question_slug
stringlengths 3
77
| title
stringlengths 1
183
| slug
stringlengths 12
45
| summary
stringlengths 1
160
⌀ | author
stringlengths 2
30
| certification
stringclasses 2
values | created_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| updated_at
stringdate 2013-10-25 17:32:12
2025-04-12 09:38:24
| hit_count
int64 0
10.6M
| has_video
bool 2
classes | content
stringlengths 4
576k
| upvotes
int64 0
11.5k
| downvotes
int64 0
358
| tags
stringlengths 2
193
| comments
int64 0
2.56k
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
last-visited-integers
|
beginner's approach
|
beginners-approach-by-albin158-mt17
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
albin158
|
NORMAL
|
2024-07-10T09:50:33.040731+00:00
|
2024-07-10T09:50:33.040761+00:00
| 6 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```\n/**\n * @param {number[]} nums\n * @return {number[]}\n */\nvar lastVisitedIntegers = function (nums) {\n const len = nums.length;\n let seen = [];\n let ans = [];\n let k = 0;\n for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {\n if (nums[i] > 0) {\n seen.unshift(nums[i]);\n k = 0;\n } else {\n if (k >= seen.length) {\n ans.push(-1);\n } else {\n ans.push(seen[k]);\n k++;\n }\n }\n }\n return ans;\n};\n\n```
| 0 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
faster than 100.00% | O(N) | (Java and C++)
|
faster-than-10000-on-java-and-c-by-iamco-kgyv
|
I am ignoring all the empty _ charcater,\n\nAs soon as i encounter any character other then _ ,\nThen the characters must be same,\n\nif It is \'L\'\n then this
|
IAmCoderrr
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T04:00:49.864421+00:00
|
2024-07-30T23:39:35.875898+00:00
| 13,930 | false |
I am ignoring all the empty _ charcater,\n\nAs soon as i encounter any character other then _ ,\nThen the characters must be same,\n\nif It is \'L\'\n then this condition must hold j>= i , if in target string it found at index i and , in st string it found at J\n because we can move \'L\' charcater to left , means left in st string , \notherwise i should return fase;\n\nsame with \'R\'\nthen this condition must hold j<= i , if in target string it found at index i and , in st string it found at J\nbecause we can move \'R\' charcater to right ,means right in st string , \notherwise i should return false;\n\n**Time complexityO(N)**\nbecause every time either i increase I , or J , or both\n\n**Space complexityO(1)**\n\n**Upvote if you find this solution helpfull**\n```\nbool canChange(string st, string tar) {\n int n=tar.length();\n int i=0,j=0;\n while(i<=n && j<=n){\n \n while(i<n && tar[i]==\'_\') i++;\n while(j<n && st[j]==\'_\') j++;\n \n if(i==n || j==n){\n return i==n && j==n;\n }\n \n if(tar[i]!=st[j]) return false;\n \n if(tar[i]==\'L\'){\n if(j<i) return false;\n }\n else{\n if(i<j) return false;\n }\n \n i++;\n j++;\n }\n return true;\n }\n\t```
| 283 | 6 |
['C', 'Java']
| 39 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
[Java/Python 3] 2 methods w/ brief explanation and analysis.
|
javapython-3-2-methods-w-brief-explanati-8lhu
|
\nIntuition:\n\nSince Ls and Rs can ONLY move to empty spaces and can NOT swap, the sequences containing all Ls and Rs and only Ls and Rs of start and target mu
|
rock
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T04:05:23.436600+00:00
|
2024-12-05T15:54:02.454428+00:00
| 7,028 | false |
\n**Intuition:**\n\nSince `L`s and `R`s can ONLY move to empty spaces and can NOT swap, the sequences containing all `L`s and `R`s and only `L`s and `R`s of `start` and `target` must be same;\nSince `L`s and `R`s can move to left and right only respectively, all positions of `L`s in `start` must be no less than the corresponding ones in `target`, and all positions of `R`s in `start` must be no greater than the corresponding ones in `target`.\n\nBased on the above conclusion we can implement an algorithm as follows:\n\n**Algorithm:**\n\n1. Check if `start` and `target` are same if without `_`\'s;\n2. Check if all positions of `L`\'s in `start` are no less than those in `target`;\n3. Check if all positions of `R`\'s in `start` are no greater than those in `target`;\n4. If all above 3 are yes, return true; otherwise return false.\n\n----\n\n**Method 1: Compare the sequences and the indices of \'L\' and \'R\'.**\n\nCredit to **@Thoyajkiran** for removal of redundant code.\n```java\n public boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n if (!(start.replaceAll("_", "")).equals(target.replaceAll("_", ""))) {\n return false;\n }\n for (int i = 0, j = 0, n = start.length(); i < n && j < n; ++i, ++j) {\n while (i < n && start.charAt(i) == \'_\') {\n ++i;\n }\n while (j < n && target.charAt(j) == \'_\') {\n ++j;\n }\n if (i < n && j < n && (start.charAt(i) == \'L\' && i < j || target.charAt(j) == \'R\' && i > j)) {\n return false;\n }\n }\n return true;\n }\n```\n```python\n def canChange(self, start: str, target: str) -> bool:\n if start.replace(\'_\', \'\') != target.replace(\'_\', \'\'):\n return False\n i = j = 0\n n = len(start)\n while i < n and j < n:\n while i < n and start[i] == \'_\':\n i += 1\n while j < n and target[j] == \'_\':\n j += 1\n if i < n and j < n and (start[i] == \'L\' and i < j or start[i] == \'R\' and i > j):\n return False\n i += 1\n j += 1\n return True\n```\n\n\n**Analysis:**\n\n`replace` and `for loop` contribute `O(n)` time complexity respectively. Each character at most visited twice, hence:\n\nTime & space: `O(n)`, where `n = start.length()`.\n\n----\n\nWe can optimize the space:\n\n```java\n public boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n int i = 0, j = 0, n = start.length();\n while (i < n || j < n) {\n while (i < n && start.charAt(i) == \'_\') {\n ++i;\n }\n while (j < n && target.charAt(j) == \'_\') {\n ++j;\n }\n if (i == n || j == n) {\n return i == j;\n }\n if (start.charAt(i) != target.charAt(j) || \n start.charAt(i) == \'L\' && i < j ||\n start.charAt(i) == \'R\' && i > j) {\n return false;\n }\n ++i;\n ++j;\n }\n return true;\n }\n```\n```python\n def canChange(self, start: str, target: str) -> bool:\n i = j = 0\n n = len(start)\n while i < n or j < n:\n while i < n and start[i] == \'_\':\n i += 1\n while j < n and target[j] == \'_\':\n j += 1\n if i == n or j == n:\n return i == j\n if start[i] != target[j] or \\\n start[i] == \'L\' and i < j or \\\n start[i] == \'R\' and i > j: \n return False\n i += 1\n j += 1\n return True\n```\n\n**Analysis:**\n\n`for loop` contribute `O(n)` time complexity. Each character visited once, hence:\n\nTime: `O(n)`, space: `O(1)`, where `n = start.length()`.\n\n----\n\n**Method 2: Count the balance of \'L\'s and \'R\'s.** -- inspired by and hence credit to **@kreakEmp** \n\n```java\n public boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n int balanceL = 0, balanceR = 0;\n for (int i = 0, n = start.length(); i < n; ++i) {\n char s = start.charAt(i), t = target.charAt(i);\n balanceL += t == \'L\' ? 1 : 0;\n balanceR += s == \'R\' ? 1 : 0;\n // If both balancers > 0, there must be different \n // \'L...R...\' subsequence between start and target.\n if (balanceL * balanceR != 0) {\n return false;\n }\n balanceL -= s == \'L\' ? 1 : 0;\n balanceR -= t == \'R\' ? 1 : 0;\n if (balanceL < 0 || balanceR < 0) {\n return false;\n }\n }\n return balanceL == 0 && balanceR == 0;\n }\n```\n```python\n def canChange(self, start: str, target: str) -> bool:\n balance_L = balance_R = 0\n for s, t in zip(start, target):\n balance_L += (t == \'L\')\n balance_R += (s == \'R\')\n # If both balancers > 0, there must be different \n # \'L...R...\'subsequence between start and target. \n if balance_L * balance_R != 0:\n return False\n balance_L -= (s == \'L\')\n balance_R -= (t == \'R\')\n if balance_L < 0 or balance_R < 0:\n return False\n return balance_L == balance_R == 0\n```\n\n**Analysis:**\n\n`for loop` contribute `O(n)` time complexity. Each character visited once, hence:\n\nTime: `O(n)`, space: `O(1)`, where `n = start.length()`.\n
| 105 | 0 |
['Java', 'Python3']
| 23 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
✅ 100% Beats | Short & Simple
|
100-beats-short-simple-by-piotr_maminski-pvmn
|
\n\n\n\n# Two Pointers (Mostly 100% [1][2][3][4][5][6][7][8][9][10])\npython3 []\nclass Solution:\n def canChange(self, start: str, target: str) -> bool:\n
|
Piotr_Maminski
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T00:22:20.784096+00:00
|
2024-12-05T02:17:19.174457+00:00
| 20,690 | false |
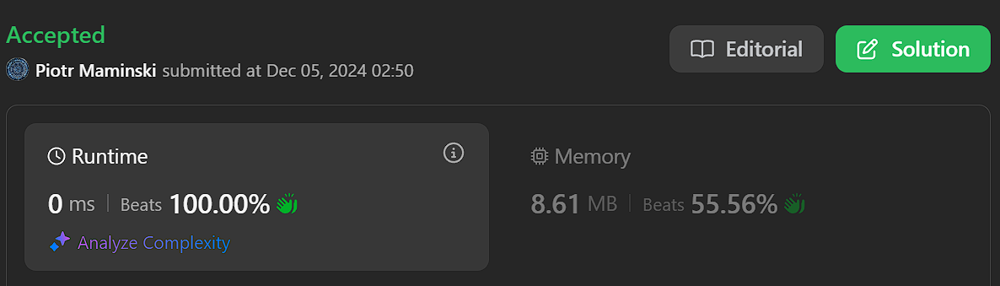\n\n\n\n# Two Pointers (Mostly 100% [[1]](https://leetcode.com/problems/move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string/submissions/1470618274)[[2]](https://leetcode.com/problems/move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string/submissions/1470617908)[[3]](https://leetcode.com/problems/move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string/submissions/1470616981)[[4]](https://leetcode.com/problems/move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string/submissions/1470616762)[[5]](https://leetcode.com/problems/move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string/submissions/1470616452)[[6]](https://leetcode.com/problems/move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string/submissions/1470620484)[[7]](https://leetcode.com/problems/move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string/submissions/1470621041)[[8]](https://leetcode.com/problems/move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string/submissions/1470621659)[[9]](https://leetcode.com/problems/move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string/submissions/1470616312)[[10]](https://leetcode.com/problems/move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string/submissions/1470622222))\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def canChange(self, start: str, target: str) -> bool:\n if start == target:\n return True\n waitL = 0 \n waitR = 0 \n\n for curr, goal in zip(start, target):\n if curr == \'R\':\n if waitL > 0:\n return False\n waitR += 1 \n if goal == \'L\':\n if waitR > 0:\n return False\n waitL += 1\n if goal == \'R\':\n if waitR == 0:\n return False\n waitR -= 1 \n if curr == \'L\':\n if waitL == 0:\n return False\n waitL -= 1 \n return waitL == 0 and waitR == 0\n```\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n if (start == target) {\n return true;\n }\n int waitL = 0;\n int waitR = 0;\n \n for (int i = 0; i < start.length(); i++) {\n char curr = start[i];\n char goal = target[i];\n if (curr == \'R\') {\n if (waitL > 0) {\n return false;\n }\n waitR++;\n }\n if (goal == \'L\') {\n if (waitR > 0) {\n return false;\n }\n waitL++;\n }\n if (goal == \'R\') {\n if (waitR == 0) {\n return false;\n }\n waitR--;\n }\n if (curr == \'L\') {\n if (waitL == 0) {\n return false;\n }\n waitL--;\n }\n }\n return waitL == 0 && waitR == 0;\n }\n};\n```\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n if (start.equals(target)) {\n return true;\n }\n int waitL = 0;\n int waitR = 0;\n \n for (int i = 0; i < start.length(); i++) {\n char curr = start.charAt(i);\n char goal = target.charAt(i);\n \n if (curr == \'R\') {\n if (waitL > 0) {\n return false;\n }\n waitR++;\n }\n if (goal == \'L\') {\n if (waitR > 0) {\n return false;\n }\n waitL++;\n }\n if (goal == \'R\') {\n if (waitR == 0) {\n return false;\n }\n waitR--;\n }\n if (curr == \'L\') {\n if (waitL == 0) {\n return false;\n }\n waitL--;\n }\n }\n \n return waitL == 0 && waitR == 0;\n }\n}\n```\n```csharp []\npublic class Solution {\n public bool CanChange(string start, string target) {\n if (start == target) return true;\n int waitL = 0, waitR = 0;\n \n for (int i = 0; i < start.Length; i++) {\n char curr = start[i];\n char goal = target[i];\n \n if (curr == \'R\') {\n if (waitL > 0) return false;\n waitR++;\n }\n if (goal == \'L\') {\n if (waitR > 0) return false;\n waitL++;\n }\n if (goal == \'R\') {\n if (waitR == 0) return false;\n waitR--;\n }\n if (curr == \'L\') {\n if (waitL == 0) return false;\n waitL--;\n }\n }\n return waitL == 0 && waitR == 0;\n }\n}\n```\n```golang []\nfunc canChange(start string, target string) bool {\n if start == target {\n return true\n }\n waitL, waitR := 0, 0\n \n for i := 0; i < len(start); i++ {\n curr := start[i]\n goal := target[i]\n \n if curr == \'R\' {\n if waitL > 0 {\n return false\n }\n waitR++\n }\n if goal == \'L\' {\n if waitR > 0 {\n return false\n }\n waitL++\n }\n if goal == \'R\' {\n if waitR == 0 {\n return false\n }\n waitR--\n }\n if curr == \'L\' {\n if waitL == 0 {\n return false\n }\n waitL--\n }\n }\n return waitL == 0 && waitR == 0\n}\n```\n```swift []\nclass Solution {\n func canChange(_ start: String, _ target: String) -> Bool {\n if start == target { return true }\n var waitL = 0, waitR = 0\n \n let startChars = Array(start)\n let targetChars = Array(target)\n \n for i in 0..<startChars.count {\n let curr = startChars[i]\n let goal = targetChars[i]\n \n if curr == "R" {\n if waitL > 0 { return false }\n waitR += 1\n }\n if goal == "L" {\n if waitR > 0 { return false }\n waitL += 1\n }\n if goal == "R" {\n if waitR == 0 { return false }\n waitR -= 1\n }\n if curr == "L" {\n if waitL == 0 { return false }\n waitL -= 1\n }\n }\n return waitL == 0 && waitR == 0\n }\n}\n```\n```javascript [JS]\n// JavaScript\n\nvar canChange = function(start, target) {\n if (start === target) return true;\n let waitL = 0, waitR = 0;\n \n for (let i = 0; i < start.length; i++) {\n const curr = start[i];\n const goal = target[i];\n \n if (curr === \'R\') {\n if (waitL > 0) return false;\n waitR++;\n }\n if (goal === \'L\') {\n if (waitR > 0) return false;\n waitL++;\n }\n if (goal === \'R\') {\n if (waitR === 0) return false;\n waitR--;\n }\n if (curr === \'L\') {\n if (waitL === 0) return false;\n waitL--;\n }\n }\n return waitL === 0 && waitR === 0;\n};\n```\n```typescript [TS]\n// TypeScript\n\nfunction canChange(start: string, target: string): boolean {\n if (start === target) return true;\n let waitL = 0, waitR = 0;\n \n for (let i = 0; i < start.length; i++) {\n const curr = start[i];\n const goal = target[i];\n \n if (curr === \'R\') {\n if (waitL > 0) return false;\n waitR++;\n }\n if (goal === \'L\') {\n if (waitR > 0) return false;\n waitL++;\n }\n if (goal === \'R\') {\n if (waitR === 0) return false;\n waitR--;\n }\n if (curr === \'L\') {\n if (waitL === 0) return false;\n waitL--;\n }\n }\n return waitL === 0 && waitR === 0;\n}\n```\n```rust []\nimpl Solution {\n pub fn can_change(start: String, target: String) -> bool {\n if start == target {\n return true;\n }\n let mut wait_l = 0;\n let mut wait_r = 0;\n \n let start_chars: Vec<char> = start.chars().collect();\n let target_chars: Vec<char> = target.chars().collect();\n \n for i in 0..start_chars.len() {\n let curr = start_chars[i];\n let goal = target_chars[i];\n \n if curr == \'R\' {\n if wait_l > 0 {\n return false;\n }\n wait_r += 1;\n }\n if goal == \'L\' {\n if wait_r > 0 {\n return false;\n }\n wait_l += 1;\n }\n if goal == \'R\' {\n if wait_r == 0 {\n return false;\n }\n wait_r -= 1;\n }\n if curr == \'L\' {\n if wait_l == 0 {\n return false;\n }\n wait_l -= 1;\n }\n }\n wait_l == 0 && wait_r == 0\n }\n}\n```\n```ruby []\ndef can_change(start, target)\n return true if start == target\n wait_l = 0\n wait_r = 0\n \n start.chars.zip(target.chars).each do |curr, goal|\n if curr == \'R\'\n return false if wait_l > 0\n wait_r += 1\n end\n if goal == \'L\'\n return false if wait_r > 0\n wait_l += 1\n end\n if goal == \'R\'\n return false if wait_r == 0\n wait_r -= 1\n end\n if curr == \'L\'\n return false if wait_l == 0\n wait_l -= 1\n end\n end\n wait_l == 0 && wait_r == 0\nend\n```\n\n\n- Complexity: Time O(n) & Space O(1)\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n# Explanation\n\n\n---\n\n\n\n## Intuition\n\n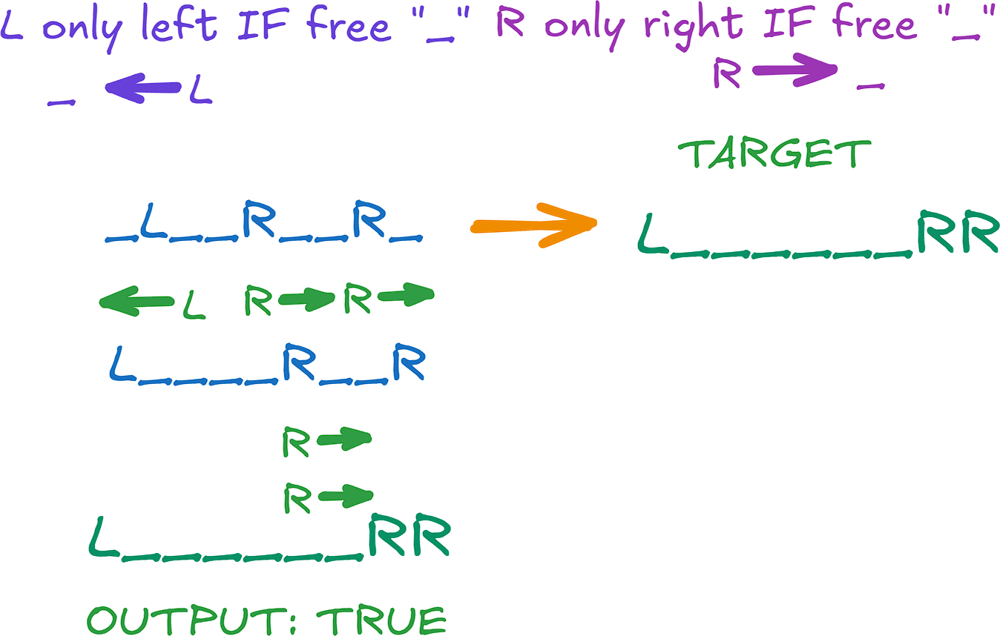\n\n- "Letters" cannot jump over another "letter"\n\n\n\n\n## Approach\n\n1. Edge Case: **IF** start = target **RETURN** True \n\n```\n if start == target:\n return True\n```\n\n- we save on efficiency, we don\'t do the rest\n\n\n\n\n`waitL` - count waiting **L**\n`waitR` - count waiting **R**\n\n2. Core\n\n- **R** on Start:\n - IF waiting **L**s return **False** ( **R** can\'t jump over **L**)\n - Increment `waitR` counter\n\n- **L** in target string:\n - IF waiting **R**s return **False** ( **L** can\'t jump over **R**)\n - Increment `waitL` counter\n\n- **R** in target string:\n - IF **NO** waiting **R**s return **False** (nothing to move)\n - Decrement `waitR` counter\n\n- **L** in target string:\n - IF **NO** waiting **L**s return **False** (nothing to move)\n - Decrement `waitL` counter\n\n3. Check if all **L** and **R** are "matched"\n\n```\nreturn waitL == 0 and waitR == 0\n```\n\nDone. \n\n\n\n**UpVote** if you think it is helpful and will help others\n\n\n---\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n# Most common String Interview Problems\nList based on my research (interviews, reddit, github) Probably not 100% accurate but very close to my recruitments. Leetcode Premium is probably more accurate [I don\'t have]\n\n**Easy:** [[20. Valid Parentheses]](https://leetcode.com/problems/valid-parentheses/solutions/6013115/solution) [[28. Find the Index of the First Occurrence in a String]](https://leetcode.com/problems/find-the-index-of-the-first-occurrence-in-a-string) [[13. Roman to Integer]](https://leetcode.com/problems/roman-to-integer/solutions/6021029/beats-100-explained-step-by-step-list-most-common-string-interview-problems/) [[125. Valid Palindrome]](https://leetcode.com/problems/valid-palindrome) [[680. Valid Palindrome II]](https://leetcode.com/problems/valid-palindrome-ii) [[67. Add Binary]](https://leetcode.com/problems/add-binary)\n\n\n\n\n**Medium/Hard:** [[8. String to Integer (atoi)]](https://leetcode.com/problems/string-to-integer-atoi/solutions/6013112/solution/) [[3. Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters]](https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-substring-without-repeating-characters/solutions/6013106/solutions/) [[5. Longest Palindromic Substring]](https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-palindromic-substring/solutions/6013111/solution/) [[937. Reorder Data in Log Files]](https://leetcode.com/problems/reorder-data-in-log-files) [[68. Text Justification]](https://leetcode.com/problems/text-justification) [[32. Longest Valid Parentheses]](https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-valid-parentheses) [[12. Integer to Roman]](https://leetcode.com/problems/integer-to-roman/solutions/6023402/solutions) [[22. Generate Parentheses]](https://leetcode.com/problems/generate-parentheses) [[65. Valid Number]](https://leetcode.com/problems/valid-number) [[49. Group Anagrams]](https://leetcode.com/problems/group-anagrams)\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n#### [Interview Questions and Answers Repository](https://github.com/RooTinfinite/Interview-questions-and-answers)\n\n
| 91 | 0 |
['Swift', 'C++', 'Java', 'Go', 'TypeScript', 'Python3', 'Rust', 'Ruby', 'JavaScript', 'C#']
| 7 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Two Pointers
|
two-pointers-by-votrubac-mqxr
|
We use two pointers to find the next non-blank space.\n\nThen, the character in the current position can be moved to the target position if:\n1. s[i] == t[j].\n
|
votrubac
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T21:53:08.679012+00:00
|
2022-07-10T21:53:08.679054+00:00
| 3,502 | false |
We use two pointers to find the next non-blank space.\n\nThen, the character in the current position can be moved to the target position if:\n1. `s[i] == t[j]`.\n2. `i >= j` for \'L\' characters.\n3. `i <= j` for \'R\' characters.\n\n**C++**\n\n```cpp\nbool canChange(string s, string t) {\n int i = 0, j = 0, n = s.size();\n for (; i < n || j < n; ++i, ++j) {\n while (i < n && s[i] == \'_\')\n ++i;\n while (j < n && t[j] == \'_\')\n ++j;\n if (i == n || j == n || s[i] != t[j] || (s[i] == \'L\' && i < j) || (s[i] == \'R\' && i > j))\n break;\n }\n return i == n && j == n;\n}\n```
| 78 | 2 |
['C']
| 9 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
2 pointers nested loop||beats 100%
|
2-pointers-nested-loopbeats-100-by-anwen-2ppe
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n2 pointers again, move i, j pointers for s, t to see when they are both not \'\'.\nC++,
|
anwendeng
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T00:39:54.506044+00:00
|
2024-12-05T16:39:09.610943+00:00
| 17,098 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n2 pointers again, move `i, j` pointers for `s, t` to see when they are both not \'_\'.\nC++, Python, C are made.\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n[Please turn English subtitles if necessary]\n[https://youtu.be/JAw_prYl0ps?si=Iyikw49MY-BJz2Nz](https://youtu.be/JAw_prYl0ps?si=Iyikw49MY-BJz2Nz)\n1. let `n` be the length for `s` &`\'t\'`\n2. Move `i, j` both for `s, t` by using for loop with increment `i++, j++`\n3. In the inner loop move i until s[i]!=\'_\'\n4. In the inner loop move j until t[j]!=\'_\'\n5. If `s[i]!=t[j]` return false\n6. If `s[i]==t[j]=\'L\'` and `i<j` return false\n7. If `s[i]==t[j]=\'R\'` and `i>j` return false\n8. end the nested loop, all conditions for `s[i]==t[j]` are passed, return true.\n# Why C, C++ s[n], t[n] cause no problem?\nFor C-string it is clear that `s[n]==\'\\0\'` which is the string terminal char. C++ string is similar. When other language is used, it needs to be modified.\n\nThe trick adding an extra char is used for the 2-pointer questions\n- [2825. Make String a Subsequence Using Cyclic Increments](https://leetcode.com/problems/make-string-a-subsequence-using-cyclic-increments/solutions/6110652/1-pass-2-pointers-beats-100/)\n- [2109. Adding Spaces to a String](https://leetcode.com/problems/adding-spaces-to-a-string/solutions/6106375/2-pointers-4ms-beats-100/)\n# Real RUN for testcase\nLet\'s consider some testcase, say `"_L__R__R_"\n"L______RR"`\nThe process is run by the submtted Python code with adding some outputs:\n```\ns[1]=L t[0]=L\ns[4]=R t[7]=R\ns[7]=R t[8]=R\ns[9]=@ t[9]=@\n=>True\n```\nOher testcase is `"_LL___R__R_"\n"L___L____RR"` with process\n```\ns[1]=L t[0]=L\ns[2]=L t[4]=L\n=>False\n```\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$O(n)$\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n$O(1)$ for C & C++\n# Code||C++ 0ms beats 100%\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n static bool canChange(string& s, string& t) {\n const int n=s.size();\n for(int i=0, j=0; i<n || j<n; i++, j++){\n while(i<n && s[i]==\'_\') i++;\n while(j<n && t[j]==\'_\') j++;\n // cout<<i<<", "<<j<<endl;\n char c=s[i];\n if (c !=t[j]) return 0;\n if (c ==\'L\' && i<j) return 0;\n if (c ==\'R\' && i>j) return 0;\n }\n return 1;\n }\n};\n\n\n\nauto init = []() {\n ios::sync_with_stdio(false);\n cin.tie(nullptr);\n cout.tie(nullptr);\n return \'c\';\n}();\n```\n```Python []\nclass Solution:\n def canChange(self, s: str, t: str) -> bool:\n n=len(s)\n s+=\'@\'\n t+=\'@\'\n i, j=0, 0\n while i<n or j<n:\n while i<n and s[i]==\'_\': i+=1\n while j<n and t[j]==\'_\': j+=1\n c=s[i]\n if c!=t[j]: return False\n if c==\'L\' and i<j: return False\n if c==\'R\' and i>j: return False\n i+=1\n j+=1\n return True\n \n \n```\n```C []\n#pragma GCC optimize("O3", "unroll-loops")\nbool canChange(char* s, char* t) {\n const int n=strlen(s);\n for (register int i=0, j=0; i<n || j<n ; i++, j++){\n while(i<n && s[i]==\'_\') i++;\n while(j<n && t[j]==\'_\') j++;\n char c=s[i];\n if (c!=t[j]) return 0;\n if (c==\'L\' && i<j) return 0;\n if (c==\'R\' && i>j) return 0;\n }\n return 1;\n}\n```
| 58 | 3 |
['Two Pointers', 'String', 'C', 'C++', 'Python3']
| 10 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Two Pointer Approach✅✅
|
two-pointer-approach-by-arunk_leetcode-zn6x
|
Intuition\nThe problem involves moving \'L\' and \'R\' characters in the start string to match the target string while adhering to specific movement constraints
|
arunk_leetcode
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T03:51:40.797766+00:00
|
2024-12-05T03:51:40.797800+00:00
| 7,705 | false |
# Intuition\nThe problem involves moving \'L\' and \'R\' characters in the `start` string to match the `target` string while adhering to specific movement constraints:\n- \'L\' can only move left.\n- \'R\' can only move right.\nThe underscores (\'_\') act as placeholders that allow movement.\n\nThe key insight is to check if each \'L\' and \'R\' character in both strings appears in the correct order and position relative to the underscores.\n\n# Approach\n1. Use two pointers `i` and `j` to traverse the `start` and `target` strings, respectively.\n2. Skip underscores in both strings by incrementing `i` and `j`.\n3. Compare the characters at the current positions of `i` and `j`.\n4. Ensure that:\n - If the character is \'L\', it should not move right (i.e., `i` should not be less than `j`).\n - If the character is \'R\', it should not move left (i.e., `i` should not be greater than `j`).\n5. Return `true` if both pointers reach the end of the strings simultaneously.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$ \n The algorithm makes a single pass through both strings, where `n` is the length of the strings.\n \n- Space complexity: $$O(1)$$ \n Only constant extra space is used for the two pointers.\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n int i = 0, j = 0, n = start.size();\n\t\n while(i < n || j < n){\n \n while(i < n && start[i] == \'_\')\n i++;\n while(j < n && target[j] == \'_\')\n j++;\n \n if(i == n || j == n)\n break;\n if(start[i] != target[j])\n return false;\n if(start[i] == \'L\')\n if(i < j)\n return false;\n if(start[i] == \'R\')\n if(i > j)\n return false;\n i++;\n j++;\n }\n\n return i == n && j == n;\n }\n};\n```\n``` Java []\nclass Solution {\n public boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n int i = 0, j = 0, n = start.length();\n \n while (i < n || j < n) {\n while (i < n && start.charAt(i) == \'_\')\n i++;\n while (j < n && target.charAt(j) == \'_\')\n j++;\n \n if (i == n || j == n)\n break;\n if (start.charAt(i) != target.charAt(j))\n return false;\n if (start.charAt(i) == \'L\' && i < j)\n return false;\n if (start.charAt(i) == \'R\' && i > j)\n return false;\n \n i++;\n j++;\n }\n \n return i == n && j == n;\n }\n}\n```\n``` JavaScript []\nvar canChange = function(start, target) {\n let i = 0, j = 0, n = start.length;\n \n while (i < n || j < n) {\n while (i < n && start[i] === \'_\')\n i++;\n while (j < n && target[j] === \'_\')\n j++;\n \n if (i === n || j === n)\n break;\n if (start[i] !== target[j])\n return false;\n if (start[i] === \'L\' && i < j)\n return false;\n if (start[i] === \'R\' && i > j)\n return false;\n \n i++;\n j++;\n }\n \n return i === n && j === n;\n};\n```\n``` Python []\nclass Solution:\n def canChange(self, start: str, target: str) -> bool:\n i, j, n = 0, 0, len(start)\n \n while i < n or j < n:\n while i < n and start[i] == \'_\':\n i += 1\n while j < n and target[j] == \'_\':\n j += 1\n \n if i == n or j == n:\n break\n if start[i] != target[j]:\n return False\n if start[i] == \'L\' and i < j:\n return False\n if start[i] == \'R\' and i > j:\n return False\n \n i += 1\n j += 1\n \n return i == n and j == n\n\n```
| 41 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'String', 'String Matching', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'Python3', 'JavaScript']
| 4 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
C++ | Explanation | Beginner Friendly | Easy-Understanding
|
c-explanation-beginner-friendly-easy-und-hi02
|
Problem states that we need to convert start string to target string by moving \'L\' to left and \'R\' to right in Start.\n\n3 observations to make here - \n\n1
|
ps1077211
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T09:09:18.215633+00:00
|
2022-07-10T09:09:18.215682+00:00
| 1,666 | false |
**Problem** states that we need to convert **start** string to **target** string by moving \'L\' to left and \'R\' to right in **Start**.\n\n**3 observations to make here** - \n\n**1. Start string can only be converted into Target string if and only if relative order of \'L\' and \'R\' is equal.**\n\nExample - \nStart = "-L-R--L-R"\nTarget = "--R--L--LR"\n\nNow here we can see that order of LR in start is -> LRLR but in Target is RLLR so it can never be converted into Target because L and R can never cross each other.\n\n\n**2. Now relative order being same doesn\'t concludes that Start can always be converted to the Target.**\n\nExample - \nStart = "L-RRL"\nTarget = "LR-RL"\n\nHere relative order is same but to convert Start to Target we will need to move R to Left which is not Possible.\n\nNow here comes our 3rd Observation\n\n**3. That although relative order is same but if need to move any R of start to Left or any L to right then also Start can never be converted into Target.**\n\nNow how to check for this??\n\nTo check (suppose for R in the above example) this we will store indexes of R from both Start and Target in say arrays - r1 (For start) and r2 for(Target) and check for every i in r1 r1[i]<=r2[i].\nSimilarly for L l1[i]>=l2[i]\n\n\n**DRY RUN -**\n\nStart = "L - R R L"\nTarget="L R - R L"\n\n**now here relative order is same** , so may be start can be converted to Target\n\nnow r1 and r2 will look like this - \n\nr1 = [2,3] r2 = [1,3]\n\nso now for i=0 r1[i]>r2[i] which simply denotes that to convert the S->T we need to move R at index 2 in Start in Left direction to make it match with R at index 1 in Target and which is not possible , Hence we cannot convert S->T.\n\n\nCode - \n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool static seqSame(string s1,string s2){\n string a,b;\n for(auto it : s1) if(it!=\'_\') a+=it;\n for(auto it : s2) if(it!=\'_\') b+=it;\n return a==b;\n }\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n int n = start.length();\n if(!seqSame(start,target)) return false;\n vector<int> l1,l2,r1,r2;\n \n for(int i=0 ; i<n ; i++){\n if(start[i]==\'L\') l1.push_back(i);\n if(start[i]==\'R\') r1.push_back(i);\n if(target[i]==\'L\') l2.push_back(i);\n if(target[i]==\'R\') r2.push_back(i);\n }\n \n for(int i=0 ; i<l1.size() ; i++) if(l1[i]<l2[i]) return false;\n for(int i=0 ; i<r1.size() ; i++) if(r1[i]>r2[i]) return false;\n \n return true;\n }\n};\n```\n\nJust in Case you like the approach and effort , **DO UPVOTE.**\n
| 41 | 0 |
['C']
| 7 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Queue | C++ | 💨 Fast & 👌 Simple!
