question_slug
stringlengths 3
77
| title
stringlengths 1
183
| slug
stringlengths 12
45
| summary
stringlengths 1
160
⌀ | author
stringlengths 2
30
| certification
stringclasses 2
values | created_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| updated_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| hit_count
int64 0
10.6M
| has_video
bool 2
classes | content
stringlengths 4
576k
| upvotes
int64 0
11.5k
| downvotes
int64 0
358
| tags
stringlengths 2
193
| comments
int64 0
2.56k
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Beats 100%
|
beats-100-by-ankitasin29-aotl
|
Code
|
Ankitasin29
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-27T04:21:45.830954+00:00
|
2024-12-27T04:21:45.830954+00:00
| 73 | false |
# Code
```golang []
func maxScoreSightseeingPair(values []int) int {
n:=len(values)
ans := 0
a := values[0]
for i:=1;i<n;i++{
b := values[i]-i
ans = max(ans,a+b)
a = max(a,values[i]+i)
}
return ans
}
```
| 3 | 0 |
['Go']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
We only need to maintain maximum maxtill (maxtill + values[i]-i) short & clean code in C++||Runs 0ms
|
we-only-need-to-maintain-maximum-maxtill-u9om
|
ApproachComplexity
Time complexity: O(N)
Space complexity: O(1)
Code
|
Harsh-X
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-27T01:02:49.381106+00:00
|
2024-12-27T01:02:49.381106+00:00
| 85 | false |
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity: **O(N)**
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity: **O(1)**
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
#pragma GCC target ("sse,sse2,sse3,ssse3,sse4,popcnt,abm,mmx,avx")
#pragma GCC optimize ("O3", "unroll-loops", "Ofast", "-ffloat-store")
static const auto harsh = []() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
return 'c';
}();
class Solution {
public:
int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {
int ans = 0;
int maxi = values[0];
for(int i = 1; i<values.size(); i++){
ans = max(ans, (maxi + values[i]-i));
maxi = max(maxi, values[i]+i);
}
return ans;
}
};
```

| 3 | 1 |
['Array', 'Greedy', 'C++']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Simple and Easy - One Pass
|
simple-and-easy-one-pass-by-mohit94596-rxkr
|
Start from first values. Take a variable to keep track of the maximum value which has already occured. As you move forward, with each step decrease 1 from the p
|
mohit94596
|
NORMAL
|
2023-08-08T10:06:50.277061+00:00
|
2023-08-08T10:06:50.277086+00:00
| 55 | false |
Start from first values. Take a variable to keep track of the maximum value which has already occured. As you move forward, with each step decrease 1 from the prevMax, because at every step i-j is increasing by 1. \nFind maxScore = max(maxScore, prevMax + values[i]). \nAlso, at every step update the prevMax as prevMax = max(prevMax, values[i])\n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, values: List[int]) -> int:\n prevMax = values[0]\n maxScore = -inf\n for i in range(1, len(values)):\n prevMax -= 1\n maxScore = max(maxScore, prevMax + values[i])\n prevMax = max(prevMax, values[i])\n return maxScore\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Python']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
🔥🚀 Kotlin/Java O(n) time & O(1) space easy solution
|
kotlinjava-on-time-o1-space-easy-solutio-ul87
|
Approach\nThe hint is to compute best first pairing for index i (at i > 0) at each run and then sum it up with current value, the maximum of these summaries is
|
Klemo1997
|
NORMAL
|
2023-02-16T21:48:39.335639+00:00
|
2023-02-16T21:48:39.335670+00:00
| 530 | false |
# Approach\nThe hint is to compute best first pairing for index i (at i > 0) at each run and then sum it up with current value, the maximum of these summaries is the answer.\n\nSo basically:\n\n1. set current optimal to values[0]\n2. at index i -> find out if it is more suitable to reuse previous currentOptimal (decremented, because it is 1 more index further) or to use previous value. This gives us optimal choice for first sigthseeing in pair. \n3. Then sum up currentOptimal + values[i]\n4. If it is larger than max, assign to max\n5. return max\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n$$O(n)$$\n\n- Space complexity:\n$$O(1)$$\n\n```kotlin []\nclass Solution {\n fun maxScoreSightseeingPair(values: IntArray): Int {\n var max = Int.MIN_VALUE\n var currentOptimal = values[0]\n\n for (i in 1 until values.size) {\n currentOptimal = maxOf(currentOptimal-1, values[i-1]-1)\n max = maxOf(max, currentOptimal+values[i])\n }\n return max\n }\n}\n```\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values) {\n int n = values.length;\n int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;\n int currentOptimal = values[0];\n\n for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {\n currentOptimal = Math.max(currentOptimal-1, values[i-1]-1);\n max = Math.max(max, currentOptimal + values[i]);\n }\n\n return max;\n }\n}\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'Java', 'Kotlin']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
c++ solution in 1 traversal ✔
|
c-solution-in-1-traversal-by-1911uttam-157c
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& arr) {\n int currMax= arr[0], ans= INT_MIN;\n \n for(int i=1;i<ar
|
1911Uttam
|
NORMAL
|
2023-01-24T12:03:24.323688+00:00
|
2023-01-24T12:03:24.323718+00:00
| 486 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& arr) {\n int currMax= arr[0], ans= INT_MIN;\n \n for(int i=1;i<arr.size();i++){\n ans= max(ans, currMax+arr[i]-i);\n currMax= max(currMax, arr[i]+i);\n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['C', 'C++']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
✔️RECURSION+MEMOIZATION || PICK OR NOT PICK INTUITIVE AND SIMPLE
|
recursionmemoization-pick-or-not-pick-in-1g5f
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<vector<int>> dp;\n int check(int i, int c,vector<int>& v)\n {\n if(i==v.size()) return -1e9;\n if(dp
|
Lash_Hope
|
NORMAL
|
2022-11-22T20:42:15.739467+00:00
|
2022-11-22T20:45:17.942864+00:00
| 579 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<vector<int>> dp;\n int check(int i, int c,vector<int>& v)\n {\n if(i==v.size()) return -1e9;\n if(dp[i][c]!=-1) return dp[i][c];\n int skip=check(i+1,c,v); // we do not consider this element for our pair and move to next element \n if(c) return dp[i][c]= max(skip,v[i]+i+check(i+1,0,v)); // we consider this as first element of our pair\n return dp[i][c]= max(skip,v[i]-i); //we consider this as our second element of our pair\n }\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {\n dp.resize(values.size(),vector<int>(2,-1));\n return check(0,1,values);\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 1 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'C']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
C++ simple different approach O(n) time + O(1) space
|
c-simple-different-approach-on-time-o1-s-fje2
|
\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {\n int ans = 0, prev = values[0];\n for(int i = 1; i < values.size(); i++){\n a
|
wowarys
|
NORMAL
|
2022-09-14T18:17:57.391785+00:00
|
2022-09-14T18:17:57.391826+00:00
| 718 | false |
```\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {\n int ans = 0, prev = values[0];\n for(int i = 1; i < values.size(); i++){\n ans = max(ans, prev - 1 + values[i]);\n prev = max(values[i], prev - 1);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n```\n\nI haven\'t seen an approach decreasing a current maximum anywhere. So the logic is at each day we decrease the current sum by 1 or pick current day as highest sum. It works because for each day `i` will be equal to `j` and `i - j == 0`.
| 3 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C', 'C++']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Simple C++ Solution || Commented
|
simple-c-solution-commented-by-rkkumar42-gely
|
Please upvote if you like my solution .\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& v) {\n // to store best start site til
|
rkkumar421
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-26T18:59:23.273318+00:00
|
2022-08-26T18:59:23.273356+00:00
| 504 | false |
**Please upvote if you like my solution .**\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& v) {\n // to store best start site till index i\n vector<int> i(v.size());\n i[0] = v[0] + 0;\n // filling array\n for(int x = 1; x<v.size();x++)\n i[x] = max(i[x-1], v[x] + x);\n int ans = 0;\n // searching best macth with every end site\n for(int x=1;x<v.size();x++)\n if(ans < v[x] - x + i[x-1]) ans = v[x] - x + i[x-1];\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
C++ | Very Easy O(n) Code with Explanation
|
c-very-easy-on-code-with-explanation-by-myyyl
|
Explanation : \n\nSuppose we have [8,1,9,2,5]\nSuppose the current index is j & second index we will take be x (x>j).\nThe value = (value[j] + j) + (values[x] -
|
ankit4601
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-29T08:36:12.415949+00:00
|
2022-07-29T08:36:12.415986+00:00
| 345 | false |
Explanation : \n\nSuppose we have [8,1,9,2,5]\nSuppose the current index is j & second index we will take be x (x>j).\nThe value = (value[j] + j) + (values[x] - x) ;\n\nSo whatever be the x, if we, moving from 0 -> n, keep track of the maximum ( index + val[index] ), then we can optimally find the best pairs. \n\nPlease Upvote :)\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {\n int j=0;\n int res=0;\n // store max of values[j] + j as you move forward. \n for(int i=1;i<values.size();i++)\n {\n res=max(res,values[i]+values[j]+j-i);\n if(values[i]+i > values[j]+j)\n j=i;\n }\n return res;\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['C', 'C++']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Best Sightseeing Pair | Explained | BruteForce and DP one pass
|
best-sightseeing-pair-explained-brutefor-byv1
|
1. Brute Force Soulution\n\nFind all the pairs and find the best score in it.\n\n\nint maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {\n int ans = 0;\n
|
raman08
|
NORMAL
|
2022-06-10T17:50:26.785033+00:00
|
2022-06-10T17:50:26.785073+00:00
| 124 | false |
**1. Brute Force Soulution**\n\nFind all the pairs and find the best score in it.\n\n```\nint maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {\n int ans = 0;\n \n for(int i = 0; i < values.size(); i++) {\n for(int j = i+1; j < values.size(); j++) {\n int score = values[i] + values[j] + i - j;\n \n ans = max(ans, score);\n }\n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n```\n\n**2. DP memorization**\n\nNote that the `score` value consists of two parts.\nWe are going to find the index of best left pair as we iterate through the values, and cache them in `bestScore`.\n\n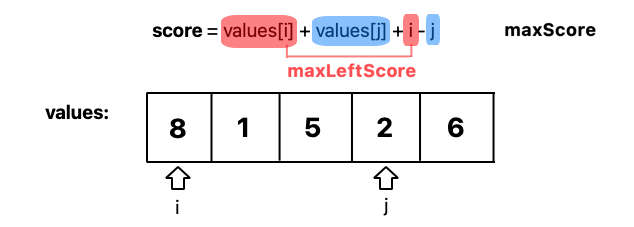\n\nAt each time we move j,\n1) Can index j-1 can be the new i? Then update `bestScore`.\n2) Update `ans` value with `max(ans, score(i,j))`.\n\n```\nint maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {\n int ans = 0;\n int bestscore = 0;\n \n for(int i = 1; i < values.size(); i++) {\n bestscore = max(bestscore, values[i-1]+i-1);\n ans = max(ans, bestscore+values[i]-i);\n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['C', 'C++']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Fully explained, Python Easy to understand, Linear time with constant space code
|
fully-explained-python-easy-to-understan-7xtk
|
See you only want to find the maximum value of ((val[i] + i) + (val[j]-j)) which is easy if we have our maximum value of (val[i] + i) being precalculated at eve
|
manav_07
|
NORMAL
|
2022-06-09T11:52:18.851996+00:00
|
2022-06-09T11:52:18.852045+00:00
| 322 | false |
See you only want to find the maximum value of ((val[i] + i) + (val[j]-j)) which is easy if we have our maximum value of (val[i] + i) being precalculated at every index. So just add (val[j]-j) to that at that "j".\nHere is a simple 8 line code for the same. \nFor better undestanding please take a simple test case and go through each and every line in the code. If you like the solution, please like and upvote it, so it can help other young coders like you. \nThankYou and Have a nice day.\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, values) -> int:\n maxAns = float("-inf") \n # precalculating the i value\n currPrevMax = values[0]+0\n for j in range(1,len(values)):\n maxAns = max(maxAns,currPrevMax+values[j]-j)\n # Update the previous max incase the current j is the new i\n currPrevMax = max(currPrevMax, values[j]+j) \n return maxAns\n
| 3 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Python']
| 1 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
C++ | Simple Dynamic Programming Solution | Easy to Understand
|
c-simple-dynamic-programming-solution-ea-kc9e
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int dp[50005][3];\n int f(vector<int>& arr,int taken,int idx){\n if(taken >= 2) return 0;\n if(idx >= arr.siz
|
LastStyleBender
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-11T12:18:05.104366+00:00
|
2022-04-11T12:18:05.104404+00:00
| 480 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int dp[50005][3];\n int f(vector<int>& arr,int taken,int idx){\n if(taken >= 2) return 0;\n if(idx >= arr.size()) return -1e7;\n else if(dp[idx][taken] != -1) return dp[idx][taken];\n\n int pick = arr[idx] + f(arr,taken+1,idx+1);\n int notPick = f(arr,taken,idx+1);\n \n if(taken == 1){\n pick = pick - idx;\n }else{\n pick += idx;\n }\n \n return dp[idx][taken] = max(pick,notPick);\n }\n \n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {\n memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp));\n return f(values,0,0);\n }\n};\n\n/**\na[i] + b[j] + i - j\na[i] + i + b[j] - j;\n\n*/\n```\n\n\nTime Complexity = O(n * 3) \nSpace Complexity = O(n * 3)
| 3 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization', 'C']
| 1 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
C++ simple solution
|
c-simple-solution-by-lekhachem-x3jq
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {\n int prefix = values[0], ans = 0, n = values.size(), i;\n for
|
lekhachem
|
NORMAL
|
2022-04-06T14:08:03.846688+00:00
|
2022-04-06T14:09:18.273683+00:00
| 87 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {\n int prefix = values[0], ans = 0, n = values.size(), i;\n for (i = 1; i < n; i++) {\n ans = max(ans, prefix + values[i] - i);\n prefix = max(prefix, values[i] + i);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
C++ | DP | T-O(N) & S-O(1) | Short & crisp solution
|
c-dp-t-on-s-o1-short-crisp-solution-by-n-ee44
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n //This question is very similar to buy and sell stock with only two transactions possible. \n int maxScoreSightseeingPair
|
nidhi_ranjan
|
NORMAL
|
2022-02-23T13:52:16.885412+00:00
|
2022-02-23T13:53:08.518763+00:00
| 144 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n //This question is very similar to buy and sell stock with only two transactions possible. \n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {\n int ci=values[0], cj=0;\n for(int i=1;i<values.size();i++){\n cj=max(cj,ci+values[i]-i); //ci stores max value of values[i]+i\n ci=max(ci,values[i]+i); //cj stores max value of ci + values[j]-j for j>i\n }\n return cj;\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C', 'C++']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
✅ One-pass, constant space || Python
|
one-pass-constant-space-python-by-johang-bg4m
|
\nclass Solution:\n def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, values: List[int]) -> int:\n max_value = 0\n i = 0\n for j in range(1, len(values)
|
johanga
|
NORMAL
|
2021-12-03T19:19:22.921643+00:00
|
2023-01-14T12:17:47.655599+00:00
| 366 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, values: List[int]) -> int:\n max_value = 0\n i = 0\n for j in range(1, len(values)):\n value = values[i] + values[j] + i - j\n max_value = max(max_value, value)\n if values[i] - (j - i) < values[j]:\n i = j\n \n return max_value\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Python']
| 1 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
C++ | Explained | Dynamic Programming
|
c-explained-dynamic-programming-by-peter-h6d4
|
Approch\nHere we are given that we have to maximize V[i] + V[j] + i - j, given i<j. In such question understanding this type of condition is very important, her
|
Peter316
|
NORMAL
|
2021-11-13T17:55:11.307456+00:00
|
2021-11-13T17:55:11.307492+00:00
| 200 | false |
# Approch\nHere we are given that we have to maximize ```V[i] + V[j] + i - j```, given ```i<j```. In such question *understanding this type of condition is very important*, here we can see that i must be less than j so, for any j ```V[ j ] - j``` is a fixed value and to maximize the given condition we must maximize ```V[i] + i``` where ```i<j``` so we keep track of this maximum value upto any j and then find the maximum of ```( V[i] + i ) + (V[ j ] - j )``` in the complete array.\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {\n return solve(values);\n }\n int solve(vector<int>& nums){\n int n = nums.size();\n\n int vi_max = nums[0];\n int ans = INT_MIN;\n for(int i=1;i<n;i++){\n ans = max(ans, vi_max + nums[i]-i);\n vi_max = max(vi_max, nums[i]+i);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
C++, O(n) time, O(1) space, single pass with explantion.
|
c-on-time-o1-space-single-pass-with-expl-n3p5
|
Consider the f(n) that needs to be maximised here, which we need to maximise the sum of two values (with the difference between their places), ie.\nf(n) = maxim
|
user4221Ir
|
NORMAL
|
2021-10-19T14:45:06.248682+00:00
|
2021-10-19T14:45:06.248720+00:00
| 120 | false |
Consider the f(n) that needs to be maximised here, which we need to maximise the sum of two values (with the difference between their places), ie.\nf(n) = maximize(value[i] + value[j] + j - i) where, j > i\n\nFor sometime, lets forget about the j-i part. So, how would you solve the problem if you were just to maximize the sum of two values? You could simply do this by keeping track of the maximum value you have seen so far, and while iterating over the array add the maximum to the current value, and see if this is the greatest result so far, and keep updating the maximum value too while iterating. The key observation here is that, if you have seen a large number while iterating, all numbers smaller than the number become useless to form the pair.\n\nNow, if we come to the question at hand, the only change is that we need to subtract the distance between the two numbers (j-i). So, instead of seeing it as the distance, you could just subtract this distance from the maximum value you have seen. In a way, the maximum value you have seen decays be 1, every time you move one step right. \n\nUsing this, you can solve the question in O(n) time, and O(1) space, and one pass.\n\nFor more help on competitive programming, join the discord here: \nhttps://discord.gg/aybzamxHWX\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {\n // Stores the maximum score to return.\n int maxScore = 0;\n \n // Stores the maximum value seen until now.\n int maxValue = 0;\n \n for(int i=0; i<values.size(); i++) {\n // Since we move one place to the right, the maximum value\n // that can form the pair decays by 1. This is to account\n // for the distance between the current number and the maximum\n // number.\n maxValue = maxValue-1;\n \n // Update the max score, if the current number can form\n // a better pair with the maximum number.\n maxScore = max(maxScore, maxValue + values[i]);\n \n // update the maximum number seen so far.\n if(values[i] > maxValue) {\n maxValue = values[i];\n }\n }\n \n return maxScore;\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
C++ || well commented
|
c-well-commented-by-spaniard_1-qmai
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {\n \n // main condition is that (i < j) \n \n int
|
Spaniard_1
|
NORMAL
|
2021-10-01T10:32:56.795328+00:00
|
2021-10-01T10:32:56.795396+00:00
| 97 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {\n \n // main condition is that (i < j) \n \n int n = values.size();\n \n // from the formula (values[i] + i) + (values[j] - j)\n int base = values[0] + 0;\n \n int ans = INT_MIN;\n \n for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)\n {\n // now if we find any value of (value[i] + i) greater than base\n \n ans = max (ans, base + values[i] - i);\n base = max(base, values[i] + i);\n }\n return ans; \n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Using some Observation and Elementary math. [O(N) Time with O(1) Space ]
|
using-some-observation-and-elementary-ma-6pop
|
Let\'s say our current maximum answer so far is ans, now if j wants to make pair with some other element it should satisfy the following condition.\n\nans < val
|
binary__search
|
NORMAL
|
2021-09-18T18:51:56.241745+00:00
|
2021-09-18T18:55:34.736198+00:00
| 103 | false |
Let\'s say our current maximum answer so far is **ans**, now if **j** wants to make pair with some other element it should satisfy the following condition.\n\n`ans < value[j]+value[i]-(j-i)` ---------------------------- (1)\n\nWhere **i** is the spot with which **j** will pair.\n\nIf we make some transformation in equation (1), we will get the following relation:\n\n`ans-value[j]+j < value[i]+i` -------------------------------(2)\n\nlets make a variable to track max of` value[i]+i `so far and call this variable **M_xi**;\n\nSo we can say that our ans will change only if equation (2) satisfy, our ans will change to:\n \t\t\t\t\n\t\t\tans=M_xi+value[j]-j;\n\n\nHere is the implementation of the approach.\n```\nint maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& a) {\n int ans=a[0]+a[1]-1,M_xi=max(a[0],a[1]+1);\n for(int i=2;i<a.size();i++){\n if(ans-a[i]+i<M_xi){\n ans=M_xi+a[i]-i;\n }\n M_xi=max(M_xi,a[i]+i);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n```\n
| 3 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming']
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Python one pass O(N) this is not a dp problem
|
python-one-pass-on-this-is-not-a-dp-prob-djo9
|
I think this is more a two pointer problem than DP.\nmax value is "values[i] + values[j] + i - j", just split to two part "values[i] + i" and "values[j] - j". W
|
herbert_cn
|
NORMAL
|
2021-08-26T05:51:52.568319+00:00
|
2021-08-26T05:51:52.568372+00:00
| 127 | false |
I think this is more a two pointer problem than DP.\nmax value is "values[i] + values[j] + i - j", just split to two part "values[i] + i" and "values[j] - j". When iterate over the array, remember that max value of value[i] + i.\n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maxScoreSightseeingPair(self, values: List[int]) -> int:\n maxPrev = values[0] + 0 # maxPrev, records max value of values[i] + i\n ans = 0 # ans, the result of max value "values[i] + values[j] + i - j"\n for i in range(1, len(values)):\n secPart = values[i] - i\n ans = max(ans, maxPrev + secPart)\n maxPrev = max(maxPrev, values[i] + i)\n return ans\n```
| 3 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
90 % faster C++ solution with explanation.
