question_slug
stringlengths 3
77
| title
stringlengths 1
183
| slug
stringlengths 12
45
| summary
stringlengths 1
160
⌀ | author
stringlengths 2
30
| certification
stringclasses 2
values | created_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| updated_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| hit_count
int64 0
10.6M
| has_video
bool 2
classes | content
stringlengths 4
576k
| upvotes
int64 0
11.5k
| downvotes
int64 0
358
| tags
stringlengths 2
193
| comments
int64 0
2.56k
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
count-items-matching-a-rule
|
JAVA + HashMap for mappings
|
java-hashmap-for-mappings-by-maxbaldin-6tfo
|
Some straightforward approach to the mapping of rule keys and indexes:\n\n\nimport java.util.HashMap;\nimport java.util.List;\nimport java.util.Map;\n\nclass So
|
maxbaldin
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-14T08:40:54.364669+00:00
|
2022-07-14T08:40:54.364704+00:00
| 104 | false |
Some straightforward approach to the mapping of rule keys and indexes:\n\n```\nimport java.util.HashMap;\nimport java.util.List;\nimport java.util.Map;\n\nclass Solution {\n Map<String, Integer> mapping = new HashMap<>() {{\n put("type", 0);\n put("color", 1);\n put("name", 2);\n }};\n\n public int countMatches(List<List<String>> items, String ruleKey, String ruleValue) {\n int count = 0;\n for (List<String> item : items) {\n if (item.get(this.mapping.get(ruleKey)).equals(ruleValue)) {\n count += 1;\n }\n }\n\n return count;\n }\n}\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
count-items-matching-a-rule
|
Easy Method || c++ |
|
easy-method-c-by-tiwariswapnil100-mpm9
|
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countMatches(vector>& items, string r1, string r2) {\n int k;\n int count =0;\n if(r1 == "type")\n
|
tiwariswapnil100
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-18T11:55:04.308375+00:00
|
2022-05-18T11:55:04.308427+00:00
| 176 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countMatches(vector<vector<string>>& items, string r1, string r2) {\n int k;\n int count =0;\n if(r1 == "type")\n k=0;\n else if(r1 == "color")\n k=1;\n else \n k=2;\n \n \n \n cout<<k;\n for(int i=0;i<items.size();i++){\n if(items[i][k]==r2)\n count++;\n }\n \n return count;\n }\n};
| 3 | 0 |
['C', 'C++']
| 0 |
count-items-matching-a-rule
|
JAVA | easy with comments |
|
java-easy-with-comments-by-akashsin63-p5a7
|
\nclass Solution {\n \n // step one we will compare it rulekey and ruleValue with every element and increase the count\n \n public int countMatches(
|
akashsin63
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-18T07:41:30.183071+00:00
|
2022-04-18T07:41:30.183096+00:00
| 219 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n \n // step one we will compare it rulekey and ruleValue with every element and increase the count\n \n public int countMatches(List<List<String>> items, String ruleKey, String ruleValue) {\n int count=0;\n for(int i=0; i<items.size(); i++){\n if(ruleKey.equals("type") && items.get(i).get(0).equals(ruleValue)){ //here we are traving at\n // row 0 and into index 0 of every element of row one if it matched requirement incre count\n count=count+1;\n }\n if(ruleKey.equals("color") && items.get(i).get(1).equals(ruleValue)){ //here we are traving at\n // row 2 and into index 1 of every element of row one if it matched requirement incre count\n count=count+1;\n }\n if(ruleKey.equals("name") && items.get(i).get(2).equals(ruleValue)){ //here we are traving at\n // row 2 and into index 2 of every element of row one if it matched requirement incre count\n count=count+1;\n }\n }\n return count;\n }\n}\n```// if you understode it than only please upvote it.. it makes me motivated to code more contribute more..
| 3 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
count-items-matching-a-rule
|
Easy Java Solution 100% faster ! Optimized Code!!
|
easy-java-solution-100-faster-optimized-3rr3h
|
Easy Solution!!\n\n\nclass Solution {\n public int countMatches(List<List<String>> items, String ruleKey, String ruleValue) \n {\n int j=0;\n
|
etishajain
|
NORMAL
|
2022-03-15T14:29:42.920570+00:00
|
2022-03-15T14:29:42.920603+00:00
| 143 | false |
**Easy Solution!!**\n\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int countMatches(List<List<String>> items, String ruleKey, String ruleValue) \n {\n int j=0;\n int count=0;\n switch(ruleKey)\n {\n case "type" -> j=0;\n case "color" -> j=1;\n default -> j=2;\n }\n for(int i=0;i<items.size();i++)\n {\n if(items.get(i).get(j).equals(ruleValue))\n count++;\n }\n return count;\n }\n}\n```\n\n**Comment if You have better Approach & found it helpful !!!**
| 3 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
count-items-matching-a-rule
|
Less memory usage 99%
|
less-memory-usage-99-by-fazliddindehkano-q9si
|
```\nclass Solution:\n def countMatches(self, items: List[List[str]], ruleKey: str, ruleValue: str) -> int:\n types = [item[0] for item in items] \n
|
fazliddindehkanoff
|
NORMAL
|
2022-03-13T15:04:13.193704+00:00
|
2022-03-13T15:04:13.193748+00:00
| 159 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def countMatches(self, items: List[List[str]], ruleKey: str, ruleValue: str) -> int:\n types = [item[0] for item in items] \n color = [item[1] for item in items] \n names = [item[2] for item in items]\n if ruleKey == \'name\':\n return names.count(ruleValue)\n elif ruleKey == \'color\':\n return color.count(ruleValue)\n else:\n return types.count(ruleValue)
| 3 | 0 |
['Python']
| 0 |
count-items-matching-a-rule
|
Java | 2 liner | Explained
|
java-2-liner-explained-by-prashant404-912k
|
Idea: Nothing clever to do here, just iterate and count\n> T/S: O(n)/O(1), where n = size(items)\n\nprivate static final Map<String, Integer> RULE_TO_INDEX = Ma
|
prashant404
|
NORMAL
|
2022-01-20T08:33:28.785744+00:00
|
2022-01-20T08:33:28.785777+00:00
| 227 | false |
**Idea:** Nothing clever to do here, just iterate and count\n> **T/S**: O(n)/O(1), where n = size(items)\n```\nprivate static final Map<String, Integer> RULE_TO_INDEX = Map.of("type", 0,\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t "color", 1,\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t "name", 2);\n\npublic int countMatches(List<List<String>> items, String ruleKey, String ruleValue) {\n\tvar ruleIndex = RULE_TO_INDEX.get(ruleKey); // get the rule\n\tvar count = 0;\n\t\n\tfor (var item : items) // iterate\n\t\tif (item.get(ruleIndex).equals(ruleValue)) // check\n\t\t\tcount++; // count\n\treturn count;\n}\n```\nVersion 2: 2 liner using streams\n```\npublic int countMatches(List<List<String>> items, String ruleKey, String ruleValue) {\n\treturn (int) items.stream()\n\t\t\t\t\t .filter(item -> item.get(RULE_TO_INDEX.get(ruleKey))\n\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t.equals(ruleValue))\n\t\t\t\t\t .count();\n}\n```\n***Please upvote if this helps***
| 3 | 0 |
['Java']
| 1 |
count-items-matching-a-rule
|
Intuitive, Go Solution
|
intuitive-go-solution-by-pradeep288-9ry4
|
\nfunc countMatches(items [][]string, ruleKey string, ruleValue string) int {\n\thashMap := make(map[string]int)\n\thashMap["type"] = 0\n\thashMap["color"] = 1\
|
pradeep288
|
NORMAL
|
2021-10-25T17:18:29.809964+00:00
|
2021-10-25T17:26:18.041353+00:00
| 165 | false |
```\nfunc countMatches(items [][]string, ruleKey string, ruleValue string) int {\n\thashMap := make(map[string]int)\n\thashMap["type"] = 0\n\thashMap["color"] = 1\n\thashMap["name"] = 2\n\n\tvar res int\n\tfor _, item := range items {\n\t\tif item[hashMap[ruleKey]] == ruleValue {\n\t\t\tres++\n\t\t}\n\t}\n\treturn res\n}\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Go']
| 2 |
count-items-matching-a-rule
|
C++ Easy to understand for beginners
|
c-easy-to-understand-for-beginners-by-ra-h233
|
Since you only have to check one thing about each item (type, color or name) you determine the index of that and then scan the array with a for loop. \n\nYou ha
|
razumihin
|
NORMAL
|
2021-08-31T10:34:08.387072+00:00
|
2021-09-01T20:07:18.249229+00:00
| 207 | false |
Since you only have to check one thing about each item (type, color or name) you determine the index of that and then scan the array with a for loop. \n\nYou have to keep track of the number of items that match the rule, so the sol varieble starts at 0 and you increment it by one everytime you see an item that matches the rule.\n\nIf you found this helpful please consider leaving an upvote.\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countMatches(vector<vector<string>>& items, string ruleKey, string ruleValue) {\n int sol = 0;\n int temp = 0;\n if(ruleKey == "color") temp = 1;\n if(ruleKey == "name") temp = 2;\n for(int i = 0; i < items.size(); i++)\n {\n if(items[i][temp] == ruleValue) sol++;\n }\n return sol;\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['C', 'C++']
| 1 |
count-items-matching-a-rule
|
Java faster than 98%
|
java-faster-than-98-by-android_devil-19nj
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int countMatches(List<List<String>> items, String ruleKey, String ruleValue) {\n \n int index = -1; \n int c
|
android_devil
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-10T19:19:33.372006+00:00
|
2021-07-10T19:19:33.372041+00:00
| 209 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int countMatches(List<List<String>> items, String ruleKey, String ruleValue) {\n \n int index = -1; \n int count = 0;\n \n \n if(ruleKey.equals("type")) index = 0; \n else if (ruleKey.equals("color")) index = 1;\n else index = 2; \n \n \n for(List<String> list : items){\n if(list.get(index).equals(ruleValue)) count++;\n \n }\n return count; \n \n }\n}\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
count-items-matching-a-rule
|
Python dict Solution
|
python-dict-solution-by-namjunwoo223-vph9
|
\nclass Solution(object):\n def countMatches(self, items, ruleKey, ruleValue):\n item_dict = {"type":0,"color":1,"name":2}\n idx = item_dict[ru
|
namjunwoo223
|
NORMAL
|
2021-06-01T02:52:41.101130+00:00
|
2021-06-01T02:52:48.658102+00:00
| 261 | false |
```\nclass Solution(object):\n def countMatches(self, items, ruleKey, ruleValue):\n item_dict = {"type":0,"color":1,"name":2}\n idx = item_dict[ruleKey]\n count = 0\n \n for i in items:\n if i[idx] == ruleValue:\n count += 1\n \n return count\n```\n\nRuntime: 180 ms, faster than 99.71% of Python online submissions for Count Items Matching a Rule.\nMemory Usage: 21.1 MB, less than 61.76% of Python online submissions for Count Items Matching a Rule.\n\n
| 3 | 1 |
['Python']
| 0 |
count-items-matching-a-rule
|
JavaScript ES6 solution (Runtime: 84 ms, faster than 94.77%)
|
javascript-es6-solution-runtime-84-ms-fa-skc5
|
Some of the top rated JS solutions for this problem use filter, but because that creates a new array for which we then access the length property, it seems like
|
dlande000
|
NORMAL
|
2021-05-07T21:44:02.980193+00:00
|
2021-07-06T13:52:40.845126+00:00
| 453 | false |
Some of the top rated JS solutions for this problem use `filter`, but because that creates a new array for which we then access the `length` property, it seems like using `reduce` to count would be more memory efficient and, given a large enough input, time efficient (for constructing the output array). \n\n1. Construct a `ruleHash` object so that we can quicky convert `ruleKey` to its corresponding index. \n2. Using reduce, iterate through the `items` array. \n3. If we find that an item\'s value matches the `ruleValue`, increment `count`. \n4. The return value of our `reduce` function will be our `count`. \n\nTime: O(n)\nSpace: O(1)\n\n```\nconst countMatches = (items, ruleKey, ruleValue) => {\n const ruleHash = {\n type: 0,\n color: 1,\n name: 2,\n }\n const ruleIdx = ruleHash[ruleKey];\n \n return items.reduce((count, item) => {\n if (item[ruleIdx] === ruleValue) count++;\n return count;\n }, 0);\n};\n```\n\nOr, written with an implicit return and a ternary (I prefer to use ternaries when assigning a variable rather than specifying a return value, but it\'s nice to collapse that logic): \n\n```\nconst countMatches = (items, ruleKey, ruleValue) => {\n const ruleHash = {\n type: 0,\n color: 1,\n name: 2,\n }\n const ruleIdx = ruleHash[ruleKey];\n \n return items.reduce((count, item) => (\n item[ruleIdx] === ruleValue ? ++count : count\n ), 0);\n};\n```\n\nFor a fake all implicit returns version, we can move the `ruleHash` constant outside of the function declaration: \n\n```\nconst RULE_HASH = {\n type: 0,\n color: 1,\n name: 2,\n};\n\nconst countMatches = (items, ruleKey, ruleValue) => (\n items.reduce((count, item) => (\n item[RULE_HASH[ruleKey]] === ruleValue ? ++count : count\n ), 0)\n);\n```\n\nThe solutions provided run between 84 ms (faster than 94.77%) and 90ms, and around 42mb for memory. \n\n... and, because why not, here\'s a solution without the hash:\n\n```\nconst countMatches = (items, ruleKey, ruleValue) => (\n items.reduce((count, item) => {\n let checkingValue;\n \n switch (ruleKey) {\n case "type":\n checkingValue = item[0];\n break;\n case "color":\n checkingValue = item[1];\n break;\n default:\n checkingValue = item[2];\n }\n\n if (checkingValue === ruleValue) count++;\n return count;\n }, 0)\n);\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
count-items-matching-a-rule
|
Python 3 line solution (%99.84 fast)
|
python-3-line-solution-9984-fast-by-furk-jtp8
|
\nclass Solution:\n def countMatches(self, items: List[List[str]], ruleKey: str, ruleValue: str) -> int:\n ruleIndex = ["type", "color", "name"].index
|
furkangulsen
|
NORMAL
|
2021-04-25T21:24:12.852708+00:00
|
2021-04-25T21:24:12.852741+00:00
| 121 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def countMatches(self, items: List[List[str]], ruleKey: str, ruleValue: str) -> int:\n ruleIndex = ["type", "color", "name"].index(ruleKey)\n reqList = [item[ruleIndex] for item in items]\n return reqList.count(ruleValue)\n```
| 3 | 0 |
[]
| 2 |
count-items-matching-a-rule
|
Kotlin 1 line
|
kotlin-1-line-by-georgcantor-s3j5
|
\nfun countMatches(l: List<List<String>>, k: String, v: String) = l.count { it[when(k){"type"->0 "color"->1 else->2}] == v }\n\n\nOr:\n\nfun countMatches(l: Lis
|
GeorgCantor
|
NORMAL
|
2021-04-14T19:38:18.398513+00:00
|
2021-11-13T13:29:20.877584+00:00
| 136 | false |
```\nfun countMatches(l: List<List<String>>, k: String, v: String) = l.count { it[when(k){"type"->0 "color"->1 else->2}] == v }\n```\n\n***Or:***\n```\nfun countMatches(l: List<List<String>>, r: String, v: String) = arrayOf("type", "color", "name").run {\n l.count { it[indexOf(r)] == v }\n}\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Kotlin']
| 0 |
count-items-matching-a-rule
|
Anybody review my JS solution?
|
anybody-review-my-js-solution-by-priyans-0rpr
|
\nvar countMatches = function(items, ruleKey, ruleValue) {\n let output = 0;\n items.forEach(item => {\n switch(ruleKey) {\n case "type"
|
priyanshu-kun
|
NORMAL
|
2021-03-24T11:10:27.595136+00:00
|
2021-03-24T11:10:27.595193+00:00
| 354 | false |
```\nvar countMatches = function(items, ruleKey, ruleValue) {\n let output = 0;\n items.forEach(item => {\n switch(ruleKey) {\n case "type":\n item[0] === ruleValue && output++;\n break;\n case "color":\n item[1] === ruleValue && output++;\n break;\n case "name":\n item[2] === ruleValue && output++;\n break;\n }\n })\n return output;\n};\n```\nPlease give a feedback how can I improve this.
| 3 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 1 |
count-items-matching-a-rule
|
Java solution
|
java-solution-by-hiunpark-a0ba
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int countMatches(List<List<String>> items, String ruleKey, String ruleValue) {\n int idx = ruleKey.equals("color") ? 1 : r
|
hiunpark
|
NORMAL
|
2021-03-03T13:48:01.243998+00:00
|
2021-03-03T13:48:01.244045+00:00
| 249 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int countMatches(List<List<String>> items, String ruleKey, String ruleValue) {\n int idx = ruleKey.equals("color") ? 1 : ruleKey.equals("name") ? 2 : 0;\n \n int ans = 0;\n for (List<String> item : items) {\n if (item.get(idx).equals(ruleValue)) {\n ans++;\n }\n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 3 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
count-items-matching-a-rule
|
javascript
|
javascript-by-chrispee-3stt
|
```\nvar countMatches = function(items, ruleKey, ruleValue) {\n const types = {\n "type": 0,\n "color": 1,\n "name": 2\n }\n \n
|
chrispee
|
NORMAL
|
2021-02-28T19:28:44.911061+00:00
|
2021-02-28T19:28:44.911103+00:00
| 320 | false |
```\nvar countMatches = function(items, ruleKey, ruleValue) {\n const types = {\n "type": 0,\n "color": 1,\n "name": 2\n }\n \n return items.filter((item) => {\n return item[types[ruleKey]] === ruleValue;\n }).length;\n};
| 3 | 1 |
[]
| 3 |
count-items-matching-a-rule
|
C# simple solution using switch pattern
|
c-simple-solution-using-switch-pattern-b-miso
|
\npublic class Solution {\n public int CountMatches(IList<IList<string>> items, string ruleKey, string ruleValue) {\n \n int res = 0;\n
|
techexplorer
|
NORMAL
|
2021-02-28T09:45:58.943007+00:00
|
2021-02-28T09:45:58.943064+00:00
| 128 | false |
```\npublic class Solution {\n public int CountMatches(IList<IList<string>> items, string ruleKey, string ruleValue) {\n \n int res = 0;\n foreach(var item in items)\n {\n res += ruleKey switch { \n "type" => item[0] == ruleValue ? 1 : 0,\n "color" => item[1] == ruleValue ? 1 : 0,\n "name" =>item[2] == ruleValue ? 1 : 0,\n _ => 0\n };\n }\n \n return res;\n }\n}\n```
| 3 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
count-items-matching-a-rule
|
[c++/python solution] simple and easy to understand with comment
|
cpython-solution-simple-and-easy-to-unde-hc2x
|
c++:\n\n\n\tclass Solution {\n\tpublic:\n\t\tint countMatches(vector>& items, string ruleKey, string ruleValue) {\n\t\t\t// take a count variable for count key
|
vishnu23kumar
|
NORMAL
|
2021-02-28T04:05:23.282758+00:00
|
2021-02-28T04:12:17.377154+00:00
| 252 | false |
c++:\n\n\n\tclass Solution {\n\tpublic:\n\t\tint countMatches(vector<vector<string>>& items, string ruleKey, string ruleValue) {\n\t\t\t// take a count variable for count key values\n\t\t\tint count = 0;\n\t\t\t// take a variable for final answer\n\t\t\tint res = 0;\n\t\t\t// Note here only 3 description type color and name so we can do one by one (brute force)\n\n\t\t\t// first we can use color as key and find all with maching color\n\t\t\tif(ruleKey=="color"){\n\t\t\t\tfor(int i = 0; i < items.size(); i++){\n\t\t\t\t\t// if color value if same as given value then increase counter\n\t\t\t\t\tif(items[i][1] == ruleValue)\n\t\t\t\t\t\tcount++;\n\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\t// update the result as maximum color matches\n\t\t\t\tres = max(res, count);\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t// if kye is not color then check for type\n\t\t\telse if(ruleKey == "type"){\n\t\t\t\t// reset counter as 0\n\t\t\t\tcount = 0;\n\t\t\t\tfor(int i = 0; i < items.size(); i++){\n\t\t\t\t\tif(items[i][0] == ruleValue)\n\t\t\t\t\t\tcount++;\n\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\t// update the result as maximum color matches\n\t\t\t\tres = max(res, count);\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t// if not color and type then check for name\n\t\t\telse if(ruleKey == "name"){\n\t\t\t\t// reinitilaze the counter\n\t\t\t\tcount = 0;\n\t\t\t\tfor(int i = 0; i < items.size(); i++){\n\t\t\t\t\tif(items[i][2] == ruleValue)\n\t\t\t\t\t\tcount++;\n\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\t// update the result as maximum color matches\n\t\t\t\tres = max(res, count);\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t// return maximum matches result \n\t\t\treturn res;\n\t\t}\n\t};\n\t\nC++ using map\n\n\tclass Solution {\n\tpublic:\n\t\tint countMatches(vector<vector<string>>& items, string ruleKey, string ruleValue) {\n\t\t\tunordered_map<string, vector<string>> mp;\n\t\t\tfor(int i = 0; i < items.size(); i++){\n\t\t\t\tmp["type"].push_back(items[i][0]);\n\t\t\t\tmp["color"].push_back(items[i][1]);\n\t\t\t\tmp["name"].push_back(items[i][2]);\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t\tint ans = 0;\n\t\t\tfor(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){\n\t\t\t\tint xx = count(mp[ruleKey].begin(), mp[ruleKey].end(), ruleValue);\n\t\t\t\tans = ans>xx? ans:xx;\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t\treturn ans;\n\n\t\t}\n\t};\n\n\nPython:\n\n\tclass Solution:\n\t\t\tdef countMatches(self, items: List[List[str]], ruleKey: str, ruleValue: str) -> int:\n\t\t\t\tdic = {}\n\t\t\t\tdic[\'type\'] = []\n\t\t\t\tdic[\'color\'] = []\n\t\t\t\tdic[\'name\'] = []\n\t\t\t\tfor item in items:\n\t\t\t\t\tdic[\'type\'].append(item[0])\n\t\t\t\t\tdic[\'color\'].append(item[1])\n\t\t\t\t\tdic[\'name\'].append(item[2])\n\n\t\t\t\treturn dic[ruleKey].count(ruleValue)\n
| 3 | 2 |
['C', 'Python']
| 1 |
count-items-matching-a-rule
|
C++ Easy Solution
|
c-easy-solution-by-rahul566-n7hh
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countMatches(vector<vector<string>>& v, string ruleKey, string ruleValue) {\n int cnt=0;\n for(int i=0;i<v.si
|
Rahul566
|
NORMAL
|
2021-02-28T04:05:05.716076+00:00
|
2021-02-28T04:05:05.716119+00:00
| 509 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int countMatches(vector<vector<string>>& v, string ruleKey, string ruleValue) {\n int cnt=0;\n for(int i=0;i<v.size();i++)\n {\n if(ruleKey=="type" && v[i][0]==ruleValue)\n cnt++;\n if(ruleKey=="color" && v[i][1]==ruleValue)\n cnt++;\n if(ruleKey=="name" && v[i][2]==ruleValue)\n cnt++;\n }\n return cnt;\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
[]
| 2 |
count-items-matching-a-rule
|
Java Easy Solution
|
java-easy-solution-by-ahmed_elsakka-17ej
|
Complexity
Time complexity:
O(n) where n is the number of items
Space complexity:
O(1)
Code
|
ahmed_elsakka
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-21T11:55:00.605206+00:00
|
2024-12-21T11:55:00.605206+00:00
| 221 | false |
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
O(n) where n is the number of items
- Space complexity:
O(1)
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
public int countMatches(List<List<String>> items, String ruleKey, String ruleValue) {
int targetIndex = 0;
int result = 0;
switch (ruleKey) {
case "type":
targetIndex = 0;
break;
case "color":
targetIndex = 1;
break;
case "name":
targetIndex = 2;
break;
}
for(List<String> item: items) {
result += item.get(targetIndex).equals(ruleValue) ? 1 : 0;
}
return result;
}
}
```
| 2 | 0 |
['String', 'String Matching', 'Java']
| 0 |
count-items-matching-a-rule
|
Very simple and easy to understand.