|
queue-c-fast-simple-by-stud_64-euhe
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string s, string t) {\n queue<pair<char, int>> ss, ts;\n \n // Fill queue with start\n
|
stud_64
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T04:03:09.369910+00:00
|
2022-07-24T04:44:02.234900+00:00
| 2,579 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string s, string t) {\n queue<pair<char, int>> ss, ts;\n \n // Fill queue with start\n for(int i=0; i<s.size(); i++){\n if(s[i] != \'_\')ss.push({s[i], i}); \n }\n \n // Fill queue with target\n for(int i=0; i<t.size(); i++){\n if(t[i] != \'_\')ts.push({t[i], i});\n }\n\n if(ss.size() != ts.size())return false;\n \n while(ss.size()){\n pair<char, int> sp, tp;\n \n sp = ss.front();\n tp = ts.front();\n \n ss.pop();\n ts.pop();\n \n// If both the letters don;t match return false, or check for the index to move Left and Right\n if(sp.first != tp.first) return false;\n if(sp.first == \'L\' && tp.second>sp.second){\n return false;\n } else if(sp.first == \'R\' && tp.second<sp.second){\n return false;\n }\n }\n \n return true;\n }\n};\n```
| 36 | 3 |
['Queue']
| 5 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Simple Java solution
|
simple-java-solution-by-10vaibhavsinghne-tc2u
|
Intuition:\nWe just need to validate the strings that we can move the chars and make target from start or not.\nWe\'ll check for all the invalid cases and at th
|
10vaibhavsinghnegi
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T04:01:29.613976+00:00
|
2022-07-10T04:05:38.636383+00:00
| 1,720 | false |
**Intuition:**\nWe just need to validate the strings that we can move the chars and make target from start or not.\nWe\'ll check for all the invalid cases and at the end return true;\n \nSo we\'ll push \'L\' and \'R\' from both the strings along with their index to their respective stacks\nwe\'ll interate the strings from end so that at the end we\'ll have string in the original order in the stacks.\n\nNow \ncase 1: is stack size is different i.e either string have extra chars so can\'t generate target from start. \ncase 2: sequence of chars are not matching i.e somewhere R is before L so can\'t generate target from start.\ncase 3: if index of L in target is to the right of L in start then we can\'t generate target from start as we can\'t move L to right.\ncase 4: if index of R in target is to the left of R in start then we can\'t generate target from start as we can\'t move R to left.\n```\nclass Solution {\n \n class Pair{\n char c;\n int idx;\n \n Pair(char cc, int idx){\n this.c = cc;\n this.idx = idx;\n }\n }\n public boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n \n int idx = 0;\n int n = start.length();\n Stack<Pair> s1 = new Stack<>();\n Stack<Pair> s2 = new Stack<>();\n \n // Fill the stacks\n for(int i = n-1; i >= 0; i--){\n \n if(start.charAt(i) == \'L\' || start.charAt(i) == \'R\'){\n s1.push(new Pair(start.charAt(i), i));\n }\n \n if(target.charAt(i) == \'L\' || target.charAt(i) == \'R\'){\n s2.push(new Pair(target.charAt(i), i));\n }\n \n }\n \n // Early return \n if(s1.size() != s2.size()){\n return false;\n }\n \n // Validates both the sequinces\n while(!s1.isEmpty()){\n \n Pair s = s1.pop();\n Pair e = s2.pop();\n \n if(s.c != e.c){\n return false;\n }\n \n if(s.c == \'L\' && e.c == \'L\'){\n if(e.idx > s.idx){\n return false;\n }\n }\n \n \n if(s.c == \'R\' && e.c == \'R\'){\n if(e.idx < s.idx){\n return false;\n }\n }\n }\n \n \n return true;\n }\n}\n```
| 28 | 0 |
['Java']
| 4 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
SIMPLE || O(n) || C++ || Explained
|
simple-on-c-explained-by-sahiltuli_31-wkq8
|
\nBasically two points are essential for our answer to be YES\n1. for all R and L in target there should be a corresponding R and L in start also.Means The rela
|
sahiltuli_31
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T04:02:24.955728+00:00
|
2022-07-10T04:13:03.863075+00:00
| 1,868 | false |
\nBasically two points are essential for our answer to be YES\n1. for all R and L in target there should be a corresponding R and L in start also.Means The relative order of L/R in start and target should be same.Becoz we cant move L beyond a R or R beyond a L.\n2. for every R and L in Target, the corresponding R/L in start can be\n\ta) Corresponding L can be ahead in start, becoz we can always bring it to left and make position equal to that of in target.\n\tb) Corresponding R can be behind in start, becoz we can always bring it to right and make position equal to that of in target.\n\telse Answer will be NO\nSo, save all chars and their position from start in a vector, and for every element L/R in target,check for above two condition if it satisfies\nwe are good to go else Answer will be NO.\n\n\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n \n\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n \n \n vector<pair<char,int >> v;\n for(int i =0 ;i < start.size();i++)\n {\n if(start[i] == \'L\' || start[i] == \'R\')\n {\n v.push_back({start[i],i});\n }\n }\n \n int i = 0;\n for(int j = 0;j < target.size();j++)\n {\n if(target[j] == \'L\' || target[j] == \'R\') // lets find its corresponding Element in start\n {\n if(i >= v.size() || v[i].first != target[j]) // Not found or Different found\n {\n return false;\n }else \n {\n \n if(v[i].first == \'L\' && v[i].second < j) // Condition a unsatisfied\n return false;\n if(v[i].first == \'R\' && v[i].second > j) // Condition b unsatisfied\n return false;\n else \n i++; // all good we move ahead in start;\n }\n \n \n }\n }\n \n return i == v.size();// all elements accounted for in start\n }\n};\n```\nConsider Upvoting.
| 27 | 0 |
['C']
| 2 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
[5 Lines] Very Elegant Functional Solution (Python)
|
5-lines-very-elegant-functional-solution-tgos
|
There are just 3 conditions:\n1. since the L and R blocks can never pass each other, their order must be the same. \n2. every L in target must be to the left or
|
elimsamazak1
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T04:58:30.508785+00:00
|
2022-07-10T05:32:22.610657+00:00
| 804 | false |
There are just 3 conditions:\n1. since the L and R blocks can never pass each other, their order must be the same. \n2. every L in `target` must be to the left or same as the corresponding L in `start` \n3. every R in `target` must be to the right or same as the corresponding R in `start` \n\n```py\nclass Solution:\n def canChange(self, A: str, B: str) -> bool:\n P = lambda c : c != \'_\'\n I = lambda s,x : [i for i,c in enumerate(s) if c==x]\n G = lambda d,p : all( p(x,y) for x,y in zip( I(A,d), I(B,d) ) )\n S = lambda : [*filter(P,A)] == [*filter(P,B)]\n return S() and G(\'L\', ge) and G(\'R\', le)\n\t\t# 1. 2. 3.\n```\n\nNotes to clear up confusion:\n1. `filter(predicate, iterable)` returns a filter object with the elements that trigger the predicate removed\n2. `[ *filter(P,A) ]` unpacks the filter object (similar to a generator/iterator) into a list\n3. `S()` returns whether or not the `\'L\'` and `\'R\'` characters appear in the same order.\n4. `I(s, x)` returns a List of the indices at which `x` occurs in `s`\n5. `G(d, p)` returns whether or not `p(x,y)` is true for all corresponding pairs `x,y` of `d`\n6. `le` and `ge` are functional equivalents of `<=` and `>=` operators, found in `operator` module\n\nPlease leave an upvote if you liked it/learned something, or comment if you have any questions!
| 21 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
One Pointer | Time O(n) | Space O(1)
|
one-pointer-time-on-space-o1-by-yunming_-tkmh
|
One Pointer | Time O(n) | Space O(1)\n\n# Code\ncpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n int n = start.leng
|
yunming_chan
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T02:56:38.020909+00:00
|
2024-12-05T02:56:38.020934+00:00
| 1,053 | false |
## One Pointer | Time O(n) | Space O(1)\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n int n = start.length();\n int l=0, r=0;\n for(int i=0; i<n; i++){\n if(start[i] == \'L\'){\n l--;\n }\n else if(start[i] == \'R\'){\n r++;\n if(l!=0) return false;\n }\n if(target[i] == \'L\'){\n l++;\n if(r!=0) return false;\n }\n else if(target[i] == \'R\'){\n r--;\n }\n\n if(l<0 || r<0) return false;\n }\n return l==0 && r==0;\n }\n};\n```
| 16 | 1 |
['C++']
| 4 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Python two-pointers O(n) solution
|
python-two-pointers-on-solution-by-bread-4q17
|
```python\nclass Solution:\n def canChange(self, start: str, target: str) -> bool:\n lcnt, rcnt = 0, 0\n for c1, c2 in zip(start, target):\n
|
breadmumu
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T04:01:18.754030+00:00
|
2022-07-11T00:39:05.492904+00:00
| 1,486 | false |
```python\nclass Solution:\n def canChange(self, start: str, target: str) -> bool:\n lcnt, rcnt = 0, 0\n for c1, c2 in zip(start, target):\n if c1 == \'L\': lcnt += 1\n if c2 == \'L\': lcnt -= 1\n if c1 == \'R\': rcnt += 1\n if c2 == \'R\': rcnt -= 1\n if lcnt or rcnt: return False\n \n s_ptr = 0\n for t_ptr in range(len(target)):\n if target[t_ptr] == \'_\':\n continue\n else:\n while s_ptr < len(start) and start[s_ptr] == \'_\':\n s_ptr += 1\n if (target[t_ptr] != start[s_ptr] or\n target[t_ptr] == \'L\' and s_ptr < t_ptr or\n target[t_ptr] == \'R\' and s_ptr > t_ptr):\n return False\n s_ptr += 1\n return True\n
| 15 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'Python']
| 1 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Python3 || 10 lines, w/ explanation || T/S: 82%/ 40%
|
python3-10-lines-w-explanation-ts-82-40-plxvn
|
Here\'s the intuition:\n\n 1. The number of Ls, number of Rs, and number of _s must be equal between the two strings.\n\n 1. The ordering of Ls and Rs in the
|
Spaulding_
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-13T03:31:41.216538+00:00
|
2024-12-05T18:56:45.716163+00:00
| 668 | false |
Here\'s the intuition:\n\n 1. The number of *L*s, number of *R*s, and number of _s must be equal between the two strings.\n\n 1. The ordering of *L*s and *R*s in the two strings must be the same.\n 2. *L*s can only move left and *R*s can only move right, so each *L* in start cannot be to the left of its corresponding *L* in target, and each *R* cannot be to the right of its corresponding *R* in target.\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def canChange(self, start: str, target: str) -> bool:\n\n # Check initial conditions\n if (len(start) != len(target)\n or start.count(\'_\') != target.count(\'_\')): return False\n\n n, i, j = len(start), 0, 0\n\n while i < n or j < n:\n # Move i and j to the next non-underscore character\n while i < n and start[i] == \'_\': i += 1\n while j < n and target[j] == \'_\': j += 1\n\n # If both indices are out of bounds, we are done\n if i == n and j == n: return True\n\n # If one index is out of bounds or characters differ, return False\n if i == n or j == n or start[i] != target[j]: return False\n\n # Check if the transformation is valid\n if start[i] == \'L\' and i < j: return False\n if start[i] == \'R\' and i > j: return False\n\n # Move to the next character\n i += 1\n j += 1\n\n return True\n```\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n // Check initial conditions\n if (count(start.begin(), start.end(), \'_\') != count(target.begin(), target.end(), \'_\')) {\n return false;\n }\n\n int n = start.size();\n int i = 0, j = 0;\n\n while (i < n || j < n) {\n // Move i and j to the next non-underscore character\n while (i < n && start[i] == \'_\') i++;\n while (j < n && target[j] == \'_\') j++;\n\n // If both indices are out of bounds, we are done\n if (i == n && j == n) return true;\n\n // If one index is out of bounds or characters differ, return false\n if (i == n || j == n || start[i] != target[j]) return false;\n\n // Check if the transformation is valid\n if (start[i] == \'L\' && i < j) return false;\n if (start[i] == \'R\' && i > j) return false;\n\n // Move to the next character\n i++;\n j++;\n }\n\n return true;\n }\n};\n\n```\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n // Check initial conditions\n if (start.length() != target.length() || countChar(start, \'_\') != countChar(target, \'_\')) {\n return false;\n }\n\n int n = start.length();\n int i = 0, j = 0;\n\n while (i < n || j < n) {\n // Move i and j to the next non-underscore character\n while (i < n && start.charAt(i) == \'_\') i++;\n while (j < n && target.charAt(j) == \'_\') j++;\n\n // If both indices are out of bounds, we are done\n if (i == n && j == n) return true;\n\n // If one index is out of bounds or characters differ, return false\n if (i == n || j == n || start.charAt(i) != target.charAt(j)) return false;\n\n // Check if the transformation is valid\n if (start.charAt(i) == \'L\' && i < j) return false;\n if (start.charAt(i) == \'R\' && i > j) return false;\n\n // Move to the next character\n i++;\n j++;\n }\n\n return true;\n }\n\n // Helper method to count occurrences of a character\n private int countChar(String s, char ch) {\n int count = 0;\n for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {\n if (c == ch) count++;\n }\n return count;\n }\n}\n\n```\n[https://leetcode.com/problems/move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string/submissions/1470587049/?envType=daily-question&envId=2024-12-05](https://leetcode.com/problems/move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string/submissions/1470587049/?envType=daily-question&envId=2024-12-05)\n\nI could be wrong, but I think that time complexity is *O*(*N*) and space complexity is ~*O*(*N*)~ *O*(1), in which *N* ~ `len(start)`.
