question_slug
stringlengths 3
77
| title
stringlengths 1
183
| slug
stringlengths 12
45
| summary
stringlengths 1
160
⌀ | author
stringlengths 2
30
| certification
stringclasses 2
values | created_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| updated_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| hit_count
int64 0
10.6M
| has_video
bool 2
classes | content
stringlengths 4
576k
| upvotes
int64 0
11.5k
| downvotes
int64 0
358
| tags
stringlengths 2
193
| comments
int64 0
2.56k
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
using map
|
using-map-by-groushan-hyt5
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
groushan
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-24T11:25:07.346443+00:00
|
2024-09-24T11:25:07.346474+00:00
| 6 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n#define ll long long\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool check(unordered_map<char, int>& mp1, unordered_map<char, int>& mp2) {\n for (auto it : mp2) {\n char c = it.first;\n int n = it.second;\n if (mp1.find(c) == mp1.end() || mp1[c] < n) return false;\n }\n return true;\n }\n\n long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) {\n unordered_map<char, int> mp2;\n for (char c : word2) {\n mp2[c]++;\n }\n\n ll ans = 0;\n unordered_map<char, int> mp1;\n int start = 0;\n\n // Sliding window\n for (int end = 0; end < word1.size(); ++end) {\n mp1[word1[end]]++; // Add current character to window\n\n \n while (end - start + 1 >= word2.size() && check(mp1, mp2)) {\n ans += word1.size() - end; \n mp1[word1[start]]--; \n if (mp1[word1[start]] == 0) {\n mp1.erase(word1[start]);\n }\n start++;\n }\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n};\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
3297. Count Substrings That Can Be Rearranged to Contain a String I. Solutions
|
3297-count-substrings-that-can-be-rearra-dqb2
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Pulatov713
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-24T09:27:55.759816+00:00
|
2024-09-24T09:27:55.759853+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public long validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n int n = word1.length();\n int m = word2.length();\n if (m > n) return 0;\n\n HashMap<Character, Integer> count2 = new HashMap<>();\n HashMap<Character, Integer> count1 = new HashMap<>();\n\n for (char c : word2.toCharArray()) {\n count2.put(c, count2.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1);\n }\n\n long result = 0;\n int required = count2.size();\n int formed = 0;\n int left = 0;\n\n for (int right = 0; right < n; ++right) {\n char c = word1.charAt(right);\n count1.put(c, count1.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1);\n\n if (count2.containsKey(c) && count1.get(c).intValue() == count2.get(c).intValue()) {\n formed++;\n }\n\n while (formed == required) {\n result += (n - right);\n char leftChar = word1.charAt(left);\n count1.put(leftChar, count1.get(leftChar) - 1);\n \n if (count2.containsKey(leftChar) && count1.get(leftChar) < count2.get(leftChar)) {\n formed--;\n }\n left++;\n }\n }\n\n return result;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Python Two Pointers
|
python-two-pointers-by-pchen36-2czm
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
pchen36
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-24T05:21:50.215846+00:00
|
2024-09-24T05:21:50.215892+00:00
| 17 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(2n1)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:O(1)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def validSubstringCount(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:\n n1, n2 = len(word1), len(word2)\n l, r = 0, 0\n f_2, f_1 = [0]*26, [0]*26\n m = n2\n ans = 0\n for c in word2:\n f_2[ord(c)-ord(\'a\')] += 1\n\n while r < n1:\n i = ord(word1[r])-ord(\'a\')\n f_1[i] += 1\n if f_2[i] != 0 and f_2[i] >= f_1[i] :\n m -= 1\n while m == 0:\n ans += n1-r\n #exclude left and move left\n i_e = ord(word1[l])-ord(\'a\')\n f_1[i_e] -= 1\n if f_2[i_e] != 0 and f_2[i_e] > f_1[i_e] :\n m += 1\n l += 1\n r += 1\n return ans\n\n\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Sliding window | C++
|
sliding-window-c-by-siddharth96shukla-eya0
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n)\n# Code\ncpp []\n#define ll long long int\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool chk(vector<int>&w1cnt, vector<int>&w2cnt){\
|
siddharth96shukla
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-24T05:07:29.023767+00:00
|
2024-09-24T05:07:29.023788+00:00
| 10 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$\n# Code\n```cpp []\n#define ll long long int\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool chk(vector<int>&w1cnt, vector<int>&w2cnt){\n for(int i=0;i<26;i++)if(w2cnt[i]>w1cnt[i])return 0;\n return 1;\n }\n\n long long validSubstringCount(string w1, string w2) {\n vector<int>w1cnt(26, 0), w2cnt(26, 0);\n for(auto c:w2)w2cnt[c-\'a\']++;\n ll ans=0;\n int l=0, r=0, n=w1.length();\n while(r<n){\n w1cnt[w1[r]-\'a\']++;\n while(chk(w1cnt, w2cnt)){\n ans+=(n-r);\n w1cnt[w1[l]-\'a\']--;\n l++;\n }\n r++;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Sliding Window', 'C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Sliding Window || Hashing || Super Simple
|
sliding-window-hashing-super-simple-by-l-i4ma
|
Code\ncpp []\nclass Solution \n{\npublic:\n long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) \n {\n map<char,long long> m1, m2;\n f
|
lotus18
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-24T04:21:23.993913+00:00
|
2024-09-24T04:21:23.993945+00:00
| 1 | false |
# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution \n{\npublic:\n long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) \n {\n map<char,long long> m1, m2;\n for(auto ch: word2) m2[ch]++;\n long long cnt=0, target=m2.size();\n long long start=0, ans=0, end=0;\n while(end<word1.size())\n {\n m1[word1[end]]++;\n if(m1[word1[end]]==m2[word1[end]]) cnt++;\n while(cnt==target)\n {\n ans+=(word1.size()-end);\n m1[word1[start]]--;\n if(m1[word1[start]]<m2[word1[start]]) cnt--;\n start++;\n }\n end++;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'Sliding Window', 'C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
C++ | Binary Search | PrefixSums for freq
|
c-binary-search-prefixsums-for-freq-by-j-qskt
|
Approach\n- Prefix Sum Array: Build a 2D prefix sum array prefixSums for word1, where prefixSums[i][j] stores the frequency of the i-th letter (\'a\' to \'z\')
|
jatindhiman05
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-23T18:13:54.837121+00:00
|
2024-09-23T18:13:54.837146+00:00
| 14 | false |
# Approach\n- **Prefix Sum Array**: Build a 2D prefix sum array prefixSums for word1, where prefixSums[i][j] stores the frequency of the i-th letter (\'a\' to \'z\') from the start of word1 up to index j.\n\n- **Binary Search for Valid Substring**: For each starting index `i` in word1, perform a binary search to find the smallest ending index k such that the substring word1[i:k] contains all characters in at least the frequency as word2(valid).\n\n- **Final Count**: Substrings after the idx k will be valid only add (n - k) to your ans. (Hence reducing the iterations)\n\n# Code\n```cpp\nclass Solution {\n vector<vector<int>> prefixSums;\n int n;\n unordered_map<int, int> freqWord_2;\n\n int binarySearch(int s) {\n int start = s;\n int end = n;\n \n while (start < end) {\n int mid = start + (end - start) / 2;\n bool valid = true;\n\n for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {\n int f = prefixSums[i][mid] - (s > 0 ? prefixSums[i][s - 1] : 0);\n if (f < freqWord_2[i]) {\n valid = false;\n break;\n }\n }\n\n if (valid) {\n end = mid; \n } else {\n start = mid + 1;\n }\n }\n\n return start;\n }\n\npublic:\n long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) {\n n = word1.length();\n prefixSums.resize(26, vector<int>(n, 0));\n\n for (char ch : word2) {\n freqWord_2[ch - \'a\']++;\n }\n\n prefixSums[word1[0] - \'a\'][0] = 1;\n for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j < 26; j++) {\n prefixSums[j][i] = prefixSums[j][i - 1];\n }\n prefixSums[word1[i] - \'a\'][i]++;\n }\n\n long long ans = 0;\n\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n int k = binarySearch(i); \n ans += (n - k);\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Simple Explanation with Images - Java
|
simple-explanation-with-images-java-by-n-hvre
|
Intuition\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\nHere\u2019s a clearer version of your explanation:\n\n"Start by identifying the windo
|
NEMARUGOMMULA
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-23T15:33:09.215615+00:00
|
2024-09-23T15:33:09.215650+00:00
| 7 | false |
# Intuition\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\nHere\u2019s a clearer version of your explanation:\n\n"Start by identifying the window that contains all the characters of `word2`. Then, begin shrinking the left boundary of the window while ensuring that the condition still holds. When the condition breaks, you\u2019ve found the minimal window that meets the criteria.\n\nAt this point, calculate the number of possible subarrays starting to the left (`leftCount`) and the number of possible subarrays to the right (`rightCount`). Multiply these two values (`leftCount * rightCount`) to determine the total number of subarrays that can be formed with this minimal window.\n\nNext, continue searching for additional minimal windows by shrinking the left boundary further. Since most of the combinations have already been accounted for in the previous calculation, you only need to focus on new possibilities."\n\n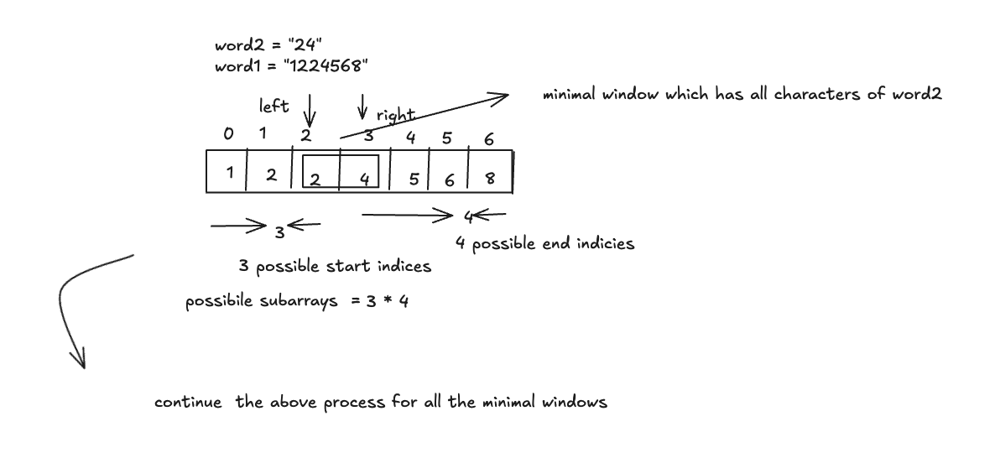\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public long validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n int word1Len = word1.length();\n int[] word2Freq = new int[26];\n Arrays.fill(word2Freq,0);\n for(char c : word2.toCharArray()){\n word2Freq[c-\'a\']++;\n }\n long ans = 0;\n int[] word1Freq = new int[26];\n Arrays.fill(word1Freq,0);\n int leftBorder = 0;\n int left = 0,right = 0;\n while(left < word1Len && right < word1Len){\n while(!doesSatisfyWordFreq(word2Freq,word1Freq) && right < word1Len){\n word1Freq[word1.charAt(right)-\'a\']++;\n ++right;\n if(doesSatisfyWordFreq(word2Freq,word1Freq))break;\n }\n if(!doesSatisfyWordFreq(word2Freq,word1Freq))break;\n while(doesSatisfyWordFreq(word2Freq,word1Freq) && left < word1Len){\n word1Freq[word1.charAt(left)-\'a\']--;\n ++left;\n if(!doesSatisfyWordFreq(word2Freq,word1Freq))break;\n }\n int leftStartPoints = left - leftBorder;\n int rightPoints = word1Len - right + 1;\n long possibilities = (long)leftStartPoints*rightPoints;\n ans += possibilities;\n leftBorder = left;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n private boolean doesSatisfyWordFreq(int[] word2Freq,int[] word1Freq){\n for(int i = 0;i< 26;++i){\n if(word2Freq[i] > word1Freq[i])return false;\n }\n return true;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Java Easy Solution
|
java-easy-solution-by-sachinsingh1451-zx9g
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
sachinsingh1451
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-23T14:47:46.476758+00:00
|
2024-09-23T14:47:46.476795+00:00
| 0 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public long validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n\n int t[] = new int[26];\n\n for(int i=0;i<word2.length();i++){\n t[word2.charAt(i)-\'a\']++;\n }\n\n int dp[] = new int[26];\n\n int j=0;\n long ans = 0l;\n for(int i=0;i<word1.length();i++){\n dp[word1.charAt(i)-\'a\']++;\n if(i-j+1 >= word2.length() && isvalid(dp, t)){\n ans += word1.length()-i;\n while(j<i && t[word1.charAt(j)-\'a\']<dp[word1.charAt(j)-\'a\']){\n dp[word1.charAt(j)-\'a\']--;\n ans+=word1.length()-i;\n j++;\n }\n dp[word1.charAt(j)-\'a\']--;\n j++;\n }\n }\n\n return ans;\n \n }\n\n private boolean isvalid(int dp[], int t[]){\n\n\n for(int i=0;i<26;i++){\n if(dp[i]<t[i])\n return false;\n }\n return true;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Very Easy to understand Solution || C++
|
very-easy-to-understand-solution-c-by-am-lefe
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
ambarr08
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-23T14:25:09.395614+00:00
|
2024-09-23T14:25:09.395648+00:00
| 8 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n\n#define ll long long\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n bool chk(vector<int> &m1, vector<int> &m2) {\n for(int i = 0 ; i < 26 ; i++) {\n if(m1[i] < m2[i]) {\n return false;\n }\n }\n return true;\n }\n\n long long validSubstringCount(string s1, string s2) {\n if(s2.size() > s1.size()) return 0LL;\n vector<int> m1(26, 0), m2(26, 0);\n for(char i : s2) {\n m2[i-\'a\']++;\n }\n int n = s1.size();\n int z = s2.size();\n int last = 0;\n ll ans = 0;\n for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) {\n char c = s1[i];\n m1[c-\'a\']++;\n if(chk(m1, m2)) {\n while(chk(m1, m2)) {\n ans += n-i;\n if(last < n) m1[s1[last]-\'a\']--;\n last++;\n }\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
c++() easy to understand solution
|
c-easy-to-understand-solution-by-zx007pi-fuct
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
zx007pi
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-23T08:30:36.734782+00:00
|
2024-09-23T08:30:36.734805+00:00
| 1 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) {\n long ans = 0;\n int t[26] = {0};\n int w[26] = {0};\n\n for(char ch: word2) t[ch - \'a\']++;\n int letters = 0, temp = 0;\n for(int j = 0; j != 26; j++)\n if(t[j]) letters++;\n\n for(int l = 0, r = 0, k, id; r != word1.size(); r++){ \n if(++w[id = word1[r] - \'a\'] == t[id]) temp++;\n if(temp < letters) continue;\n\n ans += k = word1.size() - r; \n \n while(true)\n if(--w[id = word1[l] - \'a\'] < t[id]) {l++;temp--; break;}\n else ans += k, l++; \n } \n\n return ans; \n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
[Python3] O(nlogn) Prefix count and binary search
|
python3-onlogn-prefix-count-and-binary-s-rwjt
|
Code\npython3 []\nclass Solution:\n def validSubstringCount(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:\n if len(word1) < len(word2): return 0\n pref
|
cava
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-23T02:48:22.545848+00:00
|
2024-09-23T02:48:22.545880+00:00
| 27 | false |
# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def validSubstringCount(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:\n if len(word1) < len(word2): return 0\n prefix, cnt = [[0] * (len(word1) + 1) for _ in range(26)], dict()\n for i, w in enumerate(word1):\n for c in range(26): prefix[c][i + 1] = prefix[c][i]\n prefix[ord(w) - ord(\'a\')][i + 1] += 1\n for w in word2: cnt[ord(w) - ord(\'a\')] = cnt.get(ord(w) - ord(\'a\'), 0) + 1\n ans = 0\n for i in range(len(word1) - len(word2) + 1):\n ans += len(word1) + 1 - max(bisect_left(prefix[c], prefix[c][i] + cnt[c]) for c in cnt.keys())\n return ans\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Binary Search', 'Prefix Sum', 'Python3']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
[C++] sliding window.
|
c-sliding-window-by-lovebaonvwu-6a4l
|
\ncpp []\nclass Solution {\n bool valid(const vector<int>& cnt, const vector<int>& pattern) {\n bool ret = true;\n for (int i = 0; i < pattern.
|
lovebaonvwu
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-23T01:54:27.238734+00:00
|
2024-09-23T01:54:27.238762+00:00
| 7 | false |
\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\n bool valid(const vector<int>& cnt, const vector<int>& pattern) {\n bool ret = true;\n for (int i = 0; i < pattern.size(); ++i) {\n if (cnt[i] < pattern[i]) {\n ret = false;\n break;\n }\n }\n\n return ret;\n }\npublic:\n long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) {\n vector<int> pattern(26);\n for (auto c : word2) {\n ++pattern[c - \'a\'];\n }\n\n vector<int> cnt(26);\n int m = word2.size();\n int n = word1.size();\n long long ans = 0;\n for (int i = 0, j = 0; j < n;) {\n ++cnt[word1[j] - \'a\'];\n\n if (valid(cnt, pattern)) {\n ans += n - j;\n --cnt[word1[i] - \'a\'];\n --cnt[word1[j] - \'a\'];\n ++i;\n } else {\n ++j;\n }\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Sliding Window | O(1) memory
|
sliding-window-o1-memory-by-tigprog-z87u
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n)\n Add your time complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n\n- Space complexity: O(26) = O(1)\n Add your space complexity here, e.g. O(n)
|
tigprog
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T21:52:34.519193+00:00
|
2024-09-22T21:52:34.519252+00:00
| 19 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(26) = O(1)$$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\nwhere \n`n = max(word1.length, word2.length) <= 10^6`\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def validSubstringCount(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:\n n = len(word1)\n\n data = Counter(word2)\n number_of_chars = len(data)\n for right, elem in enumerate(word1):\n if elem not in data:\n continue\n data[elem] -= 1\n if data[elem] == 0:\n number_of_chars -= 1\n if number_of_chars == 0:\n break\n \n if number_of_chars != 0:\n return 0\n\n def move_right(right, removed_elem):\n while right < n:\n elem = word1[right]\n right += 1\n if elem not in data:\n continue\n data[elem] -= 1\n if elem == removed_elem:\n return True, right\n return False, None\n\n right += 1\n result = n - right + 1\n\n for elem in word1:\n if elem in data:\n data[elem] += 1\n if data[elem] == 1:\n is_ok, right = move_right(right, elem)\n if not is_ok:\n break\n result += n - right + 1\n\n return result\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Easy Python Solution
|
easy-python-solution-by-sb012-h8qj
|
Code\npython3 []\nfrom collections import Counter, defaultdict\n\nclass Solution:\n def validSubstringCount(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:\n wo
|
sb012
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T21:34:33.587431+00:00
|
2024-09-22T21:34:33.587473+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Code\n```python3 []\nfrom collections import Counter, defaultdict\n\nclass Solution:\n def validSubstringCount(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:\n word1_count, word2_count = defaultdict(int), Counter(word2)\n\n answer = 0\n\n left = right = 0\n\n while right < len(word1):\n while right < len(word1) and any(word1_count[i] < word2_count[i] for i in word2_count):\n word1_count[word1[right]] += 1\n right += 1\n \n while left < right and all(word1_count[i] >= word2_count[i] for i in word2_count):\n answer += len(word1) + 1 - right\n word1_count[word1[left]] -= 1\n left += 1\n \n return answer\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
java beats 100%
|
java-beats-100-by-weiqyu-13o5
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
weiqyu
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T20:22:30.881398+00:00
|
2024-09-22T20:22:30.881417+00:00
| 9 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public long validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n long res = 0;\n int keys = 0;\n int len = word1.length();\n int[] count = new int[26];\n boolean[] letters = new boolean[26];\n for (char letter : word2.toCharArray()) {\n int index = letter - \'a\';\n if (count[index]++ == 0) {\n letters[index] = true;\n keys++;\n }\n }\n int start = 0, end = 0;\n while (end < len) {\n int index = word1.charAt(end) - \'a\';\n if (!letters[index]) {\n end++;\n continue;\n }\n if (--count[index] == 0) --keys;\n while (keys == 0) {\n res += len - end;\n int beginIndex = word1.charAt(start++) - \'a\';\n if (!letters[beginIndex]) continue;\n if (count[beginIndex]++ == 0) keys++;\n }\n end++;\n }\n return res; \n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
radhe radhe || simple and easy solution || beats 100%
|
radhe-radhe-simple-and-easy-solution-bea-rlb9
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
neerajofficial1919
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T19:45:25.176647+00:00
|
2024-09-22T19:45:25.176666+00:00
| 8 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) {\n vector<int> mp2(26,0);\n long long ans=0,n=word1.size();\n vector<vector<int>> mp1(n,vector<int>(26,0));\n\n mp1[0][word1[0]-\'a\']++;\n for(auto &&val:word2)mp2[val-\'a\']++;\n for(int i=1;i<n;i++){\n mp1[i]=mp1[i-1];\n mp1[i][word1[i]-\'a\']++;\n }\n\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n int s=i,e=n-1;\n while(s<=e){\n int m=s+(e-s)/2,chk=1;\n for(int j=0;j<26;j++){\n int val=mp1[m][j];\n if(i)val-=mp1[i-1][j];\n if(mp2[j]>val){\n chk=0;\n break;\n }\n }\n if(chk)e=m-1;\n else s=m+1;\n }\n ans+=n-s;\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
EASY PYTHON ( explanation inside code ) same code for 3297 and 3298
|
easy-python-explanation-inside-code-same-9atf
|
\n\n# Code\npython3 []\nclass Solution:\n def validSubstringCount(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:\n n = len(word1)\n\n dict_w2 = Counter(
|
ekambareswar1729
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T19:12:37.098711+00:00
|
2024-09-22T19:13:04.463750+00:00
| 12 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def validSubstringCount(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:\n n = len(word1)\n\n dict_w2 = Counter(word2)\n\n match, ans, l = 0, 0, 0\n check2, check1 = 1, 1\n\n dict_curr = defaultdict(int)\n for r in range(n):\n dict_curr[word1[r]] += 1\n\n if r >= len(word2) - 1 and ( not match ): # check if dict_curr matches for first time with dict_w2 them make match=1\n check1 = 1\n for k, v in dict_w2.items():\n if dict_curr[k] < dict_w2[k]:\n check1 = 0\n break\n\n match = 1 if check1 else 0\n # after first time match of dict_curr with dict_w2 (match)\n # check if we remove word1[l] from dict_curr it still matches with dict_w2 , if so l+=1\n # (l) denotes right most pointer for (r) , for which dict_curr still matches with dict_w2\n\n if match:\n check2 = 1\n while l < r and check2:\n dict_curr[word1[l]] -= 1\n if (word1[l] not in dict_w2) or (\n dict_curr[word1[l]] >= dict_w2[word1[l]]\n ):\n l += 1\n else:\n check2 = 0\n dict_curr[word1[l]] += 1\n\n if match: # substring between 0 to l (l+1 substrings)\n ans += (l + 1)\n \n return ans\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Simple Clean Solution Using Binary Search
|
simple-clean-solution-using-binary-searc-04d4
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Amit130
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T17:12:37.789351+00:00
|
2024-09-22T17:12:37.789390+00:00
| 35 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n log n)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(n)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) {\n int m=word1.length();\n int n=word2.length();\n vector<vector<int>> prefixFreq(m+1,vector<int>(26));\n for(int i=0;i<m;i++){\n prefixFreq[i+1]=prefixFreq[i];\n prefixFreq[i+1][word1[i]-\'a\']++;\n }\n\n vector<int> toSearch(26);\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++){\n toSearch[word2[j]-\'a\']++;\n }\n\n long long ans=0;\n for(int i=0;i<m;i++){\n ans+=m-binarySearch(toSearch,i,prefixFreq,m);\n toSearch[word1[i]-\'a\']++;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n\n int binarySearch(vector<int>& toSearch,int start,vector<vector<int>>& prefix,int m){\n int end = prefix.size()-2;\n int ans=m;\n while(start<=end){\n int mid = (start+end)/2;\n if(isValid(prefix[mid+1],toSearch)){\n ans=mid;\n end=mid-1;\n } else {\n start=mid+1;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n\n bool isValid(vector<int>& prefix,vector<int>& toSearch){\n for(int i=0;i<26;i++){\n if(prefix[i]<toSearch[i]){\n return false;\n }\n }\n return true;\n }\n};\n\n/*\n\n a b c a b c\n\na 1 1 1 2 2 2\nb 0 1 1 1 2 2 \nc 0 0 1 1 1 2\n\n\n*/\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'Binary Search', 'C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
749/757. Can I know where I did wrong please.