|
90-faster-c-solution-with-explanation-by-hw6n
|
As i<j so values[i] + values[j] + i - j is (values[i]+i) +( values[j]- j ) i.e for any j we just need the max of (values[i]+i)\nAt starting values[i]+i =values[
|
neemesh_17
|
NORMAL
|
2021-08-05T06:55:32.363488+00:00
|
2021-08-05T07:02:19.507583+00:00
| 102 | false |
As i<j so values[i] + values[j] + i - j is (values[i]+i) +( values[j]- j ) i.e for any j we just need the max of (values[i]+i)\nAt starting values[i]+i =values[0] then we calculate our ans for that index and keep the max of all previousally calculated ans ,simultaneousally we update our best \n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxScoreSightseeingPair(vector<int>& values) {\n int best=values[0];\n int ans=0;\n for(int j=1;j<values.size();j++)\n {\n ans=max(ans,best+values[j]-j);\n best=max(best,values[j]+j);\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
best-sightseeing-pair
|
Java || Array + DP || 1ms || beats 100% || T.C - O(N) S.C - O(1)
|
java-array-dp-1ms-beats-100-tc-on-sc-o1-1azw7
|
\n\n\t// O(n) O(1)\n\tpublic int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values) {\n\n\t\tint ans = Integer.MIN_VALUE, len = values.length, max = values[0];\n\n\t\tfor (i
|
LegendaryCoder
|
NORMAL
|
2021-07-22T09:49:48.811213+00:00
|
2021-07-22T09:49:48.811260+00:00
| 98 | false |
\n\n\t// O(n) O(1)\n\tpublic int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] values) {\n\n\t\tint ans = Integer.MIN_VALUE, len = values.length, max = values[0];\n\n\t\tfor (int j = 1; j < len; j++) {\n\t\t\tint curr = values[j] - j;\n\t\t\tif (max + curr > ans)\n\t\t\t\tans = max + curr;\n\t\t\tif (values[j] + j > max)\n\t\t\t\tmax = values[j] + j;\n\t\t}\n\n\t\treturn ans;\n\t}
| 3 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Sliding Window with Example Walkthrough
|
sliding-window-with-example-walkthrough-udkc4
|
Intuition\n1. Prefix and Rearrangement :\n- A prefix is the starting portion of a string. For example, for the string "abc", the prefix could be "a", "ab", or "
|
_sxrthakk
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T04:03:29.957268+00:00
|
2024-09-22T04:03:29.957294+00:00
| 5,198 | false |
# Intuition\n1. **Prefix and Rearrangement :**\n- A prefix is the starting portion of a string. For example, for the string "abc", the prefix could be "a", "ab", or "abc".\n- Rearrangement means that we can rearrange the characters in a substring, but when rearranged, the beginning of the rearranged string must match word2.\n\n2. **Key Insight :**\n- The problem is about finding substrings of word1 whose characters can be rearranged in such a way that word2 becomes a prefix.\n- For example, the substring "bcca" can be rearranged into "abcc", and "abc" is a prefix of "abcc". Therefore, "bcca" is a valid substring.\n\n3. **Efficient Approach :**\n- Instead of checking all possible substrings (which would take too much time), we can use a sliding window technique to check character frequencies and determine when a valid substring is formed.\n- This way, we can avoid recalculating from scratch for every substring and just adjust the window as we process each new character.\n\n# Approach\n1. **Character Frequency Calculation :**\n- First, we calculate the frequency of each character in word2 and store it in a frequency vector v of size 26 (for the 26 lowercase letters).\n \n2. **Sliding Window Setup :**\n- We maintain a sliding window over word1 to check its substrings.\n- The window will keep track of character frequencies in word1 using another vector cnt of size 26.\n- The sliding window will expand and shrink as needed. We will adjust the window as we move through the string word1.\n\n3. **Tracking Remaining Matches :**\n- We introduce a variable k which represents how many characters from word2 are yet to be matched within the window.\n- Initially, k = length(word2), and it decreases as we match characters of word2 inside the current window of word1.\n- When k == 0, it means the current window of word1 contains enough characters to potentially be rearranged into a valid substring that starts with word2.\n\n4. **Expanding the Window :**\n- For each character in word1, we:\na) Add the character to the current window (by updating cnt).\nb) If this character exists in word2 and is still needed in the window (i.e., cnt has fewer occurrences of this character than v), we reduce k by 1.\nc) If k == 0, we have a valid window that can potentially form a valid substring.\n\n5. **Counting Valid Substrings :**\n- Once we have a valid window (when k == 0), we count all substrings that can be formed by extending the window from the current position to the end of word1.\n- The total number of such substrings is given by len(word1) - i, where i is the current end of the window.\n\n6. **Shrinking the Window :**\n- After counting, we begin shrinking the window from the left by moving the start pointer.\n- As we remove characters from the left of the window, we update cnt and adjust k if necessary (i.e., if a character becomes unmatched).\n\n# Example Walkthrough \nLet\'s go through the example word1 = "bcca" and word2 = "abc" step by step using the code.\n\n## Initial Setup :\n After iterating over "abc", v looks like this:\n### v = [1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, ..., 0]\nThis indicates that word2 contains one occurrence each of the letters \'a\', \'b\', and \'c\'.\n\ncnt is initialized to track the frequency of characters in the current sliding window of word1. Initially, all elements of cnt are 0.\n\n### cnt = [0, 0, 0, ..., 0]\n### start = 0 => This represents the start of the current window.\n\n### k = 3 => This is the number of characters from word2 that still need to be matched.\n\n### c = 0 => This will store the total number of valid substrings.\n\n## Step-by-Step Walkthrough:\n\n### Iteration 1:\n**Current character :** \'b\' (at index 0)\n\n\'b\' exists in word2 (v[\'b\' - \'a\'] = 1), and its count in the window (cnt[\'b\' - \'a\'] = 0) is less than in word2. Therefore, we decrement k by 1:\nk = 2\n\n**Update cnt for \'b\' :** cnt = [0, 1, 0, ..., 0]\n\nSince k != 0, we don\'t have a valid substring yet.\n\n### Iteration 2:\n**Current character :** \'c\' (at index 1)\n\n\'c\' exists in word2 (v[\'c\' - \'a\'] = 1), and its count in the window (cnt[\'c\' - \'a\'] = 0) is less than in word2. We decrement k by 1:\nk = 1\n\n**Update cnt for \'c\' :** cnt = [0, 1, 1, ..., 0]\n\nk != 0, so still no valid substring yet.\n\n### Iteration 3:\n**Current character :** \'c\' (at index 2)\n\n\'c\' exists in word2 (v[\'c\' - \'a\'] = 1), but its count in the window (cnt[\'c\' - \'a\'] = 1) is already equal to what\u2019s required in word2. So, we don\u2019t change k.\n\n**Update cnt for \'c\' :** cnt = [0, 1, 2, ..., 0]\n\nStill, k != 0, so no valid substring yet.\n\n### Iteration 4:\n**Current character :** \'a\' (at index 3)\n\n\'a\' exists in word2 (v[\'a\' - \'a\'] = 1), and its count in the window (cnt[\'a\' - \'a\'] = 0) is less than in word2. We decrement k by 1:\nk = 0\n\n**Update cnt for \'a\' :** cnt = [1, 1, 2, ..., 0]\n\n## Now, k == 0, meaning the window from start = 0 to i = 3 forms a valid substring.\n\nWe calculate the number of valid substrings starting at start = 0 and ending at or after i = 3:\n\nThe total length of word1 is 4. Therefore, there is 4 - 3 = 1 valid substring: "bcca".\n\n**Increment c by 1 :** c = 1\n\n## Now, we shrink the window by moving start to the right and updating counts.\n\nThe leftmost character is \'b\'. Reduce the count of \'b\' in cnt:\ncnt = [1, 0, 2, ..., 0]\n\nSince we reduced the count of \'b\' below its needed count in word2, we increment k by 1:\nk = 1\n\nMove start to 1.\n\n## Final Answer:\nAfter processing all characters in word1, the total number of valid substrings is 1.\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nlong long validSubstringCount(string s1, string s2){\n vector<int> v(26,0);\n for(char c : s2){\n v[c-\'a\']++;\n }\n\n vector<int> cnt(26, 0);\n int start=0, k=s2.length();\n long long c=0;\n\n for(int i=0;i<s1.length();i++){\n char curr=s1[i];\n\n if(v[curr-\'a\']>0){\n if(cnt[curr-\'a\']<v[curr-\'a\']){\n k--;\n }\n }\n\n cnt[curr-\'a\']++;\n\n while(k==0){\n c+=s1.length()-i;\n\n char pre=s1[start];\n cnt[pre-\'a\']--;\n\n if(v[pre-\'a\']>0 and cnt[pre-\'a\']<v[pre-\'a\']){\n k++;\n }\n\n start++;\n }\n }\n\n return c;\n }\n```\n\n```Python []\ndef validSubstringCount(self,word1, word2) :\n v = [0] * 26\n for c in word2:\n v[ord(c) - ord(\'a\')] += 1\n\n cnt = [0] * 26\n start = 0\n k = len(word2)\n count = 0\n\n for i in range(len(word1)):\n curr = word1[i]\n if v[ord(curr) - ord(\'a\')] > 0:\n if cnt[ord(curr) - ord(\'a\')] < v[ord(curr) - ord(\'a\')]:\n k -= 1\n \n cnt[ord(curr) - ord(\'a\')] += 1\n\n while k == 0:\n count += len(word1) - i\n pre = word1[start]\n cnt[ord(pre) - ord(\'a\')] -= 1\n if v[ord(pre) - ord(\'a\')] > 0 and cnt[ord(pre) - ord(\'a\')] < v[ord(pre) - ord(\'a\')]:\n k += 1\n start += 1\n\n return count\n```\n\n```Java []\npublic static long validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n int[] v = new int[26];\n for (char c : word2.toCharArray()) {\n v[c - \'a\']++;\n }\n\n int[] cnt = new int[26];\n int start = 0;\n int k = word2.length();\n long count = 0;\n\n for (int i = 0; i < word1.length(); i++) {\n char curr = word1.charAt(i);\n if (v[curr - \'a\'] > 0) {\n if (cnt[curr - \'a\'] < v[curr - \'a\']) {\n k--;\n }\n }\n\n cnt[curr - \'a\']++;\n\n while (k == 0) {\n count += word1.length() - i;\n char pre = word1.charAt(start);\n cnt[pre - \'a\']--;\n if (v[pre - \'a\'] > 0 && cnt[pre - \'a\'] < v[pre - \'a\']) {\n k++;\n }\n start++;\n }\n }\n\n return count;\n }\n```\n\n
| 54 | 2 |
['Sliding Window', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java']
| 8 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Sliding Window
|
sliding-window-by-votrubac-fly8
|
Nothing new here, similar to 76. Minimum Window Substring. \n\nWe track if a string [j, i] contains all characters in w2.\n\n> For that, we decrement match when
|
votrubac
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T04:05:41.474211+00:00
|
2024-09-22T04:36:13.786970+00:00
| 1,429 | false |
Nothing new here, similar to [76. Minimum Window Substring](https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-window-substring). \n\nWe track if a string `[j, i]` contains all characters in `w2`.\n\n> For that, we decrement `match` when the remaining character count reaches zero.\n\nIf it does, we add `len(w2) - i` to the result, and increment `j`.\n\n**C++**\n```cpp\nlong long validSubstringCount(string w1, string w2) {\n long long cnt[26] = {}, j = 0, match = 0, res = 0;\n for (char ch : w2)\n match += cnt[ch - \'a\']++ == 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < w1.size(); ++i) {\n --cnt[w1[i] - \'a\'];\n match -= cnt[w1[i] - \'a\'] == 0; \n while (match == 0) {\n res += w1.size() - i;\n match += cnt[w1[j] - \'a\'] == 0;\n ++cnt[w1[j++] - \'a\'];\n }\n }\n return res;\n}\n```
| 15 | 0 |
['C']
| 5 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Effortless Sliding Window Trick !!! Striver's Approach 🔥🫣🤯
|
effortless-sliding-window-trick-strivers-lzva
|
Approach\nExplanation of Code:\n\n1.Frequency Count: count stores the frequency of each character in word2.\n2.Sliding Window: The prefix array keeps track of t
|
aroratanmay1403
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T20:26:07.010303+00:00
|
2024-09-22T20:26:07.010335+00:00
| 380 | false |
# Approach\nExplanation of Code:\n\n1.Frequency Count: count stores the frequency of each character in word2.\n2.Sliding Window: The prefix array keeps track of the character frequencies in the current window from j to i.\n3.Validity Check: The function isvalid compares the prefix (window\'s frequency) with count (required frequency for word2). If the window is valid, it counts all substrings starting from j to the end of word1.\n4.Final Answer: For every valid window, we count how many substrings can start from j and include all substrings from i to n-1\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(n)\n\n- Space complexity:O(26)+O(26)~constant\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool isvalid(vector<int>& prefix, vector<int>& count) {\n for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {\n if (prefix[i] < count[i]) {\n return false;\n }\n }\n return true;\n}\n long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) {\n vector<int>count(26,0);\n for(int i=0;i<word2.size();i++){\n count[word2[i]-\'a\']++;\n }\n long long ans=0;\n int i=0;\n int j=0;\n int n=word1.size();\n int m=word2.size();\n vector<int>prefix(26,0);\n while(i<n){\n prefix[word1[i]-\'a\']++;\n while(isvalid(prefix,count)&&j<=i){\n ans+=n-i;\n prefix[word1[j]-\'a\']--;\n j++;\n }\n i++;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 10 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'Sliding Window', 'Prefix Sum', 'C++']
| 1 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
simple two pointer approach in O(n) time and O(26) space
|
simple-two-pointer-approach-in-on-time-a-lnk1
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n- The primary task is to count how many substrings in word1 contain all characters of w
|
Reddaiah12345
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T05:32:40.778426+00:00
|
2024-09-22T05:33:05.788892+00:00
| 1,473 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n- The primary task is to count how many substrings in word1 contain all characters of word2\n- We use two arrays (represented as mpp), where:\n - mpp[x][0] keeps track of the frequency of each character in the current sliding window of word1.\n - mpp[x][1] holds the required frequency of characters based on word2.\n- The sliding window is dynamically adjusted\n - It expands when the window is too small to contain all characters from word2.\n - It contracts when all characters are present, counting valid substrings as it does so.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1. **Setup the frequency table for word2:**\n - For each character in word2, increment its frequency count in the mpp array at mpp[character][1].\n - This helps us keep track of how many occurrences of each character we need in the sliding window from word1.\n1. **Sliding Window:**\n - Initialize two pointers: l (left) and r (right) to represent the bounds of the sliding window.\n - Traverse through word1 using the r pointer. For each character at position r, check if it is part of word2:\n - If the character count in the sliding window (tracked by mpp[x][0]) is less than the count in word2, increment the size (indicating that more of the necessary characters have been found).\n - If all characters from word2 are found (size == m), begin contracting the window from the left (l) and count all valid substrings.\n1. **Count Valid Substrings:**\n For each valid window (where the window contains all characters of word2), the count of valid substrings starting at the current l and ending at any position after r is (n - r + 1) (because all substrings starting at l and ending from r to the end of the string are valid).\n1. **Final Cleanup:**\n After processing the string with the r pointer, handle any remaining valid substrings by continuing to contract the window with the l pointer until it no longer contains all characters of word2.\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(n)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:O(26)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\nimport java.util.*;\n\nclass Solution {\n public long validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n long res = 0;\n int[][] mpp = new int[26][2]; // To store frequencies of both words\n int l = 0, r = 0;\n int n = word1.length();\n int m = word2.length();\n int size = 0;\n \n // Count frequency of characters in word2\n for (char ch : word2.toCharArray()) {\n mpp[ch - \'a\'][1]++;\n }\n \n while (r < n) {\n // Slide the window while it contains all characters of word2\n while (size == m && l <= r) {\n res += (n - r + 1);\n mpp[word1.charAt(l) - \'a\'][0]--;\n if (mpp[word1.charAt(l) - \'a\'][1] > 0 && mpp[word1.charAt(l) - \'a\'][0] < mpp[word1.charAt(l) - \'a\'][1]) {\n size--;\n }\n l++;\n }\n // Expand the window\n if (mpp[word1.charAt(r) - \'a\'][1] > 0 && mpp[word1.charAt(r) - \'a\'][0] < mpp[word1.charAt(r) - \'a\'][1]) {\n size++;\n }\n mpp[word1.charAt(r) - \'a\'][0]++;\n r++;\n }\n \n // Handle remaining valid substrings\n while (size == m && l <= r) {\n res += (n - r + 1);\n mpp[word1.charAt(l) - \'a\'][0]--;\n if (mpp[word1.charAt(l) - \'a\'][1] > 0 && mpp[word1.charAt(l) - \'a\'][0] < mpp[word1.charAt(l) - \'a\'][1]) {\n size--;\n }\n l++;\n }\n \n return res;\n }\n}\n\n```\n```python []\nclass Solution:\n def validSubstringCount(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:\n res = 0\n mpp = [[0, 0] for _ in range(26)] # To store frequencies of both words\n l, r = 0, 0\n n = len(word1)\n m = len(word2)\n size = 0\n \n # Count frequency of characters in word2\n for ch in word2:\n mpp[ord(ch) - ord(\'a\')][1] += 1\n \n while r < n:\n # Slide the window while it contains all characters of word2\n while size == m and l <= r:\n res += (n - r + 1)\n mpp[ord(word1[l]) - ord(\'a\')][0] -= 1\n if mpp[ord(word1[l]) - ord(\'a\')][1] > 0 and mpp[ord(word1[l]) - ord(\'a\')][0] < mpp[ord(word1[l]) - ord(\'a\')][1]:\n size -= 1\n l += 1\n \n # Expand the window\n if mpp[ord(word1[r]) - ord(\'a\')][1] > 0 and mpp[ord(word1[r]) - ord(\'a\')][0] < mpp[ord(word1[r]) - ord(\'a\')][1]:\n size += 1\n mpp[ord(word1[r]) - ord(\'a\')][0] += 1\n r += 1\n \n # Handle remaining valid substrings\n while size == m and l <= r:\n res += (n - r + 1)\n mpp[ord(word1[l]) - ord(\'a\')][0] -= 1\n if mpp[ord(word1[l]) - ord(\'a\')][1] > 0 and mpp[ord(word1[l]) - ord(\'a\')][0] < mpp[ord(word1[l]) - ord(\'a\')][1]:\n size -= 1\n l += 1\n \n return res\n\n```\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) {\n // this problem can be solved using then concept of sliding window and two pointers\n long long res=0;\n vector<pair<int,int>>mpp(26,{0,0});\n int l,r;\n l=0;\n r=0;\n int n=word1.size();\n int m=word2.size();\n int size=0;\n for(auto ch:word2){\n mpp[ch-\'a\'].second++;\n }\n while(r<n){\n while(size==m&&l<=r){\n res+=(n-r+1);\n mpp[word1[l]-\'a\'].first--;\n if(mpp[word1[l]-\'a\'].second>0&&mpp[word1[l]-\'a\'].first<mpp[word1[l]-\'a\'].second){\n size--;\n }\n l+=1;\n }\n if(mpp[word1[r]-\'a\'].second>0&&mpp[word1[r]-\'a\'].first<mpp[word1[r]-\'a\'].second){\n size+=1;\n }\n mpp[word1[r]-\'a\'].first++;\n r+=1;\n }\n while(size==m&&l<=r){\n res+=(n-r+1);\n mpp[word1[l]-\'a\'].first--;\n if(mpp[word1[l]-\'a\'].second>0&&mpp[word1[l]-\'a\'].first<mpp[word1[l]-\'a\'].second){\n size--;\n }\n l+=1;\n }\n return res;\n }\n};\n```\n\n
| 10 | 1 |
['C++', 'Java', 'Python3']
| 1 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
[Python3] Hash Table + Sliding Window - Detailed Explanation
|
python3-hash-table-sliding-window-detail-fcmr
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\nThe provided Python c
|
dolong2110
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T16:17:22.158526+00:00
|
2024-09-22T16:17:22.158560+00:00
| 359 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\nThe provided Python code defines a function validSubstringCount that calculates the number of valid substrings in word1 that can be formed by concatenating substrings from word2. A valid substring is one where the frequency of each character in the substring is less than or equal to its frequency in word2.\n\n**1. Initialization:**\n\n- `cnt` is a counter to keep track of the frequency of characters in `word2`.\n- `match` is initialized to the number of unique characters in `word2`.\n- `res` is used to store the count of valid substrings.\n- `j` is used to keep track of the starting index of the current substring.\n\n**2. Iteration:**\n\n- The loop iterates over each character `ch` in `word1` at index `i`.\n- The frequency of `ch` in `cnt` is decremented.\n- If the frequency of `ch` becomes 0, `match` is decremented to indicate that a new unique character has been encountered.\n- While `match` is 0, it means that the current substring is valid.\n - The loop continues to increment `j` until a character is found that has a frequency greater than 0 in `cnt`.\n - The frequency of the character at index `j` is incremented in `cnt`.\n - `match` is incremented if the frequency becomes 0.\n- `res` is incremented to count the valid substring.\n\n**3. Return Value:**\n\n- The final value of `res` is returned, which represents the total number of valid substrings.\n\nIn summary, the code iterates through `word1`, maintaining a sliding window of valid substrings. The sliding window expands as long as the frequency of characters in the current substring does not exceed their frequency in `word2`. The number of valid substrings is counted based on the length of the sliding window.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(W1 + W2)$$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(26)$$ ~ $$O(1)$$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def validSubstringCount(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:\n cnt = collections.Counter(word2)\n match, res, j = len(cnt), 0, 0\n for i, ch in enumerate(word1):\n cnt[ch] -= 1\n match -= cnt[ch] == 0\n while match == 0:\n match += cnt[word1[j]] == 0\n cnt[word1[j]] += 1\n j += 1\n res += j\n return res\n```
| 8 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'Sliding Window', 'Python3']
| 1 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Sliding Window || Similar to Aditya Verma's Approach
|
sliding-window-similar-to-aditya-vermas-0rsiz
|
Reference Aditya Verma\'s video posted in comments.\n# Code\ncpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) {\
|
Rookie0934
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T04:30:52.218956+00:00
|
2024-09-22T04:30:52.218982+00:00
| 830 | false |
Reference Aditya Verma\'s video posted in comments.\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) {\n vector<int> freq(26, 0);\n int cnt = 0;\n for (char ch : word2) {\n if (freq[ch - \'a\'] == 0) {\n cnt++;\n }\n freq[ch - \'a\']++;\n }\n long long j = 0, ans = 0;\n for (long long i = 0; i < word1.size(); i++) {\n if (--freq[word1[i] - \'a\'] == 0) {\n cnt--;\n }\n while (cnt == 0) {\n ans += (word1.size() - i);\n if (++freq[word1[j] - \'a\'] == 1) {\n cnt++;\n }\n j++;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 7 | 1 |