| 13 | 0 |
['C++', 'Java', 'Python3']
| 3 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Java | Intuitive | Just traverse both Strings | O(n)
|
java-intuitive-just-traverse-both-string-ff3m
|
Approach\n\nJust traverse both the strings and check whether relative charcters (\'R\' or \'L\') are equal or not, if they are equal, then check their relative
|
arcpri
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T04:01:48.624941+00:00
|
2022-07-10T04:19:33.906168+00:00
| 1,085 | false |
**Approach**\n\nJust traverse both the strings and check whether relative charcters (\'R\' or \'L\') are equal or not, if they are equal, then check their relative positions to see whether `start` can be converted to `target` or not\n\n**e.g.** \'-R\' and \'R-\' => here, relative characters \'R\' and \'R\' are equal but index of \'R\' in `start` is greater than index of \'R\' in `target`, since \'R\' can\'t move left, hence we return false for this test case\n\n**Time Complexity** => O(n)\n\n```\npublic boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n if (start.length() != target.length()) {\n return false;\n }\n \n int i = 0, j = 0;\n \n while (i < start.length() || j < target.length()) {\n while (i < start.length() && start.charAt(i) == \'_\') {\n i++;\n }\n \n while (j < target.length() && target.charAt(j) == \'_\') {\n j++;\n }\n \n // if both i and j reach end of string\n if (i == j && i == start.length()) {\n return true;\n }\n \n if (i == start.length() || j == target.length() || start.charAt(i) != target.charAt(j)) {\n return false;\n }\n \n // if characters at both i and j are equal, check their relative positions in both start and target\n if ((target.charAt(j) == \'L\' && i < j) || (target.charAt(j) == \'R\' && i > j)) {\n return false;\n }\n \n i++;\n j++;\n }\n \n return true;\n }\n```
| 13 | 1 |
['Java']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Simple and Easy Solution | ✅Beats 100% | C++| Java | Python | JavaScript
|
simple-and-easy-solution-beats-100-c-jav-gscz
|
\u2B06\uFE0FUpvote if it helps \u2B06\uFE0F \n## Connect with me on Linkedin Bijoy Sing. \n\n## Follow me also on Codeforces: Bijoy Sing \n\n###### Solution
|
BijoySingh7
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T05:29:03.779848+00:00
|
2024-12-05T05:29:03.779885+00:00
| 1,957 | false |
# \u2B06\uFE0FUpvote if it helps \u2B06\uFE0F \n## Connect with me on Linkedin [Bijoy Sing](https://www.linkedin.com/in/bijoy-sing-236a5a1b2/). \n\n## Follow me also on Codeforces: [Bijoy Sing](https://codeforces.com/profile/BijoySingh7) \n\n###### *Solution in C++, Python, Java, and JavaScript* \n\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n int left = 0, right = 0;\n\n for (int i = 0; i < start.size(); i++) {\n if (start[i] == \'R\') {\n right++;\n if (left != 0)\n return false;\n } else if (start[i] == \'L\')\n left--;\n if (target[i] == \'R\')\n right--;\n else if (target[i] == \'L\') {\n left++;\n if (right != 0)\n return false;\n }\n if (left < 0 || right < 0)\n return false;\n }\n return left == 0 and right == 0;\n }\n};\n```\n\n```python []\nclass Solution:\n def canChange(self, start: str, target: str) -> bool:\n left = 0\n right = 0\n\n for i in range(len(start)):\n if start[i] == \'R\':\n right += 1\n if left != 0:\n return False\n elif start[i] == \'L\':\n left -= 1\n if target[i] == \'R\':\n right -= 1\n elif target[i] == \'L\':\n left += 1\n if right != 0:\n return False\n if left < 0 or right < 0:\n return False\n\n return left == 0 and right == 0\n```\n\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n int left = 0, right = 0;\n\n for (int i = 0; i < start.length(); i++) {\n if (start.charAt(i) == \'R\') {\n right++;\n if (left != 0)\n return false;\n } else if (start.charAt(i) == \'L\') {\n left--;\n }\n if (target.charAt(i) == \'R\') {\n right--;\n } else if (target.charAt(i) == \'L\') {\n left++;\n if (right != 0)\n return false;\n }\n if (left < 0 || right < 0)\n return false;\n }\n return left == 0 && right == 0;\n }\n}\n```\n\n```javascript []\nclass Solution {\n canChange(start, target) {\n let left = 0, right = 0;\n\n for (let i = 0; i < start.length; i++) {\n if (start[i] === \'R\') {\n right++;\n if (left !== 0)\n return false;\n } else if (start[i] === \'L\') {\n left--;\n }\n if (target[i] === \'R\') {\n right--;\n } else if (target[i] === \'L\') {\n left++;\n if (right !== 0)\n return false;\n }\n if (left < 0 || right < 0)\n return false;\n }\n return left === 0 && right === 0;\n }\n}\n```\nCertainly! Let\u2019s expand the explanation further to make the approach and intuition clearer:\n\n---\n\n# Intuition \nThe problem asks us to transform a `start` string into a `target` string by moving the characters \'R\' (right) and \'L\' (left), with specific movement restrictions:\n- An \'R\' can only move rightwards (i.e., it cannot be placed in a position where it would be to the left of its original position).\n- An \'L\' can only move leftwards (i.e., it cannot be placed in a position where it would be to the right of its original position).\nThus, our goal is to check if we can rearrange the characters in `start` to match those in `target`, while adhering to these movement restrictions.\n\nThe key challenge is ensuring that:\n- The relative positions of \'R\' and \'L\' remain valid.\n- If \'R\' appears before \'L\' in the `start` string, it should also appear before \'L\' in the `target` string, and vice versa. This ensures that the characters maintain their relative order.\n\n# Approach \nWe iterate through the `start` and `target` strings simultaneously. At each step, we check:\n- If we encounter an \'R\' in `start`, we ensure it can move right to its corresponding position in `target`.\n- Similarly, if we encounter an \'L\' in `start`, we ensure it can move left to its corresponding position in `target`.\n- We also keep track of the positions of \'R\' and \'L\' to ensure that they maintain the required order as they move.\n\nHere are the main conditions we check:\n1. If at any point, an \'R\' needs to move left (i.e., the number of right-moving \'R\' exceeds the number of \'R\' in `target`), return `false`.\n2. If at any point, an \'L\' needs to move right (i.e., the number of left-moving \'L\' exceeds the number of \'L\' in `target`), return `false`.\n3. Finally, at the end of the loop, we check if the counts of \'R\' and \'L\' match in both strings, ensuring that we have the same number of characters in both strings, and no illegal movement occurred.\n---\n\n### Example Walkthrough:\n\n#### Example 1:\nInput: \n`start = "_L__R__R_"`, \n`target = "L______RR"`.\n\n**Execution**:\n- `i = 0`: `start[0] = \'_\'`, `target[0] = \'L\'`, update `left++` \u2192 `left = 1`.\n- `i = 1`: `start[1] = \'L\'`, `target[1] = \'_\'`, update `left--` \u2192 `left = 0`.\n- `i = 2 to 6`: Both `start[i]` and `target[i]` are `\'_\'`.\n- `i = 7`: `start[7] = \'R\'`, `target[7] = \'_\'`, update `right++` \u2192 `right = 1`.\n- `i = 8`: `start[8] = \'R\'`, `target[8] = \'R\'`, update `right--` \u2192 `right = 0`.\n\nFinal check: `left == 0` and `right == 0` \u2192 Return `true`.\n\n---\n\n#### Example 2:\nInput: \n`start = "R_L_"`, \n`target = "__LR"`.\n\n**Execution**:\n- `i = 0`: `start[0] = \'R\'`, `target[0] = \'_\'`, update `right++` \u2192 `right = 1`.\n- `i = 1`: `start[1] = \'_\'`, `target[1] = \'_\'`.\n- `i = 2`: `start[2] = \'L\'`, `target[2] = \'L\'`, update `left--` \u2192 `left = -1`.\n\nAt `i = 2`, `left < 0` \u2192 Return `false`.\n\n---\n\n# Complexity \n\n- **Time complexity**: \n $$O(n)$$, where $$n$$ is the length of the string. This is because we only traverse the strings once, performing constant-time operations for each character.\n\n- **Space complexity**: \n $$O(1)$$, as we only use a few integer counters (`left` and `right`) to keep track of the movements of \'L\' and \'R\'. We do not use any extra data structures that scale with the size of the input.\n\n---\n\n### *If you have any questions or need further clarification, feel free to drop a comment! \uD83D\uDE0A*
| 11 | 1 |
['Array', 'Two Pointers', 'String', 'String Matching', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java', 'Python3', 'JavaScript']
| 5 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
[C++/Java] Explained - easy iterative solution O(n) || with single pointer
|
cjava-explained-easy-iterative-solution-khfjm
|
Approach\n- iterate over the start and target simultaneously\n- Take two counters lcount and rcount.\n- When we see L or R in start we increement and if we see
|
kreakEmp
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T04:31:14.746411+00:00
|
2024-12-06T12:15:01.161075+00:00
| 95 | false |
# Approach\n- iterate over the start and target simultaneously\n- Take two counters lcount and rcount.\n- When we see L or R in start we increement and if we see the same in target we decrement both l and r counter\n- Now there are 5 cases where we need to return false :\n 1. When lcount is greater than zero that means we have seen one L in start but not its equivalent in target till i which means we can not compensate it anymore so return false.\n 2. opposite of above case when we see extra R in the target i.e when the rcount is less than 0 then return false;\n 3. When we see L in start but the rcount is not zero return false;\n 4. When we see R in target but the lcount is not zero return false;\n 5. At the end of iterations if still any of rcount or lcount is not zero then return zero.\n\n- If non of the above cases found then return true;\n\n# Complexitey:\n- Time complexity : O(N)\n- Space complexity : O(1)\n\n# C++ code\n\n```\nbool canChange(string start, string target) {\n int lcount = 0, rcount = 0;\n for(int i = 0; i < start.size(); ++i){\n if(start[i] == \'L\') { lcount++; if(rcount != 0) return false; }\n if(target[i] == \'L\'){ lcount--; }\n if(start[i] == \'R\') { rcount++; }\n if(target[i] == \'R\'){ rcount--; if(lcount != 0) return false; }\n if(lcount > 0 || rcount < 0) return false;\n }\n return !(lcount != 0 || rcount != 0);\n}\n```\n\n# Java code\n\n```\npublic boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n int lcount = 0, rcount = 0;\n for(int i = 0; i < start.length(); ++i){\n if(start.charAt(i) == \'L\') { lcount++; if(rcount != 0) return false; }\n if(target.charAt(i) == \'L\'){ lcount--; }\n if(start.charAt(i) == \'R\') { rcount++; }\n if(target.charAt(i) == \'R\'){ rcount--; if(lcount != 0) return false; }\n if(lcount > 0 || rcount < 0) return false;\n }\n return !(lcount != 0 || rcount != 0);\n}\n\n```\n\n\n\n---\n\n\n<b>Here is an article of my interview experience - A Journey to FAANG Company, I recomand you to go through this to know which all resources I have used & how I cracked interview at Amazon:\nhttps://leetcode.com/discuss/interview-experience/3171859/Journey-to-a-FAANG-Company-Amazon-or-SDE2-(L5)-or-Bangalore-or-Oct-2022-Accepted\n\n\n---\n
| 9 | 0 |
['String', 'C']
| 1 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
✅ Easy to Understand | Two Pointers | Beats 100% | Detailed Video Explanation 🔥
|
easy-to-understand-two-pointers-beats-10-yg64
|
Intuition\nThe problem involves verifying whether a given string start can be transformed into another string target by moving the characters \'L\' and \'R\' un
|
sahilpcs
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T02:56:11.420964+00:00
|
2024-12-05T02:56:28.530407+00:00
| 1,295 | false |
# Intuition\nThe problem involves verifying whether a given string `start` can be transformed into another string `target` by moving the characters `\'L\'` and `\'R\'` under specific rules:\n- `\'L\'` can only move left.\n- `\'R\'` can only move right.\n- Underscores (`\'_\'`) represent empty spaces.\n\nThe key observation is that the relative order of `\'L\'` and `\'R\'` must remain unchanged, and their movements must respect the rules of directionality.\n\n---\n\n# Approach\n1. Use two pointers (`i` for `start` and `j` for `target`) to traverse both strings simultaneously.\n2. Skip any underscores in both strings, as they don\'t contribute to the logic of character matching.\n3. When encountering characters `\'L\'` or `\'R\'`, check:\n - The characters must match (`start[i] == target[j]`).\n - `\'L\'` can only move left, meaning its index in `start` must be greater than or equal to its index in `target`.\n - `\'R\'` can only move right, meaning its index in `start` must be less than or equal to its index in `target`.\n4. If any of the above conditions fail, return `false`.\n5. After completing the traversal, skip any trailing underscores in both strings.\n6. Ensure both pointers reach the end of their respective strings. If they do, return `true`; otherwise, return `false`.\n\n---\n\n# Complexity\n- **Time complexity:** \n $$O(n)$$ \n We traverse each string at most once, where \\(n\\) is the length of the strings (both assumed to be the same length).\n\n- **Space complexity:** \n $$O(1)$$ \n The algorithm uses constant space for the pointers and comparisons, with no additional data structures.\n\n\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n int i = 0, j = 0;\n int n = start.length(), m = target.length();\n\n // Traverse both strings using two pointers\n while (i < n && j < m) {\n char a = start.charAt(i);\n char b = target.charAt(j);\n\n // Skip underscores (\'_\') in both strings\n if (a == \'_\' && b == \'_\') {\n i++;\n j++;\n } \n // Skip underscores in the `start` string\n else if (a == \'_\') {\n i++;\n } \n // Skip underscores in the `target` string\n else if (b == \'_\') {\n j++;\n } \n // If characters match, ensure valid movement\n else if (\n a == b && // Characters must match\n (\n (a == \'L\' && i >= j) || // \'L\' can only move left\n (a == \'R\' && i <= j) // \'R\' can only move right\n )\n ) {\n i++;\n j++;\n } \n // If none of the above conditions are satisfied, return false\n else {\n return false;\n }\n }\n\n // Skip remaining underscores in the `start` string\n while (i < n && start.charAt(i) == \'_\') {\n i++;\n }\n\n // Skip remaining underscores in the `target` string\n while (j < m && target.charAt(j) == \'_\') {\n j++;\n }\n\n // Both pointers must reach the end for a valid transformation\n return i == n && j == m;\n }\n}\n\n```\n\nLeetCode 2337 Move Pieces to Obtain a String | String | Two Pointers | Google Amazon Interview Ques\nhttps://youtu.be/7_i0_o_BUZw
| 8 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'String', 'Java']
| 2 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Simple C++ Easy Solution | Faster than 100% | O(N)
|
simple-c-easy-solution-faster-than-100-o-jhjh
|
\nObservation 1:\nEx- _ L _ R _ _ R _ L\nLook at the example and imagine _ moving . We will notice that _ pushes L to left and it pushes R to right.\n\nWe can r
|
pk_09
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T04:15:21.027526+00:00
|
2022-07-11T18:17:23.113019+00:00
| 567 | false |
\n**Observation 1:**\nEx- _ L _ R _ _ R _ L\nLook at the example and imagine _ moving . We will notice that _ pushes L to left and it pushes R to right.\n\nWe can remove all the spaces and store the new string in s(start string without _ ) and t(target string without _ ), if s!=t the answer is false as L and R cannot cross each other so there\'s no way to make start==target.\n\n**Observation 2:**\n_ will move L only towards left, so if the index of L in start is lesser than L in target, then it is not possible to make the strings equal.\nSo in a vector(l1) we store all the indexes where start[i]=\'L\' and in another vector(l2) we store all the indexes where target[i]==\'L\'. Then we loop the vector and if at any index l1[i]<l2[i] we return false.\n\n**Observation 3:**\nSimilarly, _ will move R only towards right, so if the index of R in start is greater than R in target, then it is not possible to make the strings equal.\nSo in a vector(r1) we store all the indexes where start[i]=\'R\' and in another vector(r2) we store all the indexes where target[i]==\'R\'. Then we loop the vector and if at any index r1[i]>r2[i] we return false.\n\nCode:\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n string s,t;\n for(int i=0;i<start.size();i++){\n if(start[i]!=\'_\')s.push_back(start[i]);\n if(target[i]!=\'_\')t.push_back(target[i]);\n }\n if(s!=t)return false;\n vector<int> l1,l2;\n for(int i=0;i<start.size();i++){\n if(start[i]==\'L\')l1.push_back(i);\n if(target[i]==\'L\')l2.push_back(i);\n }\n for(int i=0;i<l1.size();i++){\n if(l1[i]<l2[i])return false;\n }\n vector<int> r1,r2;\n for(int i=0;i<start.size();i++){\n if(start[i]==\'R\')r1.push_back(i);\n if(target[i]==\'R\')r2.push_back(i);\n }\n for(int i=0;i<r1.size();i++){\n if(r1[i]>r2[i])return false;\n }\n return true;\n }\n};\n```\nPlease Upvote if you found it useful!\n
| 8 | 0 |
['Greedy', 'C']
| 1 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Keep track of the position of pieces in your start string | O(N) space and time
|
keep-track-of-the-position-of-pieces-in-22ufm
|
The idea is simple:\n\n- Use queue to keep track of the pieces and index occurance in the start string\n- Walk through the target string and when you hit a piec
|
Serined
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T04:01:40.150072+00:00
|
2022-07-10T04:11:19.099292+00:00
| 471 | false |
The idea is simple:\n\n- Use **queue** to keep track of the pieces and index occurance in the **start string**\n- Walk through the **target string** and when you hit a piece:\n\t- Make sure the queue still has pieces\n\t- Pop a piece from the queue, and make sure they match \n\t- Make sure you can move the piece to the position it occured in the **target string**; by comparing indices \n\t- Finally, only return **True** if no more pieces exist in the queue \n\n\n\n```\ndef canChange(self, start: str, target: str) -> bool:\n\tq, av = collections.deque(), set([\'L\', \'R\'])\n\n\tfor i, c in enumerate(start):\n\t\tif c in av: q.append((i, c))\n\n\tfor i, c in enumerate(target):\n\t\tif c in av:\n\t\t\tif not q: return False\n\n\t\t\tind, char = q.popleft()\n\t\t\tif c != char: return False\n\t\t\telif c == \'R\' and i < ind: return False \n\t\t\telif c == \'L\' and i > ind: return False \n\n\treturn not q \n``` \n\n\n**NOTE**\n\nIt could also be done using a stack, or by keeping track of indices in the **target string** instead of **start string.** \n
| 8 | 1 |
['Greedy', 'Queue', 'Python']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
✅ One Line Solution
|
one-line-solution-by-mikposp-o0e5
|
(Disclaimer: this is not an example to follow in a real project - it is written for fun and training mostly)Code #1Time complexity: O(n). Space complexity: O(1)
|
MikPosp
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T10:44:32.997230+00:00
|
2025-02-14T13:00:24.579653+00:00
| 1,002 | false |
(Disclaimer: this is not an example to follow in a real project - it is written for fun and training mostly)
# Code #1
Time complexity: $$O(n)$$. Space complexity: $$O(1)$$.
```python3
class Solution:
def canChange(self, s: str, t: str) -> bool:
return (f:=lambda q:(p for p in enumerate(q) if p[1]!='_')) and all(c==w and (i<=j,i>=j)[c=='L'] for (i,c),(j,w) in zip_longest(f(s),f(t),fillvalue=(0,'')))
```
<!--
# Code #1.1
Time complexity: $$O(n)$$. Space complexity: $$O(1)$$.
```python3
class Solution:
def canChange(self, s: str, t: str) -> bool:
return (f:=lambda q:(p for p in enumerate(q) if p[1]!='_')) and all((c==w)*(i<=j,i>=j)[c=='L'] for (i,c),(j,w) in zip_longest(f(s),f(t),fillvalue=(0,0)))
```
-->
# Code #2
Time complexity: $$O(n)$$. Space complexity: $$O(n)$$.
```python3
class Solution:
def canChange(self, s: str, t: str) -> bool:
return re.sub('_','',s)==re.sub('_','',t) and (f:=lambda q,s,t:min(accumulate((c==q)-(w==q) for c,w in zip(s,t)))>=0)('R',s,t) and f('L',s[::-1],t[::-1])
```
[Ref](https://leetcode.com/problems/move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string/solutions/5983924/python-one-line-solution)
---
See also similar solution: [777. Swap Adjacent in LR String](https://leetcode.com/problems/swap-adjacent-in-lr-string/solutions/6421848/one-line-solution-by-mikposp)
---
(Disclaimer 2: code above is just a product of fantasy packed into one line, it is not claimed to be 'true' oneliners - please, remind about drawbacks only if you know how to make it better)
| 7 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'String', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Python | Two-Pointer Pattern
|
python-two-pointer-pattern-by-khosiyat-mefe
|
see the Successfully Accepted Submission\n\n# Code\npython3 []\nclass Solution:\n def canChange(self, start: str, target: str) -> bool:\n # Remove \'_
|
Khosiyat
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T00:42:06.689783+00:00
|
2024-12-05T00:42:06.689818+00:00
| 767 | false |
[see the Successfully Accepted Submission](https://leetcode.com/problems/move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string/submissions/1470587258/?envType=daily-question&envId=2024-12-05)\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def canChange(self, start: str, target: str) -> bool:\n # Remove \'_\' characters and check if the relative order of \'L\' and \'R\' is the same\n if start.replace(\'_\', \'\') != target.replace(\'_\', \'\'):\n return False\n\n # Check the relative positions of \'L\' and \'R\'\n start_L_positions = []\n start_R_positions = []\n target_L_positions = []\n target_R_positions = []\n\n for i in range(len(start)):\n if start[i] == \'L\':\n start_L_positions.append(i)\n elif start[i] == \'R\':\n start_R_positions.append(i)\n if target[i] == \'L\':\n target_L_positions.append(i)\n elif target[i] == \'R\':\n target_R_positions.append(i)\n\n # Check L positions (should only move to the left)\n for s_pos, t_pos in zip(start_L_positions, target_L_positions):\n if s_pos < t_pos:\n return False\n\n # Check R positions (should only move to the right)\n for s_pos, t_pos in zip(start_R_positions, target_R_positions):\n if s_pos > t_pos:\n return False\n\n return True\n\n```\n\n\n# Explanation:\n\n### Remove Blanks and Validate Order:\n- Remove the `_` characters from both strings and check if the remaining characters (`L` and `R`) are in the same order in both `start` and `target`.\n- If not, it\'s impossible to transform `start` into `target`.\n\n### Track Positions of `L` and `R`:\n- Extract the indices of `L` and `R` from both `start` and `target`.\n\n### Check Constraints:\n1. For each `L` in `start`, ensure its target position is not to the right (as `L` can only move left).\n2. For each `R` in `start`, ensure its target position is not to the left (as `R` can only move right).\n\n### Return True or False:\n- Return `True` only if all constraints are satisfied; otherwise, return `False`.\n\n---\n\n## Complexity:\n\n- **Time Complexity**: \\(O(n)\\), where \\(n\\) is the length of the string, since we iterate over the strings a constant number of times.\n- **Space Complexity**: \\(O(n)\\) for the position lists and intermediate strings.\n\n\n
| 7 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 1 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Short & Concise | Two Pointers | C++
|
short-concise-two-pointers-c-by-tusharbh-h9ey
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string s, string t) {\n int i = 0, j = 0, n = s.size(), m = t.size();\n if(n != m) return false;\n
|
TusharBhart
|
NORMAL
|
2022-12-29T14:09:44.704804+00:00
|
2022-12-29T14:09:44.704851+00:00
| 583 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string s, string t) {\n int i = 0, j = 0, n = s.size(), m = t.size();\n if(n != m) return false;\n \n while(i < n || j < m) {\n while(i < n && s[i] == \'_\') i++;\n while(j < m && t[j] == \'_\') j++;\n \n if(s[i] != t[j]) return false;\n if(s[i] == \'R\' && i > j) return false;\n if(s[i] == \'L\' && i < j) return false;\n i++, j++;\n }\n return true;\n }\n};\n```
| 7 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'C++']
| 2 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
C++ Sweet Solution
|
c-sweet-solution-by-dracky-a1id
|
Just check the indexes and relative order of L and R and count of R\'s and L\'s\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\
|
dracky
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T04:00:41.021323+00:00
|
2022-07-16T02:49:52.992709+00:00
| 713 | false |
Just check the indexes and relative order of L and R and count of R\'s and L\'s\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n int i=0,j=0,loi=0,n=start.length();\n int SL=0,SR=0,TL=0,TR=0;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n if(start[i]==\'R\')SR++;\n else if(start[i]==\'L\')SL++;\n if(target[i]==\'L\')TL++;\n else if(target[i]==\'R\')TR++;\n }\n if(SL!= TL || SR!=TR)return false;\n while(i<n && j<n){\n while(i<n && start[i++]==\'_\');\n while(j<n && target[j++]==\'_\');\n i--;j--;\n if(start[i]!=target[j])return false;\n if(start[i]==\'L\'){\n if(i<j)return false;\n }\n if(start[i]==\'R\'){\n if(i>j)return false;\n }\n i++;j++;\n }\n return true;\n }\n};\n```
| 7 | 0 |
['C']
| 3 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
C++ | Loop Left & Right ~ O(N)
|
c-loop-left-right-on-by-geekykant-eatx
|
Track Position Together Solution (Inspired from @IAmCoderrr)\ncpp\nbool canChange(string start, string target) {\n int i = 0, j = 0, n = start.size();\n\t\n\
|
geekykant
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T04:05:41.330400+00:00
|
2022-07-10T06:24:36.506926+00:00
| 619 | false |
1. **Track Position Together Solution** (Inspired from [@IAmCoderrr](https://leetcode.com/IAmCoderrr))\n```cpp\nbool canChange(string start, string target) {\n int i = 0, j = 0, n = start.size();\n\t\n\t// we keep OR condition to execute the loop one more time till remaining \'_\' present\n while(i < n || j < n){\n while(i < n && start[i] == \'_\') i++;\n while(j < n && target[j] == \'_\') j++;\n\n\t\t// if all chars are \'_\', break\n if(i == n || j == n) break;\n\n if(start[i] != target[j]) return false;\n\t\t\n\t\t//positional conditions\n if(start[i] == \'L\') if(i < j) return false;\n if(start[i] == \'R\') if(i > j) return false;\n i++; j++;\n }\n\n return i == n && j == n;\n}\n```\n\n2. **Two Loop Solution** - Keeps making char changes live.\n```cpp\nbool canChange(string start, string target) {\n unordered_map<char, int> chars1, chars2;\n for(char& ch: start)\n chars1[ch]++;\n for(char& ch: target)\n chars2[ch]++;\n\n if(chars1 != chars2) return false;\n\n int n = start.size();\n\n //move from right to left for \'R\' changes\n for(int i=n-1; i >= 0; i--){\n if(start[i] == target[i]) continue;\n\n char req = target[i];\n if(req == \'R\'){\n int j = i;\n while(j >= 0 && start[j] == \'_\'){\n start[j] = target[j];\n j--;\n }\n if(j < 0 || start[j] == \'L\') return false;\n start[j] = \'_\';\n i = j + 1;\n }\n }\n\n //move from left to right for \'L\' changes\n for(int i=0; i < n; i++){\n if(start[i] == target[i]) continue;\n\n char req = target[i];\n if(req == \'L\'){\n int j = i;\n while(j < n && start[j] == \'_\'){\n start[j] = target[j];\n j++;\n }\n if(j == n || start[j] == \'R\') return false;\n start[j] = \'_\';\n i = j - 1;\n }\n }\n return true;\n}\n```\n
| 6 | 0 |
['C']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Move Pieces to Obtain a String | Java Solution
|
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string-java-solu-9dlv
|
\nclass Solution {\n public boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n int characs = 0; \n for (int i=0;i<start.length();i++) \n
|
shaguftashahroz09
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T04:02:25.341461+00:00
|
2022-07-10T04:02:25.341487+00:00
| 294 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n int characs = 0; \n for (int i=0;i<start.length();i++) \n { \n char ch = start.charAt(i);\n if (ch != \'_\') \n characs++; \n } \n for (int i=0;i<target.length();i++) \n { \n char ch = target.charAt(i);\n if (ch != \'_\') \n characs--; \n } \n if (characs != 0) \n return false; \n return compute(start, target); \n } \n \n public boolean compute(String start, String target) \n { \n int LStart = 0, RStart = 0; \n int LTarget = 0, RTarget = 0; \n for (int i = 0; i < start.length(); i++) \n { \n char ch1 = start.charAt(i); \n char ch2 = target.charAt(i); \n if (ch1 == \'L\') \n LStart++; \n else if(ch1 == \'R\') \n RStart++; \n if (ch2 == \'L\') \n LTarget++; \n else if(ch2 == \'R\') \n RTarget++; \n } \n \n if (LStart != LTarget || RStart != RTarget) \n return false; \n \n List<Integer> ar1 = new ArrayList<>(); \n List<Integer> ar2 = new ArrayList<>(); \n \n for (int i = 0; i < start.length(); i++) \n { \n char ch = start.charAt(i);\n if (ch != \'_\') { \n ar1.add(i); \n } \n if (target.charAt(i) != \'_\') { \n ar2.add(i); \n } \n } \n \n for (int i = 0; i < ar1.size(); i++) \n { \n if (start.charAt(ar1.get(i)) != target.charAt(ar2.get(i))) \n return false; \n \n if (start.charAt(ar1.get(i)) == \'L\') \n { \n if (ar1.get(i) < ar2.get(i)) \n return false; \n } else \n { \n if (ar1.get(i) > ar2.get(i)) \n return false; \n } \n } \n return true; \n\n }\n}\n```
| 6 | 0 |
['Java']
| 2 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
EASY C++ SOLUTION | 2337. Move Pieces to Obtain a String
|
easy-c-solution-2337-move-pieces-to-obta-acrv
|
Intuition\nThe problem involves determining whether it\'s possible to transform a string start into a string target by moving characters \'L\' (left) and \'R\'
|
shivambit
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T06:25:20.420540+00:00
|
2024-12-05T06:25:20.420589+00:00
| 357 | false |
