question_slug
stringlengths 3
77
| title
stringlengths 1
183
| slug
stringlengths 12
45
| summary
stringlengths 1
160
⌀ | author
stringlengths 2
30
| certification
stringclasses 2
values | created_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| updated_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| hit_count
int64 0
10.6M
| has_video
bool 2
classes | content
stringlengths 4
576k
| upvotes
int64 0
11.5k
| downvotes
int64 0
358
| tags
stringlengths 2
193
| comments
int64 0
2.56k
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
maximum-difference-between-increasing-elements
|
Simple C program
|
simple-c-program-by-pavithrav25-huk6
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
pavithrav25
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-01T05:13:22.082322+00:00
|
2025-01-01T05:13:22.082322+00:00
| 21 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```c []
int maximumDifference(int* nums, int numsSize) {
int maxd=-1,minval;
for(int i=0;i<numsSize-1;i++){
for(int j=i+1;j<numsSize;j++){
if(nums[i]<nums[j]){
minval=nums[j]-nums[i];
if(minval>maxd){
maxd=minval;
}}
}}
return maxd;
}
```
| 1 | 0 |
['C']
| 0 |
maximum-difference-between-increasing-elements
|
Maximum Difference Between Increasing Elements
|
maximum-difference-between-increasing-el-3hfw
|
Intuition\nThe problem requires finding the maximum difference between two elements in an array nums such that the larger element comes after the smaller elemen
|
tejdekiwadiya
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-01T11:47:46.906302+00:00
|
2024-12-01T11:47:46.906327+00:00
| 245 | false |
# Intuition\nThe problem requires finding the maximum difference between two elements in an array `nums` such that the larger element comes after the smaller element. The brute force approach naturally comes to mind\u2014comparing all pairs of elements to check the difference and updating the maximum difference whenever a larger one is found.\n\n# Approach\n1. Initialize `ans` to `-1` to store the maximum difference. If no valid pair is found, return `-1`.\n2. Iterate through the array with two nested loops:\n - The outer loop picks the first element `nums[i]`.\n - The inner loop picks a second element `nums[j]` where ( j > i ).\n3. For each pair:\n - Check if `nums[j] > nums[i]` (to satisfy the condition that the larger element comes after the smaller one).\n - If true, calculate the difference `nums[j] - nums[i]`.\n - Update `ans` if this difference is greater than the current value of `ans`.\n4. After iterating through all pairs, return the value of `ans`.\n\n# Complexity\n\n- **Time Complexity**: \n The nested loops result in a time complexity of ( O(n^2) ), where ( n ) is the length of the input array. Each element in the array is compared with every subsequent element.\n\n- **Space Complexity**: \n The space complexity is ( O(1) ) because no additional data structures are used. Only a single variable `ans` is maintained to store the result.\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumDifference(int[] nums) {\n int ans = -1;\n for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {\n for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++) {\n if (nums[j] > nums[i] && ans < nums[j] - nums[i]) {\n ans = nums[j] - nums[i];\n }\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Java']
| 0 |
maximum-difference-between-increasing-elements
|
o(n) TC o(1) SC easy python solution 99.89 % acceptance
|
on-tc-o1-sc-easy-python-solution-9989-ac-co0u
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n Describe your appr
|
bhavanabharatisingh
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-20T11:49:34.377028+00:00
|
2024-10-20T11:50:38.366485+00:00
| 20 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n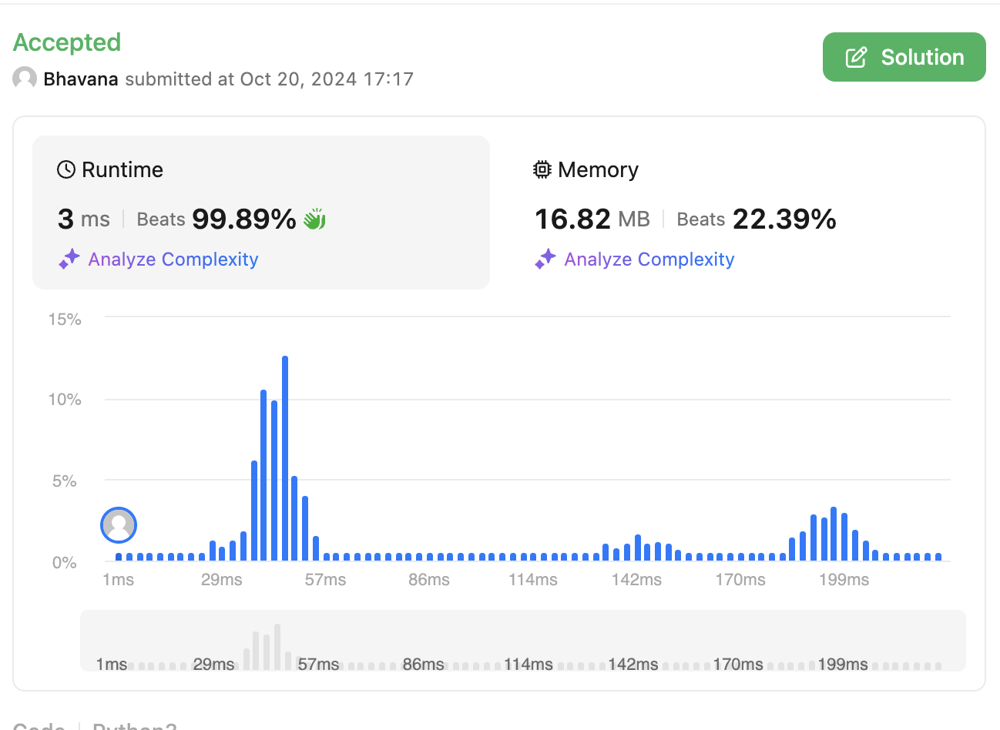\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n- we will consider every upcoming element as greater and will try to find out the difference with the minimum element .\n- Will comapre the result if max then will update \n- we will update the minimum element as well. because current element might be the smallest\n- If final result is 0 then we will return -1 \n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def maximumDifference(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n max_diff = 0\n min_ele = nums[0]\n for i in range(0, len(nums)):\n max_diff = max(max_diff, nums[i]- min_ele)\n min_ele = min(min_ele, nums[i])\n if max_diff == 0:\n return -1\n return max_diff\n\n \n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
maximum-difference-between-increasing-elements
|
max solution js
|
max-solution-js-by-joelll-ey60
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Joelll
|
NORMAL
|
2024-08-07T04:57:17.519189+00:00
|
2024-08-07T04:57:17.519212+00:00
| 18 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\n/**\n * @param {number[]} nums\n * @return {number}\n */\nvar maximumDifference = function(nums) {\n let minVal = nums[0]\n let maxDiff = -1\n\n for (let j = 1; j < nums.length; j++) {\n if (nums[j] > minVal) {\n maxDiff = Math.max(maxDiff, nums[j] - minVal)\n } else {\n minVal = nums[j]\n }\n }\n\n return maxDiff\n}\n// console.log(maximumDifference([7,1,5,4]))\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
maximum-difference-between-increasing-elements
|
one-pass
|
one-pass-by-user5285zn-ngcp
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
user5285Zn
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-30T13:01:30.540566+00:00
|
2024-07-30T13:01:30.540602+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nimpl Solution {\n pub fn maximum_difference(nums: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {\n let r = nums[1..].into_iter()\n .fold(\n (0, nums[0]), |(b, x), &y| (b.max(y-x), x.min(y))).0;\n if r == 0 {-1} else {r}\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Rust']
| 0 |
maximum-difference-between-increasing-elements
|
Similar to 121. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock
|
similar-to-121-best-time-to-buy-and-sell-835f
|
C++ || 100 BEAT || 100% EFFICIENT\uD83D\uDD25|| OPTIMAL SOLUTION || EASY TO UNDERSTAND ||\n\n- In Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock is that we don\'t need to retu
|
sonalit848
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-01T19:03:41.296936+00:00
|
2024-07-01T19:03:41.296964+00:00
| 155 | false |
# C++ || 100 BEAT || 100% EFFICIENT\uD83D\uDD25|| OPTIMAL SOLUTION || EASY TO UNDERSTAND ||\n\n- In Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock is that we don\'t need to return -1 if no profit can be made.\n# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n- The problem requires finding the maximum difference between two elements in the nums array such that the larger element appears after the smaller element. Essentially, we\'re looking for the maximum nums[j] - nums[i] where j > i.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n### Initialization:\n\n- max_diff is initialized to the first element of the array (nums[0]). This variable keeps track of the minimum value encountered so far.\nans is initialized to 0. This variable will store the maximum difference found.\n### Iterate through the array:\n\n- The for loop iterates through each element in the nums array.\n### In each iteration:\n- Update max_diff: max_diff is updated to be the minimum of the current max_diff and the current element (nums[i]). This ensures max_diff always holds the smallest value encountered up to the current index.\n- Update ans: ans is updated to be the maximum of the current ans and the difference between the current element and max_diff (nums[i] - max_diff). This calculates the potential maximum difference if the current element is considered as the selling price and max_diff as the buying price.\nReturn the Result:\n\n- After the loop, the function checks if ans is 0. If it is, it means no valid pair was found that satisfies the condition (i.e., no element was greater than any previous element). In this case, the function returns -1.\nOtherwise, it returns ans, which contains the maximum difference.\n# Return the Result:\n- After the loop, the function checks if ans is 0. If it is, it means no valid pair was found that satisfies the condition (i.e., no element was greater than any previous element). In this case, the function returns -1.\n- Otherwise, it returns ans, which contains the maximum difference.\n# Complexity\nTime complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n- The algorithm iterates through the nums array exactly once. Each iteration consists of constant-time operations (comparing and updating max_diff and ans). Therefore, the time complexity is linear, O(n), where n is the number of elements in the nums array.\n\nSpace complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n- The algorithm uses a constant amount of additional space (two integer variables max_diff and ans), regardless of the size of the input array. Therefore, the space complexity is constant, O(1).\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximumDifference(vector<int>& nums) {\n int max_diff=nums[0];\n int ans=0;\n for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){\n max_diff=min(max_diff,nums[i]);\n ans=max(ans,nums[i]-max_diff);\n }\n return (ans==0)?-1:ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 1 |
maximum-difference-between-increasing-elements
|
Easy Js Solution 😍🗝️
|
easy-js-solution-by-peermohammad-fn52
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
peermohammad
|
NORMAL
|
2024-06-13T06:36:27.764821+00:00
|
2024-06-13T06:36:27.764847+00:00
| 32 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\n/**\n * @param {number[]} nums\n * @return {number}\n */\nvar maximumDifference = function(nums) {\n let max = -1;\n for(let i=0;i<nums.length;i++){\n for(let j=i+1;j<nums.length;j++){\n if(nums[i] < nums[j]&&i < j && nums[j]-nums[i]>max){\n max = nums[j]-nums[i]\n }\n }\n }\n return max\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
maximum-difference-between-increasing-elements
|
solution with image||c++||java||easy solution||
|
solution-with-imagecjavaeasy-solution-by-vfan
|
\n\n# Code\n\nint maximumDifference(int* nums, int numsSize) {\n int dmax = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++) {\n for (int j = i + 1; j < num
|
ANKITBI1713
|
NORMAL
|
2024-03-08T14:53:56.431379+00:00
|
2024-03-08T14:53:56.431398+00:00
| 548 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```\nint maximumDifference(int* nums, int numsSize) {\n int dmax = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++) {\n for (int j = i + 1; j < numsSize; j++) {\n int diff = nums[j] - nums[i];\n if (diff > dmax) {\n dmax = diff;\n }\n }\n }\n if (dmax == 0) {\n return -1; \n } else {\n return dmax;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'C', 'C++', 'Java', 'JavaScript']
| 2 |
maximum-difference-between-increasing-elements
|
Easy solutions, beginner friendly (97 % beats rate)
|
easy-solutions-beginner-friendly-97-beat-4k90
|
Intuition\n- We aim to find the maximum difference between two elements in the array, satisfying the given conditions.\n- To find the maximum difference, we nee
|
abu_suraj
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-02T15:41:13.788024+00:00
|
2024-02-02T15:41:13.788052+00:00
| 144 | false |
# Intuition\n- We aim to find the maximum difference between two elements in the array, satisfying the given conditions.\n- To find the maximum difference, we need to identify the smallest element nums[i] where i < j and nums[i] < nums[j].\n- If such pairs exist, we calculate the difference nums[j] - nums[i] and update the maximum difference encountered so far.\nIf no such pair exists, we return -1 indicating that there is no valid difference.\n\n---\n\n\n# Approach\n- Initialize max_difference to -1, which will store the maximum difference between elements satisfying the conditions.\n- Initialize left as the first element of the array nums[0].\n- Initialize right as 1, indicating that we start considering elements from the second position.\n- Use a while loop to iterate through the array from the second position onwards (right < nums.length).\n- Inside the loop, check if left < nums[right]. If true, calculate the difference nums[right] - left and update max_difference to the maximum of the current max_difference and the calculated difference.\n- If left is not less than nums[right], update left to nums[right]. This ensures that left always points to the smallest element encountered so far.\n- Increment right to move to the next element in the array.\n- Once the loop ends, return max_difference, which holds the maximum difference between elements satisfying the conditions. If no such pair exists, the function returns -1.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:o(n)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: o(1)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nfunction maximumDifference(nums: number[]): number {\n let max_difference = -1, left= nums[0], right = 1;\n\n while(right < nums.length){\n if(left <nums[right]){\n max_difference = Math.max(max_difference, nums[right]-left);\n } else {\n left = nums[right];\n }\n right++;\n }\n return max_difference;\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++', 'TypeScript']
| 0 |
maximum-difference-between-increasing-elements
|
JAVA | EASY
|
java-easy-by-shreyaa_garg-081k
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \nkeep finding diff and u
|
shreyaa_garg
|
NORMAL
|
2024-01-06T17:15:14.332575+00:00
|
2024-01-06T17:15:14.332598+00:00
| 5 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nkeep finding diff and update min element , update maxDiff only if current diff > maxDiff and also diff !=0 as num[i] < num[j]\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(N)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(1)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumDifference(int[] nums) {\n int mini = nums[0], maxDiff=-1;\n for(int i=1;i<nums.length;i++) {\n int diff = nums[i]-mini;\n mini = Math.min(mini, nums[i]);\n if(diff>maxDiff && diff !=0 ) maxDiff = diff;\n }\n return maxDiff;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
maximum-difference-between-increasing-elements
|
C++ solution
|
c-solution-by-nick_1111-dz1f
|
\n\n# Approach \nKeep track of the minimum while traversing the array and update the answer if found a greater element than the minimum\n Describe your approach
|
nick_1111
|
NORMAL
|
2023-12-25T17:04:22.032878+00:00
|
2023-12-25T17:04:22.032920+00:00
| 14 | false |
\n\n# Approach \nKeep track of the minimum while traversing the array and update the answer if found a greater element than the minimum\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:O(1)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximumDifference(vector<int>& nums) {\n int ans=INT_MIN;\n int mi =INT_MAX;\n for(auto x:nums)\n {\n mi=min(mi,x);\n ans=max(ans,x-mi);\n }\n\n return ans==0 ? -1 : ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-difference-between-increasing-elements
|
JAVA 0MS 100.00% Better Solution
|
java-0ms-10000-better-solution-by-awes19-n5iw
|
class Solution {\n public int maximumDifference(int[] nums) {\n int ans = -1; int min = nums[0]; \n for(int i=1; i<nums.length; i++){\n
|
Awes19
|
NORMAL
|
2023-12-14T06:05:13.397095+00:00
|
2023-12-14T06:05:13.397113+00:00
| 8 | false |
class Solution {\n public int maximumDifference(int[] nums) {\n int ans = -1; int min = nums[0]; \n for(int i=1; i<nums.length; i++){\n ans = Math.max(ans,nums[i]-min);\n min = Math.min(min,nums[i]);\n }\n return ans==0?-1:ans;\n }\n}
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
maximum-difference-between-increasing-elements
|
Go easy!
