hexsha
stringlengths 40
40
| size
int64 6
14.9M
| ext
stringclasses 1
value | lang
stringclasses 1
value | max_stars_repo_path
stringlengths 6
260
| max_stars_repo_name
stringlengths 6
119
| max_stars_repo_head_hexsha
stringlengths 40
41
| max_stars_repo_licenses
list | max_stars_count
int64 1
191k
⌀ | max_stars_repo_stars_event_min_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_stars_repo_stars_event_max_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_issues_repo_path
stringlengths 6
260
| max_issues_repo_name
stringlengths 6
119
| max_issues_repo_head_hexsha
stringlengths 40
41
| max_issues_repo_licenses
list | max_issues_count
int64 1
67k
⌀ | max_issues_repo_issues_event_min_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_issues_repo_issues_event_max_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_forks_repo_path
stringlengths 6
260
| max_forks_repo_name
stringlengths 6
119
| max_forks_repo_head_hexsha
stringlengths 40
41
| max_forks_repo_licenses
list | max_forks_count
int64 1
105k
⌀ | max_forks_repo_forks_event_min_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | max_forks_repo_forks_event_max_datetime
stringlengths 24
24
⌀ | avg_line_length
float64 2
1.04M
| max_line_length
int64 2
11.2M
| alphanum_fraction
float64 0
1
| cells
list | cell_types
list | cell_type_groups
list |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
c5098d405e26429e4da50e1f9b29f0a8ceab9e68
| 24,536 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
article_prediction.ipynb
|
Jayjannoff/Article-real-or-not
|
23a39cd3c6cad4c3768769336cf142d93d1fdcff
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
article_prediction.ipynb
|
Jayjannoff/Article-real-or-not
|
23a39cd3c6cad4c3768769336cf142d93d1fdcff
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
article_prediction.ipynb
|
Jayjannoff/Article-real-or-not
|
23a39cd3c6cad4c3768769336cf142d93d1fdcff
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 32.541114 | 1,541 | 0.409398 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd \nimport numpy as np \nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nimport re\nfrom nltk.corpus import stopwords\nfrom nltk.stem.porter import PorterStemmer\nfrom sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data = pd.read_csv('drive/MyDrive/Colab Notebooks/train.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import nltk\nnltk.download('stopwords')",
"[nltk_data] Downloading package stopwords to /root/nltk_data...\n[nltk_data] Unzipping corpora/stopwords.zip.\n"
],
[
"print(stopwords.words('english'))",
"['i', 'me', 'my', 'myself', 'we', 'our', 'ours', 'ourselves', 'you', \"you're\", \"you've\", \"you'll\", \"you'd\", 'your', 'yours', 'yourself', 'yourselves', 'he', 'him', 'his', 'himself', 'she', \"she's\", 'her', 'hers', 'herself', 'it', \"it's\", 'its', 'itself', 'they', 'them', 'their', 'theirs', 'themselves', 'what', 'which', 'who', 'whom', 'this', 'that', \"that'll\", 'these', 'those', 'am', 'is', 'are', 'was', 'were', 'be', 'been', 'being', 'have', 'has', 'had', 'having', 'do', 'does', 'did', 'doing', 'a', 'an', 'the', 'and', 'but', 'if', 'or', 'because', 'as', 'until', 'while', 'of', 'at', 'by', 'for', 'with', 'about', 'against', 'between', 'into', 'through', 'during', 'before', 'after', 'above', 'below', 'to', 'from', 'up', 'down', 'in', 'out', 'on', 'off', 'over', 'under', 'again', 'further', 'then', 'once', 'here', 'there', 'when', 'where', 'why', 'how', 'all', 'any', 'both', 'each', 'few', 'more', 'most', 'other', 'some', 'such', 'no', 'nor', 'not', 'only', 'own', 'same', 'so', 'than', 'too', 'very', 's', 't', 'can', 'will', 'just', 'don', \"don't\", 'should', \"should've\", 'now', 'd', 'll', 'm', 'o', 're', 've', 'y', 'ain', 'aren', \"aren't\", 'couldn', \"couldn't\", 'didn', \"didn't\", 'doesn', \"doesn't\", 'hadn', \"hadn't\", 'hasn', \"hasn't\", 'haven', \"haven't\", 'isn', \"isn't\", 'ma', 'mightn', \"mightn't\", 'mustn', \"mustn't\", 'needn', \"needn't\", 'shan', \"shan't\", 'shouldn', \"shouldn't\", 'wasn', \"wasn't\", 'weren', \"weren't\", 'won', \"won't\", 'wouldn', \"wouldn't\"]\n"
],
[
"data.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.isnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data = data.fillna('')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.isnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data['content'] = data['author']+' '+data['title']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(data['content'])",
"0 Darrell Lucus House Dem Aide: We Didn’t Even S...\n1 Daniel J. Flynn FLYNN: Hillary Clinton, Big Wo...\n2 Consortiumnews.com Why the Truth Might Get You...\n3 Jessica Purkiss 15 Civilians Killed In Single ...\n4 Howard Portnoy Iranian woman jailed for fictio...\n ... \n20795 Jerome Hudson Rapper T.I.: Trump a ’Poster Chi...\n20796 Benjamin Hoffman N.F.L. Playoffs: Schedule, Ma...\n20797 Michael J. de la Merced and Rachel Abrams Macy...\n20798 Alex Ansary NATO, Russia To Hold Parallel Exer...\n20799 David Swanson What Keeps the F-35 Alive\nName: content, Length: 20800, dtype: object\n"
],
[
"X = data.drop('label',axis=1)\ny = data['label']\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"port_stem = PorterStemmer()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def stemming(content):\n stemmed_content = re.sub('[^a-zA-Z]',' ',content)\n stemmed_content = stemmed_content.lower()\n stemmed_content = stemmed_content.split()\n stemmed_content = [port_stem.stem(word) for word in stemmed_content if not word in stopwords.words('english')]\n stemmed_content = ' '.join(stemmed_content)\n return stemmed_content",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data['content'] = data['content'].apply(stemming)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data['content']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X = data['content'].values\nY = data['label'].values",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Y.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer()\nvectorizer.fit(X)\nX = vectorizer.transform(X)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(X,Y,test_size=0.2,stratify=Y,random_state=2)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model = LogisticRegression()\nmodel.fit(X_train,y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model.score(X_train,y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model.score(X_test,y_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x_new = X_test[59]\nprediction = model.predict(x_new)\nprint(prediction)",
"[1]\n"
],
[
"print(y_test[59])",
"1\n"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c5098ea49ace9a5d4bd7479fe150ce528f19c209
| 1,522 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Week 3/jupyter notebook/Section/Section_6.ipynb
|
Opal1031/Programming-Basics-
|
9356191a40725ff0202f13afe34d814736815991
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2022-03-07T11:34:56.000Z
|
2022-03-07T11:34:56.000Z
|
Week 3/jupyter notebook/Section/Section_6.ipynb
|
Opal1031/Programming-Basics-
|
9356191a40725ff0202f13afe34d814736815991
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Week 3/jupyter notebook/Section/Section_6.ipynb
|
Opal1031/Programming-Basics-
|
9356191a40725ff0202f13afe34d814736815991
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 16.365591 | 77 | 0.461235 |
[
[
[
"len('abc')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a = 'Hi~'\nb = len(a)\nc = '*' * b\nc",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(' ')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50992b71a87fb7dcea68f482813cbeacfc812e4
| 55,206 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
nb/.ipynb_checkpoints/first_try-checkpoint.ipynb
|
gganssle/we-are-siamese-if-you-please
|
b851d01dd83fdb54be813c0c20a4717cee534d45
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
nb/.ipynb_checkpoints/first_try-checkpoint.ipynb
|
gganssle/we-are-siamese-if-you-please
|
b851d01dd83fdb54be813c0c20a4717cee534d45
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
nb/.ipynb_checkpoints/first_try-checkpoint.ipynb
|
gganssle/we-are-siamese-if-you-please
|
b851d01dd83fdb54be813c0c20a4717cee534d45
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 55.876518 | 13,094 | 0.638264 |
[
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport torch\nimport torch.nn as nn\nfrom torch.autograd import Variable\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport torch.nn.functional as F",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"raw = pd.read_csv('../dat/schools_w_clusters.csv')\nraw = raw[['Cluster ID', 'Id', 'Site name', 'Address', 'Zip', 'Phone']]\nraw['Zip'] = raw['Zip'].astype(str)\nraw['Phone'] = raw['Phone'].astype(str)\nraw.head(15)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"inpt1 = record_formatter(raw.iloc[0])\ninpt2 = record_formatter(raw.iloc[7])\ninpt3 = record_formatter(raw.iloc[11])\n\notpt1, otpt2 = model.forward(inpt1, inpt2)\nprint(loss.forward(otpt1,otpt2,1))\n\notpt1, otpt3 = model.forward(inpt1, inpt3)\nprint(loss.forward(otpt1,otpt3,0))\n\notpt2, otpt3 = model.forward(inpt2, inpt3)\nprint(loss.forward(otpt2,otpt3,0))",
"Variable containing:\n 0\n[torch.FloatTensor of size 1]\n\nVariable containing:\n 3365.6460\n[torch.FloatTensor of size 1]\n\nVariable containing:\n 3850.2957\n[torch.FloatTensor of size 1]\n\n"
],
[
"print('name max len =', raw['Site name'].str.len().max())\nprint('address max len =', raw['Address'].str.len().max())\nprint('Zip max len =', raw['Zip'].str.len().max())\nprint('phone max len =', raw['Phone'].str.len().max())",
"name max len = 95\naddress max len = 43\nZip max len = 7\nphone max len = 9\n"
]
],
[
[
"for a total of max length 154",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## defs\nThe following insanity is how we need to convert into a useable Torch tensor of correct size and Variable...ness.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Variable(torch.from_numpy(np.random.rand(10)).float()).view(1,10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def extend_to_length(string_to_expand, length):\n extension = '~' * (length-len(string_to_expand))\n return string_to_expand + extension\n\ndef record_formatter(record):\n name = extend_to_length(record['Site name'], 95)\n addr = extend_to_length(record['Address'], 43)\n zipp = extend_to_length(record['Zip'], 7)\n phon = extend_to_length(record['Phone'], 9)\n \n strings = list(''.join((name, addr, zipp, phon)))\n characters = np.array(list(map(ord, strings)))\n \n return Variable(torch.from_numpy(characters).float()).view(1,len(characters))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class SiameseNetwork(nn.Module):\n def __init__(self):\n super(SiameseNetwork, self).__init__()\n self.fc1 = nn.Sequential(\n nn.Linear(154,100),\n nn.ReLU(inplace=True),\n nn.Linear(100, 80),\n nn.Sigmoid())\n\n def forward_once(self, x):\n return self.fc1(x)\n\n def forward(self, input1, input2):\n output1 = self.forward_once(input1)\n output2 = self.forward_once(input2)\n return output1, output2\n \nclass ContrastiveLoss(torch.nn.Module):\n def __init__(self, margin=1.0):\n super(ContrastiveLoss, self).__init__()\n self.margin = margin\n '''\n def forward(self, x0, x1, y):\n # euclidian distance\n diff = x0 - x1\n dist_sq = torch.sum(torch.pow(diff, 2), 1)\n dist = torch.sqrt(dist_sq)\n\n mdist = self.margin - dist\n dist = torch.clamp(mdist, min=0.0)\n loss = y * dist_sq + (1 - y) * torch.pow(dist, 2)\n loss = torch.sum(loss) / 2.0 / x0.size()[1]\n return loss\n '''\n \n def forward(self, output1, output2, label):\n euclidean_distance = F.pairwise_distance(output1, output2)\n loss_contrastive = torch.mean((1-label) * torch.pow(euclidean_distance, 2) +\n (label) * torch.pow(torch.clamp(self.margin - euclidean_distance, min=0.0), 2))\n return loss_contrastive",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"inpt1 = record_formatter(raw.iloc[0])\ninpt2 = record_formatter(raw.iloc[7])\n\notpt1, otpt2 = model.forward(inpt1,inpt2)\n\nloss.forward(otpt1,otpt2,1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## data characteristics",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"raw.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"raw['Cluster ID'].unique().shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## training",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model = SiameseNetwork()\nloss = ContrastiveLoss(margin=1)\noptimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.001, momentum=0.1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%%time\ndiff = 10\nloss_holder = []\n\nmodel.train()\n\nfor epoch in range(10):\n for i in range(raw.shape[0]-diff):\n # build data pairs\n inpt1 = record_formatter(raw.iloc[i])\n inpt2 = record_formatter(raw.iloc[i+diff])\n label = 1 if (raw.iloc[i]['Cluster ID'] == raw.iloc[i+diff]['Cluster ID']) else 0\n \n # forward\n otpt1, otpt2 = model.forward(inpt1, inpt2)\n optimizer.zero_grad()\n loss_calc = loss.forward(otpt1, otpt2, label)\n # reassign loss requiring gradient\n loss_calc = Variable(loss_calc.data, requires_grad=True)\n \n # backprop\n loss_calc.backward()\n optimizer.step()\n \n # console.log\n loss_holder.append(loss_calc.data[0])\n #print(label)\n if i == raw.shape[0]-diff-1:\n print('loss for epoch', epoch, 'is',\n sum(loss_holder[-raw.shape[0]:]))\n \nmodel.eval()",
"loss for epoch 0 is 9801.164808633737\nloss for epoch 1 is 9834.950611713342\nloss for epoch 2 is 9834.950611713342\nloss for epoch 3 is 9834.950611713342\nloss for epoch 4 is 9834.950611713342\nloss for epoch 5 is 9834.950611713342\nloss for epoch 6 is 9834.950611713342\nloss for epoch 7 is 9834.950611713342\nloss for epoch 8 is 9834.950611713342\nloss for epoch 9 is 9834.950611713342\nCPU times: user 1min 20s, sys: 236 ms, total: 1min 20s\nWall time: 20.2 s\n"
],
[
"model.state_dict().keys()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"inpt1.size()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"loss_calc",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model.forward(inpt1,inpt2)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.plot(loss_holder)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.plot(loss_holder[:raw.shape[0]])\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model.state_dict()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c509a126b22530a11b101e96daeefdd85e1cf0c9
| 45,078 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
HeroesOfPymoli/.ipynb_checkpoints/HeroesOfPymoli_starter-checkpoint.ipynb
|
aydinjalil/pandas-challenge
|
12d5dcc6d9417509f3ed7b6b5296889727df13df
|
[
"ADSL"
] | null | null | null |
HeroesOfPymoli/.ipynb_checkpoints/HeroesOfPymoli_starter-checkpoint.ipynb
|
aydinjalil/pandas-challenge
|
12d5dcc6d9417509f3ed7b6b5296889727df13df
|
[
"ADSL"
] | null | null | null |
HeroesOfPymoli/.ipynb_checkpoints/HeroesOfPymoli_starter-checkpoint.ipynb
|
aydinjalil/pandas-challenge
|
12d5dcc6d9417509f3ed7b6b5296889727df13df
|
[
"ADSL"
] | null | null | null | 32.688905 | 148 | 0.404721 |
[
[
[
"!cat \"../README.md\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Dependencies and Setup\n\n* Load File\n* Read Purchasing File and store into Pandas DataFrame",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\n\nfile_to_load = \"./Resources/purchase_data.csv\"\n\npurchase_data = pd.read_csv(file_to_load)\npurchase_data.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Player Count",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Display the total number of players\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Due to the possibility of players to purchase multiple items, it is important to count each player once. It can be done\n# by counting the number of unique elements either by using unique() function or value_counts(). \npurchase_data['SN'].isnull().any() # This was needed to check if there are null elements in Players column\n\nunique_players = purchase_data['SN'].nunique()\npd.DataFrame({\"Total Players\": [unique_players]})",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Purchasing Analysis (Total)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Run basic calculations to obtain number of unique items, average price, etc.\n\n\n* Create a summary data frame to hold the results\n\n\n* Optional: give the displayed data cleaner formatting\n\n\n* Display the summary data frame\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"unique_items = purchase_data['Item ID'].unique().size\naverage_price = purchase_data['Price'].mean()\npurchase_no = purchase_data['Purchase ID'].count()\ntotal_revenue = purchase_data['Price'].sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"summary_df = pd.DataFrame({\"Number of Unique Items\": [unique_items], \"Average Price\": [average_price],\\\n \"Number of Purchases\": [purchase_no], \"Total Revenue\": [total_revenue]})\nsummary_df['Average Price'] = summary_df['Average Price'].map(\"${:,.2f}\".format)\nsummary_df['Total Revenue'] = summary_df['Total Revenue'].map(\"${:,.2f}\".format)\nsummary_df",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Gender Demographics",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Percentage and Count of Male Players\n\n\n* Percentage and Count of Female Players\n\n\n* Percentage and Count of Other / Non-Disclosed\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"unique_grouped_df = purchase_data.groupby('Gender')['SN'].unique()\nmale, female, others = unique_grouped_df['Male'].size, unique_grouped_df['Female'].size, unique_grouped_df['Other / Non-Disclosed'].size\ndemographics_dict = {\"Total Count\": pd.Series([male, female, others], index = ['Male', 'Female', 'Others / Non-Disclosed']),\\\n \"Percentage of Players\": pd.Series([round(male/unique_players*100, 2), round(female/unique_players*100, 2),\\\n round(others/unique_players*100, 2)], index = ['Male', 'Female', 'Others / Non-Disclosed'])}\ndemographics_df = pd.DataFrame(demographics_dict)\ndemographics_df['Percentage of Players'] = demographics_df['Percentage of Players'].map(\"{:,.2f}%\".format)\ndemographics_df",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n## Purchasing Analysis (Gender)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Run basic calculations to obtain purchase count, avg. purchase price, avg. purchase total per person etc. by gender\n\n\n\n\n* Create a summary data frame to hold the results\n\n\n* Optional: give the displayed data cleaner formatting\n\n\n* Display the summary data frame",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\ngender_counts = np.array([female, male, others])\ngender_purchase_count = purchase_data.groupby('Gender')['Purchase ID'].count()\ngender_av_purchase = purchase_data.groupby('Gender')['Price'].mean()\ngender_purchase_total = purchase_data.groupby('Gender')['Price'].sum()\ngender_av_per_person = gender_purchase_total/gender_counts\n\npurchase_summary_dict = {\"Purchase Count\": pd.Series(gender_purchase_count),\\\n \"Average Purchase Price\": pd.Series(gender_av_purchase),\\\n \"Total Purchase Value\": pd.Series(gender_purchase_total),\\\n \"Average Total Purchase per Person\": pd.Series(gender_av_per_person)}\n\ngender_purchase_df = pd.DataFrame(purchase_summary_dict, index=['Female', 'Male', 'Other / Non-Disclosed'])\ngender_purchase_df['Average Purchase Price'] = gender_purchase_df['Average Purchase Price'].map(\"${:,.2f}\".format)\ngender_purchase_df['Total Purchase Value'] = gender_purchase_df['Total Purchase Value'].map(\"${:,.2f}\".format)\ngender_purchase_df['Average Total Purchase per Person'] = gender_purchase_df['Average Total Purchase per Person'].map(\"${:,.2f}\".format)\ngender_purchase_df",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Age Demographics",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Establish bins for ages\n\n\n* Categorize the existing players using the age bins. Hint: use pd.cut()\n\n\n* Calculate the numbers and percentages by age group\n\n\n* Create a summary data frame to hold the results\n\n\n* Optional: round the percentage column to two decimal points\n\n\n* Display Age Demographics Table\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"age_list =['<10', '10-14', '15-19', '20-24', '25-29', '30-34', '35-39', '40+']\nbins = [0, 9, 14, 19, 24, 29, 34, 39, np.inf]\n\n# First, clean the data from duplicate players\n\nno_dup = purchase_data.drop_duplicates('SN')\n\n# Sort the data according to the age ranges\n\nno_dup['age_group'] = pd.cut(no_dup['Age'], bins=bins, labels = age_list)\n\n# Find total number of players of same age group\n\ntotal_count = no_dup.groupby('age_group')['Age'].count() #no_dup.age_group.value_counts()\n\n# Calculate the percentage by dividing the total number of players of a certain age group by total number of unique players\n\npercentage_group = total_count*100/unique_players\n# Create new dataframe and display\n\nage_demog = pd.DataFrame({\"Total Count\":total_count, \"Percentage of Players\": percentage_group})\nage_demog['Percentage of Players'] = age_demog['Percentage of Players'].map(\"{:,.2f}%\".format)\nage_demog",
"D:\\Anaconda\\lib\\site-packages\\ipykernel_launcher.py:10: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy\n # Remove the CWD from sys.path while we load stuff.\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Purchasing Analysis (Age)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Bin the purchase_data data frame by age\n\n\n\n* Run basic calculations to obtain purchase count, avg. purchase price, avg. purchase total per person etc. in the table below\n\n\n* Create a summary data frame to hold the results\n\n\n* Optional: give the displayed data cleaner formatting\n\n\n* Display the summary data frame",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# We repeat the same binning process to create new age_group in the original DataFrame. The only difference now is that \n# we need duplicate data as well\n\npurchase_data['age_group'] = pd.cut(purchase_data['Age'], bins=bins, labels=age_list)\n\n# grouping data by age_group we just created. We will be using this function for this exercise.\n\nage_group_data = purchase_data.groupby('age_group')\n\n# Counting all ages that fall into each age category\n\npurchase_count = age_group_data['Age'].count()\n\n# Average purchase price for each age group\n\naverage_purchase_price = age_group_data['Price'].mean()\n\n# Total money spent by each age group\n\ntotal_purchase_value = age_group_data['Price'].sum()\n\n# Average amount of money spent given the unique set of players\n\naverage_total_ppp = age_group_data['Price'].sum()/age_group_data['SN'].nunique()\n\npurchase_df = pd.DataFrame({\"Purchase Count\": purchase_count, \"Average Purchase Price\": average_purchase_price,\\\n \"Total Purchase Value\": total_purchase_value, \"Average Total Purchase per Person\": average_total_ppp})\npurchase_df['Average Purchase Price'] = purchase_df['Average Purchase Price'].map(\"${:,.2f}\".format)\npurchase_df['Total Purchase Value'] = purchase_df['Total Purchase Value'].map(\"${:,.2f}\".format)\npurchase_df['Average Total Purchase per Person'] = purchase_df['Average Total Purchase per Person'].map(\"${:,.2f}\".format)\npurchase_df",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Top Spenders",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Run basic calculations to obtain the results in the table below\n\n\n* Create a summary data frame to hold the results\n\n\n* Sort the total purchase value column in descending order\n\n\n* Optional: give the displayed data cleaner formatting\n\n\n* Display a preview of the summary data frame\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# For this exercise we need to group the original dataframe by name of the players (\"SN\")\nsn_group_data = purchase_data.groupby('SN')\npurchase_count = sn_group_data['Purchase ID'].count()\n\naverage_pur_pr = sn_group_data['Price'].mean()\n\ntotal_pur_val = sn_group_data['Price'].sum()\n\ntop_spenders_df = pd.DataFrame({\"Purchase Count\": purchase_count, \"Average Purchase Price\": average_pur_pr,\\\n \"Total Purchase Value\": total_pur_val})\n# It is important to sort the dataframe before formatting the values in columns before. After formatting the values are \n# no longer numeric but an object and mathematical operations do not perform as expected on objects\n\ntop_spenders_df = top_spenders_df.sort_values(by=[\"Total Purchase Value\"], ascending=False)\n\ntop_spenders_df['Average Purchase Price'] = top_spenders_df['Average Purchase Price'].map(\"${:,.2f}\".format)\ntop_spenders_df['Total Purchase Value'] = top_spenders_df['Total Purchase Value'].map(\"${:,.2f}\".format)\ntop_spenders_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Most Popular Items",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Retrieve the Item ID, Item Name, and Item Price columns\n\n\n* Group by Item ID and Item Name. Perform calculations to obtain purchase count, item price, and total purchase value\n\n\n* Create a summary data frame to hold the results\n\n\n* Sort the purchase count column in descending order\n\n\n* Optional: give the displayed data cleaner formatting\n\n\n* Display a preview of the summary data frame\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"id_group_data = purchase_data.groupby(['Item ID', 'Item Name'])\n\npurchase_count = id_group_data['Purchase ID'].count()\n\n\nitem_price = id_group_data[\"Price\"].min()\nitem_price.head()\ntotal_pur_value = id_group_data['Price'].sum()\n\nmost_popular_df = pd.DataFrame({\"Purchase Count\": purchase_count, \"Item Price\": item_price,\\\n \"Total Purchase Value\": total_pur_value})\nmost_popular_df = most_popular_df.sort_values(by='Purchase Count', ascending = False)\n\nmost_popular_df['Item Price'] = most_popular_df['Item Price'].map(\"${:,.2f}\".format)\nmost_popular_df['Total Purchase Value'] = most_popular_df['Total Purchase Value'].map(\"${:,.2f}\".format)\nmost_popular_df.head()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Most Profitable Items",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Sort the above table by total purchase value in descending order\n\n\n* Optional: give the displayed data cleaner formatting\n\n\n* Display a preview of the data frame\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# This exercise almost the repetition of the above exercise with an exception that we will be sorting the data based on Total \n# Purchase Value as opposed to Purchase Count above.\n\nmost_profitable_df = pd.DataFrame({\"Purchase Count\": purchase_count, \"Item Price\": item_price,\\\n \"Total Purchase Value\": total_pur_value})\nmost_profitable_df = most_profitable_df.sort_values(by='Total Purchase Value', ascending = False)\n\nmost_profitable_df['Item Price'] = most_profitable_df['Item Price'].map(\"${:,.2f}\".format)\nmost_profitable_df['Total Purchase Value'] = most_profitable_df['Total Purchase Value'].map(\"${:,.2f}\".format)\nmost_profitable_df.head()\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c509bcbf544c2deebc0812497a4650bea0fb19f3
| 10,762 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
04_financial_feature_engineering/03_kalman_filter_and_wavelets.ipynb
|
PerrySong/ML4T
|
da16a6091223fdf5ccbfc2912ca2e3afe66da943
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
04_financial_feature_engineering/03_kalman_filter_and_wavelets.ipynb
|
PerrySong/ML4T
|
da16a6091223fdf5ccbfc2912ca2e3afe66da943
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
04_financial_feature_engineering/03_kalman_filter_and_wavelets.ipynb
|
PerrySong/ML4T
|
da16a6091223fdf5ccbfc2912ca2e3afe66da943
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 82.784615 | 1,324 | 0.672459 |
[
[
[
"import warnings\nwarnings.filterwarnings('ignore')\n%matplotlib inline\n\nfrom datetime import datetime\nimport itertools\n\nimport pandas as pd\nimport pandas_datareader.data as web\nfrom pykalman import KalmanFilter\nimport pywt\n\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn as sns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')\nsns.set_style('whitegrid')\nidx = pd.IndexSlice",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Get data\nDATA_STORE = '../data/assets.h5'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"with pd.HDFStore(DATA_STORE) as store:\n print(store.keys())\n sp500 = store['sp500/stooq'].loc['2009': '2010', 'close']",
"['/engineered_features', '/us_equities/stocks', '/stooq/us/nysemkt/stocks/prices', '/stooq/us/nysemkt/stocks/tickers', '/stooq/us/nyse/stocks/prices', '/stooq/us/nyse/stocks/tickers', '/stooq/us/nyse/etfs/prices', '/stooq/us/nyse/etfs/tickers', '/stooq/us/nasdaq/stocks/prices', '/stooq/us/nasdaq/stocks/tickers', '/stooq/us/nasdaq/etfs/prices', '/stooq/us/nasdaq/etfs/tickers', '/stooq/jp/tse/stocks/prices', '/stooq/jp/tse/stocks/tickers', '/sp500/fred', '/quandl/wiki/prices', '/quandl/wiki/stocks']\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c509c2d3c84a1c018dc37062dd49602578d330a2
| 299,398 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
ML2020_HW6/.ipynb_checkpoints/DecisionTree-checkpoint.ipynb
|
chongwen8/Machine-Learning-Courseworks
|
374210f0b77cfa166f2270cae6cce7fdd4ed62c0
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
ML2020_HW6/.ipynb_checkpoints/DecisionTree-checkpoint.ipynb
|
chongwen8/Machine-Learning-Courseworks
|
374210f0b77cfa166f2270cae6cce7fdd4ed62c0
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
ML2020_HW6/.ipynb_checkpoints/DecisionTree-checkpoint.ipynb
|
chongwen8/Machine-Learning-Courseworks
|
374210f0b77cfa166f2270cae6cce7fdd4ed62c0
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 346.926999 | 98,416 | 0.922678 |
[
[
[
"# 决策树\n\n决策树(Decision Tree)首先对数据进行处理,利用归纳算法生成可读的规则和决策树,然后使用决策对新数据进行分析,本质上是通过一系列规则对数据进行分类的过程\n\n决策树是一种典型的分类方法。其中:\n+ 每个内部结点表示一个属性上的判断\n+ 每个分支代表一个判断结果的输出\n+ 每个叶结点代表一种分类结果。\n\nCLS算法是早期提出的决策树学习算法,是很多决策树学习算法的基础框架。\n依据其中选择分类属性的策略不同,可以得到不同的决策树算法。比较常用的决策树有ID3,C4.5和CART三种和实现,其中CART一般优于其他决策树,并且可用于回归任务。\n\n下面我们将编写代码实现这三种决策树算法。",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 任务一: 导入包和创建数据集\n本实验所需的包不多\n+ log用于计算 \n+ treePlotter为已经编写好的用于可视化决策树的代码,createPlot(tree)就可以调用\n+ csv为对csv文件进行操作所需的包\n\n本实验第一个使用的是天气情况数据集,属性集合A={ 天气,温度,湿度,风速}, 类别标签有两个,类别集合L={进行(yes),取消(no)}。\n\n本实验中我们用字典嵌套的形式来表示一个决策树,如一个形如\n的决策树可表示为 {'weather': {0: {'wspeed': {0: 'yes', 2: 'no', 3: 'no'}}, 1: 'yes'}}",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from math import log\nimport treePlotter,csv \nimport numpy as np\ndef createDataSet1():\n data=[\n [0, 0, 0, 0, 'yes'],\n [0, 1, 0, 1, 'yes'],\n [0, 2, 1, 0, 'no'],\n [0, 2, 1, 1, 'no'],\n [0, 1, 1, 0, 'no'],\n [1, 2, 1, 0, 'yes'],\n [1, 0, 0, 1, 'yes'],\n [1, 1, 1, 1, 'yes'],\n [1, 2, 0, 0, 'yes'],\n [2, 1, 1, 0, 'yes'],\n [2, 0, 0, 0, 'yes'],\n [2, 1, 0, 0, 'yes'],\n [2, 0, 0, 1, 'no'],\n [2, 1, 1, 1, 'no']\n ]\n features=['weather','temperature','humidity','wspeed']\n return data,features\n\ndata1,features1 = createDataSet1()\nfeatures1",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 任务二:ID3树\n\nID3 以信息熵的增益来作为分类的依据。假设样本集D中第$k$类样本占比$p_k$,可计算其对应信息熵为:$$Ent(D)=-\\sum_k p_k log p_k$$ $Ent(D)$越小,代表数据集越有序,纯度越高。我们首先编写计算数据集香农熵的函数。\n##### 2.1完成香农熵计算函数",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def calcShannonEnt(dataSet):\n \"\"\"\n 函数:计算数据集香农熵\n 参数:dataSet:数据集\n labels:数据标签\n 返回:shannonEnt 数据集对应的香农熵\n \"\"\"\n numEntries = len(dataSet) #样本数\n labelCounts = {} #统计不同label出现次数的字典(key为label,value为出现次数)\n shannonEnt = 0.0\n \n #计算labelCounts\n for featVec in dataSet:\n # 获取当前这条数据的label值\n currentLabel = featVec[-1]\n # 是新label,则在标签字典中新建对应的key,value的对应出现的次数,初始化为0\n if currentLabel not in labelCounts.keys(): \n labelCounts[currentLabel] = 0\n # 已有则当前label出现次数+1\n labelCounts[currentLabel] += 1\n \n ### START CODE HERE ###\n\n ### END CODE HERE ### \n \n return shannonEnt",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(calcShannonEnt(data1))\ndata1[0][-1] = 'maybe' #尝试增加一个分类选项,观察熵变化\nprint(calcShannonEnt(data1)) \n#out:0.9402859586706309 ; 1.2638091738835462\n\ndata1[0][-1] = 'yes' #还原",
"0.9402859586706309\n1.2638091738835462\n"
]
],
[
[
"##### 2.2 完成基本功能函数\n+ splitDataSet:用于在决策树每个分支,将特征取某个值的所有数据划分为一个数据集",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def splitDataSet(dataSet, axis, value):\n \"\"\"\n 函数:将axis列属性值为value的组合为一个数据集,并删除第axis列特征信息\n 参数:axis:特征列索引\n value:待分离的特征取值\n 返回:retDataSet:被分割出来的数据集\n \"\"\"\n retDataSet = []\n for data in dataSet:\n # 如果数据集的第axis列值等于value,保留条数据,并删除第axis列特征信息\n if data[axis] == value:\n # 获取被降维特征前面的所有特征\n reducedFeatVec = data[:axis]\n # 接上被降维特征后面的所有特征\n reducedFeatVec.extend(data[axis + 1:])\n # 新的降维数据加入新的返回数据集中\n retDataSet.append(reducedFeatVec)\n return retDataSet\n\nsplitDataSet(data1,0,1) \n#out:[[2, 1, 0, 'yes'], [0, 0, 1, 'yes'], [1, 1, 1, 'yes'], [2, 0, 0, 'yes']]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### 2.3 用信息增益选择待分类的特征\n\n那么假设用离散属性a有V个可能值,划分能产生V个分支,每个分支包含的数据记为$D^v$。\n由此我们可以得出用属性a对样本集D划分的信息增益计算公式:\n$$Gain(D,a)=Ent(D)-\\sum_v\\frac{|D^v|}{|D|}Ent(D^v)$$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def chooseBestFeature_ID3(dataSet):\n \"\"\"\n 函数:利用香农熵,计算所有可能划分的信息增益,输出当前数据集最好的分类特征\n 参数:dataSet\n 返回:bestFeature:最优特征的index(下标)\n \"\"\"\n numFeatures = len(dataSet[0]) - 1 #特征数\n baseEntropy = calcShannonEnt(dataSet) #Ent(D)\n bestInfoGain = 0.0 #信息增益\n bestFeature = -1 #最好信息增益特征\n \n #遍历每个特征\n for i in range(numFeatures):\n featList = [example[i] for example in dataSet]\n uniqueVals = set(featList) #第i个特征的可能取值\n newEntropy = 0.0\n \n ### STARD CODE HERE ###\n\n #计算以第i个特征划分产生的infoGain\n #如果大于当前bestInfoGain,则保留当前划分为最优划分\n\n ### END CODE HERE ### \n \n return bestFeature\n\nchooseBestFeature_ID3(data1)\n#out:0",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### 2.4 生成ID3决策树\n\n接下来我们可以用 **递归** 的方法生成决策树,其基本流程如下:\n+ 划分条件:自根结点开始,通过选择出最佳属性进行划分树结构,并递归划分;\n+ 停止条件:当前结点都是同一种类型;当前结点后为空,或者所有样本在所有属性上取值相同,无法划分;\n\n这是通用的创建决策树的函数,根据参数chooseBestFeature的不同,得到不同算法的决策树,当前任务中参数为刚刚编写的 chooseBestFeature_ID3。\n\n#### 备注:\n此处代码实现的ID3树,每个结点不能选取祖先结点用过的分类特征。\n而实际上结点的不同子树,是有可能选取同样的分类特征的。\n原因在于代码实现的 del (features[bestFeat]) 会导致一个特征被选用后,之后就再不能被选用。可以通过在递归时传入features的一份复制来避免这个问题。",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def createTree(dataSet, features, chooseBestFeature):\n \"\"\"\n 函数:递归地根据数据集和数据特征名创建决策树\n 参数:chooseBestFeature:函数作为参数,通过chooseBestFeature(dataSet)调用,\n 根据参数的不同,获取由ID3或C4.5算法选择的最优特征的index\n 返回:myTree:由集合表示的决策树\n \"\"\"\n classList = [data[-1] for data in dataSet] #当前数据集的所有标签\n bestFeat = chooseBestFeature(dataSet) #当前数据集最优特征\n bestFeatName = features[bestFeat] #最优特征的标签名\n myTree = {bestFeatName: {}} #构造当前结点——最优特征:子结点集合\n bestFeatValues = set([data[bestFeat] for data in dataSet]) #最优特征可能的取值,set去重\n\n del (features[bestFeat]) #删除已用过的分类标签\n \n ### STARD CODE HERE ###\n \n # 如果当前dataSet所有的标签相同,此结点分类完毕,结束决策,返回分类标签\n # 否则,为每个最优特征取值,递归地创建子树\n\n ### END CODE HERE ### \n\n return myTree\n\ndata1, labels1 = createDataSet1()\nID3Tree = createTree(data1, labels1,chooseBestFeature_ID3)\ntreePlotter.createPlot(ID3Tree)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### <center> Sample Output:</center>\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 任务三:C4.5树\n\nID3用信息增益选择属性的方式会让他对取值数目较多的属性产生偏好,接下来我们通过一个直观的例子来说明。\n\n假设数据集变成如下所示,某个属性(如风速)变为每个样本一个值的情况,构建一个ID3树。",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def createDataSet2():\n data=[\n [0, 0, 1, 0, 'yes'],\n [1, 1, 0, 1, 'yes'],\n [0, 0, 0, 2, 'no'],\n [0, 1, 1, 3, 'no'],\n [1, 1, 1, 4, 'yes']\n ]\n features2=['weather','temperature','humidity','wspeed']\n return data,features2\ndata2, features2 = createDataSet2()\nID3Tree = createTree(data2, features2, chooseBestFeature_ID3)\ntreePlotter.createPlot(ID3Tree)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### <center> Sample Output:</center>\n\n可以观察到,ID3树利用了该属性为每一个样本创建了分支,这样得到的决策树显然泛化性会很差。\n为了进行改进,我们可以设想为信息增益增加一个类似于正则项的惩罚参数,在特征取值多时,降低信息增益。\n\n**信息增益比 = 惩罚参数 * 信息增益**\n\nC4.5算法为属性定义一个Intrinsic Value(IV)来构建这个惩罚参数:$$IV(a)=-\\sum_{v=1}^{V}\\frac{|D^v|}{|D|}log\\frac{|D^v|}{|D|}$$\n其数学意义为:以特征a作为随机变量的熵的倒数。\n\n假设某个属性将样本等分为x份,可得其$IV=-log(1/x)$\n\n观察函数图像会发现,样本划分越多,x越大,其值越大\n\n于是可将信息增益改进为信息增益比$$GainRatio(D,a)=\\frac{Gain(D,a)}{IV(a)}$$\n\n#### 任务3.1 用信息增益比选择分类特征",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def chooseBestFeature_C45(dataSet):\n \"\"\"\n 函数:计算所有可能划分的信息增益比,输出当前数据集最好的分类特征\n 参数:dataSet\n 返回:bestFeature:最优特征的index(下标)\n \"\"\"\n numFeatures = len(dataSet[0]) - 1\n baseEntropy = calcShannonEnt(dataSet)\n bestInfoGain = 0.0\n bestFeature = -1\n \n for i in range(numFeatures):\n featList = [example[i] for example in dataSet]\n uniqueVals = set(featList) \n newEntropy = 0.0\n IV = 0.0 \n \n ### STARD CODE HERE ### \n\n # 计算以第i个特征划分的infoGain,以及其IV\n # 计算GainRatio衰减\n # 如果大于当前最优,则保留当前划分为最优划分\n\n ### END CODE HERE ###\n \n return bestFeature",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### 任务3.2 生成C4.5树",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data2, labels2 = createDataSet2()\nC45Tree = createTree(data2, labels2, chooseBestFeature_C45)\ntreePlotter.createPlot(C45Tree)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### <center> Sample Output:</center>\n\n可以观察到,C4.5算法的确对特征取值较少的属性产生了更多偏好,可以有效的避免上述ID3树存在的问题。但C4.5算法分类结果还是存在一定的过拟合。",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 任务四:CART",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"前面的实验我们发现ID3和C4.5算法在用于分类问题是有效的,那么决策树可以适用于回归问题吗?\n\nCART(Classification and regression tree)如其名,便是可以既可以用于解决分类问题,又可以用于解决回归问题的决策树算法。\n\n在解决分类问题时:\n\nID3/C4.5基于信息论熵模型选择一个离散的特征进行分类,根据特征取值数目一次性划分若干子结点,然后子结点的数据集将不再包含这个特征,这个特征不再参与接下来的分类,这意味着这种决策树模型是不能直接处理连续取值的特征的,除非划分区间将其离散化。\n\nCART则根据**基尼系数(Gini Index)** 为连续或离散的特征选择一个划分点,产生左右两个分支,生成二叉树。在产生分支后,仍可以再利用这个特征,参与接下来的分类,产生下一个分支。用叶子结点样本**最多的标签**作为预测输出。\n\n在解决回归问题时:\n\nCART根据**平方损失**选择最优划分特征和划分点,并用叶子结点样本**标签均值**作为预测输出。\n\n接下来我们来具体实现CART回归树,并尝试用于解决一个分类问题。",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"##### 任务4.1 iris数据集读取和预处理\n\nIris数据集即鸢尾属植物数据集,该数据集测量了所有150个样本的4个特征,分别是:\n+ sepal length(花萼长度)\n+ sepal width(花萼宽度)\n+ petal length(花瓣长度)\n+ petal width(花瓣宽度)\n\n标签为其种属:Iris Setosa,Iris Versicolour,Iris Virginica。该数据集被广泛用于分类算法示例,我们可以看到其4个特征取值均是连续的。数据集存储在 iris.csv 文件中,我们从中手动划分一部分作为训练集。\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def createDataSetIris():\n '''\n 函数:获取鸢尾花数据集,以及预处理\n 返回:\n Data:构建决策树的数据集(因打乱有一定随机性)\n Data_test:手动划分的测试集\n featrues:特征名列表\n labels:标签名列表\n '''\n labels = [\"setosa\",\"versicolor\",\"virginica\"]\n with open('iris.csv','r') as f:\n rawData = np.array(list(csv.reader(f)))\n features = np.array(rawData[0,1:-1]) \n dataSet = np.array(rawData[1:,1:]) #去除序号和特征列\n np.random.shuffle(dataSet) #打乱(之前如果不加array()得到的会是引用,rawData会被一并打乱)\n return rawData[1:,1:], dataSet, features, labels\n\nrawData, data, features, labels = createDataSetIris()\nprint(rawData[0]) #['5.1' '3.5' '1.4' '0.2' 'setosa']\nprint(data[0])\nprint(features) #['Sepal.Length' 'Sepal.Width' 'Petal.Length' 'Petal.Width']\nprint(labels) #['setosa', 'versicolor', 'virginica']",
"['5.1' '3.5' '1.4' '0.2' 'setosa']\n['6.3' '2.3' '4.4' '1.3' 'versicolor']\n['Sepal.Length' 'Sepal.Width' 'Petal.Length' 'Petal.Width']\n['setosa', 'versicolor', 'virginica']\n"
]
],
[
[
"##### 4.2 完成基尼指数计算函数\n\n数据集D的基尼值(Gini Index)计算公式如下:\n$$Gini(D)=\\sum_{k=1}^{K}\\sum_{k'≠K}p_kp_k'=1-\\sum_{k=1}^{K}p_k^2$$\n其数学意义为,从数据集中任选两个样本,类别不一致的概率。其值越小,数据集纯度越高。\n\n数据集D某个划分a的基尼系数计算如下:\n$$GiniIndex(D,a)=\\sum_{v=1}^{V}\\frac{|D^v|}{|D|}Gini(D^v)$$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def calcGiniIndex(dataSet):\n '''\n 函数:计算数据集基尼值\n 参数:dataSet:数据集\n 返回: Gini值\n ''' \n counts = [] #每个标签在数据集中出现的次数\n count = len(dataSet) #数据集长度\n for label in labels:\n counts.append([d[-1] == label for d in dataSet].count(True))\n \n ### STARD CODE HERE ### \n \n gini = None\n \n ### END CODE HERE ###\n \n return gini\n\ncalcGiniIndex(rawData) \n#out:0.6666666666666667",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### 4.3 完成基本功能函数\n+ binarySplitDataSet: 和ID3,C4.5不同,CART每个划分均为二分,且不删除特征信息。这里由于已知数据集特征取值全是连续取值型的, 对算法的部分功能进行了并不严谨的简化。实际应用中的CART还应该判断特征取值是否离散,若离散,并把feature等于和不等于value的数据划分为两个数据集。\n+ classificationLeaf:用于分类命题,此处实现的是多数表决器,叶结点输出数据集最多的标签作为分类。如果是用于回归问题,叶结点应该输出的是数据集列的均值作为回归预测。",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def binarySplitDataSet(dataSet, feature, value):\n '''\n 函数:将数据集按特征列的某一取值换分为左右两个子数据集\n 参数:dataSet:数据集\n feature:数据集中某一特征列\n value:该特征列中的某个取值\n 返回:左右子数据集\n '''\n matLeft = [d for d in dataSet if d[feature] <= value]\n matRight = [d for d in dataSet if d[feature] > value]\n return matLeft,matRight\n\nbinarySplitDataSet(rawData,0,\"4.3\")[0]\n#out[array(['4.3', '3', '1.1', '0.1', 'setosa'], dtype='<U12')]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def classifyLeaf(dataSet, labels):\n '''\n 函数:求数据集最多的标签,用于结点分类\n 参数:dataSet:数据集\n labels:标签名列表\n 返回:该标签的index\n '''\n counts = [] \n for label in labels:\n counts.append([d[-1] == label for d in dataSet].count(True))\n return np.argmax(counts) #argmax:使counts取最大值的下标\n\nclassifyLeaf(rawData[40:120],labels) \n#out:1",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### 4.4 用基尼系数选择特征及划分点\n\nCART在这一步选择的不仅是特征,而是特征以及该特征的一个分界点。CART要遍历所有特征的所有样本取值作为分界点的Gini系数,从中找出最优特征和最优划分。\n\n在这里我们进一步地为决策树设定停止条件——阈值。当结点样本树足够小或者Gini增益足够小的时候停止划分,将结点中最多的样本作为结点的决策分类。",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def chooseBestSplit(dataSet, labels, leafType=classifyLeaf, errType=calcGiniIndex, threshold=(0.01,4)):\n '''\n 函数:利用基尼系数选择最佳划分特征及相应的划分点\n 参数:dataSet:数据集\n leafType:叶结点输出函数(当前实验为分类)\n errType:损失函数,选择划分的依据(分类问题用的就是GiniIndex)\n threshold: Gini阈值,样本阈值(结点Gini或样本数低于阈值时停止)\n 返回:bestFeatureIndex:划分特征\n bestFeatureValue:最优特征划分点\n '''\n thresholdErr = threshold[0] #Gini阈值\n thresholdSamples = threshold[1] #样本阈值\n err = errType(dataSet)\n bestErr = np.inf\n bestFeatureIndex = 0 #最优特征的index\n bestFeatureValue = 0 #最优特征划分点\n\n ### STARD CODE HERE ### \n \n #当数据中输出值都相等时,返回叶结点(即feature=None,value=结点分类)\n #尝试所有特征的所有取值,二分数据集,计算err(本实验为Gini),保留bestErr\n #检验Gini阈值,若是则不再划分,返回叶结点\n #检验左右数据集的样本数是否小于阈值,若是则不再划分,返回叶结点\n \n ### END CODE HERE ### \n \n return bestFeatureIndex,bestFeatureValue\n\nchooseBestSplit(rawData, labels)\n#out:(2, '1.9')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### 4.5 生成CART\n\n根据参数leafType,errType的不同,生成CART分类树或是CART回归树。",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def createTree_CART(dataSet, labels, leafType=classifyLeaf, errType=calcGiniIndex, threshold=(0.01,4)):\n\n '''\n 函数:建立CART树\n 参数:同上\n 返回:CART树\n '''\n feature,value = chooseBestSplit(dataSet, labels, leafType, errType, threshold)\n\n ### STARD CODE HERE ### \n\n #是叶结点则返回决策分类(chooseBestSplit返回None时表明这里是叶结点)\n #否则创建分支,递归生成子树\n leftSet,rightSet = binarySplitDataSet(dataSet, feature, value) \n myTree = {}\n myTree[features[feature]] = {}\n myTree[features[feature]]['<=' + str(value) + ' contains' + str(len(leftSet))] = None\n myTree[features[feature]]['>' + str(value) + ' contains' + str(len(rightSet))] = None\n \n ### END CODE HERE ### \n \n return myTree\n\nCARTTree = createTree_CART(data, labels, classifyLeaf, calcGiniIndex, (0.01,4))\ntreePlotter.createPlot(CARTTree)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### <center> Sample Output:</center>\n\n#### 备注:\n+ 由于实现细节,实现顺序有所不同,最终生成的树可能也不一样,之前函数的测试样例通过即可。\n+ 一个分支两个子结点分类相同是未达到Gini阈值,却达到样本阈值导致的,可以通过更改特征选择代码中,停止划分判断的顺序避免。\n\n\n从实例可以看到一些CART树的特点,如:连续属性二分划分特征,特征可重复用于结点分类等等",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
c509de2ec850fc2372d596b2924a1418b191b4a9
| 34,794 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
berlin trees/Exploring Berlin Trees part 1.ipynb
|
scrambldchannel/jupyter-notebooks
|
d96ff941a1bee5c6cdd1b10672d397abb8ba236d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
berlin trees/Exploring Berlin Trees part 1.ipynb
|
scrambldchannel/jupyter-notebooks
|
d96ff941a1bee5c6cdd1b10672d397abb8ba236d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
berlin trees/Exploring Berlin Trees part 1.ipynb
|
scrambldchannel/jupyter-notebooks
|
d96ff941a1bee5c6cdd1b10672d397abb8ba236d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 34.449505 | 1,198 | 0.484882 |
[
[
[
"The folk at [Code for Berlin](https://www.codefor.de/berlin/) have created a REST API offering access to the database of Berlin street trees and have [an issue open](https://github.com/codeforberlin/tickets/issues/3) asking people to try to do \"something\" with it. It seemed a cool way to look more deeply into the architecture of REST APIs on both the client and server side as well as playing with an interesting dataset, given I live in Berlin and like trees.\n\nThe API itself is built using the [Django REST Framework](https://www.django-rest-framework.org/) and is hosted [here](https://github.com/codeforberlin/trees-api-v2). An [interactive map](https://trees.codefor.de/) exists which uses the api to plot all the trees and allows some simple filtering on top of tiles from Open Street Map. I took a look and it proved a great intro to the data I wanted to do a deeper analysis of the data.\n\nSome of the things I wanted to look into were:\n\n* Which areas have the most trees, the oldest trees etc\n* Are there any connections between the number of trees and other datapoints (air quality, socioeconomic demographics etc)\n* Why are there no trees showing on my street even though I can see some out the window as I type this? \n\n## What sort of data is there and how can it be consumed? \n\nOne of the cool things about the Django REST Framework is the way it's API can be explored out of the box. Simply point your browser to the API using the following link:\n\nhttps://trees.codefor.de/api/v2\n\nYou should see something like this:\n\n```\n\nHTTP 200 OK\nAllow: GET, HEAD, OPTIONS\nContent-Type: application/json\nVary: Accept\n\n{\n \"trees\": \"https://trees.codefor.de/api/v2/trees/\",\n \"species\": \"https://trees.codefor.de/api/v2/species/\",\n \"genera\": \"https://trees.codefor.de/api/v2/genera/\",\n \"boroughs\": \"https://trees.codefor.de/api/v2/boroughs/\"\n}\n\n```\n\nEssetially this is telling us that we have four endpoints - trees, species, genera and boroughs. You can follow the links to each one to get more details. To explore the data available, I hacked together a simple python wrapper which you can find here: \n\nhttps://github.com/scrambldchannel/berlin-trees-api-pywrapper\n\n### Usage\n\nThe wrapper can be installed via pip:\n\n```\npip install git+https://github.com/scrambldchannel/berlin-trees-api-pywrapper.git\n```\n\n#### Setup the wrapper\n\nNote I am specifying version 2. When I look at the",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import the module and other useful libs\n\nimport json\nfrom berlintreesapiwrapper import TreesWrapper\n\n# Instantiate the api wrapper object\n# you can change the base url if you are running a local instance of the api \n\nbase_url = \"https://trees.codefor.de/api/\"\napi_version = 2\napi = TreesWrapper(api_root = base_url, version = api_version)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Calling functions\n\nThere is a function defined for each endpoint. At this stage, each function accepts only a couple of parameters. Each endpoint returns paginated results (the current config seems to return ten results per page) so the page number is a valid parameter for each function, defaulting to 1 if not supplied. See examples below. \n\n#### Trees endpoint\n\nThe most versatile endpoint is the trees endpoint which returns sets of individual trees. The endpoint allows filtering in a number of different ways (see https://github.com/codeforberlin/trees-api-v2#making-queries).\n\nMy basic wrapper function doesn't support anything other than a simple dump of all trees, by page, at this stage. This was sufficient for pulling all the data but I will look into enhancing this wrapper later, the ability to filter trees based on location is particular interesting. \n\n```python\n# Eg. request first page of all trees\n\nret_trees = api.get_trees()\n\n# Eg. request the 5000th page of all trees\n\nret_trees = api.get_trees(page=5000)\n```\n\n#### Other endpoints\n\nThe other endpoints just return a count of the trees by borough, species and genus. Results can be filtered by page and the name of the borough etc. See examples below.\n\n```python\n# Eg. request first page of the borough count\n\nret_borough = api.get_boroughs()\n\n# Eg. request the count for a specific borough\n\nret_borough = api.get_boroughs(borough = \"Friedrichshain-Kreuzberg\")\n\n# Eg. request the count for a specific species\n\nret_species = api.get_species(species = \"Fagus sylvatica\")\n\n# Eg. request a specific page of the count of genera\n\nret_genera = api.get_genera(page = 13)\n```\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n## Data exploration\n\nFirst, I need to get the data into a format I can analyse it easily. \n\n### Look at structure for a single tree\n\nI want to pull it all individual trees into a single dataframe. To do so, I returned to the trees endpoint. The relevant part of the json result is contained within \"features\" and an individual tree looks like this:\n\n```json\n\n{\n \"geometry\": {\n \"coordinates\": [\n 13.357809221770479,\n 52.56657685261005\n ],\n \"type\": \"Point\"\n },\n \"id\": 38140,\n \"properties\": {\n \"age\": 80,\n \"borough\": \"Reinickendorf\",\n \"circumference\": 251,\n \"created\": \"2018-11-11T12:22:35.506000Z\",\n \"feature_name\": \"s_wfs_baumbestand_an\",\n \"genus\": \"ACER\",\n \"height\": 20,\n \"identifier\": \"s_wfs_baumbestand_an.7329\",\n \"species\": \"Acer pseudoplatanus\",\n \"updated\": \"2018-11-11T12:22:35.506000Z\",\n \"year\": 1938\n },\n \"type\": \"Feature\"\n}\n```\n\n### Write script to pull all trees\n\nEssentially I want to pull all of these trees into a single dataframe by iterating over every page of the trees endpoint. I hacked together this code to accomplish this. It also converted the result to a geodataframe based on the long/lat information returned. Note, this was really slow, probably wasn't the best way to do it and there are other ways of sourcing the raw data. That said, I wanted to do it as a PoC.\n\n```python\n# loop over the pages until we reach the end and append the values we're interested to lists\n\nwhile True:\n this_page = api.get_trees(page=page).json()\n next_page = this_page[\"next\"]\n for row in range(len(this_page['features'])):\n ids.append(this_page['features'][row]['id'])\n age.append(this_page['features'][row]['properties']['age'])\n borough.append(this_page['features'][row]['properties']['borough'])\n circumference.append(this_page['features'][row]['properties']['circumference'])\n genus.append(this_page['features'][row]['properties']['genus'])\n height.append(this_page['features'][row]['properties']['height'])\n species.append(this_page['features'][row]['properties']['species'])\n year.append(this_page['features'][row]['properties']['year']) \n lat.append(this_page['features'][row]['geometry']['coordinates'][0])\n long.append(this_page['features'][row]['geometry']['coordinates'][1]) \n\n page = page + 1\n \n if(next_page) is None:\n break\n\n# create dataframe from resulting lists \n\ndf = pd.DataFrame(\n {'id': ids,\n 'age' : age,\n 'borough' : borough,\n 'circumference' : circumference,\n 'genus' : genus,\n 'height' : height,\n 'species' : species,\n 'year': year,\n 'Latitude': lat,\n 'Longitude': long})\n```\n\nAfter running once, I saved it to a csv for future analysis. As an aside, I've recently started using the amazing [VisiData](https://visidata.org/) for this sort of analysis of data in text form but have done it here using Pandas. \n\n### Load into Pandas dataframe",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import ilbraries\n\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport geopandas as gpd\n\n# load csv\n\ndataset_path = '../datasets/'\ndf = pd.read_csv(filepath_or_buffer = dataset_path + 'all_trees.csv', index_col = 0, encoding='utf-8')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Convert to Geopandas dataframe\n\nGiven we have lat/long for each tree, let's convert it to a Geopandas dataframe which might come in handy later.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"gdf = gpd.GeoDataFrame(df, geometry=gpd.points_from_xy(df.Longitude, df.Latitude)) ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Get an overview of the data\n\nThis gives an overview of the data which is a useful starting point and helps give insight into data quality issues there might be.\n\n#### This is what the data looks like",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"gdf.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Get a row count",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"len(gdf.index)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Use the describe method on the numeric fields",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"gdf.describe(percentiles = [.20, .40, .60, .80], include = [ 'float', 'int'])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### A number of things stand out at a glance:\n\n* All columns seem to be populated for all rows except age (ie their counts match the total row count)\n* That said, all of the value columns have zeros so there are some gaps in the data\n* The max values for all measures are clearly spurious based on the percentiles\n* There must be some duplicates in the id column which I'd believed should be unique\n* The age and the year (presuming it means the year of planting) should correspond however the percentiles don't reflect this\n* The long/lat values don't seem to have an extreme outliers\n\n#### Use the describe method on the string fields",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"gdf[['borough', 'genus', 'species']].describe()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"##### Things to note:\n\n* Population of the borough field is complete but genus and species have some gaps\n* Perhaps there is a mix of upper/lower case that might need to be normalised\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Try to address data quality\n\nLet's try to either correct the outliers (if possible) or remove them from calculations by setting the values to NaN. For the circumference and height data, this is relatively straightforward, for the age / year numbers, it might be possible to derive one from the other. \n\n#### Setting 0s to NaN\n\nDoing this should remove the 0s from the calculations while retaining any information that is available for that tree. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"gdf['age'].replace(0, np.nan, inplace=True)\ngdf['circumference'].replace(0, np.nan, inplace=True)\ngdf['height'].replace(0, np.nan, inplace=True)\ngdf['year'].replace(0, np.nan, inplace=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Deriving age from year and vice versa\n\nLet's check the assumption the age and year are connected, that is:\n\n\n```\nage = 2018 - year\n```\n\nLet's try to check that assumption, perhaps a bit of a hack but it does the trick. **There must be a better way to do this**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"total = 0\nfor i in range(0,2020):\n count = gdf[abs(gdf.age) == (i - gdf.year)]['id'].count() \n if count != 0:\n print(i, count)\n total = total + count\nprint(total)\n ",
"0 100445\n6 3\n9 2\n13 3\n15 5\n27 1\n52 1\n114 3\n2014 3\n2015 14\n2016 1141\n2017 100\n2018 136360\n238081\n"
]
],
[
[
"So there's a bit of variation but essentially, either the year is set 0 or the age is usually about equal to the number of years from the year. Let's just set the age to the 2018 - year",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"gdf['age'].replace(0, np.nan, inplace=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Get oldest tree(s)\n\ngdf[gdf['age'] == gdf['age'].max()]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# This seems to show that anything with a year has a sensible age\n\nall_trees_gdf.loc[(all_trees_gdf['age'] == 0) & (all_trees_gdf['year'] >= 1) & (all_trees_gdf['year'] < 2018)]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# but there are a lot of missing ages that have years\n\nall_trees_gdf.loc[(all_trees_gdf['age'].isnull()) & (all_trees_gdf['year'] >= 1) & (all_trees_gdf['year'] < 2018)]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# What about circumference? \n\nall_trees_gdf.loc[(all_trees_gdf['circumference'] >= 500) & (all_trees_gdf['circumference'] <= 13000)]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# this should give the oldest tree by \n\nall_trees_gdf.sort_values('age').drop_duplicates(['borough'], keep='last')[[]]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# this will give you the tree with the highest cirucmference for each borough \n\n# more columns can be added to the list passed to drop_duplicates to effectively group by more columns\n\nall_trees_gdf.sort_values('circumference').drop_duplicates(['borough'], keep='last').head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c509ead6219edec7c4c8e296d738e86559c540a2
| 443,361 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Pneumonia_The Hybrid CNN Model with FC Layers.ipynb
|
mohammadaiai/Pneumonia-Paper
|
db989bc1fc9a868bc238852ca314992ff7c0a09b
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Pneumonia_The Hybrid CNN Model with FC Layers.ipynb
|
mohammadaiai/Pneumonia-Paper
|
db989bc1fc9a868bc238852ca314992ff7c0a09b
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Pneumonia_The Hybrid CNN Model with FC Layers.ipynb
|
mohammadaiai/Pneumonia-Paper
|
db989bc1fc9a868bc238852ca314992ff7c0a09b
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 623.57384 | 396,450 | 0.933109 |
[
[
[
"# Importing the Necessary Libraries\nfrom tensorflow.keras.layers import Input, Dense, Flatten, Dropout\nfrom tensorflow.keras.models import Model\nfrom tensorflow.keras.models import load_model\nfrom tensorflow.keras.applications.vgg16 import VGG16\nfrom tensorflow.keras.applications.vgg19 import VGG19\nfrom tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator\nfrom google.colab import drive\nfrom tensorflow.keras.layers import concatenate\nfrom tensorflow.keras import optimizers\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom glob import glob\nfrom sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix\nfrom sklearn.metrics import classification_report\nfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score\nimport seaborn as sns\nfrom tensorflow.keras.callbacks import ModelCheckpoint\nfrom datetime import datetime",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Connecting to Google Drive\ndrive.mount('/content/drive')",
"Mounted at /content/drive\n"
],
[
"# Defining the Training and Test Path\ntrain_path = '/content/drive/MyDrive/Dataset/train'\ntest_path = '/content/drive/MyDrive/Dataset/test'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Checking the Number of Folders/Classes (Normal and Pneumonia)\nfolders = glob('/content/drive/MyDrive/Dataset/train/*')\nprint(len(folders))",
"2\n"
],
[
"# The Settings for Generating the Training Set\ntrain_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(\n rescale=1./255,\n shear_range=0.2,\n zoom_range=0.2,\n horizontal_flip=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# The Settings for Generating the Test Set \ntest_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(\n rescale=1./255)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Generating the Training Set \ntrain_set = train_datagen.flow_from_directory(train_path,\n target_size = (224, 224),\n batch_size=32,\n class_mode = 'categorical')",
"Found 4686 images belonging to 2 classes.\n"
],
[
"# Generating the Test Set \ntest_set = test_datagen.flow_from_directory(test_path,\n target_size = (224, 224),\n shuffle=False,\n batch_size=32,\n class_mode = 'categorical')",
"Found 1170 images belonging to 2 classes.\n"
],
[
"# Defining the Input Shape\ninput_tensor=Input(shape=(224,224,3))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Importing Model 1 (VGG16)\nbase_model1 = VGG16(input_tensor=input_tensor, weights='imagenet', include_top=False)\n# Extracting the Features\nfeatures1 = base_model1.output\nfor layer in base_model1.layers: \n layer.trainable=True # All layers are trainble\nfor layer in base_model1.layers: \n layer._name = layer._name + str('_C') # Because the names of some layers are the same in \n # both networks, a letter is assigned to prevent error",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Importing the Model 2 (VGG16)\nbase_model2 = VGG19(input_tensor=input_tensor, weights='imagenet', include_top=False)\n# Extracting the Features\nfeatures2 = base_model2.output\nfor layer in base_model2.layers:\n layer.trainable=True # All layers are trainble\nfor layer in base_model2.layers: \n layer._name = layer._name + str('_D') # Because the names of some layers are the same in \n # both networks, a letter is assigned to prevent error",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Concatenating the Features\nconcatenated=concatenate([features1,features2]) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Creating FC Layers\nx = Flatten(name='flatten')(concatenated)\nx = Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='fc1')(x)\nx = Dropout(0.5)(x)\nx = Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='fc2')(x)\nx = Dropout(0.5)(x)\nx = Dense(len(folders), activation='softmax', name='predictions')(x)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Creating the Final Hybrid CNN Model\nConcatenated_model = Model(inputs=input_tensor, outputs=x)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Showing the Architecture of the Hybrid Model\nfrom tensorflow.keras.utils import plot_model\nplot_model(Concatenated_model, show_shapes=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Checking the Model Components\nConcatenated_model.summary()",
"Model: \"model_9\"\n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nLayer (type) Output Shape Param # Connected to \n==================================================================================================\ninput_11_C_D (InputLayer) [(None, 224, 224, 3) 0 \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock1_conv1_D (Conv2D) (None, 224, 224, 64) 1792 input_11_C_D[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock1_conv2_D (Conv2D) (None, 224, 224, 64) 36928 block1_conv1_D[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock1_pool_D (MaxPooling2D) (None, 112, 112, 64) 0 block1_conv2_D[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock1_conv1_C (Conv2D) (None, 224, 224, 64) 1792 input_11_C_D[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock2_conv1_D (Conv2D) (None, 112, 112, 128 73856 block1_pool_D[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock1_conv2_C (Conv2D) (None, 224, 224, 64) 36928 block1_conv1_C[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock2_conv2_D (Conv2D) (None, 112, 112, 128 147584 block2_conv1_D[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock1_pool_C (MaxPooling2D) (None, 112, 112, 64) 0 block1_conv2_C[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock2_pool_D (MaxPooling2D) (None, 56, 56, 128) 0 block2_conv2_D[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock2_conv1_C (Conv2D) (None, 112, 112, 128 73856 block1_pool_C[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock3_conv1_D (Conv2D) (None, 56, 56, 256) 295168 block2_pool_D[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock2_conv2_C (Conv2D) (None, 112, 112, 128 147584 block2_conv1_C[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock3_conv2_D (Conv2D) (None, 56, 56, 256) 590080 block3_conv1_D[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock2_pool_C (MaxPooling2D) (None, 56, 56, 128) 0 block2_conv2_C[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock3_conv3_D (Conv2D) (None, 56, 56, 256) 590080 block3_conv2_D[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock3_conv1_C (Conv2D) (None, 56, 56, 256) 295168 block2_pool_C[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock3_conv4_D (Conv2D) (None, 56, 56, 256) 590080 block3_conv3_D[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock3_conv2_C (Conv2D) (None, 56, 56, 256) 590080 block3_conv1_C[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock3_pool_D (MaxPooling2D) (None, 28, 28, 256) 0 block3_conv4_D[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock3_conv3_C (Conv2D) (None, 56, 56, 256) 590080 block3_conv2_C[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock4_conv1_D (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 512) 1180160 block3_pool_D[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock3_pool_C (MaxPooling2D) (None, 28, 28, 256) 0 block3_conv3_C[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock4_conv2_D (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 512) 2359808 block4_conv1_D[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock4_conv1_C (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 512) 1180160 block3_pool_C[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock4_conv3_D (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 512) 2359808 block4_conv2_D[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock4_conv2_C (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 512) 2359808 block4_conv1_C[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock4_conv4_D (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 512) 2359808 block4_conv3_D[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock4_conv3_C (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 512) 2359808 block4_conv2_C[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock4_pool_D (MaxPooling2D) (None, 14, 14, 512) 0 block4_conv4_D[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock4_pool_C (MaxPooling2D) (None, 14, 14, 512) 0 block4_conv3_C[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock5_conv1_D (Conv2D) (None, 14, 14, 512) 2359808 block4_pool_D[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock5_conv1_C (Conv2D) (None, 14, 14, 512) 2359808 block4_pool_C[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock5_conv2_D (Conv2D) (None, 14, 14, 512) 2359808 block5_conv1_D[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock5_conv2_C (Conv2D) (None, 14, 14, 512) 2359808 block5_conv1_C[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock5_conv3_D (Conv2D) (None, 14, 14, 512) 2359808 block5_conv2_D[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock5_conv3_C (Conv2D) (None, 14, 14, 512) 2359808 block5_conv2_C[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock5_conv4_D (Conv2D) (None, 14, 14, 512) 2359808 block5_conv3_D[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock5_pool_C (MaxPooling2D) (None, 7, 7, 512) 0 block5_conv3_C[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nblock5_pool_D (MaxPooling2D) (None, 7, 7, 512) 0 block5_conv4_D[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nconcatenate_11 (Concatenate) (None, 7, 7, 1024) 0 block5_pool_C[0][0] \n block5_pool_D[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nflatten (Flatten) (None, 50176) 0 concatenate_11[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nfc1 (Dense) (None, 4096) 205524992 flatten[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndropout_18 (Dropout) (None, 4096) 0 fc1[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nfc2 (Dense) (None, 4096) 16781312 dropout_18[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndropout_19 (Dropout) (None, 4096) 0 fc2[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\npredictions (Dense) (None, 2) 8194 dropout_19[0][0] \n==================================================================================================\nTotal params: 257,053,570\nTrainable params: 257,053,570\nNon-trainable params: 0\n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\n"
],
[
"# Setting the Weight Optimizer and Loss Function\nsgd = optimizers.SGD()\nConcatenated_model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy',\n optimizer=sgd,\n metrics=['accuracy'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Saving the Weight Parameters, When Achieving a Higher Test Accuracy\ncheckpoint = ModelCheckpoint(filepath='/content/drive/MyDrive/ChestVGG_SGD.h5', \n monitor='val_accuracy', verbose=1, save_best_only=True)\n\ncallbacks = [checkpoint]\n\nstart = datetime.now()\n\n# Training the Hybrid Model\nConcatenated_model_history=Concatenated_model.fit(\n train_set,\n validation_data=test_set,\n epochs=20,\n callbacks=callbacks ,verbose=1)\n\nduration = datetime.now() - start\nprint(\"Training time: \", duration)",
"Epoch 1/20\n147/147 [==============================] - 295s 2s/step - loss: 0.4477 - accuracy: 0.8015 - val_loss: 0.2409 - val_accuracy: 0.9188\n\nEpoch 00001: val_accuracy improved from -inf to 0.91880, saving model to /content/drive/MyDrive/ChestVGG_SGD.h5\nEpoch 2/20\n147/147 [==============================] - 290s 2s/step - loss: 0.2189 - accuracy: 0.9108 - val_loss: 0.1443 - val_accuracy: 0.9393\n\nEpoch 00002: val_accuracy improved from 0.91880 to 0.93932, saving model to /content/drive/MyDrive/ChestVGG_SGD.h5\nEpoch 3/20\n147/147 [==============================] - 290s 2s/step - loss: 0.2167 - accuracy: 0.9159 - val_loss: 0.1265 - val_accuracy: 0.9487\n\nEpoch 00003: val_accuracy improved from 0.93932 to 0.94872, saving model to /content/drive/MyDrive/ChestVGG_SGD.h5\nEpoch 4/20\n147/147 [==============================] - 290s 2s/step - loss: 0.1580 - accuracy: 0.9381 - val_loss: 0.3235 - val_accuracy: 0.8581\n\nEpoch 00004: val_accuracy did not improve from 0.94872\nEpoch 5/20\n147/147 [==============================] - 290s 2s/step - loss: 0.1358 - accuracy: 0.9516 - val_loss: 0.0917 - val_accuracy: 0.9641\n\nEpoch 00005: val_accuracy improved from 0.94872 to 0.96410, saving model to /content/drive/MyDrive/ChestVGG_SGD.h5\nEpoch 6/20\n147/147 [==============================] - 290s 2s/step - loss: 0.1201 - accuracy: 0.9565 - val_loss: 0.0939 - val_accuracy: 0.9658\n\nEpoch 00006: val_accuracy improved from 0.96410 to 0.96581, saving model to /content/drive/MyDrive/ChestVGG_SGD.h5\nEpoch 7/20\n147/147 [==============================] - 290s 2s/step - loss: 0.1120 - accuracy: 0.9575 - val_loss: 0.1204 - val_accuracy: 0.9496\n\nEpoch 00007: val_accuracy did not improve from 0.96581\nEpoch 8/20\n147/147 [==============================] - 290s 2s/step - loss: 0.1098 - accuracy: 0.9590 - val_loss: 0.1413 - val_accuracy: 0.9427\n\nEpoch 00008: val_accuracy did not improve from 0.96581\nEpoch 9/20\n147/147 [==============================] - 290s 2s/step - loss: 0.0981 - accuracy: 0.9652 - val_loss: 0.1671 - val_accuracy: 0.9376\n\nEpoch 00009: val_accuracy did not improve from 0.96581\nEpoch 10/20\n147/147 [==============================] - 290s 2s/step - loss: 0.1019 - accuracy: 0.9650 - val_loss: 0.0736 - val_accuracy: 0.9701\n\nEpoch 00010: val_accuracy improved from 0.96581 to 0.97009, saving model to /content/drive/MyDrive/ChestVGG_SGD.h5\nEpoch 11/20\n147/147 [==============================] - 291s 2s/step - loss: 0.0935 - accuracy: 0.9682 - val_loss: 0.1031 - val_accuracy: 0.9632\n\nEpoch 00011: val_accuracy did not improve from 0.97009\nEpoch 12/20\n147/147 [==============================] - 290s 2s/step - loss: 0.1011 - accuracy: 0.9627 - val_loss: 0.0883 - val_accuracy: 0.9607\n\nEpoch 00012: val_accuracy did not improve from 0.97009\nEpoch 13/20\n147/147 [==============================] - 290s 2s/step - loss: 0.0862 - accuracy: 0.9695 - val_loss: 0.0650 - val_accuracy: 0.9735\n\nEpoch 00013: val_accuracy improved from 0.97009 to 0.97350, saving model to /content/drive/MyDrive/ChestVGG_SGD.h5\nEpoch 14/20\n147/147 [==============================] - 290s 2s/step - loss: 0.0802 - accuracy: 0.9703 - val_loss: 0.0753 - val_accuracy: 0.9701\n\nEpoch 00014: val_accuracy did not improve from 0.97350\nEpoch 15/20\n147/147 [==============================] - 290s 2s/step - loss: 0.0830 - accuracy: 0.9693 - val_loss: 0.1024 - val_accuracy: 0.9607\n\nEpoch 00015: val_accuracy did not improve from 0.97350\nEpoch 16/20\n147/147 [==============================] - 290s 2s/step - loss: 0.0772 - accuracy: 0.9716 - val_loss: 0.0579 - val_accuracy: 0.9795\n\nEpoch 00016: val_accuracy improved from 0.97350 to 0.97949, saving model to /content/drive/MyDrive/ChestVGG_SGD.h5\nEpoch 17/20\n147/147 [==============================] - 290s 2s/step - loss: 0.0740 - accuracy: 0.9750 - val_loss: 0.1201 - val_accuracy: 0.9504\n\nEpoch 00017: val_accuracy did not improve from 0.97949\nEpoch 18/20\n147/147 [==============================] - 290s 2s/step - loss: 0.0647 - accuracy: 0.9776 - val_loss: 0.1405 - val_accuracy: 0.9538\n\nEpoch 00018: val_accuracy did not improve from 0.97949\nEpoch 19/20\n147/147 [==============================] - 290s 2s/step - loss: 0.0714 - accuracy: 0.9723 - val_loss: 0.0844 - val_accuracy: 0.9675\n\nEpoch 00019: val_accuracy did not improve from 0.97949\nEpoch 20/20\n147/147 [==============================] - 290s 2s/step - loss: 0.0647 - accuracy: 0.9778 - val_loss: 0.0786 - val_accuracy: 0.9718\n\nEpoch 00020: val_accuracy did not improve from 0.97949\nTraining time: 1:38:18.073678\n"
],
[
"# Loading the Saved Model\nnetwork = load_model('/content/drive/MyDrive/ChestVGG_SGD.h5')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Creating Evaluation Set and Evaluating the Model\ntest_set_evaluation = test_datagen.flow_from_directory(test_path,\n target_size = (224, 224),\n batch_size=1,\n shuffle=False,\n class_mode = 'categorical')\nnetwork.evaluate(test_set_evaluation, steps=1170)",
"Found 1170 images belonging to 2 classes.\n1170/1170 [==============================] - 282s 233ms/step - loss: 0.0579 - accuracy: 0.9795\n"
],
[
"# Making Predictions\npredictions=network.predict(test_set_evaluation, steps=1170, verbose=1)\npreds=np.argmax(predictions, axis=1)",
"1170/1170 [==============================] - 128s 109ms/step\n"
],
[
"# Creating the Confusion Matrix\ncf_matrix=confusion_matrix(test_set_evaluation.classes, preds)\nax=plt.subplot()\nsns.heatmap(cf_matrix, cmap='Blues', annot=True, linewidths=1, fmt = 'd', ax=ax)\nax.set_xlabel('Predicted Class');ax.set_ylabel('True Class')\nax.set_title('Confusion Matrix')\nax.xaxis.set_ticklabels(['Normal', 'Pneumonia']); ax.yaxis.set_ticklabels(['Normal', 'Pneumonia'])\naccuracy_score(test_set_evaluation.classes, preds)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c509fea57f4c6d2a7d1aa4ca4c8a20b222c0e6c5
| 382,313 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
assignment3/feature-engineering-with-open-source-practice.ipynb
|
Nakulbajaj101/deploying-machine-learning-models
|
8d13fc8d1409384b469461ab2eb4fadbb06ff43e
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
assignment3/feature-engineering-with-open-source-practice.ipynb
|
Nakulbajaj101/deploying-machine-learning-models
|
8d13fc8d1409384b469461ab2eb4fadbb06ff43e
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
assignment3/feature-engineering-with-open-source-practice.ipynb
|
Nakulbajaj101/deploying-machine-learning-models
|
8d13fc8d1409384b469461ab2eb4fadbb06ff43e
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null | 111.040662 | 10,236 | 0.812133 |
[
[
[
"# Feature Engineering with Open-Source\n\nIn this notebook, we will reproduce the Feature Engineering Pipeline from the notebook 2 (02-Machine-Learning-Pipeline-Feature-Engineering), but we will replace, whenever possible, the manually created functions by open-source classes, and hopefully understand the value they bring forward.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Reproducibility: Setting the seed\n\nWith the aim to ensure reproducibility between runs of the same notebook, but also between the research and production environment, for each step that includes some element of randomness, it is extremely important that we **set the seed**.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# data manipulation and plotting\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\n# for saving the pipeline\nimport joblib\n\n# from Scikit-learn\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler, Binarizer\n\n# from feature-engine\nfrom feature_engine.imputation import (\n AddMissingIndicator,\n MeanMedianImputer,\n CategoricalImputer,\n)\n\nfrom feature_engine.encoding import (\n RareLabelEncoder,\n OrdinalEncoder,\n)\n\nfrom feature_engine.transformation import (\n LogTransformer,\n YeoJohnsonTransformer,\n)\n\nimport preprocessors as pp\n\nfrom feature_engine.selection import DropFeatures\nfrom feature_engine.wrappers import SklearnTransformerWrapper\n\n# to visualise al the columns in the dataframe\npd.pandas.set_option('display.max_columns', None)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = pd.DataFrame([('bird', 2, 2),\n ('mammal', 4, np.nan),\n ('arthropod', 8, 0),\n ('bird', 2, np.nan)],\n index=('falcon', 'horse', 'spider', 'ostrich'),\n columns=('species', 'legs', 'wings'))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df['species','legs','wings'].mode()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# load dataset\ndata = pd.read_csv('../section-04-research-and-development/train.csv')\n\n# rows and columns of the data\nprint(data.shape)\n\n# visualise the dataset\ndata.head()",
"(1460, 81)\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Separate dataset into train and test\n\nIt is important to separate our data intro training and testing set. \n\nWhen we engineer features, some techniques learn parameters from data. It is important to learn these parameters only from the train set. This is to avoid over-fitting.\n\nOur feature engineering techniques will learn:\n\n- mean\n- mode\n- exponents for the yeo-johnson\n- category frequency\n- and category to number mappings\n\nfrom the train set.\n\n**Separating the data into train and test involves randomness, therefore, we need to set the seed.**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Let's separate into train and test set\n# Remember to set the seed (random_state for this sklearn function)\n\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(\n data.drop(['Id', 'SalePrice'], axis=1), # predictive variables\n data['SalePrice'], # target\n test_size=0.1, # portion of dataset to allocate to test set\n random_state=0, # we are setting the seed here\n)\n\nX_train.shape, X_test.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Feature Engineering\n\nIn the following cells, we will engineer the variables of the House Price Dataset so that we tackle:\n\n1. Missing values\n2. Temporal variables\n3. Non-Gaussian distributed variables\n4. Categorical variables: remove rare labels\n5. Categorical variables: convert strings to numbers\n5. Standardize the values of the variables to the same range",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Target\n\nWe apply the logarithm",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"y_train = np.log(y_train)\ny_test = np.log(y_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Missing values\n\n### Categorical variables\n\nWe will replace missing values with the string \"missing\" in those variables with a lot of missing data. \n\nAlternatively, we will replace missing data with the most frequent category in those variables that contain fewer observations without values. \n\nThis is common practice.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# let's identify the categorical variables\n# we will capture those of type object\n\ncat_vars = [var for var in data.columns if data[var].dtype == 'O']\n\n# MSSubClass is also categorical by definition, despite its numeric values\n# (you can find the definitions of the variables in the data_description.txt\n# file available on Kaggle, in the same website where you downloaded the data)\n\n# lets add MSSubClass to the list of categorical variables\ncat_vars = cat_vars + ['MSSubClass']\n\n# cast all variables as categorical\nX_train[cat_vars] = X_train[cat_vars].astype('O')\nX_test[cat_vars] = X_test[cat_vars].astype('O')\n\n# number of categorical variables\nlen(cat_vars)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# make a list of the categorical variables that contain missing values\n\ncat_vars_with_na = [\n var for var in cat_vars\n if X_train[var].isnull().sum() > 0\n]\n\n# print percentage of missing values per variable\nX_train[cat_vars_with_na ].isnull().mean().sort_values(ascending=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# variables to impute with the string missing\nwith_string_missing = [\n var for var in cat_vars_with_na if X_train[var].isnull().mean() > 0.1]\n\n# variables to impute with the most frequent category\nwith_frequent_category = [\n var for var in cat_vars_with_na if X_train[var].isnull().mean() < 0.1]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# I print the values here, because it makes it easier for\n# later when we need to add this values to a config file for \n# deployment\n\nwith_string_missing",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"with_frequent_category",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# replace missing values with new label: \"Missing\"\n\n# set up the class\ncat_imputer_missing = CategoricalImputer(\n imputation_method='missing', variables=with_string_missing)\n\n# fit the class to the train set\ncat_imputer_missing.fit(X_train)\n\n# the class learns and stores the parameters\ncat_imputer_missing.imputer_dict_",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# replace NA by missing\n\n# IMPORTANT: note that we could store this class with joblib\nX_train = cat_imputer_missing.transform(X_train)\nX_test = cat_imputer_missing.transform(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# replace missing values with most frequent category\n\n# set up the class\ncat_imputer_frequent = CategoricalImputer(\n imputation_method='frequent', variables=with_frequent_category)\n\n# fit the class to the train set\ncat_imputer_frequent.fit(X_train)\n\n# the class learns and stores the parameters\ncat_imputer_frequent.imputer_dict_",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# replace NA by missing\n\n# IMPORTANT: note that we could store this class with joblib\nX_train = cat_imputer_frequent.transform(X_train)\nX_test = cat_imputer_frequent.transform(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# check that we have no missing information in the engineered variables\n\nX_train[cat_vars_with_na].isnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# check that test set does not contain null values in the engineered variables\n\n[var for var in cat_vars_with_na if X_test[var].isnull().sum() > 0]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Numerical variables\n\nTo engineer missing values in numerical variables, we will:\n\n- add a binary missing indicator variable\n- and then replace the missing values in the original variable with the mean",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# now let's identify the numerical variables\n\nnum_vars = [\n var for var in X_train.columns if var not in cat_vars and var != 'SalePrice'\n]\n\n# number of numerical variables\nlen(num_vars)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# make a list with the numerical variables that contain missing values\nvars_with_na = [\n var for var in num_vars\n if X_train[var].isnull().sum() > 0\n]\n\n# print percentage of missing values per variable\nX_train[vars_with_na].isnull().mean()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# print, makes my life easier when I want to create the config\nvars_with_na",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# add missing indicator\n\nmissing_ind = AddMissingIndicator(variables=vars_with_na)\n\nmissing_ind.fit(X_train)\n\nX_train = missing_ind.transform(X_train)\nX_test = missing_ind.transform(X_test)\n\n# check the binary missing indicator variables\nX_train[['LotFrontage_na', 'MasVnrArea_na', 'GarageYrBlt_na']].head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# then replace missing data with the mean\n\n# set the imputer\nmean_imputer = MeanMedianImputer(\n imputation_method='mean', variables=vars_with_na)\n\n# learn and store parameters from train set\nmean_imputer.fit(X_train)\n\n# the stored parameters\nmean_imputer.imputer_dict_",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_train = mean_imputer.transform(X_train)\nX_test = mean_imputer.transform(X_test)\n\n# IMPORTANT: note that we could save the imputers with joblib\n\n# check that we have no more missing values in the engineered variables\nX_train[vars_with_na].isnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# check that test set does not contain null values in the engineered variables\n\n[var for var in vars_with_na if X_test[var].isnull().sum() > 0]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Temporal variables\n\n### Capture elapsed time\n\nThere is in Feature-engine 2 classes that allow us to perform the 2 transformations below:\n\n- [CombineWithFeatureReference](https://feature-engine.readthedocs.io/en/latest/creation/CombineWithReferenceFeature.html) to capture elapsed time\n- [DropFeatures](https://feature-engine.readthedocs.io/en/latest/selection/DropFeatures.html) to drop the unwanted features\n\nWe will do the first one manually, so we take the opportunity to create 1 class ourselves for the course. For the second operation, we will use the DropFeatures class.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def elapsed_years(df, var):\n # capture difference between the year variable\n # and the year in which the house was sold\n df[var] = df['YrSold'] - df[var]\n return df",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"vars_with_temp = ['YearBuilt', 'YearRemodAdd', 'GarageYrBlt']\nsubtract_transformer = pp.SubtractTransformer(target_variable='YrSold', variables=vars_with_temp)\nsubtract_transformer.fit(X_train)\n\nX_train = subtract_transformer.transform(X_train)\nX_test = subtract_transformer.transform(X_test)\n\nX_train[vars_with_temp].head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# now we drop YrSold\ndrop_features = DropFeatures(features_to_drop=['YrSold'])\n\nX_train = drop_features.fit_transform(X_train)\nX_test = drop_features.transform(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Numerical variable transformation\n\n### Logarithmic transformation\n\nIn the previous notebook, we observed that the numerical variables are not normally distributed.\n\nWe will transform with the logarightm the positive numerical variables in order to get a more Gaussian-like distribution.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"log_transformer = LogTransformer(\n variables=[\"LotFrontage\", \"1stFlrSF\", \"GrLivArea\"])\n\nX_train = log_transformer.fit_transform(X_train)\nX_test = log_transformer.transform(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# check that test set does not contain null values in the engineered variables\n[var for var in [\"LotFrontage\", \"1stFlrSF\", \"GrLivArea\"] if X_test[var].isnull().sum() > 0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# same for train set\n[var for var in [\"LotFrontage\", \"1stFlrSF\", \"GrLivArea\"] if X_train[var].isnull().sum() > 0]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Yeo-Johnson transformation\n\nWe will apply the Yeo-Johnson transformation to LotArea.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"yeo_transformer = YeoJohnsonTransformer(\n variables=['LotArea'])\n\nX_train = yeo_transformer.fit_transform(X_train)\nX_test = yeo_transformer.transform(X_test)\n\n# the learned parameter\nyeo_transformer.lambda_dict_",
"/Users/bajajn/learn-deployml/deploying-machine-learning-models/deployml/lib/python3.8/site-packages/scipy/stats/morestats.py:1476: RuntimeWarning: divide by zero encountered in log\n loglike = -n_samples / 2 * np.log(trans.var(axis=0))\n/Users/bajajn/learn-deployml/deploying-machine-learning-models/deployml/lib/python3.8/site-packages/scipy/optimize/optimize.py:2555: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in double_scalars\n w = xb - ((xb - xc) * tmp2 - (xb - xa) * tmp1) / denom\n/Users/bajajn/learn-deployml/deploying-machine-learning-models/deployml/lib/python3.8/site-packages/scipy/optimize/optimize.py:2148: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in double_scalars\n tmp1 = (x - w) * (fx - fv)\n/Users/bajajn/learn-deployml/deploying-machine-learning-models/deployml/lib/python3.8/site-packages/scipy/optimize/optimize.py:2149: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in double_scalars\n tmp2 = (x - v) * (fx - fw)\n"
],
[
"# check absence of na in the train set\n[var for var in X_train.columns if X_train[var].isnull().sum() > 0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# check absence of na in the test set\n[var for var in X_train.columns if X_test[var].isnull().sum() > 0]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Binarize skewed variables\n\nThere were a few variables very skewed, we would transform those into binary variables.\n\nWe can perform the below transformation with open source. We can use the [Binarizer](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.preprocessing.Binarizer.html) from Scikit-learn, in combination with the [SklearnWrapper](https://feature-engine.readthedocs.io/en/latest/wrappers/Wrapper.html) from Feature-engine to be able to apply the transformation only to a subset of features.\n\nInstead, we are going to do it manually, to give us another opportunity to code the class as an in-house package later in the course.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"skewed = [\n 'BsmtFinSF2', 'LowQualFinSF', 'EnclosedPorch',\n '3SsnPorch', 'ScreenPorch', 'MiscVal'\n]\n\nbinarizer = SklearnTransformerWrapper(\n transformer=Binarizer(threshold=0), variables=skewed\n)\n\n\nX_train = binarizer.fit_transform(X_train)\nX_test = binarizer.transform(X_test)\n\nX_train[skewed].head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Categorical variables\n\n### Apply mappings\n\nThese are variables which values have an assigned order, related to quality. For more information, check Kaggle website.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# re-map strings to numbers, which determine quality\n\nqual_mappings = {'Po': 1, 'Fa': 2, 'TA': 3, 'Gd': 4, 'Ex': 5, 'Missing': 0, 'NA': 0}\n\nqual_vars = ['ExterQual', 'ExterCond', 'BsmtQual', 'BsmtCond',\n 'HeatingQC', 'KitchenQual', 'FireplaceQu',\n 'GarageQual', 'GarageCond',\n ]\nqual_mapper = pp.Mapper(qual_vars, qual_mappings)\nqual_mapper.fit(X_train)\n\nX_train=qual_mapper.transform(X_train)\nX_test=qual_mapper.transform(X_test)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"exposure_mappings = {'No': 1, 'Mn': 2, 'Av': 3, 'Gd': 4}\n\nvar = ['BsmtExposure']\n\nexposure_mapper = pp.Mapper(var,exposure_mappings)\nexposure_mapper.fit(X_train)\n\nX_train=exposure_mapper.transform(X_train)\nX_test=exposure_mapper.transform(X_test)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"finish_mappings = {'Missing': 0, 'NA': 0, 'Unf': 1, 'LwQ': 2, 'Rec': 3, 'BLQ': 4, 'ALQ': 5, 'GLQ': 6}\n\nfinish_vars = ['BsmtFinType1', 'BsmtFinType2']\n\nfinish_mapper = pp.Mapper(finish_vars, finish_mappings)\nqual_mapper.fit(X_train)\n\nX_train=finish_mapper.transform(X_train)\nX_test=finish_mapper.transform(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"garage_mappings = {'Missing': 0, 'NA': 0, 'Unf': 1, 'RFn': 2, 'Fin': 3}\n\nvar = ['GarageFinish']\n\ngarage_mapper = pp.Mapper(var, garage_mappings)\ngarage_mapper.fit(X_train)\n\nX_train=garage_mapper.transform(X_train)\nX_test=garage_mapper.transform(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fence_mappings = {'Missing': 0, 'NA': 0, 'MnWw': 1, 'GdWo': 2, 'MnPrv': 3, 'GdPrv': 4}\n\nvar = ['Fence']\n\nfence_mapper = pp.Mapper(var, fence_mappings)\nfence_mapper.fit(X_train)\n\nX_train=fence_mapper.transform(X_train)\nX_test=fence_mapper.transform(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# check absence of na in the train set\n[var for var in X_train.columns if X_train[var].isnull().sum() > 0]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Removing Rare Labels\n\nFor the remaining categorical variables, we will group those categories that are present in less than 1% of the observations. That is, all values of categorical variables that are shared by less than 1% of houses, well be replaced by the string \"Rare\".\n\nTo learn more about how to handle categorical variables visit our course [Feature Engineering for Machine Learning](https://www.udemy.com/course/feature-engineering-for-machine-learning/?referralCode=A855148E05283015CF06) in Udemy.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# capture all quality variables\n\nqual_vars = qual_vars + finish_vars + ['BsmtExposure','GarageFinish','Fence']\n\n# capture the remaining categorical variables\n# (those that we did not re-map)\n\ncat_others = [\n var for var in cat_vars if var not in qual_vars\n]\n\nlen(cat_others)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cat_others",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"rare_encoder = pp.RareLabelCategoricalEncoder(tol=0.05,variables=cat_others)\n\n# find common labels\nrare_encoder.fit(X_train)\n\n# the common labels are stored, we can save the class\n# and then use it later :)\nrare_encoder.encoder_dict_",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_train = rare_encoder.transform(X_train)\nX_test = rare_encoder.transform(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Encoding of categorical variables\n\nNext, we need to transform the strings of the categorical variables into numbers. \n\nWe will do it so that we capture the monotonic relationship between the label and the target.\n\nTo learn more about how to encode categorical variables visit our course [Feature Engineering for Machine Learning](https://www.udemy.com/course/feature-engineering-for-machine-learning/?referralCode=A855148E05283015CF06) in Udemy.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# set up the encoder\ncat_encoder = OrdinalEncoder(encoding_method='ordered', variables=cat_others)\n\n# create the mappings\ncat_encoder.fit(X_train, y_train)\n\n# mappings are stored and class can be saved\ncat_encoder.encoder_dict_",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_train = cat_encoder.transform(X_train)\nX_test = cat_encoder.transform(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# check absence of na in the train set\n[var for var in X_train.columns if X_train[var].isnull().sum() > 0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# check absence of na in the test set\n[var for var in X_test.columns if X_test[var].isnull().sum() > 0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# let me show you what I mean by monotonic relationship\n# between labels and target\n\ndef analyse_vars(train, y_train, var):\n \n # function plots median house sale price per encoded\n # category\n \n tmp = pd.concat([X_train, np.log(y_train)], axis=1)\n \n tmp.groupby(var)['SalePrice'].median().plot.bar()\n plt.title(var)\n plt.ylim(2.2, 2.6)\n plt.ylabel('SalePrice')\n plt.show()\n \nfor var in cat_others:\n analyse_vars(X_train, y_train, var)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The monotonic relationship is particularly clear for the variables MSZoning and Neighborhood. Note how, the higher the integer that now represents the category, the higher the mean house sale price.\n\n(remember that the target is log-transformed, that is why the differences seem so small).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Feature Scaling\n\nFor use in linear models, features need to be either scaled. We will scale features to the minimum and maximum values:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# create scaler\nscaler = MinMaxScaler()\n\n# fit the scaler to the train set\nscaler.fit(X_train) \n\n# transform the train and test set\n\n# sklearn returns numpy arrays, so we wrap the\n# array with a pandas dataframe\n\nX_train = pd.DataFrame(\n scaler.transform(X_train),\n columns=X_train.columns\n)\n\nX_test = pd.DataFrame(\n scaler.transform(X_test),\n columns=X_train.columns\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_train.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Conclusion\n\nWe now have several classes with parameters learned from the training dataset, that we can store and retrieve at a later stage, so that when a colleague comes with new data, we are in a better position to score it faster.\n\nStill:\n\n- we would need to save each class\n- then we could load each class\n- and apply each transformation individually.\n\nWhich sounds like a lot of work.\n\nThe good news is, we can reduce the amount of work, if we set up all the transformations within a pipeline.\n\n**IMPORTANT**\n\nIn order to set up the entire feature transformation within a pipeline, we still need to create a class that can be used within a pipeline to map the categorical variables with the arbitrary mappings, and also, to capture elapsed time between the temporal variables.\n\nWe will take that opportunity to create an in-house package.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
c509febf9270daf18c8b7cdc7aee887741e825c1
| 40,044 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Framework.ipynb
|
axa-rev-research/local-adverse-detection
|
2a4c933a8e785bf1a56ef6f0c75891ce3f607574
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Framework.ipynb
|
axa-rev-research/local-adverse-detection
|
2a4c933a8e785bf1a56ef6f0c75891ce3f607574
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Framework.ipynb
|
axa-rev-research/local-adverse-detection
|
2a4c933a8e785bf1a56ef6f0c75891ce3f607574
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 43.43167 | 2,261 | 0.594296 |
[
[
[
"import copy\nimport pandas\nimport numpy\nfrom sklearn.datasets import make_moons\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier\nfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, roc_auc_score\nfrom sklearn.metrics import euclidean_distances\n\n\"\"\"\nThis tutorial shows how to generate adversarial examples\nusing FGSM in black-box setting.\nThe original paper can be found at:\nhttps://arxiv.org/abs/1602.02697\n\"\"\"\nfrom __future__ import absolute_import\nfrom __future__ import division\nfrom __future__ import print_function\nfrom __future__ import unicode_literals\n\nfrom six.moves import xrange\n\nimport logging\nimport tensorflow as tf\nfrom tensorflow.python.platform import flags\n\nfrom cleverhans.utils_mnist import data_mnist\nfrom cleverhans.utils import to_categorical\nfrom cleverhans.utils import set_log_level\nfrom cleverhans.utils_tf import model_train, model_eval, batch_eval\nfrom cleverhans.attacks import FastGradientMethod\nfrom cleverhans.attacks_tf import jacobian_graph, jacobian_augmentation\n\nfrom cleverhans_tutorials.tutorial_models import make_basic_cnn, MLP\nfrom cleverhans_tutorials.tutorial_models import Flatten, Linear, ReLU, Softmax\nfrom cleverhans.utils import TemporaryLogLevel\n\nfrom lad import lad_Thibault as lad\nfrom scipy.spatial.distance import euclidean\n\nFLAGS = flags.FLAGS",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Functions",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"'''\nMOONS\n'''\ndef get_moon():\n X, y = make_moons(noise=0.3, random_state=1, n_samples=10000)\n y2 = numpy.zeros((X.shape[0],2))\n for k in range(len(y)):\n y2[k][y[k]] = 1\n return X, y2\n\ndef get_german():\n path_dataset='data/germancredit.csv'\n X = pandas.read_csv(path_dataset, delimiter=\",\", index_col=0)\n y = X.label\n y = y - 1\n X = X.iloc[:,X.columns != 'label']\n X = (X-X.mean())/X.std()\n y2 = numpy.zeros((X.shape[0],2)) #2= nb de classes\n for k in range(len(y)):\n y2[k][y[k]] = 1\n return numpy.array(X), numpy.array(y2)\n\nDATASETS_ = {'moons':get_moon,\n 'german': get_german}\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Training a black-box",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"'''\nPAPERNOT BB\n'''\ndef Papernot_bbox(sess, x, y, X_train, Y_train, X_test, Y_test,\n nb_epochs, batch_size, learning_rate,\n rng):\n \"\"\"\n Define and train a model that simulates the \"remote\"\n black-box oracle described in the original paper.\n :param sess: the TF session\n :param x: the input placeholder for MNIST\n :param y: the ouput placeholder for MNIST\n :param X_train: the training data for the oracle\n :param Y_train: the training labels for the oracle\n :param X_test: the testing data for the oracle\n :param Y_test: the testing labels for the oracle\n :param nb_epochs: number of epochs to train model\n :param batch_size: size of training batches\n :param learning_rate: learning rate for training\n :param rng: numpy.random.RandomState\n :return:\n \"\"\"\n\n # Define TF model graph (for the black-box model)\n model = make_basic_cnn()\n predictions = model(x)\n print(\"Defined TensorFlow model graph.\")\n\n # Train an MNIST model\n train_params = {\n 'nb_epochs': nb_epochs,\n 'batch_size': batch_size,\n 'learning_rate': learning_rate\n }\n model_train(sess, x, y, predictions, X_train, Y_train,\n args=train_params, rng=rng)\n\n # Print out the accuracy on legitimate data\n eval_params = {'batch_size': batch_size}\n accuracy = model_eval(sess, x, y, predictions, X_test, Y_test,\n args=eval_params)\n print('Test accuracy of black-box on legitimate test '\n 'examples: ' + str(accuracy))\n\n return model, predictions, accuracy\n\ndef RF_bbox(X_train, Y_train, X_test, Y_test):\n # Define RF model graph (for the black-box model)\n\n model = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100, n_jobs=-1).fit(X_train, Y_train)\n \n # Print out the accuracy on legitimate data\n #predictions = model.predict_proba(X_test)[1] TEST CHANGER PREDICTIONS > FONCTION\n predictions=lambda x: model.predict_proba(x)[1] #predict_proba required ou alors changer du code (argmax et compagnie) de papernot\n \n accuracy = accuracy_score(Y_test, model.predict(X_test))\n #roc_auc = roc_auc_score(Y_test, predictions[1][:,1])\n print('Test accuracy of black-box on legitimate test '\n 'examples: ' + str(accuracy))\n #print('Test ROC AUC of black-box on legitimate test ' 'examples: ' + str(roc_auc))\n \n \n return model, predictions, accuracy\n \nBB_MODELS_ = {'dnn': Papernot_bbox,\n 'rf': RF_bbox}\n#ne pas utiliser dnn ca marche pas pour le moment",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Papernot Surrogate",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def setup_tutorial():\n \"\"\"\n Helper function to check correct configuration of tf for tutorial\n :return: True if setup checks completed\n \"\"\"\n\n # Set TF random seed to improve reproducibility\n tf.set_random_seed(1234)\n\n return True\ndef substitute_model(img_rows=1, img_cols=2, nb_classes=2):\n \"\"\"\n Defines the model architecture to be used by the substitute. Use\n the example model interface.\n :param img_rows: number of rows in input\n :param img_cols: number of columns in input\n :param nb_classes: number of classes in output\n :return: tensorflow model\n \"\"\"\n input_shape = (None, img_rows, img_cols, 1) #on garde format d'origine parce qu'on comprend pas grand chose mais on change valeurs\n\n # Define a fully connected model (it's different than the black-box)\n '''layers2 = [Flatten(),\n Linear(200),\n ReLU(),\n Linear(200),\n ReLU(),\n Linear(nb_classes),\n Softmax()]'''\n layers1 = [Flatten(), Linear(nb_classes), Softmax()] #surrogate simplifié\n\n return MLP(layers1, input_shape)\n\n\ndef train_sub(sess, x, y, bb_model, X_sub, Y_sub, nb_classes,\n nb_epochs_s, batch_size, learning_rate, data_aug, lmbda,\n rng):\n \"\"\"\n This function creates the substitute by alternatively\n augmenting the training data and training the substitute.\n :param sess: TF session\n :param x: input TF placeholder\n :param y: output TF placeholder\n :param bbox_preds: output of black-box model predictions\n :param X_sub: initial substitute training data\n :param Y_sub: initial substitute training labels\n :param nb_classes: number of output classes\n :param nb_epochs_s: number of epochs to train substitute model\n :param batch_size: size of training batches\n :param learning_rate: learning rate for training\n :param data_aug: number of times substitute training data is augmented\n :param lmbda: lambda from arxiv.org/abs/1602.02697\n :param rng: numpy.random.RandomState instance\n :return:\n \"\"\"\n # Define TF model graph (for the black-box model)\n model_sub = substitute_model(img_cols=X_sub.shape[1])\n preds_sub = model_sub(x)\n print(\"Defined TensorFlow model graph for the substitute.\")\n\n # Define the Jacobian symbolically using TensorFlow\n grads = jacobian_graph(preds_sub, x, nb_classes)\n # Train the substitute and augment dataset alternatively\n for rho in xrange(data_aug):\n print(\"Substitute training epoch #\" + str(rho))\n train_params = {\n 'nb_epochs': nb_epochs_s,\n 'batch_size': batch_size,\n 'learning_rate': learning_rate\n }\n with TemporaryLogLevel(logging.WARNING, \"cleverhans.utils.tf\"):\n model_train(sess, x, y, preds_sub, X_sub,\n to_categorical(Y_sub, nb_classes),\n init_all=False, args=train_params, rng=rng)\n\n # If we are not at last substitute training iteration, augment dataset\n if rho < data_aug - 1:\n print(\"Augmenting substitute training data.\")\n # Perform the Jacobian augmentation\n lmbda_coef = 2 * int(int(rho / 3) != 0) - 1\n X_sub = jacobian_augmentation(sess, x, X_sub, Y_sub, grads,\n lmbda_coef * lmbda)\n \n print(\"Labeling substitute training data.\")\n # Label the newly generated synthetic points using the black-box\n Y_sub = numpy.hstack([Y_sub, Y_sub])\n X_sub_prev = X_sub[int(len(X_sub)/2):] #on a double le dataset donc prev = ce qu'il y a de nouveau = la moitie\n eval_params = {'batch_size': batch_size}\n \n #bbox_preds = tf.convert_to_tensor(bbox_preds, dtype=tf.float32) TEST CHANGER PREDICTIONS > FONCTION \n #bbox_val = batch_eval2(sess, [x], [bbox_preds], [X_sub_prev], args=eval_params)[0] TEST CHANGER PREDICTIONS > FONCTION\n \n #bbox_val = bbox_preds(X_sub_prev) #normalement batch eval sert juste à sortir les preds...?\n bbox_val = bb_model.predict(X_sub_prev)\n # Note here that we take the argmax because the adversary\n # only has access to the label (not the probabilities) output\n # by the black-box model\n Y_sub[int(len(X_sub)/2):] = numpy.argmax(bbox_val, axis=1)\n return model_sub, preds_sub ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Usage: \nprint(\"Training the substitute model.\")\n train_sub_out = train_sub(sess, x, y, bbox_preds, X_sub, Y_sub,\n nb_classes, nb_epochs_s, batch_size,\n learning_rate, data_aug, lmbda, rng=rng)\n model_sub, preds_sub = train_sub_out",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Our surrogate",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Local Fidelity",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def get_random_points_hypersphere(x_center, radius_, n_points_):\n\n res = []\n while len(res) < n_points_:\n \n n_points_left_ = n_points_ - len(res)\n # About half the points are lost in the test hypercube => hypersphere\n lbound = numpy.repeat([x_center.values-(radius_/2.)], n_points_left_*2, axis=0)\n hbound = numpy.repeat([x_center.values+(radius_/2.)], n_points_left_*2, axis=0)\n points = numpy.random.uniform(low=lbound, high=hbound)\n # Check if x_generated is within hypersphere (if kind=='hypersphere')\n for x_generated in points:\n if euclidean(x_generated, x_center.values) < radius_:\n res.append(x_generated)\n if len(res) == n_points_:\n break\n\n return pandas.DataFrame(numpy.array(res))\n \ndef generate_inside_ball(center, segment=(0,1), n=1): #verifier algo comprendre racine 1/d et rapport entre segment et radius\n d = center.shape[0]\n z = numpy.random.normal(0, 1, (n, d))\n z = numpy.array([a * b / c for a, b, c in zip(z, numpy.random.uniform(*segment, n), norm(z))])\n z = z + center\n return z \ndef norm(v):\n return numpy.linalg.norm(v, ord=2, axis=1) #array of l2 norms of vectors in v",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Framework",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\ndef main_fidelity(radius):\n accuracies = {}\n fidelities = {}\n \n \n # Seed random number generator so tutorial is reproducible\n rng = numpy.random.RandomState([2017, 8, 30])\n\n # Thibault: Tensorflow stuff\n set_log_level(logging.DEBUG)\n assert setup_tutorial()\n sess = tf.Session()\n \n \n \n # Data\n X, Y = DATASETS_['german']()\n X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.20)\n X_sub = X_test[:holdout]\n Y_sub = numpy.argmax(Y_test[:holdout], axis=1)\n\n ## Redefine test set as remaining samples unavailable to adversaries\n ### N.B Thibault: c'est pour le substitute de Papernot\n X_test = X_test[holdout:]\n Y_test = Y_test[holdout:]\n print(\"Training black box on\",X_train.shape[0], \"examples\")\n print('Testing black box and substitute on', X_test.shape[0],' examples')\n print(\"Using \", holdout, \" examples to start PP substitute\")\n ## Define input and output TF placeholders\n ### N.B. Thibault: restes de Tensorflow, utilisé pour le substitute de Papernot...\n x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(None, 20))\n y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(None, 2)) \n \n \n \n # Instance to explain\n x_toexplain = pandas.Series(X_test[0]).copy()\n support_x_ = numpy.array(get_random_points_hypersphere(x_toexplain, radius_=radius, n_points_=1000))\n \n \n \n # Simulate the black-box model\n print(\"Preparing the black-box model.\")\n prep_bbox_out = BB_MODELS_['rf'](X_train, Y_train, X_test, Y_test)\n bb_model, bbox_preds, accuracies['bbox'] = prep_bbox_out #bbox_preds fonction predict\n \n # Train PAPERNOT substitute\n print(\"Training the Pépèrenot substitute model.\")\n train_sub_pap = train_sub(sess, x, y, bb_model, X_sub, Y_sub,\n nb_classes, nb_epochs_s, batch_size,\n learning_rate, data_aug, lmbda, rng=rng)\n model_sub, preds_sub = train_sub_pap\n \n #feed_dict = {x:support_x_, y:bbox_preds(support_x_)}\n \n eval_params = {'batch_size': batch_size}\n pap_acc = model_eval(sess, x, y, preds_sub, X_test, Y_test, args=eval_params) \n pap_fid = model_eval(sess, x, y, preds_sub, support_x_, bb_model.predict(support_x_) , args=eval_params)\n accuracies['papernot'] = pap_acc\n fidelities['papernot'] = pap_fid\n \n \n # Train OUR subtitute\n print(\"Training Local Surrogate substitute model.\")\n pred = bb_model.predict\n bb_model.predict = lambda x: pred(x)[:,1]\n _, train_sub_ls = lad.LocalSurrogate(pandas.DataFrame(X), blackbox=bb_model, n_support_points=100, max_depth=3).get_local_surrogate(x_toexplain)\n #ls_acc = accuracy_score(train_sub_ls.predict(X_test), Y_test)\n ls_fid = accuracy_score(train_sub_ls.predict(support_x_), bb_model.predict(support_x_))\n #accuracies['localsurrogate'] = ls_acc\n fidelities['localsurrogate'] = ls_fid\n '''\n\n \n '''# Initialize the Fast Gradient Sign Method (FGSM) attack object.\n fgsm_par = {'eps': 0.5, 'ord': numpy.inf, 'clip_min': 0., 'clip_max': 1.} #ord: norme L1, l2 ou linfini\n fgsm = FastGradientMethod(model_sub, sess=sess)\n\n # Craft adversarial examples using the substitute\n eval_params = {'batch_size': batch_size}\n x_adv_sub = fgsm.generate(x, **fgsm_par)\n\n # Evaluate the accuracy of the \"black-box\" model on adversarial examples\n accuracy = accuracy_score(Y_test, bb_model.predict(sess.run(x_adv_sub, feed_dict={x: X_test})))\n #model_eval(sess, x, y, bb_model.predict(x_adv_sub), X_test, Y_test,\n # args=eval_params)\n print('Test accuracy of oracle on adversarial examples generated '\n 'using the substitute: ' + str(accuracy))\n accuracies['bbox_on_sub_adv_ex'] = accuracy\n \n return fidelities, accuracies\n\n\n\nnb_classes=2 #\nbatch_size=20 #\nlearning_rate=0.001 #\nnb_epochs=0 # Nombre d'itération bbox osef\nholdout=50 # Nombre d'exemples utilisés au début pour générer data (Pap-substitute)\ndata_aug=6 # Nombre d'itérations d'augmentation du dataset {IMPORTANT pour Pap-substitute}\nnb_epochs_s=10 # Nombre d'itérations pour train substitute\nlmbda=0.1 # params exploration pour augmentation data\nradius_ = 0.5 # NEW\nmain_fidelity(radius_)",
"Training black box on 800 examples\nTesting black box and substitute on 150 examples\nUsing 50 examples to start PP substitute\nPreparing the black-box model.\nTest accuracy of black-box on legitimate test examples: 0.7466666666666667\nTraining the Pépèrenot substitute model.\nDefined TensorFlow model graph for the substitute.\nSubstitute training epoch #0\n"
]
],
[
[
"\nIl faut trouver une facon de faire la boucle\n\npour radius:\n genere black box\n genere surrogate papernot\n \n pour observation dans test:\n genere local surrogate\n evalue papernot local\n evalue local surrogate local\noutputs:\npapernot: {radius: [accuracy locale de chaque point}\npareil pour ls}\n\n\nTODO: check histoire de boucle radius comment ca se goupille\nvoir si ca tourne\nfaire graphe...\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"azeazeazer\n# Seed random number generator so tutorial is reproducible\nrng = numpy.random.RandomState([2017, 8, 30])\n\n# Thibault: Tensorflow stuff\nset_log_level(logging.DEBUG)\nassert setup_tutorial()\nsess = tf.Session()\n\n\n\n# Data\nX, Y = DATASETS_['german']()\nX_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.30)\nX_sub = X_test[:holdout]\nY_sub = numpy.argmax(Y_test[:holdout], axis=1)\n\n## Redefine test set as remaining samples unavailable to adversaries\n### N.B Thibault: c'est pour le substitute de Papernot\nX_test = X_test[holdout:]\nY_test = Y_test[holdout:]\nprint(\"Training black box on\",X_train.shape[0], \"examples\")\nprint('Testing black box and substitute on', X_test.shape[0],' examples')\nprint(\"Using \", holdout, \" examples to start PP substitute\")\n## Define input and output TF placeholders\n### N.B. Thibault: restes de Tensorflow, utilisé pour le substitute de Papernot...\nx = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(None, X.shape[1]))\ny = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(None, Y.shape[1])) \n\n# Simulate the black-box model\nprint(\"Preparing the black-box model.\")\nprep_bbox_out = BB_MODELS_['rf'](X_train, Y_train, X_test, Y_test)\nbb_model, bbox_preds, _ = prep_bbox_out #bbox_preds fonction predict\n\n# Train PAPERNOT substitute\nprint(\"Training the Pépèrenot substitute model.\")\ntrain_sub_pap = train_sub(sess, x, y, bb_model, X_sub, Y_sub,\n nb_classes, nb_epochs_s, batch_size,\n learning_rate, data_aug, lmbda, rng=rng)\nmodel_sub, preds_sub = train_sub_pap\n\neval_params = {'batch_size': batch_size}\npap_acc = model_eval(sess, x, y, preds_sub, X_test, Y_test, args=eval_params) \nprint(pap_acc)\n\n\n\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import copy\nfrom multiprocessing import Pool\n\n\n\ndef pred(x):\n return bb_model.predict(x)[:,1]\n\nxs_toexplain = [pandas.Series(xi) for xi in X_test[:1000,:]]\nradius_perc=[0.05,0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4,0.5]#,0.6,0.7,0.8,0.9,1] \npapernot = {}\nlocalsurr = {}\npapernot = dict([(r, []) for r in radius_perc])\nlocalsurrogate = dict([(r, []) for r in radius_perc])\nc = 0\n\n\n\nfor x_toexplain in xs_toexplain:\n c += 1\n if c % 100 == 0:\n print('iter', c)\n \n print(\"Training Local Surrogate substitute model.\")\n \n \n _, train_sub_ls = lad.LocalSurrogate(pandas.DataFrame(X), blackbox=bb_model, n_support_points=100, max_depth=3).get_local_surrogate(x_toexplain)\n \n print(\"Calculating distances.\")\n dists = euclidean_distances(x_toexplain.to_frame().T, X)\n #dists = pandas.Series(dists[0], index=X.index)\n radius_all_ = dists.max()*numpy.array(radius_perc)\n\n \n for i in range(len(radius_all_)):\n radius = radius_all_[i]\n #support_x_ = numpy.array(get_random_points_hypersphere(x_toexplain, radius_=radius, n_points_=1000))\n support_x_ = generate_inside_ball(numpy.array(x_toexplain), segment=(0, radius), n=1000)\n \n\n pap_fid = model_eval(sess, x, y, preds_sub, support_x_, bb_model.predict(support_x_) , args=eval_params)\n papernot[radius_perc[i]].append(pap_fid)\n\n ls_fid = accuracy_score(train_sub_ls.predict(support_x_), pred(support_x_))\n localsurrogate[radius_perc[i]].append(ls_fid)\n\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_sub.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import imp\nimp.reload(lad)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"out_localsurr = pandas.DataFrame(localsurrogate)\nout_papernot = pandas.DataFrame(papernot)\n\n\n\nimport seaborn as sns\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\nsns.pointplot(data=out_papernot)\nsns.pointplot(data=out_localsurr, color='orange')\nplt.xlabel('Radius percent')\nplt.ylabel('Local Accuracy')\nplt.savefig('figures/local_fidelity_german.pdf')\nplt.show()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"out_papernot.to_csv('aze.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from multiprocessing import Pool\ndef sq(x):\n return sq[0] + sq[1] / sq[0] + sq[1]\n\nwith Pool(5) as p:\n print(p.map(sq, [xs_toexplain]))\n \nsum(xs_toexplain)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50a009709864791dce02e08b487493d7104627f
| 28,982 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
nannon-machine-learning.ipynb
|
alanhaq/nannon-machine-learning
|
c783010d3d3bc0abfaa50e7af182ca76f32b8362
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
nannon-machine-learning.ipynb
|
alanhaq/nannon-machine-learning
|
c783010d3d3bc0abfaa50e7af182ca76f32b8362
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
nannon-machine-learning.ipynb
|
alanhaq/nannon-machine-learning
|
c783010d3d3bc0abfaa50e7af182ca76f32b8362
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 27.497154 | 1,479 | 0.497895 |
[
[
[
"%load_ext autoreload\n%autoreload 2",
"The autoreload extension is already loaded. To reload it, use:\n %reload_ext autoreload\n"
],
[
"from nannon import *",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"start_pos",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"end_tuple",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"roll()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"first_roll()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pos = ((0, 0, 1), (0, 2, 3))\nprint_board(pos)\nswapped = swap_players(pos)\nprint(swapped)\nprint_board(swapped)",
" oo||o--**-||* \n((0, 2, 3), (0, 0, 1))\n o||-oo--*||** \n"
],
[
"pos = ((0, 0, 1), (0, 2, 3))\nprint_board(pos)\nprint(who_won(pos))\n\npos = ((7, 7, 7), (0, 0, 1))\nprint_board(pos)\nprint(who_won(pos))\n\npos = ((0, 0, 1), (7, 7, 7))\nprint_board(pos)\nprint(who_won(pos))",
" oo||o--**-||* \n0.5\n ||-----*||** \n1.0\n oo||o-----|| \n0.0\n"
],
[
"pos = ((0, 0, 1), (0, 2, 3))\nprint_board(pos)\nprint(legal_moves(pos, 2))\nlegal_moves(pos, 3)",
" oo||o--**-||* \n[0, 2]\n"
],
[
"pos = ((1, 2, 3), (1, 2, 3))\nprint_board(pos)\nlegal_moves(pos, 2)",
" ||ooo***|| \n"
],
[
"pos = ((0, 1, 2), (0, 1, 2))\ndie = 3\nprint('start')\nprint_board(pos)\nlm = legal_moves(pos, die)\nprint('lm with die', die, lm, '\\n')\n\nm0 = make_move(pos, 0, die)\nprint('m0')\nprint_board(m0)\n\nm1 = make_move(pos, 1, die)\nprint('m1')\nprint_board(m1)",
"start\n o||oo--**||* \nlm with die 3 [0, 1] \n\nm0\n ||ooo-**||* \nm1\n o||-o-o**||* \n"
],
[
"pos_dict = explore()\nprint(len(pos_dict))\nprint(dict(list(pos_dict.items())[:5]))",
"2530\n{((6, 7, 7), (4, 5, 6)): 0.5, ((0, 4, 7), (5, 6, 7)): 0.5, ((0, 0, 0), (1, 3, 6)): 0.5, ((3, 5, 6), (3, 5, 6)): 0.5, ((2, 7, 7), (0, 0, 2)): 0.5}\n"
],
[
"rand_play",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"die = 2\nprint_board(start_pos)\nnpos = rand_play(start_pos, die)\nprint(npos)\nprint_board(npos)",
" o||oo--**||* \n((0, 2, 3), (0, 1, 2))\n o||-oo-**||* \n"
],
[
"first_play",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"die = 2\nprint_board(start_pos)\nnpos = first_play(start_pos, die)\nprint(npos)\nprint_board(npos)",
" o||oo--**||* \n((0, 1, 4), (0, 1, 2))\n o||o--o**||* \n"
],
[
"play_game(rand_play, first_play)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"play_tourn(rand_play, first_play)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"players = [rand_play, first_play, last_play, score_play]\nround_robin(players)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import pickle\nmediocre_table = pickle.load(open('nannon/mediocre_table.p', 'rb'))\nprint(dict(list(mediocre_table.items())[:5]))\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"input_nodes = 2\nhidden_nodes = 6\noutput_nodes = 1\nlearning_rate = 0.3\n\n# Creates an instance of the scratch neural network.\n# Here we teach it how to produce correct \"XOR\" output.\nn = ScratchNetwork(input_nodes, hidden_nodes, output_nodes, learning_rate)\nX = [[0,0],\n [0,1],\n [1,0],\n [1,1]]\ny = [[0],\n [1],\n [1],\n [0]]\n\nprint('Before:', n.query(X))\nfor _ in range(5000):\n n.train(X, y)\nprint('After', n.query(X))",
"Before: [[0.60018041 0.60921318 0.74879427 0.72999071]]\nAfter [[0.02426062 0.98082423 0.97728005 0.01916943]]\n"
],
[
"# this shows the value player working\n\nprint_board(start_pos)\nnpos = value_play(start_pos, 2)\nprint(npos)\nprint_board(npos)",
" o||oo--**||* \n((0, 2, 3), (0, 1, 2))\n o||-oo-**||* \n"
],
[
"# This runs value player which is written in players.py\nplay_tourn(value_play, rand_play)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x, y = organize_input()\nnet = ScratchNetwork(6, 12, 1)\n# for pos in x:\n# print(net.query(pos))\npos_to_train = x[0]\nprint(pos_to_train)\nprint(net.query(pos_to_train))\nfor _ in range(1000):\n net.train(pos_to_train, 1)\n #print(net.query(pos_to_train))\nprint(net.query(pos_to_train))\n\n ",
"[(6, 7, 7, 4, 5, 6)]\n[[0.60889057]]\n[[0.99228565]]\n"
],
[
"# hill climbing\n#use two networks and run against each other\n#duplicate the winning position and replace loser, then add noise\n# have mutate method that takes the weights of neural network, and adds noise (small value from a random generated weight with smaller range)\n\ndef training():\n n1 = ScratchNetwork(6, 12, 1)\n n2 = ScratchNetwork(6, 12, 1)\n for i in range(0,1000): #1000\n if play_tourn(neurotest(n1), neurotest(n2)) > 0.5:\n random_init_range = pow(n1.n_input, -0.5)\n n1.weights_ih = n.weights_ih + np.random.normal(0.0, random_init_range,\n (n1.n_hidden, n1.n_input))\n n1.weights_ho = n.weights_ho + np.random.normal(0.0, random_init_range,\n (n1.n_output, n1.n_hidden))\n n2 = copy.copy(n1) \n return n1\n else:\n random_init_range = pow(n1.n_input, -0.5)\n n2.weights_ih = n.weights_ih + np.random.normal(0.0, random_init_range,\n (n2.n_hidden, n2.n_input))\n n2.weights_ho = n.weights_ho + np.random.normal(0.0, random_init_range,\n (n2.n_output, n2.n_hidden))\n n1 = copy.copy(n2)\n return n2\n\ntraining()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# this is the result of a random player vs a trained neuroplayer through hill climbing\nplay_tourn(rand_play,neurotest(training()))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# this is a test of the neuroplayer\nn = neurotest(ScratchNetwork(6, 12, 1))\nn(start_pos, 6)",
"((0, 2, 7), (0, 1, 2))\n(0, 2, 7, 0, 1, 2)\n0.8882117730281349\n((0, 1, 7), (0, 1, 2))\n(0, 1, 7, 0, 1, 2)\n0.879992541919527\n"
],
[
"# this is the neuro player algorithm that uses neural networks to value a move\ndef neurotest(n):\n def neuro_player(pos, roll):\n best_move = []\n best_val = 0\n lm = legal_moves(pos,roll)\n for moves in lm:\n move = (make_move(pos, moves, roll))\n move1 = (list(move)[0]+list(move)[1])\n value = n.query(move1)[0][0]\n if value > best_val:\n best_val = value\n best_move = move\n return best_move \n return neuro_player\n\nn = ScratchNetwork(6, 12, 1)\nplay_tourn(rand_play, neurotest(training())) \n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# This is the expectimax algorithm that finds the best possible move by minimizing the opponents strength of moves\nimport pickle\n\ndef expectimax(pos, roll):\n mediocre_table = pickle.load(open('nannon/mediocre_table.p', 'rb'))\n lm = legal_moves(pos, roll)\n candidates = []\n for move in lm:\n pos2 = swap_players(make_move(pos, move, roll))\n current = []\n for n in range(1,7):\n lm2 = legal_moves(pos2, n)\n for move2 in lm2:\n pos3 = make_move(pos2, move2, n)\n current.append((move, mediocre_table.get(pos3)))\n best_move1= max(current, key=lambda x: x[1])\n candidates.append(best_move1)\n right_move = min(candidates, key=lambda x: x[1])\n x, _ = right_move\n return make_move(pos, x, roll) \n \nexpectimax(start_pos, 2)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#This runs expectimax for starting pos\nexpectimax(start_pos,2)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#this plays a tournament with expectimax and value_play\nplay_tourn(expectimax, value_play)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#This plays a tournament with expectimax and rand_play\nplay_tourn(expectimax, rand_play)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# this is not needed\nimport random\n\nm = legal_moves(pos,roll)\n candidates = []\n pick random move\n me = make_move(pos, move, roll)\n save move to list\n candidates.append(move)\n return make_move(pos, move, roll)\n\ndef match_box_play(pos, roll):\n \n lm = legal_moves(pos, roll)\n move = random.choice(lm)\n print(move)\n print(me)\n save move to list\n return make_move(pos, move, roll)\n \nmatch_box_play(start_pos, 2)",
"2\n(0, 1, 4)\n"
],
[
"# ** I was unable to get this code to work so i wrote it out in text/pseudocode for what I was trying to do **\n\n# get all positions in the game, give each position 25 beads\n# play a game with another match_box player\n# for each move get all beads/legal moves and randomly select a bead(which determines the move to make)\n# save each move in a list for each player\n# Use a step function to weigh the values of the beads more towards later positions.\n# at the end of the game, for the winner add 3 beads to all positions moved\n# take away 1 bead to all positions from the loser moved\n# How many times to run?\n# \nimport random\n\npos_table = {}\npos_table2 = {}\nplay1_moves = []\nplay2_moves = []\n\ndef match_box(pos, roll):\n \n table = explore()\n for pos in table:\n pos_table[pos] = 25\n pos_table2 = pos_table.copy()\n play1_moves = []\n play2_moves = []\n # this will then run games between two match box players 1000 times\n # after each game in the loop, the pos_tables will be updated based on the results of the game\n # The length will be divided up into 5 sections, in step function fashion the positions made will have the number\n #of beads adjusted accordingly for the winning player\n #for example if the move list was 15 moves long, the first 3 moves would gain 1 bead, the next 3 would gain 2,\n #the next 3 would gain 3 beads and so on and so forth\n # the length of the losing player will be divided into 3 sections, and similarly lose beads in step function fashion,\n #Ex: the first 5 would lose 1 bead, next 5 would lose 2 bead, last 5 would lose 3 beads\n # after the 1000 games have finished there should remain a table with the most optimal moves given the number of beads,\n #in each position\n #this player will then match off against other players after it has finished training/learning\n \n \n \n #for n in range(1000):\n # play_game(matchbox_play(pos, roll), matchbox_play(pos,roll))\n # update tables\n #lm = legal_moves(pos, roll)\n \ndef matchbox_play(pos, roll):\n # play a game between two matchbox players\n # matchbox player 1 will select a legal move by picking randomly from the beads associated with those legal moves\n # after that move player 2 will do the same thing\n # following each move, the moves will be recorded into play1_moves and play2_moves respectivley\n # this will repeat until a player has won the game, following which the will as well as the move list will be returned\n \n lm = legal_moves(pos, roll)\n for moves in lm:\n move_list = [-1]\n for item in pos_table:\n print(make_move(pos,moves,roll))\n if make_move(pos,moves,roll) == n:\n move_list.append(n)\n move = random.choice(move_list)\n\n #save move to list\n return make_move(pos, move, roll)\n\nmatchbox_play(start_pos, 2)\n\n \n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# this is the algorithm for back propogation where moves are valued using the value table and trained against one another\n\nimport pickle\n\ndef back_prop():\n net = ScratchNetwork(6,12,1)\n mediocre_table = pickle.load(open('nannon/mediocre_table.p', 'rb'))\n lm = legal_moves(pos, roll) \n for move in lm:\n if len(lm) == 1:\n return move\n elif len(lm)==2:\n move1_val = mediocretable.get(1)\n move2_val = mediocretable.get(2)\n if move1_val > move2_val:\n train = 1\n else:\n train = 0\n for n in range(100):\n n.train[[2positions],[train]]\n #return greater val\n return move\n elif len(lm) == 3:\n move1_val = mediocretable.get(1)\n move2_val = mediocretable.get(2)\n if move1val > move2val:\n train = 1\n else:\n train = 0\n for n in range(100):\n n.train[[2positions],[train]]\n #compare greater val with move 3\n #train\n return move\n\n \n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# this is the round robin result of all the players and algorithms I got functioning\n\nplayers = [rand_play, first_play, last_play, score_play, value_play, expectimax, neurotest(training())]\nround_robin(players)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50a0b6cffe7aece7fadcea1a8b64145932a80d1
| 348,201 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Scikit - 12 Neural Network using Numpy.ipynb
|
nishantm9/machine-learning
|
3bb8f4ea29d36a1ef2fda2b71c1fa62efc2456d6
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 51 |
2017-09-28T05:38:48.000Z
|
2022-02-27T02:57:02.000Z
|
Scikit - 12 Neural Network using Numpy.ipynb
|
nishantm9/machine-learning
|
3bb8f4ea29d36a1ef2fda2b71c1fa62efc2456d6
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 2 |
2018-07-25T10:47:06.000Z
|
2019-01-16T11:22:53.000Z
|
Scikit - 12 Neural Network using Numpy.ipynb
|
nishantm9/machine-learning
|
3bb8f4ea29d36a1ef2fda2b71c1fa62efc2456d6
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 93 |
2017-08-28T08:59:49.000Z
|
2022-03-30T09:45:21.000Z
| 171.106143 | 67,108 | 0.846755 |
[
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport scipy\nimport scipy.misc\nimport scipy.ndimage\nimport pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder\nfrom datetime import datetime\n\nimport resource\n\n\nnp.set_printoptions(suppress=True, precision=5)\n\n\n\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class Laptimer: \n def __init__(self):\n self.start = datetime.now()\n self.lap = 0\n \n def click(self, message):\n td = datetime.now() - self.start\n td = (td.days*86400000 + td.seconds*1000 + td.microseconds / 1000) / 1000\n memory = resource.getrusage(resource.RUSAGE_SELF).ru_maxrss / (1024 ** 2)\n print(\"[%d] %s, %.2fs, memory: %dmb\" % (self.lap, message, td, memory))\n self.start = datetime.now()\n self.lap = self.lap + 1\n return td\n \n def reset(self):\n self.__init__()\n \n def __call__(self, message = None):\n return self.click(message)\n \ntimer = Laptimer()\ntimer()",
"[0] None, 0.00s, memory: 89mb\n"
],
[
"def normalize_fetures(X):\n return X * 0.98 / 255 + 0.01\n\ndef normalize_labels(y):\n y = OneHotEncoder(sparse=False).fit_transform(y)\n y[y == 0] = 0.01\n y[y == 1] = 0.99\n return y",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"url = \"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/makeyourownneuralnetwork/makeyourownneuralnetwork/master/mnist_dataset/mnist_train_100.csv\"\ntrain = pd.read_csv(url, header=None, dtype=\"float64\")\ntrain.sample(10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_train = normalize_fetures(train.iloc[:, 1:].values)\ny_train = train.iloc[:, [0]].values.astype(\"int32\")\ny_train_ohe = normalize_labels(y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, _ = plt.subplots(5, 6, figsize = (15, 10))\nfor i, ax in enumerate(fig.axes):\n ax.imshow(X_train[i].reshape(28, 28), cmap=\"Greys\", interpolation=\"none\")\n ax.set_title(\"T: %d\" % y_train[i])\n\nplt.tight_layout()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"url = \"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/makeyourownneuralnetwork/makeyourownneuralnetwork/master/mnist_dataset/mnist_test_10.csv\"\ntest = pd.read_csv(url, header=None, dtype=\"float64\")\ntest.sample(10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_test = normalize_fetures(test.iloc[:, 1:].values)\ny_test = test.iloc[:, 0].values.astype(\"int32\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Neural Networks Classifier\n\nAuthor: Abul Basar",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class NeuralNetwork:\n\n def __init__(self, layers, learning_rate, random_state = None):\n self.layers_ = layers\n self.num_features = layers[0]\n self.num_classes = layers[-1]\n self.hidden = layers[1:-1]\n self.learning_rate = learning_rate\n \n if not random_state:\n np.random.seed(random_state)\n \n self.W_sets = []\n for i in range(len(self.layers_) - 1):\n n_prev = layers[i]\n n_next = layers[i + 1]\n m = np.random.normal(0.0, pow(n_next, -0.5), (n_next, n_prev))\n self.W_sets.append(m)\n \n def activation_function(self, z):\n return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-z))\n \n def fit(self, training, targets):\n inputs0 = inputs = np.array(training, ndmin=2).T\n assert inputs.shape[0] == self.num_features, \\\n \"no of features {0}, it must be {1}\".format(inputs.shape[0], self.num_features)\n\n targets = np.array(targets, ndmin=2).T\n \n assert targets.shape[0] == self.num_classes, \\\n \"no of classes {0}, it must be {1}\".format(targets.shape[0], self.num_classes)\n\n \n outputs = []\n for i in range(len(self.layers_) - 1):\n W = self.W_sets[i]\n inputs = self.activation_function(W.dot(inputs))\n outputs.append(inputs)\n \n errors = [None] * (len(self.layers_) - 1)\n errors[-1] = targets - outputs[-1]\n #print(\"Last layer\", targets.shape, outputs[-1].shape, errors[-1].shape)\n #print(\"Last layer\", targets, outputs[-1])\n \n #Back propagation\n for i in range(len(self.layers_) - 1)[::-1]:\n W = self.W_sets[i]\n E = errors[i]\n O = outputs[i] \n I = outputs[i - 1] if i > 0 else inputs0\n #print(\"i: \", i, \", E: \", E.shape, \", O:\", O.shape, \", I: \", I.shape, \",W: \", W.shape)\n W += self.learning_rate * (E * O * (1 - O)).dot(I.T)\n if i > 0:\n errors[i-1] = W.T.dot(E)\n \n \n def predict(self, inputs, cls = False):\n inputs = np.array(inputs, ndmin=2).T \n assert inputs.shape[0] == self.num_features, \\\n \"no of features {0}, it must be {1}\".format(inputs.shape[0], self.num_features) \n \n for i in range(len(self.layers_) - 1):\n W = self.W_sets[i]\n input_next = W.dot(inputs)\n inputs = activated = self.activation_function(input_next)\n \n \n return np.argmax(activated.T, axis=1) if cls else activated.T \n \n def score(self, X_test, y_test):\n y_test = np.array(y_test).flatten()\n y_test_pred = nn.predict(X_test, cls=True)\n return np.sum(y_test_pred == y_test) / y_test.shape[0]\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Run neural net classifier on small dataset\n\n### Training set size: 100, testing set size 10",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"nn = NeuralNetwork([784,100,10], 0.3, random_state=0)\nfor i in np.arange(X_train.shape[0]):\n nn.fit(X_train[i], y_train_ohe[i])\n \nnn.predict(X_train[2]), nn.predict(X_train[2], cls=True)\nprint(\"Testing accuracy: \", nn.score(X_test, y_test), \", training accuracy: \", nn.score(X_train, y_train))\n#list(zip(y_test_pred, y_test))",
"Testing accuracy: 0.6 , training accuracy: 0.85\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Load full MNIST dataset. \n\n### Training set size 60,000 and test set size 10,000\n\nOriginal: http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/\n\nCSV version: \ntraining: https://pjreddie.com/media/files/mnist_train.csv\ntesting: https://pjreddie.com/media/files/mnist_test.csv",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"train = pd.read_csv(\"../data/MNIST/mnist_train.csv\", header=None, dtype=\"float64\")\nX_train = normalize_fetures(train.iloc[:, 1:].values)\ny_train = train.iloc[:, [0]].values.astype(\"int32\")\ny_train_ohe = normalize_labels(y_train)\nprint(y_train.shape, y_train_ohe.shape)\n\ntest = pd.read_csv(\"../data/MNIST/mnist_test.csv\", header=None, dtype=\"float64\")\nX_test = normalize_fetures(test.iloc[:, 1:].values)\ny_test = test.iloc[:, 0].values.astype(\"int32\")\n",
"(60000, 1) (60000, 10)\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Runt the Neural Network classifier and measure performance",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"timer.reset()\nnn = NeuralNetwork([784,100,10], 0.3, random_state=0)\nfor i in range(X_train.shape[0]):\n nn.fit(X_train[i], y_train_ohe[i])\ntimer(\"training time\")\naccuracy = nn.score(X_test, y_test)\nprint(\"Testing accuracy: \", nn.score(X_test, y_test), \", Training accuracy: \", nn.score(X_train, y_train))",
"[0] training time, 23.18s, memory: 1263mb\nTesting accuracy: 0.9285 , Training accuracy: 0.931516666667\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Effect of learning rate",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"params = 10 ** - np.linspace(0.01, 2, 10)\nscores_train = []\nscores_test = []\n\ntimer.reset()\nfor p in params:\n nn = NeuralNetwork([784,100,10], p, random_state = 0)\n for i in range(X_train.shape[0]):\n nn.fit(X_train[i], y_train_ohe[i])\n scores_train.append(nn.score(X_train, y_train))\n scores_test.append(nn.score(X_test, y_test))\n timer()\n \nplt.plot(params, scores_test, label = \"Test score\")\nplt.plot(params, scores_train, label = \"Training score\")\nplt.xlabel(\"Learning Rate\")\nplt.ylabel(\"Accuracy\")\nplt.legend()\nplt.title(\"Effect of learning rate\")",
"[0] None, 23.22s, memory: 1583mb\n[1] None, 23.83s, memory: 1583mb\n[2] None, 24.14s, memory: 1583mb\n[3] None, 23.72s, memory: 1583mb\n[4] None, 23.85s, memory: 1583mb\n[5] None, 23.08s, memory: 1583mb\n[6] None, 23.78s, memory: 1583mb\n[7] None, 23.26s, memory: 1583mb\n[8] None, 23.69s, memory: 1583mb\n[9] None, 23.20s, memory: 1583mb\n"
],
[
"print(\"Accuracy scores\")\npd.DataFrame({\"learning_rate\": params, \"train\": scores_train, \"test\": scores_test})",
"Accuracy scores\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Effect of Epochs",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"epochs = np.arange(20)\nlearning_rate = 0.077\nscores_train, scores_test = [], []\nnn = NeuralNetwork([784,100,10], learning_rate, random_state = 0)\nindices = np.arange(X_train.shape[0])\n\ntimer.reset()\nfor _ in epochs:\n np.random.shuffle(indices)\n for i in indices:\n nn.fit(X_train[i], y_train_ohe[i])\n scores_train.append(nn.score(X_train, y_train))\n scores_test.append(nn.score(X_test, y_test))\n timer(\"test score: %f, training score: %f\" % (scores_test[-1], scores_train[-1]))\n\nplt.plot(epochs, scores_test, label = \"Test score\")\nplt.plot(epochs, scores_train, label = \"Training score\")\nplt.xlabel(\"Epochs\")\nplt.ylabel(\"Accuracy\")\nplt.legend(loc = \"lower right\")\nplt.title(\"Effect of Epochs\")\n\nprint(\"Accuracy scores\")\npd.DataFrame({\"epochs\": epochs, \"train\": scores_train, \"test\": scores_test})",
"[0] test score: 0.958000, training score: 0.960850, 24.90s, memory: 1583mb\n[1] test score: 0.967000, training score: 0.972083, 24.97s, memory: 1583mb\n[2] test score: 0.970100, training score: 0.977317, 24.84s, memory: 1583mb\n[3] test score: 0.968900, training score: 0.980700, 24.63s, memory: 1583mb\n[4] test score: 0.969900, training score: 0.980733, 24.88s, memory: 1583mb\n[5] test score: 0.971500, training score: 0.983500, 24.64s, memory: 1583mb\n[6] test score: 0.971900, training score: 0.985033, 24.97s, memory: 1583mb\n[7] test score: 0.970300, training score: 0.984417, 24.71s, memory: 1583mb\n[8] test score: 0.969100, training score: 0.985050, 24.75s, memory: 1583mb\n[9] test score: 0.970600, training score: 0.986233, 24.79s, memory: 1583mb\n[10] test score: 0.967600, training score: 0.985383, 24.91s, memory: 1583mb\n[11] test score: 0.969300, training score: 0.986267, 24.80s, memory: 1583mb\n[12] test score: 0.967100, training score: 0.985833, 24.66s, memory: 1583mb\n[13] test score: 0.968900, training score: 0.987100, 24.61s, memory: 1583mb\n[14] test score: 0.963900, training score: 0.985217, 25.01s, memory: 1583mb\n[15] test score: 0.970100, training score: 0.987167, 24.56s, memory: 1583mb\n[16] test score: 0.968800, training score: 0.987417, 24.74s, memory: 1583mb\n[17] test score: 0.968400, training score: 0.988283, 24.65s, memory: 1583mb\n[18] test score: 0.965700, training score: 0.987967, 24.76s, memory: 1583mb\n[19] test score: 0.968600, training score: 0.989067, 24.68s, memory: 1583mb\nAccuracy scores\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Effect of size (num of nodes) of the single hidden layer",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"num_layers = 50 * (np.arange(10) + 1)\nlearning_rate = 0.077\nscores_train, scores_test = [], []\n\ntimer.reset()\nfor p in num_layers:\n nn = NeuralNetwork([784, p,10], learning_rate, random_state = 0)\n indices = np.arange(X_train.shape[0])\n for i in indices:\n nn.fit(X_train[i], y_train_ohe[i])\n scores_train.append(nn.score(X_train, y_train))\n scores_test.append(nn.score(X_test, y_test))\n timer(\"size: %d, test score: %f, training score: %f\" % (p, scores_test[-1], scores_train[-1]))\n\nplt.plot(num_layers, scores_test, label = \"Test score\")\nplt.plot(num_layers, scores_train, label = \"Training score\")\nplt.xlabel(\"Hidden Layer Size\")\nplt.ylabel(\"Accuracy\")\nplt.legend(loc = \"lower right\")\nplt.title(\"Effect of size (num of nodes) of the hidden layer\")\n\nprint(\"Accuracy scores\")\npd.DataFrame({\"layer\": num_layers, \"train\": scores_train, \"test\": scores_test})",
"[0] size: 50, test score: 0.944500, training score: 0.942283, 10.59s, memory: 1583mb\n[1] size: 100, test score: 0.952500, training score: 0.952617, 24.13s, memory: 1651mb\n[2] size: 150, test score: 0.952900, training score: 0.955067, 36.26s, memory: 1744mb\n[3] size: 200, test score: 0.955400, training score: 0.957283, 47.92s, memory: 1786mb\n[4] size: 250, test score: 0.957700, training score: 0.957767, 1421.18s, memory: 1786mb\n[5] size: 300, test score: 0.955100, training score: 0.957450, 137.31s, memory: 1786mb\n[6] size: 350, test score: 0.956100, training score: 0.958467, 156.60s, memory: 1786mb\n[7] size: 400, test score: 0.955800, training score: 0.956750, 204.31s, memory: 1786mb\n[8] size: 450, test score: 0.955300, training score: 0.957833, 274.12s, memory: 1786mb\n[9] size: 500, test score: 0.956200, training score: 0.957267, 339.84s, memory: 1792mb\nAccuracy scores\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Effect of using multiple hidden layers",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"num_layers = np.arange(5) + 1\nlearning_rate = 0.077\nscores_train, scores_test = [], []\n\ntimer.reset()\nfor p in num_layers:\n layers = [100] * p\n layers.insert(0, 784)\n layers.append(10)\n \n nn = NeuralNetwork(layers, learning_rate, random_state = 0)\n indices = np.arange(X_train.shape[0])\n for i in indices:\n nn.fit(X_train[i], y_train_ohe[i])\n scores_train.append(nn.score(X_train, y_train))\n scores_test.append(nn.score(X_test, y_test))\n timer(\"size: %d, test score: %f, training score: %f\" % (p, scores_test[-1], scores_train[-1]))\n\nplt.plot(num_layers, scores_test, label = \"Test score\")\nplt.plot(num_layers, scores_train, label = \"Training score\")\nplt.xlabel(\"No of hidden layers\")\nplt.ylabel(\"Accuracy\")\nplt.legend(loc = \"upper right\")\nplt.title(\"Effect of using multiple hidden layers, \\nNodes per layer=100\")\n\nprint(\"Accuracy scores\")\npd.DataFrame({\"layer\": num_layers, \"train\": scores_train, \"test\": scores_test})",
"[0] size: 1, test score: 0.952500, training score: 0.952617, 32.26s, memory: 1792mb\n[1] size: 2, test score: 0.930600, training score: 0.929183, 52.31s, memory: 1792mb\n[2] size: 3, test score: 0.542500, training score: 0.539083, 58.62s, memory: 1792mb\n[3] size: 4, test score: 0.095800, training score: 0.098633, 62.20s, memory: 1792mb\n[4] size: 5, test score: 0.095800, training score: 0.098633, 64.18s, memory: 1792mb\nAccuracy scores\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Rotation",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"img = scipy.ndimage.interpolation.rotate(X_train[110].reshape(28, 28), -10, reshape=False)\nprint(img.shape)\nplt.imshow(img, interpolation=None, cmap=\"Greys\")",
"(28, 28)\n"
],
[
"epochs = np.arange(10)\nlearning_rate = 0.077\nscores_train, scores_test = [], []\nnn = NeuralNetwork([784,250,10], learning_rate, random_state = 0)\nindices = np.arange(X_train.shape[0])\n\ntimer.reset()\nfor _ in epochs:\n np.random.shuffle(indices)\n for i in indices:\n for rotation in [-10, 0, 10]:\n img = scipy.ndimage.interpolation.rotate(X_train[i].reshape(28, 28), rotation, cval=0.01, order=1, reshape=False)\n nn.fit(img.flatten(), y_train_ohe[i])\n scores_train.append(nn.score(X_train, y_train))\n scores_test.append(nn.score(X_test, y_test))\n timer(\"test score: %f, training score: %f\" % (scores_test[-1], scores_train[-1]))\n\nplt.plot(epochs, scores_test, label = \"Test score\")\nplt.plot(epochs, scores_train, label = \"Training score\")\nplt.xlabel(\"Epochs\")\nplt.ylabel(\"Accuracy\")\nplt.legend(loc = \"lower right\")\nplt.title(\"Trained with rotation (+/- 10)\\n Hidden Nodes: 250, LR: 0.077\")\n\nprint(\"Accuracy scores\")\npd.DataFrame({\"epochs\": epochs, \"train\": scores_train, \"test\": scores_test})",
"[0] test score: 0.965700, training score: 0.965917, 469.78s, memory: 1792mb\n[1] test score: 0.970400, training score: 0.974217, 293.73s, memory: 1792mb\n[2] test score: 0.972600, training score: 0.975783, 293.26s, memory: 1792mb\n[3] test score: 0.968800, training score: 0.976300, 224.23s, memory: 1792mb\n[4] test score: 0.970900, training score: 0.978750, 220.24s, memory: 1792mb\n[5] test score: 0.966400, training score: 0.975817, 234.37s, memory: 1792mb\n[6] test score: 0.973600, training score: 0.980567, 226.90s, memory: 1792mb\n[7] test score: 0.970600, training score: 0.977233, 216.35s, memory: 1792mb\n[8] test score: 0.971800, training score: 0.981417, 215.35s, memory: 1792mb\n[9] test score: 0.972400, training score: 0.982817, 236.76s, memory: 1792mb\nAccuracy scores\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Which charaters NN was most wrong about?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"missed = y_test_pred != y_test\npd.Series(y_test[missed]).value_counts().plot(kind = \"bar\")\nplt.title(\"No of mis classification by digit\")\nplt.ylabel(\"No of misclassification\")\nplt.xlabel(\"Digit\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, _ = plt.subplots(6, 4, figsize = (15, 10))\nfor i, ax in enumerate(fig.axes):\n ax.imshow(X_test[missed][i].reshape(28, 28), interpolation=\"nearest\", cmap=\"Greys\")\n ax.set_title(\"T: %d, P: %d\" % (y_test[missed][i], y_test_pred[missed][i]))\nplt.tight_layout()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"img = scipy.ndimage.imread(\"/Users/abulbasar/Downloads/9-03.png\", mode=\"L\")\nprint(\"Original size:\", img.shape)\nimg = normalize_fetures(scipy.misc.imresize(img, (28, 28)))\nimg = np.abs(img - 0.99)\nplt.imshow(img, cmap=\"Greys\", interpolation=\"none\")\nprint(\"Predicted value: \", nn.predict(img.flatten(), cls=True))",
"Original size: (82, 82)\nPredicted value: [9]\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50a11b3449fa341b1ba29f75eb1b15c8401bbe5
| 18,802 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
paper/notebooks/figure02/.ipynb_checkpoints/som_colors-checkpoint.ipynb
|
ashishpatel26/hybrid-ensemble-method
|
2045317abd7de9f7a551fcc50aeb35bb7b816ad0
|
[
"NCSA"
] | 6 |
2015-07-21T03:05:24.000Z
|
2018-08-10T01:28:00.000Z
|
paper/notebooks/figure02/.ipynb_checkpoints/som_colors-checkpoint.ipynb
|
edwardjkim/astroclass
|
2045317abd7de9f7a551fcc50aeb35bb7b816ad0
|
[
"NCSA"
] | null | null | null |
paper/notebooks/figure02/.ipynb_checkpoints/som_colors-checkpoint.ipynb
|
edwardjkim/astroclass
|
2045317abd7de9f7a551fcc50aeb35bb7b816ad0
|
[
"NCSA"
] | 2 |
2015-06-03T16:45:25.000Z
|
2015-10-26T13:39:19.000Z
| 59.878981 | 88 | 0.77896 |
[
[
[
"%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from __future__ import print_function, division, unicode_literals\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from matplotlib import gridspec\n\ntruth_train = np.loadtxt('../../data/truth_train.dat')\nmag_i_train = np.loadtxt('../../data/mag_i_imputed.train.dat')\nclr_u_g_train = np.loadtxt('../../data/clr_u_g_imputed.train.dat')\nclr_g_r_train = np.loadtxt('../../data/clr_g_r_imputed.train.dat')\n\nn_grid = 10\nclens_som_cell = np.loadtxt('../../data/som_cells_cv.dat')\n\n# calculate mean values for each cell\ndef calc_cell_mean(x, som_cells, n_grid=10):\n x_cells = np.zeros(n_grid**2)\n for i in xrange(n_grid**2):\n i_cell = np.where(som_cells == i)\n x_cells[i] = x[i_cell].mean()\n \n return x_cells.reshape((n_grid, n_grid))\n\nmag_i_cells = calc_cell_mean(mag_i_train, clens_som_cell)\nclr_u_g_cells = calc_cell_mean(clr_u_g_train, clens_som_cell)\nclr_g_r_cells = calc_cell_mean(clr_g_r_train, clens_som_cell)\nstar_frac_cells = calc_cell_mean(truth_train, clens_som_cell)\n\ngs = gridspec.GridSpec(2, 3, height_ratios = (1, 1), width_ratios = (9, 9, 1))\n\ncmap1 = plt.cm.jet\ncmap2 = plt.cm.Spectral\n\nax1 = plt.subplot(gs[0, 0])\nim1 = ax1.matshow(mag_i_cells, cmap=cmap1)\nax1.set_xticks([])\nax1.set_yticks([])\ncb1 = plt.colorbar(im1)\ncb1.set_ticks([16, 18, 20, 22, 24])\ncb1.set_label(r'$i$')\n\nax2 = plt.subplot(gs[0, 1])\nim2 = ax2.matshow(star_frac_cells, cmap=cmap2)\nax2.set_xticks([])\nax2.set_yticks([])\ncb2 = plt.colorbar(im2)\ncb2.set_ticks([0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1])\ncb2.set_label('stellar frac.')\n\nax3 = plt.subplot(gs[1, 0])\nim3 = ax3.matshow(clr_u_g_cells, cmap=cmap2)\nax3.set_xticks([])\nax3.set_yticks([])\ncb3 = plt.colorbar(im3)\ncb3.set_ticks([0, 0.6, 1.2, 1.8, 2.4])\ncb3.set_label(r'$u-g$')\n\nax4 = plt.subplot(gs[1, 1])\nim4 = ax4.matshow(clr_g_r_cells, cmap=cmap2)\nax4.set_xticks([])\nax4.set_yticks([])\ncb4 = plt.colorbar(im4)\ncb4.set_label(r'$g-r$')\ncb4.set_ticks([0.3, 0.6, 0.9, 1.2, 1.5])\n\nplt.savefig('../../figures/som_colors.eps')\n\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50a26d7f09c2a071c7464367e90ea81670fcb95
| 210,780 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
lectures/Untitled.ipynb
|
s183910/comsocsci2021
|
d8749ebbf0bd9728d6599137de9544800b531153
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
lectures/Untitled.ipynb
|
s183910/comsocsci2021
|
d8749ebbf0bd9728d6599137de9544800b531153
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
lectures/Untitled.ipynb
|
s183910/comsocsci2021
|
d8749ebbf0bd9728d6599137de9544800b531153
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 253.951807 | 24,187 | 0.868432 |
[
[
[