# Intuition\nThe problem involves determining whether it\'s possible to transform a string start into a string target by moving characters \'L\' (left) and \'R\' (right) according to specific rules. The key insight is that:\n1. Character Movement: \'R\' can only move to the right, and \'L\' can only move to the left. Thus, if we encounter an \'R\' in start, it should not encounter an \'L\' in target before it has moved.\n2. Count Matching: The total number of \'L\'s and \'R\'s in both strings must match for a valid transformation.\n3. Order of Movement: The movement should respect the order of characters; for instance, an \'R\' should not jump over an \'L\'.\n\n# Approach\n1. Initialization: Start with two counters, left and right, initialized to zero. These will track the net movements of \'L\'s and \'R\'s respectively.\n2. Iterate through Characters:\n- For each character in both start and target, update the left and right counters based on whether the character is \'L\' or \'R\'.\n- If you encounter an \'R\', increment right. If you encounter an \'L\', decrement left.\n- Simultaneously, do the same for the target string by decrementing or incrementing the respective counters.\n3. Validation:\n- After updating the counters for both strings, check:\n - If at any point during the iteration left becomes negative (indicating more left movements than allowed) or if right becomes negative (indicating more right movements than allowed).\n - If there are any unbalanced movements after processing both strings (i.e., both counters should be zero at the end).\n4. Return Result: If all checks pass, return true; otherwise, return false.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n), where n is the length of the strings. The algorithm processes each character exactly once.\n- Space complexity: O(1), as we are using a constant amount of space for the counters regardless of input size.4\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n int left = 0, right = 0;\n\n for (int i = 0; i < start.size(); i++) {\n if (start[i] == \'R\') {\n right++;\n if (left != 0)\n return false;\n } else if (start[i] == \'L\')\n left--;\n if (target[i] == \'R\')\n right--;\n else if (target[i] == \'L\') {\n left++;\n if (right != 0)\n return false;\n }\n if (left < 0 || right < 0)\n return false;\n }\n return left == 0 and right == 0;\n }\n};\n```
| 5 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'String', 'C++', 'Python3']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Faster than 100.00 % ||CPP || O(N)
|
faster-than-10000-cpp-on-by-samuraii_sam-vo0e
|
\n\n## APPROACH EXPLAINATION :\n1. First we check if the size of both strings are same or not.\n1. If size are same:\n * Then we check for the frequency of c
|
samuraii_Sami
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T13:16:46.519820+00:00
|
2022-07-10T18:29:08.799444+00:00
| 329 | false |
\n\n## **APPROACH EXPLAINATION :**\n1. First we check if the size of both strings are same or not.\n1. If size are same:\n * Then we check for the frequency of character \'R\' ans \'L\' in both the string.\n * For string start , just add the frequency in the count_l and count_r \n and for string target, subtracts the frequency from count_l and count_r \n1. If count_l and count_r are not 0, then frequency of characters are not same , return false.\n1. Now we check if the position of characters can be changed to get the target string or not. \n* Store the index of \'R\' and \'L\' of start in a stack.\n* Iterate the string target from last and check for the foloowing\n * if char is "_" , iterate for next index.\n * if the character of target and that in the stack is not same , then start can\'t be converted to target\n * if char of target is same as the top of stack\n ! If char is "R" => Then the index on the top should be lesser then the curr iterating index, as "R" can only move to right direction, \n so this would never be moved to target\'s index position\n * Similarly we check for char "L" also.\n\n* If all\'s well then string start can be converted to target\n\n**Time complexity: O(N)\nSpace complexity : O(N)**\n\n\n\n```\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n int s=start.size(), t= target.size(); \n if(s!=t) return false;\n \n stack<int> st;\n int count_l=0,count_r=0; // Storing the frequency of characters \'L\' and \'R\'\n for(int i=0;i<s ;i++)\n {\n if(start[i]==\'L\') count_l++;\n else if(start[i]==\'R\') count_r++;\n \n if(target[i]==\'L\') count_l--;\n else if(target[i]==\'R\') count_r--;\n \n if(start[i]!=\'_\') st.push(i); // storing index values in stack\n \n }\n \n if( count_l ||count_r) // if count of characters are not same in start and target\n return false; \n \n \n //Now check if the placement of characters are in correct position \n for(int i= t-1;i>=0;i--) \n {\n if(target[i]== \'_\')\n continue;\n \n if(target[i]== start[st.top()])\n {\n if(target[i]==\'L\' && i> st.top() || target[i]==\'R\' && i<st.top()) \n return false;\n }\n else if(target[i]!= start[st.top()])\n return false;\n \n st.pop();\n }\n \n return true;\n }\n```\n\n PLEASE UPVOTE IF MY EXPLAINATION WAS HELPFUL\n 
| 5 | 0 |
['String', 'Stack', 'C++']
| 1 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
O(N) Solution
|
on-solution-by-virendra115-xyac
|
\npublic boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n int l=0,r=0,n=start.length();\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n if(start.charAt(i)=
|
virendra115
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T04:33:09.040238+00:00
|
2022-07-10T04:33:09.040268+00:00
| 212 | false |
```\npublic boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n int l=0,r=0,n=start.length();\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++){\n if(start.charAt(i)==\'L\') {\n l++;\n if(r>0) return false;\n }\n else if(start.charAt(i)==\'R\') r++;\n if(target.charAt(i)==\'L\') l--;\n else if(target.charAt(i)==\'R\') r--;\n if(l>0) return false;\n if(r<0) return false;\n }\n return l==0&&r==0;\n }\n```
| 5 | 1 |
['Java']
| 1 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Java Solution
|
java-solution-by-solved-tcz1
|
\nclass Solution {\n public boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n String onlyDirsStart = start.replace("_", "");\n String onlyDirs
|
solved
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T04:01:32.396440+00:00
|
2022-07-10T04:01:32.396493+00:00
| 210 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n String onlyDirsStart = start.replace("_", "");\n String onlyDirsTarget = target.replace("_", "");\n if (!onlyDirsStart.equals(onlyDirsTarget)) {\n return false;\n }\n int balance = 0;\n for (int i = 0; i < start.length(); i++) {\n if (target.charAt(i) == \'L\') {\n balance++;\n }\n if (start.charAt(i) == \'L\') {\n balance--;\n }\n if (balance < 0) {\n return false;\n }\n }\n balance = 0;\n for (int i = start.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {\n if (target.charAt(i) == \'R\') {\n balance++;\n }\n if (start.charAt(i) == \'R\') {\n balance--;\n } \n if(balance < 0) {\n return false;\n }\n }\n return true;\n }\n}\n```
| 5 | 1 |
['Java']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
C++ || EASY TO UNDERSTAND || Simple Solution
|
c-easy-to-understand-simple-solution-by-ijw3p
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string s, string t) {\n int n=s.size();\n string s1,s2;\n s1=s2="";\n vector<int> v1
|
aarindey
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T04:00:47.082441+00:00
|
2022-07-10T04:03:59.541904+00:00
| 237 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string s, string t) {\n int n=s.size();\n string s1,s2;\n s1=s2="";\n vector<int> v1,v2;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n char ch=s[i];\n if(ch==\'L\'||ch==\'R\')\n {\n v1.push_back(i);\n s1+=ch;\n }\n }\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n char ch=t[i];\n if(ch==\'L\'||ch==\'R\')\n {\n v2.push_back(i);\n s2+=ch;\n }\n }\n if(s1!=s2)\n return false;\n for(int i=0;i<v1.size();i++)\n {\n if(s[v1[i]]==\'L\')\n {\n if(v1[i]<v2[i])\n return false;\n }\n else\n {\n if(v1[i]>v2[i])\n return false;\n }\n }\n return true;\n }\n};\n```\n**Please upvote to motivate me in my quest of documenting all leetcode solutions. HAPPY CODING:)\nAny suggestions and improvements are always welcome**\n
| 5 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
🔥BEATS 💯 % 🎯 |✨SUPER EASY BEGINNERS 👏
|
beats-super-easy-beginners-by-codewithsp-13j4
|
\n\n---\n\nHere\u2019s the detailed explanation and solution for the problem of checking whether start can be transformed into target by moving \'L\' to the lef
|
CodeWithSparsh
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T07:26:59.606414+00:00
|
2024-12-05T11:01:03.470698+00:00
| 260 | false |
\n\n---\n\nHere\u2019s the detailed explanation and solution for the problem of checking whether `start` can be transformed into `target` by moving \'L\' to the left and \'R\' to the right, skipping the blanks represented by `_`.\n\n---\n\n# Intuition\nThe problem can be visualized as aligning two strings (`start` and `target`) by respecting movement constraints:\n1. \'L\' can only move to the left (reducing its index).\n2. \'R\' can only move to the right (increasing its index).\n3. Blank spaces `_` are ignored, and the relative order of characters must be maintained.\n\nUsing two pointers allows efficient traversal while skipping blanks and verifying the transformation.\n\n---\n\n# Approach\n1. Initialize two pointers `i` and `j` for `start` and `target`, respectively.\n2. Skip all `_` in both strings until a non-blank character is encountered or the pointer reaches the end of the string.\n3. Check:\n - If characters at `start[i]` and `target[j]` mismatch, the transformation isn\'t possible.\n - If the character is `L` and its position in `start` is greater than its position in `target`, return `false` (it can\'t move right).\n - If the character is `R` and its position in `start` is less than its position in `target`, return `false` (it can\'t move left).\n4. Repeat until both pointers reach the end. If they do, return `true`.\n\n---\n\n# Complexity\n- **Time complexity:** \n $$O(n)$$ where \\(n\\) is the length of the strings. Each character is processed once.\n \n- **Space complexity:** \n $$O(1)$$ since we only use two pointers for traversal.\n\n---\n\n\n```dart []\nclass Solution {\n bool canChange(String start, String target) {\n int n = start.length;\n int i = 0, j = 0;\n\n while (i < n || j < n) {\n // Skip blanks (\'_\') in `start`\n while (i < n && start[i] == \'_\') i++;\n // Skip blanks (\'_\') in `target`\n while (j < n && target[j] == \'_\') j++;\n\n // If one pointer reaches the end but the other doesn\'t, return false\n if (i == n || j == n) return i == n && j == n;\n\n // Compare the pieces at the current positions\n if (start[i] != target[j]) return false;\n\n // Movement constraints:\n if (start[i] == \'L\' && i < j) return false; // \'L\' can\'t move right\n if (start[i] == \'R\' && i > j) return false; // \'R\' can\'t move left\n\n // Move both pointers\n i++;\n j++;\n }\n\n return true;\n }\n}\n\n\n```\n\n```c []\n#include <stdbool.h>\n#include <string.h>\n\nbool canChange(char* start, char* target) {\n int n = strlen(start);\n int i = 0, j = 0;\n\n while (i < n || j < n) {\n while (i < n && start[i] == \'_\') i++;\n while (j < n && target[j] == \'_\') j++;\n\n if (i == n || j == n) return i == n && j == n;\n if (start[i] != target[j]) return false;\n\n if (start[i] == \'L\' && i < j) return false;\n if (start[i] == \'R\' && i > j) return false;\n\n i++;\n j++;\n }\n\n return true;\n}\n```\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n int n = start.size();\n int i = 0, j = 0;\n\n while (i < n || j < n) {\n while (i < n && start[i] == \'_\') i++;\n while (j < n && target[j] == \'_\') j++;\n\n if (i == n || j == n) return i == n && j == n;\n if (start[i] != target[j]) return false;\n\n if (start[i] == \'L\' && i < j) return false;\n if (start[i] == \'R\' && i > j) return false;\n\n i++;\n j++;\n }\n\n return true;\n }\n};\n```\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n int n = start.length();\n int i = 0, j = 0;\n\n while (i < n || j < n) {\n while (i < n && start.charAt(i) == \'_\') i++;\n while (j < n && target.charAt(j) == \'_\') j++;\n\n if (i == n || j == n) return i == n && j == n;\n if (start.charAt(i) != target.charAt(j)) return false;\n\n if (start.charAt(i) == \'L\' && i < j) return false;\n if (start.charAt(i) == \'R\' && i > j) return false;\n\n i++;\n j++;\n }\n\n return true;\n }\n}\n```\n```go []\nfunc canChange(start string, target string) bool {\n n := len(start)\n i, j := 0, 0\n\n for i < n || j < n {\n for i < n && start[i] == \'_\' {\n i++\n }\n for j < n && target[j] == \'_\' {\n j++\n }\n\n if i == n || j == n {\n return i == n && j == n\n }\n if start[i] != target[j] {\n return false\n }\n\n if start[i] == \'L\' && i < j {\n return false\n }\n if start[i] == \'R\' && i > j {\n return false\n }\n\n i++\n j++\n }\n\n return true\n}\n```\n```python []\nclass Solution:\n def canChange(self, start: str, target: str) -> bool:\n n = len(start)\n i, j = 0, 0\n\n while i < n or j < n:\n while i < n and start[i] == \'_\':\n i += 1\n while j < n and target[j] == \'_\':\n j += 1\n\n if i == n or j == n:\n return i == n and j == n\n if start[i] != target[j]:\n return False\n\n if start[i] == \'L\' and i < j:\n return False\n if start[i] == \'R\' and i > j:\n return False\n\n i += 1\n j += 1\n\n return True\n```\n```javascript []\nvar canChange = function(start, target) {\n let n = start.length, i = 0, j = 0;\n\n while (i < n || j < n) {\n while (i < n && start[i] === \'_\') i++;\n while (j < n && target[j] === \'_\') j++;\n\n if (i === n || j === n) return i === n && j === n;\n if (start[i] !== target[j]) return false;\n\n if (start[i] === \'L\' && i < j) return false;\n if (start[i] === \'R\' && i > j) return false;\n\n i++;\n j++;\n }\n\n return true;\n};\n```\n\n---\n\n {:style=\'width:250px\'}
| 4 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'String', 'C', 'C++', 'Java', 'Go', 'Python3', 'JavaScript', 'Dart']
| 1 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Transform String by Moving Pieces🔄| Easy Two Pointer | O(N) | Java | C++ | Python
|
transform-string-by-moving-pieces-easy-t-fyhg
|
\n# \uD83D\uDD0D Intuition:\nTransform start \u27A1\uFE0F target by sliding:\n\n- R \uD83D\uDC49 to the right\n- L \uD83D\uDC48 to the left\n Skip _
|
shubhamrajpoot_
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T06:09:34.336424+00:00
|
2024-12-05T06:09:34.336463+00:00
| 195 | false |
\n# \uD83D\uDD0D Intuition:\nTransform start \u27A1\uFE0F target by sliding:\n\n- R \uD83D\uDC49 to the right\n- L \uD83D\uDC48 to the left\n Skip _ (empty spaces) and ensure the rules are followed:\n- R can\u2019t move left \n- L can\u2019t move right\n\n---\n- \uD83D\uDCDD Note/Remember :: Position of \'L\' in target should be less than the position in start \n similarly, for \'R\' the position in start should be less than the postion in target.\n\n\n\n# \uD83D\uDEE0\uFE0F Approach:\n1\uFE0F\u20E3 Use two pointers to traverse start and target.\n2\uFE0F\u20E3 Skip _ in both strings \uD83C\uDFC3\u200D\u2642\uFE0F.\n3\uFE0F\u20E3 Validate:\n\nCharacters match .\n- Positions respect movement rules (\u2705 R \uD83D\uDC49, \u2705 L \uD83D\uDC48).\n4\uFE0F\u20E3 Return false if any condition breaks, else true \u2705 when traversal ends.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n- O(n)\n\n- Space complexity:\n- O(1)\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n int ind1 = 0 , ind2 = 0 ;\n while(ind1 < start.size() || ind2 < target.size())\n {\n while(ind1 < start.size() && start.at(ind1) == \'_\') ind1++ ;\n while(ind2 < target.size() && target.at(ind2) == \'_\') ind2++ ;\n\n if(ind1 == start.size() && ind2 == target.size()) return true ;\n if(ind1 == start.size() || ind2 == target.size()) return false ;\n\n if(start.at(ind1) != target.at(ind2) || (start.at(ind1) == \'R\' && ind1 > ind2) || (target.at(ind2) == \'L\' && ind1 < ind2)) return false ;\n\n ind1++ ;\n ind2++ ; \n \n }\n return true ;\n }\n};\n```\n\n```Java []\nclass Solution {\n public boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n int ind1 = 0, ind2 = 0;\n\n while (ind1 < start.length() || ind2 < target.length()) {\n while (ind1 < start.length() && start.charAt(ind1) == \'_\') ind1++;\n while (ind2 < target.length() && target.charAt(ind2) == \'_\') ind2++;\n\n if (ind1 == start.length() && ind2 == target.length()) return true;\n if (ind1 == start.length() || ind2 == target.length()) return false;\n\n if (start.charAt(ind1) != target.charAt(ind2) || \n (start.charAt(ind1) == \'R\' && ind1 > ind2) || \n (start.charAt(ind1) == \'L\' && ind1 < ind2)) return false;\n\n ind1++;\n ind2++;\n }\n\n return true;\n }\n}\n\n```\n```python []\ndef can_change(start, target):\n ind1, ind2 = 0, 0\n\n while ind1 < len(start) or ind2 < len(target):\n while ind1 < len(start) and start[ind1] == \'_\':\n ind1 += 1\n while ind2 < len(target) and target[ind2] == \'_\':\n ind2 += 1\n\n if ind1 == len(start) and ind2 == len(target):\n return True\n if ind1 == len(start) or ind2 == len(target):\n return False\n\n if start[ind1] != target[ind2] or \\\n (start[ind1] == \'R\' and ind1 > ind2) or \\\n (start[ind1] == \'L\' and ind1 < ind2):\n return False\n\n ind1 += 1\n ind2 += 1\n\n return True\n\n```\n```JavaScript []\nvar canChange = function(start, target) {\n let ind1 = 0, ind2 = 0;\n\n while (ind1 < start.length || ind2 < target.length) {\n while (ind1 < start.length && start[ind1] === \'_\') ind1++;\n while (ind2 < target.length && target[ind2] === \'_\') ind2++;\n\n if (ind1 === start.length && ind2 === target.length) return true;\n if (ind1 === start.length || ind2 === target.length) return false;\n\n if (start[ind1] !== target[ind2] || \n (start[ind1] === \'R\' && ind1 > ind2) || \n (start[ind1] === \'L\' && ind1 < ind2)) return false;\n\n ind1++;\n ind2++;\n }\n\n return true;\n};\n\n```\n```ruby []\ndef can_change(start, target)\n ind1 = 0\n ind2 = 0\n\n while ind1 < start.length || ind2 < target.length\n ind1 += 1 while ind1 < start.length && start[ind1] == \'_\'\n ind2 += 1 while ind2 < target.length && target[ind2] == \'_\'\n\n return true if ind1 == start.length && ind2 == target.length\n return false if ind1 == start.length || ind2 == target.length\n\n if start[ind1] != target[ind2] || \n (start[ind1] == \'R\' && ind1 > ind2) || \n (start[ind1] == \'L\' && ind1 < ind2) \n return false\n end\n\n ind1 += 1\n ind2 += 1\n end\n\n return true\nend\n\n```\n\n```Go []\nfunc canChange(start string, target string) bool {\n ind1, ind2 := 0, 0\n\n for ind1 < len(start) || ind2 < len(target) {\n for ind1 < len(start) && start[ind1] == \'_\' {\n ind1++\n }\n for ind2 < len(target) && target[ind2] == \'_\' {\n ind2++\n }\n\n if ind1 == len(start) && ind2 == len(target) {\n return true\n }\n if ind1 == len(start) || ind2 == len(target) {\n return false\n }\n\n if start[ind1] != target[ind2] || \n (start[ind1] == \'R\' && ind1 > ind2) || \n (start[ind1] == \'L\' && ind1 < ind2) {\n return false\n }\n\n ind1++\n ind2++\n }\n\n return true\n}\n\n```\n\n
| 4 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'String', 'String Matching', 'C++', 'Java', 'JavaScript']
| 1 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Efficient Two-Pointer Validation for Transforming start to target in Move Constraints
|
efficient-two-pointer-validation-for-tra-f44r
|
\n\n# Explanation:\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n1. Remove _ Check:\n\n - Ensure that the sequence of L and R in both strings is identic
|
anand_shukla1312
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T05:11:42.583052+00:00
|
2024-12-05T05:11:42.583074+00:00
| 88 | false |
\n\n# Explanation:\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1. **Remove _ Check**:\n\n - Ensure that the sequence of L and R in both strings is identical.\n2. **Position Validation**:\n\n - Iterate through target:\n - For L, ensure it doesn\'t move right.\n - For R, ensure it doesn\'t move left.\n - Use a pointer to traverse start and verify the positions align.\n# Complexity\n- Time : $$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space : $$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def canChange(self, start: str, target: str) -> bool:\n # Remove `_` and check the sequence of `L` and `R`\n if start.replace(\'_\', \'\') != target.replace(\'_\', \'\'):\n return False\n \n # Check valid moves for `L` and `R`\n start_pos = 0\n for i, char in enumerate(target):\n if char == \'L\':\n # Find the next `L` in `start`\n while start_pos < len(start) and start[start_pos] != \'L\':\n start_pos += 1\n # Invalid if no `L` or position is incorrect\n if start_pos >= len(start) or start_pos < i:\n return False\n start_pos += 1 # Move pointer forward\n \n elif char == \'R\':\n # Find the next `R` in `start`\n while start_pos < len(start) and start[start_pos] != \'R\':\n start_pos += 1\n # Invalid if no `R` or position is incorrect\n if start_pos >= len(start) or start_pos > i:\n return False\n start_pos += 1 # Move pointer forward\n \n return True\n\n```\n# SMALL REQUEST : If you found this post even remotely helpful, be kind enough to smash a upvote. I will be grateful.I will be motivated\uD83D\uDE0A\uD83D\uDE0A
| 4 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'String Matching', 'Python3']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
🔥Beats 100 % 🔥 | 11 MS | Tow Pointers | ✔️ Explained & Optimized Solution ✔️ |
|
beats-100-11-ms-tow-pointers-explained-o-m30s
|
\n\n---\n\n# Intuition\nThe idea is to use Two Pointers i and j to traverse the start and target strings simultaneously while skipping _ characters. For each ch
|
ntrcxst
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T03:08:11.628569+00:00
|
2024-12-05T03:08:11.628591+00:00
| 112 | false |
\n\n---\n\n# Intuition\nThe idea is to use **Two Pointers** `i` and `j` to traverse the `start` and `target` strings simultaneously while skipping `_` characters. For each characterEnsure both pointers are aligned on valid characters `L` or `R`.Check whether the character alignment violates movement constraints: `\'L\'` can only move to the **left** `\'R\'` can only move to the **right**. If all conditions are satisfied, the transformation is **valid**.\n\n# Approach\n`Step 1` **Convert start and target strings into character arrays (s and t).**\n\n`Step 2` **Initialize two pointers i and j at the start of both arrays.**\n\n`Step 3` **While Traversing :**\n- Skip `_` characters in both Arrays :\n - Increment `i` until `s[i]` points to a non-blank `\'L\'` or `\'R\'` or reaches the end.\n - Increment `j` until `t[j]` points to a non-blank or reaches the end.\n- If either pointer reaches the end:\n - Ensure both pointers have reached the end simultaneously \n `return false otherwise`.\n\n`Step 4` **For each pair of aligned Characters :**\n- Ensure the characters match `s[i] == t[j]`.\n- Check movement constraints:\n - `\'L\'` can only move to the left `i >= j`.\n - `\'R\'` can only move to the right `i <= j`.\n\n`Step 5` **If all characters align correctly, return true. Otherwise, return false**.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity : $$O(n)$$\n- Space complexity : $$O(n)$$\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution\n{\n public boolean canChange(String start, String target)\n {\n // Step 1: Convert strings to character arrays for traversal\n char[] s = start.toCharArray();\n char[] t = target.toCharArray();\n int n = s.length;\n int i = 0, j = 0; // Pointers for `start` and `target` arrays\n\n // Step 2: Traverse both arrays using pointers\n while (i <= n && j <= n)\n {\n\n // Step 3: Skip blank spaces (\'_\') in both arrays\n while (i < n && s[i] == \'_\') i++;\n while (j < n && t[j] == \'_\') j++;\n\n // Step 4: If either pointer reaches the end, ensure both are at the end\n if (i == n || j == n) return i == n && j == n;\n\n // Step 5: Compare aligned characters\n if (s[i] != t[j]) return false;\n\n // Step 6: Check movement constraints\n if (s[i] == \'L\' && i < j) return false; // \'L\' can only move to the left\n if (s[i] == \'R\' && i > j) return false; // \'R\' can only move to the right\n\n // Step 7: Move both pointers to the next character\n i++;\n j++;\n }\n\n // Step 8: If all checks pass, the transformation is valid\n return true;\n }\n}\n\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'String', 'Java']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
World's Easiest Solution 100% beats
|
worlds-easiest-solution-100-beats-by-sum-bc66
|
Intuition \uD83E\uDDE0\nThe problem can be visualized as a block alignment game, where the blocks in the start string need to be rearranged to match the target
|
Sumeet_Sharma-1
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T01:34:43.167305+00:00
|
2024-12-05T02:47:08.834959+00:00
| 1,816 | false |
# Intuition \uD83E\uDDE0\nThe problem can be visualized as a **block alignment game**, where the blocks in the `start` string need to be rearranged to match the `target` string. The blocks have special movement rules:\n\n- **`L` Block**: Moves only **left** \u2B05\uFE0F.\n- **`R` Block**: Moves only **right** \u27A1\uFE0F.\n- **`_` (Blank)**: Represents an empty space where blocks can move but doesn\'t move itself.\n\nWe must ensure:\n1. The characters in `start` and `target` match when ignoring the blanks.\n2. The movement constraints of `L` and `R` are followed correctly.\n\n---\n\n# Approach \uD83D\uDEE0\uFE0F\n\n## Step 1: Use Two Pointers \uD83D\uDD00\nWe use two pointers:\n- `startIndex` to traverse the `start` string.\n- `targetIndex` to traverse the `target` string.\n\n---\n\n### Step 2: Skip Blank Spaces \uD83D\uDE80\n- While traversing, **skip all `_`** in both strings because blanks don\'t contribute to the alignment.\n- Focus only on the `L` and `R` blocks.\n\n---\n\n### Step 3: Compare Characters \uD83E\uDDE9\n- After skipping blanks, compare the characters at `start[startIndex]` and `target[targetIndex]`:\n - If they **don\u2019t match**, transformation is not possible. \u274C\n - If they match, move forward to check movement rules.\n\n---\n\n### Step 4: Verify Movement Rules \uD83D\uDCDC\n1. **For `L` Blocks**:\n - The block in `start` **must not move right** (it can only move left).\n - If the block\'s current position (`startIndex`) is **less than** its position in `target` (`targetIndex`), return `false`.\n\n2. **For `R` Blocks**:\n - The block in `start` **must not move left** (it can only move right).\n - If the block\'s current position (`startIndex`) is **greater than** its position in `target` (`targetIndex`), return `false`.\n\n---\n\n### Step 5: Handle Remaining Characters \uD83D\uDD04\n- After one pointer finishes, check if the other string contains only blanks (`_`).\n- If not, return `false` as the strings cannot align.\n\n---\n\n# Complexity \uD83D\uDCCA\n\n- **Time Complexity**: \n Traverses both strings once, skipping blanks and verifying characters. \n **$$O(n)$$**\n\n- **Space Complexity**: \n Uses constant space for variables. \n **$$O(1)$$**\n\n---\n\n\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n int L = 0;\n int M = 0;\n int n = start.length();\n int tarspace = 0;\n int staspace = 0;\n\n while (L < n && M < n) {\n while (L < n && target[L] == \'_\') {\n tarspace++;\n L++;\n }\n while (M < n && start[M] == \'_\') {\n M++;\n staspace++;\n }\n\n if (L < n && M < n) {\n if (target[L] != start[M]) {\n return false;\n }\n if (target[L] == \'L\') {\n if (tarspace > staspace)\n return false;\n } else if (staspace > tarspace) {\n return false;\n }\n L++;\n M++;\n }\n }\n\n // Check remaining characters\n while (L < n) {\n if (target[L] != \'_\')\n return false;\n L++;\n }\n while (M < n) {\n if (start[M] != \'_\')\n return false;\n M++;\n }\n\n return true;\n }\n};\n\nvoid IO() {\n ios::sync_with_stdio(false);\n cin.tie(0);\n}\n\n```\n```Python3 []\nclass Solution(object):\n def canChange(self, start, target):\n """\n :type start: str\n :type target: str\n :rtype: bool\n """\n L = 0\n M = 0\n n = len(start)\n tarspace = 0\n staspace = 0\n\n while L < n and M < n:\n while L < n and target[L] == \'_\':\n tarspace += 1\n L += 1\n while M < n and start[M] == \'_\':\n M += 1\n staspace += 1\n\n if L < n and M < n:\n if target[L] != start[M]:\n return False\n if target[L] == \'L\':\n if tarspace > staspace:\n return False\n elif staspace > tarspace:\n return False\n L += 1\n M += 1\n\n # Check remaining characters\n while L < n:\n if target[L] != \'_\':\n return False\n L += 1\n while M < n:\n if start[M] != \'_\':\n return False\n M += 1\n\n return True\n```\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n int L = 0, M = 0;\n int n = start.length();\n int tarSpace = 0, staSpace = 0;\n\n while (L < n && M < n) {\n while (L < n && target.charAt(L) == \'_\') {\n tarSpace++;\n L++;\n }\n while (M < n && start.charAt(M) == \'_\') {\n staSpace++;\n M++;\n }\n\n if (L < n && M < n) {\n if (target.charAt(L) != start.charAt(M)) {\n return false;\n }\n if (target.charAt(L) == \'L\') {\n if (tarSpace > staSpace) {\n return false;\n }\n } else if (staSpace > tarSpace) {\n return false;\n }\n L++;\n M++;\n }\n }\n\n // Check remaining characters\n while (L < n) {\n if (target.charAt(L) != \'_\') {\n return false;\n }\n L++;\n }\n while (M < n) {\n if (start.charAt(M) != \'_\') {\n return false;\n }\n M++;\n }\n\n return true;\n }\n}\n```\n```C# []\npublic class Solution {\n public bool CanChange(string start, string target) {\n int L = 0, M = 0;\n int n = start.Length;\n int tarSpace = 0, staSpace = 0;\n\n while (L < n && M < n) {\n while (L < n && target[L] == \'_\') {\n tarSpace++;\n L++;\n }\n while (M < n && start[M] == \'_\') {\n staSpace++;\n M++;\n }\n\n if (L < n && M < n) {\n if (target[L] != start[M]) {\n return false;\n }\n if (target[L] == \'L\') {\n if (tarSpace > staSpace) {\n return false;\n }\n } else if (staSpace > tarSpace) {\n return false;\n }\n L++;\n M++;\n }\n }\n\n // Check remaining characters\n while (L < n) {\n if (target[L] != \'_\') {\n return false;\n }\n L++;\n }\n while (M < n) {\n if (start[M] != \'_\') {\n return false;\n }\n M++;\n }\n\n return true;\n }\n}\n\n```\n```Java_Script []\n/**\n * @param {string} start\n * @param {string} target\n * @return {boolean}\n */\nvar canChange = function(start, target) {\n let L = 0, M = 0;\n const n = start.length;\n let tarSpace = 0, staSpace = 0;\n\n while (L < n && M < n) {\n while (L < n && target[L] === \'_\') {\n tarSpace++;\n L++;\n }\n while (M < n && start[M] === \'_\') {\n staSpace++;\n M++;\n }\n\n if (L < n && M < n) {\n if (target[L] !== start[M]) {\n return false;\n }\n if (target[L] === \'L\') {\n if (tarSpace > staSpace) {\n return false;\n }\n } else if (staSpace > tarSpace) {\n return false;\n }\n L++;\n M++;\n }\n }\n\n // Check remaining characters\n while (L < n) {\n if (target[L] !== \'_\') {\n return false;\n }\n L++;\n }\n while (M < n) {\n if (start[M] !== \'_\') {\n return false;\n }\n M++;\n }\n\n return true;\n};\n```\n``` Rust []\nimpl Solution {\n pub fn can_change(start: String, target: String) -> bool {\n let start: Vec<char> = start.chars().collect();\n let target: Vec<char> = target.chars().collect();\n let mut l = 0;\n let mut m = 0;\n let n = start.len();\n let mut tar_space = 0;\n let mut sta_space = 0;\n\n while l < n && m < n {\n while l < n && target[l] == \'_\' {\n tar_space += 1;\n l += 1;\n }\n while m < n && start[m] == \'_\' {\n sta_space += 1;\n m += 1;\n }\n\n if l < n && m < n {\n if target[l] != start[m] {\n return false;\n }\n if target[l] == \'L\' {\n if tar_space > sta_space {\n return false;\n }\n } else if sta_space > tar_space {\n return false;\n }\n l += 1;\n m += 1;\n }\n }\n\n // Check remaining characters\n while l < n {\n if target[l] != \'_\' {\n return false;\n }\n l += 1;\n }\n while m < n {\n if start[m] != \'_\' {\n return false;\n }\n m += 1;\n }\n\n true\n }\n}\n\n```\n
| 4 | 0 |
