question_slug
stringlengths 3
77
| title
stringlengths 1
183
| slug
stringlengths 12
45
| summary
stringlengths 1
160
⌀ | author
stringlengths 2
30
| certification
stringclasses 2
values | created_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| updated_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| hit_count
int64 0
10.6M
| has_video
bool 2
classes | content
stringlengths 4
576k
| upvotes
int64 0
11.5k
| downvotes
int64 0
358
| tags
stringlengths 2
193
| comments
int64 0
2.56k
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
number-of-provinces
|
Dfs || Easy to Understand || C++
|
dfs-easy-to-understand-c-by-irahulbangar-7xom
|
\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n void dfs(int node,vector<bool> &vis, vector<int> adj[]){\n vis[node]=1;\n for(auto it=adj[node].begin();it!=adj
|
irahulbangar7
|
NORMAL
|
2023-06-04T17:37:57.235564+00:00
|
2023-06-04T17:37:57.235591+00:00
| 21 | false |
\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n void dfs(int node,vector<bool> &vis, vector<int> adj[]){\n vis[node]=1;\n for(auto it=adj[node].begin();it!=adj[node].end();it++){\n if(!vis[*it]){\n dfs(*it,vis,adj);\n }\n }\n }\n int findCircleNum(vector<vector<int>>& arr) {\n int n=arr.size();\n vector<bool> vis(n,0);\n vector<int> adj[n];\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n int m=arr[i].size();\n for(int j=0;j<m;j++){\n if(arr[i][j]==1){\n adj[i].push_back(j);\n }\n \n }\n }\n\n int ans=0;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n if(!vis[i]){\n ans++;\n dfs(i,vis,adj);\n }\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['C++']
| 2 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
DP | Memorization | easy to understand | readable | beats 99%
|
dp-memorization-easy-to-understand-reada-8ojg
|
Intuition\n\n\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nThe problem requires finding the maximum number of operations that can be performed
|
gkso07
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T16:01:58.959553+00:00
|
2024-02-17T18:39:43.271765+00:00
| 3,030 | false |
# Intuition\n\n\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThe problem requires finding the maximum number of operations that can be performed on an array of integers, such that each operation yields the same score. The operations involve selecting pairs of elements from either end or both ends of the array and summing them up.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n- Dynamic Programming with Memoization: We can solve this problem efficiently using dynamic programming with memoization. We define a recursive function that explores all possible choices of pairs of elements, keeping track of the maximum number of operations for each choice.\n\n- Recurrence Relation: The recurrence relation for our function considers three cases: selecting the first two elements, selecting the first and last elements, and selecting the last two elements. We compute the maximum number of operations possible for each case and choose the maximum among them.\n\n- Memoization: We use a 2D memoization array to store the results of subproblems. Before computing the maximum operations for a particular subarray, we check if it has already been computed. If so, we retrieve the result from the memoization table instead of recomputing it.\n\n- Base Cases: We handle base cases where the subarray has only one or no elements. In such cases, the maximum number of operations possible is zero.\n\n- Main Function: In the main function, we initialize the memoization array and call the recursive function with appropriate parameters for each of the three cases: selecting the first two elements, selecting the first and last elements, and selecting the last two elements. Finally, we return the maximum number of operations among these three cases.\n# why using only one dp table isn\'t three dp table is reqired for three case\n\nUsing only one dynamic programming (DP) table suffices because the paths corresponding to different previous sum values never collide within the DP table. At any given point where paths might intersect, only one path can pass through, and it will correspond to a specific previous sum value. Consequently, the calculated answer at that point is only relevant for future paths with the same previous sum value. Therefore, a single DP table effectively stores the results for all cases, ensuring accurate memoization and preventing interference between different cases.\nbecause of this one dp table is suffice\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nThe time complexity of this approach is O(n^2), where n is the number of elements in the input array. This is because the memoization table has dimensions of n * n, and each entry in the table is computed once.\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nThe space complexity is also O(n^2) due to the memoization table, which stores the results of subproblems. Additionally, the recursive stack can go up to O(n) levels in the worst case. Therefore, the total space complexity is dominated by the memoization table.\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\nprivate:\n int findMaxOpsHelper(std::vector<int>& nums, int left, int right, int previousSum, std::vector<std::vector<int>>& memoization) {\n if (left >= right)\n return 0;\n if (memoization[left][right] != 0)\n return memoization[left][right];\n\n int maxOps = 0;\n if (nums[left] + nums[left + 1] == previousSum)\n maxOps = std::max(maxOps, findMaxOpsHelper(nums, left + 2, right, previousSum, memoization) + 1);\n if (nums[left] + nums[right] == previousSum)\n maxOps = std::max(maxOps, findMaxOpsHelper(nums, left + 1, right - 1, previousSum, memoization) + 1);\n if (nums[right] + nums[right - 1] == previousSum)\n maxOps = std::max(maxOps, findMaxOpsHelper(nums, left, right - 2, previousSum, memoization) + 1);\n\n return memoization[left][right] = maxOps;\n }\npublic:\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n int maxOperations = 0;\n int len = nums.size();\n std::vector<std::vector<int>> memoization(len, std::vector<int>(len, 0));\n int start = 0;\n int end = len - 1;\n\n maxOperations = std::max(maxOperations,\n findMaxOpsHelper(nums, start + 2, end, nums[start] + nums[start + 1], memoization) + 1);\n maxOperations = std::max(maxOperations,\n findMaxOpsHelper(nums, start + 1, end - 1, nums[start] + nums[end], memoization) + 1);\n maxOperations = std::max(maxOperations,\n findMaxOpsHelper(nums, start, end - 2, nums[end] + nums[end - 1], memoization) + 1);\n\n return maxOperations;\n }\n};\n```\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {\n int maxOperations = 0;\n int len = nums.length;\n int[][] memoization = new int[len][len];\n int start = 0;\n int end = len - 1;\n\n maxOperations = Math.max(maxOperations,\n findMaxOpsHelper(nums, start + 2, end, nums[start] + nums[start + 1], memoization) + 1);\n maxOperations = Math.max(maxOperations,\n findMaxOpsHelper(nums, start + 1, end - 1, nums[start] + nums[end], memoization) + 1);\n maxOperations = Math.max(maxOperations,\n findMaxOpsHelper(nums, start, end - 2, nums[end] + nums[end - 1], memoization) + 1);\n\n return maxOperations;\n }\n\n private int findMaxOpsHelper(int[] nums, int left, int right, int previousSum, int[][] memoization) {\n if (left >= right)\n return 0;\n if (memoization[left][right] != 0)\n return memoization[left][right];\n\n int maxOps = 0;\n if (nums[left] + nums[left + 1] == previousSum)\n maxOps = Math.max(maxOps, findMaxOpsHelper(nums, left + 2, right, previousSum, memoization) + 1);\n if (nums[left] + nums[right] == previousSum)\n maxOps = Math.max(maxOps, findMaxOpsHelper(nums, left + 1, right - 1, previousSum, memoization) + 1);\n if (nums[right] + nums[right - 1] == previousSum)\n maxOps = Math.max(maxOps, findMaxOpsHelper(nums, left, right - 2, previousSum, memoization) + 1);\n\n return memoization[left][right] = maxOps;\n }\n}\n \n```\n```python []\nclass Solution:\n def maxOperations(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n maxOperations = 0\n length = len(nums)\n memoization = [[0] * length for _ in range(length)]\n start = 0\n end = length - 1\n\n maxOperations = max(maxOperations, self.findMaxOpsHelper(nums, start + 2, end, nums[start] + nums[start + 1], memoization) + 1)\n maxOperations = max(maxOperations, self.findMaxOpsHelper(nums, start + 1, end - 1, nums[start] + nums[end], memoization) + 1)\n maxOperations = max(maxOperations, self.findMaxOpsHelper(nums, start, end - 2, nums[end] + nums[end - 1], memoization) + 1)\n\n return maxOperations\n\n def findMaxOpsHelper(self, nums: List[int], left: int, right: int, previousSum: int, memoization: List[List[int]]) -> int:\n if left >= right:\n return 0\n if memoization[left][right] != 0:\n return memoization[left][right]\n\n maxOps = 0\n if nums[left] + nums[left + 1] == previousSum:\n maxOps = max(maxOps, self.findMaxOpsHelper(nums, left + 2, right, previousSum, memoization) + 1)\n if nums[left] + nums[right] == previousSum:\n maxOps = max(maxOps, self.findMaxOpsHelper(nums, left + 1, right - 1, previousSum, memoization) + 1)\n if nums[right] + nums[right - 1] == previousSum:\n maxOps = max(maxOps, self.findMaxOpsHelper(nums, left, right - 2, previousSum, memoization) + 1)\n\n memoization[left][right] = maxOps\n return maxOps\n\n```
| 29 | 2 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'Python3']
| 7 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
[Java/Python 3] Top-down DP: DFS cache O(n ^ 2) code w/ brief explanation and analysis.
|
javapython-3-top-down-dp-dfs-cache-on-2-j0v8m
|
For any given subarray of nums, there are 3 possible ways to get the score; Correspondingly we have the following 3 state transition functions:\n\n1. 1st 2 item
|
rock
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T16:04:37.502728+00:00
|
2024-02-20T07:14:12.813457+00:00
| 1,993 | false |
For any given subarray of `nums`, there are 3 possible ways to get the score; Correspondingly we have the following 3 state transition functions:\n\n1. 1st 2 items, if it sums to the score, we have recursion: `dfs(lo, hi) = 1 + dfs(lo + 2, hi)`;\n2. last 2 items, if it sums to the score, we have recursion: `dfs(lo, hi) = 1 + dfs(lo, hi - 2)`; \n3. 1st and last items, if it sums to the score, we have recursion: `dfs(lo, hi) = 1 + dfs(lo + 1, hi - 1)`;\n\nBase case: there are `1` or no items (`hi <= lo`) in subarray, we return `0`.\n\nIn addition, we need cache to avoid duplicate computations. Therefore, we can have the following code:\n\n\n\n```java\n public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {\n int max = 0, n = nums.length;\n for (int score : new HashSet<>(List.of(nums[0] + nums[1], nums[0] + nums[n - 1], nums[n - 2] + nums[n - 1]))) {\n max = Math.max(max, dfs(nums, 0, n - 1, score, new HashMap<String, Integer>()));\n }\n return max;\n }\n private int dfs(int[] nums, int lo, int hi, int score, Map<String, Integer> cache) {\n if (hi <= lo) {\n return 0;\n }\n String key = lo + ", " + hi;\n if (!cache.containsKey(key)) {\n int max = 0;\n if (score == nums[lo] + nums[lo + 1]) {\n max = Math.max(max, 1 + dfs(nums, lo + 2, hi, score, cache));\n }\n if (score == nums[lo] + nums[hi]) {\n max = Math.max(max, 1 + dfs(nums, lo + 1, hi - 1, score, cache));\n }\n if (score == nums[hi - 1] + nums[hi]) {\n max = Math.max(max, 1 + dfs(nums, lo, hi - 2, score, cache));\n }\n cache.put(key, max);\n }\n return cache.get(key);\n }\n```\n\n```python\n def maxOperations(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n \n def dfs(score: int, cache: Dict, lo = 0, hi = len(nums) - 1) -> int:\n if hi <= lo:\n return 0\n if (lo, hi) not in cache:\n max_ops1 = 1 + dfs(score, cache, lo + 2, hi) if score == sum(nums[lo : lo + 2]) else 0\n max_ops2 = 1 + dfs(score, cache, lo, hi - 2) if score == sum(nums[hi - 1 : hi + 1]) else 0\n max_ops3 = 1 + dfs(score, cache, lo + 1, hi - 1) if score == nums[lo] + nums[hi] else 0\n cache[lo, hi] = max(max_ops1, max_ops2, max_ops3)\n return cache[lo, hi]\n \n return max(map(dfs, \n set([sum(nums[: 2]), sum(nums[-2 :]), nums[0] + nums[-1]]), \n (defaultdict() for _ in range(3))\n )\n )\n```\nOr use built-in cache:\n```python\n def maxOperations(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n \n @lru_cache(None)\n def dfs(score: int, lo = 0, hi = len(nums) - 1) -> int:\n if hi <= lo:\n return 0\n max_ops1 = 1 + dfs(score, lo + 2, hi) if score == sum(nums[lo : lo + 2]) else 0\n max_ops2 = 1 + dfs(score, lo, hi - 2) if score == sum(nums[hi - 1 : hi + 1]) else 0\n max_ops3 = 1 + dfs(score, lo + 1, hi - 1) if score == nums[lo] + nums[hi] else 0\n return max(max_ops1, max_ops2, max_ops3)\n \n return max(map(dfs, set([sum(nums[: 2]), sum(nums[-2 :]), nums[0] + nums[-1]])))\n\n```\n\n\n----\n\n**Analysis:**\n\nSince the combinations of lower and upper bounds of the subarrays of `nums`, `lo`s and `hi`s, are at most `O(n ^ 2)`, where `n = nums.length`, we have\n\nTime & space: `O(n ^ 2)`.\n\n----\n\n**Q & A:**\n*Q1:* Why didn\'t you need to add score into the key. For a given low and high index, when computation repeats with different score value, you still need to ensure it\'s matching the current score value no ?\n\n*A1:* Because the `score` argument of `dfs` always matches the current `score` value. The code uses independent `dfs`s to compute max operations for different `scores`. As a result, both the `dfs` method and the `cache` vary from score to score. \n\nIn fact, the life cycle for both the `dfs` and the `cache` correspond to each `score`: when visiting a `score`, we call `dfs` and create `cache`, get the max operations for the `score`, then terminate `dfs`, and the memory corresponding to `cache` will lose reference handler (and eventually be gabage colleced by JVM) upon the termination of `dfs`. \n\nWhen visiting next `score`, the above procedure will repeat, untill all `3` different `score`s have been visited. \n\nThe max value out of the `3` `dfs`s\' results is the solution.
| 21 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Depth-First Search', 'Java', 'Python3']
| 8 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
c++||DP||easy solution||Memoization
|
cdpeasy-solutionmemoization-by-baibhavkr-8zt0
|
Intution\nthis is a dynamic programming problem because at every point we have to make 3 choices and take the max out of it\n Describe your first thoughts on ho
|
baibhavkr143
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T16:01:44.046231+00:00
|
2024-02-17T16:26:32.891703+00:00
| 2,336 | false |
# Intution\nthis is a dynamic programming problem because at every point we have to make 3 choices and take the max out of it\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n# Approach\n**Utilizing Dynamic Programming with Memoization**: This problem lends itself well to an efficient solution through dynamic programming with memoization. We devise a recursive function to explore various pairs of elements, maintaining the maximum number of operations for each selection.\n\n**Recurrence Relation**: Our function\'s recurrence relation examines three scenarios: selecting the first two elements, choosing the first and last elements, and opting for the last two elements. For each scenario, we compute the maximum number of operations possible and select the highest among them.\n\n**Memoization**: Employing a 2D memoization array, we store computed results of subproblems. Before evaluating the maximum operations for a particular subarray, we verify if it\'s been previously calculated. If so, we retrieve the result from the memoization table, eliminating redundant computations.\n\n**Base Cases**: We address scenarios where the subarray consists of only one or no elements. In such instances, the maximum number of operations achievable is zero.\n\n**Main Function**: Within the main function, we initialize the memoization array and invoke the recursive function for each of the three cases: selecting the first two elements, picking the first and last elements, and choosing the last two elements. Subsequently, we return the maximum number of operations among these three scenarios\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\nTime complexity:\nThis approach\'s time complexity stands at O(n^2), where n represents the number of elements in the input array. This is primarily due to the n * n dimensions of the memoization table, with each entry computed once.\n\nSpace complexity:\nThe space complexity also amounts to O(n^2) owing to the memoization table storing subproblem results. Furthermore, in the worst-case scenario, the recursive stack may extend up to O(n) levels. Consequently, the predominant factor in space complexity remains the memoization table.\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<vector<int>>dp;\n int solve(int l,int r,int score,vector<int>&nums)\n {\n if(l>=r)return 0;\n if(dp[l][r]!=-1)return dp[l][r];\n \n int ans=0;\n if(nums[l]+nums[l+1]==score)ans=max(ans,1+solve(l+2,r,score,nums));\n if(nums[r]+nums[r-1]==score)ans=max(ans,1+solve(l,r-2,score,nums));\n if(nums[l]+nums[r]==score)ans=max(ans,1+solve(l+1,r-1,score,nums));\n \n return dp[l][r]=ans;\n }\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n dp.resize(nums.size()+1,vector<int>(nums.size()+1,-1));\n int n=nums.size();\n int ans=0;\n ans=max(ans,1+solve(2,n-1,nums[0]+nums[1],nums));\n ans=max(ans,1+solve(0,n-3,nums[n-1]+nums[n-2],nums));\n ans=max(ans,1+solve(1,n-2,nums[0]+nums[n-1],nums));\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 14 | 4 |
['C++']
| 10 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Easy Approach || Recursive Approach with Memoization || C++ || Please Upvote
|
easy-approach-recursive-approach-with-me-rg87
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nThe problem aims to find the maximum number of operations that can be performed on a gi
|
Anmol_jais
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T16:07:01.193720+00:00
|
2024-02-17T16:07:01.193759+00:00
| 1,321 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThe problem aims to find the maximum number of operations that can be performed on a given array of integers, where each operation involves selecting two elements from the array that sum up to a certain value. Here\'s the intuition behind the solution:\n\n1. We can solve this problem using a recursive approach combined with memoization (dynamic programming).\n2. At each step, we consider various segment configurations of the array and try to maximize the number of operations that can be performed.\n3. We keep track of the maximum number of operations that can be performed for each segment configuration using a memoization table.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n-> Recursive Approach with Memoization:\n\n1. We define a recursive function solve that takes the current left and right indices of the array segment being considered, the target sum s, the array nums, and a memoization table dp.\n2. Base case: If the segment contains zero or one element (left >= right), the answer is 0.\n3. If the answer for the current segment [left, right] has already been calculated, it is directly returned from the memoization table.\n4. We consider three possibilities for selecting pairs:\nOne with the left index (a).\nOne with the right index (b).\nOne with both (c).\n5. Recursively, we check if pairs can be formed at different segment configurations by adjusting the indices and update the memoization table.\n6. Finally, we return the maximum number of operations that can be performed for the current segment.\n\n-> Main Function maxOperations:\n\n1. We initialize three memoization tables corresponding to different segment configurations.\n2. We calculate the initial values of segment sums based on different pairs.\n3. We invoke the solve function for each segment configuration to compute the maximum number of operations. \n4. We take the maximum of these three results as the final answer.\n5. Since the question asks for the maximum number of operations, we add 1 to the final answer before returning it.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n$$O(n^2)$$ \n\n- Space complexity:\n$$O(n^2)$$ \n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int solve(int left, int right, int s, vector<int>&nums, vector<vector<int>>&dp)\n {\n if(left>=right)\n {\n return 0;\n }\n \n if(dp[left][right]!=-1)\n {\n return dp[left][right];\n }\n \n int a=0;\n int b=0;\n int c=0;\n \n if(left+1<=right && nums[left]+nums[left+1]==s)\n {\n a=1+solve(left+2,right,s,nums,dp);\n }\n \n if(right-1>=left && nums[right]+nums[right-1]==s)\n {\n b=1+solve(left,right-2,s,nums,dp);\n }\n \n if(nums[left]+nums[right]==s)\n {\n c=1+solve(left+1,right-1,s,nums,dp);\n }\n \n return dp[left][right] = max(a,max(b,c));\n }\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n=nums.size();\n vector<vector<int>>dp1(n+1,vector<int>(n+1,-1));\n vector<vector<int>>dp2(n+1,vector<int>(n+1,-1));\n vector<vector<int>>dp3(n+1,vector<int>(n+1,-1));\n \n int s1=nums[0]+nums[1];\n int s2=nums[0]+nums[n-1];\n int s3=nums[n-2]+nums[n-1];\n \n int a=solve(2,n-1,s1,nums,dp1);\n int b=solve(0,n-3,s3,nums,dp2);\n int c=solve(1,n-2,s2,nums,dp3);\n \n int ans = max(a,max(b,c));\n ans++;\n \n return ans;\n \n \n }\n};\n```
| 12 | 2 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 5 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Python 3 || 6 lines, dp recursion w/ caching || T/S: 85% / 96%
|
python-3-6-lines-dp-recursion-w-caching-t6oez
|
\nclass Solution:\n def maxOperations(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n\n n = len(nums)\n\n @lru_cache(6000)\n def dp(i: int,j: int,targe
|
Spaulding_
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T19:53:45.555615+00:00
|
2024-06-12T03:53:41.733879+00:00
| 258 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def maxOperations(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n\n n = len(nums)\n\n @lru_cache(6000)\n def dp(i: int,j: int,target: int)-> int:\n\n if j - i < 2: return (j - i == 1 and nums[i]+nums[j]==target)\n\n return max(1+dp(i+2, j , target) if nums[i]+nums[i+1] == target else 0,\n 1+dp(i , j-2, target) if nums[j]+nums[j-1] == target else 0,\n 1+dp(i+1, j-1, target) if nums[i]+nums[j ] == target else 0)\n \n \n return 1+max(dp(2, n - 1, nums[ 0] + nums[ 1]), \n dp(0, n - 3, nums[-1] + nums[-2]), \n dp(1, n - 2, nums[ 0] + nums[-1]))\n```\n[https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii/submissions/1178202200/](https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii/submissions/1178202200/)\n\nI could be wrong, but I think that time complexity is *O*(*N*^2) and space complexity is *O*(*N*^2), in which *N* ~ `len(nums)`.