"{\n \"cells\": [\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"# Overview\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"This week we are going to learn a bit about __Data Visualization__, which is an important aspect in Computational Social Science. Why is it so important to make nice plots if we can use stats and modelling? I hope I will convince that it is _very_ important to make meaningful visualizations. Then, we will try to produce some beautiful figures using the data we downloaded last week. \"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"Here is the plan:\\n\",\n \"\\n\",\n \"* __Part 1__: Some talking from me on __why do we even care about visualizing data__. \\n\",\n \"* __Part 2__: Here is where you convince yourself that data visualization is useful by doing a __little visualization exercise__.\\n\",\n \"* __Part 3__: We will look at the relation between the attention to GME on Reddit and the evolution of the GME market indicators.\\n\",\n \"* __Part 4__: We will visualize the activity of Redditors posting about GME.\\n\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"## Part 1: Intro to visualization\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"Start by watching this short introduction video to Data Visualization.\\n\",\n \" \"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"> * _Video Lecture_: Intro to Data Visualization\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"code\",\n \"execution_count\": 80,\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"outputs\": [\n {\n \"data\": {\n \"image/jpeg\": \"/9j/4AAQSkZJRgABAQAAAQABAAD/2wCEAAUDBAgICAgICAgICAgGBwgIBwcHBwgICAgICAgICAgICAgIChALCAgOCggIDhUNDhESExMTCAsWGBYSGBASExIBBQUFBwYHDwgIDx4VEhUfGB8YHRwbGxobGhsaGhkVHh0eHR4YHx4eFhoeHx0YGh0dGBUYHRgaGRcdFR4ZGhUYG//AABEIAWgB4AMBIgACEQEDEQH/xAAcAAEAAgMBAQEAAAAAAAAAAAAABggEBQcDAgH/xABWEAABBAECAgYGBwMGCgQPAAABAAIDBAUGERIhBxMYMZTVFCJBUVRVFSMyYXGBkQhCoRYzNFKCsSQlNVNicnOSo7NDRLLFFyY2RVZ0dYOipbS1wcLR/8QAGQEBAQEBAQEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAECAwQF/8QAMREBAAECBAQDBgYDAAAAAAAAAAECEQMhMVEEEkFhgcHwE3GRobHhIzJSYtHxIiRC/9oADAMBAAIRAxEAPwCmSIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/AIzI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8AGZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/wCMyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/ABmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P8AjMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/wAZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/AIzI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8AGZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/wCMyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/ABmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P8AjMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/wAZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/AIzI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8AGZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/wCMyPlyC/6IiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIijg15hDP6KMvjfSOLg6n0+vx8e+3Bw8f29+XD3rVNFVX5YusUzOiRoiLKCIiAiIgIiICL4ErS4s4m8bQHFm44g0kgEt7wDsef3FfaAiIgIsTI5OvXMLbE8MJtztr1hNKyMzTvDnMhiDj9ZKQ1xDRz9UrKcQOZ5Ad5KtpH6i0uE1bi70r4KeRpWpoty+GtbhlkaAdieBjieEH29y3StVM0zaqLLMTGoiL4bK0uLA5pc0AuaHDiaHb8JI7wDsf0Kyj7RFiVMnXllnginiknpOjbahjka6Su6VgkiEzAd4y5hDhvtuDurYZaLX57N06EXX3rVepDxBgltTMhYXnchoc8gF2wPIc+RXricnXtxNnqzw2YJPsTV5WSxu25HZ7CQdk5ZtzWyW02uy0XxLK1u3E5reJwa3icBu49zRv3uPuX2ogiIgIiICIhKAi0+N1TjLLxHWyNCxI77Mde7XlefwZG8kr0y2o8dTeI7d+lVkcwPbHatwQPLCS0PDJXglu7XDfu3afctclV7WXlnRtEWrp6ix84jMN6nMLEroYTFbgkEszGCR8UfA88cgYQ4tHMA7rMs3oInxRyzRRyWnFleOSVjHzPa3ic2JrjvI4NBJDd+QUmmYymC0shF+OIA3PIDmSe4LT4LVeMvySQ0shStywDeWKrahmewA8JcWxuJ4d+W/crFMzEzEaERMtyi0ud1ZjKEkcN3IUqks+xiitWoYXvBPCHBsjgeHflv3LctcCAQQQRuCOYIPcQfaEmmYi8wTExm/UXm2wwyOiD2mRjGSOjDhxtZIXtY9ze8NcY5AD7eB3uKx58rWjsQ1HzxMs2mSyV67pGiWVkPD1ro2E7uDeNu+3v+4qREyWZiLSZDWGJryvgsZTHQTRECSGe/WilYS0OAfG+QOaS1zTzHcQsnC5+jd4xSu1LfU8PW+iWobHV8fFwcfVOPBvwu237+E+5WaKoi9sjlm12yREWUEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREHM/2irk7cdSpxTOrx5zM0sbcssPC6KrY610uzv3eLq2tJ9znD2rc1Oi3T8dZtUYqo6NgAD3wgzEt7nmb7fHvz33W71lpurlqU1C4wvgsgblp4Xse0h0csbv3ZGuAIP3c9wSFAYdDaqjDazNVE0mFrQ+THQOvdU0j1DYILnO2G3HvxL24dcThRRFfLMTO+fwjXp6l3pqiaIi9nzd6RMzZs5AYTEQXKODnkrWZrNswTWZ6/KeOo0NIBaQQC7ffbf27Lym6Vrt2xj6+DoV7Jy+G+ko3XbD4eocyw+GWOYRghwb1ZbyI3c4HfZZed6Mb4nvOxGblxlTNyvmyNMVopgZpRwzy1ZnevWdINyeH2nkeQA2mmejSHHX6FutMRDjMM/Ftruj3c/jnNg2DLxfaLnO3bt7e9dJq4WIvERO2u3XvfbJq+FEf380V0x0wZC19D25cXBBi85djxrZRbc+yLjmPLpGR8Ab6NxxvAB57NJ335L3i6R9Q2m5GXH4WpNXwl+/WnfLeex9llOZ7OGszg5S8DNySSN3bAHbnscV0TmDG4TH+ncX8nsw3JNm9H29IDTP8AVFnH9Wdp/tAn7PdzUN0PpLL34s/HTzE2Mgtajy8Vus+pHJxxPsO3lryvAkrvex2xLTsQARseZ6/6tV6qYi0T15tLz43s3+FN5jz3lP8ATfSW3IX8RXrwD0bOYafIiV7yJoZIZWxmAtA4XAHjBO/e3lyUE1t0h5q1XpTUYYq4g1g7GPLLksZsSV7Bjq15QG86s46zrO/h4G8jvymOS6K3RR4p2GyD8ddwNWWpDYfXjssmgn2dK2aGTlxce7gfZxHkeRH5U6JxHjqFL01z5aWfgzlm1JFxG1YjkdJKzhDh1YeXd/PbbuKxRXwtExVHwm/7vszTVhRMTHrX7Pi/r3MzZKTF4rF1bE+KrVZcy+zcdDDHYswtmFWtI1h4jwu5SEEd/Ibc4prXpDzNzBm5Wrtx8lfUf0fZDbb2TxdRbgZDESwbP6x7nRyAHYDfbdTnUmgLpyk+Vw+Vdi5slFDFk43VIrUc/UN6uGZjZeUc7WAN32I5fe7fBh6JnNw8+KOQdI6fNtyvpckO8ji2zDYLJRx+u9xiO79+ZcTsrh4nDU8tVo/53v3v010WmrCi0+7fxalucr47OZXJ5Ci2C9S0pTtZCSrakma9zpTG6rEx4DCOKGNrX8t9xvtzK2GL6RszDLj5czh4aeOzdiKtVnrWzNPVms/0ZtuNzRu1/dxN2293sUhzPR9DcyGStWZDJXzOGixc1UN4XMbHJJJ1rZd/tfWcuXItBWhxfRbfdPRGUzk2Sx+Enjnx9J1aKFxlhG1d9qZnrTuYO4nn3+8rPtOHqi9W0b7dPHfJObDmM/Pbo1DelzLCB2RdiqoxdTLnG25hck9JeTc9FbLXiLNtm8TNw483EgbAbre3de5azlLtLC4uC5Xwj2R5Cxatms6WZzQ90FXZpaHgct37gkHuGxP3L0Wl2EsYf03+k5Z2RFnqPs732XeqMfHz+zw8W/t32X3lujy8zJW72IzD8YzMFjsnX9Fish8jG8HX1nS7iCYt357HmSfuCa+FmZtERrbW3S1++pM4Wdu+/b7odqDVUuZpaUvTVxWkdrWKF0DXF3B6O67CNy4bh+zBuPYd12PWWIOQx16iJTCchTsVhM0EmMzROjD9gRuBxd243G6guL6JzBRxFL04v+g88cv1zofWsAyTv6l+8m7XfX837nct7uanuq8JFkqVmjOZGxXIXRPfC8skZvza9jh3Oa4A+7lzBG4XPHxcOaqfZzlEz4Re8M4ldN45en8uNdH9Srir+Kx2bwNelkIS+LEZ2ns+rdlbEWuD5G7Pinewnk/fck8m7gHZnpXy80FnL08LFPgKL5eOd1vq701au4ia3DERwBrQ1zuA89m9457Z+L6M8q+5j5MtnDkaeDmE9GAVGQSulY3gjfZkbzleG8tySTz953x8h0QW+CfH083PVwN2aSSfFCtE97GzPL5q8Fo/WMruJPqe47Hfc7+irE4aqu9cxM5X/NbWb26307Xu6TVhTN6vOzKvdJGSvXZKmnMfXutp1q1i3avWHV4t7cLbEMEQaN+PqnsJcTyJI25bnX1M5Ux+a1DlLNB1e3V09jbl8ssuldI50RBqiM/VB7TBEwPB2O2525k7fL9GNmGy61gMq/Dvs1a9W7H6NDaimZVjEMEzWyj6qw2MBvEO/Yd3PfOj6NmST5KS7afaZmsLUxdppZwSE1mSMdZEgcfrHl/F3ciPauUV8PEZaTEb31pvfpvZiKsOI/u/RGn9JeoK9aldvYSpFUy12jDA+K898leO5K1o9JjLN+Msdu1w2G4AIHEFuOjj/wAp9Y/7fC//AGxi1juijKzQ06tvUMlipiLdSejAaMTC5lSRrmNtSNdxzPDG8IJOw33IJ22nGm9K+h5TM5HrusGdfSf1PV8PUeiVhX24+I8fFtv3DZMTEwIoqii15jpf9VMxr2iSqrDimYjz3jdGOmvSNy7Pi8lTq1sk7Cus9bh7ruGK0yy2MF0bj6rZ2GIbcXLmO/bZ2kwevcbjsZK7E4Z9bJXM0KEuCd9Q5uWmj4vrXgFog6qPcOaACGgbN57TPpC0bbu2K2QxmSkxuRpRSQNkMYnrT15XBzop67/VPrAEO2/uaRHq3Q+59Oz6XkpZMxbyUOV+l4Y2xmC7XYY4HRQ/Z6prHObw8uTuW2w2uFi4M4VNOLOnTPeZz6THXdaKqOSIqn6+rfNpukO3fnqY8ajxFVr49S4tlJ1LITcAM7Zw6YFvrCWPhI4XbtPWAjuX3rnptkq5C5TpRY4x4lxjnfk7zq0tuZg3khpsYw7cJ9Xif3kHltzO+sdHWUuQRsymcN2avlqGQieKMUMTG0hKDAyKItDTJ1u5fzO7R3pqPoytuu3LWKyjcezLvEl6CahXuAT8IY6xVfMOKCRwHPblvz922qMThsortNr/AKrdO1/ksVYelXnZiO6VLt2bGQYXHw2HZvEyXmG7ZdCKr4rBhmbOY2u42MLHN9XmXFu2wXjW6W7tmtRgqYyOXN5C5kKjqjrJFSA4x4ZasOm4eJ0XrM2by73czwjilmK0MYMlj8h6W6U43DyY1zZImNfO6SVkpsvfHs0PJadwG8y7fdR09EckcTJKmTfVydPK5K/RyDK7HNZHkn8U1WaB7i2aLYAbn+r3cyFmmrhJyt9f3a9tGYnB2+vf7MTV/SrkcTXpwX6NGvlr89hoEl530bFWg6v/AAt8waX7PMoaI+/dr9zyG8g6HekducFuCRkDLmMcwTGnObFSeKUO6uevKWh3Du1wLSNwQOfPlgZHozv2Yak0+ZfJmsdPYkgyb6UDoDDaEYkpyUiOrfX+raR3EHcjvKkvR3pi1jmWHXbwv2LcoeXtqw1ooWhob1UEcTRwx8gdt9t9z3kk4xauG9jamI5vHfplpbvfslc4XJlr4+rM/UusMXjHMZkMhVpumY58TbU7Ii9jSA5zQ48wCR+q3DnBzOIEFrmbgjmCCNwR7wsLL4KlcLTbqVrJjBDDYgjlLQ7YkNLwdgdgs7qwG8DQGgN4QAOQG2wAHuC8c8totr1ccrRZwfod6N8NldK0ZLdOFtmaKyTkIwI7MTmWZ2xyiYbHdga3v5eqN1ptQcGU0EMtehisZOo2KnFk3xgzyQwZdldjxK71jxxl2/vL3n2qXYfobyUVNmKk1JZ+io2uY6lUpwVnPje9z5I3WBvKWPLnbgkjZxHdyU01boGC3gX4Kq4U4OrrsheGdZwCvYin5t4hxFxj5nfvcSvq1cXRGLzc9/8AK/XKM7/Hr0yeqcaIrve+d/dCH69wdOhkNIRUq0NWJ+ekkdHBG2NhldT4S8gfvENaN/uWz6Yv8s6Q/wDbM/8A9KVJekTRzcvVgjbYkqW8fZiuY+9E0OdXtQghryx3KSMhzgWHv3+5R/A6AyUmTq5POZVmQfi2yDH161VtWGJ8oDZJnNH2pCAP0C81GLRNMVVVZxFUWzvN72+u7nTXFomZ0ifnf+X3+0lclh05cETzH6VLUqyyNOxbBZtRRTc/YHMc5p+55UV6TtL0cEzTd7Gwx1rdTNUafWQtDX2a9lkjbEcxHOXcNJ3Pdu73rresNP18rRs4+00mC7EY38JAc07hzJGEjYPY9rXDf2tC59hui/Ivt0ZczmTk6uDcH46sKrID1jQGxy2XN/nZGtAG5JPI8+Z3vD41FGHETNrXvG94iPVzDriKc50v45PvpC0/p7FDKZjKxenS5hzY2wWQyaWSTqhFFToN4QWEhg22+zwkkgAleOkc9LpvSePOTa6S71Qgo0eP6+eWRzjVqAn7IawtBd3Naw+4BfWuei/J5LKtyYzbITUJGPruxsc8dRh234WTSOY+YkbmQt3Ow7gABJZOj+ter1WZ5sOYt02SMFyWEQcTZH8R2hhIYwkNYDsOfAFZxMPkpiurm0mdb5RaIi+Vt8/os1U8sRM33QPojt2KeV1NZy1pk9lmOxt66+Ih0cTRDbnkgrtBP1MLSGAD3c+Z3Oiweey1eabW2QxsNiheZHHGG2T6ZjcU6ThjdXh4Sx7fXa53MFxc4+qCdukaZ6JMXQvZCzDBC2vkaTKcdRkZaK8T2OZca1/GeJs3qEjYbFgUdd0P5N8DMRLnpJNPRSNLaBqxttOgjeJGVX2gOJ0YIHt25DkNgB3jHwKqpmZ15b5TGURnEW0n5d7N+0w5mZ93w8G16YY8LVqG+cVRv5PLPjgxsclWOSW5bmYGwF+44nRsYGucT+6wDcEhb3od0PHgscyA8Lrdk9ffma1reOd45taGgBsbPsgAbcvvX63RHHm2ZWzM2aHH02VsPS6vZtJzhtZmJJIklfwsAdy2AA/dBUzXgxMb8OMOmb9Z8o8Pr4OFVf8AjyxPv9dhEReZyEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREGp1LqGtjhVNlzmjI36+Pr8DHP3s2iWwtdw/ZaS07uPILbLmX7REj4qeHsiC1YZj9UYi3ZZRqTW5m14JJHSyCGBrnuAHuHtHvXPukbNPv5avdnOroMRPg+LT8eEq5GrJ9NMt2I7Lb9eJgkjtcDavVi0BCWF5PIu3CxyKpkmX1DTw74Z49Qy29Q6Ew9PFOhivyvjzkb7kVrr5R/k+2BPA90kpYS1m+5LdlM7eCzz5NaX60+W+k6ULINPVpLM7afHNgaHpE1Su89TNOZxIGu5tbIw7bEu3CwC0urtTUcTDFYvTNgjtXalKJx/fs3JmwQt/Ddxc4/utY8nkFxDoPeRqKm2hJq2TF/wAm7vpp1IMiKwyptY4lsfp4B9K4BJxBv1fM9WecqzenLS2T1Vl3YyCnXfi8Bj5DM7KuuVq1nJ5avLDHNVfFC70h9OsS4PaS1slpwPrR8g7Hk9S1q+Qx+MkL/SsxFemqBrN4yzHtruscb9/UO1mLb38/ctyq3WbGorjtOyipYbnsLgtbYuexJWkFc5mvVx0FKyJpYxE6G0+Bs0bzsx4c7bk07RTourZ11bNtfltQMjl0zMLpdiNQOtVso9zQ2xX+krL3yZJg60OZSLWOadweJrCAt4iqXjbmT4NKTcGonej5CeuMc1+omx3YzlomfSTbs31kLBCHOFTJBzeoL2hw3DjkZd+SbftGaXV30+dZVeKOsL/0H/J8Ziua7mdUPRPQfQ+DfY9bx8fH6vW7haxaXNamq1LuOoTGQT5t9mOnwsLmF1WD0iUSOB9T1N9veVwPTuKz8E+Nv158y6/ksvrGnPDfsXJaEVaJmZkwrZa0+8VeD0mKm9khA3EgAJaQFpejirM/L6UfwarlvVfpN2opM3FkH1K2SlxsjD1UlpvVxyOkDw0wERuaGb+twgBbBY1q/BFJBFLNFHLce6OrFJKxkliRkb5nxwMcd5XiOOR5DdyGsce4FVVyeAz9fSen5xdznFlJYJdVS2n5i5bgayrIytC6tRlZegptkDWvbAQ7cRufxetvsMDpLI5GPRUmSsZqx6Nn8qxloDJ46eDGijcfUfZD5nTMJliYxk0zhI6KZrHc3OCCwNnW+KZYx9X02J82bsXK2P6jjsRzWMeHG5CZ4GuiikjLHtIe5p4mOb3ghSJVq6JNNXcZNpuONuWbDLqzVrsgyzJdljbA2LJxUpJxLuI45A2B4c7k97w8budubKoCIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIuVSZW/quSWPD3pMZp6tLLWsZ2mGnIZaxE50U8OGlkBZVoxPDmOu8LnPexwiAa3rHavBaen0/q3F0qGQydvHagxOVmyNLJ5GfICtNjX0upvQvsuc+J8jrgjcAdjv3chsHaUREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBRvpThfJgs1HFI6KSXDZJkcrDs6N7qczWSNI7nNJBB+5SRcs/abztmHDHFY4B+W1bKMNjmcXCGC2Ort2nuHOOKKBz/rB9l0kSDSdGXSvho8Hh8fgoLWau18NQYMViIesfWd6Oxm2SuSFtXHnrGvDnTyAkh2wceRn2hNO22T2MtlnwvyuQjZD1NYudVxlGNznxY+q94DpfXcZJZyGmV5HJrGRsbzn9h7TTsXpmaCaIR3PpzJx3wCHEWKc/oLmFw5EN9G2G3LvPtK7sgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiIC4n6V9Ma4rbF7q+nRedDtwmLjo12UrL9wN/rrebkjLSR6+mwQORXWNX5uLG4+9kZ/wCZxlKxblA7yyvC+VwHvcQzYD3kLj/7LtB7Ppm/aIM1b0PFWH+z0utDJmM3IHEbnfLZzItPs/wcDkWlBJf2cbgmpZpzeYGstTbfg/KzzD+EgUX6QN9WUcldOes4TS2G9LYy1i3sbPk7NElti9PPzP0ZDLHJHHAzYzOY95cB1K5v+yF0pVINO5uOw9tnK3c9ftUcHFK03Lpu1KzwyGLfjbWEkc5fOdmRtD3vLQ0lRroA6D9T5zTrKWQyr8VpfJXIchHj2xia5bY08XHDxbCtUl9R7eMvaXRxyiM8nPC1vQI7JHTOEdl5DLkH42B9iR7nPlc14LoDO9/rPs9QYeMncl/HuT3qbrzrQtjYyNg4WRMaxjR3BrQGtH5ABeiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICrPrrXT9Q5OzXxl/LPr0L0mIxeJ03km4u1mMnWibPlL9zJFpNXDVWS12B7dw97txxBzQ7q37QGSmr4mKKKV1WLK5fF4u/kGPMbqNDIXYq1uw2UD6h5jeYmycuB07Xbt23EU6KejfB0tXZrJYaGGvDj8VQxT4Kjz6OzITOks3hwAkNkFaPFb7H7U0pPrElBlfswa5vZOLMYzKC0MhpfJmpJ6ea7rpqyhzqwty1GtgsTNMc7OujaGyNjjf3uJPY1xjoToudq3pAyDdjXsZLD0WOHcbFDG72m/i02o/zcV2dAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREHPv2ha5nwT6m+zMnlcDj5/vr3s5jqthh3/ddFK9h+55UR0vZlqdH+SvM2NzJVtQ5GMgfbu5S5flqN7xueOeuzv8AYFtP2vq9mbSOQgpNkddtXMNDSbA4tmdZfmsf1AicCC2Tj22O42Kqx0GahzdjD4agMjJYxz9eYfF5LF2I2SPq1nWquSqS15i3rYoXy1LzXsc4t+pYGgcTgQsjgP2eKdC5ZFOWvWxGVjrtylOGmfTrccMMccuN+kHykQYieSPrZYo4w+QySML+AtDe4MaGgNaAGtADWgbAAcgAB3BfqICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiIPG7VinjkhmjZNDOx0csMrGyRyRvBa9kjHgtewgkEEbEFVX6EdUvx1jWGm9J4k3LcOqrs1OaeaCDEY+CcQ0w+050gsPr15ak2zIY3l7WsaHAuDlMOn3pluR0blfTELp5I7cGMt6hkLY8dQtW52VRDTe875G+x0g4hCHti+07ctLVFOirotp4iHSuYoiavmxqCbD6hmFy1LFe6mTJ0MpE6KV/Bwek0+NpDR/NNO2+xAWH6OdKx4fHxU2yOsSl8tm9dkaGyXb9qR1i7ckA5NdJNI93D3NHC0cmhSJEQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERBEOk+UMbieLbgfqLFsfv3bmV3Vfn1vVAfeQqmZ/EXNL67txRRN+hs7qvS1p0j3cPUPu5Ka5XkY0d7WmtmoAO4Abk929mf2m4ZTpbK2K7+qs4llfLVJQATHPircGQjcAeR51tvwcVx39qTNV7+msTqeIPZXzWNbVmMW5krWJY2ZbETOLN9n1sjRdAXDfZt+wBvxcwtWijfRfqhmaw2MyrBw/SdGGd7P8ANyuaBPH94bKJG7+3hUkQEREBERAREQEREBERAUQ6acoaWnszaDp2ej4yy50lRzWWY4+rLZJK73AtZO1hc5riCA5rSVL1qdZYRmSx1/HSco8pQtU3n3NswPhJG3MEB++/3IKk9N2IfJonB6lP+CV8fcxNzEaeoyf4ux+NmcepZIS0Pu5J7ZIXSWH7bEuaxrd5HSd7wtSSbIy12M+oxesHZBpbzDqmQ03NbE/LuByVydvP2s+9cP6O87WtYLD6CzLuvsZCStFWc1h9ak708XIJDv8AU28fcp2ax5jfq6r278R4evdCGQk6/Hmy5xtZHTLMfdB34Bk9IZCbG5F3MDaWSXI+71m1gRyag7Gi53prpWrXtS5DTsdSw36Nge6LKO51LdmqawyNSEgbdZX9NqB3rE7veCG7MMnREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQQjp8idJpjPQt247WJt12cXdx2IjAzf8AtSBcE6XsDBjNJ6u0wA9tHBZDDZTFetu6DE5nKwSPja5+5d1NmPLNBO54er33JO/dOn+51ODk5gdflMHXPF3cFjOY6GX/AIb3/ouU9LNiHPZS/jK7DINSuxml4JG7jrI8LetZbUWRae59OoywysHDvsGZn7pQWLxWPgqQQ1a0TIK9SJkNeCJobHFFG0MZGxo5NaGgDb7lkoiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiCtWoOi61i9W4zLCxTOLvayfbqVWwvN2K3lcZL6dvM4cMcDpqhdwN34iWE7FqWOKxntWYOplxgb+AycGqMVlDDDYZFWyOKhZm2yVpiI5K3FYe93EdhJZa/vaFN/wBqbNTY6lgrsFd9uWrq/EOZUhG8tnjFqJ1eEf557Xua3/Sc1c16IdP4vpDkzGaydSzVfHqaKxXgjkEUsuNOHx8EVK47gJlp2IYYXvY0ji5cLtidwmH7JPR3JQpfS9u3ctvyL70uHZfI62tjMhZjsmeVvMm7c6itPIXOO20beR4+LvC/GNAAAAAaAAANgAOQAA7gv1AREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQERaDpB1PHh8fNdfG+d7XRQVKkX89cu2ZWV6dOEbH6yWeSNm/c0OLjyaSg5P+1QW5gVNLsnFaFxGa1LkiWiPE4PH8chlkcT6tiaZoEY2P8AMSEgNBcI5+y7Sfc1DbyxrtqY6HS+Ph0rjw4k0sHZv3oIDMCNhbndh5J3O4nk+lH1uZA0XSxpi/Nh9Q4/0trb1fGv1Hr3LQM4228g2m+fFabql7g5lOKKGN237kTKx23ncD2bodw3oN+1WafUxuldI4xrdubTTZmXkk+0n0kH9feg6iiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIggfS3RbYn0zG4Ahuqqs+x99PHZS40/k6uD+Sg37LUPo7K0YbwtyWidJ5AEADjsMjyFOwSfaRDFjx+YUi15rii/UeLwETutyFGO/mLXARw04W4m/VhZKf8/J6bxBneGNDjsHs4tF0AF08mnnQ79Rh+jjDV7r9vUdbybKVmtC12/OWOClLI5vsbegP7yDuCIiAiIgIiICIiDT6kwDLwj4rN+sYS4tdj79ioTxbb9Y2FwbKPVG3GDtz27ytQdGWmt4YdR56Eew8WHsOH9q7jJSfzW81NqGhjIDZyNyrRrhwZ19yxHBGXuBLWB0jgHPIB2aOZ2KhbOmzATbihJfyxHyXCZXIMJ3I2FivWMG+4P7/AC9qDeQaWvtHPUuZkPvlrad5/iIsO1ZTMHfH/nq2775KeNJ/4dVqjbteZqf+gaQyhB34ZcxfxWLi5dxLWWJ7LWnv/md/eB3L56zXFg8o9L4th2245cpmJh37gtYymwEcuYce9BKRi8iO7Kk/7ShXP/Y4V+/R+U9mSr/2sZv/AHWQo5HpfU0gPpOqWRbnl9Faep1y0e7fIzWw4/eR+S9f5CZF329XaiJ9vVw6biB/JuF5D80G9NLL+zIUf7eImP8A2cg1ebqec9mRxQ/HBWz/AN8LVDQNn26m1Gfv67FD+DcaAvx2g7f7uqdRs+8Owb/+biXINuKmb9uQxR/DCWx/3uU9HzY/63i3/d9F24/4/SDv7lqBonJtHqauz/8A7yppmT9f8Sg/xWU3T+aYPU1A6Q7d9zEUpOfvIq9Qgy5DnG/ZbiZP9Z9yH+IbIsF+Q1O1/LE4KSP+sNR345PvIjODc38uNfkOP1Qw7uyuCnb/AFDp2/XeR7AZW5p7d/v4PyXpPa1NHtwUcHa95dl79Dl7w0Y2zufuLvzQekuoMrE3eTAWZnD93HZHGS7/AIG9PWH67L0Zq1zW8VjE5ir72mpFccPyxc9jf8t14SahzETd5dPzTn2txmUx8/8AunIPqb/nsvN2veqZxW8Nn6vdu0Ys5Fw3+7CyWt/y3QZsOuMc4bvdbrgfvX8Tk6Dfx4rtaMbfesrH6uxVh3BBk8fM8ciyG9XkeD7i1ryQfuWlPSrp9gabORjx/GdgMzDZxB358uHKRQkHkeS31HIY3Jx7wT0chC4b7wywW4yPfuwuaQg2oIPMcwfaF+rQDRWJaSY8fVrvd3y04W05T9/XVeB+/wCa8XaRaxpFXI5eo4/9IMlJeIP3NzAssH4cOyCSoonJic7EW+jZipOxv225XD9ZNIPYBPj7VaOI/f1LvwXwczn4OI2MLWtsb9g4fLsfYk9+9fJwVYoj93Xu/FBL0USZr+owht2tk8a4t4nG9jLHo8YHf1mRqtlosI/238FvsFm6d+IT0bda5C7ump2IrER390kLi0/qgz0REBERARaLUmssRjf8o5TH0fcLt6vXcTtvs1srwXH7go8/pcxD9vQ2ZXJ8W3C7E4HLXYXB32S23FW9GLT7+s2HedkE+Rc+OvMvL/RNI5lwJIEmQt4WhHy32cWm/JOGnYf9Hvz7l+jLawl+xhMDVG//AFvUlyZ22/fwVsPw77ezj/NB0BFCOp1a8f0jTtc+0eg5O6B+fpkG/wDBfrcbqs9+Z0+3/V0tkXf36hCCbLlXTV18OZ0bfkcDiKWdmhvxdXxcF3JUZ8fiLb3fuxssWHM35bOstP4b92M1X7M1gCfv0rkAP1/lCVC+lHSmusljbmPju6TsRXoHRPMuNy1CaMnnHPXkbdsNZZjeGPY4ggPY0+xBq8vGf5Ia9dKeCa5l9URzyO23LevdSqF23sFOOo0f6LGrqWlIv8cZ9+3fLjYx+EdBjwB+cp/VQGn0c567pDN4vKT0GZrUclmWWWuZTSY+RlaFpceHiHG2txu4WkB0zthy2Wi11pjWt6OOxUqMxWoIzA2TK4vVdhmIsdRsDNZw81Ux2eIcTeB7CQ3g3e4MDEFh0Wu0z6b6HV+kvRvTxXiF70EyGqbIYOuNfrgH9SXbkBw3AK2KAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiIChnSlq2ahHXpY6OOxnM299fEVZSeqa5oBsX7fD6zaFZjhI8jm71GD1pApfanbFG+R52ZExz3kAuIawFzjwtBJ5A8hzVa6eLyGobdGxJKac3SDRuXZ7cbuG3i9FUJKJq4XHuHEGXLjslVlnlBABlk5O4GBBg6bt0TqJtbGiS5Dh9P6qfkNSSNH+O85N9FfSkglaNpup/wVu7Twt60Mbs1jSe8dD2JgqYTGCGJsbrGMx0thzR60szcfUgEkhPNzhFBCwe5sTGjYNAEH1niamPyOPoUYI61XG6E1aK9eFvCyNhmwDRt7S4kOJcdy4uJJJJK6hoyPgxuPaO5mPqNH5QRj/8INsiIgIi8ZLLGkji3c3va3m7fYEDYe3Yj9UHsiwXBxfC5xIJkIEYd6rR1Up57cnv5Dn3DbYe0n6vTDcRvbvHMCwvDu4n2Ebd23t/H2AoMxFhY97ml0LzuY+bHHvc3l+u27f97bntuc1Bg5PDU7T4ZLNWtYfUc51Z9ivFK6BzwGvdC6RpMbiAAS3bcBZzQANhyA5ADuAREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREAjfkeYPeCoxm+jzA3XiW3hsZPM07tsSUK5sMIIILJwzrGO3AO4cO4KToghP/g2qx8RpZDOUHO326jO37ETCfbHVyUk9aPb3CPbkOS/G6VzcIPUaotTH936WxOKstb9x+j4ajnD8Xb9/NTdEEJhp6rjPrZHT9poA5fQmRpPPv3cMrO39Gr0kt6pZ9nH4Cf7zm8jU3/sjETbfqpkiCJ1snqHb67D4oH3V9RWZh+suHiWl1Bh5rb+vsaXoS2mtc1lyLKRQ3Yw7biEN6OuyxDvsObHDuHuXRkQcDzUWv6h/xHQPVsDQyvnNSVcrBsD625mqMyD3kcuJ90j7vf5v130nxxcL9E46acDnPXzdRsLnbcy2s62ZQPuL/wA1YBEHKaUucsMByeoDid2tMjcbph1BsJ73MdfzbrlZ/wDrNA9u33bLGaHw17Z82Sv5wgbP9I1BZnrP5EEyUKU0dEk8/wDodv0XRFr8tgqNvb0unVtbd3pNaGbbbmNusaUGFpzRuIxv+T8XjqPtJpUa9ckgbbudEwFzuXeea3qjs2iqB26ttusGncMx+UyNCMe76qnYZGR9xBC8Z9K2d29RncxWa079W04y013fsHvyFCaXh5+x4PIc0EoRRSzis80AVszRO3tyOCfYcR+NPIVmg9/Ph/Jfkr9SRt9SLCXHD+tYv41p/MQWy3+KCWIolDl8+0fX4SkT7qOeM+/4G3j66+JdWZJh2Ol8xJ/pVrmnXNH4+kZaJ38EEwRRGLV90j1tNZ2M+50un3n9Ycu4fxX3/K61/wCj2b/+T+ZoJWiiMurrwG7dM52T7mzadYf+NmWr9r6ryD9//FjMxEd3X2tOgH84MxIf4IJaijgy+UdtwYfg3+JyVdm34+jtl/gvht3Pk/5NxDG/1jnbj3/nGMQB/wDEgkyKPPizbx6s+KrH3Gnbuj9Rar7/AKJ9E5SQbTZYRn2ux2NggP5C8+0B+e6CQoo4zSznDhs5TLWveTaipHb/AFsVDXI/Ec19R6NoAbPbZsD3XcnkLo/S3YegkJK8+vZ3cbPw4h//AFR2To+wLju/CYl7v60mMqPd/vPiJX4/o70+RscFhyPccTSI/QxIJOijlXQeFh/o+KoVfvp1IqjvxDqzWkH816DSsLCXQ2slC8/vDK3bDR/qw3ZZYR/uIN+i1uLx9iE+vfsWwQf6XDTDgfYWmnBCPyIP5LPgDw1okc1zwBxuYwsaXe0tYXOLR9xcfxQfa4xgKcuM1PjsQ+tIalavmJtP32NaIIsVbFWWzhpNturlq2YK4iAHCa/UD7UZLupXMrLDw8VG1ICwF8lY15mMJ728JlbM8j/RjKwP5a0dyJG5CHhPN1nC5WCMH/by1REfbzDiEEC6UHl2o3s/q9HepnD8X3cQ3/8ARdQ0x/Qaf/qdf/ksXB+krpIwNTVtGzdvMGOuaUyeLsWoI5bDIJrV6nKxk4gY50PEyB/Nw5cidhzWN+z501y2cnS01NdxebYa80NTL4mDK1ZuGhXL2PyEN+s2B0kkcLt3V5HAO2GxB3AWSREQFgvl4HS8QcAXh3FwPLdurjBJcBsBuD392yzkQYT3bvh/2h/5MqwpYSyuYiA188n1UTTuGDdvqgj93ltv/pjfbcrO9DLZIywgRscXFh/dJY9vqfdu77P6e5e1iLve1rTK1pDHP7gee2+3Pbmf1PvQY7edpxHMMg4Hfc4vDwD+IP8Aes5Y1CsY2niPE953e73nmdgdu4bn2AczyG+wyUBFQDtq6q+X6f8AB5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/RUA7auqvl+n/B5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/AEVAO2rqr5fp/wAHkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf9FQDtq6q+X6f8HkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf8ARUA7auqvl+n/AAeR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/0VAO2rqr5fp/weR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/wBFQDtq6q+X6f8AB5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/RUA7auqvl+n/B5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/AEVAO2rqr5fp/wAHkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf9FQDtq6q+X6f8HkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf8ARUA7auqvl+n/AAeR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/0VAO2rqr5fp/weR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/wBFQDtq6q+X6f8AB5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/RUA7auqvl+n/B5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/AEVAO2rqr5fp/wAHkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf9FQDtq6q+X6f8HkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf8ARUA7auqvl+n/AAeR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/0VAO2rqr5fp/weR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/wBFQDtq6q+X6f8AB5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/RUA7auqvl+n/B5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/AEVAO2rqr5fp/wAHkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf9FQDtq6q+X6f8HkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf8ARUA7auqvl+n/AAeR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/0VAO2rqr5fp/weR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/wBFQDtq6q+X6f8AB5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/RUA7auqvl+n/B5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/AEVAO2rqr5fp/wAHkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf9FQDtq6q+X6f8HkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf8ARUA7auqvl+n/AAeR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/0VAO2rqr5fp/weR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUFZkREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQf/Z\\n\",\n \"text/html\": [\n \"\\n\",\n \" <iframe\\n\",\n \" width=\\\"800\\\"\\n\",\n \" height=\\\"450\\\"\\n\",\n \" src=\\\"https://www.youtube.com/embed/oLSdlg3PUO0\\\"\\n\",\n \" frameborder=\\\"0\\\"\\n\",\n \" allowfullscreen\\n\",\n \" ></iframe>\\n\",\n \" \"\n ],\n \"text/plain\": [\n \"<IPython.lib.display.YouTubeVideo at 0x7ff95398cb50>\"\n ]\n },\n \"execution_count\": 80,\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"output_type\": \"execute_result\"\n }\n ],\n \"source\": [\n \"from IPython.display import YouTubeVideo\\n\",\n \"YouTubeVideo(\\\"oLSdlg3PUO0\\\",width=800, height=450)\\n\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"There are many types of data visualizations, serving different purposes. Today we will look at some of those types for visualizing single variable data: _line graphs_ and _histograms_. We will also use _scatter plots_ two visualize two variables against each other. \\n\",\n \"Before starting, read the following sections of the data visualization book.\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"> * _Reading_ [Sections 2,3.2 and 5 of the data visualization book](https://clauswilke.com/dataviz/aesthetic-mapping.html)\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"## Part 2: A little visualization exercise\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"Ok, but is data visualization really so necessary? Let's see if I can convince you of that with this little visualization exercise.\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"\\n\",\n \"> *Exercise 1: Visualization vs stats*\\n\",\n \"> \\n\",\n \"> Start by downloading these four datasets: [Data 1](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/suneman/socialdataanalysis2020/master/files/data1.tsv), [Data 2](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/suneman/socialdataanalysis2020/master/files/data2.tsv), [Data 3](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/suneman/socialdataanalysis2020/master/files/data3.tsv), and [Data 4](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/suneman/socialdataanalysis2020/master/files/data4.tsv). The format is `.tsv`, which stands for _tab separated values_. \\n\",\n \"> Each file has two columns (separated using the tab character). The first column is $x$-values, and the second column is $y$-values. \\n\",\n \"> \\n\",\n \"> * Using the `numpy` function `mean`, calculate the mean of both $x$-values and $y$-values for each dataset. \\n\",\n \"> * Use python string formatting to print precisely two decimal places of these results to the output cell. Check out [this _stackoverflow_ page](http://stackoverflow.com/questions/8885663/how-to-format-a-floating-number-to-fixed-width-in-python) for help with the string formatting. \\n\",\n \"> * Now calculate the variance for all of the various sets of $x$- and $y$-values (to three decimal places).\\n\",\n \"> * Use [`scipy.stats.pearsonr`](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/reference/generated/scipy.stats.pearsonr.html) to calculate the [Pearson correlation](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pearson_product-moment_correlation_coefficient) between $x$- and $y$-values for all four data sets (also to three decimal places).\\n\",\n \"> * The next step is use _linear regression_ to fit a straight line $f(x) = a x + b$ through each dataset and report $a$ and $b$ (to two decimal places). An easy way to fit a straight line in Python is using `scipy`'s `linregress`. It works like this\\n\",\n \"> ```\\n\",\n \"> from scipy import stats\\n\",\n \"> slope, intercept, r_value, p_value, std_err = stats.linregress(x,y)\\n\",\n \">```\\n\",\n \"> * Finally, it's time to plot the four datasets using `matplotlib.pyplot`. Use a two-by-two [`subplot`](http://matplotlib.org/examples/pylab_examples/subplot_demo.html) to put all of the plots nicely in a grid and use the same $x$ and $y$ range for all four plots. And include the linear fit in all four plots. (To get a sense of what I think the plot should look like, you can take a look at my version [here](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/suneman/socialdataanalysis2017/master/files/anscombe.png).)\\n\",\n \"> * Explain - in your own words - what you think my point with this exercise is.\\n\",\n \"\\n\",\n \"\\n\",\n \"Get more insight in the ideas behind this exercise by reading [here](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anscombe%27s_quartet).\\n\",\n \"\\n\",\n \"And the video below generalizes in the coolest way imaginable. It's a treat, but don't watch it until **after** you've done the exercises.\\n\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"code\",\n \"execution_count\": 81,\n \"metadata\": {\n \"scrolled\": true\n },\n \"outputs\": [\n {\n \"data\": {\n \"image/jpeg\": \"/9j/4AAQSkZJRgABAQAAAQABAAD/2wCEAAUDBAgICAgICAkICAgGCAgIBwgICAkICAgICAkICAgICAgIChwLCAgOCQgIDSENDh0dHx8fCAsgICAeIBweHx4BBQUFBwYIDQcIDRIIBwgSEhISEhISEhISEhISEhISEhISEhISEhISEhISEh4SEhISEhISEhIeHhISHh4SHh4eHv/AABEIAWgB4AMBIgACEQEDEQH/xAAdAAEAAgIDAQEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAgUEBgMHCQEI/8QARBAAAgIBAwICBgUKBQUAAQUAAQIAAwQFERITIQYxBxQiQVFSMmFxkrEVIzNCcoGR0dLwYqGissEIFiSCwvElJjRTY//EABcBAQEBAQAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAABAgP/xAAaEQEAAwEBAQAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAhIxAREh/9oADAMBAAIRAxEAPwD8ZREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERA9mIicObaa6rLAFJrrdwGbgpKqWAZ9jxXt57GBzSLOo8yB9pAmsXeMUU2gVBhV0Dv1h3FuK2Y2/s+yempVR+se3Yd5caspLLt8PiPjLznozusvzL/ER1k+ZfvCU1aHf/ANW94+U/XI9M/wBkfzmqIu+snzL94R1k+ZfvCUnTP9kfzjpn+yP5xQXfWT5l+8I6yfMv3hKTpn+yP5x0z/ZH84oLvrL8y/xEdZPmX7wlNZWe32D3j4D65Hpn+yP5xQXfWT5l+8I6yfMv3hKTpn+yP5x0z/ZH84oLvrJ8y/eEdZfmX+IlJ0z/AGR/OSRDs32fEfMv1xQXPWT5l+8I6yfMv3hKTpn+yP5x0z/ZH84oLvrJ8y/eEdZPmX7wlJ0z/ZH846Z/sj+cUF31k+ZfvCDcvzL/ABE0a/xbp6anXo7ZCjUb6urXj8X7rxazbqhemLDWjtwJ32EzM7xBg159enWZNCZ2UrWUYrWAW2IOfdR9Yrs2B8+DbeUVG29ZPmX7wjrJ8y/eEpemf7I/nPnTP9kfzigu+snzL94R1k+ZfvCUnTP9kfzjpn+yP5xQXfWT5l/iI6yfMv3hKfpnj+/4j4fbIdM/2R/OKC76yfMv3hHWT5l+8JSdM/2R/OOmf7I/nFBd9ZPmX7wgWp8y/wARKTpn+yP5yVSHkv2j3j4/bFBc9ZPmX7wklYHuCCPqlF0z/ZH85a6aNqxv8T+MnY+KyYiJkIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgJ8ZQQQQCGBBBG4IPmCPeJ9iBBaUA2CqAOOwCgAcO6/wMwNX+kv2H8ZZSt1f6S/Yfxmo6MOvz/c3+0yMlX5/ub/aZGdEIiIQiIgSs937K/hIyVnu/ZX8JGAiIgJJPJvs/wDpZGY2qapjYdL35d9GLSvFWuyLUpqDM6hQbLCF3J90KygJ1h4p9OWg4DXVl8jItxMk419dFG3Fk6gtsV72VLK0atl9k+e23bvKvxz4L8Q65q5S3PGBoWI1eTgW4hRrXfjUOwSwWjIB6xFj7qO2wO87OxfDmn1W33V4eIlubYt2VYuPXzutQsyWWHj7Thndt/izHzMg6x8SekvxHXlZlGD4cvyKsTJSunIZMkrdSxIRwqIAeqNmDqSEB9qbn6UtJ1nNwaq9Gy007LF9Vlru5UNSFcNV1a62I2dkbsO/TI8jNviUU9fhvDOVTqF1FFupUUCn17pBbT7BVyvuXfk4+IDkeUhqXhDTr9Tq1a3HVs/DU10387BxX2wN6w3TdlFj7Mw3HL7JdyVv0j9pgaX4e8K6hj63qOpXanbkYWfXxx9Pbn06G5VFSAz9NOmqOo4Ab9Uk9/O50nxTp+Xl5WDjZNduXpx2y6F5cqyG4N3K8X4v7J4k7HsdjLmad4g8PDT6tU1LQ8DHbWs6vl7Rba9zYrWey1gQE+1ZxXbkyrvCNxiU3gnJz7tPxbNTpTHz7K98qms+wjcmC7e0QpKBGK7nYsRLmBP9X9//ABISf6v7/wDiQgIiICSq+kv7Q/GRkqvpL+0PxhUZbaX+jH2n8ZUy20v9GPtP4zM8OMqIic1IiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICVur/SX7D+MqdS1fUUyb668cNRXZjrQ4x73Lq9LvZuynhsbglfNey8mLDbbe31Ye0vcDsfPf4/UJqOjCr8/wBzf7TIzkrUb+Y8m+b5T/hkeI+Yf6v6Z0RGJLiPmH+r+mOI+Yf6v6YEYkuI+Yf6v6Y4j5h/q/pgLPd+yv4SM5LFHbuPoj5vh+zI8R8w/wBX9MCMSXEfMP8AV/TOO+2uvj1Lak5sqJzbjydvoovIe05+A+ECQnV+Pn6d4y/Kuk5eHmUV6DmV7WmwVs1ytdSGBUfmrOIt3rbftap8/K/w/Gz2eIcjQjg3rXjYy3jUSW6TkpXZ+j6WwqPU4B+X0kYbTdVA2b2h5f4viv8AhkGJp+JXj01UVLwqxq66al3J4V1KERdz3OyqB3lP478XYWi4oy85rFqe5KEFVZsse11dwqrvt2Suxtz8pmw8R8w/1f0zr3xX4qxrNao8O5+mrkYebStxzMpVfE6oWyysdG6ng6hquHPffk6jaUc/gbx5fqefqGN+TsinEwq1tws5uXDNrcjpFVsrCqba2FigE9t99pq93jzxJqOjXZmmaUun5mJn9K2vUHAU4a0mx7Q2YK1XhaURifIB9u/lseoemDw7i5j6dZmcMjHvOKyjGyDUjowqs2sWrgKq7CqE+7f4SF2Lq+qZ+s6TquLVVoF2O1eJlUuVvsJanp8X5EsxHVYhlABrUdx5wZ3of1DWcrTjfra4q32XOcZsR6bK7MYqnF+WPY1bDqdUAg+QXfv57rb9I/aZTeC/DONpGDRp+IzGjF6nE2sXsZrbHusd2CAci7sdgAO8u7VG59oeZ+b+Uo44kuI+Yf6v6Y4j5h/q/pgdeYGo6pp2oanla9n6fRoltgr0nqPTTwZnJqQNxD8ugrcg5PdSR2BnYCkEbjuDsQR3BB7ggjzEovHfhDTtYxlx9RTqU0WDIXhZdU6OqupIar2tjW7jb6/jtMP0YeNNO1vFe3TurXTg2DG4XV9MqqopqKBGI6ZrK7bnft3Agbb+r+//AIkJycRx8x5/Bvh+zI8R8w/1f0wIxJcR8w/1f0xxHzD/AFf0wIyVX0l/aH4xxHzD/V/TJVKOS9x9IfN8f2YHHLbS/wBGPtP4yr4j5h/q/plrpvase/ufLf4/XMzOMmJwajQ1tNtS2PS11b1rdXt1KmdSosr5ArzUncb/AAE6t9D/AIj1fVc2yvNZqU8J476TqwVaxXqevGwdXJTbuuMmHVj3qBtudWIP0JzV2zETpL0neNdY03xNbVidTJwT4fw6asBagyrreqZWsVabl2OiGxKWv06jFLdwPW1JHYmB3bE6t9HnjW3F8MaVl6pZkanqGZdbg1jGqrOXqWaMnLrSuiolalY1Y7vu5VVWlyxABM3Hwj4rq1BcoGjKwcnTLRTn4WYlYyMd2qS+sk41r03VvVYrB6mYHcjzBADYYmmeGfSDTmZlWFZg6np1mdjXZemvqNFNK5+PjtUtz0pXe12O69eljVkqjbWr7PntW0+lvEa2/fA1ZMLC1S7R8vVXx8cYFObVlnA2JGT6xZjtfwHWrQqvUHIqQwAdixMDW9ROMlTDHycrrZFFBTFRHesX2LWci0O4C49YbmzDcgKdgfKZ8BE4c20pXY4BY1o7BQCSSqkgADuSdvITp7/p71i68YX5T1TxDbqubpFeVdpusYVGFiMx9X9ayNP46ellwpuZa9uZ2F6kghlaB3PE681HxYX8SV4K5Pq+Do9VVef2G2brGrKfyZpvIruDXi1XZJVdv/5OJv2M7DgIlH42wc/JxRRp+UMCy26gZGWEV7qcMOGyjiC1GqGW1QKK1gIHPfY7bTQ/BHi7JGl+JsynJs1XB0S7OOh6hlCsnNTEwa7sivrUIq5eNVnjIoF4HcVkbkjch2xE6e9DHiG7IysNX1XU8v8AKGkeuXY+saacI5VofH31DRnGKi+qA3OjU99hZisNt927E1lrK8igi3ISqyxTa2ytQg7KlXZN15uQORPbcwL2JW6yGH5x7zj49SMzsnEObNxx3LqRxA39keZImPZlXnFxeZNV2U9FdrAAOnPu5CkbK5A27+XKBdRKzSrLN8qoubDjWBans23IequxVcqO+zORv9kx8B7UyVpNzXnos+XuF4VWEp0+HFRw5b2ewfcoMC7ia8clvWrerblVIuRWlQWsDHI4VbK7ms/SsLDz94mwwEREBERASt1f6S/YfxllK3V/pL9h/Gajow6/P9zf7TIyVfn+5v8AaZGdEIiIQiIgSs937K/hIyVnu/ZX8JrHpM0DM1PTrMTCzX0697KnF6GxSURt2qZ6mFiK3buvyj3bwMLxx4+r0vUNJ098XIvbXLukltWwWr85XXuFI3tYFwxUbbKCZyekz0fYXiCvFrzHyK1wbmtT1exULhwFsR+aHsQo9pdiNjsZsWhYttGLjUXXNk3Y+PTVdkuOL5Fldao9zDfszkFv/aZkD6T/AH/+Z9Tyb7P/AKWRkk8m+z/6WFRmp+k3wFh+IMenGzLMitMa/rqcd0UsSjVsjCxCpBVj323H8d9siEa/d4I0Z7/WX03BfINiXG98at7jbX9Gw2MOTPuAdz5kAnvNgiICSt+kftMjNS1vx/jY2vYugtRktfqFRtS9VXoJuL2UHdubDbHs3YDYbj69ittiJpvjjxu+mahpOCuBkZa6zd0nyKiQuP7aV7hRWRay8+ZBK7KpO5hG5TRtSy9Uw9ZwMLTdLxvyNlhrdRy6qxWa7nazqtvUwSt1Vam9oEv1Nh5TeZrXpM0DL1PTrMTBzX0697KnF9ZdSURt2qL0sLEVu3dflHu3gbR+r+//AIkJjaHiW0YeNTdc2Tdj001XZLji+RZXWEe9hv2Z2Vm/fMmAiIgJKr6S/tD8ZGSq+kv7Q/GFRltpf6MfafxlTLbS/wBGPtP4zM8OPmsvkLjXtiJXblLTacWu5zVTZeEPRS2xVLV1F+ILAHYE9jOu/Rt6O8rQszFupsqvTUtPdPFFjMa7MvWVubLTVqqwuzPbblZ9bAkeycUDcJtOz4nNSath6BeniHM1Qmv1bK0XTNPrAY9UX4mZq2RaWXjsK+GdTsd/c02mIHT2b6M8x/D+kYL14WTl6DqlmpHDuvsrw81Xs1GtsZsqukvSxx9QLh+J9qpAe25mw+B/CORjYWrKuPgaLkasbBijTi+S+KoxhRj35OTaAMrKWzlZ7IAAKL325HsCIHSno49G+bh6vpWdZpek6cum4Gdi6jk4ufdnZup5WQuKq5Ntl+Itj1747tytYtve2/lubrI8B5x0HVtNBx/WNR13UNRoPUYVer5WutqlYduG62ertsQB59t/fO0YgYOsW5SLWcSqm52vpW5brmoVMZnAyLUZa252pXuwQ7bkAbjzmdEQMfUqrHpuSm3oXWVWLTfwWzo2MpCW9N/Zs4sQ3Fux2nX3h3QdbytW0vUdZrwcdvD+nahh8sLLsyvyjlag2CLckI+KnqmOEwAwQ7nfII8l3bsmIHUHiL0O2+spkYGraqoyfEVet5+Pbdg9FHLE2247fk83NYla00qjsQFrUe4TtHWLcpFrOJVTc7X0rct1zUKmMzgZFqMtbc7Ur3YIdtyANx5zOiBo3ps0DUNU01MHBSq1MnMx/wAq49uZZgDL0xOdmThjKpod6xcy1VtsO6WWjcbzI0/S8zM0nN0zNwcLR67sS3T8WvT8w51NeNbjtQCqnDqFPDlsKwCNlHebjEDrHwh4Y1izUdHzNVpwcVfDGl5unVep5luX6/dm+oI+QFtxkOLQtenqwQ7ne8jyXdt2zsXKt5Ut02qe5LBby4ulSulnT6QTZmBQjff3y4iBUari3PkVWCuu6qhN0R7TWBeW/SEcCGIUADfy5Gc2o49ttVTBUW2m2u7plyUJQndOoF3G6k99vhLGIFZh416rlWHgt+UxetA3JUK1JVWGYr3O6Ant75DQce2lVqamtF7tZaLzY9lh+k7g1gszH37y2iBT5+LlW86W6bUvdXYLS3F0rR0s6XSCbMwKbct/fLiIgIiICIiAlbq/0l+w/jKrUV1b1jI6THoG2j1cAY68a/V2D7lzydfWtmbcA8R7O5Pa21YDku5PkfIb+/7ZqOjCr8/3N/tMjOSsLv5t5N+qPlP+KR2X4n7o/qnREYktl+J+6P6o2X4n7o/qgRiS2X4n7o/qjZfifuj+qBXeLMJsnCysdMhsN8rGelMqs7PjtanBbVPIHcMw8iD8CDKz0c+Hr9K06jCyMuzPtoNhbIsDAkPYzrWodywRAwUbn3e4dhX+m7QtL1DS+jqucdOxUvotGQWqrTqqrolbi08LAQ7nifeoPum1aRj1U49FVVj2VU0VV1WMRY1laVqqO1nL84SoB5e/eQfc/Mpx0Nt9tVFSkBrLrFqrBY7KC7niCSQJg6H4jwM6zIqw8qjJswHFeUlTh2qclgA23uJRxyHbdG+E0v8A6kfDuXqeijHwMdsvITNouCqypZWipcjW1q7hLG/OBOLe6xj5ibB6OPBGnaRTyxcVcPIzacb15UtsvVbK6+9Vb3WnapbHs+jtvvvKNpkk8m+z/wCljZfifuj+qSQLs3c+Q/VHzL/igccSWy/E/dH9UbL8T90f1QIxJbL8T90f1RsvxP3R/VAjNGbw0zeKX1NdWLCjE6b6OGBapbEFYLL1fYx2cC3uvdgO82Dxt4qwNGxhl59r1UtatKcaWtd7XDsqqiHc+yjt/wCplbofgvShqt3iLGe979Wx12bmDjGu5aW6tSbcwXSqr6RI+AEg2ufR+M+7L8T90f1T6OPxP3R/VKNK9FnirUNUry31DTLtKbFyOlStvPe1diW26iAsyEAF19k8htNymneivRtaw68xdb1BNQe7I54rVgnp1bHkTyUdMOdj0huF49j3m57L8T90f1QNN0jwBXj67m68MrIezUKRQ2K23SQbUjfnvu6DojZD5c285uEqvG/r/wCTcr8lFPyhw/8AE6ypw58l5fTPDn0+e3Ptvx37SPgj1/8AJ+L+VSn5R6X/AJfRCcOfJuP0G4c+nw34dt+W3aBbxJbL8T90f1RsvxP3R/VAjJVfSX9ofjGy/E/dH9UlUF5L3P0h+qPj+1A45baX+jH2n8ZV7L8W+6P6pa6b+jG3xPmNvf8AbMzOIa1p1eXjZGLabBXmU20WNVY1VqpahRmqtQ8qrAG3Dr3BAInUnoZfV9Q1Gz8rWP8A/sWuzQuSWkV6rqdgrsu1e6pG22bTfyeyo/0Wz8udzzXPB3ho6fkazebRb+XNU/KIUJw6A9RwMHpE8j1D/wCEX5dv0m23ac1bHOi/SVZra+Lch9Ia+4jwzgYLYosJx6LNWzddqq1dqCwRjjZWHhFiNj02u28tp3pNexvDhTW8rV+qCuZpeBp3Q4d0OFlalkm7qctiGGeF47dul59+wdb+BfGP5E8I6K9znNyMvLu0zEsz8wYyW3+s57Lbn6hcpGPUuPi2uX2J9gBQSQJuvo08dDV1z0avGXK0e9KckafnJqeHb1aUyKbMTMFaGxWR9irqpBRh5bE1L+jKwaNpun15VPrmg576lhZN2IbsRr2szd68nD6wa2hsfOvqOzAgkMDuNpeaF4UyRhajjZ+VXZZrHWRjp+MuBRhU20DHWrDXk1nJRys6ljElrGI2GwAa74D9LI1DVU0q+nTqrsrGycmlMDW8fVsnF9VelbMXV6MeoLgZZW5WARrFPC0cu254q/Sln7ZeY+kVJo+ma1k6Pk5g1TlmN0NRbSzm04HqfB8cWhCytYGG9nENsC3N4L9HWo4mbpGRlZumPj+HcDK0/FxtO0l8DqpkLjIMi5mzHVXC4tY6aAAbv8QBnXejp20fUdLGUobVNXzdUF/QO1QzNXbVuia+p7ZUN0+W4+O3ugblrWRk1rUcXHTJd8ihLVfI9XFWO9gW/IDGs9R66yWFfblttuPOZ8wdYqynWsYltNLrfQ1xupa9XxlcHIqRVsXha9e6hzvsSDsfKZ0CF1qorO5CpWpZ2YhVVVG7MxPYAAE7zrD0M+IxnZWXl3tkeseJKhq+m0Wcujj+H6bPUdM4qx2ruvUNlkAb/wDm7H6InY2t6ZRm4uTh5SC3Gz6LsbJqJZRZRfW1VtZZCGUMjMNwffNK8NeivB03WU1TDNtdVOmnBrxnys3I4ObefUD5GSy9IVewKtth5jvApfSjoGN+VdCoxDkVajrOs15eRamfmAJp+lD1/PcY/X6PTsavFxSNtv8AzhO25rl3hovrlOrtaCuLpeRp1GPwO6PlZOPkX3izlt7S4lCbbfqnv3lrrFWU61jEtppdb6GuN1LXq+Mrg5FSKti8LXr3UOd9iQdj5QNI/wCoPObH0ml+WT0H1XSas6jBssrz8zEtzKq7sPD6BF1t1nIb11EMyi0DzmN6BsoXLr1dXrdeBj6y9Gn4OebxnYNPqWC99VtWUxvxqXyXyLkrfyW9NgAQBtPpD8NWanRj+r3ri5mmZuPqOBfZScihcnH5rwyKBYrW0PVbdWQrA/nNwdxMPwt4Pvpr1ezNy+pneJLTZl34CPgpjKuHTgUJhA2tZW9dNCt1SxJYk9uwAaX4L0z8meL8jHvqy8enUdOuXw6o1G7Mw7qMB8RtTuya78g216g1mXj7bjiEqIB3Lb9nLSE1BeJf87i3u4NjsvIW44Gys2y7Bj2Hxmr+F/BWorn4Ofq+oY+fZoeDlYGnnHwrMR7RmNiesZec1mU/VyWTCoHFOI3Np94C7XZhZJyBeLKAER6lU0uT03dHO56vd/za9/rPaBwa9jWWXUnpWXVJVdyWu7o+2zVcdzzHI8Vbt9czcZKcjHq4hjSyIUBZ1YADZQzBuW48u5n3Nxry4sptCHgUZLFayvz3DqquNrB3+3efcbB6WMMdGI4VGtXI78uO3MgfX32gV+gqfV8iytuK3WXPjl2LKlajp1sS5+ieHP8A9ph+GrgbqOAvTqYjPkdcvtfZyq42V8zs5BLnkvudZe0YKrjLjHuopFJI7EjhwJHwMxsDTbVsqe6xH9VqaqkJWU3DcAz2bud22rUbD64EFpCagvEv+dxb3cGx2XkLccDZWbZdgx7D4y3lXZhZJyBeLKAER6lU0uT03dHO56vd/wA2vf6z2lpAREQESFwJVuPZip49wNjt27kEDv8AUZh6KMwJ/wCYcdrN+3q4cKB39ljZ9NgAPbAG+57CBnyt1f6S/YfxllK3V/pL9h/Gajow6/P9zf7TIyVfn+5v9pkZ0QiIhCIiBr/pJ8P6bqOBZXqqFsTEHrjsrvW1Rx63LWK1R5dqmsGw9zGcfo18SafqmAlul8xi4h9TWp6zW1PQrr41cST2FTVEHc9mHv3my3KD2IBDKAQRuCCNiCD5iaL4/wDRzTqGm1abg3DRqqMpckDCoVamIDh1ail1BJL8wd/NFPeBvQE+ATSvSb4Es1nCxMRNQycI4V1VpvQGx7hWhTezjYp63fmH37HvtPvj7wM+qZOk5C6hk4Y0a/rOlYLes+1U25YWAV3fmuPMg9rX7QNzDDcjcbrsWG/cb+W492+xkuYG+5A5bKu523YspAHxPY9vqmlaR4CowdW1PXaLMm/K1OmwHFexFp5HpWcQ2253aitRy+iGaatgeHMrxdi4mVruNlaNkaLn2tj008qvWKicVubVZANlTh6+AsHyuR59it38feOtO0NMezULHrXMsaurp1NaQECtZY4X6NaBl3Pn7Q2BmJieKdQfxBfpTaZamn044tr1P8507GKVv9Ip0iC7vXwB33rJ8vLZdW0rFywgysfHyRRYt1IyKa7hXcv0bKxYp4ONz7QmZvCNM8Labr9eqarbn5lFumZG/wCSqa1Bso3feolemOHCr2SCTyOxnz0Z+GtWwcPLo1TU3z78m61qMgNY70I6BQUa/uG57vw8l8hN0mm+kHG8QPlaWdHux6sVLydVW4JyerlUR9Oslq+n1xtWQd2T7QVp/o19GOrYl2dh67m4+uaJb+dxaMpGub1nlSUtFeQC1BVVv3HI7m3f4zuMoF9lQFVPZVVACqo7KqqOwAGw2HwnwyVv0j9p/v8AGPBGa76R/EraRpuRqCY1ma2P0wKK2Kb9R1Tm9gQmuteW5bY+UssPW8O7Juw6snHsy8QK2TjJarXUq22xsrB5KPaX7y/GUvo58fYGvJk2YHXC4Vq1P1qxUWDgtXbXsx9hgrdjse3cCEXXhrUjmYeLlmmzGOZj1Xmi3tZSbEDdN+3mN/gP3SwiIE/1f3/8TSdMwddr13NysrMx20J6AMTG9kWV2bUhSR0gUIYX7sWO/UXt8u7fq/v/AOJrHpI8H067gPp99ttKWW1Wh6eJPKpuShlccbEPwP1HzEDZImo+jDxJpeZjtg6XkWZK6DXj4VjWq4sKojVU2l3UC0OMez21+Q/VNugJKr6S/tD8ZGSq+kv7Q/GFRltpf6MfafxlTLbS/wBGPtP4zM8OMlmABJIAA3JJ2AA8yT7hPhddwNxu/wBEbjdtu52+PacediVX1W0XIttORW9V1bjklldilLEdT2ZWUkbfXOjv+nRRlalqPXylzP8Asqt/Duh7rZyOm+tX89SZ7BtdbccKjDNqdt9Fu2PtGc1d7zjvuRAC7KgYhQWYKCx7BRv5k/Cck6i9NfhwvqGLqmZo6eJNHxNPycXL03hXkZWDZZbXcdTwMG8dPMtNdfSKoRYAicN9yCHbVtqoN2ZVHluxCjf4bn3ySsCAQQQe4I7gj3ETpnxlg6Xm6P4MoqYatpOTrOkrQ2eoyvW8X1HO6RyVvT86/ELuLBvuO/eXnoawqsLUPFenYlaY+Bp2sYhwsSocMfFGVo+l5eQmPUPZpqbIuts4LsN7HIHeB2XERARMDWvXOFXqXq3P1ijr+tdTj6r1B6z0ul39Y6XLjv23237TPgJGuxW34kNsdjsQdiPcdvIyGXj13V2VWqtld6NXajDdXR1KujD3qVJH751t6CdKxsG/xXi4dFOLjY/iUrTj49S001qdF0NiErrHFd2Zj2+JgdlG5OYr5KLCpYJyHMqDsWC+fHf3zkn5roqPrOq6xm6Zi204njTofluvNNevU9LUcfT8P1dPVCBp1IerHag2DklmT27+1+lIELbVQbsyqPLdiAPs3MVWq/dGVgDsSrBhv8O0wvEOi4WfQcfUMXFzcYkO1GZRVk0ck7q5qvUpyHxnUHo1xa8Twl4h1fT6qtPTXPy3rGnVYlKYteLiJjNjaW9NNShay2JhY2R2H0r2gd11XI5YKysa24uFYMVb5W2+i3fyMkXG+243+G/edG+hvBq07UdEqu0nD0jI1bw/kNiNpeYbly6sVtOsvTWaziILc9Dk12reC3fIyxv33btHJxujfdk3Y+Paj5FPG1tmvrBFNKMgKeSuN9t/eYGxMwHmQN+w3O3f4QTKjMxq7s0Jai2IuISquAyhns4swB8mKgDeQ0ypb9Oo6yi3/wAdG/OAN7Sp2Y8vM/XAugYVgd9iDt2O3uPwMqcByum1Mp2ZcFCpHuIoBBExdMx0quwemqp1sO3q8Rt1CnqzKX2+kwLudz8xgbByG+243I32377fHafZqOo8E65sQjL9drem01sW6RtqFZW7bYVivddt/iPfNugIiICIiAlbq/0l+w/jK7WdDyr7MplyV6eQuOKK+Do1BrS9GbqI/t7Pat47A8qlG47EWWqkcl7b9j+M1HRhV+f7m/2mRnJWRv5fqt7z8pkeQ+X/ADM6IjElyHy/5mOQ+X/MwIxJch8v+ZjkPl/zMBZ7v2V/CRnJYw7ez+qPefhI8h8v+ZgRmLquo4+JU1+VdTjUV7c7r7EpqXkQqhrLCFBLED94nB4o8Q4Ol4tmbqF1eLi0cRZdYW4guwRFCqOTOzMAAo98r/Emi6b4h05Krd78LLFOVRdj2shOw5VW1v8AssRsR+sYFZ6TvCWRrVOEMPVLtOGNeMg243JhfWyjgytXaN3X6Sk7j2z28pu6/rfZ/wDS/CYmkYNGJj0YtFfCjDpqooTkzcaqUFda8mO7bKo7mZiEbN7Pu+J+ZYHHE+2WooLNxVUBZmZtlVVG5ZiTsAB33PwmkeNfSEmLpQ1TScca4rZKY4GHczom4YvZY9KMwClVXYDztT3QNW8Q+NL9fvTTdCVczSc1bMLWdQqW2q/C6/Ks20vYQqItO9gchg+zKPKb36PvDNehaXVgjIe+rCF1jX2gIFVma5+KA7VUqCfZ+ozL8F6Ng4mOHw8CvTvXxXk5GOq8HS2xAxrs27Bk3K8R2Gx2AnW/ii3E8aZGTpOLlahplnhvLf1qwVA15Q5WYtnS43g12pZU/FrB+sTxPfaC98Q+KsvV9JbJ8IX05GRXlpTabaxU61qpawImcgQOedDbuPos+3faZnjTwC2sW6NlZeVbjZOiut9yYn6G289B7ekXPKr85UQH7ni7Daaxpejv4D0G5cLHu1yzI1Hqsldb461C6ta+bJXzcIBjou439q1fITtzCyTbVVa9LUtdXXY9Nh/OUs6hmqfbtzUnif2TAodJ8F6di6llatRRwztRUrkW9R2XZ2R7OFZbjWXeqskj5ftlzhYVNAcUVVUi12tsFVaVh7G+lY4Qe05+YzK5D5f8zHIfL/mZRGJLkPl/zMch8v8AmYH39X9//EhOTccfo+/4n4SPIfL/AJmB1j439G2kpk4+uBzpdeh2W6lmjDpRRk9EjJex+mOSvsjgkb7h2G3ebD4Q9Iuj6oKBi5dYvyzaKsS9lpyyat+f5gtufZUtuN9wp+B22u1UZSrIrK4Kure0rKw2Ksp7EEHbY/GadmejfSRfXnYWJThZ+FjW06fZQDXjY9jJcKrmw6yKrGR7nbuPf9Q2g3GSq+kv7Q/GdeeDNVt0PFxcPxNqmPfqOpZdq4bcrbOVZ6SLUbjUCwFjb87AAOuq79p2NURyHs/rD3n4yjiltpf6MfafxlXyHy/5mWum/oxt27n8frmZ4cR1nFsvxsimq58W3IptqryagrW472IVW+pbBwNiEhhyBG6jcGaz4f8AR7h6ffpV2C1mOui6W2j9JeJTLwt6XoGSSOTW1XVNYHHvycjf6Rm0annU4tF2TkWJTj4tb3X3WMFrqqrUvZZYx7KiqCST8DOGzWMRbcWk5FIt1JbHwq+ovPJSpFsteld97EVGRiw+dfjOas+al4o8HW5GaNRwdQyNMzDh+oX2VU4+TXdjCx7qeVOVWVW+qyy5lcf/ANzhgw2A22UXi7xjpWkLU2qZ+Hp65TlKDl5FdHVZduXDqNuwXku5HlyG8CjzvRvR+TNI0zDycjCXw5kY2ThXgVZFxsxqrqQbvWEKWF+u7E7eZ90uPBPhZNNGW5vvzcvVcn1vPzMgVLZfctNONUBXj1rVVVXj49NYVR5J33JJOT4i8U6bp2MmZn5uJiYlzIteTkX110O1il6wlrHixZVYjb4TI8Pa5h6jjpl4GTj5uNaWCZGLcl9LFSVZRZWSvIMCCPqgWEREDB1jEuuWtacmzEau+i13qrpsNtVbh7cZhehC12qChZdiOR2IMzoiBw5tbvVYldhpset1rtVVdqnZSFsCOOLFTsdm7dpqHgbwRk6ZlZmS2q5OYuq5LZmZRbi4daWZRxsbEFivRSHQCnEpHEHbsfjN1lF4c8Y6VqVttOBn4eZbigm6vGyK7XVQ7VF9kbvX1EdOQ7bqw84Gt53oxrtvvHr+WmmZup06xl6UqY/RszabKsjZck1devFsyqKr2qB7sG2IUlZuesYl1y1rTk2YjV30Wu9VdNhtqrcPbjML0IWu1QULLsRyOxBlfd4y0lM8aW+oYS6ixQDCORWMjlYjWV1mvluLGrVnCHuQpIG0voGJrOF6zjZGPzar1qi2nqptzr6qMnUTftyXlv3+AmDpnhvGp0qnRyvUw6NPr00ofZ54yUDFKnh5b1jbt8Zma5q2LgY9uXm304mLjLyuyMixaqawSFHKxzsN2IH2sBOLQNews/H9awsmjKxwzobabFsRXqO1lblT7FikbFT3EDWPCPo9OFlYmVlajl6m+j4NunaUMmvFr9Wxrzjm97GxqVOTlOuJjIbG7bVdgCSTs1ukBmb864pstW56NlINilX7ORyVCyg8ftlb4Y8f6Jql3q+nangZt/Sa7pY2TXdZ0VKK1nFG34BrEG/+IS5t1THSzotdWtpKqKy4DbvtxHH4ncfxgRzsAu4srtamwI1ZZQrckYg7EONgwI3BHxM+nA40JRS5qWtQgPFXJQLx2PMbbnz3+qcmZn008erYlfPfjyO2+22+38R/Gfbc6laxc1la1OAVsZgEbl3XZj2O4gcOn4HSp6DubUCCtQyqu1YXhx9kd+3vMhgaX03R2te3oVmqgMFHBG477lR7bkIg5H5ZnVWK6qykMrqGVh3BVhuCPqInxbkLMgYFqwpdQe68t+O492+xgYF+k82be2zo2WLc9PslS6FWGzkclQsiniPgZZyD3KrKpYBrNwik924jk2w9+wG8nAREQEREBK3V/pL9h/GWUrdX+kv2H8ZqOjDr8/3N/tMjJV+f7m/2mRnRCIiEIiIErPd+yv4SMlZ7v2V/CRgda/8AUhj6LbooTXVzGxGzKOkMDiMn1kJcVKGw9MDpdffl+7vtM2nxtoulNoWj0Lclep4uImliukmqrGsCU4YuZ2DqXOy9gT2Jbbzlp6VdNz8vSsijTRjNluajWMqum2sqtis+y5KNV1eIOxcefw8xVaB4owjn4Gjal0b/ABFiYaWW2piqaUyGx1uvTHvKfm3aoF/YAG3w8oVv+0rNC8RYObZl04mTRkW6ewry0qcM1Ll+IDge7klg3HbdGHums+EvBmNomdrGpvnWMNWZsq9cl0rqx60d7Xsdy35xU6nEWNtsoAln4J0HRcT1vO0tccDWAMm/IqyDdVaosJ51s1hSukWPZ2TYbkwK7H8bYWoaxqHhp8a8vj4r+svYF9XtqdKRbXsrc1UpkqAx8/a+re78E+FMLR8Y4mn1tVS1rXOGse13tcKpZnc7k8URf/QSyzMzHo4vdZRSb2SpGtsSvqud+nUrOfbc99lHxM1fxDk+IF1vTq8OjHfRXr//AFG5ynVR+VvPfk/MbIKeIQHcl9+3kRWeM2u8RYir4b1qrGswc1fW7qLLO4Ctshen2mAOzhfotxPeb/j46JyIVA9vE3WKio1rKOId+I7nb4ym8H+D9N0hb007HXGXLsFtwD2PyYAhFHUYlK1BOyL2HIy+gfRNO8BazreVl6tXquBXhY+Lk8NOsTlvfWXtB3LWEXbItTdRQo/OkbfDcJQekunVbNPyF0WyurUCydF7OG3DqL1QhtUothr5AFht393nCr+JXeGPWvUsUZz1W5qUVrmvRt0myVUC7jsAPp7+QHv7CWMIREQJ/q/v/wCJCT/V/f8A8SEBERApvEHhbT9QtxbszGryLdNs6uI78t6nJVv1W2deSIeLbj2B2lTp2s623iK3CswK10WuhHpzxy5vbxrb6fU4tvY1idLjuOAO+3nt8lV9Jf2h+MKjLbS/0Y+0/jKmW2l/ox9p/GZnhxz3VK6sjqHSxSrowBVlYbMrA9iCCRsZ03/0/wDhh8bUNZF+QcpPCt//AGzoSspBxNJWvG1VayxY9S415uHjmz3jTKZ3PKzRNCxsOzNtoVlfVsv13LJdmD5Hq+Pi8lDHZB0cWkcR8s5qs51n6Q9OzU1ivVNHOn6hnYelPi6joOXatV+VpuRebarcO/ucO5r8e1N7VKPwIJBXcdmTWfFXgnD1G+vKsfMxsqqh8X1nT83Iwb3xbGDtj2vjOOpXzHIb91JYqQSYGhahm4OTpXga/TKXxsC7W9KbDxrAVfGp9S1ADHdSx4vX3TYEj2Ox2l/6L1C6340RQFX8s6fZxUALzt0HR3sfiO3Jm7k++Xmq+AtNyMHB04V242Lo1lFunrhZF2JZjPjVvTSa7qHFnZLHHc99+8z/AAl4ZxNLqsqxFs/8m5sjJuvvuysnJyHVEN2Rk5Lm25+FdaDkewrQDYACBcxEQMDW8XIuStcbJOIyZFFtrrTXf1aK7Fe7GK2jZBagKcx3HLcd5nzB1jTEylrR3vQU30ZCnHyLcdmehxYqWNSwNlJI2NbdiNwQRM6Bj6nXU9FyXkCh6rFvJc1gVMpFhNikGscSfaBG06s9GeKdV1DA1nExvyd4e0HTMnS/DdTKyZGpY+W2FyzzUTvj6YKsCla0f2m5FzxHEHs/WtOqzMbIxLwWpzaLce8KxRjVejVWBXU7qeLHuJR+F/BGNp1lb0ZOq2LTV0a6MrVczKxlTiFUDHvtNe6hQAdu0Dp3EbOox9az7jp+VpdPjlxZp9uHacuxjrWJipmLqK5I6eTRacdkUIRxxApPtez+ipp+Z6ONLtzGzHXJ/PZdOoX4YzMhdOvz8fh0cy3AFnRe5TVU3lsWqrYgsAZsWsaYmUtaO96Cm+jIU4+Rbjsz0OLFSxqWBspJGxrbsRuCCIGp+mTCvso0vIoqOUdK1vAz7MNbKa7suukXI1WN6zYtVmShtW9UYjc4w277Sn9Emq9TUvGGVkY9mm1jUcK16sxqa3rrTR8AHJv6Vhrp511izudwOPLY7gb54s8O4mqYxxMxHevqVXVtXbZRfRkY9i3Y+Rj5FLCyi+u1FYOhB7TH8OeEcLBoyaK0suGpWWXahbmWvl35llta0s2TbeSbF6KJWE8gqKAAIGkYVd2B4yR3vqz6vGOm5dmM7U8btMp0U4JqxcbIW0pbhWnUbbSoUHl3JPkN3vNuO1+QllVldmTX1Kgm7Dfo45HUD+y67A7be7+GD4R9H2naXcl+P63Y+NjHCw/XM7KzRhYZZHbFxBk2Ho1k1U7nzIpqBOygC9fSaTYbCH9p1tasWMKmsXbaxq9+Jb2VP7hA+6xj+sVvjraKmcAtsOR6e/cFeQPBtiv8Zx6dkdbDrsKqpenfiv0VIUj2B7h2nPnafXawcl0dVKc6rGrYo3coSh7ruAZ9twENS0rzrrrACip2rIUDiF3U7ldvdAxtHuWvAosfstWHU7nz2VaVY/5CVvhfU0ezhzqezLRsm0q/IrYzACgfsUhB/wCpl3p2EtC8ENhUABQ7s/EKNgq8j7I29wnJ6svV63fn0+nvv248uW23x398DXLdZqGYzl696rVw60ZtmRCd8m/j7t3CLv8A/wCc2mcOTjLZw5b/AJqxbF2O3tLvsTt5jv5TmgIiICIiBjW59CsUa6pXVq1ZWsQMrXHapSpO4ZyDsPft2mNq/wBJfsP4zG1Hw6l9tlr2272MhUDhtWgpsx3qTdeyOttpJ892HfYADK1VvaXy8veN/fNR0YVfn+5v9pkZyVv38h5N7h8pkef1L90ToiMSXP6l+6I5/Uv3RCIxJc/qX7ojn9S/dEBZ7v2V/CRnJY/l2Hkv6o+Ejz+pfuiBGYf5KxfWfXPV6PXOl0fWujX6x0t9+l1uPPp7/q7zO5/Uv3RHP6l+6IHX3i30UafqmqHU8q3KJfEOJZjpYEqZSllYYOB1EAFhbgDtuoPxB1vUf+nbR7Sxqyc/HQYy1LWtldg5ixWNjmxN3Rm3Y19hudxtO5ef1L90SSv2bsvl8o+ZZPFaB4g9FemZ+n6Zp2U2U9OiJXXQ63BLbK1rSp0ubhsVdUX6ABG3Yib3Jc/qX7olF4h8Z6bp+Th4mZkV05GpvwxUNbsGPJawXdEK0qXZV3cjuT9cqLuJ1piePNY1CjXasLSvVMzTLFq0t8ojpZrNZYp4dZFrN3RqNgVSVPVr3O3c/dc1LxeumaScTGwG1ax99Xpc08K6+RFTbG3iKyNuZrJIP0Y9V2VPuQoJYHfZtwdjxIB3HYjyP1zTvSXmeIK7NO/IWPiXVvkMNS6/TBSrerp/pHG1JU37sm7eymwlB428LeLL87VrcDWKMfEyqq10+hi6NUyvQXXdaD6q2yXfnkJJ6oGw909GN/0++As7w0mo42fmY91WoZqPpyq45sVV0dtii+29Yo9gbn8031TYPAPpHp1vE1HIwsTK56WzoKLgiPkWCt7Kq0YEhLWK8Sjd15Lv5zi1f0cJqaaHbq2Rdbn6AtbPdjFK68q4HHstLhq9wDbjoeScT5+XbbflIG+yoORLHZQN2Pmx2HmfjA6303x3q1nh/J1V9GvTPx7TXVp5W5WurD0qcgVNX1+Ciywldtz6u23Y9tz8I6jfl4GJlZOO+Hfk0pZdivvypdh3U8gGHx2YA9xv3lvz+pf4CfOf1L90So+/q/v/AOJCcvL2fIefwHwkOf1L90QIxJc/qX7ojn9S/dECMlV9Jf2h+Mc/qX7okqn9pey/SHuHxhXHLbS/0Y+0/jKvn9S/wEtdNP5sfafxmZ4ccuTelSPZYy111Kz2O5CqiKCzMzHsqgAnc/Can4N9I+matctGMcyuy/HOXh+uYGXgrnYasitlYTZdSjJpBtq7r32urO2xBmT6WkZvD+uqoLM2j6mFUDcljh3gAAdySZxeFNWwOjoWOz1Nl5ulDIwAENjNjU0YYyba7VUrXX+fxhuSN+a7bzmrbInQuo5uUcLVfEB1DUE1HTfE9+nYuMubcmnriY+t16XRgPpYf1a034pRi7qXJyQysPZ23f0nYtmXq3h7B9az8bFzG1Q5iYGZfhNkLTio9ddl2M4sVQ5DboQe3n3MDsOJ1v6TsbK07wrl01ahnPk46011aibAueq2ZtKoxuQe3alThObd247tuSd9o8I+Gfya2QEzdQyqMk1PXTqGVZnNj2qHFz1ZOSxv4W7oxrJ4goeIG5EDYIkVcHfYg8Tsdjvsfgfge/8AnJQESu13TkyUqV78jHFWTj3hsbIbGaxqLFsWixkO9lDlQrVnswJBljAREpPDmRqz2XDUcXTsapdvVmwtRyM2yzu2/Wrv0+sU+zxPslvM/vCsy/SNpdWa2Cz5HKvLo0+7KXEyG0+nUMla2owrs4J0UyHFtI2J7G+pSQzAHbp0J4nsB0XXKwQbB4902soCC/N9f0O5E4+fI1Oj7fBgfKd8u4G25A3IA3O25PYDv7zArPFXiDF0zGOVls619SqmtaqrL77r8ixaaMfHopU2XX2WOqhVHv8AhMfw34sws+jIyKnepdPtspz68up8W7DtpRbbEyargDXtU6WcvIrYhBIIMo/S64X8hMxCqPEmlqWYgAGw3VVgk9t2ssRAPeXUTUrVLp6TeIL8rGRePfk6+FdMUoNvNgSBt9cDevCHpB07VLlox/W67L8b17EGXhZOF65hckQ5eIcmsdakNZVvt3HWqJGzDfZrclFsrqO/O7mUAG/ZACzE+4DdRv8A4hOn/R8+Vhal4YxjqF+q0654dzcq18pMRhjWYi6Qa7sF8ahWox7VzChrJIPSp94JO+5Ge6ZTWGu5WbIrxa96HK+rKTzKPx2LPZue3uVYF7n6jXSyIwsZrQ7KtVb2nZOIYkINwPbX+MnfmqlQtZbeLAEKKnawchvs1aryUj65iahjJbkJtfZVbVQ5Ar4jet3TdiXUggMi9vsktMyWuwktf6dlHJiBsCeJ7ge4Hz/fAzaMlHrW0H826CwMe3sMvIE7+XaY2DqlVzBV5gsvUr51vWLEGwL1lh7Q9pfvCY+nVh9NqVjxV8GtWbbfiDSATt79hMLBe1sjA5iriuNfwauw2CwcaB1Nig4IfZ/iYFq2qV9VqQtzMjKjlKXatWcKw5WKOK+y6nv8ZnTXssCrr5NF9hY5da2VEL0y5amh6ypXkTx2O4PwmwwEREBERASt1f6S/YfxllK3V/pL9h/Gajow6/P9zf7TIyVfn+5v9pkZ0QiIhCIiBKz3fsr+EjJWe79lfwkYCIiAkk8m+z/6WRkk8m+z/wClhVB4/wAXUbtOyatJurxs91T1e2z6K7WIbRyKkIzVB1DbHYsPtmoeM/Den36HV/3Tbjvm4WBZ1c+oD1hHAU22YqBN7iGFfbjsT7hvOzJ1LZpvh3xPr9lxfJvy/DinFycWxFGFkpXbkJ3W1CbES57VOxG/s+Y83RrHijwdi5XhXSMrQ31DUxoN1l2CgDCy7rZinL6mMiixWqsqYAVbEAHYnzmwnwfVq+ZfqiahZpniK/SK6svApyUsfTLsjHWr85WhGRVXxP0SRsW5ec2XSvRjh4ut16xjW2Y6UYvqtWn0oqYyKUNZCle4pJJs6e30yW3lto3gbTsTU8vV6a3XN1FGS9jYzVgWNXZaa6z2Uu9VZP7PbaTw9Ynga+rTcA4Gdq1GdmaLRZdqVz3q11FJZ7la9Xc2pUlRVQ9nmEH2S/8AD/iDC1Kj1zBvS/GdnAtAZNmQ+2rrYoasjz2YDzEpMX0eaVXnahqIoL36zTbj5i2uXoerI4HIRaj2AsNaE7/Dtt3l34f8P4Wm0ep4NCUYyM5FQLPuzn22drGLWE+W7E+QlFTiekDRrcLI1GvOpbCwX6eTeBZslhKhV4FObli6bcQd+Q23lzhavi3Yq51V1b4llJyFyN9q+iFLNYS30QADvv5bHeU+H4A0arCyNOrwaVws6zq5NANhDuCpVuZfmhUom3EjbiNtpqXoP0lcKrUtEydVxtXbFfpnCRncYmMVaqyt0t+iHZtjUu4U7jfcmPqNwxvHWkWafbqqZlRwMdjXdkcbBwsDIorNbJ1eoTZXsu256i7ecz/+4cL1H8p+sV+odH1j1nv0+j8223Lf3cdt9+228wMbwLpFen26UmHUuBkOXux+Vh52Eo3UNjP1eoDXXs2+46a7eUz/APt7B9R/Jnq9fqHR9X9W79Po+XHfflv7+W++/ffeFZHh/WMXPxKsvDtW/HyNzVanIA8SyMCrAMrBlZSrdxsZmTD8P6Pi4GJViYdS0Y+PuKqk5EDkWdiWYlmYszMWbudzMyEIiICSq+kv7Q/GRkqvpL+0PxhUZbaX+jH2n8ZUy20v9GPtP4zM8OMqUHhnwZpOmWW26dp+FhWZA42vjY9dLMnNremCi+zV1GZuA7bsTtvL+JzVr9/gnR3zhqb6dhNqAdLfWzj1m821J06ri/Hdrkr9gWHuB2B2mP4k9Hmhalket6hpen5uSEWsX5OLVdb0134oHddwo5N2/wARm0RA13WPA2jZmJjYOXp2Dk4WnBFw8W7HrsoxxXX0kFNTLxQLX7I290zPC/hnT9LqejTcTGwabrDdZXi1JSj2lUrNjKg2L8K0G/8AgEtogYenaXjYzZD0U1UtnXHJymrQKb8golZutI+nYa6q15H3IszIiBh6rpeNlrWmTTVetF1OTUtqBwmRjuLKLlDeViOoYN7iBMyIgIiIFFf4P0qzPXVHwMNtRThxzGx6zkA1q1db9Qjc2LW7oGPcBiB2ljqul42WtaZNNV60XU5NS2oHCZGO4souUN5WI6hg3uIEzIgYWt6VjZ2PbiZlFOVjZK8Lse+tbarF3DAPW42OzAH7QJDQNEw9PoGNhY9OLQrO/SorWtC9hLWWMFHtWMxJLHud+8sIgUPhnwZpOmWW26dp+FhWZI42vjY9dJZObWdPdF9mvqO7cB23ZjtLu2pX48lDcGDruN9mHkw+BEnEDHzcGm7YW1pZw3481B2389t/cfhPuTh1WIK7K0ZF2KqQOIIBA2Hu2BInPEDHwsOqkEVIlYY7kKNtyOwnzEwKKSzVVV1s/wBIqoUkb77dvIb99pkxAxnwKDYLjVWbRttZxHLcDYHf4gdt5kxEBERAREQMXVNQqxqzbcxVF8yFZz7yTxQFiAATv8FMx9X+kv2H8Zk6lg1ZNZquXmjEEgMyHt/iQg7Ebgj3gkHsZj6s5DLsSOx8jt75qOjCr8/3N/tMjOSuxt/pHyb3n5TI9RvmP8TOiIxJdRvmP8THUb5j/EwIxJdRvmP8THUb5j/EwFnu/ZH4SM5LLG7e0fJfefhI9RvmP8TAjEl1G+Y/xMdRvmP8TAjJJ5N9n/0sdRvmP8TJJYdm7t9H4n5lgccw8HSsWiy+6jHx6bs1g+VbVTXXZkOu+zXOi8rWG57t8TM7qN8x/iY6jfMf4mBGJLqN8x/iY6jfMf4mBGSt+kftMdRvmP8AEyVtjcj7R8z7zA451h6JfCOfh6tr+oahjYlR1LI3xLaHBZ6mttss4orbV1v+YY8gGLBt52j1G+Y/xMdRvmP8TAjEl1G+Y/xMdRvmP8TAfq/+3/EjOTqHj9I+fxPwkeo3zH+JgRiS6jfMf4mOo3zH+JgRkqvpL+0PxjqN8x/iZKqw8l9o+Y95+MDjltpf6MfafxlX1G+Y/wATLXTTvWN9z3P4zMsOMmIic1IiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICCIiBVeJNUGHUlnTV+dnDYv0x9Cyzs3E7u3T4Bfe1iDtvLTiPgJ9iB84j4COI+An2IHziPgJwZ9601W3MUVaK3sZrG4VqEUsS78TwQAdzsffMiIGv8Ah3xB63aajSlZFKW7rb1COSUv7S9Mcaz19gx8zTd2HGX/ABHwE+xA+cR8BHEfAT7ED5xHwE1zxF4oXDOUvR5HDoouBsZqa7epZ03VbDUV3XlT3G+5t27bGbJED5xHwEcR8BPsQPnEfARxHwEr9P1eu7Jy8ZVYPp5pFjEpxbrobFKANy2AG27Adwdt9jLGBU+LdW9QxLcrpC3omscDYtI9uxKyTYw2UANv9e2w7z7oGqjK9a9hU9Ty7sX2X6nLpEDk3sjpufPh323Xv3lrED5xHwEcR8BPsQPnEfARxHwE+xA1ZfFe+S2P0FHHL9WDG8bt+cSrdUFf6Xdi/TO3s1u2+22+0cR8BPsQPnEfARxHwE+xA+cR8BKLxD4gXEtWorQWsoa5epkCkqFyMXHLWDpkpQPWQxs77dNu0vogUvh7WxlvenSFXQTHfYvysHXVzwtr4jpWDhvtudw6H37S6AiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAieM8QPZiJ4zxA9mInjPED2YieM8QPZiJ4zxA9mInjPED2YieM8QPZiJ4zxA9mInjPED2YieM8QPZiJ4zxA9mInjPED2YieM8QPZiJ4zxA9mInjPED2YieM8QPZiJ4zxA9mInjPED2YieM8QPZiJ4zxA9mInjPED2YieM8QPZiJ4zxA9mInjPED2YieM8QPZiJ4zxA9mInjPED2YieM8QPZiJ4zxA9mInjPEBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQERED/9k=\\n\",\n \"text/html\": [\n \"\\n\",\n \" <iframe\\n\",\n \" width=\\\"800\\\"\\n\",\n \" height=\\\"450\\\"\\n\",\n \" src=\\\"https://www.youtube.com/embed/DbJyPELmhJc\\\"\\n\",\n \" frameborder=\\\"0\\\"\\n\",\n \" allowfullscreen\\n\",\n \" ></iframe>\\n\",\n \" \"\n ],\n \"text/plain\": [\n \"<IPython.lib.display.YouTubeVideo at 0x7ff95398cdc0>\"\n ]\n },\n \"execution_count\": 81,\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"output_type\": \"execute_result\"\n }\n ],\n \"source\": [\n \"from IPython.display import YouTubeVideo\\n\",\n \"YouTubeVideo(\\\"DbJyPELmhJc\\\",width=800, height=450)\\n\",\n \"\\n\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"## Prelude to Part 3: Some tips to make nicer figures.\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"Before even starting visualizing some cool data, I just want to give a few tips for making nice plots in matplotlib. Unless you are already a pro-visualizer, those should be pretty useful to make your plots look much nicer. \\n\",\n \"Paying attention to details can make an incredible difference when we present our work to others.\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"code\",\n \"execution_count\": 85,\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"outputs\": [\n {\n \"data\": {\n \"image/jpeg\": \"/9j/4AAQSkZJRgABAQAAAQABAAD/2wCEAAUDBAgICAgICAgICAgGBwgIBwcHBwgICAgICAgICAgICAgIChALCAgOCggIDhUNDhESExMTCAsWGBYSGBASExIBBQUFBwYHDwgIDx4VEhUfGB8YHRwbGxobGhsaGhkVHh0eHR4YHx4eFhoeHx0YGh0dGBUYHRgaGRcdFR4ZGhUYG//AABEIAWgB4AMBIgACEQEDEQH/xAAcAAEAAgMBAQEAAAAAAAAAAAAABggEBQcDAgH/xABWEAABBAECAgYGBwMGCgQPAAABAAIDBAUGERIhBxMYMZTVFCJBUVRVFSMyYXGBkQhCoRYzNFKCsSQlNVNicnOSo7NDRLLFFyY2RVZ0dYOipbS1wcLR/8QAGQEBAQEBAQEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAECAwQF/8QAMREBAAECBAQDBgYDAAAAAAAAAAECEQMhMVEEEkFhgcHwE3GRobHhIzJSYtHxIiRC/9oADAMBAAIRAxEAPwCmSIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/AIzI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8AGZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/wCMyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/ABmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P8AjMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/wAZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/AIzI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8AGZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/wCMyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/ABmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P8AjMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/wAZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/AIzI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8AGZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/wCMyPlyC/6IiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIijg15hDP6KMvjfSOLg6n0+vx8e+3Bw8f29+XD3rVNFVX5YusUzOiRoiLKCIiAiIgIiICL4ErS4s4m8bQHFm44g0kgEt7wDsef3FfaAiIgIsTI5OvXMLbE8MJtztr1hNKyMzTvDnMhiDj9ZKQ1xDRz9UrKcQOZ5Ad5KtpH6i0uE1bi70r4KeRpWpoty+GtbhlkaAdieBjieEH29y3StVM0zaqLLMTGoiL4bK0uLA5pc0AuaHDiaHb8JI7wDsf0Kyj7RFiVMnXllnginiknpOjbahjka6Su6VgkiEzAd4y5hDhvtuDurYZaLX57N06EXX3rVepDxBgltTMhYXnchoc8gF2wPIc+RXricnXtxNnqzw2YJPsTV5WSxu25HZ7CQdk5ZtzWyW02uy0XxLK1u3E5reJwa3icBu49zRv3uPuX2ogiIgIiICIhKAi0+N1TjLLxHWyNCxI77Mde7XlefwZG8kr0y2o8dTeI7d+lVkcwPbHatwQPLCS0PDJXglu7XDfu3afctclV7WXlnRtEWrp6ix84jMN6nMLEroYTFbgkEszGCR8UfA88cgYQ4tHMA7rMs3oInxRyzRRyWnFleOSVjHzPa3ic2JrjvI4NBJDd+QUmmYymC0shF+OIA3PIDmSe4LT4LVeMvySQ0shStywDeWKrahmewA8JcWxuJ4d+W/crFMzEzEaERMtyi0ud1ZjKEkcN3IUqks+xiitWoYXvBPCHBsjgeHflv3LctcCAQQQRuCOYIPcQfaEmmYi8wTExm/UXm2wwyOiD2mRjGSOjDhxtZIXtY9ze8NcY5AD7eB3uKx58rWjsQ1HzxMs2mSyV67pGiWVkPD1ro2E7uDeNu+3v+4qREyWZiLSZDWGJryvgsZTHQTRECSGe/WilYS0OAfG+QOaS1zTzHcQsnC5+jd4xSu1LfU8PW+iWobHV8fFwcfVOPBvwu237+E+5WaKoi9sjlm12yREWUEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREHM/2irk7cdSpxTOrx5zM0sbcssPC6KrY610uzv3eLq2tJ9znD2rc1Oi3T8dZtUYqo6NgAD3wgzEt7nmb7fHvz33W71lpurlqU1C4wvgsgblp4Xse0h0csbv3ZGuAIP3c9wSFAYdDaqjDazNVE0mFrQ+THQOvdU0j1DYILnO2G3HvxL24dcThRRFfLMTO+fwjXp6l3pqiaIi9nzd6RMzZs5AYTEQXKODnkrWZrNswTWZ6/KeOo0NIBaQQC7ffbf27Lym6Vrt2xj6+DoV7Jy+G+ko3XbD4eocyw+GWOYRghwb1ZbyI3c4HfZZed6Mb4nvOxGblxlTNyvmyNMVopgZpRwzy1ZnevWdINyeH2nkeQA2mmejSHHX6FutMRDjMM/Ftruj3c/jnNg2DLxfaLnO3bt7e9dJq4WIvERO2u3XvfbJq+FEf380V0x0wZC19D25cXBBi85djxrZRbc+yLjmPLpGR8Ab6NxxvAB57NJ335L3i6R9Q2m5GXH4WpNXwl+/WnfLeex9llOZ7OGszg5S8DNySSN3bAHbnscV0TmDG4TH+ncX8nsw3JNm9H29IDTP8AVFnH9Wdp/tAn7PdzUN0PpLL34s/HTzE2Mgtajy8Vus+pHJxxPsO3lryvAkrvex2xLTsQARseZ6/6tV6qYi0T15tLz43s3+FN5jz3lP8ATfSW3IX8RXrwD0bOYafIiV7yJoZIZWxmAtA4XAHjBO/e3lyUE1t0h5q1XpTUYYq4g1g7GPLLksZsSV7Bjq15QG86s46zrO/h4G8jvymOS6K3RR4p2GyD8ddwNWWpDYfXjssmgn2dK2aGTlxce7gfZxHkeRH5U6JxHjqFL01z5aWfgzlm1JFxG1YjkdJKzhDh1YeXd/PbbuKxRXwtExVHwm/7vszTVhRMTHrX7Pi/r3MzZKTF4rF1bE+KrVZcy+zcdDDHYswtmFWtI1h4jwu5SEEd/Ibc4prXpDzNzBm5Wrtx8lfUf0fZDbb2TxdRbgZDESwbP6x7nRyAHYDfbdTnUmgLpyk+Vw+Vdi5slFDFk43VIrUc/UN6uGZjZeUc7WAN32I5fe7fBh6JnNw8+KOQdI6fNtyvpckO8ji2zDYLJRx+u9xiO79+ZcTsrh4nDU8tVo/53v3v010WmrCi0+7fxalucr47OZXJ5Ci2C9S0pTtZCSrakma9zpTG6rEx4DCOKGNrX8t9xvtzK2GL6RszDLj5czh4aeOzdiKtVnrWzNPVms/0ZtuNzRu1/dxN2293sUhzPR9DcyGStWZDJXzOGixc1UN4XMbHJJJ1rZd/tfWcuXItBWhxfRbfdPRGUzk2Sx+Enjnx9J1aKFxlhG1d9qZnrTuYO4nn3+8rPtOHqi9W0b7dPHfJObDmM/Pbo1DelzLCB2RdiqoxdTLnG25hck9JeTc9FbLXiLNtm8TNw483EgbAbre3de5azlLtLC4uC5Xwj2R5Cxatms6WZzQ90FXZpaHgct37gkHuGxP3L0Wl2EsYf03+k5Z2RFnqPs732XeqMfHz+zw8W/t32X3lujy8zJW72IzD8YzMFjsnX9Fish8jG8HX1nS7iCYt357HmSfuCa+FmZtERrbW3S1++pM4Wdu+/b7odqDVUuZpaUvTVxWkdrWKF0DXF3B6O67CNy4bh+zBuPYd12PWWIOQx16iJTCchTsVhM0EmMzROjD9gRuBxd243G6guL6JzBRxFL04v+g88cv1zofWsAyTv6l+8m7XfX837nct7uanuq8JFkqVmjOZGxXIXRPfC8skZvza9jh3Oa4A+7lzBG4XPHxcOaqfZzlEz4Re8M4ldN45en8uNdH9Srir+Kx2bwNelkIS+LEZ2ns+rdlbEWuD5G7Pinewnk/fck8m7gHZnpXy80FnL08LFPgKL5eOd1vq701au4ia3DERwBrQ1zuA89m9457Z+L6M8q+5j5MtnDkaeDmE9GAVGQSulY3gjfZkbzleG8tySTz953x8h0QW+CfH083PVwN2aSSfFCtE97GzPL5q8Fo/WMruJPqe47Hfc7+irE4aqu9cxM5X/NbWb26307Xu6TVhTN6vOzKvdJGSvXZKmnMfXutp1q1i3avWHV4t7cLbEMEQaN+PqnsJcTyJI25bnX1M5Ux+a1DlLNB1e3V09jbl8ssuldI50RBqiM/VB7TBEwPB2O2525k7fL9GNmGy61gMq/Dvs1a9W7H6NDaimZVjEMEzWyj6qw2MBvEO/Yd3PfOj6NmST5KS7afaZmsLUxdppZwSE1mSMdZEgcfrHl/F3ciPauUV8PEZaTEb31pvfpvZiKsOI/u/RGn9JeoK9aldvYSpFUy12jDA+K898leO5K1o9JjLN+Msdu1w2G4AIHEFuOjj/wAp9Y/7fC//AGxi1juijKzQ06tvUMlipiLdSejAaMTC5lSRrmNtSNdxzPDG8IJOw33IJ22nGm9K+h5TM5HrusGdfSf1PV8PUeiVhX24+I8fFtv3DZMTEwIoqii15jpf9VMxr2iSqrDimYjz3jdGOmvSNy7Pi8lTq1sk7Cus9bh7ruGK0yy2MF0bj6rZ2GIbcXLmO/bZ2kwevcbjsZK7E4Z9bJXM0KEuCd9Q5uWmj4vrXgFog6qPcOaACGgbN57TPpC0bbu2K2QxmSkxuRpRSQNkMYnrT15XBzop67/VPrAEO2/uaRHq3Q+59Oz6XkpZMxbyUOV+l4Y2xmC7XYY4HRQ/Z6prHObw8uTuW2w2uFi4M4VNOLOnTPeZz6THXdaKqOSIqn6+rfNpukO3fnqY8ajxFVr49S4tlJ1LITcAM7Zw6YFvrCWPhI4XbtPWAjuX3rnptkq5C5TpRY4x4lxjnfk7zq0tuZg3khpsYw7cJ9Xif3kHltzO+sdHWUuQRsymcN2avlqGQieKMUMTG0hKDAyKItDTJ1u5fzO7R3pqPoytuu3LWKyjcezLvEl6CahXuAT8IY6xVfMOKCRwHPblvz922qMThsortNr/AKrdO1/ksVYelXnZiO6VLt2bGQYXHw2HZvEyXmG7ZdCKr4rBhmbOY2u42MLHN9XmXFu2wXjW6W7tmtRgqYyOXN5C5kKjqjrJFSA4x4ZasOm4eJ0XrM2by73czwjilmK0MYMlj8h6W6U43DyY1zZImNfO6SVkpsvfHs0PJadwG8y7fdR09EckcTJKmTfVydPK5K/RyDK7HNZHkn8U1WaB7i2aLYAbn+r3cyFmmrhJyt9f3a9tGYnB2+vf7MTV/SrkcTXpwX6NGvlr89hoEl530bFWg6v/AAt8waX7PMoaI+/dr9zyG8g6HekducFuCRkDLmMcwTGnObFSeKUO6uevKWh3Du1wLSNwQOfPlgZHozv2Yak0+ZfJmsdPYkgyb6UDoDDaEYkpyUiOrfX+raR3EHcjvKkvR3pi1jmWHXbwv2LcoeXtqw1ooWhob1UEcTRwx8gdt9t9z3kk4xauG9jamI5vHfplpbvfslc4XJlr4+rM/UusMXjHMZkMhVpumY58TbU7Ii9jSA5zQ48wCR+q3DnBzOIEFrmbgjmCCNwR7wsLL4KlcLTbqVrJjBDDYgjlLQ7YkNLwdgdgs7qwG8DQGgN4QAOQG2wAHuC8c8totr1ccrRZwfod6N8NldK0ZLdOFtmaKyTkIwI7MTmWZ2xyiYbHdga3v5eqN1ptQcGU0EMtehisZOo2KnFk3xgzyQwZdldjxK71jxxl2/vL3n2qXYfobyUVNmKk1JZ+io2uY6lUpwVnPje9z5I3WBvKWPLnbgkjZxHdyU01boGC3gX4Kq4U4OrrsheGdZwCvYin5t4hxFxj5nfvcSvq1cXRGLzc9/8AK/XKM7/Hr0yeqcaIrve+d/dCH69wdOhkNIRUq0NWJ+ekkdHBG2NhldT4S8gfvENaN/uWz6Yv8s6Q/wDbM/8A9KVJekTRzcvVgjbYkqW8fZiuY+9E0OdXtQghryx3KSMhzgWHv3+5R/A6AyUmTq5POZVmQfi2yDH161VtWGJ8oDZJnNH2pCAP0C81GLRNMVVVZxFUWzvN72+u7nTXFomZ0ifnf+X3+0lclh05cETzH6VLUqyyNOxbBZtRRTc/YHMc5p+55UV6TtL0cEzTd7Gwx1rdTNUafWQtDX2a9lkjbEcxHOXcNJ3Pdu73rresNP18rRs4+00mC7EY38JAc07hzJGEjYPY9rXDf2tC59hui/Ivt0ZczmTk6uDcH46sKrID1jQGxy2XN/nZGtAG5JPI8+Z3vD41FGHETNrXvG94iPVzDriKc50v45PvpC0/p7FDKZjKxenS5hzY2wWQyaWSTqhFFToN4QWEhg22+zwkkgAleOkc9LpvSePOTa6S71Qgo0eP6+eWRzjVqAn7IawtBd3Naw+4BfWuei/J5LKtyYzbITUJGPruxsc8dRh234WTSOY+YkbmQt3Ow7gABJZOj+ter1WZ5sOYt02SMFyWEQcTZH8R2hhIYwkNYDsOfAFZxMPkpiurm0mdb5RaIi+Vt8/os1U8sRM33QPojt2KeV1NZy1pk9lmOxt66+Ih0cTRDbnkgrtBP1MLSGAD3c+Z3Oiweey1eabW2QxsNiheZHHGG2T6ZjcU6ThjdXh4Sx7fXa53MFxc4+qCdukaZ6JMXQvZCzDBC2vkaTKcdRkZaK8T2OZca1/GeJs3qEjYbFgUdd0P5N8DMRLnpJNPRSNLaBqxttOgjeJGVX2gOJ0YIHt25DkNgB3jHwKqpmZ15b5TGURnEW0n5d7N+0w5mZ93w8G16YY8LVqG+cVRv5PLPjgxsclWOSW5bmYGwF+44nRsYGucT+6wDcEhb3od0PHgscyA8Lrdk9ffma1reOd45taGgBsbPsgAbcvvX63RHHm2ZWzM2aHH02VsPS6vZtJzhtZmJJIklfwsAdy2AA/dBUzXgxMb8OMOmb9Z8o8Pr4OFVf8AjyxPv9dhEReZyEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREGp1LqGtjhVNlzmjI36+Pr8DHP3s2iWwtdw/ZaS07uPILbLmX7REj4qeHsiC1YZj9UYi3ZZRqTW5m14JJHSyCGBrnuAHuHtHvXPukbNPv5avdnOroMRPg+LT8eEq5GrJ9NMt2I7Lb9eJgkjtcDavVi0BCWF5PIu3CxyKpkmX1DTw74Z49Qy29Q6Ew9PFOhivyvjzkb7kVrr5R/k+2BPA90kpYS1m+5LdlM7eCzz5NaX60+W+k6ULINPVpLM7afHNgaHpE1Su89TNOZxIGu5tbIw7bEu3CwC0urtTUcTDFYvTNgjtXalKJx/fs3JmwQt/Ddxc4/utY8nkFxDoPeRqKm2hJq2TF/wAm7vpp1IMiKwyptY4lsfp4B9K4BJxBv1fM9WecqzenLS2T1Vl3YyCnXfi8Bj5DM7KuuVq1nJ5avLDHNVfFC70h9OsS4PaS1slpwPrR8g7Hk9S1q+Qx+MkL/SsxFemqBrN4yzHtruscb9/UO1mLb38/ctyq3WbGorjtOyipYbnsLgtbYuexJWkFc5mvVx0FKyJpYxE6G0+Bs0bzsx4c7bk07RTourZ11bNtfltQMjl0zMLpdiNQOtVso9zQ2xX+krL3yZJg60OZSLWOadweJrCAt4iqXjbmT4NKTcGonej5CeuMc1+omx3YzlomfSTbs31kLBCHOFTJBzeoL2hw3DjkZd+SbftGaXV30+dZVeKOsL/0H/J8Ziua7mdUPRPQfQ+DfY9bx8fH6vW7haxaXNamq1LuOoTGQT5t9mOnwsLmF1WD0iUSOB9T1N9veVwPTuKz8E+Nv158y6/ksvrGnPDfsXJaEVaJmZkwrZa0+8VeD0mKm9khA3EgAJaQFpejirM/L6UfwarlvVfpN2opM3FkH1K2SlxsjD1UlpvVxyOkDw0wERuaGb+twgBbBY1q/BFJBFLNFHLce6OrFJKxkliRkb5nxwMcd5XiOOR5DdyGsce4FVVyeAz9fSen5xdznFlJYJdVS2n5i5bgayrIytC6tRlZegptkDWvbAQ7cRufxetvsMDpLI5GPRUmSsZqx6Nn8qxloDJ46eDGijcfUfZD5nTMJliYxk0zhI6KZrHc3OCCwNnW+KZYx9X02J82bsXK2P6jjsRzWMeHG5CZ4GuiikjLHtIe5p4mOb3ghSJVq6JNNXcZNpuONuWbDLqzVrsgyzJdljbA2LJxUpJxLuI45A2B4c7k97w8budubKoCIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIuVSZW/quSWPD3pMZp6tLLWsZ2mGnIZaxE50U8OGlkBZVoxPDmOu8LnPexwiAa3rHavBaen0/q3F0qGQydvHagxOVmyNLJ5GfICtNjX0upvQvsuc+J8jrgjcAdjv3chsHaUREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBRvpThfJgs1HFI6KSXDZJkcrDs6N7qczWSNI7nNJBB+5SRcs/abztmHDHFY4B+W1bKMNjmcXCGC2Ort2nuHOOKKBz/rB9l0kSDSdGXSvho8Hh8fgoLWau18NQYMViIesfWd6Oxm2SuSFtXHnrGvDnTyAkh2wceRn2hNO22T2MtlnwvyuQjZD1NYudVxlGNznxY+q94DpfXcZJZyGmV5HJrGRsbzn9h7TTsXpmaCaIR3PpzJx3wCHEWKc/oLmFw5EN9G2G3LvPtK7sgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiIC4n6V9Ma4rbF7q+nRedDtwmLjo12UrL9wN/rrebkjLSR6+mwQORXWNX5uLG4+9kZ/wCZxlKxblA7yyvC+VwHvcQzYD3kLj/7LtB7Ppm/aIM1b0PFWH+z0utDJmM3IHEbnfLZzItPs/wcDkWlBJf2cbgmpZpzeYGstTbfg/KzzD+EgUX6QN9WUcldOes4TS2G9LYy1i3sbPk7NElti9PPzP0ZDLHJHHAzYzOY95cB1K5v+yF0pVINO5uOw9tnK3c9ftUcHFK03Lpu1KzwyGLfjbWEkc5fOdmRtD3vLQ0lRroA6D9T5zTrKWQyr8VpfJXIchHj2xia5bY08XHDxbCtUl9R7eMvaXRxyiM8nPC1vQI7JHTOEdl5DLkH42B9iR7nPlc14LoDO9/rPs9QYeMncl/HuT3qbrzrQtjYyNg4WRMaxjR3BrQGtH5ABeiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICrPrrXT9Q5OzXxl/LPr0L0mIxeJ03km4u1mMnWibPlL9zJFpNXDVWS12B7dw97txxBzQ7q37QGSmr4mKKKV1WLK5fF4u/kGPMbqNDIXYq1uw2UD6h5jeYmycuB07Xbt23EU6KejfB0tXZrJYaGGvDj8VQxT4Kjz6OzITOks3hwAkNkFaPFb7H7U0pPrElBlfswa5vZOLMYzKC0MhpfJmpJ6ea7rpqyhzqwty1GtgsTNMc7OujaGyNjjf3uJPY1xjoToudq3pAyDdjXsZLD0WOHcbFDG72m/i02o/zcV2dAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREHPv2ha5nwT6m+zMnlcDj5/vr3s5jqthh3/ddFK9h+55UR0vZlqdH+SvM2NzJVtQ5GMgfbu5S5flqN7xueOeuzv8AYFtP2vq9mbSOQgpNkddtXMNDSbA4tmdZfmsf1AicCC2Tj22O42Kqx0GahzdjD4agMjJYxz9eYfF5LF2I2SPq1nWquSqS15i3rYoXy1LzXsc4t+pYGgcTgQsjgP2eKdC5ZFOWvWxGVjrtylOGmfTrccMMccuN+kHykQYieSPrZYo4w+QySML+AtDe4MaGgNaAGtADWgbAAcgAB3BfqICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiIPG7VinjkhmjZNDOx0csMrGyRyRvBa9kjHgtewgkEEbEFVX6EdUvx1jWGm9J4k3LcOqrs1OaeaCDEY+CcQ0w+050gsPr15ak2zIY3l7WsaHAuDlMOn3pluR0blfTELp5I7cGMt6hkLY8dQtW52VRDTe875G+x0g4hCHti+07ctLVFOirotp4iHSuYoiavmxqCbD6hmFy1LFe6mTJ0MpE6KV/Bwek0+NpDR/NNO2+xAWH6OdKx4fHxU2yOsSl8tm9dkaGyXb9qR1i7ckA5NdJNI93D3NHC0cmhSJEQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERBEOk+UMbieLbgfqLFsfv3bmV3Vfn1vVAfeQqmZ/EXNL67txRRN+hs7qvS1p0j3cPUPu5Ka5XkY0d7WmtmoAO4Abk929mf2m4ZTpbK2K7+qs4llfLVJQATHPircGQjcAeR51tvwcVx39qTNV7+msTqeIPZXzWNbVmMW5krWJY2ZbETOLN9n1sjRdAXDfZt+wBvxcwtWijfRfqhmaw2MyrBw/SdGGd7P8ANyuaBPH94bKJG7+3hUkQEREBERAREQEREBERAUQ6acoaWnszaDp2ej4yy50lRzWWY4+rLZJK73AtZO1hc5riCA5rSVL1qdZYRmSx1/HSco8pQtU3n3NswPhJG3MEB++/3IKk9N2IfJonB6lP+CV8fcxNzEaeoyf4ux+NmcepZIS0Pu5J7ZIXSWH7bEuaxrd5HSd7wtSSbIy12M+oxesHZBpbzDqmQ03NbE/LuByVydvP2s+9cP6O87WtYLD6CzLuvsZCStFWc1h9ak708XIJDv8AU28fcp2ax5jfq6r278R4evdCGQk6/Hmy5xtZHTLMfdB34Bk9IZCbG5F3MDaWSXI+71m1gRyag7Gi53prpWrXtS5DTsdSw36Nge6LKO51LdmqawyNSEgbdZX9NqB3rE7veCG7MMnREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQQjp8idJpjPQt247WJt12cXdx2IjAzf8AtSBcE6XsDBjNJ6u0wA9tHBZDDZTFetu6DE5nKwSPja5+5d1NmPLNBO54er33JO/dOn+51ODk5gdflMHXPF3cFjOY6GX/AIb3/ouU9LNiHPZS/jK7DINSuxml4JG7jrI8LetZbUWRae59OoywysHDvsGZn7pQWLxWPgqQQ1a0TIK9SJkNeCJobHFFG0MZGxo5NaGgDb7lkoiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiCtWoOi61i9W4zLCxTOLvayfbqVWwvN2K3lcZL6dvM4cMcDpqhdwN34iWE7FqWOKxntWYOplxgb+AycGqMVlDDDYZFWyOKhZm2yVpiI5K3FYe93EdhJZa/vaFN/wBqbNTY6lgrsFd9uWrq/EOZUhG8tnjFqJ1eEf557Xua3/Sc1c16IdP4vpDkzGaydSzVfHqaKxXgjkEUsuNOHx8EVK47gJlp2IYYXvY0ji5cLtidwmH7JPR3JQpfS9u3ctvyL70uHZfI62tjMhZjsmeVvMm7c6itPIXOO20beR4+LvC/GNAAAAAaAAANgAOQAA7gv1AREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQERaDpB1PHh8fNdfG+d7XRQVKkX89cu2ZWV6dOEbH6yWeSNm/c0OLjyaSg5P+1QW5gVNLsnFaFxGa1LkiWiPE4PH8chlkcT6tiaZoEY2P8AMSEgNBcI5+y7Sfc1DbyxrtqY6HS+Ph0rjw4k0sHZv3oIDMCNhbndh5J3O4nk+lH1uZA0XSxpi/Nh9Q4/0trb1fGv1Hr3LQM4228g2m+fFabql7g5lOKKGN237kTKx23ncD2bodw3oN+1WafUxuldI4xrdubTTZmXkk+0n0kH9feg6iiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIggfS3RbYn0zG4Ahuqqs+x99PHZS40/k6uD+Sg37LUPo7K0YbwtyWidJ5AEADjsMjyFOwSfaRDFjx+YUi15rii/UeLwETutyFGO/mLXARw04W4m/VhZKf8/J6bxBneGNDjsHs4tF0AF08mnnQ79Rh+jjDV7r9vUdbybKVmtC12/OWOClLI5vsbegP7yDuCIiAiIgIiICIiDT6kwDLwj4rN+sYS4tdj79ioTxbb9Y2FwbKPVG3GDtz27ytQdGWmt4YdR56Eew8WHsOH9q7jJSfzW81NqGhjIDZyNyrRrhwZ19yxHBGXuBLWB0jgHPIB2aOZ2KhbOmzATbihJfyxHyXCZXIMJ3I2FivWMG+4P7/AC9qDeQaWvtHPUuZkPvlrad5/iIsO1ZTMHfH/nq2775KeNJ/4dVqjbteZqf+gaQyhB34ZcxfxWLi5dxLWWJ7LWnv/md/eB3L56zXFg8o9L4th2245cpmJh37gtYymwEcuYce9BKRi8iO7Kk/7ShXP/Y4V+/R+U9mSr/2sZv/AHWQo5HpfU0gPpOqWRbnl9Faep1y0e7fIzWw4/eR+S9f5CZF329XaiJ9vVw6biB/JuF5D80G9NLL+zIUf7eImP8A2cg1ebqec9mRxQ/HBWz/AN8LVDQNn26m1Gfv67FD+DcaAvx2g7f7uqdRs+8Owb/+biXINuKmb9uQxR/DCWx/3uU9HzY/63i3/d9F24/4/SDv7lqBonJtHqauz/8A7yppmT9f8Sg/xWU3T+aYPU1A6Q7d9zEUpOfvIq9Qgy5DnG/ZbiZP9Z9yH+IbIsF+Q1O1/LE4KSP+sNR345PvIjODc38uNfkOP1Qw7uyuCnb/AFDp2/XeR7AZW5p7d/v4PyXpPa1NHtwUcHa95dl79Dl7w0Y2zufuLvzQekuoMrE3eTAWZnD93HZHGS7/AIG9PWH67L0Zq1zW8VjE5ir72mpFccPyxc9jf8t14SahzETd5dPzTn2txmUx8/8AunIPqb/nsvN2veqZxW8Nn6vdu0Ys5Fw3+7CyWt/y3QZsOuMc4bvdbrgfvX8Tk6Dfx4rtaMbfesrH6uxVh3BBk8fM8ciyG9XkeD7i1ryQfuWlPSrp9gabORjx/GdgMzDZxB358uHKRQkHkeS31HIY3Jx7wT0chC4b7wywW4yPfuwuaQg2oIPMcwfaF+rQDRWJaSY8fVrvd3y04W05T9/XVeB+/wCa8XaRaxpFXI5eo4/9IMlJeIP3NzAssH4cOyCSoonJic7EW+jZipOxv225XD9ZNIPYBPj7VaOI/f1LvwXwczn4OI2MLWtsb9g4fLsfYk9+9fJwVYoj93Xu/FBL0USZr+owht2tk8a4t4nG9jLHo8YHf1mRqtlosI/238FvsFm6d+IT0bda5C7ump2IrER390kLi0/qgz0REBERARaLUmssRjf8o5TH0fcLt6vXcTtvs1srwXH7go8/pcxD9vQ2ZXJ8W3C7E4HLXYXB32S23FW9GLT7+s2HedkE+Rc+OvMvL/RNI5lwJIEmQt4WhHy32cWm/JOGnYf9Hvz7l+jLawl+xhMDVG//AFvUlyZ22/fwVsPw77ezj/NB0BFCOp1a8f0jTtc+0eg5O6B+fpkG/wDBfrcbqs9+Z0+3/V0tkXf36hCCbLlXTV18OZ0bfkcDiKWdmhvxdXxcF3JUZ8fiLb3fuxssWHM35bOstP4b92M1X7M1gCfv0rkAP1/lCVC+lHSmusljbmPju6TsRXoHRPMuNy1CaMnnHPXkbdsNZZjeGPY4ggPY0+xBq8vGf5Ia9dKeCa5l9URzyO23LevdSqF23sFOOo0f6LGrqWlIv8cZ9+3fLjYx+EdBjwB+cp/VQGn0c567pDN4vKT0GZrUclmWWWuZTSY+RlaFpceHiHG2txu4WkB0zthy2Wi11pjWt6OOxUqMxWoIzA2TK4vVdhmIsdRsDNZw81Ux2eIcTeB7CQ3g3e4MDEFh0Wu0z6b6HV+kvRvTxXiF70EyGqbIYOuNfrgH9SXbkBw3AK2KAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiIChnSlq2ahHXpY6OOxnM299fEVZSeqa5oBsX7fD6zaFZjhI8jm71GD1pApfanbFG+R52ZExz3kAuIawFzjwtBJ5A8hzVa6eLyGobdGxJKac3SDRuXZ7cbuG3i9FUJKJq4XHuHEGXLjslVlnlBABlk5O4GBBg6bt0TqJtbGiS5Dh9P6qfkNSSNH+O85N9FfSkglaNpup/wVu7Twt60Mbs1jSe8dD2JgqYTGCGJsbrGMx0thzR60szcfUgEkhPNzhFBCwe5sTGjYNAEH1niamPyOPoUYI61XG6E1aK9eFvCyNhmwDRt7S4kOJcdy4uJJJJK6hoyPgxuPaO5mPqNH5QRj/8INsiIgIi8ZLLGkji3c3va3m7fYEDYe3Yj9UHsiwXBxfC5xIJkIEYd6rR1Up57cnv5Dn3DbYe0n6vTDcRvbvHMCwvDu4n2Ebd23t/H2AoMxFhY97ml0LzuY+bHHvc3l+u27f97bntuc1Bg5PDU7T4ZLNWtYfUc51Z9ivFK6BzwGvdC6RpMbiAAS3bcBZzQANhyA5ADuAREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREAjfkeYPeCoxm+jzA3XiW3hsZPM07tsSUK5sMIIILJwzrGO3AO4cO4KToghP/g2qx8RpZDOUHO326jO37ETCfbHVyUk9aPb3CPbkOS/G6VzcIPUaotTH936WxOKstb9x+j4ajnD8Xb9/NTdEEJhp6rjPrZHT9poA5fQmRpPPv3cMrO39Gr0kt6pZ9nH4Cf7zm8jU3/sjETbfqpkiCJ1snqHb67D4oH3V9RWZh+suHiWl1Bh5rb+vsaXoS2mtc1lyLKRQ3Yw7biEN6OuyxDvsObHDuHuXRkQcDzUWv6h/xHQPVsDQyvnNSVcrBsD625mqMyD3kcuJ90j7vf5v130nxxcL9E46acDnPXzdRsLnbcy2s62ZQPuL/wA1YBEHKaUucsMByeoDid2tMjcbph1BsJ73MdfzbrlZ/wDrNA9u33bLGaHw17Z82Sv5wgbP9I1BZnrP5EEyUKU0dEk8/wDodv0XRFr8tgqNvb0unVtbd3pNaGbbbmNusaUGFpzRuIxv+T8XjqPtJpUa9ckgbbudEwFzuXeea3qjs2iqB26ttusGncMx+UyNCMe76qnYZGR9xBC8Z9K2d29RncxWa079W04y013fsHvyFCaXh5+x4PIc0EoRRSzis80AVszRO3tyOCfYcR+NPIVmg9/Ph/Jfkr9SRt9SLCXHD+tYv41p/MQWy3+KCWIolDl8+0fX4SkT7qOeM+/4G3j66+JdWZJh2Ol8xJ/pVrmnXNH4+kZaJ38EEwRRGLV90j1tNZ2M+50un3n9Ycu4fxX3/K61/wCj2b/+T+ZoJWiiMurrwG7dM52T7mzadYf+NmWr9r6ryD9//FjMxEd3X2tOgH84MxIf4IJaijgy+UdtwYfg3+JyVdm34+jtl/gvht3Pk/5NxDG/1jnbj3/nGMQB/wDEgkyKPPizbx6s+KrH3Gnbuj9Rar7/AKJ9E5SQbTZYRn2ux2NggP5C8+0B+e6CQoo4zSznDhs5TLWveTaipHb/AFsVDXI/Ec19R6NoAbPbZsD3XcnkLo/S3YegkJK8+vZ3cbPw4h//AFR2To+wLju/CYl7v60mMqPd/vPiJX4/o70+RscFhyPccTSI/QxIJOijlXQeFh/o+KoVfvp1IqjvxDqzWkH816DSsLCXQ2slC8/vDK3bDR/qw3ZZYR/uIN+i1uLx9iE+vfsWwQf6XDTDgfYWmnBCPyIP5LPgDw1okc1zwBxuYwsaXe0tYXOLR9xcfxQfa4xgKcuM1PjsQ+tIalavmJtP32NaIIsVbFWWzhpNturlq2YK4iAHCa/UD7UZLupXMrLDw8VG1ICwF8lY15mMJ728JlbM8j/RjKwP5a0dyJG5CHhPN1nC5WCMH/by1REfbzDiEEC6UHl2o3s/q9HepnD8X3cQ3/8ARdQ0x/Qaf/qdf/ksXB+krpIwNTVtGzdvMGOuaUyeLsWoI5bDIJrV6nKxk4gY50PEyB/Nw5cidhzWN+z501y2cnS01NdxebYa80NTL4mDK1ZuGhXL2PyEN+s2B0kkcLt3V5HAO2GxB3AWSREQFgvl4HS8QcAXh3FwPLdurjBJcBsBuD392yzkQYT3bvh/2h/5MqwpYSyuYiA188n1UTTuGDdvqgj93ltv/pjfbcrO9DLZIywgRscXFh/dJY9vqfdu77P6e5e1iLve1rTK1pDHP7gee2+3Pbmf1PvQY7edpxHMMg4Hfc4vDwD+IP8Aes5Y1CsY2niPE953e73nmdgdu4bn2AczyG+wyUBFQDtq6q+X6f8AB5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/RUA7auqvl+n/B5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/AEVAO2rqr5fp/wAHkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf9FQDtq6q+X6f8HkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf8ARUA7auqvl+n/AAeR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/0VAO2rqr5fp/weR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/wBFQDtq6q+X6f8AB5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/RUA7auqvl+n/B5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/AEVAO2rqr5fp/wAHkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf9FQDtq6q+X6f8HkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf8ARUA7auqvl+n/AAeR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/0VAO2rqr5fp/weR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/wBFQDtq6q+X6f8AB5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/RUA7auqvl+n/B5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/AEVAO2rqr5fp/wAHkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf9FQDtq6q+X6f8HkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf8ARUA7auqvl+n/AAeR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/0VAO2rqr5fp/weR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/wBFQDtq6q+X6f8AB5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/RUA7auqvl+n/B5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/AEVAO2rqr5fp/wAHkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf9FQDtq6q+X6f8HkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf8ARUA7auqvl+n/AAeR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/0VAO2rqr5fp/weR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/wBFQDtq6q+X6f8AB5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/RUA7auqvl+n/B5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/AEVAO2rqr5fp/wAHkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf9FQDtq6q+X6f8HkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf8ARUA7auqvl+n/AAeR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/0VAO2rqr5fp/weR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUFZkREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQf/Z\\n\",\n \"text/html\": [\n \"\\n\",\n \" <iframe\\n\",\n \" width=\\\"800\\\"\\n\",\n \" height=\\\"450\\\"\\n\",\n \" src=\\\"https://www.youtube.com/embed/sdszHGaP_ag\\\"\\n\",\n \" frameborder=\\\"0\\\"\\n\",\n \" allowfullscreen\\n\",\n \" ></iframe>\\n\",\n \" \"\n ],\n \"text/plain\": [\n \"<IPython.lib.display.YouTubeVideo at 0x7ff95398c1c0>\"\n ]\n },\n \"execution_count\": 85,\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"output_type\": \"execute_result\"\n }\n ],\n \"source\": [\n \"from IPython.display import YouTubeVideo\\n\",\n \"YouTubeVideo(\\\"sdszHGaP_ag\\\",width=800, height=450)\\n\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"## Part 3: Time series of Reddit activity and market indicators.\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"It's really time to put into practice what we learnt by plotting some data! We will start by looking at the time series describing the number of comments about GME in wallstreetbets over time. We will try to see how that relates to the volume and price of GME over time, through some exploratory data visualization.\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \" We will use two datasets today: \\n\",\n \" * the _GME market data_, that you can download from [here](https://finance.yahoo.com/quote/GME/history/). \\n\",\n \" * the dataset you downloaded in Week1, Exercise 3. We will refer to this as the _comments dataset_.\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"> _Exercise 2 : Plotting prices and comments using line-graphs._\\n\",\n \"> 1. Plot the daily volume of the GME stock over time using the _GME market data_. On top of the daily data, plot the rolling average, using a 7 days window (you can use the function [``pd.rolling``](https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/reference/api/pandas.DataFrame.rolling.html)). Use a [log-scale on the y-axis](https://matplotlib.org/3.1.1/api/_as_gen/matplotlib.pyplot.yscale.html) to appreciate changes across orders of magnitude.\\n\",\n \"> 2. Now make a second plot where you plot the total number of comments on Reddit per day. Follow the same steps you followed in step 1.\\n\",\n \"> 3. Now take a minute to __look at these two figures__. Then write in a couple of lines: What are the three most important observations you can draw by looking at the figures?\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"> _Exercise 3 : Returns vs comments using scatter-plots_.\\n\",\n \"> In this exercise, we will look at the association between GME market indicators and the attention on Reddit. First, we will create the time-series of daily [returns](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Price_return). Returns measure the change in price given two given points in time (in our case two consecutive days). They really constitute the quantity of interest when it comes to stock time-series, because they tell us how much _money_ one would make if he/she bought the stock on a given day and sold it at a later time. For consistency, we will also compute returns (corresponding to daily changes) for the number of Reddit comments over time.\\n\",\n \"> 1. Compute the daily log-returns as ``np.log(Close_price(t)/Close_price(t-1))``, where ``Close_price(t)`` is the Close Price of GME on day t. You can use the function [pd.Series.shift](https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/reference/api/pandas.Series.shift.html). Working with log-returns instead of regular returns is a standard thing to do in economics, if you are interested in why, check out [this blog post](https://quantivity.wordpress.com/2011/02/21/why-log-returns/).\\n\",\n \"> 2. Compute the daily log-change in number of new submissions as ``np.log(submissions(t)/submissions(t-1))`` where ``submissions(t)`` is the number of submissions on day t. \\n\",\n \"> 3. Compute the [Pearson correlation](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/reference/generated/scipy.stats.pearsonr.html) between the series computed in step 1 and step 2 (note that you need to first remove days without any comments from the time-series). Is the correlation statistically significant? \\n\",\n \"> 4. Make a [scatter plot](https://matplotlib.org/api/_as_gen/matplotlib.pyplot.scatter.html) of the daily log-return on investment for the GME stock against the daily log-change in number of submission. Color the markers for 2020 and 2021 in different colors, and make the marker size proportional to the price. \\n\",\n \"> 5. Now take a minute to __look at the figure you just prepared__. Then write in a couple of lines: What are the three most salient observations you can draw by looking at it?\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"## Part 4 : The activity of Redditors\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"It is time to start looking at redditors activity. The [r/wallstreetbets]() subreddit has definitely become really popular in recent weeks. But probably many users only jumped on board recently, while only a few were discussing about investing on GME [for a long time](https://www.reddit.com/user/DeepFuckingValue/). Now, we wil look at the activity of redditors over time? How different are authors?\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"> _Video Lecture_: Start by watching the short video lecture below about plotting histograms in matplotlib.\\n\",\n \"\\n\",\n \"> _Reading_: [Section 7 of the Data Visualization book](https://clauswilke.com/dataviz/histograms-density-plots.html)\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"code\",\n \"execution_count\": 6,\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"outputs\": [\n {\n \"data\": {\n \"image/jpeg\": \"/9j/4AAQSkZJRgABAQAAAQABAAD/2wCEAAUDBAgICAgICAgICAgGBwgIBwcHBwgICAgICAgICAgICAgIChALCAgOCggIDhUNDhESExMTCAsWGBYSGBASExIBBQUFBwYHDwgIDx4VEhUfGB8YHRwbGxobGhsaGhkVHh0eHR4YHx4eFhoeHx0YGh0dGBUYHRgaGRcdFR4ZGhUYG//AABEIAWgB4AMBIgACEQEDEQH/xAAcAAEAAgMBAQEAAAAAAAAAAAAABggEBQcDAgH/xABWEAABBAECAgYGBwMGCgQPAAABAAIDBAUGERIhBxMYMZTVFCJBUVRVFSMyYXGBkQhCoRYzNFKCsSQlNVNicnOSo7NDRLLFFyY2RVZ0dYOipbS1wcLR/8QAGQEBAQEBAQEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAECAwQF/8QAMREBAAECBAQDBgYDAAAAAAAAAAECEQMhMVEEEkFhgcHwE3GRobHhIzJSYtHxIiRC/9oADAMBAAIRAxEAPwCmSIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/AIzI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8AGZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/wCMyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/ABmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P8AjMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/wAZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/AIzI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8AGZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/wCMyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/ABmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P8AjMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/wAZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/AIzI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8AGZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/wCMyPlyC/6IiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIijg15hDP6KMvjfSOLg6n0+vx8e+3Bw8f29+XD3rVNFVX5YusUzOiRoiLKCIiAiIgIiICL4ErS4s4m8bQHFm44g0kgEt7wDsef3FfaAiIgIsTI5OvXMLbE8MJtztr1hNKyMzTvDnMhiDj9ZKQ1xDRz9UrKcQOZ5Ad5KtpH6i0uE1bi70r4KeRpWpoty+GtbhlkaAdieBjieEH29y3StVM0zaqLLMTGoiL4bK0uLA5pc0AuaHDiaHb8JI7wDsf0Kyj7RFiVMnXllnginiknpOjbahjka6Su6VgkiEzAd4y5hDhvtuDurYZaLX57N06EXX3rVepDxBgltTMhYXnchoc8gF2wPIc+RXricnXtxNnqzw2YJPsTV5WSxu25HZ7CQdk5ZtzWyW02uy0XxLK1u3E5reJwa3icBu49zRv3uPuX2ogiIgIiICIhKAi0+N1TjLLxHWyNCxI77Mde7XlefwZG8kr0y2o8dTeI7d+lVkcwPbHatwQPLCS0PDJXglu7XDfu3afctclV7WXlnRtEWrp6ix84jMN6nMLEroYTFbgkEszGCR8UfA88cgYQ4tHMA7rMs3oInxRyzRRyWnFleOSVjHzPa3ic2JrjvI4NBJDd+QUmmYymC0shF+OIA3PIDmSe4LT4LVeMvySQ0shStywDeWKrahmewA8JcWxuJ4d+W/crFMzEzEaERMtyi0ud1ZjKEkcN3IUqks+xiitWoYXvBPCHBsjgeHflv3LctcCAQQQRuCOYIPcQfaEmmYi8wTExm/UXm2wwyOiD2mRjGSOjDhxtZIXtY9ze8NcY5AD7eB3uKx58rWjsQ1HzxMs2mSyV67pGiWVkPD1ro2E7uDeNu+3v+4qREyWZiLSZDWGJryvgsZTHQTRECSGe/WilYS0OAfG+QOaS1zTzHcQsnC5+jd4xSu1LfU8PW+iWobHV8fFwcfVOPBvwu237+E+5WaKoi9sjlm12yREWUEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREHM/2irk7cdSpxTOrx5zM0sbcssPC6KrY610uzv3eLq2tJ9znD2rc1Oi3T8dZtUYqo6NgAD3wgzEt7nmb7fHvz33W71lpurlqU1C4wvgsgblp4Xse0h0csbv3ZGuAIP3c9wSFAYdDaqjDazNVE0mFrQ+THQOvdU0j1DYILnO2G3HvxL24dcThRRFfLMTO+fwjXp6l3pqiaIi9nzd6RMzZs5AYTEQXKODnkrWZrNswTWZ6/KeOo0NIBaQQC7ffbf27Lym6Vrt2xj6+DoV7Jy+G+ko3XbD4eocyw+GWOYRghwb1ZbyI3c4HfZZed6Mb4nvOxGblxlTNyvmyNMVopgZpRwzy1ZnevWdINyeH2nkeQA2mmejSHHX6FutMRDjMM/Ftruj3c/jnNg2DLxfaLnO3bt7e9dJq4WIvERO2u3XvfbJq+FEf380V0x0wZC19D25cXBBi85djxrZRbc+yLjmPLpGR8Ab6NxxvAB57NJ335L3i6R9Q2m5GXH4WpNXwl+/WnfLeex9llOZ7OGszg5S8DNySSN3bAHbnscV0TmDG4TH+ncX8nsw3JNm9H29IDTP8AVFnH9Wdp/tAn7PdzUN0PpLL34s/HTzE2Mgtajy8Vus+pHJxxPsO3lryvAkrvex2xLTsQARseZ6/6tV6qYi0T15tLz43s3+FN5jz3lP8ATfSW3IX8RXrwD0bOYafIiV7yJoZIZWxmAtA4XAHjBO/e3lyUE1t0h5q1XpTUYYq4g1g7GPLLksZsSV7Bjq15QG86s46zrO/h4G8jvymOS6K3RR4p2GyD8ddwNWWpDYfXjssmgn2dK2aGTlxce7gfZxHkeRH5U6JxHjqFL01z5aWfgzlm1JFxG1YjkdJKzhDh1YeXd/PbbuKxRXwtExVHwm/7vszTVhRMTHrX7Pi/r3MzZKTF4rF1bE+KrVZcy+zcdDDHYswtmFWtI1h4jwu5SEEd/Ibc4prXpDzNzBm5Wrtx8lfUf0fZDbb2TxdRbgZDESwbP6x7nRyAHYDfbdTnUmgLpyk+Vw+Vdi5slFDFk43VIrUc/UN6uGZjZeUc7WAN32I5fe7fBh6JnNw8+KOQdI6fNtyvpckO8ji2zDYLJRx+u9xiO79+ZcTsrh4nDU8tVo/53v3v010WmrCi0+7fxalucr47OZXJ5Ci2C9S0pTtZCSrakma9zpTG6rEx4DCOKGNrX8t9xvtzK2GL6RszDLj5czh4aeOzdiKtVnrWzNPVms/0ZtuNzRu1/dxN2293sUhzPR9DcyGStWZDJXzOGixc1UN4XMbHJJJ1rZd/tfWcuXItBWhxfRbfdPRGUzk2Sx+Enjnx9J1aKFxlhG1d9qZnrTuYO4nn3+8rPtOHqi9W0b7dPHfJObDmM/Pbo1DelzLCB2RdiqoxdTLnG25hck9JeTc9FbLXiLNtm8TNw483EgbAbre3de5azlLtLC4uC5Xwj2R5Cxatms6WZzQ90FXZpaHgct37gkHuGxP3L0Wl2EsYf03+k5Z2RFnqPs732XeqMfHz+zw8W/t32X3lujy8zJW72IzD8YzMFjsnX9Fish8jG8HX1nS7iCYt357HmSfuCa+FmZtERrbW3S1++pM4Wdu+/b7odqDVUuZpaUvTVxWkdrWKF0DXF3B6O67CNy4bh+zBuPYd12PWWIOQx16iJTCchTsVhM0EmMzROjD9gRuBxd243G6guL6JzBRxFL04v+g88cv1zofWsAyTv6l+8m7XfX837nct7uanuq8JFkqVmjOZGxXIXRPfC8skZvza9jh3Oa4A+7lzBG4XPHxcOaqfZzlEz4Re8M4ldN45en8uNdH9Srir+Kx2bwNelkIS+LEZ2ns+rdlbEWuD5G7Pinewnk/fck8m7gHZnpXy80FnL08LFPgKL5eOd1vq701au4ia3DERwBrQ1zuA89m9457Z+L6M8q+5j5MtnDkaeDmE9GAVGQSulY3gjfZkbzleG8tySTz953x8h0QW+CfH083PVwN2aSSfFCtE97GzPL5q8Fo/WMruJPqe47Hfc7+irE4aqu9cxM5X/NbWb26307Xu6TVhTN6vOzKvdJGSvXZKmnMfXutp1q1i3avWHV4t7cLbEMEQaN+PqnsJcTyJI25bnX1M5Ux+a1DlLNB1e3V09jbl8ssuldI50RBqiM/VB7TBEwPB2O2525k7fL9GNmGy61gMq/Dvs1a9W7H6NDaimZVjEMEzWyj6qw2MBvEO/Yd3PfOj6NmST5KS7afaZmsLUxdppZwSE1mSMdZEgcfrHl/F3ciPauUV8PEZaTEb31pvfpvZiKsOI/u/RGn9JeoK9aldvYSpFUy12jDA+K898leO5K1o9JjLN+Msdu1w2G4AIHEFuOjj/wAp9Y/7fC//AGxi1juijKzQ06tvUMlipiLdSejAaMTC5lSRrmNtSNdxzPDG8IJOw33IJ22nGm9K+h5TM5HrusGdfSf1PV8PUeiVhX24+I8fFtv3DZMTEwIoqii15jpf9VMxr2iSqrDimYjz3jdGOmvSNy7Pi8lTq1sk7Cus9bh7ruGK0yy2MF0bj6rZ2GIbcXLmO/bZ2kwevcbjsZK7E4Z9bJXM0KEuCd9Q5uWmj4vrXgFog6qPcOaACGgbN57TPpC0bbu2K2QxmSkxuRpRSQNkMYnrT15XBzop67/VPrAEO2/uaRHq3Q+59Oz6XkpZMxbyUOV+l4Y2xmC7XYY4HRQ/Z6prHObw8uTuW2w2uFi4M4VNOLOnTPeZz6THXdaKqOSIqn6+rfNpukO3fnqY8ajxFVr49S4tlJ1LITcAM7Zw6YFvrCWPhI4XbtPWAjuX3rnptkq5C5TpRY4x4lxjnfk7zq0tuZg3khpsYw7cJ9Xif3kHltzO+sdHWUuQRsymcN2avlqGQieKMUMTG0hKDAyKItDTJ1u5fzO7R3pqPoytuu3LWKyjcezLvEl6CahXuAT8IY6xVfMOKCRwHPblvz922qMThsortNr/AKrdO1/ksVYelXnZiO6VLt2bGQYXHw2HZvEyXmG7ZdCKr4rBhmbOY2u42MLHN9XmXFu2wXjW6W7tmtRgqYyOXN5C5kKjqjrJFSA4x4ZasOm4eJ0XrM2by73czwjilmK0MYMlj8h6W6U43DyY1zZImNfO6SVkpsvfHs0PJadwG8y7fdR09EckcTJKmTfVydPK5K/RyDK7HNZHkn8U1WaB7i2aLYAbn+r3cyFmmrhJyt9f3a9tGYnB2+vf7MTV/SrkcTXpwX6NGvlr89hoEl530bFWg6v/AAt8waX7PMoaI+/dr9zyG8g6HekducFuCRkDLmMcwTGnObFSeKUO6uevKWh3Du1wLSNwQOfPlgZHozv2Yak0+ZfJmsdPYkgyb6UDoDDaEYkpyUiOrfX+raR3EHcjvKkvR3pi1jmWHXbwv2LcoeXtqw1ooWhob1UEcTRwx8gdt9t9z3kk4xauG9jamI5vHfplpbvfslc4XJlr4+rM/UusMXjHMZkMhVpumY58TbU7Ii9jSA5zQ48wCR+q3DnBzOIEFrmbgjmCCNwR7wsLL4KlcLTbqVrJjBDDYgjlLQ7YkNLwdgdgs7qwG8DQGgN4QAOQG2wAHuC8c8totr1ccrRZwfod6N8NldK0ZLdOFtmaKyTkIwI7MTmWZ2xyiYbHdga3v5eqN1ptQcGU0EMtehisZOo2KnFk3xgzyQwZdldjxK71jxxl2/vL3n2qXYfobyUVNmKk1JZ+io2uY6lUpwVnPje9z5I3WBvKWPLnbgkjZxHdyU01boGC3gX4Kq4U4OrrsheGdZwCvYin5t4hxFxj5nfvcSvq1cXRGLzc9/8AK/XKM7/Hr0yeqcaIrve+d/dCH69wdOhkNIRUq0NWJ+ekkdHBG2NhldT4S8gfvENaN/uWz6Yv8s6Q/wDbM/8A9KVJekTRzcvVgjbYkqW8fZiuY+9E0OdXtQghryx3KSMhzgWHv3+5R/A6AyUmTq5POZVmQfi2yDH161VtWGJ8oDZJnNH2pCAP0C81GLRNMVVVZxFUWzvN72+u7nTXFomZ0ifnf+X3+0lclh05cETzH6VLUqyyNOxbBZtRRTc/YHMc5p+55UV6TtL0cEzTd7Gwx1rdTNUafWQtDX2a9lkjbEcxHOXcNJ3Pdu73rresNP18rRs4+00mC7EY38JAc07hzJGEjYPY9rXDf2tC59hui/Ivt0ZczmTk6uDcH46sKrID1jQGxy2XN/nZGtAG5JPI8+Z3vD41FGHETNrXvG94iPVzDriKc50v45PvpC0/p7FDKZjKxenS5hzY2wWQyaWSTqhFFToN4QWEhg22+zwkkgAleOkc9LpvSePOTa6S71Qgo0eP6+eWRzjVqAn7IawtBd3Naw+4BfWuei/J5LKtyYzbITUJGPruxsc8dRh234WTSOY+YkbmQt3Ow7gABJZOj+ter1WZ5sOYt02SMFyWEQcTZH8R2hhIYwkNYDsOfAFZxMPkpiurm0mdb5RaIi+Vt8/os1U8sRM33QPojt2KeV1NZy1pk9lmOxt66+Ih0cTRDbnkgrtBP1MLSGAD3c+Z3Oiweey1eabW2QxsNiheZHHGG2T6ZjcU6ThjdXh4Sx7fXa53MFxc4+qCdukaZ6JMXQvZCzDBC2vkaTKcdRkZaK8T2OZca1/GeJs3qEjYbFgUdd0P5N8DMRLnpJNPRSNLaBqxttOgjeJGVX2gOJ0YIHt25DkNgB3jHwKqpmZ15b5TGURnEW0n5d7N+0w5mZ93w8G16YY8LVqG+cVRv5PLPjgxsclWOSW5bmYGwF+44nRsYGucT+6wDcEhb3od0PHgscyA8Lrdk9ffma1reOd45taGgBsbPsgAbcvvX63RHHm2ZWzM2aHH02VsPS6vZtJzhtZmJJIklfwsAdy2AA/dBUzXgxMb8OMOmb9Z8o8Pr4OFVf8AjyxPv9dhEReZyEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREGp1LqGtjhVNlzmjI36+Pr8DHP3s2iWwtdw/ZaS07uPILbLmX7REj4qeHsiC1YZj9UYi3ZZRqTW5m14JJHSyCGBrnuAHuHtHvXPukbNPv5avdnOroMRPg+LT8eEq5GrJ9NMt2I7Lb9eJgkjtcDavVi0BCWF5PIu3CxyKpkmX1DTw74Z49Qy29Q6Ew9PFOhivyvjzkb7kVrr5R/k+2BPA90kpYS1m+5LdlM7eCzz5NaX60+W+k6ULINPVpLM7afHNgaHpE1Su89TNOZxIGu5tbIw7bEu3CwC0urtTUcTDFYvTNgjtXalKJx/fs3JmwQt/Ddxc4/utY8nkFxDoPeRqKm2hJq2TF/wAm7vpp1IMiKwyptY4lsfp4B9K4BJxBv1fM9WecqzenLS2T1Vl3YyCnXfi8Bj5DM7KuuVq1nJ5avLDHNVfFC70h9OsS4PaS1slpwPrR8g7Hk9S1q+Qx+MkL/SsxFemqBrN4yzHtruscb9/UO1mLb38/ctyq3WbGorjtOyipYbnsLgtbYuexJWkFc5mvVx0FKyJpYxE6G0+Bs0bzsx4c7bk07RTourZ11bNtfltQMjl0zMLpdiNQOtVso9zQ2xX+krL3yZJg60OZSLWOadweJrCAt4iqXjbmT4NKTcGonej5CeuMc1+omx3YzlomfSTbs31kLBCHOFTJBzeoL2hw3DjkZd+SbftGaXV30+dZVeKOsL/0H/J8Ziua7mdUPRPQfQ+DfY9bx8fH6vW7haxaXNamq1LuOoTGQT5t9mOnwsLmF1WD0iUSOB9T1N9veVwPTuKz8E+Nv158y6/ksvrGnPDfsXJaEVaJmZkwrZa0+8VeD0mKm9khA3EgAJaQFpejirM/L6UfwarlvVfpN2opM3FkH1K2SlxsjD1UlpvVxyOkDw0wERuaGb+twgBbBY1q/BFJBFLNFHLce6OrFJKxkliRkb5nxwMcd5XiOOR5DdyGsce4FVVyeAz9fSen5xdznFlJYJdVS2n5i5bgayrIytC6tRlZegptkDWvbAQ7cRufxetvsMDpLI5GPRUmSsZqx6Nn8qxloDJ46eDGijcfUfZD5nTMJliYxk0zhI6KZrHc3OCCwNnW+KZYx9X02J82bsXK2P6jjsRzWMeHG5CZ4GuiikjLHtIe5p4mOb3ghSJVq6JNNXcZNpuONuWbDLqzVrsgyzJdljbA2LJxUpJxLuI45A2B4c7k97w8budubKoCIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIuVSZW/quSWPD3pMZp6tLLWsZ2mGnIZaxE50U8OGlkBZVoxPDmOu8LnPexwiAa3rHavBaen0/q3F0qGQydvHagxOVmyNLJ5GfICtNjX0upvQvsuc+J8jrgjcAdjv3chsHaUREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBRvpThfJgs1HFI6KSXDZJkcrDs6N7qczWSNI7nNJBB+5SRcs/abztmHDHFY4B+W1bKMNjmcXCGC2Ort2nuHOOKKBz/rB9l0kSDSdGXSvho8Hh8fgoLWau18NQYMViIesfWd6Oxm2SuSFtXHnrGvDnTyAkh2wceRn2hNO22T2MtlnwvyuQjZD1NYudVxlGNznxY+q94DpfXcZJZyGmV5HJrGRsbzn9h7TTsXpmaCaIR3PpzJx3wCHEWKc/oLmFw5EN9G2G3LvPtK7sgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiIC4n6V9Ma4rbF7q+nRedDtwmLjo12UrL9wN/rrebkjLSR6+mwQORXWNX5uLG4+9kZ/wCZxlKxblA7yyvC+VwHvcQzYD3kLj/7LtB7Ppm/aIM1b0PFWH+z0utDJmM3IHEbnfLZzItPs/wcDkWlBJf2cbgmpZpzeYGstTbfg/KzzD+EgUX6QN9WUcldOes4TS2G9LYy1i3sbPk7NElti9PPzP0ZDLHJHHAzYzOY95cB1K5v+yF0pVINO5uOw9tnK3c9ftUcHFK03Lpu1KzwyGLfjbWEkc5fOdmRtD3vLQ0lRroA6D9T5zTrKWQyr8VpfJXIchHj2xia5bY08XHDxbCtUl9R7eMvaXRxyiM8nPC1vQI7JHTOEdl5DLkH42B9iR7nPlc14LoDO9/rPs9QYeMncl/HuT3qbrzrQtjYyNg4WRMaxjR3BrQGtH5ABeiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICrPrrXT9Q5OzXxl/LPr0L0mIxeJ03km4u1mMnWibPlL9zJFpNXDVWS12B7dw97txxBzQ7q37QGSmr4mKKKV1WLK5fF4u/kGPMbqNDIXYq1uw2UD6h5jeYmycuB07Xbt23EU6KejfB0tXZrJYaGGvDj8VQxT4Kjz6OzITOks3hwAkNkFaPFb7H7U0pPrElBlfswa5vZOLMYzKC0MhpfJmpJ6ea7rpqyhzqwty1GtgsTNMc7OujaGyNjjf3uJPY1xjoToudq3pAyDdjXsZLD0WOHcbFDG72m/i02o/zcV2dAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREHPv2ha5nwT6m+zMnlcDj5/vr3s5jqthh3/ddFK9h+55UR0vZlqdH+SvM2NzJVtQ5GMgfbu5S5flqN7xueOeuzv8AYFtP2vq9mbSOQgpNkddtXMNDSbA4tmdZfmsf1AicCC2Tj22O42Kqx0GahzdjD4agMjJYxz9eYfF5LF2I2SPq1nWquSqS15i3rYoXy1LzXsc4t+pYGgcTgQsjgP2eKdC5ZFOWvWxGVjrtylOGmfTrccMMccuN+kHykQYieSPrZYo4w+QySML+AtDe4MaGgNaAGtADWgbAAcgAB3BfqICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiIPG7VinjkhmjZNDOx0csMrGyRyRvBa9kjHgtewgkEEbEFVX6EdUvx1jWGm9J4k3LcOqrs1OaeaCDEY+CcQ0w+050gsPr15ak2zIY3l7WsaHAuDlMOn3pluR0blfTELp5I7cGMt6hkLY8dQtW52VRDTe875G+x0g4hCHti+07ctLVFOirotp4iHSuYoiavmxqCbD6hmFy1LFe6mTJ0MpE6KV/Bwek0+NpDR/NNO2+xAWH6OdKx4fHxU2yOsSl8tm9dkaGyXb9qR1i7ckA5NdJNI93D3NHC0cmhSJEQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERBEOk+UMbieLbgfqLFsfv3bmV3Vfn1vVAfeQqmZ/EXNL67txRRN+hs7qvS1p0j3cPUPu5Ka5XkY0d7WmtmoAO4Abk929mf2m4ZTpbK2K7+qs4llfLVJQATHPircGQjcAeR51tvwcVx39qTNV7+msTqeIPZXzWNbVmMW5krWJY2ZbETOLN9n1sjRdAXDfZt+wBvxcwtWijfRfqhmaw2MyrBw/SdGGd7P8ANyuaBPH94bKJG7+3hUkQEREBERAREQEREBERAUQ6acoaWnszaDp2ej4yy50lRzWWY4+rLZJK73AtZO1hc5riCA5rSVL1qdZYRmSx1/HSco8pQtU3n3NswPhJG3MEB++/3IKk9N2IfJonB6lP+CV8fcxNzEaeoyf4ux+NmcepZIS0Pu5J7ZIXSWH7bEuaxrd5HSd7wtSSbIy12M+oxesHZBpbzDqmQ03NbE/LuByVydvP2s+9cP6O87WtYLD6CzLuvsZCStFWc1h9ak708XIJDv8AU28fcp2ax5jfq6r278R4evdCGQk6/Hmy5xtZHTLMfdB34Bk9IZCbG5F3MDaWSXI+71m1gRyag7Gi53prpWrXtS5DTsdSw36Nge6LKO51LdmqawyNSEgbdZX9NqB3rE7veCG7MMnREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQQjp8idJpjPQt247WJt12cXdx2IjAzf8AtSBcE6XsDBjNJ6u0wA9tHBZDDZTFetu6DE5nKwSPja5+5d1NmPLNBO54er33JO/dOn+51ODk5gdflMHXPF3cFjOY6GX/AIb3/ouU9LNiHPZS/jK7DINSuxml4JG7jrI8LetZbUWRae59OoywysHDvsGZn7pQWLxWPgqQQ1a0TIK9SJkNeCJobHFFG0MZGxo5NaGgDb7lkoiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiCtWoOi61i9W4zLCxTOLvayfbqVWwvN2K3lcZL6dvM4cMcDpqhdwN34iWE7FqWOKxntWYOplxgb+AycGqMVlDDDYZFWyOKhZm2yVpiI5K3FYe93EdhJZa/vaFN/wBqbNTY6lgrsFd9uWrq/EOZUhG8tnjFqJ1eEf557Xua3/Sc1c16IdP4vpDkzGaydSzVfHqaKxXgjkEUsuNOHx8EVK47gJlp2IYYXvY0ji5cLtidwmH7JPR3JQpfS9u3ctvyL70uHZfI62tjMhZjsmeVvMm7c6itPIXOO20beR4+LvC/GNAAAAAaAAANgAOQAA7gv1AREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQERaDpB1PHh8fNdfG+d7XRQVKkX89cu2ZWV6dOEbH6yWeSNm/c0OLjyaSg5P+1QW5gVNLsnFaFxGa1LkiWiPE4PH8chlkcT6tiaZoEY2P8AMSEgNBcI5+y7Sfc1DbyxrtqY6HS+Ph0rjw4k0sHZv3oIDMCNhbndh5J3O4nk+lH1uZA0XSxpi/Nh9Q4/0trb1fGv1Hr3LQM4228g2m+fFabql7g5lOKKGN237kTKx23ncD2bodw3oN+1WafUxuldI4xrdubTTZmXkk+0n0kH9feg6iiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIggfS3RbYn0zG4Ahuqqs+x99PHZS40/k6uD+Sg37LUPo7K0YbwtyWidJ5AEADjsMjyFOwSfaRDFjx+YUi15rii/UeLwETutyFGO/mLXARw04W4m/VhZKf8/J6bxBneGNDjsHs4tF0AF08mnnQ79Rh+jjDV7r9vUdbybKVmtC12/OWOClLI5vsbegP7yDuCIiAiIgIiICIiDT6kwDLwj4rN+sYS4tdj79ioTxbb9Y2FwbKPVG3GDtz27ytQdGWmt4YdR56Eew8WHsOH9q7jJSfzW81NqGhjIDZyNyrRrhwZ19yxHBGXuBLWB0jgHPIB2aOZ2KhbOmzATbihJfyxHyXCZXIMJ3I2FivWMG+4P7/AC9qDeQaWvtHPUuZkPvlrad5/iIsO1ZTMHfH/nq2775KeNJ/4dVqjbteZqf+gaQyhB34ZcxfxWLi5dxLWWJ7LWnv/md/eB3L56zXFg8o9L4th2245cpmJh37gtYymwEcuYce9BKRi8iO7Kk/7ShXP/Y4V+/R+U9mSr/2sZv/AHWQo5HpfU0gPpOqWRbnl9Faep1y0e7fIzWw4/eR+S9f5CZF329XaiJ9vVw6biB/JuF5D80G9NLL+zIUf7eImP8A2cg1ebqec9mRxQ/HBWz/AN8LVDQNn26m1Gfv67FD+DcaAvx2g7f7uqdRs+8Owb/+biXINuKmb9uQxR/DCWx/3uU9HzY/63i3/d9F24/4/SDv7lqBonJtHqauz/8A7yppmT9f8Sg/xWU3T+aYPU1A6Q7d9zEUpOfvIq9Qgy5DnG/ZbiZP9Z9yH+IbIsF+Q1O1/LE4KSP+sNR345PvIjODc38uNfkOP1Qw7uyuCnb/AFDp2/XeR7AZW5p7d/v4PyXpPa1NHtwUcHa95dl79Dl7w0Y2zufuLvzQekuoMrE3eTAWZnD93HZHGS7/AIG9PWH67L0Zq1zW8VjE5ir72mpFccPyxc9jf8t14SahzETd5dPzTn2txmUx8/8AunIPqb/nsvN2veqZxW8Nn6vdu0Ys5Fw3+7CyWt/y3QZsOuMc4bvdbrgfvX8Tk6Dfx4rtaMbfesrH6uxVh3BBk8fM8ciyG9XkeD7i1ryQfuWlPSrp9gabORjx/GdgMzDZxB358uHKRQkHkeS31HIY3Jx7wT0chC4b7wywW4yPfuwuaQg2oIPMcwfaF+rQDRWJaSY8fVrvd3y04W05T9/XVeB+/wCa8XaRaxpFXI5eo4/9IMlJeIP3NzAssH4cOyCSoonJic7EW+jZipOxv225XD9ZNIPYBPj7VaOI/f1LvwXwczn4OI2MLWtsb9g4fLsfYk9+9fJwVYoj93Xu/FBL0USZr+owht2tk8a4t4nG9jLHo8YHf1mRqtlosI/238FvsFm6d+IT0bda5C7ump2IrER390kLi0/qgz0REBERARaLUmssRjf8o5TH0fcLt6vXcTtvs1srwXH7go8/pcxD9vQ2ZXJ8W3C7E4HLXYXB32S23FW9GLT7+s2HedkE+Rc+OvMvL/RNI5lwJIEmQt4WhHy32cWm/JOGnYf9Hvz7l+jLawl+xhMDVG//AFvUlyZ22/fwVsPw77ezj/NB0BFCOp1a8f0jTtc+0eg5O6B+fpkG/wDBfrcbqs9+Z0+3/V0tkXf36hCCbLlXTV18OZ0bfkcDiKWdmhvxdXxcF3JUZ8fiLb3fuxssWHM35bOstP4b92M1X7M1gCfv0rkAP1/lCVC+lHSmusljbmPju6TsRXoHRPMuNy1CaMnnHPXkbdsNZZjeGPY4ggPY0+xBq8vGf5Ia9dKeCa5l9URzyO23LevdSqF23sFOOo0f6LGrqWlIv8cZ9+3fLjYx+EdBjwB+cp/VQGn0c567pDN4vKT0GZrUclmWWWuZTSY+RlaFpceHiHG2txu4WkB0zthy2Wi11pjWt6OOxUqMxWoIzA2TK4vVdhmIsdRsDNZw81Ux2eIcTeB7CQ3g3e4MDEFh0Wu0z6b6HV+kvRvTxXiF70EyGqbIYOuNfrgH9SXbkBw3AK2KAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiIChnSlq2ahHXpY6OOxnM299fEVZSeqa5oBsX7fD6zaFZjhI8jm71GD1pApfanbFG+R52ZExz3kAuIawFzjwtBJ5A8hzVa6eLyGobdGxJKac3SDRuXZ7cbuG3i9FUJKJq4XHuHEGXLjslVlnlBABlk5O4GBBg6bt0TqJtbGiS5Dh9P6qfkNSSNH+O85N9FfSkglaNpup/wVu7Twt60Mbs1jSe8dD2JgqYTGCGJsbrGMx0thzR60szcfUgEkhPNzhFBCwe5sTGjYNAEH1niamPyOPoUYI61XG6E1aK9eFvCyNhmwDRt7S4kOJcdy4uJJJJK6hoyPgxuPaO5mPqNH5QRj/8INsiIgIi8ZLLGkji3c3va3m7fYEDYe3Yj9UHsiwXBxfC5xIJkIEYd6rR1Up57cnv5Dn3DbYe0n6vTDcRvbvHMCwvDu4n2Ebd23t/H2AoMxFhY97ml0LzuY+bHHvc3l+u27f97bntuc1Bg5PDU7T4ZLNWtYfUc51Z9ivFK6BzwGvdC6RpMbiAAS3bcBZzQANhyA5ADuAREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREAjfkeYPeCoxm+jzA3XiW3hsZPM07tsSUK5sMIIILJwzrGO3AO4cO4KToghP/g2qx8RpZDOUHO326jO37ETCfbHVyUk9aPb3CPbkOS/G6VzcIPUaotTH936WxOKstb9x+j4ajnD8Xb9/NTdEEJhp6rjPrZHT9poA5fQmRpPPv3cMrO39Gr0kt6pZ9nH4Cf7zm8jU3/sjETbfqpkiCJ1snqHb67D4oH3V9RWZh+suHiWl1Bh5rb+vsaXoS2mtc1lyLKRQ3Yw7biEN6OuyxDvsObHDuHuXRkQcDzUWv6h/xHQPVsDQyvnNSVcrBsD625mqMyD3kcuJ90j7vf5v130nxxcL9E46acDnPXzdRsLnbcy2s62ZQPuL/wA1YBEHKaUucsMByeoDid2tMjcbph1BsJ73MdfzbrlZ/wDrNA9u33bLGaHw17Z82Sv5wgbP9I1BZnrP5EEyUKU0dEk8/wDodv0XRFr8tgqNvb0unVtbd3pNaGbbbmNusaUGFpzRuIxv+T8XjqPtJpUa9ckgbbudEwFzuXeea3qjs2iqB26ttusGncMx+UyNCMe76qnYZGR9xBC8Z9K2d29RncxWa079W04y013fsHvyFCaXh5+x4PIc0EoRRSzis80AVszRO3tyOCfYcR+NPIVmg9/Ph/Jfkr9SRt9SLCXHD+tYv41p/MQWy3+KCWIolDl8+0fX4SkT7qOeM+/4G3j66+JdWZJh2Ol8xJ/pVrmnXNH4+kZaJ38EEwRRGLV90j1tNZ2M+50un3n9Ycu4fxX3/K61/wCj2b/+T+ZoJWiiMurrwG7dM52T7mzadYf+NmWr9r6ryD9//FjMxEd3X2tOgH84MxIf4IJaijgy+UdtwYfg3+JyVdm34+jtl/gvht3Pk/5NxDG/1jnbj3/nGMQB/wDEgkyKPPizbx6s+KrH3Gnbuj9Rar7/AKJ9E5SQbTZYRn2ux2NggP5C8+0B+e6CQoo4zSznDhs5TLWveTaipHb/AFsVDXI/Ec19R6NoAbPbZsD3XcnkLo/S3YegkJK8+vZ3cbPw4h//AFR2To+wLju/CYl7v60mMqPd/vPiJX4/o70+RscFhyPccTSI/QxIJOijlXQeFh/o+KoVfvp1IqjvxDqzWkH816DSsLCXQ2slC8/vDK3bDR/qw3ZZYR/uIN+i1uLx9iE+vfsWwQf6XDTDgfYWmnBCPyIP5LPgDw1okc1zwBxuYwsaXe0tYXOLR9xcfxQfa4xgKcuM1PjsQ+tIalavmJtP32NaIIsVbFWWzhpNturlq2YK4iAHCa/UD7UZLupXMrLDw8VG1ICwF8lY15mMJ728JlbM8j/RjKwP5a0dyJG5CHhPN1nC5WCMH/by1REfbzDiEEC6UHl2o3s/q9HepnD8X3cQ3/8ARdQ0x/Qaf/qdf/ksXB+krpIwNTVtGzdvMGOuaUyeLsWoI5bDIJrV6nKxk4gY50PEyB/Nw5cidhzWN+z501y2cnS01NdxebYa80NTL4mDK1ZuGhXL2PyEN+s2B0kkcLt3V5HAO2GxB3AWSREQFgvl4HS8QcAXh3FwPLdurjBJcBsBuD392yzkQYT3bvh/2h/5MqwpYSyuYiA188n1UTTuGDdvqgj93ltv/pjfbcrO9DLZIywgRscXFh/dJY9vqfdu77P6e5e1iLve1rTK1pDHP7gee2+3Pbmf1PvQY7edpxHMMg4Hfc4vDwD+IP8Aes5Y1CsY2niPE953e73nmdgdu4bn2AczyG+wyUBFQDtq6q+X6f8AB5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/RUA7auqvl+n/B5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/AEVAO2rqr5fp/wAHkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf9FQDtq6q+X6f8HkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf8ARUA7auqvl+n/AAeR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/0VAO2rqr5fp/weR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/wBFQDtq6q+X6f8AB5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/RUA7auqvl+n/B5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/AEVAO2rqr5fp/wAHkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf9FQDtq6q+X6f8HkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf8ARUA7auqvl+n/AAeR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/0VAO2rqr5fp/weR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/wBFQDtq6q+X6f8AB5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/RUA7auqvl+n/B5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/AEVAO2rqr5fp/wAHkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf9FQDtq6q+X6f8HkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf8ARUA7auqvl+n/AAeR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/0VAO2rqr5fp/weR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/wBFQDtq6q+X6f8AB5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/RUA7auqvl+n/B5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/AEVAO2rqr5fp/wAHkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf9FQDtq6q+X6f8HkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf8ARUA7auqvl+n/AAeR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/0VAO2rqr5fp/weR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/wBFQDtq6q+X6f8AB5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/RUA7auqvl+n/B5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/AEVAO2rqr5fp/wAHkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf9FQDtq6q+X6f8HkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf8ARUA7auqvl+n/AAeR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/0VAO2rqr5fp/weR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUFZkREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQf/Z\\n\",\n \"text/html\": [\n \"\\n\",\n \" <iframe\\n\",\n \" width=\\\"800\\\"\\n\",\n \" height=\\\"450\\\"\\n\",\n \" src=\\\"https://www.youtube.com/embed/UpwEsguMtY4\\\"\\n\",\n \" frameborder=\\\"0\\\"\\n\",\n \" allowfullscreen\\n\",\n \" ></iframe>\\n\",\n \" \"\n ],\n \"text/plain\": [\n \"<IPython.lib.display.YouTubeVideo at 0x7ff965692040>\"\n ]\n },\n \"execution_count\": 6,\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"output_type\": \"execute_result\"\n }\n ],\n \"source\": [\n \"\\n\",\n \"YouTubeVideo(\\\"UpwEsguMtY4\\\",width=800, height=450)\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"> _Exercise 4: Authors overall activity_\\n\",\n \"> 1. Compute the total number of comments per author using the _comments dataset_. Then, make a histogram of the number of comments per author, using the function [``numpy.histogram``](https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.histogram.html), using logarithmic binning. Here are some important points on histograms (they should be already quite clear if you have watched the video above):\\n\",\n \"> * __Binning__: By default numpy makes 10 equally spaced bins, but you always have to customize the binning. The number and size of bins you choose for your histograms can completely change the visualization. If you use too few bins, the histogram doesn't portray well the data. If you have too many, you get a broken comb look. Unfortunately is no \\\"best\\\" number of bins, because different bin sizes can reveal different features of the data. Play a bit with the binning to find a suitable number of bins. Define a vector $\\\\nu$ including the desired bins and then feed it as a parameter of numpy.histogram, by specifying _bins=\\\\nu_ as an argument of the function. You always have at least two options:\\n\",\n \"> * _Linear binning_: Use linear binning, when the data is not heavy tailed, by using ``np.linspace`` to define bins.\\n\",\n \"> * _Logarithmic binning_: Use logarithmic binning, when the data is [heavy tailed](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fat-tailed_distribution), by using ``np.logspace`` to define your bins.\\n\",\n \"> * __Normalization__: To plot [probability densities](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Probability_density_function), you can set the argument _density=True_ of the ``numpy.histogram`` function.\\n\",\n \">\\n\",\n \"> 3. Compute the mean and the median value of the number of comments per author and plot them as vertical lines on top of your histogram. What do you observe? Which value do you think is more meaningful?\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"> _Exercise 5: Authors lifespan_\\n\",\n \">\\n\",\n \"> 1. For each author, find the time of publication of their first comment, _minTime_, and the time of publication of their last comment, _maxTime_, in [unix timestamp](https://www.unixtimestamp.com/). \\n\",\n \"> 2. Compute the \\\"lifespan\\\" of authors as the difference between _maxTime_ and _minTime_. Note that timestamps are measured in seconds, but it is appropriate here to compute the lifespan in days. Make a histogram showing the distribution of lifespans, choosing appropriate binning. What do you observe?\\n\",\n \"> 3. Now, we will look at how many authors joined and abandoned the discussion on GME over time. First, use the numpy function [numpy.histogram2d](https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.histogram2d.html) to create a 2-dimensional histogram for the two variables _minTime_ and _maxTime_. A 2D histogram, is nothing but a histogram where bins have two dimensions, as we look simultaneously at two variables. You need to specify two arrays of bins, one for the values along the x-axis (_minTime_) and the other for the values along the y-axis (_maxTime_). Choose bins with length 1 week.\\n\",\n \"> 4. Now, use the matplotlib function [``plt.imshow``](https://matplotlib.org/api/_as_gen/matplotlib.pyplot.imshow.html) to visualize the 2d histogram. You can follow [this example](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/2369492/generate-a-heatmap-in-matplotlib-using-a-scatter-data-set) on StackOverflow. To show dates instead of unix timestamps in the x and y axes, use [``mdates.date2num``](https://matplotlib.org/api/dates_api.html#matplotlib.dates.date2num). More details in this [StackOverflow example](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/23139595/dates-in-the-xaxis-for-a-matplotlib-plot-with-imshow), see accepted answer.\\n\",\n \"> 5. Make sure that the colormap allows to well interpret the data, by passing ``norm=mpl.colors.LogNorm()`` as an argument to imshow. This will ensure that your colormap is log-scaled. Then, add a [colorbar](https://matplotlib.org/3.1.0/gallery/color/colorbar_basics.html) on the side of the figure, with the appropriate [colorbar label](https://matplotlib.org/3.1.1/api/colorbar_api.html#matplotlib.colorbar.ColorbarBase.set_label).\\n\",\n \"> 6. As usual :) Look at the figure, and write down three key observations.\\n\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"code\",\n \"execution_count\": null,\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"outputs\": [],\n \"source\": []\n }\n ],\n \"metadata\": {\n \"anaconda-cloud\": {},\n \"kernelspec\": {\n \"display_name\": \"Python 3\",\n \"language\": \"python\",\n \"name\": \"python3\"\n },\n \"language_info\": {\n \"codemirror_mode\": {\n \"name\": \"ipython\",\n \"version\": 3\n },\n \"file_extension\": \".py\",\n \"mimetype\": \"text/x-python\",\n \"name\": \"python\",\n \"nbconvert_exporter\": \"python\",\n \"pygments_lexer\": \"ipython3\",\n \"version\": \"3.8.3\"\n }\n },\n \"nbformat\": 4,\n \"nbformat_minor\": 1\n}",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"{\n \"cells\": [\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"# Overview\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"This week we are going to learn a bit about __Data Visualization__, which is an important aspect in Computational Social Science. Why is it so important to make nice plots if we can use stats and modelling? I hope I will convince that it is _very_ important to make meaningful visualizations. Then, we will try to produce some beautiful figures using the data we downloaded last week. \"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"Here is the plan:\\n\",\n \"\\n\",\n \"* __Part 1__: Some talking from me on __why do we even care about visualizing data__. \\n\",\n \"* __Part 2__: Here is where you convince yourself that data visualization is useful by doing a __little visualization exercise__.\\n\",\n \"* __Part 3__: We will look at the relation between the attention to GME on Reddit and the evolution of the GME market indicators.\\n\",\n \"* __Part 4__: We will visualize the activity of Redditors posting about GME.\\n\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"## Part 1: Intro to visualization\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"Start by watching this short introduction video to Data Visualization.\\n\",\n \" \"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"> * _Video Lecture_: Intro to Data Visualization\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"code\",\n \"execution_count\": 80,\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"outputs\": [\n {\n \"data\": {\n \"image/jpeg\": \"/9j/4AAQSkZJRgABAQAAAQABAAD/2wCEAAUDBAgICAgICAgICAgGBwgIBwcHBwgICAgICAgICAgICAgIChALCAgOCggIDhUNDhESExMTCAsWGBYSGBASExIBBQUFBwYHDwgIDx4VEhUfGB8YHRwbGxobGhsaGhkVHh0eHR4YHx4eFhoeHx0YGh0dGBUYHRgaGRcdFR4ZGhUYG//AABEIAWgB4AMBIgACEQEDEQH/xAAcAAEAAgMBAQEAAAAAAAAAAAAABggEBQcDAgH/xABWEAABBAECAgYGBwMGCgQPAAABAAIDBAUGERIhBxMYMZTVFCJBUVRVFSMyYXGBkQhCoRYzNFKCsSQlNVNicnOSo7NDRLLFFyY2RVZ0dYOipbS1wcLR/8QAGQEBAQEBAQEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAECAwQF/8QAMREBAAECBAQDBgYDAAAAAAAAAAECEQMhMVEEEkFhgcHwE3GRobHhIzJSYtHxIiRC/9oADAMBAAIRAxEAPwCmSIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/AIzI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8AGZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/wCMyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/ABmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P8AjMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/wAZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/AIzI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8AGZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/wCMyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/ABmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P8AjMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/wAZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/AIzI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8AGZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/wCMyPlyC/6IiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIijg15hDP6KMvjfSOLg6n0+vx8e+3Bw8f29+XD3rVNFVX5YusUzOiRoiLKCIiAiIgIiICL4ErS4s4m8bQHFm44g0kgEt7wDsef3FfaAiIgIsTI5OvXMLbE8MJtztr1hNKyMzTvDnMhiDj9ZKQ1xDRz9UrKcQOZ5Ad5KtpH6i0uE1bi70r4KeRpWpoty+GtbhlkaAdieBjieEH29y3StVM0zaqLLMTGoiL4bK0uLA5pc0AuaHDiaHb8JI7wDsf0Kyj7RFiVMnXllnginiknpOjbahjka6Su6VgkiEzAd4y5hDhvtuDurYZaLX57N06EXX3rVepDxBgltTMhYXnchoc8gF2wPIc+RXricnXtxNnqzw2YJPsTV5WSxu25HZ7CQdk5ZtzWyW02uy0XxLK1u3E5reJwa3icBu49zRv3uPuX2ogiIgIiICIhKAi0+N1TjLLxHWyNCxI77Mde7XlefwZG8kr0y2o8dTeI7d+lVkcwPbHatwQPLCS0PDJXglu7XDfu3afctclV7WXlnRtEWrp6ix84jMN6nMLEroYTFbgkEszGCR8UfA88cgYQ4tHMA7rMs3oInxRyzRRyWnFleOSVjHzPa3ic2JrjvI4NBJDd+QUmmYymC0shF+OIA3PIDmSe4LT4LVeMvySQ0shStywDeWKrahmewA8JcWxuJ4d+W/crFMzEzEaERMtyi0ud1ZjKEkcN3IUqks+xiitWoYXvBPCHBsjgeHflv3LctcCAQQQRuCOYIPcQfaEmmYi8wTExm/UXm2wwyOiD2mRjGSOjDhxtZIXtY9ze8NcY5AD7eB3uKx58rWjsQ1HzxMs2mSyV67pGiWVkPD1ro2E7uDeNu+3v+4qREyWZiLSZDWGJryvgsZTHQTRECSGe/WilYS0OAfG+QOaS1zTzHcQsnC5+jd4xSu1LfU8PW+iWobHV8fFwcfVOPBvwu237+E+5WaKoi9sjlm12yREWUEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREHM/2irk7cdSpxTOrx5zM0sbcssPC6KrY610uzv3eLq2tJ9znD2rc1Oi3T8dZtUYqo6NgAD3wgzEt7nmb7fHvz33W71lpurlqU1C4wvgsgblp4Xse0h0csbv3ZGuAIP3c9wSFAYdDaqjDazNVE0mFrQ+THQOvdU0j1DYILnO2G3HvxL24dcThRRFfLMTO+fwjXp6l3pqiaIi9nzd6RMzZs5AYTEQXKODnkrWZrNswTWZ6/KeOo0NIBaQQC7ffbf27Lym6Vrt2xj6+DoV7Jy+G+ko3XbD4eocyw+GWOYRghwb1ZbyI3c4HfZZed6Mb4nvOxGblxlTNyvmyNMVopgZpRwzy1ZnevWdINyeH2nkeQA2mmejSHHX6FutMRDjMM/Ftruj3c/jnNg2DLxfaLnO3bt7e9dJq4WIvERO2u3XvfbJq+FEf380V0x0wZC19D25cXBBi85djxrZRbc+yLjmPLpGR8Ab6NxxvAB57NJ335L3i6R9Q2m5GXH4WpNXwl+/WnfLeex9llOZ7OGszg5S8DNySSN3bAHbnscV0TmDG4TH+ncX8nsw3JNm9H29IDTP8AVFnH9Wdp/tAn7PdzUN0PpLL34s/HTzE2Mgtajy8Vus+pHJxxPsO3lryvAkrvex2xLTsQARseZ6/6tV6qYi0T15tLz43s3+FN5jz3lP8ATfSW3IX8RXrwD0bOYafIiV7yJoZIZWxmAtA4XAHjBO/e3lyUE1t0h5q1XpTUYYq4g1g7GPLLksZsSV7Bjq15QG86s46zrO/h4G8jvymOS6K3RR4p2GyD8ddwNWWpDYfXjssmgn2dK2aGTlxce7gfZxHkeRH5U6JxHjqFL01z5aWfgzlm1JFxG1YjkdJKzhDh1YeXd/PbbuKxRXwtExVHwm/7vszTVhRMTHrX7Pi/r3MzZKTF4rF1bE+KrVZcy+zcdDDHYswtmFWtI1h4jwu5SEEd/Ibc4prXpDzNzBm5Wrtx8lfUf0fZDbb2TxdRbgZDESwbP6x7nRyAHYDfbdTnUmgLpyk+Vw+Vdi5slFDFk43VIrUc/UN6uGZjZeUc7WAN32I5fe7fBh6JnNw8+KOQdI6fNtyvpckO8ji2zDYLJRx+u9xiO79+ZcTsrh4nDU8tVo/53v3v010WmrCi0+7fxalucr47OZXJ5Ci2C9S0pTtZCSrakma9zpTG6rEx4DCOKGNrX8t9xvtzK2GL6RszDLj5czh4aeOzdiKtVnrWzNPVms/0ZtuNzRu1/dxN2293sUhzPR9DcyGStWZDJXzOGixc1UN4XMbHJJJ1rZd/tfWcuXItBWhxfRbfdPRGUzk2Sx+Enjnx9J1aKFxlhG1d9qZnrTuYO4nn3+8rPtOHqi9W0b7dPHfJObDmM/Pbo1DelzLCB2RdiqoxdTLnG25hck9JeTc9FbLXiLNtm8TNw483EgbAbre3de5azlLtLC4uC5Xwj2R5Cxatms6WZzQ90FXZpaHgct37gkHuGxP3L0Wl2EsYf03+k5Z2RFnqPs732XeqMfHz+zw8W/t32X3lujy8zJW72IzD8YzMFjsnX9Fish8jG8HX1nS7iCYt357HmSfuCa+FmZtERrbW3S1++pM4Wdu+/b7odqDVUuZpaUvTVxWkdrWKF0DXF3B6O67CNy4bh+zBuPYd12PWWIOQx16iJTCchTsVhM0EmMzROjD9gRuBxd243G6guL6JzBRxFL04v+g88cv1zofWsAyTv6l+8m7XfX837nct7uanuq8JFkqVmjOZGxXIXRPfC8skZvza9jh3Oa4A+7lzBG4XPHxcOaqfZzlEz4Re8M4ldN45en8uNdH9Srir+Kx2bwNelkIS+LEZ2ns+rdlbEWuD5G7Pinewnk/fck8m7gHZnpXy80FnL08LFPgKL5eOd1vq701au4ia3DERwBrQ1zuA89m9457Z+L6M8q+5j5MtnDkaeDmE9GAVGQSulY3gjfZkbzleG8tySTz953x8h0QW+CfH083PVwN2aSSfFCtE97GzPL5q8Fo/WMruJPqe47Hfc7+irE4aqu9cxM5X/NbWb26307Xu6TVhTN6vOzKvdJGSvXZKmnMfXutp1q1i3avWHV4t7cLbEMEQaN+PqnsJcTyJI25bnX1M5Ux+a1DlLNB1e3V09jbl8ssuldI50RBqiM/VB7TBEwPB2O2525k7fL9GNmGy61gMq/Dvs1a9W7H6NDaimZVjEMEzWyj6qw2MBvEO/Yd3PfOj6NmST5KS7afaZmsLUxdppZwSE1mSMdZEgcfrHl/F3ciPauUV8PEZaTEb31pvfpvZiKsOI/u/RGn9JeoK9aldvYSpFUy12jDA+K898leO5K1o9JjLN+Msdu1w2G4AIHEFuOjj/wAp9Y/7fC//AGxi1juijKzQ06tvUMlipiLdSejAaMTC5lSRrmNtSNdxzPDG8IJOw33IJ22nGm9K+h5TM5HrusGdfSf1PV8PUeiVhX24+I8fFtv3DZMTEwIoqii15jpf9VMxr2iSqrDimYjz3jdGOmvSNy7Pi8lTq1sk7Cus9bh7ruGK0yy2MF0bj6rZ2GIbcXLmO/bZ2kwevcbjsZK7E4Z9bJXM0KEuCd9Q5uWmj4vrXgFog6qPcOaACGgbN57TPpC0bbu2K2QxmSkxuRpRSQNkMYnrT15XBzop67/VPrAEO2/uaRHq3Q+59Oz6XkpZMxbyUOV+l4Y2xmC7XYY4HRQ/Z6prHObw8uTuW2w2uFi4M4VNOLOnTPeZz6THXdaKqOSIqn6+rfNpukO3fnqY8ajxFVr49S4tlJ1LITcAM7Zw6YFvrCWPhI4XbtPWAjuX3rnptkq5C5TpRY4x4lxjnfk7zq0tuZg3khpsYw7cJ9Xif3kHltzO+sdHWUuQRsymcN2avlqGQieKMUMTG0hKDAyKItDTJ1u5fzO7R3pqPoytuu3LWKyjcezLvEl6CahXuAT8IY6xVfMOKCRwHPblvz922qMThsortNr/AKrdO1/ksVYelXnZiO6VLt2bGQYXHw2HZvEyXmG7ZdCKr4rBhmbOY2u42MLHN9XmXFu2wXjW6W7tmtRgqYyOXN5C5kKjqjrJFSA4x4ZasOm4eJ0XrM2by73czwjilmK0MYMlj8h6W6U43DyY1zZImNfO6SVkpsvfHs0PJadwG8y7fdR09EckcTJKmTfVydPK5K/RyDK7HNZHkn8U1WaB7i2aLYAbn+r3cyFmmrhJyt9f3a9tGYnB2+vf7MTV/SrkcTXpwX6NGvlr89hoEl530bFWg6v/AAt8waX7PMoaI+/dr9zyG8g6HekducFuCRkDLmMcwTGnObFSeKUO6uevKWh3Du1wLSNwQOfPlgZHozv2Yak0+ZfJmsdPYkgyb6UDoDDaEYkpyUiOrfX+raR3EHcjvKkvR3pi1jmWHXbwv2LcoeXtqw1ooWhob1UEcTRwx8gdt9t9z3kk4xauG9jamI5vHfplpbvfslc4XJlr4+rM/UusMXjHMZkMhVpumY58TbU7Ii9jSA5zQ48wCR+q3DnBzOIEFrmbgjmCCNwR7wsLL4KlcLTbqVrJjBDDYgjlLQ7YkNLwdgdgs7qwG8DQGgN4QAOQG2wAHuC8c8totr1ccrRZwfod6N8NldK0ZLdOFtmaKyTkIwI7MTmWZ2xyiYbHdga3v5eqN1ptQcGU0EMtehisZOo2KnFk3xgzyQwZdldjxK71jxxl2/vL3n2qXYfobyUVNmKk1JZ+io2uY6lUpwVnPje9z5I3WBvKWPLnbgkjZxHdyU01boGC3gX4Kq4U4OrrsheGdZwCvYin5t4hxFxj5nfvcSvq1cXRGLzc9/8AK/XKM7/Hr0yeqcaIrve+d/dCH69wdOhkNIRUq0NWJ+ekkdHBG2NhldT4S8gfvENaN/uWz6Yv8s6Q/wDbM/8A9KVJekTRzcvVgjbYkqW8fZiuY+9E0OdXtQghryx3KSMhzgWHv3+5R/A6AyUmTq5POZVmQfi2yDH161VtWGJ8oDZJnNH2pCAP0C81GLRNMVVVZxFUWzvN72+u7nTXFomZ0ifnf+X3+0lclh05cETzH6VLUqyyNOxbBZtRRTc/YHMc5p+55UV6TtL0cEzTd7Gwx1rdTNUafWQtDX2a9lkjbEcxHOXcNJ3Pdu73rresNP18rRs4+00mC7EY38JAc07hzJGEjYPY9rXDf2tC59hui/Ivt0ZczmTk6uDcH46sKrID1jQGxy2XN/nZGtAG5JPI8+Z3vD41FGHETNrXvG94iPVzDriKc50v45PvpC0/p7FDKZjKxenS5hzY2wWQyaWSTqhFFToN4QWEhg22+zwkkgAleOkc9LpvSePOTa6S71Qgo0eP6+eWRzjVqAn7IawtBd3Naw+4BfWuei/J5LKtyYzbITUJGPruxsc8dRh234WTSOY+YkbmQt3Ow7gABJZOj+ter1WZ5sOYt02SMFyWEQcTZH8R2hhIYwkNYDsOfAFZxMPkpiurm0mdb5RaIi+Vt8/os1U8sRM33QPojt2KeV1NZy1pk9lmOxt66+Ih0cTRDbnkgrtBP1MLSGAD3c+Z3Oiweey1eabW2QxsNiheZHHGG2T6ZjcU6ThjdXh4Sx7fXa53MFxc4+qCdukaZ6JMXQvZCzDBC2vkaTKcdRkZaK8T2OZca1/GeJs3qEjYbFgUdd0P5N8DMRLnpJNPRSNLaBqxttOgjeJGVX2gOJ0YIHt25DkNgB3jHwKqpmZ15b5TGURnEW0n5d7N+0w5mZ93w8G16YY8LVqG+cVRv5PLPjgxsclWOSW5bmYGwF+44nRsYGucT+6wDcEhb3od0PHgscyA8Lrdk9ffma1reOd45taGgBsbPsgAbcvvX63RHHm2ZWzM2aHH02VsPS6vZtJzhtZmJJIklfwsAdy2AA/dBUzXgxMb8OMOmb9Z8o8Pr4OFVf8AjyxPv9dhEReZyEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREGp1LqGtjhVNlzmjI36+Pr8DHP3s2iWwtdw/ZaS07uPILbLmX7REj4qeHsiC1YZj9UYi3ZZRqTW5m14JJHSyCGBrnuAHuHtHvXPukbNPv5avdnOroMRPg+LT8eEq5GrJ9NMt2I7Lb9eJgkjtcDavVi0BCWF5PIu3CxyKpkmX1DTw74Z49Qy29Q6Ew9PFOhivyvjzkb7kVrr5R/k+2BPA90kpYS1m+5LdlM7eCzz5NaX60+W+k6ULINPVpLM7afHNgaHpE1Su89TNOZxIGu5tbIw7bEu3CwC0urtTUcTDFYvTNgjtXalKJx/fs3JmwQt/Ddxc4/utY8nkFxDoPeRqKm2hJq2TF/wAm7vpp1IMiKwyptY4lsfp4B9K4BJxBv1fM9WecqzenLS2T1Vl3YyCnXfi8Bj5DM7KuuVq1nJ5avLDHNVfFC70h9OsS4PaS1slpwPrR8g7Hk9S1q+Qx+MkL/SsxFemqBrN4yzHtruscb9/UO1mLb38/ctyq3WbGorjtOyipYbnsLgtbYuexJWkFc5mvVx0FKyJpYxE6G0+Bs0bzsx4c7bk07RTourZ11bNtfltQMjl0zMLpdiNQOtVso9zQ2xX+krL3yZJg60OZSLWOadweJrCAt4iqXjbmT4NKTcGonej5CeuMc1+omx3YzlomfSTbs31kLBCHOFTJBzeoL2hw3DjkZd+SbftGaXV30+dZVeKOsL/0H/J8Ziua7mdUPRPQfQ+DfY9bx8fH6vW7haxaXNamq1LuOoTGQT5t9mOnwsLmF1WD0iUSOB9T1N9veVwPTuKz8E+Nv158y6/ksvrGnPDfsXJaEVaJmZkwrZa0+8VeD0mKm9khA3EgAJaQFpejirM/L6UfwarlvVfpN2opM3FkH1K2SlxsjD1UlpvVxyOkDw0wERuaGb+twgBbBY1q/BFJBFLNFHLce6OrFJKxkliRkb5nxwMcd5XiOOR5DdyGsce4FVVyeAz9fSen5xdznFlJYJdVS2n5i5bgayrIytC6tRlZegptkDWvbAQ7cRufxetvsMDpLI5GPRUmSsZqx6Nn8qxloDJ46eDGijcfUfZD5nTMJliYxk0zhI6KZrHc3OCCwNnW+KZYx9X02J82bsXK2P6jjsRzWMeHG5CZ4GuiikjLHtIe5p4mOb3ghSJVq6JNNXcZNpuONuWbDLqzVrsgyzJdljbA2LJxUpJxLuI45A2B4c7k97w8budubKoCIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIuVSZW/quSWPD3pMZp6tLLWsZ2mGnIZaxE50U8OGlkBZVoxPDmOu8LnPexwiAa3rHavBaen0/q3F0qGQydvHagxOVmyNLJ5GfICtNjX0upvQvsuc+J8jrgjcAdjv3chsHaUREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBRvpThfJgs1HFI6KSXDZJkcrDs6N7qczWSNI7nNJBB+5SRcs/abztmHDHFY4B+W1bKMNjmcXCGC2Ort2nuHOOKKBz/rB9l0kSDSdGXSvho8Hh8fgoLWau18NQYMViIesfWd6Oxm2SuSFtXHnrGvDnTyAkh2wceRn2hNO22T2MtlnwvyuQjZD1NYudVxlGNznxY+q94DpfXcZJZyGmV5HJrGRsbzn9h7TTsXpmaCaIR3PpzJx3wCHEWKc/oLmFw5EN9G2G3LvPtK7sgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiIC4n6V9Ma4rbF7q+nRedDtwmLjo12UrL9wN/rrebkjLSR6+mwQORXWNX5uLG4+9kZ/wCZxlKxblA7yyvC+VwHvcQzYD3kLj/7LtB7Ppm/aIM1b0PFWH+z0utDJmM3IHEbnfLZzItPs/wcDkWlBJf2cbgmpZpzeYGstTbfg/KzzD+EgUX6QN9WUcldOes4TS2G9LYy1i3sbPk7NElti9PPzP0ZDLHJHHAzYzOY95cB1K5v+yF0pVINO5uOw9tnK3c9ftUcHFK03Lpu1KzwyGLfjbWEkc5fOdmRtD3vLQ0lRroA6D9T5zTrKWQyr8VpfJXIchHj2xia5bY08XHDxbCtUl9R7eMvaXRxyiM8nPC1vQI7JHTOEdl5DLkH42B9iR7nPlc14LoDO9/rPs9QYeMncl/HuT3qbrzrQtjYyNg4WRMaxjR3BrQGtH5ABeiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICrPrrXT9Q5OzXxl/LPr0L0mIxeJ03km4u1mMnWibPlL9zJFpNXDVWS12B7dw97txxBzQ7q37QGSmr4mKKKV1WLK5fF4u/kGPMbqNDIXYq1uw2UD6h5jeYmycuB07Xbt23EU6KejfB0tXZrJYaGGvDj8VQxT4Kjz6OzITOks3hwAkNkFaPFb7H7U0pPrElBlfswa5vZOLMYzKC0MhpfJmpJ6ea7rpqyhzqwty1GtgsTNMc7OujaGyNjjf3uJPY1xjoToudq3pAyDdjXsZLD0WOHcbFDG72m/i02o/zcV2dAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREHPv2ha5nwT6m+zMnlcDj5/vr3s5jqthh3/ddFK9h+55UR0vZlqdH+SvM2NzJVtQ5GMgfbu5S5flqN7xueOeuzv8AYFtP2vq9mbSOQgpNkddtXMNDSbA4tmdZfmsf1AicCC2Tj22O42Kqx0GahzdjD4agMjJYxz9eYfF5LF2I2SPq1nWquSqS15i3rYoXy1LzXsc4t+pYGgcTgQsjgP2eKdC5ZFOWvWxGVjrtylOGmfTrccMMccuN+kHykQYieSPrZYo4w+QySML+AtDe4MaGgNaAGtADWgbAAcgAB3BfqICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiIPG7VinjkhmjZNDOx0csMrGyRyRvBa9kjHgtewgkEEbEFVX6EdUvx1jWGm9J4k3LcOqrs1OaeaCDEY+CcQ0w+050gsPr15ak2zIY3l7WsaHAuDlMOn3pluR0blfTELp5I7cGMt6hkLY8dQtW52VRDTe875G+x0g4hCHti+07ctLVFOirotp4iHSuYoiavmxqCbD6hmFy1LFe6mTJ0MpE6KV/Bwek0+NpDR/NNO2+xAWH6OdKx4fHxU2yOsSl8tm9dkaGyXb9qR1i7ckA5NdJNI93D3NHC0cmhSJEQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERBEOk+UMbieLbgfqLFsfv3bmV3Vfn1vVAfeQqmZ/EXNL67txRRN+hs7qvS1p0j3cPUPu5Ka5XkY0d7WmtmoAO4Abk929mf2m4ZTpbK2K7+qs4llfLVJQATHPircGQjcAeR51tvwcVx39qTNV7+msTqeIPZXzWNbVmMW5krWJY2ZbETOLN9n1sjRdAXDfZt+wBvxcwtWijfRfqhmaw2MyrBw/SdGGd7P8ANyuaBPH94bKJG7+3hUkQEREBERAREQEREBERAUQ6acoaWnszaDp2ej4yy50lRzWWY4+rLZJK73AtZO1hc5riCA5rSVL1qdZYRmSx1/HSco8pQtU3n3NswPhJG3MEB++/3IKk9N2IfJonB6lP+CV8fcxNzEaeoyf4ux+NmcepZIS0Pu5J7ZIXSWH7bEuaxrd5HSd7wtSSbIy12M+oxesHZBpbzDqmQ03NbE/LuByVydvP2s+9cP6O87WtYLD6CzLuvsZCStFWc1h9ak708XIJDv8AU28fcp2ax5jfq6r278R4evdCGQk6/Hmy5xtZHTLMfdB34Bk9IZCbG5F3MDaWSXI+71m1gRyag7Gi53prpWrXtS5DTsdSw36Nge6LKO51LdmqawyNSEgbdZX9NqB3rE7veCG7MMnREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQQjp8idJpjPQt247WJt12cXdx2IjAzf8AtSBcE6XsDBjNJ6u0wA9tHBZDDZTFetu6DE5nKwSPja5+5d1NmPLNBO54er33JO/dOn+51ODk5gdflMHXPF3cFjOY6GX/AIb3/ouU9LNiHPZS/jK7DINSuxml4JG7jrI8LetZbUWRae59OoywysHDvsGZn7pQWLxWPgqQQ1a0TIK9SJkNeCJobHFFG0MZGxo5NaGgDb7lkoiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiCtWoOi61i9W4zLCxTOLvayfbqVWwvN2K3lcZL6dvM4cMcDpqhdwN34iWE7FqWOKxntWYOplxgb+AycGqMVlDDDYZFWyOKhZm2yVpiI5K3FYe93EdhJZa/vaFN/wBqbNTY6lgrsFd9uWrq/EOZUhG8tnjFqJ1eEf557Xua3/Sc1c16IdP4vpDkzGaydSzVfHqaKxXgjkEUsuNOHx8EVK47gJlp2IYYXvY0ji5cLtidwmH7JPR3JQpfS9u3ctvyL70uHZfI62tjMhZjsmeVvMm7c6itPIXOO20beR4+LvC/GNAAAAAaAAANgAOQAA7gv1AREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQERaDpB1PHh8fNdfG+d7XRQVKkX89cu2ZWV6dOEbH6yWeSNm/c0OLjyaSg5P+1QW5gVNLsnFaFxGa1LkiWiPE4PH8chlkcT6tiaZoEY2P8AMSEgNBcI5+y7Sfc1DbyxrtqY6HS+Ph0rjw4k0sHZv3oIDMCNhbndh5J3O4nk+lH1uZA0XSxpi/Nh9Q4/0trb1fGv1Hr3LQM4228g2m+fFabql7g5lOKKGN237kTKx23ncD2bodw3oN+1WafUxuldI4xrdubTTZmXkk+0n0kH9feg6iiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIggfS3RbYn0zG4Ahuqqs+x99PHZS40/k6uD+Sg37LUPo7K0YbwtyWidJ5AEADjsMjyFOwSfaRDFjx+YUi15rii/UeLwETutyFGO/mLXARw04W4m/VhZKf8/J6bxBneGNDjsHs4tF0AF08mnnQ79Rh+jjDV7r9vUdbybKVmtC12/OWOClLI5vsbegP7yDuCIiAiIgIiICIiDT6kwDLwj4rN+sYS4tdj79ioTxbb9Y2FwbKPVG3GDtz27ytQdGWmt4YdR56Eew8WHsOH9q7jJSfzW81NqGhjIDZyNyrRrhwZ19yxHBGXuBLWB0jgHPIB2aOZ2KhbOmzATbihJfyxHyXCZXIMJ3I2FivWMG+4P7/AC9qDeQaWvtHPUuZkPvlrad5/iIsO1ZTMHfH/nq2775KeNJ/4dVqjbteZqf+gaQyhB34ZcxfxWLi5dxLWWJ7LWnv/md/eB3L56zXFg8o9L4th2245cpmJh37gtYymwEcuYce9BKRi8iO7Kk/7ShXP/Y4V+/R+U9mSr/2sZv/AHWQo5HpfU0gPpOqWRbnl9Faep1y0e7fIzWw4/eR+S9f5CZF329XaiJ9vVw6biB/JuF5D80G9NLL+zIUf7eImP8A2cg1ebqec9mRxQ/HBWz/AN8LVDQNn26m1Gfv67FD+DcaAvx2g7f7uqdRs+8Owb/+biXINuKmb9uQxR/DCWx/3uU9HzY/63i3/d9F24/4/SDv7lqBonJtHqauz/8A7yppmT9f8Sg/xWU3T+aYPU1A6Q7d9zEUpOfvIq9Qgy5DnG/ZbiZP9Z9yH+IbIsF+Q1O1/LE4KSP+sNR345PvIjODc38uNfkOP1Qw7uyuCnb/AFDp2/XeR7AZW5p7d/v4PyXpPa1NHtwUcHa95dl79Dl7w0Y2zufuLvzQekuoMrE3eTAWZnD93HZHGS7/AIG9PWH67L0Zq1zW8VjE5ir72mpFccPyxc9jf8t14SahzETd5dPzTn2txmUx8/8AunIPqb/nsvN2veqZxW8Nn6vdu0Ys5Fw3+7CyWt/y3QZsOuMc4bvdbrgfvX8Tk6Dfx4rtaMbfesrH6uxVh3BBk8fM8ciyG9XkeD7i1ryQfuWlPSrp9gabORjx/GdgMzDZxB358uHKRQkHkeS31HIY3Jx7wT0chC4b7wywW4yPfuwuaQg2oIPMcwfaF+rQDRWJaSY8fVrvd3y04W05T9/XVeB+/wCa8XaRaxpFXI5eo4/9IMlJeIP3NzAssH4cOyCSoonJic7EW+jZipOxv225XD9ZNIPYBPj7VaOI/f1LvwXwczn4OI2MLWtsb9g4fLsfYk9+9fJwVYoj93Xu/FBL0USZr+owht2tk8a4t4nG9jLHo8YHf1mRqtlosI/238FvsFm6d+IT0bda5C7ump2IrER390kLi0/qgz0REBERARaLUmssRjf8o5TH0fcLt6vXcTtvs1srwXH7go8/pcxD9vQ2ZXJ8W3C7E4HLXYXB32S23FW9GLT7+s2HedkE+Rc+OvMvL/RNI5lwJIEmQt4WhHy32cWm/JOGnYf9Hvz7l+jLawl+xhMDVG//AFvUlyZ22/fwVsPw77ezj/NB0BFCOp1a8f0jTtc+0eg5O6B+fpkG/wDBfrcbqs9+Z0+3/V0tkXf36hCCbLlXTV18OZ0bfkcDiKWdmhvxdXxcF3JUZ8fiLb3fuxssWHM35bOstP4b92M1X7M1gCfv0rkAP1/lCVC+lHSmusljbmPju6TsRXoHRPMuNy1CaMnnHPXkbdsNZZjeGPY4ggPY0+xBq8vGf5Ia9dKeCa5l9URzyO23LevdSqF23sFOOo0f6LGrqWlIv8cZ9+3fLjYx+EdBjwB+cp/VQGn0c567pDN4vKT0GZrUclmWWWuZTSY+RlaFpceHiHG2txu4WkB0zthy2Wi11pjWt6OOxUqMxWoIzA2TK4vVdhmIsdRsDNZw81Ux2eIcTeB7CQ3g3e4MDEFh0Wu0z6b6HV+kvRvTxXiF70EyGqbIYOuNfrgH9SXbkBw3AK2KAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiIChnSlq2ahHXpY6OOxnM299fEVZSeqa5oBsX7fD6zaFZjhI8jm71GD1pApfanbFG+R52ZExz3kAuIawFzjwtBJ5A8hzVa6eLyGobdGxJKac3SDRuXZ7cbuG3i9FUJKJq4XHuHEGXLjslVlnlBABlk5O4GBBg6bt0TqJtbGiS5Dh9P6qfkNSSNH+O85N9FfSkglaNpup/wVu7Twt60Mbs1jSe8dD2JgqYTGCGJsbrGMx0thzR60szcfUgEkhPNzhFBCwe5sTGjYNAEH1niamPyOPoUYI61XG6E1aK9eFvCyNhmwDRt7S4kOJcdy4uJJJJK6hoyPgxuPaO5mPqNH5QRj/8INsiIgIi8ZLLGkji3c3va3m7fYEDYe3Yj9UHsiwXBxfC5xIJkIEYd6rR1Up57cnv5Dn3DbYe0n6vTDcRvbvHMCwvDu4n2Ebd23t/H2AoMxFhY97ml0LzuY+bHHvc3l+u27f97bntuc1Bg5PDU7T4ZLNWtYfUc51Z9ivFK6BzwGvdC6RpMbiAAS3bcBZzQANhyA5ADuAREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREAjfkeYPeCoxm+jzA3XiW3hsZPM07tsSUK5sMIIILJwzrGO3AO4cO4KToghP/g2qx8RpZDOUHO326jO37ETCfbHVyUk9aPb3CPbkOS/G6VzcIPUaotTH936WxOKstb9x+j4ajnD8Xb9/NTdEEJhp6rjPrZHT9poA5fQmRpPPv3cMrO39Gr0kt6pZ9nH4Cf7zm8jU3/sjETbfqpkiCJ1snqHb67D4oH3V9RWZh+suHiWl1Bh5rb+vsaXoS2mtc1lyLKRQ3Yw7biEN6OuyxDvsObHDuHuXRkQcDzUWv6h/xHQPVsDQyvnNSVcrBsD625mqMyD3kcuJ90j7vf5v130nxxcL9E46acDnPXzdRsLnbcy2s62ZQPuL/wA1YBEHKaUucsMByeoDid2tMjcbph1BsJ73MdfzbrlZ/wDrNA9u33bLGaHw17Z82Sv5wgbP9I1BZnrP5EEyUKU0dEk8/wDodv0XRFr8tgqNvb0unVtbd3pNaGbbbmNusaUGFpzRuIxv+T8XjqPtJpUa9ckgbbudEwFzuXeea3qjs2iqB26ttusGncMx+UyNCMe76qnYZGR9xBC8Z9K2d29RncxWa079W04y013fsHvyFCaXh5+x4PIc0EoRRSzis80AVszRO3tyOCfYcR+NPIVmg9/Ph/Jfkr9SRt9SLCXHD+tYv41p/MQWy3+KCWIolDl8+0fX4SkT7qOeM+/4G3j66+JdWZJh2Ol8xJ/pVrmnXNH4+kZaJ38EEwRRGLV90j1tNZ2M+50un3n9Ycu4fxX3/K61/wCj2b/+T+ZoJWiiMurrwG7dM52T7mzadYf+NmWr9r6ryD9//FjMxEd3X2tOgH84MxIf4IJaijgy+UdtwYfg3+JyVdm34+jtl/gvht3Pk/5NxDG/1jnbj3/nGMQB/wDEgkyKPPizbx6s+KrH3Gnbuj9Rar7/AKJ9E5SQbTZYRn2ux2NggP5C8+0B+e6CQoo4zSznDhs5TLWveTaipHb/AFsVDXI/Ec19R6NoAbPbZsD3XcnkLo/S3YegkJK8+vZ3cbPw4h//AFR2To+wLju/CYl7v60mMqPd/vPiJX4/o70+RscFhyPccTSI/QxIJOijlXQeFh/o+KoVfvp1IqjvxDqzWkH816DSsLCXQ2slC8/vDK3bDR/qw3ZZYR/uIN+i1uLx9iE+vfsWwQf6XDTDgfYWmnBCPyIP5LPgDw1okc1zwBxuYwsaXe0tYXOLR9xcfxQfa4xgKcuM1PjsQ+tIalavmJtP32NaIIsVbFWWzhpNturlq2YK4iAHCa/UD7UZLupXMrLDw8VG1ICwF8lY15mMJ728JlbM8j/RjKwP5a0dyJG5CHhPN1nC5WCMH/by1REfbzDiEEC6UHl2o3s/q9HepnD8X3cQ3/8ARdQ0x/Qaf/qdf/ksXB+krpIwNTVtGzdvMGOuaUyeLsWoI5bDIJrV6nKxk4gY50PEyB/Nw5cidhzWN+z501y2cnS01NdxebYa80NTL4mDK1ZuGhXL2PyEN+s2B0kkcLt3V5HAO2GxB3AWSREQFgvl4HS8QcAXh3FwPLdurjBJcBsBuD392yzkQYT3bvh/2h/5MqwpYSyuYiA188n1UTTuGDdvqgj93ltv/pjfbcrO9DLZIywgRscXFh/dJY9vqfdu77P6e5e1iLve1rTK1pDHP7gee2+3Pbmf1PvQY7edpxHMMg4Hfc4vDwD+IP8Aes5Y1CsY2niPE953e73nmdgdu4bn2AczyG+wyUBFQDtq6q+X6f8AB5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/RUA7auqvl+n/B5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/AEVAO2rqr5fp/wAHkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf9FQDtq6q+X6f8HkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf8ARUA7auqvl+n/AAeR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/0VAO2rqr5fp/weR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/wBFQDtq6q+X6f8AB5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/RUA7auqvl+n/B5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/AEVAO2rqr5fp/wAHkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf9FQDtq6q+X6f8HkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf8ARUA7auqvl+n/AAeR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/0VAO2rqr5fp/weR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/wBFQDtq6q+X6f8AB5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/RUA7auqvl+n/B5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/AEVAO2rqr5fp/wAHkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf9FQDtq6q+X6f8HkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf8ARUA7auqvl+n/AAeR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/0VAO2rqr5fp/weR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/wBFQDtq6q+X6f8AB5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/RUA7auqvl+n/B5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/AEVAO2rqr5fp/wAHkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf9FQDtq6q+X6f8HkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf8ARUA7auqvl+n/AAeR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/0VAO2rqr5fp/weR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/wBFQDtq6q+X6f8AB5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/RUA7auqvl+n/B5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/AEVAO2rqr5fp/wAHkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf9FQDtq6q+X6f8HkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf8ARUA7auqvl+n/AAeR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/0VAO2rqr5fp/weR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUFZkREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQf/Z\\n\",\n \"text/html\": [\n \"\\n\",\n \" <iframe\\n\",\n \" width=\\\"800\\\"\\n\",\n \" height=\\\"450\\\"\\n\",\n \" src=\\\"https://www.youtube.com/embed/oLSdlg3PUO0\\\"\\n\",\n \" frameborder=\\\"0\\\"\\n\",\n \" allowfullscreen\\n\",\n \" ></iframe>\\n\",\n \" \"\n ],\n \"text/plain\": [\n \"<IPython.lib.display.YouTubeVideo at 0x7ff95398cb50>\"\n ]\n },\n \"execution_count\": 80,\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"output_type\": \"execute_result\"\n }\n ],\n \"source\": [\n \"from IPython.display import YouTubeVideo\\n\",\n \"YouTubeVideo(\\\"oLSdlg3PUO0\\\",width=800, height=450)\\n\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"There are many types of data visualizations, serving different purposes. Today we will look at some of those types for visualizing single variable data: _line graphs_ and _histograms_. We will also use _scatter plots_ two visualize two variables against each other. \\n\",\n \"Before starting, read the following sections of the data visualization book.\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"> * _Reading_ [Sections 2,3.2 and 5 of the data visualization book](https://clauswilke.com/dataviz/aesthetic-mapping.html)\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"## Part 2: A little visualization exercise\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"Ok, but is data visualization really so necessary? Let's see if I can convince you of that with this little visualization exercise.\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"\\n\",\n \"> *Exercise 1: Visualization vs stats*\\n\",\n \"> \\n\",\n \"> Start by downloading these four datasets: [Data 1](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/suneman/socialdataanalysis2020/master/files/data1.tsv), [Data 2](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/suneman/socialdataanalysis2020/master/files/data2.tsv), [Data 3](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/suneman/socialdataanalysis2020/master/files/data3.tsv), and [Data 4](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/suneman/socialdataanalysis2020/master/files/data4.tsv). The format is `.tsv`, which stands for _tab separated values_. \\n\",\n \"> Each file has two columns (separated using the tab character). The first column is $x$-values, and the second column is $y$-values. \\n\",\n \"> \\n\",\n \"> * Using the `numpy` function `mean`, calculate the mean of both $x$-values and $y$-values for each dataset. \\n\",\n \"> * Use python string formatting to print precisely two decimal places of these results to the output cell. Check out [this _stackoverflow_ page](http://stackoverflow.com/questions/8885663/how-to-format-a-floating-number-to-fixed-width-in-python) for help with the string formatting. \\n\",\n \"> * Now calculate the variance for all of the various sets of $x$- and $y$-values (to three decimal places).\\n\",\n \"> * Use [`scipy.stats.pearsonr`](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/reference/generated/scipy.stats.pearsonr.html) to calculate the [Pearson correlation](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pearson_product-moment_correlation_coefficient) between $x$- and $y$-values for all four data sets (also to three decimal places).\\n\",\n \"> * The next step is use _linear regression_ to fit a straight line $f(x) = a x + b$ through each dataset and report $a$ and $b$ (to two decimal places). An easy way to fit a straight line in Python is using `scipy`'s `linregress`. It works like this\\n\",\n \"> ```\\n\",\n \"> from scipy import stats\\n\",\n \"> slope, intercept, r_value, p_value, std_err = stats.linregress(x,y)\\n\",\n \">```\\n\",\n \"> * Finally, it's time to plot the four datasets using `matplotlib.pyplot`. Use a two-by-two [`subplot`](http://matplotlib.org/examples/pylab_examples/subplot_demo.html) to put all of the plots nicely in a grid and use the same $x$ and $y$ range for all four plots. And include the linear fit in all four plots. (To get a sense of what I think the plot should look like, you can take a look at my version [here](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/suneman/socialdataanalysis2017/master/files/anscombe.png).)\\n\",\n \"> * Explain - in your own words - what you think my point with this exercise is.\\n\",\n \"\\n\",\n \"\\n\",\n \"Get more insight in the ideas behind this exercise by reading [here](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anscombe%27s_quartet).\\n\",\n \"\\n\",\n \"And the video below generalizes in the coolest way imaginable. It's a treat, but don't watch it until **after** you've done the exercises.\\n\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"code\",\n \"execution_count\": 81,\n \"metadata\": {\n \"scrolled\": true\n },\n \"outputs\": [\n {\n \"data\": {\n \"image/jpeg\": \"/9j/4AAQSkZJRgABAQAAAQABAAD/2wCEAAUDBAgICAgICAkICAgGCAgIBwgICAkICAgICAkICAgICAgIChwLCAgOCQgIDSENDh0dHx8fCAsgICAeIBweHx4BBQUFBwYIDQcIDRIIBwgSEhISEhISEhISEhISEhISEhISEhISEhISEhISEh4SEhISEhISEhIeHhISHh4SHh4eHv/AABEIAWgB4AMBIgACEQEDEQH/xAAdAAEAAgIDAQEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAgUEBgMHCQEI/8QARBAAAgIBAwICBgUKBQUAAQUAAQIAAwQFERITIQYxBxQiQVFSMmFxkrEVIzNCcoGR0dLwYqGissEIFiSCwvElJjRTY//EABcBAQEBAQAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAABAgP/xAAaEQEAAwEBAQAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAhIxAREh/9oADAMBAAIRAxEAPwD8ZREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERA9mIicObaa6rLAFJrrdwGbgpKqWAZ9jxXt57GBzSLOo8yB9pAmsXeMUU2gVBhV0Dv1h3FuK2Y2/s+yempVR+se3Yd5caspLLt8PiPjLznozusvzL/ER1k+ZfvCU1aHf/ANW94+U/XI9M/wBkfzmqIu+snzL94R1k+ZfvCUnTP9kfzjpn+yP5xQXfWT5l+8I6yfMv3hKTpn+yP5x0z/ZH84oLvrL8y/xEdZPmX7wlNZWe32D3j4D65Hpn+yP5xQXfWT5l+8I6yfMv3hKTpn+yP5x0z/ZH84oLvrJ8y/eEdZfmX+IlJ0z/AGR/OSRDs32fEfMv1xQXPWT5l+8I6yfMv3hKTpn+yP5x0z/ZH84oLvrJ8y/eEdZPmX7wlJ0z/ZH846Z/sj+cUF31k+ZfvCDcvzL/ABE0a/xbp6anXo7ZCjUb6urXj8X7rxazbqhemLDWjtwJ32EzM7xBg159enWZNCZ2UrWUYrWAW2IOfdR9Yrs2B8+DbeUVG29ZPmX7wjrJ8y/eEpemf7I/nPnTP9kfzigu+snzL94R1k+ZfvCUnTP9kfzjpn+yP5xQXfWT5l/iI6yfMv3hKfpnj+/4j4fbIdM/2R/OKC76yfMv3hHWT5l+8JSdM/2R/OOmf7I/nFBd9ZPmX7wgWp8y/wARKTpn+yP5yVSHkv2j3j4/bFBc9ZPmX7wklYHuCCPqlF0z/ZH85a6aNqxv8T+MnY+KyYiJkIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgJ8ZQQQQCGBBBG4IPmCPeJ9iBBaUA2CqAOOwCgAcO6/wMwNX+kv2H8ZZSt1f6S/Yfxmo6MOvz/c3+0yMlX5/ub/aZGdEIiIQiIgSs937K/hIyVnu/ZX8JGAiIgJJPJvs/wDpZGY2qapjYdL35d9GLSvFWuyLUpqDM6hQbLCF3J90KygJ1h4p9OWg4DXVl8jItxMk419dFG3Fk6gtsV72VLK0atl9k+e23bvKvxz4L8Q65q5S3PGBoWI1eTgW4hRrXfjUOwSwWjIB6xFj7qO2wO87OxfDmn1W33V4eIlubYt2VYuPXzutQsyWWHj7Thndt/izHzMg6x8SekvxHXlZlGD4cvyKsTJSunIZMkrdSxIRwqIAeqNmDqSEB9qbn6UtJ1nNwaq9Gy007LF9Vlru5UNSFcNV1a62I2dkbsO/TI8jNviUU9fhvDOVTqF1FFupUUCn17pBbT7BVyvuXfk4+IDkeUhqXhDTr9Tq1a3HVs/DU10387BxX2wN6w3TdlFj7Mw3HL7JdyVv0j9pgaX4e8K6hj63qOpXanbkYWfXxx9Pbn06G5VFSAz9NOmqOo4Ab9Uk9/O50nxTp+Xl5WDjZNduXpx2y6F5cqyG4N3K8X4v7J4k7HsdjLmad4g8PDT6tU1LQ8DHbWs6vl7Rba9zYrWey1gQE+1ZxXbkyrvCNxiU3gnJz7tPxbNTpTHz7K98qms+wjcmC7e0QpKBGK7nYsRLmBP9X9//ABISf6v7/wDiQgIiICSq+kv7Q/GRkqvpL+0PxhUZbaX+jH2n8ZUy20v9GPtP4zM8OMqIic1IiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICVur/SX7D+MqdS1fUUyb668cNRXZjrQ4x73Lq9LvZuynhsbglfNey8mLDbbe31Ye0vcDsfPf4/UJqOjCr8/wBzf7TIzkrUb+Y8m+b5T/hkeI+Yf6v6Z0RGJLiPmH+r+mOI+Yf6v6YEYkuI+Yf6v6Y4j5h/q/pgLPd+yv4SM5LFHbuPoj5vh+zI8R8w/wBX9MCMSXEfMP8AV/TOO+2uvj1Lak5sqJzbjydvoovIe05+A+ECQnV+Pn6d4y/Kuk5eHmUV6DmV7WmwVs1ytdSGBUfmrOIt3rbftap8/K/w/Gz2eIcjQjg3rXjYy3jUSW6TkpXZ+j6WwqPU4B+X0kYbTdVA2b2h5f4viv8AhkGJp+JXj01UVLwqxq66al3J4V1KERdz3OyqB3lP478XYWi4oy85rFqe5KEFVZsse11dwqrvt2Suxtz8pmw8R8w/1f0zr3xX4qxrNao8O5+mrkYebStxzMpVfE6oWyysdG6ng6hquHPffk6jaUc/gbx5fqefqGN+TsinEwq1tws5uXDNrcjpFVsrCqba2FigE9t99pq93jzxJqOjXZmmaUun5mJn9K2vUHAU4a0mx7Q2YK1XhaURifIB9u/lseoemDw7i5j6dZmcMjHvOKyjGyDUjowqs2sWrgKq7CqE+7f4SF2Lq+qZ+s6TquLVVoF2O1eJlUuVvsJanp8X5EsxHVYhlABrUdx5wZ3of1DWcrTjfra4q32XOcZsR6bK7MYqnF+WPY1bDqdUAg+QXfv57rb9I/aZTeC/DONpGDRp+IzGjF6nE2sXsZrbHusd2CAci7sdgAO8u7VG59oeZ+b+Uo44kuI+Yf6v6Y4j5h/q/pgdeYGo6pp2oanla9n6fRoltgr0nqPTTwZnJqQNxD8ugrcg5PdSR2BnYCkEbjuDsQR3BB7ggjzEovHfhDTtYxlx9RTqU0WDIXhZdU6OqupIar2tjW7jb6/jtMP0YeNNO1vFe3TurXTg2DG4XV9MqqopqKBGI6ZrK7bnft3Agbb+r+//AIkJycRx8x5/Bvh+zI8R8w/1f0wIxJcR8w/1f0xxHzD/AFf0wIyVX0l/aH4xxHzD/V/TJVKOS9x9IfN8f2YHHLbS/wBGPtP4yr4j5h/q/plrpvase/ufLf4/XMzOMmJwajQ1tNtS2PS11b1rdXt1KmdSosr5ArzUncb/AAE6t9D/AIj1fVc2yvNZqU8J476TqwVaxXqevGwdXJTbuuMmHVj3qBtudWIP0JzV2zETpL0neNdY03xNbVidTJwT4fw6asBagyrreqZWsVabl2OiGxKWv06jFLdwPW1JHYmB3bE6t9HnjW3F8MaVl6pZkanqGZdbg1jGqrOXqWaMnLrSuiolalY1Y7vu5VVWlyxABM3Hwj4rq1BcoGjKwcnTLRTn4WYlYyMd2qS+sk41r03VvVYrB6mYHcjzBADYYmmeGfSDTmZlWFZg6np1mdjXZemvqNFNK5+PjtUtz0pXe12O69eljVkqjbWr7PntW0+lvEa2/fA1ZMLC1S7R8vVXx8cYFObVlnA2JGT6xZjtfwHWrQqvUHIqQwAdixMDW9ROMlTDHycrrZFFBTFRHesX2LWci0O4C49YbmzDcgKdgfKZ8BE4c20pXY4BY1o7BQCSSqkgADuSdvITp7/p71i68YX5T1TxDbqubpFeVdpusYVGFiMx9X9ayNP46ellwpuZa9uZ2F6kghlaB3PE681HxYX8SV4K5Pq+Do9VVef2G2brGrKfyZpvIruDXi1XZJVdv/5OJv2M7DgIlH42wc/JxRRp+UMCy26gZGWEV7qcMOGyjiC1GqGW1QKK1gIHPfY7bTQ/BHi7JGl+JsynJs1XB0S7OOh6hlCsnNTEwa7sivrUIq5eNVnjIoF4HcVkbkjch2xE6e9DHiG7IysNX1XU8v8AKGkeuXY+saacI5VofH31DRnGKi+qA3OjU99hZisNt927E1lrK8igi3ISqyxTa2ytQg7KlXZN15uQORPbcwL2JW6yGH5x7zj49SMzsnEObNxx3LqRxA39keZImPZlXnFxeZNV2U9FdrAAOnPu5CkbK5A27+XKBdRKzSrLN8qoubDjWBans23IequxVcqO+zORv9kx8B7UyVpNzXnos+XuF4VWEp0+HFRw5b2ewfcoMC7ia8clvWrerblVIuRWlQWsDHI4VbK7ms/SsLDz94mwwEREBERASt1f6S/YfxllK3V/pL9h/Gajow6/P9zf7TIyVfn+5v8AaZGdEIiIQiIgSs937K/hIyVnu/ZX8JrHpM0DM1PTrMTCzX0697KnF6GxSURt2qZ6mFiK3buvyj3bwMLxx4+r0vUNJ098XIvbXLukltWwWr85XXuFI3tYFwxUbbKCZyekz0fYXiCvFrzHyK1wbmtT1exULhwFsR+aHsQo9pdiNjsZsWhYttGLjUXXNk3Y+PTVdkuOL5Fldao9zDfszkFv/aZkD6T/AH/+Z9Tyb7P/AKWRkk8m+z/6WFRmp+k3wFh+IMenGzLMitMa/rqcd0UsSjVsjCxCpBVj323H8d9siEa/d4I0Z7/WX03BfINiXG98at7jbX9Gw2MOTPuAdz5kAnvNgiICSt+kftMjNS1vx/jY2vYugtRktfqFRtS9VXoJuL2UHdubDbHs3YDYbj69ittiJpvjjxu+mahpOCuBkZa6zd0nyKiQuP7aV7hRWRay8+ZBK7KpO5hG5TRtSy9Uw9ZwMLTdLxvyNlhrdRy6qxWa7nazqtvUwSt1Vam9oEv1Nh5TeZrXpM0DL1PTrMTBzX0697KnF9ZdSURt2qL0sLEVu3dflHu3gbR+r+//AIkJjaHiW0YeNTdc2Tdj001XZLji+RZXWEe9hv2Z2Vm/fMmAiIgJKr6S/tD8ZGSq+kv7Q/GFRltpf6MfafxlTLbS/wBGPtP4zM8OPmsvkLjXtiJXblLTacWu5zVTZeEPRS2xVLV1F+ILAHYE9jOu/Rt6O8rQszFupsqvTUtPdPFFjMa7MvWVubLTVqqwuzPbblZ9bAkeycUDcJtOz4nNSath6BeniHM1Qmv1bK0XTNPrAY9UX4mZq2RaWXjsK+GdTsd/c02mIHT2b6M8x/D+kYL14WTl6DqlmpHDuvsrw81Xs1GtsZsqukvSxx9QLh+J9qpAe25mw+B/CORjYWrKuPgaLkasbBijTi+S+KoxhRj35OTaAMrKWzlZ7IAAKL325HsCIHSno49G+bh6vpWdZpek6cum4Gdi6jk4ufdnZup5WQuKq5Ntl+Itj1747tytYtve2/lubrI8B5x0HVtNBx/WNR13UNRoPUYVer5WutqlYduG62ertsQB59t/fO0YgYOsW5SLWcSqm52vpW5brmoVMZnAyLUZa252pXuwQ7bkAbjzmdEQMfUqrHpuSm3oXWVWLTfwWzo2MpCW9N/Zs4sQ3Fux2nX3h3QdbytW0vUdZrwcdvD+nahh8sLLsyvyjlag2CLckI+KnqmOEwAwQ7nfII8l3bsmIHUHiL0O2+spkYGraqoyfEVet5+Pbdg9FHLE2247fk83NYla00qjsQFrUe4TtHWLcpFrOJVTc7X0rct1zUKmMzgZFqMtbc7Ur3YIdtyANx5zOiBo3ps0DUNU01MHBSq1MnMx/wAq49uZZgDL0xOdmThjKpod6xcy1VtsO6WWjcbzI0/S8zM0nN0zNwcLR67sS3T8WvT8w51NeNbjtQCqnDqFPDlsKwCNlHebjEDrHwh4Y1izUdHzNVpwcVfDGl5unVep5luX6/dm+oI+QFtxkOLQtenqwQ7ne8jyXdt2zsXKt5Ut02qe5LBby4ulSulnT6QTZmBQjff3y4iBUari3PkVWCuu6qhN0R7TWBeW/SEcCGIUADfy5Gc2o49ttVTBUW2m2u7plyUJQndOoF3G6k99vhLGIFZh416rlWHgt+UxetA3JUK1JVWGYr3O6Ant75DQce2lVqamtF7tZaLzY9lh+k7g1gszH37y2iBT5+LlW86W6bUvdXYLS3F0rR0s6XSCbMwKbct/fLiIgIiICIiAlbq/0l+w/jKrUV1b1jI6THoG2j1cAY68a/V2D7lzydfWtmbcA8R7O5Pa21YDku5PkfIb+/7ZqOjCr8/3N/tMjOSsLv5t5N+qPlP+KR2X4n7o/qnREYktl+J+6P6o2X4n7o/qgRiS2X4n7o/qjZfifuj+qBXeLMJsnCysdMhsN8rGelMqs7PjtanBbVPIHcMw8iD8CDKz0c+Hr9K06jCyMuzPtoNhbIsDAkPYzrWodywRAwUbn3e4dhX+m7QtL1DS+jqucdOxUvotGQWqrTqqrolbi08LAQ7nifeoPum1aRj1U49FVVj2VU0VV1WMRY1laVqqO1nL84SoB5e/eQfc/Mpx0Nt9tVFSkBrLrFqrBY7KC7niCSQJg6H4jwM6zIqw8qjJswHFeUlTh2qclgA23uJRxyHbdG+E0v8A6kfDuXqeijHwMdsvITNouCqypZWipcjW1q7hLG/OBOLe6xj5ibB6OPBGnaRTyxcVcPIzacb15UtsvVbK6+9Vb3WnapbHs+jtvvvKNpkk8m+z/wCljZfifuj+qSQLs3c+Q/VHzL/igccSWy/E/dH9UbL8T90f1QIxJbL8T90f1RsvxP3R/VAjNGbw0zeKX1NdWLCjE6b6OGBapbEFYLL1fYx2cC3uvdgO82Dxt4qwNGxhl59r1UtatKcaWtd7XDsqqiHc+yjt/wCplbofgvShqt3iLGe979Wx12bmDjGu5aW6tSbcwXSqr6RI+AEg2ufR+M+7L8T90f1T6OPxP3R/VKNK9FnirUNUry31DTLtKbFyOlStvPe1diW26iAsyEAF19k8htNymneivRtaw68xdb1BNQe7I54rVgnp1bHkTyUdMOdj0huF49j3m57L8T90f1QNN0jwBXj67m68MrIezUKRQ2K23SQbUjfnvu6DojZD5c285uEqvG/r/wCTcr8lFPyhw/8AE6ypw58l5fTPDn0+e3Ptvx37SPgj1/8AJ+L+VSn5R6X/AJfRCcOfJuP0G4c+nw34dt+W3aBbxJbL8T90f1RsvxP3R/VAjJVfSX9ofjGy/E/dH9UlUF5L3P0h+qPj+1A45baX+jH2n8ZV7L8W+6P6pa6b+jG3xPmNvf8AbMzOIa1p1eXjZGLabBXmU20WNVY1VqpahRmqtQ8qrAG3Dr3BAInUnoZfV9Q1Gz8rWP8A/sWuzQuSWkV6rqdgrsu1e6pG22bTfyeyo/0Wz8udzzXPB3ho6fkazebRb+XNU/KIUJw6A9RwMHpE8j1D/wCEX5dv0m23ac1bHOi/SVZra+Lch9Ia+4jwzgYLYosJx6LNWzddqq1dqCwRjjZWHhFiNj02u28tp3pNexvDhTW8rV+qCuZpeBp3Q4d0OFlalkm7qctiGGeF47dul59+wdb+BfGP5E8I6K9znNyMvLu0zEsz8wYyW3+s57Lbn6hcpGPUuPi2uX2J9gBQSQJuvo08dDV1z0avGXK0e9KckafnJqeHb1aUyKbMTMFaGxWR9irqpBRh5bE1L+jKwaNpun15VPrmg576lhZN2IbsRr2szd68nD6wa2hsfOvqOzAgkMDuNpeaF4UyRhajjZ+VXZZrHWRjp+MuBRhU20DHWrDXk1nJRys6ljElrGI2GwAa74D9LI1DVU0q+nTqrsrGycmlMDW8fVsnF9VelbMXV6MeoLgZZW5WARrFPC0cu254q/Sln7ZeY+kVJo+ma1k6Pk5g1TlmN0NRbSzm04HqfB8cWhCytYGG9nENsC3N4L9HWo4mbpGRlZumPj+HcDK0/FxtO0l8DqpkLjIMi5mzHVXC4tY6aAAbv8QBnXejp20fUdLGUobVNXzdUF/QO1QzNXbVuia+p7ZUN0+W4+O3ugblrWRk1rUcXHTJd8ihLVfI9XFWO9gW/IDGs9R66yWFfblttuPOZ8wdYqynWsYltNLrfQ1xupa9XxlcHIqRVsXha9e6hzvsSDsfKZ0CF1qorO5CpWpZ2YhVVVG7MxPYAAE7zrD0M+IxnZWXl3tkeseJKhq+m0Wcujj+H6bPUdM4qx2ruvUNlkAb/wDm7H6InY2t6ZRm4uTh5SC3Gz6LsbJqJZRZRfW1VtZZCGUMjMNwffNK8NeivB03WU1TDNtdVOmnBrxnys3I4ObefUD5GSy9IVewKtth5jvApfSjoGN+VdCoxDkVajrOs15eRamfmAJp+lD1/PcY/X6PTsavFxSNtv8AzhO25rl3hovrlOrtaCuLpeRp1GPwO6PlZOPkX3izlt7S4lCbbfqnv3lrrFWU61jEtppdb6GuN1LXq+Mrg5FSKti8LXr3UOd9iQdj5QNI/wCoPObH0ml+WT0H1XSas6jBssrz8zEtzKq7sPD6BF1t1nIb11EMyi0DzmN6BsoXLr1dXrdeBj6y9Gn4OebxnYNPqWC99VtWUxvxqXyXyLkrfyW9NgAQBtPpD8NWanRj+r3ri5mmZuPqOBfZScihcnH5rwyKBYrW0PVbdWQrA/nNwdxMPwt4Pvpr1ezNy+pneJLTZl34CPgpjKuHTgUJhA2tZW9dNCt1SxJYk9uwAaX4L0z8meL8jHvqy8enUdOuXw6o1G7Mw7qMB8RtTuya78g216g1mXj7bjiEqIB3Lb9nLSE1BeJf87i3u4NjsvIW44Gys2y7Bj2Hxmr+F/BWorn4Ofq+oY+fZoeDlYGnnHwrMR7RmNiesZec1mU/VyWTCoHFOI3Np94C7XZhZJyBeLKAER6lU0uT03dHO56vd/za9/rPaBwa9jWWXUnpWXVJVdyWu7o+2zVcdzzHI8Vbt9czcZKcjHq4hjSyIUBZ1YADZQzBuW48u5n3Nxry4sptCHgUZLFayvz3DqquNrB3+3efcbB6WMMdGI4VGtXI78uO3MgfX32gV+gqfV8iytuK3WXPjl2LKlajp1sS5+ieHP8A9ph+GrgbqOAvTqYjPkdcvtfZyq42V8zs5BLnkvudZe0YKrjLjHuopFJI7EjhwJHwMxsDTbVsqe6xH9VqaqkJWU3DcAz2bud22rUbD64EFpCagvEv+dxb3cGx2XkLccDZWbZdgx7D4y3lXZhZJyBeLKAER6lU0uT03dHO56vd/wA2vf6z2lpAREQESFwJVuPZip49wNjt27kEDv8AUZh6KMwJ/wCYcdrN+3q4cKB39ljZ9NgAPbAG+57CBnyt1f6S/YfxllK3V/pL9h/Gajow6/P9zf7TIyVfn+5v9pkZ0QiIhCIiBr/pJ8P6bqOBZXqqFsTEHrjsrvW1Rx63LWK1R5dqmsGw9zGcfo18SafqmAlul8xi4h9TWp6zW1PQrr41cST2FTVEHc9mHv3my3KD2IBDKAQRuCCNiCD5iaL4/wDRzTqGm1abg3DRqqMpckDCoVamIDh1ail1BJL8wd/NFPeBvQE+ATSvSb4Es1nCxMRNQycI4V1VpvQGx7hWhTezjYp63fmH37HvtPvj7wM+qZOk5C6hk4Y0a/rOlYLes+1U25YWAV3fmuPMg9rX7QNzDDcjcbrsWG/cb+W492+xkuYG+5A5bKu523YspAHxPY9vqmlaR4CowdW1PXaLMm/K1OmwHFexFp5HpWcQ2253aitRy+iGaatgeHMrxdi4mVruNlaNkaLn2tj008qvWKicVubVZANlTh6+AsHyuR59it38feOtO0NMezULHrXMsaurp1NaQECtZY4X6NaBl3Pn7Q2BmJieKdQfxBfpTaZamn044tr1P8507GKVv9Ip0iC7vXwB33rJ8vLZdW0rFywgysfHyRRYt1IyKa7hXcv0bKxYp4ONz7QmZvCNM8Labr9eqarbn5lFumZG/wCSqa1Bso3feolemOHCr2SCTyOxnz0Z+GtWwcPLo1TU3z78m61qMgNY70I6BQUa/uG57vw8l8hN0mm+kHG8QPlaWdHux6sVLydVW4JyerlUR9Oslq+n1xtWQd2T7QVp/o19GOrYl2dh67m4+uaJb+dxaMpGub1nlSUtFeQC1BVVv3HI7m3f4zuMoF9lQFVPZVVACqo7KqqOwAGw2HwnwyVv0j9p/v8AGPBGa76R/EraRpuRqCY1ma2P0wKK2Kb9R1Tm9gQmuteW5bY+UssPW8O7Juw6snHsy8QK2TjJarXUq22xsrB5KPaX7y/GUvo58fYGvJk2YHXC4Vq1P1qxUWDgtXbXsx9hgrdjse3cCEXXhrUjmYeLlmmzGOZj1Xmi3tZSbEDdN+3mN/gP3SwiIE/1f3/8TSdMwddr13NysrMx20J6AMTG9kWV2bUhSR0gUIYX7sWO/UXt8u7fq/v/AOJrHpI8H067gPp99ttKWW1Wh6eJPKpuShlccbEPwP1HzEDZImo+jDxJpeZjtg6XkWZK6DXj4VjWq4sKojVU2l3UC0OMez21+Q/VNugJKr6S/tD8ZGSq+kv7Q/GFRltpf6MfafxlTLbS/wBGPtP4zM8OMlmABJIAA3JJ2AA8yT7hPhddwNxu/wBEbjdtu52+PacediVX1W0XIttORW9V1bjklldilLEdT2ZWUkbfXOjv+nRRlalqPXylzP8Asqt/Duh7rZyOm+tX89SZ7BtdbccKjDNqdt9Fu2PtGc1d7zjvuRAC7KgYhQWYKCx7BRv5k/Cck6i9NfhwvqGLqmZo6eJNHxNPycXL03hXkZWDZZbXcdTwMG8dPMtNdfSKoRYAicN9yCHbVtqoN2ZVHluxCjf4bn3ySsCAQQQe4I7gj3ETpnxlg6Xm6P4MoqYatpOTrOkrQ2eoyvW8X1HO6RyVvT86/ELuLBvuO/eXnoawqsLUPFenYlaY+Bp2sYhwsSocMfFGVo+l5eQmPUPZpqbIuts4LsN7HIHeB2XERARMDWvXOFXqXq3P1ijr+tdTj6r1B6z0ul39Y6XLjv23237TPgJGuxW34kNsdjsQdiPcdvIyGXj13V2VWqtld6NXajDdXR1KujD3qVJH751t6CdKxsG/xXi4dFOLjY/iUrTj49S001qdF0NiErrHFd2Zj2+JgdlG5OYr5KLCpYJyHMqDsWC+fHf3zkn5roqPrOq6xm6Zi204njTofluvNNevU9LUcfT8P1dPVCBp1IerHag2DklmT27+1+lIELbVQbsyqPLdiAPs3MVWq/dGVgDsSrBhv8O0wvEOi4WfQcfUMXFzcYkO1GZRVk0ck7q5qvUpyHxnUHo1xa8Twl4h1fT6qtPTXPy3rGnVYlKYteLiJjNjaW9NNShay2JhY2R2H0r2gd11XI5YKysa24uFYMVb5W2+i3fyMkXG+243+G/edG+hvBq07UdEqu0nD0jI1bw/kNiNpeYbly6sVtOsvTWaziILc9Dk12reC3fIyxv33btHJxujfdk3Y+Paj5FPG1tmvrBFNKMgKeSuN9t/eYGxMwHmQN+w3O3f4QTKjMxq7s0Jai2IuISquAyhns4swB8mKgDeQ0ypb9Oo6yi3/wAdG/OAN7Sp2Y8vM/XAugYVgd9iDt2O3uPwMqcByum1Mp2ZcFCpHuIoBBExdMx0quwemqp1sO3q8Rt1CnqzKX2+kwLudz8xgbByG+243I32377fHafZqOo8E65sQjL9drem01sW6RtqFZW7bYVivddt/iPfNugIiICIiAlbq/0l+w/jK7WdDyr7MplyV6eQuOKK+Do1BrS9GbqI/t7Pat47A8qlG47EWWqkcl7b9j+M1HRhV+f7m/2mRnJWRv5fqt7z8pkeQ+X/ADM6IjElyHy/5mOQ+X/MwIxJch8v+ZjkPl/zMBZ7v2V/CRnJYw7ez+qPefhI8h8v+ZgRmLquo4+JU1+VdTjUV7c7r7EpqXkQqhrLCFBLED94nB4o8Q4Ol4tmbqF1eLi0cRZdYW4guwRFCqOTOzMAAo98r/Emi6b4h05Krd78LLFOVRdj2shOw5VW1v8AssRsR+sYFZ6TvCWRrVOEMPVLtOGNeMg243JhfWyjgytXaN3X6Sk7j2z28pu6/rfZ/wDS/CYmkYNGJj0YtFfCjDpqooTkzcaqUFda8mO7bKo7mZiEbN7Pu+J+ZYHHE+2WooLNxVUBZmZtlVVG5ZiTsAB33PwmkeNfSEmLpQ1TScca4rZKY4GHczom4YvZY9KMwClVXYDztT3QNW8Q+NL9fvTTdCVczSc1bMLWdQqW2q/C6/Ks20vYQqItO9gchg+zKPKb36PvDNehaXVgjIe+rCF1jX2gIFVma5+KA7VUqCfZ+ozL8F6Ng4mOHw8CvTvXxXk5GOq8HS2xAxrs27Bk3K8R2Gx2AnW/ii3E8aZGTpOLlahplnhvLf1qwVA15Q5WYtnS43g12pZU/FrB+sTxPfaC98Q+KsvV9JbJ8IX05GRXlpTabaxU61qpawImcgQOedDbuPos+3faZnjTwC2sW6NlZeVbjZOiut9yYn6G289B7ekXPKr85UQH7ni7Daaxpejv4D0G5cLHu1yzI1Hqsldb461C6ta+bJXzcIBjou439q1fITtzCyTbVVa9LUtdXXY9Nh/OUs6hmqfbtzUnif2TAodJ8F6di6llatRRwztRUrkW9R2XZ2R7OFZbjWXeqskj5ftlzhYVNAcUVVUi12tsFVaVh7G+lY4Qe05+YzK5D5f8zHIfL/mZRGJLkPl/zMch8v8AmYH39X9//EhOTccfo+/4n4SPIfL/AJmB1j439G2kpk4+uBzpdeh2W6lmjDpRRk9EjJex+mOSvsjgkb7h2G3ebD4Q9Iuj6oKBi5dYvyzaKsS9lpyyat+f5gtufZUtuN9wp+B22u1UZSrIrK4Kure0rKw2Ksp7EEHbY/GadmejfSRfXnYWJThZ+FjW06fZQDXjY9jJcKrmw6yKrGR7nbuPf9Q2g3GSq+kv7Q/GdeeDNVt0PFxcPxNqmPfqOpZdq4bcrbOVZ6SLUbjUCwFjb87AAOuq79p2NURyHs/rD3n4yjiltpf6MfafxlXyHy/5mWum/oxt27n8frmZ4cR1nFsvxsimq58W3IptqryagrW472IVW+pbBwNiEhhyBG6jcGaz4f8AR7h6ffpV2C1mOui6W2j9JeJTLwt6XoGSSOTW1XVNYHHvycjf6Rm0annU4tF2TkWJTj4tb3X3WMFrqqrUvZZYx7KiqCST8DOGzWMRbcWk5FIt1JbHwq+ovPJSpFsteld97EVGRiw+dfjOas+al4o8HW5GaNRwdQyNMzDh+oX2VU4+TXdjCx7qeVOVWVW+qyy5lcf/ANzhgw2A22UXi7xjpWkLU2qZ+Hp65TlKDl5FdHVZduXDqNuwXku5HlyG8CjzvRvR+TNI0zDycjCXw5kY2ThXgVZFxsxqrqQbvWEKWF+u7E7eZ90uPBPhZNNGW5vvzcvVcn1vPzMgVLZfctNONUBXj1rVVVXj49NYVR5J33JJOT4i8U6bp2MmZn5uJiYlzIteTkX110O1il6wlrHixZVYjb4TI8Pa5h6jjpl4GTj5uNaWCZGLcl9LFSVZRZWSvIMCCPqgWEREDB1jEuuWtacmzEau+i13qrpsNtVbh7cZhehC12qChZdiOR2IMzoiBw5tbvVYldhpset1rtVVdqnZSFsCOOLFTsdm7dpqHgbwRk6ZlZmS2q5OYuq5LZmZRbi4daWZRxsbEFivRSHQCnEpHEHbsfjN1lF4c8Y6VqVttOBn4eZbigm6vGyK7XVQ7VF9kbvX1EdOQ7bqw84Gt53oxrtvvHr+WmmZup06xl6UqY/RszabKsjZck1devFsyqKr2qB7sG2IUlZuesYl1y1rTk2YjV30Wu9VdNhtqrcPbjML0IWu1QULLsRyOxBlfd4y0lM8aW+oYS6ixQDCORWMjlYjWV1mvluLGrVnCHuQpIG0voGJrOF6zjZGPzar1qi2nqptzr6qMnUTftyXlv3+AmDpnhvGp0qnRyvUw6NPr00ofZ54yUDFKnh5b1jbt8Zma5q2LgY9uXm304mLjLyuyMixaqawSFHKxzsN2IH2sBOLQNews/H9awsmjKxwzobabFsRXqO1lblT7FikbFT3EDWPCPo9OFlYmVlajl6m+j4NunaUMmvFr9Wxrzjm97GxqVOTlOuJjIbG7bVdgCSTs1ukBmb864pstW56NlINilX7ORyVCyg8ftlb4Y8f6Jql3q+nangZt/Sa7pY2TXdZ0VKK1nFG34BrEG/+IS5t1THSzotdWtpKqKy4DbvtxHH4ncfxgRzsAu4srtamwI1ZZQrckYg7EONgwI3BHxM+nA40JRS5qWtQgPFXJQLx2PMbbnz3+qcmZn008erYlfPfjyO2+22+38R/Gfbc6laxc1la1OAVsZgEbl3XZj2O4gcOn4HSp6DubUCCtQyqu1YXhx9kd+3vMhgaX03R2te3oVmqgMFHBG477lR7bkIg5H5ZnVWK6qykMrqGVh3BVhuCPqInxbkLMgYFqwpdQe68t+O492+xgYF+k82be2zo2WLc9PslS6FWGzkclQsiniPgZZyD3KrKpYBrNwik924jk2w9+wG8nAREQEREBK3V/pL9h/GWUrdX+kv2H8ZqOjDr8/3N/tMjJV+f7m/2mRnRCIiEIiIErPd+yv4SMlZ7v2V/CRgda/8AUhj6LbooTXVzGxGzKOkMDiMn1kJcVKGw9MDpdffl+7vtM2nxtoulNoWj0Lclep4uImliukmqrGsCU4YuZ2DqXOy9gT2Jbbzlp6VdNz8vSsijTRjNluajWMqum2sqtis+y5KNV1eIOxcefw8xVaB4owjn4Gjal0b/ABFiYaWW2piqaUyGx1uvTHvKfm3aoF/YAG3w8oVv+0rNC8RYObZl04mTRkW6ewry0qcM1Ll+IDge7klg3HbdGHums+EvBmNomdrGpvnWMNWZsq9cl0rqx60d7Xsdy35xU6nEWNtsoAln4J0HRcT1vO0tccDWAMm/IqyDdVaosJ51s1hSukWPZ2TYbkwK7H8bYWoaxqHhp8a8vj4r+svYF9XtqdKRbXsrc1UpkqAx8/a+re78E+FMLR8Y4mn1tVS1rXOGse13tcKpZnc7k8URf/QSyzMzHo4vdZRSb2SpGtsSvqud+nUrOfbc99lHxM1fxDk+IF1vTq8OjHfRXr//AFG5ynVR+VvPfk/MbIKeIQHcl9+3kRWeM2u8RYir4b1qrGswc1fW7qLLO4Ctshen2mAOzhfotxPeb/j46JyIVA9vE3WKio1rKOId+I7nb4ym8H+D9N0hb007HXGXLsFtwD2PyYAhFHUYlK1BOyL2HIy+gfRNO8BazreVl6tXquBXhY+Lk8NOsTlvfWXtB3LWEXbItTdRQo/OkbfDcJQekunVbNPyF0WyurUCydF7OG3DqL1QhtUothr5AFht393nCr+JXeGPWvUsUZz1W5qUVrmvRt0myVUC7jsAPp7+QHv7CWMIREQJ/q/v/wCJCT/V/f8A8SEBERApvEHhbT9QtxbszGryLdNs6uI78t6nJVv1W2deSIeLbj2B2lTp2s623iK3CswK10WuhHpzxy5vbxrb6fU4tvY1idLjuOAO+3nt8lV9Jf2h+MKjLbS/0Y+0/jKmW2l/ox9p/GZnhxz3VK6sjqHSxSrowBVlYbMrA9iCCRsZ03/0/wDhh8bUNZF+QcpPCt//AGzoSspBxNJWvG1VayxY9S415uHjmz3jTKZ3PKzRNCxsOzNtoVlfVsv13LJdmD5Hq+Pi8lDHZB0cWkcR8s5qs51n6Q9OzU1ivVNHOn6hnYelPi6joOXatV+VpuRebarcO/ucO5r8e1N7VKPwIJBXcdmTWfFXgnD1G+vKsfMxsqqh8X1nT83Iwb3xbGDtj2vjOOpXzHIb91JYqQSYGhahm4OTpXga/TKXxsC7W9KbDxrAVfGp9S1ADHdSx4vX3TYEj2Ox2l/6L1C6340RQFX8s6fZxUALzt0HR3sfiO3Jm7k++Xmq+AtNyMHB04V242Lo1lFunrhZF2JZjPjVvTSa7qHFnZLHHc99+8z/AAl4ZxNLqsqxFs/8m5sjJuvvuysnJyHVEN2Rk5Lm25+FdaDkewrQDYACBcxEQMDW8XIuStcbJOIyZFFtrrTXf1aK7Fe7GK2jZBagKcx3HLcd5nzB1jTEylrR3vQU30ZCnHyLcdmehxYqWNSwNlJI2NbdiNwQRM6Bj6nXU9FyXkCh6rFvJc1gVMpFhNikGscSfaBG06s9GeKdV1DA1nExvyd4e0HTMnS/DdTKyZGpY+W2FyzzUTvj6YKsCla0f2m5FzxHEHs/WtOqzMbIxLwWpzaLce8KxRjVejVWBXU7qeLHuJR+F/BGNp1lb0ZOq2LTV0a6MrVczKxlTiFUDHvtNe6hQAdu0Dp3EbOox9az7jp+VpdPjlxZp9uHacuxjrWJipmLqK5I6eTRacdkUIRxxApPtez+ipp+Z6ONLtzGzHXJ/PZdOoX4YzMhdOvz8fh0cy3AFnRe5TVU3lsWqrYgsAZsWsaYmUtaO96Cm+jIU4+Rbjsz0OLFSxqWBspJGxrbsRuCCIGp+mTCvso0vIoqOUdK1vAz7MNbKa7suukXI1WN6zYtVmShtW9UYjc4w277Sn9Emq9TUvGGVkY9mm1jUcK16sxqa3rrTR8AHJv6Vhrp511izudwOPLY7gb54s8O4mqYxxMxHevqVXVtXbZRfRkY9i3Y+Rj5FLCyi+u1FYOhB7TH8OeEcLBoyaK0suGpWWXahbmWvl35llta0s2TbeSbF6KJWE8gqKAAIGkYVd2B4yR3vqz6vGOm5dmM7U8btMp0U4JqxcbIW0pbhWnUbbSoUHl3JPkN3vNuO1+QllVldmTX1Kgm7Dfo45HUD+y67A7be7+GD4R9H2naXcl+P63Y+NjHCw/XM7KzRhYZZHbFxBk2Ho1k1U7nzIpqBOygC9fSaTYbCH9p1tasWMKmsXbaxq9+Jb2VP7hA+6xj+sVvjraKmcAtsOR6e/cFeQPBtiv8Zx6dkdbDrsKqpenfiv0VIUj2B7h2nPnafXawcl0dVKc6rGrYo3coSh7ruAZ9twENS0rzrrrACip2rIUDiF3U7ldvdAxtHuWvAosfstWHU7nz2VaVY/5CVvhfU0ezhzqezLRsm0q/IrYzACgfsUhB/wCpl3p2EtC8ENhUABQ7s/EKNgq8j7I29wnJ6svV63fn0+nvv248uW23x398DXLdZqGYzl696rVw60ZtmRCd8m/j7t3CLv8A/wCc2mcOTjLZw5b/AJqxbF2O3tLvsTt5jv5TmgIiICIiBjW59CsUa6pXVq1ZWsQMrXHapSpO4ZyDsPft2mNq/wBJfsP4zG1Hw6l9tlr2272MhUDhtWgpsx3qTdeyOttpJ892HfYADK1VvaXy8veN/fNR0YVfn+5v9pkZyVv38h5N7h8pkef1L90ToiMSXP6l+6I5/Uv3RCIxJc/qX7ojn9S/dEBZ7v2V/CRnJY/l2Hkv6o+Ejz+pfuiBGYf5KxfWfXPV6PXOl0fWujX6x0t9+l1uPPp7/q7zO5/Uv3RHP6l+6IHX3i30UafqmqHU8q3KJfEOJZjpYEqZSllYYOB1EAFhbgDtuoPxB1vUf+nbR7Sxqyc/HQYy1LWtldg5ixWNjmxN3Rm3Y19hudxtO5ef1L90SSv2bsvl8o+ZZPFaB4g9FemZ+n6Zp2U2U9OiJXXQ63BLbK1rSp0ubhsVdUX6ABG3Yib3Jc/qX7olF4h8Z6bp+Th4mZkV05GpvwxUNbsGPJawXdEK0qXZV3cjuT9cqLuJ1piePNY1CjXasLSvVMzTLFq0t8ojpZrNZYp4dZFrN3RqNgVSVPVr3O3c/dc1LxeumaScTGwG1ax99Xpc08K6+RFTbG3iKyNuZrJIP0Y9V2VPuQoJYHfZtwdjxIB3HYjyP1zTvSXmeIK7NO/IWPiXVvkMNS6/TBSrerp/pHG1JU37sm7eymwlB428LeLL87VrcDWKMfEyqq10+hi6NUyvQXXdaD6q2yXfnkJJ6oGw909GN/0++As7w0mo42fmY91WoZqPpyq45sVV0dtii+29Yo9gbn8031TYPAPpHp1vE1HIwsTK56WzoKLgiPkWCt7Kq0YEhLWK8Sjd15Lv5zi1f0cJqaaHbq2Rdbn6AtbPdjFK68q4HHstLhq9wDbjoeScT5+XbbflIG+yoORLHZQN2Pmx2HmfjA6303x3q1nh/J1V9GvTPx7TXVp5W5WurD0qcgVNX1+Ciywldtz6u23Y9tz8I6jfl4GJlZOO+Hfk0pZdivvypdh3U8gGHx2YA9xv3lvz+pf4CfOf1L90So+/q/v/AOJCcvL2fIefwHwkOf1L90QIxJc/qX7ojn9S/dECMlV9Jf2h+Mc/qX7okqn9pey/SHuHxhXHLbS/0Y+0/jKvn9S/wEtdNP5sfafxmZ4ccuTelSPZYy111Kz2O5CqiKCzMzHsqgAnc/Can4N9I+matctGMcyuy/HOXh+uYGXgrnYasitlYTZdSjJpBtq7r32urO2xBmT6WkZvD+uqoLM2j6mFUDcljh3gAAdySZxeFNWwOjoWOz1Nl5ulDIwAENjNjU0YYyba7VUrXX+fxhuSN+a7bzmrbInQuo5uUcLVfEB1DUE1HTfE9+nYuMubcmnriY+t16XRgPpYf1a034pRi7qXJyQysPZ23f0nYtmXq3h7B9az8bFzG1Q5iYGZfhNkLTio9ddl2M4sVQ5DboQe3n3MDsOJ1v6TsbK07wrl01ahnPk46011aibAueq2ZtKoxuQe3alThObd247tuSd9o8I+Gfya2QEzdQyqMk1PXTqGVZnNj2qHFz1ZOSxv4W7oxrJ4goeIG5EDYIkVcHfYg8Tsdjvsfgfge/8AnJQESu13TkyUqV78jHFWTj3hsbIbGaxqLFsWixkO9lDlQrVnswJBljAREpPDmRqz2XDUcXTsapdvVmwtRyM2yzu2/Wrv0+sU+zxPslvM/vCsy/SNpdWa2Cz5HKvLo0+7KXEyG0+nUMla2owrs4J0UyHFtI2J7G+pSQzAHbp0J4nsB0XXKwQbB4902soCC/N9f0O5E4+fI1Oj7fBgfKd8u4G25A3IA3O25PYDv7zArPFXiDF0zGOVls619SqmtaqrL77r8ixaaMfHopU2XX2WOqhVHv8AhMfw34sws+jIyKnepdPtspz68up8W7DtpRbbEyargDXtU6WcvIrYhBIIMo/S64X8hMxCqPEmlqWYgAGw3VVgk9t2ssRAPeXUTUrVLp6TeIL8rGRePfk6+FdMUoNvNgSBt9cDevCHpB07VLlox/W67L8b17EGXhZOF65hckQ5eIcmsdakNZVvt3HWqJGzDfZrclFsrqO/O7mUAG/ZACzE+4DdRv8A4hOn/R8+Vhal4YxjqF+q0654dzcq18pMRhjWYi6Qa7sF8ahWox7VzChrJIPSp94JO+5Ge6ZTWGu5WbIrxa96HK+rKTzKPx2LPZue3uVYF7n6jXSyIwsZrQ7KtVb2nZOIYkINwPbX+MnfmqlQtZbeLAEKKnawchvs1aryUj65iahjJbkJtfZVbVQ5Ar4jet3TdiXUggMi9vsktMyWuwktf6dlHJiBsCeJ7ge4Hz/fAzaMlHrW0H826CwMe3sMvIE7+XaY2DqlVzBV5gsvUr51vWLEGwL1lh7Q9pfvCY+nVh9NqVjxV8GtWbbfiDSATt79hMLBe1sjA5iriuNfwauw2CwcaB1Nig4IfZ/iYFq2qV9VqQtzMjKjlKXatWcKw5WKOK+y6nv8ZnTXssCrr5NF9hY5da2VEL0y5amh6ypXkTx2O4PwmwwEREBERASt1f6S/YfxllK3V/pL9h/Gajow6/P9zf7TIyVfn+5v9pkZ0QiIhCIiBKz3fsr+EjJWe79lfwkYCIiAkk8m+z/6WRkk8m+z/wClhVB4/wAXUbtOyatJurxs91T1e2z6K7WIbRyKkIzVB1DbHYsPtmoeM/Den36HV/3Tbjvm4WBZ1c+oD1hHAU22YqBN7iGFfbjsT7hvOzJ1LZpvh3xPr9lxfJvy/DinFycWxFGFkpXbkJ3W1CbES57VOxG/s+Y83RrHijwdi5XhXSMrQ31DUxoN1l2CgDCy7rZinL6mMiixWqsqYAVbEAHYnzmwnwfVq+ZfqiahZpniK/SK6svApyUsfTLsjHWr85WhGRVXxP0SRsW5ec2XSvRjh4ut16xjW2Y6UYvqtWn0oqYyKUNZCle4pJJs6e30yW3lto3gbTsTU8vV6a3XN1FGS9jYzVgWNXZaa6z2Uu9VZP7PbaTw9Ynga+rTcA4Gdq1GdmaLRZdqVz3q11FJZ7la9Xc2pUlRVQ9nmEH2S/8AD/iDC1Kj1zBvS/GdnAtAZNmQ+2rrYoasjz2YDzEpMX0eaVXnahqIoL36zTbj5i2uXoerI4HIRaj2AsNaE7/Dtt3l34f8P4Wm0ep4NCUYyM5FQLPuzn22drGLWE+W7E+QlFTiekDRrcLI1GvOpbCwX6eTeBZslhKhV4FObli6bcQd+Q23lzhavi3Yq51V1b4llJyFyN9q+iFLNYS30QADvv5bHeU+H4A0arCyNOrwaVws6zq5NANhDuCpVuZfmhUom3EjbiNtpqXoP0lcKrUtEydVxtXbFfpnCRncYmMVaqyt0t+iHZtjUu4U7jfcmPqNwxvHWkWafbqqZlRwMdjXdkcbBwsDIorNbJ1eoTZXsu256i7ecz/+4cL1H8p+sV+odH1j1nv0+j8223Lf3cdt9+228wMbwLpFen26UmHUuBkOXux+Vh52Eo3UNjP1eoDXXs2+46a7eUz/APt7B9R/Jnq9fqHR9X9W79Po+XHfflv7+W++/ffeFZHh/WMXPxKsvDtW/HyNzVanIA8SyMCrAMrBlZSrdxsZmTD8P6Pi4GJViYdS0Y+PuKqk5EDkWdiWYlmYszMWbudzMyEIiICSq+kv7Q/GRkqvpL+0PxhUZbaX+jH2n8ZUy20v9GPtP4zM8OMqUHhnwZpOmWW26dp+FhWZA42vjY9dLMnNremCi+zV1GZuA7bsTtvL+JzVr9/gnR3zhqb6dhNqAdLfWzj1m821J06ri/Hdrkr9gWHuB2B2mP4k9Hmhalket6hpen5uSEWsX5OLVdb0134oHddwo5N2/wARm0RA13WPA2jZmJjYOXp2Dk4WnBFw8W7HrsoxxXX0kFNTLxQLX7I290zPC/hnT9LqejTcTGwabrDdZXi1JSj2lUrNjKg2L8K0G/8AgEtogYenaXjYzZD0U1UtnXHJymrQKb8golZutI+nYa6q15H3IszIiBh6rpeNlrWmTTVetF1OTUtqBwmRjuLKLlDeViOoYN7iBMyIgIiIFFf4P0qzPXVHwMNtRThxzGx6zkA1q1db9Qjc2LW7oGPcBiB2ljqul42WtaZNNV60XU5NS2oHCZGO4souUN5WI6hg3uIEzIgYWt6VjZ2PbiZlFOVjZK8Lse+tbarF3DAPW42OzAH7QJDQNEw9PoGNhY9OLQrO/SorWtC9hLWWMFHtWMxJLHud+8sIgUPhnwZpOmWW26dp+FhWZI42vjY9dJZObWdPdF9mvqO7cB23ZjtLu2pX48lDcGDruN9mHkw+BEnEDHzcGm7YW1pZw3481B2389t/cfhPuTh1WIK7K0ZF2KqQOIIBA2Hu2BInPEDHwsOqkEVIlYY7kKNtyOwnzEwKKSzVVV1s/wBIqoUkb77dvIb99pkxAxnwKDYLjVWbRttZxHLcDYHf4gdt5kxEBERAREQMXVNQqxqzbcxVF8yFZz7yTxQFiAATv8FMx9X+kv2H8Zk6lg1ZNZquXmjEEgMyHt/iQg7Ebgj3gkHsZj6s5DLsSOx8jt75qOjCr8/3N/tMjOSuxt/pHyb3n5TI9RvmP8TOiIxJdRvmP8THUb5j/EwIxJdRvmP8THUb5j/EwFnu/ZH4SM5LLG7e0fJfefhI9RvmP8TAjEl1G+Y/xMdRvmP8TAjJJ5N9n/0sdRvmP8TJJYdm7t9H4n5lgccw8HSsWiy+6jHx6bs1g+VbVTXXZkOu+zXOi8rWG57t8TM7qN8x/iY6jfMf4mBGJLqN8x/iY6jfMf4mBGSt+kftMdRvmP8AEyVtjcj7R8z7zA451h6JfCOfh6tr+oahjYlR1LI3xLaHBZ6mttss4orbV1v+YY8gGLBt52j1G+Y/xMdRvmP8TAjEl1G+Y/xMdRvmP8TAfq/+3/EjOTqHj9I+fxPwkeo3zH+JgRiS6jfMf4mOo3zH+JgRkqvpL+0PxjqN8x/iZKqw8l9o+Y95+MDjltpf6MfafxlX1G+Y/wATLXTTvWN9z3P4zMsOMmIic1IiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICCIiBVeJNUGHUlnTV+dnDYv0x9Cyzs3E7u3T4Bfe1iDtvLTiPgJ9iB84j4COI+An2IHziPgJwZ9601W3MUVaK3sZrG4VqEUsS78TwQAdzsffMiIGv8Ah3xB63aajSlZFKW7rb1COSUv7S9Mcaz19gx8zTd2HGX/ABHwE+xA+cR8BHEfAT7ED5xHwE1zxF4oXDOUvR5HDoouBsZqa7epZ03VbDUV3XlT3G+5t27bGbJED5xHwEcR8BPsQPnEfARxHwEr9P1eu7Jy8ZVYPp5pFjEpxbrobFKANy2AG27Adwdt9jLGBU+LdW9QxLcrpC3omscDYtI9uxKyTYw2UANv9e2w7z7oGqjK9a9hU9Ty7sX2X6nLpEDk3sjpufPh323Xv3lrED5xHwEcR8BPsQPnEfARxHwE+xA1ZfFe+S2P0FHHL9WDG8bt+cSrdUFf6Xdi/TO3s1u2+22+0cR8BPsQPnEfARxHwE+xA+cR8BKLxD4gXEtWorQWsoa5epkCkqFyMXHLWDpkpQPWQxs77dNu0vogUvh7WxlvenSFXQTHfYvysHXVzwtr4jpWDhvtudw6H37S6AiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAieM8QPZiJ4zxA9mInjPED2YieM8QPZiJ4zxA9mInjPED2YieM8QPZiJ4zxA9mInjPED2YieM8QPZiJ4zxA9mInjPED2YieM8QPZiJ4zxA9mInjPED2YieM8QPZiJ4zxA9mInjPED2YieM8QPZiJ4zxA9mInjPED2YieM8QPZiJ4zxA9mInjPED2YieM8QPZiJ4zxA9mInjPED2YieM8QPZiJ4zxA9mInjPEBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQERED/9k=\\n\",\n \"text/html\": [\n \"\\n\",\n \" <iframe\\n\",\n \" width=\\\"800\\\"\\n\",\n \" height=\\\"450\\\"\\n\",\n \" src=\\\"https://www.youtube.com/embed/DbJyPELmhJc\\\"\\n\",\n \" frameborder=\\\"0\\\"\\n\",\n \" allowfullscreen\\n\",\n \" ></iframe>\\n\",\n \" \"\n ],\n \"text/plain\": [\n \"<IPython.lib.display.YouTubeVideo at 0x7ff95398cdc0>\"\n ]\n },\n \"execution_count\": 81,\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"output_type\": \"execute_result\"\n }\n ],\n \"source\": [\n \"from IPython.display import YouTubeVideo\\n\",\n \"YouTubeVideo(\\\"DbJyPELmhJc\\\",width=800, height=450)\\n\",\n \"\\n\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"## Prelude to Part 3: Some tips to make nicer figures.\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"Before even starting visualizing some cool data, I just want to give a few tips for making nice plots in matplotlib. Unless you are already a pro-visualizer, those should be pretty useful to make your plots look much nicer. \\n\",\n \"Paying attention to details can make an incredible difference when we present our work to others.\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"code\",\n \"execution_count\": 85,\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"outputs\": [\n {\n \"data\": {\n \"image/jpeg\": \"/9j/4AAQSkZJRgABAQAAAQABAAD/2wCEAAUDBAgICAgICAgICAgGBwgIBwcHBwgICAgICAgICAgICAgIChALCAgOCggIDhUNDhESExMTCAsWGBYSGBASExIBBQUFBwYHDwgIDx4VEhUfGB8YHRwbGxobGhsaGhkVHh0eHR4YHx4eFhoeHx0YGh0dGBUYHRgaGRcdFR4ZGhUYG//AABEIAWgB4AMBIgACEQEDEQH/xAAcAAEAAgMBAQEAAAAAAAAAAAAABggEBQcDAgH/xABWEAABBAECAgYGBwMGCgQPAAABAAIDBAUGERIhBxMYMZTVFCJBUVRVFSMyYXGBkQhCoRYzNFKCsSQlNVNicnOSo7NDRLLFFyY2RVZ0dYOipbS1wcLR/8QAGQEBAQEBAQEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAECAwQF/8QAMREBAAECBAQDBgYDAAAAAAAAAAECEQMhMVEEEkFhgcHwE3GRobHhIzJSYtHxIiRC/9oADAMBAAIRAxEAPwCmSIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/AIzI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8AGZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/wCMyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/ABmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P8AjMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/wAZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/AIzI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8AGZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/wCMyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/ABmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P8AjMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/wAZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/AIzI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8AGZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/wCMyPlyC/6IiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIijg15hDP6KMvjfSOLg6n0+vx8e+3Bw8f29+XD3rVNFVX5YusUzOiRoiLKCIiAiIgIiICL4ErS4s4m8bQHFm44g0kgEt7wDsef3FfaAiIgIsTI5OvXMLbE8MJtztr1hNKyMzTvDnMhiDj9ZKQ1xDRz9UrKcQOZ5Ad5KtpH6i0uE1bi70r4KeRpWpoty+GtbhlkaAdieBjieEH29y3StVM0zaqLLMTGoiL4bK0uLA5pc0AuaHDiaHb8JI7wDsf0Kyj7RFiVMnXllnginiknpOjbahjka6Su6VgkiEzAd4y5hDhvtuDurYZaLX57N06EXX3rVepDxBgltTMhYXnchoc8gF2wPIc+RXricnXtxNnqzw2YJPsTV5WSxu25HZ7CQdk5ZtzWyW02uy0XxLK1u3E5reJwa3icBu49zRv3uPuX2ogiIgIiICIhKAi0+N1TjLLxHWyNCxI77Mde7XlefwZG8kr0y2o8dTeI7d+lVkcwPbHatwQPLCS0PDJXglu7XDfu3afctclV7WXlnRtEWrp6ix84jMN6nMLEroYTFbgkEszGCR8UfA88cgYQ4tHMA7rMs3oInxRyzRRyWnFleOSVjHzPa3ic2JrjvI4NBJDd+QUmmYymC0shF+OIA3PIDmSe4LT4LVeMvySQ0shStywDeWKrahmewA8JcWxuJ4d+W/crFMzEzEaERMtyi0ud1ZjKEkcN3IUqks+xiitWoYXvBPCHBsjgeHflv3LctcCAQQQRuCOYIPcQfaEmmYi8wTExm/UXm2wwyOiD2mRjGSOjDhxtZIXtY9ze8NcY5AD7eB3uKx58rWjsQ1HzxMs2mSyV67pGiWVkPD1ro2E7uDeNu+3v+4qREyWZiLSZDWGJryvgsZTHQTRECSGe/WilYS0OAfG+QOaS1zTzHcQsnC5+jd4xSu1LfU8PW+iWobHV8fFwcfVOPBvwu237+E+5WaKoi9sjlm12yREWUEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREHM/2irk7cdSpxTOrx5zM0sbcssPC6KrY610uzv3eLq2tJ9znD2rc1Oi3T8dZtUYqo6NgAD3wgzEt7nmb7fHvz33W71lpurlqU1C4wvgsgblp4Xse0h0csbv3ZGuAIP3c9wSFAYdDaqjDazNVE0mFrQ+THQOvdU0j1DYILnO2G3HvxL24dcThRRFfLMTO+fwjXp6l3pqiaIi9nzd6RMzZs5AYTEQXKODnkrWZrNswTWZ6/KeOo0NIBaQQC7ffbf27Lym6Vrt2xj6+DoV7Jy+G+ko3XbD4eocyw+GWOYRghwb1ZbyI3c4HfZZed6Mb4nvOxGblxlTNyvmyNMVopgZpRwzy1ZnevWdINyeH2nkeQA2mmejSHHX6FutMRDjMM/Ftruj3c/jnNg2DLxfaLnO3bt7e9dJq4WIvERO2u3XvfbJq+FEf380V0x0wZC19D25cXBBi85djxrZRbc+yLjmPLpGR8Ab6NxxvAB57NJ335L3i6R9Q2m5GXH4WpNXwl+/WnfLeex9llOZ7OGszg5S8DNySSN3bAHbnscV0TmDG4TH+ncX8nsw3JNm9H29IDTP8AVFnH9Wdp/tAn7PdzUN0PpLL34s/HTzE2Mgtajy8Vus+pHJxxPsO3lryvAkrvex2xLTsQARseZ6/6tV6qYi0T15tLz43s3+FN5jz3lP8ATfSW3IX8RXrwD0bOYafIiV7yJoZIZWxmAtA4XAHjBO/e3lyUE1t0h5q1XpTUYYq4g1g7GPLLksZsSV7Bjq15QG86s46zrO/h4G8jvymOS6K3RR4p2GyD8ddwNWWpDYfXjssmgn2dK2aGTlxce7gfZxHkeRH5U6JxHjqFL01z5aWfgzlm1JFxG1YjkdJKzhDh1YeXd/PbbuKxRXwtExVHwm/7vszTVhRMTHrX7Pi/r3MzZKTF4rF1bE+KrVZcy+zcdDDHYswtmFWtI1h4jwu5SEEd/Ibc4prXpDzNzBm5Wrtx8lfUf0fZDbb2TxdRbgZDESwbP6x7nRyAHYDfbdTnUmgLpyk+Vw+Vdi5slFDFk43VIrUc/UN6uGZjZeUc7WAN32I5fe7fBh6JnNw8+KOQdI6fNtyvpckO8ji2zDYLJRx+u9xiO79+ZcTsrh4nDU8tVo/53v3v010WmrCi0+7fxalucr47OZXJ5Ci2C9S0pTtZCSrakma9zpTG6rEx4DCOKGNrX8t9xvtzK2GL6RszDLj5czh4aeOzdiKtVnrWzNPVms/0ZtuNzRu1/dxN2293sUhzPR9DcyGStWZDJXzOGixc1UN4XMbHJJJ1rZd/tfWcuXItBWhxfRbfdPRGUzk2Sx+Enjnx9J1aKFxlhG1d9qZnrTuYO4nn3+8rPtOHqi9W0b7dPHfJObDmM/Pbo1DelzLCB2RdiqoxdTLnG25hck9JeTc9FbLXiLNtm8TNw483EgbAbre3de5azlLtLC4uC5Xwj2R5Cxatms6WZzQ90FXZpaHgct37gkHuGxP3L0Wl2EsYf03+k5Z2RFnqPs732XeqMfHz+zw8W/t32X3lujy8zJW72IzD8YzMFjsnX9Fish8jG8HX1nS7iCYt357HmSfuCa+FmZtERrbW3S1++pM4Wdu+/b7odqDVUuZpaUvTVxWkdrWKF0DXF3B6O67CNy4bh+zBuPYd12PWWIOQx16iJTCchTsVhM0EmMzROjD9gRuBxd243G6guL6JzBRxFL04v+g88cv1zofWsAyTv6l+8m7XfX837nct7uanuq8JFkqVmjOZGxXIXRPfC8skZvza9jh3Oa4A+7lzBG4XPHxcOaqfZzlEz4Re8M4ldN45en8uNdH9Srir+Kx2bwNelkIS+LEZ2ns+rdlbEWuD5G7Pinewnk/fck8m7gHZnpXy80FnL08LFPgKL5eOd1vq701au4ia3DERwBrQ1zuA89m9457Z+L6M8q+5j5MtnDkaeDmE9GAVGQSulY3gjfZkbzleG8tySTz953x8h0QW+CfH083PVwN2aSSfFCtE97GzPL5q8Fo/WMruJPqe47Hfc7+irE4aqu9cxM5X/NbWb26307Xu6TVhTN6vOzKvdJGSvXZKmnMfXutp1q1i3avWHV4t7cLbEMEQaN+PqnsJcTyJI25bnX1M5Ux+a1DlLNB1e3V09jbl8ssuldI50RBqiM/VB7TBEwPB2O2525k7fL9GNmGy61gMq/Dvs1a9W7H6NDaimZVjEMEzWyj6qw2MBvEO/Yd3PfOj6NmST5KS7afaZmsLUxdppZwSE1mSMdZEgcfrHl/F3ciPauUV8PEZaTEb31pvfpvZiKsOI/u/RGn9JeoK9aldvYSpFUy12jDA+K898leO5K1o9JjLN+Msdu1w2G4AIHEFuOjj/wAp9Y/7fC//AGxi1juijKzQ06tvUMlipiLdSejAaMTC5lSRrmNtSNdxzPDG8IJOw33IJ22nGm9K+h5TM5HrusGdfSf1PV8PUeiVhX24+I8fFtv3DZMTEwIoqii15jpf9VMxr2iSqrDimYjz3jdGOmvSNy7Pi8lTq1sk7Cus9bh7ruGK0yy2MF0bj6rZ2GIbcXLmO/bZ2kwevcbjsZK7E4Z9bJXM0KEuCd9Q5uWmj4vrXgFog6qPcOaACGgbN57TPpC0bbu2K2QxmSkxuRpRSQNkMYnrT15XBzop67/VPrAEO2/uaRHq3Q+59Oz6XkpZMxbyUOV+l4Y2xmC7XYY4HRQ/Z6prHObw8uTuW2w2uFi4M4VNOLOnTPeZz6THXdaKqOSIqn6+rfNpukO3fnqY8ajxFVr49S4tlJ1LITcAM7Zw6YFvrCWPhI4XbtPWAjuX3rnptkq5C5TpRY4x4lxjnfk7zq0tuZg3khpsYw7cJ9Xif3kHltzO+sdHWUuQRsymcN2avlqGQieKMUMTG0hKDAyKItDTJ1u5fzO7R3pqPoytuu3LWKyjcezLvEl6CahXuAT8IY6xVfMOKCRwHPblvz922qMThsortNr/AKrdO1/ksVYelXnZiO6VLt2bGQYXHw2HZvEyXmG7ZdCKr4rBhmbOY2u42MLHN9XmXFu2wXjW6W7tmtRgqYyOXN5C5kKjqjrJFSA4x4ZasOm4eJ0XrM2by73czwjilmK0MYMlj8h6W6U43DyY1zZImNfO6SVkpsvfHs0PJadwG8y7fdR09EckcTJKmTfVydPK5K/RyDK7HNZHkn8U1WaB7i2aLYAbn+r3cyFmmrhJyt9f3a9tGYnB2+vf7MTV/SrkcTXpwX6NGvlr89hoEl530bFWg6v/AAt8waX7PMoaI+/dr9zyG8g6HekducFuCRkDLmMcwTGnObFSeKUO6uevKWh3Du1wLSNwQOfPlgZHozv2Yak0+ZfJmsdPYkgyb6UDoDDaEYkpyUiOrfX+raR3EHcjvKkvR3pi1jmWHXbwv2LcoeXtqw1ooWhob1UEcTRwx8gdt9t9z3kk4xauG9jamI5vHfplpbvfslc4XJlr4+rM/UusMXjHMZkMhVpumY58TbU7Ii9jSA5zQ48wCR+q3DnBzOIEFrmbgjmCCNwR7wsLL4KlcLTbqVrJjBDDYgjlLQ7YkNLwdgdgs7qwG8DQGgN4QAOQG2wAHuC8c8totr1ccrRZwfod6N8NldK0ZLdOFtmaKyTkIwI7MTmWZ2xyiYbHdga3v5eqN1ptQcGU0EMtehisZOo2KnFk3xgzyQwZdldjxK71jxxl2/vL3n2qXYfobyUVNmKk1JZ+io2uY6lUpwVnPje9z5I3WBvKWPLnbgkjZxHdyU01boGC3gX4Kq4U4OrrsheGdZwCvYin5t4hxFxj5nfvcSvq1cXRGLzc9/8AK/XKM7/Hr0yeqcaIrve+d/dCH69wdOhkNIRUq0NWJ+ekkdHBG2NhldT4S8gfvENaN/uWz6Yv8s6Q/wDbM/8A9KVJekTRzcvVgjbYkqW8fZiuY+9E0OdXtQghryx3KSMhzgWHv3+5R/A6AyUmTq5POZVmQfi2yDH161VtWGJ8oDZJnNH2pCAP0C81GLRNMVVVZxFUWzvN72+u7nTXFomZ0ifnf+X3+0lclh05cETzH6VLUqyyNOxbBZtRRTc/YHMc5p+55UV6TtL0cEzTd7Gwx1rdTNUafWQtDX2a9lkjbEcxHOXcNJ3Pdu73rresNP18rRs4+00mC7EY38JAc07hzJGEjYPY9rXDf2tC59hui/Ivt0ZczmTk6uDcH46sKrID1jQGxy2XN/nZGtAG5JPI8+Z3vD41FGHETNrXvG94iPVzDriKc50v45PvpC0/p7FDKZjKxenS5hzY2wWQyaWSTqhFFToN4QWEhg22+zwkkgAleOkc9LpvSePOTa6S71Qgo0eP6+eWRzjVqAn7IawtBd3Naw+4BfWuei/J5LKtyYzbITUJGPruxsc8dRh234WTSOY+YkbmQt3Ow7gABJZOj+ter1WZ5sOYt02SMFyWEQcTZH8R2hhIYwkNYDsOfAFZxMPkpiurm0mdb5RaIi+Vt8/os1U8sRM33QPojt2KeV1NZy1pk9lmOxt66+Ih0cTRDbnkgrtBP1MLSGAD3c+Z3Oiweey1eabW2QxsNiheZHHGG2T6ZjcU6ThjdXh4Sx7fXa53MFxc4+qCdukaZ6JMXQvZCzDBC2vkaTKcdRkZaK8T2OZca1/GeJs3qEjYbFgUdd0P5N8DMRLnpJNPRSNLaBqxttOgjeJGVX2gOJ0YIHt25DkNgB3jHwKqpmZ15b5TGURnEW0n5d7N+0w5mZ93w8G16YY8LVqG+cVRv5PLPjgxsclWOSW5bmYGwF+44nRsYGucT+6wDcEhb3od0PHgscyA8Lrdk9ffma1reOd45taGgBsbPsgAbcvvX63RHHm2ZWzM2aHH02VsPS6vZtJzhtZmJJIklfwsAdy2AA/dBUzXgxMb8OMOmb9Z8o8Pr4OFVf8AjyxPv9dhEReZyEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREGp1LqGtjhVNlzmjI36+Pr8DHP3s2iWwtdw/ZaS07uPILbLmX7REj4qeHsiC1YZj9UYi3ZZRqTW5m14JJHSyCGBrnuAHuHtHvXPukbNPv5avdnOroMRPg+LT8eEq5GrJ9NMt2I7Lb9eJgkjtcDavVi0BCWF5PIu3CxyKpkmX1DTw74Z49Qy29Q6Ew9PFOhivyvjzkb7kVrr5R/k+2BPA90kpYS1m+5LdlM7eCzz5NaX60+W+k6ULINPVpLM7afHNgaHpE1Su89TNOZxIGu5tbIw7bEu3CwC0urtTUcTDFYvTNgjtXalKJx/fs3JmwQt/Ddxc4/utY8nkFxDoPeRqKm2hJq2TF/wAm7vpp1IMiKwyptY4lsfp4B9K4BJxBv1fM9WecqzenLS2T1Vl3YyCnXfi8Bj5DM7KuuVq1nJ5avLDHNVfFC70h9OsS4PaS1slpwPrR8g7Hk9S1q+Qx+MkL/SsxFemqBrN4yzHtruscb9/UO1mLb38/ctyq3WbGorjtOyipYbnsLgtbYuexJWkFc5mvVx0FKyJpYxE6G0+Bs0bzsx4c7bk07RTourZ11bNtfltQMjl0zMLpdiNQOtVso9zQ2xX+krL3yZJg60OZSLWOadweJrCAt4iqXjbmT4NKTcGonej5CeuMc1+omx3YzlomfSTbs31kLBCHOFTJBzeoL2hw3DjkZd+SbftGaXV30+dZVeKOsL/0H/J8Ziua7mdUPRPQfQ+DfY9bx8fH6vW7haxaXNamq1LuOoTGQT5t9mOnwsLmF1WD0iUSOB9T1N9veVwPTuKz8E+Nv158y6/ksvrGnPDfsXJaEVaJmZkwrZa0+8VeD0mKm9khA3EgAJaQFpejirM/L6UfwarlvVfpN2opM3FkH1K2SlxsjD1UlpvVxyOkDw0wERuaGb+twgBbBY1q/BFJBFLNFHLce6OrFJKxkliRkb5nxwMcd5XiOOR5DdyGsce4FVVyeAz9fSen5xdznFlJYJdVS2n5i5bgayrIytC6tRlZegptkDWvbAQ7cRufxetvsMDpLI5GPRUmSsZqx6Nn8qxloDJ46eDGijcfUfZD5nTMJliYxk0zhI6KZrHc3OCCwNnW+KZYx9X02J82bsXK2P6jjsRzWMeHG5CZ4GuiikjLHtIe5p4mOb3ghSJVq6JNNXcZNpuONuWbDLqzVrsgyzJdljbA2LJxUpJxLuI45A2B4c7k97w8budubKoCIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIuVSZW/quSWPD3pMZp6tLLWsZ2mGnIZaxE50U8OGlkBZVoxPDmOu8LnPexwiAa3rHavBaen0/q3F0qGQydvHagxOVmyNLJ5GfICtNjX0upvQvsuc+J8jrgjcAdjv3chsHaUREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBRvpThfJgs1HFI6KSXDZJkcrDs6N7qczWSNI7nNJBB+5SRcs/abztmHDHFY4B+W1bKMNjmcXCGC2Ort2nuHOOKKBz/rB9l0kSDSdGXSvho8Hh8fgoLWau18NQYMViIesfWd6Oxm2SuSFtXHnrGvDnTyAkh2wceRn2hNO22T2MtlnwvyuQjZD1NYudVxlGNznxY+q94DpfXcZJZyGmV5HJrGRsbzn9h7TTsXpmaCaIR3PpzJx3wCHEWKc/oLmFw5EN9G2G3LvPtK7sgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiIC4n6V9Ma4rbF7q+nRedDtwmLjo12UrL9wN/rrebkjLSR6+mwQORXWNX5uLG4+9kZ/wCZxlKxblA7yyvC+VwHvcQzYD3kLj/7LtB7Ppm/aIM1b0PFWH+z0utDJmM3IHEbnfLZzItPs/wcDkWlBJf2cbgmpZpzeYGstTbfg/KzzD+EgUX6QN9WUcldOes4TS2G9LYy1i3sbPk7NElti9PPzP0ZDLHJHHAzYzOY95cB1K5v+yF0pVINO5uOw9tnK3c9ftUcHFK03Lpu1KzwyGLfjbWEkc5fOdmRtD3vLQ0lRroA6D9T5zTrKWQyr8VpfJXIchHj2xia5bY08XHDxbCtUl9R7eMvaXRxyiM8nPC1vQI7JHTOEdl5DLkH42B9iR7nPlc14LoDO9/rPs9QYeMncl/HuT3qbrzrQtjYyNg4WRMaxjR3BrQGtH5ABeiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICrPrrXT9Q5OzXxl/LPr0L0mIxeJ03km4u1mMnWibPlL9zJFpNXDVWS12B7dw97txxBzQ7q37QGSmr4mKKKV1WLK5fF4u/kGPMbqNDIXYq1uw2UD6h5jeYmycuB07Xbt23EU6KejfB0tXZrJYaGGvDj8VQxT4Kjz6OzITOks3hwAkNkFaPFb7H7U0pPrElBlfswa5vZOLMYzKC0MhpfJmpJ6ea7rpqyhzqwty1GtgsTNMc7OujaGyNjjf3uJPY1xjoToudq3pAyDdjXsZLD0WOHcbFDG72m/i02o/zcV2dAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREHPv2ha5nwT6m+zMnlcDj5/vr3s5jqthh3/ddFK9h+55UR0vZlqdH+SvM2NzJVtQ5GMgfbu5S5flqN7xueOeuzv8AYFtP2vq9mbSOQgpNkddtXMNDSbA4tmdZfmsf1AicCC2Tj22O42Kqx0GahzdjD4agMjJYxz9eYfF5LF2I2SPq1nWquSqS15i3rYoXy1LzXsc4t+pYGgcTgQsjgP2eKdC5ZFOWvWxGVjrtylOGmfTrccMMccuN+kHykQYieSPrZYo4w+QySML+AtDe4MaGgNaAGtADWgbAAcgAB3BfqICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiIPG7VinjkhmjZNDOx0csMrGyRyRvBa9kjHgtewgkEEbEFVX6EdUvx1jWGm9J4k3LcOqrs1OaeaCDEY+CcQ0w+050gsPr15ak2zIY3l7WsaHAuDlMOn3pluR0blfTELp5I7cGMt6hkLY8dQtW52VRDTe875G+x0g4hCHti+07ctLVFOirotp4iHSuYoiavmxqCbD6hmFy1LFe6mTJ0MpE6KV/Bwek0+NpDR/NNO2+xAWH6OdKx4fHxU2yOsSl8tm9dkaGyXb9qR1i7ckA5NdJNI93D3NHC0cmhSJEQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERBEOk+UMbieLbgfqLFsfv3bmV3Vfn1vVAfeQqmZ/EXNL67txRRN+hs7qvS1p0j3cPUPu5Ka5XkY0d7WmtmoAO4Abk929mf2m4ZTpbK2K7+qs4llfLVJQATHPircGQjcAeR51tvwcVx39qTNV7+msTqeIPZXzWNbVmMW5krWJY2ZbETOLN9n1sjRdAXDfZt+wBvxcwtWijfRfqhmaw2MyrBw/SdGGd7P8ANyuaBPH94bKJG7+3hUkQEREBERAREQEREBERAUQ6acoaWnszaDp2ej4yy50lRzWWY4+rLZJK73AtZO1hc5riCA5rSVL1qdZYRmSx1/HSco8pQtU3n3NswPhJG3MEB++/3IKk9N2IfJonB6lP+CV8fcxNzEaeoyf4ux+NmcepZIS0Pu5J7ZIXSWH7bEuaxrd5HSd7wtSSbIy12M+oxesHZBpbzDqmQ03NbE/LuByVydvP2s+9cP6O87WtYLD6CzLuvsZCStFWc1h9ak708XIJDv8AU28fcp2ax5jfq6r278R4evdCGQk6/Hmy5xtZHTLMfdB34Bk9IZCbG5F3MDaWSXI+71m1gRyag7Gi53prpWrXtS5DTsdSw36Nge6LKO51LdmqawyNSEgbdZX9NqB3rE7veCG7MMnREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQQjp8idJpjPQt247WJt12cXdx2IjAzf8AtSBcE6XsDBjNJ6u0wA9tHBZDDZTFetu6DE5nKwSPja5+5d1NmPLNBO54er33JO/dOn+51ODk5gdflMHXPF3cFjOY6GX/AIb3/ouU9LNiHPZS/jK7DINSuxml4JG7jrI8LetZbUWRae59OoywysHDvsGZn7pQWLxWPgqQQ1a0TIK9SJkNeCJobHFFG0MZGxo5NaGgDb7lkoiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiCtWoOi61i9W4zLCxTOLvayfbqVWwvN2K3lcZL6dvM4cMcDpqhdwN34iWE7FqWOKxntWYOplxgb+AycGqMVlDDDYZFWyOKhZm2yVpiI5K3FYe93EdhJZa/vaFN/wBqbNTY6lgrsFd9uWrq/EOZUhG8tnjFqJ1eEf557Xua3/Sc1c16IdP4vpDkzGaydSzVfHqaKxXgjkEUsuNOHx8EVK47gJlp2IYYXvY0ji5cLtidwmH7JPR3JQpfS9u3ctvyL70uHZfI62tjMhZjsmeVvMm7c6itPIXOO20beR4+LvC/GNAAAAAaAAANgAOQAA7gv1AREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQERaDpB1PHh8fNdfG+d7XRQVKkX89cu2ZWV6dOEbH6yWeSNm/c0OLjyaSg5P+1QW5gVNLsnFaFxGa1LkiWiPE4PH8chlkcT6tiaZoEY2P8AMSEgNBcI5+y7Sfc1DbyxrtqY6HS+Ph0rjw4k0sHZv3oIDMCNhbndh5J3O4nk+lH1uZA0XSxpi/Nh9Q4/0trb1fGv1Hr3LQM4228g2m+fFabql7g5lOKKGN237kTKx23ncD2bodw3oN+1WafUxuldI4xrdubTTZmXkk+0n0kH9feg6iiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIggfS3RbYn0zG4Ahuqqs+x99PHZS40/k6uD+Sg37LUPo7K0YbwtyWidJ5AEADjsMjyFOwSfaRDFjx+YUi15rii/UeLwETutyFGO/mLXARw04W4m/VhZKf8/J6bxBneGNDjsHs4tF0AF08mnnQ79Rh+jjDV7r9vUdbybKVmtC12/OWOClLI5vsbegP7yDuCIiAiIgIiICIiDT6kwDLwj4rN+sYS4tdj79ioTxbb9Y2FwbKPVG3GDtz27ytQdGWmt4YdR56Eew8WHsOH9q7jJSfzW81NqGhjIDZyNyrRrhwZ19yxHBGXuBLWB0jgHPIB2aOZ2KhbOmzATbihJfyxHyXCZXIMJ3I2FivWMG+4P7/AC9qDeQaWvtHPUuZkPvlrad5/iIsO1ZTMHfH/nq2775KeNJ/4dVqjbteZqf+gaQyhB34ZcxfxWLi5dxLWWJ7LWnv/md/eB3L56zXFg8o9L4th2245cpmJh37gtYymwEcuYce9BKRi8iO7Kk/7ShXP/Y4V+/R+U9mSr/2sZv/AHWQo5HpfU0gPpOqWRbnl9Faep1y0e7fIzWw4/eR+S9f5CZF329XaiJ9vVw6biB/JuF5D80G9NLL+zIUf7eImP8A2cg1ebqec9mRxQ/HBWz/AN8LVDQNn26m1Gfv67FD+DcaAvx2g7f7uqdRs+8Owb/+biXINuKmb9uQxR/DCWx/3uU9HzY/63i3/d9F24/4/SDv7lqBonJtHqauz/8A7yppmT9f8Sg/xWU3T+aYPU1A6Q7d9zEUpOfvIq9Qgy5DnG/ZbiZP9Z9yH+IbIsF+Q1O1/LE4KSP+sNR345PvIjODc38uNfkOP1Qw7uyuCnb/AFDp2/XeR7AZW5p7d/v4PyXpPa1NHtwUcHa95dl79Dl7w0Y2zufuLvzQekuoMrE3eTAWZnD93HZHGS7/AIG9PWH67L0Zq1zW8VjE5ir72mpFccPyxc9jf8t14SahzETd5dPzTn2txmUx8/8AunIPqb/nsvN2veqZxW8Nn6vdu0Ys5Fw3+7CyWt/y3QZsOuMc4bvdbrgfvX8Tk6Dfx4rtaMbfesrH6uxVh3BBk8fM8ciyG9XkeD7i1ryQfuWlPSrp9gabORjx/GdgMzDZxB358uHKRQkHkeS31HIY3Jx7wT0chC4b7wywW4yPfuwuaQg2oIPMcwfaF+rQDRWJaSY8fVrvd3y04W05T9/XVeB+/wCa8XaRaxpFXI5eo4/9IMlJeIP3NzAssH4cOyCSoonJic7EW+jZipOxv225XD9ZNIPYBPj7VaOI/f1LvwXwczn4OI2MLWtsb9g4fLsfYk9+9fJwVYoj93Xu/FBL0USZr+owht2tk8a4t4nG9jLHo8YHf1mRqtlosI/238FvsFm6d+IT0bda5C7ump2IrER390kLi0/qgz0REBERARaLUmssRjf8o5TH0fcLt6vXcTtvs1srwXH7go8/pcxD9vQ2ZXJ8W3C7E4HLXYXB32S23FW9GLT7+s2HedkE+Rc+OvMvL/RNI5lwJIEmQt4WhHy32cWm/JOGnYf9Hvz7l+jLawl+xhMDVG//AFvUlyZ22/fwVsPw77ezj/NB0BFCOp1a8f0jTtc+0eg5O6B+fpkG/wDBfrcbqs9+Z0+3/V0tkXf36hCCbLlXTV18OZ0bfkcDiKWdmhvxdXxcF3JUZ8fiLb3fuxssWHM35bOstP4b92M1X7M1gCfv0rkAP1/lCVC+lHSmusljbmPju6TsRXoHRPMuNy1CaMnnHPXkbdsNZZjeGPY4ggPY0+xBq8vGf5Ia9dKeCa5l9URzyO23LevdSqF23sFOOo0f6LGrqWlIv8cZ9+3fLjYx+EdBjwB+cp/VQGn0c567pDN4vKT0GZrUclmWWWuZTSY+RlaFpceHiHG2txu4WkB0zthy2Wi11pjWt6OOxUqMxWoIzA2TK4vVdhmIsdRsDNZw81Ux2eIcTeB7CQ3g3e4MDEFh0Wu0z6b6HV+kvRvTxXiF70EyGqbIYOuNfrgH9SXbkBw3AK2KAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiIChnSlq2ahHXpY6OOxnM299fEVZSeqa5oBsX7fD6zaFZjhI8jm71GD1pApfanbFG+R52ZExz3kAuIawFzjwtBJ5A8hzVa6eLyGobdGxJKac3SDRuXZ7cbuG3i9FUJKJq4XHuHEGXLjslVlnlBABlk5O4GBBg6bt0TqJtbGiS5Dh9P6qfkNSSNH+O85N9FfSkglaNpup/wVu7Twt60Mbs1jSe8dD2JgqYTGCGJsbrGMx0thzR60szcfUgEkhPNzhFBCwe5sTGjYNAEH1niamPyOPoUYI61XG6E1aK9eFvCyNhmwDRt7S4kOJcdy4uJJJJK6hoyPgxuPaO5mPqNH5QRj/8INsiIgIi8ZLLGkji3c3va3m7fYEDYe3Yj9UHsiwXBxfC5xIJkIEYd6rR1Up57cnv5Dn3DbYe0n6vTDcRvbvHMCwvDu4n2Ebd23t/H2AoMxFhY97ml0LzuY+bHHvc3l+u27f97bntuc1Bg5PDU7T4ZLNWtYfUc51Z9ivFK6BzwGvdC6RpMbiAAS3bcBZzQANhyA5ADuAREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREAjfkeYPeCoxm+jzA3XiW3hsZPM07tsSUK5sMIIILJwzrGO3AO4cO4KToghP/g2qx8RpZDOUHO326jO37ETCfbHVyUk9aPb3CPbkOS/G6VzcIPUaotTH936WxOKstb9x+j4ajnD8Xb9/NTdEEJhp6rjPrZHT9poA5fQmRpPPv3cMrO39Gr0kt6pZ9nH4Cf7zm8jU3/sjETbfqpkiCJ1snqHb67D4oH3V9RWZh+suHiWl1Bh5rb+vsaXoS2mtc1lyLKRQ3Yw7biEN6OuyxDvsObHDuHuXRkQcDzUWv6h/xHQPVsDQyvnNSVcrBsD625mqMyD3kcuJ90j7vf5v130nxxcL9E46acDnPXzdRsLnbcy2s62ZQPuL/wA1YBEHKaUucsMByeoDid2tMjcbph1BsJ73MdfzbrlZ/wDrNA9u33bLGaHw17Z82Sv5wgbP9I1BZnrP5EEyUKU0dEk8/wDodv0XRFr8tgqNvb0unVtbd3pNaGbbbmNusaUGFpzRuIxv+T8XjqPtJpUa9ckgbbudEwFzuXeea3qjs2iqB26ttusGncMx+UyNCMe76qnYZGR9xBC8Z9K2d29RncxWa079W04y013fsHvyFCaXh5+x4PIc0EoRRSzis80AVszRO3tyOCfYcR+NPIVmg9/Ph/Jfkr9SRt9SLCXHD+tYv41p/MQWy3+KCWIolDl8+0fX4SkT7qOeM+/4G3j66+JdWZJh2Ol8xJ/pVrmnXNH4+kZaJ38EEwRRGLV90j1tNZ2M+50un3n9Ycu4fxX3/K61/wCj2b/+T+ZoJWiiMurrwG7dM52T7mzadYf+NmWr9r6ryD9//FjMxEd3X2tOgH84MxIf4IJaijgy+UdtwYfg3+JyVdm34+jtl/gvht3Pk/5NxDG/1jnbj3/nGMQB/wDEgkyKPPizbx6s+KrH3Gnbuj9Rar7/AKJ9E5SQbTZYRn2ux2NggP5C8+0B+e6CQoo4zSznDhs5TLWveTaipHb/AFsVDXI/Ec19R6NoAbPbZsD3XcnkLo/S3YegkJK8+vZ3cbPw4h//AFR2To+wLju/CYl7v60mMqPd/vPiJX4/o70+RscFhyPccTSI/QxIJOijlXQeFh/o+KoVfvp1IqjvxDqzWkH816DSsLCXQ2slC8/vDK3bDR/qw3ZZYR/uIN+i1uLx9iE+vfsWwQf6XDTDgfYWmnBCPyIP5LPgDw1okc1zwBxuYwsaXe0tYXOLR9xcfxQfa4xgKcuM1PjsQ+tIalavmJtP32NaIIsVbFWWzhpNturlq2YK4iAHCa/UD7UZLupXMrLDw8VG1ICwF8lY15mMJ728JlbM8j/RjKwP5a0dyJG5CHhPN1nC5WCMH/by1REfbzDiEEC6UHl2o3s/q9HepnD8X3cQ3/8ARdQ0x/Qaf/qdf/ksXB+krpIwNTVtGzdvMGOuaUyeLsWoI5bDIJrV6nKxk4gY50PEyB/Nw5cidhzWN+z501y2cnS01NdxebYa80NTL4mDK1ZuGhXL2PyEN+s2B0kkcLt3V5HAO2GxB3AWSREQFgvl4HS8QcAXh3FwPLdurjBJcBsBuD392yzkQYT3bvh/2h/5MqwpYSyuYiA188n1UTTuGDdvqgj93ltv/pjfbcrO9DLZIywgRscXFh/dJY9vqfdu77P6e5e1iLve1rTK1pDHP7gee2+3Pbmf1PvQY7edpxHMMg4Hfc4vDwD+IP8Aes5Y1CsY2niPE953e73nmdgdu4bn2AczyG+wyUBFQDtq6q+X6f8AB5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/RUA7auqvl+n/B5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/AEVAO2rqr5fp/wAHkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf9FQDtq6q+X6f8HkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf8ARUA7auqvl+n/AAeR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/0VAO2rqr5fp/weR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/wBFQDtq6q+X6f8AB5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/RUA7auqvl+n/B5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/AEVAO2rqr5fp/wAHkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf9FQDtq6q+X6f8HkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf8ARUA7auqvl+n/AAeR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/0VAO2rqr5fp/weR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/wBFQDtq6q+X6f8AB5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/RUA7auqvl+n/B5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/AEVAO2rqr5fp/wAHkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf9FQDtq6q+X6f8HkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf8ARUA7auqvl+n/AAeR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/0VAO2rqr5fp/weR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/wBFQDtq6q+X6f8AB5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/RUA7auqvl+n/B5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/AEVAO2rqr5fp/wAHkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf9FQDtq6q+X6f8HkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf8ARUA7auqvl+n/AAeR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/0VAO2rqr5fp/weR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/wBFQDtq6q+X6f8AB5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/RUA7auqvl+n/B5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/AEVAO2rqr5fp/wAHkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf9FQDtq6q+X6f8HkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf8ARUA7auqvl+n/AAeR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/0VAO2rqr5fp/weR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUFZkREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQf/Z\\n\",\n \"text/html\": [\n \"\\n\",\n \" <iframe\\n\",\n \" width=\\\"800\\\"\\n\",\n \" height=\\\"450\\\"\\n\",\n \" src=\\\"https://www.youtube.com/embed/sdszHGaP_ag\\\"\\n\",\n \" frameborder=\\\"0\\\"\\n\",\n \" allowfullscreen\\n\",\n \" ></iframe>\\n\",\n \" \"\n ],\n \"text/plain\": [\n \"<IPython.lib.display.YouTubeVideo at 0x7ff95398c1c0>\"\n ]\n },\n \"execution_count\": 85,\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"output_type\": \"execute_result\"\n }\n ],\n \"source\": [\n \"from IPython.display import YouTubeVideo\\n\",\n \"YouTubeVideo(\\\"sdszHGaP_ag\\\",width=800, height=450)\\n\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"## Part 3: Time series of Reddit activity and market indicators.