|
go-easy-by-ganesh_raveendran-csk3
|
\n# Code\n\nfunc maximumDifference(nums []int) int {\n min:= nums[0]\n maxDiff:=-1\n for i:=1;i<len(nums);i++{\n if nums[i]<min{\n mi
|
ganesh_raveendran
|
NORMAL
|
2023-11-17T08:38:42.091768+00:00
|
2023-11-17T08:38:42.091799+00:00
| 127 | false |
\n# Code\n```\nfunc maximumDifference(nums []int) int {\n min:= nums[0]\n maxDiff:=-1\n for i:=1;i<len(nums);i++{\n if nums[i]<min{\n min=nums[i]\n }else{\n diff:= nums[i]-min\n if diff>maxDiff{\n maxDiff=diff\n }\n }\n }\n if maxDiff<=0 {\n return -1\n }\n return maxDiff\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Go']
| 0 |
maximum-difference-between-increasing-elements
|
Simple Solution
|
simple-solution-by-adwxith-eu4p
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
adwxith
|
NORMAL
|
2023-11-16T10:13:14.781279+00:00
|
2023-11-16T10:13:14.781300+00:00
| 40 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\n/**\n * @param {number[]} nums\n * @return {number}\n */\nvar maximumDifference = function(nums) {\n let max=0;\n min=nums[0]\n for(let i=0;i<nums.length;i++){\n min=Math.min(min,nums[i])\n max=Math.max(max,nums[i]-min)\n }\n return max?max:-1\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
maximum-difference-between-increasing-elements
|
simple solution and simple logic in js and Python
|
simple-solution-and-simple-logic-in-js-a-t9wn
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n\n# Complexity\n- Tim
|
amjedpulikkal
|
NORMAL
|
2023-11-16T07:01:36.616645+00:00
|
2023-11-16T07:01:36.616676+00:00
| 152 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n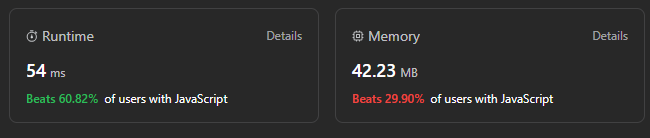\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: **54**\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: **42.23**\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\n/**\n * @param {number[]} nums\n * @return {number}\n */\nvar maximumDifference = function(nums) {\n if(nums.length <2){\n return -1\n }\n let s =-1\n \n for(let i=0;i<nums.length;i++){\n for(let j=i+1;j<nums.length;j++){\n if(nums[i]<nums[j]){\n s=Math.max(s,nums[j]-nums[i])\n }\n }\n }\n return s\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Python', 'JavaScript']
| 1 |
maximum-difference-between-increasing-elements
|
Simple python solution
|
simple-python-solution-by-gnairju-ozfa
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
gnairju
|
NORMAL
|
2023-11-16T04:14:33.424853+00:00
|
2023-11-16T04:14:33.424881+00:00
| 1,074 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maximumDifference(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n m=0\n k=0\n for i in range(len(nums)):\n for j in range(i+1,len(nums)):\n if nums[j]>nums[i]:\n k=nums[j]-nums[i]\n if k>=m:\n m=k\n if m==0:\n return -1\n return m\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
maximum-difference-between-increasing-elements
|
✅ The way you beat 🔥 100% of users 🔥
|
the-way-you-beat-100-of-users-by-nguyenl-9eic
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nJust loop.\n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n- You will
|
nguyenlinh1993
|
NORMAL
|
2023-11-07T03:57:55.380036+00:00
|
2023-11-07T03:57:55.380056+00:00
| 30 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nJust loop.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n- You will use 2 points i and j to loop the array.\n- Init: i=0, j=1, ans=-1.\n- If `(nums[i] < nums[j] && nums[j] - nums[i] > ans)` then `ans = nums[j] - nums[i]`\n- Otherwise, `i=j`\n- Note. Always increase `j++` each time loop!\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(n)$$\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(1)$$\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumDifference(int[] nums) {\n int n = nums.length;\n int ans = -1;\n int i = 0, j = 1;\n while (i < n && j < n) {\n if (nums[i] < nums[j]) {\n if (nums[j] - nums[i] > ans) {\n ans = nums[j] - nums[i];\n }\n } else {\n i = j;\n }\n j++;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Two Pointers', 'Java']
| 0 |
maximum-difference-between-increasing-elements
|
Easy solution without syntax sugar [Swift]
|
easy-solution-without-syntax-sugar-swift-2max
|
\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\n func maximumDifference(_ nums: [Int]) -> Int {\n var result = [Int]()\n \n for i in 0..<nums.count {\n
|
ArtyZenk
|
NORMAL
|
2023-08-10T06:44:34.459099+00:00
|
2023-08-10T06:44:34.459121+00:00
| 348 | false |
\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n func maximumDifference(_ nums: [Int]) -> Int {\n var result = [Int]()\n \n for i in 0..<nums.count {\n for j in (i + 1)..<nums.count {\n let diff = nums[j] - nums[i]\n if diff > 0 { result.append(diff) }\n }\n }\n \n return result.max() ?? -1\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Swift']
| 1 |
maximum-difference-between-increasing-elements
|
C++ || Simple Brute Force Solution
|
c-simple-brute-force-solution-by-princes-4svx
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(N^2)\n Add your time complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n\n- Space complexity: O(1)\n Add your space complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n\n#
|
Princesah999
|
NORMAL
|
2023-07-05T19:13:48.984100+00:00
|
2023-07-05T19:13:48.984125+00:00
| 1,244 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(N^2)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(1)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximumDifference(vector<int>& nums) {\n int maxi = 0;\n bool flag = false;\n for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){\n for(int j=i+1;j<nums.size();j++){\n if(maxi<(nums[j]-nums[i])){\n maxi = nums[j]-nums[i];\n flag = true;\n }\n }\n }\n if(flag)return maxi;\n return -1;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-difference-between-increasing-elements
|
C# || O(n) solution using for loop
|
c-on-solution-using-for-loop-by-timmok20-t1g9
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nThe main idea is to keep track of the minimum and the maximum difference while reading
|
timmok2022
|
NORMAL
|
2023-05-14T04:29:22.664826+00:00
|
2023-05-14T04:29:22.664858+00:00
| 40 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThe main idea is to keep track of the minimum and the maximum difference while reading each element from index 0 to the end of the input array.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1. declare two variables - **max** and **min**\n2. create a for loop that checks for two things - 1) if the current element is the lowest value or not 2) if the current element - **min** is greater than the existing **max** value. Use the Math.Max() method to keep **max** as the greatest difference always.\n3. once the for loop completes, check if the **max** value is greater than 0. If so, return the **max** value as is. Otherwise, return -1.\n\nThe assumption for step 2 is that the **max** value can be a negative value which is why step 3 has a logic to check if **max** is a positive value or not. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(n)\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(1)\n\n# Code\n```\npublic class Solution {\n public int MaximumDifference(int[] nums) {\n \n var max = int.MinValue;\n var min = int.MaxValue;\n \n for (int i = 0; i < nums.Length; i++)\n {\n min = Math.Min(nums[i], min); \n max = Math.Max(max, nums[i] - min);\n }\n return max > 0? max : -1;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C#']
| 0 |
maximum-difference-between-increasing-elements
|
O(N) time || O(1) space || faster than others
|
on-time-o1-space-faster-than-others-by-s-6b4u
|
\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximumDifference(vector<int>& nums) {\n //for each element store minimum in left of it\n int min
|
Shristha
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-02T05:23:35.283804+00:00
|
2023-02-02T05:23:35.283848+00:00
| 203 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maximumDifference(vector<int>& nums) {\n //for each element store minimum in left of it\n int mini=nums[0];\n int res=INT_MIN;\n for(int i=1;i<nums.size();i++){\n res=max(nums[i]-mini,res);\n mini=min(mini,nums[i]);\n }\n return (res==INT_MIN ||res<=0)?-1:res;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 1 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-difference-between-increasing-elements
|
Best java solution
|
best-java-solution-by-saha_souvik-a84a
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(N)\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(1)\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumDifference(int[] nums) {\n int ans
|
Saha_Souvik
|
NORMAL
|
2023-01-29T04:45:57.921749+00:00
|
2023-01-29T04:45:57.921799+00:00
| 1,376 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(N)\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(1)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumDifference(int[] nums) {\n int ans=-1;\n int max = nums[nums.length-1];\n\n for(int i=nums.length-2; i>=0; i--){\n max = Math.max(max, nums[i]);\n if(max <= nums[i]) continue;\n int dif = max-nums[i];\n ans = Math.max(ans, dif);\n \n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
maximum-difference-between-increasing-elements
|
Java Solution
|
java-solution-by-parshuramsudda-5frj
|
\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumDifference(int[] nums) {\n\n int min = nums[0],maxDifference=-1;\n for(int i=1;i<nums.length
|
parshuramsudda
|
NORMAL
|
2022-12-26T20:48:14.096095+00:00
|
2022-12-26T20:48:14.096133+00:00
| 1,035 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maximumDifference(int[] nums) {\n\n int min = nums[0],maxDifference=-1;\n for(int i=1;i<nums.length;i++){\n if(nums[i] <= min)\n min = nums[i];\n else\n maxDifference = Math.max(maxDifference, nums[i]-min);\n }\n return maxDifference;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
maximum-difference-between-increasing-elements
|
java brute force approach
|
java-brute-force-approach-by-callmecomde-1p7n
|
class Solution {\n public int maximumDifference(int[] arr) {\n int max=-1;\n for(int i=0;iarr[i] && ((arr[j]-arr[i])>max))\n {\n
|
callmecomder
|
NORMAL
|
2022-11-20T11:26:45.833121+00:00
|
2022-11-20T11:26:45.833160+00:00
| 11 | false |
# class Solution {\n public int maximumDifference(int[] arr) {\n int max=-1;\n for(int i=0;i<arr.length-1;i++)\n {\n for(int j=i+1;j<arr.length;j++)\n {\n if(arr[j]>arr[i] && ((arr[j]-arr[i])>max))\n {\n max=arr[j]-arr[i];\n }\n }\n }\n return max;\n }\n}
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Just brute-force
|
just-brute-force-by-cpcs-g50f
|
\n# Code\n\nclass Calculator {\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n */\n constructor(value) {\n this.result = value;\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {n
|
cpcs
|
NORMAL
|
2023-06-07T06:14:35.381139+00:00
|
2023-06-07T06:14:35.381176+00:00
| 3,473 | false |
\n# Code\n```\nclass Calculator {\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n */\n constructor(value) {\n this.result = value;\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n add(value){\n this.result += value;\n return this;\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n subtract(value){\n this.result -= value;\n return this;\n\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */ \n multiply(value) {\n this.result *= value;\n return this;\n\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n divide(value) {\n if (value === 0) {\n throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed");\n }\n this.result /= value;\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n power(value) {\n this.result **= value;\n return this;\n\n }\n \n /** \n * @return {number}\n */\n getResult() {\n return this.result;\n \n }\n}\n```
| 11 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 3 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
🗓️ Daily LeetCoding Challenge Day 30|| 🔥 JS SOL
|
daily-leetcoding-challenge-day-30-js-sol-t5wq
|
\n# Code\n\nclass Calculator {\n constructor(value) {\n this.result = value;\n }\n add(value) {\n this.result += value;\n return this;\n }\n\n sub
|
DoaaOsamaK
|
NORMAL
|
2024-06-14T19:01:00.711938+00:00
|
2024-06-14T19:01:00.711982+00:00
| 1,972 | false |
\n# Code\n```\nclass Calculator {\n constructor(value) {\n this.result = value;\n }\n add(value) {\n this.result += value;\n return this;\n }\n\n subtract(value) {\n this.result -= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n multiply(value) {\n this.result *= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n divide(value) {\n if (value === 0) {\n throw new Error(\'Division by zero is not allowed\');\n }\n this.result /= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n power(value) {\n this.result = Math.pow(this.result, value);\n return this;\n }\n\n getResult() {\n return this.result;\n }\n}\n```
| 8 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 4 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
JavaScript Solution
|
javascript-solution-by-motaharozzaman199-jo4w
|
\n\nclass Calculator {\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n */\n constructor(value) {\n this.value=value;\n\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} va
|
Motaharozzaman1996
|
NORMAL
|
2023-06-08T12:20:27.047271+00:00
|
2023-06-08T12:20:27.047324+00:00
| 1,729 | false |
\n```\nclass Calculator {\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n */\n constructor(value) {\n this.value=value;\n\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n add(value){\n this.value+=value;\n return this;\n\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n subtract(value){\n this.value-=value;\n return this;\n\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */ \n multiply(value) {\n this.value*=value;\n return this;\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n divide(value) {\n if (value==0){\n throw new Error(\'Division by zero is not allowed\');\n }\n this.value/=value;\n return this;\n\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n power(value) {\n this.value=Math.pow(this.value,value);\n return this;\n\n }\n \n /** \n * @return {number}\n */\n getResult() {\n return this.value;\n \n }\n}\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 2 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Clearly✅💯 a simple class solution
|
clearly-a-simple-class-solution-by-sardo-td0h
|
Calculator with Method Chaining...\uD83D\uDD25\n- The Calculator class has a constructor that takes an initialValue parameter, which serves as the initial value
|
SardorbekBahramov
|
NORMAL
|
2023-12-03T16:38:47.881720+00:00
|
2023-12-03T16:38:47.881745+00:00
| 843 | false |
## Calculator with Method Chaining...\uD83D\uDD25\n- The Calculator class has a constructor that takes an initialValue parameter, which serves as the initial value of the result.\n```\nconstructor(initialValue) {\n this.result = initialValue;\n}\n\n```\n- The class has methods for basic mathematical operations: add, subtract, multiply, divide, and power.\nEach of these methods takes a numeric parameter, performs the corresponding operation on the result, and returns the updated Calculator object to allow method chaining.\n- The getResult method simply returns the current value of the result.\n- Method chaining is achieved by making each method return the updated Calculator object (this). This allows consecutive operations to be performed in a single statement.\n```\nclass Calculator {\n constructor(initialValue) {\n this.result = initialValue;\n }\n\n add(value) {\n this.result += value;\n return this;\n }\n\n subtract(value) {\n this.result -= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n multiply(value) {\n this.result *= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n divide(value) {\n if (value === 0) {\n throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed");\n }\n this.result /= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n power(value) {\n this.result **= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n getResult() {\n return this.result;\n }\n}\n\n// Example usage:\nconst myCalculator = new Calculator(0); // Initialize with an initial value\nconst result = myCalculator.add(5).multiply(3).divide(2).power(2).getResult();\nconsole.log(result); // Output: 56.25\n\n```\n> ### I am always happy if it is useful to you\uD83D\uDCC8
| 4 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Detailed JavaScript Solution | Calculator with Method Chaining
|
detailed-javascript-solution-calculator-d2io5
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nWe need to design a Calculator class that supports basic arithmetic operations and meth
|
samabdullaev
|
NORMAL
|
2023-11-10T20:41:19.523981+00:00
|
2023-11-10T20:41:19.524011+00:00