| 10 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 1 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Piddi sa to Que hai (😂) || Hindi 💥 Explaination || Gadha 🫏 Majdoori krva diya || C++
|
piddi-sa-to-que-hai-hindi-explaination-g-raet
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n How i identify DP ?\n Ankh band kro...arey kro to\n thoda jayda number ko imagine krna
|
abhirai1
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T17:25:54.935595+00:00
|
2024-02-17T17:29:14.287009+00:00
| 238 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n* How i identify DP ?\n* Ankh band kro...arey kro to\n* thoda jayda number ko imagine krna\n* ab socho en tino pair bnane wale case ke baare me\n* basad machi...dimak me...kya lagta hai..\n* sabhi case se pass hona hoga..sabhi situation se gujrna hoga\n* bas lag gyi dp \n* vaise bhi esme Choice thi hmare pass...to recursion aise hi lg rha \n* esme...optimise krne ke liye DP to hai hi..\u2705\u2705\u2705\u2705\u2705\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n* intution feel hua...kya keh rhe\n* kuchh to tha hi nhi intution me \n* \uD83D\uDE02\uD83D\uDE02\uD83D\uDE02\uD83D\uDE02\n* aao sidhe, gadha majdoori ka code dekhte hai...\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int solve(int i,int j, int sum,vector<int> &ip,vector<vector<int>> &t){\n\n // dekho i start ke liye tha\n // j end ke liye\n // jab dono ek dure ko cross kiya yani \n // hmare pass, koi values hai hi nhi..\n // simple \uD83D\uDD7A\uD83D\uDD7A\uD83D\uDD7A\uD83D\uDD7A\n if(i>=j) return 0; \n\n\n // memo ka step...kyu bhai naam to suna hi hoga \n // \uD83D\uDE0A\uD83D\uDE0A\uD83D\uDE0A\uD83D\uDE0A\uD83D\uDE0A\uD83D\uDE0A\uD83D\uDE0A\uD83D\uDE0A\uD83D\uDE0A\uD83D\uDE0A\n if(t[i][j]!=-1) return t[i][j]; \n \n // itne variable ki need nhi \n // vo tumhe pta hi hai, contest time ka\n // bas type ho gya tha..\uD83D\uDE02\uD83D\uDE02\uD83D\uDE02\n int t1=0,t2=0,t3=0,t4=0,t5=0,t6=0; \n \n // ab i and j ka check krenge sum ke brabar hia ya nhi\n if(ip[i]+ip[j]==sum) t1=1+solve(i+1,j-1,sum,ip,t); \n \n // phir do pass ke element ka check karenge\n if(ip[i]+ip[i+1]==sum) t2=1+solve(i+2,j,sum,ip,t);\n\n\n // phri n, last ke do ka check kr lenge\n // usi ke hisaab se i and j move kar denge\n if(ip[j]+ip[j-1]==sum) t3=1+solve(i,j-2,sum,ip,t);\n\n\n // jo maximum hoga, vo us state ke DP me store hoga\n return t[i][j]=max({t1,t2,t3});\n \n }\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& ip) {\n int n=ip.size(); \n \n // minimum itni length to hogi hi\n // esme direct ek pair banega\n if(n==2) return 1; \n \n // dekho do dp bnayenge \n // kya abhi bhai...aisa kyu karenge ?\n // \uD83E\uDD14\uD83E\uDD14\uD83E\uDD14\uD83E\uDD14\uD83E\uDD14\uD83E\uDD14\uD83E\uDD14\uD83E\uDD14\uD83E\uDD14\uD83E\uDD14\n // smjha dunga chill...\n vector<vector<int>> tt(n,vector<int> (n,-1));\n vector<vector<int>> tt2(n,vector<int> (n,-1));\n\n int t1=0,t2=0,t3=0; \n\n\n // start ke do element ko leke dp\n // abhi ye to clear hai n.. aakhir dp hi kyu ?\n t1=solve(0,n-1,ip[0]+ip[1],ip,tt);\n\n // dusre call ke liye dp phir se -1 krna padega n\n // to esiliye ek ka help liya tha,\n // kai aur tarike hai es kaam ke\n tt=tt2; \n \n // dono aakhiri\n t2=solve(0,n-1,ip[n-1]+ip[n-2],ip,tt);\n \n // same copy paste \n // agle call ke liye....\n tt=tt2; \n \n // pehla aakhiri ke liye\n t3=solve(0,n-1,ip[0]+ip[n-1],ip,tt);\n \n // jis tarike me maximum mila, vo return kar denge\n // \u2705\u2705\u2705\u2705\u2705 Happy Happy \uD83D\uDE0A\n return max({t1,t2,t3});\n }\n};\n```
| 6 | 1 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 3 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Beats 100%🔥Top down approach || DP with memoization✅ C++ || Java || Python3
|
beats-100top-down-approach-dp-with-memoi-19ew
|
Intuition\nWe need to check all possibilies:\n1. If the first two numbers add up to score.\n2. If the last two numbers add up to score.\n3. If the first and las
|
Eshaan14_
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T17:15:45.429827+00:00
|
2024-02-17T17:15:45.429844+00:00
| 576 | false |
# Intuition\nWe need to check all possibilies:\n1. If the first two numbers add up to score.\n2. If the last two numbers add up to score.\n3. If the first and last number add up to score.\n\nWhenever we have to look for all the possibilites, recursive dp can be helpful.\n\n# Approach\nWe would require a 2D DP where the state variables would be the starting index and ending index of the array.\nWe then check for all the 3 possibilities and take the maximum of all three of them.\n\n**For case 1:** \nWe increment the starting index $$l$$ by 2 and pass the score as the addition of the first two numbers.\n\n**For case 2:** \nWe decrement the ending index $$r$$ by 2 and pass the score as the addition of the first two numbers.\n\n**For case 3:** \nWe increment the starting index $$l$$ by 1 and decrement the ending index $$r$$ by 1 and pass the score as the addition of the first two numbers.\n\nFor all the possibilities, we increment the value returned by function by 1 because we conside it as one operation.\n\nFor the recursion function, the base case would be when $$l>=r$$. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(n^2)\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(n^2)\n\n# Code\n```C++ []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n vector<vector<int>> dp;\n\n int func(int l, int r, vector<int> &nums, int num){\n if(l>=r) return 0;\n if(dp[l][r]!=-1) return dp[l][r];\n\n int ans = 0;\n if(nums[l]+nums[l+1] == num){\n ans = max(ans, 1+func(l+2, r, nums, num));\n }\n if(nums[r]+nums[r-1] == num){\n ans = max(ans, 1+func(l, r-2, nums, num));\n }\n if(nums[l]+nums[r] == num){\n ans = max(ans, 1+func(l+1, r-1, nums, num));\n }\n\n return dp[l][r] = ans;\n }\n\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n = nums.size();\n dp = vector<vector<int>>(n, vector<int>(n, -1));\n int ans = 0;\n\n ans = max(ans, 1+func(2, n-1, nums, nums[0]+nums[1]));\n ans = max(ans, 1+func(0, n-3, nums, nums[n-1]+nums[n-2]));\n ans = max(ans, 1+func(1, n-2, nums, nums[0]+nums[n-1]));\n\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\n```Java []\nclass Solution {\n int[][] dp;\n\n public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {\n int n = nums.length;\n dp = new int[n][n];\n for (int[] row : dp) {\n Arrays.fill(row, -1);\n }\n int ans = 0;\n\n ans = Math.max(ans, 1 + func(2, n - 1, nums, nums[0] + nums[1]));\n ans = Math.max(ans, 1 + func(0, n - 3, nums, nums[n - 1] + nums[n - 2]));\n ans = Math.max(ans, 1 + func(1, n - 2, nums, nums[0] + nums[n - 1]));\n\n return ans;\n }\n\n private int func(int l, int r, int[] nums, int num) {\n if (l >= r)\n return 0;\n if (dp[l][r] != -1)\n return dp[l][r];\n\n int ans = 0;\n if (nums[l] + nums[l + 1] == num) {\n ans = Math.max(ans, 1 + func(l + 2, r, nums, num));\n }\n if (nums[r] + nums[r - 1] == num) {\n ans = Math.max(ans, 1 + func(l, r - 2, nums, num));\n }\n if (nums[l] + nums[r] == num) {\n ans = Math.max(ans, 1 + func(l + 1, r - 1, nums, num));\n }\n\n return dp[l][r] = ans;\n }\n}\n\n```\n```Python []\nclass Solution:\n def maxOperations(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n def func(l, r, nums, num):\n if l >= r:\n return 0\n if dp[l][r] != -1:\n return dp[l][r]\n\n ans = 0\n if nums[l] + nums[l + 1] == num:\n ans = max(ans, 1 + func(l + 2, r, nums, num))\n if nums[r] + nums[r - 1] == num:\n ans = max(ans, 1 + func(l, r - 2, nums, num))\n if nums[l] + nums[r] == num:\n ans = max(ans, 1 + func(l + 1, r - 1, nums, num))\n\n dp[l][r] = ans\n return ans\n\n n = len(nums)\n dp = [[-1] * n for _ in range(n)]\n\n ans = 0\n ans = max(ans, 1 + func(2, n - 1, nums, nums[0] + nums[1]))\n ans = max(ans, 1 + func(0, n - 3, nums, nums[-1] + nums[-2]))\n ans = max(ans, 1 + func(1, n - 2, nums, nums[0] + nums[-1]))\n\n return ans\n\n```
| 6 | 0 |
['Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'Python3']
| 1 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Python - O(n^2) - Two Pointer - DP - Video Solution
|
python-on2-two-pointer-dp-video-solution-67ul
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nI have explained the solution entirely here https://youtu.be/k_r5JB8PWmI\n\n# Approach\
|
cheatcode-ninja
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T16:14:30.500722+00:00
|
2024-02-17T20:08:38.468511+00:00
| 553 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nI have explained the solution entirely here https://youtu.be/k_r5JB8PWmI\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n^2)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(n^2)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maxOperations(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n n= len(nums)\n \n @cache\n def dfs(l, r, score):\n if l==r or l>r:\n return 0\n \n res = 0\n if nums[l] + nums[l+1] == score:\n res = 1 + dfs(l+2, r, score)\n if nums[l] + nums[r] == score:\n res = max(res, 1 + dfs(l+1, r-1, score))\n if nums[r]+ nums[r-1] == score:\n res = max(res, 1 + dfs(l, r-2, score))\n \n return res\n \n return 1 + max( dfs(1, n-2, nums[0] +nums[-1]), dfs(2, n-1, nums[0] +nums[1]), dfs(0, n-3, nums[-1] +nums[-2]))\n```
| 6 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 2 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
🎨 The ART of Dynamic Programming
|
the-art-of-dynamic-programming-by-clayto-5dq4
|
Game Plan\n\n## \uD83C\uDFA8 The ART of Dynamic Programming:\n\n### DFS + Memo to optimally choose the maximum of 3 possibilities per i..j search-space of the i
|
claytonjwong
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T16:05:51.193079+00:00
|
2024-02-22T16:09:51.558538+00:00
| 321 | false |
# Game Plan\n\n## [\uD83C\uDFA8 The ART of Dynamic Programming:](https://leetcode.com/discuss/general-discussion/712010/The-ART-of-Dynamic-Programming-An-Intuitive-Approach%3A-from-Apprentice-to-Master)\n\n### DFS + Memo to optimally choose the maximum of 3 possibilities per `i..j` search-space of the input array `A`\n\n* **a)** Choose the first two elements of nums and delete them.\n* **b)** Choose the last two elements of nums and delete them.\n* **c)** Choose the first and the last elements of nums and delete them.\n\n# Code\n\n\n\n*Kotlin*\n```\nclass Solution {\n fun maxOperations(A: IntArray): Int {\n var N = A.size\n var dp = Array(N){ IntArray(N){ -1} }\n fun go(i: Int = 0, j: Int = N - 1, last: Int = 0): Int {\n if (j <= i)\n return 0\n if (dp[i][j] == -1) {\n var a = if (last == 0 || last == A[i] + A[i + 1]) 1 + go(i + 2, j, A[i] + A[i + 1]) else 0\n var b = if (last == 0 || last == A[j - 1] + A[j]) 1 + go(i, j - 2, A[j - 1] + A[j]) else 0\n var c = if (last == 0 || last == A[i] + A[j]) 1 + go(i + 1, j - 1, A[i] + A[j]) else 0\n dp[i][j] = listOf(a, b, c).max()\n }\n return dp[i][j]\n }\n return go()\n }\n}\n```\n\n*Javascript*\n```\nlet maxOperations = (A, N = A.length, dp = [...Array(N)].map(_ => Array(N).fill(-1))) => {\n let go = (i = 0, j = N - 1, last = 0) => {\n if (j <= i)\n return 0;\n if (dp[i][j] != -1)\n return dp[i][j];\n let a = (!last || last == A[i] + A[i + 1]) ? 1 + go(i + 2, j, A[i] + A[i + 1]) : 0,\n b = (!last || last == A[j - 1] + A[j]) ? 1 + go(i, j - 2, A[j - 1] + A[j]) : 0,\n c = (!last || last == A[i] + A[j]) ? 1 + go(i + 1, j - 1, A[i] + A[j]) : 0;\n return dp[i][j] = Math.max(a, b, c);\n };\n return go();\n};\n```\n\n*Python3*\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maxOperations(self, A: List[int]) -> int:\n @cache\n def go(i = 0, j = len(A) - 1, last = 0):\n if j <= i:\n return 0\n a = 1 + go(i + 2, j, A[i] + A[i + 1]) if not last or last == A[i] + A[i + 1] else 0\n b = 1 + go(i, j - 2, A[j - 1] + A[j]) if not last or last == A[j - 1] + A[j] else 0\n c = 1 + go(i + 1, j - 1, A[i] + A[j]) if not last or last == A[i] + A[j] else 0\n return max(a, b, c)\n return go()\n```\n\n*Rust*\n```\ntype VI = Vec<i32>;\ntype VVI = Vec<VI>;\nimpl Solution {\n pub fn max_operations(A: VI) -> i32 {\n let N = A.len();\n let mut dp = vec![vec![-1; N]; N];\n fn go(A: &VI, i: i32, j: i32, last: i32, dp: &mut VVI) -> i32 {\n if j <= i {\n return 0;\n }\n if dp[i as usize][j as usize] == -1 {\n let a = if last == 0 || last == A[i as usize] + A[i as usize + 1] { 1 + go(A, i + 2, j, A[i as usize] + A[i as usize + 1], dp) } else { 0 };\n let b = if last == 0 || last == A[j as usize- 1] + A[j as usize] { 1 + go(A, i, j - 2, A[j as usize - 1] + A[j as usize], dp) } else { 0 };\n let c = if last == 0 || last == A[i as usize] + A[j as usize] { 1 + go(A, i + 1, j - 1, A[i as usize] + A[j as usize], dp) } else { 0 };\n dp[i as usize][j as usize] = vec![a, b, c].into_iter().max().unwrap();\n }\n dp[i as usize][j as usize]\n }\n go(&A, 0, N as i32 - 1, 0, &mut dp)\n }\n}\n```\n\n*C++*\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n using VI = vector<int>;\n using VVI = vector<VI>;\n using fun = function<int(int, int, int)>;\n int maxOperations(VI& A) {\n int N = A.size();\n VVI dp(N, VI(N, -1));\n fun go = [&](auto i, auto j, auto last) {\n if (j <= i)\n return 0;\n if (dp[i][j] != -1)\n return dp[i][j];\n auto a = (!last || last == A[i] + A[i + 1]) ? 1 + go(i + 2, j, A[i] + A[i + 1]) : 0,\n b = (!last || last == A[j - 1] + A[j]) ? 1 + go(i, j - 2, A[j - 1] + A[j]) : 0,\n c = (!last || last == A[i] + A[j]) ? 1 + go(i + 1, j - 1, A[i] + A[j]) : 0;\n return dp[i][j] = max({a, b, c});\n };\n return go(0, N - 1, 0);\n }\n};\n```\n\n---\n\n# Supplemental: \uD83C\uDF5E "Breadcrumbs" for how we arrived "here" \uD83C\uDFAF\n```\n# Submission Result: Wrong Answer \n# Input:\n# [1,9,7,3,2,7,4,12,2,6]\n# Output:\n# 3\n# Expected:\n# 2\n\n# class Solution:\n# def maxOperations(self, A: List[int]) -> int:\n# N = len(A)\n# @cache\n# def go(i = 0, j = N - 1, last = 0):\n# if j <= i:\n# return 0\n# a = go(i + 2, j, A[i] + A[i + 1]) if not last or last == A[i] + A[i + 1] else 0\n# b = go(i, j - 2, A[j - 1] + A[j]) if not last or last == A[j - 1] + A[j] else 0\n# c = go(i + 1, j - 1, A[i] + A[j]) if not last or last == A[i] + A[j] else 0\n# return 1 + max(a, b, c)\n# return go()\n\n# Game Plan\n# [\uD83C\uDFA8 The ART of Dynamic Programming:](https://leetcode.com/discuss/general-discussion/712010/The-ART-of-Dynamic-Programming-An-Intuitive-Approach%3A-from-Apprentice-to-Master)\n\n# Use DFS + Memo to optimally choose from 3 possibilities:\n\n# a. Choose the first two elements of nums and delete them.\n# b. Choose the last two elements of nums and delete them.\n# c. Choose the first and the last elements of nums and delete them.\n\n# # Implementations\n# *Python3*\nclass Solution:\n def maxOperations(self, A: List[int]) -> int:\n N = len(A)\n @cache\n def go(i = 0, j = N - 1, last = 0):\n if j <= i:\n return 0\n a = 1 + go(i + 2, j, A[i] + A[i + 1]) if not last or last == A[i] + A[i + 1] else 0\n b = 1 + go(i, j - 2, A[j - 1] + A[j]) if not last or last == A[j - 1] + A[j] else 0\n c = 1 + go(i + 1, j - 1, A[i] + A[j]) if not last or last == A[i] + A[j] else 0\n return max(a, b, c)\n return go()\n\n# this is kinda silly, right?\n\n# class Solution:\n# def maxOperations(self, A: List[int], T = 2000, best = 0) -> int:\n# N = len(A)\n# dp = [[[0] * (T + 1) for _ in range(N)] for _ in range(N)]\n# for last in range(T + 1):\n# for i in range(N):\n# for j in reversed(range(i + 1, N)):\n# a = 1 + (dp[i + 2][j][A[i] + A[i + 1]] if i + 2 < N else 0) if not last or (i + 1 < N and last == A[i] + A[i + 1]) else 0\n# b = 1 + (dp[i][j - 2][A[j - 1] + A[j]] if 0 <= j - 2 else 0) if not last or (0 <= j - 1 and last == A[j - 1] + A[j]) else 0\n# c = 1 + (dp[i + 1][j - 1][A[i] + A[j]] if 0 <= j - 1 and i + 1 < N else 0) if not last or last == A[i] + A[j] else 0\n# dp[i][j][last] = max(a, b, c)\n# best = max(best, dp[i][j][last])\n# return best\n```
| 6 | 1 |
['C++', 'Python3', 'Rust', 'Kotlin', 'JavaScript']
| 2 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
C++ || Recursion + Memoization || Beginner's Method 🤩💯✅
|
c-recursion-memoization-beginners-method-v8r6
|
\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int solve(int i, int j, int score1, vector<int>&nums, vector<vector<int>>&dp){\n if(i >= j || i > nums.size()-
|
_kvschandra_2234
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T16:04:26.237249+00:00
|
2024-02-17T16:07:04.461548+00:00
| 311 | false |
\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int solve(int i, int j, int score1, vector<int>&nums, vector<vector<int>>&dp){\n if(i >= j || i > nums.size()-1 || j < 0) return 0;\n if(dp[i][j] != 1) return dp[i][j];\n int pick1 = 0;\n int pick2 = 0;\n int pick3 = 0;\n if(nums[i] + nums[j] == score1 ) pick1 = 1 + solve(i+1, j-1, score1, nums, dp);\n if(nums[i] + nums[i+1] == score1 ) pick2 = 1 +solve(i+2, j, score1, nums, dp);\n if(nums[j] + nums[j-1] == score1 ) pick3 = 1 + solve(i, j-2, score1, nums, dp);\n return dp[i][j] = max(pick1, max(pick2, pick3));\n \n }\n \n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n int i = 0;\n int j = nums.size()-1;\n int n = nums.size();\n int score1 = nums[i] + nums[j];\n int score2 = nums[i] + nums[i+1];\n int score3 = nums[j] + nums[j-1];\n vector<vector<int>>dp1(n, vector<int>(n, 1));\n vector<vector<int>>dp2(n, vector<int>(n, 1));\n vector<vector<int>>dp3(n, vector<int>(n, 1));\n int a = solve(i, j, score1, nums, dp1);\n int b = solve(i, j, score2, nums, dp2);\n int c = solve(i, j, score3, nums, dp3);\n int ans = max(a, max(b, c));\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 6 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 2 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
[C++] Top down DP
|
c-top-down-dp-by-timchen10001-lm7n
|
Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n- Base case:\n - r - l + 1 < 2: 0\n- State transformation:\n - op1Score: nums[l] + nums[l+1]\n
|
timchen10001
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T16:03:34.341421+00:00
|
2024-02-20T07:25:44.476525+00:00
| 988 | false |
# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n- Base case:\n - `r - l + 1 < 2`: `0`\n- State transformation:\n - `op1Score`: `nums[l] + nums[l+1]`\n - `op2Score`: `nums[r-1] + nums[r]`\n - `op3Score`: `nums[l] + nums[r]`\n - `op1`: op1Score == prev ? `1 + dp(prev, l+2, r)` : `0`\n - `op2`: op2Score == prev ? `1 + dp(prev, l, r-2)` : `0`\n - `op3`: op3Score == prev ? `1 + dp(prev, l+1, r-1)` : `0`\n - `dp(prev, l, r) = max(op1, op2, op3)`\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n^2)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(n^2)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n = nums.size();\n vector<vector<int>> memo(n, vector<int>(n, -1));\n function<int(int,int,int)> dp = [&](int prev, int l, int r) {\n if (r - l + 1 < 2)\n return 0;\n if (memo[l][r] != -1)\n return memo[l][r];\n int op1Score = nums[l] + nums[l+1];\n int op2Score = nums[r-1] + nums[r];\n int op3Score = nums[l] + nums[r];\n int op1 = op1Score == prev ? 1 + dp(prev, l+2, r) : 0;\n int op2 = op2Score == prev ? 1 + dp(prev, l, r-2) : 0;\n int op3 = op3Score == prev ? 1 + dp(prev, l+1, r-1) : 0;\n return memo[l][r] = max({op1, op2, op3});\n };\n return 1 + max({\n dp(nums[0]+nums[1], 2, n-1),\n dp(nums[n-2]+nums[n-1], 0, n-3),\n dp(nums[0]+nums[n-1], 1, n-2),\n });\n }\n};\n```
| 6 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 2 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Checking all the 3 possibilities.
|
checking-all-the-3-possibilities-by-mina-8mt6
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Minato_10
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T16:04:38.407675+00:00
|
2024-02-17T16:04:38.407699+00:00
| 632 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n private:\n int func(vector<int>& nums,int i,int j,vector<vector<int>>&dp,int val){\n if(i>=j) return 0;\n if(dp[i][j]!=-1) return dp[i][j];\n int op1 = 0,op2 = 0, op3 = 0;\n if(i+1<=j){\n if(nums[i]+nums[i+1]==val){\n op1 = 1 + func(nums,i+2,j,dp,val);\n }\n } \n if(nums[i]+nums[j]==val) op2 = 1 + func(nums,i+1,j-1,dp,val);\n if(j-1>=i){\n if(nums[j]+nums[j-1]==val) op3 = 1 + func(nums,i,j-2,dp,val);\n }\n return dp[i][j] = max({op1,op2,op3});\n }\npublic:\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n = nums.size();\n vector<vector<int>>dp1(n+1,vector<int>(n+1,-1));\n vector<vector<int>>dp2(n+1,vector<int>(n+1,-1));\n vector<vector<int>>dp3(n+1,vector<int>(n+1,-1));\n int v1 = nums[0]+nums[1];\n int v2 = nums[0]+nums[n-1];\n int v3 = nums[n-1]+nums[n-2];\n int ans = 0;\n ans = max(ans,func(nums,0,n-1,dp1,v1));\n ans = max(ans,func(nums,0,n-1,dp2,v2));\n ans = max(ans,func(nums,0,n-1,dp3,v3));\n return ans;\n \n }\n};\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
dp + memoisation(for 3 cases )
|
dp-memoisationfor-3-cases-by-chalobeta-g09e
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
prathamesh45_
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T16:01:49.563509+00:00
|
2024-02-17T16:01:49.563533+00:00
| 312 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int solve(int i, int j, int sum, vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& dp) {\n if (i >= j) return 0;\n if (dp[i][j] != -1) return dp[i][j];\n \n int a = 0, b = 0, c = 0;\n \n if (i + 1 <= j && nums[i] + nums[i + 1] == sum) {\n a = 1 + solve(i + 2, j, sum, nums, dp);\n }\n if (j - 1 >= i && nums[j] + nums[j - 1] == sum) {\n b = 1 + solve(i, j - 2, sum, nums, dp);\n }\n if (nums[i] + nums[j] == sum) {\n c = 1 + solve(i + 1, j - 1, sum, nums, dp);\n }\n \n return dp[i][j] = max({a, b, c});\n }\n \n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n = nums.size();\n \n vector<vector<int>> dp1(n, vector<int>(n, -1));\n vector<vector<int>> dp2(n, vector<int>(n, -1));\n vector<vector<int>> dp3(n, vector<int>(n, -1));\n \n int a = solve(2, n - 1, nums[0] + nums[1], nums, dp1);\n int b = solve(0, n - 3, nums[n - 1] + nums[n - 2], nums, dp2);\n int c = solve(1, n - 2, nums[0] + nums[n - 1], nums, dp3);\n \n return 1 + max({a, b, c});\n }\n};\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
simple java dp solution | bottom-up | tabulation
|
simple-java-dp-solution-bottom-up-tabula-tsr6
|
\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\n public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {\n\n int n = nums.length;\n long[][][] dp = new long[n + 1][n + 1][4];\n
|
guptasheenam1510
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T16:10:50.204803+00:00
|
2024-02-17T17:16:35.310931+00:00
| 447 | false |
\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {\n\n int n = nums.length;\n long[][][] dp = new long[n + 1][n + 1][4];\n \n long max = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {\n for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) {\n dp[i][j][1] = 0;\n dp[i][j][2] = 0;\n dp[i][j][3] = 0;\n }\n }\n\n long sum1 = nums[n - 1] + nums[n - 2];\n long sum2 = nums[0] + nums[1];\n long sum3 = nums[0] + nums[n - 1];\n\n for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {\n long sum = nums[i] + nums[i + 1];\n if (sum == sum1) {\n dp[i][i + 1][1] = 1;\n }\n if (sum == sum2) {\n dp[i][i + 1][2] = 1;\n }\n if (sum == sum3) {\n dp[i][i + 1][3] = 1;\n }\n }\n\n for (int l = 3; l <= n; l++) {\n int start = 0;\n while (start <= n - l) {\n int end = start + l - 1;\n\n long sum = nums[start] + nums[start + 1];\n if (sum == sum1) {\n dp[start][end][1] = Math.max(dp[start][end][1], 1 + dp[start + 2][end][1]);\n }\n if (sum == sum2) {\n dp[start][end][2] = Math.max(dp[start][end][2], 1 + dp[start + 2][end][2]);\n }\n if (sum == sum3) {\n dp[start][end][3] = Math.max(dp[start][end][3], 1 + dp[start + 2][end][3]);\n }\n\n sum = nums[end - 1] + nums[end];\n if (sum == sum1) {\n dp[start][end][1] = Math.max(dp[start][end][1], 1 + dp[start][end - 2][1]);\n }\n if (sum == sum2) {\n dp[start][end][2] = Math.max(dp[start][end][2], 1 + dp[start][end - 2][2]);\n }\n if (sum == sum3) {\n dp[start][end][3] = Math.max(dp[start][end][3], 1 + dp[start][end - 2][3]);\n }\n\n sum = nums[start] + nums[end];\n if (sum == sum1) {\n dp[start][end][1] = Math.max(dp[start][end][1], 1 + dp[start + 1][end - 1][1]);\n }\n if (sum == sum2) {\n dp[start][end][2] = Math.max(dp[start][end][2], 1 + dp[start + 1][end - 1][2]);\n }\n if (sum == sum3) {\n dp[start][end][3] = Math.max(dp[start][end][3], 1 + dp[start + 1][end - 1][3]);\n }\n\n start++;\n }\n }\n\n long ans = Math.max(Math.max(dp[0][n - 1][1], dp[0][n - 1][2]), dp[0][n - 1][3]);\n return (int) ans;\n }\n}\n\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Java']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
🔥DP || ⚡Memoization || ✅Clean Code
|
dp-memoization-clean-code-by-adish_21-rwot
|
Connect with me on LinkedIN : https://www.linkedin.com/in/aditya-jhunjhunwala-51b586195/\n\n# Complexity\n\n- Time complexity:\nO(n * n)\n\n- Space complexity:\
|
aDish_21
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T16:02:38.217398+00:00
|
2024-02-17T16:29:25.596157+00:00
| 464 | false |
## Connect with me on LinkedIN : https://www.linkedin.com/in/aditya-jhunjhunwala-51b586195/\n\n# Complexity\n```\n- Time complexity:\nO(n * n)\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(n * n)\n```\n\n# Code\n## Please Upvote if it helps\uD83E\uDD17\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int dp[2001][2001];\n int helper(int i, int j, vector<int>& nums, int score){\n if(i >= j)\n return 0;\n if(dp[i][j] != -1)\n return dp[i][j];\n int maxi = 0;\n if(nums[i] + nums[j] == score)\n maxi = max(maxi, 1 + helper(i + 1, j - 1, nums, score));\n if(nums[i] + nums[i + 1] == score)\n maxi = max(maxi, 1 + helper(i + 2, j, nums, score));\n if(nums[j] + nums[j - 1] == score)\n maxi = max(maxi, 1 + helper(i, j - 2, nums, score));\n return dp[i][j] = maxi;\n \n }\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n = nums.size(), ans = 0;\n memset(dp, -1, sizeof(dp));\n ans = max({helper(2, n - 1, nums, nums[0] + nums[1]), helper(0, n - 3, nums, nums[n - 1] + nums[n - 2]), helper(1, n - 2, nums, nums[0] + nums[n - 1])});\n return ans + 1;\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
🔥 Maximum Number of Operations with the Same Score II | Optimized DP Solution 💡
|
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-sa-m32o
|
IntuitionThe problem asks us to maximize the number of operations where pairs of elements in the array sum up to a specific value. To achieve this, we need to e
|
rshohruh
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-03T05:00:31.017666+00:00
|
2025-01-03T05:00:31.017666+00:00
| 55 | false |
### Intuition
The problem asks us to maximize the number of operations where pairs of elements in the array sum up to a specific value. To achieve this, we need to explore potential pair combinations and track valid operations efficiently. This can be solved using recursion with memoization (dynamic programming) to avoid redundant computations.
---
### Approach
1. **Recursive Function:**
- Define a function `rec(l, r, sm)` where:
- $$l$$: Left pointer.
- $$r$$: Right pointer.
- $$sm$$: Target sum for the current operation.
- Base cases:
- If $$l \geq r$$, no more pairs can be formed, return $$0$$.
- If the result for $$dp[l][r]$$ is already computed, return it.
2. **Operations:**
- Check pairs that satisfy the sum $$sm$$:
- Pair the first two elements: `nums[l] + nums[l+1]`.
- Pair the first and last elements: `nums[l] + nums[r]`.
- Pair the last two elements: `nums[r-1] + nums[r]`.
- Recur for the remaining array after removing the pair.
3. **Optimization with Memoization:**
- Use a 2D `dp` table to store intermediate results and avoid redundant calculations.
4. **Initial Calls:**
- Try all possible sums formed by the first two, first and last, or last two elements as initial target sums.
5. **Result:**
- The final answer is the maximum number of operations across all possible initial target sums.
---
### Complexity
- **Time Complexity:**
- $$O(n^2)$$: We solve at most $$O(n^2)$$ subproblems, each taking $$O(1)$$.
- **Space Complexity:**
- $$O(n^2)$$: Space required for the 2D `dp` table and recursion stack.
---
### Code
```cpp
class Solution {
public:
int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
vector dp(n, vector(n, 0)); // DP table
vector t(n, vector(n, 0)); // Temporary table
// Recursive function
auto rec = [&](auto&& rec, int l, int r, int sm) -> int {
if (l == 0 && r == n - 1) dp = t; // Reset DP for new target sum
if (l >= r) return 0; // Base case: no pairs possible
if (dp[l][r]) return dp[l][r]; // Use memoized result
int mx = 0; // Maximum operations
if (nums[l] + nums[l + 1] == sm)
mx = max(mx, rec(rec, l + 2, r, sm) + 1);
if (nums[l] + nums[r] == sm)
mx = max(mx, rec(rec, l + 1, r - 1, sm) + 1);
if (nums[r] + nums[r - 1] == sm)
mx = max(mx, rec(rec, l, r - 2, sm) + 1);
return dp[l][r] = mx; // Store result
};
// Try all possible initial target sums
int ans = max({
rec(rec, 0, n - 1, nums[0] + nums[1]),
rec(rec, 0, n - 1, nums[0] + nums[n - 1]),
rec(rec, 0, n - 1, nums[n - 1] + nums[n - 2])
});
return ans;
}
};
```
---
### Example
**Input:**
`nums = [3, 2, 3, 4, 3]`
**Execution:**
- Possible target sums are:
- $$nums[0] + nums[1] = 5$$.