['C++', 'Java', 'Python3', 'Rust', 'JavaScript', 'C#']
| 3 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
[Rust]: Iterator approach for 2-pointer
|
rust-iterator-approach-for-2-pointer-by-6b876
|
Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(n)\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(1)\n\n# Code\nrust []\nimpl Solution {\n pub fn can_change(start: String, target: String) -> b
|
discreaminant2809
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T00:54:27.856238+00:00
|
2024-12-05T00:54:27.856276+00:00
| 99 | false |
# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n$$O(n)$$\n\n- Space complexity:\n$$O(1)$$\n\n# Code\n```rust []\nimpl Solution {\n pub fn can_change(start: String, target: String) -> bool {\n #[derive(Debug, Clone, Copy)]\n enum Dir {\n Left,\n Right,\n }\n\n fn tokens(s: String) -> impl Iterator<Item = (usize, Dir)> {\n s.into_bytes()\n .into_iter()\n .enumerate()\n .filter_map(|(i, byte)| match byte {\n b\'L\' => Some((i, Dir::Left)),\n b\'R\' => Some((i, Dir::Right)),\n _ => None,\n })\n }\n\n let mut start_tokens = tokens(start);\n let mut target_tokens = tokens(target);\n\n loop {\n match (start_tokens.next(), target_tokens.next()) {\n (Some((i, Dir::Left)), Some((j, Dir::Left))) if i >= j => {}\n (Some((i, Dir::Right)), Some((j, Dir::Right))) if i <= j => {}\n (None, None) => break true,\n _ => break false,\n }\n }\n }\n}\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'Iterator', 'Rust']
| 2 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
C++ Easy Solution
|
c-easy-solution-by-retire-zdgb
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) \n {\n int n=start.size();\n vector<pair<char,int>>v1,v2;\n
|
Retire
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-15T14:59:31.978049+00:00
|
2022-07-15T14:59:31.978079+00:00
| 110 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) \n {\n int n=start.size();\n vector<pair<char,int>>v1,v2;\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n if(start[i]!=\'_\')v1.push_back({start[i],i});\n if(target[i]!=\'_\')v2.push_back({target[i],i});\n }\n if(v1.size()!=v2.size())return false;\n for(int i=0;i<v1.size();i++)\n {\n if(v1[i].first!=v2[i].first)return false;\n if(v1[i].first==\'L\')\n {\n if(v1[i].second<v2[i].second)return false;\n }else\n {\n if(v1[i].second>v2[i].second)return false;\n }\n }\n return true;\n }\n};\n```
| 4 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Java two-pointers solution, O(n) time and O(1) space
|
java-two-pointers-solution-on-time-and-o-kvnq
|
the number and order of pieces must not change\n2. for a piece \'L\', its index in the target string must be equal to or less than its index in the start string
|
Psyccc
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T04:33:03.613479+00:00
|
2022-07-10T04:39:29.413833+00:00
| 213 | false |
1. the number and order of pieces must not change\n2. for a piece \'L\', its index in the target string must be equal to or less than its index in the start string\n3. for a piece \'R\', its index in the target string must be equal to or greater than its index in the start string\n```\nclass Solution {\n public boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n int i = 0, j = 0, n = start.length();\n while(i < n && j < n) {\n while(i < n && start.charAt(i) == \'_\') i++;\n while(j < n && target.charAt(j) == \'_\') j++;\n if(i == n && j == n) return true;\n if(i == n || j == n || start.charAt(i) != target.charAt(j)) return false;\n if(start.charAt(i) == \'L\' && i < j) return false;\n if(start.charAt(i) == \'R\' && i > j) return false;\n i++;\n j++;\n }\n return true;\n }\n}\n```
| 4 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'Java']
| 1 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
two pointers comparing ✅ 14ms, 41.16MB
|
two-pointers-comparing-14ms-4116mb-by-yu-psw6
|
\n\n# Intuition\nI came up with two approaches, one is to count prefixSum and suffixSum of L and R. For example L we need suffixSum at each index that target ha
|
yunhao_liu
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T10:42:38.264465+00:00
|
2024-12-05T11:23:08.572024+00:00
| 58 | false |
\n\n# Intuition\nI came up with two approaches, one is to count prefixSum and suffixSum of `L` and `R`. For example `L` we need suffixSum at each index that target has less `L` than original. (So original has enough L to move to left.) When encountering `R` the suffixSum needs to reset to 0. It seems doable but after several testing, I can\'t pass all tests so I gave up.\n\nAnother solution is to use two pointers to compare strings directly, which is much easier to implement and more effecient.\n\n# Approach\nInitialize two pointers for the two strings, iterate within their range:\n```\n val n = start.length\n var i = 0\n var j = 0\n while (i < n && j < n) {\n```\nWhen encountering `_` we just skip it, for both strings. Because we only care about `L` and `R` and their positions.\n```\n if (start[i] == \'_\') {\n i++\n continue\n }\n if (target[j] == \'_\') {\n j++\n continue \n }\n```\nAfter skipping spaces, there are 3 invalid cases, we can directly return false:\n- pointers meet different letters: it\'s impossible to make their current letters same\n- pointers meet `L`, but `i < j`: `L` can only move to left, but i is already at left of j, it\'s impossible to move\n- pointers meet `R`, but `i > j`: `R` can only move to right, but i is already at right of j, it\'s impossible to move\n```\n if (start[i] != target[j] || \n start[i] == \'L\' && i < j || \n start[i] == \'R\' && i > j) return false\n```\notherwise increase both pointers:\n```\n i++\n j++\n```\nWhen at least one pointer reaches the end, if the other string still has spaces, skip spaces.\n```\n while (i < n && start[i] == \'_\') i++\n while (j < n && target[j] == \'_\') j++\n```\nOnly if two pointers stop at the same position (`n`) it\'s a valid case.\n```\n return i == j\n```\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n$$O(n)$$\n\n- Space complexity:\n$$O(1)$$\n\n# Code\n```kotlin []\nclass Solution {\n fun canChange(start: String, target: String): Boolean {\n val n = start.length\n var i = 0\n var j = 0\n while (i < n && j < n) {\n if (start[i] == \'_\') {\n i++\n continue\n }\n if (target[j] == \'_\') {\n j++\n continue \n }\n if (start[i] != target[j] || start[i] == \'L\' && i < j || start[i] == \'R\' && i > j) return false\n i++\n j++\n }\n while (i < n && start[i] == \'_\') i++\n while (j < n && target[j] == \'_\') j++\n return i == j\n }\n}\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'String', 'Kotlin']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
simple and easy C++ solution
|
simple-and-easy-c-solution-by-shishirrsi-stpo
|
\n# if it\'s help, please up \u2B06 vote! \u2764\uFE0F\n###### Let\'s Connect on Linkedin: www.linkedin.com/in/shishirrsiam\n\n\n\n# Code\ncpp []\nclass Solutio
|
shishirRsiam
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T04:50:53.825133+00:00
|
2024-12-05T04:50:53.825169+00:00
| 377 | false |
\n# if it\'s help, please up \u2B06 vote! \u2764\uFE0F\n###### Let\'s Connect on Linkedin: www.linkedin.com/in/shishirrsiam\n\n\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) \n {\n int idx = 0, cur = 0, n = start.size();\n\n for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)\n {\n if(start[i] == target[i]) continue;\n \n cur = max(cur, i + 1);\n if(start[i] == \'_\')\n {\n while(cur < n)\n {\n if(start[cur] == \'R\') return false;\n if(start[cur] == \'L\')\n {\n swap(start[i], start[cur++]);\n break;\n }\n cur++;\n }\n }\n \n if(start[i] == \'R\')\n {\n while(cur < n)\n {\n if(start[cur] == \'L\') return false;\n if(start[cur] == \'_\')\n {\n swap(start[i], start[cur++]);\n break;\n }\n cur++;\n }\n }\n }\n return start == target;\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'String', 'C++']
| 3 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
java easy solution
|
java-easy-solution-by-saurav840963-irnu
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
saurav840963
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T04:09:42.728313+00:00
|
2024-12-05T04:09:42.728337+00:00
| 369 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n int i=0;\n int j=0;\n int n=start.length();\n while(i<n || j<n){\n while(i<n && start.charAt(i)==\'_\')i++;\n while(j<n && target.charAt(j)==\'_\')j++;\n if(i==n || j==n) break;\n if(start.charAt(i) !=target.charAt(j)) return false;\n if (start.charAt(i) == \'L\' && i < j)\n return false;\n if (start.charAt(i) == \'R\' && i > j)\n return false;\n i++;\n j++;\n }\n if(i==n && j==n) return true;\n return false;\n }\n}\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Java']
| 1 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Move Pieces to obtain a string - Easy Solution - Nice Explanation - 🌟 Beats 100% 🌟
|
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string-easy-solu-q4wa
|
Intuition\n\n1. target string and the start string should be of same length (contains same number of characters).\n\n1. Using two pointer approach, iterate all
|
RAJESWARI_P
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T02:09:04.594419+00:00
|
2024-12-05T02:09:04.594459+00:00
| 28 | false |
# Intuition\n\n1. target string and the start string should be of same length (contains same number of characters).\n\n1. Using two pointer approach, iterate all the elements of the string.It requires less time complexity if working character array than string.Hence string is converted into character array using toCharArray().\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n\n**Initialization**:\n\nInitialize n to be the length of the string start or the string target.\n\n int n=start.length();\n\nConvert start string to character array and store it in st character array and same for target string to tar character array.\n\n char[] st=start.toCharArray();\n char[] tar=target.toCharArray();\n\nInitialize i and j to be 0, the pointer to keep track of st and tar character array.\n\n int i=0,j=0;\n\n**Checking possibility of the conversion**:\n\nIterate through all the characters of the st and the tar character array.\n\n while(i<=n && j<=n){\n\nIncrement i pointer till we encounter the character as _ and i is less than n.\n\n while(i<n && tar[i]==\'_\')\n i++;\n\nIncrement j pointer till we encounter the character as _ and j is less than n.\n\n while(j<n && st[j]==\'_\')\n j++;\n\nIf i and j reaches the end of the string, then the string contains only _, So return true .If either i or j reaches the end of the array, then return false.\n\n if(i==n || j==n)\n {\n return i==n && j==n;\n }\n\nIf st[j] and tar[i] is not equal, then return false immediately.\n\n if(st[j]!=tar[i])\n return false;\n\ncheck if character at index i of tar array is \'L\', then if j<i -> L is to left of _ in the st character array.We cannot move it to right in the tar array since blankspace is at right, so return false.\n\n if(tar[i]==\'L\')\n {\n if(j<i)\n return false;\n }\n\nOtherwise, character at index i of the tar array will be \'R\', then if i<j -> R is to right of _ in the st character array.We cannot move it to right since the blankspace is at left, so return false. \n\n else\n {\n if(i<j)\n return false;\n }\n\nIncrement i and j pointer at the end of each iteration of the outer loop.\n\n i++;\n j++;\n\n**Returning value**:\n\nIf the loop doesn\'t terminate by return condition, then string start can be converted into string target by making those moves.Hence return true.\n\n return true;\n\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n# Complexity\n- ***Time complexity***: **O(n)**.\n n -> number of the characters in the start or target string.\n\n**Outer Loop**: **O(n)**.\n\nThe outer while loop runs as long as **i and j** are within the bounds of the **string lengths**.\n\nThe total number of iterations of this loop depends on the number of characters in the strings. Thus, **at most O(n) iterations** are made in the outer loop.\n\n**Inner loop**: **O(n)**.\n\nInside the outer loop, there are two while loops:\n\n**First inner loop**: \n\nThis loop skips **underscores (_)** in the target string.\n\nEach character in target is **processed exactly once**, either by this loop (if it\u2019s _) or by the outer loop (if it\u2019s L or R).\n\n**Second inner loop**:\n\nSimilarly, this loop skips underscores (_) in the start string.\n\nEach character in start is processed exactly once.\n\n**Overall Time Complexity**: **O(n)**.\n\nSince each character is processed **exactly once** in either the outer loop or one of the inner loops, the **combined work done** by the inner and outer loops for all iterations is **O(n)**.\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- ***Space complexity***: **O(1)**.\n The program uses **constant amount of time**.\n\n**Input string**: **O(1)**.\n\nThe function does not create any additional data structures to store the strings. It processes the characters directly using the **indices i and j**.\n\n**Auxillary Space**: **O(1)**.\n\nThe program uses a **constant amount of extra space** to store variables like i, j, and the character arrays **st and tar**. \n\nThese arrays are references to the input strings, not additional copies of the data.\n\n**Overall Space complexity**: **O(1)**.\n\nThe space complexity is **O(1) as no additional space** proportional to the input size is used.\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n //2 strings : start and target : length n\n //Each string : \'L\',\'R\' and \'_\'\n // start="_L__R__R_" target="L______RR"\n\n int n=start.length();\n //same length for start and target string.\n\n char[] st=start.toCharArray();\n char[] tar=target.toCharArray();\n\n int i=0,j=0;\n\n while(i<=n && j<=n)\n {\n while(i<n && tar[i]==\'_\')\n i++;\n while(j<n && st[j]==\'_\')\n j++;\n if(i==n || j==n)\n {\n return i==n && j==n;\n }\n\n if(st[j]!=tar[i])\n return false;\n if(tar[i]==\'L\')\n {\n if(j<i)\n return false;\n }\n else\n {\n if(i<j)\n return false;\n }\n i++;\n j++;\n }\n return true;\n\n }\n}\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'String', 'Java']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
🚀Beeats 91.53%🚀✅Super Easy Two Pointer (C++/Java/Python) Solution With Detailed Explanation✅
|
beeats-9153super-easy-two-pointer-cjavap-yi7b
|
Intuition\nThe intuition of the code is to employ a two-pointer approach to traverse start and target strings simultaneously, skipping \'\' characters and ensur
|
suyogshete04
|
NORMAL
|
2024-02-18T03:33:16.012284+00:00
|
2024-02-18T03:33:16.012309+00:00
| 306 | false |
# Intuition\nThe intuition of the code is to employ a two-pointer approach to traverse `start` and `target` strings simultaneously, skipping \'_\' characters and ensuring \'L\' and \'R\' characters can only move within the constraints of their respective rules. The process checks for a one-to-one match between non-\'_\' characters in the correct order and direction, returning `true` if it\'s possible to transform `start` into `target` by adhering to movement rules, and `false` otherwise.\n\n\n\n\n# Approach\n\n1. **Initialization**: Two pointers, `i` and `j`, are initialized at the start of `start` and `target` strings respectively. These pointers will traverse the strings to compare the characters.\n\n2. **Skipping \'_\':** Both pointers skip the \'_\' characters in their respective strings since these represent empty spaces and do not affect the transformation process.\n\n3. **Comparison**:\n - If both pointers point to the same character (\'L\' or \'R\'), further checks are performed to ensure the movement rules are not violated:\n - If the character is \'L\', it can only move left. Thus, if `i < j`, the transformation is not possible because an \'L\' in `start` appearing to the right of its position in `target` cannot be achieved.\n - If the character is \'R\', it can only move right. Therefore, if `i > j`, the transformation is not possible because an \'R\' in `start` appearing to the left of its position in `target` cannot be achieved.\n - If the characters at `i` and `j` do not match, the transformation is not possible.\n\n4. **Advancement**: If none of the above conditions fail, both pointers are advanced to check the next set of non-\'_\' characters.\n\n5. **Conclusion**: After exiting the loop, if both pointers have reached the end of their respective strings, it indicates that the transformation is possible. If either pointer has not reached the end, it means there are unmatched characters, making the transformation impossible.\n\n# Complexity\n- **Time Complexity**: The algorithm has a time complexity of \\(O(n)\\), where \\(n\\) is the length of the strings. This is because each character in both strings is visited at most once by the pointers. The while loops for skipping \'_\' and the main while loop for comparison ensure that each character is involved in a constant amount of work.\n\n- **Space Complexity**: The space complexity is \\(O(1)\\). The algorithm uses a constant amount of extra space for the pointers and variables used for iteration and comparison, regardless of the input size.\n\n# Code\n```C++ []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n\n int n = start.size();\n\n int i=0;\n int j=0;\n while (i<n || j<n)\n {\n while (i<n && start[i] == \'_\')\n i++;\n\n while (j<n && target[j] == \'_\')\n j++;\n\n if (i==n || j==n)\n break;\n\n\n if (start[i] == target[j])\n {\n if (start[i] == \'L\' && i < j)\n return false;\n\n else if (start[i] == \'R\' && i > j)\n return false;\n }\n else \n return false;\n\n i++;\n j++;\n }\n\n return i==n && j==n;\n \n }\n};\n```\n```Java []\npublic class Solution {\n\n public boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n int n = start.length();\n\n int i = 0;\n int j = 0;\n while (i < n || j < n) {\n while (i < n && start.charAt(i) == \'_\')\n i++;\n\n while (j < n && target.charAt(j) == \'_\')\n j++;\n\n if (i == n || j == n)\n break;\n\n if (start.charAt(i) == target.charAt(j)) {\n if (start.charAt(i) == \'L\' && i < j)\n return false;\n\n else if (start.charAt(i) == \'R\' && i > j)\n return false;\n } else\n return false;\n\n i++;\n j++;\n }\n\n return i == n && j == n;\n }\n}\n\n```\n```Python []\nclass Solution:\n def canChange(self, start: str, target: str) -> bool:\n n = len(start)\n\n i, j = 0, 0\n while i < n or j < n:\n while i < n and start[i] == \'_\':\n i += 1\n\n while j < n and target[j] == \'_\':\n j += 1\n\n if i == n or j == n:\n break\n\n if start[i] == target[j]:\n if start[i] == \'L\' and i < j:\n return False\n\n elif start[i] == \'R\' and i > j:\n return False\n else:\n return False\n\n i += 1\n j += 1\n\n return i == n and j == n\n\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'Python', 'C++', 'Java']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
C++ || O(N) time, O(1) space intuitive and easy to understand
|
c-on-time-o1-space-intuitive-and-easy-to-jphj
|
The Idea is to iterate both strings skipping and counting how many \'underscore char\' we find and try to see if character can be moved.\nWe can hit 3 cases:\n
|
abes975
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-28T14:31:36.490138+00:00
|
2022-07-28T14:31:36.490174+00:00
| 184 | false |
The Idea is to iterate both strings skipping and counting how many \'underscore char\' we find and try to see if character can be moved.\nWe can hit 3 cases:\n1 we have different char on start and on target string...ok we are done..we can\'t continue\n2 we have L on both strings...we need to check if the position where we found this character on start string is smaller then the position where we found the same char on target. If this is the case we are done as we can\'t move a L char to the right in order to to the matching.\n3 Same of point 2 but with char R and this time the failure condition is that index on string s is bigger than index on target (as we can\'t move an R to the left\nwhen we exit from the while loop we have to check if the number of blak is equal for both string...this is neede for cases like\n"_L"\n"LL"\nas the first L can be moved to the left...but then we do not have a second L to match...\nI hope it helps\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n int i = 0;\n int j = 0;\n int cnt_s = 0;\n int cnt_t = 0;\n if(start.length() != target.length())\n return false;\n while(i < start.length() || j < target.length()) {\n while(i < start.length() && start[i] == \'_\') {\n ++i;\n ++cnt_s;\n }\n while(j < target.length() && target[j] == \'_\') {\n ++j;\n ++cnt_t;\n }\n if(start[i] == \'L\' && target[j] == \'L\')\n if(i< j)\n return false;\n if(start[i] == \'R\' && target[j] == \'R\')\n if(i > j)\n return false;\n if(start[i] != target[j])\n return false;\n ++i;\n ++j;\n }\n return cnt_s == cnt_t;\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Two Pointers']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
[Python 3] 2 pointers
|
python-3-2-pointers-by-gabhay-uths
|
\tclass Solution:\n\t\tdef canChange(self, start: str, target: str) -> bool:\n\t\t\ti=j=0\n\t\t\tn=len(start)\n\t\t\twhile i<n or j<n:\n\t\t\t\twhile ii or star
|
gabhay
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-24T14:31:41.286375+00:00
|
2022-07-24T14:31:41.286418+00:00
| 90 | false |
\tclass Solution:\n\t\tdef canChange(self, start: str, target: str) -> bool:\n\t\t\ti=j=0\n\t\t\tn=len(start)\n\t\t\twhile i<n or j<n:\n\t\t\t\twhile i<n and start[i]==\'_\':\n\t\t\t\t\ti+=1\n\t\t\t\twhile j<n and target[j]==\'_\':\n\t\t\t\t\tj+=1\n\t\t\t\tif i==n or j==n:\n\t\t\t\t\treturn i==j\n\t\t\t\tif start[i]!=target[j]:\n\t\t\t\t\treturn False\n\t\t\t\tif start[i]==\'L\' and j>i or start[i]==\'R\' and i>j: # because \'L\' cannnot move to left and vice versa and None of them can jump each other\n\t\t\t\t\treturn False\n\t\t\t\ti+=1\n\t\t\t\tj+=1\n\t\t\treturn True
| 3 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Javascript one pass O(n) runtime, O(1) space
|
javascript-one-pass-on-runtime-o1-space-yzgcm
|
\nvar canChange = function (start, target) {\n let l = 0\n let r = 0\n\n for (let i = 0; i < start.length; i++) {\n if (start[i] === "R") r++\n
|
koroja3877
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-20T08:34:36.340203+00:00
|
2022-07-20T08:34:36.340245+00:00
| 127 | false |
```\nvar canChange = function (start, target) {\n let l = 0\n let r = 0\n\n for (let i = 0; i < start.length; i++) {\n if (start[i] === "R") r++\n if (start[i] === "L") l--\n\n /**\n * If we encountered L and there is R that has not reached the target,\n * then we know that this L is blocking the way\n */\n if (target[i] === "L" && r > 0) return false\n if (start[i] === "L" && r > 0) return false\n\n if (target[i] === "L") l++\n if (target[i] === "R") r--\n\n if (l < 0 || r < 0) return false\n }\n\n /**\n * Final l and r count must be zero\n */\n return !l && !r\n\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['JavaScript']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
✔ Kotlin Solution || SIMPLE Two Pointer || EXPLAINED
|
kotlin-solution-simple-two-pointer-expla-omd9
|
check if start and target have the same amount of letters\n2. have two pointers to get the next letter in start and target\n3. check if the letter from start ca
|
PoeticIvy302543
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-14T04:40:13.255336+00:00
|
2023-01-14T19:23:30.952316+00:00
| 88 | false |
1. check if start and target have the same amount of letters\n2. have two pointers to get the next letter in start and target\n3. check if the letter from start can be moved to the same index as the letter from target\n\n```\n fun canChange(start: String, target: String): Boolean {\n val str = start.replace("_", "")\n val str2 = target.replace("_", "")\n if (str.length!=str2.length) return false\n var i = 0\n var j = -1\n while (i<target.length) {\n if (target[i] != \'_\') {\n j++\n while (j<start.length-1 && start[j]==\'_\') j++\n if (start[j]!=target[i]) return false\n\n if (start[j]==\'L\') if (i>j) return false\n if (start[j]==\'R\') if (i<j) return false\n }\n i++\n }\n return true\n }\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'Kotlin']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Simple C++ One Pass Scan Solution
|
simple-c-one-pass-scan-solution-by-srite-xz9j
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n int i=0,j=0;\n while(true)\n {\n while(i < star
|
sritesh45
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-13T13:36:16.254648+00:00
|
2022-07-13T13:36:16.254678+00:00
| 99 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n int i=0,j=0;\n while(true)\n {\n while(i < start.length() && start[i] == \'_\')\n i++;\n while(j < target.length() && target[j] == \'_\')\n j++;\n if (i == start.length() && j == target.length())\n return true;\n else if ((i != start.length() && j == target.length())\n || (i == start.length() && j != target.length()))\n return false;\n else if (start[i] != target[j])\n return false;\n else if (start[i] == \'L\' && (i>=j))\n i++,j++;\n else if (start[i] == \'R\' && (i<=j))\n i++,j++;\n else\n return false;\n }\n return false;\n }\n};\n```\n\n\nscan both the strings from start. \nlets i is the index of scanner in start string,\nj is the index of the scanner in the target string.\n\nmove i till you find an L or R.\nmove j till you find an L or R.\n\nif start[i] or target[j] don\'t match (i.e. one is R and one is L) then it is impossible to convert.\nif start[i] and target[j] both are L, then j has to be in the left (lesser) of the i as we can only shift L to left.\nSimilarly if both are R, then j has to be in the right of i (greater).\n\n
| 3 | 0 |
['C']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
O(N) solution fully Explained
|
on-solution-fully-explained-by-shivamg10-ih34
|
""" public boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n \n // Here in the problem We can See that the order in which elements appear in src
|
shivamg102000
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-13T11:01:26.901415+00:00
|
2022-07-13T11:01:26.901450+00:00
| 123 | false |
""" public boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n \n // Here in the problem We can See that the order in which elements appear in src and target must not be different \n // If the ordering is different then we can simply return false\n // this is so Bcoz Lets have src="_ R _ _ _ _ L _"\n // Then we can move R to any right place but when it is immediately before L (ie. _ _ _ _ _ RL _) then no extra space is left for\n // R to move so there is no way R can cross L and hence we can say that Relative order in which elements appear in the string \n // remains constant.\n \n int si=0;\n int ti=0;\n while(si<start.length() || ti< target.length()){\n \n // Now our main focus is to compare the elements so we can leave the indices which have \'_\' \n \n while(si<start.length() && start.charAt(si)==\'_\')\n si++;\n \n while(ti< target.length() && target.charAt(ti)==\'_\')\n ti++;\n \n // Now it might be that you reached the end of a string\n \n // So if you have reached the end of both the STrings that means that string have been fully compared and everything seems \n // Fine so we can return True \n \n if(si==start.length() && ti == target.length()){\n return true;\n }\n \n // But if you have reached the end of one string but there are still characters remaing in the other string\n // then obviously now no comparison can be made and hance we can return False\n \n if(si==start.length() || ti== target.length()){\n return false;\n }\n \n // If none of the above conditions holds true that means we are at some character\n \n // So if these characters are not same that means relative Ordering is different\n // So we can return False\n if(start.charAt(si) != target.charAt(ti))\n return false;\n \n // Since you are at this point that means characters must be matching\n \n // Now you have to check if L in src String is farther from target L or not \n // Ie src = " _ _ _ _ L" and target = " _ _ L _ _" so L in src string is at idx 4 while in target it is at 2\n // So L in src can move left to cover that place but what if \n // src=" _ _ L _ _" and target = " _ _ _ L _" now L can only move left and not right so return false for this conditions as well\n \n if(start.charAt(si)==\'L\' && si<ti )\n return false;\n \n // Similarly you can do the same thing for R as well\n \n if(start.charAt(si)==\'R\' && si > ti)\n return false;\n \n // Do this till all elements are not compared\n si++;\n ti++;\n \n }\n \n // If you are this point that means all conditions have passed well so we can now return True\n return true;\n }\n\n"""