|
749757-can-i-know-where-i-did-wrong-plea-j7im
|
Can anyone please explain where I went wrong. Only 749/757 test cases passed.\n\n# Code\njava []\nclass Solution {\n public long validSubstringCount(String w
|
Abhishek_143
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T16:22:34.394446+00:00
|
2024-09-22T16:22:34.394482+00:00
| 5 | false |
Can anyone please explain where I went wrong. Only 749/757 test cases passed.\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public long validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n int left = 0, right = 0;\n long ans = 0, temp = 0;\n char[] w1 = word1.toCharArray();\n char[] w2 = word2.toCharArray();\n HashMap<Character, Integer> w1map = new HashMap<>();\n HashMap<Character, Integer> w2map = new HashMap<>();\n int match = 0;\n\n for(char x: w2){\n w2map.put(x, w2map.getOrDefault(x, 0)+1);\n }\n\n while(right < w1.length){\n char curr = w1[right];\n if (w2map.containsKey(curr)){\n w1map.put(curr, w1map.getOrDefault(curr, 0)+1);\n if (w1map.get(curr) == w2map.get(curr)) match++;\n }\n right++;\n while (match == w2map.size()){\n char a = w1[left];\n if (w2map.containsKey(a)){\n if (w1map.get(a) == w2map.get(a)) match--;\n w1map.put(a, w1map.get(a)-1);\n }\n temp++;\n left++;\n }\n ans += temp;\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Sliding Window | Python
|
sliding-window-python-by-pragya_2305-in2z
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n+m) where n = len(word1), m=len(word2)\n\n- Space complexity: O(n+m)\n\n# Code\npython3 []\nclass Solution:\n def validSubs
|
pragya_2305
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T15:48:41.332099+00:00
|
2024-09-22T15:48:41.332121+00:00
| 20 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n+m) where n = len(word1), m=len(word2)\n\n- Space complexity: O(n+m)\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def validSubstringCount(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:\n countW2 = Counter(word2)\n need = len(countW2)\n have = 0\n ans = 0\n l = 0\n window = defaultdict(int)\n \n for r,c in enumerate(word1):\n window[c]+=1\n if c in countW2 and window[c]==countW2[c]:\n have+=1\n while have==need:\n ans+=len(word1)-r\n window[word1[l]]-=1\n if word1[l] in countW2 and window[word1[l]]<countW2[word1[l]]:\n have-=1\n l+=1\n \n return ans\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Sliding Window', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Sliding Window
|
sliding-window-by-clcwcxfwf-2k4k
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
clcwcxfwf
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T15:42:16.534320+00:00
|
2024-09-22T15:42:16.534362+00:00
| 5 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(n)$$\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(1)$$\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public long validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n int len1 = word1.length(), len2 = word2.length();\n int[] f1 = new int[26], f2 = new int[26];\n for (int i = 0; i < len2; ++i) ++f2[word2.charAt(i)-\'a\'];\n int l = 0;\n long ans = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < len1; ++i) {\n ++f1[word1.charAt(i)-\'a\'];\n while (l <= i) {\n --f1[word1.charAt(l)-\'a\'];\n if (check(f1, f2)) ++l;\n else {\n ++f1[word1.charAt(l)-\'a\'];\n break;\n }\n }\n if (l > 0) ans += l + 1;\n else if (check(f1, f2)) ans += 1;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n\n private boolean check(int[] f1, int[] f2) {\n boolean ok = true;\n for (int j = 0; j < 26; ++j) {\n if (f1[j] < f2[j]) {\n ok = false;\n break;\n }\n }\n return ok;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
🔥🔥🔥 Simple Sliding window 🔥🔥🔥
|
simple-sliding-window-by-jiaqiwangut-qmah
|
Code\npython3 []\nclass Solution:\n def validSubstringCount(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:\n dic = collections.defaultdict(int)\n window
|
JiaqiWangUT
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T15:15:38.932673+00:00
|
2024-09-22T15:15:38.932711+00:00
| 12 | false |
# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def validSubstringCount(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:\n dic = collections.defaultdict(int)\n window = collections.defaultdict(int)\n for ch in word2:\n dic[ch] += 1\n left = valid = count = 0\n size = len(word1)\n for i in range(size):\n ch = word1[i]\n if ch in dic:\n window[ch] += 1\n if window[ch] == dic[ch]:\n valid += 1\n while valid == len(dic):\n count += size - i\n removed_ch = word1[left]\n left += 1\n if removed_ch in dic:\n if window[removed_ch] == dic[removed_ch]:\n valid -= 1\n window[removed_ch] -= 1\n return count\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Sliding Window', 'Python3']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
2 priority_queue to record the end of queries, O(nlogn)
|
2-priority_queue-to-record-the-end-of-qu-onsl
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nThe thing is that you traver the nums by index, when you meet a nums that is nonzero, y
|
jerry5841314
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-23T16:00:50.949715+00:00
|
2024-11-23T16:00:50.949757+00:00
| 3,767 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThe thing is that you traver the nums by index, when you meet a nums that is nonzero, you want to choose the segment that cover this point. Whats more, the most important, you want this segment to be as far as possible. (not as long as possible, because nums before this index has already became 0).\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nYou sort the queries by their index, so that when you visit nums[i]. You know the previous part of quries cover nums[i]. Then you put all those queries cover this nums[i] into first PQ as candidate. After this, the start point of queries become no use. You only care about the end. So you only need to put the end into PQ. When you find the nums[i] is nonzero, you choose from the candidats, first PQ. And put it into second PQ, which are those queries you choose.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(nlogn)\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n sort(queries.begin(), queries.end());\n priority_queue<int> candidate;\n priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<>> chosen;\n int ans = 0;\n int n = nums.size();\n int j = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){\n while (j < queries.size() && queries[j][0] == i){\n candidate.push(queries[j][1]);\n j++;\n }\n nums[i] -= chosen.size();\n while (nums[i] > 0 && !candidate.empty() && candidate.top() >= i){\n ans++;\n chosen.push(candidate.top());\n candidate.pop();\n nums[i]--;\n } \n if (nums[i] > 0)\n return -1;\n while (!chosen.empty() && chosen.top() == i)\n chosen.pop();\n \n }\n return queries.size() - ans;\n \n }\n};\n```
| 45 | 1 |
['C++']
| 7 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
[Java/C++/Python] Take the query ending latest
|
javacpython-take-the-query-ending-latest-1uqb
|
Intuition\nItearte A,\nif we need more query,\ngreedily take the available query with biggest ending index.\n\n# Explanation\nh are ending indices of available
|
lee215
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-23T16:04:43.029989+00:00
|
2024-11-24T07:01:20.214794+00:00
| 3,123 | false |
# **Intuition**\nItearte `A`,\nif we need more query,\ngreedily take the available query with biggest ending index.\n\n# **Explanation**\n`h` are ending indices of available queries\n`cur` are number of queries currently in use.\n\nIterate each `A[i]`,\npopping out all ended query,\nupdate availble queries in `h`.\n\nWhile valid queries `cur` is smaller than required `A[i]`,\nwe need to take a query from `h` and add to `cur`.\n**the stradgy is popping out the query with biggest ending index.**\n\nRepeat this process and return the number of unused queries.\n<br>\n\n# **Complexity**\nTime `O(n + qlogq)`\nSpace `O(q)`\n<br>\n\n```Java [Java]\n public int maxRemoval(int[] A, int[][] queries) {\n int n = A.length, nq = queries.length;\n Arrays.sort(queries, (a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);\n PriorityQueue<Integer> h = new PriorityQueue<>(); // min heap\n int[] end = new int[n + 1];\n int cur = 0, j = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {\n cur -= end[i];\n while (j < nq && queries[j][0] <= i) {\n h.offer(-queries[j][1]); // Add negative for min-heap\n j++;\n }\n while (cur < A[i]) {\n if (h.isEmpty() || -h.peek() < i) {\n return -1;\n }\n end[-h.poll() + 1]++;\n cur++;\n }\n }\n return h.size();\n }\n```\n```C++ [C++]\n int maxRemoval(vector<int>& A, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n int n = A.size(), nq = queries.size();\n sort(queries.begin(), queries.end());\n priority_queue<int> h; // max heap\n vector<int> end(n + 1, 0);\n int cur = 0, j = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {\n cur -= end[i];\n while (j < nq && queries[j][0] <= i) {\n h.push(queries[j][1]);\n j++;\n }\n while (cur < A[i]) {\n if (h.empty() || h.top() < i) {\n return -1;\n }\n end[h.top() + 1]++;\n h.pop();\n cur++;\n }\n }\n return h.size();\n }\n```\n```py [Python3]\n def maxRemoval(self, A: List[int], queries: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n queries = sorted(queries)[::-1]\n ava = SortedList()\n cur = SortedList()\n for i in range(len(A)):\n while queries and queries[-1][0] <= i:\n ava.add(queries.pop()[1])\n while cur and cur[0] < i:\n cur.pop(0)\n while A[i] > len(cur):\n if not ava or ava[-1] < i:\n return -1\n cur.add(ava.pop())\n return len(ava)\n```
| 33 | 1 |
['C', 'Python', 'Java']
| 15 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Python3 || sort, heap || T/S: 99% / 92%
|
python3-sort-heap-ts-99-92-by-spaulding-9nmp
|
Here\'s the plan:\n1. We sort queries by their first elements, and we initialize arr to keep track of decrements applied to nums as we apply each query used.\n\
|
Spaulding_
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-25T20:30:32.396696+00:00
|
2024-11-25T20:32:39.426866+00:00
| 477 | false |
Here\'s the plan:\n1. We sort `queries` by their first elements, and we initialize `arr` to keep track of decrements applied to nums as we apply each query used.\n\n1. We iterate over `nums` and apply the queries for each element from the heap. We track the aggregrate decrements in `arr`. For each query applied,we decrement `ans`.\n2. If we exhaust all queries applying to an element of `nums` and that element is not zero, then no answer is possible, and we return -1.\n3. If we complete the iteration successfully, we return `ans`.\n\n\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def maxRemoval(self, nums, queries):\n \n n, decr, idx = len(nums), 0, 0\n q = ans = len(queries)\n\n arr, heap = [0] * (n + 1), []\n queries.sort(key=lambda x: x[0])\n\n for i, num in enumerate(nums):\n decr-= arr[i]\n num-= decr\n\n while q > idx and queries[idx][0] == i:\n heappush(heap, (-queries[idx][1])) \n idx+= 1\n\n while num > 0 and heap and -heap[0] >= i:\n arr[1 - heappop(heap)]+= 1\n ans-= 1\n decr+= 1\n num-= 1\n\n if num > 0: return -1\n \n return ans\n```\n[https://leetcode.com/problems/zero-array-transformation-iii/submissions/1462747331/](https://leetcode.com/problems/zero-array-transformation-iii/submissions/1462747331/)\n\nI could be wrong, but I think that time complexity is *O*(*N* + *Q* log *Q) and space complexity is *O*(*N* + *Q*), in which *N* ~ `len(nums)` and *Q* ~ `len(queries)`.
| 13 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Concise Heap Solution in Python3 with Explanation
|
concise-heap-solution-in-python3-with-ex-ar63
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nTry to construct the answer by using as few (l, r) elements as possible.\n\nMaintain th
|
metaphysicalist
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-23T16:03:14.867536+00:00
|
2024-11-23T20:01:03.218856+00:00
| 1,177 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nTry to construct the answer by using as few `(l, r)` elements as possible.\n\nMaintain three priority queues, Q, A, and W as follows:\n\n- In Q, all the input `(l, r)` are sorted by `l`.\nFor position `i`, we move all the available elements from Q to A.\n- A is another queue of `(l, r)` sorted by `r` in the descending order. \nA contains the available elements ready to select. If we want to pick up an element, it is better to the most capalable one, which is the one with the largest `r` in A. For this reason, A is sorted by `r` in the descending order. \n- The last queue W contains the currently working elements. When we move to position `i`, the first step is to retire the elements that does not work for `i`. In other words, the elements with $r < i$ should be discarded. For this reason, W is sorted by `r` in the ascending order. Then, we check the working elements is enough to cover `nums[i]`. If `nums[i] > len(W)`, we need pick up more elements from A to W. The answer will be -1 if no valid elements (i.e., $l \\le i \\le r$) can be chosen from A. \n\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\nQ should support efficient `pop()`. Thus I implement Q as a deque that initialized by `nums` sorted by `l`. A and W require both `pop()` and `push()` operations, I employ heap for both. \n \n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: The overall complexity is $O(N + M \\log M)$, where $N$ is the length of `nums` and $M$ is the length of `queries`.\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def maxRemoval(self, nums: List[int], queries: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n q = deque(sorted(queries))\n available = []\n working = []\n for i in range(len(nums)):\n while q and q[0][0] <= i:\n heappush(available, -q.popleft()[1])\n while working and working[0] < i:\n heappop(working)\n while nums[i] > len(working):\n if available and -available[0] >= i:\n heappush(working, -heappop(available))\n else:\n return -1\n return len(available)\n```\n\nThank zsq007 for his/her enlightenment suggestion to improve my code.
| 13 | 0 |
['Heap (Priority Queue)', 'Python3']
| 5 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
C++ Solution using Heap and Sorting | Explanation
|
c-solution-using-heap-and-sorting-explan-rle0
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nFor every index try to choose the seqment that covers that index also which is the fart
|
rakeshroxx
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-27T21:00:10.640397+00:00
|
2024-11-27T21:00:10.640433+00:00
| 517 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nFor every index try to choose the seqment that covers that index also which is the farthest.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nThe approach is explained along with the code \n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: n log(n)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& q) {\n priority_queue<int> availableQ; // Max Heap\n priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> appliedQ; // Min Heap\n\n // To get all the queries in a sequence\n sort(q.begin(), q.end());\n\n int qIdx = 0;\n int len = nums.size();\n int qLen = q.size();\n int successfullyAppliedQueries = 0;\n\n for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){\n // Get all the queries which can effect current idx\n // And store the end of the querie in the maxHeap which will return the \n // highest range query at the top\n while(qIdx < qLen and q[qIdx][0] == i){\n availableQ.push(q[qIdx][1]);\n qIdx++;\n }\n\n // appliedQ store the all the applied queries on this index\n // which means this many queries is effecting this perticular index\n nums[i] -= appliedQ.size();\n\n\n // new apply all the available queries and store them in the applied queue (min heap)\n // we are using the queries till the current idx become zero or there are no queries\n // available to use\n // availableQ may have more queries then needed so use till the current idx is > 0 \n while(nums[i] > 0 and not availableQ.empty() and availableQ.top() >= i){\n successfullyAppliedQueries++;\n appliedQ.push(availableQ.top());\n availableQ.pop();\n nums[i]--;\n }\n\n // after applying all the queries if still current idx is not zero then it\'s not\n // possiable to make it a zero array\n if (nums[i] > 0) return -1;\n\n // now remove all the applied queries for which the range is ended\n // Min Heap is used for this only to get the smallest range at top and remove it\n while(not appliedQ.empty() and appliedQ.top() == i){\n appliedQ.pop();\n }\n }\n\n return qLen - successfullyAppliedQueries;\n }\n};\n```
| 6 | 0 |
['Sorting', 'Heap (Priority Queue)', 'C++']
| 1 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Heap+ Queue
|
heap-queue-by-kaitou_amh-97p3
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n- assume m is the number of queries\n- sort the queries based on l (from [l,r]) and pr
|
kaitou_amh
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-24T17:49:36.446819+00:00
|
2024-11-24T17:49:36.446886+00:00
| 215 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n- assume `m` is the number of queries\n- sort the queries based on l (from `[l,r]`) and present it as a queue\n- for all those l\'s within a particular idx `i` remove them and put their `r` in a max heap\n- filtering- remove all those `r` which don\'t contain i (`r < i`)\n- put elements from max-heap to the selected, till we have the required count\n - exception: if we find insufficient `r`\'s, return -1\n- answer is `m` - ans\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n`O((m+n)logm)` where `m` is the number of queries and `n` is the number of elements in `nums`\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n`O(m)` where `m` is the number of queries\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nfrom collections import deque\nclass Solution:\n def maxRemoval(self, nums: List[int], queries: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n # Maintain a queue of sorted queries based on l from [l,r]\n q= deque(sorted(queries))\n # list to maintain max heap\n h = []\n selected =[]\n ans = 0\n # print(q)\n for i in range(len(nums)):\n # First pull out those queries for which l <= i \n # and put it\'s r into max-heap\n while q and q[0][0] <= i:\n heapq.heappush(h,-q.popleft()[1])\n\n # Before consideration, remove those r\'s from\n # selected array which are less than i ( outside the range)\n while selected and selected[0]<i:\n heapq.heappop(selected)\n \n # the number of r\'s in selected are now greater\n # than i, signifying possibility of using those\n\n # Now you can select the largest r\'s from max-heap\n # to be put into selected, in the middle if we find ineligible\n # r, return -1\n while nums[i] > len(selected):\n if h and -h[0] >= i:\n # print(-h[0],i)\n heapq.heappush(selected,-heapq.heappop(h))\n \n ans += 1\n else:\n return -1\n # ans represents minimum number of queries\n return len(queries)-ans\n\n \n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
[C++] Priority queue
|
c-priority-queue-by-bora_marian-g6cd
|
To efficiently process the queries that finish the latest:\n1. Use a priority queue to store the queries, prioritizing those that finish the latest.\n1. Apply a
|
bora_marian
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-29T15:49:31.871709+00:00
|
2024-11-29T15:49:31.871739+00:00
| 252 | false |
To efficiently process the queries that finish the latest:\n1. Use a priority queue to store the queries, prioritizing those that finish the latest.\n1. Apply a line sweep algorithm to keep track of the number of queries ending at each point:\n - For each query\'s end time, add \u22121 to represent the decrement in the active query count.\n - This approach ensures that the queries with later end times are processed first, while the line sweep manages the active query counts dynamically.\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n int n = nums.size(), qsz = queries.size();\n sort(queries.begin(), queries.end());\n priority_queue<int>pq;\n vector<int>sweep(n + 1, 0);\n int ind = 0, cs = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n cs += sweep[i];\n while (ind < qsz && queries[ind][0] <= i) {\n pq.push(queries[ind][1]);\n ind++;\n }\n while (cs < nums[i] && !pq.empty() && pq.top() >= i) {\n cs++;\n sweep[pq.top() + 1]--;\n pq.pop();\n }\n if (cs < nums[i])\n return -1;\n }\n return pq.size();\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Easy explanation (segment tree) CPP
|
easy-explanation-segment-tree-cpp-by-jmd-j8xo
|
Explanation\nWe have an array nums and a list of queries in the form of [Left, Right]. Each query allows us to decrement the elements of nums in the range [Left
|
JMDcoder1
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-23T19:05:07.005230+00:00
|
2024-11-24T13:27:47.120368+00:00
| 347 | false |
# Explanation\nWe have an array nums and a list of queries in the form of [Left, Right]. Each query allows us to decrement the elements of nums in the range [Left, Right] by 1. The goal is to determine the minimum number of queries required to make all elements in nums less than or equal to 0.\n\n\n# Intuition\n**1. Sorting the Queries**:\nIf we sort the queries based on Left, our greedy choice would be to select the query with the longest range (i.e., the maximum Right) that can affect the current index.\n\n**2. Valid Queries:**\nFor an element nums[n], only queries with Left \u2264 n and Right >= n can modify its value.\n# Approach\n**1. Using a Segment Tree:**\n\n- Create a segment tree to store the values of nums in its leaf nodes.\nImplement two additional functions:\n- One to decrement a range [L, R].\nAnother to fetch the current value of nums at any index after applying all modifications.\n\n**2. Sorting the Queries:**\n\nSort the queries first by Left in ascending order.\nFor queries with the same Left, sort them by Right in descending order.\n\n**3. Processing Each Index:**\n\nFor each index i in nums:\nPush the Right values of all queries where Left \u2264 i into a priority queue (max-heap).\nThe priority queue ensures that the query with the maximum range (Right) is processed first, providing maximum coverage.\n\n**4. Decrementing the Value:**\n\nWhile nums[i] > 0, repeatedly pop the top element of the priority queue and use the corresponding query to decrement nums[i].\nUpdate the range [i, Right] in the segment tree.\n\n**5. Edge Cases:**\n\nIf the priority queue becomes empty and nums[i] > 0, it is impossible to decrement the value further, so return -1.\n\n**6. Result Calculation:**\n\nCount the number of queries used and return queries.size() - count as the final result.\n# Complexity\n**Time Complexity:**\n\n**Sorting queries :** O(qlogq), where q is the number of queries.\n**Maintaining the priority queue:** O(nlogq), as each index can push and pop elements.\n**Segment tree operations:**(build and update): \uD835\uDC42(\uD835\uDC5Blog \uD835\uDC5B).\n**Overall complexity:** \uD835\uDC42((\uD835\uDC5B+\uD835\uDC5E)log max(n,q)).\n\n**Space Complexity:**\n\n**Segment tree:** O(n).\n**Priority queue:** O(q).\n**Total:** O(n+q).\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass ST { // Segment tree class\npublic:\n vector<int> tree;\n vector<int> ltree; // Lazy tree for lazy propagation\n\n ST(int n) {\n tree.resize(4 * n);\n ltree.resize(4 * n, 0);\n }\n\n void build(int ind, int left, int right, vector<int>& nums) {\n if (left == right) {\n tree[ind] = nums[left]; // Leaf node stores nums[i]\n return;\n }\n int mid = (left + right) / 2;\n build(2 * ind + 1, left, mid, nums); // Recursive call\n build(2 * ind + 2, mid + 1, right, nums);\n tree[ind] = max(tree[2 * ind + 1], tree[2 * ind + 2]);\n }\n\n void propagate(int ind, int left, int right) { // Lazy propagation\n if (ltree[ind] != 0) {\n tree[ind] -= ltree[ind];\n if (left != right) {\n ltree[2 * ind + 1] += ltree[ind];\n ltree[2 * ind + 2] += ltree[ind];\n }\n ltree[ind] = 0;\n }\n }\n\n void operation(int ind, int left, int right, int L, int R, int val) { // Update range [L, R]\n propagate(ind, left, right);\n if (R < left || L > right) return;\n if (L <= left && right <= R) {\n tree[ind] -= val;\n if (left != right) {\n ltree[2 * ind + 1] += val;\n ltree[2 * ind + 2] += val;\n }\n return;\n }\n int mid = (left + right) / 2;\n operation(2 * ind + 1, left, mid, L, R, val);\n operation(2 * ind + 2, mid + 1, right, L, R, val);\n tree[ind] = max(tree[2 * ind + 1], tree[2 * ind + 2]);\n }\n\n int value(int ind, int left, int right, int val) { // Get updated value at index val\n propagate(ind, left, right);\n if (val < left || val > right) return INT_MAX;\n if (left == right) return tree[ind];\n int mid = (left + right) / 2;\n return min(value(2 * ind + 1, left, mid, val), value(2 * ind + 2, mid + 1, right, val));\n }\n};\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n static bool comp(const vector<int>& a, const vector<int>& b) {\n if (a[0] != b[0]) return a[0] < b[0];\n return a[1] > b[1];\n }\n\n int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& q) {\n sort(q.begin(), q.end(), comp); // Sort queries\n priority_queue<int> pq; // Store the right-most value of queries\n int n = nums.size();\n ST st(n);\n st.build(0, 0, n - 1, nums);\n\n int count = 0, pushed = -1; // Count of queries used, index of last pushed query\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n for (int j = pushed + 1; j < q.size(); j++) {\n if (q[j][0] != i) break;\n pq.push(q[j][1]);\n pushed = j;\n }\n while (st.value(0, 0, n - 1, i) > 0) { // Decrement until nums[i] \u2264 0\n if (pq.empty() || pq.top() < i) return -1;\n int end = pq.top();\n pq.pop();\n count++;\n st.operation(0, 0, n - 1, i, end, 1); // Update range [i, end]\n }\n }\n\n return q.size() - count;\n }\n};\n\n\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Greedy', 'Segment Tree', 'Recursion', 'Heap (Priority Queue)', 'C++']
| 2 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
[Java] Track cumulative effect and use PriorityQueue
|
java-track-cumulative-effect-and-use-pri-8ruy
|
Approach\n\n1. Let\'s sort the queries by starting point ascending and by ending point descending.\n2. Let\'s say we iterate over nums array. At the point i we
|
whoawhoawhoa
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-23T16:01:12.930139+00:00
|
2024-11-23T16:11:18.812279+00:00
| 717 | false |
# Approach\n\n1. Let\'s sort the queries by starting point ascending and by ending point descending.\n2. Let\'s say we iterate over nums array. At the point $$i$$ we have an option to cover it with some queries. Let\'s greedy pick the query with farthest ending point to minimize the query usage.\n3. How to understand that the nums[i] is covered? Let\'s keep track of cumulative effect by used queries. To update this array faster we update it similar to prefix sum at every index.\n\nCheck the code comments for more insights.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n$$O(n*log(n) + m)$$\n\n- Space complexity:\n$$O(m + n)$$\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int maxRemoval(int[] nums, int[][] queries) {\n // need to iterate over queries with starting point asc\n Arrays.sort(queries, (a, b) -> a[0] == b[0] ? b[1] - a[1] : a[0] - b[0]);\n int[] effect = new int[nums.length + 1];\n int res = 0;\n // here we store active queries which we can use to cover nums[i]\n Queue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> b[1] - a[1]);\n int j = 0; // queries index\n // now for each index\n for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {\n // queries we can no longer use\n while (!pq.isEmpty() && pq.peek()[1] < i) {\n pq.poll();\n }\n\n // same here, moving j over unused queries\n while (j < queries.length && queries[j][1] < i) {\n j++;\n }\n\n // while our cumulative effect is less than the effect we need\n while (effect[i] < nums[i]) {\n boolean used = false;\n // all the queries we can potentially use go to queue\n while (j < queries.length && queries[j][0] <= i) {\n pq.add(queries[j]);\n j++;\n }\n // why we can use some query\n if (!pq.isEmpty()) {\n int[] tmp = pq.poll();\n // can\'t use it - went over its ending\n if (tmp[1] < i) {\n continue;\n }\n // now let\'s add cumulative effect\n effect[i]++;\n // at this point query ends and we need to take back the effect\n effect[tmp[1] + 1]--;\n res++; // using the query\n used = true;\n }\n // if we can\'t cover the i - we\'re out\n if (!used) {\n return -1;\n }\n }\n // works as prefix sum to cover the ending queries\n effect[i + 1] += effect[i];\n }\n // everything unused is what we can throw off\n return queries.length - res;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Greedy', 'Heap (Priority Queue)', 'Java']
| 2 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Detailed C++ Explanation with best Time complexity
|
detailed-c-explanation-with-best-time-co-fkjv
|
First Thoughts on the ProblemOn first glance it feels like a binary search or two pointers solution like part 2 of the problem, but here we can choose any queri
|
Devansh_shankhdhar
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-13T10:41:15.302876+00:00
|
2025-03-13T10:41:15.302876+00:00
| 212 | false |
# First Thoughts on the Problem
On first glance it feels like a binary search or two pointers solution like part 2 of the problem, but here we can choose any queries. For example, In part 2 if i have to choose 4 queries i can check using binary search as they would be the first 4 queries, but here i can choose any 4 queries and i just have to minimize the number of queries used to convert the array into a zero array. So we would indded go into a greedy direction here. Let's see how....