- $$nums[0] + nums[4] = 6$$.
- $$nums[3] + nums[4] = 7$$.
- For each target sum:
- Use recursive function `rec` to calculate the maximum operations.
- The maximum number of operations is returned.
**Output:**
```plaintext
2
```
---
### Edge Cases
1. **Single Element:**
`nums = [1]` → `0` (No pairs possible).
2. **All Elements Are Equal:**
`nums = [2, 2, 2, 2]` → Maximum pairs depend on the sum of two elements.
3. **No Valid Pairs:**
`nums = [1, 3, 5]` → `0` (No pairs matching any target sum).
---
### Key Insights
- Efficiently handle pair combinations using recursion and memoization.
- Test different initial target sums for the most optimal solution.
- Ensure edge cases are covered for robustness.
| 2 | 0 |
['Array', 'Two Pointers', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
c++ solution
|
c-solution-by-dilipsuthar60-zsux
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int n;\n int dp[2005][2005];\n int find(vector<int>&nums,int sum,int i,int j)\n {\n if(i>=j) return 0;\n
|
dilipsuthar17
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-25T10:45:35.574901+00:00
|
2024-02-25T10:45:35.574934+00:00
| 22 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int n;\n int dp[2005][2005];\n int find(vector<int>&nums,int sum,int i,int j)\n {\n if(i>=j) return 0;\n if(dp[i][j]!=-1) return dp[i][j];\n int ans=0;\n if(nums[i]+nums[i+1]==sum)\n {\n ans=max(ans,1+find(nums,sum,i+2,j));\n }\n if(nums[i]+nums[j]==sum)\n {\n ans=max(ans,1+find(nums,sum,i+1,j-1));\n }\n if(nums[j]+nums[j-1]==sum)\n {\n ans=max(ans,1+find(nums,sum,i,j-2));\n }\n return dp[i][j] = ans;\n }\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n n=nums.size();\n memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp));\n int firstOperation=find(nums,nums[0]+nums[1],2,n-1);\n memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp));\n int secondOperation=find(nums,nums[n-1]+nums[n-2],0,n-3);\n memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp));\n int thirdOperation=find(nums,nums[0]+nums[n-1],1,n-2);\n return 1+max({firstOperation,secondOperation,thirdOperation});\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C', 'C++']
| 1 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Easy C++ Solution || (Using DP) ✅✅
|
easy-c-solution-using-dp-by-abhi242-simm
|
Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int helper(vector<int> &nums,int i,int j,int prev,int n,vector<vector<int>> &dp){\n if(i>=j){\n return
|
Abhi242
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-19T06:52:55.654109+00:00
|
2024-02-19T07:12:51.500009+00:00
| 26 | false |
# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int helper(vector<int> &nums,int i,int j,int prev,int n,vector<vector<int>> &dp){\n if(i>=j){\n return 0;\n }\n int ans=0;\n if(dp[i][j]!=-1){\n return dp[i][j];\n }\n if((nums[i]+nums[j])==prev || prev==-1){\n ans=max(ans,1+helper(nums,i+1,j-1,nums[i]+nums[j],n,dp));\n }\n if(i+2<=j){\n if((nums[i]+nums[i+1])==prev || prev==-1){\n ans=max(ans,1+helper(nums,i+2,j,nums[i]+nums[i+1],n,dp));\n }\n }\n if(j-2>=i){\n if((nums[j]+nums[j-1])==prev || prev==-1){\n ans=max(ans,1+helper(nums,i,j-2,nums[j]+nums[j-1],n,dp));\n }\n }\n return dp[i][j]=ans;\n }\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n=nums.size();\n vector<vector<int>> dp(n,vector<int>(n,-1));\n return helper(nums,0,n-1,-1,n,dp);\n }\n};\n```\n# **PLEASE UPVOTE IF IT HELPED** \u2B06\uFE0F\n\n#\n\n
| 2 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Bottom-up DP (tabulation)
|
bottom-up-dp-tabulation-by-nikhilreddyde-erm1
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \nTabulation\n\n# Complex
|
nikhilreddydev
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-18T06:37:00.615821+00:00
|
2024-02-18T06:37:00.615852+00:00
| 56 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nTabulation\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(n^2)$$\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$$O(n^2)$$\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n = size(nums);\n set<int> s{nums[0] + nums[1], nums[0] + nums[n - 1], nums[n - 2] + nums[n - 1]};\n int res{};\n for (auto &v: s) {\n vector<vector<int>> dp(n + 1, vector<int>(n + 1));\n for (int i = 2; i <= n; ++i) {\n for (int l = 0, r = l + i - 1; r < n; ++l, ++r) {\n if (nums[l] + nums[l + 1] == v)\n dp[i][l] = max(dp[i][l], 1 + dp[i - 2][l + 2]);\n if (nums[l] + nums[r] == v)\n dp[i][l] = max(dp[i][l], 1 + dp[i - 2][l + 1]);\n if (nums[r - 1] + nums[r] == v)\n dp[i][l] = max(dp[i][l], 1 + dp[i - 2][l]);\n }\n }\n res = max(res, dp[n][0]);\n }\n\n return res;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C++']
| 1 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Easy c++ DP solution
|
easy-c-dp-solution-by-ak_invader-n7sk
|
Intuition\n\n\n\n# Approach\n\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\no(n)^2\n\n- Space complexity:\n Add your space complexity here, e.g. O(n) \no(n)^2\n\n# Cod
|
Ak_invader
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T22:46:39.031356+00:00
|
2024-02-17T22:46:39.031380+00:00
| 135 | false |
# Intuition\n\n\n\n# Approach\n\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\no(n)^2\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\no(n)^2\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int dp[2001][2001];\n\n int solve(vector<int>& nums, int i, int j, int s) {\n \n if (i >= j) return 0;\n\n if (dp[i][j] != -1) return dp[i][j];\n\n int a = 0, b = 0, c = 0;\n\n if ((nums[i] + nums[i + 1] == s || s == -1)) {\n a = solve(nums, i + 2, j, nums[i] + nums[i + 1]) + 1;\n }\n\n if ((nums[j] + nums[j - 1] == s || s == -1)) {\n b = solve(nums, i, j - 2, nums[j] + nums[j - 1]) + 1;\n }\n\n if ((nums[i] + nums[j] == s || s == -1)) {\n c = solve(nums, i + 1, j - 1, nums[i] + nums[j]) + 1;\n }\n\n return dp[i][j] = max(a, max(b, c));\n }\n\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n memset(dp, -1, sizeof(dp));\n int n = nums.size();\n\n return solve(nums, 0, n - 1, -1);\n }\n};\n\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
aao DP KARE Hindi me || DP EASY
|
aao-dp-kare-hindi-me-dp-easy-by-aman028-iv1y
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \ndekho isme sum kitne pair ka equal h count karna h\niske liye 3 tarah ka kaam kar skate
|
Aman028
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T21:07:22.139307+00:00
|
2024-02-18T10:17:13.638162+00:00
| 40 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\ndekho isme sum kitne pair ka equal h count karna h\n**iske liye** 3 tarah ka kaam kar skate h\n1.)pahle 2 ka sum\n2.)last 2 ka sum\n3.)pahle and last ka sum\n\nmaan lo pahle 2 ka sum liye uske baad sum maan lo last 2 k equal hua fir aage jaake last and first k equal hua.....aise chalte jaayega hume specifically nhi pata ki kon se 2 element ka sum equal hoga \niske liye hume all possible path try karna hoga \n**ALL POSSIBLE PATH ka matlab h RECURSION**\n\nAB SAMGH GAYE HONGE KI KYU RECURSION LAG RAHA H\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1.)SABSE PAHLE HUM FIRST AND SECOND KA SUM K LIYE MAXIMUM PAIR KHOZUNGA\n2.)FIR USKE BAAD HUM FIRST AND LAST KA SUM K LIYE MAXIMUM PAIR KHOZENGE\n3.)FIR HUM USKE BAAD LAST 2 KA SUM K LIYE MAXIMUM PAIR KHOZENGE\nJO MAXIMUM PAIR DENGE WAHI ANSWER.\n\n**Ab hum isko kaise code likhenge**\n- hum ek start index lenge jo 0 se hoga\n- hum ek end index lenge jo last index se start hoga\n- uske baad hum ek karke 3 k liye recursive call karenge\n- **ab recursion function me hum kya likhnege code me dekhte h**\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n private:\n int solve(vector<int>&nums,int start,int end,int sum,vector<vector<int>>&dp)\n {\n //agar start bada h end se toh hum 0 return karenge\n if(start>=end)\n {\n return 0;\n }\n //memoization\n if(dp[start][end]!=-1)\n {\n return dp[start][end];\n }\n \n //first 2 sum k liye\n int aage=0;\n if(nums[start]+nums[start+1]==sum)\n {\n //agar sum k equal aata h to start ko jaha h waha se 2 \n //aage badha do\n aage=1+solve(nums,start+2,end,sum,dp);\n }\n\n //last 2 sum k liye\n int piche=0;\n if(nums[end]+nums[end-1]==sum)\n {\n //agar sum k equal aata h to hum end ko end-2 shift kar \n //denge\n piche=1+solve(nums,start,end-2,sum,dp);\n }\n \n //aage piche elements ka sum k liye\n int aagpic=0;\n if(nums[start]+nums[end]==sum)\n {\n //agar eual h to start ko ek aage badha do and end ko ek \n //piche\n aagpic=1+solve(nums,start+1,end-1,sum,dp);\n }\n \n //teeno me se jo maximum pair dega woh answer.\n return dp[start][end]=max(aage,max(piche,aagpic));\n }\npublic:\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n=nums.size();\n //agr array me 2 hi element h toh 1 hi pair bana toh answer 1\n if(n==2)\n {\n return 1;\n }\n int start=0;\n int end=n-1;\n \n //vector for memoization\n vector<vector<int>>dp(n,vector<int>(n,-1));\n //first two elements ka sum\n int sum1=nums[0]+nums[1];\n //function call first 2 ka sum k liye\n int ans1=solve(nums,start,end,sum1,dp);\n\n \n //vector for memoization\n vector<vector<int>>dpp(n,vector<int>(n,-1));\n //first and last element ka sum\n int sum2=nums[0]+nums[n-1];\n //function call first and last element ka sum k liye\n int ans2=solve(nums,start,end,sum2,dpp);\n \n //vector for memoization\n vector<vector<int>>dppp(n,vector<int>(n,-1));\n //last two elements ka sum\n int sum3=nums[n-1]+nums[n-2];\n //function call last 2 element ka sum k liye\n int ans3=solve(nums,start,end,sum3,dppp);\n \n //max teeno me se!!\n return max(ans1,max(ans2,ans3));\n }\n};\n```\n\n\n
| 2 | 0 |
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 1 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Easiest Explaination (You Won't Regret) Line by Line
|
easiest-explaination-you-wont-regret-lin-fl5f
|
IntuitionAs given in the question we have to perform the operation till the sum is same for all operation .Now in starting we have 3 choices
delete the first tw
|
unvisitedNode_01
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T19:35:32.991268+00:00
|
2025-03-01T12:02:33.737795+00:00
| 196 | false |
# Intuition
#### As given in the question we have to perform the operation till the sum is same for all operation .
##### Now in starting we have 3 choices
1. delete the first two ,sum will be nums[0]+nums[1];
2. delete the last two , sum will be nums[n-1]+nums[n-2]
3. delete the first one and last one ,sum will be nums[0]+nums[n-1]
### Now you must have to perform 1 of the above 3 operations at starting
##### so there are only 3 values of sum are possible
###### Now try one by one for all 3 values,continue till the condition remains satisfied or starting<ending(as all values will be deleted if starting==ending or starting>ending),then at last return max of all three possiblilies +1
###### +1(as we have already performed one operation during sum selection)
# Approach
##### READ INTUTION ,YOU WILL UNDERSTAND ALL OF IT
###### try all sum possibilities as i have done in the main then return max of all three posibilities +1
In Recursion:-
###### There will be four parameters starting index,ending index,nums,sum value
If(s==e)return 0 as all array is traversed
Initialize the variable c=0 to count the operations
Then try all three posibilities one by one and at each call add 1 to c (1 operation completed)
Also i have added checks at each rec call to check weather the remaining array have sufficient elements to perform operations.
Now at last to avoid overlapping sub-problems I have declared 2d dp(two parameters are changing starting and endind index) set all values to -1 initially.
Initialized it with the max possible size of starting and ending index.
Now at each call before returning I saved that ans to my dp array.
At each rec call I will check weather i have solved it previously if yes then no need to solve furthur.
# Complexity
- Time complexity: o(n^2)
-Each recursive call reduces the size of the subproblem, and there are a constant number of recursive calls. Therefore, the time complexity of each recursive call is O(1).
There are a total of n^2 subproblems (since there are two parameters s and e ranging from 0 to n-1). For each subproblem, the solution is computed in O(1) time. Hence, the overall time complexity is O(n^2).
- Space complexity: o(n)
# Code
```
class Solution {
public:
int t[2001][2001];
int solve(int s,int e,vector<int>&nums,int sum){
if(s>=e){
return 0;
}
if(t[s][e]!=-1){
return t[s][e];
}
int c=0;
if(nums[s]+nums[e]==sum){
c=1+solve(s+1,e-1,nums,sum);
}
if(s+2<=e && nums[s]+nums[s+1]==sum){
c=max(c,solve(s+2,e,nums,sum)+1);
}
if(e-2>=s&& nums[e]+nums[e-1]==sum){
c=max(c,solve(s,e-2,nums,sum)+1);
}
return t[s][e]=c;
}
int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {
int n=nums.size();
memset(t,-1,sizeof(t));
int case1=nums[0]+nums[1]; // CASE 1
int k=solve(2,n-1,nums,case1);
int case2=nums[n-1]+nums[n-2]; // CASE 2
int l=solve(0,n-3,nums,case2);
int case3=nums[0]+nums[n-1]; // CASE 3
int p=solve(1,n-2,nums,case3);
return 1+max({k,l,p});
}
};
```
UPVOTE :)
| 2 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 1 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Direct solution, Dynamic Programming, O(n^2)
|
direct-solution-dynamic-programming-on2-blai2
|
Intuition\nUse DP.\n\n# Approach\nUse DP. At first create a dictionary to keep the intermediate results:\n\nvar dic = new Dictionary<(int index0, int index1), i
|
igor0
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T16:59:35.627632+00:00
|
2024-02-17T16:59:35.627668+00:00
| 78 | false |
# Intuition\nUse DP.\n\n# Approach\nUse DP. At first create a dictionary to keep the intermediate results:\n```\nvar dic = new Dictionary<(int index0, int index1), int>();\n```\nThe key in this dictionary is a tuple `(int index0, int index1)`, where `index0` and `index1` are the first and the last considered indexes in array `nums`.\nAdd a method for DP:\n```\nprivate int MaxOperations((int index0, int index1) key, Dictionary<(int index0, int index1), int> dic, int sum, int[] nums)\n```\nIn this method\n- `(int index0, int index1) key` is the key for the dictionary\n- `Dictionary<(int index0, int index1), int> dic` is the dictionary to keep the intermediate results\n- `int sum` is the sum of 2 items\n- `int[] nums` is the initial array\nCall this method recursively.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n$$O(n^2)$$\n\n- Space complexity:\n$$O(n^2)$$\n\n# Code\n```\npublic class Solution {\n public int MaxOperations(int[] nums) {\n var dic = new Dictionary<(int index0, int index1), int>();\n var sum = nums[0] + nums[1];\n var rs0 = 1 + MaxOperations((2, nums.Length - 1), dic, sum, nums);\n sum = nums[0] + nums[nums.Length - 1];\n var rs1 = 1 + MaxOperations((1, nums.Length - 2), dic, sum, nums);\n sum = nums[nums.Length - 2] + nums[nums.Length - 1];\n var rs2 = 1 + MaxOperations((0, nums.Length - 3), dic, sum, nums);\n var rs = Math.Max(Math.Max(rs0, rs1), rs2);\n return rs;\n }\n private int MaxOperations((int index0, int index1) key, Dictionary<(int index0, int index1), int> dic, int sum, int[] nums)\n {\n if (key.index1 <= key.index0) return 0;\n if (dic.ContainsKey(key)) return dic[key];\n var rs = 0;\n if (nums[key.index0] + nums[key.index0 + 1] == sum)\n {\n rs = Math.Max(rs, 1 + MaxOperations((key.index0 + 2, key.index1), dic, sum, nums));\n }\n if (nums[key.index0] + nums[key.index1] == sum)\n {\n rs = Math.Max(rs, 1 + MaxOperations((key.index0 + 1, key.index1 - 1), dic, sum, nums));\n }\n if (nums[key.index1 - 1] + nums[key.index1] == sum)\n {\n rs = Math.Max(rs, 1 + MaxOperations((key.index0, key.index1 - 2), dic, sum, nums));\n }\n if (!dic.ContainsKey(key)) dic.Add(key, rs);\n return rs;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C#']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
C++ || Easy Solution using DP
|
c-easy-solution-using-dp-by-khwaja_abdul-b3rf
|
Intuition\n\nWe can see that once we pick a sum, all operations after that must match that sum. We only have 3 initial options for the operation and so we only
|
Khwaja_Abdul_Samad
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T16:32:37.385352+00:00
|
2024-02-17T16:32:37.385388+00:00
| 108 | false |
# Intuition\n\nWe can see that once we pick a sum, all operations after that must match that sum. We only have 3 initial options for the operation and so we only have 3 possible sums.\n\nGiven an array and a target sum, we can test all three possibilities for the next operation and then recursively solve the remaining array after the deletions. For a particular starting sum, the inputs to the recursive call which varry are only the starting and ending points of the remaining array, so we can memoize this result in n^2 memory and time.\n\n# Approach\nCalculate the 3 possible sums and then recursively check the most operations that can be done with that particular sum.\n\n# Complexity\nTime complexity: O(n^2) \nSpace complexity: O(n^2)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n \n int n , sum = 0;\n \n int Solve(int i , int j , vector<int>& nums , vector<vector<int>> &dp){\n if(i>= j)\n return 0;\n if(dp[i][j] != -1)\n return dp[i][j];\n \n int ans = 0 ;\n if(sum == nums[i]+nums[i+1])\n ans = max(ans, 1 + Solve(i+2, j , nums, dp));\n if(sum == nums[i]+nums[j])\n ans = max(ans, 1 + Solve(i+1, j-1 , nums, dp));\n if(sum == nums[j-1]+nums[j])\n ans = max(ans, 1 + Solve(i, j-2 , nums, dp));\n \n return dp[i][j] = ans;\n \n }\n \n \npublic:\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n n = nums.size() ;\n vector<vector<int>> dp(n, vector<int> (n , -1));\n \n sum = nums[0]+nums[1] ;\n int op1 = Solve(2, n-1, nums, dp);\n \n sum = nums[0]+nums[n-1] ;\n dp = vector<vector<int>> (n, vector<int> (n, -1));\n int op2 = Solve(1, n-2, nums, dp );\n \n sum = nums[n-2]+nums[n-1] ;\n dp = vector<vector<int>> (n, vector<int> (n, -1));\n int op3 = Solve(0, n-3, nums, dp);\n \n return 1+max(op1 , max(op2 , op3));\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Video Explanation (Optimising brute force solution step by step)
|
video-explanation-optimising-brute-force-d14h
|
Explanation\n\nClick here for the video\n\n# Code\n\nint dp[2001][2001];\n\nclass Solution {\n \n vector<int> arr;\n \n int maxOperations (int l, in
|
codingmohan
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T16:30:53.363451+00:00
|
2024-02-17T16:30:53.363470+00:00
| 50 | false |
# Explanation\n\n[Click here for the video](https://youtu.be/9iYY33fuLSo)\n\n# Code\n```\nint dp[2001][2001];\n\nclass Solution {\n \n vector<int> arr;\n \n int maxOperations (int l, int r, const int target) {\n if (l >= r) return 0;\n \n int &ans = dp[l][r];\n if (ans != -1) return ans;\n \n ans = 0;\n if (arr[l]+arr[r] == target) ans = max (ans, 1+maxOperations(l+1, r-1, target));\n if (arr[l]+arr[l+1] == target) ans = max (ans, 1+maxOperations(l+2, r, target));\n if (arr[r]+arr[r-1] == target) ans = max (ans, 1+maxOperations(l, r-2, target));\n \n return ans;\n }\n \n int MaxOperationsWithSum (int sum) {\n memset(dp, -1, sizeof(dp));\n return maxOperations (0, arr.size()-1, sum);\n }\n \npublic:\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n arr = nums;\n int n = arr.size();\n \n if (n == 1) return 0;\n \n return max ({\n MaxOperationsWithSum(arr[0] + arr[1]),\n MaxOperationsWithSum(arr[n-1] + arr[n-2]),\n MaxOperationsWithSum(arr[0] + arr[n-1])\n });\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
simple solution
|
simple-solution-by-vinay_kumar_swami-8uxc
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
vinay_kumar_swami
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T16:27:24.195050+00:00
|
2024-02-17T16:27:24.195109+00:00
| 28 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int solve(int i, int j, int sum, vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& dp) {\n if (i >= j) return 0;\n if (dp[i][j] != -1) return dp[i][j];\n \n int a = 0, b = 0, c = 0;\n \n if (i + 1 <= j && nums[i] + nums[i + 1] == sum) {\n a = 1 + solve(i + 2, j, sum, nums, dp);\n }\n if (j - 1 >= i && nums[j] + nums[j - 1] == sum) {\n b = 1 + solve(i, j - 2, sum, nums, dp);\n }\n if (nums[i] + nums[j] == sum) {\n c = 1 + solve(i + 1, j - 1, sum, nums, dp);\n }\n \n return dp[i][j] = max({a, b, c});\n }\n \n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n = nums.size();\n \n vector<vector<int>> dp1(n, vector<int>(n, -1));\n vector<vector<int>> dp2(n, vector<int>(n, -1));\n vector<vector<int>> dp3(n, vector<int>(n, -1));\n \n int a = solve(2, n - 1, nums[0] + nums[1], nums, dp1);\n int b = solve(0, n - 3, nums[n - 1] + nums[n - 2], nums, dp2);\n int c = solve(1, n - 2, nums[0] + nums[n - 1], nums, dp3);\n \n return 1 + max({a, b, c});\n }\n};\n\n\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
[C++] Recursion + Memoization || Easy to understand
|
c-recursion-memoization-easy-to-understa-8kot
|
Recursion (TLE)\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n if(nums.size() == 2) return 1;\n int n = nums.size();\n
|
devanshsingh2222
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T16:18:38.024525+00:00
|
2024-02-17T16:19:30.066658+00:00
| 87 | false |
# Recursion (TLE)\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n if(nums.size() == 2) return 1;\n int n = nums.size();\n int ans = solve(nums , n , nums[0]+nums[1]);\n ans = max(ans , solve(nums , n , nums[0]+nums[n-1]));\n ans = max(ans , solve(nums , n , nums[n-1]+nums[n-2]));\n return ans;\n }\n int solve(vector<int>& nums , int n , int target){\n int ans = helper(nums , 0 , n-1 , target);\n return ans;\n }\n int helper(vector<int>& nums , int l , int r , int target){\n if(l >= r) return 0;\n int ans = 0;\n if(nums[l]+nums[r] == target){\n ans = max(ans , 1 + helper(nums , l+1 , r-1 , target));\n }\n if(nums[l]+nums[l+1] == target){\n ans = max(ans , 1 + helper(nums , l+2 , r , target));\n }\n if(nums[r]+nums[r-1] == target){\n ans = max(ans , 1 + helper(nums , l , r-2 , target));\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\n\n# Recursion + Memoization\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n if(nums.size() == 2) return 1;\n int n = nums.size();\n int ans = solve(nums , n , nums[0]+nums[1]);\n ans = max(ans , solve(nums , n , nums[0]+nums[n-1]));\n ans = max(ans , solve(nums , n , nums[n-1]+nums[n-2]));\n return ans;\n }\n int solve(vector<int>& nums , int n , int target){\n vector<vector<int>> dp(n , vector<int>(n , -1));\n int ans = helper(nums , 0 , n-1 , target , dp);\n return ans;\n }\n int helper(vector<int>& nums , int l , int r , int target , vector<vector<int>>& dp){\n if(l >= r) return 0;\n if(dp[l][r] != -1) return dp[l][r];\n int ans = 0;\n if(nums[l]+nums[r] == target){\n ans = max(ans , 1 + helper(nums , l+1 , r-1 , target , dp));\n }\n if(nums[l]+nums[l+1] == target){\n ans = max(ans , 1 + helper(nums , l+2 , r , target , dp));\n }\n if(nums[r]+nums[r-1] == target){\n ans = max(ans , 1 + helper(nums , l , r-2 , target , dp));\n }\n return dp[l][r] = ans;\n }\n};\n```\n# Please upvote If you find this helpfull
| 2 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
[Python3] DFS + Cache Solution, Clean & Concese
|
python3-dfs-cache-solution-clean-concese-msdx
|
Approach\nUse depth-first search and try the three possible score (first two elements of nums, last two elements of nums, first and last elements of nums as the
|
xil899
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T16:02:29.758309+00:00
|
2024-02-18T00:54:30.206270+00:00
| 202 | false |
# Approach\nUse depth-first search and try the three possible score (first two elements of `nums`, last two elements of `nums`, first and last elements of `nums` as the **score**.\n\nNote that this approach is essentially equivalent to dynamic programming.\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maxOperations(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n @cache\n def dfs(start, end, score):\n if end - start + 1 < 2:\n return 0\n ans = 0\n if nums[start] + nums[start + 1] == score:\n ans = max(ans, 1 + dfs(start + 2, end, score))\n if nums[end - 1] + nums[end] == score:\n ans = max(ans, 1 + dfs(start, end - 2, score))\n if nums[start] + nums[end] == score:\n ans = max(ans, 1 + dfs(start + 1, end - 1, score))\n return ans\n n = len(nums)\n return max(dfs(0, n - 1, nums[0] + nums[1]), dfs(0, n - 1, nums[-1] + nums[-2]), dfs(0, n - 1, nums[0] + nums[-1]))\n```
| 2 | 1 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Depth-First Search', 'Python3']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Easy Choice Based DP
|
easy-choice-based-dp-by-_sajid-hgod
|
\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\n private int solve(int arr[], int left, int right, int score, Integer dp[][]) {\n if (left >= right) return 0;\n
|
_sajid
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T16:02:24.621136+00:00
|
2024-02-17T16:02:24.621170+00:00
| 108 | false |
\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n private int solve(int arr[], int left, int right, int score, Integer dp[][]) {\n if (left >= right) return 0;\n \n if (dp[left][right] != null) return dp[left][right];\n \n int result = 0;\n \n //we have 3 choices\n \n if (arr[left] + arr[left + 1] == score)\n //chose first two\n result = 1 + solve(arr, left + 2, right, score, dp);\n \n if (arr[right] + arr[right - 1] == score)\n //chose last two\n result = Math.max(\n result,\n 1 + solve(arr, left, right - 2, score, dp)\n );\n \n if (arr[left] + arr[right] == score)\n //chose left and right\n result = Math.max(\n result,\n 1 + solve(arr, left + 1, right - 1, score, dp)\n );\n \n return dp[left][right] = result;\n }\n \n public int maxOperations(int[] arr) {\n int len = arr.length;\n \n //we have 3 different choise to start from, each choice will give different score to start with\n int score1 = arr[0] + arr[1]; //chose first two\n int score2 = arr[len - 1] + arr[len - 2]; //chose last two\n int score3 = arr[0] + arr[len - 1]; //chose first and last\n \n \n //return the result of choice which produces maximum result\n int result =\n solve(arr, 0, len - 1, score1, new Integer[len][len]);\n \n result = Math.max(\n result,\n solve(arr, 0, len - 1, score2, new Integer[len][len])\n );\n \n result = Math.max(\n result,\n solve(arr, 0, len - 1, score3, new Integer[len][len])\n );\n \n return result;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Easy to Understand and Easy Approach 😊😊
|
easy-to-understand-and-easy-approach-by-wegka
|
ApproachThe given code is designed to find the maximum number of operations that can be performed by removing two numbers at a time from the list while maintain
|
patelaviral
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-04T19:21:44.293392+00:00
|
2025-03-04T19:21:44.293392+00:00
| 33 | false |
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
The given code is designed to find the maximum number of operations that can be performed by removing two numbers at a time from the list while maintaining a sum condition. The solution follows a recursive backtracking with memoization approach.