\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"It's really time to put into practice what we learnt by plotting some data! We will start by looking at the time series describing the number of comments about GME in wallstreetbets over time. We will try to see how that relates to the volume and price of GME over time, through some exploratory data visualization.\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \" We will use two datasets today: \\n\",\n \" * the _GME market data_, that you can download from [here](https://finance.yahoo.com/quote/GME/history/). \\n\",\n \" * the dataset you downloaded in Week1, Exercise 3. We will refer to this as the _comments dataset_.\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"> _Exercise 2 : Plotting prices and comments using line-graphs._\\n\",\n \"> 1. Plot the daily volume of the GME stock over time using the _GME market data_. On top of the daily data, plot the rolling average, using a 7 days window (you can use the function [``pd.rolling``](https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/reference/api/pandas.DataFrame.rolling.html)). Use a [log-scale on the y-axis](https://matplotlib.org/3.1.1/api/_as_gen/matplotlib.pyplot.yscale.html) to appreciate changes across orders of magnitude.\\n\",\n \"> 2. Now make a second plot where you plot the total number of comments on Reddit per day. Follow the same steps you followed in step 1.\\n\",\n \"> 3. Now take a minute to __look at these two figures__. Then write in a couple of lines: What are the three most important observations you can draw by looking at the figures?\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"> _Exercise 3 : Returns vs comments using scatter-plots_.\\n\",\n \"> In this exercise, we will look at the association between GME market indicators and the attention on Reddit. First, we will create the time-series of daily [returns](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Price_return). Returns measure the change in price given two given points in time (in our case two consecutive days). They really constitute the quantity of interest when it comes to stock time-series, because they tell us how much _money_ one would make if he/she bought the stock on a given day and sold it at a later time. For consistency, we will also compute returns (corresponding to daily changes) for the number of Reddit comments over time.\\n\",\n \"> 1. Compute the daily log-returns as ``np.log(Close_price(t)/Close_price(t-1))``, where ``Close_price(t)`` is the Close Price of GME on day t. You can use the function [pd.Series.shift](https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/reference/api/pandas.Series.shift.html). Working with log-returns instead of regular returns is a standard thing to do in economics, if you are interested in why, check out [this blog post](https://quantivity.wordpress.com/2011/02/21/why-log-returns/).\\n\",\n \"> 2. Compute the daily log-change in number of new submissions as ``np.log(submissions(t)/submissions(t-1))`` where ``submissions(t)`` is the number of submissions on day t. \\n\",\n \"> 3. Compute the [Pearson correlation](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/reference/generated/scipy.stats.pearsonr.html) between the series computed in step 1 and step 2 (note that you need to first remove days without any comments from the time-series). Is the correlation statistically significant? \\n\",\n \"> 4. Make a [scatter plot](https://matplotlib.org/api/_as_gen/matplotlib.pyplot.scatter.html) of the daily log-return on investment for the GME stock against the daily log-change in number of submission. Color the markers for 2020 and 2021 in different colors, and make the marker size proportional to the price. \\n\",\n \"> 5. Now take a minute to __look at the figure you just prepared__. Then write in a couple of lines: What are the three most salient observations you can draw by looking at it?\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"## Part 4 : The activity of Redditors\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"It is time to start looking at redditors activity. The [r/wallstreetbets]() subreddit has definitely become really popular in recent weeks. But probably many users only jumped on board recently, while only a few were discussing about investing on GME [for a long time](https://www.reddit.com/user/DeepFuckingValue/). Now, we wil look at the activity of redditors over time? How different are authors?\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"> _Video Lecture_: Start by watching the short video lecture below about plotting histograms in matplotlib.\\n\",\n \"\\n\",\n \"> _Reading_: [Section 7 of the Data Visualization book](https://clauswilke.com/dataviz/histograms-density-plots.html)\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"code\",\n \"execution_count\": 6,\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"outputs\": [\n {\n \"data\": {\n \"image/jpeg\": \"/9j/4AAQSkZJRgABAQAAAQABAAD/2wCEAAUDBAgICAgICAgICAgGBwgIBwcHBwgICAgICAgICAgICAgIChALCAgOCggIDhUNDhESExMTCAsWGBYSGBASExIBBQUFBwYHDwgIDx4VEhUfGB8YHRwbGxobGhsaGhkVHh0eHR4YHx4eFhoeHx0YGh0dGBUYHRgaGRcdFR4ZGhUYG//AABEIAWgB4AMBIgACEQEDEQH/xAAcAAEAAgMBAQEAAAAAAAAAAAAABggEBQcDAgH/xABWEAABBAECAgYGBwMGCgQPAAABAAIDBAUGERIhBxMYMZTVFCJBUVRVFSMyYXGBkQhCoRYzNFKCsSQlNVNicnOSo7NDRLLFFyY2RVZ0dYOipbS1wcLR/8QAGQEBAQEBAQEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAECAwQF/8QAMREBAAECBAQDBgYDAAAAAAAAAAECEQMhMVEEEkFhgcHwE3GRobHhIzJSYtHxIiRC/9oADAMBAAIRAxEAPwCmSIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/AIzI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8AGZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/wCMyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/ABmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P8AjMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/wAZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/AIzI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8AGZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/wCMyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/ABmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P8AjMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/wAZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/4zI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/AIzI+XIKzIrM9irVXx+n/GZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8AGZHy5OxVqr4/T/jMj5cgrMisz2KtVfH6f8ZkfLk7FWqvj9P+MyPlyCsyKzPYq1V8fp/xmR8uTsVaq+P0/wCMyPlyC/6IiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIijg15hDP6KMvjfSOLg6n0+vx8e+3Bw8f29+XD3rVNFVX5YusUzOiRoiLKCIiAiIgIiICL4ErS4s4m8bQHFm44g0kgEt7wDsef3FfaAiIgIsTI5OvXMLbE8MJtztr1hNKyMzTvDnMhiDj9ZKQ1xDRz9UrKcQOZ5Ad5KtpH6i0uE1bi70r4KeRpWpoty+GtbhlkaAdieBjieEH29y3StVM0zaqLLMTGoiL4bK0uLA5pc0AuaHDiaHb8JI7wDsf0Kyj7RFiVMnXllnginiknpOjbahjka6Su6VgkiEzAd4y5hDhvtuDurYZaLX57N06EXX3rVepDxBgltTMhYXnchoc8gF2wPIc+RXricnXtxNnqzw2YJPsTV5WSxu25HZ7CQdk5ZtzWyW02uy0XxLK1u3E5reJwa3icBu49zRv3uPuX2ogiIgIiICIhKAi0+N1TjLLxHWyNCxI77Mde7XlefwZG8kr0y2o8dTeI7d+lVkcwPbHatwQPLCS0PDJXglu7XDfu3afctclV7WXlnRtEWrp6ix84jMN6nMLEroYTFbgkEszGCR8UfA88cgYQ4tHMA7rMs3oInxRyzRRyWnFleOSVjHzPa3ic2JrjvI4NBJDd+QUmmYymC0shF+OIA3PIDmSe4LT4LVeMvySQ0shStywDeWKrahmewA8JcWxuJ4d+W/crFMzEzEaERMtyi0ud1ZjKEkcN3IUqks+xiitWoYXvBPCHBsjgeHflv3LctcCAQQQRuCOYIPcQfaEmmYi8wTExm/UXm2wwyOiD2mRjGSOjDhxtZIXtY9ze8NcY5AD7eB3uKx58rWjsQ1HzxMs2mSyV67pGiWVkPD1ro2E7uDeNu+3v+4qREyWZiLSZDWGJryvgsZTHQTRECSGe/WilYS0OAfG+QOaS1zTzHcQsnC5+jd4xSu1LfU8PW+iWobHV8fFwcfVOPBvwu237+E+5WaKoi9sjlm12yREWUEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREHM/2irk7cdSpxTOrx5zM0sbcssPC6KrY610uzv3eLq2tJ9znD2rc1Oi3T8dZtUYqo6NgAD3wgzEt7nmb7fHvz33W71lpurlqU1C4wvgsgblp4Xse0h0csbv3ZGuAIP3c9wSFAYdDaqjDazNVE0mFrQ+THQOvdU0j1DYILnO2G3HvxL24dcThRRFfLMTO+fwjXp6l3pqiaIi9nzd6RMzZs5AYTEQXKODnkrWZrNswTWZ6/KeOo0NIBaQQC7ffbf27Lym6Vrt2xj6+DoV7Jy+G+ko3XbD4eocyw+GWOYRghwb1ZbyI3c4HfZZed6Mb4nvOxGblxlTNyvmyNMVopgZpRwzy1ZnevWdINyeH2nkeQA2mmejSHHX6FutMRDjMM/Ftruj3c/jnNg2DLxfaLnO3bt7e9dJq4WIvERO2u3XvfbJq+FEf380V0x0wZC19D25cXBBi85djxrZRbc+yLjmPLpGR8Ab6NxxvAB57NJ335L3i6R9Q2m5GXH4WpNXwl+/WnfLeex9llOZ7OGszg5S8DNySSN3bAHbnscV0TmDG4TH+ncX8nsw3JNm9H29IDTP8AVFnH9Wdp/tAn7PdzUN0PpLL34s/HTzE2Mgtajy8Vus+pHJxxPsO3lryvAkrvex2xLTsQARseZ6/6tV6qYi0T15tLz43s3+FN5jz3lP8ATfSW3IX8RXrwD0bOYafIiV7yJoZIZWxmAtA4XAHjBO/e3lyUE1t0h5q1XpTUYYq4g1g7GPLLksZsSV7Bjq15QG86s46zrO/h4G8jvymOS6K3RR4p2GyD8ddwNWWpDYfXjssmgn2dK2aGTlxce7gfZxHkeRH5U6JxHjqFL01z5aWfgzlm1JFxG1YjkdJKzhDh1YeXd/PbbuKxRXwtExVHwm/7vszTVhRMTHrX7Pi/r3MzZKTF4rF1bE+KrVZcy+zcdDDHYswtmFWtI1h4jwu5SEEd/Ibc4prXpDzNzBm5Wrtx8lfUf0fZDbb2TxdRbgZDESwbP6x7nRyAHYDfbdTnUmgLpyk+Vw+Vdi5slFDFk43VIrUc/UN6uGZjZeUc7WAN32I5fe7fBh6JnNw8+KOQdI6fNtyvpckO8ji2zDYLJRx+u9xiO79+ZcTsrh4nDU8tVo/53v3v010WmrCi0+7fxalucr47OZXJ5Ci2C9S0pTtZCSrakma9zpTG6rEx4DCOKGNrX8t9xvtzK2GL6RszDLj5czh4aeOzdiKtVnrWzNPVms/0ZtuNzRu1/dxN2293sUhzPR9DcyGStWZDJXzOGixc1UN4XMbHJJJ1rZd/tfWcuXItBWhxfRbfdPRGUzk2Sx+Enjnx9J1aKFxlhG1d9qZnrTuYO4nn3+8rPtOHqi9W0b7dPHfJObDmM/Pbo1DelzLCB2RdiqoxdTLnG25hck9JeTc9FbLXiLNtm8TNw483EgbAbre3de5azlLtLC4uC5Xwj2R5Cxatms6WZzQ90FXZpaHgct37gkHuGxP3L0Wl2EsYf03+k5Z2RFnqPs732XeqMfHz+zw8W/t32X3lujy8zJW72IzD8YzMFjsnX9Fish8jG8HX1nS7iCYt357HmSfuCa+FmZtERrbW3S1++pM4Wdu+/b7odqDVUuZpaUvTVxWkdrWKF0DXF3B6O67CNy4bh+zBuPYd12PWWIOQx16iJTCchTsVhM0EmMzROjD9gRuBxd243G6guL6JzBRxFL04v+g88cv1zofWsAyTv6l+8m7XfX837nct7uanuq8JFkqVmjOZGxXIXRPfC8skZvza9jh3Oa4A+7lzBG4XPHxcOaqfZzlEz4Re8M4ldN45en8uNdH9Srir+Kx2bwNelkIS+LEZ2ns+rdlbEWuD5G7Pinewnk/fck8m7gHZnpXy80FnL08LFPgKL5eOd1vq701au4ia3DERwBrQ1zuA89m9457Z+L6M8q+5j5MtnDkaeDmE9GAVGQSulY3gjfZkbzleG8tySTz953x8h0QW+CfH083PVwN2aSSfFCtE97GzPL5q8Fo/WMruJPqe47Hfc7+irE4aqu9cxM5X/NbWb26307Xu6TVhTN6vOzKvdJGSvXZKmnMfXutp1q1i3avWHV4t7cLbEMEQaN+PqnsJcTyJI25bnX1M5Ux+a1DlLNB1e3V09jbl8ssuldI50RBqiM/VB7TBEwPB2O2525k7fL9GNmGy61gMq/Dvs1a9W7H6NDaimZVjEMEzWyj6qw2MBvEO/Yd3PfOj6NmST5KS7afaZmsLUxdppZwSE1mSMdZEgcfrHl/F3ciPauUV8PEZaTEb31pvfpvZiKsOI/u/RGn9JeoK9aldvYSpFUy12jDA+K898leO5K1o9JjLN+Msdu1w2G4AIHEFuOjj/wAp9Y/7fC//AGxi1juijKzQ06tvUMlipiLdSejAaMTC5lSRrmNtSNdxzPDG8IJOw33IJ22nGm9K+h5TM5HrusGdfSf1PV8PUeiVhX24+I8fFtv3DZMTEwIoqii15jpf9VMxr2iSqrDimYjz3jdGOmvSNy7Pi8lTq1sk7Cus9bh7ruGK0yy2MF0bj6rZ2GIbcXLmO/bZ2kwevcbjsZK7E4Z9bJXM0KEuCd9Q5uWmj4vrXgFog6qPcOaACGgbN57TPpC0bbu2K2QxmSkxuRpRSQNkMYnrT15XBzop67/VPrAEO2/uaRHq3Q+59Oz6XkpZMxbyUOV+l4Y2xmC7XYY4HRQ/Z6prHObw8uTuW2w2uFi4M4VNOLOnTPeZz6THXdaKqOSIqn6+rfNpukO3fnqY8ajxFVr49S4tlJ1LITcAM7Zw6YFvrCWPhI4XbtPWAjuX3rnptkq5C5TpRY4x4lxjnfk7zq0tuZg3khpsYw7cJ9Xif3kHltzO+sdHWUuQRsymcN2avlqGQieKMUMTG0hKDAyKItDTJ1u5fzO7R3pqPoytuu3LWKyjcezLvEl6CahXuAT8IY6xVfMOKCRwHPblvz922qMThsortNr/AKrdO1/ksVYelXnZiO6VLt2bGQYXHw2HZvEyXmG7ZdCKr4rBhmbOY2u42MLHN9XmXFu2wXjW6W7tmtRgqYyOXN5C5kKjqjrJFSA4x4ZasOm4eJ0XrM2by73czwjilmK0MYMlj8h6W6U43DyY1zZImNfO6SVkpsvfHs0PJadwG8y7fdR09EckcTJKmTfVydPK5K/RyDK7HNZHkn8U1WaB7i2aLYAbn+r3cyFmmrhJyt9f3a9tGYnB2+vf7MTV/SrkcTXpwX6NGvlr89hoEl530bFWg6v/AAt8waX7PMoaI+/dr9zyG8g6HekducFuCRkDLmMcwTGnObFSeKUO6uevKWh3Du1wLSNwQOfPlgZHozv2Yak0+ZfJmsdPYkgyb6UDoDDaEYkpyUiOrfX+raR3EHcjvKkvR3pi1jmWHXbwv2LcoeXtqw1ooWhob1UEcTRwx8gdt9t9z3kk4xauG9jamI5vHfplpbvfslc4XJlr4+rM/UusMXjHMZkMhVpumY58TbU7Ii9jSA5zQ48wCR+q3DnBzOIEFrmbgjmCCNwR7wsLL4KlcLTbqVrJjBDDYgjlLQ7YkNLwdgdgs7qwG8DQGgN4QAOQG2wAHuC8c8totr1ccrRZwfod6N8NldK0ZLdOFtmaKyTkIwI7MTmWZ2xyiYbHdga3v5eqN1ptQcGU0EMtehisZOo2KnFk3xgzyQwZdldjxK71jxxl2/vL3n2qXYfobyUVNmKk1JZ+io2uY6lUpwVnPje9z5I3WBvKWPLnbgkjZxHdyU01boGC3gX4Kq4U4OrrsheGdZwCvYin5t4hxFxj5nfvcSvq1cXRGLzc9/8AK/XKM7/Hr0yeqcaIrve+d/dCH69wdOhkNIRUq0NWJ+ekkdHBG2NhldT4S8gfvENaN/uWz6Yv8s6Q/wDbM/8A9KVJekTRzcvVgjbYkqW8fZiuY+9E0OdXtQghryx3KSMhzgWHv3+5R/A6AyUmTq5POZVmQfi2yDH161VtWGJ8oDZJnNH2pCAP0C81GLRNMVVVZxFUWzvN72+u7nTXFomZ0ifnf+X3+0lclh05cETzH6VLUqyyNOxbBZtRRTc/YHMc5p+55UV6TtL0cEzTd7Gwx1rdTNUafWQtDX2a9lkjbEcxHOXcNJ3Pdu73rresNP18rRs4+00mC7EY38JAc07hzJGEjYPY9rXDf2tC59hui/Ivt0ZczmTk6uDcH46sKrID1jQGxy2XN/nZGtAG5JPI8+Z3vD41FGHETNrXvG94iPVzDriKc50v45PvpC0/p7FDKZjKxenS5hzY2wWQyaWSTqhFFToN4QWEhg22+zwkkgAleOkc9LpvSePOTa6S71Qgo0eP6+eWRzjVqAn7IawtBd3Naw+4BfWuei/J5LKtyYzbITUJGPruxsc8dRh234WTSOY+YkbmQt3Ow7gABJZOj+ter1WZ5sOYt02SMFyWEQcTZH8R2hhIYwkNYDsOfAFZxMPkpiurm0mdb5RaIi+Vt8/os1U8sRM33QPojt2KeV1NZy1pk9lmOxt66+Ih0cTRDbnkgrtBP1MLSGAD3c+Z3Oiweey1eabW2QxsNiheZHHGG2T6ZjcU6ThjdXh4Sx7fXa53MFxc4+qCdukaZ6JMXQvZCzDBC2vkaTKcdRkZaK8T2OZca1/GeJs3qEjYbFgUdd0P5N8DMRLnpJNPRSNLaBqxttOgjeJGVX2gOJ0YIHt25DkNgB3jHwKqpmZ15b5TGURnEW0n5d7N+0w5mZ93w8G16YY8LVqG+cVRv5PLPjgxsclWOSW5bmYGwF+44nRsYGucT+6wDcEhb3od0PHgscyA8Lrdk9ffma1reOd45taGgBsbPsgAbcvvX63RHHm2ZWzM2aHH02VsPS6vZtJzhtZmJJIklfwsAdy2AA/dBUzXgxMb8OMOmb9Z8o8Pr4OFVf8AjyxPv9dhEReZyEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREGp1LqGtjhVNlzmjI36+Pr8DHP3s2iWwtdw/ZaS07uPILbLmX7REj4qeHsiC1YZj9UYi3ZZRqTW5m14JJHSyCGBrnuAHuHtHvXPukbNPv5avdnOroMRPg+LT8eEq5GrJ9NMt2I7Lb9eJgkjtcDavVi0BCWF5PIu3CxyKpkmX1DTw74Z49Qy29Q6Ew9PFOhivyvjzkb7kVrr5R/k+2BPA90kpYS1m+5LdlM7eCzz5NaX60+W+k6ULINPVpLM7afHNgaHpE1Su89TNOZxIGu5tbIw7bEu3CwC0urtTUcTDFYvTNgjtXalKJx/fs3JmwQt/Ddxc4/utY8nkFxDoPeRqKm2hJq2TF/wAm7vpp1IMiKwyptY4lsfp4B9K4BJxBv1fM9WecqzenLS2T1Vl3YyCnXfi8Bj5DM7KuuVq1nJ5avLDHNVfFC70h9OsS4PaS1slpwPrR8g7Hk9S1q+Qx+MkL/SsxFemqBrN4yzHtruscb9/UO1mLb38/ctyq3WbGorjtOyipYbnsLgtbYuexJWkFc5mvVx0FKyJpYxE6G0+Bs0bzsx4c7bk07RTourZ11bNtfltQMjl0zMLpdiNQOtVso9zQ2xX+krL3yZJg60OZSLWOadweJrCAt4iqXjbmT4NKTcGonej5CeuMc1+omx3YzlomfSTbs31kLBCHOFTJBzeoL2hw3DjkZd+SbftGaXV30+dZVeKOsL/0H/J8Ziua7mdUPRPQfQ+DfY9bx8fH6vW7haxaXNamq1LuOoTGQT5t9mOnwsLmF1WD0iUSOB9T1N9veVwPTuKz8E+Nv158y6/ksvrGnPDfsXJaEVaJmZkwrZa0+8VeD0mKm9khA3EgAJaQFpejirM/L6UfwarlvVfpN2opM3FkH1K2SlxsjD1UlpvVxyOkDw0wERuaGb+twgBbBY1q/BFJBFLNFHLce6OrFJKxkliRkb5nxwMcd5XiOOR5DdyGsce4FVVyeAz9fSen5xdznFlJYJdVS2n5i5bgayrIytC6tRlZegptkDWvbAQ7cRufxetvsMDpLI5GPRUmSsZqx6Nn8qxloDJ46eDGijcfUfZD5nTMJliYxk0zhI6KZrHc3OCCwNnW+KZYx9X02J82bsXK2P6jjsRzWMeHG5CZ4GuiikjLHtIe5p4mOb3ghSJVq6JNNXcZNpuONuWbDLqzVrsgyzJdljbA2LJxUpJxLuI45A2B4c7k97w8budubKoCIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIuVSZW/quSWPD3pMZp6tLLWsZ2mGnIZaxE50U8OGlkBZVoxPDmOu8LnPexwiAa3rHavBaen0/q3F0qGQydvHagxOVmyNLJ5GfICtNjX0upvQvsuc+J8jrgjcAdjv3chsHaUREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBRvpThfJgs1HFI6KSXDZJkcrDs6N7qczWSNI7nNJBB+5SRcs/abztmHDHFY4B+W1bKMNjmcXCGC2Ort2nuHOOKKBz/rB9l0kSDSdGXSvho8Hh8fgoLWau18NQYMViIesfWd6Oxm2SuSFtXHnrGvDnTyAkh2wceRn2hNO22T2MtlnwvyuQjZD1NYudVxlGNznxY+q94DpfXcZJZyGmV5HJrGRsbzn9h7TTsXpmaCaIR3PpzJx3wCHEWKc/oLmFw5EN9G2G3LvPtK7sgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiIC4n6V9Ma4rbF7q+nRedDtwmLjo12UrL9wN/rrebkjLSR6+mwQORXWNX5uLG4+9kZ/wCZxlKxblA7yyvC+VwHvcQzYD3kLj/7LtB7Ppm/aIM1b0PFWH+z0utDJmM3IHEbnfLZzItPs/wcDkWlBJf2cbgmpZpzeYGstTbfg/KzzD+EgUX6QN9WUcldOes4TS2G9LYy1i3sbPk7NElti9PPzP0ZDLHJHHAzYzOY95cB1K5v+yF0pVINO5uOw9tnK3c9ftUcHFK03Lpu1KzwyGLfjbWEkc5fOdmRtD3vLQ0lRroA6D9T5zTrKWQyr8VpfJXIchHj2xia5bY08XHDxbCtUl9R7eMvaXRxyiM8nPC1vQI7JHTOEdl5DLkH42B9iR7nPlc14LoDO9/rPs9QYeMncl/HuT3qbrzrQtjYyNg4WRMaxjR3BrQGtH5ABeiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICrPrrXT9Q5OzXxl/LPr0L0mIxeJ03km4u1mMnWibPlL9zJFpNXDVWS12B7dw97txxBzQ7q37QGSmr4mKKKV1WLK5fF4u/kGPMbqNDIXYq1uw2UD6h5jeYmycuB07Xbt23EU6KejfB0tXZrJYaGGvDj8VQxT4Kjz6OzITOks3hwAkNkFaPFb7H7U0pPrElBlfswa5vZOLMYzKC0MhpfJmpJ6ea7rpqyhzqwty1GtgsTNMc7OujaGyNjjf3uJPY1xjoToudq3pAyDdjXsZLD0WOHcbFDG72m/i02o/zcV2dAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREHPv2ha5nwT6m+zMnlcDj5/vr3s5jqthh3/ddFK9h+55UR0vZlqdH+SvM2NzJVtQ5GMgfbu5S5flqN7xueOeuzv8AYFtP2vq9mbSOQgpNkddtXMNDSbA4tmdZfmsf1AicCC2Tj22O42Kqx0GahzdjD4agMjJYxz9eYfF5LF2I2SPq1nWquSqS15i3rYoXy1LzXsc4t+pYGgcTgQsjgP2eKdC5ZFOWvWxGVjrtylOGmfTrccMMccuN+kHykQYieSPrZYo4w+QySML+AtDe4MaGgNaAGtADWgbAAcgAB3BfqICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiIPG7VinjkhmjZNDOx0csMrGyRyRvBa9kjHgtewgkEEbEFVX6EdUvx1jWGm9J4k3LcOqrs1OaeaCDEY+CcQ0w+050gsPr15ak2zIY3l7WsaHAuDlMOn3pluR0blfTELp5I7cGMt6hkLY8dQtW52VRDTe875G+x0g4hCHti+07ctLVFOirotp4iHSuYoiavmxqCbD6hmFy1LFe6mTJ0MpE6KV/Bwek0+NpDR/NNO2+xAWH6OdKx4fHxU2yOsSl8tm9dkaGyXb9qR1i7ckA5NdJNI93D3NHC0cmhSJEQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERBEOk+UMbieLbgfqLFsfv3bmV3Vfn1vVAfeQqmZ/EXNL67txRRN+hs7qvS1p0j3cPUPu5Ka5XkY0d7WmtmoAO4Abk929mf2m4ZTpbK2K7+qs4llfLVJQATHPircGQjcAeR51tvwcVx39qTNV7+msTqeIPZXzWNbVmMW5krWJY2ZbETOLN9n1sjRdAXDfZt+wBvxcwtWijfRfqhmaw2MyrBw/SdGGd7P8ANyuaBPH94bKJG7+3hUkQEREBERAREQEREBERAUQ6acoaWnszaDp2ej4yy50lRzWWY4+rLZJK73AtZO1hc5riCA5rSVL1qdZYRmSx1/HSco8pQtU3n3NswPhJG3MEB++/3IKk9N2IfJonB6lP+CV8fcxNzEaeoyf4ux+NmcepZIS0Pu5J7ZIXSWH7bEuaxrd5HSd7wtSSbIy12M+oxesHZBpbzDqmQ03NbE/LuByVydvP2s+9cP6O87WtYLD6CzLuvsZCStFWc1h9ak708XIJDv8AU28fcp2ax5jfq6r278R4evdCGQk6/Hmy5xtZHTLMfdB34Bk9IZCbG5F3MDaWSXI+71m1gRyag7Gi53prpWrXtS5DTsdSw36Nge6LKO51LdmqawyNSEgbdZX9NqB3rE7veCG7MMnREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQQjp8idJpjPQt247WJt12cXdx2IjAzf8AtSBcE6XsDBjNJ6u0wA9tHBZDDZTFetu6DE5nKwSPja5+5d1NmPLNBO54er33JO/dOn+51ODk5gdflMHXPF3cFjOY6GX/AIb3/ouU9LNiHPZS/jK7DINSuxml4JG7jrI8LetZbUWRae59OoywysHDvsGZn7pQWLxWPgqQQ1a0TIK9SJkNeCJobHFFG0MZGxo5NaGgDb7lkoiAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiCtWoOi61i9W4zLCxTOLvayfbqVWwvN2K3lcZL6dvM4cMcDpqhdwN34iWE7FqWOKxntWYOplxgb+AycGqMVlDDDYZFWyOKhZm2yVpiI5K3FYe93EdhJZa/vaFN/wBqbNTY6lgrsFd9uWrq/EOZUhG8tnjFqJ1eEf557Xua3/Sc1c16IdP4vpDkzGaydSzVfHqaKxXgjkEUsuNOHx8EVK47gJlp2IYYXvY0ji5cLtidwmH7JPR3JQpfS9u3ctvyL70uHZfI62tjMhZjsmeVvMm7c6itPIXOO20beR4+LvC/GNAAAAAaAAANgAOQAA7gv1AREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQERaDpB1PHh8fNdfG+d7XRQVKkX89cu2ZWV6dOEbH6yWeSNm/c0OLjyaSg5P+1QW5gVNLsnFaFxGa1LkiWiPE4PH8chlkcT6tiaZoEY2P8AMSEgNBcI5+y7Sfc1DbyxrtqY6HS+Ph0rjw4k0sHZv3oIDMCNhbndh5J3O4nk+lH1uZA0XSxpi/Nh9Q4/0trb1fGv1Hr3LQM4228g2m+fFabql7g5lOKKGN237kTKx23ncD2bodw3oN+1WafUxuldI4xrdubTTZmXkk+0n0kH9feg6iiIgIiICIiAiIgIiICIiAiIggfS3RbYn0zG4Ahuqqs+x99PHZS40/k6uD+Sg37LUPo7K0YbwtyWidJ5AEADjsMjyFOwSfaRDFjx+YUi15rii/UeLwETutyFGO/mLXARw04W4m/VhZKf8/J6bxBneGNDjsHs4tF0AF08mnnQ79Rh+jjDV7r9vUdbybKVmtC12/OWOClLI5vsbegP7yDuCIiAiIgIiICIiDT6kwDLwj4rN+sYS4tdj79ioTxbb9Y2FwbKPVG3GDtz27ytQdGWmt4YdR56Eew8WHsOH9q7jJSfzW81NqGhjIDZyNyrRrhwZ19yxHBGXuBLWB0jgHPIB2aOZ2KhbOmzATbihJfyxHyXCZXIMJ3I2FivWMG+4P7/AC9qDeQaWvtHPUuZkPvlrad5/iIsO1ZTMHfH/nq2775KeNJ/4dVqjbteZqf+gaQyhB34ZcxfxWLi5dxLWWJ7LWnv/md/eB3L56zXFg8o9L4th2245cpmJh37gtYymwEcuYce9BKRi8iO7Kk/7ShXP/Y4V+/R+U9mSr/2sZv/AHWQo5HpfU0gPpOqWRbnl9Faep1y0e7fIzWw4/eR+S9f5CZF329XaiJ9vVw6biB/JuF5D80G9NLL+zIUf7eImP8A2cg1ebqec9mRxQ/HBWz/AN8LVDQNn26m1Gfv67FD+DcaAvx2g7f7uqdRs+8Owb/+biXINuKmb9uQxR/DCWx/3uU9HzY/63i3/d9F24/4/SDv7lqBonJtHqauz/8A7yppmT9f8Sg/xWU3T+aYPU1A6Q7d9zEUpOfvIq9Qgy5DnG/ZbiZP9Z9yH+IbIsF+Q1O1/LE4KSP+sNR345PvIjODc38uNfkOP1Qw7uyuCnb/AFDp2/XeR7AZW5p7d/v4PyXpPa1NHtwUcHa95dl79Dl7w0Y2zufuLvzQekuoMrE3eTAWZnD93HZHGS7/AIG9PWH67L0Zq1zW8VjE5ir72mpFccPyxc9jf8t14SahzETd5dPzTn2txmUx8/8AunIPqb/nsvN2veqZxW8Nn6vdu0Ys5Fw3+7CyWt/y3QZsOuMc4bvdbrgfvX8Tk6Dfx4rtaMbfesrH6uxVh3BBk8fM8ciyG9XkeD7i1ryQfuWlPSrp9gabORjx/GdgMzDZxB358uHKRQkHkeS31HIY3Jx7wT0chC4b7wywW4yPfuwuaQg2oIPMcwfaF+rQDRWJaSY8fVrvd3y04W05T9/XVeB+/wCa8XaRaxpFXI5eo4/9IMlJeIP3NzAssH4cOyCSoonJic7EW+jZipOxv225XD9ZNIPYBPj7VaOI/f1LvwXwczn4OI2MLWtsb9g4fLsfYk9+9fJwVYoj93Xu/FBL0USZr+owht2tk8a4t4nG9jLHo8YHf1mRqtlosI/238FvsFm6d+IT0bda5C7ump2IrER390kLi0/qgz0REBERARaLUmssRjf8o5TH0fcLt6vXcTtvs1srwXH7go8/pcxD9vQ2ZXJ8W3C7E4HLXYXB32S23FW9GLT7+s2HedkE+Rc+OvMvL/RNI5lwJIEmQt4WhHy32cWm/JOGnYf9Hvz7l+jLawl+xhMDVG//AFvUlyZ22/fwVsPw77ezj/NB0BFCOp1a8f0jTtc+0eg5O6B+fpkG/wDBfrcbqs9+Z0+3/V0tkXf36hCCbLlXTV18OZ0bfkcDiKWdmhvxdXxcF3JUZ8fiLb3fuxssWHM35bOstP4b92M1X7M1gCfv0rkAP1/lCVC+lHSmusljbmPju6TsRXoHRPMuNy1CaMnnHPXkbdsNZZjeGPY4ggPY0+xBq8vGf5Ia9dKeCa5l9URzyO23LevdSqF23sFOOo0f6LGrqWlIv8cZ9+3fLjYx+EdBjwB+cp/VQGn0c567pDN4vKT0GZrUclmWWWuZTSY+RlaFpceHiHG2txu4WkB0zthy2Wi11pjWt6OOxUqMxWoIzA2TK4vVdhmIsdRsDNZw81Ux2eIcTeB7CQ3g3e4MDEFh0Wu0z6b6HV+kvRvTxXiF70EyGqbIYOuNfrgH9SXbkBw3AK2KAiIgIiICIiAiIgIiIChnSlq2ahHXpY6OOxnM299fEVZSeqa5oBsX7fD6zaFZjhI8jm71GD1pApfanbFG+R52ZExz3kAuIawFzjwtBJ5A8hzVa6eLyGobdGxJKac3SDRuXZ7cbuG3i9FUJKJq4XHuHEGXLjslVlnlBABlk5O4GBBg6bt0TqJtbGiS5Dh9P6qfkNSSNH+O85N9FfSkglaNpup/wVu7Twt60Mbs1jSe8dD2JgqYTGCGJsbrGMx0thzR60szcfUgEkhPNzhFBCwe5sTGjYNAEH1niamPyOPoUYI61XG6E1aK9eFvCyNhmwDRt7S4kOJcdy4uJJJJK6hoyPgxuPaO5mPqNH5QRj/8INsiIgIi8ZLLGkji3c3va3m7fYEDYe3Yj9UHsiwXBxfC5xIJkIEYd6rR1Up57cnv5Dn3DbYe0n6vTDcRvbvHMCwvDu4n2Ebd23t/H2AoMxFhY97ml0LzuY+bHHvc3l+u27f97bntuc1Bg5PDU7T4ZLNWtYfUc51Z9ivFK6BzwGvdC6RpMbiAAS3bcBZzQANhyA5ADuAREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREAjfkeYPeCoxm+jzA3XiW3hsZPM07tsSUK5sMIIILJwzrGO3AO4cO4KToghP/g2qx8RpZDOUHO326jO37ETCfbHVyUk9aPb3CPbkOS/G6VzcIPUaotTH936WxOKstb9x+j4ajnD8Xb9/NTdEEJhp6rjPrZHT9poA5fQmRpPPv3cMrO39Gr0kt6pZ9nH4Cf7zm8jU3/sjETbfqpkiCJ1snqHb67D4oH3V9RWZh+suHiWl1Bh5rb+vsaXoS2mtc1lyLKRQ3Yw7biEN6OuyxDvsObHDuHuXRkQcDzUWv6h/xHQPVsDQyvnNSVcrBsD625mqMyD3kcuJ90j7vf5v130nxxcL9E46acDnPXzdRsLnbcy2s62ZQPuL/wA1YBEHKaUucsMByeoDid2tMjcbph1BsJ73MdfzbrlZ/wDrNA9u33bLGaHw17Z82Sv5wgbP9I1BZnrP5EEyUKU0dEk8/wDodv0XRFr8tgqNvb0unVtbd3pNaGbbbmNusaUGFpzRuIxv+T8XjqPtJpUa9ckgbbudEwFzuXeea3qjs2iqB26ttusGncMx+UyNCMe76qnYZGR9xBC8Z9K2d29RncxWa079W04y013fsHvyFCaXh5+x4PIc0EoRRSzis80AVszRO3tyOCfYcR+NPIVmg9/Ph/Jfkr9SRt9SLCXHD+tYv41p/MQWy3+KCWIolDl8+0fX4SkT7qOeM+/4G3j66+JdWZJh2Ol8xJ/pVrmnXNH4+kZaJ38EEwRRGLV90j1tNZ2M+50un3n9Ycu4fxX3/K61/wCj2b/+T+ZoJWiiMurrwG7dM52T7mzadYf+NmWr9r6ryD9//FjMxEd3X2tOgH84MxIf4IJaijgy+UdtwYfg3+JyVdm34+jtl/gvht3Pk/5NxDG/1jnbj3/nGMQB/wDEgkyKPPizbx6s+KrH3Gnbuj9Rar7/AKJ9E5SQbTZYRn2ux2NggP5C8+0B+e6CQoo4zSznDhs5TLWveTaipHb/AFsVDXI/Ec19R6NoAbPbZsD3XcnkLo/S3YegkJK8+vZ3cbPw4h//AFR2To+wLju/CYl7v60mMqPd/vPiJX4/o70+RscFhyPccTSI/QxIJOijlXQeFh/o+KoVfvp1IqjvxDqzWkH816DSsLCXQ2slC8/vDK3bDR/qw3ZZYR/uIN+i1uLx9iE+vfsWwQf6XDTDgfYWmnBCPyIP5LPgDw1okc1zwBxuYwsaXe0tYXOLR9xcfxQfa4xgKcuM1PjsQ+tIalavmJtP32NaIIsVbFWWzhpNturlq2YK4iAHCa/UD7UZLupXMrLDw8VG1ICwF8lY15mMJ728JlbM8j/RjKwP5a0dyJG5CHhPN1nC5WCMH/by1REfbzDiEEC6UHl2o3s/q9HepnD8X3cQ3/8ARdQ0x/Qaf/qdf/ksXB+krpIwNTVtGzdvMGOuaUyeLsWoI5bDIJrV6nKxk4gY50PEyB/Nw5cidhzWN+z501y2cnS01NdxebYa80NTL4mDK1ZuGhXL2PyEN+s2B0kkcLt3V5HAO2GxB3AWSREQFgvl4HS8QcAXh3FwPLdurjBJcBsBuD392yzkQYT3bvh/2h/5MqwpYSyuYiA188n1UTTuGDdvqgj93ltv/pjfbcrO9DLZIywgRscXFh/dJY9vqfdu77P6e5e1iLve1rTK1pDHP7gee2+3Pbmf1PvQY7edpxHMMg4Hfc4vDwD+IP8Aes5Y1CsY2niPE953e73nmdgdu4bn2AczyG+wyUBFQDtq6q+X6f8AB5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/RUA7auqvl+n/B5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/AEVAO2rqr5fp/wAHkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf9FQDtq6q+X6f8HkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf8ARUA7auqvl+n/AAeR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/0VAO2rqr5fp/weR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/wBFQDtq6q+X6f8AB5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/RUA7auqvl+n/B5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/AEVAO2rqr5fp/wAHkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf9FQDtq6q+X6f8HkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf8ARUA7auqvl+n/AAeR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/0VAO2rqr5fp/weR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/wBFQDtq6q+X6f8AB5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/RUA7auqvl+n/B5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/AEVAO2rqr5fp/wAHkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf9FQDtq6q+X6f8HkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf8ARUA7auqvl+n/AAeR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/0VAO2rqr5fp/weR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/wBFQDtq6q+X6f8AB5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/RUA7auqvl+n/B5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/AEVAO2rqr5fp/wAHkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf9FQDtq6q+X6f8HkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf8ARUA7auqvl+n/AAeR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/0VAO2rqr5fp/weR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/wBFQDtq6q+X6f8AB5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/RUA7auqvl+n/B5HzFO2rqr5fp/weR8xQX/AEVAO2rqr5fp/wAHkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf9FQDtq6q+X6f8HkfMU7auqvl+n/B5HzFBf8ARUA7auqvl+n/AAeR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUF/0VAO2rqr5fp/weR8xTtq6q+X6f8HkfMUFZkREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQEREBERAREQf/Z\\n\",\n \"text/html\": [\n \"\\n\",\n \" <iframe\\n\",\n \" width=\\\"800\\\"\\n\",\n \" height=\\\"450\\\"\\n\",\n \" src=\\\"https://www.youtube.com/embed/UpwEsguMtY4\\\"\\n\",\n \" frameborder=\\\"0\\\"\\n\",\n \" allowfullscreen\\n\",\n \" ></iframe>\\n\",\n \" \"\n ],\n \"text/plain\": [\n \"<IPython.lib.display.YouTubeVideo at 0x7ff965692040>\"\n ]\n },\n \"execution_count\": 6,\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"output_type\": \"execute_result\"\n }\n ],\n \"source\": [\n \"\\n\",\n \"YouTubeVideo(\\\"UpwEsguMtY4\\\",width=800, height=450)\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"> _Exercise 4: Authors overall activity_\\n\",\n \"> 1. Compute the total number of comments per author using the _comments dataset_. Then, make a histogram of the number of comments per author, using the function [``numpy.histogram``](https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.histogram.html), using logarithmic binning. Here are some important points on histograms (they should be already quite clear if you have watched the video above):\\n\",\n \"> * __Binning__: By default numpy makes 10 equally spaced bins, but you always have to customize the binning. The number and size of bins you choose for your histograms can completely change the visualization. If you use too few bins, the histogram doesn't portray well the data. If you have too many, you get a broken comb look. Unfortunately is no \\\"best\\\" number of bins, because different bin sizes can reveal different features of the data. Play a bit with the binning to find a suitable number of bins. Define a vector $\\\\nu$ including the desired bins and then feed it as a parameter of numpy.histogram, by specifying _bins=\\\\nu_ as an argument of the function. You always have at least two options:\\n\",\n \"> * _Linear binning_: Use linear binning, when the data is not heavy tailed, by using ``np.linspace`` to define bins.\\n\",\n \"> * _Logarithmic binning_: Use logarithmic binning, when the data is [heavy tailed](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fat-tailed_distribution), by using ``np.logspace`` to define your bins.\\n\",\n \"> * __Normalization__: To plot [probability densities](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Probability_density_function), you can set the argument _density=True_ of the ``numpy.histogram`` function.\\n\",\n \">\\n\",\n \"> 3. Compute the mean and the median value of the number of comments per author and plot them as vertical lines on top of your histogram. What do you observe? Which value do you think is more meaningful?\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"markdown\",\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"source\": [\n \"> _Exercise 5: Authors lifespan_\\n\",\n \">\\n\",\n \"> 1. For each author, find the time of publication of their first comment, _minTime_, and the time of publication of their last comment, _maxTime_, in [unix timestamp](https://www.unixtimestamp.com/). \\n\",\n \"> 2. Compute the \\\"lifespan\\\" of authors as the difference between _maxTime_ and _minTime_. Note that timestamps are measured in seconds, but it is appropriate here to compute the lifespan in days. Make a histogram showing the distribution of lifespans, choosing appropriate binning. What do you observe?\\n\",\n \"> 3. Now, we will look at how many authors joined and abandoned the discussion on GME over time. First, use the numpy function [numpy.histogram2d](https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.histogram2d.html) to create a 2-dimensional histogram for the two variables _minTime_ and _maxTime_. A 2D histogram, is nothing but a histogram where bins have two dimensions, as we look simultaneously at two variables. You need to specify two arrays of bins, one for the values along the x-axis (_minTime_) and the other for the values along the y-axis (_maxTime_). Choose bins with length 1 week.\\n\",\n \"> 4. Now, use the matplotlib function [``plt.imshow``](https://matplotlib.org/api/_as_gen/matplotlib.pyplot.imshow.html) to visualize the 2d histogram. You can follow [this example](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/2369492/generate-a-heatmap-in-matplotlib-using-a-scatter-data-set) on StackOverflow. To show dates instead of unix timestamps in the x and y axes, use [``mdates.date2num``](https://matplotlib.org/api/dates_api.html#matplotlib.dates.date2num). More details in this [StackOverflow example](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/23139595/dates-in-the-xaxis-for-a-matplotlib-plot-with-imshow), see accepted answer.\\n\",\n \"> 5. Make sure that the colormap allows to well interpret the data, by passing ``norm=mpl.colors.LogNorm()`` as an argument to imshow. This will ensure that your colormap is log-scaled. Then, add a [colorbar](https://matplotlib.org/3.1.0/gallery/color/colorbar_basics.html) on the side of the figure, with the appropriate [colorbar label](https://matplotlib.org/3.1.1/api/colorbar_api.html#matplotlib.colorbar.ColorbarBase.set_label).\\n\",\n \"> 6. As usual :) Look at the figure, and write down three key observations.\\n\"\n ]\n },\n {\n \"cell_type\": \"code\",\n \"execution_count\": null,\n \"metadata\": {},\n \"outputs\": [],\n \"source\": []\n }\n ],\n \"metadata\": {\n \"anaconda-cloud\": {},\n \"kernelspec\": {\n \"display_name\": \"Python 3\",\n \"language\": \"python\",\n \"name\": \"python3\"\n },\n \"language_info\": {\n \"codemirror_mode\": {\n \"name\": \"ipython\",\n \"version\": 3\n },\n \"file_extension\": \".py\",\n \"mimetype\": \"text/x-python\",\n \"name\": \"python\",\n \"nbconvert_exporter\": \"python\",\n \"pygments_lexer\": \"ipython3\",\n \"version\": \"3.8.3\"\n }\n },\n \"nbformat\": 4,\n \"nbformat_minor\": 1\n}",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"raw",
"code"
] |
[
[
"raw"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c50a28e544808a8b3034fc8dd8c05aa072f9ce9f
| 27,923 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
cloud/notebooks/python_sdk/deployments/spark/cars-4-you/Use Spark to recommend mitigation for car rental company.ipynb
|
kelvinlui/watson-machine-learning-samples
|
8e6dde838629a0ab8724321571f0af21079235ad
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
cloud/notebooks/python_sdk/deployments/spark/cars-4-you/Use Spark to recommend mitigation for car rental company.ipynb
|
kelvinlui/watson-machine-learning-samples
|
8e6dde838629a0ab8724321571f0af21079235ad
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
cloud/notebooks/python_sdk/deployments/spark/cars-4-you/Use Spark to recommend mitigation for car rental company.ipynb
|
kelvinlui/watson-machine-learning-samples
|
8e6dde838629a0ab8724321571f0af21079235ad
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 28.905797 | 765 | 0.574186 |
[
[
[
"# Use Spark to recommend mitigation for car rental company with `ibm-watson-machine-learning`",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"This notebook contains steps and code to create a predictive model, and deploy it on WML. This notebook introduces commands for pipeline creation, model training, model persistance to Watson Machine Learning repository, model deployment, and scoring.\n\nSome familiarity with Python is helpful. This notebook uses Python 3.6 and Apache® Spark 2.4.\n\nYou will use **car_rental_training** dataset.\n\n\n## Learning goals\n\nThe learning goals of this notebook are:\n\n- Load a CSV file into an Apache® Spark DataFrame.\n- Explore data.\n- Prepare data for training and evaluation.\n- Create an Apache® Spark machine learning pipeline.\n- Train and evaluate a model.\n- Persist a pipeline and model in Watson Machine Learning repository.\n- Deploy a model for online scoring using Wastson Machine Learning API.\n- Score sample scoring data using the Watson Machine Learning API.\n\n\n## Contents\n\nThis notebook contains the following parts:\n1. [Setup](#setup)\n2. [Load and explore data](#load)\n3. [Create an Apache Spark machine learning model](#model)\n4. [Store the model in the Watson Machine Learning repository](#persistence)\n5. [Deploy the model in the IBM Cloud](#persistence)\n6. [Score](#logging)\n7. [Clean up](#cleanup)\n8. [Summary and next steps](#summary)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Note:** This notebook works correctly with kernel `Python 3.6 with Spark 2.4`, please **do not change kernel**.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a id=\"setup\"></a>\n## 1. Set up the environment\n\nBefore you use the sample code in this notebook, you must perform the following setup tasks:\n\n- Create a <a href=\"https://console.ng.bluemix.net/catalog/services/ibm-watson-machine-learning/\" target=\"_blank\" rel=\"noopener no referrer\">Watson Machine Learning (WML) Service</a> instance (a free plan is offered and information about how to create the instance can be found <a href=\"https://dataplatform.cloud.ibm.com/docs/content/wsj/analyze-data/ml-service-instance.html?context=analytics\" target=\"_blank\" rel=\"noopener no referrer\">here</a>).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Connection to WML\n\nAuthenticate the Watson Machine Learning service on IBM Cloud. You need to provide platform `api_key` and instance `location`.\n\nYou can use [IBM Cloud CLI](https://cloud.ibm.com/docs/cli/index.html) to retrieve platform API Key and instance location.\n\nAPI Key can be generated in the following way:\n```\nibmcloud login\nibmcloud iam api-key-create API_KEY_NAME\n```\n\nIn result, get the value of `api_key` from the output.\n\n\nLocation of your WML instance can be retrieved in the following way:\n```\nibmcloud login --apikey API_KEY -a https://cloud.ibm.com\nibmcloud resource service-instance WML_INSTANCE_NAME\n```\n\nIn result, get the value of `location` from the output.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Tip**: Your `Cloud API key` can be generated by going to the [**Users** section of the Cloud console](https://cloud.ibm.com/iam#/users). From that page, click your name, scroll down to the **API Keys** section, and click **Create an IBM Cloud API key**. Give your key a name and click **Create**, then copy the created key and paste it below. You can also get a service specific url by going to the [**Endpoint URLs** section of the Watson Machine Learning docs](https://cloud.ibm.com/apidocs/machine-learning). You can check your instance location in your <a href=\"https://console.ng.bluemix.net/catalog/services/ibm-watson-machine-learning/\" target=\"_blank\" rel=\"noopener no referrer\">Watson Machine Learning (WML) Service</a> instance details.\n\nYou can also get service specific apikey by going to the [**Service IDs** section of the Cloud Console](https://cloud.ibm.com/iam/serviceids). From that page, click **Create**, then copy the created key and paste it below.\n\n**Action**: Enter your `api_key` and `location` in the following cell.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"api_key = 'PASTE YOUR PLATFORM API KEY HERE'\nlocation = 'PASTE YOUR INSTANCE LOCATION HERE'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"wml_credentials = {\n \"apikey\": api_key,\n \"url\": 'https://' + location + '.ml.cloud.ibm.com'\n}",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Install and import the `ibm-watson-machine-learning` package\n**Note:** `ibm-watson-machine-learning` documentation can be found <a href=\"http://ibm-wml-api-pyclient.mybluemix.net/\" target=\"_blank\" rel=\"noopener no referrer\">here</a>.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!pip install -U ibm-watson-machine-learning",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from ibm_watson_machine_learning import APIClient\n\nclient = APIClient(wml_credentials)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Working with spaces\n\nFirst of all, you need to create a space that will be used for your work. If you do not have space already created, you can use [Deployment Spaces Dashboard](https://dataplatform.cloud.ibm.com/ml-runtime/spaces?context=cpdaas) to create one.\n\n- Click New Deployment Space\n- Create an empty space\n- Select Cloud Object Storage\n- Select Watson Machine Learning instance and press Create\n- Copy `space_id` and paste it below\n\n**Tip**: You can also use SDK to prepare the space for your work. More information can be found [here](https://github.com/IBM/watson-machine-learning-samples/blob/master/cloud/notebooks/python_sdk/instance-management/Space%20management.ipynb).\n\n**Action**: Assign space ID below",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"space_id = 'PASTE YOUR SPACE ID HERE'",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You can use `list` method to print all existing spaces.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"client.spaces.list(limit=10)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"To be able to interact with all resources available in Watson Machine Learning, you need to set **space** which you will be using.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"client.set.default_space(space_id)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Note**: Please restart the kernel (Kernel -> Restart)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Test Spark",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"try:\n from pyspark.sql import SparkSession\nexcept:\n print('Error: Spark runtime is missing. If you are using Watson Studio change the notebook runtime to Spark.')\n raise",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id=\"load\"></a>\n## 2. Load and explore data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In this section you will load the data as an Apache Spark DataFrame and perform a basic exploration.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Read data into Spark DataFrame from DB2 database and show sample record.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Load data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import os\nfrom wget import download\n\nsample_dir = 'spark_sample_model'\nif not os.path.isdir(sample_dir):\n os.mkdir(sample_dir)\n \nfilename = os.path.join(sample_dir, 'car_rental_training_data.csv')\nif not os.path.isfile(filename):\n filename = download('https://github.com/IBM/watson-machine-learning-samples/raw/master/cloud/data/cars-4-you/car_rental_training_data.csv', out=sample_dir)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"spark = SparkSession.builder.getOrCreate()\n\ndf_data = spark.read\\\n .format('org.apache.spark.sql.execution.datasources.csv.CSVFileFormat')\\\n .option('header', 'true')\\\n .option('inferSchema', 'true')\\\n .option(\"delimiter\", \";\")\\\n .load(filename)\ndf_data.take(3)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Explore data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_data.printSchema()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"As you can see, the data contains eleven fields. `Action` field is the one you would like to predict using feedback data in `Customer_Service` field.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(\"Number of records: \" + str(df_data.count()))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"As you can see, the data set contains 243 records.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_data.select('Business_area').groupBy('Business_area').count().show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_data.select('Action').groupBy('Action').count().show(truncate=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id=\"model\"></a>\n## 3. Create an Apache Spark machine learning model\n\nIn this section you will learn how to:\n\n- [3.1 Prepare data for training a model](#prep)\n- [3.2 Create an Apache Spark machine learning pipeline](#pipe)\n- [3.3 Train a model](#train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a id=\"prep\"></a>\n### 3.1 Prepare data for training a model\n\nIn this subsection you will split your data into: train and test data set.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"train_data, test_data = df_data.randomSplit([0.8, 0.2], 24)\n\nprint(\"Number of training records: \" + str(train_data.count()))\nprint(\"Number of testing records : \" + str(test_data.count()))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 3.2 Create the pipeline<a id=\"pipe\"></a>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In this section you will create an Apache Spark machine learning pipeline and then train the model.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from pyspark.ml.feature import OneHotEncoder, StringIndexer, IndexToString, VectorAssembler, HashingTF, IDF, Tokenizer\nfrom pyspark.ml.classification import DecisionTreeClassifier\nfrom pyspark.ml.evaluation import MulticlassClassificationEvaluator\nfrom pyspark.ml import Pipeline, Model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"In the following step, use the StringIndexer transformer to convert all the string fields to numeric ones.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"string_indexer_gender = StringIndexer(inputCol=\"Gender\", outputCol=\"gender_ix\")\nstring_indexer_customer_status = StringIndexer(inputCol=\"Customer_Status\", outputCol=\"customer_status_ix\")\nstring_indexer_status = StringIndexer(inputCol=\"Status\", outputCol=\"status_ix\")\nstring_indexer_owner = StringIndexer(inputCol=\"Car_Owner\", outputCol=\"owner_ix\")\nstring_business_area = StringIndexer(inputCol=\"Business_Area\", outputCol=\"area_ix\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"assembler = VectorAssembler(inputCols=[\"gender_ix\", \"customer_status_ix\", \"status_ix\", \"owner_ix\", \"area_ix\", \"Children\", \"Age\", \"Satisfaction\"], outputCol=\"features\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"string_indexer_action = StringIndexer(inputCol=\"Action\", outputCol=\"label\").fit(df_data)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"label_action_converter = IndexToString(inputCol=\"prediction\", outputCol=\"predictedLabel\", labels=string_indexer_action.labels)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dt_action = DecisionTreeClassifier()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pipeline_action = Pipeline(stages=[string_indexer_gender, string_indexer_customer_status, string_indexer_status, string_indexer_action, string_indexer_owner, string_business_area, assembler, dt_action, label_action_converter])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model_action = pipeline_action.fit(train_data)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"predictions_action = model_action.transform(test_data)\npredictions_action.select('Business_Area','Action','probability','predictedLabel').show(2)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"evaluator = MulticlassClassificationEvaluator(labelCol=\"label\", predictionCol=\"prediction\", metricName=\"accuracy\")\naccuracy = evaluator.evaluate(predictions_action)\n\nprint(\"Accuracy = %g\" % accuracy)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id=\"persistence\"></a>\n## 4. Persist model",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In this section you will learn how to store your pipeline and model in Watson Machine Learning repository by using python client libraries.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Note**: Apache® Spark 2.4 is required.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Save training data in your Cloud Object Storage",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ibm-cos-sdk library allows Python developers to manage Cloud Object Storage (COS).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import ibm_boto3\nfrom ibm_botocore.client import Config",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Action**: Put credentials from Object Storage Service in Bluemix here.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cos_credentials = {\n \"apikey\": \"***\",\n \"cos_hmac_keys\": {\n \"access_key_id\": \"***\",\n \"secret_access_key\": \"***\"\n },\n \"endpoints\": \"***\",\n \"iam_apikey_description\": \"***\",\n \"iam_apikey_name\": \"***\",\n \"iam_role_crn\": \"***\",\n \"iam_serviceid_crn\": \"***\",\n \"resource_instance_id\": \"***\"\n }",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"connection_apikey = cos_credentials['apikey']\nconnection_resource_instance_id = cos_credentials[\"resource_instance_id\"]\nconnection_access_key_id = cos_credentials['cos_hmac_keys']['access_key_id']\nconnection_secret_access_key = cos_credentials['cos_hmac_keys']['secret_access_key']",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Action**: Define the service endpoint we will use. <br>\n**Tip**: You can find this information in Endpoints section of your Cloud Object Storage intance's dashbord.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"service_endpoint = 'https://s3.us.cloud-object-storage.appdomain.cloud'",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You also need IBM Cloud authorization endpoint to be able to create COS resource object.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"auth_endpoint = 'https://iam.cloud.ibm.com/identity/token'",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We create COS resource to be able to write data to Cloud Object Storage.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cos = ibm_boto3.resource('s3',\n ibm_api_key_id=cos_credentials['apikey'],\n ibm_service_instance_id=cos_credentials['resource_instance_id'],\n ibm_auth_endpoint=auth_endpoint,\n config=Config(signature_version='oauth'),\n endpoint_url=service_endpoint)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now you will create bucket in COS and copy `training dataset` for model from **car_rental_training_data.csv**.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from uuid import uuid4\n\nbucket_uid = str(uuid4())\n\nscore_filename = \"car_rental_training_data.csv\"\nbuckets = [\"car-rental-\" + bucket_uid]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for bucket in buckets:\n if not cos.Bucket(bucket) in cos.buckets.all():\n print('Creating bucket \"{}\"...'.format(bucket))\n try:\n cos.create_bucket(Bucket=bucket)\n except ibm_boto3.exceptions.ibm_botocore.client.ClientError as e:\n print('Error: {}.'.format(e.response['Error']['Message']))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"bucket_obj = cos.Bucket(buckets[0])\n\nprint('Uploading data {}...'.format(score_filename))\nwith open(filename, 'rb') as f:\n bucket_obj.upload_fileobj(f, score_filename)\nprint('{} is uploaded.'.format(score_filename))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 4.2 Save the pipeline and model<a id=\"save\"></a>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"training_data_references = [\n {\n \"id\":\"car-rental-training\",\n \"type\": \"s3\",\n \"connection\": {\n \"access_key_id\": connection_access_key_id,\n \"endpoint_url\": service_endpoint,\n \"secret_access_key\": connection_secret_access_key\n },\n \"location\": {\n \"bucket\": buckets[0],\n \"path\": score_filename,\n }\n }\n ]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"saved_model = client.repository.store_model(\n model=model_action, \n meta_props={\n client.repository.ModelMetaNames.NAME:\"CARS4U - Action Recommendation Model\",\n client.repository.ModelMetaNames.SPACE_UID: space_id,\n client.repository.ModelMetaNames.TYPE: \"mllib_2.4\",\n client.repository.ModelMetaNames.SOFTWARE_SPEC_UID: client.software_specifications.get_id_by_name('spark-mllib_2.4'),\n client.repository.ModelMetaNames.TRAINING_DATA_REFERENCES: training_data_references,\n client.repository.ModelMetaNames.LABEL_FIELD: \"Action\",\n }, \n training_data=train_data, \n pipeline=pipeline_action)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Get saved model metadata from Watson Machine Learning.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"published_model_id = client.repository.get_model_uid(saved_model)\n\nprint(\"Model Id: \" + str(published_model_id))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Model Id** can be used to retrive latest model version from Watson Machine Learning instance.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Below you can see stored model details.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"client.repository.get_model_details(published_model_id)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id=\"deploy\"></a>\n## 5. Deploy model in the IBM Cloud",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"You can use following command to create online deployment in cloud.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"deployment_details = client.deployments.create(\n published_model_id, \n meta_props={\n client.deployments.ConfigurationMetaNames.NAME: \"CARS4U - Action Recommendation model deployment\",\n client.deployments.ConfigurationMetaNames.ONLINE: {}\n }\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"deployment_details",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 6. Score",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"fields = ['ID', 'Gender', 'Status', 'Children', 'Age', 'Customer_Status','Car_Owner', 'Customer_Service', 'Business_Area', 'Satisfaction']\nvalues = [3785, 'Male', 'S', 1, 17, 'Inactive', 'Yes', 'The car should have been brought to us instead of us trying to find it in the lot.', 'Product: Information', 0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import json\n\npayload_scoring = {\"input_data\": [{\"fields\": fields,\"values\": [values]}]}\nscoring_response = client.deployments.score(client.deployments.get_id(deployment_details), payload_scoring)\n\nprint(json.dumps(scoring_response, indent=3))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id=\"cleanup\"></a>\n## 7. Clean up",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"If you want to clean up all created assets:\n- experiments\n- trainings\n- pipelines\n- model definitions\n- models\n- functions\n- deployments\n\nplease follow up this sample [notebook](https://github.com/IBM/watson-machine-learning-samples/blob/master/cloud/notebooks/python_sdk/instance-management/Machine%20Learning%20artifacts%20management.ipynb).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a id=\"summary\"></a>\n## 8. Summary and next steps ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
" You successfully completed this notebook! You learned how to use Apache Spark machine learning as well as Watson Machine Learning for model creation and deployment. Check out our [Online Documentation](https://dataplatform.cloud.ibm.com/docs/content/wsj/analyze-data/ml-service-instance.html?context=analytics) for more samples, tutorials, documentation, how-tos, and blog posts. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Authors\n\n**Amadeusz Masny**, Python Software Developer in Watson Machine Learning at IBM",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Copyright © 2020 IBM. This notebook and its source code are released under the terms of the MIT License.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
c50a2d54474a0866d5e5ce19c99ff667880e03f6
| 10,408 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
research/Model 1.ipynb
|
Monxun/ML-Django-API
|
61a891243c401976a6e0b94ca09f136d6b7f96ea
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
research/Model 1.ipynb
|
Monxun/ML-Django-API
|
61a891243c401976a6e0b94ca09f136d6b7f96ea
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
research/Model 1.ipynb
|
Monxun/ML-Django-API
|
61a891243c401976a6e0b94ca09f136d6b7f96ea
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 31.828746 | 343 | 0.443025 |
[
[
[
"import json # will be needed for saving preprocessing details\nimport numpy as np # for data manipulation\nimport pandas as pd # for data manipulation\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split # will be used for data split\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder # for preprocessing\nfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier # for training the algorithm\nfrom sklearn.ensemble import ExtraTreesClassifier # for training the algorithm\nimport joblib # for saving algorithm and preprocessing objects",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# load dataset\ndf = pd.read_csv('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pplonski/datasets-for-start/master/adult/data.csv', skipinitialspace=True)\nx_cols = [c for c in df.columns if c != 'income']\n# set input matrix and target column\nX = df[x_cols]\ny = df['income']\n# show first rows of data\ndf.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# data split train / test\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 0.3, random_state=1234)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# fill missing values\ntrain_mode = dict(X_train.mode().iloc[0])\nX_train = X_train.fillna(train_mode)\nprint(train_mode)",
"{'age': 31.0, 'workclass': 'Private', 'fnlwgt': 121124, 'education': 'HS-grad', 'education-num': 9.0, 'marital-status': 'Married-civ-spouse', 'occupation': 'Prof-specialty', 'relationship': 'Husband', 'race': 'White', 'sex': 'Male', 'capital-gain': 0.0, 'capital-loss': 0.0, 'hours-per-week': 40.0, 'native-country': 'United-States'}\n"
],
[
"# convert categoricals\nencoders = {}\nfor column in ['workclass', 'education', 'marital-status',\n 'occupation', 'relationship', 'race',\n 'sex','native-country']:\n categorical_convert = LabelEncoder()\n X_train[column] = categorical_convert.fit_transform(X_train[column])\n encoders[column] = categorical_convert",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# train the Random Forest algorithm\nrf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators = 100)\nrf = rf.fit(X_train, y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# train the Extra Trees algorithm\net = ExtraTreesClassifier(n_estimators = 100)\net = et.fit(X_train, y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# save preprocessing objects and RF algorithm\njoblib.dump(train_mode, \"./train_mode.joblib\", compress=True)\njoblib.dump(encoders, \"./encoders.joblib\", compress=True)\njoblib.dump(rf, \"./random_forest.joblib\", compress=True)\njoblib.dump(et, \"./extra_trees.joblib\", compress=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50a379933169d15bbcc642d382dc18b694ab358
| 5,163 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
regularExpression.ipynb
|
mmeooo/test_NLP
|
32e42d1dccc0f65ef393f0d642d33938ef45be7d
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
regularExpression.ipynb
|
mmeooo/test_NLP
|
32e42d1dccc0f65ef393f0d642d33938ef45be7d
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
regularExpression.ipynb
|
mmeooo/test_NLP
|
32e42d1dccc0f65ef393f0d642d33938ef45be7d
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 24.585714 | 74 | 0.388534 |
[
[
[
"\nhttps://regexr.com/\n\nhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Regular_expression \n\n> **`+`** : 연결되는 뒷 문장도 엮어줌. 힌트 뒤에 붙이기\n\n\n> **기호 찾기**\n\n 역슬래쉬( \\ ) 는 특수문자의 시작\n - [\\s \\]+ : '와 스페이스 빼고 선택\n - [\\S \\']+ : 스페이스포함 선택\n - [\\w ]+ : 워드 a-zA-Z\n\n\n> **숫자 찾기**\n\n1. Number Numer Nuber \n - `Nu (be|e|m) r` : 앞이 Nu + 뒤가 r인 단어 선택\n\n2. color colour colouuuur colouuhur coollouuur\n - `colou ? r` , `colou * r` : 기호 앞 문자까지동일한 단어 선택\n - `colou + r` : u가 무조건 포함된 단어 선택\n - `colou {1,3} r` : {1,3} 문자 개수 지정 \n - `[colru]` : (c|o|l|r|u) 문자 들어간 단어 선택\n\n3. `[a-z]+` = `(a|b|c|d|e...y|z)`\n4. `man | other` : man, other만 선택 \n5. `[^a-zA-Z]` : 소문자 대문자 제외 \n6. `[0-9]{3}-[0-9]{4}-[0-9]{4}` : 3자리-4자리-4자리 수 전화번호\n7. `[0-9]{2,3}-[0-9]{3,4}-[0-9]{4}` : 2,3자리-3,4자리-4자리 수 전화번호\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import re",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"phone = \"2004-959-559 # This is Phone Number\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"obj = re.findall('[0-9]+', phone)\ntype(obj), obj",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"obj = re.findall('[0-9]', phone)\ntype(obj), obj",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"re.sub('[0-9]+', '1', phone) # 0을 1로 채움",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"phone = \"2004-959-559 # This is Phone Number\"\nre.sub('[0-9]', '0', phone) # 자릿수에 맞게 0이 채워짐",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50a45893138bee005f40c2d3de84125cf46904a
| 18,304 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
intro-to-pytorch/Part 6 - Saving and Loading Models.ipynb
|
ahmedmbakr/deep-learning-v2-pytorch
|
67fbcc527e50fa5917a4fcc918863660ea255863
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
intro-to-pytorch/Part 6 - Saving and Loading Models.ipynb
|
ahmedmbakr/deep-learning-v2-pytorch
|
67fbcc527e50fa5917a4fcc918863660ea255863
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
intro-to-pytorch/Part 6 - Saving and Loading Models.ipynb
|
ahmedmbakr/deep-learning-v2-pytorch
|
67fbcc527e50fa5917a4fcc918863660ea255863
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 50.147945 | 5,068 | 0.685642 |
[
[
[
"# Saving and Loading Models\n\nIn this notebook, I'll show you how to save and load models with PyTorch. This is important because you'll often want to load previously trained models to use in making predictions or to continue training on new data.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%matplotlib inline\n%config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'retina'\n\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\nimport torch\nfrom torch import nn\nfrom torch import optim\nimport torch.nn.functional as F\nfrom torchvision import datasets, transforms\n\nimport helper\nimport fc_model",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Define a transform to normalize the data\ntransform = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor(),\n transforms.Normalize((0.5,), (0.5,))])\n# Download and load the training data\ntrainset = datasets.FashionMNIST('~/.pytorch/F_MNIST_data/', download=True, train=True, transform=transform)\ntrainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(trainset, batch_size=64, shuffle=True)\n\n# Download and load the test data\ntestset = datasets.FashionMNIST('~/.pytorch/F_MNIST_data/', download=True, train=False, transform=transform)\ntestloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(testset, batch_size=64, shuffle=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Here we can see one of the images.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"image, label = next(iter(trainloader))\nhelper.imshow(image[0,:]);",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Train a network\n\nTo make things more concise here, I moved the model architecture and training code from the last part to a file called `fc_model`. Importing this, we can easily create a fully-connected network with `fc_model.Network`, and train the network using `fc_model.train`. I'll use this model (once it's trained) to demonstrate how we can save and load models.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Create the network, define the criterion and optimizer\n\nmodel = fc_model.Network(784, 10, [512, 256, 128])\ncriterion = nn.NLLLoss()\noptimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fc_model.train(model, trainloader, testloader, criterion, optimizer, epochs=2)",
"Epoch: 1/2.. Training Loss: 1.726.. Test Loss: 0.943.. Test Accuracy: 0.650\nEpoch: 1/2.. Training Loss: 1.011.. Test Loss: 0.746.. Test Accuracy: 0.719\nEpoch: 1/2.. Training Loss: 0.861.. Test Loss: 0.710.. Test Accuracy: 0.736\nEpoch: 1/2.. Training Loss: 0.821.. Test Loss: 0.631.. Test Accuracy: 0.753\nEpoch: 1/2.. Training Loss: 0.729.. Test Loss: 0.606.. Test Accuracy: 0.768\nEpoch: 1/2.. Training Loss: 0.729.. Test Loss: 0.588.. Test Accuracy: 0.775\nEpoch: 1/2.. Training Loss: 0.736.. Test Loss: 0.580.. Test Accuracy: 0.776\nEpoch: 1/2.. Training Loss: 0.687.. Test Loss: 0.572.. Test Accuracy: 0.787\nEpoch: 1/2.. Training Loss: 0.663.. Test Loss: 0.556.. Test Accuracy: 0.798\nEpoch: 1/2.. Training Loss: 0.612.. Test Loss: 0.551.. Test Accuracy: 0.796\nEpoch: 1/2.. Training Loss: 0.592.. Test Loss: 0.519.. Test Accuracy: 0.809\nEpoch: 1/2.. Training Loss: 0.623.. Test Loss: 0.538.. Test Accuracy: 0.806\nEpoch: 1/2.. Training Loss: 0.625.. Test Loss: 0.517.. Test Accuracy: 0.807\nEpoch: 1/2.. Training Loss: 0.657.. Test Loss: 0.506.. Test Accuracy: 0.810\nEpoch: 1/2.. Training Loss: 0.621.. Test Loss: 0.512.. Test Accuracy: 0.813\nEpoch: 1/2.. Training Loss: 0.601.. Test Loss: 0.501.. Test Accuracy: 0.820\nEpoch: 1/2.. Training Loss: 0.582.. Test Loss: 0.500.. Test Accuracy: 0.816\nEpoch: 1/2.. Training Loss: 0.557.. Test Loss: 0.495.. Test Accuracy: 0.820\nEpoch: 1/2.. Training Loss: 0.579.. Test Loss: 0.486.. Test Accuracy: 0.823\nEpoch: 1/2.. Training Loss: 0.592.. Test Loss: 0.472.. Test Accuracy: 0.827\nEpoch: 1/2.. Training Loss: 0.550.. Test Loss: 0.481.. Test Accuracy: 0.825\nEpoch: 1/2.. Training Loss: 0.600.. Test Loss: 0.495.. Test Accuracy: 0.819\nEpoch: 1/2.. Training Loss: 0.563.. Test Loss: 0.495.. Test Accuracy: 0.815\nEpoch: 2/2.. Training Loss: 0.582.. Test Loss: 0.467.. Test Accuracy: 0.829\nEpoch: 2/2.. Training Loss: 0.601.. Test Loss: 0.458.. Test Accuracy: 0.829\nEpoch: 2/2.. Training Loss: 0.550.. Test Loss: 0.485.. Test Accuracy: 0.820\nEpoch: 2/2.. Training Loss: 0.547.. Test Loss: 0.475.. Test Accuracy: 0.822\nEpoch: 2/2.. Training Loss: 0.554.. Test Loss: 0.466.. Test Accuracy: 0.830\nEpoch: 2/2.. Training Loss: 0.542.. Test Loss: 0.490.. Test Accuracy: 0.822\nEpoch: 2/2.. Training Loss: 0.540.. Test Loss: 0.457.. Test Accuracy: 0.834\nEpoch: 2/2.. Training Loss: 0.570.. Test Loss: 0.470.. Test Accuracy: 0.834\nEpoch: 2/2.. Training Loss: 0.543.. Test Loss: 0.472.. Test Accuracy: 0.828\nEpoch: 2/2.. Training Loss: 0.553.. Test Loss: 0.461.. Test Accuracy: 0.834\nEpoch: 2/2.. Training Loss: 0.494.. Test Loss: 0.461.. Test Accuracy: 0.832\nEpoch: 2/2.. Training Loss: 0.494.. Test Loss: 0.478.. Test Accuracy: 0.828\nEpoch: 2/2.. Training Loss: 0.499.. Test Loss: 0.453.. Test Accuracy: 0.835\nEpoch: 2/2.. Training Loss: 0.491.. Test Loss: 0.467.. Test Accuracy: 0.832\nEpoch: 2/2.. Training Loss: 0.487.. Test Loss: 0.470.. Test Accuracy: 0.823\nEpoch: 2/2.. Training Loss: 0.501.. Test Loss: 0.451.. Test Accuracy: 0.833\nEpoch: 2/2.. Training Loss: 0.516.. Test Loss: 0.464.. Test Accuracy: 0.835\nEpoch: 2/2.. Training Loss: 0.514.. Test Loss: 0.466.. Test Accuracy: 0.824\nEpoch: 2/2.. Training Loss: 0.566.. Test Loss: 0.484.. Test Accuracy: 0.828\nEpoch: 2/2.. Training Loss: 0.543.. Test Loss: 0.443.. Test Accuracy: 0.839\nEpoch: 2/2.. Training Loss: 0.531.. Test Loss: 0.465.. Test Accuracy: 0.831\nEpoch: 2/2.. Training Loss: 0.506.. Test Loss: 0.441.. Test Accuracy: 0.842\nEpoch: 2/2.. Training Loss: 0.510.. Test Loss: 0.441.. Test Accuracy: 0.842\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Saving and loading networks\n\nAs you can imagine, it's impractical to train a network every time you need to use it. Instead, we can save trained networks then load them later to train more or use them for predictions.\n\nThe parameters for PyTorch networks are stored in a model's `state_dict`. We can see the state dict contains the weight and bias matrices for each of our layers.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(\"Our model: \\n\\n\", model, '\\n')\nprint(\"The state dict keys: \\n\\n\", model.state_dict().keys())",
"Our model: \n\n Network(\n (hidden_layers): ModuleList(\n (0): Linear(in_features=784, out_features=512, bias=True)\n (1): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=256, bias=True)\n (2): Linear(in_features=256, out_features=128, bias=True)\n )\n (output): Linear(in_features=128, out_features=10, bias=True)\n (dropout): Dropout(p=0.5, inplace=False)\n) \n\nThe state dict keys: \n\n odict_keys(['hidden_layers.0.weight', 'hidden_layers.0.bias', 'hidden_layers.1.weight', 'hidden_layers.1.bias', 'hidden_layers.2.weight', 'hidden_layers.2.bias', 'output.weight', 'output.bias'])\n"
]
],
[
[
"The simplest thing to do is simply save the state dict with `torch.save`. For example, we can save it to a file `'checkpoint.pth'`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'checkpoint.pth')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Then we can load the state dict with `torch.load`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"state_dict = torch.load('checkpoint.pth')\nprint(state_dict.keys())",
"odict_keys(['hidden_layers.0.weight', 'hidden_layers.0.bias', 'hidden_layers.1.weight', 'hidden_layers.1.bias', 'hidden_layers.2.weight', 'hidden_layers.2.bias', 'output.weight', 'output.bias'])\n"
]
],
[
[
"And to load the state dict in to the network, you do `model.load_state_dict(state_dict)`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model.load_state_dict(state_dict)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Seems pretty straightforward, but as usual it's a bit more complicated. Loading the state dict works only if the model architecture is exactly the same as the checkpoint architecture. If I create a model with a different architecture, this fails.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Try this\nmodel = fc_model.Network(784, 10, [400, 200, 100])\n# This will throw an error because the tensor sizes are wrong!\nmodel.load_state_dict(state_dict)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"This means we need to rebuild the model exactly as it was when trained. Information about the model architecture needs to be saved in the checkpoint, along with the state dict. To do this, you build a dictionary with all the information you need to compeletely rebuild the model.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"checkpoint = {'input_size': 784,\n 'output_size': 10,\n 'hidden_layers': [each.out_features for each in model.hidden_layers],\n 'state_dict': model.state_dict()}\n\ntorch.save(checkpoint, 'checkpoint.pth')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now the checkpoint has all the necessary information to rebuild the trained model. You can easily make that a function if you want. Similarly, we can write a function to load checkpoints. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def load_checkpoint(filepath):\n checkpoint = torch.load(filepath)\n model = fc_model.Network(checkpoint['input_size'],\n checkpoint['output_size'],\n checkpoint['hidden_layers'])\n model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['state_dict'])\n \n return model",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model = load_checkpoint('checkpoint.pth')\nprint(model)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50a594b54c52a42c4b98cab8264012d56e71ad6
| 499,364 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
examples/metrics/example_01_BinaryClassificationMetrics.ipynb
|
Tsmith5151/slick-ml
|
bd159386da786f94eb29724f56c7efc48e084606
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
examples/metrics/example_01_BinaryClassificationMetrics.ipynb
|
Tsmith5151/slick-ml
|
bd159386da786f94eb29724f56c7efc48e084606
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
examples/metrics/example_01_BinaryClassificationMetrics.ipynb
|
Tsmith5151/slick-ml
|
bd159386da786f94eb29724f56c7efc48e084606
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 298.48416 | 112,136 | 0.868827 |
[
[
[
"# Example 01: General Use of BinaryClassificationMetrics\n\n[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/slickml/slick-ml/blob/master/examples/metrics/example_01_BinaryClassificationMetrics.ipynb)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Google Colab Configuration",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# !git clone https://github.com/slickml/slick-ml.git\n# %cd slick-ml\n# !pip install -r requirements.txt",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Local Environment Configuration",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Change path to project root\n%cd ../..",
"/home/amirhessam/Documents/GitHub/slick-ml\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Import Python Libraries",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%load_ext autoreload\n\n# widen the screen\nfrom IPython.core.display import display, HTML\ndisplay(HTML(\"<style>.container { width:95% !important; }</style>\"))\n\n# change the path and loading class\nimport os, sys\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport seaborn as sns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%autoreload\nfrom slickml.metrics import BinaryClassificationMetrics",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"_____\n# BinaryClassificationMetrics Docstring",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"help(BinaryClassificationMetrics)",
"Help on class BinaryClassificationMetrics in module slickml.metrics:\n\nclass BinaryClassificationMetrics(builtins.object)\n | BinaryClassificationMetrics(y_true, y_pred_proba, threshold=None, average_method=None, precision_digits=None, display_df=True)\n | \n | Binary Classification Metrics.\n | This is wrapper to calculate all the binary classification\n | metrics with both arbitrary and three computed methods for\n | calculating the thresholds. Threshold computations including:\n | 1) Youden Index: (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Youden%27s_J_statistic).\n | 2) Maximizing Precision-Recall.\n | 3) Maximizing Sensitivity-Specificity.\n | \n | Parameters\n | ----------\n | y_true: numpy.array[int] or list[int]\n | List of ground truth binary values [0, 1]\n | \n | y_pred_proba: numpy.array[float] or list[float]\n | List of predicted probability for the positive class\n | (class=1 or y_pred_proba[:, 1] in scikit-learn)\n | \n | threshold: float, optional (default=0.5)\n | Threshold value for mapping y_pred_prob to y_pred\n | Note that for threshold \">\" is used instead of \">=\"\n | \n | average_method: str, optional (default=\"binary\")\n | Method to calculate the average of the metric. Possible values are\n | \"micro\", \"macro\", \"weighted\", \"binary\"\n | \n | precision_digits: int, optional (default=3)\n | The number of precision digits to format the scores' dataframe\n | \n | display_df: boolean, optional (default=True)\n | Flag to display the formatted scores' dataframe\n | \n | Attributes\n | ----------\n | y_pred_: numpy.array(int) or list[int]\n | Predicted class based on the threshold.\n | Positive class for y_pred_proba >= threshold and\n | negative for else.\n | \n | accuracy_: float value between 0. and 1.\n | Classification accuracy based on threshold value\n | \n | balanced_accuracy_: float value between 0. and 1.\n | Balanced classification accuracy based on threshold value\n | considering the prevalence of the classes\n | \n | fpr_list_: numpy.array[float] or list[float]\n | List of calculated false-positive-rates based on roc_thresholds.\n | This can be used for ROC curve plotting\n | \n | tpr_list_: numpy.array[float] or list[float]\n | List of calculated true-positive-rates based on roc_thresholds\n | This can be used for ROC curve plotting\n | \n | roc_thresholds_: numpy.array[float] or list[float]\n | List of thresholds value to calculate fpr_list_ and tpr_list_\n | \n | auc_roc_: float value between 0. and 1.\n | Area under ROC curve\n | \n | precision_list_: numpy.array[float] or list[float]\n | List of calculated precision based on pr_thresholds\n | This can be used for ROC curve plotting\n | \n | recall_list_: numpy.array[float] or list[float]\n | List of calculated recall based on pr_thresholds\n | This can be used for ROC curve plotting\n | \n | pr_thresholds_: numpy.array[float] or list[float]\n | List of thresholds value to calculate precision_list_ and recall_list_\n | \n | auc_pr_: float value between 0. and 1.\n | Area under Precision-Recall curve\n | \n | precision_: float value between 0. and 1.\n | Precision based on threshold value\n | \n | recall_: float value between 0. and 1.\n | Recall based on threshold value\n | \n | f1_: float value between 0. and 1.\n | F1-score based on threshold value (beta=1.0)\n | \n | f2_: float value between 0. and 1.\n | F2-score based on threshold value (beta=2.0)\n | \n | f05_: float value between 0. and 1.\n | F(1/2)-score based on threshold value (beta=0.5)\n | \n | average_precision_: float value between 0. and 1.\n | Avearge precision based on threshold value and class prevalence\n | \n | tn_: integer\n | True negative counts based on threshold value\n | \n | fp_: integer\n | False positive counts based on threshold value\n | \n | fn_: integer\n | False negative counts based on threshold value\n | \n | tp_: integer\n | True positive counts based on threshold value\n | \n | threat_score_: float value between 0. and 1.\n | Threat score based on threshold value\n | \n | youden_threshold_: float value between 0. and 1.\n | Threshold calculated based on Youden Index\n | \n | sens_spec_threshold_: float value between 0. and 1.\n | Threshold calculated based on maximized sensitivity-specificity\n | \n | prec_rec_threshold_: float value between 0. and 1.\n | Threshold calculated based on maximized precision-recall\n | \n | thresholds_dict_: dict()\n | Dictionary of all calculated thresholds\n | \n | metrics_dict_: dict()\n | Dictionary of all calculated metrics\n | \n | metrics_df_: pandas.DataFrame\n | Pandas DataFrame of all calculated metrics with threshold as index\n | \n | average_methods_: list[str]\n | List of all possible average methods\n | \n | plotting_dict_: dict()\n | Plotting object as a dictionary consists of all\n | calculated metrics which was used to plot the thresholds\n | \n | Methods defined here:\n | \n | __init__(self, y_true, y_pred_proba, threshold=None, average_method=None, precision_digits=None, display_df=True)\n | Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.\n | \n | plot(self, figsize=None, save_path=None)\n | Function to plot binary classification metrics.\n | This function is a helper function based on the plotting_dict\n | attribute of the BinaryClassificationMetrics class.\n | \n | Parameters\n | ----------\n | figsize: tuple, optional, (default=(12, 12))\n | Figure size\n | \n | save_path: str, optional (default=None)\n | The full or relative path to save the plot including the image format.\n | For example \"myplot.png\" or \"../../myplot.pdf\"\n | \n | ----------------------------------------------------------------------\n | Data descriptors defined here:\n | \n | __dict__\n | dictionary for instance variables (if defined)\n | \n | __weakref__\n | list of weak references to the object (if defined)\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Example 1",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# y_true values\ny_true = [0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1,\n 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1,\n 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1,\n 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0,\n 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0,\n 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1,\n 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1,\n 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0,\n 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1]\n\n# Y_pred_proba values\ny_pred_proba = [0. , 0.12, 0.78, 0.07, 1. , 0.05, 1. , 0. , 1. , 0. , 1. ,\n 0.99, 0.93, 0.88, 0.86, 1. , 0.99, 1. , 1. , 0.74, 0. , 1. ,\n 1. , 0.79, 1. , 0.58, 1. , 0.95, 1. , 1. , 1. , 0.38, 1. ,\n 0.94, 1. , 1. , 1. , 0.01, 0.81, 1. , 0.99, 1. , 0.4 , 1. ,\n 1. , 1. , 0.9 , 0.06, 0. , 0.02, 0.99, 0.45, 1. , 1. , 0.52,\n 0.99, 0.02, 0. , 1. , 0.04, 0.19, 0.99, 0. , 0. , 0.11, 1. ,\n 1. , 0.31, 1. , 0.25, 0. , 0. , 0.99, 1. , 0.01, 0.09, 0. ,\n 1. , 0.98, 0. , 0.6 , 0.1 , 1. , 1. , 0. , 1. , 0.96, 0.02,\n 1. , 0.84, 1. , 0.97, 0.01, 0.99, 0.4 , 0. , 0.18, 1. , 1. ,\n 1. , 0.96, 0.04, 1. , 0.17, 1. , 0.96, 1. , 0. , 1. , 0.06,\n 1. , 0.75, 0.64, 0.74, 0.5 , 0.97, 0.11, 0.9 , 0. , 0.15, 1. ,\n 0.11, 1. , 0.02, 1. , 0.27, 0.95, 0.91, 0.99, 0. , 1. , 0.79,\n 1. , 1. , 0.87, 1. , 1. , 0. , 0.73, 0.97, 1. , 0.82, 0.3 ,\n 0. , 0.09, 1. , 1. , 1. , 1. , 1. , 0.76, 0.75, 0.99, 0.99,\n 0.96, 0.01, 0.08, 0.98, 1. , 0. , 1. , 1. , 0.82, 0.04, 0.98,\n 0. , 1. , 1. , 0.02, 0. , 1. , 0.99, 1. , 0.96, 0. , 0. ,\n 1. , 0. , 1. , 1. , 0. , 0.83, 0. , 0.15, 1. , 0.98, 0.98,\n 1. ]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"example1 = BinaryClassificationMetrics(y_true, y_pred_proba, precision_digits=3)\nexample1.plot(figsize=(12, 12),\n save_path=None)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Example 2",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"example = BinaryClassificationMetrics(y_true, y_pred_proba, display_df=False)\n\nprint(F\"Accuracy = {example.accuracy_}\")\nprint(F\"Balanced Accuracy = {example.balanced_accuracy_}\")\nprint(F\"AUC ROC = {example.auc_roc_}\")\nprint(F\"AUC PR = {example.auc_pr_}\")\nprint(F\"Precision = {example.precision_}\")\nprint(F\"Recall = {example.recall_}\")\nprint(F\"F1-Score = {example.f1_}\")\nprint(F\"F2-Score = {example.f2_}\")\nprint(F\"F0.5-Score = {example.f05_}\")\nprint(F\"Average Precision = {example.average_precision_}\")\nprint(F\"Threat Score = {example.threat_score_}\")\nprint(F\"Metrics Dict = {example.metrics_dict_}\")\nprint(F\"Thresholds Dict = {example.thresholds_dict_}\")\n\nexample.plot()",
"Accuracy = 0.9680851063829787\nBalanced Accuracy = 0.9571428571428571\nAUC ROC = 0.9880750605326876\nAUC PR = 0.9916378326242516\nPrecision = 0.9516129032258065\nRecall = 1.0\nF1-Score = 0.9752066115702479\nF2-Score = 0.9899328859060402\nF0.5-Score = 0.9609120521172638\nAverage Precision = 0.9906638720431951\nThreat Score = 0.9516129032258065\nMetrics Dict = {'Accuracy': 0.968, 'Balanced Accuracy': 0.957, 'ROC AUC': 0.988, 'PR AUC': 0.992, 'Precision': 0.952, 'Recall': 1.0, 'F-1 Score': 0.975, 'F-2 Score': 0.99, 'F-0.50 Score': 0.961, 'Threat Score': 0.952, 'Average Precision': 0.991, 'TP': 118, 'TN': 64, 'FP': 6, 'FN': 0}\nThresholds Dict = {'Youden': 0.6, 'Sensitivity-Specificity': 0.75, 'Precision-Recall-F1': 0.74}\n"
],
[
"thresholds = example.thresholds_dict_\nmethods = example.average_methods_\n\nframes = []\nfor method in methods:\n for threshold in thresholds:\n ex = BinaryClassificationMetrics(y_true, y_pred_proba, threshold=thresholds[threshold], average_method=method, display_df=False)\n frames.append(ex.metrics_df_)\n \ndf_to_show = pd.concat(frames) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Set CSS properties\nth_props = [(\"font-size\", \"12px\"),\n (\"text-align\", \"left\"),\n (\"font-weight\", \"bold\")]\n\ntd_props = [(\"font-size\", \"12px\"),\n (\"text-align\", \"center\")]\n\n# Set table styles\nstyles = [dict(selector = \"th\", props = th_props),\n dict(selector = \"td\", props = td_props)]\ncm = sns.light_palette(\"blue\", as_cmap = True)\ndisplay(df_to_show.style.background_gradient(cmap = cm) \\\n .set_table_styles(styles))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Example 3",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# loading data from slick-ml/data\ndata = pd.read_csv(\"./data/clf_data.csv\")\ndata.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# setting up the X, y\ny = data[\"CLASS\"].values\nX = data.drop([\"CLASS\"], axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# train-test split\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, shuffle=True, stratify=y)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# train a classifier\nfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier\nclf = RandomForestClassifier()\nclf.fit(X_train, y_train)\ny_pred_proba = clf.predict_proba(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"example3 = BinaryClassificationMetrics(y_test, y_pred_proba[:,1])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"example3.plot()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"thresholds = example3.thresholds_dict_\nmethods = example3.average_methods_\n\nframes = []\nfor method in methods:\n for threshold in thresholds:\n ex = BinaryClassificationMetrics(y_test, y_pred_proba[:,1], threshold=thresholds[threshold], average_method=method, display_df=False)\n frames.append(ex.metrics_df_)\n \ndf_to_show = pd.concat(frames) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Set CSS properties\nth_props = [(\"font-size\", \"12px\"),\n (\"text-align\", \"left\"),\n (\"font-weight\", \"bold\")]\n\ntd_props = [(\"font-size\", \"12px\"),\n (\"text-align\", \"center\")]\n\n# Set table styles\nstyles = [dict(selector = \"th\", props = th_props),\n dict(selector = \"td\", props = td_props)]\n\ncm = sns.light_palette(\"blue\", as_cmap = True)\ndisplay(df_to_show.round(decimals=3).style.background_gradient(cmap = cm).set_table_styles(styles))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Example 4",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer\ndata = load_breast_cancer()\nX = data.data\ny = data.target",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# train-test split\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, shuffle=True, stratify=y)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# train a classifier\nfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier\nclf = RandomForestClassifier()\nclf.fit(X_train, y_train)\ny_pred_proba = clf.predict_proba(X_test)[:, 1]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"example4 = BinaryClassificationMetrics(y_test, y_pred_proba)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"example4.plot()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50a5980d0c9456da712d2edb7dab48f911faa66
| 54,062 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
community/algorithms/shor_algorithm.ipynb
|
Rahulmisal27/qiskit-tutorials
|
31ea17ed50f8af83b6c3fa31c10a3ea326d03f8b
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2019-04-18T13:42:25.000Z
|
2019-04-18T13:42:25.000Z
|
community/algorithms/shor_algorithm.ipynb
|
Rahulmisal27/qiskit-tutorials
|
31ea17ed50f8af83b6c3fa31c10a3ea326d03f8b
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
community/algorithms/shor_algorithm.ipynb
|
Rahulmisal27/qiskit-tutorials
|
31ea17ed50f8af83b6c3fa31c10a3ea326d03f8b
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 70.119326 | 12,388 | 0.662166 |
[
[
[
"<img src=\"../../images/qiskit-heading.gif\" alt=\"Note: In order for images to show up in this jupyter notebook you need to select File => Trusted Notebook\" width=\"500 px\" align=\"left\">",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## _*Shor's Algorithm for Integer Factorization*_ \n\nThe latest version of this tutorial notebook is available on https://github.com/qiskit/qiskit-tutorial.\n\nIn this tutorial, we first introduce the problem of [integer factorization](#factorization) and describe how [Shor's algorithm](#shorsalgorithm) solves it in detail. We then [implement](#implementation) a version of it in Qiskit.\n\n### Contributors\nAnna Phan\n***",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Integer Factorization <a id='factorization'></a>\n\nInteger factorization is the decomposition of an composite integer into a product of smaller integers, for example, the integer $100$ can be factored into $10 \\times 10$. If these factors are restricted to prime numbers, the process is called prime factorization, for example, the prime factorization of $100$ is $2 \\times 2 \\times 5 \\times 5$. \n\nWhen the integers are very large, no efficient classical integer factorization algorithm is known. The hardest factorization problems are semiprime numbers, the product of two prime numbers. In [2009](https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-642-14623-7_18), a team of researchers factored a 232 decimal digit semiprime number (768 bits), spending the computational equivalent of more than two thousand years on a single core 2.2 GHz AMD Opteron processor with 2 GB RAM:\n```\nRSA-768 = 12301866845301177551304949583849627207728535695953347921973224521517264005 \n 07263657518745202199786469389956474942774063845925192557326303453731548268 \n 50791702612214291346167042921431160222124047927473779408066535141959745985 \n 6902143413 \n \n = 33478071698956898786044169848212690817704794983713768568912431388982883793 \n 878002287614711652531743087737814467999489 \n × 36746043666799590428244633799627952632279158164343087642676032283815739666 \n 511279233373417143396810270092798736308917 \n```\nThe presumed difficulty of this semiprime factorization problem underlines many encryption algorithms, such as [RSA](https://www.google.com/patents/US4405829), which is used in online credit card transactions, amongst other applications.\n***",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Shor's Algorithm <a id='shorsalgorithm'></a>\n\nShor's algorithm, named after mathematician Peter Shor, is a polynomial time quantum algorithm for integer factorization formulated in [1994](http://epubs.siam.org/doi/10.1137/S0097539795293172). It is arguably the most dramatic example of how the paradigm of quantum computing changed our perception of which computational problems should be considered tractable, motivating the study of new quantum algorithms and efforts to design and construct quantum computers. It also has expedited research into new cryptosystems not based on integer factorization. \n\nShor's algorithm has been experimentally realised by multiple teams for specific composite integers. The composite $15$ was first factored into $3 \\times 5$ in [2001](https://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v414/n6866/full/414883a.html) using seven NMR qubits, and has since been implemented using four photon qubits in 2007 by [two](https://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.99.250504) [teams](https://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.99.250505), three solid state qubits in [2012](https://www.nature.com/nphys/journal/v8/n10/full/nphys2385.html) and five trapped ion qubits in [2016](http://science.sciencemag.org/content/351/6277/1068). The composite $21$ has also been factored into $3 \\times 7$ in [2012](http://www.nature.com/nphoton/journal/v6/n11/full/nphoton.2012.259.html) using a photon qubit and qutrit (a three level system). Note that these experimental demonstrations rely on significant optimisations of Shor's algorithm based on apriori knowledge of the expected results. In general, [$2 + \\frac{3}{2}\\log_2N$](https://link-springer-com.virtual.anu.edu.au/chapter/10.1007/3-540-49208-9_15) qubits are needed to factor the composite integer $N$, meaning at least $1,154$ qubits would be needed to factor $RSA-768$ above.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from IPython.display import HTML\nHTML('<iframe width=\"560\" height=\"315\" src=\"https://www.youtube.com/embed/hOlOY7NyMfs?start=75&end=126\" frameborder=\"0\" allowfullscreen></iframe>')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"As Peter Shor describes in the video above from [PhysicsWorld](http://physicsworld.com/cws/article/multimedia/2015/sep/30/what-is-shors-factoring-algorithm), Shor’s algorithm is composed of three parts. The first part turns the factoring problem into a period finding problem using number theory, which can be computed on a classical computer. The second part finds the period using the quantum Fourier transform and is responsible for the quantum speedup of the algorithm. The third part uses the period found to calculate the factors.\n\nThe following sections go through the algorithm in detail, for those who just want the steps, without the lengthy explanation, refer to the [blue](#stepsone) [boxes](#stepstwo) before jumping down to the [implemention](#implemention). ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### From Factorization to Period Finding\n\nThe number theory that underlines Shor's algorithm relates to periodic modulo sequences. Let's have a look at an example of such a sequence. Consider the sequence of the powers of two: \n$$1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024, ...$$\nNow let's look at the same sequence 'modulo 15', that is, the remainder after fifteen divides each of these powers of two:\n$$1, 2, 4, 8, 1, 2, 4, 8, 1, 2, 4, ...$$\nThis is a modulo sequence that repeats every four numbers, that is, a periodic modulo sequence with a period of four.\n\nReduction of factorization of $N$ to the problem of finding the period of an integer $x$ less than $N$ and greater than $1$ depends on the following result from number theory:\n\n> The function $\\mathcal{F}(a) = x^a \\bmod N$ is a periodic function, where $x$ is an integer coprime to $N$ and $a \\ge 0$.\n\nNote that two numbers are coprime, if the only positive integer that divides both of them is 1. This is equivalent to their greatest common divisor being 1. For example, 8 and 15 are coprime, as they don't share any common factors (other than 1). However, 9 and 15 are not coprime, since they are both divisible by 3 (and 1). \n\n> Since $\\mathcal{F}(a)$ is a periodic function, it has some period $r$. Knowing that $x^0 \\bmod N = 1$, this means that $x^r \\bmod N = 1$ since the function is periodic, and thus $r$ is just the first nonzero power where $x^r = 1 (\\bmod N)$.\n\nGiven this information and through the following algebraic manipulation: \n$$ x^r \\equiv 1 \\bmod N $$\n$$ x^r = (x^{r/2})^2 \\equiv 1 \\bmod N $$\n$$ (x^{r/2})^2 - 1 \\equiv 0 \\bmod N $$\nand if $r$ is an even number:\n$$ (x^{r/2} + 1)(x^{r/2} - 1) \\equiv 0 \\bmod N $$\n\nFrom this, the product $(x^{r/2} + 1)(x^{r/2} - 1)$ is an integer multiple of $N$, the number to be factored. Thus, so long as $(x^{r/2} + 1)$ or $(x^{r/2} - 1)$ is not a multiple of $N$, then at least one of $(x^{r/2} + 1)$ or $(x^{r/2} - 1)$ must have a nontrivial factor in common with $N$. \n\nSo computing $\\text{gcd}(x^{r/2} - 1, N)$ and $\\text{gcd}(x^{r/2} + 1, N)$ will obtain a factor of $N$, where $\\text{gcd}$ is the greatest common denominator function, which can be calculated by the polynomial time [Euclidean algorithm](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euclidean_algorithm). ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Classical Steps to Shor's Algorithm\n\nLet's assume for a moment that a period finding machine exists that takes as input coprime integers $x, N$ and outputs the period of $x \\bmod N$, implemented by as a brute force search below. Let's show how to use the machine to find all prime factors of $N$ using the number theory described above. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Brute force period finding algorithm\ndef find_period_classical(x, N):\n n = 1\n t = x\n while t != 1:\n t *= x\n t %= N\n n += 1\n return n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"For simplicity, assume that $N$ has only two distinct prime factors: $N = pq$.\n\n<div class=\"alert alert-block alert-info\"> <a id='stepsone'></a>\n<ol>\n<li>Pick a random integer $x$ between $1$ and $N$ and compute the greatest common divisor $\\text{gcd}(x,N)$ using Euclid's algorithm.</li>\n<li>If $x$ and $N$ have some common prime factors, $\\text{gcd}(x,N)$ will equal $p$ or $q$. Otherwise $\\text{gcd}(x,N) = 1$, meaning $x$ and $N$ are coprime. </li>\n<li>Let $r$ be the period of $x \\bmod N$ computed by the period finding machine. Repeat the above steps with different random choices of $x$ until $r$ is even.</li>\n<li>Now $p$ and $q$ can be found by computing $\\text{gcd}(x^{r/2} \\pm 1, N)$ as long as $x^{r/2} \\neq \\pm 1$.</li>\n</ol>\n</div>\n\nAs an example, consider $N = 15$. Let's look at all values of $1 < x < 15$ where $x$ is coprime with $15$:\n\n| $x$ | $x^a \\bmod 15$ | Period $r$ |$\\text{gcd}(x^{r/2}-1,15)$|$\\text{gcd}(x^{r/2}+1,15)$ | \n|:-----:|:----------------------------:|:----------:|:------------------------:|:-------------------------:|\n| 2 | 1,2,4,8,1,2,4,8,1,2,4... | 4 | 3 | 5 |\n| 4 | 1,4,1,4,1,4,1,4,1,4,1... | 2 | 3 | 5 |\n| 7 | 1,7,4,13,1,7,4,13,1,7,4... | 4 | 3 | 5 |\n| 8 | 1,8,4,2,1,8,4,2,1,8,4... | 4 | 3 | 5 |\n| 11 | 1,11,1,11,1,11,1,11,1,11,1...| 2 | 5 | 3 |\n| 13 | 1,13,4,7,1,13,4,7,1,13,4,... | 4 | 3 | 5 |\n| 14 | 1,14,1,14,1,14,1,14,1,14,1,,,| 2 | 1 | 15 |\n\nAs can be seen, any value of $x$ except $14$ will return the factors of $15$, that is, $3$ and $5$. $14$ is an example of the special case where $(x^{r/2} + 1)$ or $(x^{r/2} - 1)$ is a multiple of $N$ and thus another $x$ needs to be tried. \n\nIn general, it can be shown that this special case occurs infrequently, so on average only two calls to the period finding machine are sufficient to factor $N$. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"For a more interesting example, first let's find larger number N, that is semiprime that is relatively small. Using the [Sieve of Eratosthenes](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sieve_of_Eratosthenes) [Python implementation](http://archive.oreilly.com/pub/a/python/excerpt/pythonckbk_chap1/index1.html?page=last), let's generate a list of all the prime numbers less than a thousand, randomly select two, and muliply them.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import random, itertools\n\n# Sieve of Eratosthenes algorithm\ndef sieve( ):\n D = { }\n yield 2\n for q in itertools.islice(itertools.count(3), 0, None, 2):\n p = D.pop(q, None)\n if p is None:\n D[q*q] = q\n yield q\n else:\n x = p + q\n while x in D or not (x&1):\n x += p\n D[x] = p\n\n# Creates a list of prime numbers up to the given argument\ndef get_primes_sieve(n):\n return list(itertools.takewhile(lambda p: p<n, sieve()))\n\ndef get_semiprime(n):\n primes = get_primes_sieve(n)\n l = len(primes)\n p = primes[random.randrange(l)]\n q = primes[random.randrange(l)]\n return p*q\n\nN = get_semiprime(1000)\n\nprint(\"semiprime N =\",N)",
"semiprime N = 241001\n"
]
],
[
[
"Now implement the [above steps](#stepsone) of Shor's Algorithm:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import math\n\ndef shors_algorithm_classical(N):\n x = random.randint(0,N) # step one\n if(math.gcd(x,N) != 1): # step two\n return x,0,math.gcd(x,N),N/math.gcd(x,N)\n r = find_period_classical(x,N) # step three\n while(r % 2 != 0):\n r = find_period_classical(x,N)\n p = math.gcd(x**int(r/2)+1,N) # step four, ignoring the case where (x^(r/2) +/- 1) is a multiple of N\n q = math.gcd(x**int(r/2)-1,N)\n return x,r,p,q\n\nx,r,p,q = shors_algorithm_classical(N)\nprint(\"semiprime N = \",N,\", coprime x = \",x,\", period r = \",r,\", prime factors = \",p,\" and \",q,sep=\"\")",
"semiprime N = 241001, coprime x = 142999, period r = 1200, prime factors = 401 and 601\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Quantum Period Finding <a id='quantumperiodfinding'></a>\n\nLet's first describe the quantum period finding algorithm, and then go through a few of the steps in detail, before going through an example. This algorithm takes two coprime integers, $x$ and $N$, and outputs $r$, the period of $\\mathcal{F}(a) = x^a\\bmod N$.\n\n<div class=\"alert alert-block alert-info\"><a id='stepstwo'></a>\n<ol>\n<li> Choose $T = 2^t$ such that $N^2 \\leq T \\le 2N^2$. Initialise two registers of qubits, first an argument register with $t$ qubits and second a function register with $n = log_2 N$ qubits. These registers start in the initial state:\n$$\\vert\\psi_0\\rangle = \\vert 0 \\rangle \\vert 0 \\rangle$$ </li>\n<li> Apply a Hadamard gate on each of the qubits in the argument register to yield an equally weighted superposition of all integers from $0$ to $T$:\n$$\\vert\\psi_1\\rangle = \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{T}}\\sum_{a=0}^{T-1}\\vert a \\rangle \\vert 0 \\rangle$$ </li>\n<li> Implement the modular exponentiation function $x^a \\bmod N$ on the function register, giving the state:\n$$\\vert\\psi_2\\rangle = \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{T}}\\sum_{a=0}^{T-1}\\vert a \\rangle \\vert x^a \\bmod N \\rangle$$\nThis $\\vert\\psi_2\\rangle$ is highly entangled and exhibits quantum parallism, i.e. the function entangled in parallel all the 0 to $T$ input values with the corresponding values of $x^a \\bmod N$, even though the function was only executed once. </li>\n<li> Perform a quantum Fourier transform on the argument register, resulting in the state:\n$$\\vert\\psi_3\\rangle = \\frac{1}{T}\\sum_{a=0}^{T-1}\\sum_{z=0}^{T-1}e^{(2\\pi i)(az/T)}\\vert z \\rangle \\vert x^a \\bmod N \\rangle$$\nwhere due to the interference, only the terms $\\vert z \\rangle$ with\n$$z = qT/r $$\nhave significant amplitude where $q$ is a random integer ranging from $0$ to $r-1$ and $r$ is the period of $\\mathcal{F}(a) = x^a\\bmod N$. </li>\n<li> Measure the argument register to obtain classical result $z$. With reasonable probability, the continued fraction approximation of $T / z$ will be an integer multiple of the period $r$. Euclid's algorithm can then be used to find $r$.</li>\n</ol>\n</div>\n\nNote how quantum parallelism and constructive interference have been used to detect and measure periodicity of the modular exponentiation function. The fact that interference makes it easier to measure periodicity should not come as a big surprise. After all, physicists routinely use scattering of electromagnetic waves and interference measurements to determine periodicity of physical objects such as crystal lattices. Likewise, Shor's algorithm exploits interference to measure periodicity of arithmetic objects, a computational interferometer of sorts. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Modular Exponentiation\n\nThe modular exponentiation, step 3 above, that is the evaluation of $x^a \\bmod N$ for $2^t$ values of $a$ in parallel, is the most demanding part of the algorithm. This can be performed using the following identity for the binary representation of any integer: $x = x_{t-1}2^{t-1} + ... x_12^1+x_02^0$, where $x_t$ are the binary digits of $x$. From this, it follows that:\n\n\\begin{aligned}\nx^a \\bmod N & = x^{2^{(t-1)}a_{t-1}} ... x^{2a_1}x^{a_0} \\bmod N \\\\\n& = x^{2^{(t-1)}a_{t-1}} ... [x^{2a_1}[x^{2a_0} \\bmod N] \\bmod N] ... \\bmod N \\\\\n\\end{aligned}\n\nThis means that 1 is first multiplied by $x^1 \\bmod N$ if and only if $a_0 = 1$, then the result is multiplied by $x^2 \\bmod N$ if and only if $a_1 = 1$ and so forth, until finally the result is multiplied by $x^{2^{(s-1)}}\\bmod N$ if and only if $a_{t-1} = 1$. \n\nTherefore, the modular exponentiation consists of $t$ serial multiplications modulo $N$, each of them controlled by the qubit $a_t$. The values $x,x^2,...,x^{2^{(t-1)}} \\bmod N$ can be found efficiently on a classical computer by repeated squaring.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Quantum Fourier Transform\n\nThe Fourier transform occurs in many different versions throughout classical computing, in areas ranging from signal processing to data compression to complexity theory. The quantum Fourier transform (QFT), step 4 above, is the quantum implementation of the discrete Fourier transform over the amplitudes of a wavefunction. \n\nThe classical discrete Fourier transform acts on a vector $(x_0, ..., x_{N-1})$ and maps it to the vector $(y_0, ..., y_{N-1})$ according to the formula\n$$y_k = \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{N}}\\sum_{j=0}^{N-1}x_j\\omega_N^{jk}$$\nwhere $\\omega_N^{jk} = e^{2\\pi i \\frac{jk}{N}}$.\n\nSimilarly, the quantum Fourier transform acts on a quantum state $\\sum_{i=0}^{N-1} x_i \\vert i \\rangle$ and maps it to the quantum state $\\sum_{i=0}^{N-1} y_i \\vert i \\rangle$ according to the formula\n$$y_k = \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{N}}\\sum_{j=0}^{N-1}x_j\\omega_N^{jk}$$\nwith $\\omega_N^{jk}$ defined as above. Note that only the amplitudes of the state were affected by this transformation.\n\nThis can also be expressed as the map:\n$$\\vert x \\rangle \\mapsto \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{N}}\\sum_{y=0}^{N-1}\\omega_N^{xy} \\vert y \\rangle$$\n\nOr the unitary matrix:\n$$ U_{QFT} = \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{N}} \\sum_{x=0}^{N-1} \\sum_{y=0}^{N-1} \\omega_N^{xy} \\vert y \\rangle \\langle x \\vert$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"As an example, we've actually already seen the quantum Fourier transform for when $N = 2$, it is the Hadamard operator ($H$):\n$$H = \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{2}}\\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 1 \\\\ 1 & -1 \\end{bmatrix}$$\nSuppose we have the single qubit state $\\alpha \\vert 0 \\rangle + \\beta \\vert 1 \\rangle$, if we apply the $H$ operator to this state, we obtain the new state:\n$$\\frac{1}{\\sqrt{2}}(\\alpha + \\beta) \\vert 0 \\rangle + \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{2}}(\\alpha - \\beta) \\vert 1 \\rangle \n\\equiv \\tilde{\\alpha}\\vert 0 \\rangle + \\tilde{\\beta}\\vert 1 \\rangle$$\nNotice how the Hadamard gate performs the discrete Fourier transform for $N = 2$ on the amplitudes of the state. \n\nSo what does the quantum Fourier transform look like for larger N? Let's derive a circuit for $N=2^n$, $QFT_N$ acting on the state $\\vert x \\rangle = \\vert x_1...x_n \\rangle$ where $x_1$ is the most significant bit.\n\\begin{aligned}\nQFT_N\\vert x \\rangle & = \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{N}} \\sum_{y=0}^{N-1}\\omega_N^{xy} \\vert y \\rangle \\\\\n& = \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{N}} \\sum_{y=0}^{N-1} e^{2 \\pi i xy / 2^n} \\vert y \\rangle \\:\\text{since}\\: \\omega_N^{xy} = e^{2\\pi i \\frac{xy}{N}} \\:\\text{and}\\: N = 2^n\\\\\n& = \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{N}} \\sum_{y=0}^{N-1} e^{2 \\pi i \\left(\\sum_{k=1}^n y_k/2^k\\right) x} \\vert y_1 ... y_n \\rangle \\:\\text{rewriting in fractional binary notation}\\: y = y_1...y_k, y/2^n = \\sum_{k=1}^n y_k/2^k \\\\\n& = \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{N}} \\sum_{y=0}^{N-1} \\prod_{k=0}^n e^{2 \\pi i x y_k/2^k } \\vert y_1 ... y_n \\rangle \\:\\text{after expanding the exponential of a sum to a product of exponentials} \\\\\n& = \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{N}} \\bigotimes_{k=1}^n \\left(\\vert0\\rangle + e^{2 \\pi i x /2^k } \\vert1\\rangle \\right) \\:\\text{after rearranging the sum and products, and expanding} \\\\\n& = \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{N}} \\left(\\vert0\\rangle + e^{2 \\pi i[0.x_n]} \\vert1\\rangle\\right) \\otimes...\\otimes \\left(\\vert0\\rangle + e^{2 \\pi i[0.x_1.x_2...x_{n-1}.x_n]} \\vert1\\rangle\\right) \\:\\text{as}\\: e^{2 \\pi i x/2^k} = e^{2 \\pi i[0.x_k...x_n]} \n\\end{aligned}\n\nThis is a very useful form of the QFT for $N=2^n$ as only the last qubit depends on the the\nvalues of all the other input qubits and each further bit depends less and less on the input qubits. Furthermore, note that $e^{2 \\pi i.0.x_n}$ is either $+1$ or $-1$, which resembles the Hadamard transform.\n\nBefore we create the circuit code for general $N=2^n$, let's look at $N=8,n=3$:\n$$QFT_8\\vert x_1x_2x_3\\rangle = \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{8}} \\left(\\vert0\\rangle + e^{2 \\pi i[0.x_3]} \\vert1\\rangle\\right) \\otimes \\left(\\vert0\\rangle + e^{2 \\pi i[0.x_2.x_3]} \\vert1\\rangle\\right) \\otimes \\left(\\vert0\\rangle + e^{2 \\pi i[0.x_1.x_2.x_3]} \\vert1\\rangle\\right) $$\n\nThe steps to creating the circuit for $\\vert y_1y_2x_3\\rangle = QFT_8\\vert x_1x_2x_3\\rangle$, remembering the [controlled phase rotation gate](../tools/quantum_gates_and_linear_algebra.ipynb\n) $CU_1$, would be:\n1. Apply a Hadamard to $\\vert x_3 \\rangle$, giving the state $\\frac{1}{\\sqrt{2}}\\left(\\vert0\\rangle + e^{2 \\pi i.0.x_3} \\vert1\\rangle\\right) = \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{2}}\\left(\\vert0\\rangle + (-1)^{x_3} \\vert1\\rangle\\right)$\n2. Apply a Hadamard to $\\vert x_2 \\rangle$, then depending on $k_3$ (before the Hadamard gate) a $CU_1(\\frac{\\pi}{2})$, giving the state $\\frac{1}{\\sqrt{2}}\\left(\\vert0\\rangle + e^{2 \\pi i[0.x_2.x_3]} \\vert1\\rangle\\right)$.\n3. Apply a Hadamard to $\\vert x_1 \\rangle$, then $CU_1(\\frac{\\pi}{2})$ depending on $k_2$, and $CU_1(\\frac{\\pi}{4})$ depending on $k_3$.\n4. Measure the bits in reverse order, that is $y_3 = x_1, y_2 = x_2, y_1 = y_3$.\n\nIn Qiskit, this is:\n```\nq3 = QuantumRegister(3, 'q3')\nc3 = ClassicalRegister(3, 'c3')\n\nqft3 = QuantumCircuit(q3, c3)\nqft3.h(q[0])\nqft3.cu1(math.pi/2.0, q3[1], q3[0])\nqft3.h(q[1])\nqft3.cu1(math.pi/4.0, q3[2], q3[0])\nqft3.cu1(math.pi/2.0, q3[2], q3[1])\nqft3.h(q[2])\n```\n\nFor $N=2^n$, this can be generalised, as in the `qft` function in [tools.qi](https://github.com/Q/qiskit-terra/blob/master/qiskit/tools/qi/qi.py):\n```\ndef qft(circ, q, n):\n \"\"\"n-qubit QFT on q in circ.\"\"\"\n for j in range(n):\n for k in range(j):\n circ.cu1(math.pi/float(2**(j-k)), q[j], q[k])\n circ.h(q[j])\n```",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Example\n\nLet's factorize $N = 21$ with coprime $x=2$, following the [above steps](#stepstwo) of the quantum period finding algorithm, which should return $r = 6$. This example follows one from [this](https://arxiv.org/abs/quant-ph/0303175) tutorial. \n\n1. Choose $T = 2^t$ such that $N^2 \\leq T \\le 2N^2$. For $N = 21$, the smallest value of $t$ is 9, meaning $T = 2^t = 512$. Initialise two registers of qubits, first an argument register with $t = 9$ qubits, and second a function register with $n = log_2 N = 5$ qubits: \n$$\\vert\\psi_0\\rangle = \\vert 0 \\rangle \\vert 0 \\rangle$$\n\n2. Apply a Hadamard gate on each of the qubits in the argument register: \n$$\\vert\\psi_1\\rangle = \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{T}}\\sum_{a=0}^{T-1}\\vert a \\rangle \\vert 0 \\rangle = \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{512}}\\sum_{a=0}^{511}\\vert a \\rangle \\vert 0 \\rangle$$\n\n3. Implement the modular exponentiation function $x^a \\bmod N$ on the function register:\n\\begin{eqnarray}\n\\vert\\psi_2\\rangle \n& = & \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{T}}\\sum_{a=0}^{T-1}\\vert a \\rangle \\vert x^a \\bmod N \\rangle\n = \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{512}}\\sum_{a=0}^{511}\\vert a \\rangle \\vert 2^a \\bmod 21 \\rangle \\\\\n& = & \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{512}} \\bigg( \\;\\; \\vert 0 \\rangle \\vert 1 \\rangle + \\vert 1 \\rangle \\vert 2 \\rangle +\n\\vert 2 \\rangle \\vert 4 \\rangle + \\vert 3 \\rangle \\vert 8 \\rangle + \\;\\; \\vert 4 \\rangle \\vert 16 \\rangle + \\;\\,\n\\vert 5 \\rangle \\vert 11 \\rangle \\, + \\\\\n& & \\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\, \\vert 6 \\rangle \\vert 1 \\rangle + \\vert 7 \\rangle \\vert 2 \\rangle + \\vert 8 \\rangle \\vert 4 \\rangle + \\vert 9 \\rangle \\vert 8 \\rangle + \\vert 10 \\rangle \\vert 16 \\rangle + \\vert 11 \\rangle \\vert 11 \\rangle \\, +\\\\\n& & \\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\, \\vert 12 \\rangle \\vert 1 \\rangle + \\ldots \\bigg)\\\\\n\\end{eqnarray}\nNotice that the above expression has the following pattern: the states of the second register of each “column” are the same. Therefore we can rearrange the terms in order to collect the second register:\n\\begin{eqnarray}\n\\vert\\psi_2\\rangle \n& = & \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{512}} \\bigg[ \\big(\\,\\vert 0 \\rangle + \\;\\vert 6 \\rangle + \\vert 12 \\rangle \\ldots + \\vert 504 \\rangle + \\vert 510 \\rangle \\big) \\, \\vert 1 \\rangle \\, + \\\\\n& & \\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\; \\big(\\,\\vert 1 \\rangle + \\;\\vert 7 \\rangle + \\vert 13 \\rangle \\ldots + \\vert 505 \\rangle + \\vert 511 \\rangle \\big) \\, \\vert 2 \\rangle \\, + \\\\\n& & \\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\; \\big(\\,\\vert 2 \\rangle + \\;\\vert 8 \\rangle + \\vert 14 \\rangle \\ldots + \\vert 506 \\rangle + \\big) \\, \\vert 4 \\rangle \\, + \\\\\n& & \\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\; \\big(\\,\\vert 3 \\rangle + \\;\\vert 9 \\rangle + \\vert 15 \\rangle \\ldots + \\vert 507 \\rangle + \\big) \\, \\vert 8 \\rangle \\, + \\\\\n& & \\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\; \\big(\\,\\vert 4 \\rangle + \\vert 10 \\rangle + \\vert 16 \\rangle \\ldots + \\vert 508 \\rangle + \\big) \\vert 16 \\rangle \\, + \\\\\n& & \\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\;\\; \\big(\\,\\vert 5 \\rangle + \\vert 11 \\rangle + \\vert 17 \\rangle \\ldots + \\vert 509 \\rangle + \\big) \\vert 11 \\rangle \\, \\bigg]\\\\\n\\end{eqnarray}\n\n4. To simplify following equations, we'll measure the function register before performing a quantum Fourier transform on the argument register. This will yield one of the following numbers with equal probability: $\\{1,2,4,6,8,16,11\\}$. Suppose that the result of the measurement was $2$, then:\n$$\\vert\\psi_3\\rangle = \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{86}}(\\vert 1 \\rangle + \\;\\vert 7 \\rangle + \\vert 13 \\rangle \\ldots + \\vert 505 \\rangle + \\vert 511 \\rangle)\\, \\vert 2 \\rangle $$\nIt does not matter what is the result of the measurement; what matters is the periodic pattern. The period of the states of the first register is the solution to the problem and the quantum Fourier transform can reveal the value of the period.\n\n5. Perform a quantum Fourier transform on the argument register:\n$$\n\\vert\\psi_4\\rangle\n = QFT(\\vert\\psi_3\\rangle)\n = QFT(\\frac{1}{\\sqrt{86}}\\sum_{a=0}^{85}\\vert 6a+1 \\rangle)\\vert 2 \\rangle\n = \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{512}}\\sum_{j=0}^{511}\\bigg(\\big[ \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{86}}\\sum_{a=0}^{85} e^{-2 \\pi i \\frac{6ja}{512}} \\big] e^{-2\\pi i\\frac{j}{512}}\\vert j \\rangle \\bigg)\\vert 2 \\rangle\n$$\n\n6. Measure the argument register. The probability of measuring a result $j$ is:\n$$ \\rm{Probability}(j) = \\frac{1}{512 \\times 86} \\bigg\\vert \\sum_{a=0}^{85}e^{-2 \\pi i \\frac{6ja}{512}} \\bigg\\vert^2$$\nThis peaks at $j=0,85,171,256,341,427$. Suppose that the result of the measement yielded $j = 85$, then using continued fraction approximation of $\\frac{512}{85}$, we obtain $r=6$, as expected. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Implementation <a id='implementation'></a>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from qiskit import Aer\nfrom qiskit import QuantumCircuit, ClassicalRegister, QuantumRegister\nfrom qiskit import execute, register, get_backend, compile\nfrom qiskit.tools.visualization import plot_histogram, circuit_drawer",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"As mentioned [earlier](#shorsalgorithm), many of the experimental demonstrations of Shor's algorithm rely on significant optimisations based on apriori knowledge of the expected results. We will follow the formulation in [this](http://science.sciencemag.org/content/351/6277/1068) paper, which demonstrates a reasonably scalable realisation of Shor's algorithm using $N = 15$. Below is the first figure from the paper, showing various quantum circuits, with the following caption: _Diagrams of Shor’s algorithm for factoring $N = 15$, using a generic textbook approach (**A**) compared with Kitaev’s approach (**B**) for a generic base $a$. (**C**) The actual implementation for factoring $15$ to base $11$, optimized for the corresponding single-input state. Here $q_i$ corresponds to the respective qubit in the computational register. (**D**) Kitaev’s approach to Shor’s algorithm for the bases ${2, 7, 8, 13}$. Here, the optimized map of the first multiplier is identical in all four cases, and the last multiplier is implemented with full modular multipliers, as depicted in (**E**). In all cases, the single QFT qubit is used three times, which, together with the four qubits in the computation register, totals seven effective qubits. (**E**) Circuit diagrams of the modular multipliers of the form $a \\bmod N$ for bases $a = {2, 7, 8, 11, 13}$._\n\n<img src=\"images/shoralgorithm.png\" alt=\"Note: In order for images to show up in this jupyter notebook you need to select File => Trusted Notebook\" width=\"500 px\" align=\"center\">\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Note that we cannot run this version of Shor's algorithm on an IBM Quantum Experience device at the moment as we currently lack the ability to do measurement feedforward and qubit resetting. Thus we'll just be building the ciruits to run on the simulators for now. Based on Pinakin Padalia & Amitabh Yadav's implementation, found [here](https://github.com/amitabhyadav/Shor-Algorithm-on-IBM-Quantum-Experience)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"First we'll construct the $a^1 \\bmod 15$ circuits for $a = 2,7,8,11,13$ as in **E**:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# qc = quantum circuit, qr = quantum register, cr = classical register, a = 2, 7, 8, 11 or 13\ndef circuit_amod15(qc,qr,cr,a):\n if a == 2:\n qc.cswap(qr[4],qr[3],qr[2])\n qc.cswap(qr[4],qr[2],qr[1])\n qc.cswap(qr[4],qr[1],qr[0])\n elif a == 7:\n qc.cswap(qr[4],qr[1],qr[0])\n qc.cswap(qr[4],qr[2],qr[1])\n qc.cswap(qr[4],qr[3],qr[2])\n qc.cx(qr[4],qr[3])\n qc.cx(qr[4],qr[2])\n qc.cx(qr[4],qr[1])\n qc.cx(qr[4],qr[0])\n elif a == 8:\n qc.cswap(qr[4],qr[1],qr[0])\n qc.cswap(qr[4],qr[2],qr[1])\n qc.cswap(qr[4],qr[3],qr[2])\n elif a == 11: # this is included for completeness\n qc.cswap(qr[4],qr[2],qr[0])\n qc.cswap(qr[4],qr[3],qr[1])\n qc.cx(qr[4],qr[3])\n qc.cx(qr[4],qr[2])\n qc.cx(qr[4],qr[1])\n qc.cx(qr[4],qr[0])\n elif a == 13:\n qc.cswap(qr[4],qr[3],qr[2])\n qc.cswap(qr[4],qr[2],qr[1])\n qc.cswap(qr[4],qr[1],qr[0])\n qc.cx(qr[4],qr[3])\n qc.cx(qr[4],qr[2])\n qc.cx(qr[4],qr[1])\n qc.cx(qr[4],qr[0])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Next we'll build the rest of the period finding circuit as in **D**:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# qc = quantum circuit, qr = quantum register, cr = classical register, a = 2, 7, 8, 11 or 13\ndef circuit_aperiod15(qc,qr,cr,a):\n if a == 11:\n circuit_11period15(qc,qr,cr)\n return\n \n # Initialize q[0] to |1> \n qc.x(qr[0])\n\n # Apply a**4 mod 15\n qc.h(qr[4])\n # controlled identity on the remaining 4 qubits, which is equivalent to doing nothing\n qc.h(qr[4])\n # measure\n qc.measure(qr[4],cr[0])\n # reinitialise q[4] to |0>\n qc.reset(qr[4])\n\n # Apply a**2 mod 15\n qc.h(qr[4])\n # controlled unitary\n qc.cx(qr[4],qr[2])\n qc.cx(qr[4],qr[0])\n # feed forward\n if cr[0] == 1:\n qc.u1(math.pi/2.,qr[4])\n qc.h(qr[4])\n # measure\n qc.measure(qr[4],cr[1])\n # reinitialise q[4] to |0>\n qc.reset(qr[4])\n\n # Apply a mod 15\n qc.h(qr[4])\n # controlled unitary.\n circuit_amod15(qc,qr,cr,a)\n # feed forward\n if cr[1] == 1:\n qc.u1(math.pi/2.,qr[4])\n if cr[0] == 1:\n qc.u1(math.pi/4.,qr[4])\n qc.h(qr[4])\n # measure\n qc.measure(qr[4],cr[2])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Next we build the optimised circuit for $11 \\bmod 15$ as in **C**.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def circuit_11period15(qc,qr,cr):\n # Initialize q[0] to |1> \n qc.x(qr[0])\n\n # Apply a**4 mod 15\n qc.h(qr[4])\n # controlled identity on the remaining 4 qubits, which is equivalent to doing nothing\n qc.h(qr[4])\n # measure\n qc.measure(qr[4],cr[0])\n # reinitialise q[4] to |0>\n qc.reset(qr[4])\n\n # Apply a**2 mod 15\n qc.h(qr[4])\n # controlled identity on the remaining 4 qubits, which is equivalent to doing nothing\n # feed forward\n if cr[0] == 1:\n qc.u1(math.pi/2.,qr[4])\n qc.h(qr[4])\n # measure\n qc.measure(qr[4],cr[1])\n # reinitialise q[4] to |0>\n qc.reset(qr[4])\n\n # Apply 11 mod 15\n qc.h(qr[4])\n # controlled unitary.\n qc.cx(qr[4],qr[3])\n qc.cx(qr[4],qr[1])\n # feed forward\n if cr[1] == 1:\n qc.u1(math.pi/2.,qr[4])\n if cr[0] == 1:\n qc.u1(math.pi/4.,qr[4])\n qc.h(qr[4])\n # measure\n qc.measure(qr[4],cr[2])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's build and run a circuit for $a = 7$, and plot the results:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"q = QuantumRegister(5, 'q')\nc = ClassicalRegister(5, 'c')\n\nshor = QuantumCircuit(q, c)\ncircuit_aperiod15(shor,q,c,7)\n\nbackend = Aer.get_backend('qasm_simulator')\nsim_job = execute([shor], backend)\nsim_result = sim_job.result()\nsim_data = sim_result.get_counts(shor) \nplot_histogram(sim_data)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We see here that the period, $r = 4$, and thus calculate the factors $p = \\text{gcd}(a^{r/2}+1,15) = 3$ and $q = \\text{gcd}(a^{r/2}-1,15) = 5$. Why don't you try seeing what you get for $a = 2, 8, 11, 13$?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
c50a5a67cbbb2d8ed6d4580c6ccadb60c74c95dc
| 4,698 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
src/pyscripts/prob-dens-curr.ipynb
|
s0vereign/sesoc
|
83461ef779019ec7944bb2c5ea0a4702f4aeb32f
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2017-04-21T12:22:33.000Z
|
2019-01-22T13:14:46.000Z
|
src/pyscripts/prob-dens-curr.ipynb
|
ComputationalRadiationPhysics/QonGPU
|
83461ef779019ec7944bb2c5ea0a4702f4aeb32f
|
[
"MIT"
] | 8 |
2016-05-09T09:44:35.000Z
|
2017-03-22T15:31:13.000Z
|
src/pyscripts/prob-dens-curr.ipynb
|
ComputationalRadiationPhysics/QonGPU
|
83461ef779019ec7944bb2c5ea0a4702f4aeb32f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 24.216495 | 128 | 0.437207 |
[
[
[
"def calc_dist(x, t):\n \"\"\"\n Calculate the disturbance term \n \"\"\"\n a = 6.9314718055994524e-07\n b = 0.0069314718056\n t0 = 50.0\n w = 1.51939\n k = w/137\n I = 20.0\n res = np.zeros([t.size,x.size])\n for i in range(0, t.size):\n if t[i] < 50:\n g = t[i]/t0\n else:\n g = 1.0\n res[i] = I * np.sin(w*t[i]-k*x)*g\n return res\n\ndef int_dist(vals, h):\n \"\"\"\n \"\"\"\n res = np.zeros(vals.shape[0])\n for i in range(0, vals.shape[0]):\n res[i] = np.trapz(vals[i],dx=h)\n return res",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import Qutils\nfilepath = \"../../build/res.h5\"\nnx = np.int32(1e5)\nnt = np.int32(1e5)\nnstep = 100\nh = 0.0006 \npsi = load_vals(filepath, nt, nx, nstep)\nres = integrate_prob_current(psi, 50000, 66667, 0.0006)\n#res = integrate_prob(psi, 50000, 66667, 0.0006)\nt = np.linspace(0,100, 1000)\nx = np.linspace(0, 66667*0.0006-30.0, 5000)\nres_2 = calc_dist(x,t)\nres_2 = int_dist(res_2,h)\nres_2 *= 1/np.max(res_2)\nres *= 1/np.max(res)",
" 0% ( 900 of 100000) | | Elapsed Time: 0:00:00 ETA: 0:00:13"
],
[
"fig = plt.figure(figsize=(14,10))\nplt.plot(t, res_2, color=\"red\",label=r\"$\\int \\, dx \\, V_1(x,t)$\")\nplt.xlabel(r\"$t \\; (a.u)$\", size=20)\nplt.ylabel(r\"Integrated quantities\", size=20)\n\nplt.plot(t, -res, color=\"blue\", label=r\"$-\\int \\, dx \\, j(x)$\")\nplt.title(\"Integrated \")\nplt.legend(loc='best')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50a5c5a2d778fa3be607e1ea7bf51e280623dcc
| 20,202 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
src/main/app-resources/notebook/libexec/input.ipynb
|
ec-better/ewf-ext-03-03-03
|
da4584bb1bb94e995f7a52cca98622438d11a6b1
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
src/main/app-resources/notebook/libexec/input.ipynb
|
ec-better/ewf-ext-03-03-03
|
da4584bb1bb94e995f7a52cca98622438d11a6b1
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
src/main/app-resources/notebook/libexec/input.ipynb
|
ec-better/ewf-ext-03-03-03
|
da4584bb1bb94e995f7a52cca98622438d11a6b1
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 33.009804 | 227 | 0.547124 |
[
[
[
"## ewf-ext-03-03-03 - Flood hazard",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### <a name=\"service\">Service definition",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"service = dict([('title', 'ewf-ext-03-03-03 - Flood exposure'),\n ('abstract', 'ewf-ext-03-03-03 - Flood exposure'),\n ('id', 'ewf-ext-03-03-03')])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"start_year = dict([('id', 'start_year'),\n ('value', '2015'),\n ('title', 'start year'),\n ('abstract', 'start year')])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"end_year = dict([('id', 'end_year'),\n ('value', '2019'),\n ('title', 'end_year'),\n ('abstract', 'end_year')])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"area_of_interest = dict([('id', 'areaOfInterest'),\n ('value', 'IberianPeninsula'),\n ('title', 'Area of the region'),\n ('abstract', 'Area of the region of interest')])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"regionOfInterest = dict([('id', 'regionOfInterest'),\n ('value', 'POLYGON((-9.586 39.597,-8.100 39.597,-8.100 40.695,-9.586 40.695,-9.586 39.597))'),\n ('title', 'WKT Polygon for the Region of Interest (-1 if no crop)'),\n ('abstract', 'Set the value of WKT Polygon')])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Parameter Definition",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### <a name=\"runtime\">Runtime parameter definition",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Input identifiers**\n\nThis is the Sentinel-1 stack of products' identifiers",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"input_identifiers = ('FEI_IberianPeninsula_GHS_2015_CLC_2019.tif', 'binary_flood_map_S1A_IW_GRDH_1SDV_20191223T064251_20191223T064316_030472_037D16_1012.tif')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Input references**\n\nThis is the Sentinel-1 stack catalogue references",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"input_references = ('https://catalog.terradue.com/chirps/search?format=atom&uid=chirps-v2.0.2017.01.01','https://catalog.terradue.com/chirps/search?format=atom&uid=chirps-v2.0.2017.01.02') ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Data path**\n\nThis path defines where the data is staged-in. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data_path = \"\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"etc_path = \"/application/notebook/etc\"\n#etc_path = \"/workspace/Better_3rd_phase/Applications/EXT-03-03-03/ewf-ext-03-03-03/src/main/app-resources/notebook/etc\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"output_folder = \"\"\n#output_folder = \"/workspace/Better_3rd_phase/Applications/EXT-03-03-03/ewf-ext-03-03-03/src/main/app-resources/notebook/libexec\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"temp_folder = 'Temp'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cropped_output_folder = 'Output/Crop'",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Import Modules",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import os\nimport shutil\n\nimport sys\nimport string\nimport numpy as np\nfrom osgeo import gdal, ogr, osr\nfrom shapely.wkt import loads\nimport datetime\nimport gdal\n\nimport pdb\nfrom calendar import monthrange\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Auxiliary methods",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# remove contents of a given folder\n# used to clean a temporary folder\ndef rm_cfolder(folder):\n #folder = '/path/to/folder'\n for the_file in os.listdir(folder):\n file_path = os.path.join(folder, the_file)\n try:\n if os.path.isfile(file_path):\n os.unlink(file_path)\n elif os.path.isdir(file_path): shutil.rmtree(file_path)\n except Exception as e:\n print(e)\n \ndef crop_image(input_image, polygon_wkt, output_path):\n \n dataset = gdal.Open(input_image)\n\n polygon_ogr = ogr.CreateGeometryFromWkt(polygon_wkt)\n envelope = polygon_ogr.GetEnvelope()\n bounds = [envelope[0], envelope[3], envelope[1], envelope[2]] \n print bounds\n no_data = dataset.GetRasterBand(1).GetNoDataValue()\n gdal.Translate(output_path, dataset, outputType=gdal.GDT_Float32, projWin=bounds, projWinSRS='EPSG:4326', noData=no_data)\n\n dataset = None\n\n \ndef write_output_image(filepath, output_matrix, image_format, data_format, mask=None, output_projection=None, output_geotransform=None, no_data_value=None):\n driver = gdal.GetDriverByName(image_format)\n out_rows = np.size(output_matrix, 0)\n out_columns = np.size(output_matrix, 1)\n \n \n if mask is not None and mask is not 0:\n # TODO: check if output folder exists\n output = driver.Create(filepath, out_columns, out_rows, 2, data_format)\n mask_band = output.GetRasterBand(2)\n mask_band.WriteArray(mask)\n if no_data_value is not None:\n output_matrix[mask > 0] = no_data_value\n else:\n output = driver.Create(filepath, out_columns, out_rows, 1, data_format)\n \n if output_projection is not None:\n output.SetProjection(output_projection)\n if output_geotransform is not None:\n output.SetGeoTransform(output_geotransform)\n \n raster_band = output.GetRasterBand(1)\n if no_data_value is not None:\n raster_band.SetNoDataValue(no_data_value)\n raster_band.WriteArray(output_matrix)\n \n if filepath is None:\n print \"filepath\"\n if output is None:\n print \"output\"\n gdal.Warp(filepath, output, format=\"GTiff\", outputBoundsSRS='EPSG:4326', xRes=output_geotransform[1], yRes=-output_geotransform[5], targetAlignedPixels=True)\n\n return filepath\n\n\ndef matrix_multiply(mat1, mat2, no_data_value=None):\n #if no_data_value is not None:\n #if not isinstance(mat1, int):\n #mat1[(mat1 == no_data_value)] = 0\n #if not isinstance(mat2, int):\n #mat2[(mat2 == no_data_value)] = 0\n mats_nodata = np.logical_or(mat1 == no_data_value, mat2 == no_data_value)\n mat1 = mat1.astype('float32')\n mat2 = mat2.astype('float32')\n multiply = mat1 * mat2\n multiply = np.where(mats_nodata, no_data_value, multiply)\n return multiply\n \n\ndef get_matrix_list(image_list):\n projection = None\n geo_transform = None\n no_data = None\n mat_list = []\n for img in image_list:\n dataset = gdal.Open(img)\n print dataset\n projection = dataset.GetProjection()\n print projection\n geo_transform = dataset.GetGeoTransform()\n no_data = dataset.GetRasterBand(1).GetNoDataValue()\n product_array = dataset.GetRasterBand(1).ReadAsArray()\n mat_list.append(product_array)\n dataset = None\n return mat_list, projection, geo_transform, no_data\n \ndef write_outputs(product_name, first_date, last_date, averages, standard_deviation, image_format, projection, geo_transform, no_data_value):\n filenames = []\n areaofinterest = area_of_interest['value']\n filenames.append(product_name + '_averages_' + areaofinterest + '_' + first_date + '_' + last_date + '.tif')\n filenames.append(product_name + '_standarddeviation_' + areaofinterest + '_'+ first_date + '_' + last_date + '.tif')\n\n write_output_image(filenames[0], averages, image_format, gdal.GDT_Int16, None, projection, geo_transform, no_data_value)\n write_output_image(filenames[1], standard_deviation, image_format, gdal.GDT_Int16, None, projection, geo_transform, no_data_value)\n \n return filenames\n\ndef write_properties_file(output_name, first_date, last_date):\n \n title = 'Output %s' % output_name\n \n first_date = get_formatted_date(first_date)\n last_date = get_formatted_date(last_date)\n \n with open(output_name + '.properties', 'wb') as file:\n file.write('title=%s\\n' % title)\n file.write('date=%s/%s\\n' % (first_date, last_date))\n file.write('geometry=%s' % (regionOfInterest['value']))\n \ndef get_formatted_date(date_obj):\n date = datetime.datetime.strftime(date_obj, '%Y-%m-%dT00:00:00Z')\n return date\n\ndef reproject_image_to_master ( master, slave, dst_filename, res=None ):\n\n slave_ds = gdal.Open( slave )\n if slave_ds is None:\n raise IOError, \"GDAL could not open slave file %s \" \\\n % slave\n slave_proj = slave_ds.GetProjection()\n slave_geotrans = slave_ds.GetGeoTransform()\n data_type = slave_ds.GetRasterBand(1).DataType\n n_bands = slave_ds.RasterCount\n #no_data_value that does not exist on the image\n slave_ds.GetRasterBand(1).SetNoDataValue(-300.0)\n\n master_ds = gdal.Open( master )\n if master_ds is None:\n raise IOError, \"GDAL could not open master file %s \" \\\n % master\n master_proj = master_ds.GetProjection()\n master_geotrans = master_ds.GetGeoTransform()\n w = master_ds.RasterXSize\n h = master_ds.RasterYSize\n \n if res is not None:\n master_geotrans[1] = float( res )\n master_geotrans[-1] = - float ( res )\n \n dst_ds = gdal.GetDriverByName('GTiff').Create(dst_filename, w, h, n_bands, data_type)\n \n dst_ds.SetGeoTransform( master_geotrans )\n dst_ds.SetProjection( master_proj)\n \n gdal.ReprojectImage( slave_ds, dst_ds, slave_proj,\n master_proj, gdal.GRA_NearestNeighbour)\n \n dst_ds = None # Flush to disk\n \n return dst_filename\n\ndef project_coordinates(file, dst_filename):\n input_raster = gdal.Open(file)\n output_raster = dst_filename \n gdal.Warp(output_raster,input_raster,dstSRS='EPSG:4326')\n \ndef get_pixel_weights(mat):\n urban_fabric=[111.,112.]\n industrial_commercial_transport_units=[121.,122.,123.,124.]\n mine_dump_construction_sites=[131.,132.,133.]\n artificial_areas=[141.,142.]\n arable_land=[211.,212.,213.]\n permanent_crops=[221.,222.,223.]\n pastures=[231.]\n agricultural_areas=[241.,242.,243.,244.]\n forest=[311.,312.,313.]\n vegetation_associations=[321.,322.,323.,324.]\n little_no_vegetation=[331.,332.,333.,334.,335.]\n inland_wetlands=[411.,412.]\n coastal_wetlands=[421.,422.,423.]\n inland_waters=[511.,512.]\n marine_waters=[521.,522.,523.]\n\n exposure_dictionary = dict()\n exposure_dictionary[1.0] = urban_fabric\n exposure_dictionary[0.5] = industrial_commercial_transport_units + arable_land + permanent_crops\n exposure_dictionary[0.3] = mine_dump_construction_sites + agricultural_areas\n exposure_dictionary[0.0] = artificial_areas + marine_waters\n exposure_dictionary[0.4] = pastures\n exposure_dictionary[0.1] = forest + vegetation_associations + little_no_vegetation + inland_wetlands + coastal_wetlands + inland_waters\n\n rows = mat.shape[0]\n cols = mat.shape[1]\n\n for i in range(0, rows):\n for j in range(0, cols):\n for exposure, value_list in exposure_dictionary.iteritems():\n for value in value_list:\n if mat[i,j] == value:\n mat[i,j] = exposure\n return mat\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"if len(output_folder) > 0:\n if not os.path.isdir(output_folder):\n os.mkdir(output_folder)\n\nif not os.path.isdir(temp_folder):\n os.mkdir(temp_folder)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"area_of_interest['value'], start_year['value'], end_year['value']",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Workflow",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### Update AOI if crop not needed",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"first_year = start_year['value']\nlast_year = end_year['value']\nproduct_path_name = output_folder\nprojection = None\ngeo_transform = None\nno_data = None\nareaofinterest = area_of_interest['value']\n\nif input_identifiers[0] >=0: \n file_list = [os.path.join(etc_path, filename) for filename in input_identifiers]\n \n flood_frequency = os.path.join(temp_folder, 'flood_frequency_cropped.tif') \n crop_image(file_list[1],regionOfInterest['value'],flood_frequency)\n \n flood_exposure=file_list[0]\n image_list=[flood_exposure,flood_frequency]\n \n dst_filename = os.path.basename(flood_exposure)\n dst_filename = dst_filename.replace(\".tif\", \"_reprojected.tif\" )\n dst_filename = os.path.join(temp_folder, dst_filename)\n \n #co-registration (slave on master)\n flood_exposure_reprojected = reproject_image_to_master(flood_frequency, flood_exposure, dst_filename)\n image_list=[flood_exposure_reprojected,flood_frequency]\n mat_list, projection, geo_transform, no_data=get_matrix_list(image_list) \n \n flood_frequency_mat = mat_list[1]\n flood_exposure_mat = mat_list[0]\n no_data=-200.0\n flood_hazard = matrix_multiply(flood_frequency_mat,flood_exposure_mat, no_data)\n flood_hazard = np.where(flood_exposure==no_data, no_data, flood_hazard)\n flood_hazard = np.where(flood_hazard==0.0, no_data, flood_hazard)\n\n file = write_output_image(os.path.join(product_path_name , 'flood_hazard_' + areaofinterest + first_year + last_year + '.tif'), flood_hazard, 'GTiff', gdal.GDT_Float32, None, projection, geo_transform, no_data)\n firstdate_obj = datetime.datetime.strptime(first_year, \"%Y\").date()\n lastdate_obj = datetime.datetime.strptime(last_year, \"%Y\").date()\n \nelse:\n print \"error\" + file_list\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"if input_identifiers[0] >=0: \n if regionOfInterest['value'] == '-1':\n\n #dataset = gdal.Open('/vsigzip//vsicurl/%s' % gpd_final.iloc[0]['enclosure'])\n dataset = gdal.Open(file)\n\n geoTransform = dataset.GetGeoTransform()\n\n minx = geoTransform[0]\n maxy = geoTransform[3]\n maxx = minx + geoTransform[1] * dataset.RasterXSize\n miny = maxy + geoTransform[5] * dataset.RasterYSize\n\n regionOfInterest['value'] = 'POLYGON(({0} {1}, {2} {1}, {2} {3}, {0} {3}, {0} {1}))'.format(minx, maxy, maxx, miny)\n\n dataset = None\n else:\n crop_image(file,regionOfInterest['value'],file.split('.tif')[0] + '_cropped.tif')\n \n regionofinterest = regionOfInterest['value']\n write_properties_file(file, firstdate_obj, lastdate_obj)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Remove temporay files and folders",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"try:\n shutil.rmtree(temp_folder)\n shutil.rmtree(cropped_output_folder)\nexcept OSError as e:\n print(\"Error: %s : %s\" % (temp_folder, e.strerror))\n print(\"Error: %s : %s\" % (cropped_output_folder, e.strerror))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c50a5f20b4df0849f4ba7106cec22833692bed21
| 3,529 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
tarea8_busqueda_binaria_recursiva.ipynb
|
michelmunoz99/daa_2021_1
|
4661dbfd9b0684ee3cbe75dfe7eb5d19241f5527
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
tarea8_busqueda_binaria_recursiva.ipynb
|
michelmunoz99/daa_2021_1
|
4661dbfd9b0684ee3cbe75dfe7eb5d19241f5527
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
tarea8_busqueda_binaria_recursiva.ipynb
|
michelmunoz99/daa_2021_1
|
4661dbfd9b0684ee3cbe75dfe7eb5d19241f5527
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 30.162393 | 256 | 0.45367 |
[
[
[
"<a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/michelmunoz99/daa_2021_1/blob/master/tarea8_busqueda_binaria_recursiva.ipynb\" target=\"_parent\"><img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open In Colab\"/></a>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Binary search (Recursive)\n# Búsqueda binaria (Recursiva)\n\ndef binary_search_rec(array, x, left, right):\n if left > right:\n return -1\n \n mid = (left + right) // 2\n if array[mid] == x:\n return mid\n elif array[mid] > x:\n return binary_search_rec(array, x, left, mid - 1)\n else:\n return binary_search_rec(array, x, mid + 1, right)\n\n\narray = [1,2,3,4,5]\nx = int(input(\"Ingrese elemento para encontrar su índice: \"))\nprint(f\"Elemento '{x}' encontrado en la posición: {binary_search_rec(array, x, 0, len(array) - 1)}\")\n",
"Ingrese elemento para encontrar su índice: 4\nElemento '4' encontrado en la posición: 3\n"
],
[
"# Binary search (No recursive)\n# Búsqueda binaria (No recursiva)\n\n\ndef binary_search(array, x):\n left = 0\n right = len(array) - 1\n\n while left <= right:\n mid = (left + right) // 2\n\n if array[mid] == x:\n return mid\n elif array[mid] > x:\n right = mid - 1\n else:\n left = mid + 1\n\n return -1\n\n\narray = [1,2,3,4,5]\nx = int(input(\"Ingrese elemento para encontrar su índice: \"))\nprint(f\"Elemento '{x}' encontrado en la posición: {binary_search(array, x)}\")\n",
"Ingrese elemento para encontrar su índice: 2\nElemento '2' encontrado en la posición: 1\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50a709a3250d520163475c08083fbdddaae57df
| 5,678 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
4-1 dropout.ipynb
|
e8906482/machine-learning-project-2
|
c744f14c1feff9451f0ff54c4f56a5adbf298d74
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
4-1 dropout.ipynb
|
e8906482/machine-learning-project-2
|
c744f14c1feff9451f0ff54c4f56a5adbf298d74
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
4-1 dropout.ipynb
|
e8906482/machine-learning-project-2
|
c744f14c1feff9451f0ff54c4f56a5adbf298d74
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 31.72067 | 194 | 0.595456 |
[
[
[
"import tensorflow as tf\nfrom tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#load dataset\nmnist = input_data.read_data_sets(\"MNIST_data\",one_hot=True)\n#define batch_size\nbatch_size = 100\n#compute the number of batch\nn_batch = mnist.train.num_examples // batch_size #\n\n#define 2 placeholders\nx = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784])\ny = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10])\nkeep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)\n\nW1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([784,2000],stddev=0.1)) \nb1 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([2000])+0.1)\nL1 = tf.nn.tanh(tf.matmul(x,W1) + b1)\nL1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(L1,keep_prob)\n\nW2 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([2000,2000],stddev=0.1)) \nb2 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([2000])+0.1)\nL2 = tf.nn.tanh(tf.matmul(L1_drop,W2)+b2)\nL2_drop = tf.nn.dropout(L2,keep_prob)\n \nW3 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([2000,1000],stddev=0.1)) \nb3 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1000])+0.1)\nL3 = tf.nn.tanh(tf.matmul(L2_drop,W3)+b3)\nL3_drop = tf.nn.dropout(L3,keep_prob)\n\n\n#create a neural network\nW4 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([1000,10],stddev=0.1)) \nb4 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10])+0.1)\nprediction = tf.matmul(L3_drop,W4)+b4\n\n#quadratic cost function\n#loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y-prediction))\n#Here we use cross_entropy to define loss function instead of quadratic\nloss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y,logits=prediction))\ntrain_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.2).minimize(loss)\n\n#initialize\ninit = tf.global_variables_initializer()\n\n#compute accuracy\n#argmax will return the largest number\ncorrect_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y,1),tf.argmax(prediction,1))\n#tf.cast will change the format of correct_prediction to tf.float32\naccuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32))\n\nwith tf.Session() as sess:\n sess.run(init)\n for epoch in range(21):\n for batch in range(n_batch):\n \n batch_xs,batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)\n \n sess.run(train_step,feed_dict={x:batch_xs,y:batch_ys,keep_prob:0.6})#keep_prob:0.6 means we only let 60% of neurons to work\n \n test_acc = sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images,y:mnist.test.labels,keep_prob:1.0})\n train_acc = sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={x:mnist.train.images,y:mnist.train.labels,keep_prob:1.0})\n print(\"Iter\" + str(epoch) + \",Testing Accuracy:\" + str(test_acc)+\",Training Accuracy\"+ str(train_acc))",
"Extracting MNIST_data\\train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz\nExtracting MNIST_data\\train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz\nExtracting MNIST_data\\t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz\nExtracting MNIST_data\\t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz\nWARNING:tensorflow:From <ipython-input-3-5a8eca361376>:36: softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits (from tensorflow.python.ops.nn_ops) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version.\nInstructions for updating:\n\nFuture major versions of TensorFlow will allow gradients to flow\ninto the labels input on backprop by default.\n\nSee tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2.\n\nIter0,Testing Accuracy:0.9079,Training Accuracy0.898636\nIter1,Testing Accuracy:0.9211,Training Accuracy0.914509\n"
],
[
"\nIter0,Testing Accuracy:0.8541,Training Accuracy0.867927\nIter1,Testing Accuracy:0.9557,Training Accuracy0.969618\nIter2,Testing Accuracy:0.9627,Training Accuracy0.980218\nIter3,Testing Accuracy:0.9661,Training Accuracy0.985745\nIter4,Testing Accuracy:0.9674,Training Accuracy0.987964",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50a78d2d56ce90e303aa9f5af91ccf85b43f64b
| 2,097 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
dsi202/week11/Basic OOP.ipynb
|
wasit7/2019
|
ebe9ef4475e4534700ad5b6bf387b04cd88ad197
|
[
"BSD-2-Clause"
] | 2 |
2019-09-04T08:13:47.000Z
|
2019-09-19T07:12:18.000Z
|
dsi202/week11/Basic OOP.ipynb
|
wasit7/2019
|
ebe9ef4475e4534700ad5b6bf387b04cd88ad197
|
[
"BSD-2-Clause"
] | 9 |
2020-03-24T17:48:28.000Z
|
2022-03-12T00:02:56.000Z
|
dsi202/week11/Basic OOP.ipynb
|
wasit7/2019
|
ebe9ef4475e4534700ad5b6bf387b04cd88ad197
|
[
"BSD-2-Clause"
] | 9 |
2019-08-30T04:00:58.000Z
|
2019-11-19T04:48:07.000Z
| 23.3 | 101 | 0.468288 |
[
[
[
"class Rectangle(object): #class #instance\n def __init__(self,w=0,h=0):\n self.width=w\n self.height=h\n \n def area(self):\n return self.width*self.height\n \n def __str__(self):\n return \"[Rectangle] w: %s, h:%s, area:%.2f\"%(self.width, self.height, self.area())\n \nclass Triangle(Rectangle):\n def area(self):\n return 0.5/self.width*self.height\n \n def __str__(self):\n return \"[Triagle] w: %s, h:%s, area:%.2f\"%(self.width, self.height, self.area())\n \nclass Square(Rectangle):\n def __init__(self,w=0):\n self.width=w\n self.height=w\n \n def __str__(self):\n return \"[Square] w: %s, h:%s, area:%.2f\"%(self.width, self.height, self.area())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x = Rectangle(5,7)\ny = Triangle(3,2)\nz = Square(3)\nprint(x)\nprint(y)\nprint(z)",
"[Rectangle] w: 5, h:7, area:35.00\n[Triagle] w: 3, h:2, area:0.33\n[Square] w: 3, h:3, area:9.00\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50a8df917b26c324b08dac261ea6f3d3fd2e501
| 92,680 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/.ipynb_checkpoints/Filter_implementation-checkpoint.ipynb
|
pzinemanas/AudioMoth-Firmware-SPL
|
cbcf849e866286fe292b6647e6a3a5fe36827b38
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2022-01-12T15:00:28.000Z
|
2022-01-12T15:00:28.000Z
|
notebooks/.ipynb_checkpoints/Filter_implementation-checkpoint.ipynb
|
pzinemanas/AudioMoth-Firmware-SPL
|
cbcf849e866286fe292b6647e6a3a5fe36827b38
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2020-10-29T10:05:08.000Z
|
2020-10-30T08:05:24.000Z
|
notebooks/.ipynb_checkpoints/Filter_implementation-checkpoint.ipynb
|
pzinemanas/AudioMoth-Firmware-SPL
|
cbcf849e866286fe292b6647e6a3a5fe36827b38
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 272.588235 | 47,120 | 0.920501 |
[
[
[
"# A-weightening filter implementation",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The A-weighting transfer function is defined in the ANSI Standards S1.4-1983 and S1.42-2001:\n\n$$\nH(s) = \\frac{\\omega_4^2 s^4}{(s-\\omega_1)^2(s-\\omega_2)(s-\\omega_3)(s-\\omega_4)^2}\n$$\n\nWhere $\\omega_i = 2\\pi f_i$ are the angular frequencies defined by:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\n\nf1 = 20.598997 # Hz\nf4 = 12194.217 # Hz\nf2 = 107.65265 # Hz\nf3 = 737.86223 # Hz\n\nw1 = 2*np.pi*f1 # rad/s\nw2 = 2*np.pi*f2 # rad/s\nw3 = 2*np.pi*f3 # rad/s\nw4 = 2*np.pi*f4 # rad/s",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"In [1] ther is a method to convert this function transform to a discrete time-domain using the bilinear transform. We use a similar method, but we separate it into four filters of order one or two, in order to keep the filter stable:\n\n$$\nH(s) = \\omega_4^2 H_1(s) H_2(s) H_3(s) H_4(s),\n$$\nwhere:\n\n$$\nH_i(s) = \\left\\{ \\begin{array}{lcc}\n \\frac{s}{(s-\\omega_i)^2} & \\text{for} & i=1,4 \\\\\n \\\\ \\frac{s}{(s-\\omega_i)} & \\text{for} & i = 2,3. \\\\\n \\end{array}\n \\right.\n$$\n\nNow, we conver the $H_i(s)$ filters to their discrete-time implementation by using the bilinear transform:\n\n$$\ns \\rightarrow 2f_s\\frac{1+z^{-1}}{1-z^{-1}}.\n$$\n\nTherefore:\n\n$$\nH_i(z) = \\frac{2f_s(1-z^{-2})}{(\\omega_i-2f_s)^2z^{-2}+2(\\omega_i^2-4f_s^2)z^{-1}+(\\omega_i+2f_s)^2} \\text{ for } i = 1,4\n$$\n\n$$\nH_i(z) = \\frac{2f_s(1-z^{-1})}{(\\omega_i-2f_s)z^{-1}+(\\omega_i+2f_s)} \\text{ for } i = 2,3\n$$\n\nWe define two python functions to calculates coefficients of both types of function transforms:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def filter_first_order(w,fs): #s/(s+w)\n a0 = w + 2.0*fs \n b = 2*fs*np.array([1, -1])/a0\n a = np.array([a0, w - 2*fs])/a0\n return b,a\n\ndef filter_second_order(w,fs): #s/(s+w)^2\n a0 = (w + 2.0*fs)**2 \n b = 2*fs*np.array([1,0,-1])/a0\n a = np.array([a0,2*(w**2-4*fs**2),(w-2*fs)**2])/a0\n return b,a",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now, we calculate b and a coefficients of the four filters for some sampling rate:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"fs = 48000 #Hz\n\nb1,a1 = filter_second_order(w1,fs)\nb2,a2 = filter_first_order(w2,fs)\nb3,a3 = filter_first_order(w3,fs)\nb4,a4 = filter_second_order(w4,fs)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Then, we calculate the impulse response of the overall filter, $h[n]$, by concatenating the four filters and using the impulse signal, $\\delta[n]$, as input. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from scipy import signal\n\n# generate delta[n]\nN = 8192*2 #number of points\ndelta = np.zeros(N)\ndelta[0] = 1\n\n# apply filters\nx1 = signal.lfilter(b1,a1,delta)\nx2 = signal.lfilter(b2,a2,x1)\nx3 = signal.lfilter(b3,a3,x2)\nh = signal.lfilter(b4,a4,x3)\n\nGA = 10**(2/20.) # 0dB at 1Khz\nh = h*GA*w4**2 ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Lets find the filter's frequency response, $H(e^{j\\omega})$, by calcuating the FFT of $h[n]$.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"H = np.abs(np.fft.fft(h))[:N/2]\nH = 20*np.log10(H)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Compare the frequency response to the expresion defined in the norms:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"eps = 10**-6\nf = np.linspace(0,fs/2-fs/float(N),N/2)\ncurveA = f4**2*f**4/((f**2+f1**2)*np.sqrt((f**2+f2**2)*(f**2+f3**2))*(f**2+f4**2))\nHA = 20*np.log10(curveA+eps)+2.0",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\nfig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))\nplt.title('Digital filter frequency response')\nplt.plot(f,H, 'b',label= 'Devised filter')\nplt.plot(f,HA, 'r',label= 'Norm filter')\nplt.ylabel('Amplitude [dB]')\nplt.xlabel('Frequency [Hz]')\nplt.legend()\nplt.xscale('log')\nplt.xlim([10,fs/2.0])\nplt.ylim([-80,3])\nplt.grid()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now we also can check if the filter designed fullfill the tolerances given in the ANSI norm [2].",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import csv\n\nfreqs = []\ntol_type0_low = []\ntol_type0_high = []\ntol_type1_low = []\ntol_type1_high = []\nwith open('ANSI_tolerances.csv') as csv_file:\n csv_reader = csv.reader(csv_file, delimiter=',')\n line_count = 0\n for row in csv_reader:\n if line_count == 0:\n #print('Column names are {\", \".join(row)}')\n line_count += 1\n else:\n freqs.append(float(row[0]))\n Aw = float(row[1])\n tol_type0_low.append(Aw + float(row[2]))\n tol_type0_high.append(Aw + float(row[3]))\n tol_type1_low.append(Aw + float(row[4]))\n if row[5] != '':\n tol_type1_high.append(Aw + float(row[5])) \n else:\n tol_type1_high.append(np.Inf) \n line_count += 1\n print('Processed %d lines.'%line_count)",
"Processed 35 lines.\n"
],
[
"fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))\nplt.title('Digital filter frequency response')\nplt.plot(f,H, 'b',label= 'Devised filter')\nplt.plot(f,HA, 'r',label= 'Norm filter')\nplt.plot(freqs,tol_type0_low,'k.',label='type0 tolerances')\nplt.plot(freqs,tol_type0_high,'k.')\nplt.plot(freqs,tol_type1_low,'r.',label='type1 tolerances')\nplt.plot(freqs,tol_type1_high,'r.')\nplt.ylabel('Amplitude [dB]')\nplt.xlabel('Frequency [Hz]')\nplt.legend()\nplt.xscale('log')\nplt.xlim([10,fs/2.0])\nplt.ylim([-80,3])\nplt.grid()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## References\n[1] Rimell, Andrew; Mansfield, Neil; Paddan, Gurmail (2015). \"Design of digital filters for frequency weightings (A and C) required for risk assessments of workers exposed to noise\". Industrial Health (53): 21–27.\n\n[2] ANSI S1.4-1983. Specifications for Sound Level Meters.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
c50a9b1c28573e42e2fd795728227b6e3de378af
| 17,023 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
report/Paper_Template.ipynb
|
CSCI4850/S20-team1-project
|
3d5a2de9f2d5e42c859a76f25c63d8292b5bc1e6
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2020-03-31T20:42:00.000Z
|
2020-05-31T19:50:03.000Z
|
report/Paper_Template.ipynb
|
CSCI4850/S20-team1-project
|
3d5a2de9f2d5e42c859a76f25c63d8292b5bc1e6
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
report/Paper_Template.ipynb
|
CSCI4850/S20-team1-project
|
3d5a2de9f2d5e42c859a76f25c63d8292b5bc1e6
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2020-04-01T00:11:10.000Z
|
2020-10-01T23:29:18.000Z
| 68.092 | 1,197 | 0.708042 |
[
[
[