|
very-simple-and-easy-to-understand-by-sr-jcks
|
Code
|
srh_abhay
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-13T04:53:42.156883+00:00
|
2024-12-13T04:53:42.156883+00:00
| 200 | false |
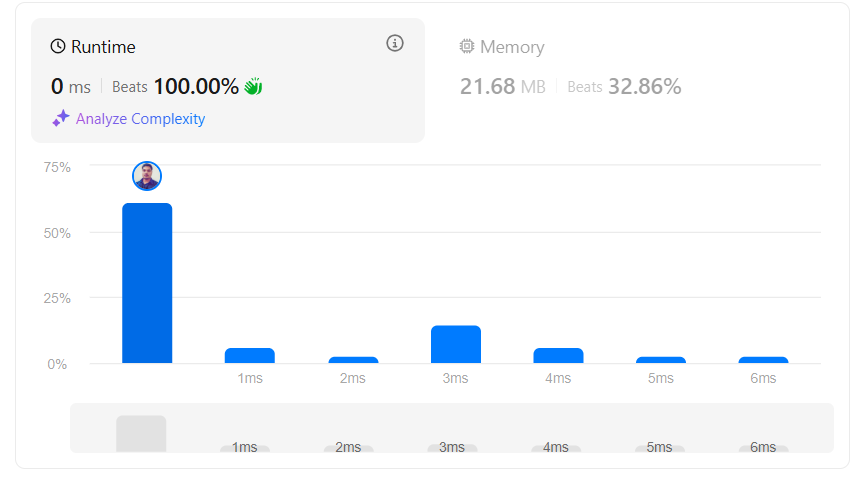\n\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def countMatches(self, items: List[List[str]], ruleKey: str, ruleValue: str) -> int:\n rule =["type", "color", "name"]\n rule_index= rule.index(ruleKey)\n count=0\n for item in items:\n if item[rule_index] == ruleValue:\n count += 1\n return count\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
count-items-matching-a-rule
|
❇ count-items-matching-a-rule👌 🏆O(1)❤️ Javascript🎯 Memory👀97.27%🕕 ++Explanation✍️ 🔴🔥 ✅ 👉
|
count-items-matching-a-rule-o1-javascrip-u0lm
|
\nTime Complexity: O(N)\nSpace Complexity: O(1)\n\n\nvar countMatches = function (items, ruleKey, ruleValue) {\n const categoryIndex = {\n type: 0,\n
|
anurag-sindhu
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-04T07:02:27.171988+00:00
|
2024-04-04T07:02:27.172021+00:00
| 438 | false |
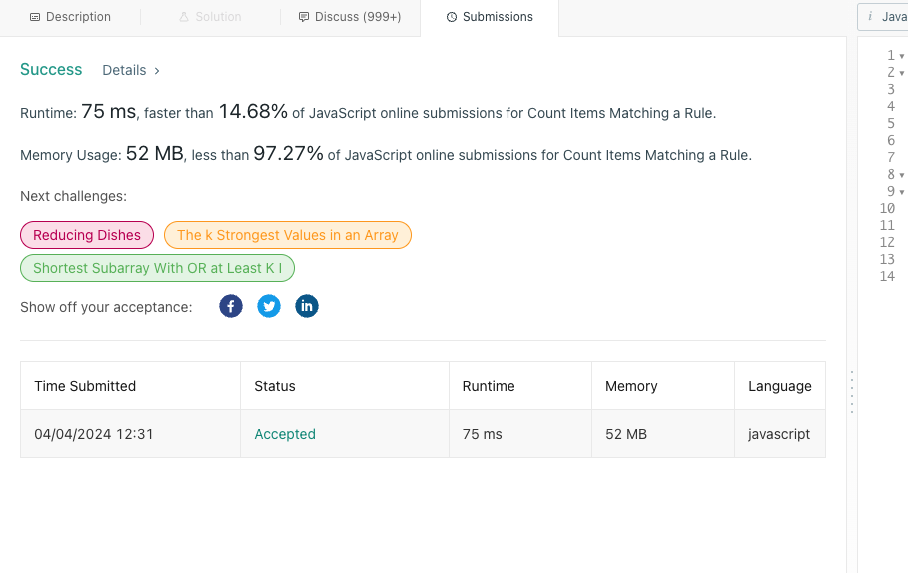\nTime Complexity: O(N)\nSpace Complexity: O(1)\n\n```\nvar countMatches = function (items, ruleKey, ruleValue) {\n const categoryIndex = {\n type: 0,\n color: 1,\n name: 2,\n };\n let count = 0;\n for (let index = 0; index < items.length; index++) {\n if (items[index][categoryIndex[ruleKey]] === ruleValue) {\n count++;\n }\n }\n return count;\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
count-items-matching-a-rule
|
JAVA || Count Items Matching a Rule
|
java-count-items-matching-a-rule-by-ruch-yh8m
|
\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\n public int countMatches(List<List<String>> items, String ruleKey, String ruleValue) {\n int count = 0 ; \n for(
|
Ruchika_Kachhawa
|
NORMAL
|
2024-03-03T18:44:13.227892+00:00
|
2024-03-03T18:44:13.227916+00:00
| 253 | false |
\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int countMatches(List<List<String>> items, String ruleKey, String ruleValue) {\n int count = 0 ; \n for( int i = 0 ; i < items.size() ; i++){\n switch (ruleKey) {\n case "type":\n if(items.get(i).get(0).equals(ruleValue)){\n count++;\n }\n break;\n case "color":\n if(items.get(i).get(1).equals(ruleValue)){\n count++;\n }\n \n break;\n case "name":\n if(items.get(i).get(2).equals(ruleValue)){\n count++;\n }\n break;\n }\n }\n return count;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
[Java/C++/Python] One Pass, O(1) space
|
javacpython-one-pass-o1-space-by-lee215-eola
|
Soluton 1\nCount the current best score in all previous sightseeing spot.\nNote that, as we go further, the score of previous spot decrement.\n\ncur will record
|
lee215
|
NORMAL
|
2019-03-24T03:05:49.166208+00:00
|
2020-08-05T03:41:17.716822+00:00
| 39,325 | false |
# **Soluton 1**\nCount the current best score in all previous sightseeing spot.\nNote that, as we go further, the score of previous spot decrement.\n\n`cur` will record the best score that we have met.\nWe iterate each value `a` in the array `A`,\nupdate `res` by `max(res, cur + a)`\n\nAlso we can update `cur` by `max(cur, a)`.\nNote that when we move forward,\nall sightseeing spot we have seen will be 1 distance further.\n\nSo for the next sightseeing spot `cur = Math.max(cur, a) - 1`\n\nThere is a feeling that,\n"A near neighbor is better than a distant cousin."\n\n**Java:**\n```java\n public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] A) {\n int res = 0, cur = 0;\n for (int a: A) {\n res = Math.max(res, cur + a);\n cur = Math.max(cur, a) - 1;\n }\n return res;\n }\n```\n\n**C++:**\n```cpp\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& A) {\n int res = 0, cur = 0;\n for (int a: A) {\n res = max(res, cur + a);\n cur = max(cur, a) - 1;\n }\n return res;\n }\n```\n\n**Python:**\n```py\n def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, A):\n cur = res = 0\n for a in A:\n res = max(res, cur + a)\n cur = max(cur, a) - 1\n return res\n```\n**Python 1-line:**\n```py\n def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, A):\n return reduce(lambda (r, c), a: [max(r, c + a), max(c, a) - 1], A, [0, 0])[0]\n```\n<br>\n\n# **Complexity**:\nOne pass,\nTime `O(N)`,\nSpace `O(1)`.\n<br>\n\n# **Soluton 2**\n**Java**\n```java\n public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] A) {\n int res = 0, imax = 0;\n for(int i = 0; i < A.length; ++i) {\n res = Math.max(res, imax + A[i] - i);\n imax = Math.max(imax, A[i] + i);\n }\n return res;\n }\n```\n**C++**\n```cpp\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& A) {\n int res = 0, imax = 0;\n for(int i = 0; i < A.size(); ++i) {\n res = max(res, imax + A[i] - i);\n imax = max(imax, A[i] + i);\n }\n return res;\n }\n```\n**Python**\n```py\n def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, A):\n res = imax = 0\n for i, a in enumerate(A):\n res = max(res, imax + A[i] - i)\n imax = max(imax, A[i] + i)\n return res\n\n```
| 455 | 22 |
[]
| 62 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Detailed Explanation using DP [O(n) Time | O(1) Space]
|
detailed-explanation-using-dp-on-time-o1-zoil
|
Intuition\n Suppose we choose the site [i,...j]. The score can be broken up into 2 parts.\n The first part is the startGain which you gain while starting at a c
|
just__a__visitor
|
NORMAL
|
2019-03-24T07:29:06.829444+00:00
|
2019-03-24T07:29:06.829487+00:00
| 12,501 | false |
**Intuition**\n* Suppose we choose the site `[i,...j]`. The score can be broken up into 2 parts.\n* The first part is the **startGain** which you gain while starting at a certain point `i`. Notice that `startGain[i] = a[i] + i`.\n* The second part is the **endGain** which is the amount you gain while ending at a certain point `j`. Notice that `endGain[i] = a[j] - j`.\n* Notice that endGain can be negative\n* The overall gain for `[i,...j]` is nothing but `startGain[i] + endGain[j]`. (This can be easily verified by the definitions).\n---\n**Constraints**\n* You cannot start at the last position\n* You cannot go left at any stage, i.e if you started at `i`, you have to end your trip at a number **strictly** bigger than `i`.\n---\n**Reduction**\n* We need to maximize the overall Gain.\n---\n\n* What are the possible positions for starting the trip? Clearly we can start at all except the last element. So, the optimal trip has to start at one of these elements.\n* Suppose, we are only allowed to start a trip at `i`. What is the maximum amount we can gain in this case? Well, since the `startGain` is fixed, we need to maximize the\n`endGain`. We can do it by stopping at an element which has the maximum `endGain` with the condition that it appears to the right of `i`.\n---\n**Setting up the DP definition**\n* As discussed above, for each i, we need to find the maximum `endGain` to the right of it. \n* `maxEndRight[i] = max(maxEndRight[i+1], endGain[i+1])` = `max(maxEndRight[i+1], a[i+1] - (i+1))`\n* `maxEndRight[i]` represent the highest `endGain` that you can get while stopping at any point **strictly** to the right of `i`. Since by definition, we already know `endGain[i+1]` (the highest gain possible by ending at any point to the right of `i+1`) we only need to check the possibility whether stopping at `i+1` would be beneficial or not. Hence, the DP definition.\n* For each valid `i`, `overallGain[i] = startGain[i] + maxEndRight[i]` = `a[i] + i + maxEndRight[i]`\n---\n**Reducing the Space complexity**\n* Notice that `maxEndRight[i]` only depends on `maxEndRight[i+1]`. Hence, we can use 2 variables to track the previous values.\n---\n**Miscellaneous**\n* Since we need the value of `maxEndRight[i+1]` to compute the value of `maxEndRight[i]`, therefore we start the iterations at the back.\n* As argued, trips cannot start at the last element, hence the `for` loop starts at `i=n-2`. For this value, `maxEndingRight` is initialized to `endGain[lastIndex]` because this is the only possible way to end the trip.\n```\nclass Solution\n{\npublic:\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& a);\n};\n\nint Solution :: maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& a)\n{\n int n = a.size();\n int maxOverallGain = INT_MIN;\n int maxEndRight = a[n-1] - (n-1);\n for(int i=n-2; i>=0; i--)\n {\n maxEndRight = max(maxEndRight, a[i+1] - (i+1));\n maxOverallGain = max(maxOverallGain, a[i] + i + maxEndRight);\n }\n return maxOverallGain;\n \n}\n```
| 222 | 6 |
[]
| 16 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Code walk through, O(n) time + O(1) space
|
code-walk-through-on-time-o1-space-by-ni-1kof
|
It took me a lot of time to understand the approach explained by people in the Discussion section. \nHere\'s an example, explaning how I understood it:\nNow, gi
|
nidhihemanth
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-17T07:44:47.845690+00:00
|
2021-09-19T18:15:12.213397+00:00
| 5,709 | false |
It took me a lot of time to understand the approach explained by people in the Discussion section. \nHere\'s an example, explaning how I understood it:\nNow, given formula for a score is\n`score = A[i] + A[j] + i - j` ; given i < j\nIt becomes more easier to group the dependant values, \ni.e `A[i] + i` and `A[j] - j`\nIn this way, when we are traversing from either sides of the array, we can just calculate that part of the score, if we maintain max of one part.\n```\nvalues = [7, 1, 6, 6, 9, 4, 3]\n```\nNow suppose I traverse the array from left to right, and decide to keep the sum `A[i] + i` maximum at each point, then I can easily use the current element value & its position to calculate the current maximum score.\nAlso, Note that at each point, we calculate `A[j] + j` and compare it to `maxLeft`, to always store the MAXIMUM of those values.\nLet\'s initialize `maxLeft = A[0] + 0 = 7`, considering `i = 0` initially. And `maxScore = 0`\n```\nwhen j = 1, \n\tscore = maxLeft + A[j] - j = 7 + 1 - 1 = 7\n\tmaxScore = max(maxScore, score) = max(0,7) = 7\n\tmaxLeft = max(maxLeft, A[j] + j) = max(7, 1+1) = 7\nwhen j = 2, \n\tscore = maxLeft + A[j] - j = 7 + 6 - 2 = 11\n\tmaxScore = max(maxScore, score) = max(7,11) = 11\n\tmaxLeft = max(maxLeft, A[j] + j) = max(7, 6+2) = 8\nwhen j = 3, \n\tscore = maxLeft + A[j] - j = 8 + 6 - 3 = 11\n\tmaxScore = max(maxScore, score) = max(11,11) = 11\n\tmaxLeft = max(maxLeft, A[j] + j) = max(8, 6+3) = 9\nwhen j = 4, \n\tscore = maxLeft + A[j] - j = 9 + 9 - 4 = 14\n\tmaxScore = max(maxScore, score) = max(11,14) = 14\n\tmaxLeft = max(maxLeft, A[j] + j) = max(9, 9+4) = 13\nwhen j = 5, \n\tscore = maxLeft + A[j] - j = 13 + 4 - 5 = 12\n\tmaxScore = max(maxScore, score) = max(14,12) = 14\n\tmaxLeft = max(maxLeft, A[j] + j) = max(13,4+5) = 13\nwhen j = 6, \n\tscore = maxLeft + A[j] - j = 13 + 3 - 6 = 10\n\tmaxScore = max(maxScore, score) = max(14,10) = 14\n\tmaxLeft = max(maxLeft, A[j] + j) = max(13, 3+6) = 13\n```\nAt the end, we return maxScore, hence our final result = 14!\n\nThe code in C++, for the same logic:\n```\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& a)\n {\n int n = a.size(), maxScore = 0;\n int maxLeft = a[0] + 0;\n for(int j = 1; j < n; j++) {\n maxScore = max(maxScore, maxLeft + a[j] - j);\n maxLeft = max(maxLeft, a[j] + j);\n }\n return maxScore;\n }\n```\nI hope my explanation helps anyone who struggled like me!\nIf I made a mistake anywhere in my explanation, kindly let me know and i\'ll edit my post :D
| 205 | 0 |
['C']
| 18 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
C++ O(n), best time to buy and sell stock
|
c-on-best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-by-uytei
|
Intuition\nIt\'s similar to Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock, but instead of min price, we track max value, and our max value decays every step due to the distan
|
votrubac
|
NORMAL
|
2019-03-24T04:05:56.932801+00:00
|
2019-03-24T04:05:56.932845+00:00
| 13,630 | false |
## Intuition\nIt\'s similar to [Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock](https://leetcode.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock/), but instead of min price, we track max value, and our max value decays every step due to the distance penalty.\n## Solution\n- Track the maximum value of ```A[i]``` as ```max_i```.\n- Every turn, decrement ```max_i```to account for ```j - i```.\n- Track and return the maximum score.\n```\nint maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& A, int res = 0) {\n for (auto j = 1, max_i = A[0] - 1; j < A.size(); ++j, --max_i) {\n res = max(res, A[j] + max_i);\n max_i = max(max_i, A[j]);\n }\n return res;\n}\n```\n## Complexity Analysis\nRuntime: *O(n)*\nMemory: *O(1)*
| 132 | 6 |
[]
| 11 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
[Java/Python] Descriptive solution.[O(N) Time | O(1) Space]. Very similar to Kadence Algo!
|
javapython-descriptive-solutionon-time-o-0zik
|
The goal is to keep track of:\n Maximum So far and add it to the cur_cell and maintain maximum result\n Here, max_so_far contains : A[i] + i\n\nOriginal Given F
|
namasteduniya
|
NORMAL
|
2019-03-24T04:24:27.091153+00:00
|
2019-03-24T04:24:27.091214+00:00
| 4,892 | false |
*The goal is to keep track of:*\n* **Maximum So far** and add it to the cur_cell and maintain maximum result\n* Here, max_so_far contains : *A[i] + i*\n\n**Original Given Formula : A[i] + A[j] + i - j**\n* Break in two parts : ***A[i] + i*** and ***A[j] -j***\n* Keep MAX_VALUE of first part among the elements seen so far\n* Add the current element to max_so_far and check the result is changing or not\n* Also, keep updating the max_so_far at each step\n\n**Java**\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] a) {\n int max_so_far = a[0];\n int result = 0;\n for(int i=1;i<a.length;i++){\n result = Math.max(result, max_so_far + a[i] - i);\n max_so_far = Math.max(max_so_far, a[i] + i);\n } \n return result;\n }\n}\n```\n\n**Python**\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, a: List[int]) -> int:\n max_so_far,result = a[0],0\n \n for i in range(1,len(a)):\n result = max(result, max_so_far + a[i] - i)\n max_so_far = max(max_so_far, a[i] + i)\n\t\t\t\n return result\n```
| 114 | 2 |
[]
| 13 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Java O(N) Easy to Understand, Clean Code beats 100%
|
java-on-easy-to-understand-clean-code-be-tx7p
|
We want to maximize A[i] + A[j] + i - j where j > i, meaning i is to the left and j is to the right\n1. One way to think about this is that we somehow make sure
|
grkulkarni
|
NORMAL
|
2019-03-24T22:12:10.374712+00:00
|
2019-03-24T22:12:10.374758+00:00
| 3,032 | false |
We want to maximize `A[i] + A[j] + i - j` where `j > i`, meaning `i` is to the left and `j` is to the right\n1. One way to think about this is that we somehow make sure that we add the best value of `A[i] + i` to `A[j] - j` as we go from left to right. So, at any point, while going towards right end, we add the best value available to the left.\n```\npublic int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] A) { \n int i=0;\n\t\tint max = A[i] + i;\n for(int j=1;j<A.length;j++){\n int curr = A[i] + A[j] + i - j;\n max = curr > max ? curr : max;\n \n // update the value of i to the one that maximizes\n if(A[i] + i < A[j] + j){\n i=j;\n }\n }\n return max;\n }\n```\n2. Other way to think is to make sure we add the best value of `A[j]-j` to `A[i] + i` as we go from right to left. So, at any point, while going towards left end, we add the best value available to the right.\n\n```\npublic int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] A) {\n int N = A.length;\n\t\tint j=N-1;\n int max = A[j] - j;\n for(int i=N-2;i>=0; i--){\n int curr = A[i] + A[j] + i - j;\n max = curr > max ? curr : max;\n \n // update the value of j to the one that maximizes\n if(A[j] - j < A[i] - i){\n j=i;\n }\n }\n return max;\n }\n```
| 74 | 1 |
[]
| 7 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
✅ 🔥 BEATS 100% PROOF🔥|| 💡 CONCISE CODE ✅ || 🌟 JAVA || 🧑💻 BEGINNER FREINDLY
|
beats-100-proof-concise-code-java-beginn-1ne3
|
📝 Proof💡 IntuitionThe formula for the score is: score = values[i] + values[j] + i - j.This can be rewritten as: score = (values[i] + i) + (values[j] - j).Here:
|
mukund_rakholiya
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-27T00:25:13.130067+00:00
|
2024-12-27T04:10:48.597372+00:00
| 11,222 | false |
```
```
# 📝 Proof
---
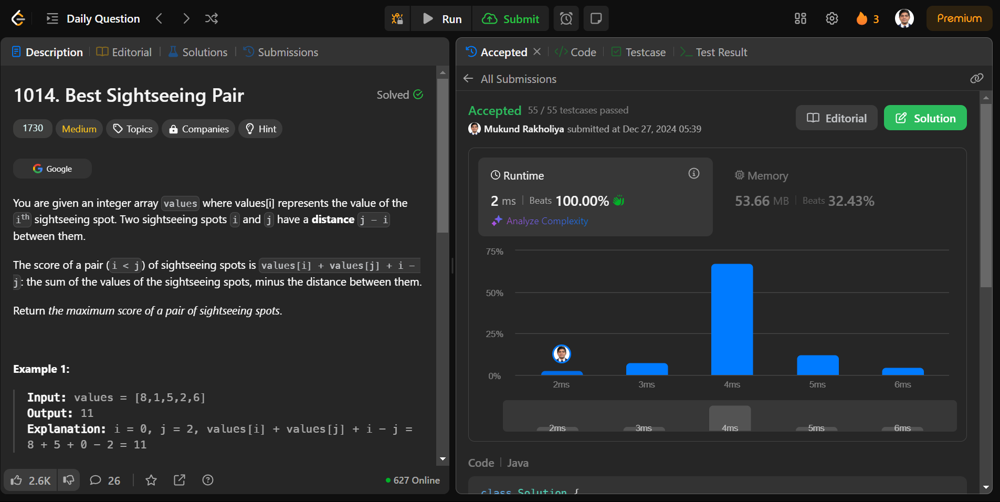
---
```
```
# 💡 Intuition
---
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
### The formula for the score is: `score = values[i] + values[j] + i - j`.
### This can be rewritten as: `score = (values[i] + i) + (values[j] - j)`.
### Here:
- `values[i] + i` represents the "potential" of the first sightseeing spot `i`.
- `values[j] - j` represents the "reduced" value of the second sightseeing spot `j` due to the distance penalty.
```
```
---
```
```
# 🧠 Approach
---
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
### 1. Keep track of the maximum value of `values[i] + i` (denoted as `m`) as you iterate through the array.
### 2. For each index `j`:
- Calculate the score using the formula: `m + values[j] - j`.