# Understanding the Problem
* We are given an array nums[], and in each operation, we remove two elements whose sum is either:
1. The sum from the first operation (if it's the first step, we choose any two elements freely).
2. The same sum from all subsequent operations.
* The goal is to maximize the number of such operations.
# Key Observations
1. Since we are allowed to remove any two elements, the brute-force solution would involve trying all possible pairs.
2. To optimize, the algorithm tries three possible pairs in each recursive call:
--> First two elements (nums[0] and nums[1])
--> Last two elements (nums[n-1] and nums[n-2])
--> First and last element (nums[0] and nums[n-1])
3. If removing a pair results in a valid sum, we recursively call the function on the remaining array.
4. Memoization (store) is used to avoid recomputation of previously seen states.
# Breakdown of the Algorithm
1. Convert nums[] into an ArrayList to facilitate removal operations.
2. Recursive function finder():
--> Base Case: If nums is empty or has less than 2 elements, return 0.
--> Check if the current state (nums + sum) is already computed in store.
--> Try the three possible valid pairs and recursively find the maximum operations.
--> Restore the original list after recursion (backtracking step).
--> Store the result in store to avoid recomputation.
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
HashMap<String, Integer> store;
public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {
ArrayList<Integer> collect = new ArrayList<>();
store = new HashMap<>();
for(int ele: nums){
collect.add(ele);
}
return finder(collect, 0);
}
public int finder(ArrayList<Integer> nums, int sum){
StringBuilder op = new StringBuilder();
op.append(nums).append("-").append(sum);
if(nums.isEmpty() || nums.size() < 2){
return 0;
}
if(store.containsKey(op.toString())){
return store.get(op.toString());
}
int ans = 0;
if(sum == 0 || nums.get(0)+nums.get(1) == sum){
int first0 = nums.get(0);
int first1 = nums.get(1);
nums.remove(0);nums.remove(0);
ans = Math.max(ans, finder(nums, first0+first1)+1);
nums.add(0, first0);nums.add(1, first1);
}
if(sum == 0 || nums.get(nums.size()-1)+nums.get(nums.size()-2) == sum){
int last0 = nums.get(nums.size()-1);
int last1 = nums.get(nums.size()-2);
nums.remove(nums.size()-1);
nums.remove(nums.size()-1);
ans = Math.max(ans, finder(nums, last0+last1)+1);
nums.add(last1);
nums.add(last0);
}
if(sum == 0 || nums.get(0)+nums.get(nums.size()-1) == sum){
int first = nums.get(0);
int last = nums.get(nums.size()-1);
nums.remove(nums.size()-1);
nums.remove(0);
ans = Math.max(ans, finder(nums, first+last)+1);
nums.add(0, first);
nums.add(last);
}
store.put(op.toString(), ans);
return ans;
}
}
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'Java']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Python Intuitive Top Down DP
|
python-intuitive-top-down-dp-by-safoan2-bivy
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
safoan2
|
NORMAL
|
2024-06-13T05:22:32.563155+00:00
|
2024-06-13T05:22:32.563208+00:00
| 72 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n**2)\n\n- Space complexity: O(n**2)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maxOperations(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n @lru_cache(None)\n def dfs(score, lo, hi):\n if lo >= hi:\n return 0\n\n maxOps1 = 1 + dfs(score, lo + 2, hi) if sum(nums[lo: lo + 2]) == score else 0\n maxOps2 = 1 + dfs(score, lo + 1, hi -1) if (nums[lo] + nums[hi]) == score else 0\n maxOps3 = 1 + dfs(score, lo, hi - 2) if sum(nums[hi-1:hi+1]) == score else 0\n\n return max(maxOps1, maxOps2, maxOps3)\n \n\n possibleScores = {sum(nums[:2]), nums[0] + nums[-1], sum(nums[-2:])}\n maxOps = -inf\n for score in possibleScores:\n maxOps = max(maxOps, dfs(score, 0, len(nums) - 1))\n \n return maxOps\n\n\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Clean Memoization Solution Beats 90 %
|
clean-memoization-solution-beats-90-by-d-dlha
|
\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\n public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {\n int n = nums.length;\n Integer[][] memo = new Integer[n + 1][n + 1];\n\
|
dhruvdangi03
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-26T06:32:34.624474+00:00
|
2024-02-26T06:32:34.624511+00:00
| 34 | false |
\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {\n int n = nums.length;\n Integer[][] memo = new Integer[n + 1][n + 1];\n\n return helper(nums, 0, n - 1, 0, memo);\n }\n\n int helper(int[] nums, int start, int end, int prev, Integer[][] memo){\n if(start >= end) return 0;\n if(memo[start][end] != null) return memo[start][end];\n\n int first = 0, last = 0, both = 0;\n\n if(nums[start] + nums[start +1] == prev || (start == 0 && end == nums.length -1)){\n first = 1 + helper(nums, start +2, end, nums[start] + nums[start +1], memo);\n }\n if(nums[end] + nums[end -1] == prev || (start == 0 && end == nums.length -1)){\n last = 1 + helper(nums, start, end -2, nums[end] + nums[end -1], memo);\n } \n if(nums[start] + nums[end] == prev || (start == 0 && end == nums.length -1)){\n both = 1 + helper(nums, start +1, end -1, nums[start] + nums[end], memo);\n }\n\n return memo[start][end] = Math.max(first, Math.max(both, last));\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'Java']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Easy Python DP solution using @cachedy
|
easy-python-dp-solution-using-cachedy-by-g8de
|
O(n^2) run time and space time since the cache is (i, j, scr) which are both bounded by n. \nn = len(nums)\nThe scr is bounded by 3 different answers so it is O
|
robert961
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-22T19:13:18.757623+00:00
|
2024-02-22T19:13:18.757650+00:00
| 42 | false |
O(n^2) run time and space time since the cache is (i, j, scr) which are both bounded by n. \nn = len(nums)\nThe scr is bounded by 3 different answers so it is O(3n^2) ~ O(n^2)\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maxOperations(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n\n @cache\n def dfs(l, r, scr):\n if l >= r: return 0\n\n ans = 0\n left = nums[l] + nums[l+1]\n right = nums[r] + nums[r-1]\n mid = nums[l] + nums[r]\n\n if scr==0 or scr == left:\n ans = max(ans, 1 + dfs(l+2, r, max(scr, left)))\n if scr == 0 or scr == right:\n ans = max(ans, 1 + dfs(l, r-2, max(scr, right)))\n if scr == 0 or scr == mid:\n ans = max(ans, 1+ dfs(l+1, r-1, max(scr, mid)))\n return ans\n\n return dfs(0, len(nums) -1, 0)\n \n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Python3']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
C++ || Easy solution using Recursion and Memoization || Faster than 100%
|
c-easy-solution-using-recursion-and-memo-58we
|
Intuition\n### Since we have 3 choices and have to choose the maximum therefore DP should be the first thought\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve th
|
Rohan1808
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-19T11:24:34.600510+00:00
|
2024-02-19T11:24:34.600540+00:00
| 17 | false |
# Intuition\n### Since we have 3 choices and have to choose the maximum therefore DP should be the first thought\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n1. Declare a 2D DP with size N*N.\n2. Call the solve function for all the 3 choices.\n3. In the function i>=j return 0 as we cannot choose 2 elements.\n4. Now check if we have already calculated or not, if yes then return it.\n5. Now check for all 3 choices if they are equal to sum call the solve function and update the ans.\n6. Store the ans in the dp to memoize.\n7. Return the ans as the maximum from all the choices.\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(N^2)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:O(N^2)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\nprivate:\n int solve(int i,int j,int sum,vector<int>& arr,vector<vector<int>>& dp)\n {\n //Base case\n if(i>=j)\n return 0;\n \n //Check if already calculated\n if(dp[i][j]!=-1)\n return dp[i][j];\n \n int ans=0;\n \n //First choice\n if(arr[i]+arr[i+1]==sum)\n ans=max(ans,solve(i+2,j,sum,arr,dp)+1);\n \n //Second choice\n if(arr[j]+arr[j-1]==sum)\n ans=max(ans,solve(i,j-2,sum,arr,dp)+1);\n \n //Third choice\n if(arr[i]+arr[j]==sum)\n ans=max(ans,solve(i+1,j-1,sum,arr,dp)+1);\n \n //Memoize\n return dp[i][j]=ans;\n \n }\npublic:\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) \n {\n int n=nums.size();\n \n //Declare the Dp\n vector<vector<int>> dp(n+2,vector<int>(n+2,-1));\n \n //Call the function for all the 3 choices\n int a=solve(2,n-1,nums[0]+nums[1],nums,dp);\n int b=solve(0,n-3,nums[n-1]+nums[n-2],nums,dp);\n int c=solve(1,n-2,nums[0]+nums[n-1],nums,dp);\n\n //Return the max of the answers\n return max(a,max(b,c))+1;\n }\n};\n```\n# Please Upvote if helps!!!
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
☑️✅Easy JAVA/C++ Solution || Beats 100%✅☑️
|
easy-javac-solution-beats-100-by-vritant-5cg6
|
PLEASE UPVOTE IF IT HELPED\n\n---\n\n\n# Intuition\nWe will use dynammic programming to solve this question.Just go through the code(explained in code) and you
|
vritant-goyal
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-19T07:16:02.673831+00:00
|
2024-02-19T07:16:51.397671+00:00
| 46 | false |
# **PLEASE UPVOTE IF IT HELPED**\n\n---\n\n\n# Intuition\nWe will use dynammic programming to solve this question.Just go through the code(explained in code) and you will understand it.\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:$$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:$$O(n^2)$$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n```Java []\nclass Solution {\n public int helper(int []nums,int l,int r,int score,int [][]dp){\n if(l>=r)return 0;\n if(dp[l][r]!=-1)return dp[l][r];\n int a1=0;\n int a2=0;\n int a3=0;\n if(nums[l]+nums[l+1]==score){\n a1=1+helper(nums,l+2,r,score,dp);\n }if(nums[l]+nums[r]==score){\n a2=1+helper(nums,l+1,r-1,score,dp);\n }if(nums[r]+nums[r-1]==score){\n a3=1+helper(nums,l,r-2,score,dp);\n }\n return dp[l][r]=Math.max(a1,Math.max(a2,a3));\n }\n public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {\n int n=nums.length;\n if(n<=1)return 0;\n int score1=nums[0]+nums[1];\n int score2=nums[n-1]+nums[n-2];\n int score3=nums[0]+nums[n-1];\n int [][]dp=new int[n][n];\n for(int []i:dp){\n Arrays.fill(i,-1);\n }\n int opr1=helper(nums,0,n-1,score1,dp);\n for(int []i:dp){\n Arrays.fill(i,-1);\n }\n int opr2=helper(nums,0,n-1,score2,dp);\n for(int []i:dp){\n Arrays.fill(i,-1);\n }\n int opr3=helper(nums,0,n-1,score3,dp);\n return Math.max(opr1,Math.max(opr2,opr3));\n }\n}\n```\n```C++ []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int helper(vector<int>& nums,int l,int r,int score,vector<vector<int>>&dp){\n if(l>=r)return 0;\n if(dp[l][r]!=-1)return dp[l][r];\n int a1=0;\n int a2=0;\n int a3=0;\n if(nums[l]+nums[l+1]==score){\n a1=1+helper(nums,l+2,r,score,dp);\n }if(nums[l]+nums[r]==score){\n a2=1+helper(nums,l+1,r-1,score,dp);\n }if(nums[r]+nums[r-1]==score){\n a3=1+helper(nums,l,r-2,score,dp);\n }\n return dp[l][r]=max(a1,max(a2,a3));\n }\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n=nums.size();\n if(n<=1)return 0;\n int score1=nums[0]+nums[1];\n int score2=nums[n-1]+nums[n-2];\n int score3=nums[0]+nums[n-1];\n\n vector<vector<int>> dp(n,vector<int>(n,-1));\n int opr1=helper(nums,0,n-1,score1,dp); \n \n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ //initializing 2d vector again with -1\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++){\n dp[i][j]=-1;\n }\n }\n int opr2=helper(nums,0,n-1,score2,dp);\n \n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ //initializing 2d vector again with -1\n for(int j=0;j<n;j++){\n dp[i][j]=-1;\n }\n }\n int opr3=helper(nums,0,n-1,score3,dp);\n return max(opr1,max(opr2,opr3));\n }\n};\n```\n# **PLEASE UPVOTE IF IT HELPED**\n\n---\n\n
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'C++', 'Java']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
With Memoization : DP : Java : Beats 50% : 136ms
|
with-memoization-dp-java-beats-50-136ms-e0bt4
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
abhinaik988
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-19T02:46:02.303759+00:00
|
2024-02-19T02:46:02.303776+00:00
| 35 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {\n //With Memoization : start [Beats 50%] [136ms]\n return withMemoization(nums);\n //With Memoization : end\n }\n \n public int withMemoization(int[] nums){\n int n = nums.length;\n int i = 0;\n int j = n-1;\n int sum1 = nums[i] + nums[i+1]; \n int sum2 = nums[i] + nums[j];\n int sum3 = nums[j-1] + nums[j];\n\n Integer[][] memo = new Integer[n+1][n+1];\n int ans = withMemo(i,j,nums,sum1,memo);\n\n memo = new Integer[n+1][n+1];\n ans = Math.max(ans, withMemo(i,j,nums,sum2,memo));\n\n memo = new Integer[n+1][n+1];\n ans = Math.max(ans, withMemo(i,j,nums,sum3,memo));\n\n return ans;\n }\n\n public int withMemo(int i,int j,int[] arr,int sum,Integer[][] memo){\n if(j <= i) return 0;\n if(memo[i][j] != null) return memo[i][j];\n\n int ans = 0;\n if(arr[i] + arr[j] == sum){\n ans = Math.max(ans,1 + withMemo(i+1,j-1,arr,sum,memo));\n }\n\n if(arr[i] + arr[i+1] == sum){\n ans = Math.max(ans,1 + withMemo(i+2,j,arr,sum,memo));\n }\n\n if(arr[j-1] + arr[j] == sum){\n ans = Math.max(ans,1 + withMemo(i,j-2,arr,sum,memo));\n }\n\n memo[i][j] = ans;\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization', 'Java']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
[C++] DP Top Down Vs. Bottom Up Solutions with 3 Base Cases, 105ms, 39.61MB
|
c-dp-top-down-vs-bottom-up-solutions-wit-vlv3
|
This is an interesting problem that, unlike its younger brother (solved here), gives us a lot of options at each turn, since we can:\n take the first 2 availabl
|
Ajna2
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-18T18:47:01.320531+00:00
|
2024-02-18T19:18:28.529314+00:00
| 20 | false |
This is an interesting problem that, unlike [its younger brother](https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-i/) ([solved here](https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-i/solutions/4748186/c-check-pair-by-pair-0ms-19-97mb/)), gives us a lot of options at each turn, since we can:\n* take the first 2 available values;\n* take the last 2 available values;\n* take the first and last available values.\n\nAnd this also complicates our starting options, since potentially we would have to go through different paths, depending on what initial value we pick.\n\nWhen we have this kind of branching logic tree with multiple options at each step that we might end up recomputing again, the best way to go it is usually to store intermediate results as we go.\n\nIn other words, we will go DP ("Dynamic Programming") all the way on this one, starting from declaring at instance level:\n* `memo` is going to be our store for precomputed values;\n* `target` will represent our current target value for all possible sums;\n* `nums` will store the input vector.\n\nIn our main function, we will indees start assigning a value to `nums`, then declare a couple of local support variables:\n* `res` will store our best score, initially set to be `0` (`1` will work too, since we will always get at least a pair, the starting one, but I preferred to have that also for ease of debugging);\n* `len` will store the length of `nums`.\n\nWe will then deal with an edge case - `nums` is made of all identical values, in which case will just `return` half the value of `len` - which is what we will get as a maximum and minimum path in this occurrence, no matter what choices we make.\n\nIt might seem trivial, but I tested and this line alone cuts my running time short by ~200ms; and, yes; I knew LC was going to throw this kind of test at us with a very long vector.\n\nNext we will check for each of the three possible scenarios we mentioned initially what is the longest possible path, by:\n* filling `memo` with the sentinel value of `-1` to mark unexplored options;\n* computing the current `target` depending from the scenario;\n* update `res` to be the maximum between its current value and `1` plus the result of calling `dfs` with the indexes of the first available values in that scenario.\n\nThe `dfs` helper function will take the indexes of the first (`st`) and last (`ed`) available index and:\n* handle the base case of when we no longer have two numbers left to match within range (ie: `st >= ed`), in which case we will `return` `0`;\n* handle the base case of when we already computed this combination (ie: `memo[st][ed] != -1`), in which case we will `return` it;\n* handle the general case in which we will:\n * declare the support variable `subRes` with initial value of `0`;\n * test \n\nOnce done, back in our main function, we can just `return` `res` :)\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n^2)$$\n- Space complexity:. $$O(n^2)$$\n\n# Code\n```cpp\nclass Solution {\n int memo[2000][2000], target;\n vector<int> nums;\n int dfs(int st, int ed) {\n // base case: done parsing!\n if (st >= ed) return 0;\n // base case: been here before!\n if (memo[st][ed] != -1) return memo[st][ed];\n // general case:\n // support variables\n int subRes = 0;\n // 1st case: first two\n if (nums[st] + nums[st + 1] == target) subRes = max(subRes, 1 + dfs(st + 2, ed));\n // 2nd case: last two\n if (nums[ed - 1] + nums[ed] == target) subRes = max(subRes, 1 + dfs(st, ed - 2));\n // 3rd case: first and last\n if (nums[st] + nums[ed] == target) subRes = max(subRes, 1 + dfs(st + 1, ed - 1));\n return memo[st][ed] = subRes;\n }\npublic:\n int maxOperations(vector<int> &tmp) {\n // populating instance variables\n swap(tmp, nums);\n // support variables\n int res = 0, len = nums.size();\n // edge case: all values are the same\n if (equal(begin(nums) + 1, end(nums), begin(nums))) return len >> 1;\n // 1st case: first two\n memset(memo, -1, sizeof(memo));\n target = nums[0] + nums[1];\n res = max(res, 1 + dfs(2, len - 1));\n // 2nd case: last two\n memset(memo, -1, sizeof(memo));\n target = nums[len - 2] + nums[len - 1];\n res = max(res, 1 + dfs(0, len - 3));\n // 3rd case: first and last\n memset(memo, -1, sizeof(memo));\n target = nums[0] + nums[len - 1];\n res = max(res, 1 + dfs(1, len - 2));\n return res;\n }\n};\n```\nSame logic, marginally DRYer code in the main function and doing `memset` to restore `memo` only as needed, going almost 4X faster!\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n^2)$$\n- Space complexity:. $$O(n^2)$$\n\n# Code\n```cpp\nclass Solution {\n int memo[2000][2000], target;\n vector<int> nums;\n int dfs(int st, int ed) {\n // base case: done parsing!\n if (st >= ed) return 0;\n // base case: been here before!\n if (memo[st][ed] != -1) return memo[st][ed];\n // general case:\n // support variables\n int subRes = 0;\n // 1st case: first two\n if (nums[st] + nums[st + 1] == target) subRes = max(subRes, 1 + dfs(st + 2, ed));\n // 2nd case: last two\n if (nums[ed - 1] + nums[ed] == target) subRes = max(subRes, 1 + dfs(st, ed - 2));\n // 3rd case: first and last\n if (nums[st] + nums[ed] == target) subRes = max(subRes, 1 + dfs(st + 1, ed - 1));\n return memo[st][ed] = subRes;\n }\npublic:\n int maxOperations(vector<int> &tmp) {\n // populating instance variables\n swap(tmp, nums);\n // support variables\n int res = 0, len = nums.size();\n array<int, 4> inputs[3];\n if (equal(begin(nums) + 1, end(nums), begin(nums))) return len >> 1;\n // creating the info for the three test cases\n inputs[0] = {0, 1, 2, len - 1};\n inputs[1] = {len - 2, len - 1, 0, len - 3};\n inputs[2] = {0, len - 1, 1, len - 2};\n // testing each different value of target\n for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {\n auto [firstIdx, secondIdx, st, ed] = inputs[i];\n target = nums[firstIdx] + nums[secondIdx];\n for (int j = 0, amt = len * sizeof(int); j < len; j++) memset(memo[j], -1, amt);\n res = max(res, 1 + dfs(st, ed));\n }\n return res;\n }\n};\n```\nMore or less same logic, with tabulation:\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n^2)$$\n- Space complexity:. $$O(n^2)$$\n\n# Code\n```cpp\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxOperations(vector<int> &nums) {\n // support variables\n int res = 0, len = nums.size(), memo[len + 1][len + 1],\n amt = (len + 1) * (len + 1) * sizeof(int);\n array<int, 4> inputs[3] = {\n {0, 1, 2, len - 1},\n {len - 2, len - 1, 0, len - 3},\n {0, len - 1, 1, len - 2}\n };\n if (equal(begin(nums) + 1, end(nums), begin(nums))) return len >> 1;\n // testing each different value of target\n for (int i = 0, subRes, target; i < 3; i++) {\n auto [firstIdx, secondIdx, st, ed] = inputs[i];\n target = nums[firstIdx] + nums[secondIdx];\n memset(memo, 0, amt);\n for (int j = 2; j <= len; j++) {\n for (int st = 0, ed = j - 1; ed < len; st++, ed++) {\n if (nums[st] + nums[st + 1] == target)\n memo[j][st] = max(memo[j][st], 1 + memo[j - 2][st + 2]);\n if (nums[st] + nums[ed] == target)\n memo[j][st] = max(memo[j][st], 1 + memo[j - 2][st + 1]);\n if (nums[ed - 1] + nums[ed] == target)\n memo[j][st] = max(memo[j][st], 1 + memo[j - 2][st]);\n }\n }\n res = max(res, memo[len][0]);\n }\n return res;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Concise JAVA Recursion
|
concise-java-recursion-by-___lovesh1808-tk07
|
\n\n# Approach\nwe can see it\'s a DP problem just by noticing we have to try all the approaches. We can fix the initital sum to reduce one extra value to memoi
|
___lovesh1808___
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-18T00:47:48.559856+00:00
|
2024-02-18T00:49:31.225354+00:00
| 31 | false |
\n\n# Approach\nwe can see it\'s a DP problem just by noticing we have to try all the approaches. We can fix the initital sum to reduce one extra value to memoize.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n Roughly O(N) where N is the lenth of the array nums \n\n- Space complexity:\n Initial 2D dp array O(N*N) {Ignoring the stack space}\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {\n int n = nums.length;\n int dp[][] = new int[n][n];\n if(n < 2)\n return 0;\n if(n == 2)\n return 1;\n for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) {\n Arrays.fill(dp[i], 0);\n }\n int max = 0;\n \n max = Math.max(max, foo(nums, nums[0] + nums[1], 2, n - 1, dp));\n for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) {\n Arrays.fill(dp[i], 0);\n }\n max = Math.max(max, foo(nums, nums[0] + nums[n-1], 1, n - 2, dp));\n for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) {\n Arrays.fill(dp[i], 0);\n }\n max = Math.max(max, foo(nums, nums[n-1] + nums[n-2], 0, n-3, dp));\n return max + 1;\n }\n int foo(int nums[], int prev, int l, int r,int dp[][]) {\n if(l >= r) {\n return 0;\n }\n if(dp[l][r] != 0) {\n return dp[l][r];\n }\n if(l + 1 <= r && nums[l] + nums[l+1] == prev) {\n dp[l][r] = Math.max(dp[l][r], 1 + foo(nums, prev, l + 2, r, dp));\n }\n if(nums[l] + nums[r] == prev) {\n dp[l][r] = Math.max(dp[l][r], 1 + foo(nums, prev, l + 1, r - 1, dp));\n }\n if(r - 1 >= l && nums[r] + nums[r-1] == prev) {\n dp[l][r] = Math.max(dp[l][r], 1 + foo(nums, prev, l, r - 2, dp));\n }\n return dp[l][r];\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization', 'Java']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Single Cache
|
single-cache-by-votrubac-b3n2
|
With a bit of coniseration, we can see that you cannot arrive at [i, j] subarray with different scores.\n\nTherefore, we only need one dp cache for 3 possible s
|
votrubac
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T20:17:41.761257+00:00
|
2024-02-17T20:17:41.761285+00:00
| 37 | false |
With a bit of coniseration, we can see that you cannot arrive at `[i, j]` subarray with different scores.\n\nTherefore, we only need one `dp` cache for `3` possible scores.\n\n**C++**\n```cpp\nint dp[2001][2001] = {};\nint dfs(int i, int j, int s, vector<int>& n) {\n if (i >= j)\n return 0;\n if (dp[i][j] == 0)\n dp[i][j] = 1 + max({\n s == 0 || n[i] + n[i + 1] == s ? 1 + dfs(i + 2, j, n[i] + n[i + 1], n) : 0,\n s == 0 || n[j] + n[j - 1] == s ? 1 + dfs(i, j - 2, n[j] + n[j - 1], n) : 0,\n s == 0 || n[i] + n[j] == s ? 1 + dfs(i + 1, j - 1, n[i] + n[j], n) : 0\n });\n return dp[i][j] - 1;\n}\nint maxOperations(vector<int>& n) {\n return dfs(0, n.size() - 1, 0, n);\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Easy to read dp solution - 277 ms
|
easy-to-read-dp-solution-277-ms-by-eforc-xsdo
|
Approach\nWe start from 3 possible cases (3 sums) and later we just find maximum using memorization. In the final result 1 + means two first sum numbers as they
|
eforce
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T19:04:16.265341+00:00
|
2024-02-17T19:04:16.265369+00:00
| 249 | false |
# Approach\nWe start from 3 possible cases (3 sums) and later we just find maximum using memorization. In the final result `1 +` means two first sum numbers as they not counted in `find` function. Memorization is required, because it will fail even on small test like:\n`[1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1]`\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n$$O(n ^ 2)$$\n\n- Space complexity:\n$$O(n ^ 2)$$\n\n# Code\n```\n/**\n * @param {number[]} nums\n * @return {number}\n */\nvar maxOperations = function(nums) {\n const dp = Array.from({ length: nums.length }, () => new Array(nums.length));\n\n const find = (l, r, sum) => {\n if (r - l < 1) return 0;\n\n if (dp[l][r] !== undefined) return dp[l][r];\n\n let ret = 0;\n\n if (nums[l] + nums[l + 1] === sum) ret = Math.max(ret, 1 + find(l + 2, r, sum));\n if (nums[l] + nums[r] === sum) ret = Math.max(ret, 1 + find(l + 1, r - 1, sum));\n if (nums[r - 1] + nums[r] === sum) ret = Math.max(ret, 1 + find(l, r - 2, sum));\n\n return dp[l][r] = ret;\n };\n\n return 1 + Math.max(\n find(2, nums.length - 1, nums[0] + nums[1]),\n find(1, nums.length - 2, nums[0] + nums[nums.length - 1]),\n find(0, nums.length - 3, nums[nums.length - 2] + nums[nums.length - 1])\n );\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 1 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Python simple DP
|
python-simple-dp-by-dkravitz78-bind
|