['Two Pointers', 'Sliding Window', 'C++']
| 3 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Binary Search | Beginner friendly approach
|
binary-search-beginner-friendly-approach-b01b
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nThe goal of the code is to count the number of valid substrings in s where any rearrang
|
Roar47
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T04:06:07.102854+00:00
|
2024-09-22T04:06:07.102885+00:00
| 507 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThe goal of the code is to count the number of valid substrings in s where any rearrangement of the substring can have word2 as a prefix. The given solution uses a combination of prefix sum arrays and binary search to achieve this efficiently.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n**Character Frequency Calculation:**\n\n- Calculate the frequency of each character in word2 and store it in the base vector.\n\n\n\n**Prefix Sum Array for Character Counts:**\n\n- Create a prefix sum array pre where pre[i] stores the cumulative counts of each character from the start of the string s up to the i-th position.\n\n\n**Find Valid Substrings Using Binary Search:**\n\n- For each starting position i in the string s, use binary search to find the shortest ending index idx such that the substring from i to idx contains all characters in word2 with the required frequency.\n\n- Calculate how many substrings can be generated from this range and add it to the result.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(NlogN)$$ \n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(1)$$\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long validSubstringCount(string s, string word2) \n {\n int n = s.size(), i, j;\n \n // Count the frequency of characters in word2\n vector<int> base(26);\n for (auto ch : word2)\n {\n base[ch - \'a\']++;\n }\n \n // Create a prefix sum array for character frequencies in s\n vector<vector<int>> pre(n + 1, vector<int>(26, 0));\n for(i = 0; i < n; i++)\n {\n pre[i + 1][s[i] - \'a\']++;\n for(j = 0; j < 26; j++)\n {\n pre[i + 1][j] += pre[i][j];\n }\n }\n \n long long ans = 0;\n \n // Iterate through each starting position in the string\n for(i = 0; i < n; i++)\n {\n int l = i, r = n - 1, idx = 1e9;\n \n // Perform binary search to find the minimum valid ending index\n while(l <= r)\n {\n int mid = (l + r) / 2;\n bool ok = true;\n \n // Check if the substring from i to mid satisfies the frequency requirement\n for(j = 0; j < 26; j++)\n {\n if(base[j] > (pre[mid + 1][j] - pre[i][j]))\n {\n ok = false;\n break;\n }\n }\n \n if(ok)\n {\n idx = mid;\n r = mid - 1;\n }\n else\n {\n l = mid + 1;\n }\n }\n \n // Count all valid substrings ending at index idx or later\n if (idx < 1e9)\n {\n ans += (n - idx);\n }\n }\n \n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 7 | 0 |
['Binary Search', 'C++']
| 2 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Sliding Window Approach in Java
|
sliding-window-approach-in-java-by-shubh-pkja
|
Approach\n1. Use a hashmap to count characters in word2.\n2. Use a sliding window approach with two pointers to find valid substrings in word1.\n3. Count how ma
|
shubhamyadav32100
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T04:03:19.187744+00:00
|
2024-09-22T04:31:10.813694+00:00
| 335 | false |
# Approach\n1. Use a hashmap to count characters in `word2`.\n2. Use a sliding window approach with two pointers to find valid substrings in `word1`.\n3. Count how many valid substrings can be formed by adjusting the window size based on character matches.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$ (where $$n$$ is the length of `word1`)\n- Space complexity: $$O(m)$$ (where $$m$$ is the length of `word2`, for storing character counts)\n\n# Code\n```java\nclass Solution {\n public long validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n int n = word1.length();\n int m = word2.length();\n if (m > n) return 0;\n\n HashMap<Character, Integer> count2 = new HashMap<>();\n HashMap<Character, Integer> count1 = new HashMap<>();\n\n for (char c : word2.toCharArray()) {\n count2.put(c, count2.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1);\n }\n\n long result = 0;\n int required = count2.size();\n int formed = 0;\n int left = 0;\n\n for (int right = 0; right < n; ++right) {\n char c = word1.charAt(right);\n count1.put(c, count1.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1);\n\n if (count2.containsKey(c) && count1.get(c).intValue() == count2.get(c).intValue()) {\n formed++;\n }\n\n while (formed == required) {\n result += (n - right);\n char leftChar = word1.charAt(left);\n count1.put(leftChar, count1.get(leftChar) - 1);\n \n if (count2.containsKey(leftChar) && count1.get(leftChar) < count2.get(leftChar)) {\n formed--;\n }\n left++;\n }\n }\n\n return result;\n }\n}\n```\n# Upvote if you found this helpful! \uD83D\uDE0A
| 7 | 0 |
['Java']
| 1 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
|| Easy Approach Using Sliding Windows || C++||
|
easy-approach-using-sliding-windows-c-by-90hv
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
bixby_0007
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T05:54:48.049069+00:00
|
2024-09-22T05:55:51.041254+00:00
| 658 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(N+M)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:O(1)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long validSubstringCount(string s, string t){\n vector<int>a(26,0);\n vector<int>b(26,0);\n for(auto x : t){\n b[x-\'a\']++;\n }\n int k=0;\n long long count=0;\n int i=0;\n bool flag=false;\n for( i=0; i<s.length(); i++){\n\n if(flag==false)\n a[s[i]-\'a\']++;\n flag = true;\n for(int i=0; i<26; i++){\n if(a[i]<b[i]){\n flag = false;\n break;\n }\n }\n if(flag){\n count+=s.length()-i;\n a[s[k]-\'a\']--;\n k++;\n i--;\n }\n \n }\n \n return count;\n \n }\n};\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['Sliding Window', 'Prefix Sum', 'C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Contest 416 || Ques-3 || Sliding window🔥
|
contest-416-ques-3-sliding-window-by-saj-b6vl
|
Approach and Intuition:\n\nThe problem asks to count valid substrings of source such that the frequency of every character in the substring is greater than or e
|
sajaltiwari007
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-24T16:48:18.142425+00:00
|
2024-09-24T16:48:18.142467+00:00
| 141 | false |
### Approach and Intuition:\n\nThe problem asks to count valid substrings of `source` such that the frequency of every character in the substring is greater than or equal to the frequency of the corresponding character in `target`.\n\n1. **Frequency Count for `target`:** \n We first create a frequency array `targetFreq` for the string `target`. This array will store the count of each character in `target`.\n\n2. **Sliding Window to Count Valid Substrings:** \n We use a sliding window approach to find valid substrings in `source`. The window expands by moving the `end` pointer and contracts by moving the `start` pointer.\n\n - For every character `end` in `source`, we increment its frequency in `currentFreq` (a frequency array for the current window).\n - We check if the current window is valid, i.e., if all characters in the window meet or exceed the frequency requirement set by `targetFreq`.\n - If valid, every suffix starting at `start` and ending after `end` is valid, so we add `(source.length() - end)` to the result.\n - We then increment `start` to try finding other possible substrings that could be valid.\n\n3. **Termination of Sliding Window:** \n The window contracts by incrementing `start` and decrementing the frequency of the character at the `start` position in `currentFreq`. We continue shrinking the window until it becomes invalid again.\n\n### Time Complexity:\n\n- **Creating the Frequency Array for `target`:** \n This takes `O(m)` time where `m` is the length of `target`.\n\n- **Sliding Window Over `source`:** \n In the worst case, the `start` pointer is moved at most once for each character in `source`, resulting in `O(n)` complexity where `n` is the length of `source`. \n Inside the loop, we check for validity by iterating over the 26 letters (constant time operation). Therefore, the complexity of checking whether the window is valid is `O(26)`, which is treated as `O(1)`.\n\n- **Overall Time Complexity:** \n The total time complexity is `O(n + m)` where `n` is the length of `source` and `m` is the length of `target`, because we process both strings once.\n\n### Space Complexity:\n\n- We use two frequency arrays (`targetFreq` and `currentFreq`), both of size 26 (constant space).\n- Hence, the space complexity is `O(1)` (constant space).\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public long validSubstringCount(String source, String target) {\n\n int[] targetFreq = new int[26];\n for (int i = 0; i < target.length(); i++) {\n char c = target.charAt(i);\n targetFreq[c - \'a\']++;\n }\n\n int start = 0;\n int[] currentFreq = new int[26];\n long validSubstrings = 0;\n for (int end = 0; end < source.length(); end++) {\n\n int charIndex = source.charAt(end) - \'a\';\n currentFreq[charIndex]++;\n\n boolean isValid = true;\n for (int j = 0; j < 26; j++) {\n if (targetFreq[j] > currentFreq[j]) {\n isValid = false;\n break;\n }\n }\n\n while (isValid) {\n validSubstrings += (long) (source.length() - end);\n charIndex = source.charAt(start) - \'a\';\n currentFreq[charIndex]--;\n start++;\n\n isValid = true;\n for (int j = 0; j < 26; j++) {\n if (targetFreq[j] > currentFreq[j]) {\n isValid = false;\n break;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n return validSubstrings;\n }\n}\n\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Sliding Window', 'Java']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Video Explanation -- Journey from O(N*N*C) --> O(N*C*logN) --> O(N*C) --> O(N)
|
video-explanation-journey-from-onnc-oncl-iya3
|
Explanation\n\nClick here for the video\n\n# Code\ncpp []\nvector<int> req(26);\nvector<int> hav(26);\nint matching_cnt = 0;\n\nclass Solution {\n \n void
|
codingmohan
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T06:57:17.362987+00:00
|
2024-09-22T06:57:17.363020+00:00
| 273 | false |
# Explanation\n\n[Click here for the video](https://youtu.be/VX2ruMTnjFk)\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nvector<int> req(26);\nvector<int> hav(26);\nint matching_cnt = 0;\n\nclass Solution {\n \n void Add (char ch) {\n int ind = ch - \'a\';\n hav[ind] ++;\n \n if (hav[ind] == req[ind]) matching_cnt ++;\n }\n \n void Remove (char ch) {\n int ind = ch - \'a\';\n hav[ind] --;\n \n if (hav[ind] == req[ind]-1) matching_cnt --;\n }\n \npublic:\n long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) {\n for (int i = 0; i < 26; i ++) req[i] = hav[i] = 0;\n matching_cnt = 0;\n \n for (auto c : word2) req[c-\'a\'] ++;\n for (int i = 0; i < 26; i ++)\n if (req[i] == 0) matching_cnt ++;\n \n int n = word1.length();\n long long ans = 0;\n int l = 0, r = -1;\n \n while (l < n) {\n while (r+1 < n && matching_cnt < 26) {\n r ++;\n Add (word1[r]);\n }\n \n if (matching_cnt == 26) ans += (n - r);\n \n Remove (word1[l]);\n l ++;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
EASY STEPWISE || STANDARD TEMPLATE || WINDOW
|
easy-stepwise-standard-template-window-b-271q
|
\n1. Frequency Arrays:\n - Two frequency arrays freq1 and freq2 are created to store the frequency of each character in word1 and word2, respectively.\n - T
|
Abhishekkant135
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-01T10:38:34.054817+00:00
|
2024-10-01T10:38:34.054843+00:00
| 32 | false |
\n1. **Frequency Arrays:**\n - Two frequency arrays `freq1` and `freq2` are created to store the frequency of each character in `word1` and `word2`, respectively.\n - The frequency of characters in `word2` is initialized.\n\n2. **Sliding Window:**\n - A sliding window approach is used to iterate through `word1`.\n - `l` and `r` represent the left and right pointers of the window.\n\n3. **Character Frequency Updates:**\n - The frequency of the current character (`word1.charAt(r)`) in `freq1` is incremented.\n - The `flag` variable is set to `true` if the current substring can form `word2`.\n - The code iterates through the frequency arrays to check if each character in `word1` has a frequency greater than or equal to its corresponding frequency in `word2`. If any character\'s frequency is less, `flag` is set to `false`.\n\n4. **Counting Valid Substrings:**\n - While `flag` is true and `l` is less than or equal to `r`:\n - The number of valid substrings (`ans`) is incremented by `m - r` (the length of the current substring).\n - The frequency of the character at index `l` in `freq1` is decremented.\n - `l` is incremented.\n - If the frequency of the current character becomes less than its corresponding frequency in `word2`, `flag` is set to `false`.\n\n5. **Sliding Window and Counting:**\n - The right pointer `r` is incremented to expand the window.\n - The process of checking frequencies and counting valid substrings is repeated until `r` reaches the end of `word1`.\n\n6. **Return Result:**\n - The final `ans` variable holds the total number of valid substrings. The code returns this value.\n\n\n\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public long validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n int m=word1.length();\n int n=word2.length();\n\n int [] freq1=new int [26];\n int [] freq2=new int [26];\n\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n freq2[word2.charAt(i)-\'a\']++;\n }\n long ans=0;\n\n int l=0;\n int r=0;\n while(r<m){\n freq1[word1.charAt(r)-\'a\']++;\n boolean flag=true;\n for(int i=0;i<26;i++){\n if(freq1[i]<freq2[i]){\n flag=false;\n break;\n }\n }\n while(flag &&l<=r){\n ans+=m-r;\n int alpha=word1.charAt(l)-\'a\';\n freq1[alpha]--;\n l++;\n if(freq1[alpha]<freq2[alpha]){\n flag=false;\n }\n }\n r++;\n }\n return ans;\n\n\n }\n}\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Sliding Window', 'Java']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
easy java solution
|
easy-java-solution-by-enkixly-dals
|
\n# Code\njava []\nimport java.util.HashMap;\n\nclass Solution {\n public long validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n HashMap<Character,
|
enkixly
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T12:53:02.954872+00:00
|
2024-09-22T12:53:02.954903+00:00
| 56 | false |
\n# Code\n```java []\nimport java.util.HashMap;\n\nclass Solution {\n public long validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n HashMap<Character, Integer> word2Count = new HashMap<>();\n for (char c : word2.toCharArray()) {\n word2Count.put(c, word2Count.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1);\n }\n\n long validCount = 0;\n int n = word1.length();\n int m = word2.length();\n HashMap<Character, Integer> currentCount = new HashMap<>();\n int left = 0;\n int matchedChars = 0;\n\n for (int right = 0; right < n; right++) {\n char rightChar = word1.charAt(right);\n currentCount.put(rightChar, currentCount.getOrDefault(rightChar, 0) + 1);\n\n if (word2Count.containsKey(rightChar) && currentCount.get(rightChar) <= word2Count.get(rightChar)) {\n matchedChars++;\n }\n\n while (matchedChars == m) {\n validCount += (n - right);\n char leftChar = word1.charAt(left);\n currentCount.put(leftChar, currentCount.get(leftChar) - 1);\n if (word2Count.containsKey(leftChar) && currentCount.get(leftChar) < word2Count.get(leftChar)) {\n matchedChars--;\n }\n left++;\n }\n }\n\n return validCount;\n }\n}\n\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Java']
| 1 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
🔥BEATS 💯 % 🎯 |✨SUPER EASY BEGINNERS 👏
|
beats-super-easy-beginners-by-codewithsp-nkmz
|
\n\n---\n\n# Intuition\nTo solve the problem of counting valid substrings of word1 that contain all characters of word2, we can leverage the sliding window tech
|
CodeWithSparsh
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T06:15:58.483276+00:00
|
2024-09-22T06:15:58.483315+00:00
| 169 | false |
\n\n---\n\n# Intuition\nTo solve the problem of counting valid substrings of `word1` that contain all characters of `word2`, we can leverage the sliding window technique. The idea is to maintain a window that counts characters from `word1` and check if it matches the character frequency in `word2`. If a valid window is found, we can count how many valid substrings can be formed from that window.\n\n# Approach\n1. **Frequency Counting**: Create frequency arrays for characters in `word2` and a sliding window in `word1`.\n2. **Sliding Window**: Use two pointers (left and right) to expand and contract the window in `word1`.\n - Expand the right pointer to include characters in the window.\n - Check if the current window satisfies the character frequency condition.\n - If valid, count all possible substrings ending at the right pointer and start shrinking the window from the left to see if it still remains valid.\n3. **Count Valid Substrings**: For each valid position of the right pointer, all characters from the left pointer to the end of `word1` form valid substrings.\n\n# Complexity\n- **Time complexity**: \n The overall time complexity is **O(n + m)**, where \\(n\\) is the length of `word1` and \\(m\\) is the length of `word2`. We iterate through `word1` once and update frequencies in constant time.\n \n- **Space complexity**: \n The space complexity is **O(1)**, as we use fixed-size arrays for character frequency (26 for lowercase letters).\n\n---\n\n# Code Implementations\n\n\n```dart []\nclass Solution {\n // Function to calculate the count of valid substrings\n int validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n // Frequency array for characters in word2\n List<int> targetFreq = List.filled(26, 0);\n for (var ch in word2.runes) {\n targetFreq[ch - \'a\'.runes.first]++;\n }\n\n // Frequency array for the sliding window in word1\n List<int> windowFreq = List.filled(26, 0);\n int result = 0;\n int left = 0, matchCount = 0;\n\n // Iterate through word1 using a sliding window\n for (int right = 0; right < word1.length; right++) {\n int charIndex = word1.codeUnitAt(right) - \'a\'.codeUnitAt(0);\n windowFreq[charIndex]++;\n\n // If the current character\'s frequency matches that in word2\n if (windowFreq[charIndex] == targetFreq[charIndex]) {\n matchCount++;\n }\n\n // Shrink window when all required characters are satisfied\n while (matchCount == targetFreq.where((count) => count > 0).length) {\n result += word1.length - right;\n\n int leftCharIndex = word1.codeUnitAt(left) - \'a\'.codeUnitAt(0);\n if (windowFreq[leftCharIndex] == targetFreq[leftCharIndex]) {\n matchCount--;\n }\n windowFreq[leftCharIndex]--;\n left++;\n }\n }\n\n return result;\n }\n}\n```\n\n\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n int[] targetFreq = new int[26];\n for (char ch : word2.toCharArray()) {\n targetFreq[ch - \'a\']++;\n }\n\n int[] windowFreq = new int[26];\n int result = 0;\n int left = 0, matchCount = 0;\n\n for (int right = 0; right < word1.length(); right++) {\n int charIndex = word1.charAt(right) - \'a\';\n windowFreq[charIndex]++;\n\n if (windowFreq[charIndex] == targetFreq[charIndex]) {\n matchCount++;\n }\n\n while (matchCount == getNonZeroCount(targetFreq)) {\n result += word1.length() - right;\n\n int leftCharIndex = word1.charAt(left) - \'a\';\n if (windowFreq[leftCharIndex] == targetFreq[leftCharIndex]) {\n matchCount--;\n }\n windowFreq[leftCharIndex]--;\n left++;\n }\n }\n return result;\n }\n\n private int getNonZeroCount(int[] freq) {\n int count = 0;\n for (int f : freq) {\n if (f > 0) count++;\n }\n return count;\n }\n}\n```\n\n\n```javascript []\nfunction validSubstringCount(word1, word2) {\n const targetFreq = Array(26).fill(0);\n for (let ch of word2) {\n targetFreq[ch.charCodeAt(0) - \'a\'.charCodeAt(0)]++;\n }\n\n const windowFreq = Array(26).fill(0);\n let result = 0;\n let left = 0;\n let matchCount = 0;\n\n for (let right = 0; right < word1.length; right++) {\n const charIndex = word1.charCodeAt(right) - \'a\'.charCodeAt(0);\n windowFreq[charIndex]++;\n\n if (windowFreq[charIndex] === targetFreq[charIndex]) {\n matchCount++;\n }\n\n while (matchCount === getNonZeroCount(targetFreq)) {\n result += word1.length - right;\n\n const leftCharIndex = word1.charCodeAt(left) - \'a\'.charCodeAt(0);\n if (windowFreq[leftCharIndex] === targetFreq[leftCharIndex]) {\n matchCount--;\n }\n windowFreq[leftCharIndex]--;\n left++;\n }\n }\n return result;\n}\n\nfunction getNonZeroCount(freq) {\n return freq.filter(f => f > 0).length;\n}\n```\n\n\n```python []\nclass Solution:\n def validSubstringCount(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:\n targetFreq = [0] * 26\n for ch in word2:\n targetFreq[ord(ch) - ord(\'a\')] += 1\n\n windowFreq = [0] * 26\n result = 0\n left = 0\n matchCount = 0\n\n for right in range(len(word1)):\n charIndex = ord(word1[right]) - ord(\'a\')\n windowFreq[charIndex] += 1\n\n if windowFreq[charIndex] == targetFreq[charIndex]:\n matchCount += 1\n\n while matchCount == sum(1 for count in targetFreq if count > 0):\n result += len(word1) - right\n\n leftCharIndex = ord(word1[left]) - ord(\'a\')\n if windowFreq[leftCharIndex] == targetFreq[leftCharIndex]:\n matchCount -= 1\n windowFreq[leftCharIndex] -= 1\n left += 1\n\n return result\n```\n\n\n```cpp []\n#include <vector>\n#include <string>\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int validSubstringCount(std::string word1, std::string word2) {\n std::vector<int> targetFreq(26, 0);\n for (char ch : word2) {\n targetFreq[ch - \'a\']++;\n }\n\n std::vector<int> windowFreq(26, 0);\n int result = 0;\n int left = 0, matchCount = 0;\n\n for (int right = 0; right < word1.length(); right++) {\n int charIndex = word1[right] - \'a\';\n windowFreq[charIndex]++;\n\n if (windowFreq[charIndex] == targetFreq[charIndex]) {\n matchCount++;\n }\n\n while (matchCount == getNonZeroCount(targetFreq)) {\n result += word1.length() - right;\n\n int leftCharIndex = word1[left] - \'a\';\n if (windowFreq[leftCharIndex] == targetFreq[leftCharIndex]) {\n matchCount--;\n }\n windowFreq[leftCharIndex]--;\n left++;\n }\n }\n return result;\n }\n\nprivate:\n int getNonZeroCount(const std::vector<int>& freq) {\n int count = 0;\n for (int f : freq) {\n if (f > 0) count++;\n }\n return count;\n }\n};\n```\n\n\n```go []\npackage main\n\nfunc validSubstringCount(word1 string, word2 string) int {\n targetFreq := make([]int, 26)\n for _, ch := range word2 {\n targetFreq[ch-\'a\']++\n }\n\n windowFreq := make([]int, 26)\n result := 0\n left, matchCount := 0, 0\n\n for right := 0; right < len(word1); right++ {\n charIndex := word1[right] - \'a\'\n windowFreq[charIndex]++\n\n if windowFreq[charIndex] == targetFreq[charIndex] {\n matchCount++\n }\n\n for matchCount == getNonZeroCount(targetFreq) {\n result += len(word1) - right\n\n leftCharIndex := word1[left] - \'a\'\n if windowFreq[leftCharIndex] == targetFreq[leftCharIndex] {\n matchCount--\n }\n windowFreq[leftCharIndex]--\n left++\n }\n }\n return result\n}\n\nfunc getNonZeroCount\n\n(freq []int) int {\n count := 0\n for _, f := range freq {\n if f > 0 {\n count++\n }\n }\n return count\n}\n```\n\n\n```typescript []\nfunction validSubstringCount(word1: string, word2: string): number {\n const targetFreq = Array(26).fill(0);\n for (let ch of word2) {\n targetFreq[ch.charCodeAt(0) - \'a\'.charCodeAt(0)]++;\n }\n\n const windowFreq = Array(26).fill(0);\n let result = 0;\n let left = 0;\n let matchCount = 0;\n\n for (let right = 0; right < word1.length; right++) {\n const charIndex = word1.charCodeAt(right) - \'a\'.charCodeAt(0);\n windowFreq[charIndex]++;\n\n if (windowFreq[charIndex] === targetFreq[charIndex]) {\n matchCount++;\n }\n\n while (matchCount === getNonZeroCount(targetFreq)) {\n result += word1.length - right;\n\n const leftCharIndex = word1.charCodeAt(left) - \'a\'.charCodeAt(0);\n if (windowFreq[leftCharIndex] === targetFreq[leftCharIndex]) {\n matchCount--;\n }\n windowFreq[leftCharIndex]--;\n left++;\n }\n }\n return result;\n}\n\nfunction getNonZeroCount(freq: number[]): number {\n return freq.filter(f => f > 0).length;\n}\n```\n\n---\n\n {:style=\'width:250px\'}