| 3 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'Java']
| 1 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
easy c++|| no queues just vectors ||explained
|
easy-c-no-queues-just-vectors-explained-zmv7z
|
```\n//Logic is store the number of L and R in with respect to their positions so that we can find if we can shift L or R accordingly \n\nclass Solution {\npubl
|
Vibhoar_Bajaj
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T05:43:23.232494+00:00
|
2022-07-10T05:43:23.232532+00:00
| 110 | false |
```\n//Logic is store the number of L and R in with respect to their positions so that we can find if we can shift L or R accordingly \n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n vector<pair<char, int>> v;\n vector<pair<char, int>> m;\n int a , b =0;\n for(int i =0;i<start.size();i++){\n if(start[i]==\'L\'){\n v.push_back({\'L\' , i});\n }\n else if ( start[i]==\'R\'){\n v.push_back({\'R\', i});\n }\n else{\n a++;\n }\n }\n \n for(int i =0;i<target.size();i++){\n if(target[i]==\'L\'){\n m.push_back({\'L\' , i});\n }\n else if ( target[i]==\'R\'){\n m.push_back({\'R\', i});\n }\n else{\n b++;\n }\n }\n\t// to check if the number of blanks are extra then we cannot obtain target \n if(a!= b){\n \n return false;\n }\n\t\t\n\t\t\n\t\t// if the element is R and it is appearing after in start with respect to target then we return false as we cannot move it left to make target .\n for(int i =0;i<v.size();i++){\n if(v[i].first == m[i].first and v[i].first == \'R\'){\n \n if(v[i].second > m[i].second){\n return false;\n }\n }\n\t\t\t// if the element is L and it is appearing before in start with respect to target then return false as we cannot move it right to make target \n else if (v[i].first == m[i].first and v[i].first == \'L\'){\n if(v[i].second <m[i].second){\n return false;\n }\n }\n\t\t\t// if the arrangement is disordered eg - LR and RL \n else{\n return false;\n }\n }\n \n return true;\n }\n\t// please upvote if you understood :)) happy coding\n};
| 3 | 0 |
['C']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Ruby T:O(n), S:O(1), faster than 100%, still exceeding time limit in the contest
|
ruby-ton-so1-faster-than-100-still-excee-y2no
|
The idea is having a pool for remaining \'L\', and remaining \'R\' in the array.\n\nThe pieces cannot be moved if:\n- Encounter any extra \'L\' in start before
|
hoangphanbk10
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T04:34:13.624673+00:00
|
2022-07-10T05:22:58.873321+00:00
| 33 | false |
The idea is having a pool for remaining \'L\', and remaining \'R\' in the array.\n\nThe pieces cannot be moved if:\n- Encounter any extra \'L\' in start before we do in target\n- Encounter any extra \'R\' in target before we do in start\n- A start\'s \'L\' waiting for a match, but we encounter a \'R\' in target\n- A target\'s \'R\' waiting for a match, but we encounter a \'L\' in start\n\nNOTE: To Leetcode mods, could we either increase Ruby compiler performance on LeetCode, or increase time for Ruby solutions? Else Ruby devs need to write a much better solutions comparing to other languages in order to be accepted\n\n```\n# @param {String} start\n# @param {String} target\n# @return {Boolean}\ndef can_change(start, target)\n l_remaining = r_remaining = i = 0\n n = start.length\n \n while i < n\n if (ti = target[i]) == \'L\'\n return false if r_remaining > 0\n l_remaining += 1\n end\n\n case start[i]\n when \'L\'\n return false if l_remaining < 1\n l_remaining -= 1\n when \'R\'\n return false if l_remaining > 0\n r_remaining += 1\n end\n\n if ti == \'R\'\n return false if r_remaining < 1\n r_remaining -= 1\n end\n\n i += 1\n end\n\n l_remaining == 0 && r_remaining == 0\nend\n```\n\nEDITED: Translated this code to Java, it actually runs in 13ms, faster than 100% and less memory than 100%\n\n```\nclass Solution {\n public boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n int lRemaining = 0, rRemaining = 0;\n int n = start.length();\n for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {\n char ti = target.charAt(i);\n char si = start.charAt(i);\n\n if (ti == \'L\') {\n if (rRemaining > 0) {\n return false;\n }\n lRemaining++;\n }\n\n if (si == \'L\') {\n if (lRemaining < 1) {\n return false;\n }\n lRemaining--;\n }\n\n if (si == \'R\') {\n if (lRemaining > 0) {\n return false;\n }\n rRemaining++;\n }\n \n if (ti == \'R\') {\n if (rRemaining < 1) {\n return false;\n }\n rRemaining--;\n }\n }\n return lRemaining == 0 && rRemaining == 0;\n }\n}\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Java', 'Ruby']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
python/java 2 pointers
|
pythonjava-2-pointers-by-akaghosting-tbrq
|
\tclass Solution:\n\t\tdef canChange(self, start: str, target: str) -> bool:\n\t\t\tif start.count("") != target.count(""):\n\t\t\t\treturn False\n\t\t\ti = 0\n
|
akaghosting
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T04:02:57.299475+00:00
|
2022-07-10T04:02:57.299505+00:00
| 79 | false |
\tclass Solution:\n\t\tdef canChange(self, start: str, target: str) -> bool:\n\t\t\tif start.count("_") != target.count("_"):\n\t\t\t\treturn False\n\t\t\ti = 0\n\t\t\tj = 0\n\t\t\twhile i < len(start) and j < len(target):\n\t\t\t\tif start[i] == "_":\n\t\t\t\t\ti += 1\n\t\t\t\t\tcontinue\n\t\t\t\tif target[j] == "_":\n\t\t\t\t\tj += 1\n\t\t\t\t\tcontinue\n\t\t\t\tif start[i] != target[j]:\n\t\t\t\t\treturn False\n\t\t\t\tif start[i] == "L" and i < j:\n\t\t\t\t\treturn False\n\t\t\t\tif start[i] == "R" and i > j:\n\t\t\t\t\treturn False\n\t\t\t\ti += 1\n\t\t\t\tj += 1\n\t\t\treturn True\n\n\n\tclass Solution {\n\t\tpublic boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n\t\t\tint cnt1 = 0;\n\t\t\tint cnt2 = 0;\n\t\t\tfor (int i = 0; i < start.length(); i ++) {\n\t\t\t\tif (start.charAt(i) == \'_\') {\n\t\t\t\t\tcnt1 ++;\n\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\tif (target.charAt(i) == \'_\') {\n\t\t\t\t\tcnt2 ++;\n\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t\tif (cnt1 != cnt2) {\n\t\t\t\treturn false;\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t\tint i = 0;\n\t\t\tint j = 0;\n\t\t\twhile (i < start.length() && j < target.length()) {\n\t\t\t\tif (start.charAt(i) == \'_\') {\n\t\t\t\t\ti ++;\n\t\t\t\t\tcontinue;\n\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\tif (target.charAt(j) == \'_\') {\n\t\t\t\t\tj ++;\n\t\t\t\t\tcontinue;\n\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\tif (start.charAt(i) != target.charAt(j)) {\n\t\t\t\t\treturn false;\n\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\tif (start.charAt(i) == \'L\' && i < j) {\n\t\t\t\t\treturn false;\n\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\tif (start.charAt(i) == \'R\' && i > j) {\n\t\t\t\t\treturn false;\n\t\t\t\t}\n\t\t\t\ti ++;\n\t\t\t\tj ++;\n\t\t\t}\n\t\t\treturn true;\n\t\t}\n\t}
| 3 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Easy C++ | Stack | Greedy Approach | O(n)
|
easy-c-stack-greedy-approach-on-by-shatr-f1cj
|
Simple Stack Solution given below:\n\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string s1, string s2) {\n stack<pair<char, int>> st1, st2;\n
|
shatrunjay4321
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T04:02:13.690397+00:00
|
2022-07-10T04:10:05.129662+00:00
| 411 | false |
Simple Stack Solution given below:\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string s1, string s2) {\n stack<pair<char, int>> st1, st2;\n int i, n = s1.size();\n for(i=0; i<n; i++)\n {\n if(s1[i]==\'L\')\n {\n st1.push({\'L\', i});\n }\n else if(s1[i]==\'R\')\n {\n st1.push({\'R\', i});\n }\n if(s2[i]==\'L\')\n {\n st2.push({\'L\', i});\n }\n else if(s2[i]==\'R\')\n {\n st2.push({\'R\', i});\n }\n }\n \n // If number of L\'s and R\'s in st1 and st2 are not same \n if(st1.size() != st2.size())\n {\n return false;\n }\n while(!st1.empty() and !st2.empty())\n {\n // If the sequence is not same, then it is always impossible\n if(st1.top().first != st2.top().first)\n {\n return false;\n }\n \n if(st1.top().first == \'R\')\n {\n // If R in s1 is ahead of R in target string, then we can never move it towards the left\n // Therefore, it is always impossible\n if(st1.top().second > st2.top().second)\n {\n return false;\n }\n }\n else\n {\n // If L in s1 is before of L in target string, then we can never move it towards the right\n // Therefore, it is always impossible\n if(st1.top().second < st2.top().second)\n {\n return false;\n }\n }\n st1.pop();\n st2.pop();\n }\n return true;\n }\n};\n```
| 3 | 0 |
['Stack', 'Greedy', 'C', 'C++']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
C++ Super Easy and Simple 2 Pointer Solution
|
c-super-easy-and-simple-2-pointer-soluti-i61r
|
Intuition\nWe will iterate through both strings, once we find a char that is not \'_\' - if they are equal, chack that it\'s on the left / right, depending on t
|
yehudisk
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-06T13:07:32.136915+00:00
|
2024-12-06T13:07:32.136937+00:00
| 8 | false |
# Intuition\nWe will iterate through both strings, once we find a char that is not \'_\' - if they are equal, chack that it\'s on the left / right, depending on the char.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n)\n\n- Space complexity: O(1)\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n int s_ptr = 0, t_ptr = 0, n = start.size();\n while (s_ptr <= n && t_ptr <= n) {\n while (s_ptr < n && start[s_ptr] == \'_\') s_ptr++;\n while (t_ptr < n && target[t_ptr] == \'_\') t_ptr++;\n\n if (s_ptr == n || t_ptr == n) return s_ptr == n && t_ptr == n;\n\n if (start[s_ptr] != target[t_ptr]) return false;\n\n if (start[s_ptr] == \'R\') {\n if (s_ptr > t_ptr) return false;\n }\n\n else if (start[s_ptr] == \'L\') {\n if (s_ptr < t_ptr) return false;\n }\n\n s_ptr++;\n t_ptr++;\n }\n return true;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Beats 50% People
|
beats-50-people-by-yashdeshmukh40-ubbi
|
Intuition\nI have used 2 Pointer but used so much If and else conditions may be this code will be beginner friendly.\n\n# Approach\n2 Pointer\n\n# Complexity\n-
|
yashdeshmukh40
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T18:01:45.995177+00:00
|
2024-12-05T18:01:45.995221+00:00
| 10 | false |
# Intuition\nI have used 2 Pointer but used so much If and else conditions may be this code will be beginner friendly.\n\n# Approach\n2 Pointer\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(N)\n\n- Space complexity:\nO(1)\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n\n int n = start.length();\n int i =0 , j =0 ;\n for( ; i < n && j <n ;){\n char sc = start.charAt(i);\n char tc = target.charAt(j);\n if(sc == tc){\n if(sc == \'L\' && i < j) {\n return false;\n }\n else if(sc == \'R\' && j < i){\n return false;\n }\n else{\n i++;\n j++;\n }\n }\n else if(tc == \'L\' && j > i){\n return false;\n } \n else if(sc == \'R\' && i > j){\n return false;\n }\n else if(tc == \'L\' && sc == \'_\'){\n i++;\n }\n else if(sc == \'R\' && tc == \'_\'){\n j++;\n }\n else if(tc == \'R\' && i < j && sc == \'_\'){\n i++;\n }\n else if(sc == \'L\' && j < i && tc == \'_\'){\n j++;\n }\n else{\n return false;\n }\n if( i != j){\n if(i < j){\n while(i != j && start.charAt(i) == \'_\'){\n i++;\n }\n }\n else if(j < i){\n while(i != j && target.charAt(j) == \'_\'){\n j++;\n }\n }\n }\n \n }\n if( i < j){\n while( i< j){\n if(start.charAt(i) != \'_\') return false;\n i++;\n }\n }\n else{\n while(j < i){\n if(target.charAt(j) != \'_\') return false;\n j++;\n }\n\n }\n return true;\n \n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'String', 'Java']
| 1 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
without 2 pointer simple loop logic and counting
|
without-2-pointer-simple-loop-logic-and-yk87q
|
\n\n# Code\ncpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n if(start.size()!=target.size()) return false;\n
|
shashwat1915
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T13:11:41.541558+00:00
|
2024-12-05T13:11:41.541582+00:00
| 72 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n if(start.size()!=target.size()) return false;\n int sl=0,sr=0,tl=0,tr=0;\n for(int i=start.size()-1;i>=0;i--){\n if(start[i]==\'L\') sl++;\n else if(start[i]==\'R\') sr++;\n if(target[i]==\'L\') tl++;\n else if(target[i]==\'R\') tr++;\n if (sl<tl || sr>tr) return false;\n if (((start[i]==\'L\'||target[i]==\'L\')&&sr!=tr) || ((start[i]==\'R\'||target[i]==\'R\')&&sl!=tl)) return false;\n }\n if(sr!=tr || tl!=sl) return false;\n return true;\n }\n};\n\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['String', 'C++']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
C++ Solution With Explanation ⭐|| Beats 90.23% ✔|| UPVOTE⬆
|
c-solution-with-explanation-beats-9023-u-ysri
|
Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n1. ### Skip Blanks:\n\n- Traverse both start and target strings while skipping all blank spaces (_).
|
Abhijithsr13
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T10:21:34.289088+00:00
|
2024-12-05T10:21:34.289114+00:00
| 8 | false |
# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1. ### Skip Blanks:\n\n- Traverse both start and target strings while skipping all blank spaces (_).\n- This allows us to focus only on the positions of \'L\' and \'R\'.\n\n2. ### Early Exit Conditions:\n\n- If one string reaches the end before the other, or if the characters at the current positions in start and target don\'t match, then it\u2019s impossible to transform start into target.\n3. ### Movement Rules:\n\n- \'L\' pieces must move left, so the index of \'L\' in start (i) must be greater than or equal to its index in target (j).\n- \'R\' pieces must move right, so the index of \'R\' in start (i) must be less than or equal to its index in target (j).\n\n4. ### Finish Traversal:\n- If both strings are fully traversed and all conditions are satisfied, return ***true***.\n Otherwise, return ***false***.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:**\uD835\uDC42(\uD835\uDC5B)**,\nEach character in the strings is processed at most once.\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:**O(1)**,\nNo additional data structures are used\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n int n = start.size();\n int i = 0, j = 0;\n\n while (i < n || j < n) {\n // Skip blank spaces in both strings\n while (i < n && start[i] == \'_\')\n i++;\n while (j < n && target[j] == \'_\')\n j++;\n\n // Check if both strings have reached the end\n if (i == n && j == n)\n return true;\n\n // Check if one string ends before the other\n if (i == n || j == n)\n return false;\n\n // Check if the characters at the current positions are different\n if (start[i] != target[j])\n return false;\n\n // Check if \'L\' or \'R\' pieces follow the movement rules\n if (start[i] == \'L\' && i < j)\n return false;\n if (start[i] == \'R\' && i > j)\n return false;\n\n // Move to the next character\n i++;\n j++;\n }\n return true;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
✅ [Python] - Quick Solution ✅
|
python-quick-solution-by-danielol-7t9q
|
Code\npython3 []\nclass Solution:\n def canChange(self, start: str, target: str) -> bool:\n if start.replace(\'_\', \'\') != target.replace(\'_\', \'\
|
DanielOL
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T08:53:18.040197+00:00
|
2024-12-05T08:53:18.040257+00:00
| 53 | false |
# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def canChange(self, start: str, target: str) -> bool:\n if start.replace(\'_\', \'\') != target.replace(\'_\', \'\'):\n return False\n \n n = len(start)\n start_positions = [(char, i) for i, char in enumerate(start) if char != \'_\']\n target_positions = [(char, i) for i, char in enumerate(target) if char != \'_\']\n \n for (s_char, s_idx), (t_char, t_idx) in zip(start_positions, target_positions):\n # \'L\' can only move to the left\n if s_char == \'L\' and s_idx < t_idx:\n return False\n # \'R\' can only move to the right\n if s_char == \'R\' and s_idx > t_idx:\n return False\n \n return True\n\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'String', 'Python3']
| 2 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
String || Two-Pointer Approach || Easy to Understand
|
string-two-pointer-approach-easy-to-unde-6e9d
|
Intuition\nWhen we want to change one string (start) into another string (target), we need to think about how we can move the characters around. The characters
|
Rohit_Pra
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T07:40:49.795053+00:00
|
2024-12-05T07:40:49.795082+00:00
| 82 | false |
# Intuition\nWhen we want to change one string (start) into another string (target), we need to think about how we can move the characters around. The characters \'L\' and \'R\' can only move left and right, respectively, and we can ignore underscores (_). Our first thought is to check if both strings have the same characters (ignoring underscores) and then see if we can rearrange them according to the movement rules.\n# Approach\n1. **Ignore Underscores:** First, we need to check if the characters in both strings (without underscores) are the same. If they are not, we cannot transform start into target.\n\n2. **Use Two Pointers:** We will use two pointers (like two fingers) to go through both strings: One pointer (i) will go through the start string.\nThe other pointer (j) will go through the target string.\n3. **Skip Underscores:** As we move our pointers, we will skip over any underscores (_) until we find a character.\n\n4. **Check Characters:** When both pointers point to characters (not underscores), we will check if they are the same. If they are not, we cannot transform start into target.\n\n**Movement Rules:** \nWe need to make sure that:\nIf we have an \'L\' in start, it should not be trying to move to the right in target.\nIf we have an \'R\' in start, it should not be trying to move to the left in target.\nFinish Check: If we reach the end of both strings at the same time, it means we can transform start into target.\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: **O(n)**\nwhere n is the length of the input strings `start` and `target`. This is because the algorithm iterates through both strings in a single pass, moving the indices `i` and `j` forward as it processes each character. The while loops for skipping underscores and the comparisons are all linear operations with respect to the length of the strings.\n- Space complexity: **O(1)**\nas the algorithm uses a constant amount of extra space. It only utilizes a few integer variables (`i`, `j`, and `n`) to keep track of indices and does not create any additional data structures that grow with the input size. Thus, the space used does not depend on the length of the input strings.\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n int i=0,j=0;\n int n=start.length();\n while(i<n || j<n){\n while(i<n && start.charAt(i)==\'_\') i++;\n while(j<n && target.charAt(j)==\'_\') j++;\n if(i==n || j==n) return i==n && j==n; \n if(start.charAt(i)!=target.charAt(j)) return false;\n if(start.charAt(i)==\'L\' && i<j) return false;\n if(start.charAt(i)==\'R\' && i>j) return false;\n i++; j++; \n }\n return true; \n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'String', 'Java']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Clear Cut Two-Pointer Solution in Python
|
clear-cut-two-pointer-solution-in-python-vbse
|
Intuition\nThe problem requires us to determine if we can transform the string start into target using valid moves for the pieces $L$ and $R$.\n\n# Approach\nKe
|
sumittripathi004
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T06:16:37.783846+00:00
|
2024-12-05T06:16:37.783875+00:00
| 44 | false |
# Intuition\nThe problem requires us to determine if we can transform the string start into target using valid moves for the pieces $L$ and $R$.\n\n# Approach\n<B>Key Observations:</B>\n1. <I>Character Equality:</I> The sequence of non-underscore characters (\'L\' and \'R\') in start and target must match, preserving their relative order. If start.replace(\'_\', \'\') != target.replace(\'_\', \'\'), the transformation is impossible.\n\n<B>Movement Rules:</B>\n\n1. An \'L\' can only move to the left, so it must not cross an \'R\' or be found further to the right than its corresponding position in target.\n2. An \'R\' can only move to the right, so it must not cross an \'L\' or be found further to the left than its corresponding position in target.\nEfficient Validation: Instead of simulating the moves, we can check if all movement constraints hold by comparing indices.\n\n<B>Plan:</B>\n1. Compare start and target after removing underscores to ensure the characters match.\n2. Use two pointers to validate the movement constraints for each \'L\' and \'R\'.\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $O(N)$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: $O(1)$\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def canChange(self, start: str, target: str) -> bool:\n # Step 1: Remove underscores and check if the character sequence matches\n if start.replace(\'_\', \'\') != target.replace(\'_\', \'\'):\n return False\n\n n = len(start)\n i, j = 0, 0\n\n # Step 2: Use two pointers to check movement constraints\n while i < n and j < n:\n # Skip underscores in start\n while i < n and start[i] == \'_\':\n i += 1\n # Skip underscores in target\n while j < n and target[j] == \'_\':\n j += 1\n\n # If both pointers are out of bounds, we\'re done\n if i == n and j == n:\n return True\n # If one pointer is out of bounds but not the other, return False\n if i == n or j == n:\n return False\n\n # Check movement constraints for \'L\' and \'R\'\n if start[i] != target[j]:\n return False\n if start[i] == \'L\' and i < j: # \'L\' cannot move to the right\n return False\n if start[i] == \'R\' and i > j: # \'R\' cannot move to the left\n return False\n\n # Move both pointers\n i += 1\n j += 1\n\n return True\n\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'String', 'Python', 'Python3']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Two pointers | O(len(target)) | Beginner Friendly
|
two-pointers-olentarget-beginner-friendl-n86h
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nusing 2 pointers to check the conditions fro both strings\n\n# Approach\n Describe your
|
chakri-34
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T05:48:16.399569+00:00
|
2024-12-05T05:48:16.399589+00:00
| 29 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nusing 2 pointers to check the conditions fro both strings\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n- \'s\' pointer for start and \'t\' pointer for target\n- Take s to first letter ("L" or "R")\n- Take t to first letter (\'L\' or \'R\')\n- conditions for furthur loop:\n 1. if s exceeds the len(start) or t exceeds the len(target), then our solution is only true if both of them happen simulatenously. So condition is **s==len(start) and t==len(target)**\n 2. if start[s]!=target[t] break the loop\n 3. if start[s]==target[t]==\'L\' , s should be greater than t ( **s>=t** )\n 4. if start[s]==target[t]==\'R , r should be greater than s ( **t>=s** )\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def canChange(self, start: str, target: str) -> bool:\n s,t=0,0\n while s<len(start) or t<len(target):\n while s<len(start) and start[s]==\'_\':\n s+=1\n while t<len(target) and target[t]==\'_\':\n t+=1\n if s==len(start) or t==len(target):\n return (s==len(start) and t==len(target))\n if (start[s]!=target[t] or (start[s]==\'L\' and s<t) or (start[s]==\'R\' and s>t)):\n return False\n s+=1\n t+=1\n return True\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'String', 'Python3']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Swift | Two Pointers | Explained
|
swift-two-pointers-explained-by-noahfeld-blwo
|
Swift suffers the most during String Week because there\'s not a way to get the character at the index of a String in Swift in O(1) without converting it to a C
|
noahfeld
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T05:17:28.176714+00:00
|
2024-12-05T05:18:07.807561+00:00
| 41 | false |
Swift suffers the most during String Week because there\'s not a way to get the character at the index of a String in Swift in $$O(1)$$ without converting it to a Character array first, which is itself an $$O(n)$$ process that results in $$O(n)$$ space complexity. Since we\'re only creating the character arrays to get around Swift\'s... unique limitations... it can be argued that solutions like this are *theoretically* $$O(1)$$ SC.\n\nAnyways, this problem, while initially difficult, can be simplified into the following rules:\n\n1. $$start$$ and $$target$$ must have the same order of L\'s and R\'s (i.e., they would be identical strings if all of their blank spaces were removed). This is because L\'s and R\'s cannot pass each other when moving pieces.\n2. An "L" in $$start$$ at index $$i$$ must have a corresponding "L" in $$target$$ at index $$j$$ such that $$i >= j$$. This is because $$start$$\'s "L" can move left but not right to match $$target$$.\n3. An "R" in $$start$$ at index $$i$$ must have a corresponding "R" in $$target$$ at index $$j$$ such that $$i <= j$$. This is because $$start$$\'s "R" can move right but not left to match $$target$$.\n\nWe can iterate two pointers through both strings, skipping blank spaces, and returning $$false$$ early if these properties are violated.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$O(n)$$\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: $$O(1)$$*\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```swift []\nclass Solution {\n func canChange(_ start: String, _ target: String) -> Bool {\n let (s, t) = (Array(start), Array(target))\n let n = s.count\n var i = 0, j = 0\n while i < n || j < n {\n while i < n && s[i] == "_" { i += 1 }\n while j < n && t[j] == "_" { j += 1 }\n if i == n || j == n { return i == n && j == n }\n if (s[i] != t[j]) || (s[i] == "L" && i < j) || (s[i] == "R" && i > j) { return false }\n (i, j) = (i+1, j+1)\n }\n return true\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Swift']
| 1 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
2 Pointer with boundries ig 😙✌🏽
|
2-pointer-with-boundries-ig-by-deepsalun-27kt
|
Intuition\nThe problem involves validating if pieces can be moved to transform start into target while adhering to specific movement constraints for \'L\' and \
|
deepsalunkhee
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T04:56:25.913889+00:00
|
2024-12-05T04:56:25.913933+00:00
| 43 | false |
# Intuition\nThe problem involves validating if pieces can be moved to transform `start` into `target` while adhering to specific movement constraints for \'L\' and \'R\'. Observing the relative order of \'L\', \'R\', and \'_\' in both strings provides insights for solving the problem.\n\n# Approach\n1. **Simultaneous Iteration**:\n - Use two pointers `sp` and `tp` to iterate through `start` and `target`, respectively.\n - Skip over \'_\' in both strings as these positions are neutral.\n\n2. **Validate Pieces**:\n - Compare characters at `sp` and `tp`:\n - If one is \'L\' and the other is \'R\', return `false`.\n - For \'L\', ensure its position in `target` does not exceed its position in `start` because \'L\' can only move left.\n - For \'R\', ensure its position in `target` does not precede its position in `start` because \'R\' can only move right.\n\n3. **Check Remaining Characters**:\n - After exiting the loop, ensure no characters other than \'_\' remain in either string. If non-\'_\' characters remain, return `false`.\n\n4. **Return Result**:\n - If all checks pass, return `true`.\n\n# Complexity\n- **Time Complexity**: \n $$O(n)$$, where \\(n\\) is the length of the strings. Both strings are traversed at most once.\n \n- **Space Complexity**: \n $$O(1)$$, as no additional data structures are used.\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n\n int sl = start.length();\n int tl = target.length();\n\n int sp = 0;\n int tp = 0;\n\n while (sp < sl && tp < tl) {\n if (start.charAt(sp) == \'_\')\n sp++;\n else if (target.charAt(tp) == \'_\')\n tp++;\n else if ((start.charAt(sp) == \'L\' && target.charAt(tp) == \'R\') || \n (start.charAt(sp) == \'R\' && target.charAt(tp) == \'L\'))\n return false;\n else if (start.charAt(sp) == \'L\' && target.charAt(tp) == \'L\') {\n if (tp > sp) return false;\n\n sp++;\n tp++;\n } else if (start.charAt(sp) == \'R\' && target.charAt(tp) == \'R\') {\n if (tp < sp) return false;\n\n sp++;\n tp++;\n }\n }\n\n // If anything is remaining in any one return false\n while (sp < sl) {\n if (start.charAt(sp) != \'_\') return false;\n sp++;\n }\n while (tp < tl) {\n if (target.charAt(tp) != \'_\') return false;\n tp++;\n }\n return true;\n }\n}\n```\n``` C++ []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n\n int sl = start.length();\n int tl = target.length();\n\n int sp = 0;\n int tp = 0;\n\n while (sp < sl && tp < tl) {\n if (start[sp] == \'_\')\n sp++;\n else if (target[tp] == \'_\')\n tp++;\n else if ((start[sp] == \'L\' && target[tp] == \'R\') || \n (start[sp] == \'R\' && target[tp] == \'L\'))\n return false;\n else if (start[sp] == \'L\' && target[tp] == \'L\') {\n if (tp > sp) return false;\n\n sp++;\n tp++;\n } else if (start[sp] == \'R\' && target[tp] == \'R\') {\n if (tp < sp) return false;\n\n sp++;\n tp++;\n }\n }\n\n // If anything is remaining in any one return false\n while (sp < sl) {\n if (start[sp] != \'_\') return false;\n sp++;\n }\n while (tp < tl) {\n if (target[tp] != \'_\') return false;\n tp++;\n }\n return true;\n }\n};\n```\n\n\n\n\n
| 2 | 0 |
['C++', 'Java']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Two Pointer Easy ✅ || C++ ✅✅
|
two-pointer-easy-c-by-yashm01-d1qa
|
"Data structures and algorithms are the building blocks of innovation." \uD83D\uDE80\n\n# Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem.