| 346 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nWe need to design a `Calculator` class that supports basic arithmetic operations and method chaining.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1. This initializes a new instance of the `Calculator` class with the provided `value` as the starting `result`\n\n ```\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n */\n constructor(value) {\n this.result = value\n }\n ```\n\n2. `add` \u2192 this method adds the given number `value` to the `result` and returns the updated `Calculator`\n\n ```\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n add(value){\n this.result += value;\n return this\n }\n ```\n\n3. `subtract` \u2192 this method subtracts the given number `value` from the `result` and returns the updated `Calculator`\n\n ```\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n subtract(value){\n this.result -= value\n return this\n }\n ```\n\n4. `multiply` \u2192 this method multiplies the `result` by the given number `value` and returns the updated `Calculator`\n\n ```\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */ \n multiply(value) {\n this.result *= value\n return this\n }\n ```\n\n5. `divide` \u2192 this method divides the `result` by the given number `value` and returns the updated `Calculator`\n\n ```\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n divide(value) {\n if(value === 0 ) throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed") \n this.result = this.result / value\n return this\n }\n ```\n\n6. `power` \u2192 this method raises the `result` to the power of the given number `value` and returns the updated `Calculator`\n\n ```\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n power(value) {\n this.result = Math.pow(this.result,value)\n return this\n }\n ```\n\n7. `getResult` \u2192 this method returns the `result`\n\n ```\n /** \n * @return {number}\n */\n getResult() {\n return this.result\n }\n ```\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $O(1)$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nThis is because the methods perform a single mathematical operation and update the variable, which takes a constant amount of time regardless of the size of the input.\n\n- Space complexity: $O(1)$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nThis is because the class only uses a single variable to store the current value.\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Calculator {\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n */\n constructor(value) {\n this.result = value\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n add(value){\n this.result += value;\n return this\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n subtract(value){\n this.result -= value\n return this\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */ \n multiply(value) {\n this.result *= value\n return this\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n divide(value) {\n if(value === 0 ) throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed") \n this.result = this.result / value\n return this\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n power(value) {\n this.result = Math.pow(this.result,value)\n return this\n }\n\n /** \n * @return {number}\n */\n getResult() {\n return this.result\n }\n}\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
JavaScript - Easy to Understand Solution ✅✅
|
javascript-easy-to-understand-solution-b-w2l8
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Shubhamjain287
|
NORMAL
|
2023-06-09T05:33:35.471921+00:00
|
2023-06-09T05:33:35.471960+00:00
| 2,621 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Calculator {\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n */\n constructor(value) {\n this.sum = value;\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n add(value){\n this.sum += value;\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n subtract(value){\n this.sum -= value;\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */ \n multiply(value) {\n this.sum *= value;\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n divide(value) {\n if(value==0){\n throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed");\n }\n this.sum /= value;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n power(value) {\n this.sum **= value;\n }\n \n /** \n * @return {number}\n */\n getResult() {\n return this.sum;\n }\n}\n```
| 3 | 1 |
['JavaScript']
| 5 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Simple TS / JS implementation
|
simple-ts-js-implementation-by-fllght-6qex
|
TypeScript\n\nclass Calculator {\n private result: number\n\n constructor(value : number) {\n this.result = value\n }\n \n add(value : number) : Cal
|
FLlGHT
|
NORMAL
|
2023-06-07T04:27:13.829132+00:00
|
2023-06-07T04:31:47.623700+00:00
| 407 | false |
## TypeScript\n```\nclass Calculator {\n private result: number\n\n constructor(value : number) {\n this.result = value\n }\n \n add(value : number) : Calculator {\n this.result += value\n return this\n }\n \n subtract(value : number) : Calculator {\n this.result -= value\n return this\n }\n \n multiply(value : number) : Calculator {\n this.result *= value\n return this\n }\n\n divide(value : number) : Calculator {\n if (value == 0)\n throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed");\n \n this.result /= value\n return this\n }\n \n power(value : number) : Calculator {\n this.result = Math.pow(this.result, value)\n return this\n }\n\n getResult() : number {\n return this.result\n }\n}\n```\n\n## JavaScript\n```\nclass Calculator {\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n */\n constructor(value) {\n this.result = value\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n add(value){\n this.result += value\n return this\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n subtract(value){\n this.result -= value\n return this\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */ \n multiply(value) {\n this.result *= value\n return this\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n divide(value) {\n if (value == 0)\n throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed");\n \n this.result /= value\n return this\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n power(value) {\n this.result = Math.pow(this.result, value)\n return this\n }\n \n /** \n * @return {number}\n */\n getResult() {\n return this.result\n }\n}\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['TypeScript', 'JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Code 2726: Calculator with Method Chaining | easy | with explanation
|
code-2726-calculator-with-method-chainin-8kc3
|
IntuitionBoiler plate is already created just need to perform operations accordingly.Approachyou just need to add basic operation.create an error so that in cas
|
dxt_ush
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-19T05:02:14.027260+00:00
|
2024-12-19T05:02:14.027260+00:00
| 518 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nBoiler plate is already created just need to perform operations accordingly.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nyou just need to add basic operation.create an error so that in case if any error encounters just add that error into that else add the value in value.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nThe time complexity of calling a method in a class depends on the operations performed inside the method. However, the act of calling the method itself is generally considered to have a constant time complexity, O(1)\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nThe act of calling a method itself doesn\'t require significant memory, so the base space complexity is constant, \nO(1)\n# Code\n```javascript []\nclass Calculator {\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n */\n constructor(value) {\n this.value = value;\n this.error = null;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n add(value){\n this.value += value;\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n subtract(value){\n this.value -= value;\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */ \n multiply(value) {\n this.value *= value;\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n divide(value) {\n if(value == 0){\n this.error = "Division by zero is not allowed"\n }else{\n this.value /= value;\n }\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n power(value) {\n this.value = Math.pow(this.value,value);\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @return {number}\n */\n getResult() {\n if(this.error){\n return this.error;\n }\n return this.value;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 1 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Simple JavaScript Calculator with Method Chaining
|
simple-javascript-calculator-with-method-0qp3
|
Intuition\nThe idea behind this code is to create a calculator that can do basic math like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and raising a number
|
aeroengg
|
NORMAL
|
2024-03-29T19:00:06.081013+00:00
|
2024-03-29T19:00:06.081040+00:00
| 903 | false |
# Intuition\nThe idea behind this code is to create a calculator that can do basic math like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and raising a number to a power. It\'s like a regular calculator but in code form.\n\n# Approach\nThe Calculator class is implemented with methods for each mathematical operation (add, subtract, multiply, divide, and power). These methods modify the result property of the Calculator instance accordingly and return this to enable method chaining. The constructor initializes the result property with the initial value provided.\n\nWhen performing division, the method checks if the divisor is zero, and if so, it throws an error message.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nEach operation in the Calculator class takes constant time complexity, as they involve simple arithmetic operations.\nMethod chaining allows multiple operations to be performed in a single expression, but the time complexity remains constant for each operation.\nTherefore, the time complexity for each operation and method chaining is O(1).\n\n- Space complexity:\nThe space complexity is also O(1) as the space used does not depend on the input size but rather on the number of variables and objects created, which is constant in this case.\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Calculator {\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n */\n constructor(value) {\n this.result = value;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n add(value){\n this.result += value;\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n subtract(value){\n this.result -= value;\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */ \n multiply(value) {\n this.result *= value;\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n divide(value) {\n if (value === 0){\n throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed");\n }\n this.result /= value;\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n power(value) {\n this.result **= value;\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @return {number}\n */\n getResult() {\n return this.result;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
A simple class solution
|
a-simple-class-solution-by-theakshaykhal-uyac
|
Code\n\nclass Calculator {\n constructor(value) {\n this.result = value;\n }\n add(value) {\n this.result += value;\n return this;\n }\n\n subtrac
|
theakshaykhale
|
NORMAL
|
2023-09-04T13:12:10.115009+00:00
|
2023-09-04T13:12:10.115038+00:00
| 3,344 | false |
# Code\n```\nclass Calculator {\n constructor(value) {\n this.result = value;\n }\n add(value) {\n this.result += value;\n return this;\n }\n\n subtract(value) {\n this.result -= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n multiply(value) {\n this.result *= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n divide(value) {\n if (value === 0) {\n throw new Error(\'Division by zero is not allowed\');\n }\n this.result /= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n power(value) {\n this.result = Math.pow(this.result, value);\n return this;\n }\n\n getResult() {\n return this.result;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Easy 🎁🎁
|
easy-by-deleted_user-5c67
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
deleted_user
|
NORMAL
|
2023-06-07T09:00:25.077246+00:00
|
2023-06-07T09:01:20.141389+00:00
| 875 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Calculator {\n constructor(value) {\n this.value = value;\n }\n\n add = (value) => {\n this.value += value;\n return this;\n };\n\n subtract = (value) => {\n this.value -= value;\n return this;\n };\n\n multiply = (value) => {\n this.value *= value;\n return this;\n };\n\n divide = (value) => {\n if (value === 0) {\n throw new Error(\'Division by zero is not allowed\');\n }\n this.value /= value;\n return this;\n };\n\n power = (value) => {\n this.value = Math.pow(this.value, value);\n return this;\n };\n\n getResult = () => {\n return this.value;\n };\n}\n\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 2 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
C#
|
c-by-adchoudhary-i26a
|
Code
|
adchoudhary
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-01T07:41:02.671634+00:00
|
2025-03-01T07:41:02.671634+00:00
| 153 | false |
# Code
```javascript []
class Calculator {
/**
* @param {number} value
*/
constructor(value) {
this.result = value;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
add(value){
this.result += value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
subtract(value){
this.result -= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
multiply(value) {
this.result *= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
divide(value) {
if(value === 0) throw "Division by zero is not allowed";
this.result /= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
power(value) {
this.result **= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @return {number}
*/
getResult() {
return this.result;
}
}
```
| 1 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Easy Explanation
|
easy-explanation-by-pratyushpanda91-13v5
|
The Calculator class is designed to provide basic mathematical operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and exponentiation) while allowing m
|
pratyushpanda91
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-30T12:00:46.136308+00:00
|
2025-01-30T12:00:46.136308+00:00
| 316 | false |
**The Calculator class is designed to provide basic mathematical operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and exponentiation) while allowing method chaining. The class constructor initializes the result variable with a given starting value. Each method (except getResult) modifies the result and returns the instance itself (this), enabling method chaining. The divide method includes an error check to prevent division by zero, throwing an error message if an attempt is made to divide by zero. The getResult method simply returns the current value of result. This design ensures that users can perform a sequence of operations fluently in a single expression.**
### Explanation:
1. Constructor (constructor(value)): Initializes the result with the provided value.
1. add(value): Adds value to result and returns this for chaining.
1. subtract(value): Subtracts value from result and returns this.
1. multiply(value): Multiplies result by value and returns this.
1. divide(value): Checks if value is 0, throws an error if so, otherwise divides result by value and returns this.
1. power(value): Raises result to the power of value and returns this.
getResult(): Returns the final computed result.
# Code
```javascript []
class Calculator {
/**
* @param {number} value
*/
constructor(value) {
this.result = value;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
add(value) {
this.result += value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
subtract(value) {
this.result -= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
multiply(value) {
this.result *= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
divide(value) {
if (value === 0) {
throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed");
}
this.result /= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
power(value) {
this.result = Math.pow(this.result, value);
return this;
}
/**
* @return {number}
*/
getResult() {
return this.result;
}
}
```
| 1 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Easy!! Thank me later :) - Calculator with Method Chaining
|
calculator-with-method-chaining-by-harry-410m
|
IntuitionMy first thought when i see the problem is we need to understand about the object oriented programming first, then we will know how to fill the empty m
|
harryakbaram
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-19T06:35:16.972439+00:00
|
2024-12-19T06:56:07.619519+00:00
| 217 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
My first thought when i see the problem is we need to understand about the object oriented programming first, then we will know how to fill the empty method in the problem.
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
- Initialize the value in the constructor, we can say this is the storage that the value we can update by the methods.
