69, 96, 126, 181]\n228 [286, 805, 318, 335, 675]\n229 [286, 805, 335, 675, 363]\n230 [286, 805, 335, 689, 432]\n231 [286, 805, 335, 705, 689]\n232 [805, 335, 286, 705, 307]\n233 [286, 805, 335, 689, 318]\n234 [286, 805, 675, 689, 563]\n235 [286, 805, 68, 432, 335]\n236 [286, 805, 335, 689, 391]\n237 [286, 805, 335, 770, 292]\n238 [805, 286, 335, 675, 563]\n239 [286, 805, 335, 689, 218]\n240 [189, 218, 286, 293, 297]\n241 [286, 805, 335, 705, 728]\n242 [805, 286, 335, 689, 675]\n243 [335, 805, 286, 705, 675]\n244 [286, 805, 363, 335, 675]\n245 [286, 805, 335, 675, 696]\n246 [805, 286, 335, 318, 363]\n247 [286, 805, 335, 705, 728]\n248 [805, 286, 363, 335, 689]\n249 [805, 286, 335, 307, 563]\n250 [286, 805, 218, 318, 335]\n251 [286, 805, 218, 335, 689]\n252 [286, 335, 705, 805, 728]\n253 [286, 805, 335, 689, 675]\n254 [286, 805, 335, 689, 728]\n255 [286, 335, 805, 705, 689]\n256 [286, 805, 675, 318, 335]\n257 [286, 805, 335, 705, 318]\n258 [286, 335, 805, 689, 218]\n259 [286, 805, 335, 318, 689]\n260 [286, 805, 391, 335, 675]\n261 [286, 335, 805, 675, 705]\n262 [286, 335, 805, 391, 318]\n263 [286, 805, 335, 675, 705]\n264 [286, 805, 432, 318, 391]\n265 [286, 307, 318, 335, 563]\n266 [805, 286, 335, 658, 307]\n267 [286, 805, 218, 299, 318]\n268 [286, 805, 335, 658, 689]\n269 [286, 805, 335, 689, 705]\n270 [286, 805, 335, 307, 218]\n271 [805, 286, 335, 705, 363]\n272 [286, 728, 842, 5, 228]\n273 [286, 805, 335, 218, 318]\n274 [16, 18, 19, 24, 26]\n275 [286, 805, 689, 335, 363]\n276 [286, 805, 335, 1091, 363]\n277 [286, 335, 805, 705, 689]\n278 [126, 144, 189, 286, 290]\n279 [805, 286, 335, 689, 675]\n280 [805, 286, 335, 1118, 689]\n281 [286, 805, 335, 563, 218]\n282 [286, 805, 335, 705, 689]\n283 [218, 286, 297, 299, 307]\n284 [218, 286, 299, 307, 318]\n285 [69, 167, 189, 197, 218]\n286 [43, 52, 68, 69, 96]\n287 [286, 805, 318, 335, 728]\n288 [286, 805, 335, 689, 318]\n289 [286, 805, 335, 318, 689]\n290 [286, 805, 318, 658, 335]\n291 [335, 286, 805, 689, 705]\n292 [69, 218, 279, 286, 297]\n293 [286, 335, 805, 391, 400]\n294 [805, 286, 335, 705, 658]\n295 [805, 335, 286, 689, 563]\n296 [286, 805, 335, 689, 425]\n297 [286, 805, 689, 675, 335]\n298 [805, 286, 705, 398, 292]\n299 [286, 805, 335, 705, 728]\n300 [318, 335, 391, 218, 805]\n301 [286, 335, 805, 675, 705]\n302 [805, 335, 286, 1091, 446]\n303 [805, 286, 335, 307, 434]\n304 [286, 805, 335, 705, 318]\n305 [286, 805, 696, 1118, 689]\n306 [286, 335, 805, 675, 705]\n307 [335, 286, 805, 728, 705]\n308 [218, 1313, 335, 286, 144]\n309 [286, 805, 689, 335, 705]\n310 [335, 286, 425, 689, 363]\n311 [286, 805, 335, 318, 689]\n312 [805, 286, 689, 318, 675]\n313 [286, 805, 705, 675, 335]\n314 [286, 805, 335, 299, 728]\n315 [68, 96, 126, 181, 189]\n316 [805, 689, 335, 286, 363]\n317 [286, 805, 658, 335, 689]\n318 [286, 805, 658, 335, 689]\n319 [286, 218, 307, 318, 1091]\n320 [286, 335, 805, 696, 292]\n321 [286, 335, 805, 299, 728]\n322 [286, 675, 805, 705, 335]\n323 [286, 705, 335, 5, 565]\n324 [286, 307, 335, 363, 398]\n325 [68, 96, 218, 279, 286]\n326 [335, 805, 286, 658, 705]\n327 [286, 335, 805, 318, 705]\n328 [286, 805, 363, 242, 335]\n329 [286, 805, 563, 335, 218]\n330 [286, 335, 805, 675, 689]\n331 [189, 286, 299, 307, 335]\n332 [286, 335, 805, 658, 689]\n333 [286, 805, 689, 675, 335]\n334 [286, 805, 335, 705, 299]\n335 [286, 805, 318, 335, 689]\n336 [286, 805, 335, 675, 705]\n337 [286, 335, 689, 805, 400]\n338 [218, 286, 307, 335, 805]\n339 [189, 197, 218, 242, 286]\n340 [286, 805, 335, 705, 728]\n341 [126, 242, 286, 293, 297]\n342 [335, 286, 805, 705, 658]\n343 [286, 805, 335, 689, 297]\n344 [805, 286, 689, 218, 335]\n345 [286, 805, 335, 689, 728]\n346 [286, 307, 335, 805, 689]\n347 [3, 4, 5, 7, 16]\n348 [286, 805, 335, 563, 728]\n349 [286, 805, 689, 335, 218]\n350 [197, 218, 286, 299, 307]\n351 [286, 335, 805, 307, 299]\n352 [805, 286, 335, 307, 363]\n353 [286, 805, 335, 675, 696]\n354 [286, 805, 335, 689, 400]\n355 [286, 689, 391, 728, 335]\n356 [286, 335, 318, 1118, 400]\n357 [286, 805, 335, 318, 689]\n358 [286, 805, 689, 335, 318]\n359 [218, 286, 318, 335, 400]\n360 [286, 335, 805, 318, 299]\n361 [211, 286, 335, 805, 5]\n362 [286, 805, 335, 689, 728]\n363 [805, 286, 335, 689, 363]\n364 [286, 335, 805, 705, 414]\n365 [286, 805, 335, 675, 307]\n366 [286, 805, 218, 335, 689]\n367 [286, 805, 335, 307, 563]\n368 [286, 675, 805, 335, 218]\n369 [286, 335, 805, 658, 318]\n370 [805, 286, 335, 689, 658]\n371 [805, 286, 335, 689, 5]\n372 [286, 335, 805, 318, 307]\n373 [286, 335, 805, 658, 446]\n374 [286, 805, 335, 307, 318]\n375 [286, 805, 1118, 689, 363]\n376 [286, 805, 335, 728, 425]\n377 [286, 335, 805, 318, 658]\n378 [286, 805, 335, 728, 689]\n379 [286, 805, 318, 335, 658]\n380 [286, 805, 335, 696, 425]\n381 [335, 805, 286, 705, 689]\n382 [286, 335, 705, 805, 299]\n383 [286, 335, 689, 805, 307]\n384 [805, 286, 705, 563, 335]\n385 [286, 805, 335, 218, 689]\n386 [286, 689, 335, 318, 805]\n387 [286, 335, 705, 675, 218]\n388 [286, 805, 675, 696, 335]\n389 [286, 805, 335, 689, 318]\n390 [286, 805, 335, 218, 696]\n391 [286, 805, 335, 689, 658]\n392 [9, 43, 52, 68, 69]\n393 [805, 286, 335, 689, 705]\n394 [805, 286, 335, 705, 689]\n395 [805, 286, 363, 335, 242]\n396 [286, 189, 400, 335, 696]\n397 [286, 805, 335, 689, 307]\n398 [286, 689, 805, 335, 728]\n399 [805, 286, 335, 696, 689]\n400 [286, 805, 335, 705, 689]\n401 [96, 197, 218, 278, 286]\n402 [286, 805, 335, 307, 696]\n403 [805, 286, 335, 658, 696]\n404 [96, 126, 218, 242, 278]\n405 [286, 805, 335, 318, 658]\n406 [96, 126, 189, 197, 218]\n407 [335, 805, 286, 689, 363]\n408 [286, 805, 675, 705, 335]\n409 [286, 805, 335, 705, 696]\n410 [286, 805, 335, 705, 299]\n411 [286, 335, 805, 307, 563]\n412 [286, 805, 318, 335, 68]\n413 [286, 805, 335, 689, 299]\n414 [286, 299, 805, 335, 675]\n415 [286, 335, 805, 696, 363]\n416 [286, 805, 689, 335, 696]\n417 [286, 805, 335, 705, 675]\n418 [286, 335, 805, 689, 696]\n419 [286, 805, 335, 689, 728]\n420 [286, 335, 805, 425, 705]\n421 [286, 805, 335, 675, 696]\n422 [286, 293, 299, 318, 335]\n423 [286, 805, 728, 335, 705]\n424 [286, 805, 218, 689, 335]\n425 [805, 286, 335, 689, 307]\n426 [286, 805, 335, 307, 728]\n427 [286, 335, 805, 689, 728]\n428 [27, 43, 52, 68, 69]\n429 [286, 335, 705, 805, 563]\n430 [286, 805, 318, 335, 705]\n431 [805, 286, 335, 218, 689]\n432 [286, 805, 335, 705, 675]\n433 [805, 335, 286, 705, 689]\n434 [286, 805, 335, 307, 705]\n435 [286, 335, 689, 805, 705]\n436 [805, 335, 728, 563, 218]\n437 [286, 307, 728, 335, 689]\n438 [286, 805, 318, 218, 689]\n439 [286, 805, 335, 293, 658]\n440 [279, 286, 292, 293, 297]\n441 [286, 335, 805, 218, 689]\n442 [805, 335, 286, 689, 563]\n443 [286, 805, 335, 705, 675]\n444 [286, 335, 805, 689, 425]\n445 [286, 805, 335, 705, 425]\n446 [286, 805, 675, 335, 689]\n447 [286, 335, 805, 705, 299]\n448 [286, 297, 335, 363, 408]\n449 [286, 805, 335, 705, 689]\n450 [286, 805, 335, 318, 689]\n451 [286, 805, 307, 218, 335]\n452 [286, 307, 335, 563, 675]\n453 [286, 805, 335, 318, 705]\n454 [286, 335, 675, 705, 805]\n455 [286, 297, 299, 307, 318]\n456 [286, 335, 391, 318, 363]\n457 [805, 286, 335, 318, 307]\n458 [286, 335, 705, 805, 563]\n459 [286, 335, 805, 307, 318]\n460 [286, 805, 335, 299, 218]\n461 [286, 805, 218, 689, 347]\n462 [286, 335, 805, 696, 218]\n463 [7, 218, 286, 318, 335]\n464 [286, 335, 705, 805, 658]\n465 [286, 335, 805, 689, 307]\n466 [335, 689, 805, 307, 728]\n467 [286, 805, 335, 1091, 307]\n468 [805, 286, 335, 307, 218]\n469 [286, 805, 335, 705, 728]\n470 [218, 286, 299, 307, 318]\n471 [286, 805, 335, 689, 432]\n472 [286, 335, 805, 414, 318]\n473 [286, 335, 805, 689, 297]\n474 [286, 805, 335, 657, 689]\n475 [286, 335, 805, 705, 307]\n476 [286, 335, 658, 805, 705]\n477 [805, 286, 335, 658, 316]\n478 [335, 805, 363, 286, 689]\n479 [335, 286, 705, 805, 689]\n480 [286, 805, 335, 705, 307]\n481 [286, 805, 335, 297, 299]\n482 [335, 805, 286, 705, 318]\n483 [805, 307, 286, 335, 705]\n484 [286, 805, 335, 689, 705]\n485 [189, 286, 318, 335, 391]\n486 [286, 335, 805, 689, 218]\n487 [286, 805, 335, 68, 696]\n488 [286, 335, 689, 705, 299]\n489 [805, 286, 689, 728, 363]\n490 [286, 335, 805, 770, 689]\n491 [286, 805, 335, 307, 705]\n492 [805, 286, 335, 307, 658]\n493 [286, 805, 335, 705, 307]\n494 [286, 805, 335, 363, 318]\n495 [805, 286, 689, 335, 299]\n496 [286, 335, 805, 728, 299]\n497 [286, 805, 335, 307, 689]\n498 [286, 689, 805, 218, 363]\n499 [286, 805, 335, 318, 705]\n500 [197, 218, 286, 299, 307]\n501 [286, 805, 335, 689, 658]\n502 [286, 805, 675, 335, 658]\n503 [68, 286, 293, 307, 335]\n504 [286, 805, 335, 705, 689]\n505 [805, 286, 335, 293, 1091]\n506 [286, 805, 335, 705, 299]\n507 [286, 299, 335, 805, 689]\n508 [286, 805, 335, 675, 696]\n509 [318, 805, 689, 391, 363]\n510 [286, 805, 335, 728, 689]\n511 [286, 335, 805, 705, 689]\n512 [286, 335, 805, 307, 728]\n513 [286, 805, 335, 658, 675]\n514 [286, 805, 335, 689, 705]\n515 [286, 335, 689, 805, 363]\n516 [286, 805, 689, 728, 335]\n517 [286, 805, 335, 299, 218]\n518 [286, 335, 446, 658, 689]\n519 [335, 286, 805, 658, 689]\n520 [286, 335, 805, 307, 318]\n521 [286, 805, 675, 335, 705]\n522 [286, 805, 335, 218, 299]\n523 [286, 335, 805, 391, 705]\n524 [286, 805, 335, 705, 696]\n525 [286, 805, 335, 318, 728]\n526 [286, 805, 335, 318, 696]\n527 [286, 307, 318, 335, 363]\n528 [286, 805, 696, 335, 400]\n529 [286, 335, 805, 658, 728]\n530 [218, 286, 299, 307, 316]\n531 [286, 805, 689, 335, 728]\n532 [286, 805, 335, 696, 1118]\n533 [805, 189, 335, 7, 689]\n534 [286, 805, 335, 189, 391]\n535 [286, 805, 658, 318, 689]\n536 [286, 335, 805, 705, 1091]\n537 [805, 286, 363, 335, 307]\n538 [286, 335, 805, 307, 658]\n539 [286, 335, 805, 689, 1091]\n540 [286, 335, 705, 805, 318]\n541 [286, 805, 335, 658, 318]\n542 [286, 335, 805, 307, 728]\n543 [286, 805, 335, 318, 391]\n544 [52, 96, 126, 144, 167]\n545 [286, 805, 335, 705, 299]\n546 [286, 335, 805, 658, 189]\n547 [805, 286, 335, 363, 689]\n548 [805, 286, 318, 307, 363]\n549 [286, 805, 335, 1091, 675]\n550 [286, 805, 218, 689, 335]\n551 [286, 805, 335, 689, 299]\n552 [286, 335, 805, 689, 705]\n553 [286, 335, 318, 805, 391]\n554 [218, 286, 335, 805, 705]\n555 [286, 297, 299, 318, 335]\n556 [286, 335, 805, 563, 218]\n557 [805, 286, 335, 689, 728]\n558 [286, 805, 335, 689, 318]\n559 [286, 805, 335, 696, 293]\n560 [805, 286, 335, 689, 563]\n561 [286, 805, 335, 318, 689]\n562 [286, 335, 689, 414, 400]\n563 [286, 805, 335, 705, 299]\n564 [335, 286, 805, 705, 689]\n565 [286, 805, 218, 335, 689]\n566 [286, 335, 805, 1091, 307]\n567 [218, 286, 318, 335, 675]\n568 [286, 805, 218, 563, 299]\n569 [805, 286, 335, 658, 728]\n570 [335, 286, 805, 689, 675]\n571 [218, 286, 307, 318, 335]\n572 [286, 335, 805, 218, 563]\n573 [805, 286, 335, 363, 689]\n574 [286, 805, 335, 675, 705]\n575 [286, 335, 805, 689, 218]\n576 [6, 27, 43, 52, 54]\n577 [286, 335, 805, 689, 770]\n578 [286, 805, 689, 432, 2]\n579 [286, 805, 335, 658, 689]\n580 [286, 318, 805, 391, 335]\n581 [286, 805, 335, 689, 363]\n582 [286, 335, 307, 805, 728]\n583 [335, 805, 286, 705, 299]\n584 [286, 805, 689, 335, 658]\n585 [286, 805, 335, 318, 432]\n586 [286, 805, 335, 689, 658]\n587 [705, 335, 728, 563, 689]\n588 [286, 318, 563, 805, 705]\n589 [286, 299, 335, 425, 705]\n590 [805, 286, 335, 705, 675]\n591 [286, 414, 705, 728, 189]\n592 [286, 318, 335, 705, 805]\n593 [286, 805, 218, 689, 335]\n594 [218, 286, 307, 318, 335]\n595 [286, 805, 335, 689, 728]\n596 [286, 805, 675, 696, 318]\n597 [286, 335, 689, 805, 299]\n598 [19, 24, 35, 43, 44]\n599 [286, 805, 335, 689, 728]\n600 [286, 307, 335, 363, 658]\n601 [286, 805, 335, 658, 689]\n602 [286, 335, 805, 318, 728]\n603 [286, 335, 563, 805, 218]\n604 [286, 335, 805, 728, 307]\n605 [286, 805, 335, 705, 728]\n606 [286, 318, 805, 696, 218]\n607 [68, 189, 218, 286, 297]\n608 [286, 335, 805, 675, 1091]\n609 [286, 805, 335, 675, 705]\n610 [218, 286, 293, 307, 318]\n611 [286, 805, 335, 307, 728]\n612 [286, 675, 805, 335, 391]\n613 [286, 805, 335, 1118, 696]\n614 [286, 805, 335, 728, 563]\n615 [805, 286, 335, 563, 658]\n616 [286, 805, 218, 318, 335]\n617 [286, 805, 335, 307, 705]\n618 [335, 805, 286, 307, 218]\n619 [286, 805, 335, 705, 307]\n620 [335, 286, 805, 705, 425]\n621 [805, 286, 335, 318, 363]\n622 [286, 805, 335, 689, 658]\n623 [286, 805, 335, 696, 400]\n624 [286, 805, 335, 696, 293]\n625 [16, 18, 19, 23, 24]\n626 [286, 278, 563, 307, 218]\n627 [286, 805, 335, 689, 318]\n628 [286, 335, 805, 705, 318]\n629 [286, 805, 335, 705, 658]\n630 [286, 805, 335, 318, 728]\n631 [286, 805, 335, 1091, 675]\n632 [52, 68, 126, 189, 286]\n633 [805, 286, 689, 335, 658]\n634 [335, 805, 286, 705, 218]\n635 [286, 335, 805, 689, 728]\n636 [286, 805, 689, 675, 189]\n637 [805, 286, 335, 705, 363]\n638 [286, 689, 805, 391, 318]\n639 [286, 805, 335, 689, 318]\n640 [805, 335, 689, 286, 218]\n641 [286, 805, 696, 335, 318]\n642 [286, 805, 335, 307, 675]\n643 [286, 805, 335, 318, 689]\n644 [805, 286, 335, 689, 299]\n645 [335, 286, 805, 563, 705]\n646 [286, 335, 805, 689, 425]\n647 [286, 805, 335, 318, 218]\n648 [286, 689, 335, 318, 805]\n649 [286, 335, 705, 805, 728]\n650 [286, 805, 335, 689, 363]\n651 [286, 335, 425, 414, 705]\n652 [286, 335, 805, 307, 1091]\n653 [286, 675, 805, 335, 318]\n654 [286, 805, 335, 318, 307]\n655 [286, 335, 805, 689, 318]\n656 [286, 805, 335, 705, 563]\n657 [286, 805, 335, 689, 728]\n658 [286, 805, 391, 696, 335]\n659 [286, 805, 218, 335, 705]\n660 [286, 805, 335, 307, 1091]\n661 [286, 689, 805, 335, 1118]\n662 [805, 286, 335, 278, 705]\n663 [286, 805, 335, 705, 689]\n664 [286, 335, 805, 307, 728]\n665 [286, 805, 335, 689, 658]\n666 [286, 805, 335, 293, 218]\n667 [286, 805, 335, 728, 307]\n668 [286, 335, 675, 689, 705]\n669 [805, 335, 286, 689, 705]\n670 [805, 335, 286, 563, 705]\n671 [286, 335, 705, 805, 391]\n672 [286, 335, 689, 805, 658]\n673 [286, 805, 307, 218, 335]\n674 [24, 35, 43, 52, 54]\n675 [189, 218, 286, 297, 307]\n676 [286, 335, 805, 675, 657]\n677 [286, 335, 805, 689, 705]\n678 [286, 805, 335, 696, 705]\n679 [286, 805, 335, 307, 563]\n680 [286, 805, 705, 675, 363]\n681 [286, 335, 805, 705, 689]\n682 [286, 805, 335, 705, 563]\n683 [286, 805, 335, 307, 728]\n684 [286, 805, 335, 218, 689]\n685 [335, 286, 805, 689, 414]\n686 [286, 805, 318, 335, 218]\n687 [11, 242, 286, 293, 297]\n688 [286, 335, 805, 675, 705]\n689 [286, 805, 335, 705, 728]\n690 [286, 805, 335, 658, 318]\n691 [52, 68, 69, 96, 126]\n692 [805, 286, 335, 675, 218]\n693 [286, 335, 805, 705, 728]\n694 [286, 335, 805, 705, 307]\n695 [286, 318, 335, 425, 563]\n696 [286, 805, 689, 728, 335]\n697 [805, 286, 335, 675, 297]\n698 [286, 805, 335, 218, 391]\n699 [286, 335, 705, 805, 728]\n700 [286, 335, 805, 705, 689]\n701 [805, 335, 286, 307, 689]\n702 [689, 286, 805, 728, 335]\n703 [286, 805, 689, 391, 335]\n704 [286, 805, 728, 297, 658]\n705 [286, 805, 689, 335, 391]\n706 [805, 286, 335, 299, 446]\n707 [286, 335, 805, 391, 299]\n708 [286, 805, 335, 299, 218]\n709 [805, 286, 335, 307, 728]\n710 [197, 218, 242, 286, 297]\n711 [286, 318, 335, 658, 705]\n712 [286, 805, 335, 307, 318]\n713 [286, 805, 335, 689, 705]\n714 [805, 335, 286, 689, 658]\n715 [286, 805, 335, 689, 696]\n716 [286, 689, 335, 805, 658]\n717 [286, 805, 335, 689, 728]\n718 [286, 805, 335, 218, 689]\n719 [335, 286, 1091, 414, 658]\n720 [286, 805, 335, 689, 318]\n721 [286, 805, 335, 689, 705]\n722 [286, 805, 335, 728, 689]\n723 [189, 286, 318, 335, 563]\n724 [24, 35, 43, 52, 68]\n725 [286, 335, 805, 218, 363]\n726 [68, 96, 126, 181, 189]\n727 [218, 286, 307, 335, 563]\n728 [286, 805, 689, 658, 363]\n729 [286, 805, 335, 318, 218]\n730 [43, 52, 68, 69, 96]\n731 [286, 805, 335, 689, 675]\n732 [286, 805, 335, 728, 689]\n733 [286, 805, 335, 689, 563]\n734 [286, 335, 805, 391, 299]\n735 [286, 805, 689, 318, 675]\n736 [805, 286, 335, 299, 689]\n737 [805, 286, 335, 689, 1118]\n738 [286, 805, 335, 705, 728]\n739 [286, 805, 335, 689, 658]\n740 [126, 197, 218, 286, 297]\n741 [286, 335, 805, 705, 307]\n742 [286, 335, 805, 689, 658]\n743 [286, 307, 318, 335, 363]\n744 [286, 335, 805, 689, 728]\n745 [286, 805, 335, 689, 696]\n746 [335, 805, 286, 705, 1173]\n747 [286, 805, 335, 689, 218]\n748 [286, 805, 335, 689, 391]\n749 [286, 805, 335, 689, 658]\n750 [286, 805, 307, 335, 318]\n751 [286, 805, 335, 696, 675]\n752 [286, 805, 689, 335, 218]\n753 [286, 335, 805, 689, 318]\n754 [286, 335, 805, 689, 658]\n755 [286, 805, 335, 318, 391]\n756 [286, 805, 689, 335, 675]\n757 [805, 286, 335, 675, 293]\n758 [286, 307, 318, 335, 414]\n759 [286, 805, 689, 675, 705]\n760 [286, 335, 805, 689, 318]\n761 [286, 675, 335, 805, 299]\n762 [189, 218, 286, 293, 299]\n763 [286, 805, 335, 675, 705]\n764 [657, 335, 728, 658, 805]\n765 [286, 805, 335, 318, 696]\n766 [286, 335, 675, 696, 414]\n767 [286, 805, 335, 675, 696]\n768 [805, 286, 335, 705, 363]\n769 [286, 68, 805, 206, 696]\n770 [286, 805, 335, 689, 705]\n771 [286, 805, 335, 728, 705]\n772 [335, 286, 805, 689, 363]\n773 [286, 335, 705, 805, 675]\n774 [52, 68, 69, 96, 126]\n775 [805, 286, 335, 696, 658]\n776 [286, 335, 805, 689, 414]\n777 [286, 805, 689, 335, 363]\n778 [805, 286, 335, 689, 658]\n779 [805, 286, 335, 696, 658]\n780 [286, 335, 805, 307, 318]\n781 [286, 293, 297, 299, 307]\n782 [286, 805, 335, 705, 689]\n783 [286, 805, 335, 318, 675]\n784 [805, 286, 335, 689, 728]\n785 [335, 286, 805, 658, 705]\n786 [286, 335, 805, 307, 318]\n787 [286, 805, 335, 705, 675]\n788 [286, 335, 805, 689, 675]\n789 [286, 335, 805, 705, 307]\n790 [286, 335, 805, 705, 318]\n791 [189, 218, 286, 297, 299]\n792 [286, 335, 805, 658, 728]\n793 [96, 126, 189, 218, 242]\n794 [218, 286, 297, 307, 318]\n795 [286, 805, 335, 307, 318]\n796 [286, 335, 805, 299, 318]\n797 [286, 805, 1091, 335, 675]\n798 [286, 805, 335, 299, 728]\n799 [286, 318, 335, 805, 728]\n800 [286, 675, 805, 1091, 405]\n801 [286, 805, 335, 318, 1091]\n802 [286, 805, 335, 705, 1091]\n803 [286, 335, 805, 307, 675]\n804 [286, 805, 335, 363, 318]\n805 [805, 335, 286, 689, 658]\n806 [286, 307, 335, 705, 805]\n807 [805, 286, 218, 563, 675]\n808 [286, 805, 391, 689, 335]\n809 [335, 805, 286, 705, 307]\n810 [286, 335, 805, 728, 689]\n811 [286, 805, 335, 705, 307]\n812 [286, 675, 398, 658, 299]\n813 [286, 335, 805, 658, 316]\n814 [805, 335, 286, 689, 363]\n815 [318, 307, 286, 363, 1118]\n816 [286, 805, 335, 307, 696]\n817 [68, 189, 218, 286, 293]\n818 [286, 805, 335, 218, 307]\n819 [286, 318, 335, 705, 805]\n820 [805, 286, 335, 705, 675]\n821 [9, 24, 43, 52, 54]\n822 [286, 805, 218, 335, 299]\n823 [286, 805, 335, 705, 675]\n824 [218, 286, 307, 318, 335]\n825 [286, 307, 335, 705, 805]\n826 [16, 24, 43, 52, 54]\n827 [286, 805, 335, 675, 318]\n828 [286, 805, 335, 689, 728]\n829 [286, 805, 696, 293, 335]\n830 [335, 253, 391, 565, 689]\n831 [286, 728, 434, 689, 189]\n832 [286, 335, 805, 299, 675]\n833 [286, 805, 335, 318, 307]\n834 [675, 286, 278, 398, 805]\n835 [218, 286, 297, 299, 307]\n836 [689, 286, 335, 805, 1173]\n837 [335, 286, 805, 658, 657]\n838 [286, 805, 335, 675, 318]\n839 [286, 335, 446, 689, 414]\n840 [43, 52, 68, 69, 96]\n841 [286, 335, 705, 658, 689]\n842 [286, 689, 705, 335, 363]\n843 [335, 286, 805, 218, 689]\n844 [286, 805, 335, 689, 728]\n845 [286, 335, 658, 299, 189]\n846 [286, 805, 696, 335, 675]\n847 [286, 805, 696, 689, 189]\n848 [286, 335, 658, 689, 728]\n849 [286, 335, 689, 705, 696]\n850 [286, 805, 335, 689, 705]\n851 [805, 286, 335, 307, 689]\n852 [286, 318, 805, 689, 363]\n853 [286, 805, 335, 318, 705]\n854 [218, 286, 307, 318, 335]\n855 [286, 805, 335, 318, 728]\n856 [286, 805, 335, 363, 705]\n857 [286, 805, 335, 675, 696]\n858 [286, 335, 805, 705, 414]\n859 [286, 299, 335, 805, 689]\n860 [286, 335, 805, 705, 689]\n861 [43, 52, 68, 69, 96]\n862 [197, 218, 286, 297, 299]\n863 [286, 675, 335, 805, 218]\n864 [286, 805, 563, 218, 335]\n865 [286, 805, 335, 363, 689]\n866 [335, 805, 286, 705, 297]\n867 [805, 563, 286, 307, 335]\n868 [286, 335, 805, 299, 705]\n869 [805, 286, 335, 705, 728]\n870 [286, 805, 335, 563, 218]\n871 [286, 805, 563, 689, 218]\n872 [335, 286, 805, 689, 705]\n873 [286, 805, 335, 299, 675]\n874 [286, 335, 705, 805, 563]\n875 [286, 805, 689, 335, 363]\n876 [286, 805, 307, 335, 318]\n877 [286, 335, 805, 689, 414]\n878 [286, 805, 335, 307, 398]\n879 [286, 805, 1118, 335, 696]\n880 [286, 805, 335, 705, 675]\n881 [805, 286, 335, 705, 563]\n882 [286, 805, 689, 728, 705]\n883 [189, 218, 286, 297, 318]\n884 [286, 335, 689, 446, 805]\n885 [286, 805, 335, 658, 689]\n886 [286, 335, 805, 689, 728]\n887 [286, 335, 675, 805, 705]\n888 [286, 805, 335, 658, 363]\n889 [286, 805, 335, 675, 218]\n890 [286, 689, 728, 805, 335]\n891 [335, 705, 689, 563, 572]\n892 [286, 805, 335, 689, 1118]\n893 [68, 218, 286, 293, 297]\n894 [286, 805, 335, 658, 675]\n895 [286, 307, 335, 705, 728]\n896 [16, 18, 19, 23, 24]\n897 [286, 705, 805, 335, 363]\n898 [286, 705, 335, 805, 675]\n899 [286, 805, 363, 335, 689]\n900 [286, 805, 335, 425, 318]\n901 [286, 805, 335, 705, 689]\n902 [286, 805, 318, 335, 728]\n903 [286, 335, 805, 675, 705]\n904 [286, 335, 805, 705, 728]\n905 [805, 335, 286, 689, 705]\n906 [286, 335, 805, 391, 705]\n907 [286, 805, 689, 335, 705]\n908 [286, 705, 805, 675, 335]\n909 [286, 805, 335, 696, 318]\n910 [805, 335, 286, 705, 425]\n911 [286, 805, 675, 218, 335]\n912 [286, 805, 335, 696, 218]\n"
]
],
[
[
"**NOTE:** \nUma observação aqui é que esses ID dos filmes estão ordenados de modo que os filmes que tiveram melhor nota (rating) sejam os primeiros.\n\n> Então, não confunda o ID dos filmes com as notas (rating).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 03.9 - Pegando previsões específicas de usuários por filme\nOk, mas como eu posso pegar uma previsão para um usuário e filme específico? Simples, vejam o código abaixo:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"user_1_predict = algo_svdpp.predict(uid=\"1\", iid=\"15\")\nuser_1_predict",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**NOTES:** \n - A primeira observação aqui e crucial é que o usuáro não tinha passado uma nota (rating) para esse filme:\n - r_ui=None\n - Nós também podemos pegar a nota (rating) que foi prevista apenas utilizando o atributo **est**:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"rating = user_1_predict.est\nprint(rating)",
"3.0028030537791928\n"
]
],
[
[
"---",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 04 - Validando nosso modelo\n\n> Ótimo, nós já treinamos um modelo; Fizemos previsões, mas falta ***validar*** esse modelo.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 04.1 - Dividindo os dados em dados de treino e dados de teste (validação)\nDa mesma maneira que a biblioteca *Scikit-Learn* tem o método **train_test_split()** a biblioteca surprise tem o mesmo para Sistemas de Recomendação.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from surprise.model_selection import train_test_split\ndf_train, df_test = train_test_split(df_surprise, test_size=0.3)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**NOTE:** \nUma observação aqui é que nós estamos passando o **df_surprise** que é um load do método **load_from_df()**:\n\n```python\ndf_surprise = surprise.Dataset.load_from_df(df, reader)\n```\n\nOu seja, nós estamos passando o conjunto de dados reais, sem dados faltantes/missing.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 04.2 - treinando o modelo com os dados de treino\nAgora o que nós vamos fazer é criar uma instância do nosso Algoritmo SVD++ e treinar nosso modelo com os dados de treino (df_train):",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model_svdpp = surprise.SVDpp(n_factors=20) # SVD++ Instance.\nmodel_svdpp = model_svdpp.fit(df_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 04.3 - Fazendo previsões com os dados de teste (validação)\nAgora que nós já treinamos nosso modelo com o método fit() e os dados de treino vamos fazer algumas predições com os dados de teste (validação):",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"general_predicts = model_svdpp.test(df_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Eu vou criar um mecanismo simples para demonstrar apenas as 10 primeiras previsões, visto que nossa saída era muito grande, vamos apenas visualizar as 10 primeiras:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"count = 0\nwhile count < 10:\n print(general_predicts[count])\n count += 1",
"user: 161 item: 352 r_ui = 2.50 est = 2.66 {'was_impossible': False}\nuser: 788 item: 3 r_ui = 3.00 est = 2.61 {'was_impossible': False}\nuser: 385 item: 211 r_ui = 3.50 est = 2.80 {'was_impossible': False}\nuser: 555 item: 10 r_ui = 3.50 est = 3.36 {'was_impossible': False}\nuser: 815 item: 121 r_ui = 0.50 est = 1.79 {'was_impossible': False}\nuser: 747 item: 250 r_ui = 3.00 est = 3.48 {'was_impossible': False}\nuser: 1454 item: 7 r_ui = 2.50 est = 2.33 {'was_impossible': False}\nuser: 669 item: 256 r_ui = 2.50 est = 2.89 {'was_impossible': False}\nuser: 91 item: 242 r_ui = 3.00 est = 3.58 {'was_impossible': False}\nuser: 830 item: 1301 r_ui = 2.50 est = 3.29 {'was_impossible': False}\n"
]
],
[
[
"**NOTE:** \nComo os dados estão divididos em **treino** e **teste (validação)** você não vai ter os dados ordenados para trabalhar. Vai receber um conjunto de dados aleatório entre treino e teste. Se for de seu interesse você pode comparar as saídas das 10 primeiras amostras pegando pelo índice da variável **general_predicts**:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"general_predicts[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**NOTE:** \nVejam que ela realmente corresponde a saída que nós tinhamos passado antes.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 04.4 - Validando o modelo com a métrica \"accuracy.rmse\"\nA biblioteca **Surprise** tem métodos de *Validação*. Vamos utilizar o método **rmse()** da classe Accuracy:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from surprise import accuracy\nrmse = accuracy.rmse(general_predicts)",
"RMSE: 0.8121\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Mas o que significa essa saída?** \nSignifica que o nosso modelo está errando a uma taxa de **0.80** mais ou menos, para cima ou para baixo.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 04.5 - Ajustando os Hiperparâmetros\nTalvez esse erro **RMSE: 0.8099** seja um pouco grande dependendo do nosso problema.\n\n> Então, como melhorar a performance do nosso Algoritmo (modelo)? **Ajustando os Hiperparâmetros!**\n\nUma das maneiras de tentar melhorar a performance do nosso modelo é **\"Ajustando os Hiperparâmetros\"**. Vamos ver como fazer isso na prática:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"start_time = datetime.now()\nparam_grid = {\n 'lr_all': [0.01, 0.001, 0.07, 0.005],\n 'reg_all': [0.02, 0.1, 1.0, 0.005]\n}\n\nsurprise_grid = surprise.model_selection.GridSearchCV(\n surprise.SVDpp, # Estimator with fit().\n param_grid, # Params.\n measures=[\"rmse\"], # Metric.\n cv=3, # Cross-Validation K-Fold.\n n_jobs=-1\n)\n\nsurprise_grid.fit(df_surprise) # Training model.\nprint(surprise_grid.best_params['rmse'])\nend_time = datetime.now()\nprint('Method runtime: {}'.format(end_time - start_time))",
"{'lr_all': 0.01, 'reg_all': 0.1}\nMethod runtime: 0:06:50.204969\n"
]
],
[
[
"**NOTES:** \n - Ótimo, agora que nós já temos os melhores valores de **lr_all** e **reg_all** é só na hora de treinar nosso modelo passar esses valores.\n - Outra observação aqui é que esse processo de encontrar os melhores hiperparâmetros demorou mais de 6 minutos e isso se dar pelo fato do Algoritmo ter que testar varias combinações possíveis com os hiperparâmetros que nós passamos.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"---",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 05 - Pegando os filmes mais semelhantes com Cosine Distance/Similarity\nAgora imagine que nós queremos pegar os 5 ou 10 filmes mais semelhantes em relação a um determinado filme. Ou seja, agora o foco é a **similaridade** entre os filmes. Como nós sabemos uma maneira de fazer isso é utilizando a abordagem ***Cosine Distance/Similarity***.\n\nVamos ver como implementar isso na prática:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from surprise import KNNBasic\n\ndf_without_missing = df_surprise.build_full_trainset()\n\n# KNN Algorithms instance.\nalgo_cosine_similarity = KNNBasic(\n sim_options = {\n 'name': 'cosine', # Name is similarity Algorithms\n # If \"user_based\" is True the algorithm calculate similarity betweem users.\n # If \"user_based\" is False the algorithm calculate similarity betweem movies (items).\n 'user_based': False\n }\n)\nalgo_cosine_similarity.fit(df_without_missing) # Training\n\n# iid (int) – The (inner) id of the user (or item) for which we want the nearest neighbors.\n# Get the top 10 nearest neighbors (k=10).\nneighbors = algo_cosine_similarity.get_neighbors(iid=343, k=10) # Get neighbors.",
"Computing the cosine similarity matrix...\nDone computing similarity matrix.\n"
],
[
"neighbors",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for movie in neighbors:\n print(movie)",
"58\n90\n102\n126\n147\n159\n168\n171\n193\n236\n"
]
],
[
[
"**NOTES:** \n - Olhando para as saídas acima nós temos que ao passar o **iid=343** ele vai retornar os top 10 filmes mais semelhantes (em Cosine Distance/Similarity) em relação ao filme com esse ID:\n - Isso é interessante porque agora nós podemos indicar (recomendar) esses filmes para quem assistir esse filme (iid=343).\n - Esse algoritmo foi treinado para pegar os vizinhos mais próximos (KNN) **baseado nos itens** e **não nos usuários**:\n - visto que nós passamos **'user_based': False**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**REFERÊNCIA:** \n[DidáticaTech](https://didatica.tech/)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Rodrigo Leite -** *drigols*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
c502949cdf01a5abd51e5d4c0b997b0a0c82eb13
| 5,996 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
examples/iterating-over-files.ipynb
|
supplyandcommand/bootcamp-py-101
|
af0c024502a68e6bec90c10df46579bad2d34a18
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
examples/iterating-over-files.ipynb
|
supplyandcommand/bootcamp-py-101
|
af0c024502a68e6bec90c10df46579bad2d34a18
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
examples/iterating-over-files.ipynb
|
supplyandcommand/bootcamp-py-101
|
af0c024502a68e6bec90c10df46579bad2d34a18
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2021-09-02T09:45:47.000Z
|
2021-09-02T14:24:59.000Z
| 26.183406 | 832 | 0.517512 |
[
[
[
"# Repeating actions with LOOPS... #",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"odds = [1, 3, 5]\nprint(odds[0])\nprint(odds[1])\nprint(odds[2])\nprint(odds[3])",
"1\n3\n5\n"
],
[
"odds = [1, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13]\nfor num in odds:\n print(num)\n\nprint('\\n***********\\n')\n\nfor metteF in odds:\n print(metteF)",
"1\n3\n5\n7\n11\n13\n\n***********\n\n1\n3\n5\n7\n11\n13\n"
],
[
"names = ['Curie', 'Darwin', 'Turing']\nfor name in names:\n print(name)\n bfor char in name:\n print(char)",
"Curie\nC\nu\nr\ni\ne\nDarwin\nD\na\nr\nw\ni\nn\nTuring\nT\nu\nr\ni\nn\ng\n"
],
[
"num_of_letters = 0\nname = 'Darth'\nfor letter in name:\n print(letter)\n num_of_letters = num_of_letters + 1\n #num_of_letters += 1\n print('Hello Mette how goes!!!')\n\nprint('number of letter in Darth is ', num_of_letters)",
"D\nHello Mette how goes!!!\na\nHello Mette how goes!!!\nr\nHello Mette how goes!!!\nt\nHello Mette how goes!!!\nh\nHello Mette how goes!!!\nnumber of letter in Darth is 5\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c502a62949d9362cdd26a9b762face4d72a273fd
| 70,511 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
final_project.ipynb
|
sortsammcdonald/edx-python_and_data_science
|
de66913541fec25f9f7981f24de45474986018fc
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
final_project.ipynb
|
sortsammcdonald/edx-python_and_data_science
|
de66913541fec25f9f7981f24de45474986018fc
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
final_project.ipynb
|
sortsammcdonald/edx-python_and_data_science
|
de66913541fec25f9f7981f24de45474986018fc
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 101.308908 | 18,786 | 0.797904 |
[
[
[
"<a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/sortsammcdonald/edx-python_and_data_science/blob/master/final_project.ipynb\" target=\"_parent\"><img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open In Colab\"/></a>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Determining Iris species based on simple metrics\n\nThis report will evaluate if it is possible for species of Iris plants to be categorised via simple meterics such as measuring sepal or petal length. The reason this is important is that it makes it more straightforward for non-experts to reliably predict the species, they simply have to record the metrics, input these into a database that an ML algorithm can parse and they should then have a correct result with small chance of error.\n\nMore broadly this could be useful as, there maybe other species this approach could be applied to and in turn if this is applied at scale it could give us insights into how plants are adjusting to changing environments.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Data set and prelimanary remarks\n\nI am using the following data set: https://www.kaggle.com/uciml/iris\n\nThis consists of data on three species of Iris:\n\n- Setosa\n- Veriscolor\n- Virginica\n\nWith 150 samples (50 per species) recorded based on the following properties:\n\n- Sepal Length\n- Sepal Width\n- Petal Length\n- Petal Width\n\nMy goal is to first review this data and see if any coralations can be drawn between these metrics and if there is sufficent clustering of the three different species for a Machine Learning algorithm to predict the Iris Species based on these metrics. If this is the case then I will train an KNN algorithm and test it's predictive power.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nfrom sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier\nfrom sklearn import metrics",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Data preparation and cleaning\n\nSince the file is in CSV format it is possible to generate a dataframe via pandas. This can be used in turn to evalutade the data and generate visualisations. However before undertaking any analysis it is necessary to check the quality of the data to ensure it is usable. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"iris_df = pd.read_csv('Iris.csv', sep=',')\niris_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"A dataframe has successfully been generated based on the CSV file.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"iris_df.info()",
"<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>\nRangeIndex: 150 entries, 0 to 149\nData columns (total 6 columns):\nId 150 non-null int64\nSepalLengthCm 150 non-null float64\nSepalWidthCm 150 non-null float64\nPetalLengthCm 150 non-null float64\nPetalWidthCm 150 non-null float64\nSpecies 150 non-null object\ndtypes: float64(4), int64(1), object(1)\nmemory usage: 7.2+ KB\n"
]
],
[
[
"There do not appear to be any null values so I can proceed with the analysis. However the Id column serves no purpose so I will remove that before proceeding.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Exploratory analysis\n\nNext I will undertake an exploratory analysis to determine if there are any correlations in the attributes within the dataframe for the species. I will also consider if there is sufficient clustering across the three species to use these metrics as a way to predict the species. To do this I will generate scatterplots showing Sepal Length vs Sepal Width and Petal Length vs Petal Width with each of the three species hightlighted in different colours.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"scatter_plot_sepal = iris_df[iris_df.Species=='Iris-setosa'].plot(kind ='scatter', x = 'SepalLengthCm', y ='SepalWidthCm',color='orange', label='Setosa') \niris_df[iris_df.Species=='Iris-versicolor'].plot(kind = 'scatter', x ='SepalLengthCm', y ='SepalWidthCm',color='blue', label='Versicolor',ax=scatter_plot_sepal)\niris_df[iris_df.Species=='Iris-virginica'].plot(kind = 'scatter', x ='SepalLengthCm', y ='SepalWidthCm',color='green', label='Virginica', ax=scatter_plot_sepal)\nscatter_plot_sepal.set_xlabel(\"Sepal Length\")\nscatter_plot_sepal.set_ylabel(\"Sepal Width\")\nscatter_plot_sepal.set_title(\"Sepal Length VS Width\")\nscatter_plot_sepal=plt.gcf()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"scatter_plot_petal = iris_df[iris_df.Species=='Iris-setosa'].plot.scatter(x = 'PetalLengthCm', y ='PetalWidthCm', color='orange', label='Setosa') \niris_df[iris_df.Species=='Iris-versicolor'].plot.scatter(x = 'PetalLengthCm', y ='PetalWidthCm', color='blue', label='Versicolor', ax = scatter_plot_petal)\niris_df[iris_df.Species=='Iris-virginica'].plot.scatter(x = 'PetalLengthCm', y ='PetalWidthCm', color='green', label='Virginica', ax = scatter_plot_petal) \nscatter_plot_petal.set_xlabel(\"Petal Length\")\nscatter_plot_petal.set_ylabel(\"Petal Width\")\nscatter_plot_petal.set_title(\"Petal Length VS Width\")\nscatter_plot_petal=plt.gcf()\nplt.show()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Visually it would appear that there are corraelations in these attributes. There is clustering among the different species in respect to Sepal Length and Width. Similarly petal length versus width shows correlatino and each species also forming their own clusters.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Testing and Training Machine Learning Algorithm\n\nIn order to train and test the predcition accuracy of a machine learning algorithm, it is divide the data into a sample for training and another for testing. Since we already know the result for the testing sample it is possible to compare the predcitions the trained algorithm makes against actual results.\n\nFor my analysis I will train a K Means alogrithm and test how accurtate its predcitions of Iris species are against the test sample.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"train, test = train_test_split(iris_df, test_size = 0.3)\nprint(train.shape)\nprint(test.shape)",
"(105, 6)\n(45, 6)\n"
]
],
[
[
"I have generated a training data set of 105 values and testing data set of 45 values",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"train_X = train[['SepalLengthCm','SepalWidthCm','PetalLengthCm','PetalWidthCm']]# taking the training data features\ntrain_y=train.Species# output of our training data\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"test_X= test[['SepalLengthCm','SepalWidthCm','PetalLengthCm','PetalWidthCm']] # taking test data features\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"test_y =test.Species #output value of test data\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"train_X.head(2)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"train_y.head() ##output of the training data\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model=KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=3) #this examines 3 neighbours for putting the new data into a class\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model.fit(train_X,train_y)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"prediction=model.predict(test_X)\nprint('The accuracy of the KNN is',metrics.accuracy_score(prediction,test_y))\n",
"The accuracy of the KNN is 0.9777777777777777\n"
],
[
"a_index=list(range(1,11))\na=pd.Series()\nx=[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]\nfor i in list(range(1,11)):\n model=KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=i) \n model.fit(train_X,train_y)\n prediction=model.predict(test_X)\n a=a.append(pd.Series(metrics.accuracy_score(prediction,test_y)))\nplt.plot(a_index, a)\nplt.xticks(x)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c502ae850c57a84049a80c71586c529a467dda98
| 274,928 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
coursera-deep-learning-homework/Improving_Deep_Neural_Networks_Hyperparameter_tuning_Regularization_and_Optimization/Week-01/Initialization.ipynb
|
chenghuiyu/DeepLearning-Examples
|
36467c3385da796723ddb12c5f774a35b439fd5d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
coursera-deep-learning-homework/Improving_Deep_Neural_Networks_Hyperparameter_tuning_Regularization_and_Optimization/Week-01/Initialization.ipynb
|
chenghuiyu/DeepLearning-Examples
|
36467c3385da796723ddb12c5f774a35b439fd5d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
coursera-deep-learning-homework/Improving_Deep_Neural_Networks_Hyperparameter_tuning_Regularization_and_Optimization/Week-01/Initialization.ipynb
|
chenghuiyu/DeepLearning-Examples
|
36467c3385da796723ddb12c5f774a35b439fd5d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 268.222439 | 57,656 | 0.901665 |
[
[
[
"# Initialization\n\nWelcome to the first assignment of \"Improving Deep Neural Networks\". \n\nTraining your neural network requires specifying an initial value of the weights. A well chosen initialization method will help learning. \n\nIf you completed the previous course of this specialization, you probably followed our instructions for weight initialization, and it has worked out so far. But how do you choose the initialization for a new neural network? In this notebook, you will see how different initializations lead to different results. \n\nA well chosen initialization can:\n- Speed up the convergence of gradient descent\n- Increase the odds of gradient descent converging to a lower training (and generalization) error \n\nTo get started, run the following cell to load the packages and the planar dataset you will try to classify.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport sklearn\nimport sklearn.datasets\nfrom init_utils import sigmoid, relu, compute_loss, forward_propagation, backward_propagation\nfrom init_utils import update_parameters, predict, load_dataset, plot_decision_boundary, predict_dec\n\n%matplotlib inline\nplt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (7.0, 4.0) # set default size of plots\nplt.rcParams['image.interpolation'] = 'nearest'\nplt.rcParams['image.cmap'] = 'gray'\n\n# load image dataset: blue/red dots in circles\ntrain_X, train_Y, test_X, test_Y = load_dataset()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You would like a classifier to separate the blue dots from the red dots.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 1 - Neural Network model ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"You will use a 3-layer neural network (already implemented for you). Here are the initialization methods you will experiment with: \n- *Zeros initialization* -- setting `initialization = \"zeros\"` in the input argument.\n- *Random initialization* -- setting `initialization = \"random\"` in the input argument. This initializes the weights to large random values. \n- *He initialization* -- setting `initialization = \"he\"` in the input argument. This initializes the weights to random values scaled according to a paper by He et al., 2015. \n\n**Instructions**: Please quickly read over the code below, and run it. In the next part you will implement the three initialization methods that this `model()` calls.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def model(X, Y, learning_rate = 0.01, num_iterations = 15000, print_cost = True, initialization = \"he\"):\n \"\"\"\n Implements a three-layer neural network: LINEAR->RELU->LINEAR->RELU->LINEAR->SIGMOID.\n \n Arguments:\n X -- input data, of shape (2, number of examples)\n Y -- true \"label\" vector (containing 0 for red dots; 1 for blue dots), of shape (1, number of examples)\n learning_rate -- learning rate for gradient descent \n num_iterations -- number of iterations to run gradient descent\n print_cost -- if True, print the cost every 1000 iterations\n initialization -- flag to choose which initialization to use (\"zeros\",\"random\" or \"he\")\n \n Returns:\n parameters -- parameters learnt by the model\n \"\"\"\n \n grads = {}\n costs = [] # to keep track of the loss\n m = X.shape[1] # number of examples\n layers_dims = [X.shape[0], 10, 5, 1]\n \n # Initialize parameters dictionary.\n if initialization == \"zeros\":\n parameters = initialize_parameters_zeros(layers_dims)\n elif initialization == \"random\":\n parameters = initialize_parameters_random(layers_dims)\n elif initialization == \"he\":\n parameters = initialize_parameters_he(layers_dims)\n\n # Loop (gradient descent)\n\n for i in range(0, num_iterations):\n\n # Forward propagation: LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID.\n a3, cache = forward_propagation(X, parameters)\n \n # Loss\n cost = compute_loss(a3, Y)\n\n # Backward propagation.\n grads = backward_propagation(X, Y, cache)\n \n # Update parameters.\n parameters = update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate)\n \n # Print the loss every 1000 iterations\n if print_cost and i % 1000 == 0:\n print(\"Cost after iteration {}: {}\".format(i, cost))\n costs.append(cost)\n \n # plot the loss\n plt.plot(costs)\n plt.ylabel('cost')\n plt.xlabel('iterations (per hundreds)')\n plt.title(\"Learning rate =\" + str(learning_rate))\n plt.show()\n \n return parameters",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 2 - Zero initialization\n\nThere are two types of parameters to initialize in a neural network:\n- the weight matrices $(W^{[1]}, W^{[2]}, W^{[3]}, ..., W^{[L-1]}, W^{[L]})$\n- the bias vectors $(b^{[1]}, b^{[2]}, b^{[3]}, ..., b^{[L-1]}, b^{[L]})$\n\n**Exercise**: Implement the following function to initialize all parameters to zeros. You'll see later that this does not work well since it fails to \"break symmetry\", but lets try it anyway and see what happens. Use np.zeros((..,..)) with the correct shapes.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# GRADED FUNCTION: initialize_parameters_zeros \n\ndef initialize_parameters_zeros(layers_dims):\n \"\"\"\n Arguments:\n layer_dims -- python array (list) containing the size of each layer.\n \n Returns:\n parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters \"W1\", \"b1\", ..., \"WL\", \"bL\":\n W1 -- weight matrix of shape (layers_dims[1], layers_dims[0])\n b1 -- bias vector of shape (layers_dims[1], 1)\n ...\n WL -- weight matrix of shape (layers_dims[L], layers_dims[L-1])\n bL -- bias vector of shape (layers_dims[L], 1)\n \"\"\"\n \n parameters = {}\n L = len(layers_dims) # number of layers in the network\n \n for l in range(1, L):\n ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)\n parameters['W' + str(l)] = np.zeros((layers_dims[l], layers_dims[l-1]))\n parameters['b' + str(l)] = np.zeros((layers_dims[l], 1))\n ### END CODE HERE ###\n return parameters",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"parameters = initialize_parameters_zeros([3,2,1])\nprint(\"W1 = \" + str(parameters[\"W1\"]))\nprint(\"b1 = \" + str(parameters[\"b1\"]))\nprint(\"W2 = \" + str(parameters[\"W2\"]))\nprint(\"b2 = \" + str(parameters[\"b2\"]))",
"W1 = [[ 0. 0. 0.]\n [ 0. 0. 0.]]\nb1 = [[ 0.]\n [ 0.]]\nW2 = [[ 0. 0.]]\nb2 = [[ 0.]]\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Expected Output**:\n\n<table> \n <tr>\n <td>\n **W1**\n </td>\n <td>\n [[ 0. 0. 0.]\n [ 0. 0. 0.]]\n </td>\n </tr>\n <tr>\n <td>\n **b1**\n </td>\n <td>\n [[ 0.]\n [ 0.]]\n </td>\n </tr>\n <tr>\n <td>\n **W2**\n </td>\n <td>\n [[ 0. 0.]]\n </td>\n </tr>\n <tr>\n <td>\n **b2**\n </td>\n <td>\n [[ 0.]]\n </td>\n </tr>\n\n</table> ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Run the following code to train your model on 15,000 iterations using zeros initialization.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"parameters = model(train_X, train_Y, initialization = \"zeros\")\nprint (\"On the train set:\")\npredictions_train = predict(train_X, train_Y, parameters)\nprint (\"On the test set:\")\npredictions_test = predict(test_X, test_Y, parameters)",
"Cost after iteration 0: 0.6931471805599453\nCost after iteration 1000: 0.6931471805599453\nCost after iteration 2000: 0.6931471805599453\nCost after iteration 3000: 0.6931471805599453\nCost after iteration 4000: 0.6931471805599453\nCost after iteration 5000: 0.6931471805599453\nCost after iteration 6000: 0.6931471805599453\nCost after iteration 7000: 0.6931471805599453\nCost after iteration 8000: 0.6931471805599453\nCost after iteration 9000: 0.6931471805599453\nCost after iteration 10000: 0.6931471805599455\nCost after iteration 11000: 0.6931471805599453\nCost after iteration 12000: 0.6931471805599453\nCost after iteration 13000: 0.6931471805599453\nCost after iteration 14000: 0.6931471805599453\n"
]
],
[
[
"The performance is really bad, and the cost does not really decrease, and the algorithm performs no better than random guessing. Why? Lets look at the details of the predictions and the decision boundary:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print (\"predictions_train = \" + str(predictions_train))\nprint (\"predictions_test = \" + str(predictions_test))",
"predictions_train = [[0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0\n 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0\n 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0\n 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0\n 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0\n 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0\n 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0\n 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0\n 0 0 0 0]]\npredictions_test = [[0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0\n 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0\n 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]]\n"
],
[
"plt.title(\"Model with Zeros initialization\")\naxes = plt.gca()\naxes.set_xlim([-1.5,1.5])\naxes.set_ylim([-1.5,1.5])\nplot_decision_boundary(lambda x: predict_dec(parameters, x.T), train_X, train_Y)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The model is predicting 0 for every example. \n\nIn general, initializing all the weights to zero results in the network failing to break symmetry. This means that every neuron in each layer will learn the same thing, and you might as well be training a neural network with $n^{[l]}=1$ for every layer, and the network is no more powerful than a linear classifier such as logistic regression. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<font color='blue'>\n**What you should remember**:\n- The weights $W^{[l]}$ should be initialized randomly to break symmetry. \n- It is however okay to initialize the biases $b^{[l]}$ to zeros. Symmetry is still broken so long as $W^{[l]}$ is initialized randomly. \n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 3 - Random initialization\n\nTo break symmetry, lets intialize the weights randomly. Following random initialization, each neuron can then proceed to learn a different function of its inputs. In this exercise, you will see what happens if the weights are intialized randomly, but to very large values. \n\n**Exercise**: Implement the following function to initialize your weights to large random values (scaled by \\*10) and your biases to zeros. Use `np.random.randn(..,..) * 10` for weights and `np.zeros((.., ..))` for biases. We are using a fixed `np.random.seed(..)` to make sure your \"random\" weights match ours, so don't worry if running several times your code gives you always the same initial values for the parameters. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# GRADED FUNCTION: initialize_parameters_random\n\ndef initialize_parameters_random(layers_dims):\n \"\"\"\n Arguments:\n layer_dims -- python array (list) containing the size of each layer.\n \n Returns:\n parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters \"W1\", \"b1\", ..., \"WL\", \"bL\":\n W1 -- weight matrix of shape (layers_dims[1], layers_dims[0])\n b1 -- bias vector of shape (layers_dims[1], 1)\n ...\n WL -- weight matrix of shape (layers_dims[L], layers_dims[L-1])\n bL -- bias vector of shape (layers_dims[L], 1)\n \"\"\"\n \n np.random.seed(3) # This seed makes sure your \"random\" numbers will be the as ours\n parameters = {}\n L = len(layers_dims) # integer representing the number of layers\n \n for l in range(1, L):\n ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)\n parameters['W' + str(l)] = np.random.randn(layers_dims[l], layers_dims[l-1]) * 10\n parameters['b' + str(l)] = np.zeros((layers_dims[l], 1))\n ### END CODE HERE ###\n\n return parameters",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"parameters = initialize_parameters_random([3, 2, 1])\nprint(\"W1 = \" + str(parameters[\"W1\"]))\nprint(\"b1 = \" + str(parameters[\"b1\"]))\nprint(\"W2 = \" + str(parameters[\"W2\"]))\nprint(\"b2 = \" + str(parameters[\"b2\"]))",
"W1 = [[ 17.88628473 4.36509851 0.96497468]\n [-18.63492703 -2.77388203 -3.54758979]]\nb1 = [[ 0.]\n [ 0.]]\nW2 = [[-0.82741481 -6.27000677]]\nb2 = [[ 0.]]\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Expected Output**:\n\n<table> \n <tr>\n <td>\n **W1**\n </td>\n <td>\n [[ 17.88628473 4.36509851 0.96497468]\n [-18.63492703 -2.77388203 -3.54758979]]\n </td>\n </tr>\n <tr>\n <td>\n **b1**\n </td>\n <td>\n [[ 0.]\n [ 0.]]\n </td>\n </tr>\n <tr>\n <td>\n **W2**\n </td>\n <td>\n [[-0.82741481 -6.27000677]]\n </td>\n </tr>\n <tr>\n <td>\n **b2**\n </td>\n <td>\n [[ 0.]]\n </td>\n </tr>\n\n</table> ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Run the following code to train your model on 15,000 iterations using random initialization.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"parameters = model(train_X, train_Y, initialization = \"random\")\nprint (\"On the train set:\")\npredictions_train = predict(train_X, train_Y, parameters)\nprint (\"On the test set:\")\npredictions_test = predict(test_X, test_Y, parameters)",
"Cost after iteration 0: inf\n"
]
],
[
[
"If you see \"inf\" as the cost after the iteration 0, this is because of numerical roundoff; a more numerically sophisticated implementation would fix this. But this isn't worth worrying about for our purposes. \n\nAnyway, it looks like you have broken symmetry, and this gives better results. than before. The model is no longer outputting all 0s. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print (predictions_train)\nprint (predictions_test)",
"[[1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1\n 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0\n 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1\n 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0\n 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1\n 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1\n 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 1\n 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1\n 1 1 1 0]]\n[[1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0\n 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1\n 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0]]\n"
],
[
"plt.title(\"Model with large random initialization\")\naxes = plt.gca()\naxes.set_xlim([-1.5,1.5])\naxes.set_ylim([-1.5,1.5])\nplot_decision_boundary(lambda x: predict_dec(parameters, x.T), train_X, train_Y)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Observations**:\n- The cost starts very high. This is because with large random-valued weights, the last activation (sigmoid) outputs results that are very close to 0 or 1 for some examples, and when it gets that example wrong it incurs a very high loss for that example. Indeed, when $\\log(a^{[3]}) = \\log(0)$, the loss goes to infinity.\n- Poor initialization can lead to vanishing/exploding gradients, which also slows down the optimization algorithm. \n- If you train this network longer you will see better results, but initializing with overly large random numbers slows down the optimization.\n\n<font color='blue'>\n**In summary**:\n- Initializing weights to very large random values does not work well. \n- Hopefully intializing with small random values does better. The important question is: how small should be these random values be? Lets find out in the next part! ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 4 - He initialization\n\nFinally, try \"He Initialization\"; this is named for the first author of He et al., 2015. (If you have heard of \"Xavier initialization\", this is similar except Xavier initialization uses a scaling factor for the weights $W^{[l]}$ of `sqrt(1./layers_dims[l-1])` where He initialization would use `sqrt(2./layers_dims[l-1])`.)\n\n**Exercise**: Implement the following function to initialize your parameters with He initialization.\n\n**Hint**: This function is similar to the previous `initialize_parameters_random(...)`. The only difference is that instead of multiplying `np.random.randn(..,..)` by 10, you will multiply it by $\\sqrt{\\frac{2}{\\text{dimension of the previous layer}}}$, which is what He initialization recommends for layers with a ReLU activation. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# GRADED FUNCTION: initialize_parameters_he\n\ndef initialize_parameters_he(layers_dims):\n \"\"\"\n Arguments:\n layer_dims -- python array (list) containing the size of each layer.\n \n Returns:\n parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters \"W1\", \"b1\", ..., \"WL\", \"bL\":\n W1 -- weight matrix of shape (layers_dims[1], layers_dims[0])\n b1 -- bias vector of shape (layers_dims[1], 1)\n ...\n WL -- weight matrix of shape (layers_dims[L], layers_dims[L-1])\n bL -- bias vector of shape (layers_dims[L], 1)\n \"\"\"\n \n np.random.seed(3)\n parameters = {}\n L = len(layers_dims) - 1 # integer representing the number of layers\n \n for l in range(1, L + 1):\n ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)\n parameters['W' + str(l)] = np.random.randn(layers_dims[l], layers_dims[l-1]) * np.sqrt(2./layers_dims[l-1]) \n parameters['b' + str(l)] = np.zeros((layers_dims[l], 1))\n ### END CODE HERE ###\n \n return parameters",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"parameters = initialize_parameters_he([2, 4, 1])\nprint(\"W1 = \" + str(parameters[\"W1\"]))\nprint(\"b1 = \" + str(parameters[\"b1\"]))\nprint(\"W2 = \" + str(parameters[\"W2\"]))\nprint(\"b2 = \" + str(parameters[\"b2\"]))",
"W1 = [[ 1.78862847 0.43650985]\n [ 0.09649747 -1.8634927 ]\n [-0.2773882 -0.35475898]\n [-0.08274148 -0.62700068]]\nb1 = [[ 0.]\n [ 0.]\n [ 0.]\n [ 0.]]\nW2 = [[-0.03098412 -0.33744411 -0.92904268 0.62552248]]\nb2 = [[ 0.]]\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Expected Output**:\n\n<table> \n <tr>\n <td>\n **W1**\n </td>\n <td>\n [[ 1.78862847 0.43650985]\n [ 0.09649747 -1.8634927 ]\n [-0.2773882 -0.35475898]\n [-0.08274148 -0.62700068]]\n </td>\n </tr>\n <tr>\n <td>\n **b1**\n </td>\n <td>\n [[ 0.]\n [ 0.]\n [ 0.]\n [ 0.]]\n </td>\n </tr>\n <tr>\n <td>\n **W2**\n </td>\n <td>\n [[-0.03098412 -0.33744411 -0.92904268 0.62552248]]\n </td>\n </tr>\n <tr>\n <td>\n **b2**\n </td>\n <td>\n [[ 0.]]\n </td>\n </tr>\n\n</table> ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Run the following code to train your model on 15,000 iterations using He initialization.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"parameters = model(train_X, train_Y, initialization = \"he\")\nprint (\"On the train set:\")\npredictions_train = predict(train_X, train_Y, parameters)\nprint (\"On the test set:\")\npredictions_test = predict(test_X, test_Y, parameters)",
"Cost after iteration 0: 0.8830537463419761\nCost after iteration 1000: 0.6879825919728063\nCost after iteration 2000: 0.6751286264523371\nCost after iteration 3000: 0.6526117768893807\nCost after iteration 4000: 0.6082958970572938\nCost after iteration 5000: 0.5304944491717495\nCost after iteration 6000: 0.4138645817071794\nCost after iteration 7000: 0.3117803464844441\nCost after iteration 8000: 0.23696215330322562\nCost after iteration 9000: 0.18597287209206836\nCost after iteration 10000: 0.1501555628037182\nCost after iteration 11000: 0.12325079292273548\nCost after iteration 12000: 0.09917746546525937\nCost after iteration 13000: 0.0845705595402428\nCost after iteration 14000: 0.07357895962677366\n"
],
[
"plt.title(\"Model with He initialization\")\naxes = plt.gca()\naxes.set_xlim([-1.5,1.5])\naxes.set_ylim([-1.5,1.5])\nplot_decision_boundary(lambda x: predict_dec(parameters, x.T), train_X, train_Y)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Observations**:\n- The model with He initialization separates the blue and the red dots very well in a small number of iterations.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 5 - Conclusions",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"You have seen three different types of initializations. For the same number of iterations and same hyperparameters the comparison is:\n\n<table> \n <tr>\n <td>\n **Model**\n </td>\n <td>\n **Train accuracy**\n </td>\n <td>\n **Problem/Comment**\n </td>\n\n </tr>\n <td>\n 3-layer NN with zeros initialization\n </td>\n <td>\n 50%\n </td>\n <td>\n fails to break symmetry\n </td>\n <tr>\n <td>\n 3-layer NN with large random initialization\n </td>\n <td>\n 83%\n </td>\n <td>\n too large weights \n </td>\n </tr>\n <tr>\n <td>\n 3-layer NN with He initialization\n </td>\n <td>\n 99%\n </td>\n <td>\n recommended method\n </td>\n </tr>\n</table> ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<font color='blue'>\n**What you should remember from this notebook**:\n- Different initializations lead to different results\n- Random initialization is used to break symmetry and make sure different hidden units can learn different things\n- Don't intialize to values that are too large\n- He initialization works well for networks with ReLU activations. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
c502af6da3dcf432fe35099fc3bfe36b15602390
| 467,579 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
week01_intro/deep_crossentropy_method(3)(1).ipynb
|
2001092236/Practical_RL
|
59090a7dd9405d283b8f626cfc29e9ec03a47e7d
|
[
"Unlicense"
] | null | null | null |
week01_intro/deep_crossentropy_method(3)(1).ipynb
|
2001092236/Practical_RL
|
59090a7dd9405d283b8f626cfc29e9ec03a47e7d
|
[
"Unlicense"
] | null | null | null |
week01_intro/deep_crossentropy_method(3)(1).ipynb
|
2001092236/Practical_RL
|
59090a7dd9405d283b8f626cfc29e9ec03a47e7d
|
[
"Unlicense"
] | null | null | null | 172.474733 | 199,200 | 0.85219 |
[
[
[
"# Deep Crossentropy method\n\nIn this section we'll extend your CEM implementation with neural networks! You will train a multi-layer neural network to solve simple continuous state space games. __Please make sure you're done with tabular crossentropy method from the previous notebook.__\n\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import sys, os\nif 'google.colab' in sys.modules and not os.path.exists('.setup_complete'):\n !wget -q https://raw.githubusercontent.com/yandexdataschool/Practical_RL/master/setup_colab.sh -O- | bash\n !touch .setup_complete\n\n# This code creates a virtual display to draw game images on.\n# It will have no effect if your machine has a monitor.\nif type(os.environ.get(\"DISPLAY\")) is not str or len(os.environ.get(\"DISPLAY\")) == 0:\n !bash ../xvfb start\n os.environ['DISPLAY'] = ':1'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from tqdm import tqdm, tqdm_notebook",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import gym\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n%matplotlib inline\n\n# if you see \"<classname> has no attribute .env\", remove .env or update gym\nenv = gym.make(\"CartPole-v0\").env\n\nenv.reset()\nn_actions = env.action_space.n\nstate_dim = env.observation_space.shape[0]\n\nplt.imshow(env.render(\"rgb_array\"))\nprint(\"state vector dim =\", state_dim)\nprint(\"n_actions =\", n_actions)",
"state vector dim = 4\nn_actions = 2\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Neural Network Policy\n\nFor this assignment we'll utilize the simplified neural network implementation from __[Scikit-learn](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.neural_network.MLPClassifier.html)__. Here's what you'll need:\n\n* `agent.partial_fit(states, actions)` - make a single training pass over the data. Maximize the probabilitity of :actions: from :states:\n* `agent.predict_proba(states)` - predict probabilities of all actions, a matrix of shape __[len(states), n_actions]__\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifier\n\nagent = MLPClassifier(\n hidden_layer_sizes=(20, 20),\n warm_start=True,\n activation='tanh',\n max_iter=1,\n)\n\n# initialize agent to the dimension of state space and number of actions\nagent.partial_fit([env.reset()] * n_actions, range(n_actions), range(n_actions))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"env.reset()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"agent.predict_proba([env.reset()])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def generate_session(env, agent, t_max=1000):\n \"\"\"\n Play a single game using agent neural network.\n Terminate when game finishes or after :t_max: steps\n \"\"\"\n states, actions = [], []\n total_reward = 0\n\n s = env.reset()\n\n for t in range(t_max):\n \n # use agent to predict a vector of action probabilities for state :s:\n probs = agent.predict_proba([s])[0] # <YOUR CODE>\n\n assert probs.shape == (env.action_space.n,), \"make sure probabilities are a vector (hint: np.reshape)\"\n \n # use the probabilities you predicted to pick an action\n # sample proportionally to the probabilities, don't just take the most likely action\n a = np.random.choice(np.arange(n_actions), p=probs) # <YOUR CODE>\n # ^-- hint: try np.random.choice\n\n new_s, r, done, info = env.step(a)\n\n # record sessions like you did before\n states.append(s)\n actions.append(a)\n total_reward += r\n\n s = new_s\n if done:\n break\n return states, actions, total_reward",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dummy_states, dummy_actions, dummy_reward = generate_session(env, agent, t_max=5)\nprint(\"states:\", np.stack(dummy_states))\nprint(\"actions:\", dummy_actions)\nprint(\"reward:\", dummy_reward)",
"states: [[-0.00694949 0.01329685 -0.0450017 0.03184425]\n [-0.00668355 0.20903429 -0.04436482 -0.2746907 ]\n [-0.00250287 0.01457249 -0.04985863 0.00367602]\n [-0.00221142 -0.17980028 -0.04978511 0.28022048]\n [-0.00580742 -0.37417801 -0.0441807 0.55679504]]\nactions: [1, 0, 0, 0, 1]\nreward: 5.0\n"
]
],
[
[
"### CEM steps\nDeep CEM uses exactly the same strategy as the regular CEM, so you can copy your function code from previous notebook.\n\nThe only difference is that now each observation is not a number but a `float32` vector.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def select_elites(states_batch, actions_batch, rewards_batch, percentile=50):\n \"\"\"\n Select states and actions from games that have rewards >= percentile\n :param states_batch: list of lists of states, states_batch[session_i][t]\n :param actions_batch: list of lists of actions, actions_batch[session_i][t]\n :param rewards_batch: list of rewards, rewards_batch[session_i]\n\n :returns: elite_states,elite_actions, both 1D lists of states and respective actions from elite sessions\n\n Please return elite states and actions in their original order \n [i.e. sorted by session number and timestep within session]\n\n If you are confused, see examples below. Please don't assume that states are integers\n (they will become different later).\n \"\"\"\n\n reward_threshold = np.percentile(rewards_batch, percentile) # <YOUR CODE: compute minimum reward for elite sessions. Hint: use np.percentile()>\n\n elite_states = []\n elite_actions = []\n for i in range(len(states_batch)):\n if rewards_batch[i] >= reward_threshold:\n elite_states += states_batch[i]\n elite_actions += actions_batch[i]\n\n return elite_states, elite_actions",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Training loop\nGenerate sessions, select N best and fit to those.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from IPython.display import clear_output\n\ndef show_progress(rewards_batch, log, percentile, reward_range=[-990, +10]):\n \"\"\"\n A convenience function that displays training progress. \n No cool math here, just charts.\n \"\"\"\n\n mean_reward = np.mean(rewards_batch)\n threshold = np.percentile(rewards_batch, percentile)\n log.append([mean_reward, threshold])\n\n clear_output(True)\n print(\"mean reward = %.3f, threshold=%.3f\" % (mean_reward, threshold))\n plt.figure(figsize=[8, 4])\n plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)\n plt.plot(list(zip(*log))[0], label='Mean rewards')\n plt.plot(list(zip(*log))[1], label='Reward thresholds')\n plt.legend()\n plt.grid()\n\n plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)\n plt.hist(rewards_batch, range=reward_range)\n plt.vlines([np.percentile(rewards_batch, percentile)],\n [0], [100], label=\"percentile\", color='red')\n plt.legend()\n plt.grid()\n\n plt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"n_sessions = 100\npercentile = 70\nlog = []\n\nfor i in range(100):\n # generate new sessions\n sessions = [ generate_session(env, agent) for i in np.arange(n_sessions) ]\n\n states_batch, actions_batch, rewards_batch = map(np.array, zip(*sessions))\n\n elite_states, elite_actions = select_elites(states_batch, actions_batch, rewards_batch, percentile) # <YOUR CODE: select elite actions just like before>\n\n #<YOUR CODE: partial_fit agent to predict elite_actions(y) from elite_states(X)>\n agent.partial_fit(elite_states, elite_actions)\n \n show_progress(rewards_batch, log, percentile, reward_range=[0, np.max(rewards_batch)])\n\n if np.mean(rewards_batch) > 190:\n print(\"You Win! You may stop training now via KeyboardInterrupt.\")",
"mean reward = 49.440, threshold=62.000\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Results",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import gym.wrappers\nenv = gym.wrappers.Monitor(gym.make(\"CartPole-v0\"), directory=\"videos\", force=True)\nsessions = [generate_session(env, agent) for _ in range(100)]\nenv.close()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Record sessions\n\nimport gym.wrappers\n\nwith gym.wrappers.Monitor(gym.make(\"CartPole-v0\"), directory=\"videos\", force=True) as env_monitor:\n sessions = [generate_session(env_monitor, agent) for _ in range(100)]",
"\u001b[31mERROR: VideoRecorder encoder exited with status 1\u001b[0m\n"
],
[
"# Show video. This may not work in some setups. If it doesn't\n# work for you, you can download the videos and view them locally.\n\nfrom pathlib import Path\nfrom base64 import b64encode\nfrom IPython.display import HTML\n\nvideo_paths = sorted([s for s in Path('videos').iterdir() if s.suffix == '.mp4'])\nvideo_path = video_paths[-1] # You can also try other indices\n\nif 'google.colab' in sys.modules:\n # https://stackoverflow.com/a/57378660/1214547\n with video_path.open('rb') as fp:\n mp4 = fp.read()\n data_url = 'data:video/mp4;base64,' + b64encode(mp4).decode()\nelse:\n data_url = str(video_path)\n\nHTML(\"\"\"\n<video width=\"640\" height=\"480\" controls>\n <source src=\"{}\" type=\"video/mp4\">\n</video>\n\"\"\".format(data_url))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Homework part I\n\n### Tabular crossentropy method\n\nYou may have noticed that the taxi problem quickly converges from -100 to a near-optimal score and then descends back into -50/-100. This is in part because the environment has some innate randomness. Namely, the starting points of passenger/driver change from episode to episode.\n\n### Tasks\n- __1.1__ (2 pts) Find out how the algorithm performance changes if you use a different `percentile` and/or `n_sessions`. Provide here some figures so we can see how the hyperparameters influence the performance.\n- __1.2__ (1 pts) Tune the algorithm to end up with positive average score.\n\nIt's okay to modify the existing code.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"```<Describe what you did here>```",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import gym\nimport numpy as np\nenv = gym.make('Taxi-v3')\nenv.reset()\nenv.render()",
"+---------+\n|R: | : :\u001b[34;1mG\u001b[0m|\n| : | : : |\n| :\u001b[43m \u001b[0m: : : |\n| | : | : |\n|Y| : |\u001b[35mB\u001b[0m: |\n+---------+\n\n"
],
[
"n_sessions = 250 # sample this many sessions\npercentile = 50 # take this percent of session with highest rewards\nlearning_rate = 0.5 # how quickly the policy is updated, on a scale from 0 to 1\n\nlog = []",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"n_states = env.observation_space.n\nn_actions = env.action_space.n\nprint(\"n_states=%i, n_actions=%i\" % (n_states, n_actions))",
"n_states=500, n_actions=6\n"
],
[
"def initialize_policy(n_states, n_actions):\n policy = np.ones((n_states, n_actions)) / n_actions\n return policy\n\npolicy = initialize_policy(n_states, n_actions)\nassert type(policy) in (np.ndarray, np.matrix)\nassert np.allclose(policy, 1./n_actions)\nassert np.allclose(np.sum(policy, axis=1), 1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def generate_session(env, policy, t_max = 10**4):\n '''\n play ONE game\n record states-actions\n compute reward\n '''\n states = []\n actions = []\n total_reward = 0.0\n \n s = env.reset()\n for t in np.arange(t_max):\n act = np.random.choice(np.arange(len(policy[s])), p=policy[s])\n new_s, r, done, info = env.step(act)\n \n states.append(s)\n actions.append(act)\n total_reward += r\n \n s = new_s\n \n if done:\n break\n return states, actions, total_reward\ns, a, r = generate_session(env, policy)\nassert type(s) == type(a) == list\nassert len(s) == len(a)\nassert type(r) in [float, np.float]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# let's see the initial reward distribution\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n%matplotlib inline\n\nsample_rewards = [generate_session(env, policy, t_max=1000)[-1] for _ in range(200)]\n\nplt.hist(sample_rewards, bins=20)\nplt.vlines([np.percentile(sample_rewards, 50)], [0], [100], label=\"50'th percentile\", color='green')\nplt.vlines([np.percentile(sample_rewards, 90)], [0], [100], label=\"90'th percentile\", color='red')\nplt.legend()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def select_elites(states_batch, actions_batch, rewards_batch, percentile):\n \"\"\"\n Select states and actions from games that have rewards >= percentile\n :param states_batch: list of lists of states, states_batch[session_i][t]\n :param actions_batch: list of lists of actions, actions_batch[session_i][t]\n :param rewards_batch: list of rewards, rewards_batch[session_i]\n\n :returns: elite_states,elite_actions, both 1D lists of states and respective actions from elite sessions\n\n Please return elite states and actions in their original order \n [i.e. sorted by session number and timestep within session]\n\n If you are confused, see examples below. Please don't assume that states are integers\n (they will become different later).\n \"\"\"\n\n reward_threshold = np.percentile(rewards_batch, percentile) # <YOUR CODE: compute minimum reward for elite sessions. Hint: use np.percentile()>\n\n elite_states = []\n elite_actions = []\n for i in range(len(states_batch)):\n if rewards_batch[i] >= reward_threshold:\n elite_states += states_batch[i]\n elite_actions += actions_batch[i]\n\n return elite_states, elite_actions",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def get_new_policy(elite_states, elite_actions):\n \"\"\"\n Given a list of elite states/actions from select_elites,\n return a new policy where each action probability is proportional to\n\n policy[s_i,a_i] ~ #[occurrences of s_i and a_i in elite states/actions]\n\n Don't forget to normalize the policy to get valid probabilities and handle the 0/0 case.\n For states that you never visited, use a uniform distribution (1/n_actions for all states).\n\n :param elite_states: 1D list of states from elite sessions\n :param elite_actions: 1D list of actions from elite sessions\n\n \"\"\"\n\n new_policy = np.zeros([n_states, n_actions])\n\n # <YOUR CODE: set probabilities for actions given elite states & actions>\n # Don't forget to set 1/n_actions for all actions in unvisited states.\n \n for i in np.arange(len(elite_states)):\n new_policy[elite_states[i]][elite_actions[i]] += 1\n \n for i in np.arange(n_states):\n summ = np.sum(new_policy[i])\n if summ == 0:\n new_policy[i] = 1 / n_actions\n else:\n new_policy[i] /= summ\n return new_policy",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from IPython.display import clear_output\n\ndef show_progress(rewards_batch, log, percentile, reward_range=[-990, +10]):\n \"\"\"\n A convenience function that displays training progress. \n No cool math here, just charts.\n \"\"\"\n\n mean_reward = np.mean(rewards_batch)\n threshold = np.percentile(rewards_batch, percentile)\n log.append([mean_reward, threshold])\n \n plt.figure(figsize=[8, 4])\n plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)\n plt.plot(list(zip(*log))[0], label='Mean rewards')\n plt.plot(list(zip(*log))[1], label='Reward thresholds')\n plt.legend()\n plt.grid()\n\n plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)\n plt.hist(rewards_batch, range=reward_range)\n plt.vlines([np.percentile(rewards_batch, percentile)],\n [0], [100], label=\"percentile\", color='red')\n plt.legend()\n plt.grid()\n clear_output(True)\n print(\"mean reward = %.3f, threshold=%.3f\" % (mean_reward, threshold))\n plt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def show_final_progress(rewards_batch, log, percentile, reward_range=[-990, +10]):\n mean_reward = np.mean(rewards_batch)\n threshold = np.percentile(rewards_batch, percentile)\n \n plt.figure(figsize=[8, 4])\n plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)\n plt.plot(list(zip(*log))[0], label='Mean rewards')\n plt.plot(list(zip(*log))[1], label='Reward thresholds')\n plt.legend()\n plt.grid()\n\n plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)\n plt.hist(rewards_batch, range=reward_range)\n plt.vlines([np.percentile(rewards_batch, percentile)],\n [0], [100], label=\"percentile\", color='red')\n plt.legend()\n plt.grid()\n clear_output(True)\n print(\"mean reward = %.3f, threshold=%.3f\" % (mean_reward, threshold))\n plt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"policy = initialize_policy(n_states, n_actions)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def get_policy_rewards_batch_log(n_sessions, percentile, learning_rate, policy=initialize_policy(n_states, n_actions)):\n log = []\n for i in tqdm(np.arange(100)):\n sessions = [ generate_session(env, policy) for i in np.arange(n_sessions) ]\n\n states_batch, actions_batch, rewards_batch = zip(*sessions)\n\n elite_states, elite_actions = select_elites(states_batch, actions_batch, rewards_batch, percentile) # <YOUR CODE: select elite states & actions>\n\n new_policy = get_new_policy(elite_states, elite_actions) # <YOUR CODE: compute new policy>\n\n policy = learning_rate * new_policy + (1 - learning_rate) * policy\n\n # display results on chart\n # show_progress(rewards_batch, log, percentile)\n mean_reward = np.mean(rewards_batch)\n threshold = np.percentile(rewards_batch, percentile)\n log.append([mean_reward, threshold])\n return policy, rewards_batch, log",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"n_sessions_tab = [50, 150, 250, 400]\npercentile_tab = [80, 60, 40, 20]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"all_policy = [[0 for i in range(len(n_sessions_tab))] for j in range(len(percentile_tab))]\nall_rewards = [[0 for i in range(len(n_sessions_tab))] for j in range(len(percentile_tab))]\nall_log = [[0 for i in range(len(n_sessions_tab))] for j in range(len(percentile_tab))]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=len(n_sessions_tab), ncols=len(percentile_tab), figsize=(25, 25))\n\nprint('n_sessions, percentile')\nfor i in tqdm_notebook(range(len(n_sessions_tab))):\n n_sessions = n_sessions_tab[i]\n for j in range(len(percentile_tab)):\n percentile = percentile_tab[j]\n policy, rewards_batch, log = get_policy_rewards_batch_log(n_sessions, percentile, learning_rate)\n \n all_policy[i][j] = policy\n all_rewards[i][j] = mean_reward\n all_log[i][j] = log\n \n mean_reward = np.mean(rewards_batch)\n threshold = np.percentile(rewards_batch, percentile)\n\n # plt.figure(figsize=[8, 4])\n # plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)\n ax[i][j].plot(list(zip(*log))[0], label='Mean rewards')\n ax[i][j].plot(list(zip(*log))[1], label='Reward thresholds')\n ax[i][j].legend()\n ax[i][j].grid()\n\n '''plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)\n plt.hist(rewards_batch, range=reward_range)\n plt.vlines([np.percentile(rewards_batch, percentile)],\n [0], [100], label=\"percentile\", color='red')\n plt.legend()\n plt.grid()\n clear_output(True)\n print(\"mean reward = %.3f, threshold=%.3f\" % (mean_reward, threshold))\n plt.show()'''\n # clear_output(True)\n \n print(\"[{0}] [{1}]\".format(n_sessions, percentile), end = ' ')\n print(\"mean reward = %.3f, threshold=%.3f\" % (mean_reward, threshold)) \n # ax[i][j].show()",
"n_sessions, percentile\n"
],
[
"opt_policy, rewards_batch, log = get_policy_rewards_batch_log(600, 20, learning_rate)\nshow_final_progress(rewards_batch, log, percentile)",
"mean reward = -763.697, threshold=-830.000\n"
],
[
"threshold",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(\"[{0}][{1}]\".format(n_sessions, percentile), end = ' ')\nprint(\"mean reward = %.3f, threshold=%.3f\" % (mean_reward, threshold))",
"[50][80] mean reward = -513.220, threshold=-65.000\n"
],
[
"n_sessions = 250 # sample this many sessions\npercentile = 50 # take this percent of session with highest rewards\nlearning_rate = 0.5 # how quickly the policy is updated, on a scale from 0 to 1\n\nlog = []\n\nfor i in range(100):\n %time sessions = [ generate_session(env, policy) for i in np.arange(n_sessions) ]\n\n states_batch, actions_batch, rewards_batch = zip(*sessions)\n\n elite_states, elite_actions = select_elites(states_batch, actions_batch, rewards_batch, percentile) # <YOUR CODE: select elite states & actions>\n\n new_policy = get_new_policy(elite_states, elite_actions) # <YOUR CODE: compute new policy>\n\n policy = learning_rate * new_policy + (1 - learning_rate) * policy\n\n # display results on chart\n show_progress(rewards_batch, log, percentile)",
"mean reward = -51.452, threshold=7.000\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Homework part II\n\n### Deep crossentropy method\n\nBy this moment you should have got enough score on [CartPole-v0](https://gym.openai.com/envs/CartPole-v0) to consider it solved (see the link). It's time to try something harder.\n\n* if you have any trouble with CartPole-v0 and feel stuck, feel free to ask us or your peers for help.\n\n### Tasks\n\n* __2.1__ (3 pts) Pick one of environments: `MountainCar-v0` or `LunarLander-v2`.\n * For MountainCar, get average reward of __at least -150__\n * For LunarLander, get average reward of __at least +50__\n\nSee the tips section below, it's kinda important.\n__Note:__ If your agent is below the target score, you'll still get most of the points depending on the result, so don't be afraid to submit it.\n \n \n* __2.2__ (up to 6 pts) Devise a way to speed up training against the default version\n * Obvious improvement: use [`joblib`](https://joblib.readthedocs.io/en/latest/). However, note that you will probably need to spawn a new environment in each of the workers instead of passing it via pickling. (2 pts)\n * Try re-using samples from 3-5 last iterations when computing threshold and training. (2 pts)\n * Experiment with the number of training iterations and learning rate of the neural network (see params). Provide some plots as in 1.1. (2 pts)\n \n__Please list what you did in Anytask submission form__. \n \n \n### Tips\n* Gym page: [MountainCar](https://gym.openai.com/envs/MountainCar-v0), [LunarLander](https://gym.openai.com/envs/LunarLander-v2)\n* Sessions for MountainCar may last for 10k+ ticks. Make sure ```t_max``` param is at least 10k.\n * Also it may be a good idea to cut rewards via \">\" and not \">=\". If 90% of your sessions get reward of -10k and 10% are better, than if you use percentile 20% as threshold, R >= threshold __fails cut off bad sessions__ whule R > threshold works alright.\n* _issue with gym_: Some versions of gym limit game time by 200 ticks. This will prevent cem training in most cases. Make sure your agent is able to play for the specified __t_max__, and if it isn't, try `env = gym.make(\"MountainCar-v0\").env` or otherwise get rid of TimeLimit wrapper.\n* If you use old _swig_ lib for LunarLander-v2, you may get an error. See this [issue](https://github.com/openai/gym/issues/100) for solution.\n* If it won't train it's a good idea to plot reward distribution and record sessions: they may give you some clue. If they don't, call course staff :)\n* 20-neuron network is probably not enough, feel free to experiment.\n\nYou may find the following snippet useful:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def visualize_mountain_car(env, agent):\n # Compute policy for all possible x and v (with discretization)\n xs = np.linspace(env.min_position, env.max_position, 100)\n vs = np.linspace(-env.max_speed, env.max_speed, 100)\n \n grid = np.dstack(np.meshgrid(xs, vs[::-1])).transpose(1, 0, 2)\n grid_flat = grid.reshape(len(xs) * len(vs), 2)\n probs = agent.predict_proba(grid_flat).reshape(len(xs), len(vs), 3).transpose(1, 0, 2)\n\n # # The above code is equivalent to the following:\n # probs = np.empty((len(vs), len(xs), 3))\n # for i, v in enumerate(vs[::-1]):\n # for j, x in enumerate(xs):\n # probs[i, j, :] = agent.predict_proba([[x, v]])[0]\n\n # Draw policy\n f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 7))\n ax.imshow(probs, extent=(env.min_position, env.max_position, -env.max_speed, env.max_speed), aspect='auto')\n ax.set_title('Learned policy: red=left, green=nothing, blue=right')\n ax.set_xlabel('position (x)')\n ax.set_ylabel('velocity (v)')\n \n # Sample a trajectory and draw it\n states, actions, _ = generate_session(env, agent)\n states = np.array(states)\n ax.plot(states[:, 0], states[:, 1], color='white')\n \n # Draw every 3rd action from the trajectory\n for (x, v), a in zip(states[::3], actions[::3]):\n if a == 0:\n plt.arrow(x, v, -0.1, 0, color='white', head_length=0.02)\n elif a == 2:\n plt.arrow(x, v, 0.1, 0, color='white', head_length=0.02)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import gym\nimport numpy as np\nimport sys, os\nfrom tqdm import tqdm, tqdm_notebook\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\nif 'google.colab' in sys.modules and not os.path.exists('.setup_complete'):\n !wget -q https://raw.githubusercontent.com/yandexdataschool/Practical_RL/master/setup_colab.sh -O- | bash\n !touch .setup_complete\n\n# This code creates a virtual display to draw game images on.\n# It will have no effect if your machine has a monitor.\nif type(os.environ.get(\"DISPLAY\")) is not str or len(os.environ.get(\"DISPLAY\")) == 0:\n !bash ../xvfb start\n os.environ['DISPLAY'] = ':1'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%matplotlib inline\n\n# if you see \"<classname> has no attribute .env\", remove .env or update gym\nenv = gym.make(\"MountainCar-v0\").env\n\nenv.reset()\nn_actions = env.action_space.n\nstate_dim = env.observation_space.shape[0]\n\nplt.imshow(env.render(\"rgb_array\"))\nprint(\"state vector dim =\", state_dim)\nprint(\"n_actions =\", n_actions)",
"state vector dim = 2\nn_actions = 3\n"
],
[
"env.reset()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifier\nagent = MLPClassifier(\n hidden_layer_sizes=(20, 20),\n warm_start=True,\n activation='tanh',\n max_iter=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"agent.partial_fit([env.reset()] * n_actions, np.arange(n_actions), np.arange(n_actions))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import pickle\nagent = pickle.load(open('saved_model_132.pkl', mode='rb'))",
"/home/ernest/anaconda3/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sklearn/base.py:310: UserWarning: Trying to unpickle estimator LabelBinarizer from version 0.22.2.post1 when using version 0.24.1. This might lead to breaking code or invalid results. Use at your own risk.\n warnings.warn(\n/home/ernest/anaconda3/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sklearn/base.py:310: UserWarning: Trying to unpickle estimator MLPClassifier from version 0.22.2.post1 when using version 0.24.1. This might lead to breaking code or invalid results. Use at your own risk.\n warnings.warn(\n"
],
[
"agent.predict_proba([env.reset()])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"agent.predict([env.reset(), [10, 2], [123, -123], [32, 23]])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from joblib import wrap_non_picklable_objects\n@wrap_non_picklable_objects\ndef generate_session(env, agent, t_max=1000):\n \"\"\"\n Play a single game using agent neural network.\n Terminate when game finishes or after :t_max: steps\n \"\"\"\n states, actions = [], []\n total_reward = 0\n\n s = env.reset()\n\n for t in range(t_max):\n \n # use agent to predict a vector of action probabilities for state :s:\n probs = agent.predict_proba([s])[0] # <YOUR CODE>\n\n assert probs.shape == (env.action_space.n,), \"make sure probabilities are a vector (hint: np.reshape)\"\n \n # use the probabilities you predicted to pick an action\n # sample proportionally to the probabilities, don't just take the most likely action\n a = np.random.choice(np.arange(n_actions), p=probs) # <YOUR CODE>\n # ^-- hint: try np.random.choice\n\n new_s, r, done, info = env.step(a)\n\n # record sessions like you did before\n states.append(s)\n actions.append(a)\n total_reward += r\n\n s = new_s\n if done:\n break\n return states, actions, total_reward",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def select_elites(states_batch, actions_batch, rewards_batch, percentile=50):\n \"\"\"\n Select states and actions from games that have rewards >= percentile\n :param states_batch: list of lists of states, states_batch[session_i][t]\n :param actions_batch: list of lists of actions, actions_batch[session_i][t]\n :param rewards_batch: list of rewards, rewards_batch[session_i]\n\n :returns: elite_states,elite_actions, both 1D lists of states and respective actions from elite sessions\n\n Please return elite states and actions in their original order \n [i.e. sorted by session number and timestep within session]\n\n If you are confused, see examples below. Please don't assume that states are integers\n (they will become different later).\n \"\"\"\n\n reward_threshold = np.percentile(rewards_batch, percentile) # <YOUR CODE: compute minimum reward for elite sessions. Hint: use np.percentile()>\n\n elite_states = []\n elite_actions = []\n for i in range(len(states_batch)):\n if rewards_batch[i] >= reward_threshold:\n for j in states_batch[i]:\n elite_states.append(j)\n for j in actions_batch[i]:\n elite_actions.append(j)\n return elite_states, elite_actions",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from IPython.display import clear_output\n\ndef show_progress(rewards_batch, log, percentile, reward_range=[-990, +10]):\n \"\"\"\n A convenience function that displays training progress. \n No cool math here, just charts.\n \"\"\"\n\n mean_reward = np.mean(rewards_batch)\n threshold = np.percentile(rewards_batch, percentile)\n log.append([mean_reward, threshold])\n\n clear_output(True)\n print(\"mean reward = %.3f, threshold=%.3f\" % (mean_reward, threshold))\n plt.figure(figsize=[8, 4])\n plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)\n plt.plot(list(zip(*log))[0], label='Mean rewards')\n plt.plot(list(zip(*log))[1], label='Reward thresholds')\n plt.legend()\n plt.grid()\n\n plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)\n plt.hist(rewards_batch, range=reward_range)\n plt.vlines([np.percentile(rewards_batch, percentile)],\n [0], [100], label=\"percentile\", color='red')\n plt.legend()\n plt.grid()\n\n plt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from joblib import Parallel, delayed\nfrom math import sqrt",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Parallel(n_jobs=2, prefer=\"threads\")(delayed(sqrt)(i ** 2) for i in range(10))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"n_sessions = 100\npercentile = 70\nlog = []\n\nfor i in range(100):\n # generate new sessions\n %time sessions = Parallel(n_jobs=1)(delayed(generate_session)(env, agent, 10000) for i in range(n_sessions))\n # [ generate_session(env, agent, 10000) for i in np.arange(n_sessions) ]\n\n states_batch, actions_batch, rewards_batch = map(np.array, zip(*sessions))\n print(states_batch.shape, actions_batch.shape)\n # <YOUR CODE: select elite actions just like before>\n elite_states, elite_actions = select_elites(states_batch, actions_batch, rewards_batch, percentile) \n \n\n #<YOUR CODE: partial_fit agent to predict elite_actions(y) from elite_states(X)>\n agent.partial_fit(elite_states, elite_actions)\n \n show_progress(rewards_batch, log, percentile, (-500, 0))",
"mean reward = -4130.420, threshold=-2462.600\n"
],
[
"with gym.make('MountainCar-v0').env as env:\n visualize_mountain_car(env, agent)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import pickle\n\n#\n# Create your model here (same as above)\n#\n\n# Save to file in the current working directory\npkl_filename = \"saved_model_132.pkl\"\nwith open(pkl_filename, 'wb') as file:\n pickle.dump(agent, file)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"n_sessions = 100\npercentile = 70\nlog = []\n\nfor i in range(100):\n # generate new sessions\n %time sessions = [ generate_session(env, agent, 10000) for i in np.arange(n_sessions) ]\n\n states_batch, actions_batch, rewards_batch = map(np.array, zip(*sessions))\n print(states_batch.shape, actions_batch.shape)\n # <YOUR CODE: select elite actions just like before>\n elite_states, elite_actions = select_elites(states_batch, actions_batch, rewards_batch, percentile) \n \n\n #<YOUR CODE: partial_fit agent to predict elite_actions(y) from elite_states(X)>\n agent.partial_fit(elite_states, elite_actions)\n \n show_progress(rewards_batch, log, percentile, (-6000, 0))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from IPython import display\n\n# Create env manually to set time limit. Please don't change this.\nTIME_LIMIT = 250\nenv = gym.wrappers.TimeLimit(\n gym.envs.classic_control.MountainCarEnv(),\n max_episode_steps=TIME_LIMIT + 1,\n)\nactions = {'left': 0, 'stop': 1, 'right': 2}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(4, 3))\ndisplay.clear_output(wait=True)\n\nobs = env.reset()\nfor t in range(TIME_LIMIT):\n plt.gca().clear()\n \n\n probs = agent.predict_proba([obs])[0] # <YOUR CODE>\n\n \n # use the probabilities you predicted to pick an action\n # sample proportionally to the probabilities, don't just take the most likely action\n action = np.random.choice(np.arange(n_actions), p=probs) # <YOUR CODE>\n\n\n # Call your policy\n obs, reward, done, _ = env.step(action) \n # Pass the action chosen by the policy to the environment\n \n # We don't do anything with reward here because MountainCar is a very simple environment,\n # and reward is a constant -1. Therefore, your goal is to end the episode as quickly as possible.\n\n # Draw game image on display.\n plt.imshow(env.render('rgb_array'))\n \n display.display(plt.gcf())\n display.clear_output(wait=True)\n\n if done:\n print(\"Well done!\")\n break\nelse:\n print(\"Time limit exceeded. Try again.\")\n\ndisplay.clear_output(wait=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Bonus tasks\n\n* __2.3 bonus__ (2 pts) Try to find a network architecture and training params that solve __both__ environments above (_Points depend on implementation. If you attempted this task, please mention it in Anytask submission._)\n\n* __2.4 bonus__ (4 pts) Solve continuous action space task with `MLPRegressor` or similar.\n * Since your agent only predicts the \"expected\" action, you will have to add noise to ensure exploration.\n * Choose one of [MountainCarContinuous-v0](https://gym.openai.com/envs/MountainCarContinuous-v0) (90+ pts to solve), [LunarLanderContinuous-v2](https://gym.openai.com/envs/LunarLanderContinuous-v2) (200+ pts to solve) \n * 4 points for solving. Slightly less for getting some results below solution threshold. Note that discrete and continuous environments may have slightly different rules aside from action spaces.\n\n\nIf you're still feeling unchallenged, consider the project (see other notebook in this folder).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
c502b95421558373019a6ef6abf074e06b404313
| 136,868 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
chapter-02/2.3-least-squares-and-nearest-neighbors.ipynb
|
leduran/ESL
|
fcb6c8268d6a64962c013006d9298c6f5a7104fe
|
[
"MIT"
] | 360 |
2019-01-28T14:05:02.000Z
|
2022-03-27T00:11:21.000Z
|
chapter-02/2.3-least-squares-and-nearest-neighbors.ipynb
|
leduran/ESL
|
fcb6c8268d6a64962c013006d9298c6f5a7104fe
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2020-07-06T16:51:40.000Z
|
2020-07-06T16:51:40.000Z
|
chapter-02/2.3-least-squares-and-nearest-neighbors.ipynb
|
leduran/ESL
|
fcb6c8268d6a64962c013006d9298c6f5a7104fe
|
[
"MIT"
] | 79 |
2019-03-21T23:48:35.000Z
|
2022-03-31T13:05:10.000Z
| 392.17192 | 44,692 | 0.938145 |
[
[
[
"# 2.3 Least Squares and Nearest Neighbors",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 2.3.3 From Least Squares to Nearest Neighbors",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"1. Generates 10 means $m_k$ from a bivariate Gaussian distrubition for each color:\n - $N((1, 0)^T, \\textbf{I})$ for <span style=\"color: blue\">BLUE</span>\n - $N((0, 1)^T, \\textbf{I})$ for <span style=\"color: orange\">ORANGE</span>\n2. For each color generates 100 observations as following:\n - For each observation it picks $m_k$ at random with probability 1/10.\n - Then generates a $N(m_k,\\textbf{I}/5)$\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%matplotlib inline\n\nimport random\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\nsample_size = 100\n\ndef generate_data(size, mean):\n identity = np.identity(2)\n m = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, identity, 10)\n return np.array([\n np.random.multivariate_normal(random.choice(m), identity / 5)\n for _ in range(size)\n ])\n\ndef plot_data(orange_data, blue_data): \n axes.plot(orange_data[:, 0], orange_data[:, 1], 'o', color='orange')\n axes.plot(blue_data[:, 0], blue_data[:, 1], 'o', color='blue')\n \nblue_data = generate_data(sample_size, [1, 0])\norange_data = generate_data(sample_size, [0, 1])\n\ndata_x = np.r_[blue_data, orange_data]\ndata_y = np.r_[np.zeros(sample_size), np.ones(sample_size)]\n\n# plotting\nfig = plt.figure(figsize = (8, 8))\naxes = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)\nplot_data(orange_data, blue_data)\n\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 2.3.1 Linear Models and Least Squares",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"$$\\hat{Y} = \\hat{\\beta_0} + \\sum_{j=1}^{p} X_j\\hat{\\beta_j}$$\n\nwhere $\\hat{\\beta_0}$ is the intercept, also know as the *bias*. It is convenient to include the constant variable 1 in X and $\\hat{\\beta_0}$ in the vector of coefficients $\\hat{\\beta}$, and then write as: \n\n$$\\hat{Y} = X^T\\hat{\\beta} $$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Residual sum of squares",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"How to fit the linear model to a set of training data? Pick the coefficients $\\beta$ to minimize the *residual sum of squares*:\n\n$$RSS(\\beta) = \\sum_{i=1}^{N} (y_i - x_i^T\\beta) ^ 2 = (\\textbf{y} - \\textbf{X}\\beta)^T (\\textbf{y} - \\textbf{X}\\beta)$$\n\nwhere $\\textbf{X}$ is an $N \\times p$ matrix with each row an input vector, and $\\textbf{y}$ is an N-vector of the outputs in the training set. Differentiating w.r.t. β we get the normal equations:\n\n$$\\mathbf{X}^T(\\mathbf{y} - \\mathbf{X}\\beta) = 0$$\n\nIf $\\mathbf{X}^T\\mathbf{X}$ is nonsingular, then the unique solution is given by: \n\n$$\\hat{\\beta} = (\\mathbf{X}^T\\mathbf{X})^{-1}\\mathbf{X}^T\\mathbf{y}$$\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class LinearRegression:\n def fit(self, X, y):\n X = np.c_[np.ones((X.shape[0], 1)), X]\n self.beta = np.linalg.inv(X.T @ X) @ X.T @ y\n\n return self\n \n def predict(self, x):\n return np.dot(self.beta, np.r_[1, x])\n\nmodel = LinearRegression().fit(data_x, data_y)\nprint(\"beta = \", model.beta)",
"beta = [ 0.52677771 -0.15145005 0.15818643]\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### Example of the linear model in a classification context\n\nThe fitted values $\\hat{Y}$ are converted to a fitted class variable $\\hat{G}$ according to the rule:\n\n$$\n\\begin{equation}\n\\hat{G} = \\begin{cases}\n\\text{ORANGE} & \\text{ if } \\hat{Y} \\gt 0.5 \\\\ \n\\text{BLUE } & \\text{ if } \\hat{Y} \\leq 0.5 \n\\end{cases}\n\\end{equation}\n$$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from itertools import filterfalse, product\n\ndef plot_grid(orange_grid, blue_grid):\n axes.plot(orange_grid[:, 0], orange_grid[:, 1], '.', zorder = 0.001,\n color='orange', alpha = 0.3, scalex = False, scaley = False)\n\n axes.plot(blue_grid[:, 0], blue_grid[:, 1], '.', zorder = 0.001,\n color='blue', alpha = 0.3, scalex = False, scaley = False)\n\nplot_xlim = axes.get_xlim()\nplot_ylim = axes.get_ylim()\n\ngrid = np.array([*product(np.linspace(*plot_xlim, 50), np.linspace(*plot_ylim, 50))])\n\nis_orange = lambda x: model.predict(x) > 0.5\n\norange_grid = np.array([*filter(is_orange, grid)])\nblue_grid = np.array([*filterfalse(is_orange, grid)])\n\naxes.clear()\naxes.set_title(\"Linear Regression of 0/1 Response\")\nplot_data(orange_data, blue_data)\nplot_grid(orange_grid, blue_grid)\n\nfind_y = lambda x: (0.5 - model.beta[0] - x * model.beta[1]) / model.beta[2]\naxes.plot(plot_xlim, [*map(find_y, plot_xlim)], color = 'black', \n scalex = False, scaley = False)\n\n\nfig",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 2.3.2 Nearest-Neighbor Methods",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"$$\\hat{Y}(x) = \\frac{1}{k} \\sum_{x_i \\in N_k(x)} y_i$$\n\nwhere $N_k(x)$ is the neighborhood of $x$ defined by the $k$ closest points $x_i$ in the training sample.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class KNeighborsRegressor:\n def __init__(self, k):\n self._k = k\n\n def fit(self, X, y):\n self._X = X\n self._y = y\n return self\n \n def predict(self, x):\n X, y, k = self._X, self._y, self._k\n distances = ((X - x) ** 2).sum(axis=1)\n \n return np.mean(y[distances.argpartition(k)[:k]])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def plot_k_nearest_neighbors(k):\n model = KNeighborsRegressor(k).fit(data_x, data_y)\n is_orange = lambda x: model.predict(x) > 0.5\n orange_grid = np.array([*filter(is_orange, grid)])\n blue_grid = np.array([*filterfalse(is_orange, grid)])\n\n axes.clear()\n axes.set_title(str(k) + \"-Nearest Neighbor Classifier\")\n\n plot_data(orange_data, blue_data)\n plot_grid(orange_grid, blue_grid)\n\nplot_k_nearest_neighbors(1)\nfig\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"It appears that k-nearest-neighbor have a single parameter (*k*), however the effective number of parameters is N/k and is generally bigger than the p parameters in least-squares fits. **Note:** if the neighborhoods\nwere nonoverlapping, there would be N/k neighborhoods and we would fit one parameter (a mean) in each neighborhood.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plot_k_nearest_neighbors(15)\n\nfig",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c502c009cdf1349a106267f72f2d7f7740c9c406
| 54,458 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
S4_3_THOR.ipynb
|
JerKeller/2022_ML_Earth_Env_Sci
|
09aecb52a71e60991207ee578e6c15ae7856ded5
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
S4_3_THOR.ipynb
|
JerKeller/2022_ML_Earth_Env_Sci
|
09aecb52a71e60991207ee578e6c15ae7856ded5
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
S4_3_THOR.ipynb
|
JerKeller/2022_ML_Earth_Env_Sci
|
09aecb52a71e60991207ee578e6c15ae7856ded5
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 61.326577 | 19,501 | 0.705222 |
[
[
[
"<a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/JerKeller/2022_ML_Earth_Env_Sci/blob/main/S4_3_THOR.ipynb\" target=\"_parent\"><img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open In Colab\"/></a>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<img src='https://unils-my.sharepoint.com/:i:/g/personal/tom_beucler_unil_ch/ESLP1e1BfUxKu-hchh7wZKcBZiG3bJnNbnt0PDDm3BK-9g?download=1'>\n\n<center> \nPhoto Credits: <a href=\"https://unsplash.com/photos/zCMWw56qseM\">Sea Foam</a> by <a href=\"https://unsplash.com/@unstable_affliction\">Ivan Bandura</a> licensed under the <a href='https://unsplash.com/license'>Unsplash License</a> \n</center>\n\n\n>*A frequently asked question related to this work is “Which mixing processes matter most for climate?” As with many alluringly comprehensive sounding questions, the answer is “it depends.”* <br>\n> $\\qquad$ MacKinnon, Jennifer A., et al. <br>$\\qquad$\"Climate process team on internal wave–driven ocean mixing.\" <br>$\\qquad$ Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society 98.11 (2017): 2429-2454.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In week 4's final notebook, we will perform clustering to identify regimes in data taken from the realistic numerical ocean model [Estimating the Circulation and Climate of the Ocean](https://www.ecco-group.org/products-ECCO-V4r4.htm). Sonnewald et al. point out that finding robust regimes is intractable with a naïve approach, so we will be using using reduced dimensionality data. \n\nIt is worth pointing out, however, that the reduction was done with an equation instead of one of the algorithms we discussed this week. If you're interested in the full details, you can check out [Sonnewald et al. (2019)](https://doi.org/10.1029/2018EA000519)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Setup",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"First, let's import a few common modules, ensure MatplotLib plots figures inline and prepare a function to save the figures. We also check that Python 3.5 or later is installed (although Python 2.x may work, it is deprecated so we strongly recommend you use Python 3 instead), as well as Scikit-Learn ≥0.20.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Python ≥3.5 is required\nimport sys\nassert sys.version_info >= (3, 5)\n\n# Scikit-Learn ≥0.20 is required\nimport sklearn\nassert sklearn.__version__ >= \"0.20\"\n\n# Common imports\nimport numpy as np\nimport os\nimport xarray as xr\nimport pooch\n\n# to make this notebook's output stable across runs\nrnd_seed = 42\nrnd_gen = np.random.default_rng(rnd_seed)\n\n# To plot pretty figures\n%matplotlib inline\nimport matplotlib as mpl\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nmpl.rc('axes', labelsize=14)\nmpl.rc('xtick', labelsize=12)\nmpl.rc('ytick', labelsize=12)\n\n# Where to save the figures\nPROJECT_ROOT_DIR = \".\"\nCHAPTER_ID = \"dim_reduction\"\nIMAGES_PATH = os.path.join(PROJECT_ROOT_DIR, \"images\", CHAPTER_ID)\nos.makedirs(IMAGES_PATH, exist_ok=True)\n\ndef save_fig(fig_id, tight_layout=True, fig_extension=\"png\", resolution=300):\n path = os.path.join(IMAGES_PATH, fig_id + \".\" + fig_extension)\n print(\"Saving figure\", fig_id)\n if tight_layout:\n plt.tight_layout()\n plt.savefig(path, format=fig_extension, dpi=resolution)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Here we're going to import the [StandardScaler](https://duckduckgo.com/sklearn.preprocessing.standardscaler) function from scikit's preprocessing tools, import the [scikit clustering library](https://duckduckgo.com/sklearn.clustering), and set up the colormap that we will use when plotting.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler\nimport sklearn.cluster as cluster\n\nfrom matplotlib.colors import LinearSegmentedColormap, ListedColormap\ncolors = ['royalblue', 'cyan','yellow', 'orange', 'magenta', 'red']\nmycmap = ListedColormap(colors)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Data Preprocessing",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The first thing we need to do is retrieve the list of files we'll be working on. We'll rely on pooch to access the files hosted on the cloud.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Retrieve the files from the cloud using Pooch.\ndata_url = 'https://unils-my.sharepoint.com/:u:/g/personal/tom_beucler_unil_ch/EUYqUzpIjoJBui02QEo6q1wBSN1Zsi1ofE6I3G4B9LJn_Q?download=1'\nhash = '3f41661c7a087fa7d7af1d2a8baf95c065468f8a415b8514baedda2f5bc18bb5'\n\nfiles = pooch.retrieve(data_url, known_hash=hash, processor=pooch.Unzip())\n[print(filename) for filename in files];",
"/root/.cache/pooch/8a10ee1ae6941d8b9bb543c954c793fa-EUYqUzpIjoJBui02QEo6q1wBSN1Zsi1ofE6I3G4B9LJn_Q.unzip/curlTau.npy\n/root/.cache/pooch/8a10ee1ae6941d8b9bb543c954c793fa-EUYqUzpIjoJBui02QEo6q1wBSN1Zsi1ofE6I3G4B9LJn_Q.unzip/curlCori.npy\n/root/.cache/pooch/8a10ee1ae6941d8b9bb543c954c793fa-EUYqUzpIjoJBui02QEo6q1wBSN1Zsi1ofE6I3G4B9LJn_Q.unzip/curlA.npy\n/root/.cache/pooch/8a10ee1ae6941d8b9bb543c954c793fa-EUYqUzpIjoJBui02QEo6q1wBSN1Zsi1ofE6I3G4B9LJn_Q.unzip/noiseMask.npy\n/root/.cache/pooch/8a10ee1ae6941d8b9bb543c954c793fa-EUYqUzpIjoJBui02QEo6q1wBSN1Zsi1ofE6I3G4B9LJn_Q.unzip/BPT.npy\n/root/.cache/pooch/8a10ee1ae6941d8b9bb543c954c793fa-EUYqUzpIjoJBui02QEo6q1wBSN1Zsi1ofE6I3G4B9LJn_Q.unzip/curlB.npy\n"
]
],
[
[
"And now that we have a set of files to load, let's set up a dictionary with the variable names as keys and the data in numpy array format as the values.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Let's read in the variable names from the filepaths\nvar_names = []\n[var_names.append(path.split('/')[-1][:-4]) for path in files]\n\n# And build a dictionary of the data variables keyed to the filenames\ndata_dict = {}\nfor idx, val in enumerate(var_names):\n data_dict[val] = np.load(files[idx]).T\n\n#We'll print the name of the variable loaded and the associated shape \n[print(f'Varname: {item[0]:<15} Shape: {item[1].shape}') for item in data_dict.items()];",
"Varname: curlTau Shape: (360, 720)\nVarname: curlCori Shape: (360, 720)\nVarname: curlA Shape: (360, 720)\nVarname: noiseMask Shape: (360, 720)\nVarname: BPT Shape: (360, 720)\nVarname: curlB Shape: (360, 720)\n"
]
],
[
[
"We now have a dictionary that uses the filename as the key! Feel free to explore the data (e.g., loading the keys, checking the shape of the arrays, plotting)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#Feel free to explore the data dictionary",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We're eventually going to have an array of cluster classes that we're going to use to label dynamic regimes in the ocean. Let's make an array full of NaN (not-a-number) values that has the same shape as our other variables and store it in the data dictionary. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data_dict['clusters'] = np.full_like(data_dict['BPT'],np.nan)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Reformatting as Xarray",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In the original paper, this data was loaded as numpy arrays. However, we'll take this opportunity to demonstrate the same procedure while relying on xarray. First, let's instantiate a blank dataset.<br><br>\n\n###**Q1) Make a blank xarray dataset.**<br>\n*Hint: Look at the xarray [documentation](https://duckduckgo.com/?q=xarray+dataset)*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Make your blank dataset here! Instantiate the class without passing any parameters.\nds = xr.Dataset",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<img src='https://unils-my.sharepoint.com/:i:/g/personal/tom_beucler_unil_ch/EZv_qqVz_h1Hio6Nq11ckScBb01bGb9jtNKzdqAg1TPrKQ?download=1'>\n<center> Image taken from the xarray <a href='https://xarray.pydata.org/en/stable/user-guide/data-structures.html#:~:text=Dataset-,xarray.,from%20the%20netCDF%20file%20format.'> <i>Data Structure documentation</i> </a> </center>\n\nIn order to build the dataset, we're going to need a set of coordinate vectors that help us map out our data! For our data, we have two axes corresponding to longitude ($\\lambda$) and latitude ($\\phi$). \n\nWe don't know much about how many lat/lon points we have, so let's explore one of the variables to make sense of the data the shape of one of the numpy arrays.\n\n###**Q2) Visualize the data using a plot and printing the shape of the data to the console output.**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#Complete the code\n# Let's print out an image of the Bottom Pressure Torques (BPT)\nplt.imshow( data_dict['BPT'] , origin='lower')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# It will also be useful to store and print out the shape of the data\ndata_shape = data_dict['BPT'].shape\nprint(data_shape)",
"(360, 720)\n"
]
],
[
[