# Recommendation
Before proceeding: Highly recommend solving the part 2 of this problem in the optimal way using 2 pointers.. else this explanation would be tough to take.
Also Highly recommend having a pen and copy while understanding the problem.. and doing dry run along with the explanation
# Intution
See first thing to observe is that to bring a value down to 0 in the given array, would need that index to be a part of atleast
nums[i] queries because each query can atmost take the value down by 1. Now if i want to choose which query should be the one taking the value down, i would obviously choose the one whose r(or ending index) is the farthest to the right as this will help in taking the values lying further ahead to 0.
So that was the greedy intution for the problem..
# Detailed Approach
***Step 1:*** First we create the difference array which we create to mark the queries. i.e if a query come with (l,r), we mark dif[l]++ and dif[r+1]--; This indicates that the values from l to r has been increased by 1 and to nullify the effect on further numbers we place -1 on r+1. The size of this dif array will be (n+1);
***Step 2:*** We then sort our queries array on basis of left index because when we will iterate from left to right, we must know which are the queries that can be used now and in future..
***Step 3:*** We would need a priority_queue (or maxheap) to store the potential queries. Now why a maxheap?? Because since we always try to choose a query with the farthest right index and this farthest index can be given to us by the maxheap.
***Step 4:*** We iterate through the entire array. On reaching the index i, we will iterate through the queries array and all the queries which have their left index less than or equal to i become the potential candidates and so we store their right indices in our maxheap. We move j to prevent doing this again and again and prevent O(n^2);
***Step 5:*** The variable sum is keeping track of how many queries are currently active for the index we are at. When we reach a index dif[i] will be 0;
Now if the value of sum is less than nums[i], it means the index as not yet been covered fully. So we start taking the elements out from the maxheap and if the maxheap gets empty in the process ,we straightaway return -1(because we cant find enough queries to cover for this index). Also if the value of element coming out from the maxheap is less than the current index, we discard it as that means that the query's range has ended before this index only.
If we pick a query, we mark dif[current_index]++, as this will help increase value of sum+dif[i] and also mark dif[r+1]-- as when our sum crosses that index, it gets reduced by 1 and the calculationsgo ahead correctly.
***Step 6:*** After doing for the index, we add the value of dif[i] to sum,as this will help in the future iterations and if the length of my query finishes it will automatically get subtracted form the sum using the values to dif[r];
***Step 7:*** The final step is to just return queries.size()-cnt, where cnt tracks the minimum number of required queries and this will give the maximum queries that can be removed...
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& q) {
int n=nums.size();
int sz=q.size();
sort(q.begin(),q.end());
vector<int>dif(n+1);
int sum=0;
int j=0;
priority_queue<int>pq;
int cnt=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
while(j<sz && q[j][0]<=i){
pq.push(q[j][1]);
j++;
}
while(sum+dif[i]<nums[i]){
if(pq.empty()){
return -1;
}
int a=pq.top();
pq.pop();
if(a>=i){
dif[i]++;
dif[a+1]--;
cnt++;
}
}
sum+=dif[i];
}
return sz-cnt;
}
};
```
# Do Upvote and Comment down the suggestions to make the explanations better!!
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Greedy', 'Sorting', 'Heap (Priority Queue)', 'Prefix Sum', 'C++']
| 1 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Heap with Linesweep Solution (With Complete Intuition, Approach and Explanation!!!)
|
heap-with-linesweep-solution-with-comple-yalr
|
IntuitionWe have to greedily find which queries can be used.
If there are multiple queries which can be used, the best one to be used would be the one which can
|
jashgandhi
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-06T07:19:57.735296+00:00
|
2025-01-06T07:19:57.735296+00:00
| 101 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
We have to greedily find which queries can be used.
If there are multiple queries which can be used, the best one to be used would be the one which can add values to a larger length of array (query having q[1] larger at same starting point)
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
To employ such format, we push all the queries in the queue, sorting them by their first index.
Whenever we are at an index, we push all the queries that **can be used for current index** in a heap, sorting them by ending index in reverse. Hence, if we have 2 queries (0,4) and (0,6), we would employ (0,6) first so that our query covers a larger set.
Via linesweep, we also store the count to be reduced once our current query's limit ends.
2 exception cases:
1. If the number is larger than the count of queries already used and the heap is empty(signifying no more queries can be used for current index), we return -1 saying we cannot convert current array to all 0.
2. If the value we pop from the heap, ends before the current index, such queries weren't used earlier, and hence, such queries can be skipped [the queries left over in the heap at the end of the traversal, are also the ones which can be counted as skipped]
# Complexity
- Time complexity: O(N+QlogQ)
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(n) would be for iterating over the array. O(QlogQ) for sorting the queries.
And also, at max we might insert Q queries in the heap and pop them. Their time will also be O(QlogQ). This will be the total time, and not specific to one index. Hence, the time complexity wont be O(N*QlogQ) but O(N+QlogQ)
- Space complexity: O(N+Q)
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
Space taken by queue will be O(Q) and space taken by heap will be O(Q)
Linesweep will need O(N).
Hence, total space required will be O(N+Q)
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def maxRemoval(self, nums: List[int], queries: List[List[int]]) -> int:
q = deque(sorted(queries))
c=0
sub=[0 for _ in range(len(nums)+1)]
countOfQueriesUsed = 0
heap=[]
for i in range(len(nums)):
c-=sub[i]
while q and q[0][0]==i:
heapq.heappush(heap,-q.popleft()[1])
while nums[i]>c:
#we will have to use heap
if not heap:
return -1
last = -heapq.heappop(heap)
if last<i:
continue
else:
c+=1
sub[last+1]+=1
countOfQueriesUsed+=1
#queries not used will be in heap
return len(queries)-countOfQueriesUsed
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Iterators using 2 heaps | 42ms
|
iterators-using-2-heaps-42ms-by-stevenyl-mshj
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
stevenylai
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-27T07:40:11.919095+00:00
|
2024-12-27T07:40:11.919095+00:00
| 7 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```rust []
impl Solution {
pub fn max_removal(nums: Vec<i32>, queries: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
use std::collections::{VecDeque, BinaryHeap};
use std::cmp::Reverse;
let mut queries = VecDeque::from(queries);
queries.make_contiguous().sort_unstable();
let mut avail = BinaryHeap::<usize>::new();
let mut working = BinaryHeap::<Reverse<usize>>::new();
let found = nums
.into_iter()
.enumerate()
.scan(true, |f, (i, n)| {
if ! *f {
return None;
}
while queries.front().is_some_and(|q| q[0] as usize <= i) {
avail.push(queries.pop_front().unwrap()[1] as usize);
}
while working.peek().is_some_and(|&Reverse(end)| end < i) {
working.pop();
}
while n as usize > working.len() {
if avail.peek().is_some_and(|&end| end >= i) {
working.push(Reverse(avail.pop().unwrap()));
} else {
*f = false;
return Some(false);
}
}
Some(true)
})
.last()
.unwrap();
if !found {-1} else {avail.len() as i32}
}
}
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Rust']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Problem intuition explained, with step by step breakdown C++| Greedy | multiset
|
problem-intuition-explained-with-step-by-3vbx
|
Tricks\nFix current index at one end and think either about indices in front or indices behind it.\nThis approach will help us maximise answer in one direction.
|
pheonixarmvel
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-28T10:34:49.031393+00:00
|
2024-11-28T10:50:50.978740+00:00
| 122 | false |
# Tricks\nFix current index at one end and think either about indices in front or indices behind it.\nThis approach will help us maximise answer in one direction.\n\nEg if we want to maximise impact on future choices, we assume all indices before current index are taken care of.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\nselect 0th index,\nselect all queries applicable on 0th index.\n--> few of these queries will be chosen to make nums[0] == 0\n--> since we are sure all queries start with 0, we have no use for starting index of queries\n--> store all applicable queries end index in **validQ**\n\nnow out of **validQ** we need to choose endIndex,\nlets store these chosen end indices in **activeQ**\n\n--> We want to choose such end indices from validQ which covers maximum possible upcoming indices.\n-->This is because we want to use up lesser queries to make upcoming indices 0. \n\nTherefore validQ needs to be sorted in descending order, so that farthest end index is chosen first. Hence multiset sorted in decending order.\n\nchoose top "nums[0]" values from **activeQ** and transfer to **validQ** and remove chosen values from activeQ.\nnote:\n--> if "nums[0]" values are not available in activeQ means we cannot reduces nums[0] to 0.\n\n\n--> nums[0] is now 0 : YAY!!\n\n\nwe have chosen indices and stored **validQ** with criteria to reuse them for the next nums elements, \nbut few of them are not valid as their query range ended at 0th index,\ntherefore we remove those **validQ** entries. \nwe use ascending order multiset to optimise this removal operation\n\nmove to next index:\nperform above operations for nums[1],\nwe dont worry about nums[0] as we are sure that it is 0.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n\n sort(queries.begin(), queries.end());\n int j = 0;\n multiset<int, greater<>> activeQ;\n multiset<int> validQ;\n int usedCount = 0;\n\n\n for(int i=0; i<nums.size(); i++){\n\n while(j<queries.size() and queries[j][0] == i){\n activeQ.insert(queries[j][1]);\n j++;\n }\n \n nums[i]-=validQ.size();\n \n \n while(nums[i]>0 and !activeQ.empty() and *activeQ.begin() >= i){\n \n validQ.insert(*activeQ.begin());\n activeQ.erase(activeQ.begin());\n \n nums[i]--;\n usedCount++;\n\n }\n \n if(nums[i]>0){\n return -1;\n }\n\n while(!validQ.empty() && (*validQ.begin() == i)){\n validQ.erase(validQ.begin());\n }\n\n }\n\n return queries.size() - usedCount;\n\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Greedy', 'Heap (Priority Queue)', 'C++']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Python3 - Two heaps
|
python3-two-heaps-by-dkravitz78-v25o
|
Keep track of 2 heaps. The first one "endings" is all b from queries [a,b] which will tell you how far you can go and still decrement. Note that values in endi
|
dkravitz78
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-25T20:19:23.760920+00:00
|
2024-11-25T20:19:23.760941+00:00
| 61 | false |
Keep track of 2 heaps. The first one "endings" is all `b` from queries `[a,b]` which will tell you how far you can go and still decrement. Note that values in endings are not used .. yet .. it\'s just where we store them. At any time we actually need to use a query, we will take the one with the furthest possible ending to get the maximum benefit beyond this current round.\n\nThe second heap is "used" which is all queries we have actually used. Again we only need the second value. If for example we are at index 5 then anything in used with an ending index >=5 wil allow us to decrease 1 from `n`.\n\nWith these heaps, simply loop through the array. Say you\'re at index `i`, anything before index `i` in used is no longer relevant so get rid of it. Anything remaining lets you decrement `n` by 1.\nIf you did this and still need to decrement `n`, keep popping queries with the furthest possible ending whose start is `<=i`. \nIf you use query `[a,b]` for some `a<=i` then you can push `i` onto `used` but you do have to subtract one from `ret` as you have now used another query. \n```\nclass Solution:\n def maxRemoval(self, nums: List[int], queries: List[List[int]]) -> int: \n queries = sorted(queries)[::-1]\n endings = []\n heapq.heapify(endings)\n used = []\n heapq.heapify(used)\n\n ret = len(queries)\n\n for i,n in enumerate(nums):\n while used and used[0]<i:\n heapq.heappop(used)\n n-=len(used)\n \n while queries and queries[-1][0]<=i:\n heapq.heappush(endings, -queries.pop()[1])\n \n while n>0 and endings and -endings[0]>=i:\n heapq.heappush(used,-heapq.heappop(endings))\n ret-=1\n n-=1\n \n if n>0: return -1\n \n return ret\n ```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
BEATS 100% USERS || VIDEO EXPLANATION || EASY EXPLANATION || C++
|
beats-100-users-video-explanation-easy-e-zfe5
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nVIDEO EXPLANATION - https://youtu.be/RVhEpnVX0jE \n# Approach\n Describe your approach
|
rsaisiddhu1106
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-25T16:47:40.954952+00:00
|
2024-11-25T16:47:40.954991+00:00
| 74 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nVIDEO EXPLANATION - https://youtu.be/RVhEpnVX0jE \n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n // SORTING the queries\n sort(queries.begin(),queries.end());\n\n // STORING the queries\n priority_queue<int> requiredQueries;\n priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> chosenQueries;\n\n int ans = 0; // to store the min no of queries\n int n = nums.size();\n int j = 0;\n\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n // iterate through queries & consider those having val equal to i\n while(j<queries.size() && queries[j][0]==i){\n requiredQueries.push(queries[j][1]);\n j++;\n }\n\n //REMOVE the size of already chosen queries from nums[i]\n nums[i]-=chosenQueries.size();\n\n while(nums[i]>0 && !requiredQueries.empty() && requiredQueries.top()>=i){\n ans++;\n chosenQueries.push(requiredQueries.top());\n // REMOVAL of used queries\n requiredQueries.pop();\n nums[i]--;\n }\n\n if(nums[i]>0) return -1; // queries are not enough to make nums as zero array so returning -1\n\n // REMOVAL of unwanted / eliminated queries\n while(!chosenQueries.empty() && chosenQueries.top()<=i){\n chosenQueries.pop();\n }\n }\n\n return queries.size()-ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 1 |
['C++']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Greedy approach
|
greedy-approach-by-ttn628826-0esw
|
Approach\n\n## Step 1: Preprocess Queries\n\nThe queries are sorted by their starting index ($l_i$) to ensure they are processed in increasing order of their ap
|
ttn628826
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-23T17:48:08.549043+00:00
|
2024-11-23T17:48:40.373777+00:00
| 214 | false |
# Approach\n\n## Step 1: Preprocess Queries\n\nThe queries are sorted by their starting index ($l_i$) to ensure they are processed in increasing order of their application range. This allows the program to efficiently add queries to the "available" queue ($availableEndIndices$) as it processes each index in $nums$.\n\n## Step 2: Manage Queries with Heaps\n\nThe code uses two priority queues to handle queries:\n\n- $availableEndIndices$ (Max-Heap):\n - This heap contains the end indices ($r_i$) of queries that could potentially be used at the current position in $nums$.\n - Queries are added to this heap when their starting index ($l_i$) matches the current position being processed.\n - The largest $r_i$ is at the top, ensuring that the code prioritizes the longest-range queries first, which are more likely to remain useful in subsequent steps.\n\n- $activeEndIndices$ (Min-Heap):\n - This heap contains the end indices ($r_i$) of queries currently being used to decrement $nums$.\n - These queries are removed from the heap when their range expires (i.e., when the current index matches their end index).\n\n## Step 3: Process Each Position in $nums$\n\n- For each position $i$ in $nums$, the value of $nums[i]$ is first reduced by the size of the $activeEndIndices$ heap, as each active query contributes a decrement of $1$ to $nums[i]$.\n- If $nums[i] > 0$ after this adjustment, the program attempts to use queries from $availableEndIndices$:\n - The largest available query (based on $r_i$) is moved to $activeEndIndices$ and contributes to decrementing $nums[i]$.\n - This process continues until $nums[i]$ is reduced to $0$ or no valid queries remain.\n- If $nums[i] > 0$ and no further queries can reduce it, the function returns $-1$ (it\'s impossible to make nums a zero array).\n\n## Step 4: Handle Expired Queries\n\nAfter processing $nums[i]$, queries in $activeEndIndices$ that expire at the current position ($i$) are removed from the heap. This ensures that only relevant queries remain in $activeEndIndices$, keeping the decrement count accurate for subsequent positions.\n\n## Step 5: Count Unused Queries\n\nThe total number of unused queries is calculated as:\n\n unused queries=total queries\u2212successful queries\n\nThis value is returned as the result.\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n // Priority queues to manage query processing\n priority_queue<int> availableEndIndices; // Max-heap for candidate queries\' end indices\n priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<>> activeEndIndices; // Min-heap for active queries\' end indices\n\n // Sort queries by their starting indices\n sort(queries.begin(), queries.end());\n\n int successfulQueries = 0; // Count of queries successfully used\n int queryPointer = 0; // Tracks the current query being processed\n\n // Process each position in nums\n for (int index = 0; index < nums.size(); ++index) {\n // Add all queries starting at the current index to the available queue\n while (queryPointer < queries.size() && queries[queryPointer][0] == index) {\n availableEndIndices.push(queries[queryPointer][1]);\n ++queryPointer;\n }\n\n // Adjust the current number by subtracting the count of active queries\n nums[index] -= activeEndIndices.size();\n\n // Use candidate queries to fulfill the current position\'s requirement\n while (nums[index] > 0 && !availableEndIndices.empty() && availableEndIndices.top() >= index) {\n ++successfulQueries;\n activeEndIndices.push(availableEndIndices.top()); // Move query from available to active\n availableEndIndices.pop();\n --nums[index];\n }\n\n // If the current position cannot be zeroed out, return -1\n if (nums[index] > 0)\n return -1;\n\n // Remove expired queries from the active queue\n while (!activeEndIndices.empty() && activeEndIndices.top() == index)\n activeEndIndices.pop();\n }\n\n // Return the number of queries that can be removed\n return queries.size() - successfulQueries;\n }\n};\n\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Easy solution with two heaps and greedy algorithm to solve in 143ms with C++ beat 100%
|
easy-solution-with-two-heaps-and-greedy-iz0nk
|
Intuition\nTo maximize utilization of query, each time we need to choose the query which have farthest ending point.\n\n# Approach\nThere is two heaps. \nOne is
|
william6715
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-23T17:17:14.946039+00:00
|
2024-11-23T17:19:14.226524+00:00
| 217 | false |
# Intuition\nTo maximize utilization of query, each time we need to choose the query which have farthest ending point.\n\n# Approach\nThere is two heaps. \nOne is max heap to record the candidate who can be use at index i. (Record its ending point)\nAnother one is min heap to record the query\'s ending point which we actually choose it to minus the nums.\n\n**Approach** \nWhen we trace to the index i, w\n1. We will put the query j into the candidate first when the query j\'s starting point is touched.\n2. [Greedy] We choose the query with maximum ending point in the candidate to add **cur** parameter until cur == val. (Because choosing any other query will reduce the impact on future indexes) And also record the choosing query\'s ending point to the end heap.\n3. Early return when cur < val because there is no enough query to reduce the nums[i].\n4. Pop the query if the ending point is at i.\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(n+ mlogm), n is nums size, m is queries size\n\n- Space complexity:\nO()\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n sort(queries.begin(), queries.end());\n int ind = 0;\n int n = nums.size();\n int cur = 0; // current index minus value\n priority_queue<int> cand; \n priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> end;\n for(int i=0; i<n; ++i){\n int val = nums[i];\n // put query into candidate\n while(ind < queries.size() && queries[ind][0] == i){\n cand.push(queries[ind][1]);\n ++ind;\n }\n // Use the candidate to be minus value\n while(cur < val && !cand.empty() && cand.top() >= i){\n ++cur;\n end.push(cand.top());\n cand.pop();\n }\n if(cur < val)\n return -1; // does not have enough candidate\n // remove the minus value when touch the end\n while(!end.empty() && end.top() == i){\n --cur;\n end.pop();\n }\n }\n return cand.size();\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
SOLVED IT JUST AFTER THE CONTEST 😭😭
|
solved-it-just-after-the-contest-by-chit-fihm
|
Code\npython3 []\nclass Solution:\n def maxRemoval(self, nums: List[int], queries: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n ans = 0\n q = sorted(queries)\n
|
chitraksh24
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-23T16:14:19.369597+00:00
|
2024-11-23T16:14:19.369621+00:00
| 488 | false |
# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def maxRemoval(self, nums: List[int], queries: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n ans = 0\n q = sorted(queries)\n e = defaultdict(int)\n curr = 0\n for i, num in enumerate(nums):\n if num<=curr:\n curr -= e[i]\n continue\n p = []\n for j, pq in enumerate(q):\n if pq[0]>i:\n break\n if pq[1]>=i:\n p.append((pq[1],j))\n p.sort(key = lambda x:-x[0])\n index = set()\n while p and q and num > curr:\n ind = p.pop(0)[1]\n x,y = q[ind]\n index.add(ind)\n if x>i:\n break\n if y<i:\n continue\n ans += 1\n curr += 1\n e[y] += 1\n q = [q[i] for i in range(len(q)) if i not in index]\n if num>curr:\n return -1\n curr -= e[i]\n return len(queries)-ans\n \n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'Sorting', 'Python3']
| 1 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Use just enough queries for each index
|
use-just-enough-queries-for-each-index-b-j0nz
|
\nimport heapq\n\nclass FenwickTree:\n def __init__(self, x):\n self.bit = x\n for i in range(len(x)):\n j = i | (i + 1)\n
|
theabbie
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-23T16:02:25.267742+00:00
|
2024-11-23T16:02:25.267765+00:00
| 357 | false |
```\nimport heapq\n\nclass FenwickTree:\n def __init__(self, x):\n self.bit = x\n for i in range(len(x)):\n j = i | (i + 1)\n if j < len(x):\n x[j] += x[i]\n\n def update(self, idx, x):\n while idx < len(self.bit):\n self.bit[idx] += x\n idx |= idx + 1\n\n def query(self, end):\n x = 0\n while end:\n x += self.bit[end - 1]\n end &= end - 1\n return x\n\nclass Solution:\n def maxRemoval(self, nums: List[int], queries: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n n = len(nums)\n queries.sort()\n dec = FenwickTree([0] * n)\n i = 0\n heap = []\n res = len(queries)\n for j in range(n):\n while i < len(queries) and queries[i][0] <= j:\n heapq.heappush(heap, (-queries[i][1], queries[i][0]))\n i += 1\n while nums[j] - dec.query(j + 1) > 0 and heap:\n res -= 1\n x = heapq.heappop(heap)\n l, r = x[1], -x[0]\n dec.update(l, 1)\n dec.update(r + 1, -1)\n if nums[j] - dec.query(j + 1) > 0:\n return -1\n \xA0 \xA0 \xA0 \xA0return res \n```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Best explained solution
|
best-explained-solution-by-wkzb0vzqfy-r0ry
|
Code
|
wkzB0vzQFy
|
NORMAL
|
2025-04-04T14:02:50.100937+00:00
|
2025-04-04T14:02:50.100937+00:00
| 6 | false |
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
// Logic:
// For each nums[idx] while traversing nums:
// -> there will be some queries which already might have efefcted nums[idx] -> chosen_options
// -> there will be some available queries which have not been explored yet -> available_options
// -> if chosen_options did not reduce nums[idx] to 0, we explore available_options optimally
// -> from available_options choose the option which have the max right_value (use max_heap)
// before all this we sort queries so that we are sure that queries are processed in order
int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {
sort(queries.begin(), queries.end());
// available_options -> stores the right_value for all the queries with effects nums[i]
priority_queue<int> available_options;
// chosen_options -> stores the right_value for all the queries we actually selected for
// nums[i] from available options
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> chosen_options;
// queries_used -> stores the number of queries actually used
int queries_used = 0;
// query_idx -> stores the index that will be processed in queries array
int query_idx = 0;
for(int idx = 0; idx < (int) nums.size(); idx++) {
// for every nums[idx]:
// we push right_values of all the queries which effect nums[idx] into available_options
// Doubt: Why queries[query_idx][0] == idx?