- add(value): update the value in constructor by adding the value from param
- substract(value): update the value in constructor by substracting the value from param
- multiply(value): update the value in constructor by multiplying the value from param
- divide(value): update the value in constructor by dividing the value from param, but if the parameter is zero, we should throw an error message because we don't handle dividing by 0
- power(value): update the value in constructor by powering the value from param
- getResult(): return the value from constructor
# Complexity
##### Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- add: O(1)
- subtract: O(1)
- multiply: O(1)
- divide: O(1)
- power: O(1)
- getResult: O(1)
##### Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- add: O(1)
- subtract: O(1)
- multiply: O(1)
- divide: O(1)
- power: O(1)
- getResult: O(1)
# Code
```javascript []
class Calculator {
/**
* @param {number} value
*/
constructor(value) {
this.result = value
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
add(value) {
this.result += value
return new Calculator(this.result)
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
subtract(value) {
this.result -= value
return new Calculator(this.result)
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
multiply(value) {
this.result *= value
return new Calculator(this.result)
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
divide(value) {
if (value === 0) {
throw 'Division by zero is not allowed'
} else {
this.result /= value
}
return new Calculator(this.result)
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
power(value) {
this.result = Math.pow(this.result, value)
return new Calculator(this.result)
}
/**
* @return {number}
*/
getResult() {
return this.result
}
}
```
| 1 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Easy | Basic - Calculator with Method Chaining by JS
|
easy-basic-calculator-with-method-chaini-dz8u
|
ApproachThis Calculator class implements a chainable API for basic arithmetic operations—addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and exponentiation—on
|
Ujjwal_Saini007
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-15T05:29:19.444318+00:00
|
2024-12-15T05:29:19.444318+00:00
| 116 | false |
# Approach\nThis Calculator class implements a chainable API for basic arithmetic operations\u2014addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and exponentiation\u2014on a result value, with built-in error handling for division by zero.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: ***O(1)***\n\n- Space complexity: ***O(1)***\n\n# Screenshot:\n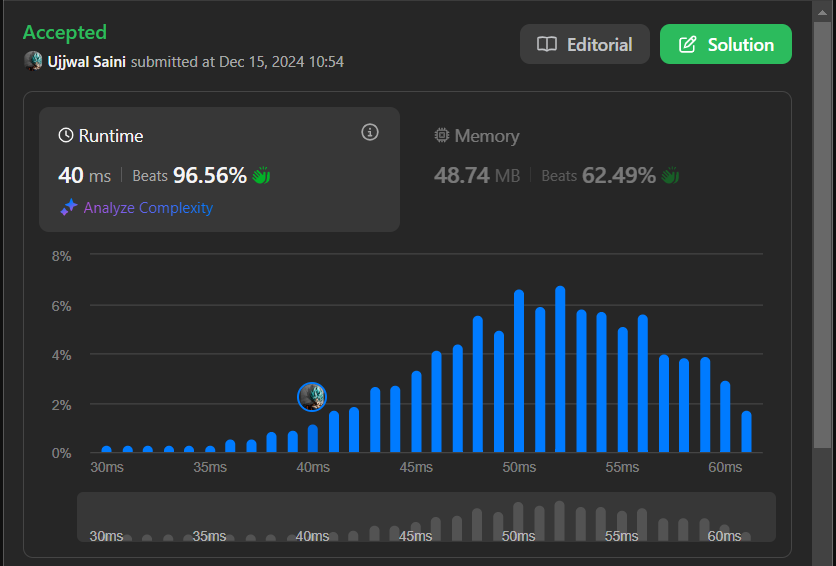\n\n\n# Code\n```javascript []\nclass Calculator {\n // @param {number} value\n constructor(value) {\n this.result = value;\n }\n \n //-------- @return {Calculator} -------- STARTS\n // @param {number} value\n add(value){\n this.result += value;\n return this;\n }\n \n // @param {number} value\n subtract(value){\n this.result -= value;\n return this;\n }\n \n // @param {number} value \n multiply(value) {\n this.result *= value;\n return this;\n }\n \n // @param {number} value\n divide(value) {\n if(value == 0) throw new Error(\'Division by zero is not allowed\');\n this.result /= value;\n return this;\n }\n \n // @param {number} value\n power(value) {\n this.result = Math.pow(this.result, value);\n return this;\n }\n \n //-------- @return {Calculator} -------- ENDS\n\n // @return {number}\n getResult() {\n return this.result;\n }\n}\n```\n
| 1 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Clear ✅TypeScript using chaining by returning "this"
|
clear-typescript-using-chaining-by-retur-p7td
|
Intuition\n\n\n# Code\n\nclass Calculator {\n #result: number\n constructor(value: number) {\n this.#result = value\n }\n \n add(value: nu
|
ovchynnikov
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-03T17:00:35.077361+00:00
|
2024-02-03T17:00:35.077383+00:00
| 38 | false |
# Intuition\n\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Calculator {\n #result: number\n constructor(value: number) {\n this.#result = value\n }\n \n add(value: number): Calculator {\n this.#result += value\n return this\n }\n \n subtract(value: number): Calculator {\n this.#result -= value\n return this\n }\n \n multiply(value: number): Calculator {\n this.#result *= value\n return this\n }\n \n divide(value: number): Calculator {\n if (value === 0) throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed")\n this.#result /= value\n return this\n }\n \n power(value: number): Calculator {\n this.#result = Math.pow(this.#result, value)\n return this\n }\n \n getResult(): number {\n return this.#result\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['TypeScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Brute force Solution
|
brute-force-solution-by-user3214w-4oc0
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
user3214w
|
NORMAL
|
2024-01-19T11:27:13.086114+00:00
|
2024-01-19T11:27:13.086149+00:00
| 161 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Calculator {\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n */\n constructor(value) {\n this.value=value\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n add(value){\n this.value+=value;\n return this\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n subtract(value){\n this.value-=value;\n return this\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */ \n multiply(value) {\n this.value*=value;\n return this\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n divide(value) {\n if(value===0){\n throw (\'Division by zero is not allowed\')\n }\n this.value/=value;\n return this\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n power(value) {\n this.value=Math.pow(this.value,value);\n return this\n }\n \n /** \n * @return {number}\n */\n getResult() {\n return this.value\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Beats 91.47%of users with JavaScript
|
beats-9147of-users-with-javascript-by-po-13la
|
\n\nclass Calculator {\n \n\tconstructor(value) {\n this.value = value;\n this.error;\n\t}\n\n\tadd(value){\n\t\tthis.value += value;\n ret
|
PoetryOfCode
|
NORMAL
|
2023-11-12T00:05:51.081973+00:00
|
2023-11-12T00:05:51.081990+00:00
| 10 | false |
\n```\nclass Calculator {\n \n\tconstructor(value) {\n this.value = value;\n this.error;\n\t}\n\n\tadd(value){\n\t\tthis.value += value;\n return this;\n\t}\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n\tsubtract(value){\n\t\tthis.value -= value;\n return this;\n\t}\n\n\tmultiply(value) {\n\t\tthis.value *= value;\n return this;\n\t}\n\n\tdivide(value) {\n if (value === 0) this.error = "Division by zero is not allowed"\n\t\tthis.value /= value;\n return this;\n\t}\n \n\tpower(value) {\n\t\tthis.value = this.value ** value;\n return this;\n\t}\n \n\tgetResult() {\n if (!this.error) return this.value\n else return this.error\n\t}\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Structured approach
|
structured-approach-by-2ziat3kywa-vbls
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
2Ziat3kYWA
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-26T12:39:20.703451+00:00
|
2025-03-26T12:39:20.703451+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```javascript []
class Calculator {
/**
* @param {number} value
*/
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.error = false;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
add(value){
this.value += value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
subtract(value){
this.value -= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
multiply(value) {
this.value *= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
divide(value) {
if(value === 0){
this.error = true;
return this;
} else {
this.value /= value;
return this;
}
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
power(value) {
this.value **= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @return {number}
*/
getResult() {
return this.error ? "Division by zero is not allowed" : this.value;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Calculator with Method Chaining
|
calculator-with-method-chaining-by-shali-93zd
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
ShaliniPaidimuddala
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-25T09:02:56.658200+00:00
|
2025-03-25T09:02:56.658200+00:00
| 1 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```javascript []
class Calculator {
constructor(value) {
this.result = value;
}
add(value) {
this.result += value;
return this;
}
subtract(value) {
this.result -= value;
return this;
}
multiply(value) {
this.result *= value;
return this;
}
divide(value) {
if (value === 0) {
throw new Error('Division by zero is not allowed');
}
this.result /= value;
return this;
}
power(value) {
this.result = Math.pow(this.result, value);
return this;
}
getResult() {
return this.result;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
javascript solution
|
javascript-solution-by-fe2-nyxar-ewa0
|
Solutionexplanation of the Solutionthe answer is self explanatory, "this" is confusing but it means the instance of class "Calculator".
it's the same as writtin
|
fe2-Nyxar
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-16T07:52:53.518119+00:00
|
2025-03-16T08:31:51.011324+00:00
| 7 | false |
# Solution
```javascript []
class Calculator {
constructor(value){
this.value = value
}
add(value){
this.value += value;
return this;
}
subtract(value){
this.value -= value;
return this;
}
power(value){
this.value **= value
return this;
}
multiply(value) {
this.value *= value
return this;
}
divide(value) {
if (value === 0 ) throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed");
this.value /= value
return this;
}
getResult(value){
return this.value
}
}
```
# explanation of the Solution
the answer is self explanatory, "this" is confusing but it means the instance of class "Calculator".
it's the same as writting this:
```javascript
class Calculator {
constructor(value){
this.value = value
}
etc...
add(value){
this.value = this.value + value;
return this.getResult();
}
getResult(value){
return this.value
}
}
let cal = new Calculator(2); // 2
console.log(cal.add(5)); // 7
console.log(cal.add(5)); // 12
```
this the same as the solution at the end but it uses a different way to call the function
```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Easy Straightforward solution
|
easy-straightforward-solution-by-ronitbl-azj4
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
RonitBL
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-15T02:49:48.526325+00:00
|
2025-03-15T02:49:48.526325+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```javascript []
class Calculator {
/**
* @param {number} value
*/
constructor(value) {
this.result = value;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
add(value){
this.result += value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
subtract(value){
this.result -= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
multiply(value) {
this.result *= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
divide(value) {
if (value === 0)
{
throw "Division by zero is not allowed";
// return value;
}
this.result /= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
power(value) {
this.result = Math.pow(this.result, value);
return this;
}
/**
* @return {number}
*/
getResult() {
return this.result;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
JavaScript Solution
|
javascript-solution-by-jayanth_br-0j6h
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
jayanth_br
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-09T06:41:04.690823+00:00
|
2025-03-09T06:41:04.690823+00:00
| 5 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```javascript []
class Calculator {
/**
* @param {number} value
*/
constructor(value) {
this.result = value;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
add(value) {
this.result += value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
subtract(value) {
this.result -= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
multiply(value) {
this.result *= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
divide(value) {
if (value != 0)
this.result /= value;
else
throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed");
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
power(value) {
this.result = Math.pow(this.result, value);
return this;
}
/**
* @return {number}
*/
getResult() {
return this.result
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
unchain the calculators
|
unchain-the-calculators-by-ecabigting-jpxy
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
ecabigting
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-07T09:20:11.792146+00:00
|
2025-03-07T09:20:11.792146+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```javascript []
class Calculator {
/**
* @param {number} value
*/
constructor(value) {
this.result = value;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
add(value){
this.result += value;
return this
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
subtract(value){
this.result -= value;
return this
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
multiply(value) {
this.result *= value;
return this
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
divide(value) {
if(value === 0)
{
throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed");
}
this.result /= value;
return this
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
power(value) {
this.result **= value;
return this
}
/**
* @return {number}
*/
getResult() {
return this.result;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Calculator with Method Chaining
|
calculator-with-method-chaining-by-gaura-bvvs
|
IntuitionApproach
Constructor (constructor(value))
Stores the initial number in this.result.
Arithmetic Methods (add,subtract,multiply,divide,power)
Updat
|
gauravkum2002
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-22T20:35:51.536948+00:00
|
2025-02-22T20:36:07.844033+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
1. Constructor (`constructor(value)`)
- Stores the initial number in this.result.
2. Arithmetic Methods (`add`, `subtract`, `multiply`, `divide`, `power`)
- Update `this.result`.
- Return `this` to allow method chaining.
3. Error Handling in `divide()`
- Throws an error if trying to divide by zero.
4. `getResult()`
- Returns the final computed value.