Score is set by first operation. Just take max of all 3 possibilities. DP simply takes the score (which doesn\'t change) and the first and last index. \n\nCom
|
dkravitz78
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T18:48:36.866884+00:00
|
2024-02-17T19:04:45.932291+00:00
| 45 | false |
Score is set by first operation. Just take max of all 3 possibilities. DP simply takes the score (which doesn\'t change) and the first and last index. \n\nComplexity and space are both theoreticaly O(n^2) but it does finish in time, note max length is 2000\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maxOperations(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n \n @cache\n def dp(score, first, last):\n if last<=first: return 0\n ret = 0\n if nums[first]+nums[first+1]==score: ret = max(ret, 1+dp(score,first+2,last))\n if nums[first]+nums[last]==score: ret = max(ret, 1+dp(score,first+1,last-1))\n if nums[last]+nums[last-1]==score: ret = max(ret, 1+dp(score,first,last-2))\n return ret\n \n \n return 1+max( dp(nums[0]+nums[1],2,len(nums)-1) , \n dp(nums[0]+nums[-1],1,len(nums)-2) , \n dp(nums[-1]+nums[-2],0,len(nums)-3) )\n\t\t```
| 1 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
C++ Top Down Recursive DP
|
c-top-down-recursive-dp-by-uchihaxmadara-3ulv
|
Code\nC++\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int n;\n int sum;\n int mem[2001][2001];\n int rec(int i, int j, vector<int> &nums) {\n if(i >= j) ret
|
uchihaXmadara
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T17:50:11.804728+00:00
|
2024-02-18T09:32:05.514649+00:00
| 40 | false |
# Code\n```C++\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int n;\n int sum;\n int mem[2001][2001];\n int rec(int i, int j, vector<int> &nums) {\n if(i >= j) return 0;\n if(mem[i][j] != -1) return mem[i][j];\n int tmp = 0;\n if(nums[i]+nums[i+1] == sum) tmp = 1+rec(i+2, j, nums);\n if(nums[j-1]+nums[j] == sum) tmp = max(tmp, 1+rec(i, j-2, nums));\n if(nums[i]+nums[j] == sum) tmp = max(tmp, 1+rec(i+1, j-1, nums));\n return mem[i][j] = tmp;\n }\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n n = nums.size();\n int sums[3];\n sums[0] = nums[0]+nums[1];\n sums[1] = nums[n-2]+nums[n-1];\n sums[2] = nums[0]+nums[n-1];\n int ans = 0;\n for(int i = 0; i<3; i++) {\n sum = sums[i];\n memset(mem, -1, sizeof(mem));\n ans = max(ans, rec(0, n-1, nums));\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```\n\n```C++\n// takes more time and memory\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n static const int lim = 2*1e3+1;\n int n;\n int mem[lim][lim][3];\n int sums[3];\n int rec(int i, int j, int prev, vector<int> &nums) {\n if(i >= j) return 0;\n if(mem[i][j][prev] != -1) return mem[i][j][prev];\n int tmp = 0;\n if(nums[i]+nums[i+1] == sums[prev]) tmp = 1+rec(i+2, j, prev, nums);\n if(nums[j-1]+nums[j] == sums[prev]) tmp = max(tmp, 1+rec(i, j-2, prev, nums));\n if(nums[i]+nums[j] == sums[prev]) tmp = max(tmp, 1+rec(i+1, j-1, prev, nums));\n return mem[i][j][prev] = tmp;\n }\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n n = nums.size();\n sums[0] = nums[0]+nums[1];\n sums[1] = nums[n-2]+nums[n-1];\n sums[2] = nums[0]+nums[n-1];\n memset(mem, -1, sizeof(mem));\n int ans = 0;\n for(int i = 0; i<3; i++) {\n ans = max(ans, rec(0, n-1, i, nums));\n }\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Recursion', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Simple 2D dp solution in cpp with proper explanation
|
simple-2d-dp-solution-in-cpp-with-proper-to7t
|
Create dp[l][r] to count the pairs having a specific sum covering the array from index l to r.\nfor transition dp[i][j] will be max of all the three posibilitie
|
magzybogues
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T16:46:37.556311+00:00
|
2024-02-17T16:46:53.114680+00:00
| 302 | false |
Create dp[l][r] to count the pairs having a specific sum covering the array from index l to r.\nfor transition dp[i][j] will be max of all the three posibilities, i.e\nselect first two elements that is 1+dp[i+2][j]\nselect last two elements that is 1+dp[i][j-2]\nand select one element from start and one from last 1+dp[i+1][j-1]\ndp[i][j] will be max of these three..\nnow use this function as black box to calculate for sum arr[0]+arr[1],arr[n-1]+arr[n-2] and arr[0]+arr[n-1].\nfinal answer will be the max of all three functions..\n\nnote: you can avoid three different dp arrays by just creating one array of dp[l][r][3]\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n int solve(int l,int r,int sum,vector<int>&nums,vector<vector<int>>&dp)\n {\n if(l>=r)\n {\n return 0;\n }\n if(dp[l][r]!=-1)\n {\n return dp[l][r];\n }\n int mx=0;\n if(nums[l]+nums[r]==sum)\n {\n mx=max(mx,1+solve(l+1,r-1,sum,nums,dp));\n }\n if(nums[l]+nums[l+1]==sum)\n {\n mx=max(mx,1+solve(l+2,r,sum,nums,dp));\n }\n if(nums[r-1]+nums[r]==sum)\n {\n mx=max(mx,1+solve(l,r-2,sum,nums,dp));\n }\n return dp[l][r]=mx;\n }\n \n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n=nums.size();\n vector<vector<int>>dp(n+1,vector<int>(n+1,-1));\n vector<vector<int>>dp1(n+1,vector<int>(n+1,-1));\n vector<vector<int>>dp2(n+1,vector<int>(n+1,-1));\n int mx=1+solve(1,n-2,nums[0]+nums[n-1],nums,dp);\n mx=max(mx,1+solve(2,n-1,nums[0]+nums[1],nums,dp1));\n mx=max(mx,1+solve(0,n-3,nums[n-1]+nums[n-2],nums,dp2));\n return mx;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Recursive DP
|
recursive-dp-by-awesson-gt5h
|
Intuition\nWe can see that once we pick a sum, all operations after that must match that sum. We only have 3 initial options for the operation and so we only ha
|
awesson
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T16:05:53.174156+00:00
|
2024-02-17T16:05:53.174182+00:00
| 27 | false |
# Intuition\nWe can see that once we pick a sum, all operations after that must match that sum. We only have 3 initial options for the operation and so we only have 3 possible sums.\n\nGiven an array and a target sum, we can test all three possibilities for the next operation and then recursively solve the remaining array after the deletions. For a particular starting sum, the inputs to the recursive call which varry are only the starting and ending points of the remaining array, so we can memoize this result in n^2 memory and time.\n\n# Approach\nCalculate the 3 possible sums and then recursively check the most operations that can be done with that particular sum.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n^2)$$\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(n^2)$$\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution\n{\npublic:\n\tint maxOperations(vector<int>& nums)\n\t{\n\t\tvector<vector<int>> uninitializeCache(nums.size(), vector<int>(nums.size(), -1));\n\n\t\tvector<vector<int>> cache = uninitializeCache;\n\t\tint firstTwo = nums[0] + nums[1];\n\t\tint ans = helper(nums, 0, nums.size() - 1, firstTwo, cache);\n\n\t\tcache = uninitializeCache;\n\t\tint firstAndLast = nums[0] + nums[nums.size() - 1];\n\t\tans = max(ans, helper(nums, 0, nums.size() - 1, firstAndLast, cache));\n\n\t\tcache = uninitializeCache;\n\t\tint lastTwo = nums[nums.size() - 2] + nums[nums.size() - 1];\n\t\tans = max(ans, helper(nums, 0, nums.size() - 1, lastTwo, cache));\n\n\t\treturn ans;\n\t}\n\n\tint helper(vector<int>& nums, int start, int end, int sum, vector<vector<int>>& cache)\n\t{\n\t\tif (start >= end)\n\t\t\treturn 0;\n\n\t\tint& ans = cache[start][end];\n\t\tif (ans >= 0)\n\t\t\treturn ans;\n\n\t\tint ansInt = 0;\n\t\tif (nums[start] + nums[start + 1] == sum)\n\t\t\tansInt = max(ansInt, 1 + helper(nums, start + 2, end, sum, cache));\n\n\t\tif (nums[start] + nums[end] == sum)\n\t\t\tansInt = max(ansInt, 1 + helper(nums, start + 1, end - 1, sum, cache));\n\n\t\tif (nums[end - 1] + nums[end] == sum)\n\t\t\tansInt = max(ansInt, 1 + helper(nums, start, end - 2, sum, cache));\n\n\t\tans = ansInt;\n\t\treturn ans;\n\t}\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 1 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
✅Easy C++ Solution || Dynamic Programming
|
easy-c-solution-dynamic-programming-by-c-2cq8
|
\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int calculate(vector<int>& a, int i, int j, int s,vector<vector<int>>& memo) {\n if (j <= i)\n re
|
conqueror24
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T16:05:18.146568+00:00
|
2024-02-26T17:02:40.034872+00:00
| 38 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int calculate(vector<int>& a, int i, int j, int s,vector<vector<int>>& memo) {\n if (j <= i)\n return 0;\n if (memo[i][j]!=-1) {\n return memo[i][j];\n }\n\n int d = 0;\n\n if (s == 0 || (s == a[i] + a[i + 1])) {\n d = max(d, 1 + calculate(a, i + 2, j, a[i] + a[i + 1], memo));\n }\n\n if (s == 0 || (s == a[i] + a[j])) {\n d = max(d, 1 + calculate(a, i + 1, j - 1, a[i] + a[j], memo));\n }\n\n if (s == 0 || (j >= 1 && s == a[j - 1] + a[j])) {\n d = max(d, 1 + calculate(a, i, j - 2, a[j] + a[j - 1], memo));\n }\n return memo[i][j] = d;\n }\n\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n vector<vector<int>> memo(nums.size(),vector<int>(nums.size(),-1));\n return calculate(nums, 0, nums.size() - 1, 0, memo);\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Memoization', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Top-Down | HashMap|Memo
|
top-down-hashmapmemo-by-abburisaikarthik-p7f2
|
\n\n# Code\n\nimport java.util.HashMap;\n\nclass Solution {\n public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {\n return helper(0, nums.length - 1, nums, -1, new
|
abburisaikarthik
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T16:03:06.181324+00:00
|
2024-02-17T16:03:06.181347+00:00
| 147 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```\nimport java.util.HashMap;\n\nclass Solution {\n public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {\n return helper(0, nums.length - 1, nums, -1, new HashMap<>());\n }\n\n int helper(int st, int en, int[] nums, int sum, HashMap<String, Integer> memo) {\n String key = st + "," + en + "," + sum;\n if (memo.containsKey(key)) {\n return memo.get(key);\n }\n int diff = en - st + 1;\n if (diff <2) {\n return 0;\n }\n if (sum == -1) {\n int op1 = 1 + helper(st + 1, en - 1, nums, nums[st] + nums[en], memo);\n int op2 = 1 + helper(st + 2, en, nums, nums[st] + nums[st + 1], memo);\n int op3 = 1 + helper(st, en - 2, nums, nums[en] + nums[en - 1], memo);\n int max = Math.max(op1, Math.max(op2, op3));\n memo.put(key, max);\n return max;\n } else {\n int val1 = nums[st] + nums[en];\n int val2 = nums[st] + nums[st + 1];\n int val3 = nums[en] + nums[en - 1];\n int op1 = (sum == val1) ? 1 + helper(st + 1, en - 1, nums, sum, memo) : Integer.MIN_VALUE;\n int op2 = (sum == val2) ? 1 + helper(st + 2, en , nums, sum, memo) : Integer.MIN_VALUE;\n int op3 = (sum == val3) ? 1 + helper(st, en - 2, nums, sum, memo) : Integer.MIN_VALUE;\n int max = Math.max(op1, Math.max(op2, op3));\n memo.put(key, max == Integer.MIN_VALUE ? 0 : max);\n return max == Integer.MIN_VALUE ? 0 : max;\n }\n }\n}\n\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Java']
| 1 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
[Python] simple DFS + @cache (memoization)
|
python-simple-dfs-cache-memoization-by-p-b2d1
|
python\nclass Solution:\n def maxOperations(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n\n @cache\n def dfs(i, j, p):\n if j - i + 1 < 2:\n
|
pbelskiy
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T16:01:12.207992+00:00
|
2024-02-17T16:04:57.315921+00:00
| 168 | false |
```python\nclass Solution:\n def maxOperations(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n\n @cache\n def dfs(i, j, p):\n if j - i + 1 < 2:\n return 0\n\n m = 0\n if nums[i] + nums[i + 1] == p: # first two\n m = max(m, dfs(i + 2, j, p) + 1)\n\n if nums[j] + nums[j - 1] == p: # last two\n m = max(m, dfs(i, j - 2, p) + 1)\n\n if nums[i] + nums[j] == p: # first and last\n m = max(m, dfs(i + 1, j - 1, p) + 1)\n\n return m\n\n return max(\n dfs(2, len(nums) - 1, nums[0] + nums[1]), # first two\n dfs(0, len(nums) - 3, nums[-1] + nums[-2]), # last two\n dfs(1, len(nums) - 2, nums[0] + nums[-1]), # first and last\n ) + 1\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
DFS + Memoization | Easy to understand
|
dfs-memoization-easy-to-understand-by-on-rg6g
|
We explore the world where the score is:\n- 2 first numbers (nums[0] + nums[1] at first, then nums[l] + nums[l+1])\n- 2 last numbers (nums[nums.size() - 1] + nu
|
onakasuita
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-17T16:01:09.096425+00:00
|
2024-02-17T16:06:23.614623+00:00
| 55 | false |
We explore the world where the score is:\n- 2 first numbers (`nums[0] + nums[1]` at first, then `nums[l] + nums[l+1]`)\n- 2 last numbers (`nums[nums.size() - 1] + nums[nums.size() - 2]` at first, then `nums[r] + nums[r-1]`)\n- 1st and the last number (`nums[0] + nums[nums.size() - 1]` at first, then `nums[l] + nums[r]`)\n\nPositions of `l` and `r` tell us where to take our numbers from. `l >= r` is the condition which makes us unable to pick 2 different numbers, so we can return 0.\n\n```cpp\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int dfs(int l, int r, int aim, vector<int>& nums, unordered_map<int, unordered_map<int, int>>& memo) {\n if(l >= r) return 0;\n if(memo[l][r]) return memo[l][r];\n\n int maxRes = 0;\n\n if(aim == nums[l] + nums[l+1]) {\n maxRes = max(maxRes, dfs(l+2, r, aim, nums, memo) + 1);\n }\n\n if(aim == nums[r] + nums[r-1]) {\n maxRes = max(maxRes, dfs(l, r-2, aim, nums, memo) + 1);\n }\n\n if(aim == nums[l] + nums[r]) {\n maxRes = max(maxRes, dfs(l+1, r-1, aim, nums, memo) + 1);\n }\n\n memo[l][r] = maxRes;\n\n return maxRes;\n }\n\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n int maxOp = 0;\n unordered_map<int, unordered_map<int, int>> memo;\n\n int score = nums[0] + nums[1];\n maxOp = max(maxOp, dfs(2, nums.size() - 1, score, nums, memo) + 1);\n\n score = nums[nums.size() - 1] + nums[nums.size() - 2];\n maxOp = max(maxOp, dfs(0, nums.size() - 3, score, nums, memo) + 1);\n\n score = nums[0] + nums[nums.size() - 1];\n maxOp = max(maxOp, dfs(1, nums.size() - 2, score, nums, memo) + 1);\n\n return maxOp;\n }\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Depth-First Search', 'Recursion', 'Memoization', 'C']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
C++ Simple & Easy Solution (memoization)
|
c-simple-easy-solution-memoization-by-ss-xhst
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
sskcorea
|
NORMAL
|
2025-03-14T14:05:40.473491+00:00
|
2025-03-14T14:05:40.473491+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {
int len = nums.size();
vector<vector<int>> m(len, vector<int>(len, 0));
function<int(int, int, int)> dfs = [&](int s, int e, int score) -> int {
if (s >= e) return 0;
if (m[s][e]) return m[s][e];
int cnt = 0;
if (s+1 < len && score == nums[s] + nums[s+1])
cnt = max (cnt, dfs(s+2, e, score) + 1);
if (score == nums[s] + nums[e])
cnt = max (cnt, dfs(s+1, e-1, score) + 1);
if (e-1 >= 0 && score == nums[e-1] + nums[e])
cnt = max (cnt, dfs(s, e-2, score) + 1);
return m[s][e] = cnt;
};
int ans = 0;
ans = max(ans, dfs(2, len-1, nums[0] + nums[1])+1);
ans = max(ans, dfs(1, len-2, nums[0] + nums[len-1])+1);
ans = max(ans, dfs(0, len-3, nums[len-2] + nums[len-1])+1);
return ans;
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Single Call || Not for Each case seperate case call
|
single-call-not-for-each-case-seperate-c-3fjl
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
skp10092001
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-20T19:35:57.463551+00:00
|
2025-02-20T19:35:57.463551+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
int solve(vector<int>& nums, int i, int j, int score,
vector<vector<int>>& dp) {
if (i >= j) {
return 0;
}
if (dp[i][j] != -1) {
return dp[i][j];
}
int ans = 0;
if (score == -1 || nums[i] + nums[i + 1] == score) {
ans =
max(ans, 1 + solve(nums, i + 2, j, nums[i] + nums[i + 1], dp));
}
if (score == -1 || nums[j] + nums[j - 1] == score) {
ans =
max(ans, 1 + solve(nums, i, j - 2, nums[j] + nums[j - 1], dp));
}
if (score == -1 || nums[i] + nums[j] == score) {
ans =
max(ans, 1 + solve(nums, i + 1, j - 1, nums[i] + nums[j], dp));
}
return dp[i][j] = ans;
}
int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
vector<vector<int>> dp(n + 3, vector<int>(n + 3, -1));
return solve(nums, 0, n - 1, -1, dp);
}
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Easy DP Soln!
|
easy-dp-soln-by-saurabhabd_360-45-x98b
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
Saurabhabd_360-45
|
NORMAL
|
2025-02-13T04:36:07.834556+00:00
|
2025-02-13T04:36:07.834556+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity:
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
public void fun(int[][] dp){
for(int[] a : dp){
Arrays.fill(a, -1);
}
}
public int func(int i, int j, int target, int[] nums, int[][] dp){
if(i >= j) return 0;
if(dp[i][j] != -1) return dp[i][j];
int ans = 0;
if((nums[i] + nums[i+1]) == target){
ans = 1 + func(i+2, j, target, nums, dp);
}
if((i+1 != j) && (nums[j] + nums[j-1] == target)){
ans = Math.max(ans, 1 + func(i, j-2, target, nums, dp));
}
if((i+1 != j) && (nums[i] + nums[j]) == target){
ans = Math.max(ans, 1 + func(i+1, j-1, target, nums, dp));
}
return dp[i][j] = ans;
}
public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {
int[][] dp = new int[nums.length][nums.length];
fun(dp);
int ans = func(0, nums.length-1, nums[0]+nums[1], nums, dp);
fun(dp);
ans = Math.max(ans, func(0, nums.length-1, nums[0]+nums[nums.length-1], nums, dp));
fun(dp);
ans = Math.max(ans, func(0, nums.length-1, nums[nums.length-2]+nums[nums.length-1], nums, dp));
return ans;
}
}
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Java']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Top Down DP
|
top-down-dp-by-cx1z0-mqfd
|
Top down
|
Cx1z0
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-18T10:08:21.069470+00:00
|
2025-01-18T10:11:52.546130+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Top down
```javascript []
const maxOperations = (nums) => {
const memo = Array.from({ length: nums.length }, () => Array(nums.length).fill(0));
function dp(left, right, prevSum) {
if (left >= right) return 0;
if (memo[left][right]) return memo[left][right];
let maxOps = 0; //Track the maximum operations
// Check if the pair at (left, left + 1) forms a valid operation
if (nums[left] + nums[left + 1] === prevSum) {
maxOps = Math.max(maxOps, dp(left + 2, right, prevSum) + 1);
}
// Check if the pair at (left, right) forms a valid operation
if (nums[left] + nums[right] === prevSum) {
maxOps = Math.max(maxOps, dp(left + 1, right - 1, prevSum) + 1);
}
// Check if the pair at (right - 1, right) forms a valid operation
if (nums[right] + nums[right - 1] === prevSum) {
maxOps = Math.max(maxOps, dp(left, right - 2, prevSum) + 1);
}
return (memo[left][right] = maxOps);
}
// Calculate the maximum operations
const end = nums.length - 1;
return Math.max(
dp(2, end, nums[0] + nums[1]) + 1, // First two elements as the target sum
dp(1, end - 1, nums[0] + nums[end]) + 1, // First and last elements as the target sum
dp(0, end - 2, nums[end] + nums[end - 1]) + 1 // Last two elements as the target sum
);
};
```
| 0 | 0 |
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'JavaScript']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
DP + Memory
|
dp-memory-by-linda2024-t4h3
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity:
Space complexity:
Code
|
linda2024
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-14T02:19:38.681590+00:00
|
2024-12-14T02:19:38.681590+00:00
| 5 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```csharp []\npublic class Solution {\n private int[,] dp;\n \n private int MaxOpts(int[] nums, int left, int right, int preSum)\n {\n if(left >= right)\n return 0;\n\n if(dp[left, right] != 0)\n return dp[left, right];\n \n int maxCnt = 0;\n if(nums[left] + nums[left+1] == preSum)\n {\n maxCnt = Math.Max(maxCnt, 1+ MaxOpts(nums, left+2, right, preSum));\n }\n\n if(nums[left] + nums[right] == preSum)\n {\n maxCnt = Math.Max(maxCnt, 1+ MaxOpts(nums, left+1, right-1, preSum));\n }\n\n if(nums[right-1] + nums[right] == preSum)\n {\n maxCnt = Math.Max(maxCnt, 1+ MaxOpts(nums, left, right-2, preSum));\n }\n\n dp[left, right] = maxCnt;\n return maxCnt;\n }\n public int MaxOperations(int[] nums) {\n int len = nums.Length;\n if(len < 2)\n return 0;\n\n HashSet<int> items = new HashSet<int>(nums);\n if(items.Count == 1)\n return len/2;\n dp = new int[len, len];\n \n int res = 1;\n res = Math.Max(res, 1+MaxOpts(nums, 1, len-2, nums[0] + nums[len-1])); \n res = Math.Max(res, 1+MaxOpts(nums, 2, len-1, nums[0] + nums[1]));\n res = Math.Max(res, 1+MaxOpts(nums, 0, len-3, nums[len-2] + nums[len-1]));\n\n return res;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C#']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
C++ Iteration Solution (No Recursion)
|
c-iteration-solution-no-recursion-by-dad-juon
|
Code\ncpp []\ntypedef struct {\n int h2 = 0, ht = 0, t2 = 0; // Check if the first two (head 2), \n // first and last (head an
|
dadin852
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-14T08:04:50.650483+00:00
|
2024-11-14T08:09:44.273780+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Code\n```cpp []\ntypedef struct {\n int h2 = 0, ht = 0, t2 = 0; // Check if the first two (head 2), \n // first and last (head and tail), \n // last two (tail 2) are calculated (\u2192visited)\n int maxop = 0; // \u7576\u524D\u6700\u5927\u7684\u64CD\u4F5C\u6B21\u6578\n} Subarr_Calc;\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n = nums.size();\n if (n == 2) return 1;\n int l, r, max_operations = 0;\n vector<vector<Subarr_Calc>> dp(n, vector<Subarr_Calc>(n)); // \u53EA\u8A2Dn-1\u5217\u4E5F\u53EF\u4EE5AC\n stack<pair<int, int>> st; // DFS\u7528\u7684stack\n set<int> bases = {nums[0] + nums[1], \n nums[0] + nums[n-1], \n nums[n-2] + nums[n-1]}; // \u53BB\u9664\u91CD\u8907\u503C\n\n for (int base : bases) {\n for (auto& row : dp) { // \u6B78\u96F6\n for (auto& cell : row) {\n cell.h2 = cell.ht = cell.t2 = 0;\n cell.maxop = 0;\n } }\n while (!st.empty())\n st.pop();\n st.push(make_pair(0, n-1)); // root\n\n int prev_op;\n while (!st.empty()) {\n auto top = st.top();\n l = top.first; r = top.second;\n\n if (r-l == 1 && nums[l] + nums[r] == base) {\n dp[l][r].maxop = 1;\n st.pop();\n l = st.top().first; r = st.top().second;\n if (2 > dp[l][r].maxop) // Backtrack +1\n dp[l][r].maxop = 2;\n continue;\n } else if (r-l <= 1) {\n st.pop();\n l = st.top().first; r = st.top().second;\n dp[l][r].maxop = 1;\n continue;\n }\n\n if ( !dp[l][r].h2) {\n if (nums[l] + nums[l+1] == base) {\n if (l+2 <= r)\n st.push(make_pair(l+2, r));\n }\n dp[l][r].h2 = 1;\n } else if ( !dp[l][r].ht) {\n if (nums[l] + nums[r] == base) {\n if (l+1 <= r-1)\n st.push(make_pair(l+1, r-1));\n }\n dp[l][r].ht = 1;\n } else if ( !dp[l][r].t2) {\n if (nums[r-1] + nums[r] == base) {\n if (l <= r-2)\n st.push(make_pair(l, r-2));\n }\n dp[l][r].t2 = 1;\n } else {\n prev_op = dp[l][r].maxop;\n st.pop();\n if (st.empty())\n break;\n l = st.top().first; r = st.top().second;\n if (prev_op + 1 > dp[l][r].maxop) // Backtrack +1\n dp[l][r].maxop = prev_op + 1;\n }\n }\n if (prev_op > max_operations)\n max_operations = prev_op;\n }\n return max_operations;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Simple Dp Memoization - explained
|
simple-dp-memoization-explained-by-abdel-gsl3
|
Intuition\nThe main challenge of this problem is to find the maximum number of operations that can be performed on the array nums such that every operation yiel
|
Abdelhak1
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-13T15:42:20.885179+00:00
|
2024-11-13T15:42:20.885218+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition\nThe main challenge of this problem is to find the maximum number of operations that can be performed on the array `nums` such that every operation yields the same score (the sum of the two deleted elements). The allowed operations involve removing either the first two elements, the last two elements, or the first and last element of the array. \n\nMy initial thought was to use a recursive approach that explores all possible deletion sequences and leverages memoization to avoid recomputing overlapping subproblems. The goal is to maximize the number of deletions while ensuring the sum remains consistent across all operations.\n\n# Approach\n1. **Recursive Depth-First Search (DFS) with Memoization**:\n - We define a recursive function `dfs(start, stop, score)` that explores different deletion combinations:\n - `start` and `stop` denote the current boundaries of the array.\n - `score` is the sum we aim to maintain for every operation.\n - The base case occurs when there are fewer than 2 elements between `start` and `stop`, which means no more operations can be performed.\n - For each call, we have three choices:\n 1. Remove the first and last elements if their sum matches `score`.\n 2. Remove the first two elements if their sum matches `score`.\n 3. Remove the last two elements if their sum matches `score`.\n - We use a cache (a dictionary) to memoize results for specific `(start, stop, score)` tuples to optimize performance and avoid recomputation.\n - Finally, we initiate the search with three potential scores:\n 1. The sum of the first two elements.\n 2. The sum of the last two elements.\n 3. The sum of the first and last element.\n - The result is the maximum number of operations found among the three initial calls.\n\n# Complexity\n- **Time Complexity**: \n - The worst-case time complexity is approximately $$O(n^3)$$ because for each combination of `start`, `stop`, and `score`, we are performing recursive calls and storing results in the cache. The memoization helps to prevent redundant calculations.\n \n- **Space Complexity**: \n - $$O(n^2)$$ due to the cache used to store results for different `(start, stop, score)` combinations, and the recursion stack can go up to a depth of $$O(n)$$ in the worst case.\n\n# Code\n```python []\nclass Solution(object):\n def maxOperations(self, nums):\n """\n :type nums: List[int]\n :rtype: int\n """\n cache = {}\n n = len(nums)\n def dfs(start, stop, score):\n if stop - start < 2:\n return 0\n if (start, stop, score) in cache:\n return cache[(start, stop, score)]\n r1, r2, r3 = 0, 0, 0\n if nums[start] + nums[stop-1] == score:\n r1 = 1 + dfs(start+1, stop-1, score)\n if nums[start] + nums[start+1] == score:\n r2 = 1 + dfs(start+2, stop, score)\n if nums[stop-2] + nums[stop-1] == score:\n r3 = 1 + dfs(start, stop-2, score)\n cache[(start, stop, score)] = max(r1, r2, r3)\n return max(r1, r2, r3)\n return max(\n dfs(0, n, nums[0]+nums[1]), \n dfs(0, n, nums[0]+nums[-1]), \n dfs(0, n, nums[-2]+nums[-1])\n )\n\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Recursion + cache | Java