|
yashm01
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T04:38:10.928457+00:00
|
2024-12-05T04:38:10.928499+00:00
| 13 | false |
# **"Data structures and algorithms are the building blocks of innovation."** \uD83D\uDE80\n\n# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThe problem revolves around validating if the positions of `L` and `R` in `start` can be adjusted to match their positions in `target` under specific movement constraints.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n1. Use two pointers, `i` and `j`, to traverse the `start` and `target` strings, respectively.\n2. Skip all `_` characters in both strings since they can be ignored for alignment purposes.\n3. Check the following conditions:\n - The current characters in both strings should match (`L` or `R`).\n - If the character is `L`, ensure `i` (from `start`) is not less than `j` (from `target`), as `L` can only move left.\n - If the character is `R`, ensure `i` is not greater than `j`, as `R` can only move right.\n4. Continue until both pointers reach the end of their respective strings, ensuring no mismatches occur.\n\n# Complexity\n- **Time complexity:** \n $$O(n)$$ \n Each string is traversed once, where `n` is the length of the strings.\n\n- **Space complexity:** \n $$O(1)$$ \n Only a few variables are used for pointer tracking.\n\n# Code\n```cpp\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n int i = 0, j = 0, n = start.size();\n\n while (i < n || j < n) {\n while (i < n && start[i] == \'_\') i++;\n while (j < n && target[j] == \'_\') j++;\n if (i == n || j == n) break;\n if (start[i] != target[j]) return false;\n if (start[i] == \'L\' && i < j) return false;\n if (start[i] == \'R\' && i > j) return false;\n i++;\n j++;\n }\n return i == n && j == n;\n }\n};\n
| 2 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'String', 'C++']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Most Simple soln | C++ | TC: O(n)
|
most-simple-soln-c-tc-on-by-shruti066-ardz
|
Intuition\n\nThink about all the cases where the conversion from start to target is not possible. Then find the generic condition where the conversion from star
|
shruti066
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T04:26:49.064601+00:00
|
2024-12-05T04:26:49.064642+00:00
| 96 | false |
# Intuition\n\nThink about all the cases where the conversion from start to target is not possible. Then find the generic condition where the conversion from start to target is not possible.\n\n# Approach\n\n1. If the sequence of L and R is not equal in both the strings then automatically we can never convert start to target.\n2. Cases where the conversion is not possible: \n i. if L in start comes before the L in target.\n ii. if R in start comes after the R in target.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n)\n\n- Space complexity: O(n)\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string s, string t) {\n string temp1="",temp2="";\n for(int i=0;i<s.size();i++){\n if(s[i]!=\'_\')temp1+=s[i];\n }\n for(int i=0;i<t.size();i++){\n if(t[i]!=\'_\')temp2+=t[i];\n }\n\n if(temp1!=temp2)return false;\n\n int sl=0,tl=0,sr=0,tr=0;\n for(int i=0,j=0;i<s.size();i++,j++){\n if(s[i]==\'L\')sl++;\n if(t[i]==\'L\')tl++;\n if(s[i]==\'R\')sr++;\n if(t[i]==\'R\')tr++;\n if(sl>tl||tr>sr)return false;\n }\n\n return true;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 1 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
C++ solution in O(n) and O(1)
|
c-solution-in-on-and-o1-by-fly_leap-lt8h
|
\n\n# Code\ncpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n int n = start.length();\n\n int cnt = 0;\n
|
fly_leap
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T04:25:59.155234+00:00
|
2024-12-05T04:25:59.155270+00:00
| 118 | false |
\n\n# Code\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n int n = start.length();\n\n int cnt = 0;\n int startcnt = 0;\n int targetcnt = 0;\n for (int i = 0;i < n;i ++) {\n startcnt += (start[i] == \'R\');\n cnt += (start[i] == \'R\');\n cnt = (start[i] == \'L\') ? 0 : cnt;\n\n if (target[i] == \'R\') {\n targetcnt ++;\n if (cnt == 0) return false;\n cnt --;\n }\n }\n\n if (startcnt != targetcnt) return false;\n\n cnt = 0;\n startcnt = 0;\n targetcnt = 0;\n for (int i = n - 1;i >= 0;i --) {\n startcnt += (start[i] == \'L\');\n cnt += (start[i] == \'L\');\n cnt = (target[i] == \'R\') ? 0 : cnt;\n\n if (target[i] == \'L\') {\n targetcnt ++;\n if (cnt == 0) return false;\n cnt --;\n }\n }\n\n return (startcnt == targetcnt);\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Rust with iterators
|
rust-with-iterators-by-minamikaze392-u5st
|
Code\nRust []\nimpl Solution {\n pub fn can_change(start: String, target: String) -> bool {\n let mut iter1 = Self::pieces(&start);\n let mut i
|
Minamikaze392
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T02:09:26.869144+00:00
|
2024-12-05T02:09:51.540849+00:00
| 16 | false |
# Code\n```Rust []\nimpl Solution {\n pub fn can_change(start: String, target: String) -> bool {\n let mut iter1 = Self::pieces(&start);\n let mut iter2 = Self::pieces(&target);\n loop {\n match (iter1.next(), iter2.next()) {\n (None, None) => return true,\n (Some((i, b1)), Some((j, b2))) => {\n if b1 != b2\n || (b1 == b\'L\' && i < j)\n || (b1 == b\'R\' && i > j) {\n return false;\n }\n }\n _ => return false,\n }\n }\n }\n\n fn pieces<\'a>(s: &\'a String) -> impl Iterator<Item=(usize, u8)> + \'a {\n s.bytes().enumerate().filter(|&(_, b)| b != b\'_\')\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'Iterator', 'Rust']
| 1 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Swift | Straightforward
|
swift-straightforward-by-pagafan7as-drm9
|
Code\nswift []\nclass Solution {\n func canChange(_ start: String, _ target: String) -> Bool {\n return start.lazy.filter { $0 != "_"} == target.lazy.
|
pagafan7as
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T00:19:37.260274+00:00
|
2024-12-06T05:27:34.072554+00:00
| 22 | false |
# Code\n```swift []\nclass Solution {\n func canChange(_ start: String, _ target: String) -> Bool {\n return start.lazy.filter { $0 != "_"} == target.lazy.filter { $0 != "_"} &&\n zip(indices("L", start), indices("L", target)).allSatisfy(>=) &&\n zip(indices("R", start), indices("R", target)).allSatisfy(<=)\n\n func indices(_ c: Character, _ s: String) -> [Int] {\n s.enumerated().lazy.filter { $0.element == c }.map { $0.offset }\n }\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Swift']
| 1 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Clear and short go solution
|
clear-and-short-go-solution-by-leetcoder-g396
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \n\n# Approach\n Describe your approach to solving the problem. \n\n# Complexity\n- Time
|
leetcoder_09
|
NORMAL
|
2024-10-19T12:33:34.447798+00:00
|
2024-10-19T12:33:34.447825+00:00
| 51 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(1)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```golang []\nfunc canChange(start string, target string) bool {\n\tln := len(start)\n\tl, r := 0, 0\n\n\tfor r < ln || l < ln {\n\t\tif r < ln && target[r] == \'_\' {\n\t\t\tr++\n\t\t} else if l < ln && start[l] == \'_\' {\n\t\t\tl++\n\t\t} else if r == ln || l == ln || start[l] != target[r] || (target[r] == \'R\' && l > r) || (target[r] == \'L\' && r > l) {\n\t\t\treturn false\n\t\t} else {\n\t\t\tr++\n\t\t\tl++\n\t\t}\n\t}\n\n\treturn true\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Go']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
O(N) time and O(1) space solution
|
on-time-and-o1-space-solution-by-random_-ijzo
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nSimilar to valid parentheses\n\nThe rules of a valid are as follow:\n1, L and R does no
|
random_code_monkey
|
NORMAL
|
2024-01-08T19:30:34.111091+00:00
|
2024-01-08T19:30:34.111120+00:00
| 117 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nSimilar to valid parentheses\n\nThe rules of a valid are as follow:\n1, L and R does not cross\n2, The index of L in start must not less than the corresponding L in target\n3, The index of R in start must not greater than the corresponding R in target\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\n\nUsing pointer for each string and check the rules mentioned above\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(N)\n\n- Space complexity:\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\nO(1)\n\n# Code\n```\nclass Solution:\n def canChange(self, start: str, target: str) -> bool:\n s_p = 0\n t_p = 0\n\n while True:\n while s_p < len(start) and start[s_p] == "_":\n s_p += 1\n while t_p < len(target) and target[t_p] == "_":\n t_p += 1\n if s_p == len(start) and t_p == len(target):\n return True\n if s_p == len(start) or t_p == len(target):\n return False\n # if not the same\n if start[s_p] != target[t_p]: return False\n # for L \n if start[s_p] == "L":\n if s_p < t_p: return False\n else:\n if s_p > t_p: return False\n s_p += 1\n t_p += 1\n return \n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
[C++] Simple C++ Code
|
c-simple-c-code-by-prosenjitkundu760-h5my
|
\n# If you like the implementation then Please help me by increasing my reputation. By clicking the up arrow on the left of my image.\n\nclass Solution {\npubli
|
_pros_
|
NORMAL
|
2022-09-01T08:45:10.239126+00:00
|
2022-09-01T08:45:10.239168+00:00
| 386 | false |
\n# **If you like the implementation then Please help me by increasing my reputation. By clicking the up arrow on the left of my image.**\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n int end = target.size();\n int ScntL = 0, ScntR = 0, TcntL = 0, TcntR = 0;\n string ss = "", st = "";\n for(int i = 0; i < end; i++)\n {\n if(start[i] != \'_\')\n ss += start[i];\n if(target[i] != \'_\')\n st += target[i];\n }\n if(ss != st) return false;\n for(int i = 0; i < end; i++)\n {\n if(start[i] == \'L\')\n ScntL++;\n if(target[i] == \'L\')\n TcntL++;\n if(ScntL > TcntL)\n return false;\n }\n if(ScntL != TcntL)\n return false;\n for(int i = 0; i < end; i++)\n {\n if(start[i] == \'R\')\n ScntR++;\n if(target[i] == \'R\')\n TcntR++;\n if(ScntR < TcntR)\n return false;\n }\n if(ScntR != TcntR)\n return false;\n return true;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C', 'C++']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Two Pointer | Easy | Fast | Commented
|
two-pointer-easy-fast-commented-by-medic-4cag
|
Thanks to koroja3877 for the answer, here is my explaination with comments for easy understanding.\n\n\tvar canChange = function (start, target) {\n\t\tlet lCou
|
Medicore
|
NORMAL
|
2022-08-25T16:54:15.728088+00:00
|
2022-08-25T16:54:48.637027+00:00
| 208 | false |
Thanks to [koroja3877](https://leetcode.com/koroja3877/) for the answer, here is my explaination with comments for easy understanding.\n\n\tvar canChange = function (start, target) {\n\t\tlet lCount = 0;//count of l\'s in target, to be consumed later in start\n\t\tlet rCount = 0;//count of r\'s in start, to be consumed later in target\n\n\t\tfor (let i = 0; i < start.length; i++) {\n\t\t\tif (start[i] === "R") rCount++;//add r to count\n\t\t\tif (start[i] === "L") lCount--;//remove l from count\n\n\t\t\tif (target[i] === "L" && rCount > 0) return false;//if L in start is blocked by R\n\t\t\tif (start[i] === "L" && rCount > 0) return false;//if there is an unsetteled R in start\n\n\t\t\tif (target[i] === "L") lCount++;//add l to count\n\t\t\tif (target[i] === "R") rCount--;//remove r from count\n\n\t\t\tif (lCount< 0 || rCount < 0) return false;//check if the requirements are less than available\n\t\t}\n\t\treturn !lCount && !rCount;//count should return to zero as all L and R are consumed\n\t};
| 2 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'JavaScript']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Easy Java Solution
|
easy-java-solution-by-amaansiddiqui739-2555
|
```\nclass Solution {\n public boolean canChange(String s, String e) {\n if(s.length() != e.length() ) return false;\n if(s.equals(e) ) return
|
amaansiddiqui739
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-18T15:23:36.822988+00:00
|
2022-07-18T15:23:36.823021+00:00
| 185 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\n public boolean canChange(String s, String e) {\n if(s.length() != e.length() ) return false;\n if(s.equals(e) ) return true;\n int n = s.length();\n \n \n if(s.replace("_","").equals(e.replace("_","")) == false) return false;\n \n // System.out.println("lll");\n int i = 0; int j = 0;\n \n while(i < n && j < n){\n while(i < n && s.charAt(i) != \'R\') i++;\n while(j < n && e.charAt(j) != \'R\') j++;\n \n if(i > j) return false;\n i++;\n j++;\n \n }\n i = 0; j = 0;\n \n while(i < n && j < n){\n while(i < n && s.charAt(i) != \'L\') i++;\n while(j < n && e.charAt(j) != \'L\') j++;\n \n if(j > i) return false;\n i++;\n j++;\n \n }\n \n return true;\n }\n}
| 2 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'Java']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Can someone comment on how did you think of the solution? Basically the thought process
|
can-someone-comment-on-how-did-you-think-kpk4
|
I took really long during the contest to think of the solution. Started with thinking of DP and then narrowed down to DFS and then thought to have two pointers
|
Smita2195
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-15T16:13:33.956065+00:00
|
2022-07-15T16:13:49.780725+00:00
| 260 | false |
**I took really long during the contest to think of the solution. Started with thinking of DP and then narrowed down to DFS and then thought to have two pointers on both ends of start string to move L and R to left and right most sides.. and so on. But I couldnt think of the solution within time. Can you guys please share your thought process here**
| 2 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'String', 'C', 'Python', 'Java']
| 1 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
C++ O(N) Time & O(1) Space
|
c-on-time-o1-space-by-rockcodz-ndzt
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n int L=0,R=0;\n for(int i=0;i<start.size();i++)\n {\n
|
RockCodz
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-14T18:45:21.111479+00:00
|
2022-07-14T18:45:21.111525+00:00
| 90 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n int L=0,R=0;\n for(int i=0;i<start.size();i++)\n {\n if(start[i]==\'R\')\n {\n if(L!=0 || R<0) return false;\n R++;\n }\n \n if(target[i]==\'R\')\n {\n if(L!=0 || R<=0) return false;\n R--;\n }\n else if(target[i]==\'L\')\n {\n if(R!=0 || L<0) return false;\n L++;\n }\n \n if(start[i]==\'L\')\n {\n if(R!=0 || L<=0) return false;\n L--;\n }\n }\n return (R==0 && L==0);\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Java | One Pass | All Test Cases Passed
|
java-one-pass-all-test-cases-passed-by-x-739o
|
There are three restrictions:\n1. the number and sequence of L and R should be equal\n2. L can not be moved to the right\n3. R can not be moved to the left\n\nT
|
xiaonitongxue
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-12T01:52:23.797535+00:00
|
2022-07-12T02:30:23.343348+00:00
| 86 | false |
There are three restrictions:\n1. the number and sequence of L and R should be equal\n2. L can not be moved to the right\n3. R can not be moved to the left\n\nThere are several new cases, say "L" and "LL".\nThe following code can pass all the test cases. Hope it helps!\n```\nclass Solution {\n public boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n int i = 0;\n int j = 0;\n int n = start.length();\n \n while (i < n || j < n) {\n while (i < n && start.charAt(i) == \'_\') i++;\n while (j < n && target.charAt(j) == \'_\') j++;\n \n // should both reach the end to check the number of L and R\n // e.g. "_L" and "LL"\n if (i == n && j == n) return true;\n if (i == n || j == n) return false; \n \n if (start.charAt(i) != target.charAt(j)) return false; // the same squence of R and L\n \n if (start.charAt(i) == \'L\' && i < j) return false; // can not move L to the right\n if (start.charAt(i) == \'R\' && i > j) return false; // can not move R to the left\n \n i++;\n j++;\n }\n \n return i == n && j == n;\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'Java']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
[C++] || space: O(1) time:O(n) || Easy Solution + Explanation
|
c-space-o1-timeon-easy-solution-explanat-n3qv
|
Approach:\n Let us think of a naive approach:\n\t We realise that if we see a L in target => our L in start string should be after the L in target string. We
|
scribble1001
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-11T07:22:31.211707+00:00
|
2022-07-11T07:39:55.232648+00:00
| 154 | false |
**Approach:**\n* Let us think of a naive approach:\n\t* We realise that if we see a `L` in target => our `L` in start string should be after the `L` in target string. We also realise all the letter b/w the start index till the target index of `L` should be `_` so that `L` in start string can move left back and reach its target location.\n\t* Similarly, if we see a `R` in target => our `R` in start string should be before the `R` in target string. Also all the indices b/w these location should contain `_`\n\t* We could intially maybe store all indices of `L` and `R` in target and start strings and check if these constraints are met. But this will be nearly O(n^2) and exceeded time limit.\n\n* Now let us see how we can solve in O(n), an optimised approach:\n\t* let us iterate through the start and target string.\n\t* if we see a `L` in target string we update the number of `L` s we need to find later on in the start string in a variable `left` . We realise if before we exhaust all `L` s that we need to find in start string, if we encounter any charecter except `_` and `L` which is basically `R` we cannot move `L` and therefore not reach target string.\n\t* similarly if we see a `R` in start string, we update the number of `R` s we need to find later on in the target string in a variable `right` . we should not encounter an `L` before we exhaust all `R`. \n\t* at the end we make sure we have exhausted all `L` and `R` . We keep this extra check in case we have more `L` or `R` in either strings.\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n int left = 0;\n int right = 0;\n int l=0;\n int r=0;\n int n = start.size();\n \n for(int i=0; i<n; i++){\n if(target[i]==\'L\') left++;\n if(start[i]==\'R\') right++;\n \n if(left && start[i]==\'R\') return 0;\n if(!left && start[i]==\'L\') return 0;\n if(left && start[i]==\'L\') left--;\n\n \n if(right && target[i]==\'L\') return 0;\n if(!right && target[i]==\'R\') return 0;\n if(right && target[i]==\'R\') right--; \n }\n \n if(!right && !left){\n return 1;\n }\n return 0;\n }\n};\n```\nHope this helps!
| 2 | 0 |
['String', 'Greedy', 'C', 'C++']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Javascript: Two Pointer Approach
|
javascript-two-pointer-approach-by-hsnim-udjv
|
\nvar canChange = function(start, target) {\n let i = 0, j = 0;\n \n while(i < start.length || j < target.length) {\n while(i < start.length &&
|
HsnImam
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T12:57:51.054526+00:00
|
2022-07-10T12:57:51.054568+00:00
| 65 | false |
```\nvar canChange = function(start, target) {\n let i = 0, j = 0;\n \n while(i < start.length || j < target.length) {\n while(i < start.length && start[i] === \'_\') {\n i++;\n }\n \n while(j < target.length && target[j] === \'_\') {\n j++;\n }\n if(start[i] !== target[j]) return false;\n \n if(start[i] === \'L\' && i < j) return false;\n \n if(start[i] === \'R\' && j < i) return false;\n \n i++;\n j++;\n }\n \n return true;\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'JavaScript']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Python - just compare
|
python-just-compare-by-ante-nrrp
|
\nclass Solution:\n def canChange(self, start: str, target: str) -> bool: \n N1, N2 = len(start), len(target) \n if N1 != N2: ret
|
Ante_
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T10:43:57.419447+00:00
|
2022-07-10T10:43:57.419491+00:00
| 51 | false |
```\nclass Solution:\n def canChange(self, start: str, target: str) -> bool: \n N1, N2 = len(start), len(target) \n if N1 != N2: return False \n if start.replace(\'_\', \'\') != target.replace(\'_\', \'\'): return False\n \n pos1 = []\n pos2 = []\n \n for i in range(N1):\n if start[i] != \'_\': pos1.append((start[i], i))\n if target[i] != \'_\': pos2.append((target[i], i))\n \n for i in range(len(pos1)):\n if pos1[i][0] == \'R\' and pos1[i][1] > pos2[i][1]: return False\n if pos1[i][0] == \'L\' and pos1[i][1] < pos2[i][1]: return False\n \n return True\n```
| 2 | 0 |
[]
| 1 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
General Approach || Faster than 100%
|
general-approach-faster-than-100-by-wise-xcye
|
Problem: We have two strings S and T. We want to achieve T from S by moving characters of S.\n\n##### Conditions that must hold:\n Size of strings must be same.