# Code
```javascript []
class Calculator {
/**
* @param {number} value
*/
constructor(value) {
this.result = value; // Store the initial value
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
add(value){
this.result += value;
return this; // Return the instance for method chaining
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
subtract(value){
this.result -= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
multiply(value) {
this.result *= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
divide(value) {
if (value === 0){
throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed");
}
this.result /= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
power(value) {
this.result = Math.pow(this.result, value);
return this;
}
/**
* @return {number}
*/
getResult() {
return this.result;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Method chaining interview question
|
method-chaining-interview-question-by-sr-7700
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
sreyajohnson
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-11T18:47:48.041688+00:00
|
2025-02-11T18:47:48.041688+00:00
| 10 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```typescript []
class Calculator {
result;
constructor(value: number) {
this.result = value;
}
add(value: number): Calculator {
this.result = this.result + value;
return this;
}
subtract(value: number): Calculator {
this.result = this.result- value;
return this;
}
multiply(value: number): Calculator {
this.result = this.result* value;
return this;
}
divide(value: number): Calculator {
if(value == 0){
this.result ="Division by zero is not allowed";
return this;
}
this.result = this.result/ value;
return this;
}
power(value: number): Calculator {
this.result = this.result** value;
return this;
}
getResult(): number {
return this.result;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['TypeScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Simple solution
|
simple-solution-by-makafsal-edr0
|
Code
|
makafsal
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-09T12:36:58.656455+00:00
|
2025-02-09T12:36:58.656455+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Code
```javascript []
class Calculator {
/**
* @param {number} value
*/
constructor(value) {
this.result = value;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
add(value){
this.result += value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
subtract(value){
this.result -= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
multiply(value) {
this.result *= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
divide(value) {
if (value === 0) {
throw 'Division by zero is not allowed';
}
this.result /= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
power(value) {
this.result = Math.pow(this.result, value);
return this;
}
/**
* @return {number}
*/
getResult() {
return this.result;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
~5min
|
5min-by-lerfich-lv2i
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
lerfich
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-06T05:00:32.299351+00:00
|
2025-02-06T05:00:32.299351+00:00
| 9 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```typescript []
class Calculator {
result = 0
constructor(value: number) {
this.result = value
}
add(value: number): Calculator {
this.result += value
return this
}
subtract(value: number): Calculator {
this.result -= value
return this
}
multiply(value: number): Calculator {
this.result *= value
return this
}
divide(value: number): Calculator {
if (!value) {
throw "Division by zero is not allowed"
}
this.result /= value
return this
}
power(value: number): Calculator {
this.result **= value
return this
}
getResult(): number {
return this.result
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['TypeScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
LC: #2726
|
lc-2726-by-jaalle-xzeg
|
Complexity
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(n)
Code
|
jaalle
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-28T03:02:17.642258+00:00
|
2025-01-28T03:02:17.642258+00:00
| 11 | false |
# Complexity
- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity: $$O(n)$$
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```typescript []
class Calculator {
private value: number;
private result: number = 0;
constructor(value: number) {
this.value = value;
this.result = value;
}
add(value: number) {
this.result += value;
return this;
}
subtract(value: number) {
this.result -= value;
return this;
}
multiply(value: number) {
this.result *= value;
return this;
}
divide(value: number) {
if (value === 0) {
throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed");
}
this.result /= value;
return this;
}
power(value: number) {
this.result **= value;
return this;
}
getResult(): number {
return this.result;
}
}
```
```javascript []
var Calculator = /** @class */ (function () {
/**
* @param {number} value
*/
function Calculator(value) {
this.result = 0;
this.value = value;
this.result = value;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @returns {Calculator}
*/
Calculator.prototype.add = function (value) {
this.result += value;
return this;
};
/**
* @param {number} value
* @returns {Calculator}
*/
Calculator.prototype.subtract = function (value) {
this.result -= value;
return this;
};
/**
* @param {number} value
* @returns {Calculator}
*/
Calculator.prototype.multiply = function (value) {
this.result *= value;
return this;
};
/**
* @param {number} value
* @returns {Calculator}
*/
Calculator.prototype.divide = function (value) {
if (value === 0) {
throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed");
}
this.result /= value;
return this;
};
/**
* @param {number} value
* @returns {Calculator}
*/
Calculator.prototype.power = function (value) {
var _a;
(_a = this).result = Math.pow(_a.result, value);
return this;
};
/**
* @returns {number}
*/
Calculator.prototype.getResult = function () {
return this.result;
};
return Calculator;
}());
```
| 0 | 0 |
['TypeScript', 'JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Simple Solution with explanation of the program and approach to solve the problem step by step
|
simple-solution-with-explanation-of-the-mjsb2
|
IntuitionUnderstand the given condition and think the logic to the given problem and the return value.ApproachWe just need a basic math calculation and operatio
|
Shashankpatelc
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-27T23:49:10.395056+00:00
|
2025-01-27T23:49:10.395056+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
Understand the given condition and think the logic to the given problem and the return value.
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
We just need a basic math calculation and operations to solve this question.We have a class `Calculator` with its methodes and We also have number `value`. On these value we perforn the opration like add, subtract, division, etc.
We have to return the error if value is 0 in division part.
# Program Breakdown
**This is the breakdown of the program given bellow of this page**
- First we need to intialise a first number using the constructor `Calculator` which take the argument `value` so we use `this.value = value` which initilize the first value, `this.error = 0` this is used to indicate the error if it appears, we initilize `0` because we don't have any error in the constructor
- To add the value we use `add()` method which accept the argument `value` and `this.value += value` which is in the form of `this.value = this.value + value` perform the addition and return `this` enables **method chaining.**
- All the method of the `Calculator` class use the same method .But we have some different things in methods :-
1. divide
2. power
- In the `divide` method we if the value is 0 we cannot divivde any other value by 0 so there is an error to solve that we use if condition to check the value of `value` is 0 or not if it is 0 we use `this.error` we created above and intialize its value by `this.error = "Division by zero is not allowed"`.
- If there is no error we prosed with `this.value /= value`.
- The power method use the `Math` to find the power because there is no operator for this `this.value = Math.pow(this.value, value)`.
- `getResult()` return the result when it is called if there is any error it return error if not it return result stored in `value`.
# Complexity
- Time complexity: $$O(1)$$
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
Calculator class is generally O(1) for each operation (add, subtract, multiply, divide, power). This is because each method performs a constant-time arithmetic operation regardless of the size of the input.
- Space complexity: $$O(1)$$
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
since the class maintains a fixed amount of state (the value and error properties) regardless of the number of operations performed or the size of the input values.
# Code
```javascript []
class Calculator {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value
this.error = 0
}
add(value) {
this.value += value
return this
}
subtract(value) {
this.value -= value
return this
}
multiply(value) {
this.value *= value
return this
}
divide(value) {
if (value === 0) {
this.error = "Division by zero is not allowed"
} else {
this.value /= value
}
return this
}
power(value) {
this.value = Math.pow(this.value, value)
return this
}
getResult() {
if (this.error) {
return this.error
}
return this.value
}
}
```
# HAVE A NICE CODING DAY
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Runtime 36 ms Beats 99.23% & Memory 48.68 MB Beats 75.58%
|
runtime-36-ms-beats-9923-memory-4868-mb-hd1oe
|
ApproachMethod chaining in JavaScript classes allows you to call multiple methods on the same instance in a single statement. This is typically achieved by havi
|
bekcodingaddict
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-25T11:11:28.753118+00:00
|
2025-01-25T11:11:28.753118+00:00
| 5 | false |
# Approach
Method chaining in JavaScript classes allows you to call multiple methods on the same instance in a single statement. This is typically achieved by having each method return the instance (this) so you can chain further method calls.
Return this: Each method returns this, which refers to the current instance of the class. This allows subsequent method calls to operate on the same instance.
Avoid Breaking the Chain: If a method returns something other than this (e.g., a primitive value), the chain will break. Make sure only methods explicitly designed to end the chain return non-instance values.
Immutability (Optional): For functional programming enthusiasts, you can return a new instance instead of modifying the original one to preserve immutability. But for simplicity, modifying the instance works well for most cases.
# Code
```javascript []
class Calculator {
/**
* @param {number} value
*/
constructor(value = 0) {
this.result = value;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
add(value) {
return new Calculator(this.result + value);
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
subtract(value) {
return new Calculator(this.result - value);
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
multiply(value) {
return new Calculator(this.result * value);
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
divide(value) {
if (value !== 0) {
return new Calculator(this.result / value);
} else {
throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed");
}
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
power(value) {
return new Calculator(this.result ** value);
}
/**
* @return {number}
*/
getResult() {
return this.result;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Runtime 58 ms Beats 17.19% & Memory 48.94 MB Beats 41.58%
|
runtime-58-ms-beats-1719-memory-4894-mb-ob0jq
|
ApproachMethod chaining in JavaScript classes allows you to call multiple methods on the same instance in a single statement. This is typically achieved by havi
|
bekcodingaddict
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-25T10:11:06.488351+00:00
|
2025-01-25T10:11:06.488351+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Approach
Method chaining in JavaScript classes allows you to call multiple methods on the same instance in a single statement. This is typically achieved by having each method return the instance (this) so you can chain further method calls.
# Code
```javascript []
class Calculator {
/**
* @param {number} value
*/
constructor(value) {
this.result = value;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
add(value) {
this.result += value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
subtract(value) {
this.result -= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
multiply(value) {
this.result *= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
divide(value) {
if (value !== 0) {
this.result /= value;
return this;
} else {
throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed");
}
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
power(value) {
this.result **= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @return {number}
*/
getResult() {
return this.result;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Fast solution ✅🚀
|
fast-solution-by-its_me_1-9vfn
|
IntuitionThe goal is to implement a chainable calculator that performs basic arithmetic operations (add, subtract, multiply, divide) and an advanced operation (
|
its_me_1
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-21T04:06:02.815963+00:00
|
2025-01-21T04:06:02.815963+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Intuition
The goal is to implement a chainable calculator that performs basic arithmetic operations (`add`, `subtract`, `multiply`, `divide`) and an advanced operation (`power`). The chaining feature allows multiple operations to be performed in a single statement. For example:
```
const calc = new Calculator(10);
calc.add(5).multiply(2).subtract(3).getResult();
```
This requires each method to return the instance of the `Calculator` class (`this`), enabling the chaining behavior.
# Approach
1. **Initialization**:
- The constructor initializes the `result` property with the given value.
2. **Arithmetic Operations**:
- Each method (`add`, `subtract`, `multiply`, `divide`, `power`) updates the `result` property based on the input value and returns `this` to allow method chaining.
3. **Division by Zero**:
- To handle invalid operations, the `divide` method checks if the divisor is `0` and throws an error if so.
4. **Retrieving the Result**:
- The `getResult` method simply returns the current value of the `result` property.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
- Each operation (add, subtract, multiply, devide, power) runs in O(1), as it performs a single arithmetic operation.
- Space complexity:
O(1), since no additional data structures are used
# Code
```javascript []
class Calculator {
/**
* @param {number} value
*/
constructor(value) {
this.result = value;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
add(value){
this.result += value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
subtract(value){
this.result -= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
multiply(value) {
this.result *= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
divide(value) {
if (value === 0) {
throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed");
}
this.result /= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
power(value) {
this.result **= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @return {number}
*/
getResult() {
return this.result;
}
}
```

| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Easy approach
|
easy-approach-by-vamsi0874-17qd
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
vamsi0874
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-20T08:25:45.085658+00:00
|
2025-01-20T08:25:45.085658+00:00
| 8 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```typescript []
class Calculator {
private value: number; // Define the value as a private property
constructor(value: number) {
this.value = value; // Initialize the value in the constructor
}
add(value: number): Calculator {
this.value += value;
return this; // Return the instance for method chaining
}
subtract(value: number): Calculator {
this.value -= value;
return this; // Return the instance for method chaining
}
multiply(value: number): Calculator {
this.value *= value;
return this; // Return the instance for method chaining
}
divide(value: number): Calculator {
if (value === 0) throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed");
this.value /= value;
return this; // Return the instance for method chaining
}
power(value: number): Calculator {
this.value = Math.pow(this.value, value); // Use Math.pow for power calculation
return this; // Return the instance for method chaining
}
getResult(): number {
return this.value; // Return the current value
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['TypeScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Calculator with Method Chaining Implementation | Dart Solution | Time O(1) | Space O(1)
|
calculator-with-method-chaining-implemen-xger
|
ApproachThe solution implements a calculator that supports method chaining:
Core Design:
Maintains running result as instance variable
Each operation returns
|
user4343mG
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-19T06:22:07.949903+00:00
|
2025-01-19T06:22:07.949903+00:00
| 4 | false |
## Approach
The solution implements a calculator that supports method chaining:
1. **Core Design**:
- Maintains running result as instance variable
- Each operation returns 'this' for chaining
- Final getResult returns computed value
2. **Operations**:
- Basic arithmetic: add, subtract, multiply, divide
- Power operation using Math.pow
- Error handling for division by zero
3. **Method Chaining**:
- Each method returns calculator instance
- Allows operations to be chained
- Maintains state between operations
## Complexity
**Time Complexity**: $$O(1)$$
- All arithmetic operations are constant time
- Power operation using Math.pow is O(1)
- getResult is simple value return
**Space Complexity**: $$O(1)$$
- Only stores single result value
- No additional space needed for operations
# Code
```javascript []
class Calculator {
/**
* @param {number} value
*/
constructor(value) {
this.result = value;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
add(value){
this.result = this.result + value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
subtract(value){
this.result = this.result - value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
multiply(value) {
this.result = this.result * value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
divide(value) {
if (value === 0) {
throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed");
}
this.result = this.result / value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
power(value) {
this.result = Math.pow(this.result, value);
return this;
}
/**
* @return {number}
*/
getResult() {
return this.result;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Calculator with method chaining
|
calculator-with-method-chaining-by-msudi-wejy
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
O(1)
Space complexity:
O(1)
Code
|
msudip738
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-18T15:52:52.358953+00:00
|
2025-01-18T15:52:52.358953+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
$$O(1)$$
- Space complexity:
$$O(1)$$
# Code
```javascript []
class Calculator {
/**
* @param {number} value
*/
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
add(value){
this.value = this.value + value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
subtract(value){
this.value = this.value - value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
multiply(value) {
this.value = this.value * value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
divide(value) {
if(value===0){
throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed");
return this;
}
this.value = this.value/value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
power(value) {
this.value = this.value**value;
return this;
}
/**
* @return {number}
*/
getResult() {
return this.value;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
#2726: Calculator with Method Chaining
|
2726-calculator-with-method-chaining-by-5jupf
|
IntuitionThe problem requires creating a wrapper around an array to enable custom behavior for arithmetic operations and string conversion. The main idea is to
|
Dheeraj7321
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-08T03:30:06.807955+00:00
|
2025-01-08T03:30:06.807955+00:00
| 6 | false |
# Intuition
The problem requires creating a wrapper around an array to enable custom behavior for arithmetic operations and string conversion. The main idea is to leverage JavaScript's built-in `valueOf` and `toString` methods to override default behavior.
# Approach
1. **Constructor (`ArrayWrapper`)**: Initialize the wrapper with the array.
2. **`valueOf` Method**: Define a custom implementation to return the sum of the array elements when the object is used in arithmetic expressions.
3. **`toString` Method**: Define a custom implementation to return the string representation of the array when the object is converted to a string.
# Complexity
- **Time complexity**:
- `valueOf`: $$O(n)$$, where `n` is the length of the array, due to summation.
- `toString`: $$O(n)$$, for converting the array to a string.
- **Space complexity**:
- `valueOf`: $$O(1)$$, as it uses constant space for computation.
- `toString`: $$O(n)$$, as it creates a new string representation of the array.
# Code
```javascript []
class Calculator {
/**
* @param {number} value
*/
constructor(value) {
this.result = value;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
add(value) {
this.result += value;
return this; // Return the instance for method chaining
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
subtract(value) {
this.result -= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
multiply(value) {
this.result *= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
divide(value) {
if (value === 0){
throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed")
}
this.result /= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
power(value) {
this.result = Math.pow(this.result, value);
return this;
}
/**
* @return {number}
*/
getResult() {
return this.result;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Solution of Calc with Method Chaining
|
solution-of-calc-with-method-chaining-by-6smv
|
IntuitionTo initalize value and error and return value in end of every fucntion.ApproachWe using simple operators in add,multiply,in divide we use if else loop
|
Danial21
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-07T16:38:23.636244+00:00
|
2025-01-07T16:38:23.636244+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition
To initalize value and error and return value in end of every fucntion.