| 3 | 0 |
['C++', 'Java', 'Go', 'TypeScript', 'Python3', 'JavaScript', 'Dart']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Beginner Friendly | Simple Java code | Beats 100%
|
beginner-friendly-simple-java-code-beats-xezf
|
Intuition\nTo solve the problem of counting valid substrings in word1 that can form word2, we need to:\n\n1. Understand Character Counting: Check if substrings
|
Ram4366
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T04:15:44.054281+00:00
|
2024-09-22T04:15:44.054327+00:00
| 71 | false |
# Intuition\nTo solve the problem of counting valid substrings in word1 that can form word2, we need to:\n\n1. Understand Character Counting: Check if substrings of word1 can contain all characters of word2 in required frequencies.\n2. Optimize for Efficient Searching: Use a sliding window technique to efficiently find and count valid substrings.\n# Approach\n## Overview\n1. Character Counting: Maintain counts of characters in both word1 and word2 to determine if a substring is valid.\n2. Sliding Window Technique: Use two pointers to define the current window in word1 and check for validity against word2.\n## Detailed Steps\n1. Initialize Character Counts:\n\n- Create a targetCount HashMap to store character frequencies of word2.\n- Initialize a windowCount HashMap to track character frequencies in the current window of word1.\n2. Setup the Sliding Window:\n\n- Use two pointers (left and right) to represent the current window in word1.\n- Expand the window by moving the right pointer and include characters in windowCount.\n3. Check for Validity:\n\n- If the current window contains all characters from word2 in required frequencies, count valid substrings and then try to contract the window from the left.\n4. Count Valid Substrings:\n\n- For each valid window, add the number of valid substrings that can be formed from the current right pointer position to the end of word1.\n5. Return the Result:\n\n- Return the total count of valid substrings.\n\n# Complexity Analysis\n## Time Complexity: \n- $$O(N)$$, where N is the length of word1. Each character is processed at most twice (once by the right pointer and once by the left pointer).\n## Space Complexity:\n- $$O(K)$$, where K is the number of unique characters in word1 and word2, since we maintain character counts in two hash maps.\n\n# Code\n```java []\nimport java.util.HashMap;\n\nclass Solution {\n public long validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n int n = word1.length();\n int m = word2.length();\n if (n < m) return 0;\n\n HashMap<Character, Integer> targetCount = new HashMap<>();\n for (char c : word2.toCharArray()) {\n targetCount.put(c, targetCount.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1);\n }\n\n long validCount = 0;\n HashMap<Character, Integer> windowCount = new HashMap<>();\n int left = 0;\n\n for (int right = 0; right < n; right++) {\n\n windowCount.put(word1.charAt(right), windowCount.getOrDefault(word1.charAt(right), 0) + 1);\n\n while (isValid(windowCount, targetCount)) {\n validCount += (n - right); \n windowCount.put(word1.charAt(left), windowCount.get(word1.charAt(left)) - 1);\n if (windowCount.get(word1.charAt(left)) == 0) {\n windowCount.remove(word1.charAt(left));\n }\n left++;\n }\n }\n\n return validCount;\n }\n\n private boolean isValid(HashMap<Character, Integer> windowCount, HashMap<Character, Integer> targetCount) {\n for (char c : targetCount.keySet()) {\n if (windowCount.getOrDefault(c, 0) < targetCount.get(c)) {\n return false;\n }\n }\n return true;\n }\n}\n\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
C++ || Easy || Binary Search || Prefix Frequency Table
|
c-easy-binary-search-prefix-frequency-ta-lczk
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nThe problem involves finding the number of valid substrings in word1 that satisfy certa
|
mohdshahid643285
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-27T12:23:15.056537+00:00
|
2024-09-27T12:25:59.101233+00:00
| 71 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThe problem involves finding the number of valid substrings in word1 that satisfy certain frequency requirements based on word2. Specifically, for any substring in word1, the frequency of each character in the substring should be greater than or equal to the frequency of the corresponding character in word2.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n**1.Frequency Array for word2:**\nWe first compute the frequency of each character in word2. This frequency array will be used to compare the character frequencies of substrings in word1.\n\n**2.Prefix Frequency Table for word1:**\nFor efficient computation of character frequencies over any substring of word1, we build a prefix frequency table. This table allows us to calculate the frequency of any character in any substring of word1 in constant time.\n\n**3.Binary Search for Valid Substring:**\nFor each starting index i in word1, we perform a binary search to find the smallest valid ending index mid. For the substring from index i to mid, we check if the frequency of each character meets or exceeds the frequency in word2.\n\n- If the current substring satisfies the condition, we try to find a smaller valid ending index to minimize the substring.\n- If it doesn\'t satisfy the condition, we move to larger substrings by increasing the ending index.\n- After determining the smallest valid mid, all substrings from i to the valid indices (mid to n-1) are counted.\n\n**4.Result:**\nWe count and accumulate all valid substrings starting from each index in word1.\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nThe overall time complexity is O(n * (log n + 26)) \u2248 O(n * log n), where n is the length of word1.\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nThe space used for the frequency array of word2 is O(26).\nThe prefix frequency table for word1 requires O(n * 26) space.\nThus, the total space complexity is O(n * 26) \u2248 O(n).\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) {\n int n = word1.size();\n int m = word2.size();\n\n // Frequency array for word2\n vector<int> freq(26, 0);\n for (auto ch : word2) {\n freq[ch - \'a\']++;\n }\n \n // Frequency table for word1\n vector<vector<int>> freqTable(26, vector<int>(n, 0));\n for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {\n int ch = word1[j] - \'a\';\n if (j > 0) {\n for (int k = 0; k < 26; k++) {\n freqTable[k][j] = freqTable[k][j-1];\n }\n }\n freqTable[ch][j]++;\n }\n\n long long ans = 0;\n \n // Iterate over each starting index in word1\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n int l = i, r = n - 1, index = -1;\n \n // Binary search for the smallest valid ending index\n while (l <= r) {\n int mid = l + (r - l) / 2;\n bool flag = true;\n \n // Check if the substring from i to mid satisfies the frequency requirement\n for (int j = 0; j < 26; j++) {\n int currFreq = freqTable[j][mid];\n \n // If i > 0, subtract the frequencies from the prefix sum up to i-1\n if (i > 0) {\n currFreq -= freqTable[j][i - 1];\n }\n \n // Check if the current character\'s frequency in the range is valid\n if (freq[j] > currFreq) {\n flag = false;\n break;\n }\n }\n \n if (flag) {\n index = mid;\n r = mid - 1; // Try to find a smaller valid index\n } else {\n l = mid + 1;\n }\n }\n\n // Count all valid substrings starting from i\n if (index != -1) {\n ans += (n - index);\n }\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n};\n\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'Binary Search', 'Prefix Sum', 'C++']
| 1 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Simple Java Solution using freq
|
simple-java-solution-using-freq-by-rajna-ro0b
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
rajnarayansharma110
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T18:46:22.054693+00:00
|
2024-09-22T18:46:22.054726+00:00
| 15 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(n+m)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:O(1)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public long validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n int n=word1.length(),m=word2.length();\n long count=0;\n int[] freq1=new int[26];\n int[] freq2=new int[26];\n for(char c:word2.toCharArray()){\n freq2[c-\'a\']++;\n }\n int l=0,validCount=0;\n for(int r=0;r<n;r++){\n freq1[word1.charAt(r)-\'a\']++;\n if(freq1[word1.charAt(r)-\'a\']<=freq2[word1.charAt(r)-\'a\']){\n validCount++;\n }\n while(validCount>=m){\n count+=n-r;\n freq1[word1.charAt(l)-\'a\']--;\n if(freq1[word1.charAt(l)-\'a\']<freq2[word1.charAt(l)-\'a\']){\n validCount--;\n }\n l++;\n }\n } \n return count;\n }\n}\n\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
🏆🏆 ✅✅BEST SOLUTION ✅✅IN PYTHON WITH PROPER COMMENTS : CHECKOUT ONCE GUYS 🏆🏆✅✅㊙️🈵
|
best-solution-in-python-with-proper-comm-fcki
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
progammersoumen
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T04:02:08.926084+00:00
|
2024-09-22T04:02:08.926119+00:00
| 304 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def validSubstringCount(self, a: str, b: str) -> int:\n # Initialize frequency arrays for characters in \'b\' and for the window in \'a\'\n cnt = [0] * 26 # Count of characters in string \'b\'\n arr = [0] * 26 # Current count of characters in window of string \'a\'\n x = 0 # Number of characters from \'b\' left to match\n n = len(a) # Length of string \'a\'\n l = 0 # Left pointer of the sliding window\n res = 0 # Result to store the number of valid substrings\n\n # Populate \'cnt\' with the frequencies of characters in \'b\'\n for c in b:\n cnt[ord(c) - ord(\'a\')] += 1\n x += 1 # Track total characters to match\n\n # Sliding window approach\n for r in range(n):\n i = ord(a[r]) - ord(\'a\') # Convert current character in \'a\' to an index\n arr[i] += 1 # Increase the count of this character in the window\n\n if arr[i] <= cnt[i]:\n x -= 1 # Decrease \'x\' if a character from \'b\' is matched\n\n # Shrink the window from the left when all characters are matched\n while x == 0:\n res += n - r # Add all possible substrings starting from this window\n i = ord(a[l]) - ord(\'a\') # Get index for the left pointer character\n arr[i] -= 1 # Remove the character from the window\n l += 1 # Move the left pointer to the right\n if arr[i] < cnt[i]:\n x += 1 # Increase \'x\' when a character is unmatched\n\n return res\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Binary search+prefix || very easy code explaination
|
binary-searchprefix-very-easy-code-expla-sw2n
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
sumit1906
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-24T16:14:42.828785+00:00
|
2024-09-24T16:14:42.828816+00:00
| 17 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(26*n*logn)\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(n*26)\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\nbool solve(const vector<vector<int>>& arr, int i, int mid, const vector<int>& count) {\n for (int j = 0; j < 26; ++j) {\n int freqInSubstring = arr[mid][j] - (i > 0 ? arr[i - 1][j] : 0);\n if (freqInSubstring < count[j]) {\n return false;\n }\n }\n return true;\n}\n\nlong long validSubstringCount(string s1, string s2) {\n vector<int> count(26, 0);\n long long ans = 0;\n\n // Frequency count for s2\n for (char c : s2) {\n count[c - \'a\']++;\n }\n\n int n = s1.size();\n \n // Create cumulative frequency array arr\n vector<vector<int>> arr(n, vector<int>(26, 0));\n\n // Initialize the frequency array\n arr[0][s1[0] - \'a\'] = 1;\n for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {\n for (int j = 0; j < 26; ++j) {\n arr[i][j] = arr[i - 1][j]; // Inherit the previous counts\n }\n arr[i][s1[i] - \'a\']++; // Increment the count of current character\n }\n\n // For each starting index i, find the maximum valid substring\n for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {\n int s = i, e = n - 1;\n int index = -1;\n\n // Binary search to find the minimum \'mid\' where the substring s1[i..mid] is valid\n while (e >= s) {\n int mid = (s + e) / 2;\n if (solve(arr, i, mid, count)) {\n e = mid - 1;\n index = mid;\n } else {\n s = mid + 1;\n }\n }\n\n // If a valid substring is found, add the number of valid substrings starting from index i\n if (index != -1) {\n ans += (n - index); // All substrings from index `i` to `n-1`\n }\n }\n\n return ans;\n}\n};\n\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Optimized Approach - O(n) Time Complexity with Constant Space
|
optimized-approach-on-time-complexity-wi-mtua
|
Intuition\nWe need to find all substrings in word1 that contain every character present in word2 with the exact required frequency. Starting from the first inde
|
isha534
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-23T06:36:06.971620+00:00
|
2024-09-23T06:36:06.971652+00:00
| 35 | false |
# Intuition\nWe need to find all substrings in word1 that contain every character present in word2 with the exact required frequency. Starting from the first index of word1, we\'ll use a sliding window approach to count the characters from word2. \n\nAs soon as our window contains all the necessary characters with their required counts, we\'ll determine how many extra characters exist before the current start index and how many potential characters remain after the current end index. By multiplying these two values, we get the total number of valid substrings that can be formed. We then add this count to our answer. Afterward, we slide the window further to the right and repeat the process until we\'ve checked all possible substrings.\n\n# Approach\nSliding Window approach\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(n)\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(26)\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) {\n\n vector<int> v(26,0);\n vector<int> v1(26,0);\n\n long long ans =0;\n\n for(auto it:word2) v[it-\'a\']++;\n\n int i=0,j=0,ct=0;\n\n while(j<word1.size()){\n if(v[word1[j]-\'a\'] && v1[word1[j]-\'a\'] < v[word1[j]-\'a\']){\n ct++;\n }\n\n v1[word1[j]-\'a\']++;\n\n if(ct==word2.size()){\n int back = 0;\n\n while(v1[word1[i]-\'a\']>v[word1[i]-\'a\']){\n v1[word1[i]-\'a\']--;\n\n back++;\n i++;\n } \n\n back++;\n\n int front = word1.size() - j;\n ans += (front * back);\n\n v1[word1[i]-\'a\']--;\n ct--;\n\n i++;\n }\n\n j++;\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n};\n\n//aabbabcabc\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Sliding Window', 'C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Sliding Window || O(N)
|
sliding-window-on-by-bora_marian-cv55
|
Approach\nCalculate for each \uD835\uDC56 the number of substrings in word1 that have at least the same character frequency as word2.\ni will contribute to the
|
bora_marian
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-23T05:08:24.073652+00:00
|
2024-09-23T05:08:24.073680+00:00
| 87 | false |
# Approach\nCalculate for each \uD835\uDC56 the number of substrings in word1 that have at least the same character frequency as word2.\n$$i$$ will contribute to the result with the substrings $$0, 1, ... , st$$ where $$st$$ is the last position satisfying the condition $$freq[i] - freq[st] >= freqWord2$$\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:$$O(n * 26)$$ => $$O(n)$$, where n is the number of characters in word1\n- Space complexity: $$O(2 * 26)$$ => $$O(1)$$\n\nSame [solution](https://leetcode.com/problems/count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-ii/solutions/5822560/sliding-window/) for the Hard problem [https://leetcode.com/problems/count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-ii](https://leetcode.com/problems/count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-ii)\n\uD83D\uDCAA\uD83D\uDE80Keep leetcoding! Keep improving!\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) {\n int freqWord2[26] = {}, freq[26] = {};\n int w2n = word2.size(), w1n = word1.size();\n for (int i = 0; i < w2n; i++) \n {\n freqWord2[word2[i] - \'a\']++;\n }\n\n int st = 0;\n long long result = 0;\n bool isBiggerOnce = false;\n for(int i = 0; i < w1n; i++) \n {\n freq[(word1[i] - \'a\')]++;\n int ch = word1[st] - \'a\';\n while(st <= i && freq[ch] - 1 >= freqWord2[ch]) \n {\n freq[ch]--;\n st++;\n ch = word1[st] - \'a\'; \n }\n //above is maintained the frequency bigger or equal so we retain if once was bigger for word2 characters.\n if (isBiggerOnce || IsBiggerOrEqual(freq, freqWord2)) { \n isBiggerOnce = true; \n result += (long long)(st + 1);\n } \n }\n\n return result;\n }\n bool IsBiggerOrEqual(int freq1[], int freq2[]) \n {\n for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) \n {\n if (freq1[i] < freq2[i]) \n return false;\n }\n return true;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Sliding window. Simple and clear solution
|
sliding-window-simple-and-clear-solution-tngn
|
\nclass Solution:\n def validSubstringCount(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:\n cnt = Counter(word2)\n ans, left, diff = 0, 0, len(cnt)\n
|
xxxxkav
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T22:57:06.356723+00:00
|
2024-09-23T07:47:51.978293+00:00
| 78 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def validSubstringCount(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:\n cnt = Counter(word2)\n ans, left, diff = 0, 0, len(cnt)\n for ch in word1:\n cnt[ch] -= 1\n if cnt[ch] == 0:\n diff -= 1\n while diff == 0:\n cnt[word1[left]] += 1\n if cnt[word1[left]] == 1:\n diff += 1\n left += 1\n ans += left\n return ans\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Sliding Window', 'Python3']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Sliding window intuition using Maps
|
sliding-window-intuition-using-maps-by-b-cvts
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nFirst get the window having all the characters required, then progressively reduce the
|
b23karali
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T18:31:46.321316+00:00
|
2024-09-22T18:31:46.321339+00:00
| 89 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nFirst get the window having all the characters required, then progressively reduce the window size ensuring the contranst are met.\nAnd substring would be word.length - index\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nSliding window to get get all lements required.\nThen get the substrings in the current position by difference of word length and current index.\nBecause if all the required chars are already prsent as prefix, rest of characters can just add to substring by selecting oneor more characters among them.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(n) where n is length of word\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(26) ~ O(1) constant space\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public long validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n Map<Character, Integer> freq = new HashMap<>();\n for(Character c : word2.toCharArray()){\n freq.put(c, freq.getOrDefault(c, 0)+1);\n }\n Map<Character, Integer> ongoing = new HashMap<>();\n int count = 0;\n int left = 0; \n int wordCount = 0;\n long answer = 0;\n int right=0;\n while(right < word1.length()){\n Character curr = word1.charAt(right);\n if(freq.containsKey(curr)){\n ongoing.put(curr,ongoing.getOrDefault(curr,0)+1);\n if(freq.get(curr).equals(ongoing.get(curr)))count++;\n }\n while(count == freq.size()){\n answer += word1.length() - right;\n Character leftChar = word1.charAt(left);\n if(freq.containsKey(leftChar)){\n ongoing.put(leftChar, ongoing.get(leftChar)-1);\n if(ongoing.get(leftChar) < freq.get(leftChar)){\n count--;\n }\n }\n left++;\n }\n right++;\n }\n return answer;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'Sliding Window', 'Java']
| 1 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Sliding Window || C++ 🔍🧩
|
sliding-window-c-by-buriburizaemon17-kd89
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nTo find valid substrings of s that can be rearranged to have p as a prefix, we need to
|
buriburizaemon17
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T05:32:26.329060+00:00
|
2024-09-22T05:32:46.716847+00:00