- Update the maximum score (`ans`) based on the current score.
### 3. Update m to be the maximum of its current value and `values[j] + j`, which accounts for the new index `j`.
### 4. Repeat this for all indices and return the maximum score.
```
```
---
```
```
# 🌟 Complexity
---
### 1. Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- $$O(n)$$, as we only traverse the array once.
---
### 2. Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- $$O(1)$$, as no extra space is used.
```
```
---
```
```
# 🏷️ Concept of Tags Used
---
### 1. Greedy Algorithm:
- The solution uses a greedy approach by maintaining the best possible value (`m`) of `values[i] + i` up to the current index. At each step, it calculates the score for index `j` and updates `m` for future iterations.
### 2. Array:
- The input is an array of integers, and the operations are performed using array indexing to calculate the required scores efficiently.
### 3. Dynamic Programming Concept:
- Although this problem does not use a formal DP table, it employs a similar concept by maintaining the maximum value of `values[i] + i` dynamically as the iteration progresses.
### 4. Two Pointers (Implicit):
- The solution indirectly mimics a two-pointer-like behavior by keeping track of the best `i` for each `j` without explicitly using two pointers.
```
```
---
```
```
# 📒 Code
---
```java []
class Solution {
public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values) {
int ans = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int m = values[0];
for (int i = 1; i < values.length; i++) {
if (values[i] - i + m > ans)
ans = values[i] - i + m;
if (values[i] + i > m)
m = values[i] + i;
}
return ans;
}
}
```
```
```
---

---
```
```
| 69 | 0 |
['Array', 'Two Pointers', 'Greedy', 'Java']
| 15 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
✅ || Very easy explanation || DP || Complexity Analysis || Python
|
very-easy-explanation-dp-complexity-anal-s3pj
|
Solution\n\n\n#### LOGIC\n\nSuppose we have a = [8,1,5,2,6]\ncreate a dp = [0, 0, 0, 0] where dp[i] represents the best possible answer if we consider all pairs
|
siddp6
|
NORMAL
|
2021-10-15T02:29:30.628814+00:00
|
2022-03-22T15:37:49.834873+00:00
| 3,972 | false |
## **Solution**\n\n\n#### **LOGIC**\n\nSuppose we have a = ```[8,1,5,2,6]```\ncreate a dp = ```[0, 0, 0, 0]``` where dp[i] represents the best possible answer if we consider all pairs forming with a[i] (like i = 3 then it will be (0, 3),(1, 3), (2, 3))\n\n* For d[0] it will be 0\n* For d[1] it will be a[0] + a[1] + 0 - 1\n* For d[2] it will be max((a[0] + a[2] + 0 - 2), (a[1] + a[2] + 1 - 2))\n* For d[3] it will be max((a[0] + a[3] + 0 - 3), (a[1] + a[3] + 1 - 3), (a[2] + a[3] + 2 - 3))\n* For d[4] it will be max(a[0] + a[4] + 0 - 4), (a[1] + a[4] + 1 - 4), (a[2] + a[4] + 2 - 4), (a[3] + a[4] + 3 - 4))\n\nRewriting above by taking about common term out of max() function\n* For d[0] it will be 0\n* For d[1] it will be a[0] + 0 + a[1] - 1\n* For d[2] it will be max((a[0] + 0), (a[1] + 1)) + a[2] - 2\n* For d[3] it will be max((a[0] + 0 ), (a[1] + 1), (a[2] + 2)) + a[3] - 3\n* For d[4] it will be max(a[0] + 0 ), (a[1] + 1), (a[2] + 2), (a[3] + 3 )) + a[4] - 4\n\nFor a minute lets ignore the part outside the max function and drop it for now, So make a new series and call it dp\n* For dp[0] it will be 0\n* For dp[1] it will be a[0] + 0\n* For dp[2] it will be max((a[0] + 0), (a[1] + 1))\n* For dp[3] it will be max((a[0] + 0 ), (a[1] + 1), (a[2] + 2))\n* For dp[4] it will be max(a[0] + 0 ), (a[1] + 1), (a[2] + 2), (a[3] + 3 ))\n\n**Here is the catch\ndp[i] = max(dp[i-1], a[i-1] + i - 1)\nYou can Clearly see this pattern in above dp series**\n\nCombining this to d series we can get:\n* For d[0] it will be 0\n* For d[1] it will be dp[0]+ a[1] - 1\n* For d[2] it will be max(dp[1], (a[1] + 1)) + a[2] - 2\n* For d[3] it will be max(dp[2], (a[2] + 2)) + a[3] - 3\n* For d[4] it will be max(dp[3], (a[3] + 3 )) + a[4] - 4\n\n**Now our answer can simply the maximum of d that is max(d), but for improving space complexity i used maxVal to keep track of maximum value**\n\n#### **Code**\n\n##### Apporach : 1 \n```cpp\nclass Solution:\n def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, values: List[int]) -> int: \n dp = [0]*(len(values))\n dp[0] = values[0]\n maxVal = 0\n \n for i in range(1, len(values)):\n dp[i] = max(dp[i-1], values[i-1]+i-1)\n maxVal = max(maxVal, dp[i]+values[i]-i)\n \n return maxVal\n```\n\n##### Apporach : 2[Memory Efficient]\n```cpp\nclass Solution:\n\n def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, values: List[int]) -> int: \n maxVal = 0\n cur = 0 \n for i in range(1, len(values)):\n cur = max(cur, values[i-1]+i-1)\n maxVal = max(maxVal, cur+values[i]-i)\n return maxVal\n\n```\n## **Complexity**\n\n##### __Apporach : 1__ \n##### Time Complexity: **O(n)**.\n\n##### Space Complexity: **O(n)**\n\n##### __Apporach : 2__ \n##### Time Complexity: **O(n)**.\n\n##### Space Complexity: **O(1)**\n<br>\n\n __Check out all [my](https://leetcode.com/siddp6/) recent solutions [here](https://github.com/sidd6p/LeetCode)__\n\n \n __Feel Free to Ask Doubts\nAnd Please Share Some Suggestions\nHAPPY CODING :)__\n\n\n
| 62 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 6 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
[Java] One pass | Easy to understand solution
|
java-one-pass-easy-to-understand-solutio-8fby
|
Divide the score into 2 parts - A[i]+i and A[j]-j. For each j value, we will check if the sum of maximum A[i]+i value found so far and current A[j]-j is greate
|
nainy
|
NORMAL
|
2020-03-14T18:38:56.453508+00:00
|
2020-03-14T18:47:24.399620+00:00
| 2,365 | false |
Divide the score into 2 parts - ```A[i]+i``` and ```A[j]-j```. For each ```j``` value, we will check if the sum of maximum ```A[i]+i``` value found so far and current ```A[j]-j``` is greater than the ```res```.\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] A) {\n\t\t//Intitialize previously seen value of A[i] + i\n int prev_max = A[0]+0;\n\t\t//Initialize the value of first pair\n int res = A[0] + A[1] - 1;\n for(int j = 1; j < A.length; j++){\n\t\t\t//update res if a higher value of prev_max+A[j]-j is found\n res = Math.max(prev_max + A[j] - j, res);\n\t\t\t//Update prev_max\n prev_max = Math.max(A[j] + j, prev_max);\n }\n return res;\n }\n}\n\n```
| 50 | 0 |
['Java']
| 4 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
C++, Dynamic Programming, O(N) time, simple with explanation
|
c-dynamic-programming-on-time-simple-wit-1uif
|
Since our task is to find max{ (A[i]+i) + (A[j]-j) } for all i<j.\nSo we can say that we want maximum of A[i]+i and maximum of A[j]-j.\nUsing Dynamic Programmin
|
trade_off
|
NORMAL
|
2019-03-24T07:10:47.509498+00:00
|
2019-03-24T07:10:47.509538+00:00
| 2,289 | false |
Since our task is to find ``max{ (A[i]+i) + (A[j]-j) }`` for all ``i<j``.\nSo we can say that we want maximum of ``A[i]+i`` and maximum of ``A[j]-j``.\n**Using Dynamic Programming**\ntime complexity: O(N)\nspace complexity: O(N)\n\nSubproblem: find max ``(A[i]-i)`` after ``i``.\nRecurrence Relation: ``max_after(i) = max{ A[i]-i, max_after(i+1) }``.\nFinally ans would be maximum of ``A[i]+i+max_after(i+1)``.\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic: \n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& A) {\n int N = A.size();\n vector<int> max_after(N,0);\n max_after[N-1] = A[N-1] - (N-1);\n for(int i=N-2;i>=0;i--)\n max_after[i] = max(max_after[i+1],A[i]-i);\n int ans = 0;\n for(int i=0;i<N-1;i++)\n ans = max(ans, A[i]+i+max_after[i+1]);\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\n\n**Without Extra space**\ntime complexity: O(N)\nspace complexity: O(1)\n\nActually we are optimizing above algorithm.\nWe see in first for loop ``max_after[i]`` is dependent on ``max_after[i+1]`` and its current element diff.\nInstead we can use a variable to store previous ``max_after`` to calculate ``ans``;\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic: \n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& A) {\n int N = A.size();\n int ans = 0;\n int max_after = A[N-1]-N+1;\n for(int i=N-2;i>=0;i--){\n max_after = max(max_after, A[i+1]-i-1);\n ans = max(ans, A[i]+i+max_after);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\n\npardon my English.\nHappy Coding!
| 45 | 1 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C']
| 3 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Code with thought process
|
code-with-thought-process-by-ravikant090-ay4d
|
The first obvious thing in the problem is that it is very easy to brute force it in O(n^2) To do better than that you can try nlogn but for that you will need a
|
ravikant0909
|
NORMAL
|
2019-08-27T22:22:29.080194+00:00
|
2019-08-27T22:22:29.080240+00:00
| 1,292 | false |
The first obvious thing in the problem is that it is very easy to brute force it in O(n^2) To do better than that you can try nlogn but for that you will need a log term which can some from sorting etc but order is important in this problem , so thats probably not possible which leaves us with O(n)\n\nFor the problem to be O(n) it implies that for every step in the brute force process when you are comparing each number with every other number there is a way to avoid all those computations making each step O(1) for the n numbers. So when looking at a pair of numbers at each step we must know exactly which number in the pair to reject for all future comparisons. So lets assume thats true and see if we can indeed do that at every step\n\nLets start with two numbers A[0] and A[1]\n\nIf A[0] <= A[1] then we can reject A[0] because every pair that A[0] will be involved in A[1] can do better in them since A[1] is bigger and closer to other numbers\n\nThe other case A[0] > A[1]. In this case we can safely reject A[1] for all future comparisons because A[0] will at least as good as A[1] for all those comparisons because A[1] is 1 closer to other numbers but A[0] is at least 1 bigger than A[1] (since the numbers are integers)\n\nSo each step we know exactly which number to reject in the current pair. This line of thinking is useful in many array problems. \nAs a trick in the code to keep track of which numbers are being compared currently I always keep them adjacent to each other by swapping when necessary and decrementing value to account for change in index\n\n```\n def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, A: List[int]) -> int:\n \n \n best_score = 0\n n = len(A)\n i = 0\n j = 1 # Dont need j but I have kept it for readabililty\n \n while i < n and j < n:\n \n score = A[i] + A[j] + i - j\n best_score = max(score, best_score)\n \n if A[i] > A[j]:\n A[i] -= 1\n A[i], A[j] = A[j], A[i]\n \n i += 1\n j += 1\n \n return best_score\n \n```
| 41 | 0 |
[]
| 4 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Only Suffix Array O(n) 100% Beats
|
only-prefix-array-on-100-beats-by-sumeet-nqcm
|
🌟 IntuitionTo maximize the sightseeing pair score, we need to recognize the key components in the formula:score = values[i] + values[j] + i - jWe can rearrange
|
Sumeet_Sharma-1
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-27T02:01:47.204065+00:00
|
2024-12-27T02:38:08.366130+00:00
| 9,908 | false |
# 🌟 Intuition
To maximize the sightseeing pair score, we need to recognize the key components in the formula:
score = values[i] + values[j] + i - j
We can rearrange this to:
score = (values[i] + i) + (values[j] - j)
This shows that:
- The first part, `values[i] + i`, is the **left part** of the score.
- The second part, `values[j] - j`, is the **right part** of the score.
### 🧠 Key Insight:
We can **precompute** the **right part** (`values[j] - j`) for all `j` and use this precomputed information when calculating the score for any `i`. This allows us to maximize the score efficiently without checking every pair.
---
# 🚀 Approach
### 1. **Suffix Array** 📊:
To efficiently track the maximum of `values[j] - j` for all possible `j > i`, we use a **suffix array**:
- This array holds the maximum value of `values[j] - j` for each index `j` starting from the end of the array.
### 2. **Iterate and Calculate** 🔄:
For each index `i`, calculate the score using the precomputed values from the suffix array:
- For each `i`, the score is the sum of `values[i] + i` (the left part) and `suffixMax[i + 1]` (the right part).
By combining these two parts, we can find the maximum score for the sightseeing pair.
### 3. **Edge Cases** ⚠️:
Handle cases with fewer than 2 elements by returning the score directly for the pair `(values[0], values[1])`.
---
# 🧠 Complexity
### Time Complexity ⏱️:
- **O(n)**: We make two passes through the array:
1. One pass to compute the `suffixMax` array.
2. Another pass to calculate the maximum score.
### Space Complexity 💾:
- **O(n)**: We store the `suffixMax` array to keep track of the maximum values of `values[j] - j`.
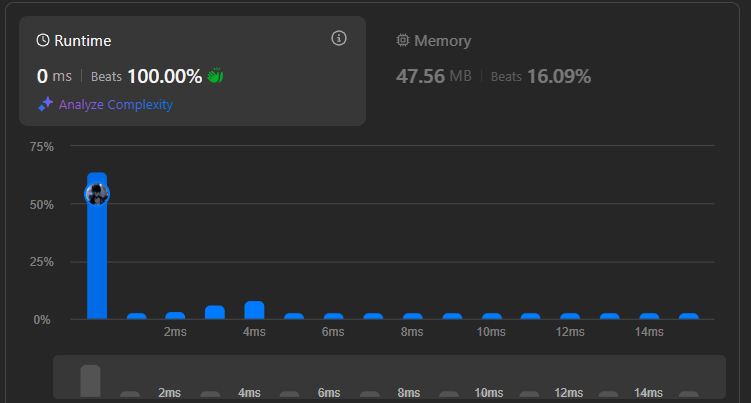
---
# 💻 Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {
int n = values.size();
if (n < 2) return values[0] + values[1] + 0 - 1;
vector<int> suffixMax(n);
suffixMax[n - 1] = values[n - 1] - (n - 1);
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
suffixMax[i] = max(suffixMax[i + 1], values[i] - i);
}
int maxScore = INT_MIN;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
maxScore = max(maxScore, values[i] + i + suffixMax[i + 1]);
}
return maxScore;
}
};
```
```Python3 []
class Solution:
def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, values: List[int]) -> int:
n = len(values)
suffixMax = [0] * n
suffixMax[n - 1] = values[n - 1] - (n - 1)
for i in range(n - 2, -1, -1):
suffixMax[i] = max(suffixMax[i + 1], values[i] - i)
maxScore = float('-inf')
for i in range(n - 1):
maxScore = max(maxScore, values[i] + i + suffixMax[i + 1])
return maxScore
```
```Java []
class Solution {
public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values) {
int n = values.length;
int[] suffixMax = new int[n];
suffixMax[n - 1] = values[n - 1] - (n - 1);
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
suffixMax[i] = Math.max(suffixMax[i + 1], values[i] - i);
}
int maxScore = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
maxScore = Math.max(maxScore, values[i] + i + suffixMax[i + 1]);
}
return maxScore;
}
}
```
```C []
int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int* values, int valuesSize) {
int* suffixMax = (int*)malloc(valuesSize * sizeof(int));
suffixMax[valuesSize - 1] = values[valuesSize - 1] - (valuesSize - 1);
for (int i = valuesSize - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
suffixMax[i] = fmax(suffixMax[i + 1], values[i] - i);
}
int maxScore = INT_MIN;
for (int i = 0; i < valuesSize - 1; i++) {
maxScore = fmax(maxScore, values[i] + i + suffixMax[i + 1]);
}
free(suffixMax);
return maxScore;
}
```
```C# []
public class Solution {
public int MaxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values) {
int n = values.Length;
int[] suffixMax = new int[n];
suffixMax[n - 1] = values[n - 1] - (n - 1);
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
suffixMax[i] = Math.Max(suffixMax[i + 1], values[i] - i);
}
int maxScore = int.MinValue;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
maxScore = Math.Max(maxScore, values[i] + i + suffixMax[i + 1]);
}
return maxScore;
}
}
```
```JavaScript []
var maxScoreSightseeingPair = function(values) {
let n = values.length;
let suffixMax = new Array(n);
suffixMax[n - 1] = values[n - 1] - (n - 1);
for (let i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
suffixMax[i] = Math.max(suffixMax[i + 1], values[i] - i);
}
let maxScore = -Infinity;
for (let i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
maxScore = Math.max(maxScore, values[i] + i + suffixMax[i + 1]);
}
return maxScore;
};
```
```Ruby []
# @param {Integer[]} values
# @return {Integer}
def max_score_sightseeing_pair(values)
n = values.length
suffix_max = Array.new(n)
suffix_max[n - 1] = values[n - 1] - (n - 1)
(n - 2).downto(0) do |i|
suffix_max[i] = [suffix_max[i + 1], values[i] - i].max
end
max_score = -Float::INFINITY
(0...n - 1).each do |i|
max_score = [max_score, values[i] + i + suffix_max[i + 1]].max
end
return max_score
end
```
| 40 | 0 |
['C', 'C++', 'Java', 'Python3', 'Ruby', 'JavaScript', 'C#']
| 9 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Recursive->Iterative DP/Greedy||beats 100%
|
recursive-dpbeats-100-by-anwendeng-h4xo
|
Intuition1st approach tries recursion (with memo). The score can be rewritten by
score=(values[i]+i)+(values[j]-j) for i<j2nd approach is an iterative DP versio
|
anwendeng
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-27T00:12:50.037408+00:00
|
2024-12-27T10:55:23.190225+00:00
| 5,509 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
1st approach tries recursion (with memo). The score can be rewritten by
`score=(values[i]+i)+(values[j]-j)` for `i<j`
2nd approach is an iterative DP version with optimized space. The interesting thing is that the 2nd solution can be interpreted also as a Greedy algorithm.(P.S. How about Kadane's Algorithm?)
3rd approach is using std::accumulate with lambda which is also fast.
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
[Please Turn on English subtitles if necessary]
[https://youtu.be/-15Q6Zc_piI?si=noYrDlAKtOxHxhkk](https://youtu.be/-15Q6Zc_piI?si=noYrDlAKtOxHxhkk)
1. Use C-array to declare state array `dp` as a global variable to store `dp[i]=max(values[k]+k for k<=i)`
2. Let `score` be a member variable
3. Define the recursive function `int f(int i, vector<int>& values)` compute `score=max(score, dp[i-1]+(values[i]-i))` & `dp[i]`.
4. In `maxScoreSightseeingPair` fill `dp` with `0`
5. Apply `f(n-1, values)`
6. `score` is the answer
7. 2nd approach is an iterative DP version with optimized space. The state array `dp` can be reduced to 1 single variable.
8. Recheck the 1st appoach, it's found there is no need for memoization to avoid of redudant computing( because the recursion has only 2 terms, current & previous). A pure recursion suffices to obtain a 0ms code.
9. C++ STL accumulate is the 3rd approach.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
$O(n)$
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
$O(n)\to O(1)$
# Code Recursion (with Memo)||both of C++ 0ms beat 100%
```cpp [Recursive C++]
class Solution {
public:
int score=0;
int f(int i, vector<int>& values){
if (i<0) return 0;
int x=values[i], prev=f(i-1, values);
score=max(score, prev+x-i);
return max(prev, x+i);
}
int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {
const int n=values.size();
f(n-1, values);
return score;
}
};
```
```cpp [C++ recursion with memo]
int dp[50000];// for max i
class Solution {
public:
int score=0;
int f(int i, vector<int>& values){
if (i<0) return 0;
if(dp[i]!=0) return dp[i];
int x=values[i], prev=f(i-1, values);
score=max(score, prev+x-i);
return dp[i]=max(prev, x+i);
}
int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {
const int n=values.size();
fill(dp, dp+n, 0);
f(n-1, values);
return score;
}
};
```
# Iterative DP/Greedy||C++ 0ms
```C++ []
class Solution {
public:
int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {
const int n=values.size();
if (n==2) return values[0]+values[1]-1;
int dp=values[0], score=0;
for(int i=1; i<n; i++){
int x=values[i];
score=max(score, dp+x-i);
dp=max(dp, x+i);
}
return score;
}
};
```
```Python []
class Solution:
def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, values: List[int]) -> int:
n=len(values)
dp, score=0, 0
for i, x in enumerate(values):
score=max(score, dp+x-i)
dp=max(dp, x+i)
return score
```
# C++ using accumulate||0ms
```
class Solution {
public:
int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {
return accumulate(values.begin(), values.end(), 0,
[dp=0, i=0](int score, int x) mutable{
score=max(score, dp+x-i);
dp=max(dp, x+i++);
return score;
});
}
};
```
# The DP/Greedy solutions are similar to Kadane's algorithm
Kadane's algorithm is used for solving some other problems which are more as follows:
[121. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock](https://leetcode.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock/solutions/3758901/c-python-greedy-explain-w-pyplot/)
[918. Maximum Sum Circular Subarray](https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-sum-circular-subarray/solutions/3722855/w-explanationc-using-kadanes-algorithm/)
[53. Maximum Subarray](https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-subarray/description/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-interview-150)
[152. Maximum Product Subarray](https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-product-subarray/solutions/3748707/c-kadane-s-algorithm/)
[2272. Substring With Largest Variance](https://leetcode.com/problems/substring-with-largest-variance/solutions/3738775/c-kadane-s-algorithm/)
| 34 | 1 |
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Greedy', 'Memoization', 'C++', 'Python3']
| 11 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Python3 easy to understand solution in one pass.
|
python3-easy-to-understand-solution-in-o-ewdu
|
The max score is defined as A[i] + A[j] + i - j, and the only constraint is i < j.\nInstead of directly comuting the score, we can find the solution by separate
|
jinjiren
|
NORMAL
|
2019-03-29T07:57:46.625205+00:00
|
2019-03-29T07:57:46.625247+00:00
| 1,739 | false |
The max score is defined as `A[i] + A[j] + i - j`, and the only constraint is `i < j`.\nInstead of directly comuting the score, we can find the solution by separate `i` and `j`.\n\n1. We maintain the maximum of `A[i] + i` for all previous visited spots\n2. We sum the maximum of `A[i] + i` with current spot `A[j]`, which is `A[i] + i + A[j] - j]`. We also maintain this value, which will become the final max score after iteration over the entire array.\n\n```py\n def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, A: List[int]) -> int:\n best_i = 0\n res = 0\n for i, v in enumerate(A):\n # here v - i is actually `A[j] - j` in the formula\n res = max(res, v - i + best_i)\n # here we store `A[i] + i`\n best_i = max(best_i, v + i)\n return res\n```
| 33 | 0 |
['Python']
| 3 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Simple & Clean Solution | ✅ Beats 100% | 💡 O(n) Approach | C++ | Java | Python | JS
|
simple-clean-solution-beats-100-on-appro-8nxr
|
⬆️Upvote if it helps ⬆️Connect with me on Linkedin [Bijoy Sing]IntuitionThe problem revolves around maximizing the score of two sightseeing spots by efficiently
|
BijoySingh7
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-27T05:00:09.814277+00:00
|
2024-12-27T05:00:09.814277+00:00
| 2,955 | false |
# ⬆️Upvote if it helps ⬆️
---
## Connect with me on Linkedin [Bijoy Sing]
---
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {
int ans = 0;
int Prev = values[0];
for (int j = 1; j < values.size(); j++) {
ans = max(ans, Prev + values[j] - j);
Prev = max(Prev, values[j] + j);
}
return ans;
}
};
```
```python []
class Solution:
def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, values: List[int]) -> int:
ans = 0
Prev = values[0]
for j in range(1, len(values)):
ans = max(ans, Prev + values[j] - j)
Prev = max(Prev, values[j] + j)
return ans
```
```java []
class Solution {
public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values) {
int ans = 0;
int Prev = values[0];
for (int j = 1; j < values.length; j++) {
ans = Math.max(ans, Prev + values[j] - j);
Prev = Math.max(Prev, values[j] + j);
}
return ans;
}
}
```
```javascript []
class Solution {
maxScoreSightseeingPair(values) {
let ans = 0;
let Prev = values[0];
for (let j = 1; j < values.length; j++) {
ans = Math.max(ans, Prev + values[j] - j);
Prev = Math.max(Prev, values[j] + j);
}
return ans;
}
}
```
---
# Intuition
The problem revolves around maximizing the score of two sightseeing spots by efficiently managing the difference between their indices and maximizing the sum of their values.