# Approach
We using simple operators in add,multiply,in divide we use if else loop to return error if division by zero is happened and use operator /.After we use Marh pow method and return value.Finally,if we got the error we return it,and return the final value.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
O(1)
- Space complexity:
O(1)
# Code
```javascript []
class Calculator {
/**
* @param {number} value
*/
constructor(value) {
this.value = value
this.error = null;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
add(value){
this.value += value
return this
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
subtract(value){
this.value -= value
return this
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
multiply(value) {
this.value *= value
return this
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
divide(value) {
if(value == 0){
this.error = "Division by zero is not allowed"
}else{
this.value /= value;
}
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
power(value) {
this.value = Math.pow(this.value, value)
return this
}
/**
* @return {number}
*/
getResult() {
if(this.error){
return this.error;
}
return this.value;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Solution of Calc with Method Chaining
|
solution-of-calc-with-method-chaining-by-7za9
|
IntuitionTo initalize value and error and return value in end of every fucntion.ApproachWe using simple operators in add,multiply,in divide we use if else loop
|
Danial21
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-07T16:38:19.243760+00:00
|
2025-01-07T16:38:19.243760+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition
To initalize value and error and return value in end of every fucntion.
# Approach
We using simple operators in add,multiply,in divide we use if else loop to return error if division by zero is happened and use operator /.After we use Marh pow method and return value.Finally,if we got the error we return it,and return the final value.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
O(1)
- Space complexity:
O(1)
# Code
```javascript []
class Calculator {
/**
* @param {number} value
*/
constructor(value) {
this.value = value
this.error = null;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
add(value){
this.value += value
return this
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
subtract(value){
this.value -= value
return this
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
multiply(value) {
this.value *= value
return this
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
divide(value) {
if(value == 0){
this.error = "Division by zero is not allowed"
}else{
this.value /= value;
}
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
power(value) {
this.value = Math.pow(this.value, value)
return this
}
/**
* @return {number}
*/
getResult() {
if(this.error){
return this.error;
}
return this.value;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
2726. Calculator with Method Chaining
|
2726-calculator-with-method-chaining-by-h0xcl
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
G8xd0QPqTy
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-06T17:43:35.933260+00:00
|
2025-01-06T17:43:35.933260+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```javascript []
class Calculator {
constructor(initialValue) {
this.result = initialValue;
}
add(value) {
this.result += value;
return this;
}
subtract(value) {
this.result -= value;
return this;
}
multiply(value) {
this.result *= value;
return this;
}
divide(value) {
if (value === 0) {
throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed");
}
this.result /= value;
return this;
}
power(value) {
this.result = Math.pow(this.result, value);
return this;
}
getResult() {
return this.result;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
easy solution
|
easy-solution-by-virendangi123-2o5e
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
Virendangi123
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-30T14:57:24.127378+00:00
|
2024-12-30T14:57:24.127378+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```javascript []
class Calculator {
/**
* @param {number} value
*/
constructor(value) {
this.result = value
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
add(value) {
this.result += value
return new Calculator(this.result)
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
subtract(value) {
this.result -= value
return new Calculator(this.result)
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
multiply(value) {
this.result *= value
return new Calculator(this.result)
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
divide(value) {
if (value === 0) {
throw 'Division by zero is not allowed'
} else {
this.result /= value
}
return new Calculator(this.result)
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
power(value) {
this.result = Math.pow(this.result, value)
return new Calculator(this.result)
}
/**
* @return {number}
*/
getResult() {
return this.result
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Javascript Solution | 🔥brute-force 🔥| ✅Easy to Understand Solution
|
javascript-solution-brute-force-easy-to-ct1jn
|
\nclass Calculator {\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n */\n constructor(value) {\n this.result = value;\n }\n \n /** \n
|
Jayendra_091
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-12T16:29:11.618423+00:00
|
2024-12-12T16:29:11.618462+00:00
| 1 | false |
```\nclass Calculator {\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n */\n constructor(value) {\n this.result = value;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n add(value){\n this.result += value;\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n subtract(value){\n this.result -= value;\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */ \n multiply(value) {\n this.result *= value;\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n divide(value) {\n if(value == 0)\n throw Error("Division by zero is not allowed");\n this.result /= value;\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n power(value) {\n this.result **= value;\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @return {number}\n */\n getResult() {\n return this.result;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Simple actions and return this.
|
simple-actions-and-return-this-by-roman_-bmtt
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
roman_gravit
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-20T13:27:32.863820+00:00
|
2024-12-20T13:27:32.863820+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```javascript []
class Calculator {
/**
* @param {number} value
*/
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
add(value){
this.value += value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
subtract(value){
this.value -= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
multiply(value) {
this.value *= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
divide(value) {
if(!value) {
throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed");
}
this.value /= value;
return this;
}
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {Calculator}
*/
power(value) {
this.value = this.value ** value;
return this;
}
/**
* @return {number}
*/
getResult() {
return this.value;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
2726. Calculator with Method Chaining
|
2726-calculator-with-method-chaining-by-adujd
|
IntuitionApproachExplanation:Error Handling in Constructor:
An error property is added to the constructor to store error messages.
divide Method:
If the diviso
|
Anikaleet
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-18T13:36:18.387040+00:00
|
2024-12-18T13:36:18.387040+00:00
| 33 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n# Explanation:\n**Error Handling in Constructor:**\n- An error property is added to the constructor to store error messages.\n\n**divide Method:**\n\n- If the divisor is zero, the error message "Division by zero is not allowed" is stored in the error property.\n\n- If the divisor is not zero, the value is divided normally.\n\n**getResult Method:**\n\n- Checks if there is an error message. If so, it returns the error message.\n\n- If no error, it returns the current value.\n\n# Example Usage:\n- In the first example, attempting to divide by zero sets the error message and getResult returns "Division by zero is not allowed".\n\n- In the second example, performing a series of valid operations and then calling getResult returns the final result of the calculations.\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:- O(1)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:- O(1)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```javascript []\nclass Calculator {\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n */\n constructor(value = 0) {\n this.value = value;\n this.error = null; // Add an error property to store error messages\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n add(value) {\n this.value += value;\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n subtract(value) {\n this.value -= value;\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */ \n multiply(value) {\n this.value *= value;\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n divide(value) {\n if (value !== 0) {\n this.value /= value;\n } else {\n this.error = "Division by zero is not allowed"; // Store the error message\n }\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n power(value) {\n this.value = Math.pow(this.value, value);\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @return {number|string}\n */\n getResult() {\n if (this.error) {\n return this.error; // Return the error message if there\'s one\n }\n return this.value;\n }\n}\n\n// Example usage:\n// const result1 = new Calculator(20)\n// .divide(0)\n// .getResult();\n\n// console.log(result1); // Output: "Division by zero is not allowed"\n\n// const result2 = new Calculator(2)\n// .add(3)\n// .subtract(1)\n// .multiply(10)\n// .divide(2)\n// .power(2)\n// .getResult();\n\n// console.log(result2); // Output: 400\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 1 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Class Calculator with method chaining
|
class-calculator-with-method-chaining-by-qhjq
| null |
koderoy
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-11T18:01:06.275005+00:00
|
2024-12-11T18:01:06.275005+00:00
| 8 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nFrom the the problem description, it was clear what needed to be done Which is to create a method for each of the operations supported by our supposed calculator. And since it has to support method chaining, meaning in each of the operations, the instance object has to be returned except in the getResult function.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nI started by creating a property in the class named `value` that will hold a number.\nThe value given to the constructor is then stored in this `value` variable. After, i defined the operation that needed to be carried out in each method one after the other and finally returned the result. In Division operation, I made sure that division by zero exception was triggered whenever we try to divide by zero.\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(1)$$\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(1)$$\n\n# Code\n```typescript []\nclass Calculator {\n value : number;\n constructor(value: number) {\n this.value = value;\n }\n \n add(value: number): Calculator {\n this.value += value;\n return this;\n }\n \n subtract(value: number): Calculator {\n this.value -= value;\n return this;\n }\n \n multiply(value: number): Calculator {\n this.value *= value;\n return this;\n }\n \n divide(value: number): Calculator {\n if (value === 0) throw Error(\'Division by zero is not allowed\')\n this.value /= value;\n return this;\n }\n \n power(value: number): Calculator {\n this.value = Math.pow(this.value, value)\n return this;\n }\n \n getResult(): number {\n return this.value;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['TypeScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Calculator with methos chaining (JS)
|
calculator-with-methos-chaining-js-by-12-23nd
| null |
123Malay
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-11T07:05:25.213200+00:00
|
2024-12-11T07:05:25.213200+00:00
| 6 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```javascript []\nclass Calculator {\n constructor(value) {\n this.result = value;\n }\n add(value) {\n this.result += value;\n return this;\n }\n\n subtract(value) {\n this.result -= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n multiply(value) {\n this.result *= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n divide(value) {\n if (value === 0) {\n throw new Error(\'Division by zero is not allowed\');\n }\n this.result /= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n power(value) {\n this.result = Math.pow(this.result, value);\n return this;\n }\n\n getResult() {\n return this.result;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
js easy
|
js-easy-by-hacker_bablu_123-75a7
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nThe goal is to implement a fluent interface for a calculator. By chaining methods (add,
|
Hacker_Bablu_123
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-03T18:58:41.840417+00:00
|
2024-12-03T18:58:41.840453+00:00
| 5 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThe goal is to implement a fluent interface for a calculator. By chaining methods (add, subtract, multiply, etc.), users can perform multiple operations in sequence on the result without needing intermediate variables or steps.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nConstructor: Initialize the Calculator with a starting value.\nMethods: Implement methods (add, subtract, etc.) that modify the result property and return the current instance (this) to enable chaining.\nValidation: Include error handling for invalid operations, such as division by zero.\nResult Retrieval: Provide a getResult method to access the current computed value.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(1)\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(1)\n\n# Code\n```javascript []\nclass Calculator {\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n */\n constructor(value) {\n this.result = value;\n \n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n add(value){\n this.result += value;\n return this;\n \n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n subtract(value){\n this.result -= value;\n return this;\n \n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */ \n multiply(value) {\n this.result *= value;\n return this;\n \n\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n divide(value) {\n if(value === 0){\n throw new Error(\'Division by zero is not allowed\');\n }\n this.result /= value\n return this\n \n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n power(value) {\n this.result = Math.pow(this.result, value)\n return this\n \n }\n \n /** \n * @return {number}\n */\n getResult() {\n return this.result;\n \n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Simple solution
|
simple-solution-by-himanshusaini0345-9dpi
|
\n# Code\ntypescript []\nclass Calculator {\n private result: number;\n constructor(value: number) {\n this.result = value;\n }\n \n add(v
|
himanshusaini0345
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-30T18:48:05.611402+00:00
|
2024-11-30T18:48:05.611431+00:00
| 3 | false |
\n# Code\n```typescript []\nclass Calculator {\n private result: number;\n constructor(value: number) {\n this.result = value;\n }\n \n add(value: number): Calculator {\n this.result += value;\n return this;\n }\n \n subtract(value: number): Calculator {\n this.result -= value;\n return this;\n }\n \n multiply(value: number): Calculator {\n this.result *= value;\n return this;\n }\n \n divide(value: number): Calculator {\n if(value == 0) throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed");\n this.result /= value;\n return this;\n }\n \n power(value: number): Calculator {\n if (value === 0){\n this.result = 1;\n return this;\n }\n\n const base = this.result;\n const isNegativeExponent = value < 0; // Track if exponent is negative\n\n this.result = 1; // Start with neutral multiplier for powers\n\n for (let i = 0; i < Math.abs(value); i++) {\n this.result *= base;\n }\n\n if (isNegativeExponent) {\n this.result = 1 / this.result; // For negative exponents, take reciprocal\n }\n return this;\n }\n \n getResult(): number {\n return this.result;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['TypeScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Chained Calculator: Fluent Arithmetic with a Twist
|
chained-calculator-fluent-arithmetic-wit-gom7
|
Intuition\nThe problem requires implementing a calculator with method chaining, allowing for multiple operations to be performed sequentially. The idea is to us
|
lenzB
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-28T12:03:10.318360+00:00
|
2024-11-28T12:03:10.318385+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition\nThe problem requires implementing a calculator with method chaining, allowing for multiple operations to be performed sequentially. The idea is to use class methods that return the object itself (`this`) to enable chaining. \n\n# Approach\n1. **Encapsulation of Value**: Store the initial value in a private property, which will be updated with each operation.\n2. **Method Chaining**: Each operation (`add`, `subtract`, `multiply`, `divide`, `power`) modifies the current value and returns the instance (`this`) to allow further operations.\n3. **Division Check**: Handle edge cases like division by zero by throwing an error.\n4. **Final Result**: Provide a `getResult` method to retrieve the computed value after a chain of operations.\n\nThis approach ensures modularity and a clean interface for performing calculations.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n - Each operation (`add`, `subtract`, `multiply`, `divide`, `power`): $$O(1)$$, as these are constant-time operations.\n - `getResult`: $$O(1)$$, as it simply returns the stored value.\n\n- Space complexity:\n - $$O(1)$$, as the operations modify the value in place without additional memory usage.\n\n# Code\n```typescript []\nclass Calculator {\n private value = 0\n \n constructor(value: number) {\n this.value = value\n }\n \n add(value: number): Calculator {\n this.value += value\n return this\n }\n \n subtract(value: number): Calculator {\n this.value -= value\n return this\n }\n \n multiply(value: number): Calculator {\n this.value *= value\n return this\n }\n \n divide(value: number): Calculator {\n if (!value) throw \'Division by zero is not allowed\'\n\n this.value /= value\n return this\n }\n \n power(value: number): Calculator {\n this.value = Math.pow(this.value, value)\n return this\n }\n \n getResult(): number {\n return this.value\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['TypeScript', 'JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Simple solution, you need to know only this