| 90 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nTo find valid substrings of $$s$$ that can be rearranged to have $$p$$ as a prefix, we need to ensure that each substring contains at least the same frequency of characters as in $$p$$. This can be efficiently tracked using a sliding window and character counts.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1. **Character Count for p:** Use an unordered map $$mpP$$ to store frequencies of characters in $$p$$\n2. **Sliding Window:** Employ two pointers ($$i$$ and $$j$$) to maintain a window in $$s$$: \n- Expand $$j$$ and update a second map $$mpS$$ for the current window.\n- When a character from $$p$$ is fully matched in $$mpS$$, increment $$cnt$$.\n\n3. **Count Valid Substrings:** If $$cnt$$ equals the unique character count from $$p$$, add $$(n - j)$$ to the result, as all remaining characters form valid substrings. Then, increment $$i$$ to narrow the window, adjusting $$mpS$$ accordingly.\n4. **Repeat Until All Characters Are Processed:** Continue until $$j$$ has processed all characters in $$s$$.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(1)$$\n# Code\n```cpp []\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n using ll = long long;\n long long validSubstringCount(string s, string p) {\n\n int n = s.size(), m = p.size();\n if (m > n) return 0;\n\n unordered_map<char, int> mpP, mpS;\n for (char c : p) \n mpP[c]++;\n\n ll ans = 0;\n int uniqCnt = mpP.size();\n int cnt = 0;\n\n int i = 0;\n for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {\n char c = s[j];\n mpS[c]++;\n if (mpP.count(c) && mpS[c] == mpP[c]) {\n cnt++;\n }\n\n while (cnt == uniqCnt) {\n ans += (n - j);\n\n char leftCh = s[i];\n mpS[leftCh]--;\n if (mpP.count(leftCh) && mpS[leftCh] < mpP[leftChar]) {\n cnt--;\n }\n i++;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n\n```
| 1 | 1 |
['Ordered Map', 'Sliding Window', 'C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Easy Java solution using hashmaps
|
easy-java-solution-using-hashmaps-by-aks-10yx
|
\n\n# Code\njava []\nclass Solution {\n long count = 0;\n public long validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n Map<Character,Integer> ma
|
akshay1610
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T04:44:46.701990+00:00
|
2024-09-22T04:44:46.702029+00:00
| 62 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n long count = 0;\n public long validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n Map<Character,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();\n Map<Character,Integer> map2 = new HashMap<>();\n for (int i = 0;i<word2.length();i++) {\n map.put(word2.charAt(i),map.getOrDefault(word2.charAt(i),0)+1);\n }\n int low= 0;\n for (int high = 0;high<word1.length();high++) {\n map2.put(word1.charAt(high),map2.getOrDefault(word1.charAt(high),0)+1);\n if (high-low+1 >=word2.length()) {\n while(helper(map,map2,low,high,word1.length())){\n \n map2.put(word1.charAt(low),map2.getOrDefault(word1.charAt(low),0)-1);\n if (map2.containsKey(word1.charAt(low)) && map2.get(word1.charAt(low))==0) {\n map2.remove(word1.charAt(low));\n }\n low++;\n }\n }\n }\n return count;\n }\n\n public boolean helper (Map<Character,Integer> map,Map<Character,Integer> map2,int low,int high,int n) {\n for (Map.Entry<Character,Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) {\n if (!map2.containsKey(entry.getKey())) {\n return false;\n }\n if (map2.get(entry.getKey()) < entry.getValue()) {\n return false;\n }\n } \n count+=(n-high);\n return true;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Two pointer | Sliding Window | Easy solution
|
two-pointer-sliding-window-easy-solution-1htq
|
Approach:\n1. Total Number of Substrings:\n\t1. The total number of substrings for a string of length n is calculated using the formula: (n*(n+1))/2\n2. Identif
|
wait_watch
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T04:44:27.395314+00:00
|
2024-09-22T05:13:15.629915+00:00
| 11 | false |
Approach:\n1. Total Number of Substrings:\n\t1. The total number of substrings for a string of length n is calculated using the formula: (n*(n+1))/2\n2. Identifying Impossible Substrings\n3. Final Step:\n\t1. Subtract the number of impossible substrings from the total number of substrings to get the desired result.\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n long long validSubstringCount(string w1, string w2) {\n long long n = w1.size();\n unordered_map<char,int>freq1;\n unordered_map<char,int>freq2;\n for(int i=0;i<w2.size();i++){\n freq2[w2[i]]++;\n }\n long long ans = (n*(n+1))/2;\n long long curr =0;\n int i =0,j=0;\n while(j<n){\n if(freq2.count(w1[j]))\n freq1[w1[j]]++;\n bool poss = true;\n auto it = freq2.begin();\n while(it!=freq2.end()){\n if(it->second>freq1[it->first]){\n poss = false;\n break;\n }\n it++;\n }\n if(poss){\n while(i<=j){\n int curr = w1[i];\n if(freq2.count(curr)){\n freq1[curr]--; \n }\n i++;\n if(freq2.count(curr) && freq2[curr]>freq1[curr])\n break;\n \n \n }\n }\n \n long long diff = j-i+1;\n curr= curr + diff;\n j++;\n\n }\n return ans-curr;\n \n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
try it--beat 90%(upvote if useful)
|
try-it-beat-90upvote-if-useful-by-bhavik-4q02
|
Intuition\nThe problem is to find the count of all valid substrings of word1 that contain at least the characters in word2. We can solve this efficiently using
|
20250406.Bhavikj
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T04:16:11.447889+00:00
|
2024-09-22T04:16:11.447927+00:00
| 30 | false |
Intuition\nThe problem is to find the count of all valid substrings of word1 that contain at least the characters in word2. We can solve this efficiently using a sliding window approach, where we track the characters in the current window of word1 and compare it with the character frequencies of word2. The idea is to keep expanding the window until it contains all the characters from word2, and then count all valid substrings starting from the current window.\n\nApproach\nPreprocessing word2:\nWe create an array word2Count to store the frequency of each character in word2. This helps us know how many times each character needs to appear in a valid substring.\nSliding window on word1:\nWe maintain a sliding window over word1 using two pointers, start and end.\nWe also maintain an array windowCount to track the frequency of characters in the current window.\nWe expand the window by moving the end pointer, adding characters to windowCount. For each character, if the count matches its required frequency in word2, we increase the matches count.\nCheck if the window is valid:\nA valid window is one where all characters in word2 have been matched (i.e., matches == required).\nOnce the window is valid, all substrings starting from start to end are valid because any longer substring will still contain the characters of word2.\nShrink the window:\nAfter counting the valid substrings for the current window, we move the start pointer to shrink the window and try to maintain validity by updating windowCount and reducing the matches count if necessary.\nComplexity\nTime complexity:\nThe time complexity is O(n), where n is the length of word1. The sliding window approach ensures that each character is processed at most twice (once when expanding the window and once when shrinking it).\n\nSpace complexity:\nThe space complexity is O(1) since the space used for word2Count and windowCount is constant (both arrays of size 26).\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) {\n vector<int> word2Count(26, 0);\n for (char c : word2) {\n word2Count[c - \'a\']++;\n }\n\n int word2Length = word2.size();\n long long result = 0;\n int required = 0;\n vector<int> windowCount(26, 0);\n\n // Count how many unique characters in word2 need to be satisfied\n for (int count : word2Count) {\n if (count > 0) required++;\n }\n\n int start = 0, matches = 0;\n\n // Sliding window over word1\n for (int end = 0; end < word1.size(); end++) {\n // Add current character to the window\n char c = word1[end];\n windowCount[c - \'a\']++;\n\n // Check if the current character satisfies the requirement from word2\n if (windowCount[c - \'a\'] == word2Count[c - \'a\']) {\n matches++;\n }\n\n // Shrink the window until it is valid\n while (matches == required) {\n // Once the window size is large enough, all substrings starting from `start` to `end` are valid\n result += word1.size() - end;\n\n // Shrink the window from the left\n char leftChar = word1[start];\n windowCount[leftChar - \'a\']--;\n\n // If the character no longer satisfies the word2 requirement, decrease match count\n if (windowCount[leftChar - \'a\'] < word2Count[leftChar - \'a\']) {\n matches--;\n }\n start++;\n }\n }\n\n return result;\n }\n};\n\n```\n
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Using sliding window | TC:O(n)| JAVA && Python
|
using-sliding-window-tcon-java-python-by-tetm
|
Intuition\nUsing the sliding window to count all the substring from right index to end.\n\n# Approach\nUsing the sliding window to maintain left index and right
|
yunjiexu
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T04:09:36.270768+00:00
|
2024-09-22T07:29:11.732006+00:00
| 113 | false |
# Intuition\nUsing the sliding window to count all the substring from right index to end.\n\n# Approach\nUsing the sliding window to maintain left index and right index, if in the window of word1 contains all the letter in word2, all the substring from current window expand to the end of the word1 is valid, so we add len(word1) - rightIndex\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(len(word1))\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(1)\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public long validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n if (word1.length() < word2.length()) {\n return 0;\n }\n int[] cnts = new int[26];\n for (char c : word2.toCharArray()) {\n cnts[c -\'a\']--;\n }\n for (int i = 0; i < word2.length(); i++) {\n cnts[word1.charAt(i) - \'a\']++;\n }\n int right = word2.length() - 1, left = 0;\n long res = 0;\n while (right < word1.length()) {\n if (isValid(cnts)) {\n res += (word1.length() - right);\n cnts[word1.charAt(left) - \'a\']--;\n left++;\n } else {\n right++;\n if (right < word1.length()) {\n cnts[word1.charAt(right) - \'a\']++;\n }\n }\n }\n return res;\n }\n\n private boolean isValid(int[] cnts) {\n for (int cnt : cnts) {\n if (cnt < 0) {\n return false;\n }\n }\n return true;\n }\n}\n```\n\n```python []\nclass Solution:\n def validSubstringCount(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:\n if len(word1) < len(word2):\n return 0\n\n # Initialize the frequency counts for each letter\n cnts = [0] * 26\n \n # Decrease counts for each character in word2\n for c in word2:\n cnts[ord(c) - ord(\'a\')] -= 1\n\n # Increase counts for the first window of word1\n for i in range(len(word2)):\n cnts[ord(word1[i]) - ord(\'a\')] += 1\n\n right = len(word2) - 1\n left = 0\n res = 0\n\n # Sliding window approach\n while right < len(word1):\n if self.isValid(cnts):\n # If valid, count all substrings from this right index to the end\n res += (len(word1) - right)\n cnts[ord(word1[left]) - ord(\'a\')] -= 1\n left += 1\n else:\n right += 1\n if right < len(word1):\n cnts[ord(word1[right]) - ord(\'a\')] += 1\n \n return res\n\n def isValid(self, cnts: list) -> bool:\n # Check if all values in cnts are non-negative\n for cnt in cnts:\n if cnt < 0:\n return False\n return True\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Sliding Window', 'Python', 'Java', 'Python3']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Easy solution using map and vector, works for part 2 also
|
easy-solution-using-map-and-vector-works-4ijm
|
Count Substrings That Can Be Rearranged to Contain a String I\n\n## Intuition\nTo solve the problem of counting how many substrings of word1 can be rearranged t
|
Rudra_hu_mai
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-22T04:06:05.425196+00:00
|
2024-09-22T14:14:09.823353+00:00
| 110 | false |
# Count Substrings That Can Be Rearranged to Contain a String I\n\n## Intuition\nTo solve the problem of counting how many substrings of `word1` can be rearranged to have `word2` as a prefix, we recognize that we need to track the frequency of characters. A substring can be rearranged to contain `word2` if it has at least the same count of each character that `word2` has. This suggests a method involving maintaining character counts and checking them as we slide through `word1`.\n\n## Approach\n1. **Frequency Maps**: Use a frequency map for `word2` to count the characters.\n2. **Sliding Window**: Traverse `word1` using a sliding window approach:\n - For each character in `word1`, decrease the count in a frequency array for characters seen so far.\n - When all characters from `word2` are matched, count all valid substrings that can be formed from the current position to the end of `word1`.\n - Adjust the left pointer of the window to explore other potential valid substrings.\n\n## Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$, where `n` is the length of `word1`. The algorithm primarily consists of a single pass through `word1`, with constant time checks for character counts.\n \n- Space complexity: $$O(1)$$ for the frequency array since the size is fixed at 26 (for the lowercase English alphabet).\n\n## Code\n```cpp\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) {\n \n int n1 = word1.size();\n int n2 = word2.size();\n\n // Array x to track frequency of characters in word2\n vector<int> x(26, 0);\n \n // If word2 is longer than word1, no valid substrings can exist\n if (n2 > n1) return 0;\n\n // Map f stores the frequency of characters in word2\n unordered_map<char, int> f;\n\n // Populate the map f and array x with frequencies of each character in word2\n for (char c : word2) {\n f[c]++;\n x[c - \'a\']++;\n }\n\n // i is the left pointer, t is the count of valid substrings\n int i = 0;\n long long t = 0;\n\n // j is the right pointer that iterates over word1\n for (int j = 0; j < n1; j++) {\n char c = word1[j];\n\n // If current character is not in word2, skip it\n if (!f.count(c))\n continue;\n\n // Decrease the frequency count of the current character\n x[c - \'a\']--;\n\n // Check if all characters from word2 are present in the window\n if (*max_element(x.begin(), x.end()) == 0) {\n // Expand the left pointer i to find all valid substrings\n while (i < n1) {\n // Add the number of valid substrings from this point\n t += n1 - j;\n\n // If word1[i] is not in word2, move the left pointer\n if (!f.count(word1[i])) {\n i++;\n continue;\n }\n\n // Restore the frequency count of the character at word1[i]\n x[word1[i] - \'a\']++;\n\n // If all characters are still covered, move the left pointer\n if (x[word1[i] - \'a\'] <= 0) {\n i++;\n } else {\n // Otherwise, break the loop as the window is no longer valid\n i++;\n break;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n\n // Return the total number of valid substrings found\n return t;\n }\n};\n\n
| 1 | 0 |
['Sliding Window', 'C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
easy solution
|
easy-solution-by-owenwu4-1te4
|
Intuitionuse sliding window with a dictionaryApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
owenwu4
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-23T15:09:07.154555+00:00
|
2025-03-23T15:09:07.154555+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
use sliding window with a dictionary
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def validSubstringCount(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:
l = 0
d = Counter()
key = Counter(word2)
res = 0
for r in range(len(word1)):
d[word1[r]] += 1
while d >= key and l <= r:
res += (len(word1) - r)
d[word1[l]] -= 1
if d[word1[l]] == 0:
del d[word1[l]]
l += 1
return res
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Java sliding window generic template solution
|
java-sliding-window-generic-template-sol-ofou
|
IntuitionUsually question would ask smallest substring - but we are asked the count here. Whatever the substrings having length > substring that obey the condit
|
anonymous63
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-22T19:15:55.293531+00:00
|
2025-03-22T19:15:55.293531+00:00
| 1 | false |
# Intuition
Usually question would ask smallest substring - but we are asked the count here. Whatever the substrings having length > substring that obey the condition should be automatically be counted.
# Approach
1. Find the smallest string string obeying the condition
2. for this solution, Add the word1.length() - endIndex will take care of string of sizes more than that.
Algo -
1. For each end index - consider the end index to update current frequency array.
2. while our substring follows the given condition - keep on reducing the start index untill it does not follow.
3. in the main while loop keep on adding end.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
$$O(n)$$
- Space complexity:
$$O(1)$$ - 26 fix size.
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
public long validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {
// count the substrings with >= frequ count as word2
int[] prefix = new int[26];
Arrays.fill(prefix, 0);
for(char c: word2.toCharArray()) {
prefix[c - 'a']++;
}
int start = 0, end = 0;
long count = 0;
int[] current = new int[26];
while(end < word1.length()) {
current[word1.charAt(end) - 'a']++;
while(isValid(current, prefix)) {
count+= (long) (word1.length() - end);
current[word1.charAt(start) - 'a']--;
start++;
}
end++;
}
return count;
}
private boolean isValid(int[] current, int[] prefix) {
for(int i=0; i< 26; i++) {
if(current[i] < prefix[i]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Best Clean Cool Solution O(n) time O(1) space
|
best-clean-cool-solution-on-time-o1-spac-s5pu
|
IntuitionWe use one array of size 26 to differentiate how many instances of a certain letter we need and how many we have (we could use one variable to keep tha
|
shmirrakhimov
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-21T17:57:56.433761+00:00
|
2025-03-21T17:57:56.433761+00:00
| 1 | false |
# Intuition
We use one array of size 26 to differentiate how many instances of a certain letter we need and how many we have (we could use one variable to keep that score, but anyways, we have two for clarity)
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
Code is readable
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity: O(n)
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity: O(1)
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```javascript []
/**
* @param {string} word1
* @param {string} word2
* @return {number}
*/
var validSubstringCount = function(word1, word2) {
let res = 0;
let freq = new Array(26).fill(0);
let left = 0;
let allScore = 0;
let curScore = 0;
for(let i = 0; i < word2.length; i++){
if(freq[word2.charCodeAt(i) - 97] == 0) allScore++;
freq[word2.charCodeAt(i) - 97]--;
}
for(let i = 0; i < word1.length; i++){
if(freq[word1.charCodeAt(i) - 97] == -1) curScore++;
freq[word1.charCodeAt(i) - 97]++;
while(allScore == curScore){
res += word1.length - i;
freq[word1.charCodeAt(left) - 97]--;
if(freq[word1.charCodeAt(left) - 97] == -1) curScore--;
left++;
}
}
return res;
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'String', 'Sliding Window', 'JavaScript']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
0ms solution
|
0ms-solution-by-kyuyeon-gi94
|
IntuitionTry to figure out the relation between valid substringsApproachA substring is defined as the interval[i, j].For a valid substring[i, j],[i + 1, j]is va
|
kyuyeon
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-22T19:03:57.252750+00:00
|
2025-02-22T19:03:57.252750+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
Try to figure out the relation between valid substrings
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
A substring is defined as the interval `[i, j]`.
For a valid substring `[i, j]`, `[i + 1, j]` is valid if `word1[i]` is not in `word2[i]`.
Instead of comparing charaters every iteration, just use keep a variable `c` that indicates whether there are any missing characters of `word2`. Since this is a frequent operation which saves 26 computations, the speedup is significant by dropping the constant multiplication in terms of time complexity.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
$$O(n_1 + n_2)$$
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
$$O(1)$$ because it uses only counter variables.
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) {
int n1 = word1.size();
int n2 = word2.size();
int c = 0;
vector<int> cnt1(256, 0);
vector<int> cnt2(256, 0);
long long ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n2; ++i) {
if (cnt2[word2[i]] == 0) {
c++;
}
cnt2[word2[i]]++;
}
long long lo = 0;
long long hi = 0;
while (hi < n1) {
cnt1[word1[hi]]++;
if (cnt1[word1[hi]] == cnt2[word1[hi]]) {
c--;
}
hi++;
while (c == 0 && lo < hi) {
ans += (n1 - hi + 1);
cnt1[word1[lo]]--;
if (cnt1[word1[lo]] < cnt2[word1[lo]]) {
c++;
}
lo++;
}
}
return ans;
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Easy Python Solution
|
easy-python-solution-by-vidhyarthisunav-j425
|
Code
|
vidhyarthisunav
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-04T10:31:56.500555+00:00
|
2025-02-04T10:31:56.500555+00:00
| 11 | false |
# Code
```python3 []
class Solution:
def validSubstringCount(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:
def check(map1, map2):
for key in map2.keys():
if map1[key] < map2[key]:
return False
return True
count1 = defaultdict(int)
count2 = Counter(word2)
n = len(word1)
count = 0
left = 0
for right in range(n):
count1[word1[right]] += 1
while check(count1, count2):
count += n - right
count1[word1[left]] -= 1
left += 1
return count
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Binary Search || prefix sum arrays || count valid substrings || C++.
|
binary-search-prefix-sum-arrays-count-va-25to
|
IntuitionThe problem requires counting substrings of word1 that contain all characters of word2 at least as many times as they appear in word2. To efficiently f
|
RishiINSANE
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-30T17:56:41.388083+00:00
|
2025-01-30T17:56:41.388083+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition
The problem requires counting substrings of word1 that contain all characters of word2 at least as many times as they appear in word2. To efficiently find such substrings, we use prefix frequency arrays and binary search. By precomputing character frequencies in word1 using a prefix sum approach, we can quickly check if a given substring satisfies the frequency requirements. Binary search helps efficiently determine the smallest valid right endpoint for each left endpoint, reducing the time complexity significantly compared to a brute-force approach.