# Approach
- Maintain a running maximum (`Prev`) of \( values[i] + i \), which represents the best value of the first spot up to the current index.
- Iterate through the array and for each index \(j\), compute the score of the pair \(i, j\) using \( Prev + values[j] - j \).
- Update the maximum score (`ans`) and `Prev` as you progress.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
$$O(n)$$, where \(n\) is the length of the `values` array, as we iterate through the array once.
- Space complexity:
$$O(1)$$, since no extra space is used apart from a few variables.
### *If you have any questions or need further clarification, feel free to drop a comment! 😊*
| 21 | 1 |
['Array', 'Sliding Window', 'Suffix Array', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'Python3', 'JavaScript']
| 16 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Python | Greedy Algorithm Pattern
|
python-greedy-algorithm-pattern-by-khosi-wf1x
|
see the Successfully Accepted SubmissionCodeExplanationInitialization:
Start with max_score = 0 to track the highest score.
Use max_i_value to store the maximum
|
Khosiyat
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-27T00:03:01.725631+00:00
|
2024-12-27T00:03:01.725631+00:00
| 1,108 | false |
[see the Successfully Accepted Submission](https://leetcode.com/problems/best-sightseeing-pair/submissions/1489297050/?envType=daily-question&envId=2024-12-27)
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, values: List[int]) -> int:
# Initialize variables
max_score = 0
max_i_value = values[0] + 0 # This is values[i] + i for the first element
# Iterate through the array starting from the second element
for j in range(1, len(values)):
# Calculate the score for the current pair (i, j)
max_score = max(max_score, max_i_value + values[j] - j)
# Update max_i_value to include the current index
max_i_value = max(max_i_value, values[j] + j)
return max_score
```
### Explanation
#### Initialization:
- Start with `max_score = 0` to track the highest score.
- Use `max_i_value` to store the maximum value of \( \text{values[i]} + i \) encountered so far.
#### Iterating Through the Array:
- For each \( j \) (starting from the second element):
- Compute the score using the current \( \text{max\_i\_value} \) and \( \text{values[j]} - j \).
- Update `max_score` if the current score is greater than the previous maximum.
- Update `max_i_value` to account for \( \text{values[j]} + j \).
#### Efficiency:
- The solution runs in \( O(n) \) time, as it involves a single loop through the array.
- The space complexity is \( O(1) \), as no additional storage proportional to the input size is used.

| 15 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 3 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Easy Python | O(n) Time, O(1) Space
|
easy-python-on-time-o1-space-by-aragorn-4tp8
|
Easy Python | O(n) Time, O(1) Space\n\nTo maximize the formula "A[i]+i+A[j]-j", we can note that for any index "j", the score is maximized by the best value of
|
aragorn_
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-27T23:27:46.879276+00:00
|
2020-08-27T23:29:20.708104+00:00
| 1,165 | false |
**Easy Python | O(n) Time, O(1) Space**\n\nTo maximize the formula "A[i]+i+A[j]-j", we can note that for any index "j", the score is maximized by the best value of "A[i]+i" seen before (since "A[j]-j" is fixed). As a result, we can make a one-pass O(n) loop remembering only the highest value of "A[i]+i" in O(1) space, and update the record score that we observe (variable "best").\n\nI hope the explanation was helpful. Cheers,\n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, A) :\n K = A[0]\n best = float(\'-inf\')\n for j in range(1,len(A)):\n x = A[j]\n best = max(best, K + x - j )\n K = max(K , x + j )\n return best\n```
| 15 | 0 |
['Python', 'Python3']
| 1 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
C++ 6 Lines One Pass With Explanation.
|
c-6-lines-one-pass-with-explanation-by-x-dupp
|
Solution\n\nThe basic way is to use mathematics.\n\nAccording to the description: The score of a pair (i < j) of sightseeing spots is values[i] + values[j] + i
|
xiaoli727
|
NORMAL
|
2021-08-26T11:33:22.361897+00:00
|
2021-08-26T11:33:51.707246+00:00
| 787 | false |
**Solution**\n\nThe basic way is to use mathematics.\n\nAccording to the description: The score of a pair (`i < j`) of sightseeing spots is `values[i] + values[j] + i - j`, and our goal it to maximize the score.\n\nThen, we just modify this formula: `values[i] + values[j] + i - j` = `(values[j] - j) + (values[i] + i) `.\n\nSo, the only thing for us is to find an anwser: `(values[j] - j) + max(values[i] + i) `, where `i < j`.\n\n**Code**\n\n```cpp\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {\n int n = values.size(), prev = values[0] + 0, ans = 0;\n for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) {\n ans = max(ans, prev + values[i] - i);\n prev = max(prev, values[i] + i);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\n\n\n**Complexity**\n\nTime complexity: O(n)\n\nSpace complexity: O(1)\n\n
| 14 | 1 |
['C']
| 2 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Java | 2 methods | Explained
|
java-2-methods-explained-by-prashant404-m0p6
|
Method 1: Bottom Up DP (Tabulation)\n Aim is to maximize MS = values[i] + values[j] + i - j for i < j, which can be rewritten as S + D where S = values[i] + i,
|
prashant404
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-17T19:47:49.258119+00:00
|
2022-08-30T23:13:58.037418+00:00
| 1,058 | false |
**Method 1:** Bottom Up DP (Tabulation)\n* Aim is to maximize MS = values[i] + values[j] + i - j for i < j, which can be rewritten as S + D where S = values[i] + i, D = values[j] - j, MS = max score\n* So if we maximize both S and D, then MS will be maximized\n* Use a 1D table to store the maximum value of S seen till any index. Then use this max value to maximize D, thereforce MS\n\n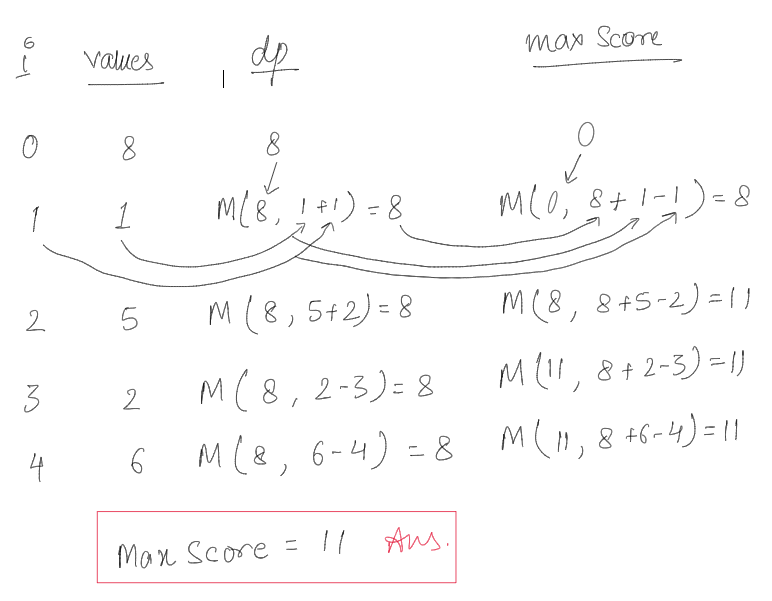\n\n>**T/S:** O(n)/O(n), where n = size(values)\n```\npublic int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values) {\n\tvar maxScore = 0;\n\tvar n = values.length;\n\tvar dp = new int[n];\n\tdp[0] = values[0];\n\n\tfor (var i = 1; i < n; i++) {\n\t\tmaxScore = Math.max(maxScore, dp[i - 1] + values[i] - i);\n\t\tdp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1], values[i] + i);\n\t}\n\treturn maxScore;\n}\n```\n\n**Version 2:** Space optimize method 1 since only 1 previous value is being used\n>**T/S:** O(n)/O(1)\n```\npublic int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values) {\n\tvar maxScore = 0;\n\n\tfor (int i = 1, sumMax = values[0]; i < values.length; i++) {\n\t\tmaxScore = Math.max(maxScore, sumMax + values[i] - i);\n\t\tsumMax = Math.max(sumMax, values[i] + i);\n\t}\n\treturn maxScore;\n}\n```\n***Please upvote if this helps***
| 13 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Java']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
C++ O(n) solution
|
c-on-solution-by-welcome2020-wwmg
|
A[i] + A[j] + i - j = (A[i] + i ) + (A[j] - j)\nWhen we iterate the array A, (A[j] - j )is known.\nFor each index j, to make (A[i] + i) + (A[j] - j) maximum,
|
welcome2020
|
NORMAL
|
2019-06-28T14:33:14.141877+00:00
|
2019-06-28T14:33:14.141951+00:00
| 624 | false |
A[i] + A[j] + i - j = (A[i] + i ) + (A[j] - j)\nWhen we iterate the array A, (A[j] - j )is known.\nFor each index j, to make (A[i] + i) + (A[j] - j) maximum, we need to find the index i such that A[i] + i is maximum. We can record the value that gives us the max A[i] + i .\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& A) {\n int maxScore = 0;\n int max_AiPlusi = A[0] + 0;\n for(int j = 1; j < A.size(); j++)\n {\n maxScore = max(maxScore, max_AiPlusi + A[j] - j);\n max_AiPlusi = max(max_AiPlusi, A[j] + j);\n }\n return maxScore;\n }\n};\n```
| 13 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Simple O(n) C++ DP Solution || Space Optimized DP
|
simple-on-c-dp-solution-space-optimized-dzc7d
|
Intuition & Logic :\nWe have the formula score = values[i] + values[j] +i -j\nNow, we are required to maximise score. So, we can modify the the formula as:\nmax
|
Debarchan_Nayek
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-12T16:30:18.999476+00:00
|
2022-05-12T16:30:18.999507+00:00
| 1,154 | false |
**Intuition & Logic :**\nWe have the formula score = values[i] + values[j] +i -j\nNow, we are required to maximise score. So, we can modify the the formula as:\nmax(score) = max(values[i] + values[j] + i - j) = max(values[i]+i) + max(values[j] - j)\n\nNow, at every index j, values[j]-j is fixed. Hence our obejctive would be to find the best previous index(i) which gives us the maximum score. We will achieve this by storing the values in a dp array, by calculating the max value between the previously stored value and current calculated value, i.e values[i] + i.\n\nFinally, we will calculate score based on our formula, where max(values[i]+i) will be stored in dp[i-1].\n\nThe **code** is given below : \n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {\n int score=INT_MIN,n=values.size();\n int dp[n];\n dp[0]=values[0];\n \n for(int i=1;i<n;i++){ \n score=max(score,dp[i-1]+values[i]-i);\t\t\n dp[i] = max(dp[i-1],values[i]+i);\n }\n \n return score;\n }\n};\n```\n\nTime Complexity : O(n)\nSpace Complexity: O(n)\n\nNow, we can reduce the extra space by storing the max(values[i]+i) in a variable instead of an array.\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {\n int score=INT_MIN,n=values.size();\n int maxLeft = values[0];\n \n for(int i=1;i<n;i++){ \n score=max(score,maxLeft+values[i]-i);\n maxLeft = max(maxLeft,values[i]+i);\n }\n \n return score;\n }\n};\n```\n\nT.C: O(n)\nS.C: O(1)\n\n**Please upvote if you liked the explanation**
| 12 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C', 'C++']
| 1 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Beats 100%✅✅ || Easy to understand solution
|
beats-100-easy-to-understand-solution-by-cyhg
|
IntuitionThe problem can be divided into two parts:
Maximizing values[i] + i for the left part.
Maximizing values[j] - j for the right part.
The best sightseein
|
arunk_leetcode
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-27T04:02:49.952408+00:00
|
2024-12-27T04:02:49.952408+00:00
| 1,689 | false |
# Intuition
The problem can be divided into two parts:
1. Maximizing `values[i] + i` for the left part.
2. Maximizing `values[j] - j` for the right part.
The best sightseeing pair can be determined by combining the maximum values from both parts.
# Approach
1. Precompute the `leftMax` array, where `leftMax[i]` stores the maximum value of `values[k] + k` for all `k <= i`.
2. Precompute the `rightMax` array, where `rightMax[i]` stores the maximum value of `values[k] - k` for all `k >= i`.
3. Iterate through the array to find the maximum sum of `leftMax[i-1] + rightMax[i]` for all valid `i`.
# Complexity
- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$, where `n` is the size of the array, as we iterate over the array a constant number of times.
- Space complexity: $$O(n)$$, for storing the `leftMax` and `rightMax` arrays.
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {
int n = values.size();
vector<int> leftMax(n), rightMax(n);
// Compute leftMax array
leftMax[0] = values[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
leftMax[i] = max(leftMax[i - 1], values[i] + i);
}
// Compute rightMax array
rightMax[n - 1] = values[n - 1] - (n - 1);
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
rightMax[i] = max(rightMax[i + 1], values[i] - i);
}
// Compute the maximum score
int maxi = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
maxi = max(maxi, leftMax[i - 1] + rightMax[i]);
}
return maxi;
}
};
```
``` Java []
class Solution {
public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values) {
int n = values.length;
int[] leftMax = new int[n];
int[] rightMax = new int[n];
// Compute leftMax array
leftMax[0] = values[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
leftMax[i] = Math.max(leftMax[i - 1], values[i] + i);
}
// Compute rightMax array
rightMax[n - 1] = values[n - 1] - (n - 1);
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
rightMax[i] = Math.max(rightMax[i + 1], values[i] - i);
}
// Compute the maximum score
int maxi = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
maxi = Math.max(maxi, leftMax[i - 1] + rightMax[i]);
}
return maxi;
}
}
```
```JavaScript []
/**
* @param {number[]} values
* @return {number}
*/
var maxScoreSightseeingPair = function(values) {
const n = values.length;
const leftMax = Array(n).fill(0);
const rightMax = Array(n).fill(0);
// Compute leftMax array
leftMax[0] = values[0];
for (let i = 1; i < n; i++) {
leftMax[i] = Math.max(leftMax[i - 1], values[i] + i);
}
// Compute rightMax array
rightMax[n - 1] = values[n - 1] - (n - 1);
for (let i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
rightMax[i] = Math.max(rightMax[i + 1], values[i] - i);
}
// Compute the maximum score
let maxi = 0;
for (let i = 1; i < n; i++) {
maxi = Math.max(maxi, leftMax[i - 1] + rightMax[i]);
}
return maxi;
};
```
```Python []
class Solution(object):
def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, values):
"""
:type values: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
n = len(values)
left_max = [0] * n
right_max = [0] * n
# Compute left_max array
left_max[0] = values[0]
for i in range(1, n):
left_max[i] = max(left_max[i - 1], values[i] + i)
# Compute right_max array
right_max[n - 1] = values[n - 1] - (n - 1)
for i in range(n - 2, -1, -1):
right_max[i] = max(right_max[i + 1], values[i] - i)
# Compute the maximum score
maxi = 0
for i in range(1, n):
maxi = max(maxi, left_max[i - 1] + right_max[i])
return maxi
```
| 11 | 0 |
['Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'Python3', 'JavaScript']
| 2 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
C++ O(N) Solution With Explanation
|
c-on-solution-with-explanation-by-pjdope-peu0
|
We will make a variable currVal which will store current maximum A[i]+i-j\n1. we will initialize currVal = A[i]\n2. we will keep it decrementing by 1 which is e
|
pjdope
|
NORMAL
|
2020-08-02T02:05:57.775595+00:00
|
2020-08-02T02:05:57.775645+00:00
| 582 | false |
We will make a variable currVal which will store current maximum A[i]+i-j\n1. we will initialize currVal = A[i]\n2. we will keep it decrementing by 1 which is equivalent to i-j\n3. if currVal is smaller than A[i], we update currVal=A[i]\n4. we find sum of A[i] and currVal for every index and return maximum value\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& A) {\n int currVal=A[0];\n int currsum;int maxsum=0;\n int n=A.size();\n for(int i=1;i<n;i++)\n {\n currVal--;\n currsum=A[i]+currVal;\n maxsum=max(currsum,maxsum);\n currVal=max(currVal,A[i]);\n }\n return maxsum;\n }\n};\n```
| 11 | 1 |
[]
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Solution for LeetCode#1014
|
solution-for-leetcode1014-by-samir023041-bauw
|
IntuitionThe problem asks to find the maximum score of a sightseeing pair, where the score is calculated as values[i] + values[j] + i - j (i < j). The key insig
|
samir023041
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-27T03:18:09.620960+00:00
|
2024-12-27T03:18:09.620960+00:00
| 586 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
The problem asks to find the maximum score of a sightseeing pair, where the score is calculated as values[i] + values[j] + i - j (i < j). The key insight is to realize that we can split this formula into (values[i] + i) + (values[j] - j) and optimize these two parts separately.
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
1. Initialize iSite with the score of the first site (values + 0).
2. Iterate through the array starting from the second element:
- Calculate the potential score if the current site is paired with the best previous site.
- Update maxScore if this potential score is higher.
- Update iSite to be the maximum of the current iSite and the score of the current site (values[i] + i).
# Complexity
- Time complexity: O(n)
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity: O(1)
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code Option-01
```java []
class Solution {
public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values) {
int n=values.length;
int iSite=values[0]+0;
int maxScore=0;
for(int i=1; i<n; i++){
maxScore=Math.max(maxScore, iSite+values[i]-i); // values[i]+i + values[j]-j where i<j
iSite=Math.max(iSite, values[i]+i);
}
return maxScore;
}
}
```
# Code Option-02
```java []
class Solution {
public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values) {
int n=values.length;
int iSite=values[0]+0;
int maxScore=0;
for(int i=1; i<n; i++){
if(maxScore<iSite+values[i]-i)
maxScore=iSite+values[i]-i; // values[i]+i + values[j]-j where i<j
if(iSite < values[i]+i)
iSite=values[i]+i;
}
return maxScore;
}
}
```
| 9 | 0 |
['Java']
| 4 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Very Easy To Understand O(n) Java Solution
|
very-easy-to-understand-on-java-solution-igew
|
Input: [8,1,5,2,6]\nOutput: 11\nExplanation: i = 0, j = 2, A[i] + A[j] + i - j = 8 + 5 + 0 - 2 = 11\nI find the equation can rewrite from A[i] + A[j] + i - j to
|
a2232189
|
NORMAL
|
2019-04-27T13:51:30.743443+00:00
|
2019-04-27T13:51:30.743488+00:00
| 592 | false |
Input: [8,1,5,2,6]\nOutput: 11\nExplanation: i = 0, j = 2, A[i] + A[j] + i - j = 8 + 5 + 0 - 2 = 11\nI find the equation can rewrite from ` A[i] + A[j] + i - j ` to ` (A[i] + i) + (A[j] - j) `\nSo in a one-pass loop, we can record the max `(A[i] + i) ` before, and calculate the possible result `res`.\n\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] A) {\n int max = A[0];\n int res = Integer.MIN_VALUE;\n for(int i = 1; i < A.length; ++i){\n res = Math.max(res, max + A[i] -i);\n max = Math.max(max, A[i] +i);\n }\n \n return res;\n }\n}\n```
| 9 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
5-lines of code ✅ Easy for beginner💡 | JavaScript || Python || C++ 😎
|
beat-9333-written-in-javascript-python-c-cldw
|
ApproachComplexity
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(1)
Code
|
yenhuynh02
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-27T03:02:19.521313+00:00
|
2024-12-27T06:34:02.878532+00:00
| 915 | false |
# Approach
# Complexity
- Time complexity: O(n)
- Space complexity: O(1)
# Code
```javascript []
/**
* @param {number[]} values
* @return {number}
*/
var maxScoreSightseeingPair = function(values) {
let maxScore = 0;
let maxI = values[0] + 0; //Initialize with index 0 of array
for (let j = 1; j < values.length; j++) {
// Calculate the score for the current pair (i, j)
maxScore = Math.max(maxScore, maxI + values[j] - j);
// Update maxI to include the current value and index
maxI = Math.max(maxI, values[j] + j);
}
return maxScore;
};
```
```python []
class Solution(object):
def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, values):
max_score = 0
max_i = values[0] # Initialize with values[0] + 0
for j in range(1, len(values)):
# Calculate the score for the current pair (i, j)
max_score = max(max_score, max_i + values[j] - j)
# Update max_i to include the current value and index
max_i = max(max_i, values[j] + j)
return max_score
```
```C++ []
class Solution {
public:
int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {
int maxScore = 0;
int maxI = values[0]; // Initialize with values[0] + 0
for (int j = 1; j < values.size(); j++) {
// Calculate the score for the current pair (i, j)
maxScore = max(maxScore, maxI + values[j] - j);
// Update maxI to include the current value and index
maxI = max(maxI, values[j] + j);
}
return maxScore;
}
};
```
| 8 | 1 |
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Python', 'C++', 'JavaScript']
| 2 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Greedy | One pass | Easy Explanation | C++
|
greedy-one-pass-easy-explanation-c-by-sa-xoj9
|
IntuitionThe problem is to find the maximum score for a pair of indices(i,j) defined as A[i] + A[j] + i -j. This equation can be derived as -
A[i] + i (dependen
|
sachanharshit
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-27T02:47:37.483956+00:00
|
2024-12-27T02:47:37.483956+00:00
| 669 | false |
# Intuition
The problem is to find the maximum score for a pair of indices(i,j) defined as A[i] + A[j] + i -j. This equation can be derived as -
1) A[i] + i (dependent on i)
2) A[j] - j (dependent on j)
The goal is to track the maximum value of **A[i] + i.**
# Approach
We use a map to track the maximum values of
A[i] + i , as we iterate through the array -
1) **Iterate** - For each index i, compute the score as max_so_far + A[i] - i , where max_so_far is the largest A[k] + k seen so far.