|
simple-solution-you-need-to-know-only-th-w0s5
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(1)\n Add your time complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n\n- Space complexity: O(1)\n Add your space complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n\n# Co
|
poperechnyi1
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-28T08:18:22.753227+00:00
|
2024-11-28T08:18:22.753262+00:00
| 6 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(1)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(1)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```typescript []\nclass Calculator {\n private value = 0\n constructor(value: number) {\n this.value = value\n }\n \n add(value: number): Calculator {\n this.value += value\n return this\n }\n \n subtract(value: number): Calculator {\n this.value -= value\n return this\n }\n \n multiply(value: number): Calculator {\n this.value *= value\n return this\n }\n \n divide(value: number): Calculator {\n if(!value)\n throw "Division by zero is not allowed"\n\n this.value /= value\n return this\n }\n \n power(value: number): Calculator {\n this.value = Math.pow(this.value, value)\n return this\n }\n \n getResult(): number {\n return this.value\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['TypeScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
js/ts solution
|
jsts-solution-by-brudnovskyi-4yr0
|
typescript []\nclass Calculator {\n value: number;\n\n constructor(value: number) {\n this.value = value\n }\n\n add(value: number): Calculat
|
brudnovskyi
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-22T06:58:09.102155+00:00
|
2024-11-22T06:58:09.102181+00:00
| 2 | false |
```typescript []\nclass Calculator {\n value: number;\n\n constructor(value: number) {\n this.value = value\n }\n\n add(value: number): Calculator {\n this.value += value;\n return this;\n }\n\n subtract(value: number): Calculator {\n this.value -= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n multiply(value: number): Calculator {\n this.value *= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n divide(value: number): Calculator {\n if (value === 0) throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed")\n\n this.value /= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n power(value: number): Calculator {\n this.value = Math.pow(this.value, value);\n return this;\n }\n\n getResult(): number {\n return this.value\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['TypeScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Calculator with Method Chaining
|
calculator-with-method-chaining-by-jayes-cfen
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
jayesh0604
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-16T16:19:54.301716+00:00
|
2024-11-16T16:19:54.301741+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```javascript []\nclass Calculator {\n constructor(value) {\n this.result = value;\n }\n add(value) {\n this.result += value;\n return this;\n }\n\n subtract(value) {\n this.result -= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n multiply(value) {\n this.result *= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n divide(value) {\n if (value === 0) {\n throw new Error(\'Division by zero is not allowed\');\n }\n this.result /= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n power(value) {\n this.result = Math.pow(this.result, value);\n return this;\n }\n\n getResult() {\n return this.result;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Chained Calculator Implementation for Sequential Operations
|
chained-calculator-implementation-for-se-tp84
|
Intuition\nMy initial thought was to create a Calculator class that could handle multiple operations in sequence, allowing each operation to be chained together
|
shubhamrachchh0
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-11T05:37:13.895930+00:00
|
2024-11-11T05:37:13.895966+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition\nMy initial thought was to create a Calculator class that could handle multiple operations in sequence, allowing each operation to be chained together. Since each action modifies a running total, I aimed to implement the class so that methods could be called consecutively on a single instance.\n\n# Approach\n1. Define the Calculator class: This class should hold the current result of calculations and implement methods for each operation (add, subtract, multiply, divide, power, getResult).\n2. Implement method chaining: Each method should modify the current result, then return this to allow chaining. The divide method includes a check to handle division by zero by setting the result to a specific error message.\n3. Use processActions function: This function initializes the Calculator with the first value in values, then iterates through actions to apply each specified operation with the corresponding value. The final result is obtained by calling getResult.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n \n\nO(n), where \n\uD835\uDC5B\nn is the number of operations. Each operation (like addition, subtraction, etc.) is a constant-time operation.\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(1), since only a fixed amount of space is used to store the result and intermediate values.\n\n# Code\n```javascript []\nclass Calculator {\n constructor(initialValue) {\n this.result = initialValue;\n }\n\n add(value) {\n this.result += value;\n return this; // Return this to allow method chaining\n }\n\n subtract(value) {\n this.result -= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n multiply(value) {\n this.result *= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n divide(value) {\n if (value === 0) {\n this.result = "Division by zero is not allowed";\n return this;\n }\n this.result /= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n power(value) {\n this.result = Math.pow(this.result, value);\n return this;\n }\n\n getResult() {\n return this.result;\n }\n}\n\nfunction processActions(actions, values) {\n let calc = new Calculator(values[0]);\n \n for (let i = 1; i < actions.length; i++) {\n let action = actions[i];\n let value = values[i - 1]; // The corresponding value for the action\n\n if (action === "add") {\n calc.add(value);\n } else if (action === "subtract") {\n calc.subtract(value);\n } else if (action === "multiply") {\n calc.multiply(value);\n } else if (action === "divide") {\n calc.divide(value);\n } else if (action === "power") {\n calc.power(value);\n }\n }\n\n return calc.getResult();\n}\n\n// Example usage:\nconsole.log(processActions(["Calculator", "add", "subtract", "getResult"], [10, 5, 7])); // Output: 8\nconsole.log(processActions(["Calculator", "multiply", "power", "getResult"], [2, 5, 2])); // Output: 100\nconsole.log(processActions(["Calculator", "divide", "getResult"], [20, 0])); // Output: "Division by zero is not allowed"\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Simple class JS
|
simple-class-js-by-fedwar-ddmd
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Fedwar
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-02T19:45:27.255668+00:00
|
2024-11-02T19:45:27.255699+00:00
| 9 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```javascript []\nclass Calculator {\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n */\n constructor(value) {\n this.value = value;\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n add(value) {\n this.value += value;\n return this;\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n subtract(value) {\n this.value -= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n multiply(value) {\n this.value *= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n divide(value) {\n this.value = !value ? "Division by zero is not allowed" : this.value / value;\n return this;\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n power(value) {\n this.value = this.value ** value;\n return this;\n }\n\n /** \n * @return {number}\n */\n getResult() {\n return this.value;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
30 day js day1
|
30-day-js-day1-by-deleted_user-5wvz
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
deleted_user
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-30T12:10:31.047617+00:00
|
2024-10-30T12:10:31.047660+00:00
| 5 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```javascript []\nclass Calculator {\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n */\n\tconstructor(value) {\n\t\tthis.x = value;\n\t}\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n\tadd(value){\n\t\tthis.x += value;\n return this\n\t}\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n\tsubtract(value){\n\t\tthis.x -= value;\n return this\n\t}\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */ \n\tmultiply(value) {\n\t\tthis.x *= value;\n return this\n\t}\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n\tdivide(value) {\n if (value === 0) {\n throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed");\n }\n this.x /= value;\n return this\n\t}\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n\tpower(value) {\n\t\tthis.x = Math.pow(this.x, value);\n return this\n\t}\n \n /** \n * @return {number}\n */\n\tgetResult() {\n\t\treturn this.x;\n\t}\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
solved
|
solved-by-ali_madad-o963
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
ali_madad
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-19T00:35:18.857603+00:00
|
2024-10-19T00:35:18.857633+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```javascript []\nclass Calculator {\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n */\n constructor(value) {\n this.result = value\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n add(value){\n this.result += value;\n return this\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n subtract(value){\n this.result -= value\n return this\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */ \n multiply(value) {\n this.result *= value\n return this\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n divide(value) {\n if(value === 0 ) throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed") \n this.result = this.result / value\n return this\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n power(value) {\n this.result = Math.pow(this.result,value)\n return this\n }\n\n /** \n * @return {number}\n */\n getResult() {\n return this.result\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
2726. Calculator with Method Chaining
|
2726-calculator-with-method-chaining-by-ohbe8
|
\n\n# Code\njavascript []\nclass Calculator {\n constructor(value) {\n this.value = value;\n }\n\n add(value) {\n this.value += value;\n
|
Maimuna_Javed
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-18T09:57:30.234568+00:00
|
2024-10-18T09:57:30.234597+00:00
| 6 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```javascript []\nclass Calculator {\n constructor(value) {\n this.value = value;\n }\n\n add(value) {\n this.value += value;\n return this;\n }\n\n subtract(value) {\n this.value -= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n multiply(value) {\n this.value *= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n divide(value) {\n if (value === 0) {\n throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed");\n }\n this.value /= value;\n\n return this;\n }\n\n power(value) {\n this.value = Math.pow(this.value, value);\n return this;\n }\n\n getResult() {\n return this.value;\n }\n}\n\ntry {\n const cal = new Calculator(10);\n console.log(cal.add(5).subtract(7).getResult());\n} catch (error) {\n console.error(error.message);\n}\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Solution for calculator with method chaining
|
solution-for-calculator-with-method-chai-mu0e
|
Code\njavascript []\nclass Calculator {\n constructor(initialValue = 0) {\n this.result = initialValue;\n }\n\n add = (value) => {\n this
|
SatyakiRaj
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-17T17:48:45.423975+00:00
|
2024-10-17T17:48:45.424037+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Code\n```javascript []\nclass Calculator {\n constructor(initialValue = 0) {\n this.result = initialValue;\n }\n\n add = (value) => {\n this.result += value;\n return this;\n }\n\n subtract = (value) => {\n this.result -= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n multiply = (value) => {\n this.result *= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n divide = (value) => {\n if (!value) throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed");\n this.result /= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n // Method to raise the result to the power of a number\n power = (value) => {\n this.result = Math.pow(this.result, value);\n return this;\n }\n\n // Method to get the current result\n getResult = () => this.result;\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Simple JS solution
|
simple-js-solution-by-alinurmamatov-8i6w
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
alinurmamatov
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-11T20:46:30.686637+00:00
|
2024-10-11T20:46:30.686669+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```javascript []\nclass Calculator {\n constructor(value) {\n this.result = value;\n }\n \n add(value){\n this.result += value;\n return this;\n }\n\n subtract(value){\n this.result -= value;\n return this;\n }\n \n multiply(value) {\n this.result *= value;\n return this;\n }\n \n divide(value) {\n if (value === 0) {\n throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed");\n } else {\n this.result /= value;\n return this;\n }\n }\n \n power(value) {\n this.result = Math.pow(this.result, value);\n return this;\n }\n\n getResult() {\n return this.result;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
!!
|
by-edogola-bh2t
|
Explanation\n# Constructor:\n The Calculator class initializes the result with the provided initialValue.\n\n# Arithmetic Methods:\n\nadd: Adds the given value
|
edogola
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-07T08:33:22.975113+00:00
|
2024-10-07T08:33:22.975142+00:00
| 1 | false |
# Explanation\n# Constructor:\n The Calculator class initializes the result with the provided initialValue.\n\n# Arithmetic Methods:\n\nadd: Adds the given value to the result and returns the current instance.\nsubtract: Subtracts the given value from the result and returns the current instance.\nmultiply: Multiplies the result by the given value and returns the current instance.\ndivide: Divides the result by the given value. It checks if the value is zero and throws an error if it is.\npower: Raises the result to the power of the given value and returns the current instance.\ngetResult: Returns the final result after all operations have been performed.\n\nExample Outputs\nThe first example shows how to chain the operations to get the final result of 8.\nThe second example demonstrates multiplication and exponentiation, yielding 100.\nThe third example illustrates error handling for division by zero.\n\nTo create the Calculator class that supports method chaining and performs various mathematical operations, you can follow these steps:\n\n# Constructor: \nThe constructor should accept a number that initializes the result.\n# Method Implementations: \nEach method (add, subtract, multiply, divide, power) should perform its respective operation, update the result, and return the current instance of the Calculator for chaining.\nError Handling: The divide method should handle division by zero by throwing an error with a specific message.\nGet Result: The getResult method should return the current result.\n# Code\n```javascript []\nclass Calculator {\n constructor(initialValue) {\n this.result = initialValue; // Initialize the result with the provided value\n }\n\n add(value) {\n this.result += value; // Add the value to the result\n return this; // Return the current instance for chaining\n }\n\n subtract(value) {\n this.result -= value; // Subtract the value from the result\n return this; // Return the current instance for chaining\n }\n\n multiply(value) {\n this.result *= value; // Multiply the result by the value\n return this; // Return the current instance for chaining\n }\n\n divide(value) {\n if (value === 0) {\n throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed"); // Handle division by zero\n }\n this.result /= value; // Divide the result by the value\n return this; // Return the current instance for chaining\n }\n\n power(value) {\n this.result **= value; // Raise the result to the power of the value\n return this; // Return the current instance for chaining\n }\n\n getResult() {\n return this.result; // Return the current result\n }\n}\n\n// Example Usage\nconsole.log(new Calculator(10).add(5).subtract(7).getResult()); // Output: 8\nconsole.log(new Calculator(2).multiply(5).power(2).getResult()); // Output: 100\ntry {\n console.log(new Calculator(20).divide(0).getResult()); // Should throw an error\n} catch (error) {\n console.log(error.message); // Output: "Division by zero is not allowed"\n}\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Solution
|
solution-by-qqama-qxxl
|
\n\n# Code\njavascript []\nclass Calculator {\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n */\n constructor(value) {\n this.value = value;\n
|
qqama
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-29T13:45:47.881630+00:00
|
2024-09-29T13:45:47.881662+00:00
| 1 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```javascript []\nclass Calculator {\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n */\n constructor(value) {\n this.value = value;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n add(value){\n this.value += value;\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n subtract(value){\n this.value -= value;\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */ \n multiply(value) {\n this.value *= value;\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n divide(value) {\n if(value == 0) throw new Error(\'Division by zero is not allowed\');\n this.value /= value;\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n power(value) {\n this.value = Math.pow(this.value, value);\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @return {number}\n */\n getResult() {\n return this.value;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Easy Solution.....