// As we sorted the queries the array, if we have observed any query whose left_value < idx,
// that query's right_value will already be present in available_options (if not chosen),
// or in chosen_options (if chosen).
// for any query, q whose left_value < idx < right_value, q will already be present in the
// queues as q would have been already processed. -> advantage of sorting the queires array
while(query_idx < (int) queries.size() && queries[query_idx][0] == idx) {
available_options.push(queries[query_idx][1]);
query_idx++;
}
// for this idx we might have already chosen some options
nums[idx] -= chosen_options.size();
// if nums[idx] is still not 0, we explore available options
while(nums[idx] > 0 && !available_options.empty() && available_options.top() >= idx) {
// we used one query
queries_used++;
// the advantage of using max priority queue is that, we are sure this right_value
// is the farthest available -> optimal choice
// we transfer this right_value from available_options to chosen_options
chosen_options.push(available_options.top());
available_options.pop();
// reduce nums[idx]
nums[idx]--;
}
// if all available_options exhaust but nums[i] > 0 -> not possible to make zero array
if(nums[idx] > 0) return -1;
// from chosen_options we remove redundant right_values -> remove right_value <= i
// hence chosen_opions is a min heap
while(!chosen_options.empty() && chosen_options.top() == idx) chosen_options.pop();
}
return (int) queries.size() - queries_used;
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
A swift solution
|
a-swift-solution-by-ramkrishnakunduece-uejo
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
O((n + q) * log q)
Space complexity:
Code
|
ramkrishnakunduece
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-28T11:30:42.443654+00:00
|
2025-03-28T11:30:42.443654+00:00
| 1 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
O((n + q) * log q)
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```swift []
class Solution {
func maxRemoval(_ nums: [Int], _ queries: [[Int]]) -> Int {
var queries = queries.sorted(by: { $0[0] < $1[0] })
var m = queries.count
var n = nums.count
var nums = nums
var maxHeap = PriorityQueue<Int>(sort: >)
var minHeap = PriorityQueue<Int>(sort: <)
var used = 0
var j = 0
for i in 0..<n {
while j < m && queries[j][0] == i {
maxHeap.enqueue(queries[j][1])
j += 1
}
nums[i] -= minHeap.count
while nums[i] > 0, let top = maxHeap.peek(), top >= i {
minHeap.enqueue(maxHeap.dequeue()!)
used += 1
nums[i] -= 1
}
if nums[i] > 0 {
return -1
}
while let top = minHeap.peek(), top == i {
minHeap.dequeue()
}
}
return m - used
}
}
// Priority Queue Implementation
struct PriorityQueue<T: Comparable> {
private var elements: [T] = []
private let sort: (T, T) -> Bool
init(sort: @escaping (T, T) -> Bool) {
self.sort = sort
}
var count: Int {
return elements.count
}
var isEmpty: Bool {
return elements.isEmpty
}
func peek() -> T? {
return elements.first
}
mutating func enqueue(_ element: T) {
elements.append(element)
siftUp(from: elements.count - 1)
}
mutating func dequeue() -> T? {
guard !elements.isEmpty else { return nil }
elements.swapAt(0, elements.count - 1)
let removed = elements.removeLast()
siftDown(from: 0)
return removed
}
mutating func remove(_ value: T) {
if let index = elements.firstIndex(of: value) {
elements.swapAt(index, elements.count - 1)
elements.removeLast()
if index < elements.count {
siftUp(from: index)
siftDown(from: index)
}
}
}
private mutating func siftUp(from index: Int) {
var child = index
var parent = (child - 1) / 2
while child > 0 && sort(elements[child], elements[parent]) {
elements.swapAt(child, parent)
child = parent
parent = (child - 1) / 2
}
}
private mutating func siftDown(from index: Int) {
var parent = index
let count = elements.count
while true {
let left = 2 * parent + 1
let right = 2 * parent + 2
var candidate = parent
if left < count && sort(elements[left], elements[candidate]) {
candidate = left
}
if right < count && sort(elements[right], elements[candidate]) {
candidate = right
}
if candidate == parent {
return
}
elements.swapAt(parent, candidate)
parent = candidate
}
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Swift']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
A swift Solution
|
a-swift-solution-by-ramkrishnakunduece-l219
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
O((n + q)*logq)
Space complexity:
Code
|
ramkrishnakunduece
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-28T11:29:20.105258+00:00
|
2025-03-28T11:29:20.105258+00:00
| 1 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
O((n + q)*logq)
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
public int maxRemoval(int[] nums, int[][] queries) {
final int n = nums.length;
final int m = queries.length;
Arrays.sort(queries, (a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
final PriorityQueue<Integer> minHeap = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> a - b);
final PriorityQueue<Integer> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> b - a);
int used = 0;
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < n; i++) {
while(j < m && queries[j][0] == i) {
maxHeap.add(queries[j++][1]);
}
nums[i] -= minHeap.size();
while(nums[i] > 0 && !maxHeap.isEmpty() && maxHeap.peek() >= i) {
minHeap.add(maxHeap.remove());
used++;
nums[i]--;
}
if (nums[i] > 0) return -1;
while(!minHeap.isEmpty() && minHeap.peek() == i) {
minHeap.remove();
}
}
return m - used;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
🔥 Most optimal solution. Beat 100%. 𝑂(𝑛+𝑚log(𝑚))
|
most-optimal-solution-beat-100-onmlogm-b-xllm
|
ApproachWe use a line sweep + max heap technique.
First, we group all queries by their start index using a hashmap edges.
We maintain a heap that stores the end
|
charleswong28
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-22T14:07:36.851259+00:00
|
2025-03-22T14:07:36.851259+00:00
| 7 | false |
# Approach
We use a line sweep + max heap technique.
- First, we group all queries by their start index using a hashmap edges.
- We maintain a heap that stores the end indices of active queries, pushed as negative values to simulate a max-heap (since Python's heapq is a min-heap).
- We iterate through each index i in nums:
- If any query starts at i, push its end into the heap.
- Track how many active decrements are available at i using a prefix sum array lines and a running current counter.
- While the available current is less than nums[i], we pop the latest-ending query from the heap to cover i, and mark its expiry in lines using lines[end + 1] -= 1.
- If at any point no valid query can cover i, return -1.
- After processing all indices, the queries left in the heap are unused. We return their count as the maximum number of removable queries.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
𝑂(𝑚+𝑛+𝑚+𝑚log𝑚) => O(𝑛+𝑚log𝑚)
- 𝑂(𝑚) to build the edges map.
- 𝑂(𝑛) to iterate through nums.
- 𝑂(𝑚+𝑚log𝑚) for at most 𝑚 insertions and deletions in the heap. It's separated from n because it will add to current at most m times and push to heap at most m times
- Space complexity:
- 𝑂(𝑛+𝑚)
- 𝑂(𝑛) for the lines prefix sum array.
- 𝑂(𝑚) for the edges map and heap storage.
# Code
```python3 []
# Line sweep + max heap
# TC: O(m + n + m + mlog(m)) => O(n + mlog(m))
# 1. m - to creat edges
# 2. n - loop nums
# 3. m + mlog(m) - separated from n because it will add to current
# at most m times and push to heap at most m times
# SC: O(n + m)
class Solution:
def maxRemoval(self, nums: list[int], queries: list[list[int]]) -> int:
n, edges = len(nums), defaultdict(list)
for start, end in queries:
edges[start].append(end)
lines, heap, current = [0] * (n + 1), [], 0
for num_index, num in enumerate(nums):
if num_index in edges:
for end in edges[num_index]: heappush(heap, -end)
current += lines[num_index]
while current < num:
if not heap or -heap[0] < num_index: return -1
end = -heappop(heap)
current += 1
lines[end + 1] -= 1
return len(heap)
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
🚀 2-heap approach
|
2-heap-approach-by-charleswong28-l4mx
|
ApproachWe use a 2-heap approach:
Sort the queries based on their start time.
Iterate through each num at num_index in nums:
2.1 For each query starting on or b
|
charleswong28
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-22T13:23:02.517157+00:00
|
2025-03-22T13:23:02.517157+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Approach
We use a 2-heap approach:
1. Sort the queries based on their start time.
2. Iterate through each num at num_index in nums:
2.1 For each query starting on or before num_index, we push its end time into a max heap (using -end to simulate max-heap behavior).
2.2 We attempt to assign the current num task to a query interval in the max heap, respecting the constraint that a task needs num available slots.
2.3 We maintain a min heap of active end times for currently assigned intervals.
2.4 If the current num is larger than the number of available slots (heap size), it’s impossible to assign, so we return -1.
2.5 Also, we evict expired intervals from the min heap as we go.
The final answer is the number of queries we failed to use (m - result), where result tracks how many tasks were successfully assigned to a query interval.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
O(mlogm+nlogm)
Sorting the queries takes 𝑂(𝑚log𝑚), and for each of the 𝑛 elements in nums, we push/pop from heaps at most 𝑂(log𝑚) time.
- Space complexity:
O(m)
We store up to m elements in the heaps.
# Code
```python3 []
# 2 heaps approach. TC: O(mlogm + nlogm) SC: O(m)
class Solution:
def maxRemoval(self, nums: List[int], queries: List[List[int]]) -> int:
n, m, min_heap, max_heap, queries_index = len(nums), len(queries), [], [], 0
result = 0
queries.sort()
for num_index, num in enumerate(nums):
while queries_index < m and num_index >= queries[queries_index][0]:
_, end = queries[queries_index]
heappush(max_heap, -end)
queries_index += 1
while max_heap and len(min_heap) < num:
end = -heappop(max_heap)
if end >= num_index:
heappush(min_heap, end)
result += 1
if num > len(min_heap): return -1
while min_heap and min_heap[0] <= num_index:
heappop(min_heap)
return m - result
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
scala solution. SortedSet
|
scala-solution-sortedset-by-vititov-i8qj
| null |
vititov
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-20T13:20:49.954965+00:00
|
2025-03-20T13:20:49.954965+00:00
| 2 | false |
```scala []
object Solution {
import scala.collection.immutable.SortedSet
def maxRemoval(nums: Array[Int], queries: Array[Array[Int]]): Int = {
val qs = queries.map(a => (a.head,a.last)).sortBy(x => (x._1,-x._2))
def f(i:Int,j:Int,aSet:Set[(Int,Int)],bSet:Set[(Int,Int)],acc:Int): Int =
if(i>=nums.length) (qs.length-j)+acc+bSet.size
else if(j<qs.length && qs(j)._1<=i) f(i,j+1,aSet,bSet+((qs(j)._2,j)),acc)
else if(aSet.headOption.exists(_._1 < i)) f(i,j,aSet.tail,bSet,acc)
else if(aSet.size>=nums(i)) f(i+1,j,aSet,bSet,acc)
else if(bSet.headOption.exists(_._1 < i)) f(i,j,aSet,bSet.tail,acc+1)
else if(bSet.nonEmpty) f(i,j,aSet+bSet.last,bSet.init,acc)
else if(j>=qs.length || qs(j)._1>i) -1
else if(qs(j)._2<j) f(i+1,j,aSet,bSet,acc+1)
else f(i,j+1,aSet,bSet+((qs(j)._2,j)),acc)
f(0,0,SortedSet(),SortedSet(),0)
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Greedy', 'Sorting', 'Heap (Priority Queue)', 'Ordered Set', 'Scala']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
C++ | Sorting + PQ + Prefix Sum
|
c-sorting-pq-prefix-sum-by-kena7-97ym
|
Code
|
kenA7
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-15T07:37:09.604114+00:00
|
2025-03-15T07:37:09.604114+00:00
| 21 | false |
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& queries)
{
sort(queries.begin(), queries.end());
int queriesUsed=0,qi=0,qn=queries.size(),n=nums.size();
vector<int>prefix(n+1,0);
priority_queue<int>maxEnd;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
prefix[i]+=(i>0)?prefix[i-1]:0;
nums[i]-=prefix[i];
while(qi<qn && queries[qi][0]<=i)
{
maxEnd.push(queries[qi][1]);
qi++;
}
while(nums[i]>0 && !maxEnd.empty())
{
if(maxEnd.top()<i)
return -1;
prefix[i]++;
nums[i]--;
prefix[maxEnd.top()+1]--;
maxEnd.pop();
queriesUsed++;
}
if(nums[i]>0)
return -1;
}
return qn-queriesUsed;
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
O(nlgm + m) two heaps
|
onlgm-m-two-heaps-by-lilongxue-kibl
|
IntuitionGo thru nums. When we encounter an "unsettled" value, we look for the query with the furthest end to cover it.Approach
Use queries to build a hashmap s
|
lilongxue
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-06T16:42:30.928302+00:00
|
2025-02-06T16:53:01.185610+00:00
| 42 | false |
# Intuition
Go thru nums. When we encounter an "unsettled" value, we look for the query with the furthest end to cover it.
# Approach
1. Use queries to build a hashmap start2ends. It maps a single start to multiple ends.
2. Create a heap availEnds. It stores ends that have not been useds. It's a max-heap.
3. Create a heap activeEnds. It stores already-in-use ends. It's a min-heap.
4. Define a variable reduceBy whose initial value is 0. It means for val: nums encountered, how much can be reduced so far.
5. Go thru nums. For each iteration of the loop, we first add newly available ends to availEnds; and delete obsolete ends from activeEnds (and decrement reduceBy).
6. For the currently encountered val, we reduce it by reduceBy. If the remaining value is still > 0, we move available ends into active ends, and increment reduceBy.
7. If there are not enough available ends, return -1.
8. result = queries.length - totally activated ends.
9. When I finished the problem, I found that the variable reduceBy is not necessary. It can be safely replaced by activeEnds.size(). By deleting it, we can avoid maintaining that information.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
O(nlgm + m)
- Space complexity:
O(n + m)
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
public int maxRemoval(int[] nums, int[][] queries) {
int len = nums.length, size = queries.length;
HashMap<Integer, LinkedList<Integer>> start2ends =
new HashMap<Integer, LinkedList<Integer>>();
for (int[] query: queries) {
Integer start = query[0], end = query[1];
if (!start2ends.containsKey(start)) {
LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<Integer>();
list.add(end);
start2ends.put(start, list);
} else {
LinkedList<Integer> existing = start2ends.get(start);
existing.add(end);
}
}
PriorityQueue<Integer> availEnds = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(
(a, b) -> b - a
);
PriorityQueue<Integer> activeEnds = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(
(a, b) -> a - b
);
int kept = 0;
int reduceBy = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// add available ends here
if (start2ends.containsKey(i)) {
LinkedList<Integer> existing = start2ends.get(i);
for (Integer end: existing) {
availEnds.offer(end);
}
}
// delete obsolete active ends here
while (activeEnds.size() > 0) {
Integer top = activeEnds.peek();
if (top < i) {
activeEnds.poll();
reduceBy--;
}
else break;
}
int val = nums[i];
int rmg = val - reduceBy;
if (rmg > 0) {
if (availEnds.size() < rmg) return -1;
for (int j = 0; j < rmg; j++) {
Integer end = availEnds.peek();
// invalid end!!
if (end < i) return -1;
activeEnds.offer(availEnds.poll());
}
reduceBy += rmg;
kept += rmg;
}
}
int result = size - kept;
return result;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
min/max heap.
|
minmax-heap-by-rishiinsane-bdjs
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
O(n+mlogm)
Space complexity:
O(m)
Code
|
RishiINSANE
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-21T19:51:52.919466+00:00
|
2025-01-21T19:51:52.919466+00:00
| 17 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
O(n+mlogm)
- Space complexity:
O(m)
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {
int n = nums.size(), m = queries.size(), ans = 0, j = 0;
priority_queue<int> candidates;
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<>> chosen;
sort(queries.begin(), queries.end());
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
while (j < m && queries[j][0] == i) {
candidates.push(queries[j][1]);
j++;
}
nums[i] -= chosen.size();
while (nums[i] > 0 && !candidates.empty() &&
candidates.top() >= i) {
chosen.push(candidates.top());
candidates.pop();
ans++;
nums[i]--;
}
if (nums[i] > 0)
return -1;
while (!chosen.empty() && chosen.top() <= i) {
chosen.pop();
}
}
return m - ans;
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Double Heap Solution Explained Clearly
|
double-heap-solution-explained-clearly-b-uw9z
|
IntuitionThe problem involves optimally choosing queries for each nums[i]. To make a selection, we need to know the context-what are our available intervals for
|
omer18
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-14T22:47:34.058801+00:00
|
2025-01-14T22:47:34.058801+00:00
| 20 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
The problem involves optimally choosing queries for each nums[i]. To make a selection, we need to know the context-what are our available intervals for some index i, and how many existing intervals already cover it. In addition, suppose we have k existing intervals that cover point i but we need n more, how should we select remaining n intervals. You should make the observation that we definitely want to priortize intervals with the farthest end point because we can hold on to them as an existing interval the longest (thus less intervals to add in the long run).
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
We will use a candidates and chosen heap. The candidates heap will hold the context-the pool of intervals that are valid for each iteration. We will take from candidates to chosen to attempt to reduce a particular value in nums. It makes sense that that candidates should be a max heap since the best available interval is one with the largest (farthest) end point within that context. To do this in python, we add negative values to the min heap to have a max heap. As we traverse nums left to right, we add the next batch of available intervals that fit within this context to candidates. But there's another thing we have to worry about: what happens of the end time for a particular interval is up, how do we remove it? The good news is we don't have to worry about that. We handle it by carefully adding to our chosen heap which will be described later.
chosen is where we will store queries that we selected from candidates. We pop from candidates to insert into chosen. Similar to the candidates heap, we will need to eliminate intervals that go out of range for chosen. Except, we will explcitily be removing them with each iterations. So how do we find out which interval to remove? If we add the end point to chosen, and make it a min heap, then the top of the heap will always give us the interval with the earliest finish time. Therefore, we continue popping from chosen until the remaining elements are valid selections. Now we guranteed that chosen will only have valid query selection, so there's a case where thats enough, or we need to draw from the candidate pool.
Suppose we need more queries from candidates. Remember that we never removed intervals that are out of range, but that's okay because candidates is a max heap sorted by farthest end point. We will just acknowledge that if we continue popping from the candidates, the farthest end point will be less than our current position i. In which case, that is all valid intervals we could take from candidates.
Note that since we need to maximize the number of queries removed, that means each query we select has to be essential. So that means the size of chosen must never exceed nums[i], and thus if we are ever short, we stop as soon as we have as many querires as nums[i]. But there could always be the case that we have no candidates to choose from, or whatever candidates remain are out of bounds, so that marks an invalid solution. Our acutal solution will be the length of queries - added, where added is increment each time we take from candidate to add to chosen.