2) **Update Answer** - Update the maximum score using the current value
3) **Insert Values** - Add A[i] + i to the map.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
0(NlogN)
- Space complexity:
0(N)
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& A) {
int n = A.size();
map<int, int> mp;
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!mp.empty()) {
auto it = mp.rbegin();
ans = max(ans, it->first + A[i] - i);
}
mp[A[i] + i]++;
}
return ans;
}
};
```
| 8 | 1 |
['Array', 'Hash Table', 'C++']
| 1 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Java Dynamic Programming with explanation and example
|
java-dynamic-programming-with-explanatio-fgxg
|
Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \nDynamic Programming\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(N)\n Add your time complexity here, e.g. O(n)
|
Kenny48620
|
NORMAL
|
2023-01-29T01:46:38.007885+00:00
|
2023-01-29T01:46:38.007929+00:00
| 532 | false |
# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nDynamic Programming\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(N)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:O(1)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] A) {\n // A[i] + A[j] + i - j = (A[i]+i) + (A[j]-j)\n // think about dividing them into two parts\n // get the max of left part and right part, then add them \n // to get the maximum score\n //\n // max(left) + max(right)\n // maximum score = max(A[i]+i) + max((A[j]-j))\n\n /* example:\n i 0 1 2 3 4\n A [8, 1, 5, 2, 6], max = 0\n \n i=1,\n left = A[0]+0 = 8\n right = A[1]-1 = 0\n => max = max(max=0, left + right=8) = 8\n Before moving to i=2, we need to update left part by \n comparing current left and right\n so ----> left = max(left=8, A[1]+1=2) = 8\n i=2,\n left = 8\n right = A[2]-2 = 3\n => max = max(max=8, left + right=11) = 11\n so ----> left = max(left=8, A[2]+2=7) = 8 \n i=3,\n left = 8\n right = A[3]-3 = 1\n => max = max(max=11, left + right=9) = 11\n so ----> left = max(left=8, A[3]+3=5) = 8 \n i=4,\n left = 8\n right = A[4]-4 = 2\n => max = max(max=11, left + right=10) = 11\n so ----> left = max(left=8, A[4]+4=10) = 8 \n end loop\n max = 11\n */\n int N = A.length;\n int left = A[0]+0;\n int right = 0; \n int max = 0;\n\n for (int i=1; i<N; i++){\n right = A[i]-i;\n max = Math.max(max, left+right);\n // before we move on, we need to update the state of left part\n // now our current right part will become left part in next round\n left = Math.max(left, A[i]+i); \n }\n return max;\n }\n}\n```
| 8 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Easy & Simple Recursion + Memoization [DP] Technique. || Intuition of Buy and Sell Stock
|
easy-simple-recursion-memoization-dp-tec-urix
|
Intuition Behind this approach . Buy and Sell Stock approach\n\n\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int dp[2][2][50001];\n int solve(vector<int>& values,int i
|
sumanpal198
|
NORMAL
|
2022-05-08T06:29:18.401564+00:00
|
2022-05-08T06:37:45.070150+00:00
| 975 | false |
[**Intuition Behind this approach . Buy and Sell Stock approach**](https://leetcode.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock/discuss/900050/Fully-explained-all-buy-and-sell-problems-C%2B%2B-oror-Recursive-oror-Memoization-oror-Minor-difference)\n\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int dp[2][2][50001];\n int solve(vector<int>& values,int index,int seen,int k)\n {\n if(index>=values.size() or k<=0)\n {\n if(k<=0) //if we have comepleted seeing two monuments ,then return 0.\n return 0;\n else //this basically means we are going out of index, in that case we will return INT_MIN\n return INT_MIN;\n }\n if(dp[seen][k][index]!=-1)\n return dp[seen][k][index];\n if(seen)\n {\n\t\t//first we will visit the monument,therefore including "values[index]+index]" and\n\t\t//making seen as opposite value,to signify that we have already seen one monument.\n\t\t//Time to see the final monument.\n return dp[seen][k][index] = max(values[index]+index + solve(values,index+1,!seen,k) , solve(values,index+1,seen,k));\n }\n else\n {\n\t\t//Time has come to see the final monument that\'s whymaking "k-1" which suignify \n\t\t//that we can see only 2 monuments at a time.\n\t\t//Including "values[index]-index" as mentioned in the question.\n return dp[seen][k][index] = max(values[index]-index + solve(values,index+1,!seen,k-1) , solve(values,index+1,seen,k));\n }\n }\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {\n int n = values.size();\n int start=0,seen=1;//we will first see the first monument therefore "seen=1"\n int k=1; //signifies that we can see sightsee two monument at a time.. \n\t\t//(k=0 -> see one monument ,k=1 -> see the final monument)\n memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp));\n return solve(values,start,seen,k);\n }\n};\n```\n\n***Please Upvote***
| 8 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization']
| 1 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
C++ simple solution without DP :)
|
c-simple-solution-without-dp-by-maninder-avyd
|
let us say we have pairs with index i and j , and ( i < j) ,, \n what are we gonna do is ,, we will start our iteration from end of an array and lets suppose t
|
ManinderSingh72
|
NORMAL
|
2022-01-25T20:09:33.823473+00:00
|
2022-01-25T20:09:33.823522+00:00
| 265 | false |
let us say we have pairs with index i and j , and ( i < j) ,, \n what are we gonna do is ,, we will start our iteration from end of an array and lets suppose to understand that the second element (present on jth index) of the pair you want to fulfill your needs is the last element as of now , and we will maintain a variable named as cur ,, which will be initially equal to value of last element (also the jth element we have chosen ) ,, then we wil start reverse iteration from back of our array ,,also at every step of iteration we will decrease value of cur by 1 (cur--) lets suppose we have found our first member of desired pair (we will understand afterwards while writing how we will get our first member ) and when we came to our first member you can realise that at present value of cur is the subtraction of value of second member of our pair and difference between first member and second member (i.e j-i) so in order to meet the need of our question ,, we just have to add the value of our first memeber ,, and we are good to go :)\n \n ```\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {\n \n int ans=INT_MIN;\n int n=values.size();\n \n int cur=values[n-1]; // taking current as last element as we decided before\n cur--;\n for(int i=n-2;i>=0;i--){\n ans=max(ans,cur+values[i]); // if we select the first member of our pair as current element of our iteration ,, if it brings out maximum ,, then we will update ans ,,else we wont update ans\n \n \n \n // now here twist comes in our story ,, if at any point we acheive element from our array whose value is greater than or equal to the current value we are carrying ,, then we will update cur with that element of array ,, this is we are doign becuase ,, there is no benefit of carrying forward our previous current because we want to acheive maximum value and we got element with whose value is greater than previous one //\n if(cur<=values[i]){ \n \n cur=values[i];\n }\n \n cur--; // decreasing cur by 1 ,, as we decided it to do before \n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n\t```\n
| 8 | 0 |
['C']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
JAVA O(N) solution with explanation
|
java-on-solution-with-explanation-by-cha-d10r
|
Approach\n1) The idea is to see the expression given that is value[i] + values[j] + i - j.\n2) Expression can also be seen as (values[i] + i) + (values[j] - j).
|
chaos_eater
|
NORMAL
|
2021-04-13T20:34:47.971002+00:00
|
2021-04-14T09:37:33.014715+00:00
| 283 | false |
Approach\n1) The idea is to see the expression given that is value[i] + values[j] + i - j.\n2) Expression can also be seen as (values[i] + i) + (values[j] - j).\n3) Now just keep the track of the maximum of (values[i] + i) upto current index and update the max answer.\n4) Below is the implementation of the same\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values) {\n int max = values[0];\n int i = 1;\n int ans = max;\n while (i < values.length) {\n ans = Math.max(ans,max + values[i] - i);\n max = Math.max(max,values[i] + i);\n i++;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 8 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
[Java] O(n) Prefix/Suffix sums with a twist
|
java-on-prefixsuffix-sums-with-a-twist-b-ae5r
|
So I had to look at the solution from other people for solving this problem in the discussion section. However, I found the "double maxxing" solution to be real
|
killedsteel
|
NORMAL
|
2021-01-18T02:59:23.107338+00:00
|
2021-01-18T02:59:23.107382+00:00
| 188 | false |
So I had to look at the solution from other people for solving this problem in the discussion section. However, I found the "double maxxing" solution to be _really_ complicated and difficult to come up with in an interview.\n\nOn one of the posts, I read a nice reformulation of the problem statement: we are interested in finding a pair `(i, j)` where `i < j`, such that:\n\n```text\nA[i] + A[j] + i - j\n```\nis **maximized**.\n\nHowever, this formula can be moved around! Specifically, you can move it around like so: **maximize:**\n```text\n(A[i] + i) + (A[j] - j)\n```\n\nNotice that both these are quantities that are computable over each individual index _without having to depend on other indices_. For example, at index `j = 10` I can compute `A[j] - j` without having to look at any other indices in the array. Now we want to compute the maximum value of this sum of 2 bracketed terms. This _really_ smells like prefix/suffix sums.\n\nThe index `i` has to be _somewhere_ within the array. So we **must** compute the sum `A[i] + i` for each individual index i. However, for one such particular `i`, what `j` to pick? Well, we pick the `j > i` such that `A[j] - j` is maximum.\n\nSo we can solve this problem by keeping an array `P` such that `P[i] = A[i] + i`. We also keep another array `S` such that `S[j] = max(A[j] - j, S[j + 1])`. That is, `S[j] = the maximum value of A[k] - k for all k >= j`.\n\nThen, to get the **maximum** possible value of a sightseeing pair where `i` is fixed, we need to simply look at the sum `P[i] + S[i + 1]`. The maximum value of this sum, is the maximum value overall of any pair!\n\nThe code in Java: \n\n```java\npublic int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] A) { \n final int n = A.length;\n \n int[] P = new int[n];\n int[] S = new int[n];\n \n S[n - 1] = A[n - 1] - (n - 1);\n \n // Prepare backward\n for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {\n S[i] = Math.max(A[i] - i, S[i + 1]); \n }\n \n // Prepare forward\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n P[i] = A[i] + i;\n }\n \n int best = Integer.MIN_VALUE;\n for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {\n // For all possible positions of i, \n // search the best j such that \n // A[j] - j was the maximum possible\n // along with A[i] + i itself\n // S[i + 1] because we cannot double\n // count index i\n best = Math.max(best, P[i] + S[i + 1]);\n }\n return best;\n }\n```\n\nHere is a pictorial form of the algorithm:\n\n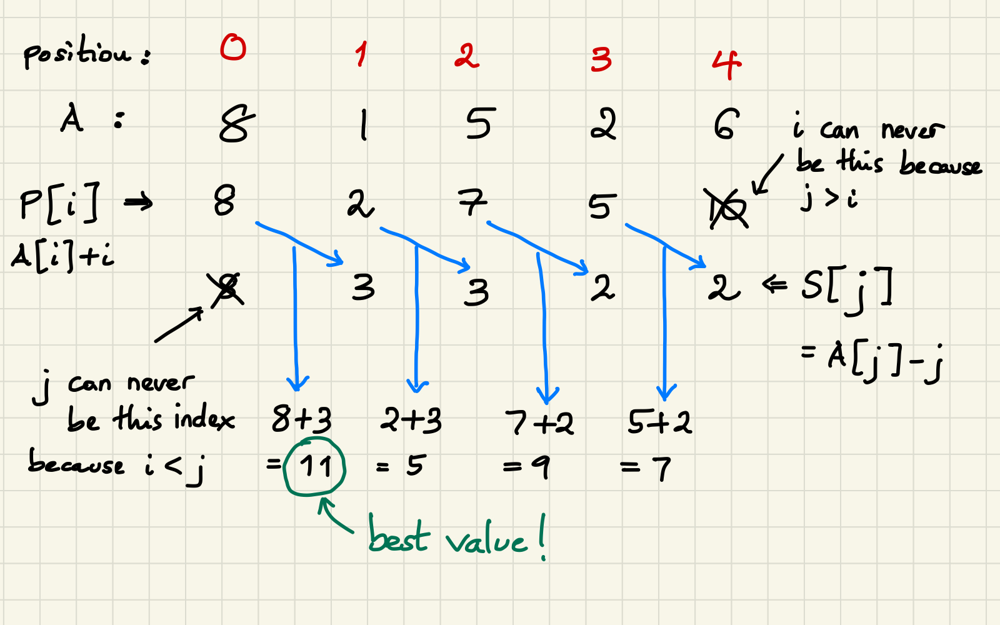\n\n\nHope this helps! This was a tough one for me :)
| 8 | 0 |
['Suffix Array']
| 1 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
With a simple rewrite of the expression, everything becomes clear
|
with-a-simple-rewrite-of-the-expression-dx39o
|
Rewrite (A[i] + A[j] + i - j) as (A[i] + i) + (A[j] - j), where i < j.\n\nFor each element A[j], you want to know the largest (A[i] + i) to its left because tha
|
timothyleong97
|
NORMAL
|
2020-12-09T12:59:56.290959+00:00
|
2022-01-20T03:12:03.252062+00:00
| 199 | false |
Rewrite `(A[i] + A[j] + i - j)` as `(A[i] + i) + (A[j] - j)`, where `i < j`.\n\nFor each element `A[j]`, you want to know the largest `(A[i] + i)` to its left because that maximises the value of `(A[i] + i) + (A[j] - j)` for the current `A[j]`. We use a variable to remember the largest `A[i] + i` seen so far.\n \nAlso, if the value of `(A[i] + i) + (A[j] - j)` for this `A[j]` is higher than the highest seen before, we update the current high score. We use another variable to remember the largest `(A[i] + i) + (A[j] - j)` seen so far.\n \n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] A) {\n // the greatest (A[i] + i) we\'ve seen so far which is A[0] + 0, but + 0 is redundant\n int max_i = A[0]; \n // the high score we want to return\n int high_score = Integer.MIN_VALUE;\n \n for (int j = 1; j < A.length; ++j) {\n // check if adding this (A[j] - j) increases the current high score\n high_score = Math.max(high_score, max_i + A[j] - j);\n // update the largest (A[i] + i) seen so far\n max_i = Math.max(max_i, A[j] + j);\n }\n \n return high_score;\n }\n}\n```
| 8 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Easy Method || Two Variable
|
easy-method-two-variable-by-muhammedniha-l539
|
IntuitionApproach
Initialize first_max as values[0]-1 (1 representing the distant to second index) and second_max as values[1].
result=first_max+second_max(=v
|
muhammednihas2218
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-27T06:14:25.261873+00:00
|
2024-12-27T06:14:25.261873+00:00
| 272 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
1. Initialize first_max as values[0]-1 (1 representing the distant to second index) and second_max as values[1].
* ```result=first_max+second_max(=values[0]+values[1]+0-1)```
2. Iterate the array from third element to last element in array.during this iteration :
* one decrement the values of first_max and second_max variable
* if the current element is higher than first_max or second_max this variable will change to current element.
* update the result also if it is higher than previouse result.
3. return the result

# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
The solution processes each element of the array once, so the time complexity is 𝑂(𝑛), where n is the length of the array.
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
The solution uses only a few variables for tracking maximum values and results, so the space complexity is 𝑂(1)
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, values: List[int]) -> int:
if len(values)==2:
return values[0]+values[1]-1
first_max,second_max=values[0]-1,values[1]
result=first_max+second_max
for k in range(2,len(values)):
first_max-=1
second_max-=1
if values[k]>first_max or values[k]>second_max:
if first_max>second_max:
second_max=values[k]
else:
first_max=values[k]
result=max(result,first_max+second_max)
return result
```
| 7 | 0 |
['Array', 'Python3']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Build Intuition with Diagram | Simple Solution | S(n): O(1) | T(n) : O(n)
|
build-intuition-with-diagram-simple-solu-w6yt
|
Here it is said that we have to maximize the value of values[i] + values[j] - ( j - i ), so if we reqarrange it a little bit we will get something like this (
|
dhiru634
|
NORMAL
|
2022-03-05T05:10:05.274808+00:00
|
2022-03-05T05:10:05.274838+00:00
| 468 | false |
Here it is said that we have to maximize the value of **values[i] + values[j] - ( j - i )**, so if we reqarrange it a little bit we will get something like this **( values[i] + i ) + ( values[j] - j )**\nNow, as we can see in the below diagram , we have to **create 2 arrays with modified values** and for each **( values[j] - j )** find the maximum **( values[i] + i )** , where **i < j**.\n\n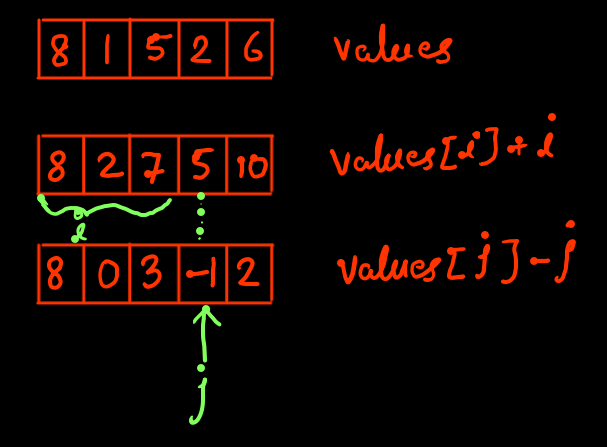\n\nWe can use either a PriorityQueue to keep the max till now , or simply keep a variable that tracks the **max(values[i] + i)** where **i < j**,\n\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values) {\n int max = -1;\n int currMax = values[0];\n for(int i =1;i<values.length;i++){\n int tempMax = currMax + (values[i] - i);\n max = Math.max(tempMax, max);\n currMax = Math.max(currMax, values[i] + i);\n }\n return max;\n }\n}\n```\n\nDo Upvote if you like the solution.\nHappy Coding !!
| 7 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Java']
| 1 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
An intuitive way to think about the problem (o(n) time+o(1) space )
|
an-intuitive-way-to-think-about-the-prob-rn21
|
The key point of the question is to get a pair of (i,j) that A[i]+A[j]+i-j is max. \nLet\'s reformat the function to (A[i]+i)+(A[j]-j). So it is clear that when
|
junchaozheng1009
|
NORMAL
|
2019-03-26T21:46:07.761618+00:00
|
2019-03-26T21:46:07.761651+00:00
| 320 | false |
The key point of the question is to get a pair of `(i,j)` that `A[i]+A[j]+i-j` is max. \nLet\'s reformat the function to `(A[i]+i)+(A[j]-j)`. So it is clear that when reaching index `j`, we want to \n1. find the maximum value of `(A[i]+i)` from `0` to `j-1`;\n2. calculate the sum of previous maximum value and `A[j]-j`.\n\nSo a clear DP solution is:\n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, A: List[int]) -> int:\n prev_max = A[0]\n res = 0\n for j in range(1, len(A)):\n res = max(prev_max+A[j]-j, res)\n prev_max = max(prev_max, A[j]+j)\n return res\n```
| 7 | 0 |
[]
| 2 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Well explained intuitive solution
|
well-explained-intuitive-solution-by-bal-6ny3
|
\n/**\n * @param {number[]} values\n * @return {number}\n */\nvar maxScoreSightseeingPair = function(values) {\n // Given formula is values[i] + values[j] +
|
balaji_sv
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-17T06:08:52.142398+00:00
|
2022-07-17T06:17:18.306978+00:00
| 311 | false |
```\n/**\n * @param {number[]} values\n * @return {number}\n */\nvar maxScoreSightseeingPair = function(values) {\n // Given formula is values[i] + values[j] + i - j;\n // Break it as values[i] + i + values[j] - j;\n \n // take the first element of the pair with the formula values[i] + i for i = 0\n let firstElementInPair = values[0] + 0;\n \n // final result;\n let resultPairValue = 0;\n \n for(let i = 1; i < values.length; i++) {\n \n // values[i] + i is computed in firstElementInPair.\n \n // Compute secondElementInPair with the formula Values[j] - j for our current i;\n const secondElementInPair = values[i] - i;\n \n // calculate the pairValue with the formula values[i] + i (FirstElementInPair) + values[j] - j (SecondElementInPair);\n const currentPairValue = firstElementInPair + secondElementInPair;\n \n // keep the best pair found so far.\n resultPairValue = Math.max(resultPairValue, currentPairValue);\n \n // update firstElementInPair, if any other better element is found\n firstElementInPair = Math.max(firstElementInPair, values[i] + i);\n }\n return resultPairValue;\n};\n```
| 6 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
C++ | O(N) Time | O(1) Space
|
c-on-time-o1-space-by-harshitparashar-ltnr
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n=nums.size();\n int prev=nums[0]; //as i<j so we can get
|
harshitparashar
|
NORMAL
|
2022-01-11T14:14:07.237201+00:00
|
2022-01-11T14:14:07.237246+00:00
| 449 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n=nums.size();\n int prev=nums[0]; //as i<j so we can get max values at each index and calclulate for i+1\n int ans=INT_MIN;\n for(int i=1;i<n;i++){\n ans=max(ans,prev+nums[i]-i); // main equation (nums[i]+i) +(nums[j]-j)\n prev=max(prev,nums[i]+i); // maximum prev update to use it in next iterations\n }\n return ans;\n \n }\n};\n```\n\nTC- O(N)\nSC- O(1)
| 6 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C', 'C++']
| 1 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
simple java solution with explaination from brute force to dp, single pass
|
simple-java-solution-with-explaination-f-omim
|
Approach 1->\nbrute force solution of trying every possible pair and keep on updating max will take o(n^2) and will result in TLE.\n\npublic int maxScoreSightse
|
kushguptacse
|
NORMAL
|
2022-01-11T11:06:00.822390+00:00
|
2022-01-11T11:09:45.094725+00:00
| 510 | false |
**Approach 1->**\nbrute force solution of trying every possible pair and keep on updating max will take o(n^2) and will result in TLE.\n```\npublic int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values) {\n int max=0;\n for(int i=0;i<values.length;i++) {\n for(int j=i+1;j<values.length;j++) {\n int spot = values[i] + values[j] + i - j;\n max=Math.max(spot,max);\n }\n }\n return max;\n }\n```\n**Approach 2 ->**\n\nIf you look at the code it is quite short. but to understand the solution it will take time.\nmaximize = (a[i]+a[j]+i-j) and i<j\nit means we cannot go back. We can write above equation as \nmax = max(a[i]+i)+max(a[j]-j)\n1. Now keep track of maximum a[i]+i till ith iteration.\n2. use that above ith max value and add it to a[j]-j to keep track of maximum answer.\n3. Now, since we are dealing with single loop we need to make sure that when we want to compute a[j]-j+maxi, maxi should point to the maximum till j-1 index.\nso, using above idea below solution will work\ninitialize maxI with 0. and when we want to compute ans, just use values[i]-i+maxI. once calculated compute maxI again for next computation. in this way maxI will always point to one less index and store the result of max(values[i]+i)\n```\npublic int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values) {\n //hold max(A[i]+i)\n int maxI=0;\n\t\t//hold the final answer\n int ans=0;\n for(int i=0;i<values.length;i++) {\n ans=Math.max(ans,maxI+values[i]-i);\n maxI=Math.max(maxI,values[i]+i);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n```
| 6 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Java']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
C++ Simple O(n) time
|
c-simple-on-time-by-jayeshbhade-6v5w
|
\tint maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector& values) {\n\t\t\tint n = values.size();\n\t\t\tint num = values[0];\n\t\t\tint ans = INT_MIN;\n\t\t\tfor (int i=1; i<n; i+
|
jayeshbhade
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-22T18:45:33.954622+00:00
|
2021-09-22T18:45:58.673712+00:00
| 183 | false |
\tint maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {\n\t\t\tint n = values.size();\n\t\t\tint num = values[0];\n\t\t\tint ans = INT_MIN;\n\t\t\tfor (int i=1; i<n; i++) {\n\t\t\t\tans = max(ans, num+values[i]-i);\n\t\t\t\tnum = max(values[i]+i, num);\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t\treturn ans;\n\t\t}
| 6 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
O(n) time and O(1) memory solution
|
on-time-and-o1-memory-solution-by-namele-sh8l
|
What we are interested in is maximize the value of A[i] + A[j] + i - j for i < j. \n\nLet\'s iterate the array from the left to the right and let\'s say we are
|
namelessghoul
|
NORMAL
|
2019-03-25T09:44:24.555167+00:00
|
2019-03-25T09:44:24.555206+00:00
| 449 | false |
What we are interested in is maximize the value of `A[i] + A[j] + i - j` for `i < j`. \n\nLet\'s iterate the array from the left to the right and let\'s say we are at index `j` at some moment. \nWe can easily calculate the value of `A[j] - j`. What we now need is to find out is what is the maximum value of `A[i] + i` where `i` was passed on some previous step. In order to do so, we can keep that previous maximum in a variable, which we will update at every iteration step:\n\n```\nint result = 0, n = a.length, bestPrev = 0;\nfor (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n result = Math.max(result, a[i] - i + bestPrev);\n bestPrev = Math.max(a[i] + i, bestPrev);\n}\nreturn result;\n```\n\nComplexity:\nTime: O(n)\nMemory: O(1)
| 6 | 1 |
[]
| 1 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
✅ One Line Solution
|
one-line-solution-by-mikposp-lt91
|
(Disclaimer: this is not an example to follow in a real project - it is written for fun and training mostly)Code #1Time complexity: O(n). Space complexity: O(1)
|
MikPosp
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-27T10:11:13.325963+00:00
|
2024-12-27T10:11:13.325963+00:00
| 397 | false |
(Disclaimer: this is not an example to follow in a real project - it is written for fun and training mostly)
# Code #1
Time complexity: $$O(n)$$. Space complexity: $$O(1)$$.