|
easy-solution-by-akashnaik7396-xtmb
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
AkashNaik7396
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-29T09:37:19.386142+00:00
|
2024-09-29T09:37:19.386164+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```javascript []\nclass Calculator {\n \n constructor(value) {\n this.result=value;\n \n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n add(value){\n this.result+=value;\n return this;\n \n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n subtract(value){\n this.result-=value;\n return this;\n \n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */ \n multiply(value) {\n this.result*=value;\n return this;\n \n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n divide(value) {\n if(value===0){\n throw new Error(\'Division by zero is not allowed\');\n }\n this.result/=value;\n return this;\n \n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n power(value) {\n this.result=Math.pow(this.result,value);\n return this;\n \n }\n \n /** \n * @return {number}\n */\n getResult() {\n return this.result;\n \n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Best Solution | Easy to Understand | Beats 90%
|
best-solution-easy-to-understand-beats-9-vgk6
|
\n# Code\njavascript []\nclass Calculator {\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n */\n constructor(value) {\n this.val = value\n }\n
|
jdszekeres
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-28T22:32:34.235732+00:00
|
2024-09-28T22:32:34.235754+00:00
| 2 | false |
\n# Code\n```javascript []\nclass Calculator {\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n */\n constructor(value) {\n this.val = value\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n add(value){\n return new Calculator(this.val + value);\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n subtract(value){\n return new Calculator(this.val - value);\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */ \n multiply(value) {\n return new Calculator(this.val * value);\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n divide(value) {\n if (value === 0) throw "Division by zero is not allowed"\n return new Calculator(this.val / value) ;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n power(value) {\n return new Calculator(this.val ** value); \n }\n \n /** \n * @return {number}\n */\n getResult() {\n return this.val\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Class object program
|
class-object-program-by-sidharajyadav157-p84n
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
sidharajyadav157
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-26T11:58:15.300432+00:00
|
2024-09-26T11:58:15.300453+00:00
| 1 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```javascript []\nclass Calculator {\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n */\n constructor(value) {\n this.result = value\n \n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n add(value){\n this.result += value\n return this\n \n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n subtract(value){\n this.result -= value\n return this\n \n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */ \n multiply(value) {\n this.result *= value\n return this\n \n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n divide(value) {\n if (value === 0) {\n throw new Error(\'Division by zero is not allowed\');\n }\n this.result /= value;\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n power(value) {\n this.result **= value\n return this\n \n }\n \n /** \n * @return {number}\n */\n getResult() {\n return this.result\n \n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Simple JS solution
|
simple-js-solution-by-p___k-0gak
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
P___K
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-25T06:16:44.491573+00:00
|
2024-09-25T06:16:44.491609+00:00
| 0 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```javascript []\nclass Calculator {\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n */\n constructor(value) {\n this.res= value;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n add(value){\n this.res+=value;\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n subtract(value){\n this.res-=value;\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */ \n multiply(value) {\n this.res*=value;\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n divide(value) {\n if(value===0){\n throw new Error(\'Division by zero is not allowed\');\n }\n this.res/=value;\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n power(value) {\n this.res**=value;\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @return {number}\n */\n getResult() {\n return this.res;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
simple solution approach
|
simple-solution-approach-by-sangram72-vz55
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
sangram72
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-20T10:54:41.926280+00:00
|
2024-09-20T10:54:41.926302+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```javascript []\nclass Calculator {\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n */\n constructor(value) {\n this.result = value;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n add(value){\n this.result +=value\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n subtract(value){\n this.result -=value\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */ \n multiply(value) {\n this.result *=value\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n divide(value) {\n if (value !== 0) {\n \n this.result /= value;\n return this;\n }else{\n throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed")\n }\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n power(value) {\n this.result = Math.pow(this.result, value);\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @return {number}\n */\n getResult() {\n return this.result;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Simple JS solution
|
simple-js-solution-by-hemilpatel-x38u
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
hemilpatel
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-18T02:35:36.544793+00:00
|
2024-09-18T02:35:36.544828+00:00
| 5 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```javascript []\nclass Calculator {\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n */\n constructor(value) {\n this.val = value\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n add(value) {\n this.val += value\n return this\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n subtract(value) {\n this.val -= value\n return this\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n multiply(value) {\n this.val *= value\n return this\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n divide(value) {\n if (value === 0) {\n this.val = "Division by zero is not allowed"\n } else {\n this.val /= value\n }\n\n return this\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n power(value) {\n this.val **= value\n return this\n }\n\n /** \n * @return {number}\n */\n getResult() {\n return this.val\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Beats 95%
|
beats-95-by-vikramsinghvsd29-28yb
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
vikramsinghvsd29
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-17T20:27:17.452446+00:00
|
2024-09-17T20:27:17.452467+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```javascript []\nclass Calculator {\n\n // public value = 0\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n */\n constructor(value) {\n this.value = value\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n add(value) {\n this.value += value\n return this\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n subtract(value) {\n this.value -= value\n\n return this\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n multiply(value) {\n this.value *= value\n return this\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n divide(value) {\n if (value === 0) throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed"\n)\n this.value /= value\n return this\n }\n\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n power(value) {\n this.value **= value\n return this\n }\n\n /** \n * @return {number}\n */\n getResult() {\n return this.value\n }\n}\n\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Method Chaining
|
method-chaining-by-arthurarakelyan-wcbu
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
ArthurArakelyan
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-13T18:35:27.885803+00:00
|
2024-09-13T18:35:27.885830+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```javascript []\nclass Calculator {\n value;\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n */\n constructor(value) {\n this.value = value;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n add(value){\n this.value += value;\n\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n subtract(value){\n this.value -= value;\n\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */ \n multiply(value) {\n this.value *= value;\n\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n divide(value) {\n if (value === 0) {\n throw "Division by zero is not allowed";\n }\n\n this.value /= value;\n\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n power(value) {\n this.value = this.value ** value;\n\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @return {number}\n */\n getResult() {\n return this.value;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
TS solution
|
ts-solution-by-rndm-sklz-sa0f
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
rndm-sklz
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-13T09:15:58.895674+00:00
|
2024-09-13T09:15:58.895700+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```typescript []\nclass Calculator {\n res: number;\n \n constructor(value: number) {\n this.res = value\n }\n \n add(value: number): Calculator {\n let calculatedValue = this.res += value\n return new Calculator(calculatedValue)\n }\n \n subtract(value: number): Calculator {\n let calculatedValue = this.res -= value\n return new Calculator(calculatedValue)\n }\n \n multiply(value: number): Calculator {\n this.res = this.res * value\n return new Calculator(this.res)\n }\n \n divide(value: number): Calculator {\n if (value === 0) {\n throw new Error(\'Division by zero is not allowed\')\n } else {\n this.res = this.res / value\n }\n \n return new Calculator(this.res)\n }\n \n power(value: number): Calculator {\n this.res = this.res ** value\n return new Calculator(this.res)\n }\n \n getResult(): number {\n return this.res\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['TypeScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
simple solution easy to understand
|
simple-solution-easy-to-understand-by-s1-6655
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
s1nju
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-12T21:44:10.117524+00:00
|
2024-09-12T21:44:10.117546+00:00
| 1 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```javascript []\nclass Calculator {\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n */\n constructor(value) {\n this.value=value;\n \n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n add(value){\n this.value+=value\n \n \n return this\n\n \n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n subtract(value){\n this.value-=value\n \n return this\n \n }\n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */ \n multiply(value) {\n this.value*=value\n \n return this\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n divide(value) {\n \n if(value==0){\n this.value= "Division by zero is not allowed"\n return this\n }else{\n this.value= this.value /value\n \n return this}\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n power(value) {\n \n this.value= Math.pow(this.value,value)\n \n return this\n }\n \n /** \n * @return {number}\n */\n getResult() {\n return this.value\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Beats 97% || Simple , easy and Beginner friendly
|
beats-97-simple-easy-and-beginner-friend-62iq
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
gautamgehani01
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-11T09:17:47.895116+00:00
|
2024-09-11T09:17:47.895149+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(1)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(1)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```javascript []\nclass Calculator {\n constructor(value) {\n this.value = value\n }\n \n add(value){\n this.value += value;\n return this;\n }\n \n subtract(value){\n this.value -= value;\n return this;\n }\n \n multiply(value) {\n this.value *= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n divide(value) {\n if (value === 0){\n throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed")\n }\n this.value /= value;\n return this;\n }\n \n power(value) {\n this.value = Math.pow(this.value, value);\n return this;\n }\n \n getResult() {\n return this.value;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Solved: Using this variable
|
solved-using-this-variable-by-choudhuryr-y2ap
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nUse of this variable in javascript\n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving th
|
choudhuryrakesh
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-08T14:25:45.532086+00:00
|
2024-09-08T14:25:45.532166+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nUse of `this` variable in javascript\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n- Inside the `constructor` add a new valriable (result) and initialise it with value.\n- Then follow the method description and remeber to return the `this` value so that the next chain function will use that `this` scope\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(1)$$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(1)$$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```javascript []\nclass Calculator {\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n */\n constructor(value) {\n this.result = value;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n add(value){\n this.result += value;\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n subtract(value){\n this.result -= value;\n return this; \n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */ \n multiply(value) {\n this.result *= value; \n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n divide(value) {\n if (value === 0) {\n throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed");\n } else {\n this.result /= value; \n return this;\n }\n }\n \n /** \n * @param {number} value\n * @return {Calculator}\n */\n power(value) {\n this.result = Math.pow(this.result, value);\n return this;\n }\n \n /** \n * @return {number}\n */\n getResult() {\n return this.result;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
Master JavaScript with This Powerful Chainable Calculator !
|
master-javascript-with-this-powerful-cha-ys3g
|
Intuition\nThe idea behind this problem is to implement a simple, chainable calculator that performs basic arithmetic operations. The goal is to allow users to
|
Asheem_Rahman
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-07T17:37:05.043093+00:00
|
2024-09-07T17:37:05.043112+00:00
| 0 | false |
# Intuition\nThe idea behind this problem is to implement a simple, chainable calculator that performs basic arithmetic operations. The goal is to allow users to perform multiple operations in a sequence while maintaining code simplicity and readability.\n\n# Approach\nWe will define a class **Calculator** that initializes with a value. Each arithmetic operation (**add, subtract, multiply, divide, and power**) will modify the internal **value** and return the instance itself, allowing method chaining. The **divide** function will handle division by zero by throwing an appropriate error. Finally, a **getResult** method will return the current value.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nEach operation (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, exponentiation) is performed in constant time. Hence, the time complexity for each operation is: \uD835\uDC42(1)\n\n- Space complexity:\nSince the calculator only stores a single value, the space complexity is also: \uD835\uDC42(1)\n\n# Code\n```javascript []\nclass Calculator {\n\n constructor(value) {\n this.value = value;\n }\n\n add(value) {\n this.value += value;\n return this;\n }\n\n subtract(value) {\n this.value -= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n multiply(value) {\n this.value *= value;\n return this;\n }\n \n divide(value) {\n if (value === 0) {\n throw new Error(\'Division by zero is not allowed\');\n }\n this.value /= value;\n return this;\n }\n \n power(value) {\n this.value = Math.pow(this.value, value);\n return this;\n }\n \n getResult() {\n return this.value;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
A simple Solution
|
a-simple-solution-by-narendra835-v1in
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
narendra835
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-06T02:59:16.972638+00:00
|
2024-09-06T02:59:16.972667+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```javascript []\nclass Calculator{\n constructor(value){\n this.result=value\n }\n add(value){\n this.result+=value\n return this\n }\n subtract(value){\n this.result-=value\n return this\n }\n multiply(value){\n this.result*=value\n return this\n }\n divide(value){\n if(value===0){\n throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed")\n }\n this.result/=value;\n return this\n }\n power(value){\n this.result**=value\n return this\n }\n getResult(){\n return this.result\n }\n\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
calculator-with-method-chaining
|
SIMPLE TO UNDERSTAND | THE EASIEST SOLUTION 🎯💯❤️🔥🏆🥇 JAVASCRIPT ✅🕶🤏📚 🧠 🎓
|
simple-to-understand-the-easiest-solutio-9gty
|
2726. Calculator with Method Chaining\n\n\uD83C\uDF31 Difficulty: Easy\n\n\uD83D\uDC81\uD83C\uDFFB\u200D\u2640\uFE0F All my solved LeetCode problems on GitHub:
|
RayanaSales
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-04T14:22:10.185078+00:00
|
2024-09-05T14:22:12.689753+00:00
| 1 | false |
# 2726. Calculator with Method Chaining\n\n\uD83C\uDF31 Difficulty: `Easy`\n\n\uD83D\uDC81\uD83C\uDFFB\u200D\u2640\uFE0F All my solved LeetCode problems on GitHub: [rayanasales/leetcode](https://github.com/rayanasales/leetcode)\n\n\u2764\uFE0F\u200D\uD83D\uDD25\u2764\uFE0F\u200D\uD83D\uDD25\u2764\uFE0F\u200D\uD83D\uDD25 If it\'s help, please up \uD83D\uDD1D vote! \u2764\uFE0F\u200D\uD83D\uDD25\u2764\uFE0F\u200D\uD83D\uDD25\u2764\uFE0F\u200D\uD83D\uDD25\n\n---\n\n# Solution\n\n```Javascript []\nclass Calculator {\n constructor(value) {\n this.result = value;\n }\n\n add(value) {\n this.result += value;\n return this;\n }\n\n subtract(value) {\n this.result -= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n multiply(value) {\n this.result *= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n divide(value) {\n if (value === 0) {\n throw new Error("Division by zero is not allowed");\n }\n this.result /= value;\n return this;\n }\n\n power(value) {\n this.result = Math.pow(this.result, value);\n return this;\n }\n\n getResult() {\n return this.result;\n }\n}\n```\n\n# Explanation\n\n### Code Explanation\n\n1. **Constructor**:\n\n - The `constructor` initializes the `Calculator` instance with an initial `result` value.\n - `this.result = value;` sets the initial value of `result` to the value passed when an instance is created.\n\n2. **Add Method**:\n\n - `add(value)` method adds the passed `value` to the current `result`.\n - It then returns `this`, allowing for method chaining. `this` refers to the current instance of the class.\n\n3. **Subtract Method**:\n\n - Similar to `add`, `subtract(value)` subtracts the passed `value` from `result`.\n - Returns `this` for continued chaining.\n\n4. **Multiply Method**:\n\n - `multiply(value)` multiplies the `result` by the passed `value`.\n - Again, it returns `this` to enable method chaining.\n\n5. **Divide Method**:\n\n - In `divide(value)`, first, there\'s a check to ensure that division by zero does not occur.\n - If `value` is `0`, it throws an `Error`, stopping execution and notifying the user.\n - Otherwise, it divides the `result` by `value` and returns `this`.\n\n6. **Power Method**:\n\n - `power(value)` uses `Math.pow` to raise `result` to the power of `value`.\n - Returns `this` for chaining.\n\n7. **Get Result Method**:\n - `getResult()` simply returns the current value of `result`.\n - This method ends the chaining by returning a primitive value (the result of computations).\n\n### How Method Chaining Works\n\nMethod chaining is possible because most methods in the `Calculator` class return `this`, which is the instance of the class. By returning `this`, you can call another method on the same instance immediately. For example, `new Calculator(10).add(5).subtract(7).getResult()` seamlessly performs several operations in one line.\n\nThis design pattern is known as the **Fluent Interface** and is commonly used in JavaScript to create more readable code. By enabling method chaining, you make the syntax more expressive and closer to natural language, which enhances readability and ease of use.\n\n---\n\n# Please UPVOTE if this was helpful \uD83D\uDD1D\uD83D\uDD1D\uD83D\uDD1D\u2764\uFE0F\u2764\uFE0F\u2764\uFE0F\n\nand check it out all my solved LeetCode problems on GitHub: [rayanasales/leetcode](https://github.com/rayanasales/leetcode) \uD83E\uDD19\uD83D\uDE1A\uD83E\uDD18\n\n\n
| 0 | 0 |
['Math', 'JavaScript']
| 0 |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.