We will traverse nums from left to right, so it makes sense to sort the queries by soonest starting time so that we know the next set of available intervals with each iteration of the for loop.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(nlogn)
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(n)
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def maxRemoval(self, nums: List[int], queries: List[List[int]]) -> int:
queries.sort() #Sort by soonest start time
candidates = []
chosen = []
j = 0
ans = 0
for i in range(len(nums)):
while j < len(queries) and queries[j][0] <= i: # with each iteration, we will encounter new valid intervals, add them
heapq.heappush(candidates,-queries[j][1])
j+= 1
while chosen and chosen[0] < i: # remove out of range selected intervals
heapq.heappop(chosen)
size = len(chosen)
need = nums[i] - size # calculate if any remaining intervals are needed, and pull from candidate as much as possible until either empty, or the next interval finishes before position i
while need > 0 and candidates and -candidates[0] >= i:
heapq.heappush(chosen,-heapq.heappop(candidates))
need -= 1
ans+= 1 # this is an interval that was necessary to add
if need > 0: # if we can't find enough intervals, invalid
return -1
return len(queries)-ans # we can subtract off the essential intervals the max number of intervals that are redundant
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Two Heapq
|
two-heapq-by-treerecursion-qnwq
|
IntuitionThink of the queries as closed intervals (inclusive of endpoints). We will select a subset of the intervals to cover nums. For each index i in range(
|
treerecursion
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-07T13:36:21.205588+00:00
|
2025-01-07T13:36:21.205588+00:00
| 11 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
Think of the queries as closed intervals (inclusive of endpoints). We will select a subset of the intervals to cover `nums`. For each index `i` in `range(len(nums))`, the number of selected intervals that cover `i` should be no less than `nums[i]`. Sort the `queries` so that the intervals are presented from left to right on the number line.
Use two heaps, one min heap, and another max heap. Both heaps store intervals. The min heap `minH` caches the intervals that are previously selected, and maintains that `minH[0]` has the smallest right endpoint. The max heap `maxH` stores candidiate intervals that may be selected (but not yet selected), and maintains that `maxH[0]` has the greatest right endpoint. Among the candidate, we greedily select `maxH[0]`, as it potentially covers more points to the right.
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
For each `i`, and corresponding `num = nums[i]`, proceed in a loop as follows.
1. As long as `minH` contains previously used intervals, if the top interval fails to cover `i`, pop `minH`.
2. After step 1, check if there are enough intervals in `minH` to cover `i` for `num` times. If so, simply continue to next loop if needed.
3. Now we know that we must select more available intervals from `queries` to cover `i`. Look at index `q` pointing to the next available interval in `queries`. As long as it cannot cover the current `i`, skip it.
4. As long as the next interval may cover `i`, push it into `maxH` as a candidate.
5. As long as there are candidates in `maxH`, we greedily pop the top out of `maxH` and push the result into `minH`, while incrementing `used`. We do this as long as we need more intervals to cover `i`.
6. After step 5, if we cannot obtain enough intervals to cover `i`, return `-1`; otherwise, go to next loop if needed.
The answer is `nq - used`.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
$O(n)$
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
$O(n)$
# Code
```python3 []
class MinElem:
def __init__(self, left, rite):
self.left = left
self.rite = rite
def __lt__(self, other):
return self.rite < other.rite
class MaxElem:
def __init__(self, left, rite):
self.left = left
self.rite = rite
def __lt__(self, other):
return self.rite > other.rite
class Solution:
def maxRemoval(self, nums: List[int], queries: List[List[int]]) -> int:
queries.sort() # queries are intervals, now sorted
nq = len(queries)
q = 0 # pointer to q-th query to be considered
maxH = [] # candidate intervals for reducing each num
minH = [] # intervals actually used to reduce each num
used = 0
for i, num in enumerate(nums): # try to reduce each num
# remove intervals that have been used but cannot help reduce the current num
while minH and minH[0].rite < i: heappop(minH)
if num <= len(minH): continue # no need to consider any more interval
while q < nq and queries[q][1] < i: q += 1 # skip non-usable queries
while q < nq and queries[q][0] <= i:
left, rite = queries[q]
heappush(maxH, MaxElem(left, rite))
q += 1
while maxH and len(minH) < num:
interval = heappop(maxH)
if i < interval.left or interval.rite < i: continue
heappush(minH, MinElem(interval.left, interval.rite))
used += 1
if len(minH) < num: return -1
return nq - used
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Two Heapq
|
two-heapq-by-treerecursion-be39
|
IntuitionThink of the queries as closed intervals (inclusive of endpoints). We will select a subset of the intervals to cover nums. For each index i in range(
|
treerecursion
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-07T13:36:18.613122+00:00
|
2025-01-07T13:36:18.613122+00:00
| 11 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
Think of the queries as closed intervals (inclusive of endpoints). We will select a subset of the intervals to cover `nums`. For each index `i` in `range(len(nums))`, the number of selected intervals that cover `i` should be no less than `nums[i]`. Sort the `queries` so that the intervals are presented from left to right on the number line.
Use two heaps, one min heap, and another max heap. Both heaps store intervals. The min heap `minH` caches the intervals that are previously selected, and maintains that `minH[0]` has the smallest right endpoint. The max heap `maxH` stores candidiate intervals that may be selected (but not yet selected), and maintains that `maxH[0]` has the greatest right endpoint. Among the candidate, we greedily select `maxH[0]`, as it potentially covers more points to the right.
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
For each `i`, and corresponding `num = nums[i]`, proceed in a loop as follows.
1. As long as `minH` contains previously used intervals, if the top interval fails to cover `i`, pop `minH`.
2. After step 1, check if there are enough intervals in `minH` to cover `i` for `num` times. If so, simply continue to next loop if needed.
3. Now we know that we must select more available intervals from `queries` to cover `i`. Look at index `q` pointing to the next available interval in `queries`. As long as it cannot cover the current `i`, skip it.
4. As long as the next interval may cover `i`, push it into `maxH` as a candidate.
5. As long as there are candidates in `maxH`, we greedily pop the top out of `maxH` and push the result into `minH`, while incrementing `used`. We do this as long as we need more intervals to cover `i`.
6. After step 5, if we cannot obtain enough intervals to cover `i`, return `-1`; otherwise, go to next loop if needed.
The answer is `nq - used`.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
$O(n)$
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
$O(n)$
# Code
```python3 []
class MinElem:
def __init__(self, left, rite):
self.left = left
self.rite = rite
def __lt__(self, other):
return self.rite < other.rite
class MaxElem:
def __init__(self, left, rite):
self.left = left
self.rite = rite
def __lt__(self, other):
return self.rite > other.rite
class Solution:
def maxRemoval(self, nums: List[int], queries: List[List[int]]) -> int:
queries.sort() # queries are intervals, now sorted
nq = len(queries)
q = 0 # pointer to q-th query to be considered
maxH = [] # candidate intervals for reducing each num
minH = [] # intervals actually used to reduce each num
used = 0
for i, num in enumerate(nums): # try to reduce each num
# remove intervals that have been used but cannot help reduce the current num
while minH and minH[0].rite < i: heappop(minH)
if num <= len(minH): continue # no need to consider any more interval
while q < nq and queries[q][1] < i: q += 1 # skip non-usable queries
while q < nq and queries[q][0] <= i:
left, rite = queries[q]
heappush(maxH, MaxElem(left, rite))
q += 1
while maxH and len(minH) < num:
interval = heappop(maxH)
if i < interval.left or interval.rite < i: continue
heappush(minH, MinElem(interval.left, interval.rite))
used += 1
if len(minH) < num: return -1
return nq - used
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Optimally select the query using Priority Queue
|
optimally-select-the-query-using-priorit-pqbk
|
Intuitionif nums[i] is greater than the queries under consideration , then we need to consider more queries .Approachhow to consider queries ?
we will sort them
|
abinashgupta712
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-07T12:55:25.522544+00:00
|
2025-01-07T12:55:25.522544+00:00
| 25 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
if nums[i] is greater than the queries under consideration , then we need to consider more queries .
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
how to consider queries ?
1. we will sort them according to the starting index
2. create eligible priority_queue which can be considered if nums[i] is greater than the queries under consideration
3. now select the query from the eligible queries optimally i.e. query with max ending index
4. keep track of queries getting considered substract the count from the no of provided queries
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
max(O(n),O(q)) as we are traversing the nums and query only once
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
O(q) as we are storing the queries in the worst case will store all queries at once .
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& q) {
// [0,3],[0,2],[1,5],[1,4]
int n=nums.size();
int m=q.size();
sort(q.begin(),q.end());
priority_queue<pair<int,int>>eligible; // store the eligible queries
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>>pq; //keep the minimum queries
int i=0;// iterate the nums
int j=0; // itereate the q
int ans=0;
while(i<n){
// cout<<i<<endl;
if(nums[i]==0) {
while(pq.size()&&i==pq.top()) pq.pop();
i++;
continue;
}
while(nums[i]>pq.size()){
// cout<<"j :"<<j<<endl;
while(j<m&&q[j][0]<=i){
// cout<<"element of pushed :"<<q[j][0]<<" "<<q[j][1]<<endl;
eligible.push({q[j][1],q[j][0]});
j++;
}
if(eligible.size()){
auto top=eligible.top();
// cout<<"top element of eligible :"<<top.first<<" "<<top.second<<endl;
if(i<=top.first){
// cout<<"pushed to pq :"<<top.first<<endl;
pq.push(top.first);
ans+=1;
}
// cout<<"current max :"<<pq.size()<<endl;
eligible.pop();
}
else return -1;
// cout<<"nums[i] :"<<nums[i]<<" "<<pq.size()<<endl;
}
if(nums[i]>pq.size()) {return -1;}
while(pq.size()&&i>=pq.top()) pq.pop();
i++;
}
return m-ans;
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Sorting', 'Heap (Priority Queue)', 'C++']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
PriorityQueue
|
priorityqueue-by-linda2024-k52r
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
linda2024
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-02T23:50:15.917070+00:00
|
2025-01-02T23:50:15.917070+00:00
| 9 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```csharp []
public class Solution {
public int MaxRemoval(int[] nums, int[][] queries) {
queries = queries.OrderBy(q => q[0]).ThenByDescending(q => q[1]).ToArray();
int len = nums.Length, res = 0, qLen = queries.Length;
PriorityQueue<int, int> pq = new();
int[] end = new int[len+1];
int cur = 0, idx = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) // Iterate each item
{
cur += end[i]; // update query freq with ended here
while (idx < qLen && queries[idx][0] <= i) // Enqueue the queries which started before cur index
{
pq.Enqueue(-queries[idx][1], -queries[idx++][1]);
}
while (cur < nums[i])
{
if (pq.Count == 0 || (-pq.Peek()) < i)
return -1;
end[-pq.Dequeue() + 1]--;
cur++;
}
}
return pq.Count;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['C#']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Should be medium greedy+: min+max heaps
|
should-be-medium-greedy-minmax-heaps-by-1l1um
|
This should be something like google medium on the harder end of mediums.\n\nGreedy logic: for each i in [0, N) pick a query with the farthest end. Why? Because
|
vokasik
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-17T11:12:58.480836+00:00
|
2024-12-17T15:14:06.739343+00:00
| 17 | false |
This should be something like `google medium` on the harder end of mediums.\n\nGreedy logic: for each `i in [0, N)` pick a query with the farthest end. Why? Because it will cover bigger ranges!\n\nImplementation is also a `piece of art`...\n\n1. group query starts by end: `start[0].append([0,1],[0,2],[0,5]])`\n2. Create 2 groups: `candidates` (sorted by max_end) and `picked` (sorted by min_end)\n3. add to the `candidates` ends with `start[i]`\n4. pick from the `candidates` ends until you get the size of the `picked` group >= nums[i]\n5. remove shorter candidates from `picked` group\n6. return total_queries - picked\n\nP.S. We can also just sort the queries by `start,-end` instead of `query_start` DS, but it\'s much slowers during runtime.\n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maxRemoval(self, nums: List[int], queries: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n query_start = defaultdict(list)\n for s,e in queries: # 1\n query_start[s].append(e)\n picked_min_end = [] # 2\n candidates_max_end = [] # 2\n used = 0\n for i in range(len(nums)):\n for e in query_start[i]: # 3\n heappush(candidates_max_end, -e)\n while picked_min_end and picked_min_end[0] < i: # 5\n heappop(picked_min_end)\n while candidates_max_end and len(picked_min_end) < nums[i]: # 4\n furthest_end = -heappop(candidates_max_end)\n if furthest_end >= i: # ignore end < i\n heappush(picked_min_end, furthest_end)\n used += 1\n nums[i] -= len(picked_min_end)\n if nums[i] > 0:\n return -1\n return len(queries) - used\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Greedy', 'Heap (Priority Queue)', 'Python3']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Python Medium
|
python-medium-by-lucasschnee-rb2l
| null |
lucasschnee
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-19T19:32:17.408443+00:00
|
2024-12-19T19:32:17.408443+00:00
| 15 | false |
```python3 []
class Solution:
def maxRemoval(self, nums: List[int], queries: List[List[int]]) -> int:
'''
can we greedily sort by the largest?
we need a O(nlogn) solution or better
things that come to mind:
difference array
segment Tree
dynamic programming
greedy
sorting queries based on size
union find
we iterate left to right in nums:
at current index, while it isnt covered, we look at unused queries that have the latest endpoint and start at current index or left of it
(1, 3), (2, 5)
if we are at index 1 and need an interval, we take (1, 3)
in other cases, we take 2, 5
heap
'''
N = len(nums)
Q = len(queries)
difference_arr = [0] * (N + 1)
h = []
queries.sort()
q = deque(queries)
used = 0
cur = 0
for index, x in enumerate(nums):
while q and q[0][0] <= index:
l, r = q.popleft()
heapq.heappush(h, -r)
cur += difference_arr[index]
while h and cur < x:
r = heapq.heappop(h) * -1
if r < index:
return -1
cur += 1
used += 1
difference_arr[r + 1] -= 1
if cur < x:
return -1
return Q - used
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
1 Max-Heap + Sorting (N log Q) simplest explanation !
|
1-max-heap-sorting-n-log-q-simplest-expl-ikrg
|
Intuitionfor any index i in nums we need to consider the query that has longest impact i + right is maxed out so more numbers ca benfit from that query being us
|
kishan_2008
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-18T11:27:35.144529+00:00
|
2024-12-18T11:27:35.144529+00:00
| 22 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nfor any index i in nums we need to consider the query that has longest impact i + right is maxed out so more numbers ca benfit from that query being used\n# Approach\n 1) sorted all the queries to effectily pick and add to valid queries list.\n 2) preSum arrary to track at with point previouly applied queries are going to be applicable.\n\n 3) for each index i in nums we add all the valid queries to the heap. we only add the right bound and add it with * -1 as we are using min heap as max heap.\n 4) if the current index needs to be adjusted using queries we pick queries one by one and increment the used queries. at times the queires could be invalid when the right bound is < than current i. this happens as we are not cleaning the heap with the old invalid queries.\n 5) we return the count of queries - usedqueires to get the count of removable queries.\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: N log Q (we do it N times & loq Q for heap ops)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: N + Q\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n\n\n\nCurious to know if there is any way to remove the invalid queries efficently as this will improve the heap operations performance.\n\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def maxRemoval(self, nums: List[int], queries: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n queries.sort(key = lambda x: x[0])\n preSum = [0] * (len(nums)+1)\n\n validQueries = []\n k = 0\n currentSum = 0\n userQueries = 0\n\n for i in range(len(nums)):\n while k < len(queries) and queries[k][0] <= i:\n heapq.heappush(validQueries, -queries[k][1])\n k+=1\n\n while currentSum + preSum[i] < nums[i]:\n if len(validQueries) == 0 or -validQueries[0] < i:\n return -1\n \n right = heapq.heappop(validQueries)\n right = -right\n\n preSum[i] += 1\n preSum[right + 1] -= 1\n userQueries += 1\n\n currentSum += preSum[i]\n return len(queries) - userQueries\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Python3 with clear explanation
|
python3-with-clear-explanation-by-mkxyz-28ds
|
Intuitionrefer to the code comments for more info.Intuition is to maintain a list of queries that covers each index. By this, I mean to say, you will need to kn
|
mkxyz
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-16T20:32:36.137243+00:00
|
2024-12-16T20:32:36.137243+00:00
| 18 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nrefer to the code comments for more info.\n\nIntuition is to maintain a list of queries that covers each index. By this, I mean to say, you will need to know the number of queries for which l <= i <= r. But We also needed to minimize the number of queries used to reduce arr[i] to 0. So, the best way is to choose the queries greedily spanning the largest (those having highest r) until you can reduce arr[i] to 0. \n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\nFor each index i, we will start adding queries with l <= i and then choose those with r >= i starting from the largest r. Once we reach number of queries == nums[i] which means we can reduce nums[i] to 0 with the chosen queries we can move to next index.\n\nTo process queries for current index, use a queue with the queries sorted in ascending order of l to make it easy to pop.\nMaintain a maxheap valid, which will be used to choose queries with the highest r among the queries which have l <=i <= r. \nWe also need a minheap active, which keeps a count of the current queries for index i. We need this because we can\'t just remove the query from valid, it can be used for next indexes (i+1, i+2, so on) as well. And a min heap because we want to remove the queries which have r<i easily.\n\nNow, for each index i:\n- add queries from queue to valid if l <= i.\n- remove queries from active if r < i.\n- keep pushing into active until we find nums[i] queries. if we can\'t return -1\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(N + Mlog(M)), m is the length of queries.\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(M)\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def maxRemoval(self, nums: List[int], queries: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n q = deque(sorted(queries)) #process queries one by one with the smallest l\n valid = [] #stores valid queries which have l<i for each index i and in maxheap. We use a maxheap because we need to choose the biggest range of valid query to maximize the number of unnecessary queries.\n active = [] #stores the chosen queries from valid queries used for each index i to reduce them to zero. We use minheap for this because we want to remove the inactive queries which have r < i (these were already used for previous indexes and are now invalid)\n\n#so basically for each index we maintain the number of queries that cover this index and to do it greedily we needed to use heaps.\n\n for i in range(len(nums)):\n #add valid queries to heap if l < i\n while q and q[0][0] <=i:\n heappush(valid, -q.popleft()[1])\n #remove inactive queries which have r < i\n while active and active[0] < i:\n heappop(active)\n #now choose queries in valid have r > i from the biggest r\n while nums[i] > len(active):\n #if there are no more valid(l<i) or the biggest r valid is < i, we dont have enough queries to reduce nums[i] to zero.\n #since each query reduces nums[i] by 1. we need len(active) to be equal to nums[i]\n if not valid or -valid[0] < i:\n return -1\n heappush(active, -heappop(valid))\n #return the number of unchosen queries\n return len(valid)\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Simp[le Commented Code, multiple Priority Queue approach
|
simple-commented-code-multiple-priority-g976s
|
Complexity
Time complexity:
O(N*logN)
Space complexity:
O(N)
Code
|
qwertyqwaf
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-16T15:48:59.790737+00:00
|
2024-12-16T15:48:59.790737+00:00
| 14 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(N*logN)\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(N)\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def maxRemoval(self, nums: List[int], queries: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n queries.sort(key = lambda x: x[0]) # sort based on start index\n queries = deque(queries) # deque makes popping faster\n queries.append([float(\'inf\'), float(\'inf\')]) # so we can avoid if cond in the while loop\n pq = [] # pq will contain valid endpoints thus far\n options = [] # these are the next options\n for i, num in enumerate(nums):\n while pq and pq[0] < i: # pop endpoints that won\'t count anymore\n heapq.heappop(pq)\n while queries[0][0] <= i: # any option that starts now or earlier is valid\n _, end = queries.popleft()\n heapq.heappush(options, -1*end) # -1*end since we\'re in \n for _ in range(max(0, num - len(pq))): # if 0 >= num - len(pq) we\'re good\n if not options or -1 * options[0] < i:\n return -1 # we ran out of options\n heapq.heappush(pq, -1*heapq.heappop(options))\n return len(options) # these are the options we didn\'t use\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Greedy', 'Heap (Priority Queue)', 'Python3']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Java O(N + KLogK) solution with Pseudo Code for explanation
|
java-on-klogk-solution-with-pseudo-code-muzwy
|
IntuitionIntution is to always use the query that impacts the largest range of indexes ahead of the current index.ApproachSort the queries array so that we can
|
codegladiator47
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-15T03:59:18.080497+00:00
|
2024-12-15T03:59:18.080497+00:00
| 55 | false |