# Approach
1. Precompute Character Frequencies:
- We maintain a prefix array where `prefix[i][ch]` stores the number of times character `ch` appears in the prefix of word1 up to index i.
- This allows quick frequency queries for any substring `[l,r]` using the formula:
`count of ch in [l,r]=prefix[r+1][ch]−prefix[l][ch]`
2. Binary Search for the Smallest Valid `r`:
- For each starting index l, we perform binary search on r (right endpoint) to find the smallest `r` such that the substring `[l,r]` contains all characters of word2 in the required count.
- The function `isGood(l, r)` checks if the substring `[l,r]` satisfies the condition using prefix sums.
- If `isGood(l, mid)` returns true, we reduce `high (high = mid - 1)`, otherwise, we increase `low (low = mid + 1)`.
- The smallest valid r found is used to count the number of valid substrings starting at l.
3. Counting Valid Substrings:
- If the smallest valid `r` for `l` is found, all substrings starting at l and ending from `r to n-1` are valid.
- The count for `l is (n - r)`, which is accumulated in `ans`.
- Finally, `ans` is returned as the total valid substring count.
This approach significantly reduces the time complexity compared to brute-force methods.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
O(NlogN)
- Space complexity:
O(26 × (N+1)) ≈ O(N).
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) {
int n = word1.size();
vector<int> cnt(26,0);
for(auto it:word2)
cnt[it-'a']++;
vector<vector<int>> prefix(n+1,vector<int>(26,0));
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
int currch = word1[i-1]-'a';
prefix[i] = prefix[i-1];
prefix[i][currch]++;
}
long long ans=0;
for(int l=0;l<n;l++)
{
int r = isGoodForLeftmostR(l,n,prefix,cnt);
ans+=(n-r)*1LL;
}
return ans;
}
int isGoodForLeftmostR(int r, int n, vector<vector<int>>& prefix, vector<int>& cnt)
{
int low = r,high = n-1;
while(low<=high)
{
int mid = (low+high)/2;
if(isGood(r, mid, prefix, cnt))
high = mid-1;
else
low = mid+1;
}
return low;
}
bool isGood(int l, int r, vector<vector<int>>& prefix, vector<int>& cnt)
{
if(r+1>prefix.size())
return false;
for(int i=0;i<26;i++)
{
if(prefix[r+1][i] - prefix[l][i] < cnt[i])
return false;
}
return true;
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
C++, sliding window, O(1)/O(n)
|
c-sliding-window-o1on-by-viktor_komarov-98ju
|
Code
|
viktor_komarov
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-03T10:19:50.403842+00:00
|
2025-01-03T10:19:50.403842+00:00
| 11 | false |
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) {
long long total = 0;
array<int, 26> target = {0};
for (size_t i = 0; i < word2.size(); ++i) {
++target[word2[i] - 'a'];
}
size_t l = 0;
for (size_t r = 0; r < word1.size(); ++r) {
--target[word1[r]-'a'];
while (isAcceptable(target)) {
total += static_cast<long long>(word1.size() - r);
++target[word1[l]-'a'];
++l;
}
}
return total;
}
bool isAcceptable(const array<int, 26>& arr) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < 26; ++i) {
if (arr[i] > 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Easy Sliding Window | C++ | Simple to understand
|
easy-sliding-window-c-simple-to-understa-7z4b
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) {\n long long ans=0;\n int i=0,j=0;\n unordered_
|
Aman786
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-25T04:04:39.712546+00:00
|
2024-12-25T04:04:39.712579+00:00
| 5 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) {\n long long ans=0;\n int i=0,j=0;\n unordered_map<int,int> freqSoFar, word2Count;\n for(auto ch: word2) {\n word2Count[ch]++;\n freqSoFar[ch]++;\n }\n \n while(j<word1.size()){\n freqSoFar[word1[j]]--;\n if(freqSoFar[word1[j]]==0){\n word2Count.erase(word1[j]);\n }\n \n while(word2Count.size()==0){\n ans+=word1.size()-j;\n freqSoFar[word1[i]]++;\n if(freqSoFar[word1[i]]>0){\n word2Count[word1[i]]++;\n i++;\n break;\n }\n i++;\n }\n j++;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Simple Solution Using Sliding Window Technique with Map
|
simple-solution-using-sliding-window-tec-nrtn
|
Complexity
Time complexity:
word1.length = n, word2.length = m, O(n+m)
Space complexity:
O(n)
Code
|
ladav
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-27T14:40:55.997104+00:00
|
2024-12-27T14:40:55.997104+00:00
| 8 | false |
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
word1.length = n, word2.length = m, $$O(n + m)$$
- Space complexity:
$$O(n)$$
# Code
```typescript []
function validSubstringCount(word1: string, word2: string): number {
const m1 = new Map();
const m2 = new Map();
for (const c of word2) {
m2.set(c, (m2.get(c) || 0) + 1);
}
let left = 0, matchCount = 0, result = 0;
for (let right = 0; right < word1.length; right++) {
const c = word1[right];
// Add/Update charcter's frequence in map m1
m1.set(c, (m1.get(c) || 0) + 1);
// Check if the current character exists in m2 and compare their frequence, to check if we found a match
if (m1.get(c) === m2.get(c)) {
matchCount++;
}
// Check if the match count is equal to count of unique characters in word2. Which mean we found a string which contain all the required character of word2 with the required frequence
// Number of unique characters in word2 = m2 size - 1 (0 index that's why - 1)
while (matchCount === m2.size) {
// All char combination which starts from left and ends on(including right as well) and after right will be considered as solutions
result += word1.length - right;
// move the window towards left and decrease the freq of character
const charLeft = word1[left];
// If this character is part of the m2 then update the match counter and decrease by 1
if (m1.get(charLeft) === m2.get(charLeft)) {
matchCount--;
}
m1.set(charLeft, m1.get(charLeft) - 1);
left++;
}
}
return result;
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['TypeScript']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Sliding PrefixSum Frequency
|
sliding-prefixsum-frequency-by-tonitanno-ok7g
|
IntuitionHow can i know if all chars of word 2 are present in a substring of word1 in O(1) timeApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
O(n)
Space complexity:
O(n
|
tonitannoury01
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-17T11:08:43.480454+00:00
|
2024-12-17T11:08:43.480454+00:00
| 15 | false |
# Intuition\nHow can i know if all chars of word 2 are present in a substring of word1 in O(1) time\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(n)\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(n)\n\n# Code\n```javascript []\n/**\n * @param {string} word1\n * @param {string} word2\n * @return {number}\n */\nvar validSubstringCount = function (word1, word2) {\n let freqs = new Map();\n for (let w of word2) {\n if (freqs.has(w)) {\n freqs.set(w, freqs.get(w) + 1);\n } else {\n freqs.set(w, 1);\n }\n }\n let strap1 = Array(26)\n .fill(0)\n .map(() => Array(word1.length).fill(0));\n for (let w = 0; w < word1.length; w++) {\n let curr = word1[w].charCodeAt(0) - 97;\n strap1[curr][w] = 1;\n }\n for (let k = 0; k < 26; k++) {\n for (let i = 1; i < strap1[k].length; i++) {\n strap1[k][i] = strap1[k][i - 1] + strap1[k][i];\n }\n }\n let p1 = 0;\n let p2 = word2.length - 1;\n let res = 0;\n while (p2 < word1.length) {\n let is = true;\n for (let k of Array.from(freqs.keys())) {\n let targetCharCode = k.charCodeAt(0) - 97;\n let neededNum = freqs.get(k);\n if (\n strap1[targetCharCode][p2] - (strap1[targetCharCode][p1 - 1] || 0) >=\n neededNum\n ) {\n continue;\n } else {\n is = false;\n break;\n }\n }\n if (is) {\n res += word1.length - p2;\n p1++;\n continue;\n }\n p2++;\n }\n return res;\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
lc problem 76 : minimum window substring will help || easy to understand || must see
|
lc-problem-76-minimum-window-substring-w-rkd4
|
Code\ncpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long validSubstringCount(string str1, string str2) {\n unordered_map<char,int>mp;\n for(int i =
|
akshat0610
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-24T12:55:10.466803+00:00
|
2024-11-24T12:55:10.466842+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long validSubstringCount(string str1, string str2) {\n unordered_map<char,int>mp;\n for(int i = 0 ; i < str2.length() ; i++)\n {\n mp[str2[i]]++;\n }\n int count = mp.size();\n\n int start = 0;\n int end = 0;\n \n long long int ans = 0;\n\n while(end < str1.length())\n {\n mp[str1[end]]--;\n if(mp[str1[end]] == 0) count--;\n else if(mp[str1[end]] < 0) {};\n\n while(count == 0)\n {\n ans = ans + 1LL + ((str1.length()-1) - (end+1) + 1);\n mp[str1[start]]++;\n if(mp[str1[start]] > 0) count++;\n start++;\n } \n \n end++; \n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'String', 'Sliding Window', 'C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Sliding Window + Frequency Dictionary
|
sliding-window-frequency-dictionary-by-i-m8ai
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(2xW1 + W2)\n- W1 = length of word1\n- W2 = length of word2\n Add your time complexity here, e.g. O(n) \n\n- Space complexity: O
|
iitjsagar
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-21T22:39:55.885729+00:00
|
2024-11-21T22:39:55.885761+00:00
| 6 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(2xW1 + W2)$$\n- W1 = length of word1\n- W2 = length of word2\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(1)$$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```python []\nclass Solution(object):\n def validSubstringCount(self, word1, word2):\n """\n :type word1: str\n :type word2: str\n :rtype: int\n """\n \n w2_dict = {}\n\n for c in word2:\n if c not in w2_dict:\n w2_dict[c] = 0\n w2_dict[c] += 1\n \n l = 0\n res = 0\n w1_dict = {}\n matching_a = 0\n for r in range(len(word1)):\n c = word1[r]\n\n if c not in w2_dict:\n continue\n \n if c not in w1_dict:\n w1_dict[c] = 0\n w1_dict[c] += 1\n\n if w1_dict[c] == w2_dict[c]:\n matching_a += 1\n \n while matching_a == len(w2_dict):\n res += len(word1) - r\n if word1[l] not in w1_dict:\n l += 1\n else:\n cl = word1[l]\n w1_dict[cl] -= 1\n if w1_dict[cl] < w2_dict[cl]:\n matching_a -= 1\n if w1_dict[cl] == 0:\n del w1_dict[cl]\n l += 1\n\n\n\n while matching_a == len(w2_dict):\n res += 1\n if word1[l] not in w1_dict:\n l += 1\n else:\n cl = word1[l]\n w1_dict[cl] -= 1\n if w1_dict[cl] < w2_dict[cl]:\n matching_a -= 1\n if w1_dict[cl] == 0:\n del w1_dict[cl]\n l += 1\n \n return res\n\n\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Using Unordered maps
|
using-unordered-maps-by-dishaswamy-fis9
|
\n\n# Code\ncpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool check(unordered_map<char,int> & mp){\n for(auto m: mp){\n if(m.second>0) return false;
|
dishaswamy
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-21T08:50:36.845931+00:00
|
2024-11-21T08:50:36.845968+00:00
| 3 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool check(unordered_map<char,int> & mp){\n for(auto m: mp){\n if(m.second>0) return false;\n }\n return true;\n }\n long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) {\n long long count = 0;\n int i=0,j=0;\n int n = word1.size(),m = word2.size();\n unordered_map<char,int> mp;\n for(int k=0;k<m;k++){\n mp[word2[k]]++;\n }\n while(j<n){\n if(mp.find(word1[j])!=mp.end()) {\n mp[word1[j]]--;\n }\n while(check(mp) && i<=j){\n count += n-j;\n if(mp.find(word1[i])!=mp.end()) mp[word1[i]]++;\n i++;\n }\n\n j++;\n\n\n }\n\n return count;\n\n \n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Sliding Window [Template]
|
sliding-window-template-by-never111-t1k6
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n sliding window \n target is the word2 set\n\n# Approach\n start from right = 0\n updat
|
never111
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-17T21:08:19.054134+00:00
|
2024-11-17T21:08:19.054159+00:00
| 12 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n* sliding window \n* target is the word2 set\n\n# Approach\n* start from `right = 0`\n* update the word status map and see if we have enough word2 set.\n* try to move left and add `len(word1) - right`.\n* update the status map since we are moving left pointer.\n* break the internal while when we don\'t have enough characters.\n* move `right += 1`\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nfrom collections import defaultdict\nclass Solution:\n def validSubstringCount(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:\n if not word2 or not word1:\n return 0\n char_freq = defaultdict(int)\n remain = set(word2)\n word2_set = set(word2)\n if len(word1) < len(word2):\n return 0\n for w in word2:\n char_freq[w] += 1\n\n res = 0\n l, r = 0, 0\n while r < len(word1):\n if word1[r] in word2_set:\n char_freq[word1[r]] -= 1\n if char_freq[word1[r]] == 0:\n remain.remove(word1[r])\n \n while len(remain) == 0 and l <= r:\n res += len(word1) - r\n if word1[l] in word2_set:\n char_freq[word1[l]] += 1\n if char_freq[word1[l]] == 1:\n remain.add(word1[l])\n l += 1\n r += 1\n return res\n\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
java very easy solution
|
java-very-easy-solution-by-trivedi_cs1-zwa4
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
trivedi_cs1
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-14T05:20:20.382362+00:00
|
2024-11-14T05:20:20.382405+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public boolean check(int fre[],int arr[])\n {\n for(int i=0;i<26;i++)\n {\n if(arr[i]<fre[i])\n {\n return false; \n }\n }\n return true;\n }\n public long validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n int n=word1.length();\n int fre[]=new int[26];\n for(int i=0;i<word2.length();i++)\n {\n char ch=word2.charAt(i);\n fre[ch-\'a\']++;\n }\n int arr[]=new int[26];\n int i=0;\n int j=0;\n long ans=0;\n while(i<n)\n {\n char ch=word1.charAt(i);\n arr[ch-\'a\']++;\n while(j<=i&&check(fre,arr))\n {\n ans+=(n-i);\n arr[word1.charAt(j)-\'a\']--;\n j++;\n }\n i++;\n }\n return ans; \n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
scala sliding window
|
scala-sliding-window-by-vititov-clqm
|
scala []\nobject Solution {\n def validSubstringCount(word1: String, word2: String): Long = {\n lazy val map2 = word2.groupMapReduce(identity)(_ => 1)(_ + _
|
vititov
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-07T17:51:14.359660+00:00
|
2024-11-07T17:51:14.359693+00:00
| 0 | false |
```scala []\nobject Solution {\n def validSubstringCount(word1: String, word2: String): Long = {\n lazy val map2 = word2.groupMapReduce(identity)(_ => 1)(_ + _)\n def f(i:Int=0, j:Int=0, map1: Map[Char,Int]=Map(), acc: Long=0L): Long = {\n lazy val incMap = map1.updatedWith(word1(j)) { case None => Some(1);case Some(v) => Some(v+1)}\n lazy val decMap = map1.updatedWith(word1(i)) { case None|Some(1) => None;case Some(v) => Some(v-1)}\n lazy val isValid = map2.forall{case (k2,v2) => map1.getOrElse(k2,0)>=v2}\n if (isValid) f(i+1, j, decMap, acc+word1.length-j+1)\n else if(j<word1.length) f(i, j+1, incMap, acc)\n else acc\n }\n f()\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'String', 'Sliding Window', 'Scala']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Sliding window and frequency counting
|
sliding-window-and-frequency-counting-by-02ib
|
Intuition\n- slide window [i, j) on word1 and count/compare its char frequency to word2\n- append \'z\'+1 to word1 to avoid edge case\n \n\n# Code\ncpp []\nclas
|
lambdacode-dev
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-31T18:31:17.064743+00:00
|
2024-10-31T18:31:17.064777+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition\n- slide window `[i, j)` on `word1` and count/compare its char frequency to `word2`\n- append `\'z\'+1` to `word1` to avoid edge case\n \n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) {\n array<int, 27> freq1 = {}, freq2 = {};\n for(auto c : word2) freq2[c-\'a\']++;\n\n auto valid = [&freq1, freq2] () {\n for(int i = 0; i < 26; ++i)\n if(freq1[i] < freq2[i])\n return false;\n return true;\n };\n long long count = 0;\n word1.push_back(\'z\'+1);\n for(int i = 0, j = 0, sz = word1.size(); j < sz;) {\n if(valid()) {\n count += sz - j; \n freq1[word1[i++]-\'a\']--;\n }\n else\n freq1[word1[j++]-\'a\']++;\n }\n return count;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Basic sliding window easy
|
basic-sliding-window-easy-by-kimhyunbin1-ry7h
|
Code\npython3 []\nfrom collections import defaultdict\n\nclass Solution:\n def validSubstringCount(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:\n word2_dict
|
kimhyunbin106
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-31T13:38:37.093844+00:00
|
2024-10-31T13:38:37.093891+00:00
| 8 | false |
# Code\n```python3 []\nfrom collections import defaultdict\n\nclass Solution:\n def validSubstringCount(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:\n word2_dict = defaultdict(int)\n for c in word2:\n word2_dict[c] += 1\n l = 0\n res = 0\n n = len(word1)\n required_matches = len(word2)\n match_count = 0 # Track how many matches we have\n\n for r in range(n):\n if word1[r] in word2_dict:\n if word2_dict[word1[r]] > 0:\n match_count += 1\n word2_dict[word1[r]] -= 1\n\n while match_count == required_matches:\n res += (n - r)\n if word1[l] in word2_dict:\n word2_dict[word1[l]] += 1\n if word2_dict[word1[l]] > 0:\n match_count -= 1\n l += 1\n\n return res\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'Sliding Window', 'Python3']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Java Solution | Sliding Window | Hash Map
|
java-solution-sliding-window-hash-map-by-f92k
|
Code\njava []\nclass Solution {\n public long validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n char check[] = word1.toCharArray();\n char pr
|
adarsh-mishra27
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-14T08:40:07.847985+00:00
|
2024-10-14T08:40:07.848016+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public long validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n char check[] = word1.toCharArray();\n char prefix[] = word2.toCharArray();\n Map<Character, Integer> map1 = new HashMap<>();\n Map<Character, Integer> map2 = new HashMap<>();\n for(char ch: prefix) {\n map2.put(ch, map2.getOrDefault(ch, 0) + 1);\n }\n long ans = 0;\n for(int j = 0, i = 0; j < check.length; j++) {\n map1.put(check[j], map1.getOrDefault(check[j], 0) + 1);\n\n while(true) {\n boolean found = true;\n for(Map.Entry<Character, Integer> e: map2.entrySet()) {\n char ch = e.getKey();\n int freq = e.getValue();\n if(freq > map1.getOrDefault(ch, 0)) {\n found = false;\n break;\n }\n }\n if(found) {\n ans += check.length - j;\n map1.put(check[i], map1.get(check[i]) - 1);\n if(map1.get(check[i]) == 0) \n map1.remove(check[i]);\n i++;\n }else {\n break;\n }\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'String', 'Sliding Window', 'Java']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
SLIDE THAT WINDOW
|
slide-that-window-by-welchj-nq4d
|
Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \nThis problem is a typical sliding window problem. \n\nA few key observations:\n1. The order of the l
|
WelchJ
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-12T01:31:25.885524+00:00
|
2024-10-12T01:31:25.885556+00:00
| 7 | false |
# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nThis problem is a typical sliding window problem. \n\nA few key observations:\n1. The order of the letters within the substring of `word1` does not matter, as we can rearrage them freely. Therefore only the frequency of the letters selected matters. Thus we keep a `freq` vector array to keep track of the letters\n2. Given observation 1, we can already construct a solution: We will first make the `freq` array store the difference between current selected letters and the frequencies of letters in `word2`, leading to a monotonous value -- the number of letters off from `word2`. Knowing that we have this value that will monotonously increase/decrease as we expand/shrink the window, we have a sliding window solution.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(N)\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(1)\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) {\n long long ans = 0;\n int l = 0;\n\n vector<int> freq (26, 0);\n int cnt = 0;\n for(auto a : word2){\n freq[a-\'a\']--;\n cnt --;\n }\n\n for(int r = 0; r < word1.length(); r++){\n char c = word1[r];\n if(freq[c-\'a\'] < 0) cnt ++;\n freq[c - \'a\']++;\n\n while(cnt >= 0 && l <= r){\n char cl = word1[l];\n if(--freq[cl-\'a\'] < 0) cnt --;\n l++;\n }\n // cout << l << " " << cnt << endl;\n if(cnt == -1){\n ans += l;\n }\n \n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Sliding window, explained
|
sliding-window-explained-by-ilya-chumako-ado5
|
Approach\nA valid substring of word1 should have all characters from word2 plus maybe some more. Let\'s think of word1 this way:\n\n\nword1 = prefix + word2 + p
|
ilya-chumakov
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-09T09:56:55.268143+00:00
|
2024-10-09T09:58:50.767507+00:00
| 6 | false |