|
wisesaint
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T10:39:28.401867+00:00
|
2022-07-10T10:39:28.401897+00:00
| 23 | false |
**Problem:** We have two strings S and T. We want to achieve T from S by moving characters of S.\n\n##### Conditions that must hold:\n* *Size of strings must be same.*\n* *Frequency of characters must be same.*\n\n##### Movements:\n* **CASE 1:** If characters can cross each other, then the above two conditions are enough.\n* **CASE 2:** If characters have restricted movements (like in this question), then the presence of characters in S should be in accordance with the restrictions.\n\n##### CASE 2 Explanation:\nLet the allowed movement says that the characters can\'t cross each other. It means, the ordering of the characters in S and T must also be same. In simple words, S = T. Very simple! That\'s why the question is allowing movements through \' _ \'. \n\nLet\'s come to the original question. \n**Movement Restrictions:** \'L\' can move only to the left and \'R\' can move only to the right. And \'L\' and \'R\' cannot cross each other.\n\nSince \'L\' and \'R\' can\'t cross each other, so if we create strings of \'L\' and \'R\' only, then that strings must be equal (say S_ = T_).\n\nSince \'L\' can move only to the left and \'R\' can move only to the right, therefore \'L\' should be in the right of required position and \'R\' should be in the left of required position in the string S_.\n\n\n**C++ implementation of the above approach:**\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string s, string t) {\n string s_, t_; // strings of L and R only\n vector<int> si, ti; // Corresponding indices of L and R.\n for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {\n if(s[i] == \'L\' or s[i] == \'R\') {\n s_.push_back(s[i]);\n si.push_back(i);\n }\n if(t[i] == \'L\' or t[i] == \'R\') {\n t_.push_back(t[i]);\n ti.push_back(i);\n }\n }\n if(s_ != t_) return false; // Ordering must be same.\n for(int i = 0; i < t_.size(); i++) {\n // L should be at or in the right of required position.\n if(t_[i] == \'L\' and si[i] < ti[i]) return false; // L is in left.\n // R should be at or in the left of required position.\n if(t_[i] == \'R\' and si[i] > ti[i]) return false; // R is in right.\n }\n return true;\n }\n};\n```\n\n**Runtime:** 89ms\n\n\n\n
| 1 | 0 |
['String']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
C++ || TC: O(n) || Stack Solution || Greedy
|
c-tc-on-stack-solution-greedy-by-theblac-cs52
|
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string a, string b) {\n if(a.size()!=b.size())\n {\n return false;\n }\n
|
theblackhoop
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T08:19:53.400922+00:00
|
2022-07-10T08:20:46.268232+00:00
| 48 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string a, string b) {\n if(a.size()!=b.size())\n {\n return false;\n }\n \n stack<pair<char,int>> st;\n int n=a.size();\n for(int i=0;i<n;i++)\n {\n if(b[i]!=\'_\')\n {\n st.push({b[i],i});\n }\n \n }\n \n for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--)\n {\n \n \n if(a[i]!=\'_\')\n {\n if(st.size()==0)\n {\n return false;\n }\n auto curr=st.top();\n char x=curr.first;\n int y=curr.second;\n if(x!=a[i])\n {\n return false;\n }\n \n if(x==\'R\' and x==a[i])\n {\n if(i<=y)\n {\n st.pop();\n \n }\n else\n {\n return false;\n }\n }\n\n if(x==\'L\' and x==a[i])\n {\n if(i>=y)\n {\n st.pop();\n \n }\n else\n {\n return false;\n }\n }\n }\n }\n if(st.size()==0)\n {\n return true;\n }\n return false;\n \n }\n};
| 2 | 0 |
['Stack', 'Greedy', 'C']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Easy to understand | O(n)
|
easy-to-understand-on-by-bansal_arun-s01v
|
Please , Upvote if you understand\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string s, string t) {\n string a="",b="";\n vector pos1,pos2
|
bansal_arun
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T08:17:10.962239+00:00
|
2022-07-10T08:17:10.962283+00:00
| 35 | false |
Please , Upvote if you understand\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string s, string t) {\n string a="",b="";\n vector<int> pos1,pos2;\n for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++)\n {\n if(s[i]!=\'_\')\n {\n a+=s[i];\n pos1.push_back(i);\n }\n }\n for(int i=0;i<t.length();i++)\n {\n if(t[i]!=\'_\')\n {\n b+=t[i];\n pos2.push_back(i);\n }\n }\n if(a!=b)\n return false;\n for(int i=0;i<a.size();i++)\n {\n if(a[i]==\'L\')\n {\n if(pos1[i]<pos2[i])return false;\n }\n else\n {\n if(pos1[i]>pos2[i])return false;\n }\n }\n return true;\n }\n};
| 2 | 0 |
['C']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
C# 17 lines, With Comments, O(n) time, O(1) space
|
c-17-lines-with-comments-on-time-o1-spac-ehir
|
\npublic class Solution \n{\n public bool CanChange(string start, string target) \n {\n int startR = 0, // free R\'s in start\n targetL
|
Rad0miR
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T05:52:40.659849+00:00
|
2022-07-10T05:55:07.898260+00:00
| 28 | false |
```\npublic class Solution \n{\n public bool CanChange(string start, string target) \n {\n int startR = 0, // free R\'s in start\n targetL = 0; // needed L\'s for target\n\t\t\t\n foreach ((int startC, int targetC) in start.Zip(target)) \n {\n if (startC == \'R\') ++startR; // we can move this R\'s to the right later\n if (targetC == \'L\') ++targetL; // we need this L\'s, hope they will come to us later\n \n if (startC == \'L\') \n {\n if (targetL == 0 || startR != 0) return false; // target doesn\'t need L, or we didn\'t finished with R\'s yet\n --targetL; // target gets L\n }\n if (targetC == \'R\')\n {\n if (startR == 0 || targetL != 0) return false; // we don\'t have free R or target want L\'s first\n --startR; // yeah we have that R for you\n } \n }\n return targetL == 0 && startR == 0; // everyone is satisfied\n }\n}\n```
| 2 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Easy Cpp Solution ✅✅
|
easy-cpp-solution-by-ayushkaushk-kyyv
|
\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool checkFreq(string start,string target)\n {\n int a1=0,a2=0,a3=0,b1=0,b2=0,b3=0;\n for(int i=0;i<start.size
|
ayushkaushk
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T05:41:40.801746+00:00
|
2022-07-10T05:41:40.805846+00:00
| 31 | false |
```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool checkFreq(string start,string target)\n {\n int a1=0,a2=0,a3=0,b1=0,b2=0,b3=0;\n for(int i=0;i<start.size();i++)\n {\n if(start[i]==\'L\')a1++;\n if(start[i]==\'R\')a2++;\n if(start[i]==\'_\')a3++;\n \n if(target[i]==\'L\')b1++;\n if(target[i]==\'R\')b2++;\n if(target[i]==\'_\')b3++;\n \n }\n return a1==b1&&a2==b2&&a3==b3;\n }\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n // Check if number of dashes L and R are equal\n if(checkFreq(start,target)==false)return false;\n \n vector<int>prevR;\n vector<int>afterL;\n \n vector<int>prevR1;\n vector<int>afterL1;\n \n //Checking if number of R before every L in start and target are same or not\n int count1=0,count2=0; \n for(int i=0;i<start.size();i++)\n {\n if(start[i]==\'R\')count1++;\n if(start[i]==\'L\')prevR.push_back(count1);\n \n if(target[i]==\'R\')count2++;\n if(target[i]==\'L\')prevR1.push_back(count2);\n \n }\n for(int i=0;i<prevR.size();i++)\n {\n if(prevR1[i]!=prevR[i])return false;\n }\n \n //Checking if number of L after every R in start and target are same or not\n count1=0;count2=0; \n for(int i=start.size()-1;i>=0;i--)\n {\n if(start[i]==\'L\')count1++;\n if(start[i]==\'R\')afterL.push_back(count1);\n \n if(target[i]==\'L\')count2++;\n if(target[i]==\'R\')afterL1.push_back(count2); \n }\n for(int i=0;i<afterL1.size();i++)\n {\n if(afterL1[i]!=afterL[i])return false;\n }\n \n// Checking if number if dashes before every L are >= than that in target\n vector<int>prevDashesStart;\n vector<int>afterDashesStart;\n vector<int>prevDashesTarget;\n vector<int>afterDashesTarget; \n count1=0;count2=0;\n for(int i=0;i<start.size();i++)\n {\n if(start[i]==\'_\')count1++;\n if(start[i]==\'L\')prevDashesStart.push_back(count1);\n \n if(target[i]==\'_\')count2++;\n if(target[i]==\'L\')prevDashesTarget.push_back(count2); \n }\n for(int i=0;i<prevDashesStart.size();i++)\n {\n if(prevDashesStart[i]<prevDashesTarget[i])return false;\n }\n // Checking if number if dashes after every R are >= than that in target\n count1=0;count2=0;\n for(int i=start.size()-1;i>=0;i--)\n {\n if(start[i]==\'_\')count1++;\n if(start[i]==\'R\')afterDashesStart.push_back(count1); \n \n if(target[i]==\'_\')count2++;\n if(target[i]==\'R\')afterDashesTarget.push_back(count2); \n }\n \n for(int i=0;i<afterDashesTarget.size();i++)\n {\n if(afterDashesStart[i]<afterDashesTarget[i])return false;\n }\n \n return true; \n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['C']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
C++ | String Simulation | Time : O(n), Space : O(1) | Easy code
|
c-string-simulation-time-on-space-o1-eas-2pll
|
Please Upvote :)\n\n\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) { \n int l=0,t=0;\n for(int i=start.length(
|
ankit4601
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T04:40:12.418864+00:00
|
2022-07-10T04:40:47.210586+00:00
| 36 | false |
Please Upvote :)\n\n```\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) { \n int l=0,t=0;\n for(int i=start.length()-1;i>=0;i--)\n {\n if(start[i]==\'L\')\n l++; \n if(target[i]==\'L\')\n t++;\n \n if(start[i]==\'R\' || target[i]==\'R\')\n {\n if(t!=l)\n return false;\n }\n if(t>l)\n return false;\n }\n if(t!=l)\n return false;\n l=0;\n t=0;\n for(int i=0;i<start.length();i++)\n {\n if(start[i]==\'R\')\n l++; \n if(target[i]==\'R\')\n t++;\n \n if(start[i]==\'L\' || target[i]==\'L\')\n {\n if(t!=l)\n return false;\n }\n if(t>l)\n return false;\n }\n if(t!=l)\n return false;\n return true;\n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['String', 'C']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
~17 lines, Simple O(N) Python soln
|
17-lines-simple-on-python-soln-by-znatha-fimy
|
Insight:\nWithout loss of generality, let\'s consider left pieces only.\n - Ls can move left, if there are spaces before the L\n - Ls can cross over lefts while
|
znathan
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T04:26:10.018552+00:00
|
2022-07-10T04:26:10.018588+00:00
| 20 | false |
Insight:\nWithout loss of generality, let\'s consider left pieces only.\n - Ls can move left, if there are spaces before the L\n - Ls can cross over lefts while moving, but cannot cross over Rs, therefore\n using a counter for number of available lefts is viable. This counter is reset to 0\n if we see a right in the way. If there\'s a left we cannot match, we return false, too.\n\n```\n def canChange(self, start, target):\n N = len(start)\n \n curr = 0\n for i in range(N - 1, -1, -1):\n if start[i] == \'L\': curr += 1\n elif start[i] == \'R\': curr = 0\n if target[i] == \'R\' and curr > 0: return False \n if target[i] == \'L\':\n if curr == 0: return False\n curr -= 1\n \n for i in range(N):\n if start[i] == \'R\': curr += 1\n elif start[i] == \'L\': curr = 0\n if target[i] == \'L\' and curr > 0: return False \n if target[i] == \'R\':\n if curr == 0: return False\n curr -= 1\n return True\n```\n
| 2 | 0 |
[]
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
C++ ✅|| Greedy🔥|| Easy Understanding
|
c-greedy-easy-understanding-by-vansh_00_-5jbw
|
UPVOTE\nwe will store all the indexes witht the characters where here is L and R in the start and target string respectively.\n\n\ntypedef vector<pair<char,int>
|
vansh_00_7
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T04:08:27.162253+00:00
|
2022-07-10T04:08:27.162288+00:00
| 40 | false |
##### ***UPVOTE***\nwe will store all the indexes witht the characters where here is L and R in the start and target string respectively.\n\n```\ntypedef vector<pair<char,int>> vi; // used to shorten the code for me little bit\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n int n = start.size();\n vi a,b;\n for(int i = 0;i < n;++i){\n if(start[i] != \'_\') a.push_back({start[i],i}); // storing L and R in start with their index\n if(target[i] != \'_\') b.push_back({target[i],i}); // storing L and R in start with their index\n }\n int op = a.size();\n int pp = b.size();\n if(op == pp){ // check if their sizes are equal if not then return false \n for(int i = 0;i < op;++i){\n if(a[i].first == b[i].first){ // elements equal we will check their position with respect to each other\n if(a[i].first == \'L\'){\n if(a[i].second < b[i].second) return false;\n }else {\n if(a[i].second > b[i].second) return false;\n }\n }else return false; // Elements not equal so we will return just false\n }\n return true;\n }\n return false; // since check the case where it can be true now we have to just return false \n }\n};\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Greedy', 'C']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Extraordinary Solution C++
|
extraordinary-solution-c-by-thedarkning-js6m
|
we are storing 2 different versions of possible strings\nfirst with only Ls on the left\nsecond with Rs on the right side \nIn the end we just check if current
|
TheDarkning
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T04:06:28.916027+00:00
|
2022-07-10T04:06:28.916057+00:00
| 119 | false |
we are storing 2 different versions of possible strings\nfirst with only Ls on the left\nsecond with Rs on the right side \nIn the end we just check if current letter is L we are looking at 1st string\nand the same for R\n```class Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n string t = start;\n int cnt = 0;\n for(int i = 0; i < start.size(); i++){\n if(start[i] == \'L\'){\n int j = i;\n while(j-- && start[j] == \'_\')\n start[j] = \'L\';\n cnt++;\n }\n else if(start[i] == \'R\'){\n i++;\n while(i < t.size() && t[i] == \'_\')\n t[i] = \'R\', i++;\n i--;\n cnt++;\n }\n }\n cout << start << \' \' << t << \' \' << target<< endl;\n for(int i = 0; i < target.size(); i++){\n if(target[i] == \'L\'){\n if(start[i] != \'L\')\n return false;\n cnt--;\n }\n \n if(target[i] == \'R\'){\n if(t[i] != \'R\')\n return false;\n cnt--;\n }\n \n }\n if(cnt)\n return false;\n return true;\n }\n};\n```\n
| 2 | 0 |
['Greedy', 'C']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Deque and position checking | Explained
|
deque-and-position-checking-explained-by-pkmp
|
We need to make the following checks for left and right ("L", "R")\n\n1. If there is a "R" between "L" actual position and it\'s final position -> return false
|
nadaralp
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T04:04:39.180193+00:00
|
2022-07-10T04:10:02.138693+00:00
| 205 | false |
We need to make the following checks for left and right ("L", "R")\n\n1. If there is a "R" between "L" actual position and it\'s final position -> `return false` since it can\'t be placed in the final location\n2. If the next "L" position is after the current index -> `return false` since we can move only left\n\nDo the same logic for the other side with "R"\n\n\n# Code\n```\nfrom collections import deque\n\nclass Solution:\n def canChange(self, start: str, target: str) -> bool:\n n = len(start)\n \n seen_left = deque([])\n seen_right = deque([])\n target_left = deque([])\n target_right = deque([])\n \n for i in range(n):\n if start[i] == "R": seen_right.append(i)\n if start[i] == "L": seen_left.append(i)\n if target[i] == "L": target_left.append(i)\n if target[i] == "R": target_right.append(i)\n \n \n for i in range(n):\n if start[i] == "L":\n if not target_left: return False\n \n next_left_target_index = target_left.popleft()\n \n if next_left_target_index > i:\n return False\n \n \n # irrelevant\n while seen_right and seen_right[0] < next_left_target_index:\n seen_right.popleft()\n \n # blocking between actual and target\n if seen_right and next_left_target_index <= seen_right[0] <= i:\n return False\n \n for i in range(n):\n cur_i = n-1-i\n if start[cur_i] == "R":\n if not target_right: return False\n \n next_right_target_index = target_right.pop()\n \n if next_right_target_index < cur_i:\n return False\n \n # irrelevant\n while seen_left and seen_left[-1] > next_right_target_index:\n seen_left.pop()\n \n # blocking between actual and target\n if seen_left and cur_i <= seen_left[-1] <= next_right_target_index:\n return False\n \n return len(target_left) == 0 and len(target_right) == 0\n\n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Queue', 'Python']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
[Python3] greedy
|
python3-greedy-by-ye15-o9w4
|
Please pull this commit for solutions of weekly 301. \n\n\nclass Solution:\n def canChange(self, s: str, e: str) -> bool:\n dl = dr = 0 \n for
|
ye15
|
NORMAL
|
2022-07-10T04:04:10.444117+00:00
|
2022-07-11T00:14:08.518932+00:00
| 293 | false |
Please pull this [commit](https://github.com/gaosanyong/leetcode/commit/f00c06cefbc1b2305f127a8cde7ff9b010197930) for solutions of weekly 301. \n\n```\nclass Solution:\n def canChange(self, s: str, e: str) -> bool:\n dl = dr = 0 \n for ss, ee in zip(s, e): \n if dl > 0 or dl < 0 and ss == \'R\' or dr < 0 or dr > 0 and ss == \'L\': return False \n dl += int(ss == \'L\') - int(ee == \'L\')\n dr += int(ss == \'R\') - int(ee == \'R\')\n return dl == dr == 0 \n```
| 2 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Unique Approach!! : Path Compression | TC: O(n) | SC: O(n) | Different approach from Editorial
|
unique-approach-path-compression-tc-on-s-2twg
|
IntuitionBasically, the problem can be re-defined as:
Each _ can shift a place with an L on its right. However, this operation is not possible if there is an R
|
PratyushJha14
|
NORMAL
|
2025-04-08T16:10:23.038000+00:00
|
2025-04-08T16:10:23.038000+00:00
| 12 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
Basically, the problem can be re-defined as:
1. Each _ can shift a place with an L on its right. However, this operation is not possible if there is an R in between the _ and the L.
2. Each R can shift a place with an _ on its right. However, this operation is not possible if there is an L in between the R and the _.
Hence, traversing from left to right, we need to know, for each position, where is the next L located on the right, and when is the next _ located on the right. This we pre-compute and store in the arrays: next_l and next_uscore.
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
- We traverse through the whole string, and check for the possibility of swaps when the individual strings do not match. If the swap is possible, we perform the operation. This, however, must change the next_l and next_uscore arrays. Hence, we do path compression so as to avoid redundant calculations (in locating the next_uscore or next_l at the required index).
- *This is worth noting that if the path compression is done recursively, it gives an "MLE" on 98th test case. Hence, the recursive stack needs to be voided, hence, the iterative path compression instead.*
# Complexity
- Time complexity: O(n)
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity: O(n)
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
vector<int> next_l, next_uscore;
int find_next_l(string& start, int idx) {
while (idx != -1 && start[idx] != 'L') {
idx = next_l[idx];
}
return idx;
}
int find_next_uscore(string& start, int idx) {
while (idx != -1 && start[idx] != '_') {
idx = next_uscore[idx];
}
return idx;
}
public:
bool canChange(string start, string target) {
int n1 = start.length(), n2 = target.length();
int l1 = 0, l2 = 0;
int l_idx = -1, uscore_idx = -1;
next_uscore.resize(n1, -1);
next_l.resize(n1,-1);
for(int i=n1-1; i>=0; i--){
next_l[i] = l_idx;
next_uscore[i] = uscore_idx;
if(start[i]=='L'){
l_idx=i;
uscore_idx = -1;
}
if(start[i]=='R'){
l_idx=-1;
}
if(start[i]=='_'){
uscore_idx = i;
}
}
while(l1<n1 and l2<n2){
if(start[l1]==target[l2]){
l1++;
l2++;
continue;
}
if(start[l1]!='_' and target[l2]!='_'){
// cout<<start;
return false;
}
if(start[l1] == 'L' or target[l2]=='R'){
// cout<<start<<" h1";
return false;
}
if(start[l1]=='R' and target[l2]=='_'){
int next_uscore_idx = find_next_uscore(start, l1);
if(next_uscore_idx != -1){
swap(start[next_uscore_idx], start[l1]);
if(l1+1<n1 and next_uscore_idx != l1+1){
next_uscore[l1+1] = next_uscore_idx;
}
l1++; l2++;
continue;
} else{
// cout<<start<<" h2 "<<l1;
return false;
}
}
if(start[l1]=='_' and target[l2]=='L'){
int next_l_idx = find_next_l(start, l1);
if(next_l_idx == -1){
// cout<<start<< " h3";
return false;
}
swap(start[l1], start[next_l_idx]);
if(l1+1<n1 and next_l_idx != l1+1){
next_l[l1+1] = next_l_idx;
}
l1++;
l2++;
continue;
}
}
return true;
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Simple and understandable java code
|
simple-and-understandable-java-code-by-s-kagl
|
Complexity
Time complexity:O(n)
Space complexity:O(1)
Code
|
samman_varshney
|
NORMAL
|
2025-01-22T10:55:39.306267+00:00
|
2025-01-22T10:55:39.306267+00:00
| 12 | false |
# Complexity
- Time complexity:O(n)
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity:O(1)
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```java []
class Solution {
public boolean canChange(String st, String tar) {
int n = st.length();
int i=0,j=0;
while(i<=n && j<=n){
while(i<n && tar.charAt(i)=='_') i++;
while(j<n && st.charAt(j)=='_') j++;
if(i==n || j==n){
return i==n && j==n;
}
if(tar.charAt(i)!=st.charAt(j)) return false;
if(tar.charAt(i)=='L'){
if(j<i) return false;
}
else{
if(i<j) return false;
}
i++;
j++;
}
return true;
}
}
```
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Simple Two Pointers | Commented | C++
|
simple-two-pointers-commented-c-by-ketan-sokr
|
IntuitionApproachComplexity
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(1)
Code
|
ketan_07
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-30T16:32:41.207676+00:00
|
2024-12-30T16:32:41.207676+00:00
| 9 | false |
# Intuition
<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->
# Approach
<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->
# Complexity
- Time complexity: O(n)
<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
- Space complexity: O(1)
<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->
# Code
```cpp []
class Solution {
public:
bool canChange(string start, string target) {
int n = target.size();
int tInd = 0; //target index
int sInd = 0; //start index
while(tInd < n || sInd < n) {
while(tInd < n && target[tInd] == '_') tInd++;
while(sInd < n && start[sInd] == '_') sInd++;
//sequence of characters should be same
if(start[sInd] != target[tInd]) return false;
//L in start should not be on the left of L in target
if(start[sInd] == 'L' && sInd < tInd) return false;
//R in start should not be on the right of R in target
if(start[sInd] == 'R' && sInd > tInd) return false;
tInd++;
sInd++;
}
return true;
}
};
```
| 1 | 0 |
['C++']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
2337. Move Pieces to Obtain a String - 100%
|
2337-move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string-100-90eb5
|
Approach\nThe approach to the solution is described in the comments in the code, perhaps it will be clearer this way.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\nO(n)\
|
user4903q
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-06T05:49:40.598479+00:00
|
2024-12-06T05:49:40.598519+00:00
| 5 | false |
# Approach\nThe approach to the solution is described in the comments in the code, perhaps it will be clearer this way.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n$$O(n)$$\n\n- Space complexity:\n$$O(1)$$\n\n# Code\n```typescript []\nfunction canChange(start: string, target: string): boolean {\n // initialize counters for encountered characters\n // if we encounter a character in target - increment\n // if we encounter a character in start - decrement\n // \'_\' characters are not important\n let countR = 0;\n let countL = 0;\n\n // if start and target are equal - immediately return true\n if (start === target) return true;\n\n for (let targetIndex = 0; targetIndex < target.length; targetIndex++) {\n // at each step, get the characters\n const letterStart = start[targetIndex];\n const letterTarget = target[targetIndex];\n\n // check the obtained values. The order of checks is important!\n // if we encounter \'R\' in target\n // 1. if we expect \'L\' in target (countL > 0) - return false, because \'R\' has blocked its path\n // 2. \'R\' can only move to the right, so if we already expect \'R\' in target (countR > 0) - \n // return false, because \'R\' from letterStart cannot move to the left\n if (letterStart === \'R\') {\n if (countL > 0) return false;\n if (countR > 0) return false;\n countR--;\n }\n\n // if we encounter \'R\' in target while already expecting \'R\' (countR > 0) return false\n // because \'R\' characters in start should appear earlier or simultaneously with target.\n // And in such a case, countR should have been <= 0\n if (letterTarget === \'R\') {\n if (countR > 0) return false;\n countR++;\n }\n\n // if we encounter \'L\' in target and \'R\' is expected after start (countR < 0),\n // the letters overlap, return false\n if (letterTarget === \'L\') {\n if (countR < 0) return false;\n countL++;\n }\n\n // if we encounter \'L\' in start and \'L\' is not needed (countL === 0), return false\n // \'L\' can move to the left, so \'L\' in target should have been encountered simultaneously\n // or earlier than in start, meaning countL would be greater than 0\n if (letterStart === \'L\') {\n if (countL === 0) return false;\n countL--;\n }\n\n }\n\n // if any counter is not equal to 0, then the number of characters in start and target do not match\n if (countL !== 0 || countR !== 0) return false;\n\n return true;\n};\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'String', 'TypeScript']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
✅10 line simple C++🎯Beats 95%⏰θ(2n)✅sp:O(1)
|
10-line-simple-cbeats-95th2nspo1-by-anja-47gb
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nTo compare the L&R characters of both string for their count of characters and order of
|
anjanakt
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-06T05:30:52.954536+00:00
|
2024-12-06T06:35:19.674316+00:00
| 15 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nTo compare the L&R characters of both string for their count of characters and order of occurances using 2 pointers.\n\n# Approach\n<!-- Describe your approach to solving the problem. -->\nBegin with two pointers for target and start string as i and j respectively. The \'_\' can be ignored as we only need to compare the character order and occurances.\n\nLoop through the target string and if an L/R is encountered, loop and obtain the next L/R character occurance in the start string by ignoring the \'_\'.\n\nWhen both pointers are pointing to the corresponding i-th L/R in the string check for the following conditions. All these conditions will make the start string impossible to shape shift to target string:\n\n1. If start string has no more L/R char even though the target has more.\n2. If the char of target doesn\'t match the corresponding char of start.\n `target[i] != start[j]`\n\n3. If both pointers are at \'L\' and start pointer j is less than target pointer i indicates that target \'L\' is positioned at the right side of start. Since L can\'t move towards right we return False.\n `start[j]==\'L\' && j<i`\n\n4. If both pointers are at \'R\' and start pointer j is greater than target pointer i indicates that target \'R\' is positioned at the left side of start. Since R can\'t move towards left we return `false`.\n\n `start[j]==\'R\' && i<j`\n\n- *Final check:*\nIf the start string passed the above loop without returning `false` it\'s time for the final check. As the target string contains no more L/R, check if start contains any additional L/R which makes that can make the frequency count of characters in both the string imbalanced.\n \n while(j<target.size()) \n if(start[j++]!=\'_\') \n return false;\n\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: $$\u03B8(2n) = O(n)$$\n- Space complexity: $$O(1)$$\n\n\n```cpp []\nclass Solution {\npublic:\n bool canChange(string start, string target) {\n\n // line#1: start string pointer\n int j=0;\n\n // line#2: Iterate the target string with i as pointer\n for(int i=0;i<target.size();i++){\n\n // We only need L & R positions of both string so:\n\n // line#3: Ignore the \'_\' in target string\n if (target[i]==\'_\') continue;\n // line#4: Ignore the \'_\' in start string\n while (j<target.size() && start[j]==\'_\') j++;\n\n // line#5: Ifc onditions of the impossibilities:\n\n // 1. If start string gets exhausted even \n if(j>=target.size() || \n // 2. If the order of LR doesn\'t match\n start[j]!=target[i] || \n // 3. L can\'t be shifted forward \n (start[j]==\'L\' && j<i) || \n // 4. R can\'t be shifted backward\n (start[j]==\'R\' && j>i) ) \n return false;\n\n // line#6: Increase the start pointer\n j++;\n }\n\n // line#7: Check if start string has any extra LR \n while(j<target.size()) \n if(start[j++]!=\'_\') \n return false;\n \n // line#8: \n return true;\n }\n};\n```\n\n```python []\nclass Solution:\n def canChange(self, start: str, target: str) -> bool:\n # line#1 \n j=0\n # line#2 \n for i in range(len(target)):\n # line#3\n if target[i]=="_": continue\n\n # line#4\n while j<len(start) and start[j]=="_": j+=1\n \n # line#5\n if j>=len(start) or start[j]!=target[i] or (start[j]=="L" and i>j) or (start[j]=="R" and j>i): \n return False\n\n # line#6\n j+=1\n \n # line#7\n while(j<len(start)):\n if start[j]!="_":\n return False\n # line#8\n j+=1\n\n # line#9\n return True\n```\n
| 1 | 0 |
['Two Pointers', 'String', 'C++', 'Python3']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Beats 36% - But Super Straightforward Solution for Understanding
|
beats-36-but-super-straightforward-solut-4sh3
|
Intuition\n Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. \nThe key intuition is that the characters \'L\' and \'R\' must appear in the same order
|
ethhix
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-06T03:02:34.913201+00:00
|
2024-12-06T03:02:34.913224+00:00
| 8 | false |
# Intuition\n<!-- Describe your first thoughts on how to solve this problem. -->\nThe key intuition is that the characters \'L\' and \'R\' must appear in the same order in both start and target when ignoring underscores (_). This allows us to iterate through both strings simultaneously and compare the characters directly. If the characters at the current positions are not equal, it means one character would need to "pass over" another, which is invalid. By ensuring that \'L\' and \'R\' appear in the same order, we can check their movement rules (\'L\' can only move left, and \'R\' can only move right) to validate the transformation.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity: O(n)\n<!-- Add your time complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n- Space complexity: O(1)\n<!-- Add your space complexity here, e.g. $$O(n)$$ -->\n\n# Code\n```java []\nclass Solution {\n public boolean canChange(String start, String target) {\n\n int startIndex = 0, targetIndex = 0;\n\n while(startIndex < start.length() && targetIndex < target.length()) {\n\n while(startIndex < start.length() && !Character.isLetter(start.charAt(startIndex))) {\n startIndex++;\n }\n\n while(targetIndex < target.length() && !Character.isLetter(target.charAt(targetIndex))) {\n targetIndex++;\n }\n \n if(startIndex < start.length() && targetIndex < target.length()) {\n\n char startChar = start.charAt(startIndex);\n char targetChar = target.charAt(targetIndex);\n\n if(startChar != targetChar) {\n return false;\n }\n \n if(start.charAt(startIndex) == \'L\' && targetIndex > startIndex) {\n return false;\n }\n\n if(start.charAt(startIndex) == \'R\' && targetIndex < startIndex) {\n return false;\n }\n startIndex++;\n targetIndex++;\n }\n }\n\n while(startIndex < start.length()) {\n if(start.charAt(startIndex) != \'_\') {\n return false;\n }\n startIndex++;\n }\n\n while(targetIndex < target.length()) {\n if(target.charAt(targetIndex) != \'_\') {\n return false;\n }\n targetIndex++;\n }\n \n return true;\n }\n}\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Java']
| 0 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
PYTHON BEATS 100% WITHOUT USING FOR OR WHILE
|
python-beats-100-without-using-for-or-wh-v5ok
|
Intuition\n\nThe problem doesn\'t require brute-forcing all possible moves to determine whether the target string can be obtained from the start string. Instead
|
bioimedpellegrino
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T20:57:09.008608+00:00
|
2024-12-05T20:57:09.008689+00:00
| 5 | false |
# Intuition\n\nThe problem doesn\'t require brute-forcing all possible moves to determine whether the target string can be obtained from the start string. Instead, we can rely on a few simple rules to verify the transformation:\n\nThe number of L and R characters in both start and target must be the same. This ensures no extra pieces are introduced or removed.\nIf an L piece is in the first position in start, it will never move to the right of its position. Similarly, if an R piece is in the last position, it cannot move to the left of its position.\nIf we remove all _ (blank spaces) from both start and target, the resulting strings must be identical. This is because the relative order of L and R pieces must remain unchanged.\n\n# Approach\n\nFilter the Characters: Remove all _ from start and target and check if the remaining strings are identical. If not, return false.\nTwo-Pointer Validation:\nUse two pointers, one for start and one for target, to verify the movement constraints of L and R.\nEnsure each L in start has a corresponding L in target at a position to its left or the same position (since L can only move left).\nEnsure each R in start has a corresponding R in target at a position to its right or the same position (since R can only move right).\nIf all constraints are satisfied, return true. Otherwise, return false.\n\n# Complexity\n- Time complexity:\n$$O(n)$$ Because of the count phase and the find phase\n\n- Space complexity:\n$$O(1)$$ Because we don\'t use any particular data structure. \n\n# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def canChange(self, start: str, target: str) -> bool:\n \n start_L, start_R = start.count("L"), start.count("R")\n target_L, target_R = target.count("L"), target.count("R")\n\n start_without_ = start.replace("_", "")\n target_without_ = target.replace("_", "")\n\n max_index_L_start = start.rfind(\'L\')\n min_index_R_start = start.find(\'R\')\n\n max_index_L_target = target.rfind(\'L\')\n min_index_R_target = target.find(\'R\')\n\n if max_index_L_target > max_index_L_start or min_index_R_target < min_index_R_start:\n return False\n \n if start_without_ != target_without_:\n return False\n\n if (start[0] == "L" and target[0] != "L") or (start[-1] == "R" and target[-1] != "R"):\n return False\n\n if start_L != target_L or start_R != target_R:\n return False\n\n\n return True\n\n \n \n```
| 1 | 0 |
['String', 'Python3']
| 1 |
move-pieces-to-obtain-a-string
|
Easy Python Solution
|
easy-python-solution-by-vidhyarthisunav-yeof
|
Code\npython3 []\nclass Solution:\n def canChange(self, start: str, target: str) -> bool:\n s_no_underscore = start.replace(\'_\', \'\')\n t_no
|
vidhyarthisunav
|
NORMAL
|
2024-12-05T20:40:25.489005+00:00
|
2024-12-05T20:40:25.489030+00:00
| 7 | false |
# Code\n```python3 []\nclass Solution:\n def canChange(self, start: str, target: str) -> bool:\n s_no_underscore = start.replace(\'_\', \'\')\n t_no_underscore = target.replace(\'_\', \'\')\n if s_no_underscore != t_no_underscore:\n return False\n n = len(start)\n i, j = 0, 0\n while i < n and j < n:\n while i < n and start[i] == \'_\':\n i += 1\n while j < n and target[j] == \'_\':\n j += 1\n if i < n and j < n:\n if start[i] != target[j] or start[i] == \'L\' and i < j or start[i] == \'R\' and i > j:\n return False\n i += 1\n j += 1\n return True\n```
| 1 | 0 |
['Python3']
| 0 |
Subsets and Splits
No community queries yet
The top public SQL queries from the community will appear here once available.