"% PACKAGES INCLUDED HERE \n% DO NOT NEED TO CHANGE\n\\documentclass[conference]{IEEEtran}\n%\\IEEEoverridecommandlockouts\n% The preceding line is only needed to identify funding in the first footnote. If that is unneeded, please comment it out.\n\\usepackage{cite}\n\\usepackage{amsmath,amssymb,amsfonts}\n\\usepackage{algorithmic}\n\\usepackage{graphicx}\n\\usepackage{textcomp}\n\\def\\BibTeX{{\\rm B\\kern-.05em{\\sc i\\kern-.025em b}\\kern-.08em\n T\\kern-.1667em\\lower.7ex\\hbox{E}\\kern-.125emX}}\n\\begin{document}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"% TITLE GOES HERE\n\n\\title{Convolutional Neural Network for Detecting Vehicles in a Parking Lot\\\\}\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\\author{\\IEEEauthorblockN{Girgis Shihataa}\n\\IEEEauthorblockA{\\textit{Department of Computer Science} \\\\\n\\textit{Middle Tennessee State University}\\\\\nMurfreesboro, United States of America \\\\\[email protected]}\n\\and\n\\IEEEauthorblockN{William Smith}\n\\IEEEauthorblockA{\\textit{Department of Computer Science} \\\\\n\\textit{Middle Tennessee State University}\\\\\nMurfreesboro United States of America \\\\\[email protected]}\n\\and\n\\IEEEauthorblockN{Michael Ketzner}\n\\IEEEauthorblockA{\\textit{Department of Computer Science} \\\\\n\\textit{Middle Tennessee State University}\\\\\nMurfreesboro, United States of America \\\\\[email protected]}\n\\and\n\\IEEEauthorblockN{Justin Hill}\n\\IEEEauthorblockA{\\textit{Department of Computer Science} \\\\\n\\textit{Middle Tennessee State University}\\\\\nMurfreesboro, United States of America \\\\\[email protected]}\n\\and\n\\IEEEauthorblockN{Mubarek Mohammed}\n\\IEEEauthorblockA{\\textit{Department of Computer Science} \\\\\n\\textit{Middle Tennessee State University}\\\\\nMurfreesboro, United States of America \\\\\[email protected]}\n\\and\n\\IEEEauthorblockN{Carolous Ghobrial}\n\\IEEEauthorblockA{\\textit{Department of Computer Science} \\\\\n\\textit{Middle Tennessee State University}\\\\\nMurfreesboro, United States of America \\\\\[email protected]}\n}\n\n\\maketitle",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"% ABSTRACT \n\n\\begin{abstract}\nMonitoring the number of open parking spaces with a camera is useful because it allows people to save time when commuting. We trained a CNN on the CNRPark-Patches data-set which contains 12,584 images of busy/free parking spaces. The accuracy of our model was .9753. Compared to other network architectures, a CNN was the best choice for this project. \n\\end{abstract}\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"% KEYWORDS\n\n\\begin{IEEEkeywords}\nMTSU, Keras, RGB, convolutional, YOLO-V3, Faster R-CNN, CNN, neural network, ReLU, LeNet\n\\end{IEEEkeywords}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"% INTRODUCTION SECTION\n\\section{Introduction and Background}\n\n\\subsection{Introduction}\nIf you are a student at MTSU, Middle Tennessee State University, and you commute, you know the struggles of finding a parking space near your class during the day. MTSU currently has a problem with parking lots for all the students who commute to campus. The number of students commuting to MTSU continues to increase every year and the problem has only increased. This always results in a large number of students funneling into and circling around parking lots at very desired locations on a daily basis. The parking lots can be completely full, but students will continue to drive around hoping they come across an empty spot. Our goal for this project was to build and train a neural network that can help provide a solution for this problem. \n\nThroughout the length of this project, we went through multiple ideas, or iterations, of the neural network. At first, we quickly recognized that for this project, we need to build and train a CNN, convolutional neural network. The main advantage for building a CNN is that it automatically detects important features without any supervision, thus allowing for more complex networks \\cite{b1}. There are many versions of convolutional networks that we researched, but eventually, we ended up with three main prospects: a basic CNN, a Faster R-CNN,or a YOLO-V3. \n\nThrough the basic CNN and the Faster R-CNN, we can achieve our neural network goal by having the neural network look at one vehicle at a time. This means that the network is binary and has the ability to observe if a vehicle is in the image or not \\cite{b1}. This opens up an avenue of methods that we can achieve our goal by. Mainly, the neural network can observe vehicles going and going out of the parking lot, or it can observe the parking lot spaces separately. The former being more efficient in hardware required, and the latter being more accurate.\n\nFor the final prospect, the YOLO-V3 neural network has the ability to detect multiple vehicles in a singular picture \\cite{b1}. This network allows us to have the most efficient setup for hardware, a singular camera on top of a post in any of the parking lots. The camera will take an aerial view picture of an entire lot, and the neural network will process the image by observing how many vehicles are in the parking lot. For obvious reasons, this has the least amount of accuracy, and thus will result in far more errors for our ideal goal.\n\n% BACKGROUND SECTION\n\\subsection{Background}\n\nParking at MTSU for students has been a rising issue in the recent years and it seems as if there will not be any solutions offered by the school in the near future. This neural network was built and trained in light of this problem as to provide a possible solution. Our plan for this project was to build a neural network that can detect vehicles in a parking lot. For the near future, we hoped that we could get in contact with MTSU's mobile development team in hopes of implementing this network into MTSU's mobile application which will receive input from the neural network as to which parking lots are open and which are full. As of now and the current quarantine situation, this is not possible.\n\nThis project can help better the lives of students commuting at MTSU, and potentially even other universities by lessening the time it takes to find a parking spot. From personal experience amongst our group, we had an average of 15 minutes to find a parking spot, and almost 90 percent of the time, it was no where near our destination building. By reducing the time it takes to find a parking spot and potentially even, at a closer lot to the destination building, this will free any and all future students from the stresses of searching for a parking space and improve the time it takes for them to commute. By reducing commute time, less students will be late because of the traffic in parking lots.\n\nAfter many deliberations, we finally decided on going through with a basic CNN for three important reasons. \n\\begin{itemize}\n \\item Simpler implementation \n \\item Less training time/epochs compared to other networks\n \\item Accuracy is within acceptable range\n\\end{itemize}\nAs listed above, the basic CNN does everything the other networks do, as good as, if not better. It is also much easier to implement than the other aforementioned networks. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"% METHODS SECTION\n\\section{Methods}\n\n\\subsection{Data}\n\nWe decided to use the CNRPark-Patches data-set. It contains a total of 12,584 images. The images were collected at varying weather conditions and light conditions \\cite{b3}. The images are taken at different perspectives and angles which helps the network generalize. Cameras will not always be mounted in the same way. The addition of noise to the images helps improve/prepare the network for noisy pictures \\cite{b2}.\n\n10\\% of the images were reserved for testing. The other 90\\% were split 80/20 for testing and validation.\n\n\n\\subsection{Input Processing}\nWe downsized the images to an input shape of 150X150 before feeding the images to the network. The image set has been divided into two batches, training and testing image data set. The training data set consists 11326 images. The testing data set consists 1258 images. We normalized the image from a scale of 0.0 to 255.0 to 0.0 to 1.0 float32 value. The normalization makes of the image data reduces the memory utilized \\cite{b4}. We utilized Keras image preprocessing tools to perform slight transformations on the image that helps in the creation of a stronger and more robust model. We performed preprocessing techniques including rotation of up to 90\\%, re-scaling factor to reduce the RGB value to range between 0.0 to 1.0 (Fig 1).\n\n\\begin{figure}[htbp]\n\\centerline{\\includegraphics[width=\\linewidth]{./random_car_transform.jpg}}\n\\caption{Pre-processed image of a car.}\n\\label{fig}\n\\end{figure}\n\n\\subsection{Convolution Neural Networks}\nFor our neural network architecture, we built a Convolution Neural Network which have been known for providing a higher accuracy of object/image recognition compared to other neural network architectures \\cite{b4}. We built our network based on further research on well known CNN architectures and a starter tutorial provided by Francois Chollet \\cite{b2}. In comparison, our architectures is built to fit a smaller scale visual recognition where the solution is binary choice between parking space being empty or full. \n\nOur architecture accepts an input image shape of 150X150 with a number of channels equal to 3. Our architecture consists of three convolution layers that are essential to extract the visual features of the image. The filters selected for the first and second convolution layers is equal to 32. We increased the filters in the third convolution layer to 64 in order to grab the image features and patterns like corners and edges \\cite{b5}. We decided upon a kernel size of 3X3 in our layers which\naligns with the objective of capturing the images features.The convolution layers are followed by rectified linear unit activation function (ReLU) and max pooling layers with a pool size of 2X2. We flattened the 3D feature maps to 1D feature vectors. We pass the flatten layer to a dense layer consisting of 64 neurons followed by rectified linear unit activation function (ReLU). We chose a larger number of neuron size to improve the CNN architectures robustness and the ability to extract patterns. The dense layer is followed by another rectified linear unit activation function (ReLU). With the target of reducing over-fitting of the training data-set, we introduced the dropout layer that turns off 50 percent of the neurons randomly during training process. The final dense layer consists of a single neuron which is the representation of the solution of our network. A single neuron represents the fact of the outcome of the network as a 0 or 1 where 0 signals an image of a busy parking space while 1 represents an image of a free parking space. The model is compiled with binary crossentropy loss function which lines with the binary classification problem of our architecture. \nFigure 2 displays the detailed structure of our CNN.\n\n\\begin{figure}[htbp]\n\\centerline{\\includegraphics[scale=1]{./model_plt.png}}\n\\caption{Detailed structure of the CNN.}\n\\label{fig}\n\\end{figure}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"% RESULTS SECTION\n\\section{Results}\n\nWe trained the model using twenty epochs, one-tenth of the training images for steps per epoch during training, and one-tenth of the validation images for steps per epoch during testing. Using this setup, the accuracy and loss were brought into acceptable ranges. The network brought a final validation accuracy of .9895 and a validation loss of .0556. The test accuracy was 0.9753 and the test loss was 2.667. This means after 20 epochs, our network was capable of identifying 98\\% of the images correctly as busy or free (car or no car present in the parking spot.)\n\nInterestingly, the number of epochs could have been decreased greatly and gotten a similar result on accuracy. As can be seen in Figure 3, the accuracy of the network maxes out at 98\\% around epoch 6 or 7. After that point, the network pretty much flat lines (there are some minor deviations). Loss is a bit of a different story. After about ten epochs, the loss drops below .1. However, while the loss has reached an acceptable value, it is still decreasing as time goes on. Also, the loss does increase from about 12 to 15, and then decreases again from then on. \n\nBased on the distribution of busy and free parking lots, the network model tended to perform better for busier parking lots (Fig. 4). For the busy parking lots, the neural network performed at ~98\\% accuracy, while only ~72\\% for the free parking lots.\n\n\\begin{figure}[htbp]\n\\centerline{\\includegraphics[scale=0.8]{./Capture.PNG}}\n\\caption{Model accuracy and loss}\n\\label{fig}\n\\end{figure}\n\n\\begin{figure}[htbp]\n\\centerline{\\includegraphics[scale=0.7]{./12.PNG}}\n\\caption{Busy vs Free lots}\n\\label{fig}\n\\end{figure}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"% DISCUSSION SECTION\n\\section{Discussion}\n\nEven though the network preforms better on busy spaces, it shouldn't affect our end goal too much. The neural network will be in use for busy parking lots during the day and it's better to error on the side of busy than free.\n\nThere were many versions of this network and many implementations, but overall, the version of a simple CNN worked the best. It gave us the best accuracy with the best potential efficiency. After the completion of the network, we were surprised to see how accurate the network was. This is one step forward to helping all students who commute, not just students at MTSU.\n\nAfter researching many implementations, our final solution for the neural net was a simple CNN. While the YOLO-V3 and the Faster R-CNN do provide good results, they are more complex and require more time to train. In comparison, the simple CNN accomplishes the goals of our project, and at very little cost compared to other network architectures.\n\nFuture work could involve utilizing real-time cameras with a resolution degree of higher magnitude which improves the image quality that is going be feed into the CNN. In order to implement the network to solve the growing parking lot congestion issue, a more robust method needs to be devised that incorporates the accuracy of the R-CNN and faster recognition property of YOLO-V3.\n\nFurther effort could be put in designing a User Interface that displays the number of spaces available based on a real-time data processed and updated. The User Interface could be included in the already functioning MTSU's mobile app.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"% REFERENCES\n% THIS IS CREATED AUTOMATICALLY\n\\bibliographystyle{IEEEtran}\n\\bibliography{References} % change if another name is used for References file",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\\end{document}",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"raw"
] |
[
[
"raw",
"raw",
"raw",
"raw",
"raw",
"raw",
"raw",
"raw",
"raw",
"raw",
"raw"
]
] |
c50a9d86cc7aa71c68528925ce81fe1a9db52799
| 879 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
cclhm0069/mod4a/sem13.ipynb
|
ericbrasiln/intro-historia-digital
|
5733dc55396beffeb916693c552fd4eb987472d0
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
cclhm0069/mod4a/sem13.ipynb
|
ericbrasiln/intro-historia-digital
|
5733dc55396beffeb916693c552fd4eb987472d0
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
cclhm0069/mod4a/sem13.ipynb
|
ericbrasiln/intro-historia-digital
|
5733dc55396beffeb916693c552fd4eb987472d0
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 19.533333 | 77 | 0.542662 |
[
[
[
"# Semana 13\n\n## Módulo 4a: Ferramentas digitais e o ensino de história\n\n**Período**: 24/01/2022 a 28/01/2022\n\n**CH**: 2h",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Atividade Assíncrona 7 (AA)\n\nTutorial 03: **Construindo apresentações interativas com Reveal.js**\n\n> EM BREVE O TUTORIAL ESTARÁ DISPONÍVEL AQUI",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
c50aa2242adc28ac58842cd47660c16016bdb253
| 287,778 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
seminar10-captioning/captioning_torch.ipynb
|
VendettaPrime/Practical_DL
|
d673eda35dfb645011745cc2d71f5c4450a573ff
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
seminar10-captioning/captioning_torch.ipynb
|
VendettaPrime/Practical_DL
|
d673eda35dfb645011745cc2d71f5c4450a573ff
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
seminar10-captioning/captioning_torch.ipynb
|
VendettaPrime/Practical_DL
|
d673eda35dfb645011745cc2d71f5c4450a573ff
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 317.285557 | 137,750 | 0.914465 |
[
[
[
"<h1 align=\"center\"> Image Captioning </h1>\n\nIn this notebook you will teach a network to do image captioning\n\n_image [source](https://towardsdatascience.com/image-captioning-in-deep-learning-9cd23fb4d8d2)_\n\n\n\n#### Alright, here's our plan:\n1. Take a pre-trained inception v3 to vectorize images\n2. Stack an LSTM on top of it\n3. Train the thing on [MSCOCO](http://cocodataset.org/#download)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Please eithrer download data from https://yadi.sk/d/b4nAwIE73TVcp5 or generate it manually with preprocess_data.\n!wget https://www.dropbox.com/s/zl9wy31p6r05j34/handout.tar.gz -O handout.tar.gz\n!tar xzf handout.tar.gz",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Data preprocessing",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%time\n# Read Dataset\nimport numpy as np\nimport json\n\nimg_codes = np.load(\"data/image_codes.npy\")\ncaptions = json.load(open('data/captions_tokenized.json'))",
"CPU times: user 404 ms, sys: 1.97 s, total: 2.38 s\nWall time: 859 ms\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Data structure\n\nTo save your time, we've already vectorized all MSCOCO17 images with a pre-trained inception_v3 network from [torchvision](https://github.com/pytorch/vision/blob/master/torchvision/models/inception.py).\n\nThe whole process takes anywhere between a day on CPU and 10min on 3x tesla m40. If you want to play with that yourself, [you're welcome](https://gist.github.com/justheuristic/11fd01f9c12c0bf960499580d104130b).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(\"Each image code is a 2048-unit vector [ shape: %s ]\" % str(img_codes.shape))\nprint(img_codes[0,:10], end='\\n\\n')\nprint(\"For each image there are 5 reference captions, e.g.:\\n\")\nprint('\\n'.join(captions[0]))",
"Each image code is a 2048-unit vector [ shape: (118287, 2048) ]\n[ 0.3659946 0.20165551 0.92457253 0.57063824 0.54726797 0.82758683\n 0.36872771 0.12085301 0.0561931 0.49758485]\n\nFor each image there are 5 reference captions, e.g.:\n\npeople shopping in an open market for vegetables .\nan open market full of people and piles of vegetables .\npeople are shopping at an open air produce market .\nlarge piles of carrots and potatoes at a crowded outdoor market .\npeople shop for vegetables like carrots and potatoes at an open air market .\n"
]
],
[
[
"As you can see, all captions are already tokenized and lowercased. We now want to split them and add some special tokens for start/end of caption.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#split descriptions into tokens\nfor img_i in range(len(captions)):\n for caption_i in range(len(captions[img_i])):\n sentence = captions[img_i][caption_i] \n captions[img_i][caption_i] = [\"#START#\"]+sentence.split(' ')+[\"#END#\"]\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You don't want your network to predict a million-size vector of probabilities at each step, so we're gotta make some cuts. \n\nWe want you to __count the occurences of each word__ so that we can decide which words to keep in our vocabulary.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Build a Vocabulary\nfrom collections import Counter\nword_counts = Counter()\n\n#Compute word frequencies for each word in captions. See code above for data structure\n<YOUR CODE HERE>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"vocab = ['#UNK#', '#START#', '#END#', '#PAD#']\nvocab += [k for k, v in word_counts.items() if v >= 5 if k not in vocab]\nn_tokens = len(vocab)\n\nassert 10000 <= n_tokens <= 10500\n\nword_to_index = {w: i for i, w in enumerate(vocab)}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"eos_ix = word_to_index['#END#']\nunk_ix = word_to_index['#UNK#']\npad_ix = word_to_index['#PAD#']\n\ndef as_matrix(sequences, max_len=None):\n \"\"\" Convert a list of tokens into a matrix with padding \"\"\"\n max_len = max_len or max(map(len,sequences))\n \n matrix = np.zeros((len(sequences), max_len), dtype='int32') + pad_ix\n for i,seq in enumerate(sequences):\n row_ix = [word_to_index.get(word, unk_ix) for word in seq[:max_len]]\n matrix[i, :len(row_ix)] = row_ix\n \n return matrix",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#try it out on several descriptions of a random image\nas_matrix(captions[1337])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Building our neural network\n\nAs we mentioned earlier, we shall build an rnn \"language-model\" conditioned on vectors from the convolutional part. \n\n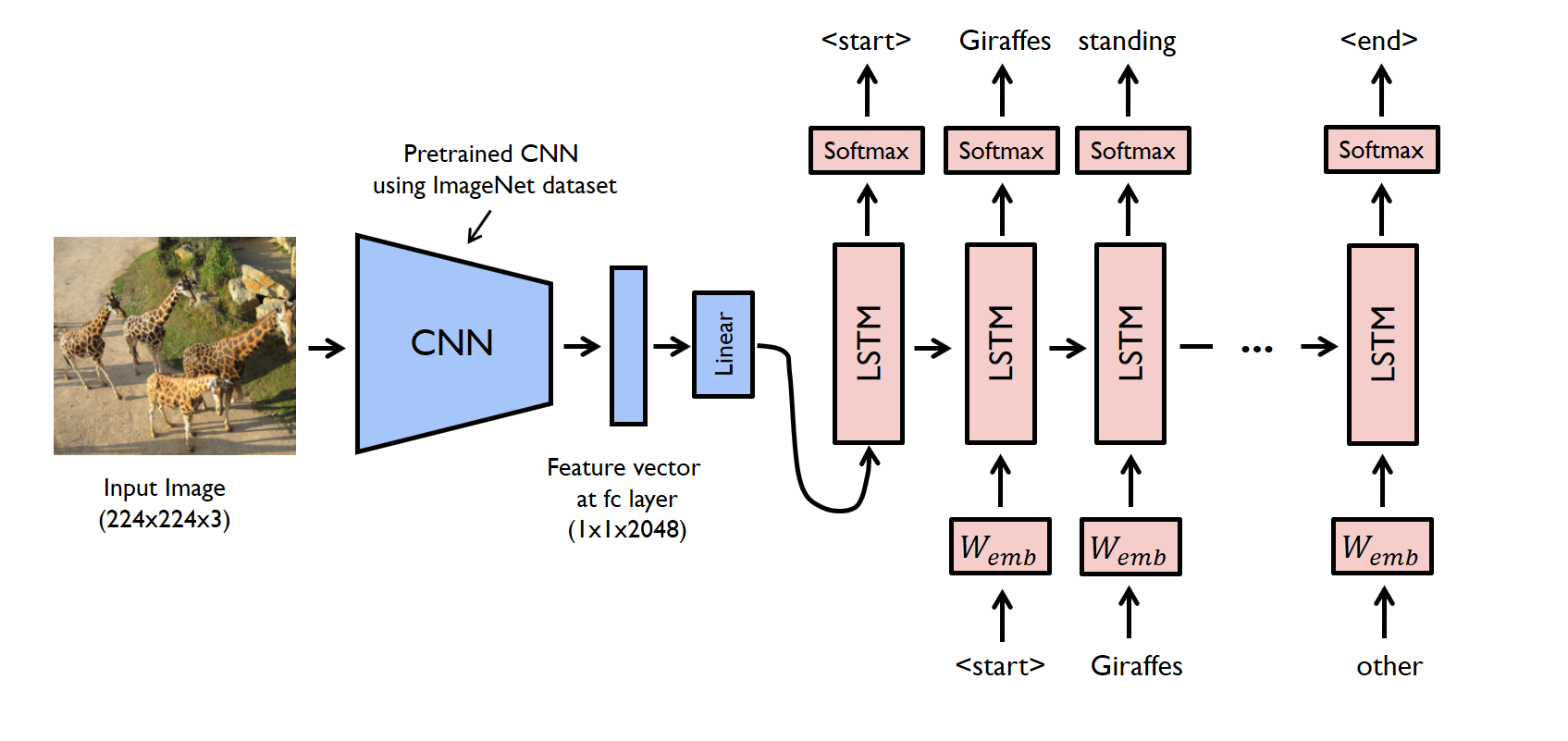\n_image: http://bit.ly/2FKnqHm_\n\n\nWe'll unbox the inception net later to save memory, for now just pretend that it's available.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import torch, torch.nn as nn\nimport torch.nn.functional as F",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class CaptionNet(nn.Module):\n def __init__(self, n_tokens=n_tokens, emb_size=128, lstm_units=256, cnn_feature_size=2048):\n \"\"\" A recurrent 'head' network for image captioning. See scheme above. \"\"\"\n super(self.__class__, self).__init__()\n \n # a layer that converts conv features to \n self.cnn_to_h0 = nn.Linear(cnn_feature_size, lstm_units)\n self.cnn_to_c0 = nn.Linear(cnn_feature_size, lstm_units)\n \n # recurrent part, please create the layers as per scheme above.\n\n # create embedding for input words. Use the parameters (e.g. emb_size).\n self.emb = <YOUR CODE> \n \n # lstm: create a recurrent core of your network. Use either LSTMCell or just LSTM. \n # In the latter case (nn.LSTM), make sure batch_first=True\n self.lstm = <YOUR CODE>\n \n # create logits: linear layer that takes lstm hidden state as input and computes one number per token\n self.logits = <YOUR CODE> \n \n def forward(self, image_vectors, captions_ix):\n \"\"\" \n Apply the network in training mode. \n :param image_vectors: torch tensor containing inception vectors. shape: [batch, cnn_feature_size]\n :param captions_ix: torch tensor containing captions as matrix. shape: [batch, word_i]. \n padded with pad_ix\n :returns: logits for next token at each tick, shape: [batch, word_i, n_tokens]\n \"\"\"\n initial_cell = self.cnn_to_c0(image_vectors)\n initial_hid = self.cnn_to_h0(image_vectors)\n \n # compute embeddings for captions_ix\n captions_emb = <YOUR CODE>\n \n # apply recurrent layer to captions_emb. \n # 1. initialize lstm state with initial_* from above\n # 2. feed it with captions. Mind the dimension order in docstring\n # 3. compute logits for next token probabilities\n # Note: if you used nn.LSTM, you can just give it (initial_cell[None], initial_hid[None]) as second arg\n\n # lstm_out should be lstm hidden state sequence of shape [batch, caption_length, lstm_units]\n lstm_out = <YOUR_CODE>\n \n # compute logits from lstm_out\n logits = <YOUR_CODE>\n \n return logits ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"network = CaptionNet(n_tokens)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dummy_img_vec = torch.randn(len(captions[0]), 2048)\ndummy_capt_ix = torch.tensor(as_matrix(captions[0]), dtype=torch.int64)\n\ndummy_logits = network.forward(dummy_img_vec, dummy_capt_ix)\n\nprint('shape:', dummy_logits.shape)\nassert dummy_logits.shape == (dummy_capt_ix.shape[0], dummy_capt_ix.shape[1], n_tokens)",
"shape: torch.Size([5, 16, 10403])\n"
],
[
"def compute_loss(network, image_vectors, captions_ix):\n \"\"\"\n :param image_vectors: torch tensor containing inception vectors. shape: [batch, cnn_feature_size]\n :param captions_ix: torch tensor containing captions as matrix. shape: [batch, word_i]. \n padded with pad_ix\n :returns: crossentropy (neg llh) loss for next captions_ix given previous ones. Scalar float tensor\n \"\"\"\n \n # captions for input - all except last cuz we don't know next token for last one.\n captions_ix_inp = captions_ix[:, :-1].contiguous()\n captions_ix_next = captions_ix[:, 1:].contiguous()\n \n # apply the network, get predictions for captions_ix_next\n logits_for_next = network.forward(image_vectors, captions_ix_inp)\n \n \n # compute the loss function between logits_for_next and captions_ix_next\n # Use the mask, Luke: make sure that predicting next tokens after EOS do not contribute to loss\n # you can do that either by multiplying elementwise loss by (captions_ix_next != pad_ix)\n # or by using ignore_index in some losses.\n \n loss = <YOUR CODE>\n \n return loss",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dummy_loss = compute_loss(network, dummy_img_vec, dummy_capt_ix)\n\nassert len(dummy_loss.shape) <= 1, 'loss must be scalar'\nassert dummy_loss.data.numpy() > 0, \"did you forget the 'negative' part of negative log-likelihood\"\n\ndummy_loss.backward()\n\nassert all(param.grad is not None for param in network.parameters()), \\\n 'loss should depend differentiably on all neural network weights'",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Create ~~adam~~ your favorite optimizer for the network.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<YOUR CODE>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Training\n\n* First implement the batch generator\n* Than train the network as usual",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\ncaptions = np.array(captions)\ntrain_img_codes, val_img_codes, train_captions, val_captions = train_test_split(img_codes, captions,\n test_size=0.1,\n random_state=42)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from random import choice\n\ndef generate_batch(img_codes, captions, batch_size, max_caption_len=None):\n \n #sample random numbers for image/caption indicies\n random_image_ix = np.random.randint(0, len(img_codes), size=batch_size)\n \n #get images\n batch_images = img_codes[random_image_ix]\n \n #5-7 captions for each image\n captions_for_batch_images = captions[random_image_ix]\n \n #pick one from a set of captions for each image\n batch_captions = list(map(choice,captions_for_batch_images))\n \n #convert to matrix\n batch_captions_ix = as_matrix(batch_captions,max_len=max_caption_len)\n \n return torch.tensor(batch_images, dtype=torch.float32), torch.tensor(batch_captions_ix, dtype=torch.int64)\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"generate_batch(img_codes,captions,3)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Main loop\n\nTrain on minibatches just as usual. Evaluate on val from time to time.\n\n##### TIps\n* If training loss has become close to 0 or model produces garbage,\n double-check that you're predicting __next__ words, not current or t+2'th words.\n* If the model generates fluent captions that have nothing to do with the images\n * this may be due to recurrent net not receiving image vectors.\n * alternatively it may be caused by gradient explosion, try clipping 'em or just restarting the training\n * finally, you may just need to train the model a bit more\n\n\n* Crossentropy is a poor measure of overfitting\n * Model can overfit validation crossentropy but keep improving validation quality.\n * Use human _(manual)_ evaluation or try automated metrics: [cider](https://github.com/vrama91/cider) or [bleu](https://www.nltk.org/_modules/nltk/translate/bleu_score.html)\n \n\n* We recommend you to periodically evaluate the network using the next \"apply trained model\" block\n * its safe to interrupt training, run a few examples and start training again\n \n* The typical loss values should be around 3~5 if you average over time, scale by length if you sum over time. The reasonable captions began appearing at loss=2.8 ~ 3.0\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"batch_size = 50 # adjust me\nn_epochs = 100 # adjust me\nn_batches_per_epoch = 50 # adjust me\nn_validation_batches = 5 # how many batches are used for validation after each epoch",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from tqdm import tqdm\n\nfor epoch in range(n_epochs):\n \n train_loss=0\n network.train(True)\n for _ in tqdm(range(n_batches_per_epoch)):\n \n loss_t = compute_loss(network, *generate_batch(train_img_codes, train_captions, batch_size))\n \n \n # clear old gradients; do a backward pass to get new gradients; then train with opt\n <YOUR CODE>\n \n train_loss += loss_t.detach().numpy()\n \n train_loss /= n_batches_per_epoch\n \n val_loss=0\n network.train(False)\n for _ in range(n_validation_batches):\n loss_t = compute_loss(network, *generate_batch(val_img_codes, val_captions, batch_size))\n val_loss += loss_t.detach().numpy()\n val_loss /= n_validation_batches\n \n print('\\nEpoch: {}, train loss: {}, val loss: {}'.format(epoch, train_loss, val_loss))\n\nprint(\"Finished!\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Apply trained model\n\nLet's unpack our pre-trained inception network and see what our model is capable of.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from beheaded_inception3 import beheaded_inception_v3\ninception = beheaded_inception_v3().train(False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Generate caption\n\nThe function below creates captions by sampling from probabilities defined by the net.\n\nThe implementation used here is simple but inefficient (quadratic in lstm steps). We keep it that way since it isn't a performance bottleneck.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def generate_caption(image, caption_prefix = (\"#START#\",), \n t=1, sample=True, max_len=100):\n \n assert isinstance(image, np.ndarray) and np.max(image) <= 1\\\n and np.min(image) >=0 and image.shape[-1] == 3\n \n image = torch.tensor(image.transpose([2, 0, 1]), dtype=torch.float32)\n \n vectors_8x8, vectors_neck, logits = inception(image[None])\n caption_prefix = list(caption_prefix)\n \n for _ in range(max_len):\n \n prefix_ix = as_matrix([caption_prefix])\n prefix_ix = torch.tensor(prefix_ix, dtype=torch.int64)\n next_word_logits = network.forward(vectors_neck, prefix_ix)[0, -1]\n next_word_probs = F.softmax(next_word_logits, -1).detach().numpy()\n \n \n assert len(next_word_probs.shape) ==1, 'probs must be one-dimensional'\n next_word_probs = next_word_probs ** t / np.sum(next_word_probs ** t) # apply temperature\n\n if sample:\n next_word = np.random.choice(vocab, p=next_word_probs) \n else:\n next_word = vocab[np.argmax(next_word_probs)]\n\n caption_prefix.append(next_word)\n\n if next_word==\"#END#\":\n break\n \n return caption_prefix",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from matplotlib import pyplot as plt\nfrom scipy.misc import imresize\n%matplotlib inline\n\n#sample image\n!wget https://pixel.nymag.com/imgs/daily/selectall/2018/02/12/12-tony-hawk.w710.h473.jpg -O data/img.jpg\nimg = plt.imread('data/img.jpg')\nimg = imresize(img, (299, 299)).astype('float32') / 255.",
"--2018-03-18 04:10:56-- https://pixel.nymag.com/imgs/daily/selectall/2018/02/12/12-tony-hawk.w710.h473.jpg\nResolving pixel.nymag.com (pixel.nymag.com)... 151.101.36.70\nConnecting to pixel.nymag.com (pixel.nymag.com)|151.101.36.70|:443... connected.\nHTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK\nLength: 107928 (105K) [image/jpeg]\nSaving to: ‘data/img.jpg’\n\ndata/img.jpg 100%[===================>] 105,40K --.-KB/s in 0,1s \n\n2018-03-18 04:10:56 (832 KB/s) - ‘data/img.jpg’ saved [107928/107928]\n\n"
],
[
"plt.imshow(img)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for i in range(10):\n print(' '.join(generate_caption(img, t=5.)[1:-1]))",
"a man in a suit is doing a trick .\na man riding a skateboard on a skateboard .\na man riding a skateboard on a skateboard .\na man is doing a trick on a skateboard .\na man is doing a trick on a skateboard .\na man in a suit and a skateboard .\na man is doing a trick on a skateboard .\na man riding a skateboard on a skateboard .\na man on a skateboard doing a trick on a skateboard .\na man is skateboarding in the air while holding a skateboard .\n"
],
[
"!wget http://ccanimalclinic.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/Cat-and-dog-1.jpg -O data/img.jpg\nimg = plt.imread('data/img.jpg')\nimg = imresize(img, (299, 299)).astype('float32') / 255.\n\nplt.imshow(img)\nplt.show()\n\nfor i in range(10):\n print(' '.join(generate_caption(img, t=5.)[1:-1]))",
"--2018-03-18 04:13:41-- http://ccanimalclinic.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/Cat-and-dog-1.jpg\nResolving ccanimalclinic.com (ccanimalclinic.com)... 64.207.177.234\nConnecting to ccanimalclinic.com (ccanimalclinic.com)|64.207.177.234|:80... connected.\nHTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK\nLength: 106870 (104K) [image/jpeg]\nSaving to: ‘data/img.jpg’\n\ndata/img.jpg 100%[===================>] 104,37K 194KB/s in 0,5s \n\n2018-03-18 04:13:42 (194 KB/s) - ‘data/img.jpg’ saved [106870/106870]\n\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Demo\n### Find at least 10 images to test it on.\n* Seriously, that's part of an assignment. Go get at least 10 pictures to get captioned\n* Make sure it works okay on __simple__ images before going to something more comples\n* Photos, not animation/3d/drawings, unless you want to train CNN network on anime\n* Mind the aspect ratio",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#apply your network on image sample you found\n#\n#",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Now what?\n\nYour model produces some captions but you still strive to improve it? You're damn right to do so. Here are some ideas that go beyond simply \"stacking more layers\". The options are listed easiest to hardest.\n\n##### Attention\nYou can build better and more interpretable captioning model with attention.\n* How it works: https://distill.pub/2016/augmented-rnns/\n* One way of doing this in captioning: https://arxiv.org/abs/1502.03044\n* You will have to create a dataset for attention with [this notebook](https://gist.github.com/justheuristic/11fd01f9c12c0bf960499580d104130b).\n\n##### Subword level captioning\nIn the base version, we replace all rare words with UNKs which throws away a lot of information and reduces quality. A better way to deal with vocabulary size problem would be to use Byte-Pair Encoding\n\n* BPE implementation you can use: [github_repo](https://github.com/rsennrich/subword-nmt). \n* Theory: https://arxiv.org/abs/1508.07909\n* It was originally built for machine translation, but it should work with captioning just as well.\n\n#### Reinforcement learning\n* After your model has been pre-trained in a teacher forced way, you can tune for captioning-speific models like CIDEr.\n* Tutorial on RL for sequence models: [practical_rl week8](https://github.com/yandexdataschool/Practical_RL/tree/master/week8_scst)\n* Theory: https://arxiv.org/abs/1612.00563",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
c50aaf2d37e9e24919c3f503639502ce2b9a1969
| 1,510 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
tests/test_notebooks/subdir/nested_basic_interact.ipynb
|
samlaf/nbinteract
|
502b0a8e5f6236ed23d4a3d0dcc22db72f6d31e4
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 214 |
2017-12-11T21:32:15.000Z
|
2022-02-07T23:18:32.000Z
|
tests/test_notebooks/subdir/nested_basic_interact.ipynb
|
samlaf/nbinteract
|
502b0a8e5f6236ed23d4a3d0dcc22db72f6d31e4
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 98 |
2017-12-21T06:48:23.000Z
|
2022-03-08T07:20:10.000Z
|
tests/test_notebooks/subdir/nested_basic_interact.ipynb
|
samlaf/nbinteract
|
502b0a8e5f6236ed23d4a3d0dcc22db72f6d31e4
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 21 |
2018-01-25T09:10:20.000Z
|
2021-04-11T21:22:38.000Z
| 18.875 | 54 | 0.523841 |
[
[
[
"# Basic Interact",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from ipywidgets import interact\n\ndef square(x): return x * x\n\ninteract(square, x=(0, 10));",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c50ab02297dbbbfcaf9d88ccc4991dae95eb67f1
| 69,275 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
nbs/02_supervised_baselines.ipynb
|
puhsu/sssupervised
|
65ba953c73639d4bf237648b66c2464259e0d948
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2020-04-12T08:22:16.000Z
|
2020-04-12T08:22:16.000Z
|
nbs/02_supervised_baselines.ipynb
|
puhsu/selfsemisupervised
|
65ba953c73639d4bf237648b66c2464259e0d948
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2021-09-28T01:36:39.000Z
|
2021-09-28T01:36:39.000Z
|
nbs/02_supervised_baselines.ipynb
|
puhsu/sssupervised
|
65ba953c73639d4bf237648b66c2464259e0d948
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 179.005168 | 53,092 | 0.873966 |
[
[
[
"# Supervised baselines\n\nNotebook with strong supervised learning baseline on cifar-10",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%reload_ext autoreload\n%autoreload 2",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You probably need to install dependencies",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# All things needed\n\n!git clone https://github.com/puhsu/sssupervised\n!pip install -q fastai2\n!pip install -qe sssupervised",
"Cloning into 'sssupervised'...\nremote: Enumerating objects: 156, done.\u001b[K\nremote: Counting objects: 0% (1/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 1% (2/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 2% (4/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 3% (5/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 4% (7/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 5% (8/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 6% (10/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 7% (11/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 8% (13/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 9% (15/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 10% (16/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 11% (18/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 12% (19/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 13% (21/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 14% (22/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 15% (24/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 16% (25/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 17% (27/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 18% (29/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 19% (30/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 20% (32/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 21% (33/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 22% (35/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 23% (36/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 24% (38/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 25% (39/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 26% (41/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 27% (43/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 28% (44/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 29% (46/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 30% (47/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 31% (49/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 32% (50/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 33% (52/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 34% (54/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 35% (55/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 36% (57/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 37% (58/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 38% (60/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 39% (61/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 40% (63/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 41% (64/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 42% (66/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 43% (68/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 44% (69/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 45% (71/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 46% (72/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 47% (74/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 48% (75/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 49% (77/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 50% (78/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 51% (80/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 52% (82/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 53% (83/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 54% (85/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 55% (86/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 56% (88/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 57% (89/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 58% (91/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 59% (93/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 60% (94/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 61% (96/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 62% (97/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 63% (99/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 64% (100/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 65% (102/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 66% (103/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 67% (105/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 68% (107/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 69% (108/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 70% (110/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 71% (111/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 72% (113/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 73% (114/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 74% (116/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 75% (117/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 76% (119/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 77% (121/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 78% (122/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 79% (124/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 80% (125/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 81% (127/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 82% (128/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 83% (130/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 84% (132/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 85% (133/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 86% (135/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 87% (136/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 88% (138/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 89% (139/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 90% (141/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 91% (142/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 92% (144/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 93% (146/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 94% (147/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 95% (149/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 96% (150/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 97% (152/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 98% (153/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 99% (155/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 100% (156/156)\u001b[K\rremote: Counting objects: 100% (156/156), done.\u001b[K\nremote: Compressing objects: 100% (126/126), done.\u001b[K\nremote: Total 156 (delta 26), reused 146 (delta 19), pack-reused 0\u001b[K\nReceiving objects: 100% (156/156), 1.34 MiB | 31.08 MiB/s, done.\nResolving deltas: 100% (26/26), done.\n\u001b[K |████████████████████████████████| 184kB 18.0MB/s \n\u001b[?25h"
]
],
[
[
"After running cell above you should restart your kernel",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sssupervised.cifar_utils import CifarFactory\nfrom sssupervised.randaugment import RandAugment\n\nfrom fastai2.data.transforms import parent_label, Categorize\n\nfrom fastai2.optimizer import ranger, Adam\n\nfrom fastai2.layers import LabelSmoothingCrossEntropy\nfrom fastai2.metrics import error_rate\n\nfrom fastai2.callback.all import *\nfrom fastai2.vision.all import *",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Baseline uses wideresnet-28-2 model with randaugment augmentation policy. It is optiimzed with RAadam with lookahead with one-cycle learning rate and momentum schedules for 200 epochs (we count epochs in number of steps on standard cifar, so we set 4000 epochs in our case, because we only have $2400$ training examples ($50000/2400 \\approx 20$)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cifar = untar_data(URLs.CIFAR)\nfiles, (train, test, unsup) = CifarFactory(n_same_cls=3, seed=42, n_labeled=400).splits_from_path(cifar)\n\nsup_ds = Datasets(files, [[PILImage.create, RandAugment, ToTensor], [parent_label, Categorize]], splits=(train, test))\nsup_dl = sup_ds.dataloaders(after_batch=[IntToFloatTensor, Normalize.from_stats(*cifar_stats)])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sup_dl.train.show_batch(max_n=9)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# https://github.com/uoguelph-mlrg/Cutout\n\nimport math\nimport torch\nimport torch.nn as nn\nimport torch.nn.functional as F\n\n\nclass BasicBlock(nn.Module):\n def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, stride, dropRate=0.0):\n super().__init__()\n self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(in_planes)\n self.relu1 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)\n self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,\n padding=1, bias=False)\n self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_planes)\n self.relu2 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)\n self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(out_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1,\n padding=1, bias=False)\n self.droprate = dropRate\n self.equalInOut = (in_planes == out_planes)\n self.convShortcut = (not self.equalInOut) and nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride,\n padding=0, bias=False) or None\n\n def forward(self, x):\n if not self.equalInOut: x = self.relu1(self.bn1(x))\n else: out = self.relu1(self.bn1(x))\n out = self.relu2(self.bn2(self.conv1(out if self.equalInOut else x)))\n if self.droprate > 0:\n out = F.dropout(out, p=self.droprate, training=self.training)\n out = self.conv2(out)\n return torch.add(x if self.equalInOut else self.convShortcut(x), out)\n\nclass NetworkBlock(nn.Module):\n def __init__(self, nb_layers, in_planes, out_planes, block, stride, dropRate=0.0):\n super().__init__()\n self.layer = self._make_layer(block, in_planes, out_planes, nb_layers, stride, dropRate)\n def _make_layer(self, block, in_planes, out_planes, nb_layers, stride, dropRate):\n layers = []\n for i in range(nb_layers):\n layers.append(block(i == 0 and in_planes or out_planes, out_planes, i == 0 and stride or 1, dropRate))\n return nn.Sequential(*layers)\n def forward(self, x): return self.layer(x)\n\nclass WideResNet(nn.Module):\n def __init__(self, depth, num_classes, widen_factor=1, dropRate=0.0):\n super().__init__()\n nChannels = [16, 16*widen_factor, 32*widen_factor, 64*widen_factor]\n assert((depth - 4) % 6 == 0)\n n = (depth - 4) // 6\n block = BasicBlock\n # 1st conv before any network block\n self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, nChannels[0], kernel_size=3, stride=1,\n padding=1, bias=False)\n self.block1 = NetworkBlock(n, nChannels[0], nChannels[1], block, 1, dropRate)\n self.block2 = NetworkBlock(n, nChannels[1], nChannels[2], block, 2, dropRate)\n self.block3 = NetworkBlock(n, nChannels[2], nChannels[3], block, 2, dropRate)\n self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(nChannels[3])\n self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)\n self.fc = nn.Linear(nChannels[3], num_classes)\n self.nChannels = nChannels[3]\n\n for m in self.modules():\n if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):\n n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels\n m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n))\n elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):\n m.weight.data.fill_(1)\n m.bias.data.zero_()\n elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear): m.bias.data.zero_()\n def forward(self, x):\n out = self.conv1(x)\n out = self.block1(out)\n out = self.block2(out)\n out = self.block3(out)\n out = self.relu(self.bn1(out))\n out = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(out, 1)\n out = out.view(-1, self.nChannels)\n return self.fc(out)\n\ndef wrn_22(): return WideResNet(depth=22, num_classes=10, widen_factor=6, dropRate=0.)\ndef wrn_22_k8(): return WideResNet(depth=22, num_classes=10, widen_factor=8, dropRate=0.)\ndef wrn_22_k10(): return WideResNet(depth=22, num_classes=10, widen_factor=10, dropRate=0.)\ndef wrn_22_k8_p2(): return WideResNet(depth=22, num_classes=10, widen_factor=8, dropRate=0.2)\ndef wrn_28(): return WideResNet(depth=28, num_classes=10, widen_factor=6, dropRate=0.)\ndef wrn_28_k8(): return WideResNet(depth=28, num_classes=10, widen_factor=8, dropRate=0.)\ndef wrn_28_k8_p2(): return WideResNet(depth=28, num_classes=10, widen_factor=8, dropRate=0.2)\ndef wrn_28_p2(): return WideResNet(depth=28, num_classes=10, widen_factor=6, dropRate=0.2)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We override default callbacks (the best way I found, to pass extra arguments to callbacks)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"defaults.callbacks = [\n TrainEvalCallback(),\n Recorder(train_metrics=True),\n ProgressCallback(),\n]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class SkipSomeValidations(Callback):\n \"\"\"Perform validation regularly, but not every epoch \n (usefull for small datasets, where training is quick)\"\"\"\n def __init__(self, n_epochs=20): self.n_epochs=n_epochs\n def begin_validate(self):\n if self.train_iter % self.n_epochs != 0:\n raise CancelValidException()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"learner = Learner(\n sup_dl, \n wrn_28(),\n CrossEntropyLossFlat(),\n opt_func=ranger, \n wd=1e-2, \n metrics=error_rate,\n cbs=[ShowGraphCallback(), SkipSomeValidations(n_epochs=20)]\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50aba3f9e7890a709c1f5c4225dc2afefc26e74
| 201,130 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Python/ml/Loan_Eligibility_Prediction.ipynb
|
kushagra1212/NeoAlgo
|
578c1e4fc054625398be3fba9b14d405f6ef1119
|
[
"MIT"
] | 897 |
2020-06-25T00:12:52.000Z
|
2022-03-24T00:49:31.000Z
|
Python/ml/Loan_Eligibility_Prediction.ipynb
|
kushagra1212/NeoAlgo
|
578c1e4fc054625398be3fba9b14d405f6ef1119
|
[
"MIT"
] | 5,707 |
2020-06-24T17:53:28.000Z
|
2022-01-22T05:03:15.000Z
|
Python/ml/Loan_Eligibility_Prediction.ipynb
|
kushagra1212/NeoAlgo
|
578c1e4fc054625398be3fba9b14d405f6ef1119
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1,817 |
2020-06-25T03:51:05.000Z
|
2022-03-29T05:14:07.000Z
| 77.149981 | 31,332 | 0.7601 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\n\nimport warnings\nwarnings.filterwarnings('ignore')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"train=pd.read_csv(r'C:\\Users\\prath\\LoanEligibilityPrediction\\Dataset\\train.csv')\ntrain.Loan_Status=train.Loan_Status.map({'Y':1,'N':0})\ntrain.isnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Loan_status=train.Loan_Status\ntrain.drop('Loan_Status',axis=1,inplace=True)\ntest=pd.read_csv(r'C:\\Users\\prath\\LoanEligibilityPrediction\\Dataset\\test.csv')\nLoan_ID=test.Loan_ID\ndata=train.append(test)\ndata.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.describe()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.isnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.Dependents.dtypes",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn as sns\n%matplotlib inline \ncorrmat=data.corr()\nf,ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(9,9))\nsns.heatmap(corrmat,vmax=.8,square=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.Gender=data.Gender.map({'Male':1,'Female':0})\ndata.Gender.value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"corrmat=data.corr()\nf,ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(9,9))\nsns.heatmap(corrmat,vmax=.8,square=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.Married=data.Married.map({'Yes':1,'No':0})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.Married.value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.Dependents=data.Dependents.map({'0':0,'1':1,'2':2,'3+':3})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.Dependents.value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"corrmat=data.corr()\nf,ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(9,9))\nsns.heatmap(corrmat,vmax=.8,square=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.Education=data.Education.map({'Graduate':1,'Not Graduate':0})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.Education.value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.Self_Employed=data.Self_Employed.map({'Yes':1,'No':0})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.Self_Employed.value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.Property_Area.value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.Property_Area=data.Property_Area.map({'Urban':2,'Rural':0,'Semiurban':1})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.Property_Area.value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"corrmat=data.corr()\nf,ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(9,9))\nsns.heatmap(corrmat,vmax=.8,square=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.Credit_History.size",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.Credit_History.fillna(np.random.randint(0,2),inplace=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.isnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.Married.fillna(np.random.randint(0,2),inplace=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.isnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.LoanAmount.fillna(data.LoanAmount.median(),inplace=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.Loan_Amount_Term.fillna(data.Loan_Amount_Term.mean(),inplace=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.isnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.Gender.value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from random import randint \ndata.Gender.fillna(np.random.randint(0,2),inplace=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.Gender.value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.Dependents.fillna(data.Dependents.median(),inplace=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.isnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"corrmat=data.corr()\nf,ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(9,9))\nsns.heatmap(corrmat,vmax=.8,square=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.Self_Employed.fillna(np.random.randint(0,2),inplace=True)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.isnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.drop('Loan_ID',inplace=True,axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.isnull().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"train_X=data.iloc[:614,]\ntrain_y=Loan_status\nX_test=data.iloc[614:,]\nseed=7",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\ntrain_X,test_X,train_y,test_y=train_test_split(train_X,train_y,random_state=seed)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import LinearDiscriminantAnalysis\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression\nfrom sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier\nfrom sklearn.svm import SVC\nfrom sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier\nfrom sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"models=[]\nmodels.append((\"logreg\",LogisticRegression()))\nmodels.append((\"tree\",DecisionTreeClassifier()))\nmodels.append((\"lda\",LinearDiscriminantAnalysis()))\nmodels.append((\"svc\",SVC()))\nmodels.append((\"knn\",KNeighborsClassifier()))\nmodels.append((\"nb\",GaussianNB()))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"seed=7\nscoring='accuracy'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.model_selection import KFold \nfrom sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score\nresult=[]\nnames=[]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for name,model in models:\n #print(model)\n kfold=KFold(n_splits=10,random_state=seed)\n cv_result=cross_val_score(model,train_X,train_y,cv=kfold,scoring=scoring)\n result.append(cv_result)\n names.append(name)\n print(\"%s %f %f\" % (name,cv_result.mean(),cv_result.std()))",
"logreg 0.747826 0.042600\ntree 0.678261 0.068608\nlda 0.763043 0.040612\nsvc 0.684783 0.060908\nknn 0.636957 0.068089\nnb 0.719565 0.032897\n"
],
[
"from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score\nfrom sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix\nfrom sklearn.metrics import classification_report\nsvc=LogisticRegression()\nsvc.fit(train_X,train_y)\npred=svc.predict(test_X)\nprint(accuracy_score(test_y,pred))\nprint(confusion_matrix(test_y,pred))\nprint(classification_report(test_y,pred))",
"0.7987012987012987\n[[25 23]\n [ 8 98]]\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.76 0.52 0.62 48\n 1 0.81 0.92 0.86 106\n\n accuracy 0.80 154\n macro avg 0.78 0.72 0.74 154\nweighted avg 0.79 0.80 0.79 154\n\n"
],
[
"df_output=pd.DataFrame()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"outp=svc.predict(X_test).astype(int)\noutp",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_output['Loan_ID']=Loan_ID\ndf_output['Loan_Status']=outp",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_output.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_output[['Loan_ID','Loan_Status']].to_csv(r'C:\\Users\\prath\\LoanEligibilityPrediction\\Dataset\\outputlr.csv',index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score\nfrom sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix\nfrom sklearn.metrics import classification_report\nsvc=DecisionTreeClassifier()\nsvc.fit(train_X,train_y)\npred=svc.predict(test_X)\nprint(accuracy_score(test_y,pred))\nprint(confusion_matrix(test_y,pred))\nprint(classification_report(test_y,pred))",
"0.6298701298701299\n[[25 23]\n [34 72]]\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.42 0.52 0.47 48\n 1 0.76 0.68 0.72 106\n\n accuracy 0.63 154\n macro avg 0.59 0.60 0.59 154\nweighted avg 0.65 0.63 0.64 154\n\n"
],
[
"df_output=pd.DataFrame()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"outp=svc.predict(X_test).astype(int)\noutp",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_output['Loan_ID']=Loan_ID\ndf_output['Loan_Status']=outp",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_output.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_output[['Loan_ID','Loan_Status']].to_csv(r'C:\\Users\\prath\\LoanEligibilityPrediction\\Dataset\\outputdt.csv',index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score\nfrom sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix\nfrom sklearn.metrics import classification_report\nsvc=LinearDiscriminantAnalysis()\nsvc.fit(train_X,train_y)\npred=svc.predict(test_X)\nprint(accuracy_score(test_y,pred))\nprint(confusion_matrix(test_y,pred))\nprint(classification_report(test_y,pred))",
"0.7922077922077922\n[[26 22]\n [10 96]]\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.72 0.54 0.62 48\n 1 0.81 0.91 0.86 106\n\n accuracy 0.79 154\n macro avg 0.77 0.72 0.74 154\nweighted avg 0.79 0.79 0.78 154\n\n"
],
[
"df_output=pd.DataFrame()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"outp=svc.predict(X_test).astype(int)\noutp",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_output['Loan_ID']=Loan_ID\ndf_output['Loan_Status']=outp",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_output.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_output[['Loan_ID','Loan_Status']].to_csv(r'C:\\Users\\prath\\LoanEligibilityPrediction\\Dataset\\outputld.csv',index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score\nfrom sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix\nfrom sklearn.metrics import classification_report\nsvc=SVC()\nsvc.fit(train_X,train_y)\npred=svc.predict(test_X)\nprint(accuracy_score(test_y,pred))\nprint(confusion_matrix(test_y,pred))\nprint(classification_report(test_y,pred))",
"0.6883116883116883\n[[ 0 48]\n [ 0 106]]\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.00 0.00 0.00 48\n 1 0.69 1.00 0.82 106\n\n accuracy 0.69 154\n macro avg 0.34 0.50 0.41 154\nweighted avg 0.47 0.69 0.56 154\n\n"
],
[
"df_output=pd.DataFrame()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"outp=svc.predict(X_test).astype(int)\noutp",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_output['Loan_ID']=Loan_ID\ndf_output['Loan_Status']=outp",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_output.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_output[['Loan_ID','Loan_Status']].to_csv(r'C:\\Users\\prath\\LoanEligibilityPrediction\\Dataset\\outputSVC.csv',index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score\nfrom sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix\nfrom sklearn.metrics import classification_report\nsvc=KNeighborsClassifier()\nsvc.fit(train_X,train_y)\npred=svc.predict(test_X)\nprint(accuracy_score(test_y,pred))\nprint(confusion_matrix(test_y,pred))\nprint(classification_report(test_y,pred))",
"0.6493506493506493\n[[ 8 40]\n [14 92]]\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.36 0.17 0.23 48\n 1 0.70 0.87 0.77 106\n\n accuracy 0.65 154\n macro avg 0.53 0.52 0.50 154\nweighted avg 0.59 0.65 0.60 154\n\n"
],
[
"df_output=pd.DataFrame()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"outp=svc.predict(X_test).astype(int)\noutp",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_output['Loan_ID']=Loan_ID\ndf_output['Loan_Status']=outp",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_output.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_output[['Loan_ID','Loan_Status']].to_csv(r'C:\\Users\\prath\\LoanEligibilityPrediction\\Dataset\\outputknn.csv',index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score\nfrom sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix\nfrom sklearn.metrics import classification_report\nsvc=GaussianNB()\nsvc.fit(train_X,train_y)\npred=svc.predict(test_X)\nprint(accuracy_score(test_y,pred))\nprint(confusion_matrix(test_y,pred))\nprint(classification_report(test_y,pred))",
"0.7337662337662337\n[[21 27]\n [14 92]]\n precision recall f1-score support\n\n 0 0.60 0.44 0.51 48\n 1 0.77 0.87 0.82 106\n\n accuracy 0.73 154\n macro avg 0.69 0.65 0.66 154\nweighted avg 0.72 0.73 0.72 154\n\n"
],
[
"df_output=pd.DataFrame()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"outp=svc.predict(X_test).astype(int)\noutp",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_output['Loan_ID']=Loan_ID\ndf_output['Loan_Status']=outp",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_output.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_output[['Loan_ID','Loan_Status']].to_csv(r'C:\\Users\\prath\\LoanEligibilityPrediction\\Dataset\\outputgnb.csv',index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50abcf3b21f0e8791c49ac6b8d64c0233c544cd
| 51,258 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Analyst Training/Exercise 10 - Network Analysis With Python/notebooks_and_constellation.ipynb
|
constellation-app/constellation-training
|
2d3085f8a9ebc32065839a0b8a51cfb1fca761ae
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 14 |
2019-08-15T06:26:47.000Z
|
2022-03-23T21:54:10.000Z
|
Analyst Training/Exercise 10 - Network Analysis With Python/notebooks_and_constellation.ipynb
|
constellation-app/constellation-training
|
2d3085f8a9ebc32065839a0b8a51cfb1fca761ae
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 2 |
2019-08-19T16:46:40.000Z
|
2021-08-20T07:27:53.000Z
|
Analyst Training/Exercise 10 - Network Analysis With Python/notebooks_and_constellation.ipynb
|
constellation-app/constellation-training
|
2d3085f8a9ebc32065839a0b8a51cfb1fca761ae
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 6 |
2019-08-15T09:23:32.000Z
|
2021-11-22T06:58:23.000Z
| 32.942159 | 618 | 0.609817 |
[
[
[
"# Jupyter Notebooks and CONSTELLATION\n\nThis notebook is an introduction to using Jupyter notebooks with CONSTELLATION. In part 1, we'll learn how to send data to CONSTELLATION to create and modify graphs. In part 2, we'll learn how to retrieve graph data from CONSTELLATION. Part 3 will be about getting and setting information about the graph itself. Part 4 will show how to call plugins. Part 5 is a quick look at types. Part 6 will be fun (and occasionally useful). Part 7 introduces some advanced graph usage.\n\nThis notebook uses Python libraries that are included in the [Python Anaconda3 distribution](https://www.anaconda.com/distribution/) version 2020.02, Python v3.7.6.\n\nTo run through the notebook, click on the triangular 'run cell' button in the toolbar to execute the current cell and move to the next cell.\n\nLet's start by seeing if we can talk to CONSTELLATION. Make sure that CONSTELLATION is running, and you've started the external scripting server (which has been done for you if you started the Jupyter notebook server from CONSTELLATION). The external scripting server makes a REST HTTP API available for use by any HTTP client.\n\nThe Python ``import`` statement looks for a library with the given name. Click the 'run cell' button to execute it.\n\n(All of the libraries used here are included in the Anaconda Python distribution.)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import io\nimport os\nimport pandas as pd\nimport PIL.Image, PIL.ImageDraw, PIL.ImageFilter, PIL.ImageFont\n\n# Also import some of the notebook display methods so we can display nice things.\n#\nfrom IPython.display import display, HTML, Image\n\n# This is a convenient Python interface to the REST API.\n#\nimport constellation_client",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cc = constellation_client.Constellation()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"When the external scripting server started, it automatically downloaded ``constellation_client.py`` into your ``.ipython`` directory. It's also important that you create a client instance **after** you start the REST server, because the server creates a secret that the client needs to know to communicate with the server.\n\nAfter the import succeeds, we then create a Python object that communicates with CONSTELLATION on our behalf. CONSTELLATION provides communication with the outside world using HTTP (as if it were a web server) and JSON (a common data format). The ``constellation_client`` library hides these details so you can just use Python.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Part 1: Sending Data to CONSTELLATION",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Typically you'll have some data in a CSV file. We'll use some Python tricks (in this case, ``io.StringIO``) to make it look like we have a separate CSV file that we're reading into a dataframe. (If your data is in an Excel spreadsheet, you could use ``read_excel()`` to read it it directly, rather than saving it to a CVS file first.)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"csv_data = '''\nfrom_address,from_country,to_address,to_country,dtg\[email protected],Brazil,[email protected],India,2017-01-01 12:34:56\[email protected],Brazil,[email protected],Zambia,2017-01-01 14:30:00\[email protected],India\n'''.strip()\ndf = pd.read_csv(io.StringIO(csv_data))\ndf",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Putting our data in a dataframe is a good idea; not only can we easily manipulate it, but it's easy to send a dataframe to CONSTELLATION, as long as we tell CONSTELLATION what data belongs where.\n\nA dataframe is a table of data, but CONSTELLATION deals with graphs, so we need to reconcile a data table and a graph. It shouldn't be too hard to notice (especially given the column names) that a row of data in the dataframe represents a transaction: the source node has the \"from\" attributes, the destination node has the \"to\" attributes, and the transaction has the dtg attribute. The first row therefore represents a connection from `[email protected]` with country value `Brazil` to `[email protected]` with country value `India`. The last row represents a node that is not connected to any other node.\n\nLet's massage the data to something that CONSTELLATION likes. All of the addresses are email addresses, which CONSTELLATION should be clever enough to recognise, but we'd prefer to be explicit, so let's add the types.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df.from_address = df.from_address + '<Email>'\ndf.to_address = df.to_address + '<Email>'\ndf",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Dataframes are clever enough to work on a column at a time; we don't have to do our own loops.\n\nLet's check the data types.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df.dtypes",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"All of the columns are of type ``object``, which in this case means \"string\". However, CONSTELLATION expects datetimes to actually be of ``datetime`` type; if we try and upload datetimes as strings, CONSTELLATION won't recognise them as datetimes.\n\nNot to worry: pandas can fix that for us.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df.dtg = pd.to_datetime(df.dtg)\ndf",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The datetimes look exactly the same, but notice that the ``Not a Number`` value in the last row has become a ``Not a Timestamp`` value. If we look at the data types again, we can see that the ``dtg`` values are now datetimes, not objects.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df.dtypes",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The ``datetime64[ns]`` type means that datetimes are stored as a 64-bit number representing a number of nanoseconds from a zero timestamp. Not that we care that much about the storage: the important thing is that ``dtg`` is now \na datetime column.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"CONSTELLATION recognises source, destination and transaction attributes by the prefixes of their names. It won't be too surprising to find out that the prefixes are ``source``, ``destination``, and ``transaction``, with a ``.`` separating the prefixes from the attribute names.\n\nLet's rename the columns to match what CONSTELLATION expects. (We didn't do this first because the column headers were valid Python identifiers, it was easier to type ``df.dtg`` than ``df['transaction.DateTime']``.)\n\nNote that we use the name ``Identifier`` for the values that uniquely identify a particular node.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df = df.rename(columns={\n 'from_address': 'source.Label',\n 'from_country': 'source.Geo.Country',\n 'to_address': 'destination.Label',\n 'to_country': 'destination.Geo.Country',\n 'dtg': 'transaction.DateTime'})\ndf",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now the dataframe is ready to be sent to CONSTELLATION. We'll create a new graph (using the ``new_graph()`` method), and send the dataframe to CONSTELLATION using the ``put_dataframe()`` method.\n\nIf you get a Python `ConnectionRefusedError` when you run this cell, you've probably forgotten to start the CONSTELLATION external scripting server in the Tools menu. If you start it now, you'll have to go back and re-execute the \"`cc = constellation_client.Constellation()`\" cell, then come back here.)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cc.new_graph()\ncc.put_dataframe(df)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"CONSTELLATION creates a new graph, accepts the contents of the dataframe, applies the schema, and automatically arranges the graph. Finally, it resets the view so you can see the complete graph.\n\nIn this simple case, it's easy to see that the first two rows of the dataframe are correctly represented as nodes with transactions between them. The third row of the dataframe does not have a destination, so there is no transaction.\n\nIf you open the `Attribute Editor` view and select a transaction, you'll see that they have the correct ``DateTime`` values.\n\nOf course, we didn't have to create a new graph. In the same graph, let's add a new node with a transaction from an existing node (`[email protected]`). We'll use another (pretend) CSV file and modify the dataframe as we did before.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"csv_data = '''\nfrom_address,from_country,to_address,to_country,dtg\[email protected],Zambia,[email protected],Brazil,2017-01-02 01:22:33\n'''.strip()\ndfn = pd.read_csv(io.StringIO(csv_data))\ndfn.from_address = dfn.from_address + '<Email>'\ndfn.to_address = dfn.to_address + '<Email>'\ndfn.dtg = pd.to_datetime(dfn.dtg)\ndfn = dfn.rename(columns={\n 'from_address': 'source.Label',\n 'from_country': 'source.Geo.Country',\n 'to_address': 'destination.Label',\n 'to_country': 'destination.Geo.Country',\n 'dtg': 'transaction.DateTime'})\ncc.put_dataframe(dfn)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Part 2: Getting Data from CONSTELLATION",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We'll use the graph that we created in Part 1 to see what happens when we get data from CONSTELLATION. Make sure that the graph is still displayed in CONSTELLATION.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df = cc.get_dataframe()\ndf.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"There seems to be more data there. Let's look at the columns.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(f'Number of columns: {len(df.columns)}')\ndf.columns",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We added five columns in part 1, but we get 50+ columns back! (The number may vary depending on the version of CONSTELLATION and your default schema.) \n\nWhat's going on?\n\nRemember that CONSTELLATION will apply the graph's schema to your data, and do an arrangement. Those other columns are the result of applying the schema, or (in the case of the x, y, z columns) applying an arrangement. The columns are in the dataframe in no particular order.\n\nLet's have a look at the data types in the dataframe.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df.dtypes",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The various ``selected`` columns are bool (that is, ``true`` or ``false`` values): an element is either selected or not selected. The ``transaction.DateTime`` is a ``datetime64[ns]`` as expected. Everything else should be unsurprising. One thing to notice is that ``source.nradius`` may be an ``int64``, even though in CONSTELLATION it's a ``float``. This is because ``nradius`` usually has integer values (typically 1.0), so the dataframe will convert it to an ``int64``. This shouldn't be a problem for us; it's still a number. This can happen for any column that only has integral values.\n\nWe can see what the CONSTELLATION types are using ``cc``'s type attribute: the ``Constellation`` instance will remember the types after each call to ``get_dataframe()``. (Usually you won't have to worry about these.)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cc.types",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"CONSTELLATION types such ``boolean``, ``datetime``, ``float``, ``int``, ``string`` convert to their obvious types in a dataframe. Other types convert to reasonable string equivalents; for example, ``icon`` converts to a string containing the name of the icon.\n\nThe ``color`` type converts to a ``[red, green, blue, alpha]`` list, where each value ranges from 0 to 1. Some people are more used to web colors (in the format #RRGGBB). The following function converts a color list to a web color.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def to_web_color(color):\n \"\"\"Convert an RGB tuple of 0..1 to a web color.\"\"\"\n \n return f'#{int(color[0]*255):02x}{int(color[1]*255):02x}{int(color[2]*255):02x}'",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"For example:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(df['source.color'])\nprint(df['source.color'].apply(to_web_color))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Which allows us to display labels using their node's schema color.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import html\nfor label,color in df[['source.Label', 'source.color']].values:\n h = '<span style=\"color:{}\">{}</span>'.format(to_web_color(color), html.escape(label))\n display(HTML(h))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Graph elements\n\nCalling ``get_dataframe()`` with no parameters gave us four rows representing the whole graph: one row for each transaction, and a row for the singleton node.\n\nSometimes we don't want all of the graph. We can ask for just the nodes.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df = cc.get_dataframe(vx=True)\ndf",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Five rows, one for each node. Note that all of the columns use the ``source`` prefix.\n\nWe can ask for just the transactions.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df = cc.get_dataframe(tx=True)\ndf",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Three rows, one for each transaction. Note that transactions always include the source and destination nodes.\n\nFinally, you can get just the elements that are selected. Before you run the next cell, use your mouse to select two nodes in the current graph.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df = cc.get_dataframe(vx=True, selected=True)\ndf",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Two rows, one for each selected node. Select some different nodes and try again. (If you don't see any rows here, it's because you didn't select any nodes. Select a couple of nodes and run the cell again.)\n\nGenerally, you'll probably want one of ``vx=True`` when you're looking at nodes, or ``tx=True`` when you're looking at transactions.\n\nSelect a couple of transactions, then run the next cell.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df = cc.get_dataframe(tx=True, selected=True)\ndf",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"When you ask for transactions, you not only get the transaction data, but the data for the modes at each end of the transaction as well.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Choosing attributes\n\nYou generally don't want all of the attributes that CONSTELLATION knows about. For example, the x,y,z coordinates are rarely useful when you're analysing data. The ``get_dataframe()`` method allows you to specify only the attributes you want. Not only does this use less space in the dataframe, but particularly for larger graphs, it can greatly reduce the time taken to get the data from the graph into a dataframe.\n\nFirst we'll find out what graph, node, and transaction attributes exist. The `get_attributes()` method returns a dictionary mapping attribute names to their CONSTELLATION types. For consistency with the other method return values, the attribute names are prefixed with `graph.`, `source.`, and `transaction.`. (Attributes that start with `graph.` are attributes of the graph itself, such as the graph's background color. You can see these in the \"Graph\" section of the Attribute Editor.)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"attrs = cc.get_attributes()\nattrs",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"To specify just the attributes you want, pass a list of attribute names using the ``attrs`` parameter.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df = cc.get_dataframe(vx=True, attrs=['source.Identifier', 'source.Type'])\ndf",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Updating the graph: nodes\n\nThere is a special attribute for each element that isn't visible in CONSTELLATION: ``source.[id]``, ``destination.[id]``, and ``transaction.[id]``. These are unique identifiers for each element. These identifiers can change whenever a graph is modified, so they can't be relied on to track an element. However, they can be used to identify a unique element when you get a dataframe, modify a value, and send the dataframe back to CONSTELLATION.\n\nFor example, suppose we want to make all nodes in the ``@example3.com`` domain larger, and color them blue. We need the ``Identifier`` attribute (for the domain name), the ``nradius`` attribute so we can modify it, and the ``source.[id]`` attribute to tell CONSTELLATION which nodes to modify. We don't need to get the color, because we don't care what it is before we change it. xx",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df = cc.get_dataframe(vx=True, attrs=['source.Identifier', 'source.nradius', 'source.[id]'])\ndf",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's filter out the ``example3.com`` nodes and double their radii.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"e3 = df[df['source.Identifier'].str.endswith('@example3.com')].copy()\ne3['source.nradius'] *= 2\ne3",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We don't need to send the ``source.Identifier`` column back to CONSTELLATION, so let's drop it. We'll also add the color column. (Fortunately, CONSTELLATION is quite forgiving about color values.)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"e3 = e3.drop('source.Identifier', axis=1)\ne3['source.color'] = 'blue'\ne3",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Finally, we can send this dataframe to CONSTELLATION.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cc.put_dataframe(e3)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The two ``example3.com`` nodes should be noticably larger. However, the colors didn't change. This is because one of the things that CONSTELLATION does for us is to apply the graph's schema whenever you call ``put_dataframe()``, so the color changes to blue, then is immediately overridden by the schema.\n\nLet's put the node sizes back to 1, and call ``put_dataframe()`` again, but this time tell CONSTELLATION not to apply the schema.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"e3['source.nradius'] = 1\ncc.put_dataframe(e3, complete_with_schema=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Better.\n\nAnother thing that CONSTELLATION does for a ``put_dataframe()`` is a simple arrangement. If you want to create your own arrangement, you have to tell CONSTELLATION not to do this using the ``arrange`` parameter.\n\nLet's arrange the nodes in a circle, just like the built-in circle arrangement. (Actually, wih only five nodes, it's more of a pentagon.) We don't need to know anything about the nodes for this one, we just need to know they exist. In particular, we don't need to know their current x, y, and z positions; we'll just create new ones.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df = cc.get_dataframe(vx=True, attrs=['source.[id]'])\ndf",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"n = len(df)\nimport numpy as np\ndf['source.x'] = n * np.sin(2*np.pi*(df.index/n))\ndf['source.y'] = n * np.cos(2*np.pi*(df.index/n))\ndf['source.z'] = 0\ndf",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cc.put_dataframe(df, arrange='')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The empty string tells CONSTELLATION not to perform any arrangement. (You could put the name of any arrangement plugin there, but there are better ways of doing that.)\n\nAlso note that the blue nodes aren't blue any more, because the schema was applied.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Updating the graph: transactions\n\nThe graph we created earlier has a problem: the transactions have the wrong type. More precisely, they don't have any type. Let's fix that. We'll get all of the transactions from the graph, give them a type, and update the graph.\n\nWhen you run this, the transactions will turn green, indicating that schema completion has happened. You can look at the Attribute Editor to see that the transactions types are now `Communication`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Get the transactions from the graph.\n#\ntx_df = cc.get_dataframe(tx=True, attrs=['transaction.[id]'])\ndisplay(tx_df)\n\n# Add the transaction type.\n#\ntx_df['transaction.Type'] = 'Communication'\ndisplay(tx_df)\n\n# Update the graph.\n#\ncc.put_dataframe(tx_df)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Updating the graph: custom attributes\n\nSometimes we want to add attributes that aren't defined in the graph's schema. For example, let's add an attribute called ``Country.Chars`` that shows the number of characters in each node's country name.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"c_df = cc.get_dataframe(vx=True, attrs=['source.[id]', 'source.Geo.Country'])\n\nc_df['source.Country.Chars'] = c_df['source.Geo.Country'].str.len()\ndisplay(c_df)\ndisplay(c_df.dtypes)\n\ncc.put_dataframe(c_df)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"If you look at the Attribute Editor, you'll see the new node attribute ``Country.Chars``. However, if you right-click on the attribute and select ``Modify Attribute``, you'll see that the new attribute is a string, not an integer, even though the value is an integer in the dataframe. This is because CONSTELLATION assumes that everything it doesn't recognise is a string.\n\nWe can fix this by suffixing a type indicator to the column name. Let's create a new attribute called ``Country.Length`` which we turn into an integer by adding ``<integer>`` to the name.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"c_df = cc.get_dataframe(vx=True, attrs=['source.[id]', 'source.Geo.Country'])\n\nc_df['source.Country.Length<integer>'] = c_df['source.Geo.Country'].str.len()\ndisplay(c_df)\n\ncc.put_dataframe(c_df)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Looking at ``Country.Length`` in the Attribute Editor, we can see that it is an integer. (Click on the Edit button to see the different dialog box.)\n\nOther useful types are ``float`` and ``datetime``. You can see the complete list of types by adding a custom attribute in the Attribute Editor and looking at the ``Attribute Type`` dropdown list.\n\n(Note that there is currently no way to delete attributes externally, so if you want to delete the ``Country.Chars`` attribute, you'll have to do it manually.)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Deleting nodes and vertices\n\nThe special identifier ``[delete]`` lets you delete nodes and transactions from the graph. It doesn't matter what value is in the ``source.[delete]`` column - just the fact that the column is there is sufficient to delete the graph elements. This means that all of the elements in the dataframe will be deleted, so be careful..\n\nLet's delete all singleton nodes. These nodes have no transactions connected to them, so when we get a dataframe, the ``destination.[id]`` value will be ``NaN``.\n\n(If we get all nodes with ``vx=True``, we won't get any data about transactions. If we get all transactions with ``tx=True``, we won't get the singleton nodes.)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Get the graph. (Names are included so we can check that the dataframe matches the graph.)\n#\ndf = cc.get_dataframe(attrs=['source.[id]', 'source.Identifier', 'destination.[id]', 'destination.Identifier'])\ndisplay(df)\n\n# Keep the singleton rows (where the destination.[id] is null).\n#\ndf = df[df['destination.[id]'].isnull()]\ndisplay(df)\n\n# Create a new dataframe with a source.[id] column containing all of the values from the df source.[id] column,\n# and a source.[delete] column containing any non-null value\n#\ndel_df = pd.DataFrame({'source.[id]': df['source.[id]'], 'source.[delete]': 0})\ndisplay(del_df)\n\n# Delete the singletons.\n#\ncc.put_dataframe(del_df)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Likewise, we can delete transactions. Let's delete all transactions originating from ``ghi`` .",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Get all transactions.\n# We don't need all of the attributes for the delete, but we'll get them to use below.\n#\ndf = cc.get_dataframe(tx=True)\ndisplay(df)\n\n# Keep the transactions originating from 'ghi'.\n#\ndf = df[df['source.Identifier'].str.startswith('ghi@')]\ndisplay(df)\n\n# Create a new dataframe containing the transaction ids in the original dataframe.\n# It doesn't matter what the value of 'transaction.[delete]' is,\n# but we have to give it something.\n#\ndel_df = pd.DataFrame({'transaction.[id]': df['transaction.[id]'], 'transaction.[delete]': 0})\ndisplay(del_df)\n\n# Delete the transactions.\n#\ncc.put_dataframe(del_df)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"And let's add a transaction that is exactly the same as the original. Remember that we originally fetched all of the attributes, so this new transaction will have the same attribute values.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cc.put_dataframe(df)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Part 3: Graph Attributes",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"As well as node and transaction attributes, we can also get graph attributes. (Graph attributes can be seen in CONSTELLATION's Attribute Editor, above the node and transaction attributes.)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df = cc.get_graph_attributes()\ndf",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"There is only one set of graph attributes, so there is one row in the dataframe.\n\nLet's display the `Geo.Country` attribute in a small size above the nodes, and the country flag as a decorator on the top-right of the node icon.\n\nA node label is defined as *``attribute-name``*``;``*``color``*``;``*``size``*, with multiple labels separated by pipes \"|\".\n\nA decorator is defined as ``\"nw\";\"ne\";\"se\";\"sw\";`` where any of the direction ordinals may be blank.\n\nWe don't care what the top labels and decorators are right now, so we'll just create a new dataframe.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"labels = 'Geo.Country;Orange;0.5'\ndf = pd.DataFrame({'node_labels_top': [labels], 'decorators': [';\"Geo.Country\";;;']})\ncc.set_graph_attributes(df)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"(You may have to zoom in to see the smaller labels.)\n\nTo add a label on the bottom in addition to the default ``Label`` attribute, you have to specify both labels.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"labels = 'Type;Teal;0.5|Label;LightBlue;1'\ndf = pd.DataFrame({'node_labels_bottom': [labels]})\ncc.set_graph_attributes(df)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Part 4: Types\n\nCONSTELLATION defines many types. Use the ``describe_type()`` method to get a description of a particular type.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"t = cc.describe_type('Communication')\nt",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Part 5: Plugins\n\nYou can call CONSTELLATION plugins from Python (if you know what they're called). Let's arrange the graph in trees.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cc.run_plugin('ArrangeInTrees')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"If we can't see all of the graph, reset the view.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cc.run_plugin('ResetView')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You can also call plugins with parameters (if you know what they are). For example, the ``AddBlaze`` plugin accepts a node id to add a blaze to.\n\nLet's add a blaze to each ``example3.com`` node.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Get all nodes and their identifiers.\n#\ndf = cc.get_dataframe(vx=True, attrs=['source.Identifier', 'source.[id]'])\n\n# Whioch nodes belong to the example3.com domain?\n#\ne3 = df[df['source.Identifier'].str.endswith('@example3.com')]\n\n# Add a blaze to those nodes.\n#\ncc.run_plugin('AddBlaze', args={'BlazeUtilities.vertex_ids': list(e3['source.[id]'])})",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's be neat and tidy and remove them again. We can reuse the dataframe.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cc.run_plugin('RemoveBlaze', args={'BlazeUtilities.vertex_ids': list(e3['source.[id]'])})",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Multichoice parameters\nWhile most parameter values are quite simple (strings, integers, etc), some are a little more complex to deal with, such as the multichoice parameter. In order to pass multichoice parameter values to a plugin, you need to know the possible choices, and you need to know how to select them. \n\nLet's use the <i>select top n</i> plugin as an example. The schema view tells us that this plugin has a multichoice parameter called <i>SelectTopNPlugin.type</i>.\n\nLooking in the Data Access View, the type options will vary depending on the value given to the <i>SelectTopN.type_category</i> parameter. For this example we we set the type category to \"Online Identifier\", which will result in the possible type options being:\n- Online Identifier \n- Email\n\nIn order to use this parameter, we need to create a string containing all options by joining each option with '\\n'. We also need to select all the options we want by prefixing them with '`✓ `' (i.e. Unicode character U+2713 (CHECK MARK) followed by character U+0020 (SPACE)). \n\nThis is obviously not an ideal system, but this is how multichoice parameters were implemented at a time when it wasn't expected that CONSTELLATION's internal workings would be exposed via scripting or a REST API.\n\n(This plugin won't do anything on this simple graph.)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Select a node.\n#\ncc.run_plugin('SelectSources')\n\n# Run the \"select top n\" plugin with a custom multichoice parameter value.\n#\nCHECK = '\\u2713'\n\noptions = ['Online Identifier', 'Communication', 'User Name']\nchecked = ['Communication']\nparameters = {\n 'SelectTopNPlugin.mode': \"Node\",\n 'SelectTopNPlugin.type_category': 'Online Location',\n 'SelectTopNPlugin.type': '\\n'.join([f'{CHECK} {v}' if v in checked else v for v in options]),\n 'SelectTopNPlugin.limit': 2\n}\n\ncc.run_plugin('SelectTopN', args=parameters)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"So how do we know what plugins exist?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plugins = cc.list_plugins()\nsorted(plugins)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Unfortunately, at the moment there is no way of using the REST API to find out what each plugin does or what parameters it takes. However, you can go the the Schema View in CONSTELLATION and look at the ``Plugins`` tab.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"If you'd like to find out what a particular plugin does:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cc.describe_plugin('ARRANGEINGRIDGENERAL')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Part 6: Data Access Plugins\n\nData Access plugins in CONSTELLATION are like any other plugins; they just have a different user interface. This means that they can be called from an external scripting client just like any other plugin.\n\nOne caveat is that many of these plugins use the global parameters (seen at the top of the Data Access View).\n\n- Query Name\n- Range\n\nLet's try running a data access plugin, although to avoid connectivity problems we'll use the <i>Test Parameters</i> plugin in the <strong>Developer</strong> category of the Data Access View. This plugin doesn't actually access any external data, but rather simply exists to test the mechanisms CONSTELLATION uses to build and use plugin parameters. The plugin has many parameters, but for this example we will focus on the following:\n\n- ``GlobalCoreParameters.query_name``: A string representing the name of the query.\n- ``GlobalCoreParameters.datetime_range``: The datetime range; see below.\n\nYou might want to try running this plugin manually on an empty graph before running the code below. The plugin will create two connected nodes containing `Comment` attribute values reflecting the values specified by the plugin parameters. (You can see these in the Attribute Editor after you've run the cell.)\n\nNote that the global parameters and plugin-specific parameters are named so they can be differentiated.\n\nRun the plugin a few times, changing the parameters each time, to satisfy yourself that this is the case. After you've done that, let's try running it programmatically.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def get_data():\n \"\"\"Display the results of the plugin.\"\"\"\n df = cc.get_dataframe()\n print('query_name :', df.loc[0, 'source.Comment'])\n print('datetime_range :', df.loc[0, 'destination.Comment'])\n print('all_parameters :', df.loc[0, 'transaction.Comment'])\n\n# Set up a counter.\n#\ncounter = 0",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cc.new_graph()\n\ncounter += 1\nparameters = {\n 'CoreGlobalParameters.query_name': f'Query {counter} from a REST client',\n 'CoreGlobalParameters.datetime_range': 'P1D',\n 'TestParametersPlugin.robot': 'Bender',\n 'TestParametersPlugin.planets': f'{CHECK} Venus\\n{CHECK} Mars'\n}\n\ncc.run_plugin('TestParameters', args=parameters)\n\nget_data()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The datetime range can be an explicit range, or a duration from the current time.\n\n### Datetime range\n\nA range is represented by two ISO 8601 datetime values separated by a semi-colon. This represents an explicit start and end point. Examples are:\n\n- ``2016-01-01T00:00:00Z;2016-12-31T23:59:59Z``\n- ``2017-06-01T12:00:00Z;2017-06-01T13:00:00Z``\n\n### Datetime duration\n\nA duration is represented by a single ISO 8601 duration. This is converted to an explicit datetime range when the query is run. Examples are:\n\n- ``P1D``: one day\n- ``P7D``: 7 days\n- ``P1M``: one month\n- ``P1Y``: one year\n- ``P1M7D``: one month and seven days\n\nNote that only years, months, and days are supported (so ``P1H`` for one hour is not a valid period, for example.) For durations other than those, use Python to determine an explicit range.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Let's try calling the plugin again.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cc.new_graph()\n\ncounter += 1\n\nparameters['CoreGlobalParameters.query_name'] = f'Query {counter} from a REST client'\nparameters['CoreGlobalParameters.datetime_range'] = '2017-07-01T00:21:15Z;2017-07-14T00:21:15Z'\n\ncc.run_plugin('TestParameters', args=parameters)\n\nget_data()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Something's wrong?\nSometimes things don't work. Like this.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cc.run_plugin('seletall')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"That's not particularly helpful. Fortunately, when something goes wrong the Python client remembers the most recent response, so we can look at what the REST server is telling us.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"HTML(cc.r.content.decode('latin1'))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"What do you mean, \"No such plugin as\"... Oh, we missed a letter. Let's try that again.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cc.run_plugin('selectall')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Part 6: Taking a Screenshot\n\nIt can be useful to include a screenshot of the graph in a notebook. It's easy to get an image encoded as data representing a PNG file.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"buf = cc.get_graph_image()\nImage(buf)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Here we used the built-in notebook facilities to display the image (which is returned from CONSTELLATION as a sequence of bytes, the encoding of the image in PNG format).\n\nIf another window overlaps CONSTELLATION's graph display, you might see that window in the image. One way of avoiding this is to resize the CONSTELLATION window slightly first. Another way is to add a sleep before the `get_graph_image()` call and click in the CONSTELLATION window to bring it to the top.\n\nWe can also use PIL (the Python Image Library) to turn the bytes into an image and manipulate it.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"img = PIL.Image.open(io.BytesIO(buf))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"You might want to resize the image to fit it into a report.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def resize(img, max_size):\n w0 = img.width\n h0 = img.height\n s = max(w0, h0)/max_size\n w1 = int(w0//s)\n h1 = int(h0//s)\n print(f'Resizing from {w0}x{h0} to {w1}x{h1}')\n \n return img.resize((w1, h1))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"small = resize(img, 512)\n\n# PIL images know how to display themselves.\n#\nsmall",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The image can be saved to a file. You can either write the bytes directly (remember the bytes are already in PNG format), or save the PIL image.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"with open('my_constellation_graph.png', 'wb') as f:\n f.write(buf)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"img.save('my_small_constellation_graph.png')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"PIL is fun.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"small.filter(PIL.ImageFilter.EMBOSS)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"w = small.width\nh = small.height\nsmall.crop((int(w*0.25), int(h*0.25), int(w*0.75), int(h*0.75)))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Fonts depend on the operating system.\n#\nif os.name=='nt':\n font = PIL.ImageFont.truetype('calibri.ttf', 20)\nelse:\n font = PIL.ImageFont.truetype('Oxygen-Sans.ttf', 20)\ndraw = PIL.ImageDraw.Draw(small)\ndraw.text((0, 0), 'This is my graph, it is mine.', (255, 200, 40), font=font)\nsmall",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Part 7: NetworkX\n\nNetworkX is a Python package for the creation, manipulation, and study of the structure, dynamics, and functions of complex networks.\n\nThis notebook isn't going to teach you how to use NetworkX, but you can extract your CONSTELLATION graph into a NetworkX graph for further analysis.\n\nWe'll start by getting a dataframe containing the graph data.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cc.run_plugin('ArrangeInGridGeneral')\ndf = cc.get_dataframe()\ndf.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The ``constellation_client`` library contains a function that converts a dataframe to a NetworkX graph. You can see the documentation for it using the notebook's built-in help mechanism.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"constellation_client.nx_from_dataframe?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"When you've looked at the help, close the help window and create a NetworkX graph from the dataframe.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"g = constellation_client.nx_from_dataframe(df)\ng",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can look at a node and see that it has the expected attributes.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"g.nodes(data=True)['0']",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can look at an edge and see that it has the expected attributes.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"list(g.edges(data=True))[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"NetworkX can draw its graphs using a plotting library called ``matplotlib``. We just need to tell ``matplotlib`` to draw in the notebook, and get the correct positions and colors from the node and edge attributes. (We can use a convenience function provided by ``constellation_client`` to get the positions.)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%matplotlib inline\nimport networkx as nx\n\npos = constellation_client.get_nx_pos(g)\nnode_colors = [to_web_color(g.nodes[n]['color']) for n in g.nodes()]\nedge_colors = [to_web_color(g.edges[e]['color']) for e in g.edges()]\n\nnx.draw(g, pos=pos, node_color=node_colors, edge_color=edge_colors)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c50acc03de885520aaaa285fe775f16ae5e3d3a8
| 121,261 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebook/Pipeline - Prepare Data.ipynb
|
sky-dust-intelligence-bv/verseagility
|
27550344c90e5339b507f0f29e20b3da8340ee0a
|
[
"MIT"
] | 15 |
2020-09-07T17:27:11.000Z
|
2021-12-16T11:17:21.000Z
|
notebook/Pipeline - Prepare Data.ipynb
|
sky-dust-intelligence-bv/verseagility
|
27550344c90e5339b507f0f29e20b3da8340ee0a
|
[
"MIT"
] | 4 |
2021-08-04T02:26:19.000Z
|
2022-01-07T01:15:52.000Z
|
notebook/Pipeline - Prepare Data.ipynb
|
sky-dust-intelligence-bv/verseagility
|
27550344c90e5339b507f0f29e20b3da8340ee0a
|
[
"MIT"
] | 8 |
2020-09-08T17:15:55.000Z
|
2021-11-10T08:17:11.000Z
| 86.061746 | 20,263 | 0.61107 |
[
[
[
"# Step 1 - Prepare Data\n\nData cleaning.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%load_ext autoreload\n%autoreload 2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import pandas as pd",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Custom Functions\nimport sys\nsys.path.append('../src')\nimport data as dt\nimport prepare as pr\nimport helper as he",
"C:\\Users\\makayser\\AppData\\Roaming\\Python\\Python36\\site-packages\\requests\\__init__.py:91: RequestsDependencyWarning: urllib3 (1.25.7) or chardet (3.0.4) doesn't match a supported version!\n RequestsDependencyWarning)\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Load Data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dt_task = dt.Data()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data = dt_task.load('fn_clean')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fn_data = he.get_config()['path']['sample_dir'] + 'data.txt'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data = pd.read_csv(fn_data, sep='\\t', encoding='utf-8')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.columns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data = data[data.answer_markedAsAnswer == True].reset_index(drop=True).copy()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.head().to_json()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"task_params = {\n 1 : {\n 'label' : 'subcat',\n 'type' : 'classification',\n 'language' : 'en',\n 'prepare' : ''\n },\n 2 : {\n 'label' : 'cat',\n 'type' : 'classification',\n 'language' : 'en',\n 'prepare' : ''\n },\n 4 : {\n 'type' : 'qa',\n 'language' : 'en',\n 'prepare' : None\n }\n}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for t in task_params.keys():\n print(t)",
"1\n2\n4\n"
],
[
"data.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cl = pr.Clean(language='en')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%%time\ntitle_clean = cl.transform(data.question_title,\n do_remove=True,\n do_placeholder=True)\n",
"Wall time: 383 ms\n"
],
[
"%%time\nbody_clean = cl.transform(data.question_text,\n do_remove=True,\n do_placeholder=True)",
"Wall time: 14.7 s\n"
],
[
"title_clean[0:20]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"body_clean[0:20]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data['text'] = title_clean",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(data[data.answer_markedAsAnswer == True])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tt = ['Asdas', 'asdasd sad asd', 'Asd ss asda asd']\n[t.split(' ') for t in tt]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"task_type_lookup = {\n 1 : 'classification',\n 2 : 'classification',\n 3 : 'ner',\n 4 : 'qa' \n }\ntask_type_lookup[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"task_type_lookup[1]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data[data.answer_upvotes > 1].head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(data)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data_red = data.drop_duplicates(subset=['text'])\ndata_red['text'] = data_red.text.replace('\\t',' ',regex=True).replace('\"','').replace(\"'\",' ').replace('\\n',' ',regex=True)\ndata_red['subcat'] = data_red.subcat.replace('\\t',' ',regex=True).replace('\"','').replace(\"'\",' ').replace('\\n',' ',regex=True)\nlen(data_red)",
"C:\\Users\\makayser\\AppData\\Local\\Continuum\\anaconda3\\envs\\nlp\\lib\\site-packages\\ipykernel_launcher.py:2: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy\n \nC:\\Users\\makayser\\AppData\\Local\\Continuum\\anaconda3\\envs\\nlp\\lib\\site-packages\\ipykernel_launcher.py:3: SettingWithCopyWarning: \nA value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.\nTry using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead\n\nSee the caveats in the documentation: http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy\n This is separate from the ipykernel package so we can avoid doing imports until\n"
],
[
"# data_red['subcat'] = data_red.subcat.str.replace(r'\\D', '')\n# data_red['text'] = data_red.text.str.replace(r'\\D', '')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data_red.subcat.value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"tt = data_red[data_red.groupby('subcat').subcat.transform('size') > 14]\ntt.subcat.value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.DataFrame(data_red.subcat.drop_duplicates())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"list(set(data.subcat.drop_duplicates()) - set(data_red.subcat.drop_duplicates()))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"list(data_red.subcat.drop_duplicates())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data_red = data_red[data_red.subcat.isin(['msoffice',\n 'edge',\n 'ie',\n 'windows',\n 'insider',\n 'mobiledevices',\n 'outlook_com',\n 'protect',\n 'skype',\n 'surface',\n 'windowslive'])].copy()\nlen(data_red)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data_red[['text','subcat']].head(6000).reset_index(drop=True).to_csv(he.get_config()['path']['sample_dir'] + 'train.txt', sep='\\t', encoding='utf-8', index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data_red[['text','subcat']].tail(7733-6000).reset_index(drop=True).to_csv(he.get_config()['path']['sample_dir'] + 'test.txt', sep='\\t', encoding='utf-8', index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50ae4d5ad101d712e451f2f6c3dc8f4de994f60
| 9,315 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
object-detection-acv/01_AzureSetup.ipynb
|
Bhaskers-Blu-Org2/deploy-MLmodels-on-iotedge
|
e27f2667347e5349206a66ac29f9919c408c7676
|
[
"MIT"
] | 13 |
2020-02-18T07:05:21.000Z
|
2022-03-28T14:23:12.000Z
|
object-detection-acv/01_AzureSetup.ipynb
|
Bhaskers-Blu-Org2/deploy-MLmodels-on-iotedge
|
e27f2667347e5349206a66ac29f9919c408c7676
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2020-01-28T23:03:09.000Z
|
2020-11-13T18:24:40.000Z
|
object-detection-acv/01_AzureSetup.ipynb
|
microsoft/deploy-MLmodels-on-iotedge
|
e27f2667347e5349206a66ac29f9919c408c7676
|
[
"MIT"
] | 8 |
2020-02-21T01:40:29.000Z
|
2022-03-28T13:34:37.000Z
| 25.732044 | 246 | 0.575953 |
[
[
[
"## Create Azure Resources¶\n\nThis notebook creates relevant Azure resources. It creates a recource group where an IoT hub with an IoT edge device identity is created. It also creates an Azure container registry (ACR).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from dotenv import set_key, get_key, find_dotenv\nfrom pathlib import Path\nimport json\nimport time",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"To create or access an Azure ML Workspace, you will need the following information:\n\n* An Azure subscription id\n* A resource group name\n* A region for your resources\n\nWe also require you to provide variable names that will be used to create these resources in later notebooks.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Azure resources\nsubscription_id = \"<subscription_id>\"\nresource_group = \"<resource_group>\" \nresource_region = \"resource_region\" # e.g. resource_region = \"eastus\"\n\n# IoT hub name - a globally UNIQUE name is required, e.g. iot_hub_name = \"myiothubplusrandomnumber\".\niot_hub_name = \"<iot_hub_name>\" \n\ndevice_id = \"<device_id>\" # the name you give to the edge device. e.g. device_id = \"mydevice\"\n\n# azure container registry name - a globally UNIQUE name is required, e.g. arc_name = \"myacrplusrandomnumber\"\nacr_name = '<acr_name>' \n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Create and initialize a dotenv file for storing parameters used in multiple notebooks.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"env_path = find_dotenv()\nif env_path == \"\":\n Path(\".env\").touch()\n env_path = find_dotenv()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"set_key(env_path, \"subscription_id\", subscription_id)\nset_key(env_path, \"resource_group\", resource_group)\nset_key(env_path, \"resource_region\", resource_region)\n\nset_key(env_path, \"iot_hub_name\", iot_hub_name)\nset_key(env_path, \"device_id\", device_id)\n\nset_key(env_path,\"acr_name\", acr_name)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"acr_login_server = '{}.azurecr.io'.format(acr_name)\nset_key(env_path,\"acr_login_server\", acr_login_server)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Create Azure Resources\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# login in your account\naccounts = !az account list --all -o tsv\nif \"Please run \\\"az login\\\" to access your accounts.\" in accounts[0]:\n !az login -o table\nelse:\n print(\"Already logged in\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Below we will reload it just to make sure that everything is working.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!az account set --subscription $subscription_id ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# create a new resource group\n!az group create -l $resource_region -n $resource_group",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Create IoT Hub",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# install az-cli iot extension - I had to use \"sudo -i\" to make it work\n!sudo -i az extension add --name azure-cli-iot-ext",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!az iot hub list --resource-group $resource_group -o table",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Command to create a Standard tier S1 hub with name `iot_hub_name` in the resource group `resource_group`.\n!az iot hub create --resource-group $resource_group --name $iot_hub_name --sku S1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Command to create a free tier F1 hub. You may encounter error \"Max number of Iot Hubs exceeded for sku = Free\" if quota is reached.\n# !az iot hub create --resource-group $resource_group --name $iot_hub_name --sku F1",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Register an IoT Edge device\nWe create a device with name `device_id` under previously created iot hub.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"time.sleep(30) # Wait 30 seconds to let IoT hub stable before creating a device\nprint(\"az iot hub device-identity create --hub-name {} --device-id {} --edge-enabled -g {}\".format(iot_hub_name,device_id,resource_group))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!az iot hub device-identity create --hub-name $iot_hub_name --device-id $device_id --edge-enabled -g $resource_group",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Obtain device_connection_string. It will be used in the next step.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(\"az iot hub device-identity show-connection-string --device-id {} --hub-name {} -g {}\".format(device_id, iot_hub_name,resource_group))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"json_data = !az iot hub device-identity show-connection-string --device-id $device_id --hub-name $iot_hub_name -g $resource_group\nprint(json_data)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"device_connection_string = json.loads(''.join([i for i in json_data if 'WARNING' not in i]))['connectionString']\nprint(device_connection_string)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"set_key(env_path, \"device_connection_string\", device_connection_string)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Create Azure Container Registry",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!az acr create -n $acr_name -g $resource_group --sku Standard --admin-enabled",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!az acr login --name $acr_name\n",
"Login Succeeded\nWARNING! Your password will be stored unencrypted in /home/mylogin/.docker/config.json.\nConfigure a credential helper to remove this warning. See\nhttps://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/login/#credentials-store\n\n\u001b[0m"
],
[
"acr_password = !az acr credential show -n $acr_name --query passwords[0].value\nacr_password = \"\".join(acr_password)\nacr_password = acr_password.strip('\\\"')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"set_key(env_path,\"acr_password\", acr_password)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"In this notebook, we created relevant Azure resources. We also created a \".env\" file to save and reuse the variables needed cross all the notebooks. We can now move on to the next notebook [02_IoTEdgeConfig.ipynb](02_IoTEdgeConfig.ipynb).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
c50ae5f8d879f1eb632513c41416b367df6708d0
| 354,904 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
content/ch-algorithms/deutsch-jozsa.ipynb
|
trietnb/qiskit-textbook
|
dff434fdf00e3daef420736ef40b39439a98384d
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
content/ch-algorithms/deutsch-jozsa.ipynb
|
trietnb/qiskit-textbook
|
dff434fdf00e3daef420736ef40b39439a98384d
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
content/ch-algorithms/deutsch-jozsa.ipynb
|
trietnb/qiskit-textbook
|
dff434fdf00e3daef420736ef40b39439a98384d
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 43.076101 | 3,971 | 0.502944 |
[
[
[
"# Deutsch-Jozsa Algorithm",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In this section, we first introduce the Deutsch-Jozsa problem, and classical and quantum algorithms to solve it. We then implement the quantum algorithm using Qiskit, and run it on a simulator and device.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Contents\n\n1. [Introduction](#introduction) \n 1.1 [Deutsch-Jozsa Problem](#djproblem) \n 1.2 [Deutsch-Jozsa Algorithm](#classical-solution) \n 1.3 [The Quantum Solution](#quantum-solution) \n 1.4 [Why Does This Work?](#why-does-this-work) \n2. [Worked Example](#example)\n3. [Creating Quantum Oracles](#creating-quantum-oracles) \n4. [Qiskit Implementation](#implementation) \n 4.1 [Constant Oracle](#const_oracle) \n 4.2 [Balanced Oracle](#balanced_oracle) \n 4.3 [The Full Algorithm](#full_alg) \n 4.4 [Generalised Circuit](#general_circs) \n5. [Running on Real Devices](#device) \n6. [Problems](#problems)\n7. [References](#references)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 1. Introduction <a id='introduction'></a>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The Deutsch-Jozsa algorithm, first introduced in Reference [1], was the first example of a quantum algorithm that performs better than the best classical algorithm. It showed that there can be advantages to using a quantum computer as a computational tool for a specific problem.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 1.1 Deutsch-Jozsa Problem <a id='djproblem'> </a>\n\nWe are given a hidden Boolean function $f$, which takes as input a string of bits, and returns either $0$ or $1$, that is:\n\n$$\nf(\\{x_0,x_1,x_2,...\\}) \\rightarrow 0 \\textrm{ or } 1 \\textrm{ , where } x_n \\textrm{ is } 0 \\textrm{ or } 1$$\n\nThe property of the given Boolean function is that it is guaranteed to either be balanced or constant. A constant function returns all $0$'s or all $1$'s for any input, while a balanced function returns $0$'s for exactly half of all inputs and $1$'s for the other half. Our task is to determine whether the given function is balanced or constant. \n\nNote that the Deutsch-Jozsa problem is an $n$-bit extension of the single bit Deutsch problem. \n\n### 1.2 The Classical Solution <a id='classical-solution'> </a>\n\nClassically, in the best case, two queries to the oracle can determine if the hidden Boolean function, $f(x)$, is balanced: \ne.g. if we get both $f(0,0,0,...)\\rightarrow 0$ and $f(1,0,0,...) \\rightarrow 1$, then we know the function is balanced as we have obtained the two different outputs. \n\nIn the worst case, if we continue to see the same output for each input we try, we will have to check exactly half of all possible inputs plus one in order to be certain that $f(x)$ is constant. Since the total number of possible inputs is $2^n$, this implies that we need $2^{n-1}+1$ trial inputs to be certain that $f(x)$ is constant in the worst case. For example, for a $4$-bit string, if we checked $8$ out of the $16$ possible combinations, getting all $0$'s, it is still possible that the $9^\\textrm{th}$ input returns a $1$ and $f(x)$ is balanced. Probabilistically, this is a very unlikely event. In fact, if we get the same result continually in succession, we can express the probability that the function is constant as a function of $k$ inputs as:\n\n\n\n$$ P_\\textrm{constant}(k) = 1 - \\frac{1}{2^{k-1}} \\qquad \\textrm{for } 1 < k \\leq 2^{n-1}$$\n\n\n\nRealistically, we could opt to truncate our classical algorithm early, say if we were over x% confident. But if we want to be 100% confident, we would need to check $2^{n-1}+1$ inputs.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 1.3 Quantum Solution <a id='quantum-solution'> </a>\n\nUsing a quantum computer, we can solve this problem with 100% confidence after only one call to the function $f(x)$, provided we have the function $f$ implemented as a quantum oracle, which maps the state $\\vert x\\rangle \\vert y\\rangle $ to $ \\vert x\\rangle \\vert y \\oplus f(x)\\rangle$, where $\\oplus$ is addition modulo $2$. Below is the generic circuit for the Deutsh-Jozsa algorithm.\n\n\n\nNow, let's go through the steps of the algorithm:\n\n<ol>\n <li>\n Prepare two quantum registers. The first is an $n$-qubit register initialized to $|0\\rangle$, and the second is a one-qubit register initialized to $|1\\rangle$:\n \n\n$$\\vert \\psi_0 \\rangle = \\vert0\\rangle^{\\otimes n} \\vert 1\\rangle$$\n\n\n </li>\n \n <li>\n Apply a Hadamard gate to each qubit:\n \n\n$$\\vert \\psi_1 \\rangle = \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{2^{n+1}}}\\sum_{x=0}^{2^n-1} \\vert x\\rangle \\left(|0\\rangle - |1 \\rangle \\right)$$\n\n\n </li>\n \n <li>\n Apply the quantum oracle $\\vert x\\rangle \\vert y\\rangle$ to $\\vert x\\rangle \\vert y \\oplus f(x)\\rangle$:\n $$\n \\begin{aligned}\n \\lvert \\psi_2 \\rangle \n & = \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{2^{n+1}}}\\sum_{x=0}^{2^n-1} \\vert x\\rangle (\\vert f(x)\\rangle - \\vert 1 \\oplus f(x)\\rangle) \\\\ \n & = \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{2^{n+1}}}\\sum_{x=0}^{2^n-1}(-1)^{f(x)}|x\\rangle ( |0\\rangle - |1\\rangle ) \n \\end{aligned}\n $$\n \nsince for each $x,f(x)$ is either $0$ or $1$.\n </li>\n\n <li>\n At this point the second single qubit register may be ignored. Apply a Hadamard gate to each qubit in the first register:\n $$\n \\begin{aligned}\n \\lvert \\psi_3 \\rangle \n & = \\frac{1}{2^n}\\sum_{x=0}^{2^n-1}(-1)^{f(x)}\n \\left[ \\sum_{y=0}^{2^n-1}(-1)^{x \\cdot y} \n \\vert y \\rangle \\right] \\\\\n & = \\frac{1}{2^n}\\sum_{y=0}^{2^n-1}\n \\left[ \\sum_{x=0}^{2^n-1}(-1)^{f(x)}(-1)^{x \\cdot y} \\right]\n \\vert y \\rangle\n \\end{aligned}\n $$\n \nwhere $x \\cdot y = x_0y_0 \\oplus x_1y_1 \\oplus \\ldots \\oplus x_{n-1}y_{n-1}$ is the sum of the bitwise product.\n </li>\n\n <li>\n Measure the first register. Notice that the probability of measuring $\\vert 0 \\rangle ^{\\otimes n} = \\lvert \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{2^n}}\\sum_{x=0}^{2^n-1}(-1)^{f(x)} \\rvert^2$, which evaluates to $1$ if $f(x)$ is constant and $0$ if $f(x)$ is balanced. \n </li>\n\n</ol>\n\n### 1.4 Why Does This Work? <a id='why-does-this-work'> </a>\n\n- **Constant Oracle**\n\nWhen the oracle is *constant*, it has no effect (up to a global phase) on the input qubits, and the quantum states before and after querying the oracle are the same. Since the H-gate is its own inverse, in Step 4 we reverse Step 2 to obtain the initial quantum state of $|00\\dots 0\\rangle$ in the first register.\n\n$$\nH^{\\otimes n}\\begin{bmatrix} 1 \\\\ 0 \\\\ 0 \\\\ \\vdots \\\\ 0 \\end{bmatrix} \n= \n\\tfrac{1}{\\sqrt{2^n}}\\begin{bmatrix} 1 \\\\ 1 \\\\ 1 \\\\ \\vdots \\\\ 1 \\end{bmatrix}\n\\quad \\xrightarrow{\\text{after } U_f} \\quad\nH^{\\otimes n}\\tfrac{1}{\\sqrt{2^n}}\\begin{bmatrix} 1 \\\\ 1 \\\\ 1 \\\\ \\vdots \\\\ 1 \\end{bmatrix}\n= \n\\begin{bmatrix} 1 \\\\ 0 \\\\ 0 \\\\ \\vdots \\\\ 0 \\end{bmatrix} \n$$\n\n- **Balanced Oracle**\n\nAfter step 2, our input register is an equal superposition of all the states in the computational basis. When the oracle is *balanced*, phase kickback adds a negative phase to exactly half these states:\n\n$$\nU_f \\tfrac{1}{\\sqrt{2^n}}\\begin{bmatrix} 1 \\\\ 1 \\\\ 1 \\\\ \\vdots \\\\ 1 \\end{bmatrix} \n= \n\\tfrac{1}{\\sqrt{2^n}}\\begin{bmatrix} -1 \\\\ 1 \\\\ -1 \\\\ \\vdots \\\\ 1 \\end{bmatrix}\n$$\n\n\nThe quantum state after querying the oracle is orthogonal to the quantum state before querying the oracle. Thus, in Step 4, when applying the H-gates, we must end up with a quantum state that is orthogonal to $|00\\dots 0\\rangle$. This means we should never measure the all-zero state. \n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 2. Worked Example <a id='example'></a>\n\nLet's go through a specific example for a two bit balanced function: \n\n<ol>\n <li> The first register of two qubits is initialized to $|00\\rangle$ and the second register qubit to $|1\\rangle$ \n \n(Note that we are using subscripts 1, 2, and 3 to index the qubits. A subscript of \"12\" indicates the state of the register containing qubits 1 and 2)\n \n\n$$\\lvert \\psi_0 \\rangle = \\lvert 0 0 \\rangle_{12} \\otimes \\lvert 1 \\rangle_{3} $$\n\n \n </li>\n \n <li> Apply Hadamard on all qubits\n \n\n$$\\lvert \\psi_1 \\rangle = \\frac{1}{2} \\left( \\lvert 0 0 \\rangle + \\lvert 0 1 \\rangle + \\lvert 1 0 \\rangle + \\lvert 1 1 \\rangle \\right)_{12} \\otimes \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{2}} \\left( \\lvert 0 \\rangle - \\lvert 1 \\rangle \\right)_{3} $$\n\n \n </li>\n \n <li> The oracle function can be implemented as $\\text{Q}_f = CX_{13}CX_{23}$, \n $$\n \\begin{align*}\n \\lvert \\psi_2 \\rangle = \\frac{1}{2\\sqrt{2}} \\left[ \\lvert 0 0 \\rangle_{12} \\otimes \\left( \\lvert 0 \\oplus 0 \\oplus 0 \\rangle - \\lvert 1 \\oplus 0 \\oplus 0 \\rangle \\right)_{3} \\\\\n + \\lvert 0 1 \\rangle_{12} \\otimes \\left( \\lvert 0 \\oplus 0 \\oplus 1 \\rangle - \\lvert 1 \\oplus 0 \\oplus 1 \\rangle \\right)_{3} \\\\\n + \\lvert 1 0 \\rangle_{12} \\otimes \\left( \\lvert 0 \\oplus 1 \\oplus 0 \\rangle - \\lvert 1 \\oplus 1 \\oplus 0 \\rangle \\right)_{3} \\\\\n + \\lvert 1 1 \\rangle_{12} \\otimes \\left( \\lvert 0 \\oplus 1 \\oplus 1 \\rangle - \\lvert 1 \\oplus 1 \\oplus 1 \\rangle \\right)_{3} \\right]\n \\end{align*}\n $$\n </li>\n \n <li>Simplifying this, we get the following: \n $$\n \\begin{aligned}\n \\lvert \\psi_2 \\rangle & = \\frac{1}{2\\sqrt{2}} \\left[ \\lvert 0 0 \\rangle_{12} \\otimes \\left( \\lvert 0 \\rangle - \\lvert 1 \\rangle \\right)_{3} - \\lvert 0 1 \\rangle_{12} \\otimes \\left( \\lvert 0 \\rangle - \\lvert 1 \\rangle \\right)_{3} - \\lvert 1 0 \\rangle_{12} \\otimes \\left( \\lvert 0 \\rangle - \\lvert 1 \\rangle \\right)_{3} + \\lvert 1 1 \\rangle_{12} \\otimes \\left( \\lvert 0 \\rangle - \\lvert 1 \\rangle \\right)_{3} \\right] \\\\\n & = \\frac{1}{2} \\left( \\lvert 0 0 \\rangle - \\lvert 0 1 \\rangle - \\lvert 1 0 \\rangle + \\lvert 1 1 \\rangle \\right)_{12} \\otimes \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{2}} \\left( \\lvert 0 \\rangle - \\lvert 1 \\rangle \\right)_{3} \\\\\n & = \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{2}} \\left( \\lvert 0 \\rangle - \\lvert 1 \\rangle \\right)_{1} \\otimes \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{2}} \\left( \\lvert 0 \\rangle - \\lvert 1 \\rangle \\right)_{2} \\otimes \\frac{1}{\\sqrt{2}} \\left( \\lvert 0 \\rangle - \\lvert 1 \\rangle \\right)_{3}\n \\end{aligned}\n $$\n </li>\n \n <li> Apply Hadamard on the first register\n \n\n$$ \\lvert \\psi_3\\rangle = \\lvert 1 \\rangle_{1} \\otimes \\lvert 1 \\rangle_{2} \\otimes \\left( \\lvert 0 \\rangle - \\lvert 1 \\rangle \\right)_{3} $$\n\n\n </li>\n \n <li> Measuring the first two qubits will give the non-zero $11$, indicating a balanced function.\n </li>\n</ol>\n\nYou can try out similar examples using the widget below. Press the buttons to add H-gates and oracles, re-run the cell and/or set `case=\"constant\"` to try out different oracles.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from qiskit_textbook.widgets import dj_widget\ndj_widget(size=\"small\", case=\"balanced\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 3. Creating Quantum Oracles <a id='creating-quantum-oracles'> </a>\n\nLet's see some different ways we can create a quantum oracle. \n\nFor a constant function, it is simple:\n\n$\\qquad$ 1. if f(x) = 0, then apply the $I$ gate to the qubit in register 2. \n$\\qquad$ 2. if f(x) = 1, then apply the $X$ gate to the qubit in register 2.\n\nFor a balanced function, there are many different circuits we can create. One of the ways we can guarantee our circuit is balanced is by performing a CNOT for each qubit in register 1, with the qubit in register 2 as the target. For example:\n\n\n\nIn the image above, the top three qubits form the input register, and the bottom qubit is the output register. We can see which input states give which output in the table below:\n\n| Input states that output 0 | Input States that output 1 |\n|:--------------------------:|:--------------------------:|\n| 000 | 001 |\n| 011 | 100 |\n| 101 | 010 |\n| 110 | 111 |\n\n\nWe can change the results while keeping them balanced by wrapping selected controls in X-gates. For example, see the circuit and its results table below:\n\n\n\n| Input states that output 0 | Input states that output 1 |\n|:--------------------------:|:--------------------------:|\n| 001 | 000 |\n| 010 | 011 |\n| 100 | 101 |\n| 111 | 110 |",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 4. Qiskit Implementation <a id='implementation'></a>\n\nWe now implement the Deutsch-Jozsa algorithm for the example of a three-bit function, with both constant and balanced oracles. First let's do our imports:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# initialization\nimport numpy as np\n\n# importing Qiskit\nfrom qiskit import IBMQ, Aer\nfrom qiskit.providers.ibmq import least_busy\nfrom qiskit import QuantumCircuit, assemble, transpile\n\n# import basic plot tools\nfrom qiskit.visualization import plot_histogram",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Next, we set the size of the input register for our oracle:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# set the length of the n-bit input string. \nn = 3",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 4.1 Constant Oracle <a id='const_oracle'></a>\nLet's start by creating a constant oracle, in this case the input has no effect on the ouput so we just randomly set the output qubit to be 0 or 1:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# set the length of the n-bit input string. \nn = 3\n\nconst_oracle = QuantumCircuit(n+1)\n\noutput = np.random.randint(2)\nif output == 1:\n const_oracle.x(n)\n\nconst_oracle.draw()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 4.2 Balanced Oracle <a id='balanced_oracle'></a>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"balanced_oracle = QuantumCircuit(n+1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Next, we create a balanced oracle. As we saw in section 1b, we can create a balanced oracle by performing CNOTs with each input qubit as a control and the output bit as the target. We can vary the input states that give 0 or 1 by wrapping some of the controls in X-gates. Let's first choose a binary string of length `n` that dictates which controls to wrap:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"b_str = \"101\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now we have this string, we can use it as a key to place our X-gates. For each qubit in our circuit, we place an X-gate if the corresponding digit in `b_str` is `1`, or do nothing if the digit is `0`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"balanced_oracle = QuantumCircuit(n+1)\nb_str = \"101\"\n\n# Place X-gates\nfor qubit in range(len(b_str)):\n if b_str[qubit] == '1':\n balanced_oracle.x(qubit)\nbalanced_oracle.draw()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Next, we do our controlled-NOT gates, using each input qubit as a control, and the output qubit as a target:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"balanced_oracle = QuantumCircuit(n+1)\nb_str = \"101\"\n\n# Place X-gates\nfor qubit in range(len(b_str)):\n if b_str[qubit] == '1':\n balanced_oracle.x(qubit)\n\n# Use barrier as divider\nbalanced_oracle.barrier()\n\n# Controlled-NOT gates\nfor qubit in range(n):\n balanced_oracle.cx(qubit, n)\n\nbalanced_oracle.barrier()\nbalanced_oracle.draw()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Finally, we repeat the code from two cells up to finish wrapping the controls in X-gates:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"balanced_oracle = QuantumCircuit(n+1)\nb_str = \"101\"\n\n# Place X-gates\nfor qubit in range(len(b_str)):\n if b_str[qubit] == '1':\n balanced_oracle.x(qubit)\n\n# Use barrier as divider\nbalanced_oracle.barrier()\n\n# Controlled-NOT gates\nfor qubit in range(n):\n balanced_oracle.cx(qubit, n)\n\nbalanced_oracle.barrier()\n\n# Place X-gates\nfor qubit in range(len(b_str)):\n if b_str[qubit] == '1':\n balanced_oracle.x(qubit)\n\n# Show oracle\nbalanced_oracle.draw()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We have just created a balanced oracle! All that's left to do is see if the Deutsch-Joza algorithm can solve it.\n\n### 4.3 The Full Algorithm <a id='full_alg'></a>\n\nLet's now put everything together. This first step in the algorithm is to initialize the input qubits in the state $|{+}\\rangle$ and the output qubit in the state $|{-}\\rangle$:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dj_circuit = QuantumCircuit(n+1, n)\n\n# Apply H-gates\nfor qubit in range(n):\n dj_circuit.h(qubit)\n\n# Put qubit in state |->\ndj_circuit.x(n)\ndj_circuit.h(n)\ndj_circuit.draw()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Next, let's apply the oracle. Here we apply the `balanced_oracle` we created above:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dj_circuit = QuantumCircuit(n+1, n)\n\n# Apply H-gates\nfor qubit in range(n):\n dj_circuit.h(qubit)\n\n# Put qubit in state |->\ndj_circuit.x(n)\ndj_circuit.h(n)\n\n# Add oracle\ndj_circuit += balanced_oracle\ndj_circuit.draw()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Finally, we perform H-gates on the $n$-input qubits, and measure our input register:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dj_circuit = QuantumCircuit(n+1, n)\n\n# Apply H-gates\nfor qubit in range(n):\n dj_circuit.h(qubit)\n\n# Put qubit in state |->\ndj_circuit.x(n)\ndj_circuit.h(n)\n\n# Add oracle\ndj_circuit += balanced_oracle\n\n# Repeat H-gates\nfor qubit in range(n):\n dj_circuit.h(qubit)\ndj_circuit.barrier()\n\n# Measure\nfor i in range(n):\n dj_circuit.measure(i, i)\n\n# Display circuit\ndj_circuit.draw()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's see the output:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# use local simulator\nqasm_sim = Aer.get_backend('qasm_simulator')\nshots = 1024\nqobj = assemble(dj_circuit, qasm_sim)\nresults = qasm_sim.run(qobj).result()\nanswer = results.get_counts()\n\nplot_histogram(answer)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can see from the results above that we have a 0% chance of measuring `000`. This correctly predicts the function is balanced. \n\n### 4.4 Generalised Circuits <a id='general_circs'></a>\n\nBelow, we provide a generalised function that creates Deutsch-Joza oracles and turns them into quantum gates. It takes the `case`, (either `'balanced'` or '`constant`', and `n`, the size of the input register:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def dj_oracle(case, n):\n # We need to make a QuantumCircuit object to return\n # This circuit has n+1 qubits: the size of the input,\n # plus one output qubit\n oracle_qc = QuantumCircuit(n+1)\n \n # First, let's deal with the case in which oracle is balanced\n if case == \"balanced\":\n # First generate a random number that tells us which CNOTs to\n # wrap in X-gates:\n b = np.random.randint(1,2**n)\n # Next, format 'b' as a binary string of length 'n', padded with zeros:\n b_str = format(b, '0'+str(n)+'b')\n # Next, we place the first X-gates. Each digit in our binary string \n # corresponds to a qubit, if the digit is 0, we do nothing, if it's 1\n # we apply an X-gate to that qubit:\n for qubit in range(len(b_str)):\n if b_str[qubit] == '1':\n oracle_qc.x(qubit)\n # Do the controlled-NOT gates for each qubit, using the output qubit \n # as the target:\n for qubit in range(n):\n oracle_qc.cx(qubit, n)\n # Next, place the final X-gates\n for qubit in range(len(b_str)):\n if b_str[qubit] == '1':\n oracle_qc.x(qubit)\n\n # Case in which oracle is constant\n if case == \"constant\":\n # First decide what the fixed output of the oracle will be\n # (either always 0 or always 1)\n output = np.random.randint(2)\n if output == 1:\n oracle_qc.x(n)\n \n oracle_gate = oracle_qc.to_gate()\n oracle_gate.name = \"Oracle\" # To show when we display the circuit\n return oracle_gate",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's also create a function that takes this oracle gate and performs the Deutsch-Joza algorithm on it:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def dj_algorithm(oracle, n):\n dj_circuit = QuantumCircuit(n+1, n)\n # Set up the output qubit:\n dj_circuit.x(n)\n dj_circuit.h(n)\n # And set up the input register:\n for qubit in range(n):\n dj_circuit.h(qubit)\n # Let's append the oracle gate to our circuit:\n dj_circuit.append(oracle, range(n+1))\n # Finally, perform the H-gates again and measure:\n for qubit in range(n):\n dj_circuit.h(qubit)\n \n for i in range(n):\n dj_circuit.measure(i, i)\n \n return dj_circuit",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Finally, let's use these functions to play around with the algorithm:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"n = 4\noracle_gate = dj_oracle('balanced', n)\ndj_circuit = dj_algorithm(oracle_gate, n)\ndj_circuit.draw()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"And see the results of running this circuit:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"transpiled_dj_circuit = transpile(dj_circuit, qasm_sim)\nqobj = assemble(transpiled_dj_circuit)\nresults = qasm_sim.run(qobj).result()\nanswer = results.get_counts()\nplot_histogram(answer)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 5. Experiment with Real Devices <a id='device'></a>\n\nWe can run the circuit on the real device as shown below. We first look for the least-busy device that can handle our circuit.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Load our saved IBMQ accounts and get the least busy backend device with greater than or equal to (n+1) qubits\nIBMQ.load_account()\nprovider = IBMQ.get_provider(hub='ibm-q')\nbackend = least_busy(provider.backends(filters=lambda x: x.configuration().n_qubits >= (n+1) and\n not x.configuration().simulator and x.status().operational==True))\nprint(\"least busy backend: \", backend)",
"/usr/local/anaconda3/lib/python3.7/site-packages/qiskit/providers/ibmq/ibmqfactory.py:192: UserWarning: Timestamps in IBMQ backend properties, jobs, and job results are all now in local time instead of UTC.\n warnings.warn('Timestamps in IBMQ backend properties, jobs, and job results '\n"
],
[
"# Run our circuit on the least busy backend. Monitor the execution of the job in the queue\nfrom qiskit.tools.monitor import job_monitor\n\nshots = 1024\ntranspiled_dj_circuit = transpile(dj_circuit, backend, optimization_level=3)\nqobj = assemble(transpiled_dj_circuit, backend)\njob = backend.run(qobj)\njob_monitor(job, interval=2)",
"Job Status: job has successfully run\n"
],
[
"# Get the results of the computation\nresults = job.result()\nanswer = results.get_counts()\n\nplot_histogram(answer)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"As we can see, the most likely result is `1111`. The other results are due to errors in the quantum computation. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 6. Problems <a id='problems'></a>\n\n1. Are you able to create a balanced or constant oracle of a different form?\n\n2. The function `dj_problem_oracle` (below) returns a Deutsch-Joza oracle for `n = 4` in the form of a gate. The gate takes 5 qubits as input where the final qubit (`q_4`) is the output qubit (as with the example oracles above). You can get different oracles by giving `dj_problem_oracle` different integers between 1 and 5. Use the Deutsch-Joza algorithm to decide whether each oracle is balanced or constant (**Note:** It is highly recommended you try this example using the `qasm_simulator` instead of a real device).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from qiskit_textbook.problems import dj_problem_oracle\noracle = dj_problem_oracle(1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 7. References <a id='references'></a>\n\n1. David Deutsch and Richard Jozsa (1992). \"Rapid solutions of problems by quantum computation\". Proceedings of the Royal Society of London A. 439: 553–558. [doi:10.1098/rspa.1992.0167](https://doi.org/10.1098%2Frspa.1992.0167).\n2. R. Cleve; A. Ekert; C. Macchiavello; M. Mosca (1998). \"Quantum algorithms revisited\". Proceedings of the Royal Society of London A. 454: 339–354. [doi:10.1098/rspa.1998.0164](https://doi.org/10.1098%2Frspa.1998.0164).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import qiskit\nqiskit.__qiskit_version__",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c50ae825414b180e7fd9af3ee5adbcfc6bace62c
| 89,544 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Lab03.ipynb
|
hoesungryu/2022_IDS507_Lab
|
0f10d6b1675c963d3b44489c1be23d4dac451ff3
|
[
"Unlicense",
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Lab03.ipynb
|
hoesungryu/2022_IDS507_Lab
|
0f10d6b1675c963d3b44489c1be23d4dac451ff3
|
[
"Unlicense",
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Lab03.ipynb
|
hoesungryu/2022_IDS507_Lab
|
0f10d6b1675c963d3b44489c1be23d4dac451ff3
|
[
"Unlicense",
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 89,544 | 89,544 | 0.859499 |
[
[
[
"# 💻IDS507 | Lab03\n<font size=5><b>Regression Analysis<b></font>\n<div align='right'>TA: 류 회 성(Hoe Sung Ryu)</div>\n\n## Concepts | 오늘 배울 개념\n---\n- 내 데이터를 train/test dataset으로 나누기\n- 내 데이터로 `Logistic regression` (로지스틱 회귀) 모델 만들어보기\n- 생성한 모델을 이용해 새로운 데이터를 예측해보기\n- 내 모델이 얼마나 잘 기능하는가?\n- Confusion Matrix, Roc Curve & AUC 계산\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 📌1.드라이브 연동",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from google.colab import drive # 드라이브 연동\ndrive.mount('/content/gdrive')",
"Mounted at /content/gdrive\n"
],
[
"import os\nos.chdir('/content/gdrive/My Drive/IDS507-00/2022_IDS507_Lab') # DataPath 설정 ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!pwd",
"/content/gdrive/My Drive/IDS507-00/2022_IDS507_Lab\n"
]
],
[
[
"## 📌2. 회귀 분석\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n### 1) 회귀(Regression)\n- 데이터의 값은 평균과 같은 기존의 경향으로 돌아가려는 경향\n- 여러 변수들 간의 상관 관계를 파악하여, 어떤 특정 변수의 값을 다른 변수들의 값을 이용하여 설명/예측하는 기법\n- 독립변수, 종속변수\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n### 2) 회귀 분석의 유형\n- 변수의 개수 및 계수의 형태에 따라 구분\n- 독립변수의 개수에 따라\n - 단순 : 독립변수가 1개인 경우\n - 다중 : 독립변수가 여러 개인 경우\n- 회귀계수의 형태에 따라\n - 선형 : 계수를 선형 결합으로 표현할 수 있는 경우\n - 비선형 : 계수를 선형 결합으로 표현할 수 없는 경우\n \n ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# sample data \n# 1. train \nX_train = [[1],[2],[3],[4],[5]] # 독립변수의 특성이 1개 밖에 없더라도 각 값들은 리스트 또는 배열의 형태\ny_train = [2.3, 3.99, 5.15, 7.89, 8.6]\n\n# 2. test\nX_test = [[6],[7]]\ny_test = [10.1, 11.9]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression\nlr = LinearRegression()\n\nreg = lr.fit(X_train,y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 3) 단순 선형 회귀\n- 독립변수가 1개이고 종속변수도 1개인 경우, 그들 간의 관계를 **선형적으로 파악**하는 회귀 방식\n- `독립변수 X`와 `종속변수 Y`의 **`관계`**를 **`Y = aX + b 형태의 1차 함수식`**으로 표현\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n#### 회귀 계수 (coefficient) → y = **`a`**x+b\n- 독립변수가 종속변수에 끼치는 영향력의 정도로서, 직선의 기울기(slope)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n#### 절편 (intercept) → y = ax+**`b`**\n- 독립변수가 0일 때의 상수 값\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n#### 잔차 (residual) → y = ax+b+**`Error`**\n- 실제 값과 회귀식의 차이에 따른 오류 값\n- 잔차 값이 작을수록, 구해진 회귀식이 데이터들을 더욱 잘 설명하고 있다",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"y_pred = reg.predict(X_test)\ny_pred",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 추정된 회귀 모형의 회귀 계수 및 절편 값을 확인\n# 회귀 계수는 coef_ 속성, 절편은 intercept_ 속성에 각각 값이 할당\nprint(\"회귀 계수 : \",reg.coef_)\nprint(\"절편 : \",reg.intercept_)\nprint(f'선형식:y= {reg.coef_[0]}X + {reg.intercept_:.4f}')",
"회귀 계수 : [1.65]\n절편 : 0.636000000000001\n선형식:y= 1.65X + 0.6360\n"
]
],
[
[
"### 4) 사이킷런으로 성능 평가 지표 확인\n\n- 회귀 분석의 평가 지표\n\n|지표|의미|대응함수|\n|---|---|---|\n|MAE|Mean Absolute Error, 즉 실제값과 예측값의 차이의 절대값들의 평균|metrics 모듈의 mean_absolute_error|\n|MSE|Mean Absolute Error, 즉 실제값과 예측값의 차이의 절대값들의 평균|metrics 모듈의 mean_squared_error|\n|RMSE|Root of MSE, 즉 MSE의 제곱근 값|math 또는 numpy 모듈의 sqrt|\n|$R^2$|결정 계수라고 하며, 실제값의 분산 대비 예측값의 분산의 비율|metrics 모듈의 r2_score 또는 LinearRegression의 score|\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 결과분석\nfrom sklearn.metrics import (mean_squared_error,\n r2_score,\n mean_absolute_error,\n)\nprint(mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred))\nprint(r2_score(y_test, y_pred))\nprint(mean_absolute_error(y_test, y_pred))\nprint(mean_absolute_error(y_test, y_pred)**(1/2))\n",
"0.13594599999999984\n0.8321654320987657\n0.36099999999999977\n0.6008327554319919\n"
],
[
"# 분석 결과 표로 표시하기 \nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nx = range(1,8)\nplt.title(\"Linear Regression\")\nplt.plot(X_train+X_test,y_train+y_test,'o',color = 'blue')\nplt.plot(x,reg.coef_*x+reg.intercept_,'--',color='red')\nplt.plot(X_test,y_pred,'x',color = 'black')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 📌3. 실제 데이터를 활용하여 로지스틱회귀 분석\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n### 1) 로지스틱 회귀란? \n- 선형 회귀 모형을 **`분류`** 에 적용한 기법\n- 데이터가 특정 레이블(클래스)에 소속될 확률을 추정\n - 이 이메일이 스팸일 확률은 얼마\n - 이번 시험에서 합격할 확률은 얼마\n- 다른 선형 회귀 모형과는 다르게, 종속변수가 수치형 (numerical)이 아니라 범주형(categorical)\n - 스팸메일, 정상메일\n - 합격, 불합격\n- 특정 클래스에 대해서 추정된 확률이 50% 이상이면 해당 데이터를 그 클래스에 속하는 것으로 분류\n- 기본적인 로지스틱 회귀는 이항형(binomial)으로서, 종속 변수의 값의 종류는 0과 1의 두 종류\n - 즉, 이 경우의 종속변수는 곧 클래스 그 자체\n - 값이 0이면 음성, 1이면 양성이라고 표현\n- 이러한 이진 데이터에 대해서 올바른 결과를 나타내는 선형 회귀를 수행하려면 다음과 같은 성질이 필요\n - 연속적인 단조 증가(monotone increasing) 함수일 것\n - 함수의 결과가 [0, 1] 사이의 값\n- 이와 같은 성질을 만족하는 함수를 시그모이드(sigmoid) 함수\n\n$$ y = \\frac{1}{1+e^{-x}} $$\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n### 2) 분류함수의 성능지표\n\n|함수명|설명|\n|---|---|\n|**accuracy_score**|정확도를 계산한다.|\n|**confusion_matrix** |오차 행렬을 도출한다.|\n|**precision_score** |정밀도를 계산한다.|\n|**recall_score** |재현율을 계산한다.|\n|**f1_score** |F1 스코어를 계산한다.|\n|**classification_report** | 정밀도, 재현율, F1 스코어를 함께 보여준다|",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib as mpl\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\nX = np.arange(-10,10,0.1)\ny = 1 / (1+np.exp(-X))\nplt.plot(X,y,label = 'Sigmoid')\nplt.plot(X,[0.5 for _ in X],color='red',label = 'Threshold')\nplt.legend()\nplt.grid()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 3) 당뇨병 데이터 불러오기\nreference:https://www.kaggle.com/saurabh00007/diabetescsv\n* Pregnancies: 임신 횟수\n* Glucose: 포도당 부하 검사 수치\n* BloodPressure: 혈압(mm Hg)\n* SkinThickness: 팔 삼두근 뒤쪽의 피하지방 측정값(mm)\n* Insulin: 혈청 인슐린(mu U/ml)\n* BMI: 체질량지수(체중(kg)/(키(m))^2)\n* DiabetesPedigreeFunction: 당뇨 내력 가중치 값\n* Age: 나이\n* Outcome: 클래스 결정 값(0또는 1)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n%matplotlib inline\n\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, precision_score, recall_score, roc_auc_score\nfrom sklearn.metrics import f1_score, confusion_matrix, precision_recall_curve, roc_curve\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler,MinMaxScaler\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression\n\ndiabetes_data = pd.read_csv('./data/diabetes.csv') # 데이터 로드\ndiabetes_data.head(3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(diabetes_data['Outcome'].value_counts())",
"0 500\n1 268\nName: Outcome, dtype: int64\n"
],
[
"# 'Glucose' 피처의 분포도\nplt.hist(diabetes_data['Glucose'], bins=10)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 4) scikit-learn 패키지를 사용하여 Train / Test 셋 분리하기\n\nparameter 설명\n\n- `train_test_split(arrays, test_size, train_size, random_state, shuffle, stratify)`의 인자(parameter)\n```\narrays : 분할시킬 데이터를 입력 (Python list, Numpy array, Pandas dataframe 등..)\ntest_size : 테스트 데이터셋의 비율(float)이나 갯수(int) (default = 0.25)\ntrain_size : 학습 데이터셋의 비율(float)이나 갯수(int) (default = test_size의 나머지)\nrandom_state : 데이터 분할시 셔플이 이루어지는데 이를 기억하기 위한 임의의 시드값 (int나 RandomState로 입력)\nshuffle : 셔플여부설정 (default = True)\nstratify : 지정한 Data의 비율을 유지한다. 예를 들어, Label Set인 Y가 25%의 0과 75%의 1로 이루어진 Binary Set일 때,\n stratify=Y로 설정하면 나누어진 데이터셋들도 0과 1을 각각 25%, 75%로 유지한 채 분할된다.\n```\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 피처 데이터 세트 X, 레이블 데이터 세트 y를 추출. \nX = diabetes_data.iloc[:, :-1]\ny = diabetes_data.iloc[:, -1]\n\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 0.2, random_state = 156, stratify=y)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 로지스틱 회귀로 학습,예측 및 평가 수행. \n\nlr_clf = LogisticRegression(max_iter=1000,)\nlr_clf.fit(X_train , y_train)\ny_pred = lr_clf.predict(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"y_pred",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test , y_pred)\nprint(\"Accuracy : \",round(accuracy,76))",
"Accuracy : 0.7987012987012987\n"
],
[
"print(500/diabetes_data['Outcome'].value_counts().sum())",
"0.6510416666666666\n"
]
],
[
[
"### 5) Confusion Matrix(오차행렬)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# #calculate AUC of model\n# pred_proba = lr_clf.predict_proba(X_test)\n# pred_proba_c1 = pred_proba[:,1].reshape(-1,1)\n# auc = roc_auc_score(y_test, pred_proba_c1)\n\n# #print AUC score\n# print(auc)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"roc_auc = roc_auc_score(y_test, pred_proba[:,1]) # calculate AUC of model\nconfusion = confusion_matrix( y_test, y_pred)\nprint('AUC score:', roc_auc)\nprint('오차 행렬')\nprint(confusion)",
"AUC score: 0.8072222222222222\n오차 행렬\n[[90 10]\n [21 33]]\n"
],
[
"import pandas as pd \nimport seaborn as sns \nmatrix = pd.DataFrame(confusion,\n columns = ['Positive','Negative'],\n index= ['True','False']\n )\nsns.heatmap(matrix, annot=True, cmap='Blues', fmt='d')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve\n\n# roc curve for models\nfpr1, tpr1, thresh1 = roc_curve(y_test, pred_proba[:,1], pos_label=1)\n# fpr2, tpr2, thresh2 = roc_curve(y_test, pred_prob2[:,1], pos_label=1)\n# \n# roc curve for tpr = fpr \n# random_probs = [0 for i in range(len(y_test))]\n# p_fpr, p_tpr, _ = roc_curve(y_test, random_probs, pos_label=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n# plt.style.use('seaborn')\n\n# plot roc curves\nplt.plot(fpr1, tpr1, linestyle='--',color='orange', label='Logistic Regression')\n# plt.plot(fpr2, tpr2, linestyle='--',color='green', label='KNN')\n# plt.plot(p_fpr, p_tpr, linestyle='--', color='blue')\nplt.plot([0,1],[0,1],linestyle='--', color='blue')\n# title\nplt.title('ROC curve for Classification')\n# x label\nplt.xlabel('False Positive Rate')\n# y label\nplt.ylabel('True Positive rate')\n\nplt.legend(loc='best')\n# plt.savefig('ROC',dpi=300)\nplt.show();",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 6) Threshold(입계값) 변경하며 성능측정하기",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"thresholds = [0.3 , 0.33 ,0.36,0.39, 0.42 , 0.45 ,0.48, 0.50]\n# pred_proba = lr_clf.predict_proba(X_test)\n\npred_proba_c1 = pred_proba[:,1].reshape(-1,1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.preprocessing import Binarizer\n\n\nfor custom_threshold in thresholds:\n binarizer = Binarizer(threshold=custom_threshold).fit(pred_proba_c1) \n custom_predict = binarizer.transform(pred_proba_c1)\n print('Threshold:',custom_threshold)\n accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test , custom_predict)\n print(\"Accuracy: \",round(accuracy,3))\n print(\" \")",
"Threshold: 0.3\nAccuracy: 0.487\n \nThreshold: 0.33\nAccuracy: 0.487\n \nThreshold: 0.36\nAccuracy: 0.494\n \nThreshold: 0.39\nAccuracy: 0.526\n \nThreshold: 0.42\nAccuracy: 0.539\n \nThreshold: 0.45\nAccuracy: 0.552\n \nThreshold: 0.48\nAccuracy: 0.558\n \nThreshold: 0.5\nAccuracy: 0.565\n \n"
]
],
[
[
"### 7) 교차검증\n\n일반적으로 회귀에는 기본 k-겹 교차검증을 사용하고, 분류에는 StratifiedKFold를 사용한다.\n데이터가 편항되어 단순 k-겹 교차검증을 사용하면 성능 평가가 잘 되지 않을 수 있기때문이다.\n\n<img src='https://jinnyjinny.github.io/assets/post_img/deep%20learning/2020-04-02-Kfold/main3.jpg'>\n<br>\n<!-- <center>leave-one-out</center>\n<center><img src='https://smlee729.github.io/img/2015-03-19-1-loocv/loocv1.png' width=70%></center> -->\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# cross_validation \nfrom sklearn.model_selection import KFold, StratifiedKFold, LeaveOneOut\n\nkfold = KFold(n_splits=5)\nsfold = StratifiedKFold()\n# loo = LeaveOneOut()\n\n\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score\n\nlr_clf = LogisticRegression(max_iter=1000,)\nkfold_score = cross_val_score(lr_clf, X, y, cv=kfold)\nsfold_score = cross_val_score(lr_clf, X, y, cv=sfold)\n# loo_score = cross_val_score(lr_clf, X, y, cv=loo)\n\nprint('Kfold 정확도: {:.2f} %'.format(kfold_score.mean()*100))\nprint('StratifiedKFold 정확도: {:.2f}'.format(sfold_score.mean()))\n# print('LeaveOneOut 정확도: {:.2f}'.format(loo_score.mean()))",
"Kfold 정확도: 77.09 %\nStratifiedKFold 정확도: 0.77\nLeaveOneOut 정확도: 0.78\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c50aea74bbf95b58bc6dc036a920e252b78c8565
| 2,374 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Intro_to_Python.ipynb
|
LamarLaiz/Elective1-3
|
dc3be15325f1c5c2108a612b4417af389b3221b7
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Intro_to_Python.ipynb
|
LamarLaiz/Elective1-3
|
dc3be15325f1c5c2108a612b4417af389b3221b7
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Intro_to_Python.ipynb
|
LamarLaiz/Elective1-3
|
dc3be15325f1c5c2108a612b4417af389b3221b7
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 23.27451 | 233 | 0.454086 |
[
[
[
"<a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/LamarLaiz/Elective1-3/blob/main/Intro_to_Python.ipynb\" target=\"_parent\"><img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open In Colab\"/></a>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"##Python Indention",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"if 5<2:\n print(\"Five is less than two\")\nelse:\n print(\"Five is greater than two\")",
"Five is greater than two\n"
]
],
[
[
"##Python Comments",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#This is a program that displays Hello, World\n\nprint(\"Hello,World\")\nprint('Welcome to Python Programming')",
"Hello,World\nWelcome to Python Programming\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c50b0dd31d60c323b425b136228c3ce189feee88
| 2,161 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/deflection/index.ipynb
|
bmcs-group/bmcs_beam
|
b53967d0d0461657ec914a3256ec40f9dcff80d5
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-05-07T11:10:27.000Z
|
2021-05-07T11:10:27.000Z
|
notebooks/deflection/index.ipynb
|
bmcs-group/bmcs_beam
|
b53967d0d0461657ec914a3256ec40f9dcff80d5
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/deflection/index.ipynb
|
bmcs-group/bmcs_beam
|
b53967d0d0461657ec914a3256ec40f9dcff80d5
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 36.627119 | 175 | 0.681629 |
[
[
[
"# **Deflection**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 1 Used packages\nExamples from some of the external libraries used here are provided in the following:\n\n* `Beam` module from `Sympy` library:\n - [General usage example](external_libraries/sympy_beam/sympy_beam_example.ipynb)\n - [Multiple beam configurations](external_libraries/sympy_beam/beam_configs_examples.ipynb)\n\n## 2 Verification studies\n- [Verification of deflection_profile module](deflection_verification/deflection_profile_verification.ipynb)\n\n## 3 Parametric studies\n- [Parametric study on deflection_profile in general](parametric_studies/deflection_parametric_study.ipynb)\n- [Parametric study using El Ghadioui beam setup](parametric_studies/deflection_parametric_study-El%20Ghadioui.ipynb)\n- [Parametric study using a cantilever modified from El Ghadioui beam setup](parametric_studies/deflection_parametric_study-El%20Ghadioui_cantilever.ipynb)\n\n## 4 Slenderness curves\nNotebooks about the concept of limiting deflections in SLS according to EC2 using slenderness $l/d$ vs reinforcement ratio $\\rho$ curves:\n- [Slenderness curves investigations](slenderness_curves/slenderness_curves.ipynb)\n- [Draft for regenerating slenderness curves according to El Ghadioui PhD dissertation](slenderness_curves/slenderness_curves_according_to_El%20Ghadioui2020_DRAFT.ipynb)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
c50b0f9bd7ff71dd47456faae741900ca38b7869
| 2,523 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
python_type_hinting.ipynb
|
tagler/Data_Science_Notebook_Tutorials_Python
|
60ec52a7159f6947ff1397e7def404c959d056fb
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-03-28T03:14:03.000Z
|
2021-03-28T03:14:03.000Z
|
python_type_hinting.ipynb
|
tagler/Data_Science_Notebook_Tutorials_Python
|
60ec52a7159f6947ff1397e7def404c959d056fb
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
python_type_hinting.ipynb
|
tagler/Data_Science_Notebook_Tutorials_Python
|
60ec52a7159f6947ff1397e7def404c959d056fb
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 18.551471 | 71 | 0.469283 |
[
[
[
"# Python Type Hinting",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from typing import List, Set, Tuple, Dict, Union, Any, Optional",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x: int = 10\ny: int = 100\nz: float = 1000\nq: str = 'asdfasdf'\nl: List[int] = [1,5,3,2,4]\ndata: Dict = {'x' : [x], 'y' : [y], 'z' : [z]}\ndf: pd.DataFrame = pd.DataFrame(data)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def test_fucntion(a: int, b: float, c: pd.DataFrame) -> float:\n return a + b",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"class MyClass:\n def __init__(self, a: int, b: int, c: int):\n self.a = a\n self.b = b\n self.c = c",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mc1 = MyClass(1,2,3)\nmc2 = MyClass(4,5,6)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def test_function_2(abc: MyClass, asdf: MyClass) -> None:\n print(abc.a)\n print(asdf.b)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"test_function_2(mc1, mc2)",
"1\n5\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50b1d141eb88ed085c314ab84b53d0579233477
| 161,377 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
benchmarking/Xgboost_XGBClassifier_Serial.ipynb
|
jashanmeet-collab/mango
|
ed1fb80fda35d00f6cdfc06e71f55b1a0a9cf4b3
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 123 |
2019-10-19T16:55:38.000Z
|
2022-03-03T02:34:17.000Z
|
benchmarking/Xgboost_XGBClassifier_Serial.ipynb
|
jashanmeet-collab/mango
|
ed1fb80fda35d00f6cdfc06e71f55b1a0a9cf4b3
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 33 |
2019-10-24T21:10:53.000Z
|
2022-03-31T00:14:47.000Z
|
benchmarking/Xgboost_XGBClassifier_Serial.ipynb
|
jashanmeet-collab/mango
|
ed1fb80fda35d00f6cdfc06e71f55b1a0a9cf4b3
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 29 |