```python3
class Solution:
def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, a: List[int]) -> int:
return reduce(lambda p,v:(max(p[0],p[1]+v),max(p[1],v)-1),a,(0,0))[0]
```
[Ref](https://leetcode.com/problems/best-sightseeing-pair/solutions/260850/JavaC++Python-One-Pass-O(1)-space/)
# Code #2
Time complexity: $$O(n)$$. Space complexity: $$O(1)$$.
```python3
class Solution:
def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, a: List[int]) -> int:
return max(map(sum,zip(a[1:],accumulate(a,lambda q,v:max(q-1,v)))))-1
```
[Ref](https://leetcode.com/problems/best-sightseeing-pair/solutions/1715803/python-2-line-solution-clean-and-concise-o-n/)
(Disclaimer 2: code above is just a product of fantasy packed into one line, it is not claimed to be 'true' oneliners - please, remind about drawbacks only if you know how to make it better)
| 5 | 0 |
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 1 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Best Easy Solution | O(n) | prefixMax needed only!! | 8 min vid solution
|
best-easy-solution-on-prefixmax-needed-o-yjhl
|
Vid SolutionIntuition
Sightseeing Pair: A sightseeing pair consists of two indices i and j in the values array, where i < j.
Score: The score of a sightseeing p
|
Atharav_s
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-27T04:08:11.616660+00:00
|
2024-12-27T05:41:11.969978+00:00
| 250 | false |
# Vid Solution
https://youtu.be/-cYzuDbn1ls
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
- Sightseeing Pair: A sightseeing pair consists of two indices i and j in the values array, where i < j.
- Score: The score of a sightseeing pair is calculated as values[i] + values[j] + i - j.
- Key Observation: To maximize the score, we need to find a balance between selecting a high values[i] and a high values[j], while also considering the i - j term which can significantly impact the score.
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
1. Initialization:
- preFixMax: Stores the maximum value of values[i] + i encountered so far. Initially, it's set to values[0].
- maxScore: Stores the maximum score found so far. Initially, it's set to 0.
2. Iteration:
- Iterate through the values array starting from index 1.
- For each index j:
- Calculate the potential score of the current pair: values[j] - j + preFixMax.
- Update maxScore if the potential score is greater than the current maxScore.
- Update preFixMax with the maximum value between the current preFixMax and values[j] + j. This step is crucial as it ensures that we always consider the best possible values[i] for the subsequent pairs.
3. Return:
- After iterating through the entire array, return the maxScore.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:O(n)
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:O(1)
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {
int preFixMax = values[0];
int maxScore = 0;
int n = values.size();
for(int j=1;j<n;j++){
maxScore = max(maxScore,preFixMax + values[j]-j);
preFixMax = max(preFixMax, values[j]+j);
}
return maxScore;
}
};
```
| 5 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Easy | Simple Greedy | C++ | O(n) | 100% Beat
|
easy-simple-approach-c-on-by-gavnish_kum-34c8
|
IntuitionBy the problem statement we know that for maximize final answer we have to maximize the difference between values and minimize the position difference.
|
gavnish_kumar
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-27T03:28:51.169045+00:00
|
2024-12-27T03:32:48.602537+00:00
| 336 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
By the problem statement we know that for maximize final answer we have to maximize the difference between values and minimize the position difference.
So, After some analysis i get to know that for any index `i` we require maximum value of `X=arr[j]-j` where `j>i`. so final answer will be max of `arr[i]+i+X`.
- I created a lastMax that maintain the value of x for each position
- Update the array by adding index position to the corresponding element.
- Final answer will be maximum of `arr[i]+lastMax(i+1)` for `0<=i<n-1`.
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:$$O(n)$$
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {
int n= values.size();
vector<int> lastMax(n); // at jth index store maximum of (arr[i]-i) for i>=j and i<n.
lastMax[n-1]=values[n-1]-n+1;
values[n-1]+=(n-1);// update by adding index to corresponding element.
for(int i=n-2;i>=0;i--){
lastMax[i]= max(lastMax[i+1],values[i]-i);
values[i]+=i;
}
int ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++){
ans=max(ans,values[i]+lastMax[i+1]);// final answer is maximum of arr[i]+lastMax[i+1]
}
return ans;
}
};
```
| 5 | 0 |
['C++']
| 1 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Easy java solution in hindi!!
|
easy-java-solution-in-hindi-by-bakree-zjqy
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \nval - varibale store ka
|
bakree
|
NORMAL
|
2024-08-17T06:37:28.703950+00:00
|
2024-08-17T06:37:28.703983+00:00
| 457 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nval - varibale store karega ki abhi tk left me max value kya possible hai \nagar apan ek element ko right shift karte rahe. Aise socho ki agar pehli value 8 hai array me aur agar apko use ek right le jana hai to uski value is now equivalent to 7 kyuki har baar right shift par ek value km hogi. Bs yahi major concept hai is question me. Fir ap compare karo ki apki jo new value hai wo us index ki value se badi hai ya choti.\n\nSimilar Question but isse thoda heavy {LC - 1937} - [https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-number-of-points-with-cost/description/?envType=daily-question&envId=2024-08-17]()\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(n)\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(1)\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values) {\n int ans = 0;\n int n = values.length;\n int val = values[0];\n for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { \n ans = Math.max(ans , values[i] + val-1);\n val = Math.max(values[i] , val-1);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Java']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Simple Explanation : DP solution O(n) time, O(1) space
|
simple-explanation-dp-solution-on-time-o-w77n
|
Very Simple Approach : \nFor each index, store the maximum score ending at current index.\nFor example :\nA = [8,1,5,2,6]\nlet B represent the maximum score su
|
niraj243
|
NORMAL
|
2022-10-27T07:39:40.443949+00:00
|
2022-10-27T07:39:40.443986+00:00
| 1,499 | false |
# Very Simple Approach : \nFor each index, store the maximum score ending at current index.\nFor example :\nA = [8,1,5,2,6]\nlet B represent the maximum score such that current index is end point (j);\nBase Cases : B[0] and B[1]\nB[0] = 0 (B[0] is not under consideration as A.size >= 2 and i>j as per question)\nB[1] = 8 + 1 - 1 = 8\nRecursive Formula : for j >= 2\nB[i] = max(B[i-1]-A[i-1] + A[i] -1, A[i-1]+A[i]-1)\nour ans is max element of B;\nB[2] = 11\nB[3] = max(11-5+2-1, 5+2-1) = 7\nB[4] = max(7-2+6-1, 2+6-1) = 10\n\nSo our ans is : max element of B = 11\n\nImplementation 1:\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& val) {\n int n = val.size();\n vector<int> vec(n,0);\n vec[1] = val[0]+val[1]-1;\n int ans = vec[1];\n for(int i=2;i<n;i++){\n vec[i] = max(vec[i-1]-val[i-1]+val[i]-1,val[i-1]+val[i]-1);\n ans = max(vec[i],ans);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n// Time Complexity : O(n)\n// Space Complexity : O(n)\n```\n\nSpace can be optimized to O(1) because only one previous val of array is being used\n\nImplementation 2:\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& val) {\n int n = val.size();\n int cur;\n cur = val[0]+val[1]-1;\n int ans = cur;\n for(int i=2;i<n;i++){\n int cur1;\n if(cur-val[i-1]+val[i]-1 > val[i-1]+val[i]-1){\n cur1 = cur-val[i-1]+val[i]-1;\n }\n else{\n cur1 = val[i-1]+val[i]-1;\n }\n ans = max(ans,cur1);\n cur = cur1;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n\t// Time Complexity : O(n)\n // Space Complexity : O(1)\n};\n```\n**Important :** Interview follow-up question can be : Return indices i and j for optimal answer.\n\nWe can also recored the value of indices (i and j) corresponding to the optimal answer.\nTry doing this, Let me know in comments if you need solution of this variant also. \n
| 5 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming']
| 1 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
✅Python 3 | O(n) | Very clearly explained!
|
python-3-on-very-clearly-explained-by-py-0v4f
|
Solution 1: Brute Force [Time Limit Exceeded]\nThe most naive solution is that we can have a brute force solution by simply getting all possible combinations of
|
PythonerAlex
|
NORMAL
|
2022-06-24T19:14:10.564813+00:00
|
2022-06-24T19:15:32.313954+00:00
| 580 | false |
***Solution 1: Brute Force [Time Limit Exceeded]***\nThe most naive solution is that we can have a brute force solution by simply getting all possible combinations of index `i` and `j`, and then finding the maximum of `values[i] + values[j] + i - j` when `i < j` for all combinations and that will be our answer. We can do this by using a 2 nested for loops keeping track of index `i` and index `j`, while skipping to the next iteration if `i >= j`. We initialize a variable `maximum` and each iteration we check to see if the current value is higher than maximum, if so, we set maximum to this new value. Returning `maximum` in the end will give us our answer.\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, values: List[int]) -> int:\n n = len(values)\n maximum = 0\n for i in range(n):\n for j in range(i+1, n):\n if i >= j: continue\n maximum = max(maximum, values[i] + values[j] + i - j)\n return maximum\n```\nTime Complexity: O(n^2)\nSpace Complexity: O(1)\n\n***Solution 2: One Pass***\n\n**Intuition**\nNotice how in the brute force solution, we skip to the next iteration if index `i >= j`. Although we skip to the next iteration using `continue`, we still iterated through many unnecessary iterations giving us a slow O(n^2) time complexity which exceeded the time limit. Thus, we can simply skip all the unnecessary iterations where `i >= j` altogether using this one pass algorithm.\n\n**Algorithm**\nWe can initialize `i` to be 0, and then this time we only need to start 1 for loop tracking the index `j`, same thing as the brute force solution, we keep track of a variable `maximum` and in the iteration if `values[i] + values[j] + i - j` is bigger than the current `maximum` we replace it with that. However, one thing we are doing differently is that instead of starting a nested for loop we write an if statement saying that `values[j] + j - i > values[i]` then we set `i=j`. Basically, you can treat `if values[j] + j - i > values[i]: i = j` the same thing as `if i >= j: continue` in the brute force solution, except we are not iterating unnecessarily.\n\n**Implementation**\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, values: List[int]) -> int:\n n = len(values)\n i = maximum = 0\n for j in range(i+1, n):\n maximum = max(maximum, values[i] + values[j] + i - j)\n if values[j] + j - i > values[i]: i = j\n return maximum\n```\nTime Complexity: O(n)\nSpace Complexity: O(1)\n\n**Please consider upvoting if this solution helped you. Good luck!**\n\n
| 5 | 0 |
['Python', 'Python3']
| 1 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Python | One Pass | O(N) | with comments
|
python-one-pass-on-with-comments-by-vish-opoy
|
\nclass Solution:\n def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, values: List[int]) -> int:\n # maintain the current max reference variable and answer variable\n
|
vishyarjun1991
|
NORMAL
|
2022-02-09T15:33:50.561283+00:00
|
2022-02-09T15:33:50.561332+00:00
| 147 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, values: List[int]) -> int:\n # maintain the current max reference variable and answer variable\n mx_ref,ans = values[0],0\n # at every index update both variables as below\n for value in values[1:]:\n # 8 at index 0 will become 7 at index 1 and 6 at index 2, so we can always keep a track of current max by comparing values[i-1]-1 with values[i].\n ans = max(ans, value+mx_ref-1)\n mx_ref = max(mx_ref-1,value)\n return ans\n```
| 5 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
C++|O(n)|Small solution with explanation
|
consmall-solution-with-explanation-by-vi-2qzr
|
Approach\nThe prime objective of this question is to find the maximum value of the following equation,\n\nA[i] + A[j] + i - j, where i < j\n\nWe can rearrange t
|
vidhayakji
|
NORMAL
|
2022-01-09T14:49:46.903247+00:00
|
2022-01-10T11:54:53.153847+00:00
| 162 | false |
# Approach\nThe prime objective of this question is to find the maximum value of the following equation,\n```\nA[i] + A[j] + i - j, where i < j\n```\nWe can rearrange this equation to take the following form,\n```\n(A[i] + i) + (A[j] - j) \n```\nNow let\'s try to optimize the above equation by fixing the value of current index, j. This comes out to be \n```\nsolution[j] = max(A[x] + x) + (A[j] - j), where x is any value less than j\n```\nIn this manner we break the solution into two parts. For the current index j, we can easily calulate the second part ,i.e, A[j] - j\nFor the first part, We need to maintain the maximum value of (A[x] + x) from the beginning to current index of this array. This can be calculated using dynamic programming, where \n```\ndp[i] = max(dp[i-1], A[i] + i) \n```\nThough this part of the solution can be optimized as we don\'t need to maintain all values of dp[i]. Instead we can use a variable that stores the current maximum value. \n\nFinally, since we don\'t know the value of j which optimizes the equation. We take the maximum of all solution[j], where 0 < j < n. \n\nAs an additional optimization, we don\'t need to store all the solution[j] values. For this, You can refer to my solution below. \n# Solution\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {\n int mx = values[0], ans = 0;\n \n for(int i=1;i<values.size();i++){\n ans = max(ans, mx + values[i] - i);\n mx = max(mx, values[i] + i);\n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\n# Complexity #\nSpace complexity - O(1)\nTime complexity - O(n)
| 5 | 0 |
['Math', 'Dynamic Programming', 'C']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Java | O(n) | solved with intuition | approach explained
|
java-on-solved-with-intuition-approach-e-96m4
|
Sorry for the bad handwritting, I am learning to use digital pen :)\nThis can be optimised more, I just thought to share a intuition behind solving this problem
|
njtnt
|
NORMAL
|
2021-12-29T08:20:04.954415+00:00
|
2021-12-29T08:20:04.954456+00:00
| 162 | false |
Sorry for the bad handwritting, I am learning to use digital pen :)\nThis can be optimised more, I just thought to share a intuition behind solving this problem.\n\n\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values) {\n int len = values.length;\n \n int[] maxLeft = new int[len];\n int[] maxRight = new int[len];\n \n int prev = 0;\n for(int i=0;i<len-1;i++){\n int val = i+values[i];\n if(val>prev){\n maxLeft[i] = val;\n prev = val;\n }else{\n maxLeft[i] = prev;\n }\n }\n \n prev = Integer.MIN_VALUE;\n for(int i=len-1;i>0;i--){\n int val = values[i]-i;\n if(val>prev){\n maxRight[i] = val;\n prev = val;\n }else{\n maxRight[i] = prev;\n }\n }\n \n return calc(maxLeft,maxRight);\n }\n \n int calc(int[] left, int[] right){\n int sum = 0;\n int max = 0;\n for(int i=0;i<left.length-1;i++){\n sum = left[i]+right[i+1];\n max = Math.max(sum,max);\n }\n return max;\n } \n}\n```
| 5 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
JAVA || Clean & Concise & Optimal Code || Dynamic Programming Technique || O(N) Time Solution
|
java-clean-concise-optimal-code-dynamic-ye9g3
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values) {\n \n int best = values[0], maxScore = 0;\n \n for (int i
|
anii_agrawal
|
NORMAL
|
2021-08-28T18:00:04.533780+00:00
|
2021-08-28T18:00:04.533821+00:00
| 183 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values) {\n \n int best = values[0], maxScore = 0;\n \n for (int i = 1; i < values.length; i++) {\n maxScore = Math.max (maxScore, values[i] + best - i);\n best = Math.max (best, values[i] + i);\n }\n \n return maxScore;\n }\n}\n```\n\nPlease help to **UPVOTE** if this post is useful for you.\nIf you have any questions, feel free to comment below.\n\n**LOVE CODING :)\nHAPPY CODING :)\nHAPPY LEARNING :)**
| 5 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
[Rust] Intuitive explanation with development from O(n^2) to O(n) time and O(1) space
|
rust-intuitive-explanation-with-developm-w2er
|
Solution 1A\n\nFor every spot i, compare it to all other spots j and calculate the score of the pair. Update the max_score found so far accordingly.\n\nrust\n
|
ticklin
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-28T04:10:08.428474+00:00
|
2021-07-28T04:10:58.872991+00:00
| 134 | false |
### Solution 1A\n\nFor every spot `i`, compare it to all other spots `j` and calculate the score of the pair. Update the `max_score` found so far accordingly.\n\n```rust\n pub fn max_score_sightseeing_pair(values: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {\n let mut max_score = i32::MIN;\n \n for i in 0..values.len() {\n for j in 0..values.len() {\n if i == j { \n continue; \n }\n let (I, J) = (i as i32, j as i32);\n max_score = cmp::max(max_score, values[i] + values[j] - (I - J).abs());\n }\n }\n max_score\n }\n```\nTime complexity: O(N^2)\n\nSpace complexity: O(1)\n\n### Solution 1B\n\nLet\'s observe that for every `i`, it is sufficient to only consider pairing with `j > i`.\nWhy ?\n- All pairs with `j < i` have already been considered since every `i` pairs with all `j > i`\n- `j == i` is not considered since they both refer to the same spot\n\n```rust\n pub fn max_score_sightseeing_pair(values: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {\n let mut max_score = i32::MIN;\n \n for i in 0..values.len() {\n for j in i + 1..values.len() {\n let (I, J) = (i as i32, j as i32);\n max_score = cmp::max(max_score, values[i] + values[j] - (I - J).abs());\n }\n }\n max_score\n }\n```\nTime complexity: O(N^2)\n\nSpace complexity: O(1)\n\n### Solution 2A\nWe observe that with the inner for loop, we\'re asking the question: \n> For every `i`, what is the maximum score possible on pairing with a `j > i` (or `j` to the right of `i`) ? We then add `value[i]` to this `max_score`\n\nHow to find this maximum to the right of `i` ?\nLet\'s define an array `max_right` to store the maximum value to the right of every `i` to be `max(values[i], max_right[i + 1] - 1`. This includes its value. This makes sense since we\'ll query `max_right[i + 1]` from `max_right[i]`. \n`- 1` is to subtract the distance between `i` and `j`. \n\nSince we need `max_right[i + 1]` to calculate `max_right[i]`, we traverse the array from back to front. We\'re propagating the `max_right` seen so far from the `right` to the `left`. Therefore, we subtract 1 to account for the left shift in this \'propagation\'.\n\nConsider the following example:\n``` rust\n let values = [8,1,5,2,6];\n```\n\nThe simplest `i` for which the above question can be answered is the last element in the array, `values[4] = 6` since there\'s no element to its right.\nWhat about `values[3] = 2` ? Only one `j` to its right so the `max_right` is `max(values[3], max_right[4] - 1) = 6 - 1 = 5`.\n\nHere\'s the complete table for all `i`:\n\n| `i` | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |\n| ----------- | - | - | - | - | - |\n| `values` | 8 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 6 |\n| `max_right` | 8 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 6 |\n\n\n``` rust\n pub fn max_score_sightseeing_pair(values: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {\n // max value to the right of i(including itself)\n let mut max_right = values.clone(); \n for i in (1..values.len() - 1).rev() {\n max_right[i] = cmp::max(values[i], max_right[i + 1] - 1);\n }\n \n let mut max_score = i32::MIN;\n for i in (0..values.len() - 1).rev() - 1 {\n max_score = cmp::max(max_score, values[i] + max_right[i + 1] - 1);\n }\n max_score\n }\n```\n> `max_right[values.len() - 1] = values[values.len() - 1]`\n\n> `max_right[i]` is calculated up to index `i = 1` only since there\'s no index `-1` to lookup `max_right[0]`\n\nTime complexity: O(N)\n\nSpace complexity: 0(N)\n\n### Solution 2B\nSince we only lookup one index ahead, `max_right` does not need to be an array\n\n``` rust\n pub fn max_score_sightseeing_pair(values: Vec<i32>) -> i32 { \n let mut max_score = i32::MIN;\n let mut max_right = values[values.len() - 1];\n\n for i in (0..values.len() - 1).rev() {\n max_score = cmp::max(max_score, values[i] + max_right - 1);\n max_right = cmp::max(values[i], max_right - 1);\n }\n max_score\n }\n```\n\nTime complexity: O(N)\n\nSpace complexity: O(1)
| 5 | 0 |
['Rust']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Java O(n), easy to understand
|
java-on-easy-to-understand-by-badding-ohp0
|
This Solution is inspired by Buy and Sell Stock. \nIn that problem we are required to work out the maximum value of A[j]-A[i]forj>i, so we need to record the mi
|
badding
|
NORMAL
|
2019-03-24T17:37:57.410689+00:00
|
2019-03-24T17:37:57.410739+00:00
| 335 | false |
This Solution is inspired by Buy and Sell Stock. \nIn that problem we are required to work out the maximum value of `A[j]-A[i]`for`j>i`, so we need to record the minimum value of `A[i]` and maximum value of `A[j]-A[i]`. \nIn this problem, `A[i]+A[j]+i-j`can be converted to`(A[j]-j)+(A[i]+i)`, so instead of record the minimum value of `A[i]`, we can use `max` to track the maximum value of `A[i]+i` and maximum value of `A[j]-j+max`.\nI think there exsits a template for this kind of problem, we can seperated `i` and `j` first and record their values.\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] A) {\n int max = 0, res = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < A.length; i ++) {\n res = Math.max(res, A[i]-i+max);\n max = Math.max(max, A[i]+i);\n }\n return res;\n }\n}\n```
| 5 | 1 |
[]
| 1 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Beats 100% || O(1) space || C++ || Greedy
|
beats-100-o1-space-c-greedy-by-akash92-k3l2
|
IntuitionAt each index we have two choices, either take the maximum element encountered previously or take the previous element, whichever is bigger adjusted wi
|
akash92
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-27T08:31:42.851086+00:00
|
2024-12-27T08:31:42.851086+00:00
| 147 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
At each index we have two choices, either take the maximum element encountered previously or take the previous element, whichever is bigger adjusted with increasing distance that increases by 1 in both cases.