|
recursion-cache-java-by-wangcai20-m6e6
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nTop-down recursion w/ cache.\n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the prob
|
wangcai20
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-10T15:17:16.853335+00:00
|
2024-11-10T15:17:37.510651+00:00
| 1 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nTop-down recursion w/ cache.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {\n Map<String, Integer> cache = new HashMap<>();\n int res = 0;\n res = Math.max(res, maxOps(nums, nums[0] + nums[1], 2, nums.length - 1, cache));\n res = Math.max(res, maxOps(nums, nums[nums.length - 1] + nums[nums.length - 2], 0, nums.length - 3, cache));\n res = Math.max(res, maxOps(nums, nums[0] + nums[nums.length - 1], 1, nums.length - 2, cache));\n return res + 1;\n }\n\n int maxOps(int[] nums, int sum, int l, int r, Map<String, Integer> cache) {\n if (l >= r)\n return 0;\n String key = sum + "-" + l + "-" + r;\n if (cache.containsKey(key)) return cache.get(key);\n int res = 0;\n res = Math.max(res, sum != nums[l] + nums[r] ? 0 : 1 + maxOps(nums, sum, l + 1, r - 1, cache));\n res = Math.max(res, sum != nums[l] + nums[l + 1] ? 0 : 1 + maxOps(nums, sum, l + 2, r, cache));\n res = Math.max(res, sum != nums[r] + nums[r - 1] ? 0 : 1 + maxOps(nums, sum, l, r - 2, cache));\n cache.put(key, res);\n //System.out.println(sum + "|" + l + "|" + r + "|" + res);\n return res;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Recursion + cache - Java
|
recursion-cache-java-by-wangcai20-m9ob
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nTop-down recursion with a map as cache.\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving
|
wangcai20
|
NORMAL
|
2024-11-10T15:16:26.288814+00:00
|
2024-11-10T15:16:26.288839+00:00
| 1 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nTop-down recursion with a `map` as cache.\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {\n Map<String, Integer> cache = new HashMap<>();\n int res = 0;\n res = Math.max(res, maxOps(nums, nums[0] + nums[1], 2, nums.length - 1, cache));\n res = Math.max(res, maxOps(nums, nums[nums.length - 1] + nums[nums.length - 2], 0, nums.length - 3, cache));\n res = Math.max(res, maxOps(nums, nums[0] + nums[nums.length - 1], 1, nums.length - 2, cache));\n return res + 1;\n }\n\n int maxOps(int[] nums, int sum, int l, int r, Map<String, Integer> cache) {\n if (l >= r)\n return 0;\n String key = sum + "-" + l + "-" + r;\n if (cache.containsKey(key)) return cache.get(key);\n int res = 0;\n res = Math.max(res, sum != nums[l] + nums[r] ? 0 : 1 + maxOps(nums, sum, l + 1, r - 1, cache));\n res = Math.max(res, sum != nums[l] + nums[l + 1] ? 0 : 1 + maxOps(nums, sum, l + 2, r, cache));\n res = Math.max(res, sum != nums[r] + nums[r - 1] ? 0 : 1 + maxOps(nums, sum, l, r - 2, cache));\n cache.put(key, res);\n //System.out.println(sum + "|" + l + "|" + r + "|" + res);\n return res;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Easy to understand Java Solution
|
easy-to-understand-java-solution-by-feli-kuk9
|
Intuition\nWe can simulate the process described on the problem, and keep repeating as long as our score is the same as the one from the first action.\nSo, for
|
FelipeA0
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-30T06:04:39.437124+00:00
|
2024-10-30T06:04:57.852098+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition\nWe can simulate the process described on the problem, and keep repeating as long as our score is the same as the one from the first action.\nSo, for the first 3 possible operations we compute the maximum between the next operations and use memoization to optimize the code.\n\n# Approach\nCreate dp array to store previous answer.\nCreate operations function which will go deep as long as we find the same score.\nCall operations function for the first 3 possible operations.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(n^2)\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(n^2)\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n int[][] dp;\n public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {\n dp = new int[2001][2001];\n int n = nums.length;\n return 1 + Math.max(operations(nums,2,n,nums[0]+nums[1]),Math.max(operations(nums,0,n-2,nums[n-1]+nums[n-2]),operations(nums,1,n-1,nums[0]+nums[n-1])));\n }\n\n public int operations(int[] nums, int start, int end, int score) {\n if (end-start < 2) {\n return 0;\n }\n\n if (dp[start][end-1] > 0) {\n return dp[start][end-1];\n }\n int max = 0;\n \n if (nums[start]+nums[start+1] == score) {\n max = Math.max(max, 1 + operations(nums,start+2,end,score));\n }\n if (nums[end-1]+nums[end-2] == score) {\n max = Math.max(max, 1 + operations(nums,start,end-2,score));\n }\n if (nums[start]+nums[end-1] == score) {\n max = Math.max(max, 1 + operations(nums,start+1,end-1,score));\n }\n dp[start][end-1]=max;\n return max;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Java']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Naive Explanation || Backtracking with Memoization 🎀
|
naive-explanation-backtracking-with-memo-dj3n
|
Approach:\n- We are allowed to either delete first 2 elements or last 2 elemets or first & last elements\n- We will explore all posibilities in all 3 cases.\n-
|
Axnjr
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-29T06:35:50.029424+00:00
|
2024-10-29T06:35:50.029459+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Approach:\n- We are allowed to either delete `first 2 elements` or `last 2 elemets` or `first & last elements`\n- We will explore all posibilities in all `3 cases`.\n- We would use 2 pointers `start` & `end` to keep track of the array, rather than actually deleting the elements of array and creating new one for every recursive call, we will just update our pointers.\n- To optimize our solution we will store the maximum operations possible `maxOps` for the 2 pointers in a `dp` matrix.\n- If we again see the `same pointers` we would just return the pre-calculated `maxOps` result.\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(N^2)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(N)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n int N;\n vector<int> nums;\n vector<vector<int>> dp; // [start, end] = maxOps;\n\n int backtrack(int start, int end, int prevScore){\n if(start >= end) return 0;\n if(dp[start][end] != -1) return dp[start][end];\n\n int case1 = 0, case2 = 0, case3 = 0;\n\n if(nums[start] + nums[end] == prevScore) case1 = backtrack(start + 1, end - 1, prevScore) + 1;\n if(nums[start] + nums[start + 1] == prevScore) case2 = backtrack(start + 2, end, prevScore) + 1;\n if(nums[end] + nums[end - 1] == prevScore) case3 = backtrack(start, end - 2, prevScore) + 1;\n\n return dp[start][end] = max({case1, case2, case3});\n }\n\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& n) {\n nums = n;\n N = nums.size();\n dp = vector<vector<int>>(N, vector<int>(N, -1));\n\n int first2EleCase = nums[0] + nums[1]; \n int first2EleCaseOps = backtrack(2, N - 1, first2EleCase);\n\n int last2EleCase = nums[N - 1] + nums[N - 2]; \n int last2EleCaseOps = backtrack(0, N - 3, last2EleCase);\n\n int firstLastEleCase = nums[0] + nums[N - 1]; \n int firstLastEleCaseOps = backtrack(1, N - 2, firstLastEleCase);\n\n return max({first2EleCaseOps, last2EleCaseOps, firstLastEleCaseOps}) + 1;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Backtracking', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii - Java Solution
|
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-sa-34gx
|
\njava []\nclass Solution {\n public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {\n //With Memoization : start [Beats 50%] [136ms]\n return withMemoization(
|
himashusharma
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-24T06:59:30.788085+00:00
|
2024-09-24T06:59:30.788117+00:00
| 0 | false |
\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {\n //With Memoization : start [Beats 50%] [136ms]\n return withMemoization(nums);\n //With Memoization : end\n }\n \n public int withMemoization(int[] nums){\n int n = nums.length;\n int i = 0;\n int j = n-1;\n int sum1 = nums[i] + nums[i+1]; \n int sum2 = nums[i] + nums[j];\n int sum3 = nums[j-1] + nums[j];\n\n Integer[][] memo = new Integer[n+1][n+1];\n int ans = withMemo(i,j,nums,sum1,memo);\n\n memo = new Integer[n+1][n+1];\n ans = Math.max(ans, withMemo(i,j,nums,sum2,memo));\n\n memo = new Integer[n+1][n+1];\n ans = Math.max(ans, withMemo(i,j,nums,sum3,memo));\n\n return ans;\n }\n\n public int withMemo(int i,int j,int[] arr,int sum,Integer[][] memo){\n if(j <= i) return 0;\n if(memo[i][j] != null) return memo[i][j];\n\n int ans = 0;\n if(arr[i] + arr[j] == sum){\n ans = Math.max(ans,1 + withMemo(i+1,j-1,arr,sum,memo));\n }\n\n if(arr[i] + arr[i+1] == sum){\n ans = Math.max(ans,1 + withMemo(i+2,j,arr,sum,memo));\n }\n\n if(arr[j-1] + arr[j] == sum){\n ans = Math.max(ans,1 + withMemo(i,j-2,arr,sum,memo));\n }\n\n memo[i][j] = ans;\n return ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'Java']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
JAVA MEMO
|
java-memo-by-staztech-9r06
|
\n# Code\njava []\nclass Solution {\n int[][] dp;\n public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {\n if(nums.length < 2) return 0;\n int n = nums.length;\n d
|
StazTech
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-07T17:27:07.931940+00:00
|
2024-09-07T17:27:07.931978+00:00
| 3 | false |
\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n int[][] dp;\n public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {\n if(nums.length < 2) return 0;\n int n = nums.length;\n dp = new int[n][n];\n\n int a = 1 + dfs(nums, 2, n - 1, nums[0] + nums[1]); \n int b = 1 + dfs(nums, 1, n - 2, nums[0] + nums[n - 1]); \n int c = 1 + dfs(nums, 0, n - 3, nums[n - 1] + nums[n - 2]); \n\n return Math.max(Math.max(a,b),c);\n }\n\n public int dfs(int[] nums, int left, int right, int sum) {\n if(right - left < 1) return 0;\n if(dp[left][right] != 0) return dp[left][right];\n\n int a = 0, b = 0, c = 0;\n if(nums[left] + nums[left+1] == sum) a = 1 + dfs(nums, left + 2, right, sum);\n if(nums[left] + nums[right] == sum) b = 1 + dfs(nums, left + 1, right - 1, sum);\n if(nums[right] + nums[right - 1] == sum) c = 1 + dfs(nums, left, right - 2, sum);\n\n return dp[left][right] = Math.max(Math.max(a,b),c);\n }\n}\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Java recursion+MAPS
|
java-recursionmaps-by-teja_07-kl13
|
\nclass Solution {\n Map<String,Integer> map=new HashMap<>();\n public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {\n return f(nums,0,nums.length-1,0);\n }\n
|
Teja_07
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-04T18:13:39.176922+00:00
|
2024-09-04T18:13:39.176957+00:00
| 5 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n Map<String,Integer> map=new HashMap<>();\n public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {\n return f(nums,0,nums.length-1,0);\n }\n public int f(int[] nums,int ind1,int ind2,int prev){\n if(ind1>=ind2) return 0;\n int max=0;\n String val=ind1+","+ind2+","+prev;\n if(map.containsKey(val)){\n return map.get(val);\n }\n int fsum=nums[ind1]+nums[ind1+1];\n if(prev==0 || fsum==prev){\n max=Math.max(max,1+f(nums,ind1+2,ind2,fsum));\n }\n int lsum=nums[ind2]+nums[ind2-1];\n if(prev==0 || lsum==prev){\n max=Math.max(max,1+f(nums,ind1,ind2-2,lsum));\n }\n int wsum=nums[ind1]+nums[ind2];\n if(prev==0 || wsum==prev){\n max=Math.max(max,1+f(nums,ind1+1,ind2-1,wsum));\n }\n map.put(val,max);\n return max;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Recursion', 'Memoization', 'Java']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Easy || Intuitive || Try all possible ways || C++ Memoisation
|
easy-intuitive-try-all-possible-ways-c-m-xewe
|
Intuition\nThere are 3 possible ways to make a move, so we will try each move one-by-one.\n\n# Code\ncpp []\nclass Solution {\nprivate:\n int solve(vector<in
|
tmohit_04
|
NORMAL
|
2024-09-04T12:52:43.136176+00:00
|
2024-09-04T12:52:43.136209+00:00
| 8 | false |
# Intuition\nThere are 3 possible ways to make a move, so we will try each move one-by-one.\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\nprivate:\n int solve(vector<int> &nums, int left, int right, int last, vector<vector<int>> &dp){\n if(left>=right) return 0;\n if(right-left==1) return (nums[left] + nums[right] == last);\n\n if(dp[left][right]!=-1) return dp[left][right];\n\n int sum1 = nums[left] + nums[left+1];\n int opt1 = 0;\n if(sum1==last) opt1 = 1 + solve(nums, left+2, right, last, dp);\n\n int sum2 = nums[right] + nums[right-1];\n int opt2 = 0;\n if(sum2==last) opt2 = 1 + solve(nums, left, right-2, last, dp);\n\n int sum3 = nums[left] + nums[right];\n int opt3 = 0;\n if(sum3==last) opt3 = 1 + solve(nums, left+1, right-1, last, dp);\n\n return dp[left][right] = max(opt1, max(opt2, opt3));\n }\npublic:\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n = nums.size();\n vector<vector<int>> dp1(n, vector<int>(n, -1));\n vector<vector<int>> dp2(n, vector<int>(n, -1));\n vector<vector<int>> dp3(n, vector<int>(n, -1));\n \n int left = 0, right = n-1;\n int sum1 = nums[left] + nums[left+1];\n int opt1 = 1 + solve(nums, left+2, right, sum1, dp1);\n\n \n int sum2 = nums[right] + nums[right-1];\n int opt2 = 1 + solve(nums, left, right-2, sum2, dp2);\n\n int sum3 = nums[left] + nums[right];\n int opt3 = 1 + solve(nums, left+1, right-1, sum3, dp3);\n\n return max(opt1, max(opt2, opt3));\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Easy Memo Solution
|
easy-memo-solution-by-roy_b-ikha
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
roy_b
|
NORMAL
|
2024-08-23T13:45:24.821416+00:00
|
2024-08-23T13:45:24.821446+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n HashMap<String,Integer> hash = new HashMap<>();\n public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {\n return f(nums,0,nums.length-1,-1);\n }\n public int f(int[] nums,int l,int r,int should){\n if(l >= r){\n return 0;\n }\n String c = l + "" + r + "" + should;\n if(hash.containsKey(c)){\n return hash.get(c);\n }\n int first = 0;\n int last = 0;\n int fl = 0;\n if(should == -1){\n first = f(nums,l+2,r,nums[l] + nums[l+1]) + 1;\n last = f(nums,l,r-2,nums[r] + nums[r-1]) + 1;\n fl = f(nums,l+1,r-1,nums[l] + nums[r]) + 1;\n }\n else{\n if(nums[l] + nums[l+1] == should){\n first = f(nums,l+2,r,should) + 1;\n }\n if(nums[r] + nums[r-1] == should){\n last = f(nums,l,r-2,should) + 1;\n }\n if(nums[l] + nums[r] == should){\n fl = f(nums,l+1,r-1,should) + 1;\n }\n }\n int d = Math.max(first,Math.max(fl,last));\n hash.put(c,d);\n return d;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization', 'Java']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
c++ top down dp solution, original
|
c-top-down-dp-solution-original-by-selma-z7mc
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nwe can use 2d dp to track of front and tail of the current interval. we can use a prev_
|
selma0817
|
NORMAL
|
2024-08-21T22:19:47.610005+00:00
|
2024-08-21T22:19:47.610033+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nwe can use 2d dp to track of front and tail of the current interval. we can use a prev_sum to make sure we can make the deletion. an elegant base case is when i>=j (when front pointer equals to or greater than the tail pointer) since we are required to have at least 2 element in the vector. \n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\n int dp[2001][2001];\npublic:\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n // delete 2 front\n // delte 2 tail\n // delete 1 front 1 tail\n\n // maximize number of operations, not total score \n // 2d dp with front and tail poiter\n memset(dp, -1, sizeof(dp));\n int n = nums.size();\n return solve(nums, 0, n-1, 0, dp);\n\n }\n int solve(vector<int>& nums, int i, int j, int prev_sum, int dp[2001][2001]){\n if(i >= j) return 0;\n if(dp[i][j] != -1) return dp[i][j];\n int result = 0;\n // delete front;\n \n int front_sum = nums[i] + nums[i+1];\n if(front_sum == prev_sum || prev_sum == 0){\n //prev_sum = prev_sum == 0 ? front_sum \n result = max(result, solve(nums, i+2, j, front_sum, dp) + 1);\n }\n \n // delete end\n int tail_sum = nums[j] + nums[j-1];\n if(tail_sum == prev_sum || prev_sum == 0){\n result = max(result, solve(nums, i, j-2, tail_sum, dp) + 1);\n }\n\n // delete both\n int both_sum = nums[i] + nums[j];\n if(both_sum == prev_sum || prev_sum == 0){\n result = max(result, solve(nums, i+1, j-1, both_sum, dp) + 1);\n }\n return dp[i][j] = result;\n\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Easy Recursive Dp Solution
|
easy-recursive-dp-solution-by-kvivekcode-brie
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
kvivekcodes
|
NORMAL
|
2024-08-17T08:40:41.477877+00:00
|
2024-08-17T08:40:41.477908+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n int solve(int i, int j, int val, vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int> >& dp){\n if(i >= j) return 0;\n\n if(dp[i][j] != -1) return dp[i][j];\n\n int ans = 0;\n if(nums[i] + nums[j] == val){\n ans = max(ans, 1+solve(i+1, j-1, val, nums, dp));\n }\n if(nums[i] + nums[i+1] == val){\n ans = max(ans, 1+solve(i+2, j, val, nums, dp));\n }\n if(nums[j-1] + nums[j] == val){\n ans = max(ans, 1+solve(i, j-2, val, nums, dp));\n }\n\n return dp[i][j] = ans;\n }\npublic:\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n = nums.size();\n int ans = 0;\n vector<vector<int> > dp(n, vector<int> (n, -1));\n ans = max(ans, 1+solve(2, n-1, nums[0]+nums[1], nums, dp));\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){\n for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) dp[i][j] = -1;\n }\n ans = max(ans, 1+solve(0, n-3, nums[n-1]+nums[n-2], nums, dp));\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){\n for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) dp[i][j] = -1;\n }\n ans = max(ans, 1+solve(1, n-2, nums[0]+nums[n-1], nums, dp));\n\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
easy and different approach for dp
|
easy-and-different-approach-for-dp-by-ja-jokk
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
jatin_leetcode
|
NORMAL
|
2024-08-01T01:53:04.552309+00:00
|
2024-08-01T01:53:04.552332+00:00
| 1 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\nint dp[2001][2001];\nint solve(vector<int>&nums,int sum,int i,int j){\n int a=0; int b=0; int c=0;\n if(j<0||i>=nums.size())return 0;\n\n if(dp[i][j]!=-1)return dp[i][j];\n if(i+1<=j&&nums[i]+nums[i+1]==sum||sum==0){\n a= 1+ solve(nums,nums[i]+nums[i+1],i+2,j);\n }\n \n if(i<j&&nums[i]+nums[j]==sum||sum==0){\n b= 1+ solve(nums,nums[i]+nums[j],i+1,j-1);\n }\n if(j-1>=i&&nums[j]+nums[j-1]==sum||sum==0){\n c= 1+ solve(nums,nums[j]+nums[j-1],i,j-2);\n }\n return dp[i][j]= max({a,b,c});\n\n}\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);\n cin.tie(nullptr);\n memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp));\n return solve(nums,0,0,nums.size()-1);\n \n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
C++ Easy Solution | Memoization | 3 ms Beats 100.00%
|
c-easy-solution-memoization-3-ms-beats-1-a7ew
|
Code\n\nclass Solution {\n int findSol(vector<int> &a,int tar,int st,int en,unordered_map<string,int> &m){\n if(st>=en) return 0;\n string temp
|
abhinandan__22
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-29T19:10:47.734072+00:00
|
2024-07-29T19:10:47.734101+00:00
| 1 | false |
# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n int findSol(vector<int> &a,int tar,int st,int en,unordered_map<string,int> &m){\n if(st>=en) return 0;\n string temp = to_string(st)+" "+to_string(en)+" "+to_string(tar);\n if(m.count(temp)) return m[temp];\n if(en-st>=3){\n if(a[st]+a[st+1]==tar&&a[en]+a[en-1]==tar){\n m[temp] = findSol(a,tar,st+2,en-2,m)+2;\n return m[temp];\n }\n }\n int ans =0 ;\n if(a[st]+a[st+1]==tar) ans = max(ans,findSol(a,tar,st+2,en,m)+1);\n if(a[st]+a[en]==tar) ans = max( ans, findSol(a,tar,st+1,en-1,m)+1);\n if(a[en]+a[en-1]==tar) ans = max(ans,findSol(a,tar,st,en-2,m)+1);\n m[temp] = ans;\n return ans;\n }\npublic:\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& a) {\n int n = a.size() ;\n unordered_map<string,int> m;\n int ans1 = findSol(a,a[0]+a[1],2,n-1,m)+1;\n int ans2 = findSol(a,a[0]+a[n-1],1,n-2,m)+1;\n int ans3 = findSol(a,a[n-1]+a[n-2],0,n-3,m)+1;\n return max({ans1,ans2,ans3});\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Kabhi kabhi to lagta hai apunich bhagwan hai
|
kabhi-kabhi-to-lagta-hai-apunich-bhagwan-d893
|
Intuition\nIntuitive\n\n\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution:\n def maxOperations(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n # convert to tuple for caching as list are
|
mukesh9
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-27T14:05:14.015950+00:00
|
2024-07-27T14:05:14.015978+00:00
| 8 | false |
# Intuition\nIntuitive\n\n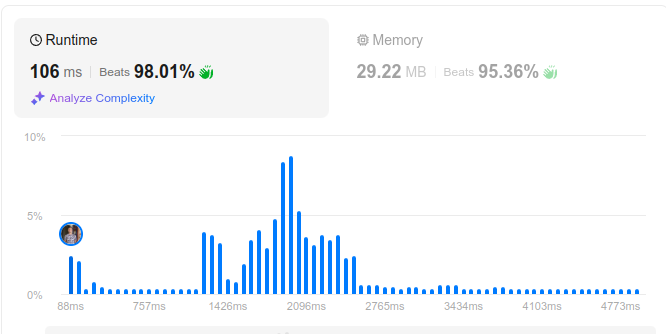\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maxOperations(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n # convert to tuple for caching as list are not hashable\n inpnums = tuple(nums)\n\n @lru_cache\n def remove(nums, expectedScore):\n first, last, both = 0, 0, 0\n if len(nums) >= 2 and expectedScore == nums[0] + nums[1]:\n first = remove(nums[2:], expectedScore)\n if len(nums) >= 2 and expectedScore == nums[-2] + nums[-1]:\n last = remove(nums[:-2], expectedScore)\n if len(nums) >= 2 and expectedScore == nums[0] + nums[-1]:\n both = remove(nums[1:-1], expectedScore)\n\n return max(first, last, both) + 1\n\n return max(\n remove(inpnums[1:-1], inpnums[0] + inpnums[-1]),\n remove(inpnums[:-2], inpnums[-2] + inpnums[-1]),\n remove(inpnums[2:], inpnums[0] + inpnums[1]),\n )\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
scala dfs recursion and memoization. and trampoline to avoid SO, thanks to broken jvm stack settings
|
scala-dfs-recursion-and-memoization-and-1unyh
|
scala dfs recursion and memoization.\nwe use trampoline to avoid SO, thanks to broken jvm stack settings\nscala\nobject Solution {\n import scala.util.chaining
|
vititov
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-15T15:13:20.627796+00:00
|
2024-07-15T15:13:20.627837+00:00
| 0 | false |
scala dfs recursion and memoization.\nwe use trampoline to avoid SO, thanks to broken jvm stack settings\n```scala\nobject Solution {\n import scala.util.chaining._\n import scala.util.control.TailCalls._\n def maxOperations(nums: Array[Int]): Int = {\n\n import scala.util.chaining._\n import scala.util.control.TailCalls._\n val cache = collection.mutable.Map.empty[(Int,Int,Int),TailRec[Int]]\n\n def g1(sum: Int, l:Int,r:Int):TailRec[Int] = {\n cache.getOrElse((sum,l,r), \n (if (r-l<1) done(0.tap(rc => cache += ((sum,l,r) -> done(rc)))) else\n for {\n l2 <- if(nums(l) + nums(l+1) == sum) tailcall(g1(sum, l + 2, r)) else done(-1)\n r2 <- if(nums(r) + nums(r-1) == sum) tailcall(g1(sum, l, r - 2)) else done(-1)\n lr <- if(nums(l) + nums(r) == sum) tailcall(g1(sum, l + 1, r - 1)) else done(-1)\n } yield {\n (1 + (l2 max r2 max lr)).tap(rc => cache += ((sum,l,r) -> done(rc)))\n }))\n }\n val ans = List(\n g1(nums(0)+nums(1),2,nums.length-1).result,\n g1(nums(nums.length-1)+nums(nums.length-2),0,nums.length-3).result,\n g1(nums(0)+nums(nums.length-1),1,nums.length-2).result\n ).maxOption.getOrElse(0)+1\n ans\n\n }\n\n\n def maxOperationsDfs(nums: Array[Int]): Int =\n import scala.util.chaining._\n val cache = collection.mutable.Map.empty[(Int,Int,Int),Int]\n def f(sum: Int, l:Int,r:Int):Int = cache.getOrElse((sum,l,r),\n (if(r-l<1) 0 else List(\n Option.when(nums(l) + nums(l+1) == sum){1+f(sum,l+2,r)},\n Option.when(nums(r) + nums(r-1) == sum){1+f(sum,l,r-2)},\n Option.when(nums(l) + nums(r) == sum){1+f(sum,l+1,r-1)}\n ).flatten.maxOption.getOrElse(0)\n ).tap(rc => cache += ((sum,l,r) -> rc)))\n List(\n f(nums(0)+nums(1),2,nums.length-1),\n f(nums(nums.length-1)+nums(nums.length-2),0,nums.length-3),\n f(nums(0)+nums(nums.length-1),1,nums.length-2)\n ).maxOption.getOrElse(0)+1\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Scala']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
DP
|
dp-by-drift_23-x4r9
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
drift_23
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-12T19:22:17.481950+00:00
|
2024-07-12T19:22:17.481978+00:00
| 4 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:O(n*n)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:O(n * n)+O((n-1)*(n-1))\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int f(int i,int j,int score,int operation,vector<int>&nums,vector<vector<int>>&dp){\n if(i>=j){\n return operation;\n }\n if((nums[i]+nums[j]!=score) &&(nums[i]+nums[i+1]!=score) &&(nums[j]+nums[j-1]!=score) && score!=0) return operation;\n if(dp[i][j]!=-1)return dp[i][j];\n int maxi=INT_MIN;\n if(score==0 ||(score==nums[i]+nums[i+1]))\n maxi=max(maxi,f(i+2,j,nums[i]+nums[i+1],operation+1,nums,dp));\n\n if(score==0 ||(score==nums[i]+nums[j]))\n maxi=max(maxi,f(i+1,j-1,nums[i]+nums[j],operation+1,nums,dp));\n\n if(score==0 ||(score==nums[j]+nums[j-1]))\n maxi=max(maxi,f(i,j-2,nums[j]+nums[j-1],operation+1,nums,dp));\n return dp[i][j]=maxi;\n }\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n=nums.size();\n int score=0;\n vector<vector<int>>dp(n,vector<int>(n,-1));\n return f(0,n-1,score,0,nums,dp);\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Answered the question which I bet you had while thinking of intuition.