"Now that we know how the resolution of our data, we can prepare a set of axis arrays. We will use these to organize the data we will feed into the dataset.\n\n###**Q3) Prepare the latitude and longitude arrays to be used as axes for our dataset**\n\n*Hint 1: You can build ordered numpy arrays using, e.g., [numpy.linspace](https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.linspace.html) and [numpy.arange](https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.arange.html)*\n\n*Hint 2: You can rely on the data_shape variable we loaded previously to know how many points you need along each axis*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#Complete the code\n# Let's prepare the lat and lon axes for our data.\nlat = np.linspace(0, data_shape[0],data_shape[0])\nlon = np.linspace(0, data_shape[1],data_shape[1])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now that we have the axes we need, we can build xarray [*data arrays*](https://xarray.pydata.org/en/stable/generated/xarray.DataArray.html) for each data variable. Since we'll be doing it several times, let's go ahead and defined a function that does this for us!\n\n###**Q4) Define a function that takes in: 1) an array name, 2) a numpy array, 3) a lat vector, and 4) a lon vector. The function should return a dataArray with lat-lon as the coordinate dimensions**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#Complete the code\ndef np_to_xr(array_name, array, lat, lon):\n #building the xarrray\n da = xr.DataArray(data = array, # Data to be stored\n \n #set the name of dimensions for the dataArray \n dims = ['lat', 'lon'],\n \n #Set the dictionary pointing the name dimensions to np arrays \n coords = {'lat':lat,\n 'lon':lon},\n \n name=array_name)\n return da",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We're now ready to build our data array! Let's iterate through the items and merge our blank dataset with the data arrays we create.\n\n###**Q5) Build the dataset from the data dictionary**\n\n*Hint: We'll be using the xarray merge command to put everything together.*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# The code in the notebook assumes you named your dataset ds. Change it to \n# whatever you used!\n\n# Complete the code\nfor key, item in data_dict.items():\n # Let's make use of our np_to_xr function to get the data as a dataArray\n da = np_to_xr(key, item, lat, lon)\n\n # Merge the dataSet with the dataArray here!\n ds = xr.merge( [ds , da] )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Congratulations! You should now have a nicely set up xarray dataset. This let's you access a ton of nice features, e.g.:\n> Data plotting by calling, e.g., `ds.BPT.plot.imshow(cmap='ocean')`\n> \n> Find statistical measures of all variables at once! (e.g.: `ds.std()`, `ds.mean()`)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Play around with the dataset here if you'd like :)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now we want to find clusters of data considering each grid point as a datapoint with 5 dimensional data. However, we went through a lot of work to get the data nicely associated with a lat and lon - do we really want to undo that?\n\nLuckily, xarray develops foresaw the need to group dimensions together. Let's create a 'flat' version of our dataset using the [`stack`](https://xarray.pydata.org/en/stable/generated/xarray.DataArray.stack.html) method. Let's make a flattened version of our dataset.\n\n###**Q6) Store a flattened version of our dataset**\n\n*Hint 1: You'll need to pass a dictionary with the 'new' stacked dimension name as the key and the 'flattened' dimensions as the values.*\n\n*Hint 2: xarrays have a ['.values' attribute](https://xarray.pydata.org/en/stable/generated/xarray.DataArray.values.html) that return their data as a numpy array.*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Complete the code\n# Let's store the stacked version of our dataset\nstacked = ds.stack( { ____ :[ ___ , ___ ] } )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# And verify the shape of our data\nprint(stacked.to_array()._____._____)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"So far we've ignored an important point - we're supposed to have 5 variables, not 6! As you may have guessed, `noiseMask` helps us throw away data we dont want (e.g., from land mass or bad pixels). \n\nWe're now going to clean up the stacked dataset using the noise mask. Relax and read through the code, since there won't be a question in this part :) ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Let's redefine stacked as all the points where noiseMask = 1, since noisemask\n# is binary data.\n\nprint(f'Dataset shape before processing: {stacked.to_array().values.shape}')\n\nprint(\"Let's do some data cleaning!\")\nprint(f'Points before cleaning: {len(stacked.BPT)}')\nstacked = stacked.where(stacked.noiseMask==1, drop=True)\nprint(f'Points after cleaning: {len(stacked.BPT)}')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# We also no longer need the noiseMask variable, so we can just drop it.\n\nprint('And drop the noisemask variable...')\nprint(f'Before dropping: {stacked.to_array().values.shape}')\nstacked = stacked.drop('noiseMask')\nprint(f'Dataset shape after processing: {stacked.to_array().values.shape}')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We now have several thousand points which we want to divide into clusters using the kmeans clustering algorithm (you can check out the documentation for scikit's implementation of kmeans [here](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.cluster.KMeans.html)).\n\nYou'll note that the algorithm expects the input data `X` to be fed as `(n_samples, n_features)`. This is the opposite of what we have! Let's go ahead and make a copy to a numpy array has the axes in the right order.\n\nYou'll need xarray's [`.to_array()`](https://xarray.pydata.org/en/stable/generated/xarray.Dataset.to_array.html) method and [`.values`](https://xarray.pydata.org/en/stable/generated/xarray.DataArray.values.html) parameter, as well as numpy's [`.moveaxis`](https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.moveaxis.html) method.\n\n###**Q7) Load the datapoints into a numpy array following the convention where the 0th axis corresponds to the samples and the 1st axis corresponds to the features.** ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Complete the code\ninput_data = np._____(stacked._____()._____, # data to reshape\n 'number', # source axis as integer, \n 'number') # destination axis as integer",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Does the input data look the way it's supposed to? Print the shape.\nprint(________)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"In previous classes we discussed the importance of the scaling the data before implementing our algorithms. Now that our data is all but ready to be fed into an algorithm, let's make sure that it's been scaled.\n\n###**Q8) Scale the input data**\n\n*Hint 1: Import the [`StandardScaler`](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.preprocessing.StandardScaler.html) class from scikit and instantiate it*\n\n*Hint 2: Update the input array to the one returned by the [`.fit_transform(X)`](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.preprocessing.StandardScaler.html#sklearn.preprocessing.StandardScaler.fit_transform) method*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#Write your scaling code here",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now we're finally ready to train our algorithm! Let's load up the kmeans model and find clusters in our data.\n\n###**Q9) Instantiate the kmeans clustering algorithm, and then fit it using 50 clusters, trying out 10 different initial centroids.**\n\n*Hint 1: `sklearn.cluster` was imported as `cluser` during the notebook setup! [Here is the scikit `KMeans` documentation](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.cluster.KMeans.html).*\n\n*Hint 2: Use the `fit_predict` method to organize the data into clusters*\n\n*Warning! : Fitting the data may take some time (under a minute during the testing of the notebook)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Complete the code\nkmeans = cluster._____(________ =50, # Number of clusters\n ________ =42, # setting a random state\n ________ =10, # Number of initial centroid states to try\n verbose = 1) # Verbosity so we know things are working",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cluster_labels = kmeans.______(____) # Feed in out scaled input data!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We now have a set of cluster labels that group the data into 50 similar groups. Let's store it in our stacked dataset!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Let's run this line\nstacked['clusters'].values = cluster_labels",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We now have a set of labels, but they're stored in a flattened array. Since we'd like to see the data as a map, we still have some work to do. Let's go back to a 2D representation of our values.\n\n###**Q10) Turn the flattened xarray back into a set of 2D fields**\n*Hint*: xarrays have an [`.unstack` method](https://xarray.pydata.org/en/stable/generated/xarray.DataArray.unstack.html) that you will find to be very useful for this.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Complete the code:\nprocessed_ds = ds.____()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now we have an unstacked dataset, and can now easily plot out the clusters we found!\n\n###**Q11) Plot the 'cluster' variable using the buil-in xarray function**\n*Hint: `.plot()` [link text](https://xarray.pydata.org/en/stable/generated/xarray.DataArray.plot.html) let's you access the xarray implementations of [`pcolormesh`](https://matplotlib.org/3.1.1/api/_as_gen/matplotlib.pyplot.pcolormesh.html) and [`imshow`](https://matplotlib.org/3.1.1/api/_as_gen/matplotlib.pyplot.imshow.html).*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Compare your results to those from the paper:\n<img src='https://unils-my.sharepoint.com/:i:/g/personal/tom_beucler_unil_ch/EdLh6Ds0yVlFivyfIOXlV74B_G35dVz87GFagzylIG-gZA?download=1'>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We now want to find the 5 most common regimes, and group the rest. This isn't straightforward, so we've gone ahead and prepared the code for you. Run through it and try to understand what the code is doing!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Make field filled with -1 vals so unprocessed points are easily retrieved.\n# Noise masked applied automatically by using previously found labels as base.\nprocessed_ds['final_clusters'] = (processed_ds.clusters * 0) - 1\n\n# Find the 5 most common cluster labels\ntop_clusters = processed_ds.groupby('clusters').count().sortby('BPT').tail(5).clusters.values\n\n#Build the set of indices for the cluster data, used for rewriting cluster labels\nfor idx, label in enumerate(top_clusters):\n #Find the indices where the label is found\n indices = (processed_ds.clusters == label)\n\n processed_ds['final_clusters'].values[indices] = 4-idx\n\n# Set the remaining unlabeled regions to category 5 \"non-linear\"\nprocessed_ds['final_clusters'].values[processed_ds.final_clusters==-1] = 5\n\n# Plot the figure\nprocessed_ds.final_clusters.plot.imshow(cmap=mycmap, figsize=(18,8));",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Feel free to use this space ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Compare it to the regimes found in the paper:\n<img src='https://unils-my.sharepoint.com/:i:/g/personal/tom_beucler_unil_ch/EehuR9cUfaJImrw4DCAzDPoBiGuG7R3Ys6453Umi1cN_OQ?download=1'>\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The authors then went on to train neural networks ***to infer in-depth dynamics from data that is largely readily available from for example CMIP6 models, using NN methods to infer the source of predictive skill*** and ***to apply the trained Ensemble MLP to a climate model in order to assess circulation changes under global heating***. \n\nFor our purposes, however, we will say goodbye to *THOR* at this point 😃",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
c502e0c483a4ac09092206ee632bab8295da6126
| 26,294 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
nbs/.ipynb_checkpoints/ergodicity-checkpoint.ipynb
|
sekunder/ergm.jl
|
3eb8b5d3868ef9ed5341f9167d37035e637753c4
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
nbs/.ipynb_checkpoints/ergodicity-checkpoint.ipynb
|
sekunder/ergm.jl
|
3eb8b5d3868ef9ed5341f9167d37035e637753c4
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
nbs/.ipynb_checkpoints/ergodicity-checkpoint.ipynb
|
sekunder/ergm.jl
|
3eb8b5d3868ef9ed5341f9167d37035e637753c4
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 87.646667 | 4,869 | 0.57979 |
[
[
[
"empty"
]
]
] |
[
"empty"
] |
[
[
"empty"
]
] |
c502ed31ca2d3ba790322b9e25bd57b36883e5c2
| 137,452 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Log Parser.ipynb
|
saifhitawala/ResNeXt
|
eb6f10e9fc274872c99a0aa082442e7be77a7634
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2019-07-20T15:22:53.000Z
|
2020-03-02T05:47:24.000Z
|
Log Parser.ipynb
|
saifhitawala/ResNeXt
|
eb6f10e9fc274872c99a0aa082442e7be77a7634
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Log Parser.ipynb
|
saifhitawala/ResNeXt
|
eb6f10e9fc274872c99a0aa082442e7be77a7634
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2018-10-25T04:10:16.000Z
|
2018-10-25T04:10:16.000Z
| 536.921875 | 39,204 | 0.935076 |
[
[
[
"import re\nimport json\nimport matplotlib.pylab as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport glob\n%matplotlib inline\nall_test_acc = []\nall_test_err = []\nall_train_loss = []\nall_test_loss = []\nall_cardinalities = []\nall_depths = []\nall_widths = []\nfor file in glob.glob('logs_cardinality/Cifar2/*.txt'):\n with open(file) as logs:\n next(logs)\n test_acc = []\n test_err = []\n train_loss = []\n test_loss = []\n i = 0\n for line in logs:\n i += 1\n if i % 2 != 0:\n for t in re.finditer(r\"\\{.*\\}\", line):\n try:\n data = json.loads(t.group())\n train_loss.append(data['train_loss'])\n test_loss.append(data['test_loss'])\n test_acc.append(data['test_accuracy'])\n test_err.append((1-data['test_accuracy'])*100)\n cardinality = data['cardinality']\n depth = data['depth']\n width = data['base_width']\n except ValueError:\n pass\n all_test_acc.append(test_acc)\n all_test_err.append(test_err)\n all_train_loss.append(train_loss)\n all_test_loss.append(test_loss)\n all_cardinalities.append(cardinality)\n all_depths.append(depth)\n all_widths.append(width)\nepochs = np.arange(0, 300, 2)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ordered_test_err = []\nordered_test_err.append(all_test_err[all_cardinalities.index(1)])\nordered_test_err.append(all_test_err[all_cardinalities.index(2)])\nordered_test_err.append(all_test_err[all_cardinalities.index(4)])\nordered_test_err.append(all_test_err[all_cardinalities.index(8)])\nordered_test_err.append(all_test_err[all_cardinalities.index(16)])\nall_cardinalities = sorted(all_cardinalities)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ordered_test_err = []\nordered_test_err.append(all_test_err[all_depths.index(20)])\nordered_test_err.append(all_test_err[all_depths.index(29)])\nall_depths = sorted(all_depths)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ordered_test_err = []\nordered_test_err.append(all_test_err[all_widths.index(32)])\nordered_test_err.append(all_test_err[all_widths.index(64)])\nall_widths = sorted(all_widths)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for file_no in range(0, 3):\n plt.plot(epochs, ordered_test_err[file_no])\nplt.legend([cardinality for cardinality in all_cardinalities[0:3]], loc='upper right')\nplt.xlabel('epochs \\n\\n (f)')\nplt.ylabel('top-1 error(%)')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for file_no in range(0, 2):\n plt.plot(epochs, ordered_test_err[file_no])\nplt.legend([depth for depth in all_depths], loc='upper right')\nplt.xlabel('epochs \\n\\n (c)')\nplt.ylabel('top-1 error(%)')\n# plt.title('(a)')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for file_no in range(0, 2):\n plt.plot(epochs, ordered_test_err[file_no])\nplt.legend([width for width in all_widths], loc='upper right')\nplt.xlabel('epochs \\n\\n (a)')\nplt.ylabel('top-1 error(%)')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cardinalities = [1, 2, 4, 8, 16]\nparams = [5.6, 9.8, 18.3, 34.4, 68.1]\ntext = ['1x64d', '2x64d', '4x64d', '8x64d', '16x64d']\ncifar29 = [[0.786, 0.797, 0.803, 0.83, 0.823], [0.886, 0.887, 0.86, 0.914, 0.92], [0.939, 0.939, 0.941, 0.946, 0.946]]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig = plt.figure()\nax = fig.add_subplot(111)\ny = [(1-val)*100 for val in cifar29[2]]\nax.plot(params, y, 'x-')\nplt.xlabel('# of parameters (M)')\nplt.ylabel('test error (%)')\nfor i, txt in enumerate(text):\n ax.annotate(txt, (params[i], y[i]))\nplt.title('CIFAR 2 Dataset')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c502f22bf31bb06416025edc5d1ff68e5562eb3b
| 233,196 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
examples/Dynamic Network Embedding.ipynb
|
iggallagher/Spectral-Embedding
|
d0ce5a277dca239341bfa133e8cd94e8bff7830a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
examples/Dynamic Network Embedding.ipynb
|
iggallagher/Spectral-Embedding
|
d0ce5a277dca239341bfa133e8cd94e8bff7830a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
examples/Dynamic Network Embedding.ipynb
|
iggallagher/Spectral-Embedding
|
d0ce5a277dca239341bfa133e8cd94e8bff7830a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 655.044944 | 81,096 | 0.946907 |
[
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport spectral_embedding as se\nimport matplotlib as mpl\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"In this example we demostrate unfolded adjacency spectral embedding for a series of stochastic block models and investigate the stability of the embedding compared to two other possible approaches; omnibus embedding and separate adjacency spectral embedding.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.random.seed(0)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We generate a dynamic stochastic block model over $T = 2$ time periods with $n=1000$ nodes and $K=4$ communities, where nodes are equally likely to be in either community, $\\pi = (0.25, 0.25, 0.25, 0.25)$. We use the following two community link probability matrices for the two time periods,\n$$\n \\textbf{B}^{(1)} = \\left( \\begin{array}{cccc}\n 0.08 & 0.02 & 0.18 & 0.10 \\\\\n 0.02 & 0.20 & 0.04 & 0.10 \\\\\n 0.18 & 0.04 & 0.02 & 0.02 \\\\\n 0.10 & 0.10 & 0.02 & 0.06\n \\end{array} \\right), \\quad\n \\textbf{B}^{(2)} = \\left( \\begin{array}{cccc}\n 0.16 & 0.16 & 0.04 & 0.10 \\\\\n 0.16 & 0.16 & 0.04 & 0.10 \\\\\n 0.04 & 0.04 & 0.09 & 0.02 \\\\\n 0.10 & 0.10 & 0.02 & 0.06\n \\end{array} \\right).\n$$\nIn the first time period, the four communities are all behaving in different ways and spectral embedding should be able to distinguish between the groups. In the second time period, communities 1 and 2 have the same link probabilities to all the other communities, so it is desirable that those nodes are embedded in the same way at this time. This is known as cross-sectional stability. Furthermore, community 4 has the same community link probabilities at time 1 and time 2, so it is desirable that these nodes are embedded in the same way between the two time periods. This is known as longitudinal stability.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"K = 4\nT = 2\nn = 1000\npi = np.repeat(1/K, K)\n\nBs = np.array([[[0.08, 0.02, 0.18, 0.10],\n [0.02, 0.20, 0.04, 0.10],\n [0.18, 0.04, 0.02, 0.02],\n [0.10, 0.10, 0.02, 0.06]],\n [[0.16, 0.16, 0.04, 0.10],\n [0.16, 0.16, 0.04, 0.10],\n [0.04, 0.04, 0.09, 0.02],\n [0.10, 0.10, 0.02, 0.06]]])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"As, Z = se.generate_SBM_dynamic(n, Bs, pi)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Colour the nodes depending on their community assignment.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"colours = np.array(list(mpl.colors.TABLEAU_COLORS.keys())[0:K])\nZcol = colours[Z]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Unfolded adjacency spectral embedding",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Embed the nodes into four dimensions by looking at the right embedding of the unfolded adjacency matrix $\\textbf{A} = (\\textbf{A}^{(1)} | \\textbf{A}^{(2)})$. Since the network is a dynamic stochastic model, we can compute the asymptotic distribution for the embedding as a Gaussian mixture model in both time periods.\n\nNote that in all the diagrams that follow, only the first two dimensions of the embeddings are shown for visualisation purposes.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"_, YAs_UASE = se.UASE(As, K)\nYs_UASE, SigmaYs_UASE = se.SBM_dynamic_distbn(As, Bs, Z, pi, K)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(9.4,4.4), sharex=True, sharey=True)\n\nfor t in range(T):\n axs[t].grid()\n axs[t].scatter(YAs_UASE[t,:,0], YAs_UASE[t,:,1], marker='.', s=5, c=Zcol)\n axs[t].scatter(Ys_UASE[t,:,0], Ys_UASE[t,:,1], marker='o', s=12, c='black')\n \n for i in range(K):\n ellipse = se.gaussian_ellipse(Ys_UASE[t,i], SigmaYs_UASE[t,i][0:2,0:2]/n)\n axs[t].plot(ellipse[0], ellipse[1],'--', color='black')\n \n axs[t].set_title('UASE, SBM ' + str(t+1), fontsize=13);",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Note that the Gaussian distributions for communities 1 and 2 (shown in blue and orange) at time 2 are identical demonstrating cross-sectional stability. Also, the Gaussian distribution for community 4 (shown in red) is the same at times 1 and 2 demonstrating longitudinal stability.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Omnibus embedding",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Embed the nodes into four dimensions using the omnibus matrix,\n$$\n \\tilde{\\textbf{A}} = \\left( \\begin{array}{cc}\n \\textbf{A}^{(1)} & \\frac{1}{2}(\\textbf{A}^{(1)} + \\textbf{A}^{(2)}) \\\\\n \\frac{1}{2}(\\textbf{A}^{(1)} + \\textbf{A}^{(2)}) & \\textbf{A}^{(2)}\n \\end{array} \\right).\n$$\nFor this technique, we do not have results about the asymptotic distribution of the embedding. However, we can still say something about the stability of the embedding.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"YAs_omni = se.omnibus(As, K)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(9.4,4.4), sharex=True, sharey=True)\n\nfor t in range(T):\n axs[t].grid()\n axs[t].scatter(YAs_omni[t,:,0], YAs_omni[t,:,1], marker='.', s=5, c=Zcol)\n axs[t].set_title('Omnibus, SBM ' + str(t+1), fontsize=13);",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Community 4 (shown in red) is approximately in the same position over the two time periods suggesting longitudinal stability, but communities 1 and 2 (shown in blue and orange) at time 2 do not have the same distribution, so no cross-sectional stability.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Separate adjacency spectral embedding",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Finally, we can always compute the spectral embedding for the adjacency matrix at each time period separately. However, since there is a choice of singular vectors in a singular value decomposition, there is no possible way these embeddings can be consistent over time, so no longitudinal stability. However, in this section we show that adjacency spectral embedding has cross-sectional stability.\n\nNote that, while the matrix $\\textbf{B}^{(1)}$ has rank 4, the matrix $\\textbf{B}^{(2)}$ has rank 3, due to the repeated rows caused by communities 1 and 2. Therefore, we need to embed the adjacency matrices into different numbers of dimensions. For example, if we tried to embed $\\textbf{A}^{(2)}$ into four dimensions, we find that the covariance matrices for the asymptotic Gaussian distributions are degenerate.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"d = [4,3]\nYAs_ASE = [se.ASE(As[0], d[0]), se.ASE(As[1], d[1])]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Y1_ASE, SigmaY1_ASE = se.SBM_distbn(As[0], Bs[0], Z, pi, d[0])\nY2_ASE, SigmaY2_ASE = se.SBM_distbn(As[1], Bs[1], Z, pi, d[1])\n\nYs_ASE = [Y1_ASE, Y2_ASE]\nSigmaYs_ASE = [SigmaY1_ASE, SigmaY2_ASE]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(9.4,4.4), sharex=True, sharey=True)\n\nfor t in range(T):\n axs[t].grid()\n axs[t].scatter(YAs_ASE[t][:,0], YAs_ASE[t][:,1], marker='.', s=5, c=Zcol)\n axs[t].scatter(Ys_ASE[t][:,0], Ys_ASE[t][:,1], marker='o', s=12, c='black')\n \n for i in range(K):\n ellipse = se.gaussian_ellipse(Ys_ASE[t][i], SigmaYs_ASE[t][i][0:2,0:2]/n)\n axs[t].plot(ellipse[0], ellipse[1],'--', color='black')\n \n axs[t].set_title('Independent ASE, SBM ' + str(t+1), fontsize=13);",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"At time 2, we see that communities 1 and 2 (shown in blue and orange) have the same distribution, so we have cross-sectional stability.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
c502ffaaf497e7d614eb433ab7733d5b9c6c092d
| 29,780 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
docs/source/application_notebooks/external_master_tutorial.ipynb
|
ianhi/pycro-manager
|
5a6a52421c4ba99bed456af174307fd21a31bccc
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 88 |
2020-05-08T16:54:24.000Z
|
2022-03-09T01:03:04.000Z
|
docs/source/application_notebooks/external_master_tutorial.ipynb
|
ianhi/pycro-manager
|
5a6a52421c4ba99bed456af174307fd21a31bccc
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 200 |
2020-05-15T13:21:44.000Z
|
2022-03-31T17:55:23.000Z
|
docs/source/application_notebooks/external_master_tutorial.ipynb
|
ianhi/pycro-manager
|
5a6a52421c4ba99bed456af174307fd21a31bccc
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 31 |
2020-04-30T03:22:50.000Z
|
2022-03-19T18:00:32.000Z
| 41.884669 | 620 | 0.610141 |
[
[
[
"# Using an external master clock for hardware control of a stage-scanning high NA oblique plane microscope \n\nTutorial provided by [qi2lab](https://www.shepherdlaboratory.org).\n\nThis tutorial uses Pycro-Manager to rapidly acquire terabyte-scale volumetric images using external hardware triggering of a stage scan optimized, high numerical aperture (NA) oblique plane microscope (OPM). The microscope that this notebook controls is described in detail in this [preprint](https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.07.030569v2), under the *stage scan OPM* section in the methods. \n \nThis high NA OPM allows for versatile, high-resolution, and large field-of-view single molecule imaging. The main application is quantifying 3D spatial gene expression in millions of cells or large pieces of intact tissue using interative RNA-FISH (see examples [here](https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-018-22297-7) and [here](https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-019-43943-8)). Because the fluidics controller for the iterative labeling is also controlled via Python (code not provided here), using Pycro-Manager greatly simplifies controlling these complex experiments.\n\nThe tutorial highlights the use of the `post_camera_hook_fn` and `post_hardware_hook_fn` functionality to allow an external controller to synchronize the microscope acquisition (external master). This is different from the standard hardware sequencing functionality in Pycro-Manager, where the acquisition engine sets up sequencable hardware and the camera serves as the master clock. \n \nThe tutorial also discusses how to structure the events and avoid timeouts to acquire >10 million of events per acquistion.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Microscope hardware",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Briefly, the stage scan high NA OPM is built around a [bespoke tertiary objective](https://andrewgyork.github.io/high_na_single_objective_lightsheet/) designed by Alfred Millet-Sikking and Andrew York at Calico Labs. Stage scanning is performed by an ASI scan optimized XY stage, an ASI FTP Z stage, and an ASI Tiger controller with a programmable logic card. Excitation light is provided by a Coherent OBIS Laser Box. A custom Teensy based DAC synchronizes laser emission and a galvanometer mirror to the scan stage motion to eliminate motion blur. Emitted fluorescence is imaged by a Photometrics Prime BSI. \n \nThe ASI Tiger controller is the master clock in this experiment. The custom Teensy DAC is setup in a closed loop with the Photometrics camera. This controller is detailed in a previous [publication](https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-017-00514-7) on adaptive light sheet microscopy.\n\nThe code to orthogonally deskew the acquired data and place it into a BigDataViewer HDF5 file that can be read stitched and fused using BigStitcher is found at the qi2lab (www.github.com/qi2lab/OPM/).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Initial setup",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Imports",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from pycromanager import Bridge, Acquisition\nimport numpy as np\nfrom pathlib import Path\nfrom time import sleep",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Create bridge to Micro-Manager",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"with Bridge() as bridge:\n core = bridge.get_core()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Define pycromanager specific hook functions for externally controlled hardware acquisition",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Post camera hook function to start external controller\nThis is run once after the camera is put into active mode in the sequence acquisition. The stage starts moving on this command and outputs a TTL pulse to the camera when it passes the preset initial position. This TTL starts the camera running at the set exposure time using internal timing. The camera acts the master signal for the galvo/laser controller using its own \"exposure out\" signal.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def post_camera_hook_(event,bridge,event_queue):\n\n \"\"\"\n Run a set of commands after the camera is started\n \n :param event: current list of events, each a dictionary, to run in this hardware sequence\n :type event: list \n :param bridge: pycro-manager java bridge\n :type bridge: pycromanager.core.Bridge\n :param event_queue: thread-safe event queue\n :type event_queue: multiprocessing.Queue\n\n :return: event_queue\n \"\"\"\n\n # acquire core from bridge\n core=bridge.get_core()\n \n # send Tiger command to start constant speed scan\n command='1SCAN'\n core.set_property('TigerCommHub','SerialCommand',command)\n\n return event",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Post hardware setup function to make sure external controller is ready\nThis is run once after the acquisition engine sets up the hardware for the non-sequencable hardware, such as the height axis stage and channel.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def post_hardware_hook(event,bridge,event_queue):\n \n \"\"\"\n Run a set of commands after the hardware setup calls by acquisition engine are finished\n \n :param event: current list of events, each a dictionary, to run in this hardware sequence\n :type event: list\n :param bridge: pycro-manager java bridge\n :type bridge: pycromanager.core.Bridge\n :param event_queue: thread-safe event queue\n :type event_queue: multiprocessing.Queue\n\n :return: event_queue\n \"\"\"\n\n # acquire core from bridge\n core = bridge.get_core()\n \n # turn on 'transmit repeated commands' for Tiger\n core.set_property('TigerCommHub','OnlySendSerialCommandOnChange','No')\n\n # check to make sure Tiger is not busy\n ready='B'\n while(ready!='N'):\n command = 'STATUS'\n core.set_property('TigerCommHub','SerialCommand',command)\n ready = core.get_property('TigerCommHub','SerialResponse')\n sleep(.500)\n\n # turn off 'transmit repeated commands' for Tiger\n core.set_property('TigerCommHub','OnlySendSerialCommandOnChange','Yes')\n\n return event",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Acquistion parameters set by user",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Select laser channels and powers",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# lasers to use\n# 0 -> inactive\n# 1 -> active\n\nstate_405 = 0\nstate_488 = 0\nstate_561 = 1\nstate_635 = 0\nstate_730 = 0\n\n# laser powers (0 -> 100%)\n\npower_405 = 0\npower_488 = 0\npower_561 = 0\npower_635 = 0\npower_730 = 0\n\n# construct arrays for laser informaton\nchannel_states = [state_405,state_488,state_561,state_635,state_730]\nchannel_powers = [power_405,power_488,power_561,power_635,power_730]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Camera parameters",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# FOV parameters.\n# x size (256) is the Rayleigh length of oblique light sheet excitation\n# y size (1600) is the high quality lateral extent of the remote image system (~180 microns)\n# camera is oriented so that cropping the x size limits the number of readout rows and therefore lowering readout time\nROI = [1024, 0, 256, 1600] #unit: pixels\n\n# camera exposure\nexposure_ms = 5 #unit: ms\n\n# camera pixel size\npixel_size_um = .115 #unit: um",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Stage scan parameters\nThe user defines these by interactively moving the XY and Z stages around the sample. At the edges of the sample, the user records the positions.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# distance between adjacent images.\nscan_axis_step_um = 0.2 #unit: um\n\n# scan axis limits. Use stage positions reported by Micromanager\nscan_axis_start_um = 0. #unit: um\nscan_axis_end_um = 5000. #unit: um\n\n# tile axis limits. Use stage positions reported by Micromanager\ntile_axis_start_um = 0. #unit: um\ntile_axis_end_um = 5000. #unit: um\n\n# height axis limits. Use stage positions reported by Micromanager\nheight_axis_start_um = 0.#unit: um\nheight_axis_end_um = 30. #unit: um",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Path to save acquistion data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"save_directory = Path('/path/to/save')\nsave_name = 'test'",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Setup hardware for stage scanning sample through oblique digitally scanned light sheet",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Calculate stage limits and speeds from user provided scan parameters\nHere, the number of events along the scan (x) axis in each acquisition, the overlap between adajcent strips along the tile (y) axis, and the overlap between adajacent strips along the height (z) axis are all calculated.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# scan axis setup\nscan_axis_step_mm = scan_axis_step_um / 1000. #unit: mm\nscan_axis_start_mm = scan_axis_start_um / 1000. #unit: mm\nscan_axis_end_mm = scan_axis_end_um / 1000. #unit: mm\nscan_axis_range_um = np.abs(scan_axis_end_um-scan_axis_start_um) # unit: um\nscan_axis_range_mm = scan_axis_range_um / 1000 #unit: mm\nactual_exposure_s = actual_readout_ms / 1000. #unit: s\nscan_axis_speed = np.round(scan_axis_step_mm / actual_exposure_s,2) #unit: mm/s\nscan_axis_positions = np.rint(scan_axis_range_mm / scan_axis_step_mm).astype(int) #unit: number of positions\n\n# tile axis setup\ntile_axis_overlap=0.2 #unit: percentage\ntile_axis_range_um = np.abs(tile_axis_end_um - tile_axis_start_um) #unit: um\ntile_axis_range_mm = tile_axis_range_um / 1000 #unit: mm\ntile_axis_ROI = ROI[3]*pixel_size_um #unit: um\ntile_axis_step_um = np.round((tile_axis_ROI) * (1-tile_axis_overlap),2) #unit: um\ntile_axis_step_mm = tile_axis_step_um / 1000 #unit: mm\ntile_axis_positions = np.rint(tile_axis_range_mm / tile_axis_step_mm).astype(int) #unit: number of positions\n\n# if tile_axis_positions rounded to zero, make sure acquisition visits at least one position\nif tile_axis_positions == 0:\n tile_axis_positions=1\n\n# height axis setup\n# this is more complicated, because the excitation is an oblique light sheet\n# the height of the scan is the length of the ROI in the tilted direction * sin(tilt angle)\nheight_axis_overlap=0.2 #unit: percentage\nheight_axis_range_um = np.abs(height_axis_end_um-height_axis_start_um) #unit: um\nheight_axis_range_mm = height_axis_range_um / 1000 #unit: mm\nheight_axis_ROI = ROI[2]*pixel_size_um*np.sin(30*(np.pi/180.)) #unit: um\nheight_axis_step_um = np.round((height_axis_ROI)*(1-height_axis_overlap),2) #unit: um\nheight_axis_step_mm = height_axis_step_um / 1000 #unit: mm\nheight_axis_positions = np.rint(height_axis_range_mm / height_axis_step_mm).astype(int) #unit: number of positions\n\n# if height_axis_positions rounded to zero, make sure acquisition visits at least one position\nif height_axis_positions==0:\n height_axis_positions=1",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Setup Coherent laser box from user provided laser parameters",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"with Bridge() as bridge:\n core = bridge.get_core()\n # turn off lasers\n # this relies on a Micro-Manager configuration group that sets all lasers to \"off\" state\n core.set_config('Coherent-State','off')\n core.wait_for_config('Coherent-State','off')\n\n # set lasers to user defined power\n core.set_property('Coherent-Scientific Remote','Laser 405-100C - PowerSetpoint (%)',channel_powers[0])\n core.set_property('Coherent-Scientific Remote','Laser 488-150C - PowerSetpoint (%)',channel_powers[1])\n core.set_property('Coherent-Scientific Remote','Laser OBIS LS 561-150 - PowerSetpoint (%)',channel_powers[2])\n core.set_property('Coherent-Scientific Remote','Laser 637-140C - PowerSetpoint (%)',channel_powers[3])\n core.set_property('Coherent-Scientific Remote','Laser 730-30C - PowerSetpoint (%)',channel_powers[4])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Setup Photometrics camera for low-noise readout and triggering\nThe camera input trigger is set to `Trigger first` mode to allow for external control and the output trigger is set to `Rolling Shutter` mode to ensure that laser light is only delivered when the entire chip is exposed. The custom Teensy DAC waits for the signal from the camera to go HIGH and then sweeps a Gaussian pencil beam once across the field-of-view. It then rapidly resets and scans again upon the next trigger. The Teensy additionally blanks the Coherent laser box emission between frames.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"with Bridge() as bridge:\n core = bridge.get_core()\n # set camera into 16bit readout mode\n core.set_property('Camera','ReadoutRate','100MHz 16bit')\n # give camera time to change modes\n sleep(5)\n\n # set camera into low noise readout mode\n core.set_property('Camera','Gain','2-CMS')\n # give camera time to change modes\n sleep(5)\n\n # set camera to give an exposure out signal\n # this signal is used by the custom DAC to synchronize blanking and a digitally swept light sheet\n core.set_property('Camera','ExposureOut','Rolling Shutter')\n # give camera time to change modes\n sleep(5)\n\n # change camera timeout.\n # this is necessary because the acquisition engine can take a long time to setup with millions of events\n # on the first run\n core.set_property('Camera','Trigger Timeout (secs)',300)\n # give camera time to change modes\n sleep(5)\n\n # set camera to internal trigger\n core.set_property('Camera','TriggerMode','Internal Trigger')\n # give camera time to change modes\n sleep(5)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Setup ASI stage control cards and programmable logic card in the Tiger controller\nHardware is setup for a constant-speed scan along the `x` direction, lateral tiling along the `y` direction, and height tiling along the `z` direction. The programmable logic card sends a signal to the camera to start acquiring once the scan (x) axis reaches the desired speed and crosses the user defined start position. \n \nDocumentation for the specific commands to setup the constant speed stage scan on the Tiger controller is at the following links,\n- [SCAN](http://asiimaging.com/docs/commands/scan)\n- [SCANR](http://asiimaging.com/docs/commands/scanr)\n- [SCANV](http://www.asiimaging.com/docs/commands/scanv)\n\n \nDocumentation for the programmable logic card is found [here](http://www.asiimaging.com/docs/tiger_programmable_logic_card?s[]=plc).\n \nThe Tiger is polled after each command to make sure that it is ready to receive another command.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"with Bridge() as bridge:\n core = bridge.get_core()\n # Setup the PLC to output external TTL when an internal signal is received from the stage scanning card\n plcName = 'PLogic:E:36'\n propPosition = 'PointerPosition'\n propCellConfig = 'EditCellConfig'\n addrOutputBNC3 = 35\n addrStageSync = 46 # TTL5 on Tiger backplane = stage sync signal\n core.set_property(plcName, propPosition, addrOutputBNC3)\n core.set_property(plcName, propCellConfig, addrStageSync)\n\n # turn on 'transmit repeated commands' for Tiger\n core.set_property('TigerCommHub','OnlySendSerialCommandOnChange','No')\n\n # set tile (y) axis speed to 25% of maximum for all moves\n command = 'SPEED Y=.25'\n core.set_property('TigerCommHub','SerialCommand',command)\n\n # check to make sure Tiger is not busy\n ready='B'\n while(ready!='N'):\n command = 'STATUS'\n core.set_property('TigerCommHub','SerialCommand',command)\n ready = core.get_property('TigerCommHub','SerialResponse')\n sleep(.500)\n\n # set scan (x) axis speed to 25% of maximum for non-sequenced moves\n command = 'SPEED X=.25'\n core.set_property('TigerCommHub','SerialCommand',command)\n\n # check to make sure Tiger is not busy\n ready='B'\n while(ready!='N'):\n command = 'STATUS'\n core.set_property('TigerCommHub','SerialCommand',command)\n ready = core.get_property('TigerCommHub','SerialResponse')\n sleep(.500)\n\n # turn off 'transmit repeated commands' for Tiger\n core.set_property('TigerCommHub','OnlySendSerialCommandOnChange','Yes')\n\n # turn on 'transmit repeated commands' for Tiger\n core.set_property('TigerCommHub','OnlySendSerialCommandOnChange','No')\n\n # set scan (x) axis speed to correct speed for constant speed movement of scan (x) axis\n # expects mm/s\n command = 'SPEED X='+str(scan_axis_speed)\n core.set_property('TigerCommHub','SerialCommand',command)\n\n # check to make sure Tiger is not busy\n ready='B'\n while(ready!='N'):\n command = 'STATUS'\n core.set_property('TigerCommHub','SerialCommand',command)\n ready = core.get_property('TigerCommHub','SerialResponse')\n sleep(.500)\n\n # set scan (x) axis to true 1D scan with no backlash\n command = '1SCAN X? Y=0 Z=9 F=0'\n core.set_property('TigerCommHub','SerialCommand',command)\n\n # check to make sure Tiger is not busy\n ready='B'\n while(ready!='N'):\n command = 'STATUS'\n core.set_property('TigerCommHub','SerialCommand',command)\n ready = core.get_property('TigerCommHub','SerialResponse')\n sleep(.500)\n\n # set range and return speed (25% of max) for constant speed movement of scan (x) axis\n # expects mm\n command = '1SCANR X='+str(scan_axis_start_mm)+' Y='+str(scan_axis_end_mm)+' R=25'\n core.set_property('TigerCommHub','SerialCommand',command)\n\n # check to make sure Tiger is not busy\n ready='B'\n while(ready!='N'):\n command = 'STATUS'\n core.set_property('TigerCommHub','SerialCommand',command)\n ready = core.get_property('TigerCommHub','SerialResponse')\n sleep(.500)\n\n # turn off 'transmit repeated commands' for Tiger\n core.set_property('TigerCommHub','OnlySendSerialCommandOnChange','Yes')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Setup and run the acquisition",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Change core timeout\nThis is necessary because of the large, slow XY stage moves.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"with Bridge() as bridge:\n core = bridge.get_core()\n # change core timeout for long stage moves\n core.set_property('Core','TimeoutMs',20000)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Move stage hardware to initial positions",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"with Bridge() as bridge:\n core = bridge.get_core()\n # move scan (x) and tile (y) stages to starting positions\n core.set_xy_position(scan_axis_start_um,tile_axis_start_um)\n core.wait_for_device(xy_stage)\n\n # move height (z) stage to starting position\n core.set_position(height_position_um)\n core.wait_for_device(z_stage)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Create event structure\nThe external controller handles all of the events in `x` for a given `yzc` position. To make sure that pycro-manager structures the acquistion this way, the value of the stage positions for `x` are kept constant for all events at a given `yzc` position. This gives the order of the loops to create the event structure as `yzcx`. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# empty event dictionary\nevents = []\n\n# loop over all tile (y) positions.\nfor y in range(tile_axis_positions):\n \n # update tile (y) axis position\n tile_position_um = tile_axis_start_um+(tile_axis_step_um*y)\n \n # loop over all height (z) positions\n for z in range(height_axis_positions):\n \n # update height (z) axis position\n height_position_um = height_axis_start_um+(height_axis_step_um*z)\n \n # loop over all channels (c)\n for c in range(len(channel_states)):\n \n # create events for all scan (x) axis positions. \n # The acquistion engine knows that this is a hardware triggered sequence because \n # the physical x position does not change when specifying the large number of x events \n for x in range(scan_axis_positions):\n \n # only create events if user sets laser to active\n # this relies on a Micromanager group 'Coherent-State' that has individual entries that correspond\n # the correct on/off state of each laser. Laser blanking and synchronization are handled by the\n # custom Teensy DAC controller.\n if channel_states[c]==1:\n if (c==0):\n evt = { 'axes': {'x': x, 'y':y, 'z':z}, 'x': scan_axis_start_um, 'y': tile_position_um, \n 'z': height_position_um, 'channel' : {'group': 'Coherent-State', 'config': '405nm'}}\n elif (c==1):\n evt = { 'axes': {'x': x, 'y':y, 'z':z}, 'x': scan_axis_start_um, 'y': tile_position_um, \n 'z': height_position_um, 'channel' : {'group': 'Coherent-State', 'config': '488nm'}}\n elif (c==2):\n evt = { 'axes': {'x': x, 'y':y, 'z':z}, 'x': scan_axis_start_um, 'y': tile_position_um, \n 'z': height_position_um, 'channel' : {'group': 'Coherent-State', 'config': '561nm'}}\n elif (c==3):\n evt = { 'axes': {'x': x, 'y':y, 'z':z}, 'x': scan_axis_start_um, 'y': tile_position_um, \n 'z': height_position_um, 'channel' : {'group': 'Coherent-State', 'config': '637nm'}}\n elif (c==4):\n evt = { 'axes': {'x': x, 'y':y, 'z':z}, 'x': scan_axis_start_um, 'y': tile_position_um, \n 'z': height_position_um, 'channel' : {'group': 'Coherent-State', 'config': '730nm'}}\n\n events.append(evt)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Run acquisition\n\n- The camera is set to `Trigger first` mode. In this mode, the camera waits for an external trigger and then runs using the internal timing. \n- The acquisition is setup and started. The initial acquisition setup by Pycro-manager and the Java acquisition engine takes a few minutes and requires at significant amount of RAM allocated to ImageJ. 40 GB of RAM seems acceptable. The circular buffer is only allocated 2 GB, because the computer for this experiment has an SSD array capable of writing up to 600 MBps.\n- At each `yzc` position, the ASI Tiger controller supplies the external master signal when the the (scan) axis has ramped up to the correct constant speed and crossed `scan_axis_start_um`. The speed is defined by `scan_axis_speed = scan_axis_step_um / camera_exposure_ms`. Acquired images are placed into the `x` axis of the Acquisition without Pycro-Manager interacting with the hardware.\n- Once the full acquisition is completed, all lasers are set to `off` and the camera is placed back in `Internal Trigger` mode.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"with Bridge() as bridge:\n core = bridge.get_core()\n # set camera to trigger first mode for stage synchronization\n # give camera time to change modes\n core.set_property('Camera','TriggerMode','Trigger first')\n sleep(5)\n\n # run acquisition\n # the acquisition needs to write data at roughly 100-500 MBps depending on frame rate and ROI\n # so the display is set to off and no multi-resolution calculations are done\n with Acquisition(directory=save_directory, name=save_name, post_hardware_hook_fn=post_hardware_hook,\n post_camera_hook_fn=post_camera_hook, show_display=False, max_multi_res_index=0) as acq:\n acq.acquire(events)\n\n # turn off lasers\n core.set_config('Coherent-State','off')\n core.wait_for_config('Coherent-State','off')\n\n # set camera to internal trigger\n core.set_property('Camera','TriggerMode','Internal Trigger')\n # give camera time to change modes\n sleep(5)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c50300c88cdb892102f33f94c3bf73b47743a497
| 323,101 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
data-visualization/seaborn/1_distributions.ipynb
|
pbgnz/ds-ml
|
45cb4756e20aa5f4e4077437faee18633ca9a0e5
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
data-visualization/seaborn/1_distributions.ipynb
|
pbgnz/ds-ml
|
45cb4756e20aa5f4e4077437faee18633ca9a0e5
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
data-visualization/seaborn/1_distributions.ipynb
|
pbgnz/ds-ml
|
45cb4756e20aa5f4e4077437faee18633ca9a0e5
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 464.225575 | 48,912 | 0.930808 |
[
[
[
"# Distribution Plots\n\nLet's discuss some plots that allow us to visualize the distribution of a data set. These plots are:\n\n* distplot\n* jointplot\n* pairplot\n* rugplot\n* kdeplot",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"___\n## Imports",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import seaborn as sns\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Data\nSeaborn comes with built-in data sets!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tips = sns.load_dataset('tips')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tips.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## distplot\n\nThe distplot shows the distribution of a univariate set of observations.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sns.distplot(tips['total_bill'])\n# Safe to ignore warnings",
"/Users/marci/anaconda/lib/python3.5/site-packages/statsmodels/nonparametric/kdetools.py:20: VisibleDeprecationWarning: using a non-integer number instead of an integer will result in an error in the future\n y = X[:m/2+1] + np.r_[0,X[m/2+1:],0]*1j\n"
]
],
[
[
"To remove the kde layer and just have the histogram use:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sns.distplot(tips['total_bill'],kde=False,bins=30)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## jointplot\n\njointplot() allows you to basically match up two distplots for bivariate data. With your choice of what **kind** parameter to compare with: \n* “scatter” \n* “reg” \n* “resid” \n* “kde” \n* “hex”",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sns.jointplot(x='total_bill',y='tip',data=tips,kind='scatter')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sns.jointplot(x='total_bill',y='tip',data=tips,kind='hex')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sns.jointplot(x='total_bill',y='tip',data=tips,kind='reg')",
"/Users/marci/anaconda/lib/python3.5/site-packages/statsmodels/nonparametric/kdetools.py:20: VisibleDeprecationWarning: using a non-integer number instead of an integer will result in an error in the future\n y = X[:m/2+1] + np.r_[0,X[m/2+1:],0]*1j\n"
]
],
[
[
"## pairplot\n\npairplot will plot pairwise relationships across an entire dataframe (for the numerical columns) and supports a color hue argument (for categorical columns). ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sns.pairplot(tips)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sns.pairplot(tips,hue='sex',palette='coolwarm')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## rugplot\n\nrugplots are actually a very simple concept, they just draw a dash mark for every point on a univariate distribution. They are the building block of a KDE plot:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sns.rugplot(tips['total_bill'])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## kdeplot\n\nkdeplots are [Kernel Density Estimation plots](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kernel_density_estimation#Practical_estimation_of_the_bandwidth). These KDE plots replace every single observation with a Gaussian (Normal) distribution centered around that value. For example:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Don't worry about understanding this code!\n# It's just for the diagram below\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom scipy import stats\n\n#Create dataset\ndataset = np.random.randn(25)\n\n# Create another rugplot\nsns.rugplot(dataset);\n\n# Set up the x-axis for the plot\nx_min = dataset.min() - 2\nx_max = dataset.max() + 2\n\n# 100 equally spaced points from x_min to x_max\nx_axis = np.linspace(x_min,x_max,100)\n\n# Set up the bandwidth, for info on this:\nurl = 'http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kernel_density_estimation#Practical_estimation_of_the_bandwidth'\n\nbandwidth = ((4*dataset.std()**5)/(3*len(dataset)))**.2\n\n\n# Create an empty kernel list\nkernel_list = []\n\n# Plot each basis function\nfor data_point in dataset:\n \n # Create a kernel for each point and append to list\n kernel = stats.norm(data_point,bandwidth).pdf(x_axis)\n kernel_list.append(kernel)\n \n #Scale for plotting\n kernel = kernel / kernel.max()\n kernel = kernel * .4\n plt.plot(x_axis,kernel,color = 'grey',alpha=0.5)\n\nplt.ylim(0,1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# To get the kde plot we can sum these basis functions.\n\n# Plot the sum of the basis function\nsum_of_kde = np.sum(kernel_list,axis=0)\n\n# Plot figure\nfig = plt.plot(x_axis,sum_of_kde,color='indianred')\n\n# Add the initial rugplot\nsns.rugplot(dataset,c = 'indianred')\n\n# Get rid of y-tick marks\nplt.yticks([])\n\n# Set title\nplt.suptitle(\"Sum of the Basis Functions\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"So with our tips dataset:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sns.kdeplot(tips['total_bill'])\nsns.rugplot(tips['total_bill'])",
"/Users/marci/anaconda/lib/python3.5/site-packages/statsmodels/nonparametric/kdetools.py:20: VisibleDeprecationWarning: using a non-integer number instead of an integer will result in an error in the future\n y = X[:m/2+1] + np.r_[0,X[m/2+1:],0]*1j\n"
],
[
"sns.kdeplot(tips['tip'])\nsns.rugplot(tips['tip'])",
"/Users/marci/anaconda/lib/python3.5/site-packages/statsmodels/nonparametric/kdetools.py:20: VisibleDeprecationWarning: using a non-integer number instead of an integer will result in an error in the future\n y = X[:m/2+1] + np.r_[0,X[m/2+1:],0]*1j\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Great Job!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
c50304dca23a322d545a018ecfa0105d0c158d38
| 165,732 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Long Short Term Memory/Part2_Music_Generation (LSTM).ipynb
|
seanjin97/Tensorflow2.0-learnbook
|
a2b02d0870f5e11f752128b2becbe280fd1c7097
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Long Short Term Memory/Part2_Music_Generation (LSTM).ipynb
|
seanjin97/Tensorflow2.0-learnbook
|
a2b02d0870f5e11f752128b2becbe280fd1c7097
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Long Short Term Memory/Part2_Music_Generation (LSTM).ipynb
|
seanjin97/Tensorflow2.0-learnbook
|
a2b02d0870f5e11f752128b2becbe280fd1c7097
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 165,732 | 165,732 | 0.624333 |
[
[
[
"<table align=\"center\">\n <td align=\"center\"><a target=\"_blank\" href=\"http://introtodeeplearning.com\">\n <img src=\"http://introtodeeplearning.com/images/colab/mit.png\" style=\"padding-bottom:5px;\" />\n Visit MIT Deep Learning</a></td>\n <td align=\"center\"><a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/aamini/introtodeeplearning/blob/master/lab1/Part2_Music_Generation.ipynb\">\n <img src=\"http://introtodeeplearning.com/images/colab/colab.png?v2.0\" style=\"padding-bottom:5px;\" />Run in Google Colab</a></td>\n <td align=\"center\"><a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://github.com/aamini/introtodeeplearning/blob/master/lab1/Part2_Music_Generation.ipynb\">\n <img src=\"http://introtodeeplearning.com/images/colab/github.png\" height=\"70px\" style=\"padding-bottom:5px;\" />View Source on GitHub</a></td>\n</table>\n\n# Copyright Information",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Copyright 2020 MIT 6.S191 Introduction to Deep Learning. All Rights Reserved.\n# \n# Licensed under the MIT License. You may not use this file except in compliance\n# with the License. Use and/or modification of this code outside of 6.S191 must\n# reference:\n#\n# © MIT 6.S191: Introduction to Deep Learning\n# http://introtodeeplearning.com\n#",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Lab 1: Intro to TensorFlow and Music Generation with RNNs\n\n# Part 2: Music Generation with RNNs\n\nIn this portion of the lab, we will explore building a Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) for music generation. We will train a model to learn the patterns in raw sheet music in [ABC notation](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ABC_notation) and then use this model to generate new music. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 2.1 Dependencies \nFirst, let's download the course repository, install dependencies, and import the relevant packages we'll need for this lab.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import Tensorflow 2.0\n%tensorflow_version 2.x\nimport tensorflow as tf \n\n\n# Download and import the MIT 6.S191 package\n!pip install mitdeeplearning\nimport mitdeeplearning as mdl\n\n# Import all remaining packages\nimport numpy as np\nimport os\nimport time\nimport functools\nfrom IPython import display as ipythondisplay\nfrom tqdm import tqdm\n!apt-get install abcmidi timidity > /dev/null 2>&1\n\n# Check that we are using a GPU, if not switch runtimes\n# using Runtime > Change Runtime Type > GPU\nassert len(tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU')) > 0",
"Requirement already satisfied: mitdeeplearning in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (0.1.2)\nRequirement already satisfied: gym in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from mitdeeplearning) (0.17.2)\nRequirement already satisfied: tqdm in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from mitdeeplearning) (4.41.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: numpy in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from mitdeeplearning) (1.18.4)\nRequirement already satisfied: regex in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from mitdeeplearning) (2019.12.20)\nRequirement already satisfied: pyglet<=1.5.0,>=1.4.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from gym->mitdeeplearning) (1.5.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: scipy in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from gym->mitdeeplearning) (1.4.1)\nRequirement already satisfied: cloudpickle<1.4.0,>=1.2.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from gym->mitdeeplearning) (1.3.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: future in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from pyglet<=1.5.0,>=1.4.0->gym->mitdeeplearning) (0.16.0)\n"
]
],
[
[
"## 2.2 Dataset\n\n\n\nWe've gathered a dataset of thousands of Irish folk songs, represented in the ABC notation. Let's download the dataset and inspect it: \n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Download the dataset\nsongs = mdl.lab1.load_training_data()\n\n# Print one of the songs to inspect it in greater detail!\nexample_song = songs[0]\nprint(\"\\nExample song: \")\nprint(example_song)",
"Found 816 songs in text\n\nExample song: \nX:2\nT:An Buachaill Dreoite\nZ: id:dc-hornpipe-2\nM:C|\nL:1/8\nK:G Major\nGF|DGGB d2GB|d2GF Gc (3AGF|DGGB d2GB|dBcA F2GF|!\nDGGB d2GF|DGGF G2Ge|fgaf gbag|fdcA G2:|!\nGA|B2BG c2cA|d2GF G2GA|B2BG c2cA|d2DE F2GA|!\nB2BG c2cA|d^cde f2 (3def|g2gf gbag|fdcA G2:|!\n"
]
],
[
[
"We can easily convert a song in ABC notation to an audio waveform and play it back. Be patient for this conversion to run, it can take some time.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Convert the ABC notation to audio file and listen to it\nmdl.lab1.play_song(example_song)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s = \"hi my name is \"\nset(s)\n# set of a string converts the string into dictionary of unique characters\n## interesting stuff",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"One important thing to think about is that this notation of music does not simply contain information on the notes being played, but additionally there is meta information such as the song title, key, and tempo. How does the number of different characters that are present in the text file impact the complexity of the learning problem? This will become important soon, when we generate a numerical representation for the text data.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Join our list of song strings into a single string containing all songs\nsongs_joined = \"\\n\\n\".join(songs) \n\n# Find all unique characters in the joined string\nvocab = sorted(set(songs_joined)) # vocab is a sorted dictionary of unique characters found in songs_joined, no values only keys\nprint(\"There are\", len(vocab), \"unique characters in the dataset\")",
"There are 83 unique characters in the dataset\n"
]
],
[
[
"## 2.3 Process the dataset for the learning task\n\nLet's take a step back and consider our prediction task. We're trying to train a RNN model to learn patterns in ABC music, and then use this model to generate (i.e., predict) a new piece of music based on this learned information. \n\nBreaking this down, what we're really asking the model is: given a character, or a sequence of characters, what is the most probable next character? We'll train the model to perform this task. \n\nTo achieve this, we will input a sequence of characters to the model, and train the model to predict the output, that is, the following character at each time step. RNNs maintain an internal state that depends on previously seen elements, so information about all characters seen up until a given moment will be taken into account in generating the prediction.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Vectorize the text\n\nBefore we begin training our RNN model, we'll need to create a numerical representation of our text-based dataset. To do this, we'll generate two lookup tables: one that maps characters to numbers, and a second that maps numbers back to characters. Recall that we just identified the unique characters present in the text.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Define numerical representation of text ###\n\n# Create a mapping from character to unique index.\n# For example, to get the index of the character \"d\", \n# we can evaluate `char2idx[\"d\"]`. \nchar2idx = {u:i for i, u in enumerate(vocab)} # assign a number to a unique character\n# Create a mapping from indices to characters. This is\n# the inverse of char2idx and allows us to convert back\n# from unique index to the character in our vocabulary.\nidx2char = np.array(vocab) # index of character in idx2char matches up with char2idx\nprint(idx2char[2])\nprint(char2idx[\"!\"])",
"!\n2\n"
]
],
[
[
"This gives us an integer representation for each character. Observe that the unique characters (i.e., our vocabulary) in the text are mapped as indices from 0 to `len(unique)`. Let's take a peek at this numerical representation of our dataset:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print('{')\nfor char,_ in zip(char2idx, range(20)):\n print(' {:4s}: {:3d},'.format(repr(char), char2idx[char])) # {:4s} and {:3d} adds padding to the print\nprint(' ...\\n}')",
"{\n '\\n': 0,\n ' ' : 1,\n '!' : 2,\n '\"' : 3,\n '#' : 4,\n \"'\" : 5,\n '(' : 6,\n ')' : 7,\n ',' : 8,\n '-' : 9,\n '.' : 10,\n '/' : 11,\n '0' : 12,\n '1' : 13,\n '2' : 14,\n '3' : 15,\n '4' : 16,\n '5' : 17,\n '6' : 18,\n '7' : 19,\n ...\n}\n"
],
[
"### Vectorize the songs string ###\n\n'''TODO: Write a function to convert the all songs string to a vectorized\n (i.e., numeric) representation. Use the appropriate mapping\n above to convert from vocab characters to the corresponding indices.\n\n NOTE: the output of the `vectorize_string` function \n should be a np.array with `N` elements, where `N` is\n the number of characters in the input string\n'''\n\ndef vectorize_string(string):\n output = np.array([char2idx[c] for c in string])\n print(output)\n return output\nvectorized_songs = vectorize_string(songs_joined)\nvectorized_songs.shape[0] - 1",
"[49 22 14 ... 22 82 2]\n"
]
],
[
[
"We can also look at how the first part of the text is mapped to an integer representation:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print ('{} ---- characters mapped to int ----> {}'.format(repr(songs_joined[:10]), vectorized_songs[:10]))\n# check that vectorized_songs is a numpy array\nassert isinstance(vectorized_songs, np.ndarray), \"returned result should be a numpy array\"",
"'X:2\\nT:An B' ---- characters mapped to int ----> [49 22 14 0 45 22 26 69 1 27]\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Create training examples and targets\n\nOur next step is to actually divide the text into example sequences that we'll use during training. Each input sequence that we feed into our RNN will contain `seq_length` characters from the text. We'll also need to define a target sequence for each input sequence, which will be used in training the RNN to predict the next character. For each input, the corresponding target will contain the same length of text, except shifted one character to the right.\n\nTo do this, we'll break the text into chunks of `seq_length+1`. Suppose `seq_length` is 4 and our text is \"Hello\". Then, our input sequence is \"Hell\" and the target sequence is \"ello\".\n\nThe batch method will then let us convert this stream of character indices to sequences of the desired size.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Batch definition to create training examples ###\n\ndef get_batch(vectorized_songs, seq_length, batch_size):\n # the length of the vectorized songs string\n n = vectorized_songs.shape[0] - 1\n # randomly choose the starting indices for the examples in the training batch\n idx = np.random.choice(n-seq_length, batch_size) # select randomly from np.arrange(n-seq_length) up till size batch_size\n print(idx)\n '''TODO: construct a list of input sequences for the training batch'''\n input_batch = [vectorized_songs[i : i+seq_length] for i in idx]\n print(input_batch)\n '''TODO: construct a list of output sequences for the training batch'''\n output_batch = [vectorized_songs[i+1 : i+seq_length+1] for i in idx]\n print(output_batch)\n # x_batch, y_batch provide the true inputs and targets for network training\n x_batch = np.reshape(input_batch, [batch_size, seq_length])\n y_batch = np.reshape(output_batch, [batch_size, seq_length])\n return x_batch, y_batch\n\n\n# Perform some simple tests to make sure your batch function is working properly! \ntest_args = (vectorized_songs, 10, 2)\nif not mdl.lab1.test_batch_func_types(get_batch, test_args) or \\\n not mdl.lab1.test_batch_func_shapes(get_batch, test_args) or \\\n not mdl.lab1.test_batch_func_next_step(get_batch, test_args): \n print(\"======\\n[FAIL] could not pass tests\")\nelse: \n print(\"======\\n[PASS] passed all tests!\")",
"[24171 6632]\n[array([27, 1, 32, 15, 82, 31, 29, 31, 1, 26]), array([32, 14, 1, 32, 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 6])]\n[array([ 1, 32, 15, 82, 31, 29, 31, 1, 26, 31]), array([14, 1, 32, 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 6, 15])]\n[PASS] test_batch_func_types\n[161623 15338]\n[array([59, 27, 60, 27, 1, 59, 27, 26, 27, 82]), array([61, 82, 62, 60, 59, 27, 1, 32, 26, 27])]\n[array([27, 60, 27, 1, 59, 27, 26, 27, 82, 59]), array([82, 62, 60, 59, 27, 1, 32, 26, 27, 32])]\n[PASS] test_batch_func_shapes\n[ 6904 164097]\n[array([60, 59, 58, 82, 27, 26, 27, 58, 1, 27]), array([30, 82, 29, 14, 31, 29, 1, 26, 29, 31])]\n[array([59, 58, 82, 27, 26, 27, 58, 1, 27, 14]), array([82, 29, 14, 31, 29, 1, 26, 29, 31, 26])]\n[PASS] test_batch_func_next_step\n======\n[PASS] passed all tests!\n"
]
],
[
[
"For each of these vectors, each index is processed at a single time step. So, for the input at time step 0, the model receives the index for the first character in the sequence, and tries to predict the index of the next character. At the next timestep, it does the same thing, but the RNN considers the information from the previous step, i.e., its updated state, in addition to the current input.\n\nWe can make this concrete by taking a look at how this works over the first several characters in our text:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x_batch, y_batch = get_batch(vectorized_songs, seq_length=5, batch_size=1)\n# np.squeeze to remove single dimension arrays, becomes a (x, ) vector\n# zip converts x and y array into an iterator of tuples of {(x1, y1)... (xn, yn)}\n# repr returns printable version of object\n# what this does is to split the sampled data into a train and test set. (X, y)\nfor i, (input_idx, target_idx) in enumerate(zip(np.squeeze(x_batch), np.squeeze(y_batch))):\n print(\"Step {:3d}\".format(i))\n print(\" input: {} ({:s})\".format(input_idx, repr(idx2char[input_idx])))\n print(\" expected output: {} ({:s})\".format(target_idx, repr(idx2char[target_idx])))",
"[112269]\n[array([27, 26, 31, 82, 29])]\n[array([26, 31, 82, 29, 31])]\nStep 0\n input: 27 ('B')\n expected output: 26 ('A')\nStep 1\n input: 26 ('A')\n expected output: 31 ('F')\nStep 2\n input: 31 ('F')\n expected output: 82 ('|')\nStep 3\n input: 82 ('|')\n expected output: 29 ('D')\nStep 4\n input: 29 ('D')\n expected output: 31 ('F')\n"
]
],
[
[
"## 2.4 The Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) model",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Now we're ready to define and train a RNN model on our ABC music dataset, and then use that trained model to generate a new song. We'll train our RNN using batches of song snippets from our dataset, which we generated in the previous section.\n\nThe model is based off the LSTM architecture, where we use a state vector to maintain information about the temporal relationships between consecutive characters. The final output of the LSTM is then fed into a fully connected [`Dense`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/layers/Dense) layer where we'll output a softmax over each character in the vocabulary, and then sample from this distribution to predict the next character. \n\nAs we introduced in the first portion of this lab, we'll be using the Keras API, specifically, [`tf.keras.Sequential`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/models/Sequential), to define the model. Three layers are used to define the model:\n\n* [`tf.keras.layers.Embedding`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/layers/Embedding): This is the input layer, consisting of a trainable lookup table that maps the numbers of each character to a vector with `embedding_dim` dimensions.\n* [`tf.keras.layers.LSTM`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/layers/LSTM): Our LSTM network, with size `units=rnn_units`. \n* [`tf.keras.layers.Dense`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/layers/Dense): The output layer, with `vocab_size` outputs.\n\n\n<img src=\"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/aamini/introtodeeplearning/2019/lab1/img/lstm_unrolled-01-01.png\" alt=\"Drawing\"/>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Define the RNN model\n\nNow, we will define a function that we will use to actually build the model.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def LSTM(rnn_units): \n return tf.keras.layers.LSTM(\n rnn_units, \n return_sequences=True, \n recurrent_initializer='glorot_uniform',\n recurrent_activation='sigmoid',\n stateful=True,\n )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The time has come! Fill in the `TODOs` to define the RNN model within the `build_model` function, and then call the function you just defined to instantiate the model!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Defining the RNN Model ###\n\n'''TODO: Add LSTM and Dense layers to define the RNN model using the Sequential API.'''\ndef build_model(vocab_size, embedding_dim, rnn_units, batch_size):\n model = tf.keras.Sequential([\n # Layer 1: Embedding layer to transform indices into dense vectors \n # of a fixed embedding size\n tf.keras.layers.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim, batch_input_shape=[batch_size, None]),\n\n # Layer 2: LSTM with `rnn_units` number of units. \n # TODO: Call the LSTM function defined above to add this layer.\n LSTM(rnn_units),\n\n # Layer 3: Dense (fully-connected) layer that transforms the LSTM output\n # into the vocabulary size. \n # TODO: Add the Dense layer.\n tf.keras.layers.Dense(vocab_size)\n ])\n\n return model\n\n# Build a simple model with default hyperparameters. You will get the \n# chance to change these later.\nmodel = build_model(len(vocab), embedding_dim=256, rnn_units=1024, batch_size=32)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Test out the RNN model\n\nIt's always a good idea to run a few simple checks on our model to see that it behaves as expected. \n\nFirst, we can use the `Model.summary` function to print out a summary of our model's internal workings. Here we can check the layers in the model, the shape of the output of each of the layers, the batch size, etc.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model.summary()",
"Model: \"sequential\"\n_________________________________________________________________\nLayer (type) Output Shape Param # \n=================================================================\nembedding (Embedding) (32, None, 256) 21248 \n_________________________________________________________________\nlstm (LSTM) (32, None, 1024) 5246976 \n_________________________________________________________________\ndense (Dense) (32, None, 83) 85075 \n=================================================================\nTotal params: 5,353,299\nTrainable params: 5,353,299\nNon-trainable params: 0\n_________________________________________________________________\n"
]
],
[
[
"We can also quickly check the dimensionality of our output, using a sequence length of 100. Note that the model can be run on inputs of any length.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x, y = get_batch(vectorized_songs, seq_length=100, batch_size=32)\npred = model(x)\nprint(\"Input shape: \", x.shape, \" # (batch_size, sequence_length)\")\nprint(\"Prediction shape: \", pred.shape, \"# (batch_size, sequence_length, vocab_size)\")",
"[137772 101304 190219 140042 100205 137561 29279 117461 199245 13999\n 56962 48388 68394 78609 158168 64465 159357 123255 147248 69069\n 70355 100869 41529 137401 130843 184340 133975 28131 105614 27479\n 89478 163448]\n[array([30, 14, 27, 30, 82, 27, 26, 31, 26, 1, 29, 15, 30, 82, 31, 29, 26,\n 29, 1, 31, 29, 31, 26, 82, 2, 0, 27, 14, 26, 59, 1, 27, 30, 30,\n 29, 82, 30, 14, 27, 30, 1, 30, 14, 27, 30, 82, 27, 26, 32, 31, 1,\n 32, 26, 27, 58, 82, 59, 27, 26, 32, 1, 31, 29, 29, 22, 82, 2, 0,\n 26, 82, 59, 14, 60, 61, 1, 62, 61, 60, 59, 82, 61, 27, 27, 14, 1,\n 61, 27, 27, 14, 82, 59, 14, 60, 61, 1, 62, 61, 60, 59, 82]), array([ 0, 38, 22, 28, 0, 37, 22, 13, 11, 20, 0, 36, 22, 26, 1, 38, 64,\n 79, 70, 67, 80, 59, 64, 56, 69, 0, 30, 26, 26, 32, 1, 30, 32, 29,\n 32, 82, 30, 26, 26, 14, 1, 61, 26, 60, 26, 82, 30, 26, 26, 32, 1,\n 30, 29, 30, 31, 82, 32, 14, 27, 32, 1, 59, 32, 27, 32, 22, 82, 2,\n 0, 26, 14, 60, 26, 1, 61, 26, 60, 26, 82, 61, 26, 60, 26, 1, 59,\n 27, 32, 27, 82, 26, 14, 60, 26, 1, 61, 26, 60, 26, 82, 59]), array([60, 82, 59, 14, 27, 1, 27, 58, 59, 82, 58, 14, 26, 1, 26, 27, 58,\n 82, 59, 14, 27, 1, 27, 15, 82, 2, 0, 60, 14, 61, 1, 62, 61, 60,\n 82, 59, 14, 27, 1, 27, 58, 59, 82, 58, 59, 58, 1, 27, 14, 26, 82,\n 27, 14, 30, 1, 30, 15, 22, 82, 0, 0, 49, 22, 14, 19, 0, 45, 22,\n 43, 70, 74, 64, 60, 1, 31, 64, 69, 69, 5, 74, 0, 51, 22, 1, 64,\n 59, 22, 59, 58, 9, 74, 67, 64, 59, 60, 9, 14, 20, 0, 38]), array([ 1, 26, 74, 63, 71, 67, 56, 69, 75, 0, 51, 22, 1, 64, 59, 22, 59,\n 58, 9, 73, 60, 60, 67, 9, 17, 0, 38, 22, 28, 0, 37, 22, 13, 11,\n 20, 0, 36, 22, 30, 1, 38, 64, 69, 70, 73, 0, 27, 30, 30, 14, 1,\n 32, 31, 32, 26, 82, 27, 30, 30, 14, 1, 27, 59, 60, 59, 82, 27, 30,\n 30, 14, 1, 59, 60, 59, 27, 82, 26, 27, 26, 31, 1, 29, 31, 26, 58,\n 22, 82, 2, 0, 27, 15, 26, 1, 32, 15, 26, 82, 27, 32, 32]), array([31, 31, 14, 1, 32, 31, 30, 31, 82, 29, 14, 31, 26, 1, 59, 26, 27,\n 32, 82, 31, 14, 26, 31, 1, 32, 31, 32, 27, 82, 26, 31, 29, 27, 8,\n 1, 26, 8, 27, 8, 28, 30, 82, 2, 0, 29, 31, 31, 14, 1, 32, 31,\n 30, 31, 82, 29, 14, 31, 26, 1, 59, 26, 27, 32, 82, 31, 14, 26, 31,\n 1, 32, 31, 32, 27, 82, 26, 31, 30, 32, 1, 31, 29, 29, 14, 22, 82,\n 2, 0, 61, 59, 59, 14, 1, 62, 14, 56, 62, 82, 61, 59, 59]), array([32, 30, 1, 29, 14, 59, 60, 82, 2, 0, 61, 59, 60, 59, 1, 26, 15,\n 32, 82, 30, 32, 32, 14, 1, 26, 27, 59, 60, 82, 61, 59, 60, 59, 1,\n 58, 26, 26, 32, 82, 30, 31, 32, 30, 1, 29, 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 31,\n 32, 82, 26, 59, 59, 60, 1, 61, 56, 62, 60, 82, 59, 61, 60, 59, 1,\n 58, 26, 26, 31, 82, 32, 15, 26, 1, 32, 30, 30, 14, 82, 60, 59, 58,\n 26, 1, 32, 30, 30, 14, 82, 2, 0, 26, 59, 59, 60, 1, 61]), array([82, 32, 31, 32, 1, 30, 31, 32, 82, 61, 60, 59, 1, 60, 58, 26, 82,\n 32, 30, 29, 1, 29, 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 26, 82, 26, 59, 59, 1, 59,\n 60, 59, 82, 24, 58, 26, 27, 1, 58, 26, 32, 82, 26, 59, 59, 1, 59,\n 60, 59, 82, 24, 58, 26, 27, 1, 58, 14, 26, 82, 2, 0, 26, 59, 59,\n 1, 59, 60, 59, 82, 24, 58, 26, 27, 1, 58, 59, 60, 82, 61, 60, 59,\n 1, 60, 58, 26, 82, 32, 30, 29, 1, 29, 14, 22, 82, 2, 0]), array([82, 60, 15, 61, 1, 60, 59, 27, 26, 82, 27, 59, 60, 61, 1, 62, 60,\n 59, 58, 82, 27, 32, 32, 14, 1, 29, 32, 32, 14, 82, 27, 60, 59, 27,\n 1, 26, 14, 27, 59, 82, 2, 0, 60, 15, 61, 1, 60, 59, 27, 26, 82,\n 27, 59, 60, 61, 1, 62, 15, 56, 82, 57, 62, 56, 61, 1, 62, 61, 60,\n 59, 82, 60, 62, 59, 27, 1, 26, 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 0, 49, 22, 13,\n 16, 19, 0, 45, 22, 33, 76, 62, 63, 64, 60, 1, 45, 73, 56]), array([82, 2, 0, 52, 13, 1, 62, 14, 1, 61, 14, 1, 60, 14, 82, 59, 14,\n 1, 58, 14, 1, 27, 14, 82, 26, 14, 1, 26, 27, 1, 26, 32, 82, 31,\n 14, 1, 32, 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 52, 14, 1, 62, 14, 1, 61, 14, 1,\n 60, 14, 82, 59, 14, 1, 58, 14, 1, 27, 14, 82, 26, 14, 1, 54, 32,\n 26, 1, 27, 58, 82, 59, 16, 82, 53, 2, 0, 58, 27, 82, 26, 14, 1,\n 61, 14, 1, 61, 14, 82, 26, 14, 1, 61, 14, 1, 61, 14, 82]), array([32, 27, 82, 6, 15, 58, 27, 26, 1, 27, 32, 1, 26, 14, 1, 6, 15,\n 29, 30, 31, 82, 2, 0, 32, 26, 1, 6, 15, 32, 31, 30, 1, 29, 32,\n 8, 27, 8, 29, 82, 32, 31, 32, 26, 1, 27, 59, 62, 61, 82, 60, 59,\n 58, 27, 1, 6, 15, 26, 27, 26, 1, 32, 26, 82, 27, 14, 32, 14, 1,\n 32, 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 0, 49, 22, 17, 16, 0, 45, 22, 44, 68, 70,\n 66, 80, 1, 28, 63, 64, 68, 69, 60, 80, 0, 51, 22, 1, 64]), array([58, 82, 59, 61, 60, 1, 59, 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 58, 82, 59, 27, 27,\n 1, 61, 27, 27, 82, 61, 62, 61, 1, 61, 60, 59, 82, 58, 26, 26, 1,\n 60, 26, 26, 82, 56, 54, 62, 56, 1, 60, 59, 58, 82, 2, 0, 59, 27,\n 27, 1, 61, 27, 27, 82, 61, 62, 61, 1, 61, 60, 59, 82, 58, 59, 58,\n 1, 26, 27, 58, 82, 59, 61, 60, 1, 59, 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 0, 49,\n 22, 13, 17, 21, 0, 45, 22, 45, 73, 64, 71, 1, 75, 70, 1]), array([75, 63, 60, 1, 43, 76, 74, 63, 60, 74, 0, 51, 22, 1, 64, 59, 22,\n 59, 58, 9, 65, 64, 62, 9, 13, 12, 16, 0, 38, 22, 18, 11, 20, 0,\n 37, 22, 13, 11, 20, 0, 36, 22, 32, 1, 38, 56, 65, 70, 73, 0, 58,\n 82, 27, 14, 32, 1, 32, 31, 32, 82, 58, 14, 26, 1, 26, 32, 26, 82,\n 27, 14, 32, 1, 32, 31, 32, 82, 58, 26, 32, 1, 31, 32, 26, 82, 2,\n 0, 27, 14, 32, 1, 27, 14, 32, 82, 58, 14, 26, 1, 26, 32]), array([82, 2, 0, 27, 58, 59, 1, 30, 32, 30, 82, 31, 32, 26, 1, 29, 31,\n 29, 82, 32, 31, 30, 1, 29, 27, 8, 29, 82, 32, 15, 1, 32, 14, 22,\n 82, 2, 0, 27, 82, 59, 60, 59, 1, 59, 60, 61, 82, 62, 15, 1, 62,\n 15, 82, 58, 59, 27, 1, 58, 59, 58, 82, 60, 15, 1, 60, 15, 82, 2,\n 0, 59, 58, 27, 1, 58, 14, 26, 82, 27, 58, 59, 1, 29, 14, 29, 82,\n 30, 31, 32, 1, 26, 31, 29, 82, 32, 15, 1, 32, 14, 22, 82]), array([ 1, 26, 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 0, 49, 22, 15, 14, 0, 45, 22, 38, 73,\n 74, 10, 1, 28, 73, 70, 78, 67, 60, 80, 5, 74, 1, 39, 70, 10, 1,\n 13, 0, 51, 22, 1, 64, 59, 22, 59, 58, 9, 71, 70, 67, 66, 56, 9,\n 14, 18, 0, 38, 22, 14, 11, 16, 0, 37, 22, 13, 11, 20, 0, 36, 22,\n 32, 1, 38, 56, 65, 70, 73, 0, 29, 32, 1, 30, 32, 11, 30, 11, 82,\n 29, 32, 1, 30, 32, 11, 30, 11, 82, 29, 32, 1, 26, 32, 11]), array([29, 31, 30, 28, 1, 29, 15, 22, 82, 2, 0, 36, 22, 29, 1, 38, 56,\n 65, 70, 73, 0, 26, 82, 59, 58, 59, 60, 1, 61, 14, 60, 59, 82, 58,\n 59, 60, 61, 1, 62, 14, 61, 60, 82, 59, 58, 59, 60, 1, 61, 14, 60,\n 59, 82, 58, 26, 32, 30, 1, 30, 29, 29, 14, 82, 2, 0, 59, 58, 59,\n 60, 1, 61, 14, 60, 59, 82, 58, 59, 60, 61, 1, 62, 14, 61, 60, 82,\n 61, 62, 61, 59, 1, 60, 61, 60, 59, 82, 58, 26, 32, 30, 1]), array([22, 82, 2, 0, 26, 27, 58, 82, 59, 14, 57, 14, 1, 56, 62, 61, 60,\n 82, 59, 14, 56, 14, 1, 58, 14, 56, 14, 82, 27, 14, 62, 27, 1, 26,\n 27, 58, 59, 82, 60, 58, 27, 26, 1, 59, 14, 59, 61, 82, 2, 0, 60,\n 59, 58, 27, 1, 58, 56, 56, 56, 82, 27, 62, 62, 62, 1, 26, 61, 61,\n 61, 82, 60, 59, 58, 27, 1, 58, 56, 56, 56, 82, 27, 62, 62, 62, 1,\n 57, 62, 57, 62, 82, 2, 0, 56, 61, 56, 61, 1, 60, 59, 58]), array([82, 60, 62, 62, 14, 1, 56, 62, 60, 61, 82, 62, 60, 59, 60, 1, 62,\n 60, 59, 27, 82, 26, 58, 27, 26, 1, 32, 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 0, 49,\n 22, 15, 13, 17, 0, 45, 22, 43, 70, 56, 73, 64, 69, 62, 1, 38, 56,\n 73, 80, 0, 51, 22, 1, 64, 59, 22, 59, 58, 9, 73, 60, 60, 67, 9,\n 14, 21, 15, 0, 38, 22, 28, 0, 37, 22, 13, 11, 20, 0, 36, 22, 29,\n 1, 38, 56, 65, 70, 73, 0, 29, 31, 31, 14, 1, 26, 31, 31]), array([58, 59, 82, 60, 59, 58, 26, 1, 27, 26, 31, 61, 82, 60, 14, 58, 59,\n 1, 60, 59, 58, 26, 82, 27, 59, 58, 26, 1, 27, 26, 31, 61, 82, 2,\n 0, 60, 14, 58, 59, 1, 60, 59, 58, 59, 82, 60, 59, 58, 26, 1, 27,\n 26, 31, 26, 82, 59, 15, 58, 1, 59, 61, 60, 59, 82, 58, 59, 27, 58,\n 1, 26, 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 0, 49, 22, 13, 19, 12, 0, 45, 22, 35,\n 70, 67, 67, 80, 1, 28, 67, 56, 68, 59, 64, 62, 62, 60, 73]), array([45, 22, 39, 64, 69, 60, 1, 41, 70, 64, 69, 75, 74, 1, 75, 70, 1,\n 43, 70, 62, 76, 60, 73, 80, 0, 51, 22, 1, 64, 59, 22, 59, 58, 9,\n 73, 60, 60, 67, 9, 14, 16, 18, 0, 38, 22, 28, 0, 37, 22, 13, 11,\n 20, 0, 36, 22, 29, 1, 38, 56, 65, 70, 73, 0, 31, 30, 82, 29, 14,\n 31, 29, 1, 32, 30, 31, 30, 82, 29, 30, 31, 32, 1, 26, 27, 26, 31,\n 82, 29, 14, 31, 29, 1, 32, 30, 31, 26, 82, 27, 30, 30, 14]), array([32, 8, 14, 22, 82, 52, 14, 1, 32, 29, 27, 8, 29, 1, 32, 8, 16,\n 82, 53, 2, 0, 0, 49, 22, 13, 16, 0, 45, 22, 37, 70, 73, 59, 1,\n 34, 69, 58, 63, 64, 72, 76, 64, 69, 0, 51, 22, 1, 64, 59, 22, 59,\n 58, 9, 70, 58, 56, 73, 70, 67, 56, 69, 9, 21, 0, 38, 22, 15, 11,\n 16, 0, 37, 22, 13, 11, 20, 0, 36, 22, 29, 1, 38, 56, 65, 70, 73,\n 0, 26, 14, 82, 59, 14, 1, 59, 60, 1, 61, 60, 82, 59, 14]), array([ 1, 26, 59, 29, 82, 27, 60, 30, 1, 60, 14, 59, 82, 2, 0, 60, 11,\n 59, 11, 27, 11, 59, 11, 60, 1, 59, 11, 27, 11, 26, 11, 27, 11, 59,\n 82, 27, 11, 26, 11, 32, 11, 26, 11, 27, 11, 32, 11, 1, 26, 31, 29,\n 82, 30, 11, 31, 11, 32, 30, 1, 31, 11, 32, 11, 26, 31, 82, 32, 11,\n 26, 11, 27, 27, 8, 1, 30, 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 0, 49, 22, 13, 19,\n 0, 45, 22, 40, 59, 60, 1, 75, 70, 1, 48, 63, 64, 74, 66]), array([ 1, 60, 59, 27, 59, 82, 60, 26, 26, 14, 1, 60, 59, 27, 58, 82, 59,\n 60, 59, 27, 1, 32, 15, 26, 82, 27, 58, 59, 62, 1, 60, 59, 27, 59,\n 82, 2, 0, 60, 26, 26, 14, 1, 60, 59, 27, 59, 82, 60, 26, 26, 14,\n 1, 60, 59, 27, 58, 82, 59, 14, 60, 61, 1, 62, 56, 56, 62, 82, 62,\n 60, 59, 27, 1, 26, 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 27, 59, 82, 60, 56, 56, 62,\n 1, 56, 14, 62, 56, 82, 57, 14, 62, 57, 1, 56, 57, 62, 60]), array([ 1, 31, 32, 31, 82, 30, 32, 27, 1, 60, 27, 32, 82, 31, 29, 31, 1,\n 26, 32, 31, 82, 2, 0, 30, 32, 27, 1, 32, 27, 60, 82, 27, 60, 62,\n 1, 60, 57, 62, 82, 61, 60, 59, 1, 26, 27, 32, 82, 31, 29, 31, 1,\n 26, 32, 31, 22, 82, 2, 0, 0, 49, 22, 21, 19, 0, 45, 22, 38, 70,\n 70, 69, 58, 70, 64, 69, 0, 51, 22, 1, 64, 59, 22, 59, 58, 9, 65,\n 64, 62, 9, 19, 21, 0, 38, 22, 18, 11, 20, 0, 37, 22, 13]), array([60, 60, 14, 82, 59, 60, 62, 56, 1, 57, 62, 62, 14, 82, 56, 62, 60,\n 59, 1, 60, 56, 62, 60, 82, 2, 0, 59, 60, 62, 56, 1, 57, 62, 62,\n 14, 82, 56, 60, 60, 14, 1, 62, 15, 56, 82, 57, 62, 56, 61, 1, 62,\n 61, 60, 59, 82, 27, 60, 60, 59, 1, 60, 14, 82, 53, 2, 0, 0, 49,\n 22, 14, 14, 16, 0, 45, 22, 38, 58, 29, 60, 73, 68, 70, 75, 75, 5,\n 74, 0, 51, 22, 1, 64, 59, 22, 59, 58, 9, 73, 60, 60, 67]), array([ 1, 27, 14, 59, 27, 82, 26, 27, 59, 60, 1, 61, 62, 61, 60, 82, 2,\n 0, 59, 27, 27, 14, 1, 61, 27, 27, 14, 82, 59, 27, 27, 14, 1, 61,\n 60, 61, 62, 82, 56, 14, 26, 31, 1, 26, 27, 26, 31, 82, 26, 27, 59,\n 60, 1, 61, 62, 61, 60, 82, 53, 2, 0, 59, 14, 61, 59, 1, 60, 61,\n 62, 60, 82, 59, 60, 61, 56, 1, 62, 14, 61, 60, 82, 59, 14, 61, 59,\n 1, 60, 61, 62, 60, 82, 61, 56, 56, 61, 1, 62, 60, 61, 60]), array([ 1, 26, 14, 59, 58, 82, 27, 26, 32, 30, 1, 29, 30, 31, 26, 82, 32,\n 14, 32, 31, 1, 32, 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 0, 49, 22, 15, 13, 0, 45,\n 22, 50, 70, 76, 62, 63, 56, 67, 1, 33, 56, 73, 57, 70, 76, 73, 0,\n 51, 22, 1, 64, 59, 22, 59, 58, 9, 74, 60, 75, 59, 56, 69, 58, 60,\n 9, 15, 14, 0, 38, 22, 28, 82, 0, 37, 22, 13, 11, 20, 0, 36, 22,\n 32, 1, 38, 56, 65, 70, 73, 0, 60, 61, 82, 62, 61, 60, 59]), array([73, 0, 29, 82, 32, 14, 59, 58, 1, 27, 29, 32, 27, 82, 29, 32, 27,\n 59, 1, 60, 26, 26, 27, 82, 32, 14, 59, 58, 1, 27, 58, 59, 60, 82,\n 59, 27, 58, 26, 1, 27, 32, 32, 22, 82, 2, 0, 59, 82, 60, 62, 61,\n 62, 1, 60, 62, 61, 60, 82, 59, 60, 61, 62, 1, 56, 61, 59, 61, 82,\n 60, 62, 61, 62, 1, 60, 61, 62, 56, 82, 57, 62, 56, 61, 1, 62, 60,\n 60, 59, 82, 2, 0, 60, 61, 62, 56, 1, 57, 62, 60, 54, 58]), array([61, 15, 1, 62, 15, 82, 56, 61, 59, 1, 58, 26, 32, 82, 31, 15, 1,\n 32, 30, 28, 82, 29, 30, 29, 1, 29, 14, 82, 53, 2, 0, 0, 49, 22,\n 16, 14, 0, 45, 22, 31, 73, 70, 74, 75, 1, 64, 74, 1, 26, 67, 67,\n 1, 40, 77, 60, 73, 1, 39, 70, 10, 1, 13, 0, 51, 22, 1, 64, 59,\n 22, 59, 58, 9, 65, 64, 62, 9, 15, 18, 0, 38, 22, 18, 11, 20, 0,\n 37, 22, 13, 11, 20, 0, 36, 22, 29, 1, 38, 56, 65, 70, 73]), array([27, 1, 32, 26, 27, 59, 82, 60, 26, 58, 26, 1, 58, 59, 60, 61, 82,\n 62, 60, 59, 27, 1, 60, 26, 26, 62, 82, 2, 0, 60, 26, 58, 26, 1,\n 60, 26, 58, 26, 82, 59, 54, 58, 59, 27, 1, 32, 26, 27, 59, 82, 58,\n 26, 59, 27, 1, 58, 59, 60, 61, 82, 62, 60, 59, 27, 1, 60, 26, 26,\n 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 56, 60, 54, 58, 60, 1, 56, 60, 58, 60, 82, 62,\n 59, 27, 59, 1, 62, 59, 27, 59, 82, 56, 60, 54, 58, 60, 1]), array([14, 24, 58, 82, 2, 0, 27, 32, 27, 1, 27, 58, 59, 82, 26, 31, 29,\n 1, 29, 31, 26, 82, 59, 58, 59, 1, 60, 56, 62, 82, 61, 59, 58, 1,\n 59, 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 0, 49, 22, 16, 12, 0, 45, 22, 31, 73, 56,\n 63, 60, 73, 5, 74, 0, 51, 22, 1, 64, 59, 22, 59, 58, 9, 65, 64,\n 62, 9, 15, 16, 0, 38, 22, 18, 11, 20, 0, 37, 22, 13, 11, 20, 0,\n 36, 22, 29, 1, 38, 64, 79, 70, 67, 80, 59, 64, 56, 69, 0]), array([62, 82, 61, 59, 59, 14, 1, 61, 59, 56, 59, 82, 61, 56, 59, 61, 1,\n 56, 14, 62, 61, 82, 62, 60, 60, 14, 1, 62, 60, 57, 60, 82, 62, 57,\n 60, 62, 1, 57, 14, 56, 62, 82, 2, 0, 61, 59, 59, 14, 1, 61, 59,\n 56, 59, 82, 59, 58, 26, 27, 1, 58, 14, 27, 58, 82, 59, 27, 58, 26,\n 1, 27, 32, 32, 58, 82, 26, 27, 58, 26, 1, 59, 14, 22, 82, 2, 0,\n 0, 49, 22, 15, 13, 0, 45, 22, 28, 56, 57, 64, 69, 1, 33]), array([59, 1, 26, 59, 61, 60, 82, 59, 60, 61, 62, 1, 56, 61, 59, 62, 82,\n 61, 56, 61, 59, 1, 61, 56, 61, 59, 82, 27, 62, 60, 58, 1, 59, 14,\n 22, 82, 2, 0, 58, 59, 82, 60, 26, 61, 26, 1, 62, 26, 56, 26, 82,\n 61, 26, 56, 61, 1, 62, 61, 60, 59, 82, 26, 26, 27, 26, 1, 58, 26,\n 59, 26, 82, 60, 61, 60, 59, 1, 58, 26, 27, 58, 82, 2, 0, 59, 59,\n 60, 59, 1, 61, 59, 62, 59, 82, 61, 59, 56, 61, 1, 62, 61])]\n[array([14, 27, 30, 82, 27, 26, 31, 26, 1, 29, 15, 30, 82, 31, 29, 26, 29,\n 1, 31, 29, 31, 26, 82, 2, 0, 27, 14, 26, 59, 1, 27, 30, 30, 29,\n 82, 30, 14, 27, 30, 1, 30, 14, 27, 30, 82, 27, 26, 32, 31, 1, 32,\n 26, 27, 58, 82, 59, 27, 26, 32, 1, 31, 29, 29, 22, 82, 2, 0, 26,\n 82, 59, 14, 60, 61, 1, 62, 61, 60, 59, 82, 61, 27, 27, 14, 1, 61,\n 27, 27, 14, 82, 59, 14, 60, 61, 1, 62, 61, 60, 59, 82, 58]), array([38, 22, 28, 0, 37, 22, 13, 11, 20, 0, 36, 22, 26, 1, 38, 64, 79,\n 70, 67, 80, 59, 64, 56, 69, 0, 30, 26, 26, 32, 1, 30, 32, 29, 32,\n 82, 30, 26, 26, 14, 1, 61, 26, 60, 26, 82, 30, 26, 26, 32, 1, 30,\n 29, 30, 31, 82, 32, 14, 27, 32, 1, 59, 32, 27, 32, 22, 82, 2, 0,\n 26, 14, 60, 26, 1, 61, 26, 60, 26, 82, 61, 26, 60, 26, 1, 59, 27,\n 32, 27, 82, 26, 14, 60, 26, 1, 61, 26, 60, 26, 82, 59, 58]), array([82, 59, 14, 27, 1, 27, 58, 59, 82, 58, 14, 26, 1, 26, 27, 58, 82,\n 59, 14, 27, 1, 27, 15, 82, 2, 0, 60, 14, 61, 1, 62, 61, 60, 82,\n 59, 14, 27, 1, 27, 58, 59, 82, 58, 59, 58, 1, 27, 14, 26, 82, 27,\n 14, 30, 1, 30, 15, 22, 82, 0, 0, 49, 22, 14, 19, 0, 45, 22, 43,\n 70, 74, 64, 60, 1, 31, 64, 69, 69, 5, 74, 0, 51, 22, 1, 64, 59,\n 22, 59, 58, 9, 74, 67, 64, 59, 60, 9, 14, 20, 0, 38, 22]), array([26, 74, 63, 71, 67, 56, 69, 75, 0, 51, 22, 1, 64, 59, 22, 59, 58,\n 9, 73, 60, 60, 67, 9, 17, 0, 38, 22, 28, 0, 37, 22, 13, 11, 20,\n 0, 36, 22, 30, 1, 38, 64, 69, 70, 73, 0, 27, 30, 30, 14, 1, 32,\n 31, 32, 26, 82, 27, 30, 30, 14, 1, 27, 59, 60, 59, 82, 27, 30, 30,\n 14, 1, 59, 60, 59, 27, 82, 26, 27, 26, 31, 1, 29, 31, 26, 58, 22,\n 82, 2, 0, 27, 15, 26, 1, 32, 15, 26, 82, 27, 32, 32, 14]), array([31, 14, 1, 32, 31, 30, 31, 82, 29, 14, 31, 26, 1, 59, 26, 27, 32,\n 82, 31, 14, 26, 31, 1, 32, 31, 32, 27, 82, 26, 31, 29, 27, 8, 1,\n 26, 8, 27, 8, 28, 30, 82, 2, 0, 29, 31, 31, 14, 1, 32, 31, 30,\n 31, 82, 29, 14, 31, 26, 1, 59, 26, 27, 32, 82, 31, 14, 26, 31, 1,\n 32, 31, 32, 27, 82, 26, 31, 30, 32, 1, 31, 29, 29, 14, 22, 82, 2,\n 0, 61, 59, 59, 14, 1, 62, 14, 56, 62, 82, 61, 59, 59, 14]), array([30, 1, 29, 14, 59, 60, 82, 2, 0, 61, 59, 60, 59, 1, 26, 15, 32,\n 82, 30, 32, 32, 14, 1, 26, 27, 59, 60, 82, 61, 59, 60, 59, 1, 58,\n 26, 26, 32, 82, 30, 31, 32, 30, 1, 29, 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 31, 32,\n 82, 26, 59, 59, 60, 1, 61, 56, 62, 60, 82, 59, 61, 60, 59, 1, 58,\n 26, 26, 31, 82, 32, 15, 26, 1, 32, 30, 30, 14, 82, 60, 59, 58, 26,\n 1, 32, 30, 30, 14, 82, 2, 0, 26, 59, 59, 60, 1, 61, 56]), array([32, 31, 32, 1, 30, 31, 32, 82, 61, 60, 59, 1, 60, 58, 26, 82, 32,\n 30, 29, 1, 29, 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 26, 82, 26, 59, 59, 1, 59, 60,\n 59, 82, 24, 58, 26, 27, 1, 58, 26, 32, 82, 26, 59, 59, 1, 59, 60,\n 59, 82, 24, 58, 26, 27, 1, 58, 14, 26, 82, 2, 0, 26, 59, 59, 1,\n 59, 60, 59, 82, 24, 58, 26, 27, 1, 58, 59, 60, 82, 61, 60, 59, 1,\n 60, 58, 26, 82, 32, 30, 29, 1, 29, 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 0]), array([60, 15, 61, 1, 60, 59, 27, 26, 82, 27, 59, 60, 61, 1, 62, 60, 59,\n 58, 82, 27, 32, 32, 14, 1, 29, 32, 32, 14, 82, 27, 60, 59, 27, 1,\n 26, 14, 27, 59, 82, 2, 0, 60, 15, 61, 1, 60, 59, 27, 26, 82, 27,\n 59, 60, 61, 1, 62, 15, 56, 82, 57, 62, 56, 61, 1, 62, 61, 60, 59,\n 82, 60, 62, 59, 27, 1, 26, 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 0, 49, 22, 13, 16,\n 19, 0, 45, 22, 33, 76, 62, 63, 64, 60, 1, 45, 73, 56, 77]), array([ 2, 0, 52, 13, 1, 62, 14, 1, 61, 14, 1, 60, 14, 82, 59, 14, 1,\n 58, 14, 1, 27, 14, 82, 26, 14, 1, 26, 27, 1, 26, 32, 82, 31, 14,\n 1, 32, 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 52, 14, 1, 62, 14, 1, 61, 14, 1, 60,\n 14, 82, 59, 14, 1, 58, 14, 1, 27, 14, 82, 26, 14, 1, 54, 32, 26,\n 1, 27, 58, 82, 59, 16, 82, 53, 2, 0, 58, 27, 82, 26, 14, 1, 61,\n 14, 1, 61, 14, 82, 26, 14, 1, 61, 14, 1, 61, 14, 82, 26]), array([27, 82, 6, 15, 58, 27, 26, 1, 27, 32, 1, 26, 14, 1, 6, 15, 29,\n 30, 31, 82, 2, 0, 32, 26, 1, 6, 15, 32, 31, 30, 1, 29, 32, 8,\n 27, 8, 29, 82, 32, 31, 32, 26, 1, 27, 59, 62, 61, 82, 60, 59, 58,\n 27, 1, 6, 15, 26, 27, 26, 1, 32, 26, 82, 27, 14, 32, 14, 1, 32,\n 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 0, 49, 22, 17, 16, 0, 45, 22, 44, 68, 70, 66,\n 80, 1, 28, 63, 64, 68, 69, 60, 80, 0, 51, 22, 1, 64, 59]), array([82, 59, 61, 60, 1, 59, 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 58, 82, 59, 27, 27, 1,\n 61, 27, 27, 82, 61, 62, 61, 1, 61, 60, 59, 82, 58, 26, 26, 1, 60,\n 26, 26, 82, 56, 54, 62, 56, 1, 60, 59, 58, 82, 2, 0, 59, 27, 27,\n 1, 61, 27, 27, 82, 61, 62, 61, 1, 61, 60, 59, 82, 58, 59, 58, 1,\n 26, 27, 58, 82, 59, 61, 60, 1, 59, 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 0, 49, 22,\n 13, 17, 21, 0, 45, 22, 45, 73, 64, 71, 1, 75, 70, 1, 26]), array([63, 60, 1, 43, 76, 74, 63, 60, 74, 0, 51, 22, 1, 64, 59, 22, 59,\n 58, 9, 65, 64, 62, 9, 13, 12, 16, 0, 38, 22, 18, 11, 20, 0, 37,\n 22, 13, 11, 20, 0, 36, 22, 32, 1, 38, 56, 65, 70, 73, 0, 58, 82,\n 27, 14, 32, 1, 32, 31, 32, 82, 58, 14, 26, 1, 26, 32, 26, 82, 27,\n 14, 32, 1, 32, 31, 32, 82, 58, 26, 32, 1, 31, 32, 26, 82, 2, 0,\n 27, 14, 32, 1, 27, 14, 32, 82, 58, 14, 26, 1, 26, 32, 26]), array([ 2, 0, 27, 58, 59, 1, 30, 32, 30, 82, 31, 32, 26, 1, 29, 31, 29,\n 82, 32, 31, 30, 1, 29, 27, 8, 29, 82, 32, 15, 1, 32, 14, 22, 82,\n 2, 0, 27, 82, 59, 60, 59, 1, 59, 60, 61, 82, 62, 15, 1, 62, 15,\n 82, 58, 59, 27, 1, 58, 59, 58, 82, 60, 15, 1, 60, 15, 82, 2, 0,\n 59, 58, 27, 1, 58, 14, 26, 82, 27, 58, 59, 1, 29, 14, 29, 82, 30,\n 31, 32, 1, 26, 31, 29, 82, 32, 15, 1, 32, 14, 22, 82, 2]), array([26, 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 0, 49, 22, 15, 14, 0, 45, 22, 38, 73, 74,\n 10, 1, 28, 73, 70, 78, 67, 60, 80, 5, 74, 1, 39, 70, 10, 1, 13,\n 0, 51, 22, 1, 64, 59, 22, 59, 58, 9, 71, 70, 67, 66, 56, 9, 14,\n 18, 0, 38, 22, 14, 11, 16, 0, 37, 22, 13, 11, 20, 0, 36, 22, 32,\n 1, 38, 56, 65, 70, 73, 0, 29, 32, 1, 30, 32, 11, 30, 11, 82, 29,\n 32, 1, 30, 32, 11, 30, 11, 82, 29, 32, 1, 26, 32, 11, 26]), array([31, 30, 28, 1, 29, 15, 22, 82, 2, 0, 36, 22, 29, 1, 38, 56, 65,\n 70, 73, 0, 26, 82, 59, 58, 59, 60, 1, 61, 14, 60, 59, 82, 58, 59,\n 60, 61, 1, 62, 14, 61, 60, 82, 59, 58, 59, 60, 1, 61, 14, 60, 59,\n 82, 58, 26, 32, 30, 1, 30, 29, 29, 14, 82, 2, 0, 59, 58, 59, 60,\n 1, 61, 14, 60, 59, 82, 58, 59, 60, 61, 1, 62, 14, 61, 60, 82, 61,\n 62, 61, 59, 1, 60, 61, 60, 59, 82, 58, 26, 32, 30, 1, 30]), array([82, 2, 0, 26, 27, 58, 82, 59, 14, 57, 14, 1, 56, 62, 61, 60, 82,\n 59, 14, 56, 14, 1, 58, 14, 56, 14, 82, 27, 14, 62, 27, 1, 26, 27,\n 58, 59, 82, 60, 58, 27, 26, 1, 59, 14, 59, 61, 82, 2, 0, 60, 59,\n 58, 27, 1, 58, 56, 56, 56, 82, 27, 62, 62, 62, 1, 26, 61, 61, 61,\n 82, 60, 59, 58, 27, 1, 58, 56, 56, 56, 82, 27, 62, 62, 62, 1, 57,\n 62, 57, 62, 82, 2, 0, 56, 61, 56, 61, 1, 60, 59, 58, 27]), array([60, 62, 62, 14, 1, 56, 62, 60, 61, 82, 62, 60, 59, 60, 1, 62, 60,\n 59, 27, 82, 26, 58, 27, 26, 1, 32, 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 0, 49, 22,\n 15, 13, 17, 0, 45, 22, 43, 70, 56, 73, 64, 69, 62, 1, 38, 56, 73,\n 80, 0, 51, 22, 1, 64, 59, 22, 59, 58, 9, 73, 60, 60, 67, 9, 14,\n 21, 15, 0, 38, 22, 28, 0, 37, 22, 13, 11, 20, 0, 36, 22, 29, 1,\n 38, 56, 65, 70, 73, 0, 29, 31, 31, 14, 1, 26, 31, 31, 14]), array([59, 82, 60, 59, 58, 26, 1, 27, 26, 31, 61, 82, 60, 14, 58, 59, 1,\n 60, 59, 58, 26, 82, 27, 59, 58, 26, 1, 27, 26, 31, 61, 82, 2, 0,\n 60, 14, 58, 59, 1, 60, 59, 58, 59, 82, 60, 59, 58, 26, 1, 27, 26,\n 31, 26, 82, 59, 15, 58, 1, 59, 61, 60, 59, 82, 58, 59, 27, 58, 1,\n 26, 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 0, 49, 22, 13, 19, 12, 0, 45, 22, 35, 70,\n 67, 67, 80, 1, 28, 67, 56, 68, 59, 64, 62, 62, 60, 73, 74]), array([22, 39, 64, 69, 60, 1, 41, 70, 64, 69, 75, 74, 1, 75, 70, 1, 43,\n 70, 62, 76, 60, 73, 80, 0, 51, 22, 1, 64, 59, 22, 59, 58, 9, 73,\n 60, 60, 67, 9, 14, 16, 18, 0, 38, 22, 28, 0, 37, 22, 13, 11, 20,\n 0, 36, 22, 29, 1, 38, 56, 65, 70, 73, 0, 31, 30, 82, 29, 14, 31,\n 29, 1, 32, 30, 31, 30, 82, 29, 30, 31, 32, 1, 26, 27, 26, 31, 82,\n 29, 14, 31, 29, 1, 32, 30, 31, 26, 82, 27, 30, 30, 14, 1]), array([ 8, 14, 22, 82, 52, 14, 1, 32, 29, 27, 8, 29, 1, 32, 8, 16, 82,\n 53, 2, 0, 0, 49, 22, 13, 16, 0, 45, 22, 37, 70, 73, 59, 1, 34,\n 69, 58, 63, 64, 72, 76, 64, 69, 0, 51, 22, 1, 64, 59, 22, 59, 58,\n 9, 70, 58, 56, 73, 70, 67, 56, 69, 9, 21, 0, 38, 22, 15, 11, 16,\n 0, 37, 22, 13, 11, 20, 0, 36, 22, 29, 1, 38, 56, 65, 70, 73, 0,\n 26, 14, 82, 59, 14, 1, 59, 60, 1, 61, 60, 82, 59, 14, 1]), array([26, 59, 29, 82, 27, 60, 30, 1, 60, 14, 59, 82, 2, 0, 60, 11, 59,\n 11, 27, 11, 59, 11, 60, 1, 59, 11, 27, 11, 26, 11, 27, 11, 59, 82,\n 27, 11, 26, 11, 32, 11, 26, 11, 27, 11, 32, 11, 1, 26, 31, 29, 82,\n 30, 11, 31, 11, 32, 30, 1, 31, 11, 32, 11, 26, 31, 82, 32, 11, 26,\n 11, 27, 27, 8, 1, 30, 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 0, 49, 22, 13, 19, 0,\n 45, 22, 40, 59, 60, 1, 75, 70, 1, 48, 63, 64, 74, 66, 60]), array([60, 59, 27, 59, 82, 60, 26, 26, 14, 1, 60, 59, 27, 58, 82, 59, 60,\n 59, 27, 1, 32, 15, 26, 82, 27, 58, 59, 62, 1, 60, 59, 27, 59, 82,\n 2, 0, 60, 26, 26, 14, 1, 60, 59, 27, 59, 82, 60, 26, 26, 14, 1,\n 60, 59, 27, 58, 82, 59, 14, 60, 61, 1, 62, 56, 56, 62, 82, 62, 60,\n 59, 27, 1, 26, 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 27, 59, 82, 60, 56, 56, 62, 1,\n 56, 14, 62, 56, 82, 57, 14, 62, 57, 1, 56, 57, 62, 60, 82]), array([31, 32, 31, 82, 30, 32, 27, 1, 60, 27, 32, 82, 31, 29, 31, 1, 26,\n 32, 31, 82, 2, 0, 30, 32, 27, 1, 32, 27, 60, 82, 27, 60, 62, 1,\n 60, 57, 62, 82, 61, 60, 59, 1, 26, 27, 32, 82, 31, 29, 31, 1, 26,\n 32, 31, 22, 82, 2, 0, 0, 49, 22, 21, 19, 0, 45, 22, 38, 70, 70,\n 69, 58, 70, 64, 69, 0, 51, 22, 1, 64, 59, 22, 59, 58, 9, 65, 64,\n 62, 9, 19, 21, 0, 38, 22, 18, 11, 20, 0, 37, 22, 13, 11]), array([60, 14, 82, 59, 60, 62, 56, 1, 57, 62, 62, 14, 82, 56, 62, 60, 59,\n 1, 60, 56, 62, 60, 82, 2, 0, 59, 60, 62, 56, 1, 57, 62, 62, 14,\n 82, 56, 60, 60, 14, 1, 62, 15, 56, 82, 57, 62, 56, 61, 1, 62, 61,\n 60, 59, 82, 27, 60, 60, 59, 1, 60, 14, 82, 53, 2, 0, 0, 49, 22,\n 14, 14, 16, 0, 45, 22, 38, 58, 29, 60, 73, 68, 70, 75, 75, 5, 74,\n 0, 51, 22, 1, 64, 59, 22, 59, 58, 9, 73, 60, 60, 67, 9]), array([27, 14, 59, 27, 82, 26, 27, 59, 60, 1, 61, 62, 61, 60, 82, 2, 0,\n 59, 27, 27, 14, 1, 61, 27, 27, 14, 82, 59, 27, 27, 14, 1, 61, 60,\n 61, 62, 82, 56, 14, 26, 31, 1, 26, 27, 26, 31, 82, 26, 27, 59, 60,\n 1, 61, 62, 61, 60, 82, 53, 2, 0, 59, 14, 61, 59, 1, 60, 61, 62,\n 60, 82, 59, 60, 61, 56, 1, 62, 14, 61, 60, 82, 59, 14, 61, 59, 1,\n 60, 61, 62, 60, 82, 61, 56, 56, 61, 1, 62, 60, 61, 60, 82]), array([26, 14, 59, 58, 82, 27, 26, 32, 30, 1, 29, 30, 31, 26, 82, 32, 14,\n 32, 31, 1, 32, 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 0, 49, 22, 15, 13, 0, 45, 22,\n 50, 70, 76, 62, 63, 56, 67, 1, 33, 56, 73, 57, 70, 76, 73, 0, 51,\n 22, 1, 64, 59, 22, 59, 58, 9, 74, 60, 75, 59, 56, 69, 58, 60, 9,\n 15, 14, 0, 38, 22, 28, 82, 0, 37, 22, 13, 11, 20, 0, 36, 22, 32,\n 1, 38, 56, 65, 70, 73, 0, 60, 61, 82, 62, 61, 60, 59, 1]), array([ 0, 29, 82, 32, 14, 59, 58, 1, 27, 29, 32, 27, 82, 29, 32, 27, 59,\n 1, 60, 26, 26, 27, 82, 32, 14, 59, 58, 1, 27, 58, 59, 60, 82, 59,\n 27, 58, 26, 1, 27, 32, 32, 22, 82, 2, 0, 59, 82, 60, 62, 61, 62,\n 1, 60, 62, 61, 60, 82, 59, 60, 61, 62, 1, 56, 61, 59, 61, 82, 60,\n 62, 61, 62, 1, 60, 61, 62, 56, 82, 57, 62, 56, 61, 1, 62, 60, 60,\n 59, 82, 2, 0, 60, 61, 62, 56, 1, 57, 62, 60, 54, 58, 82]), array([15, 1, 62, 15, 82, 56, 61, 59, 1, 58, 26, 32, 82, 31, 15, 1, 32,\n 30, 28, 82, 29, 30, 29, 1, 29, 14, 82, 53, 2, 0, 0, 49, 22, 16,\n 14, 0, 45, 22, 31, 73, 70, 74, 75, 1, 64, 74, 1, 26, 67, 67, 1,\n 40, 77, 60, 73, 1, 39, 70, 10, 1, 13, 0, 51, 22, 1, 64, 59, 22,\n 59, 58, 9, 65, 64, 62, 9, 15, 18, 0, 38, 22, 18, 11, 20, 0, 37,\n 22, 13, 11, 20, 0, 36, 22, 29, 1, 38, 56, 65, 70, 73, 0]), array([ 1, 32, 26, 27, 59, 82, 60, 26, 58, 26, 1, 58, 59, 60, 61, 82, 62,\n 60, 59, 27, 1, 60, 26, 26, 62, 82, 2, 0, 60, 26, 58, 26, 1, 60,\n 26, 58, 26, 82, 59, 54, 58, 59, 27, 1, 32, 26, 27, 59, 82, 58, 26,\n 59, 27, 1, 58, 59, 60, 61, 82, 62, 60, 59, 27, 1, 60, 26, 26, 14,\n 22, 82, 2, 0, 56, 60, 54, 58, 60, 1, 56, 60, 58, 60, 82, 62, 59,\n 27, 59, 1, 62, 59, 27, 59, 82, 56, 60, 54, 58, 60, 1, 56]), array([24, 58, 82, 2, 0, 27, 32, 27, 1, 27, 58, 59, 82, 26, 31, 29, 1,\n 29, 31, 26, 82, 59, 58, 59, 1, 60, 56, 62, 82, 61, 59, 58, 1, 59,\n 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 0, 49, 22, 16, 12, 0, 45, 22, 31, 73, 56, 63,\n 60, 73, 5, 74, 0, 51, 22, 1, 64, 59, 22, 59, 58, 9, 65, 64, 62,\n 9, 15, 16, 0, 38, 22, 18, 11, 20, 0, 37, 22, 13, 11, 20, 0, 36,\n 22, 29, 1, 38, 64, 79, 70, 67, 80, 59, 64, 56, 69, 0, 30]), array([82, 61, 59, 59, 14, 1, 61, 59, 56, 59, 82, 61, 56, 59, 61, 1, 56,\n 14, 62, 61, 82, 62, 60, 60, 14, 1, 62, 60, 57, 60, 82, 62, 57, 60,\n 62, 1, 57, 14, 56, 62, 82, 2, 0, 61, 59, 59, 14, 1, 61, 59, 56,\n 59, 82, 59, 58, 26, 27, 1, 58, 14, 27, 58, 82, 59, 27, 58, 26, 1,\n 27, 32, 32, 58, 82, 26, 27, 58, 26, 1, 59, 14, 22, 82, 2, 0, 0,\n 49, 22, 15, 13, 0, 45, 22, 28, 56, 57, 64, 69, 1, 33, 76]), array([ 1, 26, 59, 61, 60, 82, 59, 60, 61, 62, 1, 56, 61, 59, 62, 82, 61,\n 56, 61, 59, 1, 61, 56, 61, 59, 82, 27, 62, 60, 58, 1, 59, 14, 22,\n 82, 2, 0, 58, 59, 82, 60, 26, 61, 26, 1, 62, 26, 56, 26, 82, 61,\n 26, 56, 61, 1, 62, 61, 60, 59, 82, 26, 26, 27, 26, 1, 58, 26, 59,\n 26, 82, 60, 61, 60, 59, 1, 58, 26, 27, 58, 82, 2, 0, 59, 59, 60,\n 59, 1, 61, 59, 62, 59, 82, 61, 59, 56, 61, 1, 62, 61, 60])]\nInput shape: (32, 100) # (batch_size, sequence_length)\nPrediction shape: (32, 100, 83) # (batch_size, sequence_length, vocab_size)\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Predictions from the untrained model\n\nLet's take a look at what our untrained model is predicting.\n\nTo get actual predictions from the model, we sample from the output distribution, which is defined by a `softmax` over our character vocabulary. This will give us actual character indices. This means we are using a [categorical distribution](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Categorical_distribution) to sample over the example prediction. This gives a prediction of the next character (specifically its index) at each timestep.\n\nNote here that we sample from this probability distribution, as opposed to simply taking the `argmax`, which can cause the model to get stuck in a loop.\n\nLet's try this sampling out for the first example in the batch.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sampled_indices = tf.random.categorical(pred[0], num_samples=1)\nsampled_indices = tf.squeeze(sampled_indices,axis=-1).numpy()\nsampled_indices",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can now decode these to see the text predicted by the untrained model:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(\"Input: \\n\", repr(\"\".join(idx2char[x[0]])))\nprint()\nprint(\"Next Char Predictions: \\n\", repr(\"\".join(idx2char[sampled_indices])))",
"Input: \n 'E2BE|BAFA D3E|FDAD FDFA|!\\nB2Ad BEED|E2BE E2BE|BAGF GABc|dBAG FDD:|!\\nA|d2ef gfed|fBB2 fBB2|d2ef gfed|'\n\nNext Char Predictions: \n '[7oVbNNb5aiw\\'.0P^jeYt77#^8SfXhsPl-K#cctXFbNAlZ=p.hcTwSDr8OoN!sCLTZ>vpiN\\n>0r81Xg M\\n8I-rmtZR|qV\"VtV-u>'\n"
]
],
[
[
"As you can see, the text predicted by the untrained model is pretty nonsensical! How can we do better? We can train the network!",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 2.5 Training the model: loss and training operations\n\nNow it's time to train the model!\n\nAt this point, we can think of our next character prediction problem as a standard classification problem. Given the previous state of the RNN, as well as the input at a given time step, we want to predict the class of the next character -- that is, to actually predict the next character. \n\nTo train our model on this classification task, we can use a form of the `crossentropy` loss (negative log likelihood loss). Specifically, we will use the [`sparse_categorical_crossentropy`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/losses/sparse_categorical_crossentropy) loss, as it utilizes integer targets for categorical classification tasks. We will want to compute the loss using the true targets -- the `labels` -- and the predicted targets -- the `logits`.\n\nLet's first compute the loss using our example predictions from the untrained model: ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Defining the loss function ###\n\n'''TODO: define the loss function to compute and return the loss between\n the true labels and predictions (logits). Set the argument from_logits=True.'''\ndef compute_loss(labels, logits):\n loss = tf.keras.losses.sparse_categorical_crossentropy(labels, logits, from_logits=True) # TODO\n return loss\n\n'''TODO: compute the loss using the true next characters from the example batch \n and the predictions from the untrained model several cells above'''\nexample_batch_loss = compute_loss(y, pred) # TODO\n\nprint(\"Prediction shape: \", pred.shape, \" # (batch_size, sequence_length, vocab_size)\") \nprint(\"scalar_loss: \", example_batch_loss.numpy().mean())",
"Prediction shape: (32, 100, 83) # (batch_size, sequence_length, vocab_size)\nscalar_loss: 4.4186344\n"
]
],
[
[
"Let's start by defining some hyperparameters for training the model. To start, we have provided some reasonable values for some of the parameters. It is up to you to use what we've learned in class to help optimize the parameter selection here!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Hyperparameter setting and optimization ###\n\n# Optimization parameters:\nnum_training_iterations = 2000 # Increase this to train longer\nbatch_size = 4 # Experiment between 1 and 64\nseq_length = 100 # Experiment between 50 and 500\nlearning_rate = 5e-3 # Experiment between 1e-5 and 1e-1\n\n# Model parameters: \nvocab_size = len(vocab)\nembedding_dim = 256 \nrnn_units = 1024 # Experiment between 1 and 2048\n\n# Checkpoint location: \ncheckpoint_dir = './training_checkpoints'\ncheckpoint_prefix = os.path.join(checkpoint_dir, \"my_ckpt\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now, we are ready to define our training operation -- the optimizer and duration of training -- and use this function to train the model. You will experiment with the choice of optimizer and the duration for which you train your models, and see how these changes affect the network's output. Some optimizers you may like to try are [`Adam`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/optimizers/Adam?version=stable) and [`Adagrad`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/optimizers/Adagrad?version=stable).\n\nFirst, we will instantiate a new model and an optimizer. Then, we will use the [`tf.GradientTape`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/GradientTape) method to perform the backpropagation operations. \n\nWe will also generate a print-out of the model's progress through training, which will help us easily visualize whether or not we are minimizing the loss.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Define optimizer and training operation ###\n\n'''TODO: instantiate a new model for training using the `build_model`\n function and the hyperparameters created above.'''\nmodel = build_model(vocab_size, embedding_dim, rnn_units, batch_size)\n\n'''TODO: instantiate an optimizer with its learning rate.\n Checkout the tensorflow website for a list of supported optimizers.\n https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/optimizers/\n Try using the Adam optimizer to start.'''\noptimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=learning_rate, name=\"Adam\")\nprint(model.trainable_variables)\[email protected]\ndef train_step(x, y): \n # Use tf.GradientTape()\n with tf.GradientTape() as tape:\n \n '''TODO: feed the current input into the model and generate predictions'''\n y_hat = model(x)\n \n '''TODO: compute the loss!'''\n loss = compute_loss(y, y_hat)\n\n # Now, compute the gradients \n '''TODO: complete the function call for gradient computation. \n Remember that we want the gradient of the loss with respect all \n of the model parameters. \n HINT: use `model.trainable_variables` to get a list of all model\n parameters.'''\n grads = tape.gradient(loss, model.trainable_variables)\n \n # Apply the gradients to the optimizer so it can update the model accordingly\n optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, model.trainable_variables))\n return loss\n\n##################\n# Begin training!#\n##################\n\nhistory = []\nplotter = mdl.util.PeriodicPlotter(sec=2, xlabel='Iterations', ylabel='Loss')\nif hasattr(tqdm, '_instances'): tqdm._instances.clear() # clear if it exists\n\nfor iter in tqdm(range(num_training_iterations)):\n\n # Grab a batch and propagate it through the network\n x_batch, y_batch = get_batch(vectorized_songs, seq_length, batch_size)\n loss = train_step(x_batch, y_batch)\n\n # Update the progress bar\n history.append(loss.numpy().mean())\n plotter.plot(history)\n\n # Update the model with the changed weights!\n if iter % 100 == 0: \n model.save_weights(checkpoint_prefix)\n \n# Save the trained model and the weights\nmodel.save_weights(checkpoint_prefix)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 2.6 Generate music using the RNN model\n\nNow, we can use our trained RNN model to generate some music! When generating music, we'll have to feed the model some sort of seed to get it started (because it can't predict anything without something to start with!).\n\nOnce we have a generated seed, we can then iteratively predict each successive character (remember, we are using the ABC representation for our music) using our trained RNN. More specifically, recall that our RNN outputs a `softmax` over possible successive characters. For inference, we iteratively sample from these distributions, and then use our samples to encode a generated song in the ABC format.\n\nThen, all we have to do is write it to a file and listen!",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Restore the latest checkpoint\n\nTo keep this inference step simple, we will use a batch size of 1. Because of how the RNN state is passed from timestep to timestep, the model will only be able to accept a fixed batch size once it is built. \n\nTo run the model with a different `batch_size`, we'll need to rebuild the model and restore the weights from the latest checkpoint, i.e., the weights after the last checkpoint during training:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"'''TODO: Rebuild the model using a batch_size=1'''\nmodel = build_model(vocab_size, embedding_dim, rnn_units, batch_size=1)\n\n# Restore the model weights for the last checkpoint after training\nmodel.load_weights(tf.train.latest_checkpoint(checkpoint_dir))\nmodel.build(tf.TensorShape([1, None]))\n\nmodel.summary()",
"Model: \"sequential_6\"\n_________________________________________________________________\nLayer (type) Output Shape Param # \n=================================================================\nembedding_6 (Embedding) (1, None, 256) 21248 \n_________________________________________________________________\nlstm_6 (LSTM) (1, None, 1024) 5246976 \n_________________________________________________________________\ndense_6 (Dense) (1, None, 83) 85075 \n=================================================================\nTotal params: 5,353,299\nTrainable params: 5,353,299\nNon-trainable params: 0\n_________________________________________________________________\n"
]
],
[
[
"Notice that we have fed in a fixed `batch_size` of 1 for inference.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### The prediction procedure\n\nNow, we're ready to write the code to generate text in the ABC music format:\n\n* Initialize a \"seed\" start string and the RNN state, and set the number of characters we want to generate.\n\n* Use the start string and the RNN state to obtain the probability distribution over the next predicted character.\n\n* Sample from multinomial distribution to calculate the index of the predicted character. This predicted character is then used as the next input to the model.\n\n* At each time step, the updated RNN state is fed back into the model, so that it now has more context in making the next prediction. After predicting the next character, the updated RNN states are again fed back into the model, which is how it learns sequence dependencies in the data, as it gets more information from the previous predictions.\n\n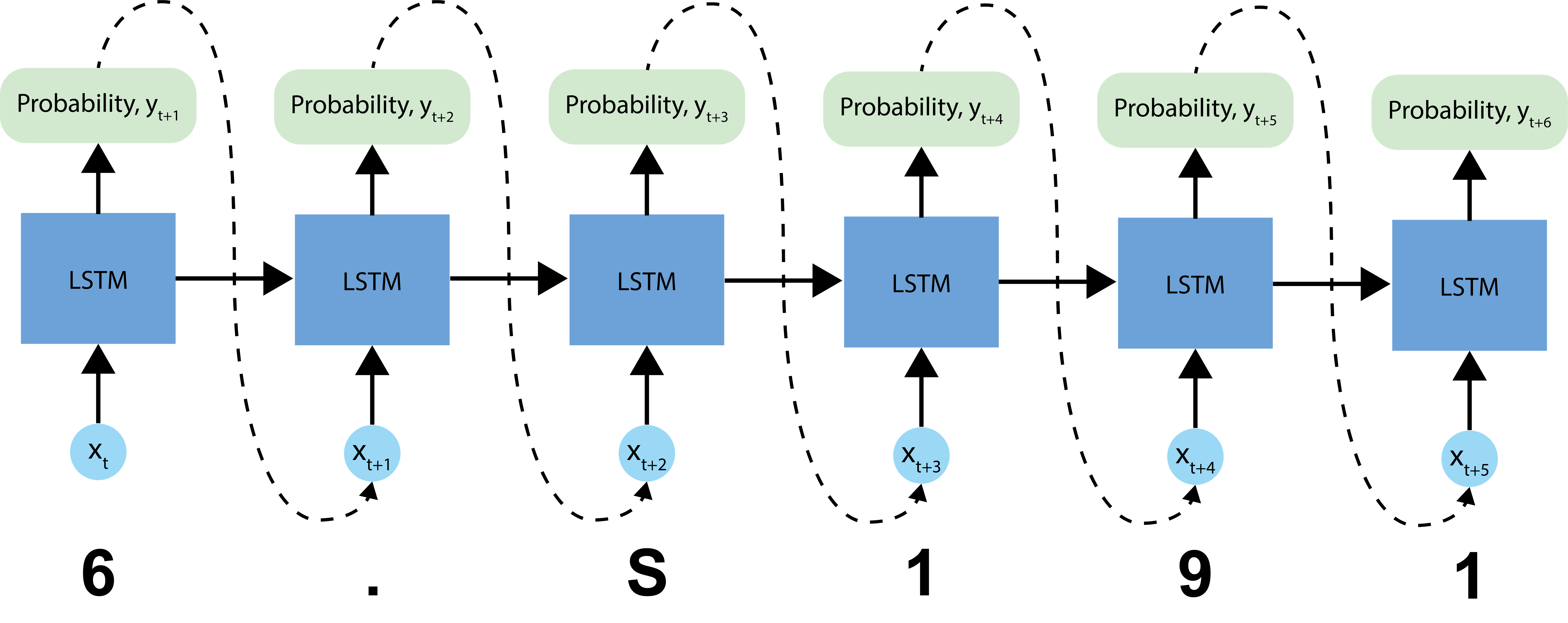\n\nComplete and experiment with this code block (as well as some of the aspects of network definition and training!), and see how the model performs. How do songs generated after training with a small number of epochs compare to those generated after a longer duration of training?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Prediction of a generated song ###\n\ndef generate_text(model, start_string, generation_length=1000):\n # Evaluation step (generating ABC text using the learned RNN model)\n\n '''TODO: convert the start string to numbers (vectorize)'''\n input_eval = [char2idx[c] for c in start_string]\n input_eval = tf.expand_dims(input_eval, 0)\n\n # Empty string to store our results\n text_generated = []\n\n # Here batch size == 1\n model.reset_states()\n tqdm._instances.clear()\n\n for i in tqdm(range(generation_length)):\n '''TODO: evaluate the inputs and generate the next character predictions'''\n predictions = model(input_eval)\n \n # Remove the batch dimension\n predictions = tf.squeeze(predictions, 0)\n \n '''TODO: use a multinomial distribution to sample'''\n predicted_id = tf.random.categorical(logits=predictions, num_samples=1)[-1,0].numpy()\n \n # Pass the prediction along with the previous hidden state\n # as the next inputs to the model\n input_eval = tf.expand_dims([predicted_id], 0)\n \n '''TODO: add the predicted character to the generated text!'''\n # Hint: consider what format the prediction is in vs. the output\n text_generated.append(idx2char[predicted_id])\n \n return (start_string + ''.join(text_generated))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"'''TODO: Use the model and the function defined above to generate ABC format text of length 1000!\n As you may notice, ABC files start with \"X\" - this may be a good start string.'''\ngenerated_text = generate_text(model, start_string=\"X\", generation_length=10000) # TODO\n# generated_text = generate_text('''TODO''', start_string=\"X\", generation_length=1000)",
"100%|██████████| 10000/10000 [01:08<00:00, 145.78it/s]\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Play back the generated music!\n\nWe can now call a function to convert the ABC format text to an audio file, and then play that back to check out our generated music! Try training longer if the resulting song is not long enough, or re-generating the song!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Play back generated songs ###\n\ngenerated_songs = mdl.lab1.extract_song_snippet(generated_text)\n\nfor i, song in enumerate(generated_songs): \n # Synthesize the waveform from a song\n waveform = mdl.lab1.play_song(song)\n\n # If its a valid song (correct syntax), lets play it! \n if waveform:\n print(\"Generated song\", i)\n ipythondisplay.display(waveform)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 2.7 Experiment and **get awarded for the best songs**!!\n\nCongrats on making your first sequence model in TensorFlow! It's a pretty big accomplishment, and hopefully you have some sweet tunes to show for it.\n\nIf you want to go further, try to optimize your model and submit your best song! Tweet us at [@MITDeepLearning](https://twitter.com/MITDeepLearning) or [email us](mailto:[email protected]) a copy of the song (if you don't have Twitter), and we'll give out prizes to our favorites! \n\nConsider how you may improve your model and what seems to be most important in terms of performance. Here are some ideas to get you started:\n\n* How does the number of training epochs affect the performance?\n* What if you alter or augment the dataset? \n* Does the choice of start string significantly affect the result? \n\nHave fun and happy listening!\n\n\n\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Example submission by a previous 6.S191 student (credit: Christian Adib) \n\n%%html\n<blockquote class=\"twitter-tweet\"><a href=\"https://twitter.com/AdibChristian/status/1090030964770783238?ref_src=twsrc%5Etfw\">January 28, 2019</a></blockquote> \n<script async src=\"https://platform.twitter.com/widgets.js\" charset=\"utf-8\"></script>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c503078d730eacf81d8ee97737f67dd3d771a318