# Intuition\nIntution is to always use the query that impacts the largest range of indexes ahead of the current index.\n\n# Approach\nSort the queries array so that we can pick up elements that actually impact current index while traversing nums array. Following is the pseudo code for the approach -\n\n sort queries array in asceneding order of left of the range.\n maxHeap = create a heap based on the right in descending order.\n range i 0 to nums.length:\n while idx < queries.length && i >= queries[idx][0]\n maxHeap.offer(queries[idx]);\n while maxHeap is not empty && nums[i] > presum + line[i]\n range = poll(maxHeap)\n if the range[1] < i \n then we return -1; // the reason for this is because we have used all the ranges that could impact i and nums[i] cannot be reduced to 0.\n update line based on the range. \n //This checks for edge case where we used all the queries and the last element could not be reduced to zero.\n if maxHeap is empty and presum + line[i] < nums[i]\n return -1;\n presum += line[i];\n return size of maxHeap;\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(N + KLogK), where N = nums.length and K = queries.length\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(N + K), where N = nums.length and K = queries.length\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int maxRemoval(int[] nums, int[][] queries) {\n int[] line = new int[nums.length + 1];\n Arrays.sort(queries, (x, y) -> x[0] - y[0]);\n PriorityQueue<int[]> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> y[1] - x[1]);\n int presum = 0;\n int ans = 0;\n int idx = 0;\n\n for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {\n while(idx < queries.length && i >= queries[idx][0]) {\n maxHeap.offer(queries[idx++]);\n }\n\n while(!maxHeap.isEmpty() && nums[i] > presum + line[i]) {\n int[] range = maxHeap.poll();\n\n // have used all ranges that could increment i\n if (range[1] < i)\n return -1;\n\n line[i]++;\n line[range[1] + 1]--;\n }\n\n // edge case\n if (maxHeap.isEmpty() && nums[i] > presum + line[i]) {\n return -1;\n }\n\n presum += line[i];\n }\n\n return maxHeap.size();\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Easy | Logical Greedy | Sort + Priority Queue
|
easy-logical-greedy-sort-priority-queue-bctym
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nIt\'s not necessary to process queries in the given order.\nSo, we can manipulate the q
|
miteshkhemani8
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-09T05:40:55.576112+00:00
|
2024-12-09T05:40:55.576143+00:00
| 27 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nIt\'s not necessary to process queries in the given order.\nSo, we can manipulate the queries ordering to our advantage.\nAt any given index, I am only interested in the queries that can help me to compute min queries needed to make that index\'s value 0.\nBasically, queries which have starting point as index+1 or more are of no use to me while dealing with value at the index.\n\nAlso, it is always always always advantageous to pick such a query (from the available pool of queries at that index) such that its ending point is the farthest. This is the greedy nature of the problem. Think why this would be the optimal everytime. (Spoiler - because in future you would potentially save some queries usage if you proceed like this.)\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nSort the queries.\nMaintain a max-heap of all the queries available till the index on which you are at currently. (MaxHeap\'s key would be the ending point of the query due to the above mentioned intuition) \n\nJust iterate through the nums array, index by index and keep count of used queries till this point. The maxHeap might also have some old queries which are of no use to us --> simply ignore and remove them whenver you encounter them as those queries can no longer help us in any way as their range doesn\'t cover the current index, we are on.\n\n**Note**\nAlso maintain the diff array to efficiently keep track of future indices which are covered when you decide to use a particular query.\nSo that, in future you do not waste queries on indices which were already covered by your used queries in the past.\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(nlogn)$$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n sort(queries.begin(), queries.end());\n priority_queue<array<int, 2>> maxHeap;\n int nidx = 0, qidx = 0, used = 0, curr = 0;\n vector<int> diff(int(nums.size())+1, 0);\n while(nidx < nums.size()) {\n curr += diff[nidx];\n while(qidx < queries.size() && queries[qidx][0] <= nidx) {\n maxHeap.push({queries[qidx][1], queries[qidx][0]});\n qidx ++;\n }\n while(nums[nidx] > curr) {\n if(!maxHeap.empty() && maxHeap.top()[1] <= nidx && maxHeap.top()[0] >= nidx) {\n curr ++;\n diff[maxHeap.top()[0] + 1] -= 1;\n used ++;\n maxHeap.pop();\n }\n else if(!maxHeap.empty()) {\n maxHeap.pop();\n }\n else return -1;\n }\n nidx ++;\n }\n return int(queries.size()) - used;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Array', 'Greedy', 'Heap (Priority Queue)', 'C++']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Sorting, MaxHeap and Partial-Difference Array
|
sorting-maxheap-and-partial-difference-a-srvq
|
Sorting and Max Heap\npython []\nclass Solution:\n # O(n + mlogm) time | O(n + m) space\n # n = length of nums\n # q = length of queries\n def maxRe
|
deydev
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-07T21:21:22.689934+00:00
|
2024-12-07T23:28:42.848605+00:00
| 51 | false |
# Sorting and Max Heap\n```python []\nclass Solution:\n # O(n + mlogm) time | O(n + m) space\n # n = length of nums\n # q = length of queries\n def maxRemoval(self, nums: List[int], queries: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n n, m = len(nums), len(queries)\n\n queries.sort()\n q_idx = 0\n max_heap = []\n end_deltas = [0] * (n + 1)\n total_possible_change = 0\n\n for i in range(n):\n total_possible_change += end_deltas[i]\n\n # add all possible intervals that start <= i\n # to max heap tracking their ends\n while q_idx < m and queries[q_idx][0] <= i:\n heappush(max_heap, -1 * queries[q_idx][1])\n q_idx += 1\n\n while nums[i] - total_possible_change > 0:\n if not max_heap:\n return -1\n\n # all queries in the max heap are guaranteed to have start <= i\n # but doesn\'t mean they\'ll have an i <= end\n farthest_end = max_heap[0] * -1\n if i > farthest_end:\n return -1\n\n # apply the best query and mark where this\n # query stops taking affect\n heappop(max_heap)\n total_possible_change += 1\n end_deltas[farthest_end + 1] -= 1\n\n return len(max_heap)\n\n```\n\n---\n\n# Min Heap and Max Heap\n``` Python []\nclass EarlierStartInterval:\n def __init__(self, start, end):\n self.start = start\n self.end = end\n\n def __lt__(self, other):\n return self.start < other.start\n\n def __iter__(self):\n yield self.start\n yield self.end\n\n\nclass LaterEndInterval:\n def __init__(self, start, end):\n self.start = start\n self.end = end\n\n def __lt__(self, other):\n return self.end > other.end\n\n def __iter__(self):\n yield self.start\n yield self.end\n\n\nclass Solution:\n # O(n + mlogm) time | O(n + m) space\n # n = length of nums\n # q = length of queries\n def maxRemoval(self, nums: List[int], queries: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n n = len(nums)\n\n earliest_starts = []\n latest_ends = []\n\n for q in queries:\n heappush(earliest_starts, EarlierStartInterval(q[0], q[1]))\n\n end_deltas = [0] * (n + 1)\n total_possible_change = 0\n\n for i in range(n):\n total_possible_change += end_deltas[i]\n\n while earliest_starts and earliest_starts[0].start <= i:\n start, end = heappop(earliest_starts)\n heappush(latest_ends, LaterEndInterval(start, end))\n\n while nums[i] - total_possible_change > 0:\n if not latest_ends or latest_ends[0].end < i:\n return -1\n\n _, end = heappop(latest_ends)\n end_deltas[end + 1] -= 1\n total_possible_change += 1\n\n return len(latest_ends)\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Array', 'Greedy', 'Sorting', 'Heap (Priority Queue)', 'Prefix Sum', 'Python3']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Classic Two Heaps Solution || Java || Clean Code || Not so easy
|
classic-two-heaps-solution-java-clean-co-7790
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
owaispatel95
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-04T18:12:05.904464+00:00
|
2024-12-04T18:12:05.904490+00:00
| 84 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int maxRemoval(int[] nums, int[][] queries) {\n final int n = nums.length;\n final int m = queries.length;\n\n Arrays.sort(queries, (a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);\n\n final PriorityQueue<Integer> minHeap = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> a - b);\n final PriorityQueue<Integer> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> b - a);\n\n int used = 0;\n\n for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < n; i++) {\n while(j < m && queries[j][0] == i) {\n maxHeap.add(queries[j++][1]);\n }\n\n nums[i] -= minHeap.size();\n\n while(nums[i] > 0 && !maxHeap.isEmpty() && maxHeap.peek() >= i) {\n minHeap.add(maxHeap.remove());\n\n used++;\n nums[i]--;\n }\n\n if (nums[i] > 0) return -1;\n\n while(!minHeap.isEmpty() && minHeap.peek() == i) {\n minHeap.remove();\n }\n }\n\n return m - used;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
It can't be Medium (Two Priority Queue + Segment Tree)
|
it-cant-be-medium-two-priority-queue-seg-89bi
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\nFirst Priority Queue is used for Finding all Intervals containing this in
|
SAYANTAN_1729
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-29T16:17:31.809010+00:00
|
2024-11-29T16:17:31.809039+00:00
| 19 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\nFirst Priority Queue is used for Finding all Intervals containing this indexed element and Second Priority Queue is used for finding the "Furthest Interval"(NOT LONGEST) containting this non-zero array value.\nSegment tree is used for Updating all the elements of the intervals even those elements which we are not currenty inspecting and Via Find operation of segment tree we can find the current value of this index before starting priority_queue operations\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(N * log N)\n\n- Space complexity: O( N )\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n#define ll int\n#define pb push_back\n vector<ll> a;\n ll seg_tree[400001][2];\n // Building segment tree\n void Build(ll l, ll r, ll node) {\n if (l == r) {\n seg_tree[node][0] = a[l];\n seg_tree[node][1] = 0;\n return;\n }\n ll mid = (l + r) / 2;\n Build(l, mid, (2 * node) + 1);\n Build(mid + 1, r, (2 * node) + 2);\n seg_tree[node][0] =\n max(seg_tree[(2 * node) + 1][0], seg_tree[(2 * node) + 2][0]);\n seg_tree[node][1] = 0;\n return;\n }\n // Query Update\n void Update(ll l, ll r, ll node, ll left, ll right) {\n if ((l > right) || (r < left)) {\n return;\n }\n if ((l >= left) && (r <= right)) {\n seg_tree[node][0]--;\n seg_tree[node][1]++;\n return;\n }\n ll mid = (l + r) / 2;\n Update(l, mid, (2 * node) + 1, left, right);\n Update(mid + 1, r, (2 * node) + 2, left, right);\n seg_tree[node][0] =\n max(seg_tree[(2 * node) + 1][0], seg_tree[(2 * node) + 2][0]) -\n seg_tree[node][1];\n }\n // Find Range_Wise Max\n ll Find(ll l, ll r, ll node, ll left, ll right) {\n if ((l > right) || (r < left)) {\n return 0;\n }\n if ((l >= left) && (r <= right)) {\n return seg_tree[node][0];\n }\n ll mid = (l + r) / 2;\n ll x = Find(l, mid, (2 * node) + 1, left, right);\n ll y = Find(mid + 1, r, (2 * node) + 2, left, right);\n ll z = max(x, y) - seg_tree[node][1];\n return z;\n }\n int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n a = nums;\n ll n = a.size();\n priority_queue<pair<ll, ll>> p, q;\n for (ll i = 0; i < queries.size(); i++) {\n ll x = -queries[i][0], y = queries[i][1];\n p.push({x, y});\n }\n Build(0, n - 1, 0);\n ll ans = 0;\n for (ll i = 0; i < a.size(); i++) {\n ll x = Find(0, n - 1, 0, 0, i);\n if (x <= 0) {\n continue;\n }\n if(!p.empty()){\n auto w = p.top();\n ll y = -w.first, z = w.second;\n while (y <= i) {\n if (z < i) {\n p.pop();\n ans++;\n } else {\n p.pop();\n q.push({z, -y});\n }\n if (p.empty()) {\n break;\n }\n w = p.top();\n y = -w.first;\n z = w.second;\n }\n }\n while (x > 0 && (!q.empty())) {\n auto w = q.top();\n ll y = -w.second;\n ll z = w.first;\n if (z < i) {\n break;\n } else {\n x--;\n Update(0, n - 1, 0, y, z);\n q.pop();\n }\n }\n if (x > 0) {\n ans = -1;\n break;\n }\n }\n if (ans == -1) {\n return ans;\n }\n ll z = (p.size()) + (q.size());\n ans += z;\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
With intution and approach 2 heap solution with explaination and algo
|
with-intution-and-approach-2-heap-soluti-08t6
|
# Intuition\n\nTransforming nums into a zero array involves applying the queries efficiently. The challenge lies in determining the maximum number of queries th
|
lav5588
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-29T10:49:17.035396+00:00
|
2024-11-29T10:49:17.035425+00:00
| 20 | false |
### **# Intuition**\n\nTransforming `nums` into a zero array involves applying the queries efficiently. The challenge lies in determining the maximum number of queries that can be excluded without preventing the transformation of `nums` to a zero array. Using a **max-heap** to prioritize queries with the largest range and a **min-heap** to track active ranges helps achieve this goal.\n\n---\n\n### **# Approach**\n\n1. **Sort the Queries**:\n - Sort the queries by their starting index (`li`) so that they can be processed sequentially with respect to the `nums` array.\n\n2. **Use Two Heaps**:\n - **Max-Heap** (`maxHeap`): Stores the ending indices (`ri`) of the queries that are currently being considered. The top element of the heap always represents the query covering the largest range.\n - **Min-Heap** (`minHeap`): Tracks active queries for the current index `i`. It helps decrement the value of `nums[i]` effectively.\n\n3. **Process `nums` Array**:\n - For each index `i` in `nums`, perform the following:\n - Push the `ri` of queries starting at or before `i` into the max-heap.\n - Remove expired ranges (queries ending before `i`) from the min-heap.\n - Reduce `nums[i]` by the number of active queries (`minHeap.size()`).\n - If `nums[i] > 0`, move additional queries from the max-heap to the min-heap to decrement `nums[i]`. If `nums[i]` cannot be reduced to zero, return `-1`.\n\n4. **Result**:\n - After processing the entire array, the size of the max-heap represents the number of unused queries, as they were not required to transform `nums` into a zero array.\n\n\n---\n\n### **# Complexity**\n\n- **Time Complexity**:\n - Sorting queries: \\(O(q \\log q)\\), where \\(q\\) is the number of queries.\n - Processing each element in `nums`:\n - Each query is pushed and popped from the heaps at most once: \\(O(q \\log q)\\).\n - Each element in `nums` is processed once: \\(O(n)\\).\n - Overall: \\(O((n + q) \\log q)\\).\n\n- **Space Complexity**:\n - Max-heap and min-heap: \\(O(q)\\).\n - Sorting storage: \\(O(q)\\).\n - Overall: \\(O(q)\\).\n\n---\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n\n sort(queries.begin(),queries.end());\n\n int n = nums.size();\n int nq = queries.size();\n\n priority_queue<int>maxHeap;\n priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>>minHeap;\n\n for(int i = 0,j = 0; i < n; i++){\n\n while(j < nq && queries[j][0] <= i){\n maxHeap.push(queries[j][1]);\n j++;\n }\n\n while(!minHeap.empty() && minHeap.top() < i){\n minHeap.pop();\n }\n\n nums[i] -= minHeap.size();\n\n if(nums[i] <= 0)continue;\n\n while( !maxHeap.empty() && maxHeap.top() >= i && nums[i] > 0 ){\n minHeap.push(maxHeap.top());\n maxHeap.pop();\n nums[i]--;\n }\n \n if(nums[i] > 0){\n return -1;\n }\n }\n\n return maxHeap.size(); \n }\n};\n```\n\nYour upvote motivates me to write more solutions to community.\n\n
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Perfect solution {:)}
|
perfect-solution-by-sachinab-8pq3
|
\n\n# Code\njava []\nclass Solution {\n public int maxRemoval(int[] nums, int[][] queries) {\n Arrays.sort(queries, (q1,q2) -> q1[0]-q2[0]);\n\n
|
sachinab
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-28T17:12:42.950597+00:00
|
2024-11-28T17:12:42.950638+00:00
| 34 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int maxRemoval(int[] nums, int[][] queries) {\n Arrays.sort(queries, (q1,q2) -> q1[0]-q2[0]);\n\n PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((q1,q2) -> q2[1]-q1[1]);\n\n int q = 0, d = 0, res = 0;\n int[] delta = new int[nums.length+1];\n for(int i=0; i<nums.length; i++){\n d+=delta[i];\n if((nums[i]-d)>0){\n while(q < queries.length && queries[q][0]<=i){\n pq.offer(queries[q++]);\n }\n }\n while((nums[i]-d)>0 && !pq.isEmpty() && pq.peek()[1]>=i){\n int[] query = pq.poll();\n res++;\n delta[query[0]]++;\n delta[query[1]+1]--;\n d++;\n }\n if(nums[i]-d>0){\n return -1;\n }\n }\n\n return queries.length - res;\n\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Simple solution using 2 priorityQueue
|
simple-solution-using-2-priorityqueue-by-9km1
|
\n# Code\njava []\nclass Solution {\n public int maxRemoval(int[] nums, int[][] queries) {\n int s=0;\n int qp=0;\n PriorityQueue<Integer
|
risabhuchiha
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-27T14:39:14.556489+00:00
|
2024-11-27T14:39:14.556527+00:00
| 23 | false |
\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int maxRemoval(int[] nums, int[][] queries) {\n int s=0;\n int qp=0;\n PriorityQueue<Integer>pq=new PriorityQueue<>((a,b)->b-a);\n PriorityQueue<Integer>pq1=new PriorityQueue<>((a,b)->a-b);\n Arrays.sort(queries,(a,b)->a[0]-b[0]);\n for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){\n int x=nums[i];\n \n while(qp<queries.length&&queries[qp][0]==i){\n \n pq.offer(queries[qp][1]);\n qp++;\n \n }\n x-=pq1.size();\n while(x>0&&pq.size()>0&&pq.peek()>=i){\n s++;\n x--;\n pq1.offer(pq.poll());\n\n }\n\n \n if(x>0)return -1;\n while(pq1.size()>0&&pq1.peek()<=i)pq1.poll();\n\n }\n return queries.length-s;\n\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Simple Solution | Sort && Priority Queue/Heap | C++
|
simple-solution-sort-priority-queueheap-p6wkz
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nFor each index, need to find all queries that can meet: ri >= i and li <= i. In those q
|
xiyang0405
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-27T08:43:16.399472+00:00
|
2024-11-27T08:43:16.399507+00:00
| 22 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nFor each index, need to find all queries that can meet: ri >= i and li <= i. In those queries, find the one with farthest ri. Pick those queries, until nums[i] == 0; Then go to the next index;\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nUse the priority_queue/heap to keep all queries, and sort them by \'ri\' in descent order.\nUse the \'curr\' to record accumulation of all queries applied so far; and use the vector \'removes\' to record all points need to be decreased from \'curr\' in the future. Similar to basic line sweep.\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(n + mlog(m))$$\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(n+m)$$\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n sort(queries.begin(), queries.end());\n \n int n = nums.size(), m = queries.size(), i = 0, j = 0, curr = 0;\n vector<int> removes(n+1, 0);\n priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, less<pair<int,int>>> pq;\n int total = 0;\n for(i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n curr -= removes[i];\n while(j < m && (queries[j][0] <= i && queries[j][1] >= i)) {\n pq.push(make_pair(queries[j][1], queries[j][0]));\n j++;\n }\n while(curr < nums[i]) {\n if(pq.empty()) {\n return -1;\n }\n auto q = pq.top();\n pq.pop();\n if(q.first >= i) {\n curr++;\n total++;\n removes[q.first+1]++;\n }\n }\n }\n return m-total;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Greedy + Heap
|
greedy-heap-by-sternentaucher-lb6f
|
Intuition\n\nPush all intervals that start before current position and only select at most a[i] intervals to cover current element. To minimize the total number
|
sternentaucher
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-25T22:44:05.085173+00:00
|
2024-11-25T22:45:55.279478+00:00
| 13 | false |
# Intuition\n\nPush all intervals that start before current position and only select at most `a[i]` intervals to cover current element. To minimize the total number, select intervals with rightmost endpoint. This can be achieved by using a Max-Heap.\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n#include <bits/stdc++.h>\nusing namespace std;\n\nstruct Comp {\n bool operator()(const array<int,2>& a, const array<int,2>& b) {\n return a[1] < b[1];\n }\n};\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxRemoval(vector<int>& a, vector<vector<int>>& qu) {\n const int n = a.size();\n const int m = qu.size();\n \n sort(qu.begin(), qu.end(), \n [](const vector<int>& l, const vector<int>& r) {\n if (l[0] == r[0]) return l[1] < r[1];\n return l[0] < r[0];\n });\n\n priority_queue<array<int,2>, vector<array<int,2>>, Comp> pq;\n vector<int> delta(n+1, 0);\n\n int curr = 0;\n int needed = 0;\n int ptr = 0;\n\n for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {\n curr -= delta[i];\n while (ptr < m && qu[ptr][0] <= i) {\n pq.push({qu[ptr][0], qu[ptr][1]});\n ptr++;\n }\n if (pq.size()+curr < a[i]) {return -1;}\n while (!pq.empty() && curr < a[i]) {\n const auto t = pq.top();\n pq.pop();\n if (t[1] < i) continue;\n curr++;\n delta[t[1]+1]++;\n needed++;\n }\n\n if (curr < a[i]) {\n return -1;\n }\n\n }\n\n return m - needed;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Priority que and line sweep
|
priority-que-and-line-sweep-by-done_87-leal
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nGredily use the longest range to meet the nums[i] requirement.\n\n# Approach\n Describe
|
done_87
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-25T16:40:15.859182+00:00
|
2024-11-25T16:42:51.723506+00:00
| 62 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nGredily use the longest range to meet the nums[i] requirement.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nThe trick how u want to create a priority heap that takes into account when you are moving through length of nums. E.G if you are at i == 2 you h have two available queries [1,3] and [2,3] both has the applicable length of 2. This can be obtained by the end value which has the value of 3. It doenst matter the length is not 2 you just want to use the same base.\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: nlog(n) time, limited by the priority heap \n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(n), linear space\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def maxRemoval(self, nums: List[int], queries: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n\n\n lit = []\n queries.sort()\n heapq.heapify(lit)\n\n sweeper = [0]*(len(nums)+1)\n cur = 0\n idx = 0\n ans = 0\n\n\n for i in range(len(nums)):\n cur += sweeper[i]\n while idx<len(queries) and queries[idx][0] <=i:\n start, end = queries[idx]\n idx +=1\n dif = end + 1\n heapq.heappush(lit, [-dif, start, end])\n \n while len(lit) > 0 and cur<nums[i]:\n diff, start, end = heapq.heappop(lit)\n if i>=start and i<=end:\n ans+=1\n cur+=1\n sweeper[end+1] -=1\n if cur<nums[i]:\n return -1\n return len(queries) - ans\n\n \n\n\n\n\n \n\n\n\n\n \n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
JAVA 78ms(beats 100%) with PQ and sort, greedy
|
java-78msbeats-100-with-pq-and-sort-gree-iwts
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
meringueee
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-25T10:48:02.987637+00:00
|
2024-11-25T10:48:02.987669+00:00
| 51 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int maxRemoval(int[] n, int[][] q) {\n Arrays.sort(q, (o1,o2)->(o1[0]-o2[0]));\n int qi=0, c=0, a=0;\n int[] d = new int[n.length+1];\n\n PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder());\n\n for(int ni=0;ni<n.length; ni++){\n c+=d[ni];\n if(c<n[ni]){\n for(; qi<q.length&&q[qi][0]<=ni; qi++){\n if(q[qi][1]<ni);\n else pq.add(q[qi][1]);\n }\n while(c<n[ni]){\n if(pq.isEmpty() || pq.peek()<ni)return -1;\n c++; d[pq.poll()+1]--; a++;\n }\n }\n }\n return q.length-a;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
C++
|
c-by-saksham0037-ucjz
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
saksham0037
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-25T09:01:21.513639+00:00
|
2024-11-25T09:01:21.513674+00:00
| 17 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n#define PII pair<int, int> \n\nclass Compare {\n public: \n bool operator()(PII a, PII b) {\n if(a.second < b.second) {\n return true;\n }\n return false;\n }\n};\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n int i = 0, n = nums.size(), nq = queries.size();\n\n sort(queries.begin(), queries.end());\n\n priority_queue<PII, vector<PII>, Compare> myPq;\n\n int count = 0, used = 0, qInd = 0;\n unordered_map<int, int> endingCount;\n\n for(i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {\n\n while(qInd < nq && queries[qInd][0] == i) {\n myPq.push({queries[qInd][0], queries[qInd][1]});\n qInd++;\n }\n\n while(nums[i] > count) {\n PII top;\n if(!myPq.empty()) {\n top = myPq.top();\n myPq.pop();\n } else {\n //cout<< "Queue got empty i:" << i << "count: " << count << \'\\n\';\n return -1;\n }\n\n if(top.second < i) {\n //cout << "The second: " << top.second << " is lesser than i: " << \'\\n\';\n return -1;\n } \n\n endingCount[top.second]++;\n count++;\n }\n\n count -= endingCount[i];\n used += endingCount[i];\n }\n\n return nq - used;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Python | one Heap | O((n+q)log(n+q))