# Approach\nA valid substring of `word1` should have all characters from `word2` plus *maybe* some more. Let\'s think of `word1` this way:\n\n```\nword1 = prefix + word2 + postfix\n```\nLet\'s check all the substrings starting from some point in `word1`. As soon as we get the first valid `prefix + word2` substring, then ALL the substrings till the rest of the `word1` are valid too, so we add the postfix length the the resulting sum. And while we have enough characters to form `word2` we can shrink `prefix` part char by char each time getting a new substring set.\n\nSo, let\'s use sliding window approach, increasing the window size till we find a valid substring, then shrinking the window till it\'s no longer valid.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(1)$$\n\n# Code\n```csharp []\npublic class Solution\n{\n public long ValidSubstringCount(string word1, string word2)\n {\n var required = new char[26];\n foreach (char c in word2)\n {\n required[c - \'a\']++;\n }\n\n int n = word1.Length;\n int l = 0;\n int r = 0;\n var window = new char[26];\n long sum = 0;\n\n while (r < n)\n {\n window[word1[r] - \'a\']++;\n \n while (l < n && IsWindowValid(window, required))\n {\n sum += n - r;\n window[word1[l] - \'a\']--;\n l++;\n }\n\n r++;\n }\n\n return sum;\n }\n\n private bool IsWindowValid(char[] window, char[] required)\n {\n for (var i = 0; i < window.Length; i++)\n {\n if (window[i] < required[i]) return false;\n }\n return true;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['String', 'Sliding Window', 'Counting Sort', 'C#']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Easy to understand using Java HashMap and classic sliding window algorithm
|
easy-to-understand-using-java-hashmap-an-qici
|
Code\njava []\nclass Solution {\n public long validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n long ans = 0;\n int n=word1.length(), m=word2
|
leet_umang
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-08T06:33:22.742330+00:00
|
2024-10-08T06:33:22.742355+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public long validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n long ans = 0;\n int n=word1.length(), m=word2.length();\n Map<Character,Integer> map1 = new HashMap<>();\n Map<Character,Integer> map2 = new HashMap<>();\n for(int i=0;i<m;i++){\n map2.put(word2.charAt(i), map2.getOrDefault(word2.charAt(i),0)+1);\n }\n int prev=0;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n char currCh = word1.charAt(i);\n map1.put(currCh, map1.getOrDefault(currCh,0)+1);\n while(itContainsAll(map1,map2)){\n ans+=n-i;\n char prevCh = word1.charAt(prev);\n if(map1.getOrDefault(prevCh,0) == 1){\n map1.remove(prevCh);\n } else{\n map1.put(prevCh, map1.getOrDefault(prevCh,0)-1);\n }\n prev++;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n\n public boolean itContainsAll(Map<Character, Integer> map1, Map<Character, Integer> map2) {\n for (Map.Entry<Character, Integer> entry : map2.entrySet()) {\n if (!map1.containsKey(entry.getKey()) || map1.get(entry.getKey()) < entry.getValue()) {\n return false;\n }\n }\n return true;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Arrays || JAVA
|
arrays-java-by-hemant-batra-h4e6
|
Code\njava []\nclass Solution {\n public long validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n int[] freq2 = freqCounter(word2); \n long tot
|
Hemant-Batra
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-08T02:22:56.950580+00:00
|
2024-10-08T02:22:56.950613+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public long validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n int[] freq2 = freqCounter(word2); \n long totalValid = 0;\n int left = 0;\n int[] currfreq = new int[26]; \n\n for (int right = 0; right < word1.length(); right++) {\n char cr = word1.charAt(right);\n currfreq[cr - \'a\']++; \n\n while (freqChecker(currfreq, freq2)) {\n totalValid += word1.length() - right; \n currfreq[word1.charAt(left) - \'a\']--; \n left++;\n }\n }\n return totalValid;\n }\n\n private int[] freqCounter(String s) {\n int[] freq = new int[26];\n for (char ch : s.toCharArray()) {\n freq[ch - \'a\']++;\n }\n return freq;\n }\n\n private boolean freqChecker(int[] more, int[] less) {\n for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {\n if (more[i] < less[i]) return false; \n }\n return true;\n }\n}\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Simple and Easy JAVA Solution using Sliding Window
|
simple-and-easy-java-solution-using-slid-x9hd
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Triyaambak
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-06T11:08:24.623341+00:00
|
2024-10-06T11:08:24.623363+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public long validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n int freq[] = new int[26];\n int n = word1.length() , m = word2.length();\n for(char ch : word2.toCharArray())\n freq[ch-\'a\']++;\n \n int count = 0;\n int left = 0 , right = 0;\n int map[] = new int[26];\n long ans = 0L;\n\n while(right < n){\n int rtCh = word1.charAt(right) - \'a\';\n map[rtCh]++;\n if(freq[rtCh] != 0 && freq[rtCh] > map[rtCh] - 1)\n count++;\n \n while(count == m){\n ans += n - right;\n int lftCh = word1.charAt(left) - \'a\';\n map[lftCh]--;\n if(freq[lftCh] != 0 && freq[lftCh] > map[lftCh] && freq[lftCh] <= map[lftCh] + 1)\n count--;\n left++;\n }\n\n right++;\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Sliding Window', 'Java']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Sliding Window and Left and Right Pointer O(n)
|
sliding-window-and-left-and-right-pointe-7rcg
|
Intuition\n\nwriting this explaination for myself\n\nSliding Window and Two Pointer Solution \nCases to cover while solving these kinds of problems \n\nCase 1 :
|
mkshv
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-05T13:29:13.474685+00:00
|
2024-10-05T13:39:22.105449+00:00
| 13 | false |
# Intuition\n\nwriting this explaination for myself\n\nSliding Window and Two Pointer Solution \nCases to cover while solving these kinds of problems \n\nCase 1 : Every substring is a valid one \n`w1 = abcabcabc` and `w1 = abc`\nThen following are the substrings which are valid \n`abcabcabc` = 9 - 3 + 1 = 7 \n`bcabcabc` = 8 - 3 + 1 = 6 \n`cabcabc` = 7 - 3 + 1 = 5\n`abcabc` = 6 - 3 + 1 = 3 \n`bcabc` = 5 - 3 + 1 = 3 \n`cabc` = 4 - 3 + 1 = 2 \n`abc` = 3 - 3 + 1 = 2 \nTotal Substrings = 28 \n\nCase 2 : \n`w1 = abcefabcefgh` and `w2 = abc`\n\nI\'m not solving for the whole string, just mentioning the calculations for corner cases (second while loop in code coveres this). \nThis is the reason we need to keep adding `res += n - j ` while the condition `i < n and is_valid(cnt,prefix_cnts)` is valid. \n\n`efabcefgh` = 9 - 3 + 1 = 7\n`fabcefgh` = 9 - 3 + 1 = 7\n\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(26n)$$ ~ $$O(n)$$\n- Space complexity: $$O(26)$$\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def validSubstringCount(self, w1: str, w2: str) -> int:\n w1,w2 = list(w1),list(w2)\n n = len(w1)\n prefix_cnts = Counter(w2)\n cnt = Counter()\n\n i = j = res = 0 \n def is_valid(cnt,pcnt):\n for w in string.ascii_lowercase:\n if cnt[w] < pcnt[w]:\n return False \n return True \n \n while j < n:\n cnt[w1[j]] += 1 \n if is_valid(cnt,prefix_cnts):\n ok = True \n while i < n and ok:\n res += n - j \n curr = w1[i]\n cnt[curr] -= 1 \n ok = cnt[curr] >= prefix_cnts[curr]\n i += 1 \n j += 1 \n return res \n \n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Python sliding window, readable and easy to understand
|
python-sliding-window-readable-and-easy-p249u
|
Python sliding window, readable and easy to understand\n\n\t\ttarget_cnt = collections.Counter(word2)\n cnt = collections.Counter()\n \n #
|
zwzbill8
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-04T18:54:14.907142+00:00
|
2024-10-04T18:59:54.809522+00:00
| 2 | false |
Python sliding window, readable and easy to understand\n\n\t\ttarget_cnt = collections.Counter(word2)\n cnt = collections.Counter()\n \n # Sliding window\n i = 0\n res = 0\n matched = 0\n for j, c in enumerate(word1):\n cnt[c] += 1\n if cnt[c] == target_cnt[c]:\n matched += 1\n \n # shrink the window if possible\n while i <= j and cnt[word1[i]] > target_cnt[word1[i]]:\n cnt[word1[i]] -= 1\n i += 1\n \n # if condition is met, accumulate the count\n if matched == len(target_cnt):\n res += i + 1\n \n return res
| 0 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Sliding window | c++
|
sliding-window-c-by-akhilcsk1111-lh2b
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
akhilcsk1111
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-04T12:31:07.460893+00:00
|
2024-10-04T12:31:07.460933+00:00
| 16 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) {\n long long counter=word2.size();\n unordered_map<char, int>mp;\n int n = word1.size(), m=word2.size();\n long long ans = 0, l=0, r=0;\n\n for(auto x:word2) mp[x]++;\n\n while(r<n) {\n if(mp[word1[r]]>0){\n counter--;\n }\n\n mp[word1[r]]--;\n\n while(counter==0) {\n ans+=(n-r); // add all after words\n mp[word1[l]]++;\n if(mp[word1[l]]>0){\n counter++;\n }\n l++;\n }\n r++;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Short Clean and Concise || Java || Sliding Window || Beats 80% ||
|
short-clean-and-concise-java-sliding-win-209i
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
owaispatel95
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-04T09:10:48.567089+00:00
|
2024-10-04T09:10:48.567113+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public long validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n final int n = word1.length();\n final int m = word2.length();\n final int[] freq1 = new int[26];\n final int[] freq2 = new int[26];\n\n for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {\n freq1[word2.charAt(i) - \'a\']++;\n }\n\n int j = 0, count = 0;\n long ans = 0;\n\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n final int curInd = word1.charAt(i) - \'a\';\n\n if (freq2[curInd] < freq1[curInd]) count++;\n if (freq1[curInd] != 0) freq2[curInd]++;\n\n while(j <= i && count >= m) {\n ans += (n - i);\n\n final int prevInd = word1.charAt(j) - \'a\';\n\n if (freq1[prevInd] != 0) freq2[prevInd]--; \n if (freq2[prevInd] < freq1[prevInd]) count--;\n\n j++;\n }\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Sliding Window
|
sliding-window-by-mz_coder-fsza
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Mz_coder
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-02T16:36:00.035126+00:00
|
2024-10-02T16:36:00.035163+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(26)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n boolean isValid(int[] freq1,int[] freq2){\n for(int i=0;i<26;i++){\n if(freq1[i] < freq2[i]){\n return false;\n }\n }\n return true;\n }\n public long validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n int[] freq1 = new int[26];\n int[] freq2 = new int[26];\n\n for(char c:word2.toCharArray()){\n freq2[c-\'a\'] += 1;\n }\n int j=0;\n long ans = 0;\n for(int i=0;i<word1.length();i++){\n char c = word1.charAt(i);\n freq1[c - \'a\'] += 1;\n\n while(isValid(freq1,freq2)){\n ans += word1.length() - i;\n c = word1.charAt(j);\n freq1[c - \'a\'] -= 1;\n j+=1;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'Sliding Window', 'Java']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Alternate simple impl of sliding window. with logic PseudoCode
|
alternate-simple-impl-of-sliding-window-l5jwc
|
\n//we store freq of word2. \n//for a substring of word1, if same freq matched then \n// we can make a prefix out of it by rearranging them.\n//so goal becomes
|
test1leetcode
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-02T05:13:39.682058+00:00
|
2024-10-02T05:13:39.682094+00:00
| 11 | false |
```\n//we store freq of word2. \n//for a substring of word1, if same freq matched then \n// we can make a prefix out of it by rearranging them.\n//so goal becomes to see if substring has enough characters to make word2 prefix.\n\n//for a window, we have two choices: add char to window or remove char from window\n//if k is count of characters remaining to match then\n\n//if k> 0 then word2 is yet to be matched\n// ADD CHAR\n//if k==0 then word2 has been matched.\n// res = wor1.length - endindexOfWindow\n// REMOVE CHAR\n// we repeat this until we are in deficit of reqFreq.\n\n//=======\n//ADD CHAR logic: \n// freq++ for that char.\n// if freq <= reqFreq for that char\n// k-- as we got one req freq. \n// if freq > reqfreq for that char\n// we added extra freq of this char. no change in k\n//-------\n//REMOVE CHAR logic\n// freq-- for that char\n// if freq < reqFreq for that char\n// k++ as we now need to fill this requirement\n// if freq >= reqFreq\n// we have extra. no change in k.\n//========\n\n//Execution stops when window reaches end.\n```\n\n# Code\n```javascript []\n/**\n * @param {string} word1\n * @param {string} word2\n * @return {number}\n */\nvar validSubstringCount = function(word1, word2) { \n let word1freq = [],word2freq = [], k = 0;\n for(let i=0; i<26; i++) {\n word2freq.push(0);\n word1freq.push(0);\n }\n function getcharindex(char) {\n let str = \'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz\';\n return str.indexOf(char);\n }\n for(let i=0; i<word2.length; i++) {\n word2freq[getcharindex(word2[i])]++;\n }\n k = word2.length;\n let start = 0, end = 0, res = 0;\n while(end < word1.length) {\n if (k > 0) {\n let charindex = getcharindex(word1[end]);\n end++;\n word1freq[charindex]++;\n if(word1freq[charindex] <= word2freq[charindex]) {\n k--;\n } else {\n //do nothing\n }\n } \n while(k == 0) {\n //word2 characters matched\n res += word1.length - (end - 1 );\n let charindex = getcharindex(word1[start]);\n start++;\n word1freq[charindex]--;\n if(word1freq[charindex] < word2freq[charindex]) {\n k++;\n } else {\n //do nothing\n }\n } \n }\n return res;\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
using prefix which has space complexity O[N][26]
|
using-prefix-which-has-space-complexity-rnhz9
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
rahulX64
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-01T11:37:16.729639+00:00
|
2024-10-01T11:37:16.729667+00:00
| 1 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution\n{\npublic:\n long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2)\n {\n int n = word1.size();\n int m = word2.size();\n vector<int> freq(26, 0);\n for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)\n {\n freq[word2[i] - \'a\']++;\n }\n vector<vector<int>> v(26, vector<int>(n + 1, 0));\n\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)\n {\n int x = word1[i] - \'a\';\n for (int j = 0; j < 26; j++)\n {\n v[j][i + 1] = v[j][i];\n }\n v[x][i + 1] = v[x][i] + 1;\n }\n long long count = 0;\n for (int i = m; i <= n; i++)\n {\n int cnt = 0;\n int mini = 1e8;\n for (int j = 0; j < 26; j++)\n {\n if (v[j][i] >= freq[j])\n cnt++;\n }\n if (cnt == 26)\n {\n for (int j = 0; j < 26; j++)\n {\n\n int r = v[j][i];\n int l = r - freq[j];\n if (r != 0)\n {\n int ind = upper_bound(v[j].begin(), v[j].end(), l) - v[j].begin();\n mini = min(mini, ind);\n }\n }\n }\n\n if(mini != 1e8) count += mini;\n }\n\n return count;\n }\n};\n\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Sliding window solution in Java
|
sliding-window-solution-in-java-by-kosty-vfo9
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
kostyan92
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-30T22:31:07.922149+00:00
|
2024-09-30T22:31:07.922180+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(n)\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(1)\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public long validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n Map<Character, Integer> symbolToCount = new HashMap<>();\n for (char c : word2.toCharArray()) {\n int count = symbolToCount.getOrDefault(c, 0);\n symbolToCount.put(c, count + 1);\n }\n int total = word2.length();\n\n long result = 0;\n\n int start = 0;\n for (int end = 0; end < word1.length(); end++) {\n char c = word1.charAt(end);\n int count = symbolToCount.getOrDefault(c, 0);\n symbolToCount.put(c, count - 1);\n\n if (symbolToCount.get(c) >= 0) {\n total--;\n }\n\n while (total == 0) {\n result += (word1.length() - 1 - end + 1);\n\n c = word1.charAt(start);\n count = symbolToCount.get(c);\n symbolToCount.put(c, count + 1);\n if (symbolToCount.get(c) > 0) {\n total++;\n }\n \n start++;\n }\n }\n\n return result;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Sliding window, hash map
|
sliding-window-hash-map-by-haque_jibon-b8l7
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
haque_jibon
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-30T17:52:30.241155+00:00
|
2024-09-30T17:52:30.241193+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```typescript []\nfunction validSubstringCount(word1: string, word2: string): number {\n let map1 = new Map<string, number>();\n let map2 = new Map<string, number>();\n\n for (let ch of word2) {\n map1.set(ch, (map1.get(ch) || 0) + 1);\n }\n\n let l = 0,\n totalSub = 0,\n count = 0;\n\n for (let i = 0; i < word1.length; i++) {\n let chr = word1.charAt(i);\n map2.set(chr, (map2.get(chr) || 0) + 1);\n\n if (map1.has(chr)) {\n if (map2.get(chr)! == map1.get(chr)!) count++;\n }\n\n while (count >= map1.size) {\n totalSub += word1.length - i;\n\n // console.log("i am calling", i);\n\n let left = word1.charAt(l);\n map2.set(left, map2.get(left)! - 1);\n\n if (map1.has(left)) {\n if (map2.get(left)! < map1.get(left)!) count--;\n }\n\n l++;\n }\n }\n\n return totalSub;\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['TypeScript']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Simple sliding window
|
simple-sliding-window-by-tuns-u0tb
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nKeep track of the smallest valid substring.\n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to s
|
tuns
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-30T07:01:56.843790+00:00
|
2024-09-30T07:22:28.813344+00:00
| 11 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nKeep track of the smallest valid substring.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nWe observe that, for example, with the valid substring "abc" in "deabc".\nthe number of valid strings are:\ndeabc\neabc\nabc\n=> We just find the last position where the substring is valid, and then there will be `lo + 1` valid substrings so far.\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:$$O(n * 26)$$\n- Space complexity: $$O(n)$$\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def validSubstringCount(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:\n count2 = Counter(word2)\n count1 = Counter()\n n1, n2 = len(word1), len(word2)\n\n ans = 0\n\n lo, hi = 0, 0\n valid = 0\n\n while hi < n1:\n c1 = word1[hi]\n count1[c1] += 1\n\n # We only count the first instance when the number of characters in both counts is equal. \n # so We can avoid duplicate counting.\n if count1[c1] == count2[c1]:\n valid += 1\n\n if valid == len(count2):\n while lo <= hi:\n if count1[word1[lo]] - 1 < count2[word1[lo]]:\n break\n count1[word1[lo]] -= 1\n lo += 1\n ans += lo + 1\n\n hi += 1\n\n return ans\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
C++ solution Sliding Window
|
c-solution-sliding-window-by-oleksam-iaig
|
\n// Please, upvote if you like it. Thanks :-)\nlong long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) {\n\tlong long res = 0, cnt = 0;\n\tunordered_map<char
|
oleksam
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-29T17:13:28.332236+00:00
|
2024-09-29T17:13:28.332268+00:00
| 13 | false |
```\n// Please, upvote if you like it. Thanks :-)\nlong long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) {\n\tlong long res = 0, cnt = 0;\n\tunordered_map<char, int> mp;\n\tfor (const char& c : word2) {\n\t\tif (mp[c] == 0)\n\t\t\tcnt++;\n\t\tmp[c]++;\n\t}\n\tint sz1 = word1.size(), i = 0, j = 0;\n\twhile (i < sz1) {\n\t\tif (--mp[word1[i]] == 0)\n\t\t\tcnt--;\n\t\twhile (cnt == 0) {\n\t\t\tres += (sz1 - i);\n\t\t\tcnt += (mp[word1[j]] == 0);\n\t\t\tmp[word1[j]]++;\n\t\t\tj++;\n\t\t}\n\t\ti++;\n\t}\n\treturn res;\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'Two Pointers', 'String', 'C', 'Sliding Window', 'C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Sliding Window || easy
|
sliding-window-easy-by-satyamshivam366-n7p4
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
satyamshivam366
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-29T05:18:20.345840+00:00
|
2024-09-29T05:23:04.406321+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\n#define ll long long\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool comp(map<char,int> &mp,map<char,int> &temp)\n {\n for(auto &it:mp){if(it.second>temp[it.first]){return false;}}\n return true;\n }\n long long validSubstringCount(string w1, string w2) {\n map<char,int> mp,temp;\n for(auto &it:w2){mp[it]++;}\n ll n=w1.length(),l=w2.length();\n ll i=0,j=0,ans=0;\n while(j<n)\n { \n if(j-i+1<l)\n {\n temp[w1[j]]++;\n j++;\n }\n else\n {\n temp[w1[j]]++;\n while(comp(mp,temp))\n {\n ans+=(n-j);\n temp[w1[i]]--;\n if(temp[w1[i]]==0){temp.erase(w1[i]);}\n i++;\n }\n j++;\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Sliding window | Java | O(n * 26)
|
sliding-window-java-on-26-by-harisht2669-yvya
|
Approach\nSliding window approch.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(n*26) \nn -> length of word1\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(26)\n\n# Code\njava []\nclass So
|
harisht26698
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-28T08:43:35.043584+00:00
|
2024-09-28T08:43:35.043609+00:00
| 7 | false |