| 520,637 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/stepperMove_doc.ipynb
|
gborelli89/BFS_flowcontrol
|
e45a3d4e222c174f713142da9d923d1a00f48b02
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/stepperMove_doc.ipynb
|
gborelli89/BFS_flowcontrol
|
e45a3d4e222c174f713142da9d923d1a00f48b02
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/stepperMove_doc.ipynb
|
gborelli89/BFS_flowcontrol
|
e45a3d4e222c174f713142da9d923d1a00f48b02
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 1,531.285294 | 234,065 | 0.958718 |
[
[
[
"empty"
]
]
] |
[
"empty"
] |
[
[
"empty"
]
] |
c5030b12401ccdfa0a93df915601c82a4a8a5d4f
| 72,536 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/euc_calibration.ipynb
|
timothyas/eccov4-euc
|
35f2251b0d471ffb152394d99c735ddab249497a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/euc_calibration.ipynb
|
timothyas/eccov4-euc
|
35f2251b0d471ffb152394d99c735ddab249497a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/euc_calibration.ipynb
|
timothyas/eccov4-euc
|
35f2251b0d471ffb152394d99c735ddab249497a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 163.369369 | 21,532 | 0.897182 |
[
[
[
"# EUC Calibration Experiment from David Halpern\n\n\n\nFor the vertical spacing, what are the ECCOv4r4 vertical layers from the surface to 400 m depth? At the equator (0°), the vertical profile of the zonal velocity component is: 0.1 m s*-1 towards the west from the sea surface at 0 m to 20 m depth; 0.5 m s*-1 towards the east at 20-170 m depth interval; and 0.1 m s-*1 towards the west at depths greater than 170 m. What would be the “algorithm” or step-by-step computational method to compute the EUC transport per unit width?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import os \nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport xarray as xr\nfrom xgcm import Grid\nfrom pych.calc import haversine",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig_dir = 'euc_figs'\nif not os.path.isdir(fig_dir):\n os.makedirs(fig_dir)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Part 1: simplified transport\n\nLet’s do a calibration calculation. Imagine the Equatorial Undercurrent at 140°W. \n- At the equator (0°), the vertical profile of the zonal velocity component is: \n - 0.1 m s*-1 towards the west from the sea surface at 0 m to 20 m depth; \n - 0.5 m s*-1 towards the east at 20-170 m depth interval; and \n - 0.1 m s*-1 towards the west at depths greater than 170 m. \n- The EUC transport per unit width is (150 m) x (0.5 m s*-1) = 75 m*2 s*-1. \n- Let’s assume that the identical velocity profile occurs at all latitudes from 1.5°S to 1.5°N. \n- For now, I’ll assume that 1° latitude between 1.5°S and 1.5°N is equal to 110 km (which is a good approximation for this exercise but not for the final computer program). \n\nThe EUC volume transport = (3°) x (110 km) x (150 m) x (0.5 m s*-1) = 24.75 x 10*6 m*3 s*-1 = 24.75 Sv.\n\nLet this EUC transport (24.75 Sv) be constant at all longitudes from 140°E to 80°W. Please make a plot of the longitudinal distribution of the EUC transport.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"lon_arr = np.concatenate((np.arange(140,180),np.arange(-180,-79)),axis=0)\nlon = xr.DataArray(lon_arr,coords={'lon':lon_arr},dims=('lon',))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lat_arr = np.arange(-1,2)\nlat = xr.DataArray(lat_arr,coords={'lat':lat_arr},dims=('lat',))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"deptharr = np.arange(1,200)-.5\ndepth = xr.DataArray(deptharr,coords={'depth':deptharr},dims=('depth',))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ds = xr.Dataset({'lon':lon,'lat':lat,'depth':depth})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ds",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ds['dyG'] = xr.DataArray(np.array([110000,110000,110000]),coords=ds.lat.coords,dims=('lat',))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ds['drF'] = xr.DataArray(np.array([1]*199),coords=ds.depth.coords,dims=('depth',))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ds = ds.set_coords(['dyG','drF'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ds['uvel'] = xr.zeros_like(ds.depth*ds.lat*ds.lon)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Create the velocity profile\n\n- At the equator (0°), the vertical profile of the zonal velocity component is: \n - 0.1 m s*-1 towards the west from the sea surface at 0 m to 20 m depth; \n - 0.5 m s*-1 towards the east at 20-170 m depth interval; and \n - 0.1 m s*-1 towards the west at depths greater than 170 m. \n- Let’s assume that the identical velocity profile occurs at all latitudes from 1.5°S to 1.5°N. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"ds['uprof'] = xr.where(ds.depth<20,-0.1,0.) + \\\n xr.where((ds.depth>=20) & (ds.depth<170),0.5,0.) + \\\n xr.where(ds.depth>=170,-0.1,0.)\nds.uprof.attrs['units'] = 'm/s'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ds.uprof.plot(y='depth',yincrease=False)\nplt.xlabel('U [m/s]')\nplt.ylabel('Depth (m)')\nplt.title('Zonal Velocity Profile')\nplt.savefig(f'{fig_dir}/simple_zonal_velocity_profile.png',bbox_inches='tight')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### \"Broadcast\" this profile to latitudes and longitudes in the domain\n\nShow a plot at two random places as verification",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"ds['uvel'],_ = xr.broadcast(ds.uprof,ds.lat*ds.lon)\nds.uvel.attrs['units'] = 'm/s'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig,axs = plt.subplots(1,2,figsize=(18,6),sharey=True)\nds.uvel.sel(lon=170).plot(ax=axs[0],yincrease=False)\nds.uvel.sel(lon=-90).plot(ax=axs[1],yincrease=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### The EUC transport per unit width is (150 m) x (0.5 m s*-1) = 75 m*2 s*-1. \n\nPlot below verifies this...",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"ds['trsp_per_width'] = (ds['uvel']*ds['drF']).where(ds.uvel>0).sum('depth')\nds.trsp_per_width.attrs['units'] = 'm^2/s'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ds.trsp_per_width.sel(lon=140).plot()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ds['trsp'] = ds['uvel']*ds['drF']*ds['dyG']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"euc = ds['trsp'].where(ds.uvel>0).sum(['lat','depth']) / 1e6\neuc.attrs['units']='Sv'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def euc_plot(xda,xcoord='XG',ax=None,xskip=10):\n \n if ax is None:\n fig,ax = plt.subplots(1,1)\n x=xda[xcoord]\n \n xbds = [140,-80]\n # Grab Pacific\n xda = xda.where((x<=xbds[0])|(x>=xbds[1]),drop=True)\n x_split=xda[xcoord]\n xda[xcoord]=xr.where(xda[xcoord]<=0,360+xda[xcoord],xda[xcoord])\n xda = xda.sortby(xcoord)\n \n xda.plot(ax=ax)\n \n xlbl = [f'{xx}' for xx in np.concatenate([np.arange(xbds[0],181),np.arange(-179,xbds[1])])]\n x_slice = slice(None,None,xskip)\n ax.xaxis.set_ticks(xda[xcoord].values[x_slice])\n ax.xaxis.set_ticklabels(xlbl[x_slice])\n ax.set_xlim([xbds[0],xbds[1]+360])\n \n return ax",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig,ax = plt.subplots(1,1,figsize=(18,6))\neuc_plot(euc,xcoord='lon',ax=ax)\nplt.title(f'EUC: {euc[0].values} {euc.attrs[\"units\"]}')\nplt.savefig(f'{fig_dir}/simplified_euc.png',bbox_inches='tight')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Part 2: The LLC90 grid with telescoping refinement near the equator\n\nThe next thought-experiment calculation will provide me with a greater appreciation of the ECCOv4r4 horizontal grid spacing, which, I believe, has a 1° x 1° horizontal grid spacing. \n\nIn the latitudinal direction, where are the grid points? \nFor example, are 0° and 1° at grid points or are 0.5° and 1.5° at grid points? \n\nIf 0° is a grid point, then is the ECCOv4r4 value of the zonal current at a specific depth, say 20 m, constant from 0.5°S to 0.5°N?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
c5030dd359c92f6b2ca6216a1516aa58d519d17e
| 222,128 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
CrossShelfTransports-CNTDIFF.ipynb
|
UBC-MOAD/outputanalysisnotebooks
|
50839cde3832d26bac6641427fed03c818fbe170
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
CrossShelfTransports-CNTDIFF.ipynb
|
UBC-MOAD/outputanalysisnotebooks
|
50839cde3832d26bac6641427fed03c818fbe170
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
CrossShelfTransports-CNTDIFF.ipynb
|
UBC-MOAD/outputanalysisnotebooks
|
50839cde3832d26bac6641427fed03c818fbe170
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 388.335664 | 74,160 | 0.921914 |
[
[
[
"Cross-shelf transport (total) of CNTDIFF experiments\n==",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"This notebook explores the similarities and differences between the 2 tracer transports for case CNTDIFF as well as canyon and no canyon cases. It looks at the transport normal to a shelf break wall<sup>1</sup>. Total Tracer Transport (TracTrans) is understood here as tracer transport (concentration * transport) per cell area; similarly, Total Transport (Trans) is transport per cell area, which is only the speed. This gives the following units:\n\n$[TracTrans] = [C]ms^{-1} $\n\n$[Trans] = [v] = ms^{-1} $\n\nTracTrans = AdvFlux + DiffFlux / cell area\n\n<sup>1</sup> Plane that goes from shelf-break depth to surface and all along the shelf break.\n\nThe base case to compare the effect of isopycnal diffusivity is a run without GMREDI and different values of $K_{iso}$ but constant vertical diffusivity (CNTDIFF). The vertical diff for tracer 1 is $10^{-5}$ $m^2s^{-1}$ and $10^{-3}$ $m^2s^{-1}$ for tracer 2. An associated no-canyon case allows to isolate the effect of the canyon (CNTDIFF run07). \n\nCNTDIFF runs include the following cases:\n\n| Run | $k_{iso}$ ($m^2s^{-1}$) | Bathymetry |\n|:-----:|:------------------------------:|:-----------------------|\n| 02 | $10^{1}$ | Barkley-like |\n| 03 | $10^{0}$ | Barkley-like |\n| 04 | $10^{-1}$ | Barkley-like |\n| 07 | $10^{0}$ | No canyon |\n\nOther runs explore the effect of bottom drag and stratification. $K_{iso}$ = 100 gave NaNs in run from first checkpoint on and I have to figure out why.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#KRM\n\nimport numpy as np\n\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\nimport matplotlib.colors as mcolors\n\nfrom math import *\n\nimport scipy.io\n\nimport scipy as spy\n\n%matplotlib inline\n\nfrom netCDF4 import Dataset\n\nimport pylab as pl\n\nimport os \n\nimport sys\n\nimport seaborn as sns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lib_path = os.path.abspath('/ocean/kramosmu/Building_canyon/BuildCanyon/PythonModulesMITgcm') # Add absolute path to my python scripts\nsys.path.append(lib_path)\n\nimport ReadOutTools_MITgcm as rout \n\nimport ShelfBreakTools_MITgcm as sb\n\nimport savitzky_golay as sg",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Base case, iso =1 , No 3d diff.\nCanyonGrid='/ocean/kramosmu/MITgcm/TracerExperiments/NOGMREDI/run02/gridGlob.nc'\nCanyonGridOut = Dataset(CanyonGrid)\n#for dimobj in CanyonGridOut.variables.values():\n# print dimobj\nCanyonState='/ocean/kramosmu/MITgcm/TracerExperiments/NOGMREDI/run02/stateGlob.nc'\nCanyonStateOut = Dataset(CanyonState)\n\nFluxTR01 = '/ocean/kramosmu/MITgcm/TracerExperiments/NOGMREDI/run02/FluxTR01Glob.nc'\nFluxOut1 = Dataset(FluxTR01)\n\nFluxTR01NoCNoR = '/ocean/kramosmu/MITgcm/TracerExperiments/NOGMREDI/run04/FluxTR01Glob.nc'\nFluxOut1NoCNoR = Dataset(FluxTR01NoCNoR)\n\nCanyonGridNoC='/ocean/kramosmu/MITgcm/TracerExperiments/CNTDIFF/run07/gridGlob.nc'\nCanyonGridOutNoC = Dataset(CanyonGridNoC)\n\nCanyonStateNoC='/ocean/kramosmu/MITgcm/TracerExperiments/CNTDIFF/run07/stateGlob.nc'\n\nFluxTR01NoC = '/ocean/kramosmu/MITgcm/TracerExperiments/CNTDIFF/run07/FluxTR01Glob.nc'\nFluxTR03NoC = '/ocean/kramosmu/MITgcm/TracerExperiments/CNTDIFF/run07/FluxTR03Glob.nc'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# General input\nnx = 360\nny = 360\nnz = 90\nnt = 19 # t dimension size \n\nz = CanyonStateOut.variables['Z']\n#print(z[10])\nTime = CanyonStateOut.variables['T']\n#print(Time[:])\n\nxc = rout.getField(CanyonGrid, 'XC') # x coords tracer cells\n\nyc = rout.getField(CanyonGrid, 'YC') # y coords tracer cells\n\nbathy = rout.getField(CanyonGrid, 'Depth')\n\nhFacC = rout.getField(CanyonGrid, 'HFacC')\nMaskC = rout.getMask(CanyonGrid, 'HFacC')\n\nhFacCNoC = rout.getField(CanyonGridNoC, 'HFacC')\nMaskCNoC = rout.getMask(CanyonGridNoC, 'HFacC')\n\ndxF = rout.getField(CanyonGrid, 'dxF')\ndrF = CanyonGridOut.variables['drF']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sns.set()\nsns.set_style('white')\nsns.set_context('talk')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"colors=['midnightblue','dodgerblue','deepskyblue','lightskyblue',\n 'darkmagenta','orchid']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"VTRAC = rout.getField(FluxTR01,'VTRAC01') # \nUTRAC = rout.getField(FluxTR01,'UTRAC01') # \n\nVTRACNoCNoR = rout.getField(FluxTR01NoCNoR,'VTRAC01') # \nUTRACNoCNoR = rout.getField(FluxTR01NoCNoR,'UTRAC01') # \n\nVTRACNoC = rout.getField(FluxTR01NoC,'VTRAC01') # \nUTRACNoC = rout.getField(FluxTR01NoC,'UTRAC01') # \n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"zlev = 29\nSBx, SBy = sb.findShelfBreak(zlev,hFacC)\nSBxx = SBx[:-1]\nSByy = SBy[:-1]\nslope, theta = sb.findSlope(xc,yc,SBxx,SByy)\nslopeFilt = sg.savitzky_golay(slope, 11, 3) # window size 11, polynomial order 3\nthetaFilt = np.arctan(slopeFilt)\n\nzlev = 29\nSBxNoC, SByNoC = sb.findShelfBreak(zlev,hFacCNoC)\nSBxxNoC = SBxNoC[:-1]\nSByyNoC = SByNoC[:-1]\nslopeNoC, thetaNoC = sb.findSlope(xc,yc,SBxxNoC,SByyNoC)\nslopeFiltNoC = sg.savitzky_golay(slopeNoC, 11, 3) # window size 11, polynomial order 3\nthetaFiltNoC = np.arctan(slopeFiltNoC)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# TRACER 1\nFluxTR01run02 = '/ocean/kramosmu/MITgcm/TracerExperiments/CNTDIFF/run02/FluxTR01Glob.nc'\nFluxOut1run02 = Dataset(FluxTR01run02)\n\nFluxTR01run03 = '/ocean/kramosmu/MITgcm/TracerExperiments/CNTDIFF/run03/FluxTR01Glob.nc'\nFluxOut1run03 = Dataset(FluxTR01run03)\n\nFluxTR01run04= '/ocean/kramosmu/MITgcm/TracerExperiments/CNTDIFF/run04/FluxTR01Glob.nc'\nFluxOut1run04 = Dataset(FluxTR01run04)\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"VTRACrun02 = rout.getField(FluxTR01run02,'VTRAC01') # \nUTRACrun02 = rout.getField(FluxTR01run02,'UTRAC01') # \n\nVTRACrun3 = rout.getField(FluxTR01run03,'VTRAC01') # \nUTRACrun3 = rout.getField(FluxTR01run03,'UTRAC01') # \n\nVTRACrun04 = rout.getField(FluxTR01run04,'VTRAC01') # \nUTRACrun04 = rout.getField(FluxTR01run04,'UTRAC01') # \n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
" ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\ntimes = range(18)\nToTalTracTransRun03=np.empty(18)\nToTalTracTransBaseNoC=np.empty(18)\nToTalTracTransBaseNoCNoR=np.empty(18)\nToTalTracTransRun02=np.empty(18)\nToTalTracTransRun04=np.empty(18)\nToTalTracTransBase=np.empty(18)\n\nfor tt in times:\n \n VTRACPlotBase = sb.MerFluxSB(SBxx,SByy,tt,VTRAC,z,xc,zlev,hFacC,MaskC)\n UTRACPlotBase = sb.ZonFluxSB(SBxx,SByy,tt,UTRAC,z,xc,zlev,hFacC,MaskC)\n \n VTRACPlotNoCNoR = sb.MerFluxSB(SBxxNoC,SByyNoC,tt,VTRACNoCNoR,z,xc,zlev,hFacCNoC,MaskCNoC)\n UTRACPlotNoCNoR = sb.ZonFluxSB(SBxxNoC,SByyNoC,tt,UTRACNoCNoR,z,xc,zlev,hFacCNoC,MaskCNoC)\n \n VTRACPlot2 = sb.MerFluxSB(SBxx,SByy,tt,VTRACrun02,z,xc,zlev,hFacC,MaskC)\n UTRACPlot2 = sb.ZonFluxSB(SBxx,SByy,tt,UTRACrun02,z,xc,zlev,hFacC,MaskC)\n \n VTRACPlot3 = sb.MerFluxSB(SBxx,SByy,tt,VTRACrun3,z,xc,zlev,hFacC,MaskC)\n UTRACPlot3 = sb.ZonFluxSB(SBxx,SByy,tt,UTRACrun3,z,xc,zlev,hFacC,MaskC)\n \n VTRACPlot4 = sb.MerFluxSB(SBxx,SByy,tt,VTRACrun04,z,xc,zlev,hFacC,MaskC)\n UTRACPlot4 = sb.ZonFluxSB(SBxx,SByy,tt,UTRACrun04,z,xc,zlev,hFacC,MaskC)\n \n \n VTRACPlotNoC = sb.MerFluxSB(SBxxNoC,SByyNoC,tt,VTRACNoC,z,xc,zlev,hFacCNoC,MaskCNoC)\n UTRACPlotNoC = sb.ZonFluxSB(SBxxNoC,SByyNoC,tt,UTRACNoC,z,xc,zlev,hFacCNoC,MaskCNoC)\n \n \n \n TracTrans2 = VTRACPlot2[:,4:-5]*np.cos(thetaFilt) + UTRACPlot2[:,4:-4]*np.sin(-thetaFilt) \n TracTrans3 = VTRACPlot3[:,4:-5]*np.cos(thetaFilt) + UTRACPlot3[:,4:-4]*np.sin(-thetaFilt) \n TracTrans4 = VTRACPlot4[:,4:-5]*np.cos(thetaFilt) + UTRACPlot4[:,4:-4]*np.sin(-thetaFilt) \n TracTransNoC = VTRACPlotNoC[:,4:-5]*np.cos(thetaFiltNoC) + UTRACPlotNoC[:,4:-4]*np.sin(-thetaFiltNoC) \n TracTransBase = VTRACPlotBase[:,4:-5]*np.cos(thetaFilt) + UTRACPlotBase[:,4:-4]*np.sin(-thetaFilt) \n TracTransNoCNoR = VTRACPlotNoCNoR[:,4:-5]*np.cos(thetaFiltNoC) + UTRACPlotNoCNoR[:,4:-4]*np.sin(-thetaFiltNoC) \n \n ToTalTracTransRun02[tt]=np.sum(TracTrans2)\n ToTalTracTransRun03[tt]=np.sum(TracTrans3)\n ToTalTracTransRun04[tt]=np.sum(TracTrans4)\n ToTalTracTransBase[tt]=np.sum(TracTransBase)\n ToTalTracTransBaseNoC[tt]=np.sum(TracTransNoC)\n ToTalTracTransBaseNoCNoR[tt]=np.sum(TracTransNoCNoR)\n \n \n \n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sns.set(context='talk', style='whitegrid', font='sans-serif', font_scale=1)\n\ntimes = range(18)# # First time element of flux is at 43200 sec, and las at 8 days \ntimes = [time/2.0+0.5 for time in times]\n\nfigSize=(10,8)\nnumCols = 1\nnumRows = 1\n\nunitsTr = '$mol \\cdot l^{-1}\\cdot ms^{-1}$'\n\n\nfig44 = plt.figure(figsize=figSize)\nplt.subplot(numRows,numCols,1)\nax = plt.gca()\nax.plot(times,ToTalTracTransRun02[:],'o-',color=colors[0],label = '$k_{iso}$ = 10 $m^2/s$')\nax.plot(times,ToTalTracTransRun03[:],'o-',color=colors[1],label = '$k_{iso}$ = 1 $m^2/s$')\nax.plot(times,ToTalTracTransRun04[:],'o-',color=colors[2],label = '$k_{iso}$ = 0.1 $m^2/s$')\nax.plot(times,ToTalTracTransBaseNoC[:],'o-',color=colors[3],label = ' NoC Run, $k_{iso}$ = 1E0 $m^2/s$ ') \nax.plot(times,ToTalTracTransBase[:],'o-',color=colors[4],label = 'Base Run, NOREDI 1E-5 $m^2/s$ ')\n\nhandles, labels = ax.get_legend_handles_labels()\ndisplay = (0,1,2,3,4)\nax.legend([handle for i,handle in enumerate(handles) if i in display],\n [label for i,label in enumerate(labels) if i in display],loc=0)\n \n \nplt.xlabel('Days')\nplt.ylabel(unitsTr)\nplt.title('Total tracer transport across shelf break - CNTDIFF runs')\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sns.set(context='talk', style='whitegrid', font='sans-serif', font_scale=1)\n\ntimes = range(18)# # First time element of flux is at 43200 sec, and las at 8 days \ntimes = [time/2.0+0.5 for time in times]\n\nfigSize=(10,8)\nnumCols = 1\nnumRows = 1\n\nunitsTr = '$mol \\cdot l^{-1}\\cdot ms^{-1}$'\n\n\nfig44 = plt.figure(figsize=figSize)\nplt.subplot(numRows,numCols,1)\nax = plt.gca()\nax.plot(times,ToTalTracTransRun02[:]-ToTalTracTransBaseNoC[:],'o-',color=colors[0],label = '10 $m^2/s$ - NoC')\nax.plot(times,ToTalTracTransRun03[:]-ToTalTracTransBaseNoC[:],'o-',color=colors[1],label = '1 $m^2/s$- NoC')\nax.plot(times,ToTalTracTransRun04[:]-ToTalTracTransBaseNoC[:],'o-',color=colors[2],label = '0.1 $m^2/s$- NoC')\nax.plot(times,ToTalTracTransBase[:]-ToTalTracTransBaseNoCNoR[:],'o-',color=colors[5],label = 'Base Run-NoC, NOREDI 1E-5 $m^2/s$ ')\n \nhandles, labels = ax.get_legend_handles_labels()\ndisplay = (0,1,2,3,4)\nax.legend([handle for i,handle in enumerate(handles) if i in display],\n [label for i,label in enumerate(labels) if i in display],loc=0)\n \n \nplt.xlabel('Days')\nplt.ylabel(unitsTr)\nplt.title('Total tracer transport across shelf break - Canyon Effect CNTDIFF')\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sns.set(context='talk', style='whitegrid', font='sans-serif', font_scale=1)\n\ntimes = range(18)# # First time element of flux is at 43200 sec, and las at 8 days \ntimes = [time/2.0+0.5 for time in times]\n\nfigSize=(10,8)\nnumCols = 1\nnumRows = 1\n\nunitsTr = '$mol \\cdot l^{-1}\\cdot ms^{-1}$'\n\n\nfig44 = plt.figure(figsize=figSize)\nplt.subplot(numRows,numCols,1)\nax = plt.gca()\n\nax.plot(times,ToTalTracTransRun02[:]-ToTalTracTransBase[:],'o-',color=colors[0],label = 'Minus Base case $k_{iso}$ = 10 $m^2/s$')\nax.plot(times,ToTalTracTransRun03[:]-ToTalTracTransBase[:],'o-',color=colors[1],label = 'Minus Base case $k_{iso}$ = 1 $m^2/s$')\nax.plot(times,ToTalTracTransRun04[:]-ToTalTracTransBase[:],'o-',color=colors[2],label = 'Minus Base case $k_{iso}$ = 0.1 $m^2/s$')\n \nhandles, labels = ax.get_legend_handles_labels()\ndisplay = (0,1,2,3,4)\nax.legend([handle for i,handle in enumerate(handles) if i in display],\n [label for i,label in enumerate(labels) if i in display],loc=0)\n \n \nplt.xlabel('Days')\nplt.ylabel(unitsTr)\nplt.title('Total tracer transport across shelf break - REDI effect')\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
c5030df62e1d6c58162011aa8c5a919b7c8aaf78
| 131,215 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
1_Rabi_Oscillations.ipynb
|
fhenneke/MSRI_Electronic_Structure_Theory
|
8c187ad8b750ad314855c7602a232271a7fcadf3
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
1_Rabi_Oscillations.ipynb
|
fhenneke/MSRI_Electronic_Structure_Theory
|
8c187ad8b750ad314855c7602a232271a7fcadf3
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
1_Rabi_Oscillations.ipynb
|
fhenneke/MSRI_Electronic_Structure_Theory
|
8c187ad8b750ad314855c7602a232271a7fcadf3
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 724.944751 | 125,943 | 0.948017 |
[
[
[
"empty"
]
]
] |
[
"empty"
] |
[
[
"empty"
]
] |
c5031ac55263a876dbf57dc9d97111f3da4bee04
| 110,025 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Modelagem/acompanhamento_score/Untitled.ipynb
|
lsawakuchi/x1
|
564a135b4fdaa687a4ef6d470ddaa4730932d429
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Modelagem/acompanhamento_score/Untitled.ipynb
|
lsawakuchi/x1
|
564a135b4fdaa687a4ef6d470ddaa4730932d429
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Modelagem/acompanhamento_score/Untitled.ipynb
|
lsawakuchi/x1
|
564a135b4fdaa687a4ef6d470ddaa4730932d429
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 42.794632 | 146 | 0.418641 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nfrom datetime import datetime\nfrom sqlalchemy import create_engine\nimport requests\nfrom time import sleep\nimport warnings\nwarnings.filterwarnings('ignore')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = pd.read_excel(\"HistoricoCobranca.xlsx\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df[\"doc\"] = df.apply(lambda x : x[\"CNPJ\"].replace(\".\", \"\").replace(\"-\", \"\").replace(\"/\", \"\"), axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df[\"MOTIVO DO CONTATO\"].unique().tolist()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df[\"JUSTIFICATIVA DO ALERTA\"].unique().tolist()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df[df['JUSTIFICATIVA DO ALERTA'].isin([\"Fechou a Loja\", \"Fechou a Empresa\"])]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"engine = create_engine(\"mysql+pymysql://capMaster:#jackpot123#@captalys.cmrbivuuu7sv.sa-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com:23306/creditoDigital\")\ncon = engine.connect()\ndfop = pd.read_sql(\"select * from desembolso\", con)\ncon.close()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_data = dfop[[\"cnpj\", \"dataDesembolso\"]]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_data[\"dataDesembolso\"] = df_data.apply(lambda x : x[\"dataDesembolso\"].date(), axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"res = df.merge(df_data, left_on='doc', right_on='cnpj', how='left')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"res[res[\"doc\"]=='11117460000110']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"res.drop(columns=[\"cnpj\"], axis=1, inplace=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"res[\"dataDesembolso\"].iloc[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"res.sort_values(\"dataDesembolso\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"res[res['dataDesembolso']<datetime(2019, 1,1).date()].shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"res.shape[0] - 13",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"res.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def get_numero_consulta(cnpj):\n engine = create_engine(\"mysql+pymysql://capMaster:#jackpot123#@captalys.cmrbivuuu7sv.sa-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com:23306/varejo\")\n con = engine.connect()\n query = \"select data_ref, numero_consulta from consultas_idwall_operacoes where cnpj_cpf='{}'\".format(cnpj)\n df = pd.read_sql(query, con)\n numero = df[df['data_ref']==df['data_ref'].max()][\"numero_consulta\"].iloc[0]\n con.close()\n \n return numero\n \n\ndef get_details(numero):\n URL = \"https://api-v2.idwall.co/relatorios\"\n authorization = \"b3818f92-5807-4acf-ade8-78a1f6d7996b\"\n url_details = URL + \"/{}\".format(numero) + \"/dados\"\n while True:\n dets = requests.get(url_details, headers={\"authorization\": authorization})\n djson = dets.json()\n sleep(1)\n if djson['result']['status'] == \"CONCLUIDO\":\n break\n\n return dets.json()\n\ndef get_idade(cnpj):\n numero = get_numero_consulta(cnpj)\n print(numero)\n js = get_details(numero)\n data_abertura = js.get(\"result\").get(\"cnpj\").get(\"data_abertura\")\n data_abertura = data_abertura.replace(\"/\", \"-\")\n data = datetime.strptime(data_abertura, \"%d-%m-%Y\").date()\n idade = ((datetime.now().date() - data).days/366)\n idade_empresa = np.around(idade, 2)\n return idade_empresa",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"get_idade(\"12549813000114\")",
"27d21972-0874-4681-926f-a5ff73400c92\n"
],
[
"res",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c5032b488ec62b92a7aff4760f3a06fe5f54e50a
| 272,911 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
research/harman_targets_without_bass.ipynb
|
vinzmc/AutoEq
|
4b42aa25e5f4933528be44e7356afe1fde75a3af
|
[
"MIT"
] | 6,741 |
2018-07-27T10:54:04.000Z
|
2022-03-31T20:22:57.000Z
|
research/harman_targets_without_bass.ipynb
|
vinzmc/AutoEq
|
4b42aa25e5f4933528be44e7356afe1fde75a3af
|
[
"MIT"
] | 428 |
2018-08-08T17:12:40.000Z
|
2022-03-31T05:53:36.000Z
|
research/harman_targets_without_bass.ipynb
|
vinzmc/AutoEq
|
4b42aa25e5f4933528be44e7356afe1fde75a3af
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1,767 |
2018-07-27T16:50:12.000Z
|
2022-03-31T19:26:39.000Z
| 1,066.058594 | 53,280 | 0.954351 |
[
[
[
"%load_ext autoreload\n%autoreload 2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import os\nimport sys\nfrom pathlib import Path\nROOT_DIR = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(Path().absolute(), os.pardir))\nsys.path.insert(1, ROOT_DIR)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import numpy as np\nimport scipy\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom frequency_response import FrequencyResponse\nfrom biquad import peaking, low_shelf, high_shelf, digital_coeffs",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"harman_overear = FrequencyResponse.read_from_csv(os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, 'compensation', 'harman_over-ear_2018.csv'))\nfig, ax = harman_overear.plot_graph(show=False, color='C0')\n\nfs = 48000\na0, a1, a2, b0, b1, b2 = low_shelf(105.0, 0.71, 6, fs=fs)\nshelf = digital_coeffs(harman_overear.frequency, fs, a0, a1, a2, b0, b1, b2)\nshelf = FrequencyResponse(name='Shelf', frequency=harman_overear.frequency.copy(), raw=shelf)\nshelf.plot_graph(fig=fig, ax=ax, show=False, color='C1')\n\nharman_overear_wo_bass = FrequencyResponse(\n name='Harman over-ear target 2018 without bass',\n frequency=harman_overear.frequency.copy(),\n raw=harman_overear.raw - shelf.raw\n)\nharman_overear_wo_bass.plot_graph(fig=fig, ax=ax, color='C2', show=False)\nax.legend(['Harman over-ear 2018', 'Low shelf', 'Harman over-ear 2018 without bass shelf'])\nax.set_ylim([-4, 10])\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"harman_inear = FrequencyResponse.read_from_csv(os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, 'compensation', 'harman_in-ear_2019v2.csv'))\nfig, ax = harman_inear.plot_graph(show=False, color='C0')\n\nfs = 48000\na0, a1, a2, b0, b1, b2 = low_shelf(105.0, 0.71, 9, fs=fs)\nshelf = digital_coeffs(harman_inear.frequency, fs, a0, a1, a2, b0, b1, b2)\nshelf = FrequencyResponse(name='Shelf', frequency=harman_inear.frequency.copy(), raw=shelf)\nshelf.plot_graph(fig=fig, ax=ax, show=False, color='C1')\n\nharman_inear_wo_bass = FrequencyResponse(\n name='Harman in-ear target 2019 without bass',\n frequency=harman_inear.frequency.copy(),\n raw=harman_inear.raw - shelf.raw\n)\nharman_inear_wo_bass.plot_graph(fig=fig, ax=ax, color='C2', show=False)\nax.legend(['Harman in-ear 2019', 'Low shelf', 'Harman in-ear target 2019 without bass'])\nax.set_ylim([-4, 10])\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = harman_overear.plot_graph(show=False, color='C0')\nharman_overear_wo_bass.plot_graph(fig=fig, ax=ax, show=False, color='C1')\nharman_overear_4_bass = harman_overear_wo_bass.copy()\nharman_overear_4_bass.raw += digital_coeffs(harman_overear_4_bass.frequency, fs, *low_shelf(105, 0.71, 4, fs=fs))\nharman_overear_4_bass.plot_graph(fig=fig, ax=ax, show=False, color='C2')\nax.legend(['Harman over-ear 2018', 'Harman over-ear 2018 without bass', 'Harman over-ear 2018 with 4 dB bass'])\nax.set_ylim([-4, 10])\nax.set_title('Harman over-ear')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = harman_inear.plot_graph(show=False, color='C0')\nharman_inear_wo_bass.plot_graph(fig=fig, ax=ax, show=False, color='C1')\nharman_inear_6_bass = harman_inear_wo_bass.copy()\nharman_inear_6_bass.raw += digital_coeffs(harman_inear_6_bass.frequency, fs, *low_shelf(105, 0.71, 4, fs=fs))\nharman_inear_6_bass.plot_graph(fig=fig, ax=ax, show=False, color='C2')\nax.legend(['Harman in-ear 2019', 'Harman in-ear 2019 without bass', 'Harman in-ear 2019 with 6 dB bass'])\nax.set_ylim([-4, 10])\nax.set_title('Harman in-ear')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# WARNING: These will overwrite the files\nharman_overear_wo_bass.write_to_csv(os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, 'compensation', 'harman_over-ear_2018_wo_bass.csv'))\nharman_overear_wo_bass.plot_graph(file_path=os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, 'compensation', 'harman_over-ear_2018_wo_bass.png'), color='C0')\nharman_inear_wo_bass.write_to_csv(os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, 'compensation', 'harman_in-ear_2019v2_wo_bass.csv'))\nharman_inear_wo_bass.plot_graph(file_path=os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, 'compensation', 'harman_in-ear_2019v2_wo_bass.png'), color='C0')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c5033490651b64e946a74e3548e3845b786fa8a6
| 641,889 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/book2/14/linreg_hierarchical_non_centered_blackjax.ipynb
|
patel-zeel/pyprobml
|
027ef3c13a2a63d958e05fdedb68fd7b8f0e0261
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/book2/14/linreg_hierarchical_non_centered_blackjax.ipynb
|
patel-zeel/pyprobml
|
027ef3c13a2a63d958e05fdedb68fd7b8f0e0261
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2022-03-27T04:59:50.000Z
|
2022-03-27T04:59:50.000Z
|
notebooks/book2/14/linreg_hierarchical_non_centered_blackjax.ipynb
|
patel-zeel/pyprobml
|
027ef3c13a2a63d958e05fdedb68fd7b8f0e0261
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2022-03-26T11:52:36.000Z
|
2022-03-27T05:17:48.000Z
| 1,040.338736 | 228,068 | 0.955935 |
[
[
[
"!pip install -q blackjax\n!pip install -q distrax",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import jax\nimport jax.numpy as jnp\nimport jax.scipy.stats as stats\nfrom jax.random import PRNGKey, split\n\ntry:\n import distrax\nexcept ModuleNotFoundError:\n %pip install -qq distrax\n import distrax\ntry:\n from tensorflow_probability.substrates.jax.distributions import HalfCauchy\nexcept ModuleNotFoundError:\n %pip install -qq tensorflow-probability\n from tensorflow_probability.substrates.jax.distributions import HalfCauchy\n\ntry:\n import blackjax.hmc as hmc\nexcept ModuleNotFoundError:\n %pip install -qq blackjax\n import blackjax.hmc as hmc\nimport blackjax.nuts as nuts\nimport blackjax.stan_warmup as stan_warmup\n\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport seaborn as sns\n\ntry:\n import arviz as az\nexcept ModuleNotFoundError:\n %pip install -qq arviz\n import arviz as az\nfrom functools import partial\n\nsns.set_style(\"whitegrid\")\nnp.random.seed(123)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"url = \"https://github.com/twiecki/WhileMyMCMCGentlySamples/blob/master/content/downloads/notebooks/radon.csv?raw=true\"\ndata = pd.read_csv(url)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"county_names = data.county.unique()\ncounty_idx = jnp.array(data.county_code.values)\nn_counties = len(county_names)\nX = data.floor.values\nY = data.log_radon.values",
"WARNING:absl:No GPU/TPU found, falling back to CPU. (Set TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL=0 and rerun for more info.)\n"
],
[
"def init_non_centered_params(n_counties, rng_key=None):\n params = {}\n\n if rng_key is None:\n rng_key = PRNGKey(0)\n\n mu_a_key, mu_b_key, sigma_a_key, sigma_b_key, a_key, b_key, eps_key = split(rng_key, 7)\n half_cauchy = distrax.as_distribution(HalfCauchy(loc=0.0, scale=5.0))\n\n params[\"mu_a\"] = distrax.Normal(0.0, 1.0).sample(seed=mu_a_key)\n params[\"mu_b\"] = distrax.Normal(0.0, 1.0).sample(seed=mu_b_key)\n\n params[\"sigma_a\"] = half_cauchy.sample(seed=sigma_a_key)\n params[\"sigma_b\"] = half_cauchy.sample(seed=sigma_b_key)\n\n params[\"a_offsets\"] = distrax.Normal(0.0, 1.0).sample(seed=a_key, sample_shape=(n_counties,))\n params[\"b_offsets\"] = distrax.Normal(0.0, 1.0).sample(seed=b_key, sample_shape=(n_counties,))\n\n params[\"eps\"] = half_cauchy.sample(seed=eps_key)\n\n return params",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def init_centered_params(n_counties, rng_key=None):\n params = {}\n\n if rng_key is None:\n rng_key = PRNGKey(0)\n\n mu_a_key, mu_b_key, sigma_a_key, sigma_b_key, a_key, b_key, eps_key = split(rng_key, 7)\n half_cauchy = distrax.as_distribution(HalfCauchy(loc=0.0, scale=5.0))\n\n params[\"mu_a\"] = distrax.Normal(0.0, 1.0).sample(seed=mu_a_key)\n params[\"mu_b\"] = distrax.Normal(0.0, 1.0).sample(seed=mu_b_key)\n\n params[\"sigma_a\"] = half_cauchy.sample(seed=sigma_a_key)\n params[\"sigma_b\"] = half_cauchy.sample(seed=sigma_b_key)\n\n params[\"b\"] = distrax.Normal(params[\"mu_b\"], params[\"sigma_b\"]).sample(seed=b_key, sample_shape=(n_counties,))\n params[\"a\"] = distrax.Normal(params[\"mu_a\"], params[\"sigma_a\"]).sample(seed=a_key, sample_shape=(n_counties,))\n\n params[\"eps\"] = half_cauchy.sample(seed=eps_key)\n\n return params",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def log_joint_non_centered(params, X, Y, county_idx, n_counties):\n log_theta = 0\n\n log_theta += distrax.Normal(0.0, 100**2).log_prob(params[\"mu_a\"]) * n_counties\n log_theta += distrax.Normal(0.0, 100**2).log_prob(params[\"mu_b\"]) * n_counties\n\n log_theta += distrax.as_distribution(HalfCauchy(0.0, 5.0)).log_prob(params[\"sigma_a\"]) * n_counties\n log_theta += distrax.as_distribution(HalfCauchy(0.0, 5.0)).log_prob(params[\"sigma_b\"]) * n_counties\n\n log_theta += distrax.Normal(0.0, 1.0).log_prob(params[\"a_offsets\"]).sum()\n log_theta += distrax.Normal(0.0, 1.0).log_prob(params[\"b_offsets\"]).sum()\n\n log_theta += jnp.sum(distrax.as_distribution(HalfCauchy(0.0, 5.0)).log_prob(params[\"eps\"]))\n\n # Linear regression\n a = params[\"mu_a\"] + params[\"a_offsets\"] * params[\"sigma_a\"]\n b = params[\"mu_b\"] + params[\"b_offsets\"] * params[\"sigma_b\"]\n radon_est = a[county_idx] + b[county_idx] * X\n\n log_theta += jnp.sum(distrax.Normal(radon_est, params[\"eps\"]).log_prob(Y))\n\n return -log_theta",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def log_joint_centered(params, X, Y, county_idx):\n log_theta = 0\n\n log_theta += distrax.Normal(0.0, 100**2).log_prob(params[\"mu_a\"]).sum()\n log_theta += distrax.Normal(0.0, 100**2).log_prob(params[\"mu_b\"]).sum()\n\n log_theta += distrax.as_distribution(HalfCauchy(0.0, 5.0)).log_prob(params[\"sigma_a\"]).sum()\n log_theta += distrax.as_distribution(HalfCauchy(0.0, 5.0)).log_prob(params[\"sigma_b\"]).sum()\n\n log_theta += distrax.Normal(params[\"mu_a\"], params[\"sigma_a\"]).log_prob(params[\"a\"]).sum()\n log_theta += distrax.Normal(params[\"mu_b\"], params[\"sigma_b\"]).log_prob(params[\"b\"]).sum()\n\n log_theta += distrax.as_distribution(HalfCauchy(0.0, 5.0)).log_prob(params[\"eps\"]).sum()\n\n # Linear regression\n radon_est = params[\"a\"][county_idx] + params[\"b\"][county_idx] * X\n log_theta += distrax.Normal(radon_est, params[\"eps\"]).log_prob(Y).sum()\n return -log_theta",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def inference_loop(rng_key, kernel, initial_state, num_samples):\n def one_step(state, rng_key):\n state, _ = kernel(rng_key, state)\n return state, state\n\n keys = jax.random.split(rng_key, num_samples)\n _, states = jax.lax.scan(one_step, initial_state, keys)\n\n return states",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def fit_hierarchical_model(\n X, Y, county_idx, n_counties, is_centered=True, num_warmup=1000, num_samples=5000, rng_key=None\n):\n if rng_key is None:\n rng_key = PRNGKey(0)\n\n init_key, warmup_key, sample_key = split(rng_key, 3)\n\n if is_centered:\n potential = partial(log_joint_centered, X=X, Y=Y, county_idx=county_idx)\n params = init_centered_params(n_counties, rng_key=init_key)\n else:\n potential = partial(log_joint_non_centered, X=X, Y=Y, county_idx=county_idx, n_counties=n_counties)\n params = init_non_centered_params(n_counties, rng_key=init_key)\n\n initial_state = nuts.new_state(params, potential)\n\n kernel_factory = lambda step_size, inverse_mass_matrix: nuts.kernel(potential, step_size, inverse_mass_matrix)\n\n last_state, (step_size, inverse_mass_matrix), _ = stan_warmup.run(\n warmup_key, kernel_factory, initial_state, num_warmup\n )\n\n kernel = kernel_factory(step_size, inverse_mass_matrix)\n\n states = inference_loop(sample_key, kernel, initial_state, num_samples)\n return states",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"states_centered = fit_hierarchical_model(X, Y, county_idx, n_counties, is_centered=True)",
"/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/jax/_src/numpy/lax_numpy.py:5847: UserWarning: Explicitly requested dtype <class 'jax._src.numpy.lax_numpy.float64'> requested in astype is not available, and will be truncated to dtype float32. To enable more dtypes, set the jax_enable_x64 configuration option or the JAX_ENABLE_X64 shell environment variable. See https://github.com/google/jax#current-gotchas for more.\n lax._check_user_dtype_supported(dtype, \"astype\")\n/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/jax/_src/numpy/lax_numpy.py:5847: UserWarning: Explicitly requested dtype <class 'jax._src.numpy.lax_numpy.float64'> requested in astype is not available, and will be truncated to dtype float32. To enable more dtypes, set the jax_enable_x64 configuration option or the JAX_ENABLE_X64 shell environment variable. See https://github.com/google/jax#current-gotchas for more.\n lax._check_user_dtype_supported(dtype, \"astype\")\n/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/jax/_src/numpy/lax_numpy.py:5847: UserWarning: Explicitly requested dtype <class 'jax._src.numpy.lax_numpy.float64'> requested in astype is not available, and will be truncated to dtype float32. To enable more dtypes, set the jax_enable_x64 configuration option or the JAX_ENABLE_X64 shell environment variable. See https://github.com/google/jax#current-gotchas for more.\n lax._check_user_dtype_supported(dtype, \"astype\")\n/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/jax/_src/numpy/lax_numpy.py:5847: UserWarning: Explicitly requested dtype <class 'jax._src.numpy.lax_numpy.float64'> requested in astype is not available, and will be truncated to dtype float32. To enable more dtypes, set the jax_enable_x64 configuration option or the JAX_ENABLE_X64 shell environment variable. See https://github.com/google/jax#current-gotchas for more.\n lax._check_user_dtype_supported(dtype, \"astype\")\n"
],
[
"states_non_centered = fit_hierarchical_model(X, Y, county_idx, n_counties, is_centered=False)",
"/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/jax/_src/numpy/lax_numpy.py:5847: UserWarning: Explicitly requested dtype <class 'jax._src.numpy.lax_numpy.float64'> requested in astype is not available, and will be truncated to dtype float32. To enable more dtypes, set the jax_enable_x64 configuration option or the JAX_ENABLE_X64 shell environment variable. See https://github.com/google/jax#current-gotchas for more.\n lax._check_user_dtype_supported(dtype, \"astype\")\n/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/jax/_src/numpy/lax_numpy.py:5847: UserWarning: Explicitly requested dtype <class 'jax._src.numpy.lax_numpy.float64'> requested in astype is not available, and will be truncated to dtype float32. To enable more dtypes, set the jax_enable_x64 configuration option or the JAX_ENABLE_X64 shell environment variable. See https://github.com/google/jax#current-gotchas for more.\n lax._check_user_dtype_supported(dtype, \"astype\")\n/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/jax/_src/numpy/lax_numpy.py:5847: UserWarning: Explicitly requested dtype <class 'jax._src.numpy.lax_numpy.float64'> requested in astype is not available, and will be truncated to dtype float32. To enable more dtypes, set the jax_enable_x64 configuration option or the JAX_ENABLE_X64 shell environment variable. See https://github.com/google/jax#current-gotchas for more.\n lax._check_user_dtype_supported(dtype, \"astype\")\n/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/jax/_src/numpy/lax_numpy.py:5847: UserWarning: Explicitly requested dtype <class 'jax._src.numpy.lax_numpy.float64'> requested in astype is not available, and will be truncated to dtype float32. To enable more dtypes, set the jax_enable_x64 configuration option or the JAX_ENABLE_X64 shell environment variable. See https://github.com/google/jax#current-gotchas for more.\n lax._check_user_dtype_supported(dtype, \"astype\")\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Centered Hierarchical Model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def plot_funnel_of_hell(x, sigma_x, k=75):\n x = pd.Series(x[:, k].flatten(), name=f\"slope b_{k}\")\n y = pd.Series(sigma_x.flatten(), name=\"slope group variance sigma_b\")\n\n sns.jointplot(x=x, y=y, ylim=(0.0, 0.7), xlim=(-2.5, 1.0));",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"samples_centered = states_centered.position\nb_centered = samples_centered[\"b\"]\nsigma_b_centered = samples_centered[\"sigma_b\"]\nplot_funnel_of_hell(b_centered, sigma_b_centered)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def plot_single_chain(x, sigma_x, name):\n fig, axs = plt.subplots(nrows=2, figsize=(16, 6))\n axs[0].plot(sigma_x, alpha=0.5)\n axs[0].set(ylabel=f\"sigma_{name}\")\n axs[1].plot(x, alpha=0.5)\n axs[1].set(ylabel=name);",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plot_single_chain(b_centered[1000:], sigma_b_centered[1000:], \"b\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Non-Centered Hierarchical Model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"samples_non_centered = states_non_centered.position\nb_non_centered = (\n samples_non_centered[\"mu_b\"][..., None]\n + samples_non_centered[\"b_offsets\"] * samples_non_centered[\"sigma_b\"][..., None]\n)\nsigma_b_non_centered = samples_non_centered[\"sigma_b\"]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plot_funnel_of_hell(b_non_centered, sigma_b_non_centered)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plot_single_chain(b_non_centered[1000:], sigma_b_non_centered[1000:], \"b\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Comparison",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"k = 75\nx_lim, y_lim = [-2.5, 1], [0, 0.7]\n\nbs = [(b_centered, sigma_b_centered, \"Centered\"), (b_non_centered, sigma_b_non_centered, \"Non-centered\")]\nncols = len(bs)\n\nfig, axs = plt.subplots(ncols=ncols, sharex=True, sharey=True, figsize=(8, 6))\n\nfor i, (b, sigma_b, model_name) in enumerate(bs):\n x = pd.Series(b[:, k], name=f\"slope b_{k}\")\n y = pd.Series(sigma_b, name=\"slope group variance sigma_b\")\n axs[i].plot(x, y, \".\")\n axs[i].set(title=model_name, ylabel=\"sigma_b\", xlabel=f\"b_{k}\")\n axs[i].set_xlim(x_lim)\n axs[i].set_ylim(y_lim)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c50334f5a03e3ededd2fb9d01def3ced4a4ab21a
| 390,091 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/Direct_Grib_Read_Demo.ipynb
|
nasa/MMM-Py
|
5f5741017e5f8bb8a0bbd46faaf395da38028e22
|
[
"NASA-1.3"
] | 47 |
2015-03-28T17:09:52.000Z
|
2022-03-17T01:12:27.000Z
|
notebooks/Direct_Grib_Read_Demo.ipynb
|
afcarl/MMM-Py
|
5f5741017e5f8bb8a0bbd46faaf395da38028e22
|
[
"NASA-1.3"
] | 2 |
2015-06-23T13:43:57.000Z
|
2016-01-25T04:59:47.000Z
|
notebooks/Direct_Grib_Read_Demo.ipynb
|
afcarl/MMM-Py
|
5f5741017e5f8bb8a0bbd46faaf395da38028e22
|
[
"NASA-1.3"
] | 36 |
2015-03-17T14:18:08.000Z
|
2022-03-17T01:12:04.000Z
| 1,045.820375 | 298,620 | 0.941178 |
[
[
[
"# Direct Grib Read ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"If you have installed more recent versions of pygrib, you can ingest grib mosaics directly without conversion to netCDF. This speeds up the ingest by ~15-20 seconds. This notebook will also demonstrate how to use MMM-Py with cartopy, and how to download near-realtime data from NCEP.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from __future__ import print_function\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport datetime as dt\nimport pandas as pd\nimport glob\nimport mmmpy\nimport cartopy.crs as ccrs\nimport cartopy.feature as cfeature\nfrom cartopy.io.img_tiles import StamenTerrain\nimport pygrib\nimport os\nimport pyart\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Download MRMS directly from NCEP",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def download_files(input_dt, max_seconds=300):\n \"\"\"\n This function takes an input datetime object, and will try to match with the closest mosaics in time\n that are available at NCEP. Note that NCEP does not archive much beyond 24 hours of data.\n \n Parameters\n ----------\n input_dt : datetime.datetime object\n input datetime object, will try to find closest file in time on NCEP server\n \n Other Parameters\n ----------------\n max_seconds : int or float\n Maximum number of seconds difference tolerated between input and selected datetimes,\n before file matching will fail\n \n Returns\n -------\n files : 1-D ndarray of strings\n Array of mosaic file names, ready for ingest into MMM-Py\n \"\"\"\n baseurl = 'http://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/'\n page1 = pd.read_html(baseurl)\n directories = np.array(page1[0][0][3:-1]) # May need to change indices depending on pandas version\n urllist = []\n files = []\n for i, d in enumerate(directories):\n print(baseurl + d)\n page2 = pd.read_html(baseurl + d)\n filelist = np.array(page2[0][0][3:-1]) # May need to change indices depending on pandas version\n dts = []\n for filen in filelist:\n # Will need to change in event of a name change\n dts.append(dt.datetime.strptime(filen[32:47], '%Y%m%d-%H%M%S'))\n dts = np.array(dts)\n diff = np.abs((dts - input_dt))\n if np.min(diff).total_seconds() <= max_seconds:\n urllist.append(baseurl + d + filelist[np.argmin(diff)])\n files.append(filelist[np.argmin(diff)])\n for url in urllist:\n print(url)\n os.system('wget ' + url)\n return np.array(files)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"files = download_files(dt.datetime.utcnow())",
"http://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_00.50/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_00.75/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_01.00/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_01.25/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_01.50/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_01.75/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_02.00/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_02.25/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_02.50/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_02.75/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_03.00/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_03.50/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_04.00/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_04.50/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_05.00/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_05.50/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_06.00/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_06.50/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_07.00/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_07.50/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_08.00/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_08.50/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_09.00/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_10.00/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_11.00/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_12.00/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_13.00/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_14.00/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_15.00/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_16.00/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_17.00/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_18.00/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_19.00/\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_00.50/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_00.50_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_00.75/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_00.75_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_01.00/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_01.00_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_01.25/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_01.25_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_01.50/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_01.50_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_01.75/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_01.75_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_02.00/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_02.00_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_02.25/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_02.25_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_02.50/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_02.50_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_02.75/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_02.75_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_03.00/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_03.00_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_03.50/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_03.50_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_04.00/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_04.00_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_04.50/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_04.50_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_05.00/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_05.00_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_05.50/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_05.50_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_06.00/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_06.00_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_06.50/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_06.50_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_07.00/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_07.00_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_07.50/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_07.50_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_08.00/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_08.00_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_08.50/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_08.50_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_09.00/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_09.00_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_10.00/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_10.00_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_11.00/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_11.00_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_12.00/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_12.00_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_13.00/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_13.00_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_14.00/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_14.00_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_15.00/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_15.00_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_16.00/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_16.00_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_17.00/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_17.00_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_18.00/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_18.00_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nhttp://mrms.ncep.noaa.gov/data/3DReflPlus/MergedReflectivityQC_19.00/MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_19.00_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Direct ingest of grib into MMM-Py",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mosaic = mmmpy.MosaicTile(files)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mosaic.diag()",
"\n********************\ndiag():\nPrinting basic metadata and making a simple plot\nData are from MRMS_MergedReflectivityQC_00.50_20170727-202238.grib2.gz\nMin, Max Latitude = 20.005 54.995\nMin, Max Longitude = -129.995 -60.0050000001\nHeights (km) = [ 0.5 0.75 1. 1.25 1.5 1.75 2. 2.25 2.5 2.75 3.\n 3.5 4. 4.5 5. 5.5 6. 6.5 7. 7.5 8. 8.5\n 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. ]\nGrid shape = (33, 3500, 7000)\nNow plotting ...\nDone!\n********************\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Plot with cartopy",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tiler = StamenTerrain()\n\next = [-130, -65, 20, 50]\nfig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))\nprojection = ccrs.PlateCarree() # ShadedReliefESRI().crs\nax = plt.axes(projection=projection)\nax.set_extent(ext)\nax.add_image(tiler, 3)\n\n# Create a feature for States/Admin 1 regions at 1:10m from Natural Earth\nstates_provinces = cfeature.NaturalEarthFeature(\n category='cultural',\n name='admin_1_states_provinces_lines',\n scale='50m',\n facecolor='none')\nax.add_feature(states_provinces, edgecolor='gray')\n\n# Create a feature for Countries 0 regions at 1:10m from Natural Earth\ncountries = cfeature.NaturalEarthFeature(\n category='cultural',\n name='admin_0_boundary_lines_land',\n scale='50m',\n facecolor='none')\nax.add_feature(countries, edgecolor='k')\n\nax.coastlines(resolution='50m')\n\nmosaic.get_comp()\nvalmask = np.ma.masked_where(mosaic.mrefl3d_comp <= 0, mosaic.mrefl3d_comp)\ncs = plt.pcolormesh(mosaic.Longitude, mosaic.Latitude, valmask, vmin=0, vmax=55,\n cmap='pyart_Carbone42', transform=projection)\nplt.colorbar(cs, label='Composite Reflectivity (dBZ)',\n orientation='horizontal', pad=0.05, shrink=0.75, fraction=0.05, aspect=30)\nplt.title(dt.datetime.utcfromtimestamp(mosaic.Time).strftime('%m/%d/%Y %H:%M UTC'))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c5033cc0ff899665e1ee06f5917e172404baf3b5
| 39,687 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
codes/labs_lecture05/lab01_mlp/mlp_demo.ipynb
|
xb-trainings/IPAM_2018
|
8927cb6be6dc112b64cb99b7bbcad4ae8c9110dd
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
codes/labs_lecture05/lab01_mlp/mlp_demo.ipynb
|
xb-trainings/IPAM_2018
|
8927cb6be6dc112b64cb99b7bbcad4ae8c9110dd
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
codes/labs_lecture05/lab01_mlp/mlp_demo.ipynb
|
xb-trainings/IPAM_2018
|
8927cb6be6dc112b64cb99b7bbcad4ae8c9110dd
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 154.424125 | 29,120 | 0.893567 |
[
[
[
"# Lab 01 : MLP -- demo\n\n# Understanding the training loop ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import torch\nimport torch.nn as nn\nimport torch.nn.functional as F\nimport torch.optim as optim\nfrom random import randint\nimport utils",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Download the data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from utils import check_mnist_dataset_exists\ndata_path=check_mnist_dataset_exists()\n\ntrain_data=torch.load(data_path+'mnist/train_data.pt')\ntrain_label=torch.load(data_path+'mnist/train_label.pt')\ntest_data=torch.load(data_path+'mnist/test_data.pt')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Make a three layer net class",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class three_layer_net(nn.Module):\n\n def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size1, hidden_size2, output_size):\n super(three_layer_net , self).__init__()\n \n self.layer1 = nn.Linear( input_size , hidden_size1 , bias=False )\n self.layer2 = nn.Linear( hidden_size1 , hidden_size2 , bias=False )\n self.layer3 = nn.Linear( hidden_size2 , output_size , bias=False )\n \n def forward(self, x):\n \n y = self.layer1(x)\n y_hat = F.relu(y)\n z = self.layer2(y_hat)\n z_hat = F.relu(z)\n scores = self.layer3(z_hat)\n \n return scores",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Build the net",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"net=three_layer_net(784, 50, 50, 10)\nprint(net)",
"three_layer_net(\n (layer1): Linear(in_features=784, out_features=50, bias=False)\n (layer2): Linear(in_features=50, out_features=50, bias=False)\n (layer3): Linear(in_features=50, out_features=10, bias=False)\n)\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Choose the criterion, optimizer, learning rate, and batch size",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()\n\noptimizer=torch.optim.SGD( net.parameters() , lr=0.01 )\n\nbs=200",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Train the network on the train set (process 5000 batches)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"for iter in range(1,5000):\n \n # Set dL/dU, dL/dV, dL/dW to be filled with zeros\n optimizer.zero_grad()\n \n # create a minibatch\n indices=torch.LongTensor(bs).random_(0,60000)\n minibatch_data = train_data[indices]\n minibatch_label= train_label[indices]\n \n #reshape the minibatch\n inputs = minibatch_data.view(bs,784)\n \n # tell Pytorch to start tracking all operations that will be done on \"inputs\"\n inputs.requires_grad_()\n\n # forward the minibatch through the net \n scores=net( inputs ) \n \n # Compute the average of the losses of the data points in the minibatch\n loss = criterion( scores , minibatch_label) \n \n # backward pass to compute dL/dU, dL/dV and dL/dW \n loss.backward()\n \n # do one step of stochastic gradient descent: U=U-lr(dL/dU), V=V-lr(dL/dU), ...\n optimizer.step()\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Choose image at random from the test set and see how good/bad are the predictions",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# choose a picture at random\nidx=randint(0, 10000-1)\nim=test_data[idx]\n\n# diplay the picture\nutils.show(im)\n\n# feed it to the net and display the confidence scores\nscores = net( im.view(1,784)) \nprob=F.softmax(scores, dim = 1)\n\nutils.show_prob_mnist(prob)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c503410afe6096a91028b8bde5657b0c00441985
| 10,836 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/.ipynb_checkpoints/vgg19-checkpoint.ipynb
|
arp95/pytorch_image_classifier
|
81db0a99b79dcebc39843869bf684c5090db6fdb
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2020-08-17T16:09:00.000Z
|
2021-02-02T04:52:17.000Z
|
notebooks/.ipynb_checkpoints/vgg19-checkpoint.ipynb
|
arp95/pytorch_image_classifier
|
81db0a99b79dcebc39843869bf684c5090db6fdb
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2020-10-14T02:21:46.000Z
|
2020-10-14T02:21:46.000Z
|
notebooks/.ipynb_checkpoints/vgg19-checkpoint.ipynb
|
arp95/cnn_architectures_image_classification
|
81db0a99b79dcebc39843869bf684c5090db6fdb
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 32.93617 | 169 | 0.502307 |
[
[
[
"# header files\nimport torch\nimport torch.nn as nn\nimport torchvision\nimport numpy as np\nfrom torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from google.colab import drive\ndrive.mount('/content/drive')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.random.seed(1234)\ntorch.manual_seed(1234)\ntorch.cuda.manual_seed(1234)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# define transforms\ntrain_transforms = torchvision.transforms.Compose([torchvision.transforms.RandomRotation(30),\n torchvision.transforms.Resize((224, 224)),\n torchvision.transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),\n torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),\n torchvision.transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# datasets\ntrain_data = torchvision.datasets.ImageFolder(\"/content/drive/My Drive/train_images/\", transform=train_transforms)\nval_data = torchvision.datasets.ImageFolder(\"/content/drive/My Drive/val_images/\", transform=train_transforms)\nprint(len(train_data))\nprint(len(val_data))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# load the data\ntrain_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_data, batch_size=32, shuffle=True, num_workers=16)\nval_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(val_data, batch_size=32, shuffle=False, num_workers=16)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class Convolution(torch.nn.Sequential):\n \n # init method\n def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, strides, padding):\n super().__init__()\n \n self.in_channels = in_channels\n self.out_channels = out_channels\n self.kernel_size = kernel_size\n self.strides = strides\n self.padding = padding\n\n self.add_module(\"conv\", torch.nn.Conv2d(self.in_channels, self.out_channels, kernel_size=self.kernel_size, stride=self.strides, padding=self.padding))\n self.add_module(\"norm\", torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(self.out_channels))\n self.add_module(\"act\", torch.nn.ReLU(inplace=True))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# define VGG19 network\nclass VGG19(torch.nn.Module):\n \n # init method\n def __init__(self, num_classes=2):\n super(VGG19, self).__init__()\n \n self.features = nn.Sequential(\n \n # first cnn block\n Convolution(3, 64, 3, 1, 1),\n Convolution(64, 64, 3, 1, 1),\n nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),\n \n # second cnn block\n Convolution(64, 128, 3, 1, 1),\n Convolution(128, 128, 3, 1, 1),\n nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),\n \n # third cnn block\n Convolution(128, 256, 3, 1, 1),\n Convolution(256, 256, 3, 1, 1),\n Convolution(256, 256, 3, 1, 1),\n Convolution(256, 256, 3, 1, 1),\n nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),\n \n # fourth cnn block\n Convolution(256, 512, 3, 1, 1),\n Convolution(512, 512, 3, 1, 1),\n Convolution(512, 512, 3, 1, 1),\n Convolution(512, 512, 3, 1, 1),\n nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),\n \n # fifth cnn block\n Convolution(512, 512, 3, 1, 1),\n Convolution(512, 512, 3, 1, 1),\n Convolution(512, 512, 3, 1, 1),\n Convolution(512, 512, 3, 1, 1),\n nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)\n )\n \n self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(7)\n \n self.classifier = nn.Sequential(\n nn.Linear(512 * 7 * 7, 4096),\n nn.ReLU(inplace = True),\n nn.Dropout(0.5),\n nn.Linear(4096, 4096),\n nn.ReLU(inplace = True),\n nn.Dropout(0.5),\n nn.Linear(4096, num_classes),\n )\n \n # forward step\n def forward(self, x):\n x = self.features(x)\n x = self.avgpool(x)\n x = x.view(x.shape[0], -1)\n x = self.classifier(x)\n return x",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Cross-Entropy loss with Label Smoothing\nclass CrossEntropyLabelSmoothingLoss(nn.Module):\n \n def __init__(self, smoothing=0.0):\n super(CrossEntropyLabelSmoothingLoss, self).__init__()\n self.smoothing = smoothing\n \n def forward(self, pred, target):\n log_prob = torch.nn.functional.log_softmax(pred, dim=-1)\n weight = input.new_ones(pred.size()) * (self.smoothing/(pred.size(-1)-1.))\n weight.scatter_(-1, target.unsqueeze(-1), (1.-self.smoothing))\n loss = (-weight * log_prob).sum(dim=-1).mean()\n return loss",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# define loss (smoothing=0 is equivalent to standard Cross-Entropy loss)\ncriterion = CrossEntropyLabelSmoothingLoss(0.0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# load model\ndevice = torch.device(\"cuda\" if torch.cuda.is_available() else \"cpu\")\nmodel = VGG19()\nmodel.to(device)\n\n# load tensorboard\n%load_ext tensorboard\n%tensorboard --logdir logs",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# optimizer to be used\noptimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.005, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=5e-4)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"best_metric = -1\nbest_metric_epoch = -1\nwriter = SummaryWriter(\"./logs/\")\n\n# train and validate\nfor epoch in range(0, 100):\n \n # train\n model.train()\n training_loss = 0.0\n total = 0\n correct = 0\n for i, (input, target) in enumerate(train_loader):\n input = input.to(device)\n target = target.to(device)\n\n optimizer.zero_grad()\n output = model(input)\n loss = criterion(output, target)\n \n loss.backward()\n optimizer.step()\n \n training_loss = training_loss + loss.item()\n _, predicted = output.max(1)\n total += target.size(0)\n correct += predicted.eq(target).sum().item()\n \n training_loss = training_loss/float(len(train_loader))\n training_accuracy = str(100.0*(float(correct)/float(total)))\n writer.add_scalar(\"Loss/train\", float(training_loss), epoch)\n writer.add_scalar(\"Accuracy/train\", float(training_accuracy), epoch)\n \n # validate\n model.eval()\n valid_loss = 0.0\n total = 0\n correct = 0\n for i, (input, target) in enumerate(val_loader):\n with torch.no_grad():\n input = input.to(device)\n target = target.to(device)\n\n output = model(input)\n loss = criterion(output, target)\n _, predicted = output.max(1)\n total += target.size(0)\n correct += predicted.eq(target).sum().item()\n \n valid_loss = valid_loss + loss.item()\n valid_loss = valid_loss/float(len(val_loader))\n valid_accuracy = str(100.0*(float(correct)/float(total)))\n writer.add_scalar(\"Loss/val\", float(valid_loss), epoch)\n writer.add_scalar(\"Accuracy/val\", float(valid_accuracy), epoch)\n\n\n # store best model\n if(float(valid_accuracy)>best_metric and epoch>=10):\n best_metric = float(valid_accuracy)\n best_metric_epoch = epoch\n torch.save(model.state_dict(), \"best_model_vgg19.pth\")\n \n print()\n print(\"Epoch\" + str(epoch) + \":\")\n print(\"Training Accuracy: \" + str(training_accuracy) + \" Validation Accuracy: \" + str(valid_accuracy))\n print(\"Training Loss: \" + str(training_loss) + \" Validation Loss: \" + str(valid_loss))\n print()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50345ee1648346d496b166848175e174d1bc3d3
| 714,404 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
1_notmnist.ipynb
|
nlharri/udacity-deep-learning
|
d9d5618638c1b24d73c6d8c9df8b15c7675765dc
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
1_notmnist.ipynb
|
nlharri/udacity-deep-learning
|
d9d5618638c1b24d73c6d8c9df8b15c7675765dc
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
1_notmnist.ipynb
|
nlharri/udacity-deep-learning
|
d9d5618638c1b24d73c6d8c9df8b15c7675765dc
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 216.486061 | 76,758 | 0.908882 |
[
[
[
"Deep Learning\n=============\n\nAssignment 1\n------------\n\nThe objective of this assignment is to learn about simple data curation practices, and familiarize you with some of the data we'll be reusing later.\n\nThis notebook uses the [notMNIST](http://yaroslavvb.blogspot.com/2011/09/notmnist-dataset.html) dataset to be used with python experiments. This dataset is designed to look like the classic [MNIST](http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/) dataset, while looking a little more like real data: it's a harder task, and the data is a lot less 'clean' than MNIST.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# These are all the modules we'll be using later. Make sure you can import them\n# before proceeding further.\nfrom __future__ import print_function\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport os\nimport sys\nimport tarfile\nfrom IPython.display import display, Image\nfrom scipy import ndimage\nimport imageio\nimport PIL.Image\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression\nfrom six.moves.urllib.request import urlretrieve\nfrom six.moves import cPickle as pickle",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"First, we'll download the dataset to our local machine. The data consists of characters rendered in a variety of fonts on a 28x28 image. The labels are limited to 'A' through 'J' (10 classes). The training set has about 500k and the testset 19.000 labelled examples. Given these sizes, it should be possible to train models quickly on any machine.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"url = 'http://yaroslavvb.com/upload/notMNIST/'\n\ndef maybe_download(filename, expected_bytes, force=False):\n \"\"\"Download a file if not present, and make sure it's the right size.\"\"\"\n if force or not os.path.exists(filename):\n filename, _ = urlretrieve(url + filename, filename)\n statinfo = os.stat(filename)\n if statinfo.st_size == expected_bytes:\n print('Found and verified', filename)\n else:\n raise Exception(\n 'Failed to verify' + filename + '. Can you get to it with a browser?')\n return filename\n\ntrain_filename = maybe_download('notMNIST_large.tar.gz', 247336696)\ntest_filename = maybe_download('notMNIST_small.tar.gz', 8458043)\nprint(\"Test file name: {}\".format(test_filename))\nprint(\"Train file name: {}\".format(train_filename))\n",
"Found and verified notMNIST_large.tar.gz\nFound and verified notMNIST_small.tar.gz\nTest file name: notMNIST_small.tar.gz\nTrain file name: notMNIST_large.tar.gz\n"
]
],
[
[
"Extract the dataset from the compressed .tar.gz file.\nThis should give you a set of directories, labelled A through J.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"num_classes = 10\nnp.random.seed(133)\n\ndef maybe_extract(filename, force=False):\n root = os.path.splitext(os.path.splitext(filename)[0])[0] # remove .tar.gz\n if os.path.isdir(root) and not force:\n # You may override by setting force=True.\n print('%s already present - Skipping extraction of %s.' % (root, filename))\n else:\n print('Extracting data for %s. This may take a while. Please wait.' % root)\n tar = tarfile.open(filename)\n sys.stdout.flush()\n tar.extractall()\n tar.close()\n data_folders = [\n os.path.join(root, d) for d in sorted(os.listdir(root))\n if os.path.isdir(os.path.join(root, d))]\n if len(data_folders) != num_classes:\n raise Exception(\n 'Expected %d folders, one per class. Found %d instead.' % (\n num_classes, len(data_folders)))\n print(data_folders)\n return data_folders\n \ntrain_folders = maybe_extract(train_filename)\ntest_folders = maybe_extract(test_filename)",
"Extracting data for notMNIST_large. This may take a while. Please wait.\n['notMNIST_large/A', 'notMNIST_large/B', 'notMNIST_large/C', 'notMNIST_large/D', 'notMNIST_large/E', 'notMNIST_large/F', 'notMNIST_large/G', 'notMNIST_large/H', 'notMNIST_large/I', 'notMNIST_large/J']\nExtracting data for notMNIST_small. This may take a while. Please wait.\n['notMNIST_small/A', 'notMNIST_small/B', 'notMNIST_small/C', 'notMNIST_small/D', 'notMNIST_small/E', 'notMNIST_small/F', 'notMNIST_small/G', 'notMNIST_small/H', 'notMNIST_small/I', 'notMNIST_small/J']\n"
]
],
[
[
"---\nProblem 1\n---------\n\nLet's take a peek at some of the data to make sure it looks sensible. Each exemplar should be an image of a character A through J rendered in a different font. Display a sample of the images that we just downloaded. Hint: you can use the package IPython.display.\n\n---",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"First of all, let's import some libraries that I will use later on and activate online display of matplotlib outputs:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import random\nimport hashlib\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def disp_samples(data_folders, sample_size):\n for folder in data_folders:\n print(folder)\n image_files = os.listdir(folder)\n image_sample = random.sample(image_files, sample_size)\n for image in image_sample:\n image_file = os.path.join(folder, image)\n i = Image(filename=image_file)\n display(i)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"disp_samples(train_folders, 5)",
"notMNIST_large/A\n"
],
[
"disp_samples(test_folders, 5)",
"notMNIST_small/A\n"
]
],
[
[
"Now let's load the data in a more manageable format. Since, depending on your computer setup you might not be able to fit it all in memory, we'll load each class into a separate dataset, store them on disk and curate them independently. Later we'll merge them into a single dataset of manageable size.\n\nWe'll convert the entire dataset into a 3D array (image index, x, y) of floating point values, normalized to have approximately zero mean and standard deviation ~0.5 to make training easier down the road. \n\nA few images might not be readable, we'll just skip them.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"image_size = 28 # Pixel width and height.\npixel_depth = 255.0 # Number of levels per pixel.\n\ndef load_letter(folder, min_num_images):\n \"\"\"Load the data for a single letter label.\"\"\"\n image_files = os.listdir(folder)\n dataset = np.ndarray(shape=(len(image_files), image_size, image_size),\n dtype=np.float32)\n image_index = 0\n print(folder)\n for image in os.listdir(folder):\n image_file = os.path.join(folder, image)\n \"\"\"Verify\"\"\"\n try:\n img = PIL.Image.open(image_file) # open the image file\n img.verify() # verify that it is, in fact an image\n image_data = (imageio.imread(image_file).astype(float) - \n pixel_depth / 2) / pixel_depth\n if image_data.shape != (image_size, image_size):\n raise Exception('Unexpected image shape: %s' % str(image_data.shape))\n dataset[image_index, :, :] = image_data\n image_index += 1\n except IOError as e:\n print('Could not read:', image_file, ':', e, '- it\\'s ok, skipping.')\n \n num_images = image_index\n dataset = dataset[0:num_images, :, :]\n if num_images < min_num_images:\n raise Exception('Many fewer images than expected: %d < %d' %\n (num_images, min_num_images))\n \n print('Full dataset tensor:', dataset.shape)\n print('Mean:', np.mean(dataset))\n print('Standard deviation:', np.std(dataset))\n return dataset\n \ndef maybe_pickle(data_folders, min_num_images_per_class, force=False):\n dataset_names = []\n for folder in data_folders:\n set_filename = folder + '.pickle'\n dataset_names.append(set_filename)\n if os.path.exists(set_filename) and not force:\n # You may override by setting force=True.\n print('%s already present - Skipping pickling.' % set_filename)\n else:\n print('Pickling %s.' % set_filename)\n dataset = load_letter(folder, min_num_images_per_class)\n try:\n with open(set_filename, 'wb') as f:\n pickle.dump(dataset, f, pickle.HIGHEST_PROTOCOL)\n except Exception as e:\n print('Unable to save data to', set_filename, ':', e)\n \n return dataset_names\n\ntrain_datasets = maybe_pickle(train_folders, 45000)\ntest_datasets = maybe_pickle(test_folders, 1800)",
"Pickling notMNIST_large/A.pickle.\nnotMNIST_large/A\nCould not read: notMNIST_large/A/RnJlaWdodERpc3BCb29rSXRhbGljLnR0Zg==.png : cannot identify image file 'notMNIST_large/A/RnJlaWdodERpc3BCb29rSXRhbGljLnR0Zg==.png' - it's ok, skipping.\nCould not read: notMNIST_large/A/Um9tYW5hIEJvbGQucGZi.png : cannot identify image file 'notMNIST_large/A/Um9tYW5hIEJvbGQucGZi.png' - it's ok, skipping.\nCould not read: notMNIST_large/A/SG90IE11c3RhcmQgQlROIFBvc3Rlci50dGY=.png : cannot identify image file 'notMNIST_large/A/SG90IE11c3RhcmQgQlROIFBvc3Rlci50dGY=.png' - it's ok, skipping.\nFull dataset tensor: (52909, 28, 28)\nMean: -0.12825038\nStandard deviation: 0.4431209\nPickling notMNIST_large/B.pickle.\nnotMNIST_large/B\nCould not read: notMNIST_large/B/TmlraXNFRi1TZW1pQm9sZEl0YWxpYy5vdGY=.png : cannot identify image file 'notMNIST_large/B/TmlraXNFRi1TZW1pQm9sZEl0YWxpYy5vdGY=.png' - it's ok, skipping.\nFull dataset tensor: (52911, 28, 28)\nMean: -0.007563031\nStandard deviation: 0.45449144\nPickling notMNIST_large/C.pickle.\nnotMNIST_large/C\nFull dataset tensor: (52912, 28, 28)\nMean: -0.14225803\nStandard deviation: 0.4398064\nPickling notMNIST_large/D.pickle.\nnotMNIST_large/D\nCould not read: notMNIST_large/D/VHJhbnNpdCBCb2xkLnR0Zg==.png : cannot identify image file 'notMNIST_large/D/VHJhbnNpdCBCb2xkLnR0Zg==.png' - it's ok, skipping.\nFull dataset tensor: (52911, 28, 28)\nMean: -0.057367746\nStandard deviation: 0.45564738\nPickling notMNIST_large/E.pickle.\nnotMNIST_large/E\n"
]
],
[
[
"---\nProblem 2\n---------\n\nLet's verify that the data still looks good. Displaying a sample of the labels and images from the ndarray. Hint: you can use matplotlib.pyplot.\n\n---",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def disp_8_img(imgs, titles):\n \"\"\"Display subplot with 8 images or less\"\"\"\n for i, img in enumerate(imgs):\n plt.subplot(2, 4, i+1)\n plt.title(titles[i])\n plt.axis('off')\n plt.imshow(img)\n\ndef disp_sample_pickles(data_folders):\n folder = random.sample(data_folders, 1)\n pickle_filename = ''.join(folder) + '.pickle'\n try:\n with open(pickle_filename, 'rb') as f:\n dataset = pickle.load(f)\n except Exception as e:\n print('Unable to read data from', pickle_filename, ':', e)\n return\n # display\n plt.suptitle(''.join(folder)[-1])\n for i, img in enumerate(random.sample(list(dataset), 8)):\n plt.subplot(2, 4, i+1)\n plt.axis('off')\n plt.imshow(img)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"disp_sample_pickles(train_folders)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"disp_sample_pickles(test_folders)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"---\nProblem 3\n---------\nAnother check: we expect the data to be balanced across classes. Verify that.\n\n---",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Data is balanced across classes if the classes have about the same number of items. Let's check the number of images by class.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def disp_number_images(data_folders):\n for folder in data_folders:\n pickle_filename = ''.join(folder) + '.pickle'\n try:\n with open(pickle_filename, 'rb') as f:\n dataset = pickle.load(f)\n except Exception as e:\n print('Unable to read data from', pickle_filename, ':', e)\n return\n print('Number of images in ', folder, ' : ', len(dataset))\n \ndisp_number_images(train_folders)\ndisp_number_images(test_folders) ",
"Number of images in notMNIST_large/A : 52909\nNumber of images in notMNIST_large/B : 52911\nNumber of images in notMNIST_large/C : 52912\nNumber of images in notMNIST_large/D : 52911\nNumber of images in notMNIST_large/E : 52912\nNumber of images in notMNIST_large/F : 52912\nNumber of images in notMNIST_large/G : 52912\nNumber of images in notMNIST_large/H : 52912\nNumber of images in notMNIST_large/I : 52912\nNumber of images in notMNIST_large/J : 52911\nNumber of images in notMNIST_small/A : 1872\nNumber of images in notMNIST_small/B : 1873\nNumber of images in notMNIST_small/C : 1873\nNumber of images in notMNIST_small/D : 1873\nNumber of images in notMNIST_small/E : 1873\nNumber of images in notMNIST_small/F : 1872\nNumber of images in notMNIST_small/G : 1872\nNumber of images in notMNIST_small/H : 1872\nNumber of images in notMNIST_small/I : 1872\nNumber of images in notMNIST_small/J : 1872\n"
]
],
[
[
"There are only minor gaps, so the classes are well balanced.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Merge and prune the training data as needed. Depending on your computer setup, you might not be able to fit it all in memory, and you can tune `train_size` as needed. The labels will be stored into a separate array of integers 0 through 9.\n\nAlso create a validation dataset for hyperparameter tuning.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def make_arrays(nb_rows, img_size):\n if nb_rows:\n dataset = np.ndarray((nb_rows, img_size, img_size), dtype=np.float32)\n labels = np.ndarray(nb_rows, dtype=np.int32)\n else:\n dataset, labels = None, None\n return dataset, labels\n\ndef merge_datasets(pickle_files, train_size, valid_size=0):\n num_classes = len(pickle_files)\n valid_dataset, valid_labels = make_arrays(valid_size, image_size)\n train_dataset, train_labels = make_arrays(train_size, image_size)\n vsize_per_class = valid_size // num_classes\n tsize_per_class = train_size // num_classes\n \n start_v, start_t = 0, 0\n end_v, end_t = vsize_per_class, tsize_per_class\n end_l = vsize_per_class+tsize_per_class\n for label, pickle_file in enumerate(pickle_files): \n try:\n with open(pickle_file, 'rb') as f:\n letter_set = pickle.load(f)\n # let's shuffle the letters to have random validation and training set\n np.random.shuffle(letter_set)\n if valid_dataset is not None:\n valid_letter = letter_set[:vsize_per_class, :, :]\n valid_dataset[start_v:end_v, :, :] = valid_letter\n valid_labels[start_v:end_v] = label\n start_v += vsize_per_class\n end_v += vsize_per_class\n \n train_letter = letter_set[vsize_per_class:end_l, :, :]\n train_dataset[start_t:end_t, :, :] = train_letter\n train_labels[start_t:end_t] = label\n start_t += tsize_per_class\n end_t += tsize_per_class\n except Exception as e:\n print('Unable to process data from', pickle_file, ':', e)\n raise\n \n return valid_dataset, valid_labels, train_dataset, train_labels\n \n \ntrain_size = 200000\nvalid_size = 10000\ntest_size = 10000\n\nvalid_dataset, valid_labels, train_dataset, train_labels = merge_datasets(\n train_datasets, train_size, valid_size)\n_, _, test_dataset, test_labels = merge_datasets(test_datasets, test_size)\n\nprint('Training:', train_dataset.shape, train_labels.shape)\nprint('Validation:', valid_dataset.shape, valid_labels.shape)\nprint('Testing:', test_dataset.shape, test_labels.shape)",
"Training: (200000, 28, 28) (200000,)\nValidation: (10000, 28, 28) (10000,)\nTesting: (10000, 28, 28) (10000,)\n"
]
],
[
[
"Next, we'll randomize the data. It's important to have the labels well shuffled for the training and test distributions to match.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def randomize(dataset, labels):\n permutation = np.random.permutation(labels.shape[0])\n shuffled_dataset = dataset[permutation,:,:]\n shuffled_labels = labels[permutation]\n return shuffled_dataset, shuffled_labels\ntrain_dataset, train_labels = randomize(train_dataset, train_labels)\ntest_dataset, test_labels = randomize(test_dataset, test_labels)\nvalid_dataset, valid_labels = randomize(valid_dataset, valid_labels)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"---\nProblem 4\n---------\nConvince yourself that the data is still good after shuffling!\n\n---",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"To be sure that the data are still fine after the merger and the randomization, I will select one item and display the image alongside the label. Note: 0 = A, 1 = B, 2 = C, 3 = D, 4 = E, 5 = F, 6 = G, 7 = H, 8 = I, 9 = J. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pretty_labels = {0: 'A', 1: 'B', 2: 'C', 3: 'D', 4: 'E', 5: 'F', 6: 'G', 7: 'H', 8: 'I', 9: 'J'}\n\ndef disp_sample_dataset(dataset, labels):\n items = random.sample(range(len(labels)), 8)\n for i, item in enumerate(items):\n plt.subplot(2, 4, i+1)\n plt.axis('off')\n plt.title(pretty_labels[labels[item]])\n plt.imshow(dataset[item])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"disp_sample_dataset(train_dataset, train_labels)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"disp_sample_dataset(valid_dataset, valid_labels)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"disp_sample_dataset(test_dataset, test_labels)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Finally, let's save the data for later reuse:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pickle_file = 'notMNIST.pickle'\n\ntry:\n f = open(pickle_file, 'wb')\n save = {\n 'train_dataset': train_dataset,\n 'train_labels': train_labels,\n 'valid_dataset': valid_dataset,\n 'valid_labels': valid_labels,\n 'test_dataset': test_dataset,\n 'test_labels': test_labels,\n }\n pickle.dump(save, f, pickle.HIGHEST_PROTOCOL)\n f.close()\nexcept Exception as e:\n print('Unable to save data to', pickle_file, ':', e)\n raise",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"statinfo = os.stat(pickle_file)\nprint('Compressed pickle size:', statinfo.st_size)",
"Compressed pickle size: 690800441\n"
]
],
[
[
"---\nProblem 5\n---------\n\nBy construction, this dataset might contain a lot of overlapping samples, including training data that's also contained in the validation and test set! Overlap between training and test can skew the results if you expect to use your model in an environment where there is never an overlap, but are actually ok if you expect to see training samples recur when you use it.\nMeasure how much overlap there is between training, validation and test samples.\n\nOptional questions:\n- What about near duplicates between datasets? (images that are almost identical)\n- Create a sanitized validation and test set, and compare your accuracy on those in subsequent assignments.\n---",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In this part, I will explore the datasets and understand better the overlap cases. There are overlaps, but there are also duplicates in the same dataset! Processing time is also critical. I will first use nested loops and matrix comparison, which is slow and then use hash function to accelerate and process the whole dataset.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def display_overlap(overlap, source_dataset, target_dataset):\n item = random.choice(overlap.keys())\n imgs = np.concatenate(([source_dataset[item]], target_dataset[overlap[item][0:7]]))\n plt.suptitle(item)\n for i, img in enumerate(imgs):\n plt.subplot(2, 4, i+1)\n plt.axis('off')\n plt.imshow(img)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def extract_overlap(dataset_1, dataset_2):\n overlap = {}\n for i, img_1 in enumerate(dataset_1):\n for j, img_2 in enumerate(dataset_2): \n if np.array_equal(img_1, img_2):\n if not i in overlap.keys():\n overlap[i] = []\n overlap[i].append(j)\n return overlap",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%time overlap_test_train = extract_overlap(test_dataset[:200], train_dataset)",
"CPU times: user 3min 27s, sys: 198 ms, total: 3min 28s\nWall time: 3min 28s\n"
],
[
"print('Number of overlaps:', len(overlap_test_train.keys()))\ndisplay_overlap(overlap_test_train, test_dataset[:200], train_dataset)",
"Number of overlaps: 24\n"
]
],
[
[
"The ``display_overlap`` function above display one of the duplicate, the first element is from the first dataset, and the next ones are from the dataset used for the comparison.\n\nNow that exact duplicates have been found, let's look for near duplicates. How to define near identical images? That's a tricky question. My first thought has been to use the ``allclose`` numpy matrix comparison. This is too restrictive, since two images can vary by one pyxel, and still be very similar even if the variation on the pyxel is large. A better solution involves some kind of average. \n\nTo keep is simple and still relevant, I will use a Manhattan norm (sum of absolute values) of the difference matrix. Since the images of the dataset have all the same size, I will not normalize the norm value. Note that it is pyxel by pyxel comparison, and therefore it will not scale to the whole dataset, but it will help to understand image similarities.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"MAX_MANHATTAN_NORM = 10\n\ndef extract_overlap_near(dataset_1, dataset_2):\n overlap = {}\n for i, img_1 in enumerate(dataset_1):\n for j, img_2 in enumerate(dataset_2):\n diff = img_1 - img_2\n m_norm = np.sum(np.abs(diff))\n if m_norm < MAX_MANHATTAN_NORM:\n if not i in overlap.keys():\n overlap[i] = []\n overlap[i].append(j)\n return overlap",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%time overlap_test_train_near = extract_overlap_near(test_dataset[:200], train_dataset)",
"CPU times: user 5min 1s, sys: 172 ms, total: 5min 1s\nWall time: 5min 1s\n"
],
[
"print('Number of near overlaps:', len(overlap_test_train_near.keys()))\ndisplay_overlap(overlap_test_train_near, test_dataset[:200], train_dataset)",
"Number of near overlaps: 53\n"
]
],
[
[
"The techniques above work well, but the performance is very low and the methods are poorly scalable to the full dataset. Let's try to improve the performance. Let's take some reference times on a small dataset.\n\nHere are some ideas:\n+ stop a the first occurence\n+ nympy function ``where`` in diff dataset\n+ hash comparison",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def extract_overlap_stop(dataset_1, dataset_2):\n overlap = {}\n for i, img_1 in enumerate(dataset_1):\n for j, img_2 in enumerate(dataset_2): \n if np.array_equal(img_1, img_2):\n overlap[i] = [j]\n break\n return overlap",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%time overlap_test_train = extract_overlap_stop(test_dataset[:200], train_dataset)",
"CPU times: user 3min 28s, sys: 430 ms, total: 3min 29s\nWall time: 3min 29s\n"
],
[
"print('Number of overlaps:', len(overlap_test_train.keys()))\ndisplay_overlap(overlap_test_train, test_dataset[:200], train_dataset)",
"Number of overlaps: 24\n"
]
],
[
[
"It is a faster, and only one duplicate from the second dataset is displayed. This is still not scalable.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"MAX_MANHATTAN_NORM = 10\n\ndef extract_overlap_where(dataset_1, dataset_2):\n overlap = {}\n for i, img_1 in enumerate(dataset_1):\n diff = dataset_2 - img_1\n norm = np.sum(np.abs(diff), axis=1)\n duplicates = np.where(norm < MAX_MANHATTAN_NORM)\n if len(duplicates[0]):\n overlap[i] = duplicates[0]\n return overlap",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"test_flat = test_dataset.reshape(test_dataset.shape[0], 28 * 28)\ntrain_flat = train_dataset.reshape(train_dataset.shape[0], 28 * 28)\n%time overlap_test_train = extract_overlap_where(test_flat[:200], train_flat)",
"CPU times: user 1min 21s, sys: 1min 14s, total: 2min 36s\nWall time: 2min 36s\n"
],
[
"print('Number of overlaps:', len(overlap_test_train.keys()))\ndisplay_overlap(overlap_test_train, test_dataset[:200], train_dataset)",
"Number of overlaps: 53\n"
]
],
[
[
"The built-in numpy function provides some improvement either, but this algorithm is still not scalable to the dataset to its full extend.\n\nTo make it work at scale, the best option is to use a hash function. To find exact duplicates, the hash functions used for the cryptography will work just fine.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def extract_overlap_hash(dataset_1, dataset_2):\n dataset_hash_1 = [hashlib.sha256(img).hexdigest() for img in dataset_1]\n dataset_hash_2 = [hashlib.sha256(img).hexdigest() for img in dataset_2]\n overlap = {}\n for i, hash1 in enumerate(dataset_hash_1):\n for j, hash2 in enumerate(dataset_hash_2):\n if hash1 == hash2:\n if not i in overlap.keys():\n overlap[i] = []\n overlap[i].append(j) ## use np.where\n return overlap",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%time overlap_test_train = extract_overlap_hash(test_dataset[:200], train_dataset)",
"CPU times: user 8.3 s, sys: 62.6 ms, total: 8.37 s\nWall time: 8.33 s\n"
],
[
"print('Number of overlaps:', len(overlap_test_train.keys()))\ndisplay_overlap(overlap_test_train, test_dataset[:200], train_dataset)",
"Number of overlaps: 24\n"
]
],
[
[
"More overlapping values could be found, this is due to the hash collisions. Several images can have the same hash but are actually different differents. This is not noticed here, and even if it happens, this is acceptable. All duplicates will be removed for sure.\n\nWe can make the processing a but faster by using the built-in numpy ``where``function.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def extract_overlap_hash_where(dataset_1, dataset_2):\n dataset_hash_1 = np.array([hashlib.sha256(img).hexdigest() for img in dataset_1])\n dataset_hash_2 = np.array([hashlib.sha256(img).hexdigest() for img in dataset_2])\n overlap = {}\n for i, hash1 in enumerate(dataset_hash_1):\n duplicates = np.where(dataset_hash_2 == hash1)\n if len(duplicates[0]):\n overlap[i] = duplicates[0]\n return overlap",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%time overlap_test_train = extract_overlap_hash_where(test_dataset[:200], train_dataset)",
"CPU times: user 2.31 s, sys: 12.2 ms, total: 2.33 s\nWall time: 2.33 s\n"
],
[
"print('Number of overlaps:', len(overlap_test_train.keys()))\ndisplay_overlap(overlap_test_train, test_dataset[:200], train_dataset)",
"Number of overlaps: 24\n"
]
],
[
[
"From my perspective near duplicates should also be removed in the sanitized datasets. My assumption is that \"near\" duplicates are very very close (sometimes just there is a one pyxel border of difference), and penalyze the training the same way the true duplicates do.\n\nThat's being said, finding near duplicates with a hash function is not obvious. There are techniques for that, like \"locally sensitive hashing\", \"perceptual hashing\" or \"difference hashing\". There even are Python library available. Unfortunatly I did not have time to try them. The sanitized dataset generated below are based on true duplicates found with a cryptography hash function.\n\nFor sanitizing the dataset, I change the function above by returning the clean dataset directly.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def sanetize(dataset_1, dataset_2, labels_1):\n dataset_hash_1 = np.array([hashlib.sha256(img).hexdigest() for img in dataset_1])\n dataset_hash_2 = np.array([hashlib.sha256(img).hexdigest() for img in dataset_2])\n overlap = [] # list of indexes\n for i, hash1 in enumerate(dataset_hash_1):\n duplicates = np.where(dataset_hash_2 == hash1)\n if len(duplicates[0]):\n overlap.append(i) \n return np.delete(dataset_1, overlap, 0), np.delete(labels_1, overlap, None)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%time test_dataset_sanit, test_labels_sanit = sanetize(test_dataset[:200], train_dataset, test_labels[:200])\nprint('Overlapping images removed: ', len(test_dataset[:200]) - len(test_dataset_sanit))",
"CPU times: user 2.63 s, sys: 21.8 ms, total: 2.65 s\nWall time: 2.66 s\nOverlapping images removed: 24\n"
]
],
[
[
"The same value is found, so we can now sanetize the test and the train datasets.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%time test_dataset_sanit, test_labels_sanit = sanetize(test_dataset, train_dataset, test_labels)\nprint('Overlapping images removed: ', len(test_dataset) - len(test_dataset_sanit))",
"CPU times: user 22.9 s, sys: 112 ms, total: 23.1 s\nWall time: 23.1 s\nOverlapping images removed: 1324\n"
],
[
"%time valid_dataset_sanit, valid_labels_sanit = sanetize(valid_dataset, train_dataset, valid_labels)\nprint('Overlapping images removed: ', len(valid_dataset) - len(valid_dataset_sanit))",
"CPU times: user 22.9 s, sys: 115 ms, total: 23 s\nWall time: 23 s\nOverlapping images removed: 1067\n"
],
[
"pickle_file_sanit = 'notMNIST_sanit.pickle'\n\ntry:\n f = open(pickle_file_sanit, 'wb')\n save = {\n 'train_dataset': train_dataset,\n 'train_labels': train_labels,\n 'valid_dataset': valid_dataset_sanit,\n 'valid_labels': valid_labels_sanit,\n 'test_dataset': test_dataset_sanit,\n 'test_labels': test_labels_sanit,\n }\n pickle.dump(save, f, pickle.HIGHEST_PROTOCOL)\n f.close()\nexcept Exception as e:\n print('Unable to save data to', pickle_file, ':', e)\n raise",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"statinfo = os.stat(pickle_file_sanit)\nprint('Compressed pickle size:', statinfo.st_size)",
"Compressed pickle size: 683292701\n"
]
],
[
[
"Since I did not have time to generate clean sanitized datasets, I did not use the datasets generated above in the training of the my NN in the next assignments.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"---\nProblem 6\n---------\n\nLet's get an idea of what an off-the-shelf classifier can give you on this data. It's always good to check that there is something to learn, and that it's a problem that is not so trivial that a canned solution solves it.\n\nTrain a simple model on this data using 50, 100, 1000 and 5000 training samples. Hint: you can use the LogisticRegression model from sklearn.linear_model.\n\nOptional question: train an off-the-shelf model on all the data!\n\n---",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"I have already used scikit-learn in a previous MOOC. It is a great tool, very easy to use!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"regr = LogisticRegression()\nX_test = test_dataset.reshape(test_dataset.shape[0], 28 * 28)\ny_test = test_labels",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sample_size = 50\nX_train = train_dataset[:sample_size].reshape(sample_size, 784)\ny_train = train_labels[:sample_size]\n%time regr.fit(X_train, y_train)\nregr.score(X_test, y_test)",
"CPU times: user 46.2 ms, sys: 1.59 ms, total: 47.8 ms\nWall time: 47 ms\n"
],
[
"pred_labels = regr.predict(X_test)\ndisp_sample_dataset(test_dataset, pred_labels)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sample_size = 100\nX_train = train_dataset[:sample_size].reshape(sample_size, 784)\ny_train = train_labels[:sample_size]\n%time regr.fit(X_train, y_train)\nregr.score(X_test, y_test)",
"CPU times: user 114 ms, sys: 1.49 ms, total: 115 ms\nWall time: 115 ms\n"
],
[
"sample_size = 1000\nX_train = train_dataset[:sample_size].reshape(sample_size, 784)\ny_train = train_labels[:sample_size]\n%time regr.fit(X_train, y_train)\nregr.score(X_test, y_test)",
"CPU times: user 2.82 s, sys: 50.1 ms, total: 2.87 s\nWall time: 2.3 s\n"
],
[
"X_valid = valid_dataset[:sample_size].reshape(sample_size, 784)\ny_valid = valid_labels[:sample_size]\nregr.score(X_valid, y_valid)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pred_labels = regr.predict(X_valid)\ndisp_sample_dataset(valid_dataset, pred_labels)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sample_size = 5000\nX_train = train_dataset[:sample_size].reshape(sample_size, 784)\ny_train = train_labels[:sample_size]\n%time regr.fit(X_train, y_train)\nregr.score(X_test, y_test)",
"CPU times: user 19.9 s, sys: 82.7 ms, total: 20 s\nWall time: 20 s\n"
]
],
[
[
"To train the model on all the data, we have to use another solver. SAG is the faster one.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"regr2 = LogisticRegression(solver='sag')\nsample_size = len(train_dataset)\nX_train = train_dataset[:sample_size].reshape(sample_size, 784)\ny_train = train_labels[:sample_size]\n%time regr2.fit(X_train, y_train)\nregr2.score(X_test, y_test)",
"CPU times: user 9min 16s, sys: 1.72 s, total: 9min 18s\nWall time: 9min 40s\n"
],
[
"pred_labels = regr.predict(X_test)\ndisp_sample_dataset(test_dataset, pred_labels)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The accuracy may be weak compared to a deep neural net, but as my first character recognition technique, I find it already impressive!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
c5034ed13ef6b986877d5b5649c0681845520d87
| 109,861 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
python/made_ASG.ipynb
|
saisenberg/mlb-asg
|
b701da9ee42bad3fe93acd980a8bf3fed9715931
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
python/made_ASG.ipynb
|
saisenberg/mlb-asg
|
b701da9ee42bad3fe93acd980a8bf3fed9715931
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
python/made_ASG.ipynb
|
saisenberg/mlb-asg
|
b701da9ee42bad3fe93acd980a8bf3fed9715931
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 39.532566 | 19,948 | 0.453509 |
[
[
[
"# MLB's Biggest All-Star Injustices",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import dependencies\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\npd.set_option('display.max_columns', 100)\npd.options.mode.chained_assignment = None\n\nfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression, SGDClassifier\nfrom sklearn.metrics import classification_report, roc_auc_score\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV, train_test_split\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler\n\nimport seaborn as sns\nimport warnings\nwarnings.simplefilter(action='ignore', category=FutureWarning)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Print accuracy of pandas crosstab\ndef crosstabAccuracy(ct):\n try:\n acc = (ct[0][0]+ct[1][1]) / (ct[0][0]+ct[1][1]+ct[0][1]+ct[1][0])\n except:\n acc = (ct[0][0]) / (ct[0][0]+ct[1][0])\n return(100*round(acc,3))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Print classification report with specified threshold\ndef thresholdReport(continuous_predictions, actual_results, threshold):\n updated_preds = np.array([1 if pred > threshold else 0 for pred in continuous_predictions])\n print(classification_report(y_pred=updated_preds, y_true=actual_results))\n print(pd.crosstab(updated_preds, actual_results))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Read data\nfh = pd.read_csv('.\\\\data\\\\firsthalf.csv')\n\n# Change 'position' to dummy variables\nposition_dummies = pd.get_dummies(fh.position)\nfh = fh.drop('position', axis=1)\nfh = pd.concat([fh, position_dummies], axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Initial df metrics\nprint(fh.shape)\nprint(fh.made_asg.value_counts(normalize=True))\nprint(fh.columns)",
"(6745, 66)\n0 0.814233\n1 0.185767\nName: made_asg, dtype: float64\nIndex(['player', 'AVG', 'BABIP', 'BB%', 'BsR', 'Def', 'G', 'HR', 'ISO', 'K%',\n 'OBP', 'Off', 'PA', 'R', 'RBI', 'SB', 'SLG', 'WAR', 'team', 'wOBA',\n 'wRC+', 'year', 'league', 'league_year_ID', 'player_year_ID',\n 'made_asg', 'num_games', 'playerID', 'started_asg', 'W-L%', 'popular',\n 'NYY', 'BOS', 'CHC', 'LAD', 'team_year_id', 'won_WS_PY', 'lost_WS_PY',\n 'played_WS_PY', 'DOB', 'years_old_SOS', 'rank_WAR', 'rank_wRC',\n 'rank_OBP', 'rank_SLG', 'rank_HR', 'rank_AVG', 'rank_Off', 'rank_Def',\n 'rank_SB', 'team_rank_WAR', 'team_rank_wRC', 'team_rank_OBP',\n 'team_rank_SLG', 'team_rank_HR', 'team_rank_AVG', 'team_rank_Off',\n 'team_rank_Def', 'team_rank_SB', '1B', '2B', '3B', 'C', 'DH', 'OF',\n 'SS'],\n dtype='object')\n"
],
[
"# Set features\nmodelcols = [\n 'AVG',\n 'Def',\n 'HR',\n 'K%',\n 'SB',\n 'WAR',\n 'popular',\n 'won_WS_PY',\n 'lost_WS_PY',\n '1B',\n '2B',\n '3B',\n 'C',\n 'DH',\n 'OF',\n 'SS'\n]\n\nY = fh.made_asg\nX = fh.loc[:,modelcols]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Correlation matrix\nsns.heatmap(X.corr(), cmap='RdBu_r')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Xtrain, Xtest, Ytrain, Ytest = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.20, \n stratify=Y, random_state=1000)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Logistic Regression (unscaled)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Train logistic regression model\nlogR = LogisticRegression(penalty='l1')\nlogR.fit(Xtrain, Ytrain)\npd.crosstab(logR.predict(Xtrain), Ytrain)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Test logistic regression model\nlogR_preds_binary = logR.predict(Xtest)\nlogR_preds_continuous = logR.predict_proba(Xtest)[:,1]\nlogR_ct = pd.crosstab(logR_preds_binary, Ytest)\nprint('Accuracy:',crosstabAccuracy(logR_ct))\nprint('AUC: {:.1f}'.format(100*roc_auc_score(y_score=logR_preds_continuous, y_true=Ytest)))\nlogR_ct",
"Accuracy: 89.0\nAUC: 92.5\n"
],
[
"# Classification report @ 0.40 threshold\nthresholdReport(continuous_predictions=logR_preds_continuous,\n actual_results=Ytest, \n threshold=0.40)",
" precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.93 0.93 0.93 1098\n 1 0.70 0.70 0.70 251\n\navg / total 0.89 0.89 0.89 1349\n\nmade_asg 0 1\nrow_0 \n0 1023 75\n1 75 176\n"
],
[
"# Feature coefficients\nprint(len(X.columns), 'features:')\nfor num, feature in enumerate(Xtrain.columns):\n print(logR.coef_[0][num], feature)",
"16 features:\n12.379747894756527 AVG\n-0.08465519851976787 Def\n0.13280894704336563 HR\n-0.08212782124728421 K%\n0.03243155022366087 SB\n1.1514895480457437 WAR\n0.3034187139195672 popular\n0.994338258269651 won_WS_PY\n1.0377194586969876 lost_WS_PY\n-1.1061999746345663 1B\n0.0 2B\n-0.2507775754295886 3B\n1.1517490471387446 C\n-1.16989673207255 DH\n-0.8091043195673008 OF\n0.5604062178846984 SS\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Lasso / Ridge / Elastic Net",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Scale all features for lasso, ridge, EN\nscaler = StandardScaler()\nXtrainscaled = pd.DataFrame(scaler.fit_transform(Xtrain))\nXtrainscaled.columns = modelcols\nXtestscaled = pd.DataFrame(scaler.transform(Xtest))\nXtestscaled.columns = modelcols",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Binary columns back to 0-1\nbinaries = ['popular', 'NYY', 'BOS', 'CHC', 'LAD', 'won_WS_PY',\n 'lost_WS_PY', 'played_WS_PY', '1B', '2B', '3B', 'C',\n 'DH', 'OF', 'SS']\nfor col in binaries:\n try:\n Xtrainscaled[col] = Xtrainscaled[col].apply(lambda x: 1 if x>0 else 0)\n Xtestscaled[col] = Xtestscaled[col].apply(lambda x: 1 if x>0 else 0)\n except:\n pass",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Conduct Lasso, Ridge, EN for different levels of alpha (never outperforms logistic)\nprint('AUCs:\\n\\n')\nfor i in np.arange(0.01, 0.50, 0.02):\n alpha = i\n print('Alpha = {:.2f}'.format(alpha))\n \n lasso_model = SGDClassifier(penalty='l1', alpha=alpha, max_iter=100, loss='modified_huber')\n lasso_model.fit(Xtrainscaled, Ytrain)\n ridge_model = SGDClassifier(penalty='l2', alpha=alpha, max_iter=100, loss='modified_huber')\n ridge_model.fit(Xtrainscaled, Ytrain)\n elastic_model = SGDClassifier(penalty='l1', alpha=alpha, l1_ratio=0.50, max_iter=100, loss='modified_huber')\n elastic_model.fit(Xtrainscaled, Ytrain)\n\n lasso_model_preds = lasso_model.predict_proba(Xtestscaled)[:,1]\n print('Lasso: {:.1f}'.format(100*roc_auc_score(y_score=lasso_model_preds, y_true=Ytest)))\n\n ridge_model_preds = ridge_model.predict_proba(Xtestscaled)[:,1]\n print('Ridge: {:.1f}'.format(100*roc_auc_score(y_score=ridge_model_preds, y_true=Ytest))) \n\n elastic_model_preds = elastic_model.predict_proba(Xtestscaled)[:,1]\n print('Elastic: {:.1f}'.format(100*roc_auc_score(y_score=elastic_model_preds, y_true=Ytest)))\n \n print('------------')",
"AUCs:\n\n\nAlpha = 0.01\nLasso: 91.3\nRidge: 92.2\nElastic: 91.6\n------------\nAlpha = 0.03\nLasso: 90.4\nRidge: 92.0\nElastic: 90.6\n------------\nAlpha = 0.05\nLasso: 90.2\nRidge: 91.9\nElastic: 90.2\n------------\nAlpha = 0.07\nLasso: 90.3\nRidge: 91.9\nElastic: 90.1\n------------\nAlpha = 0.09\nLasso: 90.1\nRidge: 91.8\nElastic: 90.3\n------------\nAlpha = 0.11\nLasso: 90.1\nRidge: 91.7\nElastic: 90.1\n------------\nAlpha = 0.13\nLasso: 90.1\nRidge: 91.6\nElastic: 90.1\n------------\nAlpha = 0.15\nLasso: 90.1\nRidge: 91.5\nElastic: 90.1\n------------\nAlpha = 0.17\nLasso: 90.1\nRidge: 91.5\nElastic: 90.1\n------------\nAlpha = 0.19\nLasso: 90.0\nRidge: 91.4\nElastic: 89.2\n------------\nAlpha = 0.21\nLasso: 89.9\nRidge: 91.4\nElastic: 90.0\n------------\nAlpha = 0.23\nLasso: 89.9\nRidge: 91.3\nElastic: 89.9\n------------\nAlpha = 0.25\nLasso: 89.1\nRidge: 91.3\nElastic: 88.7\n------------\nAlpha = 0.27\nLasso: 89.0\nRidge: 91.3\nElastic: 89.7\n------------\nAlpha = 0.29\nLasso: 89.5\nRidge: 91.2\nElastic: 89.5\n------------\nAlpha = 0.31\nLasso: 88.7\nRidge: 91.3\nElastic: 88.7\n------------\nAlpha = 0.33\nLasso: 88.7\nRidge: 91.3\nElastic: 89.1\n------------\nAlpha = 0.35\nLasso: 88.7\nRidge: 91.2\nElastic: 88.9\n------------\nAlpha = 0.37\nLasso: 88.7\nRidge: 91.2\nElastic: 88.7\n------------\nAlpha = 0.39\nLasso: 88.7\nRidge: 91.2\nElastic: 88.7\n------------\nAlpha = 0.41\nLasso: 88.7\nRidge: 91.2\nElastic: 88.7\n------------\nAlpha = 0.43\nLasso: 88.7\nRidge: 91.2\nElastic: 88.7\n------------\nAlpha = 0.45\nLasso: 88.7\nRidge: 91.2\nElastic: 88.7\n------------\nAlpha = 0.47\nLasso: 88.7\nRidge: 91.2\nElastic: 88.7\n------------\nAlpha = 0.49\nLasso: 88.7\nRidge: 91.2\nElastic: 88.7\n------------\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Random Forest",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Grid search for random forest\nparams = {\n 'max_depth':[5,6,7,8],\n 'max_features':[3,5,10,None],\n 'min_samples_leaf':[1,3,7,11],\n 'n_estimators':[301] \n}\n\nrf_for_gs = RandomForestClassifier()\ngrid_search_rf = GridSearchCV(estimator=rf_for_gs, param_grid=params, cv=7, n_jobs=4)\ngrid_search_rf.fit(Xtrain, Ytrain)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Best random forest parameters\ngrid_search_rf.best_params_",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Train model\nrf = RandomForestClassifier(max_depth=8, max_features=5, min_samples_leaf=3, \n n_estimators=1001, oob_score=True)\nrf.fit(Xtrain, Ytrain)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Training results\npd.crosstab(rf.predict(Xtrain), Ytrain)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Test results (does not outperform logistic)\nrf_probs_binary = rf.predict(Xtest)\nrf_probs_continuous = rf.predict_proba(Xtest)[:,1]\nct_rf = pd.crosstab(rf_probs_binary, Ytest)\nprint('Accuracy: {:.1f}'.format(crosstabAccuracy(ct_rf)))\nprint('AUC: {:.1f}'.format(100*roc_auc_score(y_score=rf_probs_continuous, y_true=Ytest)))\nct_rf",
"Accuracy: 87.8\nAUC: 91.5\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Full model (Logistic Regression)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Train logistic regression on full data set\nlogR_full = LogisticRegression(penalty='l1').fit(X,Y)\nfull_preds_lr = pd.Series(logR_full.predict_proba(X)[:,1])\nfh_preds = pd.concat([fh, full_preds_lr], axis=1).rename(columns={0:'pred_lr'})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Feature coefficients\nfor num, feature in enumerate(X.columns):\n print(round(logR_full.coef_[0][num],2), feature)",
"12.03 AVG\n-0.08 Def\n0.14 HR\n-0.09 K%\n0.03 SB\n1.15 WAR\n0.27 popular\n1.0 won_WS_PY\n1.17 lost_WS_PY\n-1.13 1B\n0.0 2B\n-0.31 3B\n1.07 C\n-1.26 DH\n-0.85 OF\n0.62 SS\n"
],
[
"# Reorder columns\ncols = fh_preds.columns.tolist()\ncols.insert(1, cols.pop(cols.index('year'))) # move \"year\"\ncols.insert(2, cols.pop(cols.index('made_asg'))) # move \"made_asg\"\ncols.insert(3, cols.pop(cols.index('started_asg'))) # move \"started_asg\"\ncols = cols[-1:] + cols[:-1]\nfh_preds = fh_preds[cols]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Should have made ASG, but didn't\nfh_preds[fh_preds['made_asg']==0].sort_values('pred_lr', ascending=False).head(5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Made ASG, but shouldn't have\nfh_preds[fh_preds['made_asg']==1].sort_values('pred_lr', ascending=True).head(5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fh_preds.sort_values('pred_lr', ascending=False).tail(5)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Deploy model on 2018 first-half data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import 2018 data\nfh2018_full = pd.read_csv('.\\\\data\\\\firsthalf2018.csv')\n\n# Change 'position' to dummy variables\nposition_dummies2 = pd.get_dummies(fh2018_full.position)\nfh2018_full = fh2018_full.drop(['position', 'Unnamed: 0'], axis=1)\nfh2018_full = pd.concat([fh2018_full, position_dummies2], axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Deploy logistic regression model on 2018 data\nfh2018 = fh2018_full.loc[:,modelcols]\nfh2018_full['prob_lr'] = pd.Series(logR_full.predict_proba(fh2018)[:,1])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Lowest 2018 ASG probabilities\nfh2018_full.loc[:,['player', 'prob_lr', 'AVG', 'OBP', 'SLG', 'HR', 'WAR']].sort_values('prob_lr', ascending=True).head(5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Highest 2018 ASG probabilities\nfh2018_full.loc[:,['player', 'prob_lr', 'AVG', 'OBP', 'SLG', 'HR', 'WAR']].sort_values('prob_lr', ascending=False).head(5)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c5034f835eb217ea3fe35f0b7ee765cbd4098fde
| 5,077 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
project-face-recognition/face-recognition/ANN_faceClassification/src/OpenCV1.ipynb
|
langsari/ftu-artificial-intelligence
|
fcfb2864f36639d4276d9519b421105d8ccd09d0
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
project-face-recognition/face-recognition/ANN_faceClassification/src/OpenCV1.ipynb
|
langsari/ftu-artificial-intelligence
|
fcfb2864f36639d4276d9519b421105d8ccd09d0
|
[
"MIT"
] | 7 |
2021-06-08T22:21:56.000Z
|
2022-03-12T00:48:11.000Z
|
project-face-recognition/face-recognition/ANN_faceClassification/src/OpenCV1.ipynb
|
langsari/ftu-artificial-intelligence
|
fcfb2864f36639d4276d9519b421105d8ccd09d0
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 60.440476 | 1,613 | 0.628521 |
[
[
[
"import cv2\nfaceCascade=cv2.CascadeClassifier(\"haarcascade_frontalface_default.xml\")\neyeCascade=cv2.CascadeClassifier(\"haarcascade_eye.xml\")\nnoseCascade=cv2.CascadeClassifier(\"Nariz.xml\")\nmouthCascade=cv2.CascadeClassifier(\"Mouth.xml\")\nsmileCascade=cv2.CascadeClassifier(\"haarcascade_smile.xml\")\n\ndef draw_boundary(img,classifier,scaleFactor,minNeighbors,color,text):\n gray=cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)\n features=classifier.detectMultiScale(gray,scaleFactor,minNeighbors,minSize=(55, 55))\n coords=[]\n for (x,y,w,h) in features:\n cv2.rectangle(img,(x,y),(x+w,y+h),color,2)\n cv2.putText(img,text,(x,y-4),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,0.8,color,2)\n coords=[x,y,w,h]\n return img,coords \n \ndef detect(img,faceCascade,eyeCascade,mouthCascade):\n img,coords=draw_boundary(img,faceCascade,1.1,10,(0,0,255),\"Face\")\n img,coords=draw_boundary(img,eyeCascade,1.1,10,(255,0,0),\"Eye\")\n img,coords=draw_boundary(img,mouthCascade,1.1,20,(0,255,0),\"Mouth\")\n return img\n\n \ncap = cv2.VideoCapture(\"BNK48.mp4\")\ncap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH, 1920)\ncap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT, 1080)\nwhile (True):\n ret,frame = cap.read()\n frame=detect(frame,faceCascade,eyeCascade,mouthCascade)\n cv2.imshow('frame',frame)\n if(cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF== ord('q')):\n break\ncap.release()\ncv2.destroyAllWindows()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
]
] |
c5035513456733df73ce4fed8864aad5fff8c0ba
| 79,237 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
chap2/algo_chap2.ipynb