|
python-one-heap-onqlognq-by-aryonbe-1a81
|
Code\npython3 []\nclass Solution:\n def maxRemoval(self, nums: List[int], queries: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n queries.sort(key = lambda e: (e[0],-e[1]
|
aryonbe
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-25T02:01:11.975226+00:00
|
2024-11-25T02:01:11.975256+00:00
| 22 | false |
# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def maxRemoval(self, nums: List[int], queries: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n queries.sort(key = lambda e: (e[0],-e[1]))\n events = []\n for i,num in enumerate(nums):\n events.append((i,1,num))\n for j,(l,r) in enumerate(queries):\n events.append((l,0,j))\n events.append((r,2,j))\n events.sort()\n h = []\n passed = [False]*len(queries)\n covered = set()\n overlapped = 0\n res = 0\n for e,t,j in events:\n if t == 0:\n heappush(h, (-queries[j][1],j))\n overlapped += 1\n elif t == 2:\n overlapped -= 1\n if j in covered:\n covered.remove(j)\n res += 1\n passed[j] = True\n else:\n if j > overlapped:\n return -1\n while len(covered) < j:\n while passed[h[0][1]]:\n heappop(h)\n _,k = heappop(h)\n covered.add(k)\n return len(queries) - (res + len(covered))\n\n \n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Python | heap | O((n+q)log(n+q))
|
python-heap-onqlognq-by-aryonbe-smg0
|
Code\npython3 []\nclass Solution:\n def maxRemoval(self, nums: List[int], queries: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n queries.sort(key = lambda e: (e[0],-e[1]
|
aryonbe
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-25T01:46:00.870217+00:00
|
2024-11-25T01:46:00.870239+00:00
| 6 | false |
# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def maxRemoval(self, nums: List[int], queries: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n queries.sort(key = lambda e: (e[0],-e[1]))\n events = []\n for i,num in enumerate(nums):\n events.append((i,1,num))\n for j,(l,r) in enumerate(queries):\n events.append((l,0,j))\n events.append((r,2,j))\n events.sort()\n h = []\n passed = [False]*len(queries)\n covered = set()\n overlapped = 0\n res = 0\n for e,t,j in events:\n if t == 0:\n heappush(h, (-queries[j][1],j))\n overlapped += 1\n elif t == 2:\n overlapped -= 1\n if j in covered:\n covered.remove(j)\n res += 1\n passed[j] = True\n else:\n if j > overlapped:\n return -1\n while len(covered) < j:\n while passed[h[0][1]]:\n heappop(h)\n _,k = heappop(h)\n covered.add(k)\n return len(queries) - (res + len(covered))\n\n \n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
c++
|
c-by-lyronly-cje3
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
lyronly
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-24T23:54:12.483101+00:00
|
2024-11-24T23:54:12.483125+00:00
| 13 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nstruct cmp {\n bool operator()(const int& a, const int& b) const {\n return a > b;\n }\n};\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int n = 0;\n int mx = 0;\n vector<vector<int>> dp;\n int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& qs) {\n n = nums.size();\n int m = qs.size();\n dp.resize(n);\n for (auto& q : qs)\n {\n int l = q[0];\n int r = q[1];\n dp[l].push_back(r);\n }\n multiset<int, cmp> set;\n\n vector<int> arr(n + 1, 0);\n int cur = 0;\n int cnt = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)\n {\n for (auto r : dp[i])\n {\n set.insert(r);\n }\n int a = nums[i];\n cur += arr[i];\n auto iter = set.begin();\n int d = a - cur;\n for (int x = 0; x < d; x++)\n {\n if (set.empty()) break;\n int y = *iter;\n if (y < i) return -1;\n arr[y + 1]--;\n iter = set.erase(iter);\n cnt++;\n cur++;\n }\n // cout << i << "," << cnt << "," << cur << "," << set.size() << endl;\n if (cur < a) return -1;\n \n }\n return m - cnt;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
[C++][Sort + Priority queue]
|
csort-priority-queue-by-mumrocks-s5lq
|
Intuition\n1. Sort queries\n2. for each index in nums, only add elible query in priority queue and pull the longest item from PQ first. \n\n# Code\ncpp []\nclas
|
MumRocks
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-24T20:13:55.602732+00:00
|
2024-11-24T20:13:55.602758+00:00
| 26 | false |
# Intuition\n1. Sort queries\n2. for each index in nums, only add elible query in priority queue and pull the longest item from PQ first. \n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n auto l2 = [](vector<int> a, vector<int> b) {\n return a[1]<b[1];\n };\n int usedQuery=0,sz=nums.size(),qIndex=0;;\n sort(queries.begin(),queries.end());\n priority_queue<vector<int>, vector<vector<int>>, decltype(l2)> pq(l2);\n\n vector<int> prefixSum(sz+1);\n for (int i=0;i<sz;i++){\n if (i>0) prefixSum[i]+=prefixSum[i-1];\n if (nums[i]==0 || nums[i]<=prefixSum[i]) continue;\n while(!pq.empty() && pq.top()[1]<i){\n pq.pop();\n }\n \n while(qIndex<queries.size() && queries[qIndex][0]<=i){\n pq.push(queries[qIndex++]);\n }\n \n \n for(int j=0;!pq.empty()&&prefixSum[i]<nums[i];j++){\n if (pq.top()[1]>=i){\n prefixSum[i]+=1;\n prefixSum[pq.top()[1]+1]-=1;\n usedQuery++;\n }\n pq.pop();\n }\n if (prefixSum[i]<nums[i]) return -1;\n }\n return queries.size()-usedQuery;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Simple Priority Queue | Javascript
|
simple-priority-queue-javascript-by-nish-etzn
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nThe earlier approches for iterating through the \'prefix array\' doesn\'t work here.\nI
|
nishit-mangal
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-24T17:11:35.097008+00:00
|
2024-11-24T17:14:23.165538+00:00
| 31 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThe earlier approches for iterating through the \'prefix array\' doesn\'t work here.\nI want to exhaust the nums[i] from the query covering the maximum range. If nums[i] is still > 0, I will exhaust by smaller queries.\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n- I iterate through all the elements of nums array.\n- Accumulate all the queries covering i such that the query with largest end comes on the top. Use priority queue for the above.\n- Till now I have not started to exhaust the nums[i]\n- On all the queries in priority queue, start exhausting the nums[i] till the pq is empty or the nums[i]+prefix[i] becomes 0.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(nLog(n))\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(n)\n\n# Code\n```javascript []\n/**\n * @param {number[]} nums\n * @param {number[][]} queries\n * @return {number}\n */\nvar maxRemoval = function(nums, queries) {\n queries.sort((a,b)=>a[0]-b[0]);\n let pq = new MaxPriorityQueue({compare:(a,b)=>b[1]-a[1]});\n let prefixArray = new Array(nums.length+1).fill(0);\n let i=0, j=0;\n \n while(i<nums.length){\n if(i>0)\n prefixArray[i]+=prefixArray[i-1];\n \n while(j<queries.length && queries[j][0]<=i){\n pq.enqueue(queries[j]);\n j++;\n }\n \n while(!pq.isEmpty() && nums[i]+prefixArray[i]>0 && pq.front()[1]>=i){\n let [start, end] = pq.dequeue();\n prefixArray[i]--;\n prefixArray[end+1]++;\n }\n \n if(nums[i]+prefixArray[i]>0)\n return -1;\n i++;\n }\n \n return pq.size();\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Multiset with difference arrays
|
multiset-with-difference-arrays-by-puspe-ttai
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
puspendra_09
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-24T14:40:09.013874+00:00
|
2024-11-24T14:40:09.013942+00:00
| 14 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& Q) {\n long long int n = nums.size();\n multiset<pair<long long int,long long int>> m;\n \n vector<long long int> arr(n + 1 , 0);\n\n \n sort(Q.begin() , Q.end());\n long long int ptr = 0;\n long long int q = Q.size();\n long long int ans = 0;\n for(long long int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n while(ptr < q and Q[ptr][0] == i) {\n m.insert({Q[ptr][1] , Q[ptr][0]});\n ptr++;\n } \n long long val = 0;\n if(i) arr[i] += arr[i - 1];\n val = arr[i];\n if(val < nums[i]) {\n long long int diff = nums[i] - val;\n if(m.size() < diff) return -1;\n for(long long int j = 0; j < diff; j++) {\n long long int r = m.rbegin() -> first;\n long long int l = m.rbegin() -> second;\n arr[i]++;\n arr[r + 1]--;\n m.erase(--m.end());\n ans++;\n }\n }\n while(m.size() and m.begin() -> first <= i) {\n m.erase(m.begin());\n }\n }\n return q - ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Greedy', 'C++']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Beautiful solution ;)
|
beautiful-solution-by-user7634ri-7km1
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
user7634ri
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-24T13:12:31.536709+00:00
|
2024-11-24T13:12:31.536745+00:00
| 7 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n sort(queries.begin(), queries.end());\n\n priority_queue<vector<int>> pq; // {end, start} of query\n multiset<vector<int>> aqs; // {end, start} of query.\n \n\n int num_active_queries = 0;\n\n int i = 0, j = 0;\n\n int ans = 0;\n\n while (i < nums.size()) {\n while(!aqs.empty() && (*aqs.begin())[0] < i) {\n // end reached.\n aqs.erase(aqs.find(*aqs.begin()));\n num_active_queries --;\n }\n\n while(j < queries.size()) {\n if(queries[j][0] <= i && queries[j][1] >= i) {\n pq.push({queries[j][1], queries[j][0]});\n } else if(queries[j][0] > i) {\n break;\n }\n j ++;\n }\n\n // cout << i << " " << j << " " << num_active_queries << endl;\n\n while(nums[i] > num_active_queries && !pq.empty()) {\n auto it = pq.top();\n pq.pop();\n if(it[0] >= i) {\n aqs.insert(it);\n ans ++;\n num_active_queries ++;\n }\n }\n\n if(nums[i] > num_active_queries) {\n return -1;\n }\n i ++;\n }\n\n return queries.size() - ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
My Solution
|
my-solution-by-hope_ma-59t9
|
\n/**\n * Time Complexity: O(n + n_queries * log(n_queries))\n * Space Complexity: O(n + n_queries)\n * where `n` is the length of the vector `nums`\n */\nclass
|
hope_ma
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-24T13:05:02.905570+00:00
|
2024-11-24T13:05:02.905600+00:00
| 1 | false |
```\n/**\n * Time Complexity: O(n + n_queries * log(n_queries))\n * Space Complexity: O(n + n_queries)\n * where `n` is the length of the vector `nums`\n */\nclass Solution {\n public:\n int maxRemoval(const vector<int> &nums, vector<vector<int>> &queries) {\n const int n = static_cast<int>(nums.size());\n const int n_queries = static_cast<int>(queries.size());\n sort(queries.begin(), queries.end());\n priority_queue<int> pq;\n int diffs[n + 1];\n memset(diffs, 0, sizeof(diffs));\n int used = 0;\n for (int sum = 0, i_query = 0, i = 0; i < n; ++i) {\n for (; i_query < n_queries && queries[i_query].front() < i + 1; ++i_query) {\n pq.emplace(queries[i_query].back());\n }\n \n sum += diffs[i];\n while (sum < nums[i] && !pq.empty()) {\n const int end = pq.top();\n pq.pop();\n if (end > i - 1) {\n ++used;\n ++sum;\n --diffs[end + 1];\n }\n }\n \n if (sum < nums[i]) {\n return -1;\n }\n }\n return n_queries - used;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
priority queue solution + greedy (c++)
|
priority-queue-solution-greedy-c-by-vats-os7r
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
vatsalarora
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-24T12:16:10.203899+00:00
|
2024-11-24T12:16:10.203921+00:00
| 34 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n int n = nums.size();\n int m = queries.size();\n unordered_map<int, int> mp;\n unordered_map<int, int> mp1;\n\n \n for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {\n mp[queries[i][0]]++;\n mp1[queries[i][1]]++;\n }\n\n priority_queue<int> pq; \n unordered_map<int, vector<int>> temp;\n\n \n for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {\n temp[queries[i][0]].push_back(queries[i][1]);\n }\n\n multiset<int> m2; \n int overlaps = 0, newOverlaps = 0, ans = 0, lastUsed = 0;\n\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n \n if (mp.find(i) != mp.end()) {\n overlaps += mp[i];\n newOverlaps += mp[i];\n for (int end : temp[i]) {\n pq.push(end);\n }\n }\n\n if (nums[i] == 0) {\n \n //continue;\n } else if (nums[i] - overlaps == 0) {\n \n int required = nums[i] - lastUsed;\n if (required > 0) {\n ans += required;\n int x = 0;\n while (x < required) {\n if (pq.empty()) return -1; \n int y = pq.top();\n pq.pop();\n if (y >= i) {\n m2.insert(y);\n }\n x++;\n }\n lastUsed += required;\n }\n } else if (nums[i] - overlaps < 0) {\n \n if (lastUsed < nums[i]) {\n int required = nums[i] - lastUsed;\n int x = 0;\n while (x < required) {\n if (pq.empty()) return -1; \n int y = pq.top();\n pq.pop();\n if (y >= i) {\n m2.insert(y);\n }\n x++;\n }\n ans += required;\n lastUsed += required;\n }\n }\n\n \n if (nums[i] > overlaps) return -1;\n\n \n if (mp1.find(i) != mp1.end()) {\n overlaps -= mp1[i];\n\n \n m2.erase(i);\n\n \n lastUsed = m2.size();\n }\n //cout<<overlaps<<" "<<lastUsed<<endl;\n }\n\n return m - ans;\n }\n};\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Easy Solution using multiset
|
easy-solution-using-multiset-by-kvivekco-7rxm
|
idea is to use maximum r for an index and store not used l, r into a not_used multiset for further cases.\n\n# Code\ncpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int
|
kvivekcodes
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-24T12:01:25.554937+00:00
|
2024-11-24T12:01:25.554972+00:00
| 6 | false |
idea is to use maximum r for an index and store not used l, r into a not_used multiset for further cases.\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n int n = nums.size();\n vector<pair<int, int> > v;\n for(auto it: queries) v.push_back({it[0], it[1]});\n sort(v.begin(), v.end(),[](pair<int, int>& a, pair<int, int>& b){\n if(a.first == b.first) return a.second > b.second;\n else return a.first < b.first;\n });\n\n multiset<int> ms;\n multiset<int> not_used;\n\n int ind = 0;\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){\n while(!ms.empty() && *ms.begin() < i){\n ms.erase(ms.begin());\n }\n nums[i] -= int(ms.size());\n while(ind < v.size() && v[ind].first == i){\n not_used.insert(v[ind].second);\n ind++;\n }\n\n while(nums[i] > 0){\n if(not_used.empty() || *not_used.rbegin() < i) return -1;\n auto it = --not_used.end();\n ms.insert(*it);\n not_used.erase(it);\n nums[i]--;\n }\n\n }\n\n return not_used.size();\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Python (Simple BIT)
|
python-simple-bit-by-rnotappl-akoy
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
rnotappl
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-24T07:41:32.965097+00:00
|
2024-11-24T07:41:32.965130+00:00
| 6 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass BIT:\n def __init__(self, n):\n self.ans = [0]*(n+1)\n\n def update(self, i, val):\n while i < len(self.ans):\n self.ans[i] += val \n i += i&-i\n\n def query(self, i):\n total = 0 \n\n while i > 0:\n total += self.ans[i]\n i -= i&-i\n\n return total \n\nclass Solution:\n def maxRemoval(self, nums, queries):\n n, i, ans, total = len(nums), 0, [], len(queries)\n\n queries.sort()\n \n fenwick_tree = BIT(n)\n\n for j in range(n):\n while i < len(queries) and queries[i][0] <= j:\n heapq.heappush(ans,(-queries[i][1],queries[i][0]))\n i += 1 \n\n while nums[j] - fenwick_tree.query(j+1) > 0 and ans:\n total -= 1 \n x = heapq.heappop(ans)\n fenwick_tree.update(x[1]+1,1)\n fenwick_tree.update(-x[0]+2,-1)\n\n if nums[j] - fenwick_tree.query(j+1) > 0:\n return -1\n\n return total \n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
100% faster solution in c++
|
100-faster-solution-in-c-by-balram_54321-3gw4
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Balram_54321
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-24T06:53:46.526855+00:00
|
2024-11-24T06:53:46.526897+00:00
| 42 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n- O(nlog(n))\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n- O(n)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n typedef pair<int,int> Pr;\n struct MaxHeap{\n bool operator()(Pr p1, Pr p2){\n return p1.second<p2.second;\n }\n };\n \n int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n int n = nums.size();\n\n sort(queries.begin(), queries.end());\n\n int cnt =0;\n int ind =0;\n int ans=0;\n\n priority_queue<Pr, vector<Pr>, MaxHeap> pq;\n unordered_map<int,int> m;\n\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n // pull all entries from q\n while(ind<queries.size()&&queries[ind][0]==i){\n pq.push({queries[ind][0],queries[ind][1]});\n ind++;\n }\n\n\n while(nums[i]>cnt){\n if(pq.empty()) return -1;\n Pr p = pq.top();\n pq.pop();\n\n if(p.second<i) return -1;\n\n cnt++;\n m[p.second]++;\n }\n \n // remove all close entry\n cnt-=m[i];\n ans+=m[i];\n }\n\n return queries.size()-ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Priority_queue and Ordered_set solution
|
priority_queue-and-ordered_set-solution-h40ie
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Arif2321
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-24T06:17:07.642805+00:00
|
2024-11-24T06:17:07.642844+00:00
| 21 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n#include <bits/stdc++.h>\n#include <ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>\n#include <ext/pb_ds/tree_policy.hpp>\nusing namespace std;\nusing namespace __gnu_pbds;\ntemplate<class T>\nusing ordered_set = tree<T, null_type, less<T>, rb_tree_tag, tree_order_statistics_node_update>;\ntemplate<class T>\nusing ordered_multiset = tree<T, null_type, less_equal<T>, rb_tree_tag, tree_order_statistics_node_update>;\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& queries)\n {\n ordered_multiset<int> st;\n sort(queries.begin(),queries.end(),[&](vector<int> &a, vector<int> &b){\n return a[0] < b[0];\n });\n int cnt = 0;\n int j = 0;\n priority_queue<pair<int,int>> pq;\n for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++)\n {\n while(j < queries.size() && queries[j][0] <= i)\n {\n pq.push({queries[j][1],queries[j][0]});\n j++;\n }\n int on_right = st.size() - st.order_of_key(i);\n int val = nums[i]-on_right;\n while(val > 0)\n {\n if(pq.empty() || (pq.top().first < i))\n {\n return -1;\n }\n cnt++;\n st.insert(pq.top().first);\n val--;\n pq.pop();\n }\n }\n return queries.size()-cnt;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Beginner Friendly Solution using PriorityQueue
|
beginner-friendly-solution-using-priorit-rqka
|
\nclass Solution {\n public int maxRemoval(int[] nums, int[][] queries) {\n int count = 0, n = nums.length, j = 0;\n \n // To track, Ava
|
Codewarrior_0503
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-24T06:14:58.818839+00:00
|
2024-11-24T06:14:58.818873+00:00
| 95 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public int maxRemoval(int[] nums, int[][] queries) {\n int count = 0, n = nums.length, j = 0;\n \n // To track, Available Queries - sorted in Descending order, we greedily pick farthest end point\n PriorityQueue<Integer> availableQueries = new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder()); // It stores ending point of a query\n \n // To track the Used Queries so far & check its effect is Valid or not\n PriorityQueue<Integer> usedQueries = new PriorityQueue<>(); // It stores ending point of a query\n \n // Sorting Queries, so that we can quickly find & add queries available from current index\n Arrays.sort(queries, (a,b) -> a[0] - b[0]);\n \n // To keep track of effect of the Query\n int effect = 0;\n \n \n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n \n // Picking Queries starting from this index & adding it to Available Queries list, from which queries may or may not be used\n while(j < queries.length && queries[j][0] == i)\n {\n availableQueries.add(queries[j][1]);\n j++;\n }\n \n \n // Removing the effect of Earlier Used Queries, as it is not Valid at this point, if their ending point of those queries are earlier than this index\n while(!usedQueries.isEmpty() && usedQueries.peek() < i)\n {\n effect++; // to negate the effect of the query\n usedQueries.poll(); // removing the query from used list, so we can check whether next query endpoint is Valid or not.\n }\n \n \n // Check whether nums[i] + the effect of Used Valid Queries so far and still its greater than zero, if so we can try adding few more queries which is available \n while(nums[i] + effect > 0 && !availableQueries.isEmpty() && availableQueries.peek() >= i) \n {\n usedQueries.add(availableQueries.poll()); // Greedily picking farthest end point query from Available Valid Queries & adding it to Used Queries list\n count++; // we used one more query, so adding it\n effect--; // we used one more query, so counting its effect\n if(!availableQueries.isEmpty() && availableQueries.peek() < i) // while removing the queries, we might encounter queries which has endpoint less than current index, so no point in having them further, so clear it.\n availableQueries.clear();\n \n }\n \n \n if(nums[i] + effect > 0) // check even after processing, we are not able to bring it down to zero or lesser\n return -1;\n \n }\n \n return queries.length - count; // finally our ans will be Total Queries Length - Required Queries\n \n }\n}\n\n```\n\nTime Complexity : O(N log(q)) where N = nums length and Q = Queries length\nSpace Complexity : O(Q)
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Beats 100%
|
beats-100-by-mission_conquer-ui38
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
mission_conquer
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-24T04:39:24.555991+00:00
|
2024-11-24T04:39:24.556016+00:00
| 45 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int maxRemoval(int[] nums, int[][] queries) {\n Arrays.sort(queries, (x, y) -> {\n return x[0] == y[0] ? x[1] - y[1] : x[0] - y[0];\n });\n PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<int[]>((x, y) -> {\n return y[1] - x[1];\n });\n\n int arr[] = new int[nums.length + 2];\n int n = nums.length;\n int pos = 0;\n int anss = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n while (pos < queries.length && queries[pos][0] <= i)\n pq.add(queries[pos++]);\n if (i > 0)\n arr[i] += arr[i - 1];\n nums[i] = nums[i] - arr[i];\n while (nums[i] > 0) {\n if (pq.isEmpty())\n return -1;\n int t[] = pq.poll();\n if (t[1] >= i) {\n arr[i + 1]++;\n arr[t[1] + 1]--;\n nums[i]--;\n } else\n anss++;\n }\n }\n return anss + pq.size();\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Greedy Approach on it's ^PEAK^ | Double Priority Queue + Sorting Explained Solution
|
greedy-approach-on-its-peak-double-prior-iyje
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& q) {\n // Priority queue to store potential removable indices in
|
asif_star_135
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-24T04:30:07.382485+00:00
|
2024-11-24T04:30:07.382512+00:00
| 28 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& q) {\n // Priority queue to store potential removable indices in decreasing order\n priority_queue<int> candidate;\n\n // Priority queue to store the currently "chosen" indices in increasing order\n // This helps efficiently check and remove indices that are no longer valid\n priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<>> choosen;\n\n int n = nums.size(); // Number of elements in the nums array\n\n // Sort the queries `q` based on the starting index (q[i][0]) in ascending order\n sort(q.begin(), q.end(), [](vector<int> &a, vector<int> &b) {\n return a[0] < b[0];\n });\n\n int j = 0; // Pointer for iterating through the queries\n int ans = 0; // Count of successful removals\n\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n // Remove indices from `choosen` that are no longer valid (expired)\n while (choosen.size() && choosen.top() < i) {\n choosen.pop();\n }\n\n // Adjust the allowable removals for `nums[i]` based on the size of `choosen`\n nums[i] -= choosen.size();\n\n // Add all queries that start at index `i` to the candidate queue\n while (j < q.size() && q[j][0] == i) {\n candidate.push(q[j++][1]); // Push the ending index (q[j][1]) into the candidate queue\n }\n\n // Process candidates to fulfill `nums[i]` removals\n while (nums[i] > 0 && candidate.size() && candidate.top() >= i) {\n nums[i]--; // Decrease the number of removals needed for `nums[i]`\n choosen.push(candidate.top()); // Add the index to `choosen` as it\'s now in use\n ans++; // Increment the count of successful removals\n candidate.pop(); // Remove the used candidate from the queue\n }\n\n // If there are still removals needed for `nums[i]` but no valid candidates, return -1\n if (nums[i] > 0) return -1;\n }\n\n // Return the number of unfulfilled queries\n return q.size() - ans;\n }\n};\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Greedy', 'C', 'Sorting', 'Heap (Priority Queue)']