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
Take a variable maxi, to keep track of maximum element encountered so far and then compare it with just previous element, whichever is bigger, store it in maxi.
update ans if current value + maxi is bigger than the answer
# Complexity
- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity: $$O(1)$$
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {
int maxi = values[0], ans = 0;
for(int i=1; i<values.size(); i++){
maxi = max(maxi-1, values[i-1]-1);
ans = max(ans, values[i] + maxi);
}
return ans;
}
};
auto speedup = [](){ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0); return 0;}();
```
| 4 | 0 |
['Array', 'C++']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
🌟 Dynamic Programming,🤝 the Greedy Way: 🧠 Optimized Sightseeing ||💥Beginner-Friendly✨
|
dynamic-programming-the-greedy-way-optim-au0x
|
Intuition 🌟We want to maximize the score for a sightseeing pair:By rewriting it ✍️:Key Insight 💡:To maximize the score, we keep track of the maximum value ofas
|
mansimittal935
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-27T08:21:46.129855+00:00
|
2024-12-27T08:21:46.129855+00:00
| 286 | false |
# Intuition 🌟
We want to maximize the score for a sightseeing pair:
score(i,j)=values[i]+values[j]+i−j
By rewriting it ✍️:
score(i,j)=(values[i]+i)+(values[j]−j)
Key Insight 💡:
The term (values[i]+i) depends only on i.
The term (values[j]−j) depends only on j.
To maximize the score, we keep track of the maximum value of
(values[i]+i)
as maxValue while iterating through the array. At each j, we calculate:
- score=maxValue+(values[j]−j)
and update maxValue for the next iterations.
---
# Approach 🛠️
1️⃣ Initialize:
maxValue = values[0] + 0
(track the maximum of
(values[i]+i)) 🏆.
ans = -\infty (start with the smallest possible score 🔥).
2️⃣ Iterate 🚀:
For every index
Compute the score for the current sightseeing pair:
ans=max(ans,maxValue+values[j]−j)
Update maxValue for future pairs:
maxValue=max(maxValue,values[j]+j)
3️⃣ Return the maximum score (ans) 🎯.
---
# Complexity ⏱️
- Time Complexity:
O(n) 🏃♂️
A single loop to calculate the score.
- Space Complexity:
O(1) 💾
Only a few variables are used.
---
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {
int ans = INT_MIN;
int n = values.size();
int maxValue = values[0] + 0;
for(int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
ans = max(ans, maxValue + values[j]-j);
maxValue = max(maxValue, values[j] + j);
}
return ans;
}
};
```
```java []
class Solution {
public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values) {
int maxScore = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int maxValue = values[0];
for (int j = 1; j < values.length; j++) {
maxScore = Math.max(maxScore, maxValue + values[j] - j);
maxValue = Math.max(maxValue, values[j] + j);
}
return maxScore;
}
}
```
```python []
class Solution:
def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, values: list[int]) -> int:
max_score = float('-inf')
max_value = values[0]
for j in range(1, len(values)):
max_score = max(max_score, max_value + values[j] - j)
max_value = max(max_value, values[j] + j)
return max_score
```
```javascript []
var maxScoreSightseeingPair = function(values) {
let maxScore = -Infinity;
let maxValue = values[0];
for (let j = 1; j < values.length; j++) {
maxScore = Math.max(maxScore, maxValue + values[j] - j);
maxValue = Math.max(maxValue, values[j] + j);
}
return maxScore;
};
```
```ruby []
def max_score_sightseeing_pair(values)
max_score = -Float::INFINITY
max_value = values[0]
(1...values.length).each do |j|
max_score = [max_score, max_value + values[j] - j].max
max_value = [max_value, values[j] + j].max
end
max_score
end
```
```rust []
impl Solution {
pub fn max_score_sightseeing_pair(values: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
let mut max_score = i32::MIN;
let mut max_value = values[0];
for j in 1..values.len() {
max_score = max_score.max(max_value + values[j] - j as i32);
max_value = max_value.max(values[j] + j as i32);
}
max_score
}
}
```
```c# []
public class Solution {
public int MaxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values) {
int maxScore = int.MinValue;
int maxValue = values[0];
for (int j = 1; j < values.Length; j++) {
maxScore = Math.Max(maxScore, maxValue + values[j] - j);
maxValue = Math.Max(maxValue, values[j] + j);
}
return maxScore;
}
}
```
```go []
func maxScoreSightseeingPair(values []int) int {
maxScore := -int(^uint(0) >> 1) // Smallest int
maxValue := values[0]
for j := 1; j < len(values); j++ {
maxScore = max(maxScore, maxValue + values[j] - j)
maxValue = max(maxValue, values[j] + j)
}
return maxScore
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}
```
```typescript []
function maxScoreSightseeingPair(values: number[]): number {
let maxScore = Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER;
let maxValue = values[0];
for (let j = 1; j < values.length; j++) {
maxScore = Math.max(maxScore, maxValue + values[j] - j);
maxValue = Math.max(maxValue, values[j] + j);
}
return maxScore;
}
```
```swift []
class Solution {
func maxScoreSightseeingPair(_ values: [Int]) -> Int {
var maxScore = Int.min
var maxValue = values[0]
for j in 1..<values.count {
maxScore = max(maxScore, maxValue + values[j] - j)
maxValue = max(maxValue, values[j] + j)
}
return maxScore
}
}
```
```dart []
int maxScoreSightseeingPair(List<int> values) {
int maxScore = -double.maxFinite.toInt();
int maxValue = values[0];
for (int j = 1; j < values.length; j++) {
maxScore = max(maxScore, maxValue + values[j] - j);
maxValue = max(maxValue, values[j] + j);
}
return maxScore;
}
int max(int a, int b) => (a > b) ? a : b;
```
| 4 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Greedy', 'Swift', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'Ruby', 'JavaScript', 'C#', 'Dart']
| 1 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
🔥BEATS 💯 % 🎯 |✨SUPER EASY BEGINNERS 👏
|
beats-super-easy-beginners-by-codewithsp-u3xv
|
IntuitionThe problem involves finding the maximum score between two sightseeing spots. For two indices i and j (i < j), the score is defined as:
values[i] + val
|
CodeWithSparsh
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-27T07:33:14.128414+00:00
|
2024-12-27T08:05:15.623420+00:00
| 310 | false |
---

---
### Intuition
The problem involves finding the maximum score between two sightseeing spots. For two indices `i` and `j` (`i < j`), the score is defined as:
**`values[i] + values[j] + i - j`**.
To maximize the score, we need to consider the combination of:
1. `values[i] + i` — this represents the contribution of the left sightseeing spot.
2. `values[j] - j` — this represents the contribution of the right sightseeing spot minus its positional penalty.
Thus, at each index `j`, the goal is to:
- Find the best `values[i] + i` (for all `i < j`) to maximize the score when combined with `values[j] - j`.
### Approach
1. Initialize a variable `bestLeft` to store the maximum value of `values[i] + i` seen so far as we iterate through the array.
2. Iterate through the array starting from the second element (`j = 1`):
- Calculate the score for the current pair using the formula:
**`maxScore = max(maxScore, bestLeft + values[j] - j)`**.
- Update `bestLeft` for future pairs using the formula:
**`bestLeft = max(bestLeft, values[j] + j)`**.
3. Return the maximum score after iterating through the array.
### Complexity
- **Time Complexity**: $$O(n)$$, as we traverse the array once.
- **Space Complexity**: $$O(1)$$, as no additional space is used beyond a few variables.
---
### Code
```dart []
import 'dart:math';
class Solution {
int maxScoreSightseeingPair(List<int> values) {
int maxScore = 0; // To store the maximum score
int bestLeft = values[0]; // The best "values[i] + i" seen so far
for (int j = 1; j < values.length; j++) {
// Compute the score for the current pair
maxScore = max(maxScore, bestLeft + values[j] - j);
// Update the best "values[i] + i" for future pairs
bestLeft = max(bestLeft, values[j] + j);
}
return maxScore;
}
}
```
```python []
class Solution:
def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, values):
max_score = 0
best_left = values[0] # The best "values[i] + i" seen so far
for j in range(1, len(values)):
# Compute the score for the current pair
max_score = max(max_score, best_left + values[j] - j)
# Update the best "values[i] + i" for future pairs
best_left = max(best_left, values[j] + j)
return max_score
```
```java []
class Solution {
public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values) {
int maxScore = 0;
int bestLeft = values[0]; // The best "values[i] + i" seen so far
for (int j = 1; j < values.length; j++) {
// Compute the score for the current pair
maxScore = Math.max(maxScore, bestLeft + values[j] - j);
// Update the best "values[i] + i" for future pairs
bestLeft = Math.max(bestLeft, values[j] + j);
}
return maxScore;
}
}
```
```cpp []
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {
int maxScore = 0;
int bestLeft = values[0]; // The best "values[i] + i" seen so far
for (int j = 1; j < values.size(); j++) {
// Compute the score for the current pair
maxScore = max(maxScore, bestLeft + values[j] - j);
// Update the best "values[i] + i" for future pairs
bestLeft = max(bestLeft, values[j] + j);
}
return maxScore;
}
};
```
```go []
package main
import "math"
func maxScoreSightseeingPair(values []int) int {
maxScore := 0
bestLeft := values[0] // The best "values[i] + i" seen so far
for j := 1; j < len(values); j++ {
// Compute the score for the current pair
maxScore = int(math.Max(float64(maxScore), float64(bestLeft+values[j]-j)))
// Update the best "values[i] + i" for future pairs
bestLeft = int(math.Max(float64(bestLeft), float64(values[j]+j)))
}
return maxScore
}
```
```javascript []
var maxScoreSightseeingPair = function(values) {
let maxScore = 0;
let bestLeft = values[0]; // The best "values[i] + i" seen so far
for (let j = 1; j < values.length; j++) {
// Compute the score for the current pair
maxScore = Math.max(maxScore, bestLeft + values[j] - j);
// Update the best "values[i] + i" for future pairs
bestLeft = Math.max(bestLeft, values[j] + j);
}
return maxScore;
};
```
---
 {:style='width:250px'}
| 4 | 0 |
['C', 'C++', 'Java', 'Go', 'Python3', 'JavaScript', 'Dart']
| 1 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
use hashmap sorting
|
use-hashmap-sorting-by-gowrichokkapu_123-4o47
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
O(nlogn)
Space complexity:
o(n)
Code
|
gowrichokkapu_123
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-27T07:31:51.303526+00:00
|
2024-12-27T07:31:51.303526+00:00
| 86 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
O(nlogn)
- Space complexity:
o(n)
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {
map<int,int>mp;
int maxi = INT_MIN;
for(int i=0;i<values.size();i++){
if(mp.size()>0){
maxi = max(maxi,max(mp.begin()->first-i+values[i],mp.rbegin()->first-i+values[i]));
}
mp[i+values[i]] = i;
}
return maxi;
}
};
```
| 4 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'Sorting', 'C++']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
O(n) time and O(1) space solution
|
on-time-and-o1-space-solution-by-joshdav-c6sm
|
Intuition/ApproachKeep track of a value, as we move through the array, the value decreases.
At each index, the score will be the tracked value plus the value at
|
JoshDave
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-27T00:37:19.302658+00:00
|
2024-12-27T03:19:20.756862+00:00
| 548 | false |
# Intuition/Approach
Keep track of a value, as we move through the array, the value decreases.
At each index, the score will be the tracked value plus the value at index.
If a value is found that is greater than the tracked value then use it.
# Complexity
- Time complexity: O(n)
- Space complexity: O(1)
# Code
```python []
class Solution(object):
def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, values):
max_score = 0
score = values[0]
for i in range(1, len(values)):
score -= 1
if (score + values[i] > max_score):
max_score = score + values[i]
if (values[i] > score):
score = values[i]
return max_score
```
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {
int max = 0, score = values[0];
for (int i = 1; i < values.size(); ++i) {
--score;
if (score + values[i] > max) max = score + values[i];
if (values[i] > score) score = values[i];
}
return max;
}
};
```
```java []
class Solution {
public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values) {
int max = 0, score = values[0];
for (int i = 1; i < values.length; ++i) {
--score;
if (score + values[i] > max) max = score + values[i];
if (values[i] > score) score = values[i];
}
return max;
}
}
```
```c []
int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int* values, int valuesSize) {
int max = 0, score = *values;
for (++values, --valuesSize; valuesSize; ++values, --valuesSize) {
--score;
if (score + *values > max) max = score + *values;
if (*values > score) score = *values;
}
return max;
}
```
```python3 []
class Solution:
def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, values: List[int]) -> int:
max_score = 0
score = values[0]
for i in range(1, len(values)):
score -= 1
if (score + values[i] > max_score):
max_score = score + values[i]
if (values[i] > score):
score = values[i]
return max_score
```
```csharp []
public class Solution {
public int MaxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values) {
int max = 0, score = values[0];
for (int i = 1; i < values.Length; ++i) {
--score;
if (score + values[i] > max) max = score + values[i];
if (values[i] > score) score = values[i];
}
return max;
}
}
```
```javascript []
/**
* @param {number[]} values
* @return {number}
*/
var maxScoreSightseeingPair = function(values) {
let max = 0, score = values[0];
for (let i = 1; i < values.length; ++i) {
--score;
if (score + values[i] > max) max = score + values[i];
if (values[i] > score) score = values[i];
}
return max;
};
```
```typescript []
function maxScoreSightseeingPair(values: number[]): number {
let max = 0, score = values[0];
for (let i = 1; i < values.length; ++i) {
--score;
if (score + values[i] > max) max = score + values[i];
if (values[i] > score) score = values[i];
}
return max;
};
```
weird languages
```php []
class Solution {
/**
* @param Integer[] $values
* @return Integer
*/
function maxScoreSightseeingPair($values) {
$max = 0;
$score = $values[0];
$length = count($values);
for ($i = 1; $i < $length; ++$i) {
--$score;
if ($score + $values[$i] > $max) $max = $score + $values[$i];
if ($values[$i] > $score) $score = $values[$i];
}
return $max;
}
}
```
```swift []
class Solution {
func maxScoreSightseeingPair(_ values: [Int]) -> Int {
var max = 0, score = values[0];
for i in 1..<values.count {
score -= 1;
if (score + values[i] > max) {
max = score + values[i];
}
if (values[i] > score) {
score = values[i];
}
}
return max;
}
}
```
```kotlin []
class Solution {
fun maxScoreSightseeingPair(values: IntArray): Int {
var max = 0
var score = values[0]
for (i in 1..<values.size) {
score -= 1
if (score + values[i] > max) max = score + values[i]
if (values[i] > score) score = values[i]
}
return max
}
}
```
```dart []
class Solution {
int maxScoreSightseeingPair(List<int> values) {
int max = 0, score = values[0];
for (int i = 1; i < values.length; ++i) {
--score;
if (score + values[i] > max) max = score + values[i];
if (values[i] > score) score = values[i];
}
return max;
}
}
```
```golang []
func maxScoreSightseeingPair(values []int) int {
max := 0;
score := values[0];
for i := 1; i < len(values); i++ {
score--;
if (score + values[i] > max) {
max = score + values[i];
}
if (values[i] > score) {
score = values[i];
}
}
return max;
}
```
```ruby []
# @param {Integer[]} values
# @return {Integer}
def max_score_sightseeing_pair(values)
max = 0
score = values[0]
for i in 1 ... values.length()
score -= 1
if (score + values[i] > max); max = score + values[i] end
if (values[i] > score); score = values[i] end
end
return max;
end
```
```scala []
object Solution {
def maxScoreSightseeingPair(values: Array[Int]): Int = {
var max = 0;
var score = values(0);
for (i <- 1 to (values.length - 1)) {
score -= 1;
if (score + values(i) > max) max = score + values(i);
if (values(i) > score) score = values(i);
}
return max;
}
}
```
```rust []
impl Solution {
pub fn max_score_sightseeing_pair(values: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
let mut max = 0;
let mut score = values[0];
for i in 1..values.len() {
score -= 1;
if (score + values[i] > max) { max = score + values[i] }
if (values[i] > score) { score = values[i] }
}
return max;
}
}
```
delinquent languages
```elixir []
defmodule Solution do
def max_score_sightseeing_pair(values) do
[first | rest] = values
rest
|> Enum.reduce({0, first, 1}, fn value, {max, score, i} ->
score = score - 1
new_max = max(max, score + value)
new_score = max(score, value)
{new_max, new_score, i + 1}
end)
|> elem(0)
end
end
```
```erlang []
-spec max_score_sightseeing_pair(Values :: [integer()]) -> integer().
max_score_loop([], Max, _, _) -> Max;
max_score_loop([Value | Rest], Max, Score, I) ->
NewScore = Score - 1,
NewMax = max(Max, NewScore + Value),
NextScore = max(NewScore, Value),
max_score_loop(Rest, NewMax, NextScore, I + 1).
max_score_sightseeing_pair(Values) -> [First | Rest] = Values, max_score_loop(Rest, 0, First, 1).