|
answered-the-question-which-i-bet-you-ha-egxh
|
Intuition\nYou would have thinked that using only 1 dp array of (n x n) would not work, becaue we have to check for 3 different sums.\n\nNow, if sum in second c
|
darpan_1405
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-09T16:01:49.692133+00:00
|
2024-07-09T16:01:49.692166+00:00
| 6 | false |
# Intuition\nYou would have thinked that **using only 1 dp array of (n x n) would not work**, becaue we have to check for **3 different sums**.\n\n**Now, if sum in second case is different than the first case, the pair of (i,j) for which the condition satisfies will never be marked during first iteration, because we are only applying recusrion if the scores match.**\n\n**Example:** in code, during the first call, sum that we are looking for is 5. Then recursion woud only be called for (i,j) pairs for which the score is 5. During second call, if the sum is 7, no (i,j) pairs for which sum is 5 will be encountered.\n\nThat is the reason why **using only 1 dp array works.**\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n^2)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(n^2)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n=nums.size();\n\n vector<vector<int>> dp(n,vector<int> (n,-1));\n\n int first=1+getMaxOps(2,n-1,nums,nums[0]+nums[1],dp);\n int second=1+getMaxOps(0,n-3,nums,nums[n-1]+nums[n-2],dp);\n int third=1+getMaxOps(1,n-2,nums,nums[0]+nums[n-1],dp);\n\n return max(first,max(second,third));\n }\n\nprivate:\n int getMaxOps(int i,int j,vector<int>& nums,int scoreToLook,vector<vector<int>> &dp){\n if(j-i+1<2) return 0;\n\n if(dp[i][j]!=-1) return dp[i][j];\n\n int score=0;\n if(nums[i]+nums[i+1]==scoreToLook) score=1+getMaxOps(i+2,j,nums,scoreToLook,dp);\n if(nums[j]+nums[j-1]==scoreToLook) score=max(score,1+getMaxOps(i,j-2,nums,scoreToLook,dp));\n if(nums[i]+nums[j]==scoreToLook) score=max(score,1+getMaxOps(i+1,j-1,nums,scoreToLook,dp));\n\n return dp[i][j]=score;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Top down DP in python beat 95%
|
top-down-dp-in-python-beat-95-by-miiicom-n7oe
|
\n# Code\n\nclass Solution:\n def maxOperations(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n if len(nums) == 2:\n return 1\n \n cache = d
|
miiicom
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-04T03:59:42.867579+00:00
|
2024-07-04T03:59:42.867599+00:00
| 11 | false |
\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def maxOperations(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:\n if len(nums) == 2:\n return 1\n \n cache = dict()\n\n def do_hash(arr):\n return \'\'.join(str(x) for x in arr)\n\n def dp(arr, target_sum):\n nonlocal cache\n if len(arr) <= 2:\n if len(arr) == 2:\n return int(sum(arr) == target_sum)\n return 0\n \n hashed_arr = do_hash(arr)\n if hashed_arr in cache:\n return cache[hashed_arr]\n\n temp_result = 0\n \n if arr[0] + arr[1] == target_sum:\n temp_result = max(temp_result, dp(arr[2:], target_sum) + 1)\n if arr[0] + arr[-1] == target_sum:\n temp_result = max(temp_result, dp(arr[1:-1], target_sum) + 1)\n if arr[-2] + arr[-1] == target_sum:\n temp_result = max(temp_result, dp(arr[:-2], target_sum) + 1)\n cache[hashed_arr] = temp_result\n return cache[hashed_arr]\n \n opt1_result = dp(nums[2:], nums[0] + nums[1])\n opt2_result = dp(nums[1:-1], nums[0] + nums[-1])\n opt3_result = dp(nums[:-2], nums[-2] + nums[-1])\n return max(opt1_result, opt2_result, opt3_result) + 1\n \n \n \n \n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Lo Kr Lo copy
|
lo-kr-lo-copy-by-danish_jamil-rr3g
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Danish_Jamil
|
NORMAL
|
2024-06-29T05:57:51.581788+00:00
|
2024-06-29T05:57:51.581820+00:00
| 10 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n \n // Main function to find the maximum number of operations\n public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {\n \n int maxOps = 0; // Variable to store the maximum operations\n int len = nums.length; // Length of the array\n int[][] memo = new int[len][len]; // Memoization array to store computed results\n int left = 0; // Left pointer\n int right = len - 1; // Right pointer\n\n // Checking operations with different combinations and update maxOps accordingly\n maxOps = Math.max(maxOps, maxOpsHelper(nums, left + 2, right, nums[left] + nums[left + 1], memo) + 1);\n maxOps = Math.max(maxOps, maxOpsHelper(nums, left + 1, right - 1, nums[left] + nums[right], memo) + 1);\n maxOps = Math.max(maxOps, maxOpsHelper(nums, left, right - 2, nums[right] + nums[right - 1], memo) + 1);\n\n return maxOps;\n }\n\n private int maxOpsHelper(int[] nums, int left, int right, int prevSum, int[][] memo) {\n if (left >= right)\n return 0; // Base case : no more elements to consider\n if (memo[left][right] != 0)\n return memo[left][right]; // Returning memoized result if available\n\n int ops = 0; // Variable to store the maximum operations for the current subproblem\n\n if (nums[left] + nums[left + 1] == prevSum)\n ops = Math.max(ops, maxOpsHelper(nums, left + 2, right, prevSum, memo) + 1);\n if (nums[left] + nums[right] == prevSum)\n ops = Math.max(ops, maxOpsHelper(nums, left + 1, right - 1, prevSum, memo) + 1);\n if (nums[right] + nums[right - 1] == prevSum)\n ops = Math.max(ops, maxOpsHelper(nums, left, right - 2, prevSum, memo) + 1);\n\n return memo[left][right] = ops; // Memoizing the result and return\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Easy approach | Recursion + Memoization
|
easy-approach-recursion-memoization-by-k-a4d1
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
kesarwaniankit4812
|
NORMAL
|
2024-06-16T16:23:04.029023+00:00
|
2024-06-16T16:23:04.029045+00:00
| 8 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {\n int n = nums.length;\n if (n < 2) {\n return 0;\n }\n\n int [][] dp = new int[n][n];\n for (int [] arr : dp) {\n Arrays.fill(arr, -1);\n }\n\n int firstTwo = 1 + helper(nums, 2, n - 1, nums[0] + nums[1], dp);\n int lastTwo = 1 + helper(nums, 0, n - 3, nums[n - 2] + nums[n - 1], dp);\n int firstAndLast = 1 + helper(nums, 1, n - 2, nums[0] + nums[n - 1], dp);\n\n return Math.max(firstTwo, Math.max(lastTwo, firstAndLast));\n }\n\n public int helper(int [] nums, int i, int j, int prevScore, int [][] dp) {\n if ((j - i + 1) < 2) {\n return 0;\n }\n\n if (dp[i][j] != -1) {\n return dp[i][j];\n }\n\n int firstTwo = 0;\n if (nums[i] + nums[i + 1] == prevScore) {\n firstTwo = 1 + helper(nums, i + 2, j, nums[i] + nums[i + 1], dp);\n }\n\n int lastTwo = 0;\n if (nums[j - 1] + nums[j] == prevScore) {\n lastTwo = 1 + helper(nums, i, j - 2, nums[j - 1] + nums[j], dp);\n }\n\n int firstAndLast = 0;\n if (nums[i] + nums[j] == prevScore) {\n firstAndLast = 1 + helper(nums, i + 1, j - 1, nums[i] + nums[j], dp);\n }\n\n return dp[i][j] = Math.max(firstTwo, Math.max(lastTwo, firstAndLast));\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Recursion', 'Memoization', 'Java']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Easy memoization approach✅ beats 85%
|
easy-memoization-approach-beats-85-by-sa-47zc
|
Intuition\nAs mentioned in the question we need to find the maximum number of operations we can perform that yield same score.\nwe can perform the following ope
|
saitejagorli04
|
NORMAL
|
2024-06-11T16:01:50.502264+00:00
|
2024-06-11T16:03:26.494706+00:00
| 12 | false |
# Intuition\nAs mentioned in the question we need to find the maximum number of operations we can perform that yield same score.\nwe can perform the following operations\n1. delete first two elements\n2. delete last two elements\n3. delete first and last elements\n\n\n# Approach\nso the approach is to recursively shrink the array by deleting the elements in it so we are taking two indexes **i** , **j** where\n **i** - represents starting of the array and \n**j** - represents the ending of the array\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nAs we are using memoization approach time complexity will be **O(n^2)**\n\n- Space complexity:\nwe are using an dp array which which of size **n^2**\nrecursive stack space of size **n**\nTotal space complexity is **O(n^2)**\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution(object):\n def memoization(self,i,j,score,nums,dp):\n if j<=i: # when the array is shrinked to 1 or 0 elements we simply return 0\n return 0\n if dp[i][j] !=-1:\n return dp[i][j]\n first = 0\n last = 0\n firstLast = 0 \n if (nums[i]+nums[i+1])==score:\n first = 1+self.memoization(i+2,j,score,nums,dp) #deleting the first two elements\n if (nums[i]+nums[j])==score:\n firstLast = 1+self.memoization(i+1,j-1,score,nums,dp) #deleting the first and last elements\n if (nums[j]+nums[j-1])==score:\n last = 1+self.memoization(i,j-2,score,nums,dp) #deleting the last two elements\n dp[i][j] = max(first,last,firstLast)\n return dp[i][j]\n def maxOperations(self, nums):\n n = len(nums)\n dp = [[-1]*n for _ in range(n)]\n first = self.memoization(2,n-1,nums[0]+nums[1],nums,dp)\n firstLast = self.memoization(1,n-2,nums[0]+nums[n-1],nums,dp)\n last = self.memoization(0,n-3,nums[n-1]+nums[n-2],nums,dp)\n return 1+max(first,last,firstLast)\n\n\n \n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'Python']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
No extra conditions || Tricky memoize || very simple || c++
|
no-extra-conditions-tricky-memoize-very-3blny
|
Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int n;\n int dp[2001][2001][3];\n unordered_map<int,int> indices;\n int solve(vector<int>& nums,int l,int r,int
|
shivambirla139
|
NORMAL
|
2024-06-07T14:27:37.118222+00:00
|
2024-06-07T14:27:37.118246+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int n;\n int dp[2001][2001][3];\n unordered_map<int,int> indices;\n int solve(vector<int>& nums,int l,int r,int score){\n if(r <= l) return 0;\n if(dp[l][r][indices[score]]!=-1) return dp[l][r][indices[score]];\n int ret = 0 ;\n if(score == nums[l]+nums[r]) ret = max(ret,1+solve(nums,l+1,r-1,score));\n if(score == nums[l]+nums[l+1]) ret = max(ret,1+solve(nums,l+2,r,score));\n if(score == nums[r]+nums[r-1]) ret = max(ret,1+solve(nums,l,r-2,score));\n return dp[l][r][indices[score]] = ret;\n }\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp));\n n = nums.size();\n int ans = 0;\n int l =0 , r = n-1;\n indices[nums[0]+nums[1]] = 0;\n indices[nums[n-1]+nums[n-2]] = 1;\n indices[nums[0]+nums[n-1]] = 2;\n ans = max(ans,1+solve(nums,l+2,r,nums[0]+nums[1]));\n ans = max(ans,1+solve(nums,l,r-2,nums[n-1]+nums[n-2]));\n ans = max(ans,1+solve(nums,l+1,r-1,nums[0]+nums[n-1]));\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Easy and Intuitive Top Down Dynamic Programming Solution
|
easy-and-intuitive-top-down-dynamic-prog-wsvf
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
devalpp
|
NORMAL
|
2024-06-02T17:01:45.672582+00:00
|
2024-06-02T17:01:45.672606+00:00
| 6 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n^2)$$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(n^2)$$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\n// subproblem \n// (l, r, score) -> max number of operations of this subproblem\n\n// memo only needs l and r, becuase each l + r combo will have a unique score\n\nclass Solution {\n int max;\n int[] nums;\n Integer[][] memo;\n public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {\n this.max = 0;\n this.nums = nums;\n if(nums.length == 0) return max;\n if(nums.length == 1) return max;\n\n this.memo = new Integer[nums.length][nums.length];\n dfs(0, nums.length - 1, null);\n return max;\n }\n\n private int dfs(int l, int r, Integer score) {\n if(l >= r) return 0;\n if(l == nums.length) return 0;\n if(memo[l][r] != null) return memo[l][r];\n\n int maxIfFirst2 = 0;\n int maxIfLast2 = 0;\n int maxIfFirstAndLast = 0;\n\n // delete first 2\n if(score == null || nums[l] + nums[l + 1] == score) {\n maxIfFirst2 = dfs(l + 2, r, nums[l] + nums[l + 1]) + 1;\n }\n\n // delete last 2\n if(score == null || nums[r] + nums[r - 1] == score) {\n maxIfLast2 = dfs(l, r - 2, nums[r] + nums[r - 1]) + 1;\n }\n\n // delete first and last\n if(score == null || nums[l] + nums[r] == score) {\n maxIfFirstAndLast = dfs(l + 1, r - 1, nums[l] + nums[r]) + 1;\n }\n\n int currentMax = Math.max(maxIfFirst2, Math.max(maxIfLast2, maxIfFirstAndLast));\n max = Math.max(max, currentMax);\n\n memo[l][r] = currentMax;\n\n return currentMax;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
[C++] 3d DP simple
|
c-3d-dp-simple-by-quater_nion-yuy0
|
Intuition\nwe can check for 3 different sums i.e. first 2, last 2 ans terminal elements. assign one index for each sum \nlet dp[x][y][ind] = max. operations tha
|
quater_nion
|
NORMAL
|
2024-05-22T14:34:49.577950+00:00
|
2024-05-22T14:34:49.577987+00:00
| 10 | false |
# Intuition\nwe can check for 3 different sums i.e. first 2, last 2 ans terminal elements. assign one index for each sum \nlet `dp[x][y][ind]` = max. operations that can be done in a subarray for index range `[x, y]` with sum of index `ind`.\n\n`dp[x][y][ind] = 1 + max(dp[x+1][y-1][ind], dp[x+2][y][ind] , dp[x][y-2][ind])`\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n$$O(n^2)$$\n\n- Space complexity:\n$$O(3n^2)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n \npublic:\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n=nums.size();\n int dp[2001][2001][3];\n memset(dp, -1, sizeof(dp));\n map<int, int> indexOf;\n indexOf[nums[0]+nums[1]] = 0;\n indexOf[nums[0]+nums[n-1]] = 1;\n indexOf[nums[n-2]+nums[n-1]] = 2;\n function<int(int, int, int)> solve =\n [&](int a, int b, int sum)->int {\n if(a>=b) return 0;\n int ans=0;\n if(dp[a][b][indexOf[sum]]!=-1) return dp[a][b][indexOf[sum]];\n if(nums[a]+nums[b]==sum)\n ans = max(ans, 1+ solve(a+1,b-1, sum));\n if(nums[a]+nums[a+1]==sum)\n ans = max(ans, 1+ solve(a+2,b, sum));\n if(nums[b-1]+nums[b]==sum)\n ans = max(ans, 1+ solve(a,b-2, sum));\n \n return dp[a][b][indexOf[sum]] = ans;\n };\n\n\n return max({solve(0,n-1,nums[0]+nums[1]), \n solve(0,n-1,nums[0]+nums[n-1]),\n solve(0,n-1,nums[n-2]+nums[n-1])});\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Easy sol^n
|
easy-soln-by-singhgolu933600-fo61
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
singhgolu933600
|
NORMAL
|
2024-05-20T06:25:01.553819+00:00
|
2024-05-20T06:25:01.553842+00:00
| 0 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int top_down(vector<int>& nums,int i,int j,int sum,unordered_map<int,int>&mapping,vector<vector<vector<int>>>&dp)\n {\n if(i>=j)\n {\n return 0;\n }\n if((sum!=-1)&&dp[mapping[sum]][i][j]!=-1)\n return dp[mapping[sum]][i][j];\n if(sum==-1)\n {\n int val1=0;\n int val2=0;\n int val3=0;\n if(i+1<nums.size())\n val1=1+top_down(nums,i+2,j,nums[i]+nums[i+1],mapping,dp);\n if(j-1>=0)\n val2=1+top_down(nums,i,j-2,nums[j]+nums[j-1],mapping,dp);\n val3=1+top_down(nums,i+1,j-1,nums[i]+nums[j],mapping,dp);\n return max(val1,max(val2,val3));\n }\n else\n {\n int val1=0;\n int val2=0;\n int val3=0;\n if((i+1<nums.size())&&((nums[i]+nums[i+1])==sum))\n {\n val1=1+top_down(nums,i+2,j,nums[i]+nums[i+1],mapping,dp);\n }\n if((j-1>=0)&&((nums[j]+nums[j-1])==sum))\n {\n val2=1+top_down(nums,i,j-2,nums[j]+nums[j-1],mapping,dp);\n }\n if((nums[i]+nums[j])==sum)\n val3=1+top_down(nums,i+1,j-1,nums[i]+nums[j],mapping,dp);\n dp[mapping[sum]][i][j]=max(val1,max(val2,val3));\n return dp[mapping[sum]][i][j];\n }\n }\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n unordered_map<int,int>mapping;\n mapping[nums[0]+nums[1]]=0;\n mapping[nums[nums.size()-1]+nums[nums.size()-2]]=1;\n mapping[nums[0]+nums[nums.size()-1]]=2;\n vector<vector<vector<int>>>dp(3,vector<vector<int>>(nums.size()+1,vector<int>(nums.size()+1,-1)));\n return top_down(nums,0,nums.size()-1,-1,mapping,dp); \n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
One of the simplest solution
|
one-of-the-simplest-solution-by-risabhuc-xw19
|
\n\nclass Solution {\n Integer[][][]dp;\n int[]k;\n public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {\n dp=new Integer[nums.length][nums.length][4];\n
|
risabhuchiha
|
NORMAL
|
2024-05-09T02:32:09.054314+00:00
|
2024-05-09T02:32:09.054342+00:00
| 9 | false |
\n```\nclass Solution {\n Integer[][][]dp;\n int[]k;\n public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {\n dp=new Integer[nums.length][nums.length][4];\n k=new int[4];\n k[1]=nums[nums.length-1]+nums[nums.length-2];\n k[2]=nums[0]+nums[nums.length-1];\n k[3]=nums[0]+nums[1];\n return f(0,nums.length-1,nums,0);\n }\n public int f(int l,int r,int[]nums,int s){\n if(l>=r)return 0;\n int ans=0;\n if(dp[l][r][s]!=null)return dp[l][r][s];\n\n \n // System.out.println(s+" "+ans+" "+k[s]+" "+(nums[l]+nums[r])+" "+(nums[l]+nums[l+1])+" "+(nums[r]+nums[r-1])+" "+l+" "+r);\n if(s==0){\n ans=Math.max(ans,1+f(l,r-2,nums,1));\n ans=Math.max(1+f(l+1,r-1,nums,2),ans);\n ans=Math.max(ans,1+f(l+2,r,nums,3));\n \n }\n else{\n if(k[s]==nums[l]+nums[r]){\n ans=Math.max(1+f(l+1,r-1,nums,s),ans);\n }\n if(nums[l]+nums[l+1]==k[s]){\n ans=Math.max(ans,1+f(l+2,r,nums,s));\n }\n if(nums[r]+nums[r-1]==k[s]){\n ans=Math.max(ans,1+f(l,r-2,nums,s));\n }\n }\n // System.out.println(s+" "+ans+" "+" "+(nums[l]+nums[r])+" "+(nums[l]+nums[l+1])+" "+(nums[r]+nums[r-1])+" "+l+" "+r);\n return dp[l][r][s]=ans;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Java solution using recursion with memoization (beats 98%)
|
java-solution-using-recursion-with-memoi-5pxd
|
Vote up if you like it . \n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\n\n public boolean areAllElementsSame(int[] array) {\n // Compare each element with the first
|
im_krgs
|
NORMAL
|
2024-05-05T20:30:35.357821+00:00
|
2024-05-05T20:33:59.022763+00:00
| 6 | false |
# Vote up if you like it . \n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n\n public boolean areAllElementsSame(int[] array) {\n // Compare each element with the first element\n int firstElement = array[0];\n for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {\n if (array[i] != firstElement) {\n return false; // If any element is different, return false\n }\n }\n\n return true; // If all elements are the same, return true\n }\n\n public static int sol(int[] nums, int i, int j, int score, int[][] memo) {\n // Base case\n if (i >= j)\n return 0;\n\n // If the result is already computed, return it from the memoization table\n if (memo[i][j] != -1)\n return memo[i][j];\n\n int option1 = 0, option2 = 0, option3 = 0;\n\n // Calculate scores for three options\n int score1 = nums[i] + nums[j];\n int score2 = nums[i] + nums[i + 1];\n int score3 = nums[j - 1] + nums[j];\n\n // Calculate options based on score condition\n if (score1 == score || score == -1) {\n option1 = 1 + sol(nums, i + 1, j - 1, score1,memo);\n }\n if (score2 == score || score == -1) {\n option2 = 1 + sol(nums, i + 2, j, score2,memo);\n }\n if (score3 == score || score == -1) {\n option3 = 1 + sol(nums, i, j - 2, score3,memo);\n }\n\n // Update memoization table with the maximum of the three options\n memo[i][j] = Math.max(option1, Math.max(option2, option3));\n return memo[i][j];\n }\n\n public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {\n int n = nums.length;\n //check if all the elements of the array is same if yes just return the half the number of element in the array\n if (areAllElementsSame(nums)) return n / 2;\n // Create memoization table\n int[][] memo = new int[n][n]; // memo[i][j] stores the maximum number of operations from index i to j\n \n\n // Initialize memoization table with -1\n for (int[] row : memo) {\n Arrays.fill(row, -1);\n }\n\n // Call the recursive function with memoization\n return sol(nums, 0, n - 1, -1, memo);\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Memoization', 'Java']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
JavaScript memorized search
|
javascript-memorized-search-by-lilongxue-fwhp
|
Intuition\nIt is a typical dynamic programming problem.\n# Approach\nFor simplicity of coding, we use memorized search (recursion)\n# Complexity\n- Time complex
|
lilongxue
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-30T00:42:27.439447+00:00
|
2024-04-30T00:42:27.439477+00:00
| 12 | false |
# Intuition\nIt is a typical dynamic programming problem.\n# Approach\nFor simplicity of coding, we use memorized search (recursion)\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(n ** 2)\n- Space complexity:\nO(n ** 2)\n# Code\n```\n/**\n * @param {number[]} nums\n * @return {number}\n */\nvar maxOperations = function(nums) {\n const len = nums.length\n function toKey(...args) {\n return args.join(\'|\')\n }\n const map = new Map()\n function solve(i, j, sum) {\n if (j - i < 1) return 0\n const key = toKey(i, j, sum)\n if (map.has(key)) return map.get(key)\n\n let result = 0\n const a = nums[i], b = nums[i + 1]\n if (a + b === sum)\n result = Math.max(result, 1 + solve(i + 2, j, sum))\n const c = nums[j], d = nums[j - 1]\n if (c + d === sum)\n result = Math.max(result, 1 + solve(i, j - 2, sum))\n if (a + c === sum)\n result = Math.max(result, 1 + solve(i + 1, j - 1, sum))\n\n map.set(key, result)\n return result\n }\n\n\n const a = nums[0], b = nums[1]\n const c = nums[len - 1], d = nums[len - 2]\n const resultX = 1 + solve(2, len - 1, a + b)\n const resultY = 1 + solve(0, len - 3, c + d)\n const resultZ = 1 + solve(1, len - 2, a + c)\n \n\n const result = Math.max(resultX, resultY, resultZ)\n return result\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
JavaScript memorized search
|
javascript-memorized-search-by-lilongxue-mz6t
|
Intuition\nIt is a typical dynamic programming problem.\n# Approach\nFor simplicity of coding, we use memorized search (recursion)\n# Complexity\n- Time complex
|
lilongxue
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-30T00:42:16.371450+00:00
|
2024-04-30T00:42:52.243835+00:00
| 7 | false |
# Intuition\nIt is a typical dynamic programming problem.\n# Approach\nFor simplicity of coding, we use memorized search (recursion)\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(n ** 2)\n- Space complexity:\nO(n ** 2)\n# Code\n```\n/**\n * @param {number[]} nums\n * @return {number}\n */\nvar maxOperations = function(nums) {\n const len = nums.length\n function toKey(...args) {\n return args.join(\'|\')\n }\n const map = new Map()\n function solve(i, j, sum) {\n if (j - i < 1) return 0\n const key = toKey(i, j, sum)\n if (map.has(key)) return map.get(key)\n\n let result = 0\n const a = nums[i], b = nums[i + 1]\n if (a + b === sum)\n result = Math.max(result, 1 + solve(i + 2, j, sum))\n const c = nums[j], d = nums[j - 1]\n if (c + d === sum)\n result = Math.max(result, 1 + solve(i, j - 2, sum))\n if (a + c === sum)\n result = Math.max(result, 1 + solve(i + 1, j - 1, sum))\n\n map.set(key, result)\n return result\n }\n\n\n const a = nums[0], b = nums[1]\n const c = nums[len - 1], d = nums[len - 2]\n const resultX = 1 + solve(2, len - 1, a + b)\n const resultY = 1 + solve(0, len - 3, c + d)\n const resultZ = 1 + solve(1, len - 2, a + c)\n \n\n const result = Math.max(resultX, resultY, resultZ)\n return result\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
[C++] DP [Recursion + Memoization] Easy and Straight Forward
|