|
K2OTO/HajimetenoHoge
|
adb8165a6a9686b6a593a6dbfc105a38070b906c
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2020-08-25T03:33:15.000Z
|
2020-09-29T12:29:01.000Z
|
chap2/algo_chap2.ipynb
|
K2OTO/HajimetenoHoge
|
adb8165a6a9686b6a593a6dbfc105a38070b906c
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
chap2/algo_chap2.ipynb
|
K2OTO/HajimetenoHoge
|
adb8165a6a9686b6a593a6dbfc105a38070b906c
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2020-08-25T03:34:26.000Z
|
2020-09-29T12:01:30.000Z
| 124.782677 | 14,348 | 0.84164 |
[
[
[
"import numpy as np\n%matplotlib inline\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nnp.random.seed(0)\nfrom statistics import mean",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"今回はアルゴリズムの評価が中心の章なので,学習アルゴリズム実装は後に回し、sklearnを学習アルゴリズムとして使用する。",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import sklearn",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"今回、学習に使うデータはsin関数に正規分布$N(\\varepsilon|0,0.05)$ノイズ項を加えたデータを使う",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"size = 100\nmax_degree = 11\nx_data = np.random.rand(size) * np.pi * 2\nvar_data = np.random.normal(loc=0,scale=0.1,size=size)\nsin_data = np.sin(x_data) + var_data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.ylim(-1.2,1.2)\nplt.scatter(x_data,sin_data)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n学習用のアルゴリズムは多項式回帰を使います。",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression\nfrom sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"2.2.2:**MSE**:近似の良さの評価手法。\n\n$$MSE=\\int (y(x;D) - h(x))^2p(x)dx=E\\{(y(x;D)-h(x))^2\\}$$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def MSE(y,t):\n return np.sum(np.square(y-t))/y.size",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"MSE(np.array([10,3,3]),np.array([1,2,3]))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"2.2.1 (1)**ホールドアウト法**:\n手元のデータを2つに分割し、片方をトレーニングに使い、片方をテストに使う手法。\nテストデータの数が必要",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%time\ndef holdout_method(x,y,per=0.8,value_func=MSE,degree=11):\n index = np.random.permutation(x.size)\n index_train,index_test = np.split(index,[int(x.size*per)])\n #plt.scatter(x_data[index_train],sin_data[index_train])\n test_score_list = []\n train_score_list = []\n for i in range(1,degree):\n pf = PolynomialFeatures(degree=i, include_bias=False)\n lr = LinearRegression()\n pl = Pipeline([(\"PF\", pf), (\"LR\", lr)])\n pl.fit(x[index_train].reshape(-1,1), y[index_train])\n\n pred_y_test = pl.predict(x[index_test].reshape(-1,1))\n pred_y_train = pl.predict(x[index_train].reshape(-1,1))\n score_train = value_func(pred_y_train,y[index_train])\n score_test = value_func(pred_y_test,y[index_test])\n train_score_list.append(score_train)\n test_score_list.append(score_test)\n\n return train_score_list,test_score_list",
"CPU times: user 11 µs, sys: 0 ns, total: 11 µs\nWall time: 15 µs\n"
],
[
"hold_train_score_list,hold_test_score_list = holdout_method(x_data,sin_data,degree=max_degree)\nplt.plot(np.array(range(1,max_degree)),np.array(hold_train_score_list),color='b')\nplt.plot(np.array(range(1,max_degree)),np.array(hold_test_score_list),color='r')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"(2)**交差確認法**:手元の各クラスをn分割して、n-1のグループで学習して、残りの1つのグループのデータでテストをし、その平均を誤り率とした性能評価を行う。",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def cross_validation(x,y,value_func=MSE,split_num=5,degree=1):\n assert x.size % split_num==0,\"You must use divisible number\"\n n = x.size / split_num\n train_scores =[]\n test_scores =[]\n for i in range(split_num):\n indices = [int(i*n),int(i*n+n)]\n train_x_1,test_x,train_x_2=np.split(x,indices)\n train_y_1,test_y,train_y_2=np.split(y,indices)\n\n train_x = np.concatenate([train_x_1,train_x_2])\n train_y = np.concatenate([train_y_1,train_y_2])\n \n pf = PolynomialFeatures(degree=degree, include_bias=False)\n lr = LinearRegression()\n pl = Pipeline([(\"PF\", pf), (\"LR\", lr)])\n pl.fit(train_x.reshape(-1,1), train_y)\n\n pred_y_test = pl.predict(np.array(test_x).reshape(-1,1))\n pred_y_train = pl.predict(np.array(train_x).reshape(-1,1))\n\n score_train = value_func(pred_y_train,train_y)\n #print(score_train)\n score_test = value_func(pred_y_test,test_y)\n #print(len(test_y))\n train_scores.append(score_train)\n test_scores.append(score_test)\n\n return mean(train_scores),mean(test_scores)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cross_test_score_list = []\ncross_train_score_list = []\nfor i in range(1,max_degree):\n tra,tes = cross_validation(x_data,sin_data,degree=i)\n cross_train_score_list.append(tra)\n cross_test_score_list.append(tes)\nplt.plot(np.array(range(1,max_degree)),np.array(cross_train_score_list),color='b')\nplt.plot(np.array(range(1,max_degree)),np.array(cross_test_score_list),color='r')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"(3)**一つ抜き法**:交差確認法の特別な場合で、データ数=グループの数としたものである。",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def leave_one_out(x,y,value_func=MSE,size=size,degree=1):\n return cross_validation(x,y,value_func,split_num=size,degree=degree)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"leave_test_score_list = []\nleave_train_score_list = []\nfor i in range(1,max_degree):\n tra,tes = leave_one_out(x_data,sin_data,degree=i)\n leave_train_score_list.append(tra)\n leave_test_score_list.append(tes)\nplt.plot(np.array(range(1,max_degree)),np.array(leave_train_score_list),color='b')\nplt.plot(np.array(range(1,max_degree)),np.array(leave_test_score_list),color='r')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.plot(np.array(range(1,max_degree)),np.array(hold_train_score_list),color='y')\nplt.plot(np.array(range(1,max_degree)),np.array(hold_test_score_list),color='m')\n\nplt.plot(np.array(range(1,max_degree)),np.array(cross_train_score_list),color='k')\nplt.plot(np.array(range(1,max_degree)),np.array(cross_test_score_list),color='c')\n\nplt.plot(np.array(range(1,max_degree)),np.array(leave_train_score_list),color='b')\nplt.plot(np.array(range(1,max_degree)),np.array(leave_test_score_list),color='r')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"(4)**ブートストラップ法**:N個の復元抽出をしてブートストラップサンプルを作り、そこから\n\n$bias=\\varepsilon(N^*,N^*)-N(N^*,N)$\nを推定して、それをいくつか計算してその平均でバイアスを推定する。\nその推定値を$\\overline{bias}$として、その推定値を\n\n$\\varepsilon = \\varepsilon(N,N)-\\overline{bias}$\nとする。",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def bootstrap(x,y,value_func=MSE,trial=50,degree=1):\n biases=[]\n for i in range(trial):\n boot_ind = np.random.choice(range(x.size),size=x.size,replace=True)\n pf = PolynomialFeatures(degree=degree, include_bias=False)\n lr = LinearRegression()\n pl = Pipeline([(\"PF\", pf), (\"LR\", lr)])\n pl.fit(x[boot_ind].reshape(-1,1), y[boot_ind])\n\n pred_y_boot = pl.predict(x[boot_ind].reshape(-1,1))\n pred_y_base = pl.predict(x.reshape(-1,1))\n\n score_boot = value_func(pred_y_boot,y[boot_ind])\n #print(score_train)\n score_base = value_func(pred_y_base,y)\n bias = score_base - score_boot\n #print(bias)\n biases.append(bias)\n\n pf = PolynomialFeatures(degree=degree, include_bias=False)\n lr = LinearRegression()\n pl = Pipeline([(\"PF\", pf), (\"LR\", lr)])\n pl.fit(x.reshape(-1,1), y)\n\n pred_y_base = pl.predict(x.reshape(-1,1))\n score_base = value_func(pred_y_base,y)\n return score_base + mean(biases)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"boot_score_list = []\nfor i in range(1,max_degree):\n boot_score = bootstrap(x_data,sin_data,degree=i)\n boot_score_list.append(boot_score)\nplt.plot(np.array(range(1,max_degree)),np.array(boot_score_list),color='b')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50355da7fae1391b8f2284b48eca52616f0e60c
| 32,813 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Complete-Python-3-Bootcamp-master/08-Milestone Project - 2/00-Milestone-2-Warmup-Project.ipynb
|
davidMartinVergues/PYTHON
|
dd39d3aabfc43b3cb09aadb2919e51d03364117d
|
[
"DOC"
] | 8 |
2020-09-02T03:59:02.000Z
|
2022-01-08T23:36:19.000Z
|
Complete-Python-3-Bootcamp-master/08-Milestone Project - 2/00-Milestone-2-Warmup-Project.ipynb
|
davidMartinVergues/PYTHON
|
dd39d3aabfc43b3cb09aadb2919e51d03364117d
|
[
"DOC"
] | null | null | null |
Complete-Python-3-Bootcamp-master/08-Milestone Project - 2/00-Milestone-2-Warmup-Project.ipynb
|
davidMartinVergues/PYTHON
|
dd39d3aabfc43b3cb09aadb2919e51d03364117d
|
[
"DOC"
] | 3 |
2020-11-18T12:13:05.000Z
|
2021-02-24T19:31:50.000Z
| 21.744864 | 430 | 0.459056 |
[
[
[
"___\n\n<a href='https://www.udemy.com/user/joseportilla/'><img src='../Pierian_Data_Logo.png'/></a>\n___\n<center><em>Content Copyright by Pierian Data</em></center>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Warmup Project Exercise",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Simple War Game\n\nBefore we launch in to the OOP Milestone 2 Project, let's walk through together on using OOP for a more robust and complex application, such as a game. We will use Python OOP to simulate a simplified version of the game war. Two players will each start off with half the deck, then they each remove a card, compare which card has the highest value, and the player with the higher card wins both cards. In the event of a time",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Single Card Class\n\n### Creating a Card Class with outside variables\n\nHere we will use some outside variables that we know don't change regardless of the situation, such as a deck of cards. Regardless of what round,match, or game we're playing, we'll still need the same deck of cards.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# We'll use this later\nimport random ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"suits = ('Hearts', 'Diamonds', 'Spades', 'Clubs')\nranks = ('Two', 'Three', 'Four', 'Five', 'Six', 'Seven', 'Eight', 'Nine', 'Ten', 'Jack', 'Queen', 'King', 'Ace')\nvalues = {'Two':2, 'Three':3, 'Four':4, 'Five':5, 'Six':6, 'Seven':7, 'Eight':8, \n 'Nine':9, 'Ten':10, 'Jack':11, 'Queen':12, 'King':13, 'Ace':14}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class Card:\n \n def __init__(self,suit,rank):\n self.suit = suit\n self.rank = rank\n self.value = values[rank]\n \n def __str__(self):\n return self.rank + ' of ' + self.suit",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Create an example card",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"suits[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ranks[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"two_hearts = Card(suits[0],ranks[0])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"two_hearts",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(two_hearts)",
"Two of Hearts\n"
],
[
"two_hearts.rank",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"two_hearts.value",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"values[two_hearts.rank]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Deck Class\n\n### Using a class within another class\n\nWe just created a single card, but how can we create an entire Deck of cards? Let's explore doing this with a class that utilizes the Card class.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"A Deck will be made up of multiple Cards. Which mean's we will actually use the Card class within the \\_\\_init__ of the Deck class.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class Deck:\n \n def __init__(self):\n # Note this only happens once upon creation of a new Deck\n self.all_cards = [] \n for suit in suits:\n for rank in ranks:\n # This assumes the Card class has already been defined!\n self.all_cards.append(Card(suit,rank))\n \n def shuffle(self):\n # Note this doesn't return anything\n random.shuffle(self.all_cards)\n \n def deal_one(self):\n # Note we remove one card from the list of all_cards\n return self.all_cards.pop() ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Create a Deck",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mydeck = Deck()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(mydeck.all_cards)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mydeck.all_cards[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(mydeck.all_cards[0])",
"Two of Hearts\n"
],
[
"mydeck.shuffle()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(mydeck.all_cards[0])",
"Five of Spades\n"
],
[
"my_card = mydeck.deal_one()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(my_card)",
"King of Clubs\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Player Class\n\nLet's create a Player Class, a player should be able to hold instances of Cards, they should also be able to remove and add them from their hand. We want the Player class to be flexible enough to add one card, or many cards so we'll use a simple if check to keep it all in the same method.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We'll keep this all in mind as we create the methods for the Player class.\n\n### Player Class",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class Player:\n \n def __init__(self,name):\n self.name = name\n # A new player has no cards\n self.all_cards = [] \n \n def remove_one(self):\n # Note we remove one card from the list of all_cards\n # We state 0 to remove from the \"top\" of the deck\n # We'll imagine index -1 as the bottom of the deck\n return self.all_cards.pop(0)\n \n def add_cards(self,new_cards):\n if type(new_cards) == type([]):\n self.all_cards.extend(new_cards)\n else:\n self.all_cards.append(new_cards)\n \n \n def __str__(self):\n return f'Player {self.name} has {len(self.all_cards)} cards.'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"jose = Player(\"Jose\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"jose",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(jose)",
"Player Jose has 0 cards.\n"
],
[
"two_hearts",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"jose.add_cards(two_hearts)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(jose)",
"Player Jose has 1 cards.\n"
],
[
"jose.add_cards([two_hearts,two_hearts,two_hearts])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(jose)",
"Player Jose has 4 cards.\n"
]
],
[
[
"## War Game Logic",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"player_one = Player(\"One\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"player_two = Player(\"Two\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Setup New Game",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"new_deck = Deck()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"new_deck.shuffle()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Split the Deck between players",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"len(new_deck.all_cards)/2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for x in range(26):\n player_one.add_cards(new_deck.deal_one())\n player_two.add_cards(new_deck.deal_one())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(new_deck.all_cards)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(player_one.all_cards)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(player_two.all_cards)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Play the Game",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pdb",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"game_on = True",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"round_num = 0\nwhile game_on:\n \n round_num += 1\n print(f\"Round {round_num}\")\n \n # Check to see if a player is out of cards:\n if len(player_one.all_cards) == 0:\n print(\"Player One out of cards! Game Over\")\n print(\"Player Two Wins!\")\n game_on = False\n break\n \n if len(player_two.all_cards) == 0:\n print(\"Player Two out of cards! Game Over\")\n print(\"Player One Wins!\")\n game_on = False\n break\n \n # Otherwise, the game is still on!\n \n # Start a new round and reset current cards \"on the table\"\n player_one_cards = []\n player_one_cards.append(player_one.remove_one())\n \n player_two_cards = []\n player_two_cards.append(player_two.remove_one())\n \n at_war = True\n\n while at_war:\n\n\n if player_one_cards[-1].value > player_two_cards[-1].value:\n\n # Player One gets the cards\n player_one.add_cards(player_one_cards)\n player_one.add_cards(player_two_cards)\n \n \n # No Longer at \"war\" , time for next round\n at_war = False\n \n # Player Two Has higher Card\n elif player_one_cards[-1].value < player_two_cards[-1].value:\n\n # Player Two gets the cards\n player_two.add_cards(player_one_cards)\n player_two.add_cards(player_two_cards)\n \n # No Longer at \"war\" , time for next round\n at_war = False\n\n else:\n print('WAR!')\n # This occurs when the cards are equal.\n # We'll grab another card each and continue the current war.\n \n # First check to see if player has enough cards\n \n # Check to see if a player is out of cards:\n if len(player_one.all_cards) < 5:\n print(\"Player One unable to play war! Game Over at War\")\n print(\"Player Two Wins! Player One Loses!\")\n game_on = False\n break\n\n elif len(player_two.all_cards) < 5:\n print(\"Player Two unable to play war! Game Over at War\")\n print(\"Player One Wins! Player One Loses!\")\n game_on = False\n break\n # Otherwise, we're still at war, so we'll add the next cards\n else:\n for num in range(5):\n player_one_cards.append(player_one.remove_one())\n player_two_cards.append(player_two.remove_one())\n ",
"Round 1\nRound 2\nRound 3\nRound 4\nRound 5\nRound 6\nRound 7\nRound 8\nRound 9\nRound 10\nRound 11\nRound 12\nRound 13\nRound 14\nRound 15\nRound 16\nRound 17\nRound 18\nRound 19\nRound 20\nRound 21\nRound 22\nRound 23\nRound 24\nRound 25\nRound 26\nRound 27\nPlayer One out of cards! Game Over\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Game Setup in One Cell",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"player_one = Player(\"One\")\nplayer_two = Player(\"Two\")\n\nnew_deck = Deck()\nnew_deck.shuffle()\n\nfor x in range(26):\n player_one.add_cards(new_deck.deal_one())\n player_two.add_cards(new_deck.deal_one())\n \ngame_on = True",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"round_num = 0\nwhile game_on:\n \n round_num += 1\n print(f\"Round {round_num}\")\n \n # Check to see if a player is out of cards:\n if len(player_one.all_cards) == 0:\n print(\"Player One out of cards! Game Over\")\n print(\"Player Two Wins!\")\n game_on = False\n break\n \n if len(player_two.all_cards) == 0:\n print(\"Player Two out of cards! Game Over\")\n print(\"Player One Wins!\")\n game_on = False\n break\n \n # Otherwise, the game is still on!\n \n # Start a new round and reset current cards \"on the table\"\n player_one_cards = []\n player_one_cards.append(player_one.remove_one())\n \n player_two_cards = []\n player_two_cards.append(player_two.remove_one())\n \n at_war = True\n\n while at_war:\n\n\n if player_one_cards[-1].value > player_two_cards[-1].value:\n\n # Player One gets the cards\n player_one.add_cards(player_one_cards)\n player_one.add_cards(player_two_cards)\n \n \n # No Longer at \"war\" , time for next round\n at_war = False\n \n # Player Two Has higher Card\n elif player_one_cards[-1].value < player_two_cards[-1].value:\n\n # Player Two gets the cards\n player_two.add_cards(player_one_cards)\n player_two.add_cards(player_two_cards)\n \n # No Longer at \"war\" , time for next round\n at_war = False\n\n else:\n print('WAR!')\n # This occurs when the cards are equal.\n # We'll grab another card each and continue the current war.\n \n # First check to see if player has enough cards\n \n # Check to see if a player is out of cards:\n if len(player_one.all_cards) < 5:\n print(\"Player One unable to play war! Game Over at War\")\n print(\"Player Two Wins! Player One Loses!\")\n game_on = False\n break\n\n elif len(player_two.all_cards) < 5:\n print(\"Player Two unable to play war! Game Over at War\")\n print(\"Player One Wins! Player One Loses!\")\n game_on = False\n break\n # Otherwise, we're still at war, so we'll add the next cards\n else:\n for num in range(5):\n player_one_cards.append(player_one.remove_one())\n player_two_cards.append(player_two.remove_one())\n\n ",
"Round 1\nRound 2\nWAR!\nRound 3\nWAR!\nWAR!\nRound 4\nWAR!\nRound 5\nRound 6\nRound 7\nRound 8\nRound 9\nRound 10\nRound 11\nRound 12\nRound 13\nWAR!\nRound 14\nRound 15\nWAR!\nRound 16\nRound 17\nRound 18\nRound 19\nRound 20\nRound 21\nRound 22\nRound 23\nRound 24\nRound 25\nRound 26\nRound 27\nRound 28\nRound 29\nWAR!\nRound 30\nRound 31\nRound 32\nWAR!\nRound 33\nRound 34\nRound 35\nRound 36\nRound 37\nRound 38\nRound 39\nRound 40\nRound 41\nRound 42\nWAR!\nWAR!\nRound 43\nRound 44\nRound 45\nRound 46\nRound 47\nRound 48\nRound 49\nRound 50\nRound 51\nRound 52\nRound 53\nRound 54\nRound 55\nRound 56\nRound 57\nRound 58\nRound 59\nRound 60\nRound 61\nRound 62\nRound 63\nRound 64\nRound 65\nRound 66\nRound 67\nRound 68\nRound 69\nRound 70\nRound 71\nRound 72\nRound 73\nRound 74\nRound 75\nRound 76\nRound 77\nRound 78\nRound 79\nRound 80\nRound 81\nRound 82\nRound 83\nRound 84\nRound 85\nRound 86\nRound 87\nRound 88\nRound 89\nRound 90\nRound 91\nRound 92\nRound 93\nRound 94\nRound 95\nRound 96\nRound 97\nRound 98\nRound 99\nRound 100\nRound 101\nRound 102\nRound 103\nRound 104\nRound 105\nRound 106\nRound 107\nRound 108\nWAR!\nRound 109\nRound 110\nRound 111\nRound 112\nRound 113\nRound 114\nRound 115\nRound 116\nRound 117\nRound 118\nRound 119\nRound 120\nRound 121\nRound 122\nRound 123\nRound 124\nRound 125\nRound 126\nRound 127\nRound 128\nRound 129\nRound 130\nRound 131\nRound 132\nRound 133\nRound 134\nWAR!\nRound 135\nRound 136\nWAR!\nRound 137\nWAR!\nRound 138\nRound 139\nRound 140\nRound 141\nRound 142\nRound 143\nRound 144\nRound 145\nRound 146\nRound 147\nRound 148\nRound 149\nRound 150\nRound 151\nRound 152\nRound 153\nRound 154\nRound 155\nRound 156\nRound 157\nRound 158\nRound 159\nRound 160\nRound 161\nRound 162\nRound 163\nRound 164\nRound 165\nRound 166\nRound 167\nRound 168\nRound 169\nRound 170\nRound 171\nRound 172\nRound 173\nRound 174\nRound 175\nRound 176\nRound 177\nRound 178\nRound 179\nRound 180\nRound 181\nRound 182\nRound 183\nRound 184\nRound 185\nRound 186\nRound 187\nRound 188\nRound 189\nRound 190\nRound 191\nRound 192\nRound 193\nRound 194\nRound 195\nRound 196\nRound 197\nRound 198\nRound 199\nRound 200\nRound 201\nRound 202\nRound 203\nRound 204\nRound 205\nRound 206\nRound 207\nRound 208\nRound 209\nRound 210\nRound 211\nRound 212\nRound 213\nRound 214\nRound 215\nRound 216\nRound 217\nRound 218\nRound 219\nRound 220\nRound 221\nRound 222\nRound 223\nWAR!\nRound 224\nRound 225\nRound 226\nRound 227\nRound 228\nRound 229\nRound 230\nRound 231\nRound 232\nRound 233\nRound 234\nRound 235\nRound 236\nRound 237\nRound 238\nRound 239\nRound 240\nRound 241\nRound 242\nRound 243\nRound 244\nRound 245\nRound 246\nRound 247\nRound 248\nRound 249\nRound 250\nRound 251\nRound 252\nRound 253\nRound 254\nRound 255\nRound 256\nRound 257\nWAR!\nRound 258\nRound 259\nRound 260\nRound 261\nRound 262\nRound 263\nRound 264\nRound 265\nRound 266\nRound 267\nRound 268\nRound 269\nRound 270\nRound 271\nRound 272\nRound 273\nRound 274\nRound 275\nRound 276\nRound 277\nRound 278\nRound 279\nRound 280\nRound 281\nRound 282\nRound 283\nRound 284\nRound 285\nRound 286\nRound 287\nRound 288\nRound 289\nRound 290\nRound 291\nRound 292\nRound 293\nRound 294\nRound 295\nRound 296\nRound 297\nRound 298\nRound 299\nRound 300\nRound 301\nRound 302\nRound 303\nRound 304\nRound 305\nRound 306\nRound 307\nWAR!\nRound 308\nRound 309\nRound 310\nRound 311\nRound 312\nRound 313\nRound 314\nRound 315\nWAR!\nRound 316\nRound 317\nRound 318\nRound 319\nRound 320\nRound 321\nRound 322\nRound 323\nRound 324\nRound 325\nRound 326\nRound 327\nRound 328\nRound 329\nRound 330\nRound 331\nRound 332\nRound 333\nRound 334\nRound 335\nRound 336\nRound 337\nRound 338\nRound 339\nRound 340\nRound 341\nRound 342\nRound 343\nRound 344\nRound 345\nRound 346\nRound 347\nRound 348\nRound 349\nWAR!\nRound 350\nWAR!\nPlayer Two unable to play war! Game Over at War\nPlayer One Wins! Player One Loses!\n"
],
[
"len(player_one.all_cards)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(player_two.all_cards)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(player_one_cards[-1])",
"Ace of Diamonds\n"
],
[
"print(player_two_cards[-1])",
"Four of Hearts\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Great Work!\n\nOther links that may interest you:\n* https://www.reddit.com/r/learnpython/comments/7ay83p/war_card_game/\n* https://codereview.stackexchange.com/questions/131174/war-card-game-using-classes\n* https://gist.github.com/damianesteban/6896120\n* https://lethain.com/war-card-game-in-python/\n* https://hectorpefo.github.io/2017-09-13-Card-Wars/\n* https://www.wimpyprogrammer.com/the-statistics-of-war-the-card-game",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
c5035cd070590561fff017f9bfce5987c49365be
| 64,037 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
testing_model.ipynb
|
bibliotekue/python-applied-data-analysis
|
893c9e5d7de176ce3271e01e3958797c6561d551
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
testing_model.ipynb
|
bibliotekue/python-applied-data-analysis
|
893c9e5d7de176ce3271e01e3958797c6561d551
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
testing_model.ipynb
|
bibliotekue/python-applied-data-analysis
|
893c9e5d7de176ce3271e01e3958797c6561d551
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 182.962857 | 24,804 | 0.914768 |
[
[
[
"# $\\color{black}{}$\n### 2. Testing your model\n---",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\n\ndata = pd.read_csv(\"https://milliams.com/courses/applied_data_analysis/linear.csv\")\n\nX = data[[\"x\"]]\ny = data[\"y\"]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Scikit-learn provides a built-in function, `train_test_split`, to split your data into a subset of data to fit with and a subset of data to test against.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\n\ntrain_X, test_X, train_y, test_y = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=42)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"To see that `train` and `test` are taken from the same distribution let's plot them.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\nfig, ax = plt.subplots()\n\nplt.figure(figsize=(20,20))\n\nax.scatter(train_X, train_y, color=\"red\", marker=\"o\", label=\"train\")\nax.scatter(test_X, test_y, color=\"blue\", marker=\"x\", label=\"test\")\nax.legend()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now that we have `train` and `test` we should only ever pass `train` to the `fit` function\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression\n\nmodel = LinearRegression(fit_intercept=True)\nmodel.fit(train_X, train_y)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"To find out how good the fit was, we can call the `score` method on the model. It is important here that we pass in our *test* data set as we expect that to provide an independent validation of the model.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model.score(test_X, test_y)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"A score of __1.0__ is a perfect match and anything less than that is less-well performing. A score of __0.97__ suggests we have a very good model.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### $\\color{black}{Exercise}$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# load\nfrom sklearn.datasets import load_diabetes\n\nX, y = load_diabetes(as_frame=True, return_X_y=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# split\ntrain_X, test_X, train_y, test_y = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=42)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# plot\nfig, ax = plt.subplots()\n\nax.scatter(train_X['bmi'], train_y, color='red', marker='o', label='train')\nax.scatter(test_X['bmi'], test_y, color='blue', marker='x', label='test')\nax.legend()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# fit\nmodel.fit(train_X[['bmi']], train_y)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# score\nmodel.score(test_X[['bmi']], test_y)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# regression plot\nx_fit = pd.DataFrame({'bmi': [X['bmi'].min(), X['bmi'].max()]})\ny_pred = model.predict(x_fit)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots()\n\nax.scatter(X['bmi'], y)\nax.plot(x_fit['bmi'], y_pred, linestyle=':', color='red')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c5035fce398689af1727e1ef1a1de492f1d54ae8
| 67,405 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
templates/StatsCanFinalTemplates/QuickDataExploration.ipynb
|
callysto/notebook-templates
|
e1c9a02d0cb52007f917c604737da7a1c8cb4ade
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | 1 |
2020-02-03T13:33:50.000Z
|
2020-02-03T13:33:50.000Z
|
templates/StatsCanFinalTemplates/QuickDataExploration.ipynb
|
callysto/notebook-templates
|
e1c9a02d0cb52007f917c604737da7a1c8cb4ade
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | 1 |
2018-08-30T22:30:35.000Z
|
2018-08-31T22:18:56.000Z
|
templates/StatsCanFinalTemplates/QuickDataExploration.ipynb
|
callysto/notebook-templates
|
e1c9a02d0cb52007f917c604737da7a1c8cb4ade
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | 1 |
2020-03-02T13:58:36.000Z
|
2020-03-02T13:58:36.000Z
| 81.407005 | 42,016 | 0.783562 |
[
[
[
"from IPython.display import HTML\n\nHTML('''<script>\ncode_show=true; \nfunction code_toggle() {\n if (code_show){\n $('div.input').hide();\n } else {\n $('div.input').show();\n }\n code_show = !code_show\n} \n$( document ).ready(code_toggle);\n</script>\nThe raw code for this IPython notebook is by default hidden for easier reading.\nTo toggle on/off the raw code, click <a href=\"javascript:code_toggle()\">here</a>.''')\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
" \n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<h1 align='center'>Stats Can Notebook Template: Quick Dataset Exploration</h1>\n\n<h4 align='center'>Laura Gutierrez Funderburk $\\mid$ Stats Can Notebook</h4>\n\n<h2 align='center'>Abstract</h2>\n\nThis notebook may be used to quickly explore most data sets from Stats Can. To explore the contents of a dataset, simply visit https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/en/type/data?MM=1 and select a \"Table\".\n\nTo select a table, copy the string next to Table, under the data set name. Here is an example. \n\n\n\nIn this case, the data set's table is 10-10-0122-01.\n\nSimply copy and paste that table in the box below, and press the Download Dataset button. \n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%run -i ./StatsCan/helpers.py\n%run -i ./StatsCan/scwds.py\n%run -i ./StatsCan/sc.py",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from ipywidgets import widgets, VBox, HBox, Button\nfrom ipywidgets import Button, Layout, widgets\nfrom IPython.display import display, Javascript, Markdown, HTML\nimport datetime as dt\nimport qgrid as q\nimport pandas as pd\nimport json\nimport datetime\nimport qgrid \nfrom tqdm import tnrange, tqdm_notebook\nfrom time import sleep\nimport sys\n\ngrid_features = { 'fullWidthRows': True,\n 'syncColumnCellResize': True,\n 'forceFitColumns': True,\n 'enableColumnReorder': True,\n 'enableTextSelectionOnCells': True,\n 'editable': False,\n 'filterable': True,\n 'sortable': False,\n 'highlightSelectedRow': True}\n\ndef rerun_cell( b ):\n \n display(Javascript('IPython.notebook.execute_cell_range(IPython.notebook.get_selected_index()+1,IPython.notebook.get_selected_index()+3)')) \n\n \ndef run_4cell( b ):\n \n display(Javascript('IPython.notebook.execute_cell_range(IPython.notebook.get_selected_index()+1,IPython.notebook.get_selected_index()+5)')) \n\nstyle = {'description_width': 'initial'}\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<h2 align='center'>Downloading Stats Can Data</h2>\n\nTo download a full dataset, enter a product ID and press the Download Dataset button. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"prod_ID = widgets.Text(\n value=\"10-10-0122-01\",\n placeholder='ProductID value',\n description='productID value',\n disabled=False,\n style=style\n)\n\n\nDS_button = widgets.Button(\n button_style='success',\n description=\"Download Dataset\", \n layout=Layout(width='15%', height='30px'),\n style=style\n) \nDS_button.on_click( run_4cell )\ndisplay(prod_ID)\ndisplay(DS_button)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# # Download data \nproductId = prod_ID.value\n\nif \"-\" not in productId:\n if len(productId)!=10:\n print(\"WARNING: THIS IS LIKELY A NUMBER NOT ASSOCIATED WITH A DATA TABLE. VERIFY AND TRY AGAIN\")\n sys.exit(1)\n\n \n\nelse: \n if len(productId.split(\"-\")) !=4:\n print(\"WARNING: THIS IS LIKELY A NUMBER NOT ASSOCIATED WITH A DATA TABLE. VERIFY AND TRY AGAIN\")\n sys.exit(1)\n\n \ndownload_tables(str(productId))\n\ndef download_and_store_json(productId):\n \n with open(str(productId) +'.json') as f:\n data = json.load(f)\n f.close()\n \n return data\n\nimport zipfile\n\ndef read_data_compute_df(productID):\n\n zf = zipfile.ZipFile('./' + str(productID) + '-eng.zip') \n df = pd.read_csv(zf.open(str(productID)+'.csv'))\n \n return df\n\n\n# Example\n#data = download_and_store_json(productId)\n\n# Example, we will select the study we downloaded previously \n\ndf_fullDATA = zip_table_to_dataframe(productId)\n\n\n\n\ncols = list(df_fullDATA.loc[:,'REF_DATE':'UOM'])+ ['SCALAR_FACTOR'] + ['VALUE']\ndf_less = df_fullDATA[cols]\ndf_less2 = df_less.drop([\"DGUID\"], axis=1)\ndf_less2.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"iteration_nr = df_less2.shape[1]\ncategories = []\nfor i in range(iteration_nr-1):\n categories.append(df_less2.iloc[:,i].unique())\n \n \nall_the_widgets = []\nfor i in range(len(categories)):\n if i==0:\n a_category = widgets.Dropdown(\n value = categories[i][0],\n options = categories[i], \n description ='Start Date:', \n style = style, \n disabled=False\n )\n b_category = widgets.Dropdown(\n value = categories[i][-1],\n options = categories[i], \n description ='End Date:', \n style = style, \n disabled=False\n )\n all_the_widgets.append(a_category)\n all_the_widgets.append(b_category)\n elif i==1:\n a_category = widgets.Dropdown(\n value = categories[i][0],\n options = categories[i], \n description ='Location:', \n style = style, \n disabled=False\n )\n all_the_widgets.append(a_category)\n elif i==len(categories)-1:\n a_category = widgets.Dropdown(\n value = categories[i][0],\n options = categories[i], \n description ='Scalar factor:', \n style = style, \n disabled=False\n )\n all_the_widgets.append(a_category)\n \n elif i==len(categories)-2:\n a_category = widgets.Dropdown(\n value = categories[i][0],\n options = categories[i], \n description ='Units of Measure :', \n style = style, \n disabled=False\n )\n all_the_widgets.append(a_category)\n else:\n a_category = widgets.Dropdown(\n value = categories[i][0],\n options = categories[i], \n description ='Subcategory ' + str(i), \n style = style, \n disabled=False\n )\n all_the_widgets.append(a_category)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## <h2 align='center'>Select Data Subsets: One-Dimensional Plotting</h2>\n\n\nUse the user menu below to select a cateory within the full subset you are interested in exploring. \n\nChoose a starting and end date to plot results. \n\nIf there is data available, it will appear under the headers. \n\nBe careful to select dataframes with actual data in them!. \n\nUse the Select Dataset button to help you preview the data. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"CD_button = widgets.Button(\n button_style='success',\n description=\"Preview Dataset\", \n layout=Layout(width='15%', height='30px'),\n style=style\n) \nCD_button.on_click( run_4cell )\n\ntab3 = VBox(children=[HBox(children=all_the_widgets[0:3]),\n HBox(children=all_the_widgets[3:5]),\n HBox(children=all_the_widgets[5:len(all_the_widgets)]),\n CD_button])\ntab = widgets.Tab(children=[tab3])\ntab.set_title(0, 'Load Data Subset')\ndisplay(tab)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_sub = df_less2[(df_less2[\"REF_DATE\"]>=all_the_widgets[0].value) & \n (df_less2[\"REF_DATE\"]<=all_the_widgets[1].value) &\n (df_less2[\"GEO\"]==all_the_widgets[2].value) &\n (df_less2[\"UOM\"]==all_the_widgets[-2].value) & \n (df_less2[\"SCALAR_FACTOR\"]==all_the_widgets[-1].value) ]\n\n\n\ndf_sub.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# TO HANDLE THE REST OF THE COLUMNS, SIMPLY SUBSTITUTE VALUES \ncol_name = df_sub.columns[2]\n\n# weather_data = pd.read_csv(\"DATA.csv\",sep=',')\ncol_name\n\ndf_sub_final = df_sub[(df_sub[col_name]==all_the_widgets[3].value)]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n%matplotlib inline\n\nfig1 = plt.figure(facecolor='w',figsize=(18,18))\nplt.subplot(3, 3, 1)\nplt.axis('off');\n\nplt.subplot(3, 3, 2)\nplt.plot(df_sub_final[\"REF_DATE\"],df_sub_final[\"VALUE\"],'b--',label='Value')\n#plt.plot(df_20_USA[\"REF_DATE\"],df_20_USA[\"VALUE\"],'r--',label='U.S. dollar, daily average')\nplt.xlabel('Year-Month', fontsize=20)\nplt.ylabel('Value',fontsize=20)\nplt.title(str(all_the_widgets[3].value) + \", \"+ str(all_the_widgets[2].value),fontsize=20)\nplt.xticks(rotation=90)\nplt.grid(True)\n\n\nplt.subplot(3, 3, 3);\nplt.axis('off');\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<h2 align='center'>References</h2>\n\nStatistics Canada. \n\nhttps://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/en/type/data?MM=1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
c50368ae2121becd65d8858e102840df363a5791
| 1,838 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
valid_over_underfitting.ipynb
|
shamiulshifat/Machine-Learning-with-Scratch
|
b57bd285223d11a8899625f51323fd4b50c3a204
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2020-06-22T15:00:04.000Z
|
2020-06-22T15:00:04.000Z
|
valid_over_underfitting.ipynb
|
shamiulshifat/Machine-Learning-with-Scratch
|
b57bd285223d11a8899625f51323fd4b50c3a204
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
valid_over_underfitting.ipynb
|
shamiulshifat/Machine-Learning-with-Scratch
|
b57bd285223d11a8899625f51323fd4b50c3a204
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 20.197802 | 100 | 0.500544 |
[
[
[
"dp1={'partno':100, 'maxtemp':35, 'mintemp':35, 'maxvibration':12, 'broken':0}\ndp2={'partno':101, 'maxtemp':46, 'mintemp':35, 'maxvibration':21, 'broken':0}\ndp3={'partno':130, 'maxtemp':56, 'mintemp':46, 'maxvibration':3412, 'broken':1}\ndp4={'partno':131, 'maxtemp':58, 'mintemp':48, 'maxvibration':3542, 'broken':1}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import math\ndef sigmoid(x):\n return 1/(1+math.exp(-x))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"w1=0.30\nw2=0\nw3=0\nw4=13/3412.0\n\ndef mlpredict(dp):\n return 1 if sigmoid(w1+w2*dp['maxtemp']+w3*dp['mintemp']+w4*dp['maxvibration'])>0.7 else 0",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mlpredict(dp3)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50378691b28a392c31412661ec4612c2146cf60
| 13,039 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/bubble/google_scraping.ipynb
|
janejanejam/factual-foxes
|
382c41f7007b3253b18a699acb630b1235ad2c59
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/bubble/google_scraping.ipynb
|
janejanejam/factual-foxes
|
382c41f7007b3253b18a699acb630b1235ad2c59
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/bubble/google_scraping.ipynb
|
janejanejam/factual-foxes
|
382c41f7007b3253b18a699acb630b1235ad2c59
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2020-08-11T03:27:02.000Z
|
2020-08-11T03:27:02.000Z
| 30.5363 | 121 | 0.431245 |
[
[
[
"# Import libraries and dependencies\nfrom splinter import Browser\nfrom bs4 import BeautifulSoup as bs\nimport pandas as pd\nimport requests\nimport time\nimport calendar\nimport random",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"last_day = [calendar.monthlen(2020, i+1) for i in range(12)]\n\nmonth = [i+1 for i in range(8)]\n\nzipped = list(zip(month, last_day))\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# for _zip in zipped:\n# url = f'https://trends.google.com/trends/explore?date=2020-{_zip[0]}-01%202020-{_zip[0]}-{_zip[1]}&geo=US'\n# print(url)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Mac users\nexecutable_path = {'executable_path': '/usr/local/bin/chromedriver'}\nbrowser = Browser('chrome', **executable_path, headless=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create empty list to append into\nqueries_list = []\n\n# Loop through each month\nfor _zip in zipped:\n \n # Set URL to scrape\n url = f'https://trends.google.com/trends/explore?date=2020-{_zip[0]}-01%202020-{_zip[0]}-{_zip[1]}&geo=US'\n print(url)\n browser.visit(url)\n\n # Add time delay\n time.sleep(3)\n\n # Scrape page into Soup\n html = browser.html\n soup = bs(html, \"html.parser\")\n\n # Retrieve section \n section = soup.find_all('widget', type='fe_related_queries')\n \n try:\n label_text = [div.text for div in section[1].find_all(class_='label-text')]\n \n # Loop through each row to pull elements\n# for section in sections:\n queries_dict = {}\n queries_dict['month'] = _zip[0]\n queries_dict['label text'] = label_text\n queries_list.append(queries_dict)\n except:\n next\n \n# Close the browser after scraping\nbrowser.quit()",
"https://trends.google.com/trends/explore?date=2020-1-01%202020-1-31&geo=US\nhttps://trends.google.com/trends/explore?date=2020-2-01%202020-2-29&geo=US\nhttps://trends.google.com/trends/explore?date=2020-3-01%202020-3-31&geo=US\nhttps://trends.google.com/trends/explore?date=2020-4-01%202020-4-30&geo=US\nhttps://trends.google.com/trends/explore?date=2020-5-01%202020-5-31&geo=US\nhttps://trends.google.com/trends/explore?date=2020-6-01%202020-6-30&geo=US\nhttps://trends.google.com/trends/explore?date=2020-7-01%202020-7-31&geo=US\nhttps://trends.google.com/trends/explore?date=2020-8-01%202020-8-31&geo=US\n"
],
[
"df",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_queries = pd.DataFrame(queries_list)\ndf_queries",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_queries.to_csv(path_or_buf = 'queries2020_2.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50387c2d3bbd47c80bae1e9d7d9273840fee27a
| 69,336 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
implementation/h2o-fakegame/h2o-r/demos/H2O_tutorial_eeg_eyestate_NOPASS.ipynb
|
kordikp/AutoMLprediction
|
6f87bd0b95ce78103c9f4f83ee85d831ab60a0a6
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2018-03-22T12:45:32.000Z
|
2018-03-22T12:45:32.000Z
|
implementation/h2o-fakegame/h2o-r/demos/rdemo.tutorial.eeg.eyestate.ipynb
|
kordikp/AutoMLprediction
|
6f87bd0b95ce78103c9f4f83ee85d831ab60a0a6
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
implementation/h2o-fakegame/h2o-r/demos/rdemo.tutorial.eeg.eyestate.ipynb
|
kordikp/AutoMLprediction
|
6f87bd0b95ce78103c9f4f83ee85d831ab60a0a6
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 36.358679 | 582 | 0.389134 |
[
[
[
"# H2O Tutorial: EEG Eye State Classification\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Author: Erin LeDell\n\nContact: [email protected]\n\nThis tutorial steps through a quick introduction to H2O's R API. The goal of this tutorial is to introduce through a complete example H2O's capabilities from R. \n\nMost of the functionality for R's `data.frame` is exactly the same syntax for an `H2OFrame`, so if you are comfortable with R, data frame manipulation will come naturally to you in H2O. The modeling syntax in the H2O R API may also remind you of other machine learning packages in R.\n\nReferences: [H2O R API documentation](http://h2o-release.s3.amazonaws.com/h2o/latest_stable_Rdoc.html), the [H2O Documentation landing page](http://www.h2o.ai/docs/) and [H2O general documentation](http://h2o-release.s3.amazonaws.com/h2o/latest_stable_doc.html).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Install H2O in R\n\n### Prerequisites\n\nThis tutorial assumes you have R installed. The `h2o` R package has a few dependencies which can be installed using CRAN. The packages that are required (which also have their own dependencies) can be installed in R as follows:\n```r\npkgs <- c(\"methods\",\"statmod\",\"stats\",\"graphics\",\"RCurl\",\"jsonlite\",\"tools\",\"utils\")\nfor (pkg in pkgs) {\n if (! (pkg %in% rownames(installed.packages()))) { install.packages(pkg) }\n}\n```\n\n### Install h2o\n\nOnce the dependencies are installed, you can install H2O. We will use the latest stable version of the `h2o` R package, which at the time of writing is H2O v3.8.0.4 (aka \"Tukey-4\"). The latest stable version can be installed using the commands on the [H2O R Installation](http://www.h2o.ai/download/h2o/r) page.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Start up an H2O cluster\n\nAfter the R package is installed, we can start up an H2O cluster. In a R terminal, we load the `h2o` package and start up an H2O cluster as follows:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"library(h2o)\n\n# Start an H2O Cluster on your local machine\nh2o.init(nthreads = -1) #nthreads = -1 uses all cores on your machine",
"\nH2O is not running yet, starting it now...\n\nNote: In case of errors look at the following log files:\n /var/folders/2j/jg4sl53d5q53tc2_nzm9fz5h0000gn/T//Rtmp9YYiOK/h2o_me_started_from_r.out\n /var/folders/2j/jg4sl53d5q53tc2_nzm9fz5h0000gn/T//Rtmp9YYiOK/h2o_me_started_from_r.err\n\n\nStarting H2O JVM and connecting: . Connection successful!\n\nR is connected to the H2O cluster: \n H2O cluster uptime: 1 seconds 148 milliseconds \n H2O cluster version: 3.8.0.3 \n H2O cluster name: H2O_started_from_R_me_ogz089 \n H2O cluster total nodes: 1 \n H2O cluster total memory: 3.56 GB \n H2O cluster total cores: 8 \n H2O cluster allowed cores: 8 \n H2O cluster healthy: TRUE \n H2O Connection ip: localhost \n H2O Connection port: 54321 \n H2O Connection proxy: NA \n R Version: R version 3.2.2 (2015-08-14) \n\n"
]
],
[
[
"If you already have an H2O cluster running that you'd like to connect to (for example, in a multi-node Hadoop environment), then you can specify the IP and port of that cluster as follows:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# This will not actually do anything since it's a fake IP address\n# h2o.init(ip=\"123.45.67.89\", port=54321)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Download EEG Data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The following code downloads a copy of the [EEG Eye State](http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/EEG+Eye+State#) dataset. All data is from one continuous EEG measurement with the [Emotiv EEG Neuroheadset](https://emotiv.com/epoc.php). The duration of the measurement was 117 seconds. The eye state was detected via a camera during the EEG measurement and added later manually to the file after analysing the video frames. '1' indicates the eye-closed and '0' the eye-open state. All values are in chronological order with the first measured value at the top of the data.\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We can import the data directly into H2O using the `import_file` method in the Python API. The import path can be a URL, a local path, a path to an HDFS file, or a file on Amazon S3.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#csv_url <- \"http://www.stat.berkeley.edu/~ledell/data/eeg_eyestate_splits.csv\"\ncsv_url <- \"https://h2o-public-test-data.s3.amazonaws.com/eeg_eyestate_splits.csv\"\ndata <- h2o.importFile(csv_url)",
"\r | \r | | 0%\r | \r |======================================================================| 100%\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Explore Data\nOnce we have loaded the data, let's take a quick look. First the dimension of the frame:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dim(data)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now let's take a look at the top of the frame:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"head(data)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The first 14 columns are numeric values that represent EEG measurements from the headset. The \"eyeDetection\" column is the response. There is an additional column called \"split\" that was added (by me) in order to specify partitions of the data (so we can easily benchmark against other tools outside of H2O using the same splits). I randomly divided the dataset into three partitions: train (60%), valid (%20) and test (20%) and marked which split each row belongs to in the \"split\" column.\n\nLet's take a look at the column names. The data contains derived features from the medical images of the tumors.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"names(data)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"To select a subset of the columns to look at, typical R data.frame indexing applies:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"columns <- c('AF3', 'eyeDetection', 'split')\nhead(data[columns])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now let's select a single column, for example -- the response column, and look at the data more closely:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"y <- 'eyeDetection'\ndata[y]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"It looks like a binary response, but let's validate that assumption:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"h2o.unique(data[y])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"If you don't specify the column types when you import the file, H2O makes a guess at what your column types are. If there are 0's and 1's in a column, H2O will automatically parse that as numeric by default. \n\nTherefore, we should convert the response column to a more efficient \"factor\" representation (called \"enum\" in Java) -- in this case it is a categorial variable with two levels, 0 and 1. If the only column in my data that is categorical is the response, I typically don't bother specifying the column type during the parse, and instead use this one-liner to convert it aftewards:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data[y] <- as.factor(data[y])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now we can check that there are two levels in our response column:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"h2o.nlevels(data[y])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can query the categorical \"levels\" as well ('0' and '1' stand for \"eye open\" and \"eye closed\") to see what they are:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"h2o.levels(data[y])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We may want to check if there are any missing values, so let's look for NAs in our dataset. For all the supervised H2O algorithms, H2O will handle missing values automatically, so it's not a problem if we are missing certain feature values. However, it is always a good idea to check to make sure that you are not missing any of the training labels. \n\nTo figure out which, if any, values are missing, we can use the `h2o.nacnt` (NA count) method on any H2OFrame (or column). The columns in an H2O Frame are also H2O Frames themselves, so all the methods that apply to an H2OFrame also apply to a single column.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"h2o.nacnt(data[y])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Great, no missing labels. :-)\n\nOut of curiosity, let's see if there is any missing data in any of the columsn of this frame:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"h2o.nacnt(data)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Each column returns a zero, so there are no missing values in any of the columns.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The next thing I may wonder about in a binary classification problem is the distribution of the response in the training data. Is one of the two outcomes under-represented in the training set? Many real datasets have what's called an \"imbalanace\" problem, where one of the classes has far fewer training examples than the other class. Let's take a look at the distribution:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"h2o.table(data[y])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Ok, the data is not exactly evenly distributed between the two classes -- there are more 0's than 1's in the dataset. However, this level of imbalance shouldn't be much of an issue for the machine learning algos. (We will revisit this later in the modeling section below).\n\nLet's calculate the percentage that each class represents:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"n <- nrow(data) # Total number of training samples\nh2o.table(data[y])['Count']/n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Split H2O Frame into a train and test set\n\nSo far we have explored the original dataset (all rows). For the machine learning portion of this tutorial, we will break the dataset into three parts: a training set, validation set and a test set.\n\nIf you want H2O to do the splitting for you, you can use the `split_frame` method. However, we have explicit splits that we want (for reproducibility reasons), so we can just subset the Frame to get the partitions we want. \n\nSubset the `data` H2O Frame on the \"split\" column:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"train <- data[data['split']==\"train\",]\nnrow(train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"valid <- data[data['split']==\"valid\",]\nnrow(valid)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"test <- data[data['split']==\"test\",]\nnrow(test)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Machine Learning in H2O\n\nWe will do a quick demo of the H2O software using a Gradient Boosting Machine (GBM). The goal of this problem is to train a model to predict eye state (open vs closed) from EEG data. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Train and Test a GBM model",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In the steps above, we have already created the training set and validation set, so the next step is to specify the predictor set and response variable.\n\n#### Specify the predictor set and response\n\nAs with any machine learning algorithm, we need to specify the response and predictor columns in the training set. \n\nThe `x` argument should be a vector of predictor names in the training frame, and `y` specifies the response column. We have already set `y <- \"eyeDetector\"` above, but we still need to specify `x`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"names(train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x <- setdiff(names(train), c(\"eyeDetection\", \"split\")) #Remove the 13th and 14th columns\nx",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now that we have specified `x` and `y`, we can train the GBM model using a few non-default model parameters. Since we are predicting a binary response, we set `distribution = \"bernoulli\"`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model <- h2o.gbm(x = x, y = y,\n training_frame = train,\n validation_frame = valid,\n distribution = \"bernoulli\",\n ntrees = 100,\n max_depth = 4,\n learn_rate = 0.1)",
"\r | \r | | 0%\r | \r |============= | 19%\r | \r |==================== | 29%\r | \r |=========================== | 38%\r | \r |================================ | 45%\r | \r |======================================================================| 100%\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Inspect Model\n\nThe type of results shown when you print a model, are determined by the following:\n- Model class of the estimator (e.g. GBM, RF, GLM, DL)\n- The type of machine learning problem (e.g. binary classification, multiclass classification, regression)\n- The data you specify (e.g. `training_frame` only, `training_frame` and `validation_frame`, or `training_frame` and `nfolds`)\n\nBelow, we see a GBM Model Summary, as well as training and validation metrics since we supplied a `validation_frame`. Since this a binary classification task, we are shown the relevant performance metrics, which inclues: MSE, R^2, LogLoss, AUC and Gini. Also, we are shown a Confusion Matrix, where the threshold for classification is chosen automatically (by H2O) as the threshold which maximizes the F1 score.\n\nThe scoring history is also printed, which shows the performance metrics over some increment such as \"number of trees\" in the case of GBM and RF.\n\nLastly, for tree-based methods (GBM and RF), we also print variable importance.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(model)",
"Model Details:\n==============\n\nH2OBinomialModel: gbm\nModel ID: GBM_model_R_1456125581863_170 \nModel Summary: \n number_of_trees model_size_in_bytes min_depth max_depth mean_depth min_leaves\n1 100 23828 4 4 4.00000 12\n max_leaves mean_leaves\n1 16 15.17000\n\n\nH2OBinomialMetrics: gbm\n** Reported on training data. **\n\nMSE: 0.1076065\nR^2: 0.5657448\nLogLoss: 0.3600893\nAUC: 0.9464642\nGini: 0.8929284\n\nConfusion Matrix for F1-optimal threshold:\n 0 1 Error Rate\n0 4281 635 0.129170 =635/4916\n1 537 3535 0.131876 =537/4072\nTotals 4818 4170 0.130396 =1172/8988\n\nMaximum Metrics: Maximum metrics at their respective thresholds\n metric threshold value idx\n1 max f1 0.450886 0.857802 206\n2 max f2 0.316901 0.899723 262\n3 max f0point5 0.582904 0.882212 158\n4 max accuracy 0.463161 0.870939 202\n5 max precision 0.990029 1.000000 0\n6 max recall 0.062219 1.000000 381\n7 max specificity 0.990029 1.000000 0\n8 max absolute_MCC 0.463161 0.739650 202\n9 max min_per_class_accuracy 0.448664 0.868999 207\n\nGains/Lift Table: Extract with `h2o.gainsLift(<model>, <data>)` or `h2o.gainsLift(<model>, valid=<T/F>, xval=<T/F>)`\nH2OBinomialMetrics: gbm\n** Reported on validation data. **\n\nMSE: 0.1200838\nR^2: 0.5156133\nLogLoss: 0.3894633\nAUC: 0.9238635\nGini: 0.8477271\n\nConfusion Matrix for F1-optimal threshold:\n 0 1 Error Rate\n0 1328 307 0.187768 =307/1635\n1 176 1185 0.129317 =176/1361\nTotals 1504 1492 0.161215 =483/2996\n\nMaximum Metrics: Maximum metrics at their respective thresholds\n metric threshold value idx\n1 max f1 0.425963 0.830705 227\n2 max f2 0.329543 0.887175 268\n3 max f0point5 0.606576 0.850985 156\n4 max accuracy 0.482265 0.846796 206\n5 max precision 0.980397 1.000000 0\n6 max recall 0.084627 1.000000 374\n7 max specificity 0.980397 1.000000 0\n8 max absolute_MCC 0.482265 0.690786 206\n9 max min_per_class_accuracy 0.458183 0.839089 215\n\nGains/Lift Table: Extract with `h2o.gainsLift(<model>, <data>)` or `h2o.gainsLift(<model>, valid=<T/F>, xval=<T/F>)`\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Model Performance on a Test Set\n\nOnce a model has been trained, you can also use it to make predictions on a test set. In the case above, we just ran the model once, so our validation set (passed as `validation_frame`), could have also served as a \"test set.\" We technically have already created test set predictions and evaluated test set performance. \n\nHowever, when performing model selection over a variety of model parameters, it is common for users to train a variety of models (using different parameters) using the training set, `train`, and a validation set, `valid`. Once the user selects the best model (based on validation set performance), the true test of model performance is performed by making a final set of predictions on the held-out (never been used before) test set, `test`.\n\nYou can use the `model_performance` method to generate predictions on a new dataset. The results are stored in an object of class, `\"H2OBinomialMetrics\"`. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"perf <- h2o.performance(model = model, newdata = test)\nclass(perf)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Individual model performance metrics can be extracted using methods like `r2`, `auc` and `mse`. In the case of binary classification, we may be most interested in evaluating test set Area Under the ROC Curve (AUC). ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"h2o.r2(perf)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"h2o.auc(perf)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"h2o.mse(perf)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Cross-validated Performance\n\nTo perform k-fold cross-validation, you use the same code as above, but you specify `nfolds` as an integer greater than 1, or add a \"fold_column\" to your H2O Frame which indicates a fold ID for each row.\n\nUnless you have a specific reason to manually assign the observations to folds, you will find it easiest to simply use the `nfolds` argument.\n\nWhen performing cross-validation, you can still pass a `validation_frame`, but you can also choose to use the original dataset that contains all the rows. We will cross-validate a model below using the original H2O Frame which is called `data`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cvmodel <- h2o.gbm(x = x, y = y,\n training_frame = train,\n validation_frame = valid,\n distribution = \"bernoulli\",\n ntrees = 100,\n max_depth = 4,\n learn_rate = 0.1,\n nfolds = 5)\n",
"\r | \r | | 0%\r | \r |=== | 4%\r | \r |====== | 8%\r | \r |======== | 11%\r | \r |========= | 13%\r | \r |===================== | 30%\r | \r |======================== | 34%\r | \r |========================== | 38%\r | \r |============================ | 41%\r | \r |=============================== | 45%\r | \r |========================================= | 58%\r | \r |========================================== | 61%\r | \r |============================================ | 62%\r | \r |============================================= | 64%\r | \r |================================================= | 70%\r | \r |==================================================== | 74%\r | \r |===================================================== | 75%\r | \r |====================================================== | 77%\r | \r |====================================================== | 78%\r | \r |======================================================================| 100%\n"
]
],
[
[
"This time around, we will simply pull the training and cross-validation metrics out of the model. To do so, you use the `auc` method again, and you can specify `train` or `xval` as `TRUE` to get the correct metric.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(h2o.auc(cvmodel, train = TRUE))\nprint(h2o.auc(cvmodel, xval = TRUE))",
"[1] 0.9464642\n[1] 0.9218678\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Grid Search\n\nOne way of evaluting models with different parameters is to perform a grid search over a set of parameter values. For example, in GBM, here are three model parameters that may be useful to search over:\n- `ntrees`: Number of trees\n- `max_depth`: Maximum depth of a tree\n- `learn_rate`: Learning rate in the GBM\n\nWe will define a grid as follows:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"ntrees_opt <- c(5,50,100)\nmax_depth_opt <- c(2,3,5)\nlearn_rate_opt <- c(0.1,0.2)\n\nhyper_params = list('ntrees' = ntrees_opt,\n 'max_depth' = max_depth_opt,\n 'learn_rate' = learn_rate_opt)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The `h2o.grid` function can be used to train a `\"H2OGrid\"` object for any of the H2O algorithms (specified by the `\"algorithm\"` argument.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"gs <- h2o.grid(algorithm = \"gbm\", \n grid_id = \"eeg_demo_gbm_grid\",\n hyper_params = hyper_params,\n x = x, y = y, \n training_frame = train, \n validation_frame = valid)",
"\r | \r | | 0%\r | \r |== | 3%\r | \r |=== | 5%\r | \r |==== | 6%\r | \r |====== | 8%\r | \r |======= | 10%\r | \r |======== | 11%\r | \r |============ | 17%\r | \r |============== | 20%\r | \r |=============== | 21%\r | \r |=============== | 22%\r | \r |================ | 23%\r | \r |================== | 25%\r | \r |================== | 26%\r | \r |=================== | 27%\r | \r |==================== | 28%\r | \r |========================= | 35%\r | \r |========================== | 37%\r | \r |========================== | 38%\r | \r |=========================== | 39%\r | \r |============================ | 40%\r | \r |============================= | 42%\r | \r |============================== | 43%\r | \r |=============================== | 44%\r | \r |=============================== | 45%\r | \r |===================================== | 52%\r | \r |====================================== | 54%\r | \r |======================================= | 55%\r | \r |======================================== | 56%\r | \r |========================================= | 59%\r | \r |========================================== | 60%\r | \r |=========================================== | 61%\r | \r |============================================ | 62%\r | \r |=============================================== | 68%\r | \r |================================================= | 71%\r | \r |================================================== | 72%\r | \r |=================================================== | 73%\r | \r |=================================================== | 74%\r | \r |===================================================== | 76%\r | \r |====================================================== | 77%\r | \r |======================================================= | 78%\r | \r |======================================================= | 79%\r | \r |============================================================ | 85%\r | \r |============================================================= | 87%\r | \r |============================================================== | 88%\r | \r |=============================================================== | 89%\r | \r |=============================================================== | 91%\r | \r |================================================================= | 93%\r | \r |================================================================== | 94%\r | \r |================================================================== | 95%\r | \r |=================================================================== | 95%\r | \r |======================================================================| 100%\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Compare Models",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(gs)",
"H2O Grid Details\n================\n\nGrid ID: eeg_demo_gbm_grid \nUsed hyper parameters: \n - ntrees \n - max_depth \n - learn_rate \nNumber of models: 18 \nNumber of failed models: 0 \n\nHyper-Parameter Search Summary: ordered by increasing logloss\n ntrees max_depth learn_rate model_ids logloss\n1 100 5 0.2 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_17 0.24919767209732\n2 50 5 0.2 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_16 0.321319350389403\n3 100 5 0.1 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_8 0.325041939824682\n4 100 3 0.2 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_14 0.398168927969941\n5 50 5 0.1 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_7 0.402409215186705\n6 50 3 0.2 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_13 0.455260965151754\n7 100 3 0.1 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_5 0.463893147947061\n8 50 3 0.1 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_4 0.51734929422505\n9 100 2 0.2 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_11 0.530497456235128\n10 5 5 0.2 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_15 0.548389974989351\n11 50 2 0.2 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_10 0.561668599565429\n12 100 2 0.1 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_2 0.564235794490373\n13 50 2 0.1 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_1 0.594214675563477\n14 5 5 0.1 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_6 0.600327168524549\n15 5 3 0.2 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_12 0.610367851324487\n16 5 3 0.1 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_3 0.642100038024138\n17 5 2 0.2 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_9 0.647268487315379\n18 5 2 0.1 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_0 0.663560995637836\n"
]
],
[
[
"By default, grids of models will return the grid results sorted by (increasing) logloss on the validation set. However, if we are interested in sorting on another model performance metric, we can do that using the `h2o.getGrid` function as follows:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# print out the auc for all of the models\nauc_table <- h2o.getGrid(grid_id = \"eeg_demo_gbm_grid\", sort_by = \"auc\", decreasing = TRUE)\nprint(auc_table)",
"H2O Grid Details\n================\n\nGrid ID: eeg_demo_gbm_grid \nUsed hyper parameters: \n - ntrees \n - max_depth \n - learn_rate \nNumber of models: 18 \nNumber of failed models: 0 \n\nHyper-Parameter Search Summary: ordered by decreasing auc\n ntrees max_depth learn_rate model_ids auc\n1 100 5 0.2 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_17 0.967771493797284\n2 50 5 0.2 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_16 0.949609591795923\n3 100 5 0.1 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_8 0.94941792664595\n4 50 5 0.1 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_7 0.922075196552274\n5 100 3 0.2 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_14 0.913785959685157\n6 50 3 0.2 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_13 0.887706691652792\n7 100 3 0.1 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_5 0.884064379717198\n8 5 5 0.2 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_15 0.851187402678818\n9 50 3 0.1 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_4 0.848921799270639\n10 5 5 0.1 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_6 0.825662907513139\n11 100 2 0.2 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_11 0.812030639460551\n12 50 2 0.2 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_10 0.785379521713437\n13 100 2 0.1 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_2 0.78299280750123\n14 5 3 0.2 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_12 0.774673686150002\n15 50 2 0.1 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_1 0.754834657912535\n16 5 3 0.1 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_3 0.749285131682721\n17 5 2 0.2 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_9 0.692702793188135\n18 5 2 0.1 eeg_demo_gbm_grid_model_0 0.676144542037133\n"
]
],
[
[
"The \"best\" model in terms of validation set AUC is listed first in auc_table.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"best_model <- h2o.getModel(auc_table@model_ids[[1]])\nh2o.auc(best_model, valid = TRUE) #Validation AUC for best model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The last thing we may want to do is generate predictions on the test set using the \"best\" model, and evaluate the test set AUC.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"best_perf <- h2o.performance(model = best_model, newdata = test)\nh2o.auc(best_perf)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The test set AUC is approximately 0.97. Not bad!!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
c50388f2ca21d02c214fecac552500272f47f6da
| 26,836 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
4_metrics.ipynb
|
issdl/from-data-to-solution-2021
|
b55bdcfc4a6e45a320b645a45e35c5763511846f
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2021-07-06T05:28:53.000Z
|
2021-07-06T05:28:53.000Z
|
4_metrics.ipynb
|
issdl/from-data-to-solution-2021
|
b55bdcfc4a6e45a320b645a45e35c5763511846f
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
4_metrics.ipynb
|
issdl/from-data-to-solution-2021
|
b55bdcfc4a6e45a320b645a45e35c5763511846f
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 21.589702 | 234 | 0.537524 |
[
[
[
"<a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/issdl/from-data-to-solution-2021/blob/main/4_metrics.ipynb\" target=\"_parent\"><img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open In Colab\"/></a>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Metrics",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Imports",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nnp.random.seed(2021)\nimport random\nrandom.seed(2021)\n\nfrom IPython.display import Markdown, display\n\ndef printmd(string):\n display(Markdown(string))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Create Toy Datasets",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def pc(db): # print count\n print(\"Database contains {} negative and {} positive samples\".format(db.count(0), db.count(1)))\n\nlength = 100\n\n# Balanced\ndb_balanced = [0] * (length//2) + [1] * (length//2)\npc(db_balanced)\n\n# More positives\namount = random.uniform(0.9, 0.99)\ndb_positives = [1] * int(length*amount) + [0] * int(length*(1-amount)+1)\npc(db_positives)\n\n# More negatives\namount = random.uniform(0.9, 0.99)\ndb_negatives = [0] * int(length*amount) + [1] * int(length*(1-amount)+1)\npc(db_negatives)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Dummy model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"top_no = 95\ndef dummy_model(data, threshold):\n correct=0\n output=[]\n for i, d in enumerate(data):\n if i < threshold or i > top_no :\n output.append(d)\n correct+=1\n else:\n output.append(abs(1-d))\n return output",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### *Balanced dataset*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"balanced_threshold = 80\nout_balanced = dummy_model(db_balanced, balanced_threshold)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('Labels:')\nprintmd('{}**{}**{}'.format(db_balanced[:balanced_threshold], db_balanced[balanced_threshold:top_no], db_balanced[top_no+1:],))\nprint('Predictions:')\nprintmd('{}**{}**{}'.format(out_balanced[:balanced_threshold], out_balanced[balanced_threshold:top_no], out_balanced[top_no+1:],))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### *More positives*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"positives_threshold = 80\nout_positives = dummy_model(db_positives, positives_threshold)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('Labels:')\nprintmd('{}**{}**{}'.format(db_positives[:positives_threshold], db_positives[positives_threshold:top_no], db_positives[top_no+1:]))\nprint('Predictions:')\nprintmd('{}**{}**{}'.format(out_positives[:positives_threshold], out_positives[positives_threshold:top_no], out_positives[top_no+1:]))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### *More negatives*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"negatives_threshold = 80\nout_negatives = dummy_model(db_negatives, negatives_threshold)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('Labels:')\nprintmd('{}**{}**{}'.format(db_negatives[:negatives_threshold], db_negatives[negatives_threshold:top_no], db_negatives[top_no+1:]))\nprint('Predictions:')\nprintmd('{}**{}**{}'.format(out_negatives[:negatives_threshold], out_negatives[negatives_threshold:top_no], db_negatives[top_no+1:]))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Metrics",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### **Accuracy**\n\nTasks:\n\n* Create method implementing accuracy metric",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"*Balanced dataset*\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Implement method implementing accuracy metric\n\ndef acc(labels, predictions):\n ## START\n\n ## END",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"printmd('Accuracy custom {}'.format(acc(db_balanced, out_balanced)))\nprintmd('Accuracy sklearn {}'.format(accuracy_score(db_balanced, out_balanced)))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*More positives*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"printmd('Accuracy custom {}'.format(acc(db_positives, out_positives)))\nprintmd('Accuracy sklearn {}'.format(accuracy_score(db_positives, out_positives)))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*More negatives*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"printmd('Accuracy custom {}'.format(acc(db_negatives, out_negatives)))\nprintmd('Accuracy sklearn {}'.format(accuracy_score(db_negatives, out_negatives)))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*More positives - all positive predictions*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"printmd('Accuracy {}'.format(accuracy_score(db_positives, np.ones(length))))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*More negatives - all negative predictions*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"printmd('Accuracy {}'.format(accuracy_score(db_negatives, np.zeros(length))))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### **Confusion Matrix**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, ConfusionMatrixDisplay",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*Balanced dataset*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cmd = ConfusionMatrixDisplay(confusion_matrix(db_balanced, out_balanced), display_labels=[0,1])\ncmd.plot()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*More positives*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cmd = ConfusionMatrixDisplay(confusion_matrix(db_positives, out_positives), display_labels=[0,1])\ncmd.plot()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*More negatives*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cmd = ConfusionMatrixDisplay(confusion_matrix(db_negatives, out_negatives), display_labels=[0,1])\ncmd.plot()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*More positives - all positive predictions*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cmd = ConfusionMatrixDisplay(confusion_matrix(db_positives, np.ones(length)), display_labels=[0,1])\ncmd.plot()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*More negatives - all negative predictions*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cmd = ConfusionMatrixDisplay(confusion_matrix(db_negatives, np.zeros(length)), display_labels=[0,1])\ncmd.plot()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### **Precision**\n\nTasks:\n\n* Create method implementing precision metric",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.metrics import precision_score",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Create method implementing precision metric\n\ndef precision(labels, predictions):\n ## START\n\n ## END",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*Balanced dataset*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"printmd('Precision custom {}'.format(precision(db_balanced, out_balanced)))\nprintmd('Precision sklearn {}'.format(precision_score(db_balanced, out_balanced)))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*More positives*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"printmd('Precision custom {}'.format(precision(db_positives, out_positives)))\nprintmd('Precision sklearn {}'.format(precision_score(db_positives, out_positives)))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*More negatives*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"printmd('Precision custom {}'.format(precision(db_negatives, out_negatives)))\nprintmd('Precision sklearn {}'.format(precision_score(db_negatives, out_negatives)))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*More positives - all positive predictions*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"printmd('Precision custom {}'.format(precision(db_positives, np.ones(length))))\nprintmd('Precision sklearn {}'.format(precision_score(db_positives, np.ones(length))))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*More negatives - all negative predictions*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"printmd('Precision custom {}'.format(precision(db_negatives, np.zeros(length))))\nprintmd('Precision sklearn {}'.format(precision_score(db_negatives, np.zeros(length))))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### **Recall**\n\nTasks:\n\n* Create method implementing recall metric",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.metrics import recall_score",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Create method implementing recall metric\n\ndef recall(labels, predictions):\n ## START\n\n ## END",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*Balanced dataset*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"printmd('Recall custom {}'.format(recall(db_balanced, out_balanced)))\nprintmd('Recall sklearn {}'.format(recall_score(db_balanced, out_balanced)))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*More positives*\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"printmd('Recall custom {}'.format(recall(db_positives, out_positives)))\nprintmd('Recall sklearn {}'.format(recall_score(db_positives, out_positives)))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*More negatives*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"printmd('Recall custom {}'.format(recall(db_negatives, out_negatives)))\nprintmd('Recall sklearn {}'.format(recall_score(db_negatives, out_negatives)))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*More positives - all positive predictions*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"printmd('Recall custom {}'.format(recall(db_positives, np.ones(length))))\nprintmd('Recall sklearn {}'.format(recall_score(db_positives, np.ones(length))))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*More negatives - all negative predictions*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"printmd('Recall custom {}'.format(recall(db_negatives, np.zeros(length))))\nprintmd('Recall sklearn {}'.format(recall_score(db_negatives, np.zeros(length))))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### **False Positive Rate = Specificity**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def fpr(labels, predictions):\n assert len(labels)==len(predictions)\n fp=0\n tn=0\n #fpr=fp/(fp+tn)\n for i, p in enumerate(predictions):\n if p == labels[i] and p == 0:\n tn+=1\n elif p != labels[i] and p == 1:\n fp+=1\n if (fp+tn)==0:\n return 0\n return fp/(fp+tn)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*Balanced dataset*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"printmd('fpr {}'.format(fpr(db_balanced, out_balanced)))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*More positives*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"printmd('fpr {}'.format(fpr(db_positives, out_positives)))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*More negatives*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"printmd('fpr {}'.format(fpr(db_negatives, out_negatives)))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*More positives - all positive predictions*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"printmd('fpr {}'.format(fpr(db_positives, np.ones(length))))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*More negatives - all negative predictions*",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### **True Positive Rate = Recall = Sensitivity**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### **F1 Score**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.metrics import f1_score",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def f1():\n pass",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*Balanced dataset*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"printmd('F1 sklearn {}'.format(f1_score(db_balanced, out_balanced)))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*More positives*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"printmd('F1 sklearn {}'.format(f1_score(db_positives, out_positives)))\nprintmd('F1 sklearn weighted {}'.format(f1_score(db_positives, out_positives, average='weighted')))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*More negatives*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"printmd('F1 sklearn {}'.format(f1_score(db_negatives, out_negatives)))\nprintmd('F1 sklearn weighted {}'.format(f1_score(db_negatives, out_negatives, average='weighted')))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*More positives - all positive predictions*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"printmd('F1 sklearn {}'.format(f1_score(db_positives, np.ones(length))))\nprintmd('F1 sklearn weighted {}'.format(f1_score(db_positives, np.ones(length), average='weighted')))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*More negatives - all negative predictions*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"printmd('F1 sklearn {}'.format(f1_score(db_negatives, np.zeros(length))))\nprintmd('F1 sklearn weighted {}'.format(f1_score(db_negatives, np.zeros(length), average='weighted')))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c503900b1771091553b7b55e85660039f1c7983b
| 246,426 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Models.ipynb
|
oupton/startup-ds
|
2aca6b119baabb187779f8afcb816c2bc25dc34d
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2018-04-26T03:17:11.000Z
|
2018-04-26T03:17:12.000Z
|
Models.ipynb
|
oupton/startup-ds
|
2aca6b119baabb187779f8afcb816c2bc25dc34d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Models.ipynb
|
oupton/startup-ds
|
2aca6b119baabb187779f8afcb816c2bc25dc34d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 122.295782 | 33,808 | 0.806197 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np \nimport os\nimport matplotlib\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom xgboost.sklearn import XGBRegressor\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nfrom sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, roc_auc_score, make_scorer, accuracy_score\nfrom xgboost import XGBClassifier, plot_importance\nimport math",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"main_df = pd.read_csv(os.path.join('data', 'unpacked_genres.csv')).drop('Unnamed: 0', axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lang_df = pd.read_csv(os.path.join('data', 'languages_parsed.csv')).drop('Unnamed: 0', axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"main_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lang_df.columns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"main_df['id'] = main_df['id'].astype('str')\nlang_df['id'] = lang_df['id'].astype('str')\nlang_df = lang_df[['id', u'numlang', u'cn', u'da', u'de',\n u'en', u'es', u'fr', u'hi', u'it', u'ja', u'ko', u'ml', u'ru', u'ta',\n u'zh']]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"all_df = pd.merge(main_df, lang_df, on='id')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"all_df.columns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"all_df.to_csv(os.path.join('data', 'final.csv'))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"all_df = all_df.drop(['production_countries', 'spoken_languages', 'original_language'], axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"all_df.to_csv(os.path.join('data', 'final.csv'))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"all_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"all_df.drop('original_language', axis=1).to_csv(os.path.join('data', 'final.csv'))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = pd.read_csv(os.path.join('data', 'final.csv'))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X = df.drop(['revenue', 'id', 'likes', 'dislikes'], axis=1)\ny = df.revenue",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"reg = XGBRegressor()\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"reg.fit(X_train, y_train)\nprint(math.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_test, reg.predict(X_test))))",
"114498833.086\n"
],
[
"print(reg.predict(df[df['id'] == 862].drop(['id', 'revenue'], axis=1)))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X.columns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Xp = X.drop([u'cn',\n u'da', u'de', u'es', u'fr', u'hi', u'it', u'ja', u'ko', u'ml',\n u'ru', u'ta', u'zh'], axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Xp.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"reg = XGBRegressor()\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"reg.fit(X_train, y_train)\nprint(math.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_test, reg.predict(X_test))))",
"107341968.205\n"
],
[
"import seaborn as sns\nsns.heatmap(X.corr())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.columns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sns.heatmap(df.drop([u'cn', u'da', u'de', u'es',\n u'fr', u'hi', u'it', u'ja', u'ko', u'ml', u'ru', u'ta', u'zh'], axis=1).corr())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.revenue.hist()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"profit = []\nfor i in range(len(df)):\n profit.append(df['revenue'][i] - df['budget'][i])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df['profit'] = profit",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(df[df['profit'] < 0])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"isProfitable = []\nfor i in range(len(df)):\n isProfitable.append(df['profit'][i] > 0)\ndf['isProfitable'] = isProfitable",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = pd.read_csv(os.path.join('data', 'final_clf.csv')).drop('Unnamed: 0', axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X = df.drop(['id', 'revenue', 'TV Movie', 'profit', 'isProfitable'], axis=1)\ny = df.isProfitable.astype('int')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y)\nclf = XGBClassifier()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"clf.fit(X_train, y_train)\nclf.score(X_test, y_test)",
"/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n"
],
[
"plot_importance(clf)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"roc_auc_score(y_test, np.array(clf.predict_proba(X_test))[:,1])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"roc_auc_score(y, np.array(clf.predict_proba(X))[:,1])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"all_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"all_df.drop('original_language', axis=1).to_csv(os.path.join('data', 'final.csv'))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = pd.read_csv(os.path.join('data', 'final.csv'))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X = df.drop(['revenue', 'id', 'likes', 'dislikes'], axis=1)\ny = df.revenue",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"reg = XGBRegressor()\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"reg.fit(X_train, y_train)\nprint(math.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_test, reg.predict(X_test))))",
"103448983.253\n"
],
[
"print(reg.predict(df[df['id'] == 862].drop(['id', 'revenue'], axis=1)))",
"[2.0252707e+08]\n"
],
[
"X.columns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Xp = X.drop([u'cn',\n u'da', u'de', u'es', u'fr', u'hi', u'it', u'ja', u'ko', u'ml',\n u'ru', u'ta', u'zh'], axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Xp.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"reg = XGBRegressor()\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.revenue.hist()",
"/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/sklearn/preprocessing/label.py:151: DeprecationWarning: The truth value of an empty array is ambiguous. Returning False, but in future this will result in an error. Use `array.size > 0` to check that an array is not empty.\n if diff:\n"
],
[
"profit = []\nfor i in range(len(df)):\n profit.append(df['revenue'][i] - df['budget'][i])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df['profit'] = profit",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"grid_params = {\n 'max_depth': range(5, 15, 3),\n 'n_estimators': range(50, 200, 25)\n}\nscoring = {'AUC': 'roc_auc', 'Accuracy': make_scorer(accuracy_score)}\nclf = GridSearchCV(XGBClassifier(), param_grid=grid_params, scoring=scoring, cv=5, refit='AUC')\nclf.fit(X, y)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"best_clf = clf.best_estimator_",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.columns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X = df.drop(['id', 'revenue', 'TV Movie', 'profit', 'isProfitable'], axis=1)\ny = df.isProfitable.astype('int')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y)\nclf = XGBClassifier()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"roc_auc_score(y, np.array(best_clf.predict_proba(X))[:,1])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plot_importance(best_clf)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from xgboost import plot_tree",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.daysSinceStart.plot.hist()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df['isProfitable'] = df['isProfitable'].astype('int')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(df[df['isProfitable'] == 0])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"1421.0/(len(df)-1421.0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.to_csv(os.path.join('data', 'final_clf.csv'))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c503929ec4737914c3d28efef48f9c1d58af44bf
| 50,533 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
pandas/freecodecamp/data-cleaning-rmotr-freecodecamp-master/data-cleaning-rmotr-freecodecamp-master/2 - Handling Missing Data with Pandas.ipynb
|
bruno-marcelino10/estudos-com-py
|
f82ef576b0e3fd50decbfaad652c59a6830b15bc
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
pandas/freecodecamp/data-cleaning-rmotr-freecodecamp-master/data-cleaning-rmotr-freecodecamp-master/2 - Handling Missing Data with Pandas.ipynb
|
bruno-marcelino10/estudos-com-py
|
f82ef576b0e3fd50decbfaad652c59a6830b15bc
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2022-01-11T21:04:51.000Z
|
2022-01-11T21:05:05.000Z
|
pandas/freecodecamp/data-cleaning-rmotr-freecodecamp-master/data-cleaning-rmotr-freecodecamp-master/2 - Handling Missing Data with Pandas.ipynb
|
bruno-marcelino10/estudos-com-py
|
f82ef576b0e3fd50decbfaad652c59a6830b15bc
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 22.419255 | 479 | 0.387569 |
[
[
[
"\n<hr style=\"margin-bottom: 40px;\">\n\n<img src=\"https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/7065401/39117440-24199c72-46e7-11e8-8ffc-25c6e27e07d4.jpg\"\n style=\"width:300px; float: right; margin: 0 40px 40px 40px;\"></img>\n\n# Handling Missing Data with Pandas\n\npandas borrows all the capabilities from numpy selection + adds a number of convenient methods to handle missing values. Let's see one at a time:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n\n## Hands on! ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Pandas utility functions\n\nSimilarly to `numpy`, pandas also has a few utility functions to identify and detect null values:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pd.isnull(np.nan)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.isnull(None)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.isna(np.nan)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.isna(None)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The opposite ones also exist:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pd.notnull(None)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.notnull(np.nan)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.notna(np.nan)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.notnull(3)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"These functions also work with Series and `DataFrame`s:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pd.isnull(pd.Series([1, np.nan, 7]))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.notnull(pd.Series([1, np.nan, 7]))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.isnull(pd.DataFrame({\n 'Column A': [1, np.nan, 7],\n 'Column B': [np.nan, 2, 3],\n 'Column C': [np.nan, 2, np.nan]\n}))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n### Pandas Operations with Missing Values\n\nPandas manages missing values more gracefully than numpy. `nan`s will no longer behave as \"viruses\", and operations will just ignore them completely:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pd.Series([1, 2, np.nan]).count()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.Series([1, 2, np.nan]).sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.Series([2, 2, np.nan]).mean()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Filtering missing data\n\nAs we saw with numpy, we could combine boolean selection + `pd.isnull` to filter out those `nan`s and null values:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"s = pd.Series([1, 2, 3, np.nan, np.nan, 4])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.notnull(s)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.isnull(s)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.notnull(s).sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.isnull(s).sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s[pd.notnull(s)]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"But both `notnull` and `isnull` are also methods of `Series` and `DataFrame`s, so we could use it that way:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"s.isnull()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s.notnull()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s[s.notnull()]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n### Dropping null values",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Boolean selection + `notnull()` seems a little bit verbose and repetitive. And as we said before: any repetitive task will probably have a better, more DRY way. In this case, we can use the `dropna` method:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"s",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s.dropna()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Dropping null values on DataFrames\n\nYou saw how simple it is to drop `na`s with a Series. But with `DataFrame`s, there will be a few more things to consider, because you can't drop single values. You can only drop entire columns or rows. Let's start with a sample `DataFrame`:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df = pd.DataFrame({\n 'Column A': [1, np.nan, 30, np.nan],\n 'Column B': [2, 8, 31, np.nan],\n 'Column C': [np.nan, 9, 32, 100],\n 'Column D': [5, 8, 34, 110],\n})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.info()",
"<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>\nRangeIndex: 4 entries, 0 to 3\nData columns (total 4 columns):\n # Column Non-Null Count Dtype \n--- ------ -------------- ----- \n 0 Column A 2 non-null float64\n 1 Column B 3 non-null float64\n 2 Column C 3 non-null float64\n 3 Column D 4 non-null int64 \ndtypes: float64(3), int64(1)\nmemory usage: 256.0 bytes\n"
],
[
"df.isnull()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.isnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The default `dropna` behavior will drop all the rows in which _any_ null value is present:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df.dropna()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"In this case we're dropping **rows**. Rows containing null values are dropped from the DF. You can also use the `axis` parameter to drop columns containing null values:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df.dropna(axis=1) # axis='columns' also works",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"In this case, any row or column that contains **at least** one null value will be dropped. Which can be, depending on the case, too extreme. You can control this behavior with the `how` parameter. Can be either `'any'` or `'all'`:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df2 = pd.DataFrame({\n 'Column A': [1, np.nan, 30],\n 'Column B': [2, np.nan, 31],\n 'Column C': [np.nan, np.nan, 100]\n})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.dropna(how='all')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.dropna(how='any') # default behavior",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You can also use the `thresh` parameter to indicate a _threshold_ (a minimum number) of non-null values for the row/column to be kept:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.dropna(thresh=3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.dropna(thresh=3, axis='columns')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n### Filling null values\n\nSometimes instead than dropping the null values, we might need to replace them with some other value. This highly depends on your context and the dataset you're currently working. Sometimes a `nan` can be replaced with a `0`, sometimes it can be replaced with the `mean` of the sample, and some other times you can take the closest value. Again, it depends on the context. We'll show you the different methods and mechanisms and you can then apply them to your own problem.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"s",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Filling nulls with a arbitrary value**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"s.fillna(0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s.fillna(s.mean())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Filling nulls with contiguous (close) values**\n\nThe `method` argument is used to fill null values with other values close to that null one:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"s.fillna(method='ffill')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s.fillna(method='bfill')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This can still leave null values at the extremes of the Series/DataFrame:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pd.Series([np.nan, 3, np.nan, 9]).fillna(method='ffill')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.Series([1, np.nan, 3, np.nan, np.nan]).fillna(method='bfill')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Filling null values on DataFrames\n\nThe `fillna` method also works on `DataFrame`s, and it works similarly. The main differences are that you can specify the `axis` (as usual, rows or columns) to use to fill the values (specially for methods) and that you have more control on the values passed:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.fillna({'Column A': 0, 'Column B': 99, 'Column C': df['Column C'].mean()})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.fillna(method='ffill', axis=0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.fillna(method='ffill', axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n### Checking if there are NAs\n\nThe question is: Does this `Series` or `DataFrame` contain any missing value? The answer should be yes or no: `True` or `False`. How can you verify it?\n\n**Example 1: Checking the length**\n\nIf there are missing values, `s.dropna()` will have less elements than `s`:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"s.dropna().count()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"missing_values = len(s.dropna()) != len(s)\nmissing_values",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"There's also a `count` method, that excludes `nan`s from its result:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"len(s)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s.count()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"So we could just do:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"missing_values = s.count() != len(s)\nmissing_values",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**More Pythonic solution `any`**\n\nThe methods `any` and `all` check if either there's `any` True value in a Series or `all` the values are `True`. They work in the same way as in Python:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pd.Series([True, False, False]).any()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.Series([True, False, False]).all()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.Series([True, True, True]).all()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The `isnull()` method returned a Boolean `Series` with `True` values wherever there was a `nan`:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"s.isnull()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"So we can just use the `any` method with the boolean array returned:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pd.Series([1, np.nan]).isnull().any()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.Series([1, 2]).isnull().any()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s.isnull().any()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"A more strict version would check only the `values` of the Series:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"s.isnull().values",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s.isnull().values.any()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
c503b8bb1c8d364b79be9ae1351d064d0d8ecf45
| 31,713 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
jupyter_notebooks/pandas/complex_selections.ipynb
|
manual123/Nacho-Jupyter-Notebooks
|
e75523434b1a90313a6b44e32b056f63de8a7135
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2021-02-13T05:52:05.000Z
|
2022-02-08T09:52:35.000Z
|
pandas/complex_selections.ipynb
|
manual123/Nacho-Jupyter-Notebooks
|
e75523434b1a90313a6b44e32b056f63de8a7135
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
pandas/complex_selections.ipynb
|
manual123/Nacho-Jupyter-Notebooks
|
e75523434b1a90313a6b44e32b056f63de8a7135
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 31.586653 | 309 | 0.356384 |
[
[
[
"empty"
]
]
] |
[
"empty"
] |
[
[
"empty"
]
] |
c503b9de125a62f7c4c6214bf0b0531adbf7f531
| 118,627 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
00_tensorflow_fundamentals.ipynb
|
joelweber977/Python3_TF_Certificate
|
397f6275c92d3857d29cb2c60f68604cfe3a00ef
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
00_tensorflow_fundamentals.ipynb
|
joelweber977/Python3_TF_Certificate
|
397f6275c92d3857d29cb2c60f68604cfe3a00ef
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
00_tensorflow_fundamentals.ipynb
|
joelweber977/Python3_TF_Certificate
|
397f6275c92d3857d29cb2c60f68604cfe3a00ef
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2021-09-21T11:56:19.000Z
|
2021-12-30T15:39:33.000Z
| 31.491107 | 1,643 | 0.551038 |
[
[
[
"<a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/mrdbourke/tensorflow-deep-learning/blob/main/00_tensorflow_fundamentals.ipynb\" target=\"_parent\"><img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open In Colab\"/></a>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 00. Getting started with TensorFlow: A guide to the fundamentals\n\n## What is TensorFlow?\n\n[TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/) is an open-source end-to-end machine learning library for preprocessing data, modelling data and serving models (getting them into the hands of others).\n\n## Why use TensorFlow?\n\nRather than building machine learning and deep learning models from scratch, it's more likely you'll use a library such as TensorFlow. This is because it contains many of the most common machine learning functions you'll want to use.\n\n## What we're going to cover\n\nTensorFlow is vast. But the main premise is simple: turn data into numbers (tensors) and build machine learning algorithms to find patterns in them.\n\nIn this notebook we cover some of the most fundamental TensorFlow operations, more specificially:\n* Introduction to tensors (creating tensors)\n* Getting information from tensors (tensor attributes)\n* Manipulating tensors (tensor operations)\n* Tensors and NumPy\n* Using @tf.function (a way to speed up your regular Python functions)\n* Using GPUs with TensorFlow\n* Exercises to try\n\nThings to note:\n* Many of the conventions here will happen automatically behind the scenes (when you build a model) but it's worth knowing so if you see any of these things, you know what's happening.\n* For any TensorFlow function you see, it's important to be able to check it out in the documentation, for example, going to the Python API docs for all functions and searching for what you need: https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/ (don't worry if this seems overwhelming at first, with enough practice, you'll get used to navigating the documentaiton).\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Introduction to Tensors\n\nIf you've ever used NumPy, [tensors](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/tensor) are kind of like NumPy arrays (we'll see more on this later).\n\nFor the sake of this notebook and going forward, you can think of a tensor as a multi-dimensional numerical representation (also referred to as n-dimensional, where n can be any number) of something. Where something can be almost anything you can imagine: \n* It could be numbers themselves (using tensors to represent the price of houses). \n* It could be an image (using tensors to represent the pixels of an image).\n* It could be text (using tensors to represent words).\n* Or it could be some other form of information (or data) you want to represent with numbers.\n\nThe main difference between tensors and NumPy arrays (also an n-dimensional array of numbers) is that tensors can be used on [GPUs (graphical processing units)](https://blogs.nvidia.com/blog/2009/12/16/whats-the-difference-between-a-cpu-and-a-gpu/) and [TPUs (tensor processing units)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tensor_processing_unit). \n\nThe benefit of being able to run on GPUs and TPUs is faster computation, this means, if we wanted to find patterns in the numerical representations of our data, we can generally find them faster using GPUs and TPUs.\n\nOkay, we've been talking enough about tensors, let's see them.\n\nThe first thing we'll do is import TensorFlow under the common alias `tf`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import TensorFlow\nimport tensorflow as tf\nprint(tf.__version__) # find the version number (should be 2.x+)",