# Approach\nSliding window approch.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(n*26) \nn -> length of word1\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(26)\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public long validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n long res = 0;\n int[] ct1 = new int[26], ct2 = new int[26];\n int len1 = word1.length(), len2 = word2.length(), st = 0;\n if(len2 > len1) return 0;\n\n for(int i=0; i<len2; i++){\n ct2[word2.charAt(i) - \'a\']++;\n }\n\n for(int i=0;i<len2-1;i++){\n ct1[word1.charAt(i) - \'a\']++;\n }\n\n for(int j=len2-1;j<len1;j++){\n ct1[word1.charAt(j) - \'a\']++;\n\n if(hasPrefix(ct1, ct2)){\n int k = 0, idx = word1.charAt(st) - \'a\';\n while(ct1[idx] >= ct2[idx] && (j-st+1) >= len2){\n k++;\n st++;\n ct1[idx]--;\n\n if(ct1[idx]<ct2[idx])\n break;\n\n idx = word1.charAt(st) - \'a\';\n }\n res += (len1 - j) * k;\n }\n\n }\n\n return res;\n }\n \n boolean hasPrefix(int[] ct1, int[] ct2){\n for(int i=0;i<26;i++){\n if(ct1[i] < ct2[i])\n return false;\n }\n return true;\n }\n}\n\n// cccbaaa, abc\n// 9\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'Two Pointers', 'String', 'Sliding Window', 'Java']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
From Brute Force to Elegance: Counting Rearranged Substrings Efficiently🔥
|
from-brute-force-to-elegance-counting-re-wzam
|
A Better Approach:\n\nWe can optimize the solution by using the following strategy:\n\nObservation:\n\nWe need to count the number of substrings where the count
|
tanmey
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-27T21:26:43.974013+00:00
|
2024-09-27T21:26:43.974041+00:00
| 10 | false |
**A Better Approach:**\n\nWe can optimize the solution by using the following strategy:\n\n**Observation:**\n\nWe need to count the number of substrings where the counts of each character are at least those in target. This means for every character in target, the substring must contain that character at least as many times.\n**\nAlgorithm Overview:**\n\n**Precompute Prefix Sums:**\n\nFor each character \'a\' to \'z\', compute the prefix sums in s. This allows us to get the count of any character in any substring in O(1) time.\n\n**Binary Search for Each Starting Index:**\n\nFor each starting index l in s, we can perform a binary search to find the smallest ending index r such that the substring s[l...r] covers all character counts in target.\n\n**Counting Valid Substrings:**\n\nOnce we find the minimal r for a given l, all substrings s[l...r\'], r\' >= r will be valid. So, the number of valid substrings starting at l is n - r, where n is the length of s.\n\n**Detailed Steps:**\n\nInitialize Data Structures:\n\nCreate a frequency array targetCount[26] for target.\nCompute prefix sums prefixSum[26][n + 1] for each character in s.\nProcessing Each Starting Index:\n\nFor l from 0 to n - 1:\n\nCheck Feasibility:\n\nIf the remaining characters from l to n - 1 cannot cover target, we can break early.\n\nBinary Search:\n\nInitialize lo = l, hi = n - 1, and ans = n.\nWhile lo <= hi:\nCompute mid = (lo + hi) / 2.\nFor each character c in target:\nCalculate the count of c in s[l...mid] using prefix sums.\nIf this count is less than required, break and move lo to mid + 1.\nIf all character counts are sufficient, update ans = mid and move hi to mid - 1.\nThe number of valid substrings starting at l is n - ans.\nAggregate the Result:\n\nSum up the counts from step 2 for all l to get the final answer.\n\n\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long validSubstringCount(string s, string target) {\n int n = s.size();\n vector<int> targetCount(26, 0);\n for (char c : target) targetCount[c - \'a\']++;\n\n // Compute prefix sums for each character\n vector<vector<int>> prefixSum(26, vector<int>(n + 1, 0));\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n for (int c = 0; c < 26; c++) {\n prefixSum[c][i + 1] = prefixSum[c][i];\n }\n prefixSum[s[i] - \'a\'][i + 1]++;\n }\n\n long long total = 0;\n for (int l = 0; l < n; l++) {\n int lo = l, hi = n - 1, ans = n;\n while (lo <= hi) {\n int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;\n bool valid = true;\n for (int c = 0; c < 26; c++) {\n int countInWindow = prefixSum[c][mid + 1] - prefixSum[c][l];\n if (countInWindow < targetCount[c]) {\n valid = false;\n break;\n }\n }\n if (valid) {\n ans = mid;\n hi = mid - 1;\n } else {\n lo = mid + 1;\n }\n }\n if (ans < n) {\n total += n - ans;\n }\n }\n return total;\n }\n};\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
C++ | Easy | Sliding Window Implementation
|
c-easy-sliding-window-implementation-by-t81xk
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
kaif_1995
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-27T16:28:34.794581+00:00
|
2024-09-27T16:28:34.794603+00:00
| 12 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool isValidPrefix(vector<int> &freq1, vector<int> &freq2){\n for(int i=0; i<26; i++){\n if(freq1[i] < freq2[i]){\n return false;\n }\n }\n return true;\n }\n long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) {\n vector<int> freq1(26, 0);\n vector<int> freq2(26, 0);\n for(int i=0; i<word2.size(); i++){\n freq2[word2[i]-\'a\']++;\n }\n int w1Size = word1.size();\n long long int count = 0;\n int start = 0;\n for(int end=0; end< w1Size; end++){\n freq1[word1[end]-\'a\']++;\n while(start <= end and isValidPrefix(freq1, freq2)){\n count+=(w1Size - end);\n freq1[word1[start]-\'a\']--;\n start++;\n }\n }\n return count;\n\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Esay sliding window approach
|
esay-sliding-window-approach-by-__om_pat-w6d6
|
We need to store the freq of all chars of word2 in a map,say mp.\nWe then keep a temp hashmap for storing all chars\' freq of our current window. When the count
|
__om_patil_30
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-26T05:38:44.431140+00:00
|
2024-09-26T05:38:44.431163+00:00
| 21 | false |
We need to store the freq of all chars of word2 in a map,say mp.\nWe then keep a temp hashmap for storing all chars\' freq of our current window. When the count matches all substrings from current \'end\' pointer to the end of word1 are valid. Hence, add that to the answer and shrink the window.If the outgoing element is leading to decrement of matched chars count, move out of the loop.\n\nLinear time and space complexity. \n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) {\n unordered_map<char,int> mp;\n for(char ch:word2){\n mp[ch]++;\n }\n\n int start = 0;\n int end = 0;\n\n long long ans = 0;\n\n int count = 0;\n unordered_map<char,int> temp;\n\n while(end < word1.length()){\n if(mp.find(word1[end]) != mp.end()){\n // cout << "at" << start << " " << end << endl;\n temp[word1[end]]++;\n if(temp[word1[end]] <= mp[word1[end]]){\n count++;\n }\n }\n\n while(count == word2.size()){\n ans++;\n ans += (word1.length()-(end+1)); \n //current window macthes, then all substring from end to word1.length() also are valid substrings\n // cout << start << " " << end << endl;\n\n // cout << word1.length()-(end) << " " << start << " " << end << endl;\n if(temp.find(word1[start]) != temp.end()){\n // mp[word1[start]]++;\n temp[word1[start]]--;\n if(temp[word1[start]] < mp[word1[start]]){\n count--;\n }\n }\n start++;\n }\n\n end++;\n } \n\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'Sliding Window', 'C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Python || Sliding Window || Simple Solution
|
python-sliding-window-simple-solution-by-6d8t
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
vilaparthibhaskar
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-25T23:11:57.858669+00:00
|
2024-09-25T23:11:57.858702+00:00
| 16 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(N) * 26\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(N)\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def validSubstringCount(self, word1: str, word2: str) -> int:\n l1, l2 = len(word1), len(word2)\n if l1 < l2:return 0\n c = Counter(word2)\n\n def helper(dic):\n for i , j in c.items():\n if dic[i] < j:\n return False\n return True \n\n\n l = 0\n i = 0\n hold = defaultdict(int)\n while i < l1:\n hold[word1[i]] += 1\n if helper(hold):break\n i += 1\n if i == l1:return 0\n r = i\n ans = 0\n while r < l1:\n while l < r:\n hold[word1[l]] -= 1\n if helper(hold):\n l += 1\n else:\n hold[word1[l]] += 1\n break\n ans += (l + 1)\n r += 1\n if r < l1:hold[word1[r]] += 1\n return ans\n\n \n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Hash Table', 'String', 'Sliding Window', 'Python3']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
most easy solution
|
most-easy-solution-by-sumeer7-cvnx
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n...\n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \nthis will be one o
|
Sumeer7
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-25T14:39:46.966013+00:00
|
2024-09-25T14:39:46.966055+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n...\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nthis will be one of the most simple solution\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nn\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nn\n\n# Code\n```python []\ndef is_valid(w1, w2):\n for i in w2:\n if i in w1:\n if w1[i]>= w2[i]:\n continue\n else:\n return False\n else:\n return False\n return True\nclass Solution(object):\n def validSubstringCount(self, word1, word2):\n if len(word1) < len(word2):\n return 0\n dic2 = {}\n for i in word2:\n if i in dic2:\n dic2[i] += 1\n else:\n dic2[i] = 1\n dic1 = {}\n for i in range(len(word2)):\n if word1[i] in dic1:\n dic1[word1[i]] += 1\n else:\n dic1[word1[i]] = 1\n\n ans = 0\n\n l = 0\n r = len(word2) - 1\n\n while r < len(word1):\n if is_valid(dic1, dic2):\n\n ans += len(word1) - r\n\n dic1[word1[l]] -= 1\n if dic1[word1[l]] == 0:\n del dic1[word1[l]]\n l += 1\n else:\n r += 1\n if r < len(word1):\n if word1[r] in dic1:\n dic1[word1[r]] += 1\n else:\n dic1[word1[r]] = 1\n\n return ans\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Sliding Windows Solution
|
sliding-windows-solution-by-cgl0408-8s6y
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nSolution from here:https://leetcode.com/problems/count-substrings-that-can-be-rearrange
|
cgl0408
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-25T13:24:12.538290+00:00
|
2024-09-25T13:24:12.538317+00:00
| 22 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nSolution from here:https://leetcode.com/problems/count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i/solutions/5818284/sliding-window-with-example-walkthrough/\nI just want to record what I\'ve learn. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(Len(W1))\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(1)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) {\n\n /*\n [0,2],[1,3],[2,4],[3,5]\n [0,3],[1,4],[2,5]\n [0,4],[1,5]\n [0,5]\n */\n int word1Freq[26] = {0};\n int word2Freq[26] = {0};\n //;memset(word1Freq, 0, sizeof(word1Freq));\n for(auto&c : word2){\n word2Freq[c - \'a\']+=1;\n }\n int w1Len = word1.size();\n int w2Len = word2.size();\n int remainLen = w2Len;\n int start = 0;\n long long ans = 0;\n for(int end = 0; end < w1Len; ++end){\n if(word1Freq[word1[end] - \'a\'] < word2Freq[word1[end] - \'a\']){\n remainLen-=1; \n }\n word1Freq[word1[end] - \'a\']+=1;\n while(remainLen == 0){\n //aabcde, target = \'abc\'\n //ans+=6-3 = 3 means can add postfix c,cd,cde\n //start+=1 and remainLen still equal 0 (vaild)\n //ans+=6-3 same as prev reason\n ans+=w1Len-end;\n word1Freq[word1[start] - \'a\']-=1;\n if(word1Freq[word1[start] - \'a\'] < word2Freq[word1[start] - \'a\']){\n remainLen+=1;\n }\n start+=1;\n }\n }\n\n\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Sliding Window', 'C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Sliding Window | Go
|
sliding-window-go-by-yelleti-18-xnfd
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
yelleti-18
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-25T10:27:16.787436+00:00
|
2024-09-25T10:27:16.787476+00:00
| 6 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```golang []\nfunc validSubstringCount(w1 string, w2 string) int64 {\n \n f:=make([]int,26)\n cnt:=0\n for _,i:= range w2 {\n if f[i-\'a\']==0 {\n cnt++\n }\n f[i-\'a\']++\n }\n\n j:=0;\n var ans int64 = 0;\n n:=len(w1)\n for i:=0;i<n;i++ {\n k:= w1[i]-\'a\'\n f[k]--\n if f[k] == 0 {\n cnt--\n }\n\n for cnt == 0 {\n ans+=int64(n-i)\n p:=w1[j]-\'a\'\n f[p]++\n if f[p]==1 {\n cnt++;\n }\n j++\n }\n }\n return ans;\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Sliding Window', 'Go']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Golang Sliding Window with Key observation
|
golang-sliding-window-with-key-observati-a75d
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nVery similar to Min substring. \nWe will solve using using sliding window. \n\nThe key
|
prakhar__dixit
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-25T10:11:26.190973+00:00
|
2024-09-25T10:11:26.191046+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nVery similar to Min substring. \nWe will solve using using sliding window. \n\nThe key observation that I always used to mess up was, if a substring i to j in word1 is valid, how many substrings will that add to my result. \n\nThe answer there is, if substring i to j is valid, it will add len(word1) - j substrings to my result.\n\nWhy? \n\nabcabc\nif abc is valid, abca, abcab and abcabc is also valid, since all of these can be rearragened to have abc as its prefix.\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```golang []\nfunc validSubstringCount(word1 string, word2 string) int64 {\n n := len(word1)\n\n\n w1Map := map[byte] int{} \n w2Map := map[byte] int{} \n\n for _, c := range word2 {\n w2Map[byte(c)]++\n }\n\n left, right := 0, 0 \n count := len(word2)\n\n var sCount int64 = 0\n for right < n {\n c := word1[right]\n w1Map[c]++\n if w1Map[c] <= w2Map[c] {\n count--\n }\n\n for count == 0 {\n sCount += int64(len(word1) - right)\n sChar := word1[left]\n w1Map[sChar]--\n left++ \n if w1Map[sChar] < w2Map[sChar] {\n count++\n }\n }\n\n right++\n }\n\n return sCount\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Go']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Sliding window
|
sliding-window-by-gaurav2k20-axcp
|
Intuition\nUtilize sliding window\n\n# Code\ncpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool isValid(vector<int>& f1, vector<int>& f2) {\n for(int i = 0; i <
|
gaurav2k20
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-24T19:41:08.619118+00:00
|
2024-09-24T19:41:08.619159+00:00
| 9 | false |
# Intuition\nUtilize sliding window\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool isValid(vector<int>& f1, vector<int>& f2) {\n for(int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {\n if(f1[i] > f2[i]) return false;\n }\n return true;\n }\n\n long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) {\n if(word1.size() < word2.size()) return 0;\n vector<int> freq1(26, 0);\n for(auto &it : word2) freq1[it-\'a\']++;\n\n vector<int> freq2(26, 0);\n long long ans = 0;\n int start = 0;\n for(int i = 0; i < word1.size(); i++) {\n freq2[word1[i]-\'a\']++;\n while(isValid(freq1, freq2)) {\n ans += word1.size()-i;\n freq2[word1[start]-\'a\']--;\n start++;\n }\n }\n\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Approach similar to Aditya verma
|
approach-similar-to-aditya-verma-by-kuma-itc3
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
kumarsaurav3575
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-24T18:44:22.809436+00:00
|
2024-09-24T18:44:22.809479+00:00
| 10 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n long long validSubstringCount(string word1, string word2) {\n int n=word1.size();\n int m=word2.size();\n unordered_map<char,long long>mp;\n for(int i=0;i<m;i++){\n mp[word2[i]]++;\n }\n long long count=mp.size();\n long long i=0,j=0,ans=0;\n while(j<n){\n if(mp.find(word1[j])!=mp.end()){\n mp[word1[j]]--;\n if(mp[word1[j]]==0)\n count--;\n }\n while(count==0){\n ans+=(n-j);\n if(mp.find(word1[i])!=mp.end()){\n mp[word1[i]]++;\n if(mp[word1[i]]>0)\n count++;\n }\n i++;\n }\n j++;\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Sliding window + Map
|
sliding-window-map-by-bnorbertjs-csqg
|
\n\n# Code\ntypescript []\nfunction match(w1: Map<string, number>, w2: Map<string, number>){\n return [...w2.keys()].every(w2char => w1.get(w2char) >= w2.get
|
bnorbertjs
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-24T15:02:06.694670+00:00
|
2024-09-24T15:02:06.694709+00:00
| 9 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```typescript []\nfunction match(w1: Map<string, number>, w2: Map<string, number>){\n return [...w2.keys()].every(w2char => w1.get(w2char) >= w2.get(w2char))\n}\n\nfunction validSubstringCount(word1: string, word2: string): number {\n const w2Freq = new Map()\n const w1WindowFreq = new Map()\n let count = 0\n word2.split(\'\').forEach(char => w2Freq.set(char, (w2Freq.get(char) ?? 0) + 1))\n word1.slice(0, word2.length).split(\'\').forEach(char => w1WindowFreq.set(char, (w1WindowFreq.get(char) ?? 0) + 1))\n \n let windowStart = 0, windowEnd = word2.length - 1;\n for(windowEnd; windowEnd < word1.length;) {\n if(match(w1WindowFreq, w2Freq)) {\n count += word1.length - windowEnd\n // shrink the window & remove the item on windowStart\'s index\n w1WindowFreq.set(word1[windowStart], w1WindowFreq.get(word1[windowStart]) - 1)\n if(w1WindowFreq.get(word1[windowStart]) <= 0) {\n w1WindowFreq.delete(word1[windowStart])\n }\n windowStart++\n } else {\n // increase window if theres no match\n windowEnd++\n w1WindowFreq.set(word1[windowEnd], (w1WindowFreq.get(word1[windowEnd]) ?? 0) + 1)\n }\n }\n\n return count\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['TypeScript']
| 0 |
count-substrings-that-can-be-rearranged-to-contain-a-string-i
|
Sliding Window || Beats 100% || My experience
|
sliding-window-beats-100-my-experience-b-1go2
|
Intuition\nTo be honest, the problem itself wasn\u2019t too difficult to understand, and the intuition came fairly quickly. The real challenge lay in handling s
|
Vithesh
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-24T14:58:37.615020+00:00
|
2024-09-24T14:58:37.615044+00:00
| 13 | false |
# Intuition\nTo be honest, the problem itself wasn\u2019t too difficult to understand, and the intuition came fairly quickly. The real challenge lay in handling some of the edge cases. It took me over two hours to solve it on my own. If you\u2019ve solved a few sliding window problems before, grasping the intuition is straightforward. Essentially, we maintain a window while continuously checking the frequency of elements. After each character, we verify whether the current window contains the required characters or not.\n-\n\n# Approach\nI recommend you guys to solve few easy problems on sliding window before solving this. Because even i would have felt it tough if i hadn\'t solved few problems long back\n\n1. **Initial Check**: First, we check if the length of `word1` is smaller than `word2`. If it is, we return `0` because it\'s impossible for `word1` to contain `word2` as a substring.\n\n2. **Set Up Arrays**: We convert both `word1` and `word2` into arrays of characters. Then, we create two arrays of size 26 (for each letter of the alphabet):\n - `freq`: To store the frequency of each character in `word2`.\n - `window`: To track the frequency of characters in a sliding window within `word1`.\n\n3. **Count Matching Characters**: We initialize two counters:\n - `count`: To track how many characters in the current window of `word1` match those in `word2`.\n - `strCount`: To keep the final count of valid substrings.\n\n4. **Sliding Window Approach**:\n - For each character in `word1`, we move the window forward one character at a time.\n - If the character at the current position exists in `word2` and hasn\u2019t yet reached the required frequency in the window, we increase the `count`.\n - Add the current character to the window\'s frequency count.\n\n5. **Check Valid Substrings**:\n - Once the `count` matches the length of `word2` (i.e., the window contains all characters of `word2`), we add the remaining characters from the current position to the end of `word1` to `strCount`.\n - Then, we slide the window from the left by reducing the frequency of the character at the start of the window and adjusting the `count` accordingly.\n\n6. **Final Return**: After the loop ends, `strCount` holds the total number of valid substrings where `word2` appears in `word1`, and this value is returned.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(n)\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(n)\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public long validSubstringCount(String word1, String word2) {\n if (word1.length() < word2.length())\n return 0;\n\n char[] w1 = word1.toCharArray(), w2 = word2.toCharArray();\n int[] freq = new int[26];\n\n for (char c : w2)\n freq[c - \'a\']++;\n\n int[] window = new int[26];\n long count = 0;\n\n long strCount = 0;\n int j = 0;\n\n for (int i = 0; i < w1.length; i++) {\n char c = w1[i];\n\n if (freq[c - \'a\'] != 0 && window[c - \'a\'] < freq[c - \'a\']) {\n count++;\n }\n window[c - \'a\']++;\n\n while (count == w2.length && j <= i) {\n strCount += (w1.length - i);\n\n window[w1[j] - \'a\']--;\n\n if (window[w1[j] - \'a\'] < freq[w1[j] - \'a\'])\n count--;\n\n j++;\n }\n }\n return strCount;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'Sliding Window', 'Java']
| 0 |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.