2019-10-24T19:08:50.000Z
|
2022-02-10T11:06:04.000Z
| 225.702098 | 31,680 | 0.909039 |
[
[
[
"# Example of optimizing Xgboost XGBClassifier function",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Goal is to test the objective values found by Mango",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Benchmarking Serial Evaluation: Iterations 60",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from mango.tuner import Tuner\nfrom scipy.stats import uniform\n\ndef get_param_dict():\n param_dict = {\"learning_rate\": uniform(0, 1),\n \"gamma\": uniform(0, 5),\n \"max_depth\": range(1,10),\n \"n_estimators\": range(1,300),\n \"booster\":['gbtree','gblinear','dart']\n }\n return param_dict\n\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score\nfrom xgboost import XGBClassifier\nfrom sklearn.datasets import load_wine\n\nX, Y = load_wine(return_X_y=True)\n\ncount_called = 1\n\ndef objfunc(args_list):\n global X, Y, count_called\n \n #print('count_called:',count_called)\n \n count_called = count_called + 1\n results = []\n for hyper_par in args_list:\n clf = XGBClassifier(**hyper_par)\n result = cross_val_score(clf, X, Y, scoring='accuracy').mean()\n results.append(result)\n return results\n\ndef get_conf():\n conf = dict()\n conf['batch_size'] = 1\n conf['initial_random'] = 5\n conf['num_iteration'] = 60\n conf['domain_size'] = 5000\n \n return conf\n\ndef get_optimal_x():\n param_dict = get_param_dict()\n conf = get_conf()\n tuner = Tuner(param_dict, objfunc,conf)\n results = tuner.maximize()\n return results",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"optimal_X = []\nResults = []",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"num_of_tries = 100",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for i in range(num_of_tries):\n results = get_optimal_x()\n Results.append(results)\n optimal_X.append(results['best_params']['x'])\n print(i,\":\",results['best_params']['x'])",
"0 : 0\n1 : 0\n2 : 0\n3 : 0\n4 : 0\n5 : 0\n6 : 31\n7 : 0\n8 : 0\n9 : 0\n10 : 0\n11 : 0\n12 : 0\n13 : 0\n14 : 0\n15 : 0\n16 : 0\n17 : 0\n18 : 0\n19 : 0\n20 : 0\n21 : 0\n22 : 0\n23 : 0\n24 : 0\n25 : 0\n26 : 0\n27 : 0\n28 : 0\n29 : 0\n30 : 0\n31 : -1\n32 : 0\n33 : 0\n34 : -441\n35 : 0\n36 : 0\n37 : 0\n38 : 0\n39 : 0\n40 : 0\n41 : -1162\n42 : 0\n43 : 0\n44 : 0\n45 : 0\n46 : 0\n47 : 0\n48 : 0\n49 : 0\n50 : 0\n51 : 0\n52 : 0\n53 : 0\n54 : 0\n55 : 0\n56 : 0\n57 : 0\n58 : 0\n59 : 0\n60 : 0\n61 : 0\n62 : 0\n63 : 0\n64 : 0\n65 : 0\n66 : 0\n67 : 0\n68 : 0\n69 : 0\n70 : -79\n71 : 0\n72 : 0\n73 : 0\n74 : 0\n75 : 0\n76 : 0\n77 : 0\n78 : 0\n79 : 0\n80 : 0\n81 : 0\n82 : 0\n83 : 0\n84 : 0\n85 : 0\n86 : 0\n87 : 0\n88 : 0\n89 : 0\n90 : 0\n91 : 0\n92 : 0\n93 : 0\n94 : 0\n95 : 0\n96 : 0\n97 : 0\n98 : 0\n99 : 0\n"
],
[
"# import numpy as np\n# optimal_X = np.array(optimal_X)\n\n# plot_optimal_X=[]\n# for i in range(optimal_X.shape[0]):\n# plot_optimal_X.append(optimal_X[i]['x'])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Plotting the serial run results",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\nfig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))\n\nn, bins, patches = plt.hist(optimal_X, 20, facecolor='g', alpha=0.75)\n\ndef autolabel(rects):\n \"\"\"\n Attach a text label above each bar displaying its height\n \"\"\"\n for rect in rects:\n height = rect.get_height()\n plt.text(rect.get_x() + rect.get_width()/2., 1.0*height,\n '%d' % int(height),\n ha='center', va='bottom',fontsize=15)\nplt.xlabel('X-Value',fontsize=25)\nplt.ylabel('Number of Occurence',fontsize=25)\nplt.title('Optimal Objective: Iterations 60',fontsize=20)\nplt.xticks(fontsize=20)\nplt.yticks(fontsize=20)\n\n\nplt.grid(True)\n\nautolabel(patches)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Benchmarking test with different iterations for serial executions",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from mango.tuner import Tuner\n\ndef get_param_dict():\n param_dict = {\n 'x': range(-5000, 5000)\n }\n return param_dict\n \ndef objfunc(args_list):\n results = []\n for hyper_par in args_list:\n x = hyper_par['x']\n result = -(x**2)\n results.append(result)\n return results\n\n\ndef get_conf_20():\n conf = dict()\n conf['batch_size'] = 1\n conf['initial_random'] = 5\n conf['num_iteration'] = 20\n conf['domain_size'] = 5000\n return conf\n\ndef get_conf_30():\n conf = dict()\n conf['batch_size'] = 1\n conf['initial_random'] = 5\n conf['num_iteration'] = 30\n conf['domain_size'] = 5000\n return conf\n\ndef get_conf_40():\n conf = dict()\n conf['batch_size'] = 1\n conf['initial_random'] = 5\n conf['num_iteration'] = 40\n conf['domain_size'] = 5000\n return conf\n\ndef get_conf_60():\n conf = dict()\n conf['batch_size'] = 1\n conf['initial_random'] = 5\n conf['num_iteration'] = 60\n conf['domain_size'] = 5000\n return conf\n\n\ndef get_optimal_x():\n param_dict = get_param_dict()\n conf_20 = get_conf_20()\n tuner_20 = Tuner(param_dict, objfunc,conf_20)\n \n conf_30 = get_conf_30()\n tuner_30 = Tuner(param_dict, objfunc,conf_30)\n \n conf_40 = get_conf_40()\n tuner_40 = Tuner(param_dict, objfunc,conf_40)\n \n conf_60 = get_conf_60()\n tuner_60 = Tuner(param_dict, objfunc,conf_60)\n \n \n results_20 = tuner_20.maximize()\n results_30 = tuner_30.maximize()\n results_40 = tuner_40.maximize()\n results_60 = tuner_60.maximize()\n \n return results_20, results_30, results_40 , results_60",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Store_Optimal_X = []\nStore_Results = []\nnum_of_tries = 100",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"for i in range(num_of_tries):\n results_20, results_30, results_40 , results_60 = get_optimal_x()\n Store_Results.append([results_20, results_30, results_40 , results_60])\n Store_Optimal_X.append([results_20['best_params']['x'],results_30['best_params']['x'],results_40['best_params']['x'],results_60['best_params']['x']])\n print(i,\":\",[results_20['best_params']['x'],results_30['best_params']['x'],results_40['best_params']['x'],results_60['best_params']['x']])",
"0 : [0, -4, 0, 0]\n1 : [0, 823, 0, 0]\n2 : [844, 0, 0, 0]\n3 : [5, 0, 0, 0]\n4 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n5 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n6 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n7 : [0, -70, 0, 0]\n8 : [-447, 0, 0, 0]\n9 : [421, 0, 0, 0]\n10 : [-13, 0, -31, 0]\n11 : [0, 0, 0, 245]\n12 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n13 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n14 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n15 : [-22, 0, 0, 0]\n16 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n17 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n18 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n19 : [0, -4, 0, 0]\n20 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n21 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n22 : [-391, 0, 1198, 0]\n23 : [-110, 0, 0, 0]\n24 : [0, 0, 601, 0]\n25 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n26 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n27 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n28 : [-42, 0, 0, 0]\n29 : [3, -341, 0, 0]\n30 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n31 : [-996, 0, 39, 0]\n32 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n33 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n34 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n35 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n36 : [407, -481, 0, 0]\n37 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n38 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n39 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n40 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n41 : [23, 0, 0, 0]\n42 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n43 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n44 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n45 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n46 : [0, 31, 0, 0]\n47 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n48 : [-303, 0, 0, 0]\n49 : [0, 213, 0, 0]\n50 : [0, 0, 0, 248]\n51 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n52 : [2022, 0, 163, 0]\n53 : [-248, 0, 0, 0]\n54 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n55 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n56 : [0, 0, 474, 0]\n57 : [13, 75, 0, 0]\n58 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n59 : [-5, 0, 0, 0]\n60 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n61 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n62 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n63 : [-142, 0, 0, 0]\n64 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n65 : [146, 0, 0, 0]\n66 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n67 : [1, 0, 0, 0]\n68 : [-13, 0, 0, 0]\n69 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n70 : [553, 0, 0, 0]\n71 : [24, 9, 0, 0]\n72 : [0, 44, 0, 0]\n73 : [0, -852, 0, 0]\n74 : [0, -56, 0, 0]\n75 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n76 : [-1652, 0, 0, 0]\n77 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n78 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n79 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n80 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n81 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n82 : [-605, 0, 0, 0]\n83 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n84 : [27, -1, 0, 0]\n85 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n86 : [2, 0, 0, 0]\n87 : [16, 0, 0, 0]\n88 : [0, 87, 0, 0]\n89 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n90 : [3, 0, 0, 0]\n91 : [-187, 0, 0, 0]\n92 : [0, 0, 155, 0]\n93 : [0, -168, 0, 0]\n94 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n95 : [-1, -54, 0, 0]\n96 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n97 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n98 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n99 : [0, 0, 0, 0]\n"
],
[
"import numpy as np\nStore_Optimal_X=np.array(Store_Optimal_X)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))\nn, bins, patches = plt.hist(Store_Optimal_X[:,0], 20, facecolor='g', alpha=0.75)\ndef autolabel(rects):\n \"\"\"\n Attach a text label above each bar displaying its height\n \"\"\"\n for rect in rects:\n height = rect.get_height()\n plt.text(rect.get_x() + rect.get_width()/2., 1.0*height,\n '%d' % int(height),\n ha='center', va='bottom',fontsize=15)\nplt.xlabel('X-Value',fontsize=25)\nplt.ylabel('Number of Occurence',fontsize=25)\nplt.title('Optimal Objective: Iterations 20',fontsize=20)\nplt.xticks(fontsize=20)\nplt.yticks(fontsize=20)\nplt.grid(True)\nautolabel(patches)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))\nn, bins, patches = plt.hist(Store_Optimal_X[:,1], 20, facecolor='g', alpha=0.75)\ndef autolabel(rects):\n \"\"\"\n Attach a text label above each bar displaying its height\n \"\"\"\n for rect in rects:\n height = rect.get_height()\n plt.text(rect.get_x() + rect.get_width()/2., 1.0*height,\n '%d' % int(height),\n ha='center', va='bottom',fontsize=15)\nplt.xlabel('X-Value',fontsize=25)\nplt.ylabel('Number of Occurence',fontsize=25)\nplt.title('Optimal Objective: Iterations 30',fontsize=20)\nplt.xticks(fontsize=20)\nplt.yticks(fontsize=20)\nplt.grid(True)\nautolabel(patches)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))\nn, bins, patches = plt.hist(Store_Optimal_X[:,2], 20, facecolor='g', alpha=0.75)\ndef autolabel(rects):\n \"\"\"\n Attach a text label above each bar displaying its height\n \"\"\"\n for rect in rects:\n height = rect.get_height()\n plt.text(rect.get_x() + rect.get_width()/2., 1.0*height,\n '%d' % int(height),\n ha='center', va='bottom',fontsize=15)\nplt.xlabel('X-Value',fontsize=25)\nplt.ylabel('Number of Occurence',fontsize=25)\nplt.title('Optimal Objective: Iterations 40',fontsize=20)\nplt.xticks(fontsize=20)\nplt.yticks(fontsize=20)\nplt.grid(True)\nautolabel(patches)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))\nn, bins, patches = plt.hist(Store_Optimal_X[:,3], 20, facecolor='g', alpha=0.75)\ndef autolabel(rects):\n \"\"\"\n Attach a text label above each bar displaying its height\n \"\"\"\n for rect in rects:\n height = rect.get_height()\n plt.text(rect.get_x() + rect.get_width()/2., 1.0*height,\n '%d' % int(height),\n ha='center', va='bottom',fontsize=15)\nplt.xlabel('X-Value',fontsize=25)\nplt.ylabel('Number of Occurence',fontsize=25)\nplt.title('Optimal Objective: Iterations 60',fontsize=20)\nplt.xticks(fontsize=20)\nplt.yticks(fontsize=20)\nplt.grid(True)\nautolabel(patches)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50b372f2f59b1e8d8b9e4c0d1860758fdce7dbb
| 186,543 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
opencv/OpenCV Lecture01. Image-Video.ipynb
|
mssung94/intel-basic-tutorial
|
9d7dfc3759f6d9b1334a06e47bb9fffe5ee4899d
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2019-12-16T08:59:13.000Z
|
2019-12-16T08:59:13.000Z
|
opencv/OpenCV Lecture01. Image-Video.ipynb
|
mssung94/intel-basic-tutorial
|
9d7dfc3759f6d9b1334a06e47bb9fffe5ee4899d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
opencv/OpenCV Lecture01. Image-Video.ipynb
|
mssung94/intel-basic-tutorial
|
9d7dfc3759f6d9b1334a06e47bb9fffe5ee4899d
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2020-08-29T07:18:56.000Z
|
2020-08-29T07:18:56.000Z
| 539.141618 | 114,280 | 0.943273 |
[
[
[
"<img src='./img/intel-logo.jpg' width=50%, Fig1> \n\n# OpenCV 기초강좌 \n\n<font size=5><b>01. 이미지, 비디오 입출력 <b></font>\n\n<div align='right'>성 민 석 (Minsuk Sung)</div>\n<div align='right'>류 회 성 (Hoesung Ryu)</div>\n\n<img src='./img/OpenCV_Logo_with_text.png' width=20%, Fig2> \n\n\n---",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<h1>Table of Contents<span class=\"tocSkip\"></span></h1>\n<div class=\"toc\"><ul class=\"toc-item\"><li><span><a href=\"#이미지-읽기\" data-toc-modified-id=\"이미지-읽기-1\"><span class=\"toc-item-num\">1 </span>이미지 읽기</a></span></li><li><span><a href=\"#Matplotlib을-이용해-이미지-시각화-하기\" data-toc-modified-id=\"Matplotlib을-이용해-이미지-시각화-하기-2\"><span class=\"toc-item-num\">2 </span>Matplotlib을 이용해 이미지 시각화 하기</a></span></li><li><span><a href=\"#이미지-저장하기\" data-toc-modified-id=\"이미지-저장하기-3\"><span class=\"toc-item-num\">3 </span>이미지 저장하기</a></span></li><li><span><a href=\"#웹캠을-사용하여-비디오-읽기\" data-toc-modified-id=\"웹캠을-사용하여-비디오-읽기-4\"><span class=\"toc-item-num\">4 </span>웹캠을 사용하여 비디오 읽기</a></span></li><li><span><a href=\"#영상-저장\" data-toc-modified-id=\"영상-저장-5\"><span class=\"toc-item-num\">5 </span>영상 저장</a></span></li></ul></div>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 이미지 읽기\n\n`cv2.imread(file, flag)`\n\nflag에 다양한 옵션을 주어 여러가지 형태로 불러 올 수 있습니다.\n\n1. file : 저장위치\n\n\n2. flag\n - cv2.IMREAD_ANYCOLOR: 원본 파일로 읽어옵니다. \n - cv2.IMREAD_COLOR: 이미지 파일을 Color로 읽음. 투명한 부분은 무시하며 Default 설정입니다.\n - cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE: 이미지 파일을 Grayscale로 읽음. 실제 이미지 처리시 중간 단계로 많이 사용합니다\n - cv2.IMREAD_UNCHAGED: 이미지 파일을 alpha channel 까지 포함해 읽음",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import cv2\n\n# 원본그대로 불러오기 \nimage = cv2.imread(\"./img/toy.jpg\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 회색조로 불러오기 \nimg_gray = cv2.imread(\"./img/toy.jpg\", cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Matplotlib을 이용해 이미지 시각화 하기 \n\n`jupyter notebook`에서 작업하는 경우 Matplotlib을 이용하여 시각화하는 방법을 추천합니다. \n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%matplotlib inline\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt \n\nplt.title(\"image\")\nplt.imshow(image)\nplt.xticks([]) # x축 눈금 없애기\nplt.yticks([]) # y축 눈금 없애기 \nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.title(\"image_gray\")\nplt.imshow(img_gray,cmap='gray')\nplt.xticks([]) # x축 눈금 없애기\nplt.yticks([]) # y축 눈금 없애기 \nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 이미지 저장하기 ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cv2.imwrite('./data/toy_image.jpg', image)\ncv2.imwrite('./data/toy_gray_image.jpg', img_gray)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"---\n\n## 웹캠을 사용하여 비디오 읽기 \n\n**`MAC_카탈리나` 환경에서는 창이 안닫히는 현상이 있으므로 실행하지 않는 것을 추천합니다.** \n\n\n- `cv2.VideoCapture()`: 캡쳐 객체를 생성 합니다. 소유하고 있는 웹캠의 갯수많큼 인덱스가 생기며 인덱스는 0부터 시작합니다. 예를들어, 웹캠을 하나만 가지고 있다면 0 을 입력합니다. `cv2.VideoCapture(0)`\n\n\n- `ret, fram = cap.read()`: 비디오의 한 프레임씩 읽습니다. 제대로 프레임을 읽으면 ret값이 True, 실패하면 False가 나타납니다. fram에 읽은 프레임이 나옵니다\n- `cv2.cvtColor()`: frame을 흑백으로 변환합니다\n- `cap.release()`: 오픈한 캡쳐 객체를 해제합니다\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import cv2\n\nOPTION = 'color' # gray: 흑백 \n\n\ncap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)\n\nwhile True:\n ret, frame = cap.read() \n if ret:\n if OPTION == 'gray':\n gray = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # 입력 받은 화면 Gray로 변환\n cv2.imshow('frame_gray', gray) # Gray 화면 출력\n if cv2.waitKey(1) == ord('q'): # q 를 누를시 정지 \n break\n \n elif OPTION == 'color':\n cv2.imshow('frame_color', frame) # 컬러 화면 출력\n if cv2.waitKey(1) == ord('q'):\n break\n else:\n print('error')\n \ncap.release()\ncv2.destroyAllWindows()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 영상 저장 \n\n영상을 저장하기 위해서는 `cv2.VideoWriter` Object를 생성해야 합니다.\n\n```\n\ncv2.VideoWriter(outputFile, fourcc, frame, size)\n영상을 저장하기 위한 Object\n\n Parameters:\t\n outputFile (str) – 저장될 파일명\n fourcc – Codec정보. cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc()\n frame (float) – 초당 저장될 frame\n size (list) – 저장될 사이즈(ex; 640, 480)\n```\n\n- `cv2.VideoWriter(outputFile, fourcc, frame, size)` : fourcc는 코덱 정보, frame은 초당 저장될 프레임, size는 저장될 사이즈를 뜻합니다.\n\n- `cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc('D','I','V','X')` 이런식으로소 사용하곤 합니다 적용 가능한 코덱은 DIVX, XVID, MJPG, X264, WMV1, WMV2 등이 있습니다",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import cv2\n\ncap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)\nfourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'DIVX')\nout = cv2.VideoWriter('./data/output.avi',\n fourcc,\n 25.0,\n (640, 480))\n\nwhile (cap.isOpened()):\n ret, frame = cap.read()\n\n if ret:\n\n out.write(frame)\n\n cv2.imshow('frame', frame)\n\n if cv2.waitKey(0) & 0xFF == ord('q'):\n break\n else:\n break\n\ncap.release()\nout.release()\ncv2.destroyAllWindows()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c50b3c27b453e4f89a6c5fc2d4a28bc05d8bf02d
| 7,559 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
src/literary/notebook/patch.ipynb
|
agoose77/literary
|
10245977c1c35b7ae19e42de5eb20d918d5207a5
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 10 |
2020-11-05T16:00:04.000Z
|
2022-02-04T15:53:59.000Z
|
src/literary/notebook/patch.ipynb
|
agoose77/literary
|
10245977c1c35b7ae19e42de5eb20d918d5207a5
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 33 |
2020-10-30T15:38:23.000Z
|
2021-11-10T17:31:04.000Z
|
src/literary/notebook/patch.ipynb
|
agoose77/literary
|
10245977c1c35b7ae19e42de5eb20d918d5207a5
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 1 |
2021-05-13T14:44:05.000Z
|
2021-05-13T14:44:05.000Z
| 27.190647 | 407 | 0.56952 |
[
[
[
"# Patch\n\nLiterate notebooks benefit from splitting their code and documentation across several cells. Unfortunately, the nature of the notebook-kernel execution model introduces some constraints upon this, as it is impossible to extend Python local namespaces across different cells. To facilitate this, we introduce the `patch` decorator which operates at runtime and build time to unify separate definitions.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%load_ext literary.module",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from typing import Callable, Type, TypeVar",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"T = TypeVar(\"T\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Some wrapper classes store the original object in a named attribute. Here we define a few of the common cases.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"WRAPPER_NAMES = \"fget\", \"fset\", \"fdel\", \"__func__\", \"func\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's implement the *runtime* decorator, which monkeypatches the class with the decorated function",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def patch(cls: Type) -> Callable[[T], T]:\n \"\"\"Decorator to monkey-patch additional methods to a class.\n\n At import-time, this will disappear and the source code itself will be transformed\n Inside notebooks, the implementation below will be used.\n\n :param cls:\n :return:\n \"\"\"\n\n def get_name(func):\n # Fix #4 to support patching (property) descriptors\n try:\n return func.__name__\n except AttributeError:\n # Support various descriptors\n for attr in WRAPPER_NAMES:\n try:\n return getattr(func, attr).__name__\n except AttributeError:\n continue\n\n # Raise original exception\n raise\n\n def _notebook_patch_impl(func):\n setattr(cls, get_name(func), func)\n return func\n\n return _notebook_patch_impl",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can now implement a test class to see this decorator in action",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class TestClass:\n pass",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"At runtime, an instantiated class can have new methods attached to its type",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"obj = TestClass()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"@patch(TestClass)\ndef method_a(self):\n return \"method a\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"And we can see that the method behaves as expected",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"assert obj.method_a() == \"method a\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c50b40788f1379a5972eceff1d507dcb96560b48
| 13,310 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
SCZ_sleep/explore_results_sleep.ipynb
|
vagechirkov/NI-project
|
fa0687d81ffad9b2e3737fe9115a151335bda358
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-06-01T08:06:15.000Z
|
2021-06-01T08:06:15.000Z
|
SCZ_sleep/explore_results_sleep.ipynb
|
vagechirkov/NI-project
|
fa0687d81ffad9b2e3737fe9115a151335bda358
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
SCZ_sleep/explore_results_sleep.ipynb
|
vagechirkov/NI-project
|
fa0687d81ffad9b2e3737fe9115a151335bda358
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 34.392765 | 136 | 0.562585 |
[
[
[
"import logging\nimport warnings\n\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport seaborn as sns\n\nimport neurolib.optimize.exploration.explorationUtils as eu\nimport neurolib.utils.pypetUtils as pu\nfrom neurolib.optimize.exploration import BoxSearch\n\nlogger = logging.getLogger()\nwarnings.filterwarnings(\"ignore\")\nlogger.setLevel(logging.INFO)\n\nresults_path = \"/Users/valery/Google_Drive/NI-Project/data/hdf/\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from neurolib.models.aln import ALNModel\nfrom neurolib.utils.parameterSpace import ParameterSpace\nmodel = ALNModel()\n# define the parameter space to explore\nparameters = ParameterSpace({\"mue_ext_mean\": np.linspace(0, 3, 21), # input to E\n\t\t\"mui_ext_mean\": np.linspace(0, 3, 21)}) # input to I\n\n# define exploration \nsearch = BoxSearch(model, parameters)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pu.getTrajectorynamesInFile(results_path + \"scz_sleep_reduce_abs_resolution-8.hdf\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"search.loadResults(\n filename= results_path + \"scz_sleep_reduce_abs_resolution-8.hdf\",\n trajectoryName=\"results-2021-06-25-18H-59M-03S\")\ndf = search.dfResults.copy()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"search2 = BoxSearch(model, parameters)\npu.getTrajectorynamesInFile(results_path + \"scz_sleep_Jei_resolution-50.hdf\")\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"search2.loadResults(\n filename=results_path + \"scz_sleep_Jei_resolution-50.hdf\",\n trajectoryName=\"results-2021-06-26-00H-40M-29S\")\ndf2 = search2.dfResults.copy()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"search3 = BoxSearch(model, parameters)\npu.getTrajectorynamesInFile(results_path + \"scz_sleep_resolution-50.hdf\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"search3.loadResults(\n filename=results_path + \"scz_sleep_resolution-50.hdf\",\n trajectoryName=\"results-2021-06-25-08H-34M-46S\")\ndf3 = search3.dfResults.copy()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"search4 = BoxSearch(model, parameters)\npu.getTrajectorynamesInFile(results_path + \"scz_sleep_Jii_resolution-50.hdf\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"search4.loadResults(\n filename=results_path + \"scz_sleep_Jii_resolution-50.hdf\",\n trajectoryName=\"results-2021-06-26-04H-08M-21S\")\ndf4 = search4.dfResults.copy()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"images = \"/Users/valery/Downloads/results/\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df3.loc[:, 'Global_SWS_per_min'] = df3.loc[:, 'n_global_waves']*3",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"eu.plotExplorationResults(\n df, par1=['mue_ext_mean', 'Input to E [nA]'], par2=['Jie_max', 'Synaptic current from E to I [nA]'],\n by=[\"Ke_gl\"], plot_key='SWS_per_min', plot_clim=[0, 25],\n nan_to_zero=False, plot_key_label=\"SWS/min\", one_figure=True, savename=images + \"scz_sleep1.png\")\neu.plotExplorationResults(\n df, par1=['mue_ext_mean', 'Input to E [nA]'], par2=['Jie_max', 'Synaptic current from E to I [nA]'],\n by=[\"Ke_gl\"], plot_key='perc_local_waves', plot_clim=[0, 100],\n nan_to_zero=False, plot_key_label=\"'perc_local_waves'\", one_figure=True, savename=images + \"scz_sleep1_1.png\")\neu.plotExplorationResults(\n df, par1=['mue_ext_mean', 'Input to E [nA]'], par2=['Jei_max', 'Synaptic current from I to E [nA]'],\n by=[\"Ke_gl\"], plot_key='SWS_per_min', plot_clim=[0, 25],\n nan_to_zero=False, plot_key_label=\"SWS/min\", one_figure=True, savename=images + \"scz_sleep2.png\")\neu.plotExplorationResults(\n df, par1=['mue_ext_mean', 'Input to E [nA]'], par2=['Jii_max', 'Synaptic current from I to I [nA]'],\n by=[\"Ke_gl\"], plot_key='SWS_per_min', plot_clim=[0, 25],\n nan_to_zero=False, plot_key_label=\"SWS/min\", one_figure=True, savename=images + \"scz_slee3.png\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.columns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.describe()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_2 = df.loc[df['Ke_gl'] == 200.0, \n['mue_ext_mean', 'Ke_gl','Jie_max', 'Jei_max', 'Jii_max', 'SWS_per_min',\n'perc_local_waves', 'max_output', 'normalized_up_lengths_mean', 'n_global_waves'\n]].round(decimals=2)\ndf_2['interactions'] = False\ndfdf = pd.DataFrame()\nfor n, (jie, jei, jii) in enumerate(zip(df_2['Jie_max'].unique(), df_2['Jei_max'].unique(), df_2['Jii_max'].unique())):\n mask = (df_2['Jie_max'] == jie) & (df_2['Jei_max'] == jei) & (df_2['Jii_max'] == jii)\n df_2.loc[mask, 'interactions'] = True\n df_2.loc[mask, 'J'] = 8 - n\n dfdf.loc[8-n, ['Jie_max', 'Jei_max', 'Jii_max']] = jie, jei, jii\ndf_2_interaction = df_2.loc[df_2['interactions'], :]\ndf_2_interaction.loc[:, 'global_SWS_per_min'] = df_2_interaction.loc[:, 'n_global_waves'] *3\ndfdf",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"eu.plotExplorationResults(\n df_2_interaction, par1=['mue_ext_mean', 'Input to E [nA]'], par2=['J', 'Decrease all J simultaneously'],\n by=[\"Ke_gl\"], plot_key='SWS_per_min', plot_clim=[0, 40],\n nan_to_zero=False, plot_key_label=\"SWS/min\", one_figure=True, savename=images + \"scz_sleep4.png\")\n\neu.plotExplorationResults(\n df_2_interaction, par1=['mue_ext_mean', 'Input to E [nA]'], par2=['J', 'Decrease all J simultaneously'],\n by=[\"Ke_gl\"], plot_key='perc_local_waves', plot_clim=[0, 100],\n nan_to_zero=False, plot_key_label=\"Fraction of the local waves %\", one_figure=True, savename=images + \"scz_sleep5.png\")\n\neu.plotExplorationResults(\n df_2_interaction, par1=['mue_ext_mean', 'Input to E [nA]'], par2=['J', 'Decrease all J simultaneously'],\n by=[\"Ke_gl\"], plot_key='normalized_up_lengths_mean', plot_clim=[0, 100],\n nan_to_zero=False, plot_key_label=\"Time spent in Up state %\", one_figure=True, savename=images + \"scz_sleep6.png\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"palette = sns.color_palette(\"hls\", 8)\nsns.relplot( # .relplot(\n data=df_2_interaction[(df_2_interaction[\"Ke_gl\"] == 200.)],\n x=\"mue_ext_mean\", y=\"SWS_per_min\",\n hue='J', # col='Jie_max', # size=\"choice\", size_order=[\"T1\", \"T2\"],\n kind=\"line\", # palette=palette,\n # order=3,\n height=5, aspect=1., legend=False, palette=palette\n # facet_kws=dict(sharex=False),\n)\nplt.xlim([3.32,4.5])\nplt.ylim([0, 45])\n# plt.tight_layout()\n# plt.title('All SW / min')\nplt.gcf().subplots_adjust(bottom=0.15)\nplt.savefig(images + \"scz_sleep13.png\", dpi=100)\n\npalette = sns.color_palette(\"hls\", 8)\nsns.relplot(\n data=df_2_interaction[(df_2_interaction[\"Ke_gl\"] == 200.)],\n x=\"mue_ext_mean\", y=\"global_SWS_per_min\",\n hue='J', # col='Jie_max', # size=\"choice\", size_order=[\"T1\", \"T2\"],\n kind=\"line\", # palette=palette,\n height=5, aspect=1., legend=\"full\",\n palette=palette\n # facet_kws=dict(sharex=False),\n)\nplt.xlim([3.32,4.5])\nplt.ylim([0, 45])\n# plt.tight_layout()\nplt.gcf().subplots_adjust(bottom=0.15)\n# plt.title('Global SW / min')\nplt.savefig(images + \"scz_sleep14.png\", dpi=100)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df3.columns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"eu.plotExplorationResults(\n df3, par1=['mue_ext_mean', 'Input to E [nA]'], par2=['Jie_max', 'Synaptic current from E to I [nA]'],\n by=[\"Ke_gl\"], plot_key='SWS_per_min', plot_clim=[0, 40], # plot_clim=[0.0, 100.0],\n contour=['perc_local_waves', 'normalized_up_lengths_mean'], \n contour_color=[['white'], ['red']], contour_levels=[[70], [65]], contour_alpha=[1.0, 1.0],\n contour_kwargs={0: {\"linewidths\": (2,)}, 1: {\"linewidths\": (2,)}},\n nan_to_zero=False, plot_key_label=\"SWS/min\", one_figure=True, savename=images + \"scz_sleep9.png\")\n\neu.plotExplorationResults(\n df3, par1=['mue_ext_mean', 'Input to E [nA]'], par2=['Jie_max', 'Synaptic current from E to I [nA]'],\n by=[\"Ke_gl\"], plot_key='frontal_SWS_per_min', plot_clim=[0, 40], # plot_clim=[0.0, 100.0],\n contour=['frontal_perc_local_waves', 'frontalnormalized_up_lengths_mean'], \n contour_color=[['white'], ['red']], contour_levels=[[70], [65]], contour_alpha=[1.0, 1.0],\n contour_kwargs={0: {\"linewidths\": (2,)}, 1: {\"linewidths\": (2,)}},\n nan_to_zero=False, plot_key_label=\"Frontal SWS/min\", one_figure=True, savename=images + \"scz_sleep9_1.png\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sns.lmplot( # .relplot(\n data=df3[(df3[\"Ke_gl\"] == 200.)&((df3['Jie_max'] < 1.4) | (df3['Jie_max'] == 2.6))].round(3),\n x=\"mue_ext_mean\", y=\"SWS_per_min\",\n hue='Jie_max', # col='Jie_max', # size=\"choice\", size_order=[\"T1\", \"T2\"],\n # kind=\"line\", # palette=palette,\n order=5,\n height=5, aspect=1., legend=False,\n # facet_kws=dict(sharex=False),\n)\nplt.xlim([3.32,4.5])\nplt.ylim([0, 45])\n# plt.tight_layout()\n# plt.title('All SW / min')\nplt.gcf().subplots_adjust(bottom=0.15)\nplt.savefig(images + \"scz_sleep11.png\", dpi=100)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sns.lmplot( # .relplot(\n data=df3[(df3[\"Ke_gl\"] == 200.)&((df3['Jie_max'] < 1.4) | (df3['Jie_max'] == 2.6))].round(3),\n x=\"mue_ext_mean\", y=\"Global_SWS_per_min\",\n hue='Jie_max', # col='Jie_max', # size=\"choice\", size_order=[\"T1\", \"T2\"],\n # kind=\"line\", # palette=palette,\n order=5,\n height=5, aspect=1., # legend=\"full\"\n # facet_kws=dict(sharex=False),\n)\nplt.xlim([3.32,4.5])\nplt.ylim([0, 45])\n# plt.tight_layout()\nplt.gcf().subplots_adjust(bottom=0.15)\n# plt.title('Global SW / min')\nplt.savefig(images + \"scz_sleep12.png\", dpi=100)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50b71679179df423d05877817c4c7a4c0ad8ae2
| 9,395 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/operator_upgrade.ipynb
|
marianobilli/seldon-core
|
adf6c54503da2b415800485c57c335df75be8fc5
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 3,049 |
2017-12-21T14:50:09.000Z
|
2022-03-30T18:14:15.000Z
|
notebooks/operator_upgrade.ipynb
|
marianobilli/seldon-core
|
adf6c54503da2b415800485c57c335df75be8fc5
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 3,678 |
2017-12-22T16:21:30.000Z
|
2022-03-31T20:32:31.000Z
|
notebooks/operator_upgrade.ipynb
|
marianobilli/seldon-core
|
adf6c54503da2b415800485c57c335df75be8fc5
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 714 |
2018-01-03T11:29:49.000Z
|
2022-03-31T03:49:59.000Z
| 25.255376 | 407 | 0.511229 |
[
[
[
"# Operator Upgrade Tests",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Setup Seldon Core\n\nFollow the instructions to [Setup Cluster](https://docs.seldon.io/projects/seldon-core/en/latest/examples/seldon_core_setup.html#Setup-Cluster) with [Ambassador Ingress](https://docs.seldon.io/projects/seldon-core/en/latest/examples/seldon_core_setup.html#Ambassador) and [Install Seldon Core](https://docs.seldon.io/projects/seldon-core/en/latest/examples/seldon_core_setup.html#Install-Seldon-Core).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!kubectl create namespace seldon",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!kubectl config set-context $(kubectl config current-context) --namespace=seldon",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import json\nimport time",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Install Stable Version",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!kubectl create namespace seldon-system",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!helm upgrade seldon seldon-core-operator --repo https://storage.googleapis.com/seldon-charts --namespace seldon-system --set istio.enabled=true --wait",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Launch a Range of Models",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%writefile resources/model.yaml\napiVersion: machinelearning.seldon.io/v1\nkind: SeldonDeployment\nmetadata:\n name: seldon-model\nspec:\n name: test-deployment\n predictors:\n - componentSpecs:\n - spec:\n containers:\n - image: seldonio/mock_classifier:1.9.1\n name: classifier\n graph:\n name: classifier\n type: MODEL\n endpoint:\n type: REST\n name: example\n replicas: 1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!kubectl create -f resources/model.yaml",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%%writefile ../servers/tfserving/samples/halfplustwo_rest.yaml\napiVersion: machinelearning.seldon.io/v1alpha2\nkind: SeldonDeployment\nmetadata:\n name: hpt\nspec:\n name: hpt\n protocol: tensorflow\n transport: rest\n predictors:\n - graph:\n name: halfplustwo\n implementation: TENSORFLOW_SERVER\n modelUri: gs://seldon-models/tfserving/half_plus_two\n parameters:\n - name: model_name\n type: STRING\n value: halfplustwo\n name: default\n replicas: 1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!kubectl create -f ../servers/tfserving/samples/halfplustwo_rest.yaml",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%%writefile ../examples/models/payload_logging/model_logger.yaml\napiVersion: machinelearning.seldon.io/v1\nkind: SeldonDeployment\nmetadata:\n name: model-logs\nspec:\n name: model-logs\n predictors:\n - componentSpecs:\n - spec:\n containers:\n - image: seldonio/mock_classifier_rest:1.3\n name: classifier\n imagePullPolicy: Always\n graph:\n name: classifier\n type: MODEL\n endpoint:\n type: REST\n logger:\n url: http://logger.seldon/\n mode: all\n name: logging\n replicas: 1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!kubectl create -f ../examples/models/payload_logging/model_logger.yaml",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Wait for all models to be available",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def waitStatus(desired):\n for i in range(360):\n allAvailable = True\n failedGet = False\n state = !kubectl get sdep -o json\n state = json.loads(\"\".join(state))\n for model in state[\"items\"]:\n if \"status\" in model:\n print(\"model\", model[\"metadata\"][\"name\"], model[\"status\"][\"state\"])\n if model[\"status\"][\"state\"] != \"Available\":\n allAvailable = False\n break\n else:\n failedGet = True\n if allAvailable == desired and not failedGet:\n break\n time.sleep(1)\n return allAvailable\n\n\nactual = waitStatus(True)\nassert actual == True",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Count the number of resources",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def getOwned(raw):\n count = 0\n for res in raw[\"items\"]:\n if (\n \"ownerReferences\" in res[\"metadata\"]\n and res[\"metadata\"][\"ownerReferences\"][0][\"kind\"] == \"SeldonDeployment\"\n ):\n count += 1\n return count\n\n\ndef getResourceStats():\n # Get number of deployments\n dps = !kubectl get deployment -o json\n dps = json.loads(\"\".join(dps))\n numDps = getOwned(dps)\n print(\"Number of deployments owned\", numDps)\n\n # Get number of services\n svcs = !kubectl get svc -o json\n svcs = json.loads(\"\".join(svcs))\n numSvcs = getOwned(svcs)\n print(\"Number of services owned\", numSvcs)\n\n # Get number of virtual services\n vss = !kubectl get vs -o json\n vss = json.loads(\"\".join(vss))\n numVs = getOwned(vss)\n print(\"Number of virtual services owned\", numVs)\n\n # Get number of hpas\n hpas = !kubectl get hpa -o json\n hpas = json.loads(\"\".join(hpas))\n numHpas = getOwned(hpas)\n print(\"Number of hpas owned\", numHpas)\n\n return (numDps, numSvcs, numVs, numHpas)\n\n\n(dp1, svc1, vs1, hpa1) = getResourceStats()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Upgrade to latest",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!helm upgrade seldon ../helm-charts/seldon-core-operator --namespace seldon-system --set istio.enabled=true --wait",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"actual = waitStatus(False)\nassert actual == False",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"actual = waitStatus(True)\nassert actual == True",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Give time for resources to terminate\nfor i in range(120):\n (dp2, svc2, vs2, hpa2) = getResourceStats()\n if dp1 == dp2 and svc1 == svc2 and vs1 == vs2 and hpa1 == hpa2:\n break\n time.sleep(1)\nassert dp1 == dp2\nassert svc1 == svc2\nassert vs1 == vs2\nassert hpa1 == hpa2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!kubectl delete sdep --all",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50b71899c2bb88d3baedb68e5e11044bda19e93
| 6,526 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
08_scrape8K.ipynb
|
ikedim01/secscan
|
3275e8c4c379a1f7dd0c242aaf213545b46e2192
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
08_scrape8K.ipynb
|
ikedim01/secscan
|
3275e8c4c379a1f7dd0c242aaf213545b46e2192
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
08_scrape8K.ipynb
|
ikedim01/secscan
|
3275e8c4c379a1f7dd0c242aaf213545b46e2192
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 33.295918 | 128 | 0.539841 |
[
[
[
"# default_exp scrape8K",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# scrape8K\n\n> Scrape item summaries from 8-K SEC filings.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#hide\n%load_ext autoreload\n%autoreload 2\nfrom nbdev import show_doc",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#export\n\nimport collections\nimport itertools\nimport os\nimport re\n\nfrom secscan import utils, dailyList, basicInfo, infoScraper\n\ndefault8KDir = os.path.join(utils.stockDataRoot,'scraped8K')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"8K scraper class - scrape items summary from the SEC filing:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#export\n\nitemPat = re.compile(r'item\\s*(\\d+(?:\\.\\d*)?)',re.IGNORECASE)\nexplanPat = re.compile(r'explanatory\\s*note',re.IGNORECASE)\ndef parse8K(accNo, formType=None, textLimit=basicInfo.defaultTextLimit) :\n info = basicInfo.getSecFormInfo(accNo, formType=formType, get99=True, textLimit=textLimit)\n links = info['links']\n if len(links) == 0 :\n utils.printErrInfoOrAccessNo('NO LINKS LIST in',accNo)\n return info\n if formType is None :\n formType = links[0][2]\n items = info.get('items',[])\n if len(items) == 0 :\n return info\n mainText = utils.downloadSecUrl(links[0][3], toFormat='souptext')\n if formType.lower() == '8-k/a' :\n m = explanPat.search(mainText)\n if m is not None :\n info['explanatoryNote'] = mainText[m.start():m.start()+textLimit]\n itemPosL = [0]\n info['itemTexts'] = itemTexts = [None for item in items]\n for i,item in enumerate(items) :\n m = itemPat.match(item)\n if m is None :\n utils.printErrInfoOrAccessNo(f\"unexpected format for item header {item}\",accNo)\n continue\n m = re.search(r'item\\s*' + r'\\s*'.join(m.group(1)).replace('.',r'\\.'),\n mainText[itemPosL[-1]:], re.IGNORECASE)\n if m is None :\n utils.printErrInfoOrAccessNo(f\"couldn't find {item}\",accNo)\n continue\n itemPosL.append(itemPosL[-1]+m.start())\n itemTexts[i] = ''\n # print('pos for',item,itemPosL[-1])\n itemPosL.append(len(mainText))\n j = 1\n for i in range(len(itemTexts)) :\n if itemTexts[i] is None :\n itemTexts[i] = items[i] + ' ???'\n else :\n itemTexts[i] = mainText[itemPosL[j] : min(itemPosL[j]+textLimit, itemPosL[j+1])]\n j += 1\n return info\n\nclass scraper8K(infoScraper.scraperBase) :\n @utils.delegates(infoScraper.scraperBase.__init__)\n def __init__(self, infoDir=default8KDir, **kwargs) :\n super().__init__(infoDir, '8-K', **kwargs)\n def scrapeInfo(self, accNo, formType=None) :\n return parse8K(accNo, formType), None",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Test 8-K scraper class:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"dl = dailyList.dailyList(startD='empty')\ndl.updateForDays('20210701','20210704')\nassert len(dl.getFilingsList(None,'8-K')[0])==600,\"testing 8-K scraper class (daily list count)\"\ninfo = parse8K('0001165002-21-000068', formType='8-K', textLimit=1000)\nassert (info['itemTexts'][0].startswith('ITEM 2.02: RESULTS OF OPERATIONS AND FINANCIAL CONDITION '\n +'On July 27, 2021, Westwood')\n and info['itemTexts'][0].endswith('otherwise expressly stated in such filing. ')\n and info['itemTexts'][1].startswith('ITEM 7.01: REGULATION FD DISCLOSURE Westwood')\n and info['itemTexts'][1].endswith('of record on August 6, 2021. ')\n and info['itemTexts'][2].startswith('ITEM 9.01: FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND EXHIBITS (d) ')\n and info['itemTexts'][2].endswith('Financial Officer and Treasurer')\n and info['text99'][1].startswith('EX-99.1 2 a2q21earningsrelease.htm EX-99.1 '\n +'Document Westwood Holdings Group, Inc. Reports')\n and info['text99'][1].endswith('High Income achieved a top decile ranking, Income Opportunity and Total Retur')\n ),\"testing 8-K scraper class (parsing)\"\n\ninfo = parse8K('0001606757-21-000040', formType='8-K/A', textLimit=1000)\nassert (info['explanatoryNote'].startswith('Explanatory Note This Amendment No. 1')\n and info['explanatoryNote'].endswith('Ms. Croom accepted a written offer ')\n ),\"testing 8-K scraper class (parsing explanatory note)\"",
"WEEKEND20210703 UPDATE20210702 ### list index 64 count for 20210702: 6569 * UPDATE20210701 count for 20210701: 5573 * "
],
[
"#hide\n# uncomment and run to regenerate all library Python files\n# from nbdev.export import notebook2script; notebook2script()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50b8ce9c78e430ec6905f6a50f8a977d975e5ac
| 12,155 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Pytorch Graphs .ipynb
|
JAGADEESHA-R-G/Pytroch-notebooks
|
6e4ed12420a8428fc6014360b6850728a54bfcc2
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Pytorch Graphs .ipynb
|
JAGADEESHA-R-G/Pytroch-notebooks
|
6e4ed12420a8428fc6014360b6850728a54bfcc2
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Pytorch Graphs .ipynb
|
JAGADEESHA-R-G/Pytroch-notebooks
|
6e4ed12420a8428fc6014360b6850728a54bfcc2
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 12,155 | 12,155 | 0.624846 |
[
[
[
"Practical Example of how Pytorch Graphs are constructed",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import torch \nimport numpy as np",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"a = torch.rand(10, requires_grad=True)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"b = np.asarray(a)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"we can see that when we are trying to convert a tensor to numpy, since Pytorch wont be able to assign numpy array to graph as it does not involve grad function ability, thus breaking the graph. Pytorch will show error",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"It can be resolved in few ways..",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"1. first way",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# using no_grad() : to tell pytorch that we dont include this tensor for graph\n\nwith torch.no_grad():\n a = torch.rand(10, requires_grad=True)\n b = np.asarray(a)\n print(type(b))\n print(b)",
"<class 'numpy.ndarray'>\n[0.12791282 0.8526067 0.4312092 0.638294 0.29264945 0.8066801\n 0.41793334 0.70521533 0.16463292 0.20911378]\n"
]
],
[
[
"It works successfully because Pytorch didn't add tensor to graph, thus no need to compute grad , no issue in converting to numpy",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"2. Second",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# using detach()\na = torch.rand(10, requires_grad=True)\nb = a.detach().numpy() # detaches from the graph \nprint(type(b))\nprint(b)",
"<class 'numpy.ndarray'>\n[0.47953868 0.09203494 0.20284927 0.00920457 0.01840806 0.03433728\n 0.7112533 0.408058 0.11833239 0.9942596 ]\n"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Lets see an example of how pytorch graphs work for completion",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# simple logistic example \n\nw = torch.rand(100,1, requires_grad=True) # requires_grad=True is telling pytorch to add this to graph \nx = torch.rand(1, 100)\n\nval = x@w # dot product \n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"val.backward()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"w.grad",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x.grad",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50b962a00ff45490f3054168e50efd091f6604c
| 10,319 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
_posts/scikit/decision-boundary-of-label-propagation/Decision Boundary of Label Propagation versus SVM on the Iris dataset.ipynb
|
bmb804/documentation
|
57826d25e0afea7fff6a8da9abab8be2f7a4b48c
|
[
"CC-BY-3.0"
] | 2 |
2019-06-24T23:55:53.000Z
|
2019-07-08T12:22:56.000Z
|
_posts/scikit/decision-boundary-of-label-propagation/Decision Boundary of Label Propagation versus SVM on the Iris dataset.ipynb
|
bmb804/documentation
|
57826d25e0afea7fff6a8da9abab8be2f7a4b48c
|
[
"CC-BY-3.0"
] | 15 |
2020-06-30T21:21:30.000Z
|
2021-08-02T21:16:33.000Z
|
_posts/scikit/decision-boundary-of-label-propagation/Decision Boundary of Label Propagation versus SVM on the Iris dataset.ipynb
|
bmb804/documentation
|
57826d25e0afea7fff6a8da9abab8be2f7a4b48c
|
[
"CC-BY-3.0"
] | 1 |
2019-11-10T04:01:48.000Z
|
2019-11-10T04:01:48.000Z
| 29.232295 | 316 | 0.531931 |
[
[
[
"Comparison for decision boundary generated on iris dataset between Label Propagation and SVM.\n\nThis demonstrates Label Propagation learning a good boundary even with a small amount of labeled data.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#### New to Plotly?\nPlotly's Python library is free and open source! [Get started](https://plot.ly/python/getting-started/) by downloading the client and [reading the primer](https://plot.ly/python/getting-started/).\n<br>You can set up Plotly to work in [online](https://plot.ly/python/getting-started/#initialization-for-online-plotting) or [offline](https://plot.ly/python/getting-started/#initialization-for-offline-plotting) mode, or in [jupyter notebooks](https://plot.ly/python/getting-started/#start-plotting-online).\n<br>We also have a quick-reference [cheatsheet](https://images.plot.ly/plotly-documentation/images/python_cheat_sheet.pdf) (new!) to help you get started!",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Version",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import sklearn\nsklearn.__version__",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Imports",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(__doc__)\n\nimport plotly.plotly as py\nimport plotly.graph_objs as go\nfrom plotly import tools\n\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom sklearn import datasets\nfrom sklearn import svm\nfrom sklearn.semi_supervised import label_propagation",
"Automatically created module for IPython interactive environment\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Calculations",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"rng = np.random.RandomState(0)\n\niris = datasets.load_iris()\n\nX = iris.data[:, :2]\ny = iris.target\n\n# step size in the mesh\nh = .02\n\ny_30 = np.copy(y)\ny_30[rng.rand(len(y)) < 0.3] = -1\ny_50 = np.copy(y)\ny_50[rng.rand(len(y)) < 0.5] = -1\n# we create an instance of SVM and fit out data. We do not scale our\n# data since we want to plot the support vectors\nls30 = (label_propagation.LabelSpreading().fit(X, y_30),\n y_30)\nls50 = (label_propagation.LabelSpreading().fit(X, y_50),\n y_50)\nls100 = (label_propagation.LabelSpreading().fit(X, y), y)\nrbf_svc = (svm.SVC(kernel='rbf').fit(X, y), y)\n\n# create a mesh to plot in\nx_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1\ny_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1\nx_ = np.arange(x_min, x_max, h)\ny_ = np.arange(y_min, y_max, h)\nxx, yy = np.meshgrid(x_, y_)\n\n# title for the plots\ntitles = ['Label Spreading 30% data',\n 'Label Spreading 50% data',\n 'Label Spreading 100% data',\n 'SVC with rbf kernel']",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Plot Results",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"fig = tools.make_subplots(rows=2, cols=2,\n subplot_titles=tuple(titles),\n print_grid=False)\n\ndef matplotlib_to_plotly(cmap, pl_entries):\n h = 1.0/(pl_entries-1)\n pl_colorscale = []\n \n for k in range(pl_entries):\n C = map(np.uint8, np.array(cmap(k*h)[:3])*255)\n pl_colorscale.append([k*h, 'rgb'+str((C[0], C[1], C[2]))])\n \n return pl_colorscale\ncmap = matplotlib_to_plotly(plt.cm.Paired, 6)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\nfor i, (clf, y_train) in enumerate((ls30, ls50, ls100, rbf_svc)):\n # Plot the decision boundary. For that, we will assign a color to each\n # point in the mesh [x_min, x_max]x[y_min, y_max].\n Z = clf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])\n\n # Put the result into a color plot\n Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)\n trace1 = go.Heatmap(x=x_, y=y_, z=Z,\n colorscale=cmap,\n showscale=False)\n fig.append_trace(trace1, i/2+1, i%2+1)\n # Plot also the training points\n trace2 = go.Scatter(x=X[:, 0], y=X[:, 1], \n mode='markers', \n showlegend=False,\n marker=dict(color=X[:, 0],\n colorscale=cmap,\n line=dict(width=1, color='black'))\n )\n fig.append_trace(trace2, i/2+1, i%2+1)\n\n\nfor i in map(str,range(1, 5)):\n y = 'yaxis' + i\n x = 'xaxis' + i\n fig['layout'][y].update(showticklabels=False, ticks='')\n fig['layout'][x].update(showticklabels=False, ticks='')\n \nfig['layout'].update(height=700)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"py.iplot(fig)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### License",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Authors: \n\n Clay Woolam <[email protected]>\n\nLicense: \n\n BSD",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from IPython.display import display, HTML\n\ndisplay(HTML('<link href=\"//fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Open+Sans:600,400,300,200|Inconsolata|Ubuntu+Mono:400,700\" rel=\"stylesheet\" type=\"text/css\" />'))\ndisplay(HTML('<link rel=\"stylesheet\" type=\"text/css\" href=\"http://help.plot.ly/documentation/all_static/css/ipython-notebook-custom.css\">'))\n\n! pip install git+https://github.com/plotly/publisher.git --upgrade\nimport publisher\npublisher.publish(\n 'Decision Boundary of Label Propagation versus SVM on the Iris dataset.ipynb', 'scikit-learn/plot-label-propagation-versus-svm-iris/', 'Decision Boundary of Label Propagation versus SVM on the Iris dataset | plotly',\n ' ',\n title = 'Decision Boundary of Label Propagation versus SVM on the Iris dataset | plotly',\n name = 'Decision Boundary of Label Propagation versus SVM on the Iris dataset',\n has_thumbnail='true', thumbnail='thumbnail/svm.jpg', \n language='scikit-learn', page_type='example_index',\n display_as='semi_supervised', order=3,\n ipynb= '~Diksha_Gabha/3520')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c50b975b0009b3235c605c0b0764c0a3f58d9d84
| 63,937 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Random Forest.ipynb
|
adarshkuthuru/Machine-Learning-Algorithms
|
c09c27090af3343915cc007970dc2d258682c413
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Random Forest.ipynb
|
adarshkuthuru/Machine-Learning-Algorithms
|
c09c27090af3343915cc007970dc2d258682c413
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Random Forest.ipynb
|
adarshkuthuru/Machine-Learning-Algorithms
|
c09c27090af3343915cc007970dc2d258682c413
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 68.897629 | 21,372 | 0.707587 |
[
[
[
"<h3 style='color:purple' align='center'>Random Forest Python Tutorial</h3>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Digits dataset from sklearn**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nfrom sklearn.datasets import load_digits\ndigits = load_digits()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dir(digits)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%matplotlib inline\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.gray() \nfor i in range(4):\n plt.matshow(digits.images[i]) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = pd.DataFrame(digits.data)\ndf.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df['target'] = digits.target",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df[0:12]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Train and the model and prediction**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"X = df.drop('target',axis='columns')\ny = df.target",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.2)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier\nmodel = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=20)\nmodel.fit(X_train, y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"model.score(X_test, y_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"y_predicted = model.predict(X_test)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Confusion Matrix**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix\ncm = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_predicted)\ncm",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%matplotlib inline\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn as sn\nplt.figure(figsize=(10,7))\nsn.heatmap(cm, annot=True)\nplt.xlabel('Predicted')\nplt.ylabel('Truth')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Exercise**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Use famous iris flower dataset from sklearn.datasets to predict flower species using random forest classifier.\n1. Measure prediction score using default n_estimators (10)\n2. Now fine tune your model by changing number of trees in your classifer and tell me what best score you can get using how many trees",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
c50ba3b81d81beb90d430b91a054cb01dfa85023
| 43,794 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/TAD_Week_3_Broker_Carl_1_of_2.ipynb
|
cbroker1/text-as-data
|
b28c7e48d10a155861445e9918f7ee29222e1cff
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/TAD_Week_3_Broker_Carl_1_of_2.ipynb
|
cbroker1/text-as-data
|
b28c7e48d10a155861445e9918f7ee29222e1cff
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/TAD_Week_3_Broker_Carl_1_of_2.ipynb
|
cbroker1/text-as-data
|
b28c7e48d10a155861445e9918f7ee29222e1cff
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 81.553073 | 30,180 | 0.819427 |
[
[
[
"empty"
]
]
] |
[
"empty"
] |
[
[
"empty"
]
] |
c50bc5beaa63ef684e473f46ec92a837f53f62ac
| 26,385 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
autox/autox_nlp/demo/amazon-book-price/autox.ipynb
|
OneToolsCollection/4paradigm-AutoX
|
f8e838021354de17f5bb9bc44e9d68d12dda6427
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
autox/autox_nlp/demo/amazon-book-price/autox.ipynb
|
OneToolsCollection/4paradigm-AutoX
|
f8e838021354de17f5bb9bc44e9d68d12dda6427
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
autox/autox_nlp/demo/amazon-book-price/autox.ipynb
|
OneToolsCollection/4paradigm-AutoX
|
f8e838021354de17f5bb9bc44e9d68d12dda6427
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 68.532468 | 1,390 | 0.662687 |
[
[
[
"!git clone https://github.com/4paradigm/autox.git\n!pip install ./autox",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from autox.autox_nlp import NLP_feature\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport os\nfrom tqdm import tqdm",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_train = pd.read_csv('sub_train.csv')\ndf_test = pd.read_csv('sub_val.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"use_Toknizer=True\nemb_mode = 'Bert'# TFIDF / Word2Vec / Glove / FastText / Bert\nencode_mode = 'supervise' # unsupervise / supervise\ntext_columns_name = ['Title','Synopsis']\ntarget_column = df_train['Price']\ncandidate_labels=None",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"nlp = NLP_feature()\nnlp.do_mlm = True\nnlp.mlm_epochs=3\nnlp.model_name = 'microsoft/deberta-v3-base'\nnlp.emb_size=100\nnlp.n_clusters=20\ndf = nlp.fit(df_train,\n text_columns_name,\n use_Toknizer,\n emb_mode,\n encode_mode,\n target_column,\n candidate_labels)",
"Fitting column: Title tokenizer\n"
],
[
"for column in df.columns:\n df_train[column] = df[column]\ndf_train = df_train.drop(columns=text_columns_name)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"test = nlp.transform(df_test)",
"loading configuration file ./Title_transformer/config.json\nModel config DebertaV2Config {\n \"_name_or_path\": \"./Title_transformer\",\n \"architectures\": [\n \"DebertaV2ForMaskedLM\"\n ],\n \"attention_probs_dropout_prob\": 0.1,\n \"hidden_act\": \"gelu\",\n \"hidden_dropout_prob\": 0.1,\n \"hidden_size\": 768,\n \"initializer_range\": 0.02,\n \"intermediate_size\": 3072,\n \"layer_norm_eps\": 1e-07,\n \"max_position_embeddings\": 512,\n \"max_relative_positions\": -1,\n \"model_type\": \"deberta-v2\",\n \"norm_rel_ebd\": \"layer_norm\",\n \"num_attention_heads\": 12,\n \"num_hidden_layers\": 12,\n \"output_hidden_states\": true,\n \"pad_token_id\": 0,\n \"pooler_dropout\": 0,\n \"pooler_hidden_act\": \"gelu\",\n \"pooler_hidden_size\": 768,\n \"pos_att_type\": [\n \"p2c\",\n \"c2p\"\n ],\n \"position_biased_input\": false,\n \"position_buckets\": 256,\n \"relative_attention\": true,\n \"share_att_key\": true,\n \"torch_dtype\": \"float32\",\n \"transformers_version\": \"4.16.2\",\n \"type_vocab_size\": 0,\n \"vocab_size\": 128100\n}\n\nloading weights file ./Title_transformer/pytorch_model.bin\n"
],
[
"for column in test.columns:\n df_test[column] = test[column]\ndf_test = df_test.drop(columns=text_columns_name)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_train.to_csv(f'{emb_mode}_{encode_mode}_autox_trn.csv',index=False)\ndf_test.to_csv(f'{emb_mode}_{encode_mode}_autox_val.csv',index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_val=pd.read_csv(f'{emb_mode}_{encode_mode}_autox_val.csv').drop(columns=['Price'])\ndf_val.to_csv(f'{emb_mode}_{encode_mode}_autox_tst.csv',index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from autox import AutoX\n\npath = f'.' \nautox = AutoX(target = 'Price', train_name = f'{emb_mode}_{encode_mode}_autox_trn.csv', test_name = f'{emb_mode}_{encode_mode}_autox_tst.csv', id = [], path = path)\nsub = autox.get_submit()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"val = pd.read_csv(f'sub_val.csv')\nfrom sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error\nRMSE = np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(val['Price'], sub['Price']))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"RMSE",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50bcfef19995f8b8a1753a4af4a90ba0ae5f89a
| 209,079 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
calib/SimCalibration-02 - AoverE slices.ipynb
|
ffischer42/0vbb-efficiency-analysis
|
6fded95e034279711849193d1eeb50192e654b01
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
calib/SimCalibration-02 - AoverE slices.ipynb
|
ffischer42/0vbb-efficiency-analysis
|
6fded95e034279711849193d1eeb50192e654b01
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
calib/SimCalibration-02 - AoverE slices.ipynb
|
ffischer42/0vbb-efficiency-analysis
|
6fded95e034279711849193d1eeb50192e654b01
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 151.836601 | 22,181 | 0.661912 |
[
[
[
"empty"
]
]
] |
[
"empty"
] |
[
[
"empty"
]
] |
c50be5bc15573b02fa987a6e5d3dc8518ad38148
| 358,165 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
examples/notebooks/models/pouch-cell-model.ipynb
|
priyanshuone6/PyBaMM
|
fb6ebaa12900d227d3a247afdb7acfa9f5b7c62d
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
examples/notebooks/models/pouch-cell-model.ipynb
|
priyanshuone6/PyBaMM
|
fb6ebaa12900d227d3a247afdb7acfa9f5b7c62d
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | 1 |
2022-01-15T03:51:22.000Z
|
2022-01-15T03:51:22.000Z
|
examples/notebooks/models/pouch-cell-model.ipynb
|
priyanshuone6/PyBaMM
|
fb6ebaa12900d227d3a247afdb7acfa9f5b7c62d
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null | 420.381455 | 92,240 | 0.931724 |
[
[
[
"# Pouch cell model",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In this notebook we compare the solutions of two reduced-order models of a lithium-ion pouch cell with the full solution obtained using COMSOL. This example is based on the results in [[6]](#References). The code used to produce the results in [[6]](#References) can be found [here](https://github.com/rtimms/asymptotic-pouch-cell).\n\nThe full model is based on the Doyle-Fuller-Newman model [[2]](#References) and, in the interest of simplicity, considers a one-dimensional current collector (i.e. variation in one of the current collector dimensions is ignored), resulting in a 2D macroscopic model.\n\nThe first of the reduced order models, which is applicable in the limit of large conductivity in the current collectors, solves a one-dimensional problem in the current collectors coupled to a one-dimensional DFN model describing the through-cell electrochemistry at each point. We refer to this as a 1+1D model, though since the DFN is already a pseudo-two-dimensional model, perhaps it is more properly a 1+1+1D model.\n\nThe second reduced order model, which is applicable in the limit of very large conductivity in the current collectors, solves a single (averaged) one-dimensional DFN model for the through-cell behaviour and an uncoupled problem for the distribution of potential in the current collectors (from which the resistance and heat source can be calculated). We refer to this model as the DFNCC, where the \"CC\" indicates the additional (uncoupled) current collector problem.\n\nAll of the model equations, and derivations of the reduced-order models, can be found in [[6]](#References).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Solving the reduced-order pouch cell models in PyBaMM",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We begin by importing PyBaMM along with the other packages required in this notebook",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%pip install pybamm -q # install PyBaMM if it is not installed\nimport pybamm\nimport sys\nimport pickle\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport scipy.interpolate as interp",
"Note: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.\n"
]
],
[
[
"We then need to load up the appropriate models. For the DFNCC we require a 1D model of the current collectors and an average 1D DFN model for the through-cell electrochemistry. The 1+1D pouch cell model is built directly into PyBaMM and are accessed by passing the model option \"dimensionality\" which can be 1 or 2, corresponding to 1D or 2D current collectors. This option can be passed to any existing electrochemical model (e.g. [SPM](./SPM.ipynb), [SPMe](./SPMe.ipynb), [DFN](./DFN.ipynb)). Here we choose the DFN model. \n\nFor both electrochemical models we choose an \"x-lumped\" thermal model, meaning we assume that the temperature is uniform in the through-cell direction $x$, but account for the variation in temperature in the transverse direction $z$.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cc_model = pybamm.current_collector.EffectiveResistance({\"dimensionality\": 1})\ndfn_av = pybamm.lithium_ion.DFN({\"thermal\": \"x-lumped\"}, name=\"Average DFN\")\ndfn = pybamm.lithium_ion.DFN(\n {\"current collector\": \"potential pair\", \"dimensionality\": 1, \"thermal\": \"x-lumped\"},\n name=\"1+1D DFN\",\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We then add the models to a dictionary for easy access later",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"models = {\"Current collector\": cc_model, \"Average DFN\": dfn_av, \"1+1D DFN\": dfn}",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Next we update the parameters to match those used in the COMSOL simulation. In particular, we set the current to correspond to a 3C discharge and assume uniform Newton cooling on all boundaries.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"param = dfn.default_parameter_values\nI_1C = param[\"Nominal cell capacity [A.h]\"] # 1C current is cell capacity multipled by 1 hour\nparam.update(\n {\n \"Current function [A]\": I_1C * 3, \n \"Negative electrode diffusivity [m2.s-1]\": 3.9 * 10 ** (-14),\n \"Positive electrode diffusivity [m2.s-1]\": 10 ** (-13),\n \"Negative current collector surface heat transfer coefficient [W.m-2.K-1]\": 10,\n \"Positive current collector surface heat transfer coefficient [W.m-2.K-1]\": 10,\n \"Negative tab heat transfer coefficient [W.m-2.K-1]\": 10,\n \"Positive tab heat transfer coefficient [W.m-2.K-1]\": 10,\n \"Edge heat transfer coefficient [W.m-2.K-1]\": 10,\n }\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"In this example we choose to discretise in space using 16 nodes per domain.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"npts = 16\nvar_pts = {\n \"x_n\": npts,\n \"x_s\": npts,\n \"x_p\": npts,\n \"r_n\": npts,\n \"r_p\": npts,\n \"z\": npts,\n}",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Before solving the models we load the COMSOL data so that we can request the output at the times in the COMSOL solution",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"comsol_results_path = pybamm.get_parameters_filepath(\n \"input/comsol_results/comsol_1plus1D_3C.pickle\"\n)\ncomsol_variables = pickle.load(open(comsol_results_path, \"rb\"))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Next we loop over the models, creating and solving a simulation for each.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"simulations = {}\nsolutions = {} # store solutions in a separate dict for easy access later\nfor name, model in models.items():\n sim = pybamm.Simulation(model, parameter_values=param, var_pts=var_pts)\n simulations[name] = sim # store simulation for later\n if name == \"Current collector\":\n # model is independent of time, so just solve arbitrarily at t=0 using \n # the default algebraic solver\n t_eval = np.array([0])\n solutions[name] = sim.solve(t_eval=t_eval) \n else:\n # solve at COMSOL times using Casadi solver in \"fast\" mode\n t_eval = comsol_variables[\"time\"] \n solutions[name] = sim.solve(solver=pybamm.CasadiSolver(mode=\"fast\"), t_eval=t_eval)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Creating the COMSOL model",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In this section we show how to create a PyBaMM \"model\" from the COMSOL solution. If you are just interested in seeing the comparison the skip ahead to the section \"Comparing the full and reduced-order models\".\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"To create a PyBaMM model from the COMSOL data we must create a `pybamm.Function` object for each variable. We do this by interpolating in space to match the PyBaMM mesh and then creating a function to interpolate in time. The following cell defines the function that handles the creation of the `pybamm.Function` object.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# set up times\ntau = param.evaluate(dfn.param.tau_discharge)\ncomsol_t = comsol_variables[\"time\"]\npybamm_t = comsol_t / tau\n# set up space\nmesh = simulations[\"1+1D DFN\"].mesh\nL_z = param.evaluate(dfn.param.L_z)\npybamm_z = mesh[\"current collector\"].nodes\nz_interp = pybamm_z * L_z\n\n \ndef get_interp_fun_curr_coll(variable_name):\n \"\"\"\n Create a :class:`pybamm.Function` object using the variable (interpolate in space \n to match nodes, and then create function to interpolate in time)\n \"\"\"\n\n comsol_z = comsol_variables[variable_name + \"_z\"]\n variable = comsol_variables[variable_name]\n variable = interp.interp1d(comsol_z, variable, axis=0, kind=\"linear\")(z_interp)\n\n # Make sure to use dimensional time\n fun = pybamm.Interpolant(\n comsol_t,\n variable.T,\n pybamm.t * tau,\n name=variable_name + \"_comsol\"\n )\n fun.domain = \"current collector\"\n fun.mesh = mesh.combine_submeshes(\"current collector\")\n fun.secondary_mesh = None\n \n return fun",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We then pass the variables of interest to the interpolating function",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"comsol_voltage = pybamm.Interpolant(\n comsol_t, \n comsol_variables[\"voltage\"],\n pybamm.t * tau,\n name=\"voltage_comsol\",\n)\ncomsol_voltage.mesh = None\ncomsol_voltage.secondary_mesh = None\ncomsol_phi_s_cn = get_interp_fun_curr_coll(\"phi_s_cn\")\ncomsol_phi_s_cp = get_interp_fun_curr_coll(\"phi_s_cp\")\ncomsol_current = get_interp_fun_curr_coll(\"current\")\ncomsol_temperature = get_interp_fun_curr_coll(\"temperature\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"and add them to a `pybamm.BaseModel` object",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"comsol_model = pybamm.BaseModel()\ncomsol_model.variables = {\n \"Terminal voltage [V]\": comsol_voltage,\n \"Negative current collector potential [V]\": comsol_phi_s_cn,\n \"Positive current collector potential [V]\": comsol_phi_s_cp,\n \"Current collector current density [A.m-2]\": comsol_current,\n \"X-averaged cell temperature [K]\": comsol_temperature,\n # Add spatial variables to match pybamm model\n \"z\": simulations[\"1+1D DFN\"].built_model.variables[\"z\"],\n \"z [m]\": simulations[\"1+1D DFN\"].built_model.variables[\"z [m]\"], \n}",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We then add the solution object from the 1+1D model. This is just so that PyBaMM uses the same (dimensionless) times behind the scenes when dealing with COMSOL model and the reduced-order models: the variables in `comsol_model.variables` are functions of time only that return the (interpolated in space) COMSOL solution. We also need to update the time and length scales for the COMSOL model so that any dimensionless variables are scaled correctly. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"comsol_model.timescale = simulations[\"1+1D DFN\"].model.timescale\ncomsol_model.length_scales = simulations[\"1+1D DFN\"].model.length_scales\ncomsol_solution = pybamm.Solution(solutions[\"1+1D DFN\"].t, solutions[\"1+1D DFN\"].y, comsol_model, {})",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Comparing the full and reduced-order models",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"The DFNCC requires some post-processing to extract the solution variables. In particular, we need to pass the current and voltage from the average DFN model to the current collector model in order to compute the distribution of the potential in the current collectors and to account for the effect of the current collector resistance in the terminal voltage. \n\nThis process is automated by the method `post_process` which accepts the current collector solution object, the parameters and the voltage and current from the average DFN model. The results are stored in the dictionary `dfncc_vars`",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"V_av = solutions[\"Average DFN\"][\"Terminal voltage\"]\nI_av = solutions[\"Average DFN\"][\"Total current density\"]\n\ndfncc_vars = cc_model.post_process(\n solutions[\"Current collector\"], param, V_av, I_av\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Next we create a function to create some custom plots. For a given variable the plots will show: (a) the COMSOL results as a function of position in the current collector $z$ and time $t$; (b) a comparison of the full and reduced-order models and a sequence of times; (c) the time-averaged error between the full and reduced-order models as a function of space; and (d) the space-averaged error between the full and reduced-order models as a function of time.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def plot(\n t_plot,\n z_plot,\n t_slices,\n var_name,\n units,\n comsol_var_fun,\n dfn_var_fun,\n dfncc_var_fun,\n param,\n cmap=\"viridis\",\n):\n \n fig, ax = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(13, 7))\n fig.subplots_adjust(\n left=0.15, bottom=0.1, right=0.95, top=0.95, wspace=0.4, hspace=0.8\n )\n # plot comsol var\n comsol_var = comsol_var_fun(t=t_plot, z=z_plot)\n comsol_var_plot = ax[0, 0].pcolormesh(\n z_plot * 1e3, t_plot, np.transpose(comsol_var), shading=\"gouraud\", cmap=cmap\n )\n if \"cn\" in var_name:\n format = \"%.0e\"\n elif \"cp\" in var_name:\n format = \"%.0e\"\n else:\n format = None\n fig.colorbar(\n comsol_var_plot,\n ax=ax,\n format=format,\n location=\"top\",\n shrink=0.42,\n aspect=20,\n anchor=(0.0, 0.0),\n )\n\n # plot slices\n ccmap = plt.get_cmap(\"inferno\")\n for ind, t in enumerate(t_slices):\n color = ccmap(float(ind) / len(t_slices))\n comsol_var_slice = comsol_var_fun(t=t, z=z_plot)\n dfn_var_slice = dfn_var_fun(t=t, z=z_plot)\n dfncc_var_slice = dfncc_var_fun(t=np.array([t]), z=z_plot)\n ax[0, 1].plot(\n z_plot * 1e3, comsol_var_slice, \"o\", fillstyle=\"none\", color=color\n )\n ax[0, 1].plot(\n z_plot * 1e3,\n dfn_var_slice,\n \"-\",\n color=color,\n label=\"{:.0f} s\".format(t_slices[ind]),\n )\n ax[0, 1].plot(z_plot * 1e3, dfncc_var_slice, \":\", color=color)\n # add dummy points for legend of styles\n comsol_p, = ax[0, 1].plot(np.nan, np.nan, \"ko\", fillstyle=\"none\")\n pybamm_p, = ax[0, 1].plot(np.nan, np.nan, \"k-\", fillstyle=\"none\")\n dfncc_p, = ax[0, 1].plot(np.nan, np.nan, \"k:\", fillstyle=\"none\")\n\n # compute errors\n dfn_var = dfn_var_fun(t=t_plot, z=z_plot)\n dfncc_var = dfncc_var_fun(t=t_plot, z=z_plot)\n error = np.abs(comsol_var - dfn_var)\n error_bar = np.abs(comsol_var - dfncc_var)\n\n # plot time averaged error\n ax[1, 0].plot(z_plot * 1e3, np.mean(error, axis=1), \"k-\", label=r\"$1+1$D\")\n ax[1, 0].plot(z_plot * 1e3, np.mean(error_bar, axis=1), \"k:\", label=\"DFNCC\")\n\n # plot z averaged error\n ax[1, 1].plot(t_plot, np.mean(error, axis=0), \"k-\", label=r\"$1+1$D\")\n ax[1, 1].plot(t_plot, np.mean(error_bar, axis=0), \"k:\", label=\"DFNCC\")\n\n # set ticks\n ax[0, 0].tick_params(which=\"both\")\n ax[0, 1].tick_params(which=\"both\")\n ax[1, 0].tick_params(which=\"both\")\n if var_name in [\"$\\mathcal{I}^*$\"]:\n ax[1, 0].set_yscale(\"log\")\n ax[1, 0].set_yticks = [1e-5, 1e-4, 1e-3, 1e-2, 1e-1, 1e-2, 1e-1, 1]\n else:\n ax[1, 0].ticklabel_format(style=\"sci\", scilimits=(-2, 2), axis=\"y\")\n ax[1, 1].tick_params(which=\"both\")\n if var_name in [\"$\\phi^*_{\\mathrm{s,cn}}$\", \"$\\phi^*_{\\mathrm{s,cp}} - V^*$\"]:\n ax[1, 0].ticklabel_format(style=\"sci\", scilimits=(-2, 2), axis=\"y\")\n else:\n ax[1, 1].set_yscale(\"log\")\n ax[1, 1].set_yticks = [1e-5, 1e-4, 1e-3, 1e-2, 1e-1, 1e-2, 1e-1, 1]\n\n # set labels\n ax[0, 0].set_xlabel(r\"$z^*$ [mm]\")\n ax[0, 0].set_ylabel(r\"$t^*$ [s]\")\n ax[0, 0].set_title(r\"{} {}\".format(var_name, units), y=1.5)\n ax[0, 1].set_xlabel(r\"$z^*$ [mm]\")\n ax[0, 1].set_ylabel(r\"{}\".format(var_name))\n ax[1, 0].set_xlabel(r\"$z^*$ [mm]\")\n ax[1, 0].set_ylabel(\"Time-averaged\" + \"\\n\" + r\"absolute error {}\".format(units))\n ax[1, 1].set_xlabel(r\"$t^*$ [s]\")\n ax[1, 1].set_ylabel(\"Space-averaged\" + \"\\n\" + r\"absolute error {}\".format(units))\n\n ax[0, 0].text(-0.1, 1.6, \"(a)\", transform=ax[0, 0].transAxes)\n ax[0, 1].text(-0.1, 1.6, \"(b)\", transform=ax[0, 1].transAxes)\n ax[1, 0].text(-0.1, 1.2, \"(c)\", transform=ax[1, 0].transAxes)\n ax[1, 1].text(-0.1, 1.2, \"(d)\", transform=ax[1, 1].transAxes)\n\n leg1 = ax[0, 1].legend(\n bbox_to_anchor=(0, 1.1, 1.0, 0.102),\n loc=\"lower left\",\n borderaxespad=0.0,\n ncol=3,\n mode=\"expand\",\n )\n\n leg2 = ax[0, 1].legend(\n [comsol_p, pybamm_p, dfncc_p],\n [\"COMSOL\", r\"$1+1$D\", \"DFNCC\"],\n bbox_to_anchor=(0, 1.5, 1.0, 0.102),\n loc=\"lower left\",\n borderaxespad=0.0,\n ncol=3,\n mode=\"expand\",\n )\n ax[0, 1].add_artist(leg1)\n\n ax[1, 0].legend(\n bbox_to_anchor=(0.0, 1.1, 1.0, 0.102),\n loc=\"lower right\",\n borderaxespad=0.0,\n ncol=3,\n )\n ax[1, 1].legend(\n bbox_to_anchor=(0.0, 1.1, 1.0, 0.102),\n loc=\"lower right\",\n borderaxespad=0.0,\n ncol=3,\n )",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We then set up the times and points in space to use in the plots ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"t_plot = comsol_t\nz_plot = z_interp\nt_slices = np.array([600, 1200, 1800, 2400, 3000]) / 3",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"and plot the negative current collector potential",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"var = \"Negative current collector potential [V]\"\ncomsol_var_fun = comsol_solution[var]\ndfn_var_fun = solutions[\"1+1D DFN\"][var]\n\ndfncc_var_fun = dfncc_vars[var]\nplot(\n t_plot,\n z_plot,\n t_slices,\n \"$\\phi^*_{\\mathrm{s,cn}}$\",\n \"[V]\",\n comsol_var_fun,\n dfn_var_fun,\n dfncc_var_fun,\n param,\n cmap=\"cividis\",\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"the positive current collector potential with respect to terminal voltage",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"var = \"Positive current collector potential [V]\"\ncomsol_var = comsol_solution[var]\nV_comsol = comsol_solution[\"Terminal voltage [V]\"]\n\n\ndef comsol_var_fun(t, z):\n return comsol_var(t=t, z=z) - V_comsol(t=t)\n\n\ndfn_var = solutions[\"1+1D DFN\"][var]\nV = solutions[\"1+1D DFN\"][\"Terminal voltage [V]\"]\n\n\ndef dfn_var_fun(t, z):\n return dfn_var(t=t, z=z) - V(t=t)\n\n\ndfncc_var = dfncc_vars[var]\nV_dfncc = dfncc_vars[\"Terminal voltage [V]\"]\n\ndef dfncc_var_fun(t, z):\n return dfncc_var(t=t, z=z) - V_dfncc(t)\n\n\nplot(\n t_plot,\n z_plot,\n t_slices,\n \"$\\phi^*_{\\mathrm{s,cp}} - V^*$\",\n \"[V]\",\n comsol_var_fun,\n dfn_var_fun,\n dfncc_var_fun,\n param,\n cmap=\"viridis\",\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"the through-cell current ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"var = \"Current collector current density [A.m-2]\"\ncomsol_var_fun = comsol_solution[var]\ndfn_var_fun = solutions[\"1+1D DFN\"][var]\n\nI_av = solutions[\"Average DFN\"][var]\n\n\ndef dfncc_var_fun(t, z):\n \"In the DFNCC the current is just the average current\"\n return np.transpose(np.repeat(I_av(t)[:, np.newaxis], len(z), axis=1))\n\n\nplot(\n t_plot,\n z_plot,\n t_slices,\n \"$\\mathcal{I}^*$\",\n \"[A/m${}^2$]\",\n comsol_var_fun,\n dfn_var_fun,\n dfncc_var_fun,\n param,\n cmap=\"plasma\",\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"and the temperature with respect to reference temperature",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"T_ref = param.evaluate(dfn.param.T_ref)\nvar = \"X-averaged cell temperature [K]\"\ncomsol_var = comsol_solution[var]\n\n\ndef comsol_var_fun(t, z):\n return comsol_var(t=t, z=z) - T_ref\n\n\ndfn_var = solutions[\"1+1D DFN\"][var]\n\n\ndef dfn_var_fun(t, z):\n return dfn_var(t=t, z=z) - T_ref\n\n\nT_av = solutions[\"Average DFN\"][var]\n\n\ndef dfncc_var_fun(t, z):\n \"In the DFNCC the temperature is just the average temperature\"\n return np.transpose(np.repeat(T_av(t)[:, np.newaxis], len(z), axis=1)) - T_ref\n\n\nplot(\n t_plot,\n z_plot,\n t_slices,\n \"$\\\\bar{T}^* - \\\\bar{T}_0^*$\",\n \"[K]\",\n comsol_var_fun,\n dfn_var_fun,\n dfncc_var_fun,\n param,\n cmap=\"inferno\",\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We see that the electrical conductivity of the current collectors is sufficiently\nhigh that the potentials remain fairly uniform in space, and both the 1+1D DFN and DFNCC models are able to accurately capture the potential distribution in the current collectors.\n\n\nIn the plot of the current we see that positioning both tabs at the top of the cell means that for most of the simulation the current preferentially travels through the upper part of the cell. Eventually, as the cell continues to discharge, this part becomes more (de)lithiated until the resultant local increase in through-cell resistance is sufficient for it to become preferential for the current to travel further along the current collectors and through the lower part of the cell. This behaviour is well captured by the 1+1D model. In the DFNCC formulation the through-cell current density is assumed uniform,\nso the greatest error is found at the ends of the current collectors where the current density deviates most from its average.\n\nFor the parameters used in this example we find that the temperature exhibits a relatively weak variation along the length of the current collectors. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## References\n\nThe relevant papers for this notebook are:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"pybamm.print_citations()",
"[1] Joel A. E. Andersson, Joris Gillis, Greg Horn, James B. Rawlings, and Moritz Diehl. CasADi – A software framework for nonlinear optimization and optimal control. Mathematical Programming Computation, 11(1):1–36, 2019. doi:10.1007/s12532-018-0139-4.\n[2] Marc Doyle, Thomas F. Fuller, and John Newman. Modeling of galvanostatic charge and discharge of the lithium/polymer/insertion cell. Journal of the Electrochemical society, 140(6):1526–1533, 1993. doi:10.1149/1.2221597.\n[3] Charles R. Harris, K. Jarrod Millman, Stéfan J. van der Walt, Ralf Gommers, Pauli Virtanen, David Cournapeau, Eric Wieser, Julian Taylor, Sebastian Berg, Nathaniel J. Smith, and others. Array programming with NumPy. Nature, 585(7825):357–362, 2020. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2649-2.\n[4] Scott G. Marquis, Valentin Sulzer, Robert Timms, Colin P. Please, and S. Jon Chapman. An asymptotic derivation of a single particle model with electrolyte. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 166(15):A3693–A3706, 2019. doi:10.1149/2.0341915jes.\n[5] Valentin Sulzer, Scott G. Marquis, Robert Timms, Martin Robinson, and S. Jon Chapman. Python Battery Mathematical Modelling (PyBaMM). Journal of Open Research Software, 9(1):14, 2021. doi:10.5334/jors.309.\n[6] Robert Timms, Scott G Marquis, Valentin Sulzer, Colin P. Please, and S Jonathan Chapman. Asymptotic Reduction of a Lithium-ion Pouch Cell Model. SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, 81(3):765–788, 2021. doi:10.1137/20M1336898.\n\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c50bf7954cc66c2ffdd2e1fd71be1fb5655b93e8
| 140,880 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
05_CodingDrill/reference_files/EVA4S5F1.ipynb
|
Septank766/TSAI-DeepVision-EVA4.0
|
02265d7e3e06789d0ee634a38399c6f0e01cfcbd
|
[
"MIT"
] | 22 |
2020-05-16T08:15:48.000Z
|
2021-12-30T14:38:31.000Z
|
05_CodingDrill/reference_files/EVA4S5F1.ipynb
|
Septank766/TSAI-DeepVision-EVA4.0
|
02265d7e3e06789d0ee634a38399c6f0e01cfcbd
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2020-09-07T17:10:41.000Z
|
2020-09-09T20:51:31.000Z
|
05_CodingDrill/reference_files/EVA4S5F1.ipynb
|
Septank766/TSAI-DeepVision-EVA4.0
|
02265d7e3e06789d0ee634a38399c6f0e01cfcbd
|
[
"MIT"
] | 43 |
2020-03-07T22:08:41.000Z
|
2022-03-16T21:07:30.000Z
| 128.892955 | 62,424 | 0.821522 |
[
[
[
"<a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/satyajitghana/TSAI-DeepVision-EVA4.0/blob/master/05_CodingDrill/EVA4S5F1.ipynb\" target=\"_parent\"><img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open In Colab\"/></a>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Import Libraries",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from __future__ import print_function\nimport torch\nimport torch.nn as nn\nimport torch.nn.functional as F\nimport torch.optim as optim\nfrom torchvision import datasets, transforms",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Data Transformations\n\nWe first start with defining our data transformations. We need to think what our data is and how can we augment it to correct represent images which it might not see otherwise. \n\nHere is the list of all the transformations which come pre-built with PyTorch\n\n1. Compose\n2. ToTensor\n3. ToPILImage\n4. Normalize\n5. Resize\n6. Scale\n7. CenterCrop\n8. Pad\n9. Lambda\n10. RandomApply\n11. RandomChoice\n12. RandomOrder\n13. RandomCrop\n14. RandomHorizontalFlip\n15. RandomVerticalFlip\n16. RandomResizedCrop\n17. RandomSizedCrop\n18. FiveCrop\n19. TenCrop\n20. LinearTransformation\n21. ColorJitter\n22. RandomRotation\n23. RandomAffine\n24. Grayscale\n25. RandomGrayscale\n26. RandomPerspective\n27. RandomErasing\n\nYou can read more about them [here](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/_modules/torchvision/transforms/transforms.html)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Train Phase transformations\ntrain_transforms = transforms.Compose([\n # transforms.Resize((28, 28)),\n # transforms.ColorJitter(brightness=0.10, contrast=0.1, saturation=0.10, hue=0.1),\n transforms.ToTensor(),\n transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,)) # The mean and std have to be sequences (e.g., tuples), therefore you should add a comma after the values. \n # Note the difference between (0.1307) and (0.1307,)\n ])\n\n# Test Phase transformations\ntest_transforms = transforms.Compose([\n # transforms.Resize((28, 28)),\n # transforms.ColorJitter(brightness=0.10, contrast=0.1, saturation=0.10, hue=0.1),\n transforms.ToTensor(),\n transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))\n ])\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Dataset and Creating Train/Test Split",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"train = datasets.MNIST('./data', train=True, download=True, transform=train_transforms)\ntest = datasets.MNIST('./data', train=False, download=True, transform=test_transforms)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Dataloader Arguments & Test/Train Dataloaders\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"SEED = 1\n\n# CUDA?\ncuda = torch.cuda.is_available()\nprint(\"CUDA Available?\", cuda)\n\n# For reproducibility\ntorch.manual_seed(SEED)\n\nif cuda:\n torch.cuda.manual_seed(SEED)\n\n# dataloader arguments - something you'll fetch these from cmdprmt\ndataloader_args = dict(shuffle=True, batch_size=128, num_workers=4, pin_memory=True) if cuda else dict(shuffle=True, batch_size=64)\n\n# train dataloader\ntrain_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train, **dataloader_args)\n\n# test dataloader\ntest_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(test, **dataloader_args)",
"CUDA Available? True\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Data Statistics\n\nIt is important to know your data very well. Let's check some of the statistics around our data and how it actually looks like",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# We'd need to convert it into Numpy! Remember above we have converted it into tensors already\ntrain_data = train.train_data\ntrain_data = train.transform(train_data.numpy())\n\nprint('[Train]')\nprint(' - Numpy Shape:', train.train_data.cpu().numpy().shape)\nprint(' - Tensor Shape:', train.train_data.size())\nprint(' - min:', torch.min(train_data))\nprint(' - max:', torch.max(train_data))\nprint(' - mean:', torch.mean(train_data))\nprint(' - std:', torch.std(train_data))\nprint(' - var:', torch.var(train_data))\n\ndataiter = iter(train_loader)\nimages, labels = dataiter.next()\n\nprint(images.shape)\nprint(labels.shape)\n\n# Let's visualize some of the images\n%matplotlib inline\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\nplt.imshow(images[0].numpy().squeeze(), cmap='gray_r')\n",
"/usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/torchvision/datasets/mnist.py:55: UserWarning: train_data has been renamed data\n warnings.warn(\"train_data has been renamed data\")\n"
]
],
[
[
"## MORE\n\nIt is important that we view as many images as possible. This is required to get some idea on image augmentation later on",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"figure = plt.figure()\nnum_of_images = 60\nfor index in range(1, num_of_images + 1):\n plt.subplot(6, 10, index)\n plt.axis('off')\n plt.imshow(images[index].numpy().squeeze(), cmap='gray_r')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# How did we get those mean and std values which we used above?\n\nLet's run a small experiment",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# simple transform\nsimple_transforms = transforms.Compose([\n # transforms.Resize((28, 28)),\n # transforms.ColorJitter(brightness=0.10, contrast=0.1, saturation=0.10, hue=0.1),\n transforms.ToTensor(),\n # transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,)) # The mean and std have to be sequences (e.g., tuples), therefore you should add a comma after the values. \n # Note the difference between (0.1307) and (0.1307,)\n ])\nexp = datasets.MNIST('./data', train=True, download=True, transform=simple_transforms)\nexp_data = exp.train_data\nexp_data = exp.transform(exp_data.numpy())\n\nprint('[Train]')\nprint(' - Numpy Shape:', exp.train_data.cpu().numpy().shape)\nprint(' - Tensor Shape:', exp.train_data.size())\nprint(' - min:', torch.min(exp_data))\nprint(' - max:', torch.max(exp_data))\nprint(' - mean:', torch.mean(exp_data))\nprint(' - std:', torch.std(exp_data))\nprint(' - var:', torch.var(exp_data))",
"/usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/torchvision/datasets/mnist.py:55: UserWarning: train_data has been renamed data\n warnings.warn(\"train_data has been renamed data\")\n"
]
],
[
[
"# The model\nLet's start with the model we first saw",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class Net(nn.Module):\n def __init__(self):\n super(Net, self).__init__()\n self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, 3, padding=1) #input -? OUtput? RF\n self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, 3, padding=1)\n self.pool1 = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)\n self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(64, 128, 3, padding=1)\n self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(128, 256, 3, padding=1)\n self.pool2 = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)\n self.conv5 = nn.Conv2d(256, 512, 3)\n self.conv6 = nn.Conv2d(512, 1024, 3)\n self.conv7 = nn.Conv2d(1024, 10, 3)\n\n def forward(self, x):\n x = self.pool1(F.relu(self.conv2(F.relu(self.conv1(x)))))\n x = self.pool2(F.relu(self.conv4(F.relu(self.conv3(x)))))\n x = F.relu(self.conv6(F.relu(self.conv5(x))))\n # x = F.relu(self.conv7(x))\n x = self.conv7(x)\n x = x.view(-1, 10)\n return F.log_softmax(x, dim=-1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Model Params\nCan't emphasize on how important viewing Model Summary is. \nUnfortunately, there is no in-built model visualizer, so we have to take external help",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"!pip install torchsummary\nfrom torchsummary import summary\nuse_cuda = torch.cuda.is_available()\ndevice = torch.device(\"cuda\" if use_cuda else \"cpu\")\nprint(device)\nmodel = Net().to(device)\nsummary(model, input_size=(1, 28, 28))",
"Requirement already satisfied: torchsummary in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (1.5.1)\ncuda\n----------------------------------------------------------------\n Layer (type) Output Shape Param #\n================================================================\n Conv2d-1 [-1, 32, 28, 28] 320\n Conv2d-2 [-1, 64, 28, 28] 18,496\n MaxPool2d-3 [-1, 64, 14, 14] 0\n Conv2d-4 [-1, 128, 14, 14] 73,856\n Conv2d-5 [-1, 256, 14, 14] 295,168\n MaxPool2d-6 [-1, 256, 7, 7] 0\n Conv2d-7 [-1, 512, 5, 5] 1,180,160\n Conv2d-8 [-1, 1024, 3, 3] 4,719,616\n Conv2d-9 [-1, 10, 1, 1] 92,170\n================================================================\nTotal params: 6,379,786\nTrainable params: 6,379,786\nNon-trainable params: 0\n----------------------------------------------------------------\nInput size (MB): 0.00\nForward/backward pass size (MB): 1.51\nParams size (MB): 24.34\nEstimated Total Size (MB): 25.85\n----------------------------------------------------------------\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Training and Testing\n\nAll right, so we have 6.3M params, and that's too many, we know that. But the purpose of this notebook is to set things right for our future experiments. \n\nLooking at logs can be boring, so we'll introduce **tqdm** progressbar to get cooler logs. \n\nLet's write train and test functions",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from tqdm import tqdm\n\ntrain_losses = []\ntest_losses = []\ntrain_acc = []\ntest_acc = []\n\ndef train(model, device, train_loader, optimizer, epoch):\n model.train()\n pbar = tqdm(train_loader)\n correct = 0\n processed = 0\n for batch_idx, (data, target) in enumerate(pbar):\n # get samples\n data, target = data.to(device), target.to(device)\n\n # Init\n optimizer.zero_grad()\n # In PyTorch, we need to set the gradients to zero before starting to do backpropragation because PyTorch accumulates the gradients on subsequent backward passes. \n # Because of this, when you start your training loop, ideally you should zero out the gradients so that you do the parameter update correctly.\n\n # Predict\n y_pred = model(data)\n\n # Calculate loss\n loss = F.nll_loss(y_pred, target)\n train_losses.append(loss)\n\n # Backpropagation\n loss.backward()\n optimizer.step()\n\n # Update pbar-tqdm\n \n pred = y_pred.argmax(dim=1, keepdim=True) # get the index of the max log-probability\n correct += pred.eq(target.view_as(pred)).sum().item()\n processed += len(data)\n\n pbar.set_description(desc= f'Loss={loss.item()} Batch_id={batch_idx} Accuracy={100*correct/processed:0.2f}')\n train_acc.append(100*correct/processed)\n\ndef test(model, device, test_loader):\n model.eval()\n test_loss = 0\n correct = 0\n with torch.no_grad():\n for data, target in test_loader:\n data, target = data.to(device), target.to(device)\n output = model(data)\n test_loss += F.nll_loss(output, target, reduction='sum').item() # sum up batch loss\n pred = output.argmax(dim=1, keepdim=True) # get the index of the max log-probability\n correct += pred.eq(target.view_as(pred)).sum().item()\n\n test_loss /= len(test_loader.dataset)\n test_losses.append(test_loss)\n\n print('\\nTest set: Average loss: {:.4f}, Accuracy: {}/{} ({:.2f}%)\\n'.format(\n test_loss, correct, len(test_loader.dataset),\n 100. * correct / len(test_loader.dataset)))\n \n test_acc.append(100. * correct / len(test_loader.dataset))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Let's Train and test our model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model = Net().to(device)\noptimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01, momentum=0.9)\nEPOCHS = 20\nfor epoch in range(EPOCHS):\n print(\"EPOCH:\", epoch)\n train(model, device, train_loader, optimizer, epoch)\n test(model, device, test_loader)",
"\r 0%| | 0/469 [00:00<?, ?it/s]"
],
[
"fig, axs = plt.subplots(2,2,figsize=(15,10))\naxs[0, 0].plot(train_losses)\naxs[0, 0].set_title(\"Training Loss\")\naxs[1, 0].plot(train_acc)\naxs[1, 0].set_title(\"Training Accuracy\")\naxs[0, 1].plot(test_losses)\naxs[0, 1].set_title(\"Test Loss\")\naxs[1, 1].plot(test_acc)\naxs[1, 1].set_title(\"Test Accuracy\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50bf80db5b55589a4aa7c2c21f776a9b4669680
| 894,795 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
main.ipynb
|
denisuzhva/Compressed-Sensing-Blockchain
|
a14a06dbbbe10cfbb6d9b0a6a2be974b7bf74f9c
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
main.ipynb
|
denisuzhva/Compressed-Sensing-Blockchain
|
a14a06dbbbe10cfbb6d9b0a6a2be974b7bf74f9c
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
main.ipynb
|
denisuzhva/Compressed-Sensing-Blockchain
|
a14a06dbbbe10cfbb6d9b0a6a2be974b7bf74f9c
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 1,675.646067 | 367,564 | 0.959948 |
[
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport os\n\nplt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [10.0, 5.0]\nplt.rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 220",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def rand_signal_generator(len):\n times = np.arange(0, len)\n signal = np.sin(times) + np.random.normal(scale=0.1, size=times.size) \n return signal",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def generate_block(input_data, seed_vector, m, n):\n meas_mat = np.zeros((m, n), dtype=np.float32)\n for idx, seed in enumerate(seed_vector):\n seed_int = np.asarray(seed, dtype=np.float32).view(np.uint32)\n meas_mat[idx] = np.random.RandomState(seed_int).binomial(1, .5, n) * 2 - 1\n meas_mat /= np.sqrt(m)\n out_data = meas_mat.dot(input_data)\n return out_data, meas_mat",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"dataset_path = \"./datasets/extrasensory/\"\nsample_names = os.listdir(dataset_path)[:]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"m = 8\ny = np.arange(0, m, dtype=np.float32)\ncs_blockchain = np.zeros((len(sample_names), m))\nsample_list = []\nfor idx, sample_name in enumerate(sample_names):\n sample = np.loadtxt(dataset_path + sample_name)[:, 3]\n sample_list.append(sample)\n n = sample.size\n y, _ = generate_block(sample, y, m, n)\n cs_blockchain[idx] = y ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sample = sample_list[0]\nplt.plot(sample, \"k\", linewidth=.7)\nplt.xlim([0, len(sample)])\nplt.xlabel(\"ticks\")\nplt.ylabel(\"magnitude\")\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cs_blockchain_frauded = np.zeros_like(cs_blockchain)\nfraud_idx = 100\ny = np.arange(0, m, dtype=np.float32)\nfor idx, sample in enumerate(sample_list):\n n = sample.size\n y, _ = generate_block(sample, y, m, n)\n if idx == fraud_idx:\n y += 1e-1\n cs_blockchain_frauded[idx] = y ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"y_idx = 0\nplt.plot(cs_blockchain_frauded.mean(axis=1), \"r\", linewidth=.7, label=\"malicious sub-chain\")\nplt.plot(cs_blockchain.mean(axis=1), \"g\", linewidth=.7, label=\"true chain\")\nplt.xlim([0, cs_blockchain.shape[0]-1])\nplt.xlabel(\"block #\")\nplt.ylabel(r\"mean value of $y$\")\nplt.legend()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"injects = list(np.power(10., np.arange(-38, 39)))\nl2s = []\nl2_vals = []\nfor idx, inject in enumerate(injects):\n y = np.arange(0, m, dtype=np.float32) + inject\n cs_blockchain_frauded = np.zeros_like(cs_blockchain)\n for jdx, sample in enumerate(sample_list):\n n = sample.size\n y, _ = generate_block(sample, y, m, n)\n cs_blockchain_frauded[jdx] = y\n l2_val = np.linalg.norm(cs_blockchain - cs_blockchain_frauded, ord=2, axis=1)\n l2_vals.append(l2_val)\n l2s.append(l2_val.mean())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.plot(injects, l2s, \"k\", linewidth=.7)\nplt.xscale(\"log\")\nplt.xticks(injects[0::4])\nplt.xlim([injects[0], injects[-1]])\nplt.ylim([0, 25000])\nplt.xlabel(\"injection probe magnitude\")\nplt.ylabel(r\"$\\ell_2$ distance averaged over all blocks\")\nplt.grid()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.plot(l2_vals[30], \"k\", linewidth=.7)\nplt.xlabel(\"block #\")\nplt.ylabel(r\"$\\ell_2$ distance\")\nplt.xlim([0, cs_blockchain.shape[0]-1])\nplt.grid()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(np.argwhere(l2_vals[30]))",
"[[ 0]\n [ 1]\n [ 2]\n [ 3]\n [ 4]\n [ 5]\n [ 6]\n [ 7]\n [ 8]\n [ 9]\n [ 10]\n [ 11]\n [ 12]\n [ 13]\n [ 14]\n [ 15]\n [ 16]\n [ 17]\n [ 18]\n [ 19]\n [ 20]\n [ 21]\n [ 22]\n [ 23]\n [ 24]\n [ 25]\n [ 26]\n [ 27]\n [ 28]\n [ 29]\n [ 30]\n [ 31]\n [ 32]\n [ 33]\n [ 34]\n [ 35]\n [ 36]\n [ 37]\n [ 38]\n [ 39]\n [ 40]\n [ 41]\n [ 42]\n [ 43]\n [ 44]\n [ 45]\n [ 46]\n [ 47]\n [ 48]\n [ 49]\n [ 50]\n [ 51]\n [ 52]\n [ 53]\n [ 54]\n [ 55]\n [ 56]\n [ 57]\n [ 58]\n [ 59]\n [ 60]\n [ 61]\n [ 62]\n [ 63]\n [ 64]\n [ 65]\n [ 66]\n [ 67]\n [ 68]\n [ 69]\n [ 70]\n [ 71]\n [ 72]\n [ 73]\n [ 74]\n [ 75]\n [ 76]\n [ 77]\n [ 78]\n [ 79]\n [ 80]\n [ 81]\n [ 82]\n [ 83]\n [ 84]\n [ 85]\n [ 86]\n [ 87]\n [ 88]\n [ 89]\n [ 90]\n [ 91]\n [ 92]\n [ 93]\n [ 94]\n [ 95]\n [ 96]\n [ 97]\n [ 98]\n [ 99]\n [100]\n [101]\n [102]\n [103]\n [104]\n [105]\n [106]\n [107]\n [108]\n [109]\n [110]\n [111]\n [112]\n [113]\n [114]\n [115]\n [116]\n [117]\n [118]\n [119]\n [120]\n [121]\n [122]\n [123]\n [124]\n [125]\n [126]\n [127]\n [128]\n [129]\n [130]\n [131]\n [132]\n [133]\n [134]\n [135]\n [136]\n [137]\n [138]\n [139]\n [140]\n [141]\n [142]\n [143]\n [144]\n [145]\n [146]\n [147]\n [148]\n [149]\n [150]\n [151]\n [152]\n [153]\n [154]\n [155]\n [156]\n [157]\n [158]\n [159]\n [160]\n [161]\n [162]\n [163]\n [164]\n [165]\n [166]\n [167]\n [168]\n [169]\n [170]\n [171]\n [172]\n [173]\n [174]\n [175]\n [176]\n [177]\n [178]\n [179]\n [180]\n [181]\n [182]\n [183]\n [184]\n [185]\n [186]\n [187]\n [188]\n [189]\n [190]\n [191]\n [192]\n [193]\n [194]\n [195]\n [196]\n [197]\n [198]\n [199]\n [200]\n [201]\n [202]\n [203]\n [204]\n [205]\n [206]\n [207]\n [208]\n [209]\n [210]\n [211]\n [212]\n [213]\n [214]\n [215]\n [216]\n [217]\n [218]\n [219]\n [220]\n [221]\n [222]\n [223]\n [224]\n [225]\n [226]\n [227]\n [228]\n [229]\n [230]\n [231]\n [232]\n [233]\n [234]\n [235]\n [236]\n [237]\n [238]\n [239]\n [240]\n [241]\n [242]\n [243]\n [244]\n [245]\n [246]\n [247]\n [248]\n [249]\n [250]\n [251]\n [252]\n [253]\n [254]\n [255]\n [256]\n [257]\n [258]\n [259]\n [260]\n [261]]\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50bfb67bee6064dbf792e9f458d897c2299af9d
| 18,421 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
ch05_test_datareader.ipynb
|
blockchain99/data_analysis
|
6648e63f4dca6899a643014148194015bd1707bd
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-09-04T04:38:29.000Z
|
2021-09-04T04:38:29.000Z
|
ch05_test_datareader.ipynb
|
blockchain99/data_analysis
|
6648e63f4dca6899a643014148194015bd1707bd
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
ch05_test_datareader.ipynb
|
blockchain99/data_analysis
|
6648e63f4dca6899a643014148194015bd1707bd
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 32.836007 | 95 | 0.378264 |
[
[
[
"import pandas_datareader.data as web\ntest_data = {stock: web.get_data_yahoo(stock) for stock in ['IBM', 'MSFT'] }\ntest_data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"test_data['IBM']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nprice = pd.DataFrame({key: value['Adj Close']\nfor key, value in test_data.items()})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"price",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"volume = pd.DataFrame({key: value['Volume'] \n for key, value in test_data.items()})\nvolume",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50c053c915cc344f65fbbc5394d0dbef0010460
| 20,365 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
artificial_intelligence/qsvm_kernel_multiclass.ipynb
|
chunfuchen/aqua-tutorials
|
74b0bcaac1678fc6c0de5be13e99d7ecd11b3075
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
artificial_intelligence/qsvm_kernel_multiclass.ipynb
|
chunfuchen/aqua-tutorials
|
74b0bcaac1678fc6c0de5be13e99d7ecd11b3075
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
artificial_intelligence/qsvm_kernel_multiclass.ipynb
|
chunfuchen/aqua-tutorials
|
74b0bcaac1678fc6c0de5be13e99d7ecd11b3075
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 148.649635 | 16,320 | 0.887503 |
[
[
[
"## _*Quantum SVM kernel algorithm: multiclass classifier extension*_\n\nA multiclass extension works in conjunction with an underlying binary (two class) classifier to provide multiclass classification.\n\nCurrently three different multiclass extensions are supported:\n\n* OneAgainstRest\n* AllPairs\n* ErrorCorrectingCode\n\nThese use different techniques to group the data with binary classification to achieve the final multiclass classification.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from datasets import *\nfrom qiskit_aqua.utils import split_dataset_to_data_and_labels\nfrom qiskit_aqua.input import get_input_instance\nfrom qiskit_aqua import run_algorithm\nimport numpy as np",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Here we choose the `Wine` dataset which has 3 classes.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"n = 2 # dimension of each data point\nsample_Total, training_input, test_input, class_labels = Wine(training_size=40,\n test_size=10, n=n, PLOT_DATA=True)\n\ntemp = [test_input[k] for k in test_input]\ntotal_array = np.concatenate(temp)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Now we setup an Aqua configuration dictionary to use the quantum `QSVM.Kernel` algorithm and add a multiclass extension to classify the Wine data set, since it has 3 classes.\n\nAlthough the `AllPairs` extension is used here in the example the following multiclass extensions would also work:\n\n 'multiclass_extension': {'name': 'OneAgainstRest'}\n 'multiclass_extension': {'name': 'ErrorCorrectingCode', 'code_size': 5}",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"aqua_dict = {\n 'problem': {'name': 'svm_classification', 'random_seed': 10598},\n 'algorithm': {\n 'name': 'QSVM.Kernel'\n },\n 'feature_map': {'name': 'SecondOrderExpansion', 'depth': 2, 'entangler_map': {0: [1]}},\n 'multiclass_extension': {'name': 'AllPairs'},\n 'backend': {'name': 'qasm_simulator', 'shots': 1024}\n}\n\nalgo_input = get_input_instance('SVMInput')\nalgo_input.training_dataset = training_input\nalgo_input.test_dataset = test_input\nalgo_input.datapoints = total_array\n\nresult = run_algorithm(aqua_dict, algo_input)\nfor k,v in result.items():\n print(\"'{}' : {}\".format(k, v))\n",
"'testing_accuracy' : 0.8260869565217391\n'test_success_ratio' : 0.8260869565217391\n'predicted_labels' : [0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 2 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 2 0 2]\n'predicted_classes' : ['A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'B', 'A', 'A', 'A', 'B', 'C', 'B', 'B', 'B', 'A', 'B', 'B', 'B', 'B', 'C', 'A', 'C']\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c50c0ad6dce2a585378654c303afc93ad17adcbf
| 4,909 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
hw/hw6.ipynb
|
BioSysDesign/E164
|
69f6236de2d8172e541a5b56f7807d4767f20979
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
hw/hw6.ipynb
|
BioSysDesign/E164
|
69f6236de2d8172e541a5b56f7807d4767f20979
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null |
hw/hw6.ipynb
|
BioSysDesign/E164
|
69f6236de2d8172e541a5b56f7807d4767f20979
|
[
"BSD-3-Clause"
] | null | null | null | 51.673684 | 511 | 0.688124 |
[
[
[
"# Gene Regulatory Networks \nResources:\n\n1. [week5_feedback_systems.ipynb](https://pages.hmc.edu/pandey/reading/week5_feedback_systems.ipynb): This notebook introduces the analysis of feedback systems using Python and describes the role of feedback in system design using simulations of mathematical models.\n\n1. [week6_system_analysis.ipynb](https://pages.hmc.edu/pandey/reading/week6_system_analysis.ipynb): This notebook uses analytical and computational tools to discuss functions and utilities of different gene regulatory networks. \n\n1. Python tutorials online: You are free to use any tutorials from the Internet on Numpy, Scipy, or any other Python package that you may use to solve the homework problems.\n\n1. Submit your homework to GradeScope by downloading the jupyter notebook as a PDF. Go to Files -> Download as -> PDF. If that does not work, you can go to File -> Print Preview -> Ctrl + P (to print) -> Save as PDF.\n\nDue date: 1st March on GradeScope.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Problem 1: Cascade Gene Regulation \n(Adapted from [Alon] Problem 1.4) Cascades: Consider a cascade of three activators, $X$ → $Y$ → $Z$. Protein $X$ is initially present in the cell in its inactive form. The input signal of $X$, $u_X$, appears at time $t = 0$. As a result, $X$ rapidly becomes active and binds the promoter of gene $Y$, so that protein $Y$ starts to be produced at rate $\\beta$. When $Y$ levels exceed a threshold $K_y$, gene $Z$ begins to be transcribed. All proteins have the same degradation/dilution rate $\\alpha$. \n\n(a) Write a mathematical model to model the cascade phenomena described above. You may model the system by describing the rate of change of protein concentrations. \n\n(b) Simulate your model in (a) by choosing biologically relevant parameters. What is the concentration of protein $Z$ as a function of time? \n\n(c) Compute the response time of $Z$ with respect to the time of addition of $u_X$? Discuss how you can improve the speed of the response of this system by changing parameters. To compare the response times for different parameter settings, normalize the steady-state to show a fair comparison of the response time. \n\n(d) Assume that you have a repressor cascade instead of an activation cascade. How do your conclusions change for parts (a) - (c).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Problem 2: Eukaryotic Transcriptional Control\n\nRead this short paper on eukaryotic transcriptional control:\n\nKornberg, Roger D. \"Eukaryotic transcriptional control.\" Trends in biochemical sciences 24.12 (1999): M46-M49. [URL](https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0968000499014899)\n\nWrite a one paragraph summary on key differences in transcriptional control in prokaryotes and the eukaryotes. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Problem 3: Autorepression Speeds Up Response\n\nA paper published in 2002 showed that autorepression speeds up the response times of transcription networks in cells. We discussed the autorepression mechanisms in Week 4 and Week 5. In your simulations for HW 4, you could observe that the autorepression shows faster response when compared to unregulated gene expression. The goal of this problem is to use a similar mathematical model to analytically reason about the response time. Read the paper:\n\nRosenfeld, Nitzan, Michael B. Elowitz, and Uri Alon. \"Negative autoregulation speeds the response times of transcription networks.\" Journal of molecular biology 323.5 (2002): 785-793. [URL](https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022283602009944?via%3Dihub)\n\nRe-derive the expression of rise-time as shown in this paper to analytically comment about how autorepression can lead to faster response times. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Feedback:\n\nPlease submit the feedback form on Gradescope (if you haven't yet) and write here the number of hours you needed to finish this problem set.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
c50c15e31338379adf9f7142e59ce752cc8c09bf
| 7,969 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
day02-PyTORCH-and-PyCUDA/PyCUDA/02 add with PyCUDA.ipynb
|
MeRajat/Deep-Learning-Boot-Camp
|
1734d2a07b07c2e62dc8aa19d4ec127b8c7fada5
|
[
"MIT"
] | 6 |
2018-10-30T00:53:03.000Z
|
2022-02-15T17:06:59.000Z
|
day02-PyTORCH-and-PyCUDA/PyCUDA/02 add with PyCUDA.ipynb
|
MeRajat/Deep-Learning-Boot-Camp
|
1734d2a07b07c2e62dc8aa19d4ec127b8c7fada5
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
day02-PyTORCH-and-PyCUDA/PyCUDA/02 add with PyCUDA.ipynb
|
MeRajat/Deep-Learning-Boot-Camp
|
1734d2a07b07c2e62dc8aa19d4ec127b8c7fada5
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2019-08-26T12:27:29.000Z
|
2019-08-26T12:27:29.000Z
| 23.646884 | 316 | 0.477475 |
[
[
[
"# GPU Computing for Data Scientists\n#### Using CUDA, Jupyter, PyCUDA, ArrayFire and Thrust\n\n\nhttps://github.com/QuantScientist/Data-Science-ArrayFire-GPU",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%reset -f\nimport pycuda\nfrom pycuda import compiler\nimport pycuda.driver as drv\nimport pycuda.driver as cuda",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Make sure we have CUDA",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"drv.init()\nprint(\"%d device(s) found.\" % drv.Device.count()) \nfor ordinal in range(drv.Device.count()):\n dev = drv.Device(ordinal)\n print (\"Device #%d: %s\" % (ordinal, dev.name()))\n\ndrv",
"1 device(s) found.\nDevice #0: GeForce GTX 1080\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Simple addition the GPU: compilation",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pycuda.autoinit\nimport numpy\n\nfrom pycuda.compiler import SourceModule\n\nsrcGPU = \"\"\"\n #include <stdio.h>\n __global__ void multGPU(float *dest, float *a, float *b)\n{\n const int i = threadIdx.x; \n dest[i] = a[i] * b[i];\n //dest[i] = threadIdx.x + threadIdx.y + blockDim.x;\n //dest[i] = blockDim.x;\n //printf(\"I am %d.%d\\\\n\", threadIdx.x, threadIdx.y);\n \n}\n\"\"\"\n\nsrcGPUModule = SourceModule(srcGPU)\n\nprint (srcGPUModule)",
"<pycuda.compiler.SourceModule object at 0x0000021E2268D710>\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Simple addition on the GPU: Host memory allocation",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"ARR_SIZE=16\n\na = numpy.random.randn(ARR_SIZE).astype(numpy.float32)\na=numpy.ones_like(a)*3\nb = numpy.random.randn(ARR_SIZE).astype(numpy.float32)\nb=numpy.ones_like(b)*2\n\ndest = numpy.zeros_like(a)\n# print dest",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Simple addition on the GPU: execution",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"multGPUFunc = srcGPUModule.get_function(\"multGPU\")\n\nprint (multGPUFunc)\n\nmultGPUFunc(drv.Out(dest), drv.In(a), drv.In(b),\n block=(ARR_SIZE,32,1))\nprint (dest)",
"<pycuda._driver.Function object at 0x0000021E226987A0>\n[ 6. 6. 6. 6. 6. 6. 6. 6. 6. 6. 6. 6. 6. 6. 6. 6.]\n"
],
[
"# print \"Calculating %d iterations\" % (n_iter)\nimport timeit\n\nrounds =3\nprint ('pycuda', timeit.timeit(lambda: \n multGPUFunc(drv.Out(dest), drv.In(a), drv.In(b),\n grid=(ARR_SIZE,1,1), \n block=(1,1,1)), \n number=rounds))\n# print dest\n\n# print 'pycuda', timeit.timeit(lambda: \n# multGPUFunc(drv.Out(dest), drv.In(a), drv.In(b), \n# block=(ARR_SIZE,1,1)), \n# number=rounds)\n\n# print dest\n\n\nprint ('npy', timeit.timeit(lambda:a*b , number=rounds))",
"pycuda 0.009389220357464863\nnpy 2.1461075102776825e-05\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Threads and Blocks",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"a = numpy.random.randn(4,4)\na=numpy.ones_like(a)\na = a.astype(numpy.float32)\n\na_gpu = cuda.mem_alloc(a.nbytes)\n\ncuda.memcpy_htod(a_gpu, a)\n\nmod = SourceModule(\"\"\"\n #include <stdio.h>\n __global__ void doublify(float *a)\n {\n int idx = threadIdx.x + threadIdx.y*4;\n a[idx] *= 2;\n //printf(\"I am %d.%d\\\\n\", threadIdx.x, threadIdx.y);\n \n printf(\"I am %dth thread in threadIdx.x:%d.threadIdx.y:%d blockIdx.:%d blockIdx.y:%d blockDim.x:%d blockDim.y:%d\\\\n\",(threadIdx.x+threadIdx.y*blockDim.x+(blockIdx.x*blockDim.x*blockDim.y)+(blockIdx.y*blockDim.x*blockDim.y)),threadIdx.x, threadIdx.y,blockIdx.x,blockIdx.y,blockDim.x,blockDim.y); \n }\n \"\"\")\n \nfunc = mod.get_function(\"doublify\")\nfunc(a_gpu, block=(16,1,1))\n\na_doubled = numpy.empty_like(a)\ncuda.memcpy_dtoh(a_doubled, a_gpu)\nprint (a_doubled)",
"[[ 2. 2. 2. 2.]\n [ 2. 2. 2. 2.]\n [ 2. 2. 2. 2.]\n [ 2. 2. 2. 2.]]\n"
]
],
[
[
"[block]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
c50c37713d499eb3f31e46c3173888a5f7b40145
| 86,744 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
SimLasso.ipynb
|
Pythongoras/debiascvgV2
|
f01a19f6944eb75d549fff463264db161e681b3f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
SimLasso.ipynb
|
Pythongoras/debiascvgV2
|
f01a19f6944eb75d549fff463264db161e681b3f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
SimLasso.ipynb
|
Pythongoras/debiascvgV2
|
f01a19f6944eb75d549fff463264db161e681b3f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 109.11195 | 17,212 | 0.861212 |
[
[
[
"import os\nos.chdir('/Users/yufei/Documents/2-CMU/DebiasingCvxConstrained/Code/Library')\n\nfrom math import log\nimport numpy as np\n\nfrom scipy import stats\n\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\nfrom ExperimentFunc import exp_func, beta_gen_lasso\nfrom Step1 import solve_beta_lasso\nfrom Step2 import find_v_lasso\nfrom Step3 import solve_omega, gw_l1, proj_l1_tan_cone, proj_l1_neg_tan_cone\n\nfrom collections import namedtuple\n\nfrom copy import deepcopy",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Params = namedtuple('Params', ['step1', 'step2', 'step3'])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### <span style=\"color:purple\">1) Cov(X) = I</span>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"N = 100\nn = 1000\np = 1000\nSigma_sqrt = np.eye(p)\nnoise_sd = 9\ndebias_idx = p - 1\n\ncardi = 0.005\nl1_bound = p*cardi \n\nparam_set = Params([l1_bound], \n [l1_bound], \n [gw_l1, proj_l1_tan_cone, proj_l1_neg_tan_cone])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"z, z_biased = exp_func(N,\n n,\n p, \n Sigma_sqrt, \n noise_sd, \n debias_idx,\n param_set, \n beta_gen_lasso, \n solve_beta_lasso, \n find_v_lasso, \n solve_omega)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Compare the mean of the (debiased_beta - beta) and (non-debiased_beta - beta)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mean_non_debiased = np.mean(z_biased)\nprint(\"The mean of (non_debiased_beta - beta) is: \", mean_non_debiased)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"mean_debiased = np.mean(np.array(z))\nprint(\"The mean of (debiased_beta - beta) is: \", mean_debiased)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Check if the (debiased_beta - beta) and (non-debiased_beta - beta) is standard normal",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# non-debiased\nfig = plt.figure()\nax = fig.add_subplot()\nres = stats.probplot(z_biased, plot=ax)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# debiased\nfig = plt.figure()\nax = fig.add_subplot()\nres = stats.probplot(z, plot=ax)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Save simulation results",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.save('/Users/yufei/Documents/2-CMU/DebiasingCvxConstrained/ExpResults/Lasso/identity_z_biased.npy', z_biased)\nnp.save('/Users/yufei/Documents/2-CMU/DebiasingCvxConstrained/ExpResults/Lasso/identity_z.npy', z)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### <span style=\"color:purple\">2) Cov(X) with bounded eigenvalues</span>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# other parameters are the same as cov=I case\n\n# Generate a cov matrix with bounded eigenvalues\n# generate eigenvalues\ncov_eigv = np.random.uniform(low = 0.5, high = 3.0, size = (p,))\nD_sqrt = np.diag(cov_eigv**0.5)\n# generate an orthonormal matrix\na = np.random.normal(size = (p,p))\nu, s, vh = np.linalg.svd(a.T@a, full_matrices=True)\n# generate the square root of cov matrix \nSigma_sqrt = D_sqrt @ u.T",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"z, z_biased = exp_func(N,\n n,\n p, \n Sigma_sqrt, \n noise_sd, \n debias_idx,\n param_set, \n beta_gen_lasso, \n solve_beta_lasso, \n find_v_lasso, \n solve_omega)",
"iter: 0\nThe L2 error: 1.3962876226310679\niter: 1\nThe L2 error: 1.6212450931691846\niter: 2\nThe L2 error: 2.0616743380411924\niter: 3\nThe L2 error: 1.5616911140707654\niter: 4\nThe L2 error: 1.8082677891618741\niter: 5\nThe L2 error: 1.7406434035660443\niter: 6\nThe L2 error: 1.8438038521754558\niter: 7\nThe L2 error: 1.314664899672138\niter: 8\nThe L2 error: 1.8148460920957707\niter: 9\nThe L2 error: 1.519984447714861\niter: 10\nThe L2 error: 1.9547900423392612\niter: 11\nThe L2 error: 1.994564020477562\niter: 12\nThe L2 error: 1.2373164912321177\niter: 13\nThe L2 error: 2.1575959158303024\niter: 14\nThe L2 error: 1.7224620485742632\niter: 15\nThe L2 error: 1.6518950872393625\niter: 16\nThe L2 error: 1.6408013397132837\niter: 17\nThe L2 error: 2.086708087580271\niter: 18\nThe L2 error: 1.4507243116272948\niter: 19\nThe L2 error: 1.5699433813574555\niter: 20\nThe L2 error: 1.7705919949360067\niter: 21\nThe L2 error: 1.841979893635449\niter: 22\nThe L2 error: 2.0059532934806894\niter: 23\nThe L2 error: 1.1912151196750287\niter: 24\nThe L2 error: 1.7293270093642792\niter: 25\nThe L2 error: 2.402404746247627\niter: 26\nThe L2 error: 1.698928361746332\niter: 27\nThe L2 error: 1.767478779006288\niter: 28\nThe L2 error: 1.4268300480848755\niter: 29\nThe L2 error: 1.5815115082636675\niter: 30\nThe L2 error: 1.828023755373177\niter: 31\nThe L2 error: 1.806765729599805\niter: 32\nThe L2 error: 1.367939899913461\niter: 33\nThe L2 error: 2.061954477928445\niter: 34\nThe L2 error: 1.4670370267147188\niter: 35\nThe L2 error: 1.5108908199826823\niter: 36\nThe L2 error: 1.5157640090813556\niter: 37\nThe L2 error: 1.9433183373315104\niter: 38\nThe L2 error: 1.8500642343276632\niter: 39\nThe L2 error: 2.0972047456282095\niter: 40\nThe L2 error: 1.2860163266470064\niter: 41\nThe L2 error: 1.7052327723157612\niter: 42\nThe L2 error: 1.0674076888663586\niter: 43\nThe L2 error: 1.9211825285593782\niter: 44\nThe L2 error: 2.0276936547265425\niter: 45\nThe L2 error: 1.2141321759973172\niter: 46\nThe L2 error: 1.9673109183572826\niter: 47\nThe L2 error: 1.0281370382929134\niter: 48\nThe L2 error: 2.043539325137044\niter: 49\nThe L2 error: 1.5422337188794555\niter: 50\nThe L2 error: 1.9818975904217235\niter: 51\nThe L2 error: 2.1102355838198554\niter: 52\nThe L2 error: 1.2995617625792877\niter: 53\nThe L2 error: 1.4009236063013921\niter: 54\nThe L2 error: 1.461729687237456\niter: 55\nThe L2 error: 1.8922021928462882\niter: 56\nThe L2 error: 1.4542203907257734\niter: 57\nThe L2 error: 1.795365841400416\niter: 58\nThe L2 error: 1.1360240770708356\niter: 59\nThe L2 error: 1.7708485955539215\niter: 60\nThe L2 error: 1.770808653711068\niter: 61\nThe L2 error: 1.7141829316926132\niter: 62\nThe L2 error: 1.4481938112398265\niter: 63\nThe L2 error: 1.8119043658038467\niter: 64\nThe L2 error: 1.5163103184513684\niter: 65\nThe L2 error: 1.468851533539015\niter: 66\nThe L2 error: 1.2224803664051096\niter: 67\nThe L2 error: 1.8081472432176748\niter: 68\nThe L2 error: 1.6645409311612347\niter: 69\nThe L2 error: 1.996279541191676\niter: 70\nThe L2 error: 1.6378420700696237\niter: 71\nThe L2 error: 1.9798955867910055\niter: 72\nThe L2 error: 1.5055921724501626\niter: 73\nThe L2 error: 1.6346078025153927\niter: 74\nThe L2 error: 1.83739052175347\niter: 75\nThe L2 error: 1.5972285373542745\niter: 76\nThe L2 error: 2.303766289618929\niter: 77\nThe L2 error: 1.7535130193362949\niter: 78\nThe L2 error: 1.058990348860513\niter: 79\nThe L2 error: 1.181346872645676\niter: 80\nThe L2 error: 0.939502389263943\niter: 81\nThe L2 error: 1.6372074743238763\niter: 82\nThe L2 error: 1.7842799451301012\niter: 83\nThe L2 error: 1.7767862223542565\niter: 84\nThe L2 error: 1.7830138829323445\niter: 85\nThe L2 error: 1.622700842371491\niter: 86\nThe L2 error: 1.8666451688926338\niter: 87\nThe L2 error: 2.1254768179003474\niter: 88\nThe L2 error: 2.2599193913326547\niter: 89\nThe L2 error: 0.9951423996228965\niter: 90\nThe L2 error: 1.5174953960634834\niter: 91\nThe L2 error: 2.019479899724529\niter: 92\nThe L2 error: 1.688694091121861\niter: 93\nThe L2 error: 1.7404302757487198\niter: 94\nThe L2 error: 1.5519815808926947\niter: 95\nThe L2 error: 1.8285456971771727\niter: 96\nThe L2 error: 1.4459528993830097\niter: 97\nThe L2 error: 2.0899297222648623\niter: 98\nThe L2 error: 1.7891909925957006\niter: 99\nThe L2 error: 2.1656241589092944\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### Compare the mean of the (debiased_beta - beta) and (non-debiased_beta - beta)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mean_non_debiased = np.mean(z_biased)\nprint(\"The mean of (non_debiased_beta - beta) is: \", mean_non_debiased)",
"The mean of (non_debiased_beta - beta) is: 1.249862413704363\n"
],
[
"mean_debiased = np.mean(np.array(z))\nprint(\"The mean of (debiased_beta - beta) is: \", mean_debiased)",
"The mean of (debiased_beta - beta) is: 0.0832232017251741\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### Check if the (debiased_beta - beta) and (non-debiased_beta - beta) is standard normal",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# non-debiased\nfig = plt.figure()\nax = fig.add_subplot()\nres = stats.probplot(z_biased, plot=ax)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# debiased\nfig = plt.figure()\nax = fig.add_subplot()\nres = stats.probplot(z, plot=ax)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Save the simulation results",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.save('/Users/yufei/Documents/2-CMU/DebiasingCvxConstrained/ExpResults/Lasso/bddeig_z_biased.npy', z_biased)\nnp.save('/Users/yufei/Documents/2-CMU/DebiasingCvxConstrained/ExpResults/Lasso/bddeig_z.npy', z)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### <span style = 'color:purple'>3) Cov(X) is the Cov of AR(1) Process</span>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# other parameters are the same as cov=I case\n\n# Generate the squar root of cov matrix\nrho = 0.4\nrho_vec = []\nfor i in range(p):\n rho_vec.append(rho**i)\nrho_vec = np.array(rho_vec)\n# The cholesky decomposition of cov == the squar root of cov\nSigma_sqrt = [rho_vec]\nfor i in range(1, p):\n rho_vec_shifted = np.concatenate((np.zeros(i), rho_vec[:-i]))\n# print(rho_vec_shifted)\n Sigma_sqrt.append(rho_vec_shifted * (1-rho**2)**0.5)\nSigma_sqrt = np.array(Sigma_sqrt)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"z, z_biased = exp_func(N,\n n,\n p, \n Sigma_sqrt, \n noise_sd, \n debias_idx,\n param_set, \n beta_gen_lasso, \n solve_beta_lasso, \n find_v_lasso, \n solve_omega)",
"iter: 0\nThe L2 error: 1.4151736825231735\niter: 1\nThe L2 error: 1.8331771773426064\niter: 2\nThe L2 error: 1.2564311675095525\niter: 3\nThe L2 error: 1.8777349428503398\niter: 4\nThe L2 error: 2.8526094483653446\niter: 5\nThe L2 error: 1.9689362063916973\niter: 6\nThe L2 error: 2.6821384574948937\niter: 7\nThe L2 error: 2.3361853453716295\niter: 8\nThe L2 error: 1.6417682597128638\niter: 9\nThe L2 error: 1.8273035112385507\niter: 10\nThe L2 error: 2.0094478905334965\niter: 11\nThe L2 error: 1.6340343337688603\niter: 12\nThe L2 error: 0.5331240279874784\niter: 13\nThe L2 error: 1.618860827657588\niter: 14\nThe L2 error: 1.4934864517786628\niter: 15\nThe L2 error: 2.6704601506769032\niter: 16\nThe L2 error: 2.3826547743567916\niter: 17\nThe L2 error: 1.544282918935122\niter: 18\nThe L2 error: 1.2190791789958304\niter: 19\nThe L2 error: 1.4560017790603321\niter: 20\nThe L2 error: 1.8865079912423361\niter: 21\nThe L2 error: 1.5695258914043817\niter: 22\nThe L2 error: 1.5340317418026732\niter: 23\nThe L2 error: 1.8797958968927664\niter: 24\nThe L2 error: 2.0700781697185673\niter: 25\nThe L2 error: 0.698577986451315\niter: 26\nThe L2 error: 1.844476551738138\niter: 27\nThe L2 error: 1.6071442502804014\niter: 28\nThe L2 error: 1.6876883701264649\niter: 29\nThe L2 error: 1.7844172994238918\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### Compare the mean of the (debiased_beta - beta) and (non-debiased_beta - beta)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mean_non_debiased = np.mean(z_biased)\nprint(\"The mean of (non_debiased_beta - beta) is: \", mean_non_debiased)",
"The mean of (non_debiased_beta - beta) is: 0.504885491458776\n"
],
[
"mean_debiased = np.mean(np.array(z))\nprint(\"The mean of (debiased_beta - beta) is: \", mean_debiased)",
"The mean of (debiased_beta - beta) is: -0.06248970186385651\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### Check if the (debiased_beta - beta) and (non-debiased_beta - beta) is standard normal",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# non-debiased\nfig = plt.figure()\nax = fig.add_subplot()\nres = stats.probplot(z_biased, plot=ax)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# debiased\nfig = plt.figure()\nax = fig.add_subplot()\nres = stats.probplot(z, plot=ax)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Print out (debiased beta - beta) and (non-debiased beta - beta) ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.save('/Users/yufei/Documents/2-CMU/DebiasingCvxConstrained/ExpResults/Lasso/ar1_z_biased.npy', z_biased)\nnp.save('/Users/yufei/Documents/2-CMU/DebiasingCvxConstrained/ExpResults/Lasso/ar1_z.npy', z)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c50c4f456658ec91dc07b7181f48a3812341f759
| 483,381 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
mpglue/notebooks/image_handling.ipynb
|
siu-panh/mapeo-uso-del-suelo
|
f7081a4e6784281eddceaa1a6087e0d972c92820
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
mpglue/notebooks/image_handling.ipynb
|
siu-panh/mapeo-uso-del-suelo
|
f7081a4e6784281eddceaa1a6087e0d972c92820
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
mpglue/notebooks/image_handling.ipynb
|
siu-panh/mapeo-uso-del-suelo
|
f7081a4e6784281eddceaa1a6087e0d972c92820
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 688.576923 | 162,956 | 0.935057 |
[
[
[
"## <span style=\"color:#0B3B2E;float:right;font-family:Calibri\">Jordan Graesser</span>\n\n# MpGlue\n### Handling image files with MpGlue\n---",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Opening images\n#### Everything begins with the `ropen` function.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%load_ext autoreload\n%autoreload 2\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import skimage\nimport matplotlib as mpl\n\nmpl.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (10, 10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import mpglue as gl\n\n# Setup the name of the image you want to open.\nimage2open = '../testing/data/225r85_etm_2000_0424.tif'\n\n# Load a pointer to an image and give it a variable name.\nwith gl.ropen(image2open) as i_info:\n print(dir(i_info))",
"['__class__', '__del__', '__delattr__', '__dict__', '__doc__', '__enter__', '__exit__', '__format__', '__getattribute__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__module__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', '__weakref__', '_check_band_list', '_cleanup', '_get_driver_name', '_get_file_format', '_get_hdr_info', '_open_array', '_open_dataset', '_reshape', '_reshape2predictions', 'bands', 'block_x', 'block_y', 'bottom', 'build_overviews', 'calculate_stats', 'cellX', 'cellY', 'check_clouds', 'check_corrupted', 'check_corrupted_bands', 'close', 'close_all', 'close_band', 'close_file', 'color_interpretation', 'cols', 'contains', 'contains_value', 'copy', 'datasource', 'datasource_info', 'directory', 'epsg', 'extent', 'file_format', 'file_name', 'file_open', 'filename', 'fill', 'geo_transform', 'get_band', 'get_chunk_size', 'get_image_info', 'get_metadata', 'get_stats', 'hdf_file', 'hdr_file', 'hist', 'image_mode', 'intersects', 'left', 'meta_dict', 'name', 'outside', 'parse_mtl', 'parse_xml', 'pca', 'predictions2norm', 'proj4', 'projection', 'read', 'remove_overviews', 'right', 'rotation1', 'rotation2', 'rows', 'shape', 'show', 'sp_ref', 'storage', 'top', 'translate', 'update_info', 'warp', 'within', 'write2raster', 'write_array']\n"
]
],
[
[
"* We haven't actually loaded any image data.\n* The variable, `i_info`, acts as a pointer to the GeoTiff. \n* In Python terms, it is a **class instance**. The only way you can know this is by checking the documentation of `ropen` and knowing that it creates a class object, or by checking the variable's type with the built-in **type** function.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Check the variable type\nprint(type(i_info))",
"<class 'mpglue.raster_tools.ropen'>\n"
]
],
[
[
"* A class instance of `mpglue.raster_tools`.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Getting image information\n* Now, back to `i_info`. A class instance can contain various methods, the pinnacle of object orientated programming. \n* Check the instance methods with **dir**.\n* Now we know what type of information we can get without opening the entire image.\n* Class instance methods are called as objects of the instance, which in Python is by **instance._method_**.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Get the name of the directory and file.\nwith gl.ropen(image2open) as i_info:\n \n print i_info.file_name\n print i_info.filename\n print i_info.rows, i_info.cols\n print i_info.shape\n print i_info.name\n print i_info.left, i_info.right, i_info.top, i_info.bottom\n print i_info.extent",
"../testing/data/225r85_etm_2000_0424.tif\n225r85_etm_2000_0424.tif\n224 235\n{'row_units': '224,000.00', 'rows': '224', 'col_units': '235,000.00', 'bands': 6, 'pixels': '315,840', 'columns': '235'}\nGTiff\n-45314.7978005 189685.2022 -353296.312702 -577296.312702\n{'top': -353296.31270178076, 'right': 189685.20219954854, 'bottom': -577296.3127017808, 'left': -45314.797800451466}\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Getting image data\n* Not all methods of `ropen` are information. Others are class functions.\n* For example, we can open the image as a n-dimensional array by calling `read` from the class instance itself.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Load the image as an n-dimensional array (NumPy array).\nwith gl.ropen(image2open) as i_info:\n image_array = i_info.read()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Now check the type of the variable, `image_array`.\nprint type(image_array)",
"<type 'numpy.ndarray'>\n"
]
],
[
[
"* The variable `image_array` is a **NumPy** object. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Check the shape of the image_array. *It should be the same size as the loaded image, except only one band.\nprint image_array.shape",
"(224, 235)\n"
]
],
[
[
"### What happened to the other 5 bands?\n* We need to check the documentation of `read`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print help(i_info.read)",
"Help on method read in module mpglue.raster_tools:\n\nread(self, bands2open=1, i=0, j=0, rows=-1, cols=-1, d_type=None, compute_index='none', sensor='Landsat', sort_bands2open=True, predictions=False, y=0.0, x=0.0, check_x=None, check_y=None, **viargs) method of mpglue.raster_tools.ropen instance\n Reads a raster as an array\n \n Args:\n bands2open (Optional[int or int list or dict]: Band position to open, list of bands to open, or a\n dictionary of name-band pairs. Default is 1.\n \n Examples:\n bands2open = 1 (open band 1)\n bands2open = [1,2,3] (open first three bands)\n bands2open = [4,3,2] (open bands in a specific order)\n *When opening bands in a specific order, be sure to set ``sort_bands2open`` as ``False``.\n bands2open = -1 (open all bands)\n bands2open = {'blue': 1, 'green': 2, 'nir': 4} (open bands 1, 2, and 4)\n \n i (Optional[int]): Starting row position. Default is 0, or first row.\n j (Optional[int]): Starting column position. Default is 0, or first column.\n rows (Optional[int]): Number of rows to extract. Default is -1, or all rows.\n cols (Optional[int]): Number of columns to extract. Default is -1, or all columns.\n d_type (Optional[str]): Type of array to return. Choices are ['byte', 'int16', 'uint16',\n 'int32', 'uint32', 'int64', 'uint64', 'float32', 'float64']. Default is None, or gathered\n from <i_info>.\n compute_index (Optional[str]): A spectral index to compute. Default is 'none'.\n sensor (Optional[str]): The input sensor type (used with ``compute_index``). Default is 'Landsat'.\n sort_bands2open (Optional[bool]): Whether to sort ``bands2open``. Default is True.\n predictions (Optional[bool]): Whether to return reshaped array for predictions.\n y (Optional[float]): A y index coordinate (latitude, in map units). Default is 0.\n If greater than 0, overrides ``i``.\n x (Optional[float]): A x index coordinate (longitude, in map units). Default is 0.\n If greater than 0, overrides ``j``.\n check_x (Optional[float]): Check the x offset against ``check_x``. Default is None.\n check_y (Optional[float]): Check the y offset against ``check_y``. Default is None.\n \n Attributes:\n array (ndarray)\n \n Returns:\n ``ndarray``, where shape is (rows x cols) if 1 band or (bands x rows x cols) if more than 1 band.\n \n Examples:\n >>> import mpglue as gl\n >>>\n >>> i_info = mp.ropen('image.tif')\n >>> i_info = mp.open('image.tif')\n >>>\n >>> # Open 1 band.\n >>> array = i_info.read(bands2open=1)\n >>>\n >>> # Open multiple bands.\n >>> array = i_info.read(bands2open=[1, 2, 3])\n >>> band_1 = array[0]\n >>>\n >>> # Open as a dictionary of arrays.\n >>> bands = i_info.read(bands2open={'blue': 1, 'red': 2, 'nir': 4})\n >>> red = bands['red']\n >>>\n >>> # Index an image by pixel positions.\n >>> array = i_info.read(i=1000, j=4000, rows=500, cols=500)\n >>>\n >>> # Index an image by map coordinates.\n >>> array = i_info.read(y=1200000., x=4230000., rows=500, cols=500)\n\nNone\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Now we see that the default is to only open 1 band (the first band of the image).\n* If we want to open all of the bands then we have to specify this information in the `bands2open` parameter.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# We can load the new image into the same variable and it will be overwritten.\n# Rather than open all 6 bands, we can start by loading two bands, the red and NIR.\nwith gl.ropen(image2open) as i_info:\n image_array = i_info.read(bands2open=[3, 4])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Check the array shape again.\nprint image_array.shape",
"(2, 224, 235)\n"
]
],
[
[
"### What if we only want a portion of an image?\n* First, go back to the help documentation. \n* The parameters, `i` and `j` are the starting row and column positions, respectively.\n* The parameters, `rows` and `cols` are the number of samples to load.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Open a 500 x 500 pixel array\nwith gl.ropen(image2open) as i_info:\n \n image_array = i_info.read(bands2open=[3, 4], \n i=20, \n j=30, \n rows=50, \n cols=50)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print image_array.shape",
"(2, 50, 50)\n"
]
],
[
[
"### We can also extract a subset of an image via x,y coordinates\n* To do this, use the parameters `x` and `y` in place of `i` and `j`.\n* In the example below, we are reading from the top left corner of the image.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Open a 500 x 500 pixel array\nwith gl.ropen(image2open) as i_info:\n \n image_array = i_info.read(bands2open=[3, 4], \n x=-45314.7978005, \n y=-353296.312702, \n rows=50, \n cols=50)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print image_array.shape",
"(2, 50, 50)\n"
]
],
[
[
"### MpGlue also supports parallel reading\n* This must be done with the `raster_tools` module, using `n_jobs`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from mpglue import raster_tools",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"image_array = raster_tools.read(image2open,\n bands2open=-1, \n i=20, \n j=30, \n rows=50, \n cols=50,\n n_jobs=-1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print image_array.shape",
"(6, 50, 50)\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Vegetation indexes\n* MpGlue's `read` class has built-in vegetation indices.\n\n### We see that NDVI is one option.\n* By default, `compute_index` is set to 'none'.\n* Use the `compute_index` option to return NDVI instead of the spectral bands.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"with gl.ropen(image2open) as i_info:\n image_array = i_info.read(compute_index='ndvi')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Viewing images\n* For quick visualization, you can use built-it methods.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Let's view the NDVI array\nwith gl.ropen(image2open) as i_info:\n i_info.read(compute_index='ndvi')\n i_info.show(show_which='ndvi', color_map='Greens')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# We can also view a band in greyscale, but note that\n# the array will be set as the red and NIR bands if\n# an index was computed. Here, we are viewing band 1, \n# which is the red band (1 of 2 bands in the array).\nwith gl.ropen(image2open) as i_info:\n i_info.read()\n i_info.show(color_map='Greys', band=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# In order to view any of the image's original bands,\n# reload the array. Here, we load the entire image.\nwith gl.ropen(image2open) as i_info:\n image_array = i_info.read(bands2open=-1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print i_info.array_shape",
"[6, 224, 235]\n"
],
[
"# Now view the MidIR band.\nwith gl.ropen(image2open) as i_info:\n image_array = i_info.read(bands2open=-1)\n i_info.show(band=5, color_map='afmhot')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Load the three visible bands and\n# view the true color plot.\n# !Warning! 16-bit arrays are scaled to byte\n# when displaying RGB images.\nwith gl.ropen(image2open) as i_info:\n \n image_array = i_info.read(bands2open=[3, 2, 1],\n sort_bands2open=False)\n \n i_info.show(band='rgb', clip_percentiles=(2, 98))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50c52ee7dd8e73a53777b60ab57182e3c9c476c
| 22,453 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
tutorials/tutorial05_networks.ipynb
|
weizi-li/flow
|
958b64ece8af6db715e6fb3b6042035b05b93bc2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
tutorials/tutorial05_networks.ipynb
|
weizi-li/flow
|
958b64ece8af6db715e6fb3b6042035b05b93bc2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
tutorials/tutorial05_networks.ipynb
|
weizi-li/flow
|
958b64ece8af6db715e6fb3b6042035b05b93bc2
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 46.010246 | 541 | 0.588652 |
[
[
[
"# Tutorial 05: Creating Custom Networks\n\nThis tutorial walks you through the process of generating custom networks. Networks define the network geometry of a task, as well as the constituents of the network, e.g., vehicles, traffic lights, etc... Various networks are available in Flow, depicting a diverse set of open and closed traffic networks such as ring roads, intersections, traffic light grids, straight highway merges, and more. \n\nIn this tutorial, we will recreate the ring road network, seen in the figure below.\n\n<img src=\"img/ring_scenario.png\">\n\nIn order to recreate this network, we will design a *network* class. This class creates the configuration files needed to produce a transportation network within the simulator. It also specifies the location of edge nodes in the network, as well as the positioning of vehicles at the start of a run.\n\nWe begin by creating a class that inherits the methods of Flow's base network class. The separate methods are filled in in later sections.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# import Flow's base network class\nfrom flow.networks import Network\n\n# define the network class, and inherit properties from the base network class\nclass myNetwork(Network):\n pass",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The rest of the tutorial is organized as follows: Sections 1 and 2 discuss the steps needed to specify custom traffic network geometry features and auxiliary features, respectively, while Section 3 implements the new network in a simulation for visualization and testing purposes.\n\n## 1. Specifying Traffic Network Features\n\nOne of the core responsibilities of the network class is to generate the necessary xml files needed to initialize a SUMO instance. These xml files describe specific network features such as the position and directions of nodes and edges (see the figure above). Once the base network has been inherited, specifying these features becomes very systematic. All child classes are required to define at least the following three methods: \n\n* **specify_nodes**: specifies the attributes of nodes in the network.\n* **specify_edges**: specifies the attributes of edges containing pairs of nodes in the network.\n* **specify_routes**: specifies the routes which vehicles can take starting from any edge.\n\nAdditionally, the following optional functions may also be defined:\n\n* **specify_types**: specifies the attributes of various edge types (if any exist).\n* **specify_connections**: specifies the attributes of connections. These attributes are used to describe how any specific node's incoming and outgoing edge/lane pairs are connected. If no connections are specified, SUMO will generate default connections.\n\nAll of the functions mentioned above take in as input `net_params`, and output a list of dictionary elements, with each element providing the attributes of the component to be specified.\n\nThis tutorial will cover the first three methods. For examples of `specify_types` and `specify_routes`, we refer interested users to the source code located in `flow/networks/ring.py` and `flow/networks/bridge_toll.py`, respectively.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 1.1 ADDITIONAL_NET_PARAMS\n\nThe features used to parametrize the network are specified within the `NetParams` input, as discussed in tutorial 1. Specifically, for the sake of our network, the `additional_params` attribute within `NetParams` will be responsible for storing information on the radius, number of lanes, and speed limit within each lane, as seen in the figure above. Accordingly, we define `ADDITIONAL_NET_PARAMS` as follows:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"ADDITIONAL_NET_PARAMS = {\n \"radius\": 40,\n \"num_lanes\": 1,\n \"speed_limit\": 30,\n}",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"All networks presented in Flow provide a unique `ADDITIONAL_NET_PARAMS` component containing the information needed to properly define the network parameters. We assume that these values are always provided by the user, and accordingly can be called from `net_params`. For example, if we would like to call the \"radius\" parameter, we simply type:\n\n radius = net_params.additional_params[\"radius\"]\n\n### 1.2 specify_nodes\n\nThe nodes of a network are the positions of selected points in the network. These points are connected together using edges (see section 1.4). In order to specify the location of the nodes, the function `specify_nodes` is used. This function returns a list of dictionary elements, where each dictionary depicts the attributes of a single node. These node attributes include: \n* **id**: the name of the node\n* **x**: the x coordinate of the node\n* **y**: the y coordinate of the node\n* For other SUMO-related attributes, see: http://sumo.dlr.de/wiki/Networks/Building_Networks_from_own_XML-descriptions#Node_Descriptions\n\nRefering to the figure at the top of this tutorial, we specify four nodes at the bottom (0,-r), top (0,r), left (-r,0), and right (0,r) of the ring, respectively. This is done as follows:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class myNetwork(myNetwork): # update my network class\n\n def specify_nodes(self, net_params):\n # one of the elements net_params will need is a \"radius\" value\n r = net_params.additional_params[\"radius\"]\n\n # specify the name and position (x,y) of each node\n nodes = [{\"id\": \"bottom\", \"x\": 0, \"y\": -r},\n {\"id\": \"right\", \"x\": r, \"y\": 0},\n {\"id\": \"top\", \"x\": 0, \"y\": r},\n {\"id\": \"left\", \"x\": -r, \"y\": 0}]\n\n return nodes",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 1.3 specify_edges\n\nOnce specified, the nodes are linked using directed edges. This is done through the `specify_edges` method which, similar to `specify_nodes`, returns a list of dictionary elements, with each dictionary specifying the attributes of a single edge. The attributes include:\n\n* **id**: the name of the edge\n* **from**: the name of the node the edge starts from\n* **to**: the name of the node the edges ends at\n* **length**: the length of the edge\n* **numLanes**: the number of lanes on the edge\n* **speed**: the speed limit for vehicles on the edge\n* For other SUMO-related attributes, see: http://sumo.dlr.de/wiki/Networks/Building_Networks_from_own_XML-descriptions#Edge_Descriptions.\n\nOne useful additional attribute is **shape**, which specifies the shape of the edge connecting two nodes. The shape consists of a series of subnodes (internal to SUMO) that are connected by straight lines to create a curved edge. If no shape is specified, the nodes are connected by a straight line. This attribute is needed for creating circular arcs in the system. \n\nWe now create four arcs connecting the nodes specified in Section 1.2 counter-clockwisely:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# some mathematical operations that may be used\nfrom numpy import pi, sin, cos, linspace\n\nclass myNetwork(myNetwork): # update my network class\n\n def specify_edges(self, net_params):\n r = net_params.additional_params[\"radius\"]\n edgelen = r * pi / 2\n # this will let us control the number of lanes in the network\n lanes = net_params.additional_params[\"num_lanes\"]\n # speed limit of vehicles in the network\n speed_limit = net_params.additional_params[\"speed_limit\"]\n\n edges = [\n {\n \"id\": \"edge0\",\n \"numLanes\": lanes,\n \"speed\": speed_limit, \n \"from\": \"bottom\", \n \"to\": \"right\", \n \"length\": edgelen,\n \"shape\": [(r*cos(t), r*sin(t)) for t in linspace(-pi/2, 0, 40)]\n },\n {\n \"id\": \"edge1\",\n \"numLanes\": lanes, \n \"speed\": speed_limit,\n \"from\": \"right\",\n \"to\": \"top\",\n \"length\": edgelen,\n \"shape\": [(r*cos(t), r*sin(t)) for t in linspace(0, pi/2, 40)]\n },\n {\n \"id\": \"edge2\",\n \"numLanes\": lanes,\n \"speed\": speed_limit,\n \"from\": \"top\",\n \"to\": \"left\", \n \"length\": edgelen,\n \"shape\": [(r*cos(t), r*sin(t)) for t in linspace(pi/2, pi, 40)]},\n {\n \"id\": \"edge3\", \n \"numLanes\": lanes, \n \"speed\": speed_limit,\n \"from\": \"left\", \n \"to\": \"bottom\", \n \"length\": edgelen,\n \"shape\": [(r*cos(t), r*sin(t)) for t in linspace(pi, 3*pi/2, 40)]\n }\n ]\n\n return edges",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 1.4 specify_routes\n\nThe route is a sequence of edges, which vehicles can traverse given their current positions. For example, a vehicle beginning in the edge titled \"edge0\" (see section 1.3) must traverse, in sequence, \"edge0\", \"edge1\", \"edge2\", and \"edge3\", before restarting its path.\n\nIn order to specify the routes a vehicle may take, the function `specify_routes` is used. The routes in this method can be specified in one of three ways:\n\n**1. Single route per edge:**\n\nFor deterministic routes (as is the case in the ring road scenario), the routes can be specified as a dictionary where the keys represent the starting edges and the elements represent sequences of edges that the vehicle must traverse, with the first edge corresponding to the edge that the vehicle begins on. Note that the edges must be connected for the route to be valid.\n\nFor this network, the available routes can be defined as follows:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class myNetwork(myNetwork): # update my network class\n\n def specify_routes(self, net_params):\n rts = {\"edge0\": [\"edge0\", \"edge1\", \"edge2\", \"edge3\"],\n \"edge1\": [\"edge1\", \"edge2\", \"edge3\", \"edge0\"],\n \"edge2\": [\"edge2\", \"edge3\", \"edge0\", \"edge1\"],\n \"edge3\": [\"edge3\", \"edge0\", \"edge1\", \"edge2\"]}\n\n return rts",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**2. Multiple routes per edge:**\n\nAlternatively, if the routes are meant to be stochastic, each element in the dictionary can be enriched to contain a list of (route, probability) tuples, where the first element in the tuple is one of the routes a vehicle can take from a specific starting edge, and the second element is the probability that a vehicle will choose that route. Note that, in this case, the sum of probability values for each dictionary key must sum up to one\n\nFor example, modifying the code snippet we presented above, another valid way of representing the route in a more probabilistic setting is:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class myNetwork(myNetwork): # update my network class\n\n def specify_routes(self, net_params):\n rts = {\"edge0\": [([\"edge0\", \"edge1\", \"edge2\", \"edge3\"], 1)],\n \"edge1\": [([\"edge1\", \"edge2\", \"edge3\", \"edge0\"], 1)],\n \"edge2\": [([\"edge2\", \"edge3\", \"edge0\", \"edge1\"], 1)],\n \"edge3\": [([\"edge3\", \"edge0\", \"edge1\", \"edge2\"], 1)]}\n\n return rts",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**3. Per-vehicle routes:**\n\nFinally, if you would like to assign a specific starting route to a vehicle, you can do so by adding an element into the dictionary whose key is the name of the vehicle and whose content is the list of edges the vehicle is meant to traverse as soon as being introduced to the network.\n\nAs an example, assume we have a vehicle named \\\"human_0\\\" in the network, and it is initialized on the edge named \\\"edge0\\\". Then, the route for this vehicle can be specifically added through the `specify_routes` method as follows:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"class myNetwork(myNetwork): # update my network class\n\n def specify_routes(self, net_params):\n rts = {\"edge0\": [\"edge0\", \"edge1\", \"edge2\", \"edge3\"],\n \"edge1\": [\"edge1\", \"edge2\", \"edge3\", \"edge0\"],\n \"edge2\": [\"edge2\", \"edge3\", \"edge0\", \"edge1\"],\n \"edge3\": [\"edge3\", \"edge0\", \"edge1\", \"edge2\"],\n \"human_0\": [\"edge0\", \"edge1\", \"edge2\", \"edge3\"]}\n\n return rts",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"In all three cases, the routes are ultimately represented in the class in the form described under the multiple routes setting, i.e.\n\n >>> print(network.rts)\n\n {\n \"edge0\": [\n ([\"edge0\", \"edge1\", \"edge2\", \"edge3\"], 1)\n ],\n \"edge1\": [\n ([\"edge1\", \"edge2\", \"edge3\", \"edge0\"], 1)\n ],\n \"edge2\": [\n ([\"edge2\", \"edge3\", \"edge0\", \"edge1\"], 1)\n ],\n \"edge3\": [\n ([\"edge3\", \"edge0\", \"edge1\", \"edge2\"], 1)\n ],\n \"human_0\": [\n ([\"edge0\", \"edge1\", \"edge2\", \"edge3\"], 1)\n ]\n }\n\nwhere the vehicle-specific route is only included in the third case.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## 2. Specifying Auxiliary Network Features\n\nOther auxiliary methods exist within the base network class to help support vehicle state initialization and acquisition. Of these methods, the only required abstract method is:\n\n* **specify_edge_starts**: defines edge starts for road sections with respect to some global reference.\n\nOther optional abstract methods within the base network class include:\n\n* **specify_internal_edge_starts**: defines the edge starts for internal edge nodes caused by finite length connections between road sections.\n* **specify_intersection_edge_starts**: defines edge starts for intersections with respect to some global reference frames. Only needed by environments containing intersections.\n* **gen_custom_start_pos**: used to generate a user defined set of starting positions for vehicles in the network.\n\n### 2.2 Specifying the Starting Position of Edges\n\nAll of the above functions with prefix \"specify\" receive no inputs, and return a list of tuples in which the first element of the tuple is the name of the edge/intersection/internal_link, and the second element is the distance of the link from some global reference, i.e. [(link_0, pos_0), (link_1, pos_1), ...].\n\nThe data specified in `specify_edge_starts` is used to provide a \"global\" sense of the location of vehicles, in one dimension. This is done either through the `get_x_by_id` method within an environment, or the `get_absolute_position` method in the `Vehicles` object within an environment. The `specify_internal_edge_starts` allows us to do the same to junctions/internal links when they are also located within the network (this is not the case for the ring road).\n\nIn section 1, we created a network with four edges named: \\\"edge0\\\", \\\"edge1\\\", \\\"edge2\\\", and \\\"edge3\\\". We assume \\\"edge0\\\" is the origin. Accordingly, the position of the edge start of \\\"edge0\\\" is 0. The next edge, \\\"edge1\\\", begins a quarter of the length of the network from the starting point of \\\"edge0\\\", and accordingly the position of its edge start is radius * $\\\\frac{pi}{2}$. This process continues for each of the edges. We can then define the starting position of the edges as follows:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# import some math functions we may use\nfrom numpy import pi\n\nclass myNetwork(myNetwork): # update my network class\n\n def specify_edge_starts(self):\n r = self.net_params.additional_params[\"radius\"]\n\n edgestarts = [(\"edge0\", 0),\n (\"edge1\", r * 1/2 * pi),\n (\"edge2\", r * pi),\n (\"edge3\", r * 3/2 * pi)]\n\n return edgestarts",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 3. Testing the New Network\nIn this section, we run a new sumo simulation using our newly generated network class. For information on running sumo experiments, see `exercise01_sumo.ipynb`.\n\nWe begin by defining some of the components needed to run a sumo experiment.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from flow.core.params import VehicleParams\nfrom flow.controllers import IDMController, ContinuousRouter\nfrom flow.core.params import SumoParams, EnvParams, InitialConfig, NetParams\n\nvehicles = VehicleParams()\nvehicles.add(veh_id=\"human\",\n acceleration_controller=(IDMController, {}),\n routing_controller=(ContinuousRouter, {}),\n num_vehicles=22)\n\nsumo_params = SumoParams(sim_step=0.1, render=True)\n\ninitial_config = InitialConfig(bunching=40)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"For visualizing purposes, we use the environment `AccelEnv`, as it works on any given network.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from flow.envs.ring.accel import AccelEnv, ADDITIONAL_ENV_PARAMS\n\nenv_params = EnvParams(additional_params=ADDITIONAL_ENV_PARAMS)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Next, using the `ADDITIONAL_NET_PARAMS` component see created in Section 1.1, we prepare the `NetParams` component.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"additional_net_params = ADDITIONAL_NET_PARAMS.copy()\nnet_params = NetParams(additional_params=additional_net_params)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We are ready now to create and run our network. Using the newly defined network classes, we create a network object and feed it into a `Experiment` simulation. Finally, we are able to visually confirm that are network has been properly generated.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from flow.core.experiment import Experiment\n\nnetwork = myNetwork( # we use the newly defined network class\n name=\"test_network\",\n vehicles=vehicles,\n net_params=net_params,\n initial_config=initial_config\n)\n\n# AccelEnv allows us to test any newly generated network quickly\nenv = AccelEnv(env_params, sumo_params, network)\n\nexp = Experiment(env)\n\n# run the sumo simulation for a set number of time steps\n_ = exp.run(1, 1500)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c50c56b41d5cec75e194fc30de6e82d4a146491f