"2.4.1\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Creating Tensors with `tf.constant()`\n\nAs mentioned before, in general, you usually won't create tensors yourself. This is because TensorFlow has modules built-in (such as [`tf.io`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/io) and [`tf.data`](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/data)) which are able to read your data sources and automatically convert them to tensors and then later on, neural network models will process these for us.\n\nBut for now, because we're getting familar with tensors themselves and how to manipulate them, we'll see how we can create them ourselves.\n\nWe'll begin by using [`tf.constant()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/constant).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create a scalar (rank 0 tensor)\nscalar = tf.constant(7)\nscalar",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"A scalar is known as a rank 0 tensor. Because it has no dimensions (it's just a number).\n\n> 🔑 **Note:** For now, you don't need to know too much about the different ranks of tensors (but we will see more on this later). The important point is knowing tensors can have an unlimited range of dimensions (the exact amount will depend on what data you're representing).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Check the number of dimensions of a tensor (ndim stands for number of dimensions)\nscalar.ndim",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create a vector (more than 0 dimensions)\nvector = tf.constant([10, 10])\nvector",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Check the number of dimensions of our vector tensor\nvector.ndim",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create a matrix (more than 1 dimension)\nmatrix = tf.constant([[10, 7],\n [7, 10]])\nmatrix",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"matrix.ndim",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"By default, TensorFlow creates tensors with either an `int32` or `float32` datatype.\n\nThis is known as [32-bit precision](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Precision_(computer_science) (the higher the number, the more precise the number, the more space it takes up on your computer).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create another matrix and define the datatype\nanother_matrix = tf.constant([[10., 7.],\n [3., 2.],\n [8., 9.]], dtype=tf.float16) # specify the datatype with 'dtype'\nanother_matrix",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Even though another_matrix contains more numbers, its dimensions stay the same\nanother_matrix.ndim",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# How about a tensor? (more than 2 dimensions, although, all of the above items are also technically tensors)\ntensor = tf.constant([[[1, 2, 3],\n [4, 5, 6]],\n [[7, 8, 9],\n [10, 11, 12]],\n [[13, 14, 15],\n [16, 17, 18]]])\ntensor",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tensor.ndim",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This is known as a rank 3 tensor (3-dimensions), however a tensor can have an arbitrary (unlimited) amount of dimensions.\n\nFor example, you might turn a series of images into tensors with shape (224, 224, 3, 32), where:\n* 224, 224 (the first 2 dimensions) are the height and width of the images in pixels.\n* 3 is the number of colour channels of the image (red, green blue).\n* 32 is the batch size (the number of images a neural network sees at any one time).\n\nAll of the above variables we've created are actually tensors. But you may also hear them referred to as their different names (the ones we gave them):\n* **scalar**: a single number.\n* **vector**: a number with direction (e.g. wind speed with direction).\n* **matrix**: a 2-dimensional array of numbers.\n* **tensor**: an n-dimensional arrary of numbers (where n can be any number, a 0-dimension tensor is a scalar, a 1-dimension tensor is a vector). \n\nTo add to the confusion, the terms matrix and tensor are often used interchangably.\n\nGoing forward since we're using TensorFlow, everything we refer to and use will be tensors.\n\nFor more on the mathematical difference between scalars, vectors and matrices see the [visual algebra post by Math is Fun](https://www.mathsisfun.com/algebra/scalar-vector-matrix.html).\n\n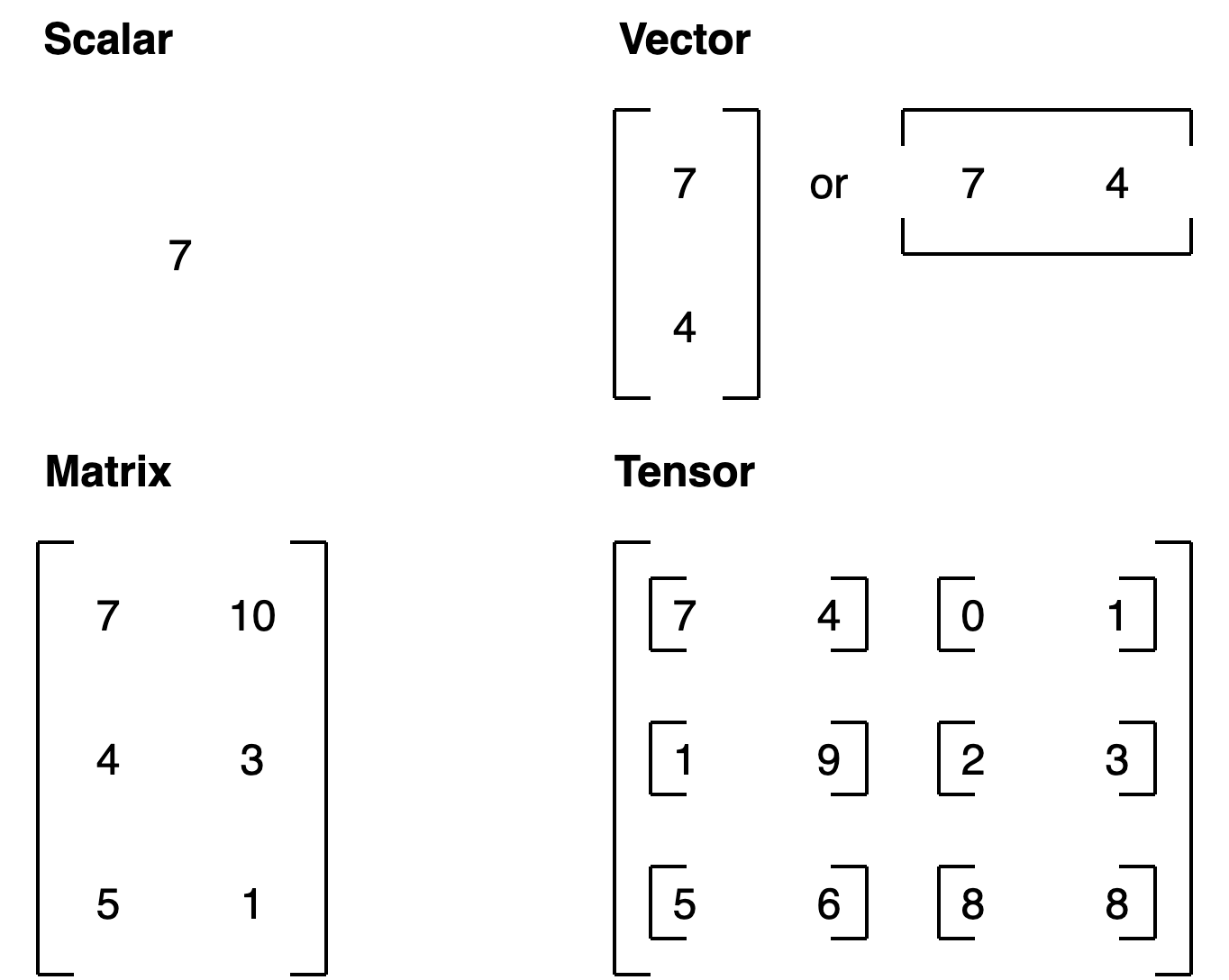",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Creating Tensors with `tf.Variable()`\n\nYou can also (although you likely rarely will, because often, when working with data, tensors are created for you automatically) create tensors using [`tf.Variable()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/Variable).\n\nThe difference between `tf.Variable()` and `tf.constant()` is tensors created with `tf.constant()` are immutable (can't be changed, can only be used to create a new tensor), where as, tensors created with `tf.Variable()` are mutable (can be changed).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create the same tensor with tf.Variable() and tf.constant()\nchangeable_tensor = tf.Variable([10, 7])\nunchangeable_tensor = tf.constant([10, 7])\nchangeable_tensor, unchangeable_tensor",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now let's try to change one of the elements of the changable tensor.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Will error (requires the .assign() method)\nchangeable_tensor[0] = 7\nchangeable_tensor",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"To change an element of a `tf.Variable()` tensor requires the `assign()` method.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Won't error\nchangeable_tensor[0].assign(7)\nchangeable_tensor",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now let's try to change a value in a `tf.constant()` tensor.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Will error (can't change tf.constant())\nunchangeable_tensor[0].assign(7)\nunchangleable_tensor",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Which one should you use? `tf.constant()` or `tf.Variable()`?\n\nIt will depend on what your problem requires. However, most of the time, TensorFlow will automatically choose for you (when loading data or modelling data).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Creating random tensors\n\nRandom tensors are tensors of some abitrary size which contain random numbers.\n\nWhy would you want to create random tensors? \n\nThis is what neural networks use to intialize their weights (patterns) that they're trying to learn in the data.\n\nFor example, the process of a neural network learning often involves taking a random n-dimensional array of numbers and refining them until they represent some kind of pattern (a compressed way to represent the original data).\n\n**How a network learns**\n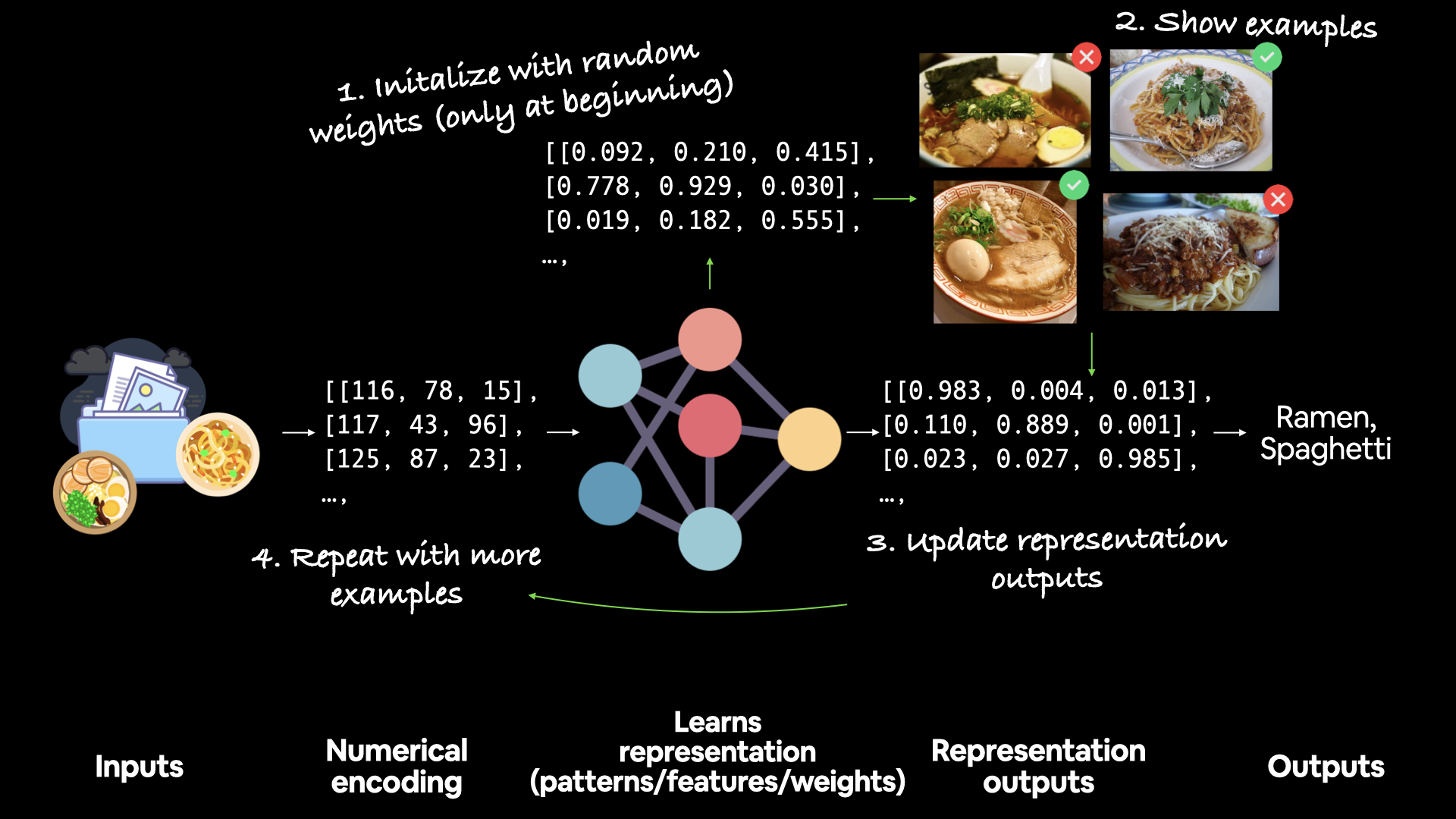\n*A network learns by starting with random patterns (1) then going through demonstrative examples of data (2) whilst trying to update its random patterns to represent the examples (3).*\n\nWe can create random tensors by using the [`tf.random.Generator`](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/random_numbers#the_tfrandomgenerator_class) class.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create two random (but the same) tensors\nrandom_1 = tf.random.Generator.from_seed(42) # set the seed for reproducibility\nrandom_1 = random_1.normal(shape=(3, 2)) # create tensor from a normal distribution \nrandom_2 = tf.random.Generator.from_seed(42)\nrandom_2 = random_2.normal(shape=(3, 2))\n\n# Are they equal?\nrandom_1, random_2, random_1 == random_2",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The random tensors we've made are actually [pseudorandom numbers](https://www.computerhope.com/jargon/p/pseudo-random.htm) (they appear as random, but really aren't).\n\nIf we set a seed we'll get the same random numbers (if you've ever used NumPy, this is similar to `np.random.seed(42)`). \n\nSetting the seed says, \"hey, create some random numbers, but flavour them with X\" (X is the seed).\n\nWhat do you think will happen when we change the seed?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create two random (and different) tensors\nrandom_3 = tf.random.Generator.from_seed(42)\nrandom_3 = random_3.normal(shape=(3, 2))\nrandom_4 = tf.random.Generator.from_seed(11)\nrandom_4 = random_4.normal(shape=(3, 2))\n\n# Check the tensors and see if they are equal\nrandom_3, random_4, random_1 == random_3, random_3 == random_4",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"What if you wanted to shuffle the order of a tensor?\n\nWait, why would you want to do that?\n\nLet's say you working with 15,000 images of cats and dogs and the first 10,000 images of were of cats and the next 5,000 were of dogs. This order could effect how a neural network learns (it may overfit by learning the order of the data), instead, it might be a good idea to move your data around.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Shuffle a tensor (valuable for when you want to shuffle your data)\nnot_shuffled = tf.constant([[10, 7],\n [3, 4],\n [2, 5]])\n# Gets different results each time\ntf.random.shuffle(not_shuffled)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Shuffle in the same order every time using the seed parameter (won't acutally be the same)\ntf.random.shuffle(not_shuffled, seed=42)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Wait... why didn't the numbers come out the same?\n\nIt's due to rule #4 of the [`tf.random.set_seed()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/random/set_seed) documentation.\n\n> \"4. If both the global and the operation seed are set: Both seeds are used in conjunction to determine the random sequence.\"\n\n`tf.random.set_seed(42)` sets the global seed, and the `seed` parameter in `tf.random.shuffle(seed=42)` sets the operation seed.\n\nBecause, \"Operations that rely on a random seed actually derive it from two seeds: the global and operation-level seeds. This sets the global seed.\"\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Shuffle in the same order every time\n\n# Set the global random seed\ntf.random.set_seed(42)\n\n# Set the operation random seed\ntf.random.shuffle(not_shuffled, seed=42)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Set the global random seed\ntf.random.set_seed(42) # if you comment this out you'll get different results\n\n# Set the operation random seed\ntf.random.shuffle(not_shuffled)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Other ways to make tensors\n\nThough you might rarely use these (remember, many tensor operations are done behind the scenes for you), you can use [`tf.ones()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/ones) to create a tensor of all ones and [`tf.zeros()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/zeros) to create a tensor of all zeros.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Make a tensor of all ones\ntf.ones(shape=(3, 2))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Make a tensor of all zeros\ntf.zeros(shape=(3, 2))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You can also turn NumPy arrays in into tensors.\n\nRemember, the main difference between tensors and NumPy arrays is that tensors can be run on GPUs.\n\n> 🔑 **Note:** A matrix or tensor is typically represented by a capital letter (e.g. `X` or `A`) where as a vector is typically represented by a lowercase letter (e.g. `y` or `b`).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nnumpy_A = np.arange(1, 25, dtype=np.int32) # create a NumPy array between 1 and 25\nA = tf.constant(numpy_A, \n shape=[2, 4, 3]) # note: the shape total (2*4*3) has to match the number of elements in the array\nnumpy_A, A",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Getting information from tensors (shape, rank, size)\n\nThere will be times when you'll want to get different pieces of information from your tensors, in particuluar, you should know the following tensor vocabulary:\n* **Shape:** The length (number of elements) of each of the dimensions of a tensor.\n* **Rank:** The number of tensor dimensions. A scalar has rank 0, a vector has rank 1, a matrix is rank 2, a tensor has rank n.\n* **Axis** or **Dimension:** A particular dimension of a tensor.\n* **Size:** The total number of items in the tensor.\n\nYou'll use these especially when you're trying to line up the shapes of your data to the shapes of your model. For example, making sure the shape of your image tensors are the same shape as your models input layer.\n\nWe've already seen one of these before using the `ndim` attribute. Let's see the rest.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create a rank 4 tensor (4 dimensions)\nrank_4_tensor = tf.zeros([2, 3, 4, 5])\nrank_4_tensor",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"rank_4_tensor.shape, rank_4_tensor.ndim, tf.size(rank_4_tensor)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Get various attributes of tensor\nprint(\"Datatype of every element:\", rank_4_tensor.dtype)\nprint(\"Number of dimensions (rank):\", rank_4_tensor.ndim)\nprint(\"Shape of tensor:\", rank_4_tensor.shape)\nprint(\"Elements along axis 0 of tensor:\", rank_4_tensor.shape[0])\nprint(\"Elements along last axis of tensor:\", rank_4_tensor.shape[-1])\nprint(\"Total number of elements (2*3*4*5):\", tf.size(rank_4_tensor).numpy()) # .numpy() converts to NumPy array",
"Datatype of every element: <dtype: 'float32'>\nNumber of dimensions (rank): 4\nShape of tensor: (2, 3, 4, 5)\nElements along axis 0 of tensor: 2\nElements along last axis of tensor: 5\nTotal number of elements (2*3*4*5): 120\n"
]
],
[
[
"You can also index tensors just like Python lists.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Get the first 2 items of each dimension\nrank_4_tensor[:2, :2, :2, :2]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Get the dimension from each index except for the final one\nrank_4_tensor[:1, :1, :1, :]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create a rank 2 tensor (2 dimensions)\nrank_2_tensor = tf.constant([[10, 7],\n [3, 4]])\n\n# Get the last item of each row\nrank_2_tensor[:, -1]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You can also add dimensions to your tensor whilst keeping the same information present using `tf.newaxis`. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Add an extra dimension (to the end)\nrank_3_tensor = rank_2_tensor[..., tf.newaxis] # in Python \"...\" means \"all dimensions prior to\"\nrank_2_tensor, rank_3_tensor # shape (2, 2), shape (2, 2, 1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You can achieve the same using [`tf.expand_dims()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/expand_dims).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tf.expand_dims(rank_2_tensor, axis=-1) # \"-1\" means last axis",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Manipulating tensors (tensor operations)\n\nFinding patterns in tensors (numberical representation of data) requires manipulating them.\n\nAgain, when building models in TensorFlow, much of this pattern discovery is done for you.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Basic operations\n\nYou can perform many of the basic mathematical operations directly on tensors using Pyhton operators such as, `+`, `-`, `*`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# You can add values to a tensor using the addition operator\ntensor = tf.constant([[10, 7], [3, 4]])\ntensor + 10",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Since we used `tf.constant()`, the original tensor is unchanged (the addition gets done on a copy).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Original tensor unchanged\ntensor",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Other operators also work.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Multiplication (known as element-wise multiplication)\ntensor * 10",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Subtraction\ntensor - 10",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You can also use the equivalent TensorFlow function. Using the TensorFlow function (where possible) has the advantage of being sped up later down the line when running as part of a [TensorFlow graph](https://www.tensorflow.org/tensorboard/graphs).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Use the tensorflow function equivalent of the '*' (multiply) operator\ntf.multiply(tensor, 10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# The original tensor is still unchanged\ntensor",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Matrix mutliplication\n\nOne of the most common operations in machine learning algorithms is [matrix multiplication](https://www.mathsisfun.com/algebra/matrix-multiplying.html).\n\nTensorFlow implements this matrix multiplication functionality in the [`tf.matmul()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/linalg/matmul) method.\n\nThe main two rules for matrix multiplication to remember are:\n1. The inner dimensions must match:\n * `(3, 5) @ (3, 5)` won't work\n * `(5, 3) @ (3, 5)` will work\n * `(3, 5) @ (5, 3)` will work\n2. The resulting matrix has the shape of the inner dimensions:\n * `(5, 3) @ (3, 5)` -> `(3, 3)`\n * `(3, 5) @ (5, 3)` -> `(5, 5)`\n\n> 🔑 **Note:** '`@`' in Python is the symbol for matrix multiplication.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Matrix multiplication in TensorFlow\nprint(tensor)\ntf.matmul(tensor, tensor)",
"tf.Tensor(\n[[10 7]\n [ 3 4]], shape=(2, 2), dtype=int32)\n"
],
[
"# Matrix multiplication with Python operator '@'\ntensor @ tensor",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Both of these examples work because our `tensor` variable is of shape (2, 2).\n\nWhat if we created some tensors which had mismatched shapes?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create (3, 2) tensor\nX = tf.constant([[1, 2],\n [3, 4],\n [5, 6]])\n\n# Create another (3, 2) tensor\nY = tf.constant([[7, 8],\n [9, 10],\n [11, 12]])\nX, Y",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Try to matrix multiply them (will error)\nX @ Y",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Trying to matrix multiply two tensors with the shape `(3, 2)` errors because the inner dimensions don't match.\n\nWe need to either:\n* Reshape X to `(2, 3)` so it's `(2, 3) @ (3, 2)`.\n* Reshape Y to `(3, 2)` so it's `(3, 2) @ (2, 3)`.\n\nWe can do this with either:\n* [`tf.reshape()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/reshape) - allows us to reshape a tensor into a defined shape.\n* [`tf.transpose()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/transpose) - switches the dimensions of a given tensor.\n\n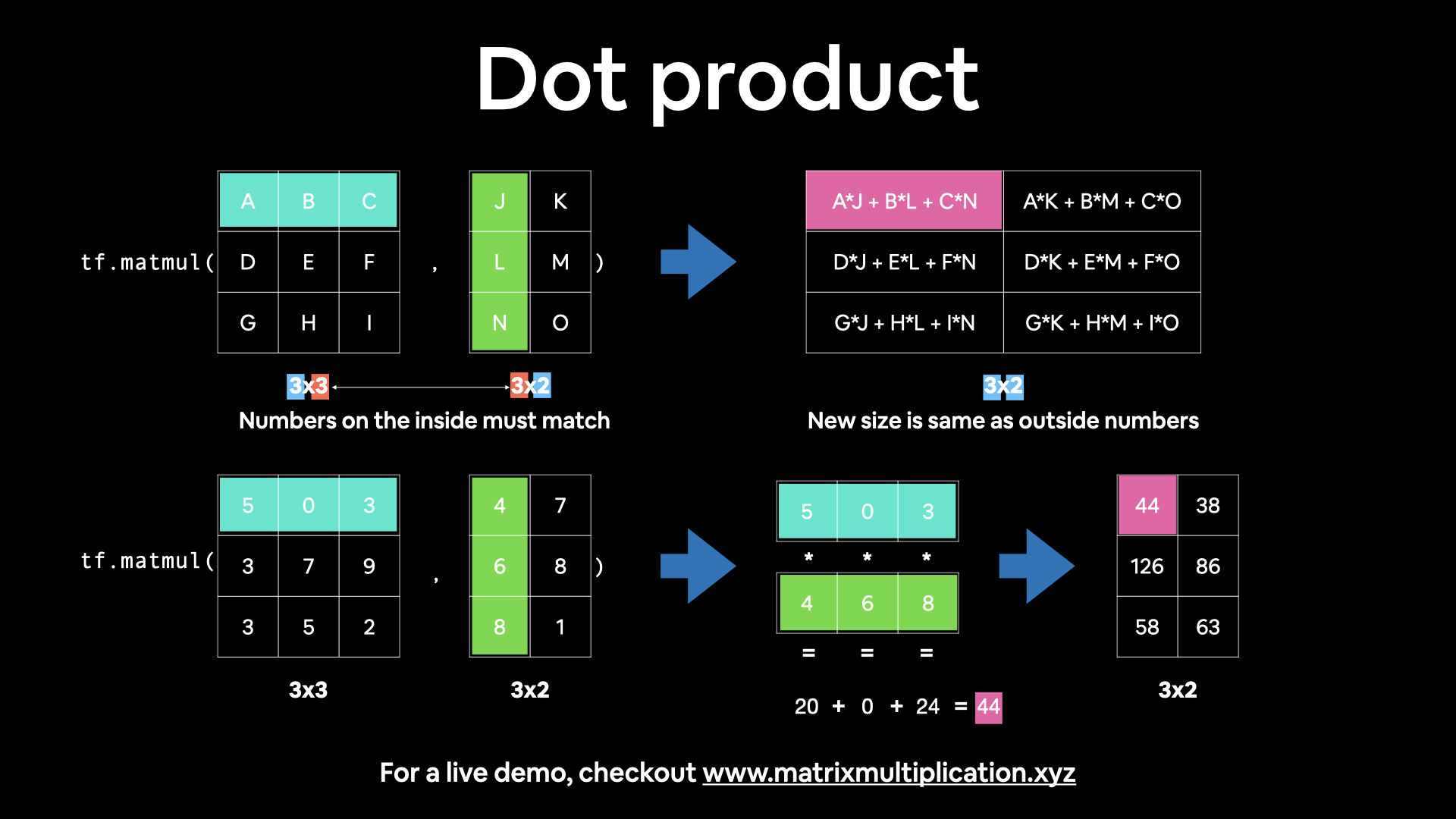\n\nLet's try `tf.reshape()` first.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Example of reshape (3, 2) -> (2, 3)\ntf.reshape(Y, shape=(2, 3))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Try matrix multiplication with reshaped Y\nX @ tf.reshape(Y, shape=(2, 3))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"It worked, let's try the same with a reshaped `X`, except this time we'll use [`tf.transpose()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/transpose) and `tf.matmul()`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Example of transpose (3, 2) -> (2, 3)\ntf.transpose(X)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Try matrix multiplication \ntf.matmul(tf.transpose(X), Y)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# You can achieve the same result with parameters\ntf.matmul(a=X, b=Y, transpose_a=True, transpose_b=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Notice the difference in the resulting shapes when tranposing `X` or reshaping `Y`.\n\nThis is because of the 2nd rule mentioned above:\n * `(3, 2) @ (2, 3)` -> `(2, 2)` done with `tf.matmul(tf.transpose(X), Y)`\n * `(2, 3) @ (3, 2)` -> `(3, 3)` done with `X @ tf.reshape(Y, shape=(2, 3))`\n\nThis kind of data manipulation is a reminder: you'll spend a lot of your time in machine learning and working with neural networks reshaping data (in the form of tensors) to prepare it to be used with various operations (such as feeding it to a model).\n\n### The dot product\n\nMultiplying matrices by eachother is also referred to as the dot product.\n\nYou can perform the `tf.matmul()` operation using [`tf.tensordot()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/tensordot). ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Perform the dot product on X and Y (requires X to be transposed)\ntf.tensordot(tf.transpose(X), Y, axes=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You might notice that although using both `reshape` and `tranpose` work, you get different results when using each.\n\nLet's see an example, first with `tf.transpose()` then with `tf.reshape()`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Perform matrix multiplication between X and Y (transposed)\ntf.matmul(X, tf.transpose(Y))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Perform matrix multiplication between X and Y (reshaped)\ntf.matmul(X, tf.reshape(Y, (2, 3)))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Hmm... they result in different values.\n\nWhich is strange because when dealing with `Y` (a `(3x2)` matrix), reshaping to `(2, 3)` and tranposing it result in the same shape.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Check shapes of Y, reshaped Y and tranposed Y\nY.shape, tf.reshape(Y, (2, 3)).shape, tf.transpose(Y).shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"But calling `tf.reshape()` and `tf.transpose()` on `Y` don't necessarily result in the same values.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Check values of Y, reshape Y and tranposed Y\nprint(\"Normal Y:\")\nprint(Y, \"\\n\") # \"\\n\" for newline\n\nprint(\"Y reshaped to (2, 3):\")\nprint(tf.reshape(Y, (2, 3)), \"\\n\")\n\nprint(\"Y transposed:\")\nprint(tf.transpose(Y))",
"Normal Y:\ntf.Tensor(\n[[ 7 8]\n [ 9 10]\n [11 12]], shape=(3, 2), dtype=int32) \n\nY reshaped to (2, 3):\ntf.Tensor(\n[[ 7 8 9]\n [10 11 12]], shape=(2, 3), dtype=int32) \n\nY transposed:\ntf.Tensor(\n[[ 7 9 11]\n [ 8 10 12]], shape=(2, 3), dtype=int32)\n"
]
],
[
[
"As you can see, the outputs of `tf.reshape()` and `tf.transpose()` when called on `Y`, even though they have the same shape, are different.\n\nThis can be explained by the default behaviour of each method:\n* [`tf.reshape()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/reshape) - change the shape of the given tensor (first) and then insert values in order they appear (in our case, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12).\n* [`tf.transpose()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/transpose) - swap the order of the axes, by default the last axis becomes the first, however the order can be changed using the [`perm` parameter](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/transpose).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"So which should you use?\n\nAgain, most of the time these operations (when they need to be run, such as during the training a neural network, will be implemented for you).\n\nBut generally, whenever performing a matrix multiplication and the shapes of two matrices don't line up, you will transpose (not reshape) one of them in order to line them up.\n\n### Matrix multiplication tidbits\n* If we transposed `Y`, it would be represented as $\\mathbf{Y}^\\mathsf{T}$ (note the capital T for tranpose).\n* Get an illustrative view of matrix multiplication [by Math is Fun](https://www.mathsisfun.com/algebra/matrix-multiplying.html).\n* Try a hands-on demo of matrix multiplcation: http://matrixmultiplication.xyz/ (shown below).\n\n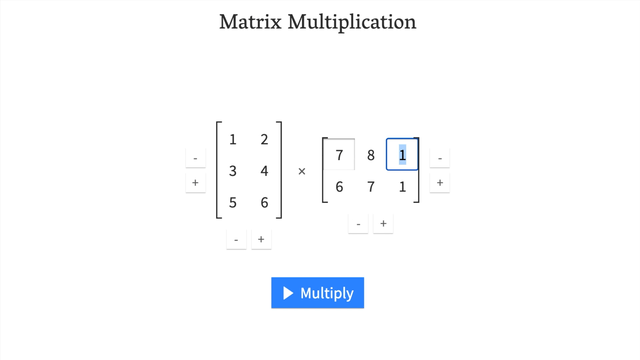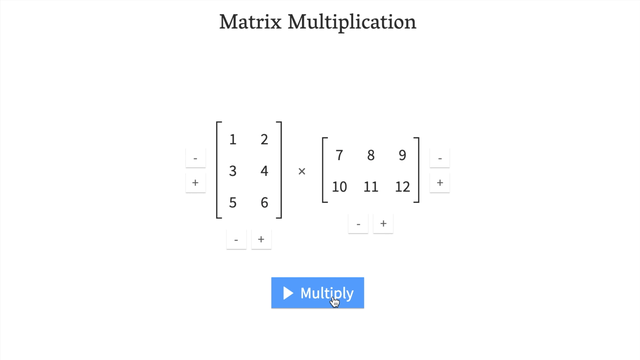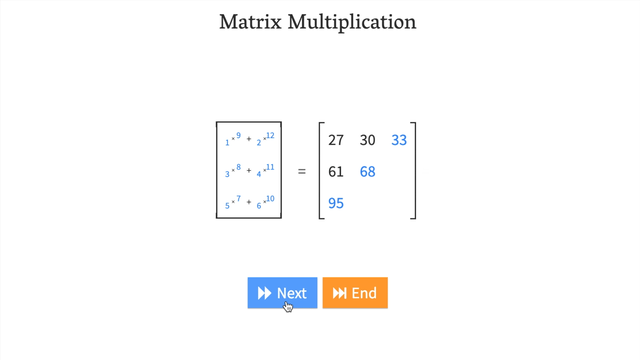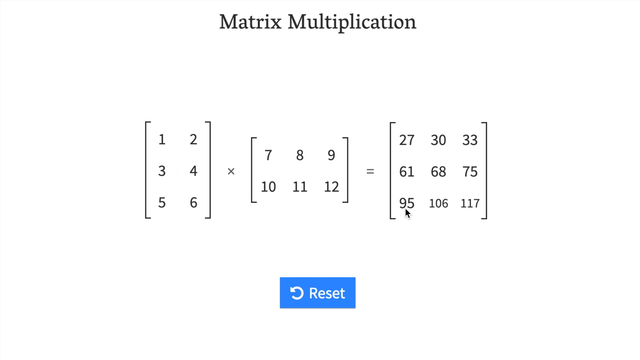",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Changing the datatype of a tensor\n\nSometimes you'll want to alter the default datatype of your tensor. \n\nThis is common when you want to compute using less precision (e.g. 16-bit floating point numbers vs. 32-bit floating point numbers). \n\nComputing with less precision is useful on devices with less computing capacity such as mobile devices (because the less bits, the less space the computations require).\n\nYou can change the datatype of a tensor using [`tf.cast()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/cast).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create a new tensor with default datatype (float32)\nB = tf.constant([1.7, 7.4])\n\n# Create a new tensor with default datatype (int32)\nC = tf.constant([1, 7])\nB, C",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Change from float32 to float16 (reduced precision)\nB = tf.cast(B, dtype=tf.float16)\nB",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Change from int32 to float32\nC = tf.cast(C, dtype=tf.float32)\nC",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Getting the absolute value\nSometimes you'll want the absolute values (all values are positive) of elements in your tensors.\n\nTo do so, you can use [`tf.abs()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/math/abs).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create tensor with negative values\nD = tf.constant([-7, -10])\nD",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Get the absolute values\ntf.abs(D)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Finding the min, max, mean, sum (aggregation)\n\nYou can quickly aggregate (perform a calculation on a whole tensor) tensors to find things like the minimum value, maximum value, mean and sum of all the elements.\n\nTo do so, aggregation methods typically have the syntax `reduce()_[action]`, such as:\n* [`tf.reduce_min()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/math/reduce_min) - find the minimum value in a tensor.\n* [`tf.reduce_max()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/math/reduce_max) - find the maximum value in a tensor (helpful for when you want to find the highest prediction probability).\n* [`tf.reduce_mean()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/math/reduce_mean) - find the mean of all elements in a tensor.\n* [`tf.reduce_sum()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/math/reduce_sum) - find the sum of all elements in a tensor.\n* **Note:** typically, each of these is under the `math` module, e.g. `tf.math.reduce_min()` but you can use the alias `tf.reduce_min()`.\n\nLet's see them in action.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create a tensor with 50 random values between 0 and 100\nE = tf.constant(np.random.randint(low=0, high=100, size=50))\nE",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Find the minimum\ntf.reduce_min(E)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Find the maximum\ntf.reduce_max(E)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Find the mean\ntf.reduce_mean(E)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Find the sum\ntf.reduce_sum(E)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You can also find the standard deviation ([`tf.reduce_std()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/math/reduce_std)) and variance ([`tf.reduce_variance()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/math/reduce_variance)) of elements in a tensor using similar methods.\n\n### Finding the positional maximum and minimum\n\nHow about finding the position a tensor where the maximum value occurs?\n\nThis is helpful when you want to line up your labels (say `['Green', 'Blue', 'Red']`) with your prediction probabilities tensor (e.g. `[0.98, 0.01, 0.01]`).\n\nIn this case, the predicted label (the one with the highest prediction probability) would be `'Green'`.\n\nYou can do the same for the minimum (if required) with the following:\n* [`tf.argmax()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/math/argmax) - find the position of the maximum element in a given tensor.\n* [`tf.argmin()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/math/argmin) - find the position of the minimum element in a given tensor.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create a tensor with 50 values between 0 and 1\nF = tf.constant(np.random.random(50))\nF",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Find the maximum element position of F\ntf.argmax(F)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Find the minimum element position of F\ntf.argmin(F)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Find the maximum element position of F\nprint(f\"The maximum value of F is at position: {tf.argmax(F).numpy()}\") \nprint(f\"The maximum value of F is: {tf.reduce_max(F).numpy()}\") \nprint(f\"Using tf.argmax() to index F, the maximum value of F is: {F[tf.argmax(F)].numpy()}\")\nprint(f\"Are the two max values the same (they should be)? {F[tf.argmax(F)].numpy() == tf.reduce_max(F).numpy()}\")",
"The maximum value of F is at position: 8\nThe maximum value of F is: 0.9749826885110175\nUsing tf.argmax() to index F, the maximum value of F is: 0.9749826885110175\nAre the two max values the same (they should be)? True\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Squeezing a tensor (removing all single dimensions)\n\nIf you need to remove single-dimensions from a tensor (dimensions with size 1), you can use `tf.squeeze()`.\n\n* [`tf.squeeze()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/squeeze) - remove all dimensions of 1 from a tensor.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create a rank 5 (5 dimensions) tensor of 50 numbers between 0 and 100\nG = tf.constant(np.random.randint(0, 100, 50), shape=(1, 1, 1, 1, 50))\nG.shape, G.ndim",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Squeeze tensor G (remove all 1 dimensions)\nG_squeezed = tf.squeeze(G)\nG_squeezed.shape, G_squeezed.ndim",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### One-hot encoding\n\nIf you have a tensor of indicies and would like to one-hot encode it, you can use [`tf.one_hot()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/one_hot).\n\nYou should also specify the `depth` parameter (the level which you want to one-hot encode to).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create a list of indices\nsome_list = [0, 1, 2, 3]\n\n# One hot encode them\ntf.one_hot(some_list, depth=4)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You can also specify values for `on_value` and `off_value` instead of the default `0` and `1`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Specify custom values for on and off encoding\ntf.one_hot(some_list, depth=4, on_value=\"We're live!\", off_value=\"Offline\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Squaring, log, square root\n\nMany other common mathematical operations you'd like to perform at some stage, probably exist.\n\nLet's take a look at:\n* [`tf.square()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/math/square) - get the square of every value in a tensor. \n* [`tf.sqrt()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/math/sqrt) - get the squareroot of every value in a tensor (**note:** the elements need to be floats or this will error).\n* [`tf.math.log()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/math/log) - get the natural log of every value in a tensor (elements need to floats).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create a new tensor\nH = tf.constant(np.arange(1, 10))\nH",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Square it\ntf.square(H)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Find the squareroot (will error), needs to be non-integer\ntf.sqrt(H)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Change H to float32\nH = tf.cast(H, dtype=tf.float32)\nH",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Find the square root\ntf.sqrt(H)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Find the log (input also needs to be float)\ntf.math.log(H)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Manipulating `tf.Variable` tensors\n\nTensors created with `tf.Variable()` can be changed in place using methods such as:\n\n* [`.assign()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/Variable#assign) - assign a different value to a particular index of a variable tensor.\n* [`.add_assign()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/Variable#assign_add) - add to an existing value and reassign it at a particular index of a variable tensor.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create a variable tensor\nI = tf.Variable(np.arange(0, 5))\nI",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Assign the final value a new value of 50\nI.assign([0, 1, 2, 3, 50])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# The change happens in place (the last value is now 50, not 4)\nI",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Add 10 to every element in I\nI.assign_add([10, 10, 10, 10, 10])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Again, the change happens in place\nI",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Tensors and NumPy\n\nWe've seen some examples of tensors interact with NumPy arrays, such as, using NumPy arrays to create tensors. \n\nTensors can also be converted to NumPy arrays using:\n\n* `np.array()` - pass a tensor to convert to an ndarray (NumPy's main datatype).\n* `tensor.numpy()` - call on a tensor to convert to an ndarray.\n\nDoing this is helpful as it makes tensors iterable as well as allows us to use any of NumPy's methods on them.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create a tensor from a NumPy array\nJ = tf.constant(np.array([3., 7., 10.]))\nJ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Convert tensor J to NumPy with np.array()\nnp.array(J), type(np.array(J))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Convert tensor J to NumPy with .numpy()\nJ.numpy(), type(J.numpy())",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"By default tensors have `dtype=float32`, where as NumPy arrays have `dtype=float64`.\n\nThis is because neural networks (which are usually built with TensorFlow) can generally work very well with less precision (32-bit rather than 64-bit).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create a tensor from NumPy and from an array\nnumpy_J = tf.constant(np.array([3., 7., 10.])) # will be float64 (due to NumPy)\ntensor_J = tf.constant([3., 7., 10.]) # will be float32 (due to being TensorFlow default)\nnumpy_J.dtype, tensor_J.dtype",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Using `@tf.function`\n\nIn your TensorFlow adventures, you might come across Python functions which have the decorator [`@tf.function`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/function).\n\nIf you aren't sure what Python decorators do, [read RealPython's guide on them](https://realpython.com/primer-on-python-decorators/).\n\nBut in short, decorators modify a function in one way or another.\n\nIn the `@tf.function` decorator case, it turns a Python function into a callable TensorFlow graph. Which is a fancy way of saying, if you've written your own Python function, and you decorate it with `@tf.function`, when you export your code (to potentially run on another device), TensorFlow will attempt to convert it into a fast(er) version of itself (by making it part of a computation graph).\n\nFor more on this, read the [Better performnace with tf.function](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/function) guide.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create a simple function\ndef function(x, y):\n return x ** 2 + y\n\nx = tf.constant(np.arange(0, 10))\ny = tf.constant(np.arange(10, 20))\nfunction(x, y)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create the same function and decorate it with tf.function\[email protected]\ndef tf_function(x, y):\n return x ** 2 + y\n\ntf_function(x, y)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"If you noticed no difference between the above two functions (the decorated one and the non-decorated one) you'd be right.\n\nMuch of the difference happens behind the scenes. One of the main ones being potential code speed-ups where possible.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Finding access to GPUs\n\nWe've mentioned GPUs plenty of times throughout this notebook.\n\nSo how do you check if you've got one available?\n\nYou can check if you've got access to a GPU using [`tf.config.list_physical_devices()`](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/gpu).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU'))",
"[PhysicalDevice(name='/physical_device:GPU:0', device_type='GPU')]\n"
]
],
[
[
"If the above outputs an empty array (or nothing), it means you don't have access to a GPU (or at least TensorFlow can't find it).\n\nIf you're running in Google Colab, you can access a GPU by going to *Runtime -> Change Runtime Type -> Select GPU* (**note:** after doing this your notebook will restart and any variables you've saved will be lost).\n\nOnce you've changed your runtime type, run the cell below.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import tensorflow as tf\nprint(tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU'))",
"[PhysicalDevice(name='/physical_device:GPU:0', device_type='GPU')]\n"
]
],
[
[
"If you've got access to a GPU, the cell above should output something like:\n\n`[PhysicalDevice(name='/physical_device:GPU:0', device_type='GPU')]`\n\nYou can also find information about your GPU using `!nvidia-smi`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!nvidia-smi",
"Mon Mar 15 22:33:50 2021 \n+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+\n| NVIDIA-SMI 460.56 Driver Version: 460.32.03 CUDA Version: 11.2 |\n|-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+\n| GPU Name Persistence-M| Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr. ECC |\n| Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap| Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. |\n| | | MIG M. |\n|===============================+======================+======================|\n| 0 Tesla T4 Off | 00000000:00:04.0 Off | 0 |\n| N/A 52C P0 29W / 70W | 224MiB / 15109MiB | 0% Default |\n| | | N/A |\n+-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+\n \n+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+\n| Processes: |\n| GPU GI CI PID Type Process name GPU Memory |\n| ID ID Usage |\n|=============================================================================|\n+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+\n"
]
],
[
[
"> 🔑 **Note:** If you have access to a GPU, TensorFlow will automatically use it whenever possible.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 🛠 Exercises\n\n1. Create a vector, scalar, matrix and tensor with values of your choosing using `tf.constant()`.\n2. Find the shape, rank and size of the tensors you created in 1.\n3. Create two tensors containing random values between 0 and 1 with shape `[5, 300]`.\n4. Multiply the two tensors you created in 3 using matrix multiplication.\n5. Multiply the two tensors you created in 3 using dot product.\n6. Create a tensor with random values between 0 and 1 with shape `[224, 224, 3]`.\n7. Find the min and max values of the tensor you created in 6.\n8. Created a tensor with random values of shape `[1, 224, 224, 3]` then squeeze it to change the shape to `[224, 224, 3]`.\n9. Create a tensor with shape `[10]` using your own choice of values, then find the index which has the maximum value.\n10. One-hot encode the tensor you created in 9.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 📖 Extra-curriculum\n\n* Read through the [list of TensorFlow Python APIs](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/), pick one we haven't gone through in this notebook, reverse engineer it (write out the documentation code for yourself) and figure out what it does.\n* Try to create a series of tensor functions to calculate your most recent grocery bill (it's okay if you don't use the names of the items, just the price in numerical form).\n * How would you calculate your grocery bill for the month and for the year using tensors?\n* Go through the [TensorFlow 2.x quick start for beginners](https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/quickstart/beginner) tutorial (be sure to type out all of the code yourself, even if you don't understand it).\n * Are there any functions we used in here that match what's used in there? Which are the same? Which haven't you seen before?\n* Watch the video [\"What's a tensor?\"](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=f5liqUk0ZTw) - a great visual introduction to many of the concepts we've covered in this notebook.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
c503c0ed3567c5ec4c99095b8cc4313a728201d5
| 1,318 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
lectures/Example.ipynb
|
fabiansinz/pydocker-template
|
61b7697340e2ee76aa2fb25bc22c292f229fab76
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2019-02-19T14:16:12.000Z
|
2019-02-19T14:16:12.000Z
|
lectures/Example.ipynb
|
mackelab/open-comp-neuro
|
61b7697340e2ee76aa2fb25bc22c292f229fab76
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
lectures/Example.ipynb
|
mackelab/open-comp-neuro
|
61b7697340e2ee76aa2fb25bc22c292f229fab76
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2018-02-15T21:03:44.000Z
|
2018-05-26T15:52:35.000Z
| 19.671642 | 52 | 0.522762 |
[
[
[
"%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn as sns\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x = np.random.randn(100)\n\nsns.set_context('notebook', font_scale=1.3)\nwith sns.axes_style('ticks'):\n fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(7,7))\n \nax.plot(x, label='noise')\n\nax.set_xlabel('index')\nax.set_ylabel('noise')\nax.set_title('example')\nsns.despine(trim=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c503c68ecdccc80f37dfd8c69c7e36bbf892a504
| 21,461 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
labs27_notebooks/mixed/PRAW_Explatory_Notebook.ipynb
|
Lambda-School-Labs/human-rights-first-d-ds
|
1acd19a78f6936d1d8f7cf92889f33af8ece6208
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2020-10-28T15:42:18.000Z
|
2020-10-28T15:42:18.000Z
|
labs27_notebooks/mixed/PRAW_Explatory_Notebook.ipynb
|
Lambda-School-Labs/human-rights-first-d-ds
|
1acd19a78f6936d1d8f7cf92889f33af8ece6208
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
labs27_notebooks/mixed/PRAW_Explatory_Notebook.ipynb
|
Lambda-School-Labs/human-rights-first-d-ds
|
1acd19a78f6936d1d8f7cf92889f33af8ece6208
|
[
"MIT"
] | 5 |
2020-11-19T23:50:30.000Z
|
2020-11-26T02:47:29.000Z
| 60.796034 | 6,937 | 0.619403 |
[
[
[
"pip install praw",
"Collecting praw\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/2c/15/4bcc44271afce0316c73cd2ed35f951f1363a07d4d5d5440ae5eb2baad78/praw-7.1.0-py3-none-any.whl (152kB)\n\r\u001b[K |██▏ | 10kB 20.2MB/s eta 0:00:01\r\u001b[K |████▎ | 20kB 5.2MB/s eta 0:00:01\r\u001b[K |██████▌ | 30kB 5.2MB/s eta 0:00:01\r\u001b[K |████████▋ | 40kB 5.9MB/s eta 0:00:01\r\u001b[K |██████████▊ | 51kB 5.8MB/s eta 0:00:01\r\u001b[K |█████████████ | 61kB 5.6MB/s eta 0:00:01\r\u001b[K |███████████████ | 71kB 5.9MB/s eta 0:00:01\r\u001b[K |█████████████████▎ | 81kB 5.9MB/s eta 0:00:01\r\u001b[K |███████████████████▍ | 92kB 6.3MB/s eta 0:00:01\r\u001b[K |█████████████████████▌ | 102kB 6.1MB/s eta 0:00:01\r\u001b[K |███████████████████████▊ | 112kB 6.1MB/s eta 0:00:01\r\u001b[K |█████████████████████████▉ | 122kB 6.1MB/s eta 0:00:01\r\u001b[K |████████████████████████████ | 133kB 6.1MB/s eta 0:00:01\r\u001b[K |██████████████████████████████▏ | 143kB 6.1MB/s eta 0:00:01\r\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 153kB 6.1MB/s \n\u001b[?25hCollecting update-checker>=0.17\n Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/0c/ba/8dd7fa5f0b1c6a8ac62f8f57f7e794160c1f86f31c6d0fb00f582372a3e4/update_checker-0.18.0-py3-none-any.whl\nCollecting prawcore<2.0,>=1.3.0\n Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/1d/40/b741437ce4c7b64f928513817b29c0a615efb66ab5e5e01f66fe92d2d95b/prawcore-1.5.0-py3-none-any.whl\nCollecting websocket-client>=0.54.0\n\u001b[?25l Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/4c/5f/f61b420143ed1c8dc69f9eaec5ff1ac36109d52c80de49d66e0c36c3dfdf/websocket_client-0.57.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl (200kB)\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 204kB 11.7MB/s \n\u001b[?25hRequirement already satisfied: requests>=2.3.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from update-checker>=0.17->praw) (2.23.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: six in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from websocket-client>=0.54.0->praw) (1.15.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: chardet<4,>=3.0.2 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from requests>=2.3.0->update-checker>=0.17->praw) (3.0.4)\nRequirement already satisfied: urllib3!=1.25.0,!=1.25.1,<1.26,>=1.21.1 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from requests>=2.3.0->update-checker>=0.17->praw) (1.24.3)\nRequirement already satisfied: idna<3,>=2.5 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from requests>=2.3.0->update-checker>=0.17->praw) (2.10)\nRequirement already satisfied: certifi>=2017.4.17 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from requests>=2.3.0->update-checker>=0.17->praw) (2020.6.20)\nInstalling collected packages: update-checker, prawcore, websocket-client, praw\nSuccessfully installed praw-7.1.0 prawcore-1.5.0 update-checker-0.18.0 websocket-client-0.57.0\n"
],
[
"!pip install colab-env -qU\nimport colab_env",
" Building wheel for colab-env (setup.py) ... \u001b[?25l\u001b[?25hdone\nGo to this URL in a browser: https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/auth?client_id=947318989803-6bn6qk8qdgf4n4g3pfee6491hc0brc4i.apps.googleusercontent.com&redirect_uri=urn%3aietf%3awg%3aoauth%3a2.0%3aoob&scope=email%20https%3a%2f%2fwww.googleapis.com%2fauth%2fdocs.test%20https%3a%2f%2fwww.googleapis.com%2fauth%2fdrive%20https%3a%2f%2fwww.googleapis.com%2fauth%2fdrive.photos.readonly%20https%3a%2f%2fwww.googleapis.com%2fauth%2fpeopleapi.readonly&response_type=code\n\nEnter your authorization code:\n··········\nMounted at /content/gdrive\n"
],
[
"!pip install colab-env -qU\nfrom colab_env import envvar_handler",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from google.colab import files\nfiles.upload()\nenv_list = ! cat .env\nfor v in env_list: \n %set_env $v",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import praw\nimport json\nimport os\nimport pandas as pd",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Reddit credentials, password stored in .env \nreddit = praw.Reddit(client_id='2RbxD2UwIMrwOA',\n client_secret=\"Ok2e494wXpQ4U0X7AV1WqiFVlnM\", password=os.getenv(\"KEY1\"),\n user_agent='Which Subreddit', username='C_Hart44')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Grabbing 100 hottest posts on Reddit at the moment. Will filter for police use of force later\n\ndata = []\n\nfor submission in reddit.subreddit(\"all\").hot(limit=100):\n data.append([submission.id, submission.title, submission.score, submission.subreddit, submission.url, \n submission.num_comments, submission.selftext, submission.created])\n\n# We'll need a way to get coordinates for a given post, before we include that in df\ncol_names = ['id', 'title', 'score', 'subreddit', 'url', \n 'num_comments', 'text', 'created']\ndf = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=col_names)\n\ndf.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c503cc26fda4414669e4ba824cb73fecaf9f8f63
| 20,341 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
textbook/content/Sparse_Matrices/Sparse_Matrices_In_Julia.ipynb
|
NoseKnowsAll/NoseKnowsAll.github.io
|
b2cff3e33cc2087770fb4aecb38b7925ad8d6e5a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
textbook/content/Sparse_Matrices/Sparse_Matrices_In_Julia.ipynb
|
NoseKnowsAll/NoseKnowsAll.github.io
|
b2cff3e33cc2087770fb4aecb38b7925ad8d6e5a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
textbook/content/Sparse_Matrices/Sparse_Matrices_In_Julia.ipynb
|
NoseKnowsAll/NoseKnowsAll.github.io
|
b2cff3e33cc2087770fb4aecb38b7925ad8d6e5a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 56.818436 | 10,038 | 0.741016 |
[
[
[
"empty"
]
]
] |
[
"empty"
] |
[
[
"empty"
]
] |
c503cd8391e2db85941385d7598f3849ed991cf1
| 8,132 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Code/src/day1/dataPreprocessing.ipynb
|
jinwei14/100-Days-Of-ML-Code
|
b0f7c345e2077e609a93f85af5db7e25b17d25ee
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Code/src/day1/dataPreprocessing.ipynb
|
jinwei14/100-Days-Of-ML-Code
|
b0f7c345e2077e609a93f85af5db7e25b17d25ee
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Code/src/day1/dataPreprocessing.ipynb
|
jinwei14/100-Days-Of-ML-Code
|
b0f7c345e2077e609a93f85af5db7e25b17d25ee
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 25.176471 | 185 | 0.484752 |
[
[
[
"## Step 1: Importing ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dataset = pd.read_csv('../../../datasets/Data.csv')\nX = dataset.iloc[ : , :-1].values\nY = dataset.iloc[ : , 3].values\nprint(X)\nprint(Y)",
"[['France' 44.0 72000.0]\n ['Spain' 27.0 48000.0]\n ['Germany' 30.0 54000.0]\n ['Spain' 38.0 61000.0]\n ['Germany' 40.0 nan]\n ['France' 35.0 58000.0]\n ['Spain' nan 52000.0]\n ['France' 48.0 79000.0]\n ['Germany' 50.0 83000.0]\n ['France' 37.0 67000.0]]\n['No' 'Yes' 'No' 'No' 'Yes' 'Yes' 'No' 'Yes' 'No' 'Yes']\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Step 2: Handling the missing data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.impute import SimpleImputer\nimputer = SimpleImputer(missing_values=np.nan, strategy='mean')\nimputer = imputer.fit(X[ : , 1:3])\nX[ : , 1:3] = imputer.transform(X[ : , 1:3])\nprint(X)",
"[['France' 44.0 72000.0]\n ['Spain' 27.0 48000.0]\n ['Germany' 30.0 54000.0]\n ['Spain' 38.0 61000.0]\n ['Germany' 40.0 63777.77777777778]\n ['France' 35.0 58000.0]\n ['Spain' 38.77777777777778 52000.0]\n ['France' 48.0 79000.0]\n ['Germany' 50.0 83000.0]\n ['France' 37.0 67000.0]]\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Step 3: Encoding categorical data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder, OneHotEncoder\nlabelencoder_X = LabelEncoder()\nX[ : , 0] = labelencoder_X.fit_transform(X[ : , 0])\nprint(X)",
"[[0 44.0 72000.0]\n [2 27.0 48000.0]\n [1 30.0 54000.0]\n [2 38.0 61000.0]\n [1 40.0 63777.77777777778]\n [0 35.0 58000.0]\n [2 38.77777777777778 52000.0]\n [0 48.0 79000.0]\n [1 50.0 83000.0]\n [0 37.0 67000.0]]\n"
],
[
"from sklearn.compose import ColumnTransformer \nct = ColumnTransformer([(\"Name_Of_Your_Step\", OneHotEncoder(),[0])], remainder=\"passthrough\") # The last arg ([0]) is the list of columns you want to transform in this step\nX = ct.fit_transform(X) \n\n# onehotencoder = OneHotEncoder(categorical_features = [0])\n# X = onehotencoder.fit_transform(X).toarray()\n\nlabelencoder_Y = LabelEncoder()\nY = labelencoder_Y.fit_transform(Y)\nprint(X)\nprint(X.shape)\nprint(Y)",
"[[1.0 0.0 0.0 44.0 72000.0]\n [0.0 0.0 1.0 27.0 48000.0]\n [0.0 1.0 0.0 30.0 54000.0]\n [0.0 0.0 1.0 38.0 61000.0]\n [0.0 1.0 0.0 40.0 63777.77777777778]\n [1.0 0.0 0.0 35.0 58000.0]\n [0.0 0.0 1.0 38.77777777777778 52000.0]\n [1.0 0.0 0.0 48.0 79000.0]\n [0.0 1.0 0.0 50.0 83000.0]\n [1.0 0.0 0.0 37.0 67000.0]]\n(10, 5)\n[0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1]\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Step 5: Splitting the datasets into training sets and Test sets",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nX_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split( X , Y , test_size = 0.2, random_state = 0)\nprint(X)\nprint(X.shape)\nprint(X_train.shape)",
"[[1.0 0.0 0.0 44.0 72000.0]\n [0.0 0.0 1.0 27.0 48000.0]\n [0.0 1.0 0.0 30.0 54000.0]\n [0.0 0.0 1.0 38.0 61000.0]\n [0.0 1.0 0.0 40.0 63777.77777777778]\n [1.0 0.0 0.0 35.0 58000.0]\n [0.0 0.0 1.0 38.77777777777778 52000.0]\n [1.0 0.0 0.0 48.0 79000.0]\n [0.0 1.0 0.0 50.0 83000.0]\n [1.0 0.0 0.0 37.0 67000.0]]\n(10, 5)\n(8, 5)\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Step 6: Feature Scaling",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler\nsc_X = StandardScaler()\nX_train = sc_X.fit_transform(X_train)\nX_test = sc_X.fit_transform(X_test)\n\nprint(X_train)\nprint(X_train.shape)\nprint(Y_train)\nprint(Y_train.shape)",
"[[-1. 2.64575131 -0.77459667 0.26306757 0.12381479]\n [ 1. -0.37796447 -0.77459667 -0.25350148 0.46175632]\n [-1. -0.37796447 1.29099445 -1.97539832 -1.53093341]\n [-1. -0.37796447 1.29099445 0.05261351 -1.11141978]\n [ 1. -0.37796447 -0.77459667 1.64058505 1.7202972 ]\n [-1. -0.37796447 1.29099445 -0.0813118 -0.16751412]\n [ 1. -0.37796447 -0.77459667 0.95182631 0.98614835]\n [ 1. -0.37796447 -0.77459667 -0.59788085 -0.48214934]]\n(8, 5)\n[1 1 1 0 1 0 0 1]\n(8,)\n"
],
[
"from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler\ndata = [[0, 0], [0, 0], [1, 1], [1, 1]]\nscaler = StandardScaler()\n\nprint(scaler.fit(data))\nprint(scaler.mean_)\nprint(scaler.var_)\nprint('std: ', np.sqrt(scaler.var_))\n\nprint(scaler.transform(data))\nprint(scaler.transform([[2, 2]]))",
"StandardScaler()\n[0.5 0.5]\n[0.25 0.25]\nstd: [0.5 0.5]\n[[-1. -1.]\n [-1. -1.]\n [ 1. 1.]\n [ 1. 1.]]\n[[3. 3.]]\n"
],
[
"# #Verify that the mean of each feature (column) is 0:\n# scaled_data.mean(axis = 0)\n# array([0., 0.])\n# #Verify that the std of each feature (column) is 1:\n# scaled_data.std(axis = 0)\n# array([1., 1.])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c503d0f579ae5dc6796a06cfbe8350f158d5b625
| 3,636 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/F1 test.ipynb
|
pschonev/deepanomaly4docs
|
c2729aff0ae57567ea0afb062547c0b8bc35a3d8
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/F1 test.ipynb
|
pschonev/deepanomaly4docs
|
c2729aff0ae57567ea0afb062547c0b8bc35a3d8
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 4 |
2021-08-23T20:51:25.000Z
|
2022-03-12T01:00:57.000Z
|
notebooks/F1 test.ipynb
|
pschonev/deepanomaly4docs
|
c2729aff0ae57567ea0afb062547c0b8bc35a3d8
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 1 |
2021-04-07T08:08:17.000Z
|
2021-04-07T08:08:17.000Z
| 19.036649 | 72 | 0.491474 |
[
[
[
"## F1",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.metrics import f1_score\n\n# 80/20 and predict all as inlier\ny_pred = [1]*10\ny_true = [1]*8 + [0]*2\nf1_score(y_true=y_true, y_pred=y_pred)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 50/50 and predict all as inlier\ny_pred = [1]*10\ny_true = [1]*5 + [0]*5\nf1_score(y_true=y_true, y_pred=y_pred)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## AUC-ROC",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score\n\n# 80/20 and predict all as inlier\ny_score = [1]*10\ny_true = [1]*8 + [0]*2\nroc_auc_score(y_true=y_true, y_score=y_score)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 50/50 and predict all as inlier\ny_score = [1]*10\ny_true = [1]*5 + [0]*5\nroc_auc_score(y_true=y_true, y_score=y_score)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## AP",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.metrics import average_precision_score\n\n# 80/20 and predict all as inlier\ny_score = [1]*10\ny_true = [1]*8 + [0]*2\naverage_precision_score(y_true=y_true, y_score=y_score)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 50/50 and predict all as inlier\ny_score = [1]*10\ny_true = [1]*5 + [0]*5\naverage_precision_score(y_true=y_true, y_score=y_score)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c503eba14cf26c1e18910e5bf788cbc9fa0775ca
| 174,102 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
examples/conditional_moons_modified.ipynb
|
robertej19/nflows
|
a17a2125a38eaaa8b6701c8e5ae4a972dcacf71b
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
examples/conditional_moons_modified.ipynb
|
robertej19/nflows
|
a17a2125a38eaaa8b6701c8e5ae4a972dcacf71b
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
examples/conditional_moons_modified.ipynb
|
robertej19/nflows
|
a17a2125a38eaaa8b6701c8e5ae4a972dcacf71b
|
[
"MIT"
] | 5 |
2021-04-19T20:43:23.000Z
|
2021-05-11T16:56:06.000Z
| 580.34 | 30,490 | 0.940678 |
[
[
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport sklearn.datasets as datasets\n\nimport torch\nfrom torch import nn\nfrom torch import optim\n\nfrom nflows.flows.base import Flow\nfrom nflows.distributions.normal import ConditionalDiagonalNormal\nfrom nflows.transforms.base import CompositeTransform\nfrom nflows.transforms.autoregressive import MaskedAffineAutoregressiveTransform\nfrom nflows.transforms.permutations import ReversePermutation\nfrom nflows.nn.nets import ResidualNet",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x, y = datasets.make_moons(128, noise=.1)\nplt.scatter(x[:, 0], x[:, 1], c=y);",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"num_layers = 5\nbase_dist = ConditionalDiagonalNormal(shape=[2], \n context_encoder=nn.Linear(1, 4))\n\ntransforms = []\nfor _ in range(num_layers):\n transforms.append(ReversePermutation(features=2))\n transforms.append(MaskedAffineAutoregressiveTransform(features=2, \n hidden_features=4, \n context_features=1))\ntransform = CompositeTransform(transforms)\n\nflow = Flow(transform, base_dist)\noptimizer = optim.Adam(flow.parameters())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"num_iter = 5000\nfor i in range(num_iter):\n x, y = datasets.make_moons(128, noise=.1)\n x = torch.tensor(x, dtype=torch.float32)\n y = torch.tensor(y, dtype=torch.float32).reshape(-1, 1)\n optimizer.zero_grad()\n loss = -flow.log_prob(inputs=x, context=y).mean()\n loss.backward()\n optimizer.step()\n \n if (i + 1) % 500 == 0:\n fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2)\n xline = torch.linspace(-1.5, 2.5)\n yline = torch.linspace(-.75, 1.25)\n xgrid, ygrid = torch.meshgrid(xline, yline)\n xyinput = torch.cat([xgrid.reshape(-1, 1), ygrid.reshape(-1, 1)], dim=1)\n\n with torch.no_grad():\n zgrid0 = flow.log_prob(xyinput, torch.zeros(10000, 1)).exp().reshape(100, 100)\n zgrid1 = flow.log_prob(xyinput, torch.ones(10000, 1)).exp().reshape(100, 100)\n\n ax[0].contourf(xgrid.numpy(), ygrid.numpy(), zgrid0.numpy())\n ax[1].contourf(xgrid.numpy(), ygrid.numpy(), zgrid1.numpy())\n plt.title('iteration {}'.format(i + 1))\n plt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c503ec2dc21ef1158b48c94a6d5e2e6b27dce066
| 86,197 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Projekty/Projekt2/Grupa1/SzczypekJakubowski/Fourier method/Generate_depth10_allPixels.ipynb
|
niladrem/2020L-WUM
|
ddccedd900e41de196612c517227e1348c7195df
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Projekty/Projekt2/Grupa1/SzczypekJakubowski/Fourier method/Generate_depth10_allPixels.ipynb
|
niladrem/2020L-WUM
|
ddccedd900e41de196612c517227e1348c7195df
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Projekty/Projekt2/Grupa1/SzczypekJakubowski/Fourier method/Generate_depth10_allPixels.ipynb
|
niladrem/2020L-WUM
|
ddccedd900e41de196612c517227e1348c7195df
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2020-06-01T23:23:16.000Z
|
2020-06-01T23:23:16.000Z
| 232.336927 | 54,888 | 0.915159 |
[
[
[
"# Libraries + DATA",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from visualizations import *\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport warnings\nfrom math import tau\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom scipy.integrate import quad\nwarnings.filterwarnings('ignore')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data = np.loadtxt(\"./../DATA/digits2k_pixels.data.gz\", ndmin=2)/255.0\ndata.shape = (data.shape[0], int(np.sqrt(data.shape[1])), int(np.sqrt(data.shape[1])))\nlabels = np.loadtxt(\"./../DATA/digits2k_pixels.labels.gz\", dtype='int')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Helpful functions",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def onlyBlackWhite(array, percentage = 0.3):\n result = array.copy()\n quantile = np.quantile(result[result>0], percentage)\n for i in range(len(result)):\n for j in range(len(result[0])):\n if (result[i,j] < quantile):\n result[i,j] = 0\n else:\n result[i,j] = 1\n return result\n## By using quantiles, we reduce some noise near the number and away from the number\n## Empiric tests show that 0.3 quantile produces some nice results",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def get_longest_array(arr_list):\n n = len(arr_list)\n max_len = 0\n max_i = 0\n for i in range(n):\n if len(arr_list[i]) > max_len:\n max_len, max_i = len(arr_list[i]), i\n return max_i",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def create_close_loop(image_array, level=[200]):\n\n # Get Contour Path and create lookup-table\n contour_paths = plt.contour(image_array, levels=level, colors='black', origin='image').collections[0].get_paths()\n contour_path = contour_paths[get_longest_array(contour_paths)]\n x_table, y_table = contour_path.vertices[:, 0], contour_path.vertices[:, 1]\n time_table = np.linspace(0, tau, len(x_table))\n\n # Simple method to center the image\n x_table = x_table - min(x_table)\n y_table = y_table - min(y_table)\n x_table = x_table - max(x_table) / 2\n y_table = y_table - max(y_table) / 2\n\n return time_table, x_table, y_table",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Some fourier series generating functions (explained in other scripts)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def f(t, time_table, x_table, y_table):\n return interp(t, time_table, x_table) + 1j*interp(t, time_table, y_table)\n\ndef coef_list(time_table, x_table, y_table, order=10):\n \"\"\"\n Counting c_n coefficients of Fourier series, of function aproximated by points (time_table, x_table + j*y_table)\n of order of magnitude = order\n \"\"\"\n coef_list = []\n for n in range(-order, order+1):\n real_coef = quad(lambda t: np.real(f(t, time_table, x_table, y_table) * np.exp(-n*1j*t)), 0, tau, limit=100, full_output=1)[0]/tau\n imag_coef = quad(lambda t: np.imag(f(t, time_table, x_table, y_table) * np.exp(-n*1j*t)), 0, tau, limit=100, full_output=1)[0]/tau\n coef_list.append([real_coef, imag_coef])\n return np.array(coef_list)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Generating",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"This time, we will use Fourier series, not to get coefficients in the result, but first points of the Fourier Shape Description, then their distances from the centroids",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Now we also need functions for: interpolation of n points from fourier series, finding radiuses of centroid distances of these points.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def DFT(t, coef_list, order=10):\n \"\"\"\n get points of Fourier series aproximation, where t is a time argument for which we want to get (from range[0, tau])\n \"\"\"\n kernel = np.array([np.exp(-n*1j*t) for n in range(-order, order+1)])\n series = np.sum( (coef_list[:,0]+1j*coef_list[:,1]) * kernel[:])\n return np.real(series), np.imag(series)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def GenerateShapePoints(coef_list, n=100):\n time_space = np.linspace(0, tau, n)\n x_DFT = [DFT(t, coef)[0] for t in time_space]\n y_DFT = [DFT(t, coef)[1] for t in time_space]\n return x_DFT, y_DFT",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### Test",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"copied = onlyBlackWhite(data[i,:,:])\ntime_table, x_table, y_table = create_close_loop(copied)\ncoef = coef_list(time_table, x_table, y_table, order=10)\nX, Y = GenerateShapePoints(coef, n=30)\nplt.plot(X, Y, '-o')\n## n = 30 describes the number well enough (we still want to do it in reasonable time)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Now a function generating centroid distances",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Maybe here is a good moment to explain why we use this method. According to https://cis.temple.edu/~lakamper/courses/cis9601_2009/etc/fourierShape.pdf it simply gives best results when comparing shapes using Fourier transformations. It's a really well written article on the topic, I strongly reccomened getting some insights.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import math",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def measureDistancesFromCentroids(coef_list, N=30):\n X, Y = GenerateShapePoints(coef_list, n=N)\n x_centroid = np.mean(X)\n y_centroid = np.mean(Y)\n centr_r = []\n \n for i in range(N):\n x_dist_sq = (X[i] - x_centroid)**2\n y_dist_sq = (Y[i] - y_centroid)**2 y\n centr_r.append(math.sqrt(x_dist_sq + y_dist_sq))\n \n return np.array(centr_r)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Let's proceed to actual generating",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"i_gen = np.linspace(0, len(data)-1, len(data)).astype(int)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"centr_radiuses = []\nfor i in i_gen:\n copied = onlyBlackWhite(data[i,:,:])\n time_table, x_table, y_table = create_close_loop(copied)\n coef = coef_list(time_table, x_table, y_table, order=10)\n centr_radiuses.append(measureDistancesFromCentroids(coef))\n if i%100 == 0:\n print(i)\n\nnp.save(file='centroid_distances', arr=centr_radiuses)",
"0\n100\n200\n300\n400\n500\n600\n700\n800\n900\n1000\n1100\n1200\n1300\n1400\n1500\n1600\n1700\n1800\n1900\n"
]
],
[
[
"GOT IT!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
c503f16649baa1638f2c24746c6cff638a0f05e8
| 8,153 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
tasks/time-series/time-series-prediction/Stock_prediction.ipynb
|
haripamuluri/ai-platform
|
6057a99b72b29fa9a7a98984d48e7db314ac95b4
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
tasks/time-series/time-series-prediction/Stock_prediction.ipynb
|
haripamuluri/ai-platform
|
6057a99b72b29fa9a7a98984d48e7db314ac95b4
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
tasks/time-series/time-series-prediction/Stock_prediction.ipynb
|
haripamuluri/ai-platform
|
6057a99b72b29fa9a7a98984d48e7db314ac95b4
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 20.958869 | 138 | 0.538697 |
[
[
[
"# Predicitng Stock/Weather prices using neural networks",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## import relevant libraries ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np # linear algebra\nimport pandas as pd # data processing, CSV file I/O (e.g. pd.read_csv)\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom keras.models import Sequential\nimport matplotlib.patches as mpatches\nfrom keras.layers import Dense\nfrom keras.layers import Dropout\nfrom keras.layers import LSTM, Bidirectional\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler\nfrom sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error\nimport os\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Load data from the file and visualize the data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df = pd.read_csv('testset.csv') # Loading the data from file\ndf.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# convert datetime columns from object type to datatime64 and set it as index",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df['datetime_utc'] = pd.to_datetime(df['datetime_utc'])\ndf.set_index('datetime_utc', inplace= True)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Resample the colums as per Day/Hour/Mins as per requirements",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df =df.resample('H').mean() #The index is based on hours and mean value of the data from that specific hour is filled in the columns",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Select the columns you want to predict",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df = df['Open' ]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Fill the empty slots ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df = df.ffill().bfill()\ndf.mean()# we will fill the null row",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Plot the data ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(20,8))\nplt.plot(df)\nplt.title('Time Series')\nplt.xlabel('Date')\nplt.ylabel('Stock')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Convert the data to float and reshape to 2D",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df=df.values\ndf = df.astype('float32')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df=df.reshape(df.shape[0],1)\ndf",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Transform the data using minmax scalr iwth the given range",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"scaler= MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(0,1))\nsc = scaler.fit_transform(df)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create Xtrain and Ytrain based on your requirements",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"timestep = 10 #Steps used to train before predicting the next point\nX=[]\nY=[]\nfor i in range(1,len(sc)- (timestep)):\n X.append(sc[i:i+timestep])\n Y.append(sc[i+timestep])\nX=np.asanyarray(X)\nY=np.asanyarray(Y)\nlength = len(sc)-100\n\n# shape of the input data varies form model to model\nXtrain = X[:length,:,:] \nXtest = X[length:,:,:] \nYtrain = Y[:length] \nYtest= Y[k-1:-1] ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import the libraries",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from keras.layers import Dense,RepeatVector\nfrom keras.layers import Flatten\nfrom keras.layers import TimeDistributed\nfrom keras.layers.convolutional import Conv1D\nfrom keras.layers.convolutional import MaxPooling1D\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Build the model Bidirectional\n\nBelow model is keras Bideirectional model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model = Sequential()\nmodel.add(Bidirectional(LSTM(100, activation='sigmoid'),input_shape=(timestep,1)))\nmodel.add(Dense(50, activation='sigmoid'))\nmodel.add(Dense(1))\nmodel.compile(loss='mse', optimizer='adam')\nmodel.fit(Xtrain,Ytrain,epochs=10, verbose=0 )\nmodel.summary()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# save model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model.save('model.h5')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# load model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model = load_model('model.h5')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Predict the results and inverse transform them",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"preds = model.predict(Xtest)\npreds = scaler.inverse_transform(preds)\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Inverse transfrom test data to compare with the predicted results",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Ytest=np.asanyarray(Ytest) \nYtest=Ytest.reshape(-1,1) \nYtest = scaler.inverse_transform(Ytest)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Mean squaled error is calculated to measure the accuracy of precdiction\n\nMeasuring accuracy varies based on the output and requirements",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mean_squared_error(Ytest,preds) ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Plot the predicted and True results to visualize",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(20,9))\nplt.plot(Ytest)\nplt.plot(preds_cnn1)\nplt.legend(('Test','Predicted'))\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c5040e10503035c1c8f7095900289e7ff7e8adb6
| 7,176 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
.ipynb_checkpoints/dl_vid-checkpoint.ipynb
|
zhiaozhou/91porn-nonmembership-download
|
98f56f3eee541d696ffa5dffb55fde0a77e31c6f
|
[
"MIT"
] | 117 |
2018-08-23T08:45:37.000Z
|
2022-03-06T07:15:33.000Z
|
.ipynb_checkpoints/dl_vid-checkpoint.ipynb
|
namigongyi/91porn-nonmembership-download
|
98f56f3eee541d696ffa5dffb55fde0a77e31c6f
|
[
"MIT"
] | 5 |
2018-07-19T07:12:40.000Z
|
2021-12-15T02:12:38.000Z
|
.ipynb_checkpoints/dl_vid-checkpoint.ipynb
|
namigongyi/91porn-nonmembership-download
|
98f56f3eee541d696ffa5dffb55fde0a77e31c6f
|
[
"MIT"
] | 36 |
2018-08-06T16:28:12.000Z
|
2020-03-30T08:10:48.000Z
| 24.325424 | 150 | 0.503066 |
[
[
[
"import re\nfrom robobrowser import RoboBrowser\nimport urllib\nimport os",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class ProgressBar(object):\n \"\"\"\n 链接:https://www.zhihu.com/question/41132103/answer/93438156\n 来源:知乎\n \"\"\"\n def __init__(self, title, count=0.0, run_status=None, fin_status=None, total=100.0, unit='', sep='/', chunk_size=1.0):\n super(ProgressBar, self).__init__()\n self.info = \"【%s】 %s %.2f %s %s %.2f %s\"\n self.title = title\n self.total = total\n self.count = count\n self.chunk_size = chunk_size\n self.status = run_status or \"\"\n self.fin_status = fin_status or \" \" * len(self.statue)\n self.unit = unit\n self.seq = sep\n\n def __get_info(self):\n \"\"\"【razorback】 下载完成 3751.50 KB / 3751.50 KB \"\"\"\n _info = self.info % (self.title, self.status, self.count/self.chunk_size, self.unit, self.seq, self.total/self.chunk_size, self.unit)\n return _info\n\n def refresh(self, count=1, status=None):\n self.count += count\n self.status = status or self.status\n end_str = \"\\r\"\n if self.count >= self.total:\n end_str = '\\n'\n self.status = status or self.fin_status\n print(self.__get_info(), end=end_str)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"path = './'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def download_video_by_url(url, path, vid_title):\n \n outfile = os.path.join(path,vid_title+'.mp4')\n with closing(requests.get(url, stream=True)) as response:\n chunk_size = 1024\n content_size = int(response.headers['content-length'])\n progress = ProgressBar(vid_title, total=content_size, unit=\"KB\", chunk_size=chunk_size, run_status=\"正在下载\", fin_status=\"下载完成\")\n assert response.status_code == 200\n with open(outfile, \"wb\") as file:\n for data in response.iter_content(chunk_size=chunk_size):\n file.write(data)\n progress.refresh(count=len(data))\n return True",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"url = 'http://91porn.com/view_video.php?viewkey=4d65b13fa47b2afb51b8'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"br = RoboBrowser(history=True,parser='lxml')\nbr.open(url)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lang = br.get_forms()[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lang['session_language'].options = ['cn_CN']\nlang['session_language'].value = 'cn_CN'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"br.submit_form(lang)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"vid_title = br.find('div',{'id':'viewvideo-title'}).text.strip()\nprint(vid_title)",
"背着老公打炮\n"
],
[
"vid_id = re.findall(r'\\d{6}',br.find('a',{'href':'#featureVideo'}).attrs['onclick'])[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"vid_real_url = 'http://192.240.120.34//mp43/{}.mp4'.format(vid_id)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"urllib.request.urlretrieve(vid_real_url,'{}.mp4'.format(vid_title))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"if download_video_by_url(vid_real_url, path, vid_title): \n print('下载成功!珍惜生命,远离黄赌毒!')",
""
],
[
"hot_videos = {}\nbr = RoboBrowser(history=True,parser='lxml')\nurl = 'http://91porn.com/v.php?category=rf&viewtype=basic&page=1'\nbr.open(url)\n\nlang = br.get_forms()[0]\nlang['session_language'].options = ['cn_CN']\nlang['session_language'].value = 'cn_CN'\nbr.submit_form(lang)\n\n# get every video's information\nvideos = br.find_all('div',{'class':'listchannel'})\n# get their titles and urls\nvideos_dict = dict([(i.find('a').find('img')['title'],i.find('a')['href']) for i in videos])\nhot_videos.update(videos_dict)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for i,j in enumerate(hot_videos.keys()):\n print(i,j)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c5041ae990b3559cd7ff18919374d2395ed6634f
| 11,448 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
NLP/NLP - Character-based LSTM Generator.ipynb
|
mcamack/ML-Notebooks
|
05709e3e3819148e6c3c701f2e6516d71cbc958b
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 3 |
2018-09-26T05:28:55.000Z
|
2019-08-16T15:32:46.000Z
|
NLP/NLP - Character-based LSTM Generator.ipynb
|
mcamack/ML-Notebooks
|
05709e3e3819148e6c3c701f2e6516d71cbc958b
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
NLP/NLP - Character-based LSTM Generator.ipynb
|
mcamack/ML-Notebooks
|
05709e3e3819148e6c3c701f2e6516d71cbc958b
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 27.854015 | 451 | 0.524371 |
[
[
[
"# Character-based LSTM",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Grab all Chesterton texts from Gutenberg",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from nltk.corpus import gutenberg\n\ngutenberg.fileids()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"text = ''\n\nfor txt in gutenberg.fileids():\n if 'chesterton' in txt:\n text += gutenberg.raw(txt).lower()\n \nchars = sorted(list(set(text)))\nchar_indices = dict((c, i) for i, c in enumerate(chars))\nindices_char = dict((i, c) for i, c in enumerate(chars))\n'corpus length: {} total chars: {}'.format(len(text), len(chars))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(text[:100])",
"[the ball and the cross by g.k. chesterton 1909]\n\n\ni. a discussion somewhat in the air\n\nthe flying s\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Create the Training set",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Build a training and test dataset. Take 40 characters and then save the 41st character. We will teach the model that a certain 40 char sequence should generate the 41st char. Use a step size of 3 so there is overlap in the training set and we get a lot more 40/41 samples.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"maxlen = 40\nstep = 3\nsentences = []\nnext_chars = []\n\nfor i in range(0, len(text) - maxlen, step):\n sentences.append(text[i: i+maxlen])\n next_chars.append(text[i + maxlen])\n \nprint(\"sequences: \", len(sentences))",
"sequences: 394855\n"
],
[
"print(sentences[0])\nprint(sentences[1])",
"[the ball and the cross by g.k. chestert\ne ball and the cross by g.k. chesterton \n"
],
[
"print(next_chars[0])",
"o\n"
]
],
[
[
"One-hot encode",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\n\nX = np.zeros((len(sentences), maxlen, len(chars)), dtype=np.bool)\ny = np.zeros((len(sentences), len(chars)), dtype=np.bool)\nfor i, sentence in enumerate(sentences):\n for t, char in enumerate(sentence):\n X[i, t, char_indices[char]] = 1\n y[i, char_indices[next_chars[i]]] = 1",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Create the Model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from keras.models import Sequential\nfrom keras.layers import Dense, Activation\nfrom keras.layers import LSTM\nfrom keras.optimizers import RMSprop\n\nmodel = Sequential()\nmodel.add(LSTM(128, input_shape=(maxlen, len(chars))))\nmodel.add(Dense(len(chars)))\nmodel.add(Activation('softmax'))\noptimizer = RMSprop(lr=0.01)\nmodel.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer=optimizer)\nmodel.summary()",
"Using TensorFlow backend.\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Train the Model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"epochs = 2\nbatch_size = 128\n\nmodel.fit(X, y, batch_size=batch_size, epochs=epochs)",
"Epoch 1/2\n394855/394855 [==============================] - 93s 235us/step - loss: 1.8309\nEpoch 2/2\n394855/394855 [==============================] - 92s 233us/step - loss: 1.57090s - loss: \n"
]
],
[
[
"## Generate new sequence",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import random\n\ndef sample(preds, temperature=1.0):\n preds = np.asarray(preds).astype('float64')\n preds = np.log(preds) / temperature\n exp_preds = np.exp(preds)\n preds = exp_preds / np.sum(exp_preds)\n probas = np.random.multinomial(1, preds, 1)\n return np.argmax(probas)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import sys\nstart_index = random.randint(0, len(text) - maxlen - 1)\nfor diversity in [0.2, 0.5, 1.0]:\n print()\n print('----- diversity:', diversity)\n generated = ''\n sentence = text[start_index: start_index + maxlen]\n generated += sentence\n print('----- Generating with seed: \"' + sentence + '\"')\n sys.stdout.write(generated)\n for i in range(400):\n x = np.zeros((1, maxlen, len(chars)))\n for t, char in enumerate(sentence):\n x[0, t, char_indices[char]] = 1.\n preds = model.predict(x, verbose=0)[0]\n next_index = sample(preds, diversity)\n next_char = indices_char[next_index]\n generated += next_char\n sentence = sentence[1:] + next_char\n sys.stdout.write(next_char)\n sys.stdout.flush()\n print()",
"\n----- diversity: 0.2\n----- Generating with seed: \"head and features. but though she was n\"\nhead and features. but though she was not believes as the still of the stood and the street of the stand of the stood and the stand of the stand of the stand of the stood and the strong face was the stare and the most contraling that the concertual and the little and the street and the little of the stand of the sense of the street of the street of the distance of the street of the stand of the still was a stand and the street of the s\n\n----- diversity: 0.5\n----- Generating with seed: \"head and features. but though she was n\"\nhead and features. but though she was not between the wall of the other ampered him was before asced and a sick off a respectains of the wild and strong concession alfeg and a sation of the tried that still that i was a cripted life that it was a lipted of the montton of his dreaming that in him. it was a monght as a man was sort of the seconds and began of the distract of the colours of the solot to he stranged to stand the state of \n\n----- diversity: 1.0\n----- Generating with seed: \"head and features. but though she was n\"\nhead and features. but though she was now, there was the withont living clother. but oscro?\"\ncansiincle the long rush packen melony only off its be. which that in the french asking to his groveter. i have pree up\nrewoutd him oy which was i took drush that creatcable long fillag alsolted himself add our side and not poledd.\"\n\n\"that i am yro?\"\n\n\"i thoudd it neteled from fam unhabled flams.--heard to be throwed kneepy,\nso a miny mind's \n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c5046a6c1178b0b6d5c0e742a7eb89a6f631ea87
| 8,313 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Fitting_a_Logistic_Regression_Model.ipynb
|
thejsuvarna/Technocolabs-Data-Science-Internship
|
9936243c927f4cdc1ea1921406ac421853f49d1b
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Fitting_a_Logistic_Regression_Model.ipynb
|
thejsuvarna/Technocolabs-Data-Science-Internship
|
9936243c927f4cdc1ea1921406ac421853f49d1b
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Fitting_a_Logistic_Regression_Model.ipynb
|
thejsuvarna/Technocolabs-Data-Science-Internship
|
9936243c927f4cdc1ea1921406ac421853f49d1b
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 24.095652 | 208 | 0.560207 |
[
[
[
"**Run the following two cells before you begin.**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%autosave 10",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nfrom sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"______________________________________________________________________\n**First, import your data set and define the sigmoid function.**\n<details>\n <summary>Hint:</summary>\n The definition of the sigmoid is $f(x) = \\frac{1}{1 + e^{-X}}$.\n</details>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import the data set\ndata = pd.read_csv(\"cleaned_data.csv\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Define the sigmoid function\ndef sigmoid(X):\n Y = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-X))\n return Y\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Now, create a train/test split (80/20) with `PAY_1` and `LIMIT_BAL` as features and `default payment next month` as values. Use a random state of 24.**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create a train/test split\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(data[['PAY_1', 'LIMIT_BAL']].values, data['default payment next month'].values,\n test_size=0.2, random_state=24)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"______________________________________________________________________\n**Next, import LogisticRegression, with the default options, but set the solver to `'liblinear'`.**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression\nlr = LogisticRegression(solver='liblinear')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"______________________________________________________________________\n**Now, train on the training data and obtain predicted classes, as well as class probabilities, using the testing data.**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Fit the logistic regression model on training data\nlr.fit(X_train,y_train)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Make predictions using `.predict()`\nmodel = lr.predict(X_test)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Find class probabilities using `.predict_proba()`\nmodel_proba = lr.predict_proba(X_test)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"______________________________________________________________________\n**Then, pull out the coefficients and intercept from the trained model and manually calculate predicted probabilities. You'll need to add a column of 1s to your features, to multiply by the intercept.**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Add column of 1s to features\nfeatures = np.hstack([np.ones((X_test.shape[0],1)), X_test])\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Get coefficients and intercepts from trained model\ncoef_inter = np.concatenate([lr.intercept_.reshape(1,1), lr.coef_], axis=1)\ncoef_inter\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Manually calculate predicted probabilities\nX_lin = np.dot(coef_inter, np.transpose(features))\nmodel_proba_manual = sigmoid(X_lin)\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"______________________________________________________________________\n**Next, using a threshold of `0.5`, manually calculate predicted classes. Compare this to the class predictions output by scikit-learn.**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Manually calculate predicted classes\nmodel_manual = model_proba_manual >= 0.5\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Compare to scikit-learn's predicted classes\nnp.array_equal(model.reshape(1,-1), model_manual)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"______________________________________________________________________\n**Finally, calculate ROC AUC using both scikit-learn's predicted probabilities, and your manually predicted probabilities, and compare.**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Use scikit-learn's predicted probabilities to calculate ROC AUC\nroc_auc_score(y_test, model_proba[:,1])\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Use manually calculated predicted probabilities to calculate ROC AUC\n\nroc_auc_score(y_test, model_proba_manual.reshape(model_proba_manual.shape[1],))\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c5046be5e6d6af7c0ad21f4a737070ba247e980c
| 556,078 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
soft_margin_svm_1.ipynb
|
ahammedshaneebnk/ML_Support_Vector_Machines_Exercises
|
73e264536a6f6226c955f76870347f65170bcb48
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
soft_margin_svm_1.ipynb
|
ahammedshaneebnk/ML_Support_Vector_Machines_Exercises
|
73e264536a6f6226c955f76870347f65170bcb48
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
soft_margin_svm_1.ipynb
|
ahammedshaneebnk/ML_Support_Vector_Machines_Exercises
|
73e264536a6f6226c955f76870347f65170bcb48
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 568.006129 | 94,625 | 0.940199 |
[
[
[
"<a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/ahammedshaneebnk/ML_Support_Vector_Machines_Exercises/blob/main/soft_margin_svm_1.ipynb\" target=\"_parent\"><img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open In Colab\"/></a>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#**Question:**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#**Answer:1(a)**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"##**Data Analysis**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"###***Read Training Set***",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# import libraries\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn as sns\nfrom sklearn import svm",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# read training set 1 and convert into pandas dataframe\ndf = pd.read_csv('train_1.txt', delim_whitespace=' ', header=None)\n\n# display the data\nprint(df)",
" 0 1 2\n0 97.855421 125.387990 1\n1 48.571973 104.501180 1\n2 80.250214 106.601290 1\n3 114.659380 76.893242 -1\n4 80.156290 92.579178 1\n... ... ... ..\n1495 117.951330 86.896305 -1\n1496 105.958030 84.619172 -1\n1497 114.405700 89.404364 -1\n1498 131.177750 93.976537 -1\n1499 81.351097 109.757670 1\n\n[1500 rows x 3 columns]\n"
]
],
[
[
"###***Basic Details***",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# rows and columns\nprint(df.shape)",
"(1500, 3)\n"
]
],
[
[
"* Number of **Rows = 1500**\n* Number of **Columns = 3**\n* Number of **Features = 2**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# basic statistical details\nprint(df.describe())",
" 0 1 2\ncount 1500.000000 1500.000000 1500.000000\nmean 106.465996 106.242949 -0.002667\nstd 22.066211 22.866386 1.000330\nmin 34.842996 41.714147 -1.000000\n25% 89.966790 88.232062 -1.000000\n50% 105.906490 106.926880 -1.000000\n75% 122.833850 124.237392 1.000000\nmax 164.854810 166.573120 1.000000\n"
]
],
[
[
"* Both features have almost same set of minimum and maximum values.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"###***Check for Null Values***",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(df.info())",
"<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>\nRangeIndex: 1500 entries, 0 to 1499\nData columns (total 3 columns):\n # Column Non-Null Count Dtype \n--- ------ -------------- ----- \n 0 0 1500 non-null float64\n 1 1 1500 non-null float64\n 2 2 1500 non-null int64 \ndtypes: float64(2), int64(1)\nmemory usage: 35.3 KB\nNone\n"
]
],
[
[
"* **No null value** is present in the dataset",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"###***Features Distribution***",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plt.figure(figsize=(14,4))\n# plot the histogram of 1st feature data\nplt.subplot(121)\nsns.histplot(data=df, x=0, kde=True)\nplt.xlabel('X1')\n# plot the histogram of 2nd feature data\nplt.subplot(122)\nsns.histplot(data=df, x=1, kde=True)\nplt.xlabel('X2')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"* Both feature values are almost normally distributed. Since both of them have almost same range too, we do not need to feature scale these.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"##**Data Visualization**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# scatter plot\n# output +1 => green and '+'\n# output -1 => red and '-'\nplt.figure(figsize=(9,7))\ndf1 = df.loc[df[2]==1]\ndf2 = df.loc[df[2]==-1]\nplt.scatter(df1[0], df1[1], color='green', marker='+', s=60)\nplt.scatter(df2[0], df2[1], color='red', marker='_', s=60)\nplt.legend(['+1 data','-1 data'])\nplt.xlabel('X1')\nplt.ylabel('X2')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##**Test Data**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"###***Read Test Data***",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# read test dataset 1 and convert into pandas dataframe\ntest_df = pd.read_csv('test_1.txt', delim_whitespace=' ', header=None)\n\n# size of the dataset\nprint(test_df.shape)\n\n# display the data\nprint(test_df)",
"(500, 3)\n 0 1 2\n0 133.437860 103.810470 -1\n1 121.698080 104.574480 -1\n2 125.708830 73.536465 -1\n3 84.161628 131.217610 1\n4 131.302240 96.246931 -1\n.. ... ... ..\n495 89.577738 111.197790 1\n496 113.859610 88.504409 -1\n497 145.776400 85.472669 -1\n498 118.437890 72.945254 -1\n499 138.236350 82.789068 -1\n\n[500 rows x 3 columns]\n"
]
],
[
[
"* There are **500** instances in the test data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"##**SVM Implementation**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"###**Function to Plot**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# this function will provide the scatter plots\n\ndef plot_fun(model, df, color1, color2, flag):\n\n # separating +1 and -1 data\n df1 = df.loc[df[2]==1]\n df2 = df.loc[df[2]==-1]\n plt.scatter(df1[0], df1[1], color=color1, marker='+', s=60)\n plt.scatter(df2[0], df2[1], color=color2, marker='_', s=60)\n plt.legend(['+1 data','-1 data'])\n plt.xlabel('X1')\n plt.ylabel('X2')\n\n # plot the decision function\n ax = plt.gca()\n xlim = ax.get_xlim()\n ylim = ax.get_ylim()\n\n # create grid to evaluate model\n xx = np.linspace(xlim[0], xlim[1], 30)\n yy = np.linspace(ylim[0], ylim[1], 30)\n XX, YY = np.meshgrid(xx, yy)\n xy = np.vstack([XX.ravel(), YY.ravel()]).T\n Z = model.decision_function(xy).reshape(XX.shape)\n\n # training set\n if flag==1:\n # plot decision boundary and margins\n ax.contour(XX, YY, Z, colors='k', levels=[-1, 0, 1], alpha=0.5,\n linestyles=['--', '-', '--'])\n # plot support vectors\n ax.scatter(model.support_vectors_[:, 0], model.support_vectors_[:, 1], s=100,\n linewidth=1, facecolors='none', edgecolors='k')\n \n # test set\n elif flag==0:\n ax.contour(XX, YY, Z, colors='k', levels=0, alpha=0.5,\n linestyles='-')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"###**Function to Find Error**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# This function will provide the error\n\ndef err_fun(model, df):\n\n # prediction with the learned model\n predicted_labels = model.predict(df.iloc[:,:-1])\n error_count = 0\n\n # comparison with actual label\n for i in range(df.shape[0]):\n if predicted_labels[i] != df.iloc[i,-1]:\n error_count = error_count + 1\n\n # returns the error percentage\n return (error_count * 100 / df.shape[0])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"###**Function to Train SVM**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# This function will train the SVM and do all other needed operations\ndef svm_fun(df, test_df, c):\n\n # training\n model = svm.SVC(kernel='linear', C = c)\n model.fit(df.iloc[:,:-1], df.iloc[:,-1])\n\n plt.figure(figsize=(15,6))\n\n # plot with training data\n plt.subplot(121)\n plt.title('Training Data, C = %s'%(c))\n plot_fun(model, df, 'green', 'red', 1)\n\n # plot with test data\n plt.subplot(122)\n plt.title('Test Data, C = %s'%(c))\n plot_fun(model, test_df, 'blue', 'magenta', 0)\n\n # support vector details\n print(f\"{30*'==='}\\n\")\n print(f\"Softmargin SVM with C = {c}\\n\")\n print(f\"There are {len(model.support_vectors_)} support vectors in total.\")\n print(f\"\\nThey are as follows:\\n\")\n for i in range(len(model.support_vectors_)):\n print(f\"{i+1}. {model.support_vectors_[i]}\\tLamda = \\\n {model.dual_coef_[0][i]/(df.iloc[model.support_[i],-1])}\")\n\n # error calculation\n print(f\"\\nTraining Error = {err_fun(model, df)} %\")\n print(f\"Testing Error = {err_fun(model, test_df)} %\\n\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"###**SVM with C = 1000**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"svm_fun(df, test_df, 1000)",
"==========================================================================================\n\nSoftmargin SVM with C = 1000\n\nThere are 3 support vectors in total.\n\nThey are as follows:\n\n1. [112.80003 105.265 ]\tLamda = 0.015821984496977397\n2. [111.43546 119.68417]\tLamda = 0.009925547121323777\n3. [ 93.95697 102.51568]\tLamda = 0.005896437375653618\n\nTraining Error = 0.0 %\nTesting Error = 0.0 %\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"###**SVM with C = 100**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"svm_fun(df, test_df, 100)",
"==========================================================================================\n\nSoftmargin SVM with C = 100\n\nThere are 3 support vectors in total.\n\nThey are as follows:\n\n1. [112.80003 105.265 ]\tLamda = 0.015821984496977397\n2. [111.43546 119.68417]\tLamda = 0.009925547121323777\n3. [ 93.95697 102.51568]\tLamda = 0.005896437375653618\n\nTraining Error = 0.0 %\nTesting Error = 0.0 %\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"###**SVM with C = 1**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"svm_fun(df, test_df, 1)",
"==========================================================================================\n\nSoftmargin SVM with C = 1\n\nThere are 3 support vectors in total.\n\nThey are as follows:\n\n1. [112.80003 105.265 ]\tLamda = 0.015821984496977397\n2. [111.43546 119.68417]\tLamda = 0.009925547121323777\n3. [ 93.95697 102.51568]\tLamda = 0.005896437375653618\n\nTraining Error = 0.0 %\nTesting Error = 0.0 %\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"###**SVM with C = 0.01**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"svm_fun(df, test_df, 0.01)",
"==========================================================================================\n\nSoftmargin SVM with C = 0.01\n\nThere are 4 support vectors in total.\n\nThey are as follows:\n\n1. [112.80003 105.265 ]\tLamda = 0.01\n2. [101.3521 93.580409]\tLamda = 0.005246330720062449\n3. [111.43546 119.68417]\tLamda = 0.006062533974598346\n4. [ 93.95697 102.51568]\tLamda = 0.009183796745464103\n\nTraining Error = 0.0 %\nTesting Error = 0.0 %\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"###**SVM with C = 0.001**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"svm_fun(df, test_df, 0.001)",
"==========================================================================================\n\nSoftmargin SVM with C = 0.001\n\nThere are 24 support vectors in total.\n\nThey are as follows:\n\n1. [112.80003 105.265 ]\tLamda = 0.001\n2. [102.16567 92.450221]\tLamda = 0.001\n3. [102.35211 92.429084]\tLamda = 3.0098280505305624e-05\n4. [111.1763 101.83797]\tLamda = 0.001\n5. [105.04054 96.025027]\tLamda = 0.001\n6. [115.19239 106.84811]\tLamda = 0.001\n7. [101.3521 93.580409]\tLamda = 0.001\n8. [125.93705 117.0811 ]\tLamda = 0.001\n9. [103.68602 95.356161]\tLamda = 0.001\n10. [102.29536 93.615224]\tLamda = 0.001\n11. [119.63533 111.34973]\tLamda = 0.001\n12. [136.27889 126.77449]\tLamda = 0.000985822920797448\n13. [ 94.100748 103.19368 ]\tLamda = 0.001\n14. [ 98.363769 108.63757 ]\tLamda = 0.001\n15. [107.30023 116.33756]\tLamda = 0.001\n16. [115.87817 125.05415]\tLamda = 0.001\n17. [80.569068 90.484681]\tLamda = 0.001\n18. [119.95112 130.32558]\tLamda = 0.001\n19. [111.43546 119.68417]\tLamda = 0.001\n20. [ 93.95697 102.51568]\tLamda = 0.001\n21. [119.53586 128.95482]\tLamda = 0.001\n22. [117.12649 127.68521]\tLamda = 1.5921201302753667e-05\n23. [88.239047 98.152622]\tLamda = 0.001\n24. [105.75989 114.33206]\tLamda = 0.001\n\nTraining Error = 0.0 %\nTesting Error = 0.0 %\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"##**Conclusion**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* The given dataset has been analyzed and the values of the features were found to be **almost normally distributed**.\n* **No null values** were present in the training data and there were **1500 instances and 2 features**. The test data has **500** instances.\n* The data set was corresponding to **binary classification** with labels -1 and +1.\n* The training data has been visualized with the help of **scatter plot** and found to be well suitable for linear SVM.\n* The softmargin SVM was implemented with linear kernel.\n* Different values for the **hyper parameter C** has been experimented and the results were noted.\n* In this particular experiment, there was no difference observed when experimented with C = 1000, 100 and 1. In these cases, there were three support vectors.\n* Althogh, **when C has been decreased** to 0.01 and further to 0.001, **more number of support vectors** were found (4 and 24 respectively. This happened because the objective function of the SVM tried to concentrate on increasing the margin and provided less priority to the misclassifications or deviations.\n* The **dual coefficient $\\lambda$ values** were also studied by displaying them and found to be greater than 0 for all the support vectors and especiallly equal to C for those do not lie on the decision boundaries.\n* In all experimented cases, both training error and test error were found to be **zero**.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"##**Submitted By:**\n\n####Ahammed Shaneeb N K\n\n####M1, AI: Roll No - 2",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
c5046e2ded0952346263204cff7bc998dccdb0f3
| 1,232 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Python/Exercicios_Curso_em_Videos/ex008.ipynb
|
rubensrabelo/Exercicios
|
af8e399a013e1b357b0cef2506c99dae8b8dd7b6
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Python/Exercicios_Curso_em_Videos/ex008.ipynb
|
rubensrabelo/Exercicios
|
af8e399a013e1b357b0cef2506c99dae8b8dd7b6
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Python/Exercicios_Curso_em_Videos/ex008.ipynb
|
rubensrabelo/Exercicios
|
af8e399a013e1b357b0cef2506c99dae8b8dd7b6
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 19.555556 | 49 | 0.458604 |
[
[
[
"m = float(input('Digite a medida[m]: '))\nkm = m / 1000\nhm = m /100\ndam = m / 10\ndm = m * 10\ncm = m * 100\nmm = m * 1000\nprint(f'A medida de {m} corresponde a:')\nprint(f'{km} km')\nprint(f'{hm} hm')\nprint(f'{dam} dam')\nprint(f'{dm} dm')\nprint(f'{cm} cm')\nprint(f'{mm} mm')",
"Digite a medida[m]: 3\nA medida de 3.0 corresponde a:\n0.003 km\n0.03 hm\n0.3 dam\n30.0 dm\n300.0 cm\n3000.0 mm\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
]
] |
c5047283b0cd6f85907f8240e67982e79fb2258b
| 190,232 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Pipeline.ipynb
|
kev-fung/KMNIST-Classifier
|
f9cf05ad7fc5cbc41b0c58eb3db25b27361a75f6
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Pipeline.ipynb
|
kev-fung/KMNIST-Classifier
|
f9cf05ad7fc5cbc41b0c58eb3db25b27361a75f6
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Pipeline.ipynb
|
kev-fung/KMNIST-Classifier
|
f9cf05ad7fc5cbc41b0c58eb3db25b27361a75f6
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 152.063949 | 75,012 | 0.832026 |
[
[
[
"# Team BackProp\nDuring exploration of the neural architecture, we used copies of this notebook to be able to easily process data whilst keeping our models intact. \n\n1. Import KMNIST Data\n2. Data preprocess and augmentate\n3. Develop neural network model\n4. Cross validate model\n - At this stage we decide whether to keep the model for full training or remodify the network again to improve it.\n5. Hyperparameter Tuning\n6. Train on full dataset\n7. Save model and submit",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Pipeline Setup",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Imports",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!pip install pycm livelossplot\n%pylab inline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import torch\nimport torch.nn as nn\nimport torch.nn.functional as F\nfrom torch.utils.data import TensorDataset, DataLoader\nfrom torch.utils.data import Dataset \nimport torchvision.transforms as transforms\nfrom torchvision.transforms import Compose, ToTensor, Normalize, RandomRotation,\\\n ToPILImage, RandomResizedCrop, RandomAffine\n\nfrom livelossplot import PlotLosses\n\nimport csv\nimport pickle\n\ndef set_seed(seed):\n \"\"\" Use this to set ALL the random seeds to a fixed value and take out any \n randomness from cuda kernels\n \"\"\"\n random.seed(seed)\n np.random.seed(seed)\n torch.manual_seed(seed)\n torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed)\n\n #uses inbuilt cudnn auto-tuner to find the fastest convolution algorithms.\n torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False \n torch.backends.cudnn.enabled = False\n\n return True\n\ndevice = 'cpu'\n\nif torch.cuda.device_count() > 0 and torch.cuda.is_available():\n print(\"Cuda installed! Running on GPU!\")\n device = 'cuda'\nelse:\n print(\"No GPU available!\")\n\nfrom google.colab import drive\ndrive.mount('/content/gdrive/')",
"Cuda installed! Running on GPU!\n"
]
],
[
[
"### KMNIST Data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Load in the datasets\nX = np.load(F\"/content/gdrive/My Drive/Colab Notebooks/Mini-Project/acse-module-8-19/kmnist-train-imgs.npy\") /255\ny = np.load(F\"/content/gdrive/My Drive/Colab Notebooks/Mini-Project/acse-module-8-19/kmnist-train-labels.npy\")\nXtest = np.load(F\"/content/gdrive/My Drive/Colab Notebooks/Mini-Project/acse-module-8-19/kmnist-test-imgs.npy\") /255\n\n# Load in the classmap as a dictionary\nclassmap = {}\nwith open('/content/gdrive/My Drive/Colab Notebooks/Mini-Project/acse-module-8-19/kmnist_classmap.csv', 'r') as csvfile:\n spamreader = csv.reader(csvfile, delimiter=',')\n next(spamreader)\n for row in spamreader:\n classmap[row[0]] = row[2]\n\n# Check if we imported correctly\nplt.imshow(X[0]);",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Image Preprocessing and Augmentation",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class CustomImageTensorDataset(Dataset):\n def __init__(self, data, targets, transform=None, mean=False, std=False):\n \"\"\"\n Args:\n data (Tensor): A tensor containing the data e.g. images\n targets (Tensor): A tensor containing all the labels\n transform (callable, optional): Optional transform to be applied\n on a sample.\n \"\"\"\n self.data = data.reshape(-1,1,28,28)\n self.targets = targets\n self.transform = transform\n\n # Find mean and standard dev\n self.mean = mean\n self.std = std\n\n self.Rotation = Compose([\n ToPILImage(),\n RandomRotation(10),\n ToTensor(), Normalize(mean=[self.mean], std=[self.std])\n ])\n\n self.RotandCrop = Compose([\n ToPILImage(),\n RandomResizedCrop(size=(28,28), scale=(0.8,1)),\n ToTensor(), Normalize(mean=[self.mean], std=[self.std])\n ])\n \n self.Affine = Compose([ToPILImage(),\n RandomAffine(10, shear=10),\n ToTensor(), Normalize(mean=[self.mean], std=[self.std])\n ])\n \n \n self.Norm = Compose([Normalize(mean=[self.mean], std=[self.std])\n ])\n \n def __len__(self):\n return len(self.data)\n\n def __getitem__(self, idx):\n sample, label = self.data[idx], self.targets[idx]\n \n assert (self.mean != False), \"Asign a mean\"\n assert (self.mean != False), \"Asign a std\"\n \n if self.transform:\n x = random.random()\n if 0<= x<0.2: # rotate\n sample = self.Rotation(sample)\n if 0.2<= x<0.4: # resize crop\n sample = self.RotandCrop(sample)\n if 0.4<= x<0.7: # shear crop\n sample= self.Affine(sample)\n \n else: # none\n sample = self.Norm(sample)\n else:\n sample = self.Norm(sample)\n \n return sample, label",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Verify if image augmentation works:\nX_train, y_train = X.astype(float), y\nX_train, y_train = torch.from_numpy(X_train).float(), torch.from_numpy(y_train)\nmean1, std1 = torch.mean(X_train), torch.std(X_train)\ndset = CustomImageTensorDataset(X_train, y_train, transform=True, mean=mean1, std=std1 )\n\n# Make a dataloader to access the PIL images of a batch size of 25\nloader = DataLoader(dset, batch_size=25, shuffle=True)\n\n# Create an iter object to cycle through dataloader\ntrain_iter = iter(loader)\nimgs, labels = train_iter.next()\n\nprint(imgs.shape)\nprint('max:',imgs.max())\n\n# plot our batch of images with labels\nfig, axarr = plt.subplots(5,5,figsize=(8,8))\nfig.tight_layout()\nfor img, label, axs in zip(imgs, labels, axarr.flatten()):\n axs.set_title(str(label.numpy()) + \" \" + str(label.numpy()))\n axs.imshow(img.numpy()[0])",