```
| 4 | 0 |
['Swift', 'C', 'PHP', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'TypeScript', 'Rust', 'JavaScript', 'C#']
| 1 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
TC : O(n) | SC : O(1) | C++ | Java | Python | Easy Solution
|
tc-on-sc-o1-c-java-python-easy-solution-y9gtt
|
Intuition\nEver been on a sightseeing trip where you\'re trying to maximize your Instagram likes? Well, this problem is kinda like that, but with less selfie st
|
coding-spidey
|
NORMAL
|
2024-08-18T10:16:37.625314+00:00
|
2024-08-18T10:16:37.625358+00:00
| 100 | false |
# Intuition\nEver been on a sightseeing trip where you\'re trying to maximize your Instagram likes? Well, this problem is kinda like that, but with less selfie sticks and more math. To find the dynamic duo of spots that\'ll make our vacation album pop. We keep track of the best spot we\'ve seen so far (let\'s call it our "selfie hotspot") and compare it with each new spot we encounter. It\'s like playing "Hot or Not" with tourist attractions!\n\n# Approach\nOur approach is to use a greedy strategy to keep track of the maximum score. We\'ll maintain two variables: `maxi`, to keep track of the index of the spot with the maximum score so far, and `ans` to store the maximum score. \nAs we iterate through the list, we\'ll update maxi whenever we find a spot with a higher score, and we\'ll update ans whenever we find a pair with a higher score. The trick is to calculate the score for each pair in O(1) time by using the fact that the score is values[i] + values[j] + i - j, where i and j are the indices of the two spots.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nThe time complexity is \uD835\uDC42(\uD835\uDC5B), where n is the number of sightseeing spots. We\'re taking a leisurely stroll through the array, no rush, just one pass!\n\n- Space complexity:\nThe space complexity is \uD835\uDC42(1) since we\'re traveling light - just a couple of variables in our backpack. Marie Kondo would be proud!\n\n# Code\n```C++ []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {\n int maxi = 0;\n int ans = 0;\n\n for(int i=1; i<values.size(); i++) {\n ans = max(ans, values[i] + values[maxi] + (maxi - i));\n\n if(values[i] + i >= values[maxi] + maxi) {\n maxi = i;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values) {\n int maxi = 0;\n int ans = 0;\n\n for(int i=1; i<values.length; i++) {\n ans = Math.max(ans, values[i] + values[maxi] + (maxi - i));\n\n if(values[i] + i >= values[maxi] + maxi) {\n maxi = i;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```\n```python []\nclass Solution:\n def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, values: List[int]) -> int:\n maxi = 0\n ans = 0\n\n for i in range(1, len(values)):\n ans = max(ans, values[i] + values[maxi] + (maxi - i))\n\n if values[i] + i >= values[maxi] + maxi:\n maxi = i\n\n return ans\n```\n\nPlease upvote if you like the solution!\n
| 4 | 0 |
['Array', 'Greedy', 'C++', 'Java', 'Python3']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
6Line code || TIME O(n) || C++ || MOST SIMPLE & OPRIMIZED
|
6line-code-time-on-c-most-simple-oprimiz-udrz
|
Code\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector& values) {\n int ans = 0, sum = values[0];\n for(int i = 1; i < values.size(); i++){\n ans
|
ganeshkumawat8740
|
NORMAL
|
2023-06-18T02:12:35.658642+00:00
|
2023-06-18T02:12:35.658664+00:00
| 787 | false |
# Code\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {\n int ans = 0, sum = values[0];\n for(int i = 1; i < values.size(); i++){\n ans = max(ans,sum+values[i]-i);\n sum = max(sum,values[i]+i);}\n return ans;\n }\n```
| 4 | 1 |
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'C++']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
✅3 Line Easy C ++ Solution✅
|
3-line-easy-c-solution-by-fiit_bhairav-zx1v
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
fiit_bhairav
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-12T06:05:01.480521+00:00
|
2023-02-12T06:05:18.613786+00:00
| 418 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {\n int maxi=values[0],ans=INT_MIN;\n for(int i=1;i<values.size();i++)\n {\n ans=max(ans,maxi+values[i]-i);\n maxi=max(maxi,values[i]+i);\n } \n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\n\n
| 4 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
recursion + Memoization || Buy/Sell stock intuition
|
recursion-memoization-buysell-stock-intu-9k64
|
Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int dp[50001][2];\n int score(vector<int>& v,int i,int f){\n if(f==-1) return 0;\n if(i==v.size()) retur
|
pklid471
|
NORMAL
|
2023-01-16T13:06:36.973863+00:00
|
2023-01-16T13:06:36.973896+00:00
| 280 | false |
# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int dp[50001][2];\n int score(vector<int>& v,int i,int f){\n if(f==-1) return 0;\n if(i==v.size()) return INT_MIN;\n if(dp[i][f]!=-1) return dp[i][f];\n\n if(f==0){\n return dp[i][f]=max(v[i]+i+score(v,i+1,1),score(v,i+1,f));\n }\n else{\n return dp[i][f]=max(v[i]-i+score(v,i+1,-1),score(v,i+1,f));\n }\n\n }\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& v) {\n memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp));\n return score(v,0,0);\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
✅✅Faster || Easy To Understand || C++ Code
|
faster-easy-to-understand-c-code-by-__kr-hwby
|
Optimized\n\n Time Complexity :- O(N)\n\n Space Complexity :- O(1)\n\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& arr) {\n
|
__KR_SHANU_IITG
|
NORMAL
|
2022-09-09T17:17:40.325075+00:00
|
2022-09-09T17:17:40.325116+00:00
| 438 | false |
* ***Optimized***\n\n* ***Time Complexity :- O(N)***\n\n* ***Space Complexity :- O(1)***\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& arr) {\n \n int n = arr.size();\n \n int maxi = INT_MIN;\n \n // left_max will keep track of max. value of (arr[i] + i)\n \n int left_max = arr[0];\n \n for(int i = 1; i < n; i++)\n {\n // find sum\n \n int sum = left_max + arr[i] - i;\n \n // update maxi\n \n maxi = max(maxi, sum);\n \n // update left_max\n \n left_max = max(left_max, arr[i] + i);\n }\n \n return maxi;\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Greedy', 'C', 'C++']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Java | In-depth Explanation | Easy to Understand
|
java-in-depth-explanation-easy-to-unders-vxqh
|
Brute force solution is very easy to come up with. We simply use a nested for-loop to try all the combination so I would skip it. Let\'s think how do we come up
|
f096t004
|
NORMAL
|
2022-06-28T14:49:23.003504+00:00
|
2022-06-28T14:49:23.003531+00:00
| 251 | false |
Brute force solution is very easy to come up with. We simply use a nested for-loop to try all the combination so I would skip it. Let\'s think how do we come up with O(n) time solution with one pass?\n \n To achieve O(n) time, it\'s obvious we need to use ONE for-loop. Then we need to use variables to track something, right? What should we keep tracking of while we iterate through values[ ]? \n \n There are two things we need to track. `max = values[i] + i` and `res` which is the result we wanna return eventually. If we found any greater `max`, we update. If `res` is greater, we also update. That\'s it !\n \n```\nclass Solution \n{\n public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values)\n {\n // O(n) time | O(1) space\n \n // initialize max and res at the pair (0, 1)\n int max = values[0] + 0;\n int res = max + (values[1] - 1);\n \n for(int i = 1; i < values.length; i++)\n {\n res = Math.max(res, max + values[i] - i);\n max = Math.max(max, values[i] + i);\n }\n return res;\n }\n}\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
C++ | O(N) | one pass Solution
|
c-on-one-pass-solution-by-karan252-021c
|
dp[i]=maximum sight score till index i\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {\n int n=values.size();\n
|
karan252
|
NORMAL
|
2022-06-19T06:01:28.462699+00:00
|
2022-06-19T06:01:28.462739+00:00
| 136 | false |
dp[i]=maximum sight score till index i\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {\n int n=values.size();\n vector<int> dp(n,0);\n int ans=0;\n for(int i=1;i<n;i++)\n {\n dp[i]=values[i]+values[i-1]-1;\n dp[i]=max(dp[i],dp[i-1]-1+values[i]-values[i-1]);\n ans=max(dp[i],ans);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
C++ Easy Solution | DP | TC O(N) | SC O(1)
|
c-easy-solution-dp-tc-on-sc-o1-by-amitti-ulzk
|
( val[i]+i ) + (val[j]-j)\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& a) {\n int maxi=a[0]+0;\n int ans=-1;\n
|
amittiwari04
|
NORMAL
|
2021-11-19T13:08:42.007191+00:00
|
2021-11-19T13:08:42.007222+00:00
| 341 | false |
( val[i]+i ) + (val[j]-j)\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& a) {\n int maxi=a[0]+0;\n int ans=-1;\n int n=a.size();\n for(int i=1;i<n;i++){\n ans=max(ans,maxi+a[i]-i);\n maxi=max(maxi,a[i]+i);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C', 'C++']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
[Javascript] O(n) time, O(1) space, kadane variation
|
javascript-on-time-o1-space-kadane-varia-ym97
|
\n var maxScoreSightseeingPair = function(values) {\n\n let prevMax = values[0], max = 0;\n\n for(let i = 1; i < values.length; i++) {\n\n prevMax-
|
_savely
|
NORMAL
|
2021-11-05T09:09:35.163457+00:00
|
2021-11-05T09:09:35.163503+00:00
| 277 | false |
```\n var maxScoreSightseeingPair = function(values) {\n\n let prevMax = values[0], max = 0;\n\n for(let i = 1; i < values.length; i++) {\n\n prevMax--;\n max = Math.max(max, prevMax + values[i]);\n prevMax = Math.max(prevMax, values[i]);\n }\n \n return max;\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 1 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Simple DP Solution | O(N) | Very easy to understand
|
simple-dp-solution-on-very-easy-to-under-t83b
|
[8,1,5,2,6]. Let\'s take this example for better understanding. Assume this is 1-metered lenses game. Each number in the input vector represents number of lense
|
ronakp01
|
NORMAL
|
2021-10-20T23:12:34.995584+00:00
|
2021-10-20T23:15:01.295286+00:00
| 324 | false |
[8,1,5,2,6]. Let\'s take this example for better understanding. Assume this is *1-metered lenses* game. Each number in the input vector represents number of lenses you get on that location (each lense can cover 1-meter distance), so 8 in [8,1,5,2,6] says, being at that position, you can cover 8-meter since you\'re having 8 1-metered lenses. You\'ve to find out the maximum distance you can cover with the help those lenses.\n\nThere are 2 rules to this game,\n* You can use maximum 2 positions\' lenses at a time. One will be in your hand and other you\'ll pick as you go to that position.\n* You lose 1 lense you currently have in your hand each time you move forward.\n\nStrategy to deal with this game is,\n1. Take all the lenses of first location. i.e. 8 in our case.\n2. Go forward, you\'ll have 7 lenses with you. Note the maximum distance you can cover with the help of lenses you kept with you and lenses you\'ve available at this position which is 7+1.\n3. Make decision of which of the lenses you want to move forward with? One you bring from previous positions or one you got from this position. (i.e. 7 lenses or 1 lense).\n4. Repeat steps 2 and 3 for all the positions. \n\nYou\'ll end up getting maximum distance you can cover with all the rules of the game.\n\n`currMx`: Lenses you\'ll be keeping in your hand each time going forward in the iteration.\n`mxScore`: Maximum distance you can cover.\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {\n int mxScore = 0;\n int currMx = values[0];\n \n for(int i=1; i<values.size(); i++){\n currMx--;\n mxScore = max(values[i]+currMx, mxScore);\n currMx = max(values[i], currMx);\n }\n \n return mxScore;\n \n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C', 'C++']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
[Py/Py3] DP Solution with comments
|
pypy3-dp-solution-with-comments-by-ssshu-8fii
|
Soln 1: Note this is more concise solution w.r.t soln 2. Soln 2 is converted to Soln 1.\n> \n\n\nfrom math import inf\n\nclass Solution:\n def maxScoreSights
|
ssshukla26
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-25T19:02:57.058290+00:00
|
2021-09-25T19:32:25.073210+00:00
| 459 | false |
> Soln 1: Note this is more concise solution w.r.t soln 2. Soln 2 is converted to Soln 1.\n> \n\n```\nfrom math import inf\n\nclass Solution:\n def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, values: List[int]) -> int:\n \n # The best value to the left of the array\n left_best = values[0]\n \n # The current best value between the pairs\n curr_best = -inf\n \n # Scan the values from index 1 onwards\n for v in values[1:]:\n \n # Compare with current best and the distance\n # betweent the best to the left of the current\n # index. Here -1 added to the value giving\n # a notion that distance increases by 1 on every\n # index\n curr_best = max(curr_best, left_best + v - 1)\n \n # The best to the left of the current index\n # must be maintained to compute the current best\n # value in the next iteration. Here also, -1\n # is added to left best to make sure to increase\n # distance from the left best for next index.\n left_best = max(left_best - 1, v)\n \n return curr_best\n```\n\n> Soln 2: A slower but an understandable solution.\n> \n\n```\nfrom math import inf\n\nclass Solution:\n \n def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, values: List[int]) -> int:\n \n # Init\n best_dist = values[0]\n prev_dist = -inf\n dist = [best_dist]\n \n # Get the best distance to the left of \n # the current index, start from index 1\n for v in values[1:]:\n \n # Get best distance to the left of the\n # currrent index\n best_dist = max(prev_dist, best_dist-1)\n \n # Append best distance at current index\n dist.append(best_dist)\n \n # Keep track of previous distance for next\n # iteration\n prev_dist = v - 1\n \n # Add the current value and the best\n # distance from the current index and\n # find the max score. Start from index 1.\n max_score = -inf\n for i,v in enumerate(values[1:],1):\n max_score = max(max_score, v + dist[i])\n \n return max_score\n```
| 4 | 1 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Java + Two Pointers
|
java-two-pointers-by-yuyuh-audr
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values) {\n int i = 0, j = 1, best = 0;\n \n while (j < values.length) {\n
|
yuyuh
|
NORMAL
|
2021-03-15T23:00:10.666582+00:00
|
2021-03-15T23:00:10.666624+00:00
| 414 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values) {\n int i = 0, j = 1, best = 0;\n \n while (j < values.length) {\n best = Math.max(best, values[i] + values[j] + i - j);\n \n if (values[i] - values[j] < j - i) {\n i = j;\n } \n \n j++;\n }\n \n return best;\n }\n}\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'Java']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
💢Faster✅💯 Lesser C++✅Python3🐍✅Java✅C✅Python🐍✅C#✅💥🔥💫Explained☠💥🔥 Beats 💯
|
faster-lesser-cpython3javacpythoncexplai-y84d
|
IntuitionApproach
JavaScript Code --> https://leetcode.com/problems/best-sightseeing-pair/submissions/1489930912
C++ Code --> https://leetcode.com/problems/best
|
Edwards310
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-27T18:08:05.214034+00:00
|
2024-12-27T18:08:05.214034+00:00
| 52 | false |

# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
- ***JavaScript Code -->*** https://leetcode.com/problems/best-sightseeing-pair/submissions/1489930912
- ***C++ Code -->*** https://leetcode.com/problems/best-sightseeing-pair/submissions/1489910874
- ***Python3 Code -->*** https://leetcode.com/problems/best-sightseeing-pair/submissions/1489928404
- ***Java Code -->*** https://leetcode.com/problems/best-sightseeing-pair/submissions/1489922798
- ***C Code -->*** https://leetcode.com/problems/best-sightseeing-pair/submissions/1489929311
- ***Python Code -->*** https://leetcode.com/problems/best-sightseeing-pair/submissions/1489926557
- ***C# Code -->*** https://leetcode.com/problems/best-sightseeing-pair/submissions/1489924062
- ***Go Code -->*** https://leetcode.com/problems/best-sightseeing-pair/submissions/1489937601
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(N) // C Solution
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(1) // C Solution
# Code

| 3 | 0 |
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'C', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'Go', 'Python3', 'JavaScript', 'C#']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Simple DP || Beats 100% || Linear Time || No Extra Space
|
simple-dp-beats-100-linear-time-no-extra-r26j
|
IntuitionIf we calculate the score using the value at index i with value at index x and x+1 (i<x), keeping the value at later indices (x and x+1) as it is, the
|
bit_mystic
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-27T11:43:11.183389+00:00
|
2024-12-27T11:43:11.183389+00:00
| 49 | false |
# Intuition
If we calculate the score using the value at index i with value at index x and x+1 (i<x), keeping the value at later indices (x and x+1) as it is, the value contributed by number at index i will be one lesser when calculated with index x+1 (arr[x+1] + arr[i]+i-x -1) compared to index x (arr[x] + arr[i]+i-x). So we can see that with each increasing index the sum contributed by previous values is getting reduced by one. We can use a varibale to store the best contribution previous elements can give to the score and add it with elements at each index to get the maximum sum till that index. After last index, we will get the score of the best pair.
# Approach
1. Use a ***curr*** variable to store maximum any previous value can contribute to the sum. Initialize it with value 0.
2. Initialize the ***ans*** variable with 0. It will store the best sum of best pair.
3. Iterate through the vector/list and at each index add the curr variable to see if exceeds the maximum score stored in ans.
4. Also, notice that the impact ***curr*** varible to the score will decrease by one for the next index. Also, if the value at present index is greater than ***curr***, we will replace ***curr*** with present value.
**Note:** The assigning of ***curr*** as maximum of ***curr*** and present value as well as decreasing the ***curr*** value has been done at single step in the solution given.
5. Return the ***ans*** variable as it contains the maximum score of the best pair.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
$$O(n)$$
- Space complexity:
$$O(1)$$
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, values: List[int]) -> int:
curr,ans=0,0
for i in values:
ans=max(ans,i+curr)
curr=max(curr-1,i-1)
return ans
```
```C++ []
class Solution {
public:
int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {
int ans=0,curr=0;
for(int i: values) {
ans=max(ans,i+curr);
curr=max(curr-1,i-1);
}
return ans;
}
};
```
# Please provide any necessary feedback and give me an upvote if you liked my explanation. Thanks.
| 3 | 0 |
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'C++', 'Python3']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Java🍵|✅Easy🔥
|
javaeasy-by-mani-26-ty5i
|
Complexity
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(1)
Code
|
mani-26
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-27T09:54:13.115110+00:00
|
2024-12-27T09:54:13.115110+00:00
| 20 | false |
# Complexity
- Time complexity: **O(n)**
- Space complexity: **O(1)**
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values) {
int n = values.length;
int max = values[0];
int res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
res = Math.max(res, (values[i] - i + max));
max = Math.max(max, values[i] + i);
}
return res;
}
}
```
| 3 | 0 |
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Java']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
✅Easy to Understand | 100% | Java | C++ | Python | Detailed Video Explanation🔥
|
easy-to-understand-100-java-c-python-det-6r70
|
IntuitionThe problem involves maximizing the score of a sightseeing pair, which is defined as values[i] + values[j] + i - j. By breaking this down, we can split
|
sahilpcs
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-27T09:48:34.223118+00:00
|
2024-12-27T09:48:34.223118+00:00
| 184 | false |
# Intuition
The problem involves maximizing the score of a sightseeing pair, which is defined as `values[i] + values[j] + i - j`. By breaking this down, we can split it into two components:
1. `(values[i] + i)`: A fixed contribution from the left side.
2. `(values[j] - j)`: A dynamic contribution from the right side as we iterate.
The goal is to efficiently keep track of the maximum possible `(values[i] + i)` encountered so far and combine it with the current `(values[j] - j)` to calculate the maximum score in \(O(n)\) time.
# Approach
1. Start by initializing a variable `first` to represent the maximum value of `(values[i] + i)` seen so far, starting with the first element.
2. Iterate through the array starting from index `1`.
- For each index `j`, compute `second = values[j] - j`.
- Update the result by checking if the sum of `first + second` is greater than the current maximum score.
- Update `first` to include the current contribution `(values[j] + j)` for potential use in future iterations.
3. Return the maximum score after processing all elements.
This approach ensures that we only iterate through the array once, keeping the computation efficient.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
$$O(n)$$
We traverse the array once, performing constant-time operations at each step.
- Space complexity:
$$O(1)$$
Only a few variables are used for computation, with no additional data structures.
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values) {
// Initialize 'first' to represent the maximum value of (values[i] + i) seen so far
int first = values[0] + 0;
// Get the size of the input array
int n = values.length;
// Initialize the answer to the minimum possible value
int ans = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
// Iterate through the array starting from index 1
for(int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
// Calculate 'second' as (values[j] - j) for the current index
int second = values[j] - j;
// Update the maximum score by considering the current 'first' and 'second'
ans = Math.max(ans, first + second);
// Update 'first' to include the current element's contribution to (values[i] + i)
first = Math.max(first, values[j] + j);
}
// Return the maximum score of a sightseeing pair
return ans;
}
}
```
```c++ []
class Solution {
public:
int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {
// Initialize 'first' to represent the maximum value of (values[i] + i) seen so far
int first = values[0] + 0;
// Initialize the answer to the minimum possible value
int ans = INT_MIN;
// Iterate through the array starting from index 1
for (int j = 1; j < values.size(); j++) {
// Calculate 'second' as (values[j] - j) for the current index
int second = values[j] - j;
// Update the maximum score by considering the current 'first' and 'second'
ans = max(ans, first + second);
// Update 'first' to include the current element's contribution to (values[i] + i)
first = max(first, values[j] + j);
}
// Return the maximum score of a sightseeing pair
return ans;
}
};
```
```python []
class Solution:
def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, values: List[int]) -> int:
# Initialize 'first' to represent the maximum value of (values[i] + i) seen so far
first = values[0] + 0
# Initialize the answer to the minimum possible value
ans = float('-inf')
# Iterate through the array starting from index 1
for j in range(1, len(values)):
# Calculate 'second' as (values[j] - j) for the current index
second = values[j] - j
# Update the maximum score by considering the current 'first' and 'second'
ans = max(ans, first + second)
# Update 'first' to include the current element's contribution to (values[i] + i)
first = max(first, values[j] + j)
# Return the maximum score of a sightseeing pair
return ans
```
LeetCode 1014 Best Sightseeing Pair | Array | DP | Asked in Google
https://youtu.be/icOKLdBEtFM
| 3 | 0 |
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java']
| 1 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Beats 97.03% || Java || Greedy || Easy approach ✅ ✅ ✅
|
beats-9703-java-greedy-easy-approach-by-uos36
|
This code solves the problem of finding the maximum score of a sightseeing pair, where the score of a pair (i, j) is defined as:Intuitionvalues[i]+i represents
|
prabhas_rakurthi
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-27T06:43:11.743844+00:00
|
2024-12-27T06:43:11.743844+00:00
| 79 | false |
This code solves the problem of finding the maximum score of a sightseeing pair, where the score of a pair (i, j) is defined as:
values[i]+values[j]+i−j
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
`values[i]+i` represents how good the left element
`values[j]−j `represents how good the right element
Combining these,
`values[i]+i+values[j]−j `
we want to maximize this score
- Get the maximum till that point that wil be `max(max,values[i]+i)`
- Check the score with current and prev res `max(max+values[i]-i,res)`
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
- Start with the first value as the best left element
- Set res to the lowest possible value.
- For each j, calculate the score of the pair `(i,j)` using the current best max.
- Update max to keep track of the best left-side value for future pairs.
- After checking all pairs, the maximum score is stored in res.
# Complexity
- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity: $$O(1)$$
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values) {
int res=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int max=values[0];
int n=values.length;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
res=Math.max(max+values[i]-i,res);
if(max < values[i]+i){
max=values[i]+i;
}
}
return res;
}
}
```
| 3 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
0 ms || Beats 100 % || One pass Solution || Space optimized DP Solution || Beginner Friendly
|
0-ms-beats-100-one-pass-solution-space-o-atoz
|
Problem Understanding:Given an integer array values where values[i] represents the value of the ith sightseeing spot, we need to find the maximum score of a pai
|
sdeepu2003
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-27T06:36:00.863750+00:00
|
2024-12-27T06:38:47.650042+00:00
| 159 | false |
# Problem Understanding:
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
Given an integer array values where values[i] represents the value of the ith sightseeing spot, we need to find the maximum score of a pair of sightseeing spots. The score of a pair (i < j) is defined as:
**$$score(i,j)=values[i]+values[j]+i−j$$**
Our goal is to find the pair (i, j) that maximizes the score, where $$i < j.$$
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
**Key Insight:**
The score formula values[i] + values[j] + i - j can be split into two components:
**$$score(i,j)=(values[i]+i)+(values[j]−j)$$**
This insight allows us to think of the problem in two parts:
1. Left part: We need to keep track of the best possible value of $$values[i] + i$$ as we iterate through the array.
2. Right part: For each j, we calculate the score by combining the best $$values[i] + i$$ seen so far with $$values[j] - j$$.
The solution involves iterating through the array while maintaining the maximum score we can achieve by selecting a j and using the best i (where i < j).
Approach:
1. **Initialize:** Start with the first element, where left = values[0] (since the first spot doesn't have any prior spot).
2. **Iterate over the array:** For each spot j starting from index 1, calculate the score using the current left (which holds the best values[i] + i up to j-1).
3. **Update:** After calculating the score for the current j, update left to reflect the best value of values[j] + j for future comparisons.
This way, we can calculate the score for all valid pairs (i, j) in one linear scan.
# Complexity
- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$ -> where n is size of array
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity: $$O(1)$$ -> no extra space required expect 3 variables
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Example:
```
values = [8, 1, 5, 2, 6]
```
1. Start with $$left = values[0] = 8$$, $$maxi = -INF$$.
2. For j = 1, calculate $$score = left + values[1] - 1 = 8 + 1 - 1 = 8$$, so $$maxi = 8$$. Update $$left = max(left, values[1] + 1) = 2$$.
3. For j = 2, calculate $$score = left + values[2] - 2 = 2 + 5 - 2 = 5$$, so $$maxi = 8$$. Update $$left = max(left, values[2] + 2) = 7$$.
4. For j = 3, calculate $$score = left + values[3] - 3 = 7 + 2 - 3 = 6$$, so $$maxi = 8$$. Update $$left = max(left, values[3] + 3) = 5$$.
5. For j = 4, calculate $$score = left + values[4] - 4 = 5 + 6 - 4 = 7$$, so $$maxi = 11$$. Final $$maxi = 11$$.
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values) {
int n = values.length;
int maxi = Integer.MIN_VALUE; // To store the maximum score
int left = values[0]; // Initialize left part as values[0] + 0
// Iterate through the array starting from index 1
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
// Update maxi by considering the score for current pair (left, j)
maxi = Math.max(maxi, left + values[j] - j);
// Update left for future pairs: values[i] + i, where i < j
left = Math.max(left, values[j] + j);
}
return maxi;
}
}
```
```python []
class Solution:
def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, values):
n = len(values)
maxi = float('-inf') # To store the maximum score
left = values[0] # Initialize left part as values[0] + 0
# Iterate through the array starting from index 1
for j in range(1, n):
# Update maxi by considering the score for current pair (left, j)
maxi = max(maxi, left + values[j] - j)
# Update left for future pairs: values[i] + i, where i < j
left = max(left, values[j] + j)
return maxi
```
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {
int n = values.size();
int maxi = INT_MIN; // To store the maximum score
int left = values[0]; // Initialize left part as values[0] + 0
// Iterate through the array starting from index 1
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
// Update maxi by considering the score for current pair (left, j)
maxi = max(maxi, left + values[j] - j);
// Update left for future pairs: values[i] + i, where i < j
left = max(left, values[j] + j);
}
return maxi;
}
};
```
| 3 | 0 |
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Greedy', 'C++', 'Java', 'Python3']
| 1 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
O(1) Space | O(N) Time | Single Pass | Beats 100%
|
o1-space-on-time-single-pass-beats-100-b-rvyx
|
IntuitionNote: In these type of problems, it is always likely to convert the given array(nums) into nums[i] (+/-) i.
i.e. update nums[i] to nums[i] + i, and the
|
fake_name
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-27T04:25:30.661379+00:00
|
2024-12-27T04:25:30.661379+00:00
| 159 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
**Note**: In these type of problems, it is always likely to convert the given array(nums) into nums[i] (+/-) i.
i.e. update nums[i] to nums[i] + i, and then appraoch problem.
- We have to maximize the value of values[i] + values[j] + (i - j). We can rewrite this as **(values[i] + i) + (values[j] - j)**.
- Now we can calculate both values for each index i.e (values[i] + i) and (values[i] - i).
- Note for any index i, we will find best j as **max(values[j] - j) for j > i**.
- Here we can notice that for every i, we need the maximum value from the **suffix**.
---
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
- Start iterating from the back, keep track of the maximum value of (values[i] - i). Call it **suffixMax**.
- For each index, calculate **values[i] + i + suffixMax**, and update the answer if this value is greater than answer.
---
# Complexity
- $$ Time Complexity: O(N) $$
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- $$ Space Complexity: O(1) $$
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
const int INF = 1e9;
int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {
int n = values.size(), ans = -INF;
int suffixMax = values[n - 1] - n + 1;
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
ans = max(ans, values[i] + i + suffixMax);
suffixMax = max(suffixMax, values[i] - i);
}
return ans;
}
};
```
| 3 | 0 |
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'C++']
| 1 |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.