| 5,512 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Untitled.ipynb
|
Paxpado/Paxpado.github.io
|
ef1f58a2bb3a4b821ffd0a30cb2ed54f2160e79a
|
[
"ADSL"
] | null | null | null |
Untitled.ipynb
|
Paxpado/Paxpado.github.io
|
ef1f58a2bb3a4b821ffd0a30cb2ed54f2160e79a
|
[
"ADSL"
] | null | null | null |
Untitled.ipynb
|
Paxpado/Paxpado.github.io
|
ef1f58a2bb3a4b821ffd0a30cb2ed54f2160e79a
|
[
"ADSL"
] | null | null | null | 27.152709 | 89 | 0.365022 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"cities_df = pd.read_csv(\"Resources/cities.csv\")\ncities_df.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"result = cities_df.to_html()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"text_file = open(\"Resources/visualizations/data2.html\",\"w\")\ntext_file.write(result)\ntext_file.close()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50c6734c2ced207e0b5bf74afa2df4f93db3e59
| 351,250 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Numerical_Analysis/LinearSys_IterMethod.ipynb
|
xiaozhouli/Jupyter
|
68d5a384dd939b3e8079da4470d6401d11b63a4c
|
[
"MIT"
] | 6 |
2020-02-27T13:09:06.000Z
|
2021-11-14T09:50:30.000Z
|
Numerical_Analysis/LinearSys_IterMethod.ipynb
|
xiaozhouli/Jupyter
|
68d5a384dd939b3e8079da4470d6401d11b63a4c
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Numerical_Analysis/LinearSys_IterMethod.ipynb
|
xiaozhouli/Jupyter
|
68d5a384dd939b3e8079da4470d6401d11b63a4c
|
[
"MIT"
] | 8 |
2018-10-18T10:20:56.000Z
|
2021-09-24T08:09:27.000Z
| 223.726115 | 243,792 | 0.902013 |
[
[
[
"# Solving Linear Systems: Iterative Methods\n<a rel=\"license\" href=\"http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/\"><img alt=\"Creative Commons License\" style=\"border-width:0\" src=\"https://licensebuttons.net/l/by/4.0/80x15.png\" /></a><br />This notebook by Xiaozhou Li is licensed under a <a rel=\"license\" href=\"http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/\">Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License</a>. \nAll code examples are also licensed under the [MIT license](http://opensource.org/licenses/MIT).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## General Form \nFor solving the linear system\n$$\n Ax = b,\n$$\nwith the exact solution $x^{*}$. The general form based on the fixed point interation:\n\\begin{equation}\n \\begin{split}\n x^{(0)} & = \\text{initial guess} \\\\\n x^{(k+1)} & = g(x^{(k)}) \\quad k = 0,1,2,\\ldots,\n \\end{split}\n\\end{equation}\nwhere\n$$\n g(x) = x - C(Ax - b).\n$$\nDifficult: find a matrix $C$ such that \n$$\n \\lim\\limits_{k\\rightarrow\\infty}x^{(k)} = x^{*}\n$$\nand the algorithm needs to be converge fast and economy. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Example 1**\n\\begin{equation*}\n A = \\left[\\begin{array}{ccc} 9& -1 & -1 \\\\ -1 & 10 & -1 \\\\ -1 & -1& 15\\end{array}\\right],\\quad b = \\left[\\begin{array}{c} 7 \\\\ 8 \\\\ 13\\end{array}\\right],\n\\end{equation*}\nhas the exact solution $x^{*} = {[1, 1, 1]}^T$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\n%matplotlib inline\n%config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'retina'\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom ipywidgets import interact, interactive, fixed, interact_manual\nimport ipywidgets as widgets\nfrom IPython.display import clear_output, display",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def IterC(A, b, C, x0, x_star, iters):\n x = np.copy(x0)\n print ('Iteration No. Numerical Solution Max norm error ')\n print (0, x, np.linalg.norm(x_star-x, np.inf))\n for i in range(iters):\n x = x + np.dot(C, b - np.dot(A,x))\n print (i+1, x, np.linalg.norm(x_star-x,np.inf))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"A = np.array([[9., -1., -1.],[-1.,10.,-1.],[-1.,-1.,15.]])\nb = np.array([7.,8.,13.])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Naive Choice** \n\nChoosing $C = I$, then \n$$g(x) = x - (Ax - b),$$\nand the fixed-point iteration\n$$x^{(k+1)} = (I - A)x^{(k)} + b \\quad k = 0,1,2,\\ldots. $$\nLet the intial guess $x_0 = [0, 0, 0]^T$.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"C = np.eye(3)\nx0 = np.zeros(3)\nx_star = np.array([1.,1.,1.])\n\nw = interactive(IterC, A=fixed(A), b=fixed(b), C=fixed(C), x0=fixed(x0), x_star=fixed(x_star), iters=widgets.IntSlider(min=0,max=20,value=0))\ndisplay(w)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Best Choice (theoretically)** \n\nChoosing $C = A^{-1}$, then \n$$g(x) = x - A^{-1}(Ax - b),$$\nand the fixed-point iteration\n$$x^{(k+1)} = A^{-1}b \\quad k = 0,1,2,\\ldots. $$\n\n* It equals to solve $Ax = b$ directly.\n* However, it gives a hint that $C$ should be close to $A^{-1}$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**First Approach** \n\nLet $D$ denote the main diagonal of $A$, $L$ denote the lower triangle of $A$ (entries below the main diagonal), and $U$ denote the upper triangle (entries above the main diagonal). Then $A = L + D + U$\n\nChoosing $C = \\text{diag}(A)^{-1} = D^{-1}$, then \n$$g(x) = x - D^{-1}(Ax - b),$$\nand the fixed-point iteration\n$$Dx^{(k+1)} = (L + U)x^{(k)} + b \\quad k = 0,1,2,\\ldots. $$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"C = np.diag(1./np.diag(A))\nx0 = np.zeros(np.size(b))\n#x0 = np.array([0,1.,0])\nx_star = np.array([1.,1.,1.])\n#IterC(A, b, C, x0, x_star, 10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"w = interactive(IterC, A=fixed(A), b=fixed(b), C=fixed(C), x0=fixed(x0), x_star=fixed(x_star), iters=widgets.IntSlider(min=0,max=20,value=0))\ndisplay(w)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Jacobi Method\n### Matrix Form:\n$$\n x^{(k+1)} = x^{(k)} - D^{-1}(Ax^{(k)} - b)\n$$\nor\n$$\n Dx^{(k+1)} = b - (L+U)x^{(k)}\n$$\n### Algorithm\n$$\n x^{(k+1)}_i = \\frac{b_i - \\sum\\limits_{j < i}a_{ij}x^{(k)}_j - \\sum\\limits_{j > i}a_{ij}x^{(k)}_j}{a_{ii}}\n$$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def Jacobi(A, b, x0, x_star, iters):\n x_old = np.copy(x0)\n x_new = np.zeros(np.size(x0))\n print (0, x_old, np.linalg.norm(x_star-x_old,np.inf))\n for k in range(iters):\n for i in range(np.size(x0)): \n x_new[i] = (b[i] - np.dot(A[i,:i],x_old[:i]) - np.dot(A[i,i+1:],x_old[i+1:]))/A[i,i]\n print (k+1, x_new, np.linalg.norm(x_star-x_new,np.inf))\n x_old = np.copy(x_new)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"w = interactive(Jacobi, A=fixed(A), b=fixed(b), x0=fixed(x0), x_star=fixed(x_star), iters=widgets.IntSlider(min=0,max=20,value=0))\ndisplay(w)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Second Approach** \n\nLet $D$ denote the main diagonal of $A$, $L$ denote the lower triangle of $A$ (entries below the main diagonal), and $U$ denote the upper triangle (entries above the main diagonal). Then $A = L + D + U$\n\nChoosing $C = (L + D)^{-1}$, then \n$$g(x) = x - (L + D)^{-1}(Ax - b),$$\nand the fixed-point iteration\n$$(L + D)x^{(k+1)} = Ux^{(k)} + b \\quad k = 0,1,2,\\ldots. $$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def GS(A, b, x0, x_star, iters):\n x = np.copy(x0)\n print (0, x, np.linalg.norm(x_star-x,np.inf))\n for k in range(iters):\n for i in range(np.size(x0)): \n x[i] = (b[i] - np.dot(A[i,:i],x[:i]) - np.dot(A[i,i+1:],x[i+1:]))/A[i,i]\n print (k+1, x, np.linalg.norm(x_star-x,np.inf))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"w = interactive(GS, A=fixed(A), b=fixed(b), x0=fixed(x0), x_star=fixed(x_star), iters=widgets.IntSlider(min=0,max=20,value=0))\ndisplay(w)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Gauss-Seidel Method\n### Algorithm\n$$\n x^{(k+1)}_i = \\frac{b_i - \\sum\\limits_{j < i}a_{ij}x^{(k+1)}_j - \\sum\\limits_{j > i}a_{ij}x^{(k)}_j}{a_{ii}}\n$$\n### Matrix Form:\n$$\n x^{(k+1)} = x^{(k)} - (L+D)^{-1}(Ax^{(k)} - b)\n$$\nor\n$$\n (L+D)x^{(k+1)} = b - Ux^{(k)}\n$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Example 2**\n\\begin{equation*}\n A = \\left[\\begin{array}{ccc} 3& 1 & -1 \\\\ 2 & 4 & 1 \\\\ -1 & 2& 5\\end{array}\\right],\\quad b = \\left[\\begin{array}{c} 4 \\\\ 1 \\\\ 1\\end{array}\\right],\n\\end{equation*}\nhas the exact solution $x^{*} = {[2, -1, 1]}^T$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"A = np.array([[3, 1, -1],[2,4,1],[-1,2,5]])\nb = np.array([4,1,1])\n\nx0 = np.zeros(np.size(b))\nx_star = np.array([2.,-1.,1.])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"w = interactive(GS, A=fixed(A), b=fixed(b), x0=fixed(x0), x_star=fixed(x_star), iters=widgets.IntSlider(min=0,max=40,value=0))\ndisplay(w)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Example 3**\n\\begin{equation*}\n A = \\left[\\begin{array}{ccc} 1& 2 & -2 \\\\ 1 & 1 & 1 \\\\ 2 & 2& 1\\end{array}\\right],\\quad b = \\left[\\begin{array}{c} 7 \\\\ 8 \\\\ 13\\end{array}\\right],\n\\end{equation*}\nhas the exact solution $x^{*} = {[-3, 8, 3]}^T$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"A = np.array([[1, 2, -2],[1,1,1],[2,2,1]])\nb = np.array([7,8,13])\n\n#x0 = np.zeros(np.size(b))\nx0 = np.array([-1,1,1])\nx_star = np.array([-3.,8.,3.])\n\nw = interactive(GS, A=fixed(A), b=fixed(b), x0=fixed(x0), x_star=fixed(x_star), iters=widgets.IntSlider(min=0,max=20,value=0))\ndisplay(w)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"B = np.eye(3) - np.dot(np.diag(1./np.diag(A)),A)\nprint(B)\nprint (np.linalg.eig(B))",
"[[ 0. -2. 2.]\n [-1. 0. -1.]\n [-2. -2. 0.]]\n(array([-6.16610918e-06+1.06799587e-05j, -6.16610918e-06-1.06799587e-05j,\n 1.23322184e-05+0.00000000e+00j]), array([[-0.57734849-6.16605800e-06j, -0.57734849+6.16605800e-06j,\n 0.57735383+0.00000000e+00j],\n [ 0.57735027+3.08300999e-06j, 0.57735027-3.08300999e-06j,\n -0.57735027+0.00000000e+00j],\n [ 0.57735205+0.00000000e+00j, 0.57735205-0.00000000e+00j,\n -0.57734671+0.00000000e+00j]]))\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Example 4**\n\\begin{equation*}\n A = \\left[\\begin{array}{cc} 1& 2 \\\\ 3 & 1 \\end{array}\\right],\\quad b = \\left[\\begin{array}{c} 5 \\\\ 5\\end{array}\\right],\n\\end{equation*}\nhas the exact solution $x^{*} = {[1, 2]}^T$\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"or\n\\begin{equation*}\n A = \\left[\\begin{array}{cc} 3& 1 \\\\ 1 & 2 \\end{array}\\right],\\quad b = \\left[\\begin{array}{c} 5 \\\\ 5\\end{array}\\right],\n\\end{equation*}",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#A = np.array([[1, 2],[3,1]])\nA = np.array([[3, 1],[1,2]])\nb = np.array([5,5])\n\n#x0 = np.zeros(np.size(b))\nx0 = np.array([0,0])\nx_star = np.array([1.,2.,])\n\nw = interactive(GS, A=fixed(A), b=fixed(b), x0=fixed(x0), x_star=fixed(x_star), iters=widgets.IntSlider(min=0,max=20,value=0))\ndisplay(w)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Example 5**\nAre Jacobi iteration and Gauss-Seidel iteration convergent for the following equations?\n\\begin{equation*}\n A_1 = \\left[\\begin{array}{ccc} 3& 0 & 4 \\\\ 7 & 4 & 2 \\\\ -1 & 1 & 2\\end{array}\\right],\\quad A_2 = \\left[\\begin{array}{ccc} -3& 3 & -6 \\\\ -4 & 7 & -8 \\\\ 5 & 7 & -9\\end{array}\\right],\n\\end{equation*}",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Consider the **spectral radius** of the iterative matrix\n* $B_J = -D^{-1}(L+U)$ and $B_{GS} = -(L+D)^{-1}U$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def Is_Jacobi_Gauss(A):\n L = np.tril(A,-1)\n U = np.triu(A,1)\n D = np.diag(np.diag(A))\n \n B_J = np.dot(np.diag(1./np.diag(A)), L+U)\n B_GS = np.dot(np.linalg.inv(L+D),U)\n \n rho_J = np.linalg.norm(np.linalg.eigvals(B_J), np.inf)\n rho_GS = np.linalg.norm(np.linalg.eigvals(B_GS), np.inf)\n \n print (\"Spectral Radius\")\n print (\"Jacobi: \", rho_J)\n print (\"Gauss Sediel: \", rho_GS)\n \nA1 = np.array([[3, 0, 4],[7, 4, 2], [-1,1,2]])\nA2 = np.array([[-3, 3, -6], [-4, 7, -8], [5, 7, -9]])\nIs_Jacobi_Gauss(A2)",
"Spectral Radius\nJacobi: 0.8133091054692768\nGauss Sediel: 1.1111111111111105\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Successive Over-Relaxation (SOR)\n### Algorithm\n$$\n x^{(k+1)}_i = x^{(k)} + \\omega \\frac{b_i - \\sum\\limits_{j < i}a_{ij}x^{(k+1)}_j - \\sum\\limits_{j \\geq i}a_{ij}x^{(k)}_j}{a_{ii}}\n$$\n### Matrix Form:\n$$\n x^{(k+1)} = x^{(k)} - \\omega(\\omega L+D)^{-1}(Ax^{(k)} - b)\n$$\nor\n$$\n (\\omega L+D)x^{(k+1)} = ((1-\\omega)D - \\omega U)x^{(k)} + \\omega b\n$$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def SOR(A, b, x0, x_star, omega, iters):\n x = np.copy(x0)\n print (0, x, np.linalg.norm(x_star-x,np.inf))\n for k in range(iters):\n for i in range(np.size(x0)): \n x[i] = x[i] + omega*(b[i] - np.dot(A[i,:i],x[:i]) - np.dot(A[i,i:],x[i:]))/A[i,i]\n print (k+1, x, np.linalg.norm(x_star-x,np.inf))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def SOR2(A, b, x0, x_star, omega, iters):\n x = np.copy(x0)\n for k in range(iters):\n for i in range(np.size(x0)): \n x[i] = x[i] + omega*(b[i] - np.dot(A[i,:i],x[:i]) - np.dot(A[i,i:],x[i:]))/A[i,i]\n return (np.linalg.norm(x_star-x,np.inf))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def SOR3(A, b, x0, x_star, omega, iters):\n x = np.copy(x0)\n print (0, np.linalg.norm(x_star-x,np.inf))\n for k in range(iters):\n for i in range(np.size(x0)): \n x[i] = x[i] + omega*(b[i] - np.dot(A[i,:i],x[:i]) - np.dot(A[i,i:],x[i:]))/A[i,i]\n print (k+1, np.linalg.norm(x_star-x,np.inf))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"A = np.array([[9., -1., -1.],[-1.,10.,-1.],[-1.,-1.,15.]])\nb = np.array([7.,8.,13.])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"x0 = np.array([0.,0.,0.])\nx_star = np.array([1.,1.,1.])\nomega = 1.01\n\nw = interactive(SOR, A=fixed(A), b=fixed(b), x0=fixed(x0), x_star=fixed(x_star), omega=fixed(omega), iters=widgets.IntSlider(min=0,max=20,value=0))\ndisplay(w)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"w = interactive(GS, A=fixed(A), b=fixed(b), x0=fixed(x0), x_star=fixed(x_star), iters=widgets.IntSlider(min=0,max=20,value=0))\ndisplay(w)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Example 6**\n\\begin{equation*}\n A = \\left[\\begin{array}{ccc} 2& -1 & 0 \\\\ -1 & 2 & -1 \\\\ 0 & -1& 2\\end{array}\\right],\\quad b = \\left[\\begin{array}{c} 1 \\\\ 0 \\\\ 1.8\\end{array}\\right],\n\\end{equation*}\nhas the exact solution $x^{*} = {[1.2, 1.4, 1.6]}^T$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"A = np.array([[2, -1, 0],[-1, 2, -1], [0, -1, 2]])\nb = np.array([1., 0, 1.8])\n\nx0 = np.array([1.,1.,1.])\nx_star = np.array([1.2,1.4,1.6])\nomega = 1.2\n\nw = interactive(SOR, A=fixed(A), b=fixed(b), x0=fixed(x0), x_star=fixed(x_star), omega=fixed(omega), iters=widgets.IntSlider(min=0,max=20,value=0))\ndisplay(w)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"w = interactive(GS, A=fixed(A), b=fixed(b), x0=fixed(x0), x_star=fixed(x_star), iters=widgets.IntSlider(min=0,max=20,value=0))\ndisplay(w)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"num = 21\nomega = np.linspace(0.8, 1.8, num)\nerr1 = np.zeros(num)\nfor i in range(num):\n err1[i] = SOR2(A, b, x0, x_star, omega[i], 10)\nprint (err1)\nplt.plot(omega, np.log10(err1), 'o')",
"[9.74407946e-03 5.97674726e-03 3.40178202e-03 1.75103265e-03\n 7.81250000e-04 2.95780635e-04 7.68649064e-05 7.55815494e-06\n 8.95664782e-08 8.45884563e-07 6.02114392e-06 1.70698528e-05\n 1.20163334e-04 4.60559853e-04 1.22304559e-03 2.67595099e-03\n 5.18204385e-03 9.23123417e-03 1.54954228e-02 2.49198480e-02\n 3.88728519e-02]\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Example 7**\n\\begin{equation*}\n A = \\left[\\begin{array}{cccc} -4& 1 & 1 & 1 \\\\ 1 & -4 & 1 & 1 \\\\ 1 & 1& -4 &1 \\\\ 1 & 1 &1 & -4\\end{array}\\right],\\quad b = \\left[\\begin{array}{c} 1 \\\\ 1 \\\\ 1 \\\\ 1\\end{array}\\right],\n\\end{equation*}\nhas the exact solution $x^{*} = {[-1, -1, -1, -1]}^T$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"A = np.array([[-4, 1, 1, 1],[1, -4, 1, 1], [1, 1, -4, 1], [1, 1, 1, -4]])\nb = np.array([1, 1, 1, 1])\n\nx0 = np.zeros(np.size(b))\nx_star = np.array([-1,-1,-1,-1])\nomega = 1.25\n\nw = interactive(SOR, A=fixed(A), b=fixed(b), x0=fixed(x0), x_star=fixed(x_star), omega=fixed(omega), iters=widgets.IntSlider(min=0,max=20,value=0))\ndisplay(w)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"w = interactive(GS, A=fixed(A), b=fixed(b), x0=fixed(x0), x_star=fixed(x_star), iters=widgets.IntSlider(min=0,max=100,value=0))\ndisplay(w)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"num = 21\nomega = np.linspace(0.8, 1.8, num)\nerr1 = np.zeros(num)\nfor i in range(num):\n err1[i] = SOR2(A, b, x0, x_star, omega[i], 10)\nprint (err1)\nplt.plot(omega, np.log10(err1), 'o')",
"[3.61803633e-02 2.42972865e-02 1.54786273e-02 9.21840054e-03\n 5.02185062e-03 2.41672275e-03 9.66046696e-04 2.82133665e-04\n 4.11422263e-05 2.97109833e-06 8.21084855e-06 3.41615422e-05\n 7.92225581e-05 2.98508851e-04 7.72804030e-04 1.47092104e-03\n 2.01360656e-03 6.50361476e-03 1.75478864e-02 4.14976604e-02\n 8.96585986e-02]\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Example 8**\n\\begin{equation*}\n A=\\begin{pmatrix}{3} & {-1} & {0} & 0 & 0 & \\frac{1}{2} \\\\ {-1} & {3} & {-1} & {0} & \\frac{1}{2} & 0\\\\ {0} & {-1} & {3} & {-1} & {0} & 0 \\\\ 0& {0} & {-1} & {3} & {-1} & {0} \\\\ {0} & \\frac{1}{2} & {0} & {-1} & {3} & {-1} \\\\ \\frac{1}{2} & {0} & 0 & 0 & {-1} & {3}\\end{pmatrix},\\,\\,b=\\begin{pmatrix}\\frac{5}{2} \\\\ \\frac{3}{2} \\\\ 1 \\\\ 1 \\\\ \\frac{3}{2} \\\\ \\frac{5}{2} \\end{pmatrix}\n\\end{equation*}\nhas the exact solution $x^{*} = {[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]}^T$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"n0 = 6\nA = 3*np.eye(n0) - np.diag(np.ones(n0-1),-1) - np.diag(np.ones(n0-1),+1)\nfor i in range(n0):\n if (abs(n0-1 - 2*i) > 1):\n A[i, n0-1-i] = - 1/2\nprint (A)\nx_star = np.ones(n0)\nb = np.dot(A, x_star)\n\nx0 = np.zeros(np.size(b))\nomega = 1.25\n\nw = interactive(SOR, A=fixed(A), b=fixed(b), x0=fixed(x0), x_star=fixed(x_star), omega=fixed(omega), iters=widgets.IntSlider(min=0,max=20,value=0))\ndisplay(w)",
"[[ 3. -1. 0. 0. 0. -0.5]\n [-1. 3. -1. 0. -0.5 0. ]\n [ 0. -1. 3. -1. 0. 0. ]\n [ 0. 0. -1. 3. -1. 0. ]\n [ 0. -0.5 0. -1. 3. -1. ]\n [-0.5 0. 0. 0. -1. 3. ]]\n"
],
[
"num = 21\nomega = np.linspace(0.8, 1.8, num)\nerr1 = np.zeros(num)\nfor i in range(num):\n err1[i] = SOR2(A, b, x0, x_star, omega[i], 10)\nprint (err1)\nplt.plot(omega, np.log10(err1), 'o')",
"[1.80518500e-02 1.09619670e-02 6.21887538e-03 3.23402618e-03\n 1.49846477e-03 5.90710685e-04 1.81660127e-04 3.52836259e-05\n 1.45462707e-05 4.93603574e-05 1.54153790e-04 3.87002370e-04\n 8.24122600e-04 1.52005198e-03 2.48178322e-03 5.69090046e-03\n 1.18481312e-02 2.27081117e-02 4.04944780e-02 6.76650388e-02\n 1.06290000e-01]\n"
],
[
"w = interactive(Jacobi, A=fixed(A), b=fixed(b), x0=fixed(x0), x_star=fixed(x_star), iters=widgets.IntSlider(min=0,max=100,value=0))\ndisplay(w)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Sparse Matrix Computations\nA coefficient matrix is called sparse if many of the matrix entries are known to be zero. Often, of the $n^2$ eligible entries in a sparse matrix, only $\\mathcal{O}(n)$ of them are nonzero. A full matrix is the opposite, where few entries may be assumed to be zero. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Example 9**\nConsider the $n$-equation version of\n\\begin{equation*}\n A=\\begin{pmatrix}{3} & {-1} & {0} & 0 & 0 & \\frac{1}{2} \\\\ {-1} & {3} & {-1} & {0} & \\frac{1}{2} & 0\\\\ {0} & {-1} & {3} & {-1} & {0} & 0 \\\\ 0& {0} & {-1} & {3} & {-1} & {0} \\\\ {0} & \\frac{1}{2} & {0} & {-1} & {3} & {-1} \\\\ \\frac{1}{2} & {0} & 0 & 0 & {-1} & {3}\\end{pmatrix}, \n\\end{equation*}\nhas the exact solution $x^{*} = {[1, 1,\\ldots, 1]}^T$ and $b = A x^{*}$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* First, let us have a look about the matrix $A$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"n0 = 10000\nA = 3*np.eye(n0) - np.diag(np.ones(n0-1),-1) - np.diag(np.ones(n0-1),+1)\nfor i in range(n0):\n if (abs(n0-1 - 2*i) > 1):\n A[i, n0-1-i] = - 1/2\n#plt.spy(A)\n#plt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"* How about the $PA = LU$ for the above matrix $A$?\n* Are the $L$ and $U$ matrices still sparse? ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import scipy.linalg\n#P, L, U = scipy.linalg.lu(A)\n\n#plt.spy(L)\n#plt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Gaussian elimination applied to a sparse matrix usually causes **fill-in**, where the coefficient matrix changes from sparse to full due to the necessary row operations. For this reason, the efficiency of Gaussian elimination and its $PA = LU$ implementation become questionable for sparse matrices, leaving iterative methods as a feasible alternative.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"* Let us solve it with SOR method",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x_star = np.ones(n0)\nb = np.dot(A, x_star)\n\nx0 = np.zeros(np.size(b))\nomega = 1.25\nw = interactive(SOR3, A=fixed(A), b=fixed(b), x0=fixed(x0), x_star=fixed(x_star), omega=fixed(omega), iters=widgets.IntSlider(min=0,max=200,value=0, step=10))\ndisplay(w)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Application for Solving Laplace's Equation\n\n### Laplace's equation\nConsider the Laplace's equation given as \n$$\n \\nabla^2 u = 0,\\quad\\quad (x,y) \\in D,\n$$\nwhere $\\nabla^2 = \\frac{\\partial^2}{\\partial x^2} + \\frac{\\partial^2}{\\partial y^2}$, and the boundary conditions are given as\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Finite Difference Approximation\nHere, we use a rectangular grid $(x_i,y_j)$, where\n$$\n x_i = i\\Delta x, \\,\\,\\text{for }\\, i = 0,1,\\ldots,N+1;\\quad y_j = j\\Delta y,\\,\\,\\text{for }\\, j = 0,1,\\ldots,M+1.\n$$\nFive-points scheme:\n$$\n -\\lambda^2 u_{i+1,j} + 2(1+\\lambda^2)u_{i,j} - \\lambda^2u_{i-1,j} - u_{i,j+1} - u_{i,j-1} = 0,\\quad\\text{for}\\,\\, i = 1,\\ldots,N,\\,\\, j = 1,\\ldots,M,\n$$\nwhere $\\lambda = \\frac{\\Delta y}{\\Delta x}$. The boundary conditions are \n- $x = 0: u_{0,j} = g_L(y_j), \\quad\\text{for }\\, j = 1,\\ldots,M$,\n- $x = a: u_{N+1,j} = g_R(y_j), \\quad\\text{for }\\, j = 1,\\ldots,M$,\n- $y = 0: u_{i,0} = g_B(x_i), \\quad\\text{for }\\, i = 1,\\ldots,N$,\n- $y = b: u_{i,M+1} = g_T(x_i), \\quad\\text{for }\\, i = 1,\\ldots,N$.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def generate_TD(N, dx, dy):\n T = np.zeros([N,N])\n a = - (dy/dx)**2\n b = 2*(1 - a)\n for i in range(N):\n T[i,i] += b\n if (i < N-1):\n T[i,i+1] += a\n if (i > 0):\n T[i,i-1] += a\n D = -np.identity(N)\n return T, D\n\ndef assemble_matrix_A(dx, dy, N, M):\n T, D = generate_TD(N, dx, dy)\n A = np.zeros([N*M, N*M])\n for j in range(M):\n A[j*N:(j+1)*N,j*N:(j+1)*N] += T\n if (j < M-1):\n A[j*N:(j+1)*N,(j+1)*N:(j+2)*N] += D\n if (j > 0):\n A[j*N:(j+1)*N,(j-1)*N:j*N] += D\n return A",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"N = 4\nM = 4\ndx = 1./(N+1)\ndy = 1./(M+1)\nT, D = generate_TD(N, dx, dy)\n#print (T)\nA = assemble_matrix_A(dx, dy, N, M)\n#print (A)\nplt.spy(A)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Set boundary conditions\ndef gL(y):\n return 0.\n\ndef gR(y):\n return 0.\n\ndef gB(x):\n return 0.\n\ndef gT(x):\n return 1.\n #return x*(1-x)*(4./5-x)*np.exp(6*x)\n \ndef assemble_vector_b(x, y, dx, dy, N, M, gL, gR, gB, gT):\n b = np.zeros(N*M)\n # Left BCs\n for j in range(M):\n b[(j-1)*N] += (dy/dx)**2*gL(y[j+1]) \n \n # Right BCs\n # b +=\n \n # Bottom BCs\n # b +=\n \n # Top BCs:\n for i in range(N):\n b[(M-1)*N+i] += gT(x[i+1])\n return b",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from mpl_toolkits import mplot3d\nfrom mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import axes3d",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def Laplace_solver(a, b, N, M, gL, gR, gB, gT):\n dx = b/(M+1)\n dy = a/(N+1)\n x = np.linspace(0, a, N+2)\n y = np.linspace(0, b, M+2)\n \n A = assemble_matrix_A(dx, dy, N, M)\n b = assemble_vector_b(x, y, dx, dy, N, M, gL, gR, gB, gT)\n \n v = np.linalg.solve(A,b)\n \n # add boundary points + plotting\n u = np.zeros([(N+2),(M+2)])\n #u[1:(N+1),1:(M+1)] = np.reshape(v, (N, M))\n # Top BCs\n for i in range(N+2):\n u[i,M+1] = gT(x[i])\n u = np.transpose(u)\n u[1:(M+1),1:(N+1)] = np.reshape(v, (M, N))\n\n \n X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)\n #Z = np.sin(2*np.pi*X)*np.sin(2*np.pi*Y)\n\n fig = plt.figure()\n #ax = plt.axes(projection='3d')\n ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1, projection='3d')\n\n ax.plot_surface(X, Y, u, rstride=1, cstride=1,\n cmap='viridis', edgecolor='none')\n ax.set_title('surface')\n plt.show()\n \nLaplace_solver(1, 1, 40, 40, gL, gR, gB, gT)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def Jacobi_tol(A, b, x0, tol):\n x_old = np.copy(x0)\n x_new = np.zeros(np.size(x0))\n for i in range(np.size(x0)): \n x_new[i] = (b[i] - np.dot(A[i,:i],x_old[:i]) - np.dot(A[i,i+1:],x_old[i+1:]))/A[i,i]\n iters = 1\n while ((np.linalg.norm(x_new-x_old,np.inf)) > tol):\n x_old = np.copy(x_new)\n for i in range(np.size(x0)): \n x_new[i] = (b[i] - np.dot(A[i,:i],x_old[:i]) - np.dot(A[i,i+1:],x_old[i+1:]))/A[i,i]\n iters += 1\n return x_new, iters",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def GS_tol(A, b, x0, tol):\n x_old = np.copy(x0)\n x = np.copy(x0)\n for i in range(np.size(x0)): \n x[i] = (b[i] - np.dot(A[i,:i],x[:i]) - np.dot(A[i,i+1:],x[i+1:]))/A[i,i]\n iters = 1\n while ((np.linalg.norm(x-x_old,np.inf)) > tol):\n x_old = np.copy(x)\n for i in range(np.size(x0)): \n x[i] = (b[i] - np.dot(A[i,:i],x[:i]) - np.dot(A[i,i+1:],x[i+1:]))/A[i,i]\n iters += 1\n return x, iters",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def SOR_tol(A, b, x0, omega, tol):\n x_old = np.copy(x0)\n x = np.copy(x0)\n for i in range(np.size(x0)): \n x[i] = x[i] + omega*(b[i] - np.dot(A[i,:i],x[:i]) - np.dot(A[i,i:],x[i:]))/A[i,i]\n iters = 1\n while ((np.linalg.norm(x-x_old,np.inf)) > tol):\n x_old = np.copy(x)\n for i in range(np.size(x0)): \n x[i] = x[i] + omega*(b[i] - np.dot(A[i,:i],x[:i]) - np.dot(A[i,i:],x[i:]))/A[i,i]\n iters += 1\n return x, iters",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def CG_tol(A, b, x0, x_star, tol):\n r_new = b - np.dot(A, x0) \n r_old = np.copy(np.size(x0))\n d_old = np.zeros(np.size(x0))\n x = np.copy(x0)\n iters = 0\n while ((np.linalg.norm(x-x_star,np.inf)) > tol):\n if (iters == 0):\n d_new = np.copy(r_new)\n else:\n beta = np.dot(r_new,r_new)/np.dot(r_old,r_old)\n d_new = r_new + beta*d_old\n Ad = np.dot(A, d_new)\n alpha = np.dot(r_new,r_new)/np.dot(d_new,Ad)\n x += alpha*d_new\n d_old = d_new\n r_old = r_new\n r_new = r_old - alpha*Ad\n iters += 1\n return x, iters",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def Iterative_solver(a, b, N, M, gL, gR, gB, gT, tol):\n dx = b/(M+1)\n dy = a/(N+1)\n x = np.linspace(0, a, N+2)\n y = np.linspace(0, b, M+2)\n \n A = assemble_matrix_A(dx, dy, N, M)\n b = assemble_vector_b(x, y, dx, dy, N, M, gL, gR, gB, gT)\n \n v = np.linalg.solve(A,b)\n #tol = 1.e-8\n v0 = np.zeros(np.size(b))\n #v_J, iters = Jacobi_tol(A, b, v0, tol)\n #print (\"Jacobi Method: %4d %7.2e\" %(iters, np.linalg.norm(v - v_J, np.inf)))\n \n #v_GS, iters = GS_tol(A, b, v0, tol)\n #print (\"Gauss Seidel : %4d %7.2e\" %(iters, np.linalg.norm(v - v_GS, np.inf)))\n \n omega = 2./(1 + np.sin(np.pi*dx))\n print (\"omega = \", omega)\n v_SOR, iters = SOR_tol(A, b, v0, omega, tol)\n print (\"SOR Method : %4d %7.2e\" %(iters, np.linalg.norm(v - v_SOR, np.inf)))\n \n v_CG, iters = CG_tol(A, b, v0, v, tol)\n print (\"CG Method : %4d %7.2e\" %(iters, np.linalg.norm(v - v_CG, np.inf)))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Iterative_solver(1, 1, 80, 80, gL, gR, gB, gT, 1.e-4)",
"omega = 1.9253440689301244\nSOR Method : 166 1.64e-04\nCG Method : 148 9.80e-05\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50c6b4c7b23fc4a623842155bec9fefd60bf748
| 2,256 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Full/Part 6 - Cloud Deployment/Deploying with Binder.ipynb
|
lucasdurand/visualization-seminar
|
4bfa263d18ac4713a0c4d8a45b2b8ab0ab8cd802
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Full/Part 6 - Cloud Deployment/Deploying with Binder.ipynb
|
lucasdurand/visualization-seminar
|
4bfa263d18ac4713a0c4d8a45b2b8ab0ab8cd802
|
[
"MIT"
] | 5 |
2019-11-26T03:47:43.000Z
|
2019-12-10T03:38:25.000Z
|
Full/Part 6 - Cloud Deployment/Deploying with Binder.ipynb
|
lucasdurand/visualization-seminar
|
4bfa263d18ac4713a0c4d8a45b2b8ab0ab8cd802
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2019-12-10T01:04:24.000Z
|
2019-12-10T01:04:24.000Z
| 32.695652 | 185 | 0.597518 |
[
[
[
"## Binder\nhttps://mybinder.org/\n\nBinder is cool. Where with HTML we get a *static* version of our notebook, Binder will launch an ephemeral notebook server to give you the full notebook experience.\n\n### How does it work?\n\nIt takes a repository and:\n\n1. Builds a `Docker` image for it\n - Docker implements *containerization*, a modern programming paradigm that allows you to create \"insulated\" processes that once created *should* work anywhere\n2. Launches a `JupyterHub` server to host your repo\n - JupyterHub is a multi-user Jupyter platform. In this case it allows us to host things externally (for a short time) and only spin it up/down when users want to access it.\n3. Gives you a re-usable link to access and share.\n\n## EXERCISE\n\n**Let's deploy this Notebook!**\n\nWe need:\n\n- This to be in a repo on Github:\n - Create a new Github repo\n - From the **Part 3** folder run `git init`\n - Follow the github instructions to `git add`, `git commit`, and `git push` the contents of this folder\n - Let's only push what we need!\n- A requirements.txt or Pipfile\n - We can steal the one from the parent project as it will have all of the dependencies we need\n - Copy `Pipfile` into this folder\n- Once everything is in place in github, deploy to Binder (https://mybinder.org/)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"To default to loading a Voila app: set the starting url to `/render/voila/path/to/file.ipynb`",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
c50c6c374f0f91e6e93721867833304360dbbd46
| 89,705 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Kesten Processes and Firm Dynamics.ipynb
|
DiogoRibeiro7/Finance
|
6babc706bd523fc83e1dd1fda7f57aef969c5347
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Kesten Processes and Firm Dynamics.ipynb
|
DiogoRibeiro7/Finance
|
6babc706bd523fc83e1dd1fda7f57aef969c5347
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Kesten Processes and Firm Dynamics.ipynb
|
DiogoRibeiro7/Finance
|
6babc706bd523fc83e1dd1fda7f57aef969c5347
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 290.307443 | 35,164 | 0.926715 |
[
[
[
"# Kesten Processes and Firm Dynamics\n\n\n<a id='index-0'></a>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n%matplotlib inline\n\nimport quantecon as qe",
"C:\\Users\\Diogo\\Anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages\\numba\\np\\ufunc\\parallel.py:355: NumbaWarning: \u001b[1mThe TBB threading layer requires TBB version 2019.5 or later i.e., TBB_INTERFACE_VERSION >= 11005. Found TBB_INTERFACE_VERSION = 10005. The TBB threading layer is disabled.\u001b[0m\n warnings.warn(problem)\n"
],
[
"from pandas.plotting import register_matplotlib_converters\nregister_matplotlib_converters()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import yfinance as yf\nimport pandas as pd\n\ns = yf.download('^IXIC', '2006-1-1', '2019-11-1')['Adj Close']\n\nr = s.pct_change()\n\nfig, ax = plt.subplots()\n\nax.plot(r, alpha=0.7)\n\nax.set_ylabel('returns', fontsize=12)\nax.set_xlabel('date', fontsize=12)\n\nplt.show()",
"[*********************100%***********************] 1 of 1 completed\n"
],
[
"μ = -0.5\nσ = 1.0\n\ndef kesten_ts(ts_length=100):\n x = np.zeros(ts_length)\n for t in range(ts_length-1):\n a = np.exp(μ + σ * np.random.randn())\n b = np.exp(np.random.randn())\n x[t+1] = a * x[t] + b\n return x\n\nfig, ax = plt.subplots()\n\nnum_paths = 10\nnp.random.seed(12)\n\nfor i in range(num_paths):\n ax.plot(kesten_ts())\n\nax.set(xlabel='time', ylabel='$X_t$')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"μ_a = -0.5 # location parameter for a\nσ_a = 0.1 # scale parameter for a\nμ_b = 0.0 # location parameter for b\nσ_b = 0.5 # scale parameter for b\nμ_e = 0.0 # location parameter for e\nσ_e = 0.5 # scale parameter for e\ns_bar = 1.0 # threshold\nT = 500 # sampling date\nM = 1_000_000 # number of firms\ns_init = 1.0 # initial condition for each firm",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"α_0 = 1e-5\nα_1 = 0.1\nβ = 0.9\n\nyears = 15\ndays = years * 250\n\ndef garch_ts(ts_length=days):\n σ2 = 0\n r = np.zeros(ts_length)\n for t in range(ts_length-1):\n ξ = np.random.randn()\n σ2 = α_0 + σ2 * (α_1 * ξ**2 + β)\n r[t] = np.sqrt(σ2) * np.random.randn()\n return r\n\nfig, ax = plt.subplots()\n\nnp.random.seed(12)\n\nax.plot(garch_ts(), alpha=0.7)\n\nax.set(xlabel='time', ylabel='$\\\\sigma_t^2$')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from numba import njit, prange\nfrom numpy.random import randn\n\n\n@njit(parallel=True)\ndef generate_draws(μ_a=-0.5,\n σ_a=0.1,\n μ_b=0.0,\n σ_b=0.5,\n μ_e=0.0,\n σ_e=0.5,\n s_bar=1.0,\n T=500,\n M=1_000_000,\n s_init=1.0):\n\n draws = np.empty(M)\n for m in prange(M):\n s = s_init\n for t in range(T):\n if s < s_bar:\n new_s = np.exp(μ_e + σ_e * randn())\n else:\n a = np.exp(μ_a + σ_a * randn())\n b = np.exp(μ_b + σ_b * randn())\n new_s = a * s + b\n s = new_s\n draws[m] = s\n\n return draws\n\ndata = generate_draws()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots()\n\nqe.rank_size_plot(data, ax, c=0.01)\n\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50c6f7cd402dc1a874c1b3c811286a7c1757ceb
| 838,544 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
P1.ipynb
|
vinothkumarmuthuraj/Finding-Lane-lines
|
effc0e76382867f73b2a116c91e50a5948abeb38
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
P1.ipynb
|
vinothkumarmuthuraj/Finding-Lane-lines
|
effc0e76382867f73b2a116c91e50a5948abeb38
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
P1.ipynb
|
vinothkumarmuthuraj/Finding-Lane-lines
|
effc0e76382867f73b2a116c91e50a5948abeb38
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 952.890909 | 128,628 | 0.952958 |
[
[
[
"# Self-Driving Car Engineer Nanodegree\n\n\n## Project: **Finding Lane Lines on the Road** \n***\nIn this project, you will use the tools you learned about in the lesson to identify lane lines on the road. You can develop your pipeline on a series of individual images, and later apply the result to a video stream (really just a series of images). Check out the video clip \"raw-lines-example.mp4\" (also contained in this repository) to see what the output should look like after using the helper functions below. \n\nOnce you have a result that looks roughly like \"raw-lines-example.mp4\", you'll need to get creative and try to average and/or extrapolate the line segments you've detected to map out the full extent of the lane lines. You can see an example of the result you're going for in the video \"P1_example.mp4\". Ultimately, you would like to draw just one line for the left side of the lane, and one for the right.\n\nIn addition to implementing code, there is a brief writeup to complete. The writeup should be completed in a separate file, which can be either a markdown file or a pdf document. There is a [write up template](https://github.com/udacity/CarND-LaneLines-P1/blob/master/writeup_template.md) that can be used to guide the writing process. Completing both the code in the Ipython notebook and the writeup template will cover all of the [rubric points](https://review.udacity.com/#!/rubrics/322/view) for this project.\n\n---\nLet's have a look at our first image called 'test_images/solidWhiteRight.jpg'. Run the 2 cells below (hit Shift-Enter or the \"play\" button above) to display the image.\n\n**Note: If, at any point, you encounter frozen display windows or other confounding issues, you can always start again with a clean slate by going to the \"Kernel\" menu above and selecting \"Restart & Clear Output\".**\n\n---",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**The tools you have are color selection, region of interest selection, grayscaling, Gaussian smoothing, Canny Edge Detection and Hough Tranform line detection. You are also free to explore and try other techniques that were not presented in the lesson. Your goal is piece together a pipeline to detect the line segments in the image, then average/extrapolate them and draw them onto the image for display (as below). Once you have a working pipeline, try it out on the video stream below.**\n\n---\n\n<figure>\n <img src=\"examples/line-segments-example.jpg\" width=\"380\" alt=\"Combined Image\" />\n <figcaption>\n <p></p> \n <p style=\"text-align: center;\"> Your output should look something like this (above) after detecting line segments using the helper functions below </p> \n </figcaption>\n</figure>\n <p></p> \n<figure>\n <img src=\"examples/laneLines_thirdPass.jpg\" width=\"380\" alt=\"Combined Image\" />\n <figcaption>\n <p></p> \n <p style=\"text-align: center;\"> Your goal is to connect/average/extrapolate line segments to get output like this</p> \n </figcaption>\n</figure>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Run the cell below to import some packages. If you get an `import error` for a package you've already installed, try changing your kernel (select the Kernel menu above --> Change Kernel). Still have problems? Try relaunching Jupyter Notebook from the terminal prompt. Also, consult the forums for more troubleshooting tips.** ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Import Packages",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#importing some useful packages\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport matplotlib.image as mpimg\nimport numpy as np\nimport cv2\n%matplotlib inline",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Read in an Image",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#reading in an image\nimage = mpimg.imread('test_images/solidWhiteRight.jpg')\n\n#printing out some stats and plotting\nprint('This image is:', type(image), 'with dimensions:', image.shape)\nplt.imshow(image) # if you wanted to show a single color channel image called 'gray', for example, call as plt.imshow(gray, cmap='gray')",
"This image is: <class 'numpy.ndarray'> with dimensions: (540, 960, 3)\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Ideas for Lane Detection Pipeline",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Some OpenCV functions (beyond those introduced in the lesson) that might be useful for this project are:**\n\n`cv2.inRange()` for color selection \n`cv2.fillPoly()` for regions selection \n`cv2.line()` to draw lines on an image given endpoints \n`cv2.addWeighted()` to coadd / overlay two images\n`cv2.cvtColor()` to grayscale or change color\n`cv2.imwrite()` to output images to file \n`cv2.bitwise_and()` to apply a mask to an image\n\n**Check out the OpenCV documentation to learn about these and discover even more awesome functionality!**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Helper Functions",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Below are some helper functions to help get you started. They should look familiar from the lesson!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import math\n\ndef grayscale(img):\n \"\"\"Applies the Grayscale transform\n This will return an image with only one color channel\n but NOTE: to see the returned image as grayscale\n (assuming your grayscaled image is called 'gray')\n you should call plt.imshow(gray, cmap='gray')\"\"\"\n return cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)\n # Or use BGR2GRAY if you read an image with cv2.imread()\n # return cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)\n\ndef hsv(image):\n return cv2.cvtColor(image,cv2.COLOR_RGB2HSV) \n \ndef canny(img, low_threshold, high_threshold):\n \"\"\"Applies the Canny transform\"\"\"\n return cv2.Canny(img, low_threshold, high_threshold)\n\ndef gaussian_blur(img, kernel_size):\n \"\"\"Applies a Gaussian Noise kernel\"\"\"\n return cv2.GaussianBlur(img, (kernel_size, kernel_size), 0)\n\ndef region_of_interest(img, vertices):\n \"\"\"\n Applies an image mask.\n \n Only keeps the region of the image defined by the polygon\n formed from `vertices`. The rest of the image is set to black.\n `vertices` should be a numpy array of integer points.\n \"\"\"\n #defining a blank mask to start with\n mask = np.zeros_like(img) \n \n #defining a 3 channel or 1 channel color to fill the mask with depending on the input image\n if len(img.shape) > 2:\n channel_count = img.shape[2] # i.e. 3 or 4 depending on your image\n ignore_mask_color = (255,) * channel_count\n else:\n ignore_mask_color = 255\n \n #filling pixels inside the polygon defined by \"vertices\" with the fill color \n cv2.fillPoly(mask, vertices, ignore_mask_color)\n \n #returning the image only where mask pixels are nonzero\n masked_image = cv2.bitwise_and(img, mask)\n return masked_image\n\n\ndef draw_lines(img, lines, color=[255, 0, 0], thickness=10):\n \"\"\"\n NOTE: this is the function you might want to use as a starting point once you want to \n average/extrapolate the line segments you detect to map out the full\n extent of the lane (going from the result shown in raw-lines-example.mp4\n to that shown in P1_example.mp4). \n \n Think about things like separating line segments by their \n slope ((y2-y1)/(x2-x1)) to decide which segments are part of the left\n line vs. the right line. Then, you can average the position of each of \n the lines and extrapolate to the top and bottom of the lane.\n \n This function draws `lines` with `color` and `thickness`. \n Lines are drawn on the image inplace (mutates the image).\n If you want to make the lines semi-transparent, think about combining\n this function with the weighted_img() function below\n \"\"\"\n x_size = img.shape[1]\n y_size = img.shape[0]\n #creating an array using points from houghspace\n lines_slope_intercept = np.zeros(shape=(len(lines),2))\n for index,line in enumerate(lines): \n for x1,y1,x2,y2 in line:\n #calculating slope and intercepts\n slope = (y2-y1)/(x2-x1)\n intercept = y1 - (x1 * slope)\n #storing the slope and intercept in a list\n lines_slope_intercept[index]=[slope,intercept]\n #finding max and min slope lines\n max_slope_line = lines_slope_intercept[lines_slope_intercept.argmax(axis=0)[0]]\n min_slope_line = lines_slope_intercept[lines_slope_intercept.argmin(axis=0)[0]]\n left_slopes = []\n left_intercepts = []\n right_slopes = []\n right_intercepts = []\n \n for line in lines_slope_intercept:\n if abs(line[0] - max_slope_line[0]) < 0.15 and abs(line[1] - max_slope_line[1]) < (0.15 * x_size):\n left_slopes.append(line[0])\n left_intercepts.append(line[1])\n elif abs(line[0] - min_slope_line[0]) < 0.15 and abs(line[1] - min_slope_line[1]) < (0.15 * x_size):\n right_slopes.append(line[0])\n right_intercepts.append(line[1])\n # left and right lines are averages of these slopes and intercepts, extrapolate lines to edges and center*\n new_lines = np.zeros(shape=(1,2,4), dtype=np.int32)\n if len(left_slopes) > 0:\n left_line = [sum(left_slopes)/len(left_slopes),sum(left_intercepts)/len(left_intercepts)]\n left_bottom_x = (y_size - left_line[1])/left_line[0]\n left_top_x = (y_size*.575 - left_line[1])/left_line[0]\n if (left_bottom_x >= 0):\n new_lines[0][0] =[left_bottom_x,y_size,left_top_x,y_size*.575]\n if len(right_slopes) > 0:\n right_line = [sum(right_slopes)/len(right_slopes),sum(right_intercepts)/len(right_intercepts)]\n right_bottom_x = (y_size - right_line[1])/right_line[0]\n right_top_x = (y_size*.575 - right_line[1])/right_line[0]\n if (right_bottom_x <= x_size):\n new_lines[0][1]=[right_bottom_x,y_size,right_top_x,y_size*.575]\n for line in new_lines:\n for x1,y1,x2,y2 in line:\n cv2.line(img, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), color, thickness)\n\n\ndef hough_lines(img, rho, theta, threshold, min_line_len, max_line_gap):\n \"\"\"\n `img` should be the output of a Canny transform.\n \n Returns an image with hough lines drawn.\n \"\"\"\n lines = cv2.HoughLinesP(img, rho, theta, threshold, np.array([]), minLineLength=min_line_len, maxLineGap=max_line_gap)\n line_img = np.zeros((img.shape[0], img.shape[1], 3), dtype=np.uint8)\n draw_lines(line_img, lines)\n return line_img\n\n# Python 3 has support for cool math symbols.\n\ndef weighted_img(img, initial_img, α=0.8, β=1., γ=0.):\n \"\"\"\n `img` is the output of the hough_lines(), An image with lines drawn on it.\n Should be a blank image (all black) with lines drawn on it.\n \n `initial_img` should be the image before any processing.\n \n The result image is computed as follows:\n \n initial_img * α + img * β + γ\n NOTE: initial_img and img must be the same shape!\n \"\"\"\n return cv2.addWeighted(initial_img, α, img, β, γ)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Test Images\n\nBuild your pipeline to work on the images in the directory \"test_images\" \n**You should make sure your pipeline works well on these images before you try the videos.**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import os\nos.listdir(\"test_images/\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Build a Lane Finding Pipeline\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Build the pipeline and run your solution on all test_images. Make copies into the `test_images_output` directory, and you can use the images in your writeup report.\n\nTry tuning the various parameters, especially the low and high Canny thresholds as well as the Hough lines parameters.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#reading in an image\nfor index, img in enumerate(os.listdir(\"test_images/\")):\n image = mpimg.imread('test_images/' + img)\n #print(image.shape)\n gray_img = grayscale(image) \n\n hsv_img = hsv(image)\n \n # define range of color in HSV\n lower_yellow = np.array([20,150,150])\n upper_yellow = np.array([40,255,255])\n lower_white = np.array([0,0,230])\n upper_white = np.array([255,255,255])\n \n # Threshold the HSV image to get only yellow/white \n yellow_mask = cv2.inRange(hsv_img, lower_yellow, upper_yellow)\n white_mask = cv2.inRange(hsv_img, lower_white, upper_white)\n # Bitwise-OR mask and original image\n full_mask = cv2.bitwise_or(yellow_mask, white_mask)\n subdued_gray = (gray_img / 2).astype('uint8')\n boosted_lanes = cv2.bitwise_or(subdued_gray, full_mask)\n #definig kernel size for gaussian smoothing/blurring\n kernel_size = 5\n blurred_img = gaussian_blur(boosted_lanes,kernel_size)\n #defining threshold for canny edge detection\n canny_low_threshold = 60\n canny_high_threshold = 150\n edges_img = canny(blurred_img,canny_low_threshold,canny_high_threshold)\n #defining vertices for fillpoly\n x = edges_img.shape[1]\n y = edges_img.shape[0]\n vertices = np.array([[(0,y),(450, 290), (490, 290), (x,y)]], dtype=np.int32)\n masked_image = region_of_interest(edges_img, vertices)\n #defining parameters for hough transform\n rho = 2.5\n theta = np.pi/180\n threshold = 68\n min_line_length = 70\n max_line_gap = 250\n hough_image = hough_lines(masked_image,rho,theta,threshold,min_line_length,max_line_gap)\n \n result = weighted_img(hough_image,image)\n \n fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6,10))\n plt.imshow(result, cmap=\"gray\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Test on Videos\n\nYou know what's cooler than drawing lanes over images? Drawing lanes over video!\n\nWe can test our solution on two provided videos:\n\n`solidWhiteRight.mp4`\n\n`solidYellowLeft.mp4`\n\n**Note: if you get an import error when you run the next cell, try changing your kernel (select the Kernel menu above --> Change Kernel). Still have problems? Try relaunching Jupyter Notebook from the terminal prompt. Also, consult the forums for more troubleshooting tips.**\n\n**If you get an error that looks like this:**\n```\nNeedDownloadError: Need ffmpeg exe. \nYou can download it by calling: \nimageio.plugins.ffmpeg.download()\n```\n**Follow the instructions in the error message and check out [this forum post](https://discussions.udacity.com/t/project-error-of-test-on-videos/274082) for more troubleshooting tips across operating systems.**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Import everything needed to edit/save/watch video clips\nfrom moviepy.editor import VideoFileClip\nfrom IPython.display import HTML",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def process_image(image):\n gray_img = grayscale(image) \n\n hsv_img = hsv(image)\n \n # define range of color in HSV\n lower_yellow = np.array([20,150,150])\n upper_yellow = np.array([40,255,255])\n lower_white = np.array([0,0,230])\n upper_white = np.array([255,255,255])\n \n # Threshold the HSV image to get only yellow/white \n yellow_mask = cv2.inRange(hsv_img, lower_yellow, upper_yellow)\n white_mask = cv2.inRange(hsv_img, lower_white, upper_white)\n # Bitwise-OR mask and original image\n full_mask = cv2.bitwise_or(yellow_mask, white_mask)\n subdued_gray = (gray_img / 2).astype('uint8')\n boosted_lanes = cv2.bitwise_or(subdued_gray, full_mask)\n #definig kernel size for gaussian smoothing/blurring\n kernel_size = 5\n blurred_img = gaussian_blur(boosted_lanes,kernel_size)\n #defining threshold for canny edge detection\n canny_low_threshold = 60\n canny_high_threshold = 150\n edges_img = canny(blurred_img,canny_low_threshold,canny_high_threshold)\n #defining vertices for fillpoly\n x = edges_img.shape[1]\n y = edges_img.shape[0]\n vertices = np.array([[(0,y),(450, 290), (490, 290), (x,y)]], dtype=np.int32)\n masked_image = region_of_interest(edges_img, vertices)\n #defining parameters for hough transform\n rho = 2.5\n theta = np.pi/180\n threshold = 68\n min_line_length = 70\n max_line_gap = 250\n hough_image = hough_lines(masked_image,rho,theta,threshold,min_line_length,max_line_gap)\n result = weighted_img(hough_image,image)\n return result",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's try the one with the solid white lane on the right first ...",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"white_output = 'test_videos_output/solidWhiteRight.mp4'\n## To speed up the testing process you may want to try your pipeline on a shorter subclip of the video\n## To do so add .subclip(start_second,end_second) to the end of the line below\n## Where start_second and end_second are integer values representing the start and end of the subclip\n## You may also uncomment the following line for a subclip of the first 5 seconds\n##clip1 = VideoFileClip(\"test_videos/solidWhiteRight.mp4\").subclip(0,5)\nclip1 = VideoFileClip(\"test_videos/solidWhiteRight.mp4\")\nwhite_clip = clip1.fl_image(process_image) #NOTE: this function expects color images!!\n%time white_clip.write_videofile(white_output, audio=False)",
"[MoviePy] >>>> Building video test_videos_output/solidWhiteRight.mp4\n[MoviePy] Writing video test_videos_output/solidWhiteRight.mp4\n"
]
],
[
[
"Play the video inline, or if you prefer find the video in your filesystem (should be in the same directory) and play it in your video player of choice.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"HTML(\"\"\"\n<video width=\"960\" height=\"540\" controls>\n <source src=\"{0}\">\n</video>\n\"\"\".format(white_output))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Improve the draw_lines() function\n\n**At this point, if you were successful with making the pipeline and tuning parameters, you probably have the Hough line segments drawn onto the road, but what about identifying the full extent of the lane and marking it clearly as in the example video (P1_example.mp4)? Think about defining a line to run the full length of the visible lane based on the line segments you identified with the Hough Transform. As mentioned previously, try to average and/or extrapolate the line segments you've detected to map out the full extent of the lane lines. You can see an example of the result you're going for in the video \"P1_example.mp4\".**\n\n**Go back and modify your draw_lines function accordingly and try re-running your pipeline. The new output should draw a single, solid line over the left lane line and a single, solid line over the right lane line. The lines should start from the bottom of the image and extend out to the top of the region of interest.**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Now for the one with the solid yellow lane on the left. This one's more tricky!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"yellow_output = 'test_videos_output/solidYellowLeft.mp4'\n## To speed up the testing process you may want to try your pipeline on a shorter subclip of the video\n## To do so add .subclip(start_second,end_second) to the end of the line below\n## Where start_second and end_second are integer values representing the start and end of the subclip\n## You may also uncomment the following line for a subclip of the first 5 seconds\n##clip2 = VideoFileClip('test_videos/solidYellowLeft.mp4').subclip(0,5)\nclip2 = VideoFileClip('test_videos/solidYellowLeft.mp4')\nyellow_clip = clip2.fl_image(process_image)\n%time yellow_clip.write_videofile(yellow_output, audio=False)",
"[MoviePy] >>>> Building video test_videos_output/solidYellowLeft.mp4\n[MoviePy] Writing video test_videos_output/solidYellowLeft.mp4\n"
],
[
"HTML(\"\"\"\n<video width=\"960\" height=\"540\" controls>\n <source src=\"{0}\">\n</video>\n\"\"\".format(yellow_output))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Writeup and Submission\n\nIf you're satisfied with your video outputs, it's time to make the report writeup in a pdf or markdown file. Once you have this Ipython notebook ready along with the writeup, it's time to submit for review! Here is a [link](https://github.com/udacity/CarND-LaneLines-P1/blob/master/writeup_template.md) to the writeup template file.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Optional Challenge\n\nTry your lane finding pipeline on the video below. Does it still work? Can you figure out a way to make it more robust? If you're up for the challenge, modify your pipeline so it works with this video and submit it along with the rest of your project!",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"challenge_output = 'test_videos_output/challenge.mp4'\n## To speed up the testing process you may want to try your pipeline on a shorter subclip of the video\n## To do so add .subclip(start_second,end_second) to the end of the line below\n## Where start_second and end_second are integer values representing the start and end of the subclip\n## You may also uncomment the following line for a subclip of the first 5 seconds\n##clip3 = VideoFileClip('test_videos/challenge.mp4').subclip(0,5)\nclip3 = VideoFileClip('test_videos/challenge.mp4')\nchallenge_clip = clip3.fl_image(process_image)\n%time challenge_clip.write_videofile(challenge_output, audio=False)",
"[MoviePy] >>>> Building video test_videos_output/challenge.mp4\n[MoviePy] Writing video test_videos_output/challenge.mp4\n"
],
[
"HTML(\"\"\"\n<video width=\"960\" height=\"540\" controls>\n <source src=\"{0}\">\n</video>\n\"\"\".format(challenge_output))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50c73a80220f9103b715e5d0bb2f333fb11a106
| 321,994 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
SNIDNewZTF/NewGraph.ipynb
|
adamamiller/supernova-spectrum-analysis
|
1f7816bdc7dadb1a9a2ee3a97a1f77dd6f0c06dd
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
SNIDNewZTF/NewGraph.ipynb
|
adamamiller/supernova-spectrum-analysis
|
1f7816bdc7dadb1a9a2ee3a97a1f77dd6f0c06dd
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
SNIDNewZTF/NewGraph.ipynb
|
adamamiller/supernova-spectrum-analysis
|
1f7816bdc7dadb1a9a2ee3a97a1f77dd6f0c06dd
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 577.050179 | 58,488 | 0.933524 |
[
[
[
"import subprocess\nimport shlex\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nfrom astropy.table import Table\nfrom astropy.table import Column\nimport os\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom matplotlib.backends.backend_pdf import PdfPages\nfrom matplotlib.ticker import MultipleLocator\nimport glob\nfrom matplotlib import pyplot\nimport matplotlib.gridspec as gridspec\nimport gc",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"basedir = \"/home/xhall/Documents/\"\n\nRedshiftClass = Table.from_pandas(pd.read_csv(basedir + \"NewZTF/ML_sample_snid200.csv\"))\nML_sample_snid_examples = Table.from_pandas(pd.read_csv(basedir + \"NewZTF/ML_sample_snid_brightexamples.csv\"))\nsample_2018 = Table.from_pandas(pd.read_csv(basedir + \"NewZTF/sample_2018/ML_sample_snid_2018.csv\"))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"source = basedir + \"NewZTF/sample_2018/SNIDoutput/\"\noutput = basedir + \"NewZTF/sample_2018/ImageOutput/\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def read_tables(files):\n matches_files = files[0:len(files)-1]\n spectra = Table.read(files[-1], format = \"ascii\", names = [\"wavelength\", \"flux\"])\n matches = []\n for i in matches_files:\n input_data = open(i,'r').readlines()[0].split()\n row = [[int(input_data[3][0]), input_data[4],input_data[5][1::],float(input_data[-3].split(\"-\")[-1]),float(input_data[-1])]]\n row.append(Table.read(i, format = \"ascii\", names = [\"redshifted_wavelength\", \"flux\"]))\n matches.append(row)\n return matches, spectra",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def plot_box_spec(wave, flux): \n flux_plot = np.repeat(flux, 2)\n wv_plot = wave.copy()\n wv_plot[:-1] += np.diff(wave)/2\n wv_plot = np.append(wave[0]-(wave[1]-wave[0])/2, \n np.append(np.repeat(wv_plot[0:-1], 2), \n wave[-1]+(wave[-1]-wave[-2])/2))\n \n return wv_plot, flux_plot",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def specplot(x,y,xi,yi,snid_type,fname,output,best_num, z_template, z_template_unc, z_snid,\n spec_num, show_redshift=False):\n fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8,4.5))\n ax.plot(xi,yi,color='#32384D',alpha=0.5,\n label='New SN')\n ax.plot(x,y,color='#217CA3',\n label='SNID template', lw=3)\n if show_redshift:\n ax.plot(x[-3],y[-3],color='white',lw=0,\n label=r'$z_\\mathrm{} = $ {:.3f}$\\,\\pm\\,${:.3f}'.format(\"{SNID}\", z_template, z_template_unc))\n ax.text(0.78, 0.955, r'$z_\\mathrm{} = ${:.4f}'.format(\"{SN}\", z_snid), \n va='center',\n fontsize=15, transform=plt.gcf().transFigure)\n else:\n ax.text(0.78, 0.955, 'Match #{d}'.format(spec_num), \n va='center',\n fontsize=15, transform=plt.gcf().transFigure)\n \n ax.plot(x[-3],y[-3],color='#217CA3', lw=3)\n ax.set_xlabel(r'Rest Frame Wavelength ($\\mathrm{\\AA}$)', fontsize=17)\n ax.set_ylabel('Relative Flux', fontsize=17)\n ax.tick_params(which='both',labelsize=15)\n \n ax.grid(axis='x', color='0.7', ls=':')\n ax.xaxis.set_minor_locator(MultipleLocator(250))\n ax.set_yticklabels([])\n\n \n ax.text(0.105, 0.955, 'SNID type: ', \n va='center',\n fontsize=15, transform=plt.gcf().transFigure)\n ax.text(0.245, 0.955, snid_type, \n color='#217CA3', weight='bold', va='center',\n fontsize=23, transform=plt.gcf().transFigure)\n\n \n \n ax.legend(fancybox=True)\n fig.subplots_adjust(left=0.055,right=0.975,top=0.925,bottom=0.145)\n fig.savefig(output + 'snidfits_emclip_' + fname + \"_\" + str(best_num) + '.png', dpi = 600)\n plt.close(fig)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def plot_best_5(source, output, spectra_name, z_snid):\n source_folder = source + spectra_name\n \n files = np.sort(glob.glob(source_folder+\"/*.dat\"))\n if(len(files)==0):\n print(spectra_name)\n return -1\n matches, spectra = read_tables(files)\n \n for spec_num, i in enumerate(matches):\n z = i[0][3]\n snid_type = i[0][2][:-1]\n \n xi, yi = plot_box_spec(spectra[\"wavelength\"], spectra[\"flux\"])\n xi /= (1+z)\n x, y = i[1][\"redshifted_wavelength\"] / (1+z), i[1][\"flux\"]\n specplot(x,y,xi,yi,snid_type,spectra_name,output,i[0][0], z, i[0][4], z_snid, spec_num)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sample_2018[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"counter = 0\nfor i in sample_2018:\n spectra_name = i[\"Version\"].split(\".\")[0]\n z_snid = i[\"z_snid\"]\n plot_best_5(source,output,spectra_name,z_snid)\n gc.collect()\n if(counter%20 == 0):\n print(counter)\n counter += 1\n break",
"/home/xhall/anaconda3/lib/python3.7/site-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:43: UserWarning: This figure includes Axes that are not compatible with tight_layout, so results might be incorrect.\n"
],
[
"pngs = glob.glob(output + \"/*.png\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(pngs)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(sample_2018)*5",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"glob.glob(source + \"/ZTF18aaxdrjn_20180531_P60_v1/*.*\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"read_tables(np.sort(glob.glob(source + \"/ZTF18aaxdrjn_20180531_P60_v1/*.dat\")))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"glob.glob(source + \"/ZTF18aabssth_20180309_P60_v1/*.dat\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plot_best_5(\"/home/xhall/Documents/RandomSNID/\",\"/home/xhall/Documents/RandomSNID/\",\"lris20201012_ZTF20acdehpz\",0.1751)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.boxplot([2 * -1, 2 * 1])\nplt.hlines(.5,.75,1.25, color = \"Blue\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50c7e91bae3074a1c4078816a02e613df12215f
| 20,699 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
lectures/markov.ipynb
|
phuijse/INFO274
|
b3145c24e7d6efa1377c2ebebe5078cd8bb31af1
|
[
"MIT"
] | 4 |
2021-06-17T16:18:26.000Z
|
2021-09-14T01:22:45.000Z
|
lectures/markov.ipynb
|
phuijse/INFO274
|
b3145c24e7d6efa1377c2ebebe5078cd8bb31af1
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-05-05T15:14:41.000Z
|
2021-05-05T15:14:41.000Z
|
lectures/markov.ipynb
|
phuijse/INFO274
|
b3145c24e7d6efa1377c2ebebe5078cd8bb31af1
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2020-11-17T17:50:18.000Z
|
2021-01-14T20:02:32.000Z
| 31.992272 | 639 | 0.578627 |
[
[
[
"import holoviews as hv\nhv.extension('bokeh')\nhv.opts.defaults(hv.opts.Curve(width=500), \n hv.opts.Histogram(width=500),\n hv.opts.HLine(alpha=0.5, color='r', line_dash='dashed'))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import numpy as np\nimport scipy.stats",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Cadenas de Markov\n\n## Introducción\n\nEn la lección anterior vimos caminatas aleatorias y definimos lo que es un proceso estocástico. En lo que sigue nos restringiremos a procesos estocásticos que sólo puede tomar valores de un conjunto discreto $\\mathcal{S}$ en tiempos $n>0$ que también son discretos.\n\nLlamaremos a $\\mathcal{S}=\\{1, 2, \\ldots, M\\}$ el conjunto de **estados** del proceso. Cada estado en particular se suele denotar por un número natural.\n\nRecordemos que para que un proceso estocástico sea considerado una **cadena de Markov** se debe cumplir \n\n$$\nP(X_{n+1}|X_{n}, X_{n-1}, \\ldots, X_{1}) = P(X_{n+1}|X_{n})\n$$\n\nque se conoce como la propiedad de Markov o propiedad markoviana.\n\n:::{important}\n\nEn una cadena de markov el estado futuro es independiente del pasado cuando conozco el presente\n\n:::\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Matriz de transición\n\nSi la cadena de Markov tiene estados discretos y es homogenea, podemos escribir\n\n$$\nP(X_{n+1}=j|X_{n}=i) = P_{ij},\n$$\n\ndonde homogeneo quiere decir que la probabilidad de transicionar de un estado a otro no cambia con el tiempo. La probabilidad $P_{i,j}$ se suele llamar probabilidad de transición \"a un paso\".",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"El conjunto con todas las posibles combinaciones $P_{ij}$ para $i,j \\in \\mathcal{S}$ forma una matriz cuadrada de $M \\times M$ que se conoce como matriz de transición\n\n$$\nP = \\begin{pmatrix} P_{11} & P_{12} & \\ldots & P_{1M} \\\\ \nP_{21} & P_{22} & \\ldots & P_{2M} \\\\\n\\vdots & \\vdots & \\ddots & \\vdots \\\\\nP_{M1} & P_{M2} & \\ldots & P_{MM}\\end{pmatrix}\n$$\n\ndonde siempre se debe cumplir que las filas sumen 1\n\n$$\n\\sum_{j \\in \\mathcal{S}} P_{ij} = 1\n$$\n\ny además todos los $P_{ij} \\geq 0$ y $P_{ij} \\in [0, 1]$.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Una matriz de transición o matriz estocástica puede representarse como un grafo dirigido donde los vertices son los estados y las aristas las probabilidades de transición o pesos.\n\nEl siguiente es un ejemplo de grafo para un sistema de cuatro estados con todas sus transiciones equivalentes e iguales a $1/2$. Las transiciones con probabilidad $0$ no se muestran.\n\n<img src=\"images/markov2.png\" width=\"300\">",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Considere ahora el siguiente ejemplo",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<img src=\"images/markov-ruin.png\" width=\"400\">",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
":::{note}\n\nSi salimos del estado $0$ o del estado $3$ ya no podemos volver a ellos. \n\n:::\n\nLos estados a los cuales no podemos retornar se conocen como estados **transitorios** o transientes. Por el contrario los estados a los que si tenemos posibilidad de retornar se llaman estados **recurrentes**.\n\nEn general cuando se tienen estados a los que no se puede retornar se dice que cadena es **reducible**. Por el contrario si podemos regresar a todos los estados se dice que la cadena es **irreducible**.\n\n:::{note}\n\nUna cadena reducible puede \"dividirse\" para crear cadenas irreducibles. \n\n:::\n\nEn el ejemplo de arriba podemos separar $\\{0\\}$, $\\{1,2\\}$ y $\\{3\\}$ en tres cadenas irreducibles [^ruina]\n\n[^ruina]: La cadena de Markov anterior modela un problema conocido como la [ruina del apostador](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gambler%27s_ruin), puedes estudiar de que se trata [aquí](http://manjeetdahiya.com/posts/markov-chains-gamblers-ruin/)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Ejemplo: Cadena de dos estados\n\nDigamos que queremos predecir el clima de Valdivia por medio utilizando una cadena de Markov. Por lo tanto asumiremos que el clima de mañana es perfectamente predecible a partir del clima de hoy. Sean dos estados\n\n- $s_A$ Luvioso\n- $s_B$ Soleado\n\nCon probabilidades condicionales $P(s_A|s_A) = 0.7$, $P(s_B|s_A) = 0.3$, $P(s_A|s_B) = 0.45$ y $P(s_B|s_B) = 0.55$. En este caso la matriz de transición es\n\n$$ \nP = \\begin{pmatrix} P(s_A|s_A) & P(s_B|s_A) \\\\ P(s_A|s_B) & P(s_B|s_B) \\end{pmatrix} = \\begin{pmatrix} 0.7 & 0.3 \\\\ 0.45 & 0.55 \\end{pmatrix} \n$$\n\nque también se puede visualizar como un mapa de transición\n\n<img src=\"images/markov1.png\" width=\"500\">\n\nSi está soleado hoy, ¿Cuál es la probabilidad de que llueva mañana, en tres dias más y en una semana más? \n\nUtilicemos `Python` y la matriz de transición para responder esta pregunta. Primero escribimos la matriz de transición como un `ndarray` de Numpy",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"P = np.array([[0.70, 0.30],\n [0.45, 0.55]])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"En segunda lugar vamos a crear un vector de estado inicial ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"s0 = np.array([0, 1]) # Estado soleado",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Luego, las probabilidades para mañana dado que hoy esta soleado pueden calcularse como\n\n$$\ns_1 = s_0 P\n$$\n\nque se conoce como transición a un paso",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.dot(s0, P)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"La probabilidad para tres días más puede calcularse como\n\n$$\ns_3 = s_2 P = s_1 P^2 = s_0 P^3\n$$\n\nque se conoce como transición a 3 pasos. Sólo necesitamos elevar la matriz al cubo y multiplicar por el estado inicial",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.dot(s0, np.linalg.matrix_power(P, 3))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"El pronóstico para una semana sería entonces la transición a 7 pasos",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.dot(s0, np.linalg.matrix_power(P, 7))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Notamos que el estado de nuestro sistema comienza a converger",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.dot(s0, np.linalg.matrix_power(P, 1000))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Esto se conoce como el estado estacionario de la cadena.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Estado estacionario de la cadena de Markov\n\nSi la cadena de Markov converge a un estado, ese estado se llama **estado estacionario**. Una cadena puede tener más de un estado estacionario.\n\nPor definición en un estado estacionario se cumple que \n\n$$\ns P = s\n$$\n\nQue corresponde al problema de valores y vectores propios.\n\n:::{note}\n\nLos estados estacionarios son los vectores propios del sistema\n\n:::\n\nPara el ejemplo anterior teniamos que\n\n$$\n\\begin{pmatrix} s_1 & s_2 \\end{pmatrix} P = \\begin{pmatrix} s_1 & s_2 \\end{pmatrix}\n$$\n\nQue resulta en las siguientes ecuaciones\n\n$$\n0.7 s_1 + 0.45 s_2 = s_1 \n$$\n\n$$\n0.3 s_1 + 0.55 s_2 = s_2\n$$\n\nAmbas nos dicen que $s_2 = \\frac{2}{3} s_1$. Si además consideramos que $s_1 + s_2 = 1$ podemos despejar y obtener\n\n- $s_1 = 3/5 = 0.6$\n- $s_2 = 0.4$\n\nQue es lo que vimos antes. Esto nos dice que en un 60\\% de los días lloverá y en el restante 40% estará soleado",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Probabilidad de transición luego de n-pasos\n\nUna pregunta interesante a responder con una cadena de Markov es\n\n> ¿Cuál es la probabilidad de llegar al estado $j$ dado que estoy en el estado $i$ si doy exactamente $n$ pasos?\n\nConsideremos por ejemplo \n\n<img src=\"images/markov3.png\" width=\"400\">\n\ndonde la matriz de transición es claramente\n\n$$\nP = \\begin{pmatrix} 1/2 & 1/4 & 1/4 \\\\ \n1/8 & 3/4 & 1/8 \\\\\n1/4 & 1/4 & 1/2\\end{pmatrix}\n$$\n\n\nPara este ejemplo particular\n\n> ¿Cúal es la probabilidad de llegar al estado $2$ desde el estado $0$ en 2 pasos?\n\nPodemos resolver esto matemáticamente como\n\n$$\n\\begin{pmatrix} P_{00} & P_{01} & P_{02} \\end{pmatrix} \\begin{pmatrix} P_{02} \\\\ P_{12} \\\\ P_{22} \\end{pmatrix} = P_{00}P_{02} + P_{01}P_{12} + P_{02}P_{22} = 0.28125 \n$$\n\nQue corresponde al elemento en la fila $0$ y columna $2$ de la matriz $P^2$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"P = np.array([[1/2, 1/4, 1/4],\n [1/8, 3/4, 1/8],\n [1/4, 1/4, 1/2]])\n\nnp.dot(P, P)[0, 2]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
":::{important}\n\nEn general la probabilidad de llegar al estado $j$ desde el estado $i$ en $n$ pasos es equivalente al elemento en la fila $i$ y columna $j$ de la matriz $P^n$\n\n:::\n\n¿Qué ocurre cuando $n$ tiene a infinito?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"display(np.linalg.matrix_power(P, 3),\n np.linalg.matrix_power(P, 5),\n np.linalg.matrix_power(P, 100))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Todas las filas convergen a un mismo valor. Este conjunto de probabilidades se conoce como $\\pi$ la distribución estacionaria de la cadena de Markov. Notar que las filas de $P^\\infty$ convergen solo si la cadena es irreducible.\n\nEl elemento $\\pi_j$ (es decir $P_{ij}^\\infty$) nos da la probabilidad de estar en $j$ luego de infinitos pasos. Notar que el subíndice $i$ ya no tiene importancia, es decir que el punto de partida ya no tiene relevancia.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Algoritmo general para simular una cadena de Markov discreta\n\nAsumiendo que tenemos un sistema con un conjunto discreto de estados $\\mathcal{S}$ y que conocemos la matriz de probabilidades de transición $P$ podemos simular su evolución con el siguiente algoritmo\n\n1. Setear $n=0$ y seleccionar un estado inicial $X_n = i$\n1. Para $n = 1,2,\\ldots,T$\n 1. Obtener la fila de $P$ que corresponde al estado actual $X_n$, es decir $P[X_n, :]$\n 1. Generar $X_{n+1}$ muestreando de una distribución multinomial con vector de probabilidad igual a la fila seleccionada \n\nEn este caso $T$ es el horizonte de la simulación. A continuación veremos como simular una cadena de Markov discreta usando Python",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Digamos que tenemos una cadena con tres estados y que la fila de $P$ asociada a $X_n$ es $[0.7, 0.2, 0.1]$. Podemos usar `scipy.stats.multinomial` para generar una aleatoriamente una variable multinomial y luego aplicar el argumento máximo para obtener el índice del estado $X_{n+1}$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.argmax(scipy.stats.multinomial.rvs(n=1, p=[0.7, 0.2, 0.1], size=1), axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Si repetimos esto 100 veces se obtiene la siguiente distribución para $X_{n+1}$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x = np.argmax(scipy.stats.multinomial.rvs(n=1, p=[0.7, 0.2, 0.1], size=100), axis=1)\nedges, bins = np.histogram(x, range=(np.amin(x)-0.5, np.amax(x)+0.5), bins=len(np.unique(x)))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"hv.Histogram((edges, bins), kdims='x', vdims='Frecuencia').opts(xticks=[0, 1, 2])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Lo cual coincide con la fila de $P$ que utilizamos",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Ahora que sabemos como obtener el estado siguiente probemos algo un poco más complicado.\n\nConsideremos el ejemplo de predicción de clima y simulemos 1000 cadenas a un horizonte de 10 pasos",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"P = np.array([[0.70, 0.30],\n [0.45, 0.55]])\n\nn_chains = 1000\nhorizon = 10\nstates = np.zeros(shape=(n_chains, horizon), dtype='int')\nstates[:, 0] = 1 # Estado inicial para todas las cadenas\n\nfor i in range(n_chains):\n for j in range(1, horizon):\n states[i, j] = np.argmax(scipy.stats.multinomial.rvs(n=1, p=P[states[i, j-1], :], size=1))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"A continuación se muestran las tres primeras simulaciones como series de tiempo",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"p =[]\nfor i in range(3):\n p.append(hv.Curve((states[i, :]), 'n', 'Estados').opts(yticks=[0, 1]))\nhv.Overlay(p)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"A continuación se muestra el estado más probable en cada paso",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"n_states = len(np.unique(states))\n\nhist = np.zeros(shape=(horizon, n_states))\nfor j in range(horizon):\n hist[j, :] = np.array([sum(states[:, j] == s) for s in range(n_states)])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"hv.Curve((np.argmax(hist, axis=1)), 'n', 'Estado más probable').opts(yticks=[0, 1]) ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Ley de los grandes números para variables no i.i.d.\n\nPreviamente vimos que el promedio de un conjunto de $N$ variables independientes e idénticamente distribuidas (iid) converge a su valor esperado cuando $N$ es grande.\n\nPor ejemplo \n\n$$\n\\lim_{N \\to \\infty} \\frac{1}{N} \\sum_{i=1}^N X_i = \\mu\n$$\n\nEn esta lección vimos que la cadena de markov, un proceso estocástico donde no se cumple el supuesto iid, puede tener en ciertos casos una distribución estacionaria \n\n:::{note}\n\nLa **distribución estacionaria** $\\pi$ de una cadena de Markov con matriz de transición $P$ es tal que $\\pi P = \\pi$\n\n:::\n\n**Teorema de ergodicidad:** Una cadena de Markov irreducible y aperiodica tiene una distribución estacionaria $\\pi$ única, independiente de valor del estado inicial y que cumple\n\n$$\n\\lim_{n\\to \\infty} s_j(n) = \\pi_j\n$$\n\ndonde los componentes de $\\pi$ representan la fracción de tiempo que la cadena estará en cada uno de los estados luego de observarla por un largo tiempo\n\n:::{important}\n\nEl límite de observar la cadena por un tiempo largo es análogo al análisis de estadísticos estáticos sobre muestras grandes. Esto es el equivalente a la ley de los grandes números para el caso de la cadena de Markov\n\n:::\n\n\n### Notas históricas\n\n- **La primera ley de los grandes números:** [Jacob Bernoulli](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jacob_Bernoulli) mostró la primera versión de la Ley de los grandes números en su Ars Conjectandi en 1713. Esta primera versión parte del supuesto de que las VAs son iid. Bernoulli era un firme creyente del destino, se oponía al libre albedrío y abogaba por el determinismo en los fenómenos aleatorios.\n- **La segunda ley de los grandes números:** En 1913 el matemático ruso [Andrei Markov](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Andrey_Markov) celebró el bicentenario de la famosa prueba de Bernoulli organizando un simposio donde presentó su nueva versión de la Ley de los grandes números que aplica sobre la clase de procesos estocásticos que hoy llamamos procesos de Markov, de esta forma extendiendo el resultado de Bernoulli a un caso que no es iid.\n- **La pugna de Markov y Nekrasov:** En aquellos tiempos Markov estaba en pugna con otro matemático ruso: [Pavel Nekrasov](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pavel_Nekrasov). Nekrasov había publicado previamente que \"la independencia era una condición necesaria para que se cumpla la ley de los grandes números\". Nekrasov mantenia que el comportamiento humano al no ser iid no podía estar guiado por la ley de los grandes números, es decir que los humanos actuan voluntariamente y con libre albedrío. Markov reaccionó a esta afirmación desarrollando un contra-ejemplo que terminó siendo lo que hoy conocemos como los procesos de Markov ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
c50c82a20bb79738cae264661811c362e2abd526
| 75,291 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/2. K-Nearest Neighbors.ipynb
|
QwertygidQ/ml-algorithms
|
2b78000bfc7e0e4874d7be4fd81f724c642a59d7
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/2. K-Nearest Neighbors.ipynb
|
QwertygidQ/ml-algorithms
|
2b78000bfc7e0e4874d7be4fd81f724c642a59d7
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/2. K-Nearest Neighbors.ipynb
|
QwertygidQ/ml-algorithms
|
2b78000bfc7e0e4874d7be4fd81f724c642a59d7
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 246.855738 | 23,808 | 0.918343 |
[
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn as sns\n\n%matplotlib inline\nnp.random.seed(0)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Model definition",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Let *k-nearest neighbors* of a new example $x$ be the $k$ examples out of the training set $X$ that minimize the distance function $d$ between $x$ and themselves.\n\n\nFor *classification* we can take the k-nearest neighbors of $x$ and assign the most popular class between them to $x$. \nFor *regression* we can take the k-nearest neighbors of $x$ and assign the average of these data points' targets to $x$. We could also use an inverse distance weighted average.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def get_k_nearest_neighbors(x, X, y, dist, k):\n sorted_X = sorted(zip(X, y), key=dist(x))\n return list(zip(*sorted_X[:k])) # [(training examples), (corresponding targets)]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let A and B be two $n$-row column vectors. \nLet's define a few distance functions:\n\n1. Euclidean distance: $d(A, B) = \\Vert {A - B}\\Vert_2 = \\sqrt{\\displaystyle \\sum_{i=1}^{n}(A_i - B_i)^2}$\n2. Manhattan distance: $d(A, B) = \\Vert {A - B}\\Vert_1 = \\displaystyle \\sum_{i=1}^{n} \\vert A_i - B_i \\vert$\n3. Chebyshev distance: $d(A, B) = \\displaystyle \\max_{i} \\vert A_i - B_i \\vert$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def d_euclidean(x):\n def d(Xi):\n return np.sqrt(np.sum((x - Xi[0]) ** 2))\n\n return d\n\ndef d_manhattan(x):\n def d(Xi):\n return np.sum(np.abs(x - Xi[0]))\n \n return d\n\ndef d_chebyshev(x):\n def d(Xi):\n return np.max(np.abs(x - Xi[0]))\n \n return d",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Let's define the classification and regression functions now.\n\nLet $X_{train}$ be the training set ($X$ in previous cells), $X_{test}$ be the test set (each row contains an example to classify), $y_{train}$ be the targets for the training set.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from scipy.stats import mode\n\ndef knn_classification(X_train, y_train, X_test, dist=d_euclidean, k=3):\n classes = []\n for x in X_test:\n k_nearest_neighbors, targets = get_k_nearest_neighbors(x, X_train, y_train, dist, k)\n classes.append(mode(targets)[0][0])\n \n return np.array(classes).reshape(-1, 1)\n\ndef knn_regression(X_train, y_train, X_test, dist=d_euclidean, k=3):\n avg_targets = []\n for x in X_test:\n k_nearest_neighbors, targets = get_k_nearest_neighbors(x, X_train, y_train, dist, k)\n avg_targets.append(np.mean(targets))\n \n return np.array(avg_targets).reshape(-1, 1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# K-Nearest Neigbors in practice",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Classification",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 1. Generating data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs\n\nX_train, y_train = make_blobs(n_samples=100, centers=3, n_features=2, random_state=1)\nsns.scatterplot(x=0, y=1, hue=y_train, data=pd.DataFrame(X_train))\n\nX_test = np.array([[-10, -1], [0, 0], [-6, -10], [-8, -6], [-5, 0]]) # some random points on the scatterplot\nplt.scatter(x=X_test[:, 0], y=X_test[:, 1], marker='X', s=20 ** 2)\n\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 2. Training the model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"sns.scatterplot(x=0, y=1, hue=y_train, data=pd.DataFrame(X_train))\n\ny_test = knn_classification(X_train, y_train, X_test)\nsns.scatterplot(x=0, y=1, hue=y_test.reshape(-1), data=pd.DataFrame(X_test), legend=False, marker='X', s=20 ** 2)\n\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Regression",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 1. Generating data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"m = 50\n\nX_train = np.linspace(-5, 5, m).reshape(-1, 1)\ny_train = -4 * X_train ** 2 - 3.5 * X_train + 7.2\n\nnoise = np.random.normal(0, 10, m).reshape(-1, 1)\ny_train += noise\n\nplt.plot(X_train, y_train, 'b.')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 2. Training the model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plt.plot(X_train, y_train, 'b.')\n\ny_test = knn_regression(X_train, y_train, X_train)\nplt.plot(X_train, y_test, 'r')\n\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c50c9719957e2711496039a2cafca606ede3e175
| 98,149 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
A/R_Poisson.ipynb
|
AskerNC/lectures-2021
|
d152450b2fee7be775892dde1a467639aa5e35ea
|
[
"MIT"
] | 13 |
2020-02-03T14:31:18.000Z
|
2022-01-14T09:04:48.000Z
|
A/R_Poisson.ipynb
|
AskerNC/lectures-2021
|
d152450b2fee7be775892dde1a467639aa5e35ea
|
[
"MIT"
] | 19 |
2020-01-06T14:43:17.000Z
|
2020-05-17T14:49:12.000Z
|
A/R_Poisson.ipynb
|
AskerNC/lectures-2021
|
d152450b2fee7be775892dde1a467639aa5e35ea
|
[
"MIT"
] | 30 |
2021-02-08T16:18:01.000Z
|
2022-02-05T17:02:35.000Z
| 81.586866 | 18,890 | 0.759804 |
[
[
[
"# The R Programming Language",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"1. **R**: Popular **open-source programming language** for statistical analysis\n2. Widely used in statistics and econometrics\n3. **User-friendly and powerful IDE**: [RStudio](https://www.rstudio.com/)\n4. Basic functionalities of **R** can be extended by **packages**\n5. Large number of packages available on the \n[Comprehensive R Archive Network](https://cran.r-project.org/) (CRAN)\n6. **Goal of this presentation:** Illustrate how to use `R` for the estimation of a\nPoisson regression model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# install.packages(\"psych\")\n# install.packages(\"wooldridge\")\n# install.packages(\"xtable\") ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Count data models",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Count data** models are used to explain dependent variables that are natural \nnumbers, i.e., positive integers such that $y_i \\in \\mathbb{N}$, where \n$\\mathbb{N} = \\{0, 1, 2,\\ldots\\}$. \n\nCount data models are frequently used in economics to study **countable events**:\nNumber of years of education, number of patent applications filed by companies, \nnumber of doctor visits, number of crimes committed in a given city, etc. \n\nThe **Poisson model** is a popular count data model.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Poisson regression model",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Given a parameter $\\lambda_i > 0$, the **Poisson model** assumes that the \nprobability of observing $Y_i=y_i$, where $y_i\\in\\mathbb{N}$, is equal to:\n$$Prob(Y_i = y_i \\mid \\lambda_i) = \\frac{\\lambda_i^{y_i}\\exp\\{-\\lambda_i\\}}{y_i!},$$\nfor $i=1,\\ldots,N$.\n\nThe mean and the variance of $Y_i$ are equal to the parameter $\\lambda_i$: \n$$E(Y_i\\mid\\lambda_i) = V(Y_i\\mid\\lambda_i) = \\lambda_i,$$\nimplying *equi-dispersion* of the data.\n\nTo control for **observed characteristics**, the parameter $\\lambda_i$ can be \nparametrized as follows (implying $\\lambda_i > 0$):\n$$E(Y_i|X_i,\\beta) \\equiv \\lambda_i = \\exp\\{X_i'\\beta\\},$$\nwhere $X_i$ is a vector containing the covariates.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Simulating data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"`R` function simulating data from Poisson regression model:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"simul_poisson <- function(n, beta) {\n k <- length(beta) # number of covariates\n x <- replicate(k - 1, rnorm(n)) # simulate covariates\n x <- cbind(1, x) # for intercept term\n lambda <- exp(x %*% beta) # individual means\n y <- rpois(n, lambda) # simulate count\n return(data.frame(y, x)) # return variables\n}",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Using function to generate data:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"set.seed(123)\nnobs <- 1000\nbeta <- c(-.5, .4, -.7)\ndata <- simul_poisson(nobs, beta)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Data description",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Descriptive statistics:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# extract variables of interest from data set\ny <- data[, 1]\nx <- as.matrix(data[, 2:4])\n\n# descriptive statistics\nlibrary(psych)\ndescribe(data)",
"Warning message:\n\"package 'psych' was built under R version 3.6.3\""
]
],
[
[
"## Data Description",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Histogram of count variable:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"barplot(table(y))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Data Description",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Relationship between count variable and covariates:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"par(mfrow = c(1, 2))\nplot(y, x[, 2])\nplot(y, x[, 3])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Likelihood Function and ML Estimator",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Individual contribution to the likelihood function:\n$$L_i(\\beta;y_i,x_i) = \\frac{\\exp\\{y_ix_i\\beta\\}\\exp\\{-\\exp\\{x_i\\beta\\}\\}}{y_i!}$$\nIndividual log-Likelihood function:\n$$\\ell_i(\\beta;y_i,x_i) = \\log L_i(\\beta;y_i,x_i) \n= y_ix_i\\beta - \\exp\\{x_i\\beta\\} - \\log(y_i!)$$\n\nMaximum Likelihood Estimator:\n$$\\hat{\\beta}_{\\text{MLE}} = \\arg\\max_{\\beta} \\sum_{i=1}^N \\ell(\\beta;y,X)$$\n\nOptimization (using *minimization* of objective function): \n$$\\hat{\\beta}_{\\text{MLE}} = \\arg\\min_{\\beta} Q(\\beta;y,X) \\qquad\nQ(\\beta;y,X) = -\\frac{1}{N}\\sum_{i=1}^N \\ell_i(\\beta;y_i,x_i)$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Coding the Objective Function",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Objective function of Poisson regression model\nobj_poisson <- function(beta, y, x) {\n lambda <- x %*% beta\n llik <- y*lambda - exp(lambda) - lfactorial(y)\n return(-mean(llik))\n}\n\n# Evaluating objective function\nbeta0 <- c(1, 2, 3)\nobj_poisson(beta0, y, x)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Maximizing the Objective Function\n\nSet starting values:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"beta0 <- rep(0, length(beta))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Optimize using quasi-Newton method (BFGS algorithm):",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"opt <- optim(beta0, obj_poisson, method = \"BFGS\", \n y = y, x = x)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Show results:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cat(\"ML estimates:\", opt$par,\n \"\\nObjective function:\", opt$value, \"\\n\")",
"ML estimates: -0.5740286 0.3921569 -0.7231029 \nObjective function: 0.9998689 \n"
]
],
[
[
"## Comparing Results to Built-in Function",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"opt_glm <- glm(y ~ 0 + x, family = poisson)\nsummary(opt_glm)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Comparing Results to Built-in Function",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Collect results from the two approaches to compare them:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"res <- cbind(\"True\" = beta, \"MLE\" = opt$par, \n \"GLM\" = opt_glm$coefficients)\nrow.names(res) <- c(\"constant\", \"x1\", \"x2\")\nres",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Question:** Our results (`MLE`) are virtually the same as those obtained \nwith the built-in function `GLM`, but not identical. Where do the small \ndifferences come from?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Empirical Illustration\n\n**Goal:** Investigate the determinants of fertility.\n\nPoisson regression model used to estimate the relationship between explanatory\nvariables and count outcome variable.\n\nBoth our estimator coded from scratch and `R` built-in function will be used.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Data\n\n**Source:** Botswana's 1988 Demographic and Health Survey.\n\nData set borrowed from Wooldridge:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"library(wooldridge)\ndata(fertil2)",
"Warning message:\n\"package 'wooldridge' was built under R version 3.6.3\""
]
],
[
[
"Outcome variable: Total number of living children:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"y_lab <- \"children\"",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Explanatory variables: Education, age, marital status, living in urban area,\nhaving electricity/TV at home:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"x_lab <- c(\"educ\", \"age\", \"agesq\", \"evermarr\", \"urban\", \n \"electric\", \"tv\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Loading data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Selecting variables and removing missing values:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"data <- fertil2[, c(y_lab, x_lab)]\ndata <- na.omit(data)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Show first 6 observations on first 8 variables:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"head(data[, 1:8], n = 6)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Descriptive Statitics",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"library(psych)\ndescribe(data)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Plot",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"attach(data)\npar(mfrow = c(1, 2))\nblue_transp <- adjustcolor(\"blue\", alpha.f = 0.1)\nplot(age, children, pch = 19, col = blue_transp)\nplot(educ, children, pch = 19, col = blue_transp)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## MLE of the Poisson Model",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Maximum likelihood function using built-in function `glm()`:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"mle <- glm(children ~ educ + age + agesq + evermarr + \n urban + electric + tv,\n family = \"poisson\", data = data)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Maximum likelihood function using our own function:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"y <- data[, y_lab]\nx <- as.matrix(data[, x_lab])\nx <- cbind(1, x) # for intercept term\nbeta0 <- rep(0, ncol(x)) # starting values\nopt <- optim(beta0, obj_poisson, method = \"BFGS\", \n y = y, x = x)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## MLE of the Poisson Model\n\n**Results different from `glm()`?**\n\nOptimization algorithms are iterative methods that rely on different criteria\nto dertermine if/when the optimum has been reached.\n\n**For example:** Change in the objective function, change in the parameter values,\nchange in the gradient, step size, etc.\n\n*[More in Advanced Microeconometrics course].*\n\n**Try to adjust tuning parameters**, for example add \n`control = list(ndeps = rep(1e-8, ncol(x)))` to `optim()` to change step size \nof gradient approximation.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Summarizing the Empirical Results",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"summary(mle)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Fitted Values",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plot(density(mle$fitted.values), \n main = \"Density of fitted mean values\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Formatting the results",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"library(xtable)\nxtable(mle)",
"Warning message:\n\"package 'xtable' was built under R version 3.6.3\""
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c50cab63c34fc5438364a9a239befe5634bd3108
| 20,028 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Ensembl-analysis/data_acquisition/ensembl_api_data/python_scripts/negative_data_extraction.ipynb
|
EnsemblGSOC/lncRNA-analysis
|
88571a150f326f706edce72be07cf5f84b309e2b
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 7 |
2019-05-29T22:18:15.000Z
|
2019-12-17T22:43:09.000Z
|
Ensembl-analysis/data_acquisition/ensembl_api_data/python_scripts/negative_data_extraction.ipynb
|
vermasrijan/srijan-gsoc-2019
|
88571a150f326f706edce72be07cf5f84b309e2b
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
Ensembl-analysis/data_acquisition/ensembl_api_data/python_scripts/negative_data_extraction.ipynb
|
vermasrijan/srijan-gsoc-2019
|
88571a150f326f706edce72be07cf5f84b309e2b
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 6 |
2019-08-23T01:48:34.000Z
|
2020-01-21T22:06:03.000Z
| 20,028 | 20,028 | 0.594967 |
[
[
[
"####################################################################################################\n\n# Copyright 2019 Srijan Verma and EMBL-European Bioinformatics Institute\n\n# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the \"License\");\n# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.\n# You may obtain a copy of the License at\n\n# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0\n\n# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software\n# distributed under the License is distributed on an \"AS IS\" BASIS,\n# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.\n# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and\n# limitations under the License.\n\n####################################################################################################",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Ensembl numeric data extraction (negative)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Below function to get Ensembl IDs from .csv and convert to a python list in JSON format",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def csv_to_id(path):\n df = pd.read_csv(path)\n ids = df.TEST_neg.tolist()\n \n for loc in ids:\n loc = str(loc) #here 'nan' is converted to a string to compare with if\n if loc != 'nan': \n cleaned_ids.append(loc)\n cleaned = json.dumps(cleaned_ids) \n correct_format = \"{\" +'\"ids\": ' + cleaned + \"}\"\n return correct_format",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport json\ncleaned_ids = []\npath = '/Training set.example.csv'\n\ncleaned_IDs = csv_to_id(path)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#print(cleaned_IDs)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Passing the list to Ensembl REST API to get JSON response ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Single request, multiple IDs\nimport requests, sys\nimport json, urllib\nserver = \"https://rest.ensembl.org\"\next = '/lookup/id/?format=full;expand=1;utr=1;phenotypes=1'\n#ext = '/lookup/id/?\nheaders = {'Content-Type' : 'application/json', \"Accept\" : 'application/json'}\n#'{\"ids\" : [\"ENSG00000255689\", \"ENSG00000254443\"]}'\n#cleaned_IDs = {\"ids\": [\"ENSG00000255689\", \"ENSG00000254443\"]}\nr = requests.post(server+ext,headers=headers, data='{0}'.format(cleaned_IDs))\n\nprint(str(r))\nprint(type(r))\n\ndecoded = r.json()\n#print(repr(decoded))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Saving JSON response on local machine and then loading the .json file",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import json\nwith open('/negative_data.json', 'w') as outfile:\n json.dump(decoded, outfile, indent=4, sort_keys=True) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"with open('/negative_data.json') as access_json:\n read_content = json.load(access_json)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## 'read_content' variable contains the json response received",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"gene_display_name = []\ngene_start = []\ngene_end = []\ngene_strand = []\ngene_seq_region_name = []\ngene_biotype = []",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Below function [get_gene_data() ] to extract 'gene' data. Data Extracted are :\n1. gene display_name\n2. gene start\n3. gene end\n4. gene strand\n5. gene seq_region_name\n6. gene biotype",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def get_gene_data():\n \n count = 0\n for i in range(len(cleaned_ids)):\n gene_display_name.append(read_content[cleaned_ids[i]]['display_name'])\n gene_start.append(read_content[cleaned_ids[i]]['start'])\n gene_end.append(read_content[cleaned_ids[i]]['end'])\n gene_strand.append(read_content[cleaned_ids[i]]['strand'])\n gene_seq_region_name.append(read_content[cleaned_ids[i]]['seq_region_name'])\n gene_biotype.append(read_content[cleaned_ids[i]]['biotype'])\n if cleaned_ids[i] in read_content:\n count = count + 1\n \n print(count) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"get_gene_data()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('No. of contents of gene_start is {0}'.format(len(gene_start)))\nprint('No. of contents of gene_end is {0}'.format(len(gene_end)))\nprint('No. of contents of gene_strand is {0}'.format(len(gene_strand)))\nprint('No. of contents of gene_seq_region_name is {0}'.format(len(gene_seq_region_name)))\nprint('No. of contents of gene_display_name is {0}'.format(len(gene_display_name)))\nprint('No. of contents of gene_biotype is {0}'.format(len(gene_biotype)))",
"No. of contents of gene_start is 832\nNo. of contents of gene_end is 832\nNo. of contents of gene_strand is 832\nNo. of contents of gene_seq_region_name is 832\nNo. of contents of gene_display_name is 832\nNo. of contents of gene_biotype is 832\n"
],
[
"no_of_transcripts = []\ngene_ids_for_transcripts = []",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Below function [ get_no_of_transcripts() ] to calculate no. of transcripts in a particular gene",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def get_no_of_transcripts():\n for i in range(len(cleaned_ids)):\n no_of_transcripts.append(len(read_content[cleaned_ids[i]]['Transcript']))\n \n for k in range(len(read_content[cleaned_ids[i]]['Transcript'])):\n gene_ids_for_transcripts.append(cleaned_ids[i])\n \n for j in range(len(cleaned_ids)):\n print('No. of transcripts in gene \"{0}\" are {1}'.format(cleaned_ids[j],no_of_transcripts[j]))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"get_no_of_transcripts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#read_content[cleaned_ids[0]]['Transcript'][0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"transcript_id = []\ntranscript_start = []\ntranscript_end = []\ntranscript_biotype = []",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#gene_ids_for_transcripts",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Below function [get_transcript_data() ] to extract 'transcript' data. Data Extracted are :\n1. transcript id\n2. transcript start\n3. transcript end\n4. transcript biotype",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def get_transcript_data():\n for i in range(len(cleaned_ids)):\n \n for j in range(len(read_content[cleaned_ids[i]]['Transcript'])):\n transcript_id.append(read_content[cleaned_ids[i]]['Transcript'][j]['id'])\n transcript_start.append(read_content[cleaned_ids[i]]['Transcript'][j]['start'])\n transcript_end.append(read_content[cleaned_ids[i]]['Transcript'][j]['end'])\n transcript_biotype.append(read_content[cleaned_ids[i]]['Transcript'][j]['biotype'])\n \n for k in range(len(gene_ids_for_transcripts)):\n print('Transcript \"{0}\" of gene ID \"{1}\" has start and end as : \"{2}\" & \"{3}\"'.format(transcript_id[k],gene_ids_for_transcripts[k],transcript_start[k],transcript_end[k]))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"get_transcript_data()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(len(transcript_id))\nprint(len(transcript_start))\nprint(len(transcript_end))\nprint(len(gene_ids_for_transcripts))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(read_content[cleaned_ids[0]]['Transcript'][0][\"Exon\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"no_of_exons = []\ntranscript_ids_for_exons = []",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Below function [ get_no_of_exons() ] to calculate no. of exons for a particular transcript",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def get_no_of_exons():\n for i in range(len(cleaned_ids)):\n for j in range(len(read_content[cleaned_ids[i]]['Transcript'])):\n no_of_exons.append(len(read_content[cleaned_ids[i]]['Transcript'][j][\"Exon\"]))\n \n for k in range(len(read_content[cleaned_ids[i]]['Transcript'][j][\"Exon\"])):\n transcript_ids_for_exons.append(read_content[cleaned_ids[i]]['Transcript'][j]['id'])\n \n for l in range(len(cleaned_ids)):\n print('No. of exons in transcript \"{0}\" are {1}'.format(transcript_id[l],no_of_exons[l]))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(read_content[cleaned_ids[0]]['Transcript'][0][\"Exon\"])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"get_no_of_exons()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"sum(no_of_exons)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(transcript_ids_for_exons)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#read_content[cleaned_ids[0]]['Transcript'][0][\"Exon\"][0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"exon_id = []\nexon_start = []\nexon_end = []\ngene_ids_for_exons = []",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Below function [get_exon_data() ] to extract 'exon' data. Data Extracted are :\n1. exon id\n2. exon start\n3. exon end",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def get_exon_data():\n for i in range(len(cleaned_ids)):\n \n for j in range(len(read_content[cleaned_ids[i]]['Transcript'])):\n for k in range(len(read_content[cleaned_ids[i]]['Transcript'][j][\"Exon\"])):\n \n \n exon_id.append(read_content[cleaned_ids[i]]['Transcript'][j][\"Exon\"][k]['id'])\n exon_start.append(read_content[cleaned_ids[i]]['Transcript'][j][\"Exon\"][k]['start'])\n exon_end.append(read_content[cleaned_ids[i]]['Transcript'][j][\"Exon\"][k]['end'])\n gene_ids_for_exons.append(cleaned_ids[i])\n \n \n for l in range(len(transcript_ids_for_exons)):\n \n print('Exon \"{0}\" of Transcript ID \"{1}\" having gene ID \"{2}\" has start and end as : \"{3}\" & \"{4}\"'.format(exon_id[l],transcript_ids_for_exons[l],gene_ids_for_exons[l],exon_start[l],exon_end[l]))\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"get_exon_data()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(exon_id)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(gene_ids_for_exons)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"transcript_len = []",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Below function[ get_transcript_length() ] to calculate length of transcript",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def get_transcript_length():\n # for i in range(transcript_id):\n # for j in range(exon)\n\n for i in range(len(cleaned_ids)):\n \n for j in range(len(read_content[cleaned_ids[i]]['Transcript'])):\n trans_len = 0\n start = 0\n end = 0\n total_exon_len = 0\n for k in range(len(read_content[cleaned_ids[i]]['Transcript'][j][\"Exon\"])):\n start = read_content[cleaned_ids[i]]['Transcript'][j][\"Exon\"][k]['start']\n end = read_content[cleaned_ids[i]]['Transcript'][j][\"Exon\"][k]['end']\n total_exon_len = total_exon_len + (end - start + 1)\n\n transcript_len.append(total_exon_len)\n \n for k in range(len(transcript_id)):\n print('Transcript ID \"{0}\" has length of {1} bps'.format(transcript_id[k], transcript_len[k]))\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(transcript_id)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"get_transcript_length()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(transcript_len)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"transcript_len[-1]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"transcript_id[-1]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"exon_len = []",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Below function[ get_exon_length() ] to calculate length of exon",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def get_exon_length():\n # for i in range(transcript_id):\n # for j in range(exon)\n#exon_id\n for i in range(len(cleaned_ids)):\n \n for j in range(len(read_content[cleaned_ids[i]]['Transcript'])):\n # exon_len = 0\n # start = 0\n # end = 0\n # exon_len = 0\n for k in range(len(read_content[cleaned_ids[i]]['Transcript'][j][\"Exon\"])):\n start = 0\n end = 0\n exon_len_sum = 0\n start = read_content[cleaned_ids[i]]['Transcript'][j][\"Exon\"][k]['start']\n end = read_content[cleaned_ids[i]]['Transcript'][j][\"Exon\"][k]['end']\n exon_len_sum = (end - start + 1)\n\n exon_len.append(exon_len_sum)\n \n for k in range(len(exon_id)):\n print('Exon ID \"{0}\" has length of {1} bps'.format(exon_id[k], exon_len[k]))\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"get_exon_length()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(exon_len)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(exon_id)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Exporting gene data to gene_data.csv file",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import csv \nheader = ['SNO', 'Gene ID', 'Display Name', 'Biotype', 'Start', 'End', 'Strand', 'Seq region Name', 'No. of Transcripts']\n\npath = '/negative_data/gene_data.csv'\n\nwith open(path, 'wt', newline ='') as file:\n writer = csv.writer(file, delimiter=',')\n writer.writerow(i for i in header)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s_no = []\nfor i in range(len(cleaned_ids)):\n s_no.append(i+1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import pandas as pd\n\ndf = pd.read_csv(path)\n\ndf[df.columns[0]] = s_no\ndf[df.columns[1]] = cleaned_ids\ndf[df.columns[2]] = gene_display_name\ndf[df.columns[3]] = gene_biotype\ndf[df.columns[4]] = gene_start\ndf[df.columns[5]] = gene_end\ndf[df.columns[6]] = gene_strand\ndf[df.columns[7]] = gene_seq_region_name\ndf[df.columns[8]] = no_of_transcripts\n\n\ndf.to_csv(path)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Exporting transcript data to transcript_data.csv file",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import csv \nheader = ['SNO', 'Gene ID', 'Transcript ID', 'Biotype', 'Transcript Start', 'Transcript End', 'Transcript Length','No. of Exons']\n\npath = '/negative_data/transcript_data.csv'\n\nwith open(path, 'wt', newline ='') as file:\n writer = csv.writer(file, delimiter=',')\n writer.writerow(i for i in header)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s_no = []\nfor i in range(len(transcript_id)):\n s_no.append(i+1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import pandas as pd\n\ndf = pd.read_csv(path)\n\ndf[df.columns[0]] = s_no\ndf[df.columns[1]] = gene_ids_for_transcripts\ndf[df.columns[2]] = transcript_id\ndf[df.columns[3]] = transcript_biotype\ndf[df.columns[4]] = transcript_start\ndf[df.columns[5]] = transcript_end\ndf[df.columns[6]] = transcript_len\ndf[df.columns[7]] = no_of_exons\n\n\n\ndf.to_csv(path)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Exporting exon data to exon_data.csv file",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import csv \nheader = ['SNO', 'Gene ID', 'Transcript ID', 'Exon ID', 'Exon Start', 'Exon End', 'Exon Length']\n\npath = '/negative_data/exon_data.csv'\n\nwith open(path, 'wt', newline ='') as file:\n writer = csv.writer(file, delimiter=',')\n writer.writerow(i for i in header)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"s_no = []\nfor i in range(len(exon_id)):\n s_no.append(i+1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import pandas as pd\n\ndf = pd.read_csv(path)\n\ndf[df.columns[0]] = s_no\ndf[df.columns[1]] = gene_ids_for_exons\ndf[df.columns[2]] = transcript_ids_for_exons\ndf[df.columns[3]] = exon_id\ndf[df.columns[4]] = exon_start\ndf[df.columns[5]] = exon_end\ndf[df.columns[6]] = exon_len\n\n\n\ndf.to_csv(path)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50cae9ade8e5539448f3cfcf4a60f16a77da00a
| 7,800 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/attack_attribute_inference_regressor.ipynb
|
tagomaru/adversarial-robustness-toolbox
|
b0d86c4489f92275d828e7cde7e9d0a34181f2fe
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2022-01-31T15:17:20.000Z
|
2022-01-31T15:17:20.000Z
|
notebooks/attack_attribute_inference_regressor.ipynb
|
proteanblank/adversarial-robustness-toolbox
|
8415d693b7bddd1d24d58d34e8b228d9c1487627
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2022-03-18T00:41:02.000Z
|
2022-03-18T00:41:02.000Z
|
notebooks/attack_attribute_inference_regressor.ipynb
|
proteanblank/adversarial-robustness-toolbox
|
8415d693b7bddd1d24d58d34e8b228d9c1487627
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2022-03-22T05:30:31.000Z
|
2022-03-22T05:30:31.000Z
| 29.657795 | 232 | 0.602051 |
[
[
[
"# Running attribute inference attacks on Regression Models",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In this tutorial we will show how to run black-box inference attacks on regression model. This will be demonstrated on the Nursery dataset (original dataset can be found here: https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/nursery). ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Preliminaries\nIn order to mount a successful attribute inference attack, the attacked feature must be categorical, and with a relatively small number of possible values (preferably binary).\n\nIn the case of the diabetes dataset, the sensitive feature we want to infer is the 'sex' feature, which is a binary feature.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Load data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import os\nimport sys\nsys.path.insert(0, os.path.abspath('..'))\n\nfrom art.utils import load_diabetes\n\n(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test), _, _ = load_diabetes(test_set=0.5)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Train MLP model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor\nfrom art.estimators.regression.scikitlearn import ScikitlearnRegressor\n\nmodel = DecisionTreeRegressor()\nmodel.fit(x_train, y_train)\nart_regressor = ScikitlearnRegressor(model)\n\nprint('Base model score: ', model.score(x_test, y_test))",
"Base model score: -0.04773984870966275\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Attack\n### Black-box attack\nThe black-box attack basically trains an additional classifier (called the attack model) to predict the attacked feature's value from the remaining n-1 features as well as the original (attacked) model's predictions.\n#### Train attack model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nfrom art.attacks.inference.attribute_inference import AttributeInferenceBlackBox\n\nattack_train_ratio = 0.5\nattack_train_size = int(len(x_train) * attack_train_ratio)\nattack_x_train = x_train[:attack_train_size]\nattack_y_train = y_train[:attack_train_size]\nattack_x_test = x_train[attack_train_size:]\nattack_y_test = y_train[attack_train_size:]\n\nattack_feature = 1 # sex\n\n# get original model's predictions\nattack_x_test_predictions = np.array([np.argmax(arr) for arr in art_regressor.predict(attack_x_test)]).reshape(-1,1)\n# only attacked feature\nattack_x_test_feature = attack_x_test[:, attack_feature].copy().reshape(-1, 1)\n# training data without attacked feature\nattack_x_test = np.delete(attack_x_test, attack_feature, 1)\n\nbb_attack = AttributeInferenceBlackBox(art_regressor, attack_feature=attack_feature)\n\n# train attack model\nbb_attack.fit(attack_x_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### Infer sensitive feature and check accuracy",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# get inferred values\nvalues = [-0.88085106, 1.]\ninferred_train_bb = bb_attack.infer(attack_x_test, pred=attack_x_test_predictions, values=values)\n# check accuracy\ntrain_acc = np.sum(inferred_train_bb == np.around(attack_x_test_feature, decimals=8).reshape(1,-1)) / len(inferred_train_bb)\nprint(train_acc)",
"0.5585585585585585\n"
]
],
[
[
"This means that for 56% of the training set, the attacked feature is inferred correctly using this attack.\nNow let's check the precision and recall:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def calc_precision_recall(predicted, actual, positive_value=1):\n score = 0 # both predicted and actual are positive\n num_positive_predicted = 0 # predicted positive\n num_positive_actual = 0 # actual positive\n for i in range(len(predicted)):\n if predicted[i] == positive_value:\n num_positive_predicted += 1\n if actual[i] == positive_value:\n num_positive_actual += 1\n if predicted[i] == actual[i]:\n if predicted[i] == positive_value:\n score += 1\n \n if num_positive_predicted == 0:\n precision = 1\n else:\n precision = score / num_positive_predicted # the fraction of predicted “Yes” responses that are correct\n if num_positive_actual == 0:\n recall = 1\n else:\n recall = score / num_positive_actual # the fraction of “Yes” responses that are predicted correctly\n\n return precision, recall\n \nprint(calc_precision_recall(inferred_train_bb, np.around(attack_x_test_feature, decimals=8), positive_value=1.))",
"(0.5483870967741935, 0.32075471698113206)\n"
]
],
[
[
"To verify the significance of these results, we now run a baseline attack that uses only the remaining features to try to predict the value of the attacked feature, with no use of the model itself.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from art.attacks.inference.attribute_inference import AttributeInferenceBaseline\n\nbaseline_attack = AttributeInferenceBaseline(attack_feature=attack_feature)\n\n# train attack model\nbaseline_attack.fit(attack_x_train)\n# infer values\ninferred_train_baseline = baseline_attack.infer(attack_x_test, values=values)\n# check accuracy\nbaseline_train_acc = np.sum(inferred_train_baseline == np.around(attack_x_test_feature, decimals=8).reshape(1,-1)) / len(inferred_train_baseline)\nprint(baseline_train_acc)",
"0.5585585585585585\n"
]
],
[
[
"In this case, the black-box attack does not do better than the baseline.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
c50cb62125fd19342151259d25a5b22da8d843d2
| 3,400 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/structured-abstract-ammar-150454388.ipynb
|
Castdeath97/csc8635-project
|
6c660f3413fd2f031cdb58ed2380e6e97464393f
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2020-09-28T16:32:28.000Z
|
2021-02-06T17:29:11.000Z
|
notebooks/structured-abstract-ammar-150454388.ipynb
|
Castdeath97/csc8635-project
|
6c660f3413fd2f031cdb58ed2380e6e97464393f
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2020-03-24T16:59:10.000Z
|
2021-02-02T21:57:35.000Z
|
notebooks/structured-abstract-ammar-150454388.ipynb
|
Castdeath97/csc8635-project
|
6c660f3413fd2f031cdb58ed2380e6e97464393f
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2020-01-20T15:34:30.000Z
|
2020-01-20T15:34:30.000Z
| 37.362637 | 477 | 0.674706 |
[
[
[
"## Context\n\nPigment skin diagnosis field has been growing due to the importance of early detection of skin conditions like skin cancer, the field has developed various detection methods that include computerised algorithms to help with this.\n \n## Objective\n\nHence, this project aim is to develop a machine learning model for the diagnosis of pigmented skin lesions. The project objectives include developing and training a models with a diverse and large dataset, and using these models with test data to evaluate their discriminatory and non-discriminatory performance to find a final model.\n\n## Method\n\nTo achieve this, the project follows the CRISP DM approach for the data mining process, specifically dividing the process up to stages and reports. The process will be used to construct and evaluate the models.\n \n## Results\n\nThe results from the process show that out of the selected three models, the logistic regression seem to perform best in the discriminatory and non-discriminatory categories, getting better accuracies, run times and confusion matricies. However, the results were still poor when it came to the consistency of classification, and the results of the other might have been effected heavily by the difficulty of tuning the SVM and the Random Forest due to poor run times. \n\t\n## Novelty\n\nOther literature usually covered discriminatory performance of models but glanced over non-discriminatory measures like fitting times and prediction times, which this project considered a priority. Moreover, this makes use of diverse and large dataset with more classes than similar projects which usually cover around 3-2 classes.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
c50cbe9479cb33dfc11360933ad35e7dfac03c67
| 26,645 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
others/third_party/fairness_aware_learning/examples/continuous_fairness_aware_learning/equalized_odds_dnn.ipynb
|
altosaar/fair_dummies
|
33b64e6a468e4d38c8992db637a9156effe3f556
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-02-15T23:48:54.000Z
|
2021-02-15T23:48:54.000Z
|
others/third_party/fairness_aware_learning/examples/continuous_fairness_aware_learning/equalized_odds_dnn.ipynb
|
altosaar/fair_dummies
|
33b64e6a468e4d38c8992db637a9156effe3f556
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
others/third_party/fairness_aware_learning/examples/continuous_fairness_aware_learning/equalized_odds_dnn.ipynb
|
altosaar/fair_dummies
|
33b64e6a468e4d38c8992db637a9156effe3f556
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2020-08-03T13:18:07.000Z
|
2022-01-13T15:08:16.000Z
| 59.608501 | 1,985 | 0.619366 |
[
[
[
"<h1><center>ERM with DNN under penalty of Equalized Odds</center></h1>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We implement here a regular Empirical Risk Minimization (ERM) of a Deep Neural Network (DNN) penalized to enforce an Equalized Odds constraint. More formally, given a dataset of size $n$ consisting of context features $x$, target $y$ and a sensitive information $z$ to protect, we want to solve\n$$\n\\text{argmin}_{h\\in\\mathcal{H}}\\frac{1}{n}\\sum_{i=1}^n \\ell(y_i, h(x_i)) + \\lambda \\chi^2|_1\n$$\nwhere $\\ell$ is for instance the MSE and the penalty is\n$$\n\\chi^2|_1 = \\left\\lVert\\chi^2\\left(\\hat{\\pi}(h(x)|y, z|y), \\hat{\\pi}(h(x)|y)\\otimes\\hat{\\pi}(z|y)\\right)\\right\\rVert_1\n$$\nwhere $\\hat{\\pi}$ denotes the empirical density estimated through a Gaussian KDE.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### The dataset\n\nWe use here the _communities and crimes_ dataset that can be found on the UCI Machine Learning Repository (http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/communities+and+crime). Non-predictive information, such as city name, state... have been removed and the file is at the arff format for ease of loading.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import sys, os\nsys.path.append(os.path.abspath(os.path.join('../..')))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from examples.data_loading import read_dataset\nx_train, y_train, z_train, x_test, y_test, z_test = read_dataset(name='crimes', fold=1)\nn, d = x_train.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### The Deep Neural Network\n\nWe define a very simple DNN for regression here",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from torch import nn\nimport torch.nn.functional as F\n\nclass NetRegression(nn.Module):\n def __init__(self, input_size, num_classes):\n super(NetRegression, self).__init__()\n size = 50\n self.first = nn.Linear(input_size, size)\n self.fc = nn.Linear(size, size)\n self.last = nn.Linear(size, num_classes)\n\n def forward(self, x):\n out = F.selu(self.first(x))\n out = F.selu(self.fc(out))\n out = self.last(out)\n return out",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### The fairness-inducing regularizer\nWe implement now the regularizer. The empirical densities $\\hat{\\pi}$ are estimated using a Gaussian KDE. The L1 functional norm is taken over the values of $y$.\n$$\n\\chi^2|_1 = \\left\\lVert\\chi^2\\left(\\hat{\\pi}(x|z, y|z), \\hat{\\pi}(x|z)\\otimes\\hat{\\pi}(y|z)\\right)\\right\\rVert_1\n$$\nThis used to enforce the conditional independence $X \\perp Y \\,|\\, Z$.\nPractically, we will want to enforce $\\text{prediction} \\perp \\text{sensitive} \\,|\\, \\text{target}$",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from facl.independence.density_estimation.pytorch_kde import kde\nfrom facl.independence.hgr import chi_2_cond\n\ndef chi_squared_l1_kde(X, Y, Z):\n return torch.mean(chi_2_cond(X, Y, Z, kde))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### The fairness-penalized ERM\n\nWe now implement the full learning loop. The regression loss used is the quadratic loss with a L2 regularization and the fairness-inducing penalty.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import torch\nimport numpy as np\nimport torch.utils.data as data_utils\n\ndef regularized_learning(x_train, y_train, z_train, model, fairness_penalty, lr=1e-5, num_epochs=10):\n # wrap dataset in torch tensors\n Y = torch.tensor(y_train.astype(np.float32))\n X = torch.tensor(x_train.astype(np.float32))\n Z = torch.tensor(z_train.astype(np.float32))\n dataset = data_utils.TensorDataset(X, Y, Z)\n dataset_loader = data_utils.DataLoader(dataset=dataset, batch_size=200, shuffle=True)\n\n # mse regression objective\n data_fitting_loss = nn.MSELoss()\n\n # stochastic optimizer\n optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=lr, weight_decay=0.01)\n\n for j in range(num_epochs):\n for i, (x, y, z) in enumerate(dataset_loader):\n def closure():\n optimizer.zero_grad()\n outputs = model(x).flatten()\n loss = data_fitting_loss(outputs, y) \n loss += fairness_penalty(outputs, z, y)\n loss.backward()\n return loss\n\n optimizer.step(closure)\n return model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Evaluation\n\nFor the evaluation on the test set, we compute two metrics: the MSE (accuracy) and HGR$|_\\infty$ (fairness).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from facl.independence.hgr import hgr_cond\n\ndef evaluate(model, x, y, z):\n Y = torch.tensor(y.astype(np.float32))\n Z = torch.Tensor(z.astype(np.float32))\n X = torch.tensor(x.astype(np.float32))\n\n prediction = model(X).detach().flatten()\n loss = nn.MSELoss()(prediction, Y)\n hgr_infty = np.max(hgr_cond(prediction, Z, Y, kde))\n return loss.item(), hgr_infty",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Running everything together\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model = NetRegression(d, 1)\n\nnum_epochs = 20\nlr = 1e-5\n\n# $\\chi^2|_1$\npenalty_coefficient = 1.0\npenalty = chi_squared_l1_kde\n\nmodel = regularized_learning(x_train, y_train, z_train, model=model, fairness_penalty=penalty, lr=lr, \\\n num_epochs=num_epochs)\n\nmse, hgr_infty = evaluate(model, x_test, y_test, z_test)\nprint(\"MSE:{} HGR_infty:{}\".format(mse, hgr_infty))",
"torch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([194])\ntorch.Size([194])\ntorch.Size([194])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([194])\ntorch.Size([194])\ntorch.Size([194])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([194])\ntorch.Size([194])\ntorch.Size([194])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([194])\ntorch.Size([194])\ntorch.Size([194])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([194])\ntorch.Size([194])\ntorch.Size([194])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([194])\ntorch.Size([194])\ntorch.Size([194])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\ntorch.Size([200])\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c50cc07338734816689ce80cbab9d7af176fc21f
| 4,899 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
RandForstDC.ipynb
|
yousifbigdata/RandomForestDC
|
c508331c1a862e34e8bfe88821f45b36b61197af
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
RandForstDC.ipynb
|
yousifbigdata/RandomForestDC
|
c508331c1a862e34e8bfe88821f45b36b61197af
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
RandForstDC.ipynb
|
yousifbigdata/RandomForestDC
|
c508331c1a862e34e8bfe88821f45b36b61197af
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 24.495 | 174 | 0.470708 |
[
[
[
"# Kernel SVM\n\n# Importing the libraries\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport pandas as pd\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Importing the dataset\ndataset = pd.read_csv('train.csv').as_matrix()",
"C:\\ProgramData\\Anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages\\ipykernel_launcher.py:2: FutureWarning: Method .as_matrix will be removed in a future version. Use .values instead.\n \n"
],
[
"X_train= dataset[0:21000,1:]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_train_label=X_train[0:21000,0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Fitting Random Forest Classification to the Training set\nfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier\nclassifier = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators = 10, criterion = 'entropy', random_state = 0)\nclassifier.fit(X_train, X_train_label)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Testing Data\nX_test=dataset[21000 : ,1 :]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"actual_label = dataset[21000: , 0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"y_pred = classifier.predict(X_test)\ncount = 0 ;\nfor i in range(0,21000):\n count+= 1 if y_pred[i] == actual_label[i] else 0\nprint(\"Accurecy = \", (count/21000)* 1000)",
"Accurecy = 99.42857142857142\n"
],
[
"# Making the Confusion Matrix\nfrom sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix\ncm = confusion_matrix(actual_label, y_pred)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cm",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"cm",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c50cc34921b2472c1dc9534b82838304cd740ae8
| 6,811 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
03_Extract-Information_NREL_WKT.ipynb
|
h2mauricio/adv-energy-processes
|
78c7e8222fc5e980fbac997a9ef6b3679d44a8ae
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
03_Extract-Information_NREL_WKT.ipynb
|
h2mauricio/adv-energy-processes
|
78c7e8222fc5e980fbac997a9ef6b3679d44a8ae
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
03_Extract-Information_NREL_WKT.ipynb
|
h2mauricio/adv-energy-processes
|
78c7e8222fc5e980fbac997a9ef6b3679d44a8ae
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 32.433333 | 613 | 0.58523 |
[
[
[
"# Extract Wind Information from NREL WKT\nBy Mauricio Hernandez",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Goal(s):\n- Collect and download data from a set of wind stations using the NREL API Wind Toolkit Data Downloads.\n- Get insights from wind speed and wind direction data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"---\nSee documentation at: https://developer.nrel.gov/docs/wind/wind-toolkit/mexico-wtk.download/ <br>\nSee examples at: https://developer.nrel.gov/docs/wind/wind-toolkit/mexico-wtk.download/#examples",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#Import libraries\nimport requests",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Read API_key\nwith open('NREL_API_Key.txt') as f:\n line = f.readline()\napi_key = lines.replace('\\n', '')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"api_key = 'RSbHTzGc9ChRkhKO3twc63rgZQ18Hkabcm67ca6o'",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"*Define longitude and latitude and other parameters*",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"lon = -100.432474084658\nlat = 20.8333616168693\nemail = '[email protected]'\nattr = 'windspeed_80m,winddirection_80m'\nyear = '2010'",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Option 1: Send HTTP requests",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#Request format\n#https://developer.nrel.gov//api/wind-toolkit/v2/wind/mexico-wtk-download.format?parameters\ntry:\n url = \"https://developer.nrel.gov/api/wind-toolkit/v2/wind/mexico-wtk-download.json?api_key=%s&attributes=%s&names=%s&utc=false&leap_day=true&email=%s&wkt=POINT(%f %f)\" % (api_key, attr, year, email, lon, lat)\n r = requests.get(url)\n print(\"HTML:\\n\", r.text)\nexcept:\n print(\"Invalid URL or some error occured while making the GET request to the specified URL\")",
"HTML:\n {\"inputs\":{\"body\":{},\"params\":{},\"query\":{\"attributes\":\"windspeed_80m,winddirection_80m\",\"names\":\"2010\",\"utc\":\"false\",\"leap_day\":\"true\",\"email\":\"[email protected]\",\"wkt\":\"POINT(-100.432474 20.833362)\"}},\"metadata\":{\"version\":\"2.0.0\",\"resultset\":{\"count\":1}},\"status\":200,\"outputs\":{\"message\":\"File generation in progress. An email will be sent to [email protected] when the download is ready.\",\"downloadUrl\":\"https://mapfiles.nrel.gov/data/wind/d7a65194be11883e07981c4409558ecd.zip\"},\"errors\":[]}\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Option 2: POST request where a very large WKT value is requiredPOST request",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"url = \"https://developer.nrel.gov/api/wind-toolkit/v2/wind/mexico-wtk-download.json?api_key=%s\" % (api_key)\n\npolygon = '(-100.3555 20.5888, -100.3555 20.3444, -100.4555 20.3444, -100.3555 20.5888)'\n\n#POLYGON instead of point\npayload = 'attributes=%s&names=2014&utc=false&leap_day=true&email=%s&wkt=POLYGON(%s)' % (attr, email, polygon)\n\nheaders = {\n 'content-type': \"application/x-www-form-urlencoded\",\n 'cache-control': \"no-cache\"\n}\n\nresponse = requests.request(\"POST\", url, data=payload, headers=headers)\n\nprint(response.text)",
"{\"inputs\":{\"body\":{\"attributes\":\"windspeed_10m,winddirection_10m\",\"names\":\"2014\",\"utc\":\"false\",\"leap_day\":\"true\",\"email\":\"[email protected]\",\"wkt\":\"POLYGON((-100.3555 20.5888, -100.3555 20.3444, -100.4555 20.3444, -100.3555 20.5888))\"},\"params\":{},\"query\":{}},\"metadata\":{\"version\":\"2.0.0\",\"resultset\":{\"count\":1}},\"status\":200,\"outputs\":{\"message\":\"File generation in progress. An email will be sent to [email protected] when the download is ready.\",\"downloadUrl\":\"https://mapfiles.nrel.gov/data/wind/d99c135cab50cada024ac351eaa5469f.zip\"},\"errors\":[]}\n"
]
],
[
[
"---\n## Activity:\n1. Use the client's location or your location and download the following data for the assigned year (2007-2014): \n- windspeed_10m, windspeed_40m, windspeed_60m, windspeed_80m, windspeed_100m, winddirection_10m, winddirection_40m, winddirection_60m, winddirection_80m, winddirection_100m.\n\n2. Obtain the descriptive statistics of the annual values of windspeeds grouped by height. i.e. average wind speed at 10 meters in 2007, average wind speed at 80 meters in 2007. Based on the data, and answer the following questions:\n- Does the average wind speed increases/decreases as the height increases?\n- Does the variability of the wind speed increases/decreases as the height increases?\n\n3. From step 3, select the data with the maximum and minimum annual average speeds (i.e heights of 10m and 60m) and obtain the descriptive statistics of the wind directions. Compare the median values from each data subset? Are they similar?",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
]
] |
c50cc34ed99cd1a5cc7eba357d806a428b725e04
| 767,166 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
_notebooks/2020-03-11-Mortality_Rate.ipynb
|
pratapvardhan/covid19-dashboard
|
2ca33bb0cf82328d84def6a2ed145b3926c520bc
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 4 |
2020-03-20T16:43:31.000Z
|
2021-04-08T14:59:00.000Z
|
_notebooks/2020-03-11-Mortality_Rate.ipynb
|
MaxCodeXTC/covid19-dashboard
|
2ca33bb0cf82328d84def6a2ed145b3926c520bc
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
_notebooks/2020-03-11-Mortality_Rate.ipynb
|
MaxCodeXTC/covid19-dashboard
|
2ca33bb0cf82328d84def6a2ed145b3926c520bc
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 4 |
2020-03-21T06:54:11.000Z
|
2020-04-29T00:59:56.000Z
| 119.440448 | 495,040 | 0.858401 |
[
[
[
"# Estimating The Mortality Rate For COVID-19\n> Using Country-Level Covariates To Correct For Testing & Reporting Biases And Estimate a True Mortality Rate.\n- author: Joseph Richards\n- image: images/corvid-mortality.png\n- comments: true\n- categories: [MCMC, mortality]\n- permalink: /covid-19-mortality-estimation/\n- toc: true",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#hide\n# ! pip install pymc3 arviz xlrd",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#hide\n\n# Setup and imports\n%matplotlib inline\n\nimport warnings\nwarnings.simplefilter('ignore')\n\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport pymc3 as pm\nfrom IPython.display import display, Markdown",
"WARNING (theano.tensor.blas): Using NumPy C-API based implementation for BLAS functions.\n"
],
[
"#hide\n\n# constants\n\nignore_countries = [\n 'Others',\n 'Cruise Ship'\n]\n\ncpi_country_mapping = {\n 'United States of America': 'US',\n 'China': 'Mainland China'\n}\n\nwb_country_mapping = {\n 'United States': 'US',\n 'Egypt, Arab Rep.': 'Egypt',\n 'Hong Kong SAR, China': 'Hong Kong',\n 'Iran, Islamic Rep.': 'Iran',\n 'China': 'Mainland China',\n 'Russian Federation': 'Russia',\n 'Slovak Republic': 'Slovakia',\n 'Korea, Rep.': 'Korea, South'\n}\n\nwb_covariates = [\n ('SH.XPD.OOPC.CH.ZS',\n 'healthcare_oop_expenditure'),\n ('SH.MED.BEDS.ZS',\n 'hospital_beds'),\n ('HD.HCI.OVRL',\n 'hci'),\n ('SP.POP.65UP.TO.ZS',\n 'population_perc_over65'),\n ('SP.RUR.TOTL.ZS',\n 'population_perc_rural')\n]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#hide\n\n# data loading and manipulation\n\nfrom datetime import datetime\nimport os\n\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\n\n\ndef get_all_data():\n '''\n Main routine that grabs all COVID and covariate data and\n returns them as a single dataframe that contains:\n\n * count of cumulative cases and deaths by country (by today's date)\n * days since first case for each country\n * CPI gov't transparency index\n * World Bank data on population, healthcare, etc. by country\n '''\n\n all_covid_data = _get_latest_covid_timeseries()\n\n covid_cases_rollup = _rollup_by_country(all_covid_data['Confirmed'])\n covid_deaths_rollup = _rollup_by_country(all_covid_data['Deaths'])\n\n todays_date = covid_cases_rollup.columns.max()\n\n # Create DataFrame with today's cumulative case and death count, by country\n df_out = pd.DataFrame({'cases': covid_cases_rollup[todays_date],\n 'deaths': covid_deaths_rollup[todays_date]})\n\n _clean_country_list(df_out)\n _clean_country_list(covid_cases_rollup)\n\n # Add observed death rate:\n df_out['death_rate_observed'] = df_out.apply(\n lambda row: row['deaths'] / float(row['cases']),\n axis=1)\n\n # Add covariate for days since first case\n df_out['days_since_first_case'] = _compute_days_since_first_case(\n covid_cases_rollup)\n\n # Add CPI covariate:\n _add_cpi_data(df_out)\n\n # Add World Bank covariates:\n _add_wb_data(df_out)\n\n # Drop any country w/o covariate data:\n num_null = df_out.isnull().sum(axis=1)\n to_drop_idx = df_out.index[num_null > 1]\n print('Dropping %i/%i countries due to lack of data' %\n (len(to_drop_idx), len(df_out)))\n df_out.drop(to_drop_idx, axis=0, inplace=True)\n\n return df_out, todays_date\n\n\ndef _get_latest_covid_timeseries():\n ''' Pull latest time-series data from JHU CSSE database '''\n\n repo = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CSSEGISandData/COVID-19/master/'\n data_path = 'csse_covid_19_data/csse_covid_19_time_series/'\n\n all_data = {}\n for status in ['Confirmed', 'Deaths', 'Recovered']:\n file_name = 'time_series_19-covid-%s.csv' % status\n all_data[status] = pd.read_csv(\n '%s%s%s' % (repo, data_path, file_name))\n\n return all_data\n\n\ndef _rollup_by_country(df):\n '''\n Roll up each raw time-series by country, adding up the cases\n across the individual states/provinces within the country\n\n :param df: Pandas DataFrame of raw data from CSSE\n :return: DataFrame of country counts\n '''\n gb = df.groupby('Country/Region')\n df_rollup = gb.sum()\n df_rollup.drop(['Lat', 'Long'], axis=1, inplace=True, errors='ignore')\n \n # Drop dates with all 0 count data\n df_rollup.drop(df_rollup.columns[df_rollup.sum(axis=0) == 0],\n axis=1,\n inplace=True)\n\n # Convert column strings to dates:\n idx_as_dt = [datetime.strptime(x, '%m/%d/%y') for x in df_rollup.columns]\n df_rollup.columns = idx_as_dt\n return df_rollup\n\n\ndef _clean_country_list(df):\n ''' Clean up input country list in df '''\n # handle recent changes in country names:\n country_rename = {\n 'Hong Kong SAR': 'Hong Kong',\n 'Taiwan*': 'Taiwan',\n 'Czechia': 'Czech Republic',\n 'Brunei': 'Brunei Darussalam',\n 'Iran (Islamic Republic of)': 'Iran',\n 'Viet Nam': 'Vietnam',\n 'Russian Federation': 'Russia',\n 'Republic of Korea': 'South Korea',\n 'Republic of Moldova': 'Moldova',\n 'China': 'Mainland China'\n }\n df.rename(country_rename, axis=0, inplace=True)\n df.drop(ignore_countries, axis=0, inplace=True, errors='ignore')\n\n\ndef _compute_days_since_first_case(df_cases):\n ''' Compute the country-wise days since first confirmed case\n\n :param df_cases: country-wise time-series of confirmed case counts\n :return: Series of country-wise days since first case\n '''\n date_first_case = df_cases[df_cases > 0].idxmin(axis=1)\n days_since_first_case = date_first_case.apply(\n lambda x: (df_cases.columns.max() - x).days)\n # Add 1 month for China, since outbreak started late 2019:\n days_since_first_case.loc['Mainland China'] += 30\n\n return days_since_first_case\n\n\ndef _add_cpi_data(df_input):\n '''\n Add the Government transparency (CPI - corruption perceptions index)\n data (by country) as a column in the COVID cases dataframe.\n\n :param df_input: COVID-19 data rolled up country-wise\n :return: None, add CPI data to df_input in place\n '''\n cpi_data = pd.read_excel(\n 'https://github.com/jwrichar/COVID19-mortality/blob/master/data/CPI2019.xlsx?raw=true',\n skiprows=2)\n cpi_data.set_index('Country', inplace=True, drop=True)\n cpi_data.rename(cpi_country_mapping, axis=0, inplace=True)\n\n # Add CPI score to input df:\n df_input['cpi_score_2019'] = cpi_data['CPI score 2019']\n\n\ndef _add_wb_data(df_input):\n '''\n Add the World Bank data covariates as columns in the COVID cases dataframe.\n\n :param df_input: COVID-19 data rolled up country-wise\n :return: None, add World Bank data to df_input in place\n '''\n wb_data = pd.read_csv(\n 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jwrichar/COVID19-mortality/master/data/world_bank_data.csv',\n na_values='..')\n\n for (wb_name, var_name) in wb_covariates:\n wb_series = wb_data.loc[wb_data['Series Code'] == wb_name]\n wb_series.set_index('Country Name', inplace=True, drop=True)\n wb_series.rename(wb_country_mapping, axis=0, inplace=True)\n\n # Add WB data:\n df_input[var_name] = _get_most_recent_value(wb_series)\n\n\ndef _get_most_recent_value(wb_series):\n '''\n Get most recent non-null value for each country in the World Bank\n time-series data\n '''\n ts_data = wb_series[wb_series.columns[3::]]\n\n def _helper(row):\n row_nn = row[row.notnull()]\n if len(row_nn):\n return row_nn[-1]\n else:\n return np.nan\n\n return ts_data.apply(_helper, axis=1)\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#hide\n\n# Load the data (see source/data.py):\ndf, todays_date = get_all_data()\n# Impute NA's column-wise:\ndf = df.apply(lambda x: x.fillna(x.mean()),axis=0)",
"Dropping 21/165 countries due to lack of data\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Observed mortality rates",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#collapse-hide\n\ndisplay(Markdown('Data as of %s' % todays_date))\n\nreported_mortality_rate = df['deaths'].sum() / df['cases'].sum()\ndisplay(Markdown('Overall reported mortality rate: %.2f%%' % (100.0 * reported_mortality_rate)))\n\ndf_highest = df.sort_values('cases', ascending=False).head(15)\nmortality_rate = pd.Series(\n data=(df_highest['deaths']/df_highest['cases']).values,\n index=map(lambda x: '%s (%i cases)' % (x, df_highest.loc[x]['cases']),\n df_highest.index))\nax = mortality_rate.plot.bar(\n figsize=(14,7), title='Reported Mortality Rate by Country (countries w/ highest case counts)')\nax.axhline(reported_mortality_rate, color='k', ls='--')\n\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Model",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Estimate COVID-19 mortality rate, controling for country factors.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#hide\n\nimport numpy as np\n\nimport pymc3 as pm\n\n\ndef initialize_model(df):\n\n # Normalize input covariates in a way that is sensible:\n\n # (1) days since first case: upper\n # mu_0 to reflect asymptotic mortality rate months after outbreak\n _normalize_col(df, 'days_since_first_case', how='upper')\n # (2) CPI score: upper\n # mu_0 to reflect scenario in absence of corrupt govts\n _normalize_col(df, 'cpi_score_2019', how='upper')\n # (3) healthcare OOP spending: mean\n # not sure which way this will go\n _normalize_col(df, 'healthcare_oop_expenditure', how='mean')\n # (4) hospital beds: upper\n # more beds, more healthcare and tests\n _normalize_col(df, 'hospital_beds', how='mean')\n # (5) hci = human capital index: upper\n # HCI measures education/health; mu_0 should reflect best scenario\n _normalize_col(df, 'hci', how='mean')\n # (6) % over 65: mean\n # mu_0 to reflect average world demographic\n _normalize_col(df, 'population_perc_over65', how='mean')\n # (7) % rural: mean\n # mu_0 to reflect average world demographic\n _normalize_col(df, 'population_perc_rural', how='mean')\n\n n = len(df)\n\n covid_mortality_model = pm.Model()\n\n with covid_mortality_model:\n\n # Priors:\n mu_0 = pm.Beta('mu_0', alpha=0.3, beta=10)\n sig_0 = pm.Uniform('sig_0', lower=0.0, upper=mu_0 * (1 - mu_0))\n beta = pm.Normal('beta', mu=0, sigma=5, shape=7)\n sigma = pm.HalfNormal('sigma', sigma=5)\n\n # Model mu from country-wise covariates:\n # Apply logit transformation so logistic regression performed\n mu_0_logit = np.log(mu_0 / (1 - mu_0))\n mu_est = mu_0_logit + \\\n beta[0] * df['days_since_first_case_normalized'].values + \\\n beta[1] * df['cpi_score_2019_normalized'].values + \\\n beta[2] * df['healthcare_oop_expenditure_normalized'].values + \\\n beta[3] * df['hospital_beds_normalized'].values + \\\n beta[4] * df['hci_normalized'].values + \\\n beta[5] * df['population_perc_over65_normalized'].values + \\\n beta[6] * df['population_perc_rural_normalized'].values\n mu_model_logit = pm.Normal('mu_model_logit',\n mu=mu_est,\n sigma=sigma,\n shape=n)\n # Transform back to probability space:\n mu_model = np.exp(mu_model_logit) / (np.exp(mu_model_logit) + 1)\n\n # tau_i, mortality rate for each country\n # Parametrize with (mu, sigma)\n # instead of (alpha, beta) to ease interpretability.\n tau = pm.Beta('tau', mu=mu_model, sigma=sig_0, shape=n)\n # tau = pm.Beta('tau', mu=mu_0, sigma=sig_0, shape=n)\n\n # Binomial likelihood:\n d_obs = pm.Binomial('d_obs',\n n=df['cases'].values,\n p=tau,\n observed=df['deaths'].values)\n\n return covid_mortality_model\n\n\ndef _normalize_col(df, colname, how='mean'):\n '''\n Normalize an input column in one of 3 ways:\n\n * how=mean: unit normal N(0,1)\n * how=upper: normalize to [-1, 0] with highest value set to 0\n * how=lower: normalize to [0, 1] with lowest value set to 0\n\n Returns df modified in place with extra column added.\n '''\n colname_new = '%s_normalized' % colname\n if how == 'mean':\n mu = df[colname].mean()\n sig = df[colname].std()\n df[colname_new] = (df[colname] - mu) / sig\n elif how == 'upper':\n maxval = df[colname].max()\n minval = df[colname].min()\n df[colname_new] = (df[colname] - maxval) / (maxval - minval)\n elif how == 'lower':\n maxval = df[colname].max()\n minval = df[colname].min()\n df[colname_new] = (df[colname] - minval) / (maxval - minval)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#hide\n\n# Initialize the model:\nmod = initialize_model(df)\n\n# Run MCMC sampler1\nwith mod:\n trace = pm.sample(300, tune=100,\n chains=3, cores=2)",
"Only 300 samples in chain.\n"
],
[
"#collapse-hide\n\nn_samp = len(trace['mu_0'])\nmu0_summary = pm.summary(trace).loc['mu_0']\nprint(\"COVID-19 Global Mortality Rate Estimation:\")\nprint(\"Posterior mean: %0.2f%%\" % (100*trace['mu_0'].mean()))\nprint(\"Posterior median: %0.2f%%\" % (100*np.median(trace['mu_0'])))\nlower = np.sort(trace['mu_0'])[int(n_samp*0.025)]\nupper = np.sort(trace['mu_0'])[int(n_samp*0.975)]\nprint(\"95%% posterior interval: (%0.2f%%, %0.2f%%)\" % (100*lower, 100*upper))\nprob_lt_reported = sum(trace['mu_0'] < reported_mortality_rate) / len(trace['mu_0'])\nprint(\"Probability true rate less than reported rate (%.2f%%) = %.2f%%\" %\n (100*reported_mortality_rate, 100*prob_lt_reported))\nprint(\"\")\n\n# Posterior plot for mu0\nprint('Posterior probability density for COVID-19 mortality rate, controlling for country factors:')\nax = pm.plot_posterior(trace, var_names=['mu_0'], figsize=(18, 8), textsize=18,\n credible_interval=0.95, bw=3.0, lw=3, kind='kde',\n ref_val=round(reported_mortality_rate, 3))",
"COVID-19 Global Mortality Rate Estimation:\nPosterior mean: 1.06%\nPosterior median: 0.86%\n95% posterior interval: (0.19%, 3.08%)\nProbability true rate less than reported rate (4.27%) = 99.67%\n\nPosterior probability density for COVID-19 mortality rate, controlling for country factors:\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Magnitude and Significance of Factors \n\nFor bias in reported COVID-19 mortality rate",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#collapse-hide\n\n# Posterior summary for the beta parameters:\nbeta_summary = pm.summary(trace).head(7)\nbeta_summary.index = ['days_since_first_case', 'cpi', 'healthcare_oop', 'hospital_beds', 'hci', 'percent_over65', 'percent_rural']\nbeta_summary.reset_index(drop=False, inplace=True)\n\nerr_vals = ((beta_summary['hpd_3%'] - beta_summary['mean']).values,\n (beta_summary['hpd_97%'] - beta_summary['mean']).values)\nax = beta_summary.plot(x='index', y='mean', kind='bar', figsize=(14, 7),\n title='Posterior Distribution of Beta Parameters',\n yerr=err_vals, color='lightgrey',\n legend=False, grid=True,\n capsize=5)\nbeta_summary.plot(x='index', y='mean', color='k', marker='o', linestyle='None',\n ax=ax, grid=True, legend=False, xlim=plt.gca().get_xlim())\n\nplt.savefig('../images/corvid-mortality.png')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# About This Analysis\n\nThis analysis was done by [Joseph Richards](https://twitter.com/joeyrichar)\n\nIn this project[^3], we attempt to estimate the true mortality rate[^1] for COVID-19 while controlling for country-level covariates[^2][^4] such as:\n* age of outbreak in the country\n* transparency of the country's government\n* access to healthcare\n* demographics such as age of population and rural vs. urban\n\nEstimating a mortality rate lower than the overall reported rate likely implies that there has been **significant under-testing and under-reporting of cases globally**.\n\n## Interpretation of Country-Level Parameters \n\n1. days_since_first_case - positive (very statistically significant). As time since outbreak increases, expected mortality rate **increases**, as expected.\n2. cpi - negative (statistically significant). As government transparency increases, expected mortality rate **decreases**. This may mean that less transparent governments under-report cases, hence inflating the mortality rate.\n3. healthcare avg. out-of-pocket spending - no significant trend.\n4. hospital beds per capita - no significant trend.\n5. Human Capital Index - no significant trend (slightly negative = mortality rates decrease with increased mobilization of the country)\n6. percent over 65 - positive (statistically significant). As population age increases, the mortality rate also **increases**, as expected.\n7. percent rural - no significant trend.\n\n\n[^1]: As of March 10, the **overall reported mortality rate is 3.5%**. However, this figure does not account for **systematic biases in case reporting and testing**. The observed mortality of COVID-19 has varied widely from country to country (as of early March 2020). For instance, as of March 10, mortality rates have ranged from < 0.1% in places like Germany (1100+ cases) to upwards of 5% in Italy (9000+ cases) and 3.9% in China (80k+ cases).\n\n[^2]: The point of our modelling work here is to **try to understand and correct for the country-to-country differences that may cause the observed discrepancies in COVID-19 country-wide mortality rates**. That way we can \"undo\" those biases and try to **pin down an overall *real* mortality rate**.\n\n[^3]: Full details about the model are available at: https://github.com/jwrichar/COVID19-mortality\n\n[^4]: The affects of these parameters are subject to change as more data are collected.\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Appendix: Model Diagnostics\n\nThe following trace plots help to assess the convergence of the MCMC sampler.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#hide_input\nimport arviz as az\naz.plot_trace(trace, compact=True);",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c50cc411d9d871ad866d0ba2afd1a3db8bcce7b2
| 68,585 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
examples/fitpredictFreq.ipynb
|
UnofficialJuliaMirrorSnapshots/RHEOS.jl-728860ae-c896-11e8-0b91-0f38ecad5046
|
2ab602ff6c69f3865ef632bde753b6b7a072b7e6
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2020-10-21T08:35:36.000Z
|
2020-10-21T08:35:36.000Z
|
examples/fitpredictFreq.ipynb
|
DwayneCao/RHEOS.jl
|
220ac83f1838ff2e60e6b577c947f0be62813cdc
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
examples/fitpredictFreq.ipynb
|
DwayneCao/RHEOS.jl
|
220ac83f1838ff2e60e6b577c947f0be62813cdc
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 210.383436 | 32,362 | 0.908624 |
[
[
[
"empty"
]
]
] |
[
"empty"
] |
[
[
"empty"
]
] |
c50cd2db8f91a83ef798b752356f828cf4e822e5
| 3,164 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Notes/Python/Defaultdict.ipynb
|
je-castelan/Personal_Jupyter_Notes
|
1d984c7ef225aa6ee5103608c205240ba3d9f0c5
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Notes/Python/Defaultdict.ipynb
|
je-castelan/Personal_Jupyter_Notes
|
1d984c7ef225aa6ee5103608c205240ba3d9f0c5
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Notes/Python/Defaultdict.ipynb
|
je-castelan/Personal_Jupyter_Notes
|
1d984c7ef225aa6ee5103608c205240ba3d9f0c5
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 18.833333 | 108 | 0.496523 |
[
[
[
"# Defaultdict",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Assuming following dictionary",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"firstdict = {1:'Peter', 2:'John', 4:'Max', 5:'Daniel'}\nfirstdict",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We will try to get the value of index 3",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"try:\n firstdict[3] # Drops error\nexcept KeyError:\n print(\"It drops KeyError\")",
"It drops KeyError\n"
]
],
[
[
"So we can try with defaultdict. It must be imported from collections.\nWe initialized it with a function which returns a default value",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from collections import defaultdict\nseconddict = defaultdict(lambda : \"Nothing here\") # Default value is a alert string",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We will set the same values",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"seconddict[1] = 'Peter'\nseconddict[2] = 'John'\nseconddict[4] = 'Max'\nseconddict[5] = 'Daniel'\nprint(seconddict)",
"defaultdict(<function <lambda> at 0x7ff5a0664550>, {1: 'Peter', 2: 'John', 4: 'Max', 5: 'Daniel'})\n"
]
],
[
[
"We will call again 3rd index",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"seconddict[3] #It returns \"nothing here\" message",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c50cd2ec405deffdad5e6b508b5857360999d231
| 4,837 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
ipynb/Germany-Niedersachsen-SK-Braunschweig.ipynb
|
skirienko/oscovida.github.io
|
eda5412d02365a8a000239be5480512c53bee8c2
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | null | null | null |
ipynb/Germany-Niedersachsen-SK-Braunschweig.ipynb
|
skirienko/oscovida.github.io
|
eda5412d02365a8a000239be5480512c53bee8c2
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | null | null | null |
ipynb/Germany-Niedersachsen-SK-Braunschweig.ipynb
|
skirienko/oscovida.github.io
|
eda5412d02365a8a000239be5480512c53bee8c2
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | null | null | null | 29.674847 | 191 | 0.521191 |
[
[
[