"torch.Size([25, 1, 28, 28])\nmax: tensor(6.1103)\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Model Development\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n### Architecture Analysis Models\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class AlexNet_Exp1(nn.Module):\n \"\"\"Based on the AlexNet paper with the same number of layers and parameters \n are rescaled down by 8x to fit with the original alexnet image size to \n our kmnist size ratio (227:28)\n \"\"\"\n \n def __init__(self):\n super(AlexNet_Exp1, self).__init__()\n self.conv_1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 6, kernel_size=11, stride=1, padding=3, bias=True)\n self.pool_2 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)\n self.conv_3 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2, bias=True)\n self.pool_4 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)\n self.conv_5 = nn.Conv2d(16, 24, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2, bias=True)\n self.conv_6 = nn.Conv2d(24, 24, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=2, bias=True)\n self.conv_7 = nn.Conv2d(24, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=2, bias=True)\n self.pool_8 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)\n self.linear_9 = nn.Linear(400, 256, bias=True)\n self.output = nn.Linear(256, 10, bias=True)\n #self.dout = nn.Dropout(p=0.25) #dropout added to prevent overfitting :0\n self.act = nn.ReLU()\n \n def forward(self, x):\n x = self.act(self.conv_1(x))\n x = self.pool_2(x)\n x = self.act(self.conv_3(x))\n x = self.pool_4(x)\n x = self.act(self.conv_5(x))\n x = self.act(self.conv_6(x))\n x = self.act(self.conv_7(x))\n x = self.pool_8(x)\n x = x.view(-1, x.size(1) * x.size(2) * x.size(3))\n x = self.act(self.linear_9(x))\n x = self.output(x) # Don't activate this output layer, we apply a softmax transformation in our training functions!\n return x",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class AlexNet_Exp3(nn.Module):\n \"\"\"Based on the AlexNet paper with the same number of layers and parameters \n are rescaled down by 4x to better fit to the labels compared to 8x scaling\n \"\"\"\n \n def __init__(self):\n super(AlexNet_Exp3, self).__init__()\n self.conv_1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 12, kernel_size=11, stride=1, padding=3, bias=True)\n self.pool_2 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)\n self.conv_3 = nn.Conv2d(12, 32, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2, bias=True)\n self.pool_4 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)\n self.conv_5 = nn.Conv2d(32, 48, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2, bias=True)\n self.conv_6 = nn.Conv2d(48, 48, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=2, bias=True)\n self.conv_7 = nn.Conv2d(48, 32, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=2, bias=True)\n self.pool_8 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)\n self.linear_9 = nn.Linear(800, 512, bias=True)\n self.output = nn.Linear(512, 10, bias=True)\n #self.dout = nn.Dropout(p=0.25) #dropout added to prevent overfitting :0\n self.act = nn.ReLU()\n \n def forward(self, x):\n x = self.act(self.conv_1(x))\n x = self.pool_2(x)\n x = self.act(self.conv_3(x))\n x = self.pool_4(x)\n x = self.act(self.conv_5(x))\n x = self.act(self.conv_6(x))\n x = self.act(self.conv_7(x))\n x = self.pool_8(x)\n x = x.view(-1, x.size(1) * x.size(2) * x.size(3))\n x = self.act(self.linear_9(x))\n x = self.output(x) # Don't activate this output layer, we apply a softmax transformation in our training functions!\n return x",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class AlexNet_Exp4(nn.Module):\n \"\"\"Based on the AlexNet paper with the same number of channels and layers \n are rescaled down by 8x to fit with the original alexnet image size to \n our kmnist size ratio (227:28)\n \n We have now provided a \"reasonable\" guess of the filters and paddings \n \n \"\"\"\n \n def __init__(self):\n super(AlexNet_Exp4, self).__init__()\n self.conv_1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 6, kernel_size=11, stride=1, padding=3, bias=True)\n self.pool_2 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)\n self.conv_3 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2, bias=True)\n self.pool_4 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)\n self.conv_5 = nn.Conv2d(16, 24, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2, bias=True)\n self.conv_6 = nn.Conv2d(24, 24, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=True)\n self.conv_7 = nn.Conv2d(24, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=True)\n self.pool_8 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)\n self.linear_9 = nn.Linear(144, 128, bias=True)\n self.output = nn.Linear(128, 10, bias=True)\n #self.dout = nn.Dropout(p=0.25) #dropout added to prevent overfitting :0\n self.act = nn.ReLU()\n \n def forward(self, x):\n x = self.act(self.conv_1(x))\n x = self.pool_2(x)\n x = self.act(self.conv_3(x))\n x = self.pool_4(x)\n x = self.act(self.conv_5(x))\n x = self.act(self.conv_6(x))\n x = self.act(self.conv_7(x))\n x = self.pool_8(x)\n x = x.view(-1, x.size(1) * x.size(2) * x.size(3))\n x = self.act(self.linear_9(x))\n x = self.output(x) # Don't activate this output layer, we apply a softmax transformation in our training functions!\n return x",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class AlexNet_Exp5(nn.Module):\n \"\"\"Based on the AlexNet paper with the same number of layers and parameters \n are rescaled down by 8x but with an addional convolutional layer \n \"\"\"\n \n def __init__(self):\n super(AlexNet_Exp5, self).__init__()\n self.conv_1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 6, kernel_size=13, stride=1, padding=6, bias=True)\n self.pool_2 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)\n self.conv_3 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, kernel_size=7, stride=1, padding=3, bias=True)\n self.pool_4 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)\n self.conv_5 = nn.Conv2d(16, 24, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2, bias=True)\n \n # additional layer\n self.conv_6 = nn.Conv2d(24, 24, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2, bias=True)\n \n self.conv_7 = nn.Conv2d(24, 24, kernel_size=4, stride=1, padding=1, bias=True)\n self.conv_8 = nn.Conv2d(24, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=True)\n self.pool_9 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)\n self.linear_10 = nn.Linear(144, 100, bias=True)\n self.output = nn.Linear(100, 10, bias=True)\n \n #self.dout = nn.Dropout(p=0.25) #dropout added to prevent overfitting :0\n self.act = nn.ReLU()\n \n \n def forward(self, x):\n x = self.act(self.conv_1(x))\n x = self.pool_2(x)\n x = self.act(self.conv_3(x))\n x = self.pool_4(x)\n x = self.act(self.conv_5(x))\n \n x = self.act(self.conv_6(x))\n \n x = self.act(self.conv_7(x))\n x = self.act(self.conv_8(x))\n x = self.pool_9(x)\n x = x.view(-1, x.size(1) * x.size(2) * x.size(3))\n x = self.act(self.linear_10(x))\n x = self.output(x) # Don't activate this output layer, we apply a softmax transformation in our training functions!\n return x",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class AlexNet_Exp6(nn.Module):\n \"\"\" Based on the AlexNet paper with the same number of channels and layers \n are rescaled down by 4x to fit with the original alexnet image size to \n our kmnist size ratio (227:28)\n \n We have now provided a \"reasonable\" guess of the filters and paddings \n \n \"\"\"\n \n def __init__(self):\n super(AlexNet_Exp6, self).__init__()\n self.conv_1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 12, kernel_size=11, stride=1, padding=3, bias=True)\n self.pool_2 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)\n self.conv_3 = nn.Conv2d(12, 32, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2, bias=True)\n self.pool_4 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)\n self.conv_5 = nn.Conv2d(32, 48, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2, bias=True)\n self.conv_6 = nn.Conv2d(48, 48, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=True)\n self.conv_7 = nn.Conv2d(48, 32, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=True)\n self.pool_8 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)\n self.linear_9 = nn.Linear(288, 200, bias=True)\n self.output = nn.Linear(200, 10, bias=True)\n #self.dout = nn.Dropout(p=0.25) #dropout added to prevent overfitting :0\n self.act = nn.ReLU()\n \n def forward(self, x):\n x = self.act(self.conv_1(x))\n x = self.pool_2(x)\n x = self.act(self.conv_3(x))\n x = self.pool_4(x)\n x = self.act(self.conv_5(x))\n x = self.act(self.conv_6(x))\n x = self.act(self.conv_7(x))\n x = self.pool_8(x)\n x = x.view(-1, x.size(1) * x.size(2) * x.size(3))\n x = self.act(self.linear_9(x))\n x = self.output(x) # Don't activate this output layer, we apply a softmax transformation in our training functions!\n return x",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class AlexNet_Exp7(nn.Module):\n \"\"\"Based on the AlexNet paper with the same number of channels and layers \n are rescaled down by 8x to fit with the original alexnet image size to \n our kmnist size ratio (227:28)\n \n +1 classification layer\n \n We provided a \"reasonable\" guess of the filters\n \n \"\"\"\n \n def __init__(self):\n super(AlexNet_Exp7, self).__init__()\n self.conv_1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 6, kernel_size=11, stride=1, padding=3, bias=True)\n self.pool_2 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)\n self.conv_3 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2, bias=True)\n self.pool_4 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)\n self.conv_5 = nn.Conv2d(16, 24, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2, bias=True)\n self.conv_6 = nn.Conv2d(24, 24, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=True)\n self.conv_7 = nn.Conv2d(24, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=True)\n self.pool_8 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)\n self.linear_9 = nn.Linear(144, 100, bias=True)\n self.linear_10 = nn.Linear(100, 70, bias=True)\n self.output = nn.Linear(70, 10, bias=True)\n #self.dout = nn.Dropout(p=0.25) #dropout added to prevent overfitting :0\n self.act = nn.ReLU()\n \n def forward(self, x):\n x = self.act(self.conv_1(x))\n x = self.pool_2(x)\n x = self.act(self.conv_3(x))\n x = self.pool_4(x)\n x = self.act(self.conv_5(x))\n x = self.act(self.conv_6(x))\n x = self.act(self.conv_7(x))\n x = self.pool_8(x)\n x = x.view(-1, x.size(1) * x.size(2) * x.size(3))\n x = self.act(self.linear_9(x))\n x = self.act(self.linear_10(x))\n x = self.output(x) # Don't activate this output layer, we apply a softmax transformation in our training functions!\n return x",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class AlexNet_Exp8(nn.Module):\n \"\"\"Based on the AlexNet paper: Modified the each part of the network\n +1 Conv layer\n +4 Classification layers\n +x4 parameters\n We have used a \"reasonable\" guess of the filters \n \n \"\"\"\n \n def __init__(self):\n super(AlexNet_Exp8, self).__init__()\n # Convolutional Layers\n self.conv_1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 12, kernel_size=13, stride=1, padding=6, bias=True)\n self.pool_2 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)\n self.conv_3 = nn.Conv2d(12, 32, kernel_size=7, stride=1, padding=3, bias=True)\n self.pool_4 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)\n self.conv_5 = nn.Conv2d(32, 48, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2, bias=True)\n self.conv_6 = nn.Conv2d(48, 48, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2, bias=True) \n self.conv_7 = nn.Conv2d(48, 48, kernel_size=4, stride=1, padding=1, bias=True)\n self.conv_8 = nn.Conv2d(48, 32, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=True)\n self.pool_9 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)\n \n # Classification Layers\n self.linear_10 = nn.Linear(288, 200, bias=True)\n self.linear_11 = nn.Linear(200, 130, bias=True)\n self.linear_12 = nn.Linear(130, 90, bias=True)\n self.linear_13 = nn.Linear(90, 60, bias=True)\n self.linear_14 = nn.Linear(60, 30, bias=True)\n self.output = nn.Linear(30, 10, bias=True)\n \n #self.dout = nn.Dropout(p=0.25) #dropout added to prevent overfitting :0\n self.act = nn.ReLU()\n \n \n def forward(self, x):\n x = self.act(self.conv_1(x))\n x = self.pool_2(x)\n x = self.act(self.conv_3(x))\n x = self.pool_4(x)\n x = self.act(self.conv_5(x))\n x = self.act(self.conv_6(x))\n x = self.act(self.conv_7(x))\n x = self.act(self.conv_8(x))\n x = self.pool_9(x)\n x = x.view(-1, x.size(1) * x.size(2) * x.size(3))\n x = self.act(self.linear_10(x))\n x = self.act(self.linear_11(x))\n x = self.act(self.linear_12(x))\n x = self.act(self.linear_13(x))\n x = self.act(self.linear_14(x))\n x = self.output(x) # Don't activate this output layer, we apply a softmax transformation in our training functions!\n return x",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class AlexNet_Exp12(nn.Module):\n \"\"\"Based on the AlexNet paper: Modified the each part of the network\n +1 Conv layer\n +5 Classification layers\n +x2 parameters - only halved the original params!\n We have used a \"reasonable\" guess of the filters \n Added batch norm\n Added drop out\n \n \"\"\"\n \n def __init__(self):\n super(AlexNet_Exp12, self).__init__()\n # Convolutional Layers\n self.conv_1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 24, kernel_size=13, stride=1, padding=6, bias=True)\n self.pool_2 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)\n self.conv_3 = nn.Conv2d(24, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=1, padding=3, bias=True)\n self.pool_4 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)\n self.conv_5 = nn.Conv2d(64, 96, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2, bias=True)\n self.conv_6 = nn.Conv2d(96, 96, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2, bias=True) \n self.conv_7 = nn.Conv2d(96, 96, kernel_size=4, stride=1, padding=1, bias=True)\n self.conv_8 = nn.Conv2d(96, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=True)\n self.pool_9 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)\n \n # Classification Layers\n self.linear_10 = nn.Linear(576, 384, bias=True)\n self.linear_11 = nn.Linear(384, 192, bias=True)\n self.linear_12 = nn.Linear(192, 128, bias=True)\n self.linear_13 = nn.Linear(128, 85, bias=True)\n self.linear_14 = nn.Linear(85, 42, bias=True)\n self.linear_15 = nn.Linear(42, 21, bias=True)\n self.output = nn.Linear(21, 10, bias=True)\n \n # Batch Normalization\n self.b1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(24)\n self.b3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)\n self.b5 = nn.BatchNorm2d(96)\n self.b6 = nn.BatchNorm2d(96)\n self.b7 = nn.BatchNorm2d(96)\n self.b8 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)\n \n self.dout = nn.Dropout(p=0.25) #dropout added to prevent overfitting :0\n self.act = nn.ReLU()\n \n \n def forward(self, x):\n x = self.act(self.b1(self.conv_1(x)))\n x = self.pool_2(x)\n x = self.act(self.b3(self.conv_3(x)))\n x = self.pool_4(x)\n x = self.act(self.b5(self.conv_5(x)))\n x = self.act(self.b6(self.conv_6(x)))\n x = self.act(self.b7(self.conv_7(x)))\n x = self.act(self.b8(self.conv_8(x)))\n x = self.pool_9(x)\n x = x.view(-1, x.size(1) * x.size(2) * x.size(3))\n x = self.act(self.dout(self.linear_10(x)))\n x = self.act(self.dout(self.linear_11(x)))\n x = self.act(self.dout(self.linear_12(x)))\n x = self.act(self.dout(self.linear_13(x)))\n x = self.act(self.dout(self.linear_14(x)))\n x = self.act(self.dout(self.linear_15(x)))\n x = self.output(x) # Don't activate this output layer, we apply a softmax transformation in our training functions!\n return x",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class AlexNet_Exp24(nn.Module):\n \"\"\"Based on the AlexNet paper: Modified the each part of the network\n +1 Conv layer\n +5 Classification layers\n +x2 parameters - only halved the original params!\n We have used a \"reasonable\" guess of the filters \n Added batch norm\n Added drop out\n \n \"\"\"\n \n def __init__(self):\n super(AlexNet_Exp24, self).__init__()\n # Convolutional Layers\n self.conv_1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 16, kernel_size=13, stride=1, padding=6, bias=True)\n self.pool_2 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)\n self.conv_3 = nn.Conv2d(16, 42, kernel_size=7, stride=1, padding=3, bias=True)\n self.pool_4 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)\n self.conv_5 = nn.Conv2d(42, 64, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2, bias=True)\n self.conv_6 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2, bias=True) \n self.conv_7 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=4, stride=1, padding=1, bias=True)\n self.conv_8 = nn.Conv2d(64, 42, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=True)\n self.pool_9 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)\n \n # Classification Layers\n self.linear_10 = nn.Linear(378, 252, bias=True)\n self.linear_11 = nn.Linear(252, 126, bias=True)\n self.linear_12 = nn.Linear(126, 84, bias=True)\n self.linear_13 = nn.Linear(84, 42, bias=True)\n self.linear_14 = nn.Linear(42, 21, bias=True)\n self.output = nn.Linear(21, 10, bias=True)\n \n # Batch Normalization\n self.b1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(16)\n self.b3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(42)\n self.b5 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)\n self.b6 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)\n self.b7 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)\n self.b8 = nn.BatchNorm2d(42)\n \n self.dout = nn.Dropout(p=0.5) #dropout added to prevent overfitting :0\n self.act = nn.ReLU()\n \n \n def forward(self, x):\n x = self.act(self.b1(self.conv_1(x)))\n x = self.pool_2(x)\n x = self.act(self.b3(self.conv_3(x)))\n x = self.pool_4(x)\n x = self.act(self.b5(self.conv_5(x)))\n x = self.act(self.b6(self.conv_6(x)))\n x = self.act(self.b7(self.conv_7(x)))\n x = self.act(self.b8(self.conv_8(x)))\n x = self.pool_9(x)\n x = x.view(-1, x.size(1) * x.size(2) * x.size(3))\n x = self.act(self.dout(self.linear_10(x)))\n x = self.act(self.dout(self.linear_11(x)))\n x = self.act(self.dout(self.linear_12(x)))\n x = self.act(self.dout(self.linear_13(x)))\n x = self.act(self.dout(self.linear_14(x)))\n x = self.output(x) # Don't activate this output layer, we apply a softmax transformation in our training functions!\n return x",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Final Model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class SimpleAlexNet_FINAL(nn.Module):\n def __init__(self):\n super(SimpleAlexNet_FINAL, self).__init__()\n self.conv_1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 36, kernel_size=3, padding=1)\n self.pool_2 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)\n self.conv_3 = nn.Conv2d(36, 72, kernel_size=3)\n self.pool_4 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)\n self.conv_5 = nn.Conv2d(72, 142, kernel_size=3, padding=1)\n self.conv_6 = nn.Conv2d(142, 284, kernel_size=3, padding=1)\n self.conv_7 = nn.Conv2d(284, 124, kernel_size=3, padding=1)\n self.pool_8 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)\n self.linear_9 = nn.Linear(1116, 400)\n self.linear_10 = nn.Linear(400, 400)\n self.linear_11 = nn.Linear(400, 10)\n self.dout = nn.Dropout(p=0.7) #dropout added to prevent overfitting :0\n self.act = nn.ReLU()\n self.b1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(36)\n self.b2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(72)\n self.b3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(142)\n self.b4 = nn.BatchNorm2d(284)\n self.b5 = nn.BatchNorm2d(124)\n \n def forward(self, x):\n x = self.act(self.b1(self.conv_1(x)))\n x = self.pool_2(x)\n x = self.act(self.b2(self.conv_3(x)))\n x = self.pool_4(x)\n x = self.act(self.b3(self.conv_5(x)))\n x = self.act(self.b4(self.conv_6(x)))\n x = self.act(self.b5(self.conv_7(x)))\n# x = self.act(self.conv_7(x)) # Added new layer\n x = self.pool_8(x)\n x = x.view(-1, x.size(1) * x.size(2) * x.size(3))\n x = self.act(self.dout(self.linear_9(x)))\n x = self.act(self.dout(self.linear_10(x)))\n # x = self.dout(x)\n x = self.act(self.linear_11(x))\n \n return x",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Cross Validation Analysis\n\nWe run holdout cross validation as it is sufficient given the amount of data we have.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from kmnist_helpers.model_selection import holdoutCV, holdout_loaders\n\n# training parameters:\nbatch = 64\ntestbatch = 1000\nepochs = 3\n\nmodel = SimpleAlexNet_FINAL().to(device)\n\ntrain_loader, val_loader = holdout_loaders(X, y, CustomImageTensorDataset, \n batch, testbatch)\nlloss, val_loss, val_acc = holdoutCV(epochs, 0.0, 1e-4, model,\n train_loader, val_loader)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Save Cross Validation Logs",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"SimpleAlexNet_FINAL_logs = lloss.logs\nf = open(F\"/content/gdrive/My Drive/Colab Notebooks/Mini-Project/Model/SimpleAlexNet_FINAL_logs.pkl\",\"wb\")\npickle.dump(SimpleAlexNet_FINAL_logs,f)\nf.close()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Random-Grid Searching for Hyperparameters\n\nWe perform a random-grid search to find optimal hyperparameters.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from kmnist_helpers.tuning import RandomSearch, GridSearch\n\ntrain_loader, val_loader = holdout_loaders(X, y, CustomImageTensorDataset, \n batch, testbatch)\n\nmodel = SimpleAlexNet_FINAL().to(device)\n\nmax_acc, rand_params = RandomSearch(5, model, 5,\n train_loader, val_loader)\n\nbest_comb, lloss, loss, acc = GridSearch(5, model, rand_params,\n train_loader, val_loader,\n pseudo=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Final Full Training\n\nWe train the model onto the full training set and use the given test dataset for Kaggle.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# =============================Load Data======================================\n\nX_train, y_train = torch.from_numpy(X).float(), torch.from_numpy(y) # Dummy Test Labels for y_test\nX_test, y_test = torch.from_numpy(Xtest).float(), torch.from_numpy(np.array(range(X_test.shape[0]))).float() \n\nmean, std = torch.mean(X_train), torch.std(X_train)\n\ntrain_ds = CustomImageTensorDataset(X_train, y_train.long(), transform=True, mean=mean, std=std)\ntest_ds = CustomImageTensorDataset(X_test, y_test.long(), transform=False, mean=mean, std=std)\n\nbatchsize = 100\ntestbatch = 1000\ntrain_loader = DataLoader(train_ds, batch_size=batchsize, shuffle=True, num_workers=4)\ntest_loader = DataLoader(test_ds, batch_size=testbatch, shuffle=False, num_workers=0)\n\n# =============================Train Model======================================\n\nepochs = 30\nmodel = SimpleAlexNet_FINAL().to(device)\nset_seed(42)\noptimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-4, betas=(0.9, 0.999),\n eps=1e-08, weight_decay=0.0, amsgrad=False)\ncriterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()\nliveloss = PlotLosses()\nfor epoch in range(epochs):\n logs = {}\n train_loss, train_accuracy = train(model, optimizer, criterion, train_loader)\n\n logs['' + 'log loss'] = train_loss.item()\n logs['' + 'accuracy'] = train_accuracy.item()\n\n logs['val_' + 'log loss'] = 0.\n logs['val_' + 'accuracy'] = 0.\n \n liveloss.update(logs)\n liveloss.draw()\n\n# ===================Train T-SNE and Logistic Regression========================\n\nidx = np.where((y_train==2) | (y_train==6))\nytrainsim = y[idx]\nXtrainsim = X[idx]\n\ntsne = TSNE(n_components=2, perplexity=3)\nxtrain2d = np.reshape(Xtrainsim, (Xtrainsim.shape[0], -1))\nxtrain2d = tsne.fit_transform(xtrain2d)\n\nclf = LogisticRegression(random_state=seed, solver='lbfgs',\n multi_class='multinomial').fit(xtrain2d, ytrainsim)\n\n# ===========================T-SNE Recorrection=================================\n\ny_predictions, _ = evaluate(model, test_loader)\nidx = np.where((y_predictions==2) | (y_predictions==6))\n\nysim = y_predictions[idx]\nXsim = X_test[idx]\n\nXsim2d = np.reshape(Xsim, (Xsim.shape[0], -1))\nXsim2d = tsne.transform(Xsim2d)\n\ny_predictions[idx] = clf.predict(Xsim2d)\n\n# ===========================Predict Model======================================\n\ny_predictions, _ = evaluate(model, test_loader)\nsubmit = np.vstack((np.array(_), np.array(y_predictions)))\nsubmit = submit.transpose()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Ensemble modelling",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from kmnist_helpers.ensemble import ensemble_validate, ensemble_score\n\nmodel_list = [] # to be filled with pre-trained models on the cpu\n\ntrain_loader_full = DataLoader(train_ds, batch_size=1000, shuffle=False, num_workers=0)\ntest_loader_full = DataLoader(test_ds, batch_size=1000, shuffle=False, num_workers=0)\n\nensemble_score = ensemble_validate(model_list, criterion=nn.CrossEntropyLoss(), data_loader=test_loader_full)\n \nprint('Score for the predictions of the ensembled models:', ensemble_score)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Save Submissions",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Save the model\nmodel_save_name = \".pt\"\npath = F\"/content/gdrive/My Drive/Colab Notebooks/Mini-Project/Model/{model_save_name}\" \ntorch.save(model.state_dict(), path)\n\n# Save the submission\noutput_save_name = \".txt\"\npath_out = F\"/content/gdrive/My Drive/Colab Notebooks/Mini-Project/{output_save_name}\"\nnp.savetxt(path_out, submit, delimiter=\",\", fmt='%d', header=\"Id,Category\", comments='')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c50473a462176f1fca9f46fc2dffdc201dcda06e
| 191,254 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
code/04.machine_learning_tasks_1998_rows_only.ipynb
|
twyunting/Deepfake_Video_Classifier
|
ad4a573ac72efba530649f03f57ebfc3e0b6667b
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
code/04.machine_learning_tasks_1998_rows_only.ipynb
|
twyunting/Deepfake_Video_Classifier
|
ad4a573ac72efba530649f03f57ebfc3e0b6667b
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
code/04.machine_learning_tasks_1998_rows_only.ipynb
|
twyunting/Deepfake_Video_Classifier
|
ad4a573ac72efba530649f03f57ebfc3e0b6667b
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 191,254 | 191,254 | 0.609279 |
[
[
[
"# Author: [Yunting Chiu](https://www.linkedin.com/in/yuntingchiu/)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import cv2\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport time\nimport pandas as pd",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#wd\n%cd /content/drive/MyDrive/American_University/2021_Fall/DATA-793-001_Data Science Practicum/data\n!pwd",
"/content/drive/MyDrive/American_University/2021_Fall/DATA-793-001_Data Science Practicum/data\n/content/drive/MyDrive/American_University/2021_Fall/DATA-793-001_Data Science Practicum/data\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Exploratory Data Analysis\n##Read the data (`.npz` file)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\"\"\"\ndata_zipped = np.load(\"np_data_all.npz\", allow_pickle=True)\n\nfor item in data_zipped.files:\n print(item)\n print(data_zipped[item])\n \nprint(data_zipped[item].shape)\ndata = data_zipped[item]\n\"\"\"",
"arr_0\n[[array([134, 131, 116, ..., 68, 60, 71], dtype=uint8) 'fake']\n [array([133, 130, 115, ..., 71, 59, 71], dtype=uint8) 'fake']\n [array([117, 113, 112, ..., 43, 31, 45], dtype=uint8) 'fake']\n ...\n [array([ 33, 20, 66, ..., 188, 155, 172], dtype=uint8) 'real']\n [array([ 51, 28, 46, ..., 116, 52, 50], dtype=uint8) 'real']\n [array([174, 140, 102, ..., 23, 39, 98], dtype=uint8) 'real']]\n(13984, 2)\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Read the data (`.npy` file)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data = np.load(\"np_data_one.npy\", allow_pickle=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Check the length of $X$ and $y$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"X = []\ny = []\nfor i in data:\n X.append(i[0])\n y.append(i[1])\nprint(len(X))\nprint(len(y))\nprint(\"The length should be \" + str((6984+7000)))",
"1998\n1998\nThe length should be 13984\n"
],
[
"print(X)\nprint(y)\nprint(\"data dimension:\",data.shape)",
"[array([133, 130, 115, ..., 71, 59, 71], dtype=uint8), array([ 49, 40, 25, ..., 111, 105, 73], dtype=uint8), array([28, 21, 15, ..., 49, 44, 40], dtype=uint8), array([ 61, 61, 53, ..., 244, 246, 243], dtype=uint8), array([15, 14, 19, ..., 88, 66, 53], dtype=uint8), array([ 1, 1, 1, ..., 18, 14, 11], dtype=uint8), array([91, 61, 63, ..., 29, 20, 67], dtype=uint8), array([250, 187, 143, ..., 100, 99, 104], dtype=uint8), array([26, 25, 31, ..., 14, 15, 20], dtype=uint8), array([36, 32, 20, ..., 38, 30, 17], dtype=uint8), array([ 51, 37, 34, ..., 179, 158, 131], dtype=uint8), array([163, 146, 164, ..., 109, 55, 104], dtype=uint8), array([ 63, 58, 65, ..., 255, 247, 253], dtype=uint8), array([ 53, 41, 29, ..., 164, 180, 196], dtype=uint8), array([110, 32, 32, ..., 188, 149, 180], dtype=uint8), array([29, 18, 52, ..., 13, 14, 8], dtype=uint8), array([ 78, 59, 65, ..., 194, 207, 239], dtype=uint8), array([101, 77, 73, ..., 34, 32, 46], dtype=uint8), array([ 83, 77, 91, ..., 153, 130, 136], dtype=uint8), array([ 11, 9, 10, ..., 152, 174, 65], dtype=uint8), array([40, 6, 4, ..., 86, 38, 16], dtype=uint8), array([131, 120, 98, ..., 61, 42, 35], dtype=uint8), array([117, 114, 107, ..., 59, 48, 56], dtype=uint8), array([ 69, 22, 28, ..., 148, 120, 99], dtype=uint8), array([149, 148, 130, ..., 58, 92, 127], dtype=uint8), array([ 4, 6, 67, ..., 113, 85, 84], dtype=uint8), array([155, 136, 140, ..., 47, 45, 46], dtype=uint8), array([116, 79, 71, ..., 72, 25, 17], dtype=uint8), array([108, 117, 112, ..., 75, 63, 65], dtype=uint8), array([20, 19, 14, ..., 6, 4, 5], dtype=uint8), array([120, 101, 87, ..., 123, 104, 97], dtype=uint8), array([ 5, 7, 55, ..., 0, 0, 24], dtype=uint8), array([ 44, 34, 42, ..., 169, 135, 107], dtype=uint8), array([ 92, 119, 140, ..., 30, 29, 35], dtype=uint8), array([127, 101, 86, ..., 96, 68, 46], dtype=uint8), array([33, 20, 12, ..., 66, 55, 51], dtype=uint8), array([167, 152, 111, ..., 5, 0, 0], dtype=uint8), array([ 47, 33, 33, ..., 121, 111, 110], dtype=uint8), array([109, 101, 99, ..., 132, 162, 188], dtype=uint8), array([ 47, 54, 47, ..., 253, 230, 236], dtype=uint8), array([ 98, 121, 127, ..., 232, 206, 219], dtype=uint8), array([133, 113, 124, ..., 151, 123, 135], dtype=uint8), array([70, 52, 42, ..., 69, 48, 43], dtype=uint8), array([84, 74, 62, ..., 26, 12, 11], dtype=uint8), array([ 6, 8, 3, ..., 24, 18, 2], dtype=uint8), array([ 63, 65, 114, ..., 60, 38, 25], dtype=uint8), array([ 56, 52, 67, ..., 142, 99, 83], dtype=uint8), array([224, 202, 223, ..., 17, 22, 15], dtype=uint8), array([203, 188, 193, ..., 182, 149, 132], dtype=uint8), array([195, 176, 159, ..., 32, 24, 11], dtype=uint8), array([82, 69, 52, ..., 75, 66, 57], dtype=uint8), array([135, 135, 147, ..., 53, 58, 64], dtype=uint8), array([ 67, 53, 42, ..., 200, 182, 180], dtype=uint8), array([72, 60, 70, ..., 14, 12, 26], dtype=uint8), array([95, 59, 35, ..., 28, 1, 6], dtype=uint8), array([33, 28, 22, ..., 13, 8, 12], dtype=uint8), array([69, 44, 37, ..., 49, 20, 14], dtype=uint8), array([51, 45, 47, ..., 16, 5, 3], dtype=uint8), array([166, 173, 183, ..., 78, 30, 82], dtype=uint8), array([59, 49, 48, ..., 13, 8, 5], dtype=uint8), array([35, 35, 27, ..., 18, 17, 13], dtype=uint8), array([59, 44, 47, ..., 38, 36, 50], dtype=uint8), array([ 53, 32, 37, ..., 119, 25, 49], dtype=uint8), array([70, 63, 47, ..., 51, 54, 85], dtype=uint8), array([121, 107, 106, ..., 37, 33, 48], dtype=uint8), array([192, 220, 231, ..., 128, 110, 106], dtype=uint8), array([ 55, 72, 56, ..., 160, 117, 98], dtype=uint8), array([180, 179, 174, ..., 36, 8, 0], dtype=uint8), array([ 0, 12, 45, ..., 42, 34, 21], dtype=uint8), array([ 98, 154, 237, ..., 108, 110, 158], dtype=uint8), array([83, 62, 33, ..., 56, 49, 39], dtype=uint8), array([ 60, 76, 102, ..., 32, 32, 40], dtype=uint8), array([114, 117, 100, ..., 174, 159, 138], dtype=uint8), array([173, 156, 172, ..., 22, 22, 24], dtype=uint8), array([32, 16, 26, ..., 92, 63, 57], dtype=uint8), array([20, 24, 9, ..., 75, 55, 18], dtype=uint8), array([224, 224, 214, ..., 21, 16, 10], dtype=uint8), array([33, 34, 20, ..., 48, 49, 41], dtype=uint8), array([222, 210, 188, ..., 241, 241, 253], dtype=uint8), array([33, 29, 28, ..., 38, 32, 36], dtype=uint8), array([ 82, 82, 116, ..., 230, 225, 245], dtype=uint8), array([ 66, 59, 40, ..., 251, 255, 255], dtype=uint8), array([18, 17, 15, ..., 52, 54, 53], dtype=uint8), array([13, 44, 72, ..., 0, 27, 52], dtype=uint8), array([116, 106, 107, ..., 80, 34, 34], dtype=uint8), array([81, 28, 24, ..., 90, 18, 21], dtype=uint8), array([105, 89, 74, ..., 252, 248, 223], dtype=uint8), array([46, 36, 37, ..., 81, 83, 98], dtype=uint8), array([28, 27, 32, ..., 19, 20, 25], dtype=uint8), array([157, 157, 155, ..., 0, 5, 19], dtype=uint8), array([80, 58, 34, ..., 29, 9, 2], dtype=uint8), array([104, 105, 91, ..., 87, 75, 59], dtype=uint8), array([68, 60, 49, ..., 52, 44, 42], dtype=uint8), array([14, 2, 6, ..., 57, 74, 20], dtype=uint8), array([57, 42, 39, ..., 42, 68, 95], dtype=uint8), array([35, 15, 8, ..., 20, 16, 13], dtype=uint8), array([76, 65, 43, ..., 8, 1, 9], dtype=uint8), array([101, 96, 66, ..., 63, 52, 34], dtype=uint8), array([47, 25, 14, ..., 71, 35, 21], dtype=uint8), array([81, 67, 56, ..., 60, 39, 38], dtype=uint8), array([28, 30, 45, ..., 4, 4, 6], dtype=uint8), array([ 25, 38, 54, ..., 230, 220, 208], dtype=uint8), array([ 40, 45, 41, ..., 227, 200, 189], dtype=uint8), array([21, 22, 17, ..., 32, 38, 38], dtype=uint8), array([91, 74, 84, ..., 75, 60, 65], dtype=uint8), array([159, 158, 174, ..., 87, 79, 92], dtype=uint8), array([51, 46, 17, ..., 0, 4, 7], dtype=uint8), array([ 32, 36, 35, ..., 215, 210, 230], dtype=uint8), array([ 46, 56, 55, ..., 145, 116, 98], dtype=uint8), array([52, 51, 57, ..., 25, 20, 16], dtype=uint8), array([ 40, 41, 25, ..., 140, 109, 81], dtype=uint8), array([ 87, 57, 129, ..., 74, 49, 106], dtype=uint8), array([97, 85, 87, ..., 35, 35, 37], dtype=uint8), array([228, 47, 64, ..., 25, 6, 25], dtype=uint8), array([173, 168, 162, ..., 29, 23, 25], dtype=uint8), array([111, 100, 96, ..., 57, 30, 19], dtype=uint8), array([ 66, 61, 42, ..., 151, 126, 217], dtype=uint8), array([ 29, 38, 33, ..., 119, 88, 86], dtype=uint8), array([142, 133, 124, ..., 99, 61, 52], dtype=uint8), array([187, 178, 145, ..., 11, 12, 7], dtype=uint8), array([49, 57, 70, ..., 22, 26, 29], dtype=uint8), array([130, 90, 55, ..., 94, 51, 34], dtype=uint8), array([17, 7, 6, ..., 50, 26, 14], dtype=uint8), array([127, 110, 82, ..., 136, 112, 66], dtype=uint8), array([25, 21, 38, ..., 54, 53, 69], dtype=uint8), array([ 24, 26, 23, ..., 87, 109, 120], dtype=uint8), array([214, 68, 69, ..., 142, 107, 88], dtype=uint8), array([46, 24, 27, ..., 36, 15, 10], dtype=uint8), array([69, 43, 28, ..., 66, 38, 27], dtype=uint8), array([ 87, 40, 12, ..., 211, 190, 187], dtype=uint8), array([109, 58, 27, ..., 128, 138, 140], dtype=uint8), array([48, 46, 60, ..., 26, 24, 29], dtype=uint8), array([13, 12, 17, ..., 21, 19, 33], dtype=uint8), array([93, 69, 57, ..., 60, 47, 54], dtype=uint8), array([146, 141, 111, ..., 76, 61, 40], dtype=uint8), array([53, 46, 54, ..., 11, 28, 12], dtype=uint8), array([ 15, 10, 7, ..., 185, 182, 173], dtype=uint8), array([ 60, 25, 23, ..., 228, 228, 230], dtype=uint8), array([127, 88, 81, ..., 119, 99, 90], dtype=uint8), array([168, 152, 152, ..., 23, 22, 20], dtype=uint8), array([ 21, 11, 12, ..., 191, 152, 119], dtype=uint8), array([43, 34, 29, ..., 56, 42, 31], dtype=uint8), array([142, 30, 55, ..., 135, 123, 123], dtype=uint8), array([155, 178, 222, ..., 251, 247, 248], dtype=uint8), array([68, 55, 73, ..., 95, 67, 53], dtype=uint8), array([118, 82, 60, ..., 5, 7, 6], dtype=uint8), array([ 75, 69, 71, ..., 129, 133, 144], dtype=uint8), array([ 11, 74, 145, ..., 1, 0, 6], dtype=uint8), array([ 85, 89, 127, ..., 71, 33, 22], dtype=uint8), array([118, 90, 78, ..., 95, 69, 56], dtype=uint8), array([90, 59, 41, ..., 50, 29, 12], dtype=uint8), array([51, 49, 62, ..., 66, 44, 33], dtype=uint8), array([ 67, 59, 56, ..., 200, 200, 136], dtype=uint8), array([ 51, 43, 41, ..., 215, 235, 223], dtype=uint8), array([192, 109, 93, ..., 91, 58, 79], dtype=uint8), array([ 29, 35, 21, ..., 205, 201, 176], dtype=uint8), array([117, 92, 183, ..., 53, 47, 59], dtype=uint8), array([ 65, 34, 16, ..., 209, 201, 199], dtype=uint8), array([102, 80, 82, ..., 41, 42, 44], dtype=uint8), array([ 8, 31, 45, ..., 160, 131, 115], dtype=uint8), array([39, 31, 52, ..., 40, 37, 44], dtype=uint8), array([186, 166, 165, ..., 240, 193, 201], dtype=uint8), array([69, 37, 40, ..., 25, 10, 13], dtype=uint8), array([119, 101, 89, ..., 94, 93, 88], dtype=uint8), array([100, 81, 74, ..., 40, 29, 27], dtype=uint8), array([182, 156, 155, ..., 46, 26, 27], dtype=uint8), array([44, 48, 49, ..., 33, 18, 13], dtype=uint8), array([111, 97, 114, ..., 93, 61, 62], dtype=uint8), array([54, 39, 60, ..., 0, 1, 19], dtype=uint8), array([100, 60, 58, ..., 137, 110, 99], dtype=uint8), array([ 6, 8, 7, ..., 63, 47, 48], dtype=uint8), array([41, 38, 49, ..., 53, 42, 50], dtype=uint8), array([52, 39, 48, ..., 53, 45, 60], dtype=uint8), array([46, 50, 53, ..., 45, 49, 61], dtype=uint8), array([ 37, 34, 29, ..., 255, 252, 228], dtype=uint8), array([ 22, 3, 7, ..., 7, 6, 136], dtype=uint8), array([224, 224, 224, ..., 38, 16, 2], dtype=uint8), array([ 9, 1, 0, ..., 149, 113, 115], dtype=uint8), array([136, 110, 93, ..., 20, 78, 53], dtype=uint8), array([ 2, 10, 0, ..., 145, 132, 126], dtype=uint8), array([144, 110, 127, ..., 136, 94, 118], dtype=uint8), array([ 5, 4, 2, ..., 63, 36, 15], dtype=uint8), array([178, 143, 111, ..., 195, 130, 112], dtype=uint8), array([ 36, 67, 157, ..., 216, 218, 207], dtype=uint8), array([19, 17, 18, ..., 44, 38, 38], dtype=uint8), array([ 99, 87, 97, ..., 125, 122, 143], dtype=uint8), array([ 13, 13, 47, ..., 255, 250, 246], dtype=uint8), array([75, 73, 74, ..., 49, 39, 40], dtype=uint8), array([114, 94, 83, ..., 80, 44, 28], dtype=uint8), array([41, 41, 39, ..., 26, 30, 33], dtype=uint8), array([111, 87, 75, ..., 128, 76, 52], dtype=uint8), array([ 1, 167, 253, ..., 42, 49, 67], dtype=uint8), array([56, 57, 49, ..., 23, 25, 24], dtype=uint8), array([137, 120, 92, ..., 131, 105, 70], dtype=uint8), array([ 9, 11, 8, ..., 12, 12, 2], dtype=uint8), array([199, 162, 144, ..., 168, 113, 93], dtype=uint8), array([169, 143, 84, ..., 69, 42, 13], dtype=uint8), array([113, 96, 106, ..., 163, 97, 111], dtype=uint8), array([114, 95, 97, ..., 78, 70, 59], dtype=uint8), array([127, 103, 116, ..., 38, 19, 47], dtype=uint8), array([ 92, 107, 146, ..., 164, 126, 115], dtype=uint8), array([22, 7, 30, ..., 45, 35, 60], dtype=uint8), array([72, 57, 60, ..., 72, 63, 54], dtype=uint8), array([158, 166, 155, ..., 164, 125, 232], dtype=uint8), array([40, 50, 60, ..., 11, 30, 62], dtype=uint8), array([128, 129, 121, ..., 7, 14, 20], dtype=uint8), array([46, 50, 51, ..., 84, 57, 40], dtype=uint8), array([223, 253, 255, ..., 146, 145, 151], dtype=uint8), array([141, 176, 208, ..., 43, 28, 33], dtype=uint8), array([ 37, 30, 4, ..., 110, 74, 40], dtype=uint8), array([ 69, 69, 69, ..., 37, 197, 149], dtype=uint8), array([ 26, 24, 25, ..., 118, 66, 42], dtype=uint8), array([83, 54, 20, ..., 83, 48, 10], dtype=uint8), array([74, 62, 64, ..., 28, 32, 31], dtype=uint8), array([116, 183, 202, ..., 42, 30, 32], dtype=uint8), array([67, 47, 46, ..., 63, 37, 20], dtype=uint8), array([90, 79, 77, ..., 60, 43, 36], dtype=uint8), array([120, 58, 73, ..., 44, 29, 22], dtype=uint8), array([27, 22, 16, ..., 86, 86, 98], dtype=uint8), array([ 75, 51, 27, ..., 176, 162, 159], dtype=uint8), array([231, 225, 227, ..., 218, 133, 188], dtype=uint8), array([135, 125, 133, ..., 145, 178, 187], dtype=uint8), array([54, 41, 51, ..., 21, 23, 48], dtype=uint8), array([179, 153, 190, ..., 155, 162, 255], dtype=uint8), array([48, 52, 2, ..., 30, 26, 23], dtype=uint8), array([181, 189, 228, ..., 100, 99, 115], dtype=uint8), array([43, 55, 55, ..., 85, 97, 97], dtype=uint8), array([138, 102, 78, ..., 61, 43, 33], dtype=uint8), array([11, 10, 8, ..., 18, 32, 93], dtype=uint8), array([ 38, 24, 15, ..., 117, 104, 96], dtype=uint8), array([ 4, 124, 236, ..., 31, 34, 43], dtype=uint8), array([218, 179, 164, ..., 182, 132, 125], dtype=uint8), array([125, 166, 152, ..., 19, 13, 15], dtype=uint8), array([218, 199, 156, ..., 64, 60, 61], dtype=uint8), array([156, 151, 158, ..., 11, 11, 13], dtype=uint8), array([23, 11, 15, ..., 44, 3, 7], dtype=uint8), array([149, 159, 161, ..., 89, 69, 44], dtype=uint8), array([37, 66, 84, ..., 22, 34, 34], dtype=uint8), array([138, 144, 170, ..., 9, 9, 11], dtype=uint8), array([58, 49, 34, ..., 20, 11, 2], dtype=uint8), array([160, 149, 129, ..., 206, 211, 189], dtype=uint8), array([ 68, 66, 77, ..., 143, 130, 124], dtype=uint8), array([52, 59, 65, ..., 33, 28, 24], dtype=uint8), array([143, 125, 101, ..., 229, 233, 216], dtype=uint8), array([ 0, 9, 89, ..., 107, 83, 83], dtype=uint8), array([ 52, 51, 47, ..., 102, 92, 91], dtype=uint8), array([71, 51, 44, ..., 74, 45, 41], dtype=uint8), array([ 88, 85, 70, ..., 116, 111, 81], dtype=uint8), array([141, 126, 123, ..., 102, 62, 54], dtype=uint8), array([60, 51, 42, ..., 63, 41, 28], dtype=uint8), array([106, 115, 130, ..., 22, 6, 7], dtype=uint8), array([ 46, 32, 32, ..., 107, 71, 49], dtype=uint8), array([ 1, 1, 3, ..., 144, 161, 171], dtype=uint8), array([54, 49, 43, ..., 44, 32, 34], dtype=uint8), array([23, 24, 16, ..., 38, 24, 21], dtype=uint8), array([66, 46, 37, ..., 83, 52, 50], dtype=uint8), array([177, 159, 123, ..., 92, 55, 49], dtype=uint8), array([15, 18, 25, ..., 13, 7, 7], dtype=uint8), array([130, 174, 237, ..., 115, 88, 61], dtype=uint8), array([105, 91, 88, ..., 23, 19, 20], dtype=uint8), array([43, 56, 64, ..., 27, 27, 19], dtype=uint8), array([ 75, 81, 103, ..., 35, 21, 12], dtype=uint8), array([33, 19, 18, ..., 92, 87, 83], dtype=uint8), array([ 20, 10, 1, ..., 141, 139, 140], dtype=uint8), array([ 74, 163, 255, ..., 52, 37, 30], dtype=uint8), array([111, 111, 111, ..., 44, 30, 29], dtype=uint8), array([39, 39, 39, ..., 82, 71, 69], dtype=uint8), array([104, 87, 59, ..., 9, 11, 8], dtype=uint8), array([15, 25, 34, ..., 11, 15, 24], dtype=uint8), array([167, 151, 118, ..., 171, 124, 94], dtype=uint8), array([192, 156, 82, ..., 225, 203, 164], dtype=uint8), array([75, 68, 84, ..., 42, 61, 93], dtype=uint8), array([175, 205, 213, ..., 70, 41, 61], dtype=uint8), array([137, 135, 122, ..., 123, 70, 36], dtype=uint8), array([157, 151, 151, ..., 77, 52, 48], dtype=uint8), array([61, 50, 48, ..., 61, 49, 49], dtype=uint8), array([196, 179, 110, ..., 78, 76, 98], dtype=uint8), array([211, 212, 206, ..., 168, 101, 196], dtype=uint8), array([ 37, 47, 49, ..., 242, 233, 228], dtype=uint8), array([ 82, 67, 124, ..., 53, 22, 82], dtype=uint8), array([64, 50, 39, ..., 20, 6, 3], dtype=uint8), array([46, 23, 9, ..., 12, 8, 7], dtype=uint8), array([116, 89, 96, ..., 24, 33, 50], dtype=uint8), array([ 71, 47, 45, ..., 168, 164, 178], dtype=uint8), array([169, 134, 104, ..., 21, 23, 22], dtype=uint8), array([153, 142, 124, ..., 38, 40, 52], dtype=uint8), array([96, 64, 17, ..., 0, 4, 0], dtype=uint8), array([ 10, 18, 215, ..., 65, 33, 56], dtype=uint8), array([ 4, 9, 13, ..., 0, 2, 0], dtype=uint8), array([ 44, 40, 29, ..., 101, 43, 21], dtype=uint8), array([47, 21, 24, ..., 11, 0, 1], dtype=uint8), array([37, 27, 26, ..., 63, 30, 21], dtype=uint8), array([189, 163, 150, ..., 113, 91, 77], dtype=uint8), array([107, 68, 35, ..., 59, 23, 0], dtype=uint8), array([ 78, 64, 53, ..., 205, 147, 101], dtype=uint8), array([ 0, 0, 0, ..., 83, 48, 54], dtype=uint8), array([92, 81, 63, ..., 16, 7, 0], dtype=uint8), array([146, 119, 90, ..., 96, 72, 38], dtype=uint8), array([80, 78, 81, ..., 58, 44, 44], dtype=uint8), array([126, 98, 74, ..., 84, 46, 27], dtype=uint8), array([50, 10, 8, ..., 24, 24, 22], dtype=uint8), array([ 68, 56, 58, ..., 144, 143, 187], dtype=uint8), array([53, 50, 35, ..., 17, 20, 27], dtype=uint8), array([90, 82, 69, ..., 21, 9, 11], dtype=uint8), array([149, 118, 90, ..., 192, 171, 214], dtype=uint8), array([134, 118, 103, ..., 37, 19, 17], dtype=uint8), array([ 0, 104, 212, ..., 17, 19, 5], dtype=uint8), array([23, 29, 43, ..., 36, 23, 7], dtype=uint8), array([27, 27, 29, ..., 18, 19, 11], dtype=uint8), array([ 45, 56, 60, ..., 126, 93, 74], dtype=uint8), array([ 63, 45, 41, ..., 155, 113, 97], dtype=uint8), array([43, 34, 29, ..., 76, 54, 31], dtype=uint8), array([ 76, 78, 90, ..., 106, 106, 98], dtype=uint8), array([ 60, 50, 123, ..., 132, 68, 66], dtype=uint8), array([247, 224, 180, ..., 231, 199, 148], dtype=uint8), array([212, 205, 176, ..., 172, 143, 113], dtype=uint8), array([21, 16, 12, ..., 24, 15, 10], dtype=uint8), array([226, 212, 201, ..., 37, 27, 26], dtype=uint8), array([17, 13, 12, ..., 13, 0, 8], dtype=uint8), array([ 65, 28, 19, ..., 101, 123, 100], dtype=uint8), array([92, 75, 32, ..., 1, 0, 5], dtype=uint8), array([123, 164, 160, ..., 84, 80, 79], dtype=uint8), array([ 84, 57, 36, ..., 254, 255, 247], dtype=uint8), array([ 0, 0, 0, ..., 44, 1, 46], dtype=uint8), array([32, 28, 27, ..., 29, 24, 20], dtype=uint8), array([63, 47, 50, ..., 56, 36, 29], dtype=uint8), array([55, 49, 49, ..., 68, 59, 44], dtype=uint8), array([113, 92, 89, ..., 53, 24, 26], dtype=uint8), array([129, 106, 62, ..., 166, 110, 87], dtype=uint8), array([26, 21, 27, ..., 24, 19, 23], dtype=uint8), array([59, 47, 61, ..., 48, 48, 50], dtype=uint8), array([30, 20, 10, ..., 14, 10, 1], dtype=uint8), array([ 36, 57, 50, ..., 251, 250, 245], dtype=uint8), array([91, 82, 73, ..., 50, 34, 37], dtype=uint8), array([113, 110, 91, ..., 8, 0, 14], dtype=uint8), array([166, 143, 135, ..., 169, 161, 150], dtype=uint8), array([ 71, 82, 114, ..., 47, 24, 18], dtype=uint8), array([ 72, 48, 62, ..., 131, 103, 89], dtype=uint8), array([148, 140, 155, ..., 87, 55, 58], dtype=uint8), array([132, 72, 61, ..., 62, 25, 33], dtype=uint8), array([35, 21, 36, ..., 45, 33, 37], dtype=uint8), array([159, 144, 123, ..., 31, 8, 2], dtype=uint8), array([160, 135, 94, ..., 219, 201, 177], dtype=uint8), array([ 90, 115, 179, ..., 96, 161, 189], dtype=uint8), array([90, 92, 87, ..., 41, 43, 38], dtype=uint8), array([71, 53, 33, ..., 32, 1, 0], dtype=uint8), array([34, 31, 24, ..., 0, 0, 0], dtype=uint8), array([90, 78, 56, ..., 93, 73, 66], dtype=uint8), array([ 11, 6, 2, ..., 125, 90, 58], dtype=uint8), array([253, 252, 255, ..., 121, 42, 35], dtype=uint8), array([123, 93, 83, ..., 139, 128, 108], dtype=uint8), array([ 2, 63, 117, ..., 245, 241, 255], dtype=uint8), array([ 55, 46, 65, ..., 250, 205, 226], dtype=uint8), array([ 75, 61, 58, ..., 145, 39, 113], dtype=uint8), array([122, 124, 139, ..., 59, 46, 27], dtype=uint8), array([50, 67, 75, ..., 53, 41, 41], dtype=uint8), array([ 0, 59, 209, ..., 112, 76, 112], dtype=uint8), array([77, 88, 90, ..., 6, 0, 2], dtype=uint8), array([ 50, 116, 200, ..., 59, 59, 71], dtype=uint8), array([125, 133, 118, ..., 58, 53, 49], dtype=uint8), array([ 8, 9, 4, ..., 21, 17, 8], dtype=uint8), array([ 6, 7, 27, ..., 12, 85, 190], dtype=uint8), array([125, 97, 86, ..., 133, 161, 211], dtype=uint8), array([83, 44, 27, ..., 32, 0, 6], dtype=uint8), array([69, 58, 56, ..., 46, 34, 34], dtype=uint8), array([ 59, 71, 121, ..., 76, 0, 38], dtype=uint8), array([ 91, 87, 86, ..., 169, 170, 227], dtype=uint8), array([ 32, 37, 31, ..., 136, 97, 92], dtype=uint8), array([ 45, 28, 46, ..., 116, 79, 53], dtype=uint8), array([173, 48, 92, ..., 255, 209, 255], dtype=uint8), array([ 10, 24, 27, ..., 168, 186, 210], dtype=uint8), array([53, 35, 31, ..., 25, 13, 17], dtype=uint8), array([ 94, 75, 61, ..., 230, 222, 201], dtype=uint8), array([49, 58, 53, ..., 55, 65, 75], dtype=uint8), array([ 1, 3, 2, ..., 25, 56, 87], dtype=uint8), array([185, 164, 145, ..., 184, 145, 138], dtype=uint8), array([149, 149, 141, ..., 102, 68, 56], dtype=uint8), array([192, 142, 89, ..., 206, 52, 54], dtype=uint8), array([ 66, 72, 94, ..., 254, 250, 215], dtype=uint8), array([ 78, 35, 18, ..., 169, 113, 80], dtype=uint8), array([163, 130, 111, ..., 42, 28, 28], dtype=uint8), array([ 69, 55, 44, ..., 14, 39, 142], dtype=uint8), array([164, 129, 109, ..., 50, 46, 47], dtype=uint8), array([48, 29, 22, ..., 24, 14, 12], dtype=uint8), array([38, 29, 14, ..., 50, 42, 53], dtype=uint8), array([95, 57, 44, ..., 49, 10, 3], dtype=uint8), array([183, 146, 120, ..., 91, 70, 51], dtype=uint8), array([55, 39, 16, ..., 47, 25, 12], dtype=uint8), array([98, 82, 67, ..., 64, 67, 72], dtype=uint8), array([ 92, 106, 143, ..., 27, 45, 67], dtype=uint8), array([ 46, 53, 37, ..., 213, 219, 245], dtype=uint8), array([ 55, 55, 43, ..., 223, 220, 213], dtype=uint8), array([30, 43, 33, ..., 42, 92, 55], dtype=uint8), array([ 63, 66, 109, ..., 44, 43, 48], dtype=uint8), array([ 85, 68, 78, ..., 255, 218, 177], dtype=uint8), array([131, 104, 87, ..., 17, 14, 7], dtype=uint8), array([224, 219, 163, ..., 178, 152, 77], dtype=uint8), array([140, 123, 93, ..., 100, 66, 39], dtype=uint8), array([ 52, 38, 38, ..., 20, 45, 249], dtype=uint8), array([99, 81, 69, ..., 34, 36, 57], dtype=uint8), array([15, 10, 4, ..., 89, 90, 82], dtype=uint8), array([128, 129, 121, ..., 86, 67, 37], dtype=uint8), array([ 91, 64, 43, ..., 239, 221, 217], dtype=uint8), array([255, 214, 171, ..., 105, 63, 51], dtype=uint8), array([129, 134, 127, ..., 117, 112, 119], dtype=uint8), array([192, 192, 192, ..., 37, 23, 22], dtype=uint8), array([229, 196, 163, ..., 248, 225, 235], dtype=uint8), array([ 38, 86, 106, ..., 123, 123, 149], dtype=uint8), array([33, 33, 35, ..., 64, 41, 0], dtype=uint8), array([47, 36, 40, ..., 10, 5, 1], dtype=uint8), array([79, 46, 31, ..., 35, 11, 24], dtype=uint8), array([137, 128, 121, ..., 68, 97, 235], dtype=uint8), array([ 11, 11, 9, ..., 164, 159, 165], dtype=uint8), array([51, 30, 37, ..., 36, 6, 8], dtype=uint8), array([37, 54, 72, ..., 64, 73, 80], dtype=uint8), array([228, 229, 224, ..., 40, 32, 43], dtype=uint8), array([255, 255, 255, ..., 197, 148, 118], dtype=uint8), array([ 77, 70, 88, ..., 194, 195, 241], dtype=uint8), array([25, 26, 20, ..., 25, 12, 6], dtype=uint8), array([182, 151, 107, ..., 17, 22, 25], dtype=uint8), array([162, 171, 154, ..., 76, 82, 80], dtype=uint8), array([72, 46, 33, ..., 66, 47, 33], dtype=uint8), array([232, 214, 190, ..., 157, 83, 120], dtype=uint8), array([172, 183, 177, ..., 39, 30, 33], dtype=uint8), array([185, 182, 175, ..., 198, 206, 193], dtype=uint8), array([ 62, 135, 186, ..., 94, 75, 79], dtype=uint8), array([226, 236, 199, ..., 39, 56, 48], dtype=uint8), array([ 20, 27, 20, ..., 166, 132, 97], dtype=uint8), array([125, 30, 28, ..., 93, 87, 91], dtype=uint8), array([106, 91, 84, ..., 17, 16, 32], dtype=uint8), array([34, 13, 22, ..., 25, 28, 45], dtype=uint8), array([ 31, 28, 11, ..., 178, 180, 177], dtype=uint8), array([165, 138, 121, ..., 90, 54, 32], dtype=uint8), array([76, 49, 40, ..., 6, 2, 1], dtype=uint8), array([ 91, 101, 222, ..., 108, 95, 125], dtype=uint8), array([ 51, 21, 31, ..., 154, 86, 83], dtype=uint8), array([12, 31, 64, ..., 63, 77, 88], dtype=uint8), array([ 62, 57, 38, ..., 207, 208, 202], dtype=uint8), array([44, 45, 40, ..., 33, 14, 8], dtype=uint8), array([164, 131, 88, ..., 111, 85, 86], dtype=uint8), array([ 55, 47, 28, ..., 123, 132, 131], dtype=uint8), array([178, 163, 140, ..., 136, 109, 79], dtype=uint8), array([240, 202, 191, ..., 94, 48, 61], dtype=uint8), array([61, 51, 52, ..., 36, 22, 21], dtype=uint8), array([ 64, 60, 61, ..., 127, 98, 80], dtype=uint8), array([ 63, 76, 108, ..., 75, 47, 35], dtype=uint8), array([ 33, 30, 61, ..., 220, 188, 209], dtype=uint8), array([ 24, 52, 56, ..., 163, 117, 104], dtype=uint8), array([62, 68, 82, ..., 12, 21, 30], dtype=uint8), array([ 78, 88, 100, ..., 152, 178, 213], dtype=uint8), array([123, 88, 30, ..., 103, 84, 67], dtype=uint8), array([205, 179, 156, ..., 21, 16, 20], dtype=uint8), array([40, 37, 44, ..., 23, 17, 17], dtype=uint8), array([19, 10, 1, ..., 36, 31, 25], dtype=uint8), array([10, 10, 20, ..., 8, 3, 10], dtype=uint8), array([ 65, 65, 65, ..., 203, 174, 179], dtype=uint8), array([174, 186, 184, ..., 98, 75, 41], dtype=uint8), array([53, 31, 20, ..., 29, 22, 16], dtype=uint8), array([ 54, 42, 44, ..., 172, 249, 255], dtype=uint8), array([180, 168, 170, ..., 18, 49, 33], dtype=uint8), array([ 42, 35, 42, ..., 112, 83, 69], dtype=uint8), array([22, 18, 7, ..., 67, 54, 37], dtype=uint8), array([ 56, 53, 108, ..., 27, 21, 25], dtype=uint8), array([17, 16, 14, ..., 72, 36, 24], dtype=uint8), array([66, 36, 25, ..., 75, 50, 45], dtype=uint8), array([144, 126, 114, ..., 115, 96, 90], dtype=uint8), array([80, 79, 87, ..., 94, 95, 97], dtype=uint8), array([128, 166, 167, ..., 46, 32, 32], dtype=uint8), array([44, 36, 34, ..., 35, 17, 15], dtype=uint8), array([98, 96, 83, ..., 58, 49, 44], dtype=uint8), array([143, 172, 232, ..., 35, 23, 37], dtype=uint8), array([18, 35, 51, ..., 3, 14, 36], dtype=uint8), array([ 9, 1, 42, ..., 255, 255, 255], dtype=uint8), array([52, 32, 34, ..., 68, 31, 25], dtype=uint8), array([111, 88, 98, ..., 92, 87, 83], dtype=uint8), array([123, 98, 102, ..., 177, 120, 113], dtype=uint8), array([246, 207, 190, ..., 168, 88, 81], dtype=uint8), array([45, 55, 44, ..., 67, 72, 65], dtype=uint8), array([66, 47, 40, ..., 54, 37, 43], dtype=uint8), array([142, 124, 86, ..., 49, 39, 38], dtype=uint8), array([38, 34, 25, ..., 1, 5, 14], dtype=uint8), array([178, 139, 157, ..., 150, 112, 91], dtype=uint8), array([34, 33, 39, ..., 51, 50, 55], dtype=uint8), array([34, 31, 62, ..., 55, 54, 62], dtype=uint8), array([137, 116, 85, ..., 73, 61, 49], dtype=uint8), array([ 71, 45, 32, ..., 134, 90, 53], dtype=uint8), array([198, 171, 150, ..., 56, 51, 55], dtype=uint8), array([22, 21, 35, ..., 16, 15, 20], dtype=uint8), array([ 17, 13, 10, ..., 235, 247, 247], dtype=uint8), array([44, 48, 49, ..., 7, 8, 12], dtype=uint8), array([ 1, 6, 26, ..., 18, 0, 1], dtype=uint8), array([ 41, 26, 21, ..., 153, 143, 133], dtype=uint8), array([87, 73, 73, ..., 86, 86, 96], dtype=uint8), array([ 2, 0, 1, ..., 241, 215, 192], dtype=uint8), array([50, 38, 40, ..., 85, 46, 41], dtype=uint8), array([71, 62, 57, ..., 74, 44, 33], dtype=uint8), array([224, 228, 239, ..., 221, 221, 231], dtype=uint8), array([38, 30, 19, ..., 4, 2, 3], dtype=uint8), array([18, 13, 10, ..., 26, 23, 6], dtype=uint8), array([227, 74, 94, ..., 40, 53, 98], dtype=uint8), array([192, 172, 165, ..., 200, 113, 86], dtype=uint8), array([61, 34, 23, ..., 56, 27, 32], dtype=uint8), array([ 50, 50, 58, ..., 196, 172, 160], dtype=uint8), array([ 60, 63, 36, ..., 124, 98, 65], dtype=uint8), array([51, 33, 29, ..., 18, 17, 12], dtype=uint8), array([146, 142, 157, ..., 95, 85, 83], dtype=uint8), array([178, 168, 169, ..., 164, 136, 159], dtype=uint8), array([79, 66, 60, ..., 95, 73, 62], dtype=uint8), array([105, 116, 134, ..., 35, 37, 49], dtype=uint8), array([111, 103, 127, ..., 43, 32, 28], dtype=uint8), array([242, 196, 233, ..., 235, 184, 243], dtype=uint8), array([158, 192, 194, ..., 110, 77, 72], dtype=uint8), array([247, 228, 247, ..., 112, 86, 73], dtype=uint8), array([253, 255, 227, ..., 135, 106, 98], dtype=uint8), array([179, 140, 171, ..., 24, 22, 23], dtype=uint8), array([ 35, 38, 31, ..., 253, 235, 223], dtype=uint8), array([111, 124, 140, ..., 178, 186, 249], dtype=uint8), array([162, 164, 161, ..., 56, 23, 14], dtype=uint8), array([ 47, 47, 111, ..., 104, 111, 104], dtype=uint8), array([183, 160, 119, ..., 138, 96, 71], dtype=uint8), array([194, 159, 127, ..., 144, 98, 83], dtype=uint8), array([ 70, 68, 90, ..., 154, 145, 162], dtype=uint8), array([ 45, 52, 60, ..., 166, 176, 188], dtype=uint8), array([22, 21, 27, ..., 18, 16, 19], dtype=uint8), array([198, 154, 119, ..., 127, 112, 109], dtype=uint8), array([136, 95, 91, ..., 19, 13, 17], dtype=uint8), array([252, 226, 235, ..., 243, 180, 137], dtype=uint8), array([44, 52, 55, ..., 82, 26, 27], dtype=uint8), array([ 40, 44, 29, ..., 153, 121, 100], dtype=uint8), array([43, 38, 35, ..., 33, 29, 20], dtype=uint8), array([23, 26, 31, ..., 37, 40, 45], dtype=uint8), array([ 42, 30, 18, ..., 108, 105, 98], dtype=uint8), array([ 47, 52, 46, ..., 168, 138, 130], dtype=uint8), array([213, 215, 212, ..., 88, 53, 33], dtype=uint8), array([43, 44, 36, ..., 0, 0, 0], dtype=uint8), array([ 5, 6, 0, ..., 9, 1, 16], dtype=uint8), array([149, 157, 193, ..., 115, 118, 133], dtype=uint8), array([54, 53, 95, ..., 70, 64, 92], dtype=uint8), array([255, 253, 226, ..., 117, 119, 157], dtype=uint8), array([71, 43, 39, ..., 90, 63, 54], dtype=uint8), array([133, 170, 248, ..., 49, 49, 51], dtype=uint8), array([164, 132, 91, ..., 219, 170, 129], dtype=uint8), array([73, 58, 61, ..., 28, 18, 17], dtype=uint8), array([130, 99, 79, ..., 158, 106, 84], dtype=uint8), array([197, 200, 179, ..., 29, 24, 28], dtype=uint8), array([172, 170, 171, ..., 8, 8, 10], dtype=uint8), array([102, 99, 94, ..., 76, 56, 49], dtype=uint8), array([160, 65, 63, ..., 100, 107, 113], dtype=uint8), array([210, 236, 209, ..., 197, 175, 134], dtype=uint8), array([134, 90, 61, ..., 89, 53, 29], dtype=uint8), array([207, 203, 191, ..., 21, 8, 18], dtype=uint8), array([67, 50, 0, ..., 10, 14, 15], dtype=uint8), array([59, 88, 58, ..., 1, 16, 11], dtype=uint8), array([109, 120, 152, ..., 18, 17, 12], dtype=uint8), array([137, 109, 88, ..., 68, 40, 28], dtype=uint8), array([157, 141, 108, ..., 169, 212, 219], dtype=uint8), array([73, 51, 40, ..., 91, 85, 95], dtype=uint8), array([92, 82, 73, ..., 8, 7, 13], dtype=uint8), array([15, 20, 16, ..., 68, 85, 92], dtype=uint8), array([253, 229, 185, ..., 170, 107, 92], dtype=uint8), array([30, 25, 22, ..., 7, 20, 29], dtype=uint8), array([92, 74, 72, ..., 55, 16, 17], dtype=uint8), array([119, 110, 101, ..., 146, 109, 91], dtype=uint8), array([229, 229, 229, ..., 40, 27, 18], dtype=uint8), array([116, 86, 58, ..., 144, 92, 55], dtype=uint8), array([152, 150, 163, ..., 99, 89, 124], dtype=uint8), array([36, 27, 28, ..., 88, 59, 51], dtype=uint8), array([47, 32, 29, ..., 58, 34, 22], dtype=uint8), array([ 94, 80, 69, ..., 236, 203, 184], dtype=uint8), array([78, 66, 70, ..., 18, 18, 28], dtype=uint8), array([ 0, 0, 0, ..., 75, 77, 126], dtype=uint8), array([113, 97, 84, ..., 135, 132, 143], dtype=uint8), array([183, 182, 178, ..., 116, 112, 100], dtype=uint8), array([ 6, 6, 6, ..., 167, 197, 221], dtype=uint8), array([165, 116, 75, ..., 201, 141, 91], dtype=uint8), array([16, 17, 12, ..., 49, 38, 32], dtype=uint8), array([ 28, 31, 36, ..., 157, 106, 77], dtype=uint8), array([ 20, 19, 24, ..., 103, 103, 103], dtype=uint8), array([ 0, 94, 130, ..., 48, 17, 12], dtype=uint8), array([53, 36, 46, ..., 34, 24, 33], dtype=uint8), array([48, 36, 38, ..., 77, 77, 87], dtype=uint8), array([139, 134, 128, ..., 42, 39, 48], dtype=uint8), array([69, 73, 84, ..., 83, 83, 91], dtype=uint8), array([158, 150, 131, ..., 220, 223, 242], dtype=uint8), array([43, 31, 33, ..., 54, 23, 28], dtype=uint8), array([109, 100, 105, ..., 195, 155, 119], dtype=uint8), array([113, 84, 66, ..., 60, 58, 59], dtype=uint8), array([ 73, 49, 49, ..., 148, 95, 81], dtype=uint8), array([44, 39, 35, ..., 58, 50, 39], dtype=uint8), array([ 79, 82, 97, ..., 74, 50, 126], dtype=uint8), array([243, 247, 250, ..., 44, 38, 40], dtype=uint8), array([128, 102, 75, ..., 144, 110, 75], dtype=uint8), array([ 54, 41, 33, ..., 145, 117, 96], dtype=uint8), array([157, 130, 109, ..., 26, 26, 26], dtype=uint8), array([51, 47, 48, ..., 87, 85, 99], dtype=uint8), array([116, 109, 90, ..., 29, 33, 36], dtype=uint8), array([146, 138, 221, ..., 144, 83, 64], dtype=uint8), array([ 92, 74, 52, ..., 170, 121, 89], dtype=uint8), array([183, 156, 127, ..., 121, 101, 77], dtype=uint8), array([45, 59, 85, ..., 64, 29, 23], dtype=uint8), array([ 22, 24, 10, ..., 187, 162, 122], dtype=uint8), array([167, 146, 127, ..., 114, 90, 66], dtype=uint8), array([31, 24, 14, ..., 64, 56, 43], dtype=uint8), array([17, 17, 17, ..., 27, 16, 20], dtype=uint8), array([ 6, 33, 202, ..., 40, 40, 50], dtype=uint8), array([ 75, 72, 83, ..., 192, 188, 213], dtype=uint8), array([44, 36, 34, ..., 23, 23, 23], dtype=uint8), array([31, 22, 39, ..., 35, 36, 64], dtype=uint8), array([ 50, 33, 23, ..., 189, 131, 111], dtype=uint8), array([ 9, 8, 24, ..., 230, 197, 190], dtype=uint8), array([64, 73, 80, ..., 39, 21, 17], dtype=uint8), array([ 5, 1, 2, ..., 22, 11, 17], dtype=uint8), array([30, 17, 26, ..., 2, 1, 7], dtype=uint8), array([ 98, 174, 234, ..., 170, 178, 181], dtype=uint8), array([54, 44, 32, ..., 44, 40, 55], dtype=uint8), array([110, 93, 85, ..., 29, 28, 42], dtype=uint8), array([81, 43, 22, ..., 32, 2, 2], dtype=uint8), array([77, 48, 30, ..., 12, 0, 0], dtype=uint8), array([81, 62, 47, ..., 21, 17, 18], dtype=uint8), array([114, 87, 68, ..., 56, 23, 18], dtype=uint8), array([ 3, 0, 4, ..., 171, 138, 123], dtype=uint8), array([30, 24, 10, ..., 6, 11, 5], dtype=uint8), array([138, 129, 124, ..., 111, 108, 117], dtype=uint8), array([ 31, 28, 57, ..., 35, 74, 177], dtype=uint8), array([32, 20, 22, ..., 15, 5, 4], dtype=uint8), array([23, 12, 8, ..., 6, 7, 1], dtype=uint8), array([82, 62, 35, ..., 30, 7, 0], dtype=uint8), array([211, 198, 216, ..., 21, 25, 73], dtype=uint8), array([15, 37, 78, ..., 25, 52, 99], dtype=uint8), array([68, 60, 47, ..., 84, 60, 36], dtype=uint8), array([89, 77, 89, ..., 50, 32, 20], dtype=uint8), array([ 57, 47, 38, ..., 112, 120, 123], dtype=uint8), array([151, 81, 117, ..., 217, 204, 230], dtype=uint8), array([237, 232, 238, ..., 230, 232, 231], dtype=uint8), array([ 33, 12, 29, ..., 169, 143, 126], dtype=uint8), array([ 2, 0, 14, ..., 104, 79, 108], dtype=uint8), array([143, 156, 173, ..., 162, 159, 150], dtype=uint8), array([33, 24, 43, ..., 29, 11, 9], dtype=uint8), array([54, 40, 40, ..., 0, 6, 18], dtype=uint8), array([ 36, 39, 22, ..., 182, 138, 127], dtype=uint8), array([ 25, 27, 68, ..., 157, 126, 106], dtype=uint8), array([194, 167, 124, ..., 161, 114, 70], dtype=uint8), array([162, 158, 131, ..., 229, 239, 241], dtype=uint8), array([116, 144, 241, ..., 123, 133, 182], dtype=uint8), array([59, 48, 54, ..., 53, 57, 69], dtype=uint8), array([ 88, 63, 58, ..., 140, 95, 98], dtype=uint8), array([59, 52, 46, ..., 14, 12, 15], dtype=uint8), array([211, 222, 205, ..., 57, 15, 39], dtype=uint8), array([36, 48, 46, ..., 54, 60, 86], dtype=uint8), array([122, 98, 74, ..., 48, 57, 64], dtype=uint8), array([132, 102, 91, ..., 114, 83, 62], dtype=uint8), array([27, 20, 36, ..., 38, 33, 37], dtype=uint8), array([163, 184, 231, ..., 205, 194, 198], dtype=uint8), array([111, 81, 89, ..., 26, 12, 45], dtype=uint8), array([ 1, 1, 1, ..., 177, 141, 119], dtype=uint8), array([27, 25, 12, ..., 17, 3, 3], dtype=uint8), array([ 86, 60, 37, ..., 126, 83, 64], dtype=uint8), array([39, 34, 28, ..., 61, 51, 41], dtype=uint8), array([72, 34, 25, ..., 45, 7, 4], dtype=uint8), array([15, 19, 22, ..., 10, 11, 6], dtype=uint8), array([136, 123, 133, ..., 50, 52, 75], dtype=uint8), array([104, 103, 137, ..., 85, 82, 99], dtype=uint8), array([ 9, 62, 106, ..., 62, 165, 162], dtype=uint8), array([103, 101, 102, ..., 170, 169, 165], dtype=uint8), array([81, 67, 64, ..., 14, 0, 0], dtype=uint8), array([ 67, 30, 24, ..., 119, 135, 210], dtype=uint8), array([116, 96, 85, ..., 38, 22, 35], dtype=uint8), array([32, 43, 3, ..., 78, 60, 38], dtype=uint8), array([ 6, 0, 224, ..., 0, 11, 181], dtype=uint8), array([112, 109, 100, ..., 170, 248, 252], dtype=uint8), array([30, 21, 6, ..., 11, 8, 1], dtype=uint8), array([26, 16, 24, ..., 33, 54, 49], dtype=uint8), array([122, 97, 75, ..., 33, 23, 22], dtype=uint8), array([199, 158, 112, ..., 200, 157, 112], dtype=uint8), array([1, 1, 1, ..., 0, 0, 0], dtype=uint8), array([110, 103, 85, ..., 17, 7, 8], dtype=uint8), array([222, 182, 60, ..., 165, 116, 75], dtype=uint8), array([ 38, 25, 69, ..., 240, 247, 253], dtype=uint8), array([145, 127, 91, ..., 150, 109, 81], dtype=uint8), array([ 17, 34, 41, ..., 196, 191, 195], dtype=uint8), array([52, 35, 28, ..., 35, 24, 20], dtype=uint8), array([126, 62, 63, ..., 189, 180, 149], dtype=uint8), array([ 71, 62, 53, ..., 219, 219, 231], dtype=uint8), array([ 9, 11, 10, ..., 24, 10, 10], dtype=uint8), array([139, 83, 96, ..., 181, 180, 186], dtype=uint8), array([ 83, 79, 130, ..., 33, 31, 42], dtype=uint8), array([ 73, 43, 35, ..., 129, 118, 132], dtype=uint8), array([ 7, 16, 25, ..., 86, 70, 73], dtype=uint8), array([144, 93, 62, ..., 176, 13, 78], dtype=uint8), array([48, 31, 21, ..., 22, 16, 4], dtype=uint8), array([71, 57, 74, ..., 55, 38, 54], dtype=uint8), array([30, 30, 22, ..., 36, 27, 18], dtype=uint8), array([ 93, 86, 68, ..., 247, 229, 205], dtype=uint8), array([153, 134, 140, ..., 102, 92, 100], dtype=uint8), array([39, 39, 31, ..., 9, 12, 5], dtype=uint8), array([ 13, 13, 23, ..., 109, 116, 109], dtype=uint8), array([217, 210, 192, ..., 91, 84, 65], dtype=uint8), array([28, 27, 23, ..., 55, 31, 27], dtype=uint8), array([131, 184, 178, ..., 95, 69, 54], dtype=uint8), array([114, 76, 67, ..., 65, 24, 20], dtype=uint8), array([80, 70, 69, ..., 86, 68, 48], dtype=uint8), array([133, 81, 59, ..., 70, 41, 33], dtype=uint8), array([28, 29, 24, ..., 32, 34, 31], dtype=uint8), array([ 14, 12, 0, ..., 86, 79, 121], dtype=uint8), array([ 10, 11, 6, ..., 65, 91, 114], dtype=uint8), array([ 25, 14, 10, ..., 171, 144, 115], dtype=uint8), array([22, 21, 19, ..., 8, 8, 8], dtype=uint8), array([170, 131, 92, ..., 95, 95, 87], dtype=uint8), array([137, 108, 92, ..., 14, 10, 9], dtype=uint8), array([ 94, 84, 82, ..., 143, 153, 202], dtype=uint8), array([154, 137, 121, ..., 155, 136, 121], dtype=uint8), array([52, 27, 31, ..., 76, 49, 32], dtype=uint8), array([ 78, 48, 37, ..., 125, 132, 176], dtype=uint8), array([ 47, 42, 36, ..., 111, 74, 55], dtype=uint8), array([ 49, 40, 145, ..., 195, 172, 178], dtype=uint8), array([ 2, 18, 201, ..., 138, 99, 66], dtype=uint8), array([ 7, 17, 42, ..., 69, 67, 81], dtype=uint8), array([ 75, 54, 51, ..., 130, 96, 94], dtype=uint8), array([69, 37, 22, ..., 29, 0, 4], dtype=uint8), array([124, 66, 202, ..., 202, 169, 128], dtype=uint8), array([ 61, 52, 55, ..., 219, 220, 224], dtype=uint8), array([ 45, 26, 28, ..., 152, 74, 88], dtype=uint8), array([36, 18, 14, ..., 17, 13, 10], dtype=uint8), array([187, 147, 111, ..., 22, 43, 96], dtype=uint8), array([ 90, 69, 64, ..., 111, 154, 199], dtype=uint8), array([71, 54, 44, ..., 92, 59, 44], dtype=uint8), array([124, 129, 125, ..., 97, 63, 88], dtype=uint8), array([46, 32, 21, ..., 71, 57, 54], dtype=uint8), array([237, 232, 210, ..., 117, 114, 99], dtype=uint8), array([34, 32, 17, ..., 13, 18, 22], dtype=uint8), array([ 6, 12, 2, ..., 26, 12, 3], dtype=uint8), array([43, 33, 32, ..., 21, 9, 21], dtype=uint8), array([ 90, 67, 61, ..., 100, 62, 43], dtype=uint8), array([143, 120, 76, ..., 168, 140, 100], dtype=uint8), array([107, 98, 99, ..., 205, 193, 203], dtype=uint8), array([ 31, 36, 40, ..., 189, 186, 195], dtype=uint8), array([175, 151, 139, ..., 106, 96, 104], dtype=uint8), array([105, 79, 144, ..., 90, 61, 43], dtype=uint8), array([11, 20, 29, ..., 10, 0, 0], dtype=uint8), array([19, 19, 19, ..., 1, 1, 1], dtype=uint8), array([64, 59, 63, ..., 13, 11, 14], dtype=uint8), array([129, 88, 84, ..., 68, 46, 49], dtype=uint8), array([134, 102, 91, ..., 183, 195, 149], dtype=uint8), array([28, 26, 37, ..., 40, 28, 28], dtype=uint8), array([38, 40, 29, ..., 27, 32, 26], dtype=uint8), array([122, 102, 95, ..., 78, 72, 74], dtype=uint8), array([93, 69, 65, ..., 45, 44, 49], dtype=uint8), array([11, 19, 21, ..., 63, 68, 62], dtype=uint8), array([ 49, 43, 53, ..., 182, 196, 225], dtype=uint8), array([54, 69, 62, ..., 41, 50, 67], dtype=uint8), array([128, 108, 117, ..., 86, 59, 38], dtype=uint8), array([39, 25, 22, ..., 1, 0, 0], dtype=uint8), array([ 78, 68, 58, ..., 142, 132, 120], dtype=uint8), array([72, 63, 46, ..., 75, 83, 70], dtype=uint8), array([ 58, 80, 117, ..., 180, 178, 215], dtype=uint8), array([ 78, 81, 60, ..., 191, 197, 171], dtype=uint8), array([246, 218, 196, ..., 29, 28, 34], dtype=uint8), array([255, 216, 189, ..., 162, 115, 99], dtype=uint8), array([ 66, 80, 109, ..., 229, 230, 222], dtype=uint8), array([156, 158, 171, ..., 88, 57, 54], dtype=uint8), array([32, 41, 40, ..., 18, 9, 10], dtype=uint8), array([56, 54, 42, ..., 33, 33, 35], dtype=uint8), array([16, 14, 17, ..., 33, 28, 32], dtype=uint8), array([35, 37, 26, ..., 45, 43, 67], dtype=uint8), array([ 30, 29, 35, ..., 161, 104, 75], dtype=uint8), array([ 91, 173, 255, ..., 12, 7, 11], dtype=uint8), array([187, 182, 188, ..., 134, 134, 142], dtype=uint8), array([ 58, 84, 107, ..., 0, 9, 22], dtype=uint8), array([54, 49, 45, ..., 28, 28, 28], dtype=uint8), array([75, 78, 71, ..., 25, 13, 13], dtype=uint8), array([ 4, 14, 41, ..., 144, 165, 168], dtype=uint8), array([64, 57, 88, ..., 57, 38, 57], dtype=uint8), array([ 21, 54, 157, ..., 28, 79, 158], dtype=uint8), array([223, 148, 145, ..., 30, 28, 52], dtype=uint8), array([ 42, 32, 20, ..., 190, 175, 204], dtype=uint8), array([83, 89, 79, ..., 40, 35, 32], dtype=uint8), array([113, 102, 84, ..., 92, 70, 59], dtype=uint8), array([ 97, 117, 126, ..., 214, 189, 159], dtype=uint8), array([137, 108, 102, ..., 52, 23, 27], dtype=uint8), array([5, 1, 0, ..., 2, 2, 2], dtype=uint8), array([186, 185, 219, ..., 160, 121, 80], dtype=uint8), array([ 90, 73, 65, ..., 144, 85, 71], dtype=uint8), array([233, 234, 226, ..., 50, 49, 44], dtype=uint8), array([92, 60, 75, ..., 69, 33, 35], dtype=uint8), array([81, 57, 33, ..., 85, 57, 45], dtype=uint8), array([77, 49, 61, ..., 12, 12, 12], dtype=uint8), array([ 0, 0, 0, ..., 52, 106, 212], dtype=uint8), array([ 25, 38, 134, ..., 45, 119, 204], dtype=uint8), array([223, 225, 224, ..., 14, 8, 8], dtype=uint8), array([105, 103, 104, ..., 72, 67, 61], dtype=uint8), array([43, 44, 62, ..., 29, 20, 21], dtype=uint8), array([ 71, 76, 80, ..., 111, 121, 97], dtype=uint8), array([131, 112, 108, ..., 68, 59, 78], dtype=uint8), array([ 59, 115, 252, ..., 59, 63, 90], dtype=uint8), array([ 53, 33, 32, ..., 161, 108, 92], dtype=uint8), array([157, 149, 170, ..., 181, 144, 135], dtype=uint8), array([ 39, 34, 30, ..., 196, 133, 116], dtype=uint8), array([25, 25, 13, ..., 96, 61, 33], dtype=uint8), array([ 13, 49, 65, ..., 163, 149, 122], dtype=uint8), array([239, 244, 240, ..., 77, 78, 73], dtype=uint8), array([33, 24, 19, ..., 42, 34, 23], dtype=uint8), array([116, 104, 118, ..., 73, 0, 19], dtype=uint8), array([140, 79, 12, ..., 44, 36, 51], dtype=uint8), array([29, 29, 21, ..., 17, 17, 17], dtype=uint8), array([ 93, 101, 147, ..., 156, 109, 99], dtype=uint8), array([251, 251, 249, ..., 242, 215, 248], dtype=uint8), array([ 81, 100, 80, ..., 85, 67, 55], dtype=uint8), array([157, 148, 141, ..., 0, 3, 23], dtype=uint8), array([51, 56, 52, ..., 48, 46, 51], dtype=uint8), array([ 27, 56, 134, ..., 62, 104, 202], dtype=uint8), array([174, 158, 143, ..., 14, 7, 14], dtype=uint8), array([75, 71, 72, ..., 27, 14, 24], dtype=uint8), array([230, 211, 194, ..., 134, 102, 103], dtype=uint8), array([111, 81, 53, ..., 144, 130, 117], dtype=uint8), array([199, 199, 199, ..., 6, 0, 0], dtype=uint8), array([ 71, 46, 42, ..., 131, 117, 116], dtype=uint8), array([80, 70, 68, ..., 38, 17, 14], dtype=uint8), array([ 39, 34, 54, ..., 229, 177, 140], dtype=uint8), array([54, 42, 30, ..., 29, 26, 11], dtype=uint8), array([172, 150, 137, ..., 182, 134, 94], dtype=uint8), array([ 76, 63, 55, ..., 129, 120, 111], dtype=uint8), array([125, 115, 103, ..., 55, 51, 74], dtype=uint8), array([79, 70, 71, ..., 41, 36, 33], dtype=uint8), array([36, 37, 58, ..., 12, 10, 11], dtype=uint8), array([ 62, 24, 5, ..., 160, 82, 59], dtype=uint8), array([145, 142, 137, ..., 152, 151, 147], dtype=uint8), array([ 81, 104, 88, ..., 160, 155, 152], dtype=uint8), array([141, 251, 248, ..., 167, 172, 210], dtype=uint8), array([138, 128, 116, ..., 203, 39, 74], dtype=uint8), array([157, 110, 58, ..., 12, 12, 12], dtype=uint8), array([19, 9, 36, ..., 16, 16, 16], dtype=uint8), array([ 61, 51, 111, ..., 129, 186, 255], dtype=uint8), array([ 3, 2, 0, ..., 96, 161, 15], dtype=uint8), array([ 49, 51, 64, ..., 143, 126, 116], dtype=uint8), array([112, 81, 60, ..., 30, 12, 10], dtype=uint8), array([139, 125, 99, ..., 165, 123, 101], dtype=uint8), array([ 56, 52, 53, ..., 104, 95, 80], dtype=uint8), array([ 53, 56, 39, ..., 146, 144, 145], dtype=uint8), array([84, 50, 41, ..., 66, 47, 49], dtype=uint8), array([121, 84, 78, ..., 214, 219, 155], dtype=uint8), array([63, 50, 42, ..., 84, 71, 62], dtype=uint8), array([42, 7, 1, ..., 33, 4, 6], dtype=uint8), array([28, 28, 40, ..., 26, 24, 29], dtype=uint8), array([ 89, 73, 57, ..., 249, 220, 202], dtype=uint8), array([121, 123, 122, ..., 10, 5, 2], dtype=uint8), array([181, 154, 99, ..., 243, 216, 189], dtype=uint8), array([122, 120, 125, ..., 224, 236, 250], dtype=uint8), array([160, 155, 159, ..., 56, 50, 114], dtype=uint8), array([ 8, 19, 64, ..., 23, 22, 30], dtype=uint8), array([52, 48, 47, ..., 36, 52, 88], dtype=uint8), array([29, 20, 15, ..., 62, 65, 70], dtype=uint8), array([149, 59, 110, ..., 50, 39, 73], dtype=uint8), array([227, 239, 251, ..., 31, 32, 60], dtype=uint8), array([39, 43, 72, ..., 62, 54, 75], dtype=uint8), array([80, 56, 22, ..., 42, 21, 4], dtype=uint8), array([51, 40, 34, ..., 24, 10, 89], dtype=uint8), array([47, 32, 29, ..., 14, 8, 8], dtype=uint8), array([ 0, 0, 0, ..., 73, 95, 116], dtype=uint8), array([27, 33, 19, ..., 50, 54, 57], dtype=uint8), array([ 55, 98, 210, ..., 138, 111, 92], dtype=uint8), array([107, 96, 113, ..., 43, 40, 57], dtype=uint8), array([ 84, 117, 98, ..., 144, 105, 100], dtype=uint8), array([101, 129, 213, ..., 0, 3, 77], dtype=uint8), array([125, 103, 79, ..., 12, 26, 37], dtype=uint8), array([ 88, 73, 76, ..., 123, 93, 85], dtype=uint8), array([ 47, 113, 51, ..., 70, 56, 43], dtype=uint8), array([177, 144, 125, ..., 120, 92, 71], dtype=uint8), array([165, 166, 160, ..., 52, 36, 23], dtype=uint8), array([48, 41, 59, ..., 62, 7, 26], dtype=uint8), array([69, 67, 72, ..., 55, 41, 54], dtype=uint8), array([ 6, 77, 61, ..., 139, 111, 99], dtype=uint8), array([ 85, 40, 43, ..., 111, 86, 92], dtype=uint8), array([148, 209, 240, ..., 158, 181, 222], dtype=uint8), array([ 90, 75, 68, ..., 195, 198, 191], dtype=uint8), array([ 47, 28, 14, ..., 253, 255, 244], dtype=uint8), array([ 30, 22, 11, ..., 126, 138, 134], dtype=uint8), array([253, 254, 255, ..., 207, 196, 132], dtype=uint8), array([105, 68, 50, ..., 44, 40, 41], dtype=uint8), array([92, 77, 80, ..., 28, 21, 37], dtype=uint8), array([63, 50, 41, ..., 40, 38, 41], dtype=uint8), array([24, 20, 21, ..., 48, 14, 2], dtype=uint8), array([ 33, 37, 36, ..., 109, 43, 45], dtype=uint8), array([145, 142, 199, ..., 4, 0, 0], dtype=uint8), array([1, 3, 2, ..., 0, 0, 0], dtype=uint8), array([129, 95, 83, ..., 135, 78, 123], dtype=uint8), array([170, 144, 121, ..., 170, 161, 156], dtype=uint8), array([249, 230, 200, ..., 216, 193, 187], dtype=uint8), array([28, 17, 23, ..., 99, 66, 57], dtype=uint8), array([ 81, 90, 71, ..., 169, 205, 239], dtype=uint8), array([79, 76, 61, ..., 53, 57, 68], dtype=uint8), array([ 23, 107, 171, ..., 240, 225, 230], dtype=uint8), array([106, 125, 131, ..., 83, 80, 89], dtype=uint8), array([90, 71, 77, ..., 0, 19, 78], dtype=uint8), array([ 37, 48, 66, ..., 102, 107, 100], dtype=uint8), array([130, 132, 129, ..., 48, 51, 56], dtype=uint8), array([163, 139, 91, ..., 113, 67, 18], dtype=uint8), array([229, 183, 123, ..., 87, 47, 35], dtype=uint8), array([138, 138, 128, ..., 28, 24, 25], dtype=uint8), array([42, 38, 39, ..., 38, 18, 7], dtype=uint8), array([128, 104, 76, ..., 34, 39, 19], dtype=uint8), array([82, 83, 67, ..., 20, 6, 5], dtype=uint8), array([35, 54, 58, ..., 5, 1, 2], dtype=uint8), array([69, 59, 49, ..., 31, 37, 33], dtype=uint8), array([ 72, 71, 67, ..., 140, 113, 102], dtype=uint8), array([ 90, 64, 41, ..., 106, 74, 49], dtype=uint8), array([201, 178, 137, ..., 82, 47, 28], dtype=uint8), array([255, 244, 250, ..., 241, 242, 247], dtype=uint8), array([127, 99, 78, ..., 136, 95, 49], dtype=uint8), array([150, 125, 61, ..., 150, 130, 105], dtype=uint8), array([ 4, 10, 8, ..., 3, 12, 21], dtype=uint8), array([33, 44, 62, ..., 26, 23, 40], dtype=uint8), array([46, 43, 34, ..., 57, 38, 58], dtype=uint8), array([141, 137, 134, ..., 20, 6, 6], dtype=uint8), array([125, 104, 75, ..., 164, 158, 158], dtype=uint8), array([106, 109, 142, ..., 39, 36, 63], dtype=uint8), array([48, 43, 37, ..., 72, 59, 51], dtype=uint8), array([130, 40, 75, ..., 46, 44, 65], dtype=uint8), array([ 20, 16, 5, ..., 135, 103, 114], dtype=uint8), array([158, 169, 171, ..., 108, 159, 238], dtype=uint8), array([44, 33, 31, ..., 42, 35, 51], dtype=uint8), array([157, 133, 107, ..., 165, 129, 97], dtype=uint8), array([ 40, 21, 49, ..., 114, 104, 105], dtype=uint8), array([53, 16, 0, ..., 25, 6, 0], dtype=uint8), array([84, 37, 9, ..., 36, 28, 5], dtype=uint8), array([64, 34, 26, ..., 67, 41, 26], dtype=uint8), array([110, 110, 122, ..., 65, 46, 48], dtype=uint8), array([ 19, 25, 49, ..., 129, 102, 93], dtype=uint8), array([25, 11, 11, ..., 40, 31, 50], dtype=uint8), array([28, 15, 6, ..., 30, 17, 11], dtype=uint8), array([56, 44, 32, ..., 10, 10, 12], dtype=uint8), array([ 14, 3, 11, ..., 122, 99, 115], dtype=uint8), array([106, 81, 85, ..., 246, 240, 228], dtype=uint8), array([76, 59, 49, ..., 36, 24, 12], dtype=uint8), array([101, 65, 29, ..., 135, 101, 73], dtype=uint8), array([121, 123, 112, ..., 183, 184, 179], dtype=uint8), array([152, 126, 91, ..., 69, 53, 40], dtype=uint8), array([ 69, 36, 21, ..., 131, 96, 68], dtype=uint8), array([228, 214, 205, ..., 153, 124, 108], dtype=uint8), array([133, 132, 130, ..., 6, 4, 5], dtype=uint8), array([211, 168, 125, ..., 221, 180, 134], dtype=uint8), array([66, 30, 30, ..., 50, 25, 29], dtype=uint8), array([ 29, 37, 138, ..., 141, 116, 75], dtype=uint8), array([ 37, 27, 17, ..., 238, 229, 220], dtype=uint8), array([47, 61, 64, ..., 79, 73, 23], dtype=uint8), array([198, 151, 141, ..., 182, 127, 106], dtype=uint8), array([144, 135, 130, ..., 76, 36, 11], dtype=uint8), array([ 89, 83, 67, ..., 236, 207, 212], dtype=uint8), array([171, 138, 129, ..., 117, 102, 121], dtype=uint8), array([ 92, 94, 107, ..., 49, 31, 27], dtype=uint8), array([ 64, 60, 49, ..., 177, 125, 111], dtype=uint8), array([ 50, 31, 25, ..., 139, 55, 45], dtype=uint8), array([115, 116, 146, ..., 105, 81, 77], dtype=uint8), array([106, 72, 60, ..., 45, 28, 21], dtype=uint8), array([97, 83, 74, ..., 85, 63, 40], dtype=uint8), array([161, 217, 244, ..., 29, 30, 35], dtype=uint8), array([ 41, 36, 42, ..., 100, 66, 56], dtype=uint8), array([42, 26, 63, ..., 68, 43, 39], dtype=uint8), array([76, 65, 63, ..., 10, 13, 20], dtype=uint8), array([ 87, 117, 167, ..., 41, 23, 21], dtype=uint8), array([101, 110, 89, ..., 22, 24, 23], dtype=uint8), array([ 3, 17, 82, ..., 10, 9, 15], dtype=uint8), array([213, 228, 225, ..., 38, 34, 5], dtype=uint8), array([ 78, 63, 56, ..., 246, 216, 224], dtype=uint8), array([105, 73, 60, ..., 46, 44, 49], dtype=uint8), array([151, 133, 119, ..., 53, 35, 33], dtype=uint8), array([ 10, 12, 0, ..., 110, 86, 38], dtype=uint8), array([43, 50, 42, ..., 76, 85, 84], dtype=uint8), array([245, 200, 179, ..., 43, 40, 23], dtype=uint8), array([ 32, 32, 30, ..., 128, 150, 171], dtype=uint8), array([101, 81, 74, ..., 15, 15, 17], dtype=uint8), array([163, 113, 102, ..., 19, 17, 28], dtype=uint8), array([ 48, 45, 30, ..., 156, 123, 104], dtype=uint8), array([38, 19, 15, ..., 40, 28, 28], dtype=uint8), array([ 96, 91, 85, ..., 141, 140, 145], dtype=uint8), array([54, 34, 0, ..., 33, 33, 33], dtype=uint8), array([190, 204, 213, ..., 161, 171, 180], dtype=uint8), array([ 91, 101, 103, ..., 145, 139, 173], dtype=uint8), array([155, 142, 133, ..., 193, 168, 163], dtype=uint8), array([106, 103, 254, ..., 171, 111, 87], dtype=uint8), array([ 0, 7, 0, ..., 91, 66, 59], dtype=uint8), array([ 52, 56, 42, ..., 141, 144, 135], dtype=uint8), array([ 75, 41, 39, ..., 105, 62, 55], dtype=uint8), array([163, 145, 135, ..., 4, 187, 255], dtype=uint8), array([74, 40, 30, ..., 82, 46, 30], dtype=uint8), array([110, 109, 140, ..., 53, 49, 48], dtype=uint8), array([228, 223, 220, ..., 162, 134, 113], dtype=uint8), array([ 11, 93, 239, ..., 113, 97, 108], dtype=uint8), array([70, 70, 58, ..., 46, 51, 55], dtype=uint8), array([48, 38, 28, ..., 40, 26, 26], dtype=uint8), array([63, 80, 44, ..., 29, 19, 20], dtype=uint8), array([ 95, 48, 54, ..., 228, 209, 192], dtype=uint8), array([112, 96, 71, ..., 17, 20, 25], dtype=uint8), array([48, 47, 42, ..., 15, 51, 87], dtype=uint8), array([20, 10, 9, ..., 27, 14, 24], dtype=uint8), array([ 0, 18, 9, ..., 130, 102, 101], dtype=uint8), array([45, 30, 71, ..., 57, 43, 56], dtype=uint8), array([ 20, 28, 51, ..., 184, 167, 175], dtype=uint8), array([122, 108, 99, ..., 182, 128, 92], dtype=uint8), array([192, 135, 105, ..., 37, 67, 117], dtype=uint8), array([21, 22, 26, ..., 18, 19, 23], dtype=uint8), array([49, 41, 20, ..., 60, 52, 33], dtype=uint8), array([ 39, 27, 27, ..., 163, 147, 134], dtype=uint8), array([173, 138, 171, ..., 117, 64, 110], dtype=uint8), array([ 56, 49, 56, ..., 158, 135, 151], dtype=uint8), array([ 31, 28, 13, ..., 150, 181, 184], dtype=uint8), array([104, 34, 26, ..., 208, 174, 224], dtype=uint8), array([34, 23, 66, ..., 71, 58, 65], dtype=uint8), array([ 78, 57, 64, ..., 175, 192, 222], dtype=uint8), array([124, 90, 81, ..., 24, 22, 33], dtype=uint8), array([ 91, 85, 99, ..., 131, 118, 127], dtype=uint8), array([ 31, 34, 13, ..., 158, 178, 65], dtype=uint8), array([45, 14, 9, ..., 90, 39, 18], dtype=uint8), array([176, 161, 166, ..., 38, 17, 12], dtype=uint8), array([100, 91, 86, ..., 48, 49, 53], dtype=uint8), array([ 56, 44, 32, ..., 106, 83, 75], dtype=uint8), array([148, 144, 132, ..., 10, 26, 41], dtype=uint8), array([ 1, 4, 73, ..., 87, 77, 86], dtype=uint8), array([66, 65, 70, ..., 23, 13, 12], dtype=uint8), array([134, 104, 106, ..., 77, 32, 9], dtype=uint8), array([106, 115, 110, ..., 69, 57, 61], dtype=uint8), array([184, 175, 180, ..., 8, 6, 7], dtype=uint8), array([ 83, 78, 75, ..., 114, 89, 85], dtype=uint8), array([ 8, 56, 132, ..., 0, 0, 28], dtype=uint8), array([ 40, 40, 40, ..., 174, 140, 103], dtype=uint8), array([103, 121, 141, ..., 101, 92, 97], dtype=uint8), array([113, 89, 77, ..., 103, 75, 54], dtype=uint8), array([59, 60, 55, ..., 50, 43, 37], dtype=uint8), array([106, 92, 83, ..., 21, 20, 28], dtype=uint8), array([53, 42, 40, ..., 37, 23, 12], dtype=uint8), array([ 87, 91, 100, ..., 0, 7, 18], dtype=uint8), array([ 51, 53, 40, ..., 254, 229, 235], dtype=uint8), array([ 95, 102, 110, ..., 145, 126, 145], dtype=uint8), array([ 76, 67, 68, ..., 184, 138, 140], dtype=uint8), array([59, 40, 36, ..., 61, 32, 26], dtype=uint8), array([52, 42, 30, ..., 14, 17, 24], dtype=uint8), array([27, 28, 20, ..., 57, 42, 23], dtype=uint8), array([177, 164, 155, ..., 60, 46, 35], dtype=uint8), array([ 55, 50, 70, ..., 222, 219, 226], dtype=uint8), array([196, 192, 207, ..., 23, 24, 19], dtype=uint8), array([204, 189, 192, ..., 18, 13, 10], dtype=uint8), array([199, 178, 161, ..., 150, 132, 50], dtype=uint8), array([ 95, 81, 68, ..., 113, 102, 100], dtype=uint8), array([196, 198, 197, ..., 117, 121, 122], dtype=uint8), array([ 59, 39, 28, ..., 196, 184, 184], dtype=uint8), array([84, 70, 87, ..., 15, 9, 35], dtype=uint8), array([50, 38, 26, ..., 47, 17, 15], dtype=uint8), array([137, 141, 142, ..., 180, 136, 97], dtype=uint8), array([71, 46, 39, ..., 50, 27, 13], dtype=uint8), array([57, 57, 57, ..., 16, 11, 5], dtype=uint8), array([11, 18, 26, ..., 3, 3, 5], dtype=uint8), array([50, 53, 60, ..., 78, 48, 40], dtype=uint8), array([61, 60, 55, ..., 2, 2, 2], dtype=uint8), array([113, 111, 133, ..., 36, 34, 47], dtype=uint8), array([ 68, 42, 53, ..., 116, 43, 60], dtype=uint8), array([73, 66, 50, ..., 62, 63, 94], dtype=uint8), array([169, 161, 158, ..., 88, 81, 99], dtype=uint8), array([192, 221, 225, ..., 126, 112, 111], dtype=uint8), array([ 89, 130, 112, ..., 48, 36, 24], dtype=uint8), array([143, 148, 126, ..., 134, 87, 59], dtype=uint8), array([136, 183, 227, ..., 129, 82, 72], dtype=uint8), array([ 27, 67, 139, ..., 130, 139, 194], dtype=uint8), array([92, 81, 49, ..., 79, 74, 52], dtype=uint8), array([57, 75, 97, ..., 27, 25, 38], dtype=uint8), array([114, 117, 100, ..., 164, 162, 141], dtype=uint8), array([174, 159, 166, ..., 25, 25, 27], dtype=uint8), array([31, 15, 25, ..., 12, 1, 0], dtype=uint8), array([59, 52, 23, ..., 93, 70, 28], dtype=uint8), array([230, 229, 224, ..., 38, 23, 16], dtype=uint8), array([52, 53, 37, ..., 62, 59, 42], dtype=uint8), array([ 36, 38, 37, ..., 156, 102, 116], dtype=uint8), array([86, 36, 45, ..., 50, 37, 46], dtype=uint8), array([222, 245, 255, ..., 57, 48, 79], dtype=uint8), array([ 40, 32, 21, ..., 249, 252, 255], dtype=uint8), array([32, 33, 25, ..., 95, 67, 63], dtype=uint8), array([ 16, 62, 96, ..., 62, 121, 153], dtype=uint8), array([114, 104, 102, ..., 84, 34, 35], dtype=uint8), array([205, 161, 136, ..., 90, 18, 21], dtype=uint8), array([ 80, 65, 44, ..., 109, 103, 115], dtype=uint8), array([ 49, 41, 28, ..., 103, 90, 81], dtype=uint8), array([ 9, 34, 54, ..., 27, 67, 93], dtype=uint8), array([158, 159, 154, ..., 3, 13, 25], dtype=uint8), array([72, 46, 23, ..., 65, 37, 16], dtype=uint8), array([109, 106, 91, ..., 97, 74, 68], dtype=uint8), array([179, 170, 165, ..., 48, 33, 36], dtype=uint8), array([19, 7, 11, ..., 0, 7, 0], dtype=uint8), array([53, 34, 36, ..., 0, 63, 91], dtype=uint8), array([45, 28, 20, ..., 28, 12, 0], dtype=uint8), array([73, 78, 56, ..., 11, 1, 2], dtype=uint8), array([ 78, 111, 104, ..., 91, 82, 65], dtype=uint8), array([215, 209, 195, ..., 81, 57, 55], dtype=uint8), array([74, 49, 42, ..., 66, 46, 39], dtype=uint8), array([43, 37, 49, ..., 2, 2, 2], dtype=uint8), array([ 26, 43, 73, ..., 233, 219, 208], dtype=uint8), array([160, 165, 158, ..., 164, 159, 155], dtype=uint8), array([13, 22, 17, ..., 19, 24, 28], dtype=uint8), array([94, 72, 74, ..., 41, 26, 31], dtype=uint8), array([112, 127, 158, ..., 127, 108, 130], dtype=uint8), array([ 80, 64, 12, ..., 113, 111, 122], dtype=uint8), array([ 33, 33, 33, ..., 140, 142, 165], dtype=uint8), array([34, 51, 45, ..., 74, 45, 37], dtype=uint8), array([ 46, 46, 46, ..., 86, 99, 108], dtype=uint8), array([ 47, 49, 46, ..., 146, 111, 83], dtype=uint8), array([ 72, 58, 179, ..., 81, 60, 77], dtype=uint8), array([93, 81, 91, ..., 26, 14, 16], dtype=uint8), array([234, 52, 64, ..., 28, 7, 26], dtype=uint8), array([180, 171, 156, ..., 38, 23, 26], dtype=uint8), array([136, 123, 104, ..., 112, 85, 68], dtype=uint8), array([ 59, 52, 34, ..., 175, 138, 216], dtype=uint8), array([81, 86, 79, ..., 23, 23, 23], dtype=uint8), array([145, 150, 154, ..., 110, 64, 48], dtype=uint8), array([189, 181, 144, ..., 26, 24, 25], dtype=uint8), array([39, 47, 60, ..., 27, 26, 32], dtype=uint8), array([172, 132, 96, ..., 86, 55, 37], dtype=uint8), array([17, 7, 6, ..., 26, 12, 12], dtype=uint8), array([ 46, 60, 34, ..., 143, 122, 79], dtype=uint8), array([26, 22, 39, ..., 39, 31, 42], dtype=uint8), array([ 63, 100, 108, ..., 68, 86, 98], dtype=uint8), array([ 77, 58, 52, ..., 122, 90, 69], dtype=uint8), array([48, 28, 27, ..., 21, 14, 0], dtype=uint8), array([134, 100, 75, ..., 110, 64, 51], dtype=uint8), array([ 85, 36, 4, ..., 178, 155, 149], dtype=uint8), array([126, 67, 27, ..., 131, 140, 137], dtype=uint8), array([38, 35, 56, ..., 48, 63, 70], dtype=uint8), array([ 6, 0, 2, ..., 53, 48, 54], dtype=uint8), array([98, 74, 62, ..., 56, 45, 53], dtype=uint8), array([149, 160, 130, ..., 68, 55, 36], dtype=uint8), array([57, 46, 50, ..., 0, 20, 9], dtype=uint8), array([15, 10, 7, ..., 59, 62, 43], dtype=uint8), array([ 66, 37, 29, ..., 146, 129, 135], dtype=uint8), array([61, 40, 39, ..., 42, 27, 22], dtype=uint8), array([164, 152, 136, ..., 22, 22, 20], dtype=uint8), array([ 21, 11, 9, ..., 178, 139, 100], dtype=uint8), array([33, 22, 18, ..., 15, 5, 0], dtype=uint8), array([139, 29, 58, ..., 105, 91, 88], dtype=uint8), array([61, 34, 49, ..., 83, 52, 57], dtype=uint8), array([110, 73, 55, ..., 2, 2, 4], dtype=uint8), array([109, 107, 86, ..., 180, 176, 177], dtype=uint8), array([ 51, 84, 103, ..., 2, 3, 8], dtype=uint8), array([ 2, 131, 235, ..., 64, 35, 31], dtype=uint8), array([142, 120, 107, ..., 34, 15, 8], dtype=uint8), array([87, 59, 37, ..., 52, 25, 18], dtype=uint8), array([62, 61, 57, ..., 3, 4, 0], dtype=uint8), array([ 46, 21, 27, ..., 205, 204, 140], dtype=uint8), array([ 43, 40, 35, ..., 215, 225, 235], dtype=uint8), array([221, 129, 114, ..., 94, 61, 82], dtype=uint8), array([ 39, 40, 35, ..., 206, 204, 179], dtype=uint8), array([129, 100, 193, ..., 50, 52, 67], dtype=uint8), array([ 83, 49, 12, ..., 217, 207, 208], dtype=uint8), array([133, 126, 84, ..., 48, 50, 49], dtype=uint8), array([ 9, 71, 110, ..., 9, 21, 21], dtype=uint8), array([43, 41, 52, ..., 33, 30, 39], dtype=uint8), array([123, 98, 102, ..., 207, 165, 169], dtype=uint8), array([77, 46, 51, ..., 28, 12, 15], dtype=uint8), array([102, 84, 72, ..., 127, 142, 147], dtype=uint8), array([108, 89, 82, ..., 35, 21, 20], dtype=uint8), array([155, 133, 136, ..., 49, 29, 28], dtype=uint8), array([53, 54, 56, ..., 32, 17, 10], dtype=uint8), array([ 48, 70, 107, ..., 117, 84, 77], dtype=uint8), array([61, 66, 86, ..., 14, 9, 31], dtype=uint8), array([119, 73, 73, ..., 126, 54, 66], dtype=uint8), array([ 6, 8, 3, ..., 146, 134, 136], dtype=uint8), array([43, 39, 53, ..., 37, 32, 36], dtype=uint8), array([36, 35, 49, ..., 49, 32, 40], dtype=uint8), array([183, 187, 186, ..., 52, 50, 61], dtype=uint8), array([ 43, 37, 21, ..., 252, 250, 253], dtype=uint8), array([20, 7, 14, ..., 1, 0, 10], dtype=uint8), array([223, 223, 221, ..., 3, 2, 0], dtype=uint8), array([ 9, 5, 2, ..., 153, 109, 98], dtype=uint8), array([158, 135, 117, ..., 15, 74, 52], dtype=uint8), array([20, 18, 21, ..., 29, 23, 25], dtype=uint8), array([141, 100, 118, ..., 137, 95, 119], dtype=uint8), array([32, 32, 32, ..., 63, 35, 21], dtype=uint8), array([ 22, 15, 5, ..., 145, 108, 79], dtype=uint8), array([ 29, 64, 146, ..., 198, 199, 194], dtype=uint8), array([22, 21, 19, ..., 48, 43, 40], dtype=uint8), array([164, 168, 195, ..., 133, 130, 151], dtype=uint8), array([ 27, 11, 74, ..., 127, 82, 79], dtype=uint8), array([85, 83, 84, ..., 48, 43, 47], dtype=uint8), array([107, 94, 85, ..., 89, 61, 37], dtype=uint8), array([58, 52, 52, ..., 36, 32, 33], dtype=uint8), array([168, 109, 69, ..., 142, 89, 58], dtype=uint8), array([ 0, 163, 254, ..., 10, 28, 38], dtype=uint8), array([72, 73, 68, ..., 32, 28, 25], dtype=uint8), array([136, 133, 98, ..., 145, 120, 79], dtype=uint8), array([10, 12, 9, ..., 13, 13, 3], dtype=uint8), array([185, 149, 125, ..., 166, 116, 91], dtype=uint8), array([170, 145, 91, ..., 70, 51, 34], dtype=uint8), array([ 17, 4, 13, ..., 164, 146, 146], dtype=uint8), array([102, 82, 93, ..., 77, 69, 58], dtype=uint8), array([111, 98, 105, ..., 32, 11, 28], dtype=uint8), array([ 98, 114, 148, ..., 171, 127, 116], dtype=uint8), array([78, 70, 91, ..., 42, 46, 45], dtype=uint8), array([73, 48, 70, ..., 21, 17, 50], dtype=uint8), array([185, 183, 188, ..., 45, 35, 34], dtype=uint8), array([163, 164, 166, ..., 150, 114, 202], dtype=uint8), array([17, 17, 5, ..., 3, 21, 45], dtype=uint8), array([101, 101, 93, ..., 3, 10, 16], dtype=uint8), array([125, 128, 135, ..., 81, 61, 50], dtype=uint8), array([220, 251, 254, ..., 139, 137, 148], dtype=uint8), array([146, 165, 197, ..., 37, 26, 34], dtype=uint8), array([34, 21, 5, ..., 80, 47, 28], dtype=uint8), array([ 37, 37, 37, ..., 45, 188, 144], dtype=uint8), array([ 89, 59, 48, ..., 135, 95, 60], dtype=uint8), array([125, 225, 251, ..., 98, 53, 11], dtype=uint8), array([72, 60, 62, ..., 29, 30, 32], dtype=uint8), array([144, 193, 200, ..., 43, 32, 30], dtype=uint8), array([87, 62, 66, ..., 61, 45, 32], dtype=uint8), array([ 26, 15, 11, ..., 168, 152, 119], dtype=uint8), array([111, 75, 79, ..., 47, 33, 33], dtype=uint8), array([ 27, 23, 20, ..., 151, 149, 160], dtype=uint8), array([ 84, 60, 36, ..., 171, 157, 154], dtype=uint8), array([210, 206, 207, ..., 177, 157, 156], dtype=uint8), array([145, 133, 137, ..., 114, 66, 46], dtype=uint8), array([ 47, 41, 41, ..., 176, 167, 196], dtype=uint8), array([108, 104, 127, ..., 226, 238, 255], dtype=uint8), array([ 89, 101, 27, ..., 22, 22, 10], dtype=uint8), array([ 50, 51, 82, ..., 117, 109, 124], dtype=uint8), array([ 51, 57, 55, ..., 92, 104, 100], dtype=uint8), array([137, 120, 74, ..., 1, 8, 34], dtype=uint8), array([17, 13, 48, ..., 13, 20, 72], dtype=uint8), array([32, 29, 14, ..., 69, 45, 41], dtype=uint8), array([ 3, 123, 236, ..., 1, 118, 214], dtype=uint8), array([255, 253, 254, ..., 249, 235, 226], dtype=uint8), array([115, 115, 117, ..., 16, 16, 16], dtype=uint8), array([ 72, 73, 67, ..., 109, 109, 107], dtype=uint8), array([155, 150, 156, ..., 9, 9, 11], dtype=uint8), array([25, 8, 14, ..., 62, 21, 17], dtype=uint8), array([144, 140, 111, ..., 71, 54, 26], dtype=uint8), array([ 97, 231, 234, ..., 30, 42, 42], dtype=uint8), array([161, 165, 194, ..., 10, 10, 8], dtype=uint8), array([37, 33, 21, ..., 5, 5, 3], dtype=uint8), array([161, 161, 133, ..., 200, 205, 183], dtype=uint8), array([ 69, 67, 78, ..., 146, 130, 131], dtype=uint8), array([103, 107, 119, ..., 31, 32, 24], dtype=uint8), array([172, 154, 130, ..., 189, 201, 179], dtype=uint8), array([ 41, 73, 150, ..., 93, 62, 67], dtype=uint8), array([ 42, 30, 34, ..., 166, 147, 143], dtype=uint8), array([12, 0, 2, ..., 26, 24, 37], dtype=uint8), array([ 81, 82, 64, ..., 132, 138, 124], dtype=uint8), array([139, 137, 200, ..., 169, 132, 114], dtype=uint8), array([69, 56, 48, ..., 70, 52, 40], dtype=uint8), array([167, 171, 170, ..., 15, 16, 20], dtype=uint8), array([54, 37, 30, ..., 20, 19, 33], dtype=uint8), array([ 2, 1, 6, ..., 144, 133, 131], dtype=uint8), array([77, 78, 73, ..., 45, 34, 32], dtype=uint8), array([20, 20, 18, ..., 53, 41, 41], dtype=uint8), array([197, 164, 147, ..., 112, 91, 86], dtype=uint8), array([148, 131, 101, ..., 99, 59, 33], dtype=uint8), array([24, 28, 31, ..., 46, 36, 37], dtype=uint8), array([124, 173, 231, ..., 127, 103, 67], dtype=uint8), array([131, 117, 117, ..., 21, 20, 18], dtype=uint8), array([93, 90, 71, ..., 30, 31, 17], dtype=uint8), array([187, 204, 224, ..., 24, 12, 0], dtype=uint8), array([193, 184, 153, ..., 135, 109, 96], dtype=uint8), array([ 19, 9, 0, ..., 161, 157, 158], dtype=uint8), array([74, 50, 40, ..., 83, 56, 49], dtype=uint8), array([105, 91, 82, ..., 53, 38, 31], dtype=uint8), array([ 48, 46, 47, ..., 97, 98, 118], dtype=uint8), array([37, 33, 22, ..., 19, 14, 20], dtype=uint8), array([16, 22, 20, ..., 2, 1, 6], dtype=uint8), array([132, 122, 147, ..., 0, 14, 136], dtype=uint8), array([245, 203, 127, ..., 152, 126, 77], dtype=uint8), array([ 55, 58, 73, ..., 158, 210, 250], dtype=uint8), array([174, 202, 216, ..., 21, 19, 32], dtype=uint8), array([183, 174, 145, ..., 118, 72, 38], dtype=uint8), array([143, 145, 132, ..., 100, 77, 69], dtype=uint8), array([54, 52, 53, ..., 37, 31, 33], dtype=uint8), array([14, 22, 43, ..., 4, 10, 36], dtype=uint8), array([237, 237, 229, ..., 91, 68, 78], dtype=uint8), array([134, 142, 145, ..., 122, 122, 132], dtype=uint8), array([ 79, 58, 123, ..., 147, 118, 184], dtype=uint8), array([67, 50, 40, ..., 16, 10, 0], dtype=uint8), array([64, 34, 26, ..., 14, 6, 3], dtype=uint8), array([93, 72, 79, ..., 26, 33, 49], dtype=uint8), array([161, 173, 199, ..., 189, 184, 188], dtype=uint8), array([159, 128, 108, ..., 218, 214, 203], dtype=uint8), array([137, 131, 115, ..., 99, 104, 123], dtype=uint8), array([46, 39, 47, ..., 48, 46, 70], dtype=uint8), array([39, 44, 48, ..., 0, 0, 0], dtype=uint8), array([ 56, 57, 43, ..., 211, 215, 214], dtype=uint8), array([41, 24, 17, ..., 9, 2, 0], dtype=uint8), array([19, 15, 12, ..., 23, 27, 26], dtype=uint8), array([ 55, 50, 31, ..., 123, 103, 92], dtype=uint8), array([215, 189, 140, ..., 56, 20, 4], dtype=uint8), array([127, 114, 82, ..., 179, 144, 90], dtype=uint8), array([ 57, 49, 47, ..., 131, 114, 106], dtype=uint8), array([106, 101, 82, ..., 118, 76, 52], dtype=uint8), array([132, 116, 82, ..., 91, 70, 25], dtype=uint8), array([75, 64, 70, ..., 49, 37, 41], dtype=uint8), array([103, 75, 53, ..., 95, 59, 35], dtype=uint8), array([20, 16, 13, ..., 16, 16, 18], dtype=uint8), array([ 52, 40, 42, ..., 88, 70, 118], dtype=uint8), array([39, 32, 14, ..., 14, 22, 11], dtype=uint8), array([95, 87, 74, ..., 19, 7, 7], dtype=uint8), array([254, 217, 191, ..., 189, 168, 207], dtype=uint8), array([161, 141, 116, ..., 39, 19, 18], dtype=uint8), array([ 4, 114, 225, ..., 78, 97, 129], dtype=uint8), array([ 20, 27, 35, ..., 145, 118, 91], dtype=uint8), array([63, 50, 34, ..., 18, 18, 18], dtype=uint8), array([42, 55, 61, ..., 91, 59, 48], dtype=uint8), array([ 88, 71, 64, ..., 152, 114, 103], dtype=uint8), array([39, 34, 30, ..., 62, 46, 23], dtype=uint8), array([ 33, 31, 42, ..., 144, 154, 143], dtype=uint8), array([139, 151, 253, ..., 160, 96, 131], dtype=uint8), array([215, 186, 142, ..., 116, 84, 43], dtype=uint8), array([234, 236, 223, ..., 179, 152, 125], dtype=uint8), array([118, 172, 94, ..., 3, 2, 0], dtype=uint8), array([46, 33, 24, ..., 37, 27, 26], dtype=uint8), array([ 6, 7, 2, ..., 251, 236, 243], dtype=uint8), array([ 67, 27, 25, ..., 112, 132, 107], dtype=uint8), array([205, 201, 189, ..., 1, 0, 5], dtype=uint8), array([51, 21, 23, ..., 85, 81, 80], dtype=uint8), array([135, 97, 60, ..., 252, 253, 247], dtype=uint8), array([ 9, 9, 9, ..., 49, 7, 45], dtype=uint8), array([199, 204, 200, ..., 21, 15, 15], dtype=uint8), array([55, 43, 53, ..., 82, 55, 46], dtype=uint8), array([56, 50, 50, ..., 37, 28, 13], dtype=uint8), array([130, 112, 110, ..., 56, 33, 25], dtype=uint8), array([123, 95, 55, ..., 171, 113, 93], dtype=uint8), array([26, 23, 34, ..., 29, 18, 22], dtype=uint8), array([59, 47, 61, ..., 48, 48, 50], dtype=uint8), array([28, 24, 12, ..., 14, 10, 9], dtype=uint8), array([ 51, 74, 66, ..., 174, 112, 101], dtype=uint8), array([101, 92, 83, ..., 47, 33, 32], dtype=uint8), array([ 63, 81, 181, ..., 155, 141, 174], dtype=uint8), array([157, 143, 140, ..., 169, 161, 150], dtype=uint8), array([17, 20, 51, ..., 32, 15, 8], dtype=uint8), array([ 69, 46, 54, ..., 124, 96, 72], dtype=uint8), array([163, 154, 137, ..., 87, 54, 63], dtype=uint8), array([151, 84, 67, ..., 61, 16, 21], dtype=uint8), array([41, 29, 53, ..., 58, 47, 53], dtype=uint8), array([211, 184, 141, ..., 35, 23, 11], dtype=uint8), array([157, 129, 92, ..., 160, 144, 111], dtype=uint8), array([ 93, 118, 184, ..., 77, 134, 161], dtype=uint8), array([69, 75, 65, ..., 24, 31, 24], dtype=uint8), array([80, 59, 38, ..., 90, 63, 42], dtype=uint8), array([34, 34, 26, ..., 0, 0, 0], dtype=uint8), array([84, 72, 50, ..., 98, 69, 71], dtype=uint8), array([255, 250, 226, ..., 150, 111, 72], dtype=uint8), array([251, 255, 252, ..., 144, 44, 54], dtype=uint8), array([118, 90, 76, ..., 104, 88, 72], dtype=uint8), array([ 81, 105, 109, ..., 220, 221, 239], dtype=uint8), array([ 46, 38, 59, ..., 228, 186, 224], dtype=uint8), array([ 54, 51, 46, ..., 209, 205, 228], dtype=uint8), array([126, 135, 142, ..., 76, 60, 35], dtype=uint8), array([57, 80, 96, ..., 51, 39, 41], dtype=uint8), array([ 11, 75, 211, ..., 131, 130, 208], dtype=uint8), array([41, 47, 37, ..., 0, 1, 23], dtype=uint8), array([ 56, 119, 198, ..., 55, 58, 67], dtype=uint8), array([103, 91, 69, ..., 81, 35, 19], dtype=uint8), array([ 0, 4, 0, ..., 103, 72, 52], dtype=uint8), array([ 7, 7, 43, ..., 10, 83, 188], dtype=uint8), array([102, 73, 59, ..., 18, 49, 104], dtype=uint8), array([49, 32, 25, ..., 87, 50, 23], dtype=uint8), array([91, 78, 70, ..., 46, 34, 34], dtype=uint8), array([38, 48, 75, ..., 30, 18, 30], dtype=uint8), array([81, 71, 70, ..., 29, 30, 34], dtype=uint8), array([40, 46, 44, ..., 64, 48, 49], dtype=uint8), array([ 41, 24, 40, ..., 108, 71, 45], dtype=uint8), array([66, 38, 61, ..., 29, 8, 64], dtype=uint8), array([ 16, 24, 27, ..., 161, 187, 204], dtype=uint8), array([51, 32, 34, ..., 18, 16, 19], dtype=uint8), array([255, 255, 255, ..., 95, 75, 68], dtype=uint8), array([87, 87, 85, ..., 55, 65, 77], dtype=uint8), array([ 1, 1, 1, ..., 26, 58, 97], dtype=uint8), array([171, 153, 133, ..., 49, 24, 27], dtype=uint8), array([ 86, 86, 76, ..., 195, 184, 166], dtype=uint8), array([213, 234, 225, ..., 196, 133, 92], dtype=uint8), array([ 36, 37, 58, ..., 252, 255, 226], dtype=uint8), array([96, 38, 18, ..., 53, 25, 4], dtype=uint8), array([163, 130, 111, ..., 16, 11, 8], dtype=uint8), array([82, 72, 62, ..., 46, 42, 59], dtype=uint8), array([158, 131, 110, ..., 49, 47, 48], dtype=uint8), array([48, 28, 19, ..., 34, 20, 17], dtype=uint8), array([35, 23, 23, ..., 40, 29, 33], dtype=uint8), array([ 25, 1, 0, ..., 176, 107, 91], dtype=uint8), array([184, 168, 117, ..., 76, 46, 35], dtype=uint8), array([41, 62, 29, ..., 74, 45, 29], dtype=uint8), array([144, 132, 132, ..., 52, 46, 58], dtype=uint8), array([ 75, 84, 117, ..., 20, 40, 64], dtype=uint8), array([ 30, 42, 28, ..., 222, 222, 248], dtype=uint8), array([ 15, 20, 13, ..., 241, 210, 192], dtype=uint8), array([25, 38, 28, ..., 30, 28, 39], dtype=uint8), array([ 55, 70, 101, ..., 48, 47, 55], dtype=uint8), array([ 87, 63, 77, ..., 254, 215, 172], dtype=uint8), array([140, 105, 85, ..., 15, 5, 3], dtype=uint8), array([226, 221, 163, ..., 184, 160, 86], dtype=uint8), array([149, 127, 103, ..., 107, 77, 49], dtype=uint8), array([ 37, 48, 44, ..., 134, 174, 255], dtype=uint8), array([79, 72, 54, ..., 36, 41, 45], dtype=uint8), array([14, 15, 9, ..., 86, 91, 85], dtype=uint8), array([124, 116, 103, ..., 83, 72, 52], dtype=uint8), array([115, 87, 66, ..., 247, 216, 214], dtype=uint8), array([188, 136, 97, ..., 124, 84, 58], dtype=uint8), array([126, 133, 125, ..., 141, 128, 138], dtype=uint8), array([192, 191, 196, ..., 128, 117, 121], dtype=uint8), array([232, 196, 162, ..., 237, 224, 234], dtype=uint8), array([ 34, 88, 135, ..., 169, 159, 183], dtype=uint8), array([49, 38, 34, ..., 54, 40, 13], dtype=uint8), array([40, 30, 29, ..., 10, 5, 1], dtype=uint8), array([97, 76, 49, ..., 50, 20, 28], dtype=uint8), array([118, 109, 114, ..., 56, 62, 210], dtype=uint8), array([ 7, 7, 5, ..., 138, 131, 138], dtype=uint8), array([42, 22, 13, ..., 26, 16, 25], dtype=uint8), array([34, 47, 56, ..., 74, 72, 73], dtype=uint8), array([232, 227, 224, ..., 213, 211, 214], dtype=uint8), array([251, 255, 254, ..., 240, 241, 246], dtype=uint8), array([ 74, 89, 128, ..., 194, 193, 237], dtype=uint8), array([ 15, 20, 14, ..., 106, 71, 31], dtype=uint8), array([119, 106, 72, ..., 20, 24, 25], dtype=uint8), array([163, 171, 160, ..., 44, 56, 56], dtype=uint8), array([76, 55, 36, ..., 69, 50, 35], dtype=uint8), array([229, 212, 182, ..., 172, 98, 133], dtype=uint8), array([183, 205, 192, ..., 31, 25, 29], dtype=uint8), array([ 29, 22, 16, ..., 189, 191, 167], dtype=uint8), array([ 0, 30, 46, ..., 98, 86, 96], dtype=uint8), array([183, 187, 154, ..., 75, 69, 45], dtype=uint8), array([ 27, 29, 24, ..., 250, 251, 246], dtype=uint8), array([127, 33, 23, ..., 161, 162, 206], dtype=uint8), array([152, 182, 232, ..., 17, 5, 17], dtype=uint8), array([ 31, 20, 0, ..., 135, 121, 94], dtype=uint8), array([126, 95, 75, ..., 99, 62, 43], dtype=uint8), array([48, 26, 15, ..., 40, 26, 15], dtype=uint8), array([ 87, 99, 209, ..., 188, 154, 168], dtype=uint8), array([ 62, 30, 33, ..., 249, 142, 198], dtype=uint8), array([ 1, 11, 36, ..., 17, 31, 57], dtype=uint8), array([ 65, 57, 34, ..., 115, 114, 109], dtype=uint8), array([43, 44, 48, ..., 29, 17, 17], dtype=uint8), array([164, 123, 69, ..., 126, 95, 101], dtype=uint8), array([ 72, 81, 64, ..., 128, 135, 143], dtype=uint8), array([166, 145, 118, ..., 136, 105, 85], dtype=uint8), array([237, 205, 194, ..., 150, 113, 105], dtype=uint8), array([77, 65, 67, ..., 77, 67, 65], dtype=uint8), array([ 16, 16, 14, ..., 121, 93, 71], dtype=uint8), array([ 71, 89, 113, ..., 56, 44, 32], dtype=uint8), array([12, 11, 25, ..., 33, 34, 55], dtype=uint8), array([ 13, 122, 165, ..., 55, 49, 63], dtype=uint8), array([37, 35, 36, ..., 11, 17, 29], dtype=uint8), array([ 91, 99, 122, ..., 67, 77, 104], dtype=uint8), array([131, 98, 47, ..., 126, 92, 57], dtype=uint8), array([215, 185, 161, ..., 56, 42, 41], dtype=uint8), array([31, 30, 35, ..., 28, 22, 22], dtype=uint8), array([38, 21, 13, ..., 58, 45, 39], dtype=uint8), array([17, 12, 32, ..., 10, 1, 2], dtype=uint8), array([ 14, 8, 20, ..., 193, 158, 164], dtype=uint8), array([141, 149, 128, ..., 92, 76, 43], dtype=uint8), array([59, 32, 23, ..., 17, 16, 12], dtype=uint8), array([ 53, 43, 34, ..., 121, 122, 166], dtype=uint8), array([168, 153, 156, ..., 133, 93, 101], dtype=uint8), array([31, 32, 26, ..., 44, 0, 1], dtype=uint8), array([26, 17, 12, ..., 57, 44, 28], dtype=uint8), array([ 59, 51, 110, ..., 6, 1, 0], dtype=uint8), array([17, 16, 12, ..., 57, 40, 30], dtype=uint8), array([110, 79, 85, ..., 151, 122, 88], dtype=uint8), array([143, 124, 118, ..., 120, 100, 91], dtype=uint8), array([80, 79, 84, ..., 90, 91, 95], dtype=uint8), array([133, 174, 170, ..., 66, 31, 37], dtype=uint8), array([38, 29, 24, ..., 52, 32, 25], dtype=uint8), array([98, 94, 83, ..., 54, 47, 39], dtype=uint8), array([156, 204, 244, ..., 67, 55, 75], dtype=uint8), array([ 0, 32, 57, ..., 75, 193, 231], dtype=uint8), array([ 0, 2, 47, ..., 196, 184, 206], dtype=uint8), array([38, 24, 24, ..., 84, 41, 35], dtype=uint8), array([ 83, 78, 134, ..., 69, 69, 77], dtype=uint8), array([108, 86, 89, ..., 129, 79, 82], dtype=uint8), array([196, 64, 75, ..., 175, 75, 77], dtype=uint8), array([ 53, 57, 40, ..., 113, 74, 43], dtype=uint8), array([231, 234, 251, ..., 36, 23, 32], dtype=uint8), array([123, 110, 78, ..., 18, 0, 0], dtype=uint8), array([59, 61, 56, ..., 6, 6, 16], dtype=uint8), array([165, 131, 147, ..., 149, 107, 91], dtype=uint8), array([34, 32, 37, ..., 51, 54, 63], dtype=uint8), array([113, 132, 188, ..., 108, 109, 137], dtype=uint8), array([121, 105, 72, ..., 108, 92, 79], dtype=uint8), array([128, 110, 90, ..., 91, 63, 42], dtype=uint8), array([224, 218, 204, ..., 54, 52, 53], dtype=uint8), array([ 25, 24, 6, ..., 172, 165, 173], dtype=uint8), array([24, 26, 39, ..., 29, 28, 33], dtype=uint8), array([226, 223, 208, ..., 161, 176, 179], dtype=uint8), array([57, 56, 62, ..., 5, 11, 9], dtype=uint8), array([ 85, 128, 118, ..., 67, 44, 38], dtype=uint8), array([ 36, 29, 21, ..., 158, 147, 141], dtype=uint8), array([110, 93, 83, ..., 94, 76, 72], dtype=uint8), array([ 4, 0, 0, ..., 233, 209, 175], dtype=uint8), array([56, 36, 38, ..., 60, 29, 27], dtype=uint8), array([69, 69, 67, ..., 96, 66, 56], dtype=uint8), array([224, 228, 237, ..., 236, 239, 244], dtype=uint8), array([ 22, 22, 10, ..., 232, 233, 228], dtype=uint8), array([ 26, 8, 4, ..., 213, 195, 173], dtype=uint8), array([232, 88, 113, ..., 38, 51, 95], dtype=uint8), array([157, 147, 137, ..., 157, 103, 77], dtype=uint8), array([165, 112, 72, ..., 25, 25, 25], dtype=uint8), array([62, 62, 62, ..., 98, 49, 44], dtype=uint8), array([74, 69, 40, ..., 94, 67, 38], dtype=uint8), array([171, 152, 122, ..., 13, 19, 17], dtype=uint8), array([240, 242, 241, ..., 77, 82, 88], dtype=uint8), array([180, 168, 168, ..., 241, 211, 237], dtype=uint8), array([ 99, 89, 79, ..., 253, 251, 228], dtype=uint8), array([101, 112, 130, ..., 21, 26, 45], dtype=uint8), array([115, 107, 120, ..., 56, 42, 31], dtype=uint8), array([243, 192, 235, ..., 51, 40, 118], dtype=uint8), array([98, 80, 68, ..., 88, 60, 57], dtype=uint8), array([233, 152, 193, ..., 101, 59, 43], dtype=uint8), array([253, 253, 255, ..., 126, 106, 97], dtype=uint8), array([177, 136, 170, ..., 24, 24, 26], dtype=uint8), array([ 20, 21, 16, ..., 250, 239, 221], dtype=uint8), array([ 65, 79, 108, ..., 91, 85, 87], dtype=uint8), array([162, 164, 161, ..., 62, 36, 23], dtype=uint8), array([ 47, 28, 231, ..., 102, 109, 102], dtype=uint8), array([234, 216, 168, ..., 133, 98, 70], dtype=uint8), array([201, 169, 130, ..., 197, 175, 152], dtype=uint8), array([ 54, 59, 81, ..., 103, 108, 130], dtype=uint8), array([33, 44, 64, ..., 10, 19, 36], dtype=uint8), array([20, 19, 24, ..., 17, 15, 18], dtype=uint8), array([207, 170, 162, ..., 91, 51, 43], dtype=uint8), array([49, 27, 14, ..., 2, 1, 17], dtype=uint8), array([254, 224, 236, ..., 230, 165, 127], dtype=uint8), array([ 2, 9, 25, ..., 89, 25, 25], dtype=uint8), array([ 27, 31, 17, ..., 179, 138, 120], dtype=uint8), array([55, 49, 51, ..., 46, 41, 38], dtype=uint8), array([30, 37, 55, ..., 18, 18, 28], dtype=uint8), array([ 40, 26, 25, ..., 110, 112, 99], dtype=uint8), array([ 42, 46, 49, ..., 208, 214, 246], dtype=uint8), array([211, 207, 204, ..., 153, 139, 113], dtype=uint8), array([58, 63, 66, ..., 0, 0, 0], dtype=uint8), array([ 11, 0, 28, ..., 191, 173, 199], dtype=uint8), array([ 55, 62, 114, ..., 148, 137, 154], dtype=uint8), array([56, 54, 94, ..., 59, 62, 81], dtype=uint8), array([255, 252, 223, ..., 102, 107, 139], dtype=uint8), array([56, 46, 47, ..., 90, 65, 60], dtype=uint8), array([118, 158, 230, ..., 38, 37, 43], dtype=uint8), array([167, 143, 107, ..., 167, 118, 78], dtype=uint8), array([71, 57, 56, ..., 29, 21, 19], dtype=uint8), array([166, 128, 117, ..., 151, 105, 82], dtype=uint8), array([204, 210, 176, ..., 15, 20, 26], dtype=uint8), array([172, 170, 171, ..., 1, 1, 3], dtype=uint8), array([ 32, 29, 22, ..., 107, 90, 82], dtype=uint8), array([169, 71, 70, ..., 57, 55, 56], dtype=uint8), array([209, 232, 206, ..., 224, 220, 191], dtype=uint8), array([135, 91, 66, ..., 79, 42, 23], dtype=uint8), array([205, 207, 193, ..., 23, 14, 17], dtype=uint8), array([176, 111, 17, ..., 16, 18, 17], dtype=uint8), array([ 78, 93, 62, ..., 188, 209, 236], dtype=uint8), array([ 79, 110, 200, ..., 18, 14, 15], dtype=uint8), array([118, 102, 79, ..., 95, 78, 68], dtype=uint8), array([169, 150, 118, ..., 172, 220, 234], dtype=uint8), array([ 82, 62, 51, ..., 126, 118, 131], dtype=uint8), array([76, 70, 58, ..., 7, 19, 31], dtype=uint8), array([16, 16, 16, ..., 49, 62, 70], dtype=uint8), array([254, 236, 186, ..., 205, 141, 141], dtype=uint8), array([ 59, 45, 34, ..., 104, 97, 113], dtype=uint8), array([56, 47, 66, ..., 94, 76, 76], dtype=uint8), array([121, 116, 110, ..., 144, 120, 136], dtype=uint8), array([229, 229, 229, ..., 58, 45, 36], dtype=uint8), array([223, 192, 148, ..., 164, 112, 73], dtype=uint8), array([156, 154, 167, ..., 23, 21, 43], dtype=uint8), array([ 36, 24, 24, ..., 68, 74, 108], dtype=uint8), array([39, 28, 26, ..., 53, 33, 24], dtype=uint8), array([166, 152, 143, ..., 87, 54, 37], dtype=uint8), array([54, 32, 44, ..., 41, 44, 53], dtype=uint8), array([ 0, 0, 0, ..., 186, 210, 244], dtype=uint8), array([140, 137, 144, ..., 100, 88, 64], dtype=uint8), array([99, 61, 14, ..., 0, 5, 1], dtype=uint8), array([191, 142, 110, ..., 203, 139, 93], dtype=uint8), array([ 14, 15, 10, ..., 117, 102, 97], dtype=uint8), array([ 23, 23, 23, ..., 155, 6, 8], dtype=uint8), array([209, 203, 177, ..., 28, 23, 20], dtype=uint8), array([ 18, 86, 123, ..., 55, 25, 14], dtype=uint8), array([95, 68, 47, ..., 49, 27, 30], dtype=uint8), array([52, 37, 40, ..., 28, 28, 36], dtype=uint8), array([163, 160, 153, ..., 44, 43, 39], dtype=uint8), array([ 64, 68, 71, ..., 164, 145, 139], dtype=uint8), array([125, 112, 93, ..., 186, 179, 187], dtype=uint8), array([41, 25, 25, ..., 55, 24, 29], dtype=uint8), array([ 32, 49, 103, ..., 195, 155, 119], dtype=uint8), array([ 94, 96, 83, ..., 201, 192, 193], dtype=uint8), array([62, 38, 36, ..., 74, 35, 53], dtype=uint8), array([47, 33, 22, ..., 57, 47, 38], dtype=uint8), array([ 88, 79, 100, ..., 82, 34, 120], dtype=uint8), array([225, 238, 246, ..., 42, 33, 38], dtype=uint8), array([107, 87, 60, ..., 90, 64, 27], dtype=uint8), array([ 38, 28, 27, ..., 217, 219, 218], dtype=uint8), array([158, 133, 111, ..., 139, 97, 75], dtype=uint8), array([ 22, 17, 21, ..., 112, 111, 125], dtype=uint8), array([116, 109, 90, ..., 29, 33, 36], dtype=uint8), array([ 65, 53, 77, ..., 157, 90, 74], dtype=uint8), array([18, 9, 4, ..., 17, 34, 42], dtype=uint8), array([161, 138, 106, ..., 118, 97, 68], dtype=uint8), array([37, 49, 71, ..., 22, 20, 21], dtype=uint8), array([132, 138, 104, ..., 60, 38, 27], dtype=uint8), array([93, 82, 78, ..., 77, 55, 41], dtype=uint8), array([40, 27, 21, ..., 62, 50, 36], dtype=uint8), array([31, 30, 28, ..., 34, 21, 15], dtype=uint8), array([ 9, 58, 187, ..., 36, 35, 49], dtype=uint8), array([ 71, 69, 80, ..., 173, 176, 193], dtype=uint8), array([ 98, 81, 87, ..., 115, 111, 144], dtype=uint8), array([30, 23, 39, ..., 28, 26, 40], dtype=uint8), array([211, 180, 188, ..., 227, 190, 171], dtype=uint8), array([17, 14, 25, ..., 36, 0, 0], dtype=uint8), array([103, 91, 75, ..., 62, 44, 34], dtype=uint8), array([ 5, 8, 25, ..., 47, 36, 44], dtype=uint8), array([39, 26, 36, ..., 42, 31, 39], dtype=uint8), array([ 93, 172, 241, ..., 146, 152, 186], dtype=uint8), array([187, 173, 147, ..., 39, 35, 52], dtype=uint8), array([95, 83, 69, ..., 28, 25, 42], dtype=uint8), array([77, 45, 30, ..., 58, 19, 14], dtype=uint8), array([69, 42, 23, ..., 13, 4, 0], dtype=uint8), array([84, 60, 36, ..., 2, 9, 17], dtype=uint8), array([114, 88, 61, ..., 39, 4, 0], dtype=uint8), array([ 0, 1, 2, ..., 159, 133, 110], dtype=uint8), array([51, 41, 31, ..., 34, 19, 12], dtype=uint8), array([114, 110, 107, ..., 145, 141, 142], dtype=uint8), array([22, 22, 46, ..., 32, 28, 55], dtype=uint8), array([64, 45, 47, ..., 29, 15, 15], dtype=uint8), array([35, 21, 12, ..., 12, 7, 1], dtype=uint8), array([95, 75, 48, ..., 25, 8, 0], dtype=uint8), array([13, 4, 21, ..., 27, 39, 87], dtype=uint8), array([119, 103, 90, ..., 41, 35, 37], dtype=uint8), array([113, 97, 81, ..., 76, 65, 37], dtype=uint8), array([ 63, 38, 31, ..., 163, 164, 158], dtype=uint8), array([55, 52, 37, ..., 62, 70, 83], dtype=uint8), array([237, 158, 203, ..., 158, 117, 131], dtype=uint8), array([239, 239, 241, ..., 229, 231, 230], dtype=uint8), array([100, 99, 107, ..., 20, 20, 28], dtype=uint8), array([ 7, 36, 92, ..., 105, 95, 120], dtype=uint8), array([ 4, 11, 19, ..., 154, 127, 100], dtype=uint8), array([36, 24, 38, ..., 24, 7, 0], dtype=uint8), array([59, 35, 35, ..., 3, 5, 20], dtype=uint8), array([ 49, 41, 30, ..., 172, 154, 170], dtype=uint8), array([ 39, 47, 86, ..., 159, 122, 104], dtype=uint8), array([164, 142, 95, ..., 191, 148, 93], dtype=uint8), array([ 42, 34, 21, ..., 213, 206, 180], dtype=uint8), array([118, 143, 243, ..., 99, 120, 209], dtype=uint8), array([37, 30, 37, ..., 62, 60, 63], dtype=uint8), array([34, 36, 49, ..., 35, 8, 17], dtype=uint8), array([53, 46, 40, ..., 25, 17, 14], dtype=uint8), array([149, 142, 150, ..., 72, 27, 47], dtype=uint8), array([61, 73, 69, ..., 52, 53, 81], dtype=uint8), array([ 92, 71, 44, ..., 94, 98, 107], dtype=uint8), array([154, 126, 115, ..., 110, 68, 56], dtype=uint8), array([28, 22, 34, ..., 22, 18, 19], dtype=uint8), array([169, 186, 229, ..., 252, 244, 255], dtype=uint8), array([108, 83, 86, ..., 187, 158, 188], dtype=uint8), array([2, 1, 0, ..., 3, 0, 7], dtype=uint8), array([11, 8, 1, ..., 14, 5, 0], dtype=uint8), array([ 69, 42, 21, ..., 104, 65, 48], dtype=uint8), array([30, 20, 19, ..., 39, 31, 18], dtype=uint8), array([87, 49, 36, ..., 44, 14, 12], dtype=uint8), array([14, 16, 15, ..., 13, 14, 9], dtype=uint8), array([100, 106, 128, ..., 50, 51, 72], dtype=uint8), array([ 92, 87, 110, ..., 97, 96, 104], dtype=uint8), array([ 10, 67, 112, ..., 91, 138, 156], dtype=uint8), array([ 65, 67, 64, ..., 133, 90, 71], dtype=uint8), array([44, 17, 6, ..., 14, 0, 0], dtype=uint8), array([ 73, 33, 23, ..., 121, 137, 215], dtype=uint8), array([68, 76, 65, ..., 95, 86, 71], dtype=uint8), array([60, 79, 0, ..., 67, 51, 28], dtype=uint8), array([ 1, 35, 228, ..., 1, 55, 215], dtype=uint8), array([ 97, 83, 70, ..., 249, 254, 255], dtype=uint8), array([49, 44, 24, ..., 17, 7, 5], dtype=uint8), array([18, 16, 19, ..., 40, 74, 58], dtype=uint8), array([148, 4, 14, ..., 28, 23, 19], dtype=uint8), array([203, 158, 116, ..., 189, 148, 104], dtype=uint8), array([ 6, 4, 5, ..., 13, 2, 6], dtype=uint8), array([110, 103, 85, ..., 25, 14, 20], dtype=uint8), array([217, 168, 65, ..., 175, 126, 83], dtype=uint8), array([175, 222, 250, ..., 205, 207, 245], dtype=uint8), array([ 66, 48, 28, ..., 152, 112, 86], dtype=uint8), array([ 22, 38, 64, ..., 209, 206, 233], dtype=uint8), array([48, 33, 28, ..., 32, 23, 16], dtype=uint8), array([128, 64, 65, ..., 209, 208, 178], dtype=uint8), array([201, 178, 184, ..., 207, 205, 216], dtype=uint8), array([12, 6, 10, ..., 72, 64, 77], dtype=uint8), array([ 25, 17, 30, ..., 219, 219, 217], dtype=uint8), array([70, 65, 85, ..., 33, 31, 42], dtype=uint8), array([ 67, 41, 40, ..., 140, 133, 149], dtype=uint8), array([ 32, 39, 55, ..., 108, 99, 92], dtype=uint8), array([145, 99, 65, ..., 189, 22, 92], dtype=uint8), array([39, 37, 24, ..., 37, 24, 7], dtype=uint8), array([187, 189, 248, ..., 74, 53, 70], dtype=uint8), array([48, 39, 40, ..., 87, 77, 65], dtype=uint8), array([115, 101, 88, ..., 223, 215, 204], dtype=uint8), array([156, 136, 135, ..., 92, 90, 104], dtype=uint8), array([24, 18, 2, ..., 26, 12, 12], dtype=uint8), array([11, 13, 8, ..., 83, 84, 79], dtype=uint8), array([183, 176, 158, ..., 89, 80, 49], dtype=uint8), array([ 40, 31, 26, ..., 113, 98, 101], dtype=uint8), array([136, 187, 180, ..., 41, 20, 15], dtype=uint8), array([237, 217, 208, ..., 63, 35, 31], dtype=uint8), array([ 97, 103, 89, ..., 94, 69, 49], dtype=uint8), array([148, 98, 89, ..., 86, 36, 27], dtype=uint8), array([ 45, 38, 28, ..., 226, 226, 218], dtype=uint8), array([ 79, 59, 24, ..., 159, 117, 153], dtype=uint8), array([ 8, 10, 7, ..., 54, 81, 111], dtype=uint8), array([ 23, 13, 11, ..., 184, 155, 123], dtype=uint8), array([20, 16, 7, ..., 1, 1, 1], dtype=uint8), array([106, 82, 58, ..., 68, 64, 61], dtype=uint8), array([97, 84, 76, ..., 20, 15, 21], dtype=uint8), array([102, 91, 95, ..., 156, 138, 138], dtype=uint8), array([159, 140, 123, ..., 78, 59, 45], dtype=uint8), array([ 35, 23, 27, ..., 135, 100, 68], dtype=uint8), array([66, 40, 23, ..., 44, 0, 35], dtype=uint8), array([ 55, 45, 43, ..., 185, 145, 133], dtype=uint8), array([ 23, 30, 121, ..., 193, 163, 173], dtype=uint8), array([101, 85, 86, ..., 5, 0, 6], dtype=uint8), array([ 19, 15, 32, ..., 83, 83, 109], dtype=uint8), array([53, 38, 41, ..., 94, 47, 57], dtype=uint8), array([86, 63, 49, ..., 35, 6, 0], dtype=uint8), array([245, 182, 239, ..., 199, 164, 132], dtype=uint8), array([79, 62, 54, ..., 65, 60, 67], dtype=uint8), array([ 45, 31, 31, ..., 158, 105, 121], dtype=uint8), array([2, 1, 0, ..., 0, 0, 0], dtype=uint8), array([187, 152, 120, ..., 25, 42, 94], dtype=uint8), array([ 78, 65, 48, ..., 112, 143, 207], dtype=uint8), array([82, 62, 53, ..., 68, 44, 20], dtype=uint8), array([113, 119, 115, ..., 111, 69, 93], dtype=uint8), array([68, 51, 35, ..., 49, 37, 21], dtype=uint8), array([ 85, 81, 46, ..., 132, 131, 111], dtype=uint8), array([47, 65, 69, ..., 64, 69, 98], dtype=uint8), array([185, 190, 193, ..., 20, 7, 0], dtype=uint8), array([84, 75, 76, ..., 13, 2, 10], dtype=uint8), array([77, 66, 62, ..., 92, 58, 46], dtype=uint8), array([161, 139, 102, ..., 167, 142, 101], dtype=uint8), array([100, 94, 94, ..., 52, 73, 92], dtype=uint8), array([ 91, 99, 101, ..., 31, 29, 40], dtype=uint8), array([157, 161, 170, ..., 99, 91, 88], dtype=uint8), array([157, 127, 129, ..., 95, 63, 50], dtype=uint8), array([ 20, 24, 35, ..., 164, 101, 83], dtype=uint8), array([22, 20, 23, ..., 0, 0, 0], dtype=uint8), array([36, 32, 33, ..., 12, 7, 13], dtype=uint8), array([128, 89, 84, ..., 48, 23, 27], dtype=uint8), array([17, 15, 26, ..., 78, 72, 74], dtype=uint8), array([50, 49, 67, ..., 34, 31, 38], dtype=uint8), array([ 52, 49, 44, ..., 206, 197, 200], dtype=uint8), array([115, 88, 81, ..., 142, 109, 102], dtype=uint8), array([92, 62, 60, ..., 87, 85, 98], dtype=uint8), array([ 9, 18, 15, ..., 160, 159, 154], dtype=uint8), array([ 36, 29, 37, ..., 212, 218, 234], dtype=uint8), array([ 89, 100, 94, ..., 42, 53, 71], dtype=uint8), array([98, 80, 60, ..., 54, 26, 14], dtype=uint8), array([18, 17, 12, ..., 7, 3, 0], dtype=uint8), array([ 64, 55, 40, ..., 102, 140, 153], dtype=uint8), array([83, 72, 54, ..., 46, 48, 69], dtype=uint8), array([ 72, 128, 189, ..., 21, 25, 70], dtype=uint8), array([169, 174, 144, ..., 219, 190, 174], dtype=uint8), array([244, 218, 193, ..., 19, 24, 27], dtype=uint8), array([245, 212, 171, ..., 172, 115, 95], dtype=uint8), array([ 17, 95, 118, ..., 129, 209, 242], dtype=uint8), array([116, 111, 131, ..., 97, 63, 61], dtype=uint8), array([ 77, 77, 87, ..., 126, 109, 102], dtype=uint8), array([86, 72, 61, ..., 50, 52, 51], dtype=uint8), array([16, 16, 18, ..., 22, 19, 12], dtype=uint8), array([13, 10, 1, ..., 26, 27, 47], dtype=uint8), array([ 35, 38, 55, ..., 145, 87, 65], dtype=uint8), array([ 7, 39, 80, ..., 3, 8, 12], dtype=uint8), array([221, 222, 227, ..., 213, 227, 230], dtype=uint8), array([180, 132, 96, ..., 87, 99, 121], dtype=uint8), array([47, 25, 11, ..., 63, 62, 67], dtype=uint8), array([182, 178, 177, ..., 42, 38, 37], dtype=uint8), array([122, 124, 113, ..., 179, 181, 194], dtype=uint8), array([41, 35, 63, ..., 67, 49, 63], dtype=uint8), array([ 14, 68, 158, ..., 109, 128, 184], dtype=uint8), array([222, 160, 163, ..., 31, 29, 43], dtype=uint8), array([60, 47, 39, ..., 42, 40, 41], dtype=uint8), array([81, 91, 83, ..., 41, 31, 32], dtype=uint8), array([107, 109, 104, ..., 104, 82, 69], dtype=uint8), array([ 65, 84, 88, ..., 207, 182, 152], dtype=uint8), array([128, 99, 93, ..., 54, 25, 30], dtype=uint8), array([5, 1, 0, ..., 0, 0, 0], dtype=uint8), array([120, 90, 62, ..., 165, 123, 85], dtype=uint8), array([101, 83, 79, ..., 156, 106, 83], dtype=uint8), array([81, 72, 67, ..., 64, 55, 46], dtype=uint8), array([92, 56, 70, ..., 79, 37, 39], dtype=uint8), array([108, 74, 46, ..., 77, 8, 13], dtype=uint8), array([46, 28, 26, ..., 13, 2, 10], dtype=uint8), array([ 0, 0, 0, ..., 61, 118, 199], dtype=uint8), array([ 23, 38, 141, ..., 19, 49, 135], dtype=uint8), array([222, 220, 221, ..., 0, 0, 0], dtype=uint8), array([158, 158, 158, ..., 73, 62, 58], dtype=uint8), array([108, 82, 65, ..., 18, 14, 5], dtype=uint8), array([ 69, 80, 76, ..., 104, 120, 110], dtype=uint8), array([23, 25, 14, ..., 82, 57, 78], dtype=uint8), array([ 69, 96, 177, ..., 48, 51, 70], dtype=uint8), array([ 45, 23, 25, ..., 139, 88, 71], dtype=uint8), array([149, 141, 162, ..., 100, 73, 56], dtype=uint8), array([ 32, 40, 87, ..., 148, 70, 48], dtype=uint8), array([ 40, 37, 22, ..., 110, 75, 43], dtype=uint8), array([ 44, 43, 41, ..., 131, 127, 124], dtype=uint8), array([222, 237, 234, ..., 96, 97, 91], dtype=uint8), array([24, 23, 19, ..., 30, 20, 10], dtype=uint8), array([35, 23, 33, ..., 83, 2, 19], dtype=uint8), array([140, 79, 12, ..., 48, 48, 60], dtype=uint8), array([38, 36, 23, ..., 17, 17, 17], dtype=uint8), array([ 95, 95, 147, ..., 160, 111, 97], dtype=uint8), array([253, 253, 253, ..., 203, 178, 244], dtype=uint8), array([78, 84, 84, ..., 74, 80, 78], dtype=uint8), array([161, 172, 176, ..., 91, 111, 118], dtype=uint8), array([88, 93, 89, ..., 79, 84, 90], dtype=uint8), array([ 9, 73, 197, ..., 37, 71, 168], dtype=uint8), array([149, 137, 115, ..., 16, 5, 13], dtype=uint8), array([229, 237, 240, ..., 27, 17, 25], dtype=uint8), array([238, 211, 194, ..., 149, 106, 100], dtype=uint8), array([118, 116, 103, ..., 159, 149, 124], dtype=uint8), array([196, 196, 196, ..., 14, 7, 15], dtype=uint8), array([ 66, 45, 40, ..., 118, 103, 96], dtype=uint8), array([78, 63, 60, ..., 51, 32, 28], dtype=uint8), array([ 57, 42, 63, ..., 198, 144, 108], dtype=uint8), array([64, 53, 49, ..., 22, 16, 4], dtype=uint8), array([163, 126, 99, ..., 194, 149, 108], dtype=uint8), array([ 77, 75, 62, ..., 121, 113, 102], dtype=uint8), array([111, 95, 82, ..., 155, 127, 168], dtype=uint8), array([72, 69, 76, ..., 39, 33, 35], dtype=uint8), array([ 67, 72, 153, ..., 0, 0, 2], dtype=uint8), array([ 40, 7, 2, ..., 156, 82, 55], dtype=uint8), array([141, 138, 131, ..., 162, 161, 157], dtype=uint8), array([ 83, 107, 85, ..., 163, 162, 157], dtype=uint8), array([228, 239, 222, ..., 113, 87, 96], dtype=uint8), array([136, 126, 114, ..., 161, 21, 58], dtype=uint8), array([157, 106, 51, ..., 6, 6, 6], dtype=uint8), array([41, 42, 99, ..., 19, 17, 18], dtype=uint8), array([143, 200, 255, ..., 161, 161, 255], dtype=uint8), array([1, 0, 6, ..., 2, 1, 6], dtype=uint8), array([50, 43, 84, ..., 72, 75, 82], dtype=uint8), array([108, 67, 39, ..., 21, 7, 4], dtype=uint8), array([127, 109, 87, ..., 95, 68, 41], dtype=uint8), array([ 56, 50, 50, ..., 106, 94, 80], dtype=uint8), array([ 51, 55, 32, ..., 144, 145, 140], dtype=uint8), array([113, 73, 71, ..., 91, 70, 126], dtype=uint8), array([121, 99, 60, ..., 121, 73, 59], dtype=uint8), array([53, 39, 36, ..., 80, 70, 60], dtype=uint8), array([43, 10, 3, ..., 28, 2, 5], dtype=uint8), array([30, 28, 42, ..., 40, 40, 38], dtype=uint8), array([ 70, 58, 44, ..., 240, 214, 197], dtype=uint8), array([196, 201, 195, ..., 10, 3, 0], dtype=uint8), array([156, 125, 60, ..., 233, 189, 160], dtype=uint8), array([155, 165, 167, ..., 221, 252, 254], dtype=uint8), array([123, 115, 112, ..., 45, 48, 63], dtype=uint8), array([13, 21, 58, ..., 26, 26, 36], dtype=uint8), array([ 54, 69, 74, ..., 47, 60, 105], dtype=uint8), array([35, 29, 29, ..., 9, 7, 10], dtype=uint8), array([136, 67, 114, ..., 39, 25, 84], dtype=uint8), array([238, 241, 250, ..., 82, 89, 117], dtype=uint8), array([ 32, 37, 67, ..., 112, 84, 109], dtype=uint8), array([31, 7, 0, ..., 27, 17, 7], dtype=uint8), array([ 74, 52, 41, ..., 17, 17, 113], dtype=uint8), array([46, 29, 22, ..., 10, 10, 10], dtype=uint8), array([196, 162, 137, ..., 60, 45, 40], dtype=uint8), array([188, 190, 179, ..., 112, 99, 90], dtype=uint8), array([28, 38, 30, ..., 23, 44, 65], dtype=uint8), array([33, 34, 26, ..., 34, 33, 38], dtype=uint8), array([ 71, 105, 195, ..., 32, 13, 6], dtype=uint8), array([113, 96, 89, ..., 26, 23, 30], dtype=uint8), array([239, 244, 247, ..., 164, 118, 105], dtype=uint8), array([39, 46, 56, ..., 31, 43, 93], dtype=uint8), array([ 56, 58, 44, ..., 145, 159, 159], dtype=uint8), array([50, 34, 35, ..., 24, 13, 21], dtype=uint8), array([ 91, 135, 84, ..., 75, 61, 48], dtype=uint8), array([200, 171, 155, ..., 77, 47, 57], dtype=uint8), array([ 12, 20, 39, ..., 111, 61, 36], dtype=uint8), array([ 95, 92, 109, ..., 56, 0, 18], dtype=uint8), array([ 66, 72, 104, ..., 92, 74, 72], dtype=uint8), array([ 10, 102, 81, ..., 58, 69, 65], dtype=uint8), array([ 54, 34, 36, ..., 111, 86, 92], dtype=uint8), array([ 7, 63, 172, ..., 104, 111, 121], dtype=uint8), array([ 94, 85, 80, ..., 215, 217, 212], dtype=uint8), array([ 33, 18, 11, ..., 253, 253, 245], dtype=uint8), array([48, 30, 16, ..., 48, 21, 4], dtype=uint8), array([231, 237, 253, ..., 209, 195, 130], dtype=uint8), array([177, 163, 152, ..., 218, 187, 156], dtype=uint8), array([ 82, 91, 186, ..., 31, 23, 44], dtype=uint8), array([18, 12, 14, ..., 55, 53, 56], dtype=uint8), array([31, 25, 27, ..., 39, 20, 16], dtype=uint8), array([ 94, 44, 33, ..., 129, 99, 88], dtype=uint8), array([143, 140, 197, ..., 1, 1, 1], dtype=uint8), array([0, 0, 0, ..., 0, 0, 0], dtype=uint8), array([146, 114, 91, ..., 88, 58, 50], dtype=uint8), array([159, 142, 116, ..., 172, 163, 154], dtype=uint8), array([252, 226, 199, ..., 205, 182, 176], dtype=uint8), array([ 24, 13, 17, ..., 137, 95, 73], dtype=uint8), array([ 57, 69, 67, ..., 164, 199, 241], dtype=uint8), array([72, 79, 72, ..., 48, 57, 64], dtype=uint8), array([ 94, 135, 201, ..., 222, 221, 229], dtype=uint8), array([115, 85, 57, ..., 195, 196, 214], dtype=uint8), array([ 0, 26, 70, ..., 17, 39, 80], dtype=uint8), array([ 79, 100, 117, ..., 81, 107, 144], dtype=uint8), array([106, 112, 108, ..., 54, 57, 72], dtype=uint8), array([162, 171, 154, ..., 100, 68, 29], dtype=uint8), array([184, 140, 139, ..., 64, 47, 40], dtype=uint8), array([166, 162, 151, ..., 26, 22, 23], dtype=uint8), array([58, 53, 60, ..., 26, 14, 0], dtype=uint8), array([127, 101, 74, ..., 39, 42, 21], dtype=uint8), array([82, 78, 66, ..., 19, 4, 7], dtype=uint8), array([90, 58, 37, ..., 6, 0, 0], dtype=uint8), array([56, 53, 38, ..., 32, 38, 28], dtype=uint8), array([116, 134, 110, ..., 223, 205, 193], dtype=uint8), array([95, 67, 45, ..., 65, 33, 22], dtype=uint8), array([199, 170, 130, ..., 86, 60, 43], dtype=uint8), array([239, 242, 247, ..., 232, 236, 245], dtype=uint8), array([152, 127, 107, ..., 142, 101, 69], dtype=uint8), array([124, 127, 100, ..., 163, 148, 127], dtype=uint8), array([ 4, 7, 12, ..., 63, 55, 52], dtype=uint8), array([ 37, 37, 91, ..., 145, 148, 163], dtype=uint8), array([43, 36, 44, ..., 70, 46, 68], dtype=uint8), array([142, 134, 132, ..., 13, 3, 2], dtype=uint8), array([107, 86, 59, ..., 155, 156, 151], dtype=uint8), array([43, 27, 37, ..., 44, 40, 63], dtype=uint8), array([50, 39, 35, ..., 72, 56, 57], dtype=uint8), array([136, 20, 55, ..., 52, 49, 68], dtype=uint8), array([ 26, 25, 21, ..., 209, 172, 213], dtype=uint8), array([137, 142, 146, ..., 128, 176, 250], dtype=uint8), array([35, 16, 22, ..., 34, 36, 48], dtype=uint8), array([ 27, 44, 38, ..., 132, 112, 87], dtype=uint8), array([ 40, 21, 53, ..., 116, 104, 106], dtype=uint8), array([58, 22, 6, ..., 23, 5, 3], dtype=uint8), array([75, 29, 6, ..., 45, 24, 5], dtype=uint8), array([42, 28, 19, ..., 74, 46, 34], dtype=uint8), array([103, 113, 125, ..., 67, 51, 52], dtype=uint8), array([ 19, 27, 76, ..., 104, 83, 82], dtype=uint8), array([ 22, 10, 12, ..., 133, 135, 158], dtype=uint8), array([15, 12, 5, ..., 59, 46, 37], dtype=uint8), array([73, 59, 48, ..., 10, 5, 2], dtype=uint8), array([117, 88, 93, ..., 96, 86, 111], dtype=uint8), array([128, 99, 104, ..., 23, 17, 31], dtype=uint8), array([77, 60, 53, ..., 28, 23, 19], dtype=uint8), array([118, 82, 46, ..., 142, 108, 81], dtype=uint8), array([111, 108, 99, ..., 177, 176, 174], dtype=uint8), array([164, 132, 83, ..., 66, 50, 37], dtype=uint8), array([124, 92, 69, ..., 106, 75, 55], dtype=uint8), array([ 92, 66, 53, ..., 152, 122, 111], dtype=uint8), array([130, 129, 127, ..., 7, 5, 6], dtype=uint8), array([170, 136, 101, ..., 212, 168, 121], dtype=uint8), array([93, 52, 46, ..., 51, 27, 23], dtype=uint8), array([ 50, 51, 141, ..., 113, 93, 69], dtype=uint8), array([ 56, 45, 39, ..., 102, 103, 95], dtype=uint8), array([32, 26, 10, ..., 26, 24, 3], dtype=uint8), array([173, 133, 123, ..., 105, 67, 56], dtype=uint8), array([ 84, 89, 109, ..., 115, 68, 38], dtype=uint8), array([93, 89, 88, ..., 42, 53, 36], dtype=uint8), array([150, 118, 97, ..., 94, 78, 91], dtype=uint8), array([ 1, 1, 1, ..., 145, 140, 147], dtype=uint8), array([ 73, 68, 62, ..., 179, 128, 109], dtype=uint8), array([ 56, 52, 49, ..., 133, 41, 46], dtype=uint8), array([55, 54, 68, ..., 7, 8, 13], dtype=uint8), array([126, 87, 70, ..., 44, 27, 19], dtype=uint8), array([100, 82, 70, ..., 75, 53, 40], dtype=uint8), array([ 72, 169, 126, ..., 34, 24, 33], dtype=uint8), array([ 18, 13, 17, ..., 211, 191, 203], dtype=uint8), array([34, 30, 57, ..., 99, 71, 57], dtype=uint8), array([73, 61, 65, ..., 37, 50, 59], dtype=uint8), array([34, 38, 47, ..., 25, 14, 18], dtype=uint8), array([106, 116, 91, ..., 21, 23, 22], dtype=uint8), array([ 10, 84, 207, ..., 15, 9, 9], dtype=uint8), array([209, 230, 225, ..., 28, 9, 11], dtype=uint8), array([ 47, 28, 22, ..., 253, 241, 245], dtype=uint8), array([111, 94, 84, ..., 42, 32, 33], dtype=uint8), array([127, 106, 87, ..., 55, 33, 35], dtype=uint8), array([109, 101, 90, ..., 100, 73, 43], dtype=uint8), array([38, 46, 48, ..., 57, 59, 72], dtype=uint8), array([181, 150, 145, ..., 74, 46, 34], dtype=uint8), array([131, 132, 136, ..., 255, 235, 255], dtype=uint8), array([126, 106, 95, ..., 12, 8, 23], dtype=uint8), array([121, 95, 82, ..., 19, 18, 23], dtype=uint8), array([ 64, 43, 38, ..., 153, 127, 104], dtype=uint8), array([ 20, 16, 13, ..., 117, 96, 93], dtype=uint8), array([100, 96, 84, ..., 152, 148, 137], dtype=uint8), array([153, 142, 112, ..., 44, 38, 26], dtype=uint8), array([197, 210, 216, ..., 166, 169, 204], dtype=uint8), array([ 9, 42, 77, ..., 34, 38, 65], dtype=uint8), array([156, 142, 139, ..., 16, 5, 11], dtype=uint8), array([104, 106, 253, ..., 105, 101, 134], dtype=uint8), array([157, 158, 153, ..., 0, 0, 0], dtype=uint8), array([ 6, 24, 2, ..., 168, 159, 162], dtype=uint8), array([77, 36, 44, ..., 11, 9, 14], dtype=uint8), array([124, 108, 95, ..., 13, 185, 251], dtype=uint8), array([ 61, 98, 140, ..., 39, 15, 3], dtype=uint8), array([ 94, 94, 120, ..., 254, 255, 250], dtype=uint8), array([216, 215, 210, ..., 156, 125, 104], dtype=uint8), array([ 1, 114, 246, ..., 109, 91, 107], dtype=uint8), array([144, 136, 115, ..., 42, 37, 41], dtype=uint8), array([56, 42, 29, ..., 31, 17, 17], dtype=uint8), array([48, 85, 33, ..., 30, 16, 16], dtype=uint8), array([127, 68, 74, ..., 222, 210, 194], dtype=uint8), array([96, 99, 72, ..., 61, 11, 14], dtype=uint8), array([31, 36, 29, ..., 23, 47, 81], dtype=uint8), array([18, 13, 10, ..., 16, 11, 8], dtype=uint8), array([ 54, 59, 78, ..., 80, 118, 155], dtype=uint8), array([37, 24, 33, ..., 42, 35, 66], dtype=uint8), array([ 49, 51, 50, ..., 134, 124, 159], dtype=uint8), array([116, 107, 102, ..., 160, 116, 91], dtype=uint8), array([58, 46, 32, ..., 26, 16, 6], dtype=uint8), array([ 7, 29, 254, ..., 110, 72, 51], dtype=uint8), array([134, 130, 118, ..., 26, 18, 33], dtype=uint8), array([ 36, 34, 9, ..., 126, 109, 91], dtype=uint8), array([22, 23, 15, ..., 51, 58, 84], dtype=uint8), array([ 68, 68, 60, ..., 244, 246, 243], dtype=uint8), array([ 63, 64, 120, ..., 146, 114, 101], dtype=uint8), array([33, 37, 40, ..., 18, 17, 15], dtype=uint8), array([81, 51, 41, ..., 38, 27, 69], dtype=uint8)]\n['fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'fake', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real', 'real']\ndata dimension: (1998, 2)\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Visualization",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"fake_cnt = 0\nreal_cnt = 0\nfor i in data:\n if i[1] == \"fake\":\n fake_cnt += 1\n else:\n real_cnt += 1\n\n#print(fake_cnt)\n#print(real_cnt)\ndf = [['fake', fake_cnt], ['real', real_cnt]]\ndf = pd.DataFrame(df, columns=['image_type', 'count'])\n#ax = df.plot.bar(x='video_type', y='count', rot=0)\n#fig = plt.figure()\nplt.bar(df['image_type'], df['count'])\nplt.xlabel(\"Image Type\")\nplt.ylabel(\"Count\")\nplt.savefig('count_type.png')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Machine Learning Task\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nfrom sklearn.svm import SVC\nfrom sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler # standardize features by removing the mean and scaling to unit variance.\nfrom sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix\n#from sklearn.metrics import plot_confusion_matrix\nfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score\nfrom sklearn.metrics import classification_report\nfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression\nfrom sklearn.metrics import roc_curve\nfrom sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Support Vector Machine",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"start_time = time.time()\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 0.2, random_state = 42) # 80% for training, 20 for of testing\nsvm_clf = make_pipeline(StandardScaler(), SVC(gamma='scale', C = 1)) # clf = classifer\nsvm_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)\ny_pred = svm_clf.predict(X_test)\n\nprint(\"--- %s seconds ---\" % (time.time() - start_time))\nprint(confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### SVM Confusion Matrix\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#plot_confusion_matrix(svm_clf, X_test, y_test, values_format = '.0f') \n#plt.figure(figsize=(12,8))\n#plt.show()\nconf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_true = y_test, y_pred = y_pred)\n# Print the confusion matrix using Matplotlib\n\nfig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(7.5, 7.5))\nax.matshow(conf_matrix, cmap=plt.cm.Blues, alpha=0.3)\nfor i in range(conf_matrix.shape[0]):\n for j in range(conf_matrix.shape[1]):\n ax.text(x=j, y=i,s=conf_matrix[i, j], va='center', ha='center', size='xx-large')\n \nplt.xlabel('Predictions', fontsize=18)\nplt.ylabel('Actuals', fontsize=18)\nplt.title('Confusion Matrix', fontsize=18)\nplt.show()\nplt.savefig('Confusion_Matrix.png')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### ROC curves\n- ROC Curves summarize the trade-off between the true positive rate and false positive rate for a predictive model using different probability thresholds.\n- Precision-Recall curves summarize the trade-off between the true positive rate and the positive predictive value for a predictive model using different probability thresholds.\n- ROC curves are appropriate when the observations are balanced between each class, whereas precision-recall curves are appropriate for imbalanced datasets.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\"\"\"\n# generate a no skill prediction (majority class)\nns_probs = [0 for _ in range(len(y_test))]\nlr_probs = svm_clf.predict_proba(X_test)\n# keep probabilities for the positive outcome only\nlr_probs = lr_probs[:, 1]\n# calculate scores\nns_auc = roc_auc_score(y_test, ns_probs)\nlr_auc = roc_auc_score(y_test, lr_probs)\n# summarize scores\nprint('No Skill: ROC AUC=%.3f' % (ns_auc))\nprint('Logistic: ROC AUC=%.3f' % (lr_auc))\n# calculate roc curves\nns_fpr, ns_tpr, _ = roc_curve(y_test, ns_probs)\nlr_fpr, lr_tpr, _ = roc_curve(y_test, lr_probs)\n# plot the roc curve for the model\nplt.plot(ns_fpr, ns_tpr, linestyle='--', label='No Skill')\nplt.plot(lr_fpr, lr_tpr, marker='.', label='Logistic')\n# axis labels\nplt.xlabel('False Positive Rate')\nplt.ylabel('True Positive Rate')\n# show the legend\nplt.legend()\n# show the plot\nplt.show()\nplt.savefig('ROC_AUC_Plot.png')\n\"\"\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### SVM Accuracy Score",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(\"----------Accuracy Score----------------\")\nprint(accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred))\n\ntarget_names = ['fake', 'real']\nprint(classification_report(y_test, y_pred, target_names=target_names))",