| 1 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Segment Tree (with Lazy Update, needed for last few test cases)
|
segment-tree-with-lazy-update-needed-for-1m4b
|
Intuition\nThe size constraints rule out an O(n^2) solution.\nFirst thoughts were to use a Binary Search, but the range updates pointed strongly to segment tree
|
LYjwjScNHF
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-23T21:37:49.504980+00:00
|
2024-11-23T21:37:49.505023+00:00
| 34 | false |
# Intuition\nThe size constraints rule out an O(n^2) solution.\nFirst thoughts were to use a Binary Search, but the range updates pointed strongly to segment trees.\nHave attached an LLM generated documentation of the code I wrote below -\n\n\nThe class `Solution` contains:\n\t\u2022\tPrivate Members:\n\t\u2022\t`vector<int> seg`: This is the segment tree array that stores the maximum values for segments of the input array.\n\t\u2022\t`vector<int> lseg`: This is the lazy propagation array that helps manage delayed updates to ranges in the segment tree.\n\nKey Functions\n\t1.\t`buildTree`:\n\t\u2022\tThis function constructs the segment tree.\n\t\u2022\tIt recursively divides the array into segments and computes the maximum value for each segment.\n\t\u2022\tThe base case occurs when `low` equals `high`, meaning it has reached a leaf node, and it assigns the corresponding value from `nums`.\n\t2.\t`lazyupdate`:\n\t\u2022\tThis function applies any pending updates stored in the `lseg` array to the segment tree.\n\t\u2022\tIf there are pending updates (i.e., `lsegindex != 0`), it updates the current segment\u2019s value and propagates the update to its children if necessary.\n\t3.\t`update`:\n\t\u2022\tThis function updates a range of indices in the segment tree.\n\t\u2022\tIt first calls `lazyupdate` to apply any pending updates.\n\t\u2022\tIf the update range (`ll`, `hh`) does not overlap with the current segment (`low`, `high`), it returns early.\n\t\u2022\tIf the current segment is fully within the update range, it decrements the segment value and marks its children for lazy updates.\n\t\u2022\tIf only part of the current segment is within the update range, it recursively updates its left and right children.\n\t4.\t`val`:\n\t\u2022\tThis function retrieves the value at a specific index in the original array while applying any pending updates.\n\t\u2022\tIt checks if the index is out of bounds and then applies lazy updates before returning the value.\n\t5.\t`numVal`:\n\t\u2022\tA convenience function that calls `val` with appropriate parameters to get the value at a specific index.\n\t6.\t`maxRemoval`:\n\t\u2022\tThis is the main function that processes a series of queries on an input array `nums`.\n\t\u2022\tIt initializes the segment tree and sorts queries based on their first element.\n\t\u2022\tIt uses a priority queue to manage ranges for removal based on queries.\n\t\u2022\tThe outer loop iterates through each index of `nums`, while inner loops handle adding new queries to the priority queue and updating segments until all possible removals are completed or no more valid removals can be made.\n\nDetailed Explanation of `maxRemoval`\n\t\u2022\tThe function starts by initializing the segment tree and lazy propagation arrays based on the size of `nums`.\n\t\u2022\tIt sorts queries in ascending order based on their starting index.\n\t\u2022\tA priority queue is used to manage end indices of queries, allowing efficient access to which ranges can be processed for removal.\n\t\u2022\tThe outer loop iterates over each index in `nums`, checking if there are any queries that can be processed at that index.\n\t\u2022\tFor each index, while there are still values greater than zero (indicating elements that can be removed), it pops from the priority queue and applies updates to decrement those elements in that range, marking them as removed.\n\t\u2022\tThe process continues until either all elements are removed or no more valid removals can be made.\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\nprivate:\n vector<int> seg;\n vector<int> lseg;\npublic:\n void buildTree(int index, int low, int high, vector<int>& nums){\n if(low==high){\n seg[index] = nums[low];\n return;\n }\n int mid = (low+high)/2;\n buildTree(2*index+1, low, mid, nums);\n buildTree(2*index+2, mid+1, high, nums);\n seg[index] = max(seg[2*index+1], seg[2*index+2]);\n }\n void lazyupdate(int index, int low, int high){\n if(lseg[index]!=0){\n seg[index] -= lseg[index];\n if(low!=high){\n lseg[2*index+1] += lseg[index];\n lseg[2*index+2] += lseg[index];\n }\n lseg[index]=0;\n }\n }\n void update(int index, int low, int high, int ll, int hh){\n lazyupdate(index, low, high);\n if(ll>high || hh<low) return;\n if(low==high){\n seg[index] = seg[index]-1;\n return;\n }\n if(low>=ll && high<=hh){\n seg[index]-=1;\n lseg[2*index+1]+=1;\n lseg[2*index+2]+=1;\n return;\n }\n int mid = (low+high)/2;\n update(2*index+1, low, mid, ll, hh);\n update(2*index+2, mid+1, high, ll, hh);\n seg[index] = max(seg[2*index+1], seg[2*index+2]);\n return;\n }\n int val(int index, int low, int high, int idx){\n lazyupdate(index, low, high);\n if(idx<low || idx>high) return INT_MAX;\n if(low==high && low==idx){\n return seg[index];\n }\n int mid = (low+high)/2;\n int left = val(2*index+1, low, mid, idx);\n int right = val(2*index+2, mid+1, high, idx);\n return right==INT_MAX ? left : right;\n }\n int numVal(int idx, int n){\n return val(0, 0, n-1, idx);\n }\n int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& q) {\n int n = nums.size();\n seg = vector<int>(4*n + 1, 0);\n lseg = vector<int>(4*n + 1, 0);\n buildTree(0, 0, n-1, nums);\n sort(q.begin(), q.end());\n priority_queue<int> pq;\n int count = q.size();\n int index = 0;\n int qi = 0;\n cout<<"qsize"<<q.size()<<endl;\n while(index<nums.size()){\n while(qi<q.size() && q[qi][0]<=index){\n pq.push(q[qi][1]);\n qi++;\n }\n while(numVal(index, n)>0){\n if(pq.empty()) return -1;\n int r = pq.top(); pq.pop();\n if(r<index){\n continue;\n }\n update(0, 0, n-1, index, r);\n // for(int i=0; i<n; i++){\n // cout<<numVal(i, n)<<" ";\n // }\n // cout<<endl;\n count--;\n }\n index++;\n }\n return count;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
[C++] Difference + Greedy
|
c-difference-greedy-by-projectcoder-dljc
|
CODE:\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& queries) { int n = nums.size(), T = queries.size();\n
|
projectcoder
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-23T17:57:00.421429+00:00
|
2024-11-23T18:01:11.967787+00:00
| 88 | false |
**CODE:**\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& queries) { int n = nums.size(), T = queries.size();\n // Prework 0: \n int a[n+10];\n for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) a[i] = nums[i-1];\n\n // Prework 1: Sort all queries\n for (auto& e : queries) e[0]++, e[1]++;\n sort(queries.begin(), queries.end(), [&](auto& l, auto& r){ return l[0]==r[0]?l[1]<r[1]:l[0]<r[0]; });\n\n // Max-Heap \n priority_queue<int> que;\n\n\n int d[n+10]; \n memset(d, 0, sizeof(d));\n\n int ans = 0, pos = 0;\n for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { \n // Difference Array \n d[i] += d[i-1];\n\n // Push [i, r] into the heap \n while (pos < T && queries[pos][0] == i) que.push(queries[pos++][1]);\n\n // Greedy: Choose the interval that covers the furthest position currently\n while (!que.empty() && d[i] < a[i]) {\n int e = que.top(); que.pop(); \n if (e < i) { ans++; continue; } \n \n d[i]++;\n d[e+1]--;\n }\n\n if (d[i] < a[i]) return -1;\n }\n\n return ans + que.size() + (T - pos);\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
sorting, priority_queue, c++
|
sorting-priority_queue-c-by-kamal__nath-q4a9
|
solved after contest;\nhere we make individual element zero\nand first we consider the longest end point that constains current point greedily\n# Complexity\n-
|
reporite
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-23T17:13:56.951991+00:00
|
2024-11-23T17:26:47.179919+00:00
| 56 | false |
solved after contest;\nhere we make individual element zero\nand first we consider the longest end point that constains current point greedily\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n // to check if it possible make zero array with all queries\n bool ispos(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& qu){\n int n = nums.size();\n vector<int> diff(n + 1, 0);\n for(auto v : qu){\n diff[v[0]]--;\n diff[v[1] + 1]++;\n }\n for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){\n diff[i] += diff[i - 1];\n }\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){\n if(nums[i] + diff[i] > 0) return false;\n }\n return true;\n }\n int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& qu) {\n //to the queries in order we sort\n sort(qu.begin(), qu.end());\n if(!ispos(nums, qu)) return -1;\n int n = nums.size(), q = qu.size(), used = 0;\n priority_queue<pair<int, int>> pq;\n vector<int> diff(n + 1, 0);\n for(int i = 0, j = 0; i < n; i++){\n if(i != 0){\n diff[i] += diff[i - 1];\n }\n int curr = nums[i];\n curr += diff[i];\n //pushing all queries thats constains i\n while(j < q and qu[j][0] <= i){\n pq.push({qu[j][1], qu[j++][0]});\n }\n while(curr > 0 and !pq.empty()){\n auto [r, l] = pq.top();\n pq.pop();\n // the query wont effect current element\n if(r < i){\n continue;\n }\n used++;\n curr -= 1;\n diff[i] -= 1;\n diff[r + 1] += 1;\n }\n }\n return q - used;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
C++ | Beats 100% | Priority_queue + Sweep Line
|
c-beats-100-priority_queue-sweep-line-by-ahle
|
Intuition\nI was unable to solve the problem during contest but just after the contest i was able to do it felt bad. for every index we need atleast nums[index]
|
n1kh1l
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-23T16:40:15.348628+00:00
|
2024-11-23T16:40:15.348646+00:00
| 125 | false |
# Intuition\nI was unable to solve the problem during contest but just after the contest i was able to do it felt bad. for every index we need atleast nums[index] queries to make it 0. sort the queries processing from first index will make life easy. Push the queries in your queue as long as they contain that index in the range and sort them with furthermost index so if we process any query it can effect maximum ranges, only process till your current value becomes zero, now sweeping the line for whole array will result in counting some values multiple times so only process the values for current index, do this before starting to push your values in max heap so that if the value already became zero you do not need to process it the size of the max heap is the unprocessed queries\n\n# Approach\nuse priority_queue sort the ranges for each index as you process based on max length and then pop the values subtracting the 1 from each range\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(NlogN)\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(N)\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n\n ios::sync_with_stdio(false);\n cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);\n priority_queue<pair<int,int>> pq;\n int n = queries.size();\n sort(queries.begin(), queries.end());\n vector<int> v(nums.size() + 1, 0);\n int i = 0, k = 0;\n while (k < nums.size()) {\n if (k > 0)\n v[k] += v[k - 1];\n while (i < n && queries[i][0] <= k)\n pq.push({queries[i][1], queries[i][0]}), i++;\n while (k < nums.size() && !pq.empty() && nums[k] + v[k] > 0 && pq.top().first >= k) {\n v[k] -= 1;\n v[pq.top().first + 1] += 1;\n pq.pop();\n }\n if (nums[k] + v[k] > 0)\n return -1;\n \n k++;\n }\n\n return pq.size();\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
sort + heap + sweepline
|
sort-heap-sweepline-by-andimeo-uc53
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
andimeo
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-23T16:28:03.755052+00:00
|
2024-11-23T16:28:03.755074+00:00
| 121 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nfrom sortedcontainers import SortedList\n\nclass Solution:\n def maxRemoval(self, nums: List[int], queries: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n n = len(nums)\n queries.sort(key=lambda q: q[0])\n\n d = [0] * (n + 1)\n hp = []\n cnt = 0\n j = 0\n for i in range(n):\n while j < len(queries) and queries[j][0] <= i:\n heappush(hp, -queries[j][1])\n j += 1\n k = 0\n cnt += d[i]\n while cnt < nums[i]:\n if len(hp) == 0:\n break\n e = -heappop(hp)\n if e < i:\n break\n cnt += 1\n d[e+1] += -1\n if cnt < nums[i]:\n return -1\n return len(hp)\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
100% beat in all
|
100-beat-in-all-by-somenath___singh-cogl
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n log(n))\n Add your time complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n\n- Space complexity: O(n)\n Add your space complexity here, e.g. O(n) \
|
alpha_numerics
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-23T16:22:33.969952+00:00
|
2024-11-23T16:22:33.969985+00:00
| 54 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n log(n))\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(n)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n static bool comp(vector<int>&a,vector<int>&b){\n return a[0]<b[0];\n }\n int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& q) {\n sort(q.begin(),q.end(),comp);\n vector<int>t(nums.size(),0);\n priority_queue<int>l;\n int tn=0;\n int in=0;\n for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){\n nums[i]=max(0,nums[i]-tn);\n while(in<q.size() && q[in][0]==i){\n l.push(q[in][1]);\n in++;\n }\n while(nums[i] && !l.empty() && l.top()>=i)nums[i]--,tn++,t[l.top()]++,l.pop();\n if(nums[i])return -1;\n tn-=t[i];\n }\n return l.size();\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
BEATS 100% || Java Solution || Optimum Solution
|
beats-100-java-solution-optimum-solution-4lwp
|
Intuition\n- The problem aims to determine the maximum number of elements that can be removed from an array given a set of constraints defined by queries. Each
|
yallavamsipavan1234
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-23T16:19:39.928392+00:00
|
2024-11-23T16:19:39.928429+00:00
| 175 | false |
# Intuition\n- The problem aims to determine the maximum number of elements that can be removed from an array given a set of constraints defined by queries. Each query specifies a range within which removals can be made. The goal is to ensure that the constraints are satisfied while maximizing the number of elements removed.\n\n# Approach\n- Sort the Queries: The queries are sorted based on their starting index. This helps in processing them in a sequential manner.\n\n- Priority Queue for End Points: A max-priority queue (max-heap) is used to keep track of the end points of the active queries. This allows efficient retrieval of the maximum end point.\n\n- Difference Array: A difference array diffs is maintained to track the number of removals to be adjusted.\n\n- Processing Elements:\n\n - For each element in the nums array, the current difference (cur) is adjusted using the difference array.\n\n - While the current removals are less than the required removals (nums[i]), the max-heap is used to find a range that can still be used for removals, and adjustments are made to the difference array.\n\n - If it\'s impossible to satisfy the removal requirement for any element, the function returns -1.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: `O(Q*logQ)`\n\n- Space complexity: `O(N*logQ)`\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int maxRemoval(int[] nums, int[][] queries) {\n Arrays.sort(queries, (a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);\n PriorityQueue<Integer> last = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> b - a);\n int[] diffs = new int[nums.length + 1];\n int idx = 0;\n int cur = 0;\n for(int i=0; i<nums.length; i++) {\n while(idx < queries.length && queries[idx][0] == i) {\n last.add(queries[idx][1]);\n idx++;\n }\n cur += diffs[i];\n while(cur < nums[i] && !last.isEmpty() && last.peek() >= i) {\n cur++;\n diffs[last.poll() + 1]--;\n }\n if(cur < nums[i]) {\n return -1;\n }\n }\n return last.size(); \n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Sorting', 'Heap (Priority Queue)', 'Java']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Segment Tree Solution | | C++
|
segment-tree-solution-c-by-adiipareek-hykc
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
adiipareek
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-23T16:06:17.273369+00:00
|
2024-11-23T16:06:17.273403+00:00
| 266 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass SegmentTree {\nprivate:\n vector<int> tree, lazy;\n int n;\n\n void propagate(int node, int start, int end) {\n if (lazy[node] != 0) {\n tree[node] += lazy[node]; // Apply the pending update\n\n // If not a leaf node, propagate the laziness to the children\n if (start != end) {\n lazy[2 * node + 1] += lazy[node]; // Left child\n lazy[2 * node + 2] += lazy[node]; // Right child\n }\n\n // Clear the lazy value for the current node\n lazy[node] = 0;\n }\n }\n\n void build(const vector<int>& arr, int node, int start, int end) {\n if (start == end) {\n tree[node] = arr[start];\n } else {\n int mid = start + (end - start) / 2;\n int leftChild = 2 * node + 1;\n int rightChild = 2 * node + 2;\n build(arr, leftChild, start, mid);\n build(arr, rightChild, mid + 1, end);\n tree[node] = max(tree[leftChild], tree[rightChild]);\n }\n }\n\n int query(int node, int start, int end, int l, int r) {\n propagate(node, start, end); // Apply any pending updates\n\n if (r < start || end < l) {\n return INT_MIN;\n }\n if (l <= start && end <= r) {\n return tree[node];\n }\n\n int mid = start + (end - start) / 2;\n int leftChild = 2 * node + 1;\n int rightChild = 2 * node + 2;\n int leftMin = query(leftChild, start, mid, l, r);\n int rightMin = query(rightChild, mid + 1, end, l, r);\n return max(leftMin, rightMin);\n }\n\n void update(int node, int start, int end, int l, int r, int value) {\n propagate(node, start, end); // Apply any pending updates\n\n if (r < start || end < l) {\n return;\n }\n if (l <= start && end <= r) {\n tree[node] += value;\n if (start != end) {\n lazy[2 * node + 1] += value; // Mark left child for update\n lazy[2 * node + 2] += value; // Mark right child for update\n }\n return;\n }\n\n int mid = start + (end - start) / 2;\n int leftChild = 2 * node + 1;\n int rightChild = 2 * node + 2;\n update(leftChild, start, mid, l, r, value);\n update(rightChild, mid + 1, end, l, r, value);\n tree[node] = max(tree[leftChild], tree[rightChild]);\n }\n\npublic:\n SegmentTree(const vector<int>& arr) {\n n = arr.size();\n tree.resize(4 * n, INT_MIN);\n lazy.resize(4 * n, 0); // Initialize the lazy array with 0\n build(arr, 0, 0, n - 1);\n }\n\n int query(int l, int r) {\n return query(0, 0, n - 1, l, r);\n }\n\n void update(int l, int r, int value) {\n update(0, 0, n - 1, l, r, value);\n }\n};\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& q) {\n int n = nums.size();\n int m = q.size();\n\n vector<int> prefixSum(n + 1, 0);\n for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {\n int l = q[i][0], r = q[i][1];\n prefixSum[l] -= 1;\n prefixSum[r + 1] += 1;\n }\n\n int current = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {\n current += prefixSum[i];\n nums[i] += current;\n if (nums[i] > 0) return -1;\n }\n\n SegmentTree segTree(nums);\n int removableCount = 0;\n sort(q.begin(), q.end(), [](auto a, auto b) {\n return a[1] - a[0] == b[1] - b[0] ? a[0] == b[0] ? a[1] < b[1] : a[0] < b[0] : a[1] - a[0] < b[1] - b[0];\n });\n\n for (const auto& query : q) {\n int l = query[0], r = query[1];\n if (segTree.query(l, r) < 0) {\n ++removableCount;\n segTree.update(l, r, 1); // Remove the query by updating the range\n }\n }\n\n return removableCount;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Segment Tree', 'C++']
| 2 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Heap
|
heap-by-mustafaansari-7c1q
|
\n# Code\npython3 []\nfrom heapq import heappush, heappop\n\nclass Solution:\n def maxRemoval(self, nums, queries):\n queries.sort()\n candidat
|
mustafaansari
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-23T16:05:03.682323+00:00
|
2024-11-23T16:05:03.682359+00:00
| 71 | false |
\n# Code\n```python3 []\nfrom heapq import heappush, heappop\n\nclass Solution:\n def maxRemoval(self, nums, queries):\n queries.sort()\n candidate = [] \n chosen = [] \n ans = 0\n n = len(nums)\n j = 0\n \n for i in range(n):\n while j < len(queries) and queries[j][0] == i:\n heappush(candidate, -queries[j][1]) \n j += 1\n \n nums[i] -= len(chosen)\n \n while nums[i] > 0 and candidate and -candidate[0] >= i:\n ans += 1\n heappush(chosen, -heappop(candidate)) \n nums[i] -= 1\n \n if nums[i] > 0:\n return -1\n \n while chosen and chosen[0] == i:\n heappop(chosen)\n \n return len(queries) - ans\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Greedy: use query with furthest endpoint
|
greedy-use-query-with-furthest-endpoint-xj6d8
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
evanhe1
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-23T16:02:32.024653+00:00
|
2024-11-23T16:06:20.832046+00:00
| 241 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(n\\log n)$$\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(n)$$\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxRemoval(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {\n multiset<int> pool;\n multiset<int> used;\n sort(queries.begin(), queries.end(), [](vector<int>& a, vector<int>& b) {\n if (a[0] != b[0]) {\n return a[0] < b[0];\n }\n return a[1] > b[1];\n });\n\n int cur = 0;\n int j = 0;\n int sol = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {\n while (used.size() && *used.begin() == i) {\n cur--;\n used.erase(used.begin());\n }\n while (pool.size() && * pool.begin() == i) {\n pool.erase(pool.begin());\n }\n while (cur < nums[i] && (j < queries.size() && queries[j][0] <= i || pool.size())) {\n if (j < queries.size() && queries[j][0] == i && pool.size()) {\n auto p = *pool.rbegin();\n auto q = queries[j];\n if (p > q[1]) {\n used.insert(p);\n pool.erase(prev(pool.end()));\n } else {\n used.insert(q[1]+1);\n j++;\n }\n } else if (pool.size()) {\n auto p = *pool.rbegin();\n used.insert(p);\n pool.erase(prev(pool.end()));\n } else if (j < queries.size() && queries[j][0] <= i) {\n auto q = queries[j];\n used.insert(q[1]+1);\n j++;\n }\n cur++;\n sol++;\n }\n if (cur < nums[i]) return -1;\n\n while (j < queries.size() && queries[j][0] == i) {\n pool.insert(queries[j][1]+1);\n j++;\n }\n \n }\n return queries.size()-sol;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
zero-array-transformation-iii
|
Go || Two heap
|
go-two-heap-by-ligt-cga7
|
\nThis problem similar to last week \nCheckout my other, use heap as well\nhttps://leetcode.com/problems/zero-array-transformation-ii/solutions/6053396/go-min-h
|
ligt
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-23T16:01:50.211643+00:00
|
2024-11-23T16:28:43.455060+00:00
| 52 | false |
\nThis problem similar to last week \nCheckout my other, use heap as well\nhttps://leetcode.com/problems/zero-array-transformation-ii/solutions/6053396/go-min-heap/\n\n# Code\n```golang []\nfunc maxRemoval(nums []int, queries [][]int) int {\n\tslices.SortFunc(queries, func(a, b []int) int {\n\t\tif a[0] == b[0] {\n\t\t\treturn b[1] - a[1] \n\t\t}\n\t\treturn a[0] - b[0] \n\t})\n\n\tused := priorityqueue.New[int]() \n\tq := priorityqueue.NewWith(func(x, y int) int { return y - x }) \n\n\tqueryIndex := 0\n\tusedCount := 0\n\n\tfor i := range nums {\n\t\tfor !used.Empty() {\n\t\t\ttop, _ := used.Peek()\n\t\t\tif i <= top {\n\t\t\t\tbreak\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t\tused.Dequeue()\n\t\t}\n\n\t\tfor queryIndex < len(queries) {\n\t\t\tstart, end := queries[queryIndex][0], queries[queryIndex][1]\n\t\t\tif end < i {\n\t\t\t\tqueryIndex++\n\t\t\t\tcontinue\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t\tif start > i {\n\t\t\t\tbreak\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t\tq.Enqueue(end)\n\t\t\tqueryIndex++\n\t\t}\n\n\t\tfor used.Size() < nums[i] {\n\t\t\ttop, ok := q.Peek()\n\t\t\tif !ok || top < i {\n\t\t\t\treturn -1\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t\tused.Enqueue(top)\n\t\t\tq.Dequeue()\n\t\t\tusedCount++\n\t\t}\n\t}\n\n\treturn len(queries) - usedCount\n}\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Heap (Priority Queue)', 'Go']
| 0 |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.