"# Germany: SK Braunschweig (Niedersachsen)\n\n* Homepage of project: https://oscovida.github.io\n* Plots are explained at http://oscovida.github.io/plots.html\n* [Execute this Jupyter Notebook using myBinder](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/oscovida/binder/master?filepath=ipynb/Germany-Niedersachsen-SK-Braunschweig.ipynb)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import datetime\nimport time\n\nstart = datetime.datetime.now()\nprint(f\"Notebook executed on: {start.strftime('%d/%m/%Y %H:%M:%S%Z')} {time.tzname[time.daylight]}\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"%config InlineBackend.figure_formats = ['svg']\nfrom oscovida import *",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"overview(country=\"Germany\", subregion=\"SK Braunschweig\", weeks=5);",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"overview(country=\"Germany\", subregion=\"SK Braunschweig\");",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"compare_plot(country=\"Germany\", subregion=\"SK Braunschweig\", dates=\"2020-03-15:\");\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# load the data\ncases, deaths = germany_get_region(landkreis=\"SK Braunschweig\")\n\n# compose into one table\ntable = compose_dataframe_summary(cases, deaths)\n\n# show tables with up to 500 rows\npd.set_option(\"max_rows\", 500)\n\n# display the table\ntable",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Explore the data in your web browser\n\n- If you want to execute this notebook, [click here to use myBinder](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/oscovida/binder/master?filepath=ipynb/Germany-Niedersachsen-SK-Braunschweig.ipynb)\n- and wait (~1 to 2 minutes)\n- Then press SHIFT+RETURN to advance code cell to code cell\n- See http://jupyter.org for more details on how to use Jupyter Notebook",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Acknowledgements:\n\n- Johns Hopkins University provides data for countries\n- Robert Koch Institute provides data for within Germany\n- Atlo Team for gathering and providing data from Hungary (https://atlo.team/koronamonitor/)\n- Open source and scientific computing community for the data tools\n- Github for hosting repository and html files\n- Project Jupyter for the Notebook and binder service\n- The H2020 project Photon and Neutron Open Science Cloud ([PaNOSC](https://www.panosc.eu/))\n\n--------------------",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(f\"Download of data from Johns Hopkins university: cases at {fetch_cases_last_execution()} and \"\n f\"deaths at {fetch_deaths_last_execution()}.\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# to force a fresh download of data, run \"clear_cache()\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(f\"Notebook execution took: {datetime.datetime.now()-start}\")\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50cd601686a0ae95109b6e445d73b4d419ccc04
| 28,713 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
.ipynb_checkpoints/RANplayground-checkpoint.ipynb
|
SelinZ/machinelearning
|
105273b2cf5907b23a2ee2b4c076d89f215c38ff
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-12-07T12:38:33.000Z
|
2021-12-07T12:38:33.000Z
|
.ipynb_checkpoints/RANplayground-checkpoint.ipynb
|
SelinZ/machinelearning
|
105273b2cf5907b23a2ee2b4c076d89f215c38ff
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
.ipynb_checkpoints/RANplayground-checkpoint.ipynb
|
SelinZ/machinelearning
|
105273b2cf5907b23a2ee2b4c076d89f215c38ff
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 36.90617 | 211 | 0.543552 |
[
[
[
"Building the dataset of numerical data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#### STOP - ONLY if needed\n# Allows printing full text\nimport pandas as pd\npd.set_option('display.max_colwidth', None)\n\n\n#mid_keywords = best_keywords(data, 1, 0.49, 0.51) # same as above, but for average papers\n#low_keywords = best_keywords(data, 1, 0.03, 0.05) # same as above, but for poor papers\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### PUT MAIN HERE ###",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Machine Learning Challenge\n# Course: Machine Learning (880083-M-6)\n# Group 58\n \n##########################################\n# Import packages #\n##########################################\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom scipy.stats import pearsonr\nimport yake #NOTE: with Anaconda: conda install -c conda-forge yake\n\n##########################################\n# Import self-made functions #\n##########################################\nfrom CODE.data_preprocessing.split_val import split_val\nfrom CODE.data_preprocessing.find_outliers_tukey import find_outliers_tukey\n\n#feature based on the title of the paper\nfrom CODE.features.length_title import length_title\n\n# features based on 'field_of_study' column \nfrom CODE.features.field_variety import field_variety \nfrom CODE.features.field_popularity import field_popularity\nfrom CODE.features.field_citations_avarage import field_citations_avarage \n\n# features based on the topics of the paper\nfrom CODE.features.topic_citations_avarage import topic_citations_avarage\nfrom CODE.features.topic_variety import topics_variety\nfrom CODE.features.topic_popularity import topic_popularity\nfrom CODE.features.topic_citations_avarage import topic_citations_avarage\n\n# features based on the abstract of the paper\nfrom CODE.features.keywords import best_keywords\nfrom CODE.features.abst_words import abst_words\nfrom CODE.features.abst_words import abst_count\n\n# features based on the venue of the paper\nfrom CODE.features.venue_popularity import venue_popularity\nfrom CODE.features.venue_citations import venues_citations\n\nfrom CODE.features.age import age\n\n# features based on the authors of the paper\nfrom CODE.features.author_h_index import author_h_index\nfrom CODE.features.paper_h_index import paper_h_index\nfrom CODE.features.team_size import team_size\nfrom CODE.features.author_database import author_database\n\n\n##########################################\n# Load datasets #\n##########################################\n# Main datasets\ndata = pd.read_json('DATA/train.json') # Training set\ntest = pd.read_json('DATA/test.json') # Test set\n\n# Author-centric datasets\n# These datasets were made using our self-made functions 'citations_per_author' (for the author_citation_dic)\n# These functions took a long time to make (ballpark ~10 minutes on a laptop in 'silent mode'), so instead we \n# decided to run this function once, save the data, and reload the datasets instead of running the function again. \nimport pickle\nwith open('my_dataset1.pickle', 'rb') as dataset:\n author_citation_dic = pickle.load(dataset)\nwith open('my_dataset2.pickle', 'rb') as dataset2:\n author_db = pickle.load(dataset2)\n\n\n##########################################\n# Missing values handling #\n##########################################\n\n# Missing values for feature 'fields_of_study'\ndata.loc[data['fields_of_study'].isnull(), 'fields_of_study'] = \"\"\n\n# Missing values for feature 'title'\ndata.loc[data['title'].isnull(), 'title'] = \"\"\n\n# Missing values for feature 'abstract'\ndata.loc[data['abstract'].isnull(), 'abstract'] = \"\"\n \n# Missing values for features 'authors'\ndata.loc[data['authors'].isnull(), 'authors'] = \"\"\n\n# Missing values for feature 'venue'\ndata.loc[data['venue'].isnull(), 'venue'] = \"\"\n \n# Missing values for feature 'year'\n# data.loc[data['fields_of_study'].isnull(), 'fields_of_study'] = mean(year) \n # Take mean by venue instead\n # If venue not known, take something else?\n\n# Missing values for feature 'references'\ndata.loc[data['references'].isnull(), 'references'] = \"\"\n\n# Missing values for feature 'topics'\ndata.loc[data['topics'].isnull(), 'topics'] = \"\"\n\n# Missing values for feature 'is_open_access'\n#data.loc[data['is_open_access'].isnull(), 'is_open_access'] = \"\" \n # Take most frequent occurrence for venue\n # If venue not known, do something else?\n \n##########################################\n# Create basic numeric df #\n##########################################\nend = len(data)\nnum_X = data.loc[ 0:end+1 , ('doi', 'citations', 'year', 'references') ] ##REMOVE DOI\n\n\n##########################################\n# Feature creation #\n##########################################\n\"\"\"\nFEATURE DATAFRAME: num_X\n\nALL: After writing a funtion to create a feature, please incorporate your new feature as a column on the dataframe below.\nThis is the dataframe we will use to train the models.\n\nDO NOT change the order in this section if at all possible\n\"\"\"\nnum_X['title_length'] = length_title(data) # returns a numbered series\nnum_X['field_variety'] = field_variety(data) # returns a numbered series \nnum_X['field_popularity'] = field_popularity(data) # returns a numbered series\n# num_X['field_citations_avarage'] = field_citations_avarage(data) # returns a numbered series\nnum_X['team_sz'] = team_size(data) # returns a numbered series\nnum_X['topic_var'] = topics_variety(data) # returns a numbered series\nnum_X['topic_popularity'] = topic_popularity(data) # returns a numbered series\nnum_X['topic_citations_avarage'] = topic_citations_avarage(data) # returns a numbered series\nnum_X['venue_popularity'], num_X['venue'] = venue_popularity(data) # returns a numbered series and a pandas.Series of the 'venues' column reformatted \nnum_X['open_access'] = pd.get_dummies(data[\"is_open_access\"], drop_first = True) # returns pd.df (True = 1)\nnum_X['age'] = age(data) # returns a numbered series. Needs to be called upon AFTER the venues have been reformed (from venue_frequency)\nnum_X['venPresL'] = venues_citations(data) # returns a numbered series. Needs to be called upon AFTER the venues have been reformed (from venue_frequency)\nkeywords = best_keywords(data, 1, 0.954, 0.955) # from [data set] get [integer] keywords from papers btw [lower bound] and [upper bound] quantiles; returns list\nnum_X['has_keyword'] = abst_words(data, keywords)#returns a numbered series: 1 if any of the words is present in the abstract, else 0\nnum_X['keyword_count'] = abst_count(data, keywords) # same as above, only a count (noot bool)\n\n# Author H-index\nauthor_db, reformatted_authors = author_database(data)\ndata['authors'] = reformatted_authors\nnum_X['h_index'] = paper_h_index(data, author_citation_dic) # Returns a numbered series. Must come after author names have been reformatted.\n\nfield_avg_cit = num_X.groupby('field_variety').citations.mean()\nfor field, field_avg in zip(field_avg_cit.index, field_avg_cit):\n num_X.loc[num_X['field_variety'] == field, 'field_cit'] = field_avg\n\n\n\"\"\"\nEND do not reorder\n\"\"\"\n\n##########################################\n# Deal with specific missing values #\n##########################################\n# Open_access, thanks to jreback (27th of July 2016) https://github.com/pandas-dev/pandas/issues/13809\nOpAc_by_venue = num_X.groupby('venue').open_access.apply(lambda x: x.mode()) # Take mode for each venue\nOpAc_by_venue = OpAc_by_venue.to_dict()\nmissing_OpAc = num_X.loc[num_X['open_access'].isnull(),]\nfor i, i_paper in missing_OpAc.iterrows():\n venue = i_paper['venue']\n doi = i_paper['doi']\n index = num_X[num_X['doi'] == doi].index[0]\n if venue in OpAc_by_venue.keys(): # If a known venue, append the most frequent value for that venue\n num_X[num_X['doi'] == doi]['open_access'] = OpAc_by_venue[venue] # Set most frequent occurrence \n else: # Else take most occurring value in entire dataset\n num_X.loc[index,'open_access'] = num_X.open_access.mode()[0] # Thanks to BENY (2nd of February, 2018) https://stackoverflow.com/questions/48590268/pandas-get-the-most-frequent-values-of-a-column\n\n### Drop columns containing just strings\nnum_X = num_X.drop(['venue', 'doi', 'field_variety'], axis = 1)\nnum_X = num_X.dropna()\n\n\n##########################################\n# Train/val split #\n##########################################\n\n## train/val split\nX_train, X_val, y_train, y_val = split_val(num_X, target_variable = 'citations')\n\n\n\"\"\"\nINSERT outlier detection on X_train here - ALBERT\n\"\"\"\n\n##########################################\n# Outlier detection #\n##########################################\n### MODEL code for outlier detection\n### names: X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val\n\n# print(list(X_train.columns))\n\nout_y = (find_outliers_tukey(x = y_train['citations'], top = 93, bottom = 0))[0]\nout_rows = out_y\n\n# out_X = (find_outliers_tukey(x = X_train['team_sz'], top = 99, bottom = 0))[0]\n# out_rows = out_y + out_X\n\nout_rows = sorted(list(set(out_rows)))\n\n# print(\"X_train:\")\n# print(X_train.shape)\nX_train = X_train.drop(labels = out_rows)\n# print(X_train.shape)\n# print()\n# print(\"y_train:\")\n# print(y_train.shape)\ny_train = y_train.drop(labels = out_rows)\n# print(y_train.shape)\n\n# Potential features to get rid of: team_sz\n\n\n##########################################\n# Model implementations #\n##########################################\n\"\"\"\nIMPLEMENT models here\nNOTE: Please do not write over X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val in your model - make new variables if needed\n\n\n\"\"\"\n\n#-----------simple regression, all columns\n\"\"\"\nMODEL RESULTS:\nR2: 0.03724\nMSE: 33.38996\n\"\"\"\n#-----------logistic regression, all columns\n\"\"\"\nMODEL RESULTS:\nR2: 0.006551953988217396\nMSE: 34.07342328208346\n\"\"\"\n#-----------SGD regression, all columns\n\"\"\"\n# MODEL RESULTS:\n# Best outcome: ('constant', 0.01, 'squared_error', 35.74249957361433, 0.04476790061780822)\n\"\"\"\n\n#-----------polynomial regression, all columns\n\"\"\"\n\"\"\"\n\n\n#model.fit(X_train, y_train)\n#print('Best score: ', model.best_score_)\n#print('Best parameters: ', model.best_params_)\n#y_pred = model.predict(X_val)\n\n#from sklearn.metrics import r2_score\n#print(r2_score(y_val,y_pred))\n\n\n# import json\n#with open(\"sample.json\", \"w\") as outfile:\n #json.dump(dictionary, outfile)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\"\"\"\n-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n------------------------------ LETS EXPLORE!!! ------------------------------------------------------------\n-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n\"\"\"\n\"\"\"\n\"\"\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### FOR: exploring the new dataframe with numerical columns\n# --> NOTE: it would be more efficient to combine these first and only expand the df once (per addition type)\n\nnum_X",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### FOR: explore data train/val split (should be 6470 train rows and 3188 validation rows)\n# names: X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val\nprint(\"number of keywords:\", len(keywords))\nprint(\"total train rows:\", X_train.shape)\nprint(\"numer w keyword:\", sum(X_train['has_keyword']))\nprint()\nprint(keywords)\n\n#X_val\n#y_train\n#y_val\n#6210 of 6313\n#6136 (of 6313) for 1 keyword from the top 1% of papers\n#4787 for 2 keywords from top .01% of papers (correlation: 0.036)\n#2917 for 1 keyword from top .01% of papers (correlation: 0.049)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\"\"\"\nLook at some correlations - full num_X\n\"\"\"\n# names: X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val\n\n# From: https://www.kaggle.com/ankitjha/comparing-regression-models\nimport seaborn as sns\ncorr_mat = num_X.corr(method='pearson')\nplt.figure(figsize=(20,10))\nsns.heatmap(corr_mat,vmax=1,square=True,annot=True,cmap='cubehelix')\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\"\"\"\nLook at some correlations - X_train\nNOTE: there is no y here\n\"\"\"\n# names: X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val\n\n#temp = y_train hstack X_train\n\n\n# From: https://www.kaggle.com/ankitjha/comparing-regression-models\ncorr_mat = X_train.corr(method='pearson')\nplt.figure(figsize=(20,10))\nsns.heatmap(corr_mat,vmax=1,square=True,annot=True,cmap='cubehelix')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\"\"\"\n-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n------------------------- LETS CODE!!! --------------------------------------------------------------------\n-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n\"\"\"\n\"\"\"\n\"\"\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print(list(X_train.columns))\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\"\"\"\nChoose your columns\n\"\"\"\n\n#X_train_small = X_train.loc[ : , 'topic_var':'h_index'].copy()\n#X_val_small = X_val.loc[ : , 'topic_var':'h_index'].copy()\n\ndrops = ['year', 'team_sz', 'has_keyword']\nX_train_small = X_train.copy()\nX_train_small.drop(drops, inplace = True, axis=1)\n\nX_val_small = X_val.copy()\nX_val_small.drop(drops, inplace = True, axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler\nfrom sklearn.metrics import r2_score, mean_absolute_error",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from CODE.models.regression import simple_linear\nfrom CODE.models.regression import log_reg\n\nsummaries = list(X_train.columns)\nprint(summaries)\n\nfor i in range(len(summaries)):\n# fs = summaries[:i] + summaries[i+1:]\n X_train_small = X_train.copy()\n X_val_small = X_val.copy()\n drops = summaries[i]\n X_train_small.drop(drops, inplace = True, axis=1)\n X_val_small.drop(drops, inplace = True, axis=1)\n\n print(\"dropped:\", summaries[i])\n \n# simple_linear(X_train_small, y_train, X_val_small, y_val) #dropping venue_popularity helps a tiny bit\n log_reg(X_train_small, y_train, X_val_small, y_val)\n\n # print('r2:', r2_score(y_val, y_pred_val)) # 0.006551953988217396\n # print(\"MAE:\", mean_absolute_error(y_val, y_pred_val)) # 34.07342328208346\n # print()\n \n# helps to drop: year, field_popularity, team_size, topic_var, age, has_keyword, keyword_count\n# hurts to drop: references, title length, topic_popularity, opic_citations_avarage, venue_popularity(!), \n# venPresL(!), h_index(!), field_cit",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_train_small\n#X_val_small",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def abst_categories (the_data, keywords, mid_keywords, low_keywords):\n abst = the_data['abstract']\n counts = []\n abst_key = [] \n\n for i in abst:\n if i == None:\n abst_key.append(0)\n continue\n else:\n high = 0\n for word in keywords:\n if word in i.lower():\n high += 1\n \n mid = 0\n for word in mid_keywords:\n if word in i.lower():\n mid += 1\n\n low = 0\n for word in low_keywords:\n if word in i.lower():\n low +=1\n\n \n# abst_key = np.argmax(abst_key)\n# abst_key = (max(abst_key)).index\n\n\n return pd.Series(abst_key) \n \n \nprint(sum(abst_categories (data, keywords, mid_keywords, low_keywords))) #9499 rows",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\"\"\"\nRemove outliers\nNOTE: can't rerun this code without restarting the kernal\n\"\"\"\n#names: X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val\n#print(list(X_train.columns))\n\n# print(\"citations:\", find_outliers_tukey(x = y_train['citations'], top = 93, bottom = 0))\n\n# print(\"year:\", find_outliers_tukey(X_train['year'], top = 74, bottom = 25)) # seems unnecessary\n# print(\"references:\", find_outliers_tukey(X_train['references'], top = 90, bottom = 10)) # seems unnecessary\n# print(\"team_size:\", find_outliers_tukey(X_train['team_size'], top = 99, bottom = 0)) # Meh\n# print(\"topic_variety:\", find_outliers_tukey(X_train['topic_variety'], top = 75, bottom = 10)) # not much diff btw top and normal\n# print(\"age:\", find_outliers_tukey(X_train['age'], top = 90, bottom = 10)) # Meh\n# print(\"open_access:\", find_outliers_tukey(X_train['open_access'], top = 100, bottom = 0)) # Not necessary: boolean\n# print(\"has_keyword:\", find_outliers_tukey(X_train['has_keyword'], top = 100, bottom = 0)) # Not necessary: boolean\n# print(\"title_length:\", find_outliers_tukey(X_train['title_length'], top = 90, bottom = 10)) # Meh\n# print(\"field_variety:\", find_outliers_tukey(X_train['field_variety'], top = 90, bottom = 10)) # seems unnecessary\n# print(\"venue_freq:\", find_outliers_tukey(X_train['venue_freq'], top = 90, bottom = 10)) # seems unnecessary\n\n\nout_y = (find_outliers_tukey(x = y_train['citations'], top = 95, bottom = 0))[0]\n#out_X = (find_outliers_tukey(x = X_train['team_size'], top = 99, bottom = 0))[0]\nout_rows = out_y\n#out_rows = out_y + out_X\nout_rows = sorted(list(set(out_rows)))\n\nprint(\"X_train:\")\nprint(X_train.shape)\nX_train = X_train.drop(labels = out_rows)\nprint(X_train.shape)\nprint()\nprint(\"y_train:\")\nprint(y_train.shape)\ny_train = y_train.drop(labels = out_rows)\nprint(y_train.shape)\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_train",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Create a mini version of the main 'data' dataframe\n\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\n# %pwd\n# %cd C:\\Users\\r_noc\\Desktop\\Python\\GIT\\machinelearning\n \nplay = data.sample(100, replace = False, axis = 0, random_state = 123) \n\n\nprint(play.shape)\n# print(play['abstract'])\n\nprint(list(play.columns))\n# play['has_keyword'] = np.nan\n# print(play.shape)\n# play",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.linear_model import PoissonRegressor\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler\n\nscaler = StandardScaler()\nX_train_z = scaler.fit_transform(X_train_small)\nX_val_z =scaler.transform(X_val_small)\n\npolynomial_features = PolynomialFeatures(degree = 2)\nx_train_poly = polynomial_features.fit_transform(X_train_z)\nx_val_poly = polynomial_features.transform(X_val_z)\n\nmodel = LinearRegression()\nmodel.fit(x_train_poly, y_train)\ny_poly_pred = model.predict(x_val_poly)\n\nprint(r2_score(y_val, y_poly_pred)) # -0.04350391168707901\nprint(mean_absolute_error(y_val, y_poly_pred)) # 32.65668266590838",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler\n\nscaler = StandardScaler()\nX_train_z = scaler.fit_transform(X_train_small)\nX_val_z =scaler.transform(X_val_small)\n\nmodel = PolynomialFeatures(degree = 2)\nX_poly = model.fit_transform(X_train_z)\nmodel.fit(X_poly, y_train)\nmodel2 = LinearRegression()\nmodel2.fit(X_poly, y_train)\n\ny_pred_val = model2.predict(model.fit_transform(X_val_z))\n\nprint(r2_score(y_val, y_pred_val)) #0.03724015197555319\nprint(mean_absolute_error(y_val, y_pred_val)) #33.38996938585591",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#names: X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val\n\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import SGDRegressor\n\nscaler = StandardScaler()\nX_train_z = scaler.fit_transform(X_train_small)\nX_val_z =scaler.transform(X_val_small)\ny_ravel = np.ravel(y_train)\nlr = [ 1.1, 1, .1, .01, .001, .0001]\nsettings = []\nfor learning_rate in ['constant', 'optimal', 'invscaling']:\n for loss in ['squared_error', 'huber']:\n for eta0 in lr:\n model = SGDRegressor(learning_rate=learning_rate, eta0=eta0, loss=loss,random_state=666, max_iter=5000)\n model.fit(X_train_z, y_ravel)\n y_pred = model.predict(X_val_z)\n \n mae = mean_absolute_error(y_val, y_pred)\n r2 = r2_score(y_val, y_pred)\n settings.append((learning_rate, eta0, loss, mae, r2))\n print(settings[-1])\n\n# Best outcome: ('constant', 0.01, 'squared_error', 35.74249957361433, 0.04476790061780822)\n# With small: ('invscaling', 1, 'squared_error', 48.92137807970932, 0.05128477811871335)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_train\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50cd916e9dd0d8eb21ba0393ec4b593fc838570
| 27,562 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
python/Untitled.ipynb
|
lafamila/lafamila
|
1ed2463c6d6143fd5aee69820c371cb4641f0d2a
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2017-12-29T05:51:30.000Z
|
2018-11-25T22:04:22.000Z
|
python/Untitled.ipynb
|
lafamila/lafamila
|
1ed2463c6d6143fd5aee69820c371cb4641f0d2a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
python/Untitled.ipynb
|
lafamila/lafamila
|
1ed2463c6d6143fd5aee69820c371cb4641f0d2a
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2021-04-15T07:41:25.000Z
|
2021-04-15T07:41:25.000Z
| 56.479508 | 1,114 | 0.546187 |
[
[
[
"import requests\nimport json\n\nheaders = {'content-type': 'application/json'}\nurl = 'https://nid.naver.com/nidlogin.login'\n\ndata = {\"eventType\": \"AAS_PORTAL_START\", \"data\": {\"id\": \"lafamila\", \"pw\": \"als01060\"}}\n#params = {'sessionKey': '9ebbd0b25760557393a43064a92bae539d962103', 'format': 'xml', 'platformId': 1}\n\n#requests.post(url, params=params, data=json.dumps(data), headers=headers)\nsource = requests.post(url, data=json.dumps(data), headers=headers)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<b>params</b> is for GET-style URL parameters, <b>data</b> is for POST-style body information",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"form = \"\"\"\n<form name=\"frmNIDLogin\" id=\"frmNIDLogin\" action=\"https://nid.naver.com/nidlogin.login\" method=\"post\" target=\"_top\">\n <input name=\"enctp\" id=\"enctp\" type=\"hidden\" value=\"1\">\n <input name=\"encpw\" id=\"encpw\" type=\"hidden\" value=\"\">\n <input name=\"encnm\" id=\"encnm\" type=\"hidden\" value=\"\">\n <input name=\"svctype\" id=\"svctype\" type=\"hidden\" value=\"0\">\n <input name=\"url\" id=\"url\" type=\"hidden\" value=\"https://www.naver.com/\">\n <input name=\"enc_url\" id=\"enc_url\" type=\"hidden\" value=\"https%3A%2F%2Fwww.naver.com%2F\">\n <input name=\"postDataKey\" id=\"postDataKey\" type=\"hidden\" value=\"\">\n <input name=\"nvlong\" id=\"nvlong\" type=\"hidden\" value=\"\">\n <input name=\"saveID\" id=\"saveID\" type=\"hidden\" value=\"\">\n <input name=\"smart_level\" id=\"smart_level\" type=\"hidden\" value=\"1\">\n <fieldset>\n <legend class=\"blind\">로그인</legend>\n <div class=\"htmlarea\" id=\"flasharea\" style=\"visibility: hidden;\"><object width=\"148\" height=\"67\" id=\"flashlogin\" classid=\"clsid:d27cdb6e-ae6d-11cf-96b8-444553540000\" codebase=\"https://fpdownload.macromedia.com/pub/shockwave/cabs/flash/swflash.cab#version=9,0,0,0\" style=\"visibility: hidden;\"><param name=\"allowScriptAccess\" value=\"always\"><param name=\"quality\" value=\"high\"><param name=\"menu\" value=\"false\"><param name=\"movie\" value=\"https://static.nid.naver.com/loginv3/commonLoginF_201505.swf\"><param name=\"wmode\" value=\"window\"><param name=\"bgcolor\" value=\"#f7f7f7\"><param name=\"FlashVars\" value=\"null\"><param name=\"allowFullScreen\" value=\"false\"><embed name=\"flashlogin\" width=\"148\" height=\"67\" align=\"middle\" pluginspage=\"https://www.macromedia.com/go/getflashplayer\" src=\"https://static.nid.naver.com/loginv3/commonLoginF_201505.swf\" type=\"application/x-shockwave-flash\" allowscriptaccess=\"always\" allowfullscreen=\"false\" bgcolor=\"#f7f7f7\" flashvars=\"null\" menu=\"false\" wmode=\"window\" quality=\"high\"></object>\n <div class=\"error_box_v2\" id=\"div_capslock2\" style=\"left: -14px; top: 59px; display: none; position: absolute;\">\n <p><strong>Caps Lock</strong>이 켜져 있습니다.</p>\n </div>\n </div>\n <div class=\"htmlarea\" id=\"htmlarea\" style=\"display: block;\">\n <div class=\"input_box\"><label class=\"lbl_in\" id=\"label_id\" for=\"id\">아이디</label><input name=\"id\" title=\"아이디\" class=\"int\" id=\"id\" accesskey=\"L\" style=\"-ms-ime-mode: disabled;\" type=\"text\" maxlength=\"41\" placeholder=\"아이디\"></div>\n <div class=\"input_box\"><label class=\"lbl_in\" id=\"label_pw\" for=\"pw\">비밀번호</label><input name=\"pw\" title=\"비밀번호\" class=\"int\" id=\"pw\" type=\"password\" maxlength=\"16\" placeholder=\"비밀번호\">\n <div class=\"error_box_v2\" id=\"div_capslock\" style=\"display: none;\">\n <p><strong>Caps Lock</strong>이 켜져 있습니다.</p>\n </div>\n </div>\n </div>\n <div class=\"chk_id_login\">\n <input title=\"로그인 상태유지\" class=\"chk_login\" id=\"chk_log\" type=\"checkbox\">\n <label class=\"lbl_long\" id=\"lbl_long\" for=\"chk_log\"><i class=\"ico_chk\"></i>로그인 상태 유지</label>\n </div>\n <div class=\"login_help\">\n <div class=\"chk_ip\"><a title=\"\" id=\"ip_guide\" href=\"https://static.nid.naver.com/loginv3/help_ip.html\" target=\"_blank\">IP보안</a> <span class=\"ip_box\"><input title=\"IP 보안이 켜져 있습니다. IP보안을 사용하지 않으시려면 선택을 해제해주세요.\" class=\"chb_b\" id=\"ckb_type\" type=\"checkbox\"><label class=\"lbl_type on\" id=\"lbl_type\" for=\"ckb_type\">IP보안 체크</label></span></div>\n </div>\n <span class=\"btn_login\"><input title=\"로그인\" type=\"submit\" value=\"로그인\"></span>\n <a class=\"btn_dis\" href=\"https://nid.naver.com/nidlogin.login?mode=number&svctype=&logintp=&viewtype=&url=https://www.naver.com\" target=\"_top\">일회용 로그인</a>\n <p class=\"btn_lnk\">\n <a class=\"btn_join\" href=\"https://nid.naver.com/nidregister.form?url=https://www.naver.com\" target=\"_blank\">회원가입</a>\n <a class=\"btn_id\" href=\"https://nid.naver.com/user/help.nhn?todo=idinquiry\" target=\"_blank\">아이디<span class=\"blind\">찾기</span></a>/<a href=\"https://nid.naver.com/nidreminder.form\" target=\"_blank\">비밀번호 찾기</a>\n </p>\n </fieldset>\n </form>\n\"\"\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from bs4 import BeautifulSoup\nsoup = BeautifulSoup(form, 'html.parser')\nvalues = soup.find_all('input')\ndatas = {}\nfor val in values:\n inputs = str(val).split(\"\\n\")[0]\n inp = BeautifulSoup(inputs, 'html.parser')\n if \"name\" in str(inp):\n name = inp.find('input')['name'].decode('utf-8').encode('utf-8')\n if \"value\" not in str(inp):\n datas[name] = raw_input(name)\n else:\n datas[name] = inp.find('input')['value'].decode('utf-8').encode('utf-8')\nprint datas",
"idlafamila\npwals01060\n{'postDataKey': '', 'encpw': '', 'pw': 'als01060', 'url': 'https://www.naver.com/', 'enctp': '1', 'encnm': '', 'nvlong': '', 'smart_level': '1', 'enc_url': 'https%3A%2F%2Fwww.naver.com%2F', 'svctype': '0', 'id': 'lafamila', 'saveID': ''}\n"
],
[
"import requests\nimport json\n\nheaders = {'content-type': 'application/json'}\nurl = 'https://nid.naver.com/nidlogin.login'\n\ndata = {\"data\": datas}\n#params = {'sessionKey': '9ebbd0b25760557393a43064a92bae539d962103', 'format': 'xml', 'platformId': 1}\n\n#requests.post(url, params=params, data=json.dumps(data), headers=headers)\nsource = requests.post(url, data=json.dumps(data), headers=headers)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print source.text",
"<!DOCTYPE html>\n<html lang=\"ko\">\n<head>\n\t<meta charset=\"UTF-8\">\n\t<meta name=\"viewport\" content=\"width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0, user-scalable=no\">\n\t<title>네이버 : 로그인</title>\n\t<link rel=\"stylesheet\" type=\"text/css\" href=\"/login/css/global/desktop/w_20161104.css?dt=20161214\">\n\t<link rel=\"stylesheet\" type=\"text/css\" href=\"/login/css/global/desktop/e_20161104.css?dt=20161214\">\n</head>\n<body >\n<script type=\"text/javascript\">\nfunction swapViewDiv(objname)\n{\n\tvar theme_setting_message = document.getElementById(objname);\n\tif (theme_setting_message.style.display=='block'||theme_setting_message.style.display=='')\n\t{\n\t\ttheme_setting_message.style.display='none';\n\t}\n\telse\n\t{\n\t\ttheme_setting_message.style.display='block';\n\t}\n}\nfunction swapViewDiv2(objname)\n{\n\tif (document.getElementById('themeCampaignLayer').style.display=='none')\n\t{\n\t\tswapViewDiv(objname);\n\t}\n}\n</script>\n<div class=\"theme_txt\" id=\"theme_txt_message\" >\n\t<p><strong>안전한 네이버 로그인을 위해 주소창의 URL과 자물쇠 마크를 확인하세요!</strong><br>보다 안전한 로그인을 위해 로그인 테마 설정을 추천합니다. 이미 로그인 테마를 사용하고 있었다면? <a href=\"javascript:swapViewDiv2('theme_setting_message');\" class=\"sp link\">자세히 보기</a></p>\n\t<a href=\"javascript:swapViewDiv('theme_txt_message');\" class=\"btn_closed\"><span class=\"blind\">로그인 테마 삭제 메세지 닫기</span></a>\n</div>\n<div class=\"theme_setting_message theme_dm\" id=\"theme_setting_message\" style=\"display:none;\">\n\t<div class=\"theme_error_view\">\n\t\t<h3 class=\"theme_h3\">로그인 테마를 설정해 주세요!</h3>\n\t\t<a href=\"javascript:swapViewDiv('theme_setting_message');\" class=\"btn_closed\"><span class=\"blind\">로그인 테마 삭제 안내창 닫기</span></a>\n\t\t<h4 class=\"theme_h4\">01. 기기의 설정 변경 등으로 이미지가 삭제된 것으로 판단됩니다!</h4>\n\t\t<p class=\"theme_view_txt\">브라우저 설정에서 검색/방문 기록을 삭제하거나 클리너/백신 프로그램의 PC 최적화 기능을 이용하여 쿠키/캐시를 삭제한 경우 설정했던 로그인 배경 이미지가 함께 삭제될 수 있습니다. <a href=\"https://help.naver.com/support/contents/contents.nhn?serviceNo=532&categoryNo=11003\" class=\"sp link\">자세히보기</a></p>\n\t\t<h4 class=\"theme_h4\">02. 지금 접속하신 페이지가 네이버가 맞는지 걱정 되시나요?</h4>\n\t\t<p class=\"theme_view_txt_url\">조금이라도 의심스럽다면, <strong>주소창의 URL</strong>(https://nid.naver.com)과 <strong>자물쇠</strong>를 꼭 확인하세요!</p>\n\t\t<p class=\"theme_view_txt_strong\">※ 주소창의 URL과 자물쇠를 확인하셨다면, 로그인 테마를 다시 설정하세요!</p>\n\t\t<a href=\"javascript:swapViewDiv('theme_setting_message');LoginTheme.openThemeCampaign()\" class=\"btn_theme_setting\">다시 설정하기</a>\n\t</div>\n</div>\n\n<div id=\"wrap\">\n\t<!-- header -->\n\t<div id=\"header\">\n\t\t<h1><a href=\"http://www.naver.com\" class=\"sp h_logo\" tabindex=\"1\" onclick=\"nclks('log.naver',this,event)\">NAVER</a></h1>\n\t\t<div class=\"theme_setting\" style=\"display:none\" onmouseover=\"LoginTheme.openLayer()\" onmouseout=\"LoginTheme.closeLayer()\">\n\t\t\t<a href=\"javascript:LoginTheme.redirectConfigWindow()\" onclick=\"nclks('ltg.setting',this,event)\" class=\"sp btn_setting\"><span class=\"blind\">로그인 테마 설정</span></a>\n\t\t\t<div id=\"theme_set\" class=\"ly_v3\">\n\t\t\t\t<div class=\"ly_box\">\n\t\t\t\t\t<strong>나만의 개성을 담아, 더 안전한 로그인!</strong>\n\t\t\t\t\t<p>간단한 설정으로 나만의 로그인 페이지를 만들어, 피싱 페이지로부터 안전하게 개인정보를 지킬 수 있습니다. <a href=\"https://help.naver.com/support/contents/contents.nhn?serviceNo=532&categoryNo=11001\" target=\"_blank\" class=\"\"><span class=\"sp btn_help\">도움말</span></a></p>\n\t\t\t\t\t<a href=\"javascript:LoginTheme.redirectConfigWindow()\" class=\"sp link\" onclick=\"nclks('ltg.setting',this,event)\">설정하기</a>\n\t\t\t\t</div>\n\t\t\t\t<span class=\"sp ly_point\"></span>\n\t\t\t</div>\n\t\t</div>\n\t\t<div class=\"lang\">\n\t\t\t<select id=\"locale_switch\" name=\"locale_switch\" title=\"언어선택\" tabindex=\"2\" class=\"sel\" onchange=\"switchlocale();nclks_select(this.value,'',{'ko_KR':'log.lankr','en_US':'log.lanen','zh-Hans_CN':'log.lancn','zh-Hant_TW':'log.lantw'},this,event);\">\n\t\t\t\t<option value=\"ko_KR\" selected>한국어</option>\n\t\t\t\t<option value=\"en_US\" >English</option>\n\t\t\t\t<option value=\"zh-Hans_CN\" >中文(简体)</option>\n\t\t\t\t<option value=\"zh-Hant_TW\" >中文(台灣)</option>\n\t\t\t</select>\n\t\t</div>\n\t</div>\n\t<!-- //header -->\n\t<!-- container -->\n\t<div id=\"container\">\n\t\t<!-- content -->\n\t\t<div id=\"content\">\n\t\t\t<div class=\"title\">\n\t\t\t\t<p></p>\n\t\t\t</div>\n\t\t\t<div class=\"link_info\">\n\t\t\t\t<span class=\"link_group\">\n\t\t\t\t\t<a href=\"https://help.naver.com/support/contents/contents.nhn?serviceNo=532&categoryNo=1577\" target=\"_blank\" tabindex=\"6\" onclick=\"nclks('log.groupidlogin',this,event)\">단체아이디 로그인 방법</a>\n\t\t\t\t</span>\n\t\t\t</div>\n <form id=\"frmNIDLogin\" name=\"frmNIDLogin\" target=\"_top\" AUTOCOMPLETE=\"off\" action=\"https://nid.naver.com/nidlogin.login\" method=\"post\" onsubmit=\"return confirmSubmit();\">\n <input type=\"hidden\" name=\"enctp\" id=\"enctp\" value=\"2\">\n <input type=\"hidden\" name=\"encpw\" id=\"encpw\" value=\"\">\n <input type=\"hidden\" name=\"encnm\" id=\"encnm\" value=\"\">\n <input type=\"hidden\" name=\"svctype\" id=\"svctype\" value=\"0\">\n <input type=\"hidden\" name=\"svc\" id=\"svc\" value=\"\">\n <input type=\"hidden\" name=\"viewtype\" id=\"viewtype\" value=\"0\">\n <input type=\"hidden\" name=\"locale\" id=\"locale\" value=\"ko_KR\">\n <input type=\"hidden\" name=\"postDataKey\" id=\"postDataKey\" value=\"\">\n <input type=\"hidden\" name=\"smart_LEVEL\" id=\"smart_LEVEL\" value=\"-1\">\n <input type=\"hidden\" name=\"logintp\" id=\"logintp\" value=\"\">\n <input type=\"hidden\" name=\"url\" id=\"url\" value=\"http://www.naver.com\">\n <input type=\"hidden\" name=\"localechange\" id=\"localechange\" value=\"\">\n <input type=\"hidden\" name=\"theme_mode\" id=\"theme_mode\" value=\"\">\n <input type=\"hidden\" name=\"ls\" id=\"ls\" value=\"\">\n <input type=\"hidden\" name=\"pre_id\" id=\"pre_id\" value=\"\">\n <input type=\"hidden\" name=\"resp\" id=\"resp\" value=\"\">\n <input type=\"hidden\" name=\"exp\" id=\"exp\" value=\"\">\n <input type=\"hidden\" name=\"ru\" id=\"ru\" value=\"\">\n\t\t\t\t<fieldset class=\"login_form\">\n\t\t\t\t\t<legend class=\"blind\">로그인</legend>\n\t\t\t\t\t<div class=\"input_row\" id=\"id_area\">\n\t\t\t\t\t\t<span class=\"input_box\">\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t<label for=\"id\" id=\"label_id_area\" class=\"lbl\" >아이디</label>\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t<input type=\"text\" id=\"id\" name=\"id\" tabindex=\"7\" accesskey=\"L\" placeholder=\"아이디\" class=\"int\" maxlength=\"41\" value=\"\">\n\t\t\t\t\t\t</span>\n\t\t\t\t\t\t<button type=\"button\" disabled=\"\" title=\"delete\" id=\"id_clear\" class=\"wrg\">삭제</button>\n\t\t\t\t\t</div>\n\t\t\t\t\t<div id=\"err_empty_id\" class=\"error\" style=\"display:none;\">아이디를 입력해주세요.</div>\n\t\t\t\t\t<div class=\"input_row\" id=\"pw_area\">\n\t\t\t\t\t\t<span class=\"input_box\">\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t<label for=\"pw\" id=\"label_pw_area\" class=\"lbl\">비밀번호</label>\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t<input type=\"password\" id=\"pw\" name=\"pw\" tabindex=\"8\" placeholder=\"비밀번호\" class=\"int\" maxlength=\"16\" onkeypress=\"capslockevt(event);getKeysv2();\" onkeyup=\"checkShiftUp(event);\" onkeydown=\"checkShiftDown(event);\" >\n\t\t\t\t\t\t</span>\n\t\t\t\t\t\t<button type=\"button\" disabled=\"\" title=\"delete\" id=\"pw_clear\" class=\"wrg\">삭제</button>\n\t\t\t\t\t\t<div class=\"ly_v2\" id=\"err_capslock\" style=\"display:none;\">\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t<div class=\"ly_box\">\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t<p><strong>Caps Lock</strong>이 켜져 있습니다.</p>\t\t\t\t\t\t\t</div>\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t<span class=\"sp ly_point\"></span>\n\t\t\t\t\t\t</div>\n\t\t\t\t\t</div>\n\t\t\t\t\t<div class=\"error\" id=\"err_empty_pw\" style=\"display:none;\">비밀번호를 입력해주세요.</div>\n\t\t\t\t\t<input type=\"submit\" title=\"로그인\" alt=\"로그인\" tabindex=\"12\" value=\"로그인\" class=\"btn_global\" onclick=\"nclks('log.login',this,event)\">\n\t\t\t\t\t<div class=\"check_info\" >\n\t\t\t\t\t\t<div class=\"login_check\">\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t<span class=\"login_check_box\">\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t<input type=\"checkbox\" id=\"login_chk\" name=\"nvlong\" class=\"\" tabindex=\"9\" value=\"off\" onchange=\"savedLong(this);nclks_chk('login_chk', 'log.keepon', 'log.keepoff',this,event)\" onclick=\"msieblur(this);\"/>\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t<label for=\"login_chk\" id=\"label_login_chk\" class=\"sp\">로그인 상태 유지</label>\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t</span>\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t<div class=\"ly_v2\" id=\"persist_usage\" style=\"display:none;\">\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t<div class=\"ly_box\">\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t<p>개인정보 보호를 위해 <strong>개인 PC에서만 사용하세요.</strong> <a href=\"https://help.naver.com/support/contents/contents.nhn?serviceNo=532&categoryNo=1523\" target=\"_blank\" class=\"sp btn_check_help\">도움말보기</a></p>\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t</div>\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t<span class=\"sp ly_point\"></span>\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t</div>\n\t\t\t\t\t\t</div>\n\t\t\t\t\t\t<div class=\"pc_check\">\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t<span class=\"ip_check\">\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t<a href=\"/login/ext/help_ip3.html\" target=\"_blank\" onclick=\"window.open(this.href, 'IPGUIDE', 'titlebar=1, resizable=1, scrollbars=yes, width=537, height=750'); return false;\" title=\"\" tabindex=\"10\">IP보안</a>\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t<span class=\"ip_ch\">\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t<input type=\"checkbox\" id=\"ip_on\" checked=\"checked\" tabindex=\"11\" onchange=\"ipCheck(this,event);nclks_chk('ip_on', 'log.iponset', 'log.ipoffset',this,event)\" onclick=\"msieblur(this);\" class=\"\"/>\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t<label for=\"ip_on\" id=\"label_ip_on\" class=\"sp\">on</label>\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t</span>\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t</span>\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t<span class=\"bar\">|</span>\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t<span class=\"dis_di\">\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t<a href=\"#\" onclick=\"onetime(); nclks('log.otn',this,event); return false;\" title=\"일회용 로그인\">일회용 로그인</a><a href=\"javascript:viewOnetime();\" onclick=\"nclks('log.otnhelp',this,event)\" title=\"도움말\" class=\"sp btn_help\">도움말</a>\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t<div class=\"ly\" id=\"onetime_usage\" style=\"display:none;\" onclick=\"javascript:viewOnetime()\">\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t<div class=\"ly_box\">\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t<p>네이버앱에서 생성된 일회용 로그인 번호를 입력하면, 앱에 로그인된 계정으로 PC에서 로그인할 수 있어요. 아이디/비밀번호를 입력하지 않아 간편하고 더욱 안전합니다.</p>\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t</div>\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t<span class=\"sp ly_point\"></span>\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t</div>\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t</span>\n\t\t\t\t\t\t</div>\n\t\t\t\t\t</div>\n\t\t\t\t</fieldset>\n\t\t\t</form>\n\t\t\t<div class=\"position_a\">\n\t\t\t\t<div class=\"find_info\">\n\t\t\t\t\t<a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://nid.naver.com/user/help.nhn?todo=idinquiry\" onclick=\"try{nclks('log.searchid',this,event)}catch(e){}\">아이디 찾기</a> <span class=\"bar\">|</span> <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://nid.naver.com/nidreminder.form\" onclick=\"try{nclks('log.searchpass',this,event)}catch(e){}\">비밀번호 찾기</a> <span class=\"bar\">|</span> <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://nid.naver.com/user/join.html?lang=ko_KR\" onclick=\"try{nclks('log.registration',this,event)}catch(e){}\">회원가입</a>\t\t\t\t</div>\n\t\t\t</div>\n\t\t\t<!-- tg-lang -->\n\t\t</div>\n\t\t<!-- //content -->\n\t</div>\n\t<!-- //container -->\n\t<!-- footer -->\n\t<div id=\"footer\">\n\t\t<ul>\n\t\t<li><a target=\"_blank\" href=\"http://www.naver.com/rules/service.html\" onclick=\"nclks('fot.agreement',this,event)\">이용약관</a></li>\n\t\t<li><strong><a target=\"_blank\" href=\"http://www.naver.com/rules/privacy.html\" onclick=\"nclks('fot.privacy',this,event)\">개인정보처리방침</a></strong></li>\n\t\t<li><a target=\"_blank\" href=\"http://www.naver.com/rules/disclaimer.html\" onclick=\"nclks('fot.disclaimer',this,event)\">책임의 한계와 법적고지</a></li>\n\t\t<li><a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://help.naver.com/support/service/main.nhn?serviceNo=532\" onclick=\"nclks('fot.help',this,event)\">회원정보 고객센터</a></li>\n\t\t</ul>\n\t\n\t\t<address><em><a target=\"_blank\" href=\"http://www.navercorp.com\" class=\"logo\" onclick=\"nclks('fot.naver',this,event)\"><span class=\"blind\">naver</span></a></em><em class=\"copy\">Copyright</em> <em class=\"u_cri\">©</em> <a target=\"_blank\" href=\"http://www.navercorp.com\" class=\"u_cra\" onclick=\"nclks('fot.navercorp',this,event)\">NAVER Corp.</a> <span class=\"all_r\">All Rights Reserved.</span></address>\t</div>\n\t<!-- //footer -->\n\t\n</div>\n<div class=\"theme_setting_message\" id=\"themeCampaignLayer\" style=\"display:none\">\n\t<div class=\"setting_message\">\n\t\t<h3 class=\"blind\">로그인 테마 설정 안내</h3>\n\t\t<a href=\"javascript:LoginTheme.closeThemeCampaign()\" onclick=\"nclks('ltg.close',this,event)\" class=\"btn_closed\"><span class=\"blind\">로그인 테마 설정 안내창 닫기</span></a>\n\t\t<p class=\"blind\"><strong><span>나만의 개성을 담아,</span><br>더 안전한 로그인!</strong></p>\n\t\t<p class=\"blind\">늘 보는 밋밋한 로그인 페이지는 이제 그만! 개성 넘치는 나만의 로그인 페이지 설정하고, 안전하게 로그인 하세요. 가짜 로그인 화면과 구별되어 피싱으로부터 안전해집니다.</p>\n\t\t<a href=\"https://help.naver.com/support/contents/contents.nhn?serviceNo=532&categoryNo=11001\" onclick=\"javascript:nclks('ltg.help',this,event)\" target=\"_blank\" class=\"btn_view\"><span class=\"blind\">자세히 보기</span></a>\n\t\t<p class=\"setting_message_txt\">이제 내가 설정한 이미지가 나오는지 꼭 확인하고 로그인 하세요!<strong><span class=\"sp ico_error\"></span>안보인다면? 피싱페이지일 수 있습니다!</strong></p>\n\t\t<a href=\"javascript:LoginTheme.redirectConfigWindow()\" onclick=\"nclks('ltg.setting',this,event)\" class=\"btn_theme_setting\">지금 설정하기</a>\n\t</div>\n</div>\n<script type=\"text/javascript\" src=\"https://nid.naver.com/login/js/common.all.js?141216\"> </script>\n<script type=\"text/javascript\" src=\"https://nid.naver.com/login/js/logintheme.js?150109\"> </script>\n<script type=\"text/javascript\">\nvar disp_stat = \"20\";\nvar session_keys = \"\";\nvar pc_keyboard_close=\"<span class=\\\"sp\\\">PC 키보드 닫기</span>\";\nvar pc_keyboard_open=\"<span class=\\\"sp\\\">PC 키보드 보기</span>\";\nvar view_char=\"한글 보기\";\nvar view_symbol=\"특수기호 보기\";\n\naddInputEvent('id', 'id_area');\naddInputEvent('pw', 'pw_area');\n\ninitSmartLevel();\nvar login_chk = $('login_chk');\nif(login_chk.attachEvent) {\n\tlogin_chk.attachEvent(\"onchange\", function(){persist_usage();});\n} else if (login_chk.addEventListener) {\n\tlogin_chk.addEventListener(\"change\", function(){persist_usage();}, false);\n}\nfunction persist_usage()\n{\n\tvar login_chk = $(\"login_chk\");\n\tif (login_chk.checked==true)\n\t{\n\t\tshow(\"persist_usage\");\n\t\thide('onetime_usage');\n\t\tview_onetimeusage = false;\n\t}\n\telse\n\t{\n\t\thide(\"persist_usage\");\n\t}\n}\nvar view_onetimeusage = false;\nfunction viewOnetime()\n{\n\tif (view_onetimeusage)\n\t{\n\t\thide('onetime_usage');\n\t\tview_onetimeusage = false;\n\t}\n\telse\n\t{\n\t\thide(\"persist_usage\");\n\t\tshow('onetime_usage');\n\t\tview_onetimeusage = true;\n\t}\n}\ntry{\n\tif (navigator.appVersion.toLowerCase().indexOf(\"win\") != -1) {\n\t\t$('id').style.imeMode = \"disabled\";\n\t\tdocument.msCapsLockWarningOff = true;\n\t}\n}catch(e) {}\ntry{\n\tif ( $('id').value.length == 0 )\n\t{\n\t\t$('id').focus();\n\t}\n\telse\n\t{\n\t\t$('pw').focus();\n\t}\n}catch (e){}\ntry{\n\tvar nid_buk = localStorage.getItem(\"nid_buk\");\n\tif (nid_buk!=null && nid_buk.length>0)\n\t{\n\t\tLoginTheme.setCookieNameValue(\"nid_buk\", escape(nid_buk));\n\t}\n\telse\n\t{\n\t\tnid_nnb = getCookie('NNB');\n\t\tif (nid_nnb!=null && nid_nnb.length>0)\n\t\t{\n\t\t\tlocalStorage.setItem(\"nid_buk\", nid_nnb);\n\t\t\tLoginTheme.setCookieNameValue(\"nid_buk\", escape(nid_nnb));\n\t\t}\n\t}\n}catch(e){}\n\n</script>\n<script type=\"text/javascript\" src=\"https://nid.naver.com/login/js/common.util.js\"></script>\n<script type=\"text/javascript\"> lcs_do(); </script>\n<script type=\"text/javascript\">\nvar nsc = \"nid.login_kr\";\n</script>\n<div id=\"nv_stat\" style=\"display:none;\">20</div>\n</body>\n</html>\n\n"
],
[
"#https://gist.github.com/blmarket/9012444",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50cd94633f8630b8bad855d44ac69dede8b6af3
| 188,127 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
hw1/Ketchum_HW1_incom.ipynb
|
dgketchum/csci547
|
bbba91c1cd09f672342b11280f79e551968a0037
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
hw1/Ketchum_HW1_incom.ipynb
|
dgketchum/csci547
|
bbba91c1cd09f672342b11280f79e551968a0037
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null |
hw1/Ketchum_HW1_incom.ipynb
|
dgketchum/csci547
|
bbba91c1cd09f672342b11280f79e551968a0037
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | null | null | null | 363.882012 | 43,364 | 0.936352 |
[
[
[
"# 1A See Handwritten Notes",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 1B",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\nimport os\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport matplotlib as mpl\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nmpl.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [12,8]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# sine wave with noise, aka swell with wind chop\narr = np.linspace(0, 20, 50)\nts = np.sin(arr) * 5 + np.random.uniform(-1, 1, len(arr))\nplt.plot(arr, ts, 'r+')\nplt.show()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"data = pd.DataFrame(data={'Time': arr, 'Wave Height': ts})\nx = data['Time'].as_matrix().astype(float)\ny = data['Wave Height'].as_matrix().astype(float)\n\nX = np.column_stack([np.ones_like(x),x])\nw = np.linalg.solve(np.dot(X.T,X),np.dot(X.T,y))\n\nxhat = np.linspace(x.min(),x.max(),101)\nXhat = np.column_stack([np.ones_like(xhat),xhat])\nyhat = np.dot(Xhat,w)\n\nx_tilde = 2*(x - x.min())/(x.max()-x.min()) - 1\nxhat = 2*(xhat - x.min())/(x.max()-x.min()) - 1\n\nx = x_tilde\n\ndegree = 10\n\nX = np.vander(x,degree+1,increasing=True)\n\ngamma = 1e-4\nEye = np.eye(X.shape[1])\nEye[0,0] = 0\n\nw = np.linalg.solve(np.dot(X.T,X),np.dot(X.T,y))\n\nXhat = np.vander(xhat,degree+1,increasing=True)\nyhat = np.dot(Xhat,w)\n\navg_rmse = np.sqrt(np.sum((np.dot(X,w) - y)**2)/len(y))\nprint(avg_rmse)\nplt.plot(xhat,yhat,'k-')\nplt.plot(x,y,'ro')\nplt.show()",
"0.9996401024440149\n"
]
],
[
[
"## 1C",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"test_path = 'PC1_test.csv'\ntraining_path = 'PC1_training.csv'\n\ndegree = 3\n\ntest_series = pd.read_csv(test_path, names=['Test'])\ntraining_series = pd.read_csv(training_path, names=['Training'])\ny = training_series['Training'].values\nx = training_series['Training'].index\n\nx_tilde = 2*(x - x.min())/(x.max()-x.min()) - 1\nxhat = 2*(xhat - x.min())/(x.max()-x.min()) - 1\n\nx = x_tilde\n\nX = np.vander(x, degree+1, increasing=True)\n\ngamma = 1e-4\nEye = np.eye(X.shape[1])\nEye[0,0] = 0\n\nw = np.linalg.solve(np.dot(X.T,X) + gamma*Eye, np.dot(X.T,y))\n\nXhat = np.vander(xhat,degree+1,increasing=True)\nyhat = np.dot(Xhat, w)\n\n\navg_rmse = np.sqrt(np.sum((np.dot(X,w) - y)**2)/len(y))\n\nplt.plot(x,y,'ro')\nplt.plot(xhat,yhat,'k-')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 1D",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\ntraining_rmse = []\nfor degree in range(0, 15):\n X = np.vander(x, degree+1, increasing=True)\n w = np.linalg.solve(np.dot(X.T,X), np.dot(X.T,y))\n Xhat = np.vander(xhat,degree+1,increasing=True)\n yhat = np.dot(Xhat, w)\n avg_rmse = np.sqrt(np.sum((np.dot(X,w) - y)**2)/len(y))\n training_rmse.append(avg_rmse)\n\n \nyt = test_series['Test'].values\nxt = test_series['Test'].index \n\ntest_rmse = []\nfor degree in range(0, 15):\n X = np.vander(x, degree+1, increasing=True)\n w = np.linalg.solve(np.dot(X.T,X), np.dot(X.T,yt))\n Xhat = np.vander(xhat,degree+1,increasing=True)\n yhat = np.dot(Xhat, w)\n avg_rmse = np.sqrt(np.sum((np.dot(X,w) - yt)**2)/len(yt))\n test_rmse.append(avg_rmse)\n\nrmse_hat = [x for x in range(0, 15)]\n\nplt.ylabel('Avg. RMSE')\nplt.xlabel('Polygon Order')\nplt.plot(rmse_hat, test_rmse, 'k-')\nplt.plot(rmse_hat, training_rmse, 'b-')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 1E",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"degree = 15\n\ngamma_arr = [x for x in np.logspace(-5, 1, 10)]\n\ntraining_rmse = []\nfor gamma in np.logspace(-5, 1, 10):\n X = np.vander(x, degree+1, increasing=True)\n Eye = np.eye(X.shape[1])\n Eye[0,0] = 0\n w = np.linalg.solve(np.dot(X.T,X) + gamma*Eye,np.dot(X.T,y))\n avg_rmse = np.sqrt(np.sum((np.dot(X,w) - y)**2)/len(y))\n training_rmse.append(avg_rmse)\n \ntest_rmse = []\nfor gamma in np.logspace(-5, 1, 10):\n X = np.vander(xt, degree+1, increasing=True)\n Eye = np.eye(X.shape[1])\n Eye[0,0] = 0\n w = np.linalg.solve(np.dot(X.T,X) + gamma*Eye,np.dot(X.T,yt))\n avg_rmse = np.sqrt(np.sum((np.dot(X,w) - yt)**2)/len(yt))\n test_rmse.append(avg_rmse)\n\nplt.ylabel('Avg. RMSE')\nplt.xlabel('Gamma')\nplt.semilogx(gamma_arr, training_rmse, 'b-')\nplt.semilogx(gamma_arr, test_rmse, 'k-')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 1F",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn import linear_model\n\nN = 11\ndegree = 15\n\ngamma_arr = [x for x in np.logspace(-5, 1, 10)]\n\ntraining_rmse = []\nfor gamma in np.logspace(-5, 1, 10):\n X = np.vander(x,degree)[:,1:]\n lasso = linear_model.Lasso(alpha=gamma,max_iter=100000)\n lasso.fit(X,y)\n rmse = np.sqrt(np.sum((lasso.predict(X) - y)**2)/N)\n training_rmse.append(rmse)\n\ntest_rmse = []\nfor gamma in np.logspace(-5, 1, 10):\n X = np.vander(xt,degree)[:,1:]\n lasso = linear_model.Lasso(alpha=gamma,max_iter=100000)\n lasso.fit(X,yt)\n rmse = np.sqrt(np.sum((lasso.predict(X) - yt)**2)/N)\n test_rmse.append(rmse)\n \nplt.ylabel('Avg. RMSE')\nplt.xlabel('Gamma')\nplt.semilogx(gamma_arr, training_rmse, 'b-')\nplt.semilogx(gamma_arr, test_rmse, 'k-')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 1G",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy.polynomial.legendre as leg\n\ntraining_rmse = []\nfor degree in range(0, 20):\n X = np.vander(x, degree+1, increasing=True)\n w = np.linalg.solve(np.dot(X.T,X), np.dot(X.T,y))\n Xhat = np.vander(xhat,degree+1,increasing=True)\n yhat = np.dot(Xhat, w)\n avg_rmse = np.sqrt(np.sum((np.dot(X,w) - y)**2)/len(y))\n training_rmse.append(avg_rmse)\n \nlegendre_rmse = []\nfor degree in range(0, 20):\n X = leg.legvander(x,degree)\n w = np.linalg.solve(np.dot(X.T,X),np.dot(X.T,y))\n avg_rmse = np.sqrt(np.sum((np.dot(X,w) - y)**2)/len(y))\n legendre_rmse.append(avg_rmse) \n\nrmse_hat = [x for x in range(0, 20)]\nplt.ylabel('Avg. RMSE')\nplt.xlabel('Polygon Order')\nplt.plot(rmse_hat, legendre_rmse, 'ko')\nplt.plot(rmse_hat, training_rmse, 'b-')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 3A",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Can ignore denominator because probability of a class is proportional to numerator, and the denominator is the same for each class, so the classifier can just choose the class with the highest valued numerator without normalizing each case.\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# 3B",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from sklearn.datasets import load_digits\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nfrom sklearn.naive_bayes import BernoulliNB\n\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport pprint\n\ndigits = load_digits()\nX = np.round(digits.data/16.)\ny = digits.target\nprint(y)\nn = y.shape[0]\n\nX, X_test, y, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.33,\n random_state=42)\n\nprint(len(y_test))\nm = X.shape[0] \nm_test = X_test.shape[0] \nN = 10 \n\nmu_array = np.zeros((n,N))\nsigma2_array = np.zeros((n,N))\nprior_array = np.zeros((N))\n\nfor i in \n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.figure(1, figsize=(3, 3))\nplt.imshow(digits.images[-1], cmap=plt.cm.gray_r, interpolation='nearest')\nplt.show()\n\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50ceae19a8baeb98606d74cb417ea03d1089b0f
| 21,079 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
0 - Visualization-and-analysis/1. Numpy/00-NumPy-Arrays.ipynb
|
yashodeepchikte/Machine-Learning
|
82eb3e2bc5bdc72acfefa1c3e3098d86705d3ed5
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2020-08-14T13:42:03.000Z
|
2020-08-19T20:32:29.000Z
|
0 - Visualization-and-analysis/1. Numpy/.ipynb_checkpoints/00-NumPy-Arrays-checkpoint.ipynb
|
yashodeepchikte/Machine-Learning
|
82eb3e2bc5bdc72acfefa1c3e3098d86705d3ed5
|
[
"MIT"
] | 5 |
2021-05-12T03:00:56.000Z
|
2022-02-10T04:52:10.000Z
|
0 - Visualization-and-analysis/1. Numpy/00-NumPy-Arrays.ipynb
|
yashodeepchikte/Machine-Learning
|
82eb3e2bc5bdc72acfefa1c3e3098d86705d3ed5
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 20.80849 | 268 | 0.455619 |
[
[
[
"# NumPy \n\nNumPy is also incredibly fast, as it has bindings to C libraries. For more info on why you would want to use arrays instead of lists, check out this great [StackOverflow post](http://stackoverflow.com/questions/993984/why-numpy-instead-of-python-lists).",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# NumPy Arrays\n\nNumPy arrays is the main way in which Numpy arrays are used.<br/> \nNumPy arrays essentially come in two flavors: vectors and matrices.<br/>\nVectors are strictly 1-dimensional (1D) arrays and matrices are 2D (but you should note a matrix can still have only one row or one column).\n\n\n## Creating NumPy Arrays\n\n### From a Python List\n\nWe can create an array by directly converting a list or list of lists:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"my_list = [1,2,3]\nmy_list",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.array(my_list)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"my_matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]\nmy_matrix",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.array(my_matrix)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Built-in Methods\n\nThere are lots of built-in ways to generate arrays.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### arange\n\nReturn evenly spaced values within a given interval. [[reference](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy-1.15.0/reference/generated/numpy.arange.html)]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.arange(0,10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.arange(0,11,2)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### zeros and ones\n\nGenerate arrays of zeros or ones. [[reference](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy-1.15.0/reference/generated/numpy.zeros.html)]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.zeros(3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.zeros((5,5))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.ones(3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.ones((3,3))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### linspace \nReturn evenly spaced numbers over a specified interval. [[reference](https://www.numpy.org/devdocs/reference/generated/numpy.linspace.html)]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.linspace(0,10,3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.linspace(0,5,20)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<font color=green>Note that `.linspace()` *includes* the stop value. To obtain an array of common fractions, increase the number of items:</font>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.linspace(0,5,21)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### eye\n\nCreates an identity matrix [[reference](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy-1.15.0/reference/generated/numpy.eye.html)]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.eye(4)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Random \nNumpy also has lots of ways to create random number arrays:\n\n### rand\nCreates an array of the given shape and populates it with random samples from a uniform distribution over ``[0, 1)``. [[reference](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy-1.15.0/reference/generated/numpy.random.rand.html)]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.random.rand(2)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.random.rand(5,5)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### randn\n\nReturns a sample (or samples) from the \"standard normal\" distribution [σ = 1]. Unlike **rand** which is uniform, values closer to zero are more likely to appear. [[reference](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy-1.15.0/reference/generated/numpy.random.randn.html)]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.random.randn(2)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.random.randn(5,5)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### randint\nReturns random integers from `low` (inclusive) to `high` (exclusive). [[reference](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy-1.15.0/reference/generated/numpy.random.randint.html)]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.random.randint(1,100)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.random.randint(1,100, (10, 10))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### seed\nCan be used to set the random state, so that the same \"random\" results can be reproduced. [[reference](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy-1.15.0/reference/generated/numpy.random.seed.html)]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"np.random.seed(42)\nnp.random.rand(4)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.random.seed(42)\nnp.random.rand(4)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Array Attributes and Methods\n\nLet's discuss some useful attributes and methods for an array:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"arr = np.arange(25)\nranarr = np.random.randint(0,50,10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"arr",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ranarr",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Reshape\nReturns an array containing the same data with a new shape. [[reference](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy-1.15.0/reference/generated/numpy.reshape.html)]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"arr.reshape(5,5)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### max, min, argmax, argmin\n\nThese are useful methods for finding max or min values. Or to find their index locations using argmin or argmax",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"ranarr",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ranarr.max()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ranarr.argmax()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ranarr.min()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"ranarr.argmin()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Shape\n\nShape is an attribute that arrays have (not a method): [[reference](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy-1.15.0/reference/generated/numpy.ndarray.shape.html)]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Vector\narr.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Notice the two sets of brackets\narr.reshape(1,25)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"arr.reshape(1,25).shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"arr.reshape(25,1)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"arr.reshape(25,1).shape",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### dtype\n\nYou can also grab the data type of the object in the array: [[reference](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy-1.15.0/reference/generated/numpy.ndarray.dtype.html)]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"arr.dtype",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"arr2 = np.array([1.2, 3.4, 5.6])\narr2.dtype",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50d0bcfb199a5660e18bdd022ab876bca2a1bf1
| 19,826 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Trail.ipynb
|
DaanMatch/Codebook
|
7c910062b3db59018b37ca15295ca4f32e64eccd
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Trail.ipynb
|
DaanMatch/Codebook
|
7c910062b3db59018b37ca15295ca4f32e64eccd
|
[
"MIT"
] | 20 |
2021-06-15T04:59:04.000Z
|
2021-10-05T23:00:11.000Z
|
Trail.ipynb
|
DaanMatch/Codebook
|
7c910062b3db59018b37ca15295ca4f32e64eccd
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2021-09-30T01:25:02.000Z
|
2021-09-30T02:07:47.000Z
| 37.908222 | 145 | 0.427166 |
[
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"raw = pd.read_csv(\"Trial.txt\", names=['Column Names', 'Data'])\nraw",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Strip Leading and trailing whitespace\nraw[\"Column Names\"] = raw[\"Column Names\"].apply(lambda x: x.strip())\nraw[\"Data\"] = raw[\"Data\"].apply(lambda x: x.strip())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# List of all the headers\nheaders = raw[\"Column Names\"].unique()\nheaders",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Groupby the headers and convert to dictionary\nraw_dict = raw.groupby(\"Column Names\")[\"Data\"].apply(list).to_dict()\nraw_dict",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Convert dictionary to dataframe, and expand list\nraw_final = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(raw_dict,orient='index').transpose()\nraw_final.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50d14d7683664df3660938fbfa6950c30e514ed
| 4,960 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
part-5.ipynb
|
willingc/intro-to-python
|
9822315d28c603b17d7475c09925146d704a571c
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | 13 |
2015-05-11T06:20:24.000Z
|
2017-04-13T19:47:54.000Z
|
part-5.ipynb
|
willingc/intro-to-python
|
9822315d28c603b17d7475c09925146d704a571c
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | null | null | null |
part-5.ipynb
|
willingc/intro-to-python
|
9822315d28c603b17d7475c09925146d704a571c
|
[
"CC-BY-4.0"
] | 10 |
2016-04-16T19:28:22.000Z
|
2018-06-15T14:56:57.000Z
| 20.411523 | 97 | 0.47379 |
[
[
[
"empty"
]
]
] |
[
"empty"
] |
[
[
"empty"
]
] |
c50d16790fb82580a5ed77a1403a28b6d81c6ed5
| 496,443 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
LS_DS_123_Make_Explanatory_Visualizations.ipynb
|
Scott-Huston/DS-Unit-1-Sprint-2-Data-Wrangling-and-Storytelling
|
23b16a29b749fa6185202b2e1d884ee549f7ed0f
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2019-07-15T19:09:25.000Z
|
2019-07-15T19:09:25.000Z
|
LS_DS_123_Make_Explanatory_Visualizations.ipynb
|
Scott-Huston/DS-Unit-1-Sprint-2-Data-Wrangling-and-Storytelling
|
23b16a29b749fa6185202b2e1d884ee549f7ed0f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
LS_DS_123_Make_Explanatory_Visualizations.ipynb
|
Scott-Huston/DS-Unit-1-Sprint-2-Data-Wrangling-and-Storytelling
|
23b16a29b749fa6185202b2e1d884ee549f7ed0f
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 71.072727 | 93,732 | 0.553067 |
[
[
[
"<a href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/Scott-Huston/DS-Unit-1-Sprint-2-Data-Wrangling-and-Storytelling/blob/master/LS_DS_123_Make_Explanatory_Visualizations.ipynb\" target=\"_parent\"><img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open In Colab\"/></a>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"_Lambda School Data Science_\n\n# Make Explanatory Visualizations\n\n### Objectives\n\n- identify misleading visualizations and how to fix them\n- use Seaborn to visualize distributions and relationships with continuous and discrete variables\n- add emphasis and annotations to transform visualizations from exploratory to explanatory\n- remove clutter from visualizations\n\n### Links\n\n- [How to Spot Visualization Lies](https://flowingdata.com/2017/02/09/how-to-spot-visualization-lies/)\n- [Visual Vocabulary - Vega Edition](http://ft.com/vocabulary)\n- [Choosing a Python Visualization Tool flowchart](http://pbpython.com/python-vis-flowchart.html)\n- [Searborn example gallery](http://seaborn.pydata.org/examples/index.html) & [tutorial](http://seaborn.pydata.org/tutorial.html)\n- [Strong Titles Are The Biggest Bang for Your Buck](http://stephanieevergreen.com/strong-titles/)\n- [Remove to improve (the data-ink ratio)](https://www.darkhorseanalytics.com/blog/data-looks-better-naked)\n- [How to Generate FiveThirtyEight Graphs in Python](https://www.dataquest.io/blog/making-538-plots/)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Avoid Misleading Visualizations\n\nDid you find/discuss any interesting misleading visualizations in your Walkie Talkie?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## What makes a visualization misleading?\n\n[5 Ways Writers Use Misleading Graphs To Manipulate You](https://venngage.com/blog/misleading-graphs/)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Two y-axes\n\n<img src=\"https://kieranhealy.org/files/misc/two-y-by-four-sm.jpg\" width=\"800\">\n \n Other Examples: \n - [Spurious Correlations](https://tylervigen.com/spurious-correlations)\n - <https://blog.datawrapper.de/dualaxis/>\n - <https://kieranhealy.org/blog/archives/2016/01/16/two-y-axes/>\n - <http://www.storytellingwithdata.com/blog/2016/2/1/be-gone-dual-y-axis>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Y-axis doesn't start at zero.\n\n<img src=\"https://i.pinimg.com/originals/22/53/a9/2253a944f54bb61f1983bc076ff33cdd.jpg\" width=\"600\">",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Pie Charts are bad\n\n<img src=\"https://i1.wp.com/flowingdata.com/wp-content/uploads/2009/11/Fox-News-pie-chart.png?fit=620%2C465&ssl=1\" width=\"600\">",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Pie charts that omit data are extra bad\n \n- A guy makes a misleading chart that goes viral\n\n What does this chart imply at first glance? You don't want your user to have to do a lot of work in order to be able to interpret you graph correctly. You want that first-glance conclusions to be the correct ones.\n\n <img src=\"https://pbs.twimg.com/media/DiaiTLHWsAYAEEX?format=jpg&name=medium\" width='600'>\n \n <https://twitter.com/michaelbatnick/status/1019680856837849090?lang=en>\n \n- It gets picked up by overworked journalists (assuming incompetency before malice)\n \n <https://www.marketwatch.com/story/this-1-chart-puts-mega-techs-trillions-of-market-value-into-eye-popping-perspective-2018-07-18>\n \n- Even after the chart's implications have been refuted, it's hard a bad (although compelling) visualization from being passed around.\n\n <https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/good-bad-pie-charts-karthik-shashidhar/>\n\n**[\"yea I understand a pie chart was probably not the best choice to present this data.\"](https://twitter.com/michaelbatnick/status/1037036440494985216)**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Pie Charts that compare unrelated things are next-level extra bad\n\n<img src=\"http://www.painting-with-numbers.com/download/document/186/170403+Legalizing+Marijuana+Graph.jpg\" width=\"600\">\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Be careful about how you use volume to represent quantities:\n\nradius vs diameter vs volume\n\n<img src=\"https://static1.squarespace.com/static/5bfc8dbab40b9d7dd9054f41/t/5c32d86e0ebbe80a25873249/1546836082961/5474039-25383714-thumbnail.jpg?format=1500w\" width=\"600\">",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Don't cherrypick timelines or specific subsets of your data:\n\n<img src=\"https://wattsupwiththat.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/Figure-1-1.png\" width=\"600\">\n\nLook how specifically the writer has selected what years to show in the legend on the right side.\n\n<https://wattsupwiththat.com/2019/02/24/strong-arctic-sea-ice-growth-this-year/>\n\nTry the tool that was used to make the graphic for yourself\n\n<http://nsidc.org/arcticseaicenews/charctic-interactive-sea-ice-graph/>\n ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Use Relative units rather than Absolute Units\n\n<img src=\"https://imgs.xkcd.com/comics/heatmap_2x.png\" width=\"600\">",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Avoid 3D graphs unless having the extra dimension is effective\n\nUsually you can Split 3D graphs into multiple 2D graphs\n\n3D graphs that are interactive can be very cool. (See Plotly and Bokeh)\n\n<img src=\"https://thumbor.forbes.com/thumbor/1280x868/https%3A%2F%2Fblogs-images.forbes.com%2Fthumbnails%2Fblog_1855%2Fpt_1855_811_o.jpg%3Ft%3D1339592470\" width=\"600\">",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Don't go against typical conventions\n\n<img src=\"http://www.callingbullshit.org/twittercards/tools_misleading_axes.png\" width=\"600\">",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Tips for choosing an appropriate visualization:",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Use Appropriate \"Visual Vocabulary\"\n\n[Visual Vocabulary - Vega Edition](http://ft.com/vocabulary)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## What are the properties of your data?\n- Is your primary variable of interest continuous or discrete?\n- Is in wide or long (tidy) format?\n- Does your visualization involve multiple variables?\n- How many dimensions do you need to include on your plot?\n\nCan you express the main idea of your visualization in a single sentence?\n\nHow hard does your visualization make the user work in order to draw the intended conclusion?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Which Visualization tool is most appropriate? \n\n[Choosing a Python Visualization Tool flowchart](http://pbpython.com/python-vis-flowchart.html)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Anatomy of a Matplotlib Plot",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom matplotlib.ticker import AutoMinorLocator, MultipleLocator, FuncFormatter\n\nnp.random.seed(19680801)\n\nX = np.linspace(0.5, 3.5, 100)\nY1 = 3+np.cos(X)\nY2 = 1+np.cos(1+X/0.75)/2\nY3 = np.random.uniform(Y1, Y2, len(X))\n\nfig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))\nax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1, aspect=1)\n\n\ndef minor_tick(x, pos):\n if not x % 1.0:\n return \"\"\n return \"%.2f\" % x\n\nax.xaxis.set_major_locator(MultipleLocator(1.000))\nax.xaxis.set_minor_locator(AutoMinorLocator(4))\nax.yaxis.set_major_locator(MultipleLocator(1.000))\nax.yaxis.set_minor_locator(AutoMinorLocator(4))\nax.xaxis.set_minor_formatter(FuncFormatter(minor_tick))\n\nax.set_xlim(0, 4)\nax.set_ylim(0, 4)\n\nax.tick_params(which='major', width=1.0)\nax.tick_params(which='major', length=10)\nax.tick_params(which='minor', width=1.0, labelsize=10)\nax.tick_params(which='minor', length=5, labelsize=10, labelcolor='0.25')\n\nax.grid(linestyle=\"--\", linewidth=0.5, color='.25', zorder=-10)\n\nax.plot(X, Y1, c=(0.25, 0.25, 1.00), lw=2, label=\"Blue signal\", zorder=10)\nax.plot(X, Y2, c=(1.00, 0.25, 0.25), lw=2, label=\"Red signal\")\nax.plot(X, Y3, linewidth=0,\n marker='o', markerfacecolor='w', markeredgecolor='k')\n\nax.set_title(\"Anatomy of a figure\", fontsize=20, verticalalignment='bottom')\nax.set_xlabel(\"X axis label\")\nax.set_ylabel(\"Y axis label\")\n\nax.legend()\n\n\ndef circle(x, y, radius=0.15):\n from matplotlib.patches import Circle\n from matplotlib.patheffects import withStroke\n circle = Circle((x, y), radius, clip_on=False, zorder=10, linewidth=1,\n edgecolor='black', facecolor=(0, 0, 0, .0125),\n path_effects=[withStroke(linewidth=5, foreground='w')])\n ax.add_artist(circle)\n\n\ndef text(x, y, text):\n ax.text(x, y, text, backgroundcolor=\"white\",\n ha='center', va='top', weight='bold', color='blue')\n\n# Minor tick\ncircle(0.50, -0.10)\ntext(0.50, -0.32, \"Minor tick label\")\n\n# Major tick\ncircle(-0.03, 4.00)\ntext(0.03, 3.80, \"Major tick\")\n\n# Minor tick\ncircle(0.00, 3.50)\ntext(0.00, 3.30, \"Minor tick\")\n\n# Major tick label\ncircle(-0.15, 3.00)\ntext(-0.15, 2.80, \"Major tick label\")\n\n# X Label\ncircle(1.80, -0.27)\ntext(1.80, -0.45, \"X axis label\")\n\n# Y Label\ncircle(-0.27, 1.80)\ntext(-0.27, 1.6, \"Y axis label\")\n\n# Title\ncircle(1.60, 4.13)\ntext(1.60, 3.93, \"Title\")\n\n# Blue plot\ncircle(1.75, 2.80)\ntext(1.75, 2.60, \"Line\\n(line plot)\")\n\n# Red plot\ncircle(1.20, 0.60)\ntext(1.20, 0.40, \"Line\\n(line plot)\")\n\n# Scatter plot\ncircle(3.20, 1.75)\ntext(3.20, 1.55, \"Markers\\n(scatter plot)\")\n\n# Grid\ncircle(3.00, 3.00)\ntext(3.00, 2.80, \"Grid\")\n\n# Legend\ncircle(3.70, 3.80)\ntext(3.70, 3.60, \"Legend\")\n\n# Axes\ncircle(0.5, 0.5)\ntext(0.5, 0.3, \"Axes\")\n\n# Figure\ncircle(-0.3, 0.65)\ntext(-0.3, 0.45, \"Figure\")\n\ncolor = 'blue'\nax.annotate('Spines', xy=(4.0, 0.35), xytext=(3.3, 0.5),\n weight='bold', color=color,\n arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle='->',\n connectionstyle=\"arc3\",\n color=color))\n\nax.annotate('', xy=(3.15, 0.0), xytext=(3.45, 0.45),\n weight='bold', color=color,\n arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle='->',\n connectionstyle=\"arc3\",\n color=color))\n\nax.text(4.0, -0.4, \"Made with http://matplotlib.org\",\n fontsize=10, ha=\"right\", color='.5')\n\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Making Explanatory Visualizations with Seaborn",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Today we will reproduce this [example by FiveThirtyEight:](https://fivethirtyeight.com/features/al-gores-new-movie-exposes-the-big-flaw-in-online-movie-ratings/)\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from IPython.display import display, Image\n\nurl = 'https://fivethirtyeight.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/09/mehtahickey-inconvenient-0830-1.png'\nexample = Image(url=url, width=400)\n\ndisplay(example)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Using this data: https://github.com/fivethirtyeight/data/tree/master/inconvenient-sequel",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Links\n- [Strong Titles Are The Biggest Bang for Your Buck](http://stephanieevergreen.com/strong-titles/)\n- [Remove to improve (the data-ink ratio)](https://www.darkhorseanalytics.com/blog/data-looks-better-naked)\n- [How to Generate FiveThirtyEight Graphs in Python](https://www.dataquest.io/blog/making-538-plots/)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Make prototypes\n\nThis helps us understand the problem",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%matplotlib inline\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport numpy as np\nimport pandas as pd\n\n\nplt.style.use('fivethirtyeight')\n\nfake = pd.Series([38, 3, 2, 1, 2, 4, 6, 5, 5, 33], \n index=range(1,11))\n\nfake.plot.bar(color='C1', width=0.9);",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fake2 = pd.Series(\n [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,\n 2, 2, 2, \n 3, 3, 3,\n 4, 4,\n 5, 5, 5,\n 6, 6, 6, 6,\n 7, 7, 7, 7, 7,\n 8, 8, 8, 8,\n 9, 9, 9, 9, \n 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10])\n\nfake2.value_counts().sort_index().plot.bar(color='C1', width=0.9);",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Annotate with text",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"plt.style.use('fivethirtyeight')\n\nfig = plt.figure()\n\nfig.patch.set_facecolor('white')\n\nax = fake.plot.bar(color='#ED713A', width = .9)\n\nax.set(facecolor = 'white')\n\nax.text(x=-2,y = 46, s=\"'An Inconvenient Sequel: Truth To Power' is divisive\", fontweight = 'bold')\nax.text(x=-2, y = 43, s = 'IMDb ratings for the film as of Aug. 29')\n\nax.set_xticklabels(range(1,11), rotation = 0, color = '#A3A3A3')\nax.set_yticklabels(['0', '10', '20', '30', '40%'], color = '#A3A3A3')\nax.set_yticks(range(0,50,10))\n\nplt.ylabel('Percent of total votes', fontweight = 'bold', fontsize = '12')\nplt.xlabel('Rating', fontweight = 'bold', fontsize = '12')\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Reproduce with real data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df = pd.read_csv('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/fivethirtyeight/data/master/inconvenient-sequel/ratings.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pd.set_option('display.max_columns', 50)\nprint(df.shape)\ndf.head(20)",
"(80053, 27)\n"
],
[
"df.sample(1).T",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.tail()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.dtypes",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df['timestamp'] = pd.to_datetime(df['timestamp'])\ndf.timestamp.describe()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.dtypes",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.set_index(df['timestamp'], inplace = True)\ndf['2017-08-29']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lastday = df['2017-08-29']\nlastday_filtered = lastday[lastday['category']=='IMDb users']\nlastday_filtered.tail(30)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df.category.value_counts()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lastday_filtered.respondents.plot()\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"final = lastday_filtered.tail(1)\nfinal.T",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pct_columns = ['1_pct', '2_pct', '3_pct', '4_pct', '5_pct','6_pct','7_pct','8_pct','9_pct','10_pct']\nfinal = final[pct_columns]\nfinal.T",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plot_data = final.T\nplot_data.index = range(1,11)\nplot_data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.style.use('fivethirtyeight')\n\nfig = plt.figure()\n\nfig.patch.set_facecolor('white')\n\nax = plot_data.plot.bar(color='#ED713A', width = .9, legend = False)\n\nax.set(facecolor = 'white')\n\nax.text(x=-2,y = 46, s=\"'An Inconvenient Sequel: Truth To Power' is divisive\", fontweight = 'bold')\nax.text(x=-2, y = 43, s = 'IMDb ratings for the film as of Aug. 29')\n\nax.set_xticklabels(range(1,11), rotation = 0, color = '#A3A3A3')\nax.set_yticklabels(['0', '10', '20', '30', '40%'], color = '#A3A3A3')\nax.set_yticks(range(0,50,10))\n\nplt.ylabel('Percent of total votes', fontweight = 'bold', fontsize = '12')\nplt.xlabel('Rating', fontweight = 'bold', fontsize = '12', labelpad = 15)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# ASSIGNMENT\n\nReplicate the lesson code. I recommend that you [do not copy-paste](https://docs.google.com/document/d/1ubOw9B3Hfip27hF2ZFnW3a3z9xAgrUDRReOEo-FHCVs/edit).\n\n# STRETCH OPTIONS\n\n#### 1) Reproduce another example from [FiveThityEight's shared data repository](https://data.fivethirtyeight.com/).\n\n#### 2) Reproduce one of the following using a library other than Seaborn or Matplotlib.\n\nFor example:\n- [thanksgiving-2015](https://fivethirtyeight.com/features/heres-what-your-part-of-america-eats-on-thanksgiving/) (try the [`altair`](https://altair-viz.github.io/gallery/index.html#maps) library)\n- [candy-power-ranking](https://fivethirtyeight.com/features/the-ultimate-halloween-candy-power-ranking/) (try the [`statsmodels`](https://www.statsmodels.org/stable/index.html) library)\n- or another example of your choice!\n\n#### 3) Make more charts!\n\nChoose a chart you want to make, from [Visual Vocabulary - Vega Edition](http://ft.com/vocabulary).\n\nFind the chart in an example gallery of a Python data visualization library:\n- [Seaborn](http://seaborn.pydata.org/examples/index.html)\n- [Altair](https://altair-viz.github.io/gallery/index.html)\n- [Matplotlib](https://matplotlib.org/gallery.html)\n- [Pandas](https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/visualization.html)\n\nReproduce the chart. [Optionally, try the \"Ben Franklin Method.\"](https://docs.google.com/document/d/1ubOw9B3Hfip27hF2ZFnW3a3z9xAgrUDRReOEo-FHCVs/edit) If you want, experiment and make changes.\n\nTake notes. Consider sharing your work with your cohort!\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Stretch option #1\n\n!pip install pandas==0.23.4\nimport pandas as pd\n\nfrom IPython.display import display, Image\n\n# url = 'https://fivethirtyeight.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/09/mehtahickey-inconvenient-0830-1.png'\n# example = Image(url=url, width=400)\n\n# example = Image(filename = '/Users/scotthuston/Desktop/FTE_image')\n\n# display(example)\n\n\n\n",
"Requirement already satisfied: pandas==0.23.4 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (0.23.4)\nRequirement already satisfied: pytz>=2011k in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from pandas==0.23.4) (2018.9)\nRequirement already satisfied: numpy>=1.9.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from pandas==0.23.4) (1.16.4)\nRequirement already satisfied: python-dateutil>=2.5.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from pandas==0.23.4) (2.5.3)\nRequirement already satisfied: six>=1.5 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from python-dateutil>=2.5.0->pandas==0.23.4) (1.12.0)\n"
],
[
"FTE = pd.read_csv('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/fivethirtyeight/checking-our-work-data/master/mlb_games.csv')\nFTE.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"prob1_bins = pd.cut(FTE['prob1'],13)\n\nct = pd.crosstab(FTE['prob1_outcome'], [prob1_bins])\n\n\n\n\n# FTE.boxplot(column = 'prob1')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df1 = FTE[FTE['prob1'] <= .278]\ndf2 = FTE[(FTE['prob1'] <= .322) & (FTE['prob1']>.278)]\ndf3 = FTE[(FTE['prob1'] <= .367) & (FTE['prob1']>.322)]\ndf4 = FTE[(FTE['prob1'] <= .411) & (FTE['prob1']>.367)]\ndf5 = FTE[(FTE['prob1'] <= .456) & (FTE['prob1']>.411)]\ndf6 = FTE[(FTE['prob1'] <= .501) & (FTE['prob1']>.456)]\ndf7 = FTE[(FTE['prob1'] <= .545) & (FTE['prob1']>.501)]\ndf8 = FTE[(FTE['prob1'] <= .59) & (FTE['prob1']>.545)]\ndf9 = FTE[(FTE['prob1'] <= .634) & (FTE['prob1']>.59)]\ndf10 = FTE[(FTE['prob1'] <= .679) & (FTE['prob1']>.634)]\ndf11= FTE[(FTE['prob1'] <= .723) & (FTE['prob1']>.679)]\ndf12 = FTE[(FTE['prob1'] <= .768) & (FTE['prob1']>.723)]\ndf13 = FTE[(FTE['prob1'] <= .812) & (FTE['prob1']>.768)]\ndf1.head()\ndf2.head(10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport seaborn as sns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"plt.errorbar(df1['prob1'],df1['prob1_outcome'], xerr = df1['prob1_outcome']-df1['prob1'])\n\nsns.set(style=\"darkgrid\")\n\nlst = []\nfor i in len(df2.prob1_outcome):\n lst.append(1)\n\nsns.pointplot(lst, y=\"prob1_outcome\", data=df2)\n# df2['prob1_outcome']",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50d215a292a4879771539d540a10a6655e0887a
| 12,113 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
analysis/contig_blast_analysis/bloodmeal_calling.ipynb
|
wolfQK/california-mosquito-study
|
b158c887b61032dc327f45f776a93300b20644a5
|
[
"MIT"
] | 8 |
2020-06-02T12:15:04.000Z
|
2021-11-06T15:48:40.000Z
|
analysis/contig_blast_analysis/bloodmeal_calling.ipynb
|
wolfQK/california-mosquito-study
|
b158c887b61032dc327f45f776a93300b20644a5
|
[
"MIT"
] | 19 |
2018-10-15T20:40:51.000Z
|
2020-02-06T23:07:26.000Z
|
analysis/contig_blast_analysis/bloodmeal_calling.ipynb
|
wolfQK/california-mosquito-study
|
b158c887b61032dc327f45f776a93300b20644a5
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2021-09-27T11:54:57.000Z
|
2021-11-11T13:14:33.000Z
| 28.771971 | 373 | 0.494675 |
[
[
[
"# Bloodmeal Calling\n\nIn this notebook, we analyze contigs from each bloodfed mosquito sample with LCA in *Vertebrata*. The potential bloodmeal call is the lowest taxonomic group consistent with the LCAs of all such contigs in a sample.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nfrom ete3 import NCBITaxa\nimport boto3\nimport tempfile\nimport subprocess\nimport os\nimport io\nimport re\nimport time\nimport json\nncbi = NCBITaxa()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df = pd.read_csv('../../figures/fig3/all_contigs_df.tsv', sep='\\t', \n dtype={'taxid': np.int})\ndf = df[df['group'] == 'Metazoa']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def taxid2name(taxid):\n return ncbi.get_taxid_translator([taxid])[taxid]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"There is a partial order on taxa: $a < b$ if $a$ is an ancestor of $b$. A taxon $t$ is admissible as a bloodmeal call for a given sample if it is consistent with all *Vertebrata* LCA taxa $b$: $t < b$ or $b < t$ for all $b$. That is, a taxon is admissable if t in lineage(b) or b in lineage(t) for all b.\n\nWe will report the lowest admissable taxon for each sample.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def get_lowest_admissable_taxon(taxa):\n lineages = [ncbi.get_lineage(taxid) for taxid in taxa]\n \n if len(lineages) == 0:\n return 0\n \n all_taxa = np.unique([taxid for lineage in lineages for taxid in lineage])\n non_leaf_taxa = np.unique([taxid for lineage in lineages for taxid in lineage[:-1]])\n leaf_taxa = [taxid for taxid in all_taxa if taxid not in non_leaf_taxa]\n \n leaf_lineages = [ncbi.get_lineage(taxid) for taxid in leaf_taxa]\n leaf_common_ancestors = set.intersection(*[set(l) for l in leaf_lineages])\n lca = [taxid for taxid in leaf_lineages[0] if taxid in leaf_common_ancestors][-1]\n \n return lca",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def filter_taxon(taxid, exclude = [], # drop these taxa\n exclude_children = [], # drop children of these taxa\n parent=None # only keep children of the parent\n ):\n if taxid in exclude:\n return False\n \n lineage = ncbi.get_lineage(taxid)\n \n exclude_children = set(exclude_children)\n \n if len(set(lineage) & set(exclude_children)) > 0:\n return False\n \n if parent and parent not in lineage:\n return False\n \n return True",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"vertebrate_taxid = 7742\nprimate_taxid = 9443",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"euarchontoglires_taxid = 314146",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df['filter_taxon'] = df['taxid'].apply(lambda x: filter_taxon(x, \n exclude = [euarchontoglires_taxid],\n exclude_children = [primate_taxid],\n parent = vertebrate_taxid))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"How many nonprimate vertebrate contigs per sample? 1 to 11.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%pprint\nsorted(df[df['filter_taxon']].groupby('sample').count()['taxid'])",
"Pretty printing has been turned OFF\n"
],
[
"sorted(df[df['filter_taxon']].groupby('sample')['reads'].sum())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lowest_admissable_taxa = []\nfor sample in df['sample'].unique():\n taxid = get_lowest_admissable_taxon(df[(df['sample'] == sample) & df['filter_taxon']]['taxid'])\n name = taxid2name(taxid) if taxid else \"NA\"\n lowest_admissable_taxa.append({'sample': sample, 'name': name, 'taxid': taxid})\nlowest_admissable_taxa = pd.DataFrame(lowest_admissable_taxa).sort_values('sample')\nlowest_admissable_taxa = lowest_admissable_taxa[['sample', 'taxid', 'name']]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"lowest_admissable_taxa.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"partition = \"Pecora Carnivora Homininae Rodentia Leporidae Aves\".split()\npartition = ncbi.get_name_translator(partition)\npartition = {v[0]: k for k, v in partition.items()}\n\ndef get_category(taxid):\n if not taxid:\n return None\n lineage = ncbi.get_lineage(taxid)\n for k in partition:\n if k in lineage:\n return partition[k]\n else:\n return 'NA'",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"The ranks of the categories are:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"ncbi.get_rank(partition.keys())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"bloodmeal_calls = lowest_admissable_taxa\n\nbloodmeal_calls['category'] = bloodmeal_calls['taxid'].apply(get_category)\n\nbloodmeal_calls = bloodmeal_calls[bloodmeal_calls['category'] != 'NA']\nbloodmeal_calls = bloodmeal_calls[bloodmeal_calls['name'] != 'NA']\n\nbloodmeal_calls = bloodmeal_calls[['sample', 'category', 'name']]\nbloodmeal_calls = bloodmeal_calls.sort_values('sample')\nbloodmeal_calls = bloodmeal_calls.rename(columns={'sample': 'Sample',\n 'category': 'Bloodmeal Category',\n 'name': 'Bloodmeal Call'})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"metadata = pd.read_csv('../../data/metadata/CMS001_CMS002_MergedAnnotations.csv')\nmetadata = metadata[['NewIDseqName', 'Habitat', 'collection_lat', 'collection_long', 'ska_genus', 'ska_species']].rename(\n columns = {'NewIDseqName': 'Sample',\n 'ska_genus': 'Genus',\n 'ska_species': 'Species',\n 'collection_lat': 'Lat',\n 'collection_long': 'Long'})",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"bloodmeal_calls = bloodmeal_calls.merge(metadata, on='Sample', how='left')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"bloodmeal_calls.to_csv(\n '../../figures/fig4/bloodmeal_calls.csv', index=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50d2818acfe29df7b88731e79b767be30a56941
| 86,792 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
courses/machine_learning/deepdive2/structured/solutions/4b_keras_dnn_babyweight.ipynb
|
jonesevan007/training-data-analyst
|
774446719316599cf221bdc5a67b00ec4c0b3ad0
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2019-11-23T14:38:33.000Z
|
2019-11-23T14:38:33.000Z
|
courses/machine_learning/deepdive2/structured/solutions/4b_keras_dnn_babyweight.ipynb
|
jonesevan007/training-data-analyst
|
774446719316599cf221bdc5a67b00ec4c0b3ad0
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 11 |
2020-01-28T23:13:27.000Z
|
2022-03-12T00:11:30.000Z
|
courses/machine_learning/deepdive2/structured/solutions/4b_keras_dnn_babyweight.ipynb
|
jonesevan007/training-data-analyst
|
774446719316599cf221bdc5a67b00ec4c0b3ad0
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 1 |
2020-07-17T15:42:26.000Z
|
2020-07-17T15:42:26.000Z
| 112.863459 | 31,052 | 0.836805 |
[
[
[
"# LAB 4b: Create Keras DNN model.\n\n**Learning Objectives**\n\n1. Set CSV Columns, label column, and column defaults\n1. Make dataset of features and label from CSV files\n1. Create input layers for raw features\n1. Create feature columns for inputs\n1. Create DNN dense hidden layers and output layer\n1. Create custom evaluation metric\n1. Build DNN model tying all of the pieces together\n1. Train and evaluate\n\n\n## Introduction \nIn this notebook, we'll be using Keras to create a DNN model to predict the weight of a baby before it is born.\n\nWe'll start by defining the CSV column names, label column, and column defaults for our data inputs. Then, we'll construct a tf.data Dataset of features and the label from the CSV files and create inputs layers for the raw features. Next, we'll set up feature columns for the model inputs and build a deep neural network in Keras. We'll create a custom evaluation metric and build our DNN model. Finally, we'll train and evaluate our model.\n\nEach learning objective will correspond to a __#TODO__ in this student lab notebook -- try to complete this notebook first and then review the [solution notebook](../solutions/4b_keras_dnn_babyweight.ipynb).",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Load necessary libraries",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import datetime\nimport os\nimport shutil\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport tensorflow as tf\nprint(tf.__version__)",
"2.0.0\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Verify CSV files exist\n\nIn the seventh lab of this series [4a_sample_babyweight](../solutions/4a_sample_babyweight.ipynb), we sampled from BigQuery our train, eval, and test CSV files. Verify that they exist, otherwise go back to that lab and create them.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"%%bash\nls *.csv",
"eval.csv\ntest.csv\ntrain.csv\n"
],
[
"%%bash\nhead -5 *.csv",
"==> eval.csv <==\n6.87621795178,False,33,Single(1),40\n7.7492485093,Unknown,21,Single(1),38\n8.86699217764,False,22,Single(1),38\n6.60504936952,False,32,Single(1),40\n8.313631900019999,True,36,Single(1),39\n\n==> test.csv <==\n7.5618555866,True,40,Twins(2),43\n9.3586230219,Unknown,22,Single(1),40\n8.5539357656,True,26,Single(1),37\n5.81138522632,Unknown,36,Multiple(2+),36\n7.06140625186,Unknown,23,Single(1),40\n\n==> train.csv <==\n10.18756112702,Unknown,23,Single(1),33\n8.93754010148,True,40,Single(1),41\n6.9996768185,Unknown,23,Single(1),38\n8.65975765136,Unknown,19,Single(1),42\n4.2549216566,True,20,Single(1),33\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Create Keras model",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Set CSV Columns, label column, and column defaults.\n\nNow that we have verified that our CSV files exist, we need to set a few things that we will be using in our input function.\n* `CSV_COLUMNS` are going to be our header names of our columns. Make sure that they are in the same order as in the CSV files\n* `LABEL_COLUMN` is the header name of the column that is our label. We will need to know this to pop it from our features dictionary.\n* `DEFAULTS` is a list with the same length as `CSV_COLUMNS`, i.e. there is a default for each column in our CSVs. Each element is a list itself with the default value for that CSV column.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Determine CSV, label, and key columns\n# Create list of string column headers, make sure order matches.\nCSV_COLUMNS = [\"weight_pounds\",\n \"is_male\",\n \"mother_age\",\n \"plurality\",\n \"gestation_weeks\"]\n\n# Add string name for label column\nLABEL_COLUMN = \"weight_pounds\"\n\n# Set default values for each CSV column as a list of lists.\n# Treat is_male and plurality as strings.\nDEFAULTS = [[0.0], [\"null\"], [0.0], [\"null\"], [0.0]]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Make dataset of features and label from CSV files.\n\nNext, we will write an input_fn to read the data. Since we are reading from CSV files we can save ourself from trying to recreate the wheel and can use `tf.data.experimental.make_csv_dataset`. This will create a CSV dataset object. However we will need to divide the columns up into features and a label. We can do this by applying the map method to our dataset and popping our label column off of our dictionary of feature tensors.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def features_and_labels(row_data):\n \"\"\"Splits features and labels from feature dictionary.\n\n Args:\n row_data: Dictionary of CSV column names and tensor values.\n Returns:\n Dictionary of feature tensors and label tensor.\n \"\"\"\n label = row_data.pop(LABEL_COLUMN)\n\n return row_data, label # features, label\n\n\ndef load_dataset(pattern, batch_size=1, mode=tf.estimator.ModeKeys.EVAL):\n \"\"\"Loads dataset using the tf.data API from CSV files.\n\n Args:\n pattern: str, file pattern to glob into list of files.\n batch_size: int, the number of examples per batch.\n mode: tf.estimator.ModeKeys to determine if training or evaluating.\n Returns:\n `Dataset` object.\n \"\"\"\n # Make a CSV dataset\n dataset = tf.data.experimental.make_csv_dataset(\n file_pattern=pattern,\n batch_size=batch_size,\n column_names=CSV_COLUMNS,\n column_defaults=DEFAULTS)\n\n # Map dataset to features and label\n dataset = dataset.map(map_func=features_and_labels) # features, label\n\n # Shuffle and repeat for training\n if mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN:\n dataset = dataset.shuffle(buffer_size=1000).repeat()\n\n # Take advantage of multi-threading; 1=AUTOTUNE\n dataset = dataset.prefetch(buffer_size=1)\n\n return dataset",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Create input layers for raw features.\n\nWe'll need to get the data read in by our input function to our model function, but just how do we go about connecting the dots? We can use Keras input layers [(tf.Keras.layers.Input)](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/Input) by defining:\n* shape: A shape tuple (integers), not including the batch size. For instance, shape=(32,) indicates that the expected input will be batches of 32-dimensional vectors. Elements of this tuple can be None; 'None' elements represent dimensions where the shape is not known.\n* name: An optional name string for the layer. Should be unique in a model (do not reuse the same name twice). It will be autogenerated if it isn't provided.\n* dtype: The data type expected by the input, as a string (float32, float64, int32...)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def create_input_layers():\n \"\"\"Creates dictionary of input layers for each feature.\n\n Returns:\n Dictionary of `tf.Keras.layers.Input` layers for each feature.\n \"\"\"\n inputs = {\n colname: tf.keras.layers.Input(\n name=colname, shape=(), dtype=\"float32\")\n for colname in [\"mother_age\", \"gestation_weeks\"]}\n\n inputs.update({\n colname: tf.keras.layers.Input(\n name=colname, shape=(), dtype=\"string\")\n for colname in [\"is_male\", \"plurality\"]})\n\n return inputs",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Create feature columns for inputs.\n\nNext, define the feature columns. `mother_age` and `gestation_weeks` should be numeric. The others, `is_male` and `plurality`, should be categorical. Remember, only dense feature columns can be inputs to a DNN.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def categorical_fc(name, values):\n \"\"\"Helper function to wrap categorical feature by indicator column.\n\n Args:\n name: str, name of feature.\n values: list, list of strings of categorical values.\n Returns:\n Indicator column of categorical feature.\n \"\"\"\n cat_column = tf.feature_column.categorical_column_with_vocabulary_list(\n key=name, vocabulary_list=values)\n\n return tf.feature_column.indicator_column(categorical_column=cat_column)\n\n\ndef create_feature_columns():\n \"\"\"Creates dictionary of feature columns from inputs.\n\n Returns:\n Dictionary of feature columns.\n \"\"\"\n feature_columns = {\n colname : tf.feature_column.numeric_column(key=colname)\n for colname in [\"mother_age\", \"gestation_weeks\"]\n }\n\n feature_columns[\"is_male\"] = categorical_fc(\n \"is_male\", [\"True\", \"False\", \"Unknown\"])\n feature_columns[\"plurality\"] = categorical_fc(\n \"plurality\", [\"Single(1)\", \"Twins(2)\", \"Triplets(3)\",\n \"Quadruplets(4)\", \"Quintuplets(5)\", \"Multiple(2+)\"])\n\n return feature_columns",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Create DNN dense hidden layers and output layer.\n\nSo we've figured out how to get our inputs ready for machine learning but now we need to connect them to our desired output. Our model architecture is what links the two together. Let's create some hidden dense layers beginning with our inputs and end with a dense output layer. This is regression so make sure the output layer activation is correct and that the shape is right.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def get_model_outputs(inputs):\n \"\"\"Creates model architecture and returns outputs.\n\n Args:\n inputs: Dense tensor used as inputs to model.\n Returns:\n Dense tensor output from the model.\n \"\"\"\n # Create two hidden layers of [64, 32] just in like the BQML DNN\n h1 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(64, activation=\"relu\", name=\"h1\")(inputs)\n h2 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(32, activation=\"relu\", name=\"h2\")(h1)\n\n # Final output is a linear activation because this is regression\n output = tf.keras.layers.Dense(\n units=1, activation=\"linear\", name=\"weight\")(h2)\n\n return output",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Create custom evaluation metric.\n\nWe want to make sure that we have some useful way to measure model performance for us. Since this is regression, we would like to know the RMSE of the model on our evaluation dataset, however, this does not exist as a standard evaluation metric, so we'll have to create our own by using the true and predicted labels.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def rmse(y_true, y_pred):\n \"\"\"Calculates RMSE evaluation metric.\n\n Args:\n y_true: tensor, true labels.\n y_pred: tensor, predicted labels.\n Returns:\n Tensor with value of RMSE between true and predicted labels.\n \"\"\"\n return tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_mean((y_pred - y_true) ** 2))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Build DNN model tying all of the pieces together.\n\nExcellent! We've assembled all of the pieces, now we just need to tie them all together into a Keras Model. This is a simple feedforward model with no branching, side inputs, etc. so we could have used Keras' Sequential Model API but just for fun we're going to use Keras' Functional Model API. Here we will build the model using [tf.keras.models.Model](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/Model) giving our inputs and outputs and then compile our model with an optimizer, a loss function, and evaluation metrics.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def build_dnn_model():\n \"\"\"Builds simple DNN using Keras Functional API.\n\n Returns:\n `tf.keras.models.Model` object.\n \"\"\"\n # Create input layer\n inputs = create_input_layers()\n\n # Create feature columns\n feature_columns = create_feature_columns()\n\n # The constructor for DenseFeatures takes a list of numeric columns\n # The Functional API in Keras requires: LayerConstructor()(inputs)\n dnn_inputs = tf.keras.layers.DenseFeatures(\n feature_columns=feature_columns.values())(inputs)\n\n # Get output of model given inputs\n output = get_model_outputs(dnn_inputs)\n\n # Build model and compile it all together\n model = tf.keras.models.Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=output)\n model.compile(optimizer=\"adam\", loss=\"mse\", metrics=[rmse, \"mse\"])\n\n return model\n\nprint(\"Here is our DNN architecture so far:\\n\")\nmodel = build_dnn_model()\nprint(model.summary())",
"Here is our DNN architecture so far:\n\nWARNING:tensorflow:From /usr/local/lib/python3.5/dist-packages/tensorflow_core/python/feature_column/feature_column_v2.py:4276: IndicatorColumn._variable_shape (from tensorflow.python.feature_column.feature_column_v2) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version.\nInstructions for updating:\nThe old _FeatureColumn APIs are being deprecated. Please use the new FeatureColumn APIs instead.\nWARNING:tensorflow:From /usr/local/lib/python3.5/dist-packages/tensorflow_core/python/feature_column/feature_column_v2.py:4331: VocabularyListCategoricalColumn._num_buckets (from tensorflow.python.feature_column.feature_column_v2) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version.\nInstructions for updating:\nThe old _FeatureColumn APIs are being deprecated. Please use the new FeatureColumn APIs instead.\nModel: \"model\"\n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nLayer (type) Output Shape Param # Connected to \n==================================================================================================\ngestation_weeks (InputLayer) [(None,)] 0 \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nis_male (InputLayer) [(None,)] 0 \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nmother_age (InputLayer) [(None,)] 0 \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nplurality (InputLayer) [(None,)] 0 \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\ndense_features (DenseFeatures) (None, 11) 0 gestation_weeks[0][0] \n is_male[0][0] \n mother_age[0][0] \n plurality[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nh1 (Dense) (None, 64) 768 dense_features[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nh2 (Dense) (None, 32) 2080 h1[0][0] \n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nweight (Dense) (None, 1) 33 h2[0][0] \n==================================================================================================\nTotal params: 2,881\nTrainable params: 2,881\nNon-trainable params: 0\n__________________________________________________________________________________________________\nNone\n"
]
],
[
[
"We can visualize the DNN using the Keras plot_model utility.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"tf.keras.utils.plot_model(\n model=model, to_file=\"dnn_model.png\", show_shapes=False, rankdir=\"LR\")",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Run and evaluate model",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### Train and evaluate.\n\nWe've built our Keras model using our inputs from our CSV files and the architecture we designed. Let's now run our model by training our model parameters and periodically running an evaluation to track how well we are doing on outside data as training goes on. We'll need to load both our train and eval datasets and send those to our model through the fit method. Make sure you have the right pattern, batch size, and mode when loading the data. Also, don't forget to add the callback to TensorBoard.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"TRAIN_BATCH_SIZE = 32\nNUM_TRAIN_EXAMPLES = 10000 * 5 # training dataset repeats, it'll wrap around\nNUM_EVALS = 5 # how many times to evaluate\n# Enough to get a reasonable sample, but not so much that it slows down\nNUM_EVAL_EXAMPLES = 10000\n\ntrainds = load_dataset(\n pattern=\"train*\",\n batch_size=TRAIN_BATCH_SIZE,\n mode=tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN)\n\nevalds = load_dataset(\n pattern=\"eval*\",\n batch_size=1000,\n mode=tf.estimator.ModeKeys.EVAL).take(count=NUM_EVAL_EXAMPLES // 1000)\n\nsteps_per_epoch = NUM_TRAIN_EXAMPLES // (TRAIN_BATCH_SIZE * NUM_EVALS)\n\nlogdir = os.path.join(\n \"logs\", datetime.datetime.now().strftime(\"%Y%m%d-%H%M%S\"))\ntensorboard_callback = tf.keras.callbacks.TensorBoard(\n log_dir=logdir, histogram_freq=1)\n\nhistory = model.fit(\n trainds,\n validation_data=evalds,\n epochs=NUM_EVALS,\n steps_per_epoch=steps_per_epoch,\n callbacks=[tensorboard_callback])",
"WARNING:tensorflow:From /usr/local/lib/python3.5/dist-packages/tensorflow_core/python/data/experimental/ops/readers.py:521: parallel_interleave (from tensorflow.python.data.experimental.ops.interleave_ops) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version.\nInstructions for updating:\nUse `tf.data.Dataset.interleave(map_func, cycle_length, block_length, num_parallel_calls=tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE)` instead. If sloppy execution is desired, use `tf.data.Options.experimental_determinstic`.\nWARNING:tensorflow:From /usr/local/lib/python3.5/dist-packages/tensorflow_core/python/data/experimental/ops/readers.py:215: shuffle_and_repeat (from tensorflow.python.data.experimental.ops.shuffle_ops) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version.\nInstructions for updating:\nUse `tf.data.Dataset.shuffle(buffer_size, seed)` followed by `tf.data.Dataset.repeat(count)`. Static tf.data optimizations will take care of using the fused implementation.\nTrain for 312 steps, validate for 10 steps\nEpoch 1/5\n312/312 [==============================] - 5s 16ms/step - loss: 4.2510 - rmse: 1.5391 - mse: 4.2510 - val_loss: 1.3007 - val_rmse: 1.1402 - val_mse: 1.3007\nEpoch 2/5\n312/312 [==============================] - 3s 9ms/step - loss: 1.1924 - rmse: 1.0779 - mse: 1.1924 - val_loss: 1.2050 - val_rmse: 1.0974 - val_mse: 1.2050\nEpoch 3/5\n312/312 [==============================] - 4s 12ms/step - loss: 1.2077 - rmse: 1.0884 - mse: 1.2077 - val_loss: 1.1679 - val_rmse: 1.0804 - val_mse: 1.1679\nEpoch 4/5\n312/312 [==============================] - 4s 11ms/step - loss: 1.1964 - rmse: 1.0829 - mse: 1.1964 - val_loss: 1.2209 - val_rmse: 1.1047 - val_mse: 1.2209\nEpoch 5/5\n312/312 [==============================] - 3s 9ms/step - loss: 1.1474 - rmse: 1.0607 - mse: 1.1474 - val_loss: 1.1566 - val_rmse: 1.0752 - val_mse: 1.1566\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Visualize loss curve",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Plot\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nnrows = 1\nncols = 2\nfig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))\n\nfor idx, key in enumerate([\"loss\", \"rmse\"]):\n ax = fig.add_subplot(nrows, ncols, idx+1)\n plt.plot(history.history[key])\n plt.plot(history.history[\"val_{}\".format(key)])\n plt.title(\"model {}\".format(key))\n plt.ylabel(key)\n plt.xlabel(\"epoch\")\n plt.legend([\"train\", \"validation\"], loc=\"upper left\");",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### Save the model",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"OUTPUT_DIR = \"babyweight_trained\"\nshutil.rmtree(OUTPUT_DIR, ignore_errors=True)\nEXPORT_PATH = os.path.join(\n OUTPUT_DIR, datetime.datetime.now().strftime(\"%Y%m%d%H%M%S\"))\ntf.saved_model.save(\n obj=model, export_dir=EXPORT_PATH) # with default serving function\nprint(\"Exported trained model to {}\".format(EXPORT_PATH))",
"WARNING:tensorflow:From /usr/local/lib/python3.5/dist-packages/tensorflow_core/python/ops/resource_variable_ops.py:1781: calling BaseResourceVariable.__init__ (from tensorflow.python.ops.resource_variable_ops) with constraint is deprecated and will be removed in a future version.\nInstructions for updating:\nIf using Keras pass *_constraint arguments to layers.\nINFO:tensorflow:Assets written to: babyweight_trained/20191119050541/assets\nExported trained model to babyweight_trained/20191119050541\n"
],
[
"!ls $EXPORT_PATH",
"assets\tsaved_model.pb\tvariables\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Monitor and experiment with training",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"To begin TensorBoard from within AI Platform Notebooks, click the + symbol in the top left corner and select the **Tensorboard** icon to create a new TensorBoard. Before you click make sure you are in the directory of your TensorBoard log_dir.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"In TensorBoard, look at the learned embeddings. Are they getting clustered? How about the weights for the hidden layers? What if you run this longer? What happens if you change the batchsize?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Lab Summary: \nIn this lab, we started by defining the CSV column names, label column, and column defaults for our data inputs. Then, we constructed a tf.data Dataset of features and the label from the CSV files and created inputs layers for the raw features. Next, we set up feature columns for the model inputs and built a deep neural network in Keras. We created a custom evaluation metric and built our DNN model. Finally, we trained and evaluated our model.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Copyright 2019 Google Inc. Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the \"License\"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an \"AS IS\" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
]
] |
c50d64a1c8ee73bc766ff27dfc5d6e75bb6e1c7b
| 177,007 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/ridgeplot.ipynb
|
gpp-rnd/gpplot
|
627a2feb398fe8de5539ee6d0ae3150079578a7a
|
[
"MIT"
] | 2 |
2020-06-19T19:35:14.000Z
|
2020-07-22T17:24:02.000Z
|
notebooks/ridgeplot.ipynb
|
gpp-rnd/gpplot
|
627a2feb398fe8de5539ee6d0ae3150079578a7a
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2020-08-23T21:47:57.000Z
|
2020-08-23T21:47:57.000Z
|
notebooks/ridgeplot.ipynb
|
gpp-rnd/gpplot
|
627a2feb398fe8de5539ee6d0ae3150079578a7a
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 578.454248 | 18,192 | 0.949205 |
[
[
[
"# Ridge Plot",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Author: Ruth Hanna\n\nThis notebook demonstrates how to make overlapping kde plots (\"ridgeplots\") using gpplot. The code for ridgeplots was based on the example found here: https://seaborn.pydata.org/examples/kde_ridgeplot",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import gpplot\nimport seaborn as sns",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"iris = sns.load_dataset('iris')\ng = gpplot.ridgeplot(iris, 'sepal_width', 'species')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can modify the position of the label text with the text_xpos, text_ypos, text_ha, text_va arguments.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Move the text to the right\ng = gpplot.ridgeplot(iris, 'sepal_width', 'species', text_xpos=1, text_ha='right')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can also change the opacity of the kde plots by changing alpha.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Really light\ng = gpplot.ridgeplot(iris, 'sepal_width', 'species', alpha = 0.5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Really dark\ng = gpplot.ridgeplot(iris, 'sepal_width', 'species', alpha = 1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"To modify the overlap of the subplots, we make changes to the FacetGrid after the ridgeplots function returns a FacetGrid.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# More overlap\ng = gpplot.ridgeplot(iris, 'sepal_width', 'species')\ng.fig.subplots_adjust(hspace=-0.5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Less overlap\ng = gpplot.ridgeplot(iris, 'sepal_width', 'species',)\ng.fig.subplots_adjust(hspace=0)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Finally, we can also supply other parameters to FacetGrid via **kwargs. For example, we could specify the order of the kde plots via hue_order and row_order.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Just changing row order keeps the colors the same\ng = gpplot.ridgeplot(iris, 'sepal_width', 'species', row_order=['versicolor','setosa','virginica'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Change the colors by also specifying hue_order\ng = gpplot.ridgeplot(iris, 'sepal_width', 'species', row_order=['versicolor','setosa','virginica'], hue_order=['versicolor','setosa','virginica'])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"We can also change the color palette with palette",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Paired color palette\ng = gpplot.ridgeplot(iris, 'sepal_width', 'species', palette = sns.color_palette('Paired'))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Set 2 color palette\ng = gpplot.ridgeplot(iris, 'sepal_width', 'species', palette = sns.color_palette('Set2'))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50d68b66af19dc68a9198cbfa7f9179c0e9d4f1
| 683,288 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
task_01/Task-1.ipynb
|
svinkapeppa/image_recognition
|
22b30aed91f4e6b8d858fc1e0b5d7d9e4f66263d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
task_01/Task-1.ipynb
|
svinkapeppa/image_recognition
|
22b30aed91f4e6b8d858fc1e0b5d7d9e4f66263d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
task_01/Task-1.ipynb
|
svinkapeppa/image_recognition
|
22b30aed91f4e6b8d858fc1e0b5d7d9e4f66263d
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 345.094949 | 182,992 | 0.925695 |
[
[
[
"# Часть 1. k-Nearest Neighbor (kNN) классификатор\n\nkNN классификатор:\n- Во время обучения получает данные и просто запоминает их\n- Во время тестирования каждое тестовое изображение сравнивается с каждым обучающим. Итоговая метка получается на основе анализа меток k ближайших обучающих изображений\n- Значение k подбирается с помощью кросс-валидации.\n\nПервое упражнение разминочное. Направлено на поминимание pipeline классификации изображений, кросс-валидации и получения практики написания эффективного векторизованного кода, осознания его эффективности.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Run some setup code for this notebook.\nimport random\nimport numpy as np\nfrom cs231n.data_utils import load_CIFAR10\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\nfrom __future__ import print_function\n\n# This is a bit of magic to make matplotlib figures appear inline in the notebook\n# rather than in a new window.\n%matplotlib inline\nplt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (10.0, 8.0) # set default size of plots\nplt.rcParams['image.interpolation'] = 'nearest'\nplt.rcParams['image.cmap'] = 'gray'\n\n# Some more magic so that the notebook will reload external python modules;\n# see http://stackoverflow.com/questions/1907993/autoreload-of-modules-in-ipython\n%load_ext autoreload\n%autoreload 2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Load the raw CIFAR-10 data.\ncifar10_dir = 'cs231n/datasets/cifar-10-batches-py'\n\n# Cleaning up variables to prevent loading data multiple times (which may cause memory issue)\ntry:\n del X_train, y_train\n del X_test, y_test\n print('Clear previously loaded data.')\nexcept:\n pass\n\nX_train, y_train, X_test, y_test = load_CIFAR10(cifar10_dir)\n\n# As a sanity check, we print out the size of the training and test data.\nprint('Training data shape: ', X_train.shape)\nprint('Training labels shape: ', y_train.shape)\nprint('Test data shape: ', X_test.shape)\nprint('Test labels shape: ', y_test.shape)",
"Training data shape: (50000, 32, 32, 3)\nTraining labels shape: (50000,)\nTest data shape: (10000, 32, 32, 3)\nTest labels shape: (10000,)\n"
],
[
"# Visualize some examples from the dataset.\n# We show a few examples of training images from each class.\nclasses = ['plane', 'car', 'bird', 'cat', 'deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck']\nnum_classes = len(classes)\nsamples_per_class = 7\nfor y, cls in enumerate(classes):\n idxs = np.flatnonzero(y_train == y)\n idxs = np.random.choice(idxs, samples_per_class, replace=False)\n for i, idx in enumerate(idxs):\n plt_idx = i * num_classes + y + 1\n plt.subplot(samples_per_class, num_classes, plt_idx)\n plt.imshow(X_train[idx].astype('uint8'))\n plt.axis('off')\n if i == 0:\n plt.title(cls)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Subsample the data for more efficient code execution in this exercise\nnum_training = 5000\nmask = list(range(num_training))\nX_train = X_train[mask]\ny_train = y_train[mask]\n\nnum_test = 500\nmask = list(range(num_test))\nX_test = X_test[mask]\ny_test = y_test[mask]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Reshape the image data into rows\nX_train = np.reshape(X_train, (X_train.shape[0], -1))\nX_test = np.reshape(X_test, (X_test.shape[0], -1))\nprint(X_train.shape, X_test.shape)",
"(5000, 3072) (500, 3072)\n"
],
[
"from cs231n.classifiers import KNearestNeighbor\n\n# Create a kNN classifier instance. \n# Remember that training a kNN classifier is a noop: \n# the Classifier simply remembers the data and does no further processing \nclassifier = KNearestNeighbor()\nclassifier.train(X_train, y_train)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Нам хочется классифицировать данные с помощью kNN. Вспомним, что этот процесс можно разбить на 2 шага:\n\n1. Посчитать расстояние между каждым обучающим и каждым тестовым примером.\n2. Имея эти расстояния для каждого тестового примера найти k ближайших примеров и дать им проголосовать за итоговую метку.\n\nНачать стоит с подсчета матрицы расстояний между всеми обучающими и всеми тестовыми примерами. Например, если у вас **Ntr** обучающих примеров и **Nte** тестовых примеров, то на этом этапе у вас должна получиться матрица из **Nte x Ntr** элементов, где элемент (i, j) равен расстоянию от i-ого обучающего до j-ого тестового примера.\n\nОткройте файл `cs231n/classifiers/k_nearest_neighbor.py` и реализуйте в нём функцию `compute_distances_two_loops`, используя (крайне неэффективный) вложенный цикл по всем парам из (test, train), подсчитывая по одному элементу матрицы за одну итерацию.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Open cs231n/classifiers/k_nearest_neighbor.py and implement\n# compute_distances_two_loops.\n\n# Test your implementation:\ndists = classifier.compute_distances_two_loops(X_test)\nprint(dists.shape)",
"(500, 5000)\n"
],
[
"# We can visualize the distance matrix: each row is a single test example and\n# its distances to training examples\nplt.imshow(dists, interpolation='none')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Вопрос №1** Обратите внимание на структурные элементы в матрице расстояний. Какие-то строки и столбцы являются более яркими. (При этом в цветовой схеме по умолчанию чёрный свет соответсвует малым расстояниям, а белый - большим.)\n\n- Что именно в данных приводит к тому, что некоторые строчки отчётливо яркие?\n- А столбцы?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Ваш ответ**: Разница между столбцами и строками заключается в том, что одни отвечают за обучающую выборку, а другие - за тестовую. Поэтому приведу рассуждения для строк.\n\n\"Белая строка\" означает, что данный объект находится далеко от всех объектов тестовой выборки. Так как объекты - это вектора, представляющие исходные изображения, логично предположить, что это происходит из-за того, что некоторые объекты отличаются по признакам, связанным исключительно со значениями компонент векторов (т.е. с интенсивностью цвета). Простой пример - самолет часто легко отличить от лягушки, потому что самолет - это белые и синие цвета, а лягушка - зеленые и коричневые. Как мне кажется, проблема происходит из-за того, что когда мы сэмплировали выборку, мы не делали никакого решафла, а в исходных данных были какие-то неочевидные зависимости между номерами изображений.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Далее нужно реализовать функцию `\npredict_labels`, и запустить следующий код. Получим accuracy для `k = 1`",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Now implement the function predict_labels and run the code below:\n# We use k = 1 (which is Nearest Neighbor).\ny_test_pred = classifier.predict_labels(dists, k=1)\n\n# Compute and print the fraction of correctly predicted examples\nnum_correct = np.sum(y_test_pred == y_test)\naccuracy = float(num_correct) / num_test\nprint('Got %d / %d correct => accuracy: %f' % (num_correct, num_test, accuracy))",
"Got 137 / 500 correct => accuracy: 0.274000\n"
]
],
[
[
"Должно получится где-то `27%` accuracy. Теперь попробуем большее значение `k`, например `k = 5`:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"y_test_pred = classifier.predict_labels(dists, k=5)\nnum_correct = np.sum(y_test_pred == y_test)\naccuracy = float(num_correct) / num_test\nprint('Got %d / %d correct => accuracy: %f' % (num_correct, num_test, accuracy))",
"Got 139 / 500 correct => accuracy: 0.278000\n"
]
],
[
[
"Должно стать немного лучше, чем с `k = 1`.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Вопрос №2**\n\nМожно также попробовать другую метрику расстояний, например L1.\nКачество классификатора по ближайшему соседу с L1 расстоянием не изменится, если (Выберите все подходящие варианты):\n1. Данные предобработаны вычитанием среднего.\n2. Данные предобработаны вычитанием среднего и делением на дисперсию.\n3. Координатные оси данных повёрнуты.\n4. Ни одно из вышеперечисленного.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Ваш ответ**: Верными являются утверждения #1 и #2.\n\n_Подробнее по каждому пункту:_\n1. $||x - y|| = ||(x - mean) - (y - mean)||$ \nТаким образом, при поиске соседей в матрице расстояний получим те же самые значения. Тогда качество не изменится, так как ответы будут теми же самыми.\n2. $\\cfrac{||x - y||}{variance} = \\left|\\left|\\cfrac{x - mean}{variance} - \\cfrac{y - mean}{variance}\\right|\\right|$ \nВ данном случае матрица расстояний будет уменьшена в `variance` раз. Но это не повлияет на поиск ближайших соседей - качество останется прежним.\n3. `L1`-метрика не является симметричной\n\nПри повороте осей матрица расстояний изменится, и ответы классификатора (т.е. качество) могут измениться.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Теперь нужно немного ускорить подсчёт матрицы расстояний, ограничив число циклов до одного. Реализуйте функцию `compute_distances_one_loop` и запустите код ниже",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Now lets speed up distance matrix computation by using partial vectorization\n# with one loop. Implement the function compute_distances_one_loop and run the\n# code below:\ndists_one = classifier.compute_distances_one_loop(X_test)\n\n# To ensure that our vectorized implementation is correct, we make sure that it\n# agrees with the naive implementation. There are many ways to decide whether\n# two matrices are similar; one of the simplest is the Frobenius norm. In case\n# you haven't seen it before, the Frobenius norm of two matrices is the square\n# root of the squared sum of differences of all elements; in other words, reshape\n# the matrices into vectors and compute the Euclidean distance between them.\ndifference = np.linalg.norm(dists - dists_one, ord='fro')\nprint('Difference was: %f' % (difference, ))\nif difference < 0.001:\n print('Good! The distance matrices are the same')\nelse:\n print('Uh-oh! The distance matrices are different')",
"Difference was: 0.000000\nGood! The distance matrices are the same\n"
]
],
[
[
"Наконец реализуем полностью векторизованную версию: `compute_distances_no_loops`",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Now implement the fully vectorized version inside compute_distances_no_loops\n# and run the code\ndists_two = classifier.compute_distances_no_loops(X_test)\n\n# check that the distance matrix agrees with the one we computed before:\ndifference = np.linalg.norm(dists - dists_two, ord='fro')\nprint('Difference was: %f' % (difference, ))\nif difference < 0.001:\n print('Good! The distance matrices are the same')\nelse:\n print('Uh-oh! The distance matrices are different')",
"Difference was: 0.000000\nGood! The distance matrices are the same\n"
]
],
[
[
"Осталось сравнить эффективность всех 3 написанных версий",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Let's compare how fast the implementations are\ndef time_function(f, *args):\n \"\"\"\n Call a function f with args and return the time (in seconds) that it took to execute.\n \"\"\"\n import time\n tic = time.time()\n f(*args)\n toc = time.time()\n return toc - tic\n\ntwo_loop_time = time_function(classifier.compute_distances_two_loops, X_test)\nprint('Two loop version took %f seconds' % two_loop_time)\n\none_loop_time = time_function(classifier.compute_distances_one_loop, X_test)\nprint('One loop version took %f seconds' % one_loop_time)\n\nno_loop_time = time_function(classifier.compute_distances_no_loops, X_test)\nprint('No loop version took %f seconds' % no_loop_time)\n\n# you should see significantly faster performance with the fully vectorized implementation",
"Two loop version took 30.070831 seconds\nOne loop version took 27.681288 seconds\nNo loop version took 0.248711 seconds\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Cross-validation\n\nМы построили классификатор, используя k = 5 по умолчанию. Теперь подберём оптимальное значение гиперпараметра с использованием кросс-валидации методом k-fold. Требуется разбить ваши данные на группы (folds) и для каждой группы посчитать accuracy, когда она выделяется как тестовая.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"num_folds = 5\nk_choices = [1, 3, 5, 8, 10, 12, 15, 20, 50, 100]\n\nX_train_folds = np.array_split(X_train, num_folds)\ny_train_folds = np.array_split(y_train, num_folds)\n\n# A dictionary holding the accuracies for different values of k that we find\n# when running cross-validation. After running cross-validation,\n# k_to_accuracies[k] should be a list of length num_folds giving the different\n# accuracy values that we found when using that value of k.\nk_to_accuracies = {}\n\nfor k in k_choices:\n accuracies = []\n for val_fold in range(num_folds):\n classifier.train(np.delete(X_train_folds, val_fold, 0).reshape(-1, X_train_folds[0].shape[1]),\n np.delete(y_train_folds, val_fold, 0).reshape(-1,))\n y_val_pred = classifier.predict(X_train_folds[val_fold], k=k)\n num_correct = np.sum(y_val_pred == y_train_folds[val_fold])\n accuracies.append(float(num_correct) / num_test)\n k_to_accuracies[k] = accuracies\n\n# Print out the computed accuracies\nfor k in sorted(k_to_accuracies):\n for accuracy in k_to_accuracies[k]:\n print('k = %d, accuracy = %f' % (k, accuracy))",
"k = 1, accuracy = 0.526000\nk = 1, accuracy = 0.514000\nk = 1, accuracy = 0.528000\nk = 1, accuracy = 0.556000\nk = 1, accuracy = 0.532000\nk = 3, accuracy = 0.478000\nk = 3, accuracy = 0.498000\nk = 3, accuracy = 0.480000\nk = 3, accuracy = 0.532000\nk = 3, accuracy = 0.508000\nk = 5, accuracy = 0.496000\nk = 5, accuracy = 0.532000\nk = 5, accuracy = 0.560000\nk = 5, accuracy = 0.584000\nk = 5, accuracy = 0.560000\nk = 8, accuracy = 0.524000\nk = 8, accuracy = 0.564000\nk = 8, accuracy = 0.546000\nk = 8, accuracy = 0.580000\nk = 8, accuracy = 0.546000\nk = 10, accuracy = 0.530000\nk = 10, accuracy = 0.592000\nk = 10, accuracy = 0.552000\nk = 10, accuracy = 0.568000\nk = 10, accuracy = 0.560000\nk = 12, accuracy = 0.520000\nk = 12, accuracy = 0.590000\nk = 12, accuracy = 0.558000\nk = 12, accuracy = 0.566000\nk = 12, accuracy = 0.560000\nk = 15, accuracy = 0.504000\nk = 15, accuracy = 0.578000\nk = 15, accuracy = 0.556000\nk = 15, accuracy = 0.564000\nk = 15, accuracy = 0.548000\nk = 20, accuracy = 0.540000\nk = 20, accuracy = 0.558000\nk = 20, accuracy = 0.558000\nk = 20, accuracy = 0.564000\nk = 20, accuracy = 0.570000\nk = 50, accuracy = 0.542000\nk = 50, accuracy = 0.576000\nk = 50, accuracy = 0.556000\nk = 50, accuracy = 0.538000\nk = 50, accuracy = 0.532000\nk = 100, accuracy = 0.512000\nk = 100, accuracy = 0.540000\nk = 100, accuracy = 0.526000\nk = 100, accuracy = 0.512000\nk = 100, accuracy = 0.526000\n"
]
],
[
[
"Построим график зависимости качества от k",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# plot the raw observations\nfor k in k_choices:\n accuracies = k_to_accuracies[k]\n plt.scatter([k] * len(accuracies), accuracies)\n\n# plot the trend line with error bars that correspond to standard deviation\naccuracies_mean = np.array([np.mean(v) for k,v in sorted(k_to_accuracies.items())])\naccuracies_std = np.array([np.std(v) for k,v in sorted(k_to_accuracies.items())])\nplt.errorbar(k_choices, accuracies_mean, yerr=accuracies_std)\nplt.title('Cross-validation on k')\nplt.xlabel('k')\nplt.ylabel('Cross-validation accuracy')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Наконец, выберите лучшее значение k и переобучите классификатор с использованием всех данных для обучения.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Based on the cross-validation results above, choose the best value for k, \n# retrain the classifier using all the training data, and test it on the test\n# data. You should be able to get above 28% accuracy on the test data.\nbest_k = 10\n\nclassifier = KNearestNeighbor()\nclassifier.train(X_train, y_train)\ny_test_pred = classifier.predict(X_test, k=best_k)\n\n# Compute and display the accuracy\nnum_correct = np.sum(y_test_pred == y_test)\naccuracy = float(num_correct) / num_test\nprint('Got %d / %d correct => accuracy: %f' % (num_correct, num_test, accuracy))",
"Got 141 / 500 correct => accuracy: 0.282000\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Вопрос №3**\nКакие утверждения про классификатор $k$-Nearest Neighbor ($k$-NN) верны, и для всех ли значений $k$?\n1. Качество на обучающих данных будет для 1-NN всегда выше, чем для 5-NN.\n2. Качество на тестовых данных будет для 1-NN всегда выше, чем для 5-NN.\n3. Разделяющие поверхности k-NN классификатора линейные.\n4. Время нужное для классификации тестового примера k-NN классификатором растёт с ростом размера обучающей выборки.\n5. Ничего из вышеперечисленного.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Ваш ответ**: Верными являются утверждения #1 и #4.\n\n_Подробнее по каждому пункту_:\n1. В случае `1-NN` во время `predict` будет рассматриваться только одна метка из обучающей выборки. Если подать на вход элемент из обучающей выборки, то ближайшей для него точкой из обучающей выборки будет сама эта точка. Как следствие - отсутствие ошибок при классификации обучающей выборки. В случае `5-NN` во время `predict` будут рассматриваться уже 5 меток - это может сместить классификацию; точность может уменьшиться.\n2. Рассмотрим следующий случай: пусть в обучающей выборке один объект первого типа, и 100 объектов второго типа, а в тестовой - 10 объектов второго типа, причем ближайшей для них точкой из обучающей выборки является объект первого типа. Тогда `1-NN` будет постоянно ошибаться, а `5-NN` - правильно классифицировать.\n\n3. Для начала посмотрим на такой случай: пусть у нас в обучающей выборке всего два объекта, причем эти объекты имеют разные метки. Тогда классификатор поделит всю плоскость на две части следующим образом: проведет серединную гиперплоскость, точки со стороны первого объекта будут получать его метку, а с другой стороны - метку второго объекта. В этом примере получим, что разделяющая гиперплоскость будет линейной. \nЕсли посмотреть на [этот пример](https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/iris), то видим, что разделяющие поверхности здесь не являются линейными (хотя части поверхностей, несомненно, являются прямыми линиями)\n\nГоворим про гиперплоскости, т.к. признаков у объектов может быть неограниченное количество.\n4. Во время `predict` рассчитывается расстояние от тестового примера до всех объектов обучающей выборки. Время прямо пропорционально зависит от размера обучающей выборки.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Часть 2. SVM классификатор\n\nВ этом упражнении вы:\n\n- реализуете полностью векторизованную **функцию потерь** для SVM классификатора\n- реализуете полностью векторизованное представление его **аналитического градиента**\n- **проверите реализацию** числовым градиентом\n- используете валидационное множество **чтобы подобрать параметр learning rate и силу регуляризации**\n- **оптимизируете** функцию потерь с помощью **SGD**\n- **визуализируете** итоговые полученные веса\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Загружаем и предобрабатываем данные",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Load the raw CIFAR-10 data.\ncifar10_dir = 'cs231n/datasets/cifar-10-batches-py'\n\n# Cleaning up variables to prevent loading data multiple times (which may cause memory issue)\ntry:\n del X_train, y_train\n del X_test, y_test\n print('Clear previously loaded data.')\nexcept:\n pass\n\nX_train, y_train, X_test, y_test = load_CIFAR10(cifar10_dir)\n\n# As a sanity check, we print out the size of the training and test data.\nprint('Training data shape: ', X_train.shape)\nprint('Training labels shape: ', y_train.shape)\nprint('Test data shape: ', X_test.shape)\nprint('Test labels shape: ', y_test.shape)",
"Clear previously loaded data.\nTraining data shape: (50000, 32, 32, 3)\nTraining labels shape: (50000,)\nTest data shape: (10000, 32, 32, 3)\nTest labels shape: (10000,)\n"
],
[
"# Visualize some examples from the dataset.\n# We show a few examples of training images from each class.\nclasses = ['plane', 'car', 'bird', 'cat', 'deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck']\nnum_classes = len(classes)\nsamples_per_class = 7\nfor y, cls in enumerate(classes):\n idxs = np.flatnonzero(y_train == y)\n idxs = np.random.choice(idxs, samples_per_class, replace=False)\n for i, idx in enumerate(idxs):\n plt_idx = i * num_classes + y + 1\n plt.subplot(samples_per_class, num_classes, plt_idx)\n plt.imshow(X_train[idx].astype('uint8'))\n plt.axis('off')\n if i == 0:\n plt.title(cls)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Split the data into train, val, and test sets. In addition we will\n# create a small development set as a subset of the training data;\n# we can use this for development so our code runs faster.\nnum_training = 49000\nnum_validation = 1000\nnum_test = 1000\nnum_dev = 500\n\n# Our validation set will be num_validation points from the original\n# training set.\nmask = range(num_training, num_training + num_validation)\nX_val = X_train[mask]\ny_val = y_train[mask]\n\n# Our training set will be the first num_train points from the original\n# training set.\nmask = range(num_training)\nX_train = X_train[mask]\ny_train = y_train[mask]\n\n# We will also make a development set, which is a small subset of\n# the training set.\nmask = np.random.choice(num_training, num_dev, replace=False)\nX_dev = X_train[mask]\ny_dev = y_train[mask]\n\n# We use the first num_test points of the original test set as our\n# test set.\nmask = range(num_test)\nX_test = X_test[mask]\ny_test = y_test[mask]\n\nprint('Train data shape: ', X_train.shape)\nprint('Train labels shape: ', y_train.shape)\nprint('Validation data shape: ', X_val.shape)\nprint('Validation labels shape: ', y_val.shape)\nprint('Test data shape: ', X_test.shape)\nprint('Test labels shape: ', y_test.shape)",
"Train data shape: (49000, 32, 32, 3)\nTrain labels shape: (49000,)\nValidation data shape: (1000, 32, 32, 3)\nValidation labels shape: (1000,)\nTest data shape: (1000, 32, 32, 3)\nTest labels shape: (1000,)\n"
],
[
"# Preprocessing: reshape the image data into rows\nX_train = np.reshape(X_train, (X_train.shape[0], -1))\nX_val = np.reshape(X_val, (X_val.shape[0], -1))\nX_test = np.reshape(X_test, (X_test.shape[0], -1))\nX_dev = np.reshape(X_dev, (X_dev.shape[0], -1))\n\n# As a sanity check, print out the shapes of the data\nprint('Training data shape: ', X_train.shape)\nprint('Validation data shape: ', X_val.shape)\nprint('Test data shape: ', X_test.shape)\nprint('dev data shape: ', X_dev.shape)",
"Training data shape: (49000, 3072)\nValidation data shape: (1000, 3072)\nTest data shape: (1000, 3072)\ndev data shape: (500, 3072)\n"
],
[
"# Preprocessing: subtract the mean image\n# first: compute the image mean based on the training data\nmean_image = np.mean(X_train, axis=0)\nprint(mean_image[:10]) # print a few of the elements\nplt.figure(figsize=(4,4))\nplt.imshow(mean_image.reshape((32,32,3)).astype('uint8')) # visualize the mean image\nplt.show()",
"[130.64189796 135.98173469 132.47391837 130.05569388 135.34804082\n 131.75402041 130.96055102 136.14328571 132.47636735 131.48467347]\n"
],
[
"# second: subtract the mean image from train and test data\nX_train -= mean_image\nX_val -= mean_image\nX_test -= mean_image\nX_dev -= mean_image",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# third: append the bias dimension of ones (i.e. bias trick) so that our SVM\n# only has to worry about optimizing a single weight matrix W.\nX_train = np.hstack([X_train, np.ones((X_train.shape[0], 1))])\nX_val = np.hstack([X_val, np.ones((X_val.shape[0], 1))])\nX_test = np.hstack([X_test, np.ones((X_test.shape[0], 1))])\nX_dev = np.hstack([X_dev, np.ones((X_dev.shape[0], 1))])\n\nprint(X_train.shape, X_val.shape, X_test.shape, X_dev.shape)",
"(49000, 3073) (1000, 3073) (1000, 3073) (500, 3073)\n"
]
],
[
[
"## SVM Classifier\n\nВесь дальнейший код нужно будет реализовать в файле **cs231n/classifiers/linear_svm.py**. \n\nФункция `svm_loss_naive` в данном случае уже частично реализована за вас и производит неэффективный подсчёт самого значения loss-а.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Evaluate the naive implementation of the loss we provided for you:\nfrom cs231n.classifiers.linear_svm import svm_loss_naive\nimport time\n\n# generate a random SVM weight matrix of small numbers\nW = np.random.randn(3073, 10) * 0.0001 \n\nloss, grad = svm_loss_naive(W, X_dev, y_dev, 0.000005)\nprint('loss: %f' % (loss, ))",
"loss: 9.068982\n"
]
],
[
[
"Значение `grad`, возаращаемое из функции сейчас состоит из нулей. Реализуйте подсчёт градиента и добавьте его в функцию `svm_loss_naive`.\n\nДля проверки корректности вычисленного градента, можно использовать сравнение с численным градиентом. Код ниже проводит тестирование:",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Once you've implemented the gradient, recompute it with the code below\n# and gradient check it with the function we provided for you\n\n# Compute the loss and its gradient at W.\nloss, grad = svm_loss_naive(W, X_dev, y_dev, 0.0)\n\n# Numerically compute the gradient along several randomly chosen dimensions, and\n# compare them with your analytically computed gradient. The numbers should match\n# almost exactly along all dimensions.\nfrom cs231n.gradient_check import grad_check_sparse\nf = lambda w: svm_loss_naive(w, X_dev, y_dev, 0.0)[0]\ngrad_numerical = grad_check_sparse(f, W, grad)\n\n# do the gradient check once again with regularization turned on\n# you didn't forget the regularization gradient did you?\nloss, grad = svm_loss_naive(W, X_dev, y_dev, 5e1)\nf = lambda w: svm_loss_naive(w, X_dev, y_dev, 5e1)[0]\ngrad_numerical = grad_check_sparse(f, W, grad)",
"numerical: 16.289530 analytic: 16.289530, relative error: 2.030656e-11\nnumerical: 19.209084 analytic: 19.209084, relative error: 1.685604e-11\nnumerical: 19.375548 analytic: 19.375548, relative error: 2.122776e-11\nnumerical: 1.764973 analytic: 1.764973, relative error: 7.133026e-11\nnumerical: 26.980030 analytic: 26.980030, relative error: 1.225935e-12\nnumerical: -4.737275 analytic: -4.737275, relative error: 1.297012e-10\nnumerical: -1.420379 analytic: -1.420379, relative error: 2.123416e-10\nnumerical: 2.222812 analytic: 2.222812, relative error: 1.137687e-10\nnumerical: -17.610159 analytic: -17.555463, relative error: 1.555386e-03\nnumerical: -21.828563 analytic: -21.828563, relative error: 3.355281e-12\nnumerical: -43.299073 analytic: -43.267220, relative error: 3.679589e-04\nnumerical: 13.433475 analytic: 13.433475, relative error: 4.650722e-12\nnumerical: 12.085845 analytic: 12.037438, relative error: 2.006641e-03\nnumerical: 15.809217 analytic: 15.809217, relative error: 3.886043e-13\nnumerical: 14.444902 analytic: 14.444902, relative error: 3.382363e-11\nnumerical: -16.543332 analytic: -16.543332, relative error: 1.266833e-11\nnumerical: -0.584348 analytic: -0.584348, relative error: 3.616100e-10\nnumerical: -27.742445 analytic: -27.742445, relative error: 5.570571e-12\nnumerical: -5.319729 analytic: -5.319729, relative error: 7.860261e-11\nnumerical: 20.457781 analytic: 20.457781, relative error: 3.348787e-12\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Вопрос №1**\nИногда бывает так, что в какой-то момент одно из измерений при сравнении градиентов не будет подностью совпадать. Что может приводить к подобному разбросу? Стоит ли по этому поводу волноваться? Можно ли привести простой пример, в котором сравнение градиентов в одном из измерений сработает неправильно? Как можно повлиять на частоту возникновения подобных граничных эффектов? *Подсказка: SVM loss строго говоря не дифференцируется*",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Ваш ответ:**\nОшибки могут быть связаны с погрешностью вычислений. Для вычисления производной используется следующая приближенная формула\n$$f'(x) = \\cfrac{f(x+h) - f(x-h)}{2h}$$\nПогрешность этой формулы имеет второй порядок по `h`. Тогда, при $h = 10^{-5}$ погрешность численной производной будет $10^{-10}$. При расчетах с использованием `double` точность измеряется в пределах $2^{-64} \\approx 10^{-19}$. Видим, что при вычислении градиента с использованием точной формулы погрешность значительно меньше.\n\nЭта проблема не является существенной - при изменении параметров моделей с помощью градиентного спуска мы все равно будем смещаться в нужную сторону.\n\nПростой пример, когда возникает проблема: возьмем какую-нибудь недифференцируемую в нуле функцию\n$$x \\cdot I\\{x > 0\\}$$\nВ случае с точной формулой мы вообще мало что можем сделать (логично, наверное, доопределить каким-то значением). При вычислении по численной формуле получим\n$$f'(x)_{x=x_{0}} = 0.5$$\n\nСтандартный прием борьбы с такими проблемами - использование штрафных и барьерных функций.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Далее нужно реализовать векторизованную версию кода: `svm_loss_vectorized`.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Next implement the function svm_loss_vectorized; for now only compute the loss;\n# we will implement the gradient in a moment.\ntic = time.time()\nloss_naive, grad_naive = svm_loss_naive(W, X_dev, y_dev, 0.000005)\ntoc = time.time()\nprint('Naive loss: %e computed in %fs' % (loss_naive, toc - tic))\n\nfrom cs231n.classifiers.linear_svm import svm_loss_vectorized\ntic = time.time()\nloss_vectorized, _ = svm_loss_vectorized(W, X_dev, y_dev, 0.000005)\ntoc = time.time()\nprint('Vectorized loss: %e computed in %fs' % (loss_vectorized, toc - tic))\n\n# The losses should match but your vectorized implementation should be much faster.\nprint('difference: %f' % (loss_naive - loss_vectorized))",
"Naive loss: 9.068982e+00 computed in 0.120869s\nVectorized loss: 9.068982e+00 computed in 0.016371s\ndifference: -0.000000\n"
],
[
"# Complete the implementation of svm_loss_vectorized, and compute the gradient\n# of the loss function in a vectorized way.\n\n# The naive implementation and the vectorized implementation should match, but\n# the vectorized version should still be much faster.\ntic = time.time()\n_, grad_naive = svm_loss_naive(W, X_dev, y_dev, 0.000005)\ntoc = time.time()\nprint('Naive loss and gradient: computed in %fs' % (toc - tic))\n\ntic = time.time()\n_, grad_vectorized = svm_loss_vectorized(W, X_dev, y_dev, 0.000005)\ntoc = time.time()\nprint('Vectorized loss and gradient: computed in %fs' % (toc - tic))\n\n# The loss is a single number, so it is easy to compare the values computed\n# by the two implementations. The gradient on the other hand is a matrix, so\n# we use the Frobenius norm to compare them.\ndifference = np.linalg.norm(grad_naive - grad_vectorized, ord='fro')\nprint('difference: %f' % difference)",
"Naive loss and gradient: computed in 0.127521s\nVectorized loss and gradient: computed in 0.005606s\ndifference: 0.000000\n"
]
],
[
[
"### Stochastic Gradient Descent\n\nТеперь мы умеем эффективно считать выражения для loss-а и его градиента, причём градиент совпадает с численным. Теперь мы готовы к оптимизации loss-а.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Реализуйте функцию `LinearClassifier.train()` в файле `linear_classifier.py`",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# In the file linear_classifier.py, implement SGD in the function\n# LinearClassifier.train() and then run it with the code below.\nfrom cs231n.classifiers import LinearSVM\nsvm = LinearSVM()\ntic = time.time()\nloss_hist = svm.train(X_train, y_train, learning_rate=1e-7, reg=2.5e4,\n num_iters=1500, verbose=True)\ntoc = time.time()\nprint('That took %fs' % (toc - tic))",
"iteration 0 / 1500: loss 775.912711\niteration 100 / 1500: loss 284.835462\niteration 200 / 1500: loss 107.309465\niteration 300 / 1500: loss 42.152784\niteration 400 / 1500: loss 18.673201\niteration 500 / 1500: loss 10.054205\niteration 600 / 1500: loss 6.803731\niteration 700 / 1500: loss 6.024163\niteration 800 / 1500: loss 5.804819\niteration 900 / 1500: loss 5.113340\niteration 1000 / 1500: loss 5.440761\niteration 1100 / 1500: loss 5.955665\niteration 1200 / 1500: loss 5.577010\niteration 1300 / 1500: loss 5.849262\niteration 1400 / 1500: loss 5.161636\nThat took 13.950493s\n"
],
[
"# A useful debugging strategy is to plot the loss as a function of\n# iteration number:\nplt.plot(loss_hist)\nplt.xlabel('Iteration number')\nplt.ylabel('Loss value')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"А теперь потребуется реализацию функции `LinearClassifier.predict()`",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Write the LinearSVM.predict function and evaluate the performance on both the\n# training and validation set\ny_train_pred = svm.predict(X_train)\nprint('training accuracy: %f' % (np.mean(y_train == y_train_pred), ))\ny_val_pred = svm.predict(X_val)\nprint('validation accuracy: %f' % (np.mean(y_val == y_val_pred), ))",
"training accuracy: 0.369673\nvalidation accuracy: 0.374000\n"
]
],
[
[
"Подберите значения гиперпараметров: силы регуляризации и скорости обучения",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Use the validation set to tune hyperparameters (regularization strength and\n# learning rate). You should experiment with different ranges for the learning\n# rates and regularization strengths; if you are careful you should be able to\n# get a classification accuracy of about 0.4 on the validation set.\nlearning_rates = np.arange(1.6e-7, 1.8e-7, 0.3e-8)\nregularization_strengths = np.arange(4e3, 6e3, 3e2)\n\n# results is dictionary mapping tuples of the form\n# (learning_rate, regularization_strength) to tuples of the form\n# (training_accuracy, validation_accuracy). The accuracy is simply the fraction\n# of data points that are correctly classified.\nresults = {}\nbest_val = -1 # The highest validation accuracy that we have seen so far.\nbest_svm = None # The LinearSVM object that achieved the highest validation rate.\n\nfor lr in learning_rates:\n for reg in regularization_strengths:\n clf = LinearSVM()\n clf.train(X_train, y_train, learning_rate=lr, reg=reg, num_iters=1000)\n \n y_train_pred = clf.predict(X_train)\n train_acc = np.mean(y_train == y_train_pred)\n \n y_val_pred = clf.predict(X_val)\n val_acc = np.mean(y_val == y_val_pred)\n \n results[(lr, reg)] = (train_acc, val_acc)\n \n if val_acc > best_val:\n best_val = val_acc\n best_svm = clf\n \n# Print out results.\nfor lr, reg in sorted(results):\n train_accuracy, val_accuracy = results[(lr, reg)]\n print('lr %e reg %e train accuracy: %f val accuracy: %f' % (\n lr, reg, train_accuracy, val_accuracy))\n \nprint('best validation accuracy achieved during cross-validation: %f' % best_val)",
"lr 1.600000e-07 reg 4.000000e+03 train accuracy: 0.366776 val accuracy: 0.364000\nlr 1.600000e-07 reg 4.300000e+03 train accuracy: 0.371143 val accuracy: 0.363000\nlr 1.600000e-07 reg 4.600000e+03 train accuracy: 0.373041 val accuracy: 0.377000\nlr 1.600000e-07 reg 4.900000e+03 train accuracy: 0.364204 val accuracy: 0.371000\nlr 1.600000e-07 reg 5.200000e+03 train accuracy: 0.373571 val accuracy: 0.365000\nlr 1.600000e-07 reg 5.500000e+03 train accuracy: 0.376449 val accuracy: 0.372000\nlr 1.600000e-07 reg 5.800000e+03 train accuracy: 0.380510 val accuracy: 0.404000\nlr 1.630000e-07 reg 4.000000e+03 train accuracy: 0.370694 val accuracy: 0.367000\nlr 1.630000e-07 reg 4.300000e+03 train accuracy: 0.370429 val accuracy: 0.351000\nlr 1.630000e-07 reg 4.600000e+03 train accuracy: 0.367939 val accuracy: 0.372000\nlr 1.630000e-07 reg 4.900000e+03 train accuracy: 0.373857 val accuracy: 0.378000\nlr 1.630000e-07 reg 5.200000e+03 train accuracy: 0.377204 val accuracy: 0.377000\nlr 1.630000e-07 reg 5.500000e+03 train accuracy: 0.380143 val accuracy: 0.377000\nlr 1.630000e-07 reg 5.800000e+03 train accuracy: 0.381306 val accuracy: 0.389000\nlr 1.660000e-07 reg 4.000000e+03 train accuracy: 0.364449 val accuracy: 0.376000\nlr 1.660000e-07 reg 4.300000e+03 train accuracy: 0.373122 val accuracy: 0.377000\nlr 1.660000e-07 reg 4.600000e+03 train accuracy: 0.374755 val accuracy: 0.381000\nlr 1.660000e-07 reg 4.900000e+03 train accuracy: 0.379633 val accuracy: 0.381000\nlr 1.660000e-07 reg 5.200000e+03 train accuracy: 0.374592 val accuracy: 0.366000\nlr 1.660000e-07 reg 5.500000e+03 train accuracy: 0.378959 val accuracy: 0.381000\nlr 1.660000e-07 reg 5.800000e+03 train accuracy: 0.376449 val accuracy: 0.377000\nlr 1.690000e-07 reg 4.000000e+03 train accuracy: 0.367857 val accuracy: 0.374000\nlr 1.690000e-07 reg 4.300000e+03 train accuracy: 0.368796 val accuracy: 0.368000\nlr 1.690000e-07 reg 4.600000e+03 train accuracy: 0.375837 val accuracy: 0.380000\nlr 1.690000e-07 reg 4.900000e+03 train accuracy: 0.377327 val accuracy: 0.384000\nlr 1.690000e-07 reg 5.200000e+03 train accuracy: 0.374531 val accuracy: 0.382000\nlr 1.690000e-07 reg 5.500000e+03 train accuracy: 0.373612 val accuracy: 0.374000\nlr 1.690000e-07 reg 5.800000e+03 train accuracy: 0.370653 val accuracy: 0.360000\nlr 1.720000e-07 reg 4.000000e+03 train accuracy: 0.360163 val accuracy: 0.355000\nlr 1.720000e-07 reg 4.300000e+03 train accuracy: 0.371020 val accuracy: 0.374000\nlr 1.720000e-07 reg 4.600000e+03 train accuracy: 0.371082 val accuracy: 0.389000\nlr 1.720000e-07 reg 4.900000e+03 train accuracy: 0.379327 val accuracy: 0.393000\nlr 1.720000e-07 reg 5.200000e+03 train accuracy: 0.374510 val accuracy: 0.357000\nlr 1.720000e-07 reg 5.500000e+03 train accuracy: 0.376122 val accuracy: 0.390000\nlr 1.720000e-07 reg 5.800000e+03 train accuracy: 0.381408 val accuracy: 0.378000\nlr 1.750000e-07 reg 4.000000e+03 train accuracy: 0.371633 val accuracy: 0.401000\nlr 1.750000e-07 reg 4.300000e+03 train accuracy: 0.374408 val accuracy: 0.379000\nlr 1.750000e-07 reg 4.600000e+03 train accuracy: 0.371796 val accuracy: 0.375000\nlr 1.750000e-07 reg 4.900000e+03 train accuracy: 0.375571 val accuracy: 0.384000\nlr 1.750000e-07 reg 5.200000e+03 train accuracy: 0.374163 val accuracy: 0.368000\nlr 1.750000e-07 reg 5.500000e+03 train accuracy: 0.373816 val accuracy: 0.384000\nlr 1.750000e-07 reg 5.800000e+03 train accuracy: 0.382286 val accuracy: 0.381000\nlr 1.780000e-07 reg 4.000000e+03 train accuracy: 0.372429 val accuracy: 0.361000\nlr 1.780000e-07 reg 4.300000e+03 train accuracy: 0.377918 val accuracy: 0.378000\nlr 1.780000e-07 reg 4.600000e+03 train accuracy: 0.373571 val accuracy: 0.382000\nlr 1.780000e-07 reg 4.900000e+03 train accuracy: 0.376796 val accuracy: 0.385000\nlr 1.780000e-07 reg 5.200000e+03 train accuracy: 0.380653 val accuracy: 0.377000\nlr 1.780000e-07 reg 5.500000e+03 train accuracy: 0.380510 val accuracy: 0.385000\nlr 1.780000e-07 reg 5.800000e+03 train accuracy: 0.382388 val accuracy: 0.375000\nbest validation accuracy achieved during cross-validation: 0.404000\n"
],
[
"# Visualize the cross-validation results\nimport math\nx_scatter = [math.log10(x[0]) for x in results]\ny_scatter = [math.log10(x[1]) for x in results]\n\n# plot training accuracy\nmarker_size = 100\ncolors = [results[x][0] for x in results]\nplt.subplot(2, 1, 1)\nplt.scatter(x_scatter, y_scatter, marker_size, c=colors)\nplt.colorbar()\nplt.xlabel('log learning rate')\nplt.ylabel('log regularization strength')\nplt.title('CIFAR-10 training accuracy')\n\n# plot validation accuracy\ncolors = [results[x][1] for x in results] # default size of markers is 20\nplt.subplot(2, 1, 2)\nplt.scatter(x_scatter, y_scatter, marker_size, c=colors)\nplt.colorbar()\nplt.xlabel('log learning rate')\nplt.ylabel('log regularization strength')\nplt.title('CIFAR-10 validation accuracy')\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# Evaluate the best svm on test set\ny_test_pred = best_svm.predict(X_test)\ntest_accuracy = np.mean(y_test == y_test_pred)\nprint('linear SVM on raw pixels final test set accuracy: %f' % test_accuracy)",
"linear SVM on raw pixels final test set accuracy: 0.374000\n"
]
],
[
[