"----------Accuracy Score----------------\n0.6475\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n fake 0.68 0.60 0.64 207\n real 0.62 0.70 0.66 193\n\n accuracy 0.65 400\n macro avg 0.65 0.65 0.65 400\nweighted avg 0.65 0.65 0.65 400\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Random Forest Classifier",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"start_time = time.time()\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 0.2, random_state = 42) # 80% for training, 20 for of testing\n#rf_clf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100, random_state=42, bootstrap=True)\n#rf_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)\n#y_pred = rf_clf.predict(X_test)\n\n#print(\"--- %s seconds ---\" % (time.time() - start_time))\n#print(confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Random Forest Accuracy Score",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred))",
"0.7257142857142858\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Logistic Regression",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"start_time = time.time()\nlg_clf = LogisticRegression(random_state=42, C=1)\nlg_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)\ny_pred = lg_clf.predict(X_test)\n\nprint(\"--- %s seconds ---\" % (time.time() - start_time))\nprint(confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred))",
"/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/sklearn/linear_model/_logistic.py:940: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge (status=1):\nSTOP: TOTAL NO. of ITERATIONS REACHED LIMIT.\n\nIncrease the number of iterations (max_iter) or scale the data as shown in:\n https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/preprocessing.html\nPlease also refer to the documentation for alternative solver options:\n https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/linear_model.html#logistic-regression\n extra_warning_msg=_LOGISTIC_SOLVER_CONVERGENCE_MSG)\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Logistic Regression Accuracy Score",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred))",
"0.6528571428571428\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Nested Cross-Validation (Testing Zone)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.datasets import make_classification\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import KFold\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV\nfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier\nfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# manual nested cross-validation for random forest on a classification dataset\nfrom numpy import mean\nfrom numpy import std\nfrom sklearn.datasets import make_classification\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import KFold\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV\nfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier\n# create dataset\n\n#X, y = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=20, random_state=1, n_informative=10, n_redundant=10)\n#print(X.shape)\n#print(y.shape)\n\n# configure the cross-validation procedure\ncv_inner = KFold(n_splits=3, shuffle=True, random_state=1)\n# define the model\nmodel = RandomForestClassifier(random_state=42)\n# define search space\nspace = dict()\nspace['n_estimators'] = [10, 100, 500]\n#space['max_features'] = [2, 4, 6]\n# define search\nsearch = GridSearchCV(model, space, scoring='accuracy', n_jobs=1, cv=cv_inner, refit=True)\n# configure the cross-validation procedure\ncv_outer = KFold(n_splits=10, shuffle=True, random_state=1)\n# execute the nested cross-validation\nscores = cross_val_score(search, X_train, y_train, scoring='accuracy', cv=cv_outer, n_jobs=-1)\n# report performance\nprint('Accuracy: %.3f (%.3f)' % (mean(scores), std(scores)))\n\n\nresult = search.fit(X_train, y_train)\n# get the best performing model fit on the whole training set\nbest_model = result.best_estimator_\n# evaluate model on the hold out dataset\nyhat = best_model.predict(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"space = {}\nspace['n_estimators'] = list(range(1, 1001))\nprint(space)",
"{'n_estimators': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76, 77, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88, 89, 90, 91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98, 99, 100, 101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107, 108, 109, 110, 111, 112, 113, 114, 115, 116, 117, 118, 119, 120, 121, 122, 123, 124, 125, 126, 127, 128, 129, 130, 131, 132, 133, 134, 135, 136, 137, 138, 139, 140, 141, 142, 143, 144, 145, 146, 147, 148, 149, 150, 151, 152, 153, 154, 155, 156, 157, 158, 159, 160, 161, 162, 163, 164, 165, 166, 167, 168, 169, 170, 171, 172, 173, 174, 175, 176, 177, 178, 179, 180, 181, 182, 183, 184, 185, 186, 187, 188, 189, 190, 191, 192, 193, 194, 195, 196, 197, 198, 199, 200, 201, 202, 203, 204, 205, 206, 207, 208, 209, 210, 211, 212, 213, 214, 215, 216, 217, 218, 219, 220, 221, 222, 223, 224, 225, 226, 227, 228, 229, 230, 231, 232, 233, 234, 235, 236, 237, 238, 239, 240, 241, 242, 243, 244, 245, 246, 247, 248, 249, 250, 251, 252, 253, 254, 255, 256, 257, 258, 259, 260, 261, 262, 263, 264, 265, 266, 267, 268, 269, 270, 271, 272, 273, 274, 275, 276, 277, 278, 279, 280, 281, 282, 283, 284, 285, 286, 287, 288, 289, 290, 291, 292, 293, 294, 295, 296, 297, 298, 299, 300, 301, 302, 303, 304, 305, 306, 307, 308, 309, 310, 311, 312, 313, 314, 315, 316, 317, 318, 319, 320, 321, 322, 323, 324, 325, 326, 327, 328, 329, 330, 331, 332, 333, 334, 335, 336, 337, 338, 339, 340, 341, 342, 343, 344, 345, 346, 347, 348, 349, 350, 351, 352, 353, 354, 355, 356, 357, 358, 359, 360, 361, 362, 363, 364, 365, 366, 367, 368, 369, 370, 371, 372, 373, 374, 375, 376, 377, 378, 379, 380, 381, 382, 383, 384, 385, 386, 387, 388, 389, 390, 391, 392, 393, 394, 395, 396, 397, 398, 399, 400, 401, 402, 403, 404, 405, 406, 407, 408, 409, 410, 411, 412, 413, 414, 415, 416, 417, 418, 419, 420, 421, 422, 423, 424, 425, 426, 427, 428, 429, 430, 431, 432, 433, 434, 435, 436, 437, 438, 439, 440, 441, 442, 443, 444, 445, 446, 447, 448, 449, 450, 451, 452, 453, 454, 455, 456, 457, 458, 459, 460, 461, 462, 463, 464, 465, 466, 467, 468, 469, 470, 471, 472, 473, 474, 475, 476, 477, 478, 479, 480, 481, 482, 483, 484, 485, 486, 487, 488, 489, 490, 491, 492, 493, 494, 495, 496, 497, 498, 499, 500, 501, 502, 503, 504, 505, 506, 507, 508, 509, 510, 511, 512, 513, 514, 515, 516, 517, 518, 519, 520, 521, 522, 523, 524, 525, 526, 527, 528, 529, 530, 531, 532, 533, 534, 535, 536, 537, 538, 539, 540, 541, 542, 543, 544, 545, 546, 547, 548, 549, 550, 551, 552, 553, 554, 555, 556, 557, 558, 559, 560, 561, 562, 563, 564, 565, 566, 567, 568, 569, 570, 571, 572, 573, 574, 575, 576, 577, 578, 579, 580, 581, 582, 583, 584, 585, 586, 587, 588, 589, 590, 591, 592, 593, 594, 595, 596, 597, 598, 599, 600, 601, 602, 603, 604, 605, 606, 607, 608, 609, 610, 611, 612, 613, 614, 615, 616, 617, 618, 619, 620, 621, 622, 623, 624, 625, 626, 627, 628, 629, 630, 631, 632, 633, 634, 635, 636, 637, 638, 639, 640, 641, 642, 643, 644, 645, 646, 647, 648, 649, 650, 651, 652, 653, 654, 655, 656, 657, 658, 659, 660, 661, 662, 663, 664, 665, 666, 667, 668, 669, 670, 671, 672, 673, 674, 675, 676, 677, 678, 679, 680, 681, 682, 683, 684, 685, 686, 687, 688, 689, 690, 691, 692, 693, 694, 695, 696, 697, 698, 699, 700, 701, 702, 703, 704, 705, 706, 707, 708, 709, 710, 711, 712, 713, 714, 715, 716, 717, 718, 719, 720, 721, 722, 723, 724, 725, 726, 727, 728, 729, 730, 731, 732, 733, 734, 735, 736, 737, 738, 739, 740, 741, 742, 743, 744, 745, 746, 747, 748, 749, 750, 751, 752, 753, 754, 755, 756, 757, 758, 759, 760, 761, 762, 763, 764, 765, 766, 767, 768, 769, 770, 771, 772, 773, 774, 775, 776, 777, 778, 779, 780, 781, 782, 783, 784, 785, 786, 787, 788, 789, 790, 791, 792, 793, 794, 795, 796, 797, 798, 799, 800, 801, 802, 803, 804, 805, 806, 807, 808, 809, 810, 811, 812, 813, 814, 815, 816, 817, 818, 819, 820, 821, 822, 823, 824, 825, 826, 827, 828, 829, 830, 831, 832, 833, 834, 835, 836, 837, 838, 839, 840, 841, 842, 843, 844, 845, 846, 847, 848, 849, 850, 851, 852, 853, 854, 855, 856, 857, 858, 859, 860, 861, 862, 863, 864, 865, 866, 867, 868, 869, 870, 871, 872, 873, 874, 875, 876, 877, 878, 879, 880, 881, 882, 883, 884, 885, 886, 887, 888, 889, 890, 891, 892, 893, 894, 895, 896, 897, 898, 899, 900, 901, 902, 903, 904, 905, 906, 907, 908, 909, 910, 911, 912, 913, 914, 915, 916, 917, 918, 919, 920, 921, 922, 923, 924, 925, 926, 927, 928, 929, 930, 931, 932, 933, 934, 935, 936, 937, 938, 939, 940, 941, 942, 943, 944, 945, 946, 947, 948, 949, 950, 951, 952, 953, 954, 955, 956, 957, 958, 959, 960, 961, 962, 963, 964, 965, 966, 967, 968, 969, 970, 971, 972, 973, 974, 975, 976, 977, 978, 979, 980, 981, 982, 983, 984, 985, 986, 987, 988, 989, 990, 991, 992, 993, 994, 995, 996, 997, 998, 999, 1000]}\n"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# References\n- https://learning.oreilly.com/library/view/hands-on-machine-learning/9781492032632/ch05.html#idm45022165153592\n- https://github.com/scikit-learn/scikit-learn/issues/16127\n- https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.ensemble.RandomForestClassifier.html\n- https://pandas.pydata.org/docs/reference/api/pandas.DataFrame.plot.bar.html\n- https://machinelearningmastery.com/roc-curves-and-precision-recall-curves-for-classification-in-python/\n- https://machinelearningmastery.com/nested-cross-validation-for-machine-learning-with-python/",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
c5047415654d2d3764010cfce380bcf3e9a2f2f1
| 200,118 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
jupyter/history.ipynb
|
jesserobertson/maxr
|
7b60da6781e06e95a8355505ebbde291cbe6d61a
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 2 |
2020-12-08T01:01:20.000Z
|
2021-09-15T13:52:14.000Z
|
jupyter/history.ipynb
|
jesserobertson/maxr
|
7b60da6781e06e95a8355505ebbde291cbe6d61a
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
jupyter/history.ipynb
|
jesserobertson/maxr
|
7b60da6781e06e95a8355505ebbde291cbe6d61a
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 1 |
2021-09-15T13:52:16.000Z
|
2021-09-15T13:52:16.000Z
| 206.307216 | 65,314 | 0.671004 |
[
[
[
"Check coefficients for integration schemes - they should all line up nicely for values in the middle and vary smoothly",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from bokeh import plotting, io, models, palettes\nio.output_notebook()\n\nimport numpy\nfrom maxr.integrator import history\n\nnmax = 5\nfigures = []\npalette = palettes.Category10[3]\nfor n in range(1, nmax):\n fig = plotting.figure(height=100, width=600,\n active_drag='pan', active_scroll='wheel_zoom')\n for order, color in zip((1, 2, 3), palette):\n try:\n coeffs = history.coefficients(n, order=order)\n ticks = range(len(coeffs))\n fig.line(ticks, coeffs, alpha=0.9, color=color)\n fig.circle(ticks, coeffs, alpha=0.9, color=color)\n except ValueError:\n # Skip orders if we don't have enough coefficients to calculate these\n continue\n fig.yaxis.axis_label = 'n={0}'.format(n)\n fig.toolbar.logo = None\n fig.toolbar_location = None\n figures.append(fig)\n \n # Set up scaling\n if len(figures) == 1:\n figures[0].x_range = models.Range1d(0, nmax - 1)\n figures[0].y_range = models.Range1d(0, 2)\n else:\n figures[-1].x_range = figures[0].x_range\n figures[-1].y_range = figures[0].y_range\n\nio.show(models.Column(*figures))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Define some timesteps to integrate over",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tmin, tmax = 0, 30\nts = numpy.linspace(tmin, tmax, 1000)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Check we can integrate things!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"expected = -1.2492166377597749",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"history.integrator(numpy.sin(ts), ts) - expected < 1e-5",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Turn this into a history integrator for a python function",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def evaluate_history_integral(f, ts, order=1):\n \"\"\" Evaluate the history integral for a given driving function f\n \"\"\"\n return numpy.array([0] + [\n history.integrator(f(ts[:idx+1]), ts[:idx+1], order=order)\n for idx in range(1, len(ts))])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"results = evaluate_history_integral(numpy.sin, ts)\n\nfigure = plotting.figure(height=300)\nfigure.line(ts, results)\nfigure.title.text = \"∫sin(t)/√(t-𝜏)d𝜏\"\nio.show(figure)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Check accuracy of convergence. We use a sinusoidal forcing and plot the response\n$$ \n\\int_0^{t} \\frac{\\sin{(\\tau)}}{\\sqrt{t - \\tau}}d\\tau = \\sqrt{2 \\pi}\\left[C{\\left(\\sqrt{\\frac{2t}{\\pi}}\\right)}\\sin{t} - S{\\left(\\sqrt{\\frac{2t}{\\pi}}\\right)}\\cos{t}\\right]\n$$\nwhere $C$ is the Fresnel C (cos) integral, and $S$ is the Fresnel $S$ (sin) integral. Note the solution in the paper is **WRONG**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from scipy.special import fresnel\n\ndef solution(t):\n ssc, csc = fresnel(numpy.sqrt(2 * t / numpy.pi)) \n return numpy.sqrt(2 * numpy.pi) * (\n csc * numpy.sin(t) - ssc * numpy.cos(t))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Show the solution",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"figure = plotting.figure(height=300)\nfigure.line(ts, numpy.sin(ts), legend='Source function sin(t)', color=palette[1], alpha=0.7)\nfigure.line(ts, solution(ts), legend='Analytic ∫sin(t)/√(t-𝜏)d𝜏', color=palette[0], alpha=0.7)\nfigure.line(ts, evaluate_history_integral(numpy.sin, ts), legend='Numerical ∫sin(t)/√(t-𝜏)d𝜏', color=palette[2], alpha=0.7)\nio.show(figure)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"and try integration numerically",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"nsteps = 30\norder = 3\ntmin = 0\ntmax = 40\n\n# Evaluate solution \nts = numpy.linspace(tmin, tmax, nsteps)\nnumeric = evaluate_history_integral(numpy.sin, ts, order=order)\nexact = solution(ts)\n\nfigure = plotting.figure(height=300)\nfigure.line(ts, exact, legend='Analytic', color=palette[0], alpha=0.7)\nfigure.line(ts, numeric, legend='Numerical', color=palette[2], alpha=0.7)\nio.show(figure)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"numpy.mean(numeric - exact)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now we loop through by order and computer the error",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from collections import defaultdict\n\n# Set up steps\nnstepstep = 50\nnsteps = numpy.arange(nstepstep, 500, nstepstep)\nspacing = 10 / (nsteps - 1)\n\n# Calculate error\nerror = defaultdict(list)\nfor order in (1, 2, 3):\n for N in nsteps:\n ts = numpy.linspace(0, tmax, N)\n err = evaluate_history_integral(numpy.sin, ts, order=order) - solution(ts)\n error[order].append(abs(err).max())\n\n# Convert to arrays\nfor key, value in error.items():\n error[key] = numpy.asarray(value)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can plot how the error changes with spacing",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"figure = plotting.figure(height=300, x_axis_type='log', y_axis_type='log')\nfor order, color in zip((1, 2, 3), palette):\n figure.line(spacing, error[order], legend='Order = {0}'.format(order),\n color=color, alpha=0.9)\nfigure.xaxis.axis_label = 'Timestep (𝛿t)'\nfigure.yaxis.axis_label = 'Error (𝜀)'\nfigure.legend.location = 'bottom_right'\nio.show(figure)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"check that we get reasonable scaling (should be about $\\epsilon\\sim\\delta t ^{\\text{order} + 1}$)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def slope(rise, run):\n return (rise[1:] - rise[0]) / (run[1:] - run[0])\n\nfigure = plotting.figure(height=300, x_axis_type='log')\nfor order, color in zip((1, 2, 3), palette):\n figure.line(spacing[1:], \n slope(numpy.log(error[order]), numpy.log(spacing)), \n legend='Order = {0}'.format(order),\n color=color, alpha=0.9)\nfigure.xaxis.axis_label = 'Timestep (𝛿t)'\nfigure.yaxis.axis_label = 'Scaling exponent'\nfigure.legend.location = 'center_right'\nio.show(figure)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c50487da83f8fb57bab42ca00a8c4cfca948e3e6
| 38,981 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Operations_on_word_vectors_v2a.ipynb
|
osamaa-mustafa/Operations_on_word_vectors_v2a
|
67232c749ce5349194511cc43a41574d6e3989a2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Operations_on_word_vectors_v2a.ipynb
|
osamaa-mustafa/Operations_on_word_vectors_v2a
|
67232c749ce5349194511cc43a41574d6e3989a2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Operations_on_word_vectors_v2a.ipynb
|
osamaa-mustafa/Operations_on_word_vectors_v2a
|
67232c749ce5349194511cc43a41574d6e3989a2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 42.370652 | 1,843 | 0.574972 |
[
[
[
"# Operations on Word Vectors\n\nWelcome to your first assignment of Week 2, Course 5 of the Deep Learning Specialization! \n\nBecause word embeddings are very computationally expensive to train, most ML practitioners will load a pre-trained set of embeddings. In this notebook you'll try your hand at loading, measuring similarity between, and modifying pre-trained embeddings. \n\n**After this assignment you'll be able to**:\n\n* Explain how word embeddings capture relationships between words\n* Load pre-trained word vectors\n* Measure similarity between word vectors using cosine similarity\n* Use word embeddings to solve word analogy problems such as Man is to Woman as King is to ______. \n\nAt the end of this notebook you'll have a chance to try an optional exercise, where you'll modify word embeddings to reduce their gender bias. Reducing bias is an important consideration in ML, so you're encouraged to take this challenge! ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Table of Contents\n\n- [Packages](#0)\n- [1 - Load the Word Vectors](#1)\n- [2 - Embedding Vectors Versus One-Hot Vectors](#2)\n- [3 - Cosine Similarity](#3)\n - [Exercise 1 - cosine_similarity](#ex-1)\n- [4 - Word Analogy Task](#4)\n - [Exercise 2 - complete_analogy](#ex-2)\n- [5 - Debiasing Word Vectors (OPTIONAL/UNGRADED)](#5)\n - [5.1 - Neutralize Bias for Non-Gender Specific Words](#5-1)\n - [Exercise 3 - neutralize](#ex-3)\n - [5.2 - Equalization Algorithm for Gender-Specific Words](#5-2)\n - [Exercise 4 - equalize](#ex-4)\n- [6 - References](#6)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a name='0'></a>\n## Packages\n\nLet's get started! Run the following cell to load the packages you'll need.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nfrom w2v_utils import *",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a name='1'></a>\n## 1 - Load the Word Vectors\n\nFor this assignment, you'll use 50-dimensional GloVe vectors to represent words. \nRun the following cell to load the `word_to_vec_map`. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"words, word_to_vec_map = read_glove_vecs('data/glove.6B.50d.txt')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You've loaded:\n- `words`: set of words in the vocabulary.\n- `word_to_vec_map`: dictionary mapping words to their GloVe vector representation.\n\n<a name='2'></a>\n## 2 - Embedding Vectors Versus One-Hot Vectors\nRecall from the lesson videos that one-hot vectors don't do a good job of capturing the level of similarity between words. This is because every one-hot vector has the same Euclidean distance from any other one-hot vector.\n\nEmbedding vectors, such as GloVe vectors, provide much more useful information about the meaning of individual words. \nNow, see how you can use GloVe vectors to measure the similarity between two words! ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a name='3'></a>\n## 3 - Cosine Similarity\n\nTo measure the similarity between two words, you need a way to measure the degree of similarity between two embedding vectors for the two words. Given two vectors $u$ and $v$, cosine similarity is defined as follows: \n\n$$\\text{CosineSimilarity(u, v)} = \\frac {u \\cdot v} {||u||_2 ||v||_2} = cos(\\theta) \\tag{1}$$\n\n* $u \\cdot v$ is the dot product (or inner product) of two vectors\n* $||u||_2$ is the norm (or length) of the vector $u$\n* $\\theta$ is the angle between $u$ and $v$. \n* The cosine similarity depends on the angle between $u$ and $v$. \n * If $u$ and $v$ are very similar, their cosine similarity will be close to 1.\n * If they are dissimilar, the cosine similarity will take a smaller value. \n\n<img src=\"images/cosine_sim.png\" style=\"width:800px;height:250px;\">\n<caption><center><font color='purple'><b>Figure 1</b>: The cosine of the angle between two vectors is a measure of their similarity.</font></center></caption>\n\n<a name='ex-1'></a>\n### Exercise 1 - cosine_similarity\n\nImplement the function `cosine_similarity()` to evaluate the similarity between word vectors.\n\n**Reminder**: The norm of $u$ is defined as $ ||u||_2 = \\sqrt{\\sum_{i=1}^{n} u_i^2}$\n\n#### Additional Hints\n* You may find [np.dot](https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.dot.html), [np.sum](https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.sum.html), or [np.sqrt](https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.sqrt.html) useful depending upon the implementation that you choose.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# UNQ_C1 (UNIQUE CELL IDENTIFIER, DO NOT EDIT)\n# GRADED FUNCTION: cosine_similarity\n\ndef cosine_similarity(u, v):\n \"\"\"\n Cosine similarity reflects the degree of similarity between u and v\n \n Arguments:\n u -- a word vector of shape (n,) \n v -- a word vector of shape (n,)\n\n Returns:\n cosine_similarity -- the cosine similarity between u and v defined by the formula above.\n \"\"\"\n \n # Special case. Consider the case u = [0, 0], v=[0, 0]\n if np.all(u == v):\n return 1\n \n ### START CODE HERE ###\n # Compute the dot product between u and v (≈1 line)\n dot = np.dot(u.T, v)\n # Compute the L2 norm of u (≈1 line)\n norm_u = np.sqrt(np.sum(np.power(u, 2)))\n\n # Compute the L2 norm of v (≈1 line)\n norm_v = np.sqrt(np.sum(np.power(v, 2)))\n # Compute the cosine similarity defined by formula (1) (≈1 line)\n cosine_similarity = np.divide(dot, norm_u * norm_v)\n ### END CODE HERE ###\n \n return cosine_similarity",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# START SKIP FOR GRADING\nfather = word_to_vec_map[\"father\"]\nmother = word_to_vec_map[\"mother\"]\nball = word_to_vec_map[\"ball\"]\ncrocodile = word_to_vec_map[\"crocodile\"]\nfrance = word_to_vec_map[\"france\"]\nitaly = word_to_vec_map[\"italy\"]\nparis = word_to_vec_map[\"paris\"]\nrome = word_to_vec_map[\"rome\"]\n\nprint(\"cosine_similarity(father, mother) = \", cosine_similarity(father, mother))\nprint(\"cosine_similarity(ball, crocodile) = \",cosine_similarity(ball, crocodile))\nprint(\"cosine_similarity(france - paris, rome - italy) = \",cosine_similarity(france - paris, rome - italy))\n# END SKIP FOR GRADING\n\n# PUBLIC TESTS\ndef cosine_similarity_test(target):\n a = np.random.uniform(-10, 10, 10)\n b = np.random.uniform(-10, 10, 10)\n c = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, 23)\n \n assert np.isclose(cosine_similarity(a, a), 1), \"cosine_similarity(a, a) must be 1\"\n assert np.isclose(cosine_similarity((c >= 0) * 1, (c < 0) * 1), 0), \"cosine_similarity(a, not(a)) must be 0\"\n assert np.isclose(cosine_similarity(a, -a), -1), \"cosine_similarity(a, -a) must be -1\"\n assert np.isclose(cosine_similarity(a, b), cosine_similarity(a * 2, b * 4)), \"cosine_similarity must be scale-independent. You must divide by the product of the norms of each input\"\n\n print(\"\\033[92mAll test passed!\")\n \ncosine_similarity_test(cosine_similarity)",
"cosine_similarity(father, mother) = 0.8909038442893615\ncosine_similarity(ball, crocodile) = 0.2743924626137942\ncosine_similarity(france - paris, rome - italy) = -0.6751479308174201\n\u001b[92mAll test passed!\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### Try different words!\n\nAfter you get the correct expected output, please feel free to modify the inputs and measure the cosine similarity between other pairs of words! Playing around with the cosine similarity of other inputs will give you a better sense of how word vectors behave.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a name='4'></a>\n## 4 - Word Analogy Task\n\n* In the word analogy task, complete this sentence: \n <font color='brown'>\"*a* is to *b* as *c* is to **____**\"</font>. \n\n* An example is: \n <font color='brown'> '*man* is to *woman* as *king* is to *queen*' </font>. \n\n* You're trying to find a word *d*, such that the associated word vectors $e_a, e_b, e_c, e_d$ are related in the following manner: \n $e_b - e_a \\approx e_d - e_c$\n* Measure the similarity between $e_b - e_a$ and $e_d - e_c$ using cosine similarity. \n\n<a name='ex-2'></a>\n### Exercise 2 - complete_analogy\n\nComplete the code below to perform word analogies!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# UNQ_C2 (UNIQUE CELL IDENTIFIER, DO NOT EDIT)\n# GRADED FUNCTION: complete_analogy\n\ndef complete_analogy(word_a, word_b, word_c, word_to_vec_map):\n \"\"\"\n Performs the word analogy task as explained above: a is to b as c is to ____. \n \n Arguments:\n word_a -- a word, string\n word_b -- a word, string\n word_c -- a word, string\n word_to_vec_map -- dictionary that maps words to their corresponding vectors. \n \n Returns:\n best_word -- the word such that v_b - v_a is close to v_best_word - v_c, as measured by cosine similarity\n \"\"\"\n \n # convert words to lower case\n word_a, word_b, word_c = word_a.lower(), word_b.lower(), word_c.lower()\n \n ### START CODE HERE ###\n # Get the word embeddings v_a, v_b and v_c (≈1-3 lines)\n e_a, e_b, e_c = word_to_vec_map[word_a],word_to_vec_map[word_b],word_to_vec_map[word_c] # transform words into vectors\n ### END CODE HERE ###\n \n words = word_to_vec_map.keys()\n max_cosine_sim = -100 # Initialize max_cosine_sim to a large negative number\n best_word = None # Initialize best_word with None, it will help keep track of the word to output\n\n # loop over the whole word vector set\n for w in words: \n # to avoid best_word being one of the input words, pass on them.\n if w in [word_a, word_b, word_c] :\n continue\n \n ### START CODE HERE ###\n # Compute cosine similarity between the vector (e_b - e_a) and the vector ((w's vector representation) - e_c) (≈1 line)\n cosine_sim = cosine_similarity(e_b-e_a, word_to_vec_map[w] - e_c)\n \n # If the cosine_sim is more than the max_cosine_sim seen so far,\n # then: set the new max_cosine_sim to the current cosine_sim and the best_word to the current word (≈3 lines)\n if cosine_sim > max_cosine_sim:\n max_cosine_sim = cosine_sim\n best_word = w\n ### END CODE HERE ###\n \n return best_word",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# PUBLIC TEST\ndef complete_analogy_test(target):\n a = [3, 3] # Center at a\n a_nw = [2, 4] # North-West oriented vector from a\n a_s = [3, 2] # South oriented vector from a\n \n c = [-2, 1] # Center at c\n # Create a controlled word to vec map\n word_to_vec_map = {'a': a,\n 'synonym_of_a': a,\n 'a_nw': a_nw, \n 'a_s': a_s, \n 'c': c, \n 'c_n': [-2, 2], # N\n 'c_ne': [-1, 2], # NE\n 'c_e': [-1, 1], # E\n 'c_se': [-1, 0], # SE\n 'c_s': [-2, 0], # S\n 'c_sw': [-3, 0], # SW\n 'c_w': [-3, 1], # W\n 'c_nw': [-3, 2] # NW\n }\n \n # Convert lists to np.arrays\n for key in word_to_vec_map.keys():\n word_to_vec_map[key] = np.array(word_to_vec_map[key])\n \n assert(target('a', 'a_nw', 'c', word_to_vec_map) == 'c_nw')\n assert(target('a', 'a_s', 'c', word_to_vec_map) == 'c_s')\n assert(target('a', 'synonym_of_a', 'c', word_to_vec_map) != 'c'), \"Best word cannot be input query\"\n assert(target('a', 'c', 'a', word_to_vec_map) == 'c')\n\n print(\"\\033[92mAll tests passed\")\n \ncomplete_analogy_test(complete_analogy)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Run the cell below to test your code. Patience, young grasshopper...this may take 1-2 minutes.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# START SKIP FOR GRADING\ntriads_to_try = [('italy', 'italian', 'spain'), ('india', 'delhi', 'japan'), ('man', 'woman', 'boy'), ('small', 'smaller', 'large')]\nfor triad in triads_to_try:\n print ('{} -> {} :: {} -> {}'.format( *triad, complete_analogy(*triad, word_to_vec_map)))\n\n# END SKIP FOR GRADING",
"italy -> italian :: spain -> portugal\nindia -> delhi :: japan -> japanese\nman -> woman :: boy -> girl\nsmall -> smaller :: large -> larger\n"
]
],
[
[
"Once you get the output, try modifying the input cells above to test your own analogies. \n\n**Hint**: Try to find some other analogy pairs that will work, along with some others where the algorithm doesn't give the right answer:\n * For example, you can try small->smaller as big->?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Congratulations!\n\nYou've come to the end of the graded portion of the assignment. By now, you've: \n\n* Loaded some pre-trained word vectors\n* Measured the similarity between word vectors using cosine similarity\n* Used word embeddings to solve word analogy problems such as Man is to Woman as King is to __.\n\nCosine similarity is a relatively simple and intuitive, yet powerful, method you can use to capture nuanced relationships between words. These exercises should be helpful to you in explaining how it works, and applying it to your own projects! ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<font color='blue'>\n <b>What you should remember</b>:\n\n- Cosine similarity is a good way to compare the similarity between pairs of word vectors.\n - Note that L2 (Euclidean) distance also works.\n- For NLP applications, using a pre-trained set of word vectors is often a great way to get started. </font>\n\nEven though you've finished the graded portion, please take a look at the rest of this notebook to learn about debiasing word vectors.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a name='5'></a>\n## 5 - Debiasing Word Vectors (OPTIONAL/UNGRADED) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In the following exercise, you'll examine gender biases that can be reflected in a word embedding, and explore algorithms for reducing the bias. In addition to learning about the topic of debiasing, this exercise will also help hone your intuition about what word vectors are doing. This section involves a bit of linear algebra, though you can certainly complete it without being an expert! Go ahead and give it a shot. This portion of the notebook is optional and is not graded...so just have fun and explore. \n\nFirst, see how the GloVe word embeddings relate to gender. You'll begin by computing a vector $g = e_{woman}-e_{man}$, where $e_{woman}$ represents the word vector corresponding to the word *woman*, and $e_{man}$ corresponds to the word vector corresponding to the word *man*. The resulting vector $g$ roughly encodes the concept of \"gender\". \n\nYou might get a more accurate representation if you compute $g_1 = e_{mother}-e_{father}$, $g_2 = e_{girl}-e_{boy}$, etc. and average over them, but just using $e_{woman}-e_{man}$ will give good enough results for now.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"g = word_to_vec_map['woman'] - word_to_vec_map['man']\nprint(g)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now, consider the cosine similarity of different words with $g$. What does a positive value of similarity mean, versus a negative cosine similarity? ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print ('List of names and their similarities with constructed vector:')\n\n# girls and boys name\nname_list = ['john', 'marie', 'sophie', 'ronaldo', 'priya', 'rahul', 'danielle', 'reza', 'katy', 'yasmin']\n\nfor w in name_list:\n print (w, cosine_similarity(word_to_vec_map[w], g))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"As you can see, female first names tend to have a positive cosine similarity with our constructed vector $g$, while male first names tend to have a negative cosine similarity. This is not surprising, and the result seems acceptable. \n\nNow try with some other words:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print('Other words and their similarities:')\nword_list = ['lipstick', 'guns', 'science', 'arts', 'literature', 'warrior','doctor', 'tree', 'receptionist', \n 'technology', 'fashion', 'teacher', 'engineer', 'pilot', 'computer', 'singer']\nfor w in word_list:\n print (w, cosine_similarity(word_to_vec_map[w], g))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Do you notice anything surprising? It is astonishing how these results reflect certain unhealthy gender stereotypes. For example, we see “computer” is negative and is closer in value to male first names, while “literature” is positive and is closer to female first names. Ouch! \n\nYou'll see below how to reduce the bias of these vectors, using an algorithm due to [Boliukbasi et al., 2016](https://arxiv.org/abs/1607.06520). Note that some word pairs such as \"actor\"/\"actress\" or \"grandmother\"/\"grandfather\" should remain gender-specific, while other words such as \"receptionist\" or \"technology\" should be neutralized, i.e. not be gender-related. You'll have to treat these two types of words differently when debiasing.\n\n<a name='5-1'></a>\n### 5.1 - Neutralize Bias for Non-Gender Specific Words \n\nThe figure below should help you visualize what neutralizing does. If you're using a 50-dimensional word embedding, the 50 dimensional space can be split into two parts: The bias-direction $g$, and the remaining 49 dimensions, which is called $g_{\\perp}$ here. In linear algebra, we say that the 49-dimensional $g_{\\perp}$ is perpendicular (or \"orthogonal\") to $g$, meaning it is at 90 degrees to $g$. The neutralization step takes a vector such as $e_{receptionist}$ and zeros out the component in the direction of $g$, giving us $e_{receptionist}^{debiased}$. \n\nEven though $g_{\\perp}$ is 49-dimensional, given the limitations of what you can draw on a 2D screen, it's illustrated using a 1-dimensional axis below. \n\n<img src=\"images/neutral.png\" style=\"width:800px;height:300px;\">\n<caption><center><font color='purple'><b>Figure 2</b>: The word vector for \"receptionist\" represented before and after applying the neutralize operation.</font> </center></caption>\n\n<a name='ex-3'></a>\n### Exercise 3 - neutralize\n\nImplement `neutralize()` to remove the bias of words such as \"receptionist\" or \"scientist.\"\n\nGiven an input embedding $e$, you can use the following formulas to compute $e^{debiased}$: \n\n$$e^{bias\\_component} = \\frac{e \\cdot g}{||g||_2^2} * g\\tag{2}$$\n$$e^{debiased} = e - e^{bias\\_component}\\tag{3}$$\n\nIf you are an expert in linear algebra, you may recognize $e^{bias\\_component}$ as the projection of $e$ onto the direction $g$. If you're not an expert in linear algebra, don't worry about this. ;) \n\n<!-- \n**Reminder**: a vector $u$ can be split into two parts: its projection over a vector-axis $v_B$ and its projection over the axis orthogonal to $v$:\n$$u = u_B + u_{\\perp}$$\nwhere : $u_B = $ and $ u_{\\perp} = u - u_B $\n!--> ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def neutralize(word, g, word_to_vec_map):\n \"\"\"\n Removes the bias of \"word\" by projecting it on the space orthogonal to the bias axis. \n This function ensures that gender neutral words are zero in the gender subspace.\n \n Arguments:\n word -- string indicating the word to debias\n g -- numpy-array of shape (50,), corresponding to the bias axis (such as gender)\n word_to_vec_map -- dictionary mapping words to their corresponding vectors.\n \n Returns:\n e_debiased -- neutralized word vector representation of the input \"word\"\n \"\"\"\n \n ### START CODE HERE ###\n # Select word vector representation of \"word\". Use word_to_vec_map. (≈ 1 line)\n e = None\n \n # Compute e_biascomponent using the formula given above. (≈ 1 line)\n e_biascomponent = None\n \n # Neutralize e by subtracting e_biascomponent from it \n # e_debiased should be equal to its orthogonal projection. (≈ 1 line)\n e_debiased = None\n ### END CODE HERE ###\n \n return e_debiased",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"e = \"receptionist\"\nprint(\"cosine similarity between \" + e + \" and g, before neutralizing: \", cosine_similarity(word_to_vec_map[\"receptionist\"], g))\n\ne_debiased = neutralize(\"receptionist\", g, word_to_vec_map)\nprint(\"cosine similarity between \" + e + \" and g, after neutralizing: \", cosine_similarity(e_debiased, g))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Expected Output**: The second result is essentially 0, up to numerical rounding (on the order of $10^{-17}$).\n\n\n<table>\n <tr>\n <td>\n <b>cosine similarity between receptionist and g, before neutralizing:</b> :\n </td>\n <td>\n 0.330779417506\n </td>\n </tr>\n <tr>\n <td>\n <b>cosine similarity between receptionist and g, after neutralizing</b> :\n </td>\n <td>\n -4.442232511624783e-17\n </tr>\n</table>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a name='5-2'></a>\n### 5.2 - Equalization Algorithm for Gender-Specific Words\n\nNext, let's see how debiasing can also be applied to word pairs such as \"actress\" and \"actor.\" Equalization is applied to pairs of words that you might want to have differ only through the gender property. As a concrete example, suppose that \"actress\" is closer to \"babysit\" than \"actor.\" By applying neutralization to \"babysit,\" you can reduce the gender stereotype associated with babysitting. But this still does not guarantee that \"actor\" and \"actress\" are equidistant from \"babysit.\" The equalization algorithm takes care of this. \n\nThe key idea behind equalization is to make sure that a particular pair of words are equidistant from the 49-dimensional $g_\\perp$. The equalization step also ensures that the two equalized steps are now the same distance from $e_{receptionist}^{debiased}$, or from any other work that has been neutralized. Visually, this is how equalization works: \n\n<img src=\"images/equalize10.png\" style=\"width:800px;height:400px;\">\n\n\nThe derivation of the linear algebra to do this is a bit more complex. (See Bolukbasi et al., 2016 in the References for details.) Here are the key equations: \n\n\n$$ \\mu = \\frac{e_{w1} + e_{w2}}{2}\\tag{4}$$ \n\n$$ \\mu_{B} = \\frac {\\mu \\cdot \\text{bias_axis}}{||\\text{bias_axis}||_2^2} *\\text{bias_axis}\n\\tag{5}$$ \n\n$$\\mu_{\\perp} = \\mu - \\mu_{B} \\tag{6}$$\n\n$$ e_{w1B} = \\frac {e_{w1} \\cdot \\text{bias_axis}}{||\\text{bias_axis}||_2^2} *\\text{bias_axis}\n\\tag{7}$$ \n$$ e_{w2B} = \\frac {e_{w2} \\cdot \\text{bias_axis}}{||\\text{bias_axis}||_2^2} *\\text{bias_axis}\n\\tag{8}$$\n\n\n$$e_{w1B}^{corrected} = \\sqrt{ |{1 - ||\\mu_{\\perp} ||^2_2} |} * \\frac{e_{\\text{w1B}} - \\mu_B} {||(e_{w1} - \\mu_{\\perp}) - \\mu_B||_2} \\tag{9}$$\n\n\n$$e_{w2B}^{corrected} = \\sqrt{ |{1 - ||\\mu_{\\perp} ||^2_2} |} * \\frac{e_{\\text{w2B}} - \\mu_B} {||(e_{w2} - \\mu_{\\perp}) - \\mu_B||_2} \\tag{10}$$\n\n$$e_1 = e_{w1B}^{corrected} + \\mu_{\\perp} \\tag{11}$$\n$$e_2 = e_{w2B}^{corrected} + \\mu_{\\perp} \\tag{12}$$\n\n\n<a name='ex-4'></a>\n### Exercise 4 - equalize\n\nImplement the `equalize()` function below. \n\nUse the equations above to get the final equalized version of the pair of words. Good luck!\n\n**Hint**\n- Use [np.linalg.norm](https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.linalg.norm.html)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def equalize(pair, bias_axis, word_to_vec_map):\n \"\"\"\n Debias gender specific words by following the equalize method described in the figure above.\n \n Arguments:\n pair -- pair of strings of gender specific words to debias, e.g. (\"actress\", \"actor\") \n bias_axis -- numpy-array of shape (50,), vector corresponding to the bias axis, e.g. gender\n word_to_vec_map -- dictionary mapping words to their corresponding vectors\n \n Returns\n e_1 -- word vector corresponding to the first word\n e_2 -- word vector corresponding to the second word\n \"\"\"\n \n ### START CODE HERE ###\n # Step 1: Select word vector representation of \"word\". Use word_to_vec_map. (≈ 2 lines)\n w1, w2 = None\n e_w1, e_w2 = None\n \n # Step 2: Compute the mean of e_w1 and e_w2 (≈ 1 line)\n mu = None\n\n # Step 3: Compute the projections of mu over the bias axis and the orthogonal axis (≈ 2 lines)\n mu_B = None\n mu_orth = None\n\n # Step 4: Use equations (7) and (8) to compute e_w1B and e_w2B (≈2 lines)\n e_w1B = None\n e_w2B = None\n \n # Step 5: Adjust the Bias part of e_w1B and e_w2B using the formulas (9) and (10) given above (≈2 lines)\n corrected_e_w1B = None\n corrected_e_w2B = None\n\n # Step 6: Debias by equalizing e1 and e2 to the sum of their corrected projections (≈2 lines)\n e1 = None\n e2 = None\n \n ### END CODE HERE ###\n \n return e1, e2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(\"cosine similarities before equalizing:\")\nprint(\"cosine_similarity(word_to_vec_map[\\\"man\\\"], gender) = \", cosine_similarity(word_to_vec_map[\"man\"], g))\nprint(\"cosine_similarity(word_to_vec_map[\\\"woman\\\"], gender) = \", cosine_similarity(word_to_vec_map[\"woman\"], g))\nprint()\ne1, e2 = equalize((\"man\", \"woman\"), g, word_to_vec_map)\nprint(\"cosine similarities after equalizing:\")\nprint(\"cosine_similarity(e1, gender) = \", cosine_similarity(e1, g))\nprint(\"cosine_similarity(e2, gender) = \", cosine_similarity(e2, g))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Expected Output**:\n\ncosine similarities before equalizing:\n<table>\n <tr>\n <td>\n <b>cosine_similarity(word_to_vec_map[\"man\"], gender)</b> =\n </td>\n <td>\n -0.117110957653\n </td>\n </tr>\n <tr>\n <td>\n <b>cosine_similarity(word_to_vec_map[\"woman\"], gender)</b> =\n </td>\n <td>\n 0.356666188463\n </td>\n </tr>\n</table>\n\ncosine similarities after equalizing:\n<table>\n <tr>\n <td>\n <b>cosine_similarity(e1, gender)</b> =\n </td>\n <td>\n -0.7004364289309388\n </td>\n </tr>\n <tr>\n <td>\n <b>cosine_similarity(e2, gender)</b> =\n </td>\n <td>\n 0.7004364289309387\n </td>\n </tr>\n</table>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Go ahead and play with the input words in the cell above, to apply equalization to other pairs of words. \n\nHint: Try...\n\nThese debiasing algorithms are very helpful for reducing bias, but aren't perfect and don't eliminate all traces of bias. For example, one weakness of this implementation was that the bias direction $g$ was defined using only the pair of words _woman_ and _man_. As discussed earlier, if $g$ were defined by computing $g_1 = e_{woman} - e_{man}$; $g_2 = e_{mother} - e_{father}$; $g_3 = e_{girl} - e_{boy}$; and so on and averaging over them, you would obtain a better estimate of the \"gender\" dimension in the 50 dimensional word embedding space. Feel free to play with these types of variants as well! ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Congratulations!\n\nYou have come to the end of both graded and ungraded portions of this notebook, and have seen several of the ways that word vectors can be applied and modified. Great work pushing your knowledge in the areas of neutralizing and equalizing word vectors! See you next time.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a name='6'></a>\n## 6 - References\n\n- The debiasing algorithm is from Bolukbasi et al., 2016, [Man is to Computer Programmer as Woman is to\nHomemaker? Debiasing Word Embeddings](https://papers.nips.cc/paper/6228-man-is-to-computer-programmer-as-woman-is-to-homemaker-debiasing-word-embeddings.pdf)\n- The GloVe word embeddings were due to Jeffrey Pennington, Richard Socher, and Christopher D. Manning. (https://nlp.stanford.edu/projects/glove/)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
c5048ad3da9600a8cf8f04a53aa604823d1ccbda
| 237,834 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
20190909_TA_Restaurants_V1.ipynb
|
Dysentrieb/TripadAdvisor_Euro-Restaurants
|
6af3fbcfbd218f9fb4d85487630bfb27d54b0aec
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2019-09-09T12:30:47.000Z
|
2019-09-19T08:11:37.000Z
|
20190909_TA_Restaurants_V1.ipynb
|
Dysentrieb/TripadAdvisor_Euro-Restaurants
|
6af3fbcfbd218f9fb4d85487630bfb27d54b0aec
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
20190909_TA_Restaurants_V1.ipynb
|
Dysentrieb/TripadAdvisor_Euro-Restaurants
|
6af3fbcfbd218f9fb4d85487630bfb27d54b0aec
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 110.057381 | 22,952 | 0.779914 |
[
[
[
"### Notebook for the Udacity Project \"Write A Data Science Blog Post\"\n\n#### Dataset used: \"TripAdvisor Restaurants Info for 31 Euro-Cities\"\nhttps://www.kaggle.com/damienbeneschi/krakow-ta-restaurans-data-raw\nhttps://www.kaggle.com/damienbeneschi/krakow-ta-restaurans-data-raw/downloads/krakow-ta-restaurans-data-raw.zip/5",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 1.: Business Understanding according to CRISP-DM\n\nI was in south-western Poland recently and while searching for a good place to eat on Google Maps I noticed, that there were a lot of restaurants that had really good ratings and reviews in the 4+ region, in cities as well as at the countryside. This made me thinking, because in my hometown Munich there is also many great places, but also a lot that are in not-so-good-region around 3 stars. In general, ratings seemed to be better there compared to what I know. So I thought, maybe people just rate more mildly there. Then I had my first lunch at one of those 4+ places and not only the staff was so friendly and the food looked really nicely, it also tasted amazing at a decent pricetag. Okay, I was lucky I thought. On the evening of the same day I tried another place and had the same great experience.\n\nI had even more great eats. So is the quality of the polish restaurants on average better than the quality of the bavarian ones? Subjectively… Yes, it seemed so. But what does data science say? Are there differences in average ratings and number of ratings between regions? To answer this question, I used the TripAdvisor Restaurants Info for 31 Euro-Cities from Kaggle. This dataset contains the TripAdvisor reviews and ratings for 111927 restaurants in 31 European cities.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Problem Definition / Research Questions:\n\n- RQ 1: Are there differences in average ratings and number of ratings between cities?\n- RQ 2: Are there more vegetarian-friendly cities and if so, are they locally concentrated?\n- RQ 3: Is local cuisine rated better than foreign cusine and if so, is there a difference between cities?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import Statements\n\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Load in dataset\n\ndata_raw = pd.read_csv(\"TA_restaurants_curated.csv\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 2.: Data Understanding according to CRISP-DM\n\nIn the following, we have a look at the raw data of the dataset.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Having a first look at the data\n\ndata_raw.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data_raw.describe()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Which cities are included in the dataset?\n\ncities = data_raw.City.unique()\ncities",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Manually add the name of the local cuisines into an array (needed for RQ3)\n\nlocal_cuisine = ['Dutch', 'Greek', 'Spanish', 'German', 'Eastern European', 'Belgian', 'Hungarian', 'Danish', 'Irish', 'Scottish', 'Swiss', 'German', 'Scandinavian', 'Polish', 'Portuguese', 'Slovenian', 'British', 'European', 'French', 'Spanish', 'Italian', 'German', 'Portuguese', 'Norwegian', 'French', 'Czech', 'Italian', 'Swedish', 'Austrian', 'Polish', 'Swiss']",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"As I live in Munich, I will want to have a closer look on the data for the city of Munich. So I will filter for the Munich data and have a first look on it.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Function to return data for a specific city\n\ndef getRawData(city):\n '''Returns the data for a specific city, which is given to the function via the city argument.'''\n data_raw_city = data_raw[(data_raw.City == \"Munich\")]\n return data_raw_city\n\n# Filter for Munich data and have a first look\ncity = \"Munich\"\ndata_raw_city = getRawData(city)\ndata_raw_city.head(10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data_raw_city.tail(10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data_raw_city.describe()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Dealing with missing data:\n\nIt can be seen, that some restaurants, especially the last ones, don't have any Ranking, Rating, Price Ranges or reviews. How to deal with that data? I have chosen to ignore those restaurants in the relevant questions. If, for example, the average rating of a cities restaurant is needed, I only use that restaurants, that actually have a rating. The other restaurants without rating are ignored.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 3. and 4.: Data Preparation and Modeling according to CRISP-DM\n\n### Calculate the data for RQ 1 - 3\n\nIn the following code, the data is first prepared by only selecting relevant and non-NaN data. Afterwards, data is modelled by calculating the relevant statistical numbers. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Loop through entries for each city\n\n# Create empty lists\nnum_entries = []\nnum_rated = []\nperc_rated = []\navg_num_ratings = []\navg_rating = []\navg_veg_available = []\navg_loc_available = []\navg_loc_rating = []\navg_non_loc_rating = []\ndiff_loc_rating = []\ntotal_local_rating = []\ntotal_non_local_rating = []\n\n# Initialize city number\nn_city = -1\n\nfor city in cities:\n n_city = n_city + 1\n \n # Compute Data for RQ1\n # Select data for one city\n data_1city = data_raw[(data_raw.City == city)]\n ratings = data_1city.Rating\n data_1city_non_NaN = data_1city[data_1city['Rating'].notnull()]\n ratings_non_NaN = data_1city_non_NaN.Rating\n \n # Compute Data for RQ2 & RQ3\n # Initialize lists for the current city\n veg_available = []\n loc_available = []\n rating_local = []\n rating_non_local = []\n data_1city_stl_non_Nan = data_1city[data_1city['Cuisine Style'].notnull()]\n \n # Iterate through every restaurant and check if they offer vegetarian/vegan food.\n for i in range(len(data_1city_stl_non_Nan)):\n veg_true = 0\n styles = data_1city_stl_non_Nan.iloc[i, 3]\n if 'Vegetarian' in styles:\n veg_true = 1\n #print('Veg Found')\n elif 'Vegan' in styles:\n veg_true = 1\n veg_available.append(veg_true)\n \n # For RQ3 check if the current restaurant offers local food and add the rating to the respective list.\n loc_true = 0\n if local_cuisine[n_city] in styles:\n loc_true = 1\n if ~np.isnan(data_1city_stl_non_Nan.iloc[i, 5]):\n rating_local.append(data_1city_stl_non_Nan.iloc[i, 5])\n total_local_rating.append(data_1city_stl_non_Nan.iloc[i, 5])\n else:\n if ~np.isnan(data_1city_stl_non_Nan.iloc[i, 5]):\n rating_non_local.append(data_1city_stl_non_Nan.iloc[i, 5])\n total_non_local_rating.append(data_1city_stl_non_Nan.iloc[i, 5])\n \n loc_available.append(loc_true) \n \n \n \n # Add to lists / caluclate aggregated values\n num_entries.append(len(data_1city))\n num_rated.append(len(data_1city_non_NaN))\n perc_rated.append(len(data_1city_non_NaN) / len(data_1city))\n avg_num_ratings.append(np.mean(data_1city_non_NaN['Number of Reviews']))\n avg_rating.append(np.mean(data_1city_non_NaN['Rating']))\n avg_veg_available.append(np.mean(veg_available))\n avg_loc_available.append(np.mean(loc_available))\n avg_loc_rating.append(np.mean(rating_local))\n avg_non_loc_rating.append(np.mean(rating_non_local))\n diff_loc_rating.append(np.mean(rating_local) - np.mean(rating_non_local))\n \n \n# Create Dataframe\ndata_RQ1 = pd.DataFrame({'City': cities, 'Local_Cuisine': local_cuisine, 'Num_Entries': num_entries, 'Num_Rated': num_rated, 'Perc_Rated': perc_rated, 'Avg_Num_Ratings': avg_num_ratings, 'Avg_Rating': avg_rating, 'Avg_Veg_Av': avg_veg_available, 'Avg_Loc_Av': avg_loc_available, 'Avg_loc_rating': avg_loc_rating, 'Avg_non_loc_rating': avg_non_loc_rating, 'Diff_loc_rating': diff_loc_rating})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Show the before computed data for RQ 1, 2 and 3.\ndata_RQ1.head(31)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 5.: Evaluate the Results according to CRISP-DM\n\nIn the following, for every research questions relevant plots and statistical numbers are plotted to interpret the results. Afterward the plots, results are discussed.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### RQ 1: Are there differences in average ratings and number of ratings between cities?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data_RQ1.plot.bar(x='City', y='Avg_Rating', rot=0, figsize=(30,6))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('Lowest Average Rating: {:.3f}'.format(min(data_RQ1.Avg_Rating)))\nprint('Highest Average Rating: {:.3f}'.format(max(data_RQ1.Avg_Rating)))\nprint('Difference from lowest to highest average Rating: {:.3f}'.format(max(data_RQ1.Avg_Rating) - min(data_RQ1.Avg_Rating)))",
"Lowest Average Rating: 3.797\nHighest Average Rating: 4.232\nDifference from lowest to highest average Rating: 0.435\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### As it can clearly be seen, there is a difference in average ratings by citiy. The highest average rating is 4.232 for the city of Rome and 3.797 for the city of Madrid. An interesting follow-up question would be, wether the general quality of restaurants is better in Rome or if reviewers give better ratings in Rome compared to Madrid. Another more vague explaination would be that Tripadvisor is more often used by Tourists than locals, and that tourists rate Italian food better, as they are better used to it since it is better known in the world compared to spanish food.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data_RQ1.plot.bar(x='City', y='Avg_Num_Ratings', rot=0, figsize=(30,6))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('Lowest Average Number of Ratings: {:.3f}'.format(min(data_RQ1.Avg_Num_Ratings)))\nprint('Highest Average Number of Ratings: {:.3f}'.format(max(data_RQ1.Avg_Num_Ratings)))\nprint('Difference from lowest to highest number of Ratings: {:.3f}'.format(max(data_RQ1.Avg_Num_Ratings) - min(data_RQ1.Avg_Num_Ratings)))",
"Lowest Average Number of Ratings: 45.942\nHighest Average Number of Ratings: 293.896\nDifference from lowest to highest number of Ratings: 247.954\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### Also with the number of ratings it can be noted, that there definitely is a a difference in number of ratings. The highest average number of ratings with 293.896 is (again) seen in the city of Rome, while Hamburg with 45.942 has the lowest average number of ratings, which makes up of a difference of close to 248 in average ratings - that means rome has 6 times the average number of ratings as Hamburg, which can't be explained by the difference in inhabitants, which is 2.872.800 for Rome (Wikipedia) and 1.841.179 for Hamburg (Wikipedia). Other explainations would be that certain regions are more rating-friendly, prefer Tripadvisor or other tools such as Google Maps or that the probably higher number of tourists in Rome uses Tripadvisor more often.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### RQ 2: Are there more vegetarian-friendly cities and if so, are they locally concentrated?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data_RQ1.plot.bar(x='City', y='Avg_Veg_Av', rot=0, figsize=(30,6))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('Lowest Average Number of Vegetarian/Vegan Available: {:.3f}'.format(min(data_RQ1.Avg_Veg_Av)))\nprint('Highest Average Number of Vegetarian/Vegan Available: {:.3f}'.format(max(data_RQ1.Avg_Veg_Av)))\nprint('Difference from lowest to highest number: {:.3f}'.format(max(data_RQ1.Avg_Veg_Av) - min(data_RQ1.Avg_Veg_Av)))",
"Lowest Average Number of Vegetarian/Vegan Available: 0.129\nHighest Average Number of Vegetarian/Vegan Available: 0.569\nDifference from lowest to highest number: 0.440\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### It seems that there are also great differences in average number of restaurants with vegetarian/vegan option available: Edinburgh has the highest number of restaurants that offer veg, with 56.9%, Lyon on the other hand with 12,9% is a lot less veg-friendly. A clear local pattern can not be distinguished.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### RQ 3: Is local cuisine rated better than foreign cusine and if so, is there a difference between cities?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data_RQ1.plot.bar(x='City', y='Avg_Loc_Av', rot=0, figsize=(30,6))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data_RQ1.plot.bar(x='City', y='Avg_loc_rating', rot=0, figsize=(30,6))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data_RQ1.plot.bar(x='City', y='Avg_non_loc_rating', rot=0, figsize=(30,6))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data_RQ1.plot.bar(x='City', y='Diff_loc_rating', rot=0, figsize=(30,6))\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('Lowest Rating Difference: {:.3f}'.format(min(data_RQ1.Diff_loc_rating)))\nprint('Highest Rating Difference: {:.3f}'.format(max(data_RQ1.Diff_loc_rating)))\nprint('Average Total Rating Difference: {:.3f}'.format(np.mean(data_RQ1.Diff_loc_rating)))\nprint()\nprint('Total Local Ratings: {}'.format(len(total_local_rating)))\nprint('Total Local Rating Mean: {}'.format(np.mean(total_local_rating)))\nprint('Total Non-Local Ratings: {}'.format(len(total_non_local_rating)))\nprint('Total Non-Local Rating Mean: {}'.format(np.mean(total_non_local_rating)))\nprint('Total Non-Local Rating Mean Difference: {}'.format(np.mean(total_local_rating) - np.mean(total_non_local_rating)))",
"Lowest Rating Difference: -0.231\nHighest Rating Difference: 0.220\nAverage Total Rating Difference: 0.026\n\nTotal Local Ratings: 38385\nTotal Local Rating Mean: 4.0122052885241635\nTotal Non-Local Ratings: 50664\nTotal Non-Local Rating Mean: 3.9966248223590717\nTotal Non-Local Rating Mean Difference: 0.015580466165091789\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### Although there is a difference with local restaurants being rated better than restaurants not serving local food (aggregated difference is 0.026 / total difference is 0.0155), it is quite small and not neccessarily statistically significant in general. Yet it is interesting to notive, that for some cities the hypothesis is true. Especially Copenhagen, Edicnburgh, Helsinki, Ljubliana and Lyana show more significant differences with local restaurants being favored and cities like Barcelona, Berlin, Bratislava, Brussels and Prahgue, where local restaurants are rated less good, in the case of Bratislava the difference is greater than 0.2.\n\nSo, again, this can have multiple reasons. It is possible that people who use Tripadvisor, which are often tourists, prefer certain cousines that they are familiar to. Also it is possible, that certain local cuisines are \"easier\" for the non local. Other reasons are thinkable.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
c50499ab273ba71b70ec7585cb25cf2cf8f6bb4e
| 4,655 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
examples/formulas.ipynb
|
kmedian/pctl_scale
|
18642882d685600bf4c4c5596ad44ee776089695
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
examples/formulas.ipynb
|
kmedian/pctl_scale
|
18642882d685600bf4c4c5596ad44ee776089695
|
[
"MIT"
] | 5 |
2019-08-22T10:51:43.000Z
|
2019-12-01T10:47:12.000Z
|
examples/formulas.ipynb
|
kmedian/pctl_scale
|
18642882d685600bf4c4c5596ad44ee776089695
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 30.032258 | 115 | 0.480344 |
[
[
[
"## Formulas\nLet $x \\in \\mathbb{R}$ the variable subject to scaling, \n$b \\in \\{q \\in \\mathbb{R} | 0 < q < 1\\}$ a given upper percentile,\n$v_b \\in \\mathbb{R}$ the corresponding upper percentile value,\n$a \\in \\{q \\in \\mathbb{R} | 0 < q < b < 1\\}$ a given lower percentile,\n$v_a \\in \\mathbb{R}$ the corresponding lower percentile value\n\n## Scaling\n(1) In a first step, $x$ is scaled by distance between the upper and lower percentile values $v_b - v_a$. \n\n$$\ny = a + b \\, \\left(\\frac{x - v_a}{v_b - v_a}\\right)\n$$\n\nValues between $x \\in [v_a, v_b]$ are scaled as $y \\in [a, b]$ what is similar to min-max scaling.\n\n(2) However, values below the lower percentile value $x < v_a$ might have values below 0, \nand values above the upper percentile value $x > v_b$ might have values above 1.\n\nIn both cases growth saturations formulas are used to enforce the interval boundaries 0 and 1\n\n$$\nz = \n\\begin{cases}\n \\frac{a}{\\exp\\left(\\frac{a - y}{a}\\right)}, & \\text{if } y < a \\\\\n y, & \\text{else if } a \\leq y \\leq b \\\\\n \\frac{b}{b + (1 - b) \\exp\\left(\\frac{b - y}{1 - b}\\right)}, & \\text{else if } y > b\n\\end{cases}\n$$\n\n## Inverse Transform\n$\\forall z < a$\n\n$$\nz = \\frac{a}{\\exp\\left(\\frac{a-y}{a}\\right)} \\\\\n\\Leftrightarrow\nz = d \\cdot \\exp\\left(\\frac{-a + y}{a}\\right) \\\\\n\\Leftrightarrow\n\\ln{z} = \\ln{a} + \\frac{y - a}{a} \\\\\n\\Leftrightarrow\ny = (\\ln{z} - \\ln{a}) \\cdot a + a \\\\\n\\Leftrightarrow\ny = a \\cdot \\ln{\\frac{z}{a}} + a \\\\\n\\Leftrightarrow\ny = a \\cdot \\left( \\ln{\\frac{z}{a}} + 1 \\right)\n$$\n\n$\\forall z > b$\n\n$$\nz = \\frac{b}{b + (1 - b) \\exp\\left(\\frac{b - y}{1 - b}\\right)} \\\\\n\\Leftrightarrow\nb + (1 - b) \\exp\\left(\\frac{b - y}{1 - b}\\right) = \\frac{b}{z}\\\\\n\\Leftrightarrow\n\\exp\\left(\\frac{b - y}{1 - b}\\right) = \\frac{\\frac{b}{z} - b}{1 -b} \\\\\n\\Leftrightarrow\n\\frac{b - y}{1 - b} = \\ln{\\frac{\\frac{b}{z} - b}{1 -b}} \\\\\n\\Leftrightarrow\nb - y = (1 - b) \\cdot \\ln{\\frac{\\frac{b}{z} - b}{1 -b}} \\\\\n\\Leftrightarrow\ny = b - (1 - b) \\cdot \\ln{\\frac{\\frac{b}{z} - b}{1 -b}} \\\\\n$$\n\nInverse simple scaling\n\n$$\ny = a + b \\, \\left(\\frac{x - v_a}{v_b - v_a}\\right) \\\\\n\\Leftrightarrow\n\\frac{y - a}{b} = \\frac{x - v_a}{v_b - v_a} \\\\\n\\Leftrightarrow\n\\left(\\frac{y - a}{b}\\right) \\cdot (v_b - v_a) = x - v_a \\\\\n\\Leftrightarrow\nx = \\left(\\frac{y - a}{b}\\right) \\cdot (v_b - v_a) + v_a\n$$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
]
] |
c504af97b5175101fe3e8583f960524edf2b2dc3
| 4,124 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Plants Python3/2_Making_requests_with_python.ipynb
|
fabiolib/rest-api-jupyter-course
|
c3fd4a36cbfd86ce1571d1056a78ffef93395df6
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 4 |
2020-09-02T08:00:32.000Z
|
2021-02-16T09:51:38.000Z
|
Plants Python3/2_Making_requests_with_python.ipynb
|
fabiolib/rest-api-jupyter-course
|
c3fd4a36cbfd86ce1571d1056a78ffef93395df6
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Plants Python3/2_Making_requests_with_python.ipynb
|
fabiolib/rest-api-jupyter-course
|
c3fd4a36cbfd86ce1571d1056a78ffef93395df6
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 3 |
2020-09-02T14:56:32.000Z
|
2022-03-08T15:21:31.000Z
| 41.24 | 564 | 0.56935 |
[
[
[
"# Making requests with Python\n\nTo make a request, you'll need to specify the server and extension, using the requests module.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import requests, sys\n\nserver = \"http://rest.ensembl.org\"\next = \"/lookup/id/TraesCS3D02G007500\"\n \nr = requests.get(server+ext, headers={ \"Content-Type\" : \"application/json\"})\n\nprint (r)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Never assume that your request has worked. If it doesn't work, you should check the response code.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import requests, sys\n\nserver = \"http://rest.ensembl.org\"\next = \"/lookup/id/TraesCS3D02G007500\"\n \nr = requests.get(server+ext, headers={ \"Content-Type\" : \"application/json\"})\n\nif not r.ok:\n r.raise_for_status()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"If you get responses in json (recommended), you can then decode them. I've also imported the pretty print (pprint) module from python, which makes my json easy to read. You'll find this useful during the exercises to see how the json looks.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import requests, sys, json\nfrom pprint import pprint\n\nserver = \"http://rest.ensembl.org\"\next = \"/lookup/id/TraesCS3D02G007500\"\n \nr = requests.get(server+ext, headers={ \"Content-Type\" : \"application/json\"})\n\nif not r.ok:\n r.raise_for_status()\n\ndecoded = r.json()\n\npprint (decoded)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The helper function allows you to call the request, check the status and decode the json in a single line in your script. If you're using lots of REST calls in your script, creating the function at the beginning of your script will save you a lot of time.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import requests, sys, json\nfrom pprint import pprint\n\ndef fetch_endpoint(server, request, content_type):\n\n r = requests.get(server+request, headers={ \"Content-Type\" : content_type})\n\n if not r.ok:\n r.raise_for_status()\n sys.exit()\n\n if content_type == 'application/json':\n return r.json()\n else:\n return r.text\n\n\nserver = \"http://rest.ensembl.org/\"\next = \"lookup/id/TraesCS3D02G007500?\"\ncon = \"application/json\"\nget_gene = fetch_endpoint(server, ext, con)\n\npprint (get_gene)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Exercises 2\n\n1. Write a script to **lookup** the gene called *BCH1* in barley and print the results in json.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Exercise 2.1",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"[Next page: Exercises 2 – answers](2_Making_requests_with_python_answers.ipynb)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
c504b19f15e1b93be41321c63864bfc1956e6c23
| 35,863 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Generate_dataset_ohara2017/generate_dataset.ipynb
|
sjk0709/Electrophysiology
|
d7d9eb9e8ee787ed9b3d675afb85456b3f340357
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Generate_dataset_ohara2017/generate_dataset.ipynb
|
sjk0709/Electrophysiology
|
d7d9eb9e8ee787ed9b3d675afb85456b3f340357
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Generate_dataset_ohara2017/generate_dataset.ipynb
|
sjk0709/Electrophysiology
|
d7d9eb9e8ee787ed9b3d675afb85456b3f340357
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 67.285178 | 17,108 | 0.716114 |
[
[
[
"import os, sys, time, copy\nimport random\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\nimport multiprocessing\nfrom functools import partial\nfrom tqdm import tqdm\n\n\nimport myokit\nsys.path.append('../')\nsys.path.append('../Protocols')\nsys.path.append('../Models')\nsys.path.append('../Lib')\nimport protocol_lib\nimport mod_trace\n\nimport simulator_myokit\nimport simulator_scipy\nimport vc_protocols",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def find_closest_index(array, t):\n \"\"\"Given an array, return the index with the value closest to t.\"\"\"\n return (np.abs(np.array(array) - t)).argmin()\n\n# def get_currents_with_constant_dt(xs, window=1, step_size=1):\n \n# times = xs[0]\n# currents = xs[1:]\n \n# data_li = []\n# for I in currents: \n# data_temp = []\n# t = 0\n# while t <= times[-1] - window:\n# start_index = find_closest_index(times, t)\n# end_index = find_closest_index(times, t + window) \n# I_window = I[start_index: end_index + 1] \n# data_temp.append(sum(I_window)/len(I_window)) \n# t += step_size\n# data_li.append(data_temp) \n \n# return data_li\n\ndef get_currents_with_constant_dt(xs, window=1, step_size=1):\n \n times = xs[0]\n i_ion = xs[1]\n \n i_ion_window = []\n t = 0\n while t <= times[-1] - window:\n start_index = find_closest_index(times, t)\n end_index = find_closest_index(times, t + window) \n I_window = i_ion[start_index: end_index + 1] \n i_ion_window.append(sum(I_window)/len(I_window)) \n t += step_size\n \n return i_ion_window",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cell_types = {\n 'Endocardial' : 0,\n 'Epicardial' : 1,\n 'Mid-myocardial' : 2,\n}",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Create Voltage Protocol",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"'''\nleemV1\n'''\n# VC_protocol = vc_protocols.hERG_CiPA()\n# VC_protocol = vc_protocols.cav12_CiPA()\n# VC_protocol = vc_protocols.lateNav15_CiPA()\n\nVC_protocol = protocol_lib.VoltageClampProtocol() # steps=steps\nVC_protocol.add( protocol_lib.VoltageClampStep(voltage=-80, duration=100) )\nVC_protocol.add( protocol_lib.VoltageClampStep(voltage=-90, duration=100) )\nVC_protocol.add( protocol_lib.VoltageClampStep(voltage=-80, duration=100) )\nVC_protocol.add( protocol_lib.VoltageClampStep(voltage=-35, duration=40) )\nVC_protocol.add( protocol_lib.VoltageClampStep(voltage=-80, duration=200) )\nVC_protocol.add( protocol_lib.VoltageClampStep(voltage=-40, duration=40) )\nVC_protocol.add( protocol_lib.VoltageClampStep(voltage=0, duration=40) ) # <- why?? vo\nVC_protocol.add( protocol_lib.VoltageClampStep(voltage=40, duration=500) )\nVC_protocol.add( protocol_lib.VoltageClampRamp(voltage_start=40, voltage_end=-120, duration=200)) # ramp step\n# VC_protocol.add( protocol_lib.VoltageClampStep(voltage=-80, duration=100) )\n# VC_protocol.add( protocol_lib.VoltageClampStep(voltage=0, duration=100) )\n# VC_protocol.add( protocol_lib.VoltageClampStep(voltage=60, duration=500) )\n# VC_protocol.add( protocol_lib.VoltageClampRamp(voltage_start=60, voltage_end=-80, duration=200)) # ramp step\n\nvhold = -80 # VC_protocol.steps[0].voltage\n\nprint(f'The protocol is {VC_protocol.get_voltage_change_endpoints()[-1]} ms')",
"The protocol is 1320 ms\n"
],
[
"# '''\n# SongV1\n# '''\n# VC_protocol = protocol_lib.VoltageClampProtocol() # steps=steps\n\n# VC_protocol.add( protocol_lib.VoltageClampStep(voltage=-80, duration=100) )\n# VC_protocol.add( protocol_lib.VoltageClampStep(voltage=-120, duration=20) ) \n# VC_protocol.add( protocol_lib.VoltageClampStep(voltage=-40, duration=200) )\n# VC_protocol.add( protocol_lib.VoltageClampStep(voltage=60, duration=200) )\n# VC_protocol.add( protocol_lib.VoltageClampStep(voltage=0, duration=200) ) # <- why?? vo\n# VC_protocol.add( protocol_lib.VoltageClampStep(voltage=50, duration=200) )\n# VC_protocol.add( protocol_lib.VoltageClampStep(voltage=-10, duration=200) )\n# VC_protocol.add( protocol_lib.VoltageClampStep(voltage=-80, duration=50) )\n# VC_protocol.add( protocol_lib.VoltageClampRamp(voltage_start=30, voltage_end=-50, duration=100)) # ramp step\n\n# vhold = -80\n\n# print(f'The protocol is {VC_protocol.get_voltage_change_endpoints()[-1]} ms')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"start_time = time.time()\n\nmodel, p, s = myokit.load(\"../mmt-model-files/ohara-cipa-v1-2017_JK-v2.mmt\") \nsim = simulator_myokit.Simulator(model, VC_protocol, max_step=1.0, abs_tol=1e-06, rel_tol=1e-6, vhold=vhold) # 1e-12, 1e-14 # 1e-08, 1e-10\nsim.name = \"ohara2017\" \n\nf = 1.5\nparams = { \n 'cell.mode': cell_types['Mid-myocardial'],\n 'setting.simType': 1, # 0: AP | 1: VC \n \n 'ina.gNa' : 75.0 * f, \n 'inal.gNaL' : 0.0075 * 2.661 * f, \n 'ito.gto' : 0.02 * 4 * f,\n 'ical.PCa' : 0.0001 * 1.007 * 2.5 * f,\n 'ikr.gKr' : 4.65854545454545618e-2 * 1.3 * f, # [mS/uF]\n 'iks.gKs' : 0.0034 * 1.87 * 1.4 * f,\n 'ik1.gK1' : 0.1908 * 1.698 * 1.3 * f,\n 'inaca.gNaCa' : 0.0008 * 1.4,\n 'inak.PNaK' : 30 * 0.7,\n 'ikb.gKb' : 0.003,\n 'inab.PNab' : 3.75e-10,\n 'icab.PCab' : 2.5e-8,\n 'ipca.GpCa' : 0.0005,\n}\nsim.set_simulation_params(params)\n\nprint(\"--- %s seconds ---\"%(time.time()-start_time))",
"--- 3.5311107635498047 seconds ---\n"
],
[
"for key, value in params.items():\n print(f'{key} : {value}')",
"cell.mode : 2\nsetting.simType : 1\nina.gNa : 112.5\ninal.gNaL : 0.029936249999999998\nito.gto : 0.12\nical.PCa : 0.0003776249999999999\nikr.gKr : 0.0908416363636364\niks.gKs : 0.0133518\nik1.gK1 : 0.6317578800000001\ninaca.gNaCa : 0.00112\ninak.PNaK : 21.0\nikb.gKb : 0.003\ninab.PNab : 3.75e-10\nicab.PCab : 2.5e-08\nipca.GpCa : 0.0005\n"
],
[
"def gen_dataset( gen_params, datasetNo=1): \n '''\n type = 'AP' or 'I\" \n params = {\n 'times': 1, \n 'log_li' : [],\n 'nData' : 10000, \n 'dataset_dir' : './dataset',\n 'data_file_name' : 'current',\n 'scale' : 2,\n } \n '''\n random.seed(datasetNo * 84)\n np.random.seed(datasetNo * 86)\n\n print(\"-----Dataset%d generation starts.-----\"%(datasetNo))\n\n d = None \n result_li = []\n param_li = []\n current_nData = 0\n \n simulation_error_count = 0\n with tqdm(total = gen_params['nData']) as pbar: \n while (current_nData < gen_params['nData']): \n g_adj = np.random.uniform(0, 1, 7) \n \n g_adj_li= { \n 'ina.g_adj' : g_adj[0],\n 'inal.g_adj' : g_adj[1],\n 'ito.g_adj' : g_adj[2],\n 'ical.g_adj' : g_adj[3],\n 'ikr.g_adj' : g_adj[4],\n 'iks.g_adj' : g_adj[5],\n 'ik1.g_adj' : g_adj[6],\n # 'if.g_adj' : g_fc[7] \n } \n sim.set_simulation_params(g_adj_li) \n # log_li = ['membrane.V']\n # if len(log_li)>0:\n # log_li = gen_params['log_li']\n try : \n sim.pre_simulate(5000, sim_type=1)\n d = sim.simulate( gen_params['end_time'], extra_log=gen_params['log_li']) \n\n # temp = [d['engine.time']]\n # for log in gen_params['save_log_li'] : \n # temp.append(d[log]) \n # temp = get_currents_with_constant_dt(temp, window=gen_params['window'], step_size=gen_params['step_size'])\n\n temp = [d['engine.time'], d['membrane.i_ion']] \n\n if (gen_params['window']>0) and (gen_params['step_size']>0):\n temp = get_currents_with_constant_dt(temp, window=gen_params['window'], step_size=gen_params['step_size'])\n result_li.append( np.array(temp) )\n else:\n result_li.append( temp ) \n\n param_li.append( g_adj )\n current_nData+=1 \n\n except :\n simulation_error_count += 1\n print(\"There is a simulation error.\")\n continue\n \n pbar.update(1) \n \n if gen_params['window'] != None and gen_params['step_size']:\n result_li = np.array(result_li) \n else:\n result_li = np.array(result_li, dtype=object) \n \n param_li = np.array(param_li) \n \n np.save(os.path.join(gen_params['dataset_dir'], f\"{gen_params['data_file_name']}{datasetNo}\" ) , result_li)\n np.save(os.path.join(gen_params['dataset_dir'], f'parameter{datasetNo}' ), param_li )\n\n result_li = []\n param_li = []\n\n print(\"=====Dataset%d generation End. & %d simulation errors occured.=====\"%(datasetNo, simulation_error_count)) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"if __name__=='__main__':\n start_time = time.time() \n nCPU = os.cpu_count() \n print(\"The number of process :\", nCPU ) \n \n multi = False\n \n gen_params = {\n 'end_time': VC_protocol.get_voltage_change_endpoints()[-1], \n 'log_li' : ['membrane.i_ion', 'ina.INa', 'inal.INaL', 'ito.Ito', 'ical.ICaL', 'ical.ICaNa', 'ical.ICaK', 'ikr.IKr', 'iks.IKs', 'ik1.IK1', 'inaca.INaCa', 'inacass.INaCa_ss', 'inak.INaK', 'ikb.IKb', 'inab.INab', 'icab.ICab', 'ipca.IpCa'],\n 'save_log_li' : ['membrane.i_ion'],\n 'nData' : 1000, \n 'dataset_dir' : './ohara2017_LeemV1_fixed_concentrations',\n 'data_file_name' : 'currents',\n 'window' : None,\n 'step_size' : None,\n 'startNo' : 71,\n 'nDataset' : 1,\n } \n gen_params['dataset_dir'] = gen_params['dataset_dir'] #+ f\"_w{gen_params['window']}_s{gen_params['step_size']}\"\n\n datasetNo_li = list(range(gen_params['startNo'], gen_params['startNo']+gen_params['nDataset'])) # Core 수만큼 [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10] \n print(datasetNo_li) \n \n try:\n if not os.path.exists(gen_params['dataset_dir']):\n os.makedirs(gen_params['dataset_dir'])\n print('\"%s\" has been created.'%(gen_params['dataset_dir']))\n else:\n print(\"The folder already exists.\")\n except OSError:\n print('Error: create_folder(). : ' + gen_params['dataset_dir'])\n \n \n '''\n Plot\n '''\n fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,1, figsize=(10,3)) \n # fig.suptitle(sim.name, fontsize=14)\n # ax.set_title('Simulation %d'%(simulationNo))\n # axes[i].set_xlim(model_scipy.times.min(), model_scipy.times.max())\n # ax.set_ylim(ylim[0], ylim[1])\n ax.set_xlabel('Time (ms)') \n ax.set_ylabel(f'Voltage') \n times = np.linspace(0, VC_protocol.get_voltage_change_endpoints()[-1], 10000) \n ax.plot( times, VC_protocol.get_voltage_clamp_protocol(times), label='VC', color='k', linewidth=5) \n ax.legend()\n ax.grid()\n # ax[-1].set_ylim(-5, 5)\n\n plt.subplots_adjust(left=0.07, bottom=0.05, right=0.95, top=0.95, wspace=0.5, hspace=0.15)\n plt.show()\n fig.savefig(os.path.join(gen_params['dataset_dir'], \"aVC.jpg\" ), dpi=100)\n \n if multi : \n pool = multiprocessing.Pool(processes=32 )\n func = partial(gen_dataset, gen_params)\n pool.map(func, datasetNo_li)\n pool.close()\n pool.join()\n else:\n for No in datasetNo_li :\n gen_dataset(gen_params, No)\n \n # print(\"Dataset has been generated.\")\n \n print(\"--- %s seconds ---\"%(time.time()-start_time))\n \n # \n\n # # Set parameter transformation\n # transform_to_model_param = log_transform_to_model_param # return np.exp(out)\n # transform_from_model_param = log_transform_from_model_param # return np.log(out)\n \n # logprior = LogPrior(transform_to_model_param, transform_from_model_param)\n \n # p = logprior.sample_without_inv_transform()\n # print(p)\n \n # print(logprior.rmax)\n # print(logprior.rmin)\n # print(5e5)\n\n ",
"The number of process : 72\n[71]\n\"./ohara2017_LeemV1\" has been created.\n"
],
[
"print(\"Finish\")",
"Finish\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c504c15d030dacd45b838575308844a8d0ead894
| 371,881 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
content/sections/section4/notebook/cs109a_section_4.ipynb
|
songdavidb/2019-CS109A
|
5cd50e7a3f84b0d6b6668fb80732fb91bfec6cea
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
content/sections/section4/notebook/cs109a_section_4.ipynb
|
songdavidb/2019-CS109A
|
5cd50e7a3f84b0d6b6668fb80732fb91bfec6cea
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
content/sections/section4/notebook/cs109a_section_4.ipynb
|
songdavidb/2019-CS109A
|
5cd50e7a3f84b0d6b6668fb80732fb91bfec6cea
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 83.418798 | 27,168 | 0.678343 |
[
[
[
"empty"
]
]
] |
[
"empty"
] |
[
[
"empty"
]
] |
c504c3ae92b936e11b2f8397540540c1051492e3
| 4,190 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
sourmash-collections.ipynb
|
ctb/2019-upr-kmers
|
dfc8aa922facf66dfce90210e1c7d0866f14790a
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 2 |
2019-02-15T12:51:44.000Z
|
2019-02-15T20:14:45.000Z
|
sourmash-collections.ipynb
|
ctb/2019-upr-kmers
|
dfc8aa922facf66dfce90210e1c7d0866f14790a
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
sourmash-collections.ipynb
|
ctb/2019-upr-kmers
|
dfc8aa922facf66dfce90210e1c7d0866f14790a
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 1 |
2019-04-13T12:47:27.000Z
|
2019-04-13T12:47:27.000Z
| 20.339806 | 94 | 0.542005 |
[
[
[
"# sourmash: working with private collections of signatures",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## download a bunch of genomes",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!mkdir -p big_genomes\n!curl -L https://osf.io/8uxj9/?action=download | (cd big_genomes && tar xzf -)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## compute signatures for each file",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!cd big_genomes/ && sourmash compute -k 31 --scaled=1000 --name-from-first *.fa",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Compare them all",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!sourmash compare big_genomes/*.sig -o compare_all.mat\n!sourmash plot compare_all.mat",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from IPython.display import Image\nImage(filename='compare_all.mat.matrix.png') ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## make a fast(er) search database for all of them",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!sourmash index -k 31 all-genomes big_genomes/*.sig",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You can now use this to search, and gather.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!sourmash search shew_os185.fa.sig all-genomes --threshold=0.001",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# (make fake metagenome again, just in case)\n!cat genomes/*.fa > fake-metagenome.fa\n!sourmash compute -k 31 --scaled=1000 fake-metagenome.fa",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!sourmash gather fake-metagenome.fa.sig all-genomes",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# build a database with taxonomic information --\n\nfor this, we need to provide a metadata file that contains accession => tax information.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas\ndf = pandas.read_csv('podar-lineage.csv')\ndf",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!sourmash lca index podar-lineage.csv taxdb big_genomes/*.sig -C 3 --split-identifiers",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This database 'taxdb.lca.json' can be used for search and gather as above:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!sourmash gather fake-metagenome.fa.sig taxdb.lca.json",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"...but can also be used for taxonomic summarization:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!sourmash lca summarize --query fake-metagenome.fa.sig --db taxdb.lca.json",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c504d0e5bb3564779504f423fc1e3ce9df492765
| 461,742 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Applied_Machine_Learning_S22/aml-08-gradient-boosting-calibration/aml-11-calibration.ipynb
|
pratoolbharti/pratoolb
|
2f1380fea637c7c1570c502cf27a13d9a7ca5b43
|
[
"MIT"
] | 315 |
2019-01-16T03:10:25.000Z
|
2022-02-12T16:10:59.000Z
|
Applied_Machine_Learning_S22/aml-08-gradient-boosting-calibration/aml-11-calibration.ipynb
|
pratoolbharti/pratoolb
|
2f1380fea637c7c1570c502cf27a13d9a7ca5b43
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2019-02-07T15:21:30.000Z
|
2019-05-22T18:45:15.000Z
|
Applied_Machine_Learning_S22/aml-08-gradient-boosting-calibration/aml-11-calibration.ipynb
|
pratoolbharti/pratoolb
|
2f1380fea637c7c1570c502cf27a13d9a7ca5b43
|
[
"MIT"
] | 147 |
2019-01-23T19:15:42.000Z
|
2022-02-12T16:11:03.000Z
| 511.909091 | 161,852 | 0.938416 |
[
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n% matplotlib inline\nplt.rcParams[\"savefig.dpi\"] = 300\nplt.rcParams[\"savefig.bbox\"] = \"tight\"\nnp.set_printoptions(precision=3, suppress=True)\nimport pandas as pd\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nfrom sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import scale, StandardScaler",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# toy plot\nplt.plot([.3, 0, 1])\nplt.xticks((0, 1, 2), (\"0 (.16)\", \"1 (.5)\", \"2 (.84)\"))\nplt.xlabel(\"Bin index (expected positive)\")\nplt.ylabel(\"Observed positive in bin\")\nplt.savefig(\"images/calib_curve.png\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.datasets import fetch_covtype\nfrom sklearn.utils import check_array\n\ndef load_data(dtype=np.float32, order='C', random_state=13):\n ######################################################################\n # Load covertype dataset (downloads it from the web, might take a bit)\n data = fetch_covtype(download_if_missing=True, shuffle=True,\n random_state=random_state)\n X = check_array(data['data'], dtype=dtype, order=order)\n # make it bineary classification\n y = (data['target'] != 1).astype(np.int)\n\n # Create train-test split (as [Joachims, 2006])\n n_train = 522911\n X_train = X[:n_train]\n y_train = y[:n_train]\n X_test = X[n_train:]\n y_test = y[n_train:]\n\n # Standardize first 10 features (the numerical ones)\n mean = X_train.mean(axis=0)\n std = X_train.std(axis=0)\n mean[10:] = 0.0\n std[10:] = 1.0\n X_train = (X_train - mean) / std\n X_test = (X_test - mean) / std\n return X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test\n\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = load_data()\n\n# subsample training set by a factor of 10:\nX_train = X_train[::10]\ny_train = y_train[::10]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegressionCV\nprint(X_train.shape)\nprint(np.bincount(y_train))\nlr = LogisticRegressionCV().fit(X_train, y_train)",
"(52292, 54)\n[19036 33256]\n"
],
[
"lr.C_",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(lr.predict_proba(X_test)[:10])\nprint(y_test[:10])",
"[[0.681 0.319]\n [0.049 0.951]\n [0.706 0.294]\n [0.536 0.464]\n [0.819 0.181]\n [0. 1. ]\n [0.794 0.206]\n [0.676 0.324]\n [0.727 0.273]\n [0.597 0.403]]\n[0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1]\n"
],
[
"from sklearn.calibration import calibration_curve\nprobs = lr.predict_proba(X_test)[:, 1]\nprob_true, prob_pred = calibration_curve(y_test, probs, n_bins=5)\nprint(prob_true)\nprint(prob_pred)",
"[0.199 0.304 0.458 0.709 0.934]\n[0.138 0.306 0.498 0.701 0.926]\n"
],
[
"def plot_calibration_curve(y_true, y_prob, n_bins=5, ax=None, hist=True, normalize=False):\n prob_true, prob_pred = calibration_curve(y_true, y_prob, n_bins=n_bins, normalize=normalize)\n if ax is None:\n ax = plt.gca()\n if hist:\n ax.hist(y_prob, weights=np.ones_like(y_prob) / len(y_prob), alpha=.4,\n bins=np.maximum(10, n_bins))\n ax.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], ':', c='k')\n curve = ax.plot(prob_pred, prob_true, marker=\"o\")\n\n ax.set_xlabel(\"predicted probability\")\n ax.set_ylabel(\"fraction of positive samples\")\n\n ax.set(aspect='equal')\n return curve\n\n \nplot_calibration_curve(y_test, probs)\nplt.title(\"n_bins=5\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(16, 6))\nfor ax, n_bins in zip(axes, [5, 20, 50]):\n plot_calibration_curve(y_test, probs, n_bins=n_bins, ax=ax)\n ax.set_title(\"n_bins={}\".format(n_bins))\nplt.savefig(\"images/influence_bins.png\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC, SVC\nfrom sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier\nfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier\nfig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(8, 8))\nfor ax, clf in zip(axes, [LogisticRegressionCV(), DecisionTreeClassifier(),\n RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100)]):\n # use predict_proba is the estimator has it\n scores = clf.fit(X_train, y_train).predict_proba(X_test)[:, 1]\n plot_calibration_curve(y_test, scores, n_bins=20, ax=ax)\n ax.set_title(clf.__class__.__name__)\n\nplt.tight_layout()\nplt.savefig(\"images/calib_curve_models.png\")",
"/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/model_selection/_split.py:2058: FutureWarning: The default value of cv will change from 3 to 5 in version 0.22. Specify it explicitly to silence this warning.\n warnings.warn(CV_WARNING, FutureWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n"
],
[
"# same thing but with bier loss shown. Why do I refit the models? lol\nfrom sklearn.metrics import brier_score_loss\nfig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(10, 4))\nfor ax, clf in zip(axes, [LogisticRegressionCV(), DecisionTreeClassifier(), RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100)]):\n # use predict_proba is the estimator has it\n scores = clf.fit(X_train, y_train).predict_proba(X_test)[:, 1]\n plot_calibration_curve(y_test, scores, n_bins=20, ax=ax)\n ax.set_title(\"{}: {:.2f}\".format(clf.__class__.__name__, brier_score_loss(y_test, scores)))\n\nplt.tight_layout()\nplt.savefig(\"images/models_bscore.png\")",
"/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/model_selection/_split.py:2058: FutureWarning: The default value of cv will change from 3 to 5 in version 0.22. Specify it explicitly to silence this warning.\n warnings.warn(CV_WARNING, FutureWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/linear_model/logistic.py:947: ConvergenceWarning: lbfgs failed to converge. Increase the number of iterations.\n \"of iterations.\", ConvergenceWarning)\n"
],
[
"from sklearn.calibration import CalibratedClassifierCV\nX_train_sub, X_val, y_train_sub, y_val = train_test_split(X_train, y_train,\n stratify=y_train, random_state=0)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"rf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100).fit(X_train_sub, y_train_sub)\nscores = rf.predict_proba(X_test)[:, 1]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plot_calibration_curve(y_test, scores, n_bins=20)\nplt.title(\"{}: {:.3f}\".format(clf.__class__.__name__, brier_score_loss(y_test, scores)))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cal_rf = CalibratedClassifierCV(rf, cv=\"prefit\", method='sigmoid')\ncal_rf.fit(X_val, y_val)\nscores_sigm = cal_rf.predict_proba(X_test)[:, 1]\n\ncal_rf_iso = CalibratedClassifierCV(rf, cv=\"prefit\", method='isotonic')\ncal_rf_iso.fit(X_val, y_val)\nscores_iso = cal_rf_iso.predict_proba(X_test)[:, 1]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"scores_rf = cal_rf.predict_proba(X_val)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.plot(scores_rf[:, 1], y_val, 'o', alpha=.01)\nplt.xlabel(\"rf.predict_proba\")\nplt.ylabel(\"True validation label\")\nplt.savefig(\"images/calibration_val_scores.png\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sigm = cal_rf.calibrated_classifiers_[0].calibrators_[0]\nscores_rf_sorted = np.sort(scores_rf[:, 1])\nsigm_scores = sigm.predict(scores_rf_sorted)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"iso = cal_rf_iso.calibrated_classifiers_[0].calibrators_[0]\niso_scores = iso.predict(scores_rf_sorted)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.plot(scores_rf[:, 1], y_val, 'o', alpha=.01)\nplt.plot(scores_rf_sorted, sigm_scores, label='sigm')\nplt.plot(scores_rf_sorted, iso_scores, label='iso')\n\nplt.xlabel(\"rf.predict_proba\")\nplt.ylabel(\"True validation label\")\nplt.legend()\nplt.savefig(\"images/calibration_val_scores_fitted.png\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(10, 4))\n\nfor name, s, ax in zip(['no callibration', 'sigmoid', 'isotonic'],\n [scores, scores_sigm, scores_iso], axes):\n plot_calibration_curve(y_test, s, n_bins=20, ax=ax)\n ax.set_title(\"{}: {:.3f}\".format(name, brier_score_loss(y_test, s)))\nplt.tight_layout()\nplt.savefig(\"images/types_callib.png\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cal_rf_iso_cv = CalibratedClassifierCV(rf, method='isotonic')\ncal_rf_iso_cv.fit(X_train, y_train)\nscores_iso_cv = cal_rf_iso_cv.predict_proba(X_test)[:, 1]",
"/home/andy/checkout/scikit-learn/sklearn/model_selection/_split.py:2058: FutureWarning: The default value of cv will change from 3 to 5 in version 0.22. Specify it explicitly to silence this warning.\n warnings.warn(CV_WARNING, FutureWarning)\n"
],
[
"fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(10, 4))\n\nfor name, s, ax in zip(['no callibration', 'isotonic', 'isotonic cv'],\n [scores, scores_iso, scores_iso_cv], axes):\n plot_calibration_curve(y_test, s, n_bins=20, ax=ax)\n ax.set_title(\"{}: {:.3f}\".format(name, brier_score_loss(y_test, s)))\nplt.tight_layout()\nplt.savefig(\"images/types_callib_cv.png\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# http://scikit-learn.org/dev/auto_examples/calibration/plot_calibration_multiclass.html\n\n# Author: Jan Hendrik Metzen <[email protected]>\n# License: BSD Style.\n\n\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\nimport numpy as np\n\nfrom sklearn.datasets import make_blobs\nfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier\nfrom sklearn.calibration import CalibratedClassifierCV\nfrom sklearn.metrics import log_loss, brier_score_loss\n\nnp.random.seed(0)\n\n# Generate data\nX, y = make_blobs(n_samples=1000, n_features=2, random_state=42,\n cluster_std=5.0)\nX_train, y_train = X[:600], y[:600]\nX_valid, y_valid = X[600:800], y[600:800]\nX_train_valid, y_train_valid = X[:800], y[:800]\nX_test, y_test = X[800:], y[800:]\n\n# Train uncalibrated random forest classifier on whole train and validation\n# data and evaluate on test data\nclf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=25)\nclf.fit(X_train_valid, y_train_valid)\nclf_probs = clf.predict_proba(X_test)\nscore = log_loss(y_test, clf_probs)\n#score = brier_score_loss(y_test, clf_probs[:, 1])\n\n# Train random forest classifier, calibrate on validation data and evaluate\n# on test data\nclf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=25)\nclf.fit(X_train, y_train)\nclf_probs = clf.predict_proba(X_test)\nsig_clf = CalibratedClassifierCV(clf, method=\"sigmoid\", cv=\"prefit\")\nsig_clf.fit(X_valid, y_valid)\nsig_clf_probs = sig_clf.predict_proba(X_test)\nsig_score = log_loss(y_test, sig_clf_probs)\n#sig_score = brier_score_loss(y_test, sig_clf_probs[:, 1])\n\n# Plot changes in predicted probabilities via arrows\nplt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))\nplt.subplot(1, 2, 1)\ncolors = [\"r\", \"g\", \"b\"]\nfor i in range(clf_probs.shape[0]):\n plt.arrow(clf_probs[i, 0], clf_probs[i, 1],\n sig_clf_probs[i, 0] - clf_probs[i, 0],\n sig_clf_probs[i, 1] - clf_probs[i, 1],\n color=colors[y_test[i]], head_width=1e-2)\n\n# Plot perfect predictions\nplt.plot([1.0], [0.0], 'ro', ms=20, label=\"Class 1\")\nplt.plot([0.0], [1.0], 'go', ms=20, label=\"Class 2\")\nplt.plot([0.0], [0.0], 'bo', ms=20, label=\"Class 3\")\n\n# Plot boundaries of unit simplex\nplt.plot([0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0], [0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0], 'k', label=\"Simplex\")\n\n# Annotate points on the simplex\nplt.annotate(r'($\\frac{1}{3}$, $\\frac{1}{3}$, $\\frac{1}{3}$)',\n xy=(1.0/3, 1.0/3), xytext=(1.0/3, .23), xycoords='data',\n arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', shrink=0.05),\n horizontalalignment='center', verticalalignment='center')\nplt.plot([1.0/3], [1.0/3], 'ko', ms=5)\nplt.annotate(r'($\\frac{1}{2}$, $0$, $\\frac{1}{2}$)',\n xy=(.5, .0), xytext=(.5, .1), xycoords='data',\n arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', shrink=0.05),\n horizontalalignment='center', verticalalignment='center')\nplt.annotate(r'($0$, $\\frac{1}{2}$, $\\frac{1}{2}$)',\n xy=(.0, .5), xytext=(.1, .5), xycoords='data',\n arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', shrink=0.05),\n horizontalalignment='center', verticalalignment='center')\nplt.annotate(r'($\\frac{1}{2}$, $\\frac{1}{2}$, $0$)',\n xy=(.5, .5), xytext=(.6, .6), xycoords='data',\n arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', shrink=0.05),\n horizontalalignment='center', verticalalignment='center')\nplt.annotate(r'($0$, $0$, $1$)',\n xy=(0, 0), xytext=(.1, .1), xycoords='data',\n arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', shrink=0.05),\n horizontalalignment='center', verticalalignment='center')\nplt.annotate(r'($1$, $0$, $0$)',\n xy=(1, 0), xytext=(1, .1), xycoords='data',\n arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', shrink=0.05),\n horizontalalignment='center', verticalalignment='center')\nplt.annotate(r'($0$, $1$, $0$)',\n xy=(0, 1), xytext=(.1, 1), xycoords='data',\n arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', shrink=0.05),\n horizontalalignment='center', verticalalignment='center')\n# Add grid\nplt.grid(\"off\")\nfor x in [0.0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, 1.0]:\n plt.plot([0, x], [x, 0], 'k', alpha=0.2)\n plt.plot([0, 0 + (1-x)/2], [x, x + (1-x)/2], 'k', alpha=0.2)\n plt.plot([x, x + (1-x)/2], [0, 0 + (1-x)/2], 'k', alpha=0.2)\n\nplt.title(\"Change of predicted probabilities after sigmoid calibration\")\nplt.xlabel(\"Probability class 1\")\nplt.ylabel(\"Probability class 2\")\nplt.xlim(-0.05, 1.05)\nplt.ylim(-0.05, 1.05)\nplt.legend(loc=\"best\")\n\nprint(\"Log-loss of\")\nprint(\" * uncalibrated classifier trained on 800 datapoints: %.3f \"\n % score)\nprint(\" * classifier trained on 600 datapoints and calibrated on \"\n \"200 datapoint: %.3f\" % sig_score)\n\n# Illustrate calibrator\nplt.subplot(1, 2, 2)\n# generate grid over 2-simplex\np1d = np.linspace(0, 1, 20)\np0, p1 = np.meshgrid(p1d, p1d)\np2 = 1 - p0 - p1\np = np.c_[p0.ravel(), p1.ravel(), p2.ravel()]\np = p[p[:, 2] >= 0]\n\ncalibrated_classifier = sig_clf.calibrated_classifiers_[0]\nprediction = np.vstack([calibrator.predict(this_p)\n for calibrator, this_p in\n zip(calibrated_classifier.calibrators_, p.T)]).T\nprediction /= prediction.sum(axis=1)[:, None]\n\n# Plot modifications of calibrator\nfor i in range(prediction.shape[0]):\n plt.arrow(p[i, 0], p[i, 1],\n prediction[i, 0] - p[i, 0], prediction[i, 1] - p[i, 1],\n head_width=1e-2, color=colors[np.argmax(p[i])])\n# Plot boundaries of unit simplex\nplt.plot([0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0], [0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0], 'k', label=\"Simplex\")\n\nplt.grid(\"off\")\nfor x in [0.0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, 1.0]:\n plt.plot([0, x], [x, 0], 'k', alpha=0.2)\n plt.plot([0, 0 + (1-x)/2], [x, x + (1-x)/2], 'k', alpha=0.2)\n plt.plot([x, x + (1-x)/2], [0, 0 + (1-x)/2], 'k', alpha=0.2)\n\nplt.title(\"Illustration of sigmoid calibrator\")\nplt.xlabel(\"Probability class 1\")\nplt.ylabel(\"Probability class 2\")\nplt.xlim(-0.05, 1.05)\nplt.ylim(-0.05, 1.05)\n\nplt.savefig(\"images/multi_class_calibration.png\")",
"/home/andy/anaconda3/envs/py37/lib/python3.7/site-packages/matplotlib/cbook/__init__.py:424: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning: \nPassing one of 'on', 'true', 'off', 'false' as a boolean is deprecated; use an actual boolean (True/False) instead.\n warn_deprecated(\"2.2\", \"Passing one of 'on', 'true', 'off', 'false' as a \"\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c504d1ce93218c557338bad4639b2cb93a890c26
| 126,916 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
model.ipynb
|
hlappal/catalysis_data_project
|
5cace5280b4b83a2d60bc08848719d1b1f34201c
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
model.ipynb
|
hlappal/catalysis_data_project
|
5cace5280b4b83a2d60bc08848719d1b1f34201c
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
model.ipynb
|
hlappal/catalysis_data_project
|
5cace5280b4b83a2d60bc08848719d1b1f34201c
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 130.437821 | 17,436 | 0.819841 |
[
[
[
"# Imports\n\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport pickle\nimport os\nfrom scipy.stats import linregress\nfrom sklearn_pandas import DataFrameMapper\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder, LabelBinarizer\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, GridSearchCV, RandomizedSearchCV\nfrom sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error\nfrom sklearn.kernel_ridge import KernelRidge as KRR\nfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor as RFR\nfrom sklearn.gaussian_process.kernels import WhiteKernel, ExpSineSquared\n\n# Define the project root directory\nROOT_DIR = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), os.pardir)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Load the data\ndf = pd.read_pickle(f\"{ROOT_DIR}/data/data.csv\")\nprint(f\"Loaded raw data of shape {df.shape}\")",
"Loaded raw data of shape (1892, 14)\n"
],
[
"plt.plot(df[\"Reaction Energy\"], df[\"Activation Energy\"], \"b.\")\nplt.xlabel(\"Reaction Energy [eV]\")\nplt.ylabel(\"Activation Energy [eV]\")\nplt.savefig(f\"{ROOT_DIR}/data/images/er_ea_correlation.png\")\nplt.show()\ndf.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Separate metals, non-metals, and semiconductors",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"metals = [\n \"Sc\", \"Ti\", \"V\", \"Cr\", \"Mn\", \"Fe\", \"Co\", \"Ni\", \"Cu\", \"Zn\",\n \"Y\", \"Zr\", \"Nb\", \"Mo\", \"Tc\", \"Ru\", \"Rh\", \"Pd\", \"Ag\", \"Cd\",\n \"Hf\", \"Ta\", \"W\", \"Re\", \"Os\", \"Ir\", \"Pt\", \"Au\", \"Hg\",\n \"Rf\", \"Db\", \"Sg\", \"Bh\", \"Hs\", \"Mt\", \"Ds\", \"Rg\", \"Cn\",\n \"Al\", \"Ga\", \"In\", \"Sn\", \"Tl\", \"Pb\", \"Bi\", \"Nh\", \"Fl\", \"Mc\", \"Lv\",\n \"Y-fcc\", \"Zr-fcc\", \"Nb-fcc\", \"Mo-fcc\", \"Tc-fcc\", \"Ru-fcc\", \"Rh-fcc\", \"Pd-fcc\", \"Ag-fcc\", \"Cd-fcc\",\n \"Sc-fcc\", \"Ti-fcc\", \"V-fcc\", \"Cr-fcc\", \"Mn-fcc\", \"Fe-fcc\", \"Co-fcc\", \"Ni-fcc\", \"Cu-fcc\", \"Zn-fcc\",\n \"Hf-fcc\", \"Ta-fcc\", \"W-fcc\", \"Re-fcc\", \"Os-fcc\", \"Ir-fcc\", \"Pt-fcc\", \"Au-fcc\", \"Hg-fcc\",\n \"Rf-fcc\", \"Db-fcc\", \"Sg-fcc\", \"Bh-fcc\", \"Hs-fcc\", \"Mt-fcc\", \"Ds-fcc\", \"Rg-fcc\", \"Cn-fcc\",\n \"Al-fcc\", \"Ga-fcc\", \"In-fcc\", \"Sn-fcc\", \"Tl-fcc\", \"Pb-fcc\", \"Bi-fcc\", \"Nh-fcc\", \"Fl-fcc\", \"Mc-fcc\", \"Lv-fcc\"\n]\n\nindices = []\n\nfor i in range(df.shape[0]):\n if df.iloc[i][\"Chemical Composition\"] in metals or df.iloc[i][\"Surface Composition\"] in metals:\n indices.append(i)\ndf = df.iloc[indices]\n\nprint(f\"Found {df.shape[0]} reaction on pure metal catalyst surfaces.\")",
"Found 1826 reaction on pure metal catalyst surfaces.\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Transform feature labels to binary one-hot arrays with DataFrameMapper and LabelBinarizer",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_bin = df.copy()\nprint(f\"Converted {df_bin.shape[1] - 1} features into \", end=\"\")\n\nbin_mapper = DataFrameMapper([\n (\"Reactant 1\", LabelBinarizer()),\n (\"Reactant 2\", LabelBinarizer()),\n (\"Reactant 3\", LabelBinarizer()),\n (\"Product 1\", LabelBinarizer()),\n (\"Product 2\", LabelBinarizer()),\n (\"Chemical Composition\", LabelBinarizer()),\n (\"Surface Composition\", LabelBinarizer()),\n (\"Facet\", LabelBinarizer()),\n (\"Adsorption Site\", LabelBinarizer()),\n (\"Reaction Equation\", LabelBinarizer()),\n ([\"Reaction Energy\"], None),\n ([\"Activation Energy\"], None),\n], df_out=True)\n\ndf_bin = bin_mapper.fit_transform(df_bin)\nprint(f\"{df_bin.shape[1] - 1} features.\")\ndf_bin.head()",
"Converted 13 features into 527 features.\n"
]
],
[
[
"### OR Transform feature labels to integer values with LabelEncoder",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_enc = df.copy()\n\nenc_mapper = DataFrameMapper([\n ('Reactant 1', LabelEncoder()),\n ('Reactant 2', LabelEncoder()),\n ('Reactant 3', LabelEncoder()),\n ('Product 1', LabelEncoder()),\n ('Product 2', LabelEncoder()),\n ('Chemical Composition', LabelEncoder()),\n ('Surface Composition', LabelEncoder()),\n ('Facet', LabelEncoder()),\n ('Adsorption Site', LabelEncoder()),\n ('Reaction Equation', LabelEncoder()),\n (['Reaction Energy'], None),\n (['Activation Energy'], None),\n], df_out=True)\n\ndf_enc = enc_mapper.fit_transform(df_enc)\ndf_enc = df_enc.drop_duplicates(ignore_index=True)\ndf_enc.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Split the data into training and test sets",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"train_set_enc, test_set_enc = train_test_split(df_enc, test_size=0.2)\ntrain_set_bin, test_set_bin = train_test_split(df_bin, test_size=0.2)\n\ny_train_enc = train_set_enc[\"Activation Energy\"]\nX_train_enc = train_set_enc.drop(\"Activation Energy\", axis=1)\ny_train_bin = train_set_bin[\"Activation Energy\"]\nX_train_bin = train_set_bin.drop(\"Activation Energy\", axis=1)\n\ny_test_enc = test_set_enc[\"Activation Energy\"]\nX_test_enc = test_set_enc.drop(\"Activation Energy\", axis=1)\ny_test_bin = test_set_bin[\"Activation Energy\"]\nX_test_bin = test_set_bin.drop(\"Activation Energy\", axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Kernel Ridge Regression",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"param_grid = {\"alpha\": [1e0, 1e-1, 1e-2, 1e-3],\n \"gamma\": np.logspace(-2, 2, 5),\n \"kernel\": [\"rbf\", \"linear\"]}\n\nkrr_enc = GridSearchCV(KRR(), param_grid=param_grid)\nkrr_enc.fit(X_train_enc, y_train_enc)\nkrr_enc_best = krr_enc.best_estimator_\nkrr_enc_score = krr_enc_best.score(X_test_enc, y_test_enc)\nkrr_enc_pred = krr_enc_best.predict(X_test_enc)\n\nkrr_bin = GridSearchCV(KRR(), param_grid=param_grid)\nkrr_bin.fit(X_train_bin, y_train_bin)\nkrr_bin_best = krr_bin.best_estimator_\nkrr_bin_score = krr_bin_best.score(X_test_bin, y_test_bin)\nkrr_bin_pred = krr_bin_best.predict(X_test_bin)\n\nprint(f\"KRR score with label encoded data: {krr_enc_score}, using parameters: {krr_enc_best.get_params()}\")\nprint(f\"KRR score with label binarized data: {krr_bin_score}, using parameters: {krr_bin_best.get_params()}\")",
"KRR score with label encoded data: 0.7344589224984097, using parameters: {'alpha': 1.0, 'coef0': 1, 'degree': 3, 'gamma': 0.01, 'kernel': 'linear', 'kernel_params': None}\nKRR score with label binarized data: 0.9508332111666689, using parameters: {'alpha': 0.01, 'coef0': 1, 'degree': 3, 'gamma': 0.01, 'kernel': 'rbf', 'kernel_params': None}\n"
],
[