c-dp-recursion-memoization-easy-and-stra-h6ar
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int solve(vector<vector<int>> &dp, vector<int> &nums, int l, int r, int val, int taken)\n {\n int n = nums.size(), an
|
ranjan_him212
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-22T13:48:54.509053+00:00
|
2024-04-22T13:48:54.509087+00:00
| 2 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int solve(vector<vector<int>> &dp, vector<int> &nums, int l, int r, int val, int taken)\n {\n int n = nums.size(), ans = taken;\n if(l > n || r < 0 || l >= r)return taken;\n if(dp[l][r]!=-1)return dp[l][r];\n if(l+1 < n && nums[l+1] + nums[l] == val)ans = max(ans, solve(dp, nums, l+2, r, val, 1 + taken));\n if(nums[r] + nums[l] == val)ans = max(ans, solve(dp, nums, l+1, r-1, val, taken + 1));\n if(r-1 >= 0 && nums[r-1] + nums[r] == val)ans = max(ans, solve(dp, nums, l, r-2, val, taken + 1));\n return dp[l][r] = ans;\n }\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n = nums.size();\n vector<vector<int>> dp1(n+1, vector<int> (n+1, -1));\n vector<vector<int>> dp2(n+1, vector<int> (n+1, -1));\n vector<vector<int>> dp3(n+1, vector<int> (n+1, -1));\n return max({solve(dp1, nums, 0, n-1, nums[0]+nums[1], 0), \n solve(dp2, nums, 0, n-1, nums[0]+nums[n-1], 0),solve(dp3, nums, 0, n-1, nums[n-1]+nums[n-2], 0)});\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'C']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Java Recursion + Memorization
|
java-recursion-memorization-by-arkadeepg-uvgq
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \nRecursion + Memorizatio
|
arkadeepgr
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-20T14:18:58.650339+00:00
|
2024-04-20T14:18:58.650362+00:00
| 0 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nRecursion + Memorization\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution { \n\n public static HashMap<Integer,int[][]> topCache = new HashMap<Integer,int[][]>();\n\n public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {\n topCache.clear();\n int start = 0;\n int end = nums.length-1;\n\n int first = nums[start];\n int second = nums[start+1];\n int last = nums[end]; \n int secondLast = nums[end-1];\n \n int A = first + second;\n int B = last + secondLast;\n int C = first + last;\n\n topCache.put(A,new int[nums.length][nums.length]);\n topCache.put(B,new int[nums.length][nums.length]);\n topCache.put(C,new int[nums.length][nums.length]);\n\n int resA = 1 + solve(nums,start+2,end,A,topCache.get(A));\n int resB = 1 + solve(nums,start,end-2,B,topCache.get(B));\n int resC = 1 + solve(nums,start+1,end-1,C,topCache.get(C));\n \n return Math.max(resA,Math.max(resB,resC)); \n }\n\n public int solve(int[] nums,int start,int end,int match,int[][] cache){\n\n if(end-start < 1)\n return 0;\n \n if(cache[start][end] != 0)\n return cache[start][end];\n \n int first = nums[start];\n int second = nums[start+1];\n int last = nums[end]; \n int secondLast = nums[end - 1];\n\n int A = first + second;\n int B = last + secondLast;\n int C = first + last;\n \n int res = 0;\n\n if(A == match){\n int tempRes = 1 + solve(nums,start+2,end,A,cache);\n if(tempRes >= res){\n res = tempRes;\n }\n }\n if(B == match){\n int tempRes = 1 + solve(nums,start,end-2,B,cache);\n if(tempRes >= res){\n res = tempRes;\n }\n }\n \n if(C == match){\n int tempRes = 1 + solve(nums,start+1,end-1,C,cache);\n if(tempRes >= res){\n res = tempRes;\n }\n }\n\n cache[start][end] = res;\n\n return res; \n }\n}\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
simple code
|
simple-code-by-nithi_0805-42wa
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Nithi_0805
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-19T08:52:07.491499+00:00
|
2024-04-19T08:52:07.491517+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n int[][][] arr;\n int sum1;\n int sum2;\n int sum3;\n public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {\n arr=new int[nums.length][nums.length][3];\n int sum1=nums[0]+nums[1];\n int sum2=nums[nums.length-1]+nums[nums.length-2];\n int sum3=nums[0]+nums[nums.length-1];\n for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++)\n {\n for(int j=0;j<arr[0].length;j++)\n {\n for(int k=0;k<3;k++)\n {\n arr[i][j][k]=-1;\n }\n }\n }\n int temp1= 1+ope(nums,2,nums.length-1,nums[0]+nums[1]);\n int temp2= 1+ope(nums,0,nums.length-3,nums[nums.length-1]+nums[nums.length-2]);\n int temp3= 1+ope(nums,1,nums.length-2,nums[0]+nums[nums.length-1]);\n \n return Math.max(temp1,Math.max(temp2,temp3));\n }\n\n int ope(int[] nums,int start,int end,int sum)\n { int res=0;\n \n if(start==end || start<0 || start>=nums.length || end<0 || end>=nums.length)\n return 0;\n \n int val=0;\n if(sum==sum1)\n val=0;\n else if(sum==sum2)\n val=1;\n else if(sum==sum3)\n val=3;\n\n if(arr[start][end][val] != -1)\n return arr[start][end][val];\n\n if((end-start >= 1) && (nums[start]+nums[start+1]) == sum)\n {\n res=Math.max(res,1+ope(nums,start+2,end,sum));\n }\n\n if((end-start >= 1) && (nums[end]+nums[end-1]) == sum)\n {\n res=Math.max(res,1+ope(nums,start,end-2,sum));\n }\n\n if((end-start >= 1) && (nums[start]+nums[end]) == sum)\n {\n res=Math.max(res,1+ope(nums,start+1,end-1,sum));\n }\n\n return arr[start][end][val]= res;\n }\n\n} \n\n\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Very Easy DP Solution
|
very-easy-dp-solution-by-fenil_vaghasiya-gked
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
Fenil_Vaghasiya
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-14T09:16:08.555377+00:00
|
2024-04-14T09:16:08.555412+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int fun(int sum,int i,int j,vector<int> &a,vector<vector<int>> &dp){\n if(i>=j) return 0;\n // cout<<i<<" "<<j<<endl;\n\n if(dp[i][j]!=-1) return dp[i][j];\n\n int a1=0,a2=0,a3=0;\n if(a[i]+a[i+1]==sum) a1=fun(sum,i+2,j,a,dp)+1;\n if(a[i]+a[j]==sum) a2=fun(sum,i+1,j-1,a,dp)+1;\n if(a[j]+a[j-1]==sum) a3=fun(sum,i,j-2,a,dp)+1;\n\n // cout<<a1<<" "<<a2<<" "<<a3<<endl;\n dp[i][j]=max(a1,max(a2,a3));\n return dp[i][j];\n }\n\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& a) {\n int n=a.size();\n vector<vector<int>> dp(n,vector<int>(n,-1));\n\n int ans1=fun(a[0]+a[1],2,n-1,a,dp)+1;\n int ans2=fun(a[0]+a[n-1],1,n-2,a,dp)+1;\n int ans3=fun(a[n-1]+a[n-2],0,n-3,a,dp)+1;\n\n int ans=max(ans1,max(ans2,ans3));\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
EASY C++ SOLUTION || MEMORISATION || 2D DP
|
easy-c-solution-memorisation-2d-dp-by-ha-b6hs
|
EASY C++ SOLUTION || MEMORISATION\n# Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nreally easy and understandable\n# Approach\n Descr
|
harshh_raj
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-12T19:05:27.798747+00:00
|
2024-04-12T19:05:27.798775+00:00
| 1 | false |
EASY C++ SOLUTION || MEMORISATION\n# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nreally easy and understandable\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int f(int i,int j,vector<int>& nums,int sum, vector<vector<int>>&dp){\n if(i>j)return 0;\n if(dp[i][j]!=-1)return dp[i][j];\n int l=0;\n if(i+1<=j){\n int ss=nums[i]+nums[i+1];\n if(sum==0 || ss==sum)l=1+f(i+2,j,nums,ss,dp);\n }\n int r=0;\n if(i<=j-1){\n int ss=nums[j]+nums[j-1];\n if(sum==0 || ss==sum)r=1+f(i,j-2,nums,ss,dp);\n }\n int m=0;\n if(i!=j){\n int ss=nums[i]+nums[j];\n if(sum==0 || ss==sum)m=1+f(i+1,j-1,nums,ss,dp);\n }\n return dp[i][j]=max(l,max(r,m));\n }\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n=nums.size();\n vector<vector<int>>dp(n,vector<int>(n,-1));\n return f(0,n-1,nums,0,dp);\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Simple Java | DP | Memoization | O(n^2) | Beats 98.77%
|
simple-java-dp-memoization-on2-beats-987-fdkm
|
Approach\nTry All possible paths and maintain a 2-D matrix to store the results.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n^2)\n\n- Space complexity: O(n^2)\n\n# C
|
pathetic_
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-12T08:29:06.896760+00:00
|
2024-04-12T08:29:06.896783+00:00
| 5 | false |
# Approach\nTry All possible paths and maintain a 2-D matrix to store the results.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n^2)\n\n- Space complexity: O(n^2)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {\n int [][] map = new int[nums.length][nums.length];\n int start = getMax(nums, 2, nums.length - 1, nums[0] + nums[1], map) + 1;\n int end = getMax(nums, 0, nums.length - 3, nums[nums.length - 1] + nums[nums.length - 2], map) + 1;\n int both = getMax(nums, 1, nums.length - 2, nums[0] + nums[nums.length - 1], map) + 1;\n return Math.max(start, Math.max(end, both));\n }\n private int getMax(int nums[], int start, int end, int pastVal, int[][] map) {\n if (start >= end) {\n return 0;\n }\n if (map[start][end] != 0) {\n return map[start][end];\n }\n int max = 0;\n int startVal = nums[start] + nums[start + 1];\n if (startVal == pastVal) {\n max = Math.max(max, getMax(nums, start + 2, end, pastVal, map) + 1);\n }\n int endVal = nums[end] + nums[end - 1];\n if (endVal == pastVal) {\n max = Math.max(max, getMax(nums, start, end - 2, pastVal, map) + 1);\n }\n int both = nums[start] + nums[end];\n if (both == pastVal) {\n max = Math.max(max, getMax(nums, start + 1, end - 1, pastVal, map) + 1);\n }\n map[start][end] = max;\n return max;\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
java 85% beats
|
java-85-beats-by-krish25052004-5ora
|
Intuition\nusing dynamic programming(recursive method)\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\no(n2)\n\n- Space complexity:\no(n2)\n\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\
|
krish25052004
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-06T11:36:06.839313+00:00
|
2024-04-06T11:36:06.839344+00:00
| 5 | false |
# Intuition\nusing dynamic programming(recursive method)\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\no(n2)\n\n- Space complexity:\no(n2)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n public int maxOperations(int[] nums) {\n int n=nums.length;\n int[][] dp=new int[nums.length][nums.length];\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n Arrays.fill(dp[i],-1);\n }\n int x=helper(nums,0,n-3,nums[n-1]+nums[n-2],dp);\n \n int y=helper(nums,1,n-2,nums[n-1]+nums[0],dp);\n \n int z=helper(nums,2,n-1,nums[0]+nums[1],dp);\n return Math.max(x,Math.max(y,z))+1;\n }\n public int helper(int[] nums,int i,int j,int sum,int[][] dp){\n if(i>=j){\n return 0;\n }\n int x=0;\n int y=0;\n int z=0;\n if(dp[i][j]!=-1){\n return dp[i][j];\n }\n if(nums[i]+nums[j]==sum){\n x=helper(nums,i+1,j-1,sum,dp)+1;\n }\n if(nums[i]+nums[i+1]==sum){\n y=helper(nums,i+2,j,sum,dp)+1;\n }\n if(nums[j]+nums[j-1]==sum){\n z=helper(nums,i,j-2,sum,dp)+1;\n }\n dp[i][j]=Math.max(x,Math.max(y,z));\n return dp[i][j];\n }\n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Dynamic Programming', 'Recursion', 'Java']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Memoization | C++
|
memoization-c-by-katkadeharsh-43p7
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
katkadeharsh
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-05T16:50:42.091395+00:00
|
2024-04-05T16:50:42.091423+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int ans;\n int helper(vector<int>& nums,int left,int right,int score,int ops,vector<vector<int>>& dp){\n if((right-left+1)<2){\n return 0;\n }\n if(dp[left][right]!=-1){\n return dp[left][right];\n }\n int takeFront=0,takeRear=0,takeOne=0;\n if(nums[left]+nums[left+1]==score || score==INT_MIN){\n ans=max(ans,ops+1);\n takeFront=nums[left]+nums[left+1]+helper(nums,left+2,right,nums[left]+nums[left+1],ops+1,dp);\n }\n if(nums[right]+nums[right-1]==score || score==INT_MIN){\n ans=max(ans,ops+1);\n takeFront=nums[right]+nums[right-1]+helper(nums,left,right-2,nums[right]+nums[right-1],ops+1,dp);\n }\n if(nums[left]+nums[right]==score || score==INT_MIN){\n ans=max(ans,ops+1);\n takeFront=nums[left]+nums[right]+helper(nums,left+1,right-1,nums[left]+nums[right],ops+1,dp);\n }\n return dp[left][right]=max({takeFront,takeRear,takeOne});\n } \n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n ans=0;\n vector<vector<int>> dp(nums.size()+1,vector<int>(nums.size()+1,-1));\n helper(nums,0,nums.size()-1,INT_MIN,0,dp);\n return ans;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
12 MS C++ solution. Beat 99.84%
|
12-ms-c-solution-beat-9984-by-intermsof-2j7f
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
intermsof
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-03T02:29:24.440699+00:00
|
2024-04-03T02:29:24.440730+00:00
| 1 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n struct Node {\n size_t i;\n size_t j;\n int s;\n int d;\n };\n typedef pair<int, int> P;\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n stack<Node> s({{0, nums.size() - 1, -1, 0}});\n set<P> seen;\n int result = 0;\n while (!s.empty()) {\n const Node f = s.top();\n s.pop();\n if (f.d > result) result = f.d;\n if (f.j > f.i) {\n const int a = nums[f.i] + nums[f.i + 1];\n const int b = nums[f.j] + nums[f.j - 1];\n const int c = nums[f.i] + nums[f.j];\n vector<Node> next;\n \n if ( (f.s == -1 || f.s == a)) next.push_back({f.i + 2, f.j, a, f.d + 1});\n if ( (f.s == -1 || f.s == b) && f.j > 1) next.push_back({f.i, f.j - 2, b, f.d + 1});\n if ( (f.s == -1 || f.s == c)) next.push_back({f.i + 1, f.j - 1, c, f.d + 1});\n\n for (auto node : next) {\n P p = make_pair(node.i, node.j);\n if (seen.find(p) == seen.end()) {\n seen.insert(p);\n s.push(node);\n }\n }\n } else {\n return result;\n }\n }\n return result;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
2d dp c++ | top down approach
|
2d-dp-c-top-down-approach-by-warril-w53c
|
\n\n# Code\n\nstatic const bool __boost = [](){\n cin.tie(nullptr);\n cout.tie(nullptr);\n return ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);\n}();\nclass Soluti
|
warril
|
NORMAL
|
2024-04-02T05:10:05.012206+00:00
|
2024-04-02T05:10:05.012269+00:00
| 1 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```\nstatic const bool __boost = [](){\n cin.tie(nullptr);\n cout.tie(nullptr);\n return ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);\n}();\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n // map<pair<pair<int,int>,int>,int>m;\n int dp[2001][2001];\n int rec (int i, int j,vector<int>&nums,int sum)\n {\n \n if(j-i<=0)\n {return 1;}\n\n // if(m.find({{i,j},sum})!=m.end())\n // return m[{{i,j},sum}];\n if(dp[i][j]!=-1)\n return dp[i][j];\n int a=0;\n if(nums[i]+nums[i+1]==sum)\n a = max(a, rec(i+2,j,nums,sum));\n if(nums[j]+nums[j-1]==sum)\n a =max(a,rec(i,j-2,nums,sum)); \n if(nums[i]+nums[j]==sum) \n a = max(a,rec (i+1,j-1,nums,sum));\n \n // m[{{i,j},sum}]=a+1;\n return dp[i][j]=a+1;\n\n \n\n }\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) \n {\n int ans =0;\n int i=0,j=nums.size()-1;\n if(j<3)\n return 1;\n memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp));\n int a = rec(i+2,j,nums,nums[0]+nums[1]);\n \n int b = rec(i,j-2,nums,nums[j-1]+nums[j]); \n\n int c = rec (i+1,j-1,nums,nums[i]+nums[j]); \n\n\n a=max(a,b);\n a=max(a,c);\n return a;\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Clean Swift - O(n^2) - DP - Recursion.
|
clean-swift-on2-dp-recursion-by-timcheng-q9wv
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nWe can construct a decision tree for the problem where each node has 3 children based o
|
timchenggu123
|
NORMAL
|
2024-03-25T20:09:54.664322+00:00
|
2024-03-25T20:09:54.664352+00:00
| 10 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nWe can construct a decision tree for the problem where each node has 3 children based on the 3 actions we can take. We want to find the height of the tree. The height of each node on the tree is 1 + <the max height of the three sub trees>. Each node is also associated with a subarray that we need to check, denoted with [i,j] where i < j. A node is a leaf when i >= j. From here, we simply need to conduct a tree walk resursively, and update the value of each node based on the max of its three children. DP comes into play since multiple paths may lead to the same node, so if we already know the value of the node we can simply store it in an array. \n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\n func subHeight(_ i: Int, _ j: Int, _ val: Int, _ nums:[Int], _ dp: inout [[Int]], _ first: Bool) -> Int{\n if i >= j {return 0}\n if dp[i][j] != -1 {return dp[i][j]}\n \n var op1 = 0; var op2 = 0; var op3 = 0\n var v = nums[i] + nums[i+1]\n if first || v == val {\n op1 = 1 + subHeight(i+2, j, v, nums, &dp, false)\n }\n v = nums[j] + nums[j-1]\n if first || v == val{\n op2 = 1 + subHeight(i, j-2, v, nums, &dp, false)\n }\n v = nums[i] + nums[j]\n if first || v == val{\n op3 = 1 + subHeight(i+1, j-1, v, nums, &dp, false)\n }\n var ans = max(op1, op2, op3)\n dp[i][j] = ans\n return ans\n \n }\n func maxOperations(_ nums: [Int]) -> Int {\n var i = 0; var j = nums.count-1; var val = 0;\n var dp = Array(repeating: Array(repeating: -1, count: nums.count), count: nums.count)\n return subHeight(0, nums.count - 1, 0, nums, &dp, true)\n } \n}\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Swift']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
C++ | Easy 3D DP
|
c-easy-3d-dp-by-prakash868-hccc
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
prakash868
|
NORMAL
|
2024-03-19T19:34:32.519199+00:00
|
2024-03-19T19:34:32.519234+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int dp[2000][2000][3];\n int solve(int i,int j,int sumInd,vector<int>&nums,vector<int>&sum)\n {\n if(i>=j)return 0;\n \n if(dp[i][j][sumInd]!=-1)return dp[i][j][sumInd];\n int maxi=0;\n int sum1=nums[i]+nums[i+1];\n int sum2=nums[j-1]+nums[j];\n int sum3=nums[i]+nums[j];\n \n int Sum=sum[sumInd];\n if(Sum==sum1)\n {\n maxi=max(maxi,1+solve(i+2,j,sumInd,nums,sum));\n }\n if(Sum==sum2)\n {\n maxi=max(maxi,1+solve(i,j-2,sumInd,nums,sum));\n }\n if(Sum==sum3)\n {\n maxi=max(maxi,1+solve(i+1,j-1,sumInd,nums,sum));\n }\n return dp[i][j][sumInd]=maxi;\n \n }\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n=nums.size();\n int sum1=nums[0]+nums[1];\n int sum2=nums[n-2]+nums[n-1];\n int sum3=nums[0]+nums[n-1];\n vector<int>sum={sum1,sum2,sum3};\n // vector<vector<vector<int>>>dp(n,vector<vector<int>>(n,vector<int>(3,-1)));\n memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp));\n int ans=0;\n for(int i=0;i<3;i++)\n ans=max(ans,solve(0,n-1,i,nums,sum));\n return ans;\n \n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
3040. Maximum Number of Operations With the Same Score II
|
3040-maximum-number-of-operations-with-t-o13m
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
prs19524
|
NORMAL
|
2024-03-19T17:08:31.421698+00:00
|
2024-03-19T17:08:31.421736+00:00
| 2 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int f(vector<int>& nums,int i,int j, int val,vector<vector<int>>& dp){\n if(j-i<1) return 0;\n\n if(dp[i][j]!=-1) return dp[i][j];\n int maxVal = 0;\n // cout<<"\\n";\n // for(int x = i;x<=j;x++){\n // cout<<x<<" ";\n // }\n if(val>-1){\n if((nums[i]+nums[i+1]) == val){\n maxVal = max(maxVal,f(nums,i+2,j,val,dp)+1);\n }\n if((nums[j]+nums[j-1]) == val){\n maxVal = max(maxVal,f(nums,i,j-2,val,dp)+1);\n }\n if((nums[i]+nums[j]) == val){\n maxVal = max(maxVal,f(nums,i+1,j-1,val,dp)+1);\n }\n }\n else{\n maxVal = max(f(nums,i+2,j,nums[i]+nums[i+1],dp)+1,f(nums,i,j-2,nums[j]+nums[j-1],dp)+1);\n maxVal = max(maxVal,f(nums,i+1,j-1,nums[i]+nums[j],dp)+1);\n }\n return dp[i][j] = maxVal;\n }\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n vector<vector<int>> dp(nums.size()+1,vector<int>(nums.size()+1,-1));\n int ans = f(nums,0,nums.size()-1,-1,dp);\n return ans;\n }\n};\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Clean Code | Recursion + Memo | C++
|
clean-code-recursion-memo-c-by-natani-df0k
|
\n# Code\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int solve(int i,int j,int sum,vector<int>&nums,vector<vector<int>> &dp){\n if(i>=j) return 0;\n if(dp[i
|
natani
|
NORMAL
|
2024-03-15T18:55:35.124527+00:00
|
2024-03-15T18:55:35.124550+00:00
| 3 | false |
\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n int solve(int i,int j,int sum,vector<int>&nums,vector<vector<int>> &dp){\n if(i>=j) return 0;\n if(dp[i][j]!=-1) return dp[i][j]; \n int ans1=0,ans2=0,ans3=0;\n if(nums[i]+nums[i+1]==sum) ans1 = 1 + solve(i+2,j,sum,nums,dp);\n if(nums[j]+nums[j-1]==sum) ans2 = 1 + solve(i,j-2,sum,nums,dp);\n if(nums[i]+nums[j]==sum) ans3 = 1 + solve(i+1,j-1,sum,nums,dp);\n return dp[i][j] = max(ans1,max(ans2,ans3));\n }\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n = nums.size();\n vector<vector<int>> dp1(n+1,vector<int>(n+1,-1));\n vector<vector<int>> dp2(n+1,vector<int>(n+1,-1));\n vector<vector<int>> dp3(n+1,vector<int>(n+1,-1));\n int ans1 = solve(2,n-1,nums[0]+nums[1],nums,dp1) + 1;\n int ans2 = solve(0,n-3,nums[n-1]+nums[n-2],nums,dp2) + 1;\n int ans3 = solve(1,n-2,nums[0]+nums[n-1],nums,dp3) + 1;\n return max(ans1,max(ans2,ans3));\n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
maximum-number-of-operations-with-the-same-score-ii
|
Very Easy & Intuitive C++ Solution Approach
|
very-easy-intuitive-c-solution-approach-uuhcx
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
ambarr08
|
NORMAL
|
2024-03-15T13:25:47.478883+00:00
|
2024-03-15T13:25:47.478919+00:00
| 3 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n\n int dp[2000][2000];\n\n\n int f(vector<int> &nums, int l, int r, int sum, int n) {\n \n if(!(l <= r-1)) {\n return 0;\n }\n if(sum == -1) {\n return dp[l][r] = 1 + max(f(nums, l+1, r-1, nums[l]+nums[r], n), max(f(nums, l+2, r, nums[l]+nums[l+1], n), f(nums , l , r-2, nums[r]+nums[r-1], n)));\n }\n if(dp[l][r] != -1) {\n return dp[l][r];\n }\n if(l <= r-1) {\n if(nums[l] + nums[l+1] == sum && nums[r] + nums[r-1] == sum && nums[r] + nums[l] == sum) {\n return dp[l][r] = 1 + max(f(nums, l+1, r-1, nums[l]+nums[r], n), max(f(nums, l+2, r, nums[l]+nums[l+1], n), f(nums , l , r-2, nums[r]+nums[r-1], n)));\n }\n else if((nums[l] + nums[l+1] == sum && nums[r] + nums[r-1] == sum)) {\n return dp[l][r] = 1 + max(f(nums, l+2, r, nums[l]+nums[l+1], n), f(nums , l , r-2, nums[r]+nums[r-1], n));\n }\n else if(nums[r] + nums[r-1] == sum && nums[r] + nums[l] == sum) {\n return dp[l][r] = 1 + max(f(nums, l, r-2, sum, n), f(nums , l+1 , r-1, sum, n));\n }\n else if(nums[l] + nums[l+1] == sum && nums[r] + nums[l] == sum) {\n return dp[l][r] = 1 + max(f(nums, l+2, r, nums[l]+nums[l+1], n), f(nums, l+1, r-1, nums[l]+nums[r], n));\n }\n else if(nums[l] + nums[l+1] == sum) {\n return dp[l][r] = 1 + f(nums, l+2, r, sum , n);\n }\n else if(nums[l] + nums[r] == sum) {\n return dp[l][r] = 1 + f(nums, l+1, r-1, sum , n);\n }\n else if(nums[r] + nums[r-1] == sum) {\n return dp[l][r] = 1 + f(nums, l, r-2, sum , n);\n }\n else{\n return dp[l][r] = 0;\n }\n }\n else{\n return 0;\n }\n }\n\n int maxOperations(vector<int>& nums) {\n int n = nums.size();\n memset(dp, -1, sizeof(dp));\n return f(nums, 0, n-1, -1, n); \n }\n};\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['Array', 'Dynamic Programming', 'Memoization', 'C++']
| 0 |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.