"Осталось визуализировать обученные веса для всех классов",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Visualize the learned weights for each class.\n# Depending on your choice of learning rate and regularization strength, these may\n# or may not be nice to look at.\nw = best_svm.W[:-1,:] # strip out the bias\nw = w.reshape(32, 32, 3, 10)\nw_min, w_max = np.min(w), np.max(w)\nclasses = ['plane', 'car', 'bird', 'cat', 'deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck']\nfor i in range(10):\n plt.subplot(2, 5, i + 1)\n \n # Rescale the weights to be between 0 and 255\n wimg = 255.0 * (w[:, :, :, i].squeeze() - w_min) / (w_max - w_min)\n plt.imshow(wimg.astype('uint8'))\n plt.axis('off')\n plt.title(classes[i])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Часть 3. Softmax классификатор\n\nВ этом упражнении вы:\n\n- реализуете полностью векторизованную **функцию потерь** для Softmax классификатора\n- реализуете полностью векторизованное представление его **аналитического градиента**\n- **проверите реализацию** числовым градиентом\n- используете валидационное множество **чтобы подобрать параметр learning rate и силу регуляризации**\n- **оптимизируете** функцию потерь с помощью **SGD**\n- **визуализируете** итоговые полученные веса\n\nПримечание: требуется код, написанный в части 2.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def get_CIFAR10_data(num_training=49000, num_validation=1000, num_test=1000, num_dev=500):\n \"\"\"\n Load the CIFAR-10 dataset from disk and perform preprocessing to prepare\n it for the linear classifier. These are the same steps as we used for the\n SVM, but condensed to a single function. \n \"\"\"\n # Load the raw CIFAR-10 data\n cifar10_dir = 'cs231n/datasets/cifar-10-batches-py'\n \n X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test = load_CIFAR10(cifar10_dir)\n \n # subsample the data\n mask = list(range(num_training, num_training + num_validation))\n X_val = X_train[mask]\n y_val = y_train[mask]\n mask = list(range(num_training))\n X_train = X_train[mask]\n y_train = y_train[mask]\n mask = list(range(num_test))\n X_test = X_test[mask]\n y_test = y_test[mask]\n mask = np.random.choice(num_training, num_dev, replace=False)\n X_dev = X_train[mask]\n y_dev = y_train[mask]\n \n # Preprocessing: reshape the image data into rows\n X_train = np.reshape(X_train, (X_train.shape[0], -1))\n X_val = np.reshape(X_val, (X_val.shape[0], -1))\n X_test = np.reshape(X_test, (X_test.shape[0], -1))\n X_dev = np.reshape(X_dev, (X_dev.shape[0], -1))\n \n # Normalize the data: subtract the mean image\n mean_image = np.mean(X_train, axis = 0)\n X_train -= mean_image\n X_val -= mean_image\n X_test -= mean_image\n X_dev -= mean_image\n \n # add bias dimension and transform into columns\n X_train = np.hstack([X_train, np.ones((X_train.shape[0], 1))])\n X_val = np.hstack([X_val, np.ones((X_val.shape[0], 1))])\n X_test = np.hstack([X_test, np.ones((X_test.shape[0], 1))])\n X_dev = np.hstack([X_dev, np.ones((X_dev.shape[0], 1))])\n \n return X_train, y_train, X_val, y_val, X_test, y_test, X_dev, y_dev\n\n\n# Cleaning up variables to prevent loading data multiple times (which may cause memory issue)\ntry:\n del X_train, y_train\n del X_test, y_test\n print('Clear previously loaded data.')\nexcept:\n pass\n\n# Invoke the above function to get our data.\nX_train, y_train, X_val, y_val, X_test, y_test, X_dev, y_dev = get_CIFAR10_data()\nprint('Train data shape: ', X_train.shape)\nprint('Train labels shape: ', y_train.shape)\nprint('Validation data shape: ', X_val.shape)\nprint('Validation labels shape: ', y_val.shape)\nprint('Test data shape: ', X_test.shape)\nprint('Test labels shape: ', y_test.shape)\nprint('dev data shape: ', X_dev.shape)\nprint('dev labels shape: ', y_dev.shape)",
"Clear previously loaded data.\nTrain data shape: (49000, 3073)\nTrain labels shape: (49000,)\nValidation data shape: (1000, 3073)\nValidation labels shape: (1000,)\nTest data shape: (1000, 3073)\nTest labels shape: (1000,)\ndev data shape: (500, 3073)\ndev labels shape: (500,)\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Softmax Classifier\n\nКод в этой секции нужно писать в файле **cs231n/classifiers/softmax.py**. \nДля начала реализуйте функцию `softmax_loss_naive`",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# First implement the naive softmax loss function with nested loops.\n# Open the file cs231n/classifiers/softmax.py and implement the\n# softmax_loss_naive function.\n\nfrom cs231n.classifiers.softmax import softmax_loss_naive\nimport time\n\n# Generate a random softmax weight matrix and use it to compute the loss.\nW = np.random.randn(3073, 10) * 0.0001\nloss, grad = softmax_loss_naive(W, X_dev, y_dev, 0.0)\n\n# As a rough sanity check, our loss should be something close to -log(0.1).\nprint('loss: %f' % loss)\nprint('sanity check: %f' % (-np.log(0.1)))",
"loss: 2.372887\nsanity check: 2.302585\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Вопрос №1**\nПочему мы ожидаем значение функции потерь -log(0.1)? Дайте краткий ответ.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Ваш ответ**: В начале все классы имеют почти одинаковый `score` (близкий к 0), поэтому значения `softmax` будут похожими. Так как классов 10, то получим\n$$Loss \\approx -log\\left(\\cfrac{e^{0}}{\\sum_{1}^{10}e^{0}}\\right) \\approx -log(0.1)$$",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Допишите вашу реализацию, чтобы она также возвращала и корректный градиент. Ячейка ниже проверит его на корректность по сравнению с числовым градиентом.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Complete the implementation of softmax_loss_naive and implement a (naive)\n# version of the gradient that uses nested loops.\nloss, grad = softmax_loss_naive(W, X_dev, y_dev, 0.0)\n\n# As we did for the SVM, use numeric gradient checking as a debugging tool.\n# The numeric gradient should be close to the analytic gradient.\nfrom cs231n.gradient_check import grad_check_sparse\nf = lambda w: softmax_loss_naive(w, X_dev, y_dev, 0.0)[0]\ngrad_numerical = grad_check_sparse(f, W, grad, 10)\n\n# similar to SVM case, do another gradient check with regularization\nloss, grad = softmax_loss_naive(W, X_dev, y_dev, 5e1)\nf = lambda w: softmax_loss_naive(w, X_dev, y_dev, 5e1)[0]\ngrad_numerical = grad_check_sparse(f, W, grad, 10)",
"numerical: -6.753812 analytic: -6.753813, relative error: 9.017098e-10\nnumerical: -1.038043 analytic: -1.038043, relative error: 6.496176e-08\nnumerical: 0.336065 analytic: 0.336065, relative error: 7.895096e-08\nnumerical: 2.549307 analytic: 2.549307, relative error: 2.144710e-08\nnumerical: 0.659773 analytic: 0.659772, relative error: 8.497040e-08\nnumerical: -1.056757 analytic: -1.056757, relative error: 9.399436e-08\nnumerical: 0.367526 analytic: 0.367526, relative error: 1.354265e-07\nnumerical: -2.499379 analytic: -2.499379, relative error: 1.530929e-08\nnumerical: 3.552621 analytic: 3.552621, relative error: 3.283463e-10\nnumerical: 0.207585 analytic: 0.207585, relative error: 1.505460e-08\nnumerical: 1.361501 analytic: 1.361501, relative error: 1.317494e-08\nnumerical: -2.532388 analytic: -2.532388, relative error: 1.254853e-08\nnumerical: -0.824894 analytic: -0.824894, relative error: 7.747554e-08\nnumerical: -2.178519 analytic: -2.178519, relative error: 3.531246e-08\nnumerical: -0.627476 analytic: -0.627476, relative error: 3.760837e-08\nnumerical: -3.752354 analytic: -3.752354, relative error: 4.936916e-09\nnumerical: 0.512406 analytic: 0.512406, relative error: 3.280518e-08\nnumerical: 1.126067 analytic: 1.126067, relative error: 1.349936e-08\nnumerical: 1.239027 analytic: 1.239027, relative error: 1.567394e-08\nnumerical: 0.322134 analytic: 0.322134, relative error: 6.765403e-08\n"
]
],
[
[
"Теперь реализуйте функцию `softmax_loss_vectorized` - подсчёт того же самого значения и градиента с использованием векторных операций.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Now that we have a naive implementation of the softmax loss function and its gradient,\n# implement a vectorized version in softmax_loss_vectorized.\n# The two versions should compute the same results, but the vectorized version should be\n# much faster.\ntic = time.time()\nloss_naive, grad_naive = softmax_loss_naive(W, X_dev, y_dev, 0.000005)\ntoc = time.time()\nprint('naive loss: %e computed in %fs' % (loss_naive, toc - tic))\n\nfrom cs231n.classifiers.softmax import softmax_loss_vectorized\ntic = time.time()\nloss_vectorized, grad_vectorized = softmax_loss_vectorized(W, X_dev, y_dev, 0.000005)\ntoc = time.time()\nprint('vectorized loss: %e computed in %fs' % (loss_vectorized, toc - tic))\n\n# As we did for the SVM, we use the Frobenius norm to compare the two versions\n# of the gradient.\ngrad_difference = np.linalg.norm(grad_naive - grad_vectorized, ord='fro')\nprint('Loss difference: %f' % np.abs(loss_naive - loss_vectorized))\nprint('Gradient difference: %f' % grad_difference)",
"naive loss: 2.372887e+00 computed in 0.103603s\nvectorized loss: 2.372887e+00 computed in 0.010390s\nLoss difference: 0.000000\nGradient difference: 0.000000\n"
]
],
[
[
"Используйте валидационное множество для подбора гиперпараметров силы регуляризации и скорости обучения.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Use the validation set to tune hyperparameters (regularization strength and\n# learning rate). You should experiment with different ranges for the learning\n# rates and regularization strengths; if you are careful you should be able to\n# get a classification accuracy of over 0.35 on the validation set.\nfrom cs231n.classifiers import Softmax\nresults = {}\nbest_val = -1\nbest_softmax = None\nlearning_rates = np.arange(1.6e-7, 1.8e-7, 0.3e-8)\nregularization_strengths = np.arange(4e3, 6e3, 3e2)\n\nfor lr in learning_rates:\n for reg in regularization_strengths:\n clf = Softmax()\n clf.train(X_train, y_train, learning_rate=lr, reg=reg, num_iters=1000)\n \n y_train_pred = clf.predict(X_train)\n train_acc = np.mean(y_train == y_train_pred)\n \n y_val_pred = clf.predict(X_val)\n val_acc = np.mean(y_val == y_val_pred)\n \n results[(lr, reg)] = (train_acc, val_acc)\n \n if val_acc > best_val:\n best_val = val_acc\n best_softmax = clf\n \n# Print out results.\nfor lr, reg in sorted(results):\n train_accuracy, val_accuracy = results[(lr, reg)]\n print('lr %e reg %e train accuracy: %f val accuracy: %f' % (\n lr, reg, train_accuracy, val_accuracy))\n \nprint('best validation accuracy achieved during cross-validation: %f' % best_val)",
"lr 1.600000e-07 reg 4.000000e+03 train accuracy: 0.323857 val accuracy: 0.335000\nlr 1.600000e-07 reg 4.300000e+03 train accuracy: 0.329571 val accuracy: 0.339000\nlr 1.600000e-07 reg 4.600000e+03 train accuracy: 0.331184 val accuracy: 0.349000\nlr 1.600000e-07 reg 4.900000e+03 train accuracy: 0.336388 val accuracy: 0.345000\nlr 1.600000e-07 reg 5.200000e+03 train accuracy: 0.339796 val accuracy: 0.354000\nlr 1.600000e-07 reg 5.500000e+03 train accuracy: 0.343224 val accuracy: 0.329000\nlr 1.600000e-07 reg 5.800000e+03 train accuracy: 0.341714 val accuracy: 0.367000\nlr 1.630000e-07 reg 4.000000e+03 train accuracy: 0.325265 val accuracy: 0.319000\nlr 1.630000e-07 reg 4.300000e+03 train accuracy: 0.336245 val accuracy: 0.327000\nlr 1.630000e-07 reg 4.600000e+03 train accuracy: 0.338633 val accuracy: 0.322000\nlr 1.630000e-07 reg 4.900000e+03 train accuracy: 0.341286 val accuracy: 0.342000\nlr 1.630000e-07 reg 5.200000e+03 train accuracy: 0.342449 val accuracy: 0.340000\nlr 1.630000e-07 reg 5.500000e+03 train accuracy: 0.346429 val accuracy: 0.348000\nlr 1.630000e-07 reg 5.800000e+03 train accuracy: 0.348000 val accuracy: 0.366000\nlr 1.660000e-07 reg 4.000000e+03 train accuracy: 0.331816 val accuracy: 0.332000\nlr 1.660000e-07 reg 4.300000e+03 train accuracy: 0.334735 val accuracy: 0.357000\nlr 1.660000e-07 reg 4.600000e+03 train accuracy: 0.336571 val accuracy: 0.333000\nlr 1.660000e-07 reg 4.900000e+03 train accuracy: 0.340776 val accuracy: 0.349000\nlr 1.660000e-07 reg 5.200000e+03 train accuracy: 0.342612 val accuracy: 0.352000\nlr 1.660000e-07 reg 5.500000e+03 train accuracy: 0.344959 val accuracy: 0.349000\nlr 1.660000e-07 reg 5.800000e+03 train accuracy: 0.349367 val accuracy: 0.366000\nlr 1.690000e-07 reg 4.000000e+03 train accuracy: 0.330143 val accuracy: 0.334000\nlr 1.690000e-07 reg 4.300000e+03 train accuracy: 0.335653 val accuracy: 0.353000\nlr 1.690000e-07 reg 4.600000e+03 train accuracy: 0.340633 val accuracy: 0.363000\nlr 1.690000e-07 reg 4.900000e+03 train accuracy: 0.340816 val accuracy: 0.347000\nlr 1.690000e-07 reg 5.200000e+03 train accuracy: 0.347102 val accuracy: 0.353000\nlr 1.690000e-07 reg 5.500000e+03 train accuracy: 0.352633 val accuracy: 0.353000\nlr 1.690000e-07 reg 5.800000e+03 train accuracy: 0.350939 val accuracy: 0.360000\nlr 1.720000e-07 reg 4.000000e+03 train accuracy: 0.331571 val accuracy: 0.337000\nlr 1.720000e-07 reg 4.300000e+03 train accuracy: 0.340755 val accuracy: 0.354000\nlr 1.720000e-07 reg 4.600000e+03 train accuracy: 0.341490 val accuracy: 0.331000\nlr 1.720000e-07 reg 4.900000e+03 train accuracy: 0.343184 val accuracy: 0.367000\nlr 1.720000e-07 reg 5.200000e+03 train accuracy: 0.348551 val accuracy: 0.359000\nlr 1.720000e-07 reg 5.500000e+03 train accuracy: 0.350306 val accuracy: 0.357000\nlr 1.720000e-07 reg 5.800000e+03 train accuracy: 0.353245 val accuracy: 0.353000\nlr 1.750000e-07 reg 4.000000e+03 train accuracy: 0.338388 val accuracy: 0.339000\nlr 1.750000e-07 reg 4.300000e+03 train accuracy: 0.339531 val accuracy: 0.361000\nlr 1.750000e-07 reg 4.600000e+03 train accuracy: 0.343694 val accuracy: 0.335000\nlr 1.750000e-07 reg 4.900000e+03 train accuracy: 0.347776 val accuracy: 0.341000\nlr 1.750000e-07 reg 5.200000e+03 train accuracy: 0.347898 val accuracy: 0.344000\nlr 1.750000e-07 reg 5.500000e+03 train accuracy: 0.351286 val accuracy: 0.363000\nlr 1.750000e-07 reg 5.800000e+03 train accuracy: 0.352327 val accuracy: 0.353000\nlr 1.780000e-07 reg 4.000000e+03 train accuracy: 0.335633 val accuracy: 0.340000\nlr 1.780000e-07 reg 4.300000e+03 train accuracy: 0.342612 val accuracy: 0.361000\nlr 1.780000e-07 reg 4.600000e+03 train accuracy: 0.344612 val accuracy: 0.354000\nlr 1.780000e-07 reg 4.900000e+03 train accuracy: 0.349592 val accuracy: 0.373000\nlr 1.780000e-07 reg 5.200000e+03 train accuracy: 0.350469 val accuracy: 0.354000\nlr 1.780000e-07 reg 5.500000e+03 train accuracy: 0.352327 val accuracy: 0.359000\nlr 1.780000e-07 reg 5.800000e+03 train accuracy: 0.352449 val accuracy: 0.354000\nbest validation accuracy achieved during cross-validation: 0.373000\n"
]
],
[
[
"Наконец посчитайте значение accuracy для лучшего классификатора.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# evaluate on test set\n# Evaluate the best softmax on test set\ny_test_pred = best_softmax.predict(X_test)\ntest_accuracy = np.mean(y_test == y_test_pred)\nprint('softmax on raw pixels final test set accuracy: %f' % (test_accuracy, ))",
"softmax on raw pixels final test set accuracy: 0.360000\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Вопрос №2**\nВозможно ли, что при добавлении нового примера в обучающих данных SVM loss бы не изменился, но Softmax loss при этом бы поменялся?",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Ваш ответ**: Возможно.\n\n_Подробнее_: Допустим, что мы решаем задачу трехклассовой классификации, и что в выборке сейчас два примера:\n\n| Scores | Object 1 | Object 2 |\n|---------|----------|----------|\n| Class 1 | **3.2** | 2.2 |\n| Class 2 | 5.1 | 2.5 |\n| Class 3 | -1.7 | **-3.1** |\n\n| Object Loss | Object 1 | Object 2 |\n|--------------|----------|----------|\n| SVM Loss | 2.9 | 12.9 |\n| Softmax Loss | 2.04 | 6.16 |\n\n| Total Loss | SVM | Softmax |\n|------------|---------|---------|\n| Value | 7.9 | 4.1 |\n\nДобавим еще один объект в выборку:\n\n| Scores | Object 1 | Object 2 | Object 3 |\n|---------|----------|----------|----------|\n| Class 1 | **3.2** | 2.2 | 7.0 |\n| Class 2 | 5.1 | 2.5 | **1.0** |\n| Class 3 | -1.7 | **-3.1** | 0.9 |\n\n| Object Loss | Object 1 | Object 2 | Object 3 |\n|--------------|----------|----------|----------|\n| SVM Loss | 2.9 | 12.9 | 7.9 |\n| Softmax Loss | 2.04 | 6.16 | 6.0 |\n\n| Total Loss | SVM | Softmax |\n|------------|---------|---------|\n| Value | 7.9 | 4.73 |\n\nКак видим, `SVM TotalLoss` остался прежним, а `Softmax TotalLoss` изменился.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Осталось визуализировать обученные веса для всех классов",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# Visualize the learned weights for each class\nw = best_softmax.W[:-1,:] # strip out the bias\nw = w.reshape(32, 32, 3, 10)\n\nw_min, w_max = np.min(w), np.max(w)\n\nclasses = ['plane', 'car', 'bird', 'cat', 'deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck']\nfor i in range(10):\n plt.subplot(2, 5, i + 1)\n \n # Rescale the weights to be between 0 and 255\n wimg = 255.0 * (w[:, :, :, i].squeeze() - w_min) / (w_max - w_min)\n plt.imshow(wimg.astype('uint8'))\n plt.axis('off')\n plt.title(classes[i])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c50d6faede9dcafadfb2fef950058487072bbfe0
| 245,331 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
src/video_summarizer.ipynb
|
ayushtyagi188/face-emotion-recognition
|
26323fbf7eed504990c765a0ee61ae8ba8582538
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 90 |
2021-04-02T03:23:38.000Z
|
2022-03-28T01:41:35.000Z
|
src/video_summarizer.ipynb
|
ayushtyagi188/face-emotion-recognition
|
26323fbf7eed504990c765a0ee61ae8ba8582538
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 10 |
2021-06-23T07:42:55.000Z
|
2022-03-09T06:50:06.000Z
|
src/video_summarizer.ipynb
|
ayushtyagi188/face-emotion-recognition
|
26323fbf7eed504990c765a0ee61ae8ba8582538
|
[
"Apache-2.0"
] | 34 |
2021-04-02T10:40:34.000Z
|
2022-03-23T10:44:54.000Z
| 154.978522 | 173,988 | 0.832426 |
[
[
[
"%env CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=1",
"env: CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=1\n"
],
[
"DATA_DIR='/home/HDD6TB/datasets/emotions/zoom/'",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import os\nfrom PIL import Image\nimport cv2\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split\nfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier,RandomForestRegressor\nfrom sklearn import svm,metrics,preprocessing\nfrom sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier\nfrom sklearn.decomposition import PCA\nfrom sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline\nfrom sklearn.metrics.pairwise import pairwise_distances\n\nfrom collections import defaultdict\nimport os\nimport random\nimport numpy as np\nfrom tqdm import tqdm\nimport time\nimport pickle\nimport pandas as pd\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"compare_filenames=lambda x: int(os.path.splitext(x)[0])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"video_path=os.path.join(DATA_DIR,'videos/4.mp4')\nprint(video_path)\nfaces_path=os.path.join(DATA_DIR,'faces/mtcnn_new/4')",
"/home/HDD6TB/datasets/emotions/zoom/videos/4.mp4\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Face detection + OCR",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import tensorflow as tf\n\nprint(tf.__version__)\nfrom tensorflow.compat.v1.keras.backend import set_session \nconfig = tf.compat.v1.ConfigProto()\nconfig.gpu_options.allow_growth = True\nsess=tf.compat.v1.Session(config=config)\nset_session(sess)\n\nfrom facial_analysis import FacialImageProcessing\nimgProcessing=FacialImageProcessing(False)",
"2.4.1\n"
],
[
"import numpy as np\nimport cv2\nimport math\nfrom skimage import transform as trans\ndef get_iou(bb1, bb2):\n \"\"\"\n Calculate the Intersection over Union (IoU) of two bounding boxes.\n\n Parameters\n ----------\n bb1 : array\n order: {'x1', 'y1', 'x2', 'y2'}\n The (x1, y1) position is at the top left corner,\n the (x2, y2) position is at the bottom right corner\n bb2 : array\n order: {'x1', 'y1', 'x2', 'y2'}\n The (x1, y1) position is at the top left corner,\n the (x2, y2) position is at the bottom right corner\n\n Returns\n -------\n float\n in [0, 1]\n \"\"\"\n\n # determine the coordinates of the intersection rectangle\n x_left = max(bb1[0], bb2[0])\n y_top = max(bb1[1], bb2[1])\n x_right = min(bb1[2], bb2[2])\n y_bottom = min(bb1[3], bb2[3])\n\n if x_right < x_left or y_bottom < y_top:\n return 0.0\n\n # The intersection of two axis-aligned bounding boxes is always an\n # axis-aligned bounding box\n intersection_area = (x_right - x_left) * (y_bottom - y_top)\n\n # compute the area of both AABBs\n bb1_area = (bb1[2] - bb1[0]) * (bb1[3] - bb1[1])\n bb2_area = (bb2[2] - bb2[0]) * (bb2[3] - bb2[1])\n\n # compute the intersection over union by taking the intersection\n # area and dividing it by the sum of prediction + ground-truth\n # areas - the interesection area\n iou = intersection_area / float(bb1_area + bb2_area - intersection_area)\n return iou\n\n#print(get_iou([10,10,20,20],[15,15,25,25]))\n\ndef preprocess(img, bbox=None, landmark=None, **kwargs):\n M = None\n image_size = [224,224]\n src = np.array([\n [30.2946, 51.6963],\n [65.5318, 51.5014],\n [48.0252, 71.7366],\n [33.5493, 92.3655],\n [62.7299, 92.2041] ], dtype=np.float32 )\n if image_size[1]==224:\n src[:,0] += 8.0\n src*=2\n if landmark is not None:\n dst = landmark.astype(np.float32)\n\n tform = trans.SimilarityTransform()\n #dst=dst[:3]\n #src=src[:3]\n #print(dst.shape,src.shape,dst,src)\n tform.estimate(dst, src)\n M = tform.params[0:2,:]\n #M = cv2.estimateRigidTransform( dst.reshape(1,5,2), src.reshape(1,5,2), False)\n #print(M)\n\n if M is None:\n if bbox is None: #use center crop\n det = np.zeros(4, dtype=np.int32)\n det[0] = int(img.shape[1]*0.0625)\n det[1] = int(img.shape[0]*0.0625)\n det[2] = img.shape[1] - det[0]\n det[3] = img.shape[0] - det[1]\n else:\n det = bbox\n margin = 0#kwargs.get('margin', 44)\n bb = np.zeros(4, dtype=np.int32)\n bb[0] = np.maximum(det[0]-margin//2, 0)\n bb[1] = np.maximum(det[1]-margin//2, 0)\n bb[2] = np.minimum(det[2]+margin//2, img.shape[1])\n bb[3] = np.minimum(det[3]+margin//2, img.shape[0])\n ret = img[bb[1]:bb[3],bb[0]:bb[2],:]\n if len(image_size)>0:\n ret = cv2.resize(ret, (image_size[1], image_size[0]))\n return ret \n else: #do align using landmark\n assert len(image_size)==2\n warped = cv2.warpAffine(img,M,(image_size[1],image_size[0]), borderValue = 0.0)\n return warped",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import pytesseract\nif not os.path.exists(faces_path):\n os.mkdir(faces_path)\n\ncap = cv2.VideoCapture(video_path)\nfps = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)\ntotal_frames = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT))\nprint('total_frames:',total_frames)\ncap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_POS_FRAMES,1)\n\nframe_count = 0\ncounter=0\nbboxes,all_text=[],[]\n\nfor frame_count in tqdm(range(total_frames-1)):\n ret, frame_bgr = cap.read()\n counter+=1\n if not ret:\n #cap.release()\n #break\n continue\n frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame_bgr, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)\n bounding_boxes, points = imgProcessing.detect_faces(frame)\n points = points.T\n if len(bounding_boxes)!=0:\n sorted_indices=bounding_boxes[:,0].argsort()\n bounding_boxes=bounding_boxes[sorted_indices]\n points=points[sorted_indices]\n\n faces_folder=os.path.join(faces_path, str(counter)) \n if not os.path.exists(faces_folder):\n os.mkdir(faces_folder)\n for i,b in enumerate(bounding_boxes):\n outfile=os.path.join(faces_folder, str(i)+'.png')\n if not os.path.exists(outfile):\n if True:\n p=None\n else:\n p=points[i]\n p = p.reshape((2,5)).T\n face_img=preprocess(frame_bgr,b,p)\n\n if np.prod(face_img.shape)==0:\n print('Empty face ',b,' found for ',filename)\n continue\n cv2.imwrite(outfile, face_img) \n bboxes.append(bounding_boxes)\n \n frame = cv2.resize(frame, None, fx=2.0, fy=2.0, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)\n results=pytesseract.image_to_data(frame,lang='rus+eng',output_type=pytesseract.Output.DICT)\n frame_text=[]\n for i in range(0, len(results[\"text\"])):\n x = results[\"left\"][i]\n y = results[\"top\"][i]\n w = results[\"width\"][i]\n h = results[\"height\"][i]\n text = results[\"text\"][i].strip()\n conf = float(results[\"conf\"][i])\n if conf > 0 and len(text)>1:\n frame_text.append((text,int(x/frame.shape[1]*frame_bgr.shape[1]),int(y/frame.shape[0]*frame_bgr.shape[0]),\n int(w/frame.shape[1]*frame_bgr.shape[1]),int(h/frame.shape[0]*frame_bgr.shape[1])))\n all_text.append(frame_text)\n \ncap.release() ",
"\r 0%| | 0/1700 [00:00<?, ?it/s]"
]
],
[
[
"## Text processing ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def combine_words(photo_text):\n #print(photo_text)\n if len(photo_text)>0:\n new_text=[photo_text[0]]\n for word_ind in range(1,len(photo_text)):\n prev_text,x1,y1,w1,h1=new_text[-1]\n center1_x,center1_y=x1+w1,y1+h1/2\n cur_text,x2,y2,w2,h2=photo_text[word_ind]\n center2_x,center2_y=x2,y2+h2/2\n dist=abs(center1_x-center2_x)+abs(center1_y-center2_y)\n #print(prev_text,cur_text,dist)\n if dist>=7: #0.01:\n new_text.append(photo_text[word_ind])\n else:\n new_text[-1]=(prev_text+' '+cur_text,x1,y1,x2+w2-x1,y2+h2-y1)\n else:\n new_text=[]\n return new_text",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def get_closest_texts(bboxes,photo_text):\n best_texts,best_distances=[],[]\n for (x1,y1,x2,y2,_) in bboxes:\n face_x,face_y=x1,y2\n #print(x1,y1,x2,y2)\n best_dist=10000\n best_text=''\n for (text,x,y,w,h) in photo_text:\n if y>y1:\n dist_y=abs(face_y-y)\n if face_x<x:\n dist_x=x-face_x\n elif face_x>x+w:\n dist_x=face_x-x-w\n else:\n dist_x=0\n #print(text,dist_x, dist_y,x,y,w,h)\n if dist_x<best_dist and dist_y<1.5*(y2-y1):\n best_dist=dist_x\n best_text=text\n #print(best_text,best_dist,(x2-x1))\n if best_dist>=(x2-x1)*2:\n best_text=''\n if best_text!='':\n for i,prev_txt in enumerate(best_texts):\n if prev_txt==best_text:\n if best_distances[i]<best_dist:\n best_text=''\n break\n else:\n best_texts[i]=''\n best_texts.append(best_text)\n best_distances.append(best_dist)\n return best_texts",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# FaceId ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import torch\nfrom PIL import Image\nfrom torchvision import datasets, transforms\n\nprint(f\"Torch: {torch.__version__}\")\ndevice = 'cuda'",
"Torch: 1.7.1+cu110\n"
],
[
"import timm\nmodel=timm.create_model('tf_efficientnet_b0_ns', pretrained=False)\nmodel.classifier=torch.nn.Identity()\nmodel.load_state_dict(torch.load('../models/pretrained_faces/state_vggface2_enet0_new.pt'))\n\nmodel=model.to(device)\nmodel.eval()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"test_transforms = transforms.Compose(\n [\n transforms.Resize((224,224)),\n transforms.ToTensor(),\n transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],\n std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])\n ]\n)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"embeddings=[]\ni=0\nfor filename in tqdm(sorted(os.listdir(faces_path), key=compare_filenames)):\n faces_dir=os.path.join(faces_path,filename)\n imgs=[]\n for img_name in sorted(os.listdir(faces_dir), key=compare_filenames):\n img = Image.open(os.path.join(faces_dir,img_name))\n img_tensor = test_transforms(img)\n imgs.append(img_tensor)\n\n if len(imgs)>0: \n scores = model(torch.stack(imgs, dim=0).to(device))\n scores=scores.data.cpu().numpy()\n else:\n scores=[]\n\n embeddings.append(scores)\n if len(scores)!=len(bboxes[i]):\n print('Error',videoname,filename,i,len(scores),len(bboxes[i]))\n i+=1\n\nprint(len(embeddings))",
"100%|██████████| 1650/1650 [00:29<00:00, 56.49it/s]"
]
],
[
[
"## Faces only ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"face_files=[]\nsubjects=None\nX_recent_features=None\nfor i,filename in enumerate(sorted(os.listdir(faces_path), key=compare_filenames)):\n f=preprocessing.normalize(embeddings[i],norm='l2')\n if X_recent_features is None:\n for face_ind in range(len(f)):\n face_files.append([(i,filename,face_ind)])\n X_recent_features=f\n else:\n dist_matrix=pairwise_distances(f,X_recent_features)\n sorted_indices=dist_matrix.argsort(axis=1)\n for face_ind,sorted_inds in enumerate(sorted_indices):\n closest_ind=sorted_inds[0]\n min_dist=dist_matrix[face_ind][closest_ind]\n if min_dist<0.85 or (len(sorted_inds)>1 and min_dist<dist_matrix[face_ind][sorted_inds[1]]-0.1):\n X_recent_features[closest_ind]=f[face_ind]\n face_files[closest_ind].append((i,filename,face_ind))\n else:\n face_files.append([(i,filename,face_ind)])\n X_recent_features=np.concatenate((X_recent_features,[f[face_ind]]),axis=0)\nprint(len(face_files), [len(files) for files in face_files])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"## Faces+bboxes",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def get_square(bb):\n return abs((bb[2]-bb[0])*(bb[3]-bb[1]))\nSQUARE_THRESHOLD=900",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"face_files=[]\nsubjects=None\nX_recent_features=None\nrecent_bboxes=[]\nfor i,filename in enumerate(sorted(os.listdir(faces_path), key=compare_filenames)):\n f=preprocessing.normalize(embeddings[i],norm='l2')\n if X_recent_features is None:\n large_face_indices=[]\n for face_ind in range(len(f)):\n if get_square(bboxes[i][face_ind])>SQUARE_THRESHOLD:\n large_face_indices.append(face_ind)\n recent_bboxes.append(bboxes[i][face_ind])\n face_files.append([(i,filename,face_ind)])\n if len(large_face_indices)>0:\n X_recent_features=f[np.array(large_face_indices)]\n #print(X_recent_features.shape)\n #recent_bboxes=list(deepcopy(bboxes[i]))\n else:\n matched_faces=[]\n for face_ind,face_bbox in enumerate(bboxes[i]):\n closest_ind=-1\n best_iou=0\n for ind, bbox in enumerate(recent_bboxes):\n iou=get_iou(face_bbox,bbox)\n if iou>best_iou:\n best_iou=iou\n closest_ind=ind\n if best_iou>0.15:\n d=np.linalg.norm(f[face_ind]-X_recent_features[closest_ind])\n if d<1.0:\n X_recent_features[closest_ind]=f[face_ind]\n face_files[closest_ind].append((i,filename,face_ind))\n recent_bboxes[closest_ind]=bboxes[i][face_ind]\n matched_faces.append(face_ind)\n if len(matched_faces)<len(bboxes[i]):\n dist_matrix=pairwise_distances(f,X_recent_features)\n sorted_indices=dist_matrix.argsort(axis=1)\n for face_ind,sorted_inds in enumerate(sorted_indices):\n if face_ind in matched_faces or get_square(bboxes[i][face_ind])<=SQUARE_THRESHOLD:\n continue\n closest_ind=sorted_inds[0]\n min_dist=dist_matrix[face_ind][closest_ind]\n if min_dist<0.85:# or (len(sorted_inds)>1 and min_dist<dist_matrix[face_ind][sorted_inds[1]]-0.1):\n X_recent_features[closest_ind]=f[face_ind]\n face_files[closest_ind].append((i,filename,face_ind))\n recent_bboxes[closest_ind]=bboxes[i][face_ind]\n else:\n face_files.append([(i,filename,face_ind)])\n X_recent_features=np.concatenate((X_recent_features,[f[face_ind]]),axis=0)\n recent_bboxes.append(bboxes[i][face_ind])\n #print(filename,i,X_recent_features.shape,face_ind,closest_ind,dist_matrix[face_ind][closest_ind])\n #print(dist_matrix)\nprint(len(face_files), [len(files) for files in face_files])",
"8 [1650, 3, 401, 1599, 51, 155, 348, 14]\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Text + faces",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import editdistance\ndef levenstein(txt1,txt2):\n if txt1=='' or txt2=='':\n return 1\n #return editdistance.eval(txt1,txt2)\n return (editdistance.eval(txt1,txt2))/(max(len(txt1),len(txt2)))\n\ndef get_name(name2count):\n #print(name2count)\n return max(name2count, key=name2count.get)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"face_files=[]\nrecent_texts=[]\nX_recent_features=[]\n\nfor i,filename in enumerate(sorted(os.listdir(faces_path), key=compare_filenames)):\n photo_text=combine_words(all_text[i])\n best_texts=get_closest_texts(bboxes[i],photo_text)\n f=preprocessing.normalize(embeddings[i],norm='l2')\n\n if len(recent_texts)==0:\n for face_ind,txt in enumerate(best_texts):\n if len(txt)>=4:\n recent_texts.append({txt:1})\n face_files.append([(i,filename,face_ind)])\n X_recent_features.append(f[face_ind])\n else:\n for face_ind,txt in enumerate(best_texts):\n if len(txt)>=4:\n closest_ind=-1\n best_d_txt=1\n for ind,recent_text_set in enumerate(recent_texts):\n d_txt=min([levenstein(txt,recent_text) for recent_text in recent_text_set])\n if d_txt<best_d_txt:\n best_d_txt=d_txt\n closest_ind=ind\n\n face_dist=np.linalg.norm(X_recent_features[closest_ind]-f[face_ind])\n if (best_d_txt<=0.45 and face_dist<=1.0) or face_dist<=0.8:\n if txt in recent_texts[closest_ind]:\n recent_texts[closest_ind][txt]+=1\n else:\n recent_texts[closest_ind][txt]=1\n face_files[closest_ind].append((i,filename,face_ind))\n X_recent_features[closest_ind]=f[face_ind]\n elif best_d_txt>0.45:\n recent_texts.append({txt:1})\n face_files.append([(i,filename,face_ind)])\n X_recent_features.append(f[face_ind])\n #print(videoname,filename,i,face_ind,face_dist,txt,best_d_txt,recent_texts[closest_ind])\n\nsubjects=[get_name(name2count) for name2count in recent_texts]",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"---------------",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import random\nplt_ind=1\nminNoPhotos=20\nmin_num_files=100\nno_clusters=len([i for i,files in enumerate(face_files) if len(files)>min_num_files])\nplt.figure(figsize=(10,10))\nfor i,files in enumerate(face_files):\n if len(files)>min_num_files:\n print(i,len(files),files[0])\n for j in range(minNoPhotos):\n f=random.choice(files)\n fpath=os.path.join(faces_path,f[1],str(f[2])+'.png')\n plt.subplot(no_clusters,minNoPhotos,plt_ind)\n if j==0 and subjects is not None:\n plt.title(subjects[i])\n plt.imshow(Image.open(fpath))\n plt.axis('off')\n plt_ind+=1\nplt.show()",
"0 1506 (0, '1', 0)\n1 977 (14, '15', 1)\n2 1476 (20, '21', 1)\n3 953 (40, '41', 2)\n4 628 (73, '74', 1)\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Emotions",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"if False:\n model_name='enet_b2_8'\n IMG_SIZE=260 #224 #\nelse:\n model_name='enet_b0_8_best_afew'\n IMG_SIZE=224\nPATH='../models/affectnet_emotions/'+model_name+'.pt'\ntest_transforms = transforms.Compose(\n [\n transforms.Resize((IMG_SIZE,IMG_SIZE)),\n #transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),\n transforms.ToTensor(),\n transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],\n std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])\n ]\n)\nfeature_extractor_model = torch.load(PATH)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"classifier_weights=feature_extractor_model.classifier[0].weight.cpu().data.numpy()\nclassifier_bias=feature_extractor_model.classifier[0].bias.cpu().data.numpy()\nprint(classifier_weights.shape,classifier_weights)\nprint(classifier_bias.shape,classifier_bias)",
"(8, 1280) [[ 0.00515123 -0.00972202 -0.01203173 ... 0.05333852 -0.06858566\n -0.12183831]\n [ 0.05973773 -0.01306326 -0.00981904 ... 0.04521868 0.03189689\n 0.16130415]\n [-0.02749952 -0.1972647 0.02720864 ... 0.18251328 -0.03125019\n -0.07623435]\n ...\n [-0.15567695 0.09653756 -0.02194299 ... -0.07001057 0.00730149\n 0.11114535]\n [ 0.08313771 -0.16218805 -0.10610525 ... -0.05499801 -0.00550514\n 0.12355816]\n [-0.04981646 0.23458022 -0.16780637 ... -0.24049994 0.02247157\n -0.10648516]]\n(8,) [-0.02634053 0.05532073 -0.09343545 0.01225835 0.05623824 0.05436933\n -0.0242617 0.02030101]\n"
],
[
"feature_extractor_model.classifier=torch.nn.Identity()\nfeature_extractor_model.eval()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def get_probab(features):\n x=np.dot(features,np.transpose(classifier_weights))+classifier_bias\n #print(x)\n e_x = np.exp(x - np.max(x,axis=0))\n return e_x / e_x.sum(axis=1)[:,None]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"if len(classifier_bias)==7:\n idx_to_class={0: 'Anger', 1: 'Disgust', 2: 'Fear', 3: 'Happiness', 4: 'Neutral', 5: 'Sadness', 6: 'Surprise'}\n INTERESTING_STATES=[0,1,2,3,6]\nelse:\n idx_to_class={0: 'Anger', 1: 'Contempt', 2: 'Disgust', 3: 'Fear', 4: 'Happiness', 5: 'Neutral', 6: 'Sadness', 7: 'Surprise'}\n INTERESTING_STATES=[0,2,3,4,7]\nprint(idx_to_class)",
"{0: 'Anger', 1: 'Contempt', 2: 'Disgust', 3: 'Fear', 4: 'Happiness', 5: 'Neutral', 6: 'Sadness', 7: 'Surprise'}\n"
],
[
"X_global_features,X_scores=[],[]\nfor filename in tqdm(sorted(os.listdir(faces_path), key=compare_filenames)):\n faces_dir=os.path.join(faces_path,filename)\n imgs=[]\n for img_name in sorted(os.listdir(faces_dir), key=compare_filenames):\n img = Image.open(os.path.join(faces_dir,img_name))\n img_tensor = test_transforms(img)\n if img.size:\n imgs.append(img_tensor)\n\n if len(imgs)>0:\n features = feature_extractor_model(torch.stack(imgs, dim=0).to(device))\n features=features.data.cpu().numpy()\n scores=get_probab(features)\n #print(videoname,filename,features.shape,scores.shape)\n X_global_features.append(features)\n X_scores.append(scores)",
"100%|██████████| 1650/1650 [00:29<00:00, 56.47it/s]\n"
]
],
[
[
"# Create gifs ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"from IPython import display\nfrom PIL import Image, ImageFont, ImageDraw \nmin_num_files=100\nunicode_font = ImageFont.truetype(\"DejaVuSans.ttf\", 8)\ngif=[]\nno_clusters=len([i for i,files in enumerate(face_files) if len(files)>min_num_files])\nfor subject_ind,files in enumerate(face_files):\n if len(files)>min_num_files:\n print(len(files),files[0])\n prev_filename_ind=-1\n start_i=0\n current_scores,current_features=[],[]\n current_emotion=-1\n emotion2longest_sequence={}\n for i,(file_ind,filename,face_ind) in enumerate(files):\n filename_ind=int(filename)\n if prev_filename_ind==-1:\n prev_filename_ind=filename_ind-1\n new_emotion=np.argmax(X_scores[file_ind][face_ind])\n #print('check',prev_filename_ind,filename_ind-1, new_emotion,current_emotion)\n if prev_filename_ind!=filename_ind-1 or new_emotion!=current_emotion or new_emotion not in INTERESTING_STATES:\n if len(current_scores)>=10:\n emotion=np.argmax(np.mean(current_scores,axis=0))\n if emotion in emotion2longest_sequence:\n if emotion2longest_sequence[emotion][0]<len(current_scores):\n emotion2longest_sequence[emotion]=(len(current_scores),start_i,i-1)\n else:\n emotion2longest_sequence[emotion]=(len(current_scores),start_i,i-1)\n #print(start_i,i-1,idx_to_class[emotion])\n start_i=i\n current_scores,current_features=[],[]\n prev_filename_ind=filename_ind\n current_emotion=new_emotion\n current_scores.append(X_scores[file_ind][face_ind])\n current_features.append(X_global_features[file_ind][face_ind])\n\n if len(emotion2longest_sequence)>0:\n for emotion, (_,start_i, end_i) in emotion2longest_sequence.items():\n print(idx_to_class[emotion],start_i,end_i,len(files))\n for i in range(start_i,min(start_i+20,end_i)+1):\n #print(files[i])\n fpath=os.path.join(faces_path,files[i][1],str(files[i][2])+'.png')\n img=Image.open(fpath)\n img = img.resize((112,112), Image.ANTIALIAS)\n draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img) \n draw.text((0, 0), subjects[subject_ind], align =\"left\", font=unicode_font,fill=(0,0,255,255))\n draw.text((0, 10), idx_to_class[emotion], align =\"left\",font=unicode_font, fill=(0,255,0,255))\n gif.append(img.convert(\"P\",palette=Image.ADAPTIVE))\n\nif False:\n for img in gif:\n display.clear_output(wait=True)\n plt.axis('off')\n plt.imshow(img)\n plt.show()\nif True and len(gif)>0:\n gif[0].save('emo.gif', save_all=True,optimize=False, append_images=gif[1:],disposal=2)",
"1506 (0, '1', 0)\nAnger 409 442 1506\nDisgust 326 357 1506\nHappiness 1267 1309 1506\n977 (14, '15', 1)\nFear 896 912 977\nAnger 177 238 977\n1476 (20, '21', 1)\nFear 53 79 1476\nHappiness 226 260 1476\nAnger 1315 1336 1476\n953 (40, '41', 2)\nHappiness 247 270 953\nAnger 751 789 953\nSurprise 652 663 953\n628 (73, '74', 1)\nHappiness 116 131 628\nFear 289 318 628\nAnger 521 550 628\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c50d73a38efb09ccdb7fb41e2ec6cf1d40206550
| 33,759 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Addendum/Extended_SQuAD_Dataset.ipynb
|
sudarshan-rags/CS685_Project
|
2015a3e1b26e0d164a9957969c8c7024a13409c1
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Addendum/Extended_SQuAD_Dataset.ipynb
|
sudarshan-rags/CS685_Project
|
2015a3e1b26e0d164a9957969c8c7024a13409c1
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Addendum/Extended_SQuAD_Dataset.ipynb
|
sudarshan-rags/CS685_Project
|
2015a3e1b26e0d164a9957969c8c7024a13409c1
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 39.623239 | 715 | 0.419177 |
[
[
[
"\nimport numpy as np # linear algebra\nimport pandas as pd # data processing, CSV file I/O (e.g. pd.read_csv)\nimport json # to read json\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\ndef squad_json_to_dataframe_train(input_file_path, record_path = ['data','paragraphs','qas','answers'],\n verbose = 1):\n \"\"\"\n input_file_path: path to the squad json file.\n record_path: path to deepest level in json file default value is\n ['data','paragraphs','qas','answers']\n verbose: 0 to suppress it default is 1\n \"\"\"\n if verbose:\n print(\"Reading the json file\") \n file = json.loads(open(input_file_path).read())\n if verbose:\n print(\"processing...\")\n # parsing different level's in the json file\n js = pd.io.json.json_normalize(file , record_path )\n m = pd.io.json.json_normalize(file, record_path[:-1] )\n r = pd.io.json.json_normalize(file,record_path[:-2])\n \n #combining it into single dataframe\n idx = np.repeat(r['context'].values, r.qas.str.len())\n ndx = np.repeat(m['id'].values,m['answers'].str.len())\n m['context'] = idx\n js['q_idx'] = ndx\n main = pd.concat([ m[['id','question','context']].set_index('id'),js.set_index('q_idx')],1,sort=False).reset_index()\n main['c_id'] = main['context'].factorize()[0]\n if verbose:\n print(\"shape of the dataframe is {}\".format(main.shape))\n print(\"Done\")\n return main",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!wget https://rajpurkar.github.io/SQuAD-explorer/dataset/train-v2.0.json",
"--2020-11-13 04:41:50-- https://rajpurkar.github.io/SQuAD-explorer/dataset/train-v2.0.json\nResolving rajpurkar.github.io (rajpurkar.github.io)... 185.199.108.153, 185.199.109.153, 185.199.110.153, ...\nConnecting to rajpurkar.github.io (rajpurkar.github.io)|185.199.108.153|:443... connected.\nHTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK\nLength: 42123633 (40M) [application/json]\nSaving to: ‘train-v2.0.json’\n\ntrain-v2.0.json 100%[===================>] 40.17M 122MB/s in 0.3s \n\n2020-11-13 04:41:50 (122 MB/s) - ‘train-v2.0.json’ saved [42123633/42123633]\n\n"
],
[
"input_file_path = 'train-v2.0.json'\nrecord_path = ['data','paragraphs','qas','answers']\ntrain = squad_json_to_dataframe_train(input_file_path=input_file_path,record_path=record_path)",
"Reading the json file\nprocessing...\n"
],
[
"train.head()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"contexts = train['context'].unique()\n\ncontexts_size = contexts.size\n\nprint('The total number of unique contexts are = ', contexts_size)\n",
"Beyoncé Giselle Knowles-Carter (/biːˈjɒnseɪ/ bee-YON-say) (born September 4, 1981) is an American singer, songwriter, record producer and actress. Born and raised in Houston, Texas, she performed in various singing and dancing competitions as a child, and rose to fame in the late 1990s as lead singer of R&B girl-group Destiny's Child. Managed by her father, Mathew Knowles, the group became one of the world's best-selling girl groups of all time. Their hiatus saw the release of Beyoncé's debut album, Dangerously in Love (2003), which established her as a solo artist worldwide, earned five Grammy Awards and featured the Billboard Hot 100 number-one singles \"Crazy in Love\" and \"Baby Boy\".\nThe total number of unique contexts are = 19029\n"
],
[
"import random\ntotal_text = []\n\nnumber_of_contexts = 30 # Set the number of contexts you want to concatenate to create the data\n\nfor index, row in train.iterrows():\n\n text = \"\"\n\n for i in range(number_of_contexts):\n\n curr_ques = row['question']\n curr_context = row['context']\n\n random_int = random.randint(0, context_size-1)\n context_text = contexts[random_int]\n\n if context_text!=curr_context:\n text=text+context_text\n\n if i==number_of_contexts/2:\n text=text+curr_context\n\n total_text.append(text)\n\ntrain['total_text']=total_text\n\ntrain.head()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"final_data = train[['question', 'context', 'total_text','text']].copy()\n\nfinal_data = final_data.rename(columns={'text': 'answer'})\n\nfinal_data.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"from google.colab import files\n\nfinal_data.to_csv('final_data')\nfiles.download('final_data')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"!wget https://rajpurkar.github.io/SQuAD-explorer/dataset/dev-v2.0.json",
"--2020-11-13 04:41:58-- https://rajpurkar.github.io/SQuAD-explorer/dataset/dev-v2.0.json\nResolving rajpurkar.github.io (rajpurkar.github.io)... 185.199.109.153, 185.199.108.153, 185.199.110.153, ...\nConnecting to rajpurkar.github.io (rajpurkar.github.io)|185.199.109.153|:443... connected.\nHTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK\nLength: 4370528 (4.2M) [application/json]\nSaving to: ‘dev-v2.0.json’\n\ndev-v2.0.json 100%[===================>] 4.17M --.-KB/s in 0.1s \n\n2020-11-13 04:41:58 (30.6 MB/s) - ‘dev-v2.0.json’ saved [4370528/4370528]\n\n"
],
[
"def squad_json_to_dataframe_dev(input_file_path, record_path = ['data','paragraphs','qas','answers'],\n verbose = 1):\n \"\"\"\n input_file_path: path to the squad json file.\n record_path: path to deepest level in json file default value is\n ['data','paragraphs','qas','answers']\n verbose: 0 to suppress it default is 1\n \"\"\"\n if verbose:\n print(\"Reading the json file\") \n file = json.loads(open(input_file_path).read())\n if verbose:\n print(\"processing...\")\n # parsing different level's in the json file\n js = pd.io.json.json_normalize(file , record_path )\n m = pd.io.json.json_normalize(file, record_path[:-1] )\n r = pd.io.json.json_normalize(file,record_path[:-2])\n \n #combining it into single dataframe\n idx = np.repeat(r['context'].values, r.qas.str.len())\n# ndx = np.repeat(m['id'].values,m['answers'].str.len())\n m['context'] = idx\n# js['q_idx'] = ndx\n main = m[['id','question','context','answers']].set_index('id').reset_index()\n main['c_id'] = main['context'].factorize()[0]\n if verbose:\n print(\"shape of the dataframe is {}\".format(main.shape))\n print(\"Done\")\n return main",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"input_file_path = 'dev-v2.0.json'\nrecord_path = ['data','paragraphs','qas','answers']\nverbose = 0\ndev = squad_json_to_dataframe_dev(input_file_path=input_file_path,record_path=record_path)",
"Reading the json file\nprocessing...\n"
],
[
"dev.head()\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50d87e19f24c9cd467d65da1b5e85dfe1dfebb7
| 850,264 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Arvind/Capstone Project.ipynb
|
Arvind-collab/Data-Science
|
4d7027c308adba2b414f97abfe151c8881674da4
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Arvind/Capstone Project.ipynb
|
Arvind-collab/Data-Science
|
4d7027c308adba2b414f97abfe151c8881674da4
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
Arvind/Capstone Project.ipynb
|
Arvind-collab/Data-Science
|
4d7027c308adba2b414f97abfe151c8881674da4
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 86.172494 | 71,696 | 0.786475 |
[
[
[
"<table align=\"center\" width=100%>\n <tr>\n <td width=\"15%\">\n <img src=\"edaicon.png\">\n </td>\n <td>\n <div align=\"center\">\n <font color=\"#21618C\" size=24px>\n <b>Exploratory Data Analysis\n </b>\n </font>\n </div>\n </td>\n </tr>\n</table>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Problem Statement\n\nThe zomato exploratory data analysis is for the foodies to find the best restaurants, value for money restaurants in their locality. It also helps to find their required cuisines in their locality. ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Data Definition\n\n**res_id**: The code given to a restaurant (Categorical) \n\n**name**: Name of the restaurant (Categorical)\n\n**establishment**: Represents the type of establishment (Categorical)\n\n**url**: The website of the restaurant (Categorical)\n\n**address**: The address of the restaurant (Categorical)\n\n**city**: City in which the restaurant located (Categorical)\n\n**city_id**: The code given to a city (Categorical)\n\n**locality**: Locality of the restaurant (Categorical)\n\n**latitude**: Latitude of the restaurant (Categorical)\n\n**longitude**: Longitude of the restaurant (Categorical)\n\n**zipcode**: Zipcode of the city in which the restaurant located (Categorical)\n\n**country_id**: Country code in which the restaurant located (Categorical)\n\n**locality_verbose**: Locality along with the city in which the restaurant located (Categorical)\n\n**cuisines**: The cuisines a restaurant serves (Categorical)\n\n**timings**: The working hours of a restaurant (Categorical)\n\n**average_cost_for_two**: The average amount expected for 2 people (Numerical)\n\n**price_range**: The categories for average cost (Categories - 1,2,3,4) (Categorical)\n\n**currency**: The currency in which a customer pays (Categorical)\n\n**highlights**: The facilities of the restaurant (Categorical)\n\n**aggregate_rating**: The overall rating a restaurant has got (Numerical) \n\n**rating_text**: Categorized ratings (Categorical)\n\n**votes**: Number of votes received by the restaurant from customers (Numerical)\n\n**photo_count**: The number of photos of a restaurant (Numerical)\n\n**opentable_support**: Restaurant reservation from Opentable (Categorical)\n\n**delivery**: The restaurant deliver an order or not (Categorical)\n\n**takeaway**: The restaurant allows a 'takeaway' of an order or not (Categorical)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"## Table of Contents\n\n1. **[Import Libraries](#import_lib)** \n2. **[Set Options](#set_options)** \n3. **[Read Data](#Read_Data)** \n4. **[Understand and Prepare the Data](#Understand_Data)**\n5. **[Understand the variables](#Understanding_variables)**\n6. **[Check for Missing Values](#missing)**\n7. **[Study Correlation](#correlation)**\n8. **[Detect Outliers](#outliers)**\n9. **[Create a new variable 'region'](#region)**\n10. **[Some more analysis](#more)** \n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<a id='import_lib'></a>\n## 1. Import Libraries",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<table align =\"left\">\n <tr>\n <td width=\"8%\">\n <img src=\"todo.png\">\n </td>\n <td>\n <div align=\"left\", style=\"font-size:120%\">\n <font color=\"#21618C\">\n <b> Import the required libraries and functions\n </b>\n </font>\n </div>\n </td>\n </tr>\n</table>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import seaborn as sns\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nimport os",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id='set_options'></a>\n## 2. Set Options",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<table align=\"left\">\n <tr>\n <td width=\"8%\">\n <img src=\"todo.png\">\n </td>\n <td>\n <div align=\"left\", style=\"font-size:120%\">\n <font color=\"#21618C\">\n <b>Make necessary changes to :<br><br>\nSet the working directory \n </b>\n </font>\n </div>\n </td>\n </tr>\n</table>",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"os.chdir('C:\\\\Users\\\\Kejri\\\\Downloads\\\\files\\\\Capstone')\nos.getcwd()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id='Read_Data'></a>\n## 3. Read Data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_restaurants = pd.read_csv('ZomatoRestaurantsIndia.csv')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id='Understand_Data'></a>\n## 4. Understand and Prepare the Data",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"A well-prepared data proves beneficial for analysis as it limits errors and inaccuracies that can occur during analysis. The processed data is more accessible to users.<br> <br>\n Data understanding is the process of getting familiar with the data, to identify data type, to discover first insights into the data, or to detect interesting subsets to form hypotheses about hidden information. Whereas, data preparation is the process of cleaning and transforming raw data before analysis. It is an important step before processing and often involves reformatting data, making corrections to data. <br> <br>\n Data preparation is often a lengthy process, but it is essential as a prerequisite to put data in context to get insights and eliminate bias resulting from poor data quality.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<table align=\"left\">\n <tr>\n <td width=\"8%\">\n <img src=\"todo.png\">\n </td>\n <td>\n <div align=\"left\", style=\"font-size:120%\">\n <font color=\"#21618C\">\n <b> Analyze and prepare data:<br>\n 1. Check dimensions of the dataframe <br>\n 2. View the head of the data<br>\n 3. Note the redundant variables and drop them <br>\n 4. Check the data types. Refer to data definition to ensure your data types are correct. If data types are not as per business context, change the data types as per requirement <br>\n 5. Check for duplicates<br>\n Note: It is an art to explore data and one will need more and more practice to gain expertise in this area\n </b>\n </font>\n </div>\n </td>\n </tr>\n</table>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### -------------------------*** Provide the inference's from the output of every code executed.***----------------------------",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**1. Check dimensions of the dataframe in terms of rows and columns**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_restaurants.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants.info()",
"<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>\nRangeIndex: 211944 entries, 0 to 211943\nData columns (total 26 columns):\nres_id 211944 non-null int64\nname 211944 non-null object\nestablishment 207117 non-null object\nurl 211944 non-null object\naddress 211810 non-null object\ncity 211944 non-null object\ncity_id 211944 non-null int64\nlocality 211944 non-null object\nlatitude 211944 non-null float64\nlongitude 211944 non-null float64\nzipcode 48757 non-null object\ncountry_id 211944 non-null int64\nlocality_verbose 211944 non-null object\ncuisines 210553 non-null object\ntimings 208070 non-null object\naverage_cost_for_two 211944 non-null int64\nprice_range 211944 non-null int64\ncurrency 211944 non-null object\nhighlights 209875 non-null object\naggregate_rating 211944 non-null float64\nrating_text 211944 non-null object\nvotes 211944 non-null int64\nphoto_count 211944 non-null int64\nopentable_support 211896 non-null float64\ndelivery 211944 non-null int64\ntakeaway 211944 non-null int64\ndtypes: float64(4), int64(9), object(13)\nmemory usage: 42.0+ MB\n"
],
[
"print('The dataframe has 211944 rows and 26 columns. Also in some columns, such as, \\'establishment\\', \\'zipcode\\', \\'highlights\\' etc., the number of rows are less.')",
"The dataframe has 211944 rows and 26 columns. Also in some columns, such as, 'establishment', 'zipcode', 'highlights' etc., the number of rows are less.\n"
]
],
[
[
"**2. View the head of the data**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_restaurants.head(5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('Each locality has a latitude and longitude, that lie in a certain city and a certain country; Has various restaurant names which have an address and url to their website and many more such variables')",
"Each locality has a latitude and longitude, that lie in a certain city and a certain country; Has various restaurant names which have an address and url to their website and many more such variables\n"
]
],
[
[
"**3. Note the redundant variables and drop them**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_restaurants.columns.duplicated().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#i=0\n#for var in df_restaurants_copy.columns:\n# print(i+1,\". \",var, \": \", df_restaurants_copy[var].unique())\n# i+=1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants['currency'].unique(), df_restaurants['currency'].shape[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants['country_id'].unique(), df_restaurants['currency'].shape[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants['opentable_support'].isna().sum(), df_restaurants['currency'].shape[0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy = df_restaurants.drop(['locality_verbose','currency','country_id','takeaway','res_id'], axis=1).copy()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('We have two separate columns \\'locality\\' and \\'city\\', we can later derive \\'locality_verbose\\' from these two, so we drop \\'locality_verbose\\', since we might later need to make analysis city or locality wise also. Also, since \\'currency\\', \\'country_id\\', \\'takeaway\\' has same value for all restaurants, i.e, Rs., 1, -1 respectively, we decide to drop these. Also, \\'res_id\\' would not be needed since we don\\'t have any other dataframe to map to and we have default index for this dataframe as well, so we drop this also.')",
"We have two separate columns 'locality' and 'city', we can later derive 'locality_verbose' from these two, so we drop 'locality_verbose', since we might later need to make analysis city or locality wise also. Also, since 'currency', 'country_id', 'takeaway' has same value for all restaurants, i.e, Rs., 1, -1 respectively, we decide to drop these. Also, 'res_id' would not be needed since we don't have any other dataframe to map to and we have default index for this dataframe as well, so we drop this also.\n"
]
],
[
[
"**4. Check the data types. Refer to data definition to ensure your data types are correct. If data types are not as per business context, change the data types as per requirement**\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_restaurants_copy.dtypes",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('Here, we have searched for datatypes that have been described as numerical in data definition, but wrongly made categorical in dataframe. No such variable found. Regarding variables that have been marked as categorical in data definition, but are not \\'object\\' data type in dataframe, all such variables can be excluded in numerical calculations on dataframe, so no need to convert them to object.')",
"Here, we have searched for datatypes that have been described as numerical in data definition, but wrongly made categorical in dataframe. No such variable found. Regarding variables that have been marked as categorical in data definition, but are not 'object' data type in dataframe, all such variables can be excluded in numerical calculations on dataframe, so no need to convert them to object.\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### Change the incorrect data type",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#df_restaurants_copy[['city_id','latitude','longitude','price_range','opentable_support','delivery']] = df_restaurants_copy[['city_id','latitude','longitude','price_range','opentable_support','delivery']].astype('object')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('All datatypes which are numerical in data definition, are also numerical in dataframe')",
"All datatypes which are numerical in data definition, are also numerical in dataframe\n"
]
],
[
[
"**5. Check for Duplicates**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_restaurants_copy.duplicated().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy.duplicated(keep=\"last\")]\n#df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['name']=='Peshawri - ITC Mughal']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy.drop_duplicates(keep='first',inplace=True)\ndf_restaurants_copy.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['name']=='Peshawri - ITC Mughal']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('Dropped all duplicate rows, retaining the first one')",
"Dropped all duplicate rows, retaining the first one\n"
]
],
[
[
"<a id = 'Understanding_variables'> </a>\n## 5. Understand the variables",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**1. Variable 'name'**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_restaurants_copy['name'].isna().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['name'].duplicated().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['name'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**2. Variable 'establishment'**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_restaurants_copy['establishment'].isna().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['establishment'].duplicated().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['establishment'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**3. Variable 'city'**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_restaurants_copy['city'].isna().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['city'].duplicated().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"i = 0\nfor var in df_restaurants_copy['city'].unique():\n print(var)",
"Agra\nAhmedabad\nGandhinagar\nAjmer\nAlappuzha\nAllahabad\nAmravati\nAmritsar\nAurangabad\nBangalore\nBhopal\nBhubaneshwar\nChandigarh\nMohali\nPanchkula\nZirakpur\nNayagaon\nChennai\nCoimbatore\nCuttack\nDarjeeling\nDehradun\nNew Delhi\nGurgaon\nNoida\nFaridabad\nGhaziabad\nGreater Noida\nDharamshala\nGangtok\nGoa\nGorakhpur\nGuntur\nGuwahati\nGwalior\nHaridwar\nHyderabad\nSecunderabad\nIndore\nJabalpur\nJaipur\nJalandhar\nJammu\nJamnagar\nJamshedpur\nJhansi\nJodhpur\nJunagadh\nKanpur\nKharagpur\nKochi\nKolhapur\nKolkata\nHowrah\nKota\nLucknow\nLudhiana\nMadurai\nManali\nMangalore\nManipal\nUdupi\nMeerut\nMumbai\nThane\nNavi Mumbai\nMussoorie\nMysore\nNagpur\nNainital\nNashik\nNeemrana\nOoty\nPalakkad\nPatiala\nPatna\nPuducherry\nPune\nPushkar\nRaipur\nRajkot\nRanchi\nRishikesh\nSalem\nShimla\nSiliguri\nSrinagar\nSurat\nThrissur\nTirupati\nTrichy\nTrivandrum\nUdaipur\nVaranasi\nVellore\nVijayawada\nVizag\nVadodara\n"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['city'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Let us find the count of restaurants in each city**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_restaurants_copy['name'].isna().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy.groupby(['city'])[['city','name']].head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"i = 0\nfor var in df_restaurants_copy['city'].unique():\n print(var , ' has ', len(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['city'] == var]['name']), ' restaurants.')",
"Agra has 893 restaurants.\nAhmedabad has 1329 restaurants.\nGandhinagar has 96 restaurants.\nAjmer has 470 restaurants.\nAlappuzha has 267 restaurants.\nAllahabad has 567 restaurants.\nAmravati has 440 restaurants.\nAmritsar has 692 restaurants.\nAurangabad has 693 restaurants.\nBangalore has 2365 restaurants.\nBhopal has 971 restaurants.\nBhubaneshwar has 792 restaurants.\nChandigarh has 681 restaurants.\nMohali has 333 restaurants.\nPanchkula has 174 restaurants.\nZirakpur has 154 restaurants.\nNayagaon has 15 restaurants.\nChennai has 2612 restaurants.\nCoimbatore has 1019 restaurants.\nCuttack has 293 restaurants.\nDarjeeling has 116 restaurants.\nDehradun has 805 restaurants.\nNew Delhi has 1847 restaurants.\nGurgaon has 662 restaurants.\nNoida has 273 restaurants.\nFaridabad has 81 restaurants.\nGhaziabad has 95 restaurants.\nGreater Noida has 22 restaurants.\nDharamshala has 259 restaurants.\nGangtok has 132 restaurants.\nGoa has 1169 restaurants.\nGorakhpur has 526 restaurants.\nGuntur has 319 restaurants.\nGuwahati has 784 restaurants.\nGwalior has 606 restaurants.\nHaridwar has 401 restaurants.\nHyderabad has 866 restaurants.\nSecunderabad has 97 restaurants.\nIndore has 1093 restaurants.\nJabalpur has 598 restaurants.\nJaipur has 1456 restaurants.\nJalandhar has 643 restaurants.\nJammu has 549 restaurants.\nJamnagar has 425 restaurants.\nJamshedpur has 615 restaurants.\nJhansi has 371 restaurants.\nJodhpur has 731 restaurants.\nJunagadh has 231 restaurants.\nKanpur has 836 restaurants.\nKharagpur has 116 restaurants.\nKochi has 1027 restaurants.\nKolhapur has 567 restaurants.\nKolkata has 1413 restaurants.\nHowrah has 50 restaurants.\nKota has 622 restaurants.\nLucknow has 1290 restaurants.\nLudhiana has 992 restaurants.\nMadurai has 578 restaurants.\nManali has 185 restaurants.\nMangalore has 584 restaurants.\nManipal has 162 restaurants.\nUdupi has 61 restaurants.\nMeerut has 580 restaurants.\nMumbai has 2538 restaurants.\nThane has 300 restaurants.\nNavi Mumbai has 256 restaurants.\nMussoorie has 190 restaurants.\nMysore has 585 restaurants.\nNagpur has 1102 restaurants.\nNainital has 246 restaurants.\nNashik has 758 restaurants.\nNeemrana has 26 restaurants.\nOoty has 276 restaurants.\nPalakkad has 178 restaurants.\nPatiala has 505 restaurants.\nPatna has 683 restaurants.\nPuducherry has 583 restaurants.\nPune has 1911 restaurants.\nPushkar has 183 restaurants.\nRaipur has 833 restaurants.\nRajkot has 587 restaurants.\nRanchi has 689 restaurants.\nRishikesh has 258 restaurants.\nSalem has 418 restaurants.\nShimla has 241 restaurants.\nSiliguri has 483 restaurants.\nSrinagar has 125 restaurants.\nSurat has 1001 restaurants.\nThrissur has 405 restaurants.\nTirupati has 277 restaurants.\nTrichy has 505 restaurants.\nTrivandrum has 617 restaurants.\nUdaipur has 775 restaurants.\nVaranasi has 598 restaurants.\nVellore has 341 restaurants.\nVijayawada has 530 restaurants.\nVizag has 721 restaurants.\nVadodara has 1002 restaurants.\n"
]
],
[
[
"**4. Variable 'locality'**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_restaurants_copy['locality'].isna().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['locality'].duplicated().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['locality'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**4. Variable 'latitude'**\n\nFrom the variable 'latitude', we know the latitudinal location of the restaurant\n\nThe Latitudinal extent of India 8º4‛N to 37º6‛ N. \n\nWe must check whether we have any points beyond this extent.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_restaurants_copy['latitude'].isna().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['latitude'].duplicated().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(df_restaurants_copy[(df_restaurants_copy['latitude'] < 8.066667) | (df_restaurants_copy['latitude'] > 37.1)])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"- We need to replace all these values with NaN's.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def replacement(x):\n if((x < 8.066667) | (x > 37.1)):\n return np.nan\n else:\n return x\ndf_restaurants_copy['latitude'] = df_restaurants_copy['latitude'].transform(lambda x: replacement(x))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"- check if the values are replace by NaN's",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"len(df_restaurants_copy[(df_restaurants_copy['latitude'] < 8.066667) | (df_restaurants_copy['latitude'] > 37.1)])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['latitude'].isna().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('Now, the number of nan values has become same as number of values in the result above i.e. 955, which means all the qualifying values have been replaced with nan values')",
"Now, the number of nan values has become same as number of values in the result above i.e. 955, which means all the qualifying values have been replaced with nan values\n"
]
],
[
[
"- We see all the values are replaced by NaN's",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['latitude'].isna()]['latitude'].head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**5. Variable 'longitude'**\n\nFrom the variable 'longitude', we know the longitudinal location of the restaurant\n\nThe Longitudinal extent of India is from 68°7'E to 97°25'E\n\nWe must check whether we have any points beyond this extent.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_restaurants_copy['longitude'].isna().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['longitude'].duplicated().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(df_restaurants_copy[(df_restaurants_copy['longitude'] < 68.1166667) | (df_restaurants_copy['longitude'] > 97.41666667)])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"- We need to replace all these values with NaN's.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def replacement2(x):\n if((x < 68.1166667) | (x > 97.41666667)):\n return np.nan\n else:\n return x\ndf_restaurants_copy['longitude'] = df_restaurants_copy['longitude'].transform(lambda x: replacement2(x))",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"- Check if the values are replace by NaN's",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"len(df_restaurants_copy[(df_restaurants_copy['longitude'] < 68.1166667) | (df_restaurants_copy['longitude'] > 97.41666667)])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['longitude'].isna().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('Now, the number of nan values has become same as number of values in the result above i.e. 957, which means all the qualifying values have been replaced with nan values')",
"Now, the number of nan values has become same as number of values in the result above i.e. 957, which means all the qualifying values have been replaced with nan values\n"
]
],
[
[
"- From variable 'latitude' and 'longitude', plot the location of restaurants.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_temp = df_restaurants_copy[['latitude','longitude']].dropna()\ndf_temp.isna().sum().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6,10))\nplt.scatter(df_temp['longitude'],df_temp['latitude'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"pip install gmplot",
"Requirement already satisfied: gmplot in c:\\users\\kejri\\anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages (1.2.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: requests in c:\\users\\kejri\\anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages (from gmplot) (2.22.0)\nRequirement already satisfied: urllib3!=1.25.0,!=1.25.1,<1.26,>=1.21.1 in c:\\users\\kejri\\anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages (from requests->gmplot) (1.24.2)\nRequirement already satisfied: chardet<3.1.0,>=3.0.2 in c:\\users\\kejri\\anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages (from requests->gmplot) (3.0.4)\nRequirement already satisfied: idna<2.9,>=2.5 in c:\\users\\kejri\\anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages (from requests->gmplot) (2.8)\nRequirement already satisfied: certifi>=2017.4.17 in c:\\users\\kejri\\anaconda3\\lib\\site-packages (from requests->gmplot) (2019.9.11)\nNote: you may need to restart the kernel to use updated packages.\n"
],
[
"import gmplot",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#lat, long, zoom\ngoogle_map = gmplot.GoogleMapPlotter(28.7041,77.1025, 5, apikey=\"\" )",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#google_map.apikey = \"\"",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"google_map.scatter(df_temp['latitude'],df_temp['longitude'], '#cb202d', size = 35, marker = False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"google_map.draw(\"location.html\")",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"import webbrowser \nwebbrowser.open('location.html')",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**6. Variable 'cuisines'**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_restaurants_copy['cuisines'].isna().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['cuisines'].duplicated().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"- To find the unique cusines we write a small user defined function.\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_restaurants_copy['cuisines']",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def cuisines(x):\n x=x.dropna()\n x=np.asarray(x.transform(lambda x: x.split(\", \")).to_numpy())\n x= pd.Series(np.concatenate(x, axis=0))\n print(x.unique())\ncuisines(df_restaurants_copy['cuisines'])",
"['North Indian' 'South Indian' 'Mithai' 'Street Food' 'Desserts' 'Mughlai'\n 'Rolls' 'Chinese' 'Fast Food' 'Bakery' 'Continental' 'Italian' 'Pizza'\n 'Cafe' 'Burger' 'Wraps' 'Beverages' 'Rajasthani' 'Mexican' 'Healthy Food'\n 'Sandwich' 'Salad' 'Momos' 'Lebanese' 'Mediterranean' 'Thai' 'Gujarati'\n 'Indian' 'Finger Food' 'European' 'Tea' 'Asian' 'Bar Food' 'Kebab' 'Paan'\n 'Biryani' 'Juices' 'Ice Cream' 'Japanese' 'Korean' 'Afghan' 'Awadhi'\n 'Hyderabadi' 'Lucknowi' 'Roast Chicken' 'Drinks Only' 'Coffee' 'American'\n 'BBQ' 'Maharashtrian' 'Modern Indian' 'Andhra' 'Konkan' 'Kerala' 'Sushi'\n 'Parsi' 'Greek' 'Bengali' 'Seafood' 'Frozen Yogurt' 'Arabian'\n 'Indonesian' 'Sindhi' 'Hot dogs' 'Goan' 'Charcoal Chicken' 'Raw Meats'\n 'Grill' 'Malwani' 'Cantonese' 'Pakistani' 'Steak' 'Vietnamese'\n 'Singaporean' 'Middle Eastern' 'British' 'French' 'Burmese' 'Kashmiri'\n 'Mangalorean' 'Malaysian' 'Tex-Mex' 'Spanish' 'Chettinad' 'Tibetan'\n 'German' 'Belgian' 'Turkish' 'Bihari' 'Odia' 'Naga' 'Bubble Tea'\n 'Moroccan' 'Sri Lankan' 'Mandi' 'Coffee and Tea' 'Cafe Food' 'Oriental'\n 'Cuisine Varies' 'Pan Asian' 'Mishti' 'Portuguese' 'Iranian'\n 'North Eastern' 'Mongolian' 'Irish' 'Tamil' 'Russian' 'Panini'\n 'South American' 'Fusion' 'Nepalese' 'International' 'Modern Australian'\n 'Poké' 'Falafel' 'Armenian' 'Peruvian' 'Brazilian' 'Himachali' 'Israeli'\n 'Bohri' 'Assamese' 'Bangladeshi' 'African' 'Egyptian' 'Crepes'\n 'Fried Chicken' 'Swedish' 'Cake' 'Garhwali' 'Vegan' 'Afghani']\n"
],
[
"cuisines(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['city'] == 'Agra']['cuisines'])",
"['North Indian' 'South Indian' 'Mithai' 'Street Food' 'Desserts' 'Mughlai'\n 'Rolls' 'Chinese' 'Fast Food' 'Bakery' 'Continental' 'Italian' 'Pizza'\n 'Cafe' 'Burger' 'Wraps' 'Beverages' 'Rajasthani' 'Mexican' 'Healthy Food'\n 'Sandwich' 'Salad' 'Momos' 'Lebanese' 'Mediterranean' 'Thai' 'Gujarati'\n 'Indian' 'Finger Food' 'European' 'Tea' 'Asian' 'Bar Food' 'Kebab' 'Paan'\n 'Biryani' 'Juices' 'Ice Cream' 'Japanese' 'Korean' 'Afghan' 'Awadhi'\n 'Hyderabadi' 'Lucknowi' 'Roast Chicken' 'Drinks Only' 'Coffee']\n"
],
[
"cuisines(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['city'] == 'Srinagar']['cuisines'])",
"['Cafe' 'Pizza' 'Continental' 'North Indian' 'South Indian' 'Kashmiri'\n 'Fast Food' 'Italian' 'Mughlai' 'Chinese' 'Desserts' 'Beverages'\n 'Sandwich' 'Street Food' 'Mithai' 'Bakery' 'Tibetan' 'Afghan' 'Asian'\n 'Burger' 'Ice Cream' 'European' 'American' 'Thai' 'Finger Food' 'BBQ'\n 'Biryani' 'Tea']\n"
],
[
"cuisines(df_restaurants_copy[(df_restaurants_copy['city'] == 'Srinagar') & (df_restaurants_copy['name'] == 'Winterfell Cafe')]['cuisines'])",
"['Cafe']\n"
],
[
"cuisines(df_restaurants_copy[(df_restaurants_copy['city'] == 'Srinagar') & (df_restaurants_copy['name'] == 'Nathus Sweets')]['cuisines'])",
"['North Indian' 'South Indian' 'Chinese' 'Street Food' 'Fast Food'\n 'Mithai' 'Desserts']\n"
]
],
[
[
"- find out the frequency of each cuisine",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def cuisines_freq(x):\n x=x.dropna()\n x=np.asarray(x.transform(lambda x: x.split(\", \")).to_numpy())\n x= pd.Series(np.concatenate(x, axis=0))\n print(x.value_counts())\ncuisines_freq(df_restaurants_copy['cuisines'])",
"North Indian 21259\nChinese 14139\nFast Food 13191\nDesserts 7755\nBeverages 7486\n ... \nAfrican 2\nInternational 1\nVegan 1\nMandi 1\nSwedish 1\nLength: 133, dtype: int64\n"
],
[
"cuisines_freq(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['city'] == 'Srinagar']['cuisines'])",
"North Indian 44\nChinese 22\nKashmiri 19\nMughlai 16\nFast Food 15\nBakery 13\nCafe 13\nItalian 9\nContinental 8\nMithai 6\nPizza 6\nSouth Indian 5\nDesserts 4\nBeverages 3\nAsian 2\nIce Cream 2\nStreet Food 2\nAmerican 1\nSandwich 1\nBurger 1\nAfghan 1\nThai 1\nTea 1\nBBQ 1\nBiryani 1\nFinger Food 1\nTibetan 1\nEuropean 1\ndtype: int64\n"
]
],
[
[
"**8. Variable 'average_cost_for_two'**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_restaurants_copy['average_cost_for_two'].isna().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['average_cost_for_two'].duplicated().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"len(df_restaurants_copy['average_cost_for_two'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['average_cost_for_two'].min(), round(df_restaurants_copy['average_cost_for_two'].mean(),2), df_restaurants_copy['average_cost_for_two'].max()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**9. Variable 'price_range'**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_restaurants_copy['price_range'].isna().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['price_range'].duplicated().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['price_range'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"- visualize a exploded pie chart.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"labels = 1,2,3,4\nsizes = [len(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['price_range']==1]['price_range']), len(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['price_range']==2]['price_range']), len(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['price_range']==3]['price_range']), len(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['price_range']==4]['price_range'])]\nexplode = (0, 0, 0, 0.3)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots()\nax.pie(sizes, labels=labels, explode=explode, autopct='%1.1f%%', shadow=True, startangle=90, radius = 2)\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**10. Variable 'highlights'**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_restaurants_copy['highlights'].isna().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['highlights'].duplicated().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['highlights'].head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"\n\n- write a small function to know the number of times a facility has appeared in the 'Highlights'.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def highlights_freq(x):\n x=x.dropna()\n x=np.asarray(x.transform(lambda x: x.split(\", \")).to_numpy())\n x= pd.Series(np.concatenate(x, axis=0))\n print(x.value_counts())\nhighlights_freq(df_restaurants_copy['highlights'])",
"Cash 57533\nTakeaway Available 51010\nIndoor Seating 44847\nDinner 41685\nLunch 40012\n ... \nMembers Only 3\nBira 91 Beer 2\nAlipay Accepted 1\nSubscription Required 1\nSubscription Available 1\nLength: 103, dtype: int64\n"
]
],
[
[
"- Now we find out which facility occurs most number of in the data.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def highlights_freq_max(x):\n x=x.dropna()\n x=np.asarray(x.transform(lambda x: x.split(\", \")).to_numpy())\n x= pd.Series(np.concatenate(x, axis=0))\n print(x.value_counts().head(1))\nhighlights_freq_max(df_restaurants_copy['highlights'])",
"Cash 57533\ndtype: int64\n"
]
],
[
[
"**11. Variable 'aggregate_rating'** \n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_restaurants_copy['aggregate_rating'].isna().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['aggregate_rating'].duplicated().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['aggregate_rating'].head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"round(df_restaurants_copy['aggregate_rating'].mean(),2)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**12. Variable 'rating_text'**\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_restaurants_copy['rating_text'].isna().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['rating_text'].duplicated().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['rating_text'].head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['rating_text'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['rating_text'] == \"Very Good\"]['aggregate_rating'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['rating_text'] == \"Excellent\"]['aggregate_rating'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['rating_text'] == \"Good\"]['aggregate_rating'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['rating_text'] == \"Average\"]['aggregate_rating'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['rating_text'] == \"Not rated\"]['aggregate_rating'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['rating_text'] == \"Poor\"]['aggregate_rating'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"Creating a New feature for better understanding of ratings\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def ratings(x): \n if x>=4.5:\n return \"Excellent\"\n elif ((x<4.5) & (x>=4)):\n return \"Very Good\"\n elif ((x<4) & (x>=3.5)):\n return 'Good'\n elif ((x<3.5) & (x>=2.5)):\n return 'Average'\n elif ((x<2.5) & (x>0)):\n return 'Poor'\n else:\n return 'Not Rated'\ndf_restaurants_copy['new_ratings'] = np.nan\ndf_restaurants_copy['new_ratings'].head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['new_ratings'] = df_restaurants_copy['aggregate_rating'].transform(lambda x: ratings(x))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['rating_text'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['new_ratings'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['new_ratings'].head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy = df_restaurants_copy.drop(['rating_text'], axis=1)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**13. Variable 'votes'**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_restaurants_copy['votes'].isna().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['votes'].duplicated().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['votes'].min(), round(df_restaurants_copy['votes'].mean(),2), df_restaurants_copy['votes'].max()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['votes'].head()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**14. Variable 'photo_count'**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_restaurants_copy['photo_count'].isna().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['photo_count'].duplicated().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['photo_count'].min(), round(df_restaurants_copy['photo_count'].mean(),2), df_restaurants_copy['photo_count'].max()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**15. Variable 'delivery'**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_restaurants_copy['delivery'].isna().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['delivery'].duplicated().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['delivery'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id ='missing'></a>\n## 6. Check for missing values",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_restaurants_copy.isna().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy.isna().sum().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**6. Study summary statistics**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Let us check the summary statistics for numerical variables.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_restaurants_copy[[\"average_cost_for_two\",\"aggregate_rating\",\"votes\",\"photo_count\"]].describe()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('Sum')\ndf_restaurants_copy[[\"average_cost_for_two\",\"aggregate_rating\",\"votes\",\"photo_count\"]].sum()",
"Sum\n"
],
[
"print('Mode')\ndf_restaurants_copy[[\"average_cost_for_two\",\"aggregate_rating\",\"votes\",\"photo_count\"]].mode()",
"Mode\n"
]
],
[
[
"<a id = 'correlation'> </a>\n## 7. Study correlation",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_restaurants_copy[[\"average_cost_for_two\",\"aggregate_rating\",\"votes\",\"photo_count\"]].duplicated().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_temp = df_restaurants_copy[[\"average_cost_for_two\",\"aggregate_rating\",\"votes\",\"photo_count\"]].drop_duplicates()\ndf_temp_copy = df_temp.copy()\ndf_temp_copy2 = df_temp.copy()\ndf_temp.shape",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_temp.isna().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_temp.corr()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#ax.get_ylim()\nax=sns.heatmap(df_temp.corr(), annot=True, vmin=-1, vmax=1, center= 0, cmap= 'coolwarm') \nax.set_ylim(4.0, 0) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('Without removing the outliers, the restaurants that have more number of photos also have more number of votes')",
"Without removing the outliers, the restaurants that have more number of photos also have more number of votes\n"
],
[
"def replace_outliers(x): \n Q1 = df_temp[x].quantile(0.25)\n Q3 = df_temp[x].quantile(0.75)\n IQR = Q3 - Q1\n print(\"Outliers Number in \", x, \": \", ((df_temp[x] < (Q1 - 1.5 * IQR)) | (df_temp[x] > (Q3 + 1.5 * IQR))).sum(), \"out of \", df_temp[x].shape[0])\n ##Replaced outliers in HDI for year\n whisker1=Q1-1.5*IQR\n for i in (np.where((df_temp[x] < whisker1))):\n df_temp.iloc[i, df_temp.columns.get_loc(x)]= whisker1\n whisker2=Q3+1.5*IQR\n for i in (np.where((df_temp[x] > whisker2))): \n df_temp.iloc[i, df_temp.columns.get_loc(x)]= whisker2\n print('Outliers left: ',len(np.where((((df_temp[x] <(Q1-1.5*IQR)) | (df_temp[x] >(Q3+1.5*IQR)))))[0]))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"replace_outliers('average_cost_for_two')\nreplace_outliers('aggregate_rating')\nreplace_outliers('votes')\nreplace_outliers('photo_count')",
"Outliers Number in average_cost_for_two : 4267 out of 41726\nOutliers left: 0\nOutliers Number in aggregate_rating : 1131 out of 41726\nOutliers left: 0\nOutliers Number in votes : 4914 out of 41726\nOutliers left: 0\nOutliers Number in photo_count : 6155 out of 41726\nOutliers left: 0\n"
],
[
"#ax.get_ylim()\nax=sns.heatmap(df_temp.corr(), annot=True, vmin=-1, vmax=1, center= 0, cmap= 'coolwarm') \nax.set_ylim(4.0, 0) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('After replacing outliers with whiskers, new correlations have been found')",
"After replacing outliers with whiskers, new correlations have been found\n"
],
[
"def del_outliers(x):\n Q1 = df_temp[x].quantile(0.25)\n Q3 = df_temp[x].quantile(0.75)\n IQR = Q3 - Q1\n print(\"Outliers Number in (rows being dropped)\", x, \": \", ((df_temp[x] < (Q1 - 1.5 * IQR)) | (df_temp[x] > (Q3 + 1.5 * IQR))).sum(), \"out of \", df_temp[x].shape[0])\n whisker1=Q1-1.5*IQR\n whisker2=Q3+1.5*IQR\n ##Deleting rows having outliers in HDI for year or suicides_no based on IQR Score method\n for i in (np.where((df_temp_copy[x] < whisker1) | (df_temp_copy[x] > whisker2))):\n df_temp_copy.drop(df_temp_copy.index[i],inplace=True) \n print('Outliers left: ', len(np.where((((df_temp_copy[x] <(Q1-1.5*IQR)) | (df_temp_copy[x] >(Q3+1.5*IQR)))))[0]))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"del_outliers('average_cost_for_two')\ndel_outliers('aggregate_rating')\ndel_outliers('votes')\ndel_outliers('photo_count')",
"Outliers Number in (rows being dropped) average_cost_for_two : 0 out of 41726\nOutliers left: 0\nOutliers Number in (rows being dropped) aggregate_rating : 0 out of 41726\nOutliers left: 0\nOutliers Number in (rows being dropped) votes : 0 out of 41726\nOutliers left: 0\nOutliers Number in (rows being dropped) photo_count : 0 out of 41726\nOutliers left: 0\n"
],
[
"#ax.get_ylim()\nax=sns.heatmap(df_temp_copy.corr(), annot=True, vmin=-1, vmax=1, center= 0, cmap= 'coolwarm') \nax.set_ylim(4.0, 0) ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('After deleting rows having outliers, new correlations have been found')",
"After deleting rows having outliers, new correlations have been found\n"
]
],
[
[
"<a id='outliers'> </a>\n## 8. Detect outliers",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def detect_outliers(x):\n Q1 = df_temp_copy2[x].quantile(0.25)\n Q3 = df_temp_copy2[x].quantile(0.75)\n IQR = Q3 - Q1\n print(\"Number of Outliers in \", x, \": \", ((df_temp_copy2[x] < (Q1 - 1.5 * IQR)) | (df_temp_copy2[x] > (Q3 + 1.5 * IQR))).sum(), \"out of \", df_temp_copy2[x].shape[0])\n #whisker1=Q1-1.5*IQR\n #whisker2=Q3+1.5*IQR\n sns.boxplot(x=df_temp_copy2[x])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"detect_outliers('average_cost_for_two')",
"Number of Outliers in average_cost_for_two : 4267 out of 41726\n"
],
[
"detect_outliers('aggregate_rating')",
"Number of Outliers in aggregate_rating : 1131 out of 41726\n"
],
[
"detect_outliers('votes')",
"Number of Outliers in votes : 4914 out of 41726\n"
],
[
"detect_outliers('photo_count')",
"Number of Outliers in photo_count : 6155 out of 41726\n"
]
],
[
[
"<a id='region'> </a>\n## 9. Create a new variable 'region'\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"Create a variable 'region' with four categories 'northern','eastern', 'southern', 'western' and 'central'. To do so, use the 'city' column, group all cities belonging to the same region. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#Manually created an excel file from data available at the source url: http://www.indianventurez.com/city_list.htm\ndf=pd.read_excel('cities.xlsx')\ndf.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df=df.dropna()\ndf['Category'] = df['Category'].replace('WEST INDIA\\xa0',\"WEST INDIA\").replace('SOUTH INDIA\\xa0',\"SOUTH INDIA\").replace('NORTH-EAST INDIA',\"EAST INDIA\").replace('NORTH EAST INDIA',\"EAST INDIA\").replace('WESTERN REGION',\"WEST INDIA\")\ndf['Category'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df['CITY']= df['CITY'].transform(lambda x: x.title())\ndf.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df[df['Category']=='NORTH INDIA']['CITY'].values",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df[df['Category']=='EAST INDIA']['CITY'].values",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df[df['Category']=='SOUTH INDIA']['CITY'].values",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df[df['Category']=='WEST INDIA']['CITY'].values",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df[df['Category']=='CENTRAL INDIA']['CITY'].values",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"northern=['Agra', 'Allahabad', 'Almora', 'Ambala', 'Amritsar', 'Auli',\n 'Baddi', 'Badrinath', 'Balrampur', 'Bareilly', 'Betalghat',\n 'Bhimtal', 'Binsar', 'Chail', 'Chamba', 'Chandigarh',\n 'Corbett National Park', 'Dalhousie', 'Dehradun', 'Dharamshala',\n 'Faridabad', 'Firozabad', 'Gangotri', 'Garhmukteshwar', 'Garhwal',\n 'Ghaziabad', 'Greater Noida', 'Gulmarg', 'Gurgaon', 'Hansi',\n 'Haridwar', 'Jalandhar', 'Jammu', 'Jhansi', 'Kanatal', 'Kargil',\n 'Karnal', 'Kasauli', 'Kashipur', 'Katra', 'Kausani', 'Kaza',\n 'Kedarnath', 'Khajjiar', 'Kufri', 'Kullu', 'Kushinagar', 'Leh',\n 'Lucknow', 'Ludhiana', 'Manali', 'Manesar', 'Marchula', 'Mathura',\n 'Mcleodganj', 'Mohali', 'Moradabad', 'Mukteshwar', 'Mussoorie',\n 'Nahan', 'Nainital', 'Naldhera', 'New Delhi', 'Noida', 'Palampur',\n 'Pahalgam', 'Panchkula', 'Pantnagar', 'Parwanoo', 'Patiala',\n 'Pathankot', 'Patnitop', 'Phagwara', 'Pinjore', 'Pragpur',\n 'Rai Bareilly', 'Ram Nagar', 'Ranikhet', 'Rishikesh', 'Sattal',\n 'Shimla', 'Solan', 'Sonauli', 'Srinagar', 'Udhampur', 'Uttarkashi',\n 'Varanasi', 'Yamunotri','Zirakpur','Nayagaon','Meerut']\neastern=['Agartala', 'Aizwal', 'Barbil', 'Berhampur', 'Bhilai',\n 'Bhubaneshwar', 'Bodhgaya', 'Cuttack', 'Darjeeling', 'Dibrugarh',\n 'Digha', 'Dooars', 'Durgapur', 'Gangtok', 'Gaya', 'Gorakhpur',\n 'Guwahati', 'Imphal', 'Jamshedpur', 'Jorhat', 'Kalimpong',\n 'Kanpur', 'Kaziranga', 'Kolkata', 'Kurseong', 'Lachung',\n 'Mandormoni', 'Patna', 'Pelling', 'Puri', 'Raichak', 'Rajgir',\n 'Ranchi', 'Ravangla', 'Rishyap', 'Rourkela', 'Shillong',\n 'Shimlipal', 'Siliguri', 'Sunderban', 'Tarapith', 'Yuksom', 'Howrah', 'Kharagpur']\nsouthern=['Alleppey', 'Ashtamudi', 'Bandipur', 'Bangalore', 'Belgaum',\n 'Calicut', 'Canannore', 'Chennai', 'Chikmagalur', 'Coimbatore',\n 'Coonoor', 'Coorg', 'Dandeli', 'Gokharna', 'Guruvayoor', 'Halebid',\n 'Hampi', 'Hassan', 'Hospet', 'Hosur', 'Hubli', 'Hyderabad',\n 'Idukki', 'Kabini', 'Kanchipuram', 'Kanyakumari', 'Karur',\n 'Karwar', 'Kasargod', 'Kochin', 'Kodaikanal', 'Kollam', 'Kotagiri',\n 'Kottayam', 'Kovalam', 'Kumarakom', 'Kumbakonam', 'Kumily',\n 'Lakshadweep', 'Madurai', 'Mahabalipuram', 'Malappuram', 'Malpe',\n 'Mararri', 'Mangalore', 'Munnar', 'Mysore', 'Nadukani',\n 'Nagapattinam', 'Nagarhole', 'Nilgiri', 'Ooty', 'Pallakad',\n 'Pondicherry', 'Poovar', 'Port Blair', 'Puttaparthi',\n 'Rajahmundry', 'Rameshwaram', 'Ranny', 'Salem', 'Secunderabad',\n 'Sharavanbelgola', 'Shivanasamudra', 'Sivaganga District',\n 'Tanjore', 'Thekkady', 'Thirvannamalai', 'Thiruvananthapuram',\n 'Tiruchirapalli', 'Tirupur', 'Tirupati', 'Thrissur', 'Udupi',\n 'Vagamon', 'Varkala', 'Velankanni', 'Vellore', 'Vijayawada',\n 'Vishakapatnam', 'Wayanad', 'Yercaud','Alappuzha', 'Amravati', 'Guntur',\n 'Kochi', 'Manipal', 'Palakkad', 'Puducherry', 'Trichy','Trivandrum', 'Vizag']\nwestern=['Ahmedabad', 'Ajmer', 'Alibaug', 'Alsisar', 'Alwar', 'Anand',\n 'Ankleshwar', 'Aurangabad', 'Balasinor', 'Bambora', 'Behror',\n 'Bharatpur', 'Bhandardara', 'Bharuch', 'Bhavangadh', 'Bhavnagar',\n 'Bhuj', 'Bikaner', 'Bundi', 'Chiplun', 'Chittorgarh', 'Dabhosa',\n 'Daman', 'Dapoli', 'Dausa', 'Diu', 'Dive Agar', 'Durshet',\n 'Dwarka', 'Ganapatipule', 'Gandhidham', 'Gandhinagar', 'Goa',\n 'Gondal', 'Igatpuri', 'Jaipur', 'Jaisalmer', 'Jalgaon',\n 'Jambugodha', 'Jamnagar', 'Jawhar', 'Jodhpur', 'Jojawar',\n 'Junagadh', 'Karjat', 'Kashid', 'Khandala', 'Khimsar', 'Kolhapur',\n 'Kota', 'Kumbalgarh', 'Lonavala', 'Lothal', 'Mahabaleshwar',\n 'Malshej Ghat', 'Malvan', 'Mandavi', 'Mandawa', 'Manmad',\n 'Matheran', 'Mount Abu', 'Morbi', 'Mumbai', 'Mundra',\n 'Murud Janjira', 'Nagaur Fort', 'Nagothane', 'Nagpur', 'Nanded',\n 'Napne', 'Nasik', 'Navi Mumbai', 'Neral', 'Osian', 'Palanpur',\n 'Pali', 'Palitana', 'Panchgani', 'Panhala', 'Panvel', 'Pench',\n 'Phalodi', 'Porbandar', 'Poshina', 'Pune', 'Puskhar', 'Rajasthan',\n 'Rajkot', 'Rajpipla', 'Rajsamand', 'Ramgarh', 'Ranakpur',\n 'Ranthambore', 'Ratnagiri', 'Rohetgarh', 'Sajan', 'Saputara',\n 'Sasan Gir', 'Sawai Madhopur', 'Sawantwadi', 'Shirdi', 'Siana',\n 'Silvassa', 'Surat', 'Tapola', 'Thane', 'Udaipur', 'Vadodara',\n 'Vapi', 'Veraval', 'Vikramgadh', 'Wankaner','Nashik','Neemrana','Pushkar']\ncentral=['Amla', 'Bandhavgarh', 'Bhopal', 'Chitrakoot', 'Gwalior', 'Indore',\n 'Jabalpur', 'Kanha', 'Khajuraho', 'Orchha', 'Pachmarhi', 'Panna',\n 'Raipur', 'Ujjain']\ndef region(x):\n #northern=['Delhi','Jaipur','Lucknow','Kanpur','Ghaziabad','Ludhiana','Agra','Allahabad','Faridabad','Meerut','Varanasi','Srinagar','Amritsar','Jodhpur','Chandigarh','Kota','Bareily','Moradabad','Gurgaon','Aligarh','Jalandhar','Saharanpur','Gorakhpur','Bikaner','Noida','Firozabad','Dehradun','Ajmer','Lonni','Jhansi','Jammu']\n if x in northern:\n return 'northern'\n elif x in eastern:\n return 'eastern'\n elif x in southern:\n return 'southern'\n elif x in western:\n return 'western'\n elif x in central:\n return 'central'\n else:\n return np.nan\ndf_restaurants_copy['region'] = np.nan\ndf_restaurants_copy['region'].head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['city'].isna().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['region'] = df_restaurants_copy['city'].transform(lambda x: region(x))",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['region'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['region'].isna()]['city'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('Let\\'s add these leftover cities manually to their respective lists')",
"Let's add these leftover cities manually to their respective lists\n"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy['region'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy.groupby('region')[['region','city']].head(2)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_restaurants_copy.groupby('region')['city'].first()",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"<a id='more'> </a>\n## 10. Some more Analysis",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"<b>Lets us explore the data some more now that we have extrapolated and removed the missing values <br>\nWe now conduct analysis to compare the regions.</b>",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 1. To find which cities have expensive restaurants \n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#METHOD 1: Based on average 'average cost for two' of all restaurants per city for cities which have expensive restaurants\ndef detect_res(x, y):\n Q1 = df_restaurants_copy[x].quantile(0.25)\n Q3 = df_restaurants_copy[x].quantile(0.75)\n IQR = Q3 - Q1\n if y==1:\n return df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy[x] > (Q3 + 1.5 * IQR)][['city','latitude','longitude','average_cost_for_two']].drop_duplicates(keep=\"first\") \n else:\n return df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy[x] > (Q3 + 1.5 * IQR)][['city','latitude','longitude','average_cost_for_two']].groupby(['city']).mean().sort_values(by=\"average_cost_for_two\",ascending=False).reset_index().drop_duplicates(keep=\"first\").reset_index()\nprint(\"The cities which have expensive restaurants: \\n\", detect_res('average_cost_for_two',1)['city'].unique())\nprint(len(detect_res('average_cost_for_two',1)['city'].unique()),\" out of \", len(df_restaurants_copy['city'].unique()),\" cities have expensive restaurants\")\n#detect_res('average_cost_for_two',2)",
"The cities which have expensive restaurants: \n ['Agra' 'Ahmedabad' 'Gandhinagar' 'Ajmer' 'Alappuzha' 'Allahabad'\n 'Amritsar' 'Aurangabad' 'Bangalore' 'Bhopal' 'Bhubaneshwar' 'Chandigarh'\n 'Panchkula' 'Mohali' 'Zirakpur' 'Nayagaon' 'Chennai' 'Coimbatore'\n 'Cuttack' 'Darjeeling' 'Dehradun' 'New Delhi' 'Gurgaon' 'Noida'\n 'Ghaziabad' 'Faridabad' 'Greater Noida' 'Dharamshala' 'Gangtok' 'Goa'\n 'Gorakhpur' 'Guntur' 'Guwahati' 'Gwalior' 'Haridwar' 'Hyderabad'\n 'Secunderabad' 'Indore' 'Jabalpur' 'Jaipur' 'Jalandhar' 'Jammu'\n 'Jamshedpur' 'Jhansi' 'Jodhpur' 'Kanpur' 'Kochi' 'Kolhapur' 'Kolkata'\n 'Howrah' 'Kota' 'Lucknow' 'Ludhiana' 'Madurai' 'Manali' 'Mangalore'\n 'Manipal' 'Meerut' 'Mumbai' 'Thane' 'Navi Mumbai' 'Mussoorie' 'Mysore'\n 'Nagpur' 'Nainital' 'Nashik' 'Neemrana' 'Ooty' 'Patiala' 'Patna'\n 'Puducherry' 'Pune' 'Pushkar' 'Raipur' 'Rajkot' 'Ranchi' 'Rishikesh'\n 'Salem' 'Shimla' 'Siliguri' 'Srinagar' 'Surat' 'Thrissur' 'Trichy'\n 'Trivandrum' 'Udaipur' 'Varanasi' 'Vellore' 'Vijayawada' 'Vizag'\n 'Vadodara']\n91 out of 98 cities have expensive restaurants\n"
]
],
[
[
"- plot the cities which have costliest restaurants. ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6,10))\nplt.scatter(detect_res('average_cost_for_two',2)['longitude'],detect_res('average_cost_for_two',2)['latitude'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"detect_res('average_cost_for_two',2).head(5)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6,25))\n#plt.xticks(rotation=90)\nsns.barplot(y=detect_res('average_cost_for_two',2)['city'], x=detect_res('average_cost_for_two',2)['average_cost_for_two'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"detect_res('average_cost_for_two',2)[detect_res('average_cost_for_two',2)['average_cost_for_two']>=2000]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6,8))\nax = sns.barplot(y=detect_res('average_cost_for_two',2)[detect_res('average_cost_for_two',2)['average_cost_for_two']>=2000]['city'], x=detect_res('average_cost_for_two',2)[detect_res('average_cost_for_two',2)['average_cost_for_two']>=2000]['average_cost_for_two'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(2,4))\nax = plt.scatter(y=detect_res('average_cost_for_two',2)[detect_res('average_cost_for_two',2)['average_cost_for_two']>=2000]['longitude'], x=detect_res('average_cost_for_two',2)[detect_res('average_cost_for_two',2)['average_cost_for_two']>=2000]['latitude'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#Method 2: Based on cities having atleast 1 expensive restaurant:\ndf_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['average_cost_for_two']>=6000]['city'].unique()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df1 = df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['average_cost_for_two']>=6000].drop_duplicates().groupby('city')[['latitude','longitude','average_cost_for_two']].mean().sort_values(by=\"average_cost_for_two\", ascending=False).reset_index()\ndf1",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6,8))\nax = sns.barplot(x=df1['average_cost_for_two'],y=df1['city'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#METHOD 3: MEAN AVERAGE COST FOR TWO INCLUDING BOTH EXPENSIVE AND NON-EXPENSIVE RESTAURANTS\ndf2 = df_restaurants_copy.drop_duplicates().groupby('city')[['latitude','longitude','average_cost_for_two']].mean().sort_values(by=\"average_cost_for_two\", ascending=False).head(10).reset_index()\ndf2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(4,6))\nax = sns.barplot(x=df2['average_cost_for_two'],y=df2['city'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"#METHOD 4: MEDIAN AVERAGE COST FOR TWO INCLUDING BOTH EXPENSIVE AND NON-EXPENSIVE RESTAURANTS\ndf2 = df_restaurants_copy.drop_duplicates().groupby('city')[['latitude','longitude','average_cost_for_two']].median().sort_values(by=\"average_cost_for_two\", ascending=False).head(10).reset_index()\ndf2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('METHOD 4')\nfig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(4,6))\nax = sns.barplot(x=df2['average_cost_for_two'],y=df2['city'])",
"METHOD 4\n"
],
[
"#METHOD 5: MEAN AVERAGE COST FOR TWO INCLUDING EXPENSIVE RESTAURANTS ONLY\ndf2 = df_restaurants_copy.drop_duplicates().sort_values(by=\"average_cost_for_two\", ascending=False).head(20).groupby('city')[['latitude','longitude','average_cost_for_two']].mean().sort_values(by=\"average_cost_for_two\", ascending=False).reset_index()\ndf2",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('METHOD 5')\nfig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(4,6))\nax = sns.barplot(x=df2['average_cost_for_two'],y=df2['city'])",
"METHOD 5\n"
]
],
[
[
"### 2. Comparing regions",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"### 2a. Highlights available in restaurants for different regions",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"To cater our analysis we define the regions as nothern, eastern, western and southern.",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We first need to select the unique facilities available in each region and sort according to their frequencies.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def highlights_sort(x):\n x=x.dropna()\n x=np.asarray(x.transform(lambda x: x.split(\", \")).to_numpy())\n x= pd.Series(np.concatenate(x, axis=0))\n z = x.value_counts().reset_index()\n z = z.rename(columns={'index': 'highlights', 0: 'frequency'})\n return z",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Highlights of the northern region**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(highlights_sort(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['region'] == \"northern\"]['highlights']))",
" highlights frequency\n0 Cash 14080\n1 Takeaway Available 12702\n2 Dinner 10765\n3 Indoor Seating 10747\n4 Lunch 10565\n.. ... ...\n90 Unlimited Pizza 3\n91 Members Only 2\n92 Gin Bar 2\n93 Wine Tasting 1\n94 Couple Entry Only 1\n\n[95 rows x 2 columns]\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Highlights of the eastern region**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(highlights_sort(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['region'] == \"eastern\"]['highlights']))",
" highlights frequency\n0 Cash 7261\n1 Takeaway Available 6418\n2 Indoor Seating 5421\n3 Dinner 5061\n4 Lunch 4914\n.. ... ...\n89 Dark Kitchen 1\n90 Gin Bar 1\n91 Keto Options 1\n92 Alipay Accepted 1\n93 Couple Entry Only 1\n\n[94 rows x 2 columns]\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Highlights of the southern region**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(highlights_sort(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['region'] == \"southern\"]['highlights']))",
" highlights frequency\n0 Cash 14971\n1 Takeaway Available 13198\n2 Indoor Seating 12712\n3 Dinner 10988\n4 Lunch 10583\n.. ... ...\n93 Wine Tasting 3\n94 BYOB 3\n95 Celebrity Frequented 2\n96 Members Only 1\n97 Dark Kitchen 1\n\n[98 rows x 2 columns]\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Highlights of the western region**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(highlights_sort(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['region'] == \"western\"]['highlights']))",
" highlights frequency\n0 Cash 17230\n1 Takeaway Available 14883\n2 Indoor Seating 12997\n3 Dinner 12154\n4 Lunch 11345\n.. ... ...\n95 Bira 91 Beer 2\n96 BYOB 2\n97 Dark Kitchen 1\n98 Subscription Available 1\n99 Subscription Required 1\n\n[100 rows x 2 columns]\n"
]
],
[
[
"#### Plot the barplot for different regions",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"We shall now plot the graphs for top 10 highlights.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print('Northern: ')\nfig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6,6)) \nsns.barplot(y=highlights_sort(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['region'] == \"northern\"]['highlights'])['highlights'].head(10), x=highlights_sort(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['region'] == \"northern\"]['highlights'])['frequency'].head(10))",
"Northern: \n"
],
[
"print('Western:')\nfig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6,6)) \nsns.barplot(y=highlights_sort(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['region'] == \"western\"]['highlights'])['highlights'].head(10), x=highlights_sort(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['region'] == \"western\"]['highlights'])['frequency'].head(10))",
"Western:\n"
],
[
"print('Eastern: ')\nfig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6,6)) \nsns.barplot(y=highlights_sort(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['region'] == \"eastern\"]['highlights'])['highlights'].head(10), x=highlights_sort(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['region'] == \"eastern\"]['highlights'])['frequency'].head(10))",
"Eastern: \n"
],
[
"print('Southern: ')\nfig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6,6)) \nsns.barplot(y=highlights_sort(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['region'] == \"southern\"]['highlights'])['highlights'].head(10), x=highlights_sort(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['region'] == \"southern\"]['highlights'])['frequency'].head(10))",
"Southern: \n"
]
],
[
[
"### 2b. Cuisines available in restaurants for different regions",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def cuisines_freq2(x):\n x=x.dropna()\n x=np.asarray(x.transform(lambda x: x.split(\", \")).to_numpy())\n x= pd.Series(np.concatenate(x, axis=0))\n z = x.value_counts().reset_index()\n z = z.rename(columns={'index': 'cuisines', 0: 'frequency'})\n return z ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**Cuisines in the northern region**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(cuisines_freq2(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['region'] == \"northern\"]['cuisines']))",
" cuisines frequency\n0 North Indian 6444\n1 Chinese 3584\n2 Fast Food 3524\n3 Continental 1550\n4 Beverages 1547\n.. ... ...\n108 Crepes 1\n109 Swedish 1\n110 Egyptian 1\n111 Peruvian 1\n112 Fusion 1\n\n[113 rows x 2 columns]\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Cuisines in the eastern region**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(cuisines_freq2(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['region'] == \"eastern\"]['cuisines']))",
" cuisines frequency\n0 North Indian 2652\n1 Chinese 2329\n2 Fast Food 1601\n3 Desserts 893\n4 Bakery 736\n.. ... ...\n94 Pan Asian 1\n95 African 1\n96 Russian 1\n97 Oriental 1\n98 Cafe Food 1\n\n[99 rows x 2 columns]\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Cuisines in the southern region**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(cuisines_freq2(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['region'] == \"southern\"]['cuisines']))",
" cuisines frequency\n0 North Indian 4444\n1 South Indian 4048\n2 Chinese 3587\n3 Fast Food 2541\n4 Beverages 2300\n.. ... ...\n108 Coffee and Tea 1\n109 Mishti 1\n110 Pakistani 1\n111 Naga 1\n112 Irish 1\n\n[113 rows x 2 columns]\n"
]
],
[
[
"**Cuisines in the western region** ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(cuisines_freq2(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['region'] == \"western\"]['cuisines']))",
" cuisines frequency\n0 North Indian 6075\n1 Fast Food 4349\n2 Chinese 3698\n3 Desserts 2646\n4 Beverages 2456\n.. ... ...\n105 Grill 1\n106 Fried Chicken 1\n107 Cafe Food 1\n108 Sri Lankan 1\n109 Bohri 1\n\n[110 rows x 2 columns]\n"
]
],
[
[
"- Plot the barplot for top 10 cuisines served in the four regions",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print('Northern: ')\nfig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6,6)) \nsns.barplot(y=cuisines_freq2(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['region'] == \"northern\"]['cuisines'])['cuisines'].head(10), x=cuisines_freq2(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['region'] == \"northern\"]['cuisines'])['frequency'].head(10))",
"Northern: \n"
],
[
"print('Western: ')\nfig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6,6)) \nsns.barplot(y=cuisines_freq2(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['region'] == \"western\"]['cuisines'])['cuisines'].head(10), x=cuisines_freq2(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['region'] == \"western\"]['cuisines'])['frequency'].head(10))",
"Western: \n"
],
[
"print('Eastern: ')\nfig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6,6)) \nsns.barplot(y=cuisines_freq2(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['region'] == \"eastern\"]['cuisines'])['cuisines'].head(10), x=cuisines_freq2(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['region'] == \"eastern\"]['cuisines'])['frequency'].head(10))",
"Eastern: \n"
],
[
"print('Southern: ')\nfig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6,6)) \nsns.barplot(y=cuisines_freq2(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['region'] == \"southern\"]['cuisines'])['cuisines'].head(10), x=cuisines_freq2(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['region'] == \"southern\"]['cuisines'])['frequency'].head(10))",
"Southern: \n"
]
],
[
[
"### 3. The Northern Region",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**Now we shall consider only the northern region**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"**1. The top 10 cuisines served in Restaurants** ",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(cuisines_freq2(df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['region'] == \"northern\"]['cuisines']).head(10))",
" cuisines frequency\n0 North Indian 6444\n1 Chinese 3584\n2 Fast Food 3524\n3 Continental 1550\n4 Beverages 1547\n5 Desserts 1492\n6 Cafe 1209\n7 Bakery 1177\n8 Italian 1139\n9 Street Food 1062\n"
]
],
[
[
"**2. Do restaurants with more photo counts and votes have better rating?**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_temp1 = df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['region']=='northern'][[\"aggregate_rating\",\"votes\",\"photo_count\"]].copy()\ndf_temp1.duplicated().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_temp1 = df_temp1.drop_duplicates()\ndf_temp1.isna().sum()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_temp1.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_temp1.corr().iloc[1:,0]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('We need not always delete outliers. Without treating outliers, we see a very small positive correlation between \"votes and aggregate_rating\" and \"photo_count and aggregate_rating\".\\nClearly, more votes and more photo_count result in less, though a positive impact on aggregate rating.\\nSo the answer is, Very likely, yes! Maybe there is an indirect effect working here. Let\\'s understand how this happens, below:')",
"We need not always delete outliers. Without treating outliers, we see a very small positive correlation between \"votes and aggregate_rating\" and \"photo_count and aggregate_rating\".\nClearly, more votes and more photo_count result in less, though a positive impact on aggregate rating.\nSo the answer is, Very likely, yes! Maybe there is an indirect effect working here. Let's understand how this happens, below:\n"
],
[
"df_votes = df_temp1.groupby('aggregate_rating').sum().sort_values(by=\"votes\", ascending=False)['votes'].reset_index()\ndf_votes",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_photo = df_temp1.groupby('aggregate_rating').sum().sort_values(by=\"photo_count\", ascending=False)['photo_count'].reset_index()\ndf_photo",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"- Plot a boxplots for the above table",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(\"Categorical distribution plot between aggregate_rating and votes: \")\nfig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10,5))\nax = sns.barplot(y=\"votes\", x=\"aggregate_rating\", data=df_votes)",
"Categorical distribution plot between aggregate_rating and votes: \n"
],
[
"print('So,it is clear that maximum number of votes are for ratings between 3.7 and 4.6')",
"So,it is clear that maximum number of votes are for ratings between 3.7 and 4.6\n"
],
[
"print(\"Categorical distribution plot between aggregate_rating and photo_count: \")\nfig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10,5))\nax = sns.barplot(y=\"photo_count\", x=\"aggregate_rating\", data=df_photo)",
"Categorical distribution plot between aggregate_rating and photo_count: \n"
],
[
"print('Almost same trend also holds true here. So, maximum photo count is for ratings between 3.9 and 4.5')",
"Almost same trend also holds true here. So, maximum photo count is for ratings between 3.9 and 4.5\n"
],
[
"print('Now let\\'s draw boxplot for each variable:')",
"Now let's draw boxplot for each variable:\n"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(7,3))\nsns.boxplot(x=df_temp1['aggregate_rating'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(15,2))\nsns.boxplot(x=df_temp1['votes'])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(15,2))\nsns.boxplot(x=df_temp1['photo_count'])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 4. The Mumbai city",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"consider the city mumbai and get a better insights of restuarants in Mumbai.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_mumbai = df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['city']=='Mumbai'].drop_duplicates(keep=\"first\").copy()\ndf_mumbai.head(2)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**1. Expensive restaurants in Mumbai**\n\n- Define the costliest restaurants whose average cost of two people exceeds Rs.5000 .\n- Plot the restaurants which are costliest based on their average cost for two .\n\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_m_expensive = df_mumbai[df_mumbai['average_cost_for_two']>5000].sort_values(by=\"average_cost_for_two\", ascending=False).reset_index()\ndf_m_expensive.head(2)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6,5))\nax = sns.barplot(y=\"name\", x=\"average_cost_for_two\", data=df_m_expensive)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**2.To find the top 20 cuisines of Mumbai**",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"- select unique cuisines available at restaurants in Mumbai\n\n\n- sort cuisines based on frequency\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"print(cuisines_freq2(df_mumbai['cuisines']))",
" cuisines frequency\n0 North Indian 765\n1 Fast Food 564\n2 Chinese 561\n3 Desserts 532\n4 Italian 403\n.. ... ...\n87 Frozen Yogurt 2\n88 Assamese 1\n89 Cafe Food 1\n90 Charcoal Chicken 1\n91 German 1\n\n[92 rows x 2 columns]\n"
]
],
[
[
"**3. To find the popular localities in Mumbai**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_popular = df_mumbai.groupby('locality')['votes'].sum().sort_values(ascending=False).reset_index().head(10)\ndf_popular",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6,5))\nax = sns.barplot(y=\"locality\", x=\"votes\", data=df_popular)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**4. Check for relationship between 'aggregate_rating' and 'average_cost_for_two'**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"df_mumbai[['aggregate_rating','average_cost_for_two']].corr().iloc[0,1]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('Weak Positive Correlation exists between the two as shown below:')",
"Weak Positive Correlation exists between the two as shown below:\n"
],
[
"df_mumbai_agg = df_mumbai.groupby('aggregate_rating').sum().sort_values(by=\"average_cost_for_two\", ascending=False)['average_cost_for_two'].reset_index()\ndf_mumbai_agg ",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10,5))\nax = sns.barplot(y=\"average_cost_for_two\", x=\"aggregate_rating\", data=df_mumbai_agg)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**5. Multiple box plot for photo_counts based on establishment type.**\n\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10,15))\nax = sns.boxplot(x=\"photo_count\", y=\"establishment\", data=df_mumbai)",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"**6. Check for payments method offered in restaurants**",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"payments = ['Cash','Debit Card','Credit Card','Digital Payments Accepted', 'Alipay Accepted']\ndef get_payment_method(x):\n val=\"\"\n x=x.split(\", \")\n for var in x:\n if var in payments:\n val = val + \", \" + var\n else: \n continue\n if val==\"\":\n return val\n else: \n return val[2:]",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_payments = df_mumbai[['name','highlights','latitude','longitude']].drop_duplicates().copy()\nfor i in range(df_payments['highlights'].shape[0]): \n df_payments.iloc[i,df_payments.columns.get_loc('highlights')] = get_payment_method(df_payments.iloc[i,df_payments.columns.get_loc('highlights')])\n\ndf_payments = df_payments.rename(columns={'name': 'restaurant', 'highlights': 'payment methods'})\ndf_payments[['restaurant','payment methods','latitude','longitude']].head(10)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"print('These restaurants accept Only Cash (So, maybe take enough cash while visiting them):')\ndf_payments[df_payments['payment methods']=='Cash'][['restaurant','payment methods','latitude','longitude']]",
"These restaurants accept Only Cash (So, maybe take enough cash while visiting them):\n"
],
[
"print('verify for first restaurant:\\n')\ndf_mumbai[df_mumbai['name']=='Drinkery 51'].drop_duplicates().iloc[0,df_mumbai[df_mumbai['name']=='Drinkery 51'].columns.get_loc('highlights')]",
"verify for first restaurant:\n\n"
],
[
"df_payments[df_payments['restaurant']=='Drinkery 51'].drop_duplicates()['payment methods']",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"- select unique facilities available at restaurants in western region\n- sort facilities based on frequency\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"#Western Region of Mumbai\nprint(\"Latitudinal extent of Mumbai according to data available: \",df_mumbai['latitude'].min(),\" degree E to \",df_mumbai['latitude'].max(),\" degree E\")\nprint(\"\\nWe assume that left 35% and middle 50% is Western Region, which has latitude from \",df_mumbai['latitude'].min(),\" degree E to \",df_mumbai['latitude'].quantile(0.35),\" degree E and longitude from \",df_mumbai['longitude'].quantile(0.25),\" degree N to \", df_mumbai['longitude'].quantile(0.75),\" degree N\")",
"Latitudinal extent of Mumbai according to data available: 18.9131928 degree E to 19.46439399 degree E\n\nWe assume that left 35% and middle 50% is Western Region, which has latitude from 18.9131928 degree E to 19.06537549 degree E and longitude from 72.82946885 degree N to 72.86466 degree N\n"
],
[
"#Unique facilities (sorted)\nprint(highlights_sort(df_mumbai[(df_mumbai['latitude'] < df_mumbai['latitude'].quantile(0.35)) & (df_mumbai['longitude'] < df_mumbai['longitude'].quantile(0.75)) & (df_mumbai['longitude'] > df_mumbai['longitude'].quantile(0.25))]['highlights']))",
" highlights frequency\n0 Cash 440\n1 Indoor Seating 377\n2 Dinner 354\n3 Credit Card 345\n4 Takeaway Available 345\n.. ... ...\n75 Available for Functions 2\n76 Seaside 1\n77 Craft Beer 1\n78 Bira 91 Beer 1\n79 Rooftop 1\n\n[80 rows x 2 columns]\n"
],
[
"df_mumbai_unique = highlights_sort(df_mumbai[(df_mumbai['latitude'] < df_mumbai['latitude'].quantile(0.35)) & (df_mumbai['longitude'] < df_mumbai['longitude'].quantile(0.75)) & (df_mumbai['longitude'] > df_mumbai['longitude'].quantile(0.25))]['highlights']).copy()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_not_mumbai = df_restaurants_copy[df_restaurants_copy['city']!='Mumbai'].drop_duplicates(keep=\"first\").copy()\ndf_not_mumbai.head(2)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"df_not_mumbai_unique = highlights_sort(df_not_mumbai['highlights']).copy()\ndf_not_mumbai_unique.head()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"val=\"\"\nfor var in df_mumbai_unique['highlights'].values:\n if var in df_not_mumbai_unique['highlights'].values: \n continue\n else: \n val = val + \", \" + var\n val = val[2:]\nif val ==\"\":\n val=\"None\"\nprint(\"Values exclusive to Mumbai are: \",val)",
"Values exclusive to Mumbai are: None\n"
],
[
"print(\"Thank you :)\")",
"Thank you :)\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown",
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50d933d2736a03ce62b5e83014f4b616996d461
| 4,336 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
test/async/test2.ipynb
|
ancient-data/text-fabric
|
c1ccd4a4dc451e94a789f138576576c5d7f13474
|
[
"MIT"
] | 10 |
2017-10-30T22:38:00.000Z
|
2018-12-12T06:10:10.000Z
|
test/async/test2.ipynb
|
ancient-data/text-fabric
|
c1ccd4a4dc451e94a789f138576576c5d7f13474
|
[
"MIT"
] | 37 |
2017-10-19T12:06:54.000Z
|
2018-12-13T10:18:23.000Z
|
test/async/test2.ipynb
|
ancient-data/text-fabric
|
c1ccd4a4dc451e94a789f138576576c5d7f13474
|
[
"MIT"
] | 3 |
2018-02-28T12:37:21.000Z
|
2018-06-23T08:32:54.000Z
| 21.15122 | 92 | 0.483625 |
[
[
[
"from tf.server.kernel import makeTfConnection\nfrom tf.applib.appmake import findAppConfig\nfrom tf.core.helpers import console",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"config = findAppConfig('bhsa')",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"TIMEOUT = 5",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"TF = makeTfConnection(config.host, config.port, TIMEOUT)\nkernelApi = TF.connect()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"querySlow = '''\np:phrase\n =: wFirst:word\n wLast:word\n :=\n\nwGap:word\nwFirst < wGap\nwLast > wGap\n\np || wGap\n\nv:verse\n\nv [[ wFirst\nv [[ wGap\n'''\n\nqueryFast = '''\nverse\n p:phrase\n wPreGap:word lex=L\n wLast:word\n :=\n\nwGap:word\nwPreGap <: wGap\nwGap < wLast\np || wGap\n'''",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def search(query):\n try:\n (results, messages) = kernelApi.rawSearch(query)\n except TimeoutError:\n messages = f'Aborted query because it takes longer than {TIMEOUT} seconds.'\n results = ()\n if messages:\n console(messages, error=True)\n else:\n console(f'{len(results)} results')\n return results",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"def search(query):\n results = kernelApi.rawSearch(query)\n console(f'{len(results)} results')\n return results",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"search(queryFast)",
"13 results\n"
],
[
"search(querySlow)",
"Aborted query because it takes longer than 5 seconds.\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50d949a698c691538b07ebccb90175e7df660d8
| 332,866 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
notebooks/k_nearest_neighbors.ipynb
|
Joshua-Robison/eCornell
|
5c4044b1a58074f9b88ce99efb408b1f346c19c4
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/k_nearest_neighbors.ipynb
|
Joshua-Robison/eCornell
|
5c4044b1a58074f9b88ce99efb408b1f346c19c4
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
notebooks/k_nearest_neighbors.ipynb
|
Joshua-Robison/eCornell
|
5c4044b1a58074f9b88ce99efb408b1f346c19c4
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 702.248945 | 72,654 | 0.945206 |
[
[
[
"# K Nearest Neighbors\n\nThis notebook uses scikit-learn's knn model to train classifiers to associate images of peoples' faces and images of handwritten digits.",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# import libraries\nimport numpy as np\nfrom scipy.io import loadmat\nfrom scipy.stats import mode\n\n%matplotlib inline\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# settings\nseed = 421\nnp.random.seed(seed)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"def loaddata(filename: str):\n \"\"\"This function returns X,y training and testing data from the given filename.\"\"\"\n data = loadmat(filename)\n X_train = data['xTr']\n y_train = np.round(data['yTr'])\n X_test = data['xTe']\n y_test = np.round(data['yTe'])\n \n return X_train.T, y_train.T, X_test.T, y_test.T",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test = loaddata('../data/faces.mat')\n\ndef plotdata(X, xdim=38, ydim=31):\n n, d = X.shape\n f, axes = plt.subplots(1, n, sharey=True)\n f.set_figwidth(10 * n)\n f.set_figheight(n)\n \n if n > 1:\n for i in range(n):\n axes[i].imshow(X[i,:].reshape(ydim, xdim).T, cmap=plt.cm.binary_r)\n else:\n axes.imshow(X[0,:].reshape(ydim, xdim).T, cmap=plt.cm.binary_r)\n\nplt.figure(figsize=(11,8))\nplotdata(X_train[:9,:])",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# get unique face labels\nprint(np.unique(y_train))",
"[ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24\n 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40]\n"
],
[
"def subsetdata(X, y, c):\n \"\"\"This function returns the X features for y == class c.\"\"\"\n mask = np.squeeze(y == c)\n sample = X[mask,:]\n \n return sample",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# test function\nsample = subsetdata(X_train, y_train, 35)\nplotdata(sample)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# import sklearn model\nfrom sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier\n\n# build and fit a k=1 nearest neighbor model\nclf = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=1).fit(X_train, y_train.ravel())",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# import scoring function\nfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score\n\n# get the performance on the test data\nscore = accuracy_score(y_test, clf.predict(X_test))\nprint('Accuracy score = {:.2%}'.format(score))",
"Accuracy score = 95.83%\n"
],
[
"# see performance for a few cases\nfor c in range(1, 40, 10):\n sample = subsetdata(X_test, y_test, c)\n preds = clf.predict(sample)\n print(f'Actual class = {c} Predictions = {preds}')\n plotdata(sample)",
"Actual class = 1 Predictions = [1 1 1]\nActual class = 11 Predictions = [11 11 11]\nActual class = 21 Predictions = [21 21 21]\nActual class = 31 Predictions = [31 31 31]\n"
]
],
[
[
"## Repeat the process with the digit data",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# load the training and testing sets\nX_train, y_train, X_test, y_test = loaddata('../data/digits.mat')\n\n# preview some samples\nplt.figure(figsize=(11,8))\nplotdata(X_train[:9,:], ydim=16, xdim=16)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# get the class labels\nprint(np.unique(y_train))",
"[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]\n"
],
[
"# preview '7' images\nsample = subsetdata(X_train, y_train, 7)\nplotdata(sample[:7], ydim=16, xdim=16)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"# make and fit an instance of a knn model with k=1\nclf = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=1).fit(X_train, y_train.ravel())\n\n# compute and print accuracy on test set\nscore = accuracy_score(y_test, clf.predict(X_test))\nprint('Accuracy score = {:.2%}'.format(score))",
"Accuracy score = 95.02%\n"
],
[
"# see performance\nfor c in range(0, 9, 4):\n sample = subsetdata(X_test, y_test, c)\n preds = clf.predict(sample)\n print(f'Actual class = {c} Predictions = {preds}')\n plotdata(sample[:5], ydim=16, xdim=16)",
"Actual class = 0 Predictions = [0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0\n 9 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0\n 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0\n 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 6 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0\n 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0\n 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 7 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0\n 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0\n 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0\n 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0\n 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]\nActual class = 4 Predictions = [4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 9 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4\n 4 4 4 4 5 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 9 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4\n 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 1 4 4 2 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 7 4 4 4 4 4 4\n 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 6\n 9 4 4 9 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 9 9 4 4 8 4 4 9 9 4 4 4 4 6\n 4 4 4 4 4 7 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4]\nActual class = 8 Predictions = [3 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 0 8 8 8 0 8 2 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 9 8 8 8 8\n 8 0 8 8 8 8 8 4 3 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 9 8 8 8 8 8 8 8\n 8 8 8 8 8 8 3 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 5 8 8 8 8 3 8 8 8 8 8 8\n 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 3 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8\n 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 9 0 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8]\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50d957c9720a17ad73d55fa24d063f896a0449d
| 33,776 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
example.ipynb
|
AlbertiPot/NAS-Bench-201
|
57a494007a41c7f032a3d4a0a08b8eb7765f0bc6
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
example.ipynb
|
AlbertiPot/NAS-Bench-201
|
57a494007a41c7f032a3d4a0a08b8eb7765f0bc6
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
example.ipynb
|
AlbertiPot/NAS-Bench-201
|
57a494007a41c7f032a3d4a0a08b8eb7765f0bc6
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 50.11276 | 399 | 0.476522 |
[
[
[
"from nas_201_api import NASBench201API as API\n\napi = API('./data/NAS-Bench-201-v1_1-096897.pth', verbose=False)",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"num = len(api)\nfor i, arch_str in enumerate(api):\n print ('{:5d}/{:5d} : {:}'.format(i, len(api), arch_str))\n if i ==5:\n break",
" 0/15625 : |avg_pool_3x3~0|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|skip_connect~2|\n 1/15625 : |nor_conv_3x3~0|+|nor_conv_3x3~0|avg_pool_3x3~1|+|skip_connect~0|nor_conv_3x3~1|skip_connect~2|\n 2/15625 : |avg_pool_3x3~0|+|nor_conv_3x3~0|nor_conv_3x3~1|+|avg_pool_3x3~0|avg_pool_3x3~1|avg_pool_3x3~2|\n 3/15625 : |avg_pool_3x3~0|+|skip_connect~0|none~1|+|none~0|none~1|skip_connect~2|\n 4/15625 : |skip_connect~0|+|skip_connect~0|nor_conv_1x1~1|+|skip_connect~0|skip_connect~1|nor_conv_1x1~2|\n 5/15625 : |nor_conv_1x1~0|+|skip_connect~0|nor_conv_1x1~1|+|nor_conv_3x3~0|none~1|avg_pool_3x3~2|\n"
],
[
"# show all information for a specific architecture\nindex = 5\napi.show(index)",
">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 012 epochs >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>\n|nor_conv_1x1~0|+|skip_connect~0|nor_conv_1x1~1|+|nor_conv_3x3~0|none~1|avg_pool_3x3~2|\ndatasets : ['cifar10-valid', 'cifar10', 'cifar100', 'ImageNet16-120'], extra-info : None\ncifar10-valid FLOP= 51.04 M, Params=0.372 MB, latency=17.48 ms.\ncifar10-valid train : [loss = 0.682, top1 = 75.70%], valid : [loss = 0.756, top1 = 73.58%]\ncifar10 FLOP= 51.04 M, Params=0.372 MB, latency=17.48 ms.\ncifar10 train : [loss = 0.528, top1 = 81.56%], test : [loss = 0.588, top1 = 79.54%]\ncifar100 FLOP= 51.04 M, Params=0.378 MB, latency=16.61 ms.\ncifar100 train : [loss = 1.986, top1 = 46.21%], valid : [loss = 2.079, top1 = 43.98%], test : [loss = 2.104, top1 = 43.70%]\nImageNet16-120 FLOP= 12.77 M, Params=0.379 MB, latency=15.98 ms.\nImageNet16-120 train : [loss = 3.002, top1 = 26.04%], valid : [loss = 3.026, top1 = 26.50%], test : [loss = 3.049, top1 = 25.63%]\n>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 200 epochs >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>\n|nor_conv_1x1~0|+|skip_connect~0|nor_conv_1x1~1|+|nor_conv_3x3~0|none~1|avg_pool_3x3~2|\ndatasets : ['cifar10-valid', 'cifar10', 'cifar100', 'ImageNet16-120'], extra-info : None\ncifar10-valid FLOP= 51.04 M, Params=0.372 MB, latency=17.48 ms.\ncifar10-valid train : [loss = 0.005, top1 = 99.95%], valid : [loss = 0.575, top1 = 87.81%]\ncifar10 FLOP= 51.04 M, Params=0.372 MB, latency=17.48 ms.\ncifar10 train : [loss = 0.010, top1 = 99.81%], test : [loss = 0.391, top1 = 91.09%]\ncifar100 FLOP= 51.04 M, Params=0.378 MB, latency=16.61 ms.\ncifar100 train : [loss = 0.182, top1 = 95.89%], valid : [loss = 1.496, top1 = 66.23%], test : [loss = 1.484, top1 = 66.30%]\nImageNet16-120 FLOP= 12.77 M, Params=0.379 MB, latency=15.98 ms.\nImageNet16-120 train : [loss = 2.062, top1 = 46.21%], valid : [loss = 2.472, top1 = 37.88%], test : [loss = 2.499, top1 = 38.74%]\n<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<------------<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<\n"
],
[
"# show the mean loss and accuracy of an architecture\ninfo = api.query_meta_info_by_index(index, '200') # This is an instance of `ArchResults`\n# res_metrics = info.get_metrics('cifar10', 'train') # This is a dict with metric names as keys\ncost_metrics_cifar10 = info.get_compute_costs('cifar10')\ncost_metrics_cifar100 = info.get_compute_costs('cifar100') # This is a dict with metric names as keys, e.g., flops, params, latency\ncost_metrics_imagenet16 = info.get_compute_costs('ImageNet16-120')\nprint(cost_metrics_cifar10)\nprint(cost_metrics_cifar100)\nprint(cost_metrics_imagenet16)",
"{'flops': 51.03681, 'params': 0.372346, 'latency': 0.017475859114998264, 'T-train@epoch': 19.92486000061035, 'T-train@total': 3984.9720001220703, 'T-ori-test@epoch': 1.2974819569360643, 'T-ori-test@total': 259.49639138721284}\n{'flops': 51.04265999999999, 'params': 0.378196, 'latency': 0.016608317693074543, 'T-train@epoch': 19.92486000061035, 'T-train@total': 3984.9720001220703, 'T-ori-test@epoch': 1.2974819569360643, 'T-ori-test@total': 259.49639138721284, 'T-x-valid@epoch': 0.6487409784680321, 'T-x-valid@total': 129.74819569360642, 'T-x-test@epoch': 0.6487409784680321, 'T-x-test@total': 129.74819569360642}\n{'flops': 12.76684, 'params': 0.379496, 'latency': 0.01598209540049235, 'T-train@epoch': 60.45202524185183, 'T-train@total': 12090.405048370367, 'T-ori-test@epoch': 0.7784891741616385, 'T-ori-test@total': 155.69783483232771, 'T-x-valid@epoch': 0.38924458708081927, 'T-x-valid@total': 77.84891741616386, 'T-x-test@epoch': 0.38924458708081927, 'T-x-test@total': 77.84891741616386}\n"
],
[
"# get the detailed information\nresults = api.query_by_index(0, 'cifar10','200') # a dict of all trials for 1st net on cifar100, where the key is the seed\nprint ('There are {:} trials for this architecture [{:}] on cifar100'.format(len(results), api[0]))\nfor seed, result in results.items():\n print ('Latency : {:}'.format(result.get_latency()))\n print ('Train Info : {:}'.format(result.get_train()))\n# print ('Valid Info : {:}'.format(result.get_eval('x-valid')))\n# print ('Test Info : {:}'.format(result.get_eval('x-test')))\n # for the metric after a specific epoch\n print ('Train Info [10-th epoch] : {:}'.format(result.get_train(10)))",
"There are 3 trials for this architecture [|avg_pool_3x3~0|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|skip_connect~2|] on cifar100\nLatency : 0.0139359758611311\nTrain Info : {'iepoch': 199, 'loss': 0.27533122161865237, 'accuracy': 90.446, 'cur_time': 14.442185997962952, 'all_time': 2888.4371995925903}\nTrain Info [10-th epoch] : {'iepoch': 10, 'loss': 1.0130011839294433, 'accuracy': 63.858, 'cur_time': 14.442185997962952, 'all_time': 158.86404597759247}\nLatency : 0.0139359758611311\nTrain Info : {'iepoch': 199, 'loss': 0.27072189832687377, 'accuracy': 90.74, 'cur_time': 14.442185997962952, 'all_time': 2888.4371995925903}\nTrain Info [10-th epoch] : {'iepoch': 10, 'loss': 1.0328740346527099, 'accuracy': 62.964, 'cur_time': 14.442185997962952, 'all_time': 158.86404597759247}\nLatency : 0.0139359758611311\nTrain Info : {'iepoch': 199, 'loss': 0.26770111352920534, 'accuracy': 90.82, 'cur_time': 14.442185997962952, 'all_time': 2888.4371995925903}\nTrain Info [10-th epoch] : {'iepoch': 10, 'loss': 1.0447258094978333, 'accuracy': 62.606, 'cur_time': 14.442185997962952, 'all_time': 158.86404597759247}\n"
],
[
"index = api.query_index_by_arch('|avg_pool_3x3~0|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|skip_connect~2|')\nprint(index)\napi.show(index)",
"0\n>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 012 epochs >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>\n|avg_pool_3x3~0|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|skip_connect~2|\ndatasets : ['cifar10-valid', 'cifar10', 'cifar100', 'ImageNet16-120'], extra-info : None\ncifar10-valid FLOP= 15.65 M, Params=0.129 MB, latency=13.94 ms.\ncifar10-valid train : [loss = 0.990, top1 = 64.45%], valid : [loss = 1.034, top1 = 63.36%]\ncifar10 FLOP= 15.65 M, Params=0.129 MB, latency=13.94 ms.\ncifar10 train : [loss = 0.818, top1 = 71.08%], test : [loss = 0.865, top1 = 69.55%]\ncifar100 FLOP= 15.65 M, Params=0.135 MB, latency=13.18 ms.\ncifar100 train : [loss = 2.588, top1 = 33.09%], valid : [loss = 2.654, top1 = 31.84%], test : [loss = 2.656, top1 = 31.26%]\nImageNet16-120 FLOP= 3.92 M, Params=0.136 MB, latency=12.98 ms.\nImageNet16-120 train : [loss = 3.479, top1 = 17.66%], valid : [loss = 3.427, top1 = 18.47%], test : [loss = 3.475, top1 = 17.00%]\n>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 200 epochs >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>\n|avg_pool_3x3~0|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|skip_connect~2|\ndatasets : ['cifar10-valid', 'cifar10', 'cifar100', 'ImageNet16-120'], extra-info : None\ncifar10-valid FLOP= 15.65 M, Params=0.129 MB, latency=13.94 ms.\ncifar10-valid train : [loss = 0.319, top1 = 88.92%], valid : [loss = 0.566, top1 = 81.98%]\ncifar10 FLOP= 15.65 M, Params=0.129 MB, latency=13.94 ms.\ncifar10 train : [loss = 0.271, top1 = 90.67%], test : [loss = 0.430, top1 = 85.86%]\ncifar100 FLOP= 15.65 M, Params=0.135 MB, latency=13.18 ms.\ncifar100 train : [loss = 1.511, top1 = 57.73%], valid : [loss = 1.742, top1 = 52.70%], test : [loss = 1.736, top1 = 52.91%]\nImageNet16-120 FLOP= 3.92 M, Params=0.136 MB, latency=12.98 ms.\nImageNet16-120 train : [loss = 2.925, top1 = 28.14%], valid : [loss = 2.944, top1 = 28.21%], test : [loss = 2.989, top1 = 26.63%]\n<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<------------<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<\n"
],
[
"config = api.get_net_config(0, 'cifar10') # obtain the network configuration for the 123-th architecture on the CIFAR-10 dataset\nprint(config)\nfrom xautodl.models import get_cell_based_tiny_net # this module is in ./models\nnetwork = get_cell_based_tiny_net(config) # create the network from configurration\nprint(network) # show the structure of this architecture\nprint(type(network))",
"{'name': 'infer.tiny', 'C': 16, 'N': 5, 'arch_str': '|avg_pool_3x3~0|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|skip_connect~2|', 'num_classes': 10}\nTinyNetwork(\n TinyNetwork(C=16, N=5, L=17)\n (stem): Sequential(\n (0): Conv2d(3, 16, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (1): BatchNorm2d(16, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n (cells): ModuleList(\n (0): InferCell(\n info :: nodes=4, inC=16, outC=16, [1<-(I0-L0) | 2<-(I0-L1,I1-L2) | 3<-(I0-L3,I1-L4,I2-L5)], |avg_pool_3x3~0|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|skip_connect~2|\n (layers): ModuleList(\n (0): POOLING(\n (op): AvgPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)\n )\n (1): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(16, 16, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(16, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (2): Identity()\n (3): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(16, 16, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(16, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (4): Identity()\n (5): Identity()\n )\n )\n (1): InferCell(\n info :: nodes=4, inC=16, outC=16, [1<-(I0-L0) | 2<-(I0-L1,I1-L2) | 3<-(I0-L3,I1-L4,I2-L5)], |avg_pool_3x3~0|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|skip_connect~2|\n (layers): ModuleList(\n (0): POOLING(\n (op): AvgPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)\n )\n (1): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(16, 16, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(16, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (2): Identity()\n (3): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(16, 16, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(16, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (4): Identity()\n (5): Identity()\n )\n )\n (2): InferCell(\n info :: nodes=4, inC=16, outC=16, [1<-(I0-L0) | 2<-(I0-L1,I1-L2) | 3<-(I0-L3,I1-L4,I2-L5)], |avg_pool_3x3~0|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|skip_connect~2|\n (layers): ModuleList(\n (0): POOLING(\n (op): AvgPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)\n )\n (1): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(16, 16, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(16, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (2): Identity()\n (3): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(16, 16, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(16, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (4): Identity()\n (5): Identity()\n )\n )\n (3): InferCell(\n info :: nodes=4, inC=16, outC=16, [1<-(I0-L0) | 2<-(I0-L1,I1-L2) | 3<-(I0-L3,I1-L4,I2-L5)], |avg_pool_3x3~0|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|skip_connect~2|\n (layers): ModuleList(\n (0): POOLING(\n (op): AvgPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)\n )\n (1): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(16, 16, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(16, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (2): Identity()\n (3): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(16, 16, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(16, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (4): Identity()\n (5): Identity()\n )\n )\n (4): InferCell(\n info :: nodes=4, inC=16, outC=16, [1<-(I0-L0) | 2<-(I0-L1,I1-L2) | 3<-(I0-L3,I1-L4,I2-L5)], |avg_pool_3x3~0|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|skip_connect~2|\n (layers): ModuleList(\n (0): POOLING(\n (op): AvgPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)\n )\n (1): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(16, 16, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(16, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (2): Identity()\n (3): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(16, 16, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(16, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (4): Identity()\n (5): Identity()\n )\n )\n (5): ResNetBasicblock(\n ResNetBasicblock(inC=16, outC=32, stride=2)\n (conv_a): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(16, 32, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (conv_b): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(32, 32, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (downsample): Sequential(\n (0): AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0)\n (1): Conv2d(16, 32, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)\n )\n )\n (6): InferCell(\n info :: nodes=4, inC=32, outC=32, [1<-(I0-L0) | 2<-(I0-L1,I1-L2) | 3<-(I0-L3,I1-L4,I2-L5)], |avg_pool_3x3~0|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|skip_connect~2|\n (layers): ModuleList(\n (0): POOLING(\n (op): AvgPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)\n )\n (1): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(32, 32, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (2): Identity()\n (3): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(32, 32, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (4): Identity()\n (5): Identity()\n )\n )\n (7): InferCell(\n info :: nodes=4, inC=32, outC=32, [1<-(I0-L0) | 2<-(I0-L1,I1-L2) | 3<-(I0-L3,I1-L4,I2-L5)], |avg_pool_3x3~0|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|skip_connect~2|\n (layers): ModuleList(\n (0): POOLING(\n (op): AvgPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)\n )\n (1): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(32, 32, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (2): Identity()\n (3): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(32, 32, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (4): Identity()\n (5): Identity()\n )\n )\n (8): InferCell(\n info :: nodes=4, inC=32, outC=32, [1<-(I0-L0) | 2<-(I0-L1,I1-L2) | 3<-(I0-L3,I1-L4,I2-L5)], |avg_pool_3x3~0|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|skip_connect~2|\n (layers): ModuleList(\n (0): POOLING(\n (op): AvgPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)\n )\n (1): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(32, 32, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (2): Identity()\n (3): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(32, 32, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (4): Identity()\n (5): Identity()\n )\n )\n (9): InferCell(\n info :: nodes=4, inC=32, outC=32, [1<-(I0-L0) | 2<-(I0-L1,I1-L2) | 3<-(I0-L3,I1-L4,I2-L5)], |avg_pool_3x3~0|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|skip_connect~2|\n (layers): ModuleList(\n (0): POOLING(\n (op): AvgPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)\n )\n (1): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(32, 32, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (2): Identity()\n (3): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(32, 32, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (4): Identity()\n (5): Identity()\n )\n )\n (10): InferCell(\n info :: nodes=4, inC=32, outC=32, [1<-(I0-L0) | 2<-(I0-L1,I1-L2) | 3<-(I0-L3,I1-L4,I2-L5)], |avg_pool_3x3~0|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|skip_connect~2|\n (layers): ModuleList(\n (0): POOLING(\n (op): AvgPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)\n )\n (1): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(32, 32, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (2): Identity()\n (3): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(32, 32, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (4): Identity()\n (5): Identity()\n )\n )\n (11): ResNetBasicblock(\n ResNetBasicblock(inC=32, outC=64, stride=2)\n (conv_a): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (conv_b): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (downsample): Sequential(\n (0): AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0)\n (1): Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)\n )\n )\n (12): InferCell(\n info :: nodes=4, inC=64, outC=64, [1<-(I0-L0) | 2<-(I0-L1,I1-L2) | 3<-(I0-L3,I1-L4,I2-L5)], |avg_pool_3x3~0|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|skip_connect~2|\n (layers): ModuleList(\n (0): POOLING(\n (op): AvgPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)\n )\n (1): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (2): Identity()\n (3): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (4): Identity()\n (5): Identity()\n )\n )\n (13): InferCell(\n info :: nodes=4, inC=64, outC=64, [1<-(I0-L0) | 2<-(I0-L1,I1-L2) | 3<-(I0-L3,I1-L4,I2-L5)], |avg_pool_3x3~0|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|skip_connect~2|\n (layers): ModuleList(\n (0): POOLING(\n (op): AvgPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)\n )\n (1): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (2): Identity()\n (3): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (4): Identity()\n (5): Identity()\n )\n )\n (14): InferCell(\n info :: nodes=4, inC=64, outC=64, [1<-(I0-L0) | 2<-(I0-L1,I1-L2) | 3<-(I0-L3,I1-L4,I2-L5)], |avg_pool_3x3~0|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|skip_connect~2|\n (layers): ModuleList(\n (0): POOLING(\n (op): AvgPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)\n )\n (1): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (2): Identity()\n (3): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (4): Identity()\n (5): Identity()\n )\n )\n (15): InferCell(\n info :: nodes=4, inC=64, outC=64, [1<-(I0-L0) | 2<-(I0-L1,I1-L2) | 3<-(I0-L3,I1-L4,I2-L5)], |avg_pool_3x3~0|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|skip_connect~2|\n (layers): ModuleList(\n (0): POOLING(\n (op): AvgPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)\n )\n (1): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (2): Identity()\n (3): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (4): Identity()\n (5): Identity()\n )\n )\n (16): InferCell(\n info :: nodes=4, inC=64, outC=64, [1<-(I0-L0) | 2<-(I0-L1,I1-L2) | 3<-(I0-L3,I1-L4,I2-L5)], |avg_pool_3x3~0|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|+|nor_conv_1x1~0|skip_connect~1|skip_connect~2|\n (layers): ModuleList(\n (0): POOLING(\n (op): AvgPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)\n )\n (1): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (2): Identity()\n (3): ReLUConvBN(\n (op): Sequential(\n (0): ReLU()\n (1): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)\n (2): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n )\n )\n (4): Identity()\n (5): Identity()\n )\n )\n )\n (lastact): Sequential(\n (0): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)\n (1): ReLU(inplace=True)\n )\n (global_pooling): AdaptiveAvgPool2d(output_size=1)\n (classifier): Linear(in_features=64, out_features=10, bias=True)\n)\n<class 'xautodl.models.cell_infers.tiny_network.TinyNetwork'>\n"
]
]
] |
[
"code"
] |
[
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
c50db35be1c44581c67f4c9b7b3a326457c6994b
| 6,115 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
Deep_Learning_with_TensorFlow/1.4.0/Chapter10/3. Keras-CNN.ipynb
|
Asurada2015/TensorFlow_Google_Practice
|
0ea7d52a4056e5e53391a452a9bbd468175af7f5
|
[
"MIT"
] | 14 |
2018-03-07T00:44:25.000Z
|
2019-08-25T03:06:58.000Z
|
Deep_Learning_with_TensorFlow/1.4.0/Chapter10/3. Keras-CNN.ipynb
|
Asurada2015/TensorFlow_Google_Practice
|
0ea7d52a4056e5e53391a452a9bbd468175af7f5
|
[
"MIT"
] | 1 |
2018-10-15T12:04:05.000Z
|
2018-10-15T12:04:05.000Z
|
Deep_Learning_with_TensorFlow/1.4.0/Chapter10/3. Keras-CNN.ipynb
|
Asurada2015/TensorFlow_Google_Practice
|
0ea7d52a4056e5e53391a452a9bbd468175af7f5
|
[
"MIT"
] | 10 |
2018-05-20T10:46:56.000Z
|
2020-04-17T11:50:40.000Z
| 31.520619 | 137 | 0.528046 |
[
[
[
"### 1. 数据预处理",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import keras\nfrom keras.datasets import mnist\nfrom keras.models import Sequential\nfrom keras.layers import Dense, Flatten, Conv2D, MaxPooling2D\nfrom keras import backend as K\n\nnum_classes = 10\nimg_rows, img_cols = 28, 28\n \n# 通过Keras封装好的API加载MNIST数据。其中trainX就是一个60000 * 28 * 28的数组,\n# trainY是每一张图片对应的数字。\n(trainX, trainY), (testX, testY) = mnist.load_data()\n\n# 根据对图像编码的格式要求来设置输入层的格式。\nif K.image_data_format() == 'channels_first':\n trainX = trainX.reshape(trainX.shape[0], 1, img_rows, img_cols)\n testX = testX.reshape(testX.shape[0], 1, img_rows, img_cols)\n input_shape = (1, img_rows, img_cols)\nelse:\n trainX = trainX.reshape(trainX.shape[0], img_rows, img_cols, 1)\n testX = testX.reshape(testX.shape[0], img_rows, img_cols, 1)\n input_shape = (img_rows, img_cols, 1)\n \ntrainX = trainX.astype('float32')\ntestX = testX.astype('float32')\ntrainX /= 255.0\ntestX /= 255.0\n \n# 将标准答案转化为需要的格式(one-hot编码)。\ntrainY = keras.utils.to_categorical(trainY, num_classes)\ntestY = keras.utils.to_categorical(testY, num_classes)",
"Using TensorFlow backend.\n"
]
],
[
[
"### 2. 通过Keras的API定义卷机神经网络。",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"# 使用Keras API定义模型。\nmodel = Sequential()\nmodel.add(Conv2D(32, kernel_size=(5, 5), activation='relu', input_shape=input_shape))\nmodel.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))\nmodel.add(Conv2D(64, (5, 5), activation='relu'))\nmodel.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))\nmodel.add(Flatten())\nmodel.add(Dense(500, activation='relu'))\nmodel.add(Dense(num_classes, activation='softmax'))\n \n# 定义损失函数、优化函数和评测方法。\nmodel.compile(loss=keras.losses.categorical_crossentropy,\n optimizer=keras.optimizers.SGD(),\n metrics=['accuracy'])",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"### 3. 通过Keras的API训练模型并计算在测试数据上的准确率。",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"model.fit(trainX, trainY,\n batch_size=128,\n epochs=10,\n validation_data=(testX, testY))\n \n# 在测试数据上计算准确率。\nscore = model.evaluate(testX, testY)\nprint('Test loss:', score[0])\nprint('Test accuracy:', score[1])",
"Train on 60000 samples, validate on 10000 samples\nEpoch 1/10\n60000/60000 [==============================] - 183s 3ms/step - loss: 1.0468 - acc: 0.7266 - val_loss: 0.3387 - val_acc: 0.8909\nEpoch 2/10\n60000/60000 [==============================] - 189s 3ms/step - loss: 0.2722 - acc: 0.9181 - val_loss: 0.2052 - val_acc: 0.9397\nEpoch 3/10\n60000/60000 [==============================] - 192s 3ms/step - loss: 0.1915 - acc: 0.9428 - val_loss: 0.1493 - val_acc: 0.9556\nEpoch 4/10\n60000/60000 [==============================] - 191s 3ms/step - loss: 0.1498 - acc: 0.9559 - val_loss: 0.1152 - val_acc: 0.9677\nEpoch 5/10\n60000/60000 [==============================] - 189s 3ms/step - loss: 0.1229 - acc: 0.9638 - val_loss: 0.1147 - val_acc: 0.9663\nEpoch 6/10\n60000/60000 [==============================] - 212s 4ms/step - loss: 0.1055 - acc: 0.9683 - val_loss: 0.0835 - val_acc: 0.9765\nEpoch 7/10\n60000/60000 [==============================] - 277s 5ms/step - loss: 0.0934 - acc: 0.9720 - val_loss: 0.0803 - val_acc: 0.9748\nEpoch 8/10\n60000/60000 [==============================] - 260s 4ms/step - loss: 0.0838 - acc: 0.9749 - val_loss: 0.0747 - val_acc: 0.9781\nEpoch 9/10\n60000/60000 [==============================] - 247s 4ms/step - loss: 0.0765 - acc: 0.9767 - val_loss: 0.0693 - val_acc: 0.9788\nEpoch 10/10\n60000/60000 [==============================] - 242s 4ms/step - loss: 0.0711 - acc: 0.9788 - val_loss: 0.0659 - val_acc: 0.9804\n10000/10000 [==============================] - 19s 2ms/step\n('Test loss:', 0.065869684981741006)\n('Test accuracy:', 0.98040000000000005)\n"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code",
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
],
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code"
]
] |
c50db3d54a8d0236efdb0cad08f6a6f2011d253c
| 80,596 |
ipynb
|
Jupyter Notebook
|
code/Overfitting vs Underfitting.ipynb
|
zeran4/justdoit
|
00ba46262f1fd636d9fde15812e341d73ced41ae
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
code/Overfitting vs Underfitting.ipynb
|
zeran4/justdoit
|
00ba46262f1fd636d9fde15812e341d73ced41ae
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null |
code/Overfitting vs Underfitting.ipynb
|
zeran4/justdoit
|
00ba46262f1fd636d9fde15812e341d73ced41ae
|
[
"MIT"
] | null | null | null | 634.614173 | 77,210 | 0.929041 |
[
[
[
"# Overfitting vs Underfitting\n## From Sklearn \nhttp://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/model_selection/plot_underfitting_overfitting.html\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
],
[
[
"import numpy as np\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nfrom sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline\nfrom sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures\nfrom sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression\nfrom sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"np.random.seed(0)\n\nn_samples = 30\ndegrees = [1, 4, 15]\n\ntrue_fun = lambda X: np.cos(1.5 * np.pi * X)\nX = np.sort(np.random.rand(n_samples))\ny = true_fun(X) + np.random.randn(n_samples) * 0.1\n",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\nplt.figure(figsize=(14, 5))\nfor i in range(len(degrees)):\n ax = plt.subplot(1, len(degrees), i + 1)\n plt.setp(ax, xticks=(), yticks=())\n\n polynomial_features = PolynomialFeatures(degree=degrees[i],\n include_bias=False)\n linear_regression = LinearRegression()\n pipeline = Pipeline([(\"polynomial_features\", polynomial_features),\n (\"linear_regression\", linear_regression)])\n pipeline.fit(X[:, np.newaxis], y)\n\n # Evaluate the models using crossvalidation\n scores = cross_val_score(pipeline, X[:, np.newaxis], y,\n scoring=\"neg_mean_squared_error\", cv=10)\n\n X_test = np.linspace(0, 1, 100)\n plt.plot(X_test, pipeline.predict(X_test[:, np.newaxis]), label=\"Model\")\n plt.plot(X_test, true_fun(X_test), label=\"True function\")\n plt.scatter(X, y, label=\"Samples\")\n plt.xlabel(\"x\")\n plt.ylabel(\"y\")\n plt.xlim((0, 1))\n plt.ylim((-2, 2))\n plt.legend(loc=\"best\")\n plt.title(\"Degree {}\\nMSE = {:.2e}(+/- {:.2e})\".format(\n degrees[i], -scores.mean(), scores.std()))\nplt.show()",
"_____no_output_____"
],
[
"\n",
"_____no_output_____"
]
]
] |
[
"markdown",
"code"
] |
[
[
"markdown"
],
[
"code",
"code",
"code",
"code"
]
] |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.