"# Plot the label encoded KRR predictions against the test set target values\n\nres = linregress(krr_enc_pred, y_test_enc)\nx = np.arange(-1, 8, 1)\ny = x*res[0] + res[1]\nfig = plt.figure()\nax = fig.add_subplot(111)\nplt.plot(krr_enc_pred, y_test_enc, \"b.\")\nplt.plot(x, y, \"r-\")\nplt.xlabel(\"$E_A$ ML [eV]\")\nplt.ylabel(\"$E_A$ DFT [eV]\")\nplt.xlim(xmin=min(krr_enc_pred), xmax=max(krr_enc_pred))\nplt.ylim(ymin=min(y_test_enc), ymax=max(y_test_enc))\nax.set_aspect(\"equal\")\nplt.savefig(f\"{ROOT_DIR}/data/images/krr_enc_pred.png\")\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Plot the binarized KRR predictions against the test set target values\n\nres = linregress(krr_bin_pred, y_test_bin)\nx = np.arange(0, 8, 1)\ny = x*res[0] + res[1]\nfig = plt.figure()\nax = fig.add_subplot(111)\nplt.plot(krr_bin_pred, y_test_bin, \"b.\")\nplt.plot(x, y, \"r-\")\nplt.xlabel(\"$E_A$ ML [eV]\")\nplt.ylabel(\"$E_A$ DFT [eV]\")\nplt.xlim(xmin=min(krr_bin_pred), xmax=max(krr_bin_pred))\nplt.ylim(ymin=min(y_test_bin), ymax=max(y_test_bin))\nax.set_aspect(\"equal\")\nplt.savefig(f\"{ROOT_DIR}/data/images/krr_bin_pred.png\")\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Random Forest",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"n_estimators = [50, 100, 150, 200, 250, 300]\nmax_features = [\"auto\", \"sqrt\", \"log2\"]\nmax_depth = [10, 20, 30, 40]\nmax_depth.append(None)\nmin_samples_split = [2, 5, 10, 15, 20]\nmin_samples_leaf = [1, 2, 5, 10, 15, 20]\n\nparam_grid = {\n \"n_estimators\": n_estimators,\n \"max_features\": max_features,\n \"max_depth\": max_depth,\n \"min_samples_split\": min_samples_split,\n \"min_samples_leaf\": min_samples_leaf\n}\n\nrfr_enc = RandomizedSearchCV(RFR(), param_distributions=param_grid, n_iter=400, cv=5, verbose=1, n_jobs=-1)\nrfr_enc.fit(X_train_enc, y_train_enc)\n\nrfr_bin = RandomizedSearchCV(RFR(), param_distributions=param_grid, n_iter=400, cv=5, verbose=1, n_jobs=-1)\nrfr_bin.fit(X_train_bin, y_train_bin)",
"Fitting 5 folds for each of 400 candidates, totalling 2000 fits\nFitting 5 folds for each of 400 candidates, totalling 2000 fits\n"
],
[
"rfr_enc_best = rfr_enc.best_estimator_\nrfr_enc_score = rfr_enc_best.score(X_test_enc, y_test_enc)\nrfr_enc_pred = rfr_enc_best.predict(X_test_enc)\n\nrfr_bin_best = rfr_bin.best_estimator_\nrfr_bin_score = rfr_bin_best.score(X_test_bin, y_test_bin)\nrfr_bin_pred = rfr_bin_best.predict(X_test_bin)\n\nprint(f\"Random Forest score with label encoded data: {rfr_enc_score}, using parameters: {rfr_enc_best.get_params()}\")\nprint(f\"Random Forest score with label binarized data: {rfr_bin_score}, using parameters: {rfr_bin_best.get_params()}\")",
"Random Forest score with label encoded data: 0.9045524895605336, using parameters: {'bootstrap': True, 'ccp_alpha': 0.0, 'criterion': 'mse', 'max_depth': None, 'max_features': 'log2', 'max_leaf_nodes': None, 'max_samples': None, 'min_impurity_decrease': 0.0, 'min_impurity_split': None, 'min_samples_leaf': 1, 'min_samples_split': 2, 'min_weight_fraction_leaf': 0.0, 'n_estimators': 300, 'n_jobs': None, 'oob_score': False, 'random_state': None, 'verbose': 0, 'warm_start': False}\nRandom Forest score with label binarized data: 0.9052001179537059, using parameters: {'bootstrap': True, 'ccp_alpha': 0.0, 'criterion': 'mse', 'max_depth': 30, 'max_features': 'auto', 'max_leaf_nodes': None, 'max_samples': None, 'min_impurity_decrease': 0.0, 'min_impurity_split': None, 'min_samples_leaf': 1, 'min_samples_split': 2, 'min_weight_fraction_leaf': 0.0, 'n_estimators': 150, 'n_jobs': None, 'oob_score': False, 'random_state': None, 'verbose': 0, 'warm_start': False}\n"
],
[
"res = linregress(rfr_enc_pred, y_test_enc)\nx = np.arange(0, 8, 1)\ny = x*res[0] + res[1]\nfig = plt.figure()\nax = fig.add_subplot(111)\nplt.plot(rfr_enc_pred, y_test_enc, \"b.\")\nplt.plot(x, y, \"r-\")\nplt.xlabel(\"E$_A$ ML [eV]\")\nplt.ylabel(\"E$_A$ DFT [eV]\")\nplt.xlim(xmin=min(rfr_enc_pred), xmax=max(rfr_enc_pred))\nplt.ylim(ymin=min(y_test_enc), ymax=max(y_test_enc))\nax.set_aspect(\"equal\")\nplt.savefig(f\"{ROOT_DIR}/data/images/rfr_enc_pred.png\")\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"res = linregress(rfr_bin_pred, y_test_bin)\nx = np.arange(0, 8, 1)\ny = x*res[0] + res[1]\nfig = plt.figure()\nax = fig.add_subplot(111)\nplt.plot(rfr_bin_pred, y_test_bin, \"b.\")\nplt.plot(x, y, \"r-\")\nplt.xlabel(\"E$_A$ ML [eV]\")\nplt.ylabel(\"E$_A$ DFT [eV]\")\nplt.xlim(xmin=min(rfr_bin_pred), xmax=max(rfr_bin_pred))\nplt.ylim(ymin=min(y_test_bin), ymax=max(y_test_bin))\nax.set_aspect(\"equal\")\nplt.savefig(f\"{ROOT_DIR}/data/images/rfr_bin_pred.png\")\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Save the trained models",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Save the label encoded RFR model\nwith open(f\"{ROOT_DIR}/data/rfr_enc.pkl\", \"wb\") as rfr_enc_file:\n pickle.dump(rfr_enc_best, rfr_enc_file)\n \n# Save the label binarized RFR model\nwith open(f\"{ROOT_DIR}/data/rfr_bin.pkl\", \"wb\") as rfr_bin_file:\n pickle.dump(rfr_bin_best, rfr_bin_file)\n \n# Save the label encoded KRR model\nwith open(f\"{ROOT_DIR}/data/krr_enc.pkl\", \"wb\") as krr_enc_file:\n pickle.dump(krr_enc_best, krr_enc_file)\n \n# Save the label binarized KRR model\nwith open(f\"{ROOT_DIR}/data/krr_bin.pkl\", \"wb\") as krr_bin_file:\n pickle.dump(krr_bin_best, krr_bin_file)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Inspect the freature importances",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"fimportances = rfr_enc_best.feature_importances_\nfi_data = np.array([X_train_enc.columns,fimportances]).T\nfi_data = fi_data[fi_data[:,1].argsort()]\n\nplt.barh(fi_data[:,0], fi_data[:,1])\nplt.xlabel(\"Feature weight\")\nplt.savefig(f\"{ROOT_DIR}/data/images/feature_importances.png\", bbox_inches=\"tight\")\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c504d8bb5fa4c9e35395741f0180c19c4d44ce2d
| 604,885 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/illustrate_std_demo.ipynb
|
fomightez/pymol-binder
|
63b8132dd980bdcbb0c66d64422d0c70f5602636
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2021-04-11T17:36:00.000Z
|
2021-10-12T04:32:30.000Z
|
notebooks/illustrate_std_demo.ipynb
|
fomightez/pymol-binder
|
63b8132dd980bdcbb0c66d64422d0c70f5602636
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/illustrate_std_demo.ipynb
|
fomightez/pymol-binder
|
63b8132dd980bdcbb0c66d64422d0c70f5602636
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2022-02-01T16:05:33.000Z
|
2022-02-01T16:05:33.000Z
| 2,043.530405 | 593,684 | 0.959951 |
[
[
[
"# David Goodsell's ILLUSTRATE - Biomolecular Illustration Tool standard hemoglobin demo\n\nThis uses the included input script and PDB file for hemoglobin to run through using the Fortran code to generate output. The output `.pnm ` file is then converted to a `PNG`.\n\nEverything is installed and ready to run if you are accessing this using a link that involves MyBinder.org.\n\nLearn more about David Goodsell's work and software [here](https://ccsb.scripps.edu/illustrate/) and [here](https://github.com/ccsb-scripps/Illustrate).\n\nYou can exectute `Run all` to run the code all in one step or step through each cell entering `shift-enter` to trigger running each.\n\n----\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Preparation\n\nCopy the input files from the previously cloned repository to the current working directory. (See `postBuild` for previous set-up steps and compiling.)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cp ~/.local/bin/Illustrate/* .",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Show the compiled fortran code for `illustrate` is now in the working directory along with input files, `2hhb.inp` (script file) and `2hhb.pdb` (standard [structure file](https://www.rcsb.org/structure/2hhb) in PDB format).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!ls ",
"2hhb_image.png\t\tdemo_colors.ipynb illustrate_std_demo.ipynb\n2hhb.inp\t\tdemo_fetch.ipynb image.png\n2hhb.pdb\t\tdemo_orient.ipynb LICENSE\n2hhb.pnm\t\tdemo_palette.ipynb README.md\nconverted_image.png\tillustrate\ndemo_apply_combo.ipynb\tillustrate.f\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Run Illustrate",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!./illustrate < 2hhb.inp",
" atom descriptors: 15\n type, color, radius 1 0.500000000 0.500000000 0.500000000 0.00000000 \n type, color, radius 2 0.500000000 0.500000000 0.500000000 0.00000000 \n type, color, radius 3 0.500000000 0.500000000 0.500000000 0.00000000 \n type, color, radius 4 1.00000000 0.600000024 0.600000024 1.60000002 \n type, color, radius 5 1.00000000 0.500000000 0.500000000 1.79999995 \n type, color, radius 6 1.00000000 0.500000000 0.500000000 1.50000000 \n type, color, radius 7 1.00000000 0.600000024 0.600000024 1.60000002 \n type, color, radius 8 1.00000000 0.500000000 0.500000000 1.79999995 \n type, color, radius 9 1.00000000 0.500000000 0.500000000 1.50000000 \n type, color, radius 10 1.00000000 0.800000012 0.600000024 1.60000002 \n type, color, radius 11 1.00000000 0.699999988 0.500000000 1.79999995 \n type, color, radius 12 1.00000000 0.699999988 0.500000000 1.50000000 \n type, color, radius 13 1.00000000 0.800000012 0.00000000 1.79999995 \n type, color, radius 14 1.00000000 0.300000012 0.300000012 1.60000002 \n type, color, radius 15 1.00000000 0.100000001 0.100000001 1.50000000 \n Number of BIOMT 0\n Chains in Biological Assembly\n 1 A\n 2 B\n 3 C\n 4 D\n\n Number of BIOMT 1\n BIOMAT 1 1.00000000 0.00000000 0.00000000 0.00000000 \n BIOMAT 1 0.00000000 1.00000000 0.00000000 0.00000000 \n BIOMAT 1 0.00000000 0.00000000 1.00000000 0.00000000 \n atoms read: 4556 from: 2hhb.pdb \n number of subunits: 8\n \n translation vector : 0.00000000 0.00000000 0.00000000 \n\n scale factor : 12.0000000 \n\n z rotation : 90.0000000 \n background inten. : 1.00 1.00 1.00\n fog intensity : 1.00 1.00 1.00\n upper fog percent : 100.00\n lower fog percent : 100.00\n draw conical shadow\n input value for image size -30 -30\n illustration parameters\n l parameters: 3.00000000 10.0000000 \n g parameters: 3.00000000 8.00000000 \n\n *begin calculation*\n\n min coordinates : -26.4710026 -34.0060005 -29.9990005 \n max coordinates : 27.4800034 34.3030014 29.9880009 \n automating centering\n centering vector : -0.504499435 -0.148502350 -52.5879974 \n\n applying autosizing\n x and y frame width: 30 30\n xsize and ysize: 750 922\n\n output pnm filename: 2hhb.pnm \n 0 spheres added of type: 1\n 0 spheres added of type: 2\n 0 spheres added of type: 3\n 685 spheres added of type: 4\n 3 spheres added of type: 5\n 381 spheres added of type: 6\n 685 spheres added of type: 7\n 3 spheres added of type: 8\n 381 spheres added of type: 9\n 1448 spheres added of type: 10\n 6 spheres added of type: 11\n 792 spheres added of type: 12\n 4 spheres added of type: 13\n 136 spheres added of type: 14\n 32 spheres added of type: 15\n shading maps written into depth buffer\n zpix_min,zpix_max -818.827271 -253.199951 \n Pixel processing beginning \n99999999999999999999999999999999999999999999999\n99999999999999109884999990095999999999999999999\n99999999999999995899999999989887799999999999999\n99999999999968994878899999768789976999999999999\n99999999992798889999693957746519995999999999999\n99999999967697998982898045194898995999999999999\n99999999907698999989989986889899688890999999999\n99999990778888980888989957688988888888999999999\n99999977776708981729999979967888777788828999999\n99999288869898870988588809978807089656788999999\n99990998799977868929888789878869997859967809999\n99976499709898998979899889577059999789978879999\n99979888889988990887839899007748699889978709999\n99999989987899867881880888885769997899668999999\n99999099987999989998988986900549998905678999999\n99997588762888886998089869998969989989378999999\n99997687086899889896269887899988988998567879999\n99999909989999998899889988888999498890895999999\n99999904638900996999787908989958798899816999999\n99995885499998999998994639881989598888561699999\n99999886099989999099998800448728885886789978099\n99999884899899999696969995898178889908898538999\n99999877999978154776599998909998888308908999999\n99998987763296668870007999989906759890968979999\n99968846367760650998088897888878999899898709999\n99999667688887756998099995890989987491078879999\n99999878778088987488899989998970078867578989999\n99999789798509998298485788479957888888889999999\n99999999888888882665446889988772888086832999999\n99999999979998958862059988977268899967899999999\n99999999989998989986769948908897884578999999999\n99999999908999989906778808978898978657999999999\n99999999999999556876899999787909959799999999999\n99999999999056588788999999188568986799999999999\n99999999999999887998999999997977999999999999999\n99999999999999999999999999999999999999999999999\n99999999999999999999999999999999999999999999999\n"
]
],
[
[
"That produces the file `2hhb.pnm`, which is in the `portable anymap format`, see [here](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Netpbm_format).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!ls 2hhb.pnm",
"2hhb.pnm\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Convert output from `portable anymap format` to standard PNG format\n\nConversion uses the Netpbm project's `pnmtopng`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!pnmtopng 2hhb.pnm > 2hhb_image.png",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Display the output here.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from IPython.display import Image\nImage(\"2hhb_image.png\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c504dc725582523c0c1321f45e67f5886a3dc182
| 6,404 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Tutorials/SBPLAT/Setup_API_environment.ipynb
|
sbg/okAPI
|
4dbf9e917e2a53241fc2a58ddb51ccc9a990b348
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | 23 |
2016-04-03T13:44:35.000Z
|
2020-11-19T13:18:33.000Z
|
Tutorials/SBPLAT/Setup_API_environment.ipynb
|
sbg/okAPI
|
4dbf9e917e2a53241fc2a58ddb51ccc9a990b348
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | 8 |
2016-07-06T21:42:35.000Z
|
2022-03-05T01:06:32.000Z
|
Tutorials/SBPLAT/Setup_API_environment.ipynb
|
sbg/okAPI
|
4dbf9e917e2a53241fc2a58ddb51ccc9a990b348
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | 17 |
2016-03-23T12:36:24.000Z
|
2021-10-30T17:35:21.000Z
| 30.641148 | 267 | 0.582761 |
[
[
[
"# How to setup Seven Bridges Public API python library\n## Overview\nHere you will learn the three possible ways to setup Seven Bridges Public API Python library.\n\n## Prerequisites\n\n1. You need to install _sevenbridges-python_ library. Library details are available [here](http://sevenbridges-python.readthedocs.io/en/latest/sevenbridges/)\n\n The easiest way to install sevenbridges-python is using pip:\n\n $ pip install sevenbridges-python\n\n Alternatively, you can get the code. sevenbridges-python is actively developed on GitHub, where the [code](https://github.com/sbg/sevenbridges-python) is always available. To clone the public repository :\n\n $ git clone git://github.com/sbg/sevenbridges-python.git\n\n Once you have a copy of the source, you can embed it in your Python\n package, or install it into your site-packages by invoking:\n\n $ python setup.py install\n\n2. You need your _authentication token_ which you can get [here](https://igor.sbgenomics.com/developer/token)\n\n \n### Notes and Compatibility\n\nPython package is intended to be used with Python 3.6+ versions.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import the library\nimport sevenbridges as sbg",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Initialize the library\n\nYou can initialize the library explicitly or by supplying the necessary information in the $HOME/.sevenbridges/credentials file\n\nThere are generally three ways to initialize the library:\n 1. Explicitly, when calling api constructor, like:\n ``` python\n api = sbg.Api(url='https://api.sbgenomics.com/v2', token='MY AUTH TOKEN')\n ```\n \n 2. By using OS environment to store the url and authentication token\n ```\n export AUTH_TOKEN=<MY AUTH TOKEN>\n export API_ENDPOINT='https://api.sbgenomics.com/v2'\n ```\n 3. By using ini file $HOME/.sevenbridges/credentials (for MS Windows, the file should be located in \\%UserProfile\\%.sevenbridges\\credentials) and specifying a profile to use. The format of the credentials file is standard ini file format, as shown below:\n\n ```bash\n [sbpla]\n api_endpoint = https://api.sbgenomics.com/v2\n auth_token = 700992f7b24a470bb0b028fe813b8100\n\n [cgc]\n api_endpoint = https://cgc-api.sbgenomics.com/v2\n auth_token = 910975f5b24a470bb0b028fe813b8100\n ```\n \n 0. to **create** this file<sup>1</sup>, use the following steps in your _Terminal_:\n 1.\n ```bash\n cd ~\n mkdir .sevenbridges\n touch .sevenbridges/credentials\n vi .sevenbridges/credentials\n ```\n 2. Press \"i\" then enter to go into **insert mode**\n 3. write the text above for each environment. \n 4. Press \"ESC\" then type \":wq\" to save the file and exit vi\n \n<sup>1</sup> If the file already exists, omit the _touch_ command",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Test if you have stored the token correctly\nBelow are the three options presented above, test **one** of them. Logically, if you have only done **Step 3**, then testing **Step 2** will return an error.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# (1.) You can also instantiate library by explicitly \n# specifying API url and authentication token\napi_explicitly = sbg.Api(url='https://api.sbgenomics.com/v2',\n token='<MY TOKEN HERE>')\napi_explicitly.users.me()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# (2.) If you have not specified profile, the python-sbg library \n# will search for configuration in the environment\nc = sbg.Config()\napi_via_environment = sbg.Api(config=c)\napi_via_environment.users.me()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# (3.) If you have credentials setup correctly, you only need to specify the profile\nconfig_file = sbg.Config(profile='sbpla')\napi_via_ini_file = sbg.Api(config=config_file)\napi_via_ini_file.users.me()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### PROTIP\n* We _recommend_ the approach with configuration file (the **.sevenbridges/credentials** file in option #3), especially if you are using multiple environments (like SBPLA and CGC).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
c504e8f71beb0e540b04f2c0398abc7bdcc66547
| 30,336 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
00_02_numbers_in_python.ipynb
|
Price-L/Comp_Phys
|
40ec1ddf10dad0d7109fcb8845fe93b578027533
|
[
"MIT"
] | 104 |
2015-09-13T19:38:37.000Z
|
2022-03-26T15:36:14.000Z
|
00_02_numbers_in_python.ipynb
|
Price-L/Comp_Phys
|
40ec1ddf10dad0d7109fcb8845fe93b578027533
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2019-09-13T17:41:21.000Z
|
2021-03-06T06:20:12.000Z
|
00_02_numbers_in_python.ipynb
|
Price-L/Comp_Phys
|
40ec1ddf10dad0d7109fcb8845fe93b578027533
|
[
"MIT"
] | 54 |
2015-09-15T14:20:24.000Z
|
2022-02-27T22:40:07.000Z
| 29.085331 | 397 | 0.490968 |
[
[
[
"Manipulating numbers in Python\n================\n\n**_Disclaimer_: Much of this section has been transcribed from <a href=\"https://pymotw.com/2/math/\">https://pymotw.com/2/math/</a>** \n\nEvery computer represents numbers using the <a href=\"https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IEEE_floating_point\">IEEE floating point standard</a>. The **math** module implements many of the IEEE functions that would normally be found in the native platform C libraries for complex mathematical operations using floating point values, including logarithms and trigonometric operations. \n\nThe fundamental information about number representation is contained in the module **sys**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import sys \n\nsys.float_info",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"From here we can learn, for instance:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sys.float_info.max",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Similarly, we can learn the limits of the IEEE 754 standard\n\nLargest Real = 1.79769e+308, 7fefffffffffffff // -Largest Real = -1.79769e+308, ffefffffffffffff\n\nSmallest Real = 2.22507e-308, 0010000000000000 // -Smallest Real = -2.22507e-308, 8010000000000000\n\nZero = 0, 0000000000000000 // -Zero = -0, 8000000000000000\n\neps = 2.22045e-16, 3cb0000000000000 // -eps = -2.22045e-16, bcb0000000000000",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Interestingly, one could define an even larger constant (more about this below)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"infinity = float(\"inf\")\ninfinity",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"infinity/10000",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Special constants\n\nMany math operations depend on special constants. **math** includes values for $\\pi$ and $e$.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import math\n\nprint ('π: %.30f' % math.pi)\nprint ('e: %.30f' % math.e)\nprint('nan: {:.30f}'.format(math.nan))\nprint('inf: {:.30f}'.format(math.inf))",
"π: 3.141592653589793115997963468544\ne: 2.718281828459045090795598298428\nnan: nan\ninf: inf\n"
]
],
[
[
"Both values are limited in precision only by the platform’s floating point C library.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Testing for exceptional values\n\nFloating point calculations can result in two types of exceptional values. INF (“infinity”) appears when the double used to hold a floating point value overflows from a value with a large absolute value.\nThere are several reserved bit patterns, mostly those with all ones in the exponent field. These allow for tagging special cases as Not A Number—NaN. If there are all ones and the fraction is zero, the number is Infinite.\n\nThe IEEE standard specifies:\n\nInf = Inf, 7ff0000000000000 // -Inf = -Inf, fff0000000000000\n\nNaN = NaN, fff8000000000000 // -NaN = NaN, 7ff8000000000000\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"float(\"inf\")-float(\"inf\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import math\n\nprint('{:^3} {:6} {:6} {:6}'.format(\n 'e', 'x', 'x**2', 'isinf'))\nprint('{:-^3} {:-^6} {:-^6} {:-^6}'.format(\n '', '', '', ''))\n\nfor e in range(0, 201, 20):\n x = 10.0 ** e\n y = x * x\n print('{:3d} {:<6g} {:<6g} {!s:6}'.format(\n e, x, y, math.isinf(y),))",
" e x x**2 isinf \n--- ------ ------ ------\n 0 1 1 False \n 20 1e+20 1e+40 False \n 40 1e+40 1e+80 False \n 60 1e+60 1e+120 False \n 80 1e+80 1e+160 False \n100 1e+100 1e+200 False \n120 1e+120 1e+240 False \n140 1e+140 1e+280 False \n160 1e+160 inf True \n180 1e+180 inf True \n200 1e+200 inf True \n"
]
],
[
[
"When the exponent in this example grows large enough, the square of x no longer fits inside a double, and the value is recorded as infinite. Not all floating point overflows result in INF values, however. Calculating an exponent with floating point values, in particular, raises OverflowError instead of preserving the INF result.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x = 10.0 ** 200\n\nprint('x =', x)\nprint('x*x =', x*x)\ntry:\n print('x**2 =', x**2)\nexcept OverflowError as err:\n print(err)",
"x = 1e+200\nx*x = inf\n(34, 'Result too large')\n"
]
],
[
[
"This discrepancy is caused by an implementation difference in the library used by C Python.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Division operations using infinite values are undefined. The result of dividing a number by infinity is NaN (“not a number”).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import math\n\nx = (10.0 ** 200) * (10.0 ** 200)\ny = x/x\n\nprint('x =', x)\nprint('isnan(x) =', math.isnan(x))\nprint('y = x / x =', x/x)\nprint('y == nan =', y == float('nan'))\nprint('isnan(y) =', math.isnan(y))",
"x = inf\nisnan(x) = False\ny = x / x = nan\ny == nan = False\nisnan(y) = True\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Comparing\nComparisons for floating point values can be error prone, with each step of the computation potentially introducing errors due to the numerical representation. The isclose() function uses a stable algorithm to minimize these errors and provide a way for relative as well as absolute comparisons. The formula used is equivalent to\n\nabs(a-b) <= max(rel_tol * max(abs(a), abs(b)), abs_tol)\nBy default, isclose() uses relative comparison with the tolerance set to 1e-09, meaning that the difference between the values must be less than or equal to 1e-09 times the larger absolute value between a and b. Passing a keyword argument rel_tol to isclose() changes the tolerance. In this example, the values must be within 10% of each other.\n\nThe comparison between 0.1 and 0.09 fails because of the error representing 0.1.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import math\n\nINPUTS = [\n (1000, 900, 0.1),\n (100, 90, 0.1),\n (10, 9, 0.1),\n (1, 0.9, 0.1),\n (0.1, 0.09, 0.1),\n]\n\nprint('{:^8} {:^8} {:^8} {:^8} {:^8} {:^8}'.format(\n 'a', 'b', 'rel_tol', 'abs(a-b)', 'tolerance', 'close')\n)\nprint('{:-^8} {:-^8} {:-^8} {:-^8} {:-^8} {:-^8}'.format(\n '-', '-', '-', '-', '-', '-'),\n)\n\nfmt = '{:8.2f} {:8.2f} {:8.2f} {:8.2f} {:8.2f} {!s:>8}'\n\nfor a, b, rel_tol in INPUTS:\n close = math.isclose(a, b, rel_tol=rel_tol)\n tolerance = rel_tol * max(abs(a), abs(b))\n abs_diff = abs(a - b)\n print(fmt.format(a, b, rel_tol, abs_diff, tolerance, close))",
" a b rel_tol abs(a-b) tolerance close \n-------- -------- -------- -------- -------- --------\n 1000.00 900.00 0.10 100.00 100.00 True\n 100.00 90.00 0.10 10.00 10.00 True\n 10.00 9.00 0.10 1.00 1.00 True\n 1.00 0.90 0.10 0.10 0.10 True\n 0.10 0.09 0.10 0.01 0.01 False\n"
]
],
[
[
"To use a fixed or \"absolute\" tolerance, pass abs_tol instead of rel_tol.\n\nFor an absolute tolerance, the difference between the input values must be less than the tolerance given.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import math\n\nINPUTS = [\n (1.0, 1.0 + 1e-07, 1e-08),\n (1.0, 1.0 + 1e-08, 1e-08),\n (1.0, 1.0 + 1e-09, 1e-08),\n]\n\nprint('{:^8} {:^11} {:^8} {:^10} {:^8}'.format(\n 'a', 'b', 'abs_tol', 'abs(a-b)', 'close')\n)\nprint('{:-^8} {:-^11} {:-^8} {:-^10} {:-^8}'.format(\n '-', '-', '-', '-', '-'),\n)\n\nfor a, b, abs_tol in INPUTS:\n close = math.isclose(a, b, abs_tol=abs_tol)\n abs_diff = abs(a - b)\n print('{:8.2f} {:11} {:8} {:0.9f} {!s:>8}'.format(\n a, b, abs_tol, abs_diff, close))",
" a b abs_tol abs(a-b) close \n-------- ----------- -------- ---------- --------\n 1.00 1.0000001 1e-08 0.000000100 False\n 1.00 1.00000001 1e-08 0.000000010 True\n 1.00 1.000000001 1e-08 0.000000001 True\n"
]
],
[
[
"nan and inf are special cases.\nnan is never close to another value, including itself. inf is only close to itself.\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import math\n\nprint('nan, nan:', math.isclose(math.nan, math.nan))\nprint('nan, 1.0:', math.isclose(math.nan, 1.0))\nprint('inf, inf:', math.isclose(math.inf, math.inf))\nprint('inf, 1.0:', math.isclose(math.inf, 1.0))",
"nan, nan: False\nnan, 1.0: False\ninf, inf: True\ninf, 1.0: False\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Converting to Integers\n\nThe math module includes three functions for converting floating point values to whole numbers. Each takes a different approach, and will be useful in different circumstances.\n\nThe simplest is trunc(), which truncates the digits following the decimal, leaving only the significant digits making up the whole number portion of the value. floor() converts its input to the largest preceding integer, and ceil() (ceiling) produces the largest integer following sequentially after the input value.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import math\n\nprint('{:^5} {:^5} {:^5} {:^5} {:^5}'.format('i', 'int', 'trunk', 'floor', 'ceil'))\nprint('{:-^5} {:-^5} {:-^5} {:-^5} {:-^5}'.format('', '', '', '', ''))\n\nfmt = ' '.join(['{:5.1f}'] * 5)\n\nfor i in [ -1.5, -0.8, -0.5, -0.2, 0, 0.2, 0.5, 0.8, 1 ]:\n print (fmt.format(i, int(i), math.trunc(i), math.floor(i), math.ceil(i)))",
" i int trunk floor ceil \n----- ----- ----- ----- -----\n -1.5 -1.0 -1.0 -2.0 -1.0\n -0.8 0.0 0.0 -1.0 0.0\n -0.5 0.0 0.0 -1.0 0.0\n -0.2 0.0 0.0 -1.0 0.0\n 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0\n 0.2 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0\n 0.5 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0\n 0.8 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0\n 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Alternate Representations\n\n**modf()** takes a single floating point number and returns a tuple containing the fractional and whole number parts of the input value.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import math\n\nfor i in range(6):\n print('{}/2 = {}'.format(i, math.modf(i/2.0)))",
"0/2 = (0.0, 0.0)\n1/2 = (0.5, 0.0)\n2/2 = (0.0, 1.0)\n3/2 = (0.5, 1.0)\n4/2 = (0.0, 2.0)\n5/2 = (0.5, 2.0)\n"
]
],
[
[
"**frexp()** returns the mantissa and exponent of a floating point number, and can be used to create a more portable representation of the value. It uses the formula x = m \\* 2 \\*\\* e, and returns the values m and e.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import math\n\nprint('{:^7} {:^7} {:^7}'.format('x', 'm', 'e'))\nprint('{:-^7} {:-^7} {:-^7}'.format('', '', ''))\n\nfor x in [ 0.1, 0.5, 4.0 ]:\n m, e = math.frexp(x)\n print('{:7.2f} {:7.2f} {:7d}'.format(x, m, e))",
" x m e \n------- ------- -------\n 0.10 0.80 -3\n 0.50 0.50 0\n 4.00 0.50 3\n"
]
],
[
[
"**ldexp()** is the inverse of frexp(). Using the same formula as frexp(), ldexp() takes the mantissa and exponent values as arguments and returns a floating point number.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import math\n\nprint('{:^7} {:^7} {:^7}'.format('m', 'e', 'x'))\nprint('{:-^7} {:-^7} {:-^7}'.format('', '', ''))\n\nfor m, e in [ (0.8, -3),\n (0.5, 0),\n (0.5, 3),\n ]:\n x = math.ldexp(m, e)\n print('{:7.2f} {:7d} {:7.2f}'.format(m, e, x))",
" m e x \n------- ------- -------\n 0.80 -3 0.10\n 0.50 0 0.50\n 0.50 3 4.00\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Positive and Negative Signs\n\nThe absolute value of number is its value without a sign. Use **fabs()** to calculate the absolute value of a floating point number.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import math\n\nprint(math.fabs(-1.1))\nprint(math.fabs(-0.0))\nprint(math.fabs(0.0))\nprint(math.fabs(1.1))",
"1.1\n0.0\n0.0\n1.1\n"
]
],
[
[
"To determine the sign of a value, either to give a set of values the same sign or simply for comparison, use **copysign()** to set the sign of a known good value. An extra function like copysign() is needed because comparing NaN and -NaN directly with other values does not work.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import math\n\nprint\nprint('{:^5} {:^5} {:^5} {:^5} {:^5}'.format('f', 's', '< 0', '> 0', '= 0'))\nprint('{:-^5} {:-^5} {:-^5} {:-^5} {:-^5}'.format('', '', '', '', ''))\n\nfor f in [ -1.0,\n 0.0,\n 1.0,\n float('-inf'),\n float('inf'),\n float('-nan'),\n float('nan'),\n ]:\n s = int(math.copysign(1, f))\n print('{:5.1f} {:5d} {!s:5} {!s:5} {!s:5}'.format(f, s, f < 0, f > 0, f==0))",
" f s < 0 > 0 = 0 \n----- ----- ----- ----- -----\n -1.0 -1 True False False\n 0.0 1 False False True \n 1.0 1 False True False\n -inf -1 True False False\n inf 1 False True False\n nan -1 False False False\n nan 1 False False False\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Commonly Used Calculations\n\nRepresenting precise values in binary floating point memory is challenging. Some values cannot be represented exactly, and the more often a value is manipulated through repeated calculations, the more likely a representation error will be introduced. math includes a function for computing the sum of a series of floating point numbers using an efficient algorithm that minimize such errors.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import math\n\nvalues = [ 0.1 ] * 10\n\nprint('Input values:', values)\n\nprint('sum() : {:.20f}'.format(sum(values)))\n\ns = 0.0\nfor i in values:\n s += i\nprint('for-loop : {:.20f}'.format(s))\n \nprint('math.fsum() : {:.20f}'.format(math.fsum(values)))",
"Input values: [0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1]\nsum() : 0.99999999999999988898\nfor-loop : 0.99999999999999988898\nmath.fsum() : 1.00000000000000000000\n"
]
],
[
[
"Given a sequence of ten values each equal to 0.1, the expected value for the sum of the sequence is 1.0. Since 0.1 cannot be represented exactly as a floating point value, however, errors are introduced into the sum unless it is calculated with **fsum()**.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**factorial()** is commonly used to calculate the number of permutations and combinations of a series of objects. The factorial of a positive integer n, expressed n!, is defined recursively as (n-1)! * n and stops with 0! == 1. **factorial()** only works with whole numbers, but does accept float arguments as long as they can be converted to an integer without losing value.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import math\n\nfor i in [ 0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 6.1 ]:\n try:\n print('{:2.0f} {:6.0f}'.format(i, math.factorial(i)))\n except ValueError as err:\n print('Error computing factorial(%s):' % i, err)",
" 0 1\n 1 1\n 2 2\n 3 6\n 4 24\n 5 120\nError computing factorial(6.1): factorial() only accepts integral values\n"
]
],
[
[
"The modulo operator (%) computes the remainder of a division expression (i.e., 5 % 2 = 1). The operator built into the language works well with integers but, as with so many other floating point operations, intermediate calculations cause representational issues that result in a loss of data. fmod() provides a more accurate implementation for floating point values.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import math\n\nprint('{:^4} {:^4} {:^5} {:^5}'.format('x', 'y', '%', 'fmod'))\nprint('---- ---- ----- -----')\n\nfor x, y in [ (5, 2),\n (5, -2),\n (-5, 2),\n ]:\n print('{:4.1f} {:4.1f} {:5.2f} {:5.2f}'.format(x, y, x % y, math.fmod(x, y)))",
" x y % fmod \n---- ---- ----- -----\n 5.0 2.0 1.00 1.00\n 5.0 -2.0 -1.00 1.00\n-5.0 2.0 1.00 -1.00\n"
]
],
[
[
"A potentially more frequent source of confusion is the fact that the algorithm used by fmod for computing modulo is also different from that used by %, so the sign of the result is different. mixed-sign inputs.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Exponents and Logarithms\n\nExponential growth curves appear in economics, physics, and other sciences. Python has a built-in exponentiation operator (“\\*\\*”), but pow() can be useful when you need to pass a callable function as an argument.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import math\n\nfor x, y in [\n # Typical uses\n (2, 3),\n (2.1, 3.2),\n\n # Always 1\n (1.0, 5),\n (2.0, 0),\n\n # Not-a-number\n (2, float('nan')),\n\n # Roots\n (9.0, 0.5),\n (27.0, 1.0/3),\n ]:\n print('{:5.1f} ** {:5.3f} = {:6.3f}'.format(x, y, math.pow(x, y)))",
" 2.0 ** 3.000 = 8.000\n 2.1 ** 3.200 = 10.742\n 1.0 ** 5.000 = 1.000\n 2.0 ** 0.000 = 1.000\n 2.0 ** nan = nan\n 9.0 ** 0.500 = 3.000\n 27.0 ** 0.333 = 3.000\n"
]
],
[
[
"Raising 1 to any power always returns 1.0, as does raising any value to a power of 0.0. Most operations on the not-a-number value nan return nan. If the exponent is less than 1, pow() computes a root.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Since square roots (exponent of 1/2) are used so frequently, there is a separate function for computing them.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import math\n\nprint(math.sqrt(9.0))\nprint(math.sqrt(3))\ntry:\n print(math.sqrt(-1))\nexcept ValueError as err:\n print('Cannot compute sqrt(-1):', err)\n ",
"3.0\n1.7320508075688772\nCannot compute sqrt(-1): math domain error\n"
]
],
[
[
"Computing the square roots of negative numbers requires complex numbers, which are not handled by math. Any attempt to calculate a square root of a negative value results in a ValueError.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"There are two variations of **log()**. Given floating point representation and rounding errors the computed value produced by **log(x, b)** has limited accuracy, especially for some bases. **log10()** computes **log(x, 10)**, using a more accurate algorithm than **log()**.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import math\n\nprint('{:2} {:^12} {:^20} {:^20} {:8}'.format('i', 'x', 'accurate', 'inaccurate', 'mismatch'))\nprint('{:-^2} {:-^12} {:-^20} {:-^20} {:-^8}'.format('', '', '', '', ''))\n\nfor i in range(0, 10):\n x = math.pow(10, i)\n accurate = math.log10(x)\n inaccurate = math.log(x, 10)\n match = '' if int(inaccurate) == i else '*'\n print('{:2d} {:12.1f} {:20.18f} {:20.18f} {:^5}'.format(i, x, accurate, inaccurate, match))",
"i x accurate inaccurate mismatch\n-- ------------ -------------------- -------------------- --------\n 0 1.0 0.000000000000000000 0.000000000000000000 \n 1 10.0 1.000000000000000000 1.000000000000000000 \n 2 100.0 2.000000000000000000 2.000000000000000000 \n 3 1000.0 3.000000000000000000 2.999999999999999556 * \n 4 10000.0 4.000000000000000000 4.000000000000000000 \n 5 100000.0 5.000000000000000000 5.000000000000000000 \n 6 1000000.0 6.000000000000000000 5.999999999999999112 * \n 7 10000000.0 7.000000000000000000 7.000000000000000000 \n 8 100000000.0 8.000000000000000000 8.000000000000000000 \n 9 1000000000.0 9.000000000000000000 8.999999999999998224 * \n"
]
],
[
[
"The lines in the output with trailing * highlight the inaccurate values.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"As with other special-case functions, the function **exp()** uses an algorithm that produces more accurate results than the general-purpose equivalent math.pow(math.e, x).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import math\n\nx = 2\n\nfmt = '%.20f'\nprint(fmt % (math.e ** 2))\nprint(fmt % math.pow(math.e, 2))\nprint(fmt % math.exp(2))",
"7.38905609893064951876\n7.38905609893064951876\n7.38905609893065040694\n"
]
],
[
[
"For more information about other mathematical functions, including trigonometric ones, we refer to <a href=\"https://pymotw.com/2/math/\">https://pymotw.com/2/math/</a>\n\nThe python references can be found at <a href=\"https://docs.python.org/2/library/math.html\">https://docs.python.org/2/library/math.html</a>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
c504ef3464376c9a80f90847015124959cee4316
| 6,169 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
examples/testfaster/demo.ipynb
|
combinator-ml/terraform-k8s-seldon
|
8886af97f8d340ee5b346c60dbe462fc1d40745e
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
examples/testfaster/demo.ipynb
|
combinator-ml/terraform-k8s-seldon
|
8886af97f8d340ee5b346c60dbe462fc1d40745e
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2021-06-24T15:45:23.000Z
|
2021-06-24T15:45:23.000Z
|
examples/testfaster/demo.ipynb
|
combinator-ml/terraform-k8s-seldon
|
8886af97f8d340ee5b346c60dbe462fc1d40745e
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2022-02-22T01:58:46.000Z
|
2022-02-22T01:58:46.000Z
| 29.516746 | 295 | 0.555357 |
[
[
[
"# Seldon-Core Component Demo\n\nIf you are reading this then you are about to take Seldon-Core, a model serving framework, for a test drive.\n\nSeldon-Core has been packaged as a [combinator component](https://combinator.ml/components/introduction/), which makes it easy to spin up a combination of MLOps components to make a stack. This notebook is running within the cluster, next to the Seldon-Core installation.\n\nThe following demo is a very short introduction to show you how to connect to seldon-core. But I recommend that you follow the [official documentation](https://docs.seldon.io/projects/seldon-core/en/latest/workflow/github-readme.html) for a comprehensive guide.\n\n## Prerequisites\n\nYou will primarily interact with Seldon-Core via the Kubernetes API. This means we need to download `kubectl`.\n\n`kubectl` usage, however, requires permission. This notebook needs permission to perform actions on the Kubernetes API. This is acheived in the test drive codebase by connecting the seldon-core operator cluster role to the default service account.\n\n:warning: Connecting pre-existing cluster roles to default service accounts is not a good idea! :warning:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!wget -q -O /tmp/kubectl https://dl.k8s.io/release/v1.21.2/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl \n!cp /tmp/kubectl /opt/conda/bin # Move the binary to somewhere on the PATH\n!chmod +x /opt/conda/bin/kubectl",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Deploy a Pre-Trained Model\n\nThe manifest below defines a `SeldonDeployment` using a pre-trained sklearn model. This leverages Seldon-Core's sklearn server implementation.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%writefile deployment.yaml\napiVersion: machinelearning.seldon.io/v1\nkind: SeldonDeployment\nmetadata:\n name: iris-model\n namespace: seldon\nspec:\n name: iris\n predictors:\n - graph:\n implementation: SKLEARN_SERVER\n modelUri: gs://seldon-models/sklearn/iris\n name: classifier\n name: default\n replicas: 1",
"Writing deployment.yaml\n"
]
],
[
[
"And apply the manifest to the seldon namespace.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!kubectl -n seldon apply -f deployment.yaml",
"seldondeployment.machinelearning.seldon.io/iris-model created\r\n"
],
[
"!kubectl -n seldon rollout status deployment/iris-model-default-0-classifier",
"deployment \"iris-model-default-0-classifier\" successfully rolled out\r\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Call The Model\n\nThe model container has downloaded a pre-trained model and instantiated it inside a serving container. You can now call the hosted endpoint.\n\nSeldon-core uses a service mesh to call the endpoint, so here you need to point the call towards the ingress gateway of your service mesh. In this case it's the default Istio ingress gateway and I'm able to use the internal Kubernetes DNS because this notebook is running in the cluster.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import json, urllib\n\nurl = \"http://istio-ingressgateway.istio-system.svc/seldon/seldon/iris-model/api/v1.0/predictions\"\ndata = { \"data\": { \"ndarray\": [[1,2,3,4]] } }\nparams = json.dumps(data).encode('utf8')\nreq = urllib.request.Request(url,\n data=params,\n headers={'content-type': 'application/json'})\nresponse = urllib.request.urlopen(req)\nprint(json.dumps(json.loads(response.read()), indent=4, sort_keys=True))",
"{\n \"data\": {\n \"names\": [\n \"t:0\",\n \"t:1\",\n \"t:2\"\n ],\n \"ndarray\": [\n [\n 0.0006985194531162841,\n 0.003668039039435755,\n 0.9956334415074478\n ]\n ]\n },\n \"meta\": {\n \"requestPath\": {\n \"classifier\": \"seldonio/sklearnserver:1.9.0\"\n }\n }\n}\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c504f958dcde39312c2820b3e146c3cc2325094a
| 841 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
HelloGithub.ipynb
|
Grajes-pl/dw_matrix
|
8243e09504bbbb94157b7efc6231ac6eda4de991
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
HelloGithub.ipynb
|
Grajes-pl/dw_matrix
|
8243e09504bbbb94157b7efc6231ac6eda4de991
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
HelloGithub.ipynb
|
Grajes-pl/dw_matrix
|
8243e09504bbbb94157b7efc6231ac6eda4de991
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 841 | 841 | 0.689655 |
[
[
[
"print(\"Hello Github\")",
"Hello Github\n"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c504fe5b7f2e6ffad5ded84ddd0ab0acb62431a6
| 66,558 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
nn/processjams.ipynb
|
m-walters/mcmd
|
9ceabfd70def27d18643bd07da3911ad0a8cd711
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2020-02-17T18:31:22.000Z
|
2020-02-17T18:31:22.000Z
|
nn/processjams.ipynb
|
m-walters/mcmd
|
9ceabfd70def27d18643bd07da3911ad0a8cd711
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
nn/processjams.ipynb
|
m-walters/mcmd
|
9ceabfd70def27d18643bd07da3911ad0a8cd711
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 47.070721 | 85 | 0.634124 |
[
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport random\ntwopi = 2.*np.pi\noneOver2Pi = 1./twopi",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import time\n\ndef time_usage(func):\n def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):\n beg_ts = time.time()\n retval = func(*args, **kwargs)\n end_ts = time.time() \n print(\"elapsed time: %f\" % (end_ts - beg_ts))\n return retval\n return wrapper",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#\n# For the jam multiruns\n# [iso, D, T, X, U, L]\n\nmode = \"edge_3\"\nruns = {1:\"edge_3_7.00\", 0:\"edge_3_14.00\"}\nin_dir = \"/home/walterms/project/walterms/mcmd/output/scratch/\"+mode+\"/\"\ntrn_dir = \"/home/walterms/project/walterms/mcmd/nn/data/train/\"\ntest_dir = \"/home/walterms/project/walterms/mcmd/nn/data/test/\"\nunlabeled_dir = \"/home/walterms/project/walterms/mcmd/nn/data/unlbl/\"\n\njidx = np.arange(2,18)\ntestidxs = np.arange(0,2) # want 400 ea\nnblSkip = 1 # Skip first image\n\n# noiseLvl: sigma of Gaussian in units of rod length\nrodlen = 1.0\nnoiseLvl = 0.00*rodlen\nthnoise = 0.00\nnoiseappend = \"\"\nif noiseLvl > 0.0:\n noiseappend = \"_\"+str(noiseLvl)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"processTrain(noise=noiseLvl)",
"processing edge_3_14.00_2 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_3 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_4 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_5 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_6 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_7 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_8 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_9 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_10 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_11 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_12 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_13 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_14 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_15 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_16 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_17 for training data\nDone processing training files\nprocessing edge_3_7.00_2 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_7.00_3 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_7.00_4 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_7.00_5 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_7.00_6 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_7.00_7 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_7.00_8 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_7.00_9 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_7.00_10 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_7.00_11 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_7.00_12 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_7.00_13 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_7.00_14 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_7.00_15 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_7.00_16 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_7.00_17 for training data\nDone processing training files\nelapsed time: 95.798936\n"
],
[
"@time_usage\ndef processTrain(noise=0.):\n for lbl in runs:\n name = runs[lbl] \n trnlim = -1\n trnfnames = [name+\"_\"+str(i) for i in jidx]\n fout = open(trn_dir+name+noiseappend,'w') #erases file\n fout.close()\n for f in trnfnames:\n fin = open(in_dir+f,'r')\n print \"processing \" + f + noiseappend + \" for training data\"\n fout = open(trn_dir+name+noiseappend,'a')\n\n # find width from file header\n width, height = 0., 0.\n l = fin.readline().split(\"|\")\n for ll in l:\n if \"boxEdge\" in ll:\n width = float(ll.split()[1])\n height = width\n fin.seek(0)\n\n if width == 0.:\n # calculate edge length based on vertices of first block\n block = []\n for line in fin.readlines():\n if line == \"\\n\": break\n if line[0].isalpha(): continue\n block.append(line)\n fin.seek(0)\n width, height = edgeLenCalc(block)\n\n if not (fin.readline()[0].isalpha()): fin.seek(0)\n\n thNorm = oneOver2Pi\n normX, normY = 1./width, 1./height # normalize x and y\n\n nbl = 0\n fRot = 0. # rotation factor: 0,1,2,3. Multiplied by pi/2\n block = []\n for line in fin.readlines():\n if line == \"\\n\":\n if nbl < nblSkip:\n nbl+=1\n block = []\n continue\n fRot = random.randint(0,3)\n for l in block:\n fout.write('%f %f %f\\n' % (l[0], l[1], l[2]))\n fout.write('label %f\\n\\n' % (lbl))\n block = []\n nbl+=1\n continue\n\n rndxy = [0.,0.]\n rndth = 0.\n if noise > 0.:\n # Gen three random numbers\n rndxy = np.random.normal(0,noise,2)\n rndth = np.random.normal(0,twopi*thnoise,1)\n # rndxy = [0.,0.]\n # rndth = 0.\n\n spt = [float(x) for x in line.split()]\n x,y,th = spt[2],spt[3],spt[4]\n # Rotate block\n # note thetas should be [0,2pi] initially\n th_ = fRot*twopi*0.25\n th += th_ + rndth\n if th > twopi: th-=twopi\n th *= thNorm\n\n x = np.cos(th_)*spt[2] - np.sin(th_)*spt[3] + rndxy[0]\n y = np.sin(th_)*spt[2] + np.cos(th_)*spt[3] + rndxy[1]\n # shift and normalize\n x *= normX\n y *= normY\n\n block.append([x,y,th])\n\n fout.close()\n fin.close()\n print \"Done processing training files\" ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"r = np.random.normal(0,noiseLvl,2)\nr[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"processTest()",
"processing edge_3_14.00_0 for testing data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_1 for testing data\nDone processing testing files\nprocessing edge_3_7.00_0 for testing data\nprocessing edge_3_7.00_1 for testing data\nDone processing testing files\nelapsed time: 11.643448\n"
],
[
"@time_usage\ndef processTest():\n for lbl in runs:\n name = runs[lbl]\n testfnames = [name+\"_\"+str(i) for i in testidxs]\n fout = open(test_dir+name,'w') #erases file\n fout.close()\n for f in testfnames:\n fin = open(in_dir+f,'r')\n print \"processing \" + f + \" for testing data\"\n fout = open(test_dir+name,'a')\n\n # find width from file header\n width, height = 0., 0.\n l = fin.readline().split(\"|\")\n for ll in l:\n if \"boxEdge\" in ll:\n width = float(ll.split()[1])\n height = width\n fin.seek(0)\n\n if width == 0.:\n # calculate edge length based on vertices of first block\n block = []\n for line in fin.readlines():\n if line == \"\\n\": break\n if line[0].isalpha(): continue\n block.append(line)\n fin.seek(0)\n width, height = edgeLenCalc(block)\n\n if not (fin.readline()[0].isalpha()): fin.seek(0)\n\n thNorm = oneOver2Pi\n normX, normY = 1./width, 1./height # normalize x and y\n\n nbl = 0\n fRot = 0. # rotation factor: 0,1,2,3. Multiplied by pi/2\n block = []\n for line in fin.readlines():\n if line == \"\\n\":\n if nbl < 1:\n nbl+=1\n block = []\n continue\n fRot = random.randint(0,3)\n for l in block:\n fout.write('%f %f %f\\n' % (l[0], l[1], l[2]))\n fout.write('label %f\\n\\n' % (lbl))\n block = []\n nbl+=1\n continue\n\n spt = [float(x) for x in line.split()]\n x,y,th = spt[2],spt[3],spt[4]\n # Rotate block\n # note thetas should be [0,2pi] initially\n th_ = fRot*twopi*0.25\n th += th_\n if th > twopi: th-=twopi\n th *= thNorm\n\n x = np.cos(th_)*spt[2] - np.sin(th_)*spt[3]\n y = np.sin(th_)*spt[2] + np.cos(th_)*spt[3]\n # shift and normalize\n x *= normX\n y *= normY\n\n block.append([x,y,th])\n\n fout.close()\n fin.close()\n print \"Done processing testing files\" ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"edges = []\nein = open(\"/home/walterms/mcmd/edge_3\",'r')\nfor line in ein.readlines():\n edges.append(float(line))\nunlblnames = [mode+\"_\"+\"%.2f\"%(e) for e in edges]\nuidx = np.arange(0,18)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"processUnlbl()",
"processing edge_3_14.00_0 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_1 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_2 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_3 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_4 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_5 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_6 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_7 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_8 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_9 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_10 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_11 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_12 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_13 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_14 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_15 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_16 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_14.00_17 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.59_0 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.59_1 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.59_2 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.59_3 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.59_4 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.59_5 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.59_6 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.59_7 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.59_8 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.59_9 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.59_10 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.59_11 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.59_12 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.59_13 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.59_14 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.59_15 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.59_16 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.59_17 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.22_0 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.22_1 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.22_2 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.22_3 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.22_4 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.22_5 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.22_6 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.22_7 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.22_8 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.22_9 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.22_10 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.22_11 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.22_12 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.22_13 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.22_14 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.22_15 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.22_16 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_13.22_17 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.87_0 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.87_1 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.87_2 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.87_3 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.87_4 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.87_5 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.87_6 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.87_7 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.87_8 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.87_9 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.87_10 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.87_11 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.87_12 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.87_13 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.87_14 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.87_15 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.87_16 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.87_17 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.55_0 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.55_1 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.55_2 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.55_3 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.55_4 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.55_5 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.55_6 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.55_7 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.55_8 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.55_9 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.55_10 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.55_11 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.55_12 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.55_13 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.55_14 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.55_15 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.55_16 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.55_17 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.25_0 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.25_1 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.25_2 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.25_3 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.25_4 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.25_5 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.25_6 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.25_7 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.25_8 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.25_9 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.25_10 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.25_11 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.25_12 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.25_13 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.25_14 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.25_15 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.25_16 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_12.25_17 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.97_0 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.97_1 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.97_2 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.97_3 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.97_4 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.97_5 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.97_6 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.97_7 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.97_8 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.97_9 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.97_10 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.97_11 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.97_12 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.97_13 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.97_14 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.97_15 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.97_16 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.97_17 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.71_0 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.71_1 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.71_2 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.71_3 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.71_4 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.71_5 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.71_6 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.71_7 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.71_8 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.71_9 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.71_10 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.71_11 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.71_12 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.71_13 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.71_14 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.71_15 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.71_16 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.71_17 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.47_0 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.47_1 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.47_2 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.47_3 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.47_4 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.47_5 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.47_6 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.47_7 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.47_8 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.47_9 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.47_10 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.47_11 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.47_12 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.47_13 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.47_14 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.47_15 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.47_16 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.47_17 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.24_0 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.24_1 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.24_2 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.24_3 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.24_4 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.24_5 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.24_6 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.24_7 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.24_8 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.24_9 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.24_10 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.24_11 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.24_12 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.24_13 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.24_14 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.24_15 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.24_16 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.24_17 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.03_0 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.03_1 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.03_2 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.03_3 for training data\nprocessing edge_3_11.03_4 for training data\n"
],
[
"@time_usage\ndef processUnlbl(noise=0.):\n nlimPerFile = 270+nblSkip\n for run in unlblnames:\n fnames = [run+\"_\"+str(i) for i in uidx]\n fout = open(unlabeled_dir+run+noiseappend,'w') #erases file\n fout.close()\n for f in fnames:\n fin = open(in_dir+f,'r')\n print \"processing \" + f + noiseappend + \" for training data\"\n fout = open(unlabeled_dir+run+noiseappend,'a')\n\n # find width from file header\n width, height = 0., 0.\n l = fin.readline().split(\"|\")\n for ll in l:\n if \"boxEdge\" in ll:\n width = float(ll.split()[1])\n height = width\n fin.seek(0)\n\n if width == 0.:\n # calculate edge length based on vertices of first block\n block = []\n for line in fin.readlines():\n if line == \"\\n\": break\n if line[0].isalpha(): continue\n block.append(line)\n fin.seek(0)\n width, height = edgeLenCalc(block)\n\n if not (fin.readline()[0].isalpha()): fin.seek(0)\n\n thNorm = oneOver2Pi\n normX, normY = 1./width, 1./height # normalize x and y\n\n nbl = 0\n fRot = 0. # rotation factor: 0,1,2,3. Multiplied by pi/2\n block = []\n for line in fin.readlines():\n if line == \"\\n\":\n if nbl < nblSkip:\n nbl+=1\n block = []\n continue\n fRot = random.randint(0,3)\n for l in block:\n fout.write('%f %f %f\\n' % (l[0], l[1], l[2]))\n fout.write('\\n')\n block = []\n nbl+=1\n if nbl == nlimPerFile:\n break\n else:\n continue\n\n rndxy = [0.,0.]\n rndth = 0.\n if noise > 0.:\n # Gen three random numbers\n rndxy = np.random.normal(0,noise,2)\n rndth = np.random.normal(0,twopi*thnoise,1)\n # rndxy = [0.,0.]\n # rndth = 0.\n\n spt = [float(x) for x in line.split()]\n x,y,th = spt[2],spt[3],spt[4]\n # Rotate block\n # note thetas should be [0,2pi] initially\n th_ = fRot*twopi*0.25\n th += th_ + rndth\n if th > twopi: th-=twopi\n th *= thNorm\n\n x = np.cos(th_)*spt[2] - np.sin(th_)*spt[3] + rndxy[0]\n y = np.sin(th_)*spt[2] + np.cos(th_)*spt[3] + rndxy[1]\n # shift and normalize\n x *= normX\n y *= normY\n\n block.append([x,y,th])\n\n fout.close()\n fin.close()\n print \"Done processing unlbl files\" ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c505058428f96677d08a18cbd70ec964ebfd512a
| 30,270 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
site/en/tutorials/structured_data/imbalanced_data.ipynb
|
sriyogesh94/docs
|
b2e7670f95d360c64493d1b3a9ff84c96d285ca4
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2021-02-01T21:01:37.000Z
|
2021-02-01T21:01:37.000Z
|
site/en/tutorials/structured_data/imbalanced_data.ipynb
|
sriyogesh94/docs
|
b2e7670f95d360c64493d1b3a9ff84c96d285ca4
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
site/en/tutorials/structured_data/imbalanced_data.ipynb
|
sriyogesh94/docs
|
b2e7670f95d360c64493d1b3a9ff84c96d285ca4
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2019-09-15T17:30:32.000Z
|
2019-09-15T17:30:32.000Z
| 40.306258 | 852 | 0.583251 |
[
[
[
"#### Copyright 2019 The TensorFlow Authors.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#@title Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the \"License\");\n# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.\n# You may obtain a copy of the License at\n#\n# https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0\n#\n# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software\n# distributed under the License is distributed on an \"AS IS\" BASIS,\n# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.\n# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and\n# limitations under the License.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Classification on imbalanced data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<table class=\"tfo-notebook-buttons\" align=\"left\">\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/structured_data/imbalanced_data\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/tf_logo_32px.png\" />View on TensorFlow.org</a>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/tensorflow/docs/blob/master/site/en/tutorials/structured_data/imbalanced_data.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/colab_logo_32px.png\" />Run in Google Colab</a>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://github.com/tensorflow/docs/blob/master/site/en/tutorials/structured_data/imbalanced_data.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/GitHub-Mark-32px.png\" />View source on GitHub</a>\n </td>\n <td>\n <a href=\"https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow_docs/docs/site/en/tutorials/structured_data/imbalanced_data.ipynb\"><img src=\"https://www.tensorflow.org/images/download_logo_32px.png\" />Download notebook</a>\n </td>\n</table>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"This tutorial demonstrates how to classify a highly imbalanced dataset in which the number of examples in one class greatly outnumbers the examples in another. You will work with the [Credit Card Fraud Detection](https://www.kaggle.com/mlg-ulb/creditcardfraud) dataset hosted on Kaggle. The aim is to detect a mere 492 fraudulent transactions from 284,807 transactions in total. You will use [Keras](../../guide/keras/overview.ipynb) to define the model and [class weights](https://www.tensorflow.org/versions/r2.0/api_docs/python/tf/keras/Model) to help the model learn from the imbalanced data. You will display metrics for precision, recall, true positives, false positives, true negatives, false negatives, and AUC while training the model. These are more informative than accuracy when working with imbalanced datasets classification.\n\nThis tutorial contains complete code to:\n\n* Load a CSV file using Pandas.\n* Create train, validation, and test sets.\n* Define and train a model using Keras (including setting class weights).\n* Evaluate the model using various metrics (including precision and recall).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Import TensorFlow and other libraries",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"try:\n # %tensorflow_version only exists in Colab.\n %tensorflow_version 2.x\nexcept Exception:\n pass",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!pip install imblearn",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import tensorflow as tf\nfrom tensorflow import keras\n\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nfrom sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler\nfrom scikit_learn_contrib.imbalanced_learn.over_sampling import SMOTE",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Use Pandas to get the Kaggle Credit Card Fraud data set\n\nPandas is a Python library with many helpful utilities for loading and working with structured data and can be used to download CSVs into a dataframe.\n\nNote: This dataset has been collected and analysed during a research collaboration of Worldline and the [Machine Learning Group](http://mlg.ulb.ac.be) of ULB (Université Libre de Bruxelles) on big data mining and fraud detection. More details on current and past projects on related topics are available [here](https://www.researchgate.net/project/Fraud-detection-5) and the page of the [DefeatFraud](https://mlg.ulb.ac.be/wordpress/portfolio_page/defeatfraud-assessment-and-validation-of-deep-feature-engineering-and-learning-solutions-for-fraud-detection/) project",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"raw_df = pd.read_csv('https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/creditcard.csv')\nraw_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Split the dataframe into train, validation, and test\n\nSplit the dataset into train, validation, and test sets. The validation set is used during the model fitting to evaluate the loss and any metrics, however the model is not fit with this data. The test set is completely unused during the training phase and is only used at the end to evaluate how well the model generalizes to new data. This is especially important with imbalanced datasets where [overfitting](https://developers.google.com/machine-learning/crash-course/generalization/peril-of-overfitting) is a significant concern from the lack of training data.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Use a utility from sklearn to split and shuffle our dataset.\ntrain_df, test_df = train_test_split(raw_df, test_size=0.2)\ntrain_df, val_df = train_test_split(train_df, test_size=0.2)\n\n# Form np arrays of labels and features.\ntrain_labels = np.array(train_df.pop('Class'))\nval_labels = np.array(val_df.pop('Class'))\ntest_labels = np.array(test_df.pop('Class'))\n\ntrain_features = np.array(train_df)\nval_features = np.array(val_df)\ntest_features = np.array(test_df)\n\n# Normalize the input features using the sklearn StandardScaler.\n# This will set the mean to 0 and standard deviation to 1.\nscaler = StandardScaler()\ntrain_features = scaler.fit_transform(train_features)\nval_features = scaler.transform(val_features)\ntest_features = scaler.transform(test_features)\n\nprint('Training labels shape:', train_labels.shape)\nprint('Validation labels shape:', val_labels.shape)\nprint('Test labels shape:', test_labels.shape)\n\nprint('Training features shape:', train_features.shape)\nprint('Validation features shape:', val_features.shape)\nprint('Test features shape:', test_features.shape)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Examine the class label imbalance\n\nLet's look at the dataset imbalance:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"neg, pos = np.bincount(train_labels)\ntotal = neg + pos\nprint('{} positive samples out of {} training samples ({:.2f}% of total)'.format(\n pos, total, 100 * pos / total))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This shows a small fraction of positive samples.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Define the model and metrics\n\nDefine a function that creates a simple neural network with three densely connected hidden layers, an output sigmoid layer that returns the probability of a transaction being fraudulent, and two [dropout](https://developers.google.com/machine-learning/glossary/#dropout_regularization) layers as an effective way to reduce overfitting.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def make_model():\n model = keras.Sequential([\n keras.layers.Dense(256, activation='relu',\n input_shape=(train_features.shape[-1],)),\n keras.layers.Dense(256, activation='relu'),\n keras.layers.Dropout(0.3),\n keras.layers.Dense(256, activation='relu'),\n keras.layers.Dropout(0.3),\n keras.layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'),\n ])\n\n metrics = [\n keras.metrics.Accuracy(name='accuracy'),\n keras.metrics.TruePositives(name='tp'),\n keras.metrics.FalsePositives(name='fp'),\n keras.metrics.TrueNegatives(name='tn'),\n keras.metrics.FalseNegatives(name='fn'),\n keras.metrics.Precision(name='precision'),\n keras.metrics.Recall(name='recall'),\n keras.metrics.AUC(name='auc')\n ]\n\n model.compile(\n optimizer='adam',\n loss='binary_crossentropy',\n metrics=metrics)\n \n return model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Understanding useful metrics\n\nNotice that there are a few metrics defined above that can be computed by the model that will be helpful when evaluating the performance.\n\n\n\n* **False** negatives and **false** positives are samples that were **incorrectly** classified\n* **True** negatives and **true** positives are samples that were **correctly** classified\n* **Accuracy** is the percentage of examples correctly classified\n> $\\frac{\\text{true samples}}{\\text{total samples}}$\n* **Precision** is the percentage of **predicted** positives that were correctly classified\n> $\\frac{\\text{true positives}}{\\text{true positives + false positives}}$\n* **Recall** is the percentage of **actual** positives that were correctly classified\n> $\\frac{\\text{true positives}}{\\text{true positives + false negatives}}$\n* **AUC** refers to the Area Under the Curve of a Receiver Operating Characteristic curve (ROC-AUC). This metric is equal to the probability that a classifier will rank a random positive sample higher than than a random negative sample.\n\n<br>\n\nRead more:\n* [True vs. False and Positive vs. Negative](https://developers.google.com/machine-learning/crash-course/classification/true-false-positive-negative)\n* [Accuracy](https://developers.google.com/machine-learning/crash-course/classification/accuracy)\n* [Precision and Recall](https://developers.google.com/machine-learning/crash-course/classification/precision-and-recall)\n* [ROC-AUC](https://developers.google.com/machine-learning/crash-course/classification/roc-and-auc)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Train a baseline model\n\nNow create and train your model using the function that was defined earlier. Notice that the model is fit using a larger than default batch size of 2048, this is important to ensure that each batch has a decent chance of containing a few positive samples. If the batch size was too small, they would likely have no fraudelent transactions to learn from.\n\n\nNote: this model will not handle the class imbalance well. You will improve it later in this tutorial.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model = make_model()\n\nEPOCHS = 10\nBATCH_SIZE = 2048\n\nhistory = model.fit(\n train_features,\n train_labels,\n batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,\n epochs=EPOCHS,\n validation_data=(val_features, val_labels))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Plot metrics on the training and validation sets\nIn this section, you will produce plots of your model's accuracy and loss on the training and validation set. These are useful to check for overfitting, which you can learn more about in this [tutorial](https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/keras/overfit_and_underfit).\n\nAdditionally, you can produce these plots for any of the metrics you created above. False negatives are included as an example.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"epochs = range(EPOCHS)\n\nplt.title('Accuracy')\nplt.plot(epochs, history.history['accuracy'], color='blue', label='Train')\nplt.plot(epochs, history.history['val_accuracy'], color='orange', label='Val')\nplt.xlabel('Epoch')\nplt.ylabel('Accuracy')\nplt.legend()\n\n_ = plt.figure()\nplt.title('Loss')\nplt.plot(epochs, history.history['loss'], color='blue', label='Train')\nplt.plot(epochs, history.history['val_loss'], color='orange', label='Val')\nplt.xlabel('Epoch')\nplt.ylabel('Loss')\nplt.legend()\n\n_ = plt.figure()\nplt.title('False Negatives')\nplt.plot(epochs, history.history['fn'], color='blue', label='Train')\nplt.plot(epochs, history.history['val_fn'], color='orange', label='Val')\nplt.xlabel('Epoch')\nplt.ylabel('False Negatives')\nplt.legend()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Evaluate the baseline model\n\nEvaluate your model on the test dataset and display results for the metrics you created above.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"results = model.evaluate(test_features, test_labels)\nfor name, value in zip(model.metrics_names, results):\n print(name, ': ', value)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"It looks like the precision is relatively high, but the recall and AUC aren't as high as you might like. Classifiers often face challenges when trying to maximize both precision and recall, which is especially true when working with imbalanced datasets. However, because missing fraudulent transactions (false negatives) may have significantly worse business consequences than incorrectly flagging fraudulent transactions (false positives), recall may be more important than precision in this case.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Examine the confusion matrix\n\nYou can use a [confusion matrix](https://developers.google.com/machine-learning/glossary/#confusion_matrix) to summarize the actual vs. predicted labels where the X axis is the predicted label and the Y axis is the actual label.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"predicted_labels = model.predict(test_features)\ncm = confusion_matrix(test_labels, np.round(predicted_labels))\n\nplt.matshow(cm, alpha=0)\nplt.title('Confusion matrix')\nplt.ylabel('Actual label')\nplt.xlabel('Predicted label')\n\nfor (i, j), z in np.ndenumerate(cm):\n plt.text(j, i, str(z), ha='center', va='center')\n \nplt.show()\n\nprint('Legitimate Transactions Detected (True Negatives): ', cm[0][0])\nprint('Legitimate Transactions Incorrectly Detected (False Positives): ', cm[0][1])\nprint('Fraudulent Transactions Missed (False Negatives): ', cm[1][0])\nprint('Fraudulent Transactions Detected (True Positives): ', cm[1][1])\nprint('Total Fraudulent Transactions: ', np.sum(cm[1]))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"If the model had predicted everything perfectly, this would be a [diagonal matrix](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diagonal_matrix) where values off the main diagonal, indicating incorrect predictions, would be zero. In this case the matrix shows that you have relatively few false positives, meaning that there were relatively few legitimate transactions that were incorrectly flagged. However, you would likely want to have even fewer false negatives despite the cost of increasing the number of false positives. This trade off may be preferable because false negatives would allow fraudulent transactions to go through, whereas false positives may cause an email to be sent to a customer to ask them to verify their card activity.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Using class weights for the loss function\n\nThe goal is to identify fradulent transactions, but you don't have very many of those positive samples to work with, so you would want to have the classifier heavily weight the few examples that are available. You can do this by passing Keras weights for each class through a parameter. These will cause the model to \"pay more attention\" to examples from an under-represented class.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\nweight_for_0 = 1 / neg\nweight_for_1 = 1 / pos\n\nclass_weight = {0: weight_for_0, 1: weight_for_1}\n\nprint('Weight for class 0: {:.2e}'.format(weight_for_0))\nprint('Weight for class 1: {:.2e}'.format(weight_for_1))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Train a model with class weights\n\nNow try re-training and evaluating the model with class weights to see how that affects the predictions.\n\nNote: Using `class_weights` changes the range of the loss. This may affect the stability of the training depending on the optimizer. Optimizers who's step size is dependent on the magnitude of the gradient, like `optimizers.SGD`, may fail. The optimizer used here, `optimizers.Adam`, is unaffected by the scaling change. Also note that because of the weighting, the total losses are not comparable between the two models.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"weighted_model = make_model()\n\nweighted_history = weighted_model.fit(\n train_features,\n train_labels,\n batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,\n epochs=EPOCHS,\n validation_data=(val_features, val_labels),\n class_weight=class_weight)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"weighted_results = weighted_model.evaluate(test_features, test_labels)\nfor name, value in zip(weighted_model.metrics_names, weighted_results):\n print(name, ': ', value)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Here you can see that with class weights the accuracy and precision are lower because there are more false positives, but conversely the recall and AUC are higher because the model also found more true positives. Despite having lower overall accuracy, this approach may be better when considering the consequences of failing to identify fraudulent transactions driving the prioritization of recall. Depending on how bad false negatives are, you might use even more exaggerated weights to further improve recall while dropping precision.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Oversampling the minority class\n\nA related approach would be to resample the dataset by oversampling the minority class, which is the process of creating more positive samples using something like sklearn's [imbalanced-learn library](https://github.com/scikit-learn-contrib/imbalanced-learn). This library provides methods to create new positive samples by simply duplicating random existing samples, or by interpolating between them to generate synthetic samples using variations of [SMOTE](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oversampling_and_undersampling_in_data_analysis#Oversampling_techniques_for_classification_problems). TensorFlow also provides a way to do [Random Oversampling](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/data/experimental/sample_from_datasets).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# with default args this will oversample the minority class to have an equal\n# number of observations\nsmote = SMOTE()\nres_features, res_labels = smote.fit_sample(train_features, train_labels)\n\nres_neg, res_pos = np.bincount(res_labels)\nres_total = res_neg + res_pos\nprint('{} positive samples out of {} training samples ({:.2f}% of total)'.format(\n res_pos, res_total, 100 * res_pos / res_total))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Train and evaluate a model on the resampled data\n\nNow try training the model with the resampled data set instead of using class weights to see how these methods compare.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"resampled_model = make_model()\n\nresampled_history = resampled_model.fit(\n res_features,\n res_labels,\n batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,\n epochs=EPOCHS,\n validation_data=(val_features, val_labels))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"resampled_results = resampled_model.evaluate(test_features, test_labels)\nfor name, value in zip(resampled_model.metrics_names, resampled_results):\n print(name, ': ', value)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This approach can be worth trying, but may not provide better results than using class weights because the synthetic examples may not accurately represent the underlying data. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Applying this tutorial to your problem\n\nImbalanced data classification is an inherantly difficult task since there are so few samples to learn from. You should always start with the data first and do your best to collect as many samples as possible and give substantial thought to what features may be relevant so the model can get the most out of your minority class. At some point your model may struggle to improve and yield the results you want, so it is important to keep in mind the context of the problem to evaluate how bad your false positives or negatives really are.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
c5050606c3a5dde07c885e12471f584fab1775bb
| 4,826 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
materials/homeworks/into_course_03.ipynb
|
Rajk-Prog1/prog1_2021_fall
|
bf7983cfd146b91b5788ed9874f6b415c33cc4c4
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-09-08T10:25:23.000Z
|
2021-09-08T10:25:23.000Z
|
materials/homeworks/into_course_03.ipynb
|
Rajk-Prog1/prog1_2021_fall
|
bf7983cfd146b91b5788ed9874f6b415c33cc4c4
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
materials/homeworks/into_course_03.ipynb
|
Rajk-Prog1/prog1_2021_fall
|
bf7983cfd146b91b5788ed9874f6b415c33cc4c4
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2021-09-05T00:13:22.000Z
|
2021-09-08T10:25:31.000Z
| 92.807692 | 2,502 | 0.830501 |
[
[
[
"empty"
]
]
] |
[
"empty"
] |
[
[
"empty"
]
] |
c5050cb4b688c7c200f2b966ab7e3b947bff276a
| 6,562 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
files/course_material/comp_models/TD2/TD2_M2_modeling_immuno.ipynb
|
ibalelli/ibalelli.github.io
|
44ab09efe7f9790b54c2e56cd8e6f4e2040de1c4
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
files/course_material/comp_models/TD2/TD2_M2_modeling_immuno.ipynb
|
ibalelli/ibalelli.github.io
|
44ab09efe7f9790b54c2e56cd8e6f4e2040de1c4
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
files/course_material/comp_models/TD2/TD2_M2_modeling_immuno.ipynb
|
ibalelli/ibalelli.github.io
|
44ab09efe7f9790b54c2e56cd8e6f4e2040de1c4
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 37.284091 | 123 | 0.573301 |
[
[
[
"# Génération de données synthétiques",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nfrom math import exp, log, log10, sqrt\nfrom scipy.integrate import odeint\nfrom scipy.stats import norm, lognorm\n\n# The Complete model\ndef deriv(y, t, phiS, phiL, deltaS, deltaL, deltaAb):\n dydt = phiS * exp(-deltaS * t) + phiL * exp(-deltaL * t) - deltaAb * y\n return dydt\n\ndef analytic(A0, time, phiS, phiL, deltaS, deltaL, deltaAb):\n y = []\n for t in time:\n A=(A0-phiS/(deltaAb-deltaS)-phiL/(deltaAb-deltaL))*exp(-deltaAb*t)\\\n +phiS/(deltaAb-deltaS)*exp(-deltaS*t)+phiL/(deltaAb-deltaL)*exp(-deltaL*t)\n y.append(A)\n return y\n\ndef sample_id_params(pop_params,groupHav720 = False):\n # sample parameters from their distributions\n A0 = norm.rvs(model_params['A0_mean'],model_params['A0_std'])\n phiS = exp(norm.rvs(model_params['ln_phiS_mean'],model_params['ln_phiS_std']))\n deltaAb = exp(norm.rvs(model_params['ln_deltaAb_mean'],model_params['ln_deltaAb_std']))\n \n if groupHav720: \n phiL = exp(norm.rvs(model_params['ln_phiL_mean'],model_params['ln_phiL_std'])+\n model_params['beta_phiL_Hav720'])\n deltaS = exp(norm.rvs(model_params['ln_deltaS_mean'],model_params['ln_deltaS_std'])+\n model_params['beta_deltaS_Hav720'])\n deltaL = exp(norm.rvs(model_params['ln_deltaL_mean'],model_params['ln_deltaL_std'])+\n model_params['beta_deltaL_Hav720'])\n else:\n phiL = exp(norm.rvs(model_params['ln_phiL_mean'],model_params['ln_phiL_std']))\n deltaS = exp(norm.rvs(model_params['ln_deltaS_mean'],model_params['ln_deltaS_std']))\n deltaL = exp(norm.rvs(model_params['ln_deltaL_mean'],model_params['ln_deltaL_std']))\n \n return A0, (phiS, phiL, deltaS, deltaL, deltaAb)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# True parameters: we suppose that they are log-normal distributed\nln_phiS_mean = log(1)\nln_phiS_std = 0.2\n\nln_phiL_mean = log(0.54)\nln_phiL_std = 0.1\n\nln_deltaS_mean = log(0.069)\nln_deltaS_std = 0.5\n\nln_deltaL_mean = log(1.8e-6)\nln_deltaL_std = 1\n\nln_deltaAb_mean = log(0.79)\nln_deltaAb_std = 0.1\n\nbeta_phiL_Hav720 = -1\nbeta_deltaS_Hav720 = -0.5\nbeta_deltaL_Hav720 = 3\n\n# Initial conditions on A0 is supposed to be normally distributed:\nA0_mean = 8\nA0_std = 0.1\n\n# Finally, we will add an additive error to log_10 transformed data. The error follows a standard gaussian,\n# distribution with variance:\nsigma2 = 0.01\n\nmodel_params = {'ln_phiS_mean':ln_phiS_mean,'ln_phiL_mean':ln_phiL_mean,'ln_deltaS_mean':ln_deltaS_mean,\n 'ln_deltaL_mean':ln_deltaL_mean,'ln_deltaAb_mean':ln_deltaAb_mean,\n 'ln_phiS_std':ln_phiS_std,'ln_phiL_std':ln_phiL_std,'ln_deltaS_std':ln_deltaS_std,\n 'ln_deltaL_std':ln_deltaL_std,'ln_deltaAb_std':ln_deltaAb_std,\n 'beta_phiL_Hav720':beta_phiL_Hav720,'beta_deltaS_Hav720':beta_deltaS_Hav720,\n 'beta_deltaL_Hav720':beta_deltaL_Hav720,'A0_mean':A0_mean,'A0_std':A0_std}\n\n# Time points: we suppose that all participants have observation at all time points. Note: here time is in months.\ntime = np.linspace(0,36,10)\n \n# We are going to generate 100 patients form HavrixTM 1440 dataset and 100 patients from HavrixTM 720 dataset\nN1, N2 = 100, 100\n\ndata = []\nfor n in range(N1+N2):\n if n < N1:\n A0, id_params = sample_id_params(model_params,groupHav720 = False)\n error = norm.rvs(0,sqrt(sigma2))\n phiS, phiL, deltaS, deltaL, deltaAb = id_params\n y_t = analytic(A0, time, phiS, phiL, deltaS, deltaL, deltaAb)\n #ret = odeint(deriv, A0, time, args=id_params)\n #y_t = ret.T[0]\n for t in range(len(y_t)):\n data.append([n+1,time[t],log10(y_t[t])+error,A0,0])\n else:\n A0, id_params = sample_id_params(model_params,groupHav720 = True)\n error = norm.rvs(0,sqrt(sigma2))\n phiS, phiL, deltaS, deltaL, deltaAb = id_params\n y_t = analytic(A0, time, phiS, phiL, deltaS, deltaL, deltaAb)\n #ret = odeint(deriv, A0, time, args=id_params)\n #y_t = ret.T[0]\n for t in range(len(y_t)):\n data.append([n+1,time[t],log10(y_t[t])+error,A0,1])\n \ndataframe = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=['ID', 'TIME', 'OBS', 'OBS_0', 'GROUP'])\n\n# Save the obtained dataframe as simulated_AB_response.csv\ndataframe.to_csv('simulated_AB_response.csv',sep=',',index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"####if you are using Colab:\nfrom google.colab import files \nfiles.download('simulated_AB_response.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50513c5efa177d29c32908470370a271cdad7ca
| 338,847 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
discretization/Discretization_Solution.ipynb
|
Jeyhooon/deep-reinforcement-learning
|
7a6f1974493a2058635539a4868512cdf3fb5bdb
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
discretization/Discretization_Solution.ipynb
|
Jeyhooon/deep-reinforcement-learning
|
7a6f1974493a2058635539a4868512cdf3fb5bdb
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
discretization/Discretization_Solution.ipynb
|
Jeyhooon/deep-reinforcement-learning
|
7a6f1974493a2058635539a4868512cdf3fb5bdb
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 353.702505 | 70,168 | 0.928204 |
[
[
[
"# Discretization\n\n---\n\nIn this notebook, you will deal with continuous state and action spaces by discretizing them. This will enable you to apply reinforcement learning algorithms that are only designed to work with discrete spaces.\n\n### 1. Import the Necessary Packages",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import sys\nimport gym\nimport numpy as np\n\nimport pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\n# Set plotting options\n%matplotlib inline\nplt.style.use('ggplot')\nnp.set_printoptions(precision=3, linewidth=120)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 2. Specify the Environment, and Explore the State and Action Spaces\n\nWe'll use [OpenAI Gym](https://gym.openai.com/) environments to test and develop our algorithms. These simulate a variety of classic as well as contemporary reinforcement learning tasks. Let's use an environment that has a continuous state space, but a discrete action space.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create an environment and set random seed\nenv = gym.make('MountainCar-v0')\nenv.seed(505);",
"\u001b[33mWARN: gym.spaces.Box autodetected dtype as <class 'numpy.float32'>. Please provide explicit dtype.\u001b[0m\n"
]
],
[
[
"Run the next code cell to watch a random agent.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"state = env.reset()\nscore = 0\nfor t in range(200):\n action = env.action_space.sample()\n env.render()\n state, reward, done, _ = env.step(action)\n score += reward\n if done:\n break \nprint('Final score:', score)\nenv.close()",
"Final score: -200.0\n"
]
],
[
[
"In this notebook, you will train an agent to perform much better! For now, we can explore the state and action spaces, as well as sample them.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Explore state (observation) space\nprint(\"State space:\", env.observation_space)\nprint(\"- low:\", env.observation_space.low)\nprint(\"- high:\", env.observation_space.high)",
"State space: Box(2,)\n- low: [-1.2 -0.07]\n- high: [0.6 0.07]\n"
],
[
"# Generate some samples from the state space \nprint(\"State space samples:\")\nprint(np.array([env.observation_space.sample() for i in range(10)]))",
"State space samples:\n[[-0.622 -0.039]\n [-0.946 -0.056]\n [ 0.571 -0.034]\n [-0.233 -0.007]\n [-1.021 -0.021]\n [-0.355 0.048]\n [ 0.428 -0.065]\n [-0.285 -0.047]\n [ 0.202 0.051]\n [-0.459 -0.05 ]]\n"
],
[
"# Explore the action space\nprint(\"Action space:\", env.action_space)\n\n# Generate some samples from the action space\nprint(\"Action space samples:\")\nprint(np.array([env.action_space.sample() for i in range(10)]))",
"Action space: Discrete(3)\nAction space samples:\n[1 1 1 2 2 2 0 1 2 1]\n"
]
],
[
[
"### 3. Discretize the State Space with a Uniform Grid\n\nWe will discretize the space using a uniformly-spaced grid. Implement the following function to create such a grid, given the lower bounds (`low`), upper bounds (`high`), and number of desired `bins` along each dimension. It should return the split points for each dimension, which will be 1 less than the number of bins.\n\nFor instance, if `low = [-1.0, -5.0]`, `high = [1.0, 5.0]`, and `bins = (10, 10)`, then your function should return the following list of 2 NumPy arrays:\n\n```\n[array([-0.8, -0.6, -0.4, -0.2, 0.0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8]),\n array([-4.0, -3.0, -2.0, -1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0])]\n```\n\nNote that the ends of `low` and `high` are **not** included in these split points. It is assumed that any value below the lowest split point maps to index `0` and any value above the highest split point maps to index `n-1`, where `n` is the number of bins along that dimension.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def create_uniform_grid(low, high, bins=(10, 10)):\n \"\"\"Define a uniformly-spaced grid that can be used to discretize a space.\n \n Parameters\n ----------\n low : array_like\n Lower bounds for each dimension of the continuous space.\n high : array_like\n Upper bounds for each dimension of the continuous space.\n bins : tuple\n Number of bins along each corresponding dimension.\n \n Returns\n -------\n grid : list of array_like\n A list of arrays containing split points for each dimension.\n \"\"\"\n # TODO: Implement this\n grid = [np.linspace(low[dim], high[dim], bins[dim] + 1)[1:-1] for dim in range(len(bins))]\n print(\"Uniform grid: [<low>, <high>] / <bins> => <splits>\")\n for l, h, b, splits in zip(low, high, bins, grid):\n print(\" [{}, {}] / {} => {}\".format(l, h, b, splits))\n return grid\n\n\nlow = [-1.0, -5.0]\nhigh = [1.0, 5.0]\ncreate_uniform_grid(low, high) # [test]",
"Uniform grid: [<low>, <high>] / <bins> => <splits>\n [-1.0, 1.0] / 10 => [-0.8 -0.6 -0.4 -0.2 0. 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8]\n [-5.0, 5.0] / 10 => [-4. -3. -2. -1. 0. 1. 2. 3. 4.]\n"
]
],
[
[
"Now write a function that can convert samples from a continuous space into its equivalent discretized representation, given a grid like the one you created above. You can use the [`numpy.digitize()`](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy-1.9.3/reference/generated/numpy.digitize.html) function for this purpose.\n\nAssume the grid is a list of NumPy arrays containing the following split points:\n```\n[array([-0.8, -0.6, -0.4, -0.2, 0.0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8]),\n array([-4.0, -3.0, -2.0, -1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0])]\n```\n\nHere are some potential samples and their corresponding discretized representations:\n```\n[-1.0 , -5.0] => [0, 0]\n[-0.81, -4.1] => [0, 0]\n[-0.8 , -4.0] => [1, 1]\n[-0.5 , 0.0] => [2, 5]\n[ 0.2 , -1.9] => [6, 3]\n[ 0.8 , 4.0] => [9, 9]\n[ 0.81, 4.1] => [9, 9]\n[ 1.0 , 5.0] => [9, 9]\n```\n\n**Note**: There may be one-off differences in binning due to floating-point inaccuracies when samples are close to grid boundaries, but that is alright.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def discretize(sample, grid):\n \"\"\"Discretize a sample as per given grid.\n \n Parameters\n ----------\n sample : array_like\n A single sample from the (original) continuous space.\n grid : list of array_like\n A list of arrays containing split points for each dimension.\n \n Returns\n -------\n discretized_sample : array_like\n A sequence of integers with the same number of dimensions as sample.\n \"\"\"\n # TODO: Implement this\n return list(int(np.digitize(s, g)) for s, g in zip(sample, grid)) # apply along each dimension\n\n\n# Test with a simple grid and some samples\ngrid = create_uniform_grid([-1.0, -5.0], [1.0, 5.0])\nsamples = np.array(\n [[-1.0 , -5.0],\n [-0.81, -4.1],\n [-0.8 , -4.0],\n [-0.5 , 0.0],\n [ 0.2 , -1.9],\n [ 0.8 , 4.0],\n [ 0.81, 4.1],\n [ 1.0 , 5.0]])\ndiscretized_samples = np.array([discretize(sample, grid) for sample in samples])\nprint(\"\\nSamples:\", repr(samples), sep=\"\\n\")\nprint(\"\\nDiscretized samples:\", repr(discretized_samples), sep=\"\\n\")",
"Uniform grid: [<low>, <high>] / <bins> => <splits>\n [-1.0, 1.0] / 10 => [-0.8 -0.6 -0.4 -0.2 0. 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8]\n [-5.0, 5.0] / 10 => [-4. -3. -2. -1. 0. 1. 2. 3. 4.]\n\nSamples:\narray([[-1. , -5. ],\n [-0.81, -4.1 ],\n [-0.8 , -4. ],\n [-0.5 , 0. ],\n [ 0.2 , -1.9 ],\n [ 0.8 , 4. ],\n [ 0.81, 4.1 ],\n [ 1. , 5. ]])\n\nDiscretized samples:\narray([[0, 0],\n [0, 0],\n [1, 1],\n [2, 5],\n [5, 3],\n [9, 9],\n [9, 9],\n [9, 9]])\n"
]
],
[
[
"### 4. Visualization\n\nIt might be helpful to visualize the original and discretized samples to get a sense of how much error you are introducing.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import matplotlib.collections as mc\n\ndef visualize_samples(samples, discretized_samples, grid, low=None, high=None):\n \"\"\"Visualize original and discretized samples on a given 2-dimensional grid.\"\"\"\n\n fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 10))\n \n # Show grid\n ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(plt.FixedLocator(grid[0]))\n ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(plt.FixedLocator(grid[1]))\n ax.grid(True)\n \n # If bounds (low, high) are specified, use them to set axis limits\n if low is not None and high is not None:\n ax.set_xlim(low[0], high[0])\n ax.set_ylim(low[1], high[1])\n else:\n # Otherwise use first, last grid locations as low, high (for further mapping discretized samples)\n low = [splits[0] for splits in grid]\n high = [splits[-1] for splits in grid]\n\n # Map each discretized sample (which is really an index) to the center of corresponding grid cell\n grid_extended = np.hstack((np.array([low]).T, grid, np.array([high]).T)) # add low and high ends\n grid_centers = (grid_extended[:, 1:] + grid_extended[:, :-1]) / 2 # compute center of each grid cell\n locs = np.stack(grid_centers[i, discretized_samples[:, i]] for i in range(len(grid))).T # map discretized samples\n\n ax.plot(samples[:, 0], samples[:, 1], 'o') # plot original samples\n ax.plot(locs[:, 0], locs[:, 1], 's') # plot discretized samples in mapped locations\n ax.add_collection(mc.LineCollection(list(zip(samples, locs)), colors='orange')) # add a line connecting each original-discretized sample\n ax.legend(['original', 'discretized'])\n\n \nvisualize_samples(samples, discretized_samples, grid, low, high)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now that we have a way to discretize a state space, let's apply it to our reinforcement learning environment.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create a grid to discretize the state space\nstate_grid = create_uniform_grid(env.observation_space.low, env.observation_space.high, bins=(10, 10))\nstate_grid",
"Uniform grid: [<low>, <high>] / <bins> => <splits>\n [-1.2000000476837158, 0.6000000238418579] / 10 => [-1.02 -0.84 -0.66 -0.48 -0.3 -0.12 0.06 0.24 0.42]\n [-0.07000000029802322, 0.07000000029802322] / 10 => [-0.056 -0.042 -0.028 -0.014 0. 0.014 0.028 0.042 0.056]\n"
],
[
"# Obtain some samples from the space, discretize them, and then visualize them\nstate_samples = np.array([env.observation_space.sample() for i in range(10)])\ndiscretized_state_samples = np.array([discretize(sample, state_grid) for sample in state_samples])\nvisualize_samples(state_samples, discretized_state_samples, state_grid,\n env.observation_space.low, env.observation_space.high)\nplt.xlabel('position'); plt.ylabel('velocity'); # axis labels for MountainCar-v0 state space",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You might notice that if you have enough bins, the discretization doesn't introduce too much error into your representation. So we may be able to now apply a reinforcement learning algorithm (like Q-Learning) that operates on discrete spaces. Give it a shot to see how well it works!\n\n### 5. Q-Learning\n\nProvided below is a simple Q-Learning agent. Implement the `preprocess_state()` method to convert each continuous state sample to its corresponding discretized representation.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class QLearningAgent:\n \"\"\"Q-Learning agent that can act on a continuous state space by discretizing it.\"\"\"\n\n def __init__(self, env, state_grid, alpha=0.02, gamma=0.99,\n epsilon=1.0, epsilon_decay_rate=0.9995, min_epsilon=.01, seed=505):\n \"\"\"Initialize variables, create grid for discretization.\"\"\"\n # Environment info\n self.env = env\n self.state_grid = state_grid\n self.state_size = tuple(len(splits) + 1 for splits in self.state_grid) # n-dimensional state space\n self.action_size = self.env.action_space.n # 1-dimensional discrete action space\n self.seed = np.random.seed(seed)\n print(\"Environment:\", self.env)\n print(\"State space size:\", self.state_size)\n print(\"Action space size:\", self.action_size)\n \n # Learning parameters\n self.alpha = alpha # learning rate\n self.gamma = gamma # discount factor\n self.epsilon = self.initial_epsilon = epsilon # initial exploration rate\n self.epsilon_decay_rate = epsilon_decay_rate # how quickly should we decrease epsilon\n self.min_epsilon = min_epsilon\n \n # Create Q-table\n self.q_table = np.zeros(shape=(self.state_size + (self.action_size,)))\n print(\"Q table size:\", self.q_table.shape)\n\n def preprocess_state(self, state):\n \"\"\"Map a continuous state to its discretized representation.\"\"\"\n # TODO: Implement this\n return tuple(discretize(state, self.state_grid))\n\n def reset_episode(self, state):\n \"\"\"Reset variables for a new episode.\"\"\"\n # Gradually decrease exploration rate\n self.epsilon *= self.epsilon_decay_rate\n self.epsilon = max(self.epsilon, self.min_epsilon)\n\n # Decide initial action\n self.last_state = self.preprocess_state(state)\n self.last_action = np.argmax(self.q_table[self.last_state])\n return self.last_action\n \n def reset_exploration(self, epsilon=None):\n \"\"\"Reset exploration rate used when training.\"\"\"\n self.epsilon = epsilon if epsilon is not None else self.initial_epsilon\n\n def act(self, state, reward=None, done=None, mode='train'):\n \"\"\"Pick next action and update internal Q table (when mode != 'test').\"\"\"\n state = self.preprocess_state(state)\n if mode == 'test':\n # Test mode: Simply produce an action\n action = np.argmax(self.q_table[state])\n else:\n # Train mode (default): Update Q table, pick next action\n # Note: We update the Q table entry for the *last* (state, action) pair with current state, reward\n self.q_table[self.last_state + (self.last_action,)] += self.alpha * \\\n (reward + self.gamma * max(self.q_table[state]) - self.q_table[self.last_state + (self.last_action,)])\n\n # Exploration vs. exploitation\n do_exploration = np.random.uniform(0, 1) < self.epsilon\n if do_exploration:\n # Pick a random action\n action = np.random.randint(0, self.action_size)\n else:\n # Pick the best action from Q table\n action = np.argmax(self.q_table[state])\n\n # Roll over current state, action for next step\n self.last_state = state\n self.last_action = action\n return action\n\n \nq_agent = QLearningAgent(env, state_grid)",
"Environment: <TimeLimit<MountainCarEnv<MountainCar-v0>>>\nState space size: (10, 10)\nAction space size: 3\nQ table size: (10, 10, 3)\n"
]
],
[
[
"Let's also define a convenience function to run an agent on a given environment. When calling this function, you can pass in `mode='test'` to tell the agent not to learn.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def run(agent, env, num_episodes=20000, mode='train'):\n \"\"\"Run agent in given reinforcement learning environment and return scores.\"\"\"\n scores = []\n max_avg_score = -np.inf\n for i_episode in range(1, num_episodes+1):\n # Initialize episode\n state = env.reset()\n action = agent.reset_episode(state)\n total_reward = 0\n done = False\n\n # Roll out steps until done\n while not done:\n state, reward, done, info = env.step(action)\n total_reward += reward\n action = agent.act(state, reward, done, mode)\n\n # Save final score\n scores.append(total_reward)\n \n # Print episode stats\n if mode == 'train':\n if len(scores) > 100:\n avg_score = np.mean(scores[-100:])\n if avg_score > max_avg_score:\n max_avg_score = avg_score\n if i_episode % 100 == 0:\n print(\"\\rEpisode {}/{} | Max Average Score: {}\".format(i_episode, num_episodes, max_avg_score), end=\"\")\n sys.stdout.flush()\n\n return scores\n\nscores = run(q_agent, env)",
"Episode 20000/20000 | Max Average Score: -137.36"
]
],
[
[
"The best way to analyze if your agent was learning the task is to plot the scores. It should generally increase as the agent goes through more episodes.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Plot scores obtained per episode\nplt.plot(scores); plt.title(\"Scores\");",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"If the scores are noisy, it might be difficult to tell whether your agent is actually learning. To find the underlying trend, you may want to plot a rolling mean of the scores. Let's write a convenience function to plot both raw scores as well as a rolling mean.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def plot_scores(scores, rolling_window=100):\n \"\"\"Plot scores and optional rolling mean using specified window.\"\"\"\n plt.plot(scores); plt.title(\"Scores\");\n rolling_mean = pd.Series(scores).rolling(rolling_window).mean()\n plt.plot(rolling_mean);\n return rolling_mean\n\nrolling_mean = plot_scores(scores)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You should observe the mean episode scores go up over time. Next, you can freeze learning and run the agent in test mode to see how well it performs.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Run in test mode and analyze scores obtained\ntest_scores = run(q_agent, env, num_episodes=100, mode='test')\nprint(\"[TEST] Completed {} episodes with avg. score = {}\".format(len(test_scores), np.mean(test_scores)))\n_ = plot_scores(test_scores)",
"[TEST] Completed 100 episodes with avg. score = -176.1\n"
]
],
[
[
"It's also interesting to look at the final Q-table that is learned by the agent. Note that the Q-table is of size MxNxA, where (M, N) is the size of the state space, and A is the size of the action space. We are interested in the maximum Q-value for each state, and the corresponding (best) action associated with that value.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def plot_q_table(q_table):\n \"\"\"Visualize max Q-value for each state and corresponding action.\"\"\"\n q_image = np.max(q_table, axis=2) # max Q-value for each state\n q_actions = np.argmax(q_table, axis=2) # best action for each state\n\n fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 10))\n cax = ax.imshow(q_image, cmap='jet');\n cbar = fig.colorbar(cax)\n for x in range(q_image.shape[0]):\n for y in range(q_image.shape[1]):\n ax.text(x, y, q_actions[x, y], color='white',\n horizontalalignment='center', verticalalignment='center')\n ax.grid(False)\n ax.set_title(\"Q-table, size: {}\".format(q_table.shape))\n ax.set_xlabel('position')\n ax.set_ylabel('velocity')\n\n\nplot_q_table(q_agent.q_table)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 6. Modify the Grid\n\nNow it's your turn to play with the grid definition and see what gives you optimal results. Your agent's final performance is likely to get better if you use a finer grid, with more bins per dimension, at the cost of higher model complexity (more parameters to learn).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# TODO: Create a new agent with a different state space grid\nstate_grid_new = create_uniform_grid(env.observation_space.low, env.observation_space.high, bins=(20, 20))\nq_agent_new = QLearningAgent(env, state_grid_new)\nq_agent_new.scores = [] # initialize a list to store scores for this agent",
"Uniform grid: [<low>, <high>] / <bins> => <splits>\n [-1.2000000476837158, 0.6000000238418579] / 20 => [-1.11 -1.02 -0.93 -0.84 -0.75 -0.66 -0.57 -0.48 -0.39 -0.3 -0.21 -0.12 -0.03 0.06 0.15 0.24 0.33 0.42 0.51]\n [-0.07000000029802322, 0.07000000029802322] / 20 => [-0.063 -0.056 -0.049 -0.042 -0.035 -0.028 -0.021 -0.014 -0.007 0. 0.007 0.014 0.021 0.028 0.035 0.042 0.049\n 0.056 0.063]\nEnvironment: <TimeLimit<MountainCarEnv<MountainCar-v0>>>\nState space size: (20, 20)\nAction space size: 3\nQ table size: (20, 20, 3)\n"
],
[
"# Train it over a desired number of episodes and analyze scores\n# Note: This cell can be run multiple times, and scores will get accumulated\nq_agent_new.scores += run(q_agent_new, env, num_episodes=50000) # accumulate scores\nrolling_mean_new = plot_scores(q_agent_new.scores)",
"Episode 50000/50000 | Max Average Score: -109.87"
],
[
"# Run in test mode and analyze scores obtained\ntest_scores = run(q_agent_new, env, num_episodes=100, mode='test')\nprint(\"[TEST] Completed {} episodes with avg. score = {}\".format(len(test_scores), np.mean(test_scores)))\n_ = plot_scores(test_scores)",
"[TEST] Completed 100 episodes with avg. score = -107.66\n"
],
[
"# Visualize the learned Q-table\nplot_q_table(q_agent_new.q_table)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 7. Watch a Smart Agent",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"state = env.reset()\nscore = 0\nfor t in range(200):\n action = q_agent_new.act(state, mode='test')\n env.render()\n state, reward, done, _ = env.step(action)\n score += reward\n if done:\n break \nprint('Final score:', score)\nenv.close()",
"Final score: -110.0\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c5051529c6af664fb7710fd2dc86fc75aa89be1b
| 3,197 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
samples/notebooks/fsharp/Docs/Displaying output.ipynb
|
haraldsteinlechner/interactive
|
0fb8d88fc6a400e0f0507629067a32c8d3724a8d
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2020-07-25T20:10:29.000Z
|
2020-07-26T18:23:30.000Z
|
samples/notebooks/fsharp/Docs/Displaying output.ipynb
|
Keboo/interactive
|
fb89048f73d2cb66505b090c8f55bb8b97b863b3
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
samples/notebooks/fsharp/Docs/Displaying output.ipynb
|
Keboo/interactive
|
fb89048f73d2cb66505b090c8f55bb8b97b863b3
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 23.858209 | 239 | 0.558649 |
[
[
[
"[this doc on github](https://github.com/dotnet/interactive/tree/master/samples/notebooks/fsharp/Docs)\n\n# Displaying output in a .NET (F#) notebook",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"When writing F# in a .NET notebook, you can write code similar to how you would with the F# Interactive tool.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"1 + 3",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The last value in a cell has its output displayed.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"let r = System.Random()\nr.Next(0,10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\"Hello, world!\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"When you end a cell with an expression evaluation like this, it is the return value of the cell. There can only be a single return value for a cell. If you add more code after a return value expression, you'll see a compile error.\n\nThere are also several ways to display information without using the return value. The most intuitive one for many .NET users is to write to the console:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"System.Console.WriteLine(\"Hello, world!\")\nprintfn \"Hello, world!\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"But a more familiar API for many notebook users would be the `display` method.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"display(\"Hello, world!\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Each call to `display` writes an additional display data value to the notebook.\nYou can also update an existing displayed value by calling `Update` on the object returned by a call to `display`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"let fruitOutput = display(\"Let's get some fruit!\");\nlet basket = [| \"apple\"; \"orange\"; \"coconut\"; \"pear\"; \"peach\" |]\n\nfor fruit in basket do\n System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(1000);\n let updateMessage = sprintf \"I have 1 %s\" fruit\n fruitOutput.Update(updateMessage)\n\nSystem.Threading.Thread.Sleep(1000);\n\nfruitOutput.Update(basket);",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.